
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lights are reflected on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft during illumination testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A Ball Aerospace and Technology worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers conduct a light test on the solar array panels of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Ball Aerospace and Technology workers adjust the light cast on solar array panels during illumination testing of NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Kepler will hunt for planets using a specialized one-meter diameter telescope called a photometer to measure the small changes in brightness caused by the transits. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
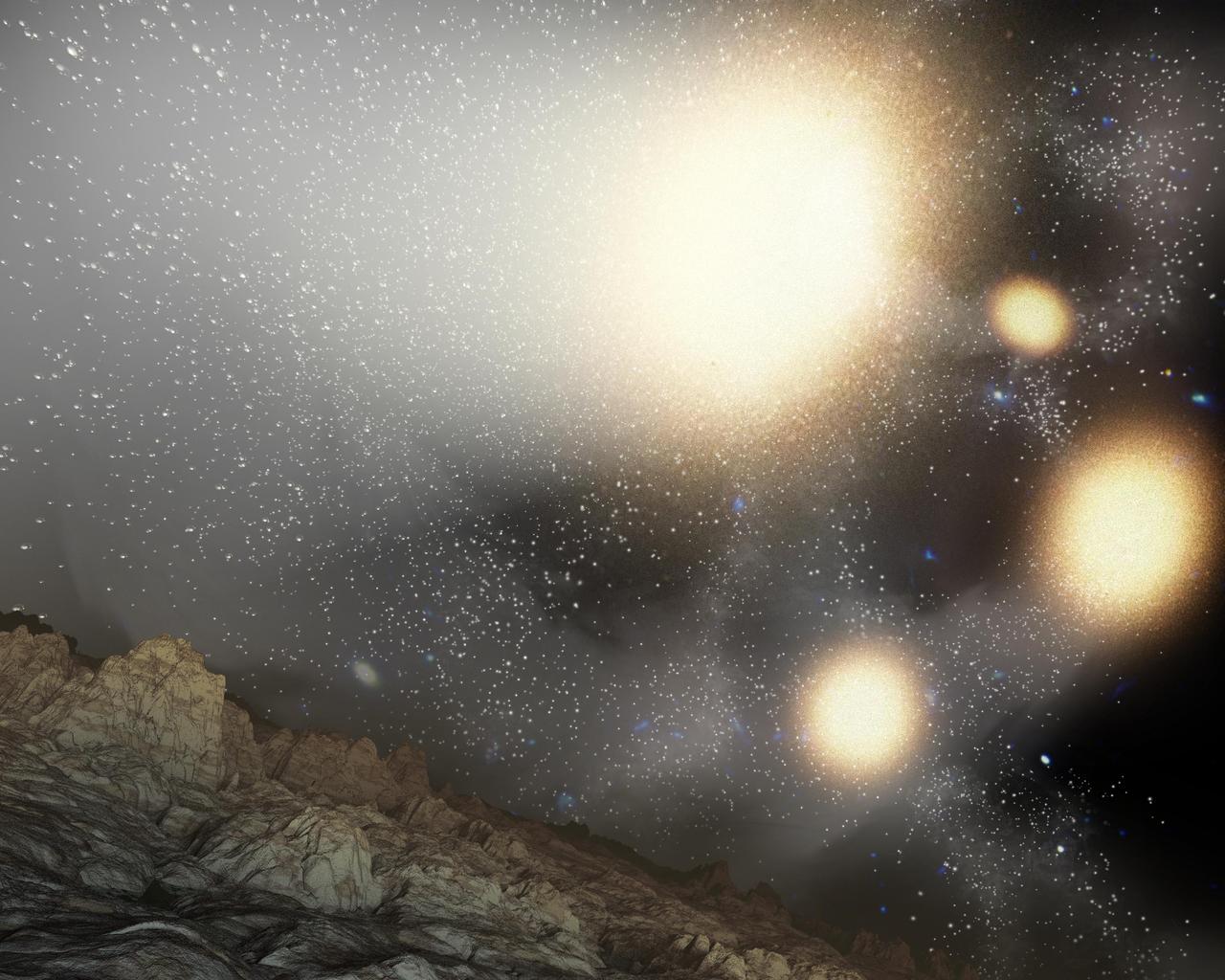

This artist concept shows what the night sky might look like from a hypothetical planet around a star tossed out of an ongoing four-way collision between big galaxies.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
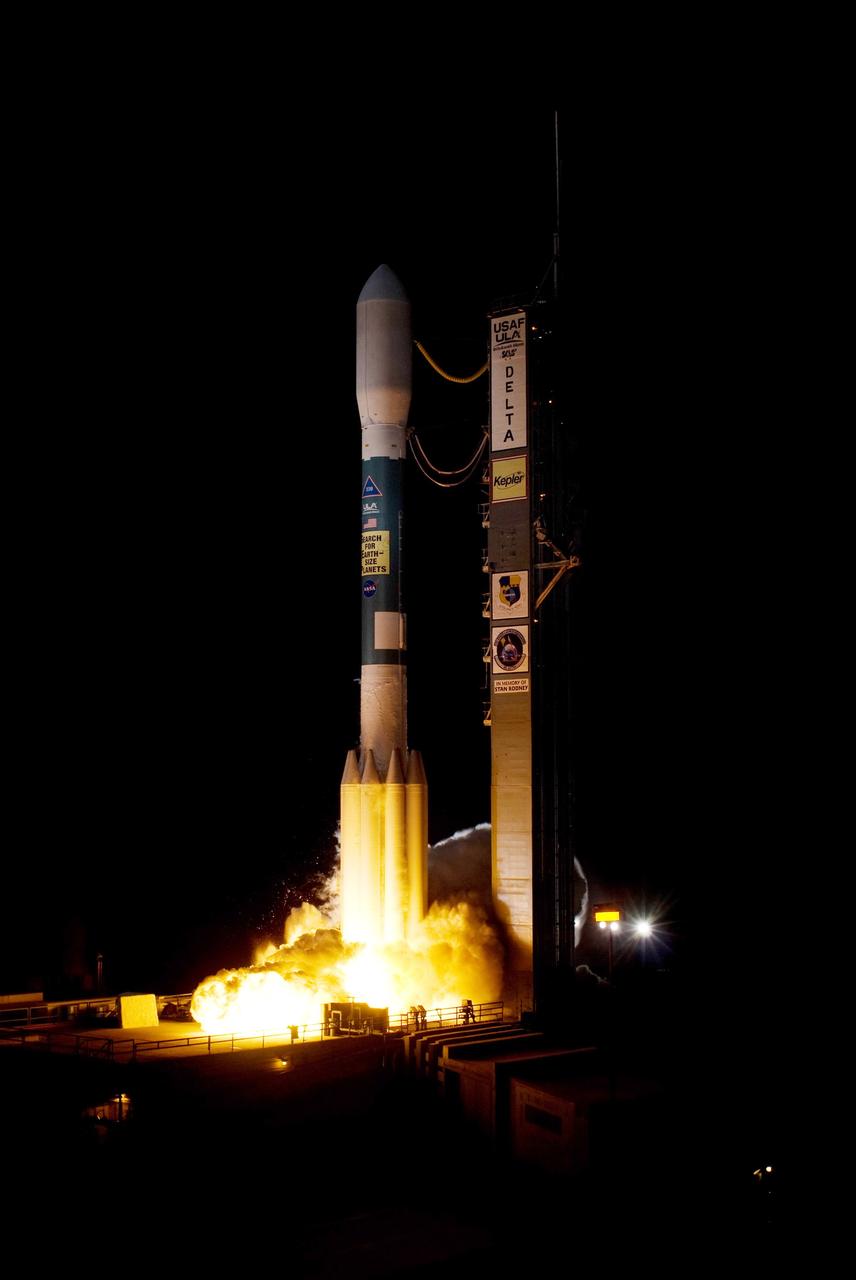

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the engines on United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
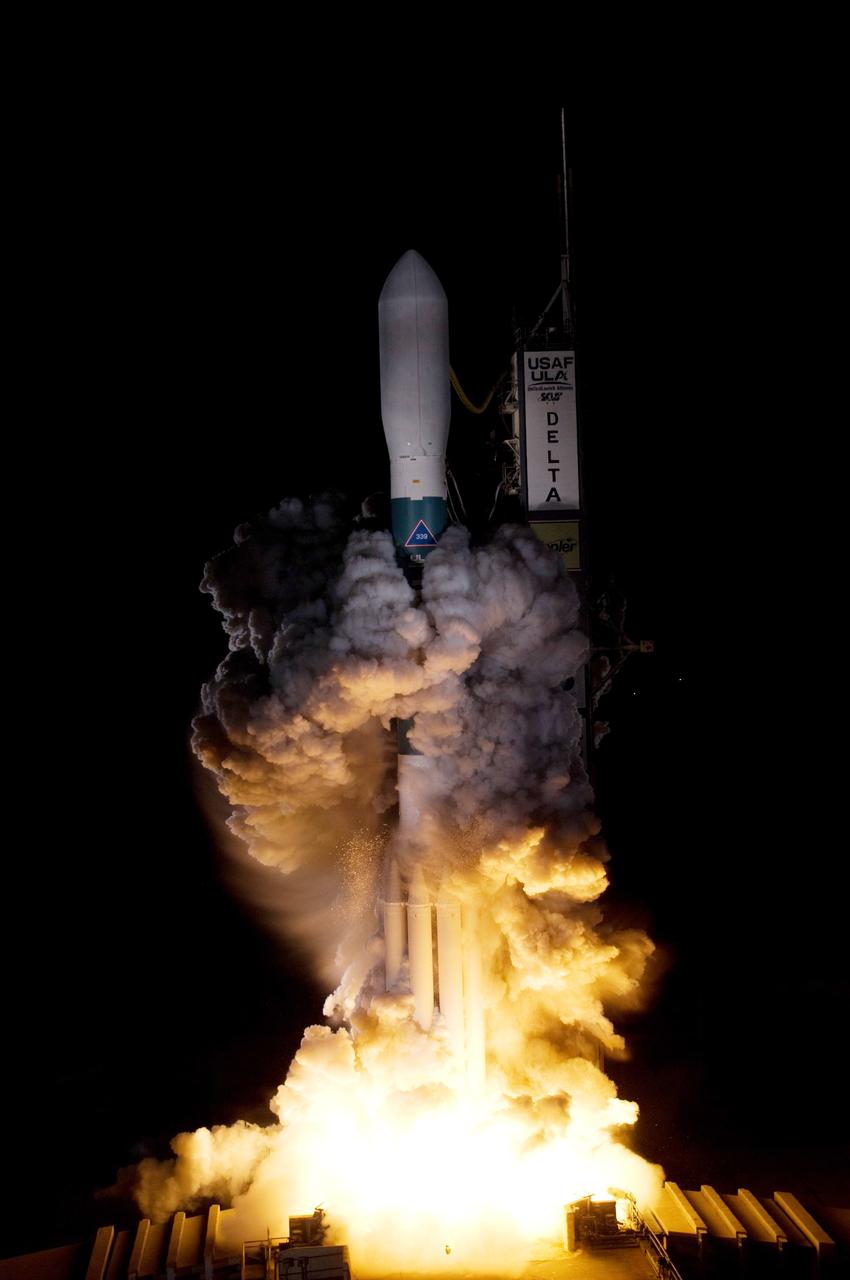

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft rises through the exhaust cloud created by the firing of the rocket’s engines. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Regina Mitchell-Ryall, Tom Farrar
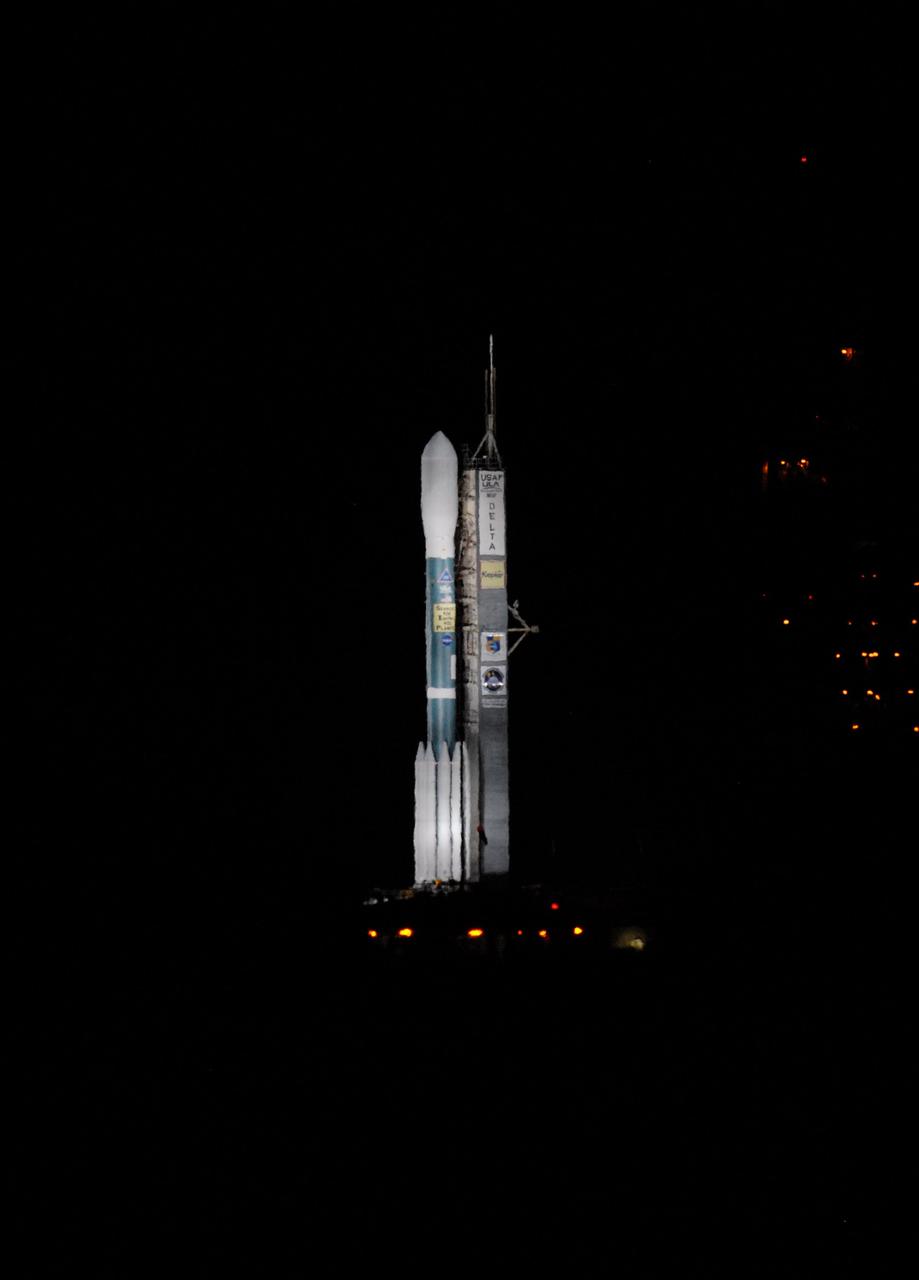

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket, with NASA's Kepler spacecraft aboard, is bathed in light on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida prior to launch. Liftoff is planned for 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
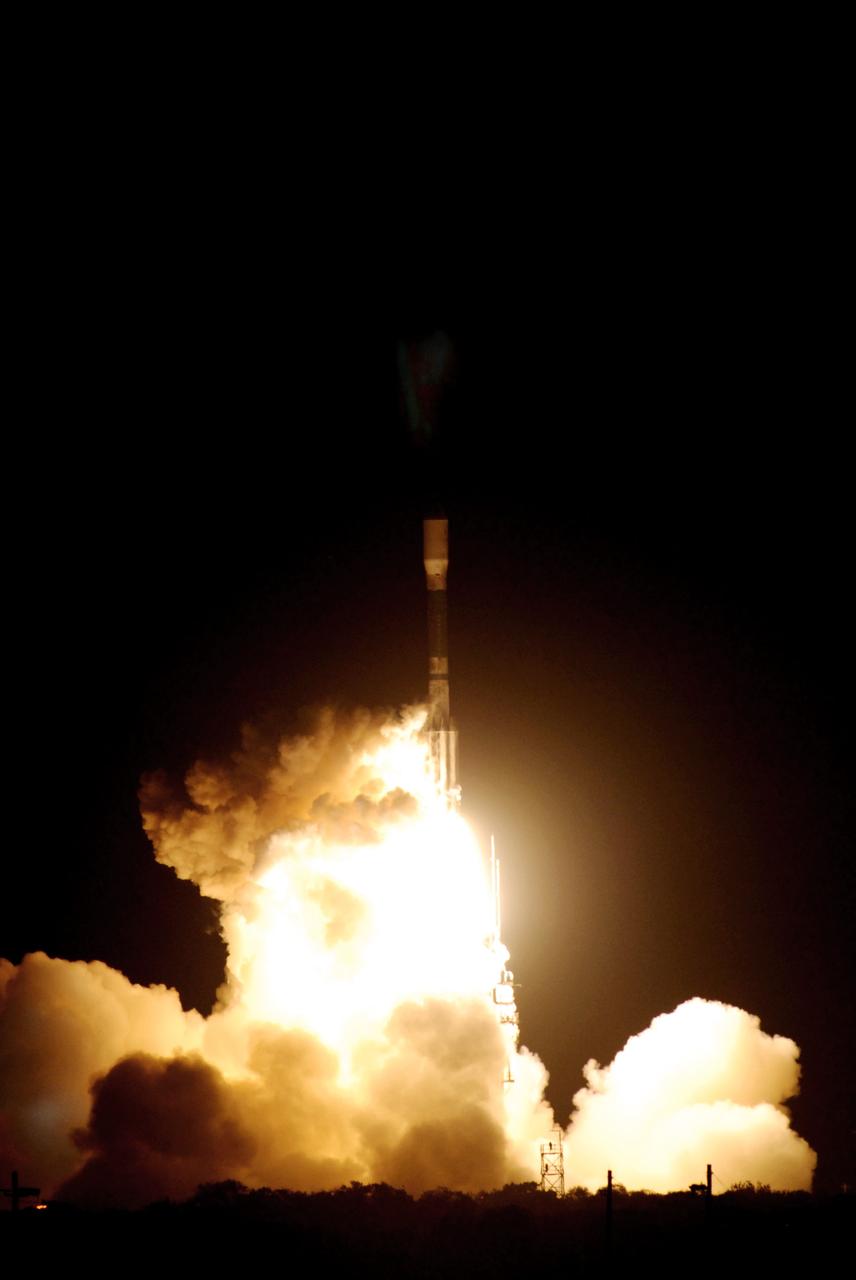

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket roars into the night sky carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
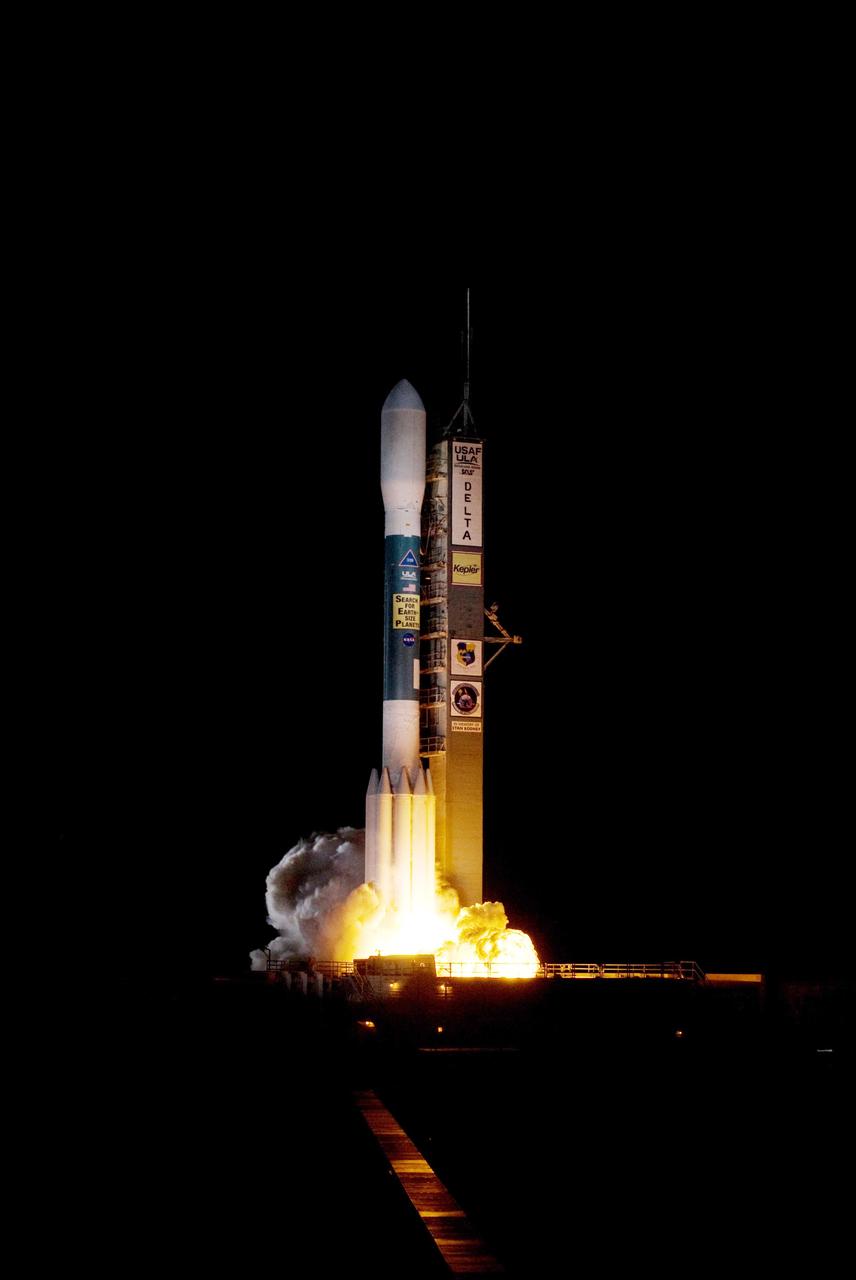

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, exhaust clouds cascade around the base of United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft as the rocket’s engines ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph, Kevin O'Connell
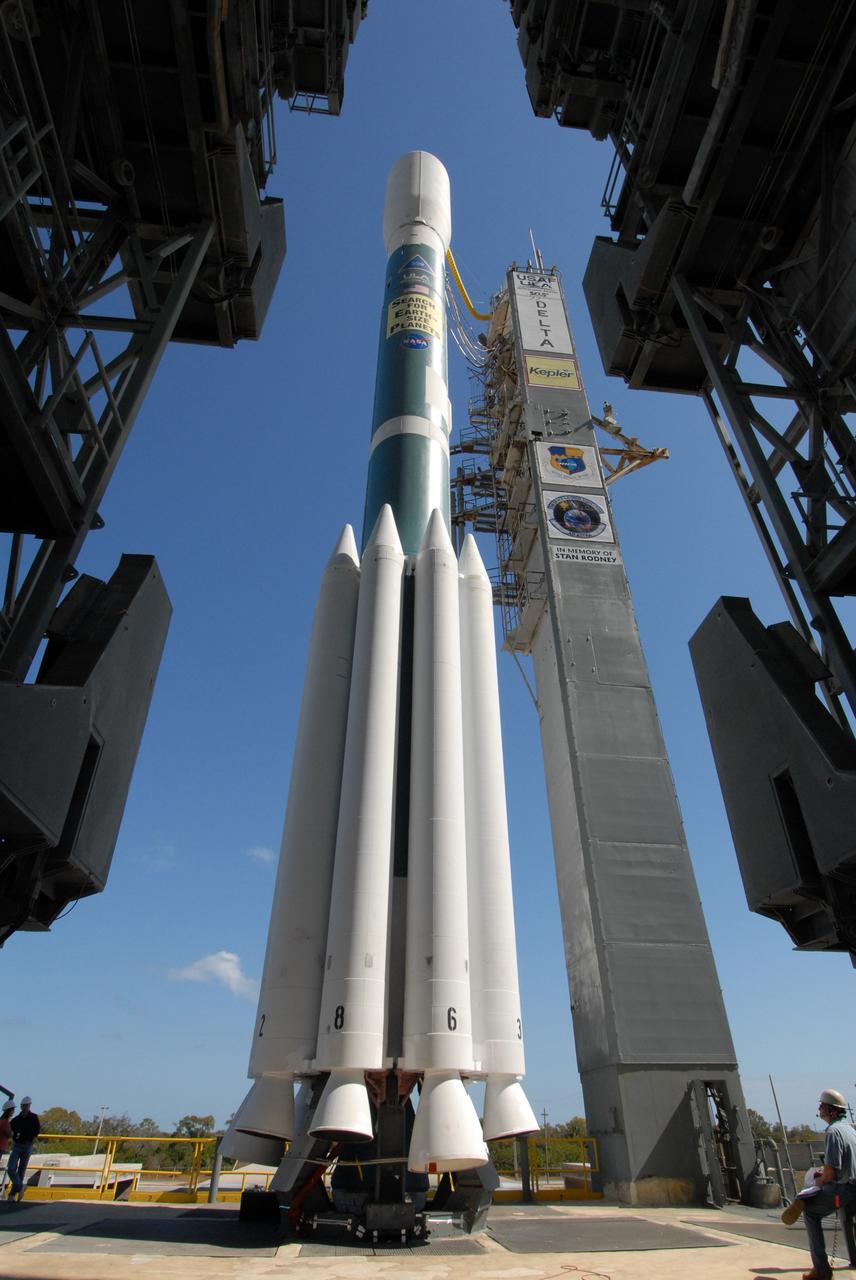

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
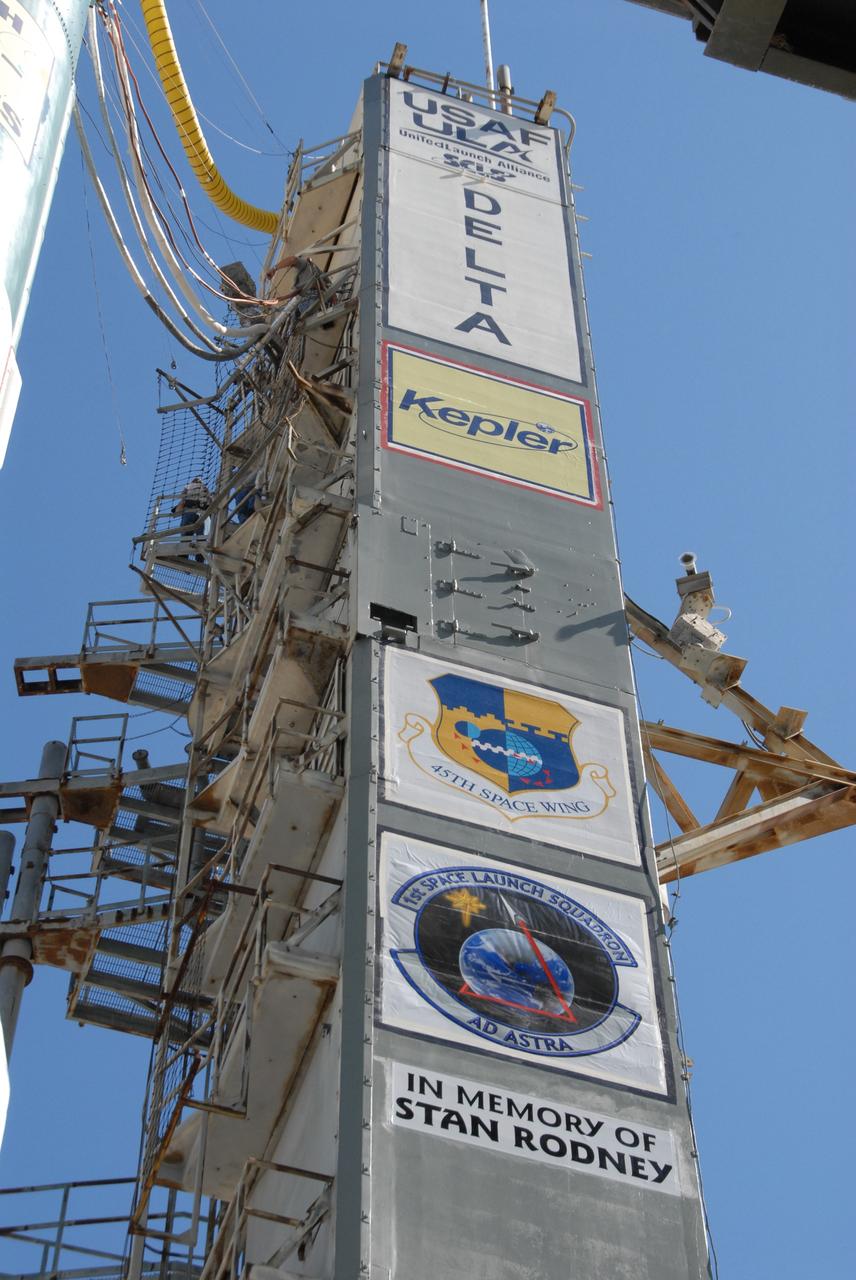

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The gantry on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida shows the various logos of NASA's Kepler spacecraft launch. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
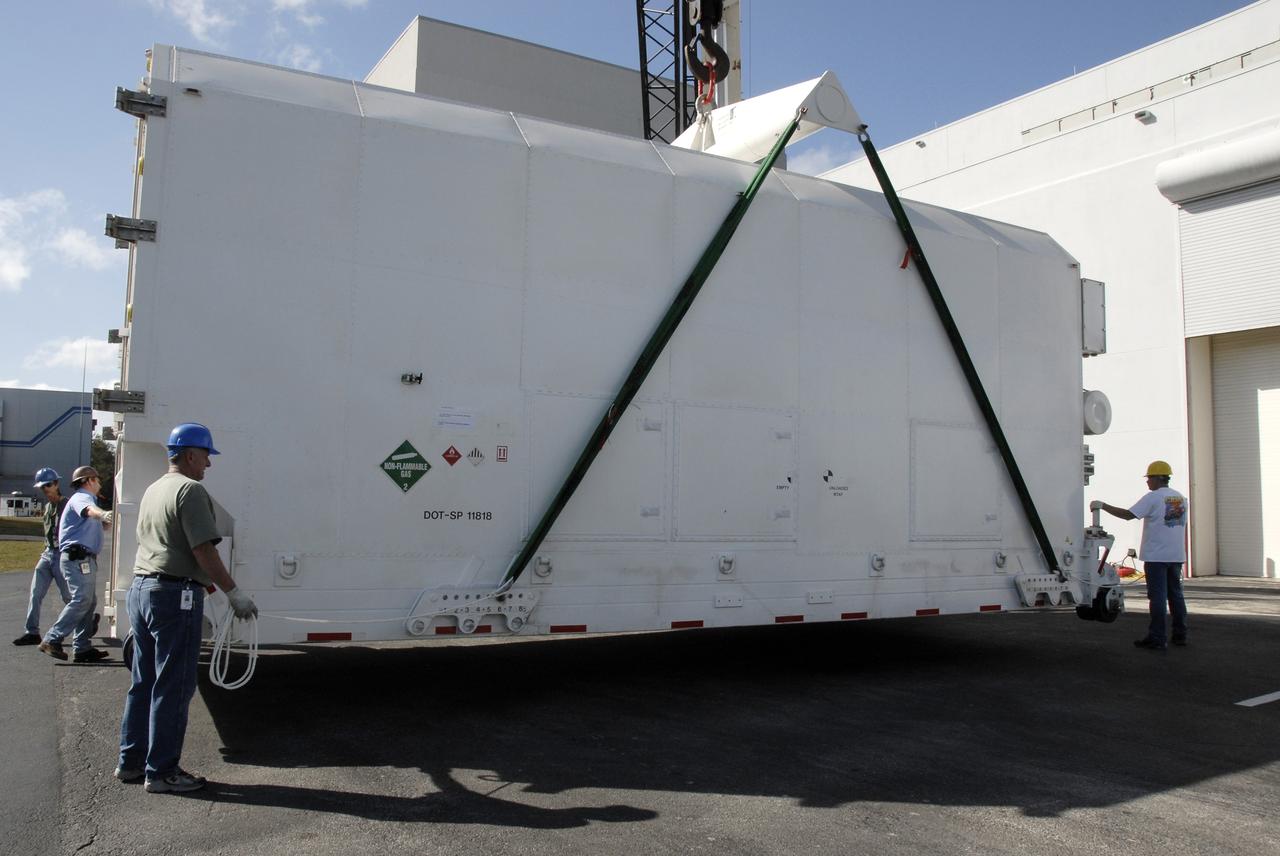

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
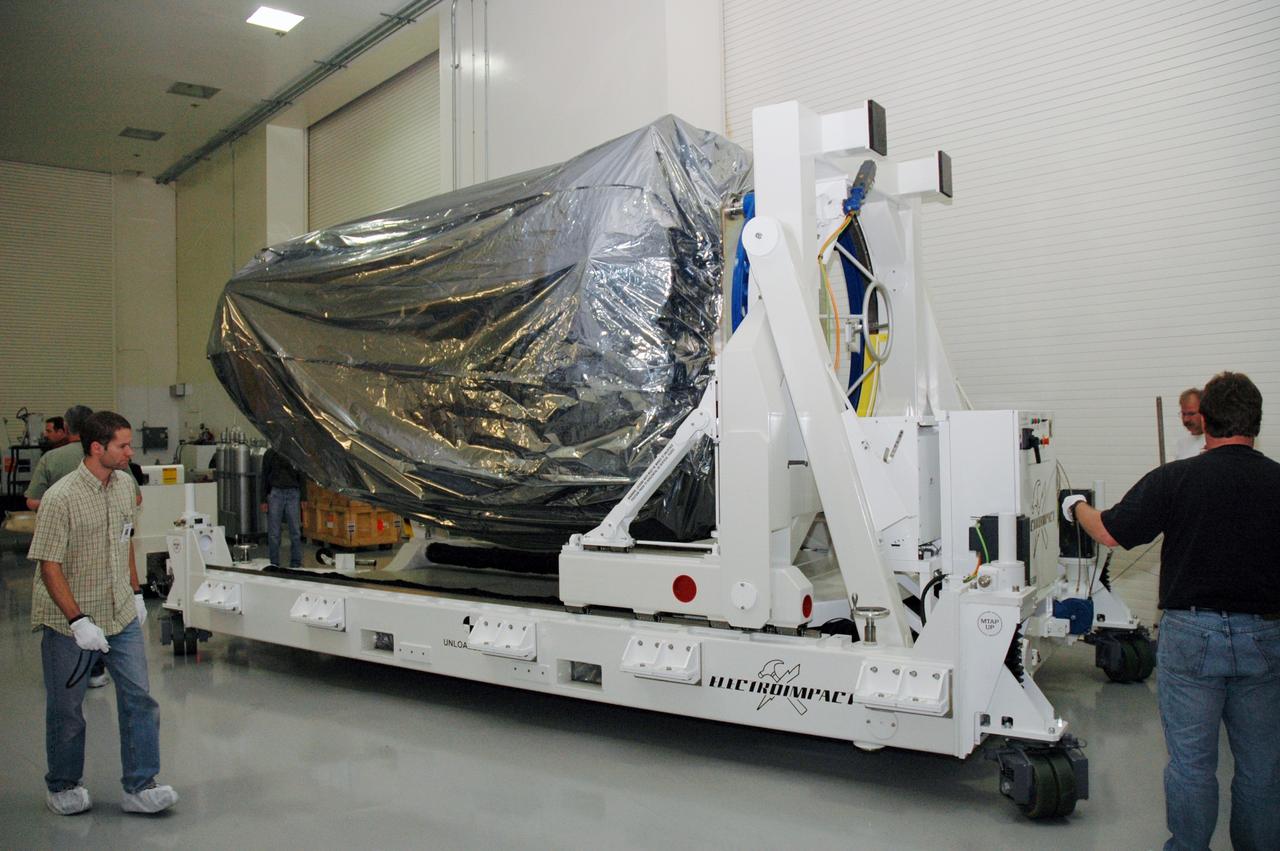

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is rolled into a clean room. The spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
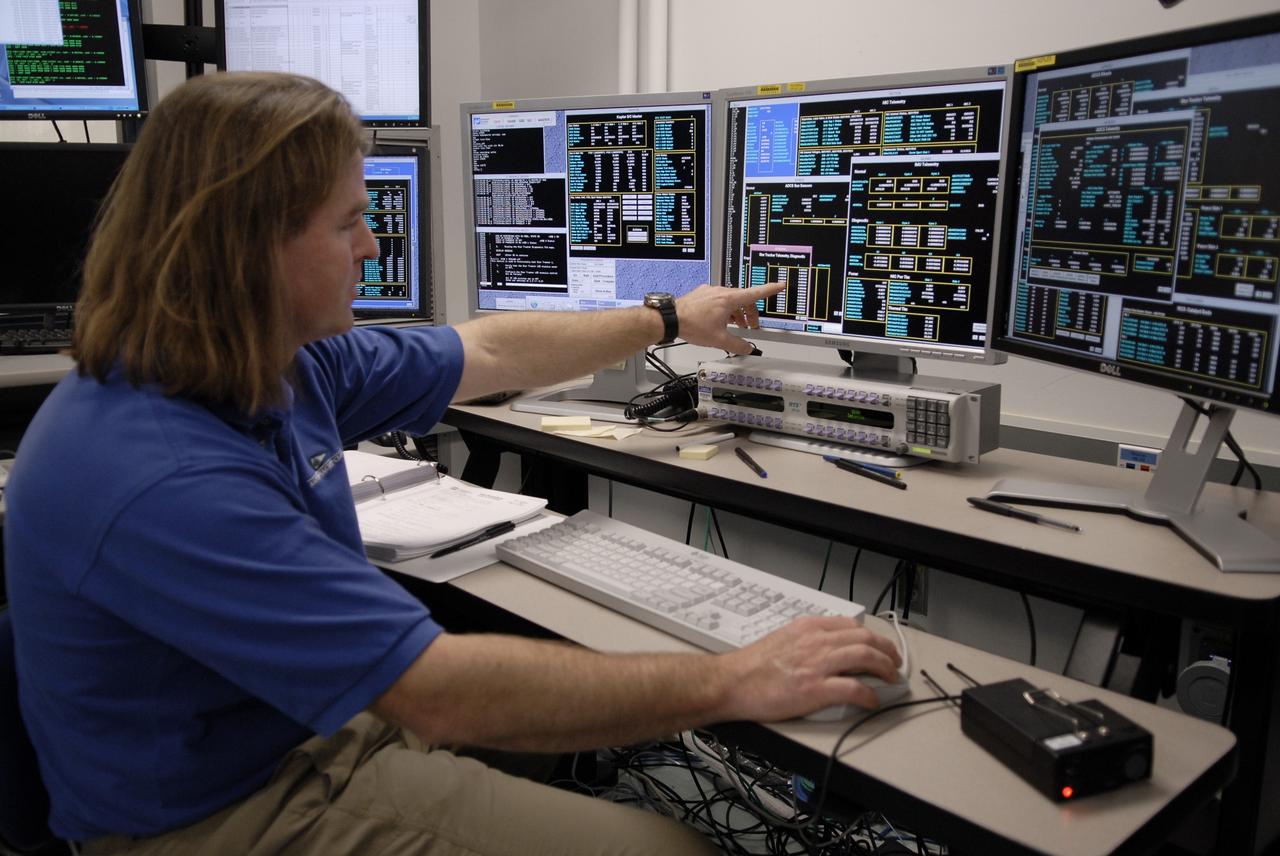

