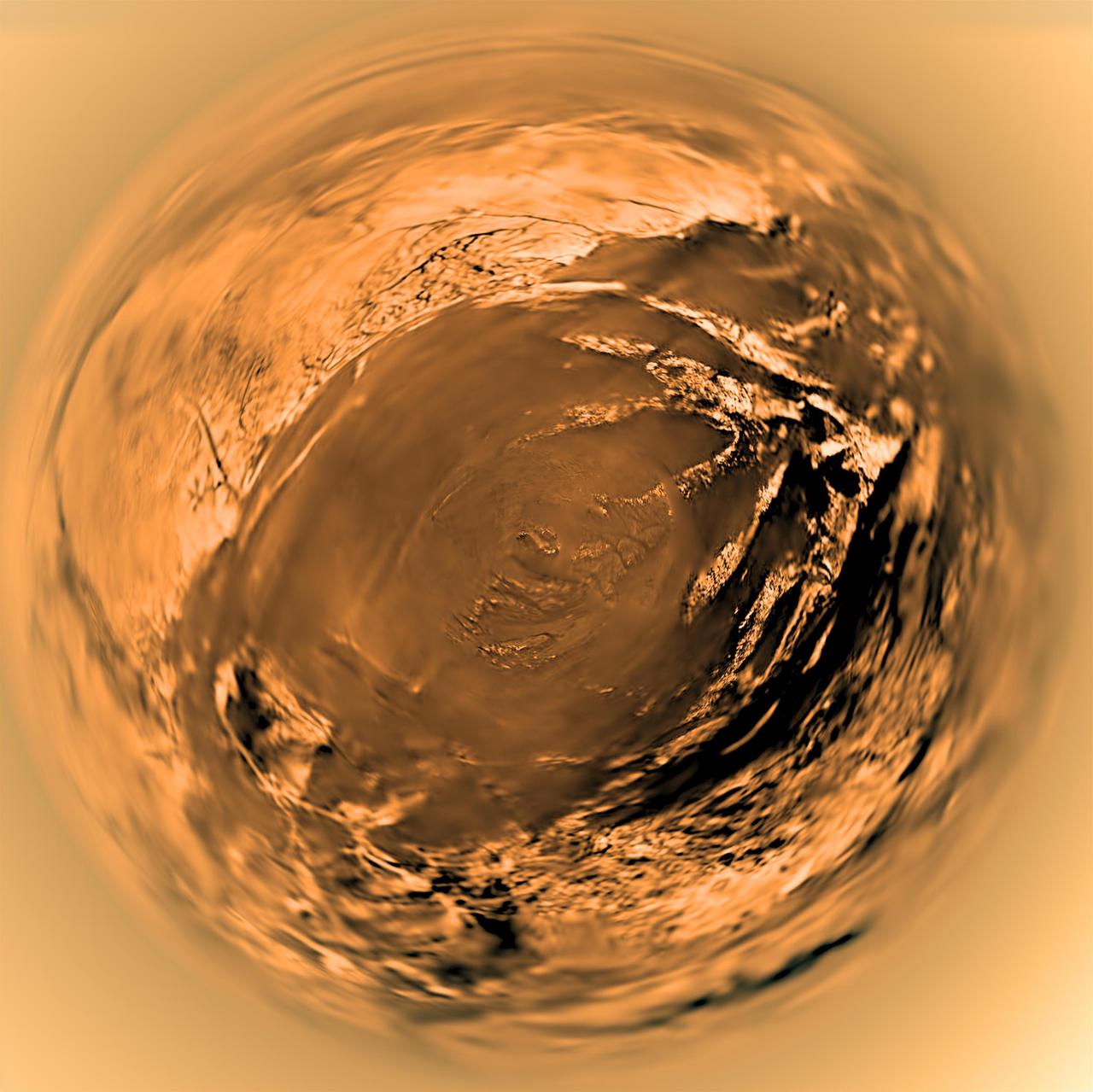
Fish-eye View of Titan Surface
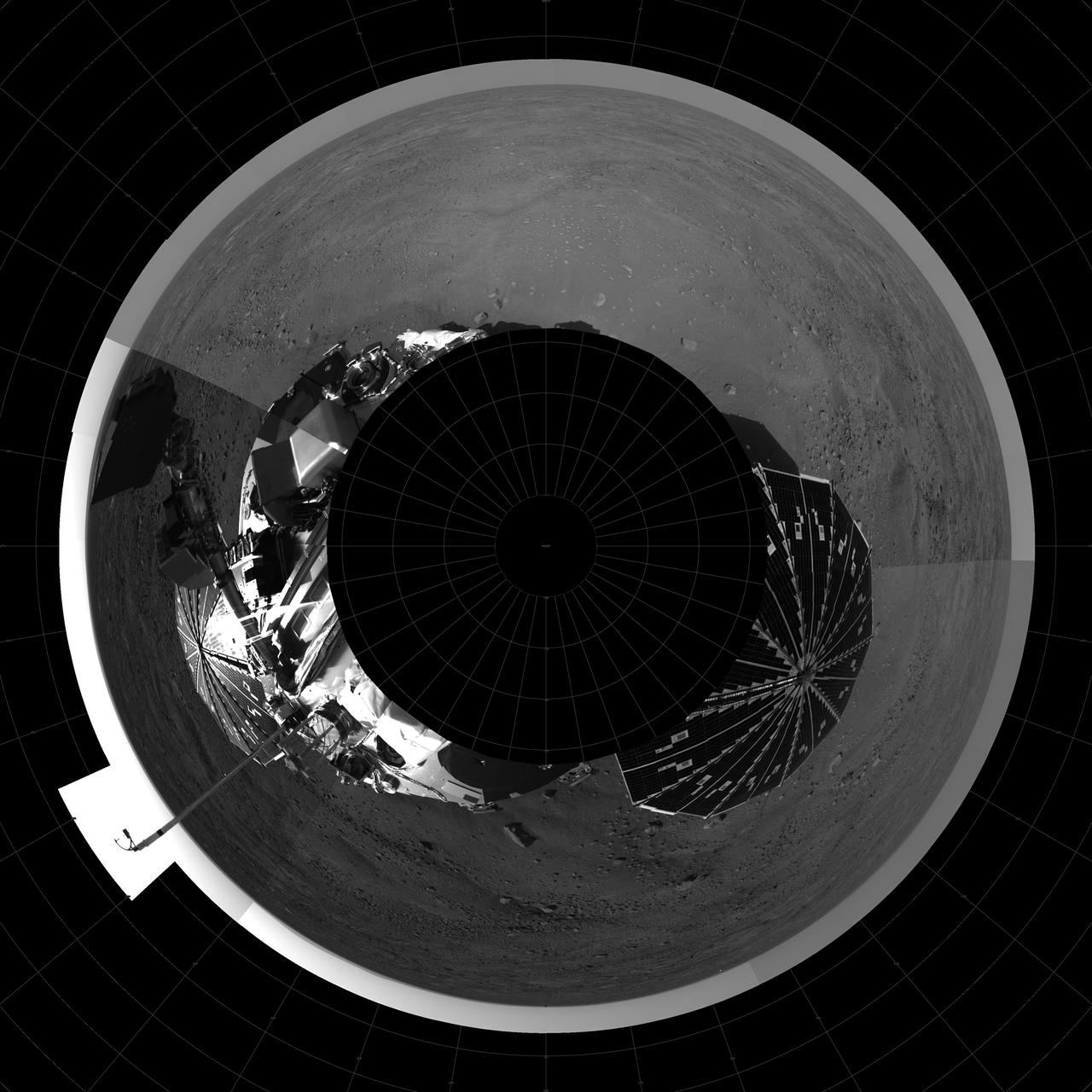

Fish Eye View of Horizon and Lander
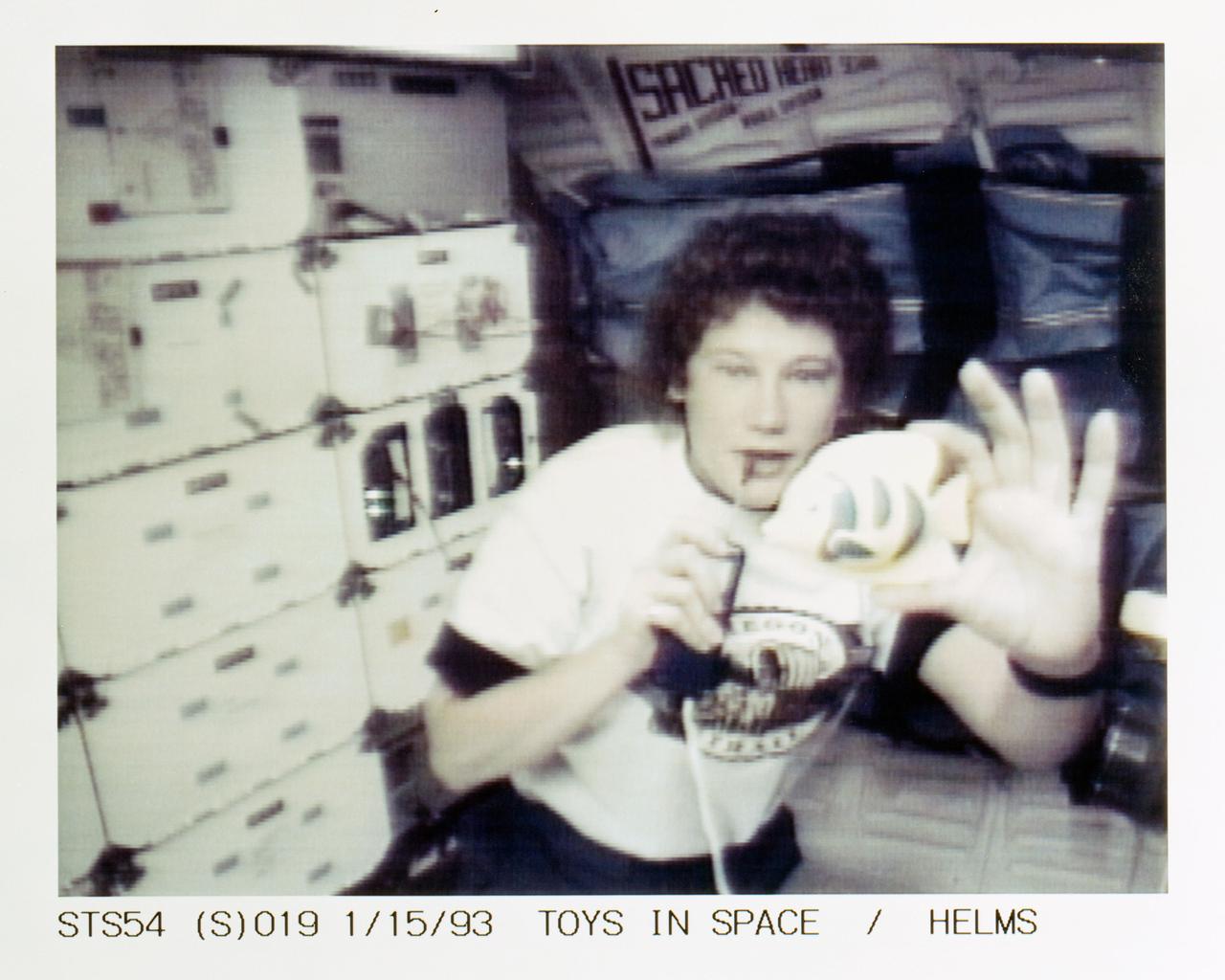

STS054-S-019 (15 Jan 1993) --- Helms with a fish toy on the middeck demonstrates some of the physics of toys to students watching on television. Four schools were chosen to ask questions of the astronauts during the lengthy program. Helms fielded questions from students at Shaver Elementary School in Portland, Oregon. The fish was used to demonstrate Newton's third law of motion and the conservation of angular momentum. The entire collection of toys will be videotaped for an educational program to be distributed to schools in the fall of this year. The scene was recorded at 17:50:08:27 GMT, Jan. 15, 1993.
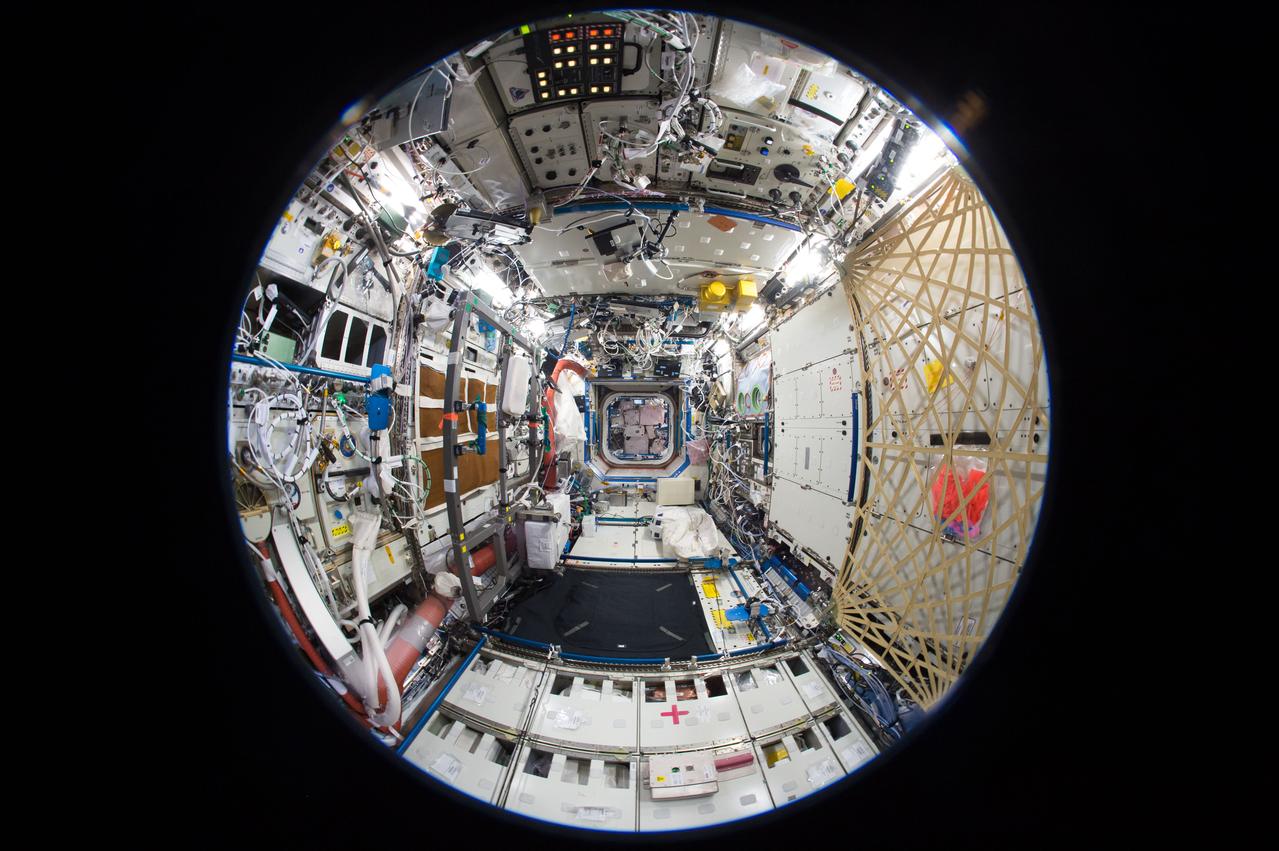

iss050e050873 (2/19/2017) --- A fish-eye view of the U.S. Laboratory taken for a Google Street View of the ISS.

View of Johnson Space Center Administrative Building 1 taken from across the fish pond.
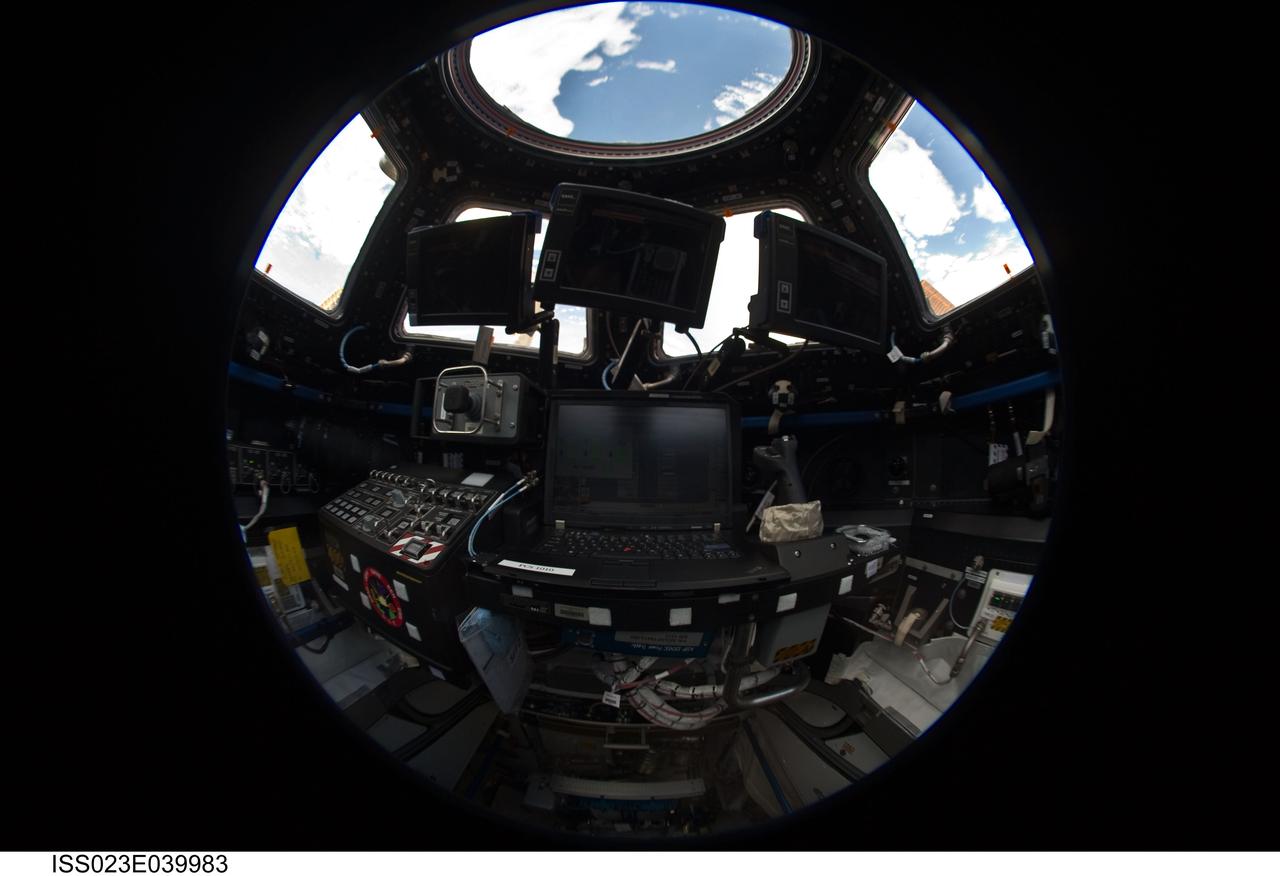

ISS023-E-039983 (8 May 2010) --- A fish-eye lens attached to an electronic still camera was used by an Expedition 23 crew member to capture this image of the robotic workstation in the Cupola of the International Space Station.
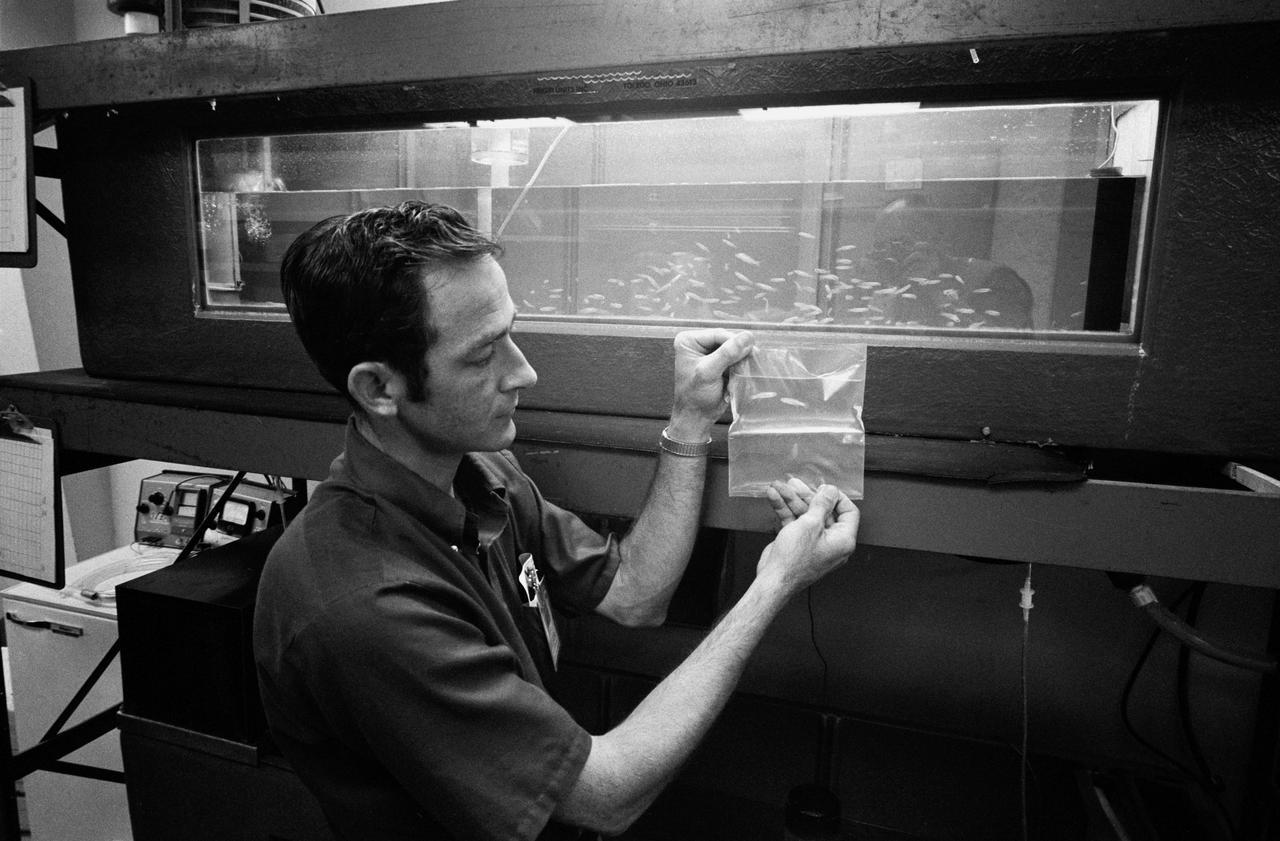

S73-30856 (29 June 1973) --- John Boyd observes a bag with two ?brackish water? minnows known as ?Mummichog Minnows? which will be onboard Skylab 3 with astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma. The fish were added to the flight at the request of scientist-astronaut Dr. Owen K. Garriott, science pilot. Fifty eggs from the minnows will also be included in the bag. The objective of this experiment is to show what disorientation the fish will experience when exposed to weightlessness. Many fish have vestibular apparatus quite similar to man. Even though they live in an environment usually considered to resemble weightlessness, they do perceive a gravity vector. An aquarium of the minnows, caught off the coast of Beaufort, North Carolina, is in the background. Photo credit: NASA
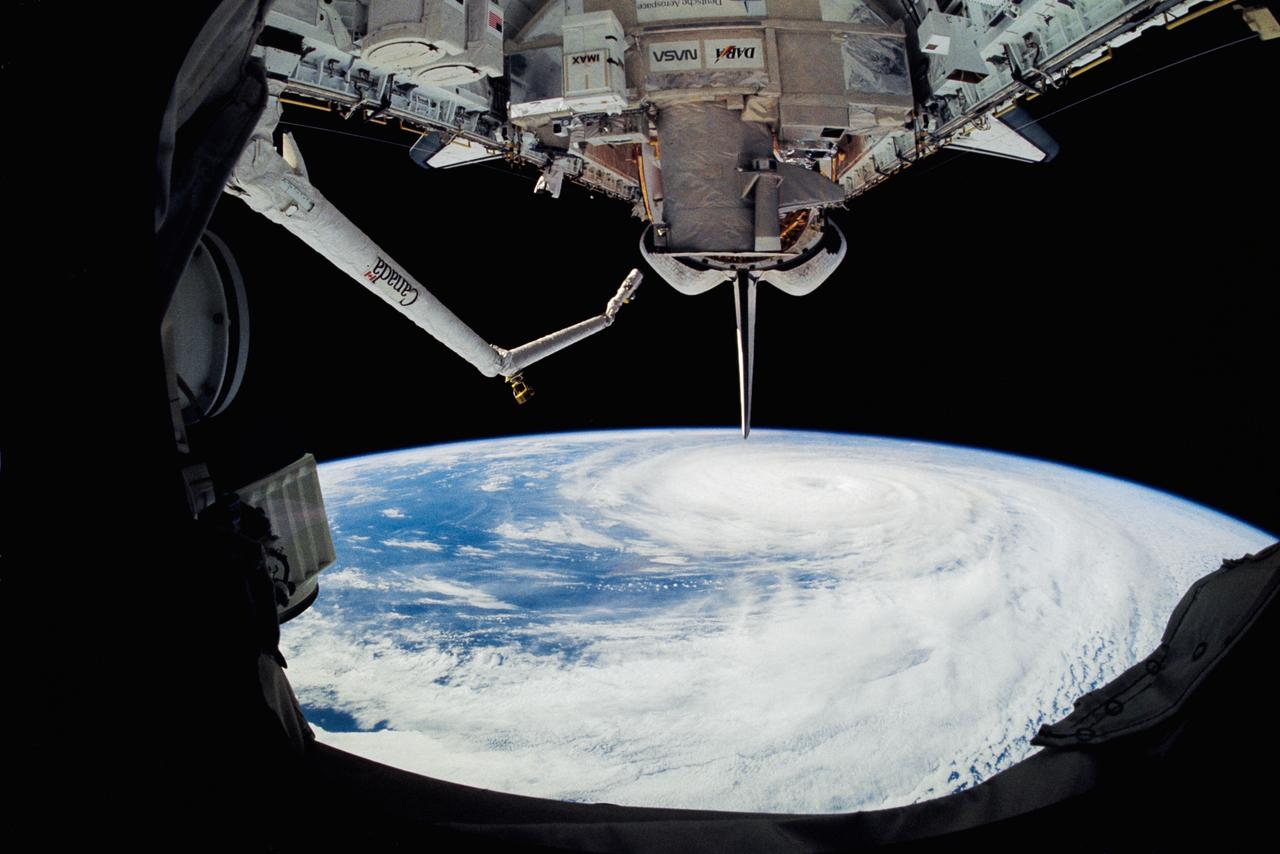

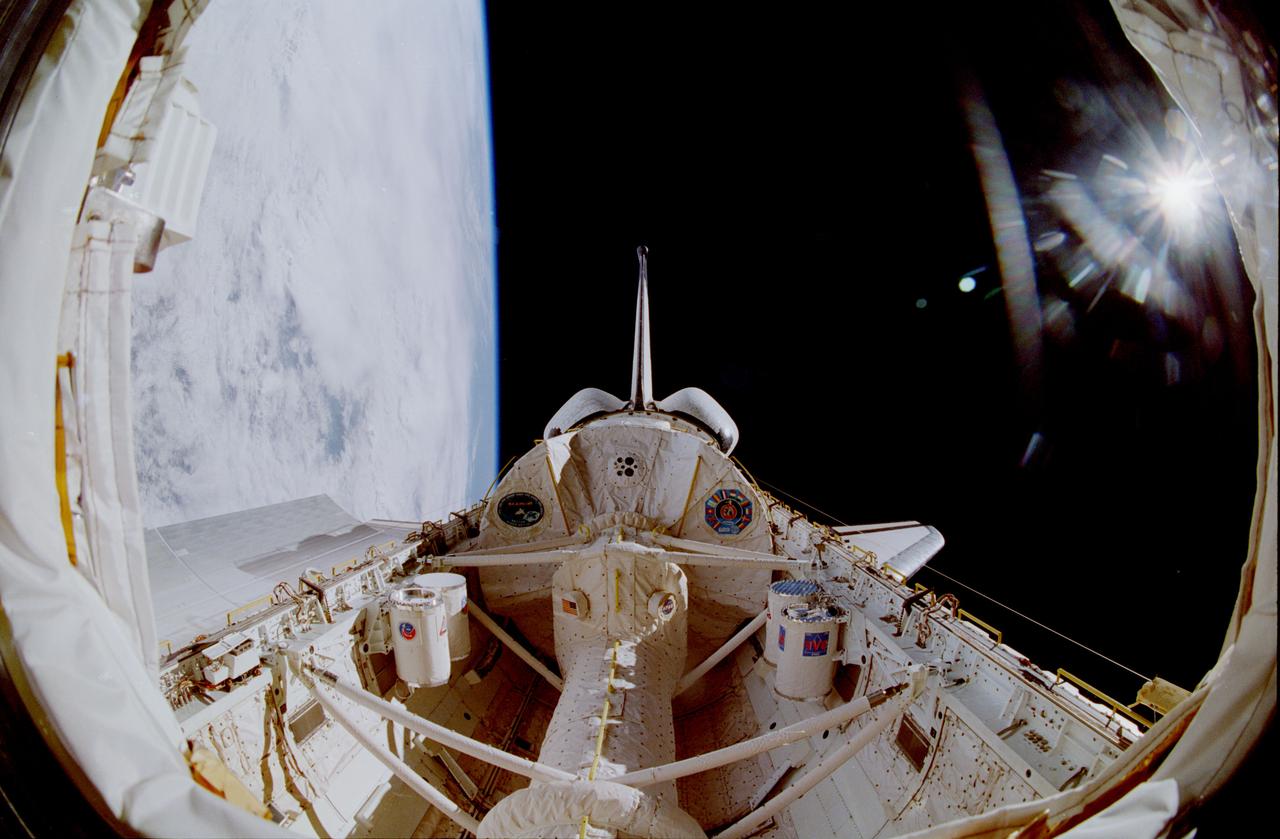
One of the STS-51 astronauts used a "fish-eye" lens on a 35mm cmaera to photograph this view of Hurricane Kenneth in the Pacific Ocean. The Orbiting Retrievable Far and Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer/Shuttle Pallet Satellite (ORFEUS/SPAS) is still in the cargo bay. The Remote Manipulator System (RMS) is extended towards the open payload bay.

iss073e0222649 (May 26, 2025) --- Jakarta, Indonesia, with a metropolitan population of about 32.6 million including its suburbs, and fishing boats illuminated on the Java Sea are pictured at approximately 11:47 p.m. local time from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above the Indian Ocean.
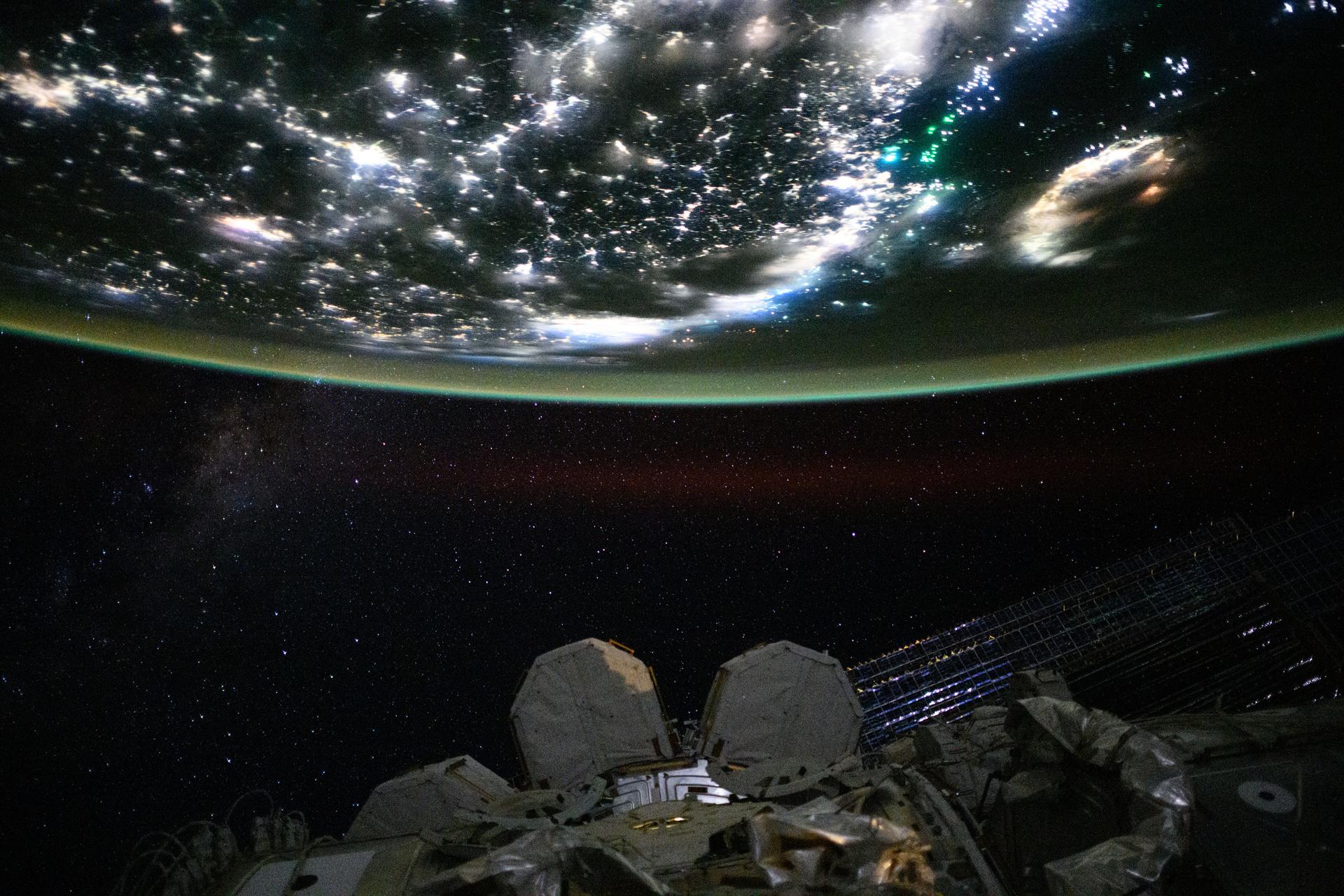

iss073e0848542 (Sept. 17, 2025) --- Green fishing boat lights lure squid, mackerel, and amberjack in the Taiwan Strait near China’s coast, glowing with white LED city lights from Fuzhou to Shenzhen. In contrast, Taiwan’s coast (right) from Taipei to Kaohsiung glows amber from sodium streetlights. The International Space Station captured this view from 261 miles above the East China Sea at 11:55 p.m. local time.
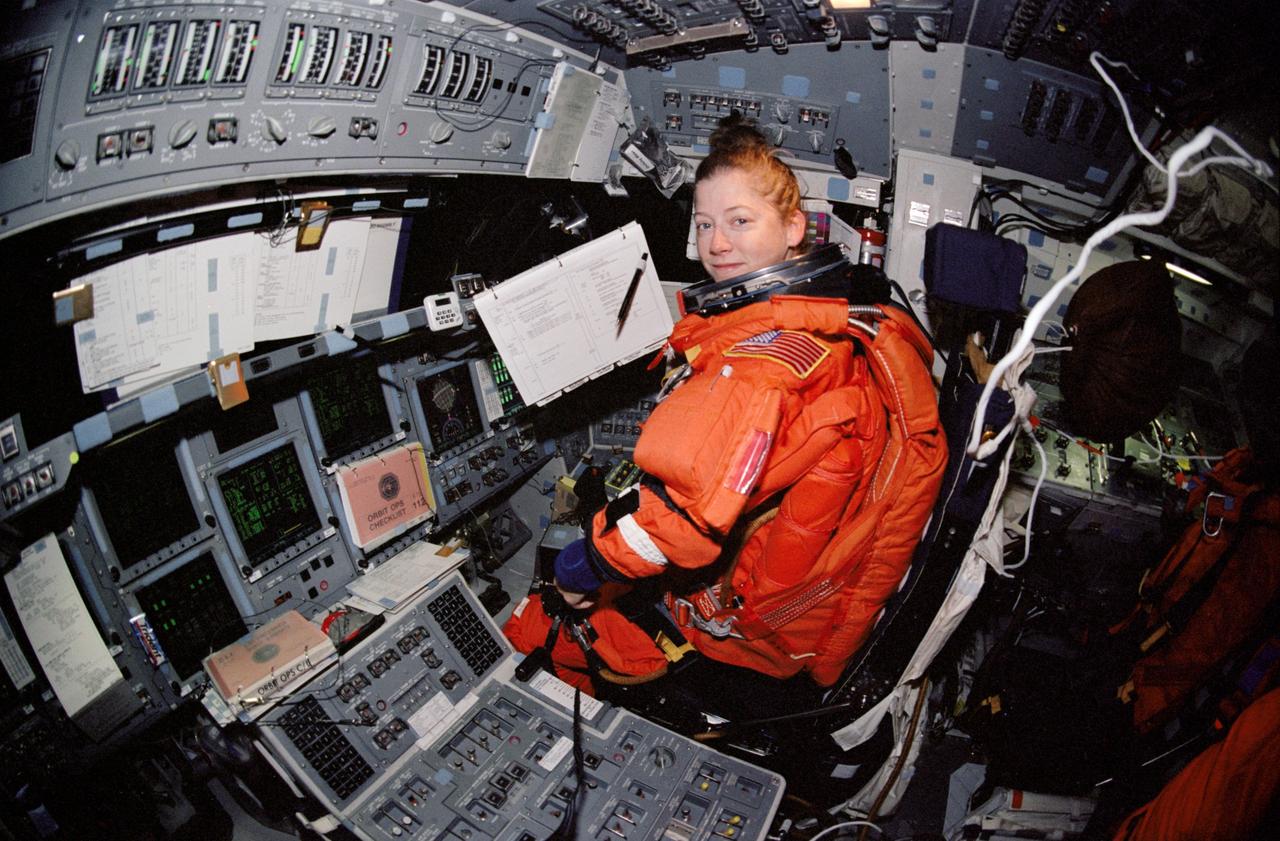

