
The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that will launch NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission arrived in Florida Tuesday, July 14, 2020. The rocket was shipped from the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas, and will now undergo prelaunch processing in the company’s facility on nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
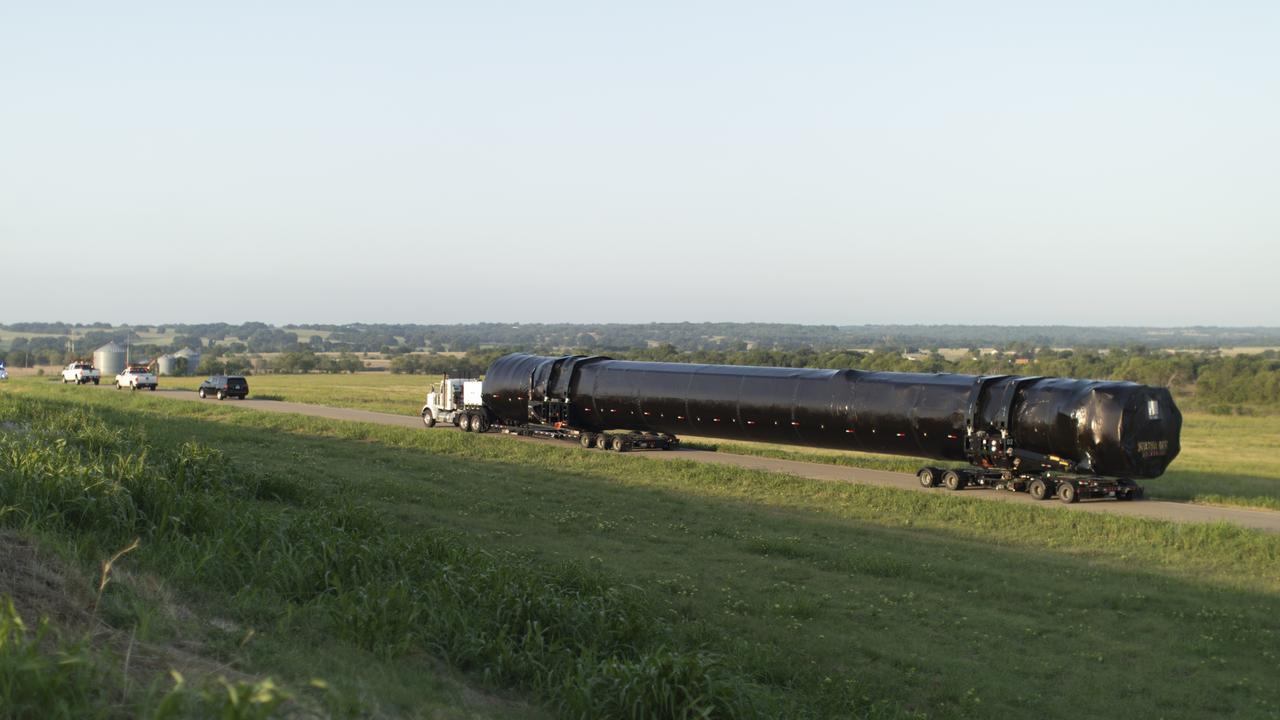

The SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster that will launch NASA’s SpaceX Crew-1 mission arrived in Florida Tuesday, July 14, 2020. The rocket was shipped from the SpaceX facility in McGregor, Texas, and will now undergo prelaunch processing in the company’s facility on nearby Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
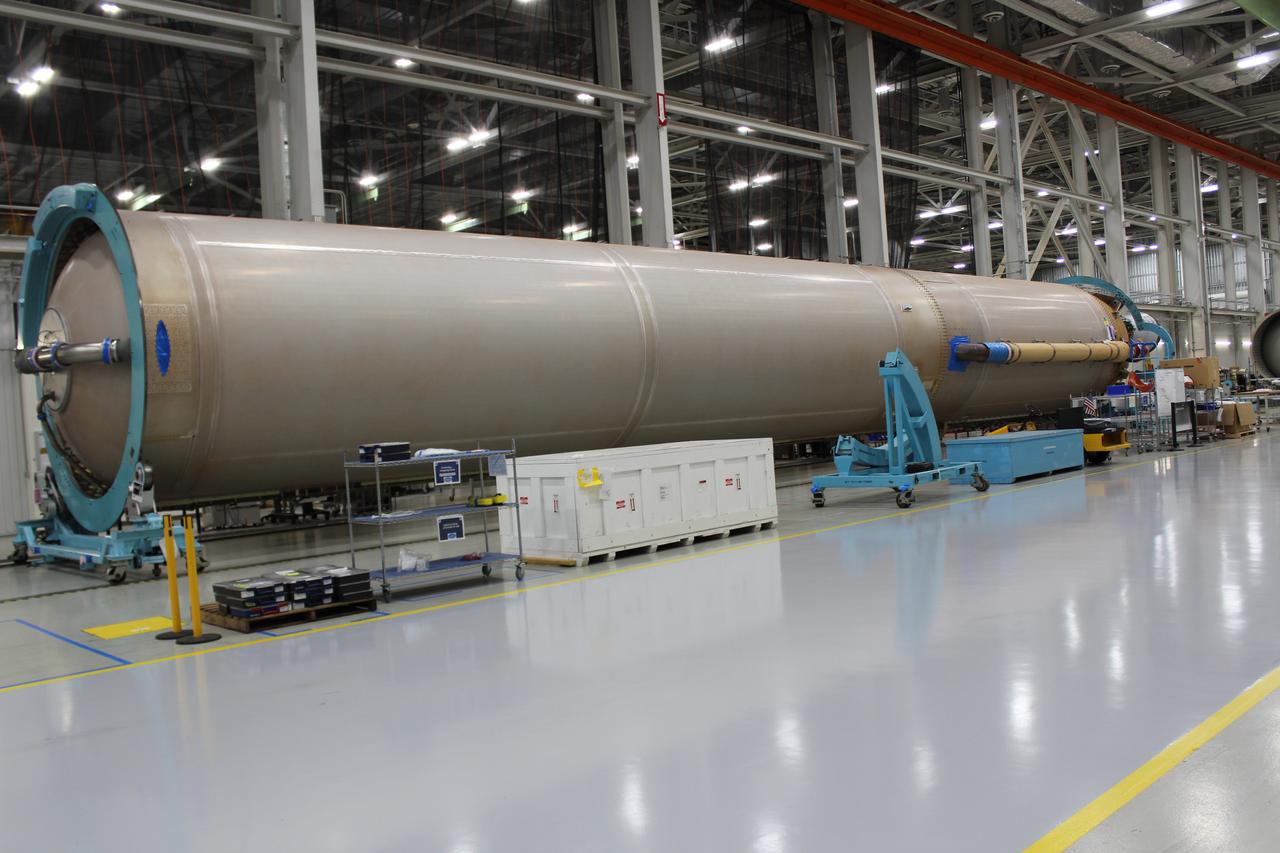

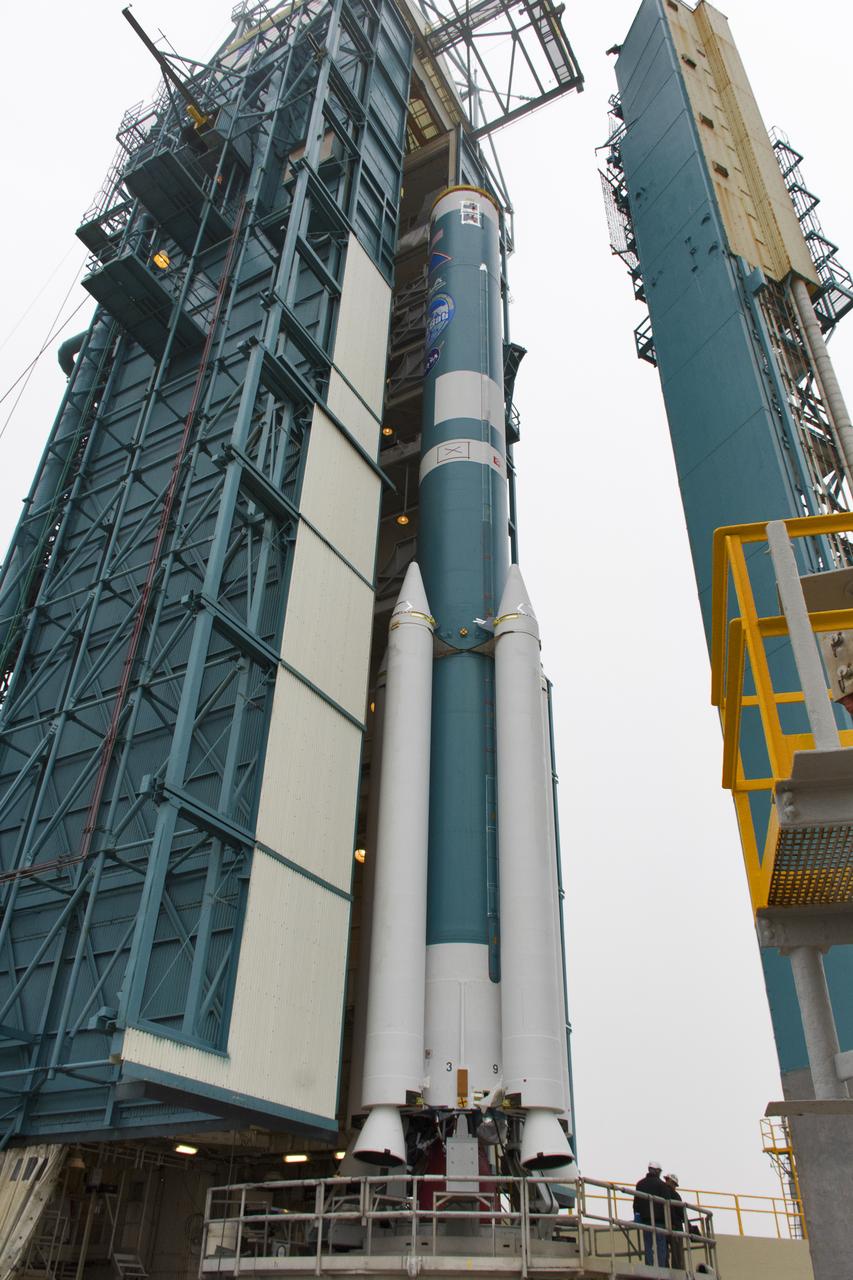
The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster for the Crew Flight Test of Boeing’s CST-100 Starliner is in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. Soon the booster will be assembled with the dual engine Centaur upper stage. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.
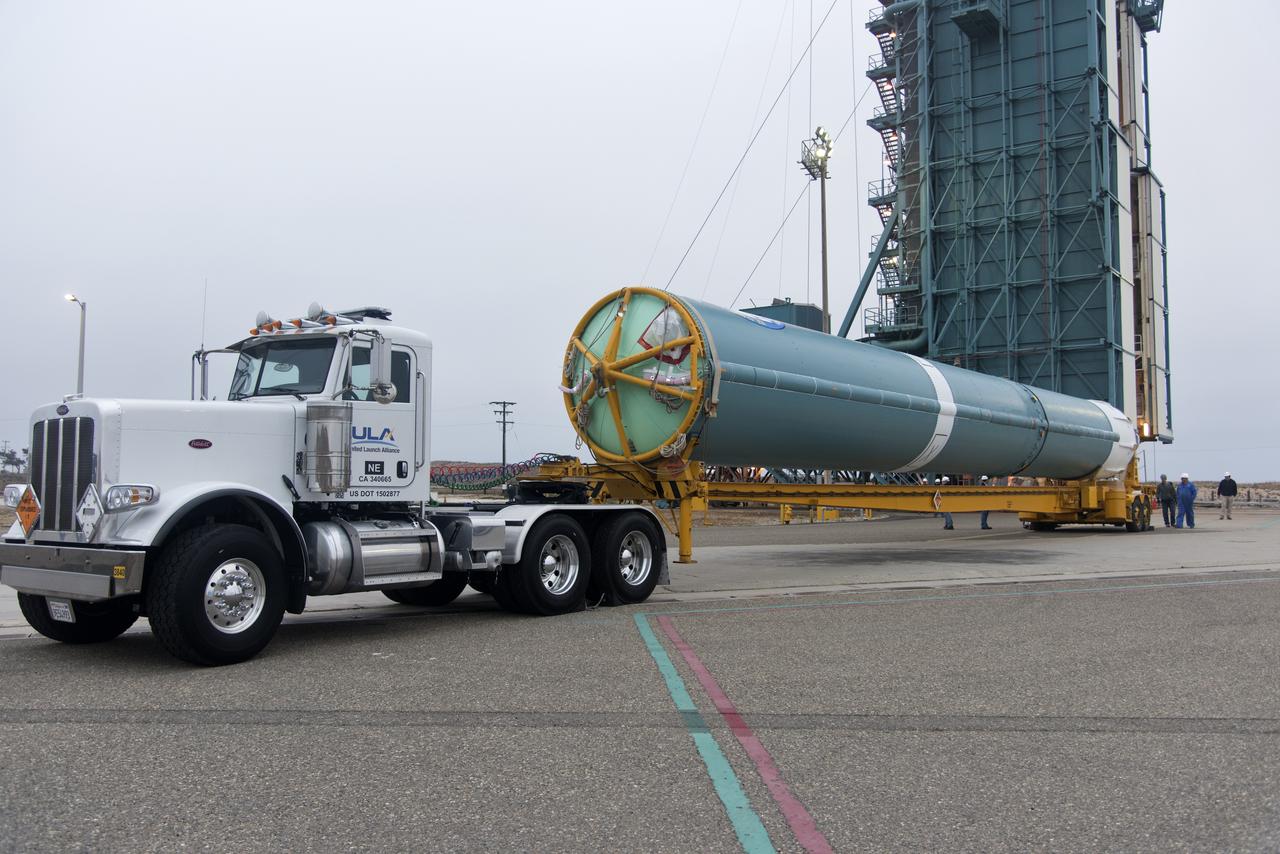

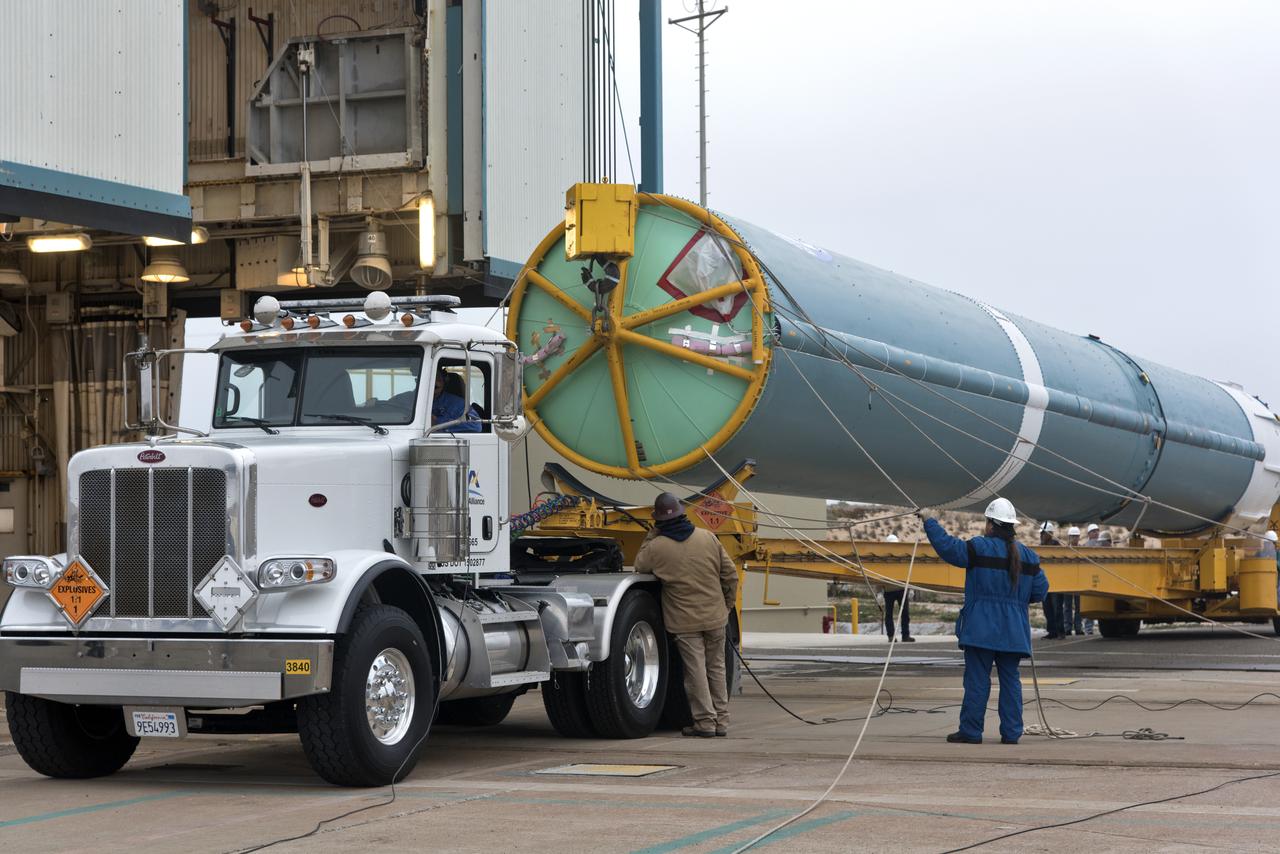
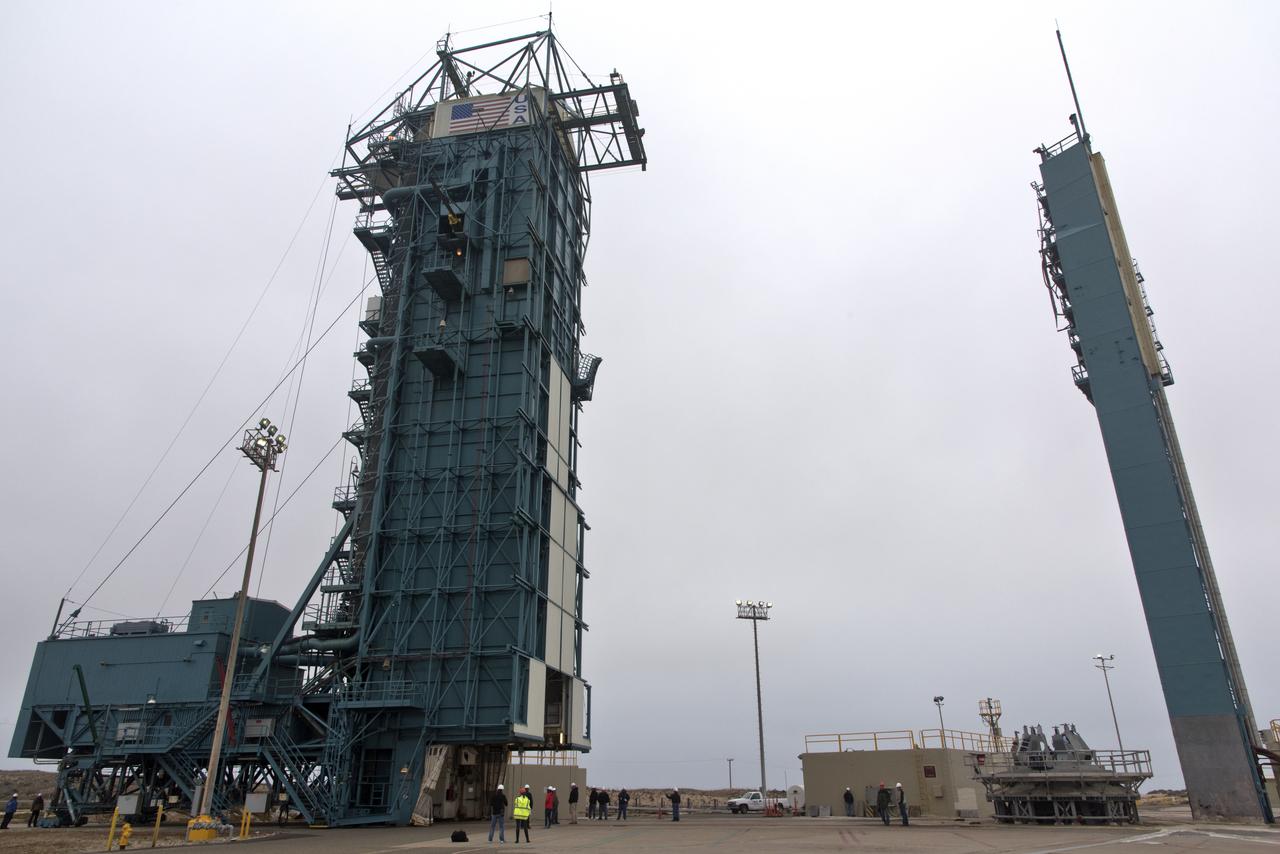
The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical on the stand at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
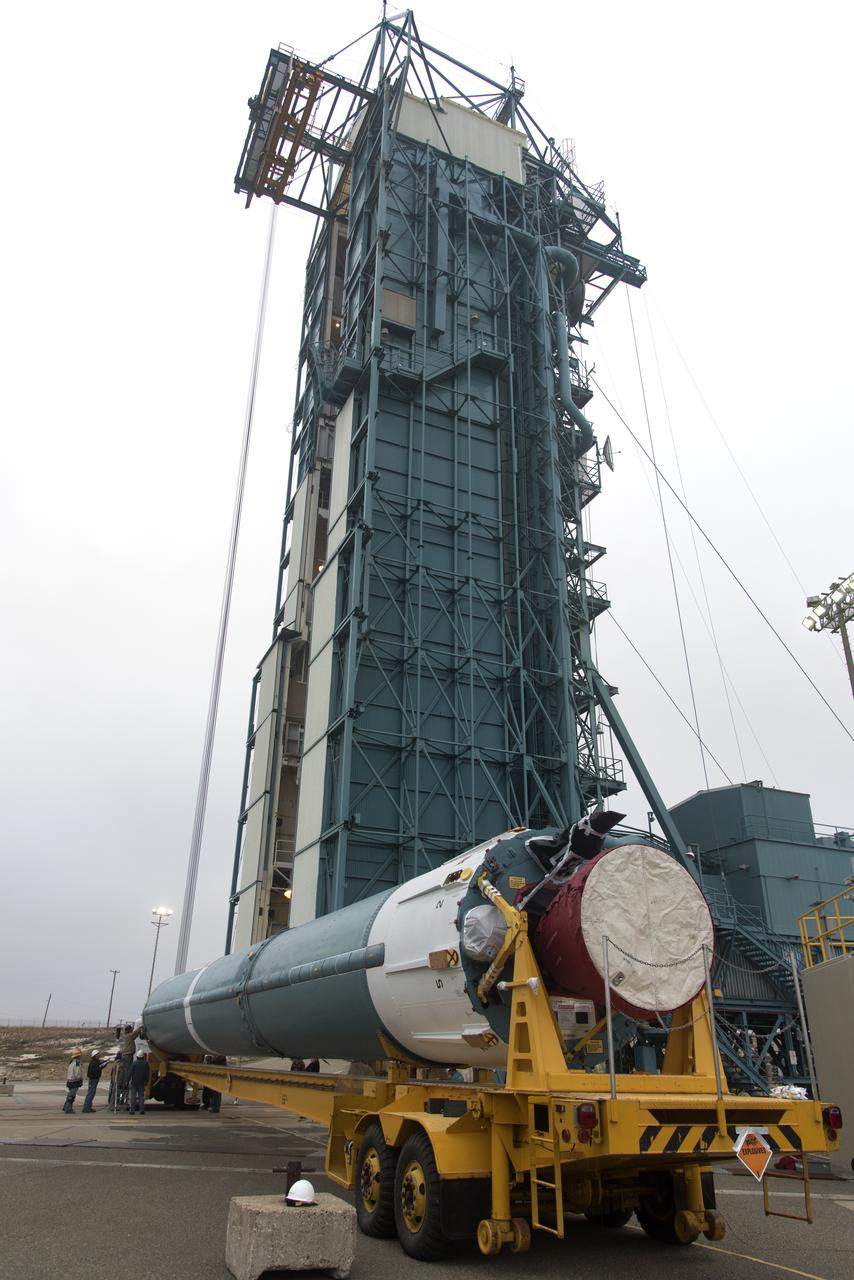

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage arrives at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be lifted to vertical and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
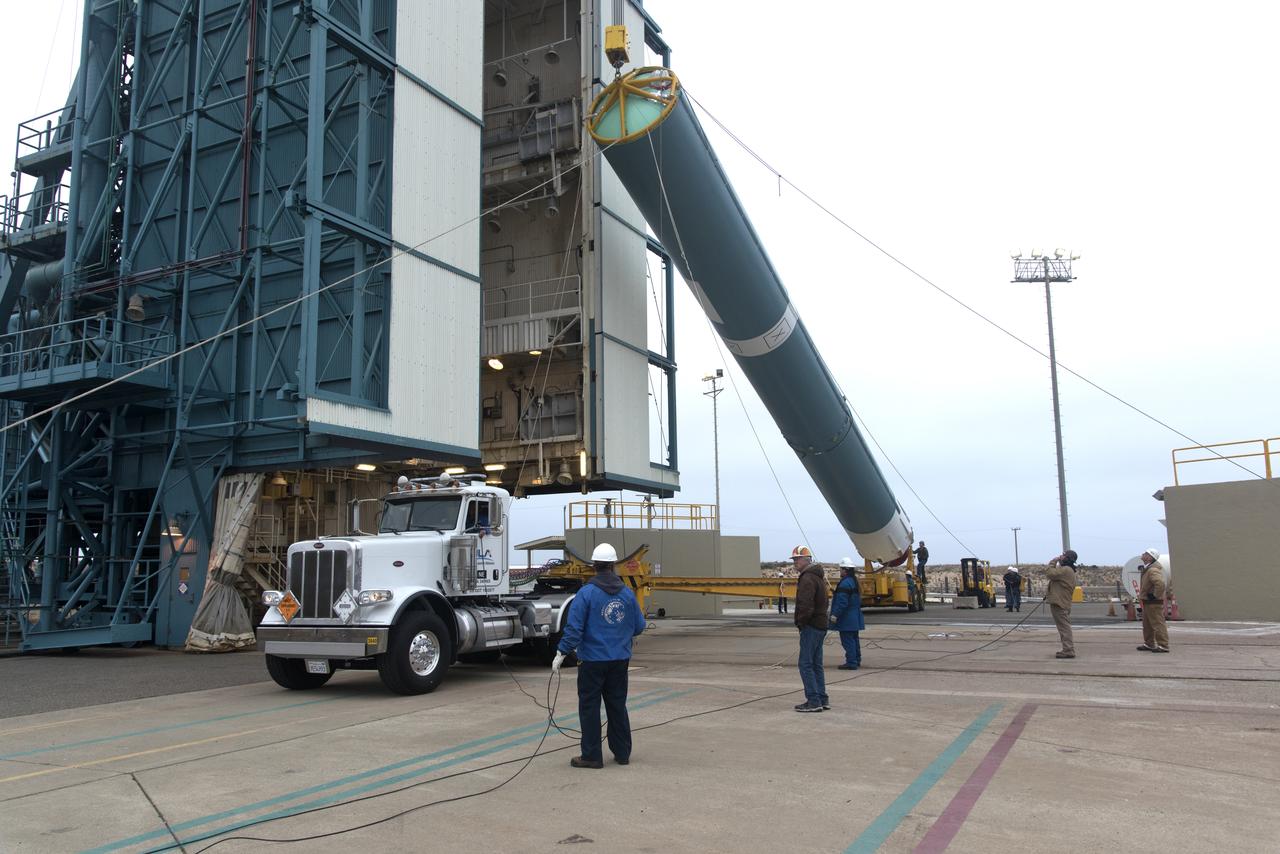

United Launch Alliance (ULA) workers assist as the Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

United Launch Alliance (ULA) workers assist as the Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The booster will be moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
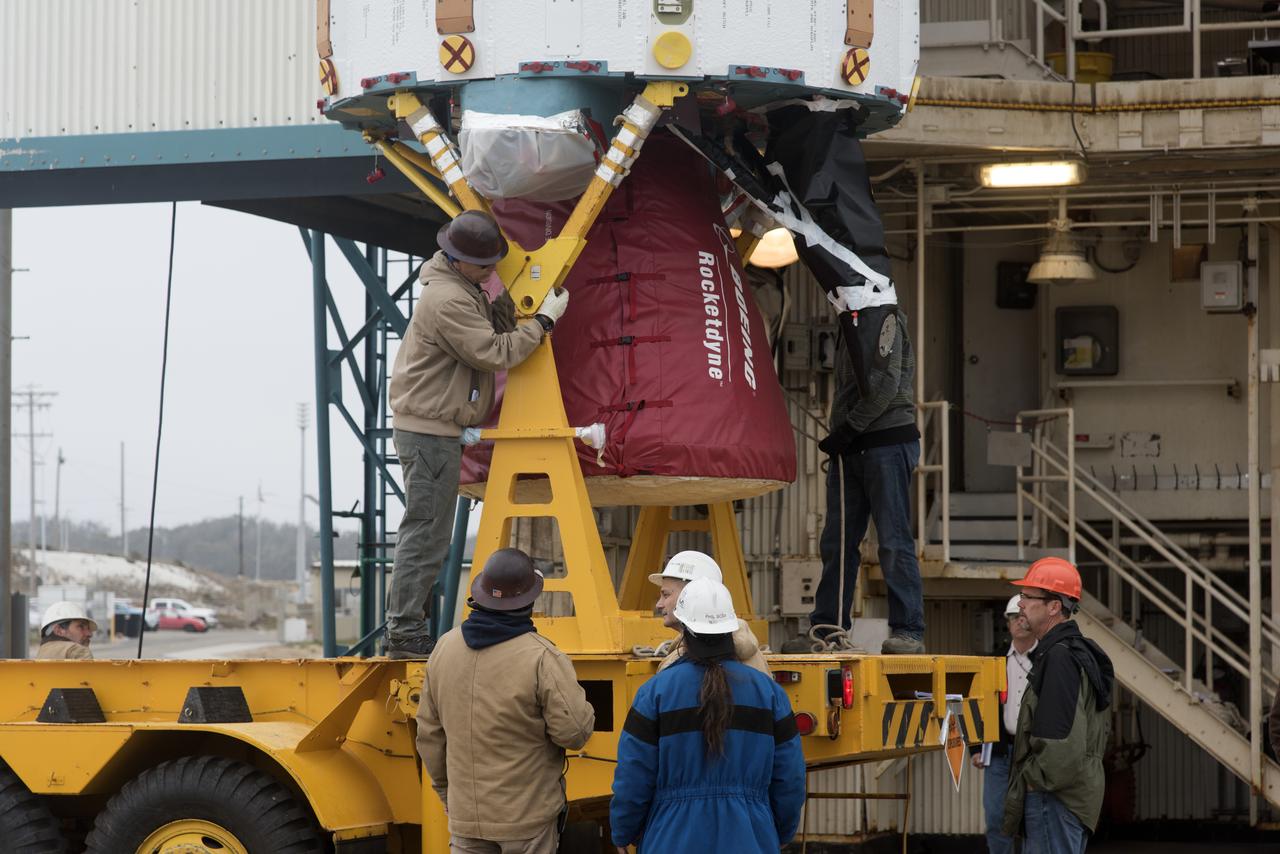

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted to vertical at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. ULA workers make adjustments so the booster can be lifted up from its stand and moved into the mobile service tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
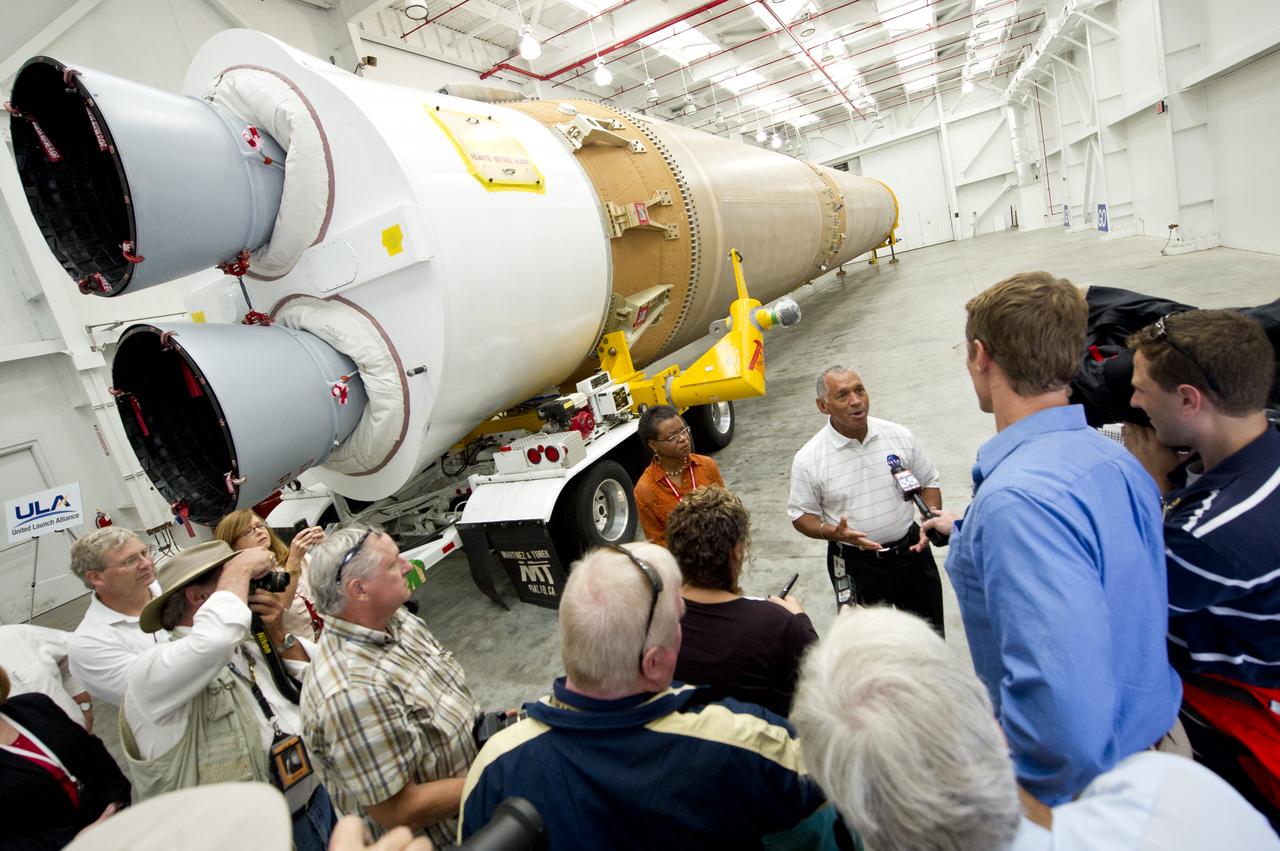