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. technician Phil Mislinski checks data from the light sensor test conducted on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Ball Aerospace was responsible for the flight segment design and fabrication. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
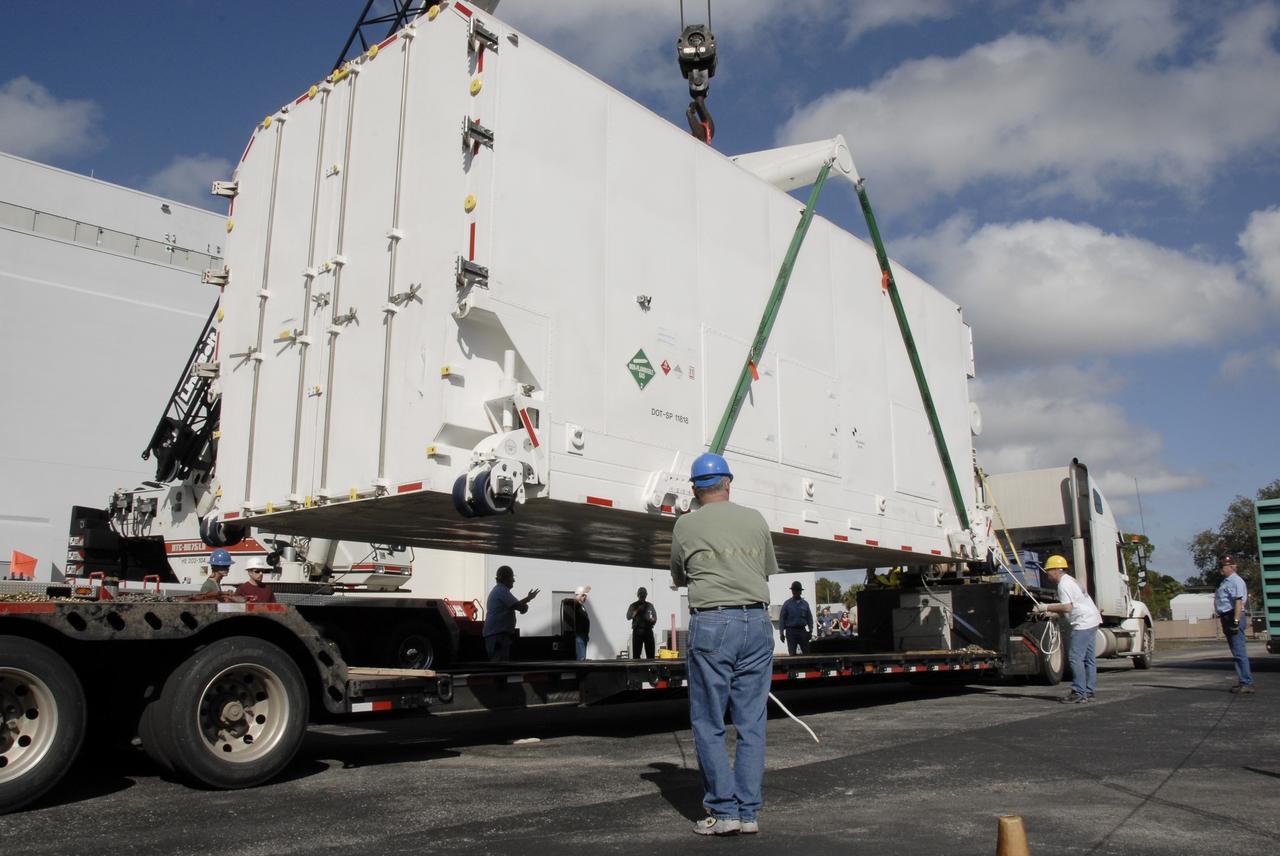

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is lifted off the trailer outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
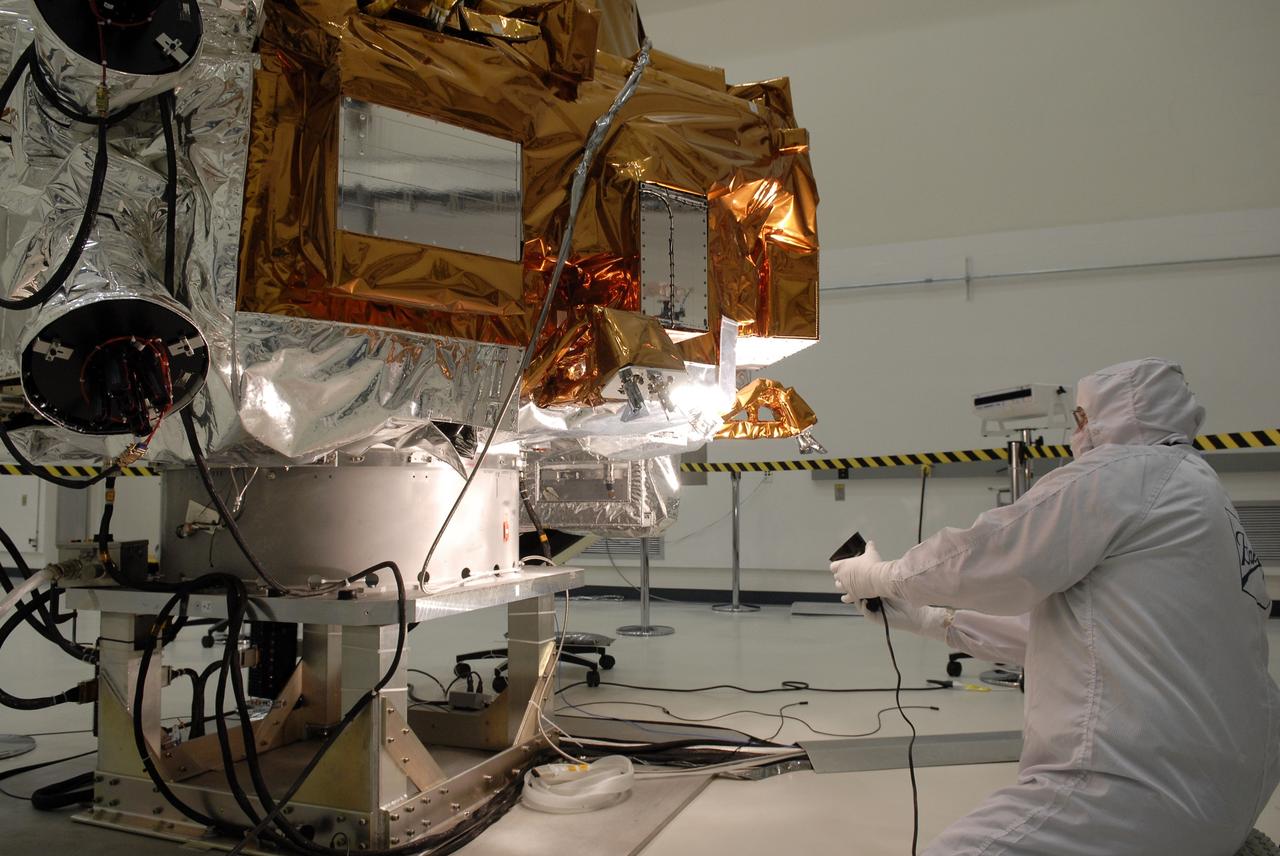

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
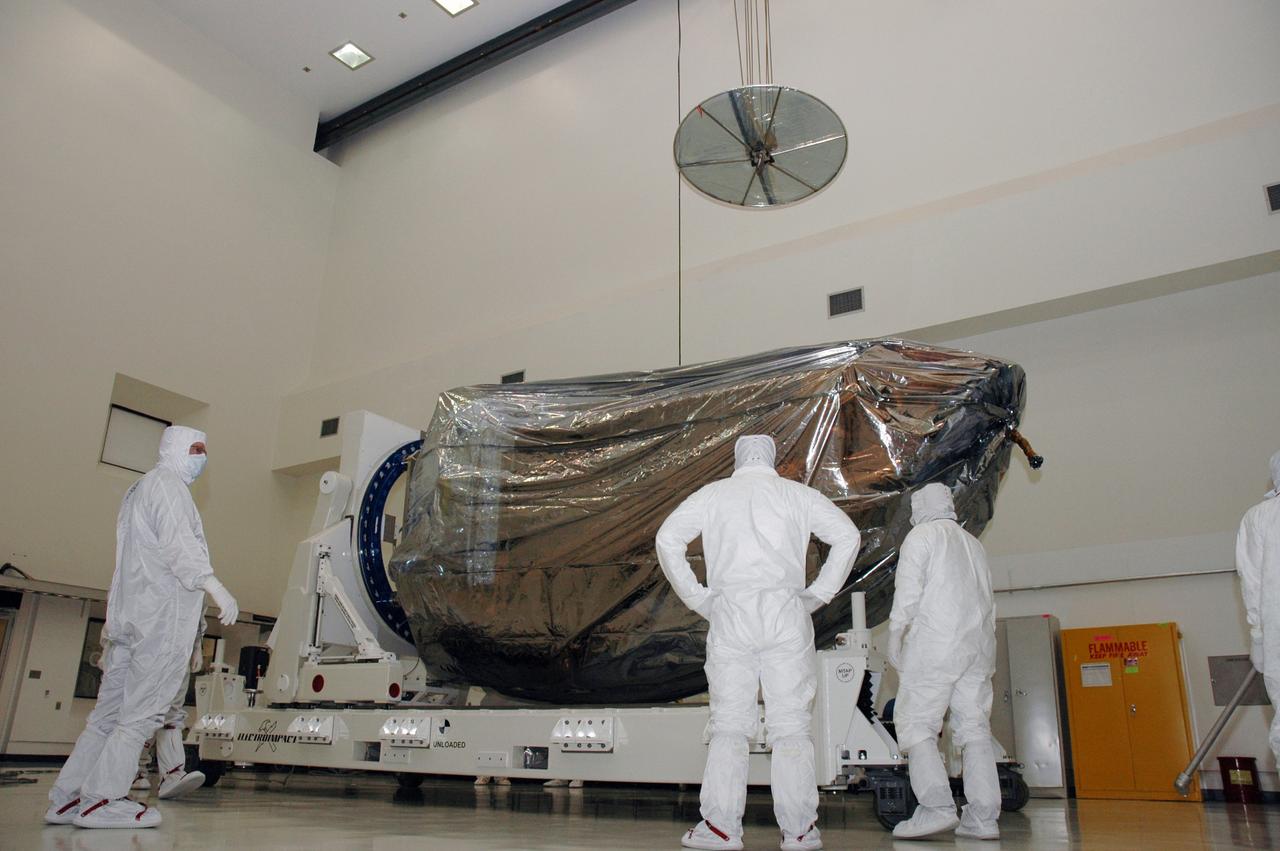

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In a clean room at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare to rotate NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will then be uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
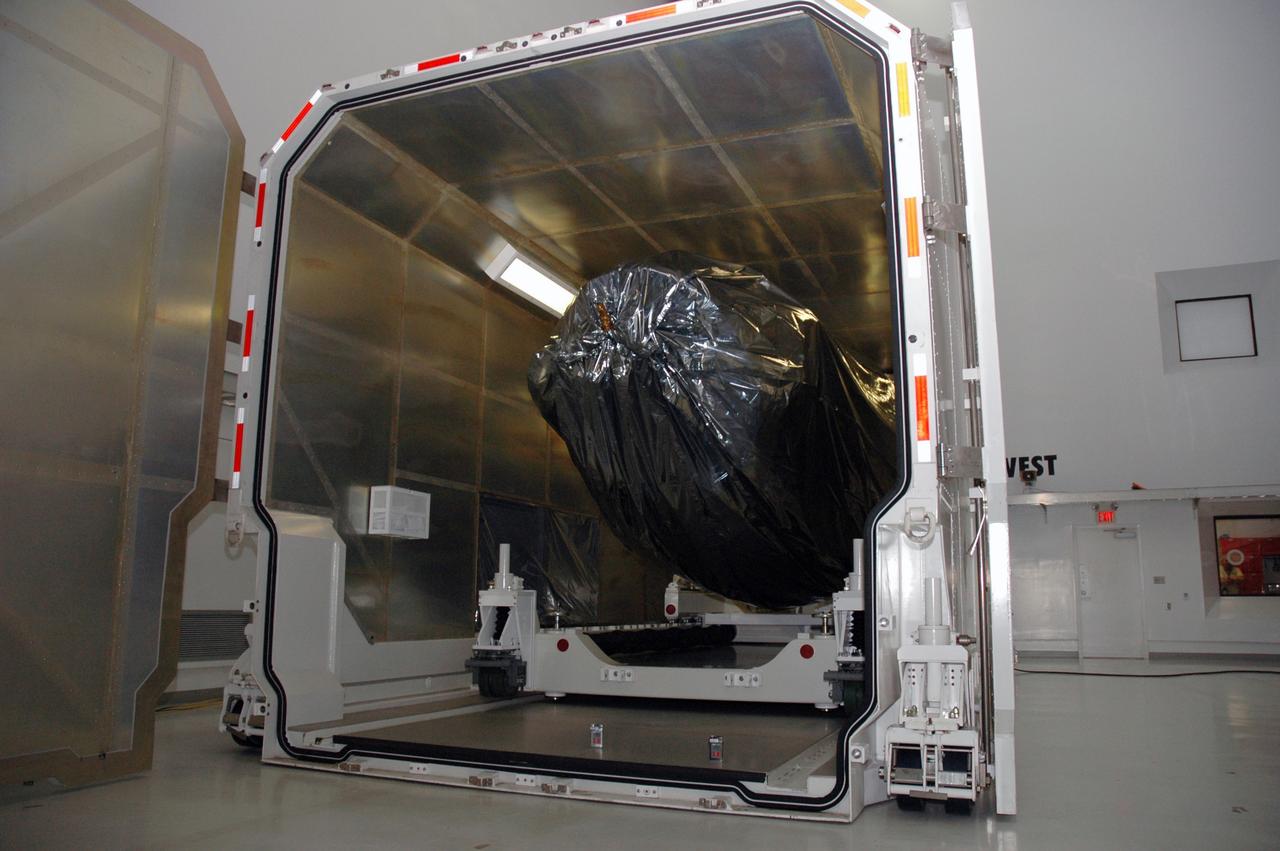

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the open doors of the shipping container reveal NASA's Kepler spacecraft. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
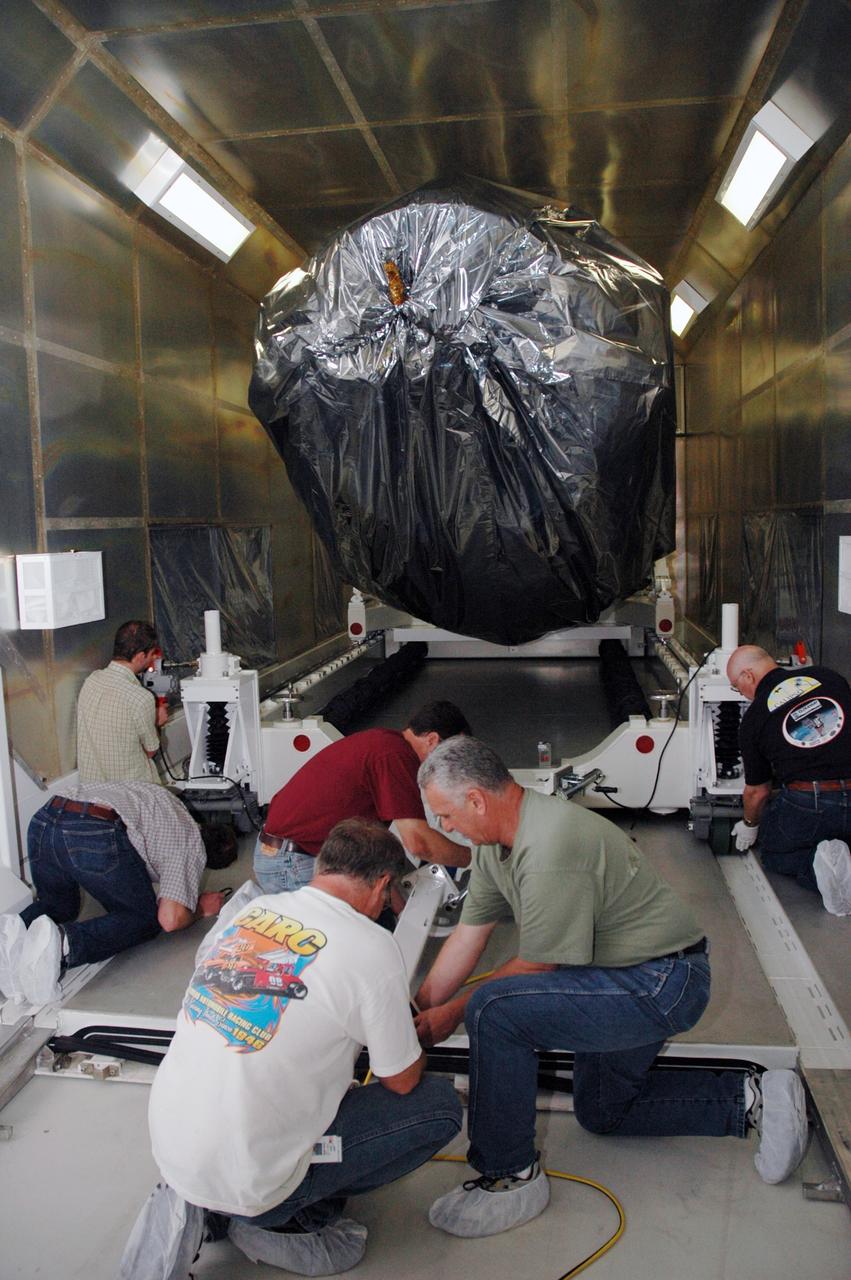

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare the mobile stand for removal of NASA's Kepler spacecraft from its shipping container. After its removal, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
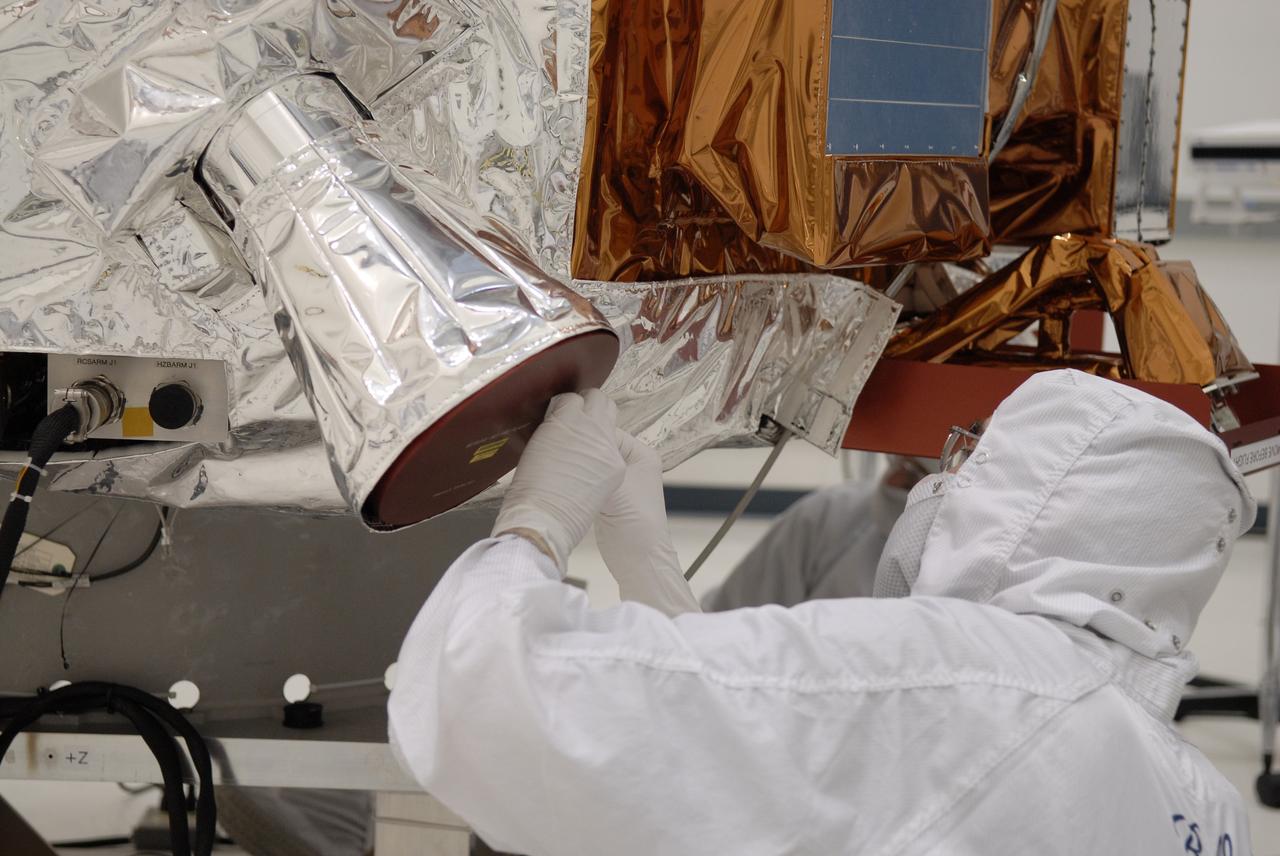

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
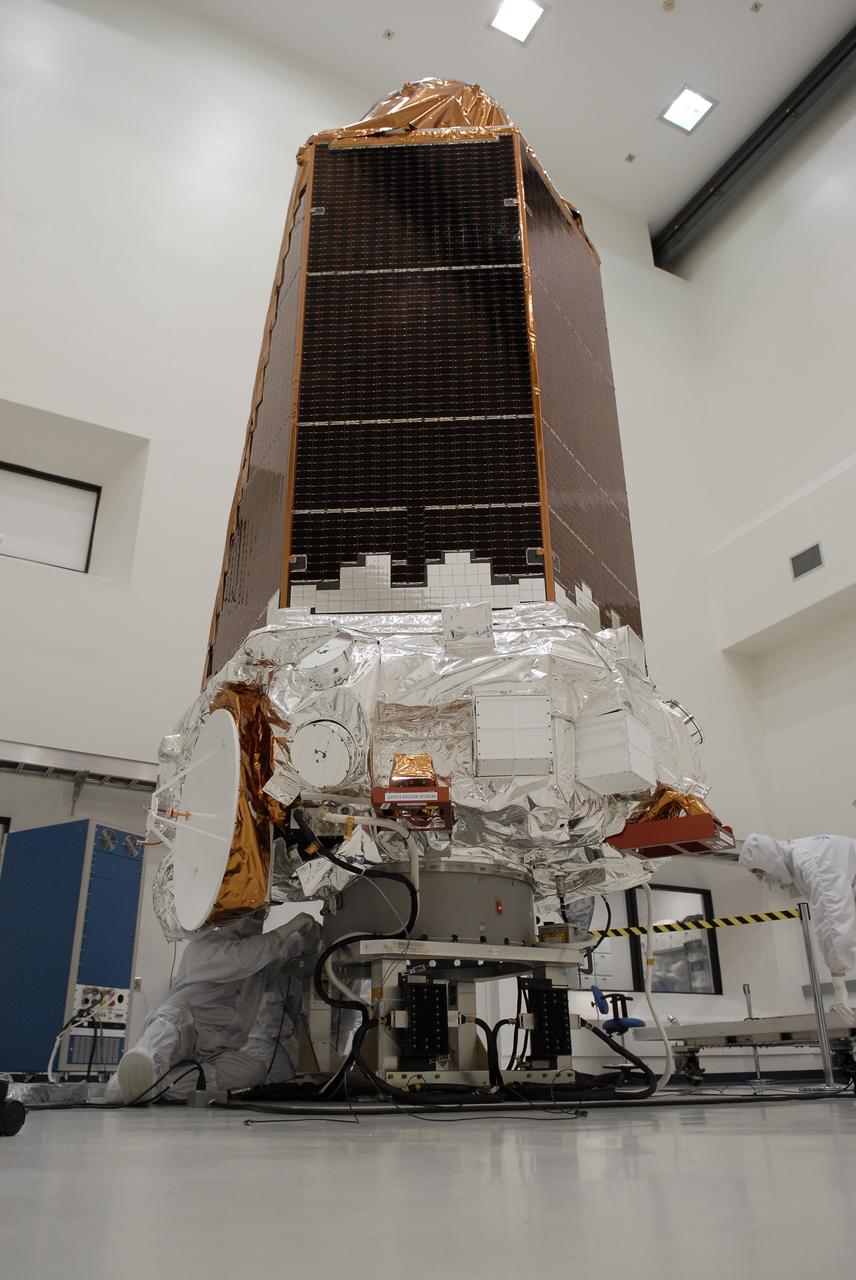

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
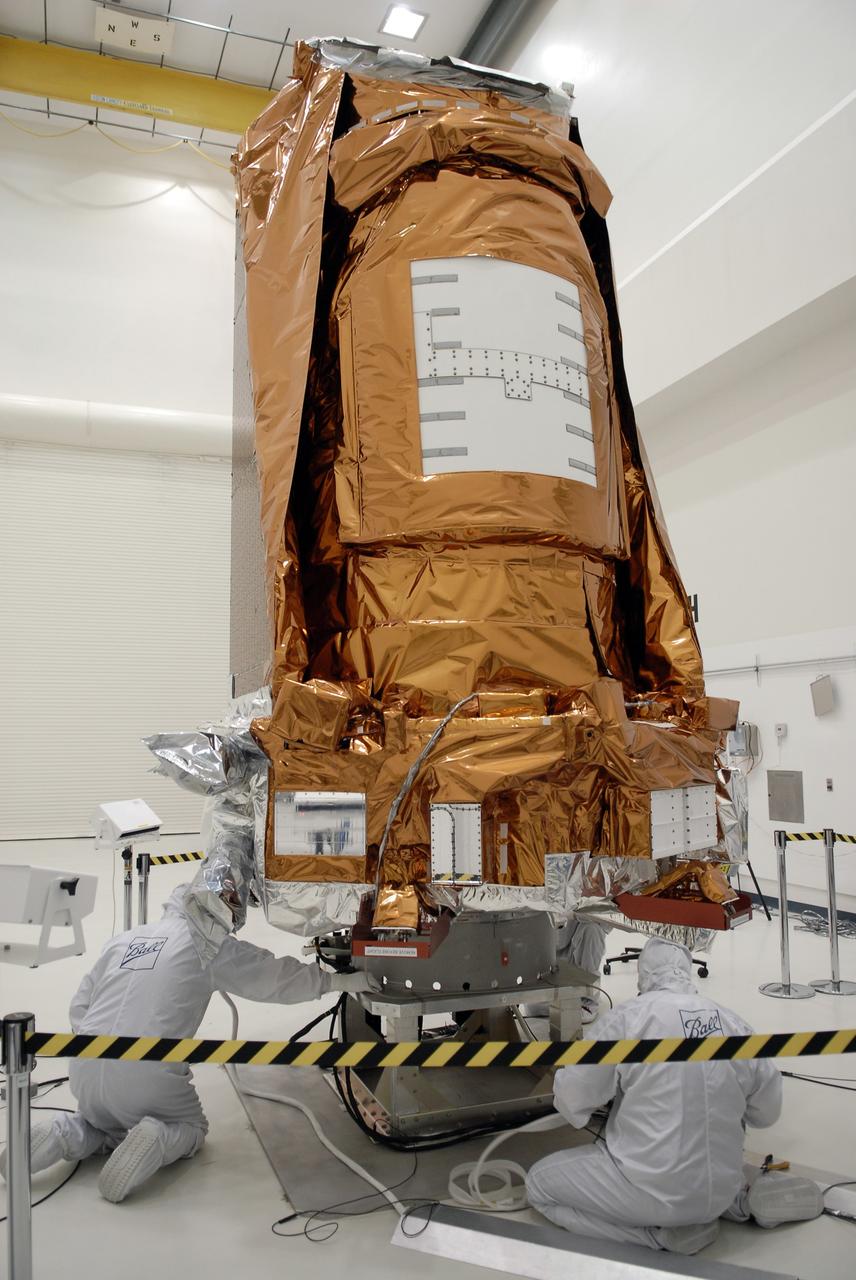

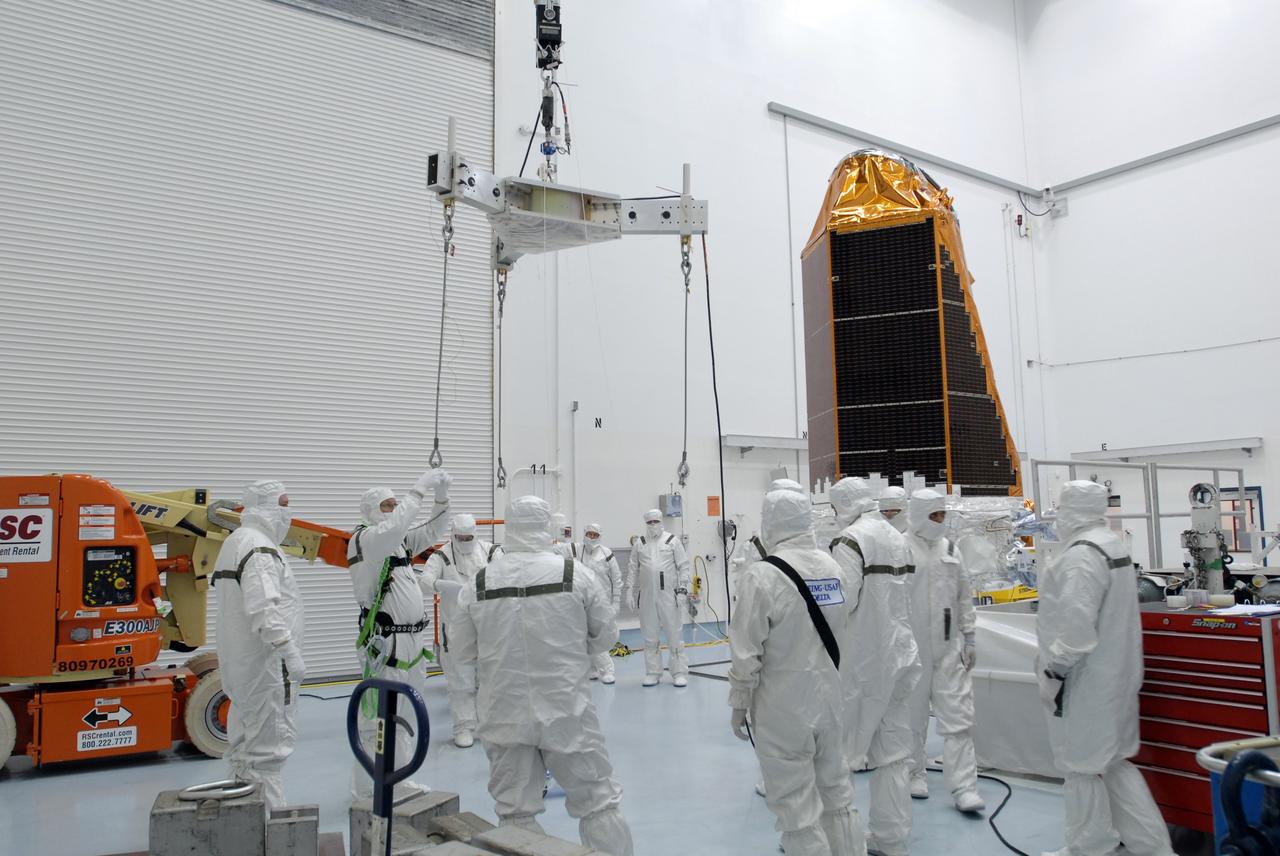
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers from Ball Aerospace check the Star Trackers on NASA's Kepler spacecraft before testing. Star Trackers are small aperture, space-qualified optical products which assure a spacecraft’s accurate navigation in space. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
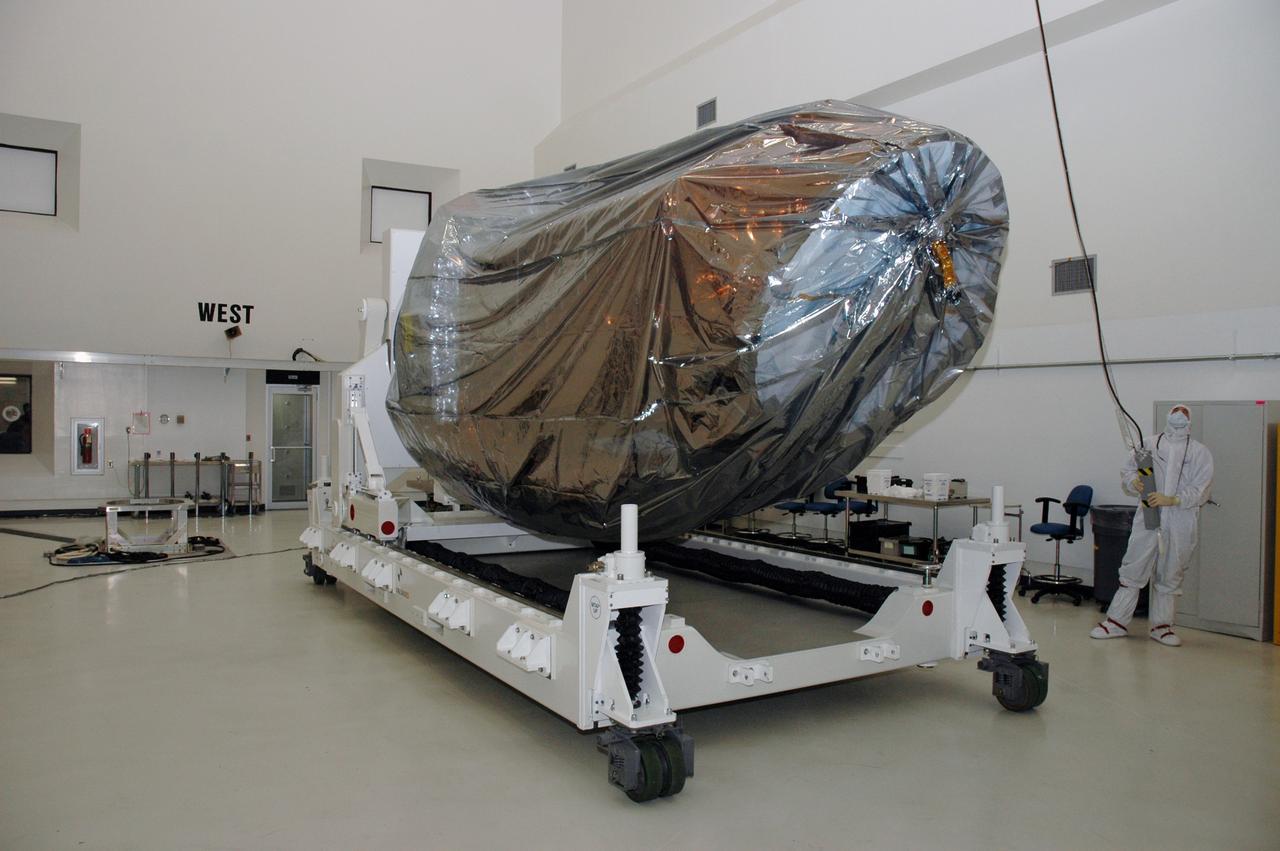

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In a clean room at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare to rotate NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will then be uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
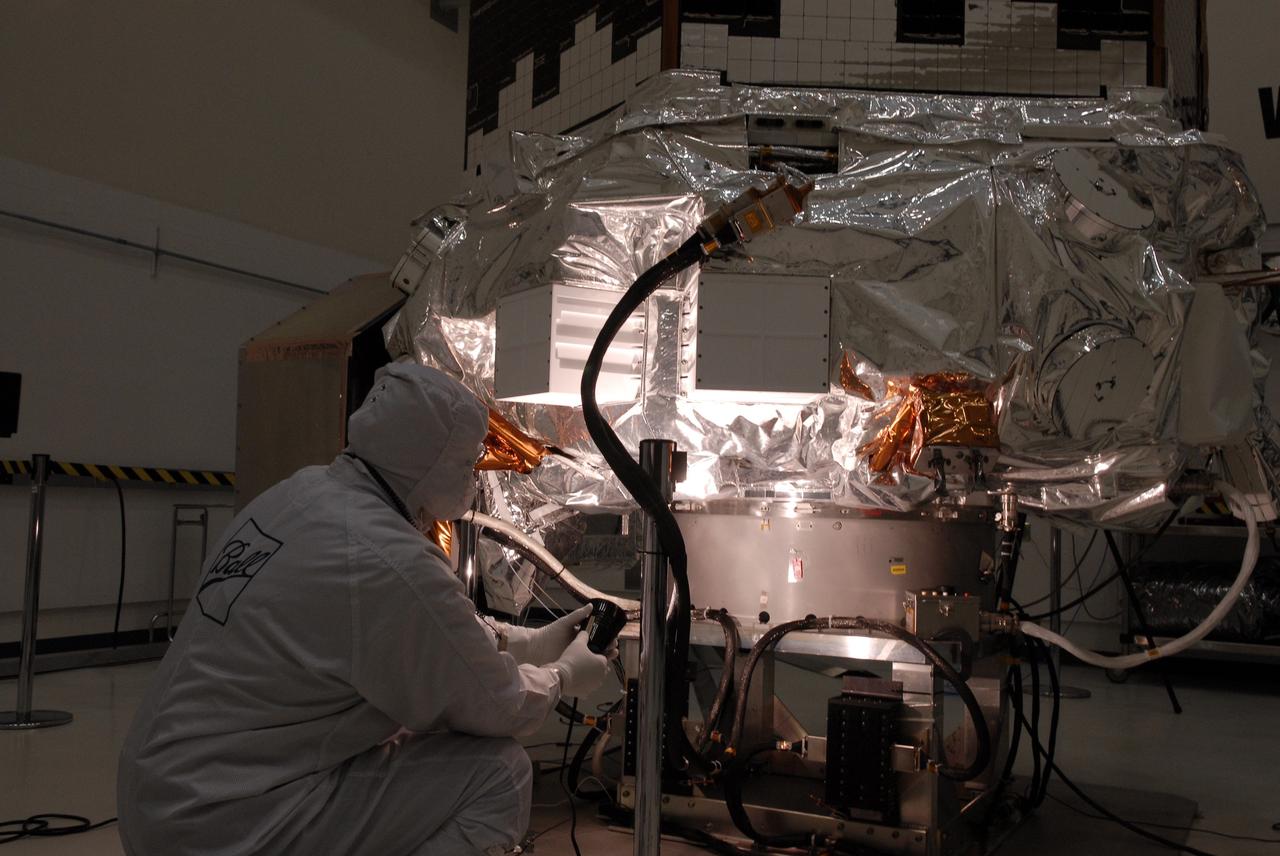

