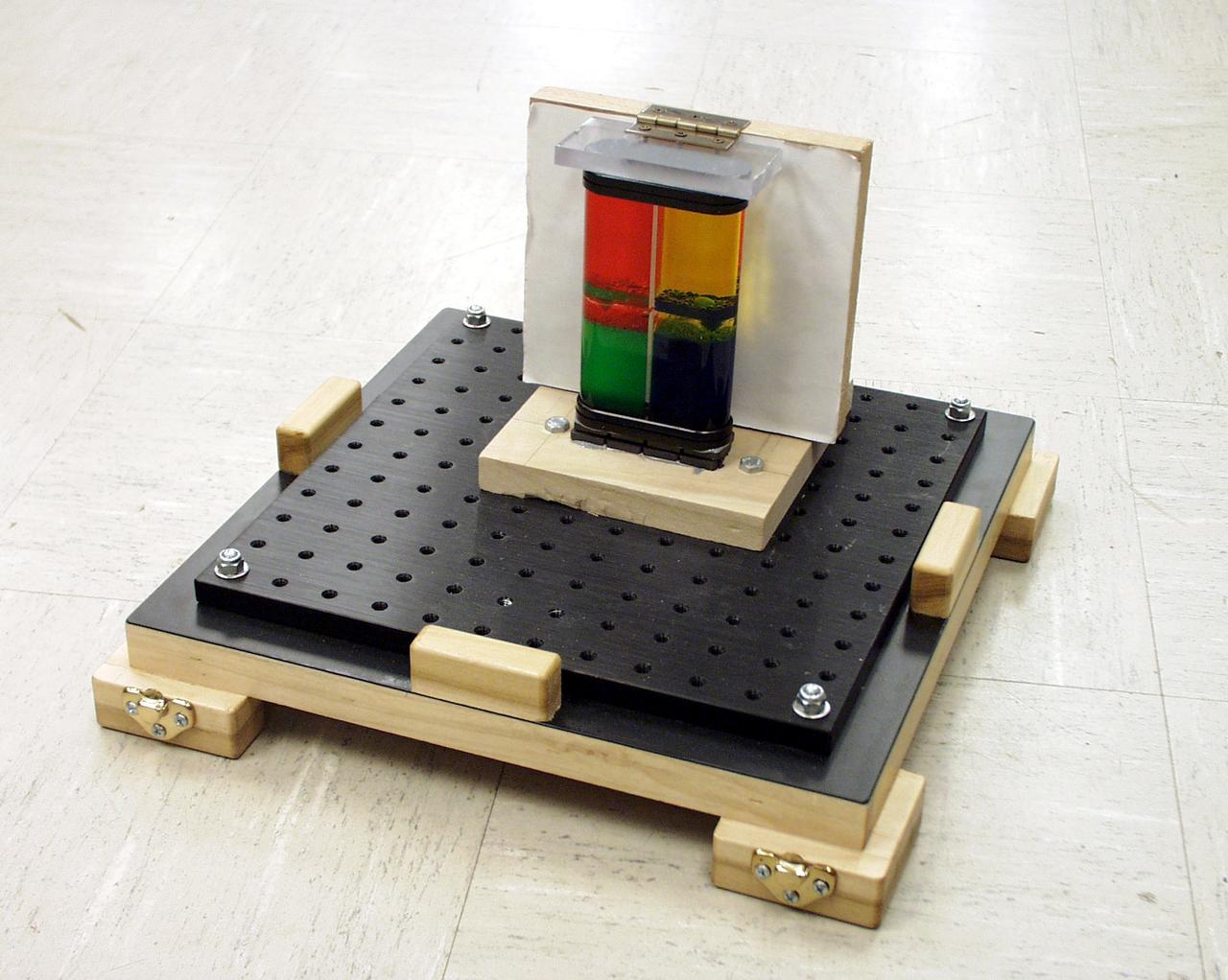
Colored oil flow toy was part of a student-designed apparatus used in the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
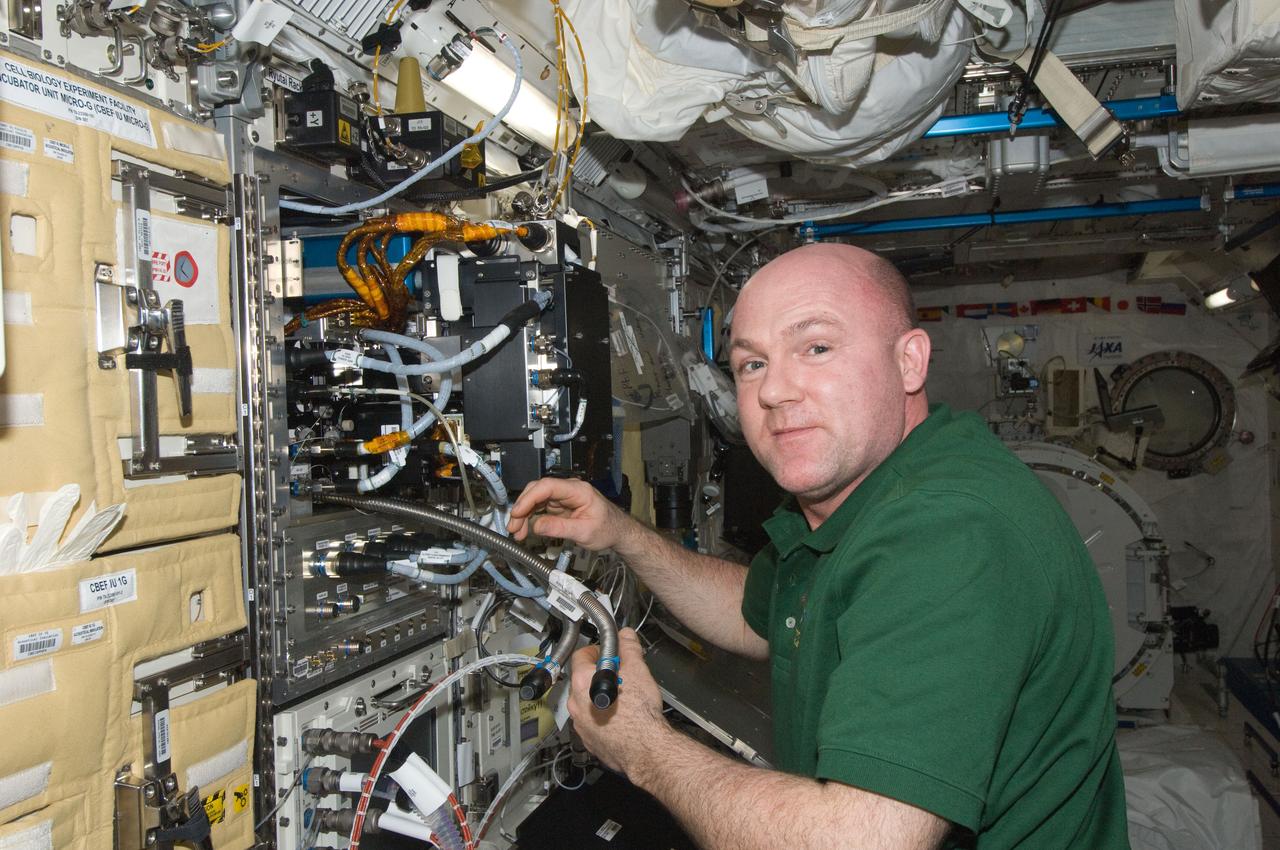

ISS030-E-142784 (15 March 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Surface fluid physics experiment from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
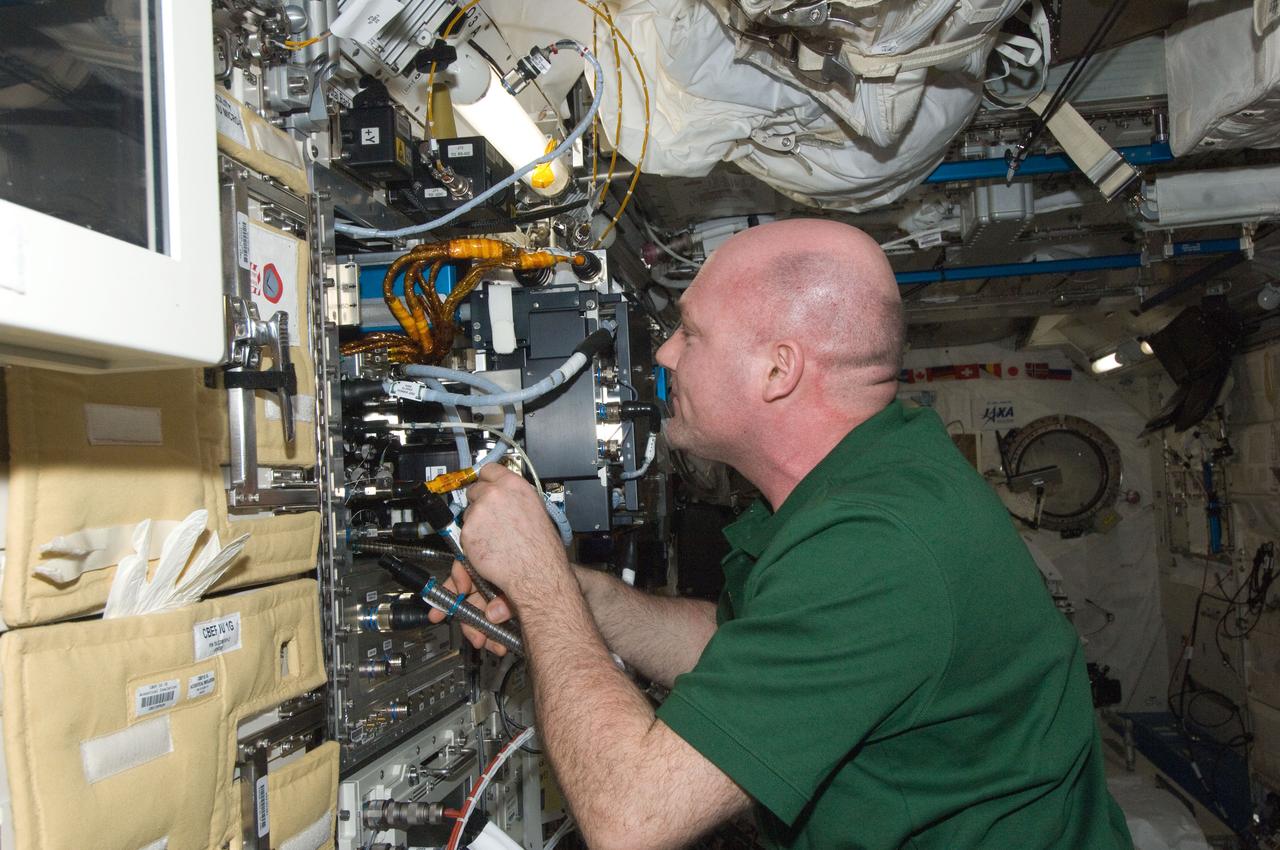

ISS030-E-142785 (15 March 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Surface fluid physics experiment from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
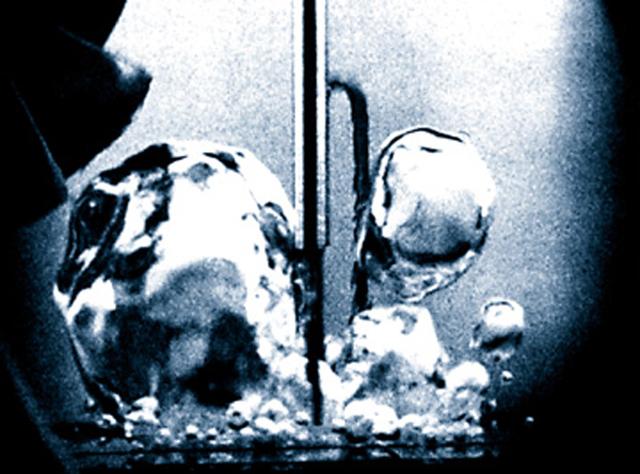
Fluid Physics is study of the motion of fluids and the effects of such motion. When a liquid is heated from the bottom to the boiling point in Earth's microgravity, small bubbles of heated gas form near the bottom of the container and are carried to the top of the liquid by gravity-driven convective flows. In the same setup in microgravity, the lack of convection and buoyancy allows the heated gas bubbles to grow larger and remain attached to the container's bottom for a significantly longer period.
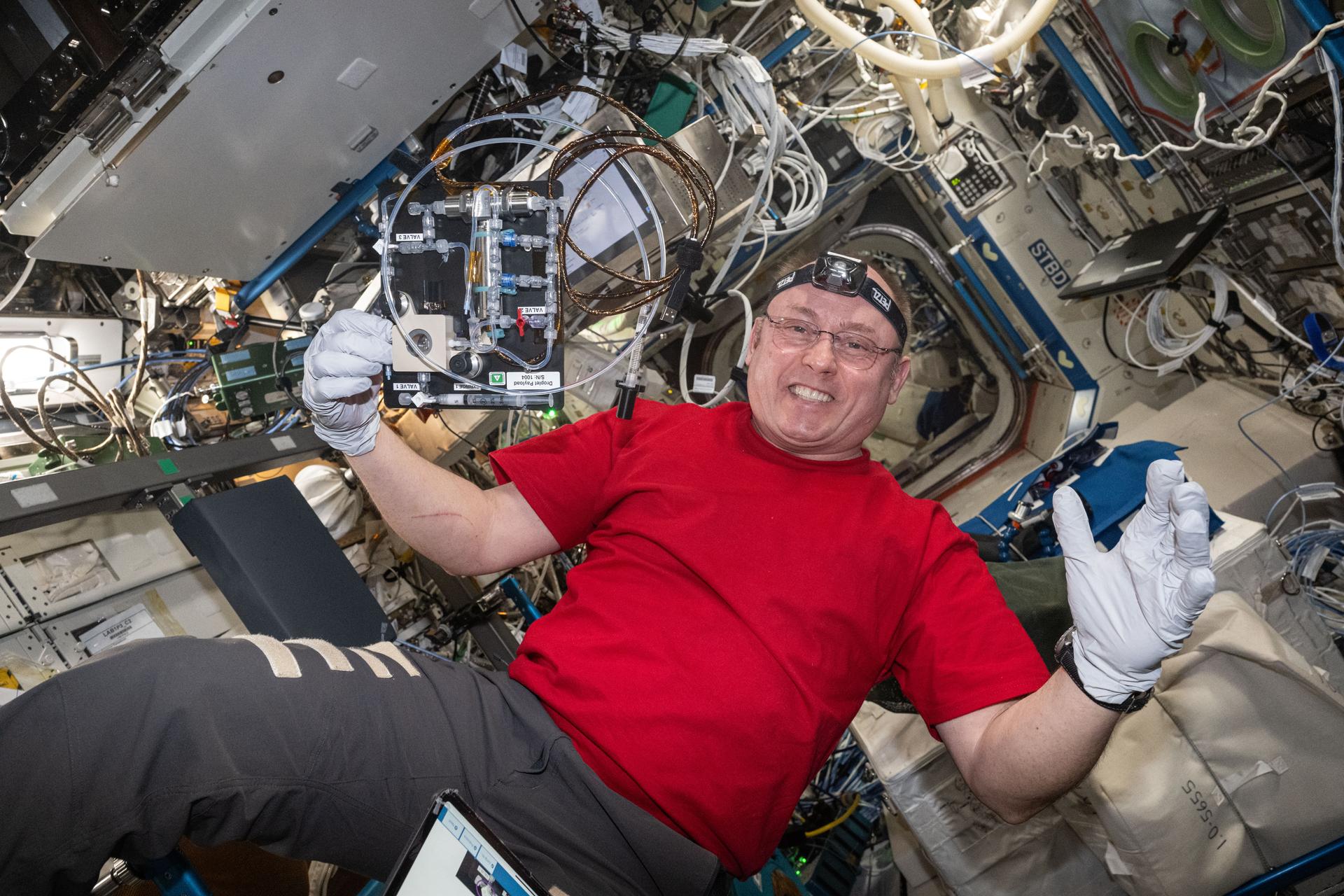

iss073e1193970 (Nov. 25, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Mike Fincke smiles for a portrait during research operations for the Droplets fluid physics investigation. Fincke was inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module exploring how particles behave inside fluids. The microgravity study may inform commercial in-space manufacturing techniques and improve optical materials and pollution removal operations.
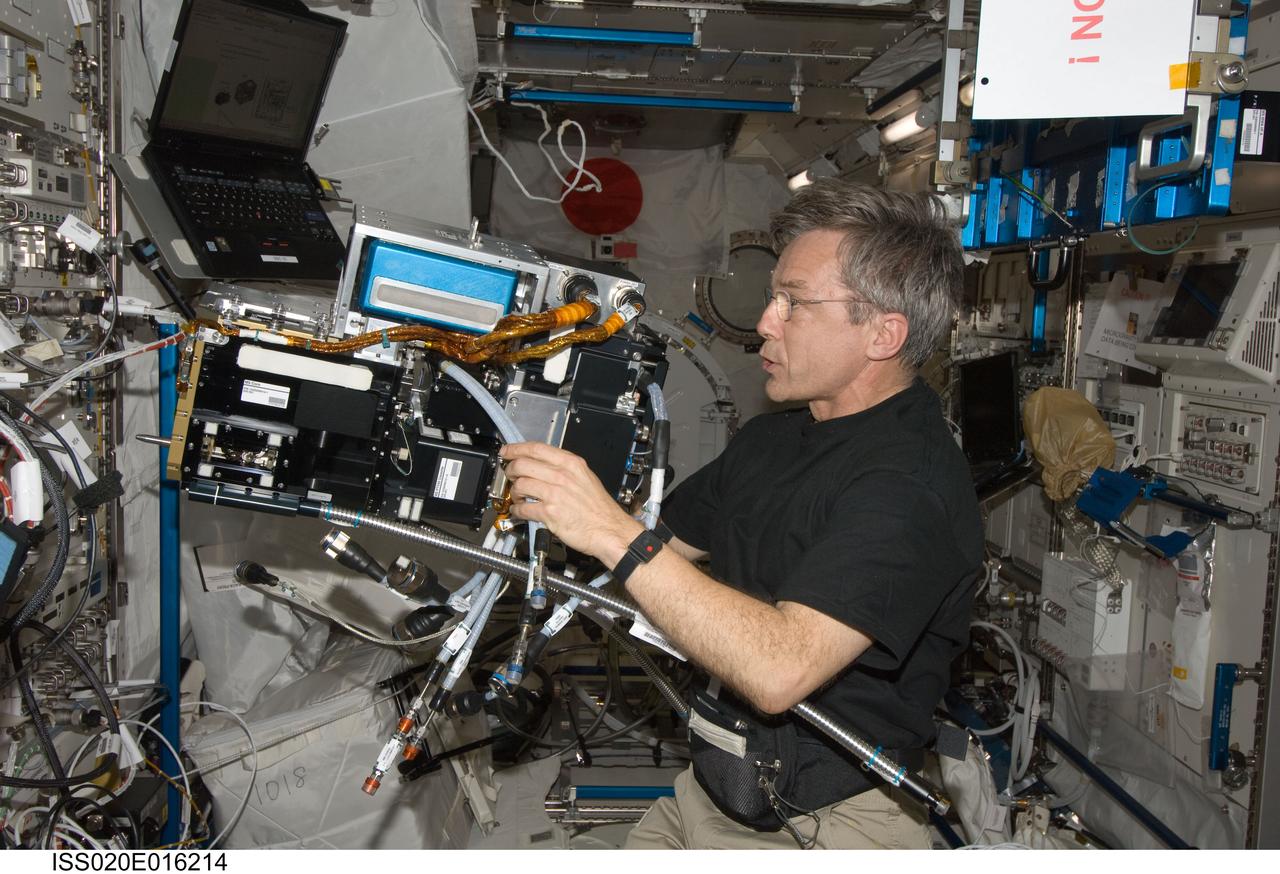

ISS020-E-016214 (1 July 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk, Expedition 20 flight engineer, prepares the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) for the planned Marangoni Surface experiment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
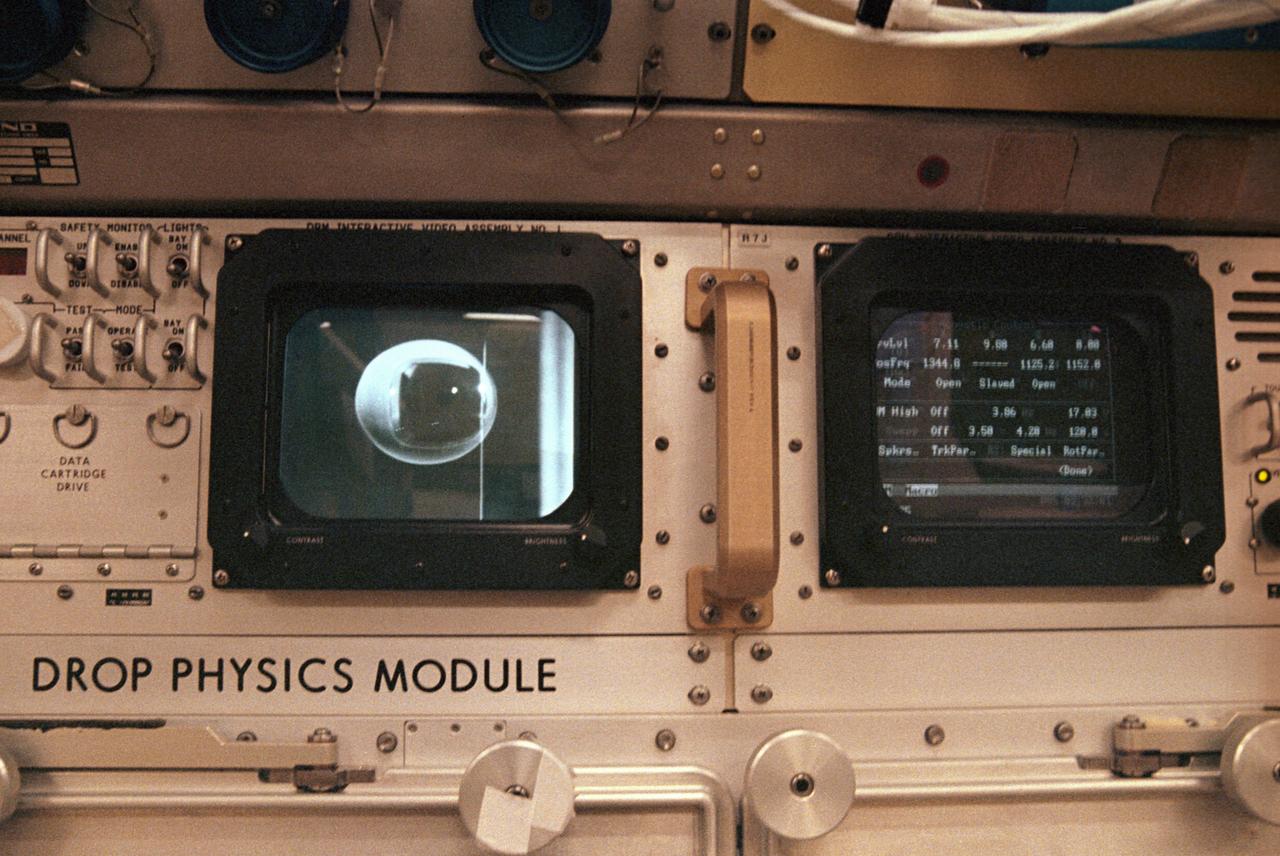
The first United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-1) was one of NASA's science and technology programs that provided scientists an opportunity to research various scientific investigations in a weightlessness environment inside the Spacelab module. It also provided demonstrations of new equipment to help prepare for advanced microgravity research and processing aboard the Space Station. The USML-1 flew in orbit for extended periods, providing greater opportunities for research in materials science, fluid dynamics, biotechnology (crystal growth), and combustion science. This is a close-up view of the Drop Physics Module (DPM) in the USML science laboratory. The DPM was dedicated to the detailed study of the dynamics of fluid drops in microgravity: their equilibrium shapes, the dynamics of their flows, and their stable and chaotic behaviors. It also demonstrated a technique known as containerless processing. The DPM and microgravity combine to remove the effects of the container, such as chemical contamination and shape, on the sample being studied. Sound waves, generating acoustic forces, were used to suspend a sample in microgravity and to hold a sample of free drops away from the walls of the experiment chamber, which isolated the sample from potentially harmful external influences. The DPM gave scientists the opportunity to test theories of classical fluid physics, which have not been confirmed by experiments conducted on Earth. This image is a close-up view of the DPM. The USML-1 flew aboard the STS-50 mission on June 1992, and was managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center.
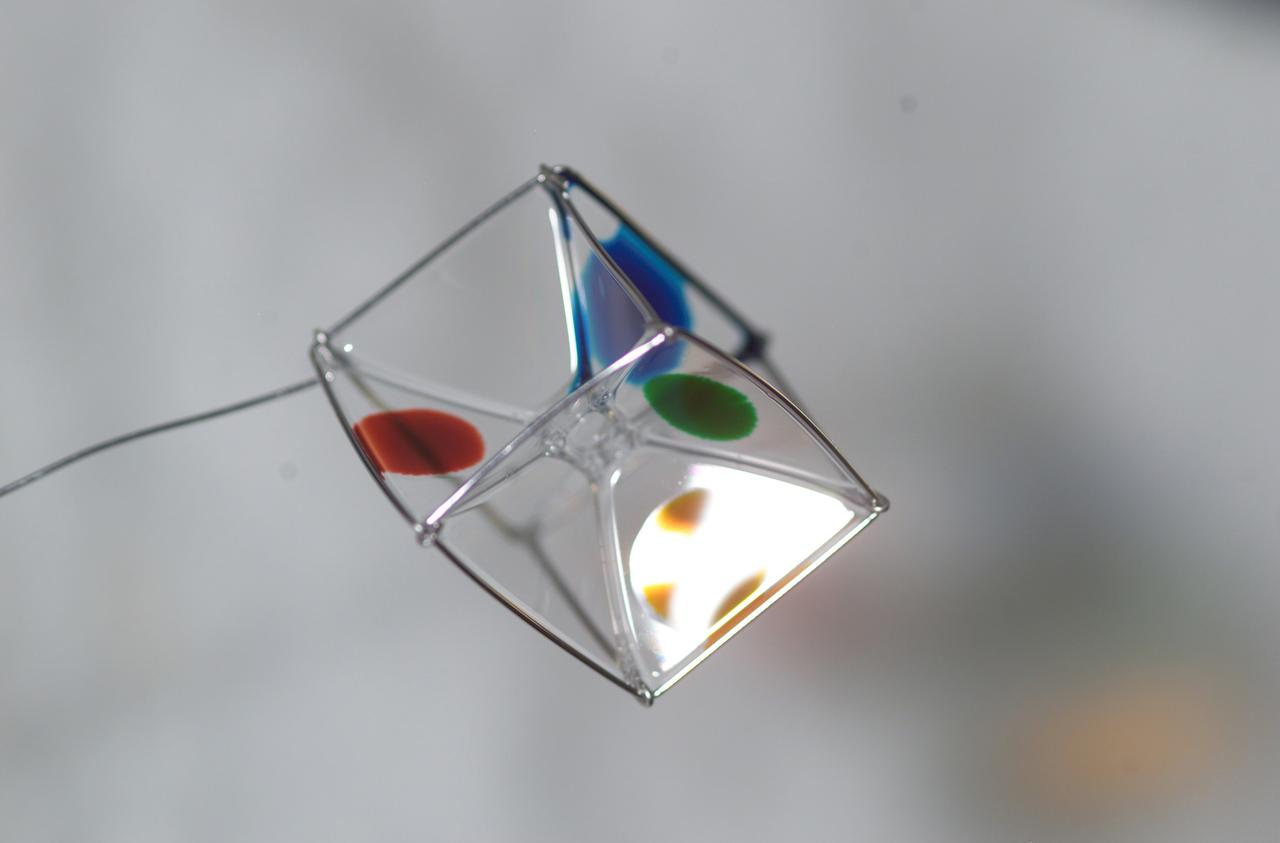
Expedition 6 astronaut Dr. Don Pettit photographed a cube shaped wire frame supporting a thin film made from a water-soap solution during his Saturday Morning Science aboard the International Space Station’s (ISS) Destiny Laboratory. Food coloring was added to several faces to observe the effects of diffusion within the film.
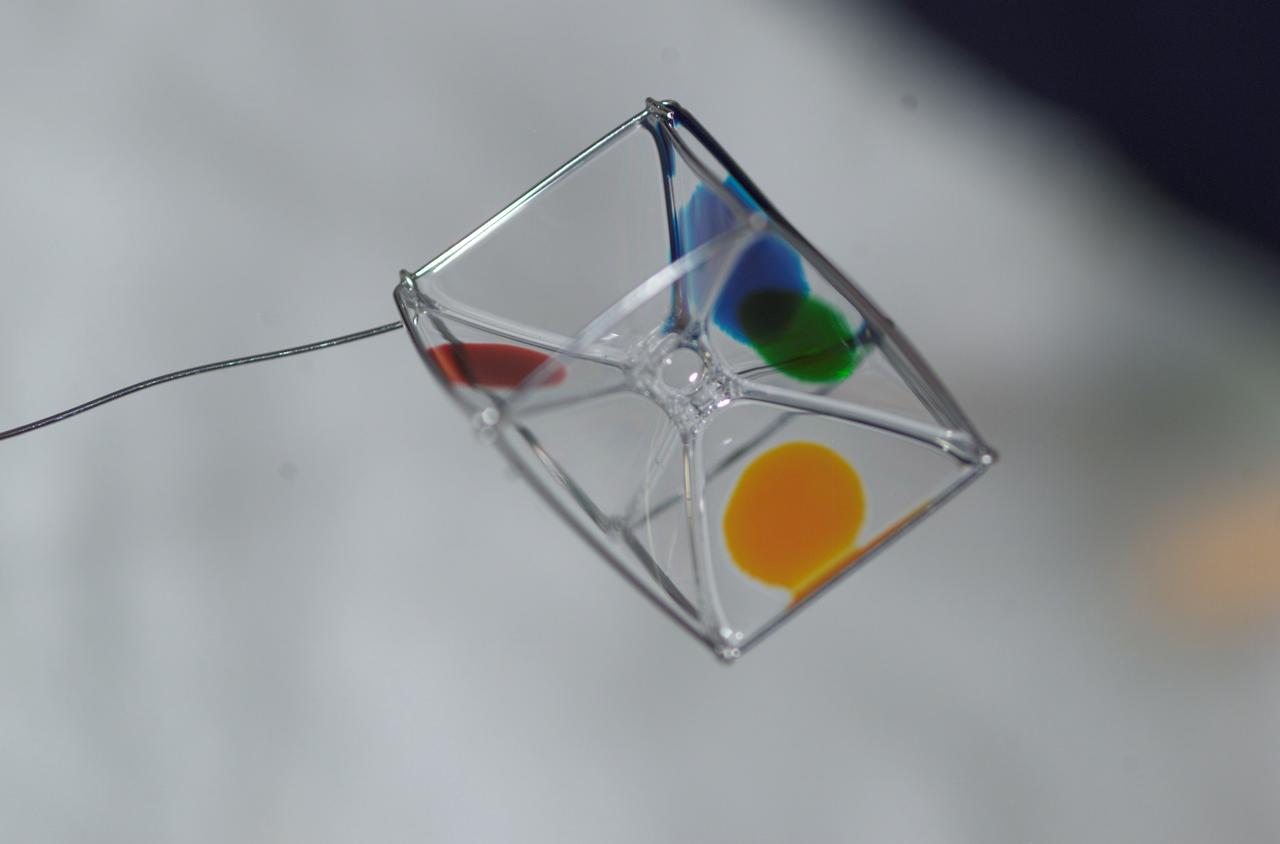

Expedition 6 astronaut Dr. Don Pettit photographed a cube shaped wire frame supporting a thin film made from a water-soap solution during his Saturday Morning Science aboard the International Space Station’s (ISS) Destiny Laboratory. Food coloring was added to several faces to observe the effects of diffusion within the film.

Whipped cream and the filling for pumpkin pie are two familiar materials that exhibit the shear-thinning effect seen in a range of industrial applications. It is thick enough to stand on its own atop a piece of pie, yet flows readily when pushed through a tube. This demonstrates the shear-thinning effect that was studied with the Critical Viscosity of Xenon Experiment (CVX-2) on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002. CVX observed the behavior of xenon, a heavy inert gas used in flash lamps and ion rocket engines, at its critical point. The principal investigator was Dr. Robert Berg of the National Institutes of Standards and Technology in Gaithersburg, MD.
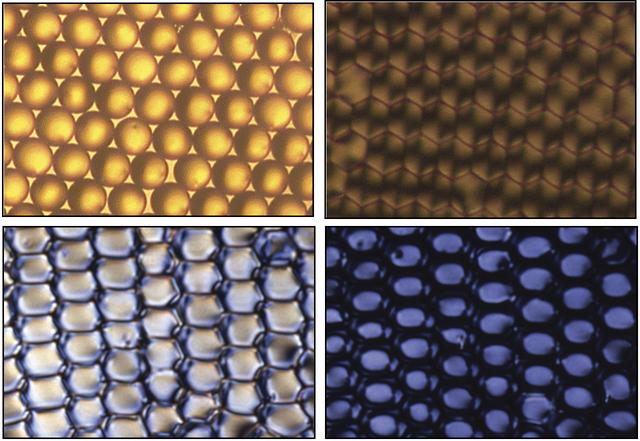
These images, from David Weitz’s liquid crystal research, show ordered uniform sized droplets (upper left) before they are dried from their solution. After the droplets are dried (upper right), they are viewed with crossed polarizers that show the deformation caused by drying, a process that orients the bipolar structure of the liquid crystal within the droplets. When an electric field is applied to the dried droplets (lower left), and then increased (lower right), the liquid crystal within the droplets switches its alignment, thereby reducing the amount of light that can be scattered by the droplets when a beam is shone through them.
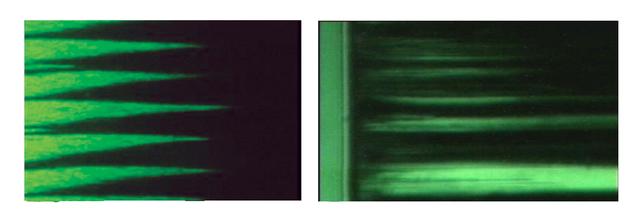
These are video microscope images of magnetorheological (MR) fluids, illuminated with a green light. Those on Earth, left, show the MR fluid forming columns or spikes structures. On the right, the fluids in microgravity aboard the International Space Station (ISS), formed broader columns.
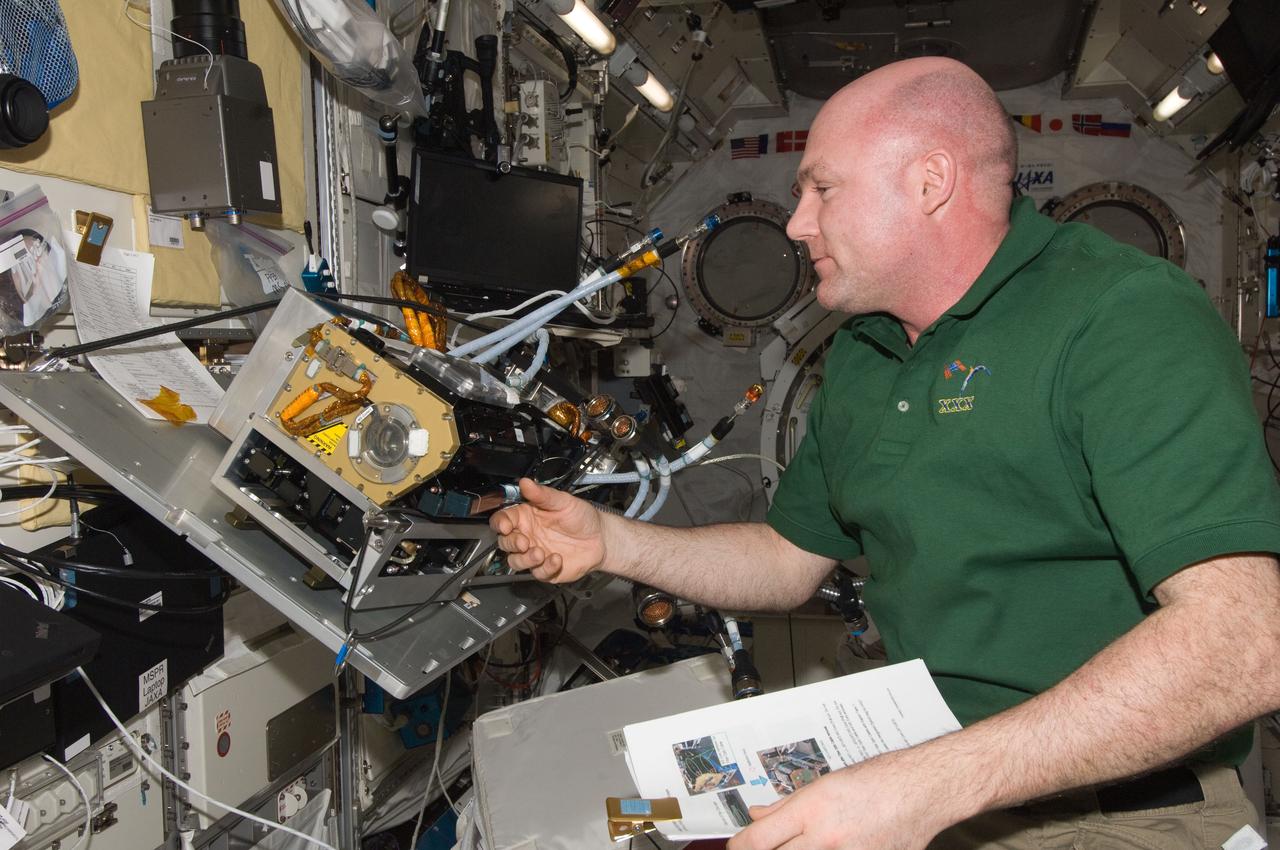

ISS030-E-142827 (15 March 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Surface fluid physics experiment from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
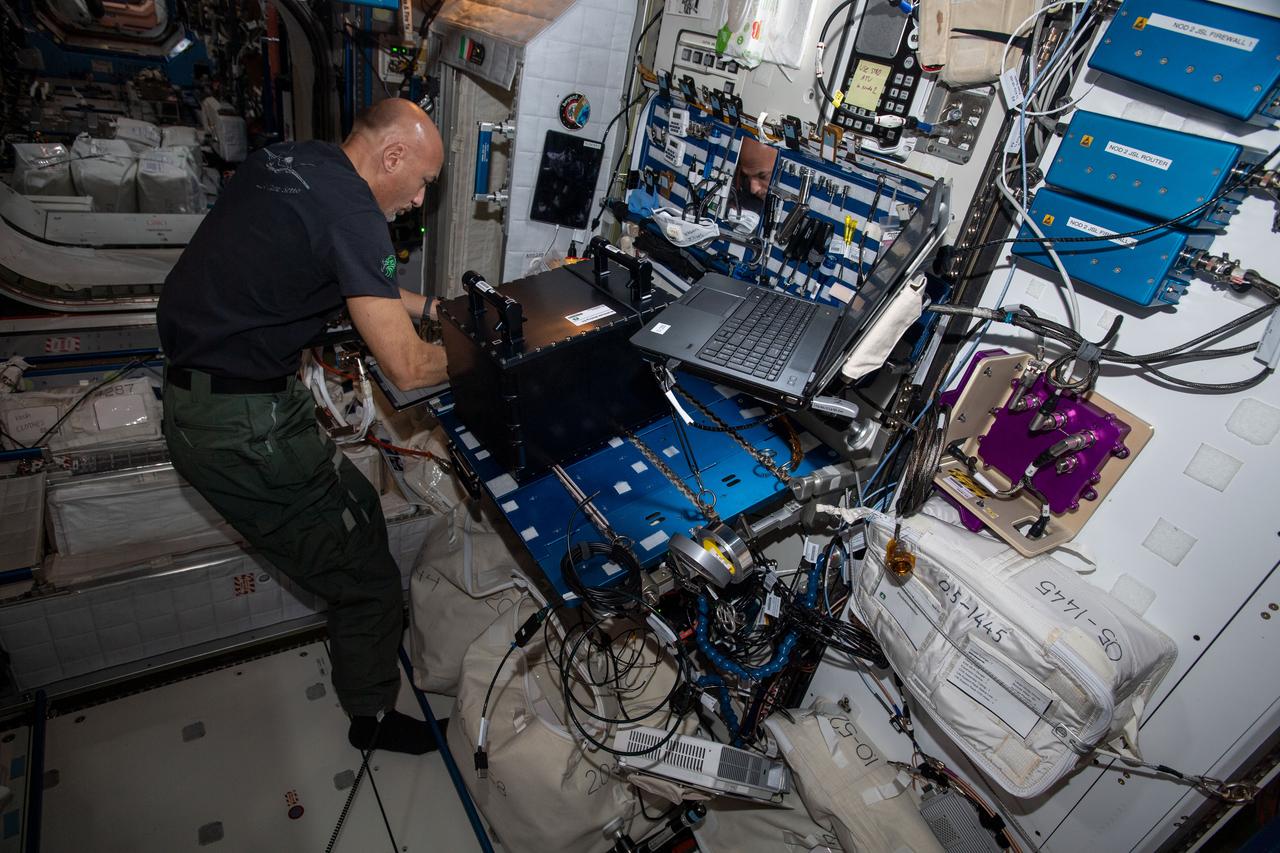

iss060e032989 (Aug. 9, 2019) --- Expedition 60 Flight Engineer Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency configures and installs hardware in the Fluid Science Laboratory to continue ongoing fluid physics research in microgravity.
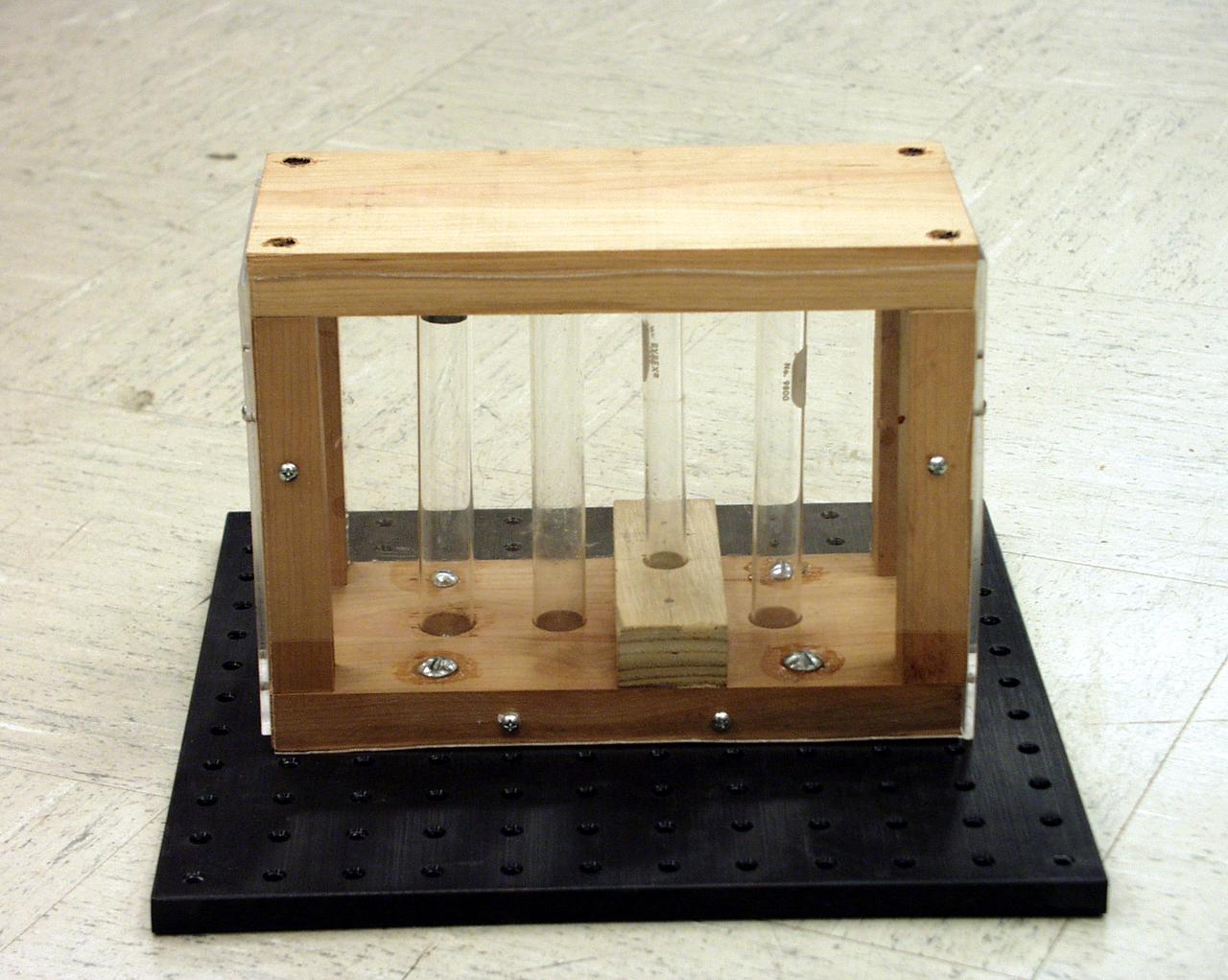
Test tubes to hold different types of fluids while in free-fall were among the student-designed items for the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
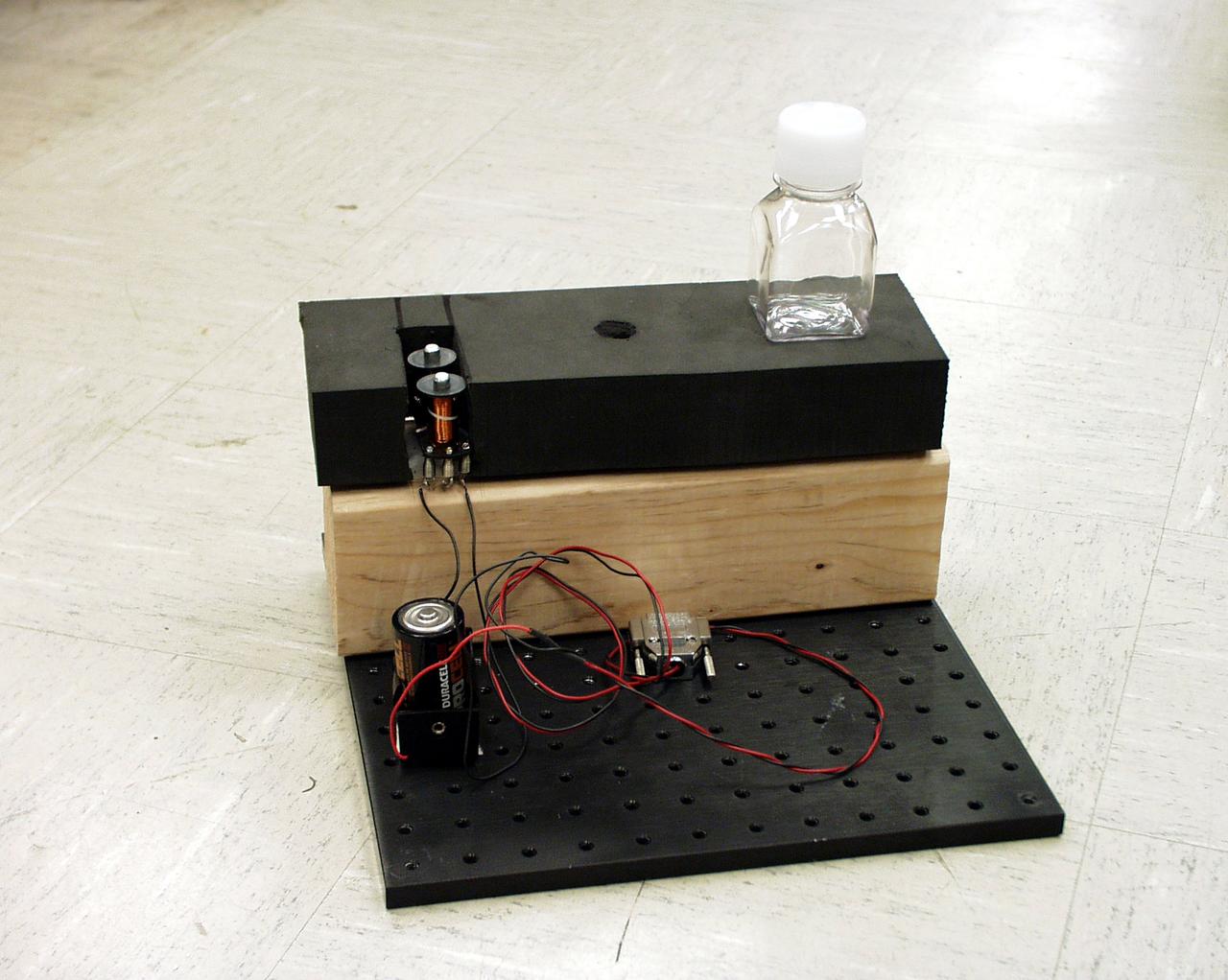
Student-designed and -built apparatus for the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
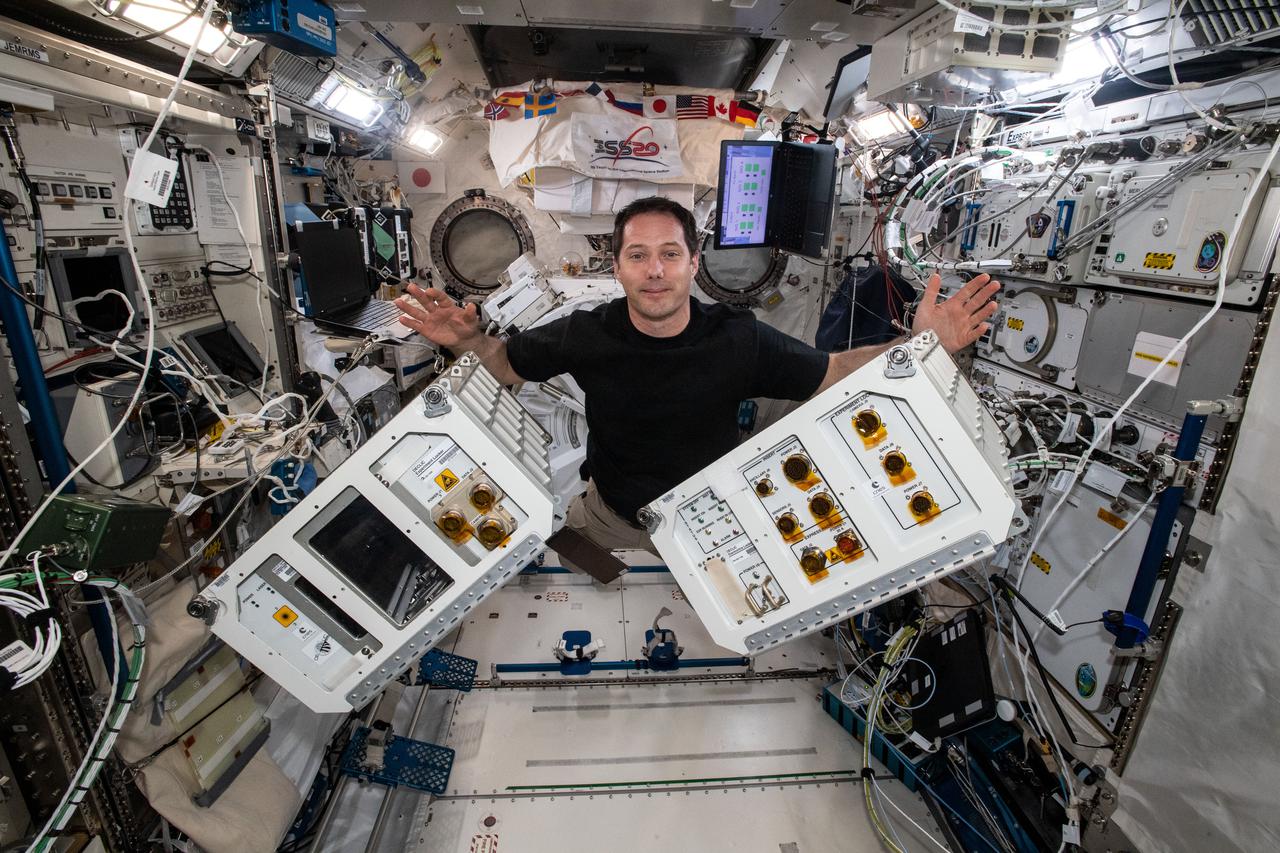

iss065e442803 (10/7/2021) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet gathers fluid physics and materials research hardware inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Device for the Study of Critical Liquids and Crystallization (DECLIC) is a multi-user facility developed by the agency Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (French Space Agency, CNES) and flown in collaboration with NASA. It is designed to support experiments in the fields of fluid physics and materials science. Special inserts allow researchers to study both ambient temperature critical point fluids and high temperature super-critical fluids. Another class of insert studies the dynamics and morphology of the fronts that form as a liquid material solidifies.
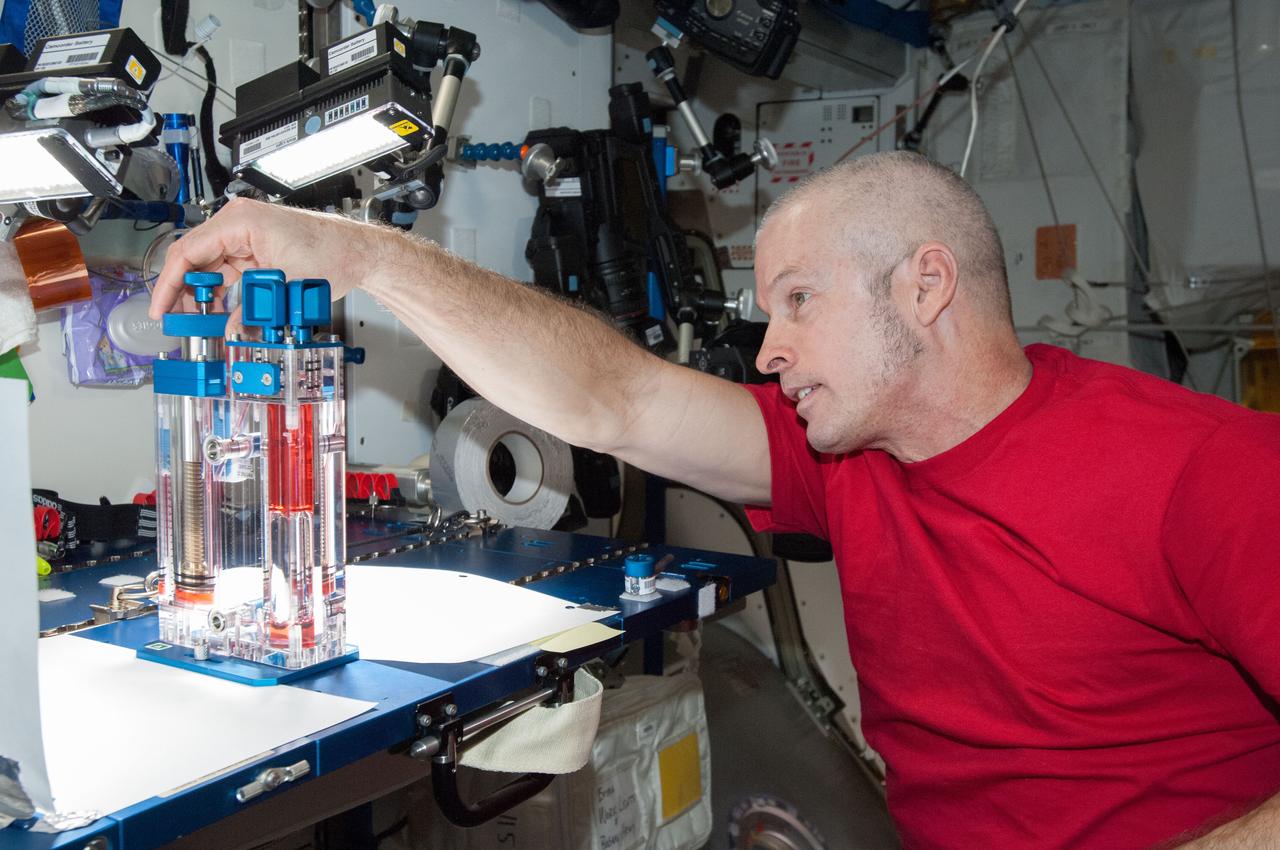

ISS040-E-032827 (3 July 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids move up surfaces in microgravity. The results aim to improve current computer models that are used by designers of low gravity fluid systems and may improve fluid transfer systems for water on future spacecraft.
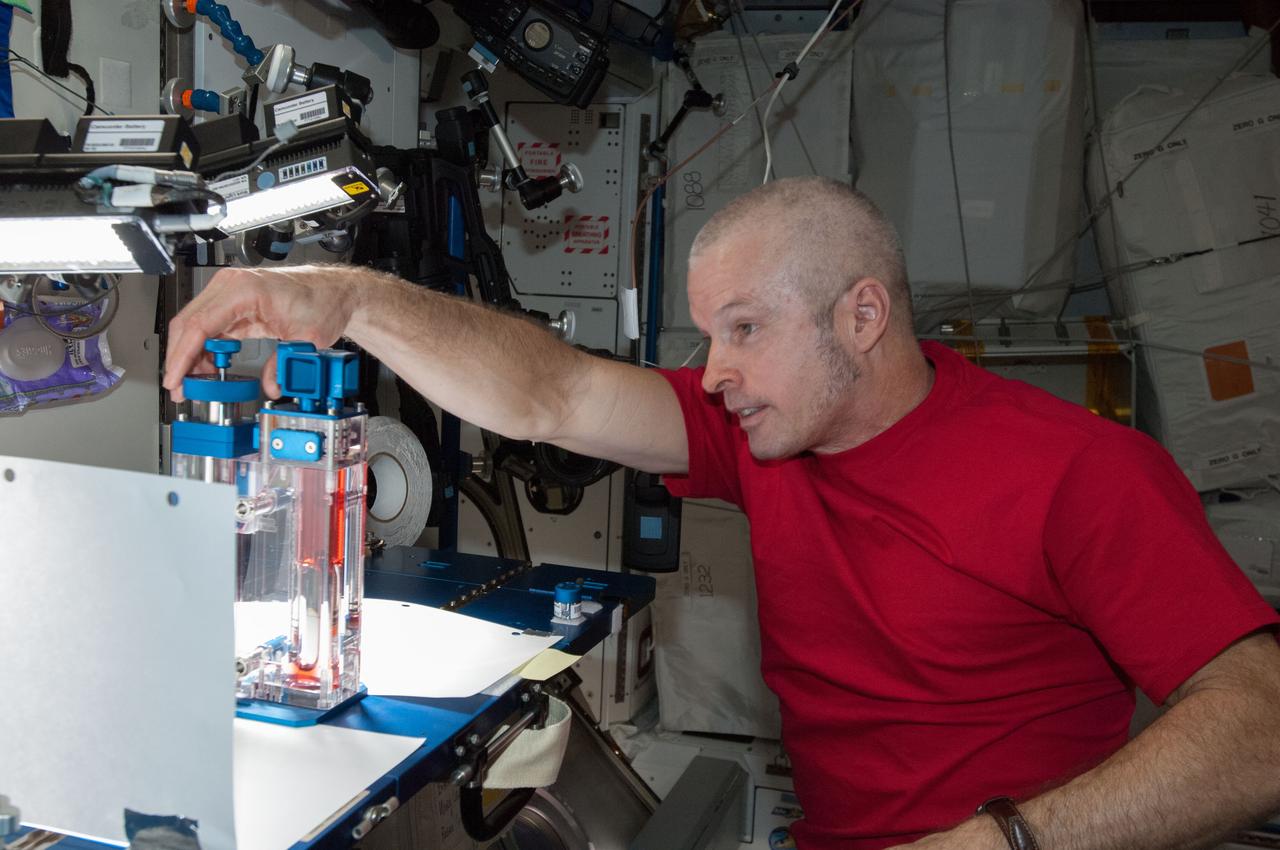

ISS040-E-032825 (3 July 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids move up surfaces in microgravity. The results aim to improve current computer models that are used by designers of low gravity fluid systems and may improve fluid transfer systems for water on future spacecraft.
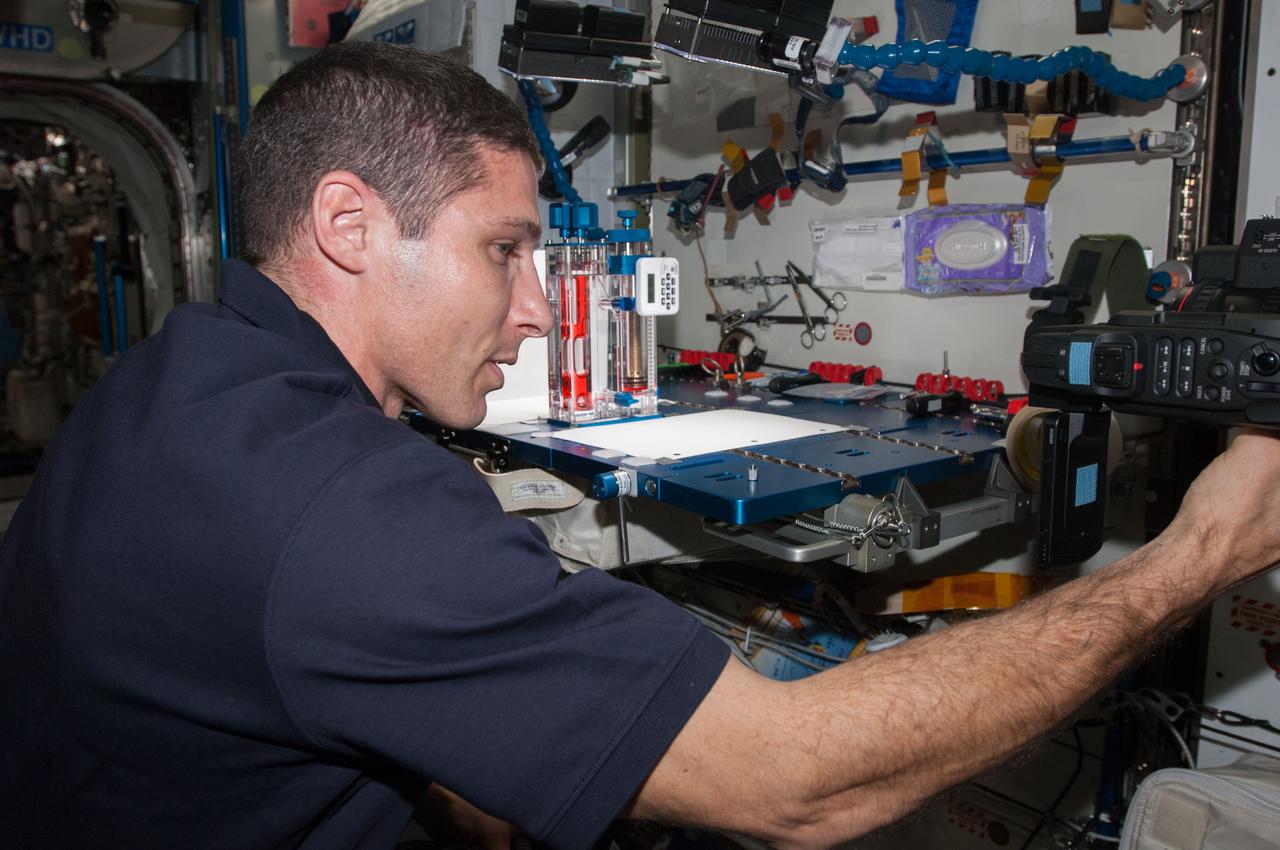

ISS038-E-000269 (11 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids move up surfaces in microgravity. The results aim to improve current computer models that are used by designers of low gravity fluid systems and may improve fluid transfer systems for water on future spacecraft.
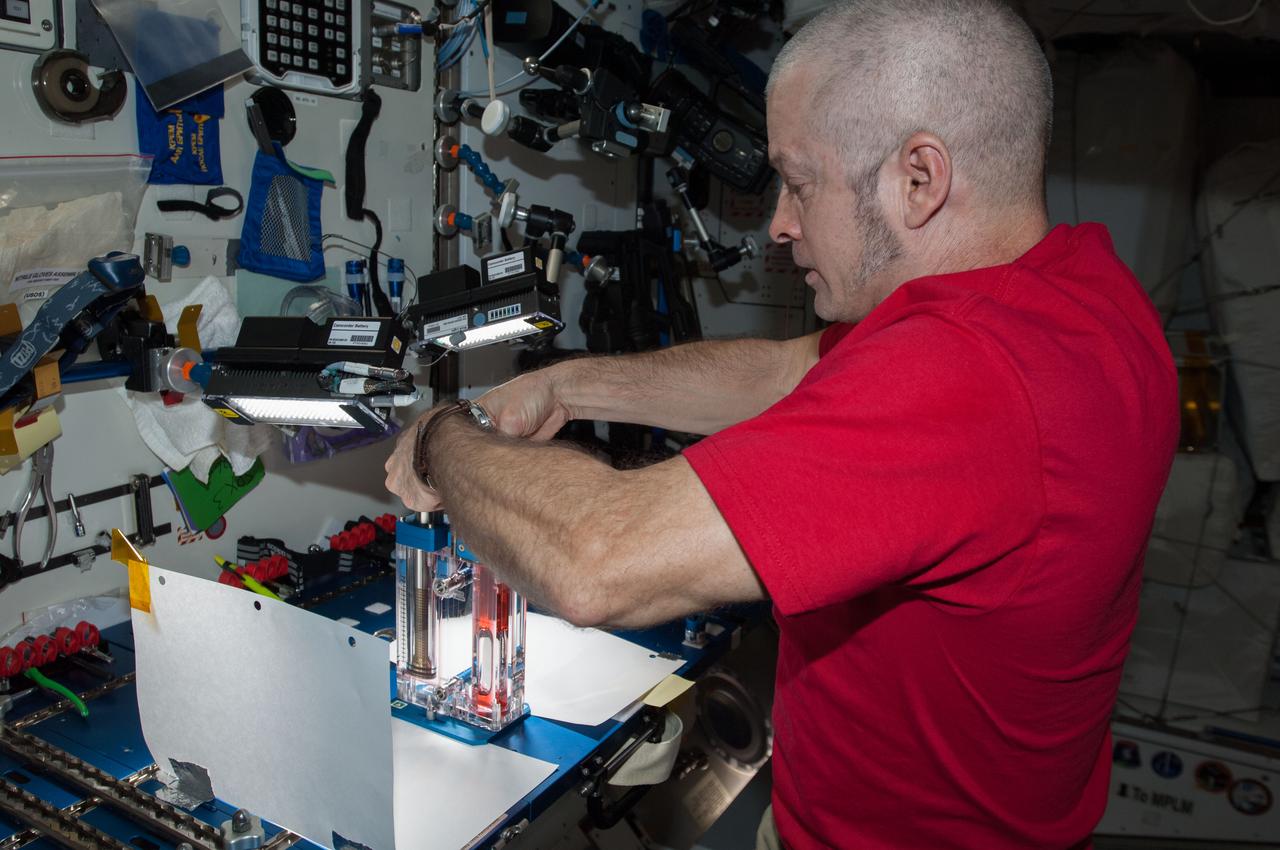

ISS040-E-032820 (3 July 2014) --- NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids move up surfaces in microgravity. The results aim to improve current computer models that are used by designers of low gravity fluid systems and may improve fluid transfer systems for water on future spacecraft.
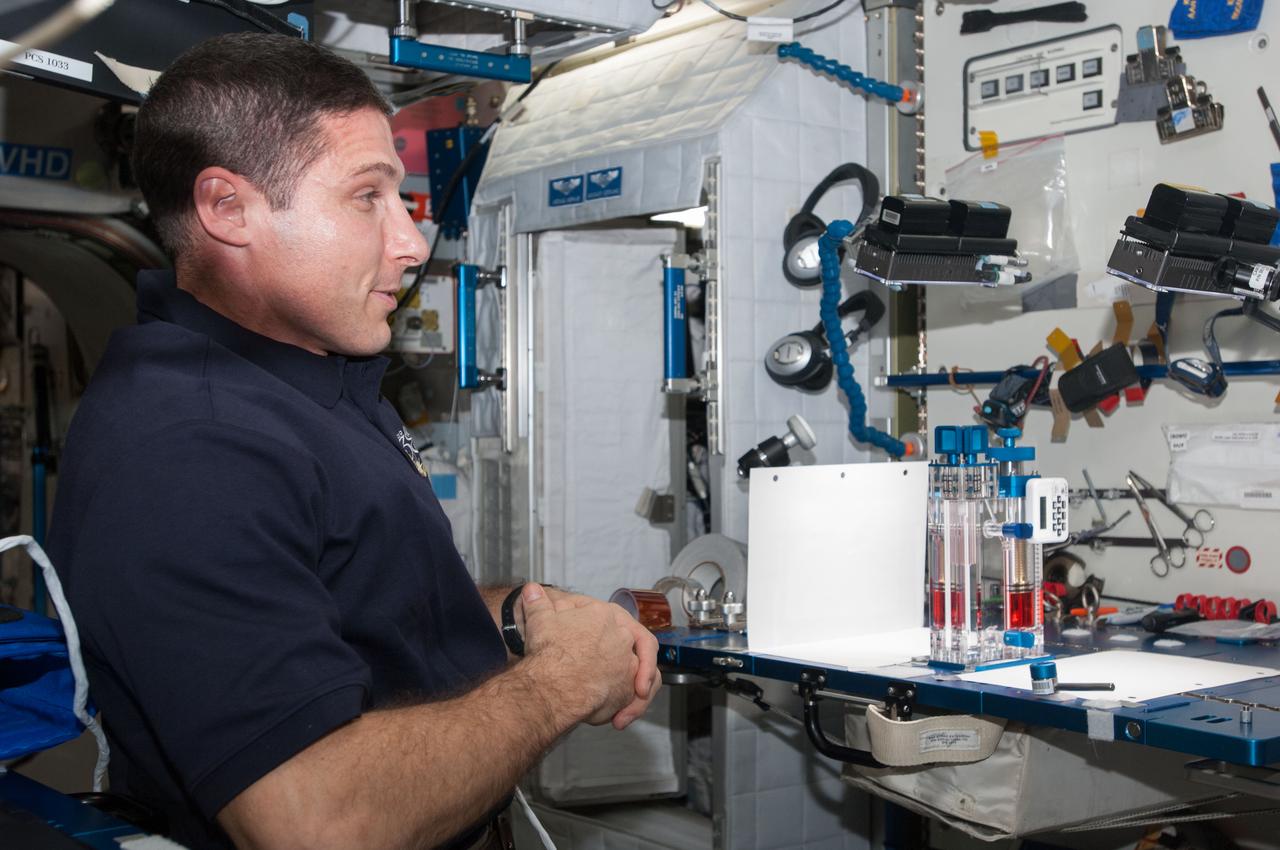

ISS038-E-000263 (11 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids move up surfaces in microgravity. The results aim to improve current computer models that are used by designers of low gravity fluid systems and may improve fluid transfer systems for water on future spacecraft.

iss060e054549 -- Expedition 60 flight engineer Luca Parmitano of ESA (European Space Agency) works on swapping out a power cable located in the Fluid Science Laboratory, which is a facility designed by ESA for conducting fluid physics research in microgravity.
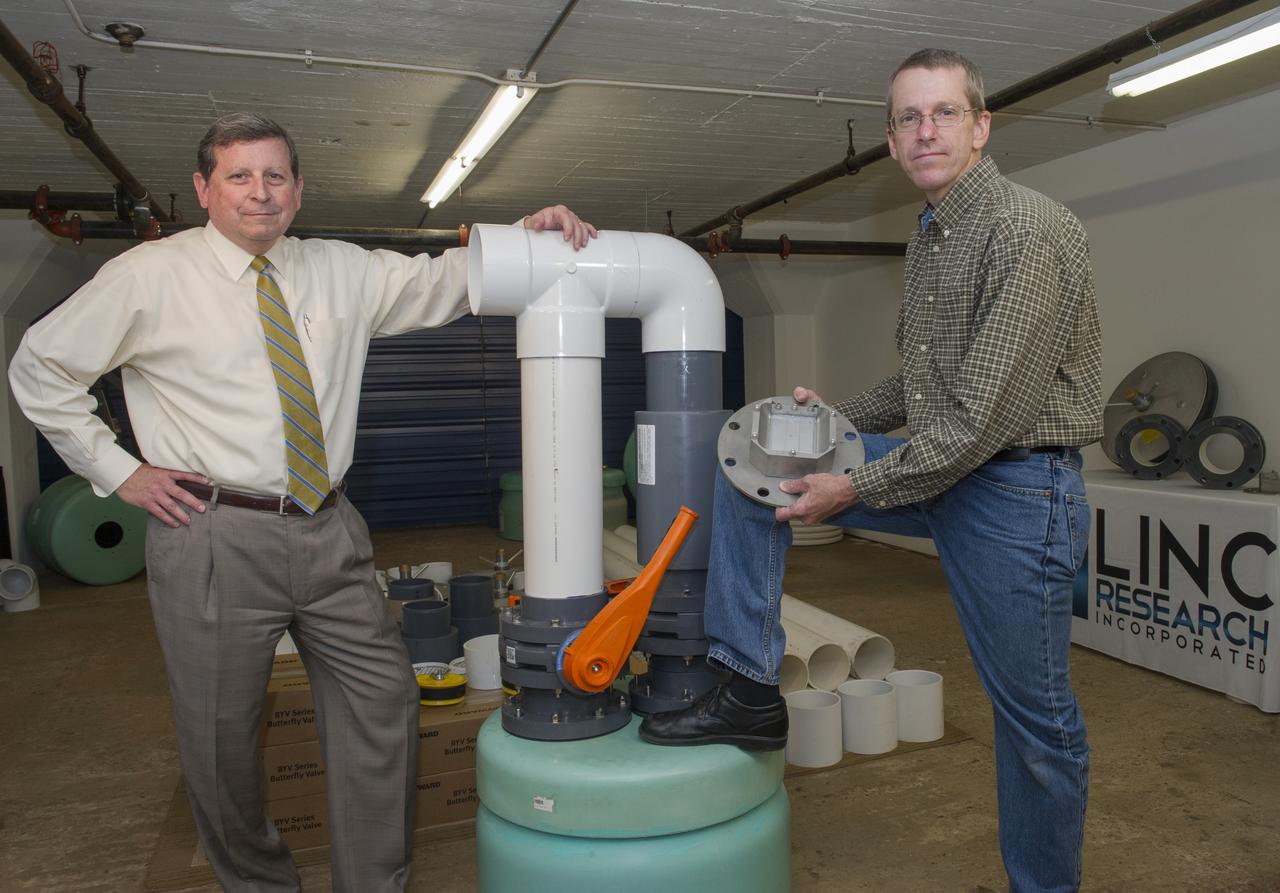

CURTIS O. TAYLOR, PRESIDENT OF LINC RESEARCH CORP, (L), AND JEFF LINDNER, CHIEF ENGINEER, POSE WITH HARDWARE FOR THEIR PATENTED TECHNOLOGY, FLUID STRUCTURE COUPLING, WHICH USES SIMPLE PHYSICS TO DAMPEN POTENTIALLY HARMFUL SHAKING IN STRUCTURES. INSTALLATION OF THE FLUID STRUCTURE COUPLING TECHNOLOGY IN A BUILDING WILL TAKE PLACE IN SUMMER OF 2016.
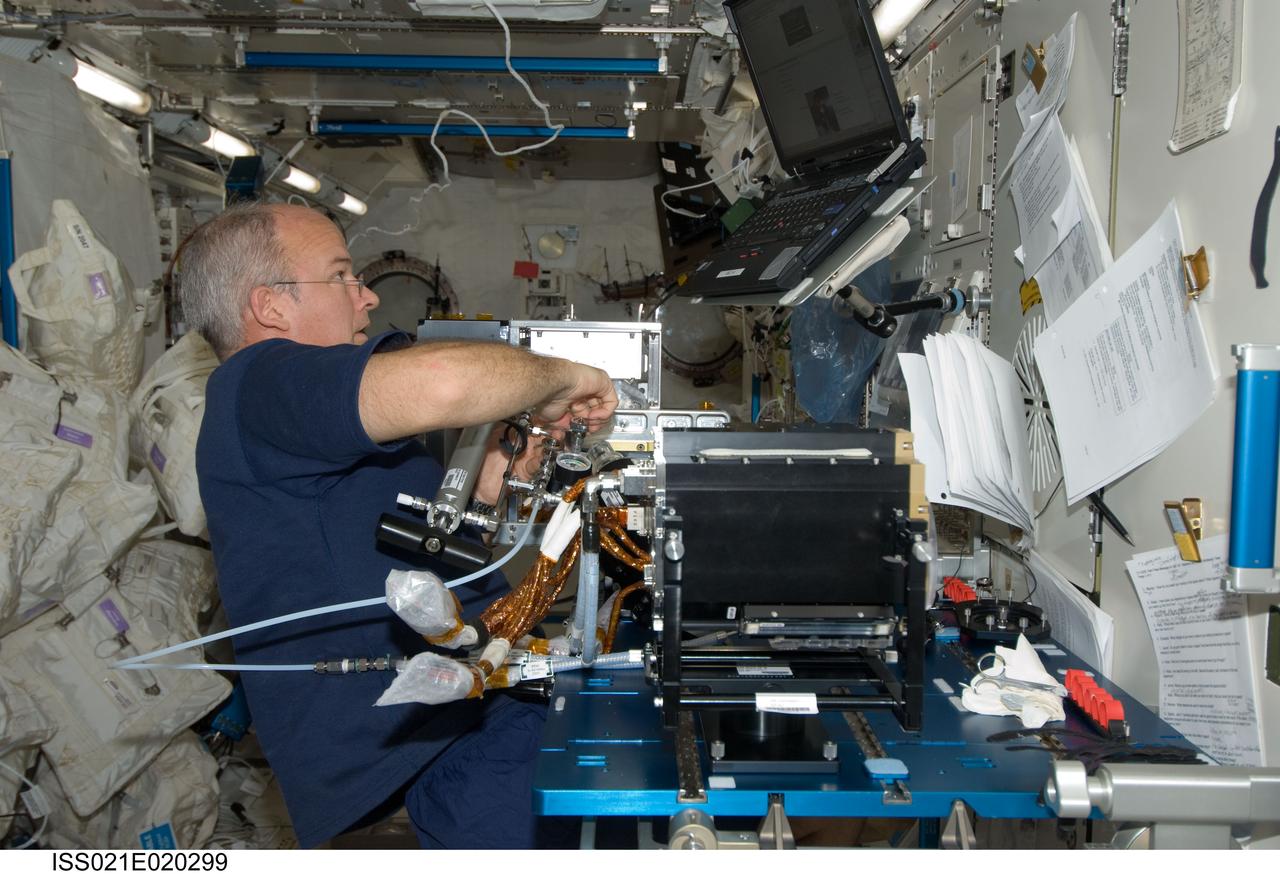

ISS021-E-020299 (5 Nov. 2009) --- NASA astronaut Jeffrey Williams, Expedition 21 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
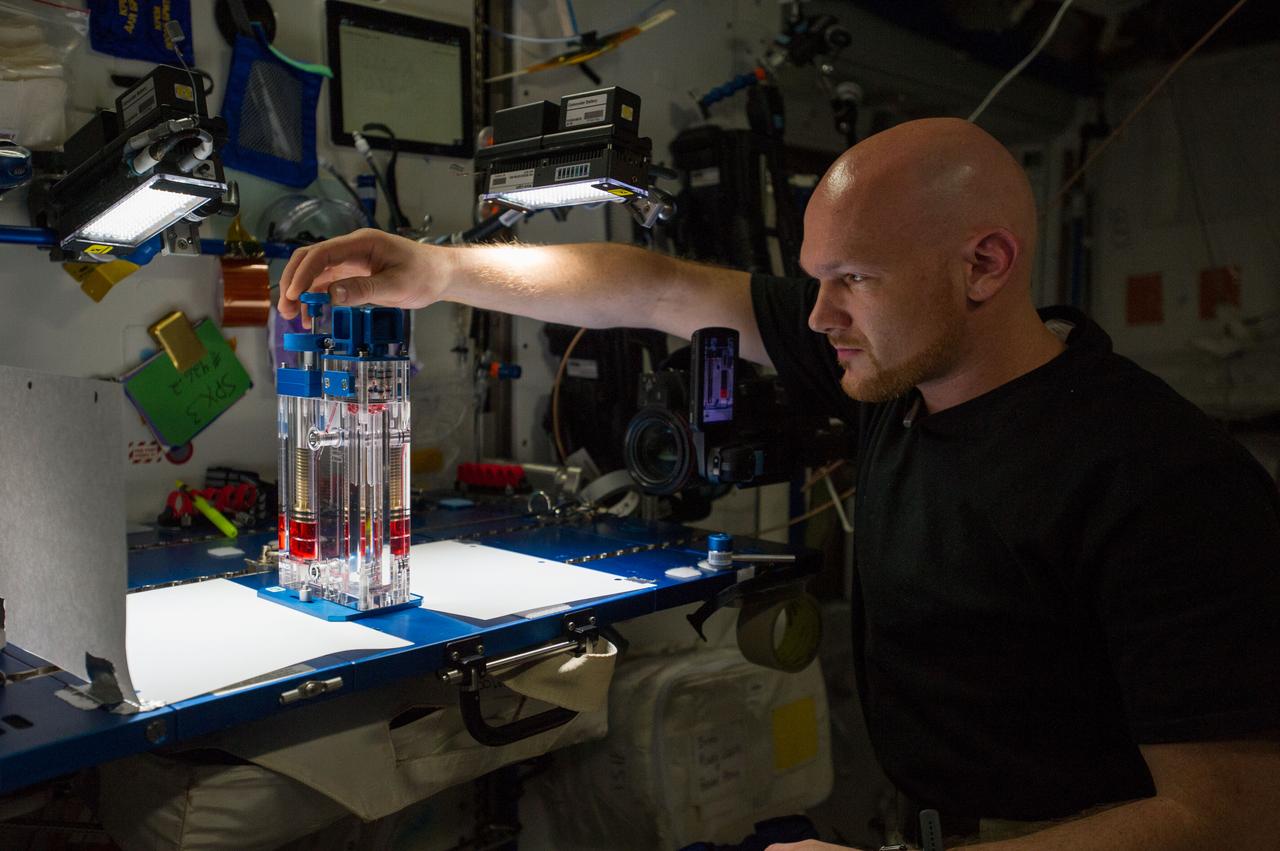
ISS040-E-015543 (19 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
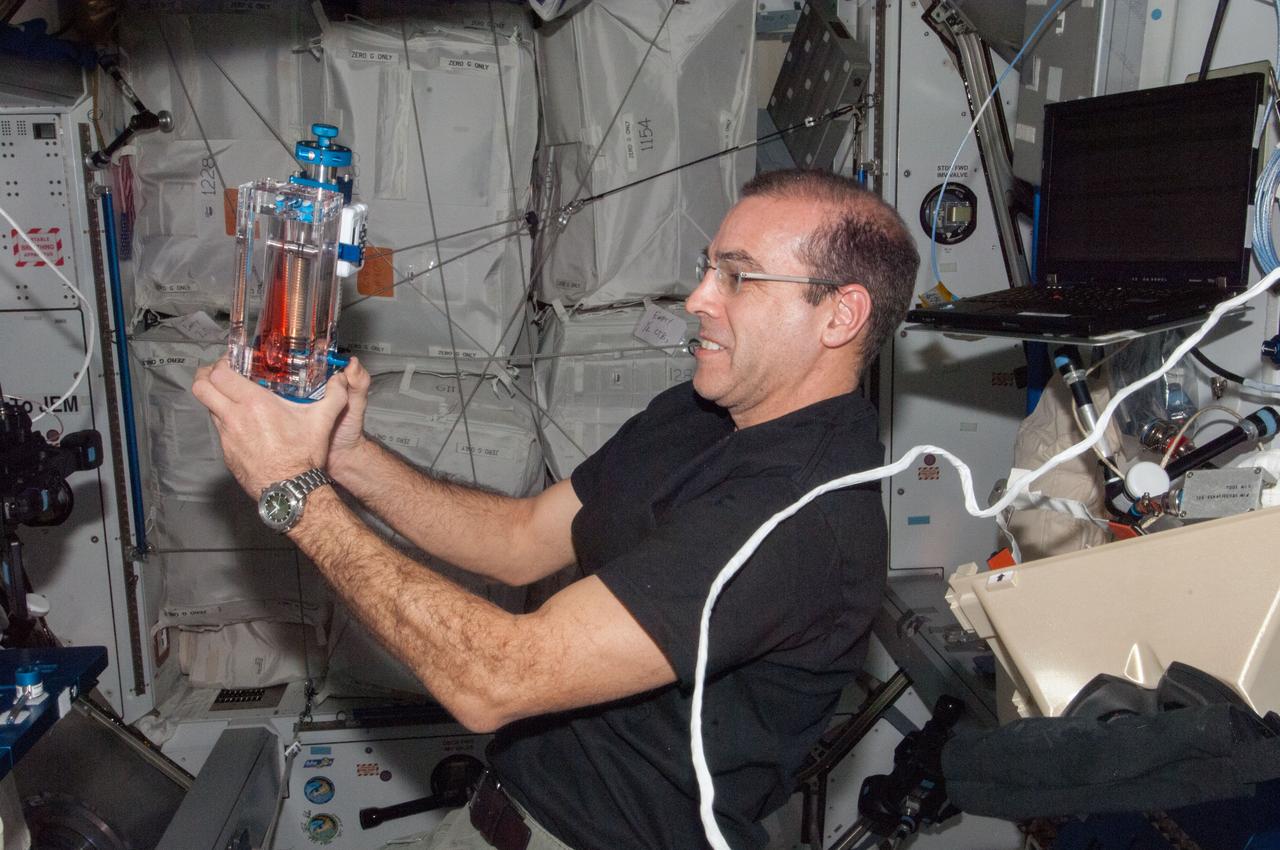

ISS038-E-025016 (3 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
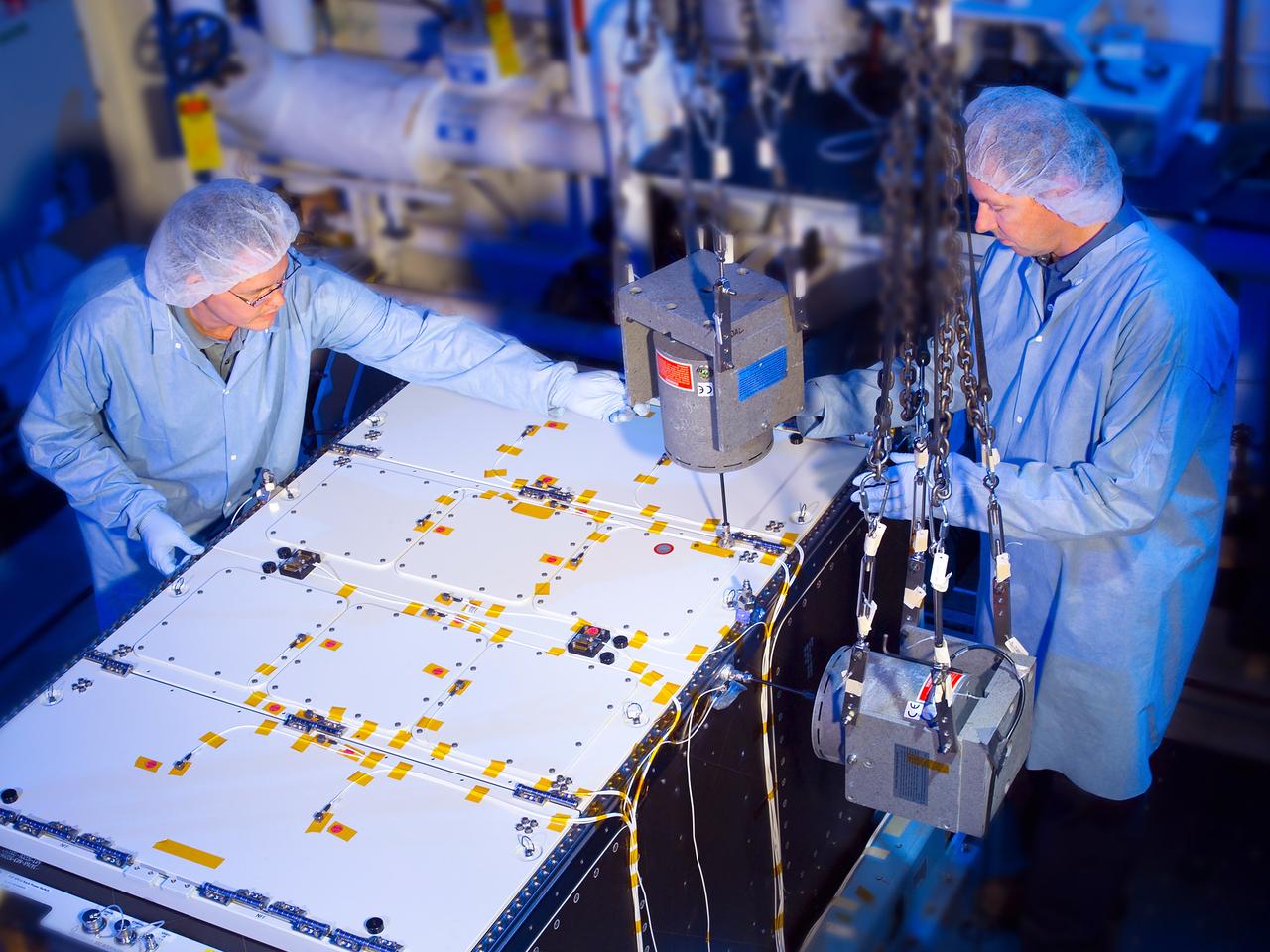
Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF), Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) during testing in the Structural Dynamics Laboratory (SDL). The Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) is a set of two International Space Station (ISS) research facilities designed to support physical and biological experiments in support of technology development and validation in space. The FCF consists of two modular, reconfigurable racks called the Combustion Integration Rack (CIR) and the Fluids Integration Rack (FIR). The CIR and FIR were developed at NASAʼs Glenn Research Center.
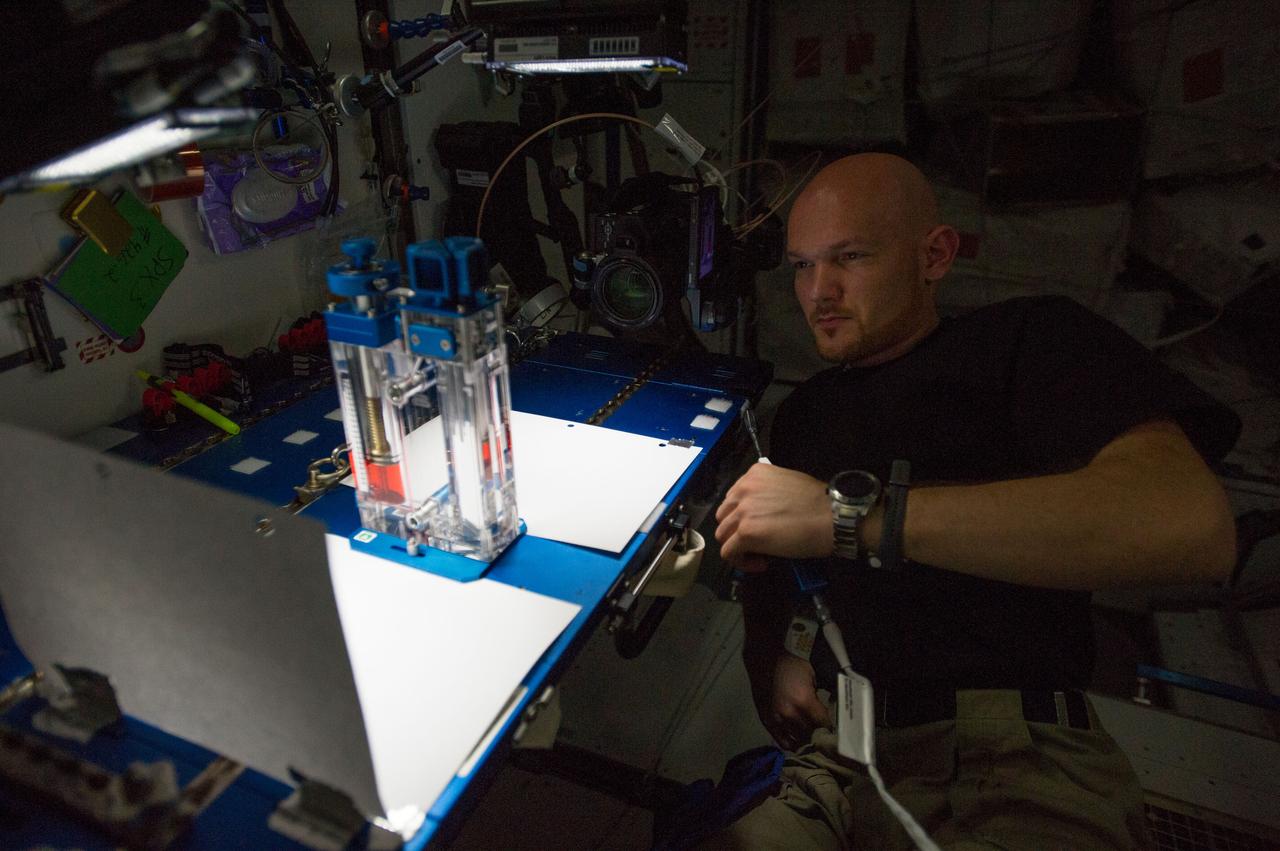
ISS040-E-015532 (19 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
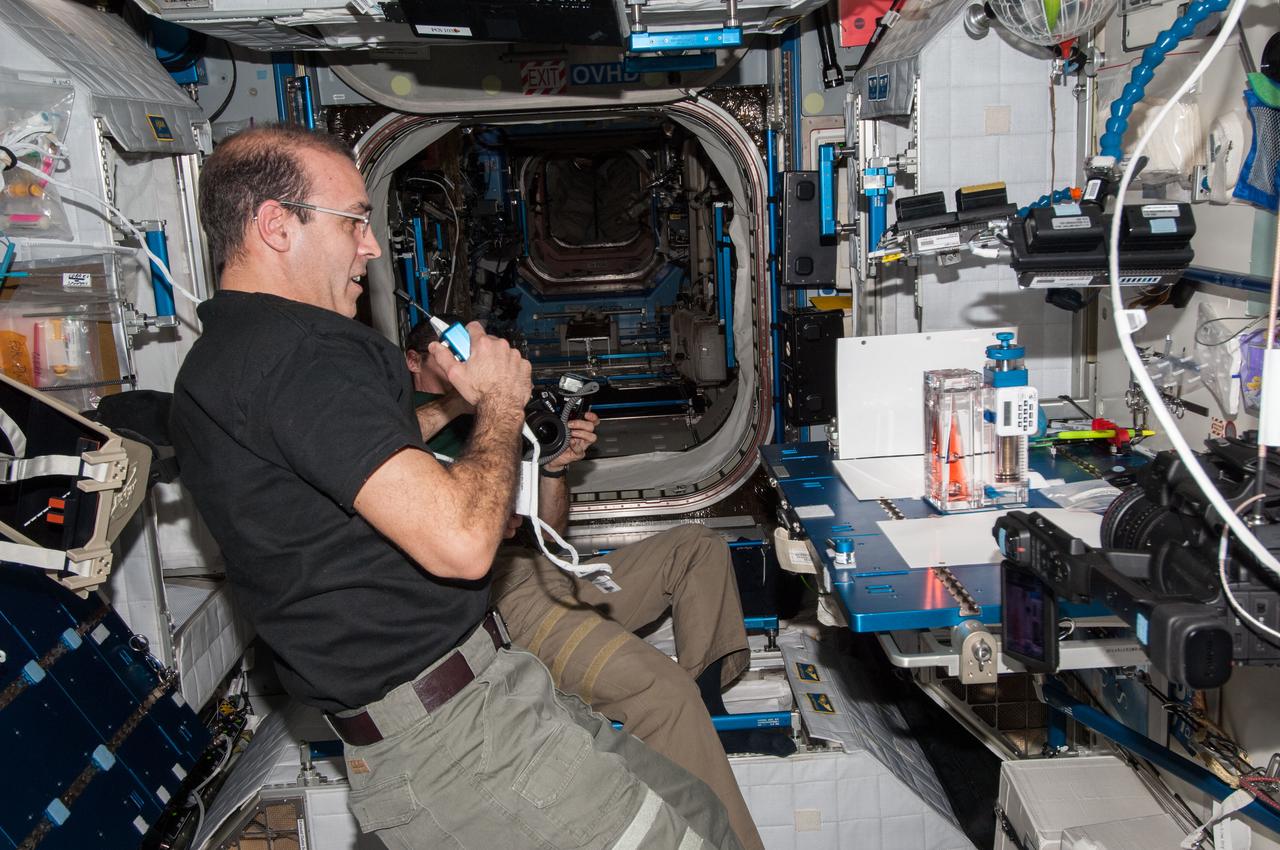

ISS038-E-025000 (3 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, Expedition 38 flight engineer, speaks in a microphone while conducting a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
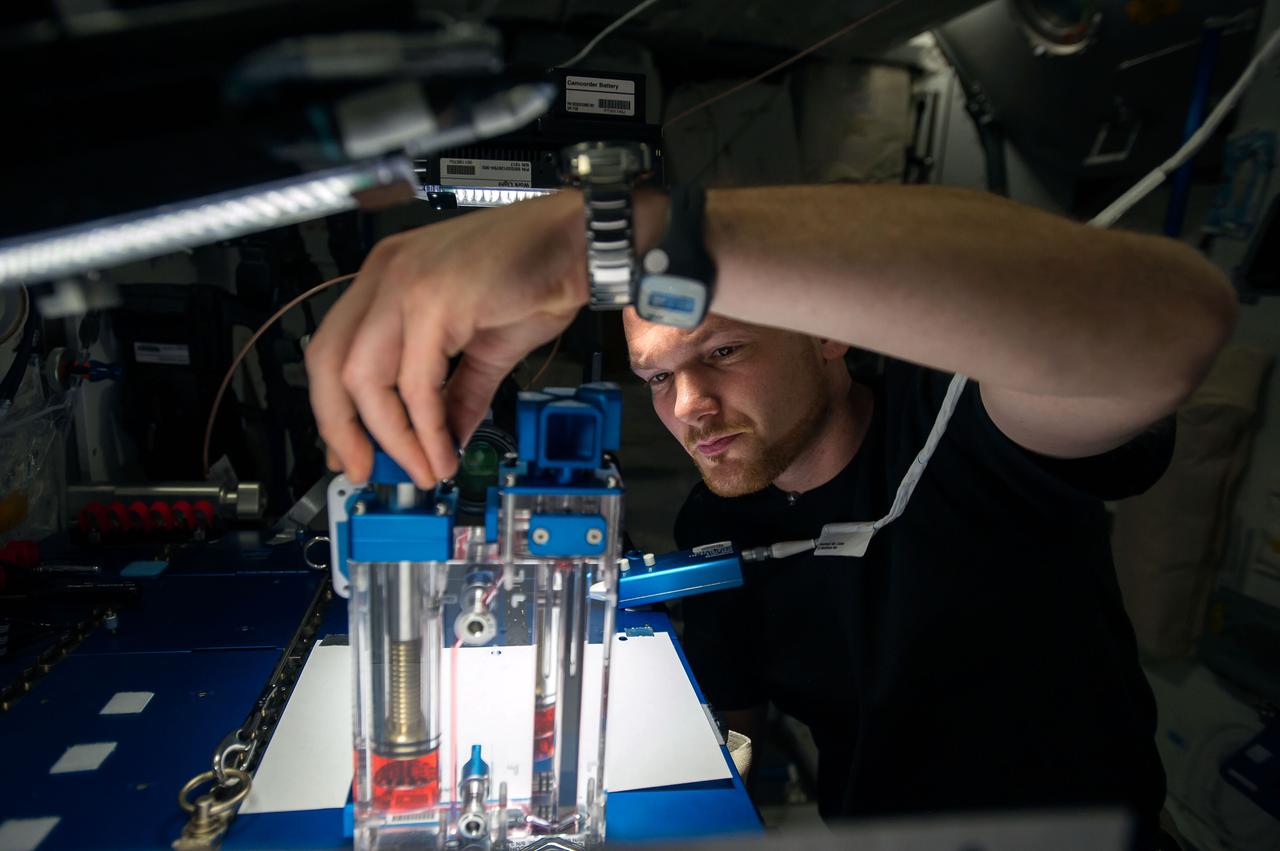

ISS040-E-015536 (19 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
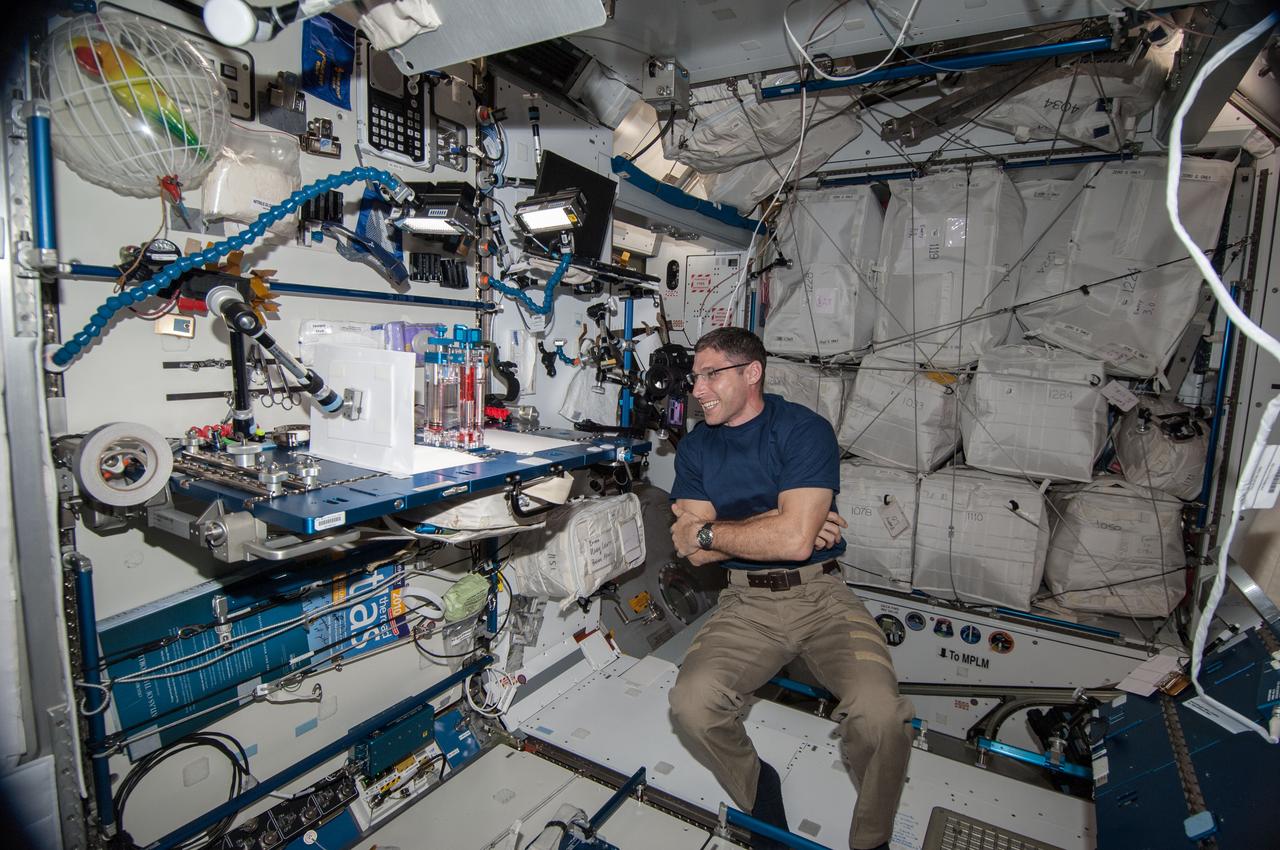

ISS038-E-005962 (19 Nov. 2013) --- NASA astronaut Michael Hopkins, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the Capillary Flow Experiment-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
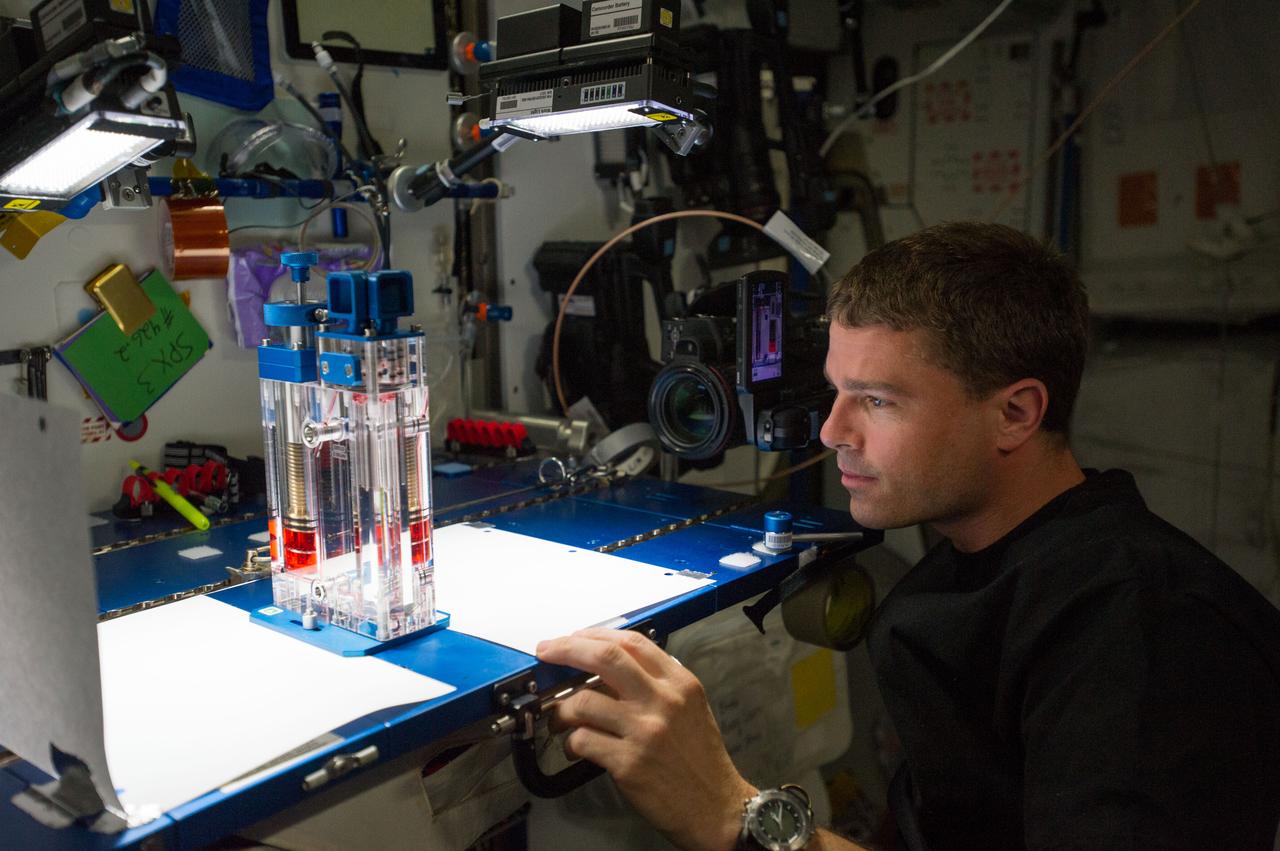
ISS040-E-015539 (19 June 2014) --- NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
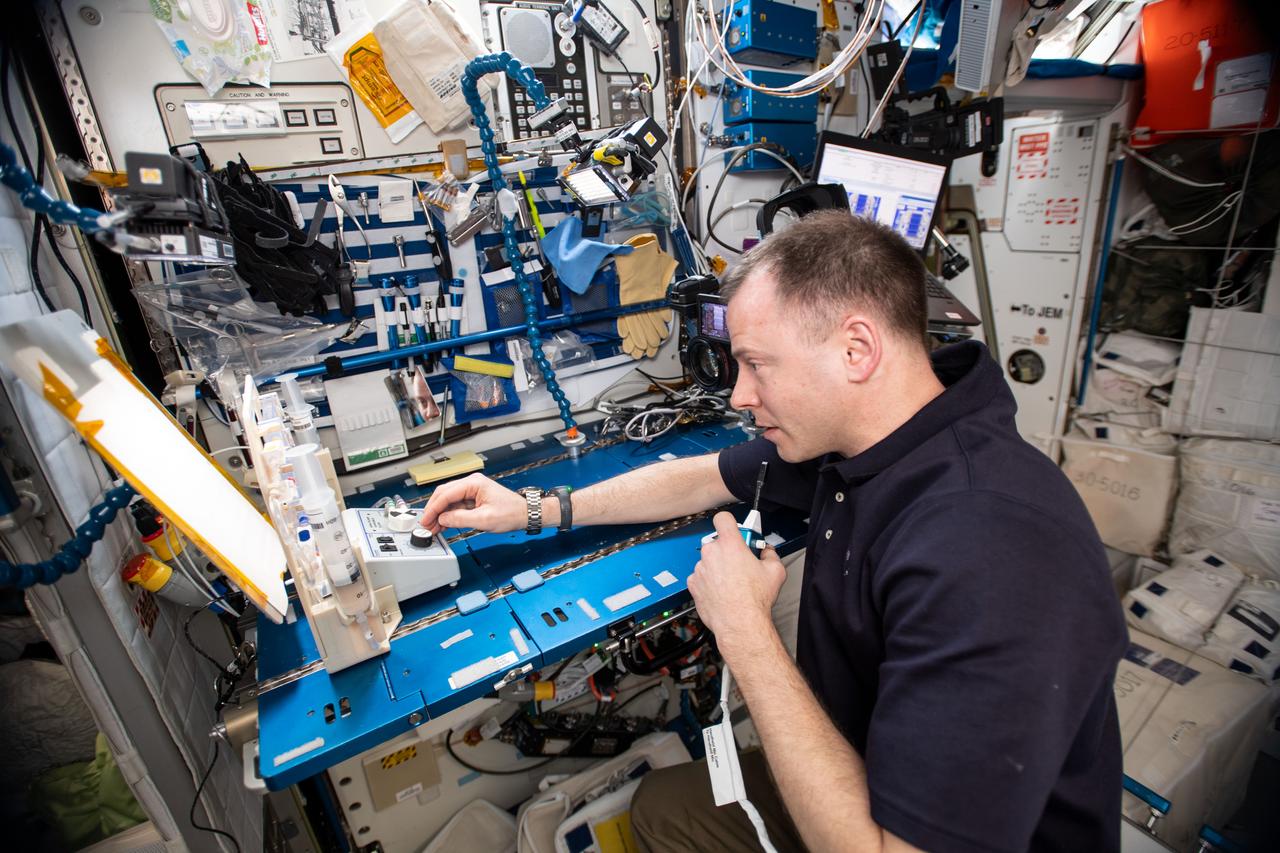

iss059e112425 (June 18, 2019) --- Flight Engineer Nick Hague is supporting research for the Capillary Structures experiment that uses specialized hardware to demonstrate the flow of fluid and gas mixtures using surface tension and fluid dynamics. The fluid physics study is helping NASA evaluate technologies for a lightweight, advanced life support system that can recover water and remove carbon dioxide in space.

iss065e442823 (Oct. 7, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) installs a fluid physics and materials research device inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Also called DECLIC, or Device for the Study of Critical Liquids and Crystallization, the device allows researchers to study ambient temperature critical point fluids, high temperature super-critical fluids, and the dynamics and morphology of the fronts that form as a liquid material solidifies.
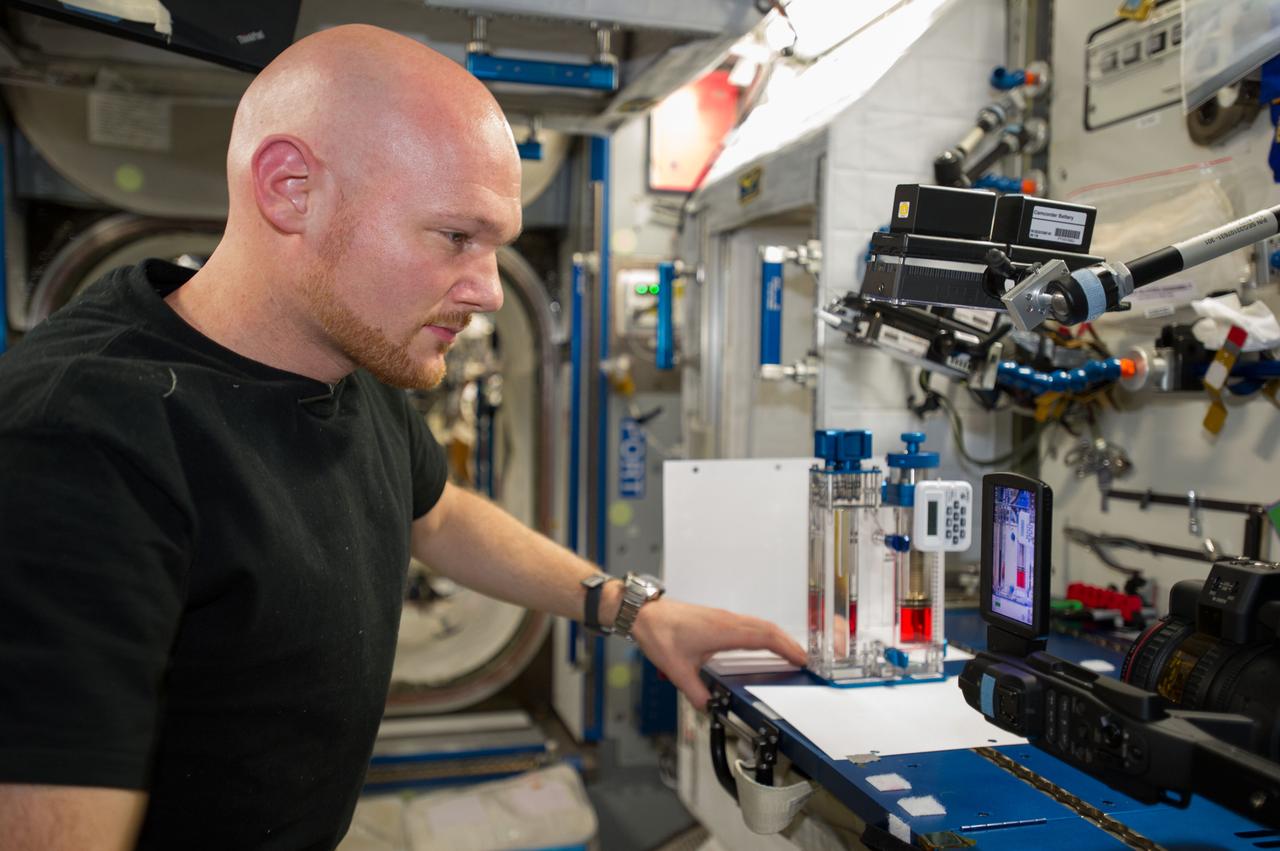

ISS040-E-015523 (19 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
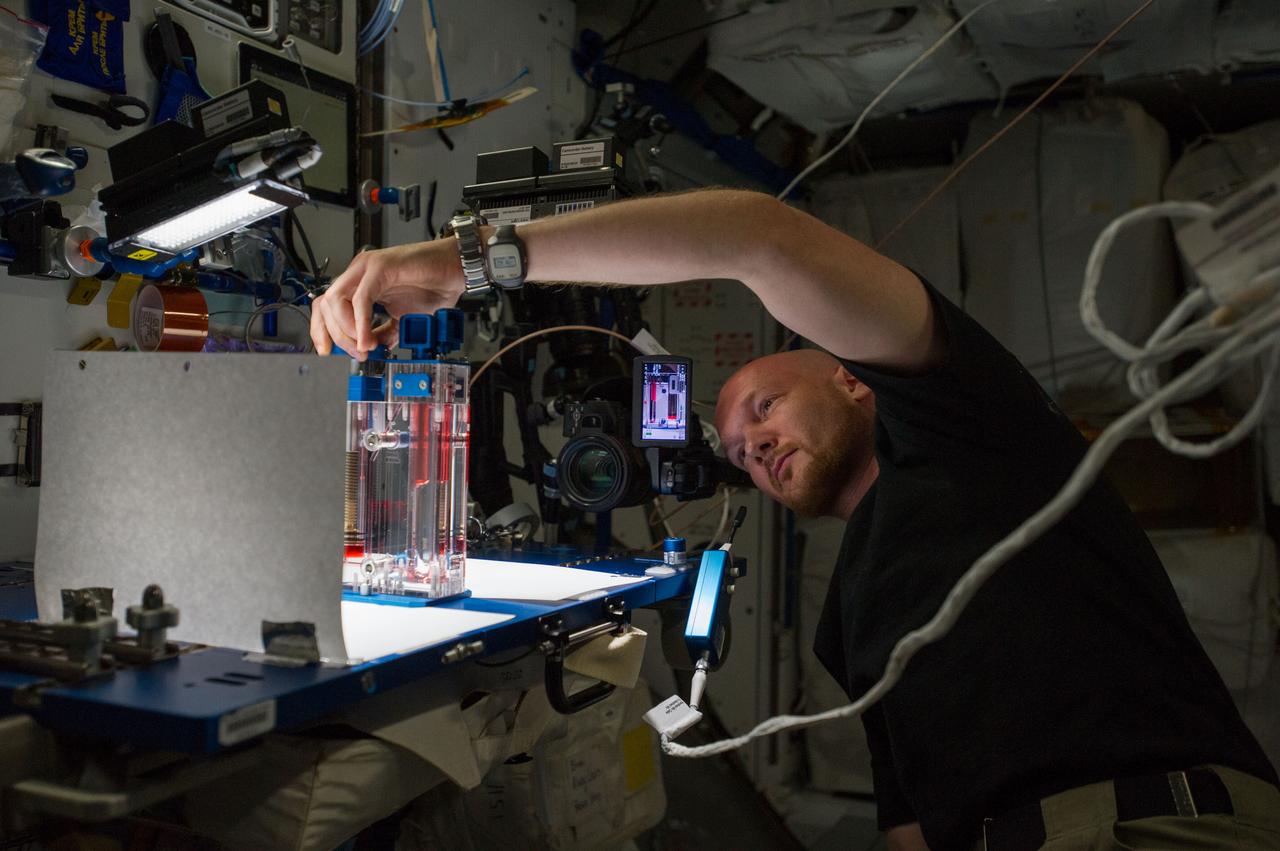

ISS040-E-015545 (19 June 2014) --- European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, Expedition 40 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry.
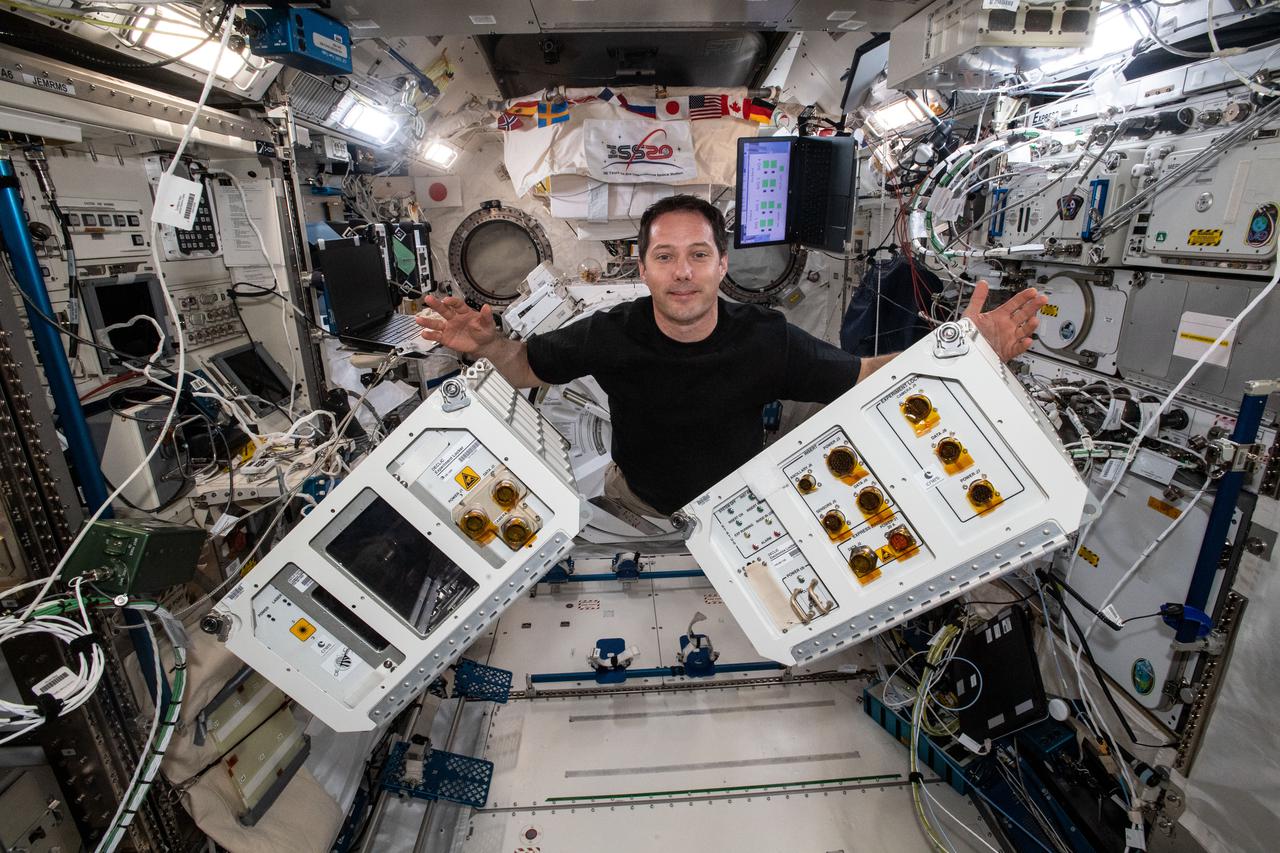

iss065e442804 (Oct. 7, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Commander Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) gathers fluid physics and materials research hardware inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module. Also called DECLIC, or Device for the Study of Critical Liquids and Crystallization, the science gear allows researchers to study ambient temperature critical point fluids, high temperature super-critical fluids, and the dynamics and morphology of the fronts that form as a liquid material solidifies.
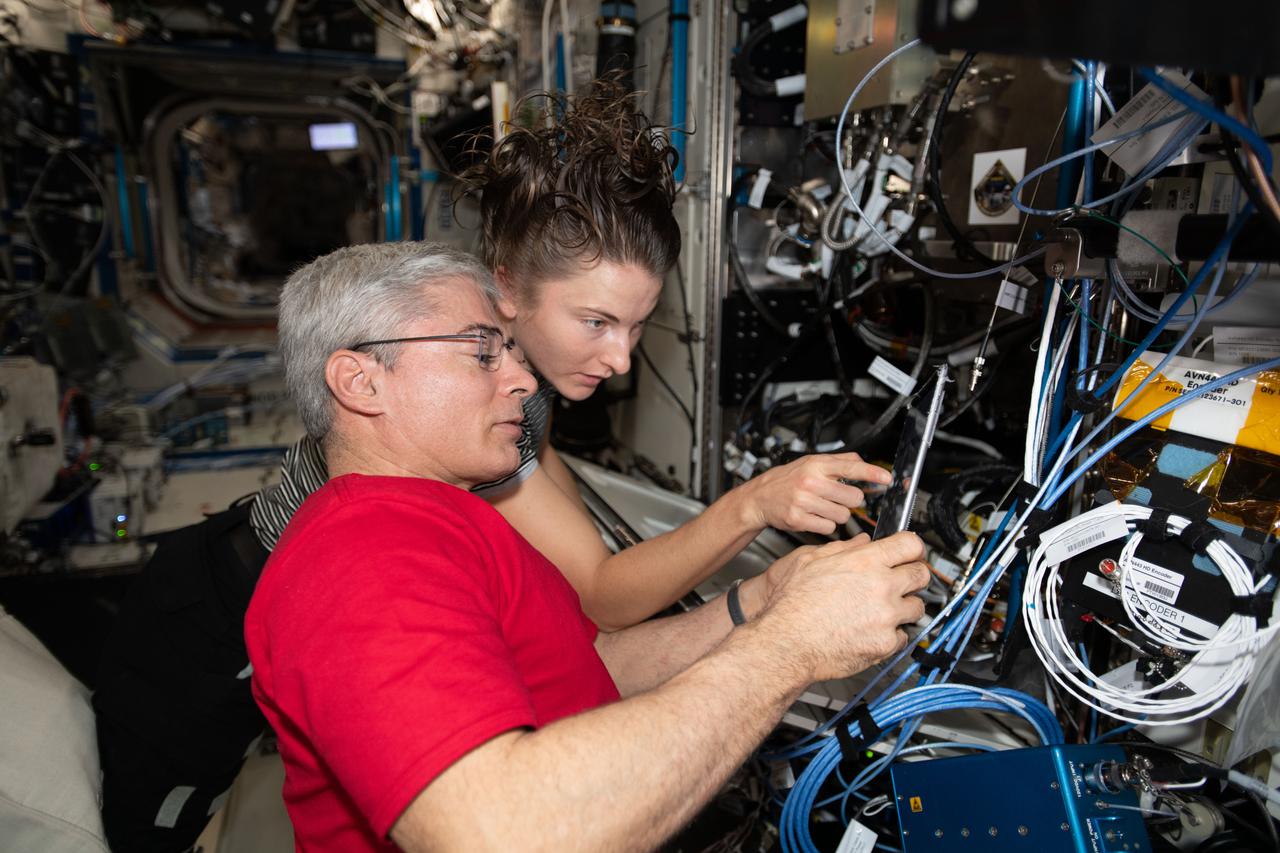

iss066e088377 (Dec. 9, 2021) --- NASA astronauts Mark Vande Hei and Kayla Barron set up the Fluids Integrated Rack for a space physics study that may improve thermal systems for Earth and other planetary environments.
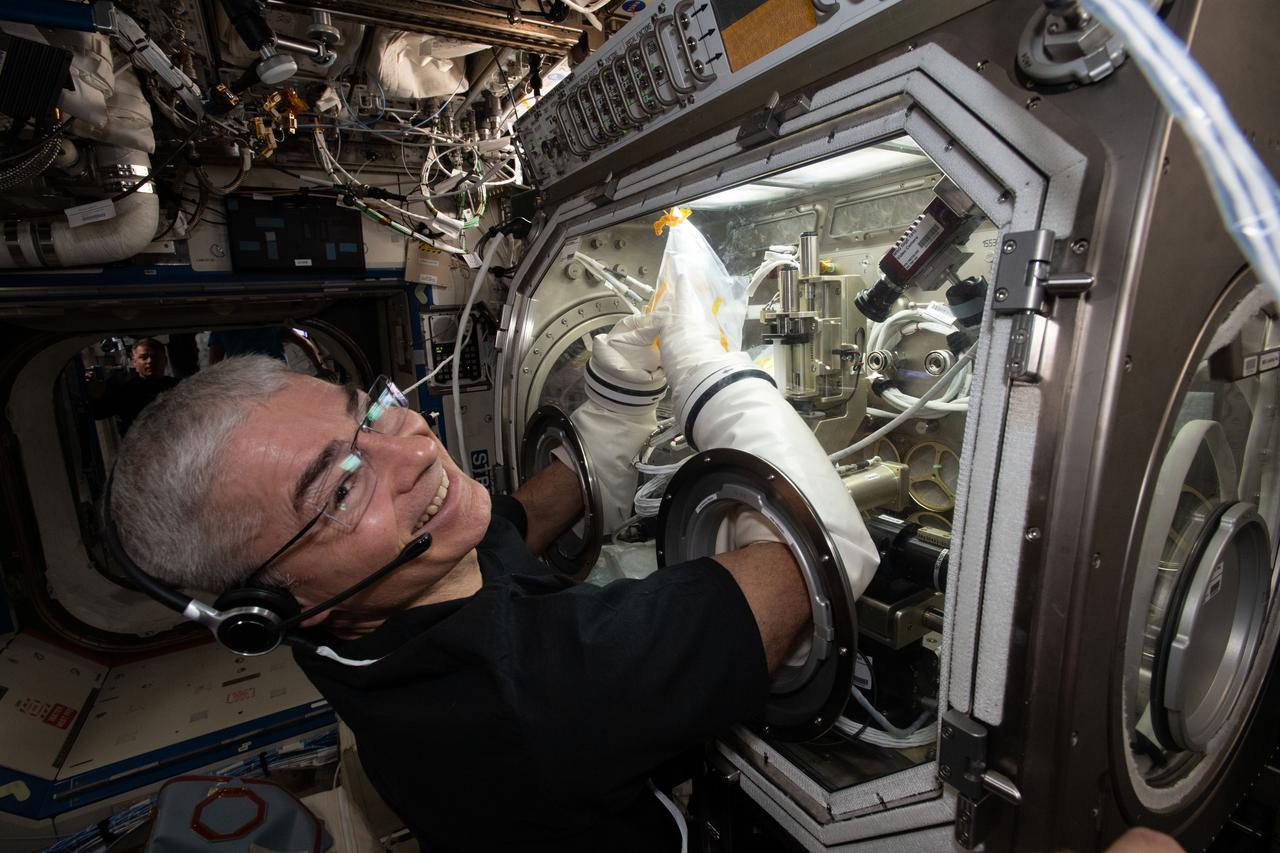

iss065e276849 (Aug. 16, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei works inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Ring Sheared Drop fluid physics study.
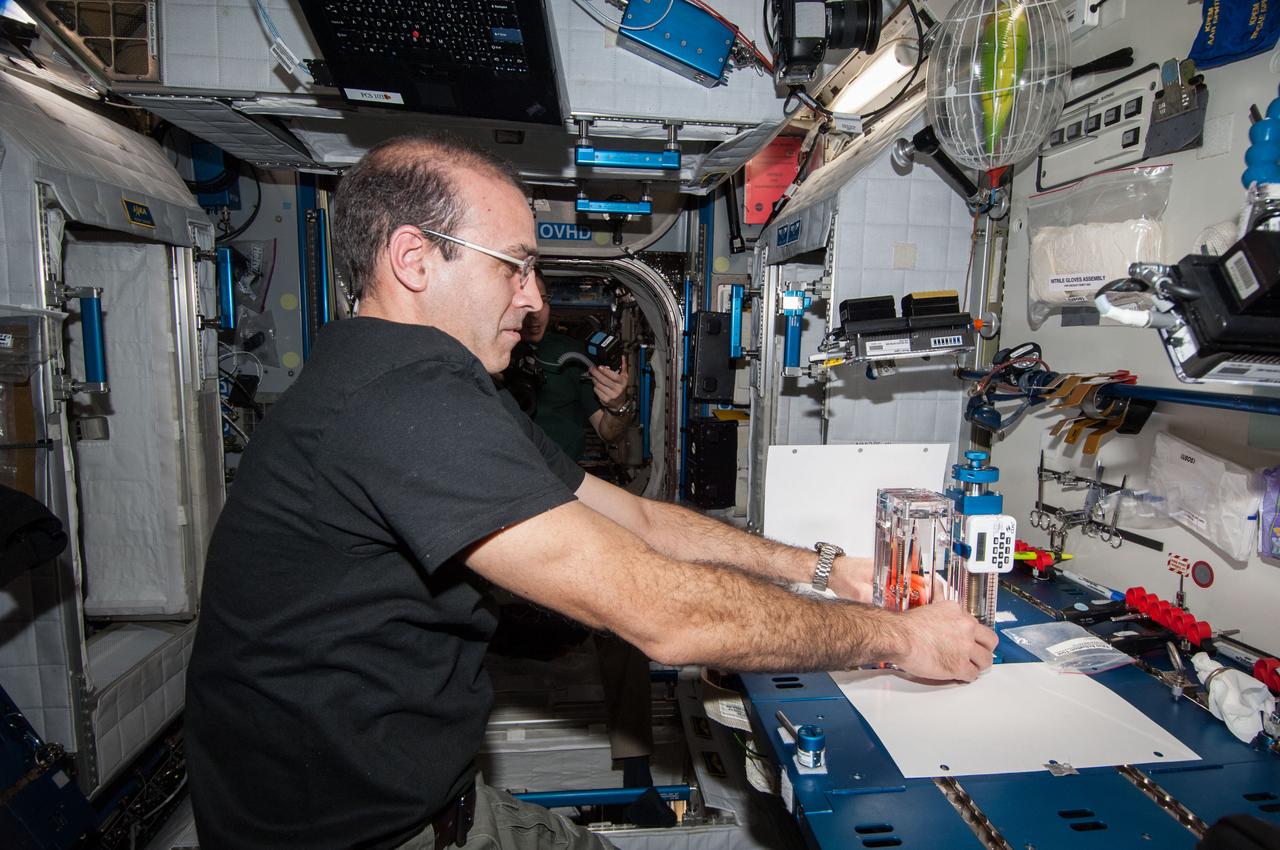

ISS038-E-025002 (3 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry. NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins (mostly obscured in the background), flight engineer, uses a still camera to photograph the session.
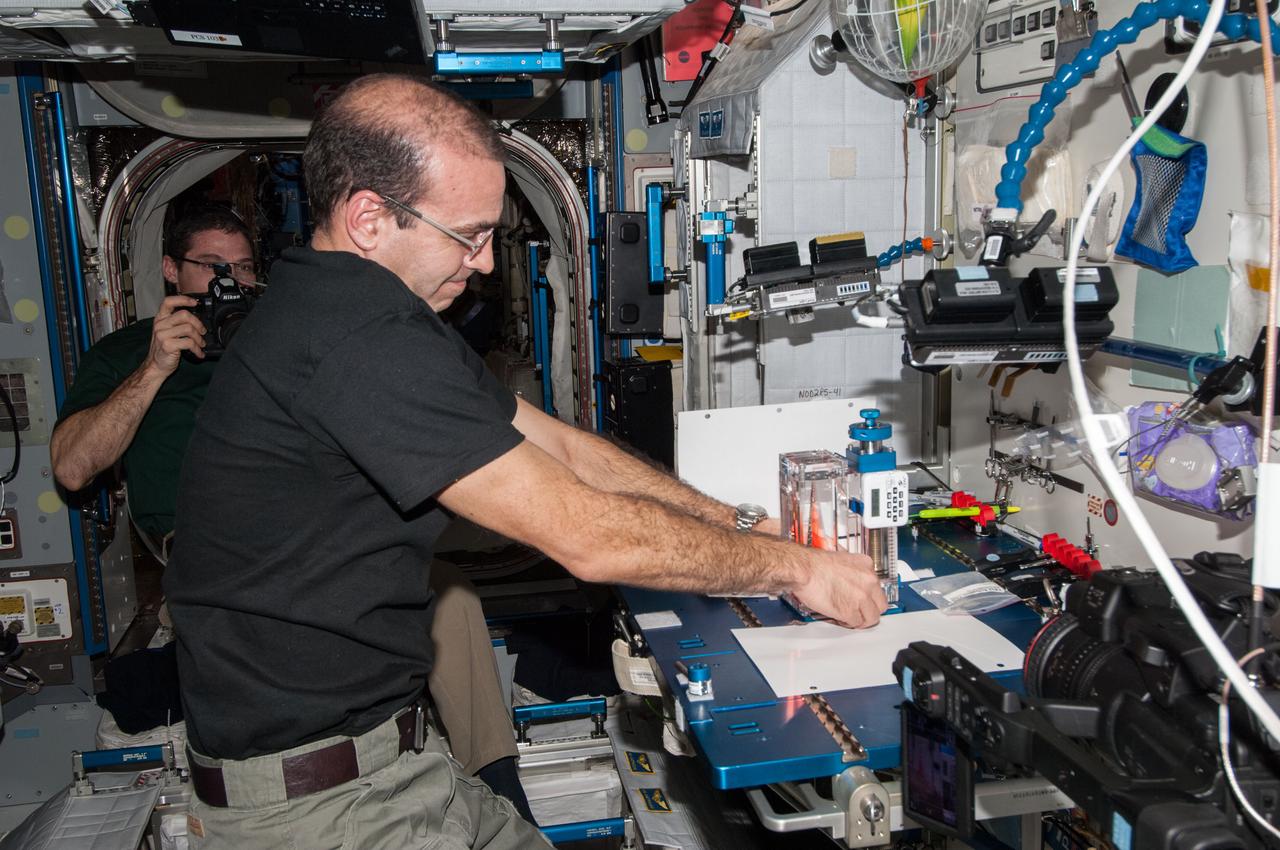

ISS038-E-025002 (3 Jan. 2014) --- NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, Expedition 38 flight engineer, conducts a session with the Capillary Flow Experiment (CFE-2) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. CFE is a suite of fluid physics experiments that investigate how fluids behave in microgravity which could benefit water and fuel delivery systems on future spacecraft. Scientists designed the CFE-2 to study properties of fluids and bubbles inside containers with a specific 3-D geometry. NASA astronaut Mike Hopkins (mostly obscured in the background), flight engineer, uses a still camera to photograph the session.
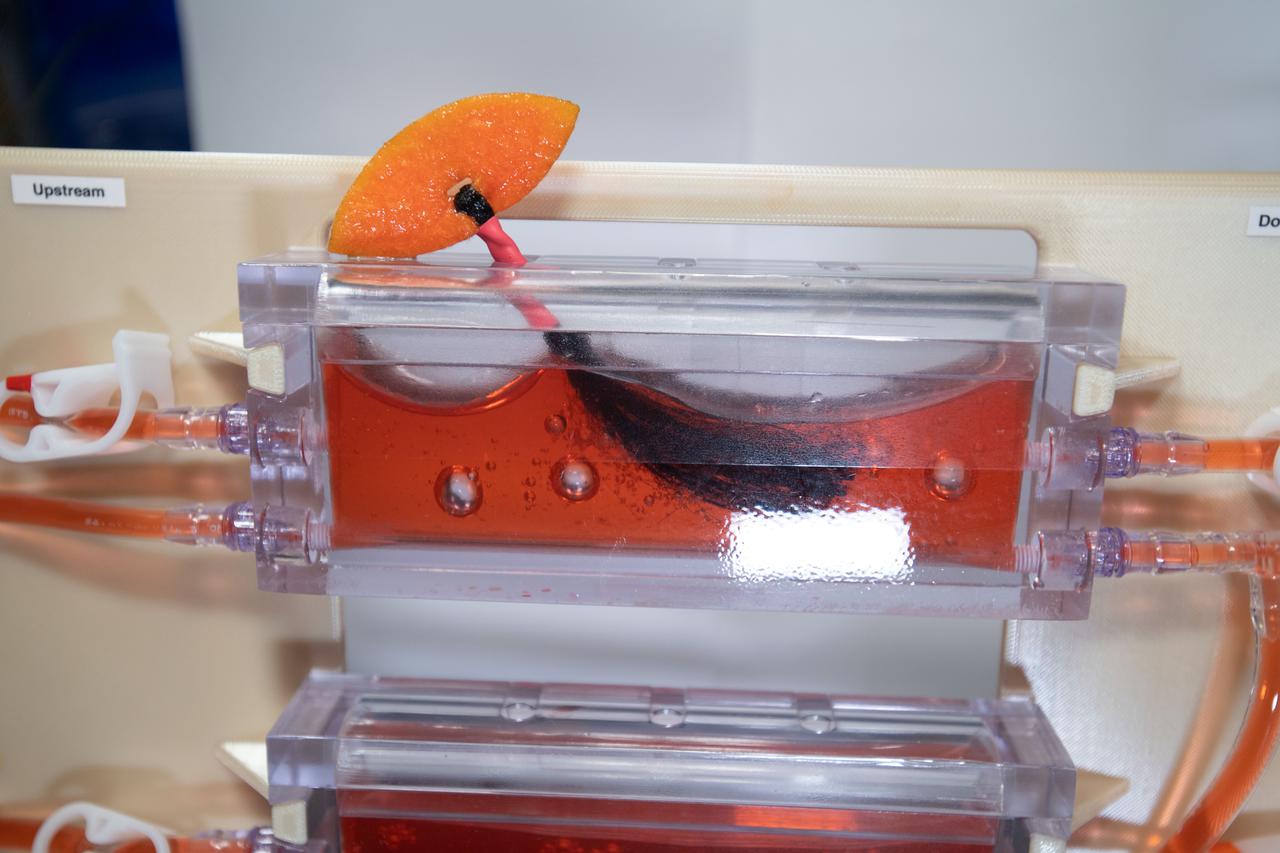

iss064e049400 (3/31/2021) --- A view of the Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation aboard the International space Station (ISS). The Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation demonstrates passive measures for controlling fluid delivery and uptake in plant growth systems. Reduced gravity creates challenges in providing adequate fluid and nutrition for plant growth. This investigation examines using other physical properties such as surface tension, wetting and system geometry to replace the role of gravity.
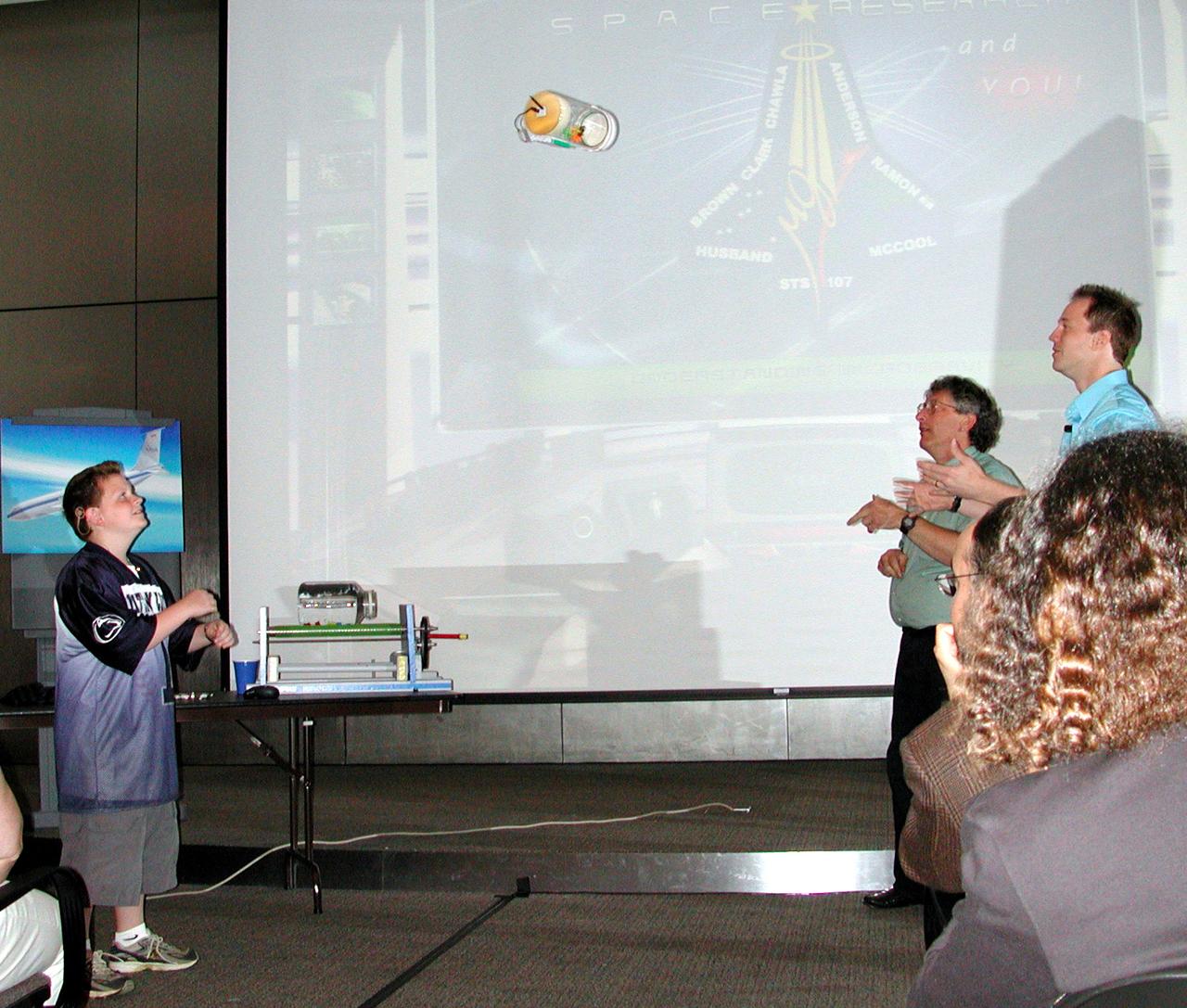

A student gets ready to catch a plastic tube carrying a small fluid bottle and a wireless video camera. As it arced through the air, the container was in free-fall -- just like astronauts in space -- and the TV camera broadcast images of how the fluid behaved. The activity was part of the Space Research and You education event held by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Research on June 25, 2002, in Arlington, VA, to highlight the research that will be conducted on STS-107. (Digital camera image; no film original.
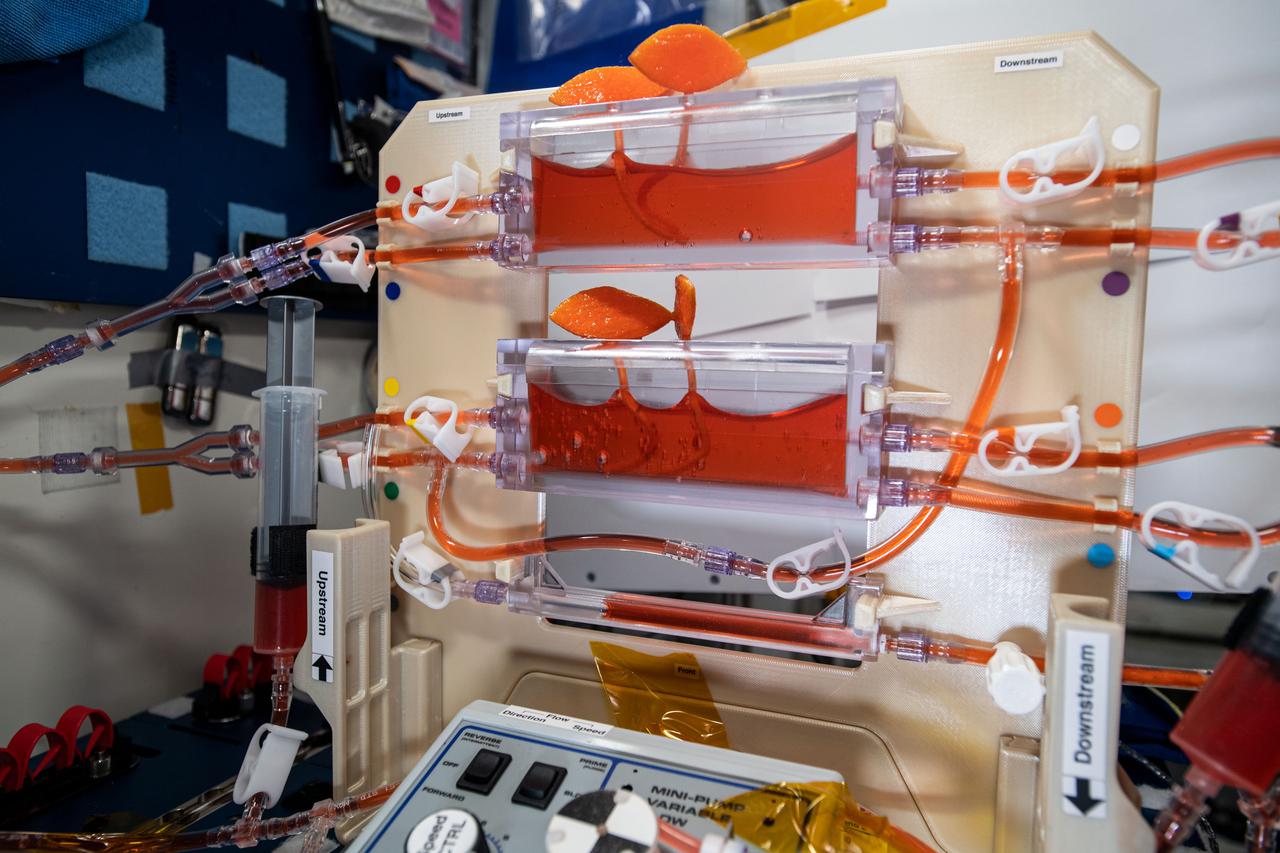

iss064e049289 (3/30/2021) --- A view of the Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation aboard the International space Station (ISS). The Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation demonstrates passive measures for controlling fluid delivery and uptake in plant growth systems. Reduced gravity creates challenges in providing adequate fluid and nutrition for plant growth. This investigation examines using other physical properties such as surface tension, wetting and system geometry to replace the role of gravity.
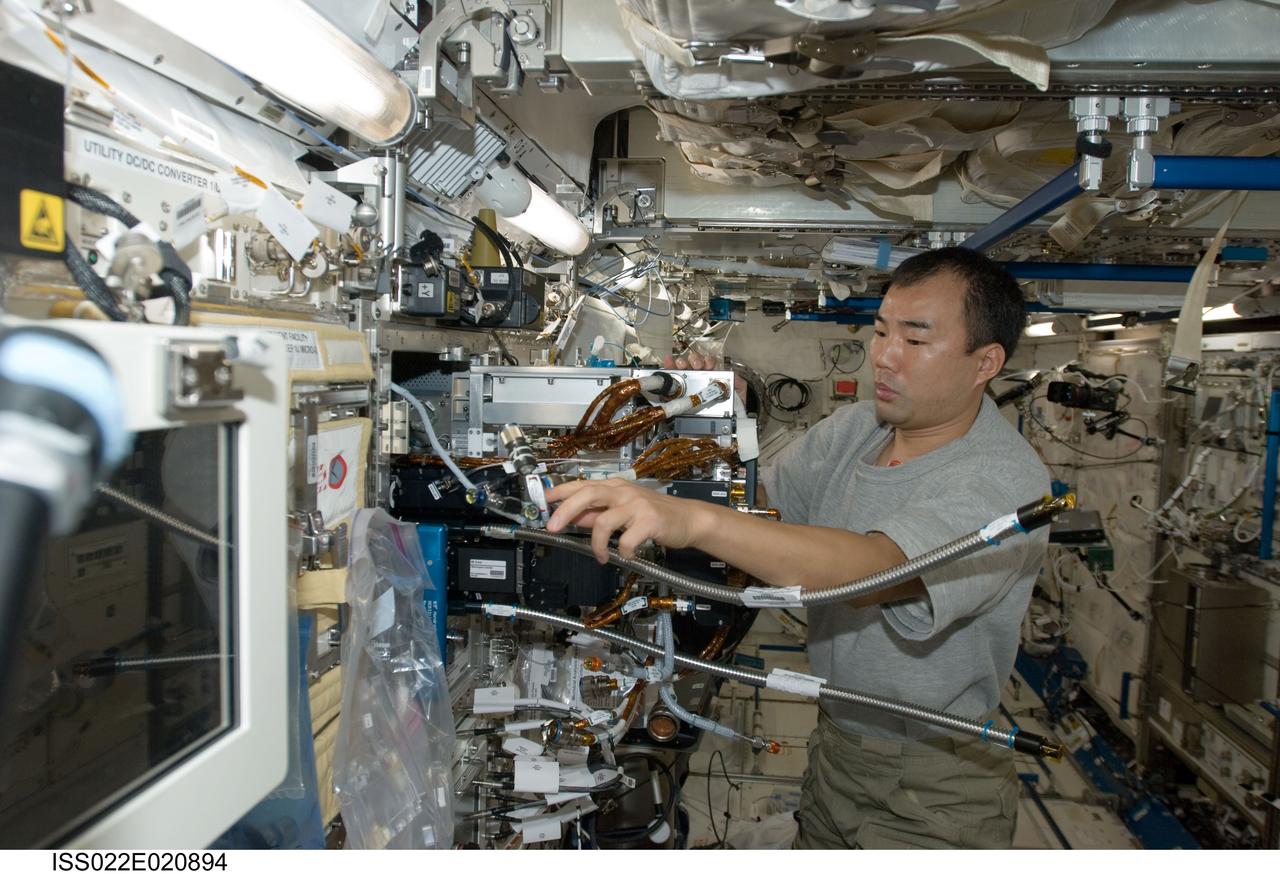

ISS022-E-020894 (11 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
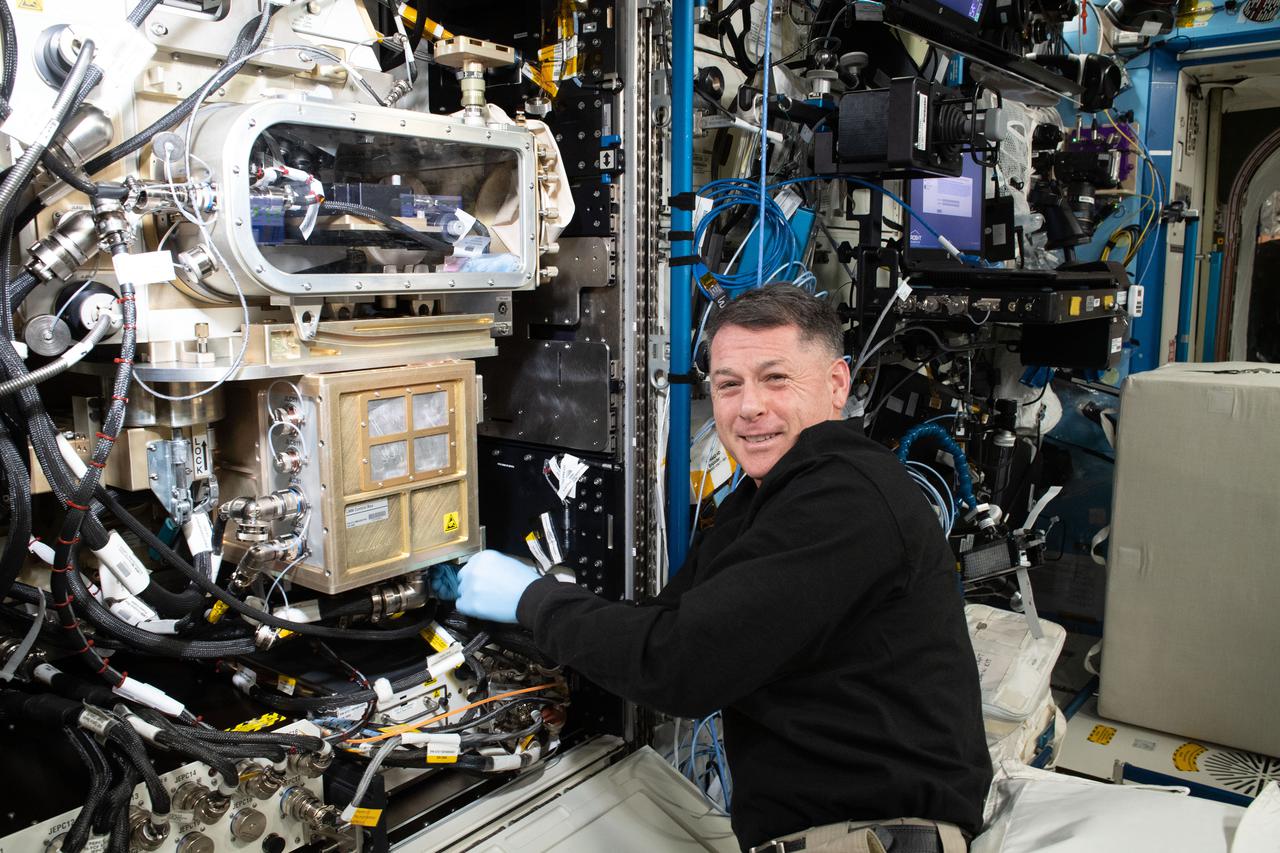

iss065e257486 (Aug. 17, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough installs and configures a new Advanced Colloids Experiment module inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR). The work supports the ACE-T9 fluid physics study that uses the FIR's Light Microscopy Module to image colloidal molecules for insights into the development of advanced materials not possible to produce in Earth's gravity.
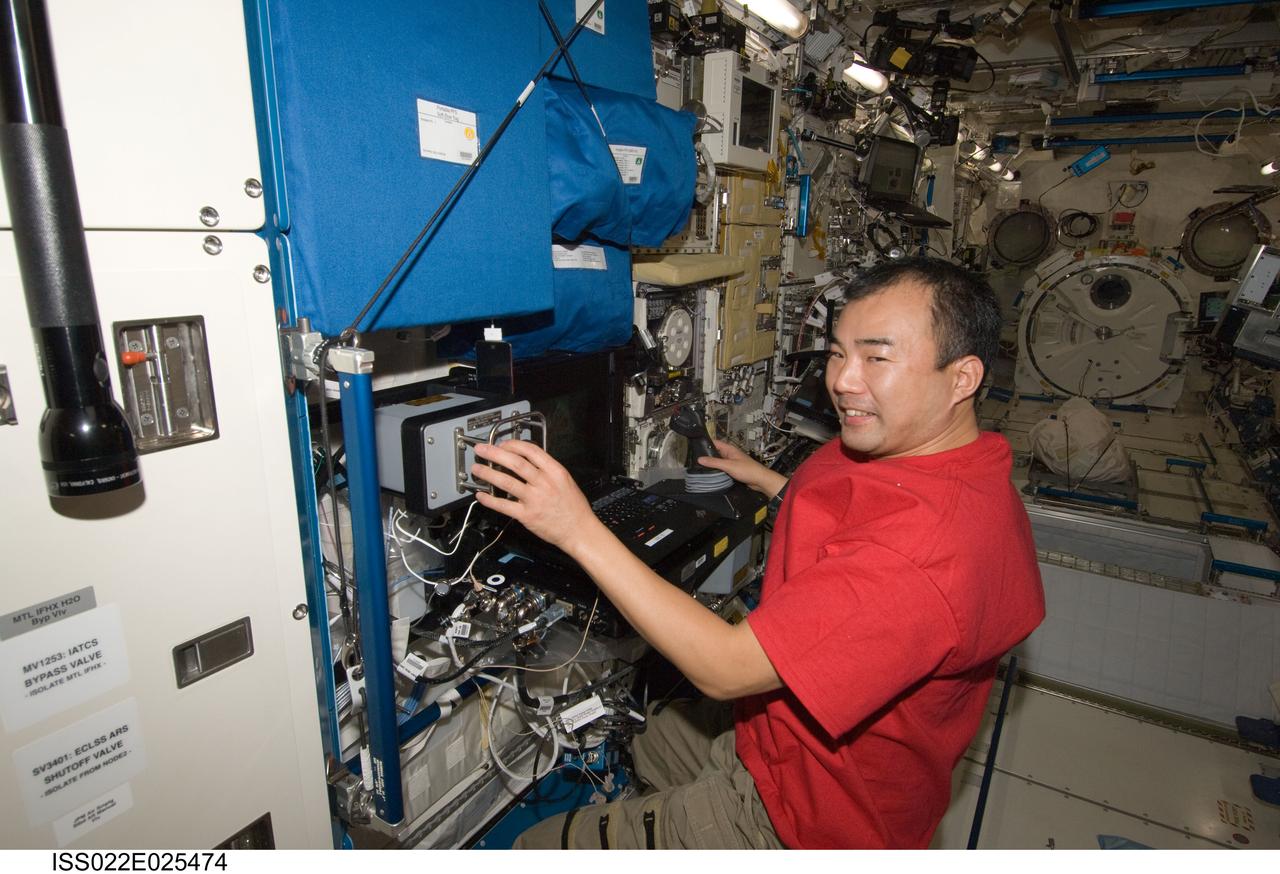

ISS022-E-025474 (14 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, services the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
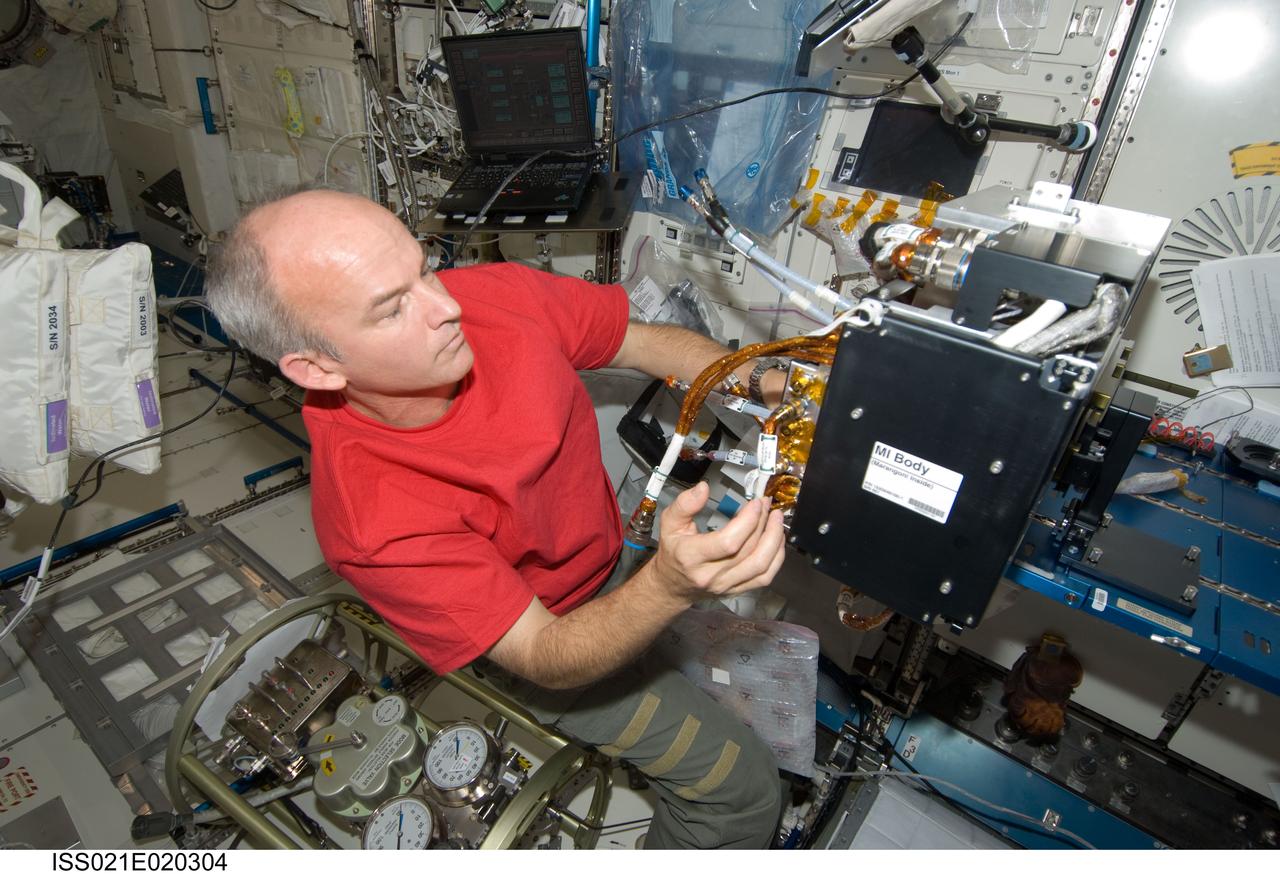

ISS021-E-020304 (5 Nov. 2009) --- NASA astronaut Jeffrey Williams, Expedition 21 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Williams first inserted the Marangoni Inside (MI) cassette in the MI Core for a leak check, and then installed the MI Core into the FPEF MI Body. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
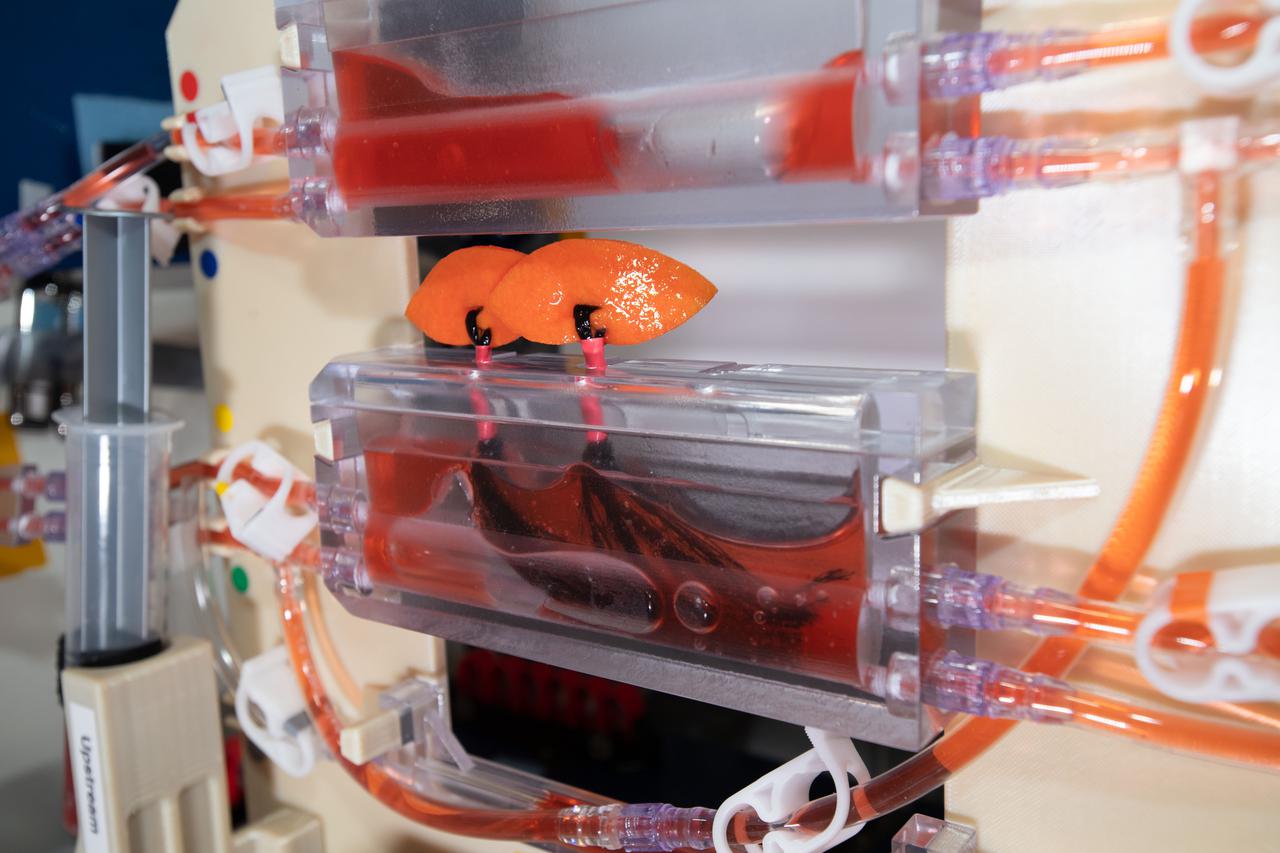

iss064e049484 (3/31/2021) --- A view of the Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation aboard the International space Station (ISS). The Plant Water Management 3 and 4 investigation demonstrates passive measures for controlling fluid delivery and uptake in plant growth systems. Reduced gravity creates challenges in providing adequate fluid and nutrition for plant growth. This investigation examines using other physical properties such as surface tension, wetting and system geometry to replace the role of gravity.
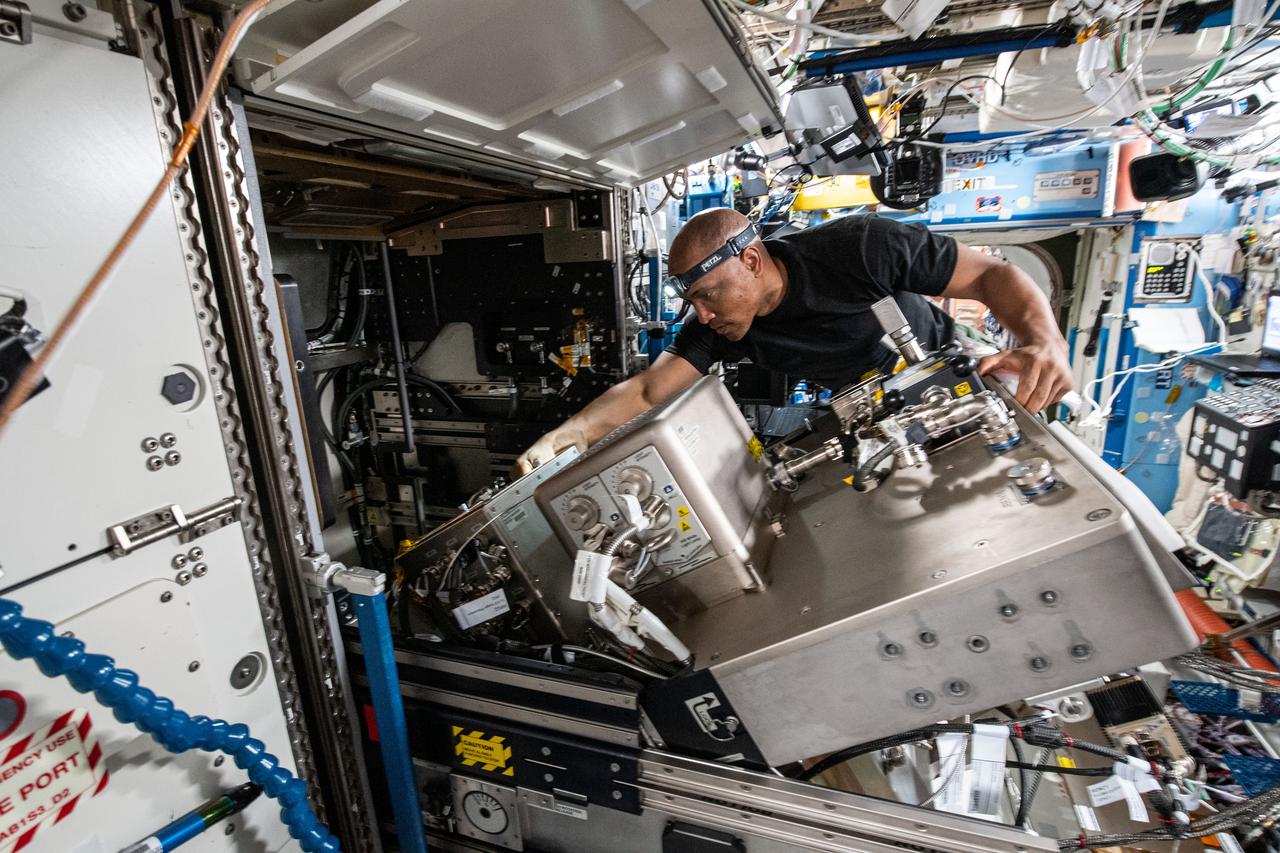

iss064e044807 (March 19, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Victor Glover replaces hardware inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR). The FIR supports fluid physics research in microgravity observing phenomena such as colloids, gels, bubbles, wetting and capillary action, and phase changes, including boiling and condensation.
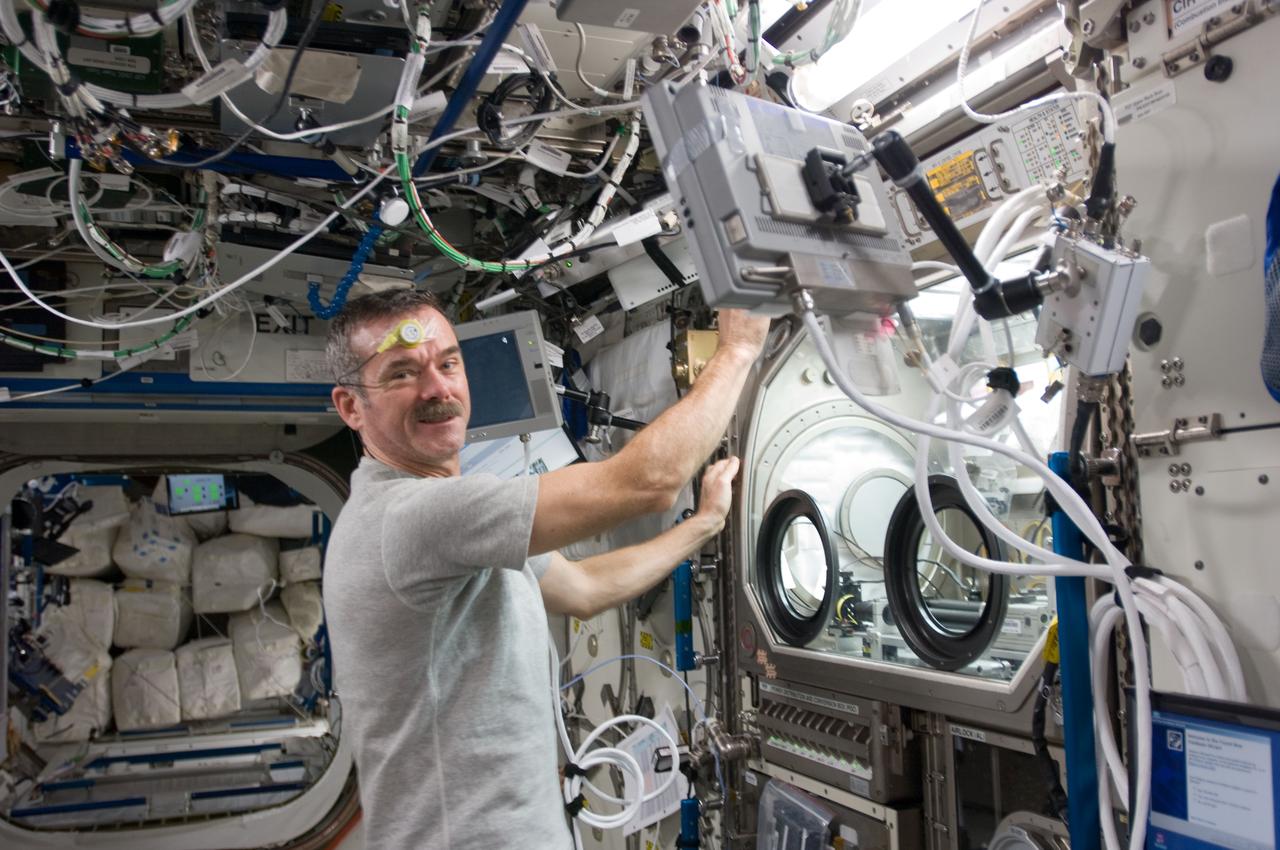

View of Canadian Space Agency (CSA) Chris Hadfield,Expedition 34 Flight Engineer (FE), during the Investigating the Structure of Paramagnetic Aggregates from Colloidal Emulsions 3 (InSPACE-3) experiment. InSPACE-3 collects and records data on fluids containing ellipsoid-shaped particles that change the physical properties of the fluids in response to magnetic fields. Photo was taken during Expedition 34.
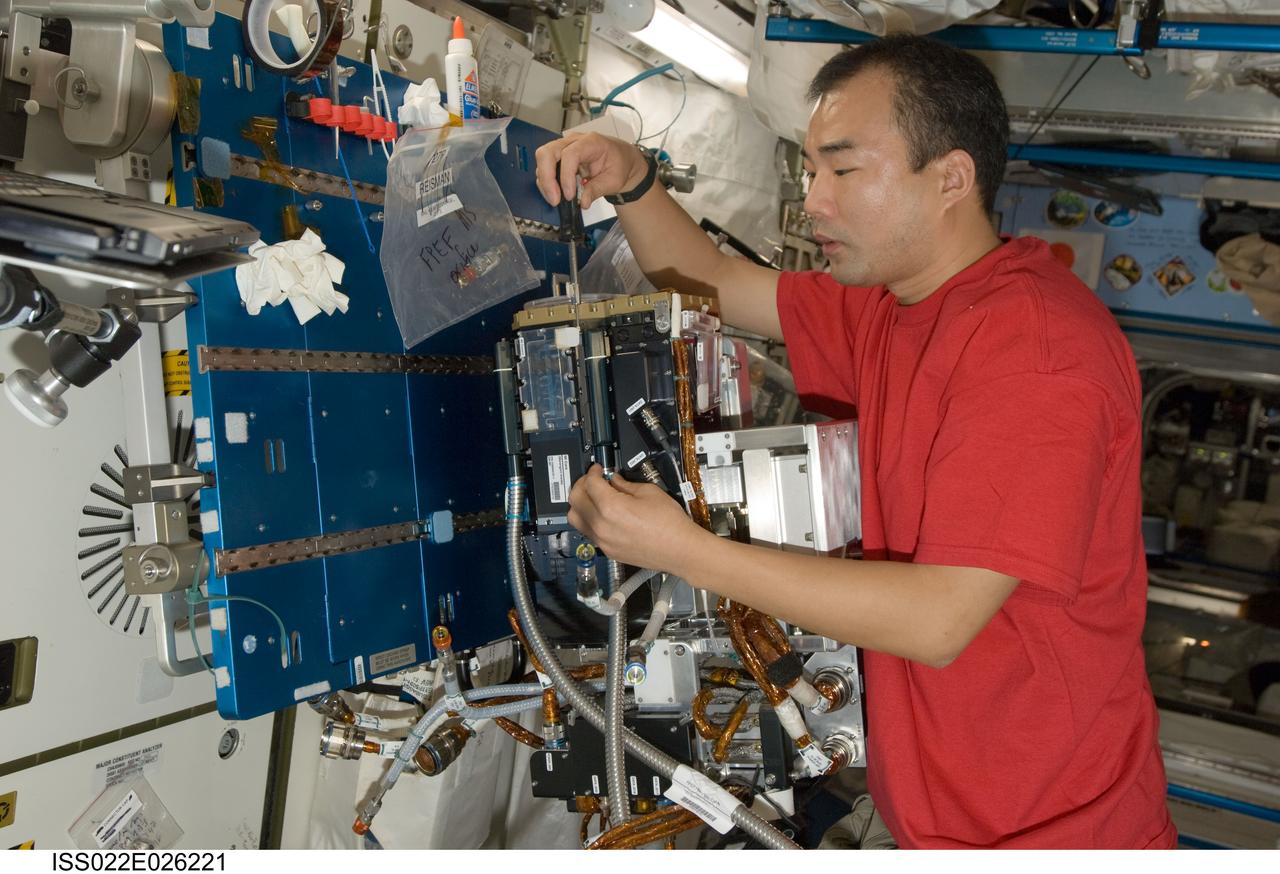

ISS022-E-026221 (15 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, services the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
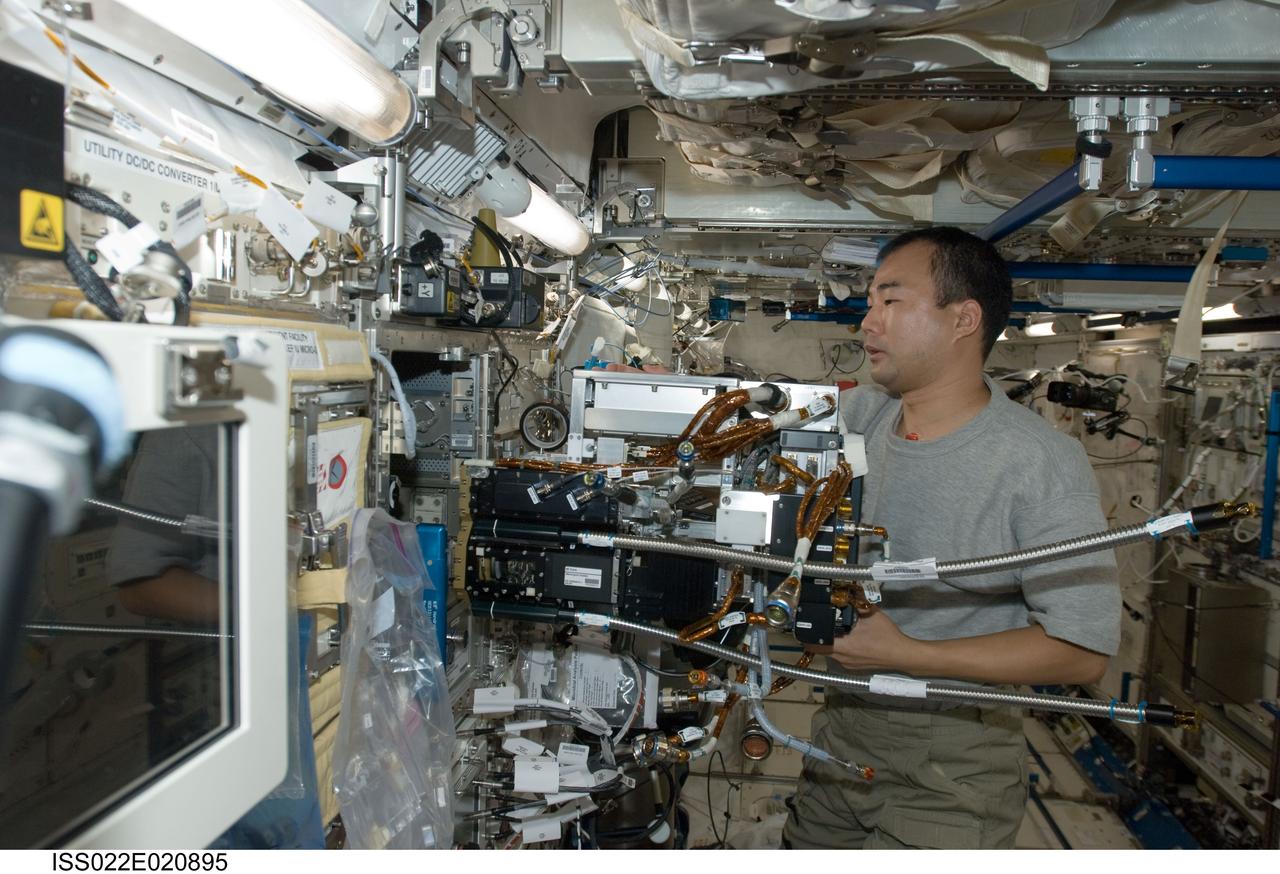

ISS022-E-020895 (11 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.

ISS028-E-048923 (13 Sept. 2011) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, Expedition 28 flight engineer, works with the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
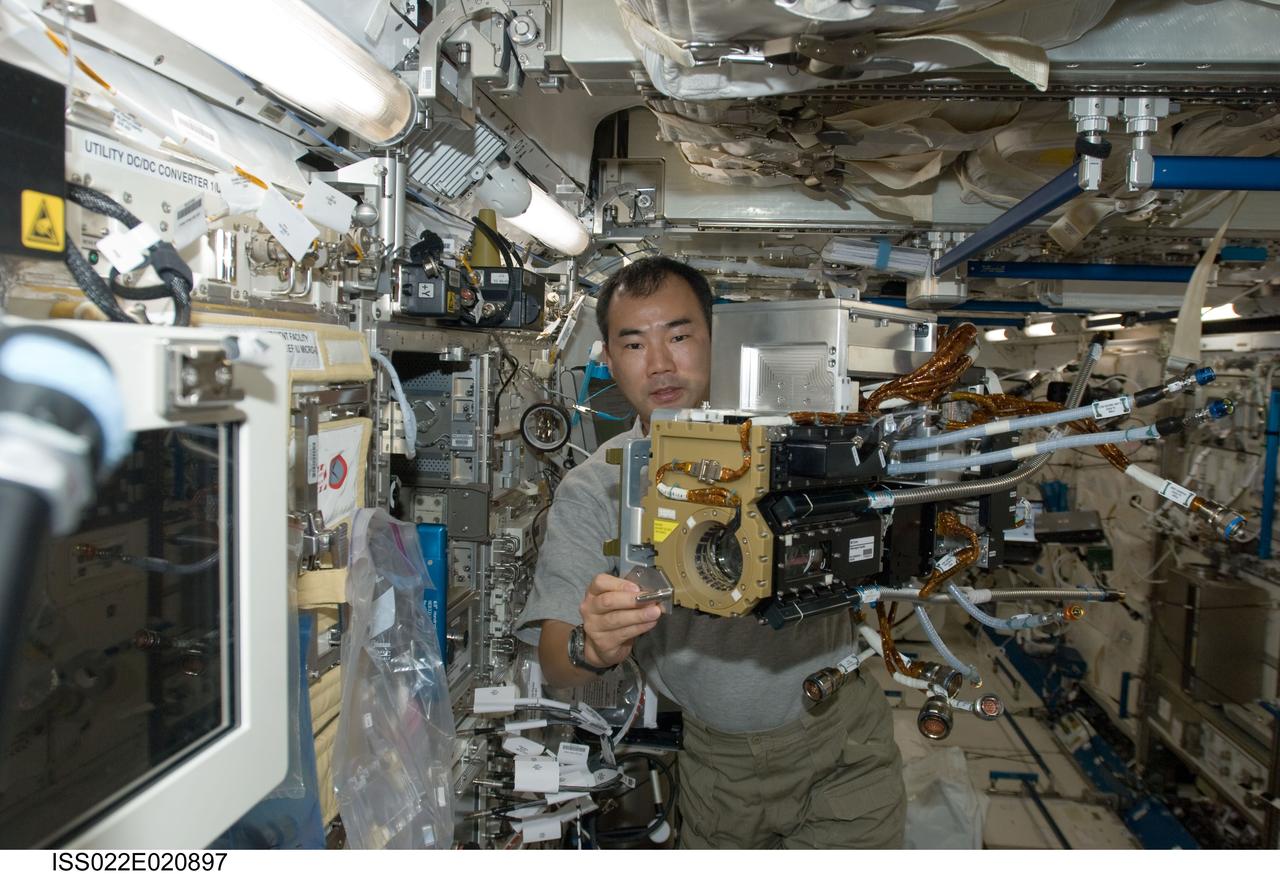

ISS022-E-020897 (11 Jan. 2010) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, Expedition 22 flight engineer, works with Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. The Marangoni convection experiment in the FPEF examines fluid tension flow in micro-G.
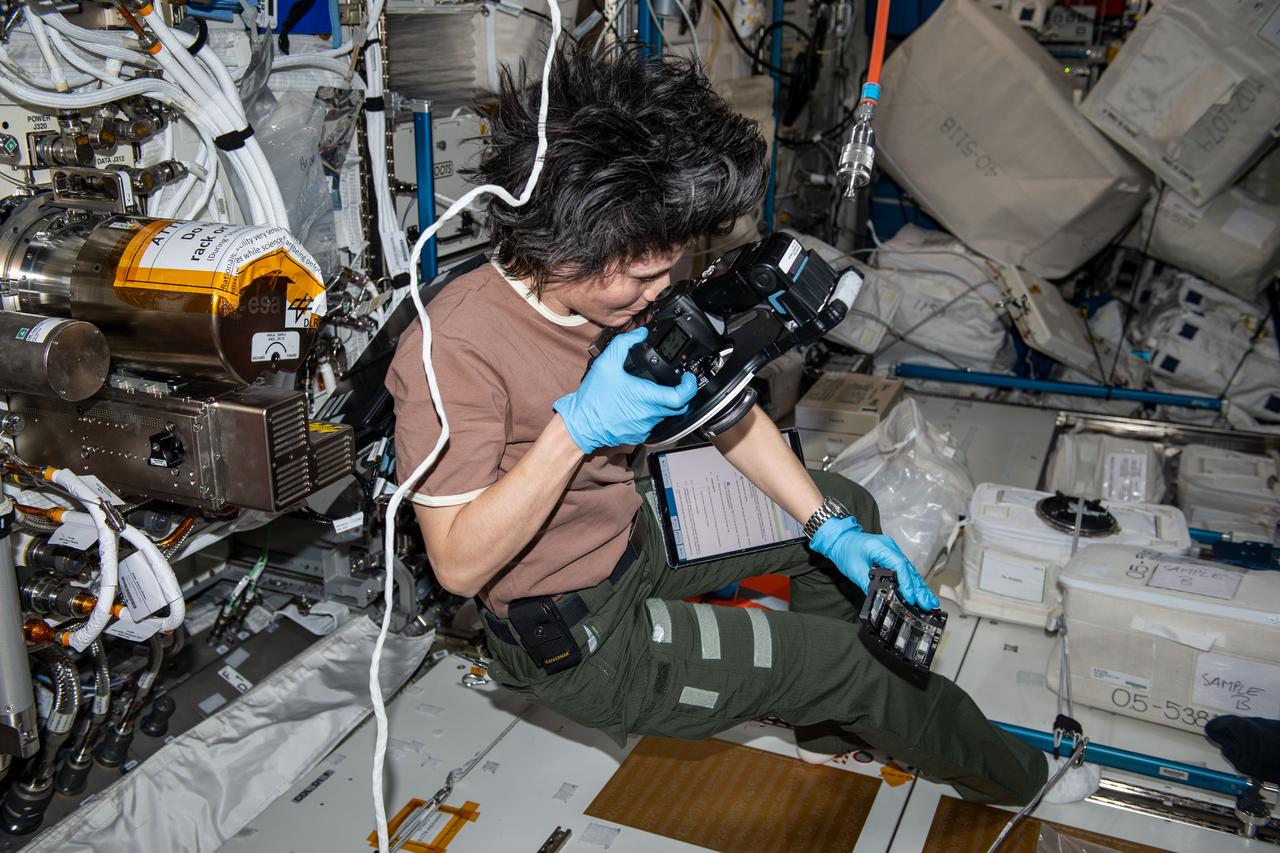

iss067e253397 (Dec. 2, 2024) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 67 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti photographs and exchanges samples for the Fluids Science Laboratory Soft Matter Dynamics space physics experiment aboard the Intenational Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. The microgravity environment enables the observation of "wet" foams and the study of rearrangement phenomena, such as coarsening and coalescence, disentangled from drainage issues caused by Earth's gravity. Results may benefit Earth and space industries.
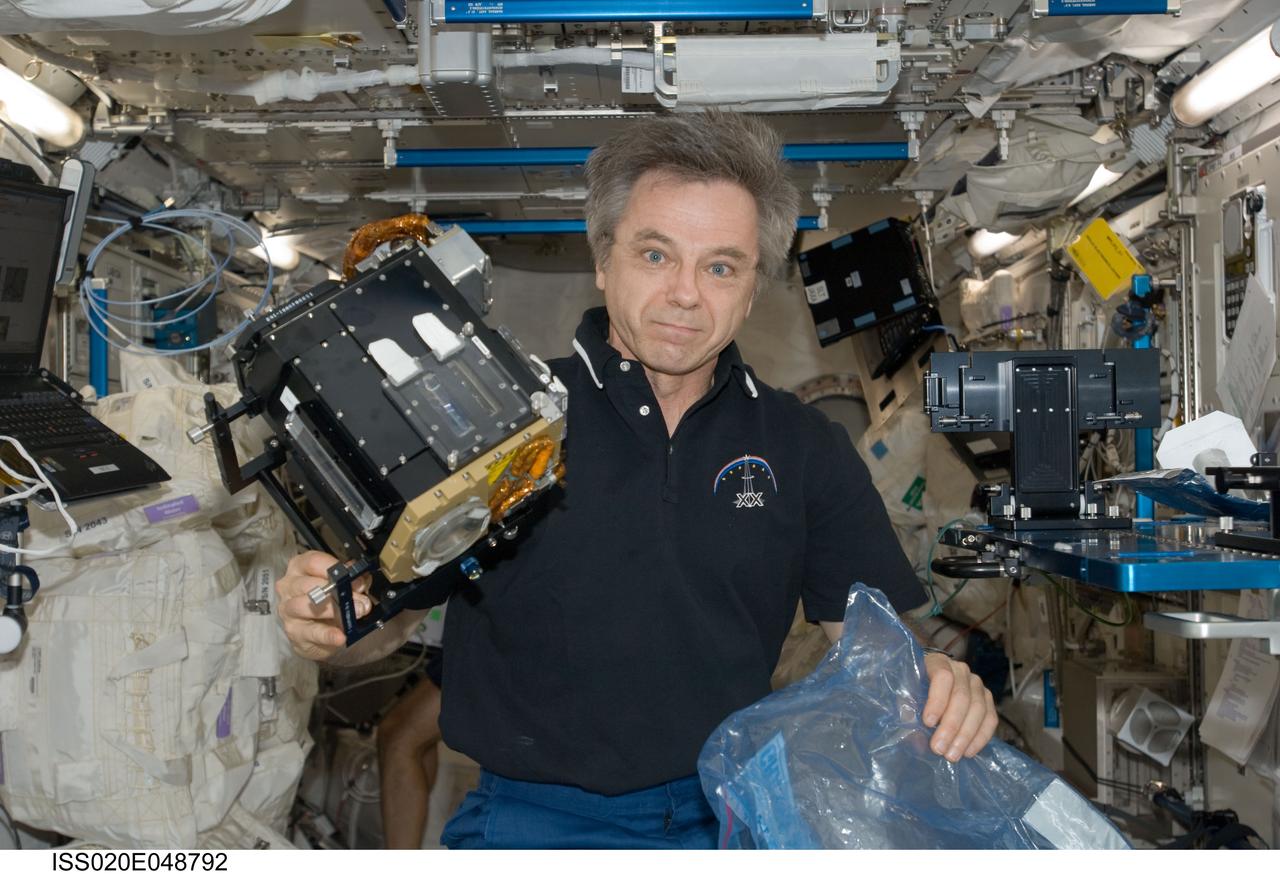

ISS020-E-048792 (7 Oct. 2009) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut Robert Thirsk, Expedition 20/21 flight engineer, holds Fluid Physics Experiment Facility/Marangoni Surface (FPEF MS) Core hardware in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
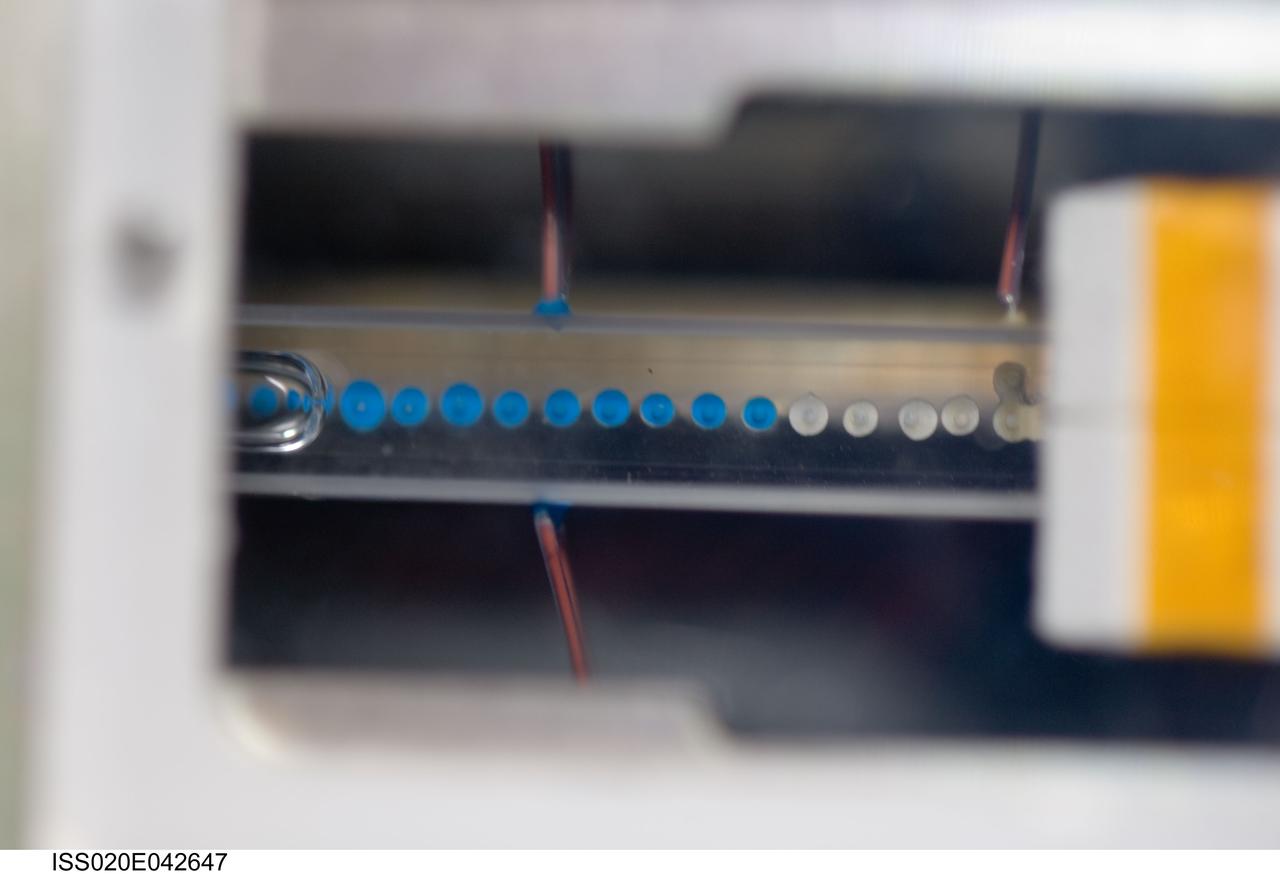

iss020e042647 (Sep. 26, 2009) --- Constrained Vapor Bubble (CVB) module with the science sample on the Fluids Integrated Rack (FIR). CVB aims to better understand the physics of evaporation and condensation to help create an efficient and highly reliable cooling equipment for space, where replacement parts are difficult or impossible.
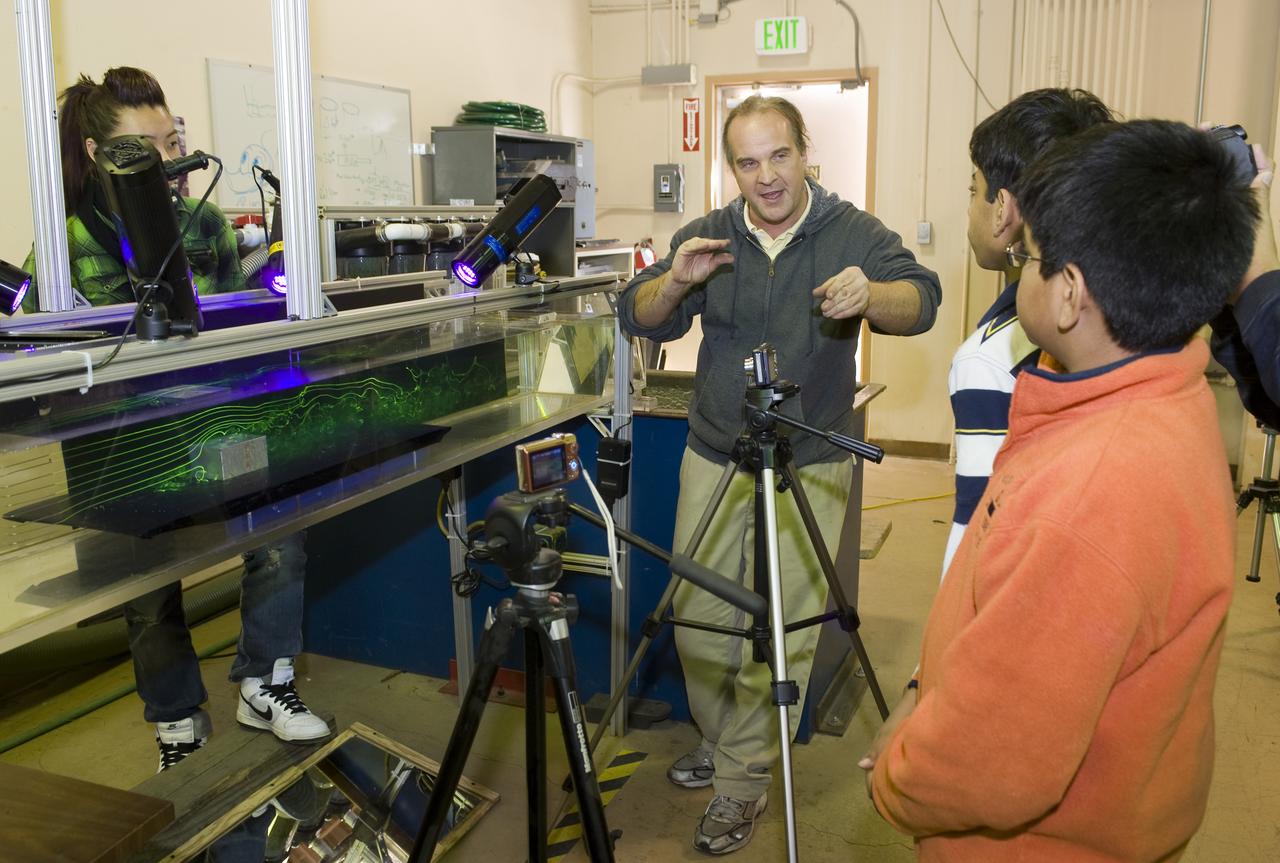

Students, Ajay Ramesh and Prithvi Aiyaswamy in 7th grade, Chaboya Middle School, San Jose, have entered the Intel Inernational Science Fair (May 2010) They are here at the Ames Research center to test the drag of race cars in the Fluid Mechanics Lab (FML) with the guidance of Kurt Long of the Experimental Aero-Physics Branch.
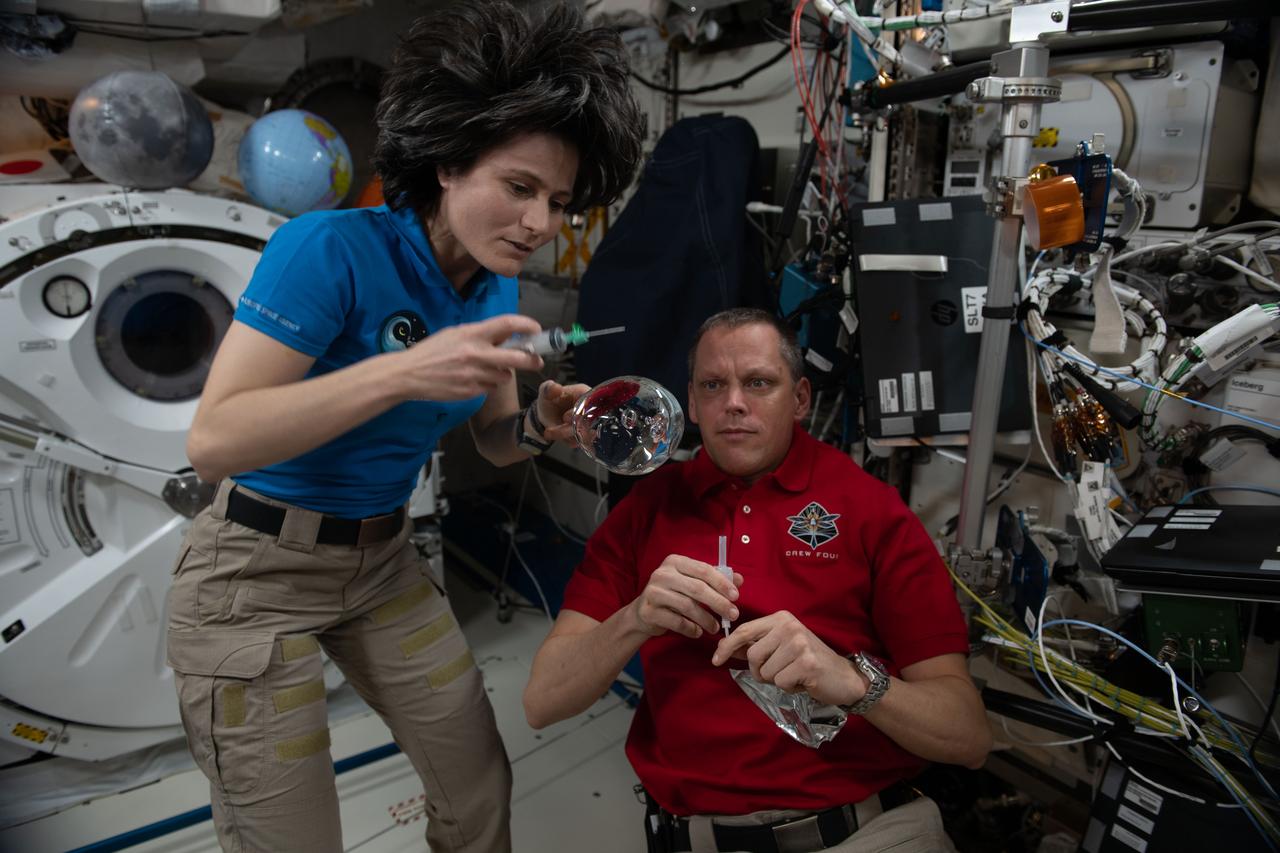

iss068e006399 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- Expedition 68 Flight Engineers Samantha Cristoforetti of ESA (European Space Agency) and Bob Hines of NASA have fun with fluid physics as they observe the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
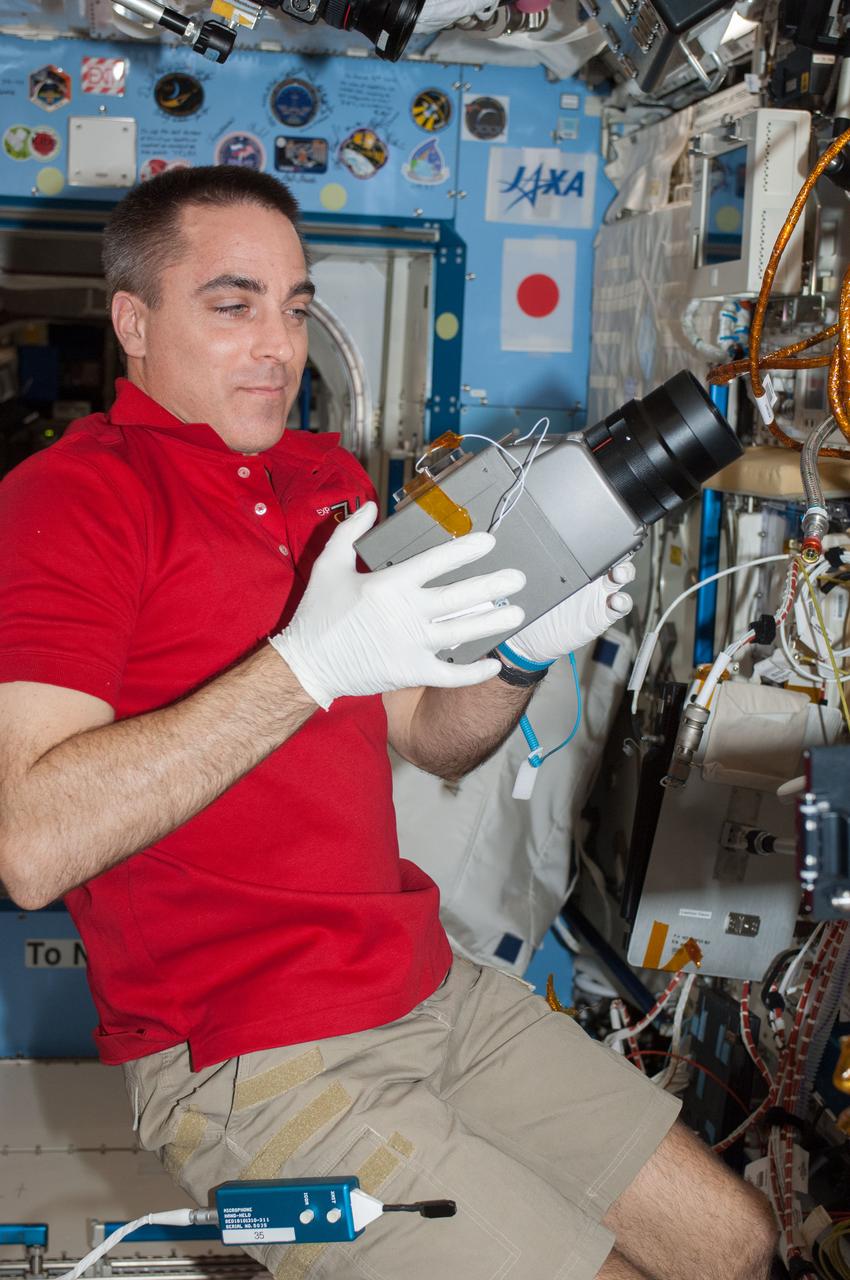

ISS036-E-025489 (24 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Marangoni Inside experiment in the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) which is part of a Japanese science rack in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory.
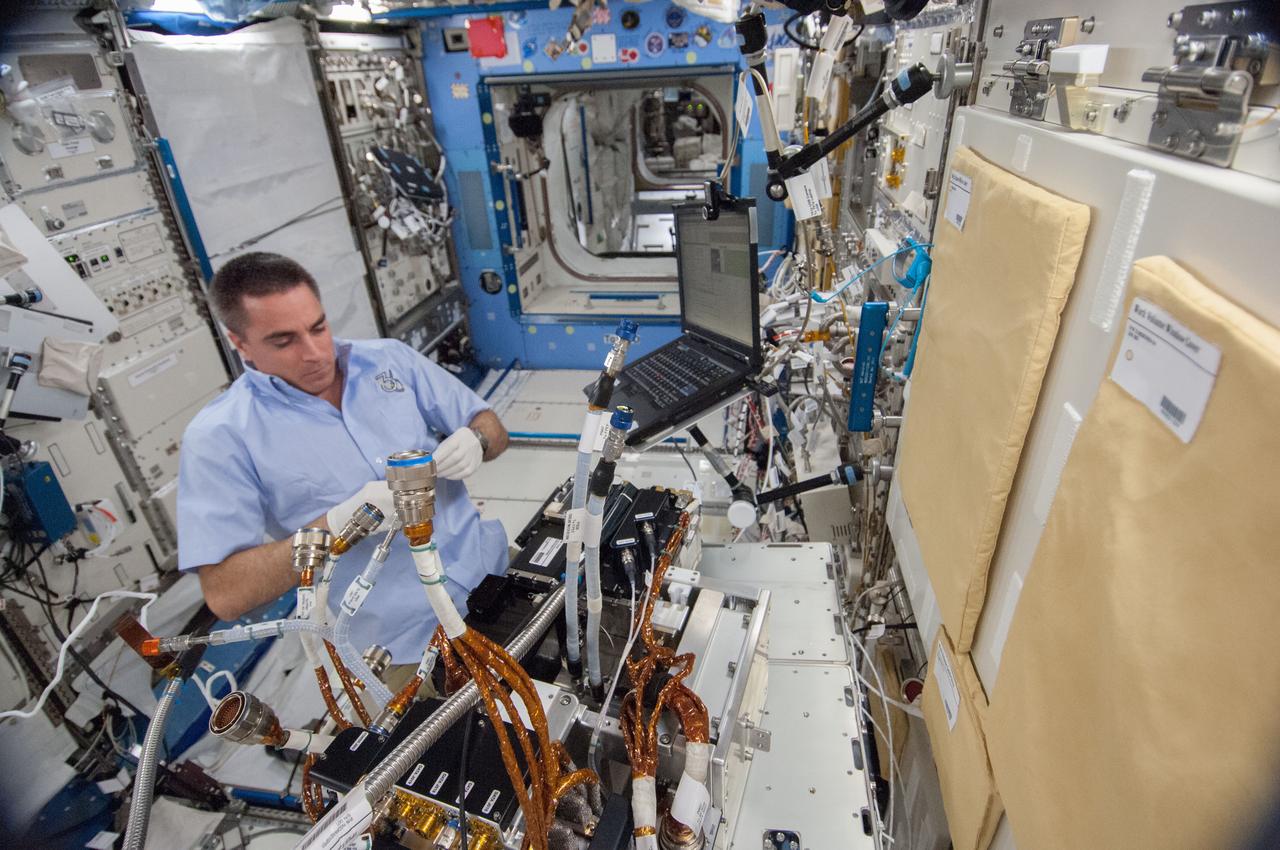

ISS036-E-023070 (23 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Inside (MI) from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
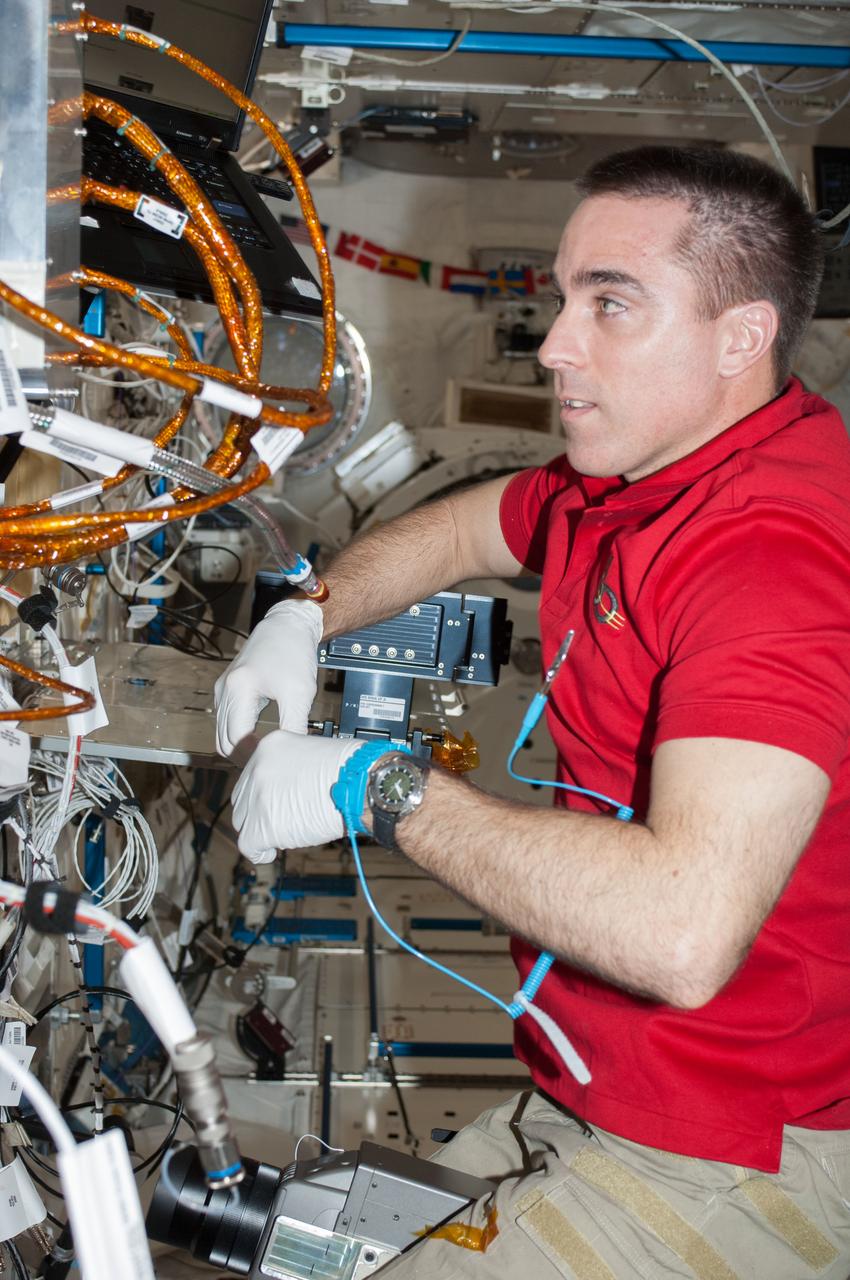

ISS036-E-025484 (24 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Marangoni Inside experiment in the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) which is part of a Japanese science rack in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory.
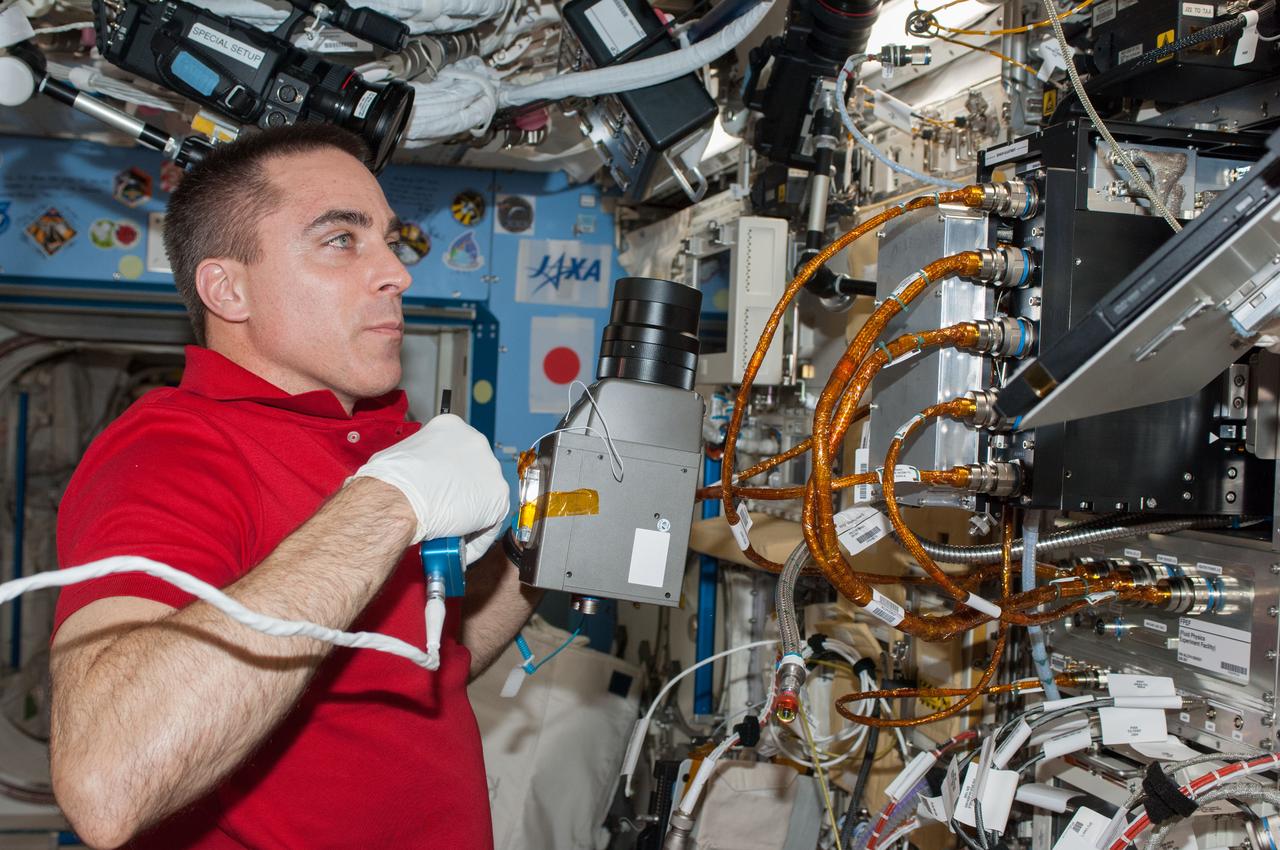

ISS036-E-025491 (24 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Marangoni Inside experiment in the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) which is part of a Japanese science rack in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory.
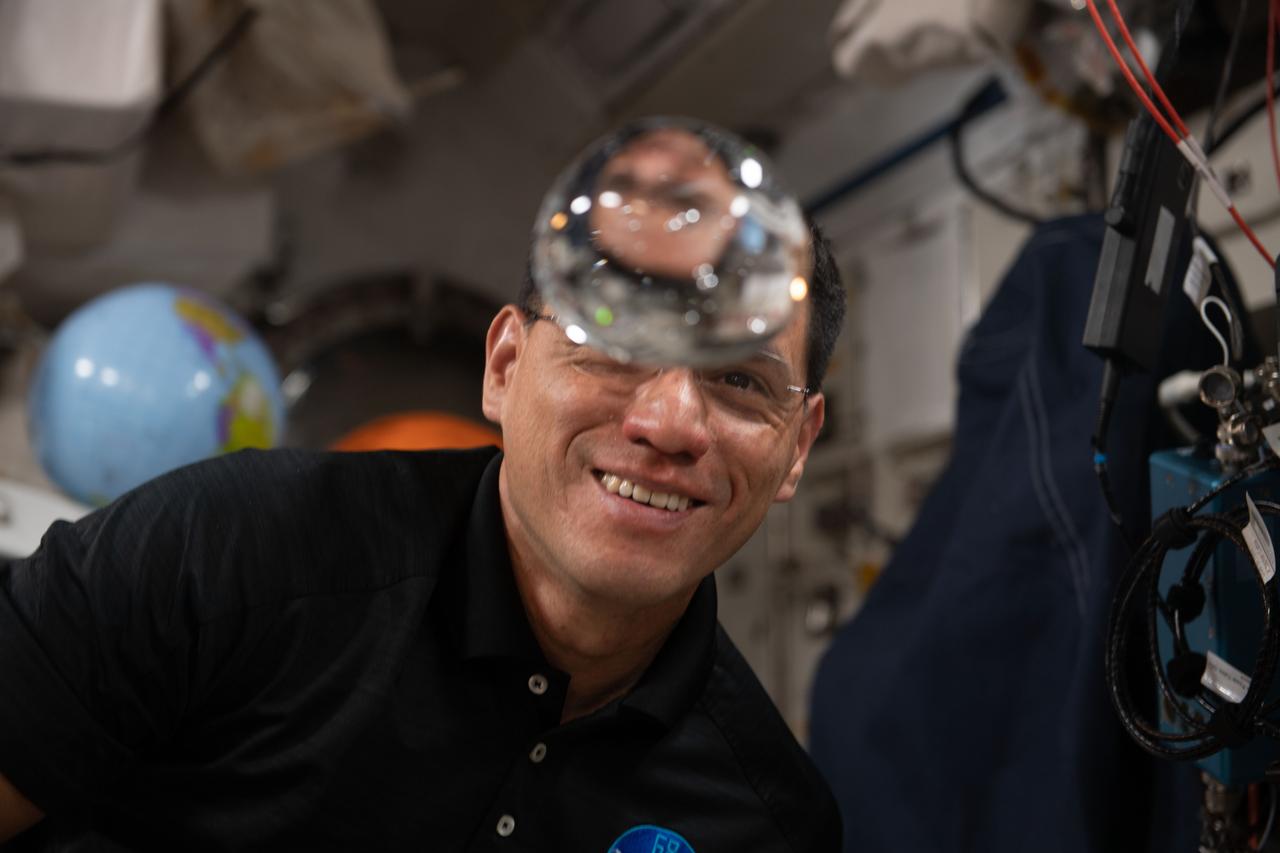

iss068e006386 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Frank Rubio has fun with fluid physics as he observes the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
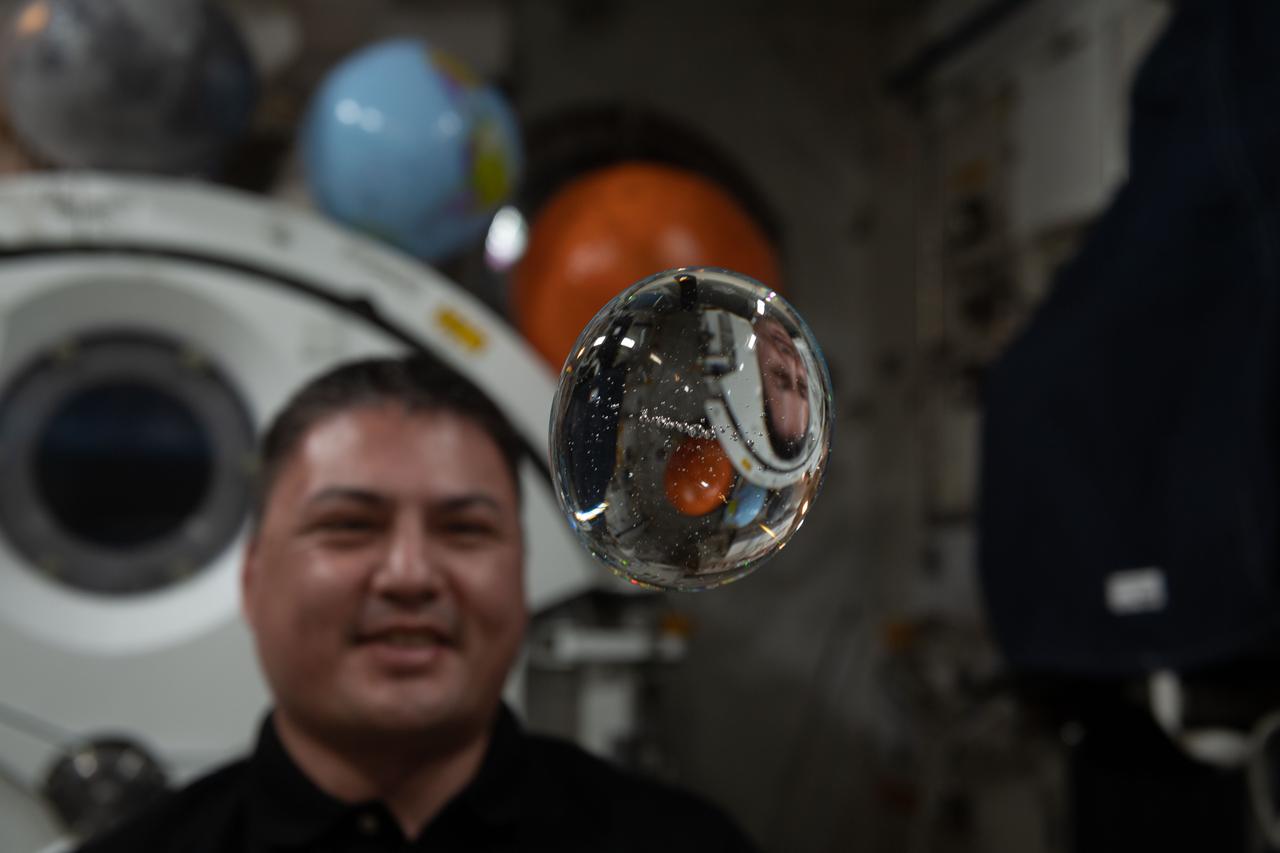

iss068e006306 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Kjell Lindgren has fun with fluid physics as he observes the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
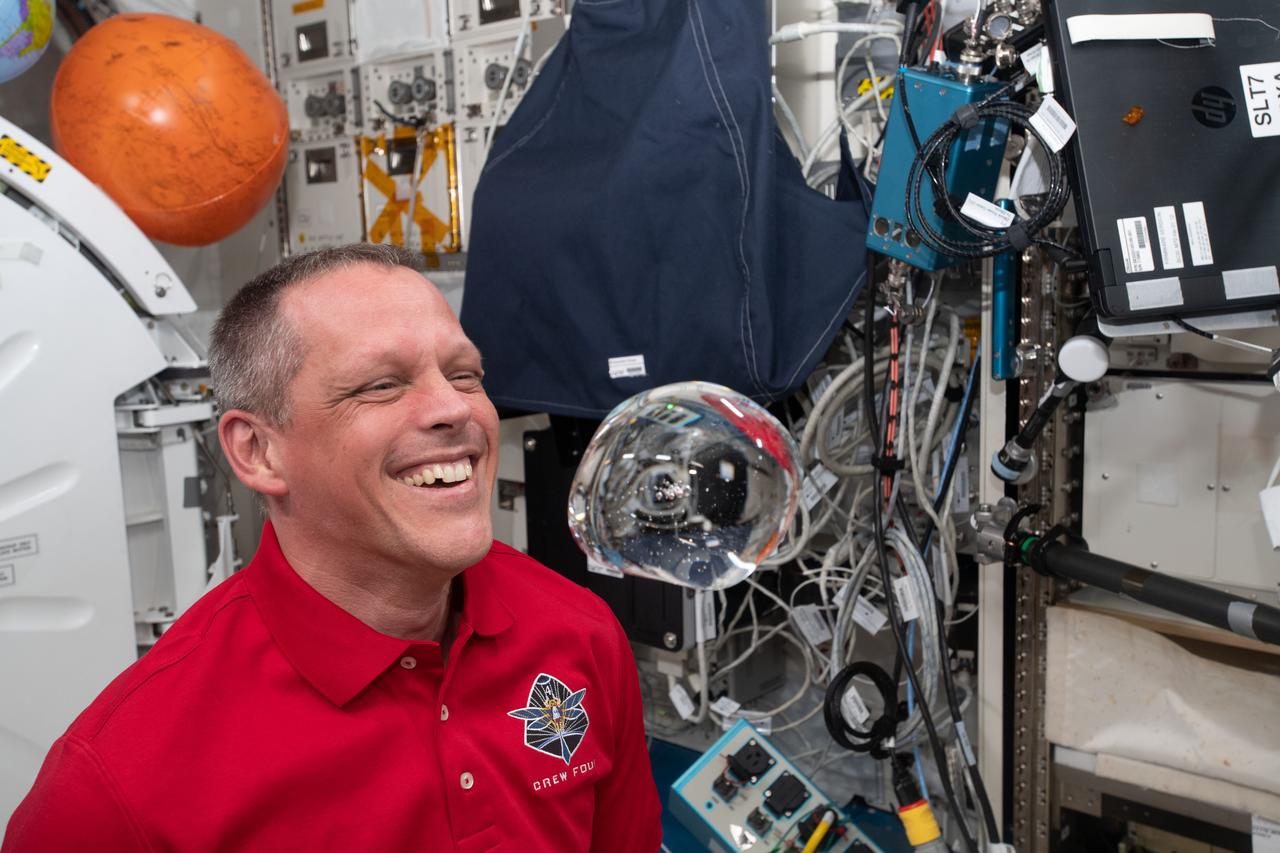

iss068e005874 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Bob Hines has fun with fluid physics as he observes the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
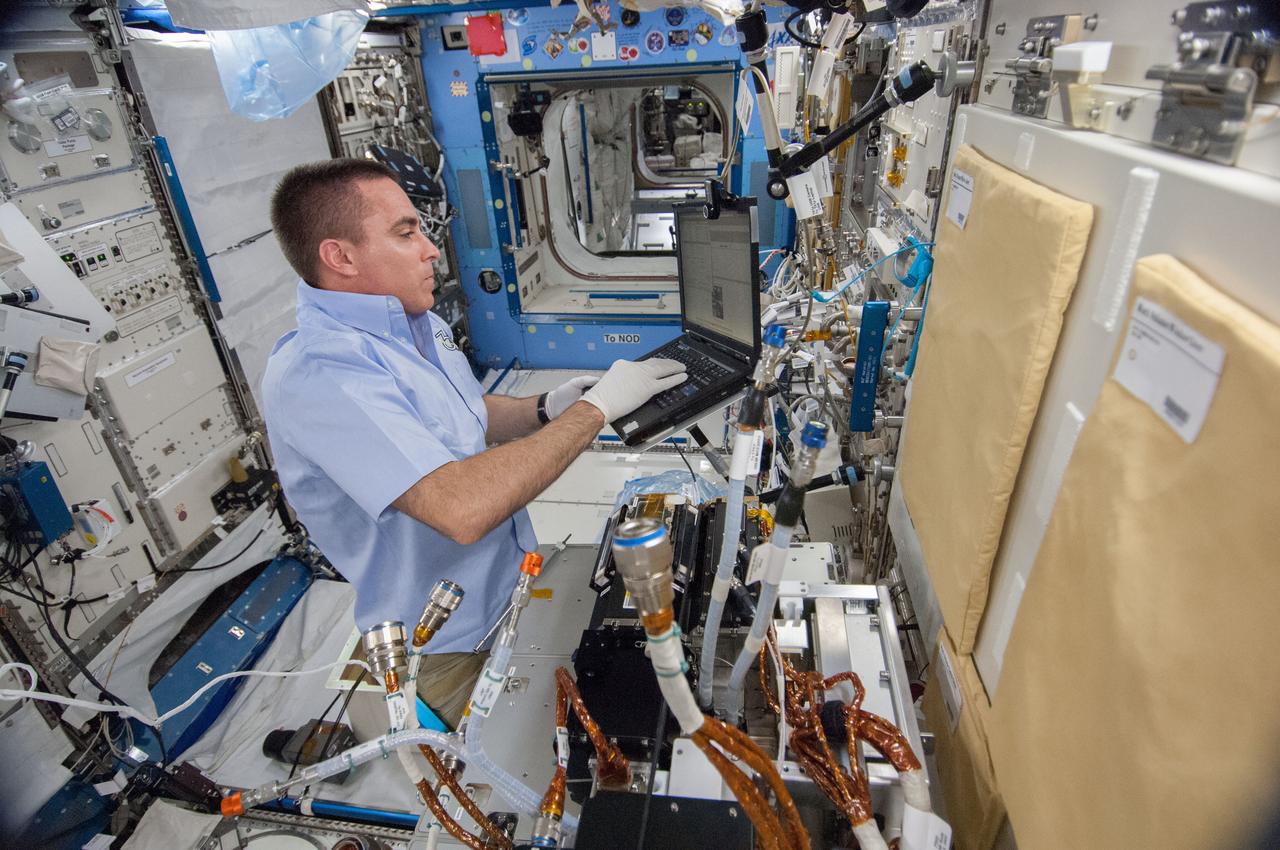

ISS036-E-023083 (23 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Inside (MI) from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
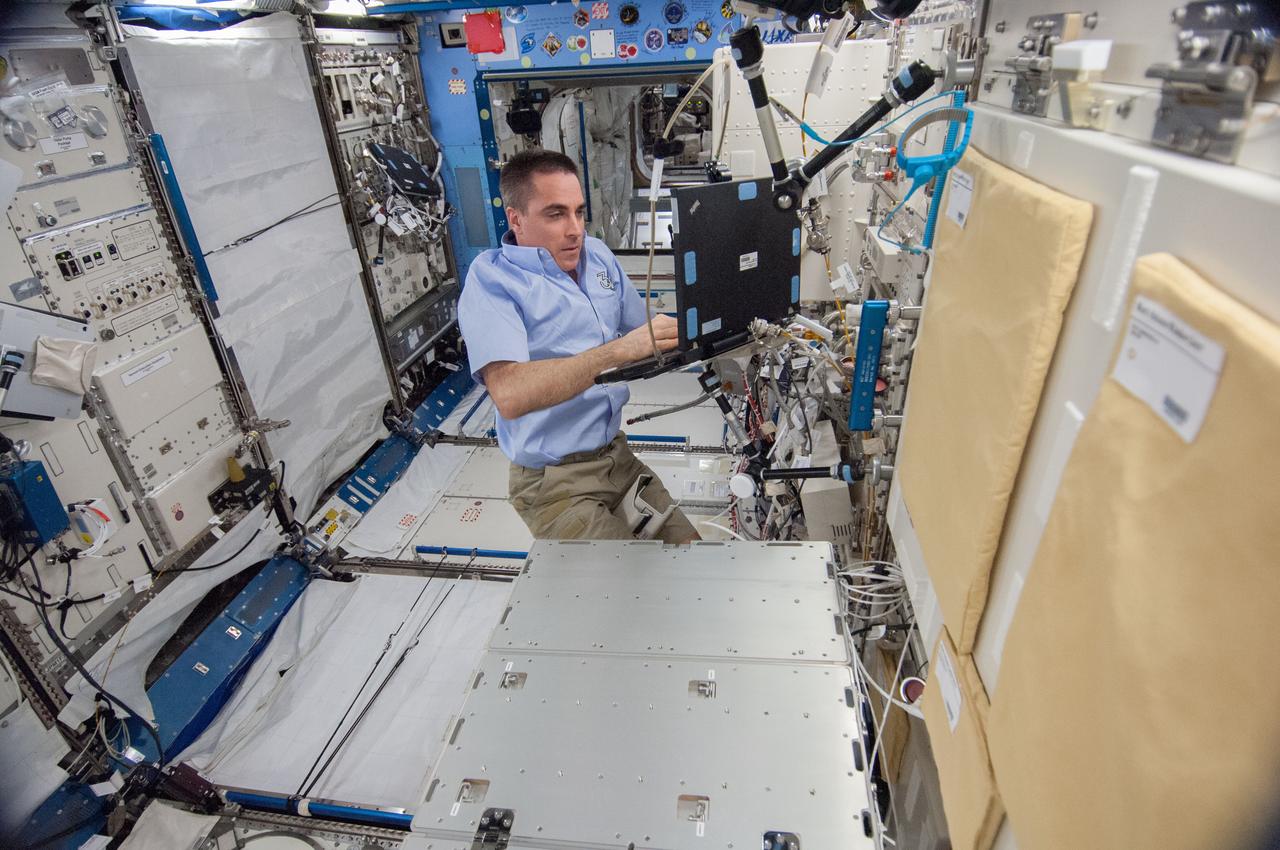

ISS036-E-023006 (23 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, uses a computer as he works to remove the Marangoni Inside (MI) from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
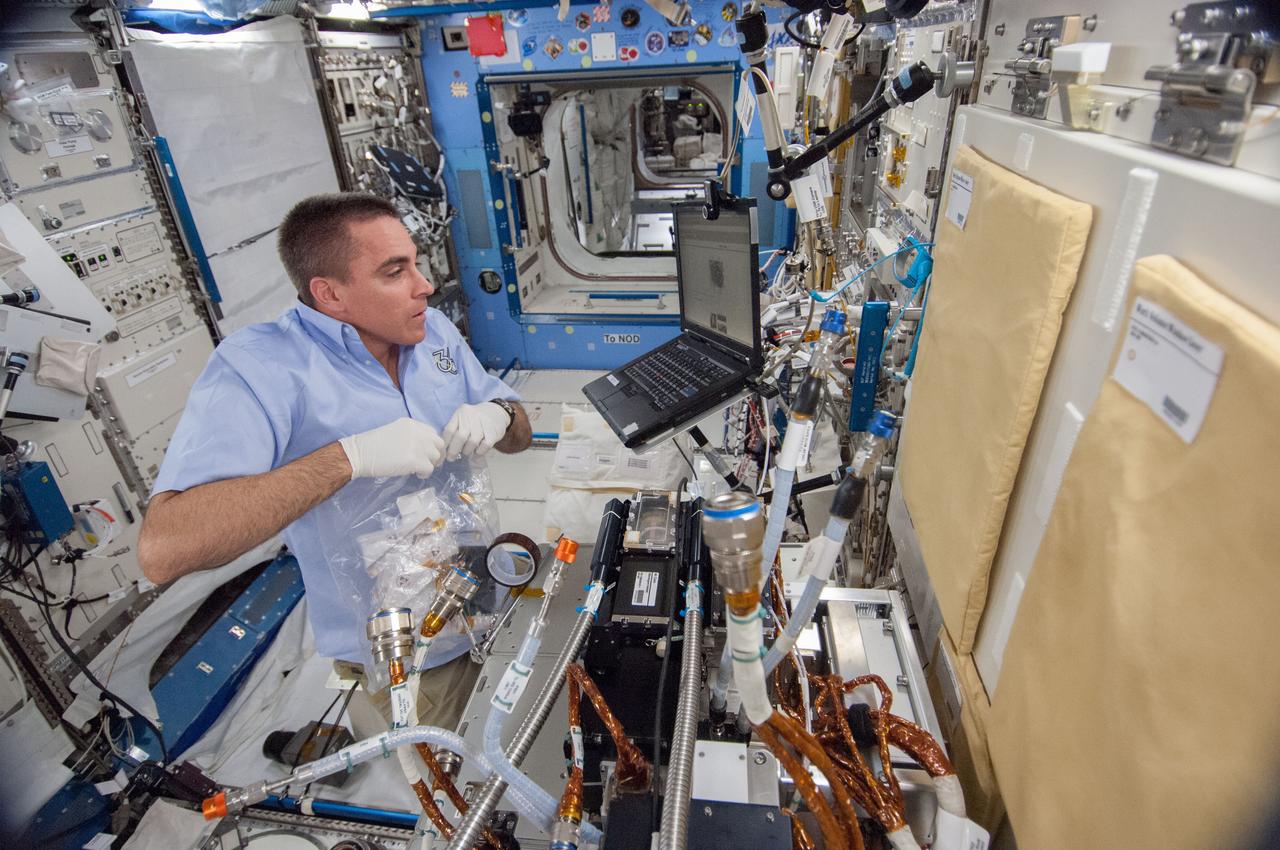

ISS036-E-023061 (23 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works to remove the Marangoni Inside (MI) from the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
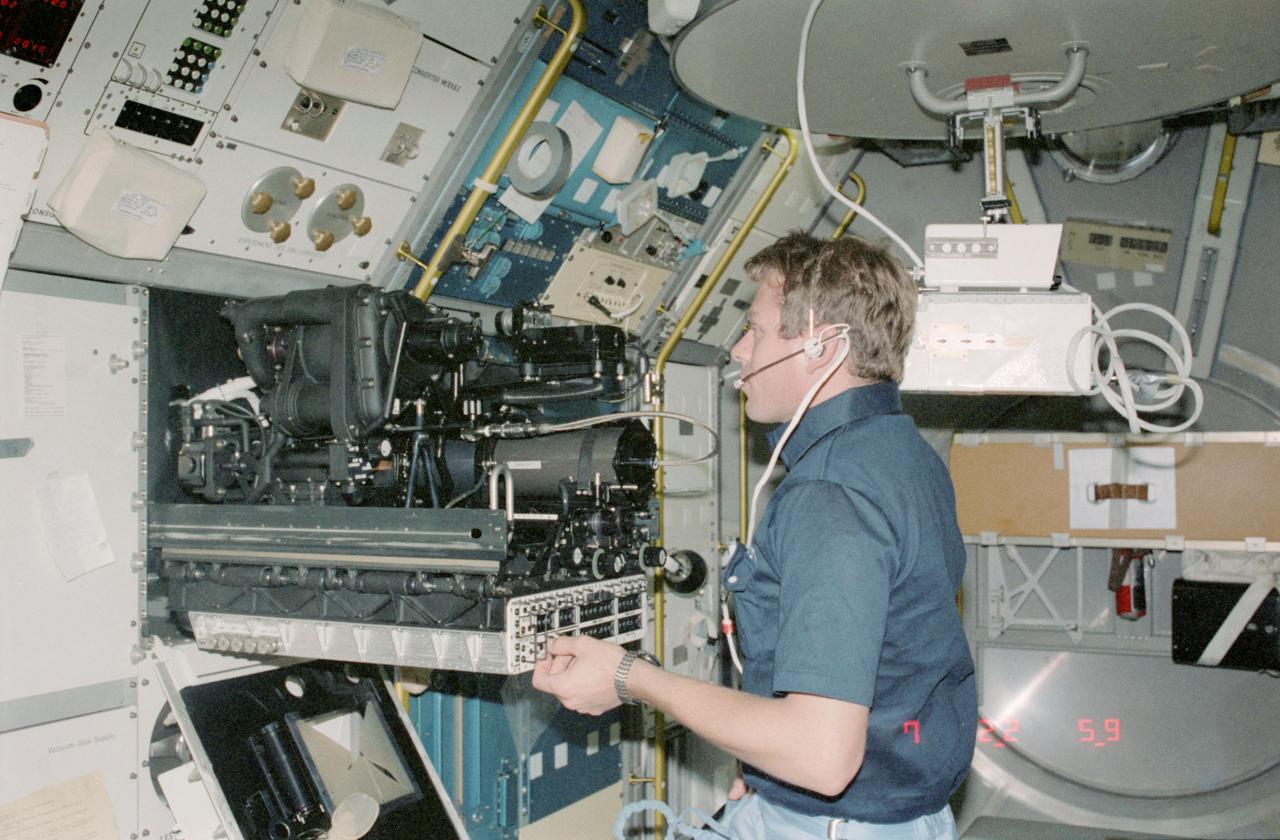

STS009-125-427 (28 Nov 1983) --- Payload Specialist Byron K. Lichtenberg carries out an experiment at the fluid physics module on the busy materials science double rack facility. Two beverage containers can be seen just above the biomedical engineer's head.
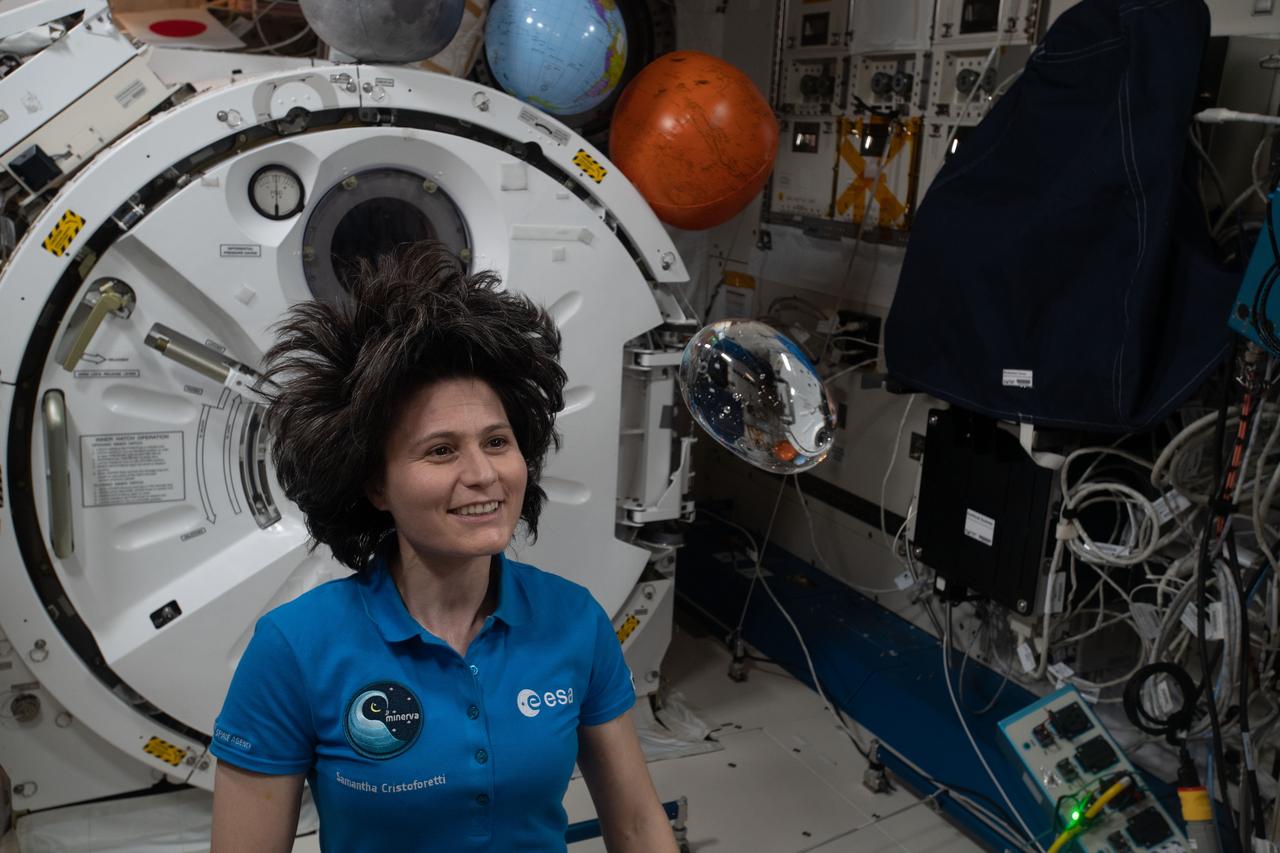

iss068e005884 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti has fun with fluid physics as she observes the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
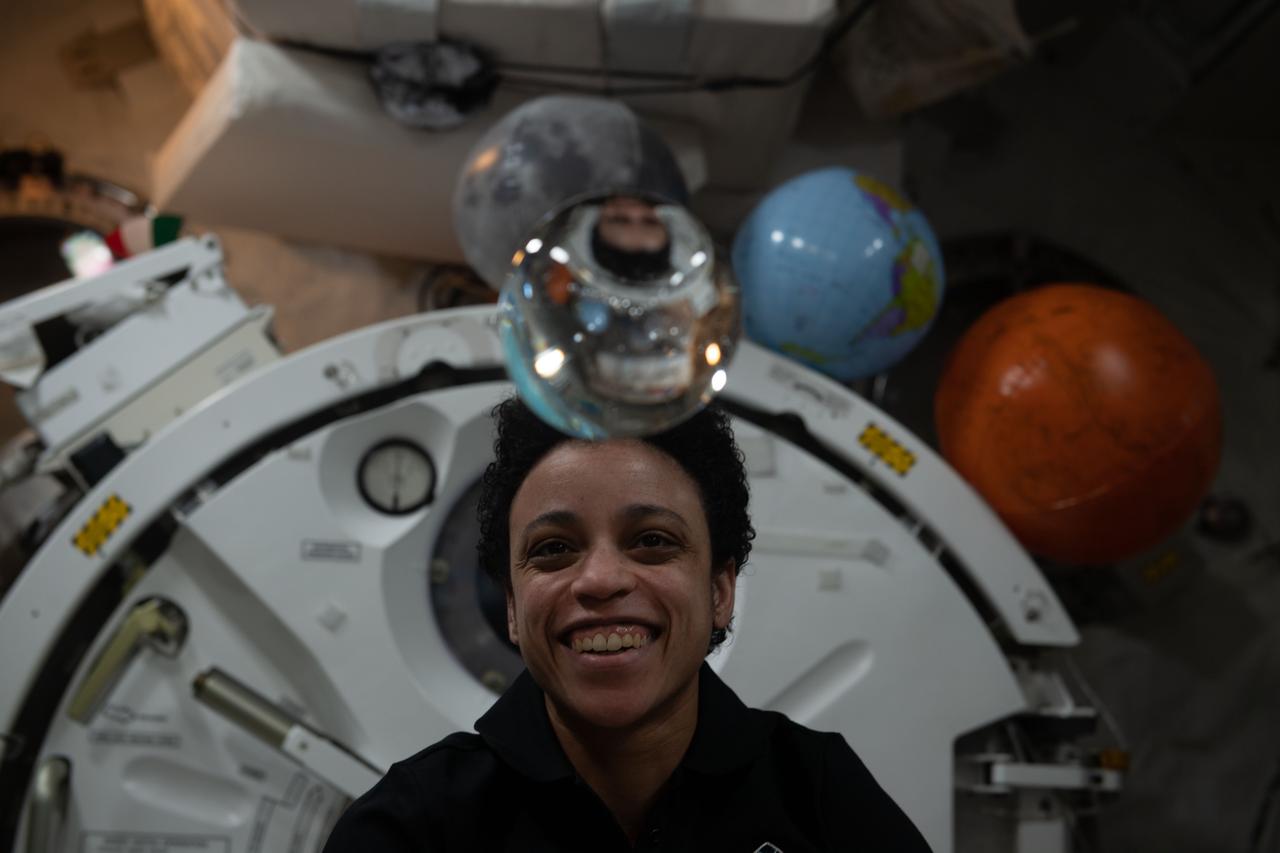

iss068e006271 (Oct. 1, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Jessica Watkins has fun with fluid physics as she observes the behavior of a free-flying water bubble inside the International Space Station's Kibo laboratory module.
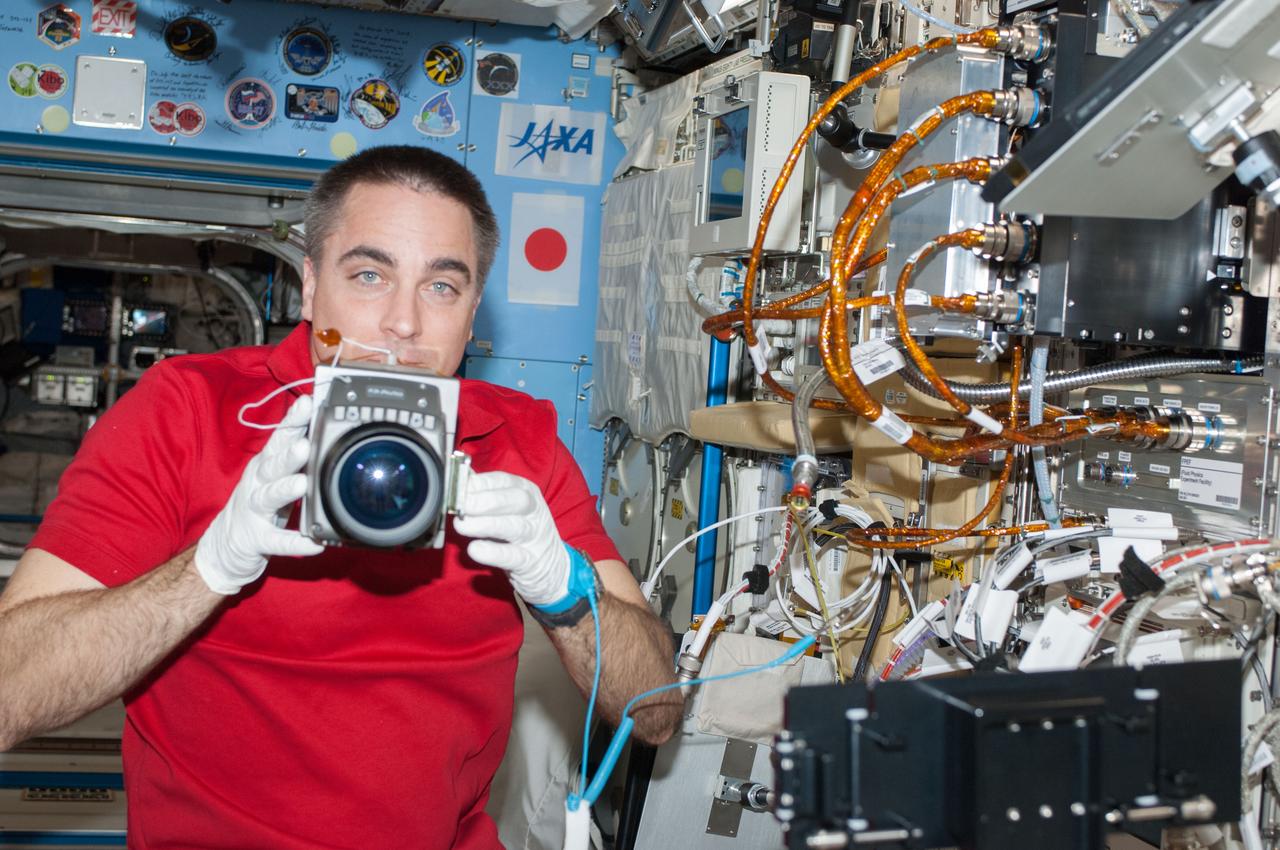

ISS036-E-025487 (24 July 2013) --- NASA astronaut Chris Cassidy, Expedition 36 flight engineer, performs in-flight maintenance on the Marangoni Inside experiment in the Fluid Physics Experiment Facility (FPEF) which is part of a Japanese science rack in the International Space Station?s Kibo laboratory.

iss067e378812 (Sept. 21, 2022) --- Expedition 67 Flight Engineer and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti works inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox removing hardware that supported the Ring Sheared Drop experiment. The fluid physics study observes the formation of destructive protein clusters that may be responsible for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
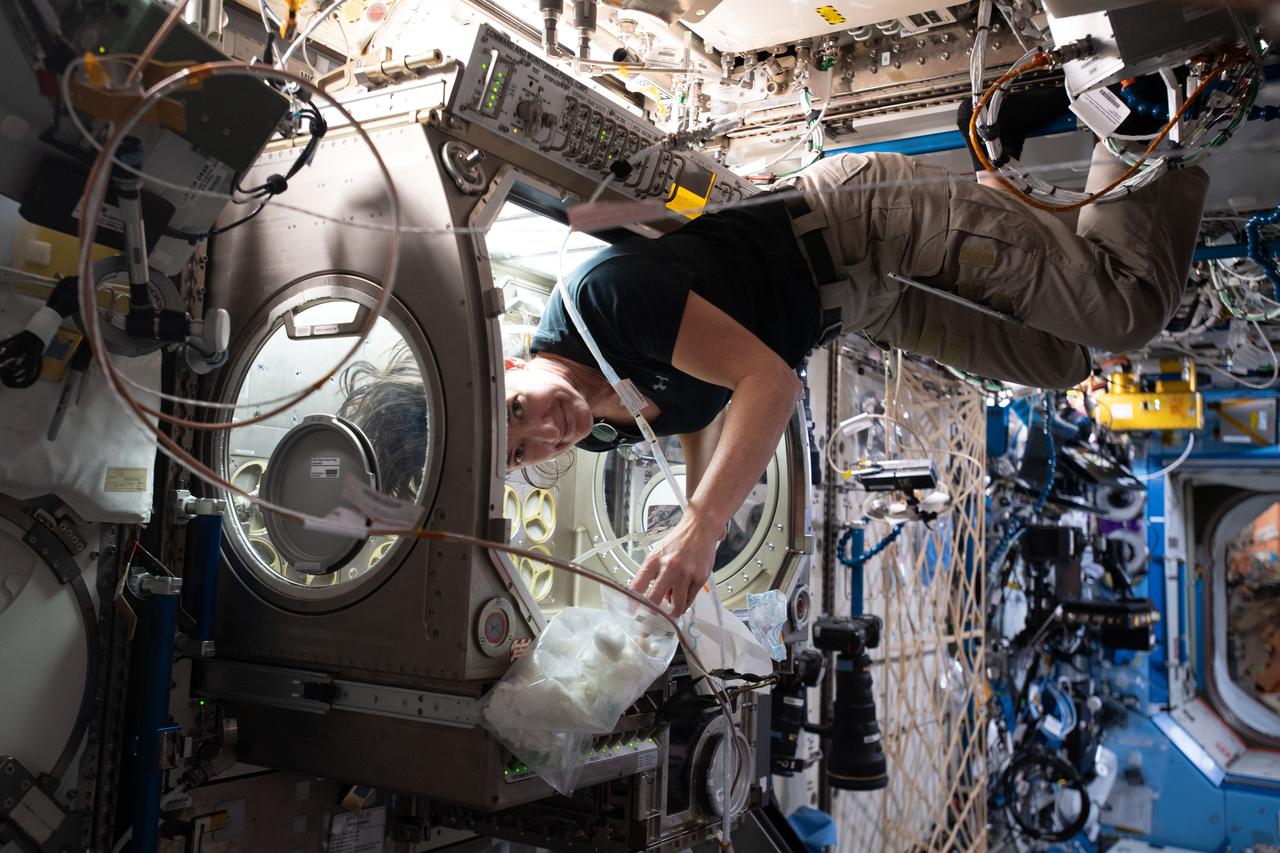

iss065e017714 (May 3, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur cleans the inside of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG). Located in the International Space Station's U.S. Destiny laboratory module, the MSG supports a variety of research disciplines including biotechnology, combustion science, fluid physics, fundamental physics, and materials science.
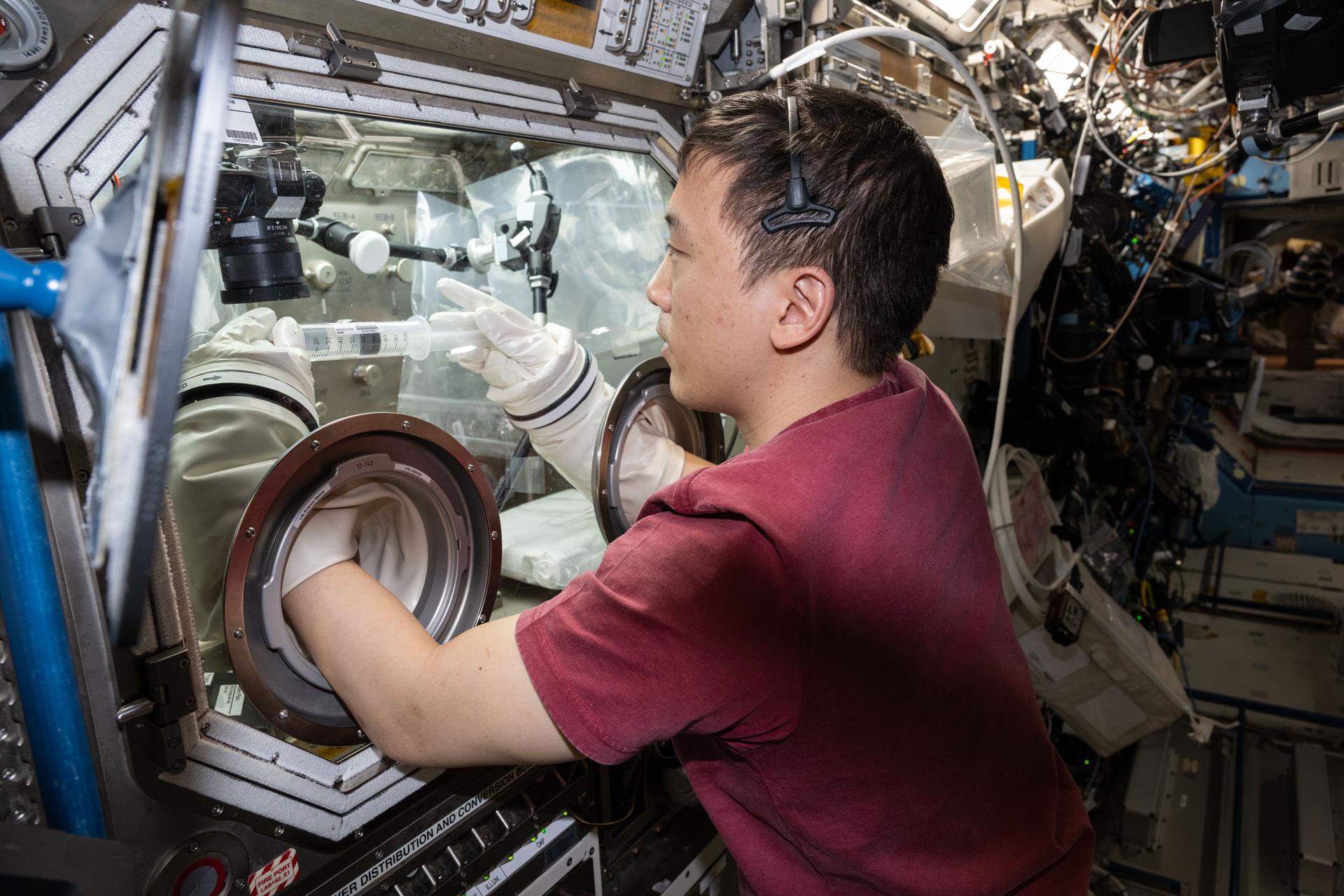

iss073e0917782 (Oct. 23, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim conducts research operations for the Fluid Particles investigation inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The fluid physics experiment may help researchers understand how particles in a liquid interface come together to form larger structures or clusters in microgravity advancing fire suppression, lunar dust control, and plant growth in space. Earth benefits may include insights into pollen behavior, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transfer during storms.
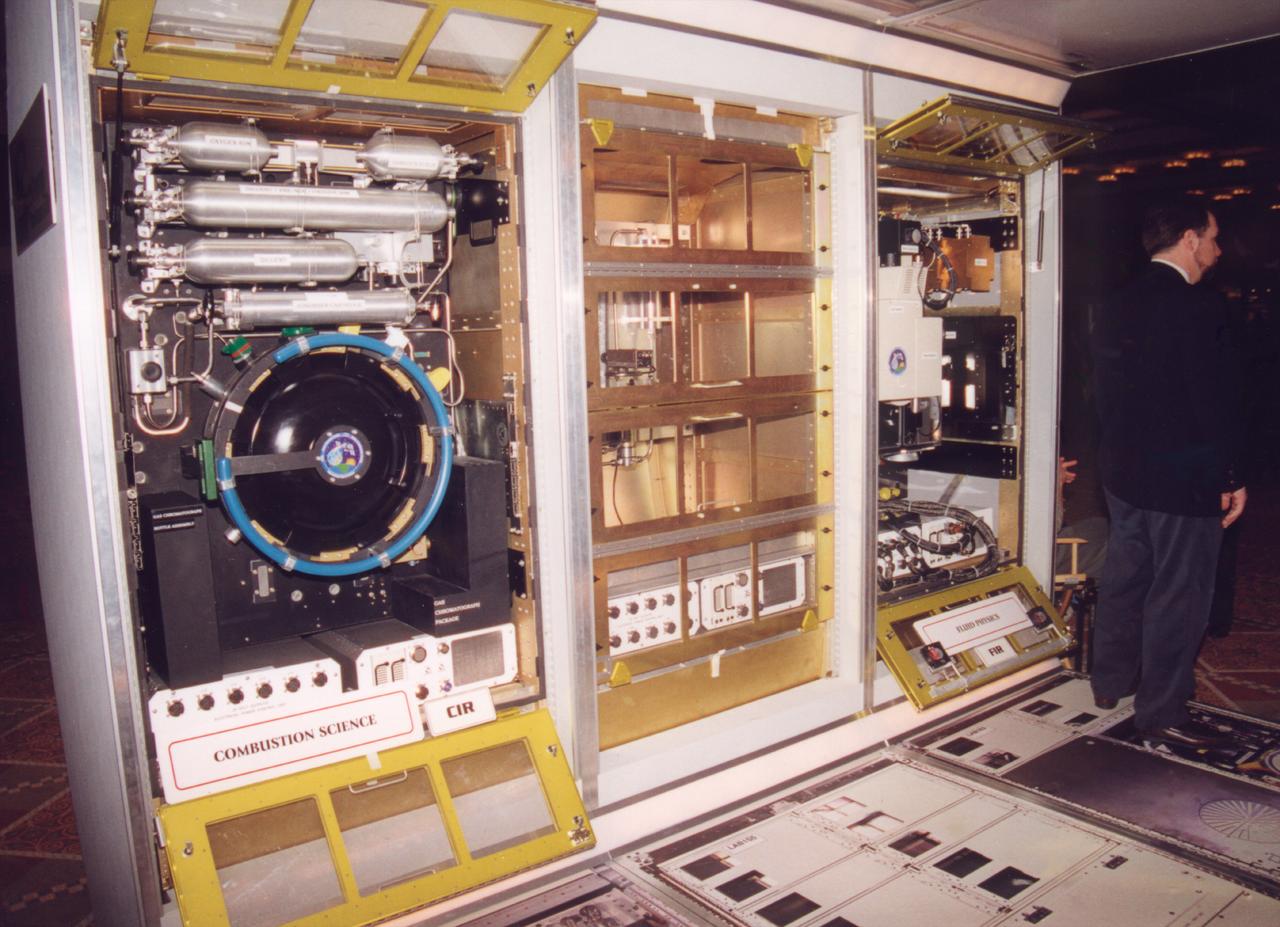
The Fluids and Combustion Facility (FCF) is a modular, multi-user facility to accommodate microgravity science experiments on board Destiny, the U.S. Laboratory Module for the International Space Station (ISS). The FCF will be a permanet facility aboard the ISS, and will be capable of accommodating up to ten science investigations per year. It will support the NASA Science and Technology Research Plans for the International Space Station (ISS) which require sustained systematic research of the effects of reduced gravity in the areas of fluid physics and combustion science. From left to right are the Combustion Integrated Rack, the Shared Rack, and the Fluids Integrated Rack. The FCF is being developed by the Microgravity Science Division (MSD) at the NASA Glenn Research Center. (Photo Credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to 1 meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No.1 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one-meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 3 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)

An experiment vehicle plunges into the deceleration pit at the end of a 5.18-second drop in the Zero-Gravity Research Facility at NASA's Glenn Research Center. The Zero-Gravity Research Facility was developed to support microgravity research and development programs that investigate various physical sciences, materials, fluid physics, and combustion and processing systems. Payloads up to one meter in diameter and 455 kg in weight can be accommodated. The facility has a 145-meter evacuated shaft to ensure a disturbance-free drop. This is No. 4 of a sequence of 4 images. (Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center)
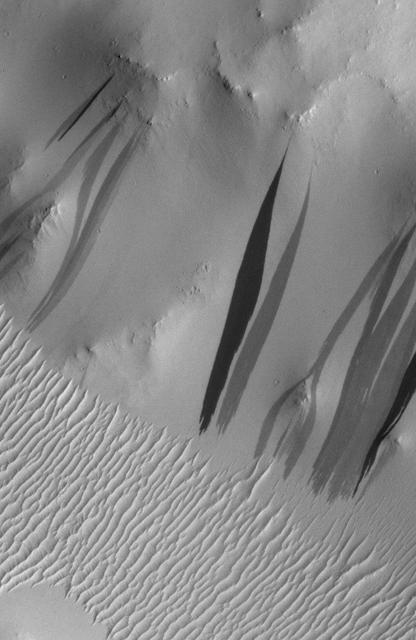

The light-toned deposits that formed in two gully sites on Mars during the Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC) mission in the 1999 to 2005 period are considered to be the result of sediment transport by a fluid with the physical properties of liquid water. The young, light-toned gully deposits were found in a crater in Terra Sirenum (see PIA09027 or MOC2-1618) and in a crater east of the Hellas basin in the Centauri Montes region (see PIA09028 or MOC2-1619). In their study of how the light-toned gully deposits may have formed, the MOC team considered their resemblance to light- and dark-toned slope streaks found elsewhere on Mars. Slope streaks are most commonly believed to have formed by downslope movement of extremely dry, very fine-grained dust, through processes thought by some to be analogous to terrestrial snow avalanche formation. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA09030
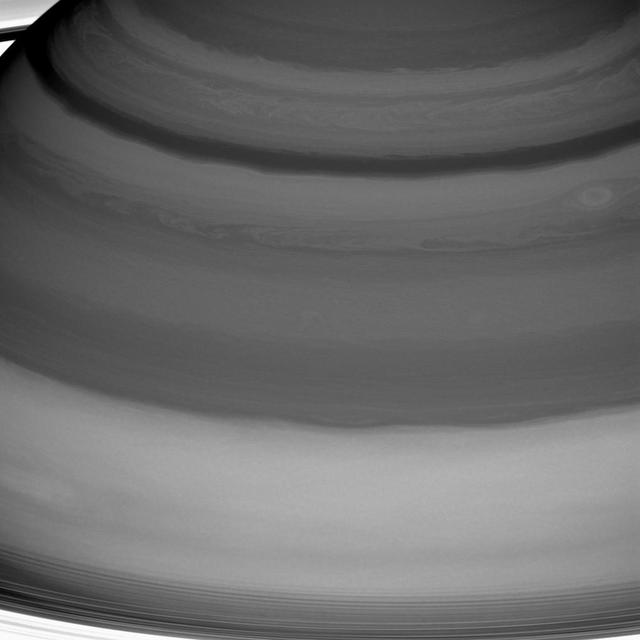

Saturn's clouds are full of raw beauty, but they also represent a playground for a branch of physics called fluid dynamics, which seeks to understand the motion of gases and liquids. Saturn's lack of a solid planetary surface (as on Earth, Mars or Venus) means that its atmosphere is free to flow around the planet essentially without obstruction. This is one factor that generates Saturn's pattern of alternating belts and zones -- one of the main features of its dynamic atmosphere. Winds in the belts blow at speeds different from those in the adjacent zones, leading to the formation of vortices along the boundaries between the two. And vigorous convection occasionally leads to storms and waves. Saturn's innermost rings are just visible at the bottom and in the upper left corner. This view is centered on clouds at 25 degrees north latitude on Saturn. The image was taken with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on July 20, 2016 using a spectral filter which preferentially admits wavelengths of near-infrared light centered at 728 nanometers. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 752,000 miles (1.21 million kilometers) from Saturn and at a Sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 6 degrees. Image scale is 45 miles (72 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20503
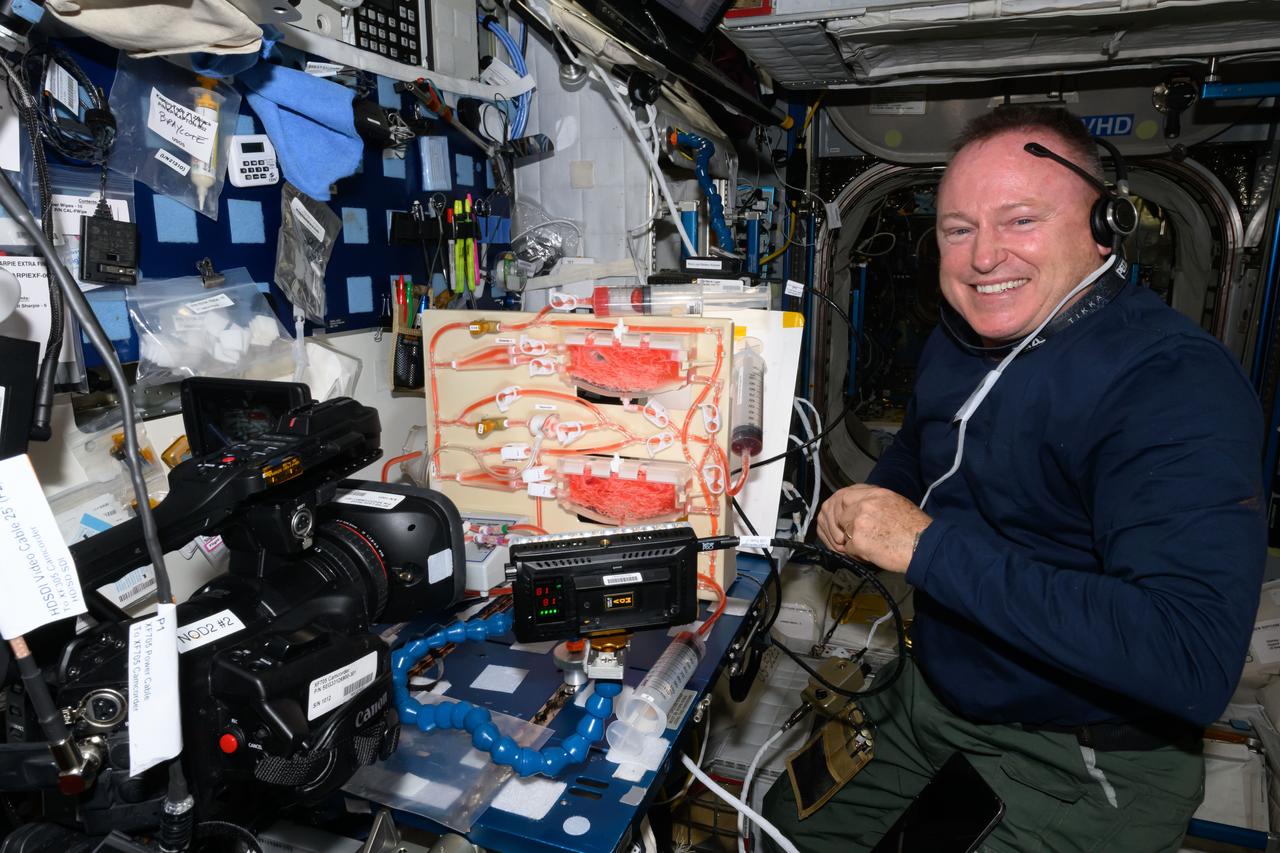

iss071e364248 (July 16, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test Commander Butch Wilmore investigates using fluid physics techniques such as surface tension, as well as hydroponics and air circulation, to overcome the lack of gravity when watering and nourishing plants grown in space. The Plant Water Management investigation uses facilities in the International Space Station's Harmony module to promote space agricultural activities on spacecraft and space habitats.

Interior lights give the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) the appearance of a high-tech juke box. The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC

iss065e084906 (June 1, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) swaps samples inside the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox for an experiment called Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA. The physics investigation explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
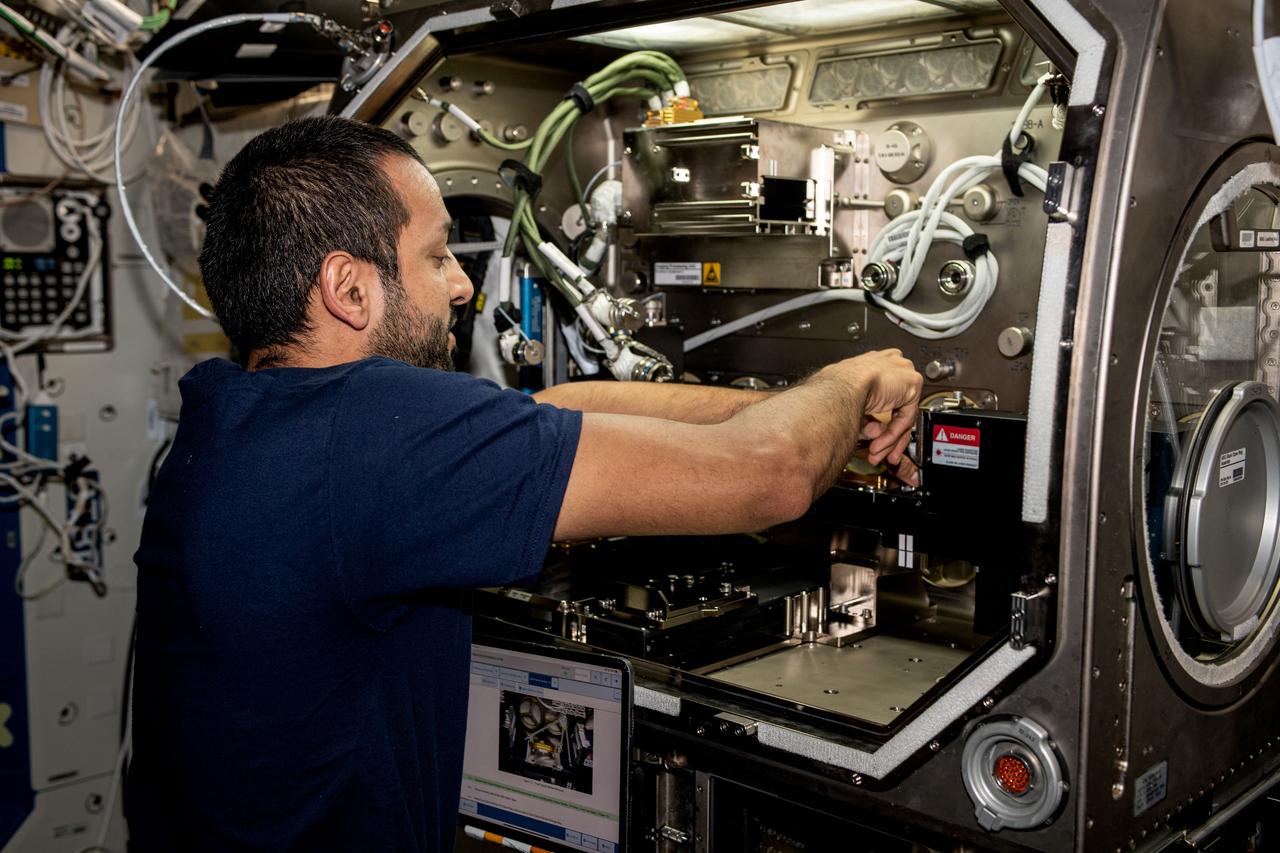

iss069e008883 (May 5, 2023) --- UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi removes physics research hardware from inside the Destiny laboratory module's Microgravity Science Glovebox. The Particle Vibrations experiment investigated the self-organization mechanisms of particles in fluids potentially providing insights into new manufacturing techniques and the formation of planets and asteroids.
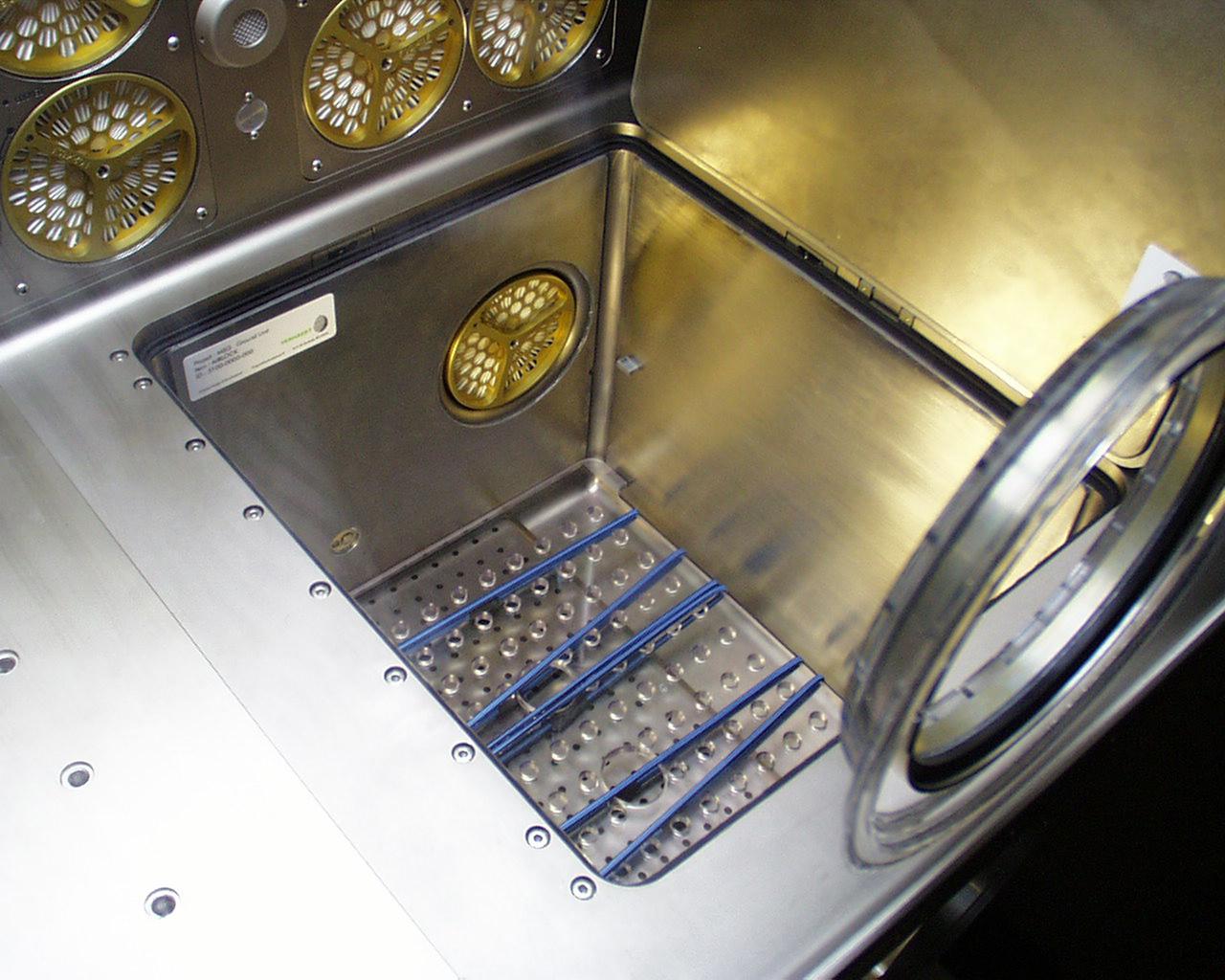

This photo shows the access through the internal airlock (bottom right) on the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) being developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The airlock will allow the insertion or removal of equipment and samples without opening the working volume of the glovebox. Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
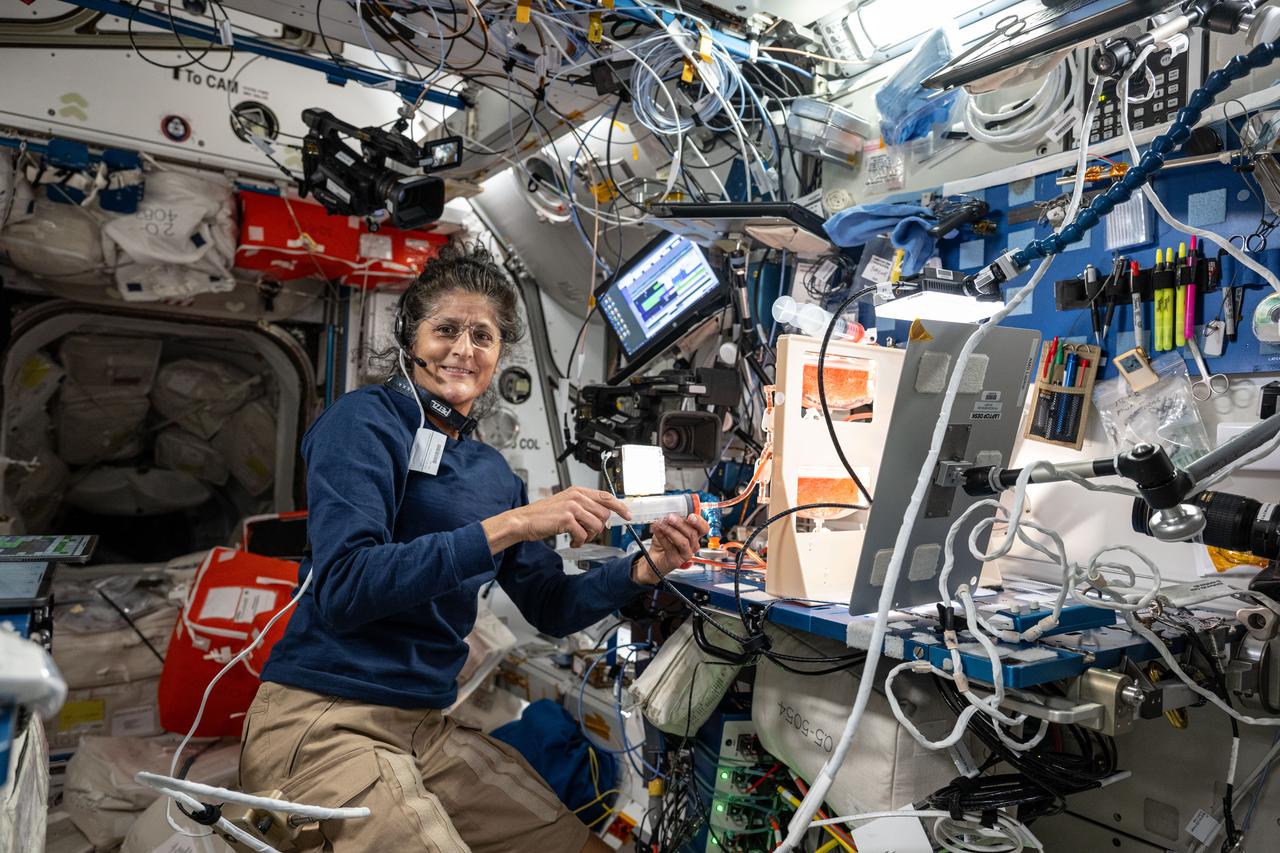

iss071e356675 (July 16, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Boeing Crew Flight Test Pilot Suni Williams investigates using fluid physics techniques such as surface tension, as well as hydroponics and air circulation, to overcome the lack of gravity when watering and nourishing plants grown in space. The Plant Water Management investigation uses facilities in the International Space Station's Harmony module to promote space agricultural activities on spacecraft and space habitats.
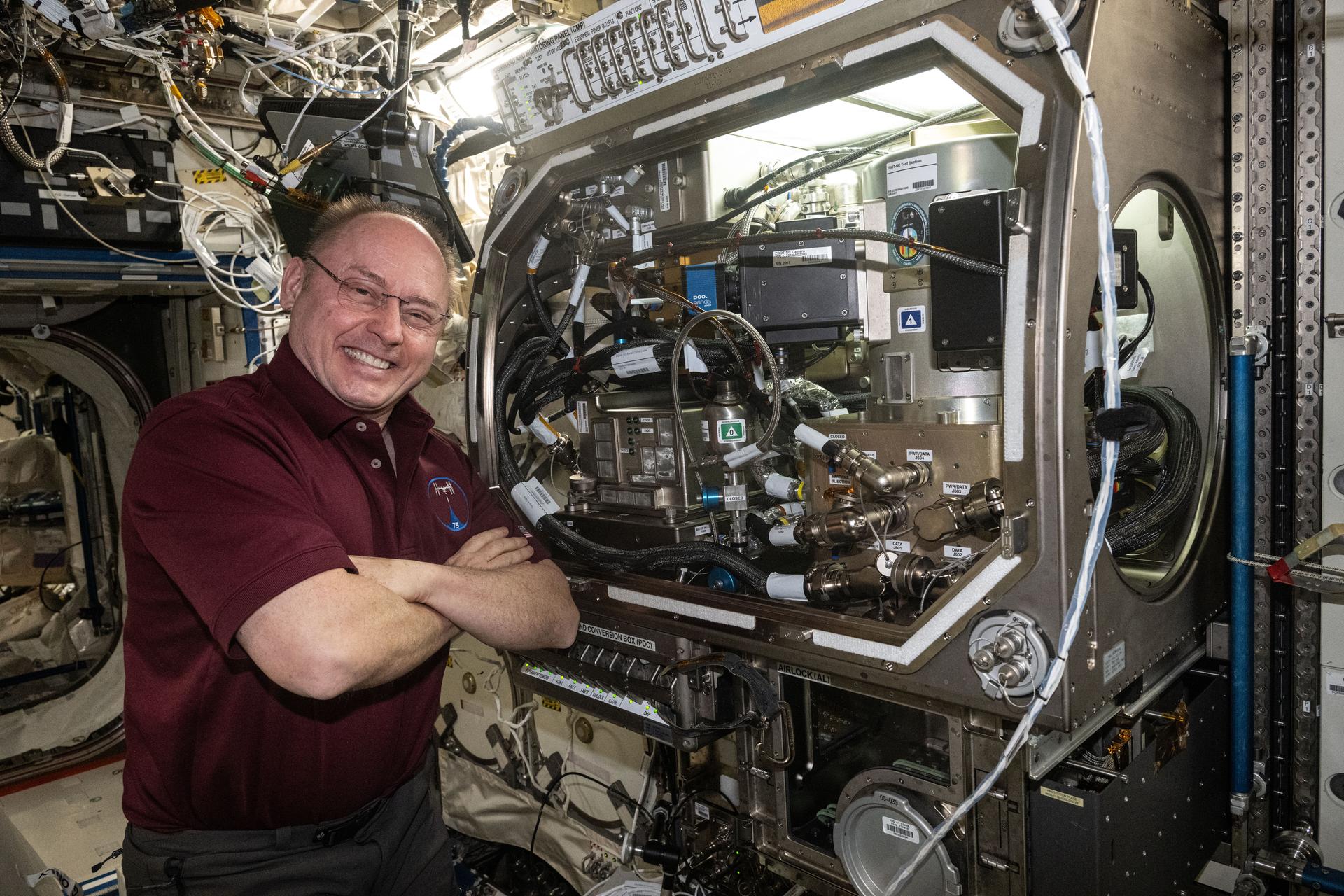
iss073e0982894 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Mike Fincke poses for a portrait next to the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module. Fincke had just completed configuring research hardware for the Zero Boil-Off Tank physics investigation, which explores methods for storing cryogenic fluids. The experiment supports advancements in spacecraft propulsion and life support systems, as well as biotechnological, medical, and industrial applications on Earth.
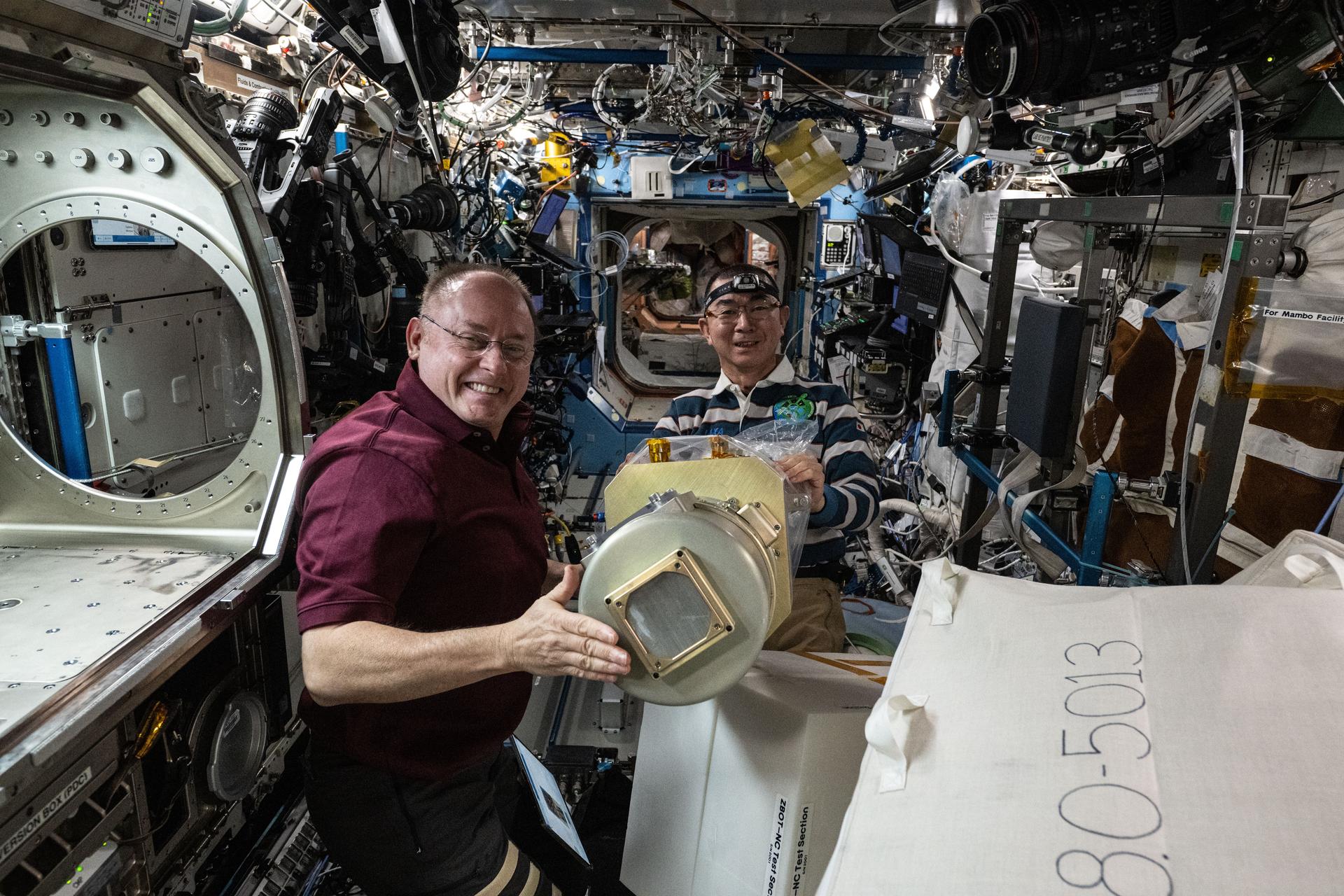

iss073e0982900 (Oct. 28, 2025) --- Expedition 73 Flight Engineers Mike Fincke of NASA and Kimiya Yui of JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) work together to configure research hardware for the Zero Boil-Off Tank physics investigation inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station. The experiment explores methods for storing cryogenic fluids and supports advancements in spacecraft propulsion and life support systems, as well as biotechnological, medical, and industrial applications on Earth.
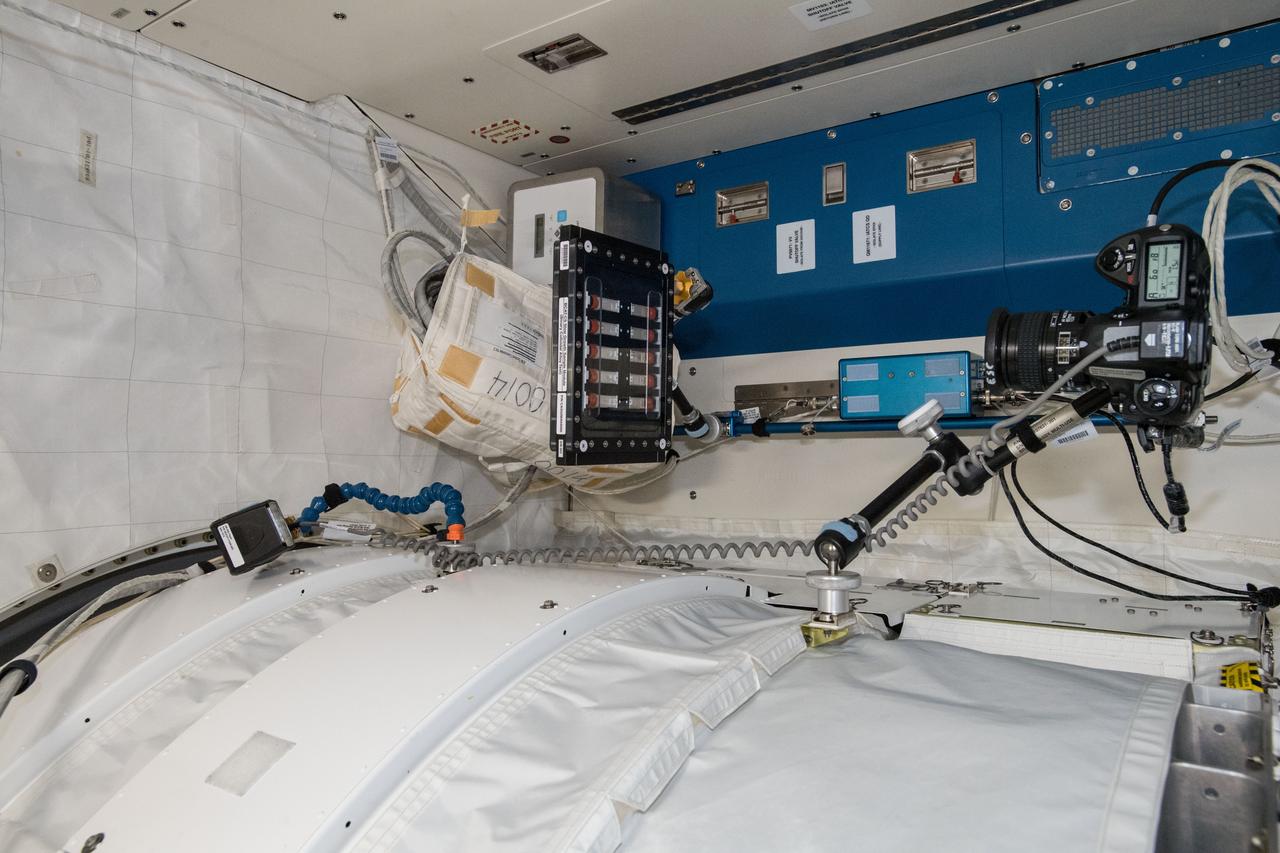

iss056e098988 (July 26, 2018) --- Photographic documentation of the Binary Colloidal Alloy Test-Cohesive Sedimentation investigation (BCAT-CS). The fluid physics research explores the sedimentary properties of quartz and clay particles. Mixed quartz and clay samples are suspended in a liquid for photographic and video downlink to scientists on Earth helping guide future geological studies of unexplored planets and improving petroleum exploration here on Earth.
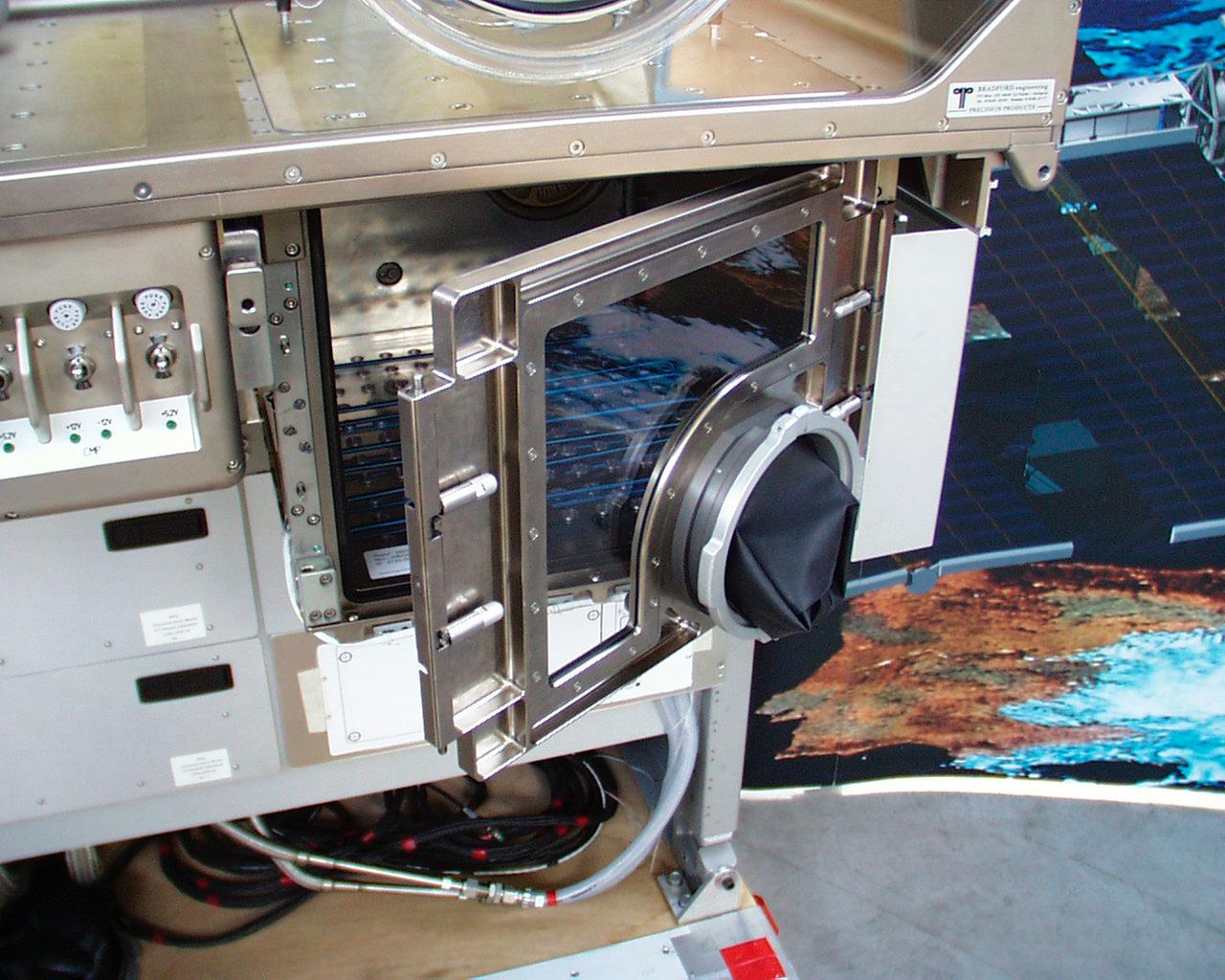

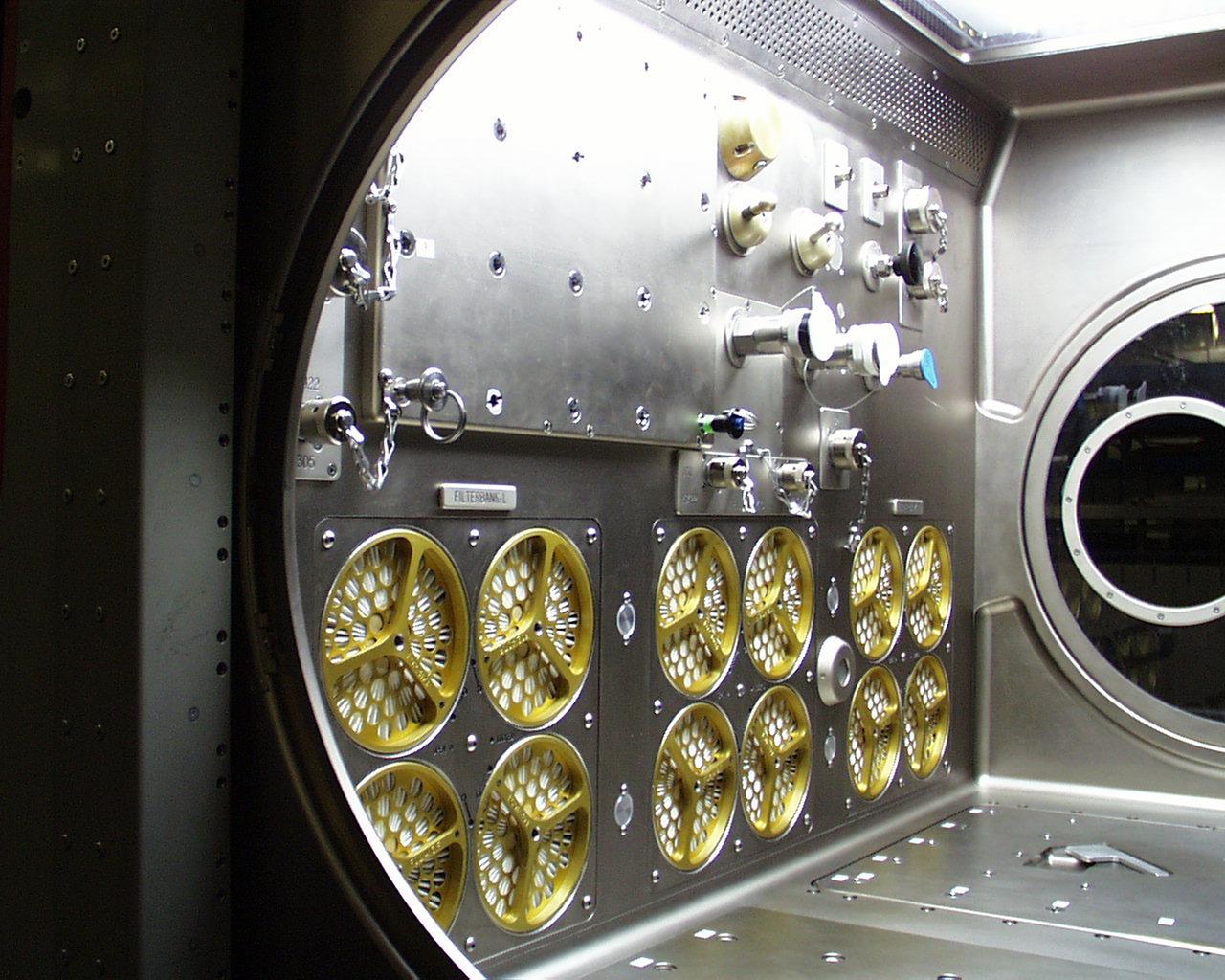
Once the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) is sealed, additional experiment items can be inserted through a small airlock at the bottom right of the work volume. It is shown here with the door open. The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
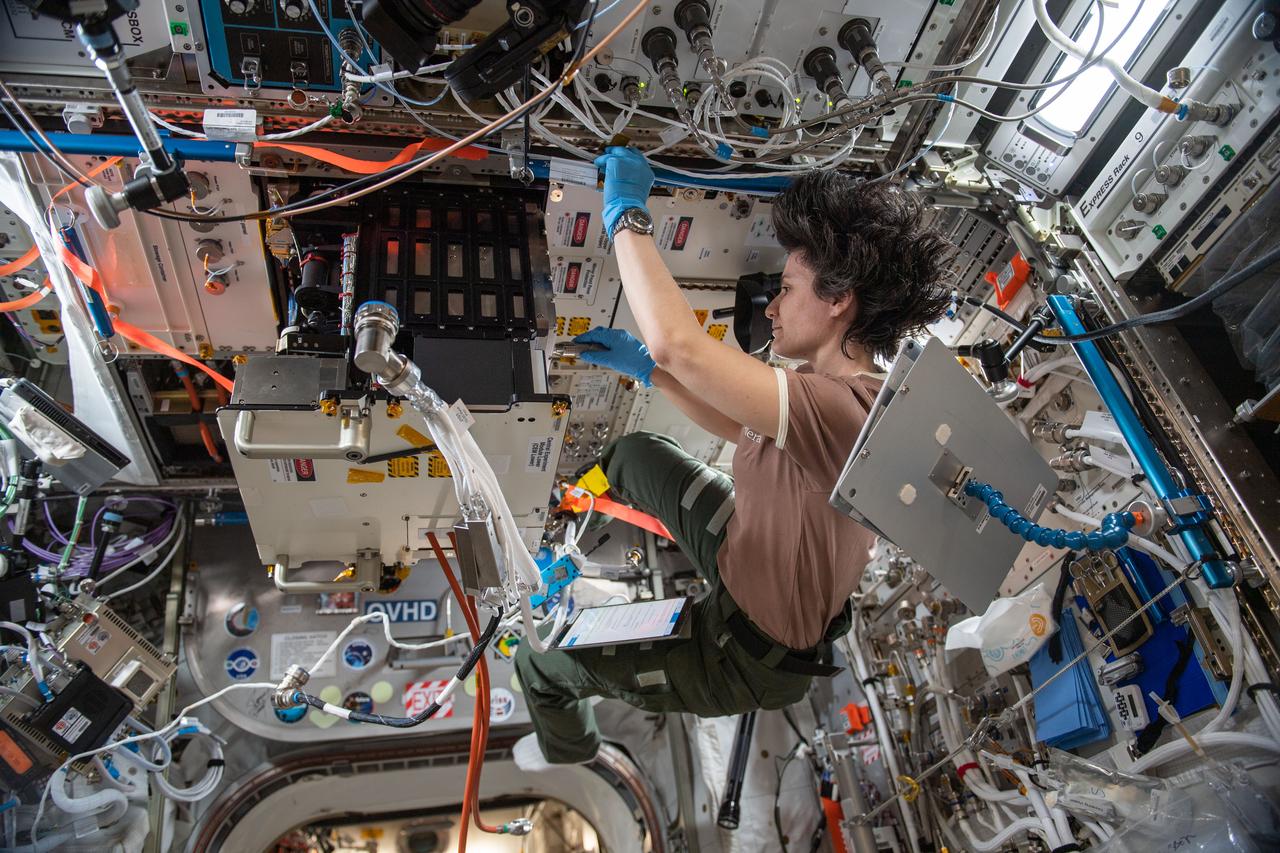

iss067e253411 (Aug. 10, 2022) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 67 Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti swaps samples inside the Fluid Science Laboratory’s Soft Matter Dynamics experiment container. The space physics study takes place aboard the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module and explores the dynamics of foams, droplets, and granular materials with implications for future planetary travel and industries on Earth.
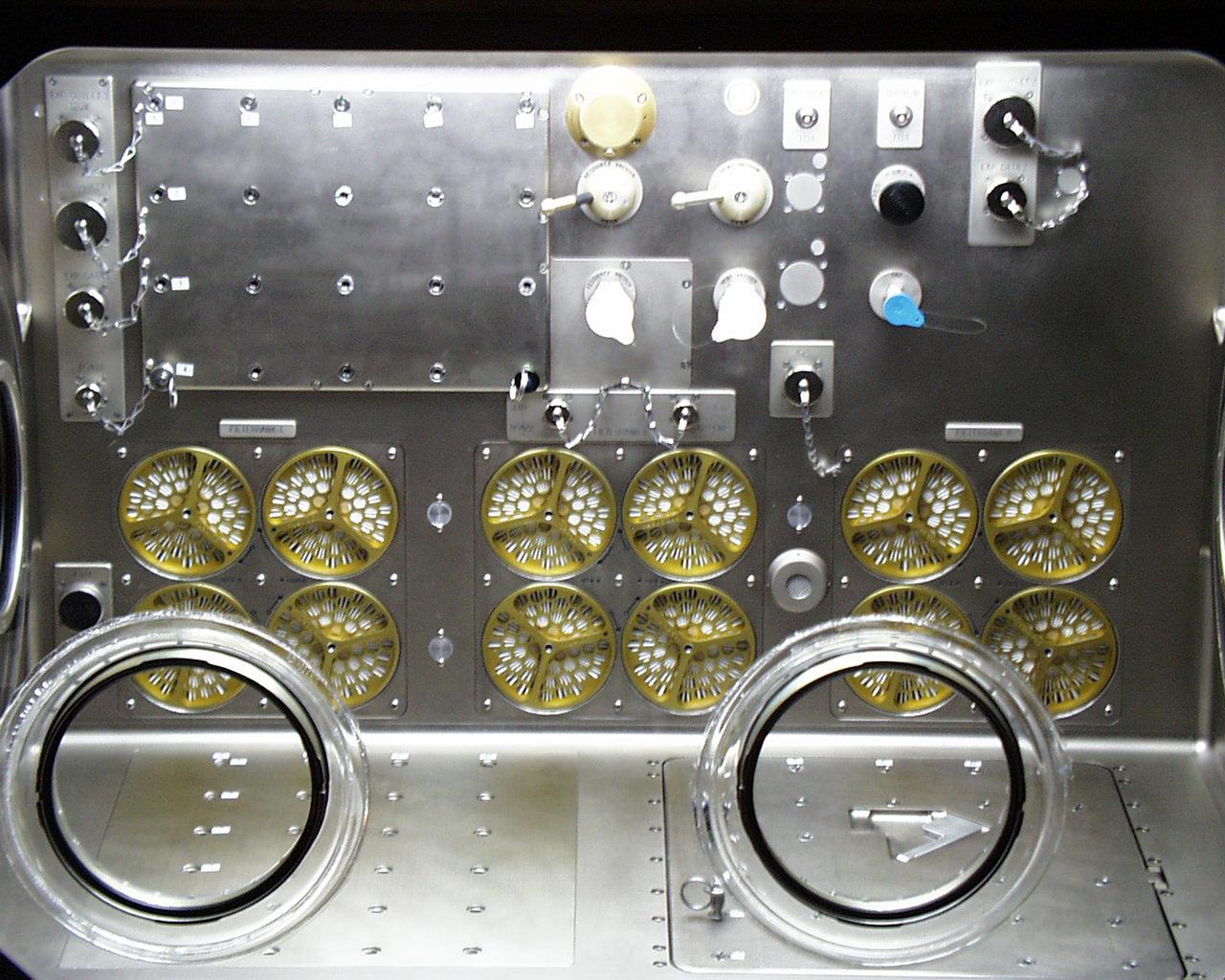

Interior lights give the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) the appearance of a high-tech juke box. The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
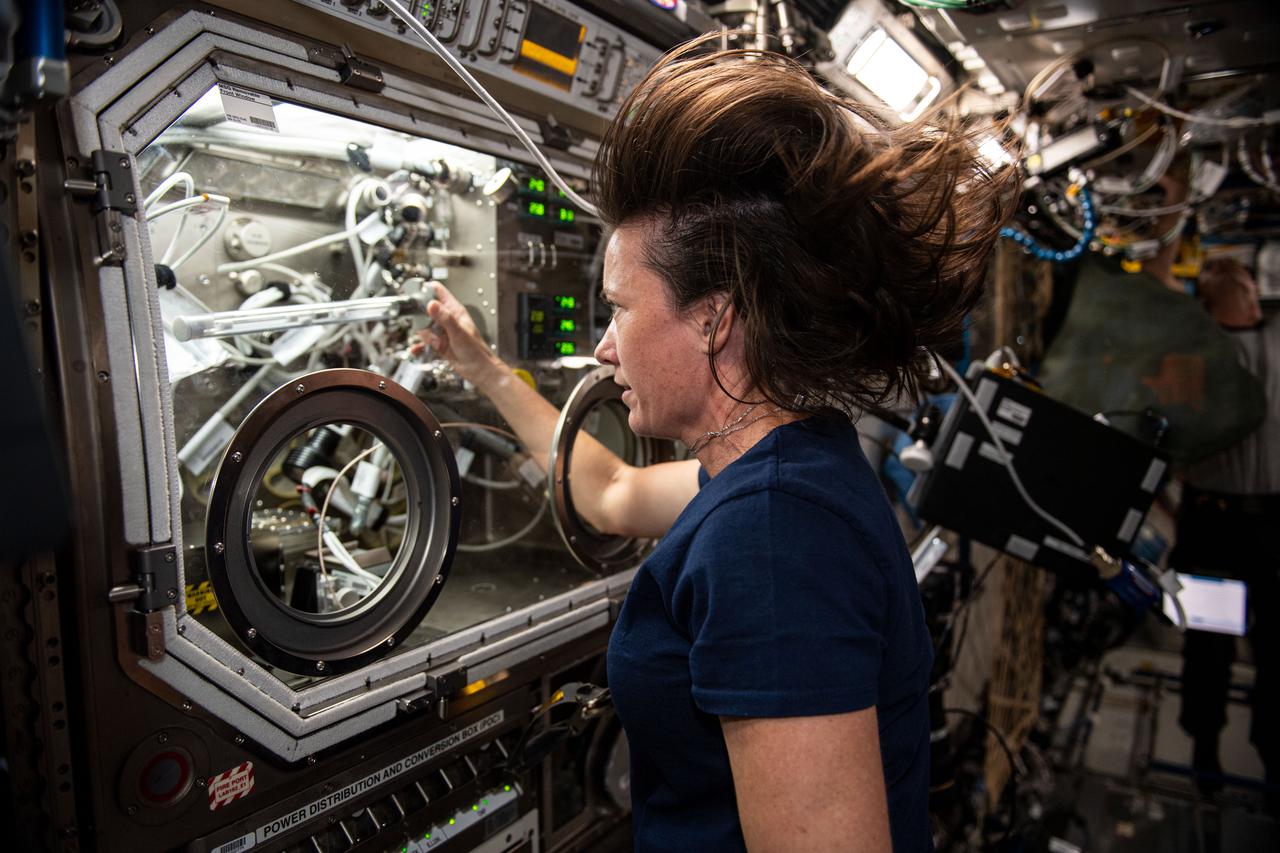

iss065e061407 (May 24, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur works in the Microgravity Science Glovebox swapping samples for an experiment called Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA. The physics investigation explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
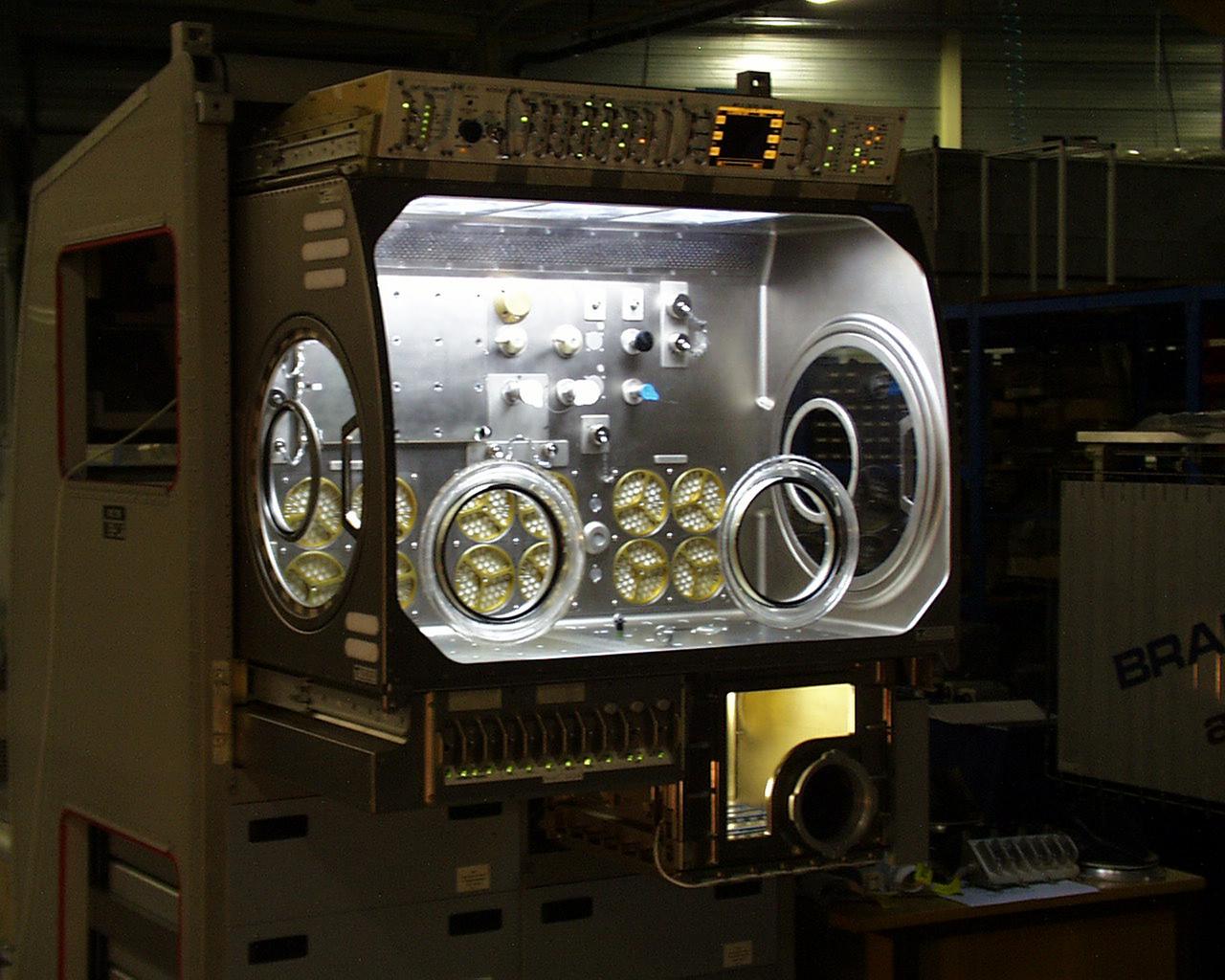

Interior lights give the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) the appearance of a high-tech juke box. The European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA are developing the MSG for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
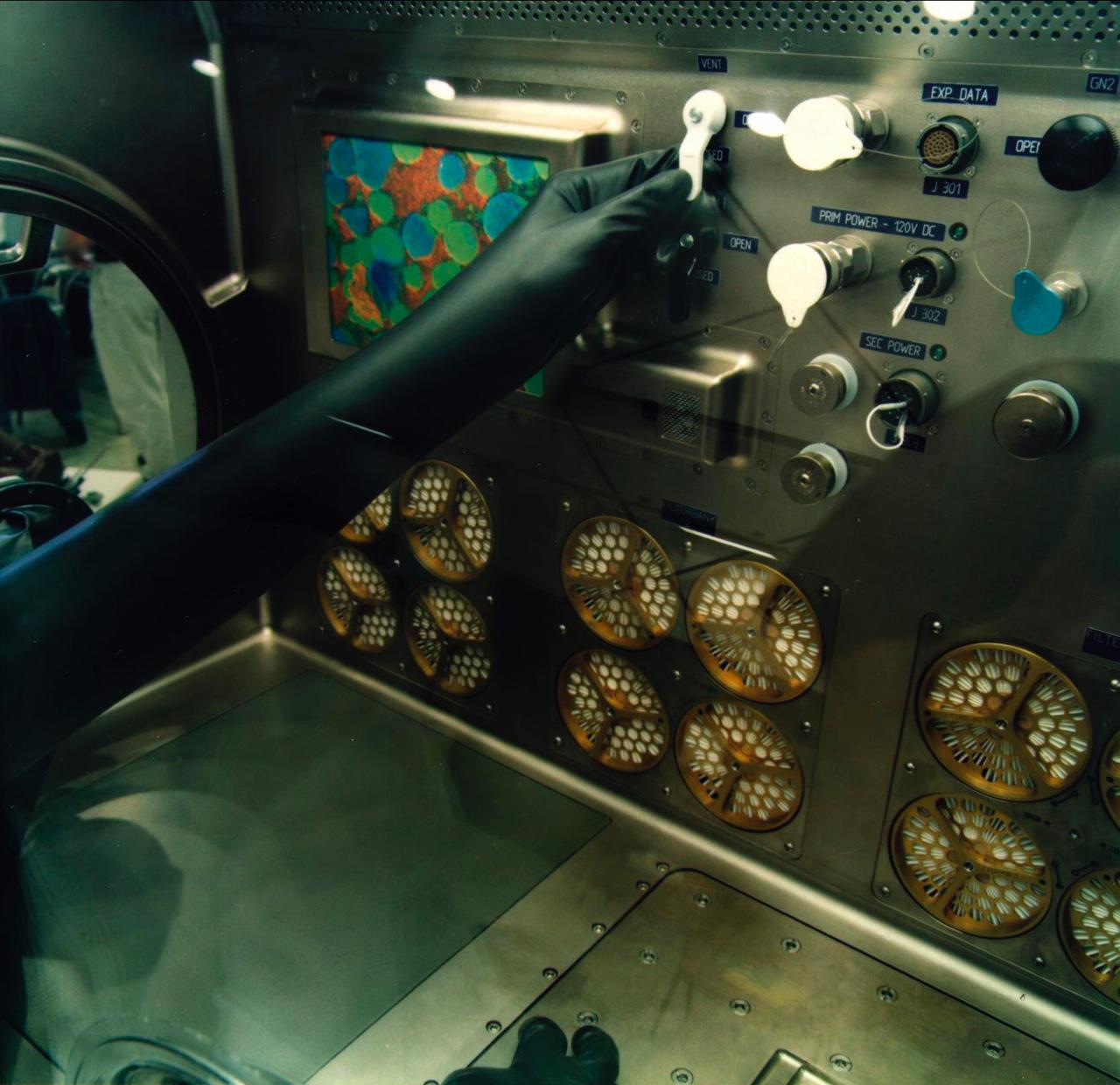

This photo shows the interior reach in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) being developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA for use aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Scientists will use the MSG to carry out multidisciplinary studies in combustion science, fluid physics and materials science. The MSG is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Photo Credit: NASA/MSFC
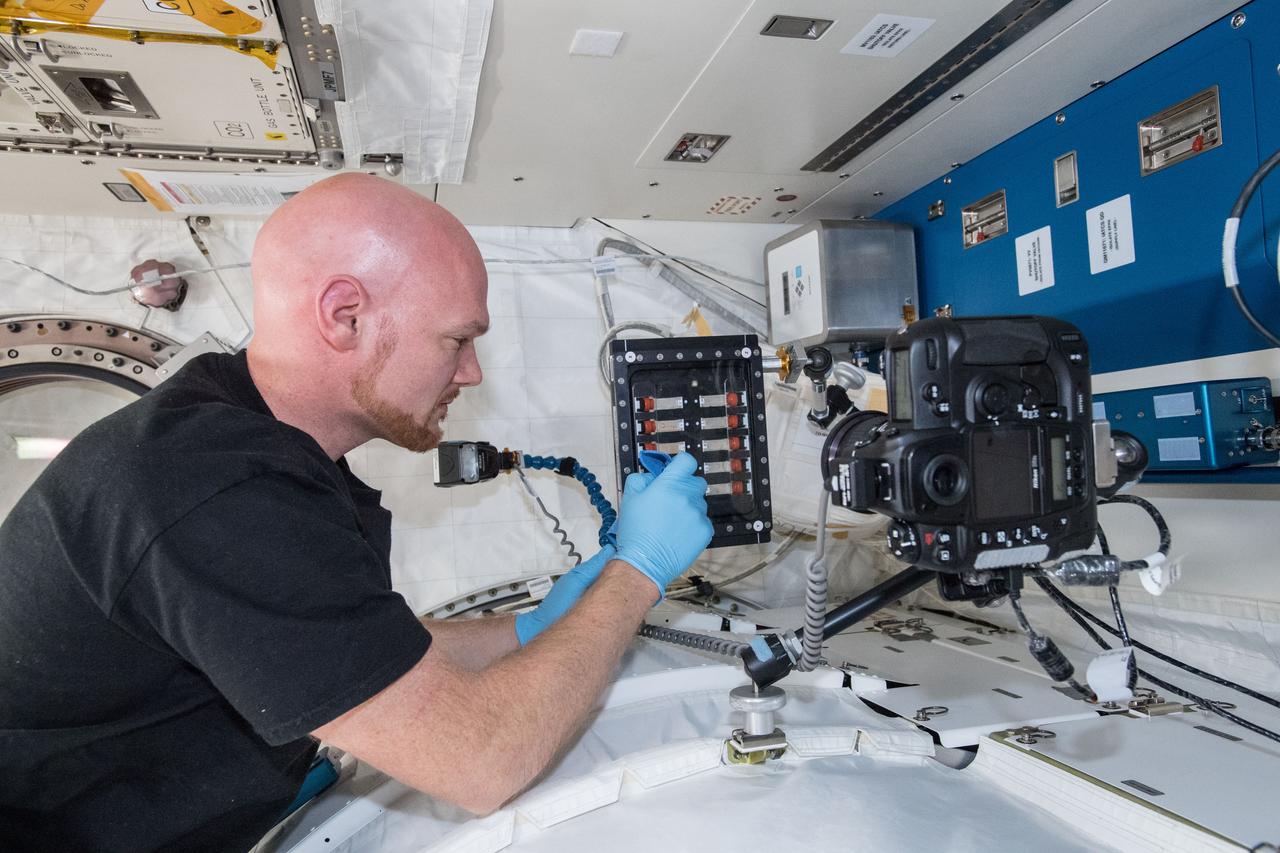

iss056e098995 (July 26, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module taking pictures of samples for the Binary Colloidal Alloy Test-Cohesive Sedimentation investigation (BCAT-CS). The fluid physics research explores the sedimentary properties of quartz and clay particles. Mixed quartz and clay samples are suspended in a liquid for photographic and video downlink to scientists on Earth helping guide future geological studies of unexplored planets and improving petroleum exploration here on Earth.