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, stands in front of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage booster while taking questions from the media, Wednesday, Sept. 7, 2011, at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The booster will help send NASA's Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover to Mars later this year. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

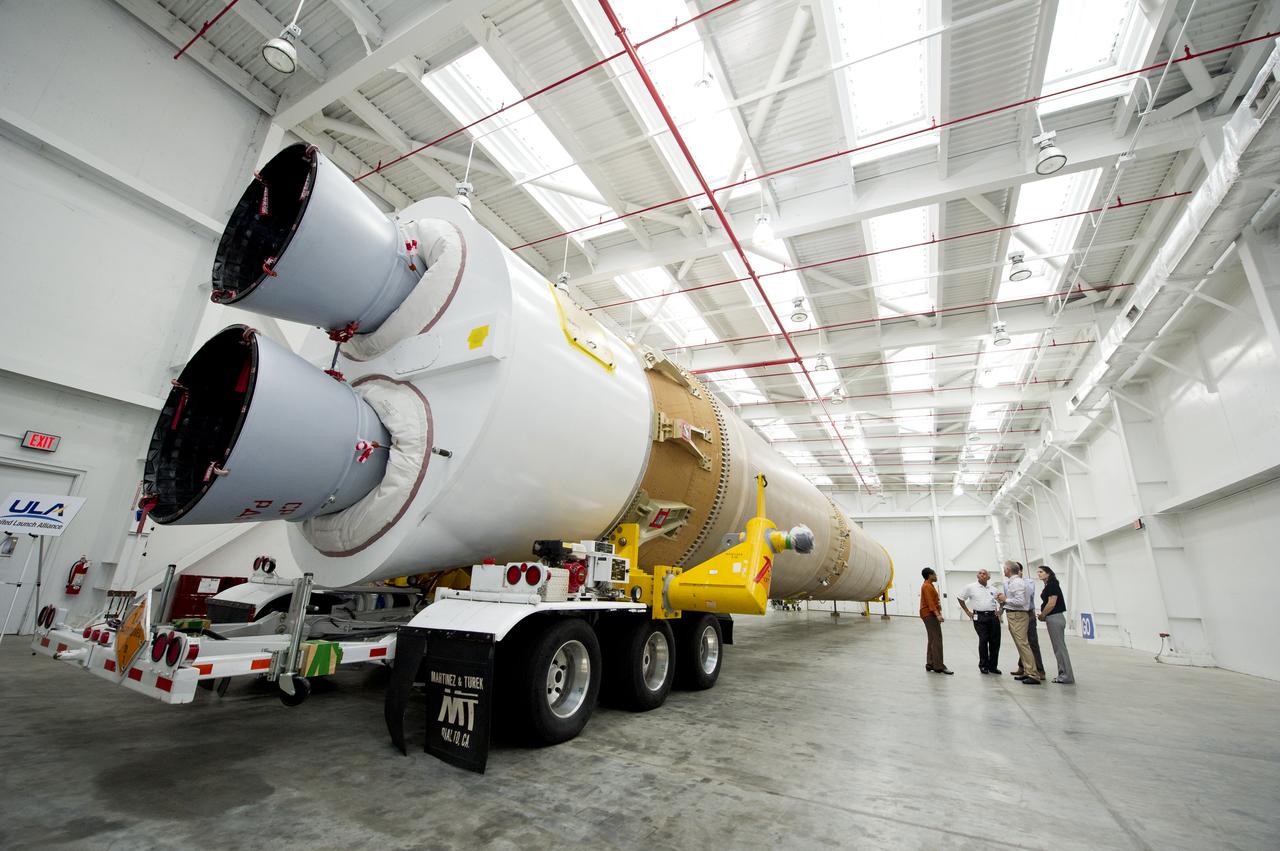
NASA Administrator Charles Bolden walks around the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage booster with United Launch Alliance Vice President of Mission operations Jim Sponnick, NASA Mission Manager for Launch Services Wanda Harding, NASA Senior Advisor Mike French, and White House Fellow Debra Kurshan, Wednesday, Sept. 7, 2011, at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The booster will help send NASA's Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover to Mars later this year. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, second from left, talks with United Launch Alliance Vice President of Mission operations Jim Sponnick, along with NASA Mission Manager for Launch Services Wanda Harding, left, White House Fellow Debra Kurshan, right, and NASA Senior Advisor Mike French, background, in front of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage booster, Wednesday, Sept. 7, 2011, at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The booster will help send NASA's Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover to Mars later this year. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
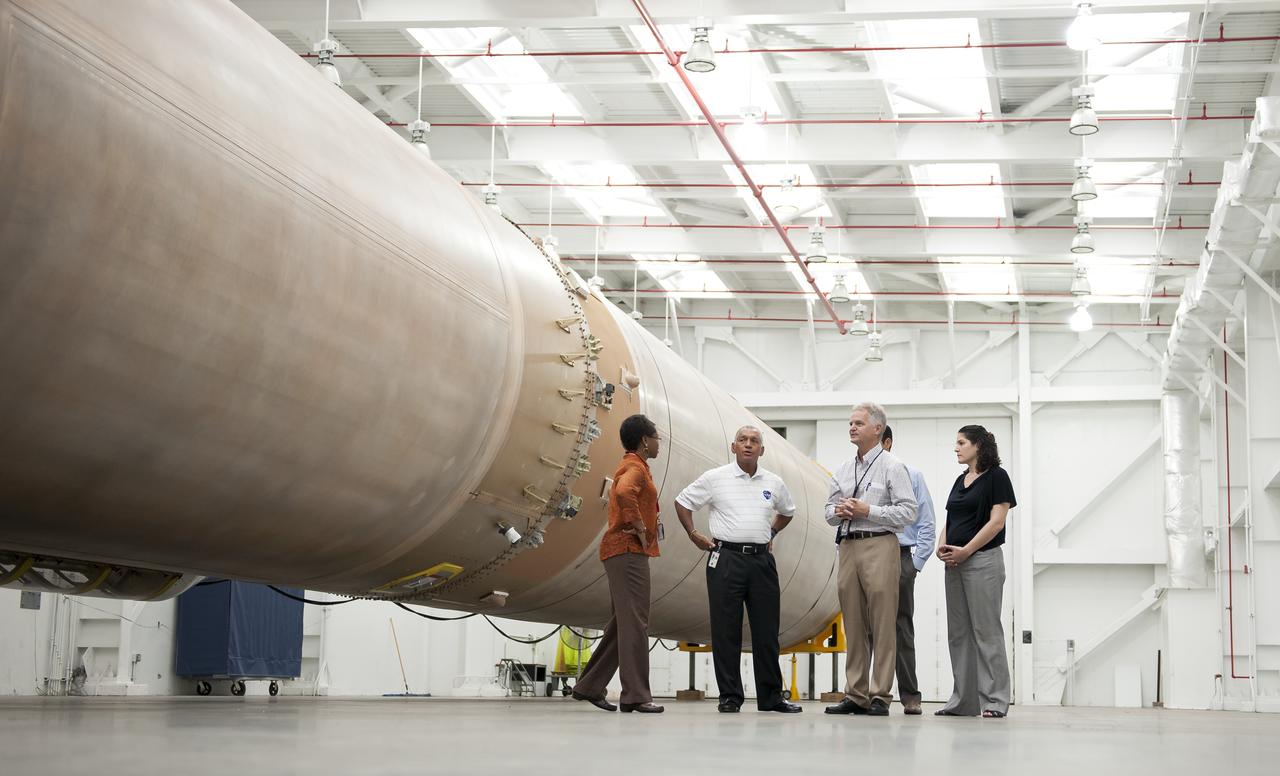

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, second from left, talks with United Launch Alliance Vice President of Mission operations Jim Sponnick, along with NASA Mission Manager for Launch Services Wanda Harding, left, White House Fellow Debra Kurshan, right, and NASA Senior Advisor Mike French, background, in front of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V first stage booster, Wednesday, Sept. 7, 2011, at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Cape Canaveral, Fla. The booster will help send NASA's Mars Science Laboratory Curiosity rover to Mars later this year. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
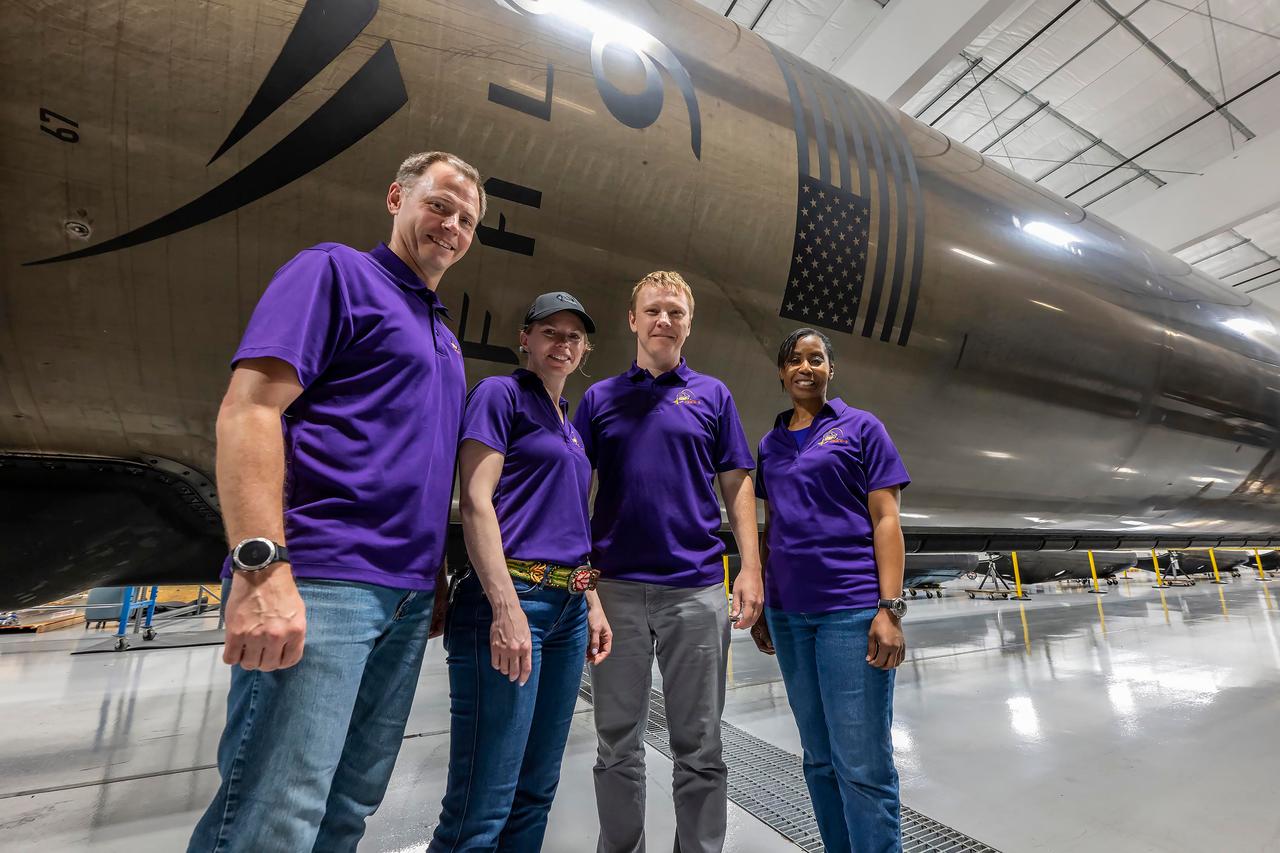

jsc2024e050140 (May 13, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 members stand in front of a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are, Pilot Nick Hague from NASA; Commander Zena Cardman from NASA; Mission Spedialist Alexsandr Gorbunov from Roscosmos; and Mission Specialist Stephanie Wilson from NASA. Credit: SpaceX
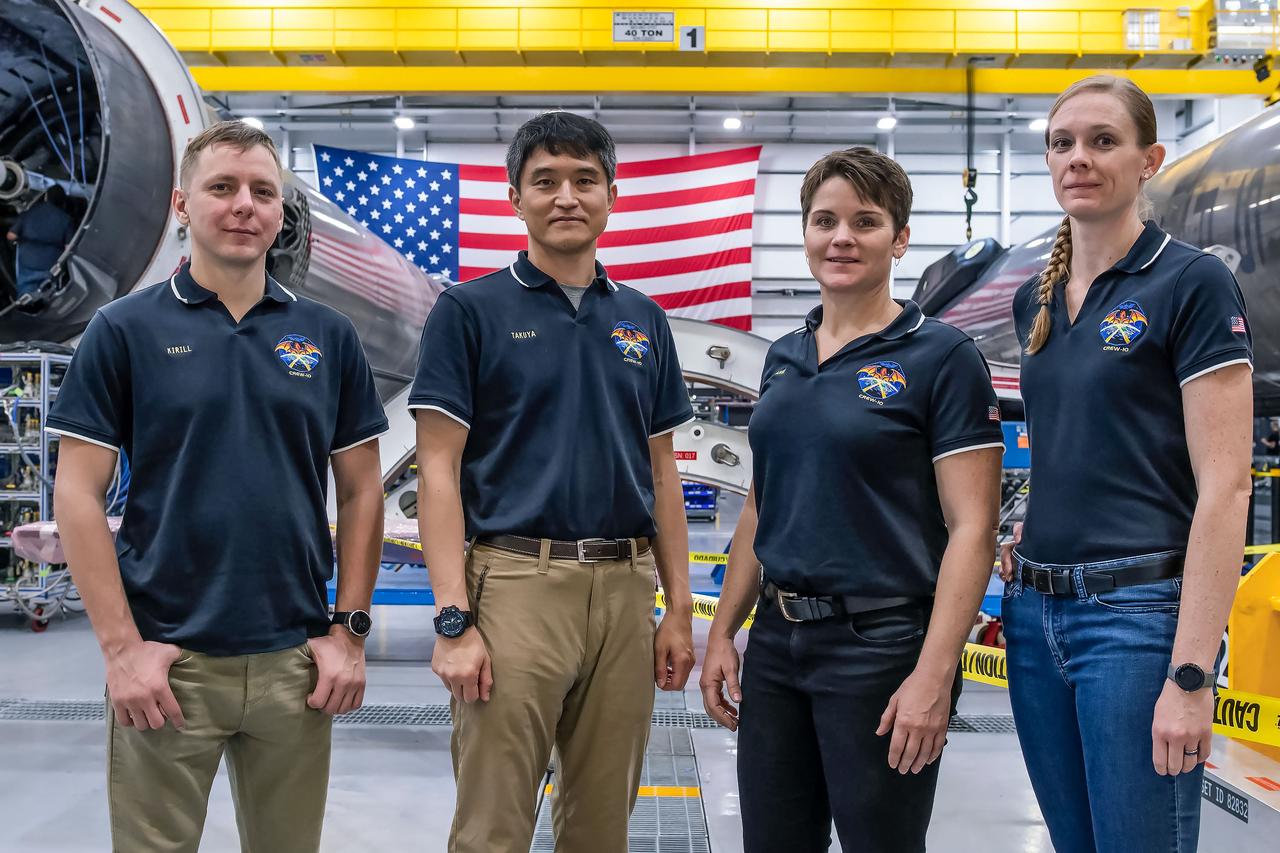

jsc2024e080751 (Nov. 18, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 members stand between Falcon 9 first-stage boosters at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Mission Specialist Kirill Peskov of Roscosmos, Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), along with NASA Astronauts Commander Anne McClain and Pilot Nichole Ayers. Credit: SpaceX
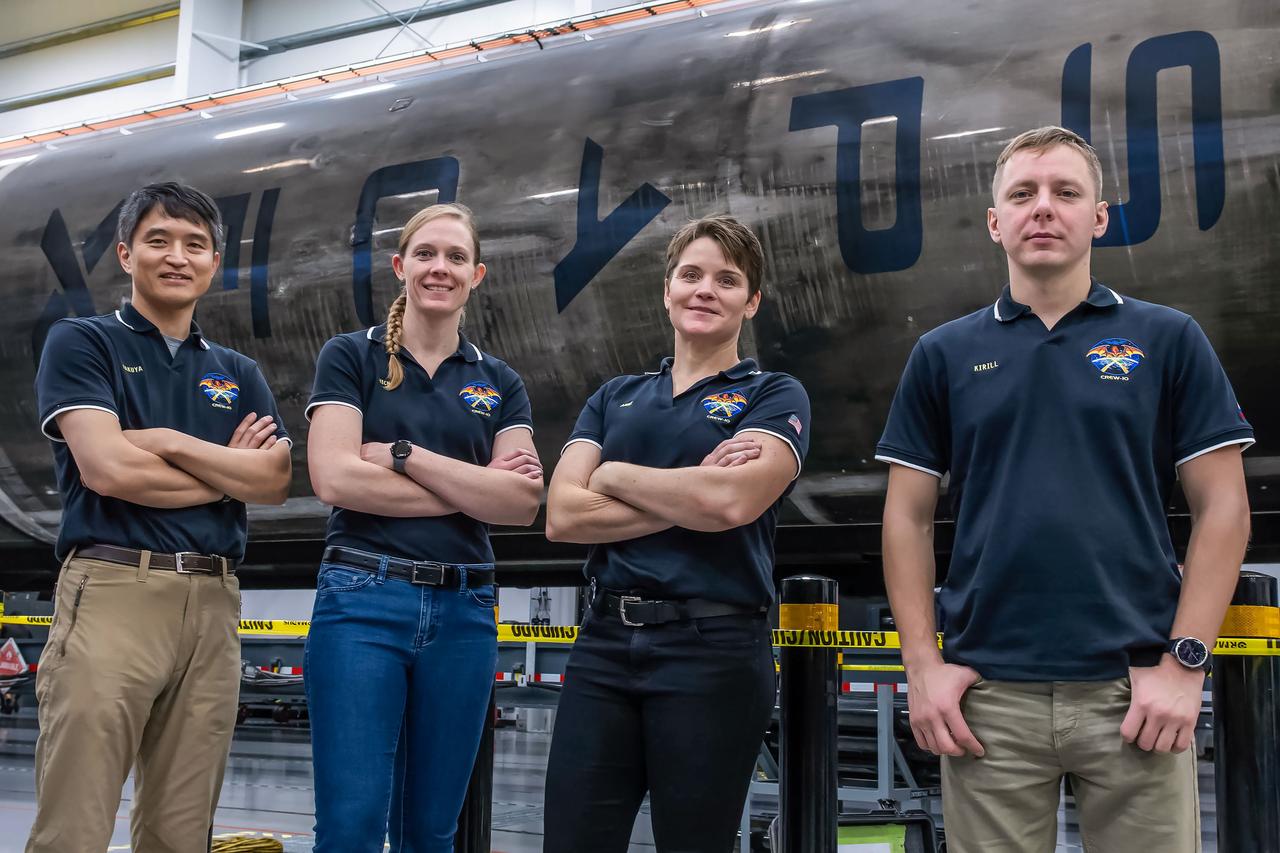

jsc2024e080752 (Nov. 18, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 members stand in front of a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), Commander Anne McClain of NASA, Pilot Nichole Ayers of NASA, and Mission Specialist Kirill Peskov of Roscosmos. Credit: SpaceX
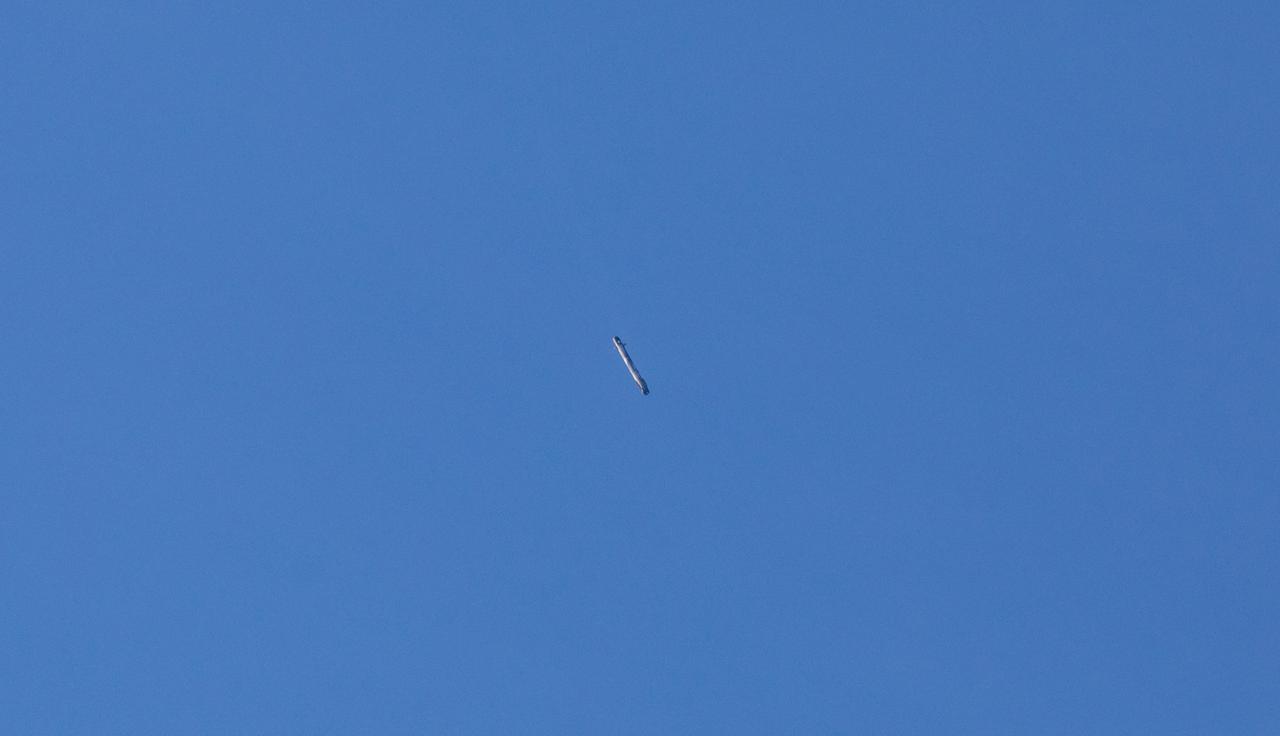

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down toward a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
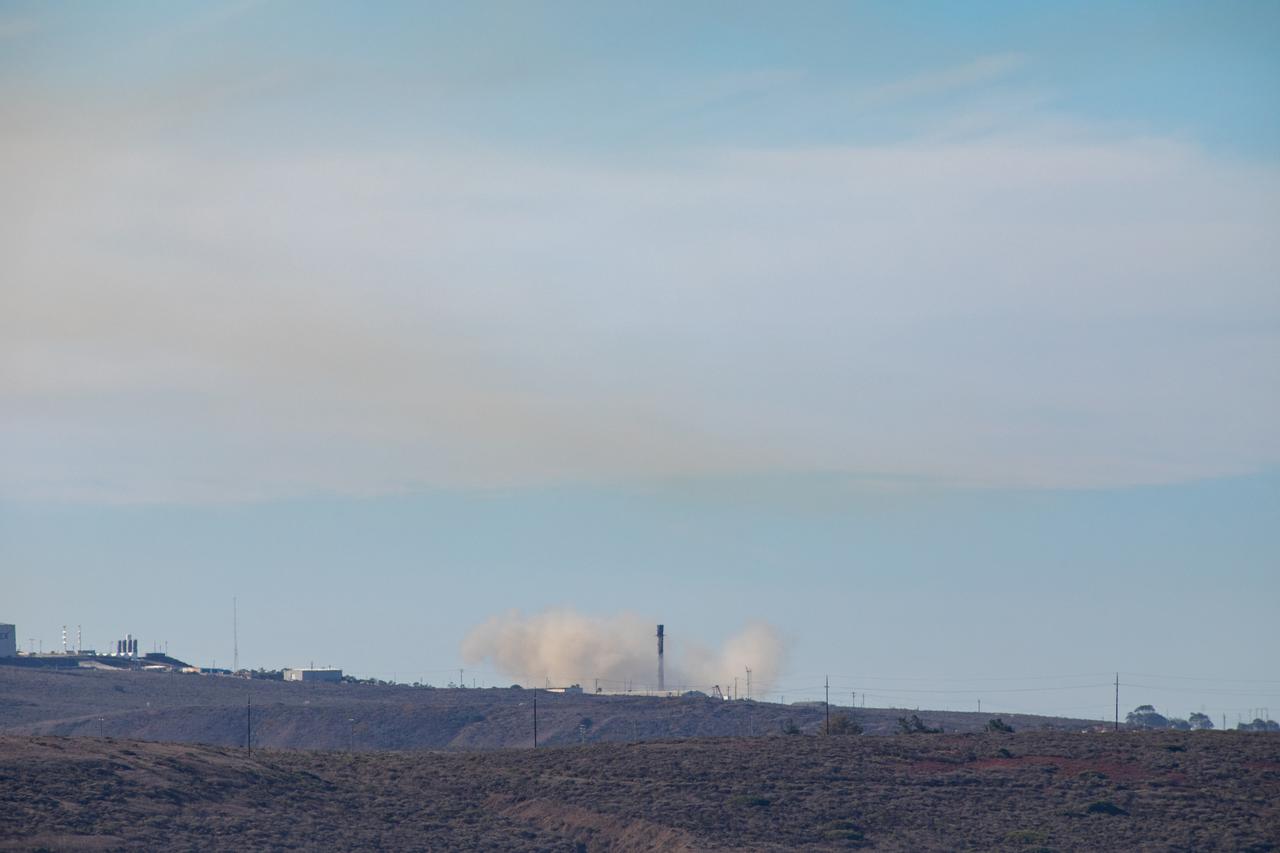

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
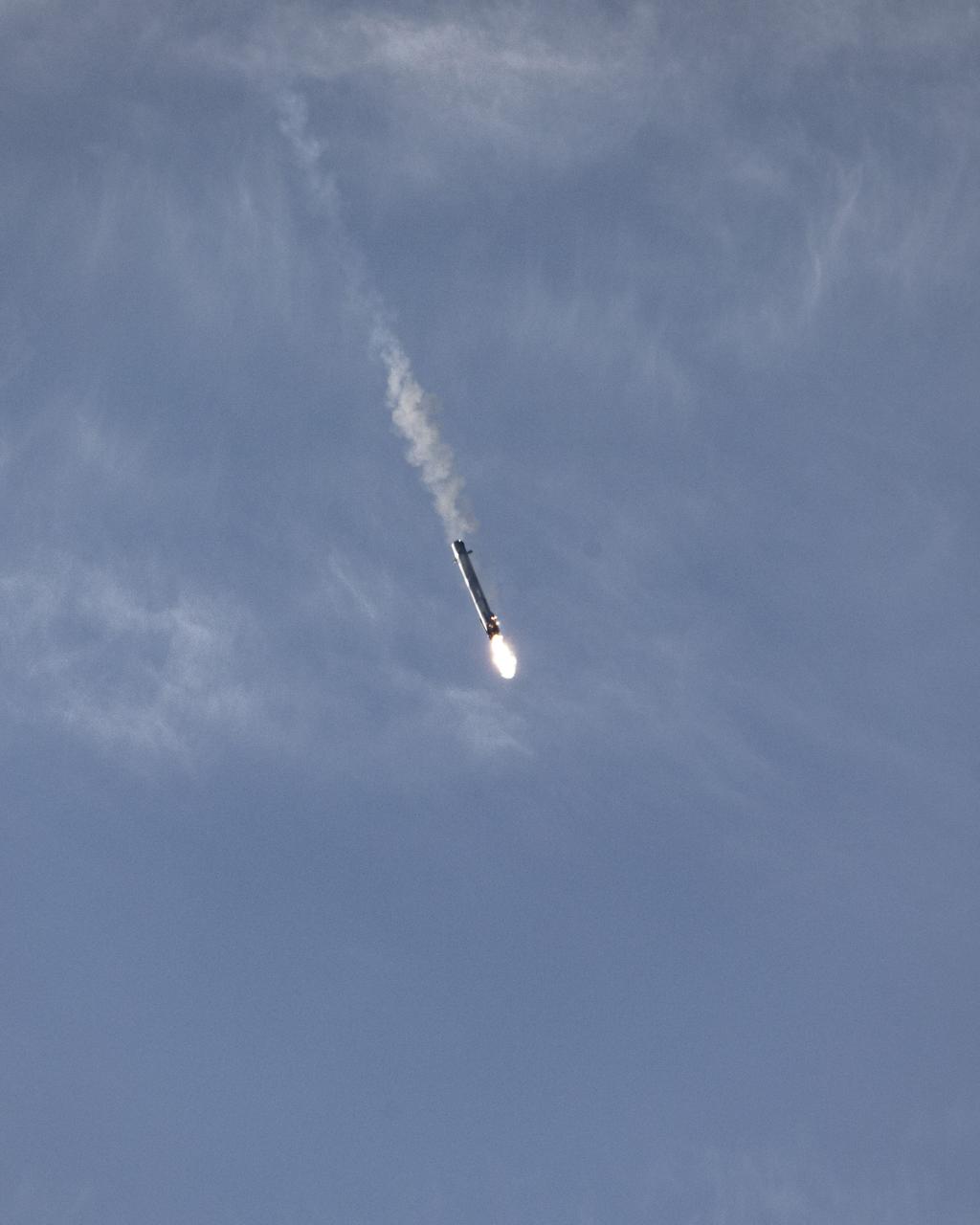

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Falcon 9 carrying the satellite lifted off from Vandenberg’s Space Launch Complex 4 on Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 a.m. PST (12:17 p.m. EST). The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
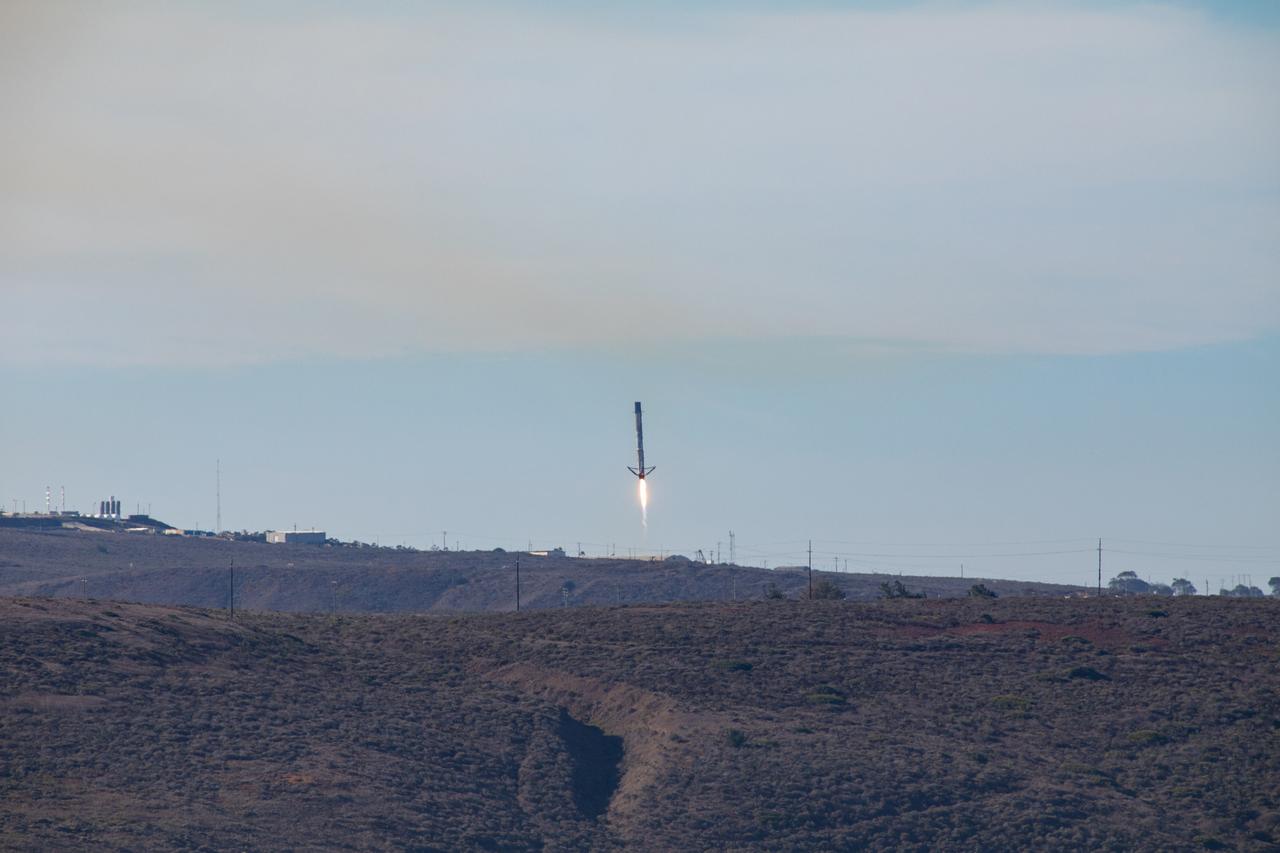