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
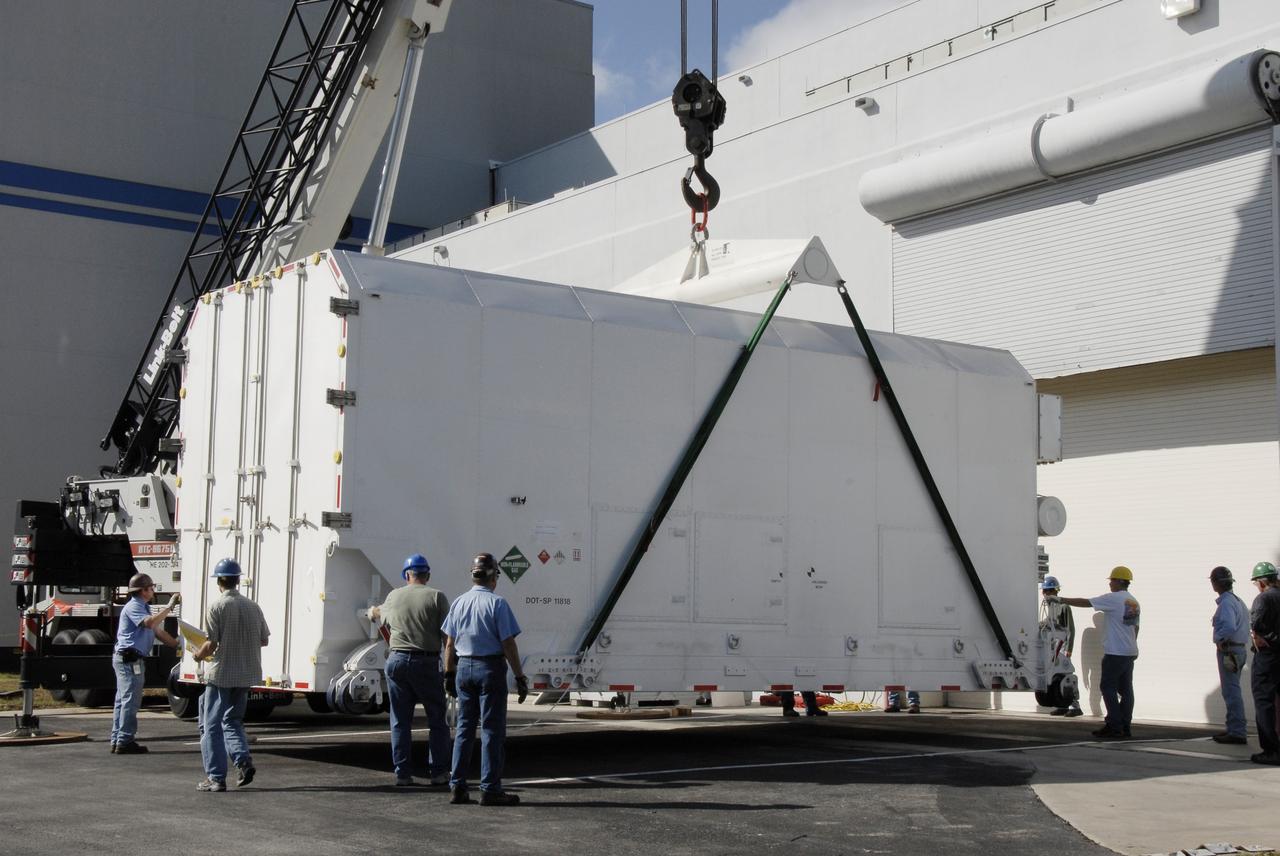

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
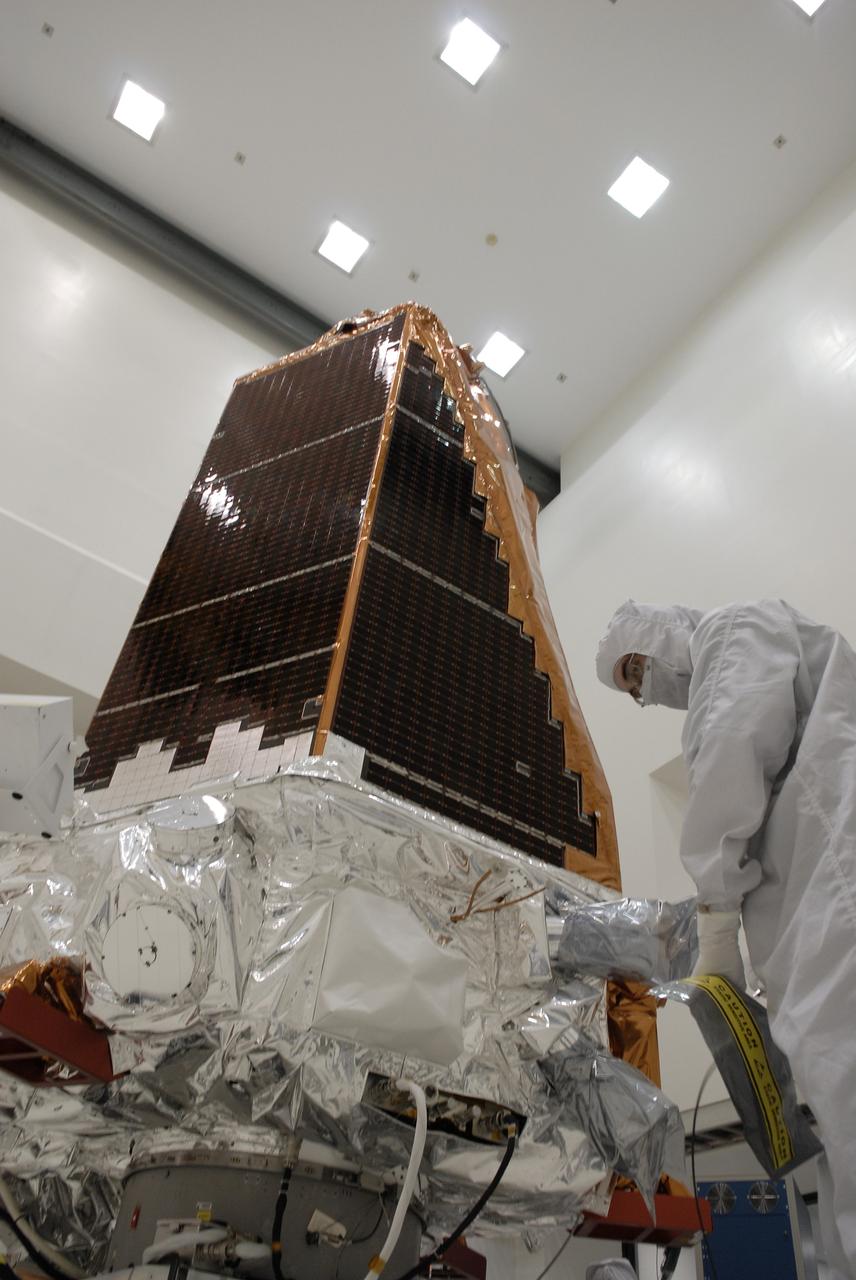

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
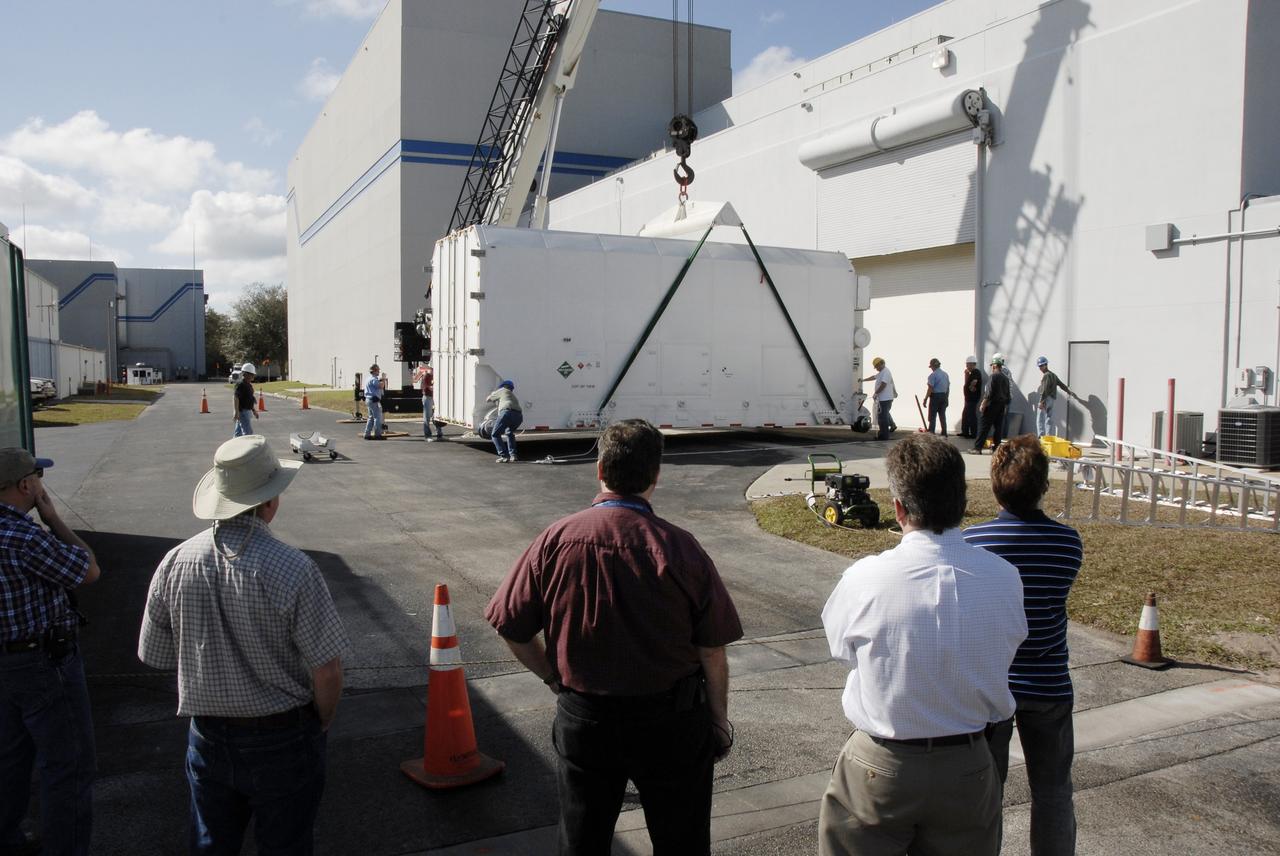

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
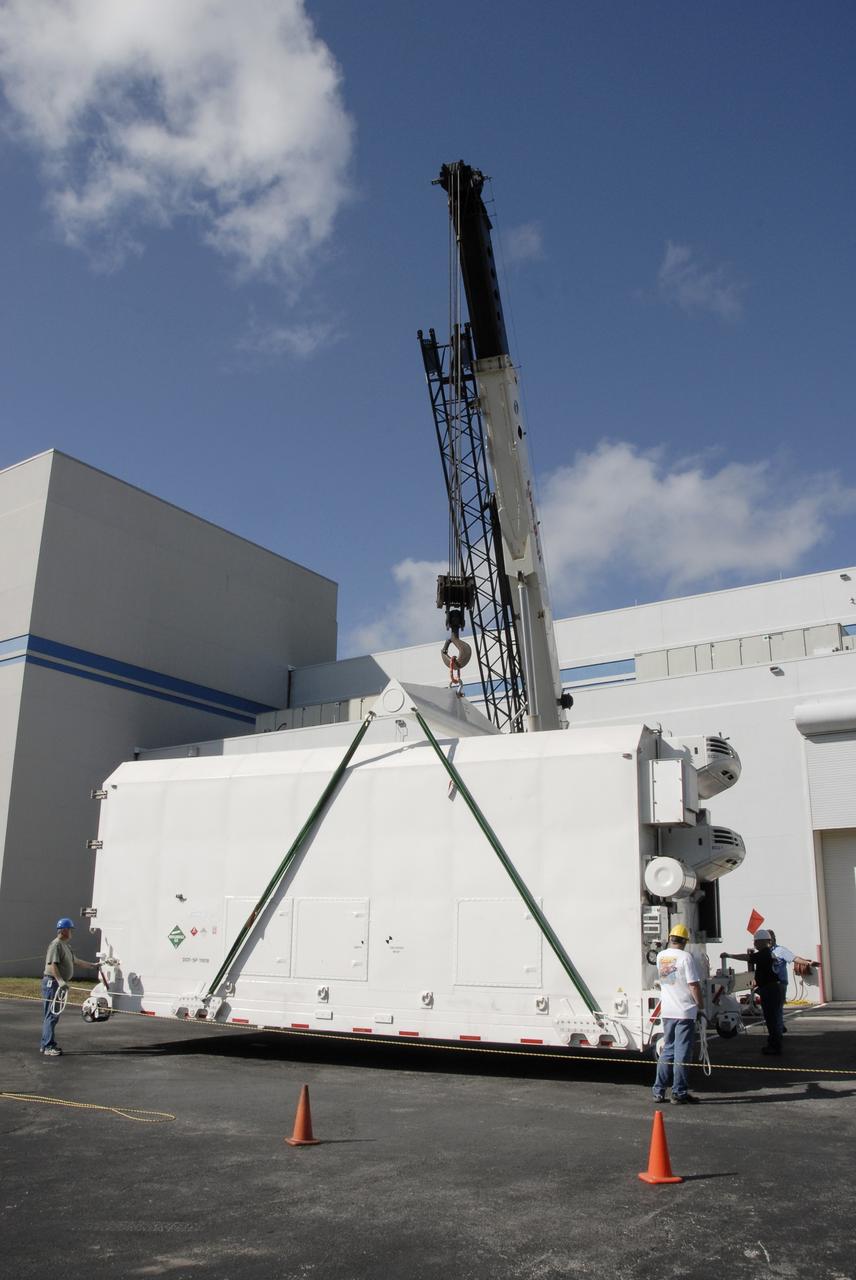

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The shipping container holding the Kepler spacecraft is placed on the tarmac outside Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., before being moved inside. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
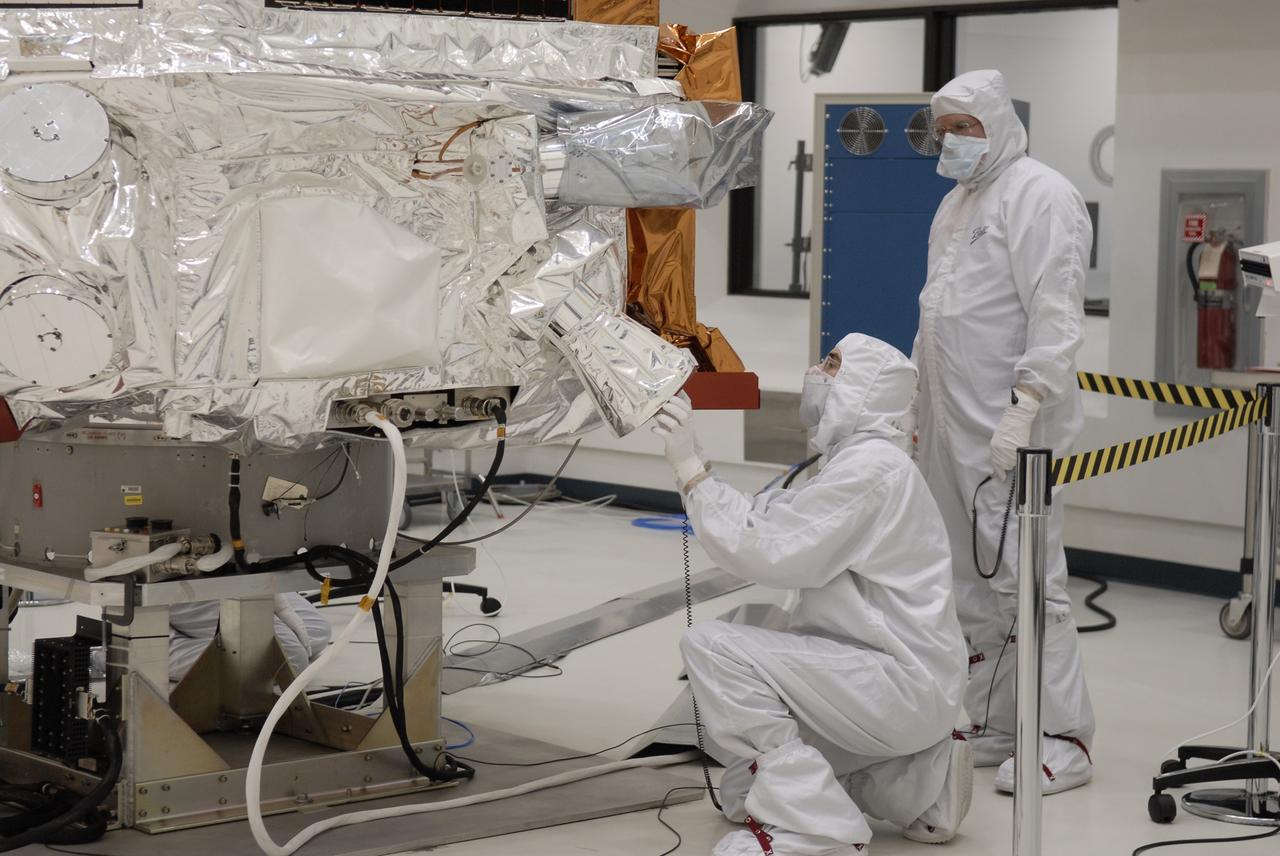

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is prepared for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
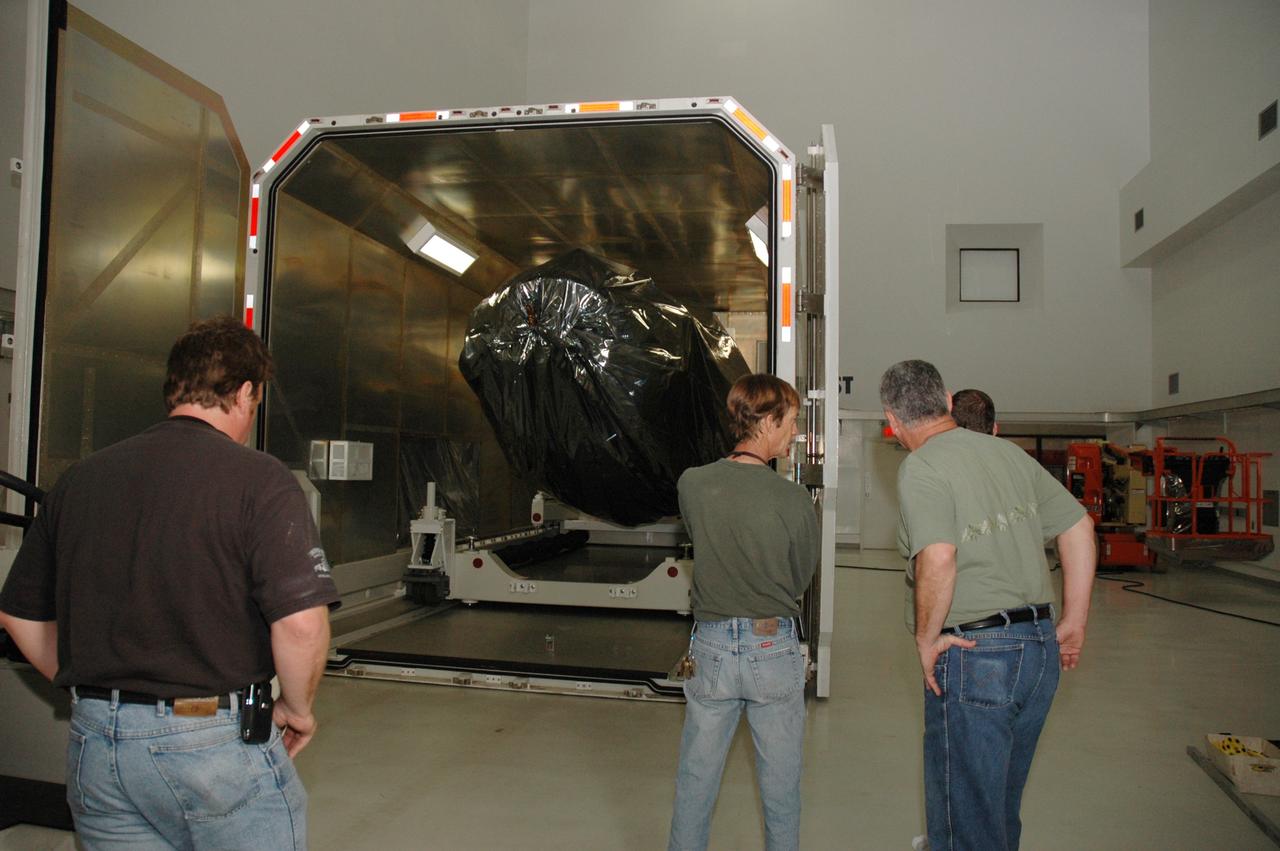

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., doors are opened on the shipping container holding NASA's Kepler spacecraft. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
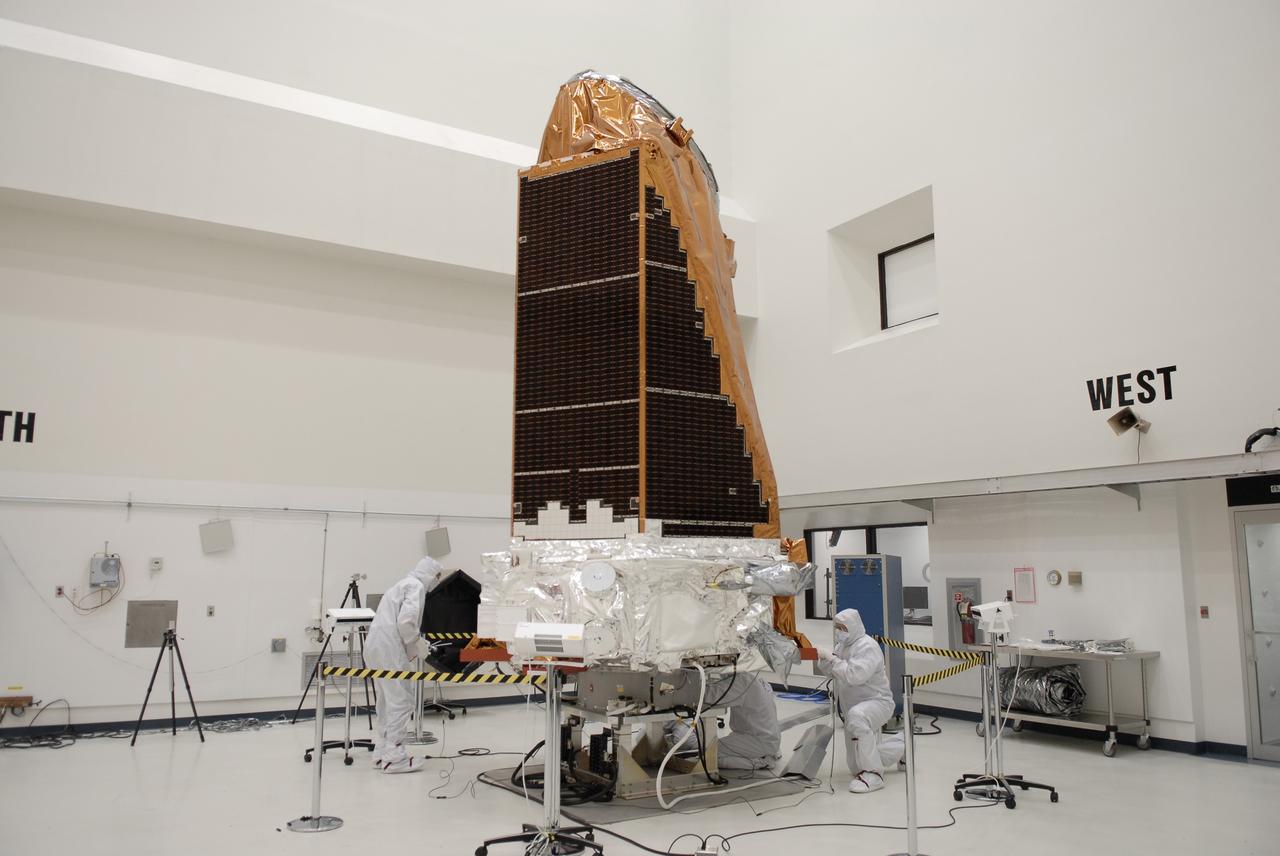

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., workers from Ball Aerospace check the star trackers on NASA's Kepler spacecraft before testing. Star Trackers are small aperture, space-qualified optical products which assure a spacecraft’s accurate navigation in space. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
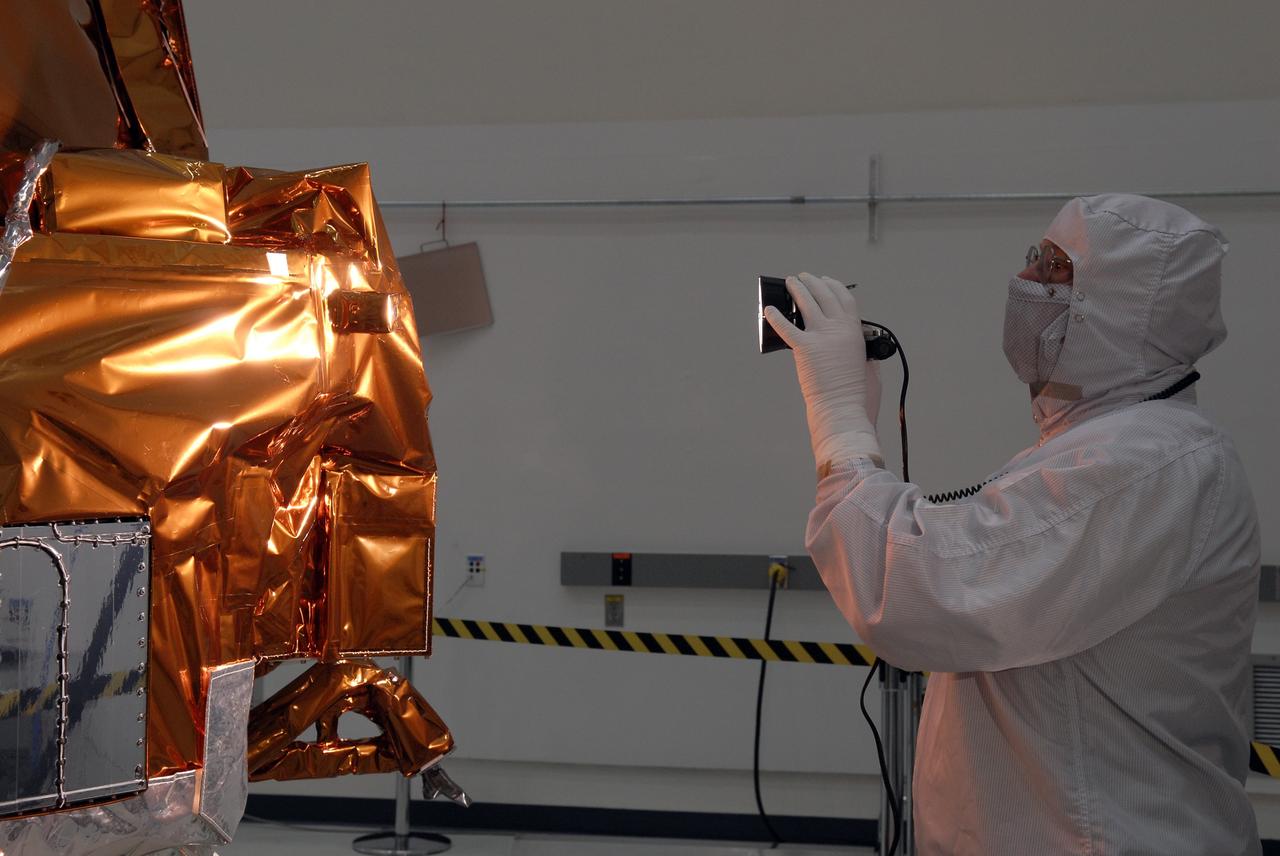

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
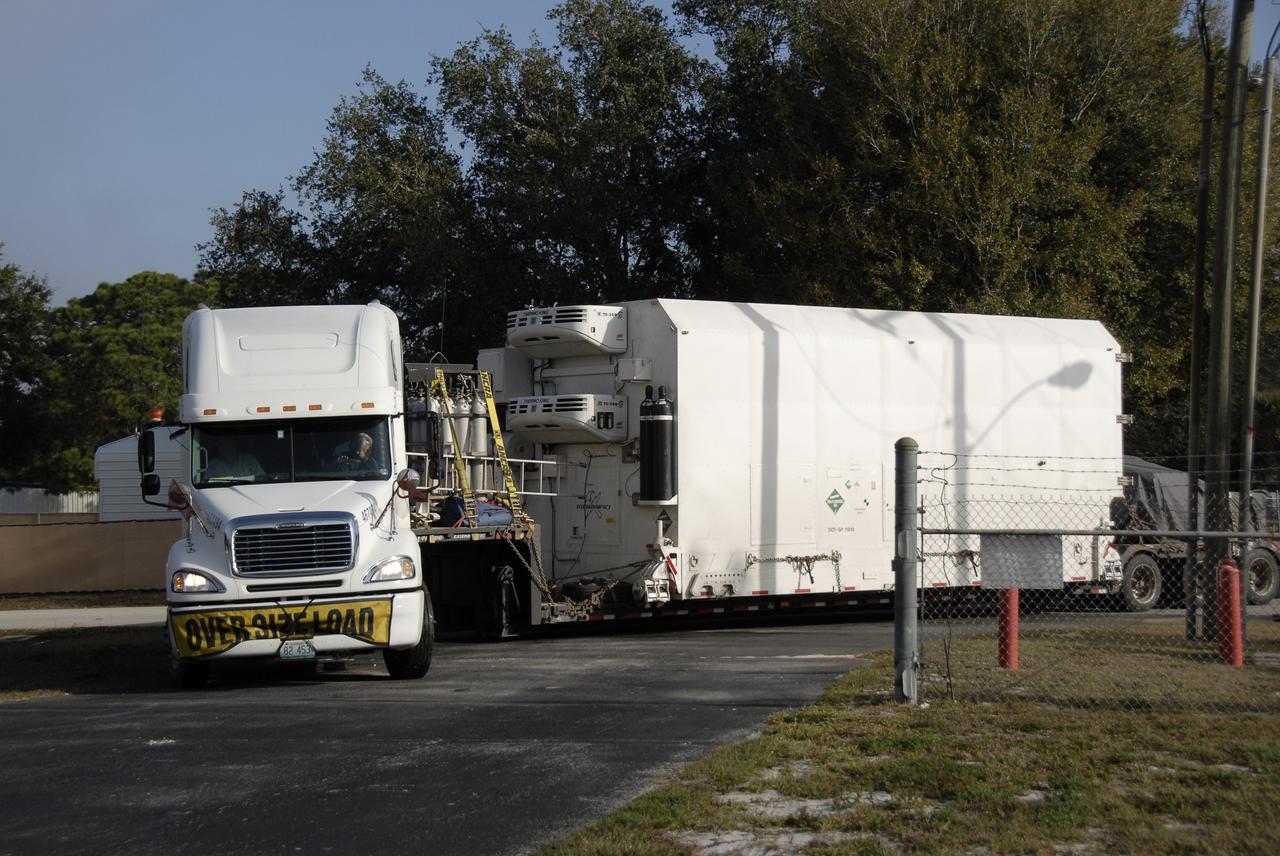

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A truck with the Kepler spacecraft in tow arrives at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. The spacecraft will be processed at Astrotech before being carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009, atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
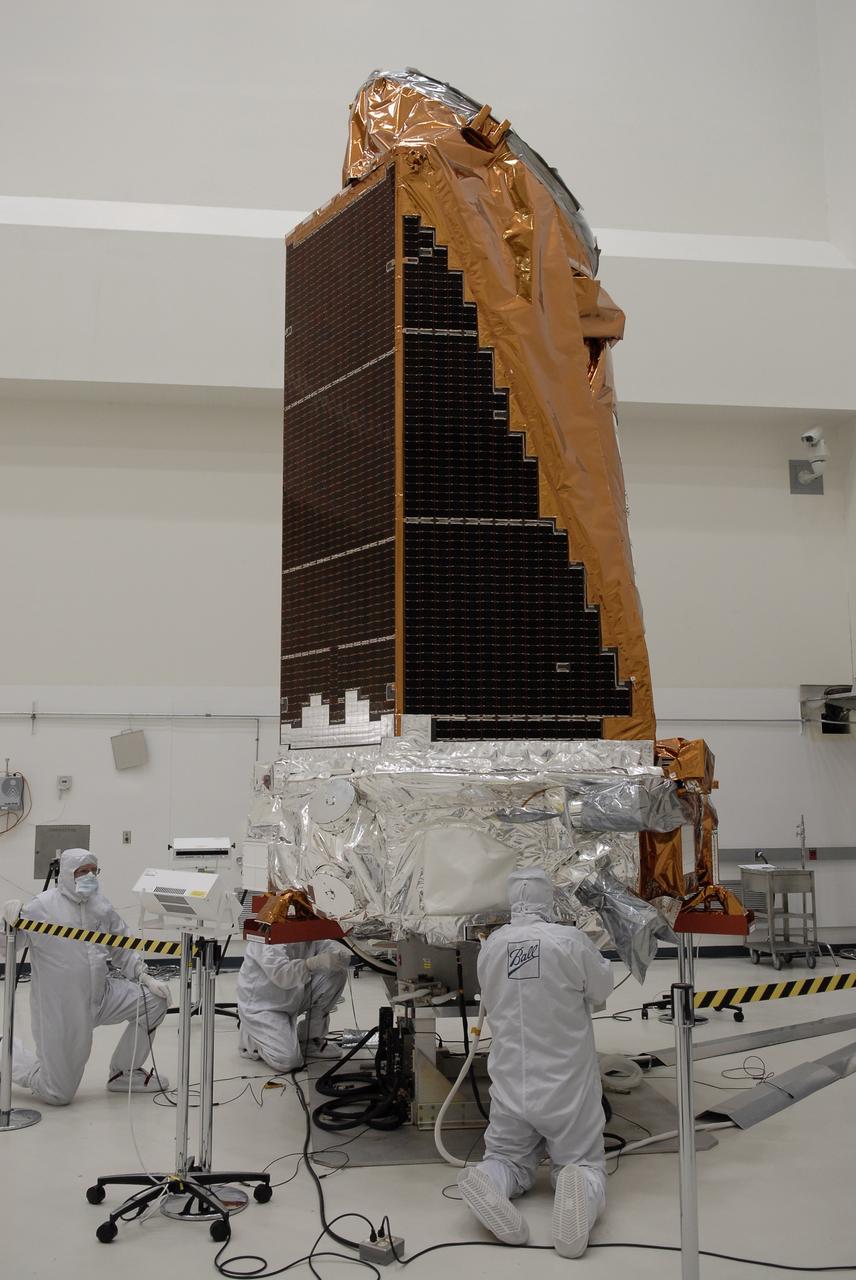

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is unbagged. The spacecraft will undergo initial testing before launch. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
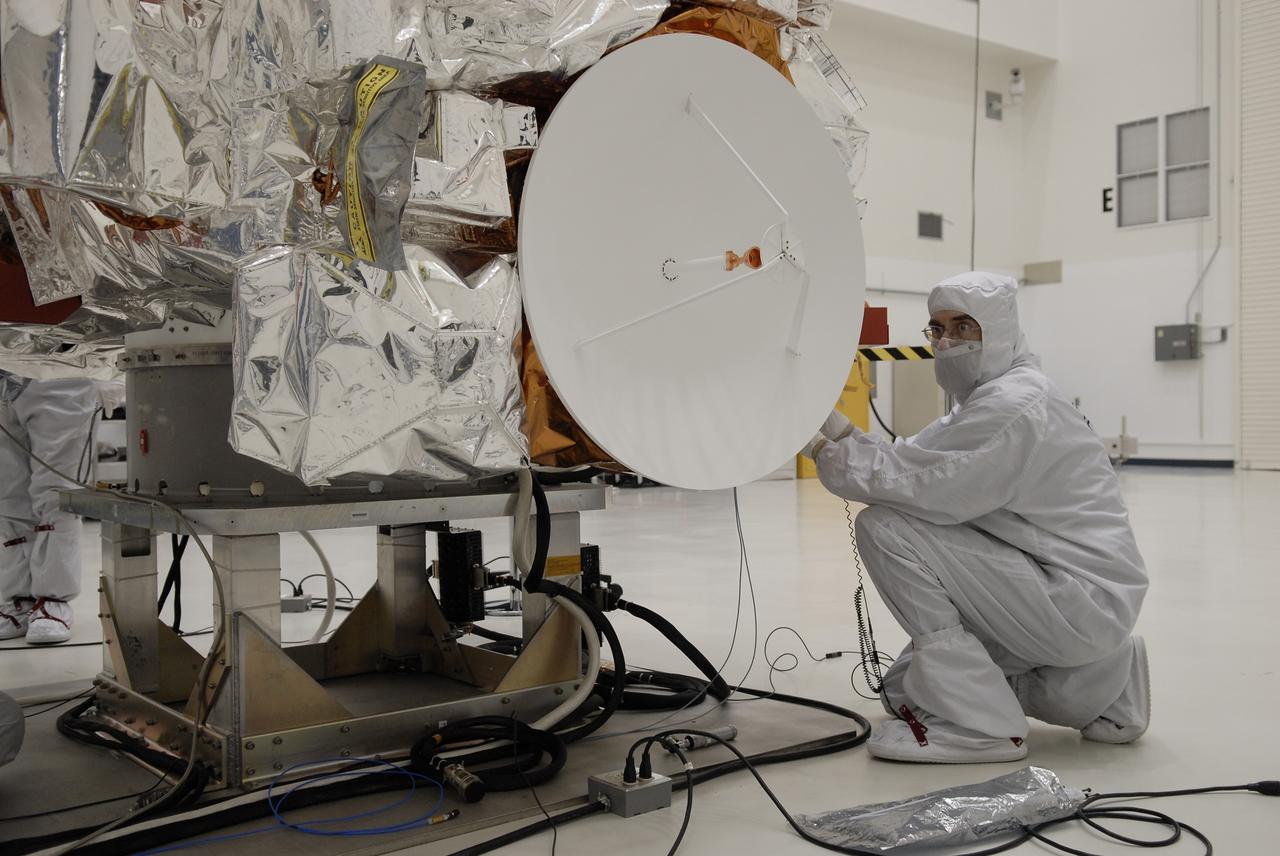