STS112-337-034 (18 October 2002) --- A “fish-eye” lens on a 35mm camera records astronaut Pamela A. Melroy, STS-112 pilot, at the pilot’s station on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Melroy, attired in her shuttle launch and entry suit, looks over a checklist prior to the entry phase of the flight.
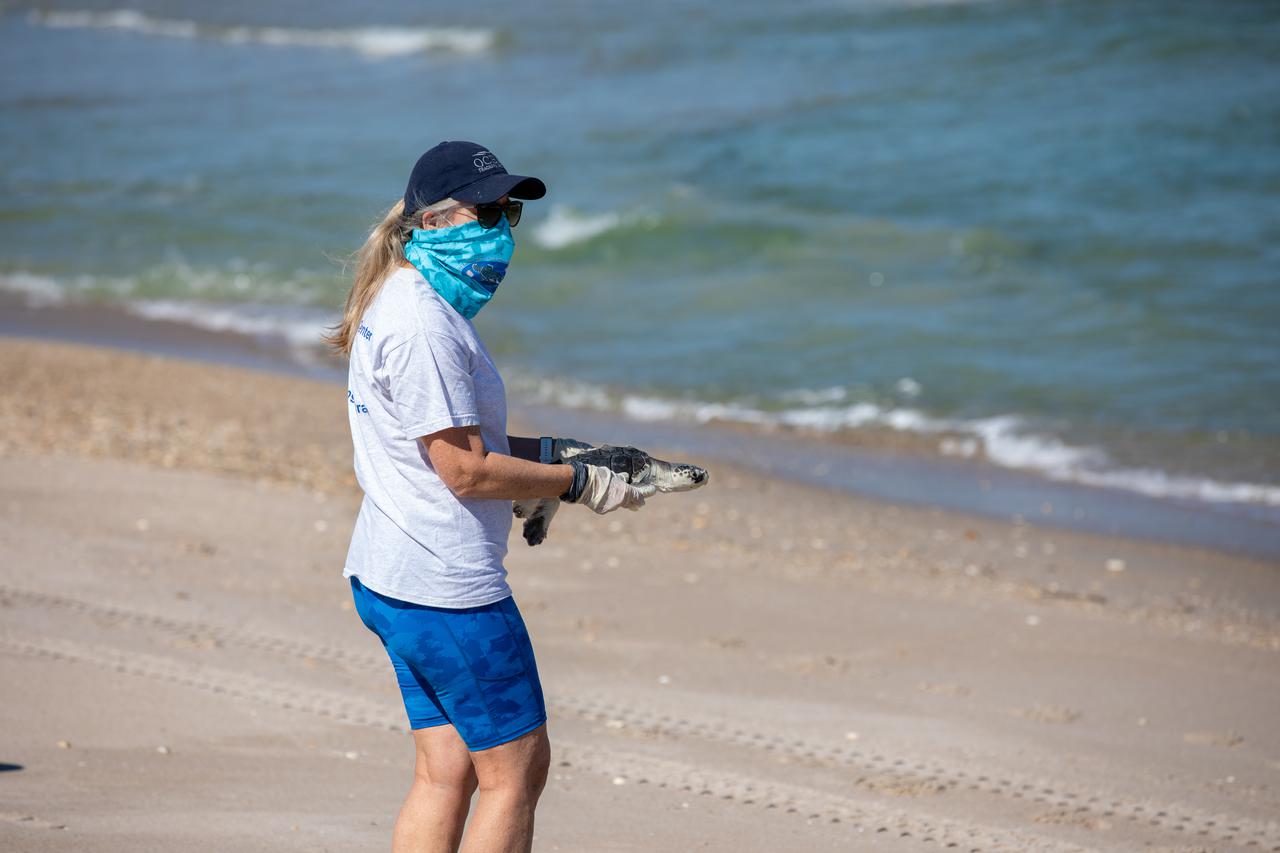

A biologist with Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, prepares to release Kemp’s ridley sea turtles into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
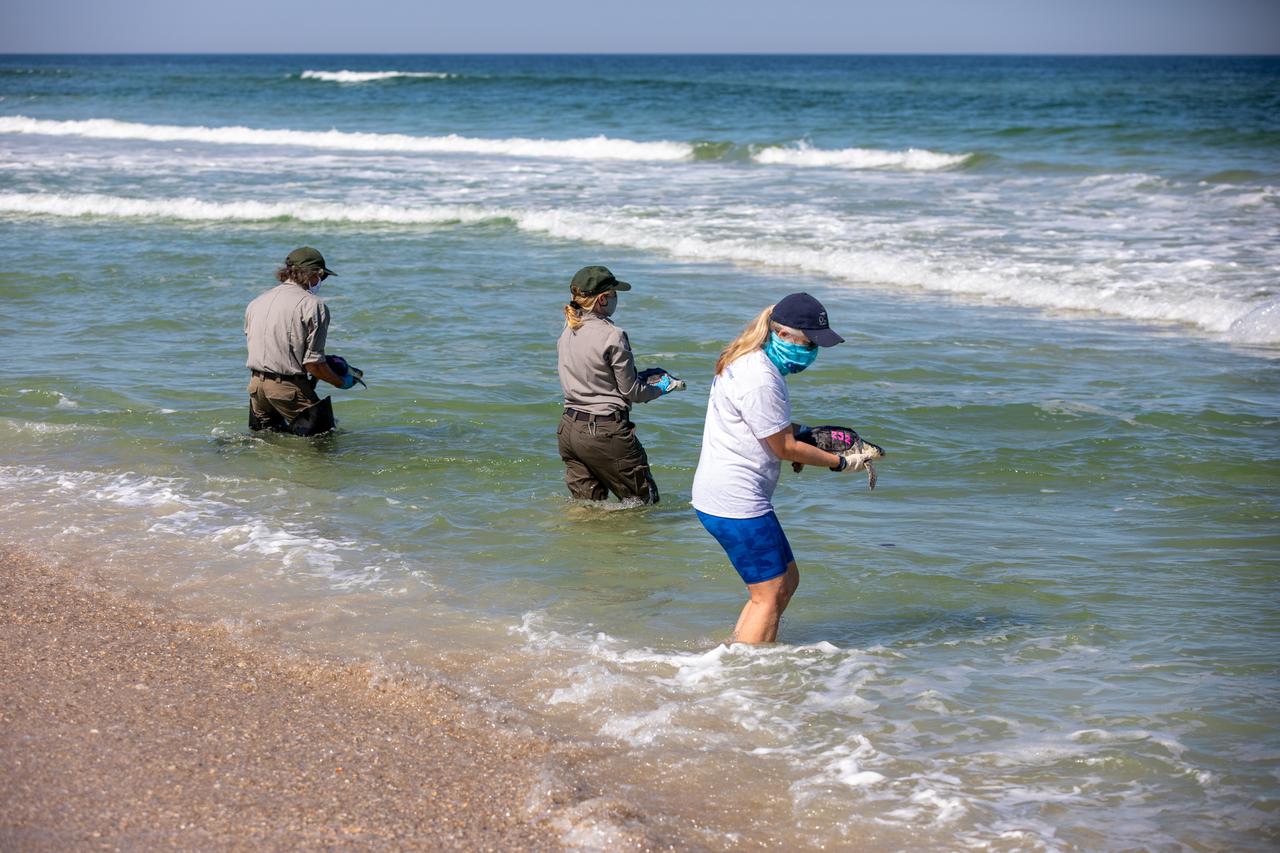

Staff with NASA, the National Park Service, Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, and others, prepare to release Kemp’s ridley sea turtles into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
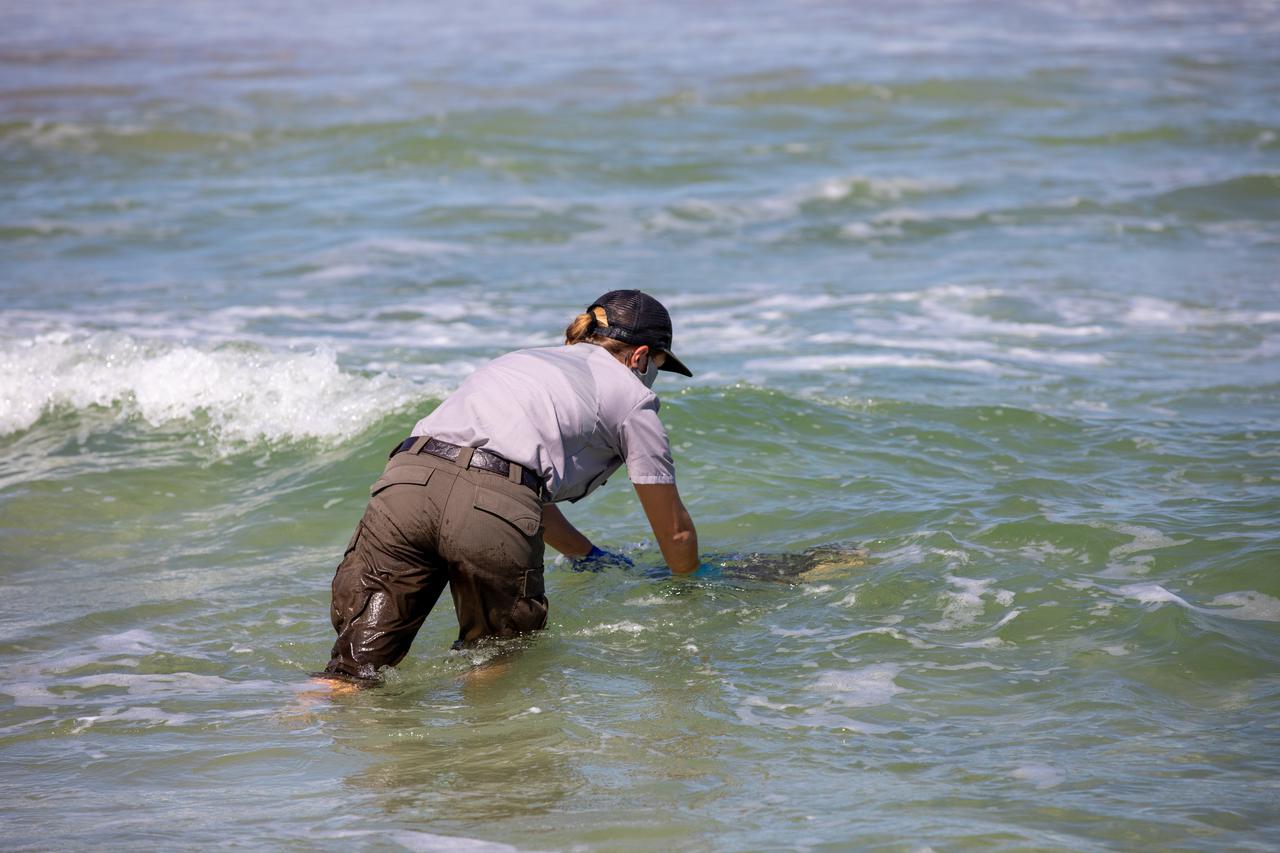

A National Park Service staff member releases a Kemp’s ridley sea turtle into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
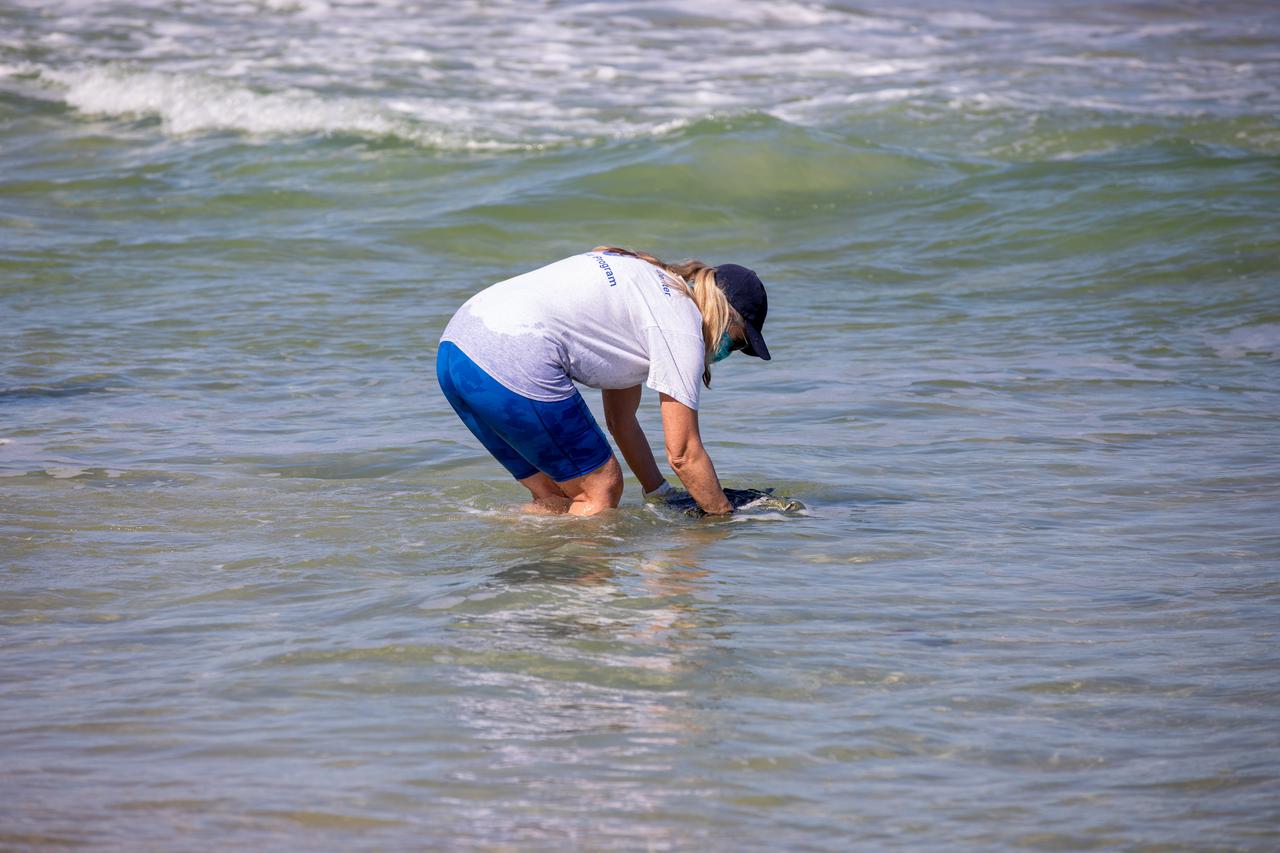

A biologist with Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, releases a Kemp’s ridley sea turtle into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
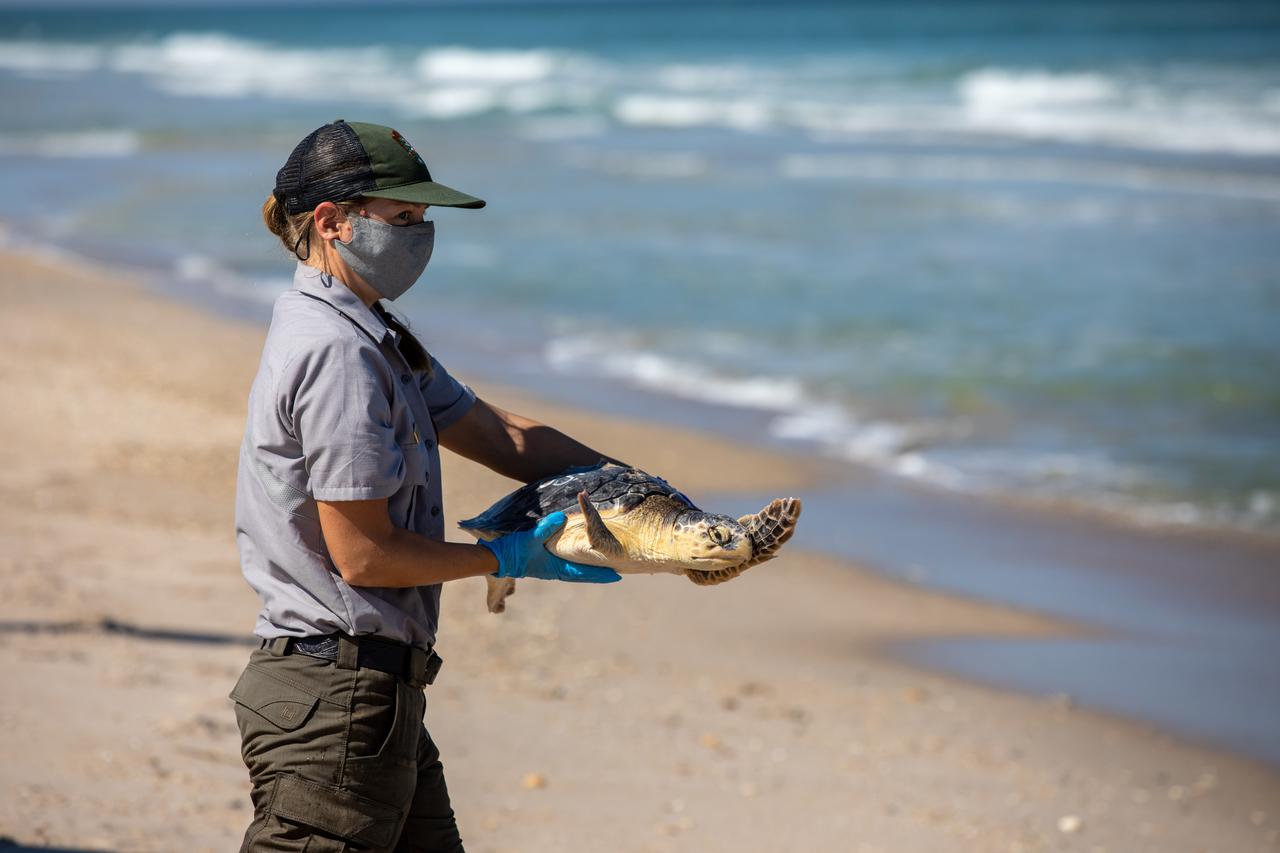

A National Park Service staff member prepares to release a Kemp’s ridley sea turtle into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
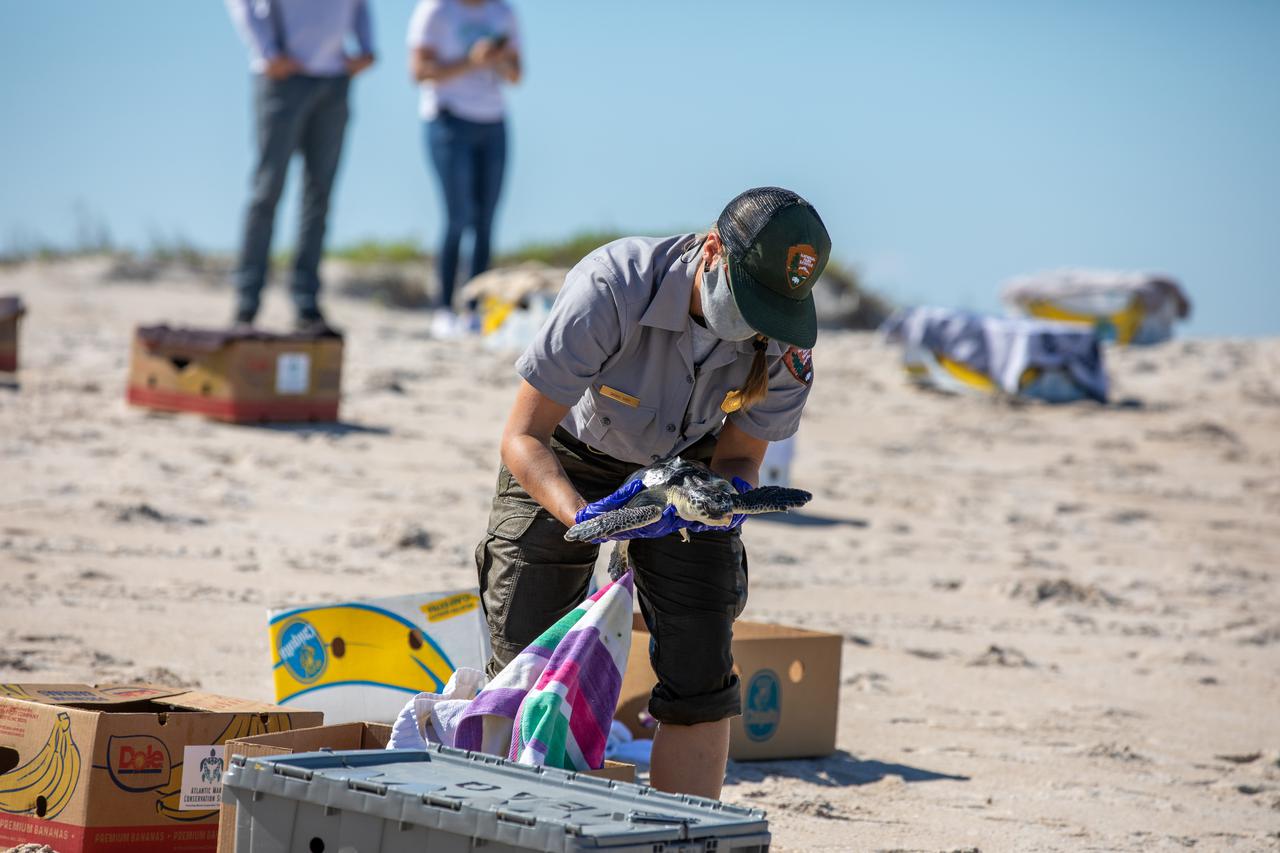

Staff with NASA, the National Park Service, Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, and others, prepare to release Kemp’s ridley sea turtles into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
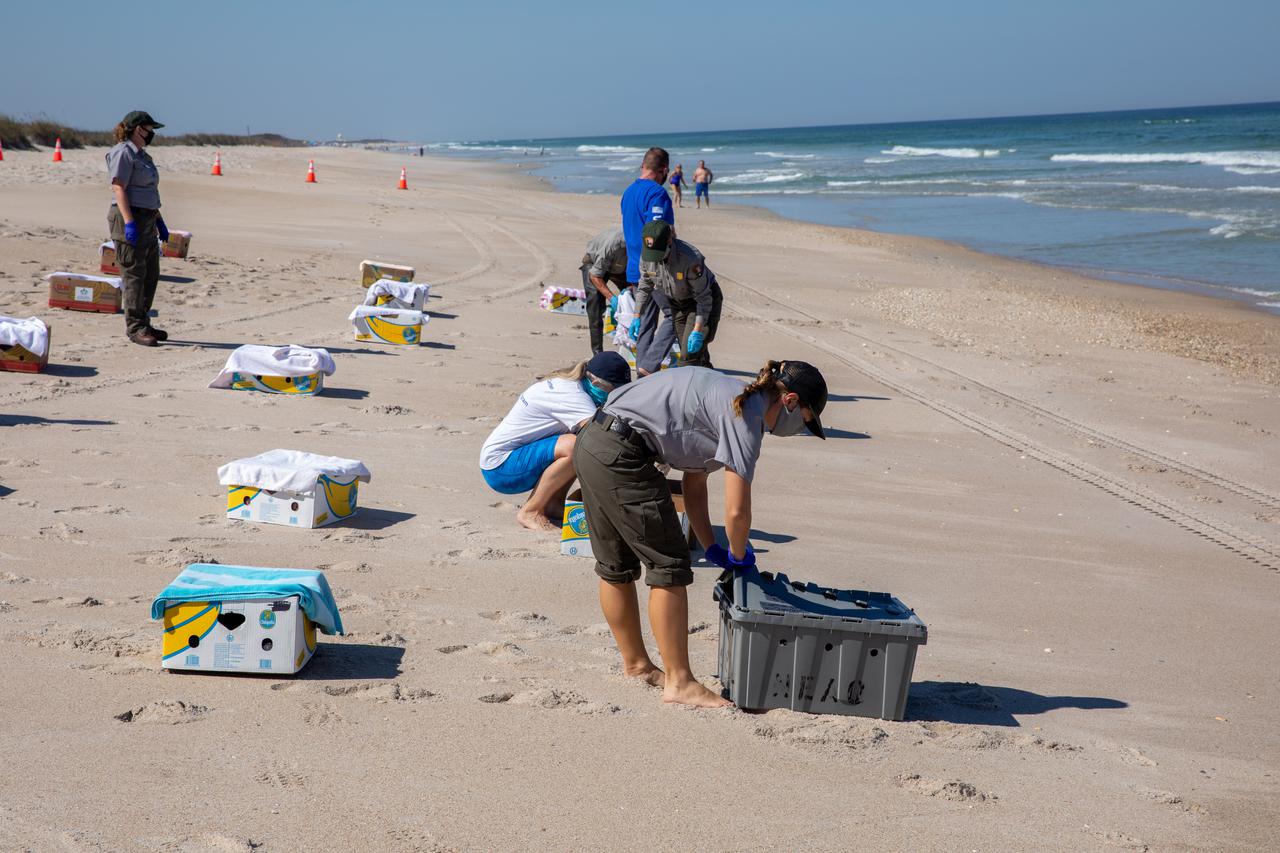

Staff with NASA, the National Park Service, Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, and others, prepare to release Kemp’s ridley sea turtles into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
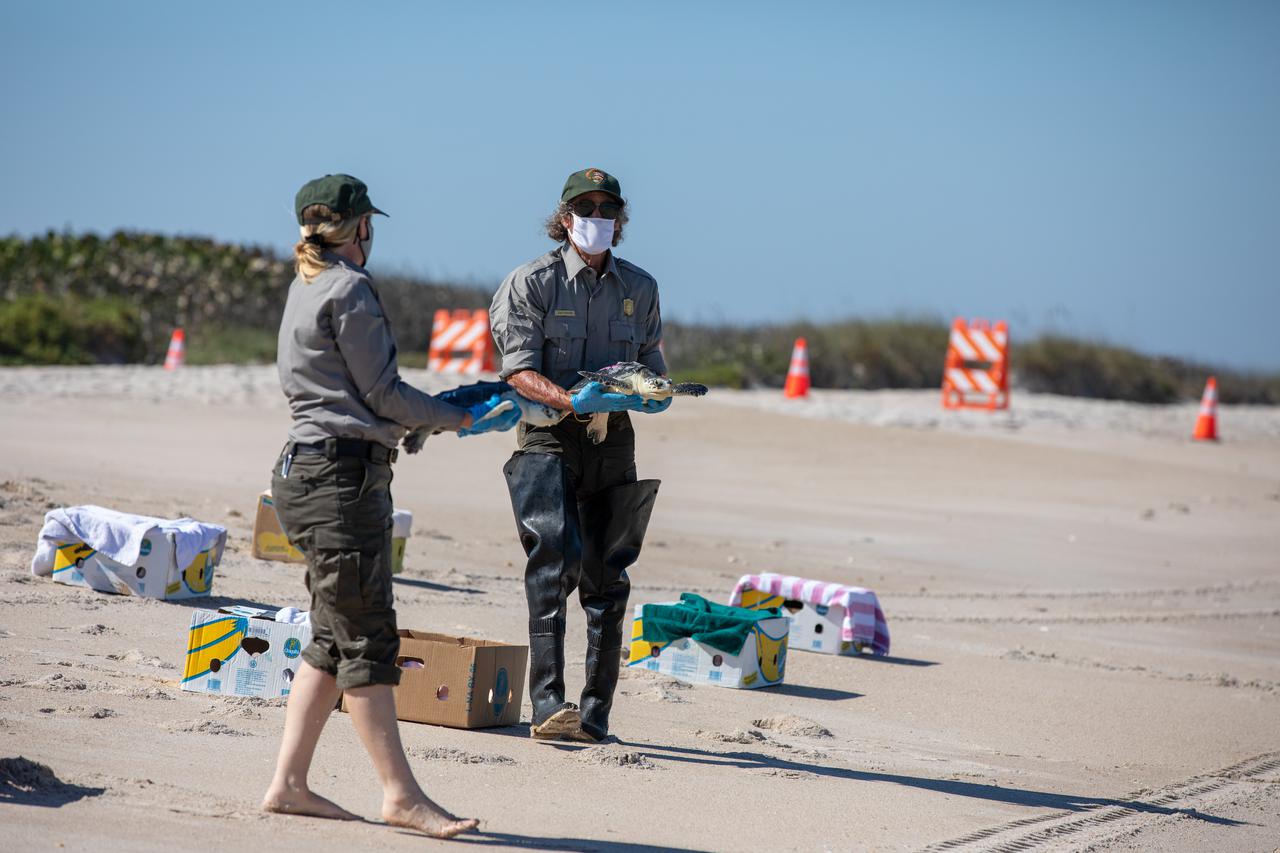

Staff with NASA, the National Park Service, Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, and others, prepare to release Kemp’s ridley sea turtles into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
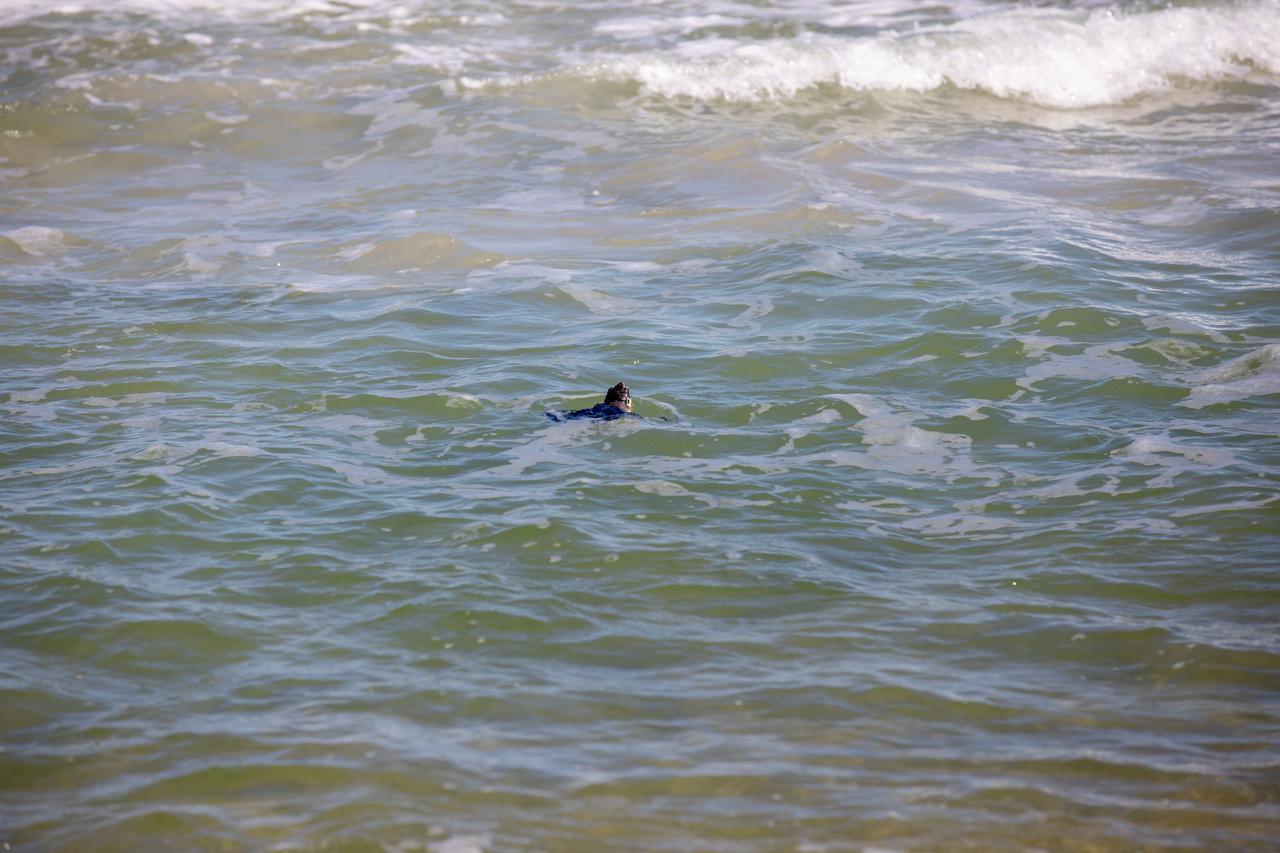

A Kemp’s ridley sea turtle swims in the surf after it is released into the Atlantic Ocean at the Canaveral National Seashore near Kennedy Space Center on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York to the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
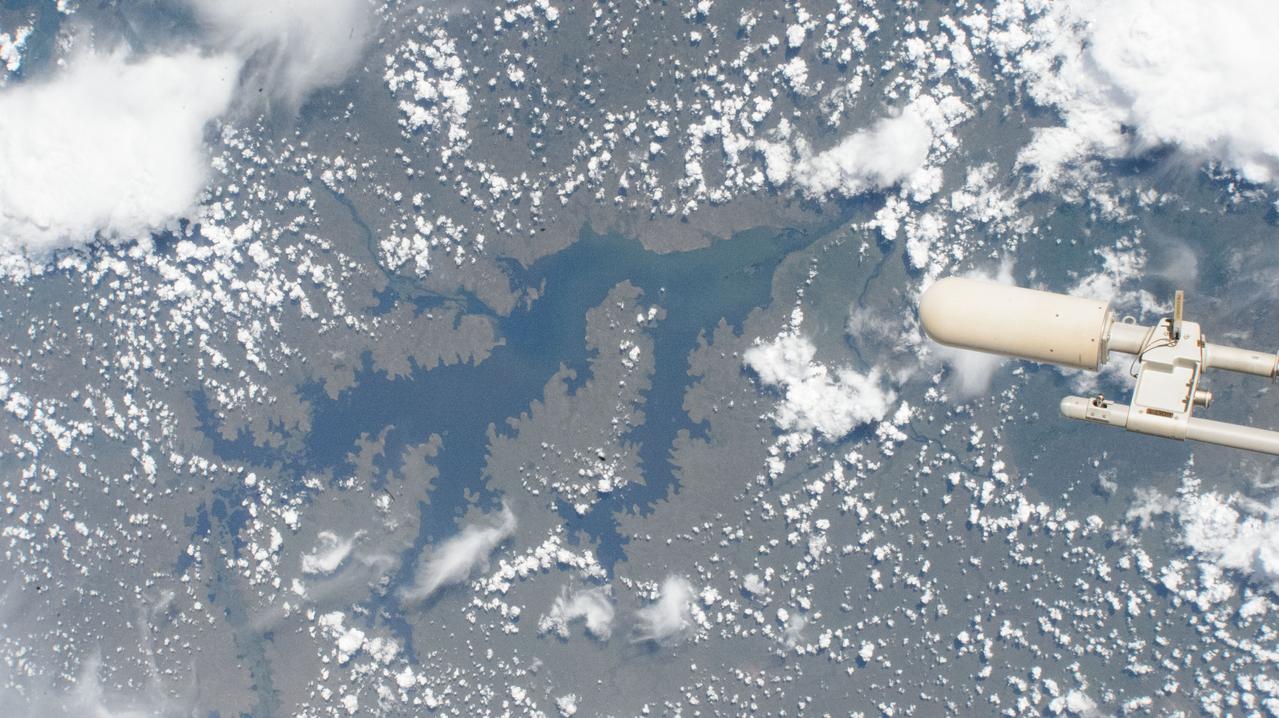

iss072e073616 (Oct. 19, 2024) --- Uganda's Lake Kyoga, hosting crocodiles, and numerous fish and plant species, extends into Lake Kwania, Lake Kojweri, and other lakes in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above the African nation.
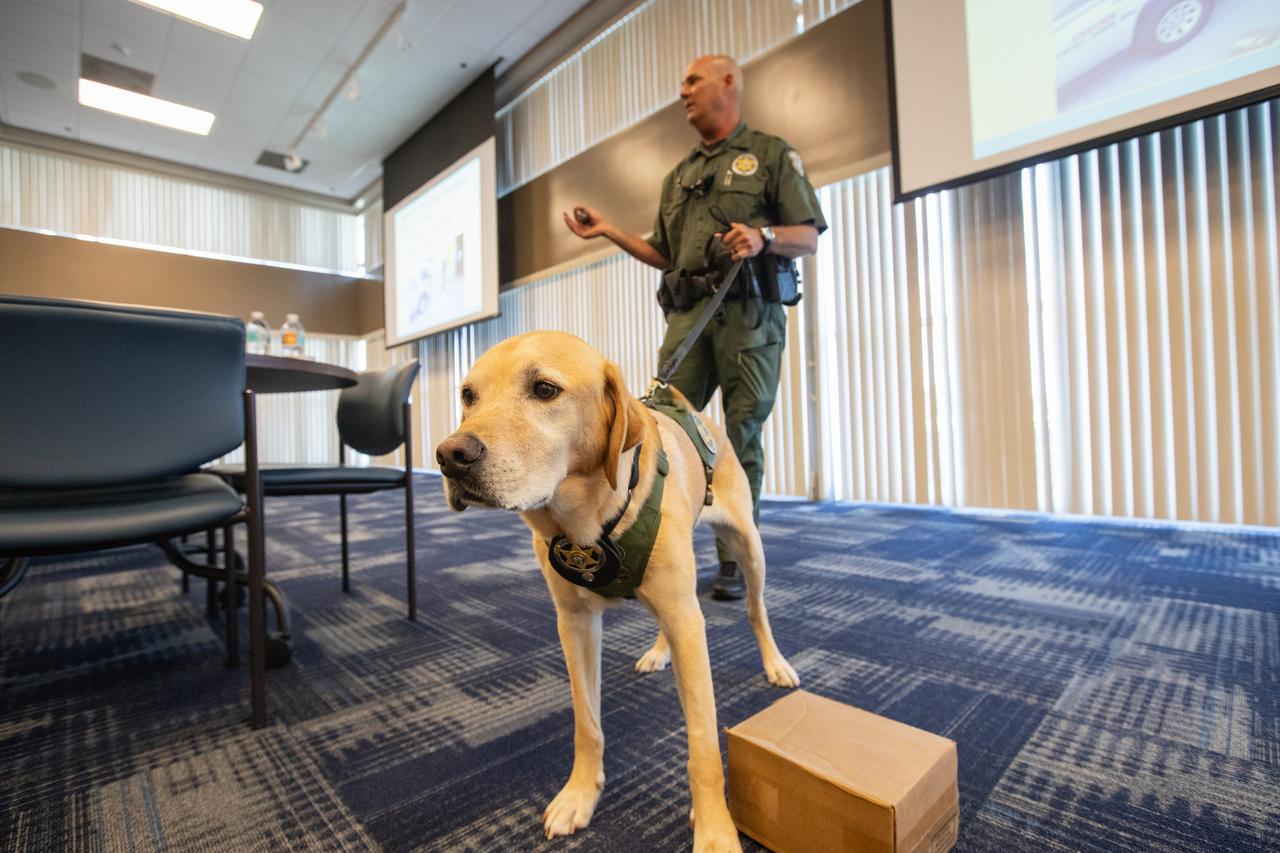

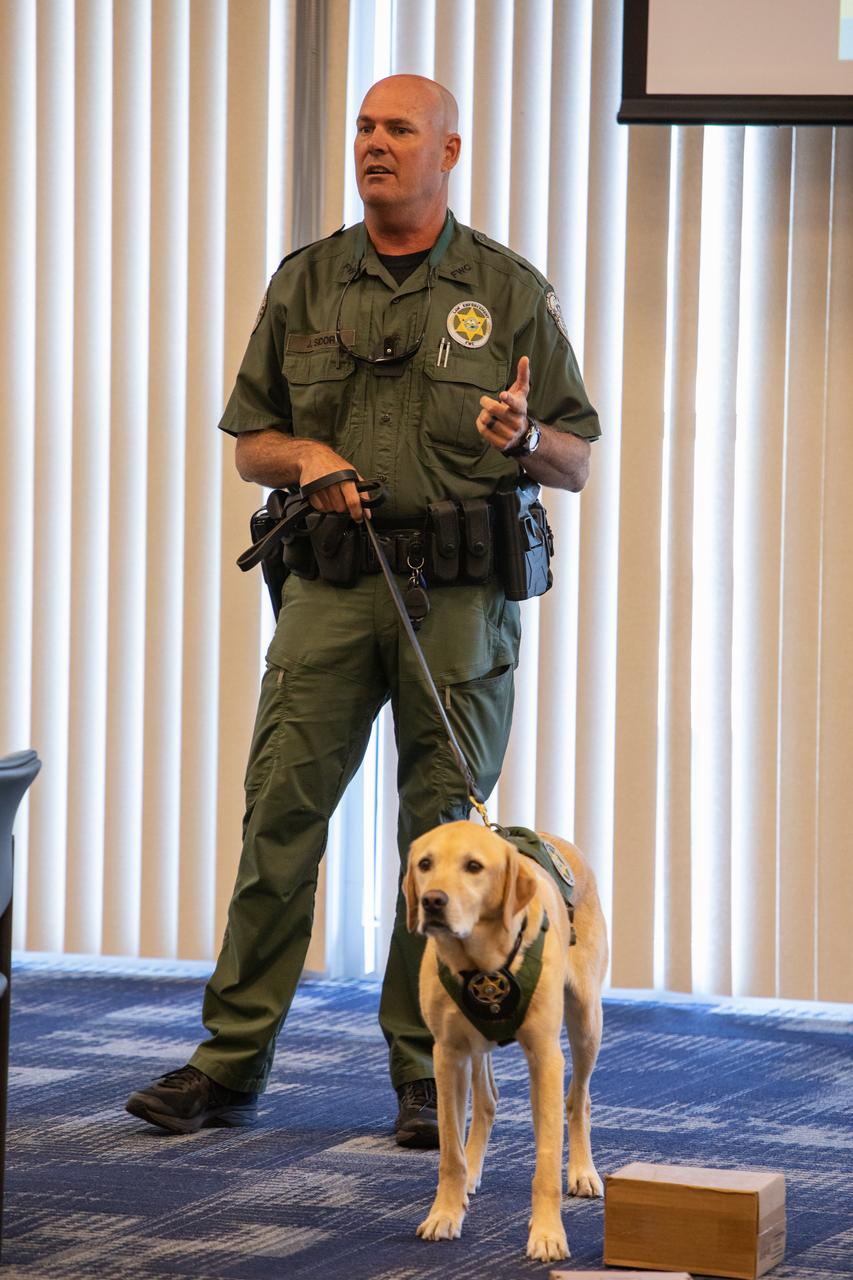
Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
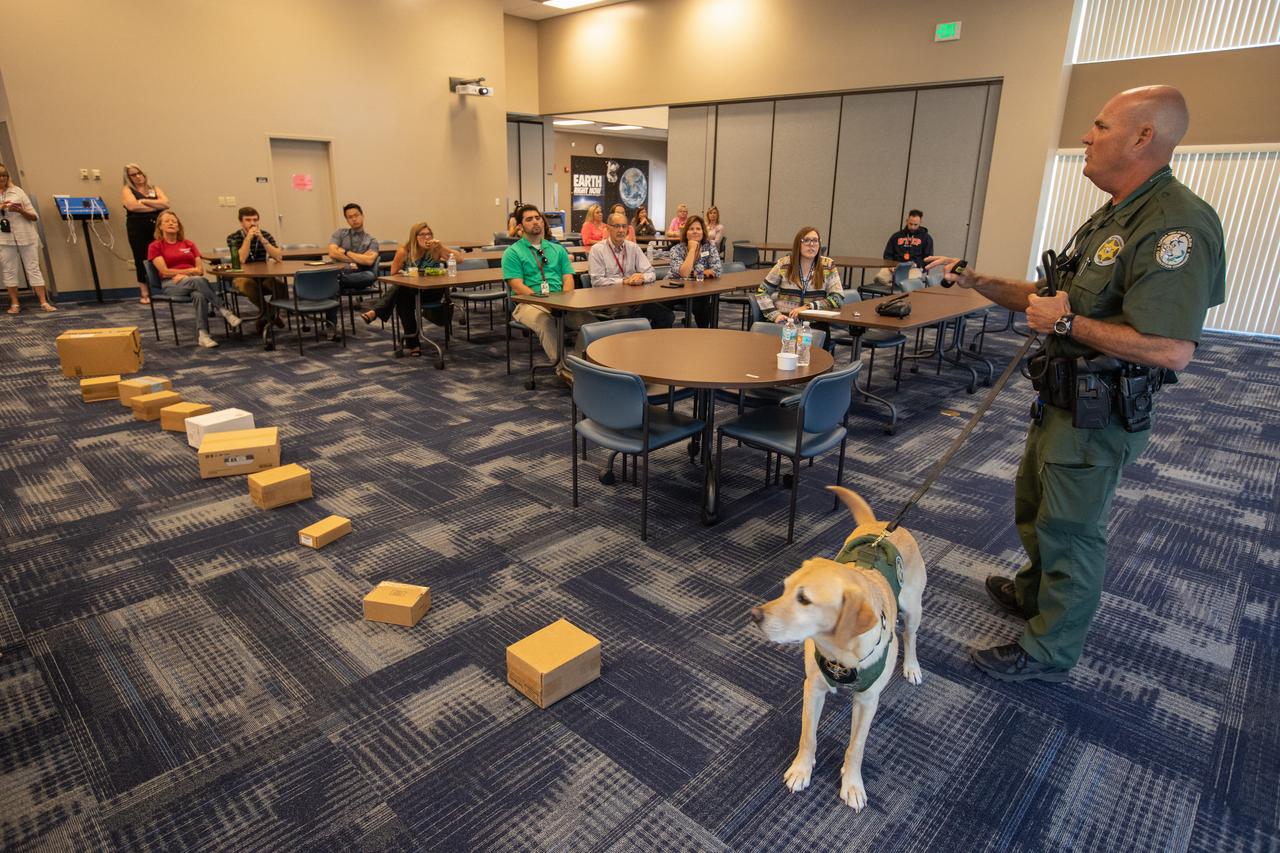

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
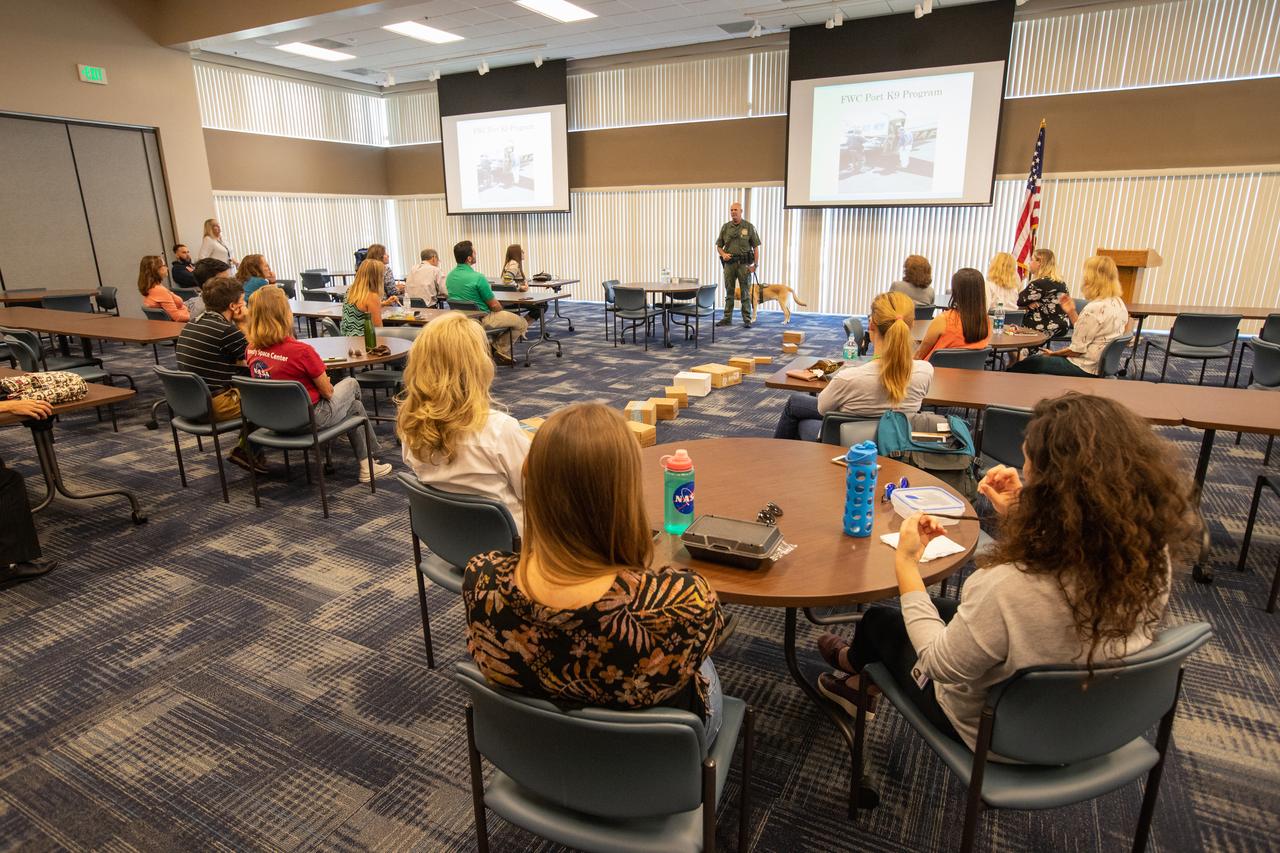

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.

Back by popular demand: THEMIS ART IMAGE #61 With an impact crater for an eye - this layer of material resembles a large fish
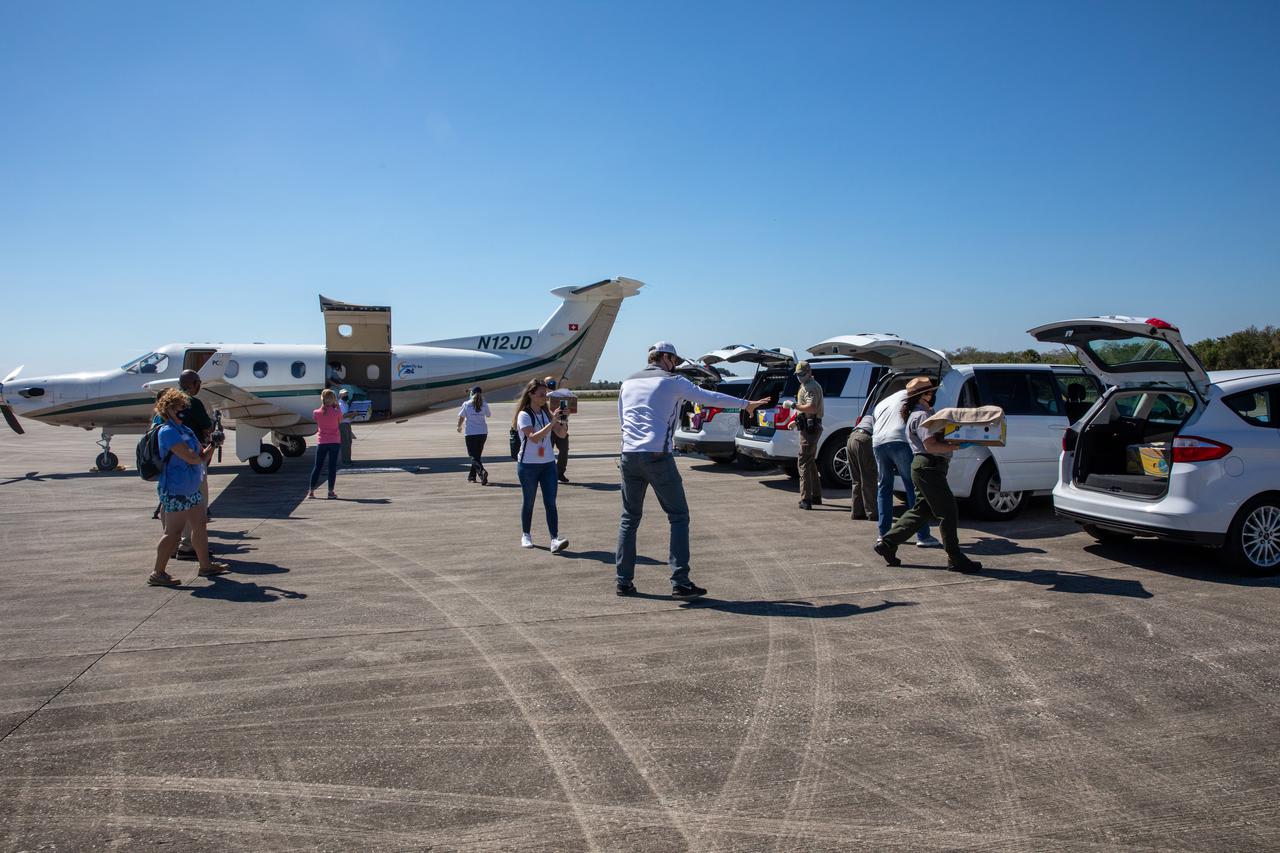

Staff with NASA and partner agencies help to unpack the containers of Kemp’s ridley and other sea turtles from the PC12 aircraft that arrived at the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York. The containers of turtles will be transferred to vehicles for the short trip to the Canaveral National Seashore, where they will be released into the Atlantic Ocean. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
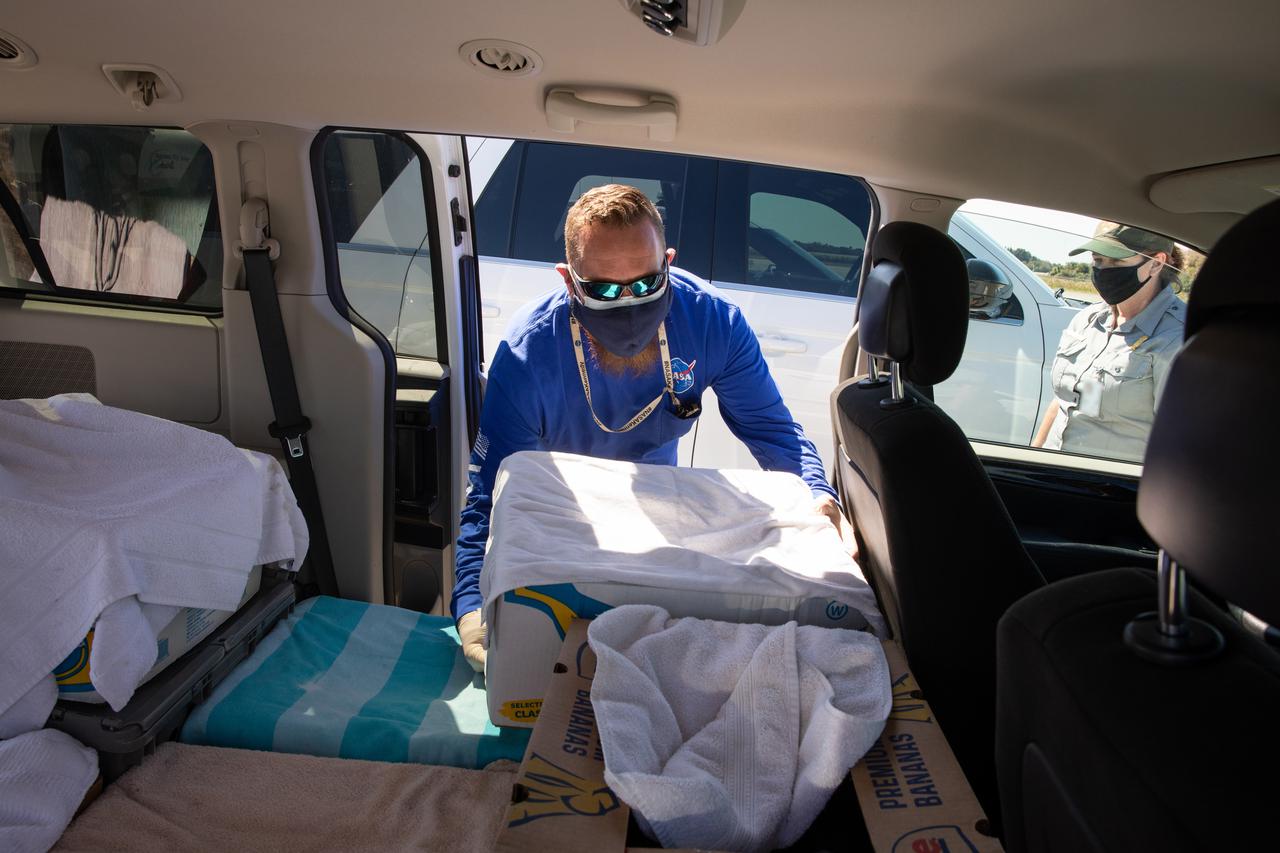

Staff with NASA and partner agencies help to unpack the containers of Kemp’s ridley and other sea turtles from the PC12 aircraft that arrived at the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York. The containers of turtles will be transferred to vehicles for the short trip to the Canaveral National Seashore, where they will be released into the Atlantic Ocean. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
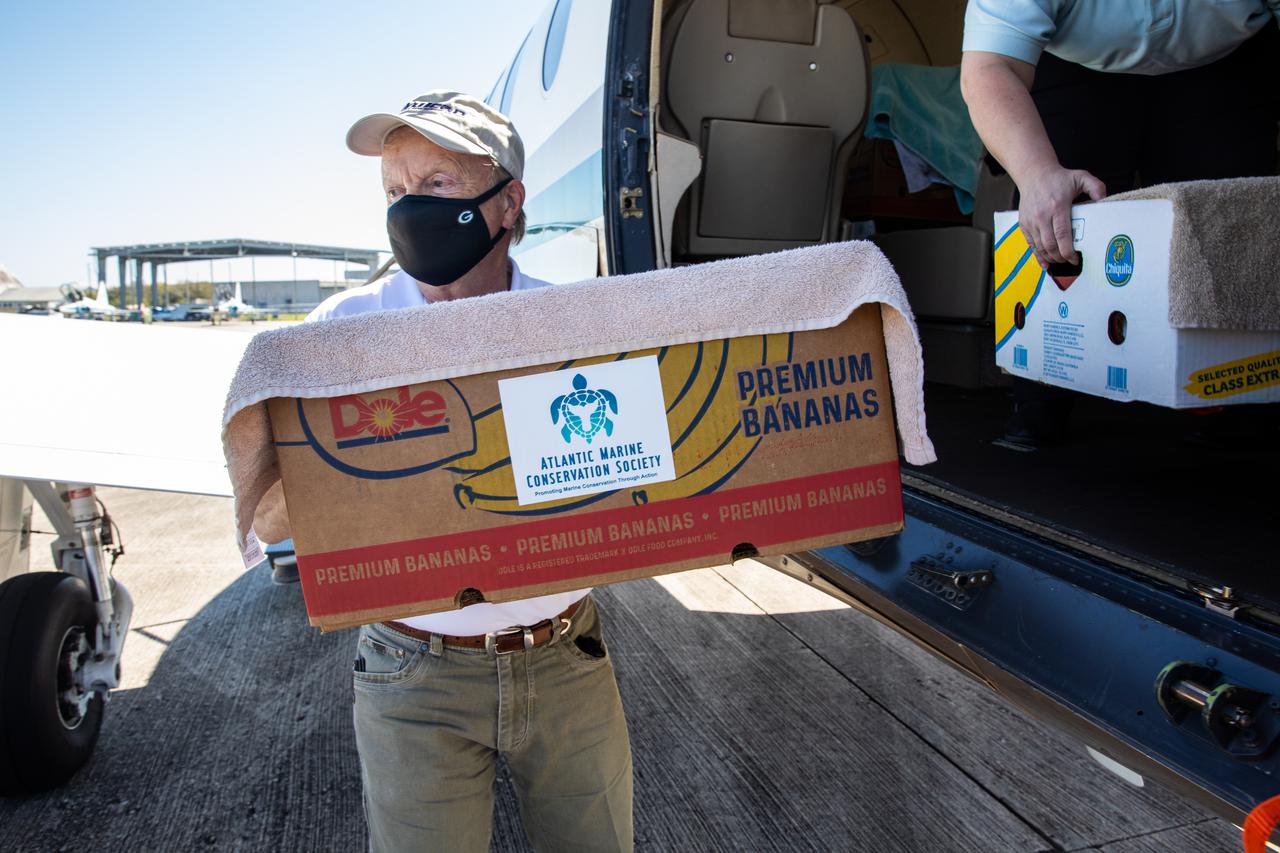

Staff with NASA and partner agencies help to unpack the containers of Kemp’s ridley and other sea turtles from the PC12 aircraft that arrived at the Launch and Landing Facility, managed by Space Florida, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 26, 2021. The rescued and rehabilitated turtles were flown from aquatic centers in Massachusetts and New York. The containers of turtles will be transferred to vehicles for the short trip to the Canaveral National Seashore, where they will be released into the Atlantic Ocean. NASA, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, NOAA Fisheries, Space Florida, and Herndon Solutions Group, the center’s environmental services contractor, provided support. The Turtles Fly Too organization provided the flight to Kennedy. All marine turtle footage/images was obtained with the approval of the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) under conditions not harmful to marine turtles. Footage was acquired while conducting authorized conservation activities pursuant to: FWC 2021 Consent Permit, MTP-21-005 and MTP-21-114.
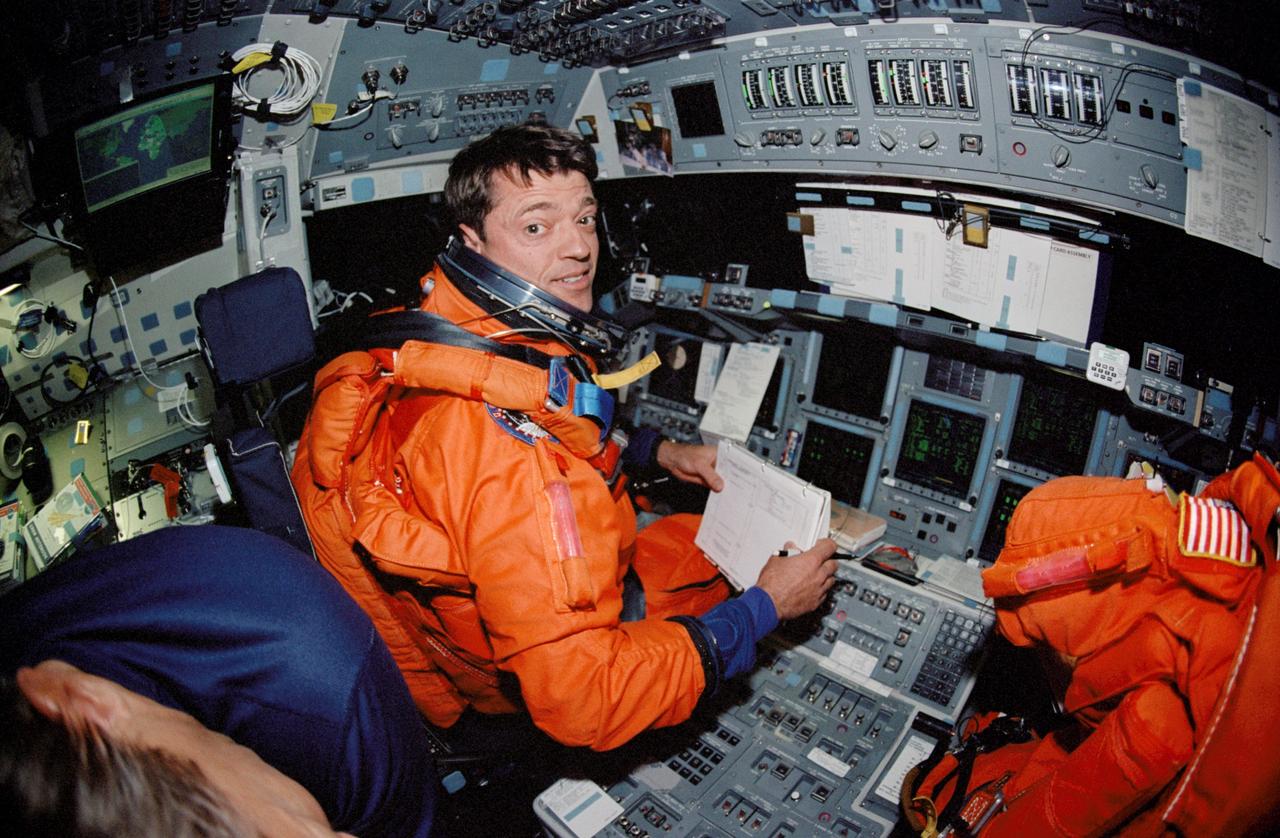

STS112-347-001 (18 October 2002) --- A “fish-eye” lens on a 35mm camera records astronaut Jeffrey S. Ashby, STS-112 mission commander, at the commander’s station on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Ashby, attired in his shuttle launch and entry suit, looks over a checklist prior to the entry phase of the flight.
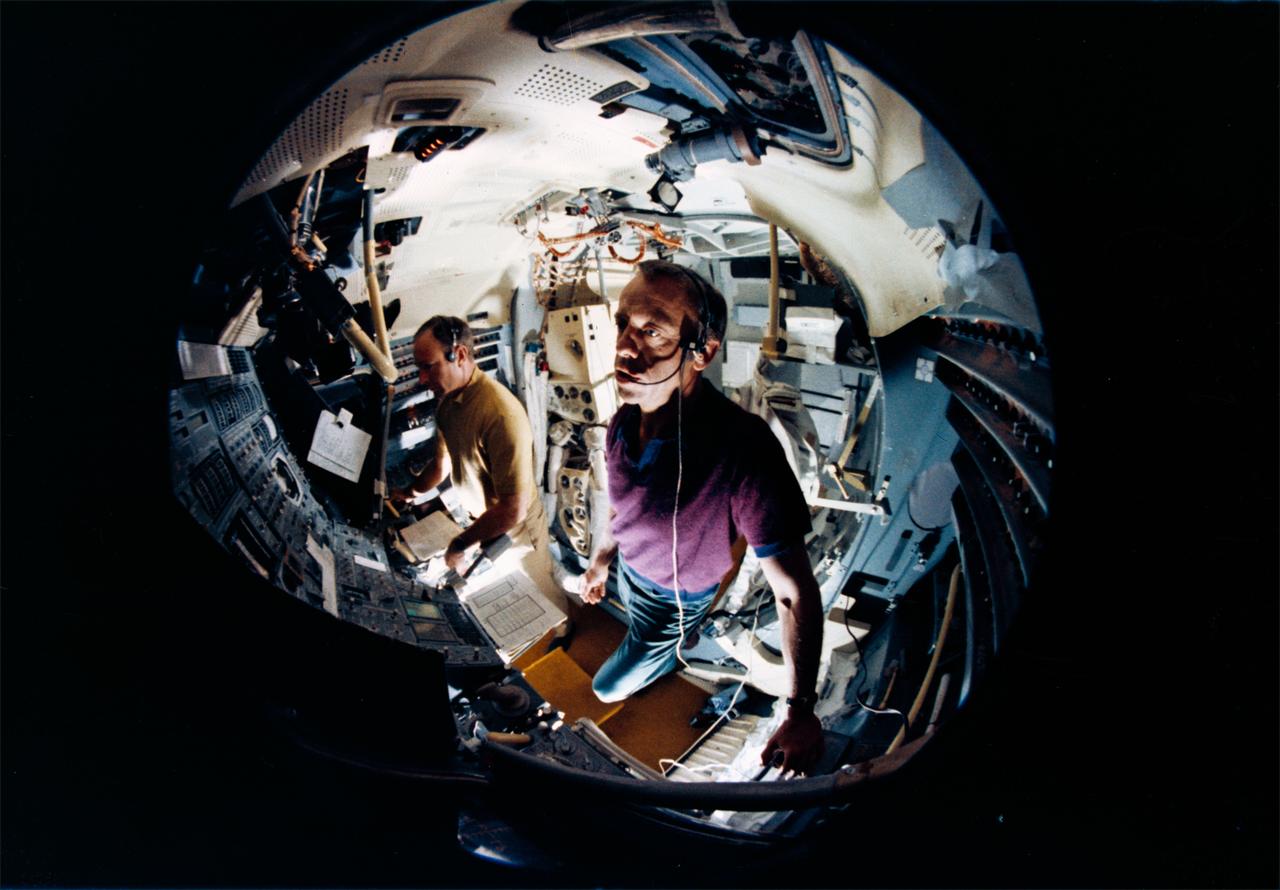

S70-45555 (July 1970) --- A fish-eye lens view showing astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (foreground) and Edgar D. Mitchell in the Apollo lunar module mission simulator at the Kennedy Space Center during preflight training for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Shepard is the Apollo 14 commander; and Mitchell is the lunar module pilot.
STS090-361-022 (17 April - 3 May 1998) --- A special lens on a 35mm camera gives a fish-eye effect to this out-the-window view from the Space Shuttle Columbia's cabin. The Spacelab Science Module, hosting 16-days of Neurolab research, is in frame center. This picture clearly depicts the configuration of the tunnel that leads from the cabin to the module in the center of the cargo bay.
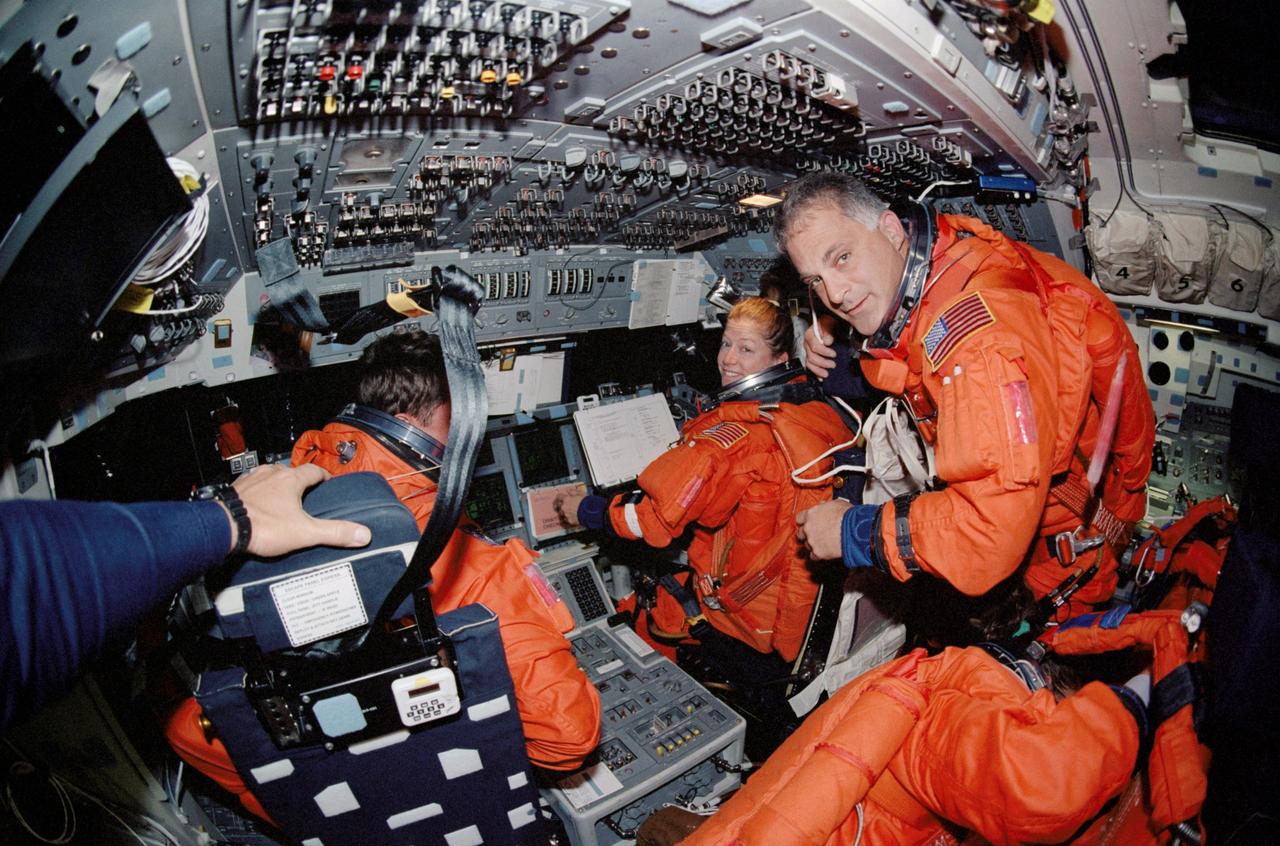

STS112-337-036 (18 October 2002) --- A “fish-eye” lens on a 35mm camera records astronauts Jeffrey S. Ashby (left), STS-112 mission commander; Pamela A. Melroy, pilot; and David A. Wolf, mission specialist, on the forward flight deck of the Space Shuttle Atlantis. Attired in their shuttle launch and entry suits, the crew prepares for the entry phase of the flight.
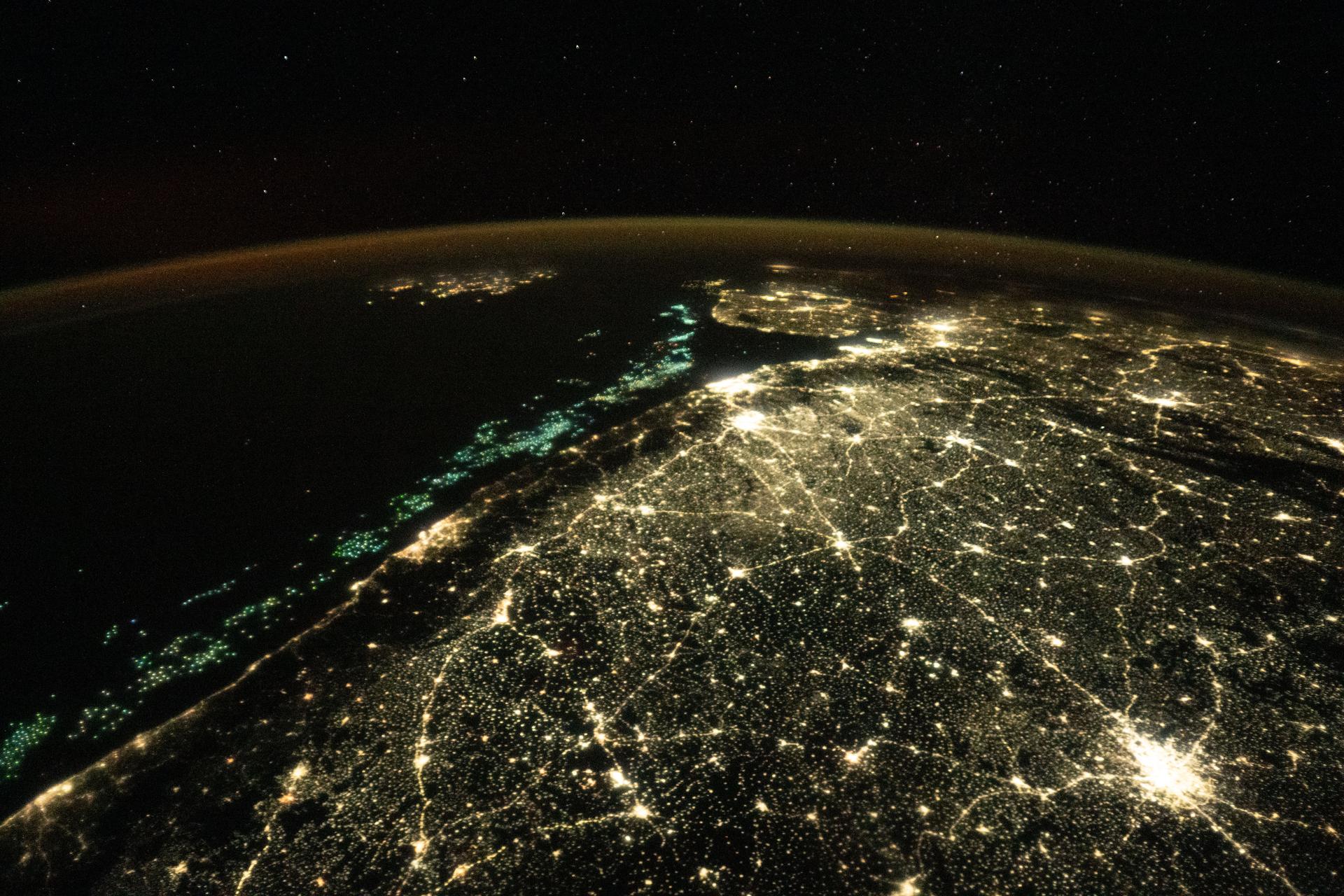

iss074e0044675 (Dec. 25, 2025) --- Fishing boats illuminate the Arabian Sea along India’s west coast with green lights designed to attract squid, shrimp, sardines, and mackerel in this nighttime photograph from the International Space Station, orbiting 259 miles above Earth. At lower right, the city lights of Hyderabad—renowned for its historic diamond and pearl trade—stretch westward toward the Mumbai Metropolitan Region, home to over 26 million people and the heart of Bollywood.

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
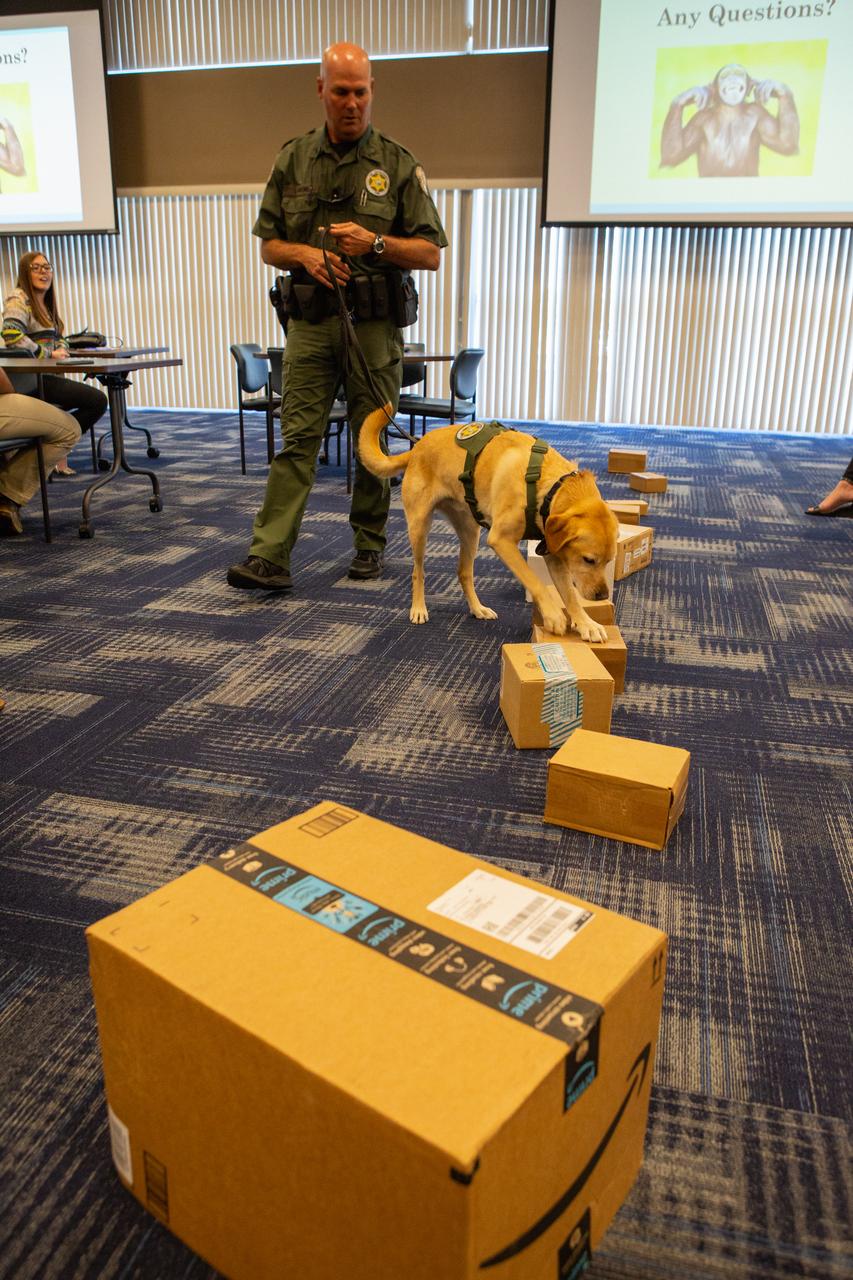

Inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center, Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor and K9 Harry demonstrate how specially trained dogs are used to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration, held April 23, 2019, involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. Prior to the demonstration, Officer Sidor presented information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.

Inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center, Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor and K9 Harry demonstrate how specially trained dogs are used to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration, held April 23, 2019, involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. Prior to the demonstration, Officer Sidor presented information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.

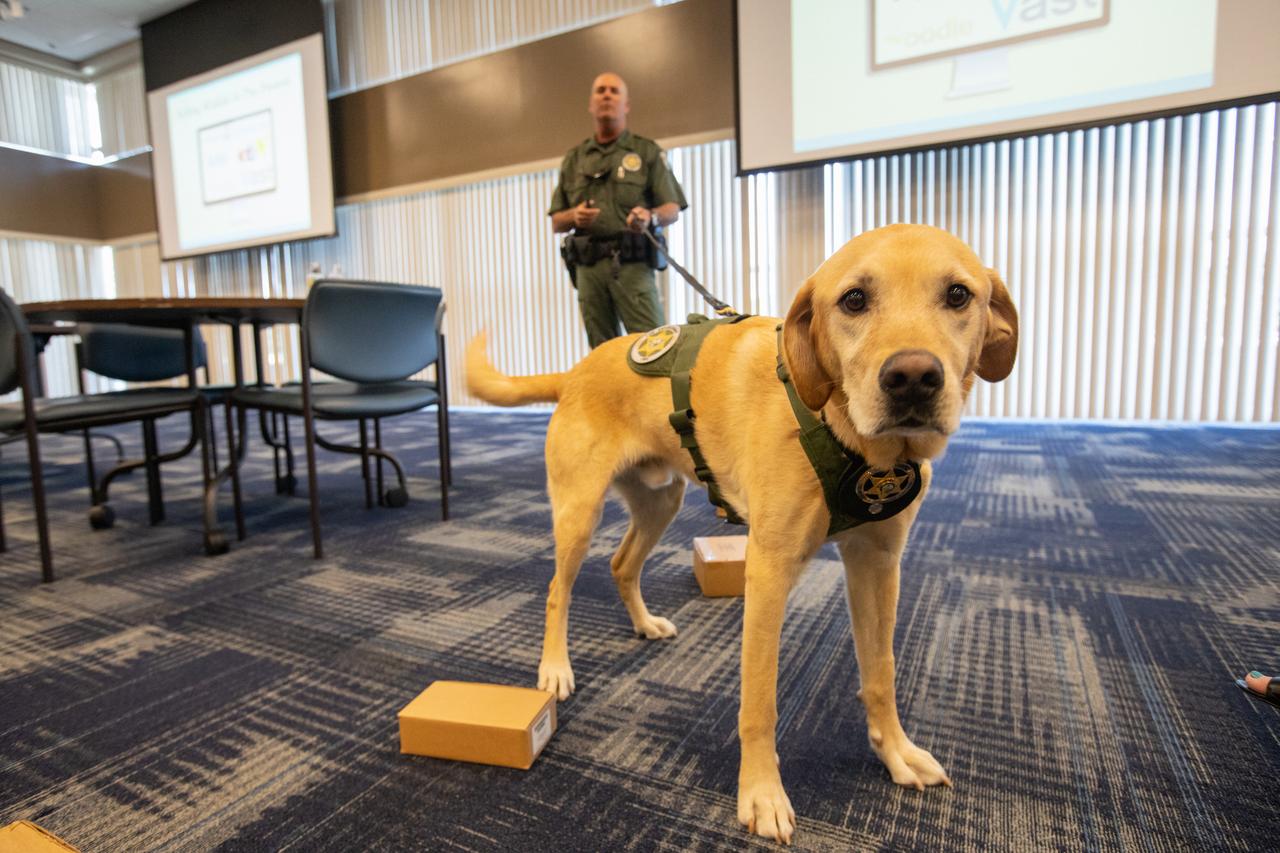
Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Port K9, Harry, lies inside Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center. FWC Officer Jeff Sidor presented information on the commission’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees on April 23, 2019, and brought Harry along for a demonstration. Following the presentation, Officer Sidor demonstrated how FWC is using specially trained dogs such as Harry in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
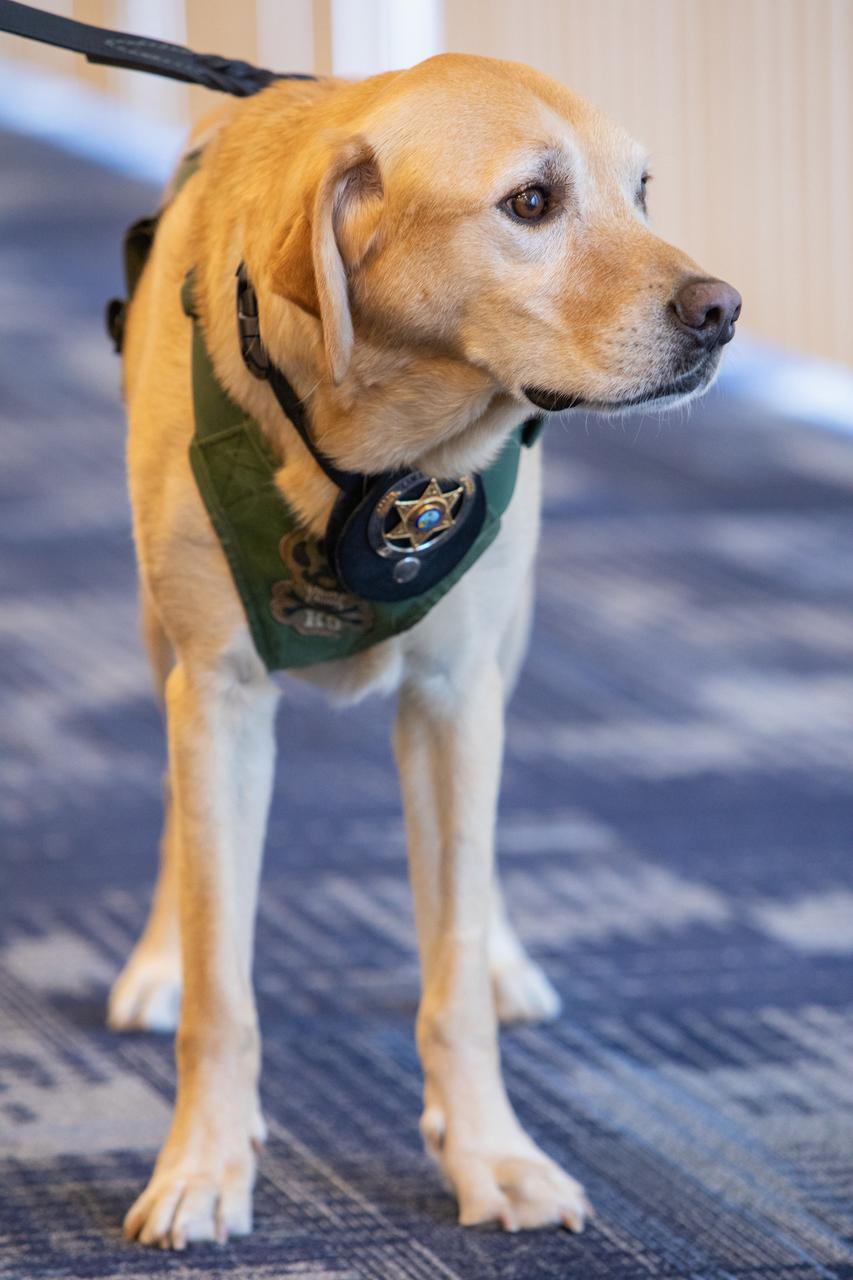

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Port K9, Harry, stands in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center. FWC Officer Jeff Sidor presented information on the commission’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees on April 23, 2019, and brought Harry along for a demonstration. Following the presentation, Officer Sidor demonstrated how FWC is using specially trained dogs such as Harry in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
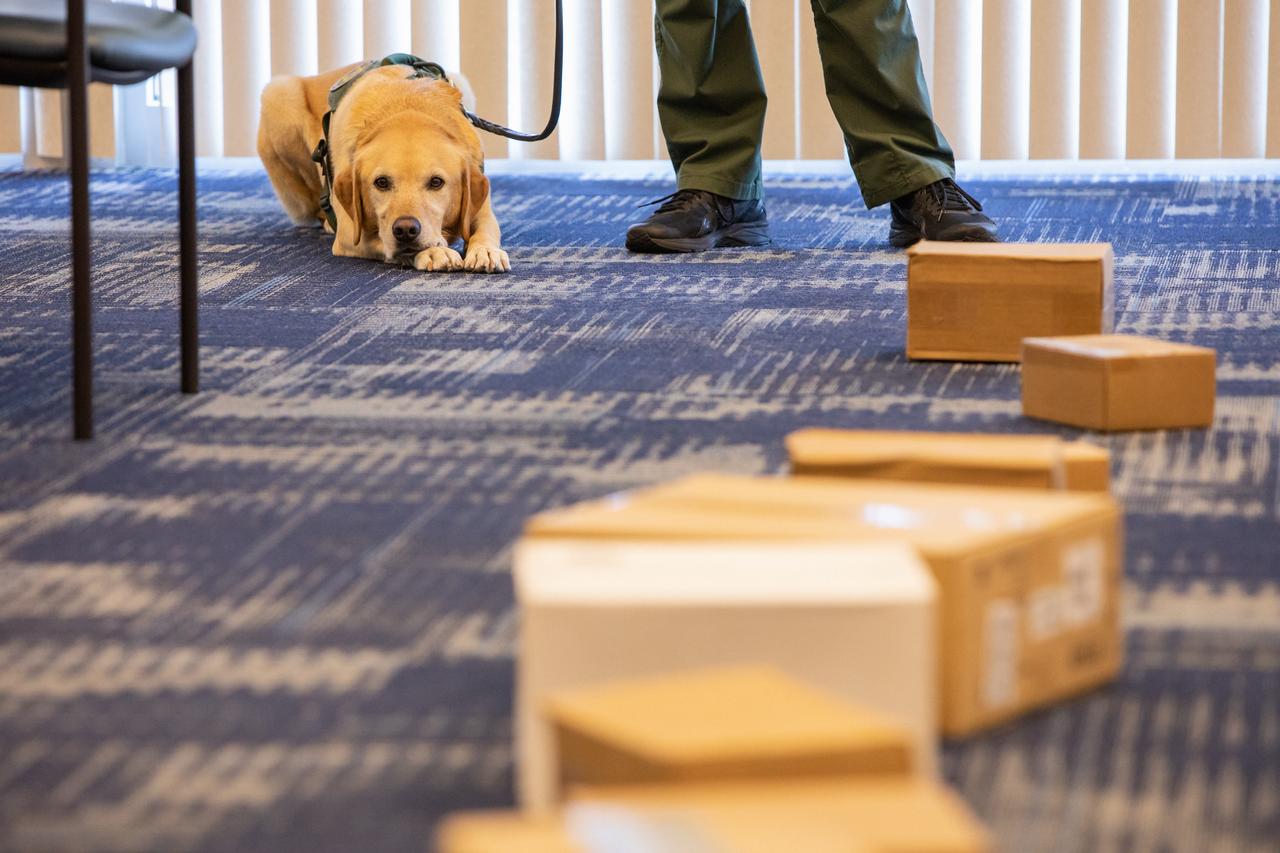

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) K9 Harry rests during FWC Officer Jeff Sidor’s presentation on the commission’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees on April 23, 2019. Following the presentation in the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center, Officer Sidor demonstrated how FWC is using specially trained dogs such as Harry in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
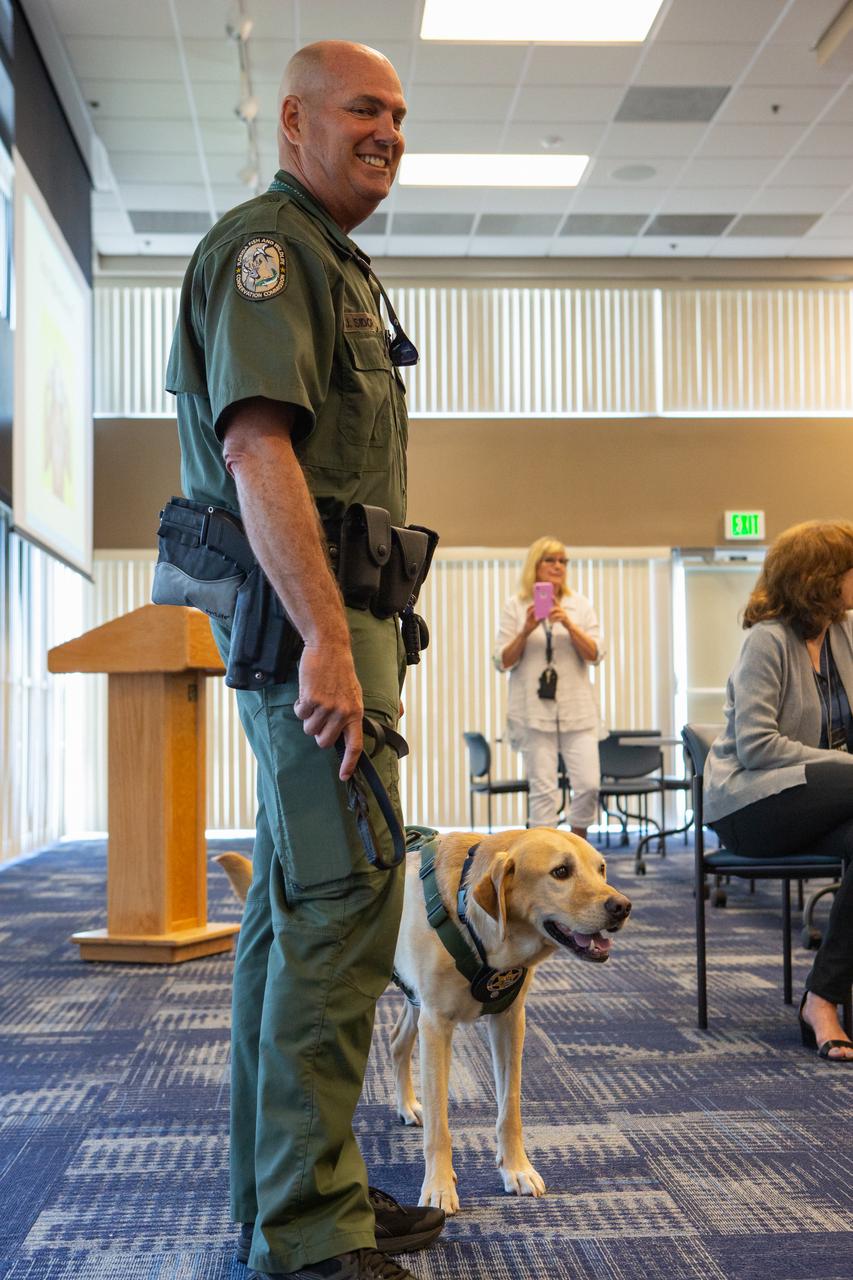

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
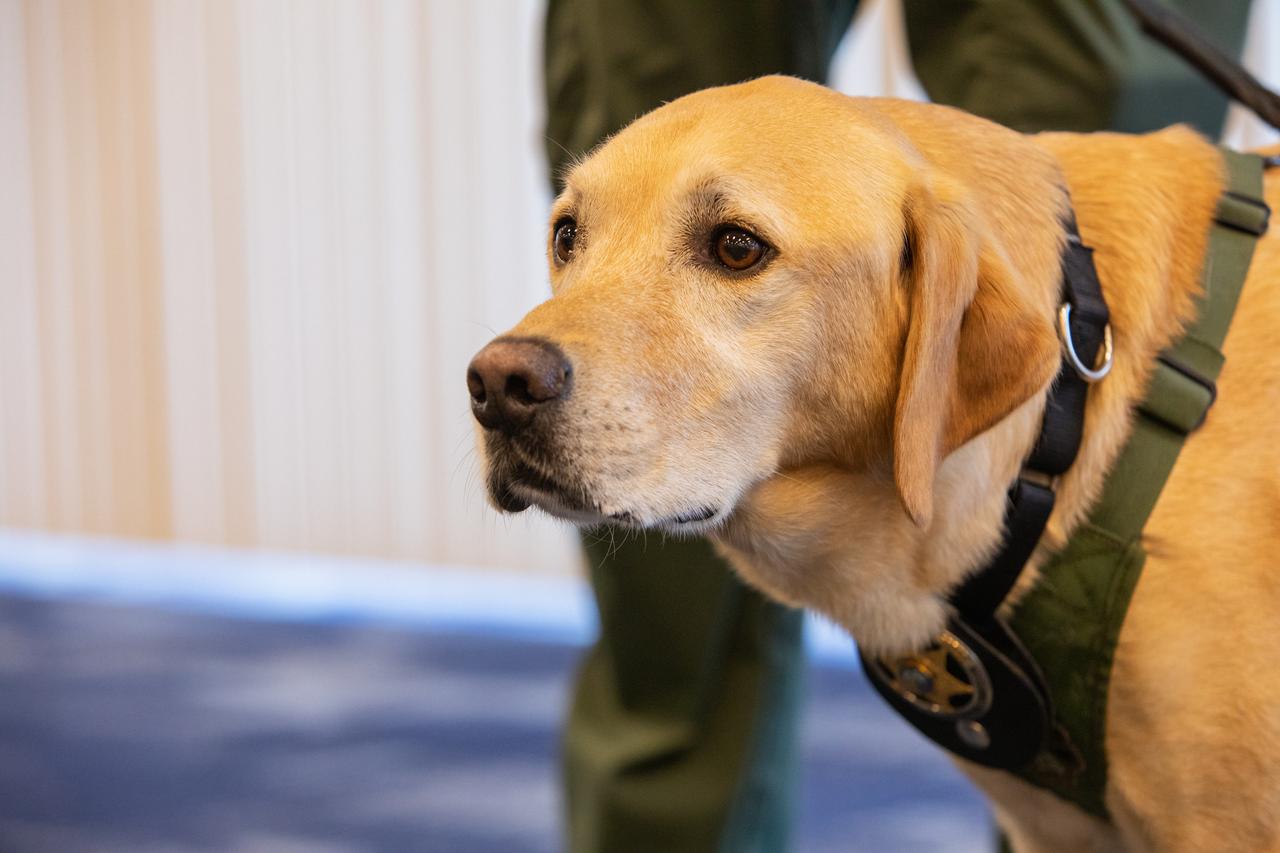

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Port K9, Harry, stands in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center. FWC Officer Jeff Sidor presented information on the commission’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees on April 23, 2019, and brought Harry along for a demonstration. Following the presentation, Officer Sidor demonstrated how FWC is using specially trained dogs such as Harry in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
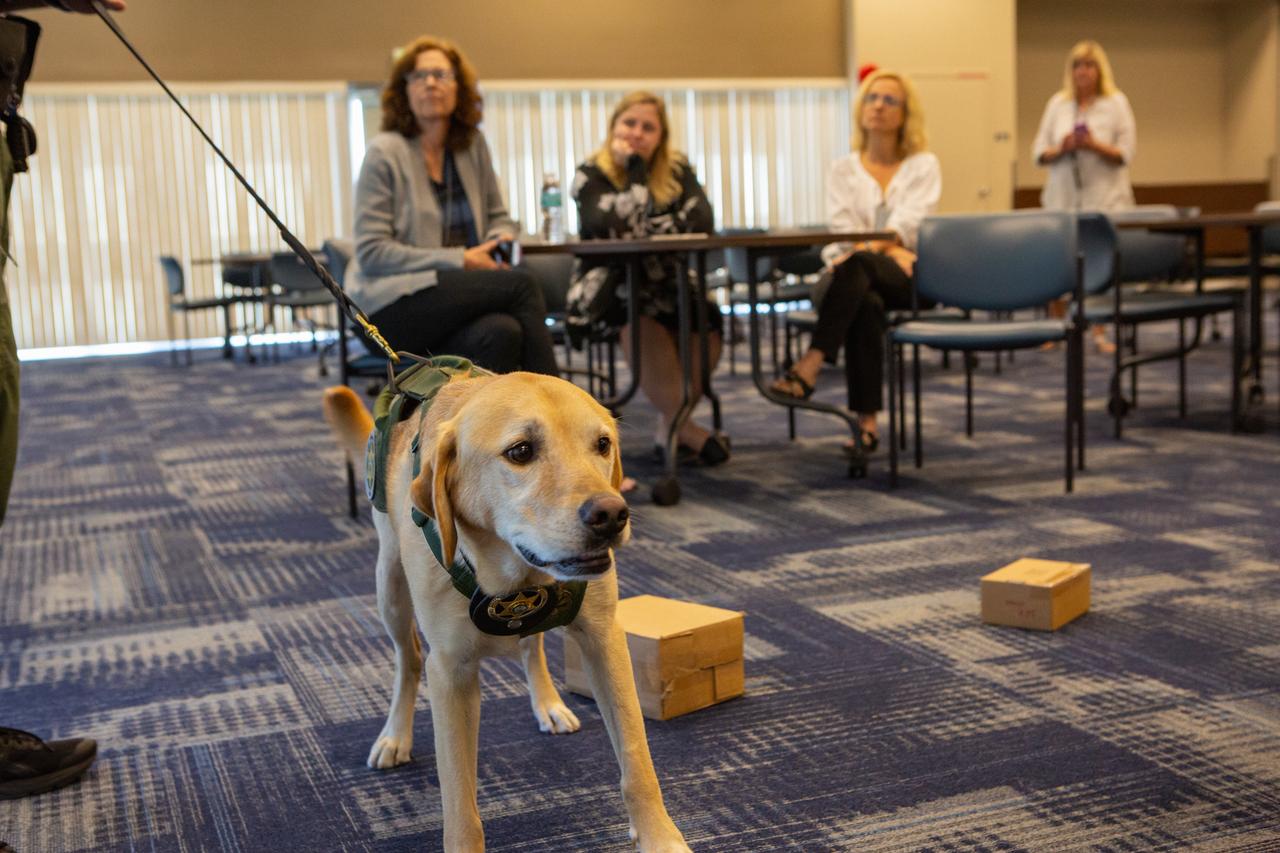

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission’s (FWC) Port K9, Harry, stands in Kennedy Space Center’s Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center. FWC Officer Jeff Sidor presented information on the commission’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy employees on April 23, 2019, and brought Harry along for a demonstration. Following the presentation, Officer Sidor demonstrated how FWC is using specially trained dogs such as Harry in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
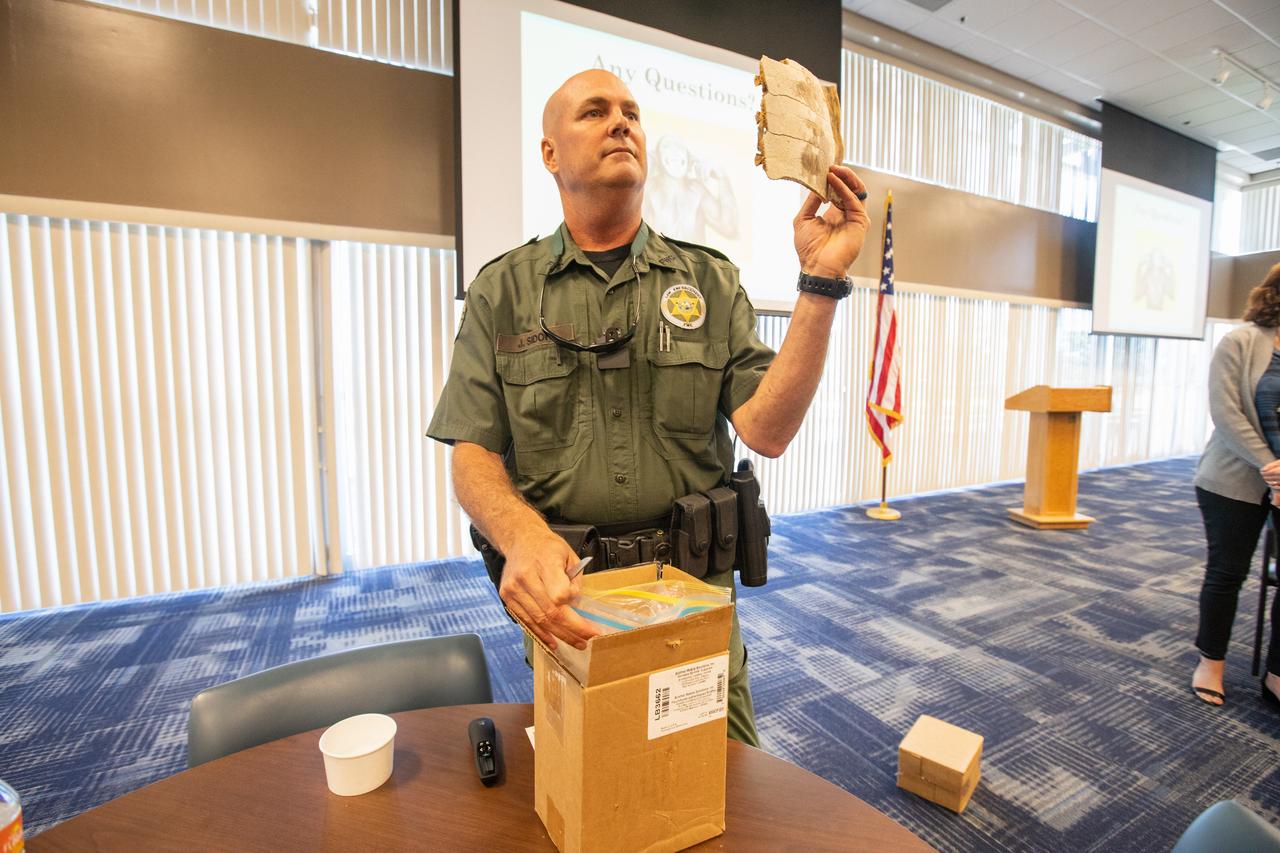

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor holds up a piece of turtle shell during a presentation and demonstration to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained the turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.
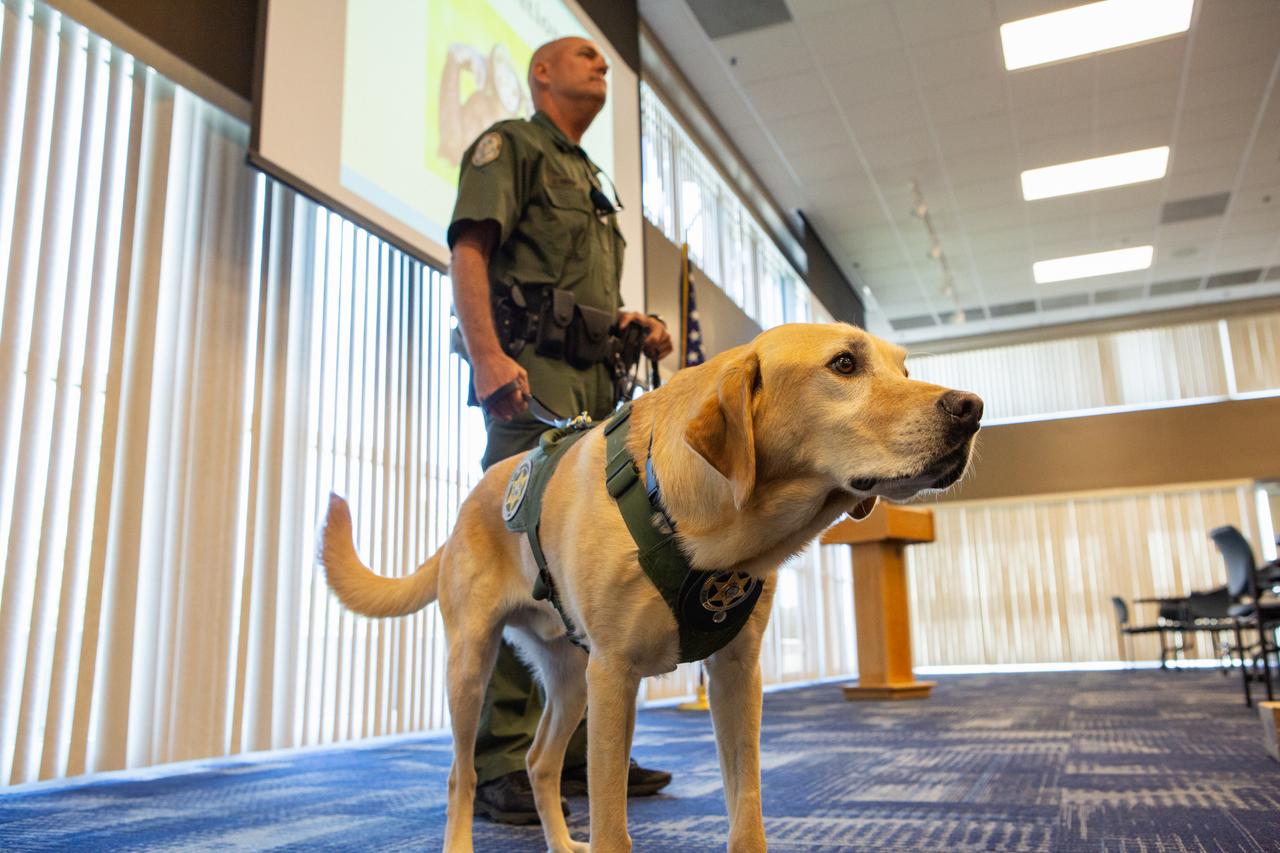

Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (FWC) Officer Jeff Sidor presents information on FWC’s Port K9 Program to Kennedy Space Center employees in the Space Station Processing Facility Conference Center on April 23, 2019. Officer Sidor brought a special K9, Harry, to demonstrate how FWC is using specially trained dogs in airports, seaports and mail facilities to detect illegal and invasive fish and wildlife species shipping into Florida. The demonstration involved Harry distinguishing which box, among many, contained a turtle shell. This lunch and learn was available for employees to attend as part of Kennedy’s Earth Day events.

Do you see what I see? A giant fish with open mouth looks to the left in the center of this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
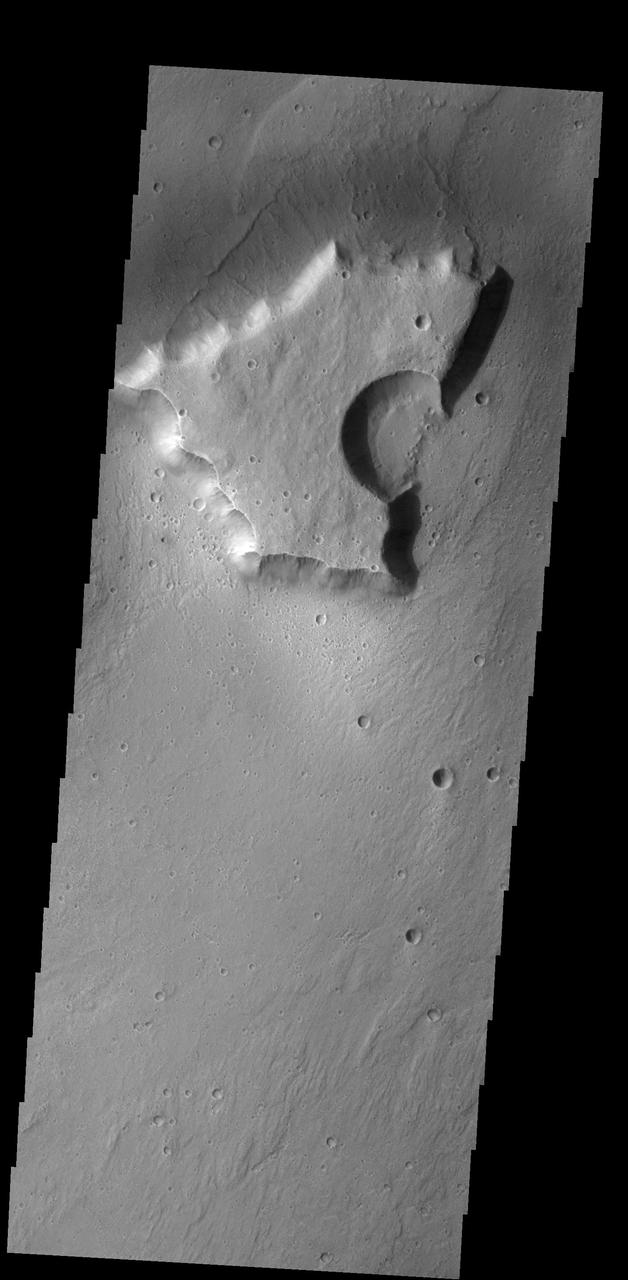

In this image, NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft spies what looks like a deep water fish yelling. Orbit Number: 52146 Latitude: 31.751 Longitude: 306.831 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2013-09-15 16:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21685
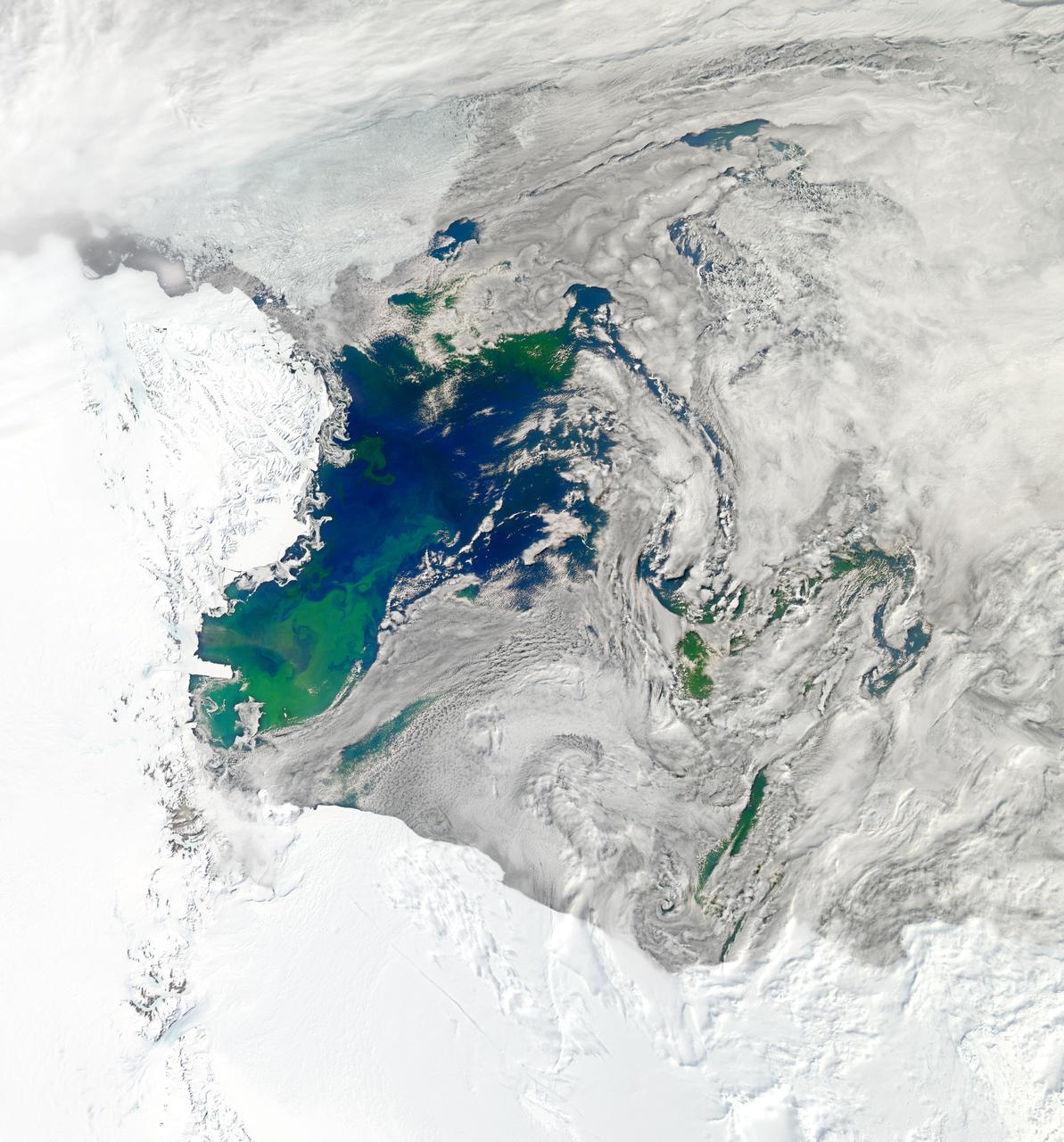

NASA image acquired January 22, 2011 To see a detail of this image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5398237910">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5398237910</a> Every southern spring and summer, after the Sun has risen into its 24-hour circuit around the skies of Antarctica, the Ross Sea bursts with life. Floating, microscopic plants, known as phytoplankton, soak up the sunlight and the nutrients stirring in the Southern Ocean and grow into prodigious blooms. Those blooms become a great banquet for krill, fish, penguins, whales, and other marine species who carve out a living in the cool waters of the far south. This true-color image captures such a bloom in the Ross Sea on January 22, 2011, as viewed by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. Bright greens of plant-life have replaced the deep blues of open ocean water. The Ross Sea is a relatively shallow bay in the Antarctic coastline and due south from New Zealand. As the spring weather thaws the sea ice around Antarctica, areas of open water surrounded by ice—polynyas—open up on the continental shelf. In this open water, sunlight provides the fuel and various current systems provide nutrients from deeper waters to form blooms that can stretch 100 to 200 kilometers (60 to 120 miles). These blooms are among the largest in extent and abundance in the world. Scientists have hypothesized that the Modified Circumpolar Deep Water is the engine behind the blooms, stirring up just the right mix of trace metals and minerals from the deep to sustain plankton growth. This month, researchers aboard the U.S. icebreaking ship Nathaniel B. Palmer are cruising in the Ross Sea in search of the signatures of this current system. NASA image courtesy Norman Kuring, Ocean Color Team at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz, with information from Hugh Powell, COSEE-NOW. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
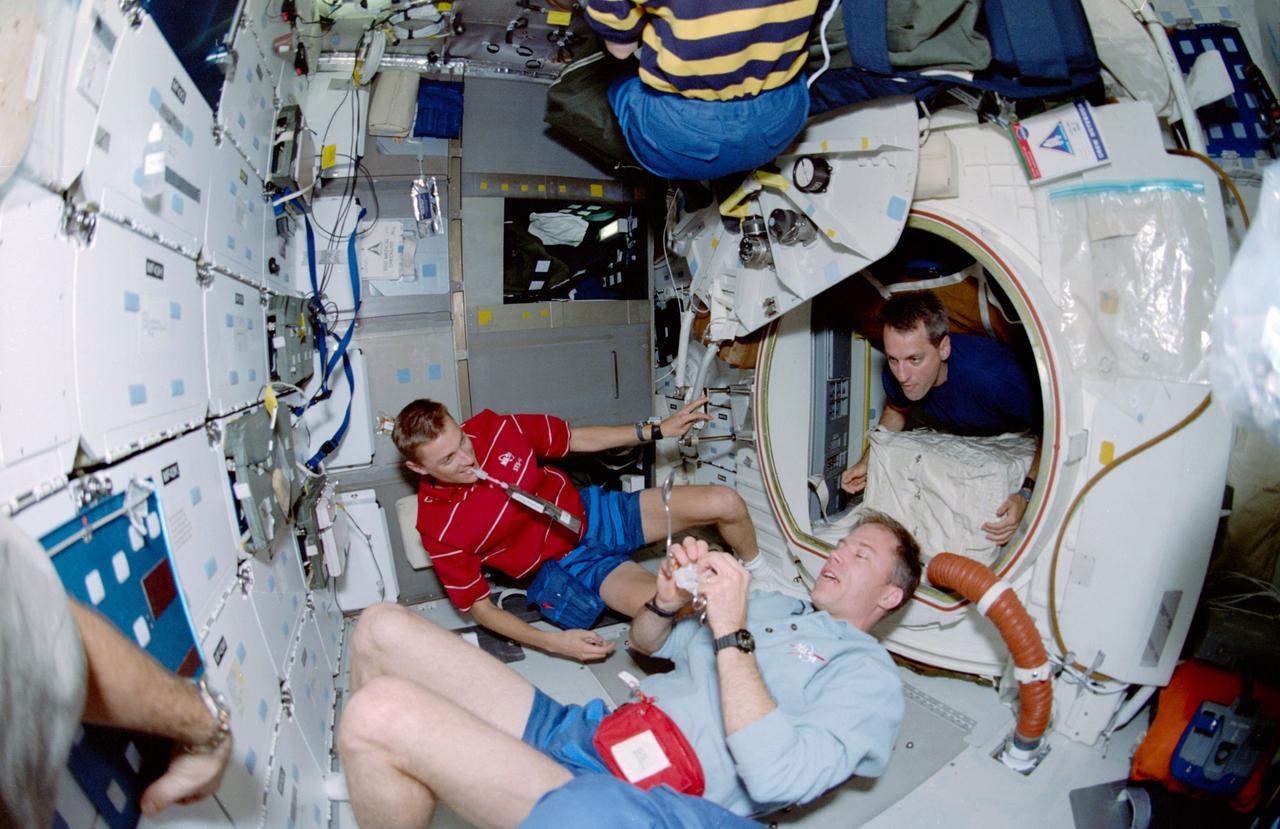

STS090-351-009 (17 April - 3 May 1998) --- Three members of the Neurolab crew were photographed during off-duty time on the mid-deck aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Left to right are James A. (Jim) Pawelczyk, payload specialist, and astronauts Richard A. Searfoss, mission commander; and Richard M. Linnehan, payload commander. Linnehan is in the hatchway of the tunnel that connected the crew members to the Spacelab Science Module in Columbia's cargo bay. A "fish-eye" lens on a 35mm camera gives the scene a slightly distorted look. Five NASA astronauts and two payload specialists went on to spend a little more than 16-days in Earth-orbit in support of the Neurolab mission.
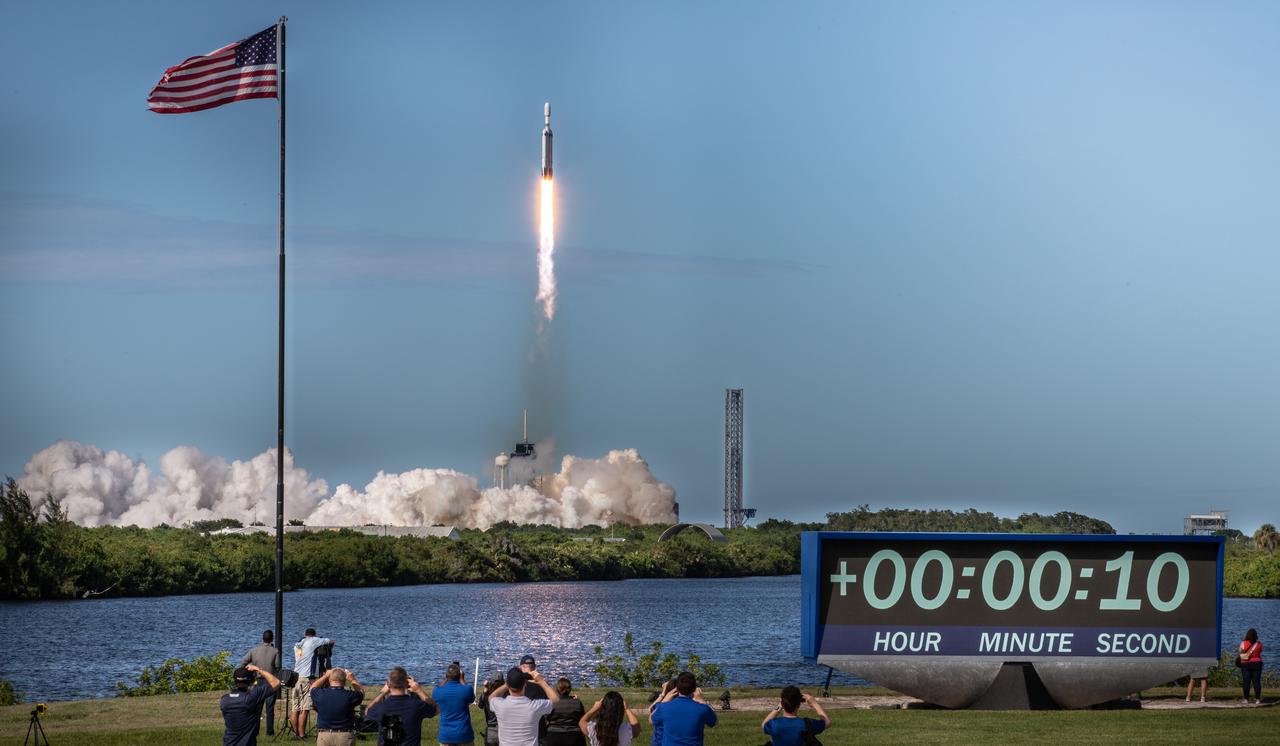

A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket carrying the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) GOES-U (Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite U) lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, June 25, 2024. The GOES-U satellite is the final satellite in the GOES-R series, which serves a critical role in providing continuous coverage of the Western Hemisphere, including monitoring tropical systems in the eastern Pacific and Atlantic oceans.
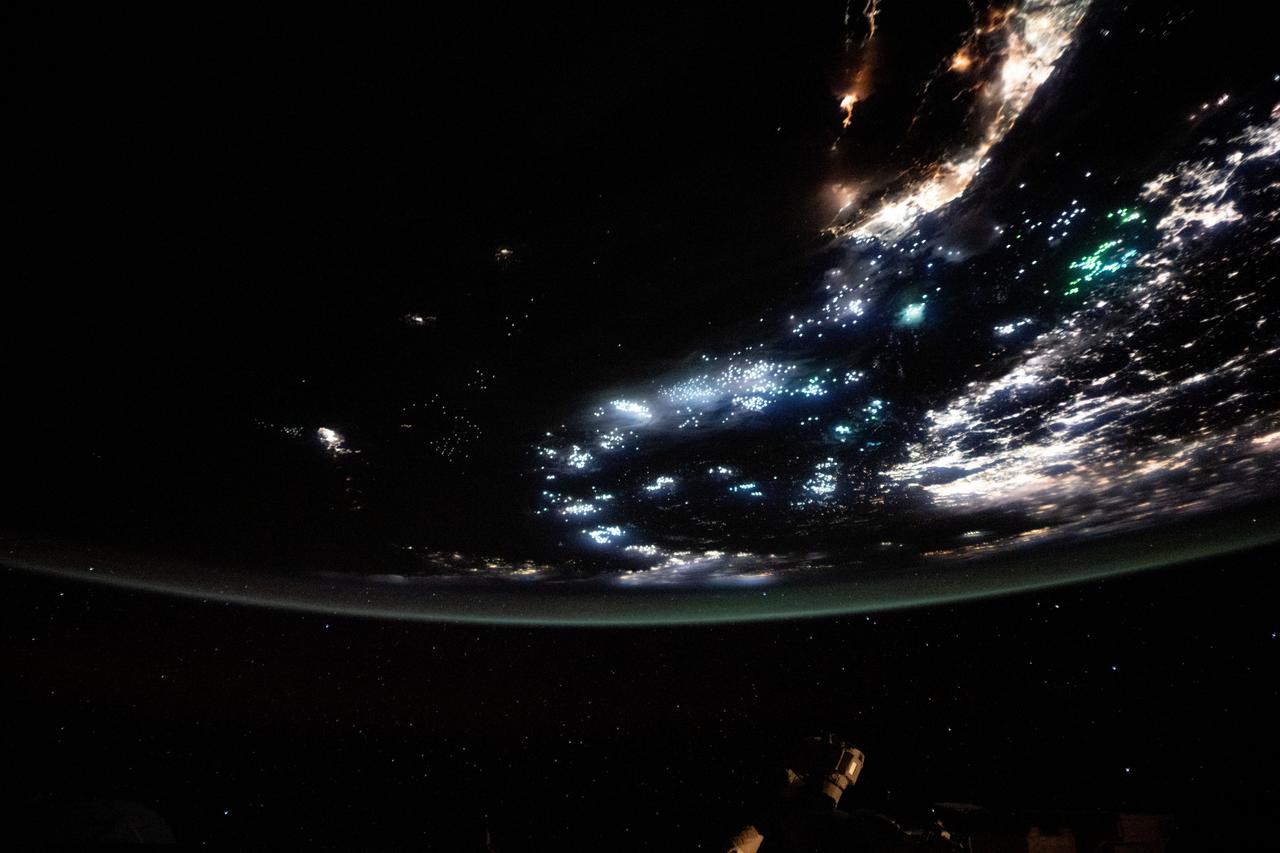

iss073e0688699 (Aug. 26, 2025) --- The blue-green lights of fishing boats, designed to lure squid, sardines, or mackerel, dot the East China Sea and the Taiwan Strait contrasting with the coastal city lights of Taiwan and China. The International Space Station was orbiting 259 miles above the South China Sea just south of Taiwan at approximately 11:53 p.m. local time when this photograph was taken.
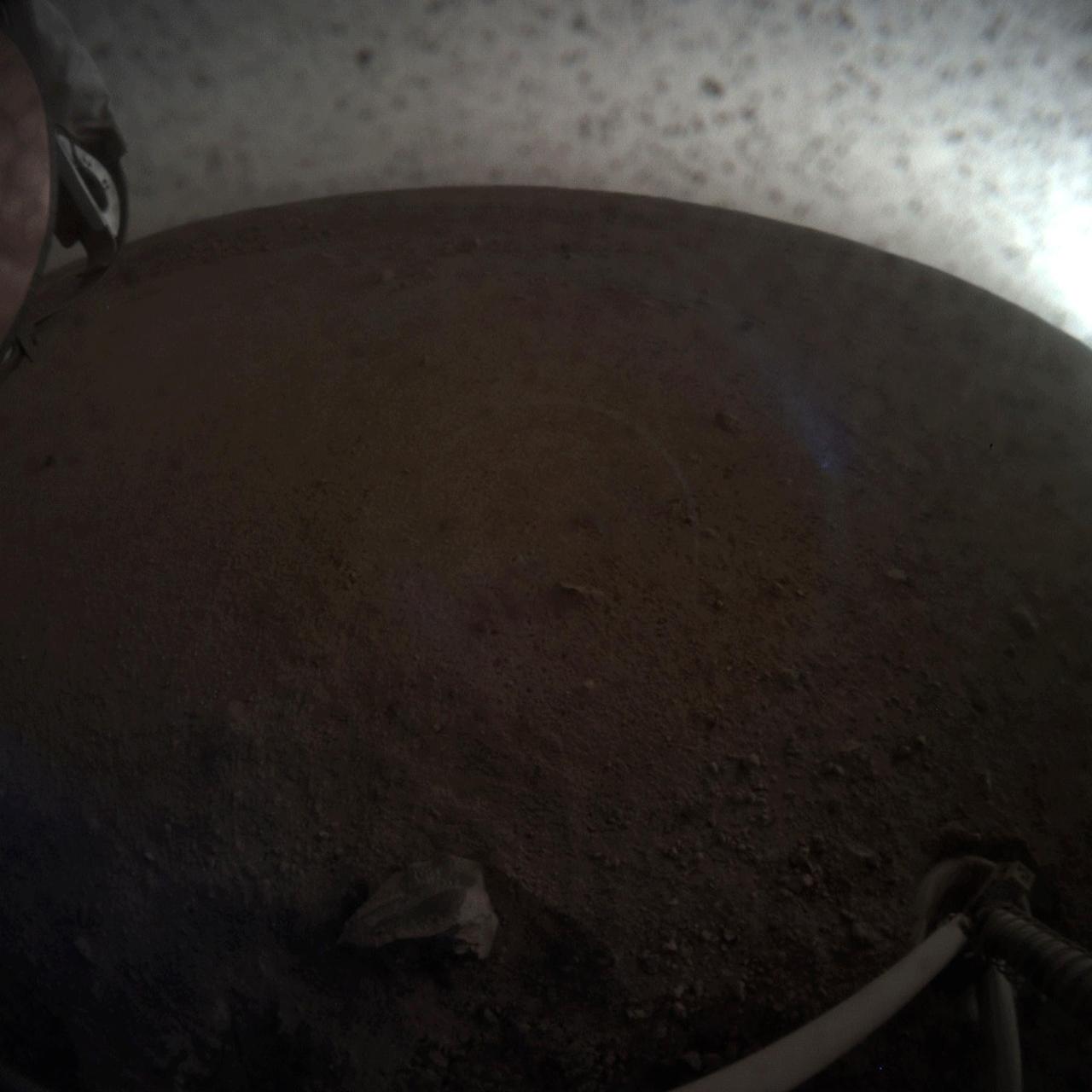

A fish-eye view of NASA's InSight lander deploying its first instrument onto the surface of Mars. InSight's robotic arm placed the seismometer on Dec. 19, 2018, around the time of dusk on Mars. These images were taken by the Instrument Context Camera (ICC), a fish-eye camera under the spacecraft's deck. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22978
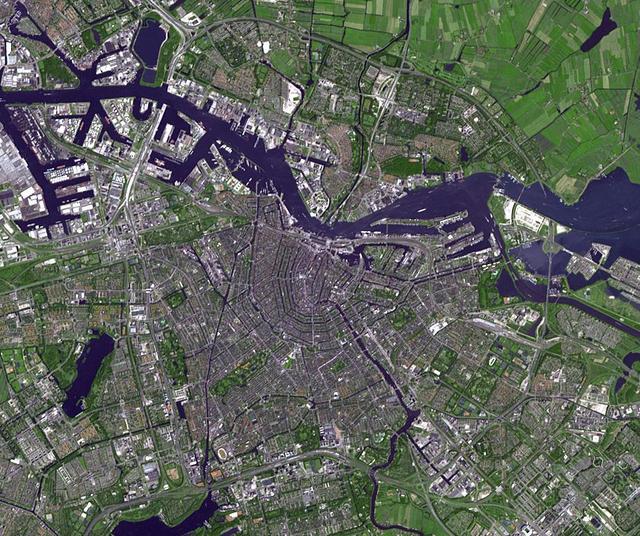

Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. Its name derives from a dam in the river Amstel. Founded in the 12th century as a fishing village, Amsterdam was one of the most important ports in the world in the 17th century.
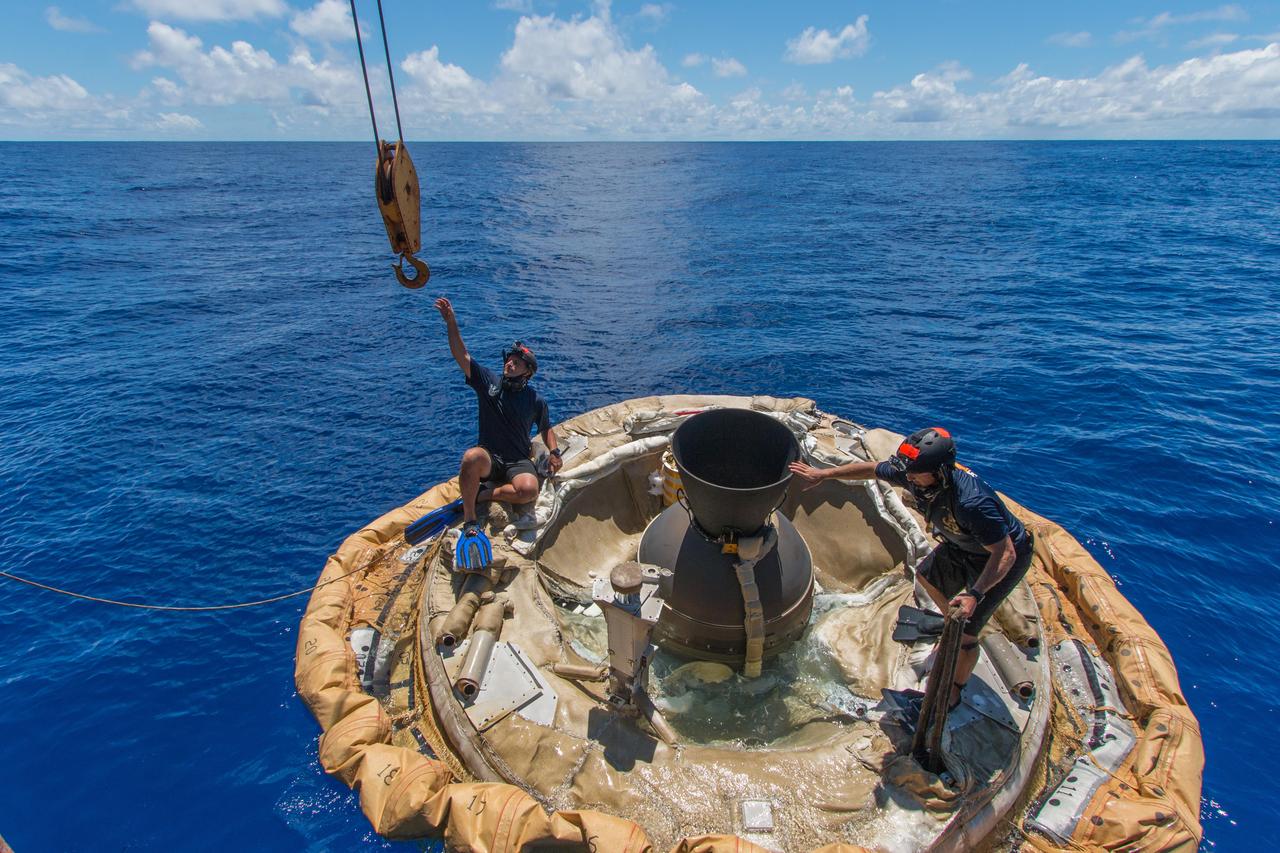

Divers retrieve the test vehicle for NASA Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator off the coast of the U.S. Navy Pacific Missile Range Facility in Kauai, Hawaii.
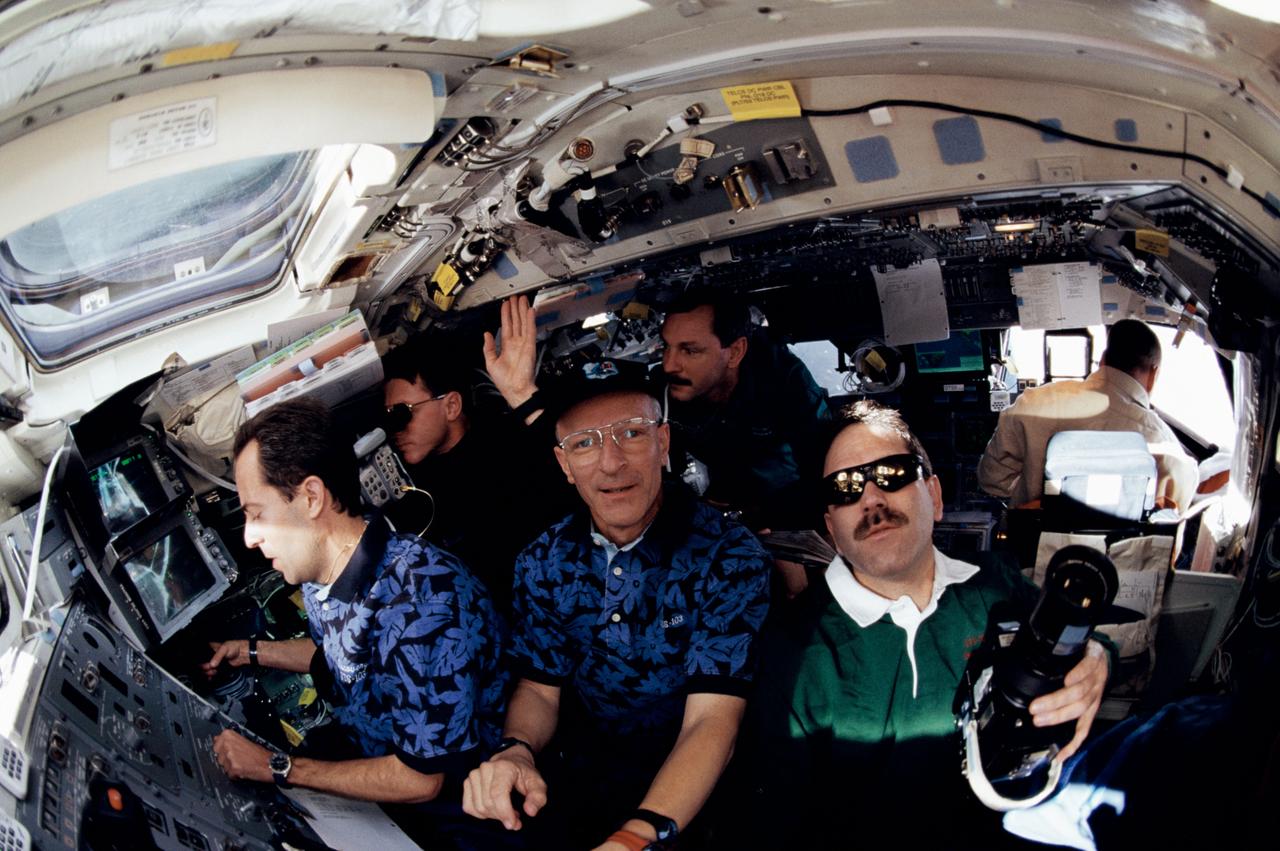

STS103-375-019 (19-27 December 1999) ---.Six members of the STS-103 crew are seen in this "fish-eye" lens scene taken on Discovery's flight deck during the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). From left are astronauts Jean-Francois Clervoy, C. Michael Foale, Claude Nicollier, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., John M. Grunsfeld and Scott J. Kelly. Brown and Kelly are commander and pilot, respectively. All the others are mission specialists, with international MS Nicollier and Clervoy representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Astronaut Steven L. Smith, payload commander, took the photo.
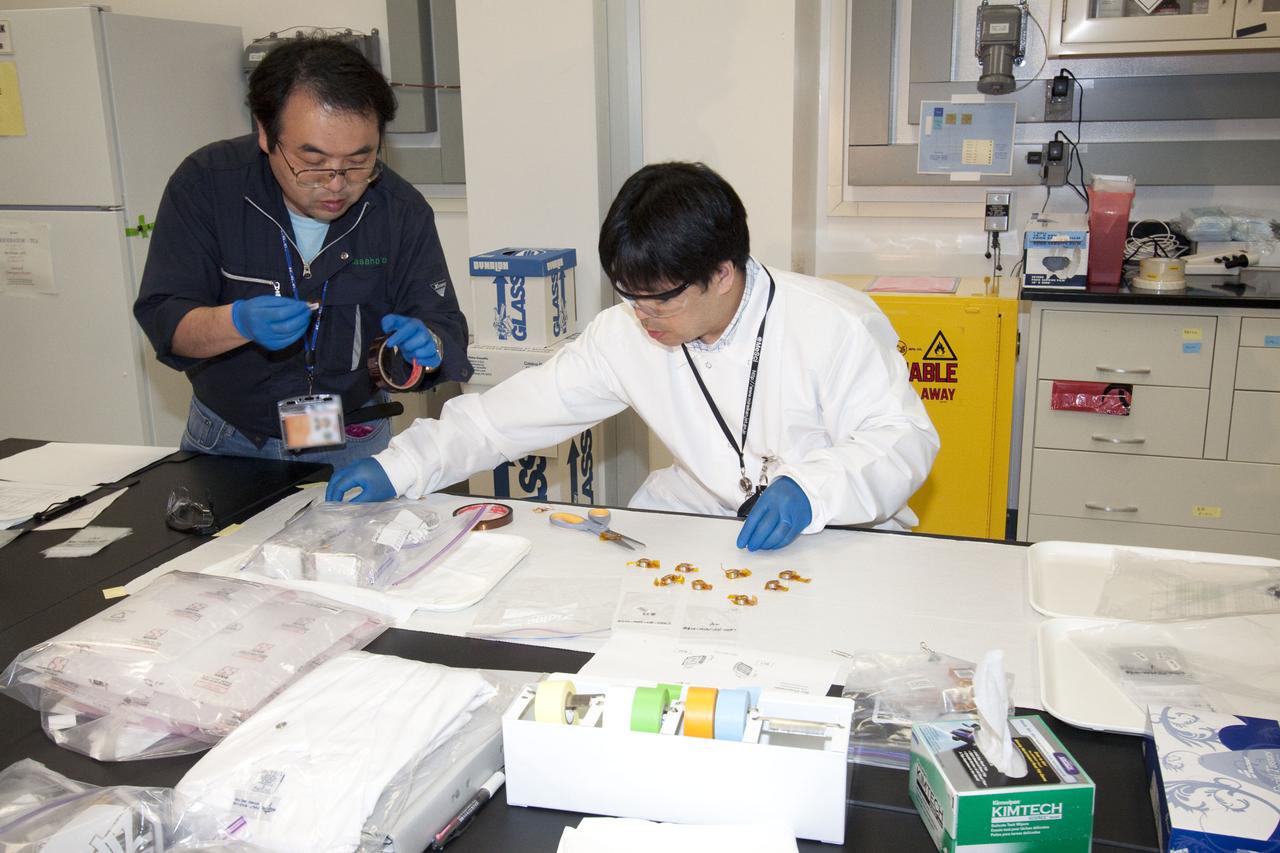

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
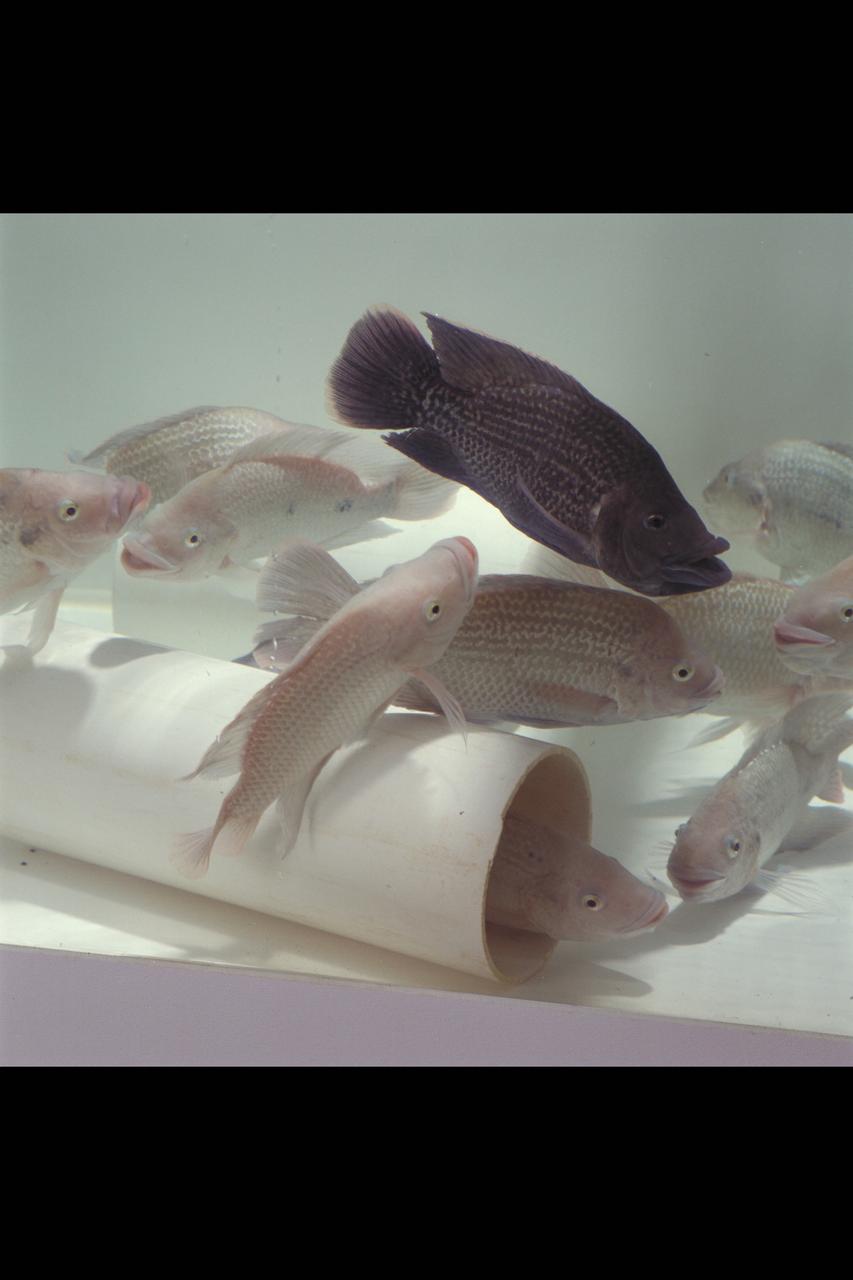

Ames Life Sciences Experiments: Tilapia fish Aquaculture
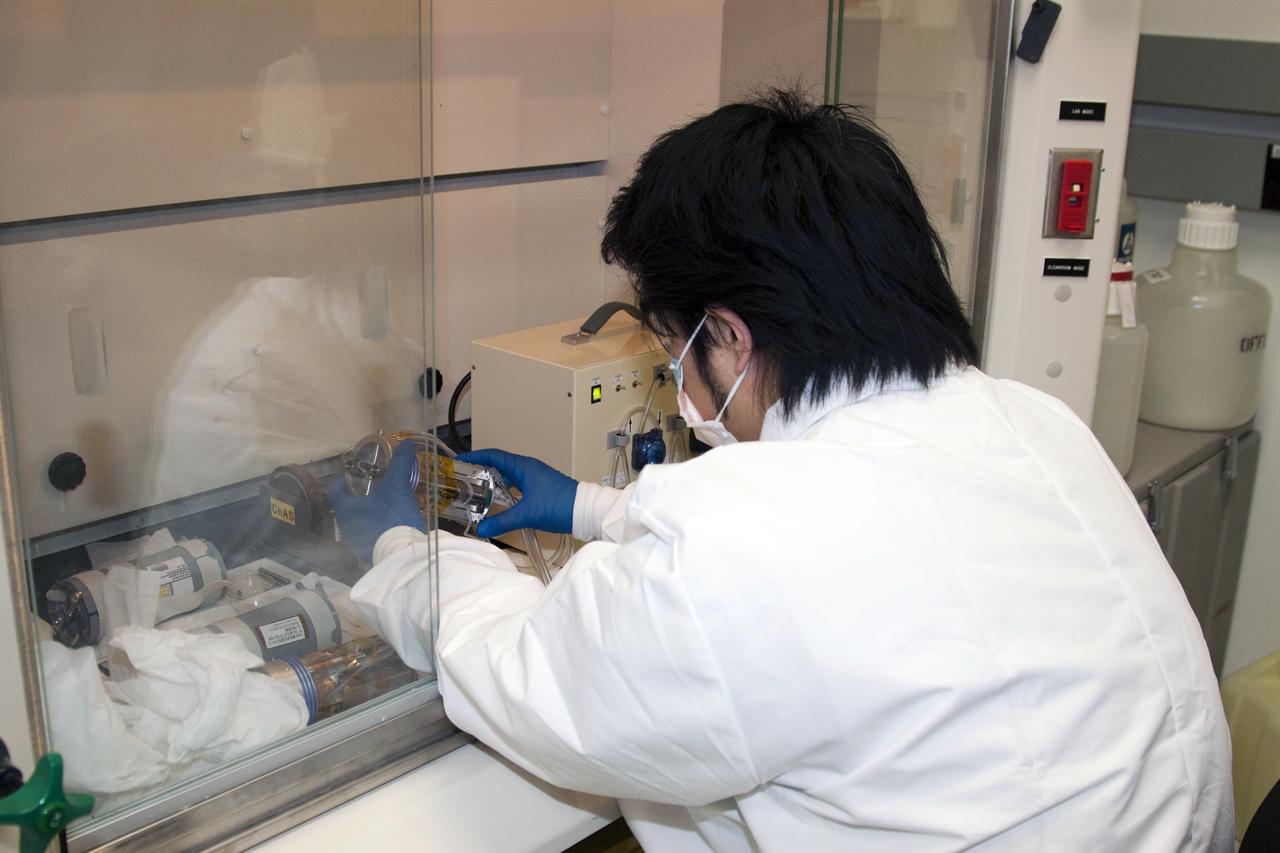

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
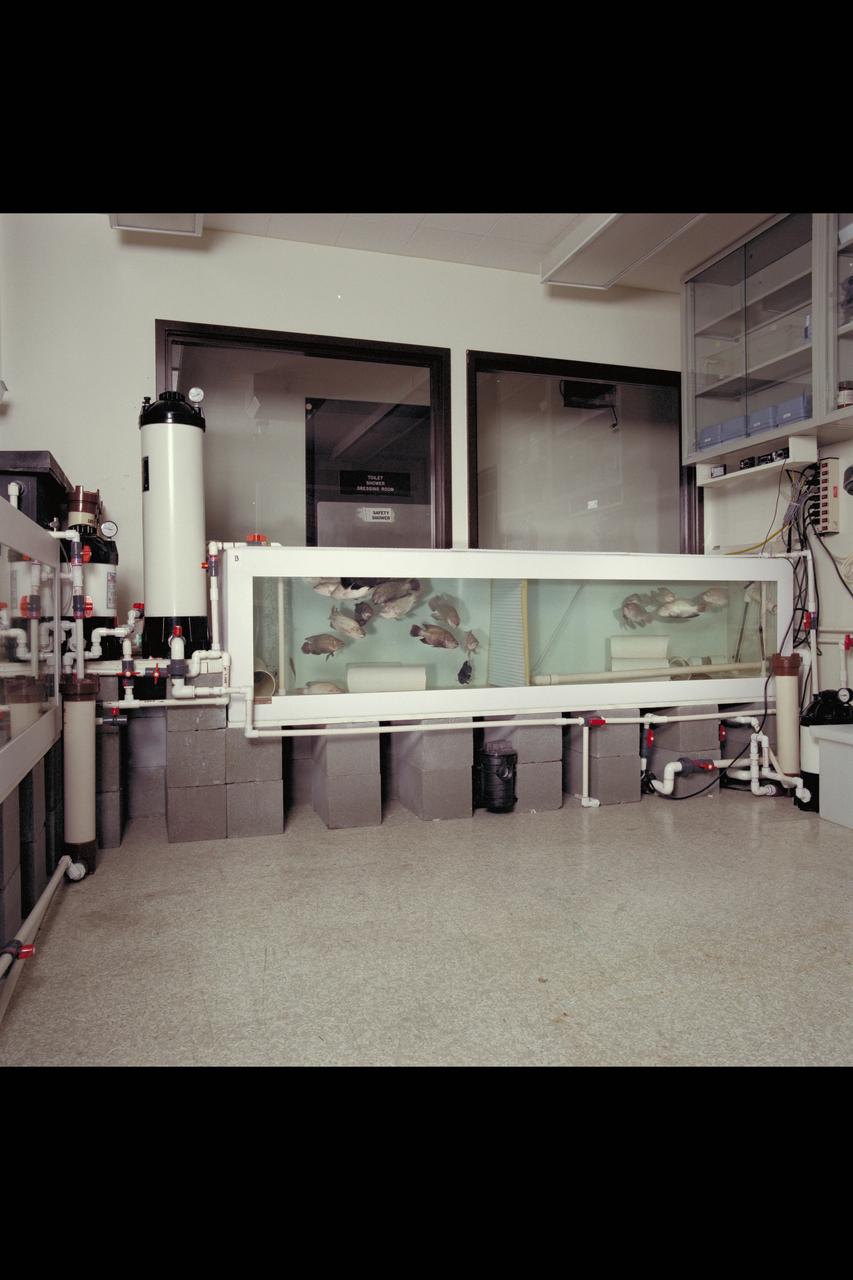
Ames Life Sciences Experiments: Tilapia fish Aquaculture
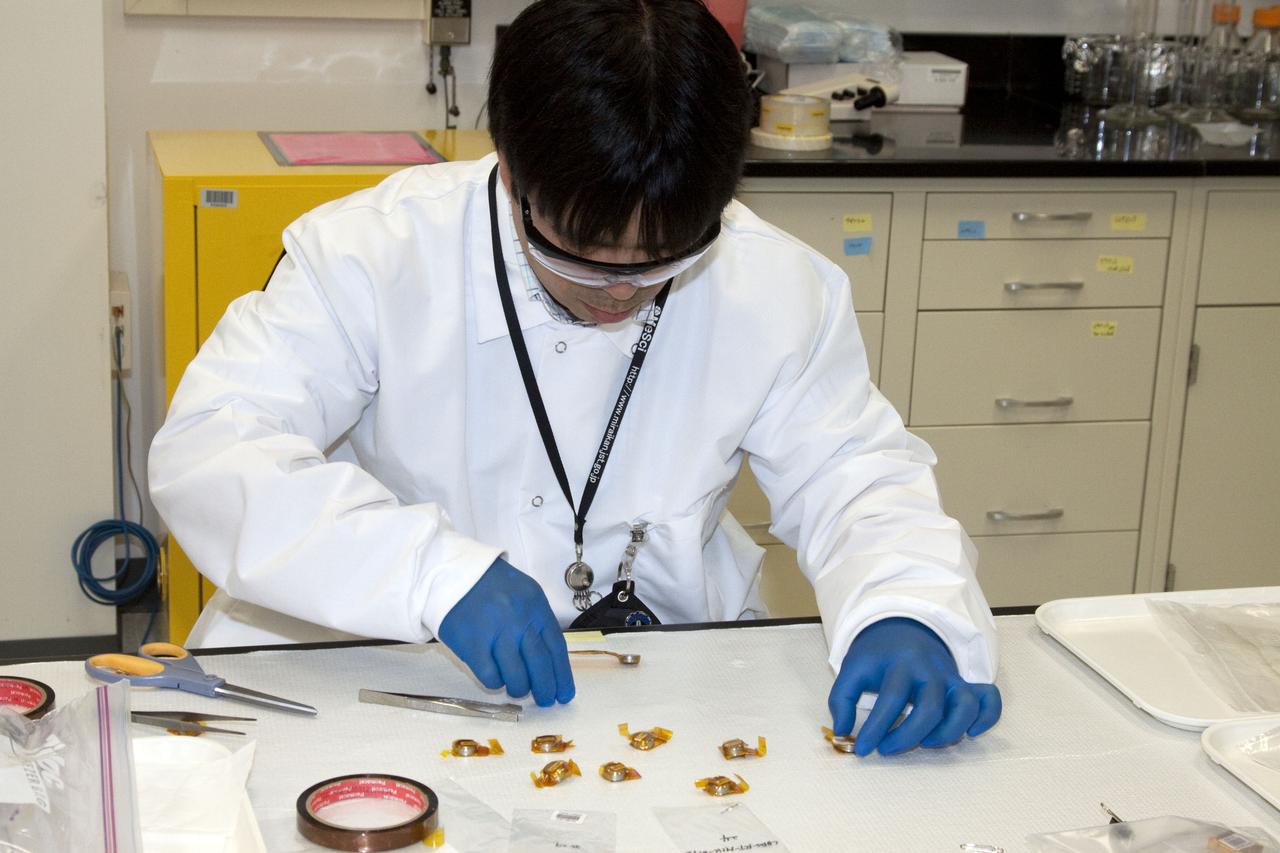

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
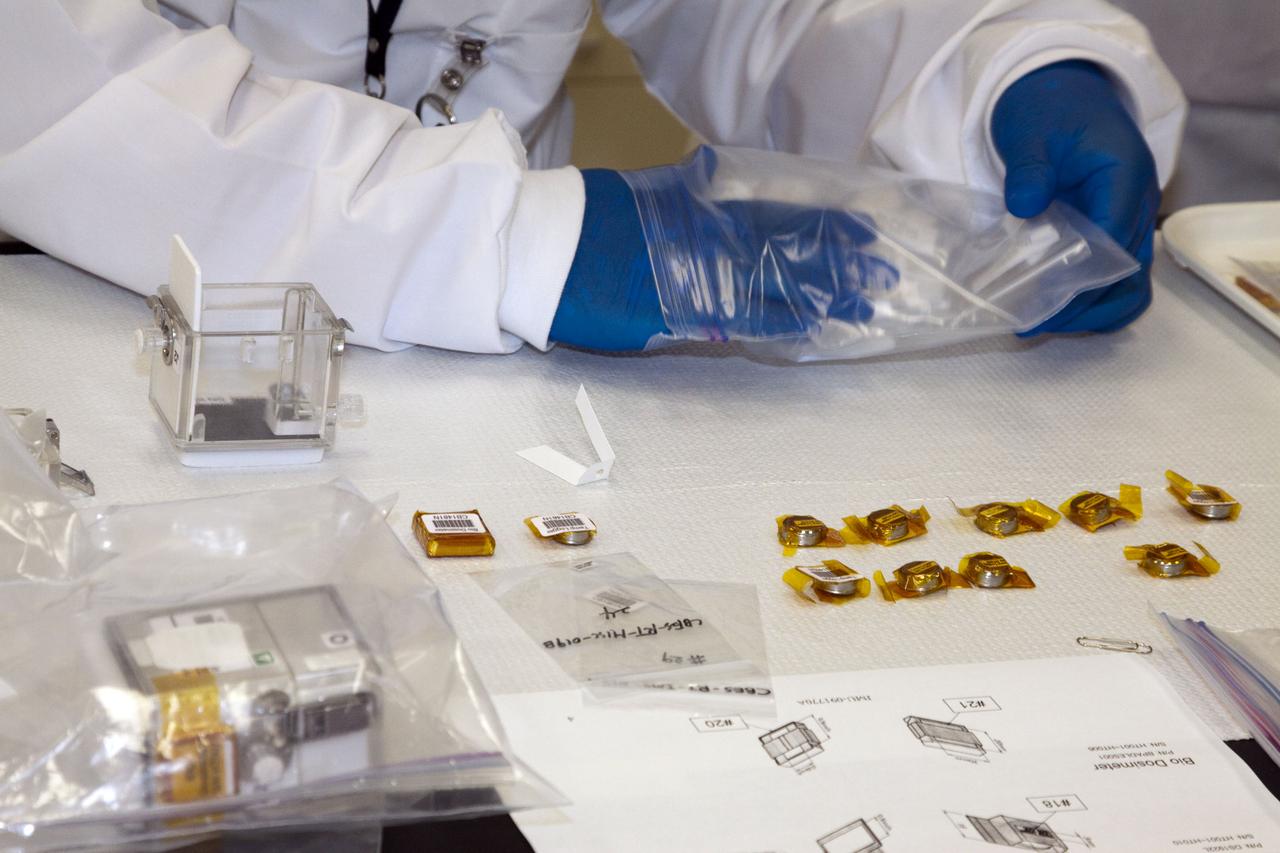

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
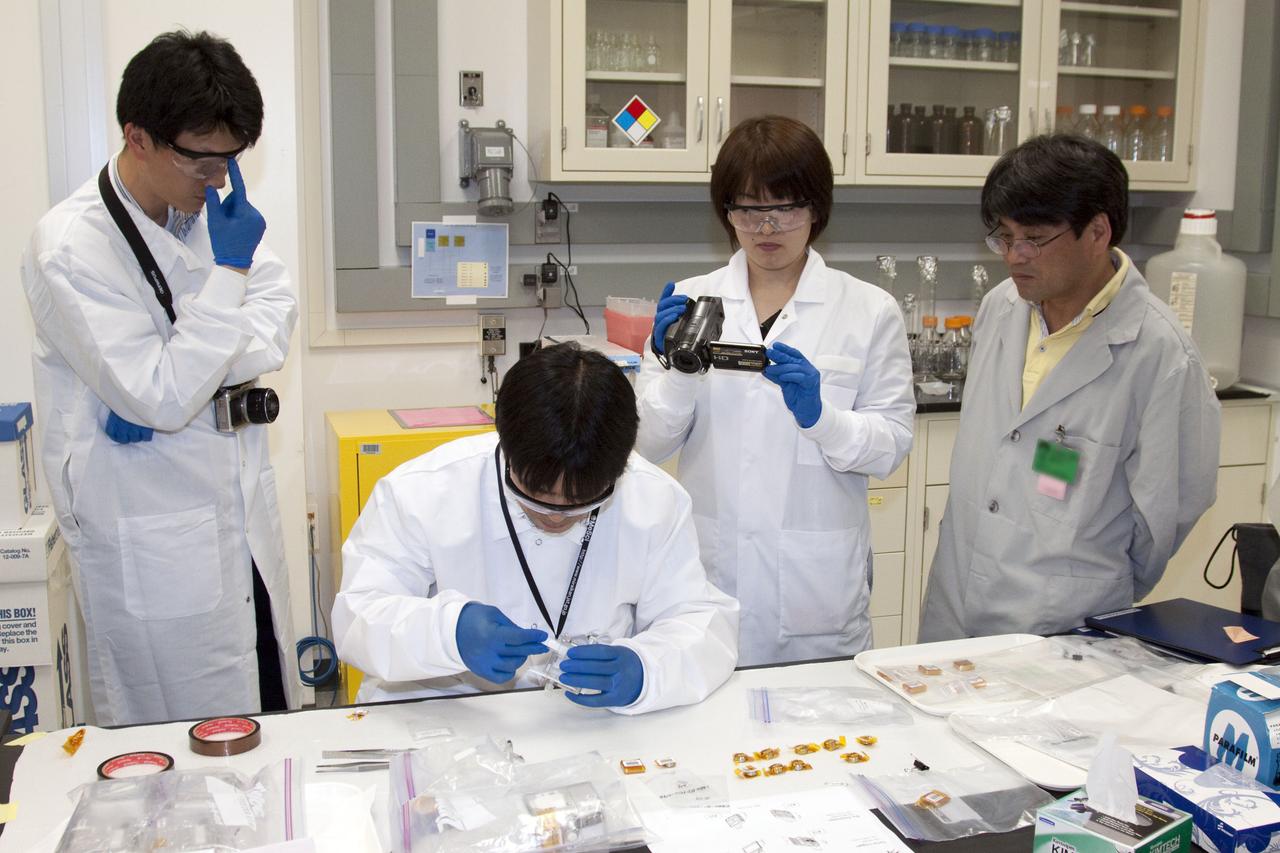

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
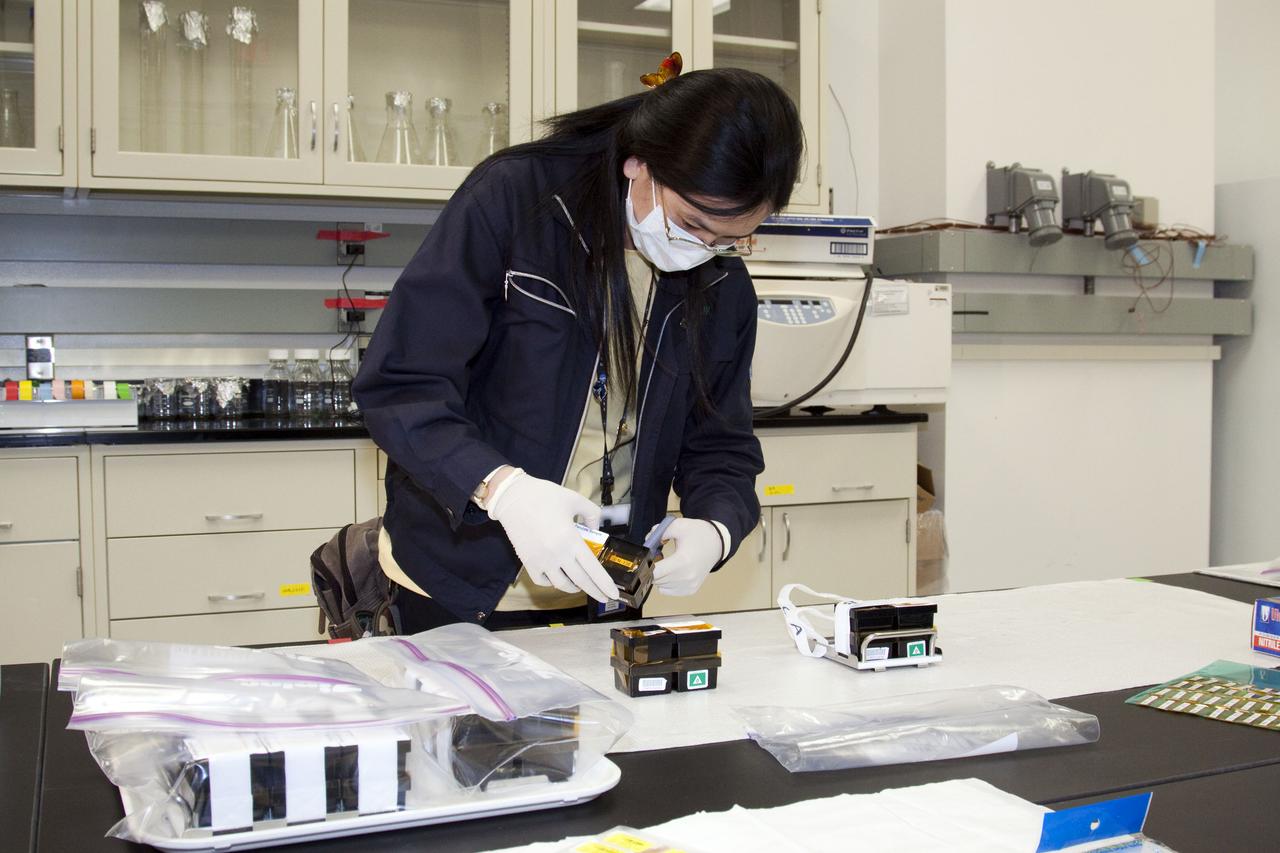

STS-132 JAXA FISH SCALES & HYDROTROP EXPERIMENTS
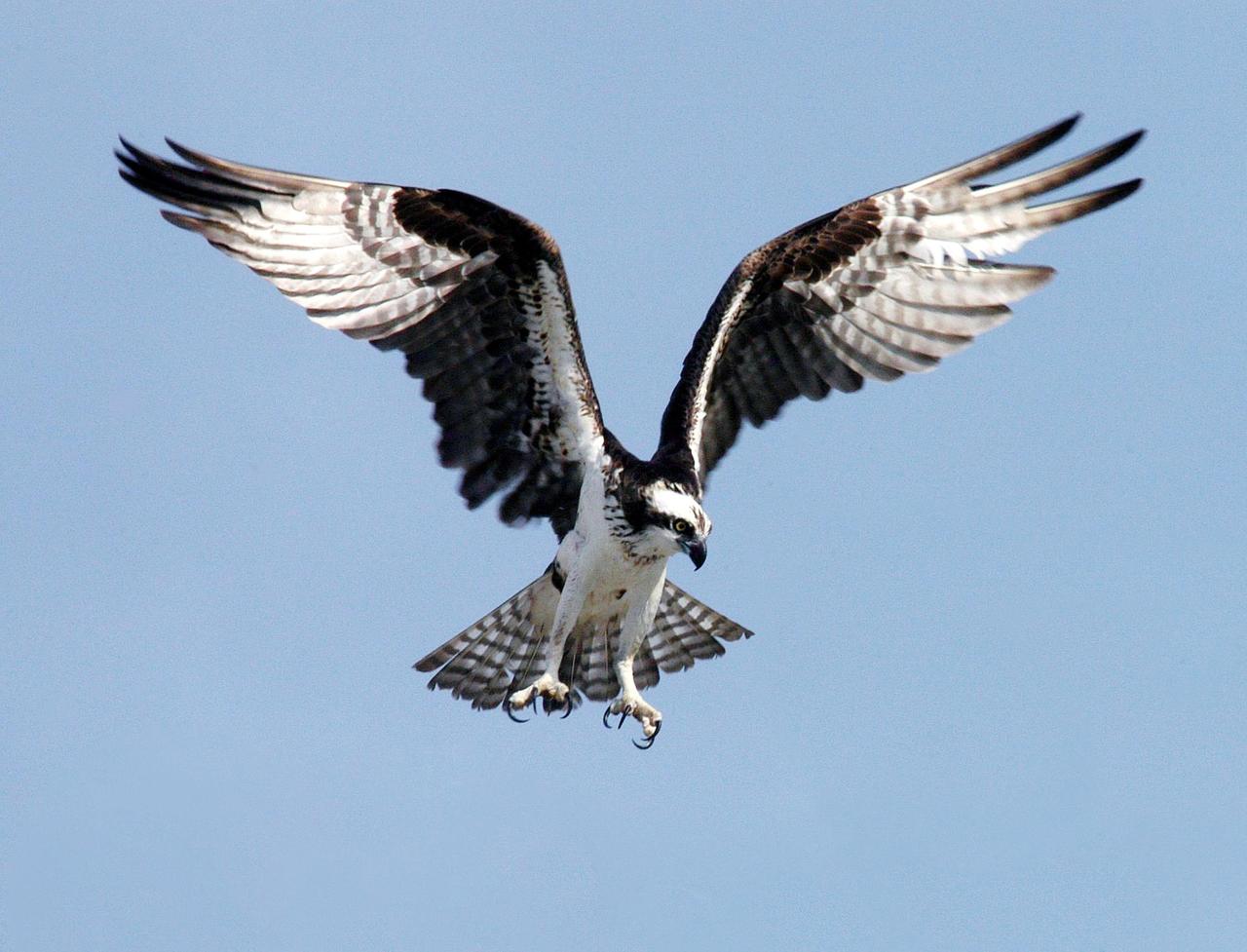

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - An osprey stares intently at prey as it extends its talons. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground, often near water. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge.
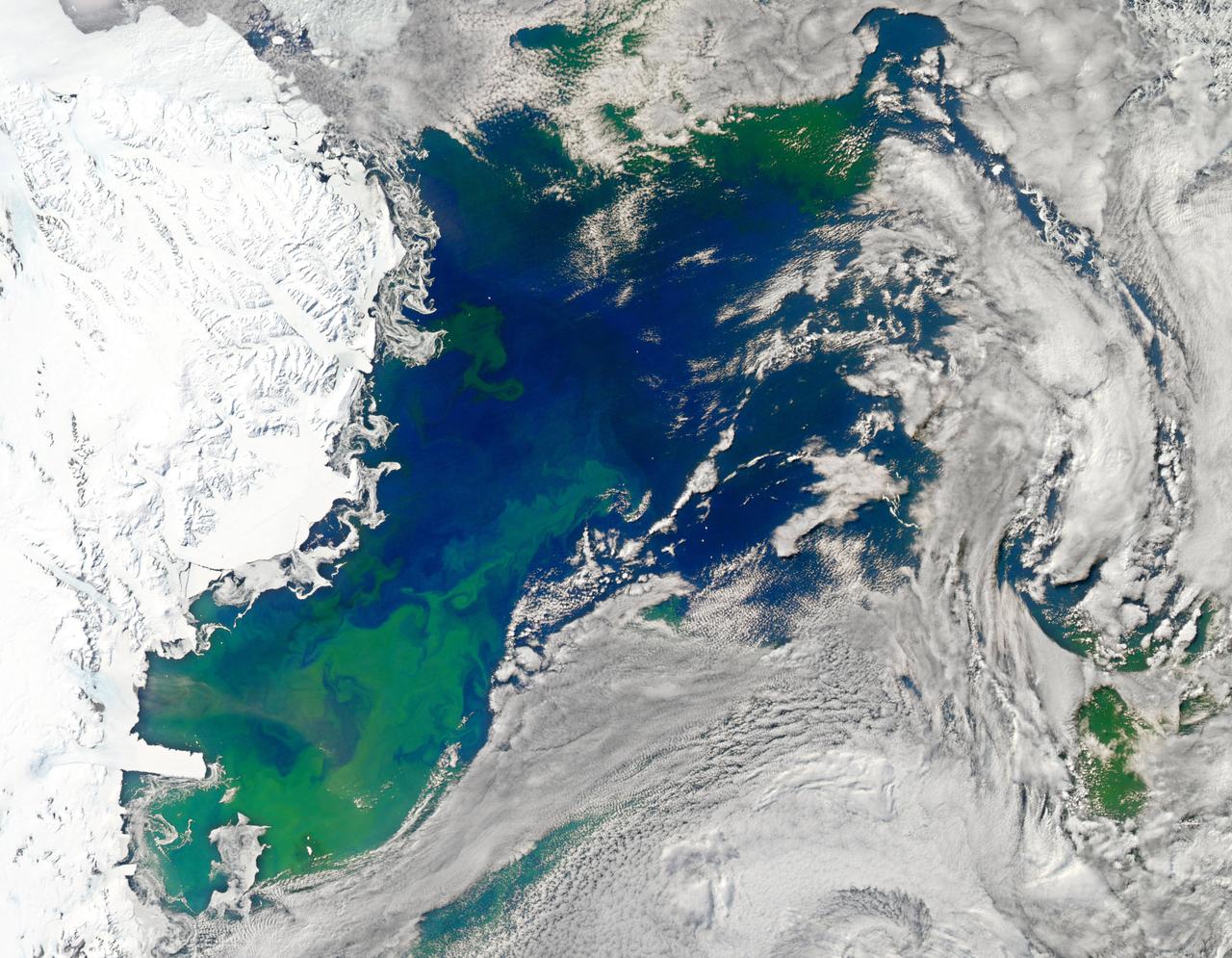
NASA image acquired January 22, 2011 To view the full image go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5397636843">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5397636843</a> Every southern spring and summer, after the Sun has risen into its 24-hour circuit around the skies of Antarctica, the Ross Sea bursts with life. Floating, microscopic plants, known as phytoplankton, soak up the sunlight and the nutrients stirring in the Southern Ocean and grow into prodigious blooms. Those blooms become a great banquet for krill, fish, penguins, whales, and other marine species who carve out a living in the cool waters of the far south. This true-color image captures such a bloom in the Ross Sea on January 22, 2011, as viewed by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. Bright greens of plant-life have replaced the deep blues of open ocean water. The Ross Sea is a relatively shallow bay in the Antarctic coastline and due south from New Zealand. As the spring weather thaws the sea ice around Antarctica, areas of open water surrounded by ice—polynyas—open up on the continental shelf. In this open water, sunlight provides the fuel and various current systems provide nutrients from deeper waters to form blooms that can stretch 100 to 200 kilometers (60 to 120 miles). These blooms are among the largest in extent and abundance in the world. Scientists have hypothesized that the Modified Circumpolar Deep Water is the engine behind the blooms, stirring up just the right mix of trace metals and minerals from the deep to sustain plankton growth. This month, researchers aboard the U.S. icebreaking ship Nathaniel B. Palmer are cruising in the Ross Sea in search of the signatures of this current system. NASA image courtesy Norman Kuring, Ocean Color Team at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz, with information from Hugh Powell, COSEE-NOW. Instrument: Aqua - MODIS For more info go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=48949</a> Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
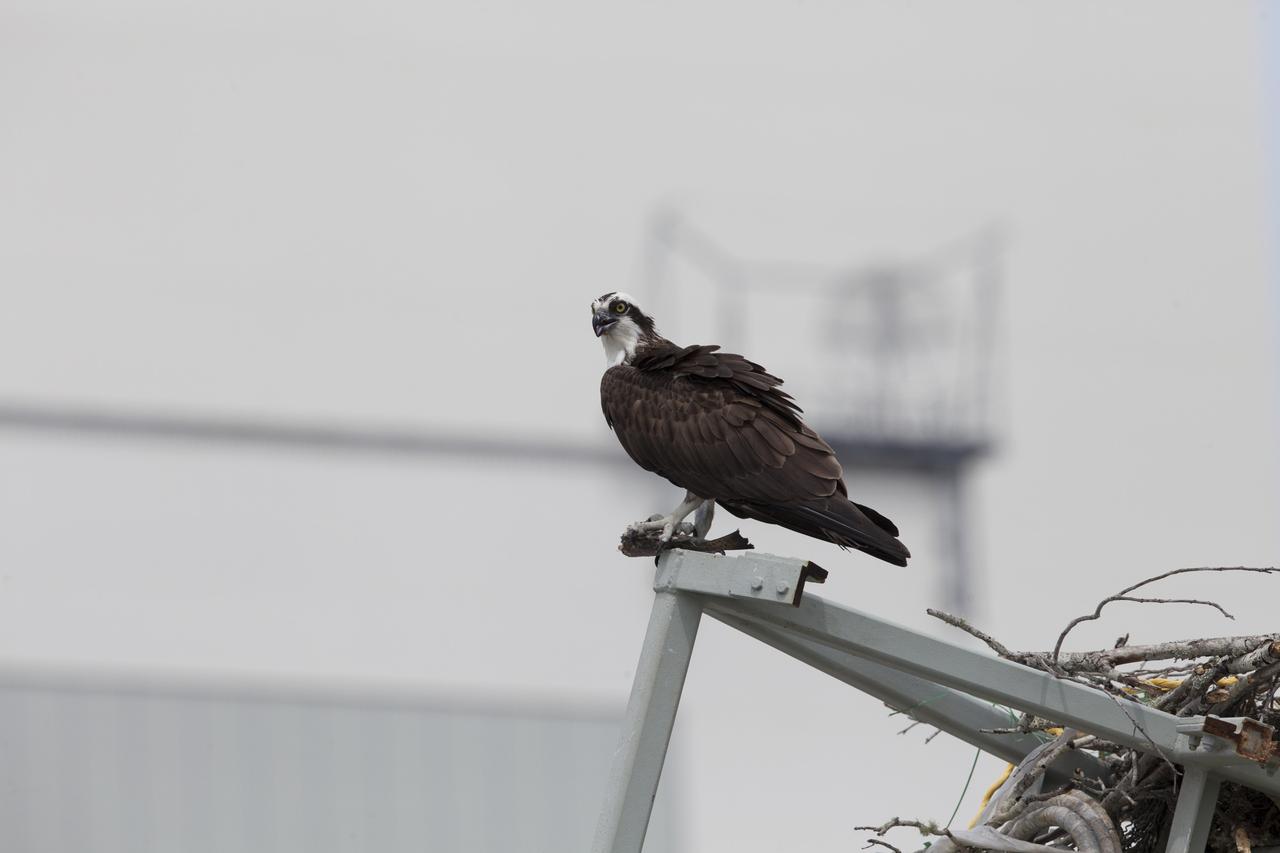

An osprey, clutching a fish, pauses for a meal atop a metal structure at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spaceport shares boundaries with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
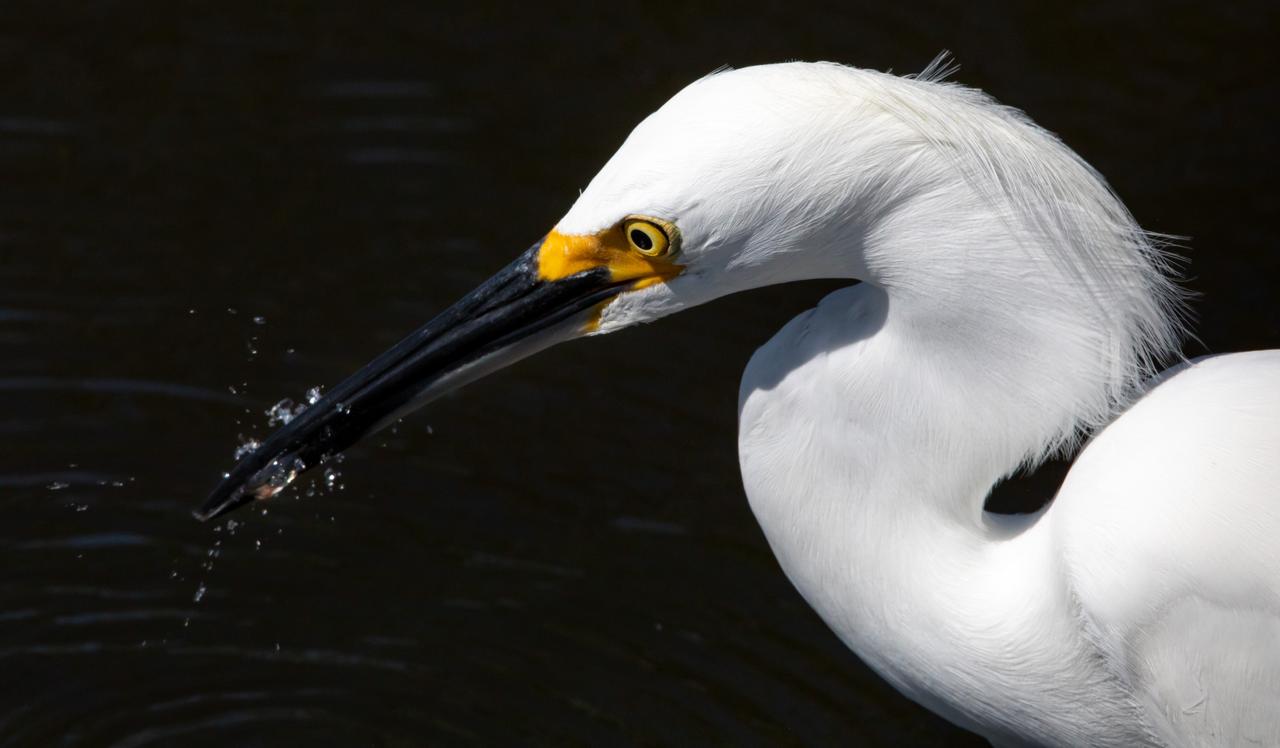

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
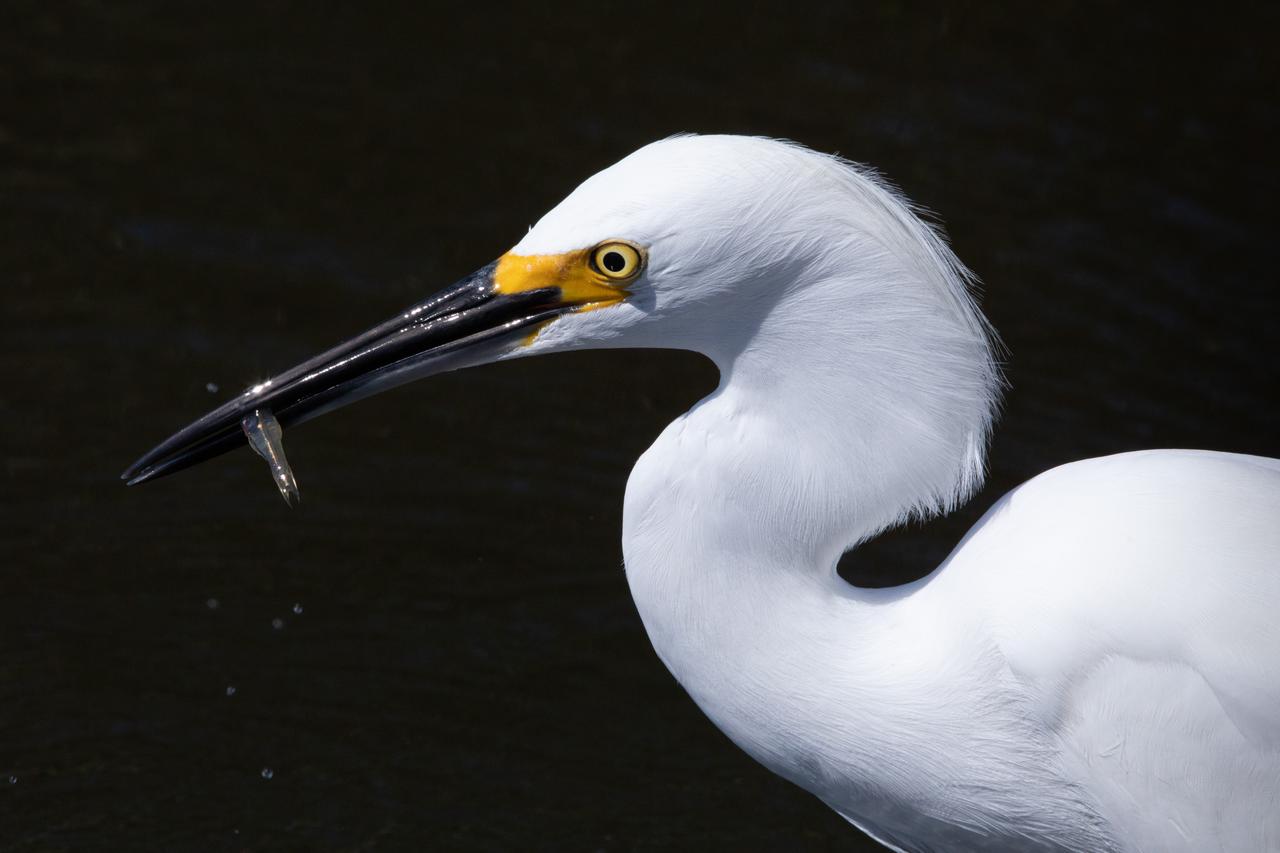

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
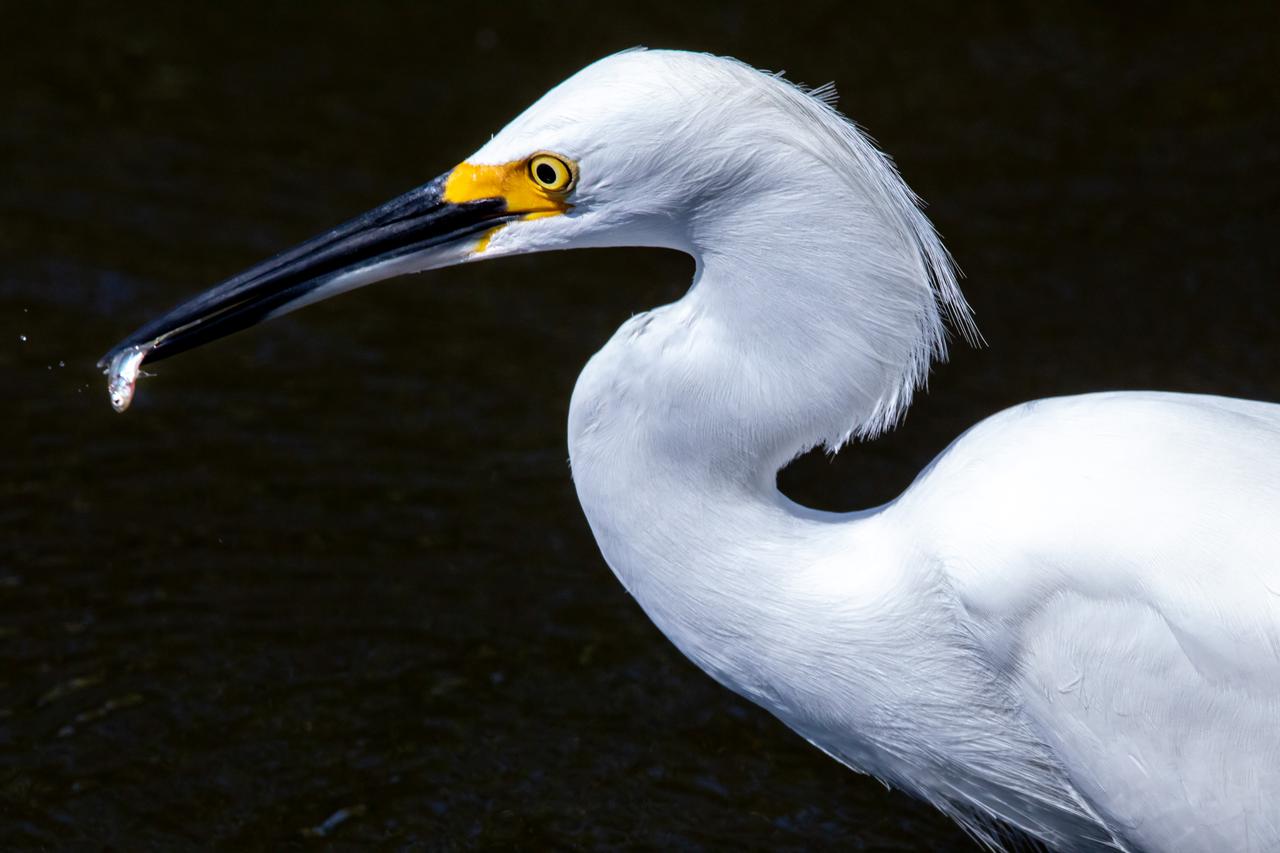

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
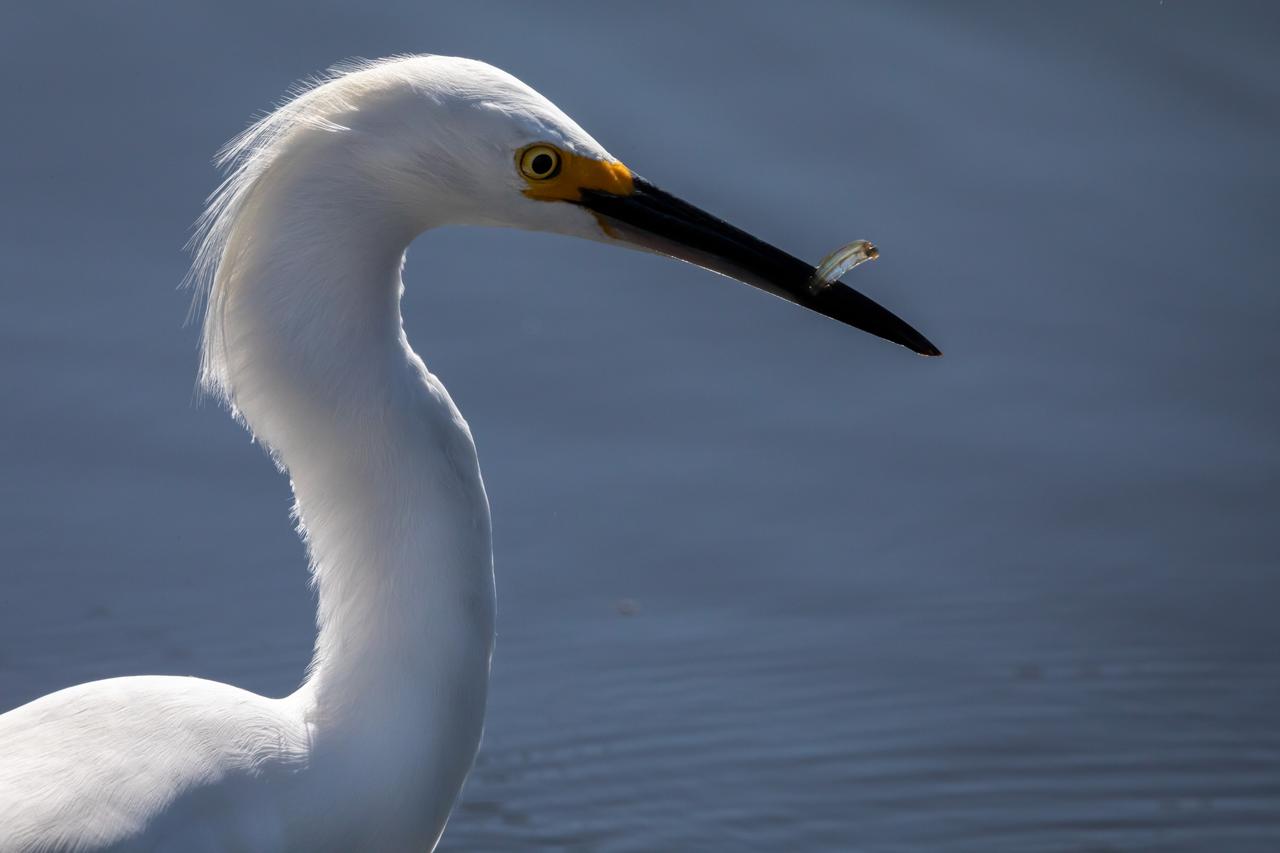

A Great Egret catches a small fish in a waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The center shares a border with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. More than 330 native and migratory bird species, 25 mammal, 117 fish and 65 amphibian and reptile species call Kennedy and the wildlife refuge home.
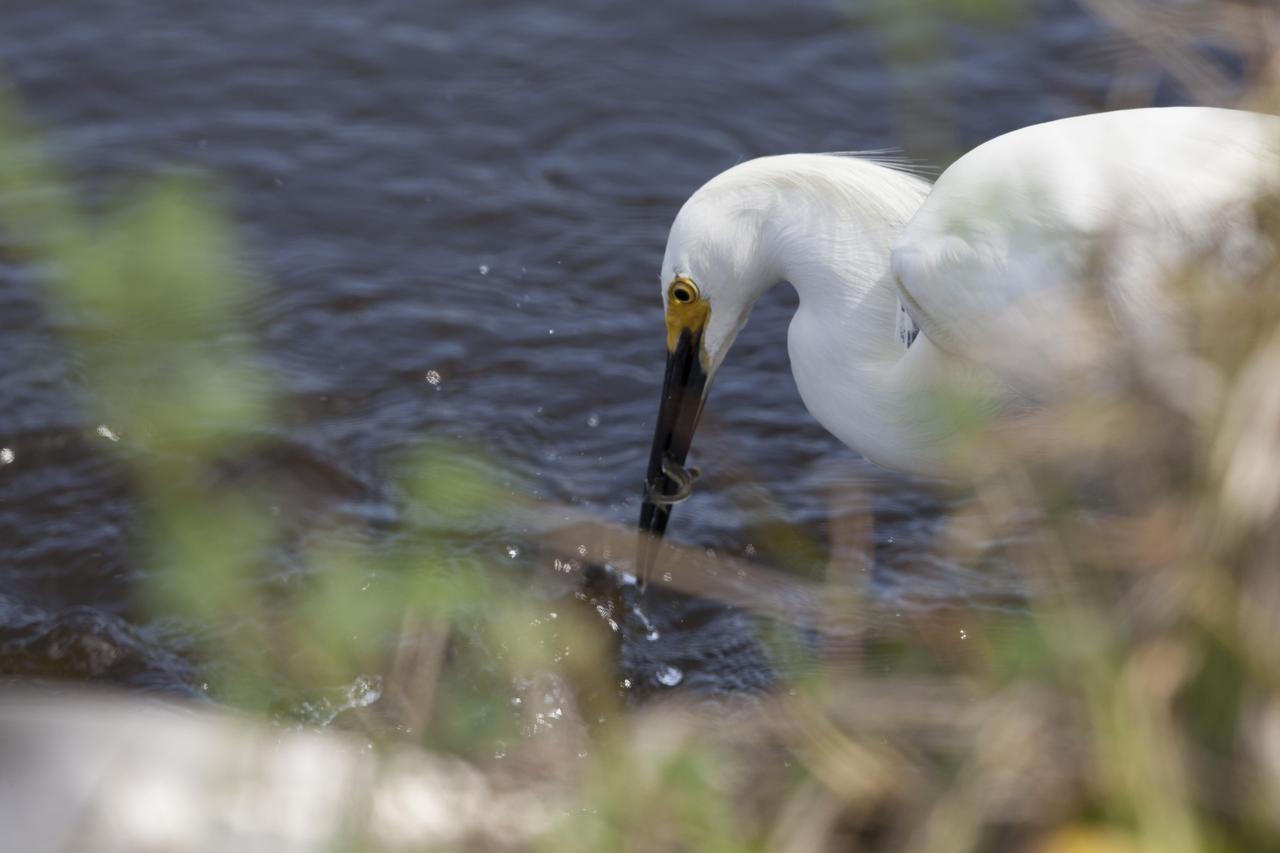

A snowy egret successfully catches a small fish in a shallow waterway at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
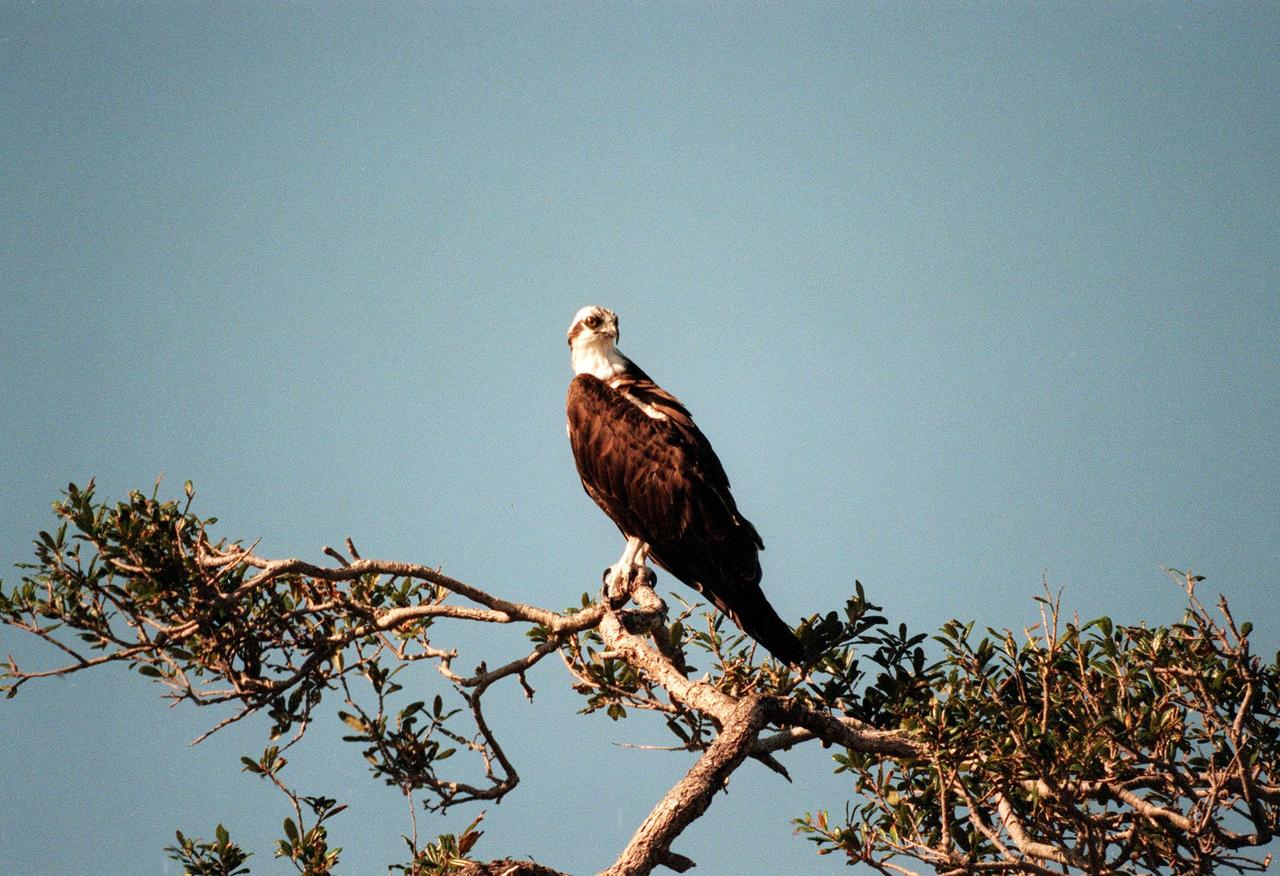

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- An osprey perches on a treetop at Kennedy Space Center. This long-winged "fish hawk" inhabits lakes, rivers and seacoasts, surviving solely on fish which it captures from the water, grasping them in its talons when they near the surface. They range from Alaska and Newfoundland south to Florida and the Gulf Coast
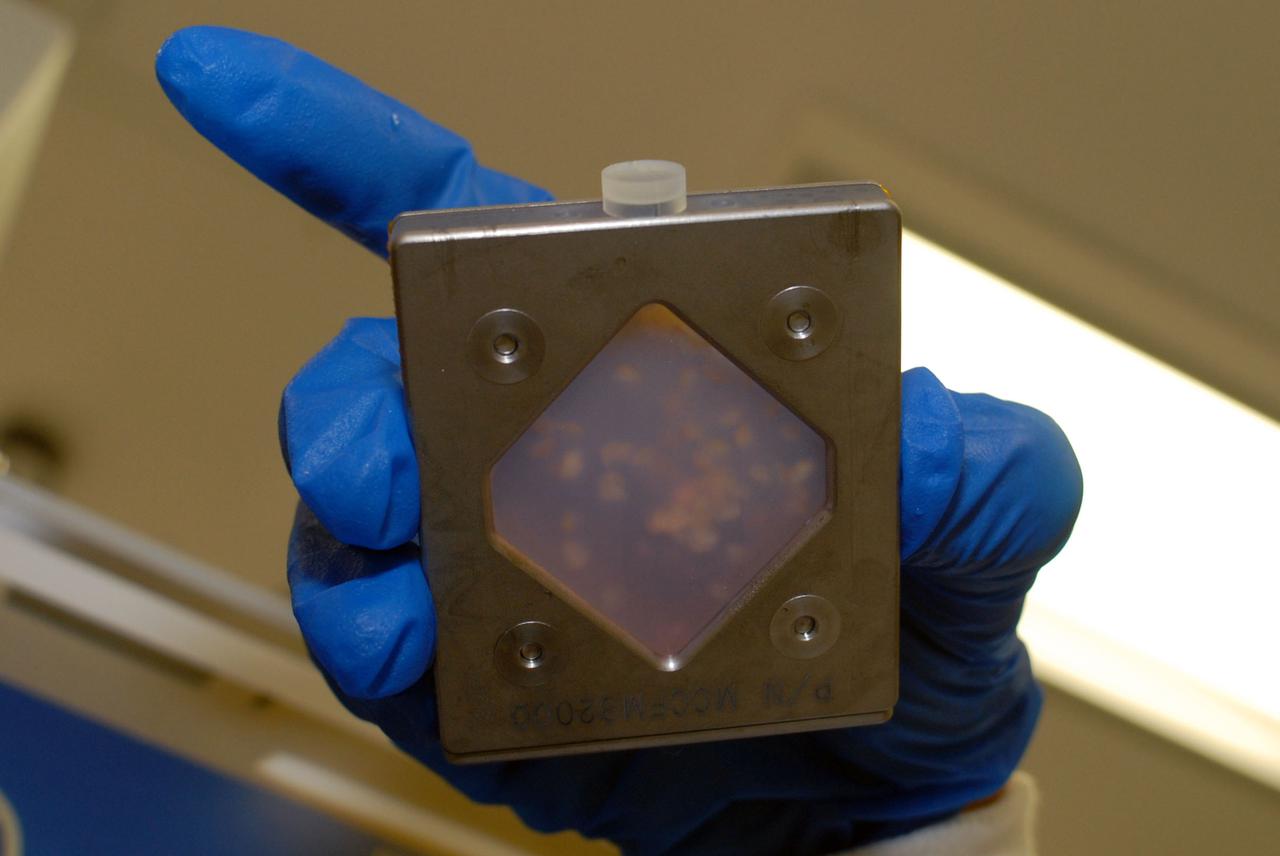
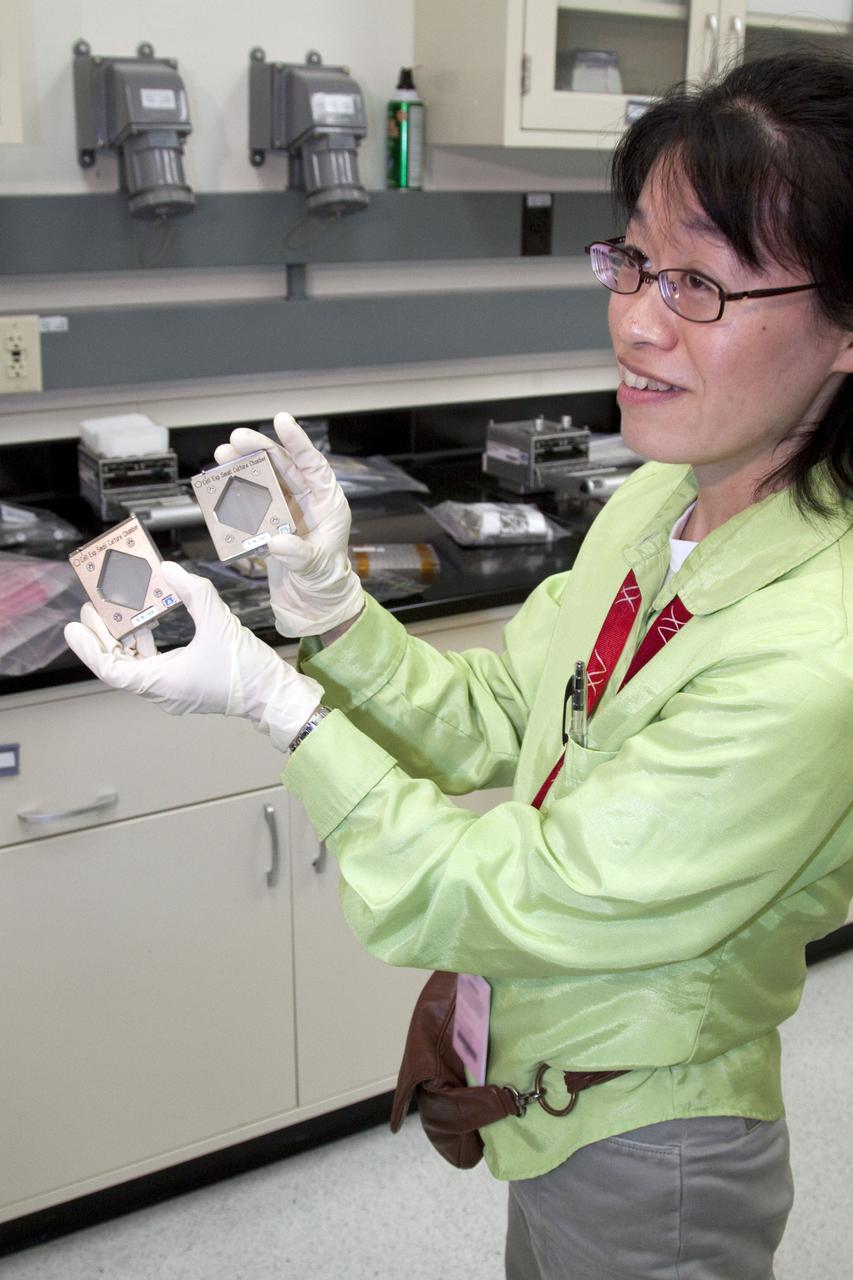
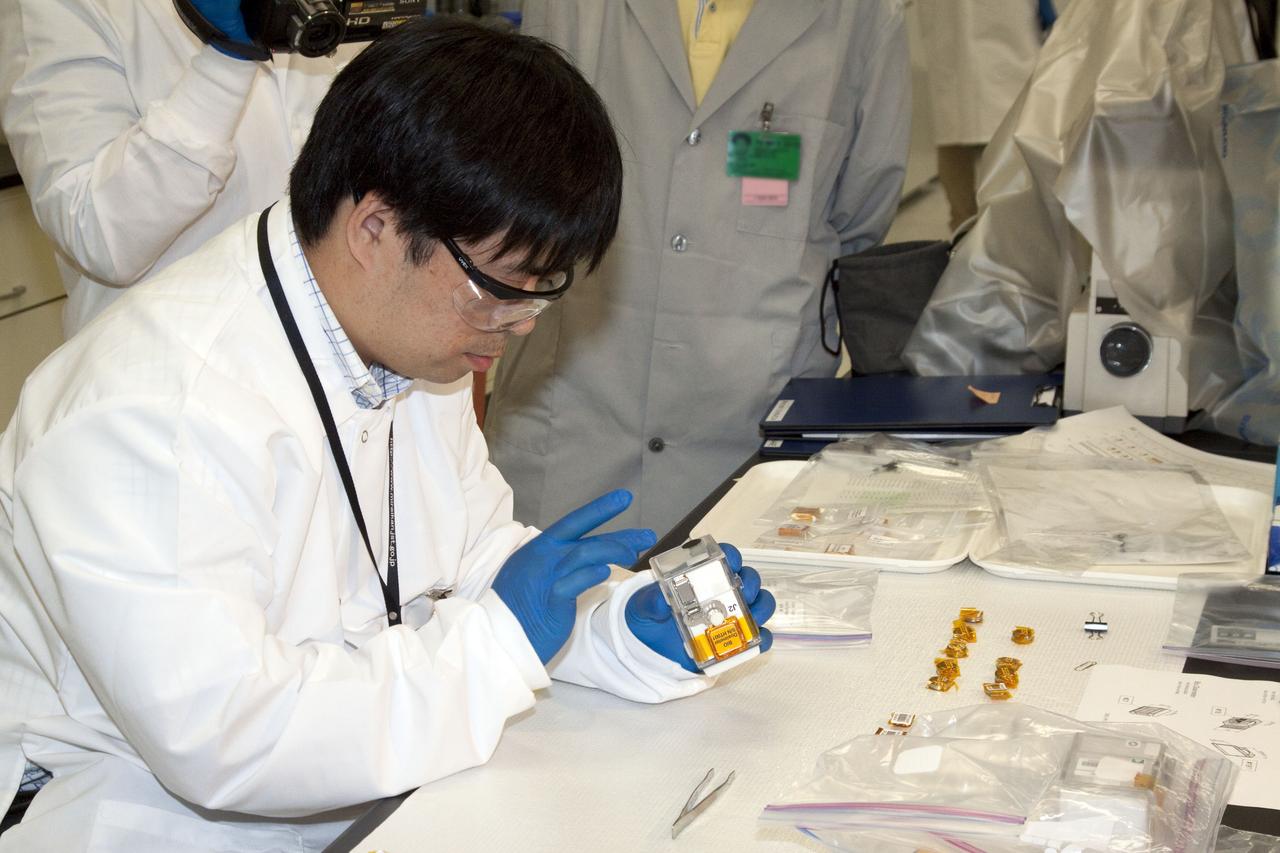
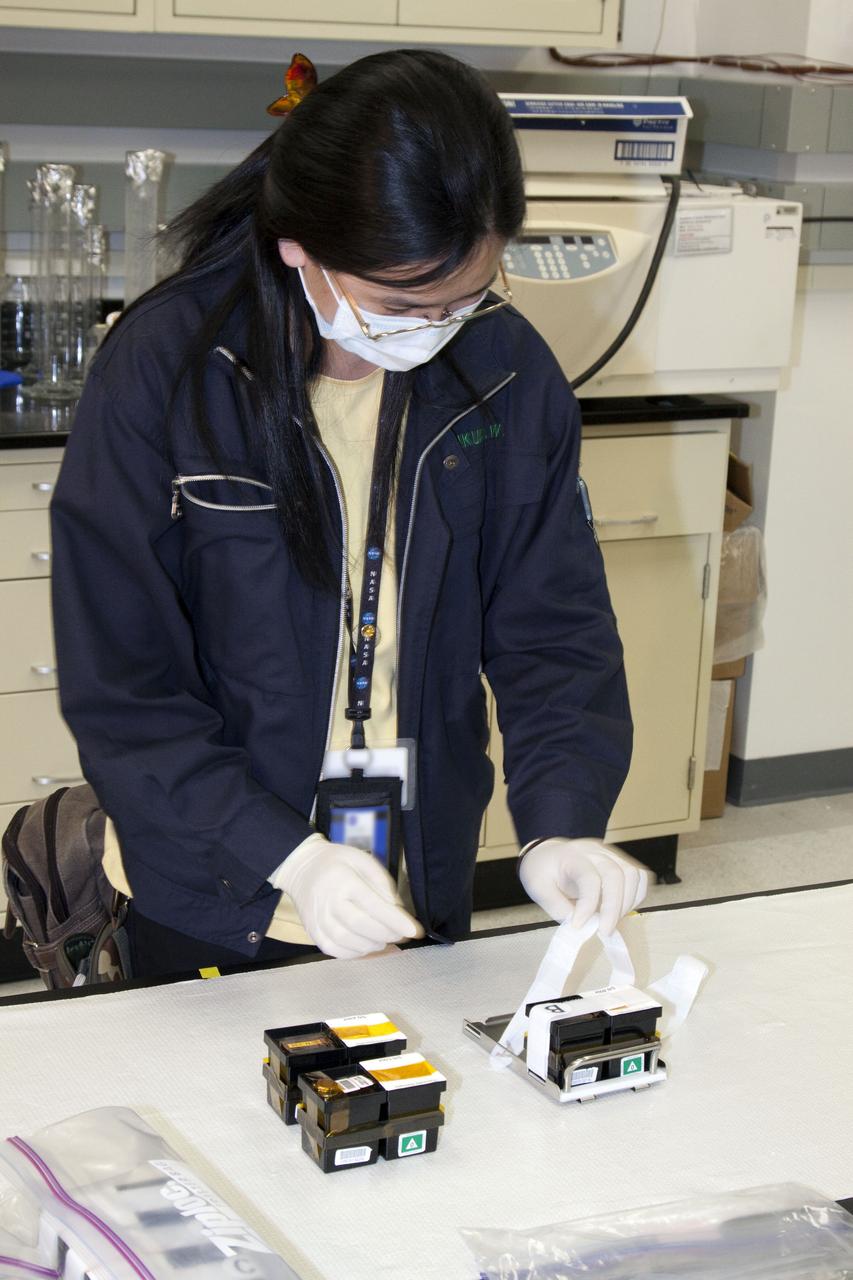
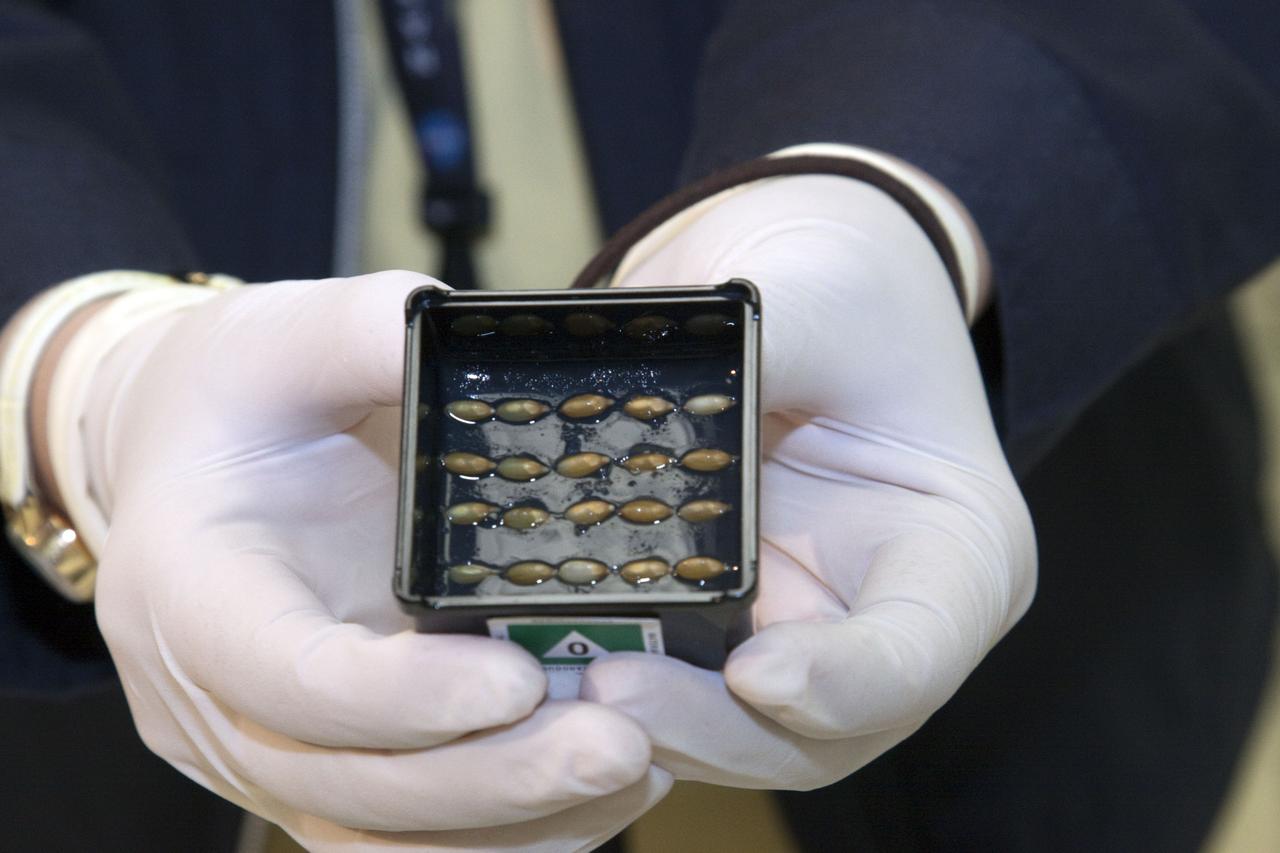
jsc2010e08036p (5/12/2010) --- A preflight image of the Fish Scales Culture Chambers with samples inside. The Osteoclastic and Osteoblastic Responses to Microgravity Using Goldfish Scales (Fish Scales) investigation will examine regenerating scales collected from anesthetized goldfish in microgravity, the results will be compared with ground controls.
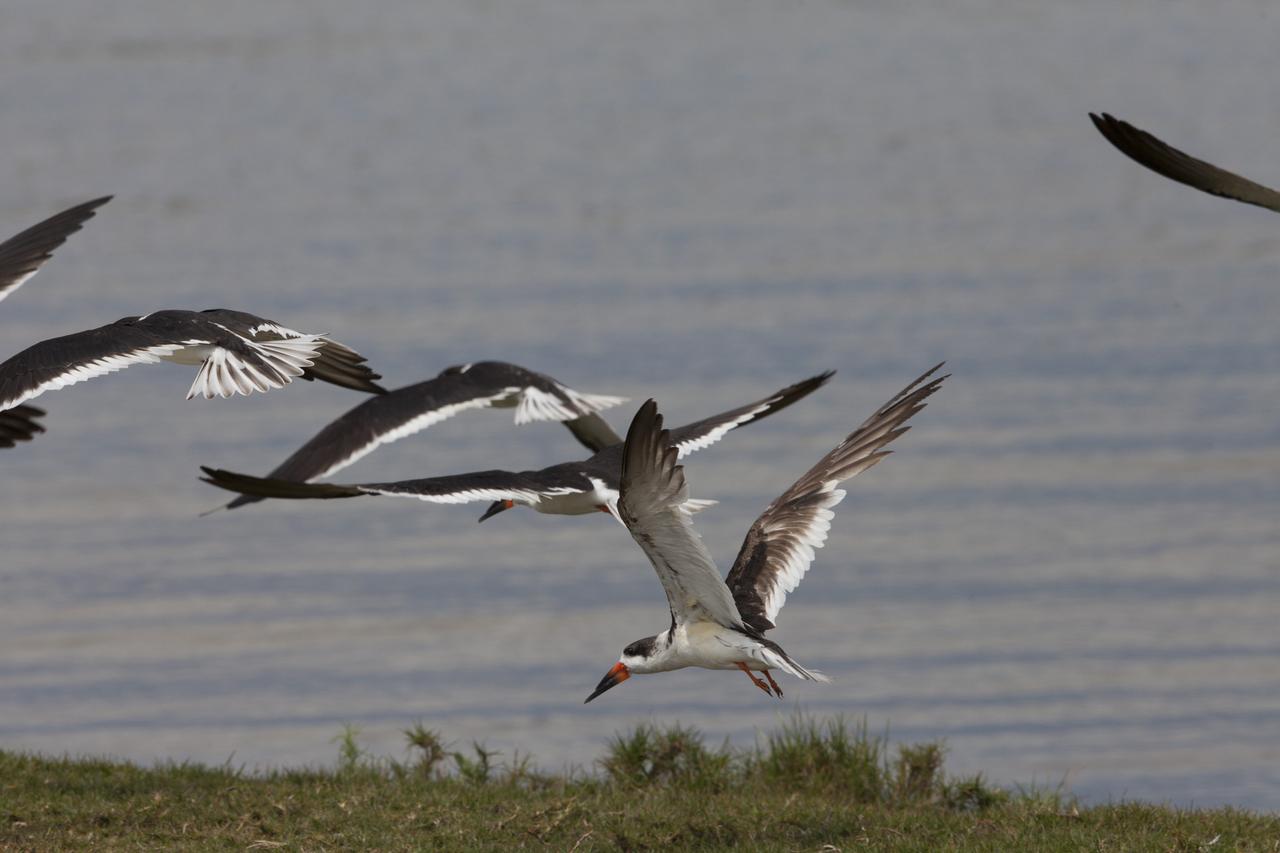

Black skimmers fly just above the waterline as they hunt for fish at Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge in Florida. NASA’s Kennedy Space Center shares boundaries with the refuge, which is home to more than 330 native and migratory bird species, along with 25 mammal, 117 fish, and 65 amphibian and reptile species.
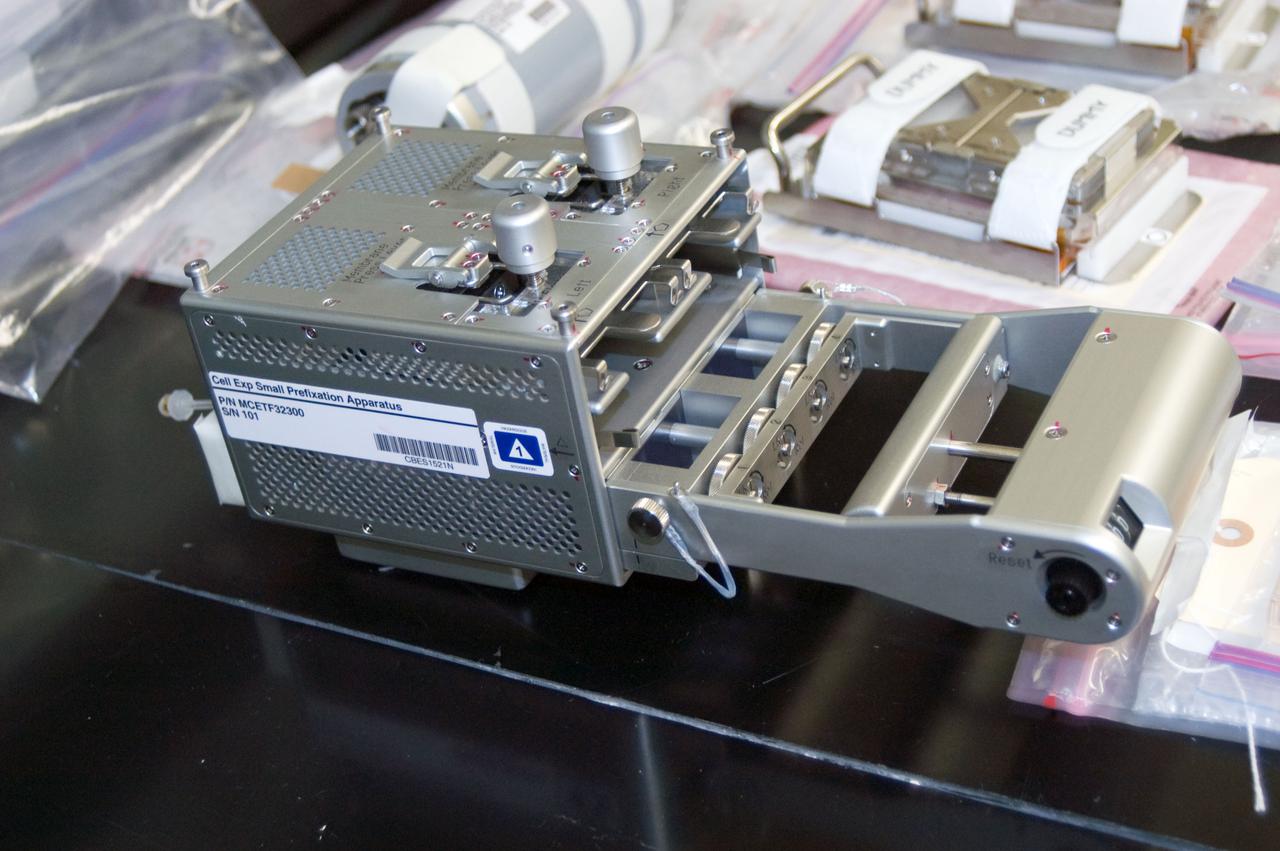

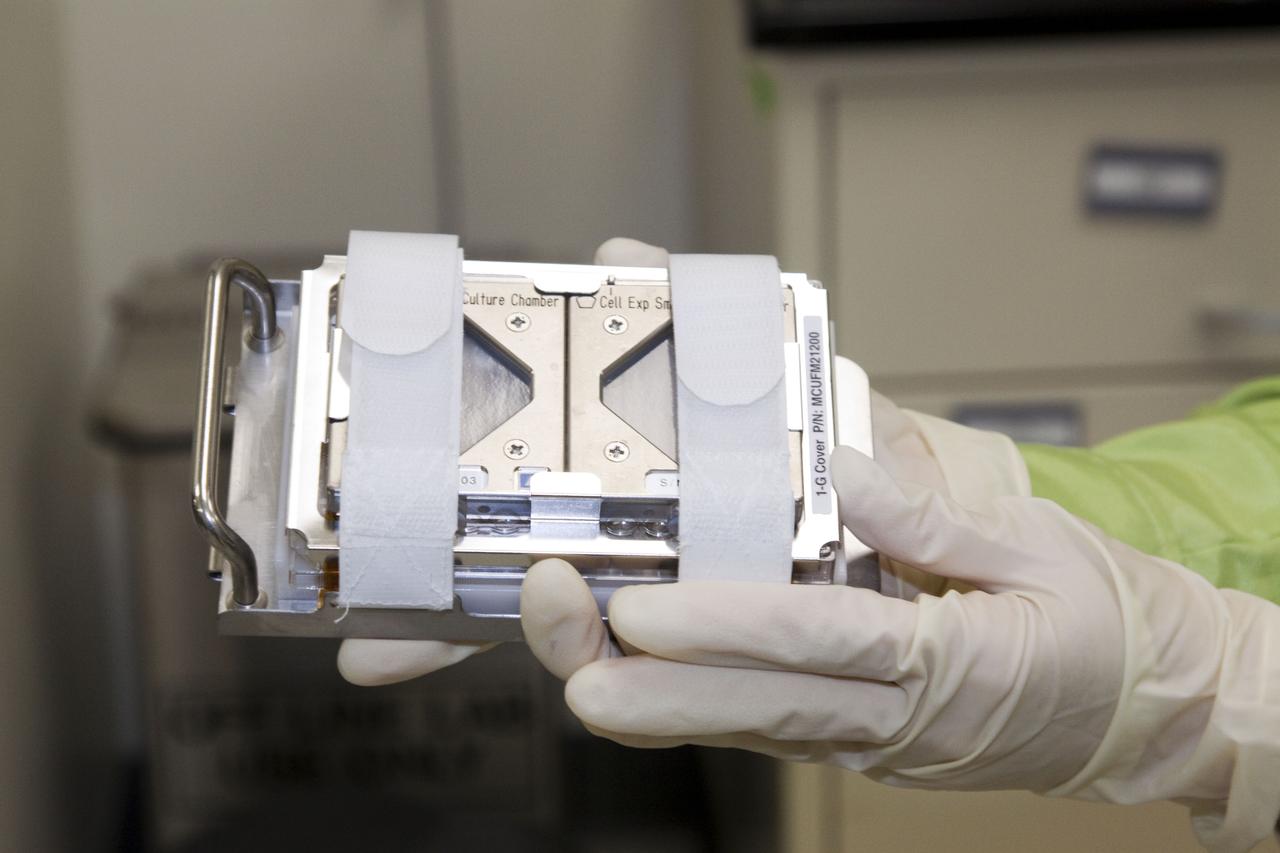
jsc2010e089995 (6/7/2010) --- A preflight image of the Cell Experiment Small Prefixation Apparatus for Fish Scales. The Osteoclastic and Osteoblastic Responses to Microgravity Using Goldfish Scales (Fish Scales) investigation will examine regenerating scales collected from anesthetized goldfish in microgravity, the results will be compared with ground controls.
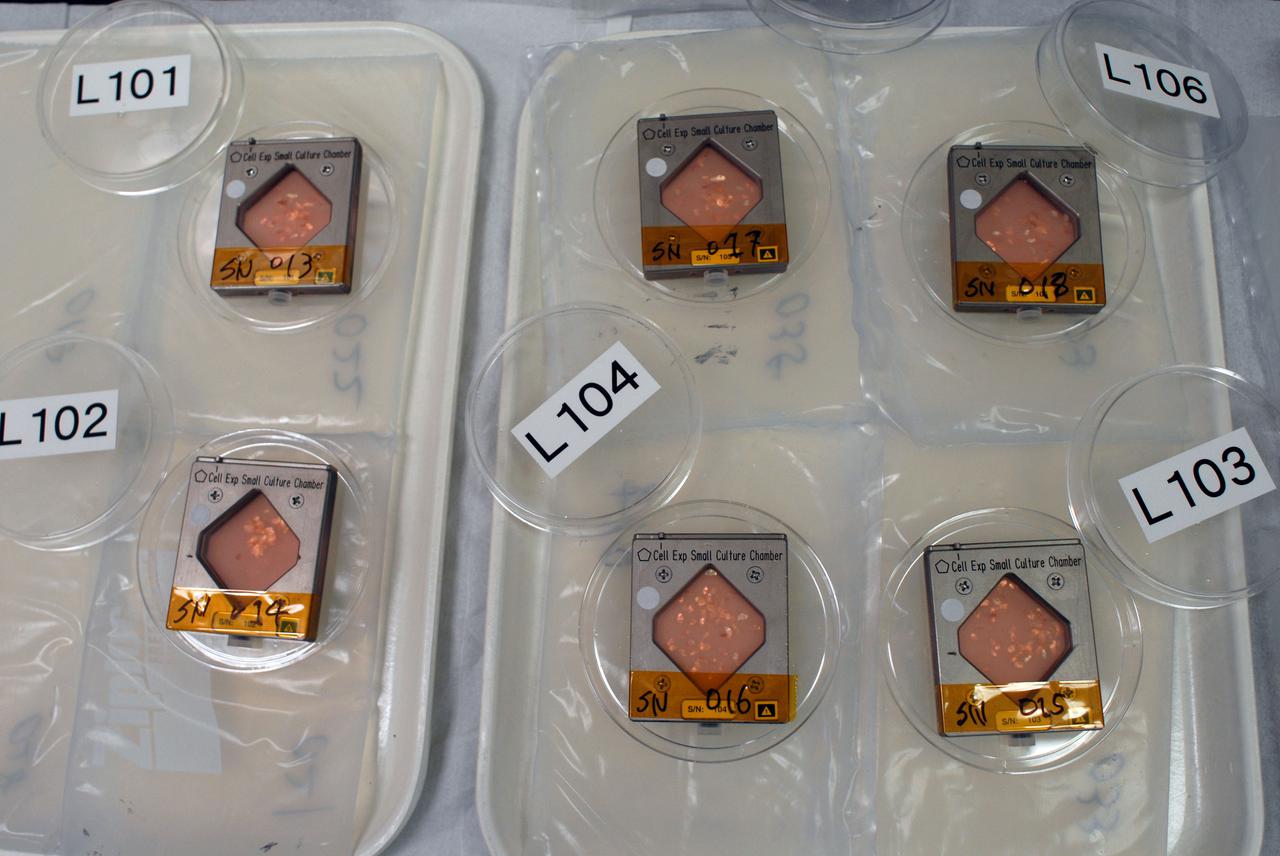

jsc2010e080368 (5/12/2010) --- A preflight image of the Fish Scales Culture Chambers with samples inside. The Osteoclastic and Osteoblastic Responses to Microgravity Using Goldfish Scales (Fish Scales) investigation will examine regenerating scales collected from anesthetized goldfish in microgravity, the results will be compared with ground controls.

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to
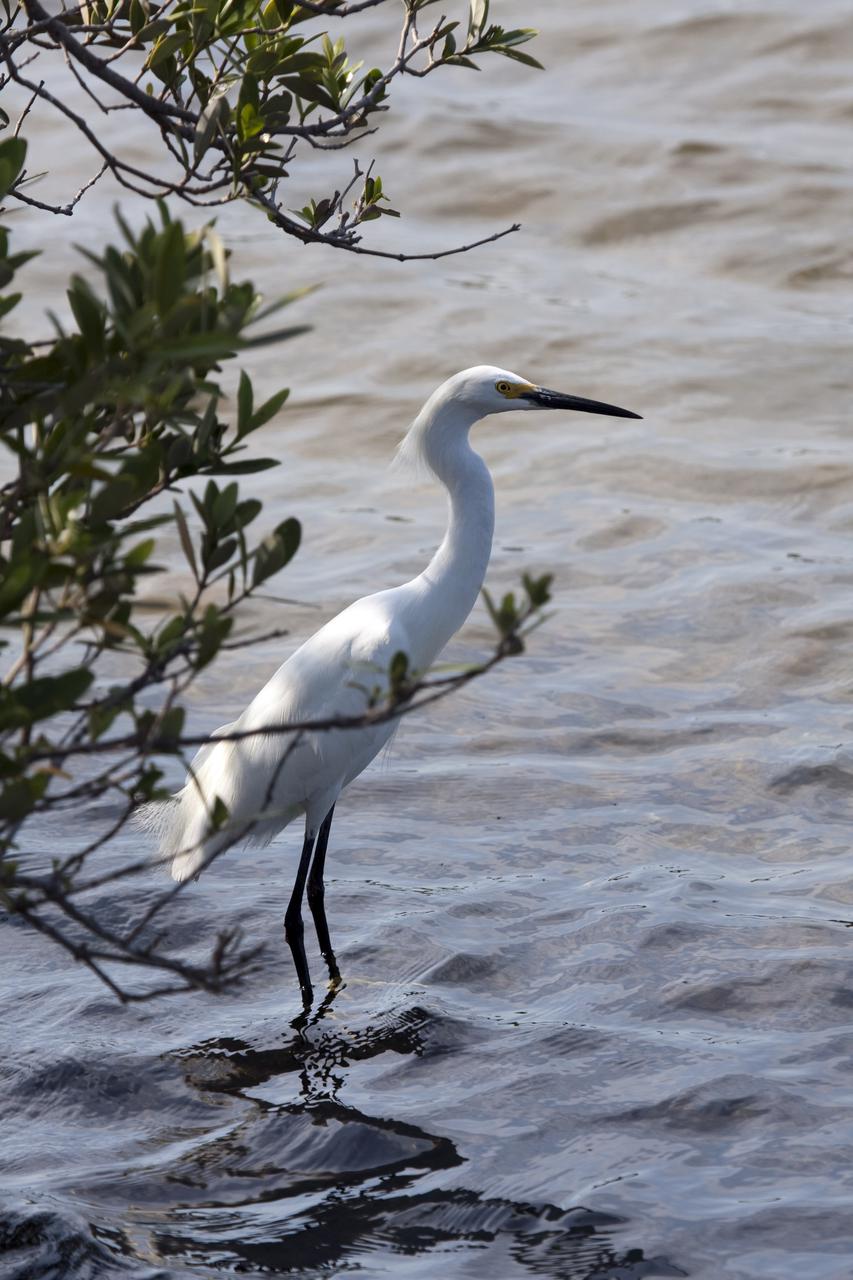

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a great white egret fishes in Launch Complex 39. Egrets use a foot-foraging method to fish, standing motionless in the shallows and raking the bottom to attract fish which they quickly capture in their bills. The Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge overlaps with Kennedy Space Center property and provides a habitat for 330 species of birds, including egrets. A variety of other wildlife - 117 kinds of fish, 65 types of amphibians and reptiles, 31 different mammals, and 1,045 species of plants - also inhabit the refuge. For information on the refuge, visit http:__www.fws.gov_merrittisland_Index.html. For information on Kennedy Space Center, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_kennedy. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
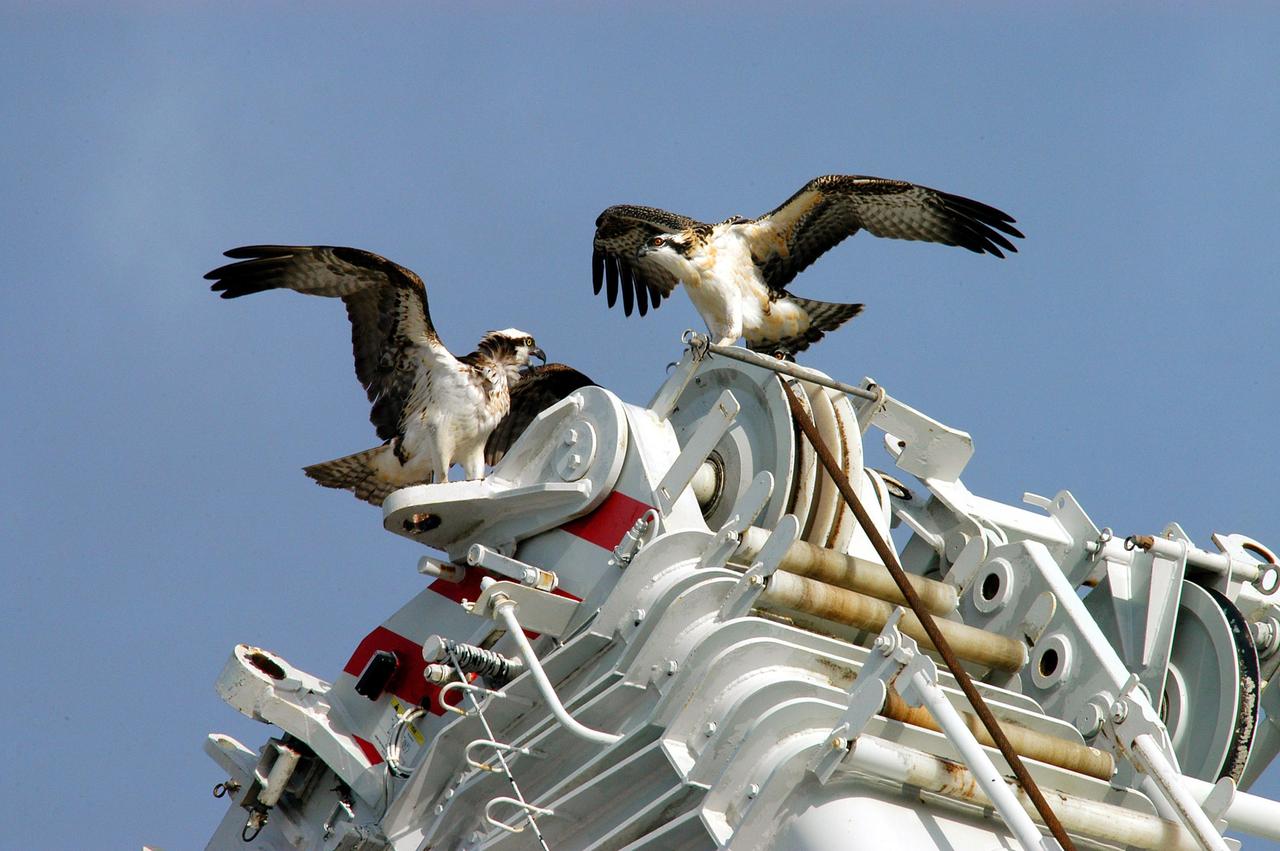

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- - Two young ospreys flex their wings for flight. Their nest is located in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
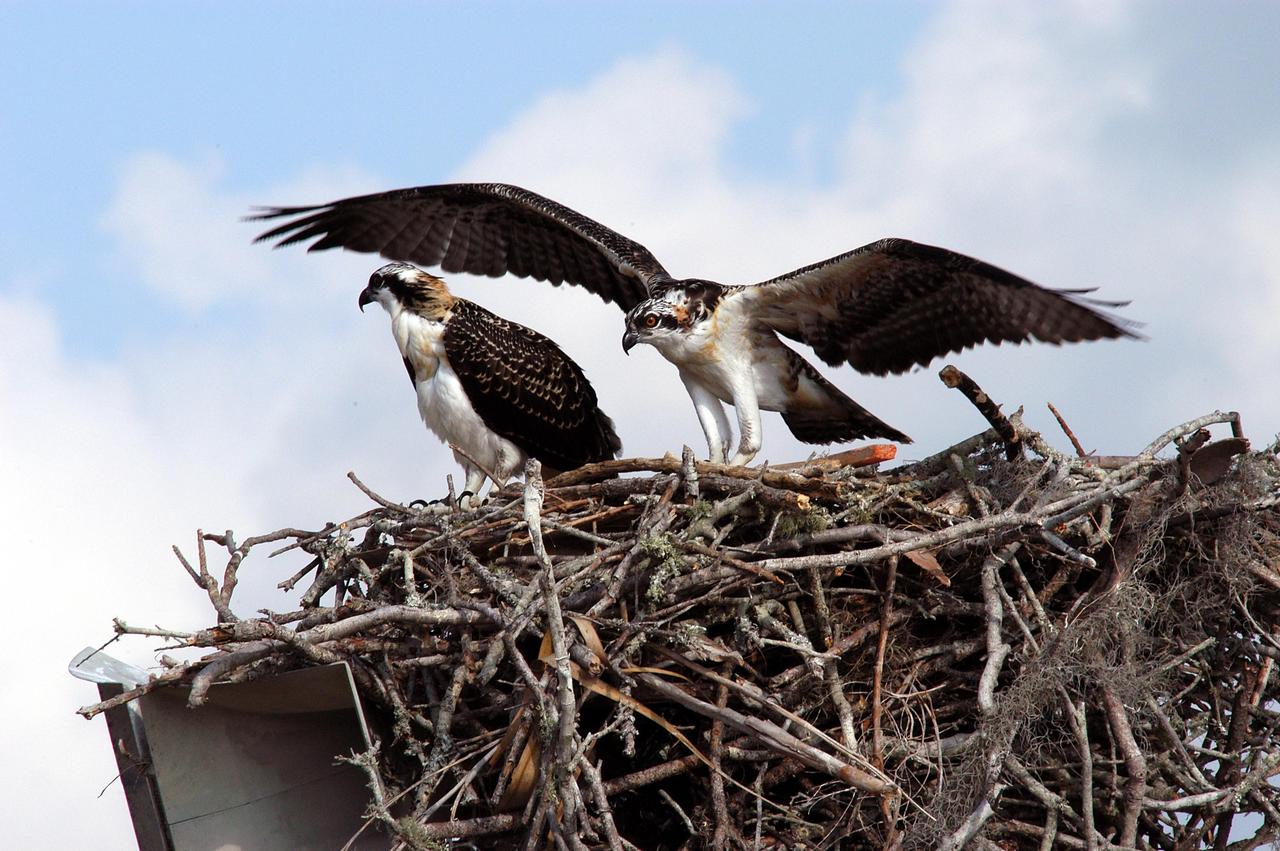

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of two fledgling ospreys still in the nest stretches its wings to fly away. The stick-built nest is located in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
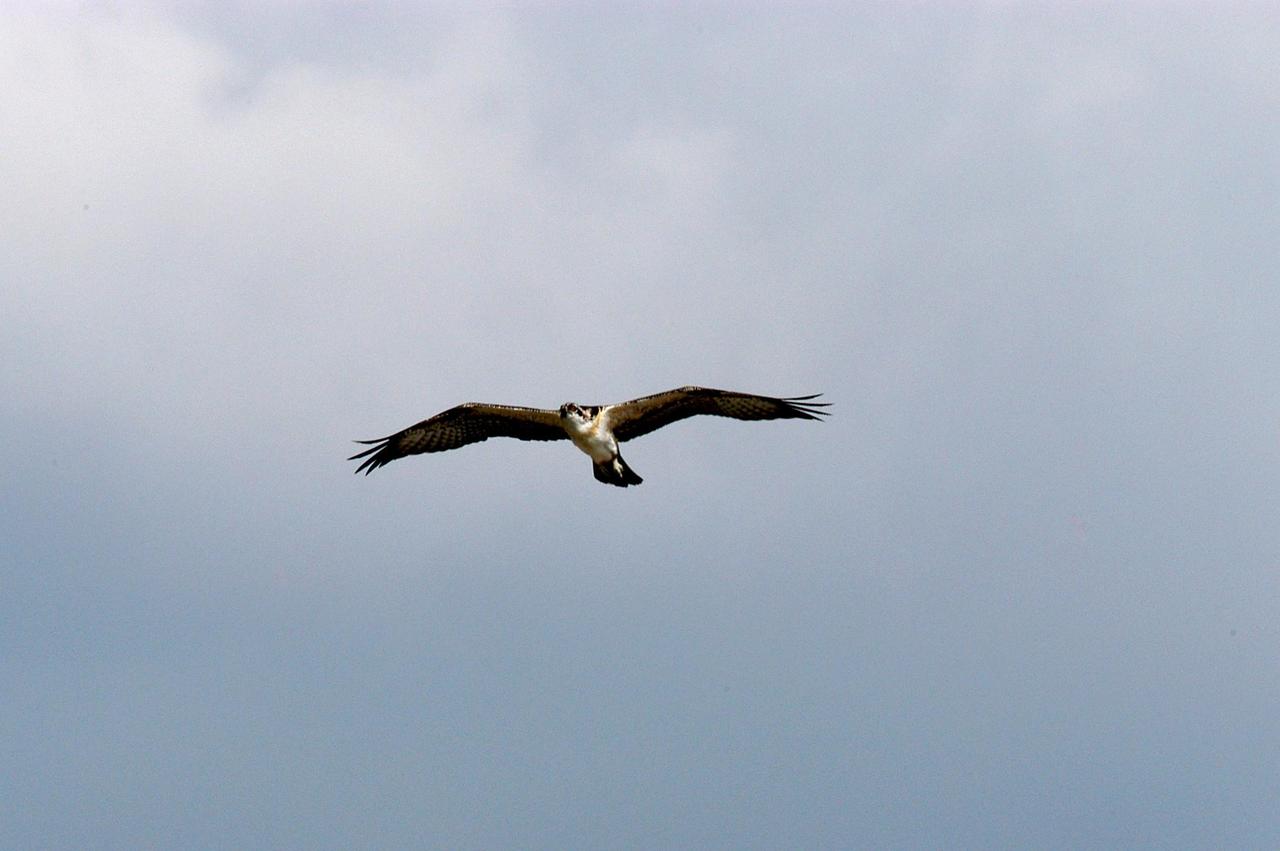

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A fledgling osprey soars above its nest, located in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
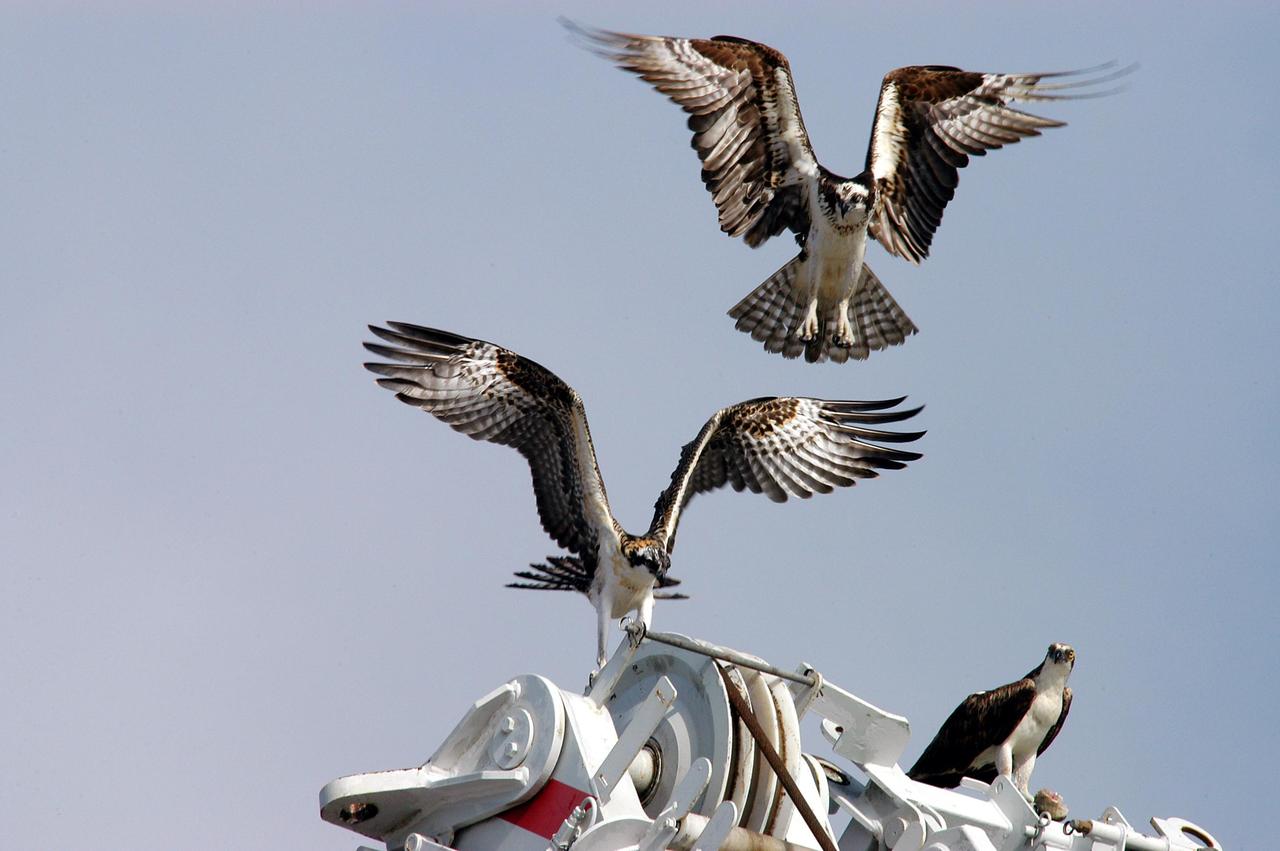

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Two fledgling ospreys begin flight lessons with their parent nearby (right). Their nest is located in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
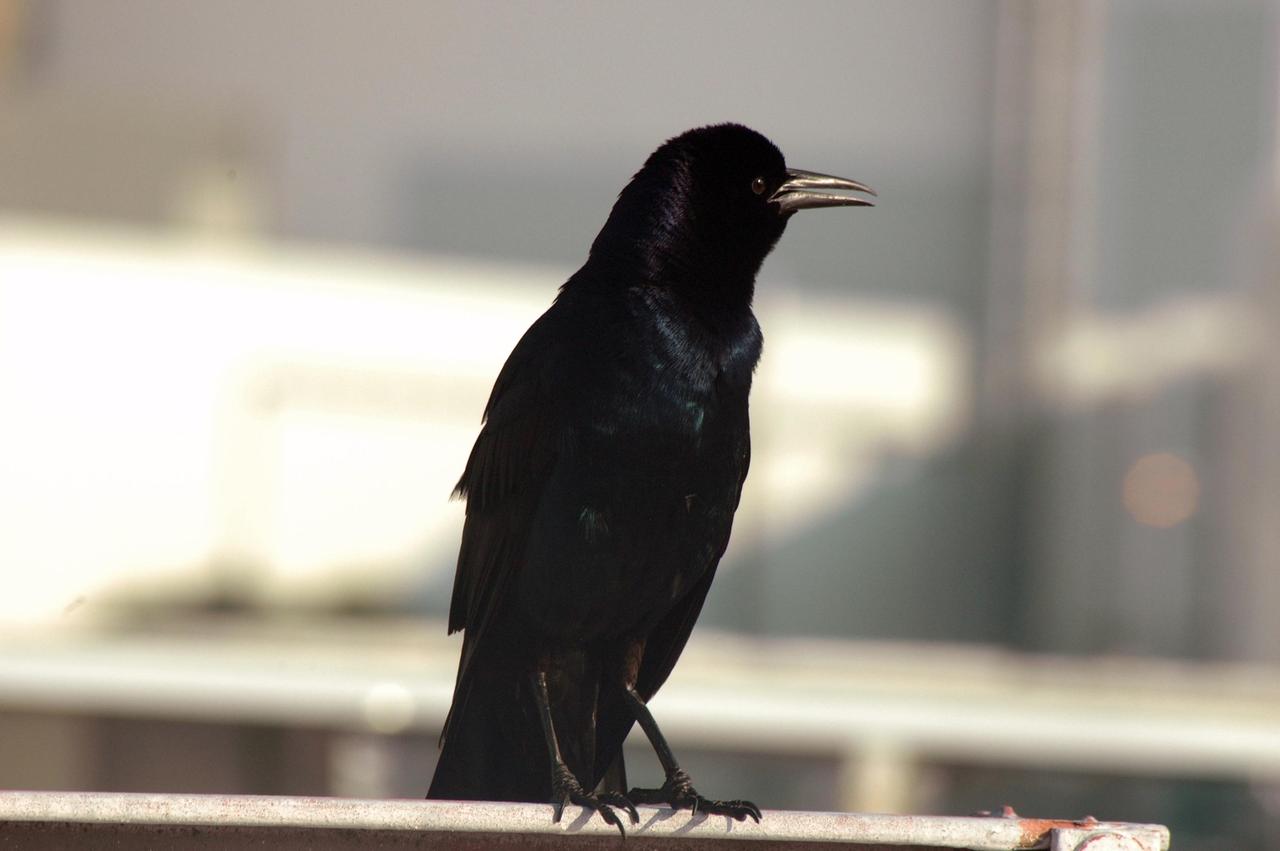

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This black bird photographed at the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center is likely a fish crow, somewhat smaller than the American Crow. Fish crows inhabit low coastal country, as well as lakes, rivers and swamps inland. They are common around KSC. The Center shares a boundary with the Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, which is a habitat for more than 310 species of birds, 25 mammals, 117 fishes and 65 amphibians and reptiles. In addition, the Refuge supports 19 endangered or threatened wildlife species on Federal or State lists, more than any other single refuge in the U.S. Photo credit: NASA/Ken Thornsley
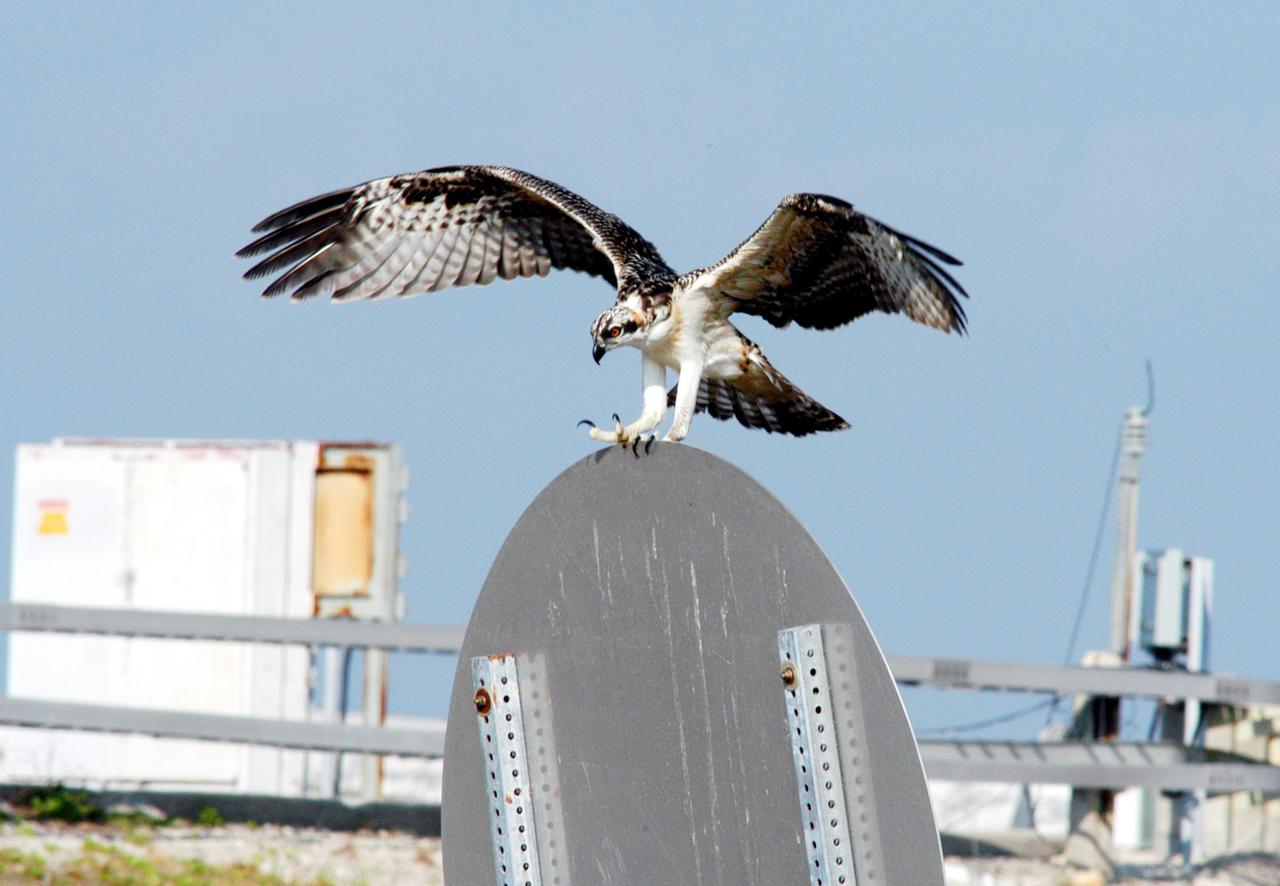

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of the fledgling ospreys from the nest in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot lands on a sign after testing its wings. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
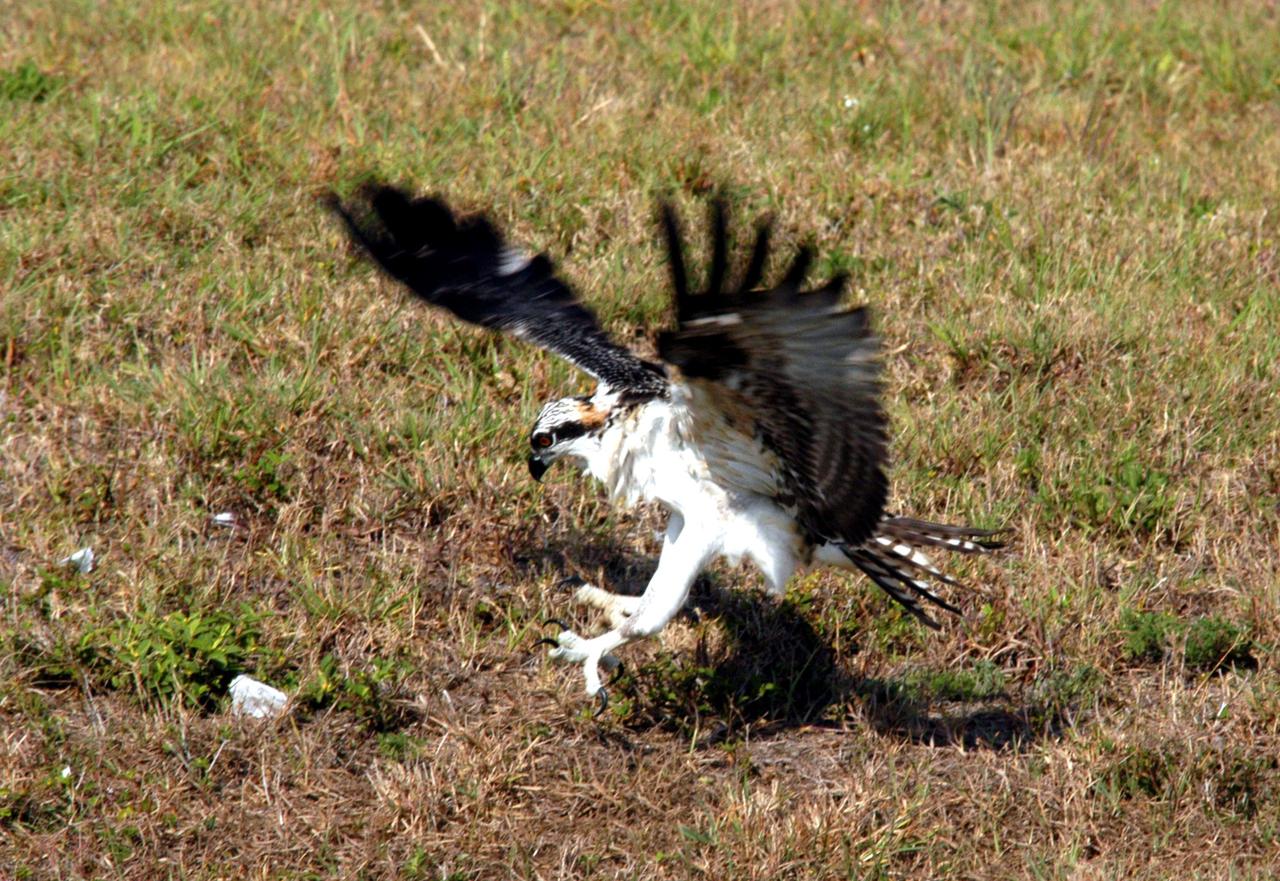

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One of the fledgling ospreys from the nest in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot comes down for a rough landing in the nearby grass. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska and Newfoundland to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.
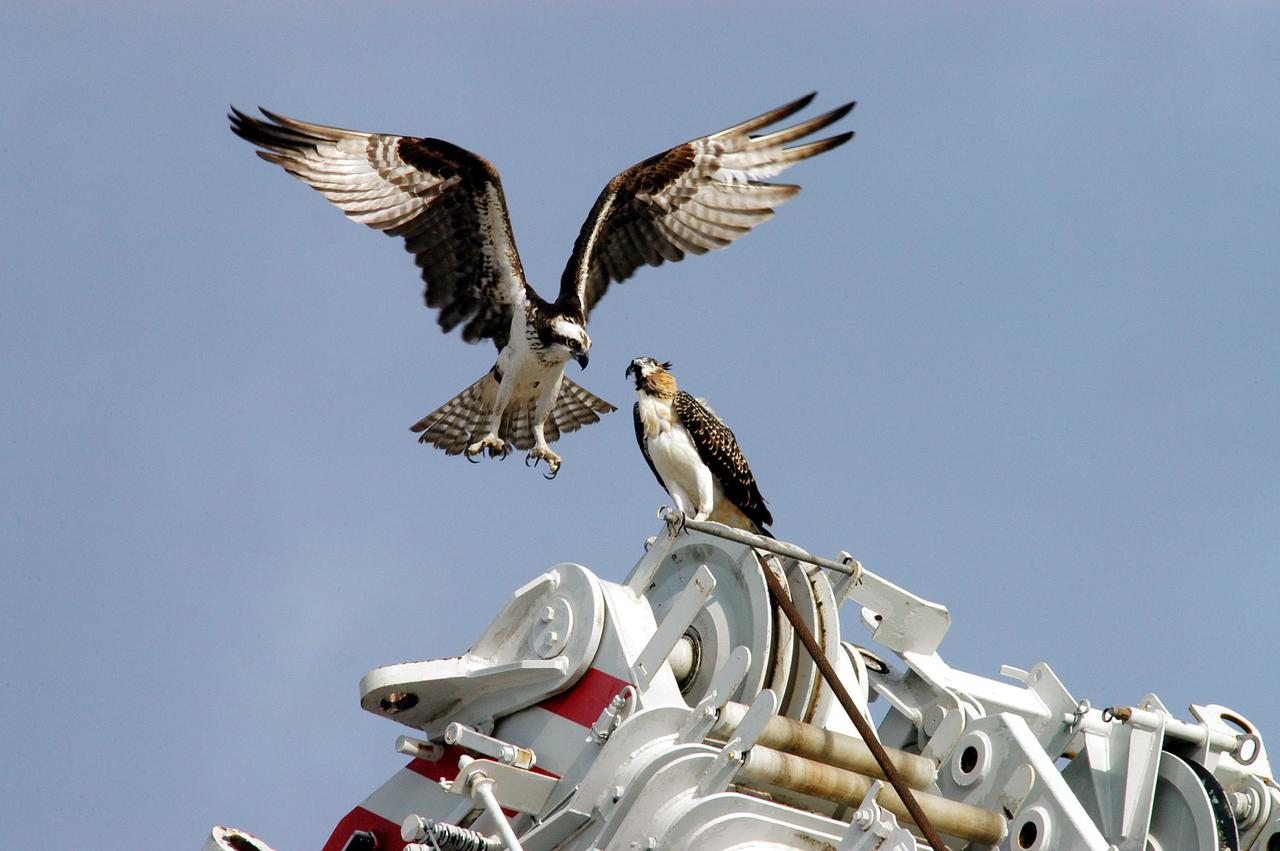

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- One young osprey tests its wings while another waits nearby. Their nest is located in the NASA KSC News Center parking lot. Ospreys select nesting sites of opportunity, from trees and telephone poles to rocks or even flat ground. In the United States they are found from Alaska to Florida and the Gulf Coast. Osprey nests are found throughout the Kennedy Space Center and nearby Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge. Known as a fish hawk, ospreys often can be seen flying overhead with a fish in their talons. Fish are their sole source of food.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A fish-eye view of the flight deck of STS-95 Space Shuttle Discover
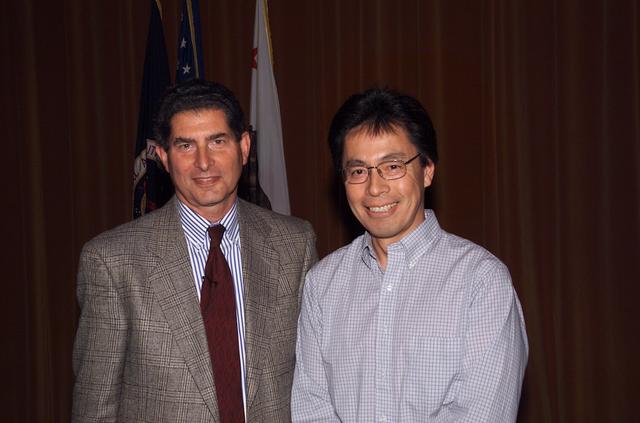

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A fish-eye view of the flight deck of STS-95 Space Shuttle Discovery
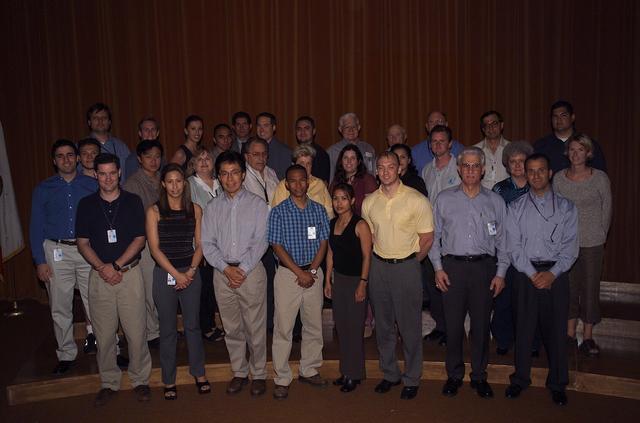

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja
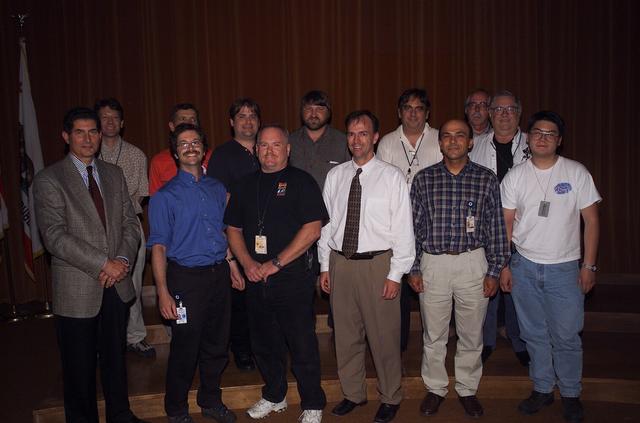

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja
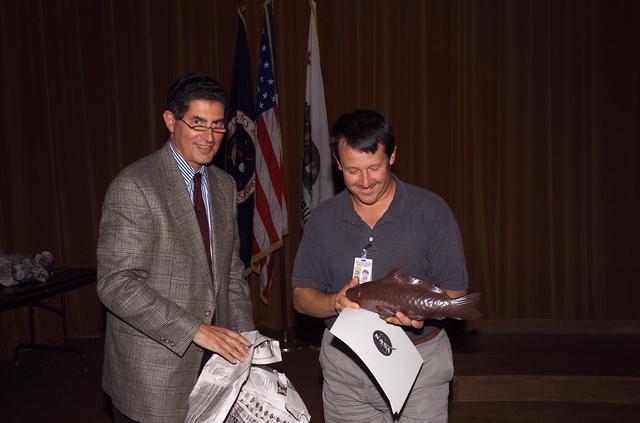

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja

Technology Infusion Award (Code I) 'Golden Fish' presented by Steve Zornitzer to Ja