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down to a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
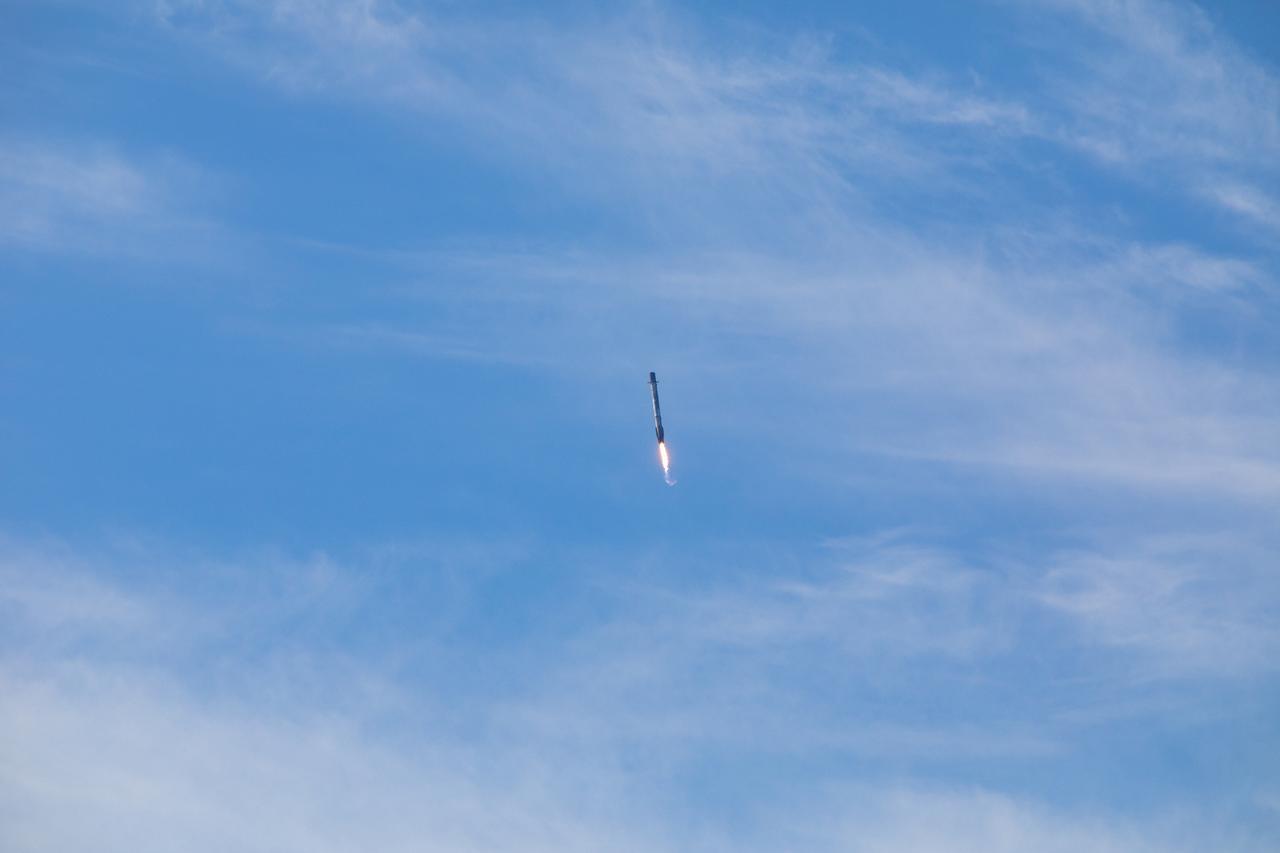

The first-stage booster of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket flies down toward a landing at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during the launch of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich mission. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS (Continuity of Service) mission consists of the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite, which will be followed by its twin, the Sentinel-6B satellite, in 2025. The Sentinel-6/Jason-CS mission is part of Copernicus, the European Union’s Earth observation program, managed by the European Commission. Continuing the legacy of the Jason series missions, Sentinel-6/Jason-CS will extend the records of sea level into their fourth decade, collecting accurate measurements of sea surface height for more than 90% of the world’s seas, and providing crucial information for operational oceanography, marine meteorology, and climate studies. Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich launched Nov. 21, 2020, at 9:17 PST (12:17 EST). NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center was responsible for launch management.
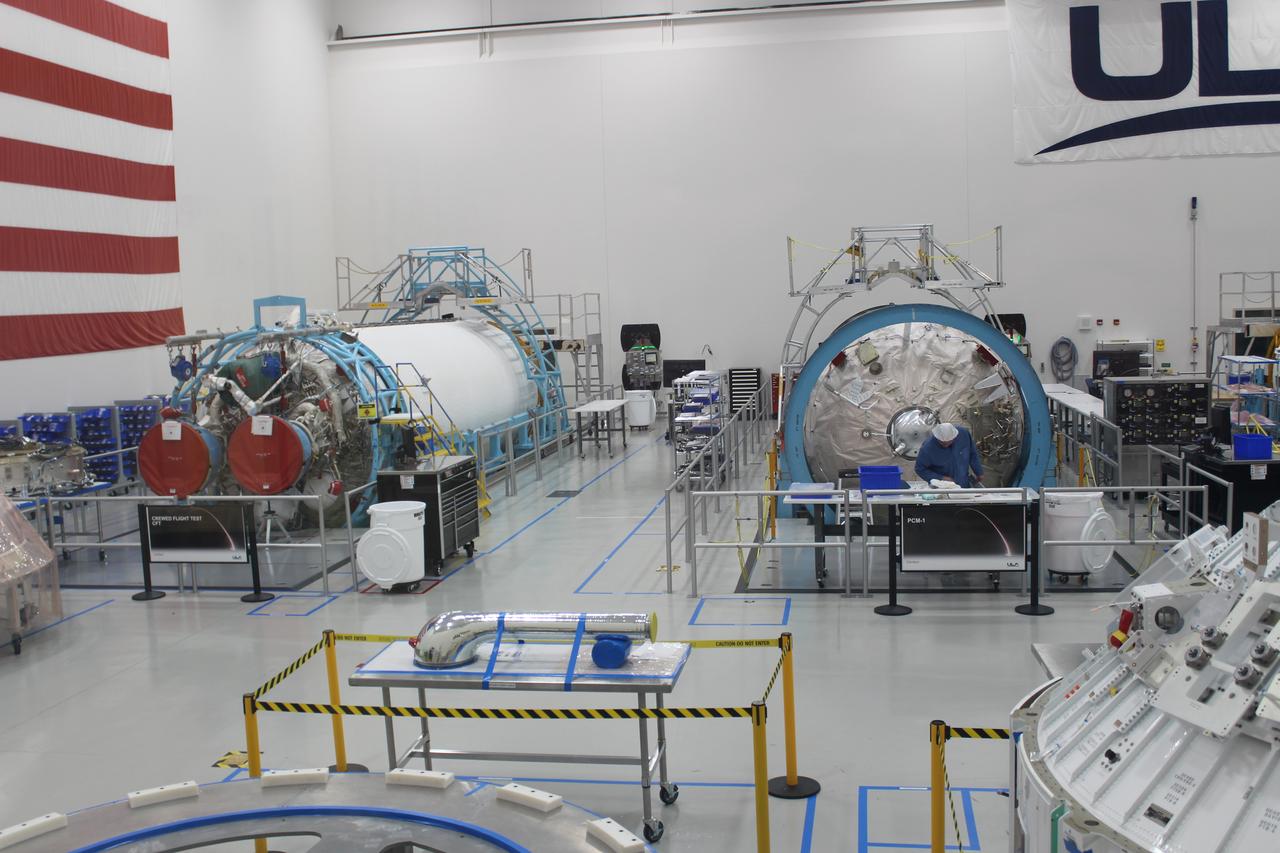

Two United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V dual engine Centaur upper stages are in production in ULA's factory in Decatur, Alabama on March 1, 2019. One is for Boeing’s Crew Flight Test on the CST-100 Starliner, and the other will be used for the first crew rotation mission on the Starliner. One of the Centaur upper stages will be assembled to the first stage booster. They will be shipped aboard the company’s Mariner cargo ship to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Starliner and the Atlas V rockets that will launch the spacecraft, are key to restoring the nation’s capability to send astronauts to the space station from U.S. soil with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. NASA astronauts Mike Fincke and Nicole Mann, and Boeing astronaut Chris Ferguson will launch to the space station aboard the Starliner for the Crew Flight Test.

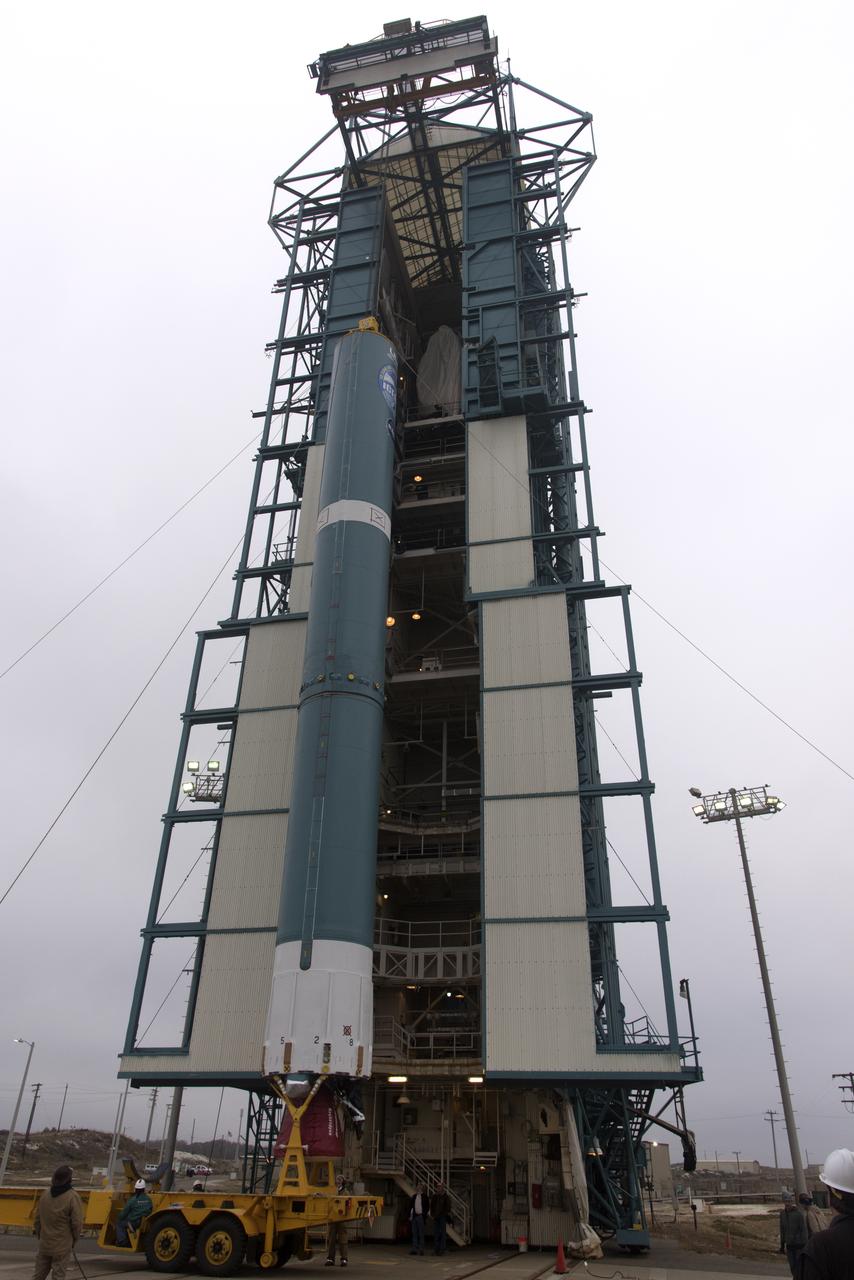
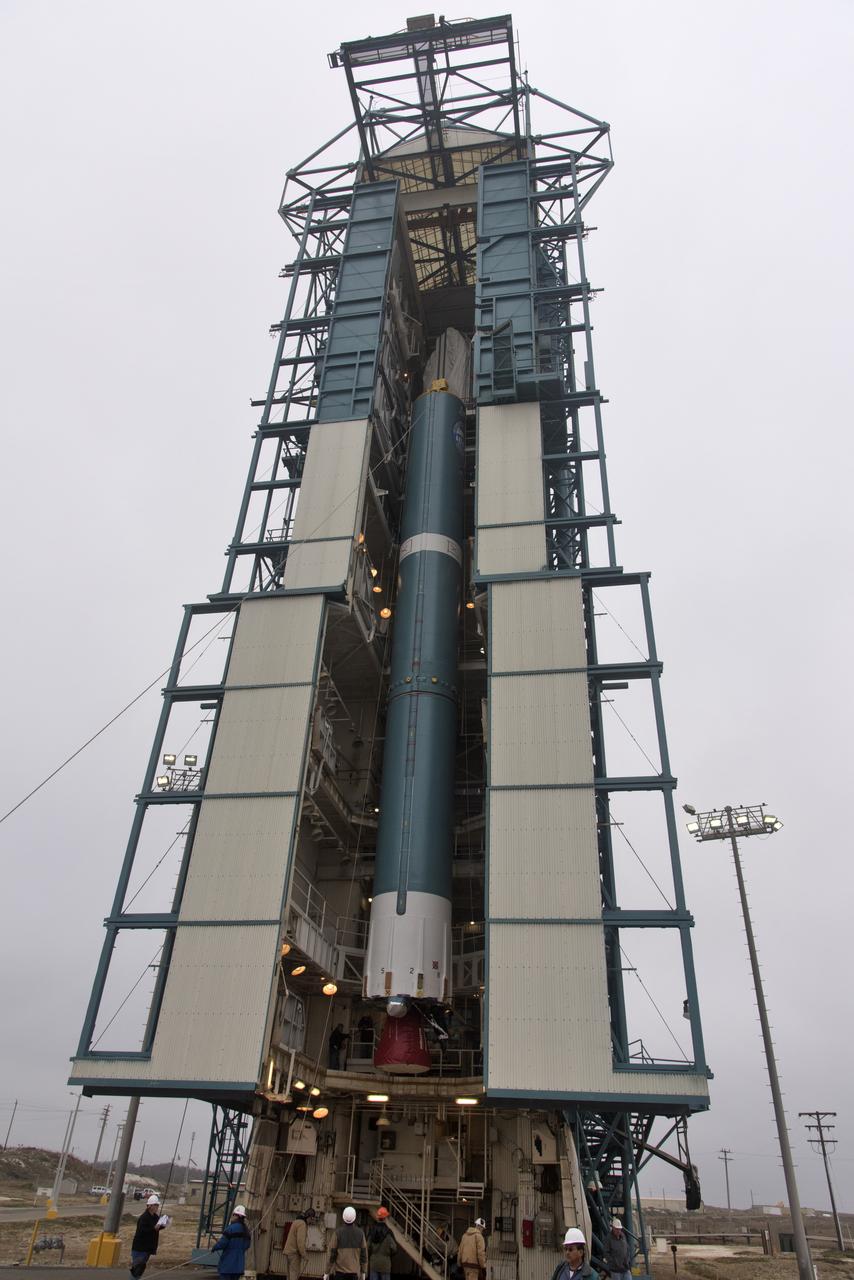
Protective doors have been closed on the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on June 8, 2018. The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up and secured inside the tower. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up from its stand and moved into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II first stage is lifted up and into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 8, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

United Launch Alliance workers prepare the first stage of the Delta II second stage to be lifted up in the Vertical Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage, of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
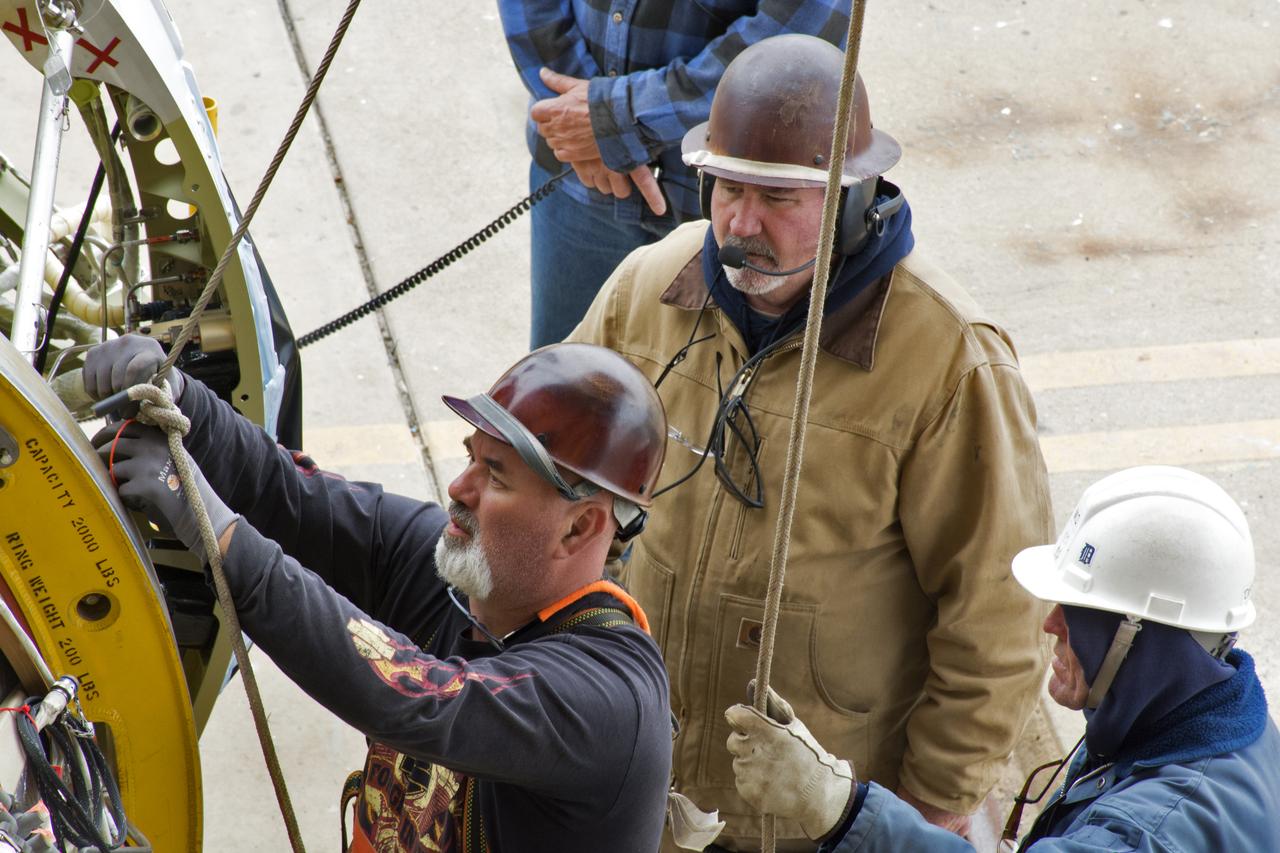

United Launch Alliance workers prepare the first stage of the Delta II second stage to be lifted up in the Vertical Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage, of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
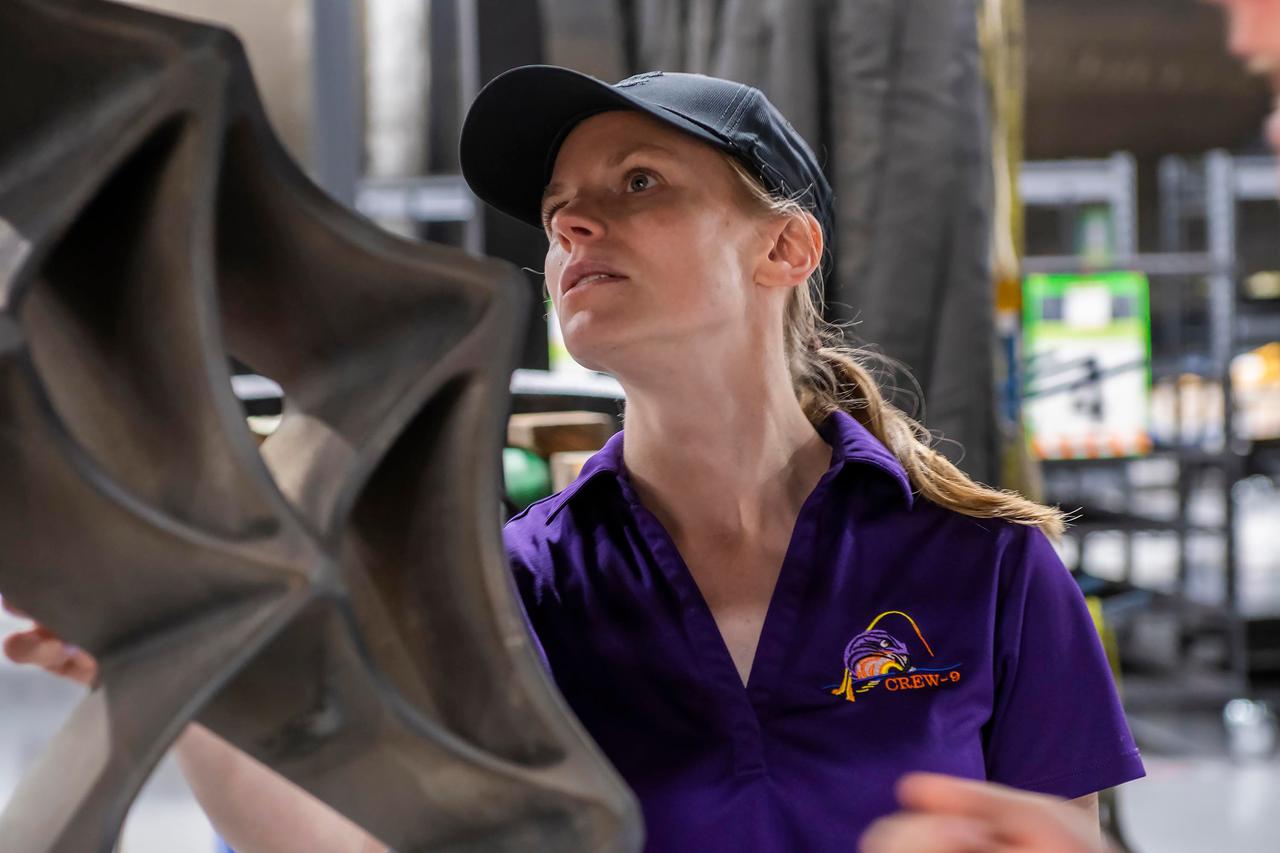

jsc2024e050142 (May 13, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 Commander Zena Cardman checks out a grid fin on a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Credit: SpaceX
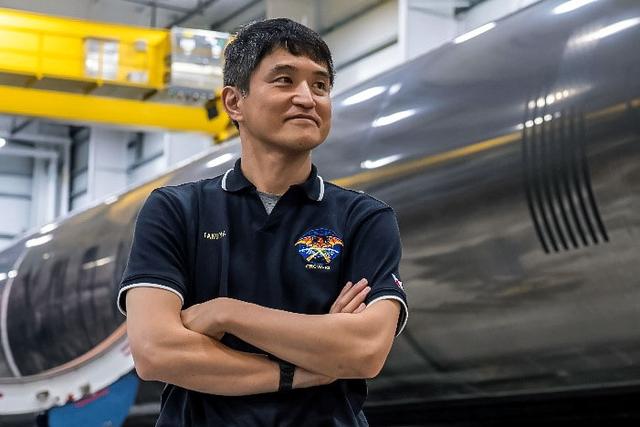

jsc2024e080749 (Dec. 13, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Mission Specialist Takuya Onishi of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), stands in front of a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Credit: SpaceX
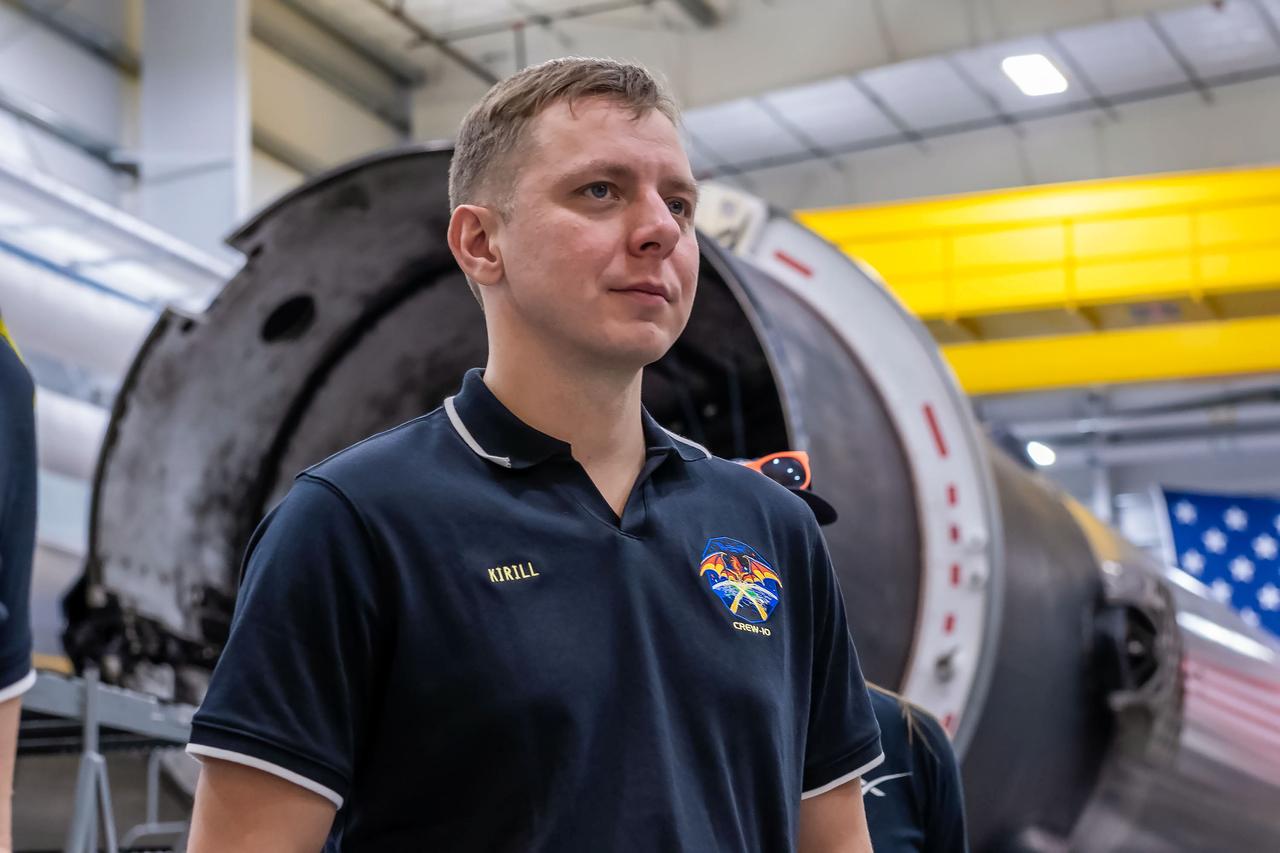

jsc2024e080750 (Nov. 18, 2024) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-10 Mission Specialist Kirill Peskov of Roscosmos stands in front of a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Credit: SpaceX
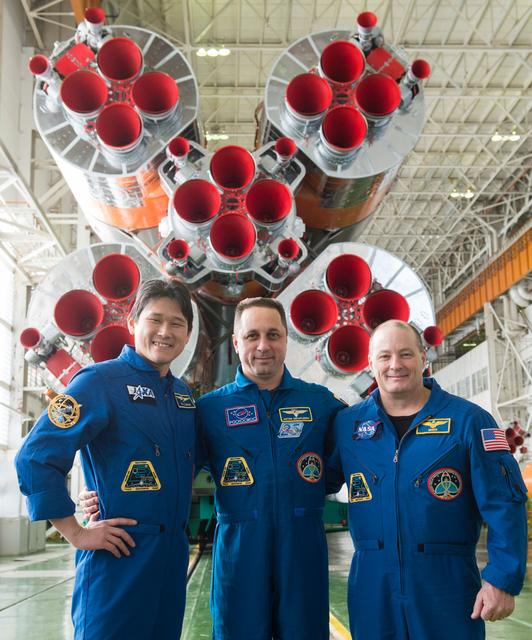

jsc2017e138119 - In the Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, the Expedition 54-55 prime crewmembers pose for pictures Dec. 13 in front of the first stage of the Soyuz booster rocket. From left to right are Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Scott Tingle of NASA and Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), who will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin/Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.
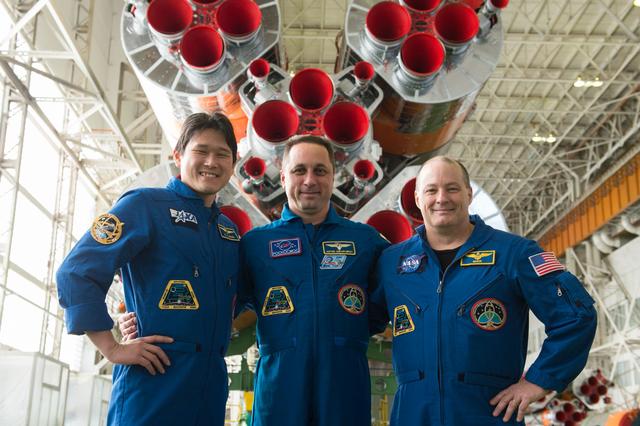

jsc2017e138118 - In the Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, the Expedition 54-55 prime crewmembers pose for pictures Dec. 13 in front of the first stage of the Soyuz booster rocket. From left to right are Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Scott Tingle of NASA and Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), who will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin/Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.

The second stage of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility, at left, at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket, which is being moved out of the Mobile Service Tower, at right. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.