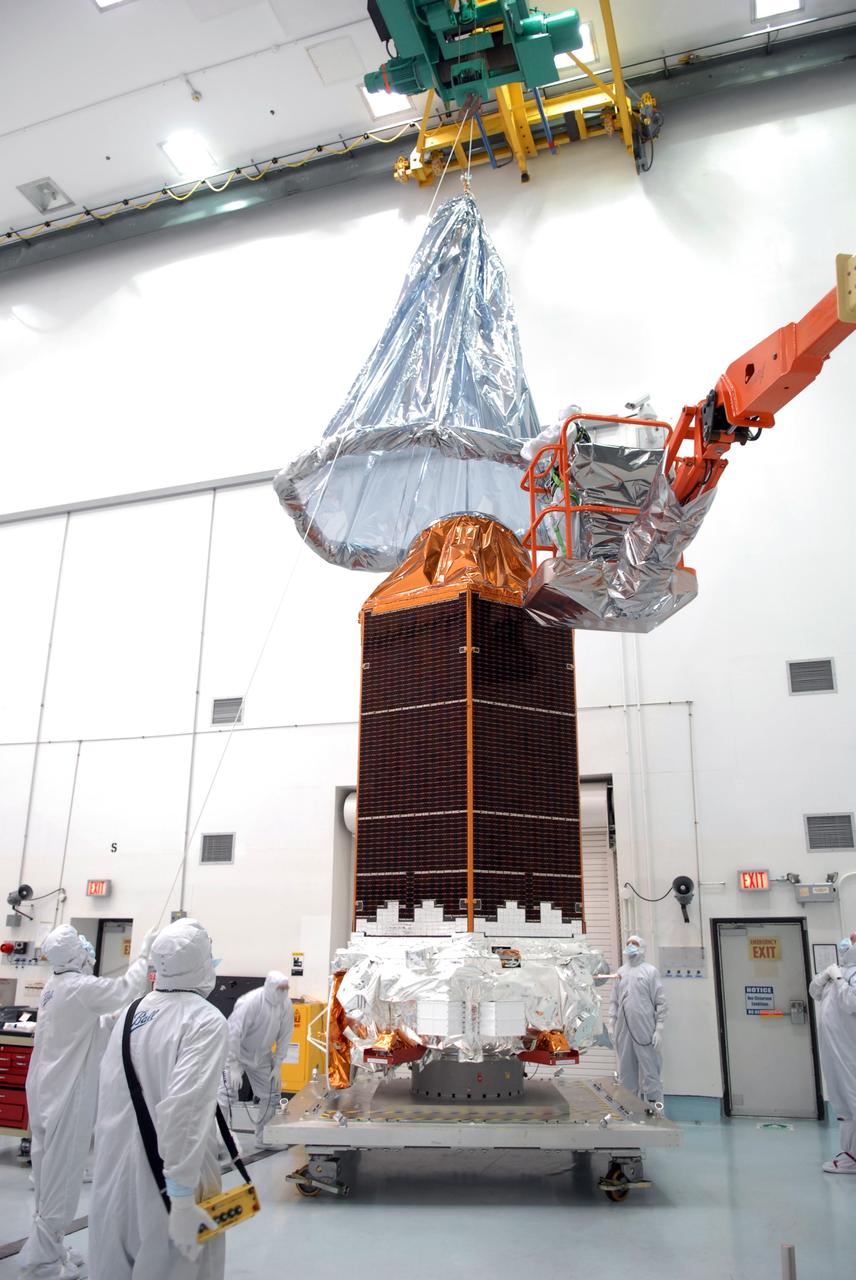
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a worker inspects the high-gain antenna on NASA's Kepler spacecraft in preparation for testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
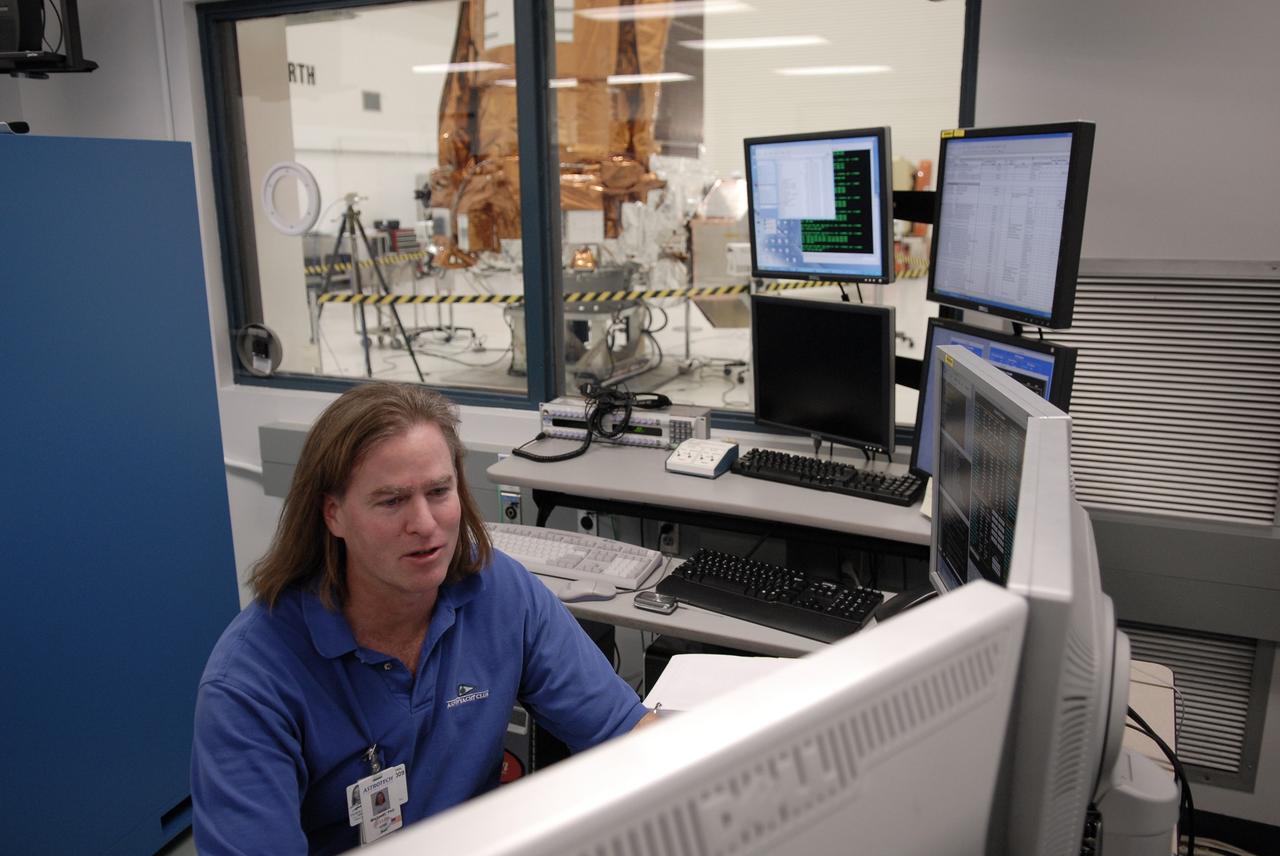

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. technician Phil Mislinski checks data from the light sensor test conducted on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Ball Aerospace was responsible for the flight segment design and fabrication. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
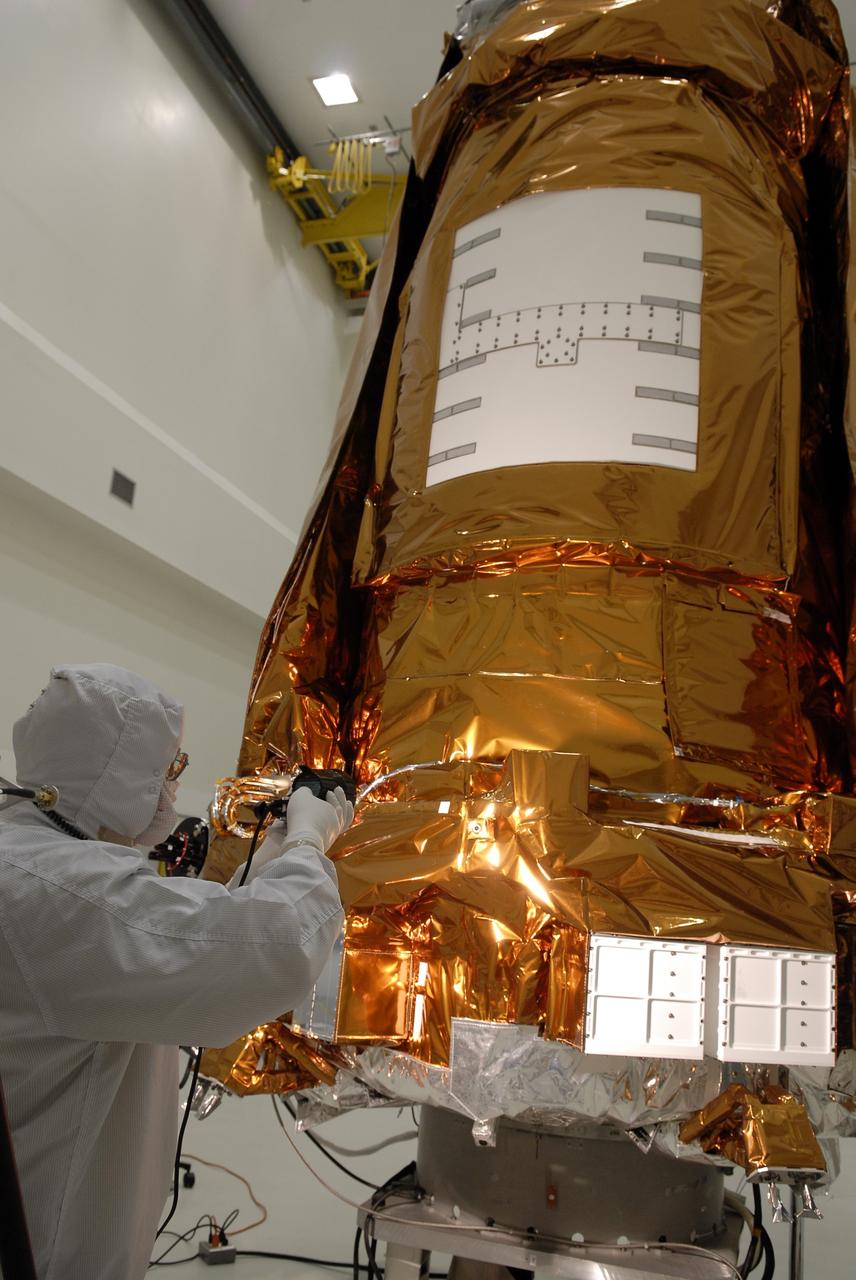

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
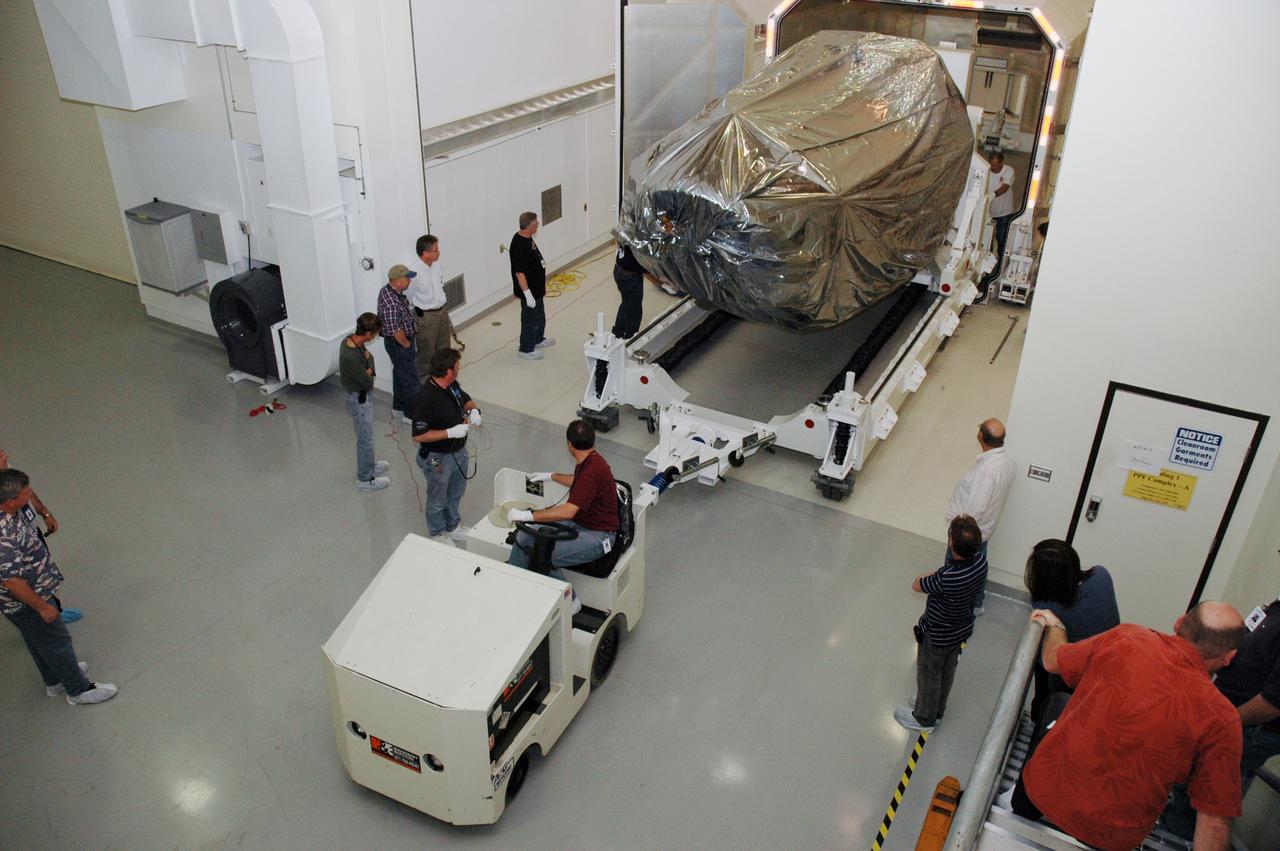

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is rolled out of its shipping container. The spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
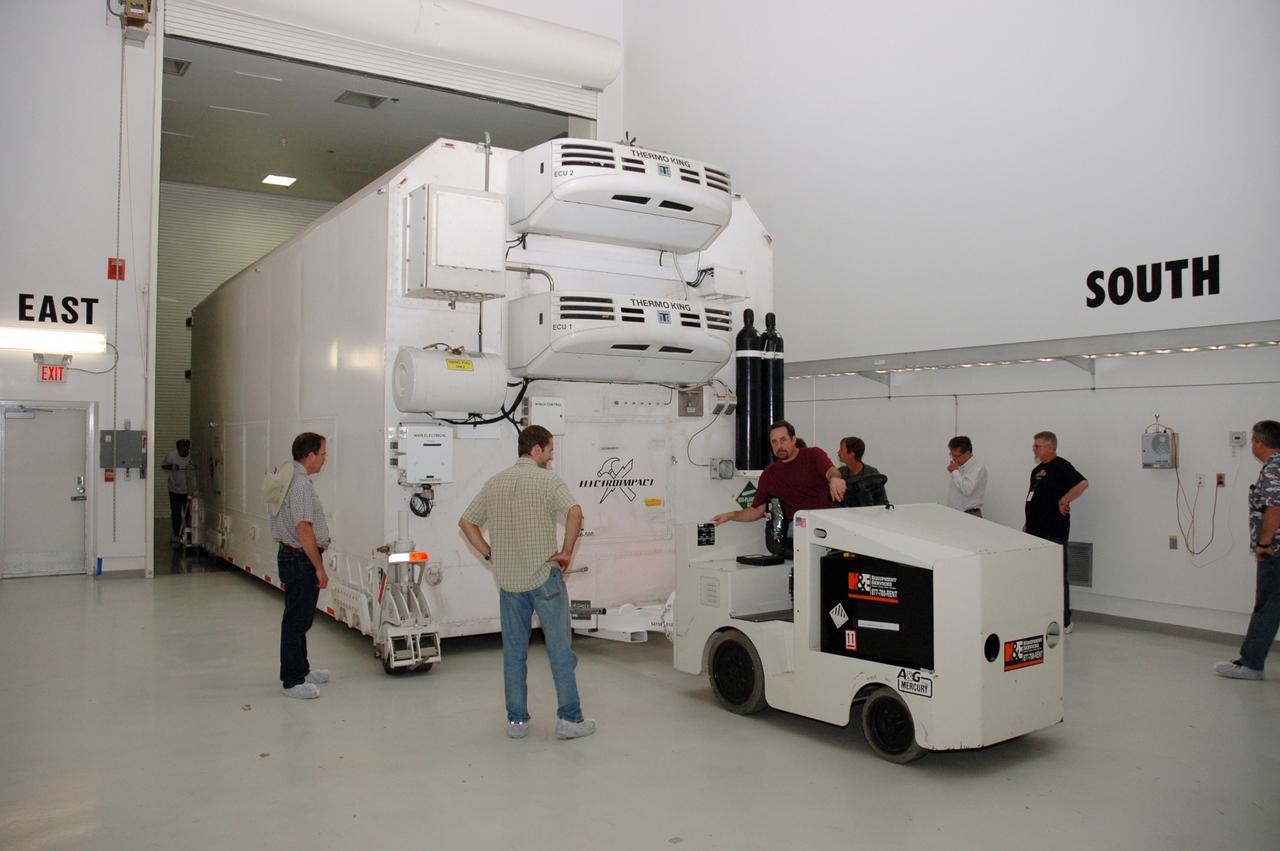

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., the shipping container holding NASA's Kepler spacecraft is moved into a clean room. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
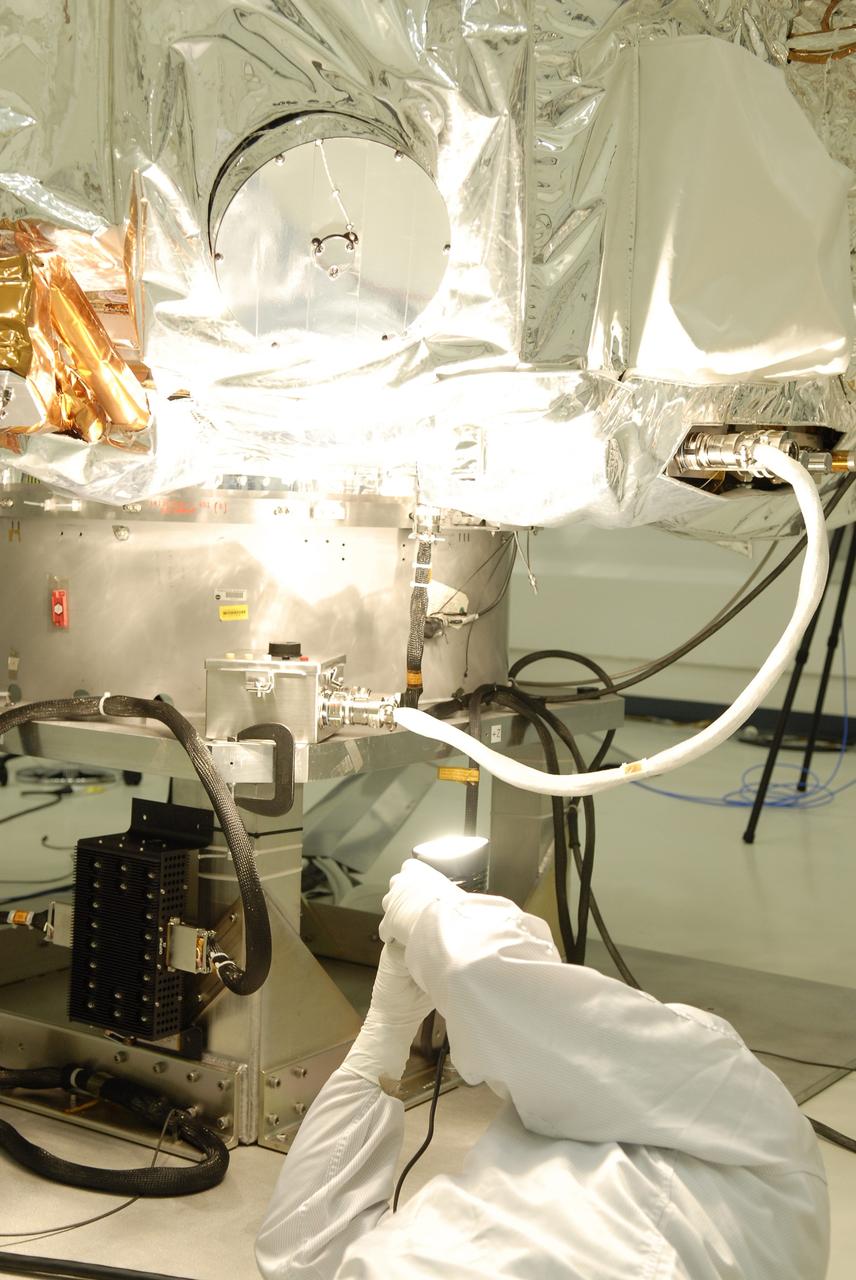

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. worker conducts a light sensor test on NASA's Kepler spacecraft. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. .NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
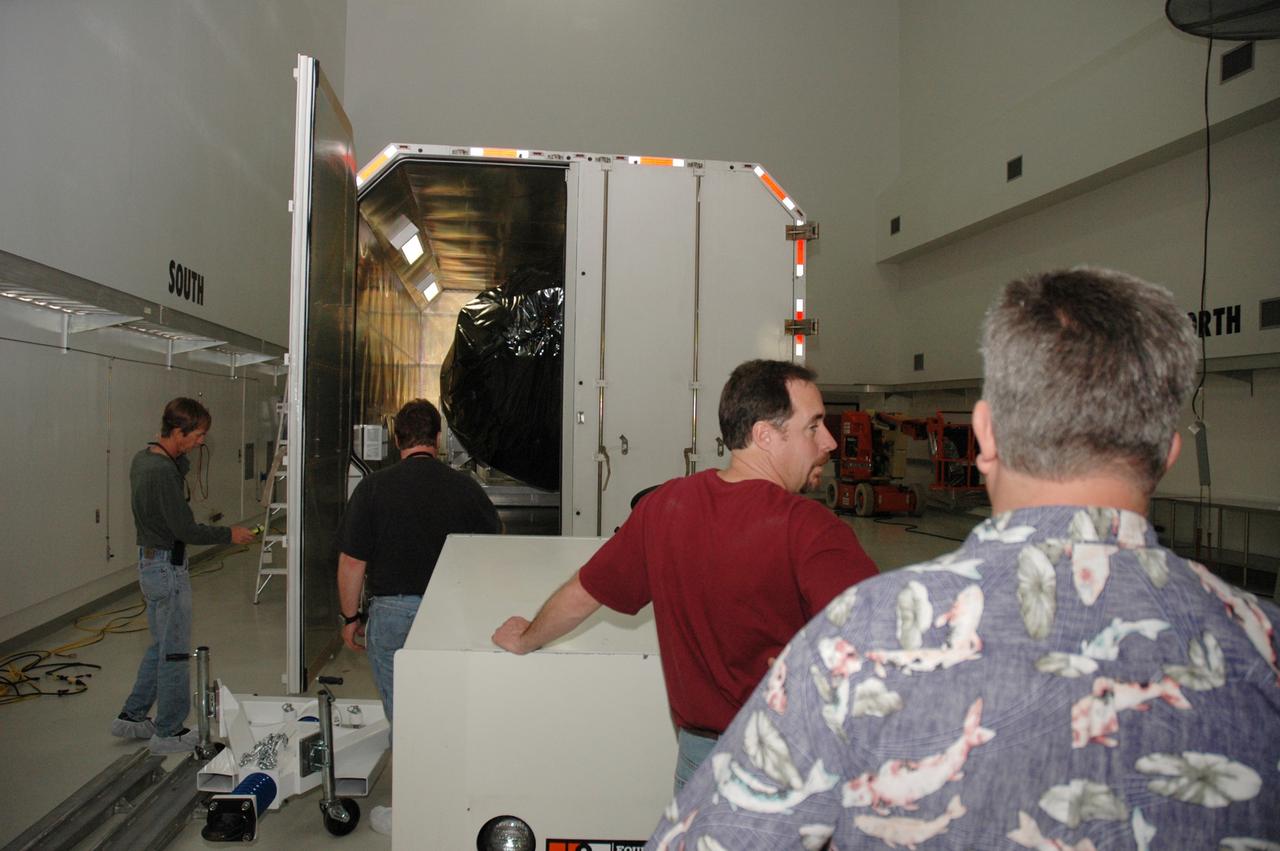

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., doors are opened on the shipping container holding NASA's Kepler spacecraft. After removal from the container, the spacecraft will be rotated to vertical, uncovered and prepared for initial testing. A NASA Discovery mission, Kepler is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. After processing at Astrotech, Kepler will be carried to its launch pad at Cape Canaveral. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5 atop a Delta II rocket. Photo credit: NASA/Chris Rhodes
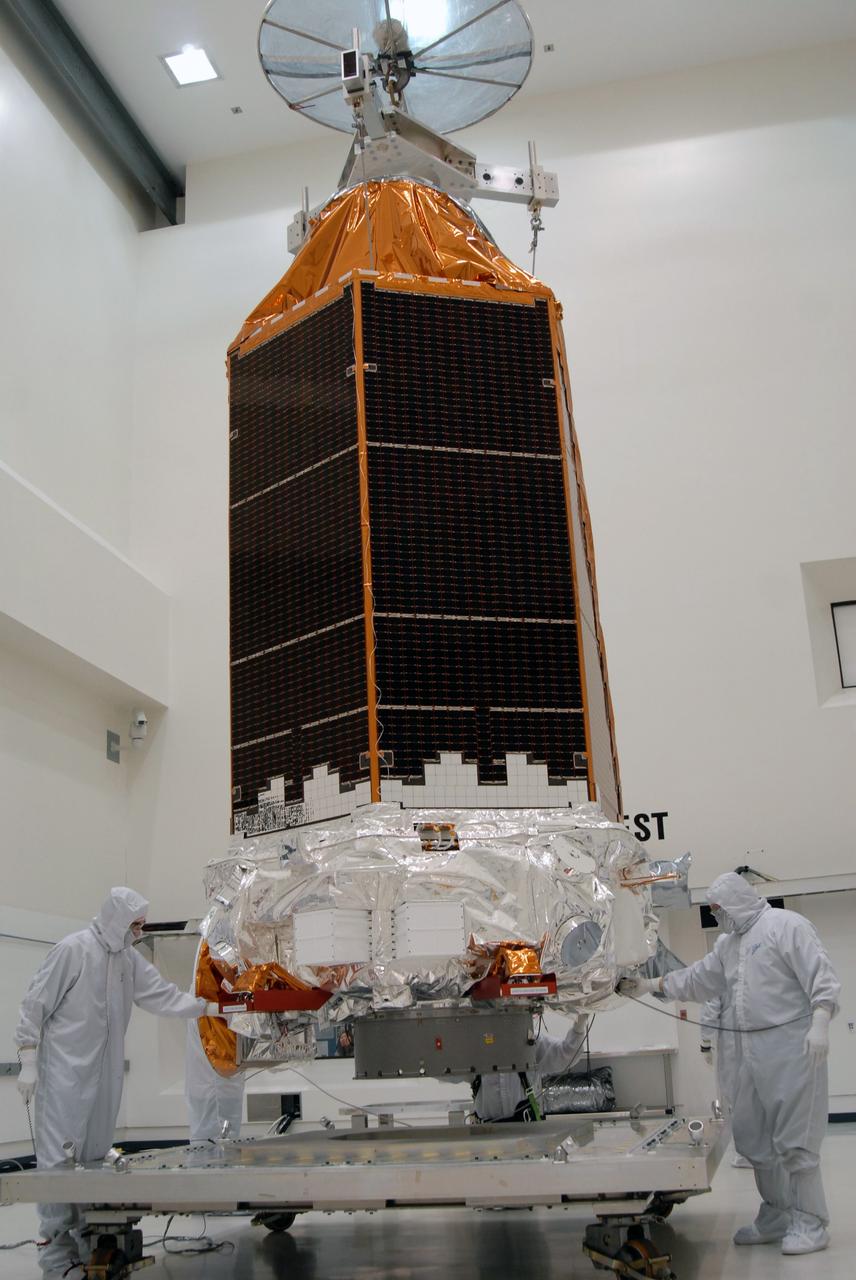

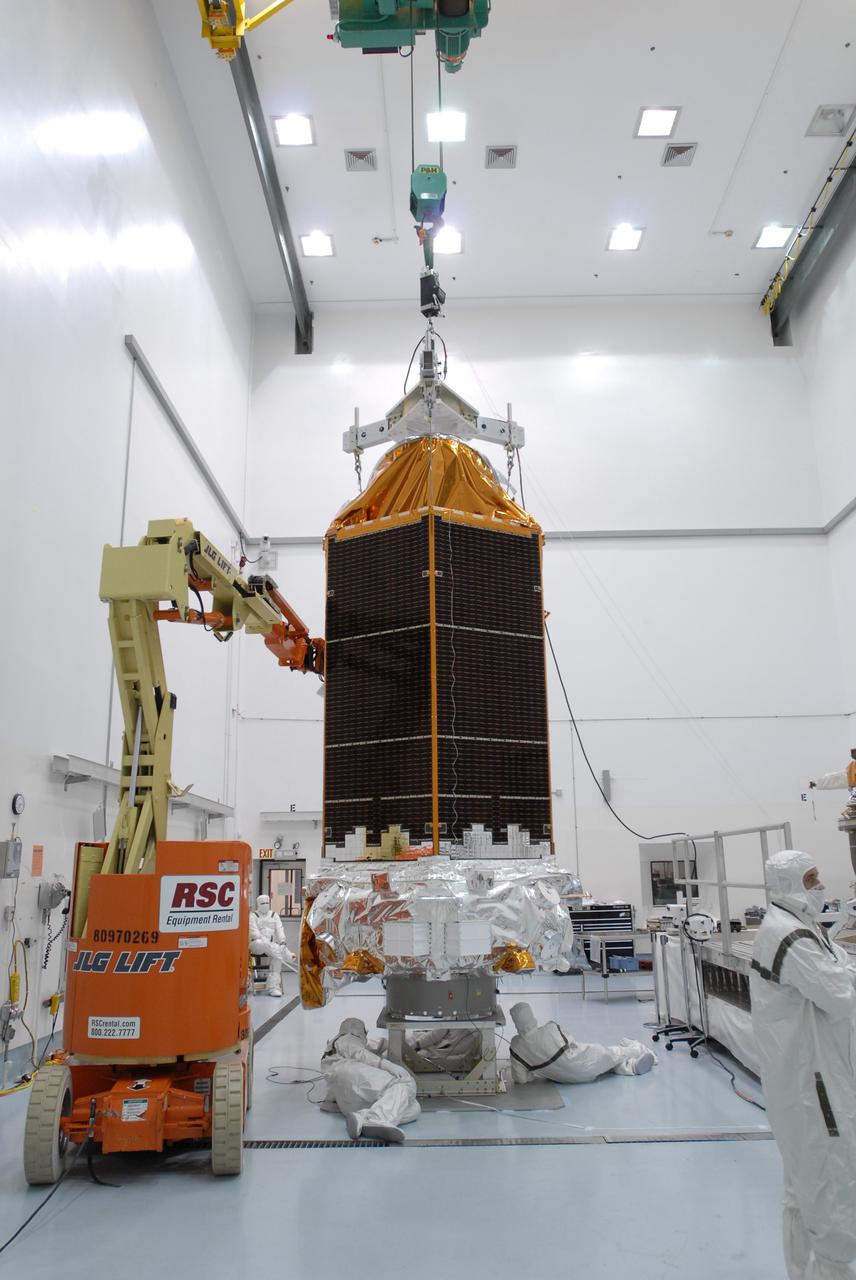
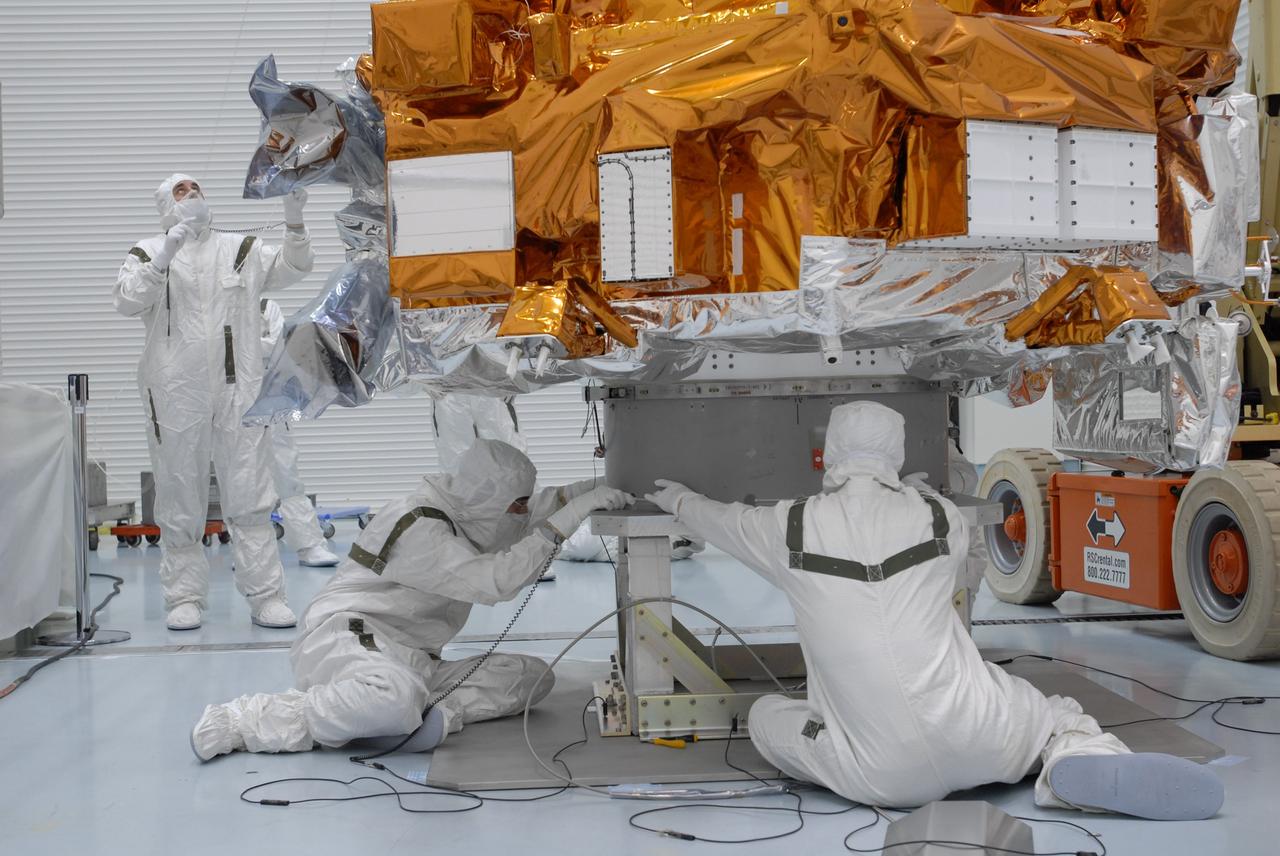
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, an overhead crane carries NASA's Kepler spacecraft toward a mobile stand to be covered and moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
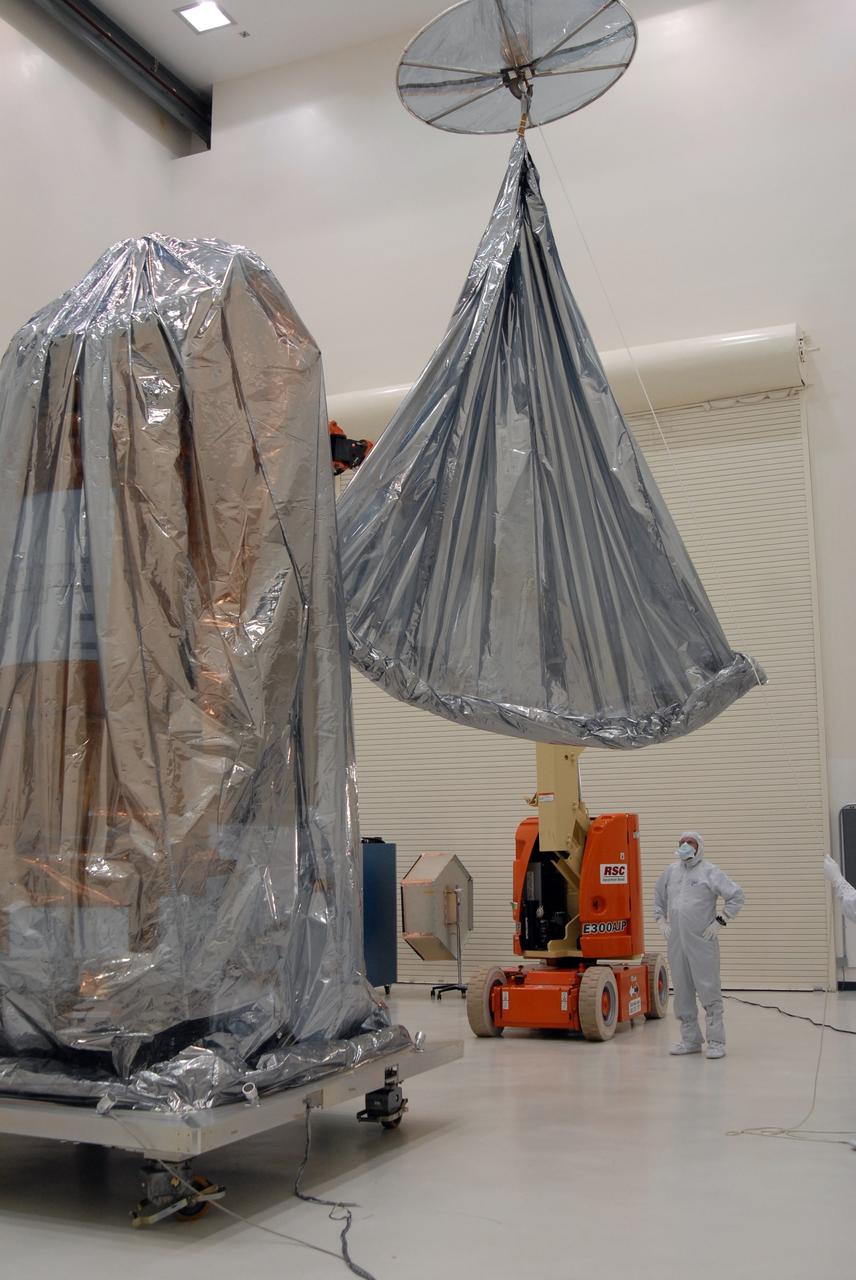

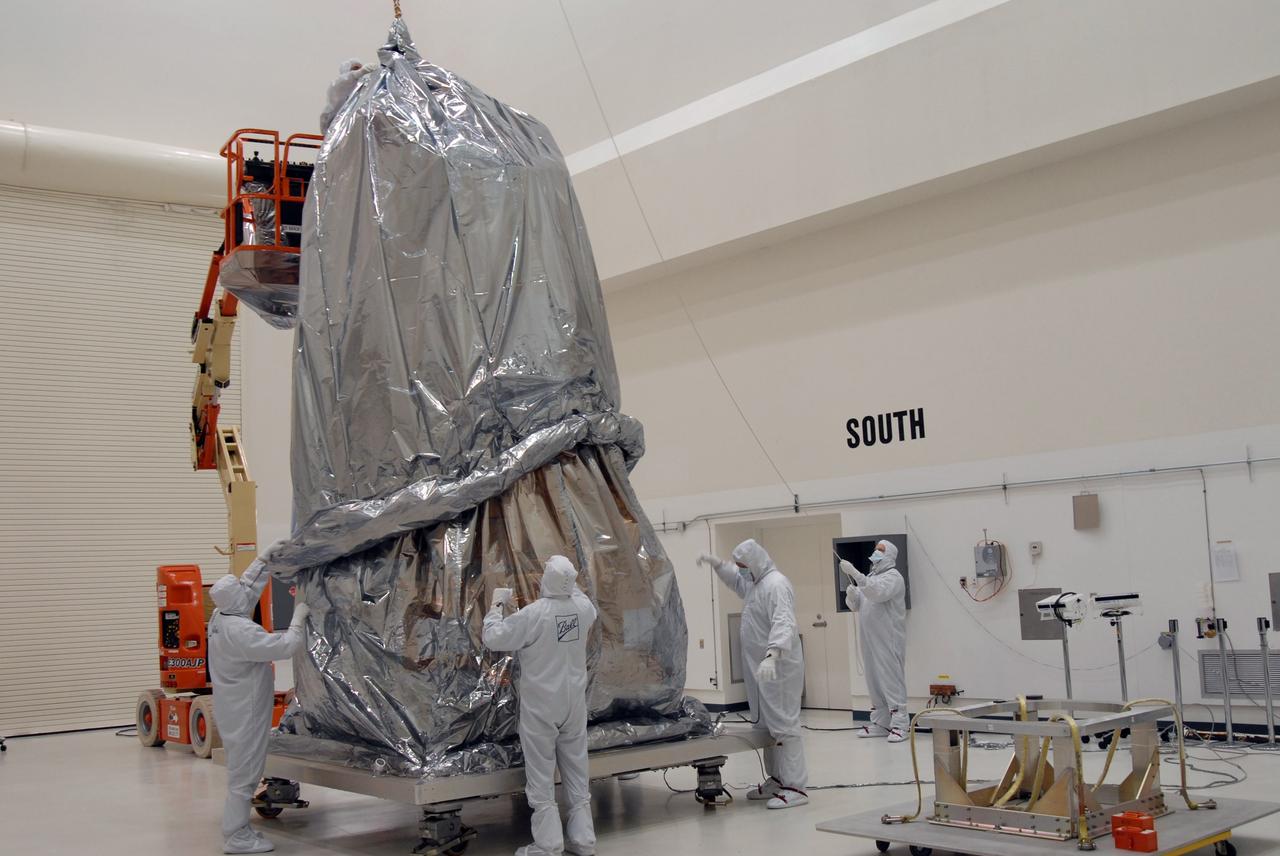
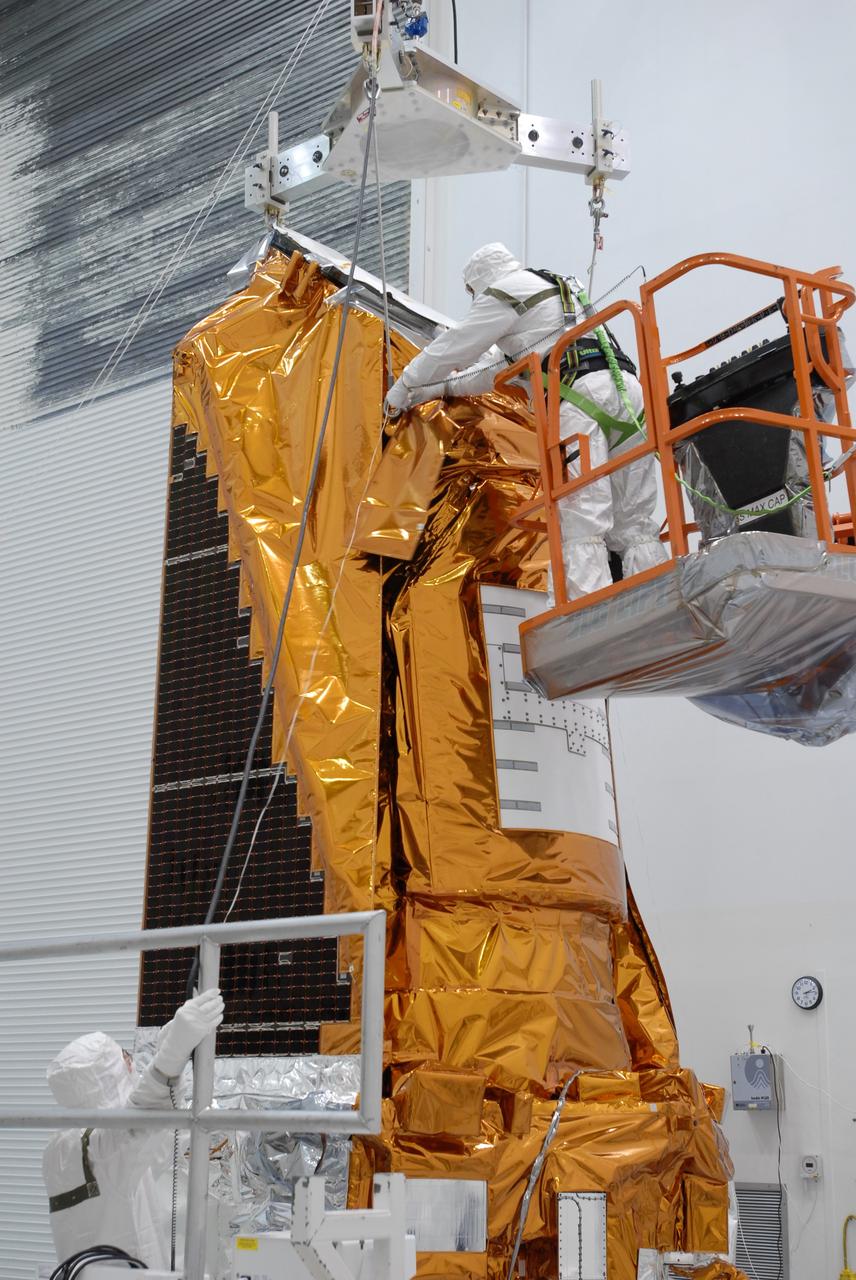
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, another protective cover is lowered over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. When covered, Kepler will be moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
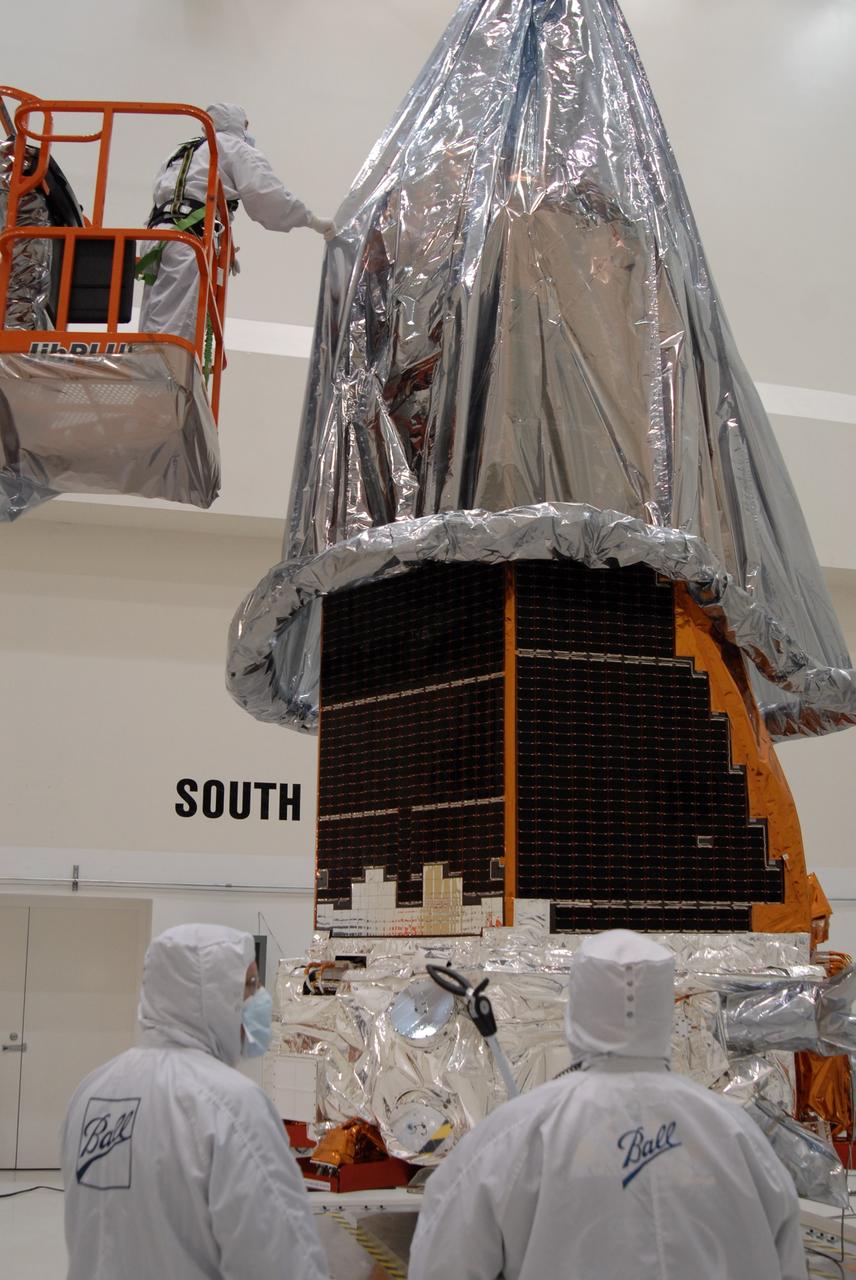

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, the protective cover is lowered over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. When covered, Kepler will be moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
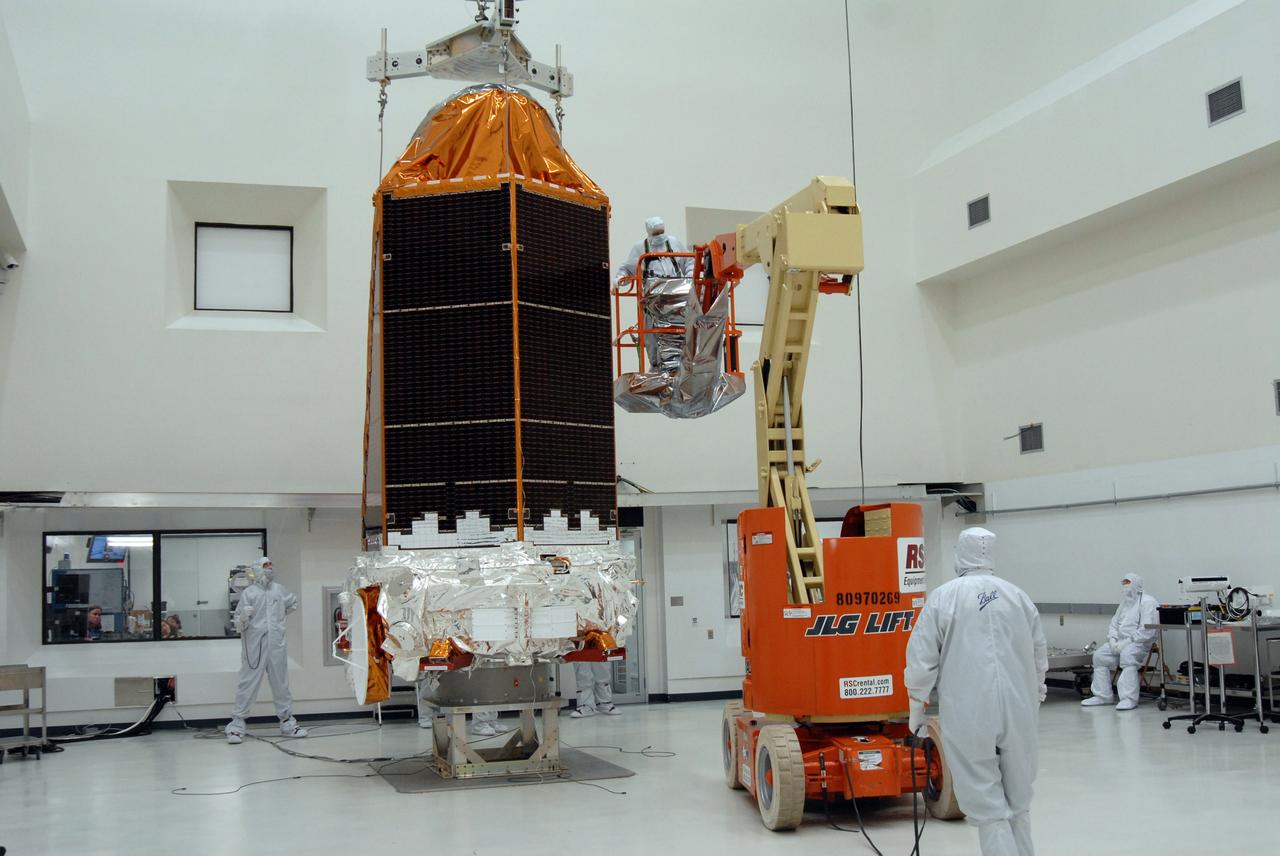

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, an overhead crane lifts NASA's Kepler spacecraft from a work stand. Kepler will be moved to a mobile stand to be covered and moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
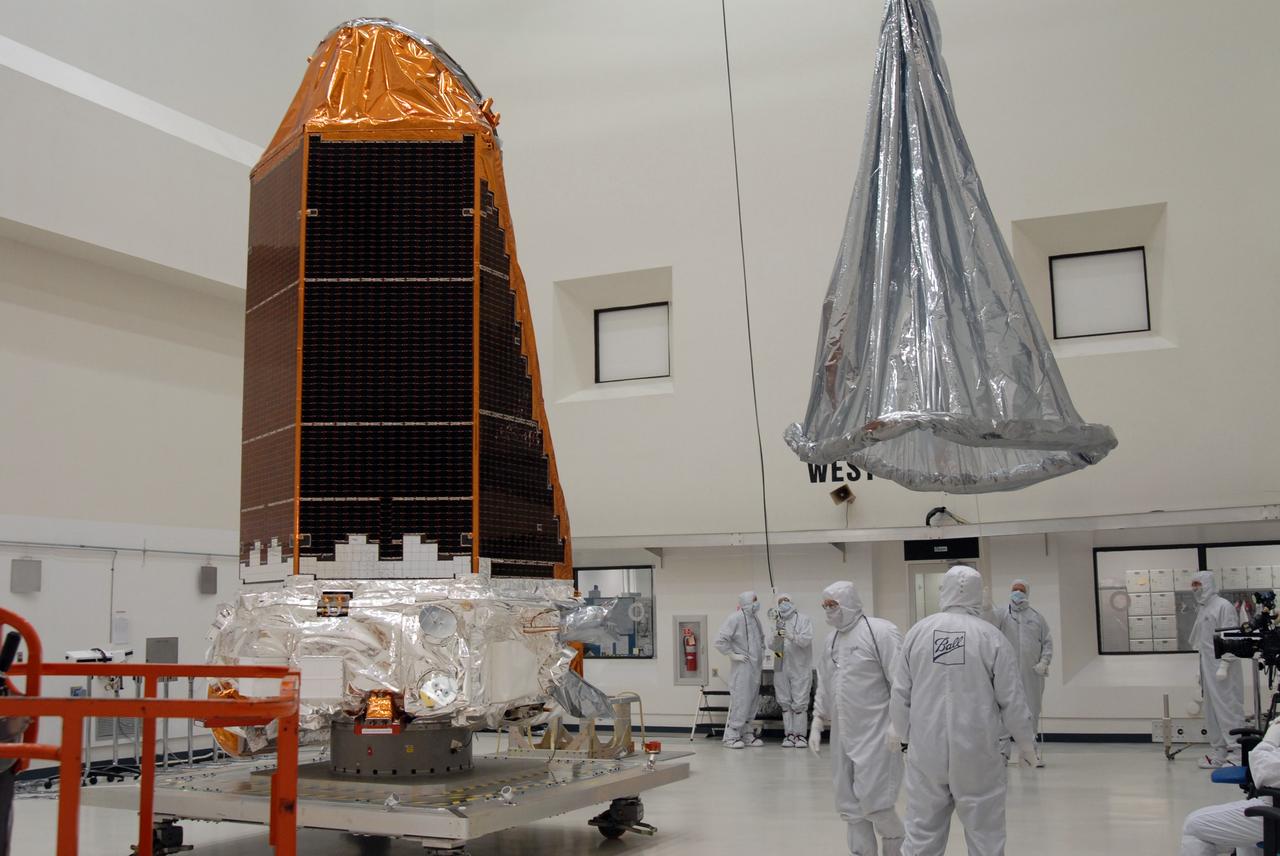

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, the protective cover at right is lifted toward NASA's Kepler spacecraft at left. When covered, Kepler will be moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
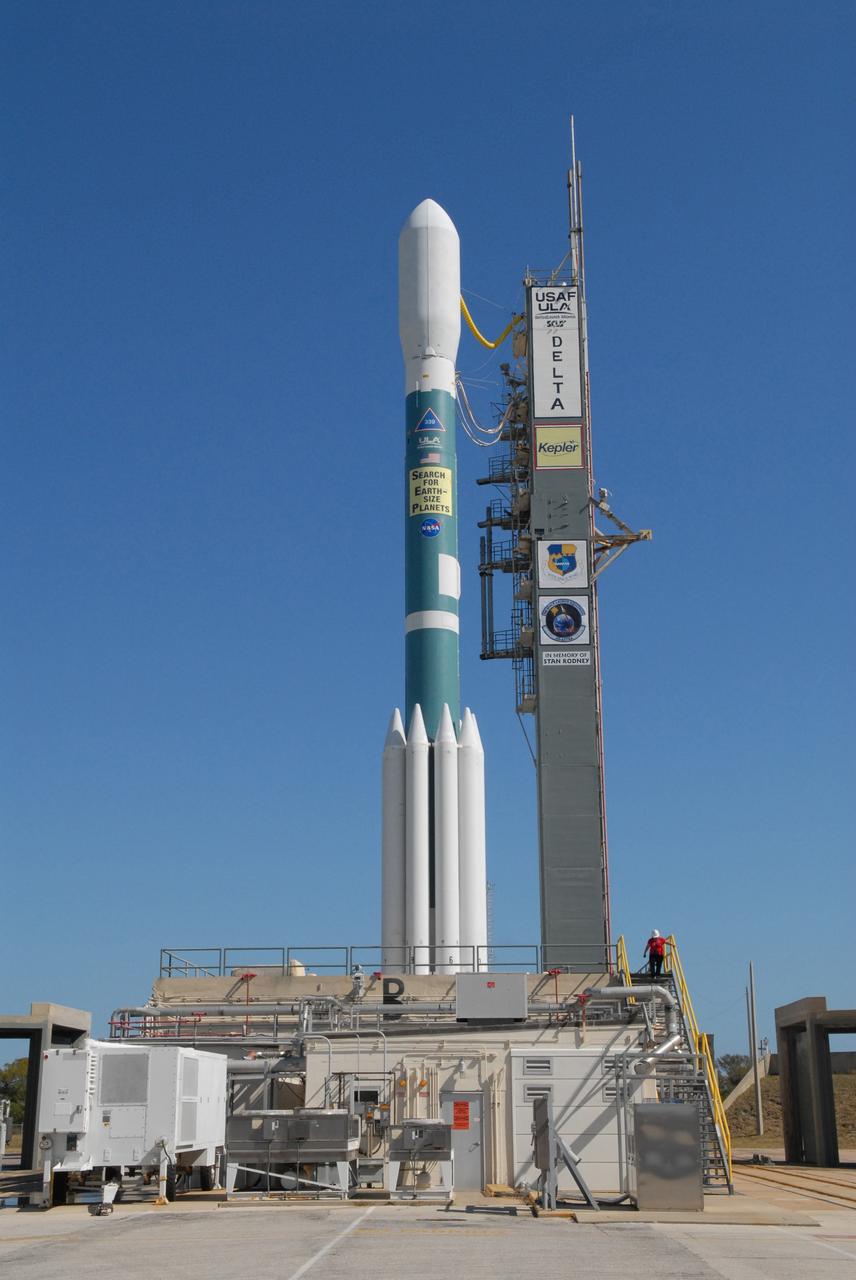

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
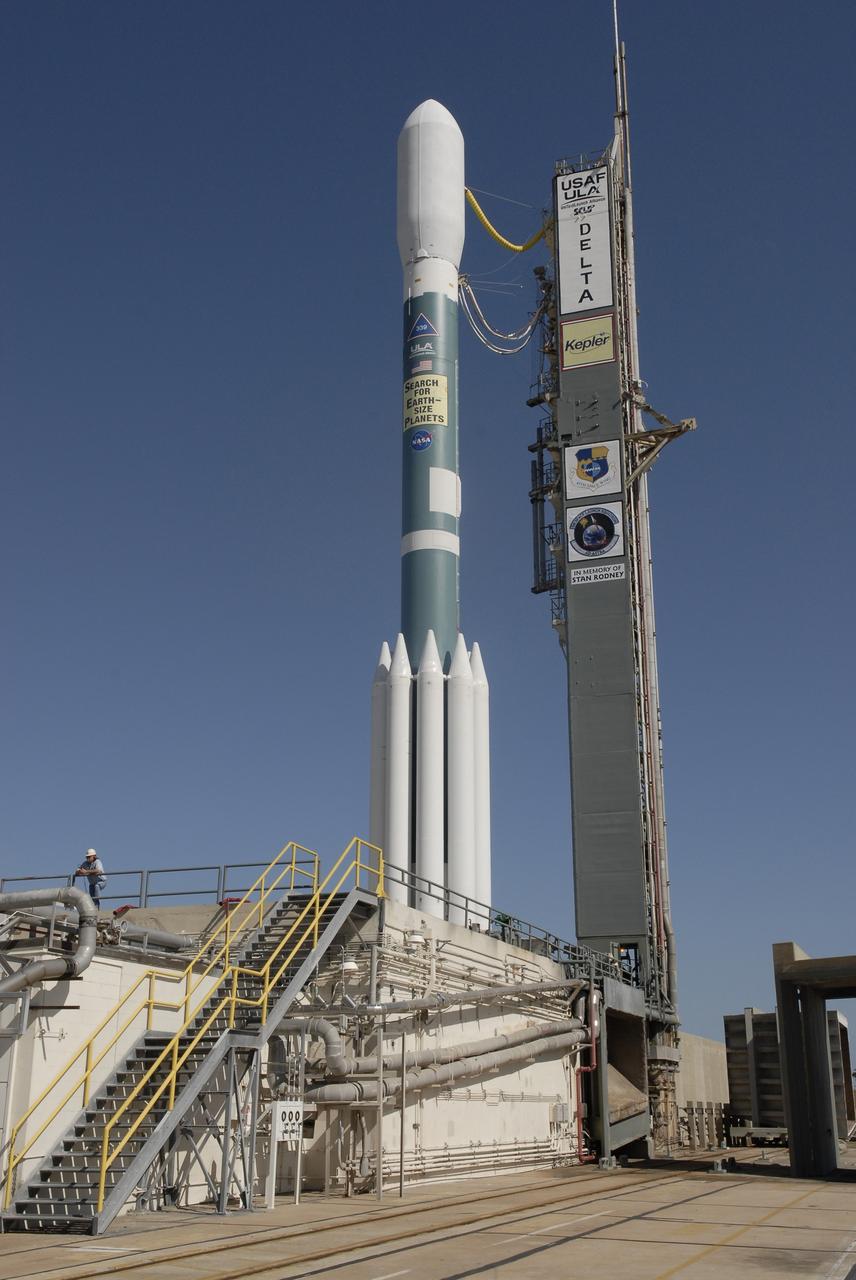

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
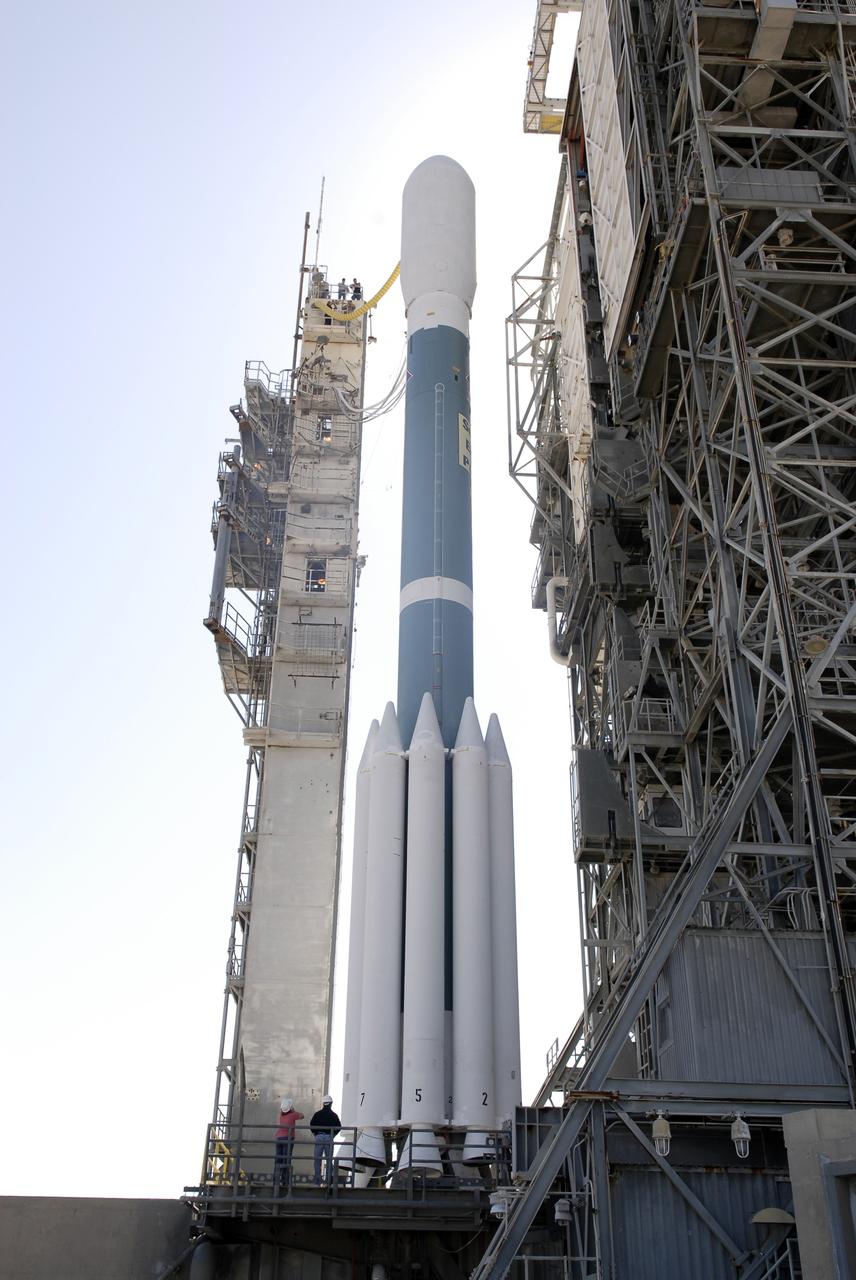

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B, in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
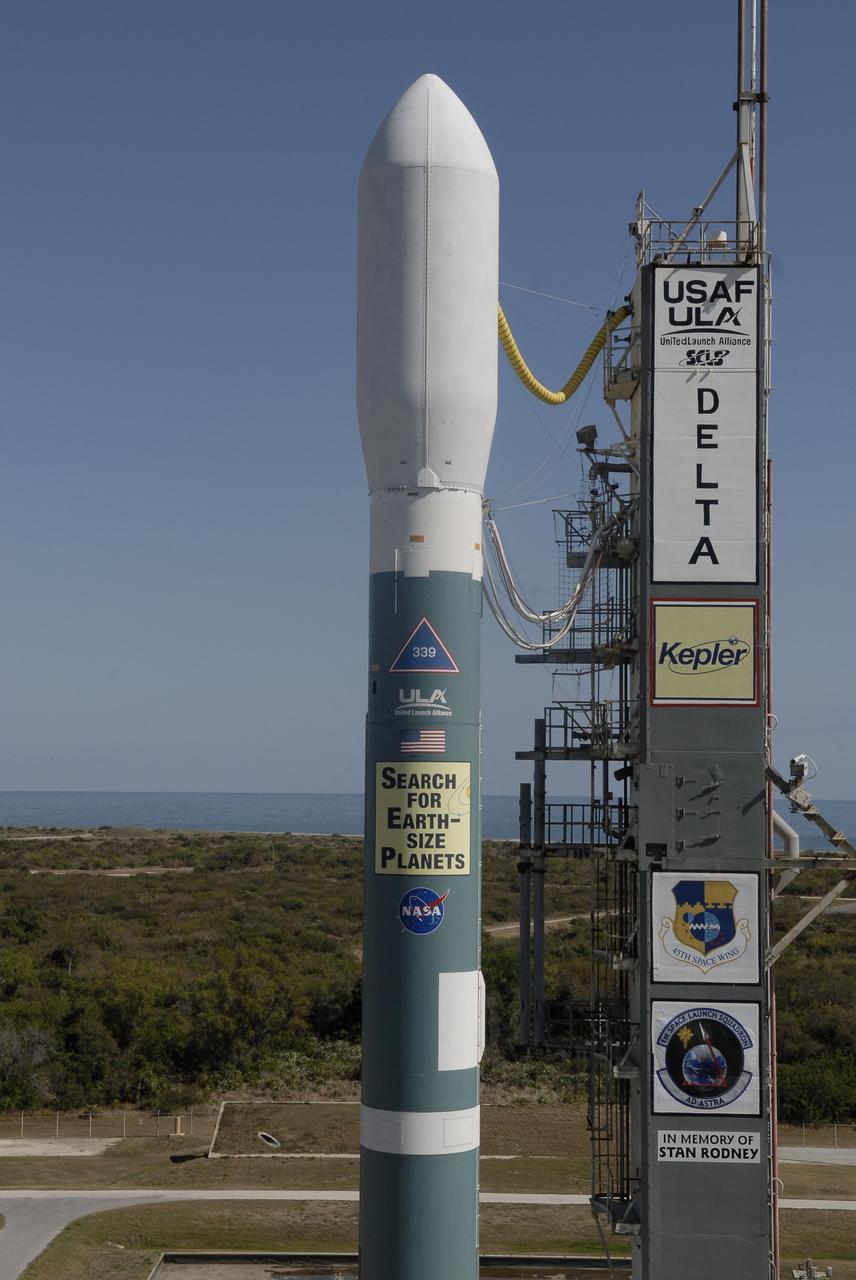

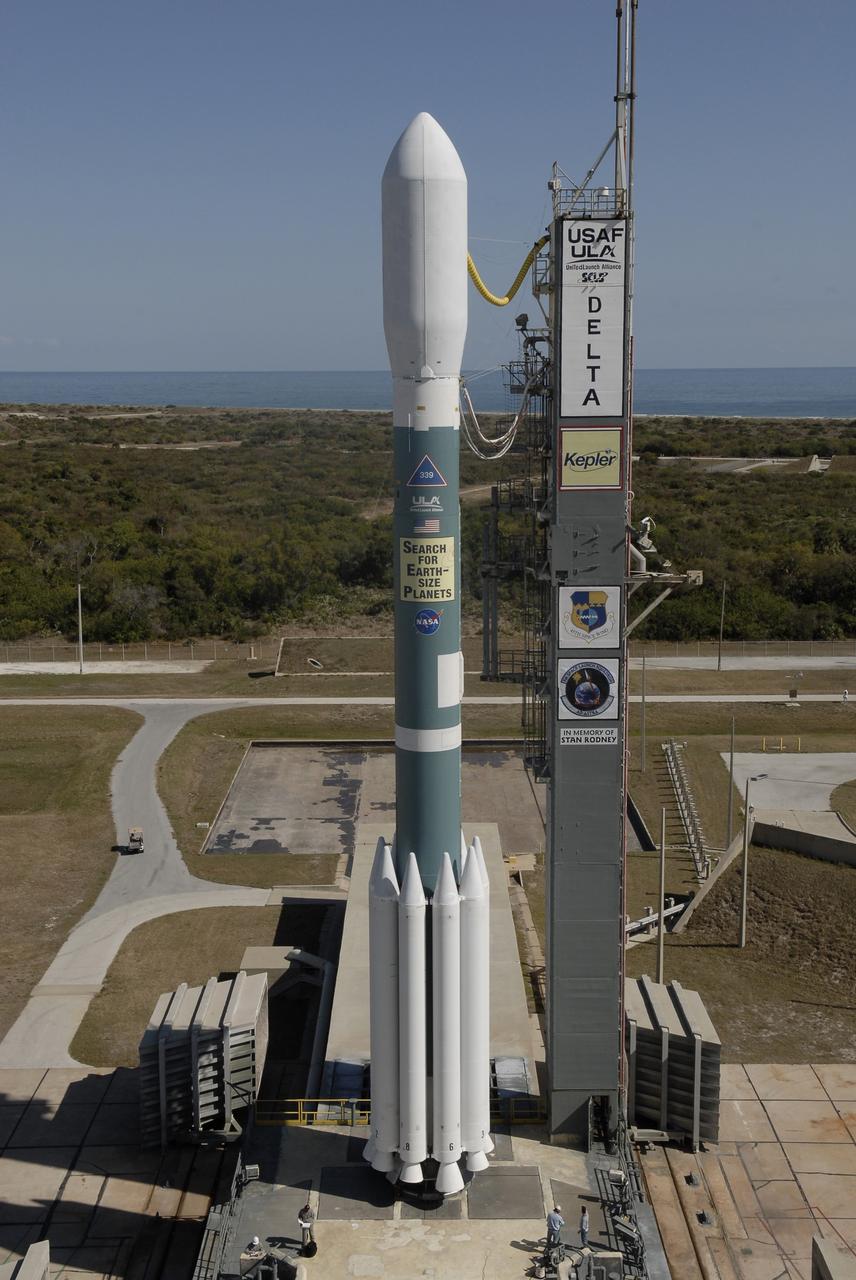
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Against the backdrop of the Atlantic Ocean, the Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
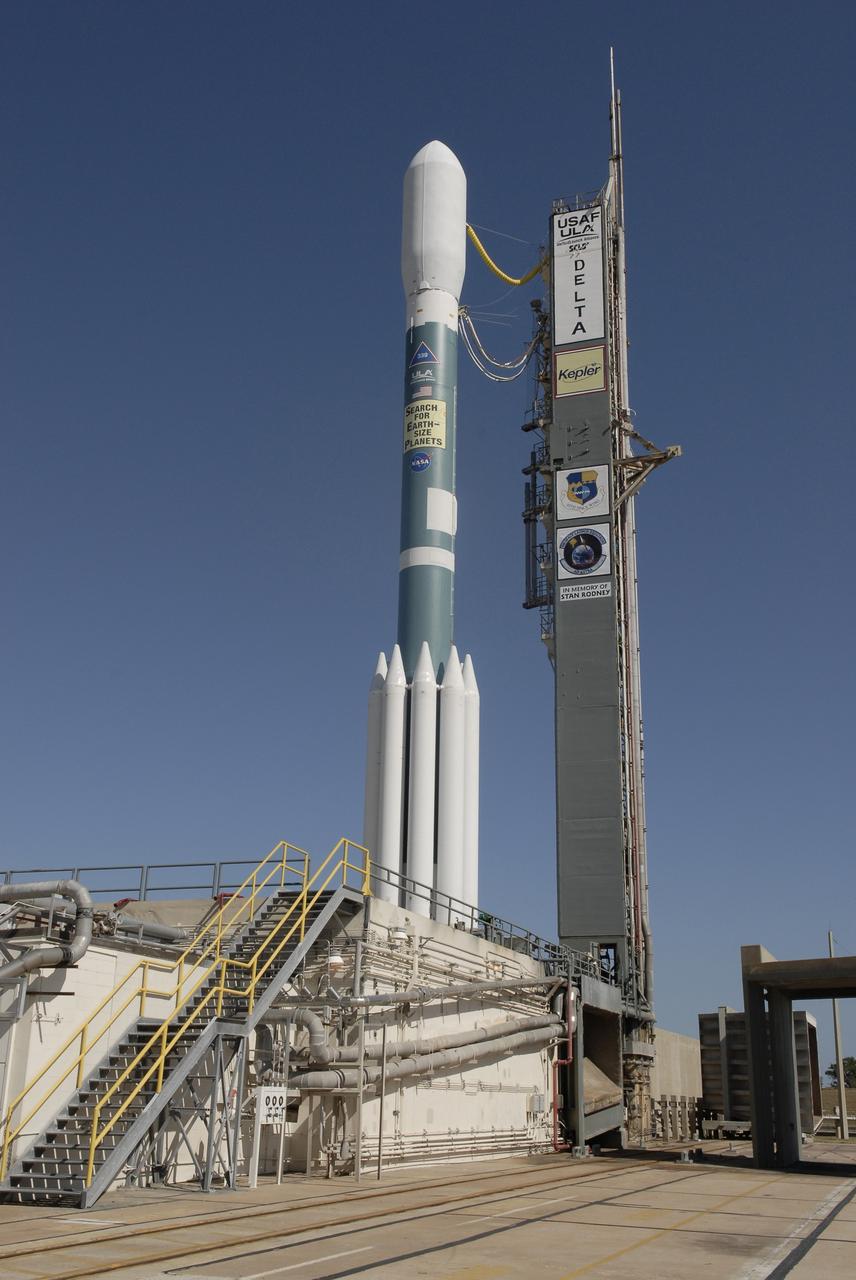

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
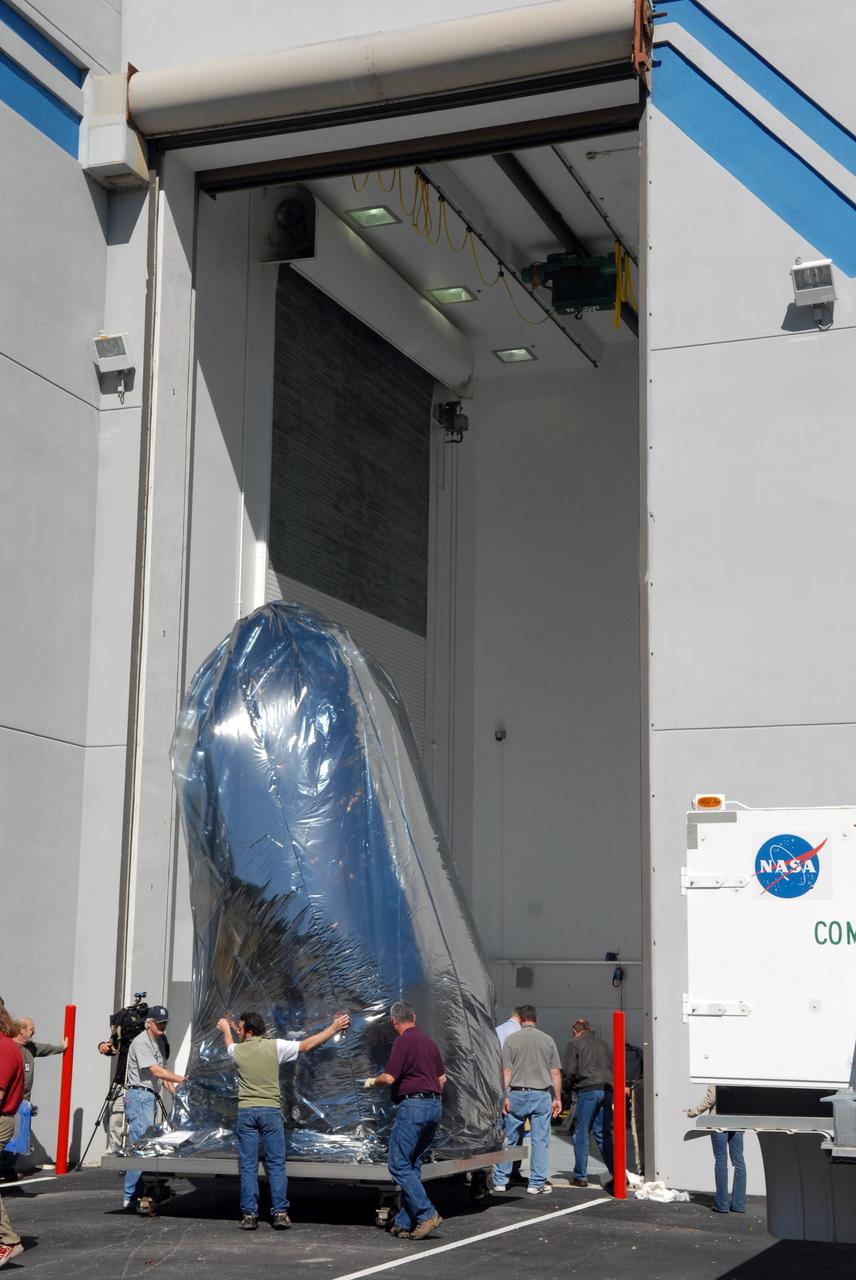

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Thoroughly wrapped for travel, NASA's Kepler spacecraft is moved into the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
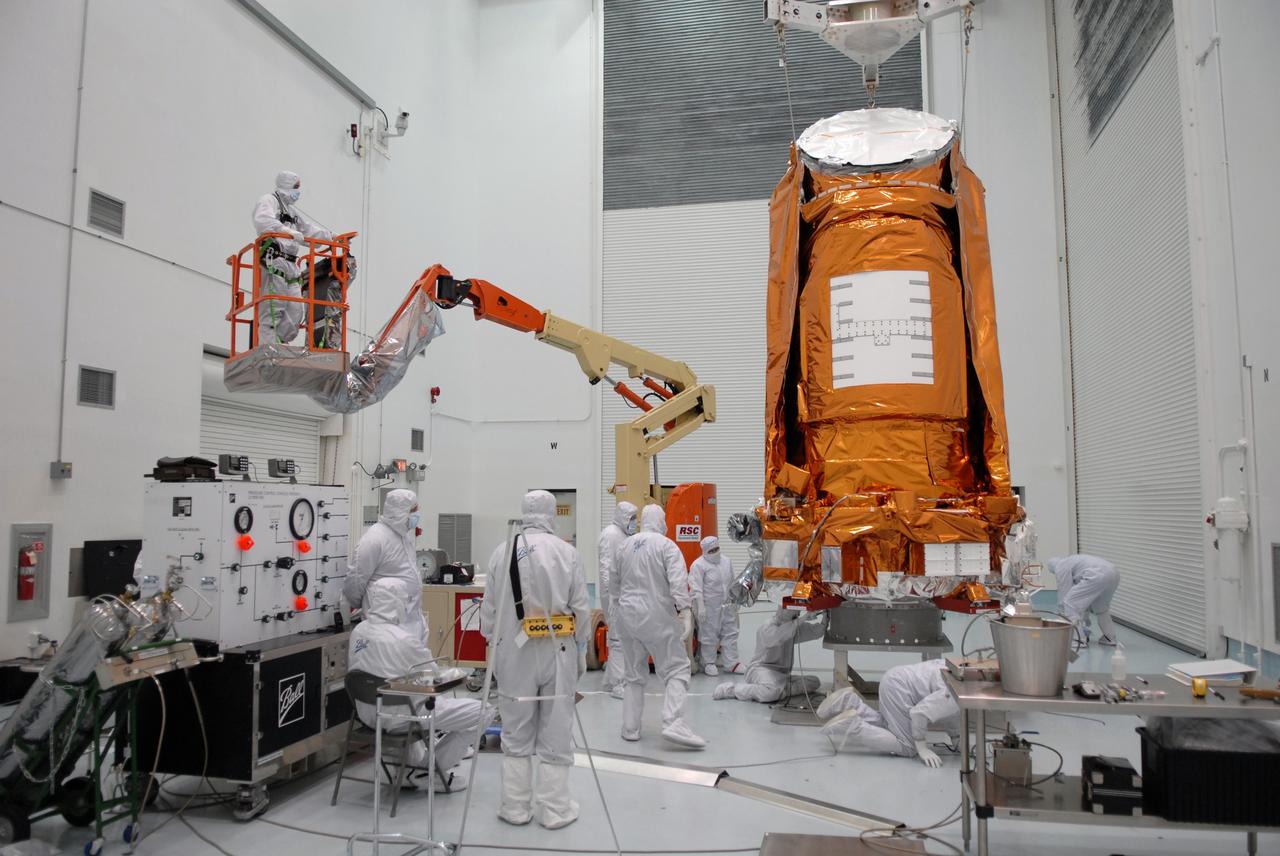

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is placed on a stand for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is being moved to another stand for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare the crane and scale that will be used to weigh the Kepler spacecraft, in the background at right. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, the second cover is placed over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will be moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the final cover is removed from NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will be fueled for launch. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers check the Kepler spacecraft as it is lifted for weighing. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
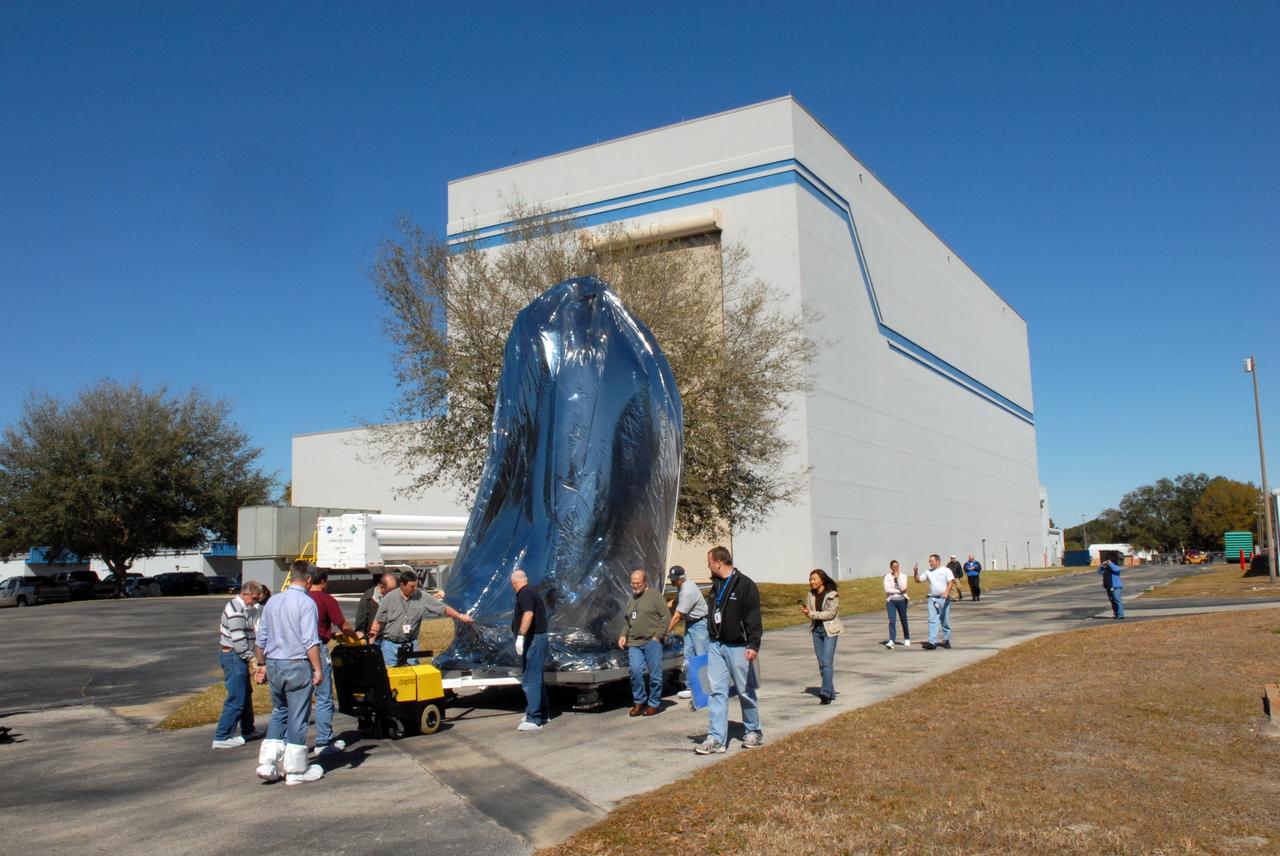

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Thoroughly wrapped for travel, NASA's Kepler spacecraft is moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers prepare the scale that will be used to weigh the Kepler spacecraft, in the background. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
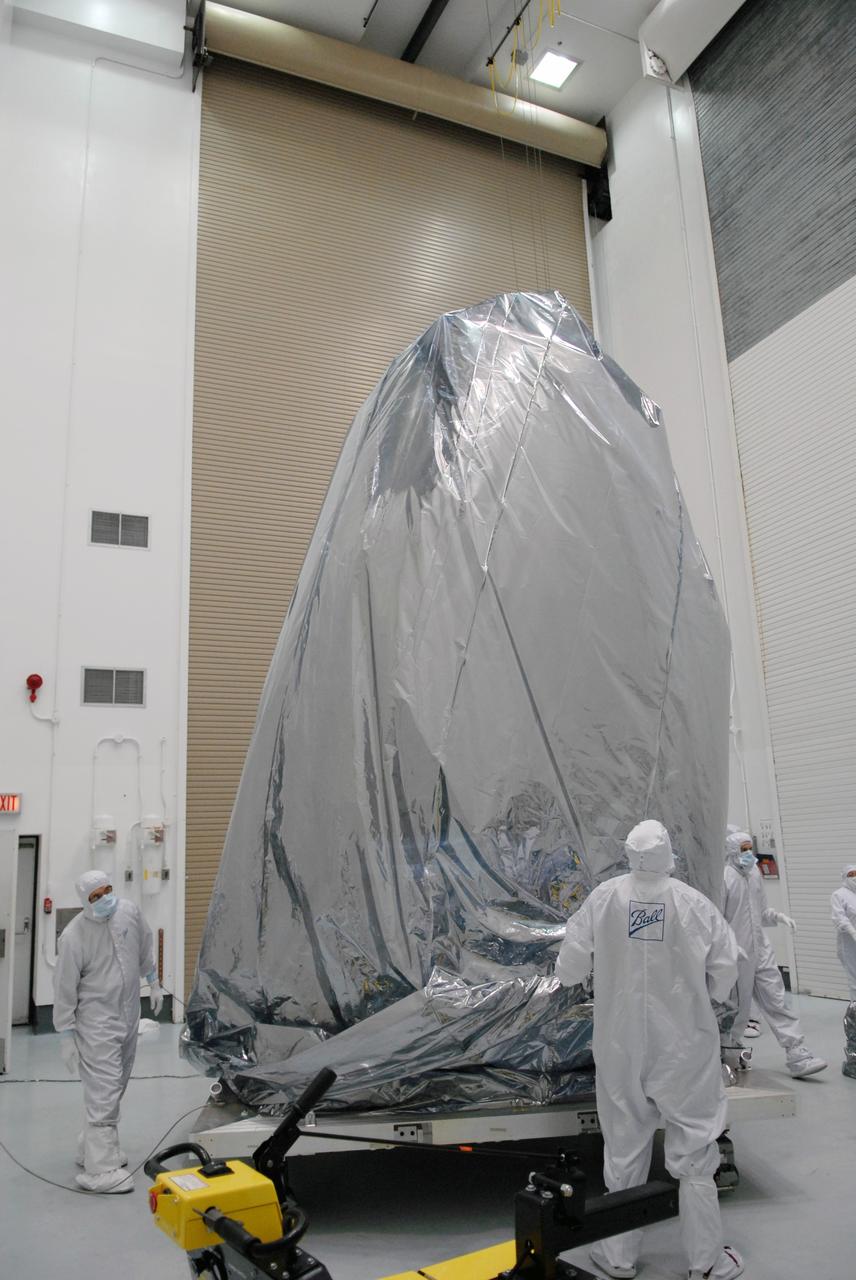

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is being unwrapped to prepare for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

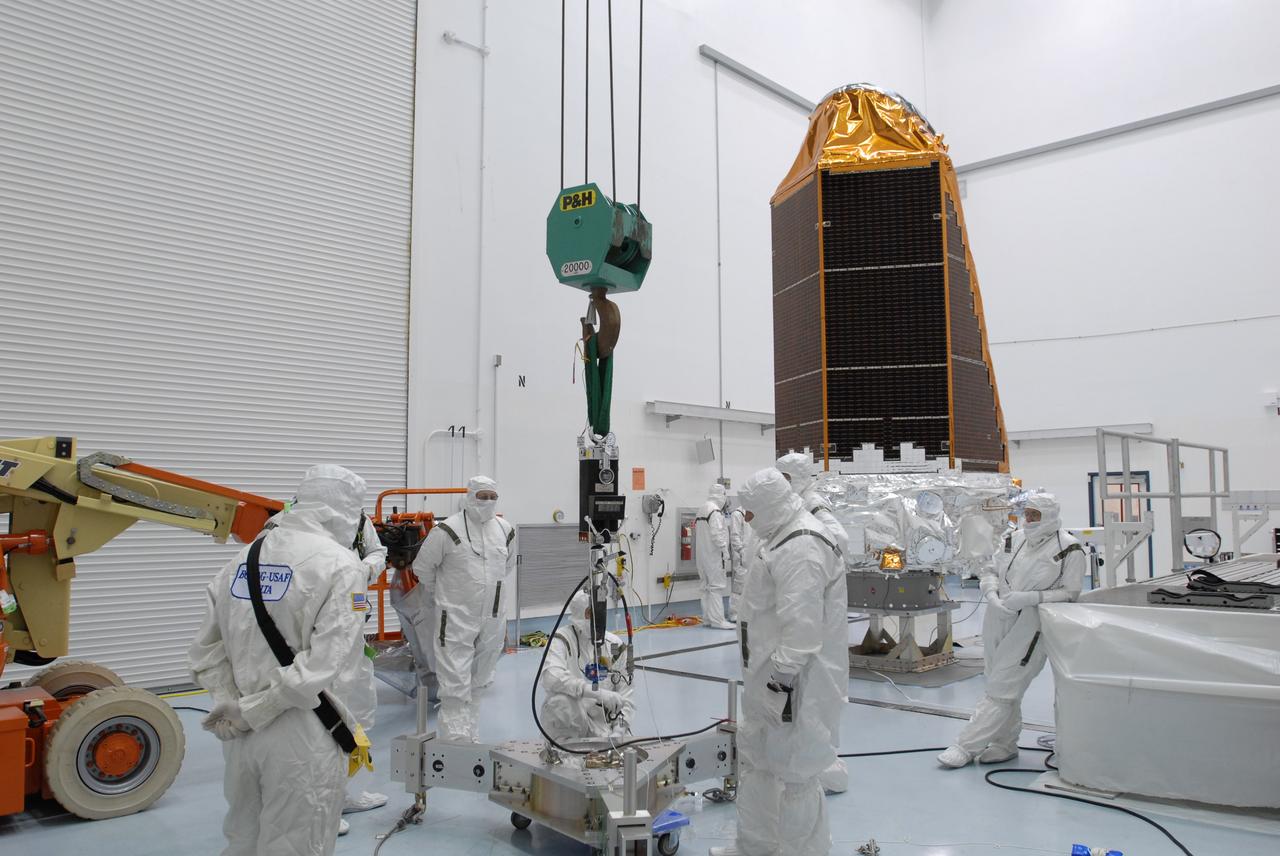
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the Kepler spacecraft is lifted by the overhead crane. Special equipment on the crane will weigh the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
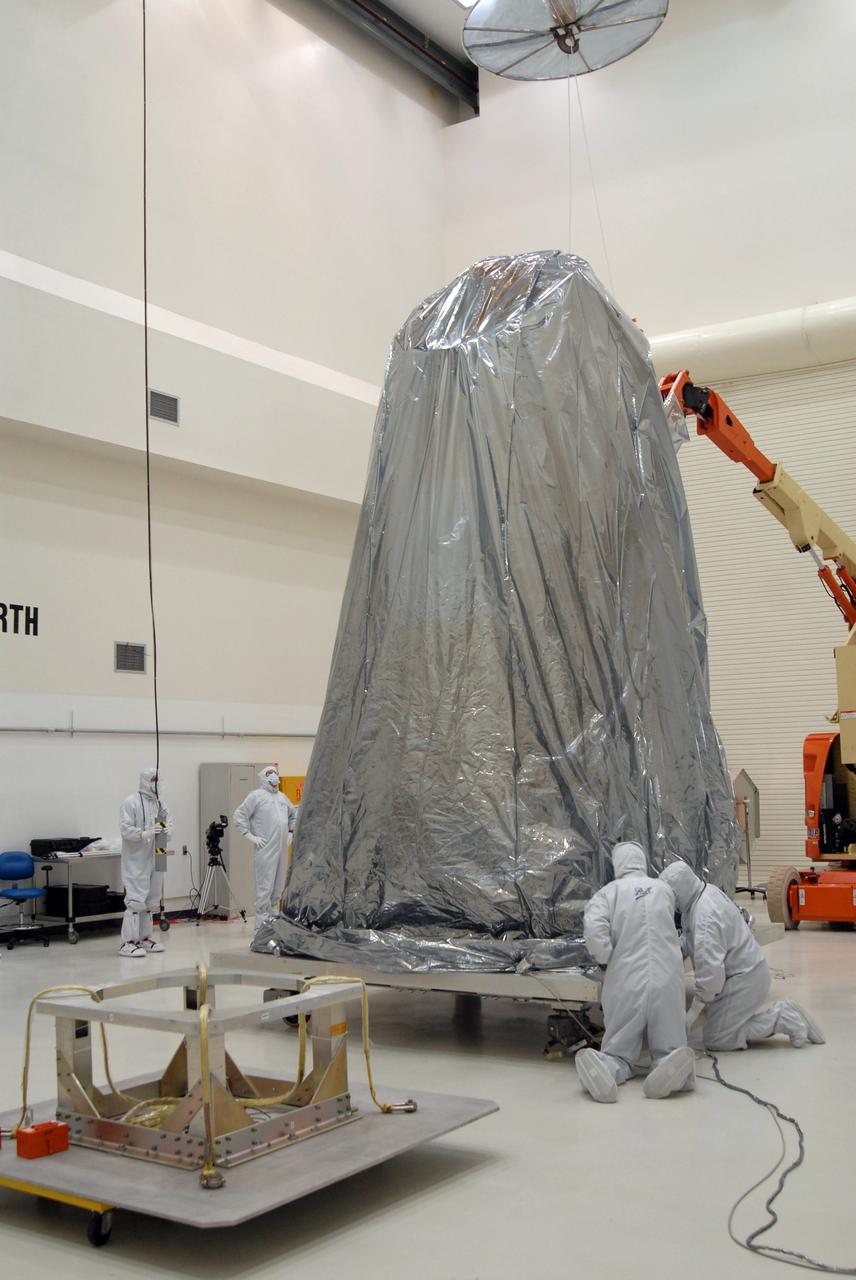

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astrotech payload processing facility, technicians secure the protective cover over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler will be moved to the Hazardous Processing Facility for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers check the Kepler spacecraft as it is lifted for weighing. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers attach cables from the overhead crane onto the Kepler spacecraft. The crane will lift and weigh the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., workers attach cables from the overhead crane onto the Kepler spacecraft. The crane will lift and weigh the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
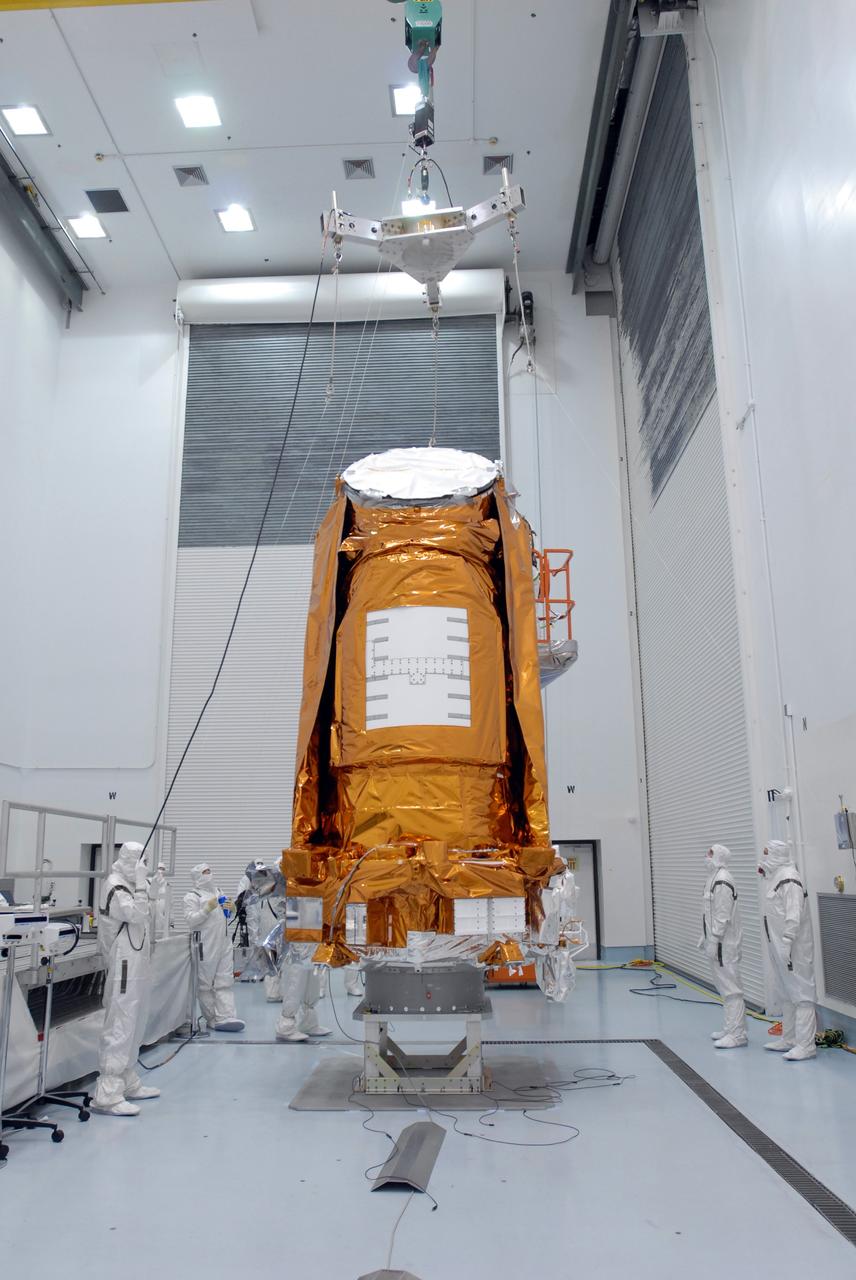

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., the crane-scale is moved into place above the Kepler spacecraft. The spacecraft will be lifted and weighed. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently targeted for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
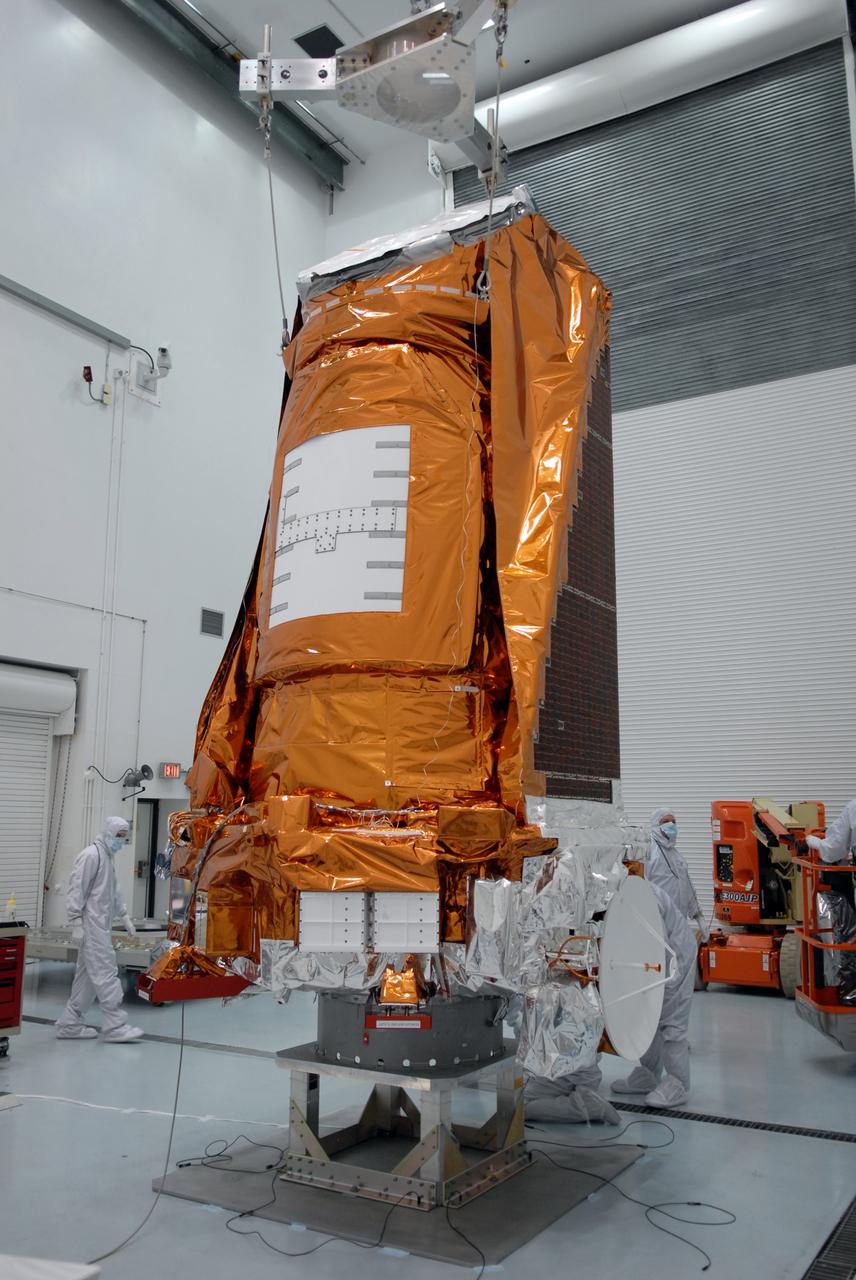

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is lowered onto a stand for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
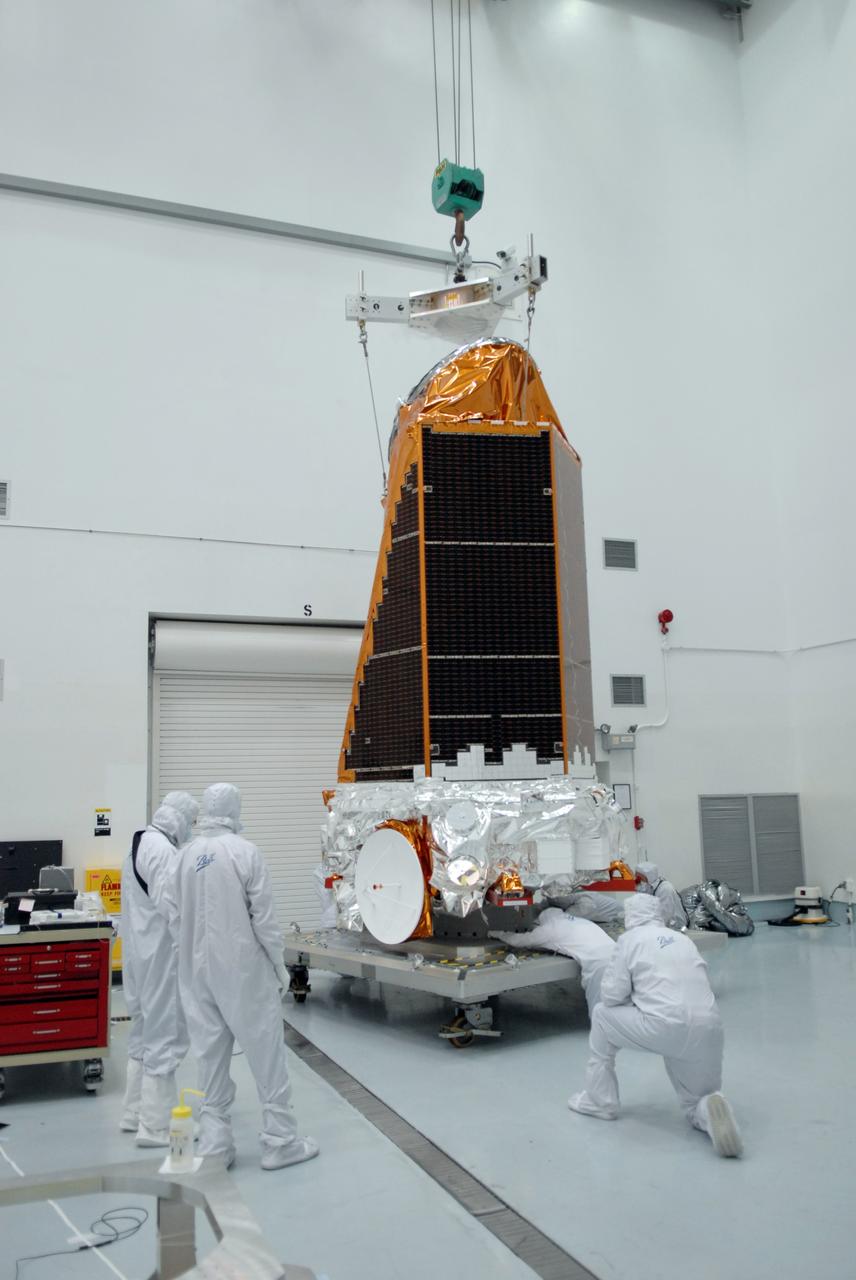

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Inside the Hazardous Processing Facility at Astrotech in Titusville, Fla., NASA's Kepler spacecraft is being moved to another stand for fueling. Kepler is designed to survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
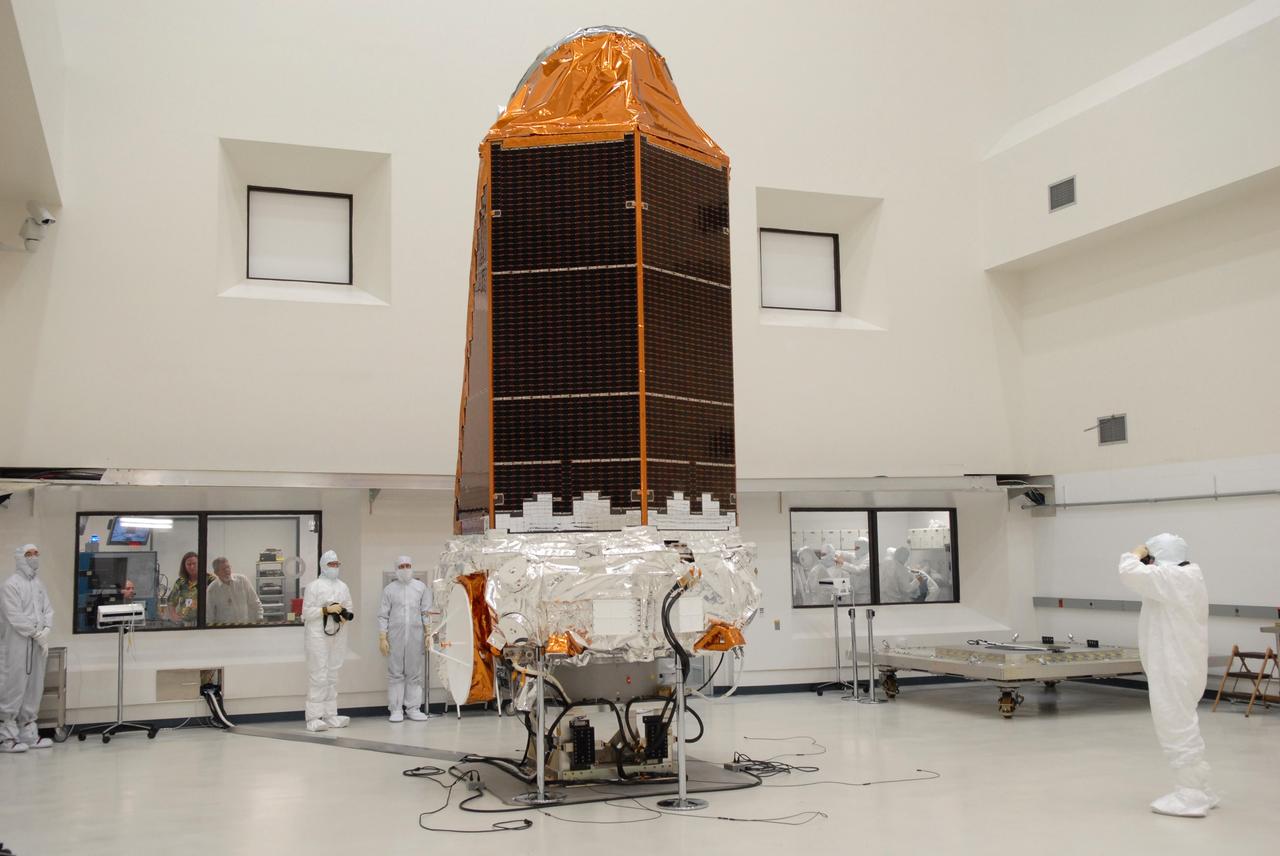

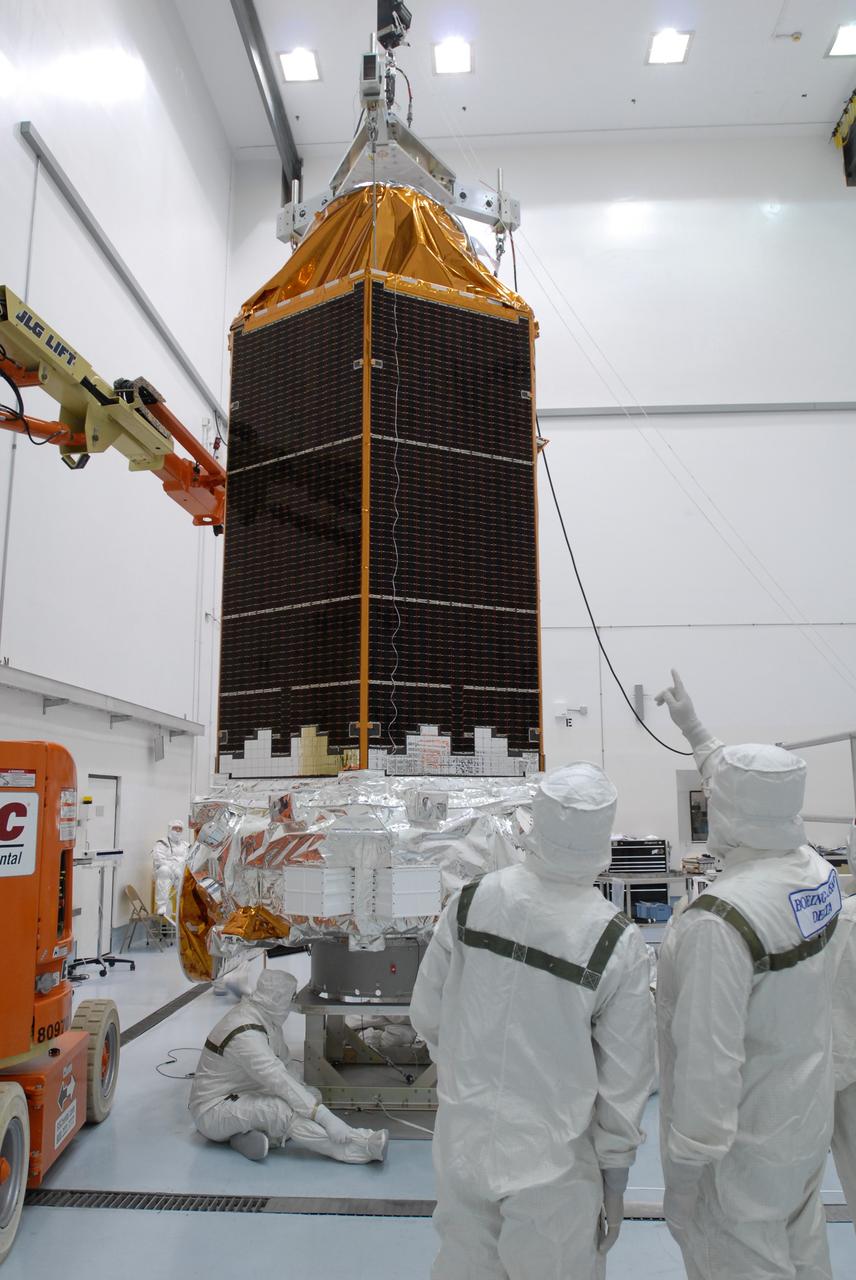
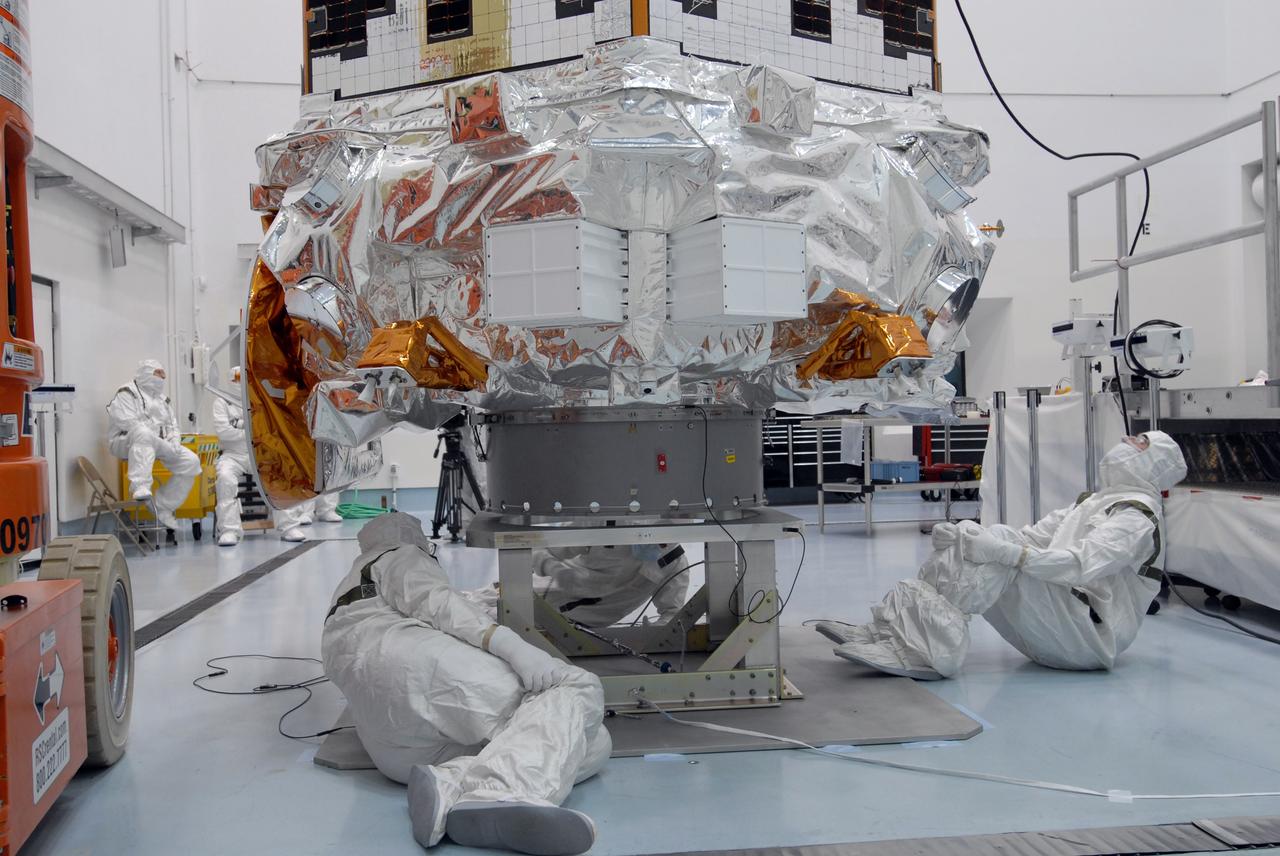
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Kepler spacecraft, that will be launched in March aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, is photographed by journalists dressed in clean-room suits. Visible are the solar arrays on top and the high-gain antenna at lower left. The event, being held at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., provides media representatives an opportunity to photograph the space telescope and to interview project officials from NASA and Ball Aerospace, builder of the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more that 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
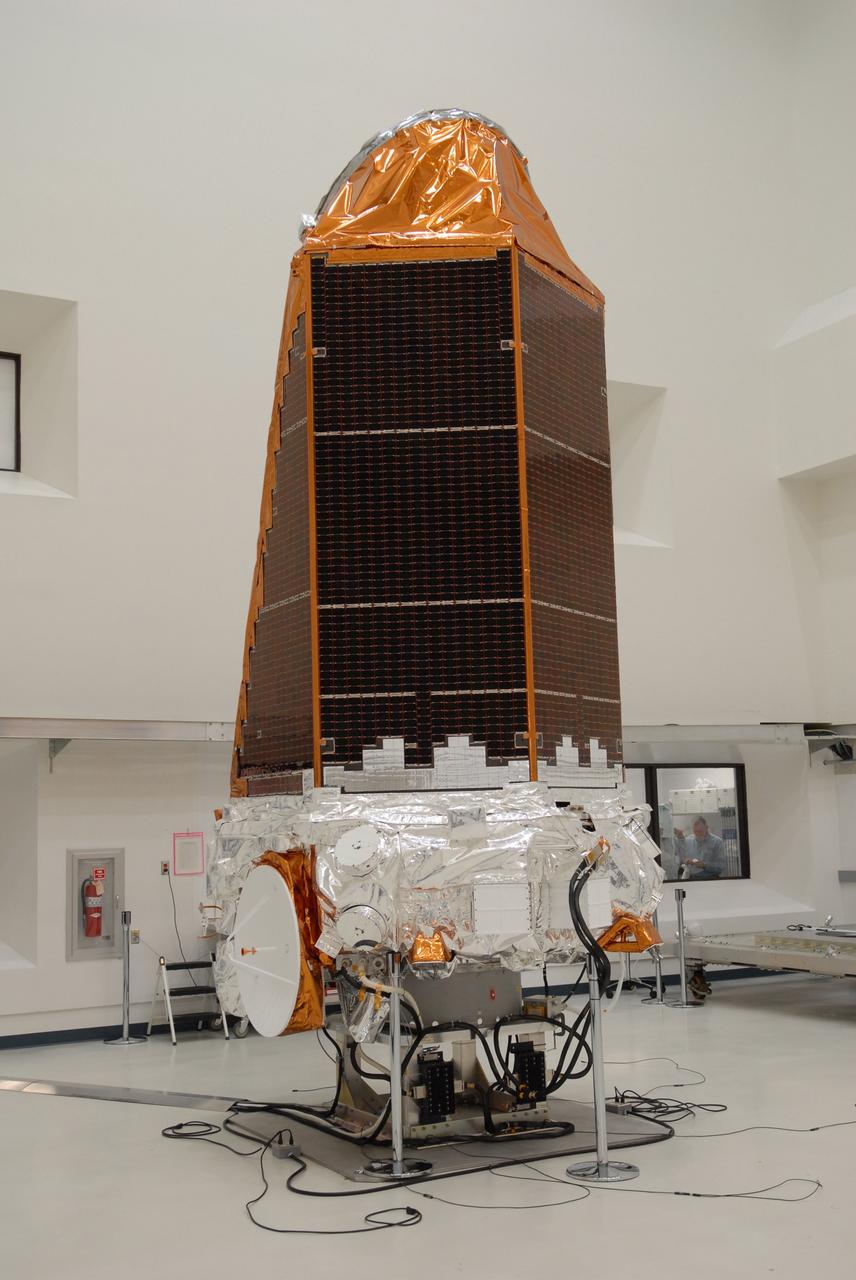

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Kepler spacecraft, that will be launched in March aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, is ready for the media opportunity Jan. 30. Visible are the solar arrays on top and the high-gain antenna at lower left. The event, being held at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., will provide media representatives an opportunity to photograph the space telescope and to interview project officials from NASA and Ball Aerospace, builder of the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more that 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
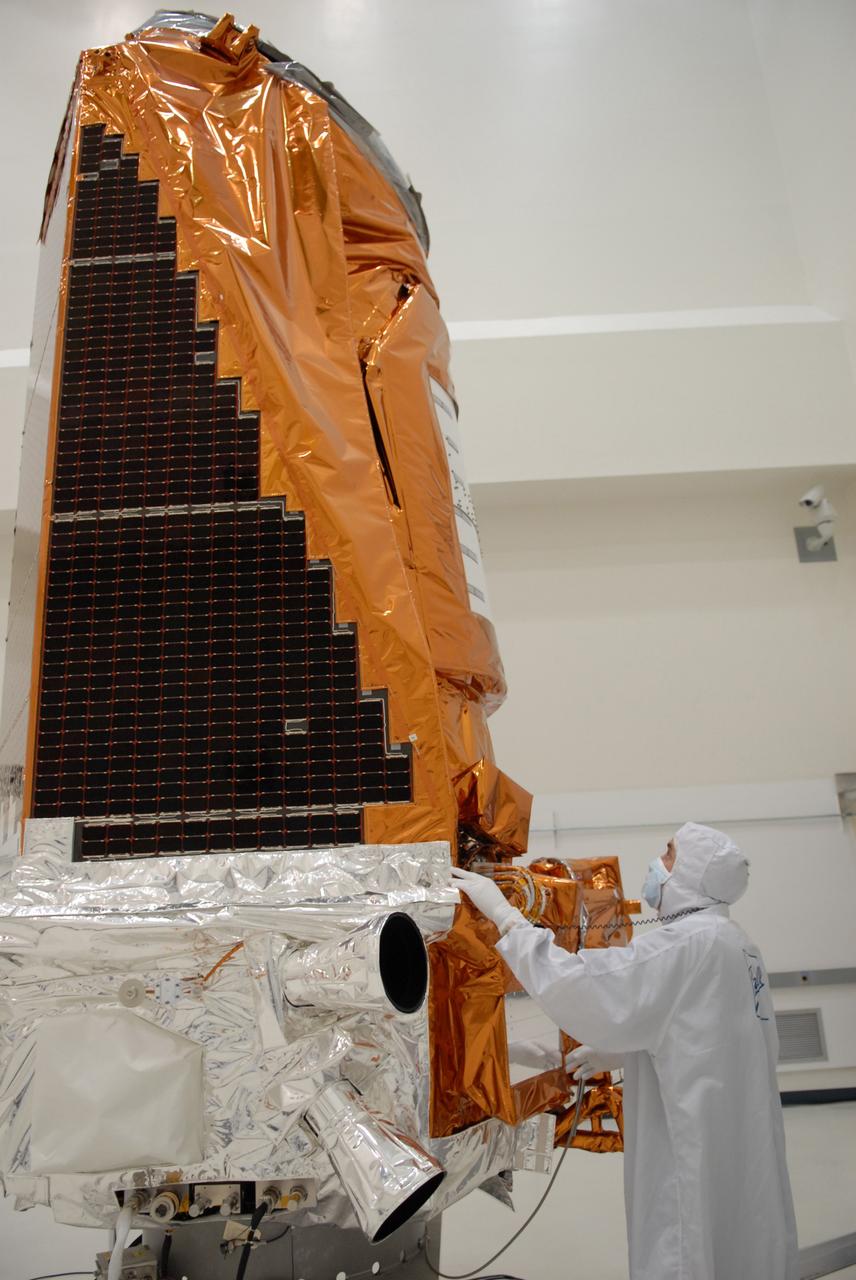

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a media event at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace technician looks over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Visible on top are the solar arrays. The event provided media representatives an opportunity to photograph the space telescope and to interview project officials from NASA and Ball Aerospace, builder of the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more that 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
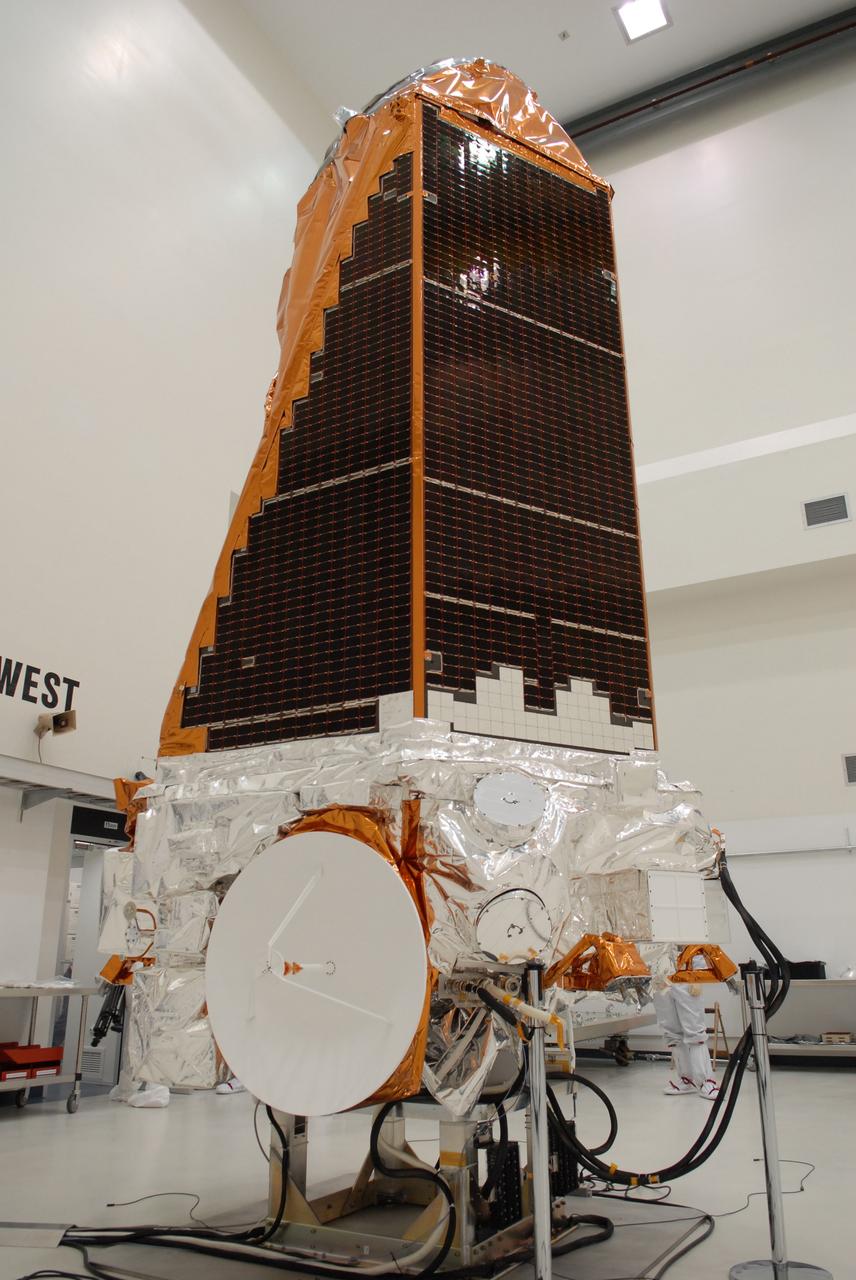
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA's Kepler spacecraft, that will be launched in March aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, is ready for the media opportunity Jan. 30. Visible are the solar arrays on top and the high-gain antenna at lower left. The event, being held at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., will provide media representatives an opportunity to photograph the space telescope and to interview project officials from NASA and Ball Aerospace, builder of the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more that 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
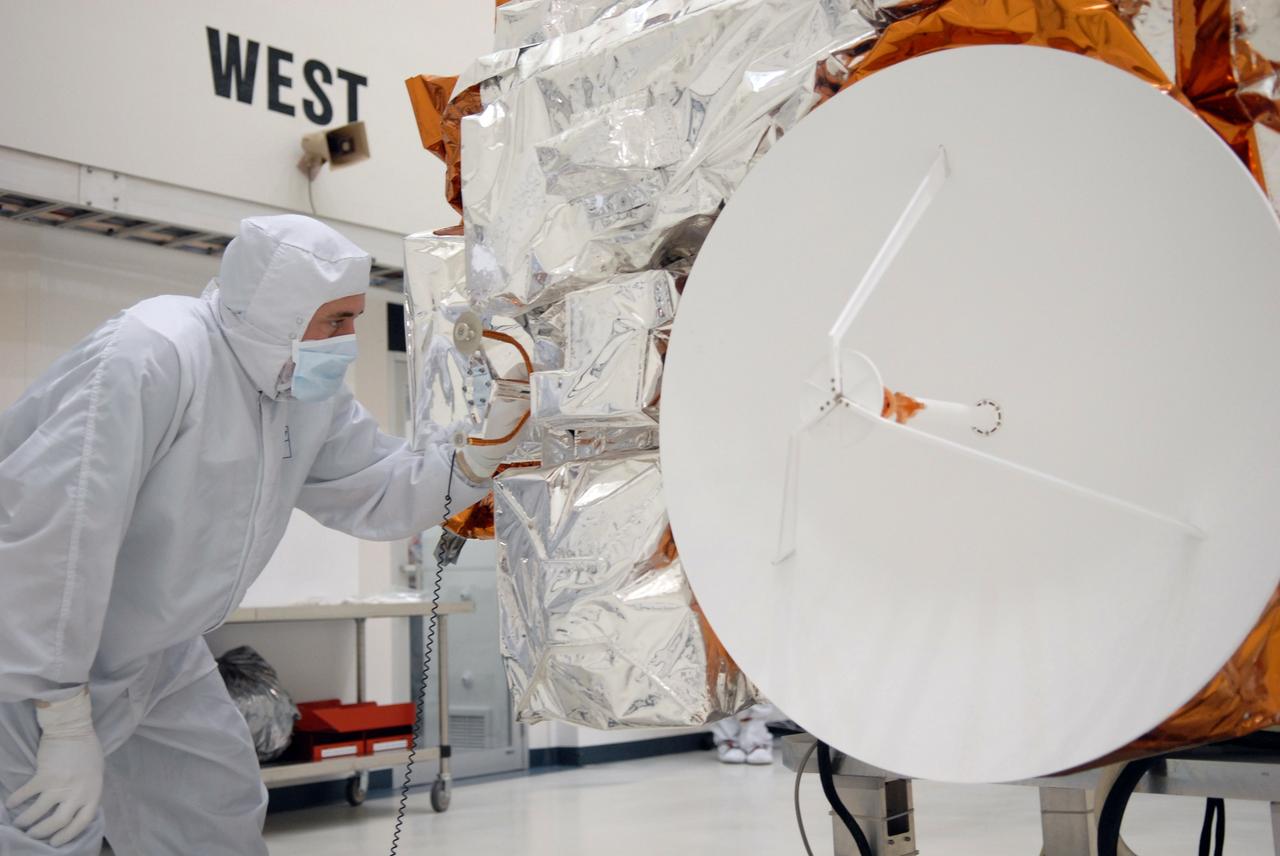

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a media event at the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Fla., a Ball Aerospace technician looks over NASA's Kepler spacecraft. At right is the high-gain antenna. The event provided media representatives an opportunity to photograph the space telescope and to interview project officials from NASA and Ball Aerospace, builder of the spacecraft. Kepler is designed to survey more that 100,000 stars in our galaxy to determine the number of sun-like stars that have Earth-size and larger planets, including those that lie in a star's "habitable zone," a region where liquid water, and perhaps life, could exist. If these Earth-size worlds do exist around stars like our sun, Kepler is expected to be the first to find them and the first to measure how common they are. The liftoff of Kepler aboard a Delta II rocket is currently planned for 10:48 p.m. EST March 5 from Space Launch Complex 17 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
NASA Kepler mission has discovered a world where two suns set over the horizon instead of just one. The planet, called Kepler-16b, is the most Tatooine-like planet yet found in our galaxy and is depicted here in this artist concept.
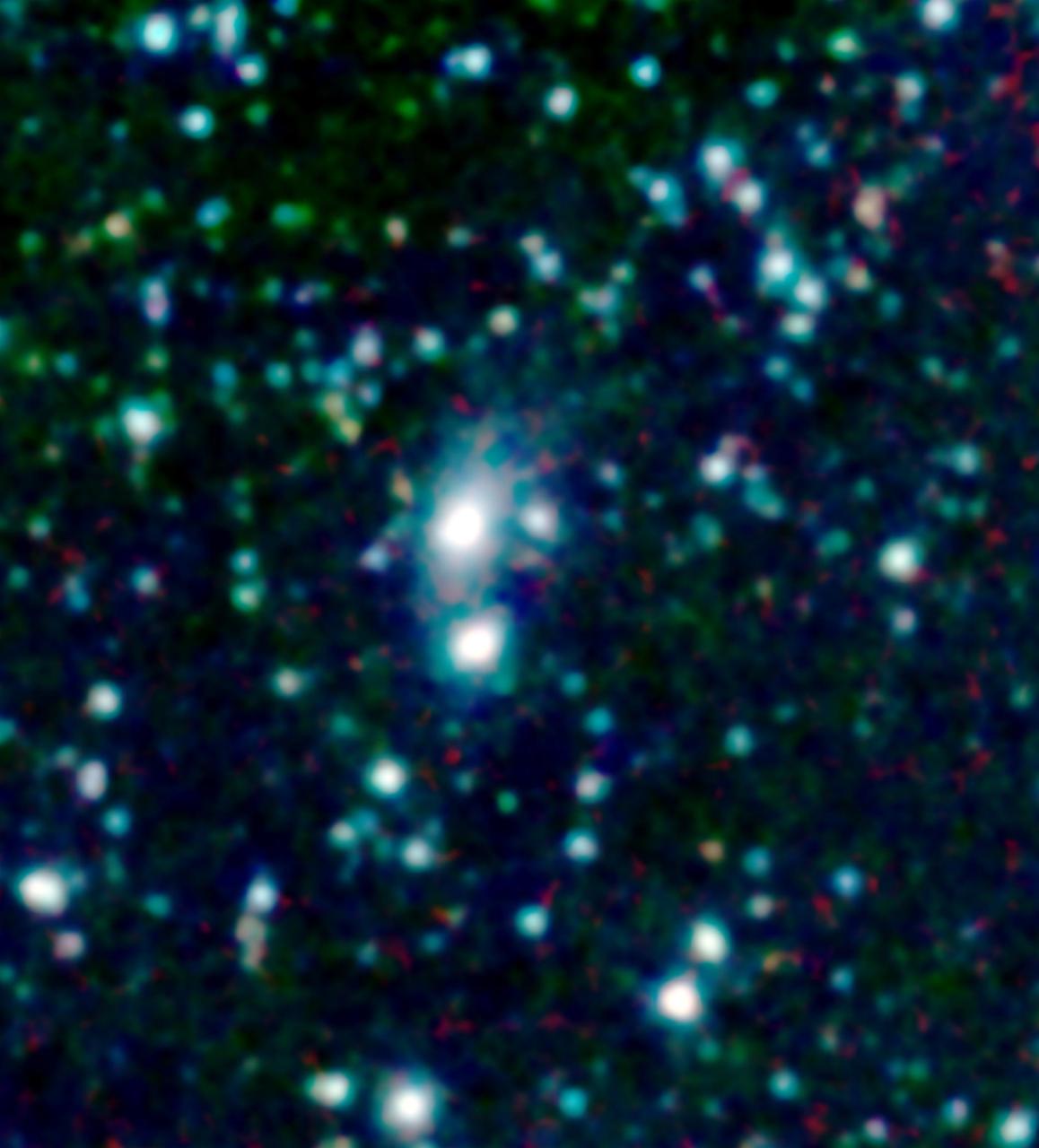

A big galaxy is stealing gas right off the back of its smaller companion in this new image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. The stolen gas is hot, but it might eventually cool down to make new stars and planets.

This artist concept illustrates a young, red dwarf star surrounded by three planets. NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer is helping to identify young, red dwarf stars that are close to us by detecting their ultraviolet light.
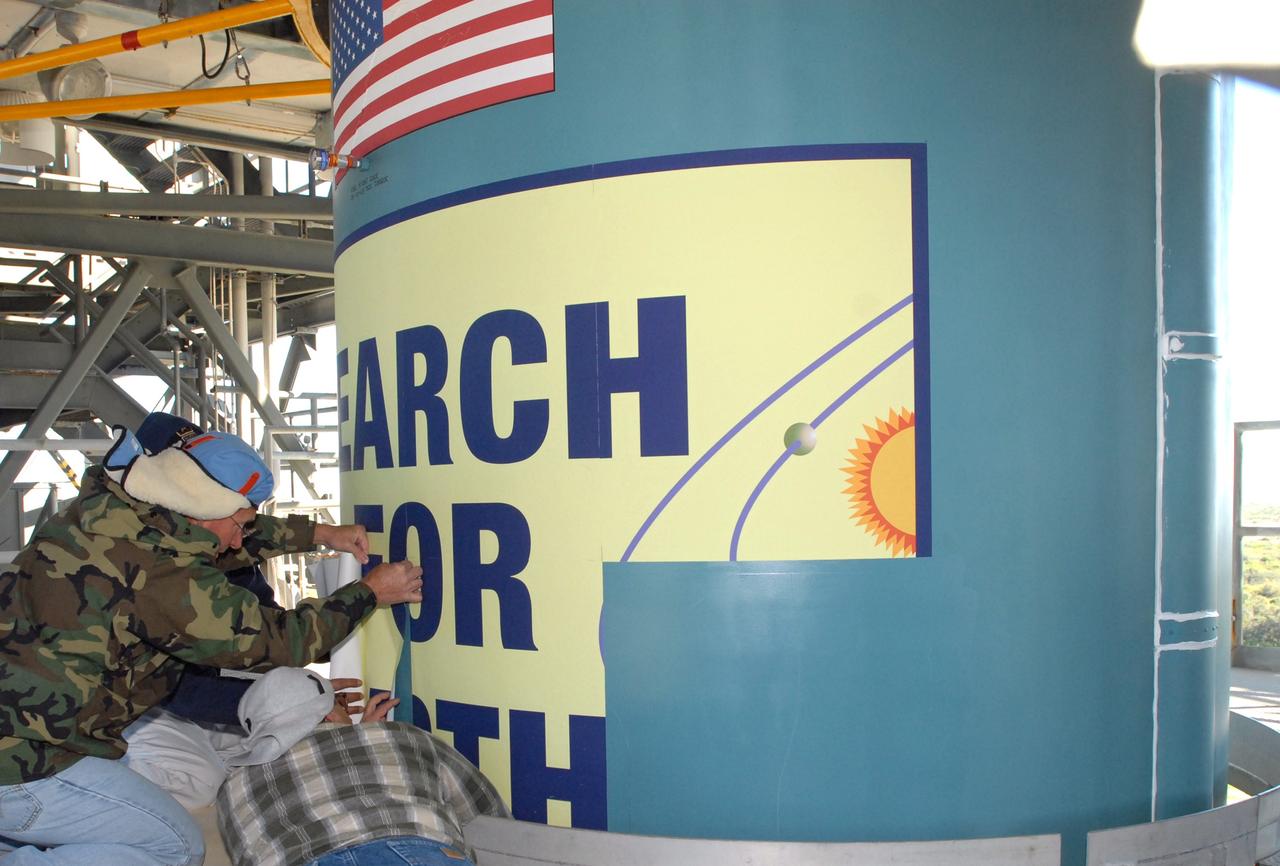

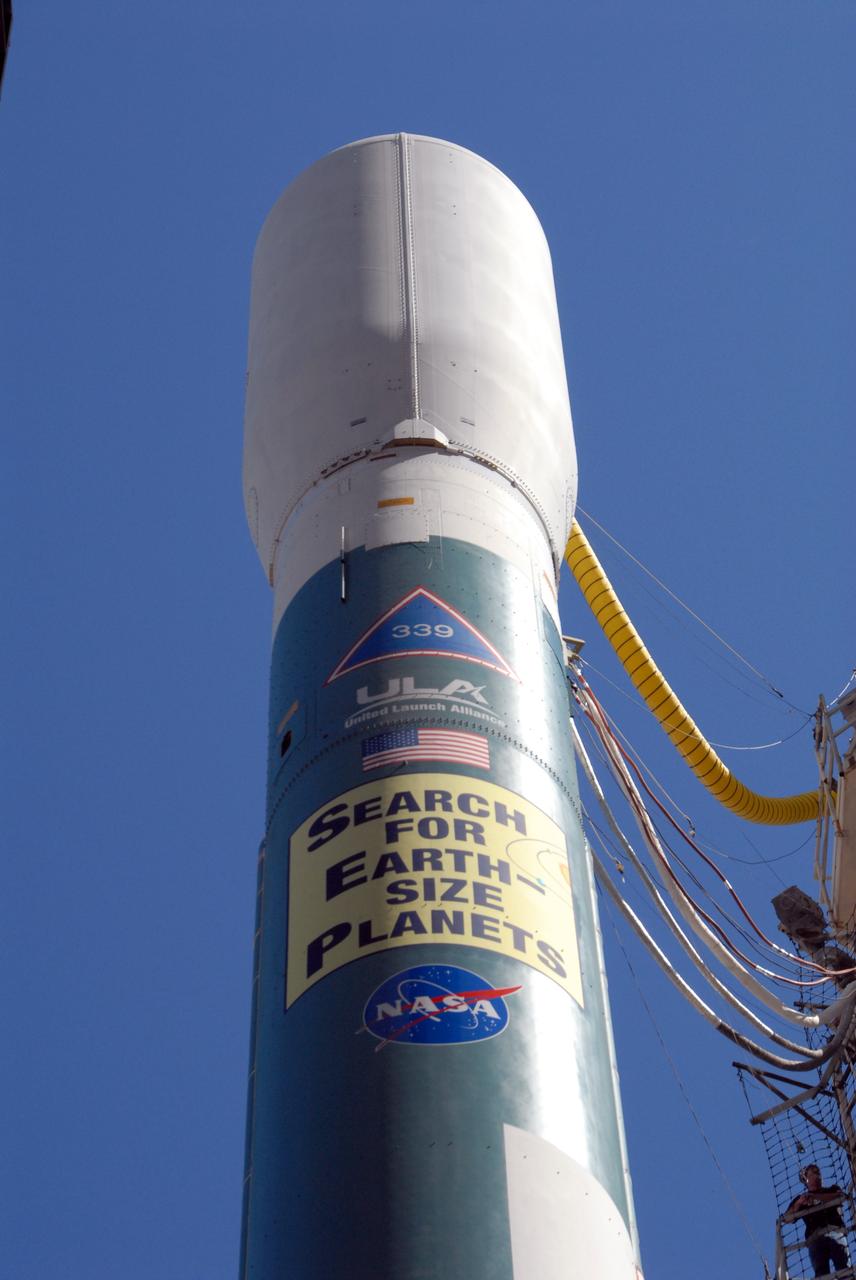
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers at Launch Complex 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida place the large patch on the Delta 2 rocket that describes the Kepler spacecraft mission to be launched by the rocket. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
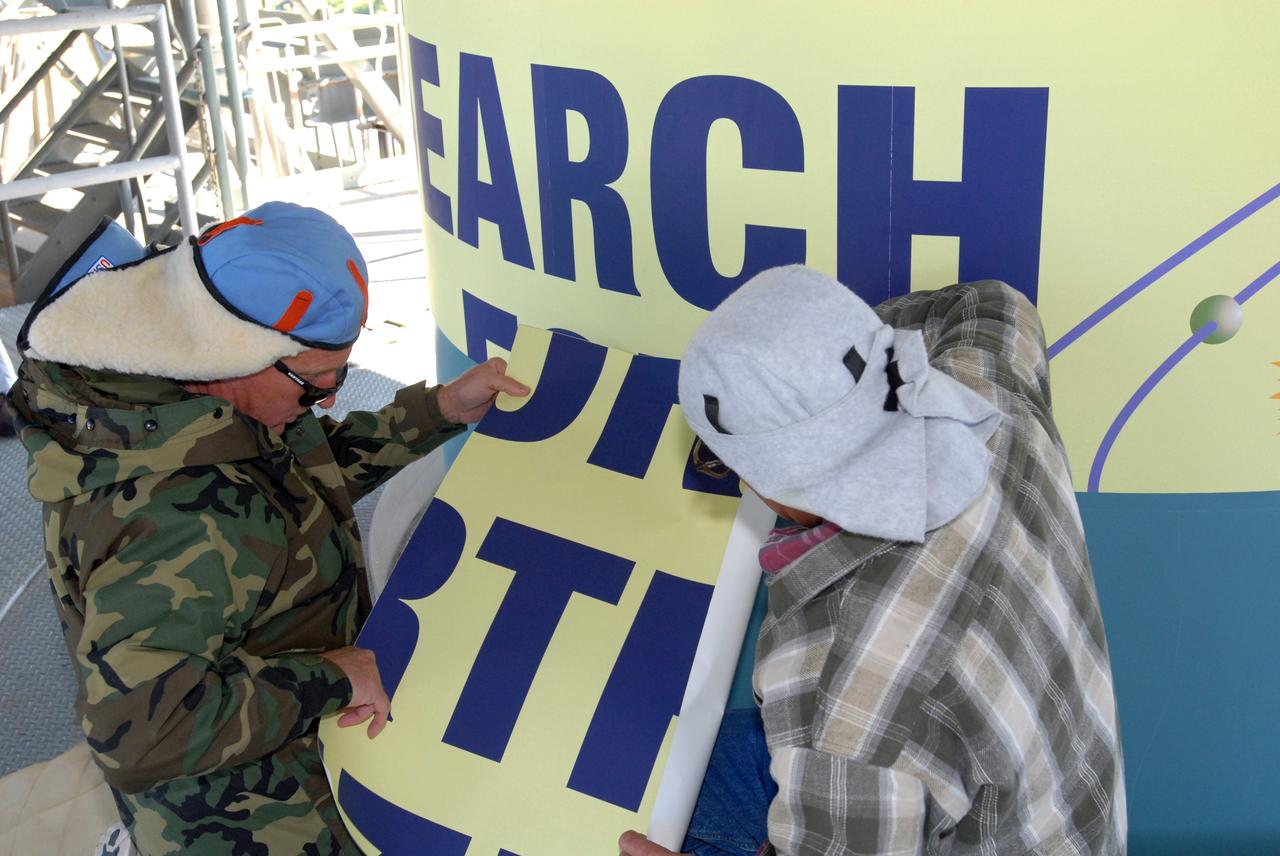

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers at Launch Complex 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida place sections of the large patch that describes the Kepler spacecraft mission to be launched by the Delta 2 rocket. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
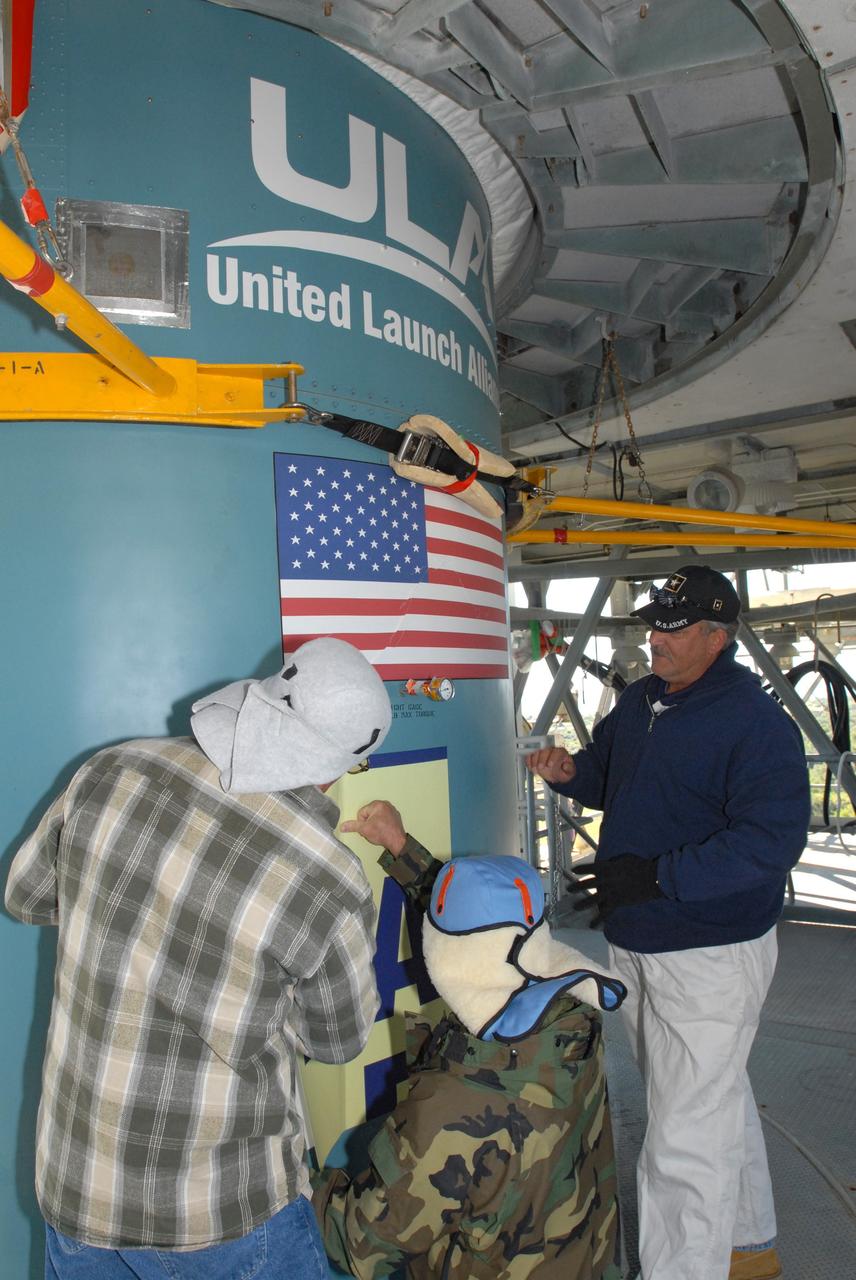

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers at Launch Complex 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida place the large patch that describes the Kepler spacecraft mission to be launched on the Delta 2 rocket. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
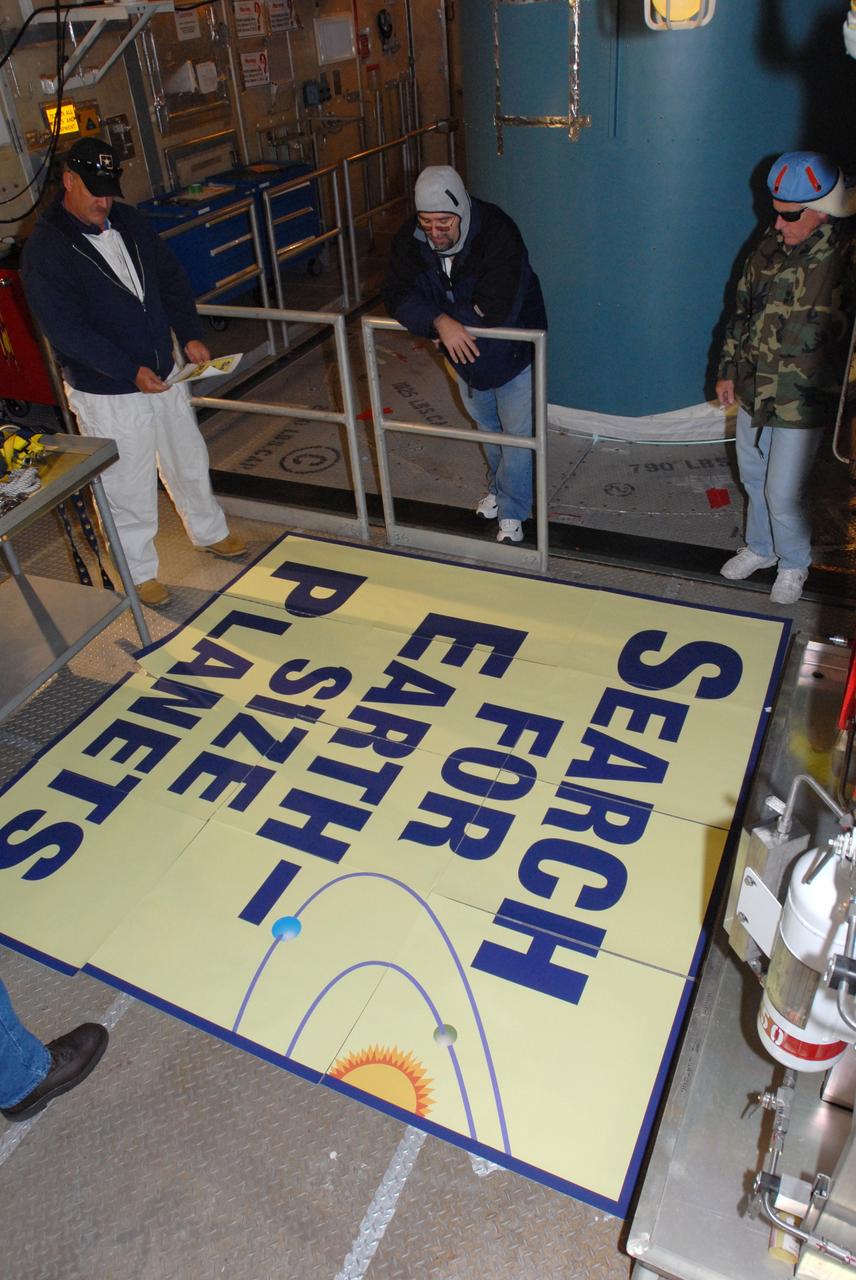

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers at Launch Complex 17-B on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida check the large patch they will place on the Delta 2 rocket (behind them). The patch describes the Kepler spacecraft mission that will be launched by the rocket. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

Planets having atmospheres rich in helium may be common in our galaxy, according to a new theory based on data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. These planets would be around the mass of Neptune, or lighter, and would orbit close to their stars, basking in their searing heat. According to the new theory, radiation from the stars would boil off hydrogen in the planets' atmospheres. Both hydrogen and helium are common ingredients of gas planets like these. Hydrogen is lighter than helium and thus more likely to escape. After billions of years of losing hydrogen, the planet's atmosphere would become enriched with helium. Scientists predict the planets would appear covered in white or gray clouds. This is in contrast to our own Neptune, which is blue due to the presence of methane. Methane absorbs the color red, leaving blue. Neptune is far from our sun and hasn't lost its hydrogen. The hydrogen bonds with carbon to form methane. This artist's concept depicts a proposed helium-atmosphere planet called GJ 436b, which was found by Spitzer to lack in methane -- a first clue about its lack of hydrogen. The planet orbits every 2.6 days around its star, which is cooler than our sun and thus appears more yellow-orange in color. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19344
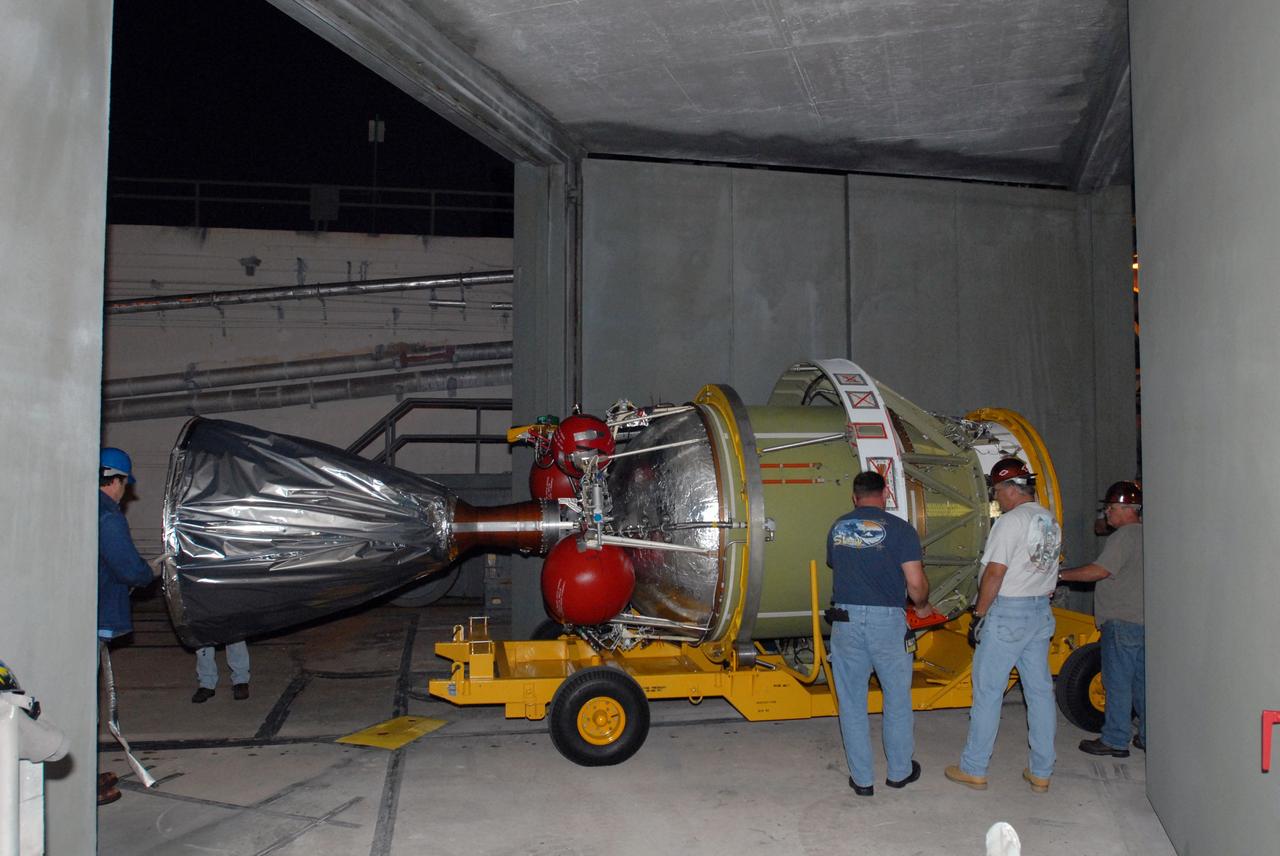

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The second stage of the Delta 2 rocket for the launch of NASA's Kepler spacecraft arrives on Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The second stage will be lifted into the mobile service tower for mating with the first stage. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
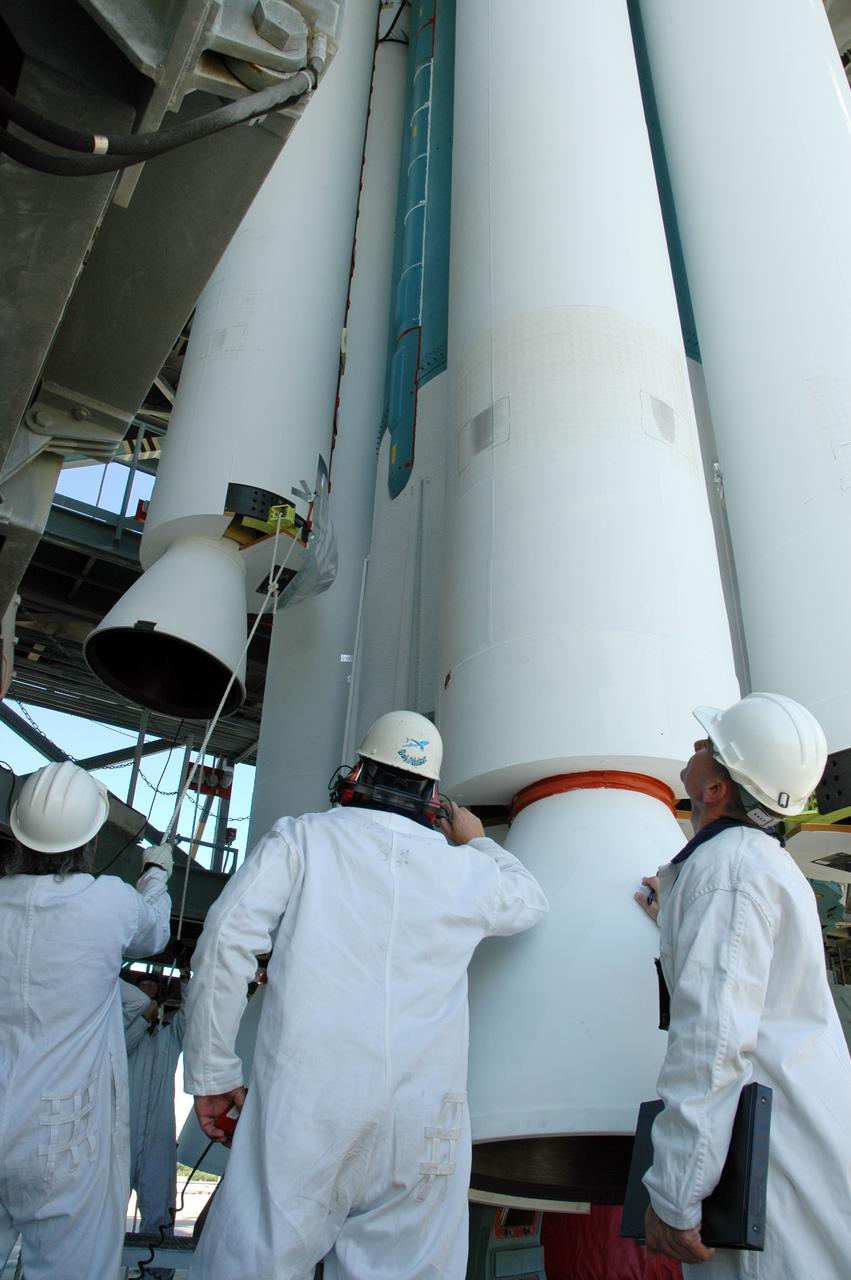

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers oversee the lifting of an air-lit strap-on solid rocket booster that will be mated to the Delta 2 launch vehicle that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, an air-lit strap-on solid rocket booster is lifted up for mating onto the Delta 2 launch vehicle that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers get ready to lift an air-lit strap-on solid rocket booster to be mated onto the Delta 2 launch vehicle that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
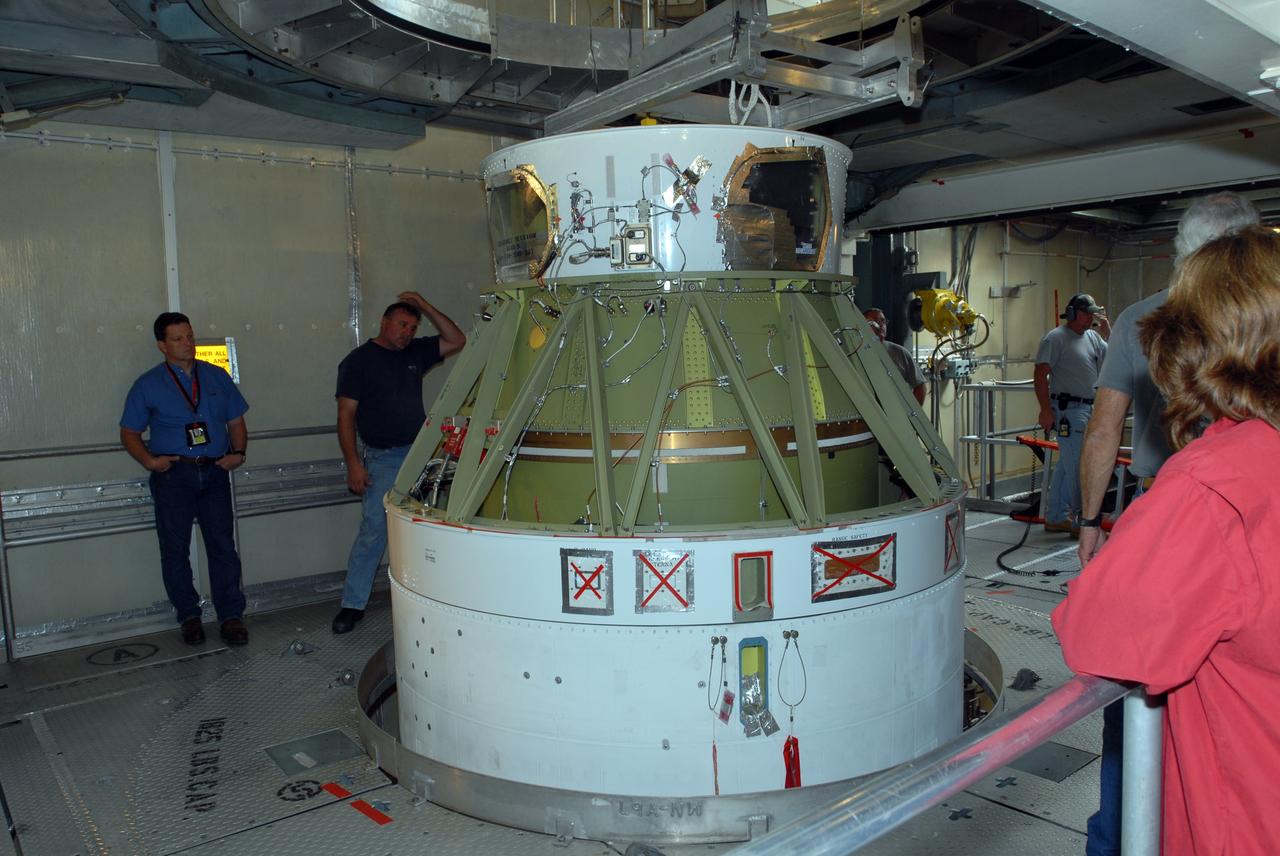

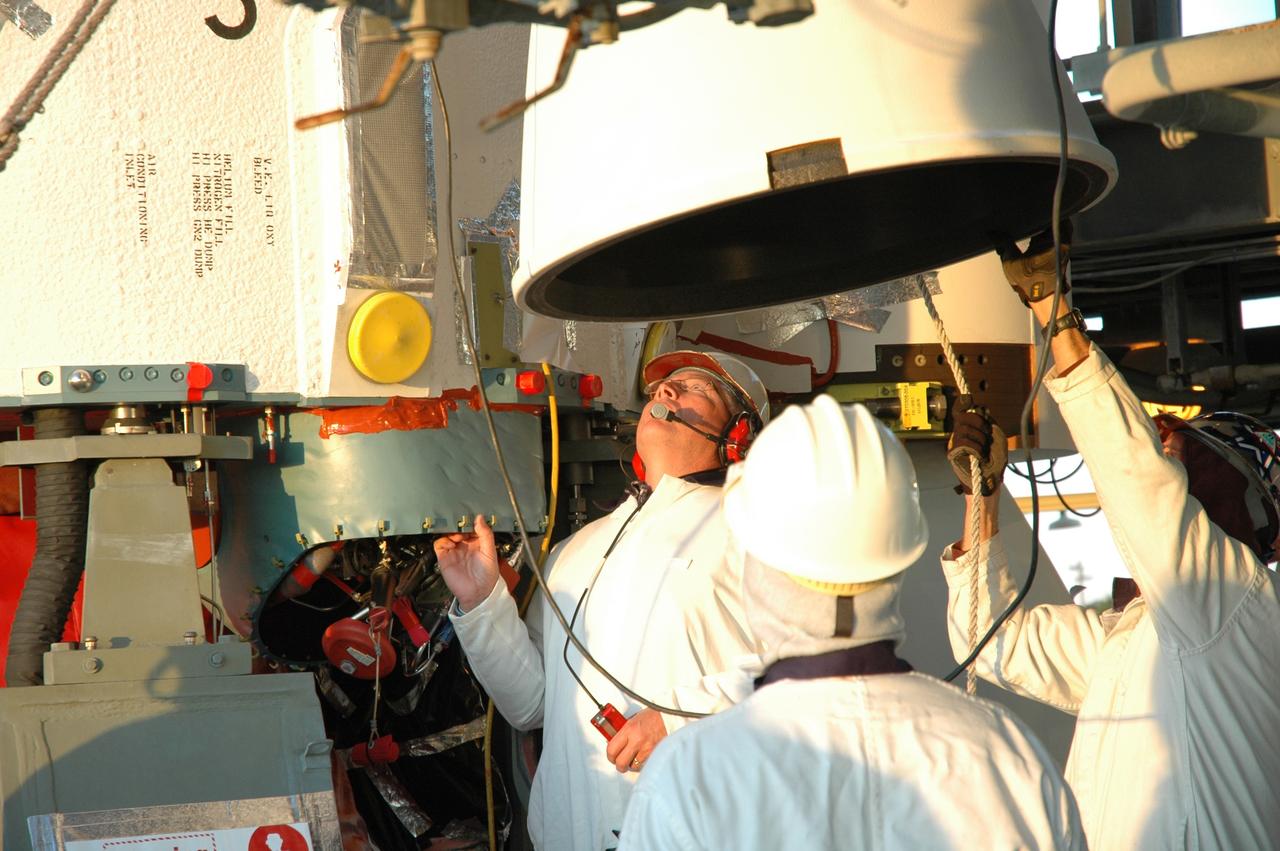
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the second stage has been mated to the first stage of the Delta 2 rocket that will launch NASA's Kepler spacecraft. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
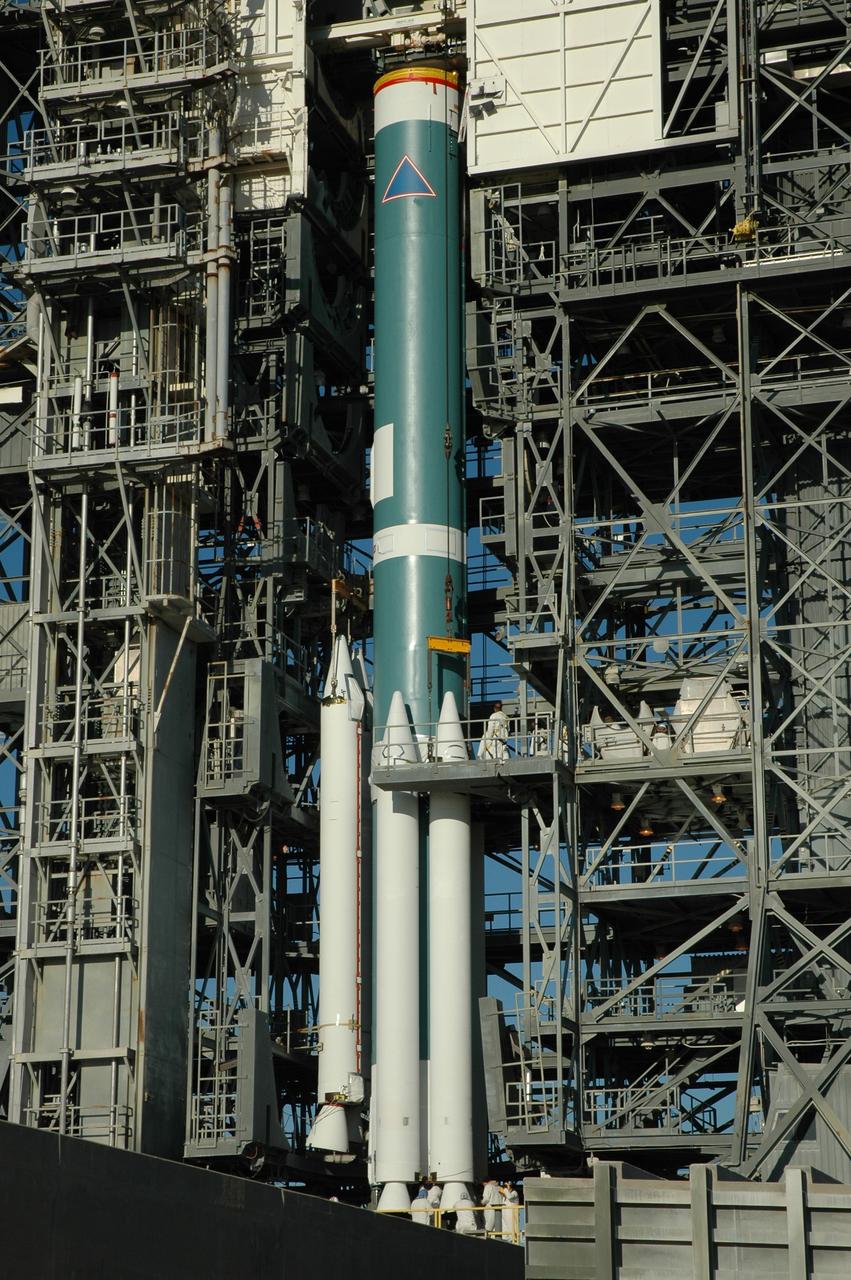

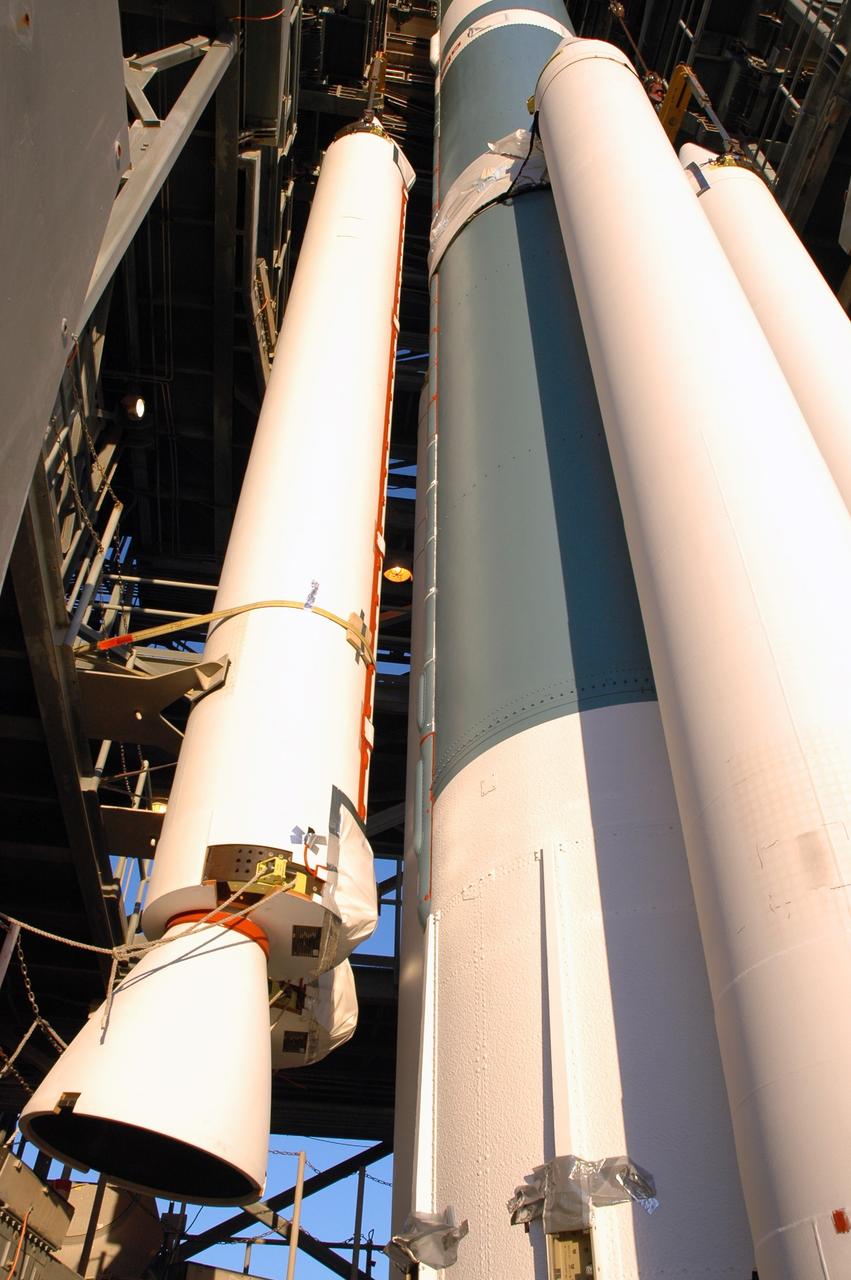
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, air-lit strap-on solid rocket boosters are being added to the first stage of the Delta 2 launch vehicle (seen here) that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
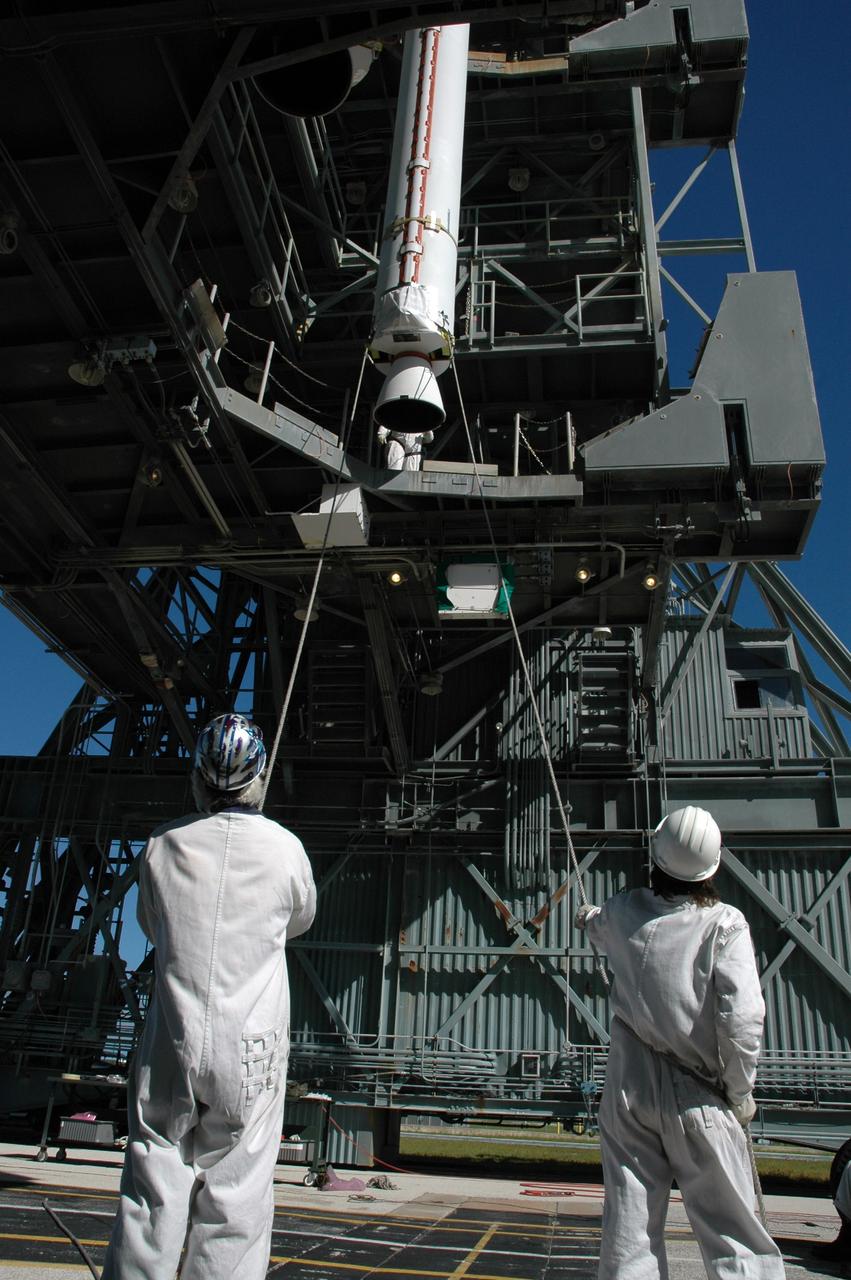

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, another solid rocket booster is being lifted into the mobile service tower for mating to the first stage of the Kepler's Delta 2 launch vehicle. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, air-lit strap-on solid rocket boosters are being added to the first stage of the Delta 2 launch vehicle (seen here) that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
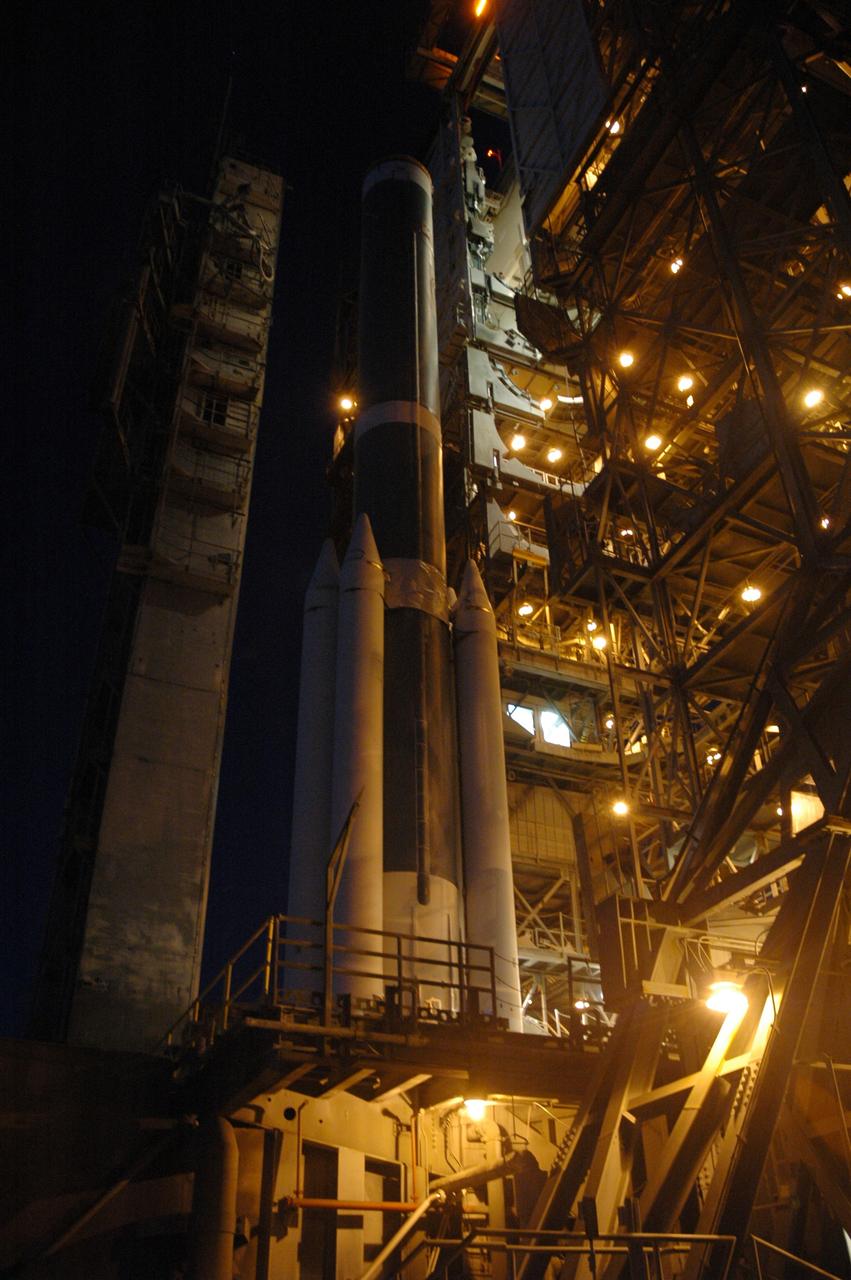

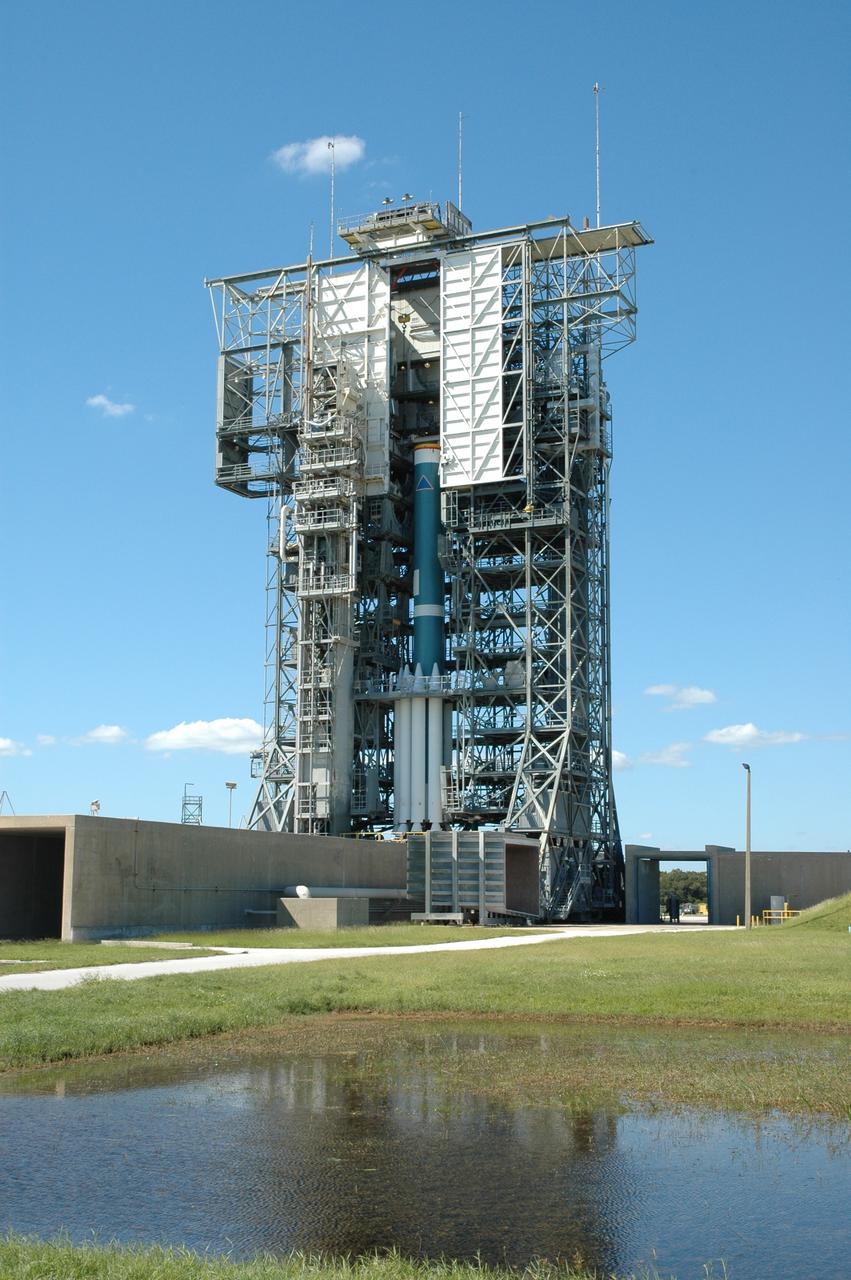
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the first stage of the Delta 2 launch vehicle that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit waits for the installation of the final solid rocket boosters. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
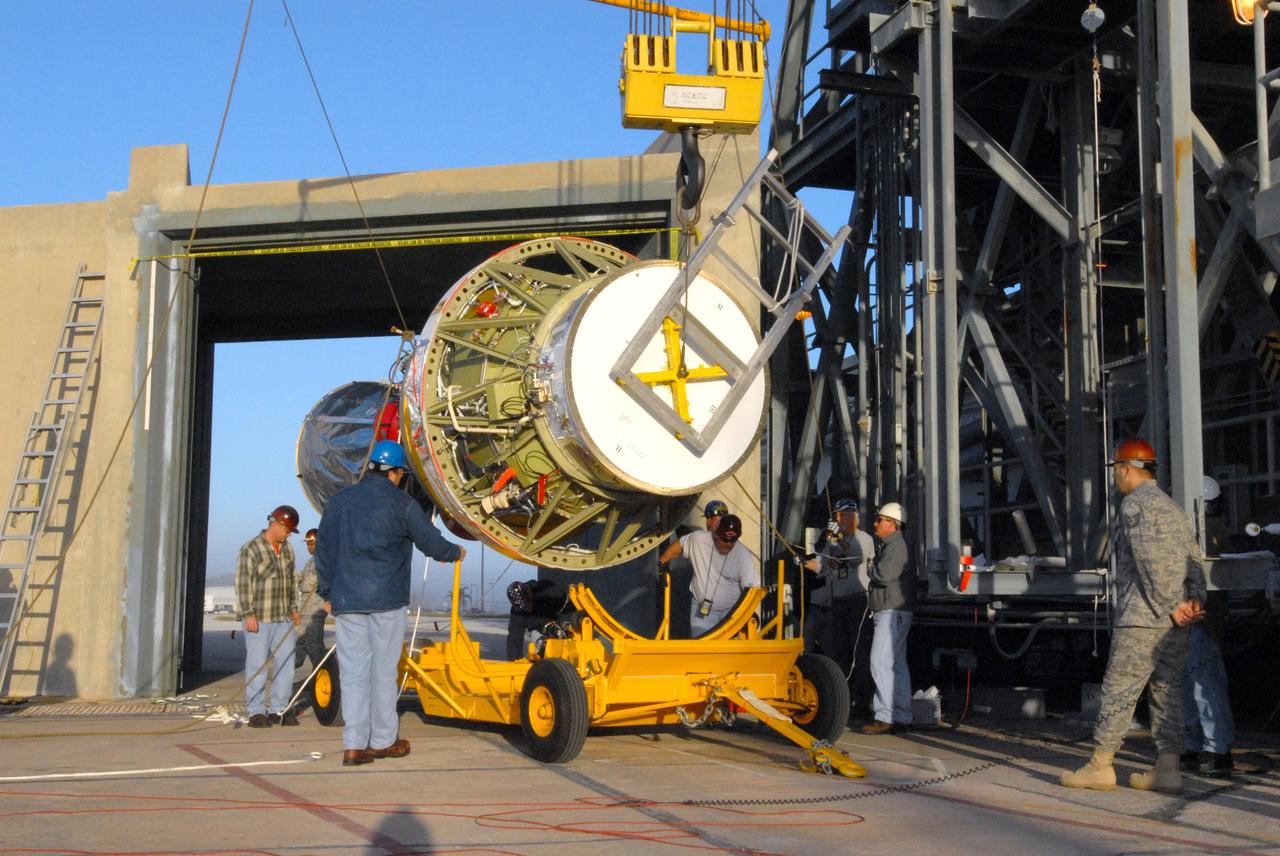

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- On Complex 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a crane lifts the second stage of the Delta 2 rocket off its transporter. The second stage will be lifted into the mobile service tower for mating with the first stage of the Delta 2, which is the launch vehicle for NASA's Kepler spacecraft. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
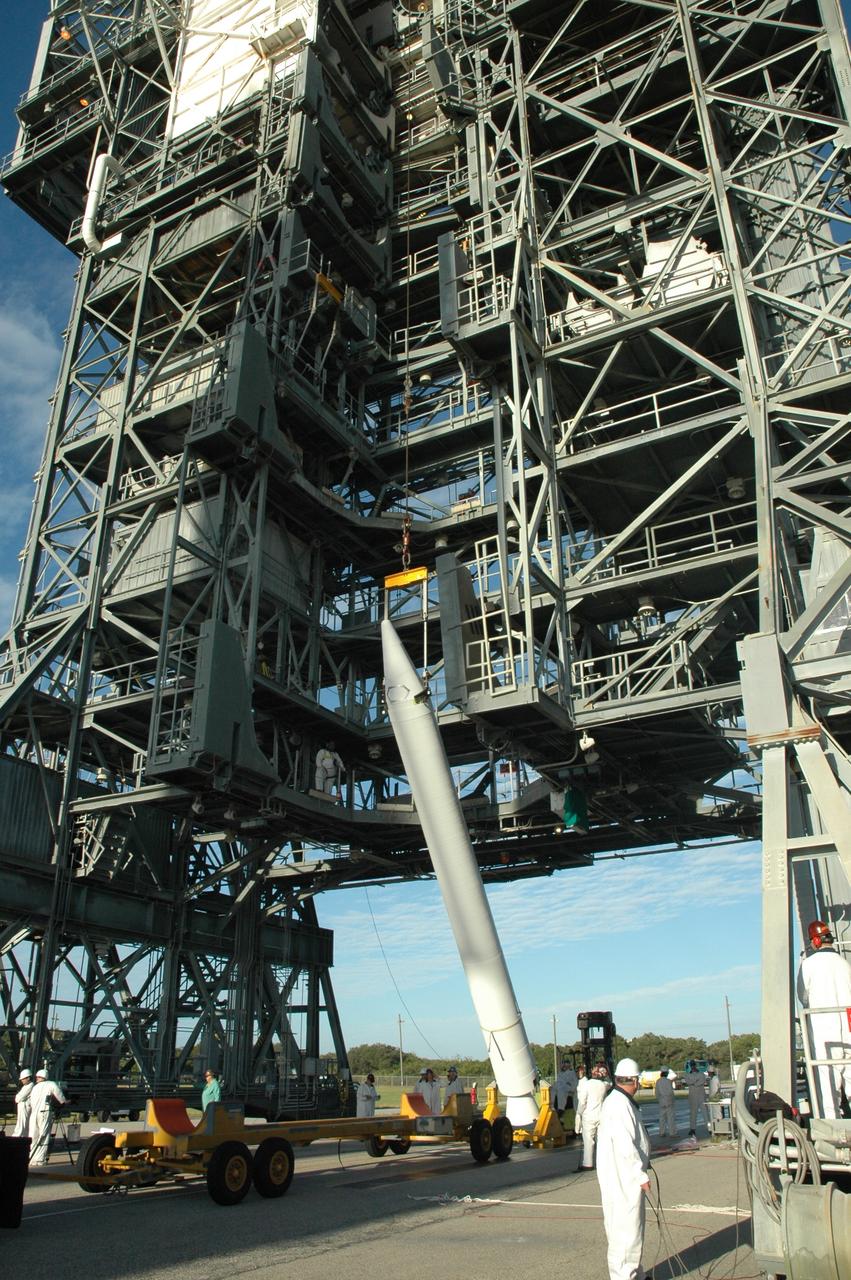

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a solid rocket booster is nearly vertical. It will be lifted into the mobile service tower for mating to the first stage of the Kepler's Delta 2 launch vehicle. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, workers on an upper level of the launch tower watch as a strap-on solid rocket booster is lifted into place to mate to the first stage of the Delta 2 launch vehicle that will carry the Kepler spacecraft into orbit. The Kepler mission is specifically designed to survey our region of the Milky Way galaxy to discover hundreds of Earth-size and smaller planets in or near the habitable zone and determine how many of the billions of stars in our galaxy have such planets. Results from this mission will allow us to place our solar system within the continuum of planetary systems in the Galaxy. NASA's planet-hunting Kepler mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than March 5, 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann