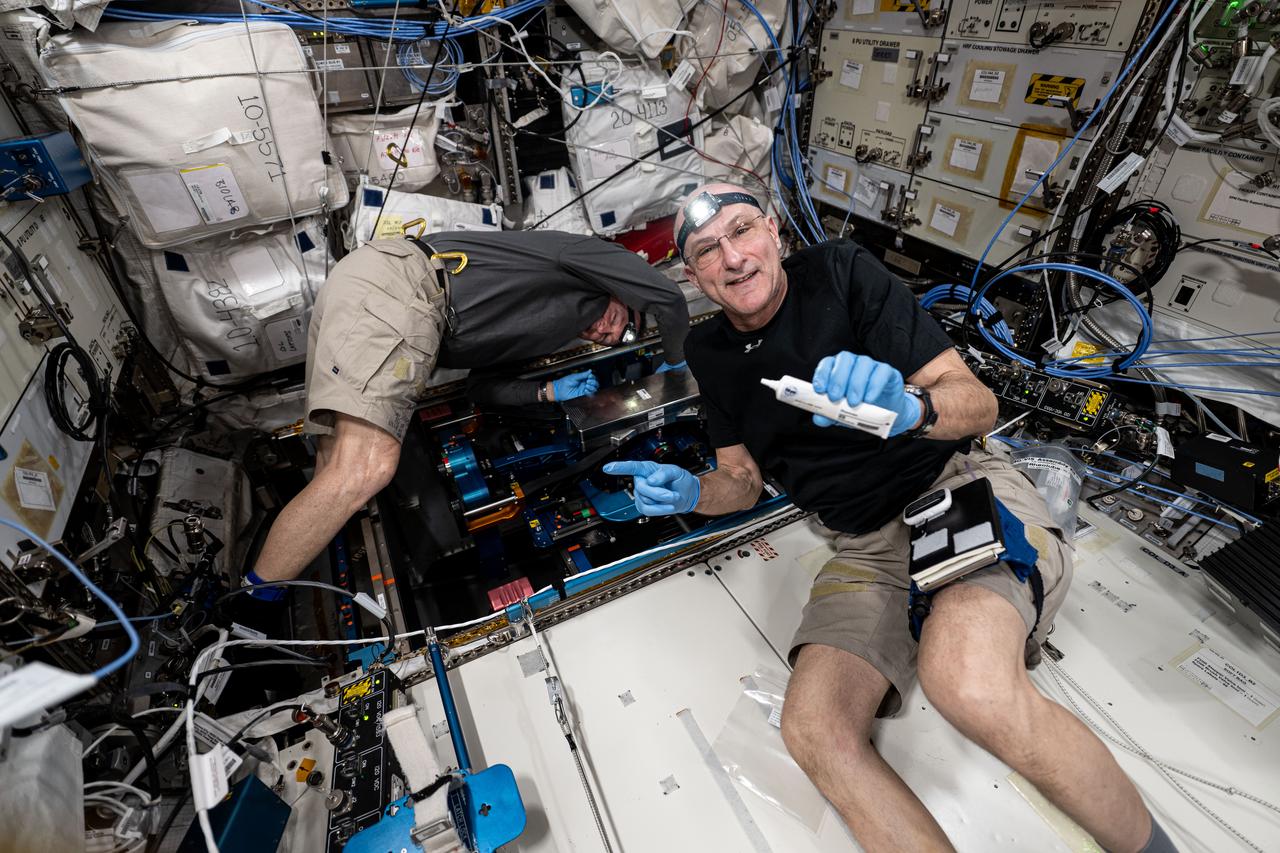

iss072e397047 (Dec. 19, 2024) --- NASA astronauts (from left) Butch Wilmore and Don Pettit, both Expedition 72 flight engineers, install the European Enhanced Exploration Exercise Device inside the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. The futuristic exercise gear will be tested by the station crew using its advanced bicycling, rowing, and resistive capabilities. The small and compact workout gear will be evaluated in the orbital outpost’s microgravity environment before being used on longer term missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
Artwork Artist conception of a hypersonic futuristic space vehicle re-entry
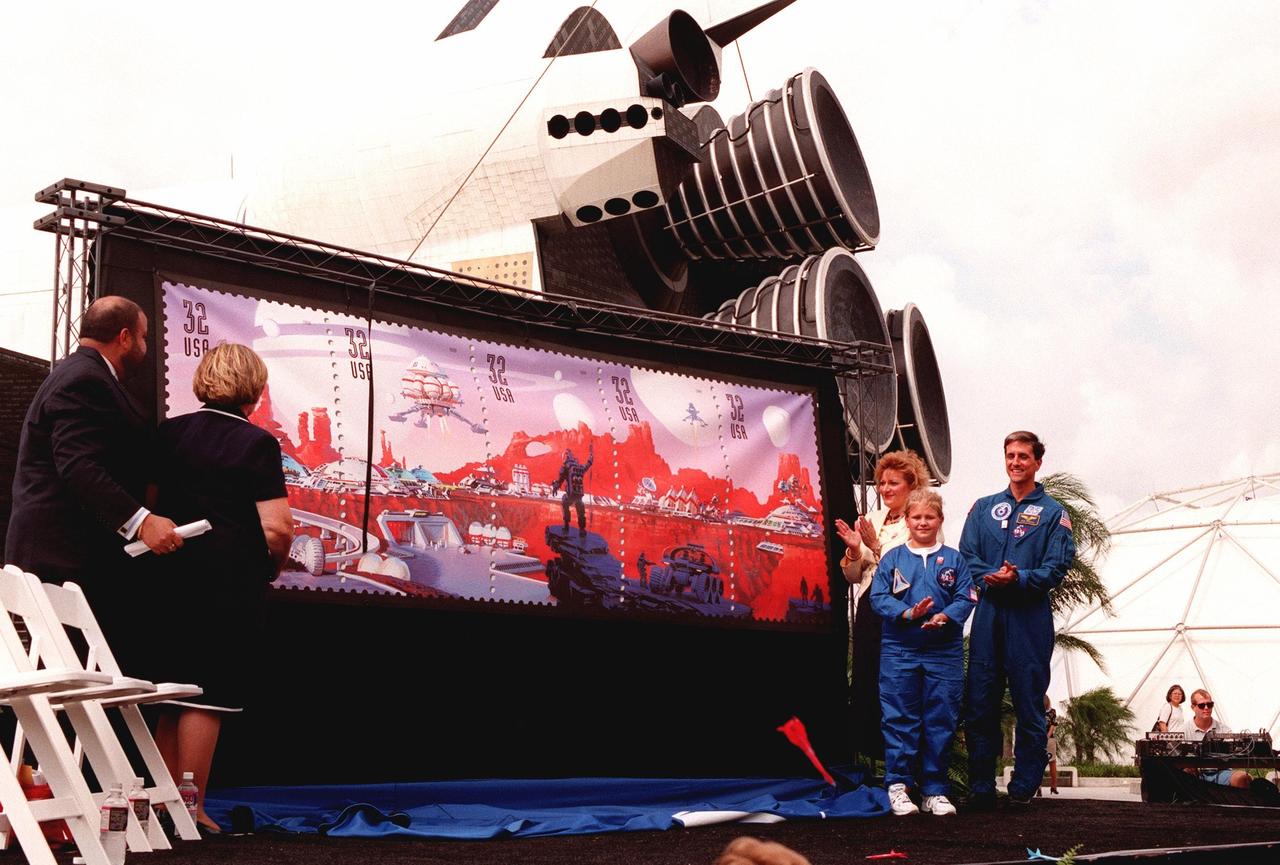

Applauding the unveiling of the U.S. Postal Service's newest series of stamps, Space Discovery, are are (left to right) Barry Ziehl, U.S. Postal Service; JoAnn Morgan, KSC associate director of advanced development and shuttle upgrades; Karla Corcoran, Postal Service inspector general; Kristene A. Graves, a student from Lewis Carroll Elementary School; and Dr. Donald Thomas, astronaut and veteran of four Shuttle missions. During the ceremony, Kristene read her essay "My Stamp Adventure" that she had written for an area-wide contest for the event. The unveiling took place at the KSC Visitor Complex and coincided with NASA's 40th anniversary on this date. Behind the large display can be seen the mockup of an orbiter. The stamps were designed by renowned aerospace artist Attila Heija. The strip of five individual stamps together make up a futuristic scene complete with space vehicles, a futuristic space city, and space explorers. The stamps are available nationwide beginning Oct. 1
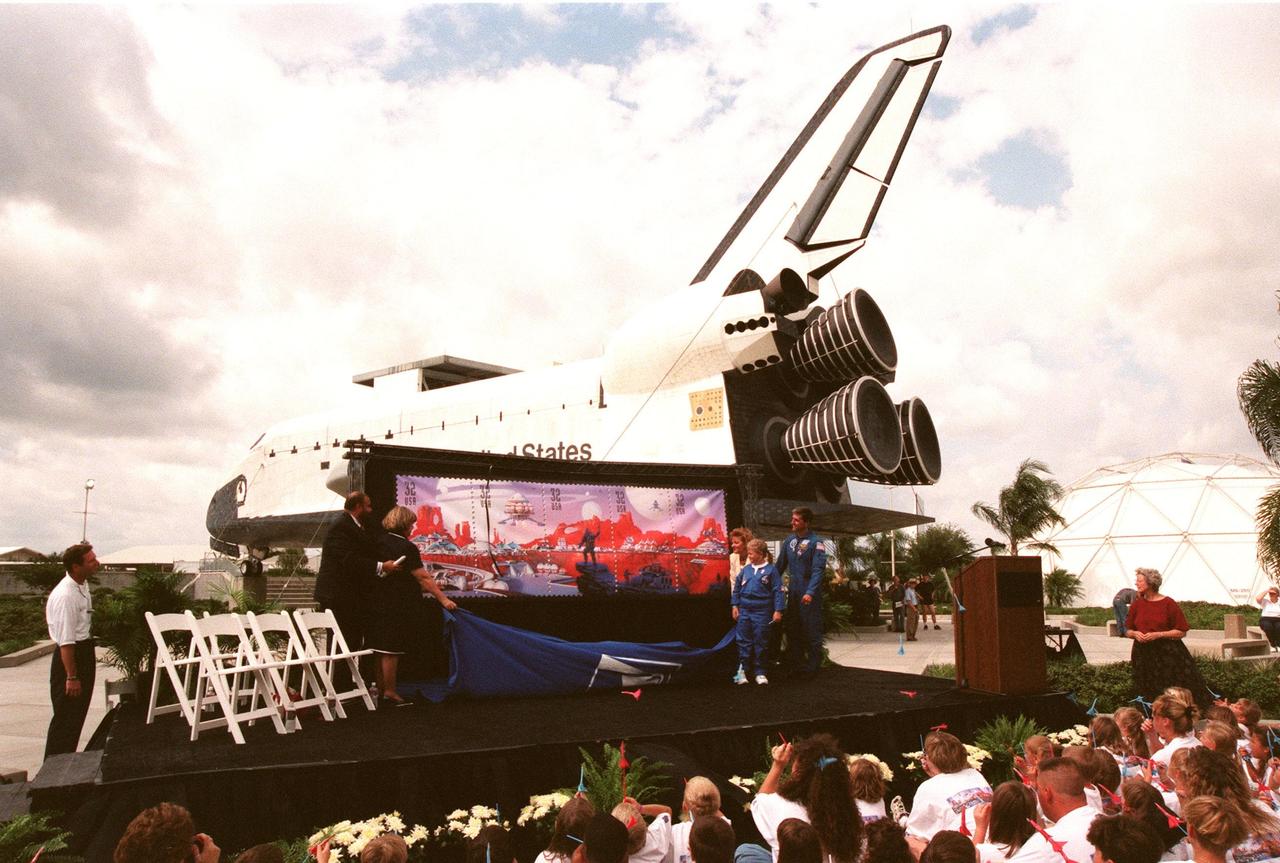

The U.S. Postal Service unveils its newest series of stamps, Space Discovery, at the KSC Visitor Complex. The event coincided with NASA's 40th anniversary on this date. Participating in the unveiling are (left to right) Barry Ziehl, U.S. Postal Service; JoAnn Morgan, KSC associate director of advanced development and shuttle upgrades; Karla Corcoran, Postal Service inspector general; Kristene A. Graves, a student from Lewis Carroll Elementary School ; and Dr. Donald Thomas, astronaut and veteran of four Shuttle missions. Behind them is the mockup of an orbiter. During the ceremony, Kristene read her essay "My Stamp Adventure" that she had written for an area-wide contest for the event. The stamps were designed by renowned aerospace artist Attila Heija. The strip of five individual stamps together make up a futuristic scene complete with space vehicles, a futuristic space city, and space explorers. The stamps are available nationwide beginning Oct. 1
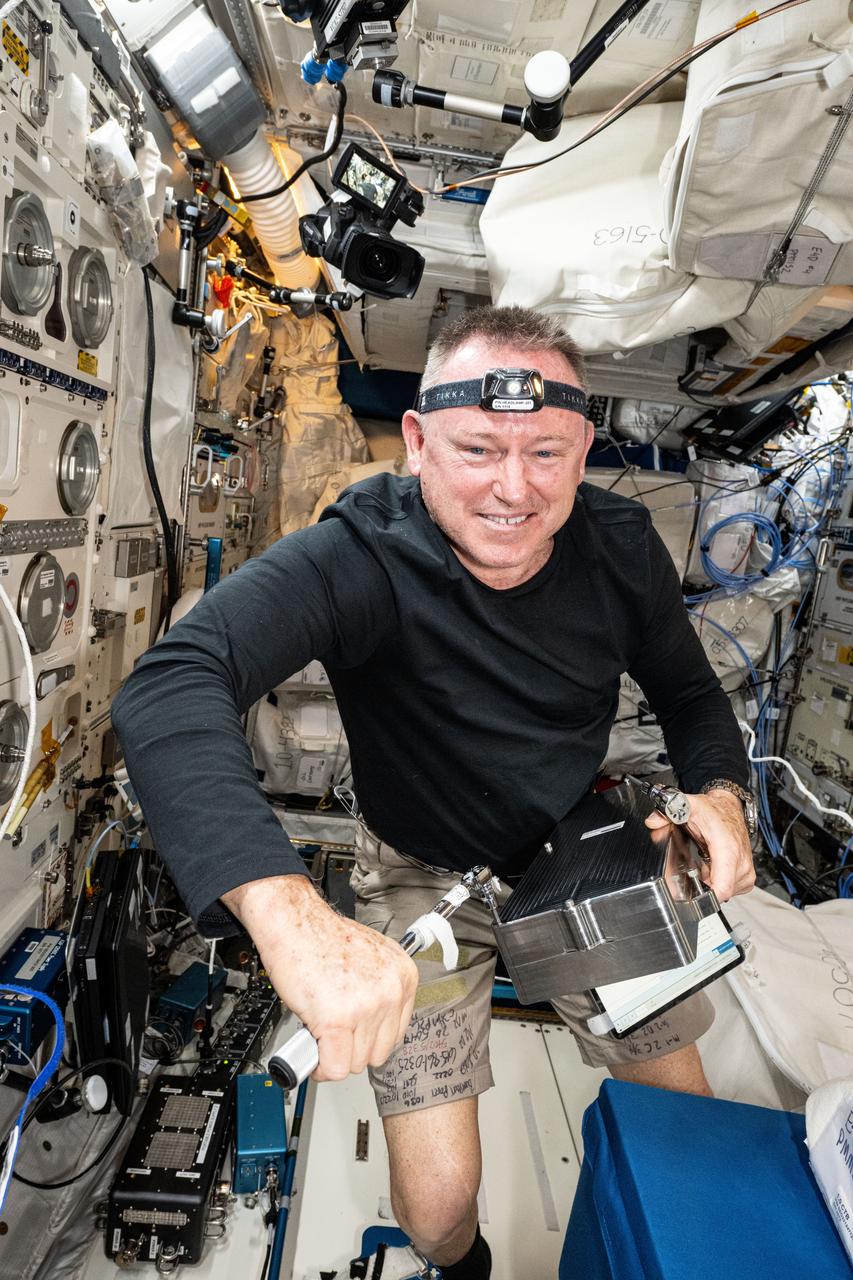

iss072e391444 (Dec. 18, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Butch Wilmore works inside the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module to begin installing the European Enhanced Exploration Exercise Device. The futuristic exercise gear will be tested by the station crew using its advanced bicycling, rowing, and resistive capabilities. The small and compact workout gear will be evaluated in the orbital outpost’s microgravity environment before being used on longer term missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
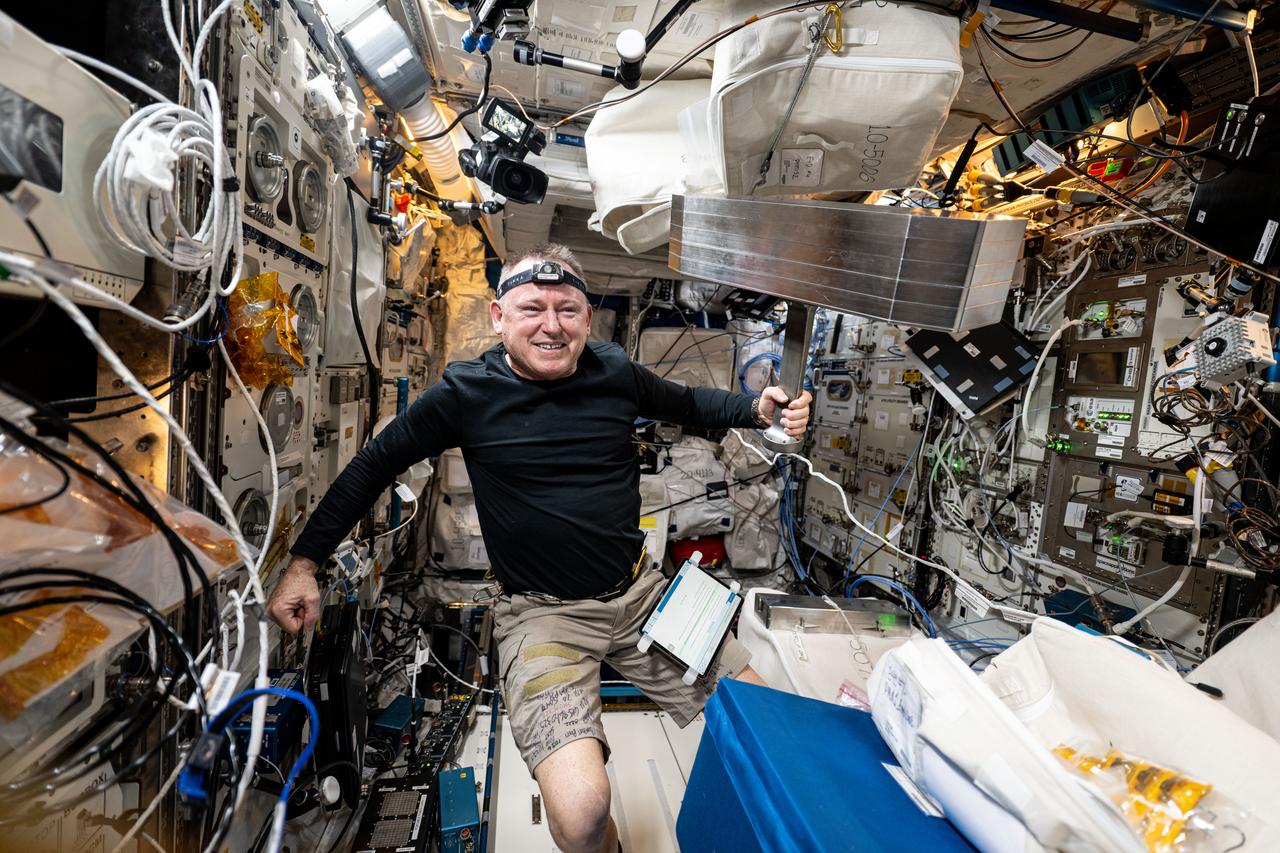

iss072e391382 (Dec. 18, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 72 Flight Engineer Butch Wilmore works inside the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module to begin installing the European Enhanced Exploration Exercise Device. The futuristic exercise gear will be tested by the station crew using its advanced bicycling, rowing, and resistive capabilities. The small and compact workout gear will be evaluated in the orbital outpost’s microgravity environment before being used on longer term missions to the Moon, Mars, and beyond.

iss073e0420094 (July 3, 2025) --- Shanghai, China—the nation's largest city with a metropolitan population of approximately 24.9 million—is seen from the International Space Station at around 9:55 p.m. local time. Located where the Yangtze River meets the Yellow Sea, the city glows with urban energy. Notable landmarks include Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport near the top center and Shanghai Pudong International Airport at the bottom. The Huangpu River winds through the heart of downtown, dividing the historic Bund from the futuristic skyline of Lujiazui.
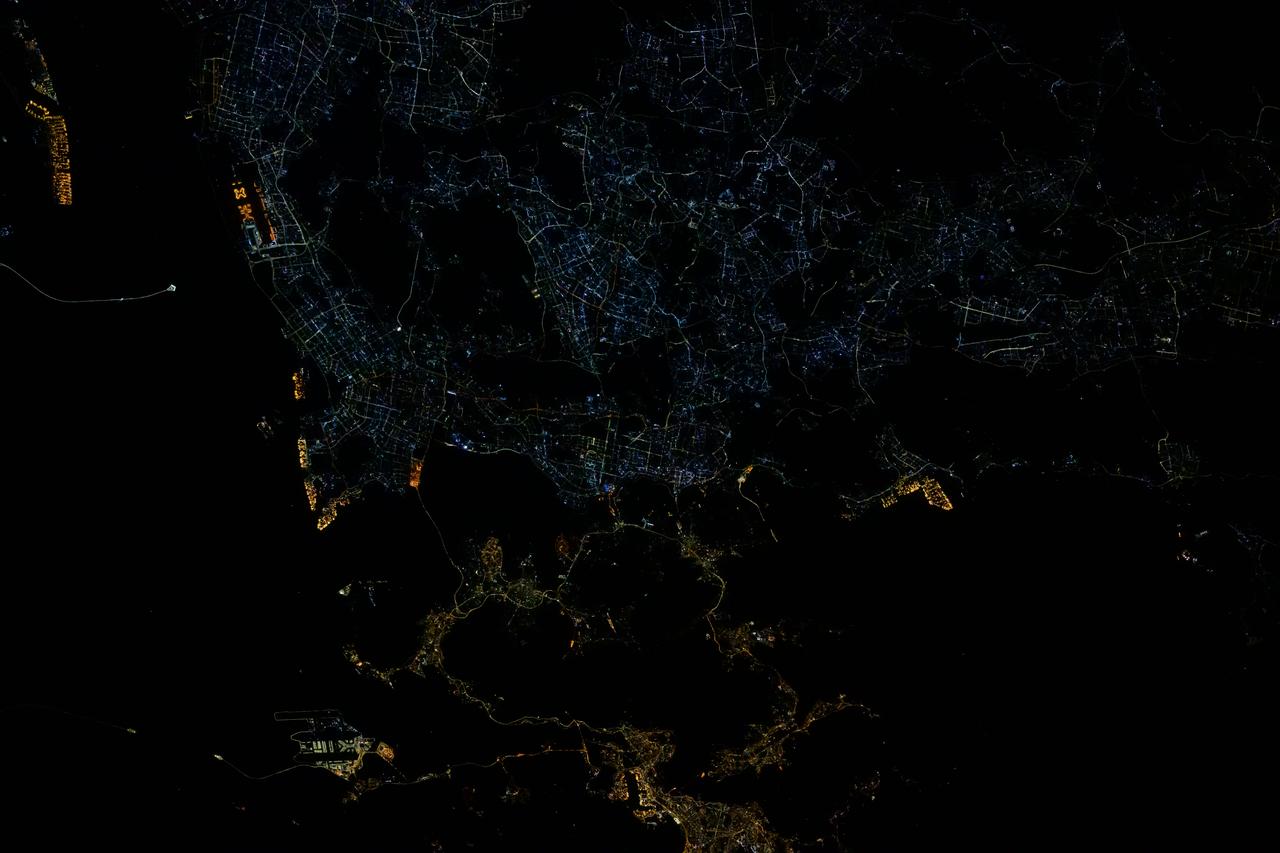

iss072e399613 (Dec. 20, 2024) --- The city lights of Hong Kong (bottom center) and Shenzhen, China, are different colors due to their historical differences. Shenzhen is a younger, more futuristic city, while Hong Kong is an older city illuminating its historical landmarks and its harbor. The International Space Station was orbiting 255 miles above southeastern China at the time of this photograph.
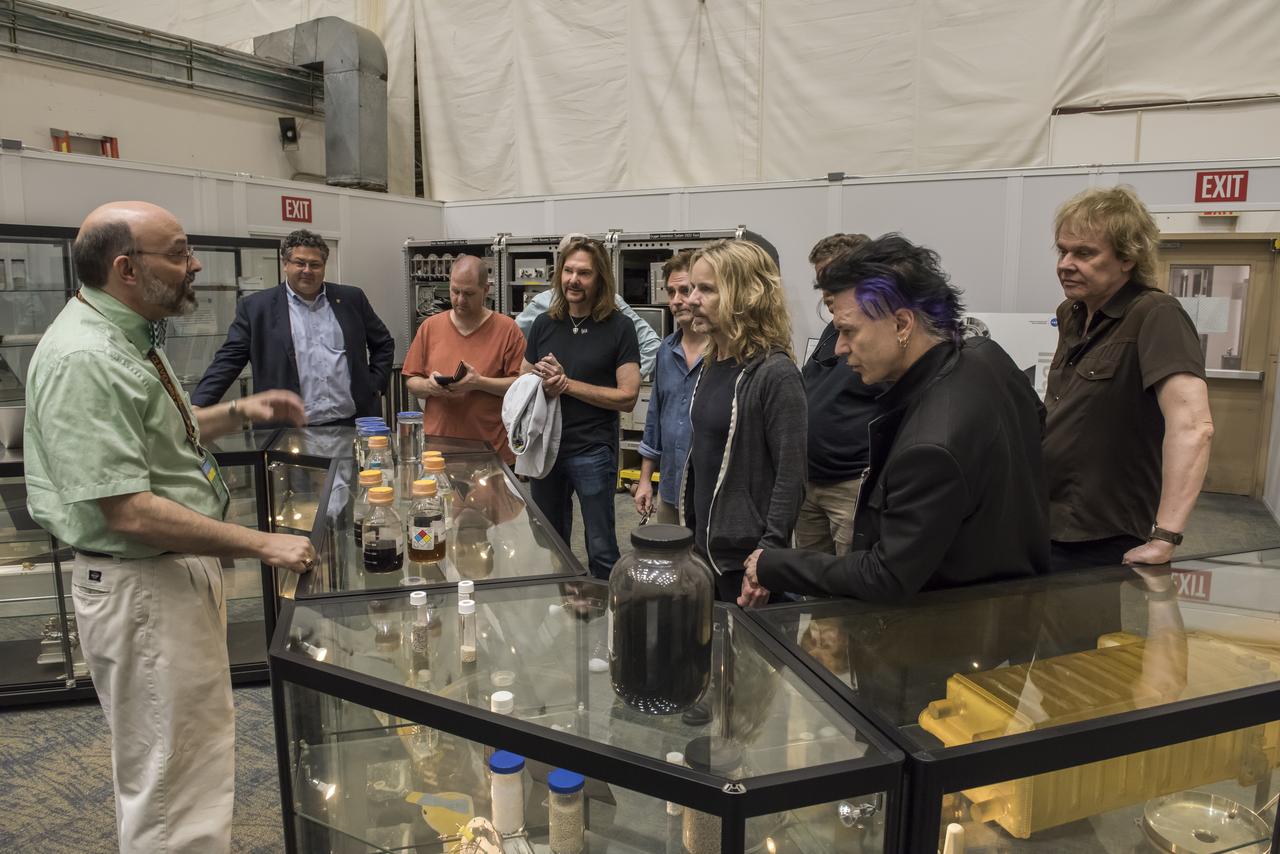

Keith Parrish, left, of the Space Systems Department at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, discusses the process of the Environmental Control and Life Support System with Marshall Center Director Todd May, second from left, and members of the legendary rock band Styx during a tour of Marshall April 27. Inspired by NASA’s goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s, the band’s upcoming album, "The Mission," musically chronicles a futuristic, crewed mission to Mars. While Styx’s mission may be only realized through their iconic sound, NASA’s mission is well underway with the new Space Launch System

This is a computer generated image of a Shuttle launch utilizing 2nd generation Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) flyback boosters, a futuristic concept that is currently undergoing study by NASA's Space Launch Initiative (SLI) Propulsion Office, managed by the Marshall Space Fight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, working in conjunction with the Agency's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Currently, after providing thrust to the Space Shuttle, the solid rocket boosters are parachuted into the sea and are retrieved for reuse. The SLI is considering vehicle concepts that would fly first-stage boosters back to a designated landing site after separation from the orbital vehicle. These flyback boosters would be powered by several jet engines integrated into the booster capable of providing over 100,000 pounds of thrust. The study will determine the requirements for the engines, identify risk mitigation activities, and identify costs associated with risk mitigation and jet engine development and production, as well as determine candidate jet engine options to pursue for the flyback booster.
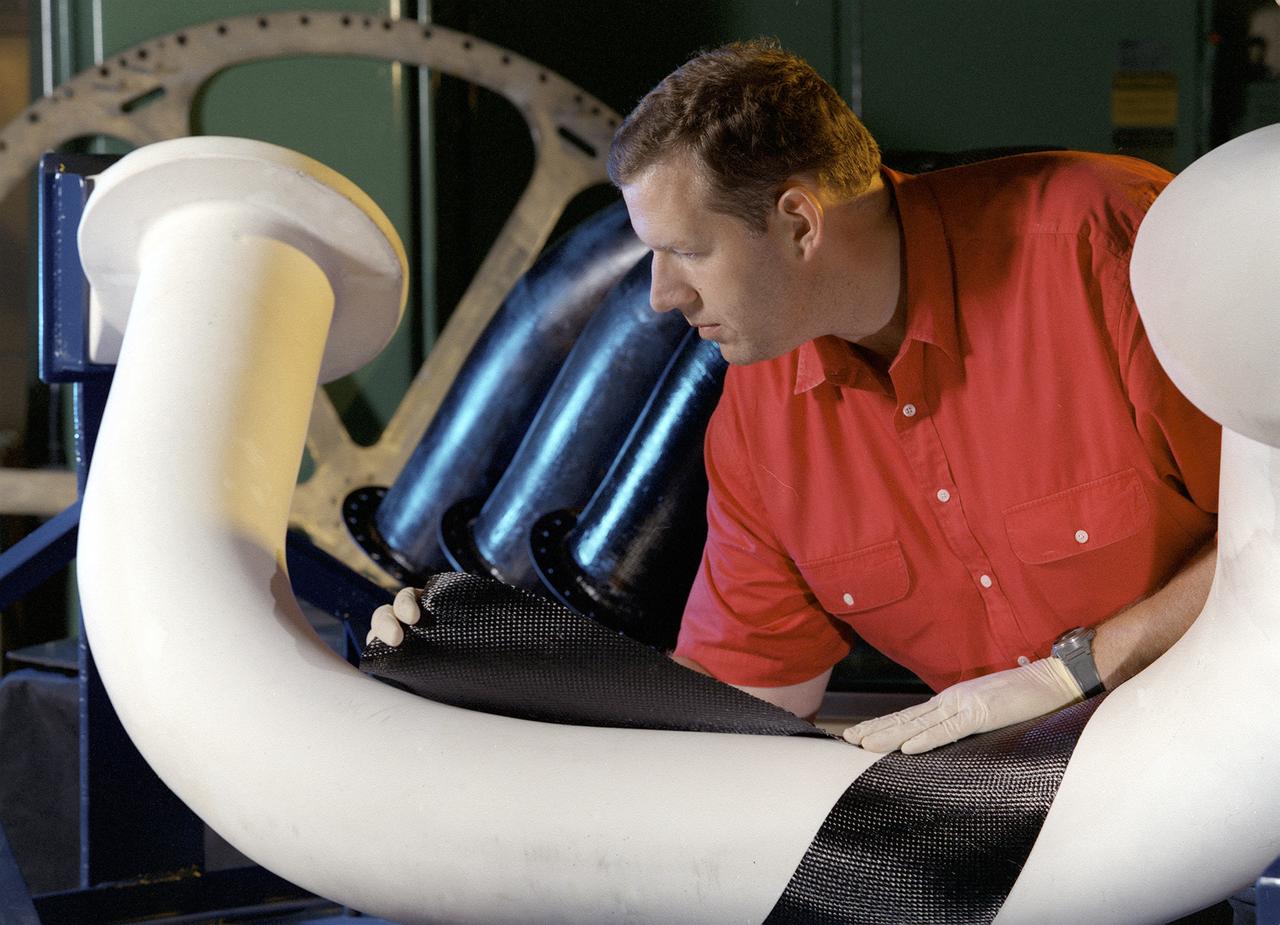

Engineers at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are working with industry partners to develop a new generation of more cost-efficient space vehicles. Lightweight fuel tanks and components under development will be the critical elements in tomorrow's reusable launch vehicles and will tremendously curb the costs of getting to space. In this photo, Tom DeLay, a materials processes engineer for MSFC, uses a new graphite epoxy technology to create lightweight cryogenic fuel lines for futuristic reusable launch vehicles. He is wrapping a water-soluble mandrel, or mold, with a graphite fabric coated with an epoxy resin. Once wrapped, the pipe will be vacuum-bagged and autoclave-cured. The disposable mold will be removed to reveal a thin-walled fuel line. In addition to being much lighter and stronger than metal, this material won't expand or contract as much in the extreme temperatures encountered by launch vehicles.

The official patch of the International Space Station's Expedition 70 crew. The Expedition 70 patch is designed around the central yin-yang symbol representing balance; first and foremost, the balance of our beautiful planet Earth that is encircled by the yin-yang symbol and which forms part of the Expedition number. In our exploration of space, we are reminded of the uniqueness of Earth; the further we push the boundaries of human existence, the stronger our longing for our home planet grows. As our understanding of the cosmos expands, so does our understanding of Earth, and although we live in an ever-changing world, we recognize the need for a planet in balance to ensure our future. Space exploration is also about creating the future of our dreams. The tentative first steps we take today will hopefully become a well-trodden path in the future. This is represented stylistically by the “retro-futuristic” design of the patch, which mimics the design of the posters depicting the future from the early days of the space age. It is also emphasized by the yellow, orange, and red colors suggesting a sunrise. Lastly, the dynamism in the depiction of the number 7 suggests not only the physical launch into space, but also humanity’s progress towards the future.

A model of a tiny, wedge-shaped robot designed to explore subsurface oceans of icy moons, right, sits beside a large waterproof capsule containing electronics and sensors for testing below glacial ice at the Juneau Icefield in Alaska in July 2023. The model, about 5 inches (12 centimeters) long, was 3D-printed to show the final envisioned size of a futuristic NASA mission concept called SWIM, short for Sensing With Independent Micro-swimmers. Led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory from spring 2021 to fall 2024, SWIM envisions a swarm of dozens of self-propelled, cellphone-size robots exploring the waters of icy moons like Jupiter's Europa and Saturn's Enceladus. Delivered to the subsurface ocean by an ice-melting cryobot, the tiny robots would zoom away to look for chemical and temperature signals that could point to life. The capsule shown here contains the first generation of an ocean composition sensor built for the SWIM robots by a team at Georgia Tech. The final version of the sensor would enable each robot to simultaneously measure temperature, pressure, acidity or alkalinity, conductivity, and chemical makeup. During the Alaska field test, the team lowered the capsule through a borehole in the ice and measured pressure and conductivity down to a depth of 164 feet (50 meters). This field test was conducted as part of a JPL-managed project called ORCAA (Ocean Worlds Reconnaissance and Characterization of Astrobiological Analogs). Known as an analog mission, ORCAA is working to answer science questions and test technology in preparation for a potential future mission to explore the surface or subsurface of icy moons. ORCAA is funded by NASA's Planetary Science and Technology from Analog Research program. SWIM was supported by Phase I and II funding from NASA's Innovative Advanced Concepts program under the agency's Space Technology Mission Directorate. JPL is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, California. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26424
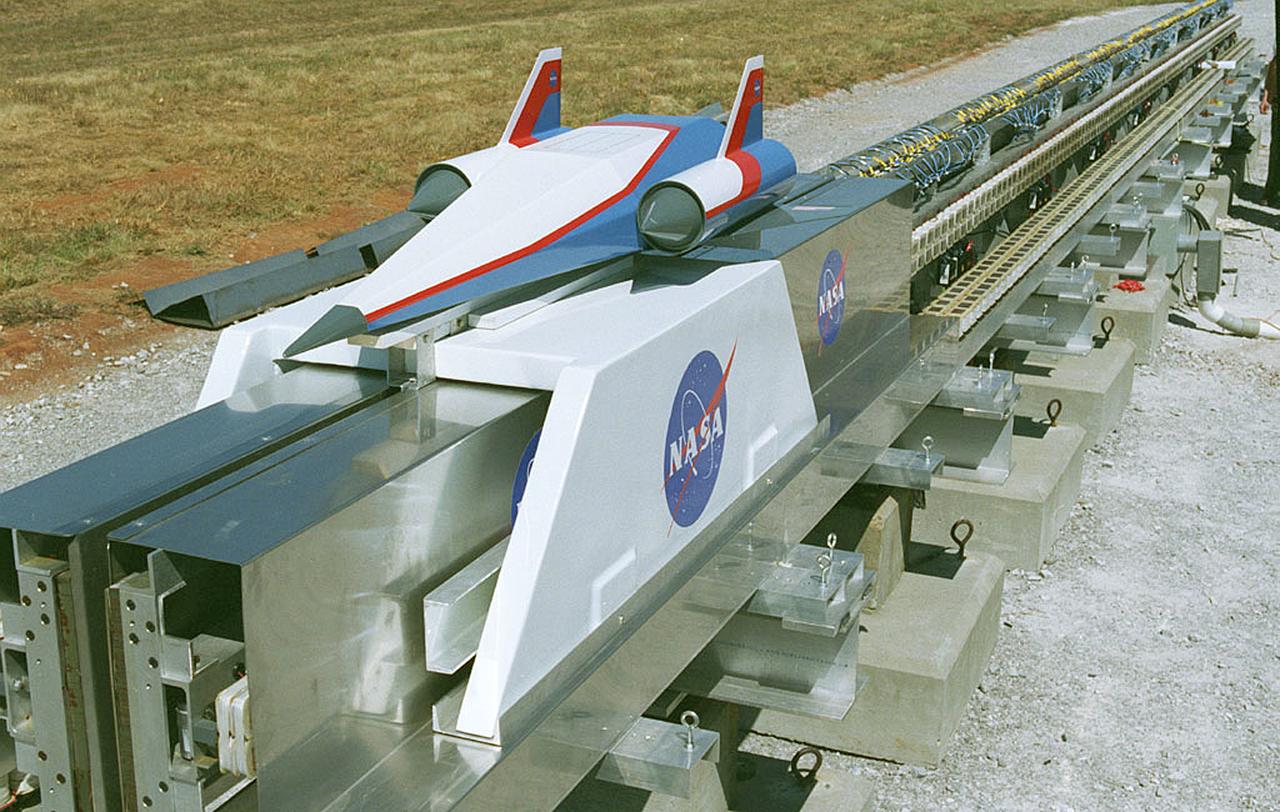

In this photograph, a futuristic spacecraft model sits atop a carrier on the Magnetic Launch Assist System, formerly known as the Magnetic Levitation (MagLev) System, experimental track at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Engineers at MSFC have developed and tested Magnetic Launch Assist technologies that would use magnetic fields to levitate and accelerate a vehicle along a track at very high speeds. Similar to high-speed trains and roller coasters that use high-strength magnets to lift and propel a vehicle a couple of inches above a guideway, a Magnetic Launch Assist system would electromagnetically drive a space vehicle along the track. A full-scale, operational track would be about 1.5-miles long and capable of accelerating a vehicle to 600 mph in 9.5 seconds. This track is an advanced linear induction motor. Induction motors are common in fans, power drills, and sewing machines. Instead of spinning in a circular motion to turn a shaft or gears, a linear induction motor produces thrust in a straight line. Mounted on concrete pedestals, the track is 100-feet long, about 2-feet wide, and about 1.5-feet high. The major advantages of launch assist for NASA launch vehicles is that it reduces the weight of the take-off, the landing gear, the wing size, and less propellant resulting in significant cost savings. The US Navy and the British MOD (Ministry of Defense) are planning to use magnetic launch assist for their next generation aircraft carriers as the aircraft launch system. The US Army is considering using this technology for launching target drones for anti-aircraft training.
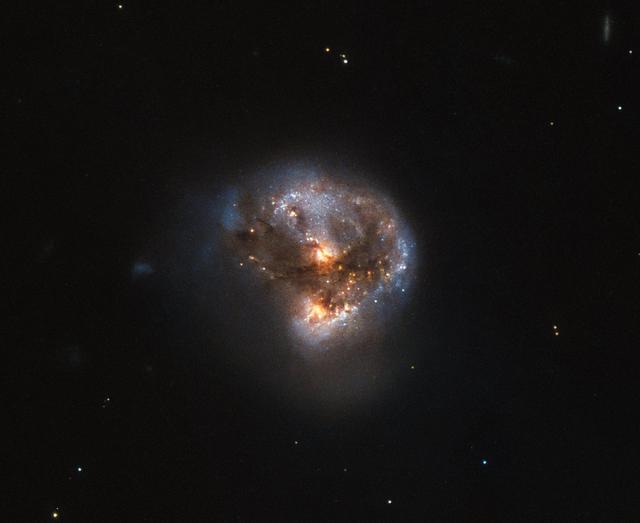

This galaxy has a far more exciting and futuristic classification than most — it hosts a megamaser. Megamasers are intensely bright, around 100 million times brighter than the masers found in galaxies like the Milky Way. The entire galaxy essentially acts as an astronomical laser that beams out microwave emission rather than visible light (hence the ‘m’ replacing the ‘l’). A megamaser is a process that involves some components within the galaxy (like gas) that is in the right physical condition to cause the amplification of light (in this case, microwaves). But there are other parts of the galaxy (like stars for example) that aren’t part of the maser process. This megamaser galaxy is named IRAS 16399-0937 and is located over 370 million light-years from Earth. This NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image belies the galaxy’s energetic nature, instead painting it as a beautiful and serene cosmic rosebud. The image comprises observations captured across various wavelengths by two of Hubble’s instruments: the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), and the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS). NICMOS’s superb sensitivity, resolution, and field of view gave astronomers the unique opportunity to observe the structure of IRAS 16399-0937 in detail. They found it hosts a double nucleus — the galaxy’s core is thought to be formed of two separate cores in the process of merging. The two components, named IRAS 16399N and IRAS 16399S for the northern and southern parts respectively, sit over 11,000 light-years apart. However, they are both buried deep within the same swirl of cosmic gas and dust and are interacting, giving the galaxy its peculiar structure. The nuclei are very different. IRAS 16399S appears to be a starburst region, where new stars are forming at an incredible rate. IRAS 16399N, however, is something known as a LINER nucleus (Low Ionization Nuclear Emission Region), which is a region whose emission mostly stems from weakly-ionized or neutral atoms of particular gases. The northern nucleus also hosts a black hole with some 100 million times the mass of the sun! Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Judy Schmidt (geckzilla) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
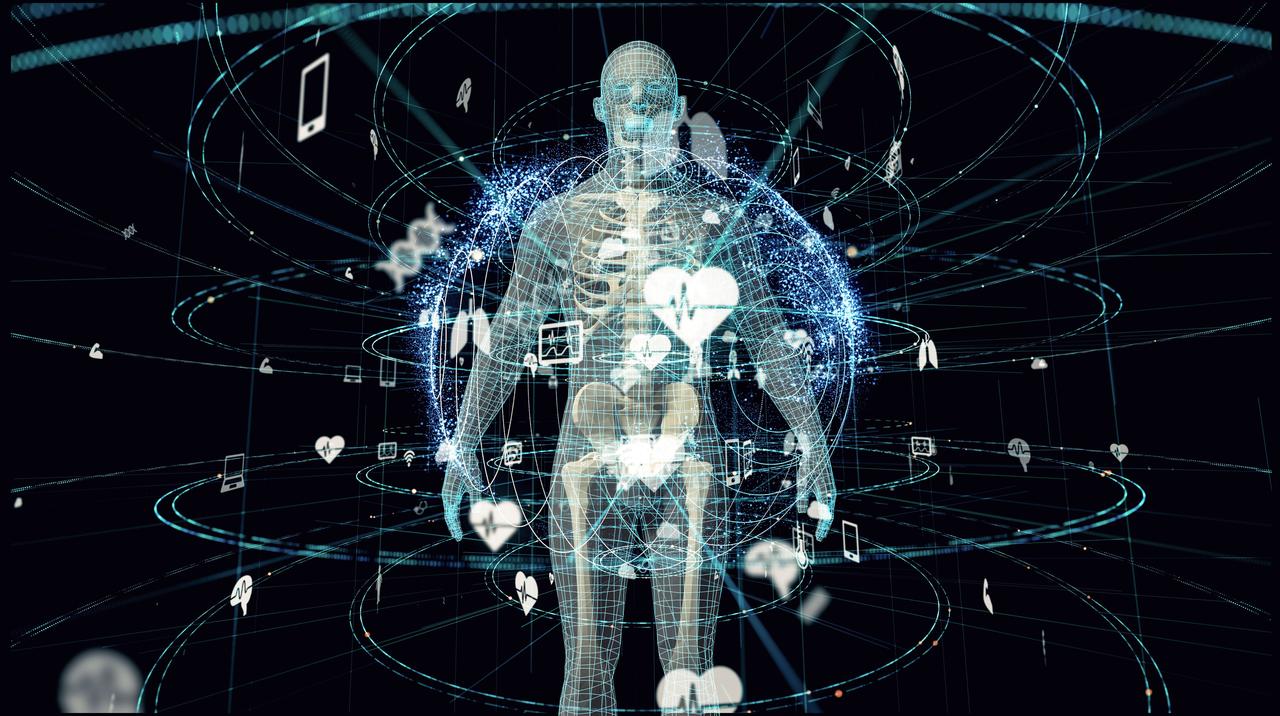
jsc2022e062020 (6/30/2022) --- Space Health will create a digital twin of the astronaut from the data collected by the Bio-Monitor and demonstrate how this could be used for autonomous health monitoring on future space missions. (Image courtesy of CSA)