The United Launch Alliance Delta II second stage is lifted high up at the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 12, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be attached to the top of the booster, or first stage of the rocket. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
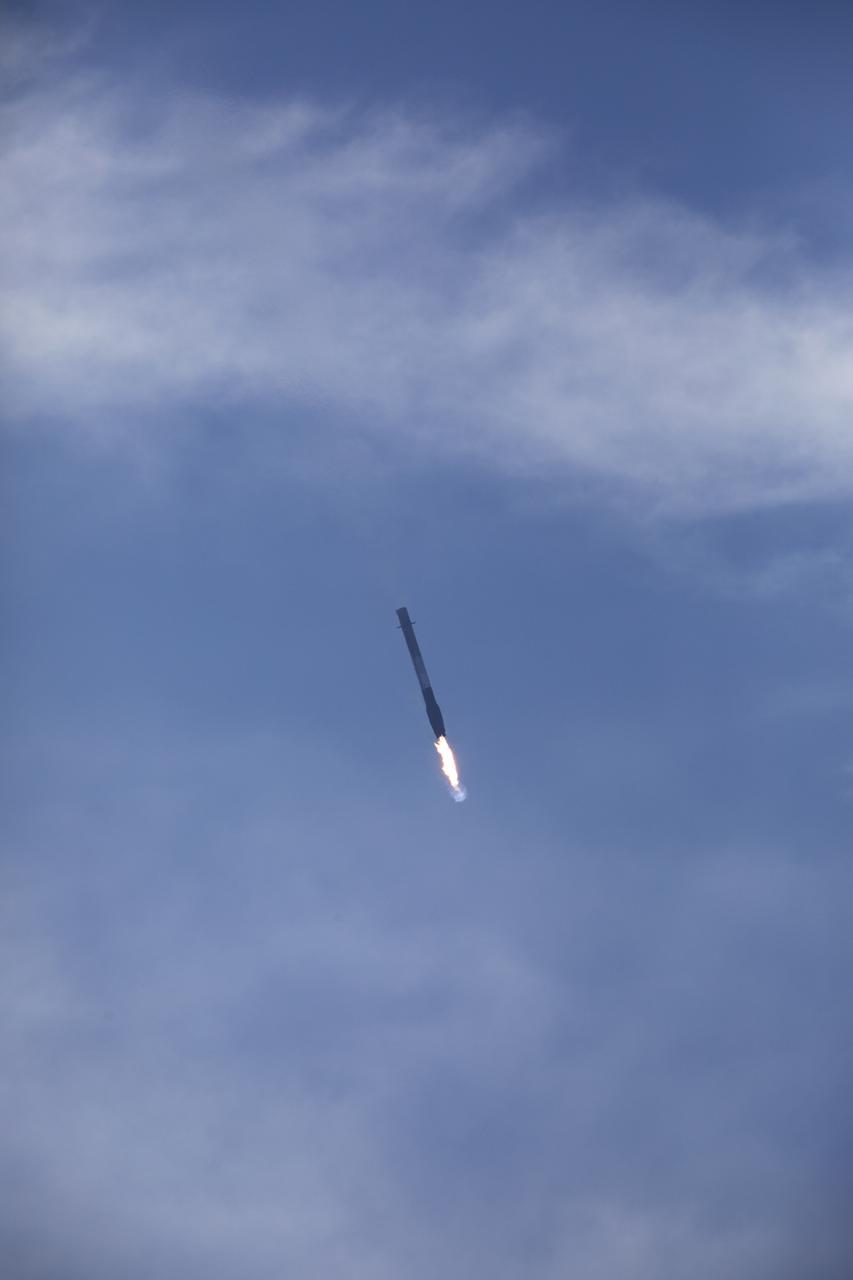

After boosting a Dragon spacecraft on its way to the International Space Staton for the SpaceX CRS-13 mission, the Falcon 9 first stage returns to Landin Zone 1 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket lifted off moments earlier from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape on the company's 13th commercial resupply services mission to the space station. Dragon will deliver additional supplies and research experiments that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
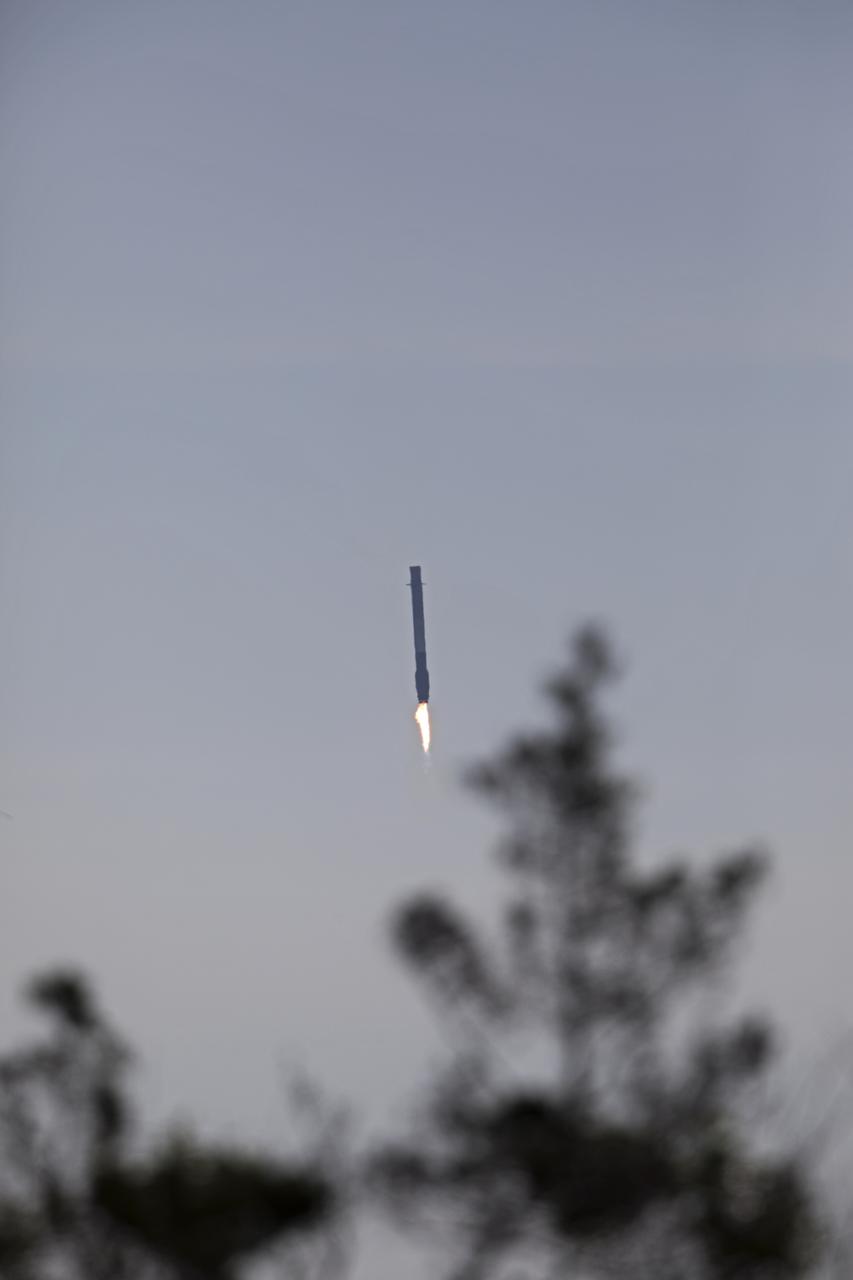

After boosting a Dragon spacecraft on its way to the International Space Staton for the SpaceX CRS-13 mission, the Falcon 9 first stage returns to Landin Zone 1 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket lifted off moments earlier from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape on the company's 13th commercial resupply services mission to the space station. Dragon will deliver additional supplies and research experiments that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.
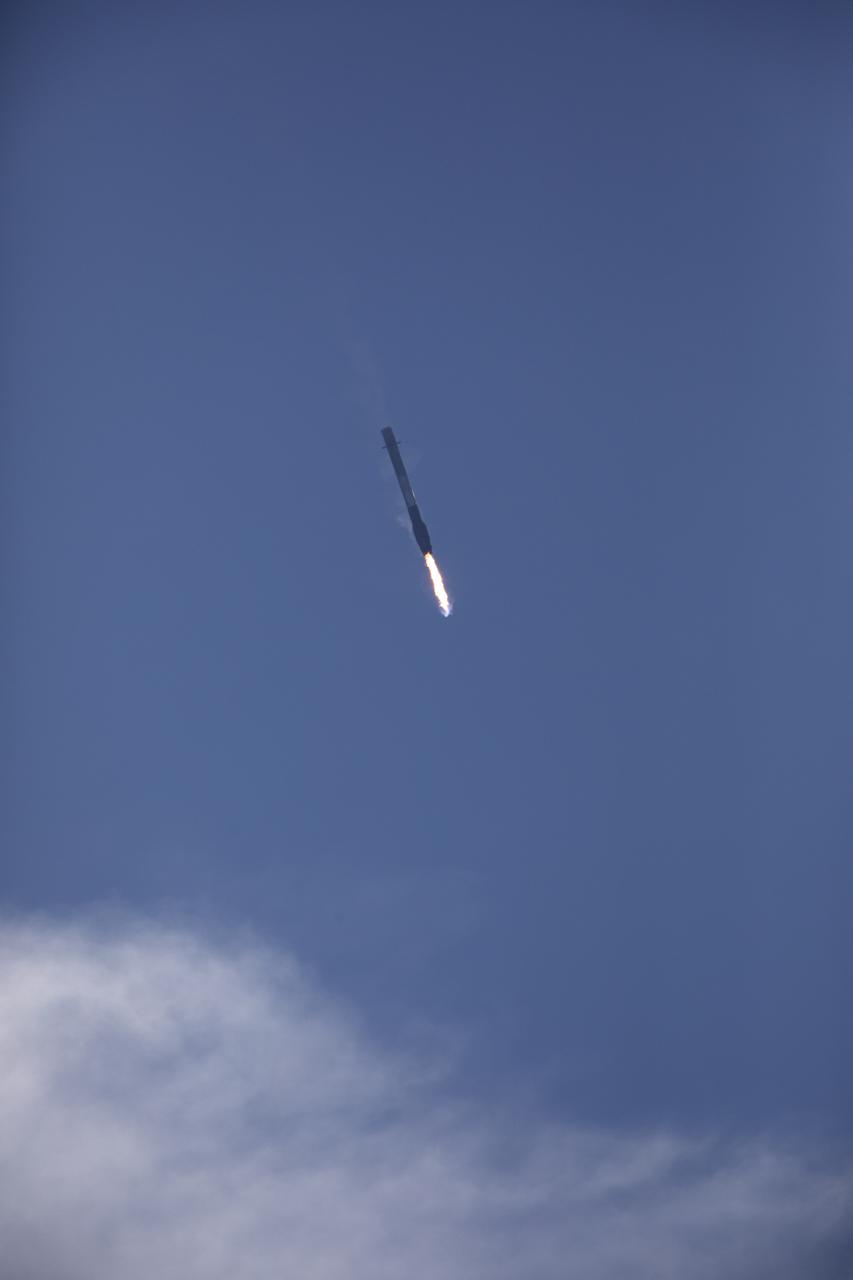

After boosting a Dragon spacecraft on its way to the International Space Staton for the SpaceX CRS-13 mission, the Falcon 9 first stage returns to Landin Zone 1 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket lifted off moments earlier from Space Launch Complex 40 at the Cape on the company's 13th commercial resupply services mission to the space station. Dragon will deliver additional supplies and research experiments that improve life on Earth and drive progress toward future space exploration.

The first stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lands at Vandenberg Space Force Base's landing zone 4 following the successful launch of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite on Dec. 16, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. The satellite will help researchers understand how much water flows in and out of Earth’s freshwater bodies and will provide insight into the ocean’s role in climate change. The instruments onboard will measure the height of water in lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and the ocean, and will observe ocean features in higher definition than ever before. NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, is managing the launch service.
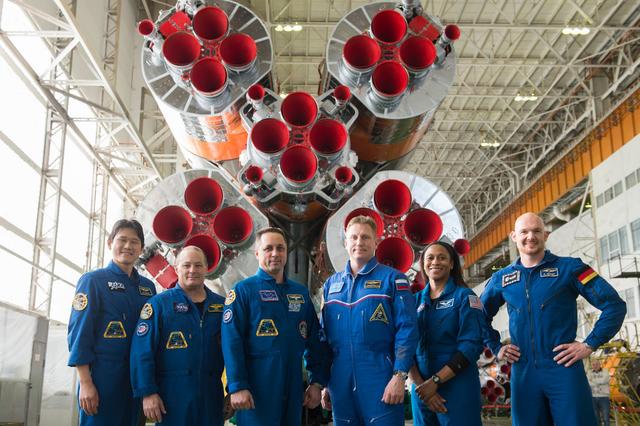

jsc2017e138124 - In the Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, the Expedition 54-55 prime and backup crewmembers pose for pictures Dec. 13 in front of the first stage of the Soyuz booster rocket. From left to right are prime crewmembers Norishige Kanai of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), Scott Tingle of NASA and Anton Shkaplerov of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos), and backup crewmembers Sergey Prokopyev of Roscosmos, Jeanette Epps of NASA and Alexander Gerst of the European Space Agency. Kanai, Tingle and Shkaplerov will launch Dec. 17 on the Soyuz MS-07 spacecraft for a five month mission on the International Space Station...Andrey Shelepin/Gagarin Cosmonaut Training Center.
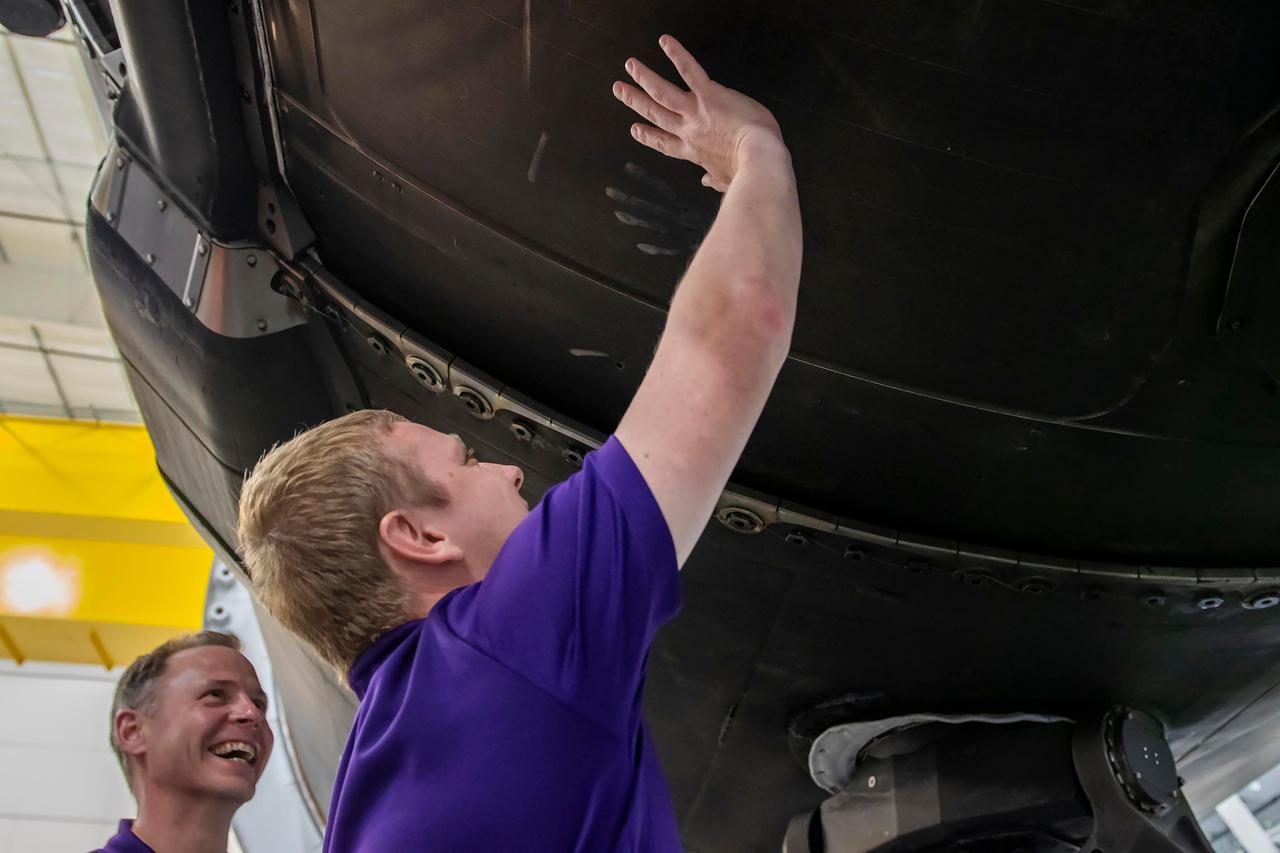

jsc2024e050143 (May 13, 2024) --- From left, SpaceX Crew-9 Pilot Nick Hague from NASA and Mission Specialist Aleksandr Gorbunov check out a Falcon 9 first-stage booster at SpaceX’s HangarX facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Credit: SpaceX

The United Launch Alliance Delta II booster, or first stage, with the interstage attached on top is moved out of the Vertical Integration Facility (VIF) at Space Launch Complex 2 on June 21, 2018, at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The second stage will be lifted up at the VIF. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) will launch on the final Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry a single instrument, the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System. ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, is changing in a warming climate.
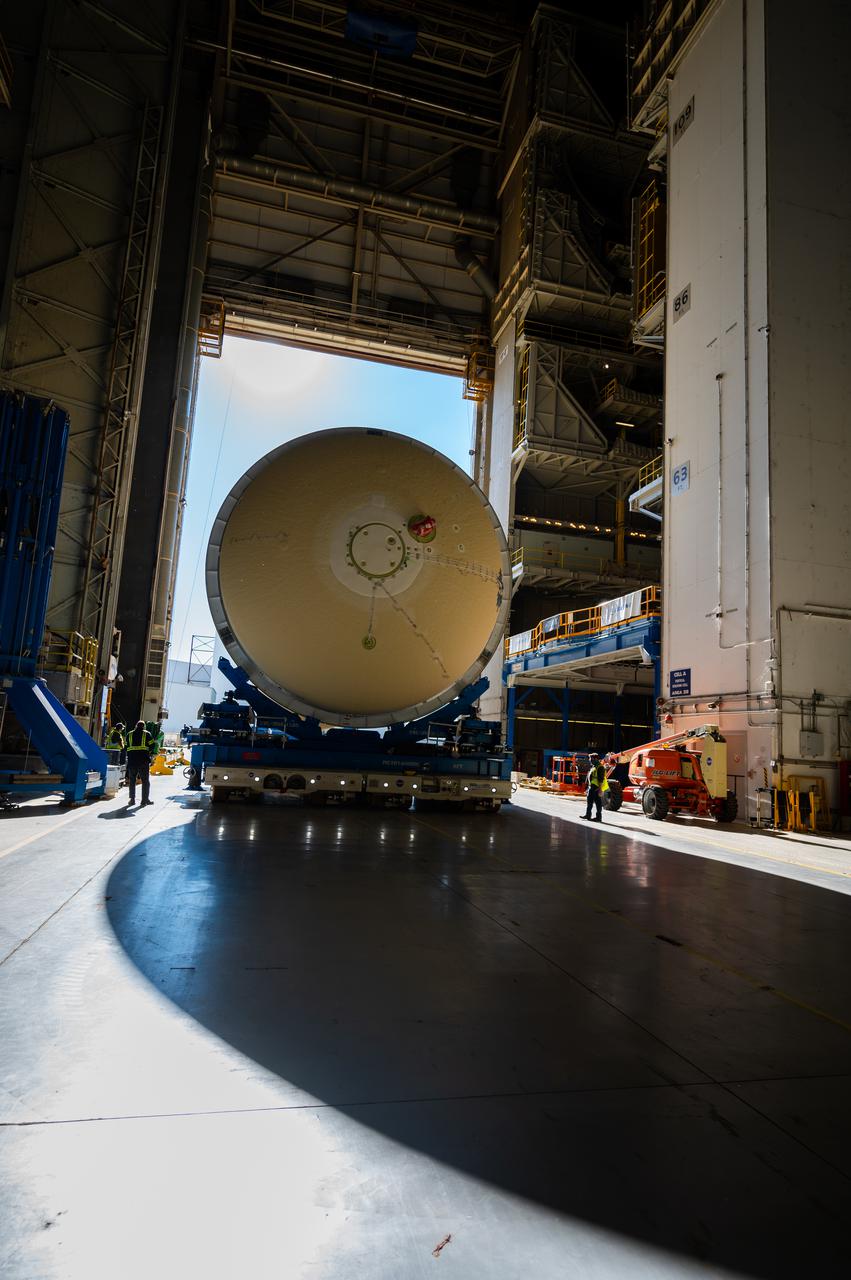

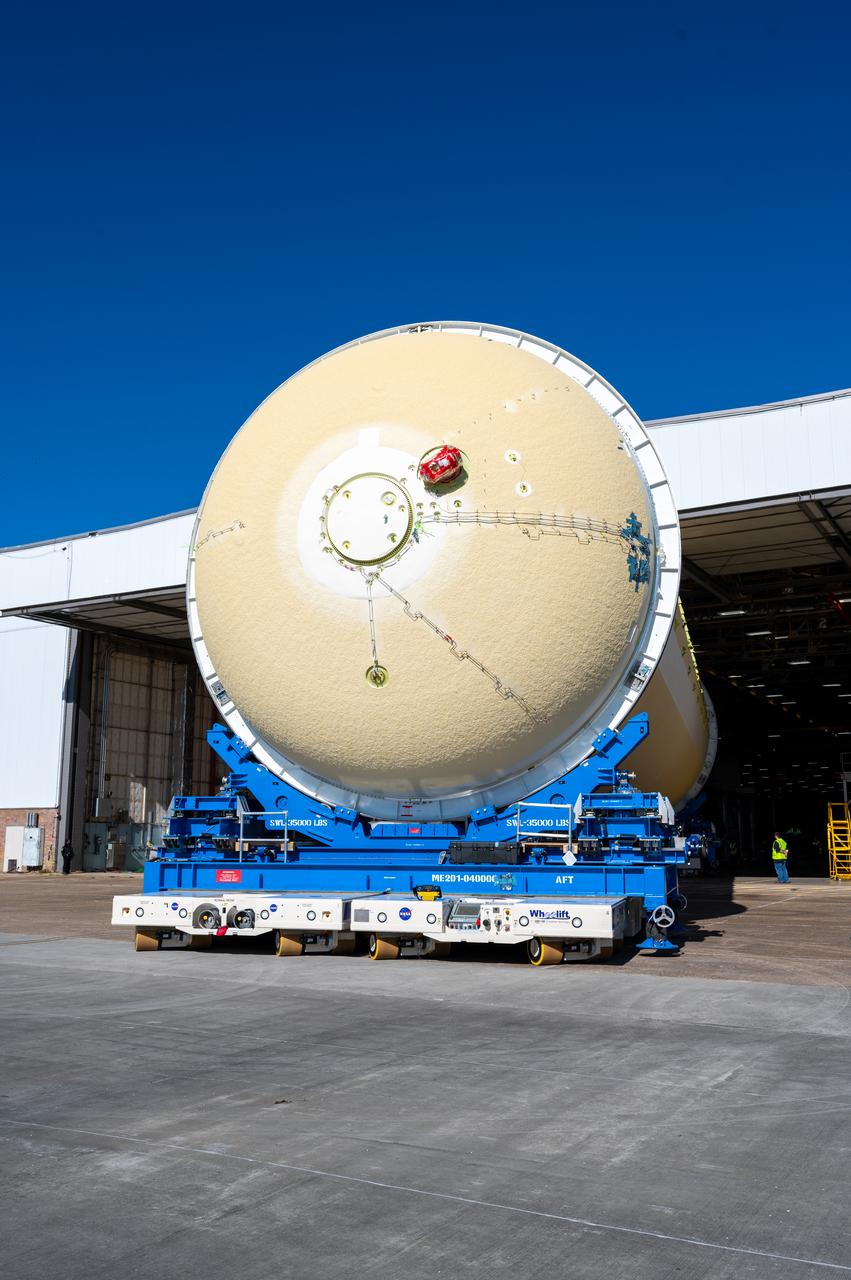
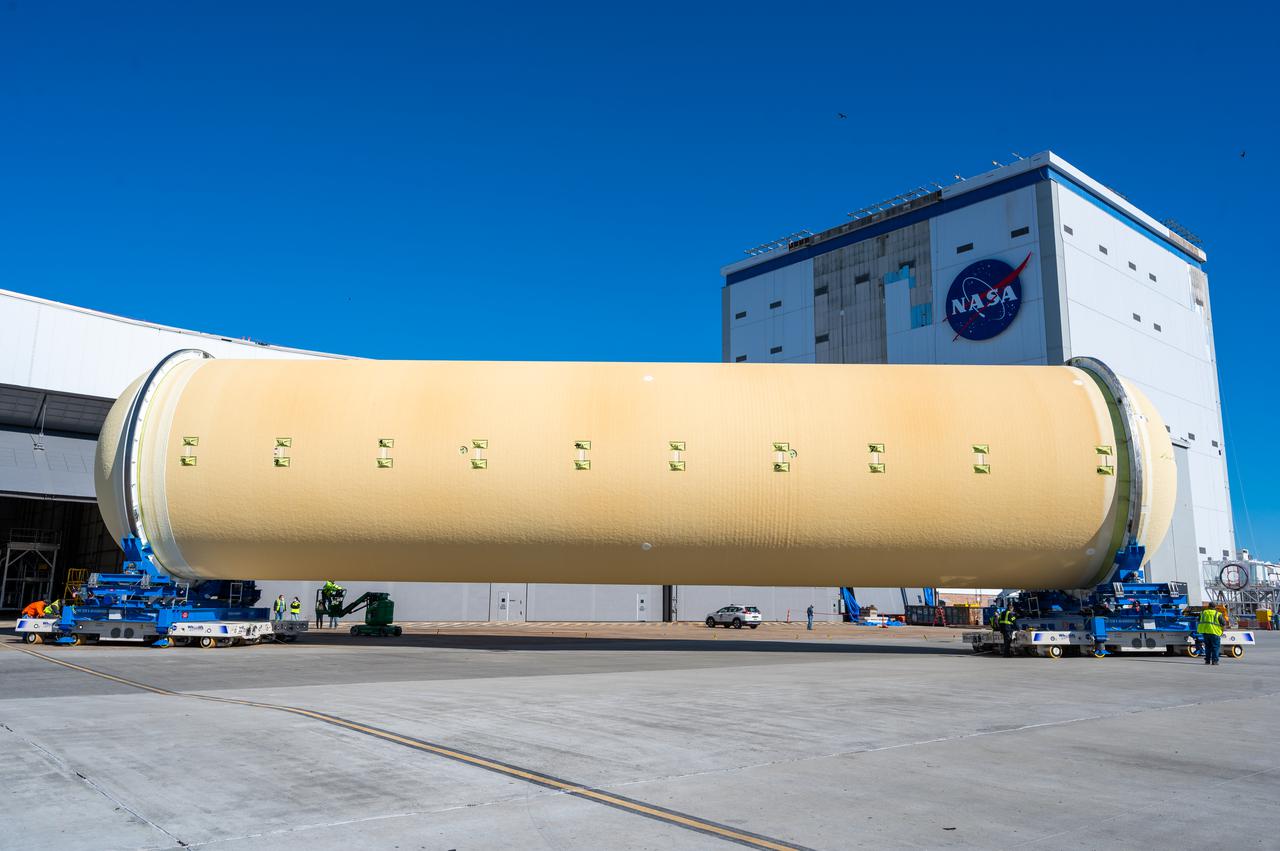
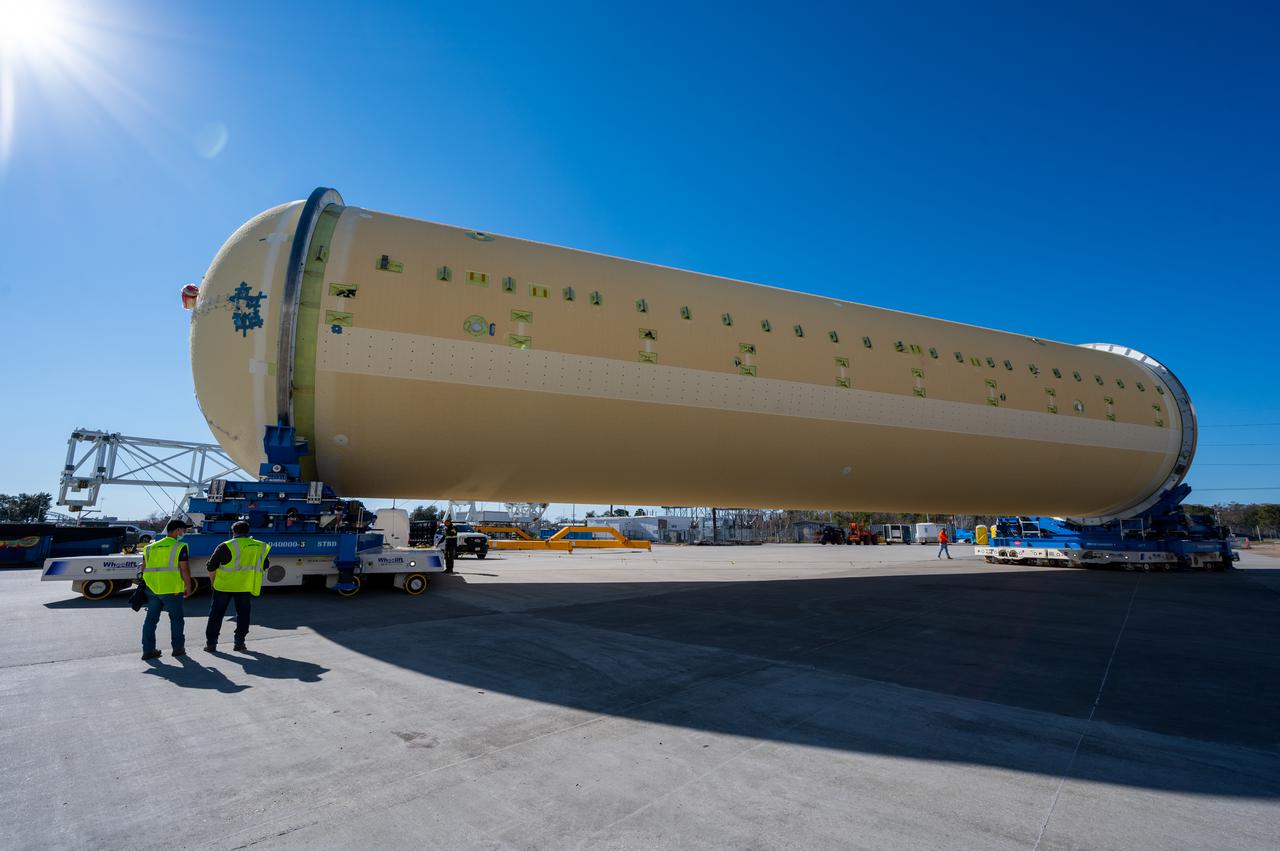
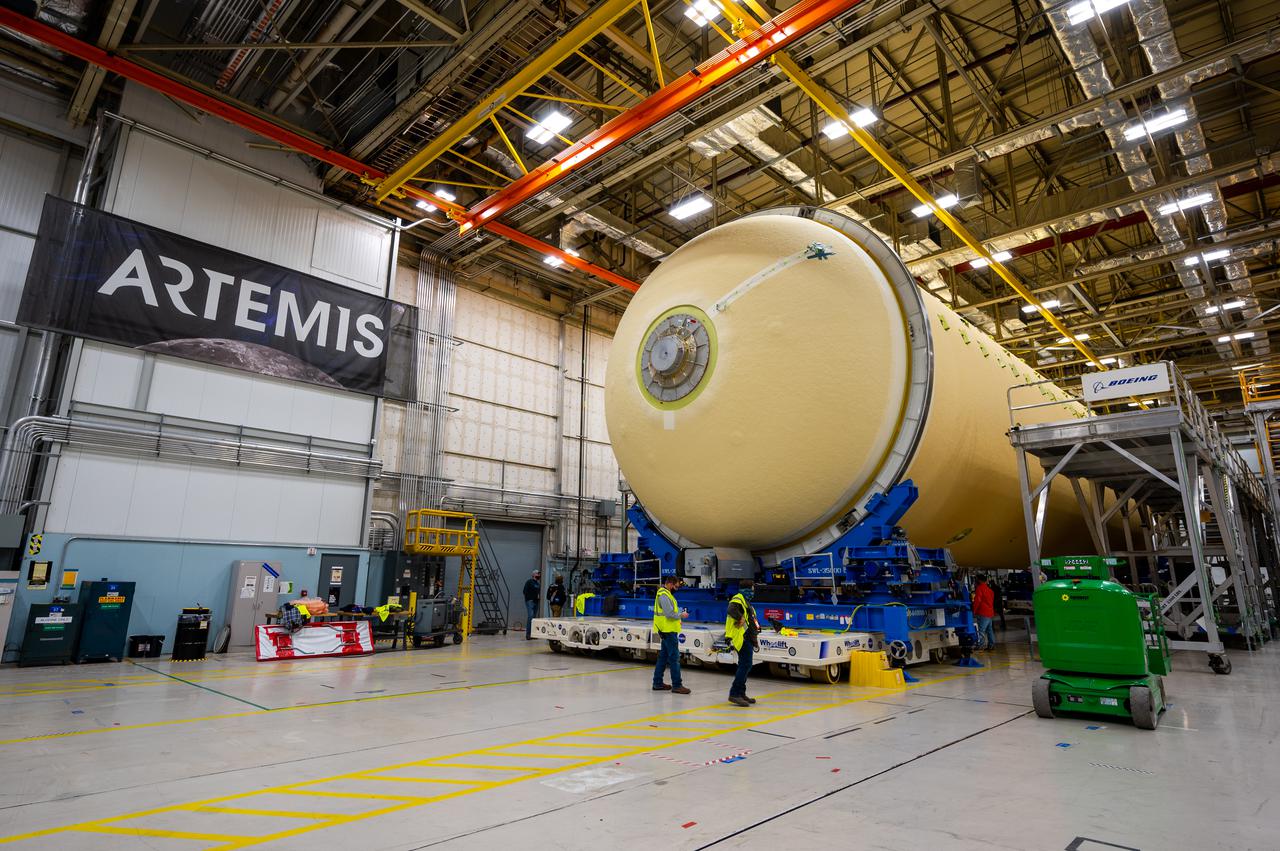
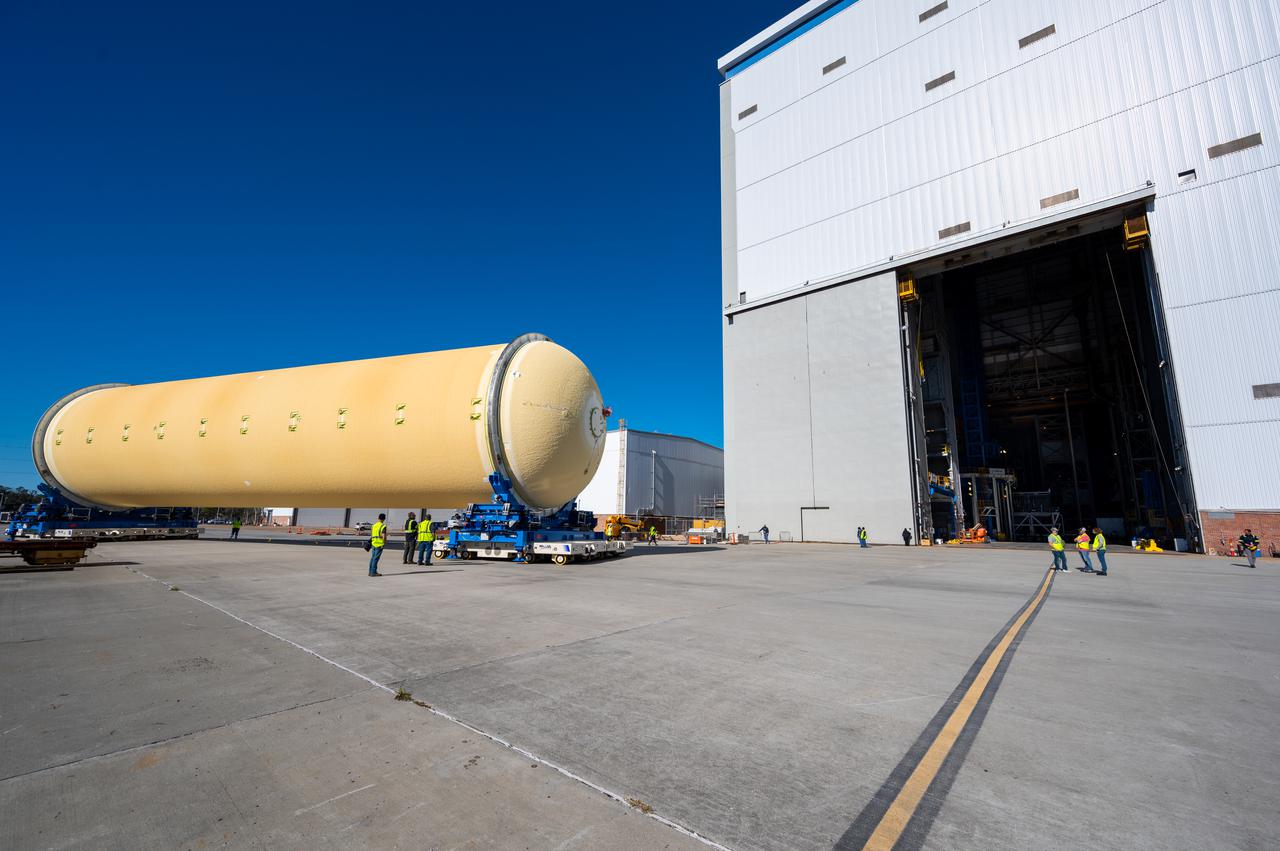
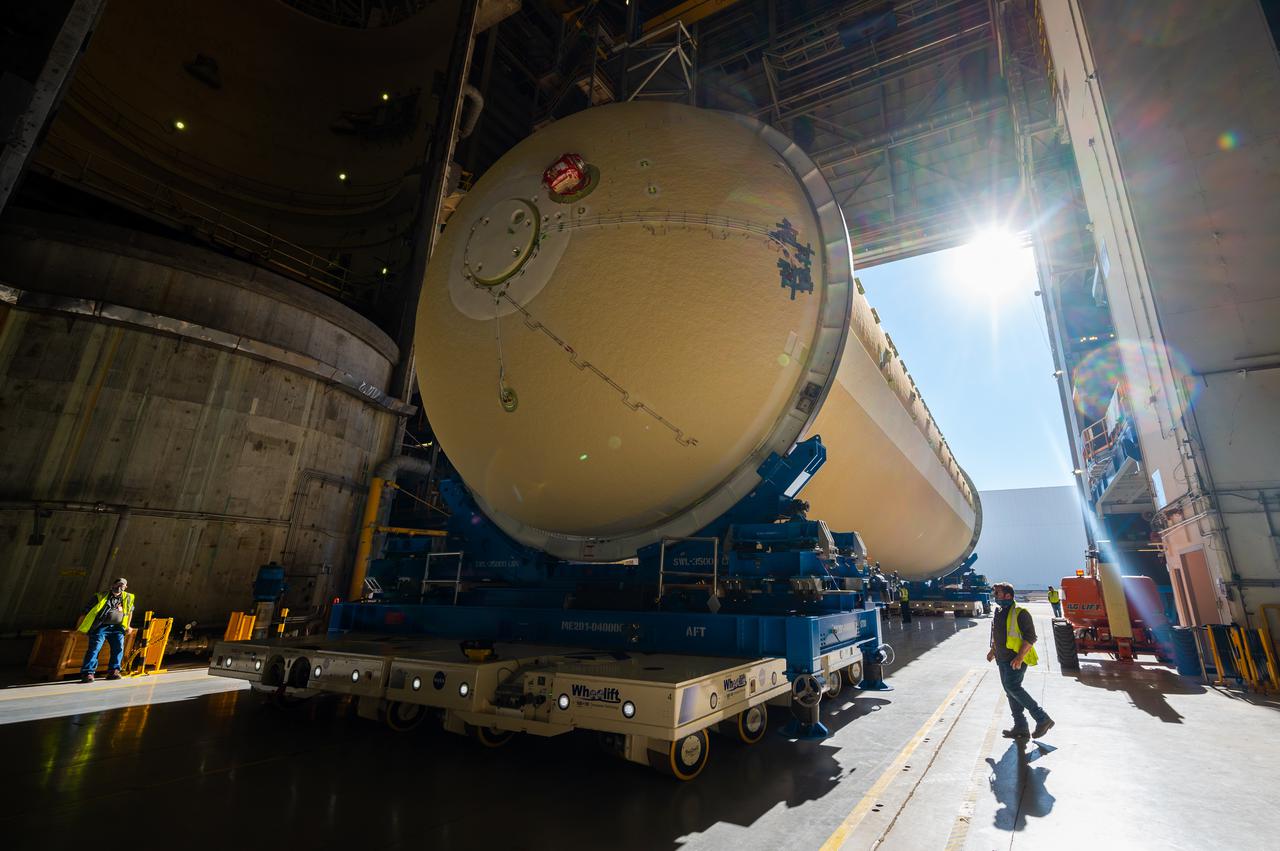
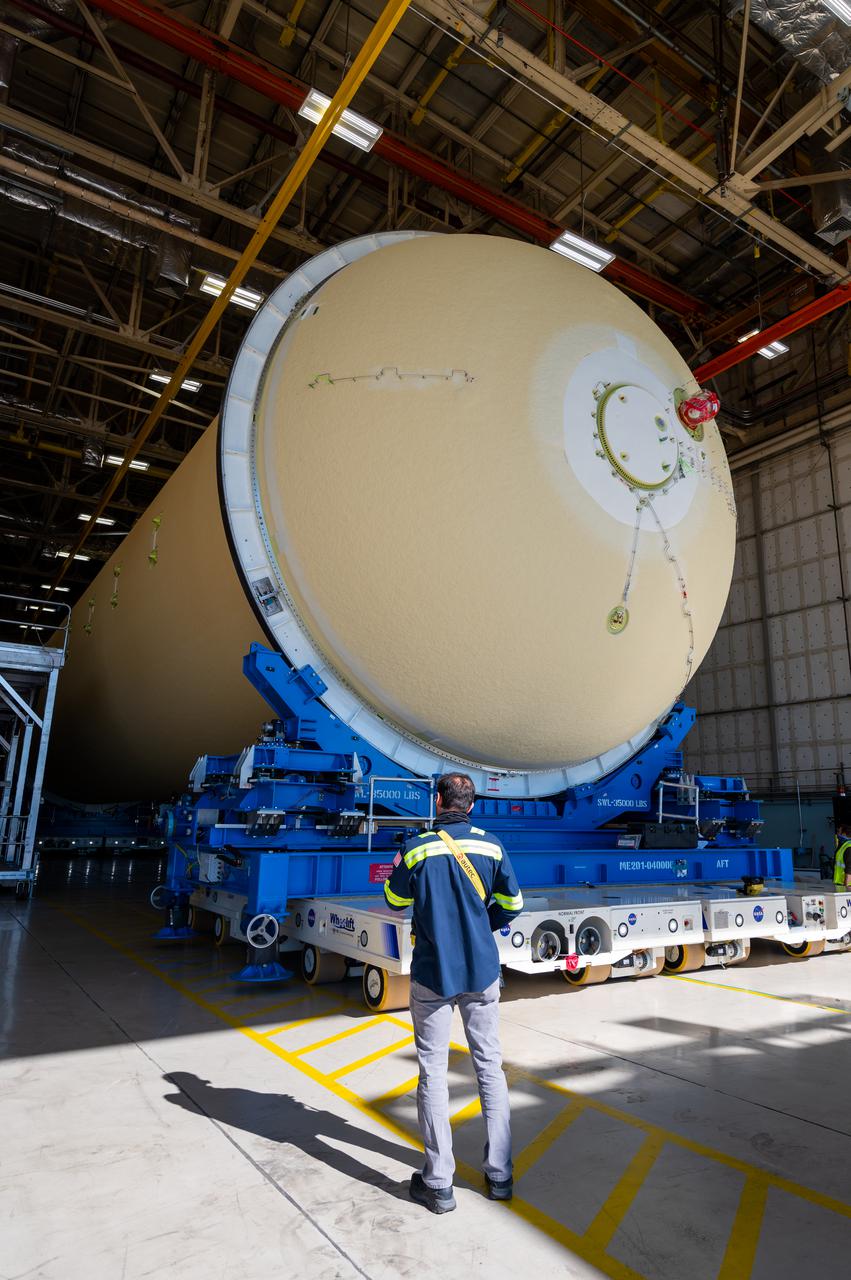
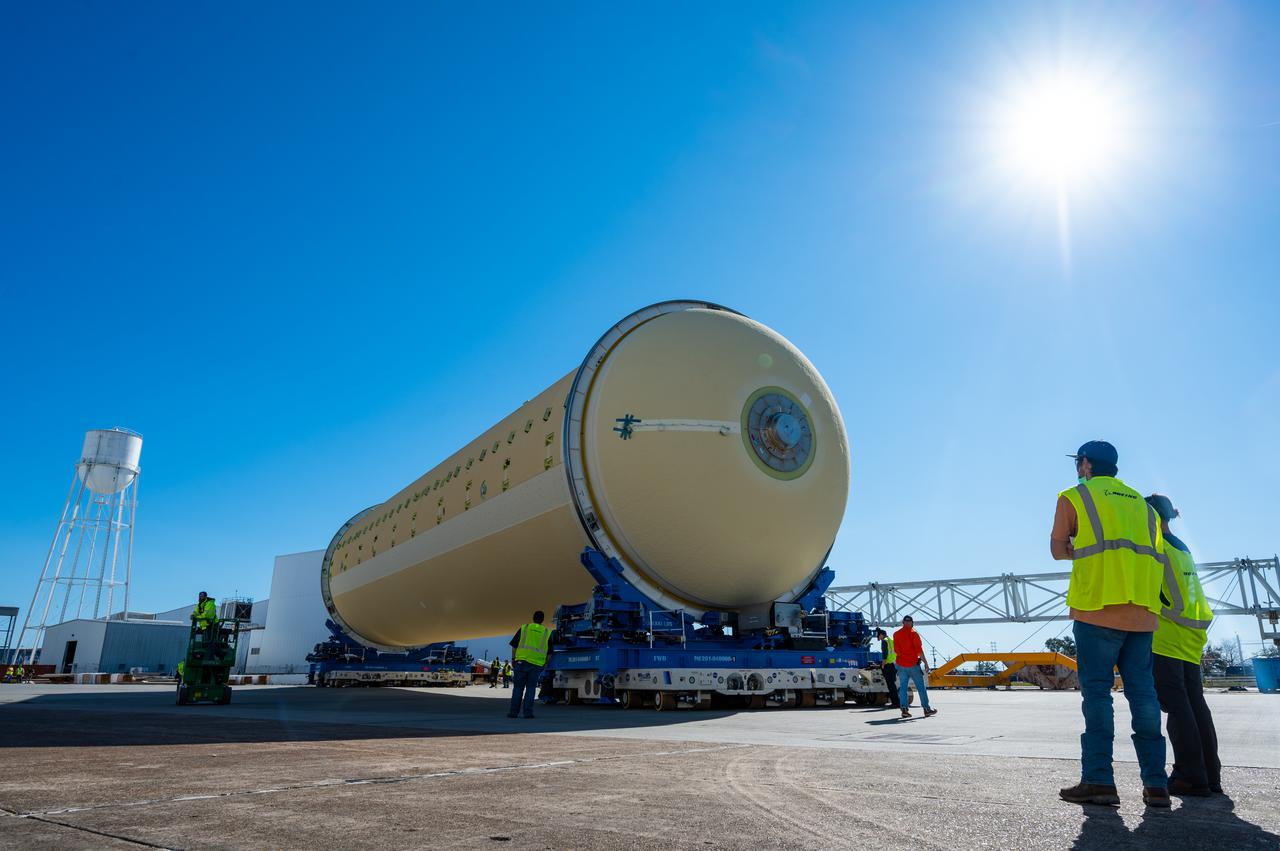
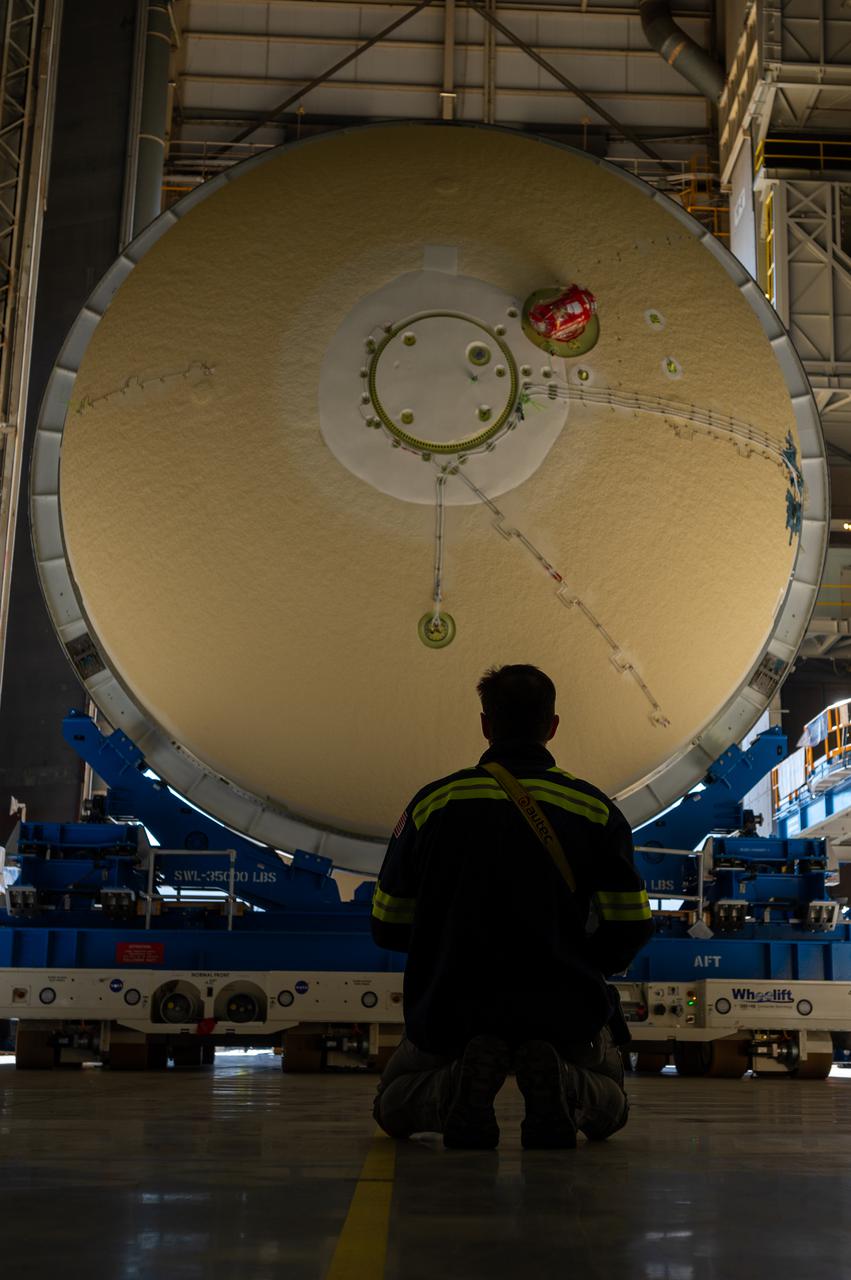
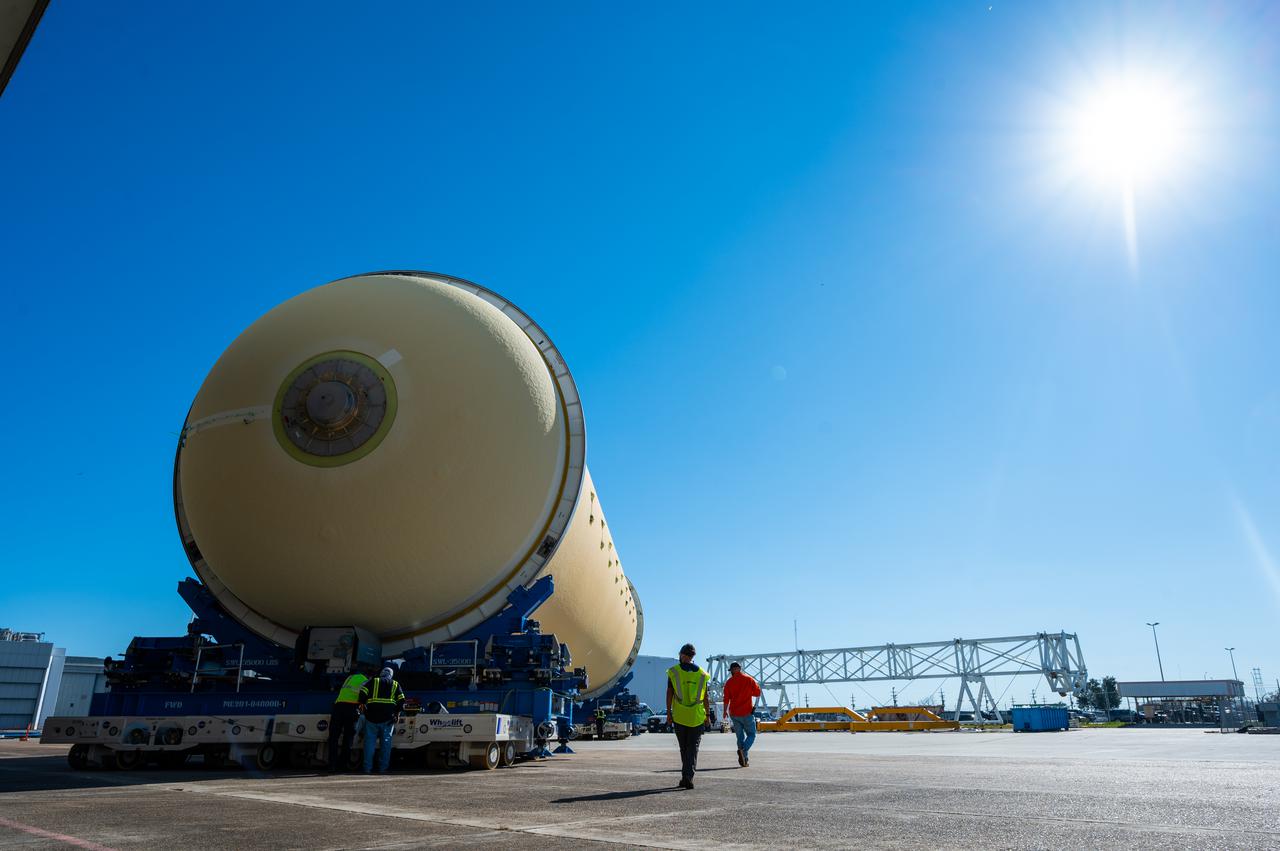
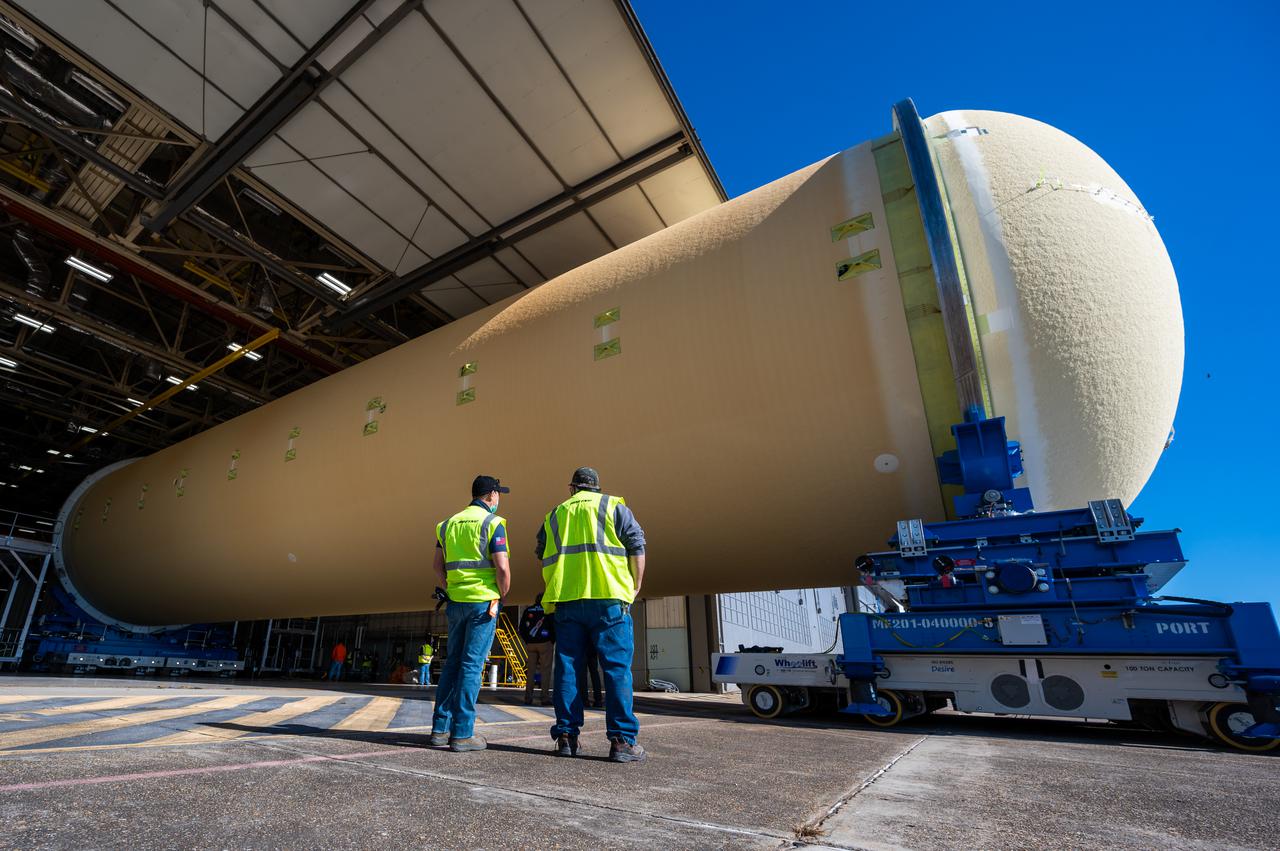
Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
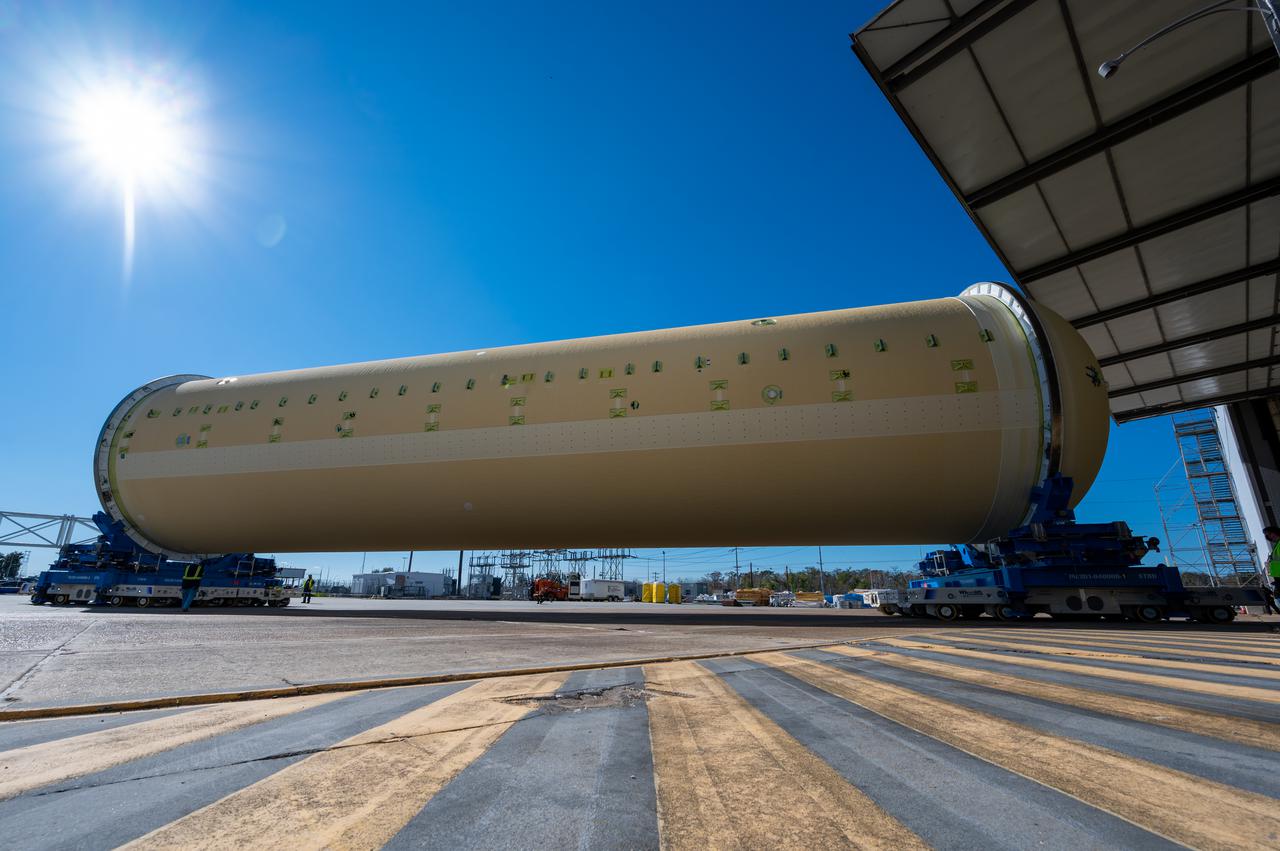

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
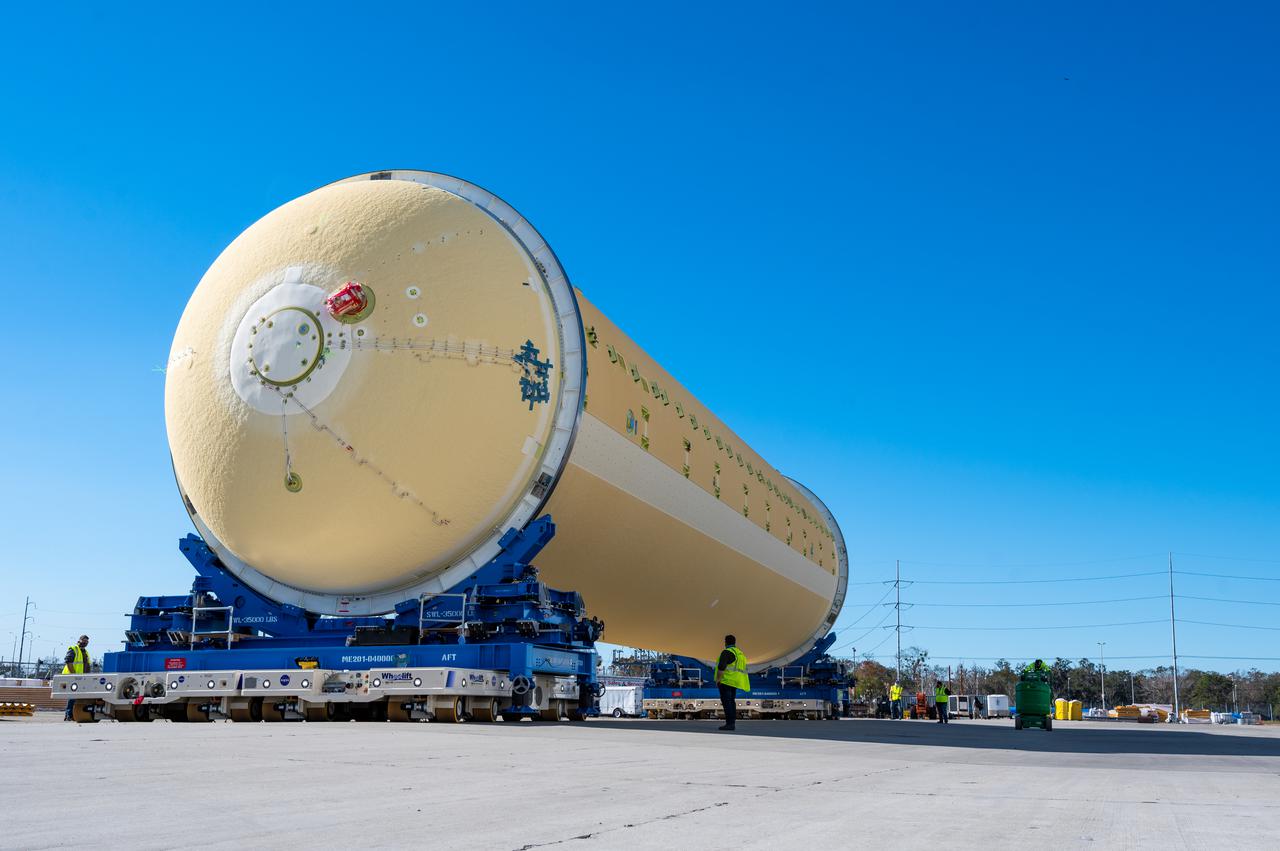

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
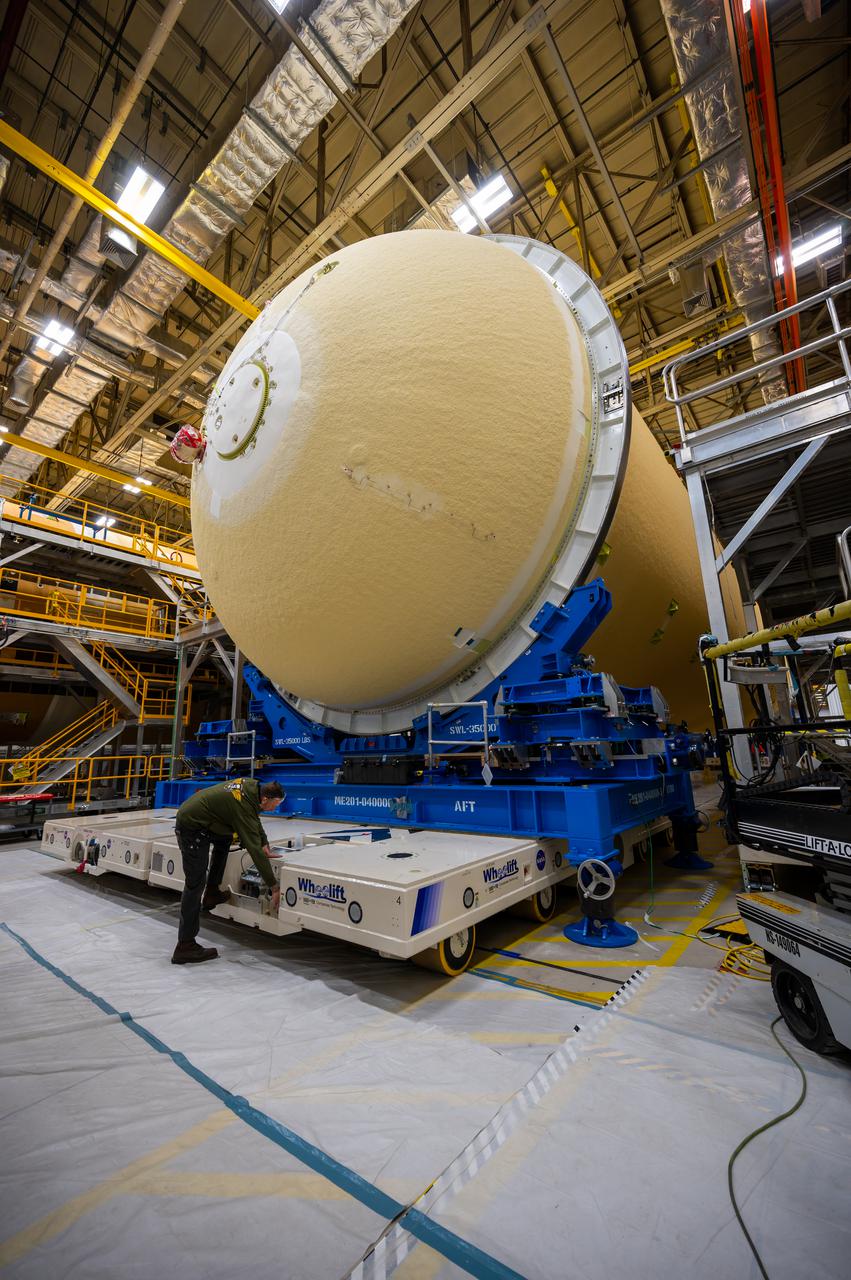

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

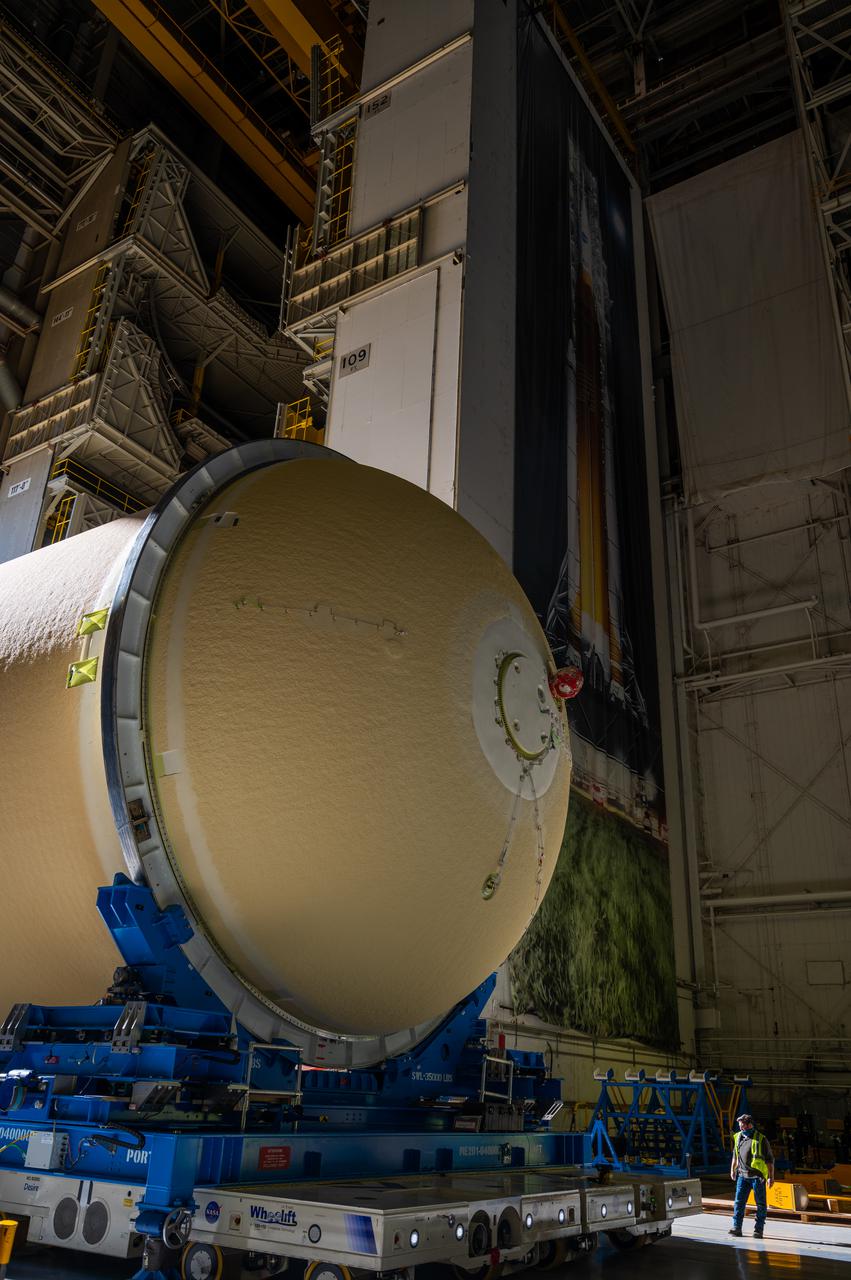
Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

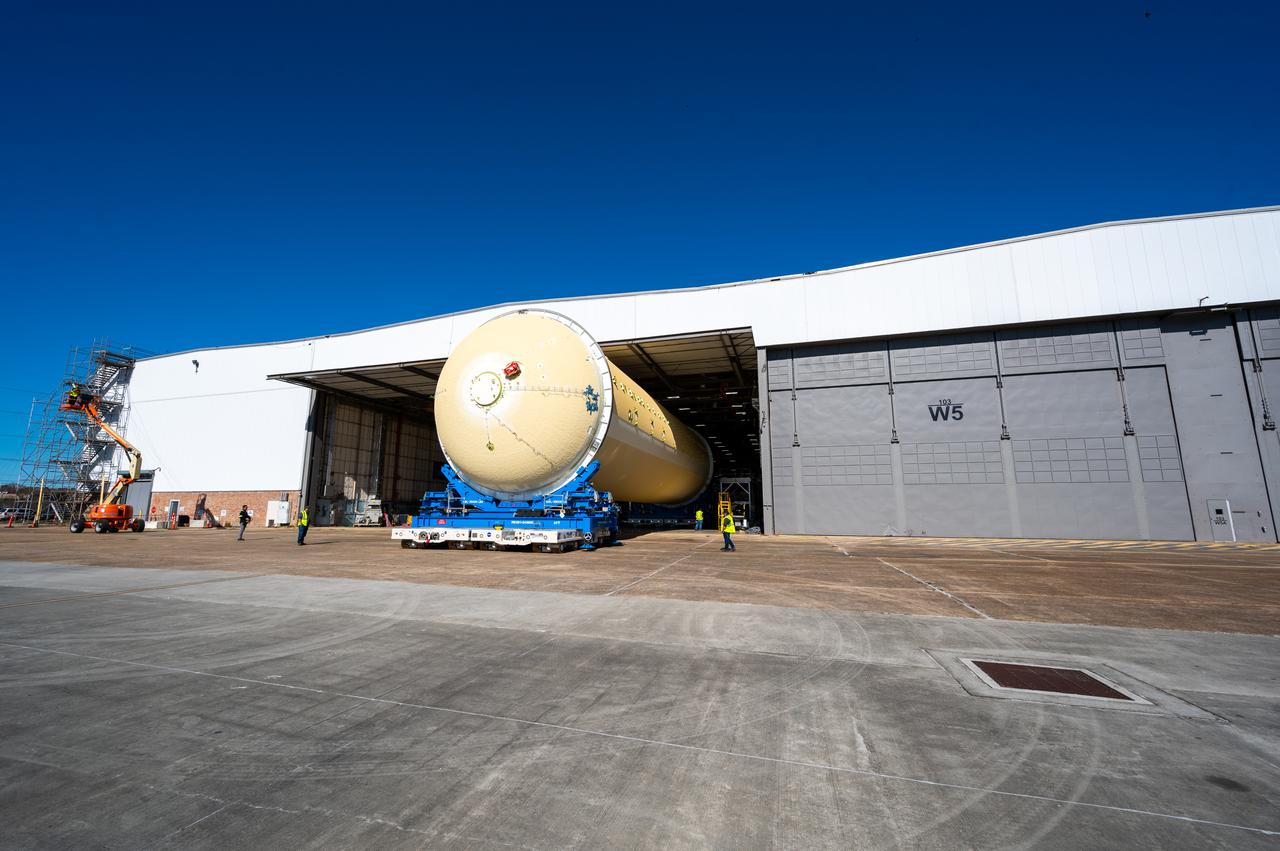
Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
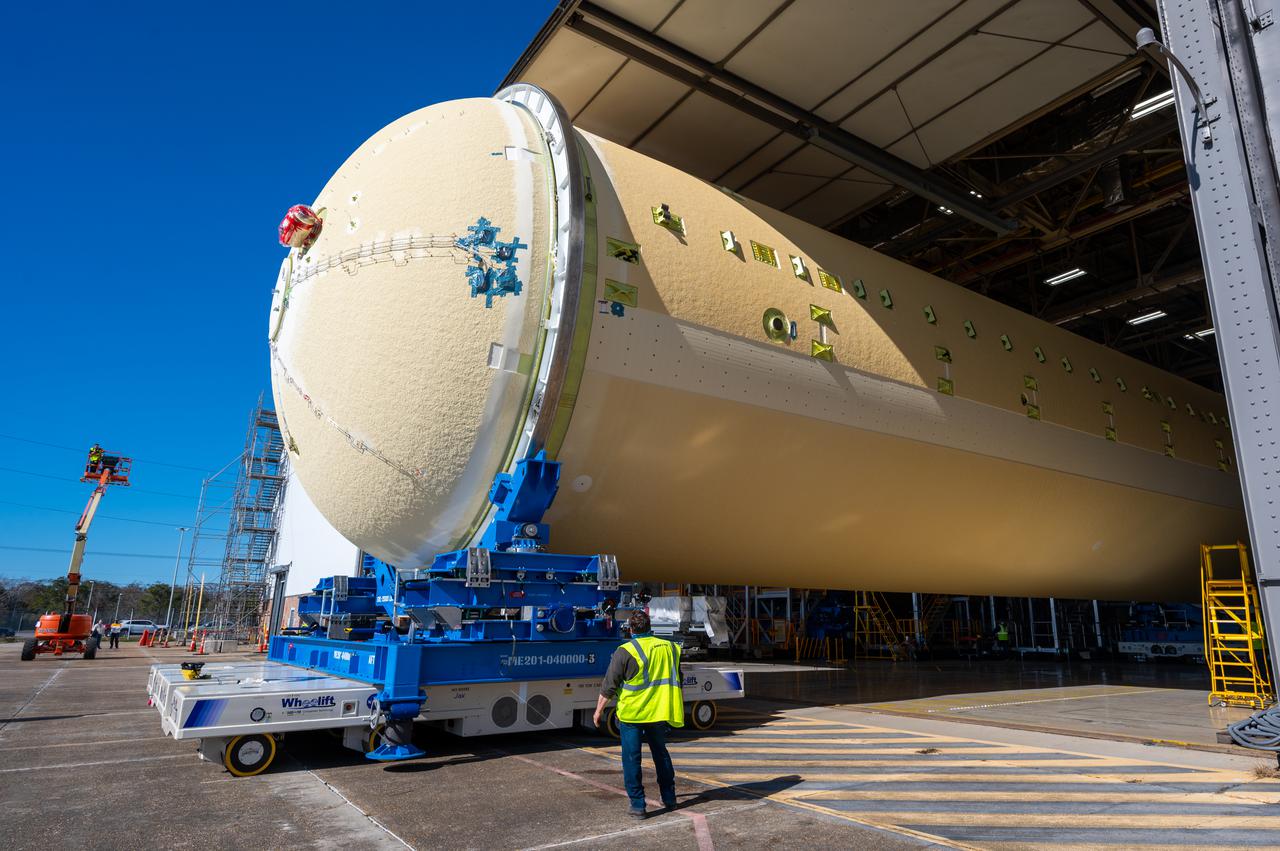

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
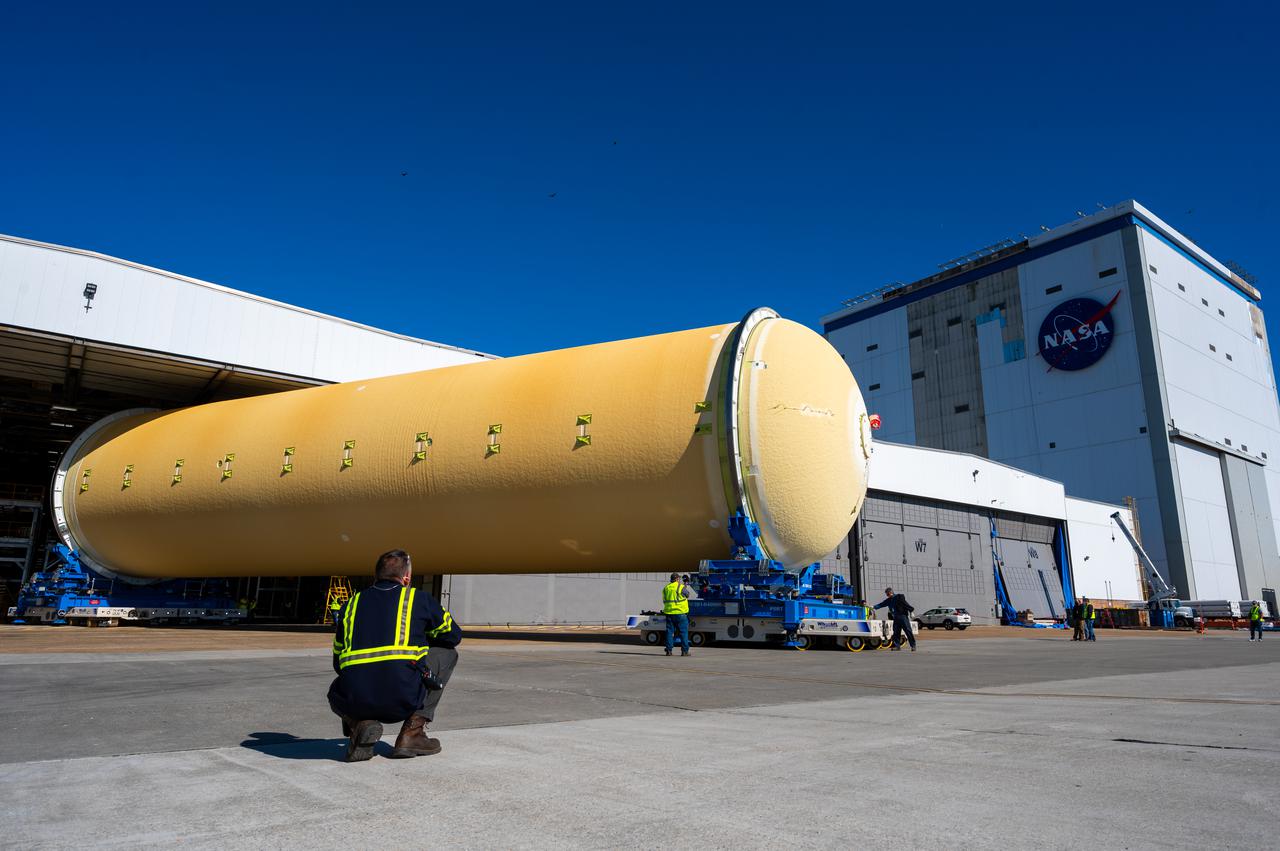

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
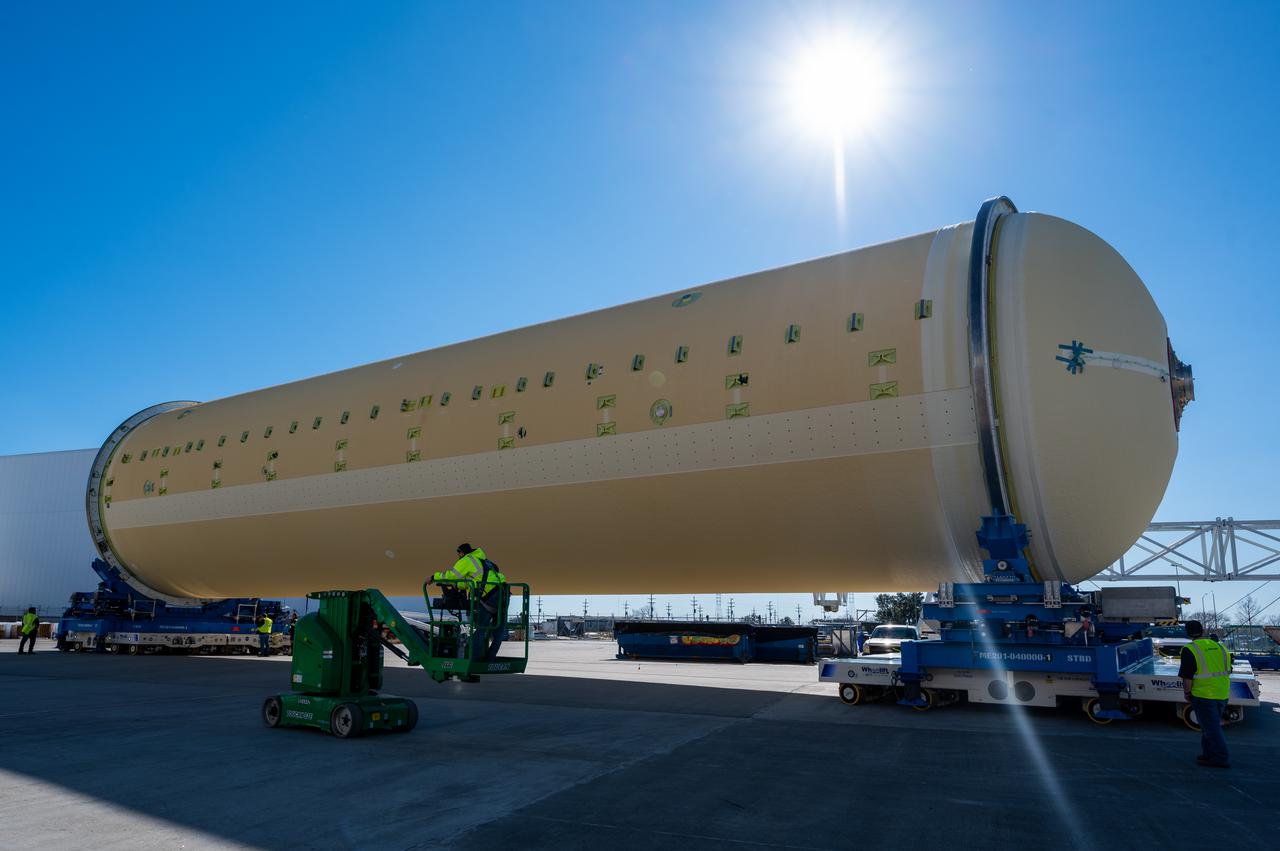

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
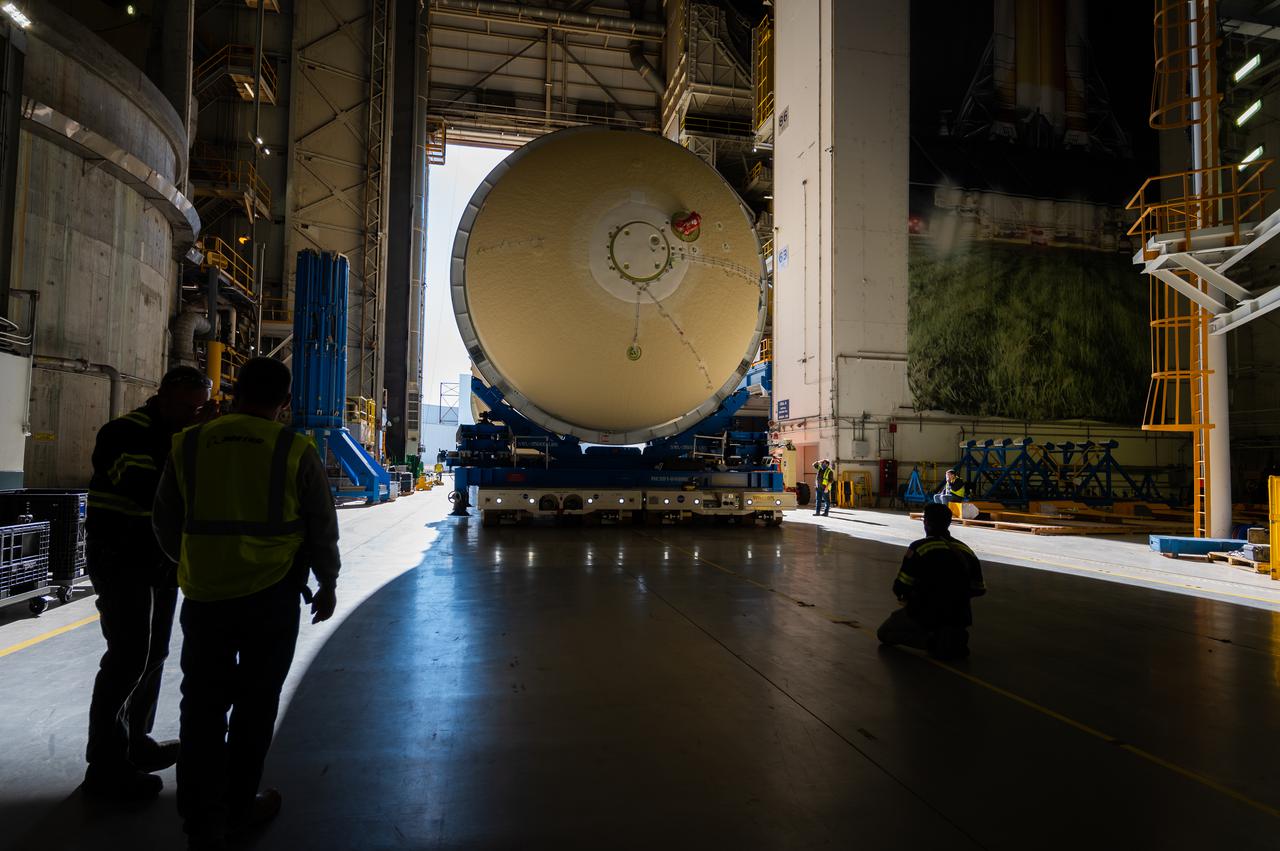

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
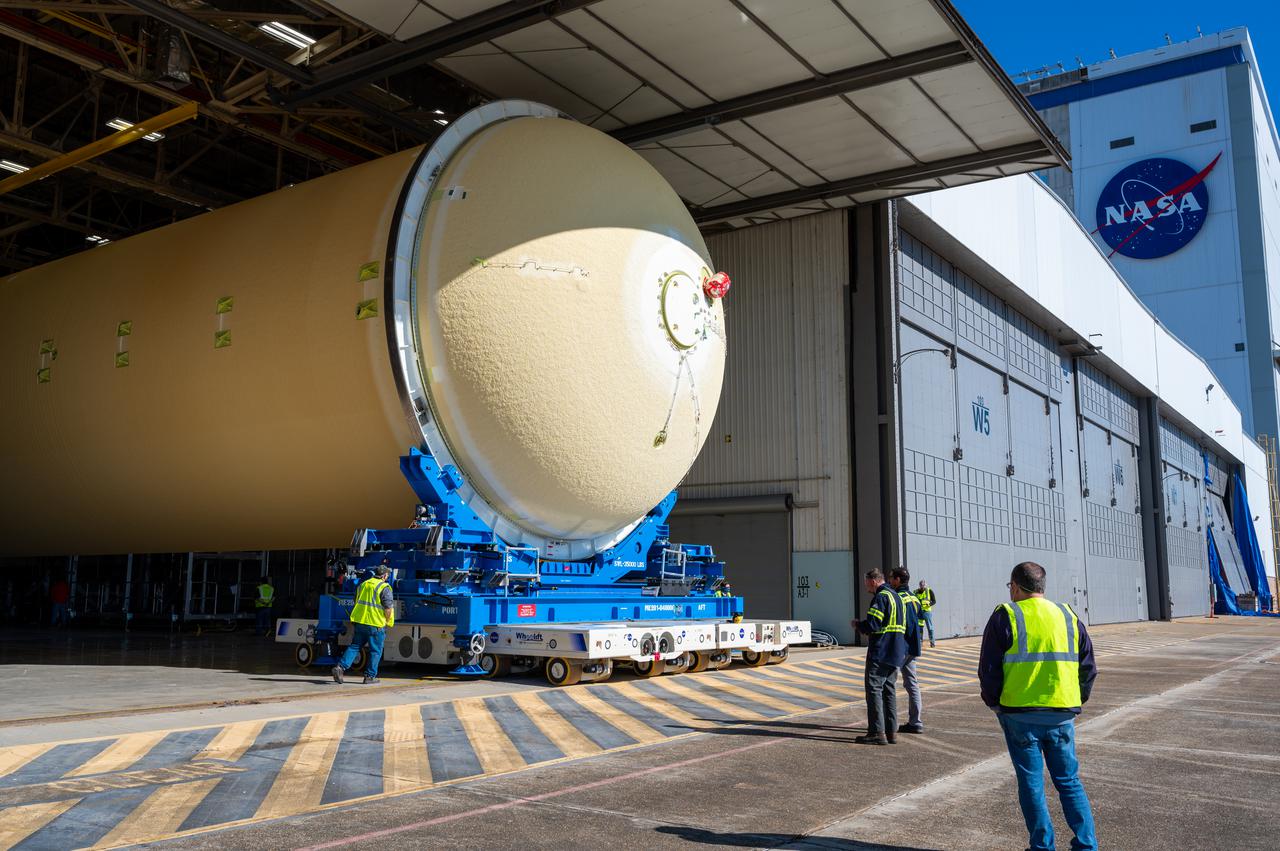

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
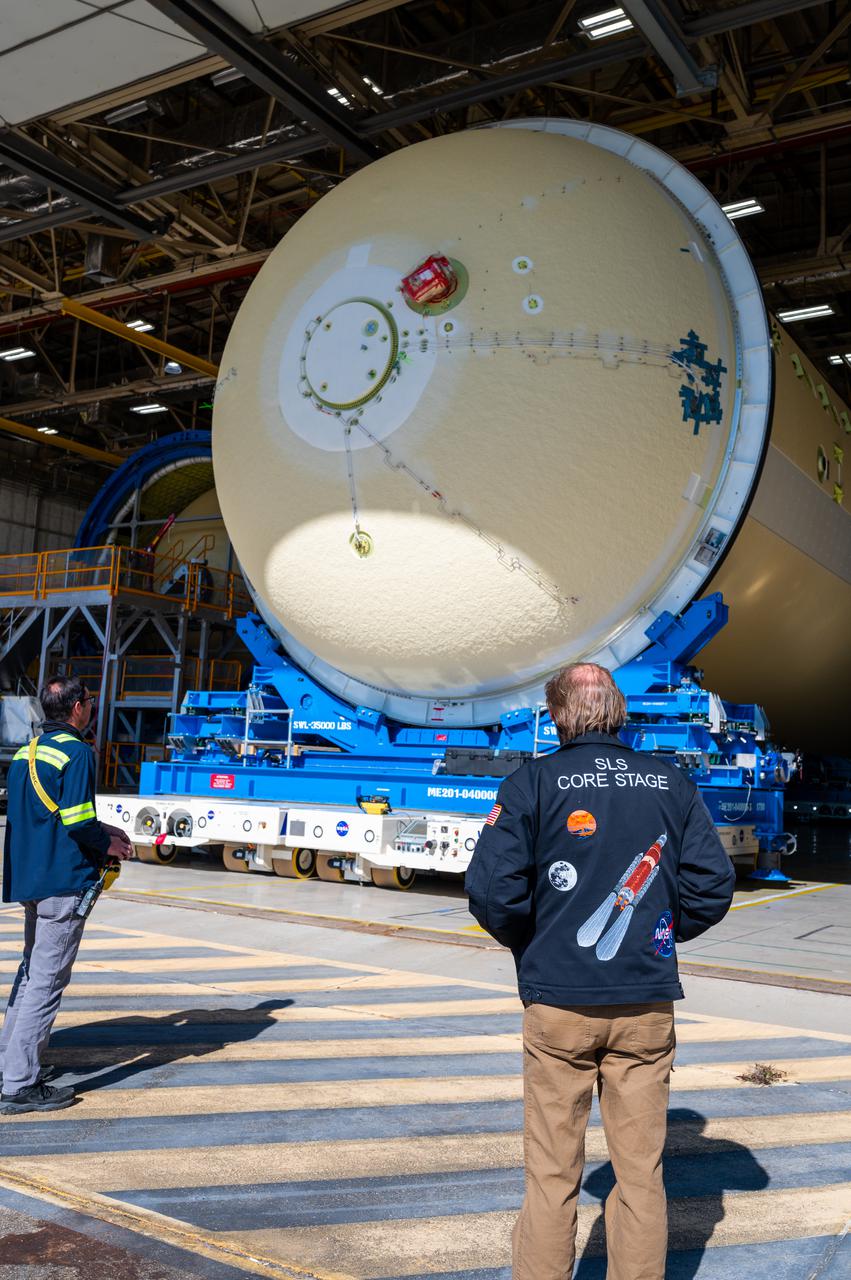

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
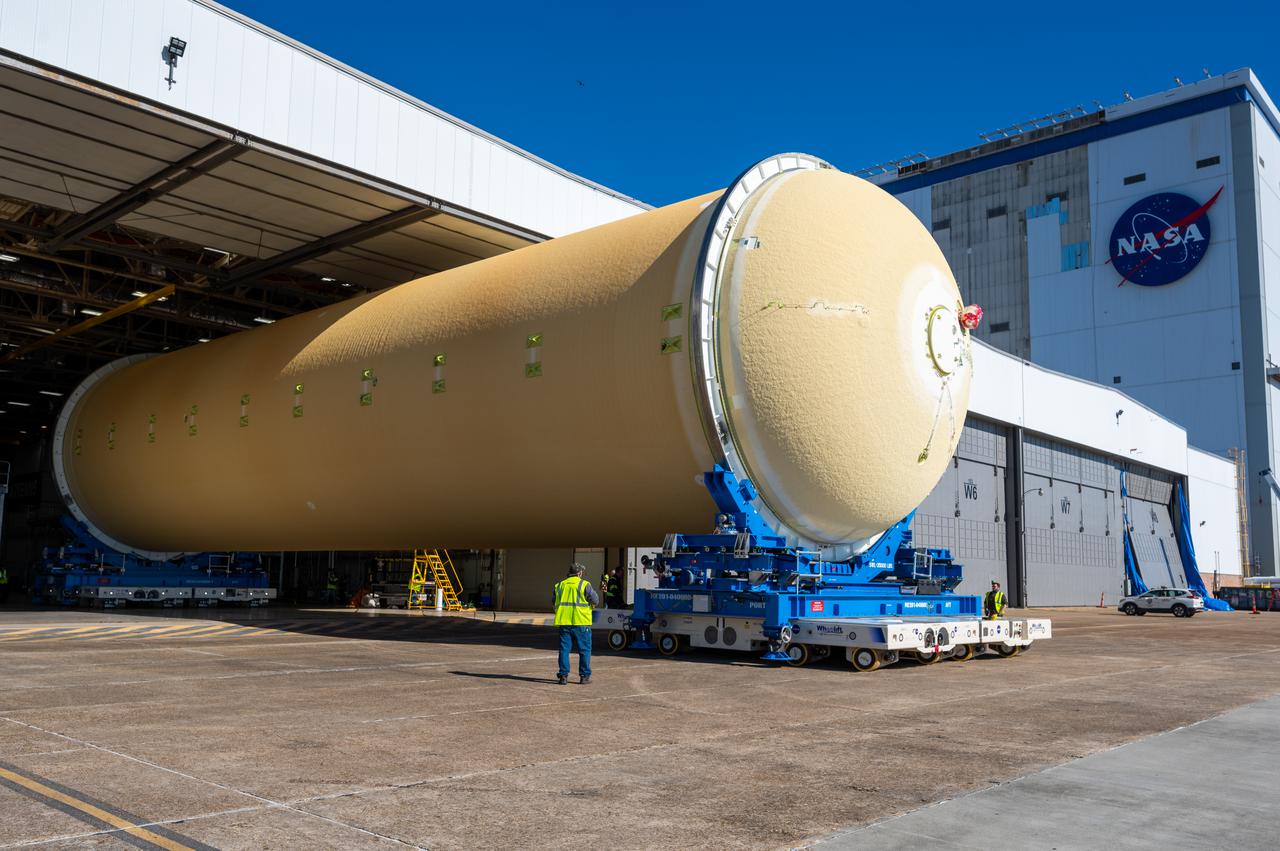

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
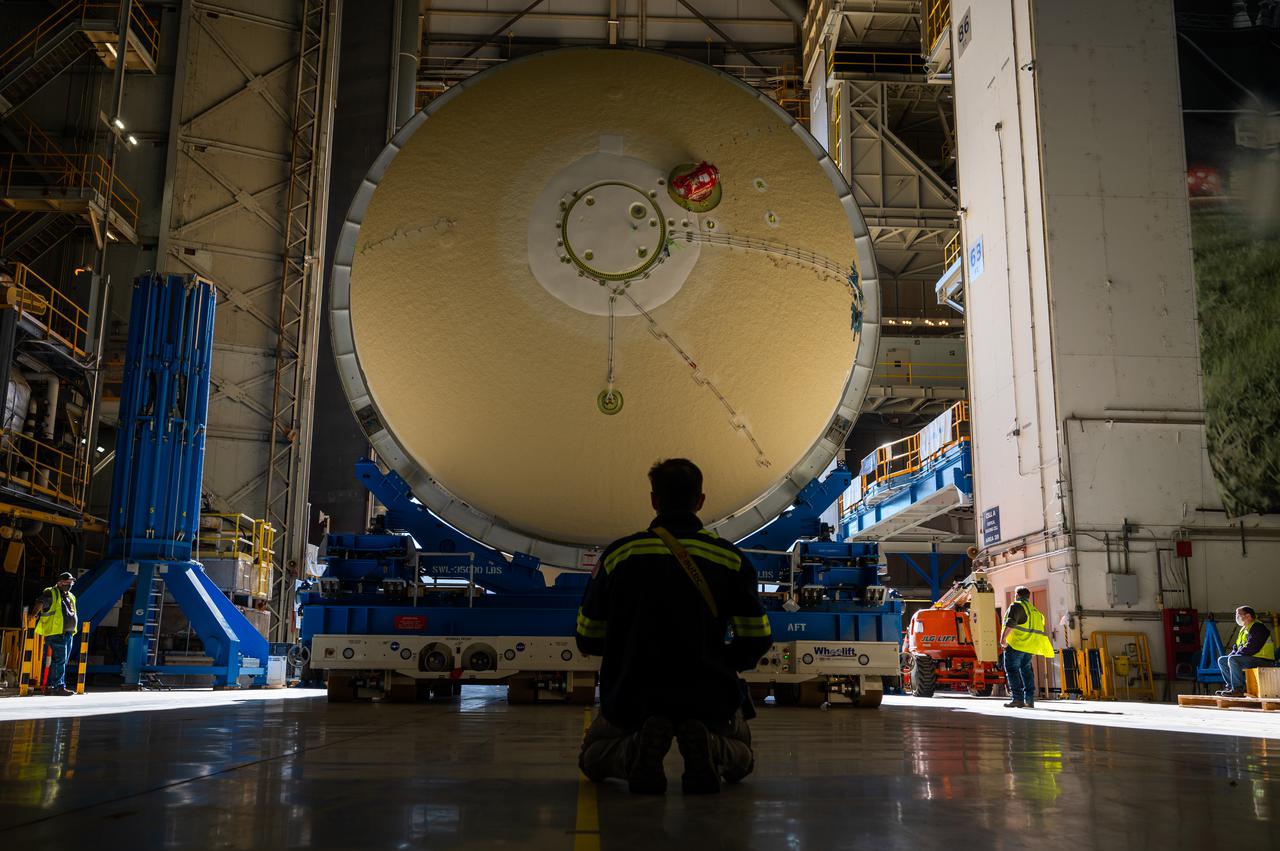

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
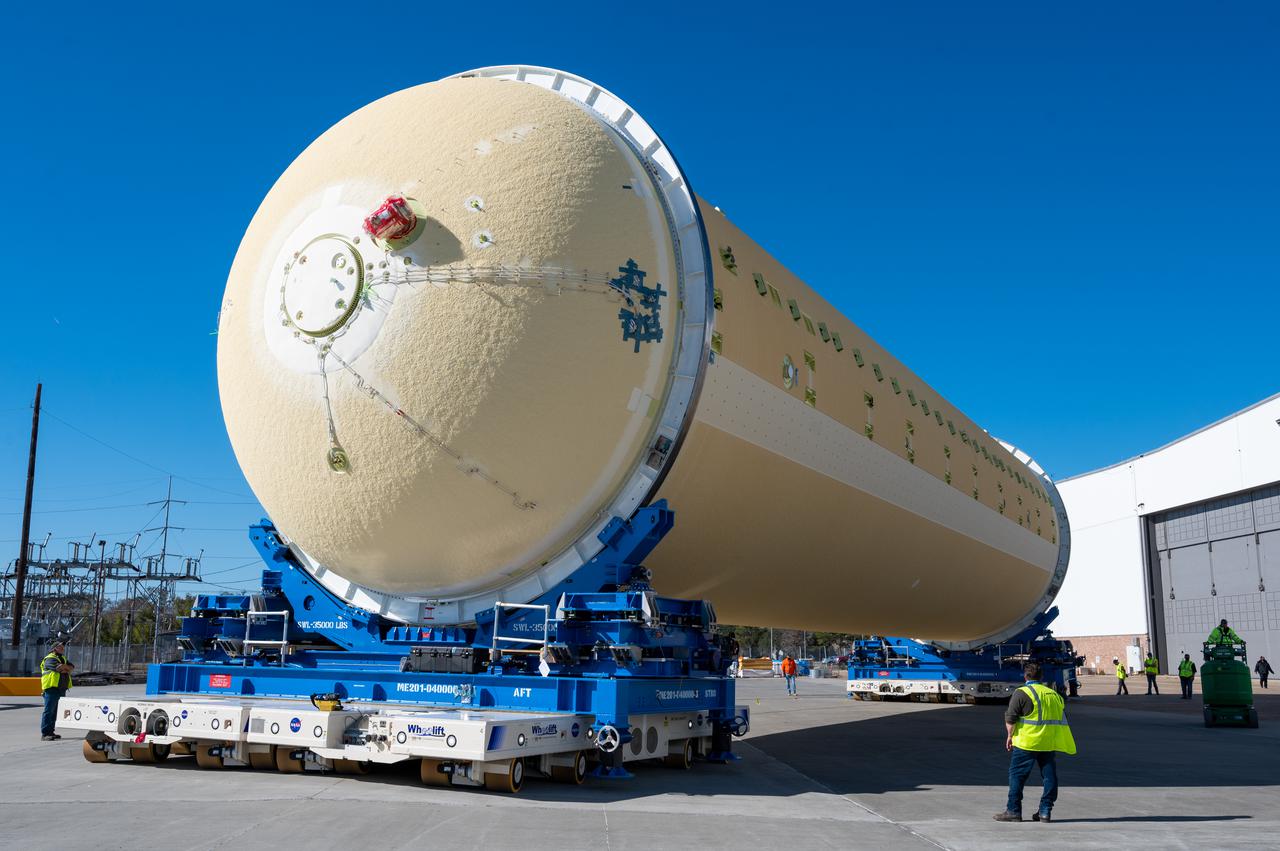

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
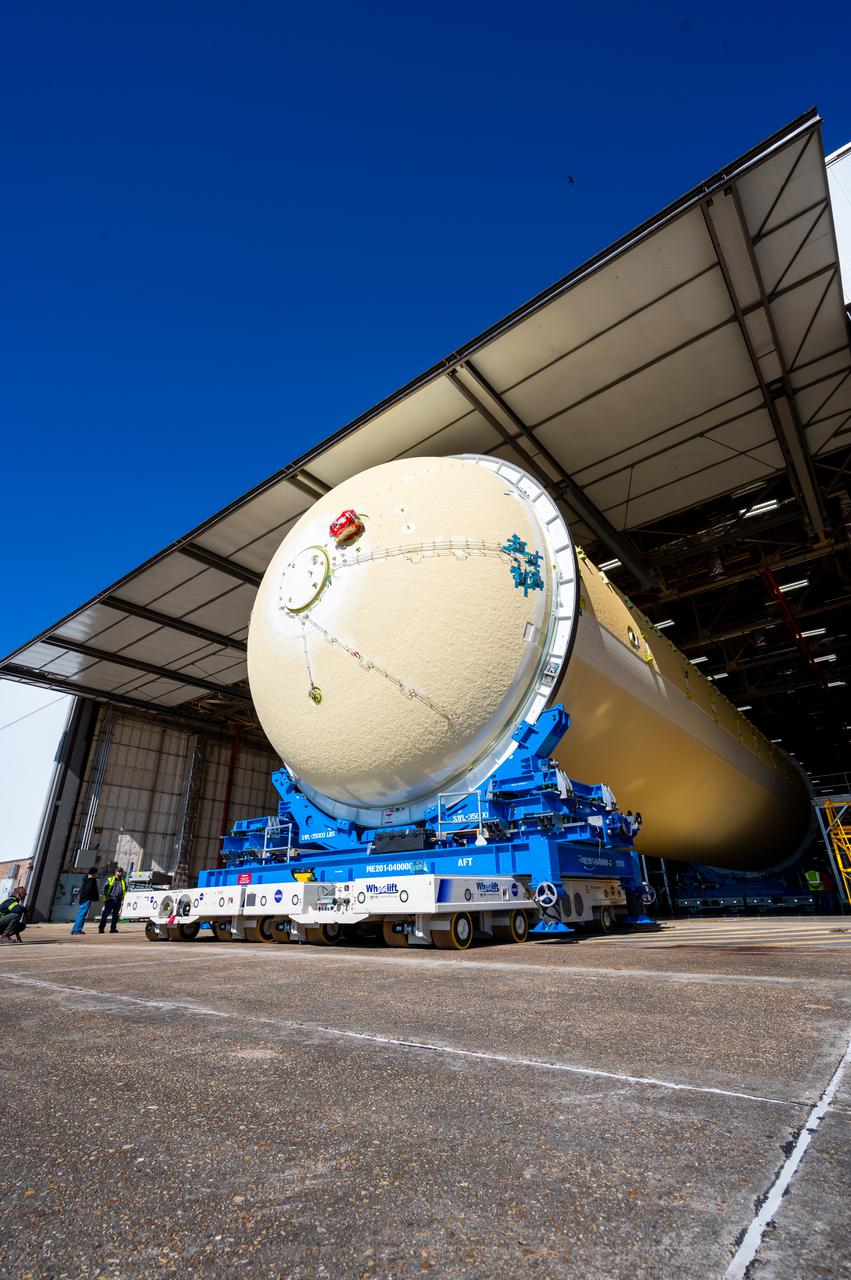

Technicians transported the assembled upper part of the Artemis II core stage to the final assembly area inside the factory at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On Jan 10, the forward assembly, left was moved next to the Artemis II liquid hydrogen tank, which has been undergoing assembly. Next, Boeing, the lead core stage contractor, will join the forward assembly and the liquid hydrogen tank to complete most of the core stage for the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket that will send the first crew on an Artemis mission. The core stage consists of five major structures that are built, outfitted, and then connected to form the final stage. The forward skirt, liquid oxygen and intertank were connected and tested to form the 66-foot forward assembly. After the forward assembly is joined with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank, only the engine section, the fifth piece of the stage, will need to be added to complete the Artemis II core stage. The core stage serves as the backbone of the rocket, supporting the weight of the payload, upper stage, and crew vehicle, as well as the thrust of its four RS-25 engines and two five-segment solid rocket boosters attached to the engine and intertank sections. On Artemis II, the SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft and a crew, sending them into lunar orbit, in preparation for later Artemis missions that will enable the first woman and first person of color to land on the Moon.
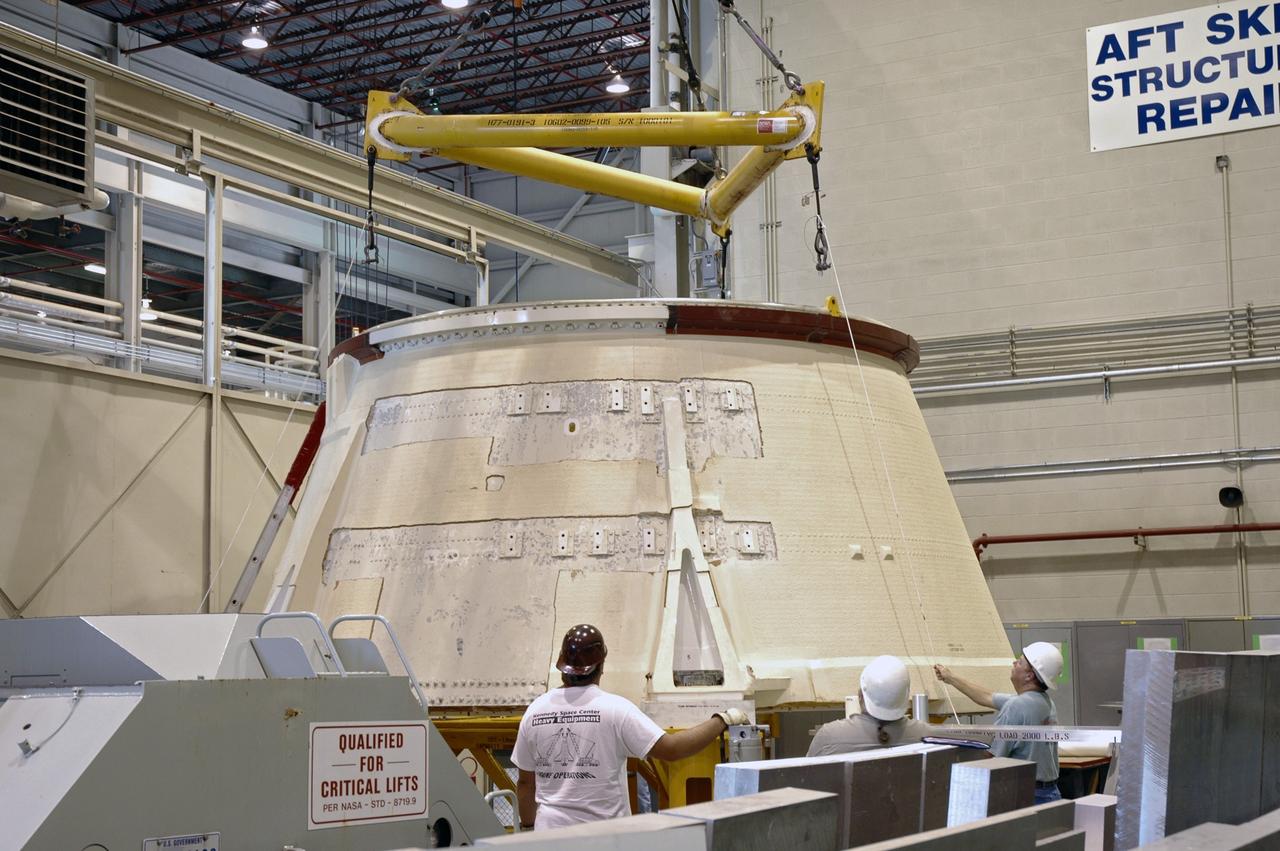

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Assembly and Refurbishment Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a crane is lowered over the aft skirt for the Ares 1-X rocket. The segment is being lifted into a machine shop work stand for drilling modifications. The modifications will prepare it for the installation of the auxiliary power unit controller, the reduced-rate gyro unit, the booster decelerator motors and the booster tumble motors. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. Ares I-X is a test rocket. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
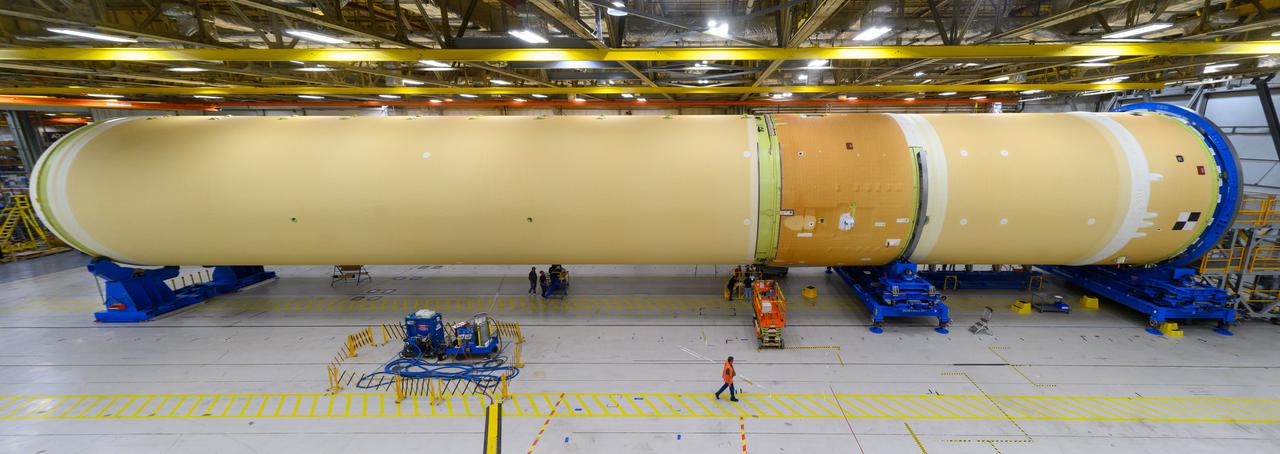

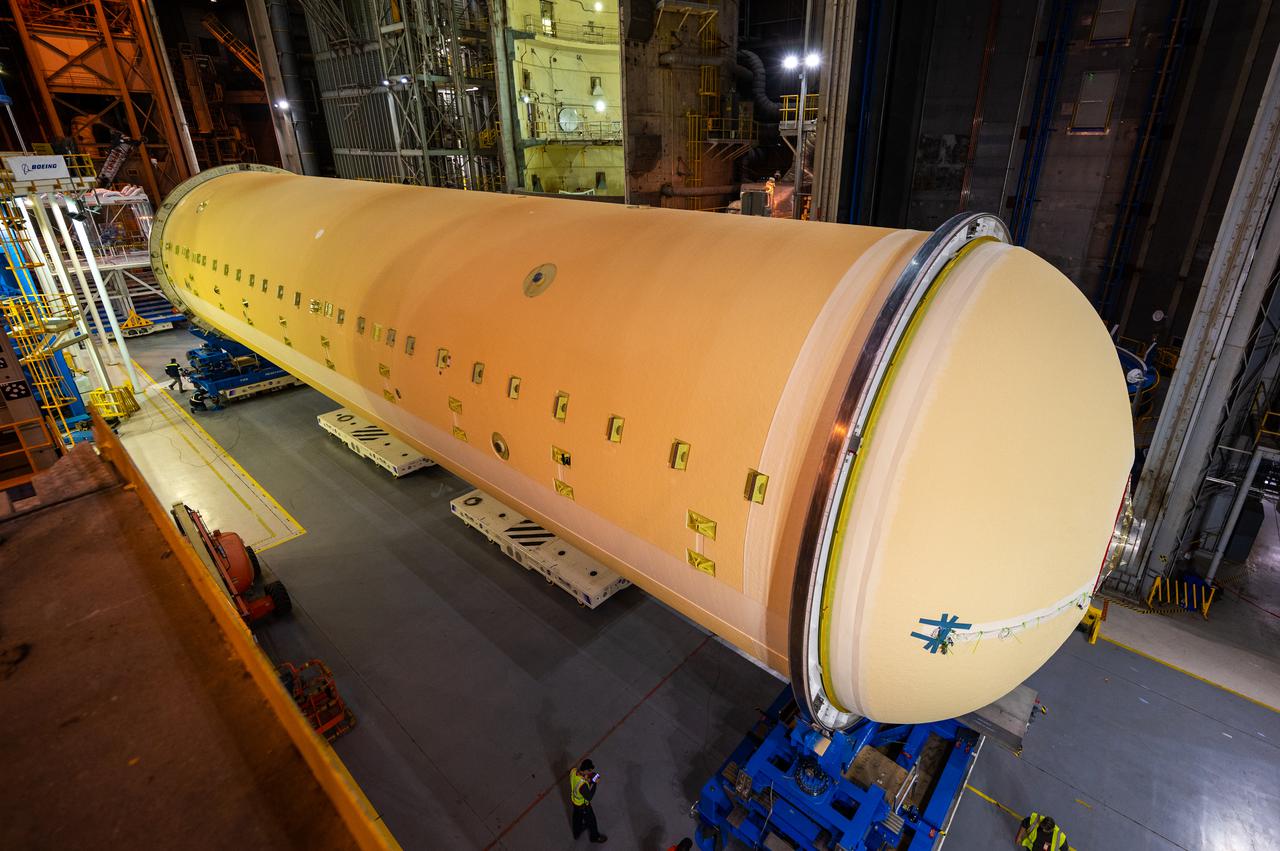
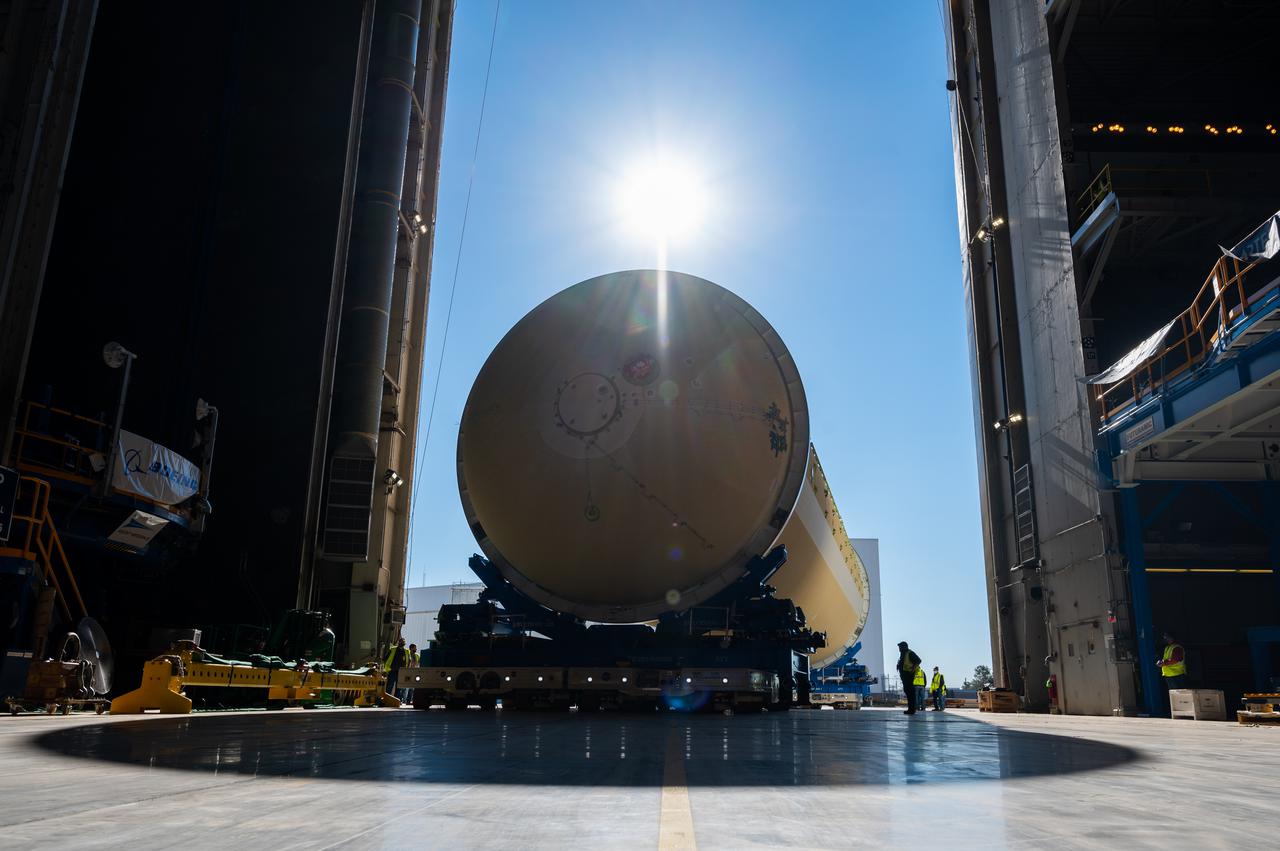
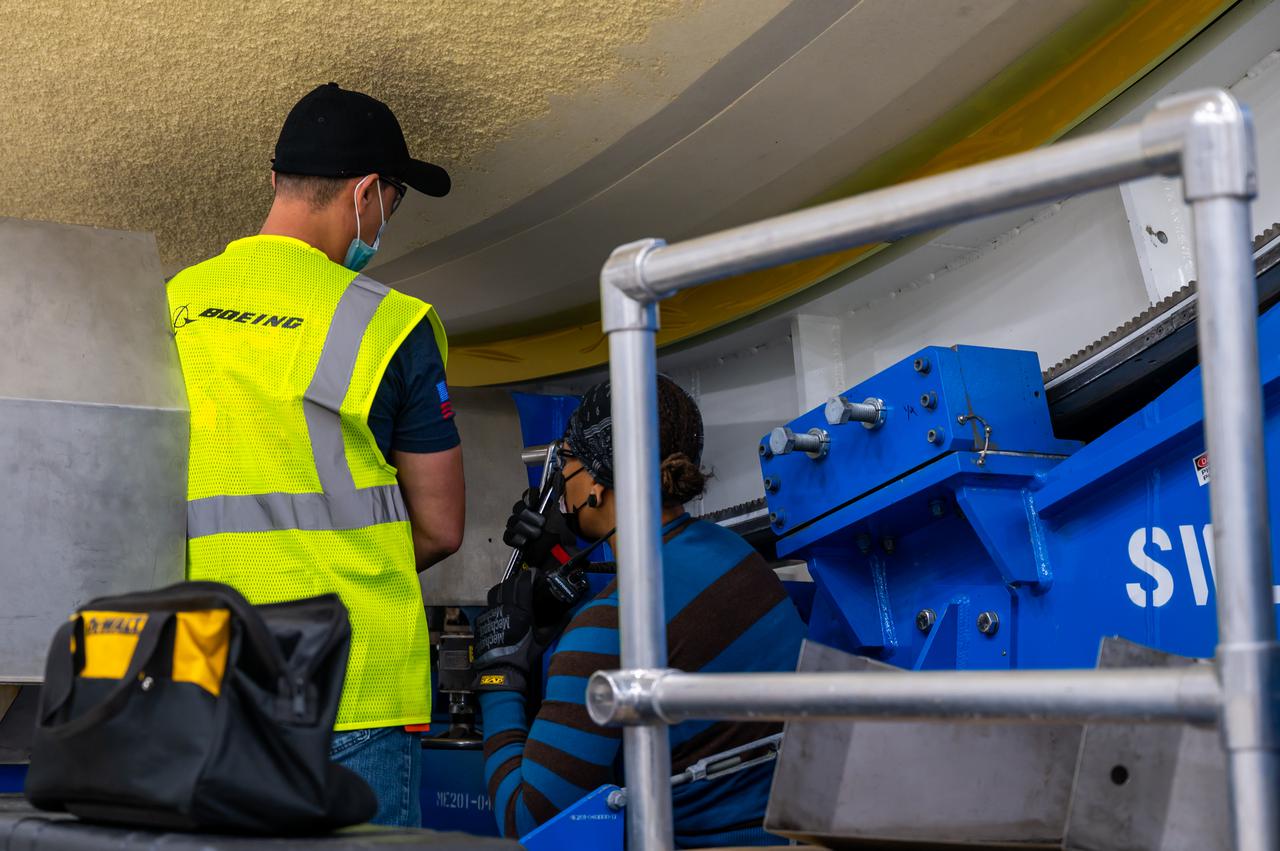
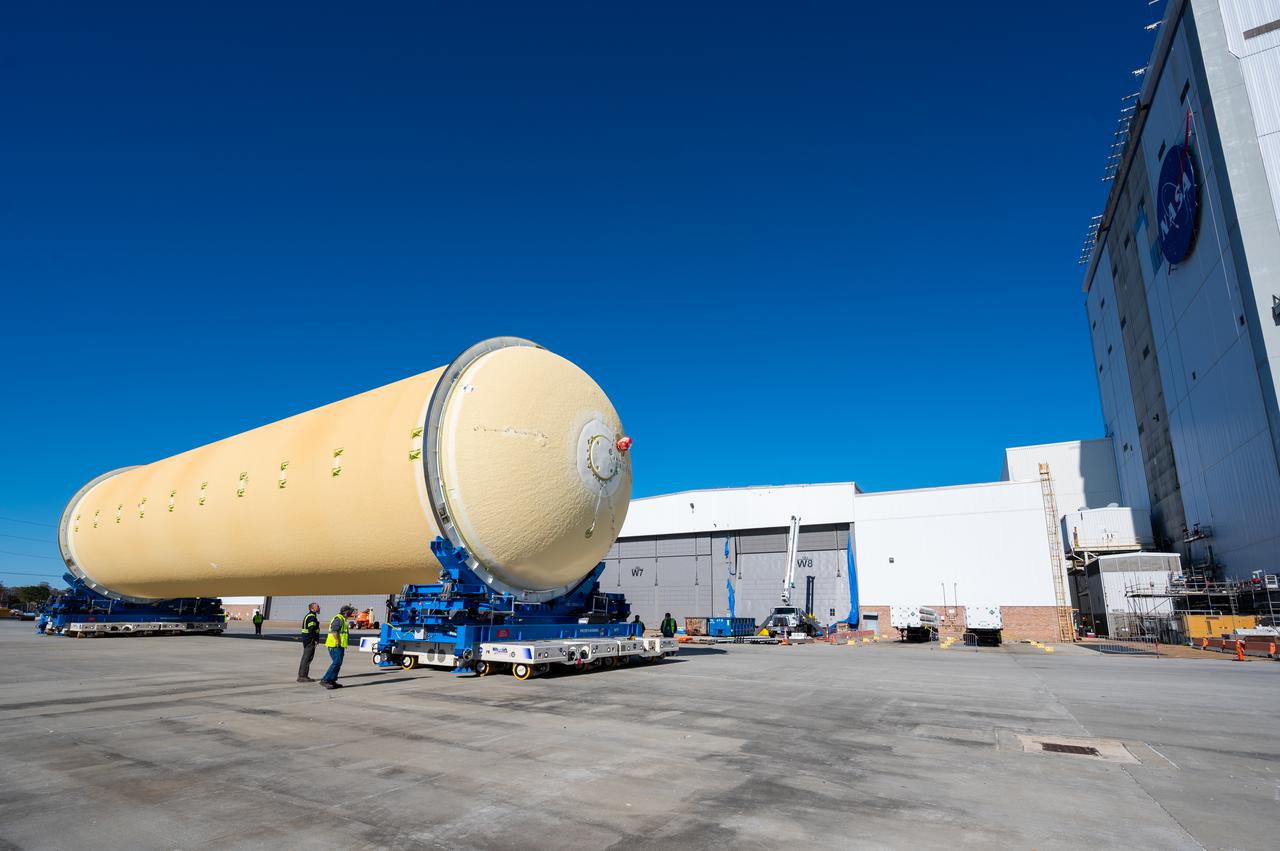
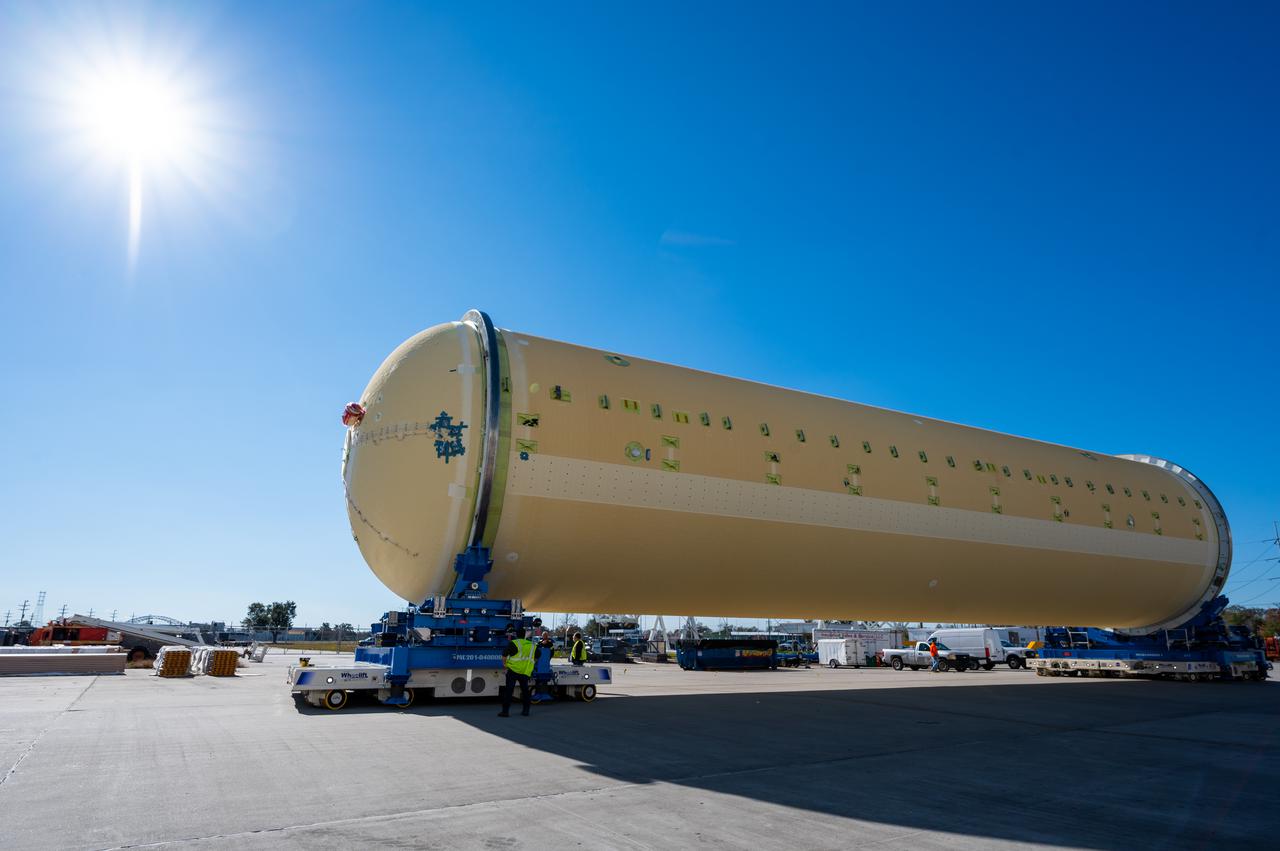
NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.

NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.
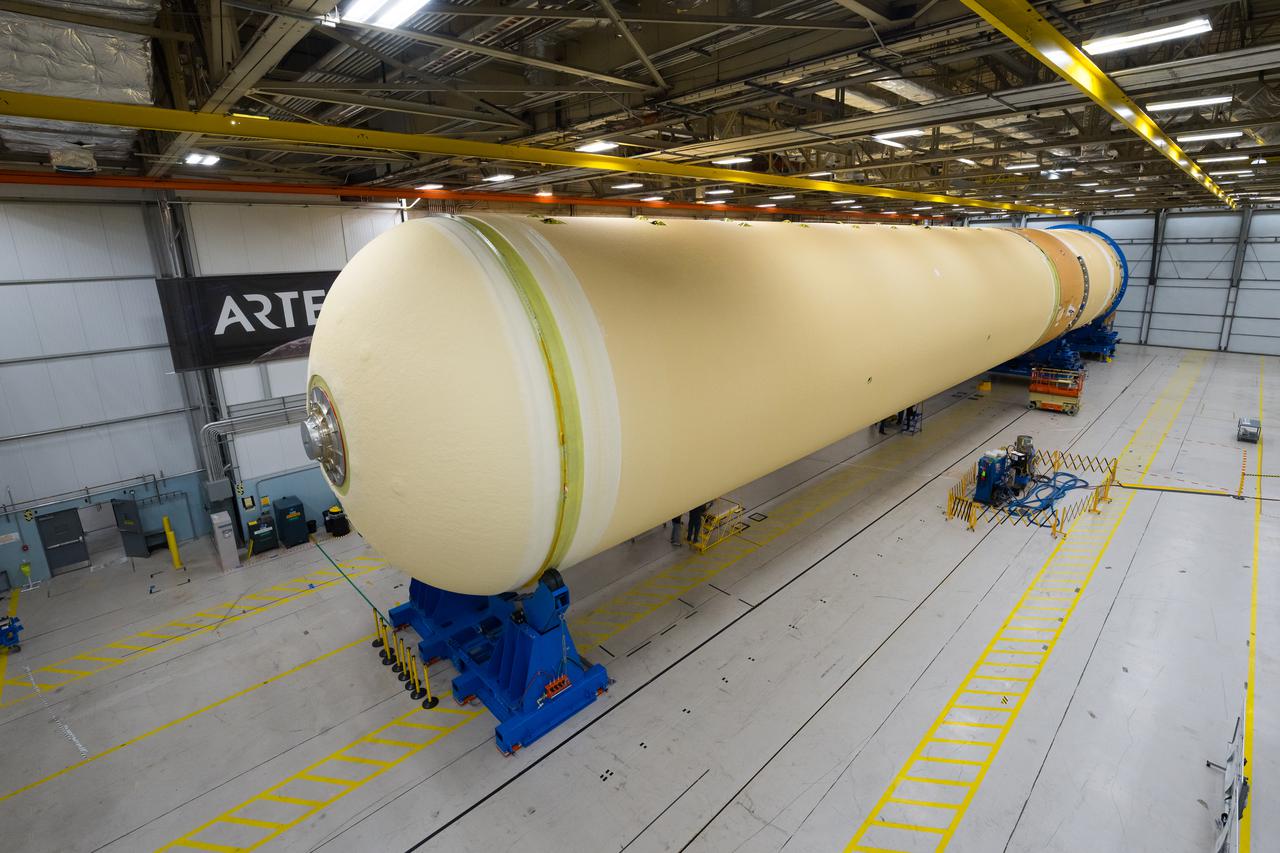

NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.

Shown is an illustration of the Ares I concept. The first stage will be a single, five-segment solid rocket booster derived from the space shuttle programs reusable solid rocket motor. The first stage is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama for NASA's Constellation program.
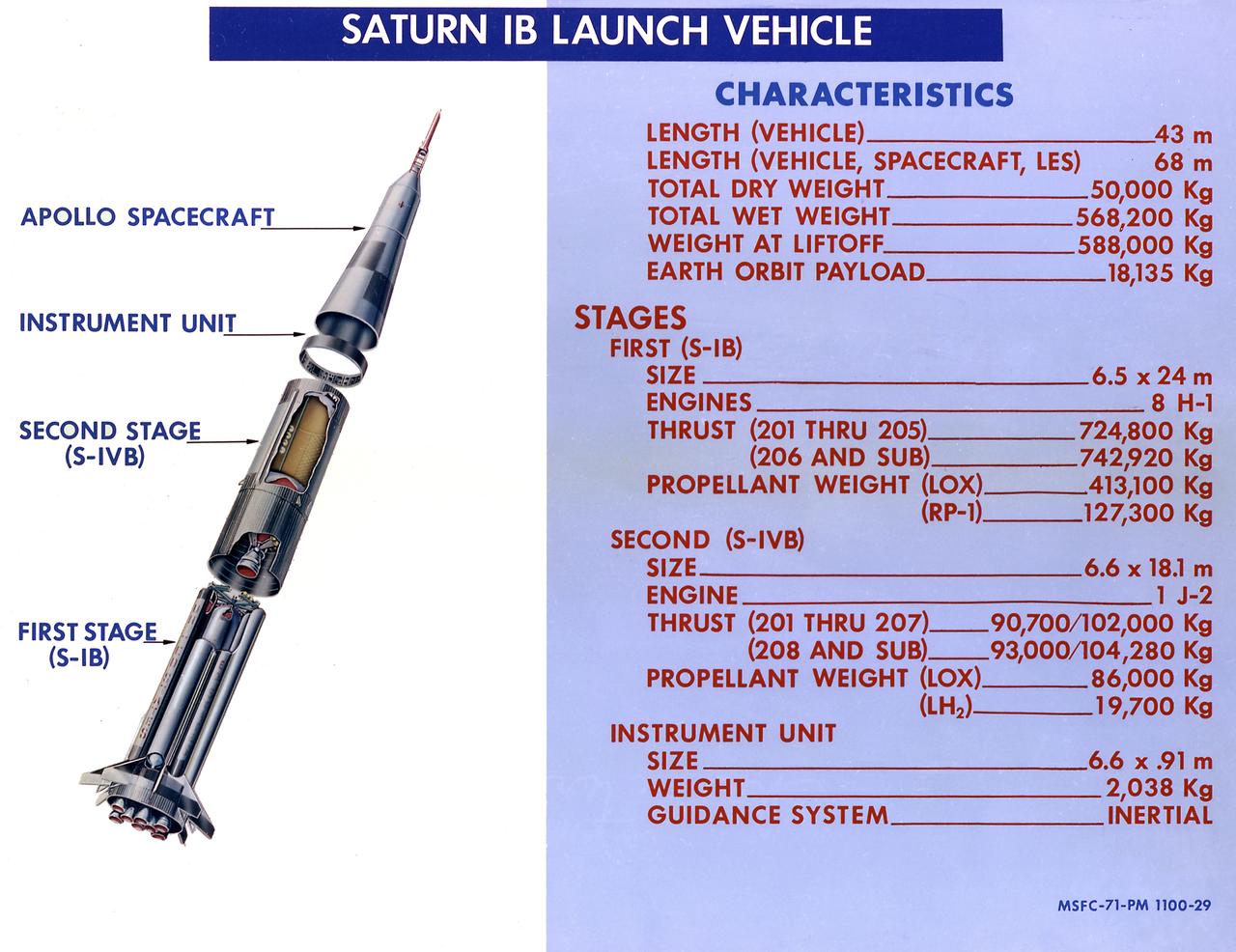
This 1968 cutaway drawing illustrates the Saturn IB launch vehicle with its two booster stages, the S-IB (first stage) and S-IVB (second stage), and provides the vital statistics in metric units. Developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) as an interim vehicle in MSFC's "building block" approach to the Saturn rocket development, the Saturn IB utilized Saturn I technology to further develop and refine the larger boosters and the Apollo spacecraft capabilities required for the marned lunar missions.
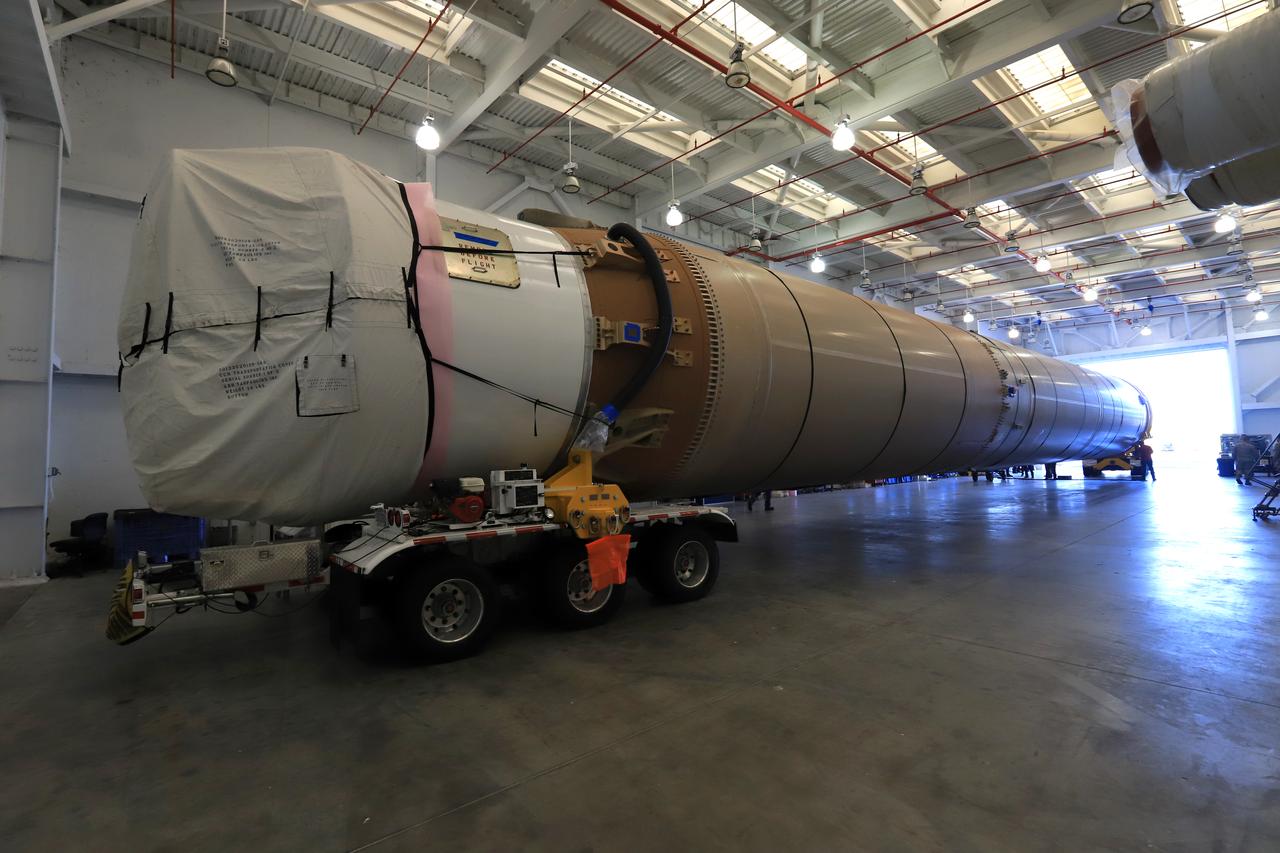

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
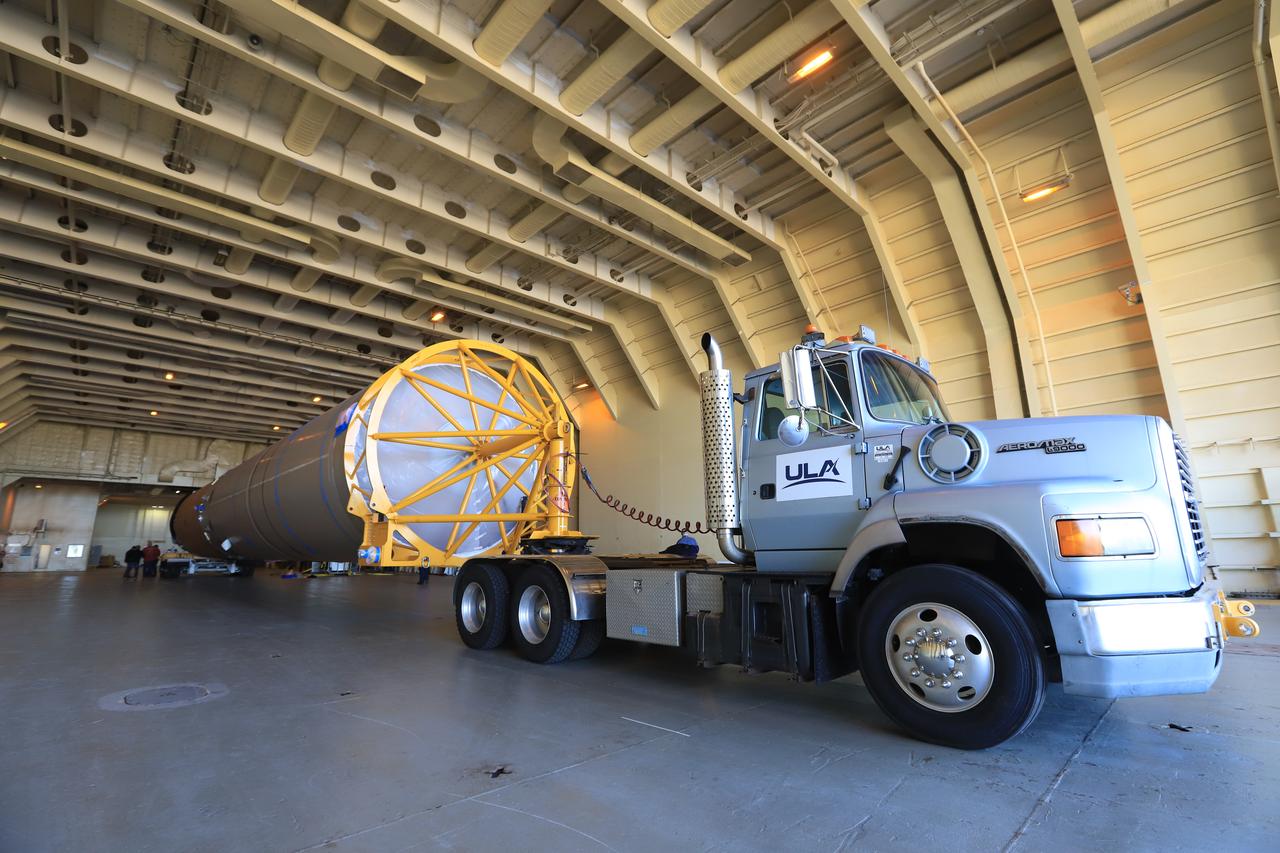

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrived at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
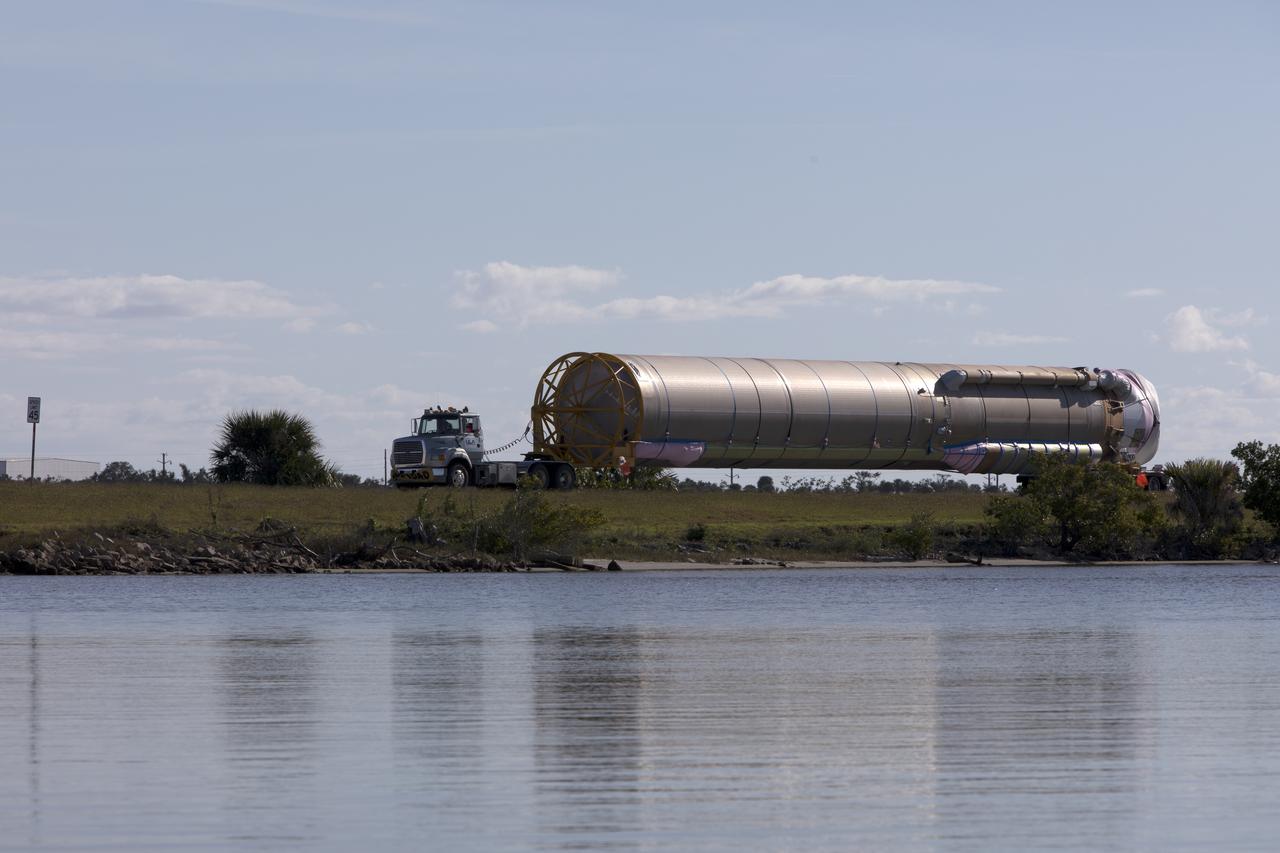

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.

(31 March 2011) --- Technicians at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan pore over the Soyuz TMA-21 spacecraft encapsulated in the first stage of the Soyuz booster rocket March 31, 2011 as preparations continue for the launch April 5 (Kazakhstan time) of Expedition 27 crew members -- Ron Garan of NASA, Soyuz commander Alexander Samokutyaev and Andrey Borisenko, both of Russia, to the International Space Station. The first stage of the Soyuz booster is emblazoned with the name “Gagarin” and the likeness of Yuri Gagarin. The launch is dedicated to the 50th anniversary of the launching of Gagarin from Baikonur April 12, 1961 to become the first human to fly in space. Photo credit: NASA/Victor Zelentsov

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Mariner cargo vessel arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018, carrying the first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
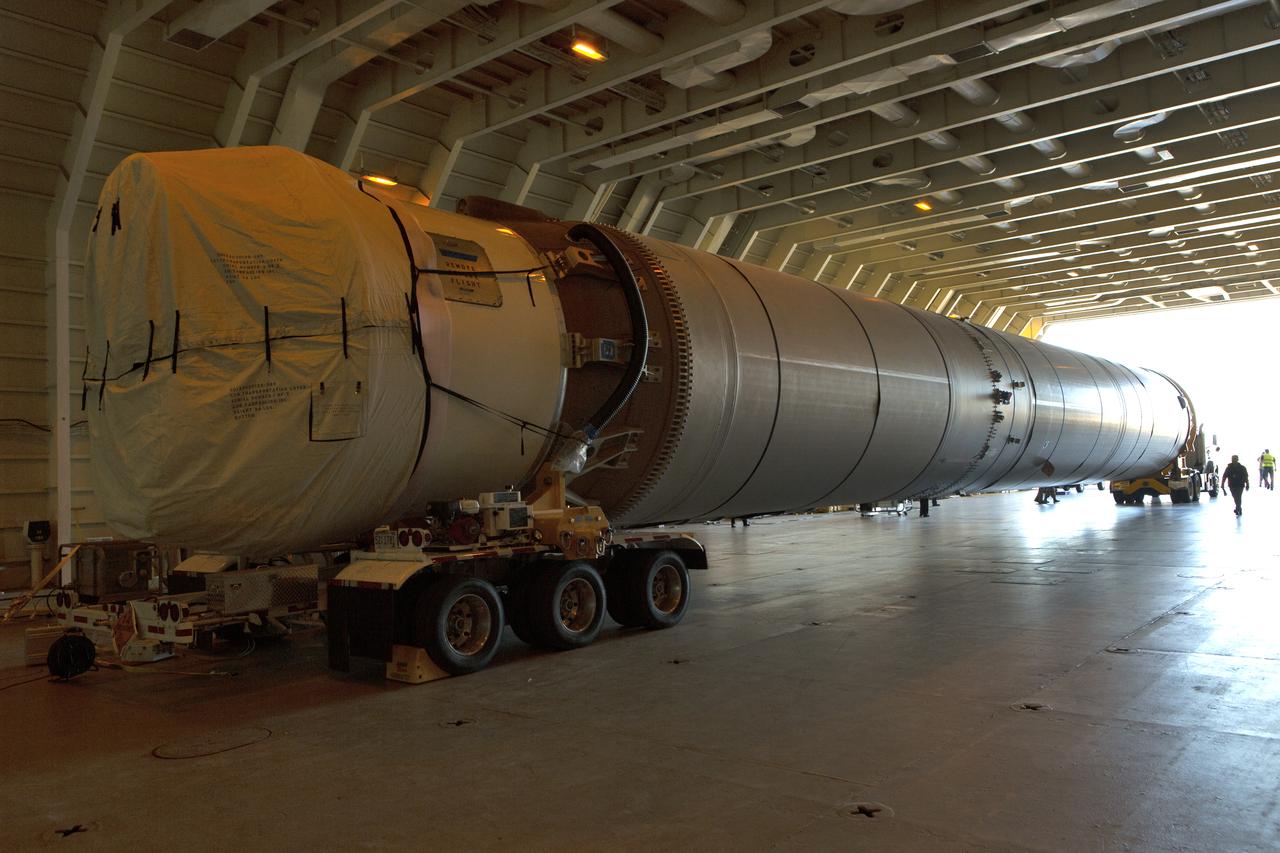

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.
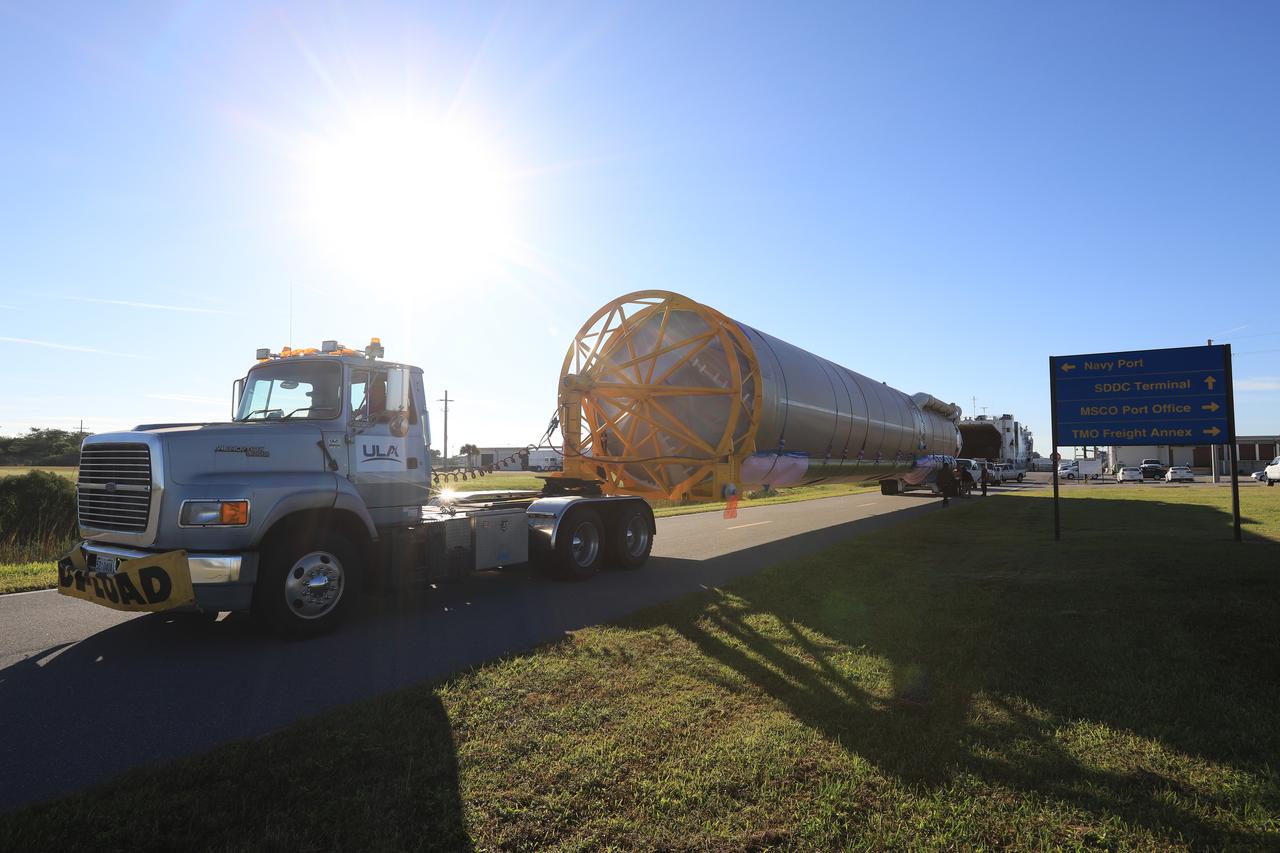

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
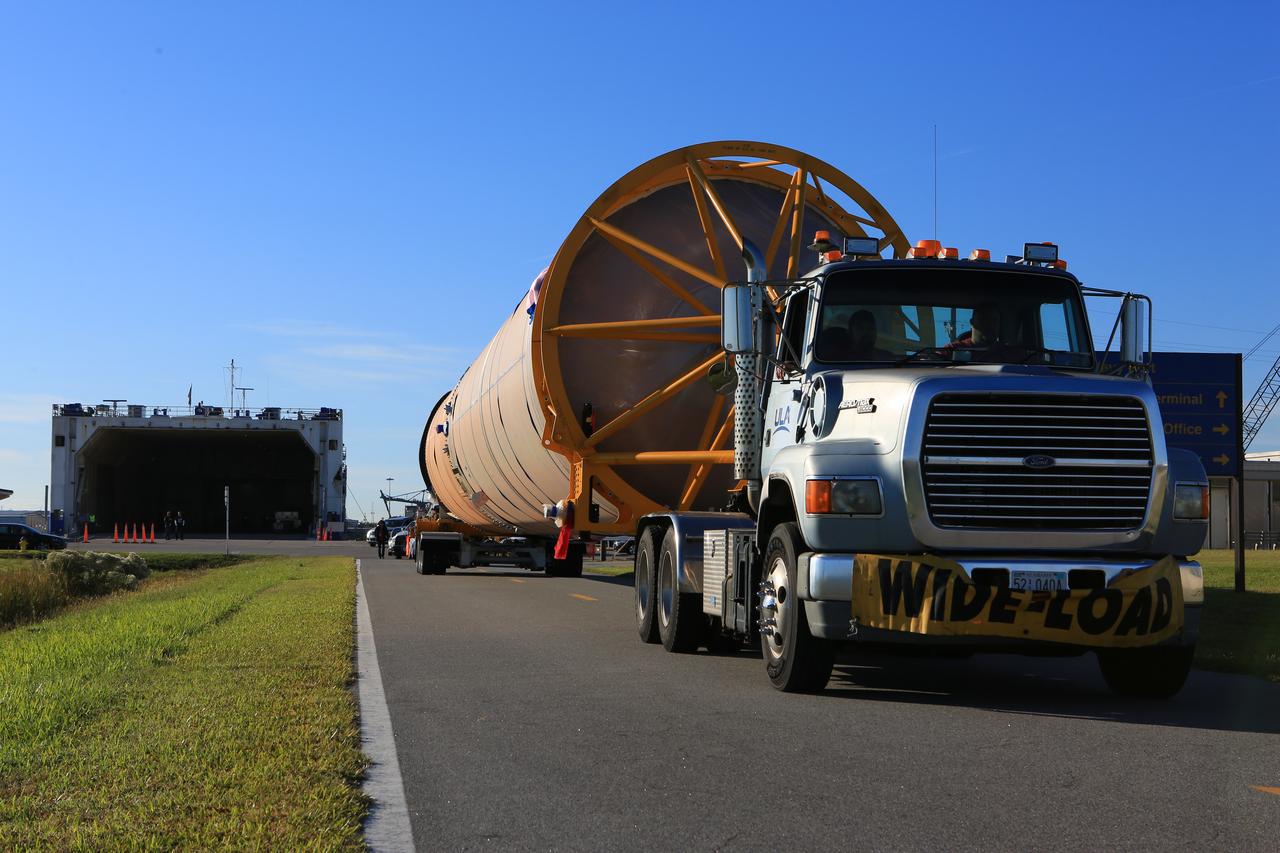

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test arrives at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard ULA's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. The booster will be transported to the Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center for receiving inspections and checkout.

The first stage of the rocket that will launch Boeing's CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the International Space Station on the company's uncrewed Orbital Flight Test is on its way to the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas Spaceflight Operations Center (ASOC) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida on Dec. 7, 2018. The ULA Atlas V first stage booster was shipped aboard the company's Mariner cargo vessel from the company's manufacturing plant in Decatur, Alabama. It is the final piece of hardware that ULA needs to launch the first Boeing Starliner. Inside the ASOC, the booster will be inspected and checked out.
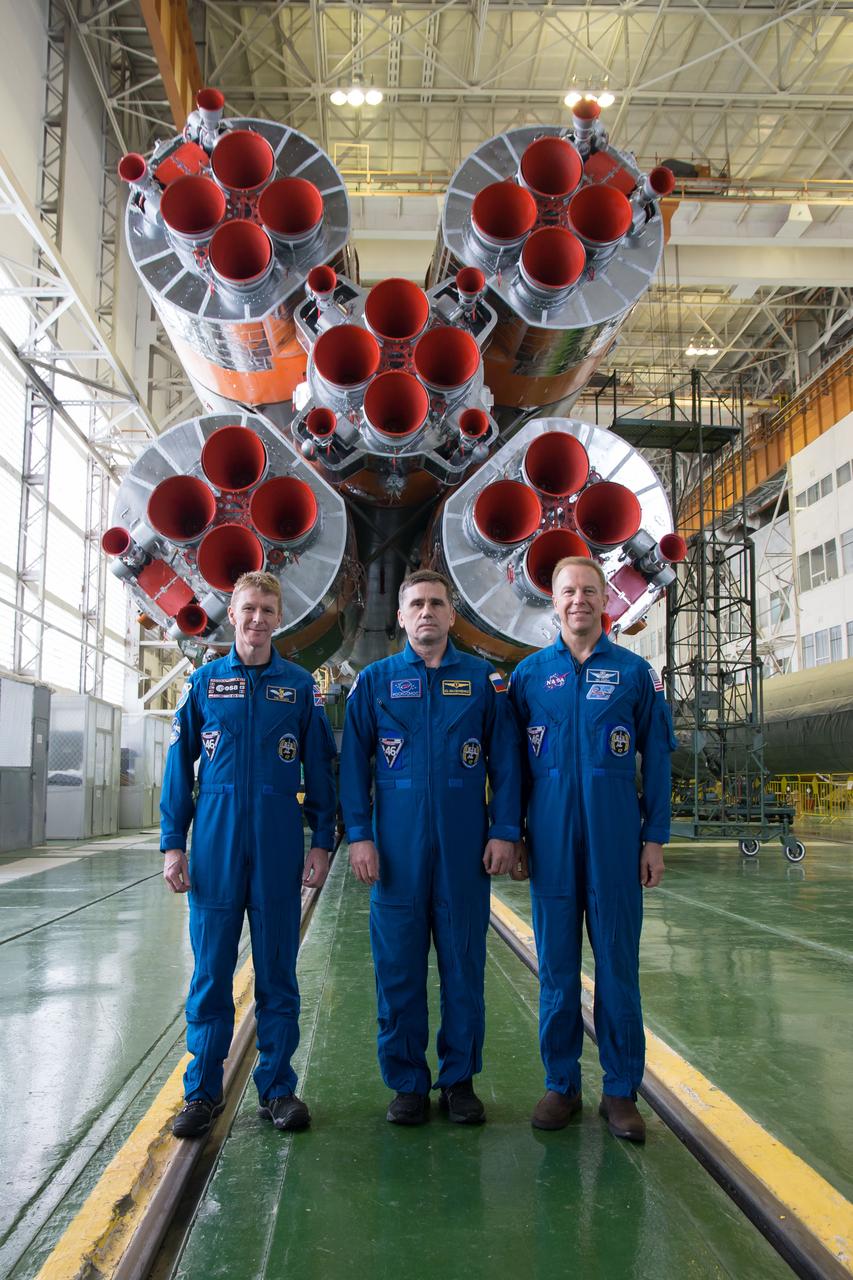

In the Integration Facility at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, Expedition 46-47 crewmembers Tim Peake of the European Space Agency (left), Yuri Malenchenko of the Russian Federal Space Agency (Roscosmos, center) and Tim Kopra of NASA (right) posed for pictures Dec. 10 in front of the first stage of the Soyuz booster rocket during final pre-launch training. Kopra, Peake and Malenchenko will launch Dec. 15 on the Soyuz TMA-19M spacecraft for a six-month mission on the International Space Station. NASA/Victor Zelentsov
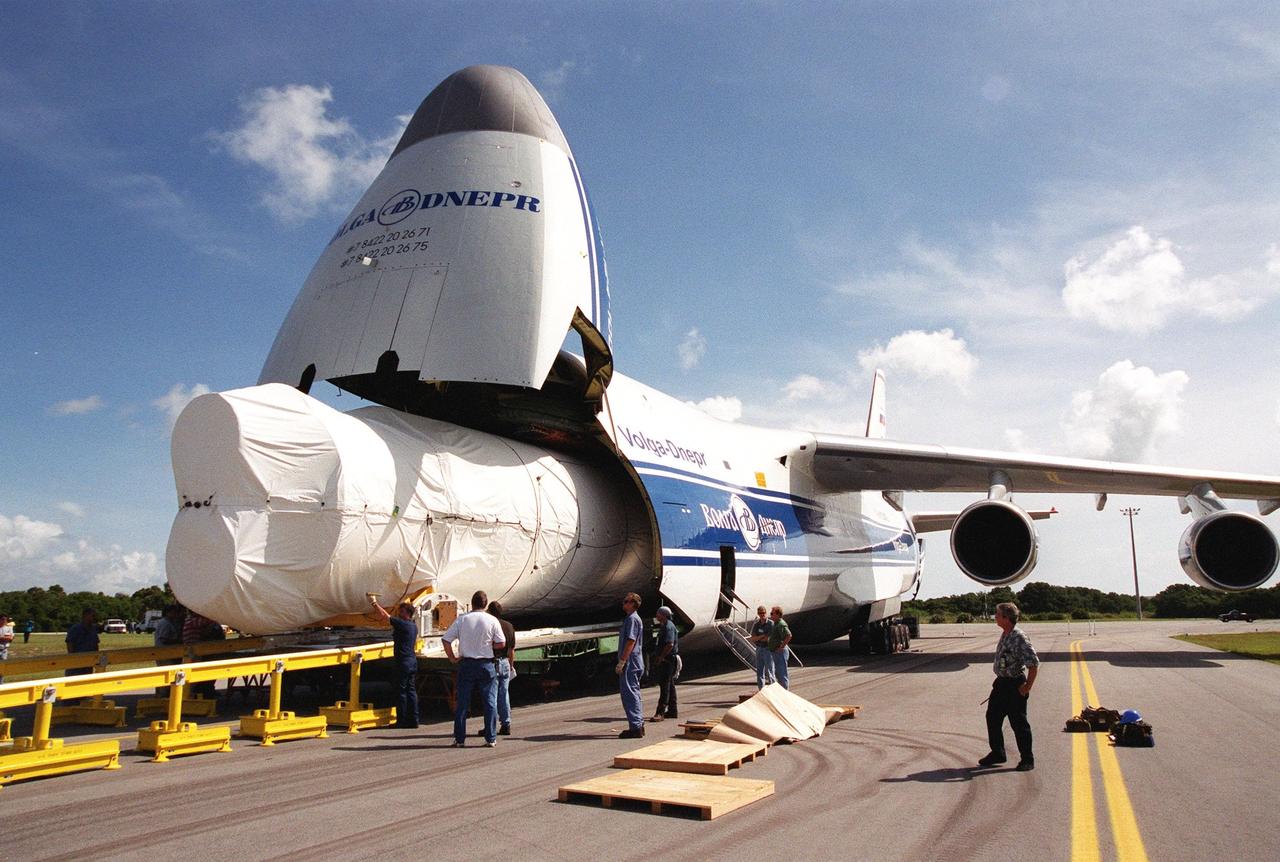

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- Stages of the first Atlas V rocket are offloaded from a Russian Antonov AN-124 aircraft after their arrival at the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The booster will be joined to its Centaur upper stage for testing and checkout in preparation for launch in May 2002

Shown is a concept illustration of Ares I which is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion Crew Exploration Vehicle to low earth orbit. Orion will accommodate as many as six astronauts. The first stage will consist of the five-segment solid rocket booster.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers prepare a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker measures straps for parachutes being prepared for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker sews a parachute being prepared for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A worker prepares a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers prepare a parachute for an upcoming test at the Parachute Refurbishment Facility. The first stage of the new Ares I rocket and Orion spacecraft will use parachutes to return to Earth. Current tests are being performed in Arizona to make sure the designs can safely handle their intended weight. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the shuttle. As with the shuttle, this booster will fall away when spent, lowered by parachute into the Atlantic Ocean where it can be retrieved for re-use. Unlike the shuttle, the booster will be flying faster, at Mach 6, when its separation from the rest of Ares I occurs. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett