
Gamma Rays for You and Me

This visualization shows gamma rays detected during 3C 279's big flare by the LAT instrument on NASA's Fermi satellite. Gamma rays are represented as expanding circles reminiscent of raindrops on water. The flare is an abrupt shower of "rain" that trails off toward the end of the movie. Both the maximum size of the circle and its color represent the energy of the gamma ray, with white lowest and magenta highest. In a second version of the visualization, a background map shows how the LAT detects 3C 279 and other sources by accumulating high-energy photons over time (brighter squares reflect higher numbers of gamma rays). The movie starts on June 14 and ends June 17. The area shown is a region of the sky five degrees on a side and centered on the position of 3C 279. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1TqximF" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1TqximF</a> Credits: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration

This view of the gamma-ray sky constructed from one year of Fermi LAT observations is the best view of the extreme universe to date. The map shows the rate at which the LAT detects gamma rays with energies above 300 million electron volts -- about 120 million times the energy of visible light -- from different sky directions. Brighter colors equal higher rates. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration Full story: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/first_year.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/first_year.html</a>
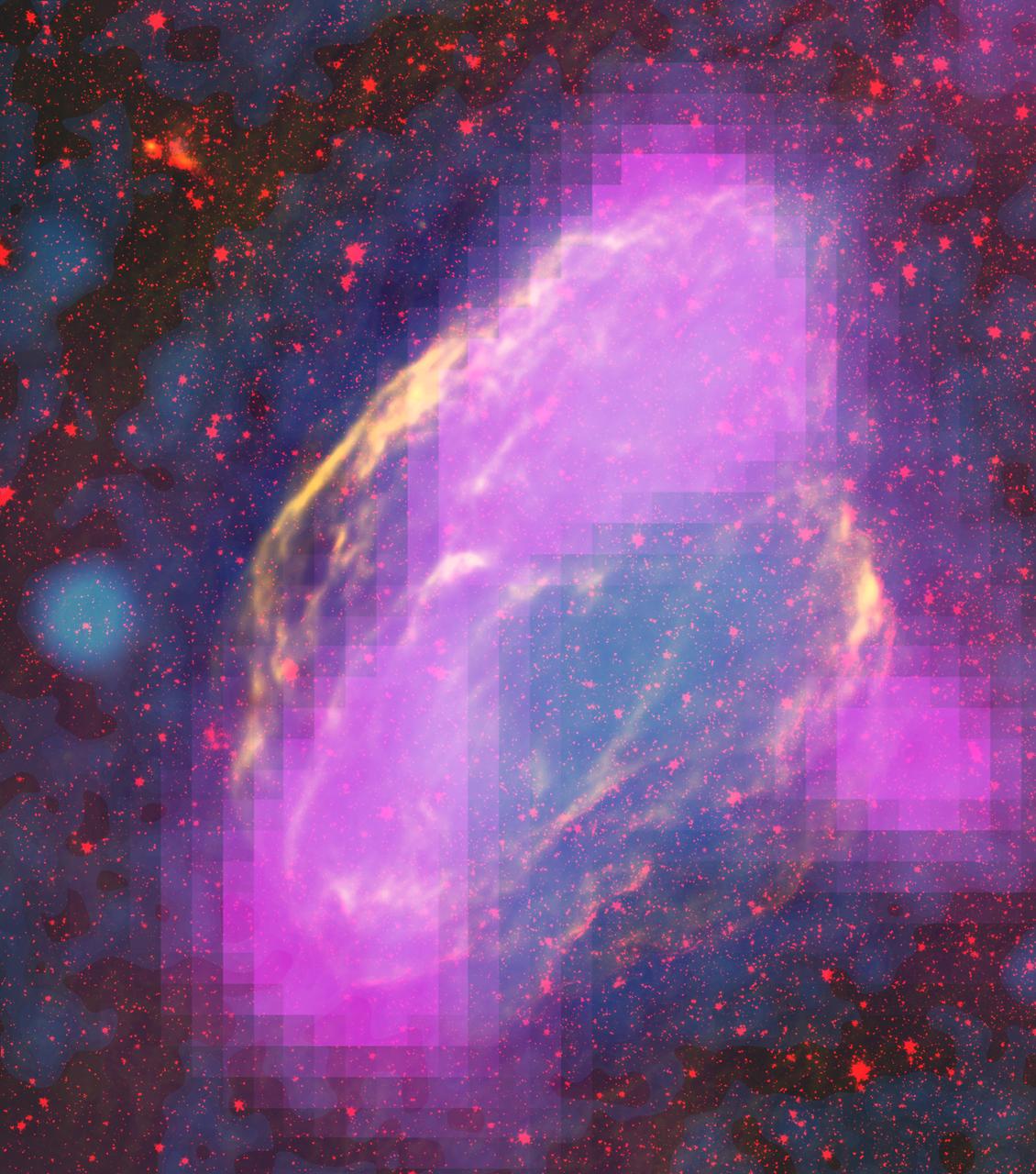

NASA's Fermi Closes on Source of Cosmic Rays New images from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope show where supernova remnants emit radiation a billion times more energetic than visible light. The images bring astronomers a step closer to understanding the source of some of the universe's most energetic particles -- cosmic rays. Fermi mapped GeV-gamma-ray emission regions (magenta) in the W44 supernova remnant. The features clearly align with filaments detectable in other wavelengths. This composite merges X-rays (blue) from the Germany-led ROSAT mission, infrared (red) from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, and radio (orange) from the Very Large Array near Socorro, N.M. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration, ROSAT, JPL-Caltech, and NRAO/AUI For more information: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cosmic-rays-source.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/cosmic-rays-source....</a>
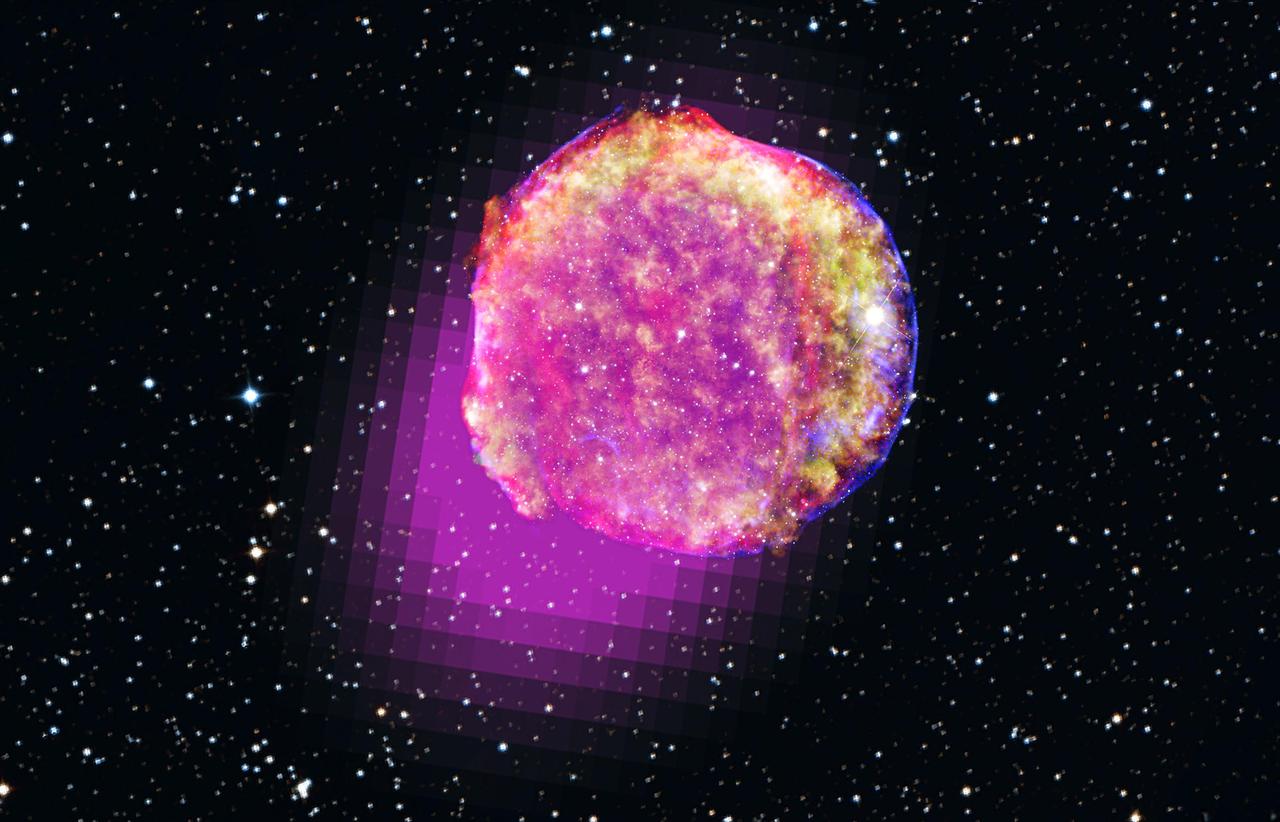

NASA image relase December 13, 2011 Gamma-rays detected by Fermi's LAT show that the remnant of Tycho's supernova shines in the highest-energy form of light. This portrait of the shattered star includes gamma rays (magenta), X-rays (yellow, green, and blue), infrared (red) and optical data. Credit: Gamma ray, NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration; X-ray, NASA/CXC/SAO; Infrared, NASA/JPL-Caltech; Optical, MPIA, Calar Alto, O. Krause et al. and DSS To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/tycho-star.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/tycho-star.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Blazar 3C 279's historic gamma-ray flare can be seen in this image from the Large Area Telescope (LAT) on NASA's Fermi satellite. Gamma rays with energies from 100 million to 100 billion electron volts (eV) are shown; for comparison, visible light has energies between 2 and 3 eV. The image spans 150 degrees, is shown in a stereographic projection, and represents an exposure from June 11 at 00:28 UT to June 17 at 08:17 UT. Credit: NASA/DOE/Fermi LAT Collaboration
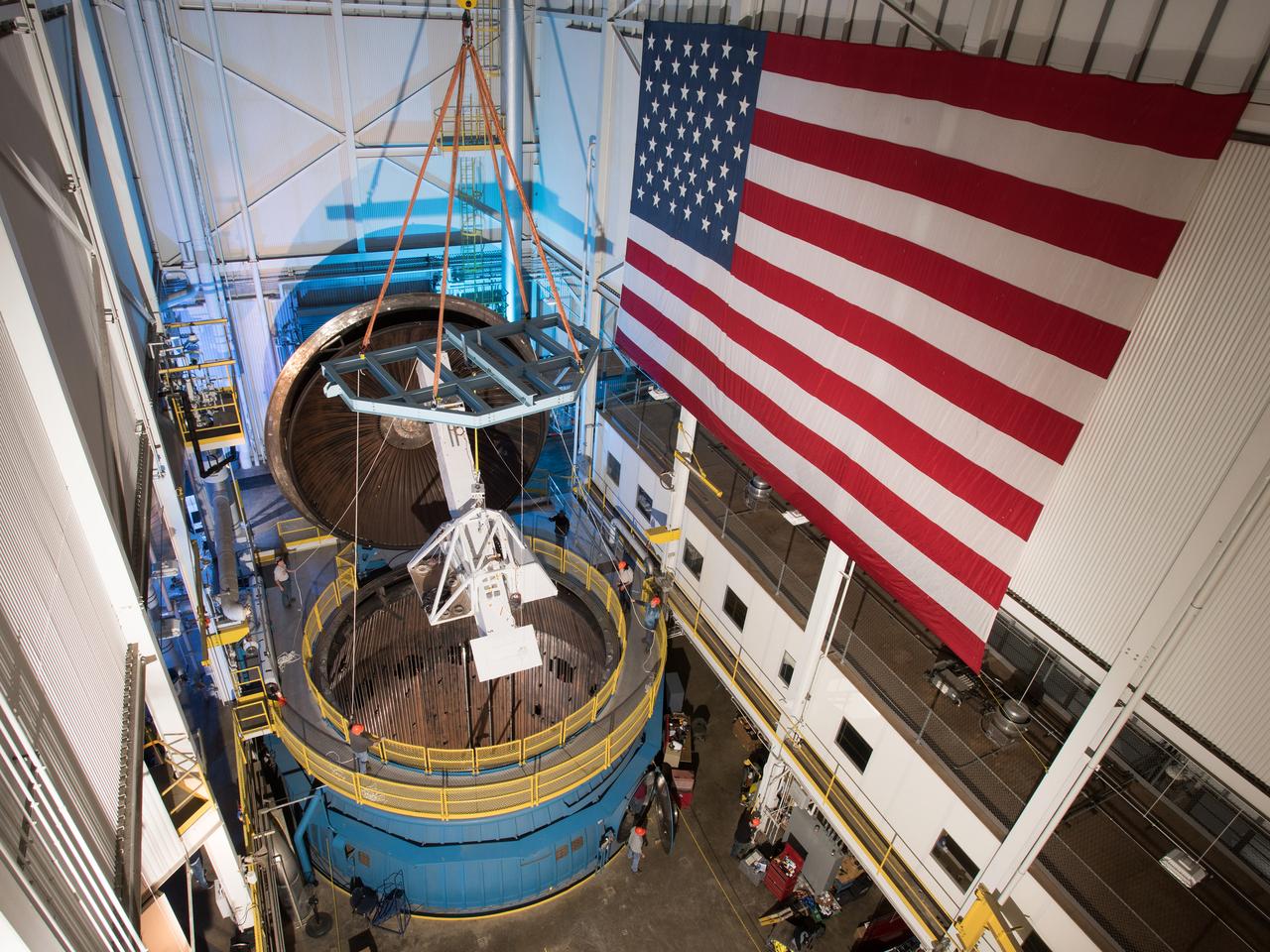
The Gamma-Ray Imager/Polarimeter for Solar flares (GRIPS) instrument is installed in the B-2 vacuum chamber for a full-instrument thermal-vacuum test in 2015. The GRIPS telescope was launched via balloon in January 2016 on a high-altitude flight over Antarctica to study the acceleration and transport of solar flare particles.
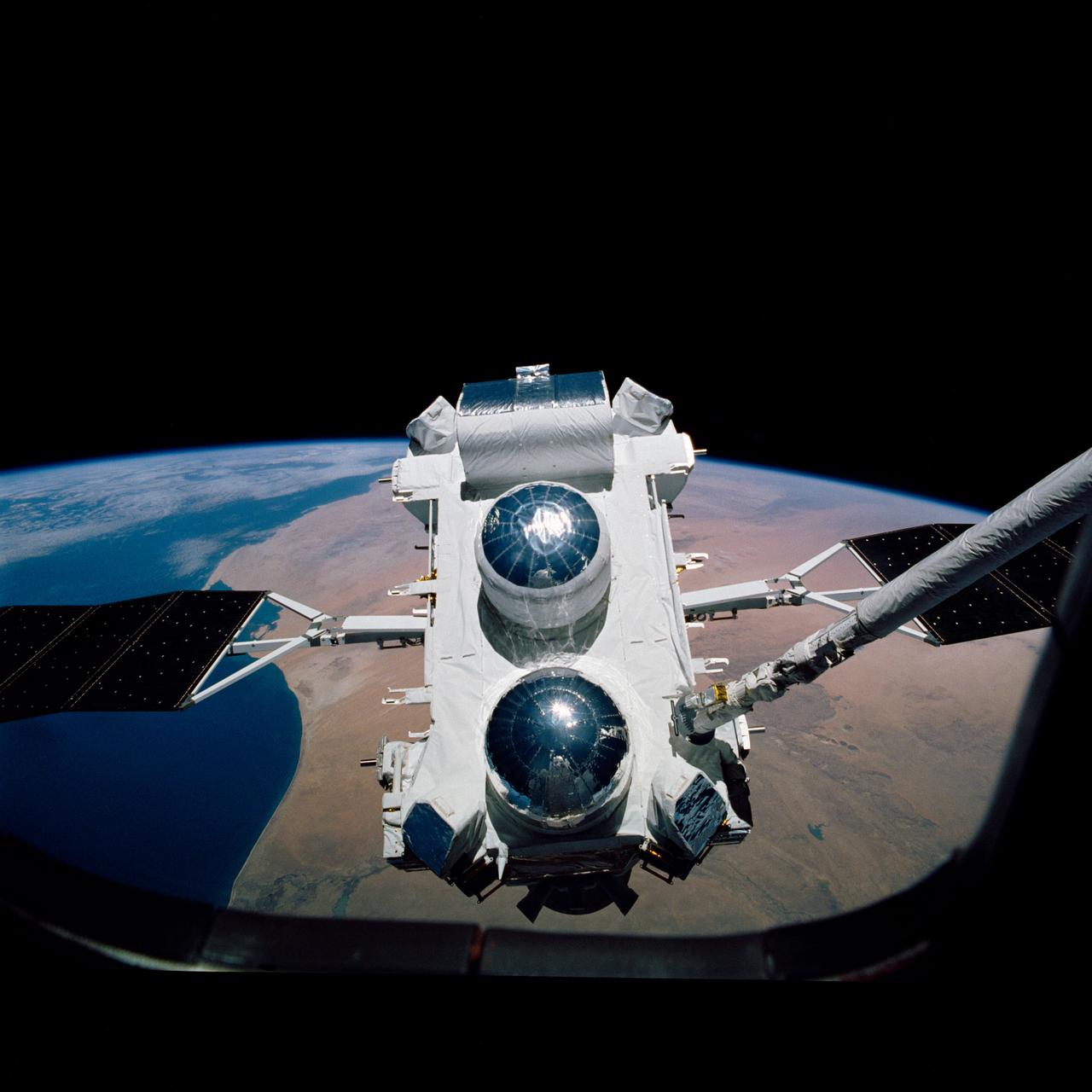

Backdropped against the Earth's surface, the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) with its solar array (SA) panels deployed is grappled by the remote manipulator system (RMS) during STS-37 systems checkout. GRO's four complement instruments are visible: the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET) (at the bottom); the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL) (center); the Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSE) (top); and Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) (on four corners). The view was taken by STS-37 crew through an aft flight deck overhead window.
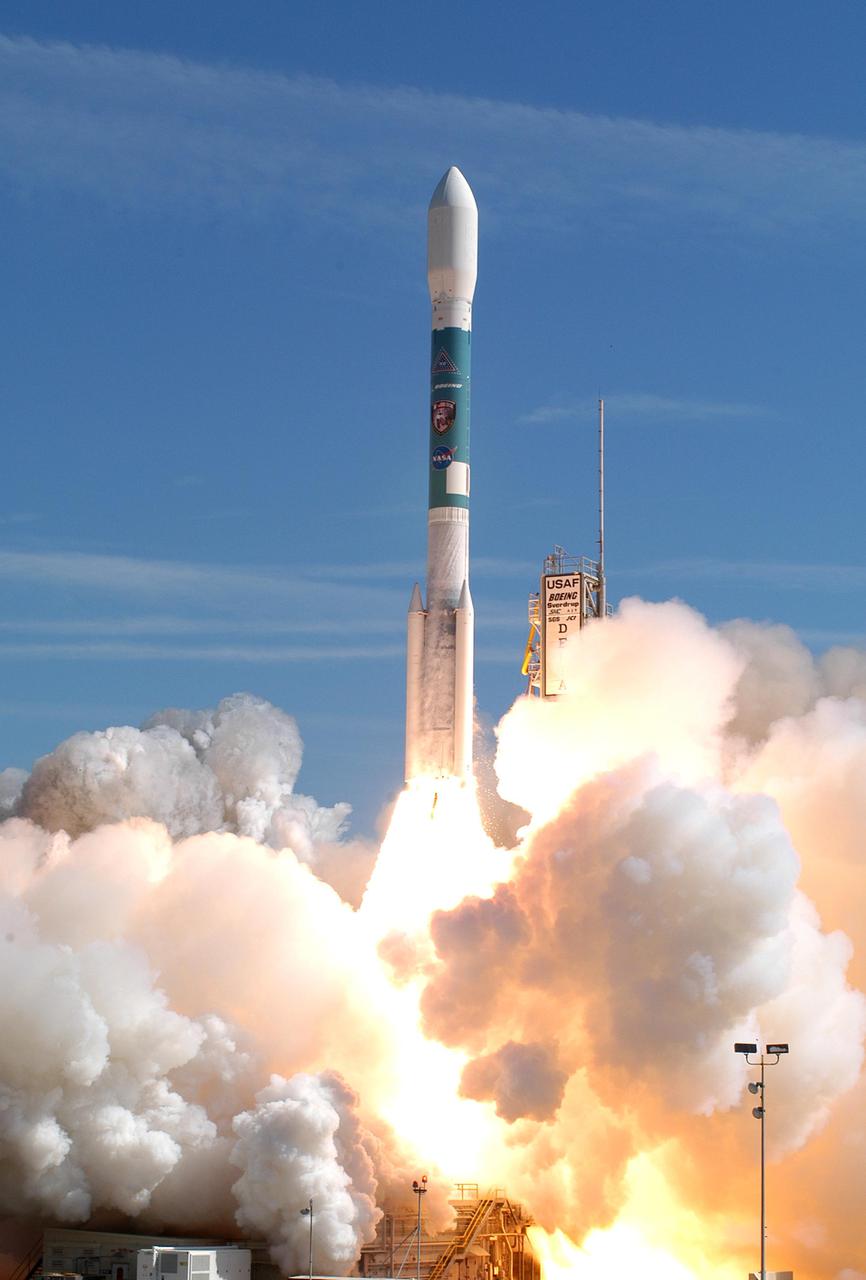

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Clouds of exhaust form around a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle as it blasts NASA's Swift spacecraft on its mission at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
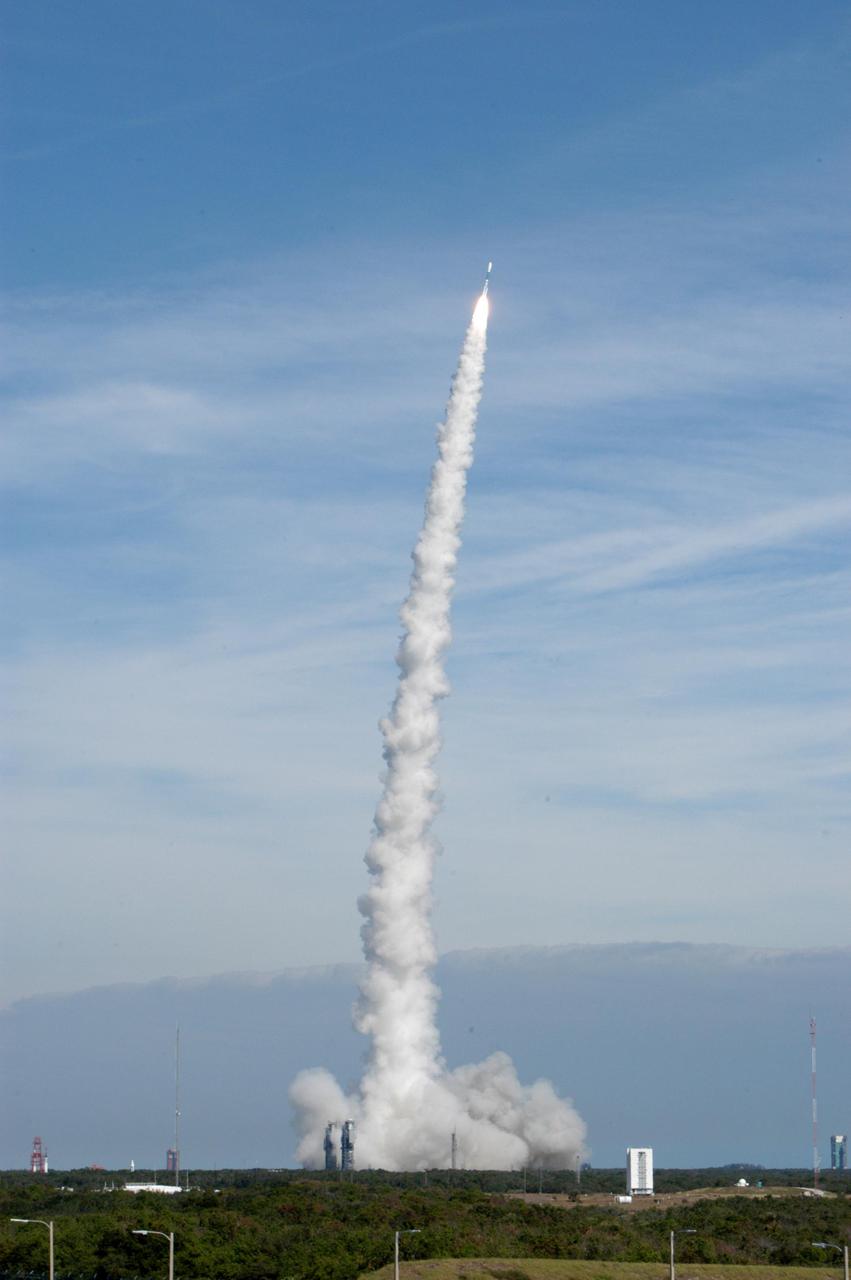

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Seen from a distance, NASA's Swift spacecraft lifts off from Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST aboard a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
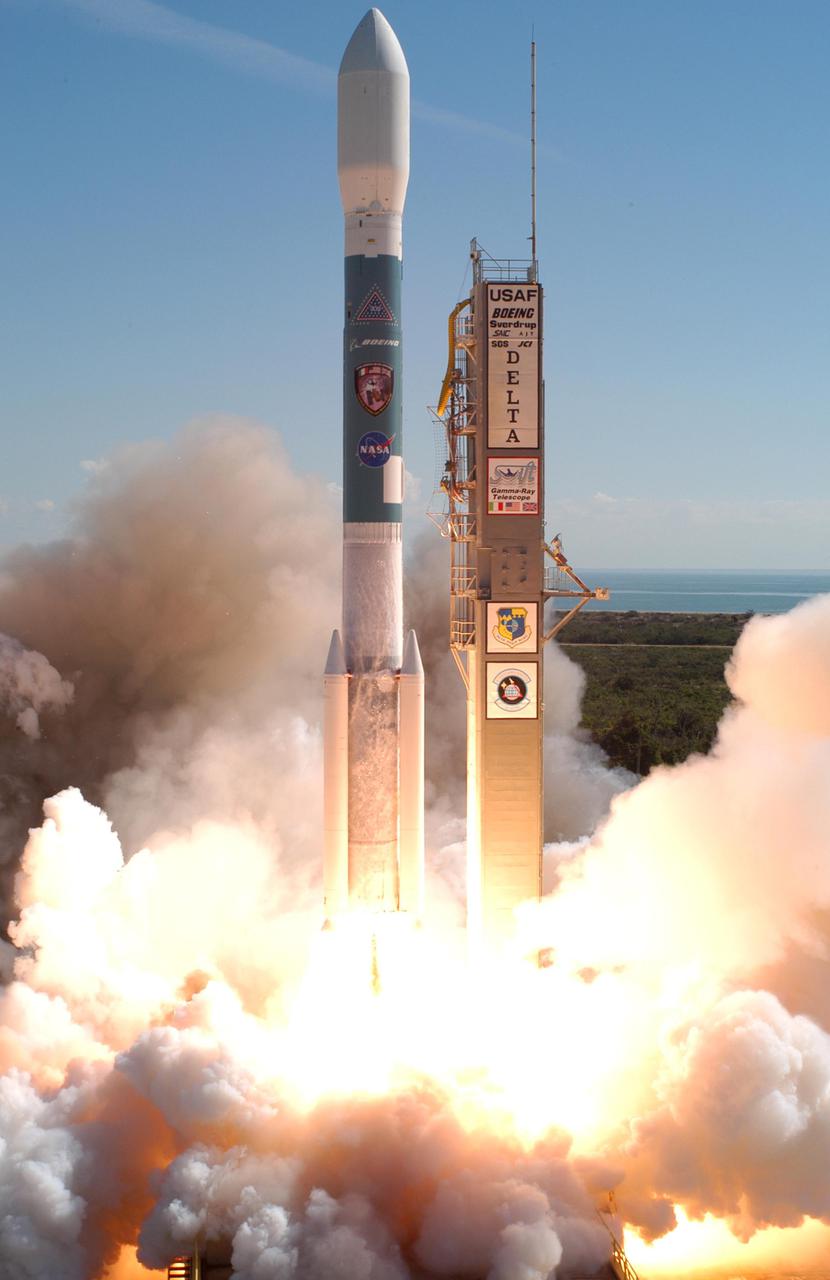

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The engines of a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle ignite to blast NASA's Swift spacecraft on its way at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
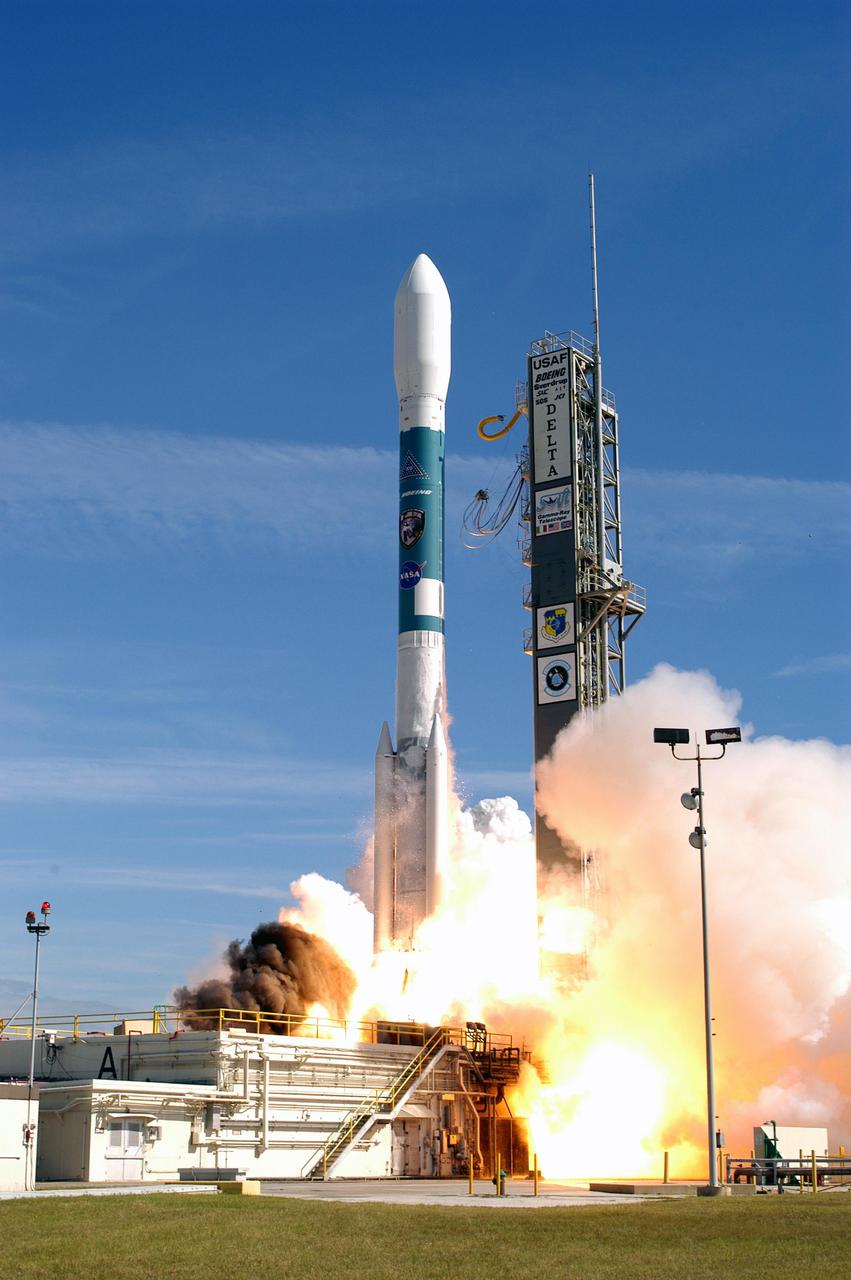

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Swift spacecraft lifts off from Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in sunny Florida, on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST aboard a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
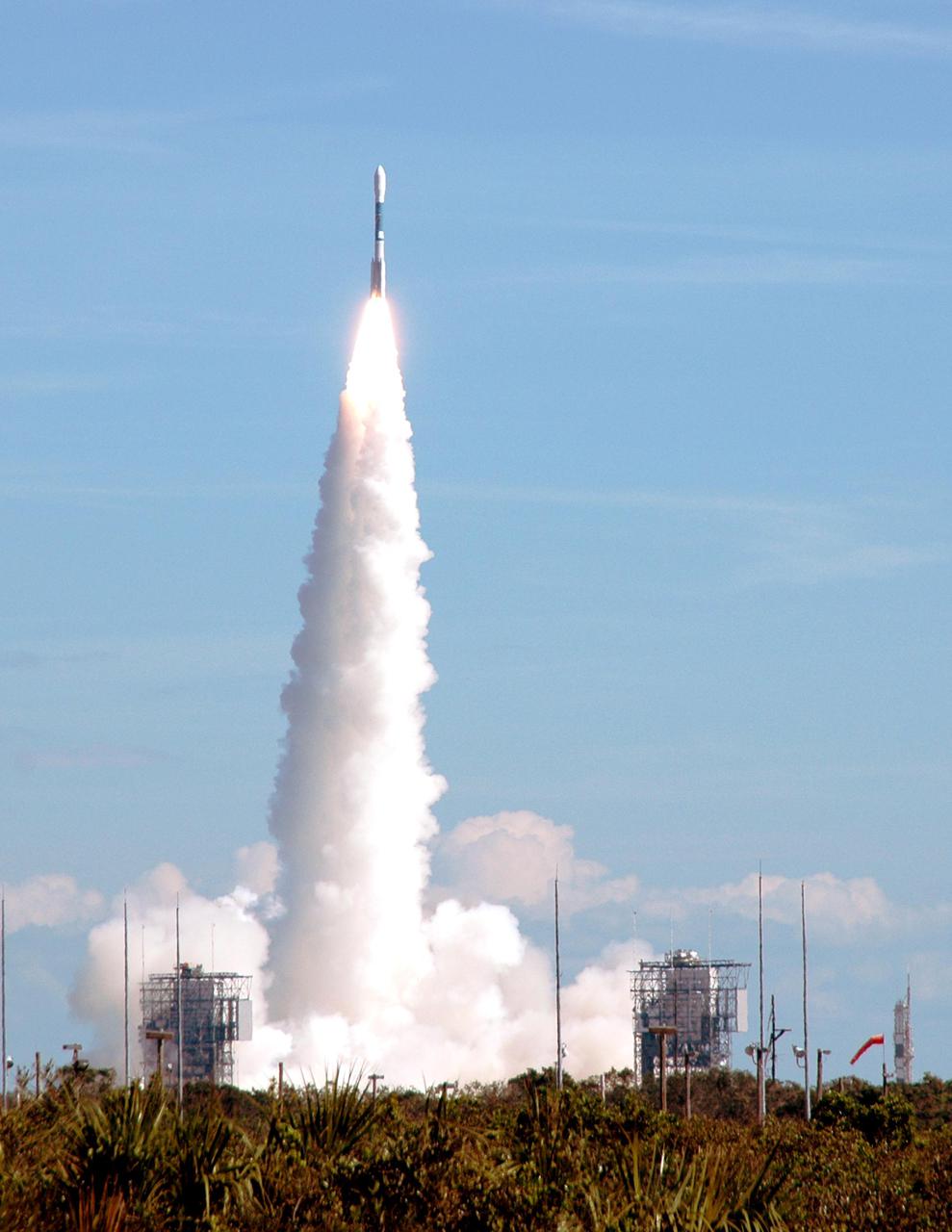

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Swift spacecraft blasts off from Complex 17A into the beautiful blue sky above Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST aboard a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
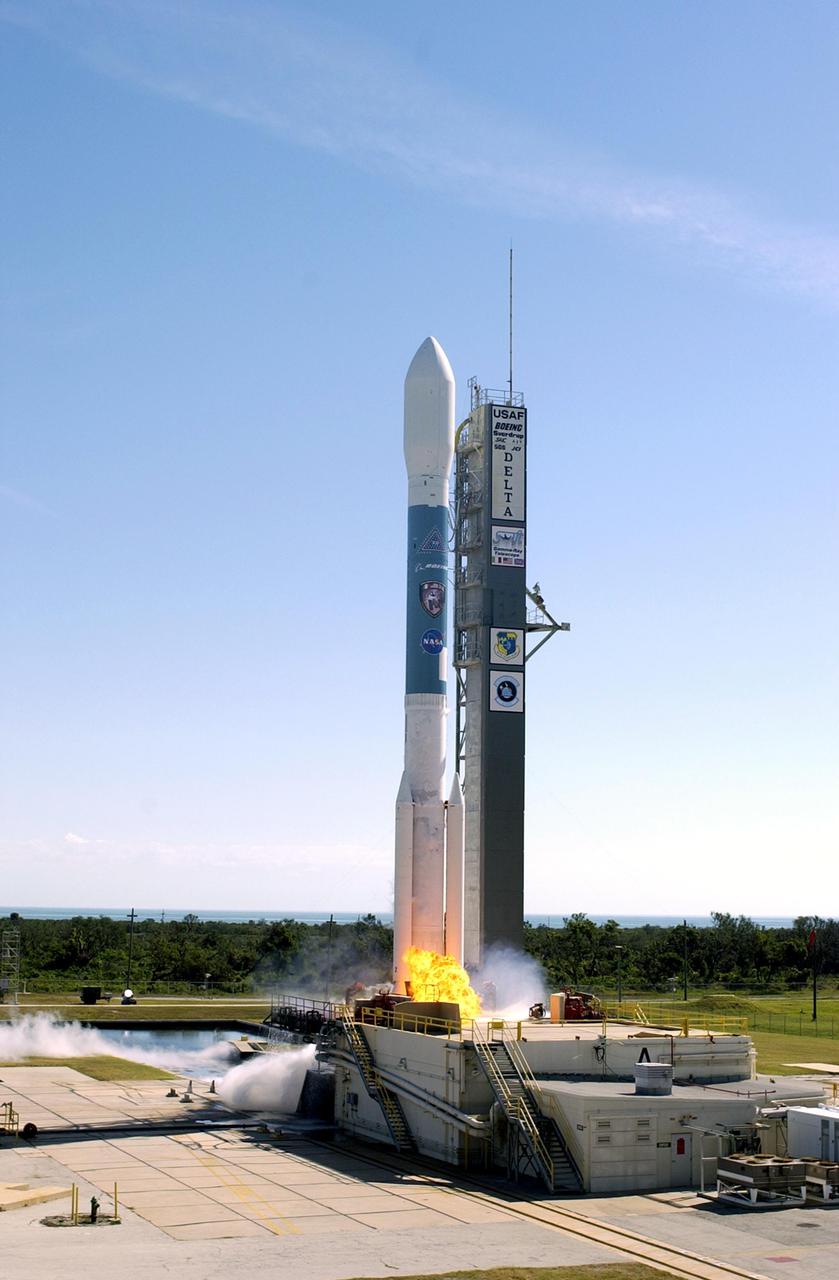

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA's Swift spacecraft lifts off from Complex 17A into the beautiful blue sky above Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST aboard a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
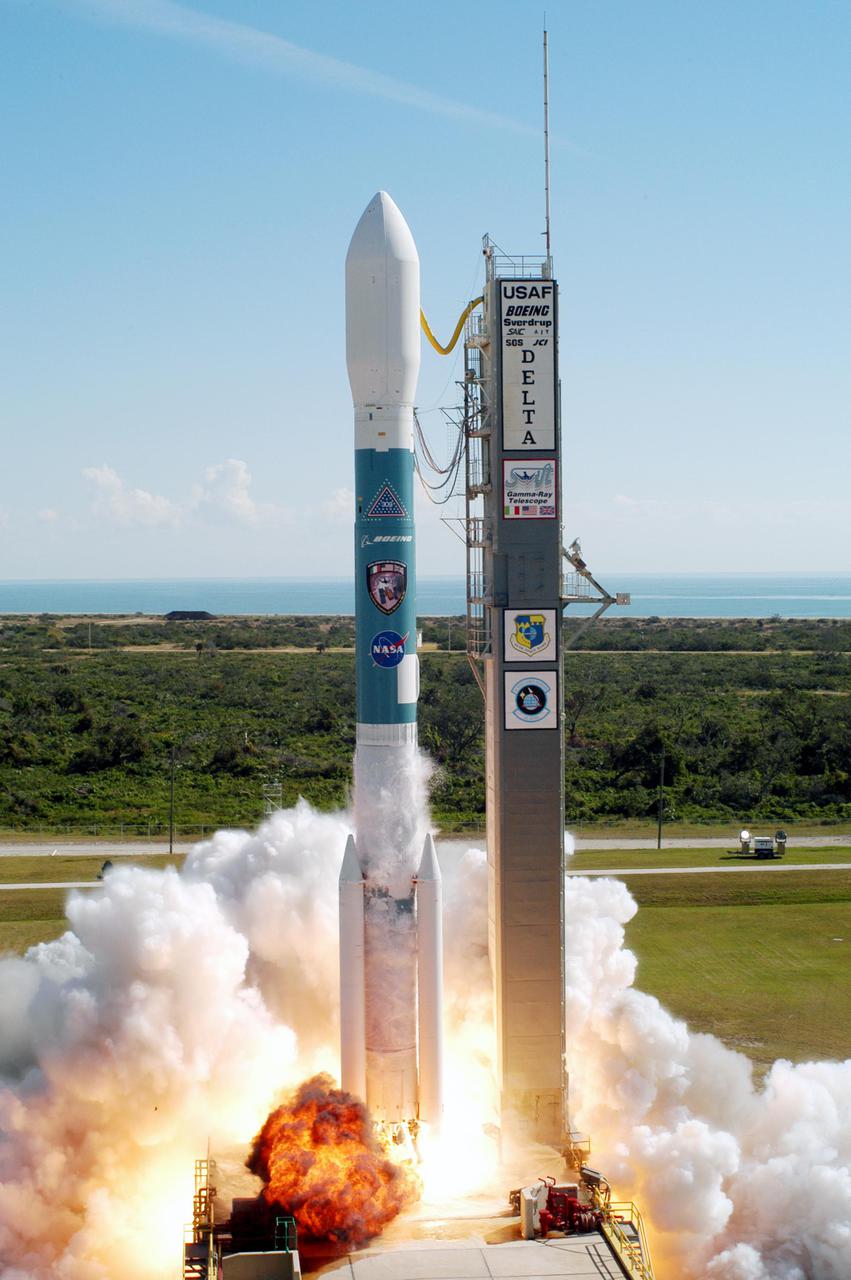

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The engines of a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle ignite to blast NASA's Swift spacecraft on its way at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.
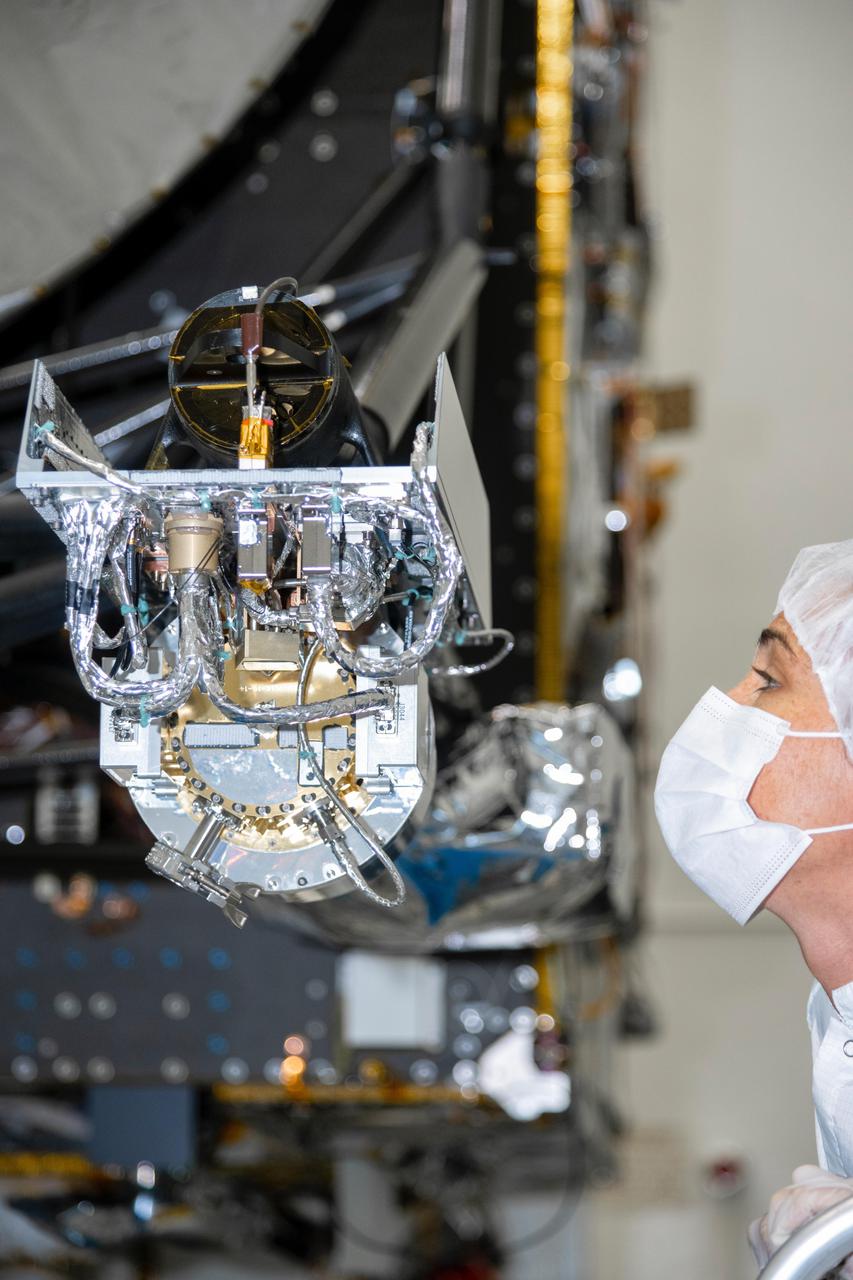
An engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California inspects the gamma ray and neutron spectrometer instrument as it is integrated into the agency's Psyche spacecraft on Aug. 23, 2021. Psyche, set to launch in August 2022, will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. The spacecraft will use the GRNS to study the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the asteroid's surface to help determine its elemental composition. As cosmic rays and high energy particles impact the surface of Psyche, the elements that make up the surface material absorb the energy and in response emit neutrons and gamma rays of varying energy levels. These emitted neutrons and gamma rays can be detected by the GRNS and analyzed by scientists, who can match their properties to those emitted by known elements to determine what Psyche is made of. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24892
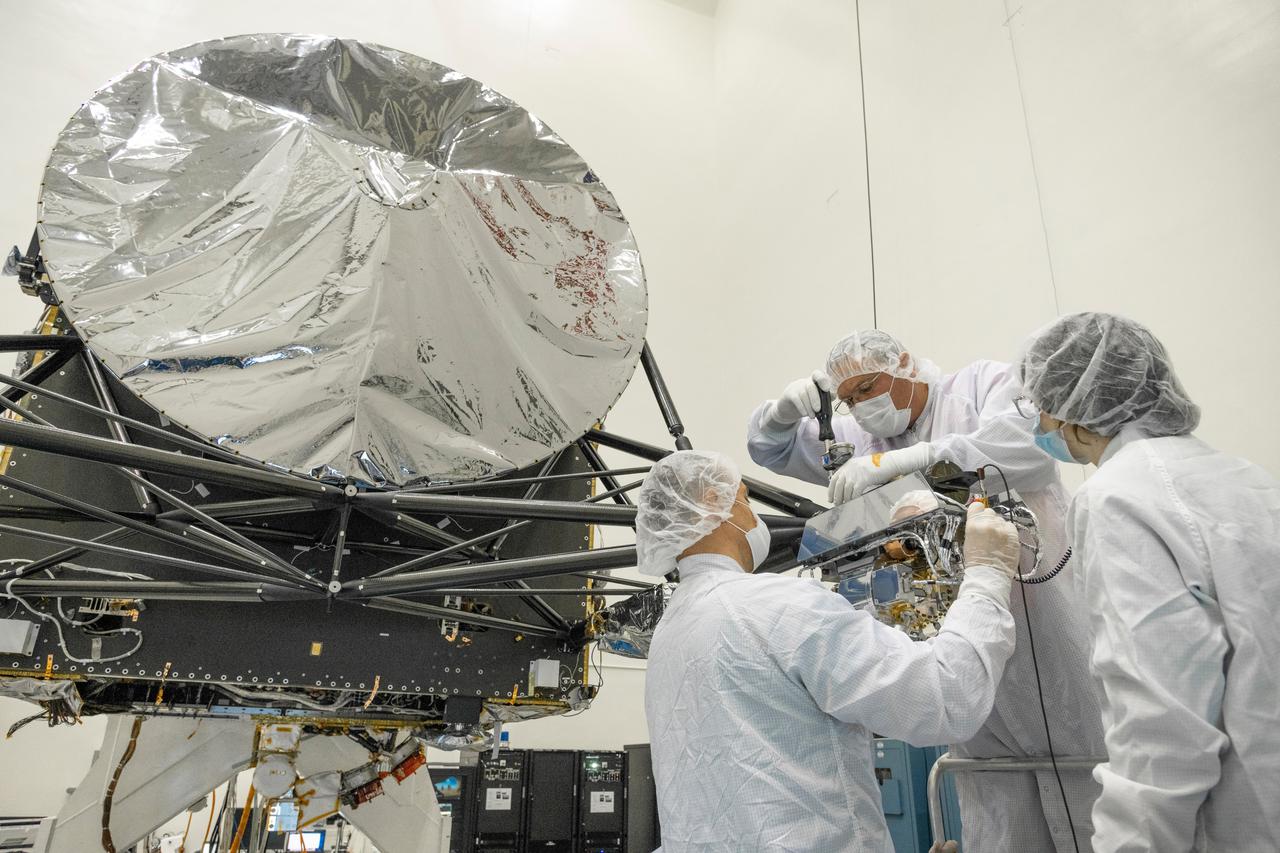

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California integrate the gamma ray and neutron spectrometer instrument into the agency's Psyche spacecraft on Aug. 23, 2021. Psyche, set to launch in August 2022, will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. The spacecraft will use the GRNS to study the neutrons and gamma rays coming from the asteroid's surface to help determine its elemental composition. As cosmic rays and high energy particles impact the surface of Psyche, the elements that make up the surface material absorb the energy and in response emit neutrons and gamma rays of varying energy levels. These emitted neutrons and gamma rays can be detected by the GRNS and analyzed by scientists, who can match their properties to those emitted by known elements to determine what Psyche is made of. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24891
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Clouds of exhaust form around a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle as it blasts NASA’s Swift spacecraft on its mission from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST Nov. 20 . Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/04pd2356/04pd2356~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Clouds of exhaust form around a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle as it blasts NASA’s Swift spacecraft on its mission from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST Nov. 20 . Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The engines of a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle ignite to blast NASA’s Swift spacecraft on its way from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST Nov. 20 . Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/04pd2357/04pd2357~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The engines of a Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle ignite to blast NASA’s Swift spacecraft on its way from Complex 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST Nov. 20 . Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]
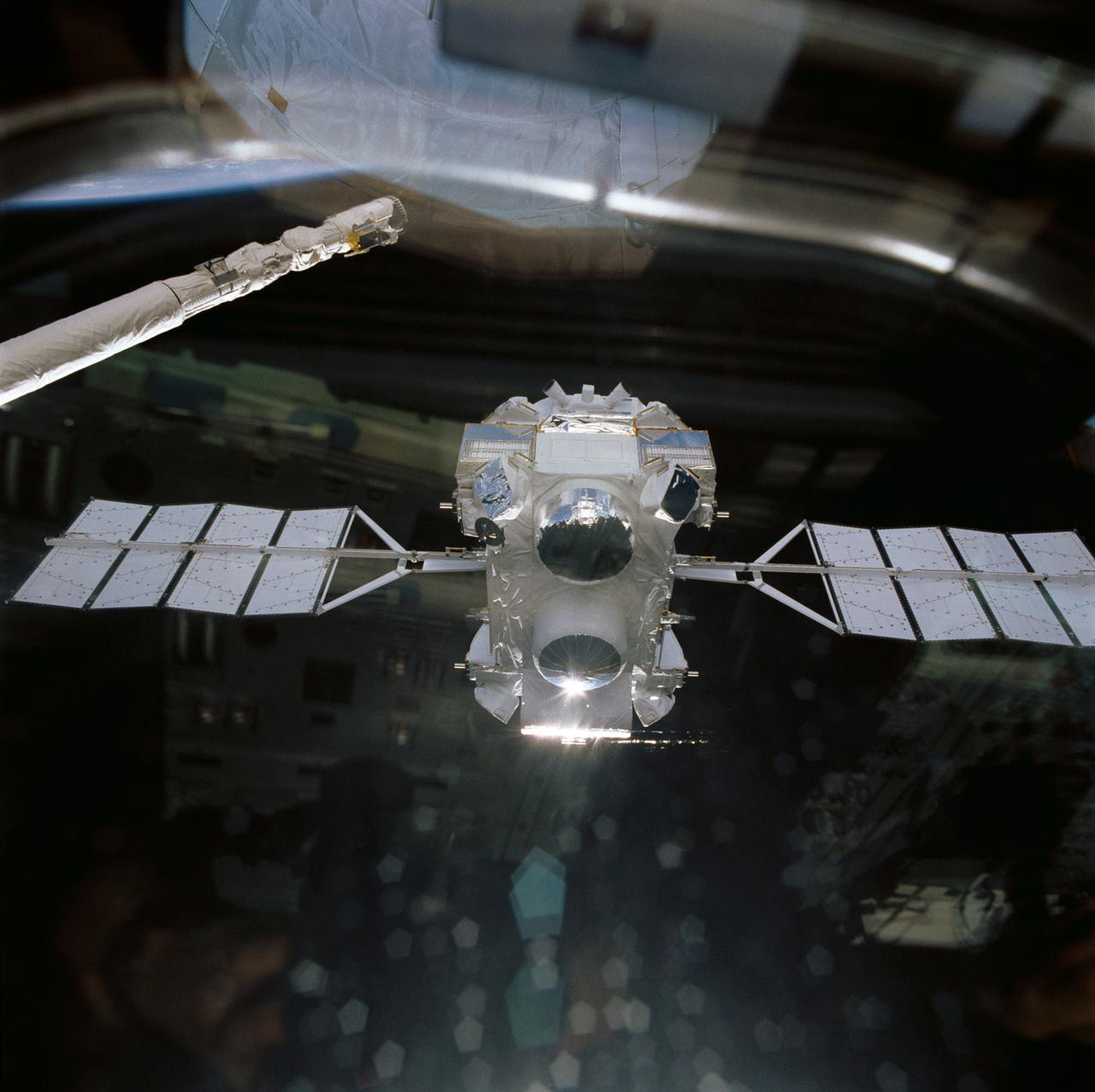

Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, remote manipulator system (RMS) releases Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) during STS-37 deployment. Visible on the GRO as it drifts away from the RMS end effector are the four complement instruments: the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment (bottom); Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL) (center); Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSE) (top); and Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) (at four corners). GRO's solar array (SA) panels are extended and are in orbit configuration. View was taken through aft flight deck window which reflects some of the crew compartment interior.

NASA image release November 9, 2010 To view a video about this story go to: <a href="http://www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062">www.flickr.com/photos/gsfc/5162413062</a> Using data from NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, scientists have recently discovered a gigantic, mysterious structure in our galaxy. This never-before-seen feature looks like a pair of bubbles extending above and below our galaxy's center. But these enormous gamma-ray emitting lobes aren't immediately visible in the Fermi all-sky map. However, by processing the data, a group of scientists was able to bring these unexpected structures into sharp relief. Each lobe is 25,000 light-years tall and the whole structure may be only a few million years old. Within the bubbles, extremely energetic electrons are interacting with lower-energy light to create gamma rays, but right now, no one knows the source of these electrons. Are the bubbles remnants of a massive burst of star formation? Leftovers from an eruption by the supermassive black hole at our galaxy's center? Or or did these forces work in tandem to produce them? Scientists aren't sure yet, but the more they learn about this amazing structure, the better we'll understand the Milky Way. To learn more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/GLAST/news/new-structure.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> Credit: <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio</a>
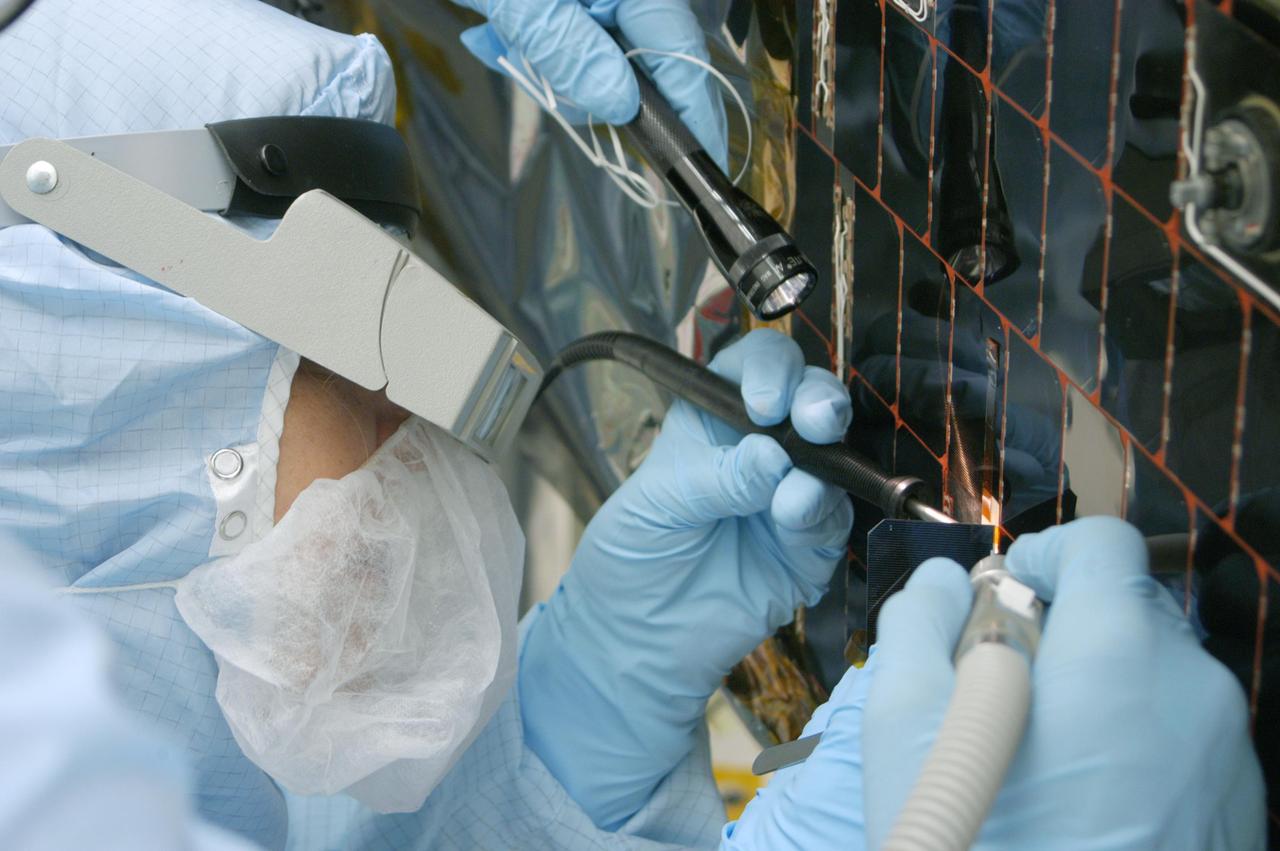

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a Spectrolab technician, Anna Herrera, removes one of the solar cells that will be replaced on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
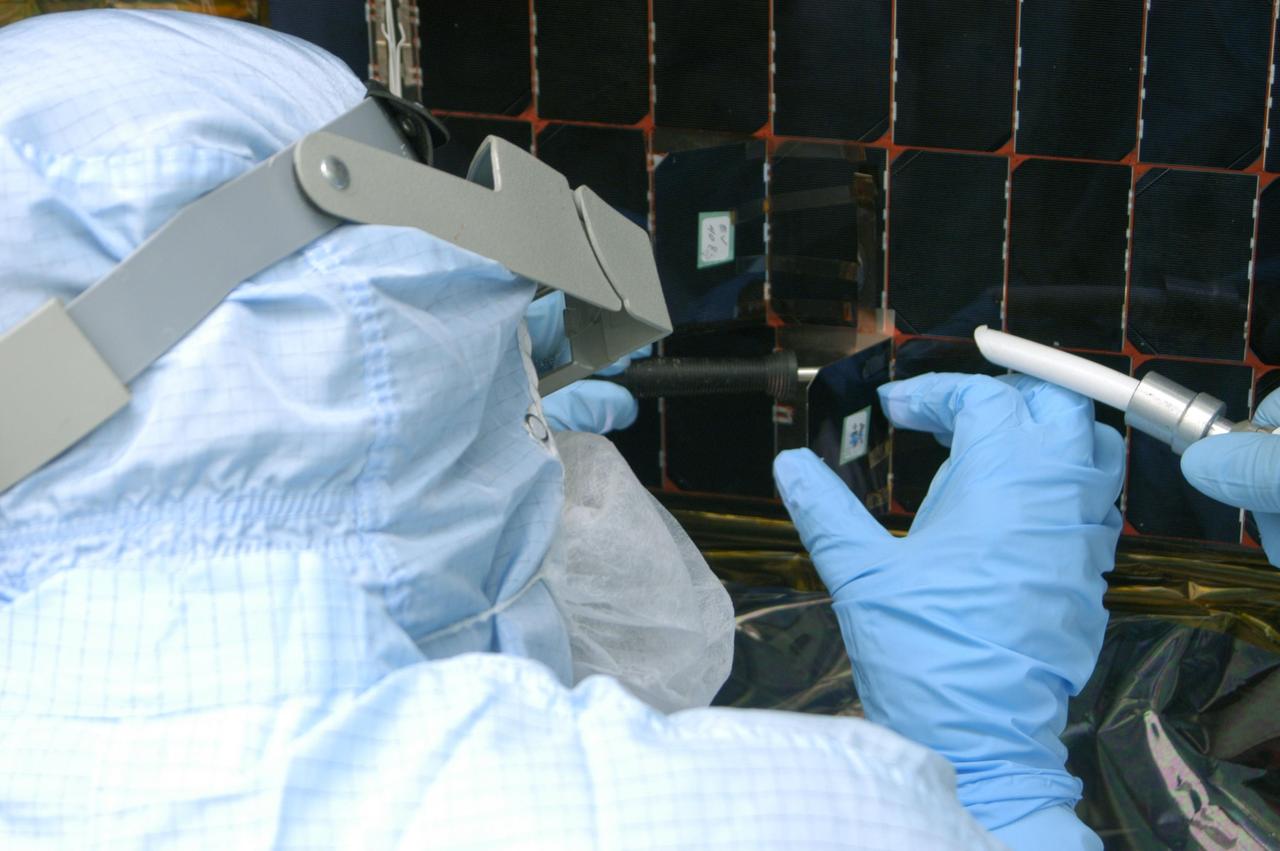

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a Spectrolab technician, Anna Herrera, places a new solar cell on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
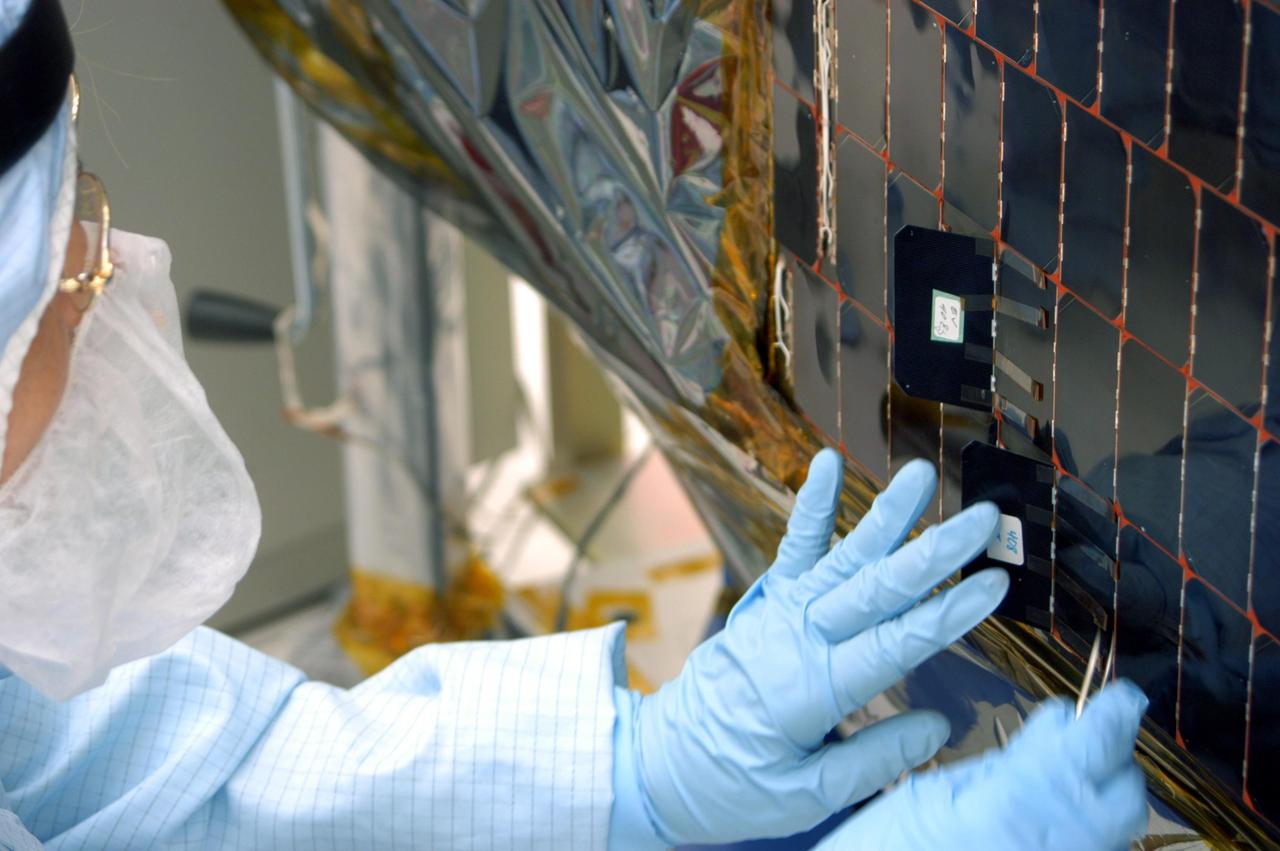

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a Spectrolab technician, Anna Herrera, places a new solar cell on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
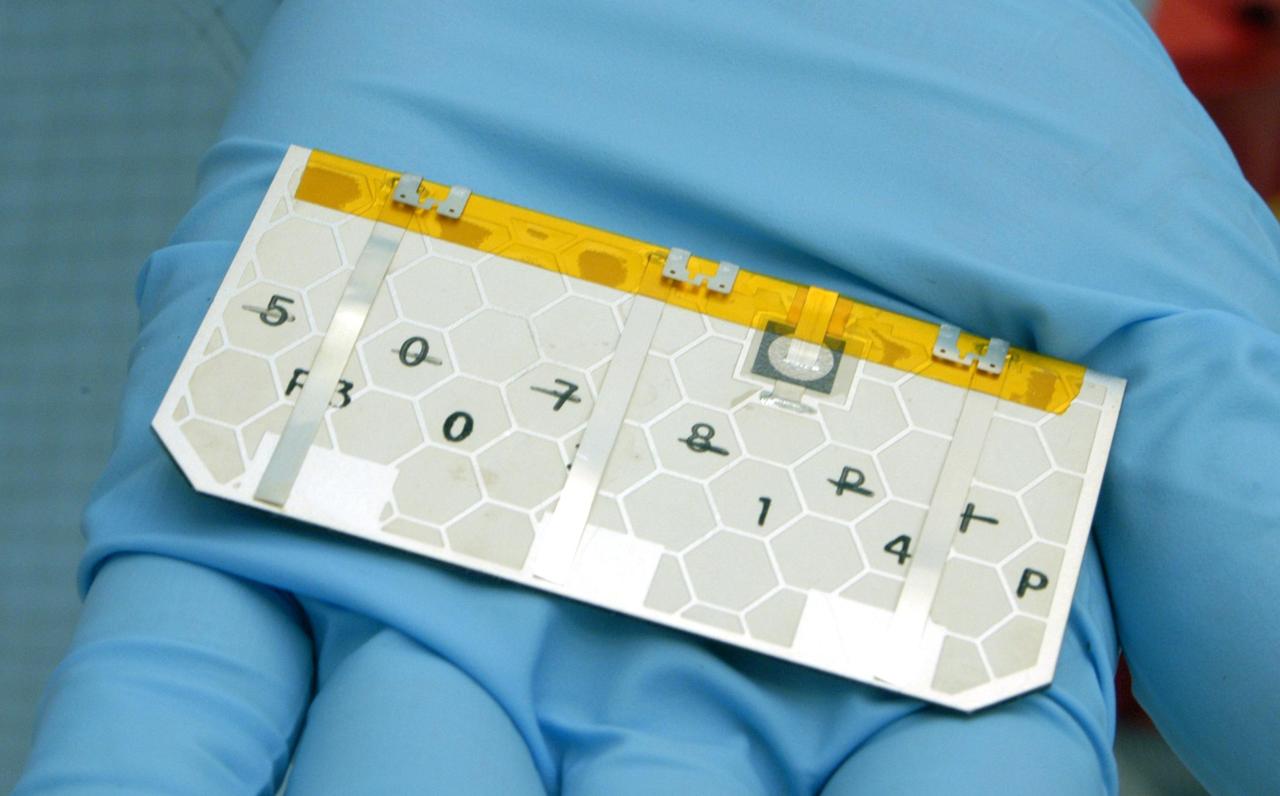

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A closeup of one of the solar cells that will be removed and replaced on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
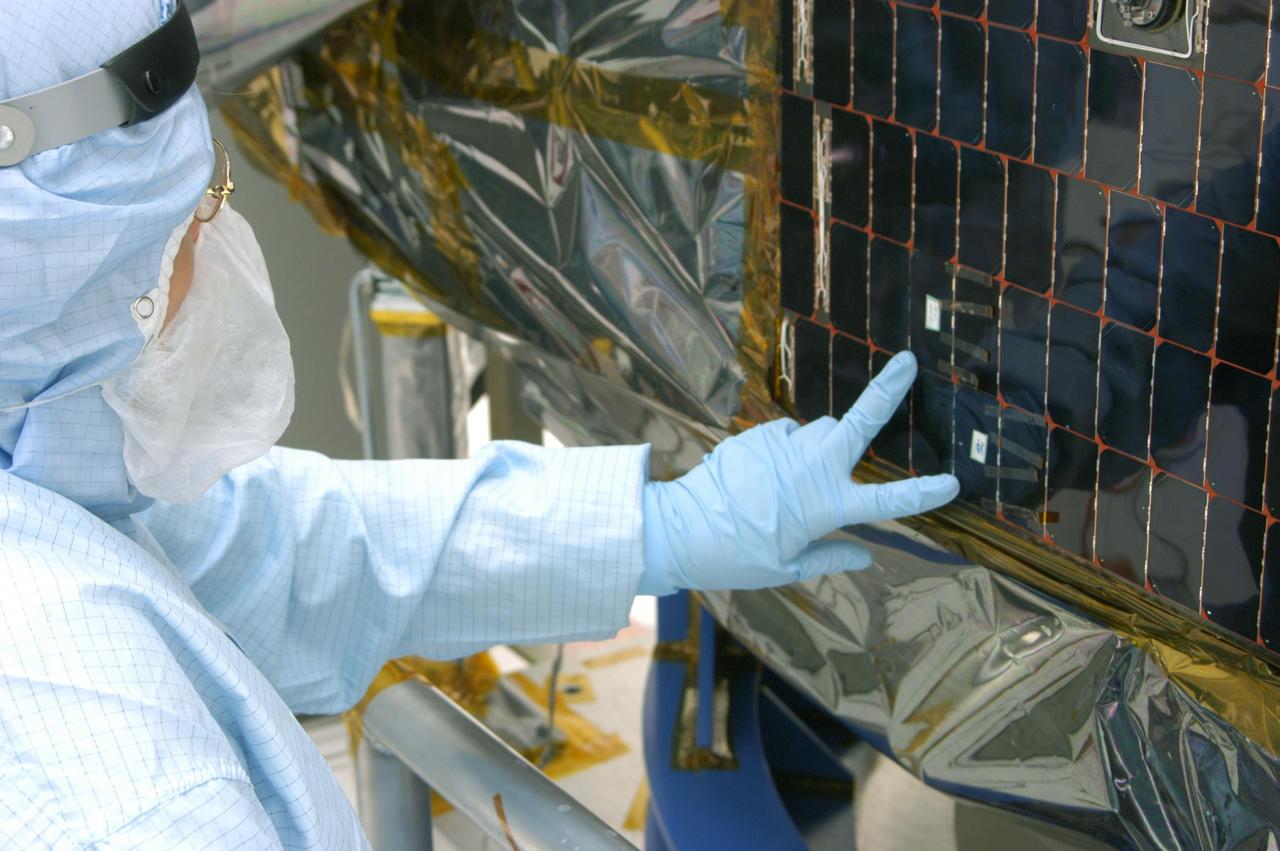

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a Spectrolab technician, Anna Herrera, points to the two new solar cells removed and replaced on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
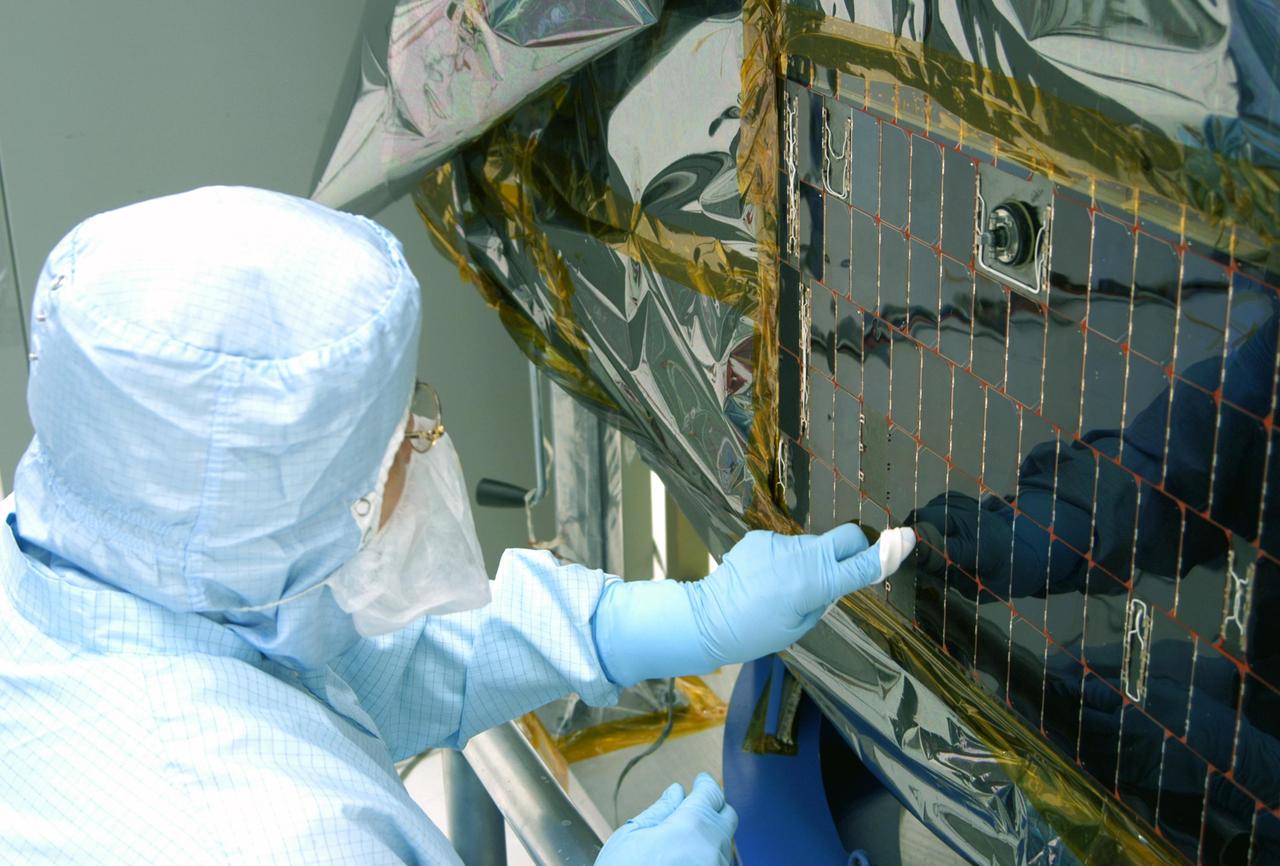

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), a Spectrolab technician, Anna Herrera, points to an area on the Swift spacecraft’s solar array where cells will be removed and replaced. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
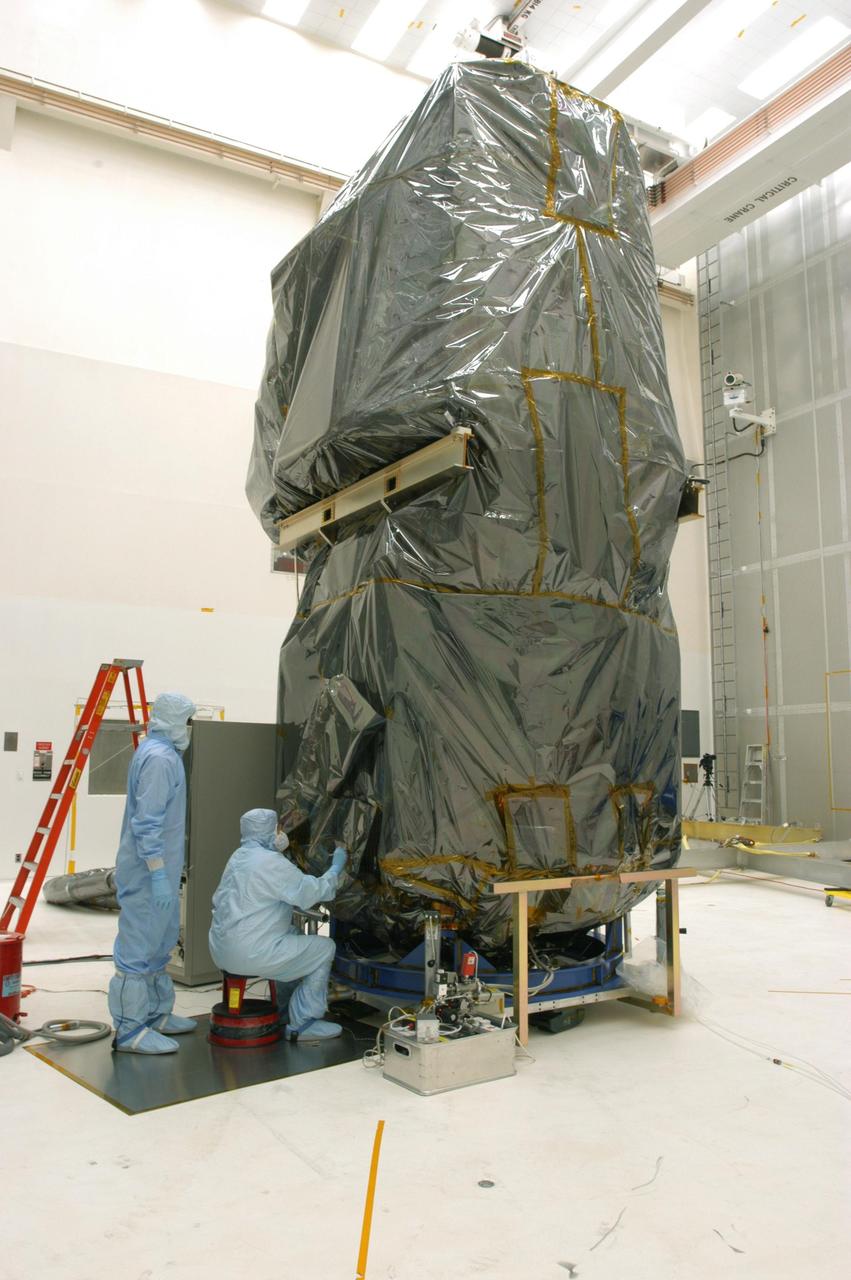

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the clean room at NASA’s Hangar AE on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS), Spectrolab technicians begin lifting the protective cover from the Swift spacecraft. Two of Swift’s solar cells on the solar array will be removed and replaced. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The main mission objectives for Swift are to determine the origin of gamma-ray bursts, classify gamma-ray bursts and search for new types, determine how the blast wave evolves and interacts with the surroundings, use gamma-ray bursts to study the early universe and perform the first sensitive hard X-ray survey of the sky. Swift is scheduled to launch Oct. 26 from Launch Pad 17-A, CCAFS, on a Boeing Delta 7320 rocket.
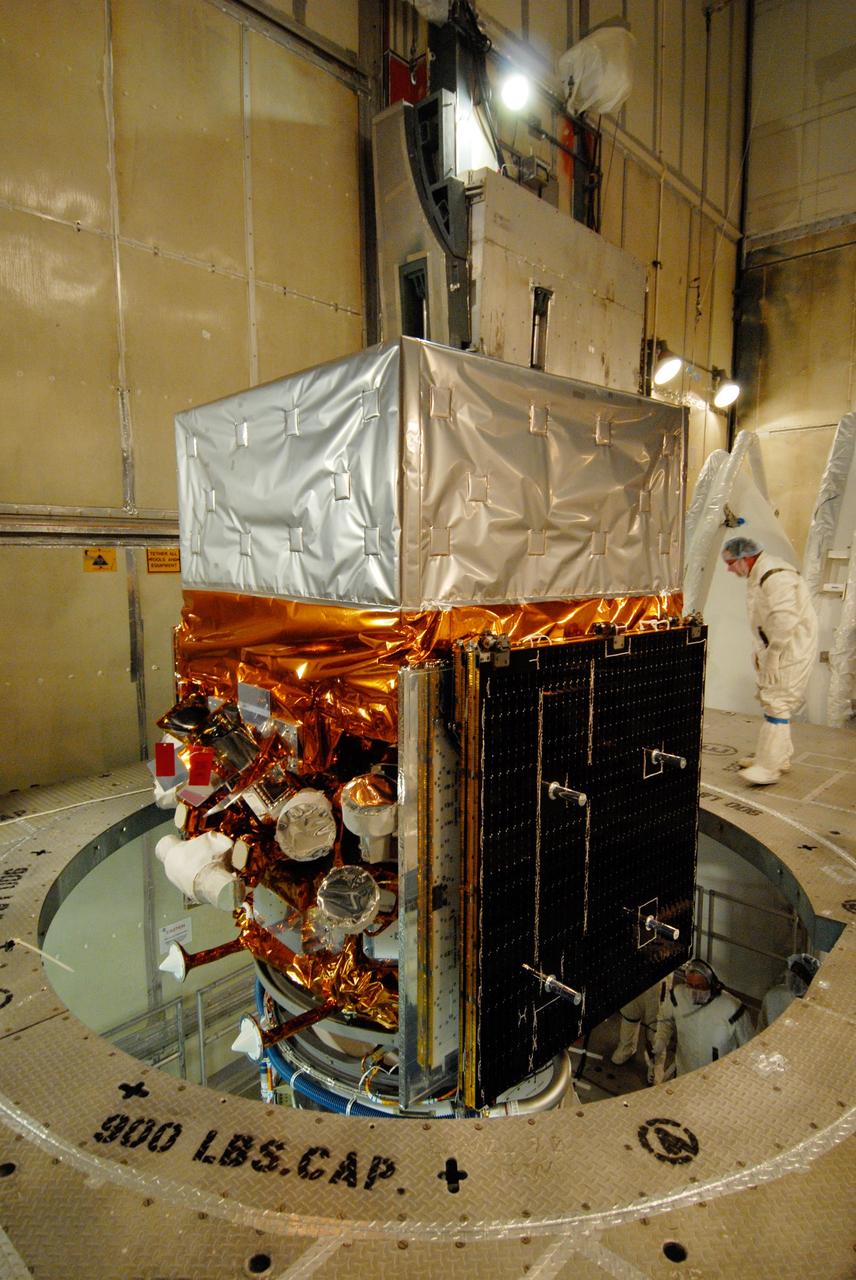

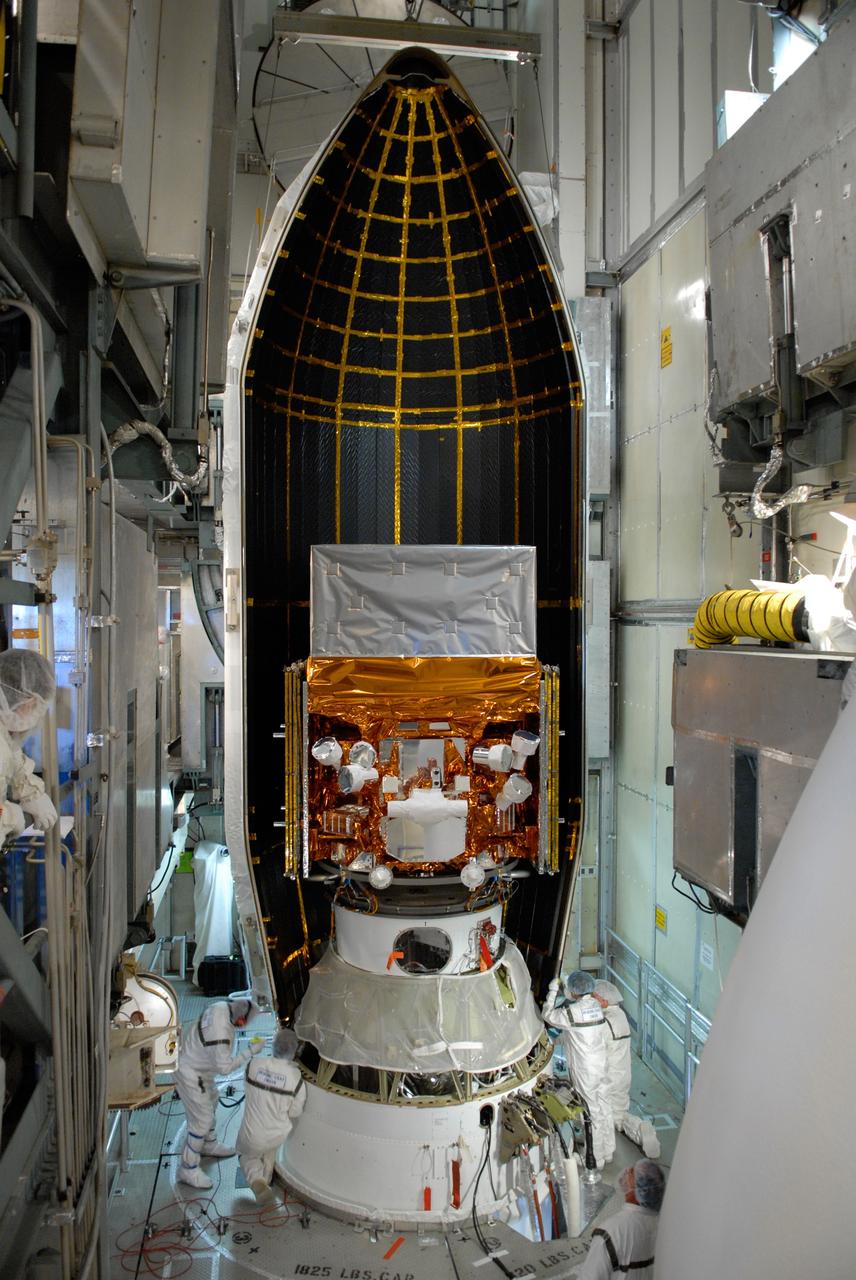
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST, is ready for encapsulation in the payload fairing. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
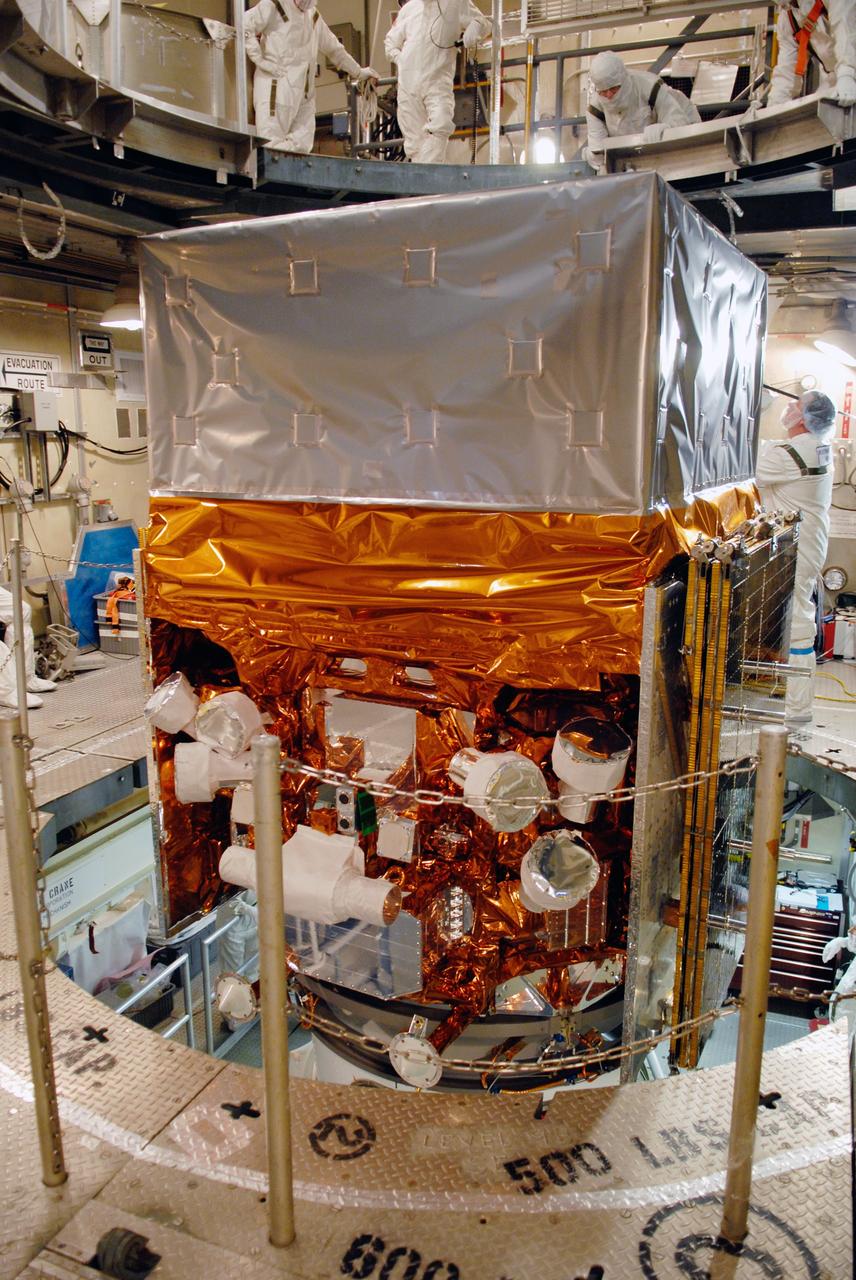
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST, is ready for encapsulation in the payload fairing. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Spectrum Astro workers look over the Swift spacecraft while removing its protective cover. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Swift spacecraft is revealed. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft is being unwrapped in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft is being unwrapped in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Swift spacecraft waits for final removal of the protective cover (at top). Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Spectrum Astro workers look at the final pieces of protective cover on the Swift spacecraft that must be removed. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft is being unwrapped in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Spectrum Astro workers remove the final pieces of protective cover on the Swift spacecraft. Swift is a first-of-its-kind, multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray and optical wavebands. Swift is part of NASA’s medium explorer (MIDEX) program being developed by an international collaboration. During its nominal 2-year mission, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 bursts, which will represent the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglow to date. It is scheduled for launch into a low-Earth orbit on a Delta 7320 rocket on Oct. 7.
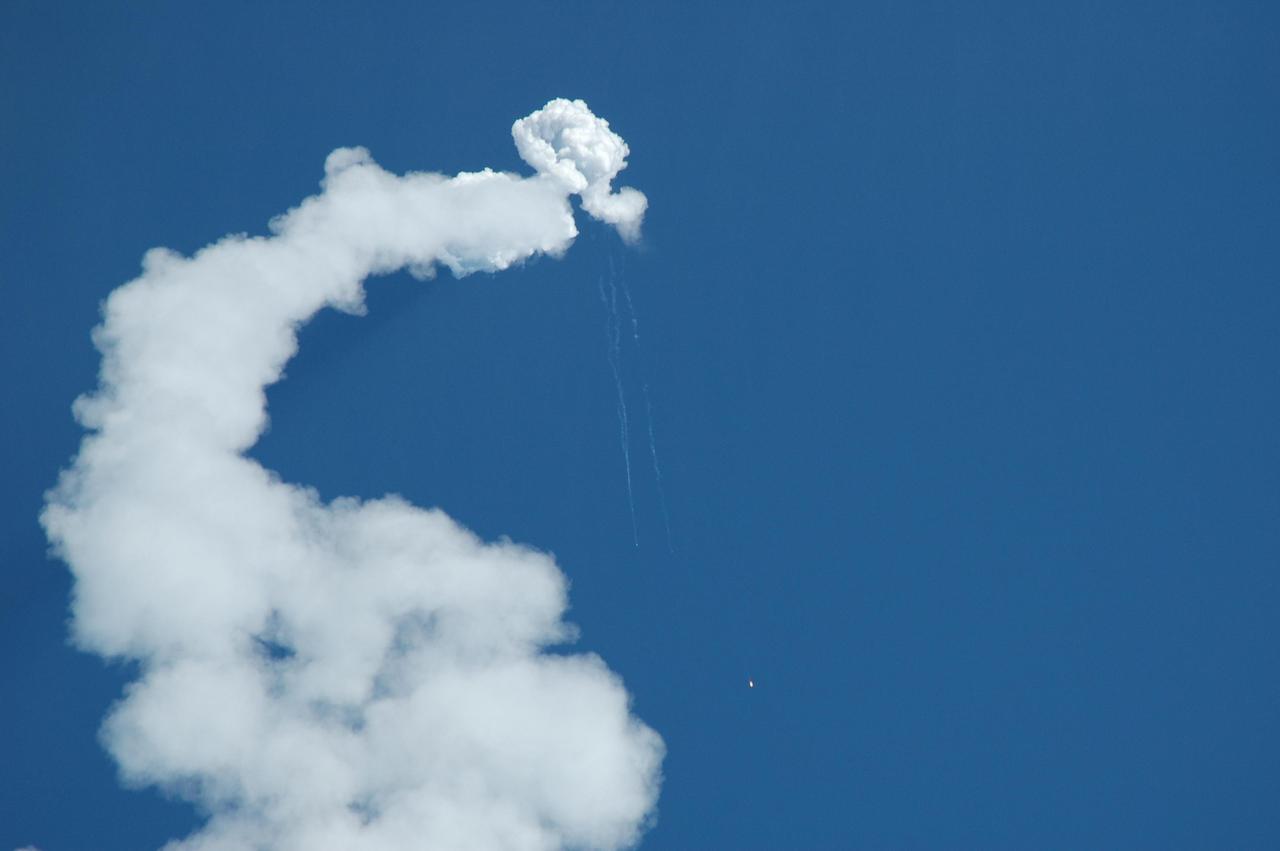

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Solid Rocket Boosters of the Boeing Delta II rocket, used to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft, fall toward the Atlantic Ocean as the rocket continues on its path down range. The successful launch took place at Complex 17A at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on Nov. 20 at 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands.

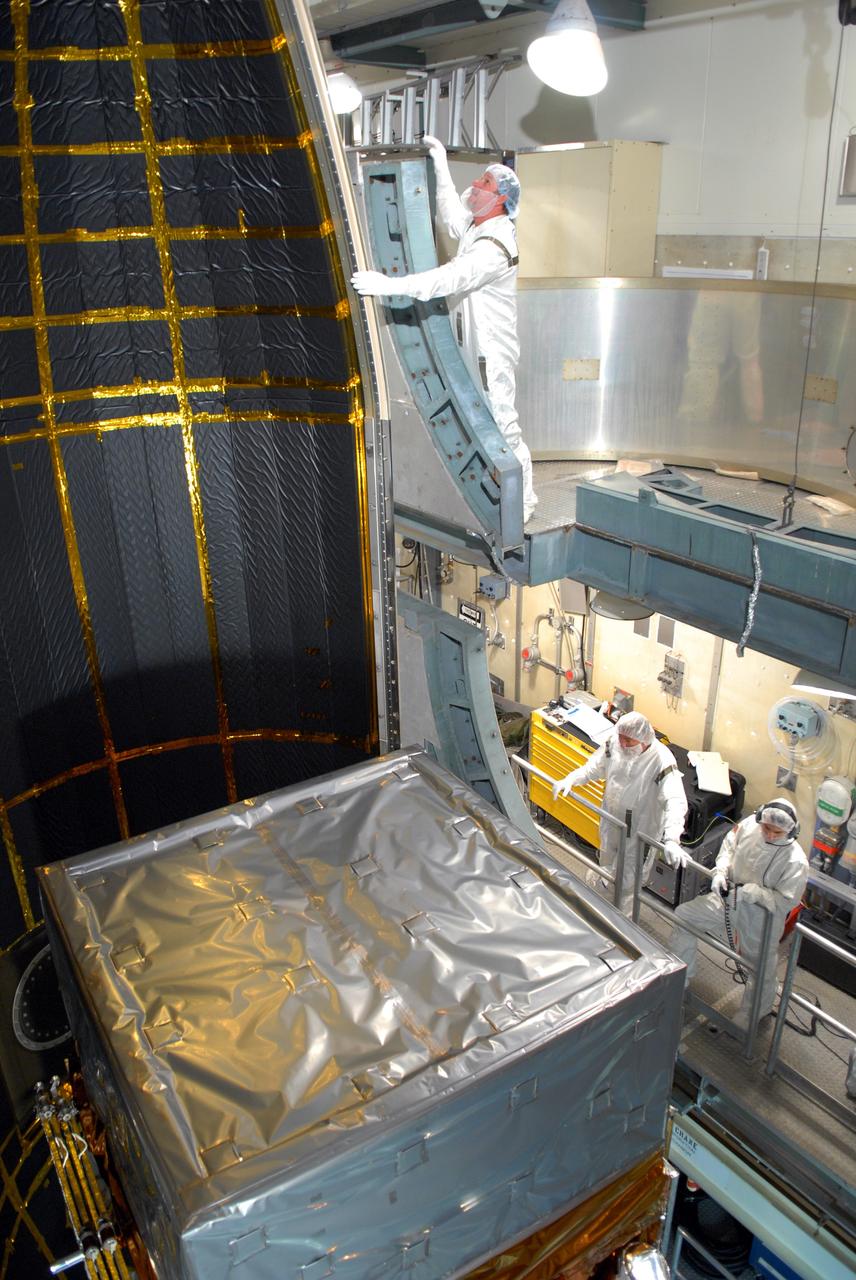
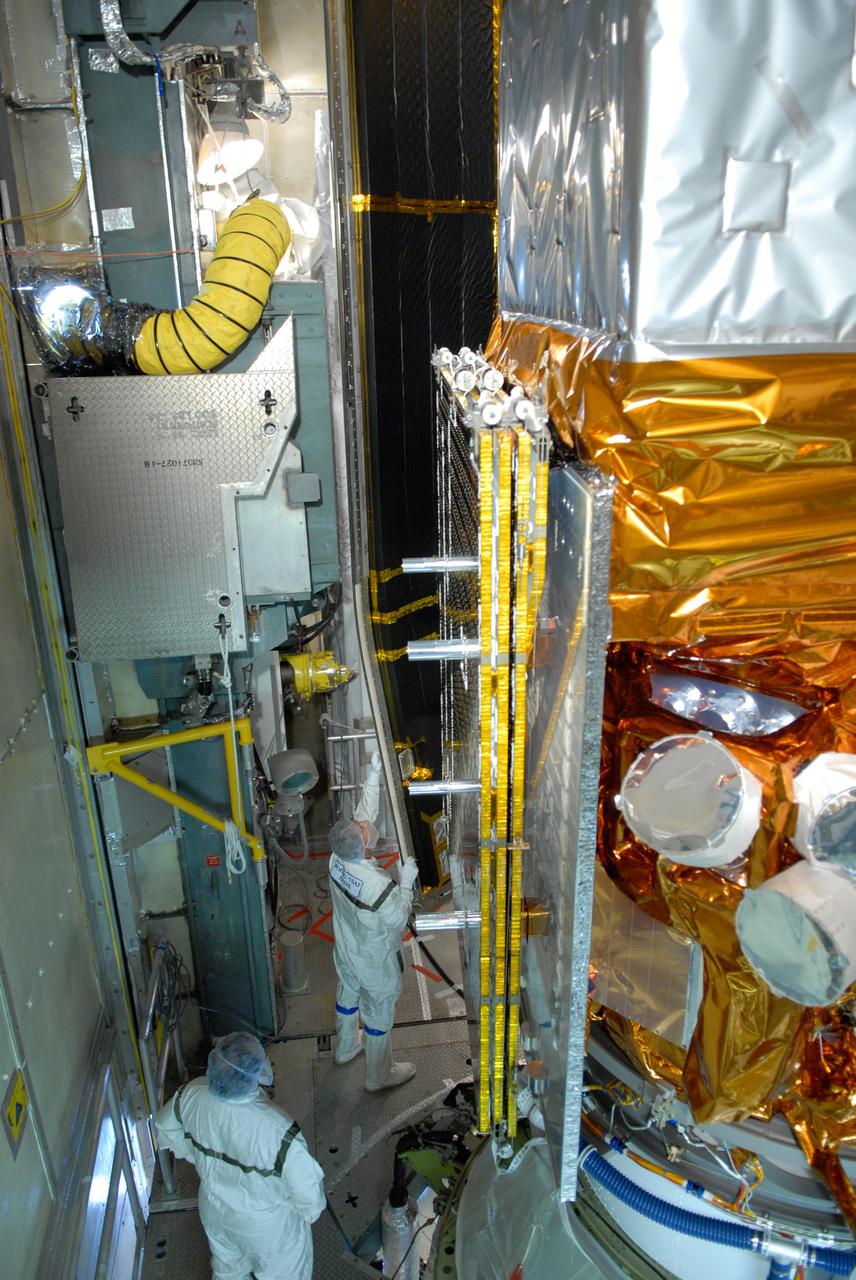
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help guide the second section of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The first half is seen at left. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

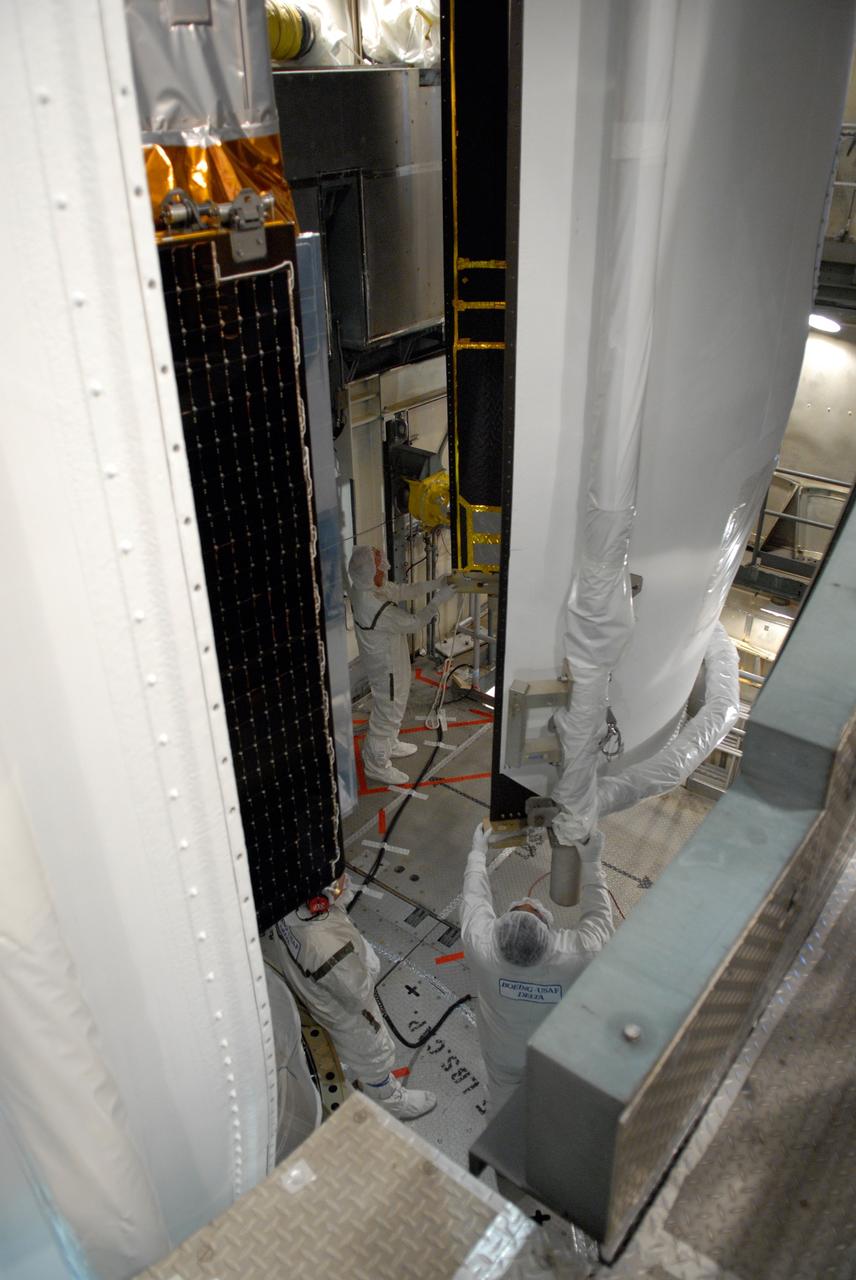
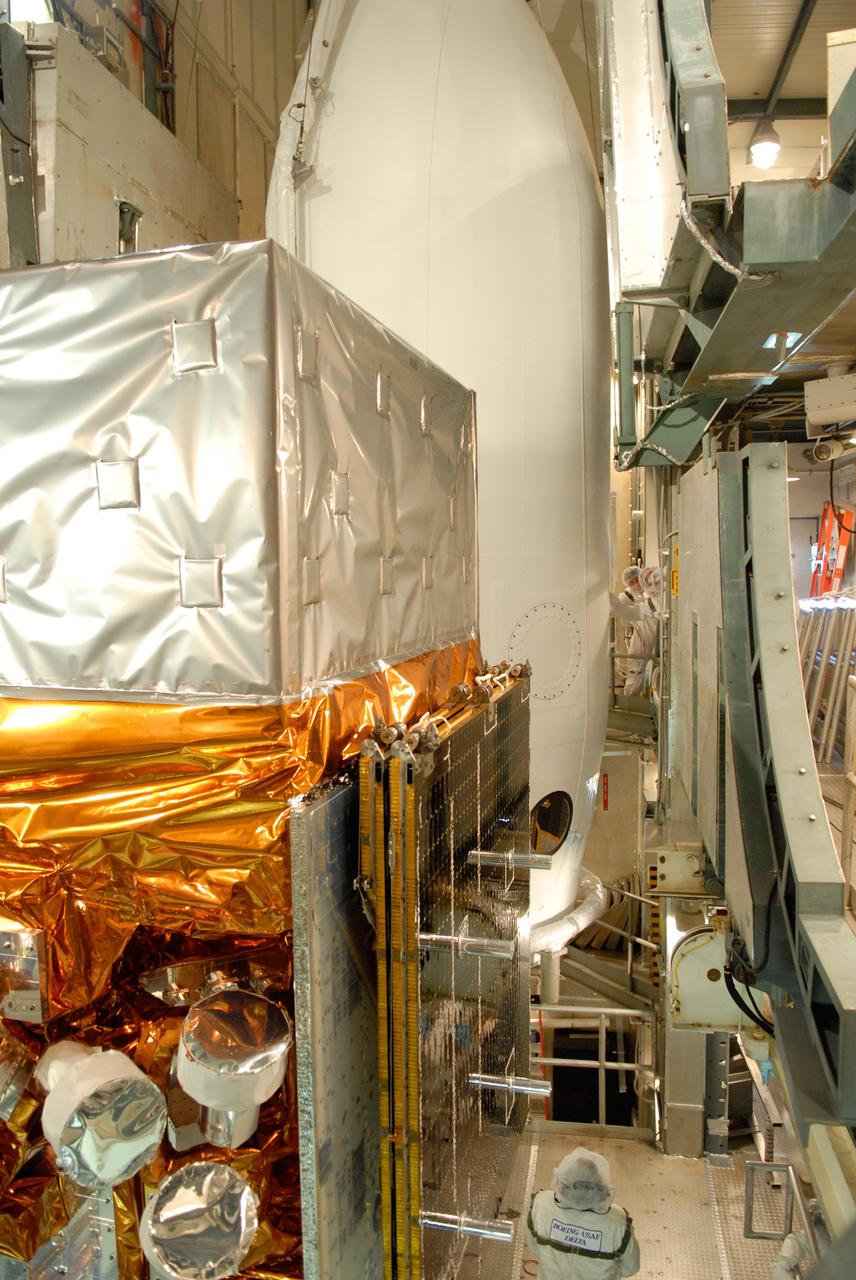
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help guide one section of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first half of the payload fairing is moved into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope within the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The first half of the payload fairing is ready to be moved around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST, within the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

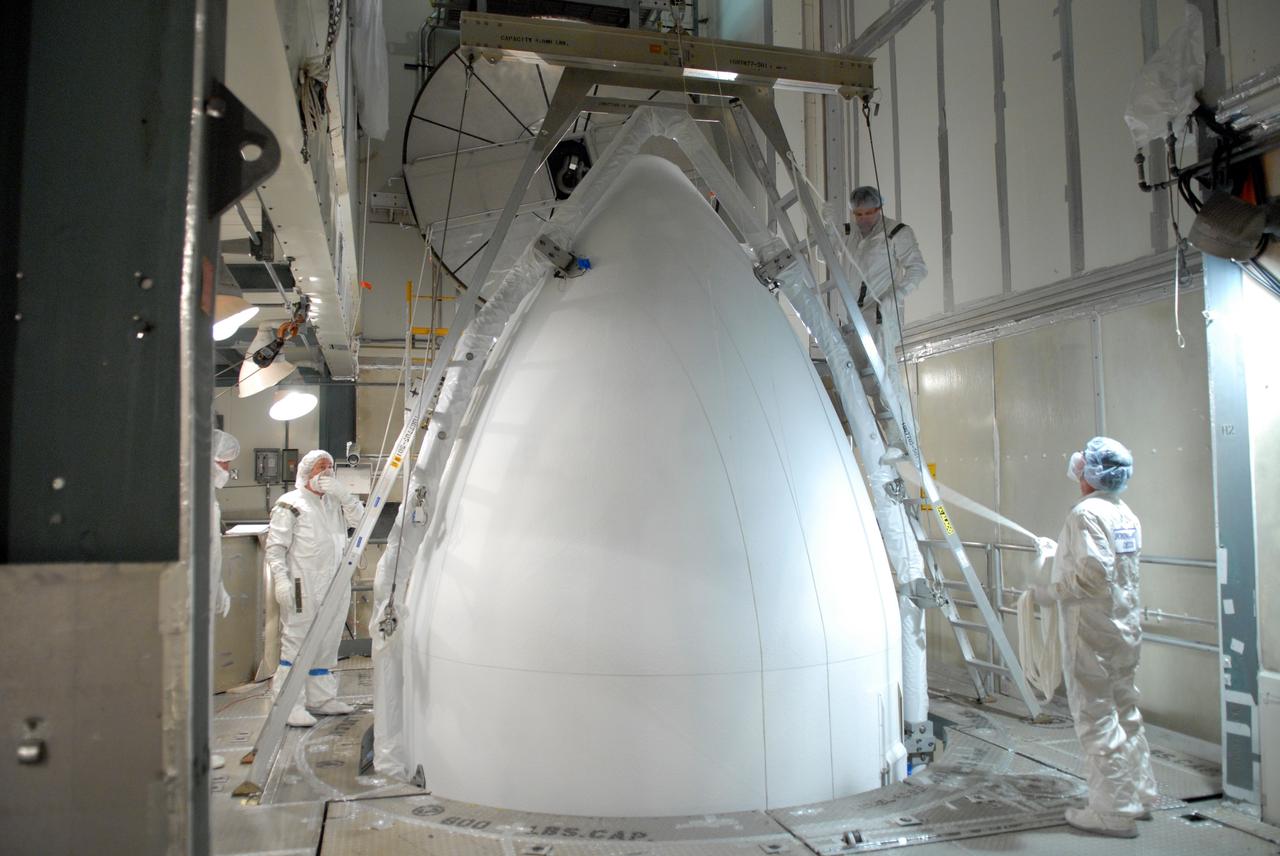
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers connect the two sections of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
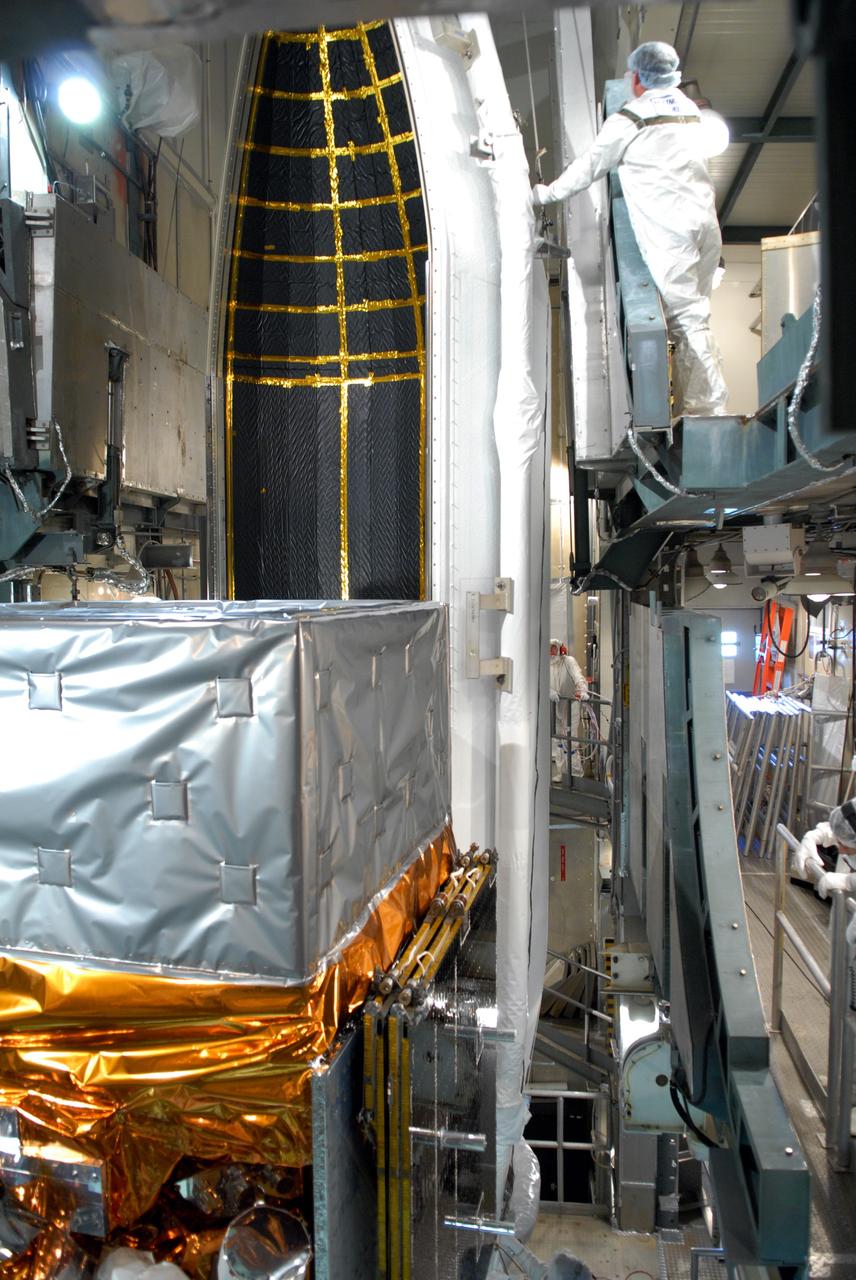
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help guide one section of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers help guide one section of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

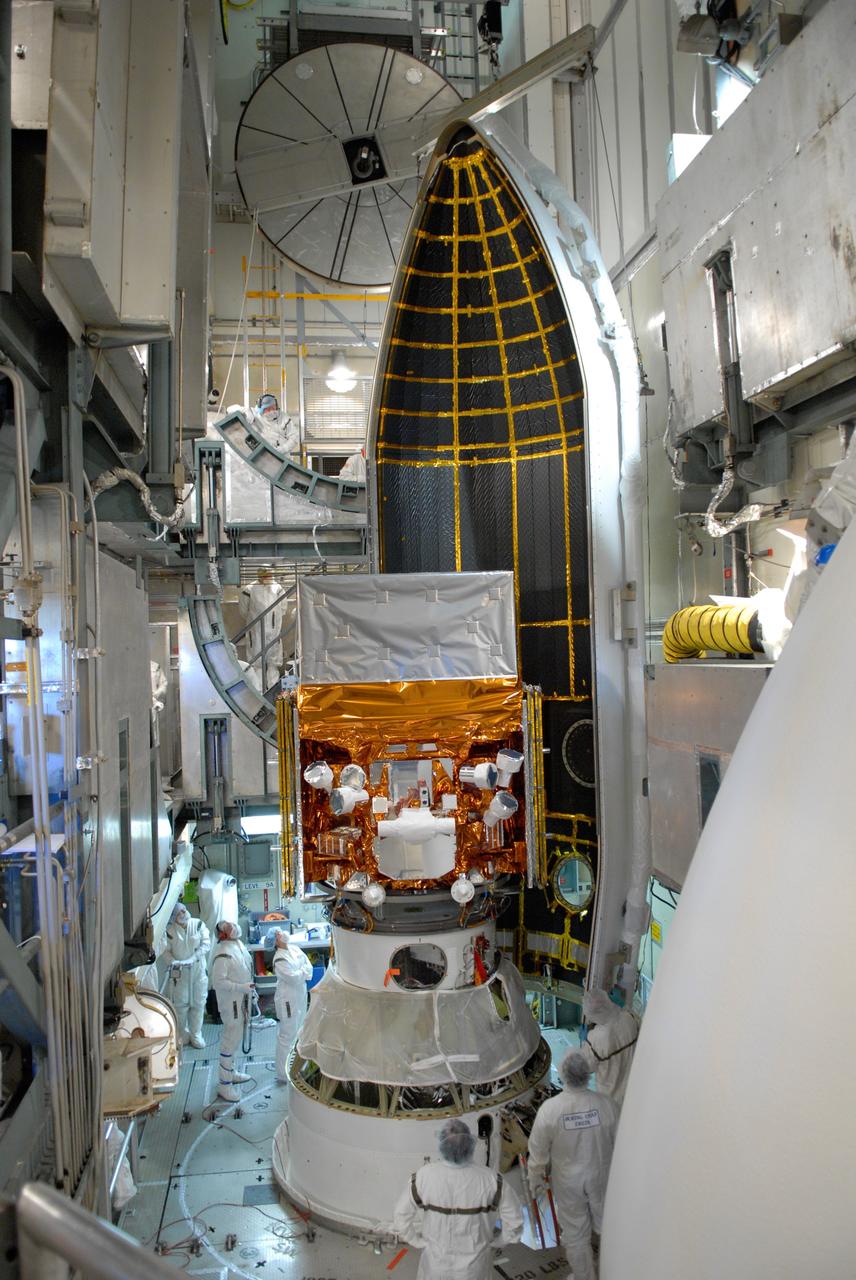
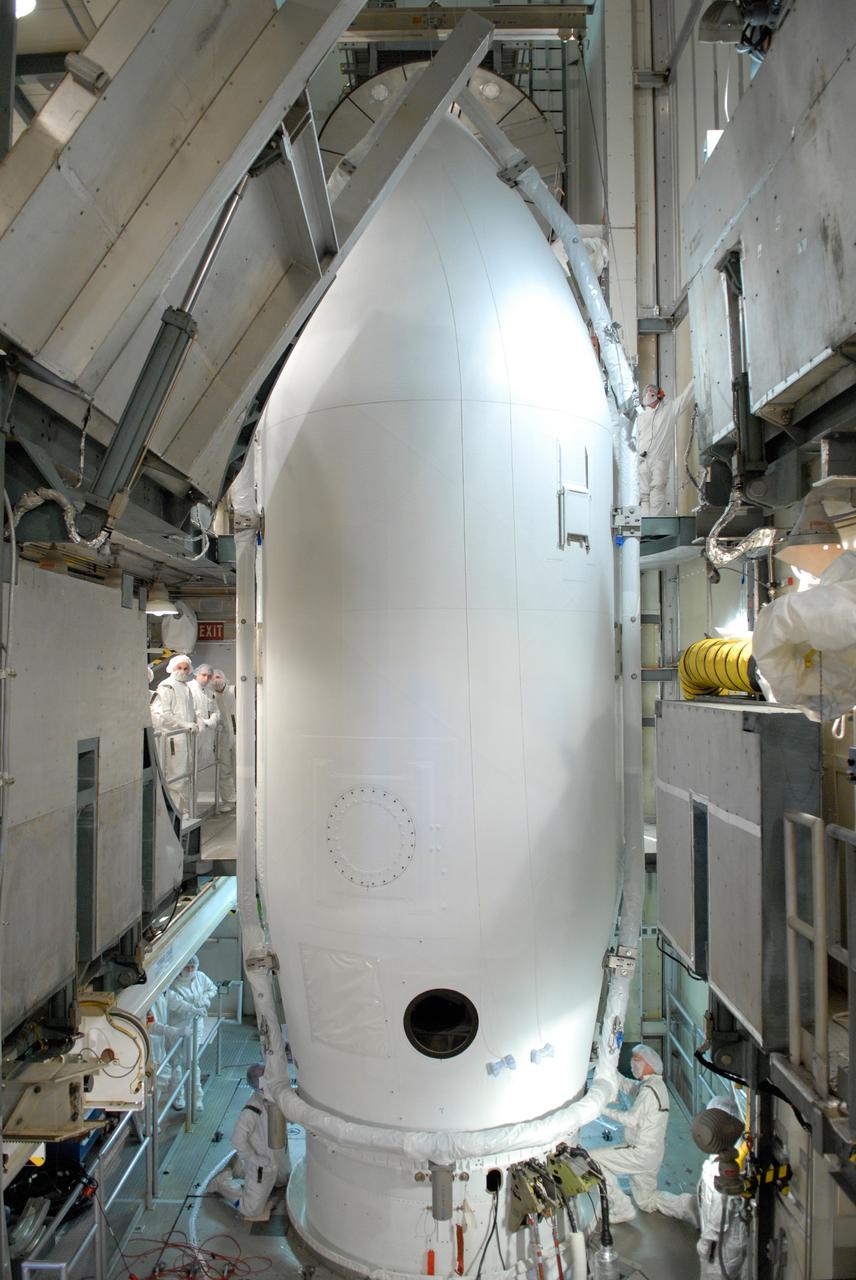
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST, is ready for encapsulation in the payload fairing, which is seen behind it. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers secure the top of the payload fairing into place around NASA's Gamma-Ray Large Area Space Telescope, or GLAST. The fairing is a molded structure that fits flush with the outside surface of the Delta II upper stage booster and forms an aerodynamically smooth nose cone, protecting the spacecraft during launch and ascent. GLAST is a powerful space observatory that will explore the Universe's ultimate frontier, where nature harnesses forces and energies far beyond anything possible on Earth; probe some of science's deepest questions, such as what our Universe is made of, and search for new laws of physics; explain how black holes accelerate jets of material to nearly light speed; and help crack the mystery of stupendously powerful explosions known as gamma-ray bursts. The launch date is targeted no earlier than June 3. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

This photograph shows the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory being released from the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis during the STS-35 mission in April 1991. The GRO reentered the Earth's atmosphere and ended its successful mission in June 2000. For nearly 9 years, GRO's Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center, kept an unblinking watch on the universe to alert scientist to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts that had puzzled them for decades. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of star, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. In January 1999, the instrument, via the Internet, cued a computer-controlled telescope at Las Alamos National Laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, within 20 seconds of registering a burst. With this capability, the gamma-ray experiment came to serve as a gamma-ray burst alert for the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and major gound-based observatories around the world. Thirty-seven universities, observatories, and NASA centers in 19 states, and 11 more institutions in Europe and Russia, participated in BATSE's science program.
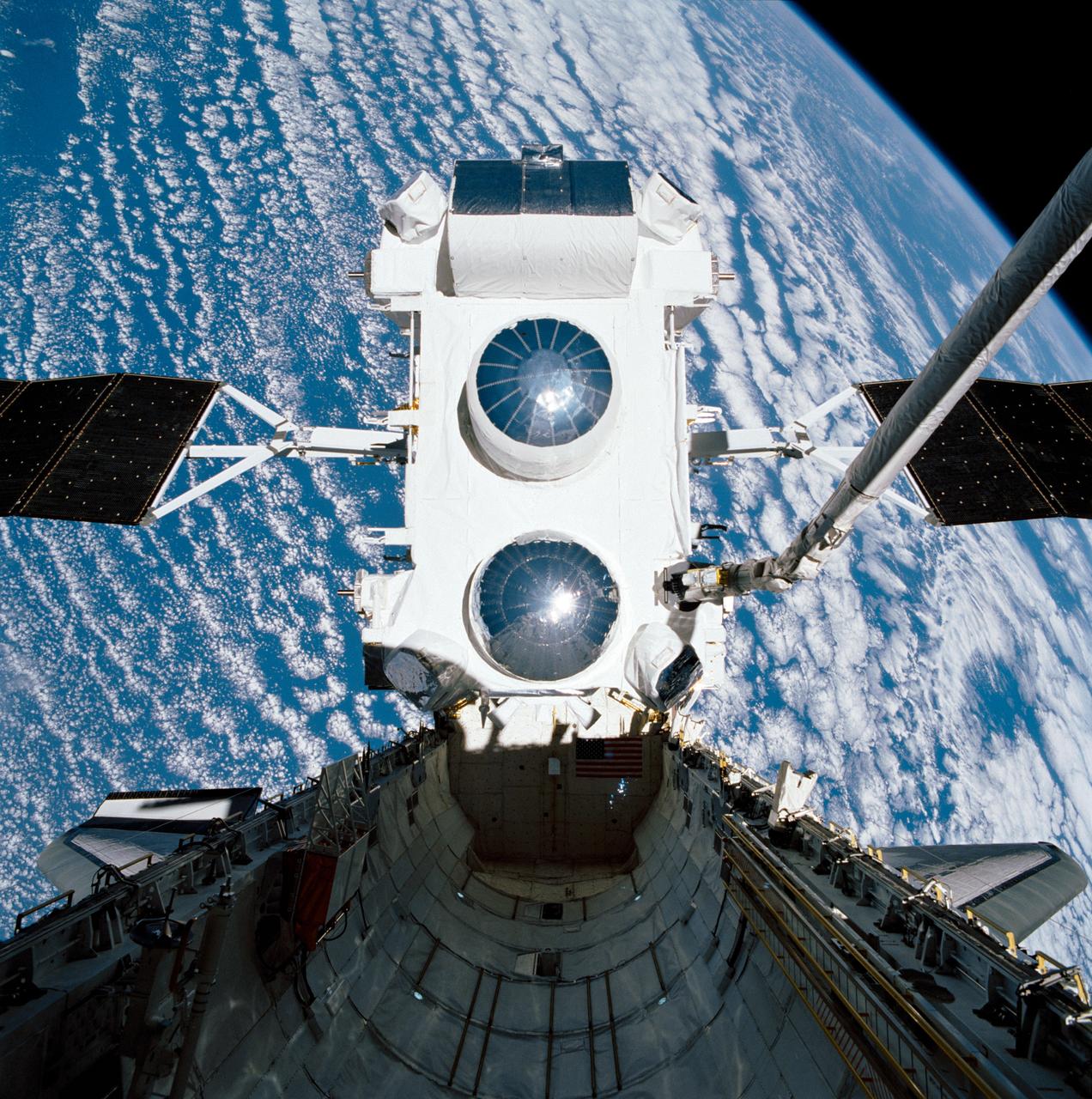

STS037-99-098 (7 April 1991) --- Backdropped against clouds over water, the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) is still in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Atlantis' Remote Manipulator System (RMS) in this 70mm scene. A special Extravehicular Activity (EVA) was required by astronauts Jerry L. Ross and Jerome (Jay) Apt to manually extend the high-gain antenna on GRO. The five-member crew capped off a busy Flight Day 3 by releasing the heavy payload.

This photograph shows the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (GRO) being deployed by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis during the STS-37 mission in April 1991. The GRO reentered Earth atmosphere and ended its successful mission in June 2000. For nearly 9 years, the GRO Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), kept an unblinking watch on the universe to alert scientists to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts that had puzzled them for decades. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of stars, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. In January 1999, the instrument, via the Internet, cued a computer-controlled telescope at Las Alamos National Laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, within 20 seconds of registering a burst. With this capability, the gamma-ray experiment came to serve as a gamma-ray burst alert for the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and major gound-based observatories around the world. Thirty-seven universities, observatories, and NASA centers in 19 states, and 11 more institutions in Europe and Russia, participated in the BATSE science program.
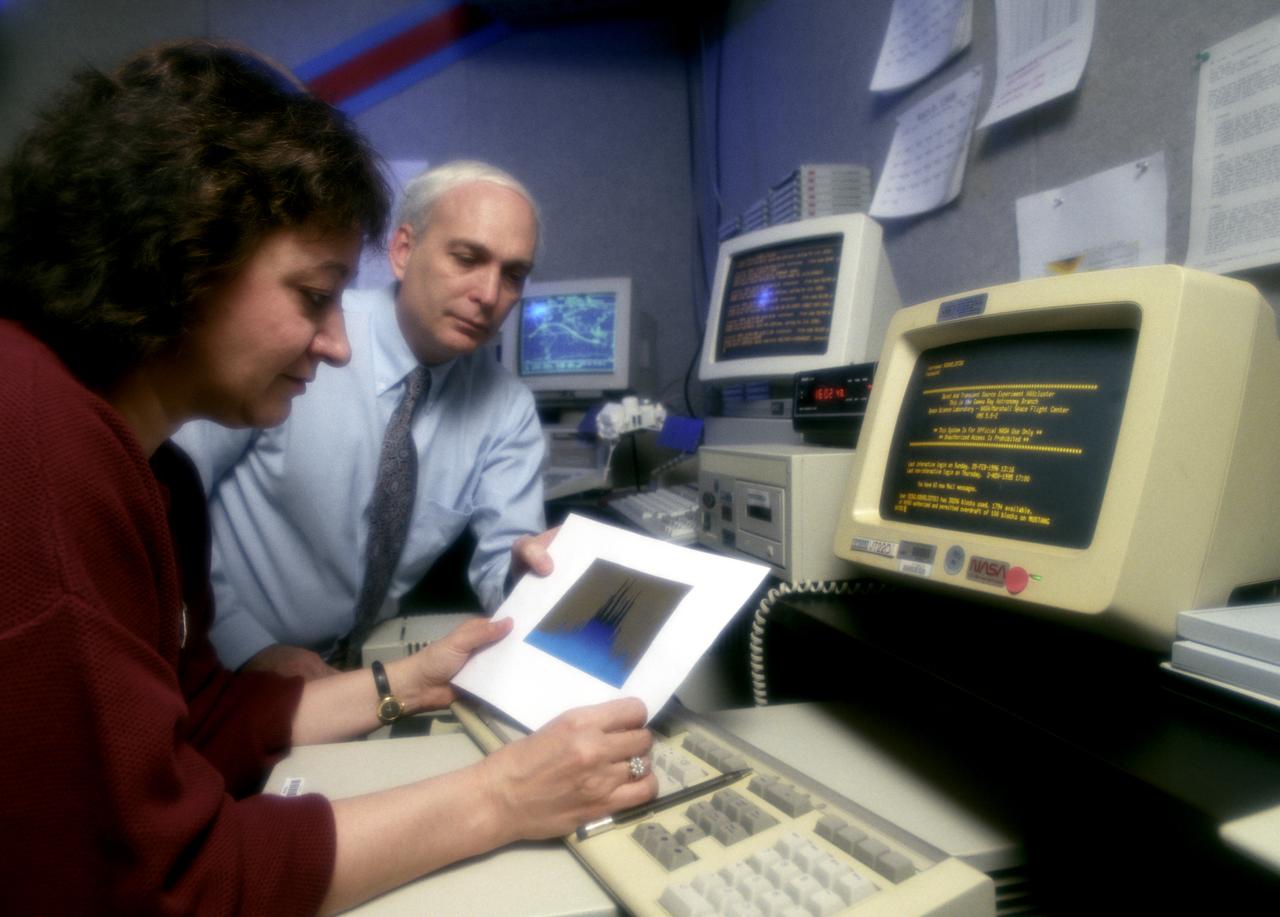

In this photograph, Dr. Gerald Fishman of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), a principal investigator of the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory's (GRO's) instrument, the Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), and Dr. Chryssa Kouveliotou of Universities Space Research Associates review data from the BATSE. For nearly 9 years, GRO's Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center, kept a blinking watch on the universe to alert scientist to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of stars, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. Because gamma-rays are so powerful, they pass through conventional telescope mirrors. Instead of a mirror, the heart of each BATSE module was a large, flat, transparent crystal that generated a tiny flash of light when struck by a gamma-ray. With an impressive list of discoveries and diverse accomplishments, BATSE could claim to have rewritten astronomy textbooks. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis during the STS-35 mission in April 1991, the GRO reentered the Earth's atmosphere and ended its successful 9-year mission in June 2000.
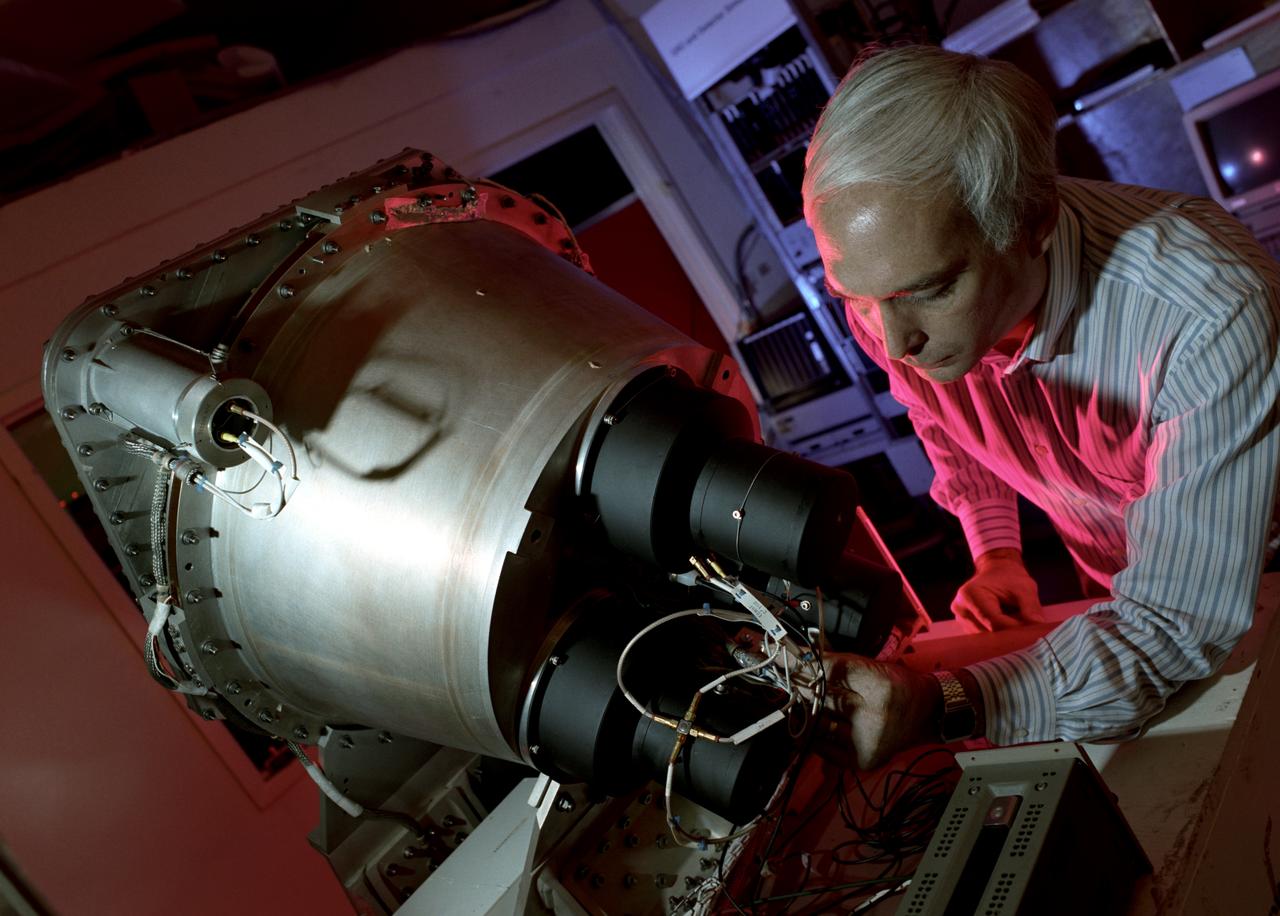

In this photograph, Dr. Gerald Fishman of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), a principal investigator of the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory's (GRO's) instrument, the Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), works on the BATSE detector module. For nearly 9 years, GRO's BATSE, designed and built by MSFC, kept an unblinking watch on the universe to alert scientist to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of star, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. Because gamma-rays are so powerful, they pass through conventional telescope mirrors. Instead of a mirror, the heart of each BATSE module was a large, flat, transparent crystal that generated a tiny flash of light when struck by a gamma-ray. With an impressive list of discoveries and diverse accomplishments, BATSE could claim to have rewritten astronomy textbooks. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis during the STS-35 mission in April 1991, the GRO reentered the Earth's atmosphere and ended its successful 9-year mission in June 2000.
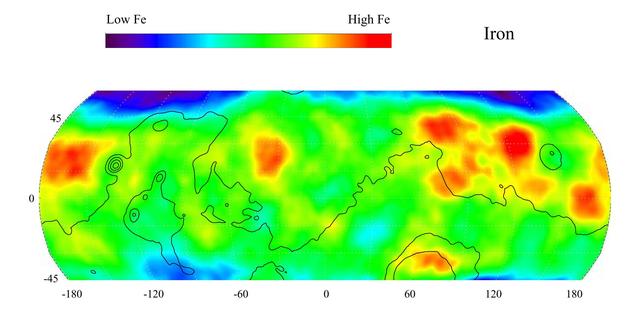
This gamma ray spectrometer map from NASA Mars Odyssey of the mid-latitude region of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element iron, one of the most abundant elements on Mars and Earth. It is responsible for the red color on the surface of Mars.
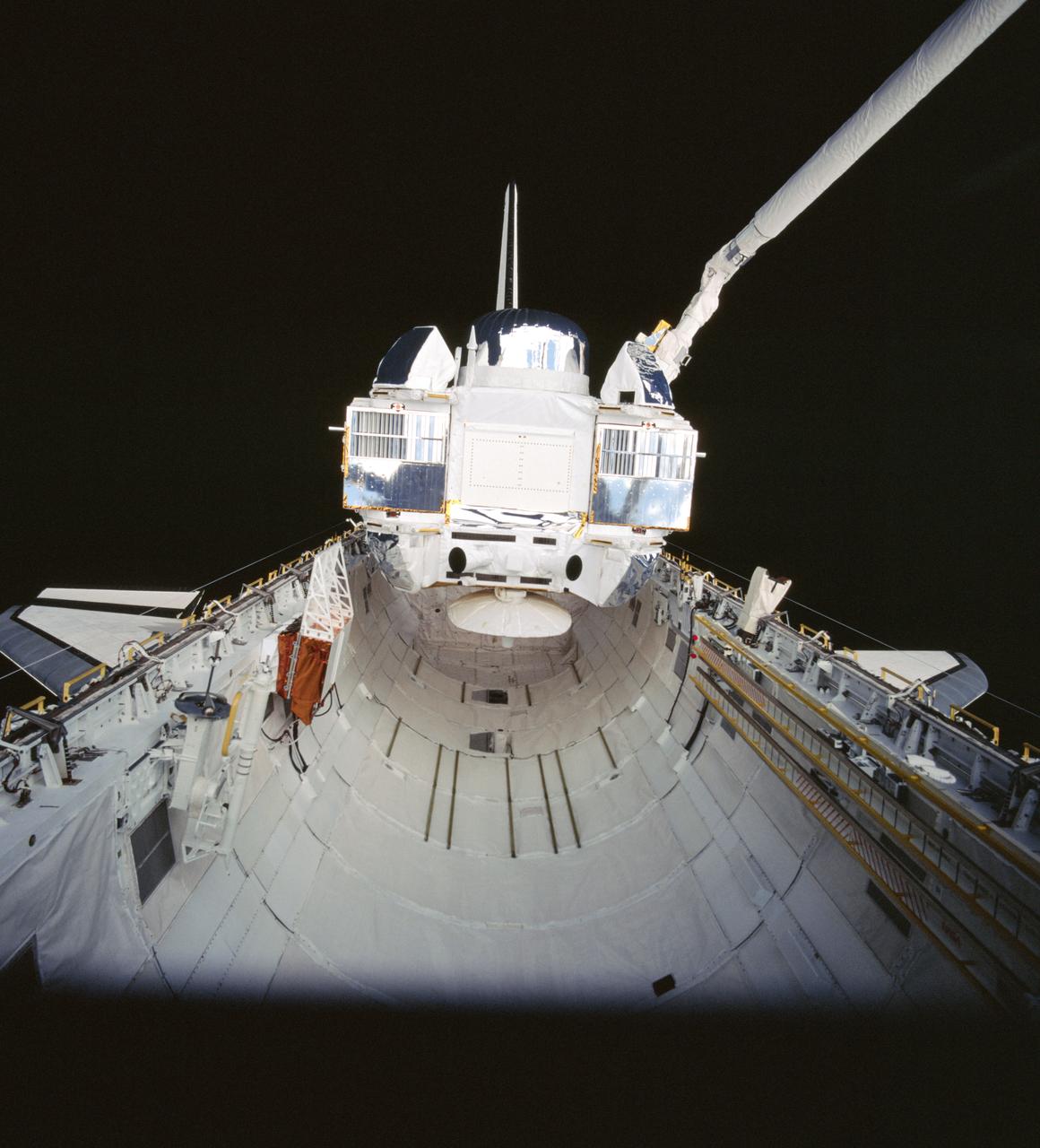

STS037-99-031 (7 April 1991) --- The Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) is still in the grasp of Atlantis' remote manipulator system (RMS) in this 70mm scene, photographed from inside the crew cabin. A special extravehicular activity (EVA) was required by astronauts Jerry L. Ross and Jerome (Jay) Apt to manually extend the high-gain antenna on GRO. The solar array panels are not yet deployed in this scene. The five-member crew capped off a busy Flight Day 3 by releasing the heavy payload.
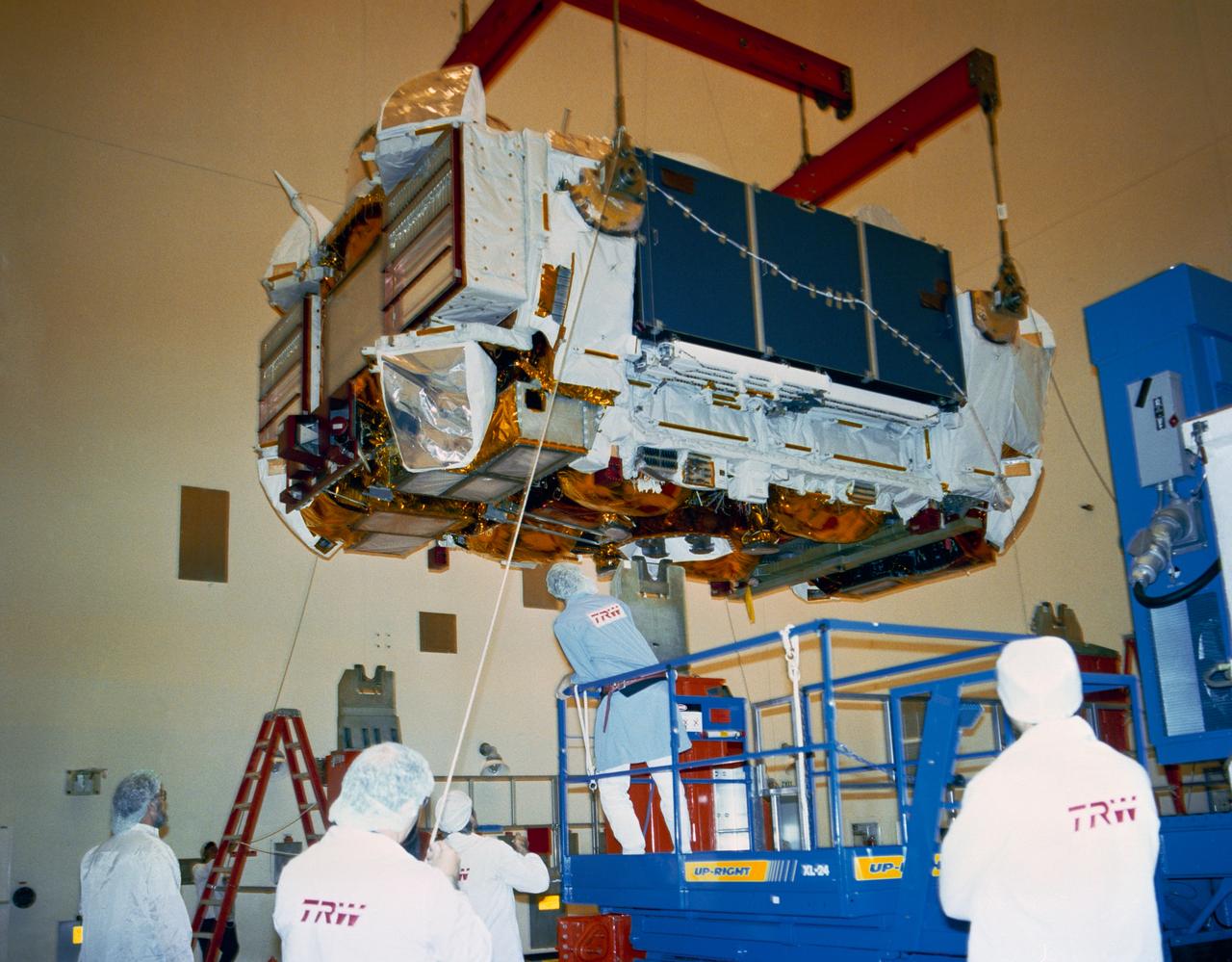

S90-36709 (8 Feb 8, 1990) --- Workers at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility are removing the Gamma Ray Observatory from its storage container. GRO, one of four NASA Great Observatories, arrived at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) February 6 from the California plant of builder TRW. Weighing a massive 34,700 pounds, GRO will be the heaviest payload without an upper stage ever carried aboard the space shuttle. It is scheduled for deployment from the orbiter Atlantis during STS-37 in November 1990.
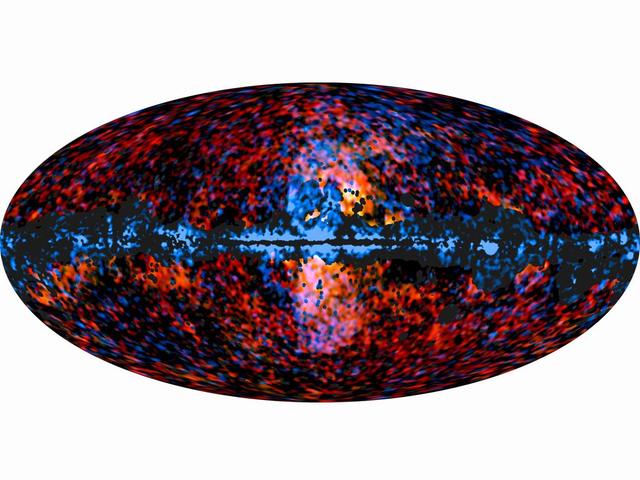
This all-sky image shows the distribution of the galactic haze seen by ESA Planck mission at microwave frequencies superimposed over the high-energy sky, as seen by NASA Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.

STS037-18-032 (7 April 1991) --- Astronaut Jerry L. Ross, mission specialist, peers into Space Shuttle Atlantis' cabin and is photographed by a fellow crew member using a 35mm camera. Ross was in the space shuttle's cargo bay to join astronaut Jerome (Jay) Apt in accomplishing a repair task on the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO), seen in left frame. The two had been called upon to manually extend the high-gain antenna on GRO.
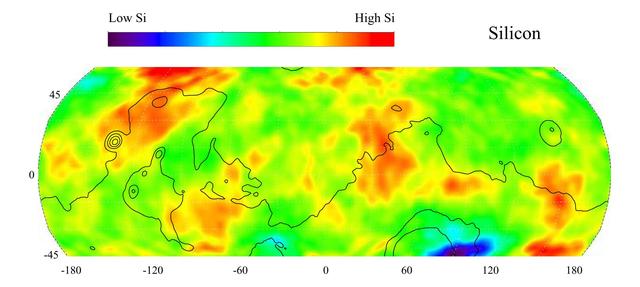
This gamma ray spectrometer map of the mid-latitude region of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element silicon. Silicon is one of the most abundant elements on the surface of both Mars and Earth (second only to oxygen). The most extensive region of highest silicon content, shown in red, is located in the high latitudes north of Tharsis (centered near 45 degrees latitude, -120 degrees longitude). The area of lowest silicon content, shown in blue, lies just to the east of the Hellas Basin (-45 degrees latitude, 90 degrees longitude). Contours of constant surface elevation are also shown. The long continuous contour line running from east to west marks the approximate separation of the younger lowlands in the north from the older highlands in the south. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04256
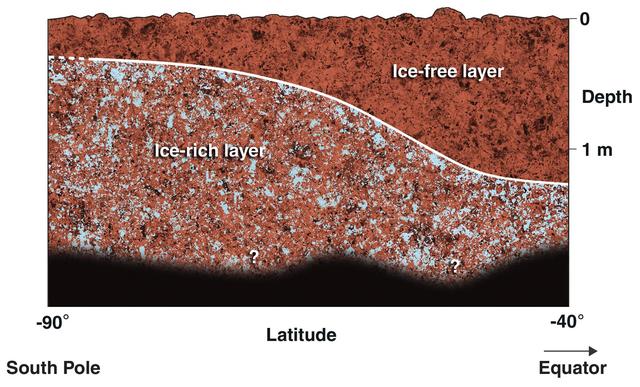
This diagram shows a possible configuration of ice-rich and dry soil in the upper meter 3 feet of Mars. The ice-rich soil was detected by the gamma ray spectrometer suite of instruments aboard NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
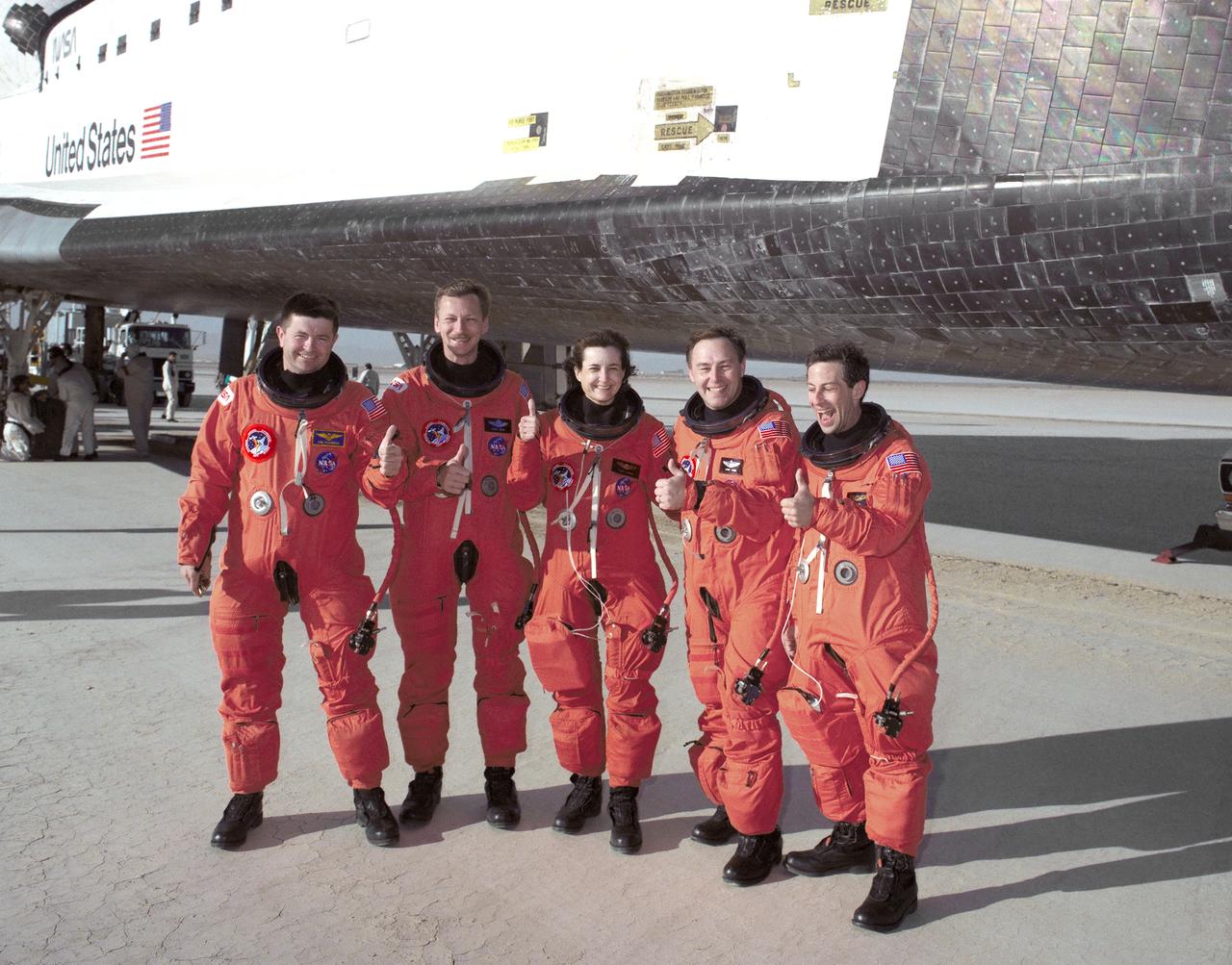

The crew of the Space Shuttle Atlantis gives the "all's well" thumb's-up sign after leaving the 100-ton orbiter following their landing at 6:55 a.m. (PDT), 11 April 1991, at NASA's Ames Dryden Flight Research Facility (later redesignated Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, to conclude mission STS-37. They are, from left, Kenneth D. Cameron, pilot; Steven R. Nagel, mission commander; and mission specialists Linda M. Godwin, Jerry L. Ross, and Jay Apt. During the mission,which began with launch April 5 at Kennedy Space Center, Florida, the crew deployed the Gamma Ray Observatory. Ross and Jay also carried out two spacewalks, one to deploy an antenna on the Gamma Ray Observatory and the other to test equipment and mobility techniques for the construction of the future Space Station. The planned five-day mission was extended one day because of high winds at Edwards.
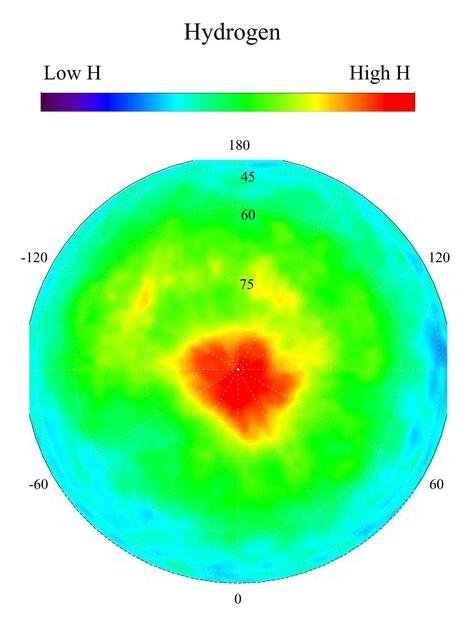
This gamma ray spectrometer map centered on the north pole of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element hydrogen. In this region, hydrogen is mainly in the form of water ice. Regions of high ice content are shown in red and those low in ice content are shown in blue. The very ice-rich region at the north pole is due to a permanent polar cap of water ice on the surface. Elsewhere in this region, the ice is buried under several to a few tens of centimeters of dry soil. The sub-surface ice is not uniformly distributed in the north, but varies with both latitude and longitude. In the north, the soil is well over 50 percent ice, which is more than can be accommodated by just filling the pore space in pre-existing soil. This high ice content implies that the ice may have been slowly co-deposited with dust in the past when conditions were wetter. Deposition of ice by this process means it is more likely that the ice deposits are very thick and may even be deep enough to have liquid water at their base. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04254

This Atlas/Centaur launch vehicle, carrying the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3, lifted off on September 20, 1979. The HEAO-3's mission was to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit.

This schematic details the third High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3. The HEAO-3's mission was to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit.
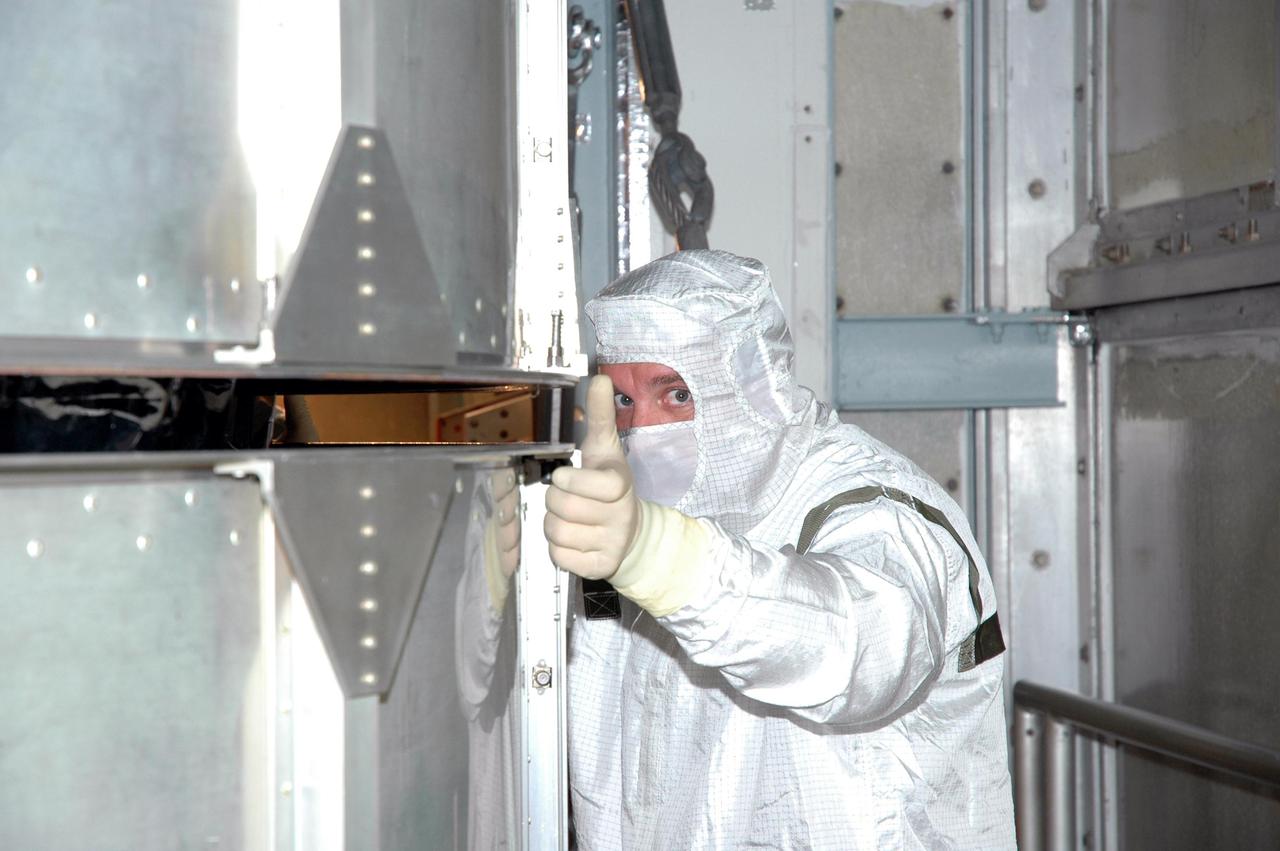

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A , Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., a Boeing technician gives the signal to lift the transport canister surrounding the Swift spacecraft. A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. It is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. Swift is scheduled to launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST Nov. 17.
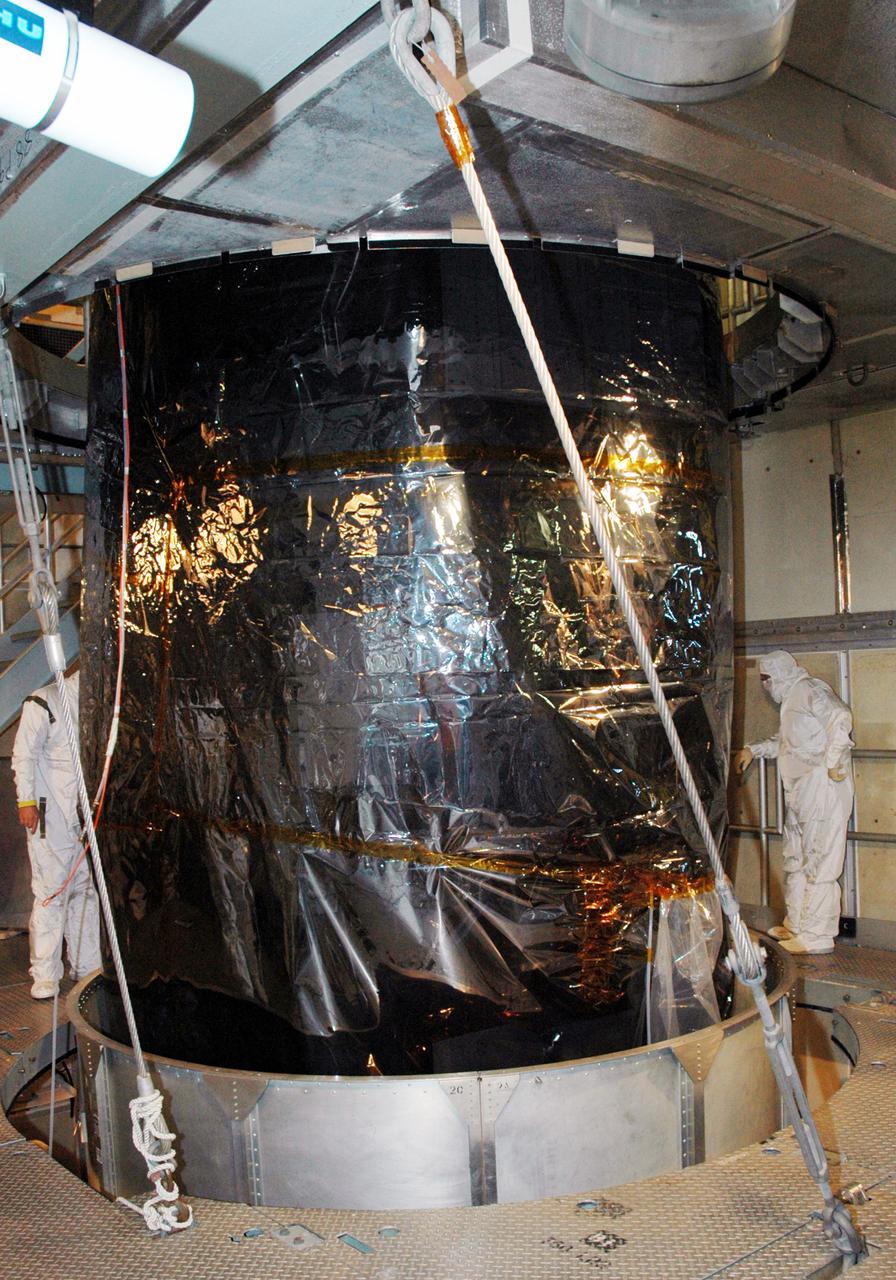

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A , Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., the Swift spacecraft still remains covered by plastic as Boeing technicians work to remove the rest of the transport canister surrounding it. A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. It is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. Swift is scheduled to launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST Nov. 17.
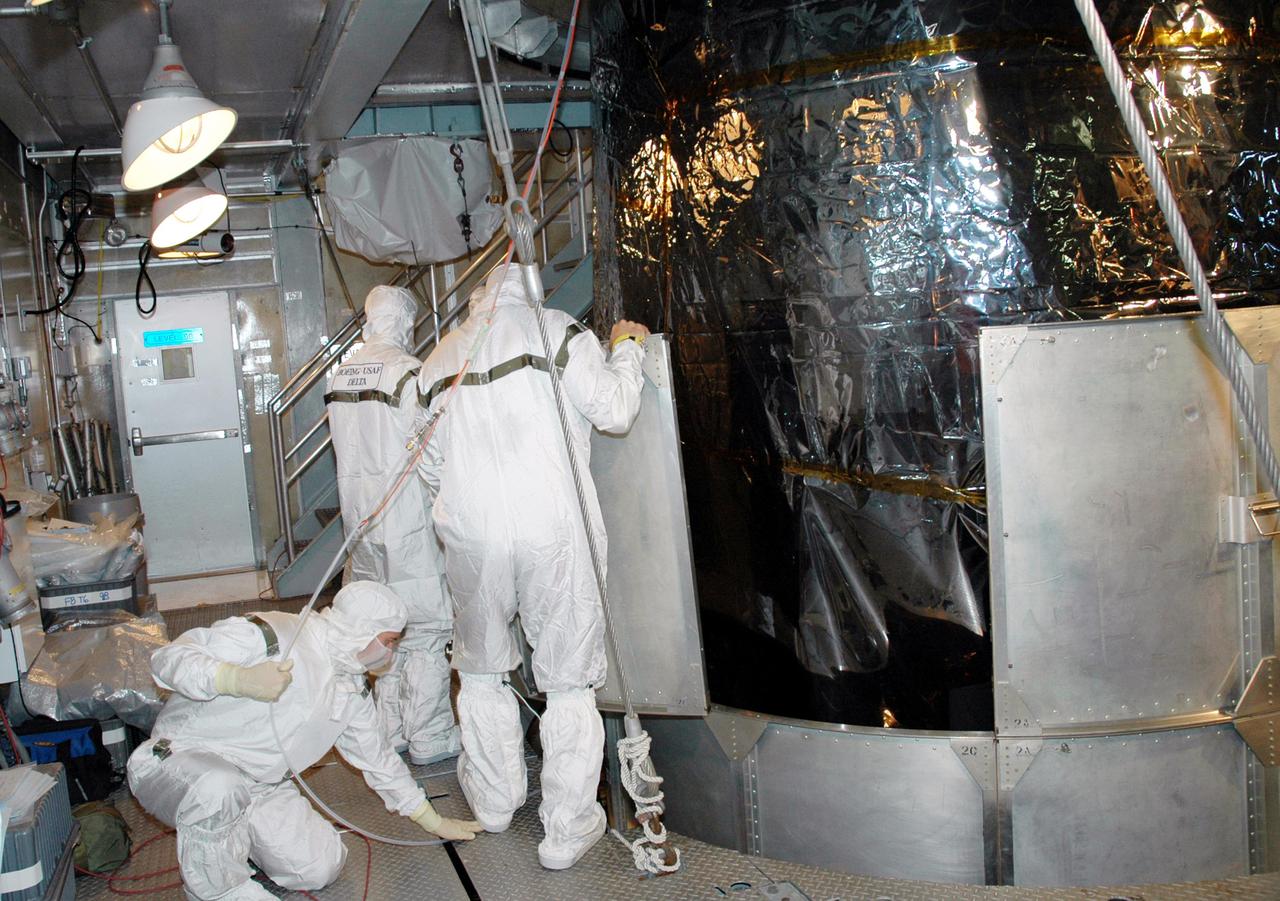

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A , Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Boeing technicians remove the lower portion of the transport canister from the Swift spacecraft. A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. It is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. Swift is scheduled to launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST Nov. 17.
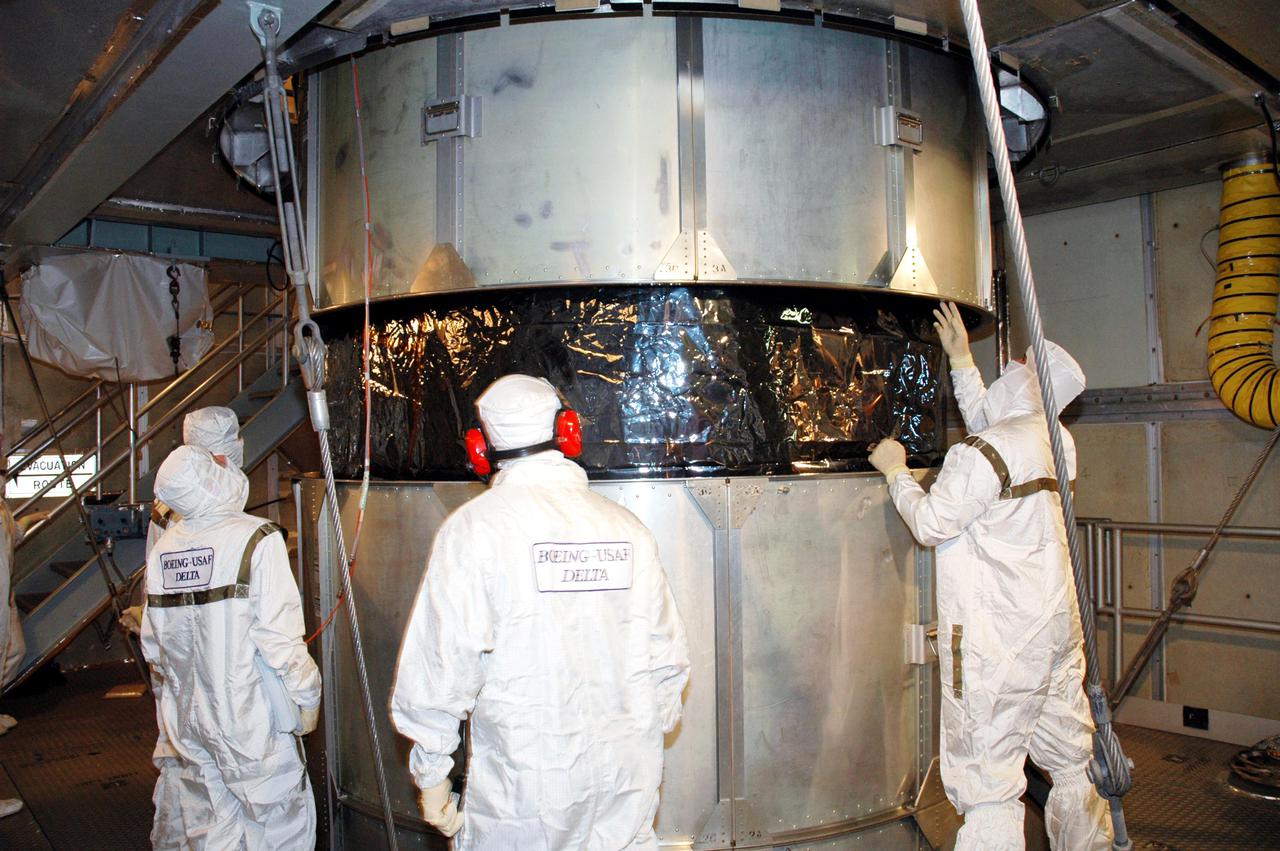

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A , Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Boeing technicians observe the lifting of the transport canister surrounding the Swift spacecraft. A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. It is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. Swift is scheduled to launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST Nov. 17.
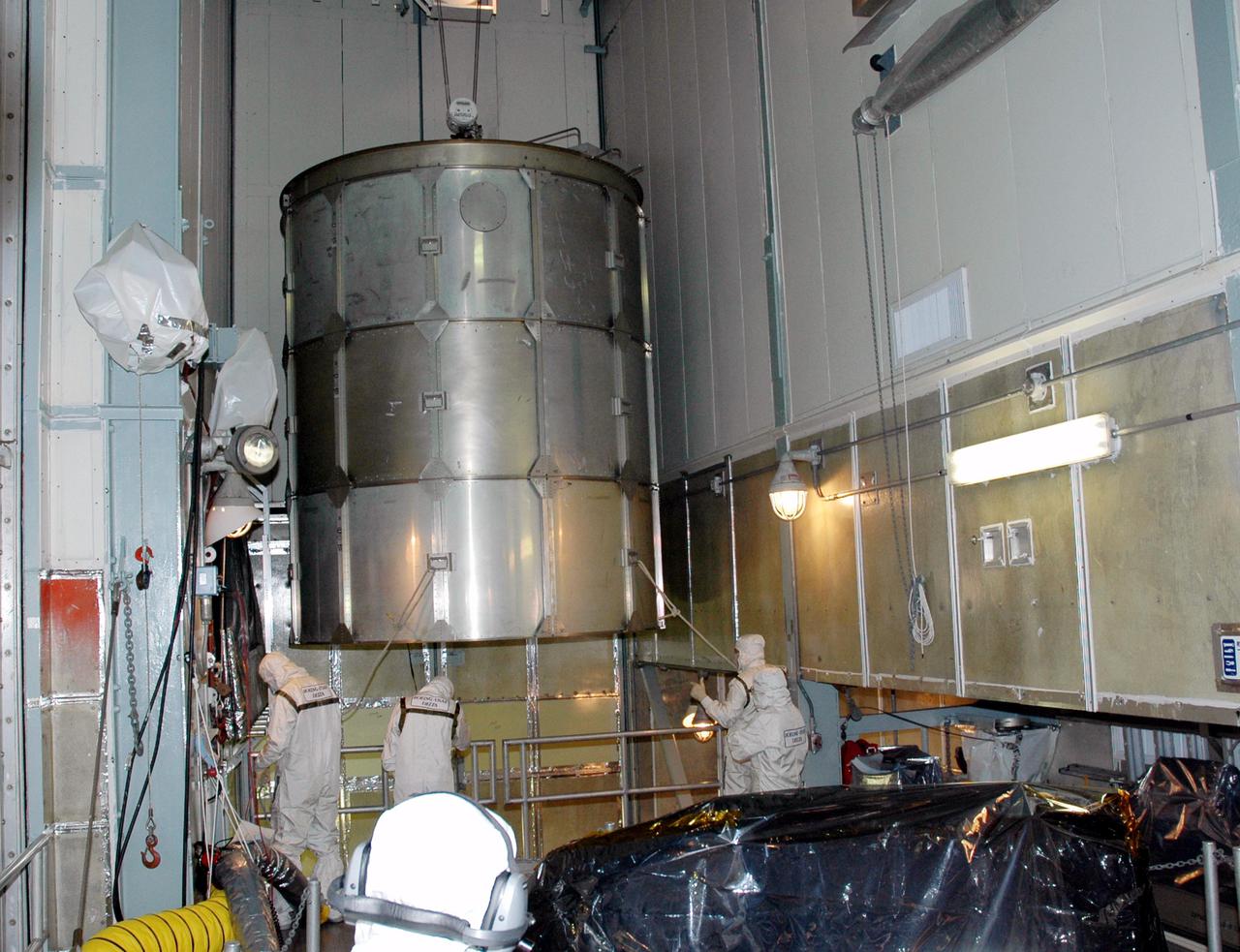

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A , Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., the upper portion of the transport canister is moved away after being lifted from the Swift spacecraft (lower right). A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. It is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes. Swift is scheduled to launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST Nov. 17.
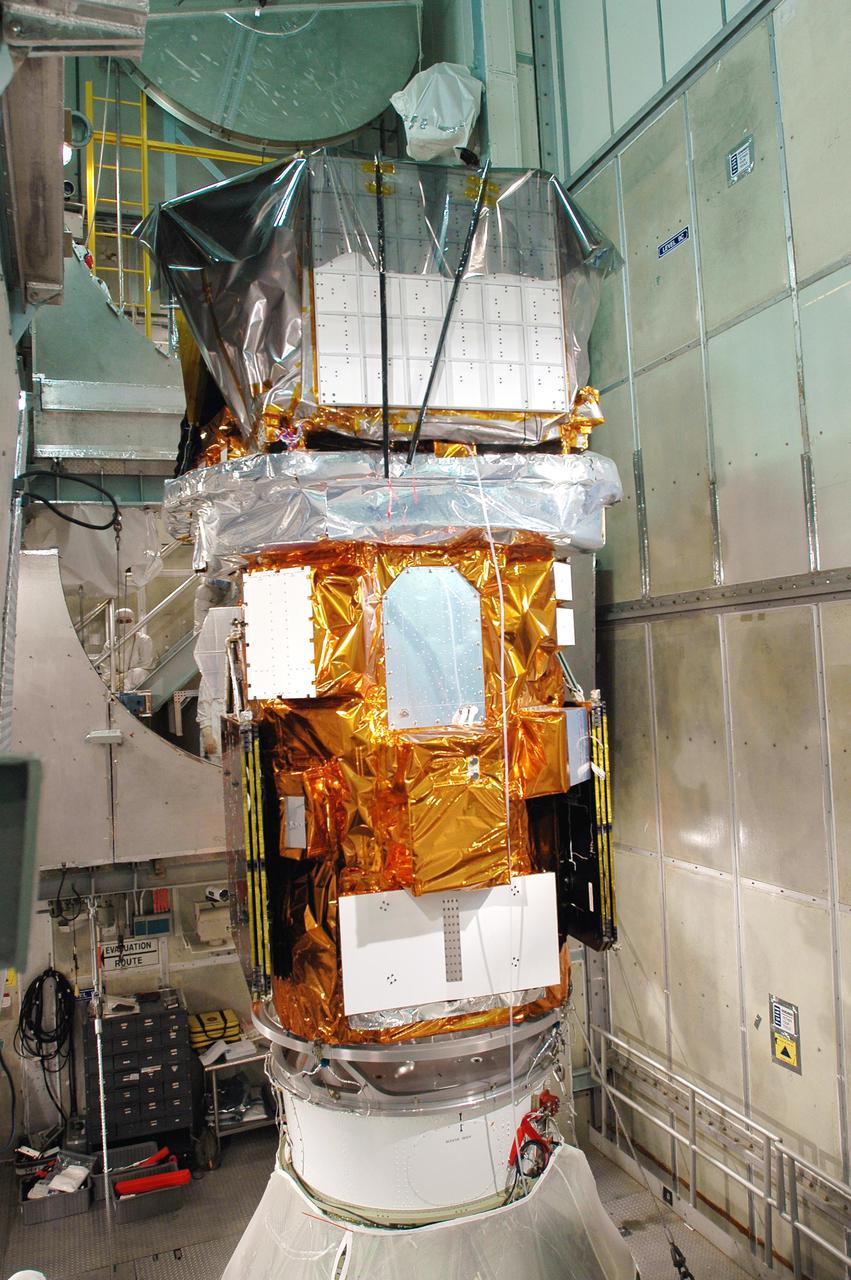

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Swift spacecraft (on top) is ready for fairing encapsulation. The fairing is being installed around the payload for protection during launch and ascent. A Boeing Delta II rocket is the launch vehicle for the Swift spacecraft and its Gamma-Ray Burst Mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 17 at 12:09 p.m. EST.
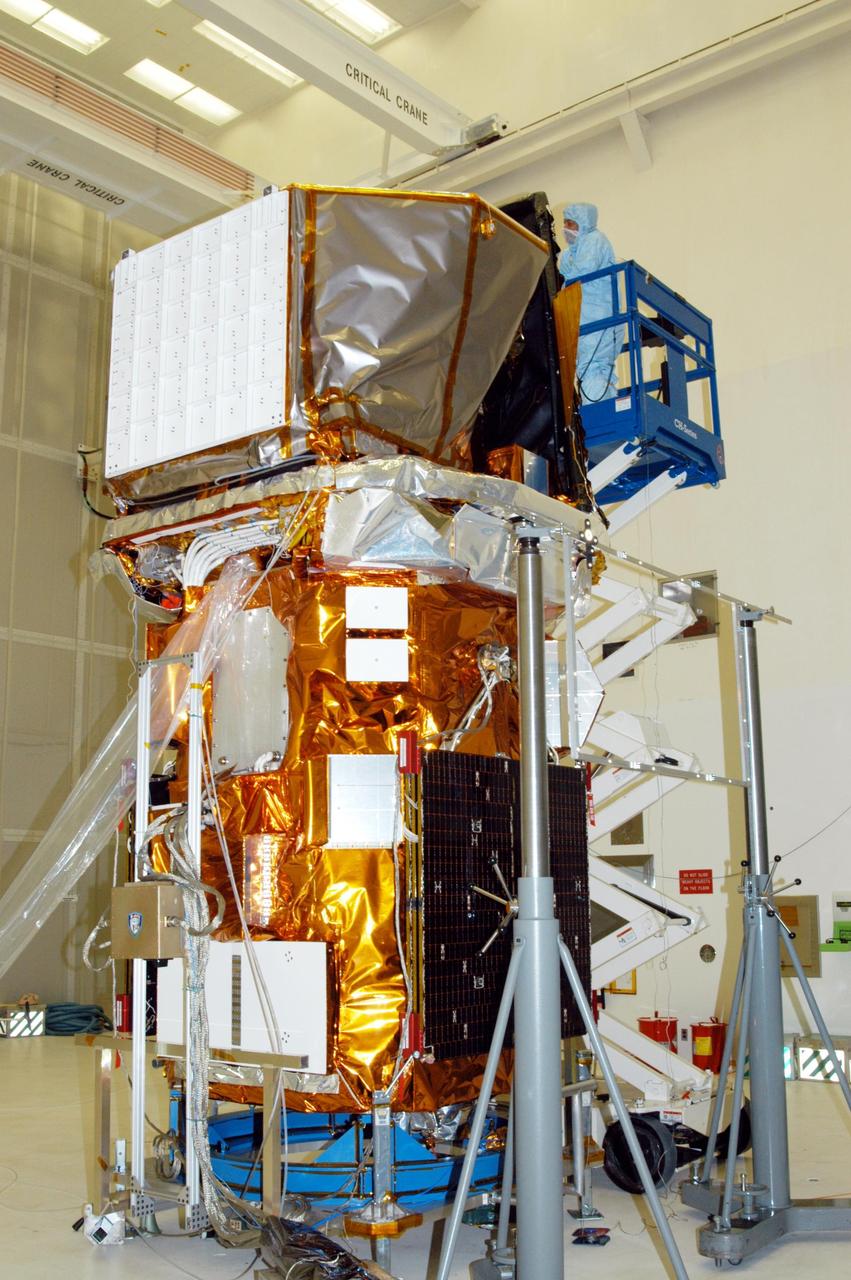

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician performs blanket closeouts on the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
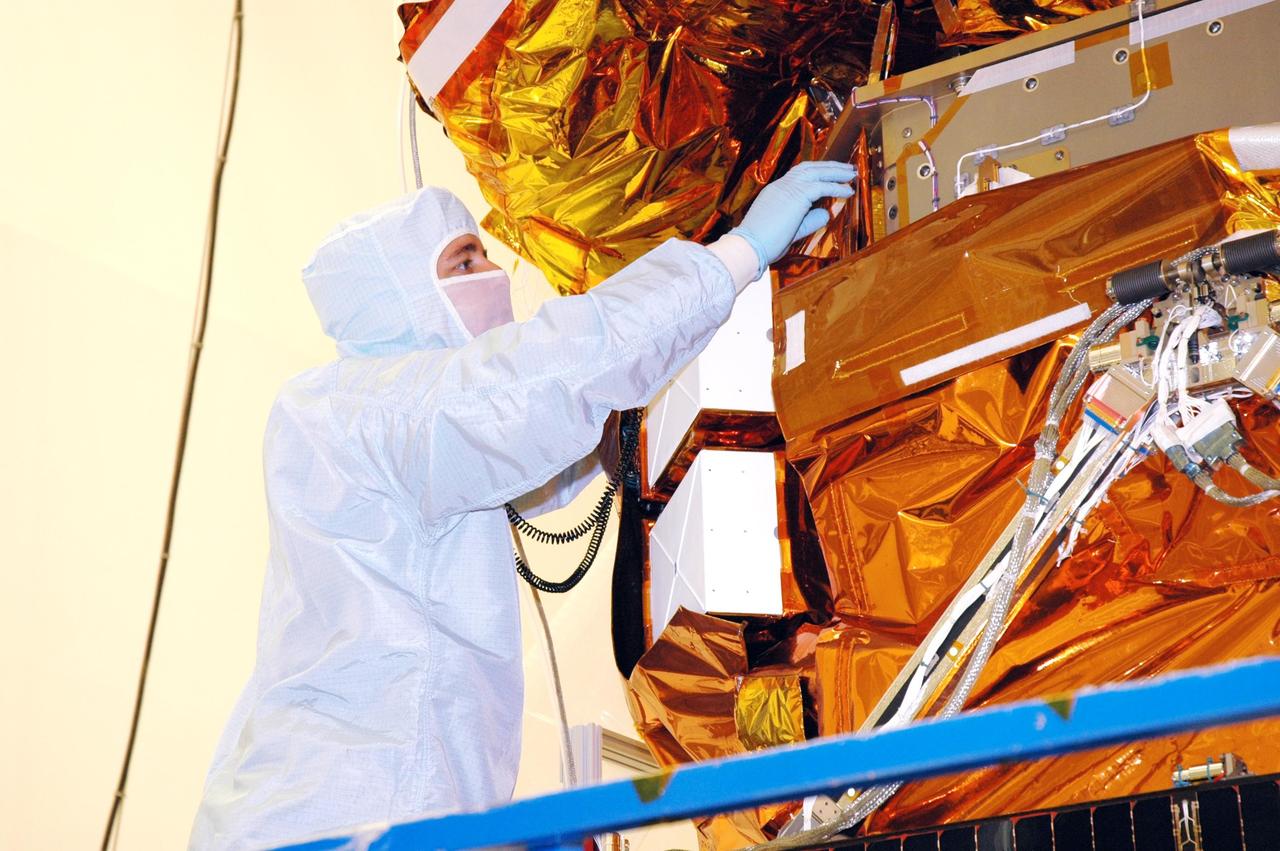

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician works on a blanket installed around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician installs the blankets around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.
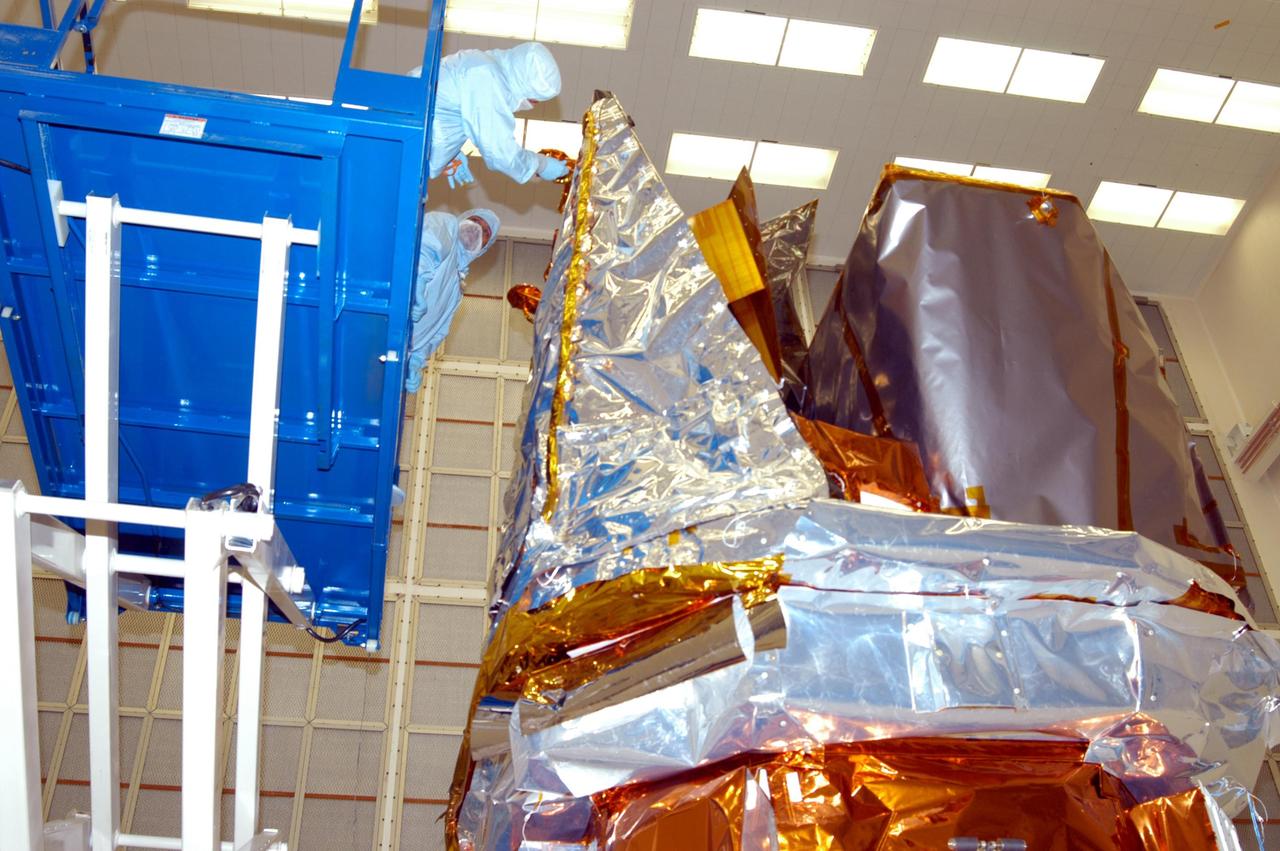

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, technicians perform blanket closeouts on the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
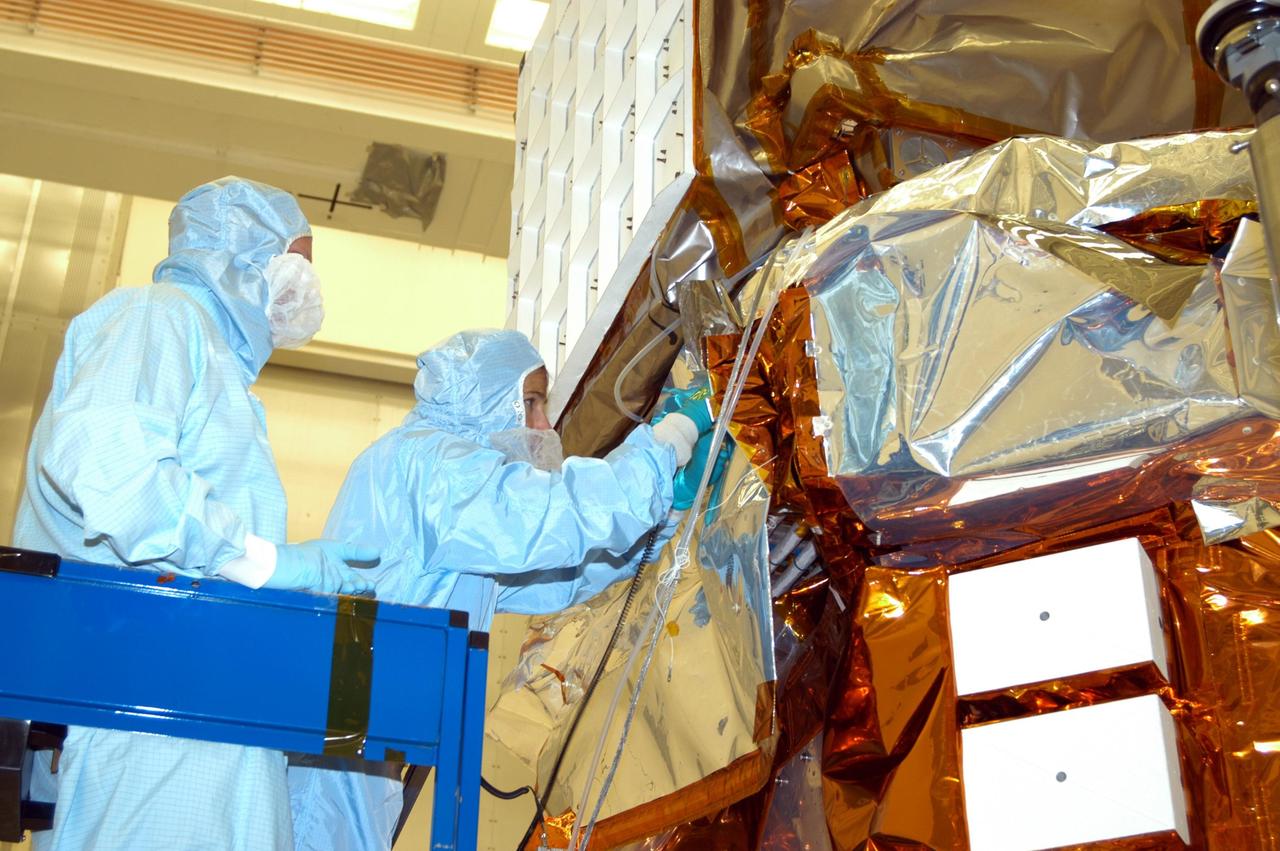

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, technicians take a final look at the blankets installed on the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
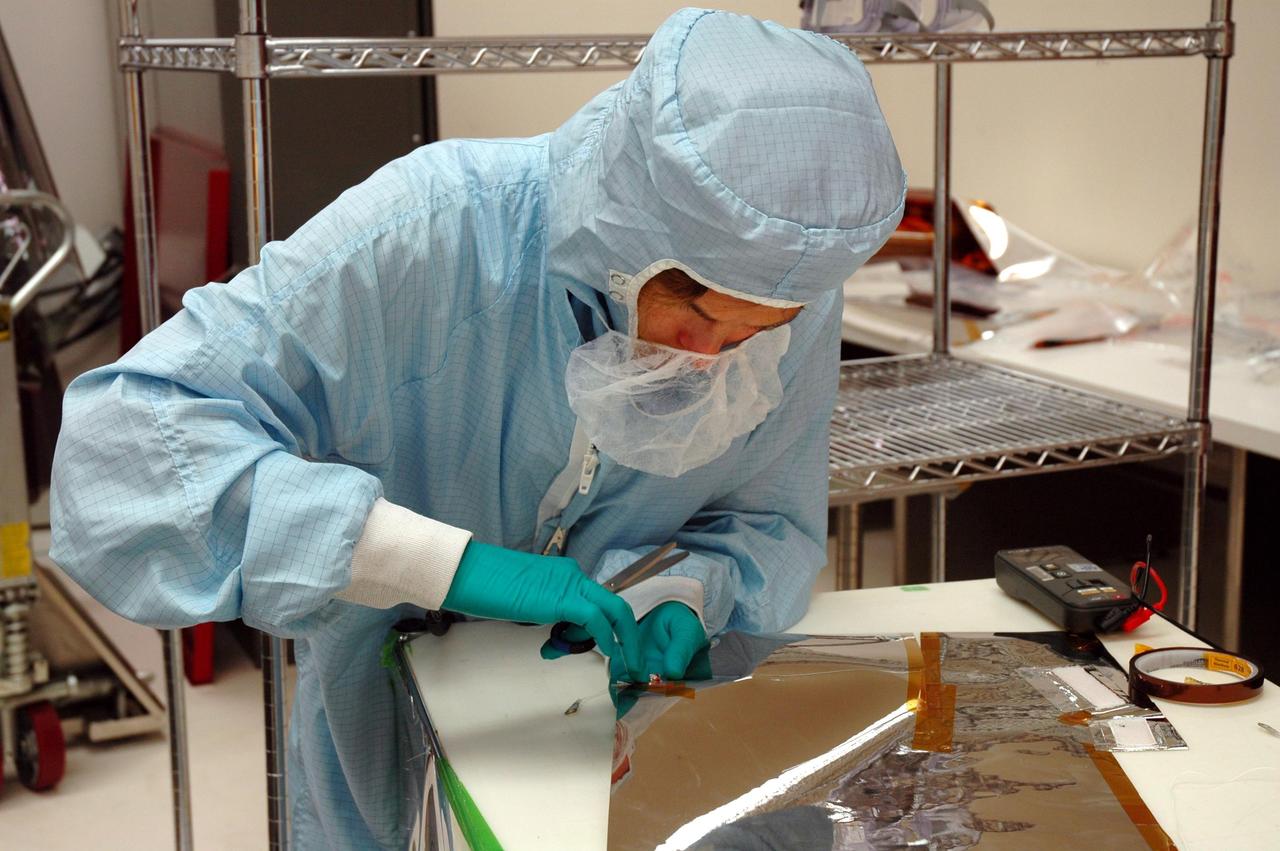

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician trims blanket material that will be installed around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.
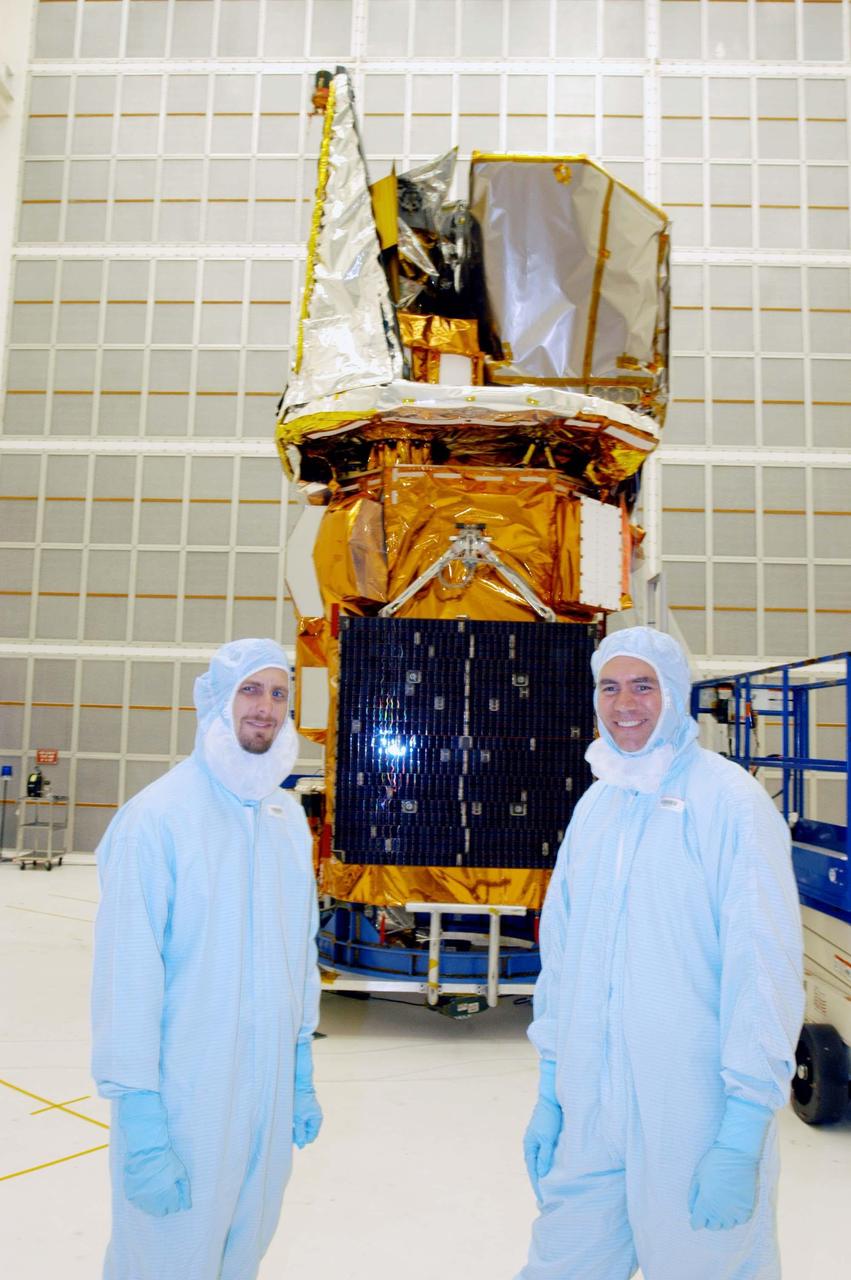

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Project managers Mike Miller and Rex Eberhardt stand in front of the Swift spacecraft in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift has been wrapped with blankets to provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
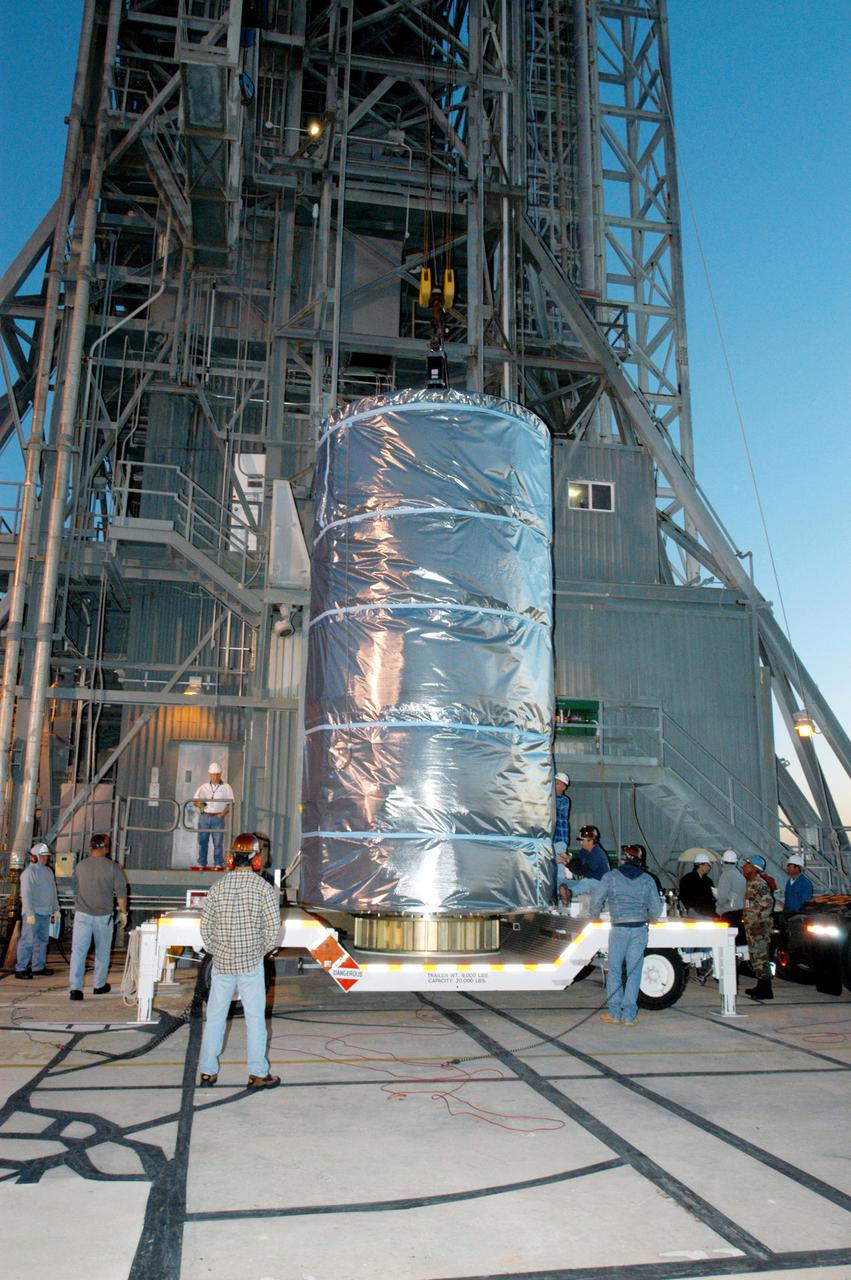

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Wrapped inside a protective cover, the Swift spacecraft arrives at Launch Pad 17-A on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 17. The liftoff aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is targeted at the opening of a one-hour launch window beginning at 12:09 p.m. EST. A first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science, Swift’s three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Gamma-ray bursts are distant, yet fleeting explosions that appear to signal the births of black holes.
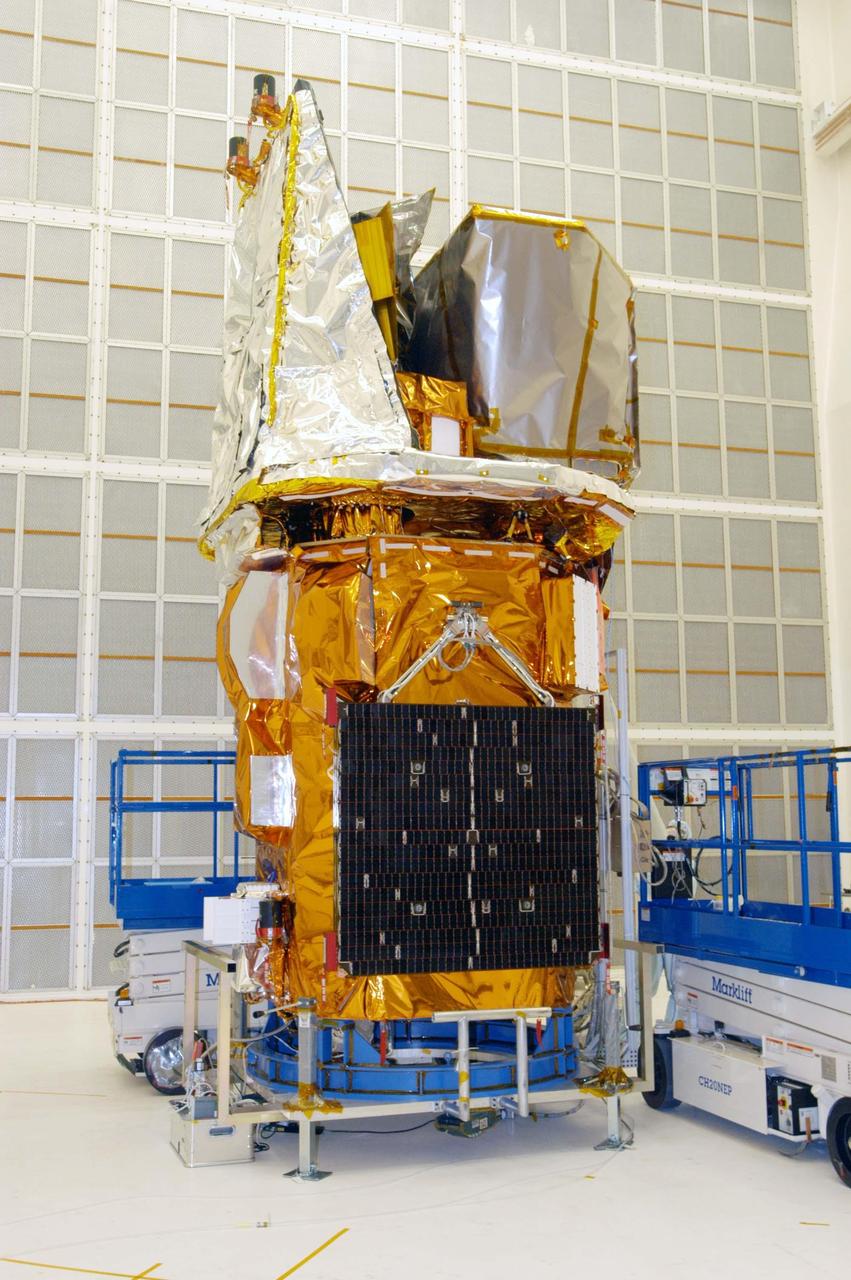

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Swift spacecraft is in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift has been wrapped with blankets to provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician works on a blanket installed around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.
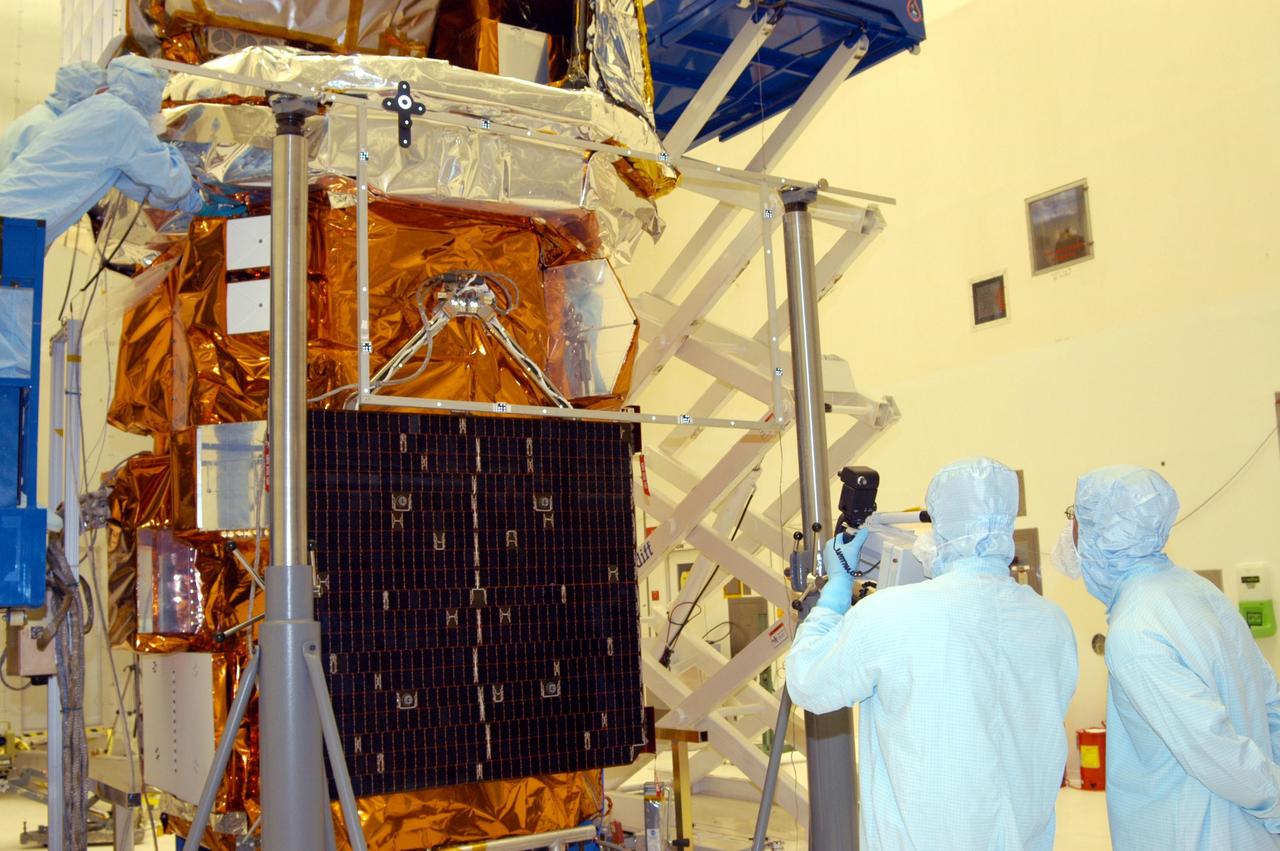

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, technicians perform blanket closeouts on the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technician Grace Miller-Swales does touch-up work on the Swift spacecraft in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is wrapped with blankets to provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
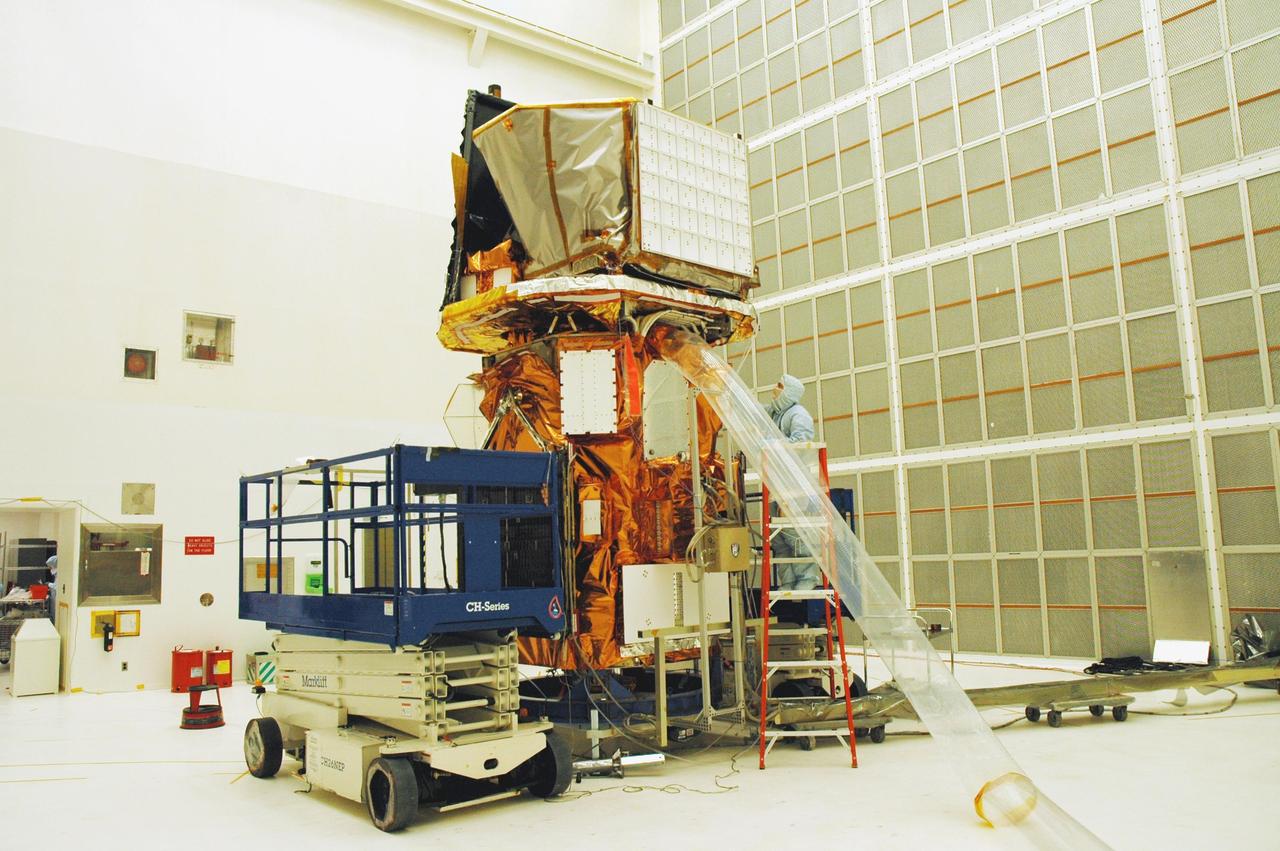

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, technicians install the blankets around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.
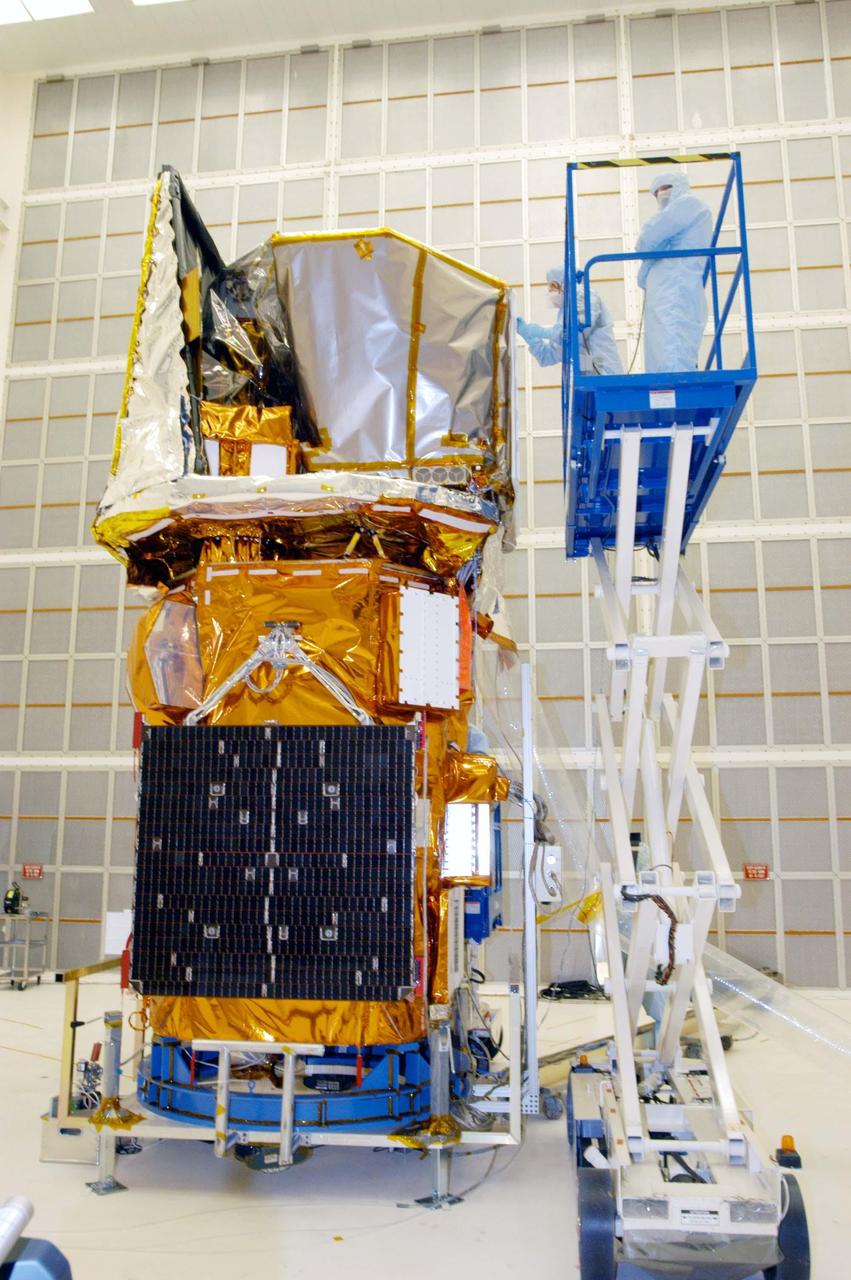

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technician Grace Miller-Swales (left) does touch-up work on the Swift spacecraft in Hangar AE at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. John DiBatilito is at right. Swift is wrapped with blankets to provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma-ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. The most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date, Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts during its 2-year mission.
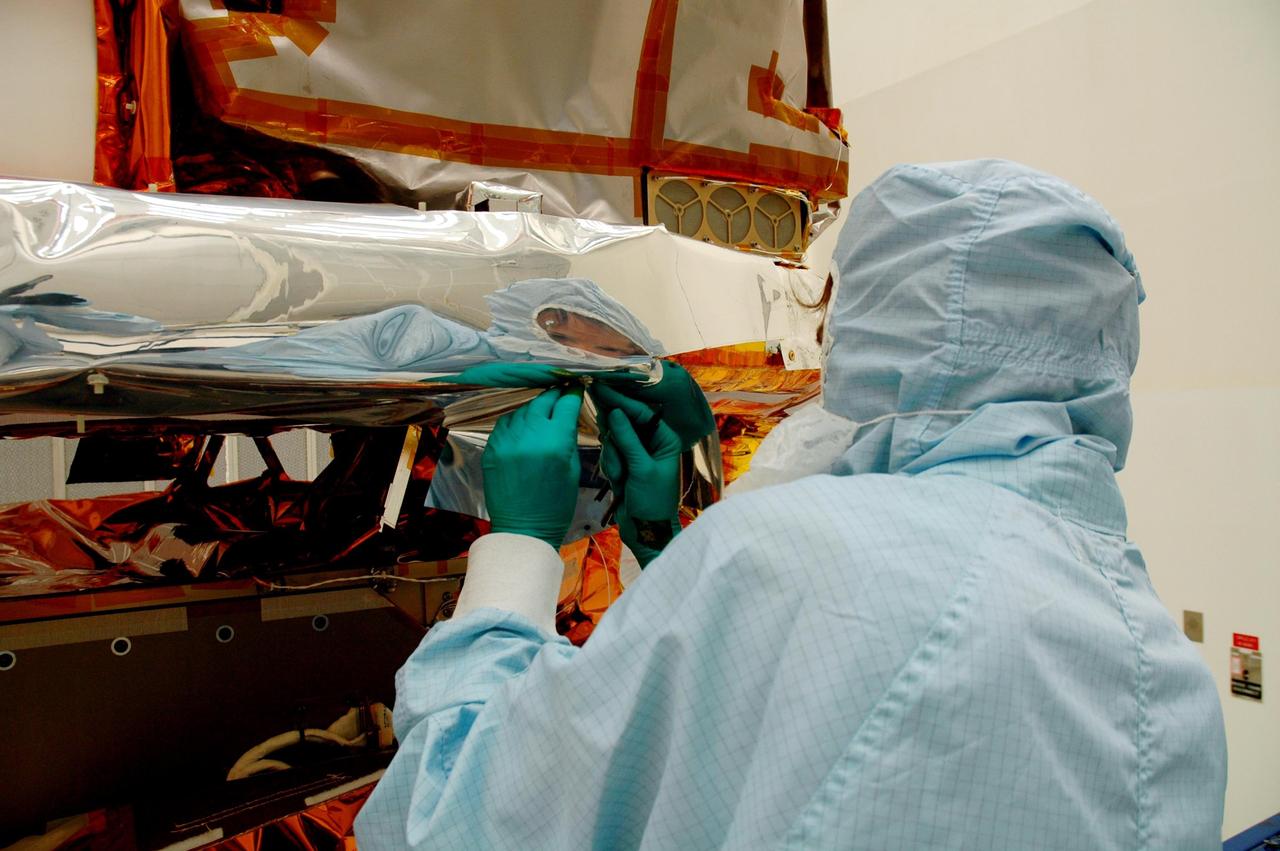

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Hangar AE, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, a technician (right) watches while another completes installation of the blankets around the Swift spacecraft. The blankets provide thermal stability during the mission. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst (GRB) science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is expected to observe more than 200 gamma-ray bursts - the most comprehensive study of GRB afterglows to date - during its 2-year mission.
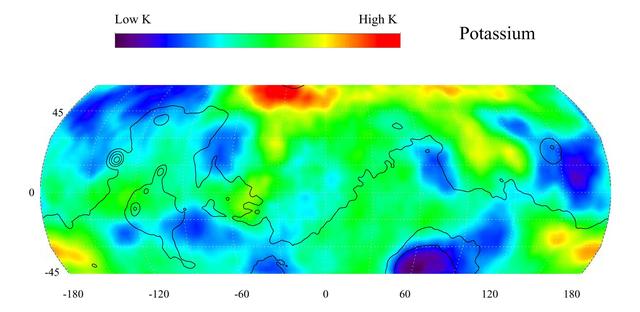
This gamma ray spectrometer map of the mid-latitude region of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element potassium. Potassium, having the chemical symbol K, is a naturally radioactive element and is a minor constituent of rocks on the surface of both Mars and Earth. The region of highest potassium content, shown in red, is concentrated in the northern part of Acidalia Planitia (centered near 55 degrees N, -30 degrees). Several areas of low potassium content, shown in blue, are distributed across the mid-latitudes, with two significant low concentrations, one associated with the Hellas Basin (centered near 35 degrees S, 70 degrees) and the other lying southeast of Elysium Mons (centered near 10 degrees N, 160 degrees). Contours of constant surface elevation are also shown. The long continuous line running from east to west marks the approximate separation of the younger lowlands in the north from the older highlands in the south. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04255
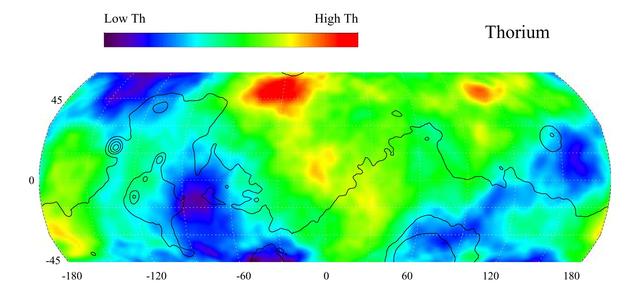
This gamma ray spectrometer map of the mid-latitude region of Mars is based on gamma-rays from the element thorium. Thorium is a naturally radioactive element that exists in rocks and soils in extremely small amounts. The region of highest thorium content, shown in red, is found in the northern part of Acidalia Planitia (50 degrees latitude, -30 degrees longitude). Areas of low thorium content, shown in blue, are spread widely across the planet with significant low abundances located to the north of Olympus Mons (near 55 degrees latitude, -155 degrees longitude), to the east of the Tharsis volcanoes (-10 degrees latitude, -80 degrees longitude) and to the south and east of Elysium Mons (20 degrees latitude, 160 degrees longitude). Contours of constant surface elevation are also shown. The long continuous contour line running from east to west marks the approximate separation of the younger lowlands in the north from the older highlands in the south. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04257
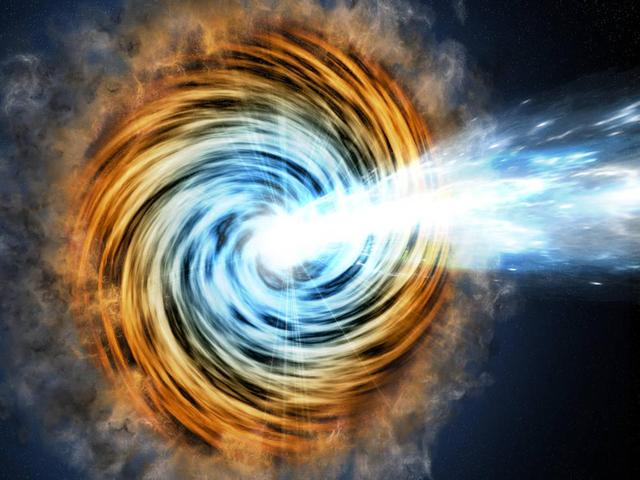

Black-hole-powered galaxies called blazars are the most common sources detected by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope. As matter falls toward the supermassive black hole at the galaxy's center, some of it is accelerated outward at nearly the speed of light along jets pointed in opposite directions. When one of the jets happens to be aimed in the direction of Earth, as illustrated here, the galaxy appears especially bright and is classified as a blazar. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20912

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.
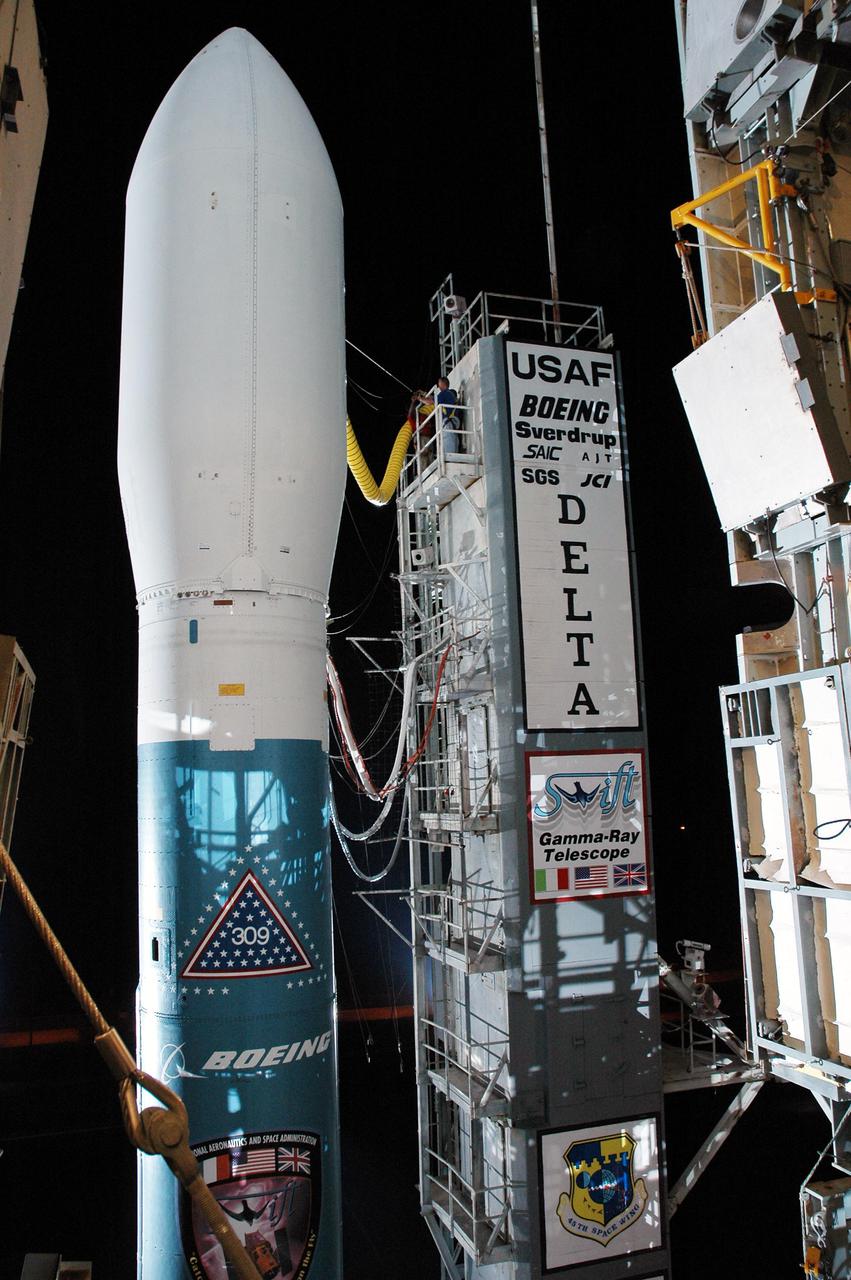

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.
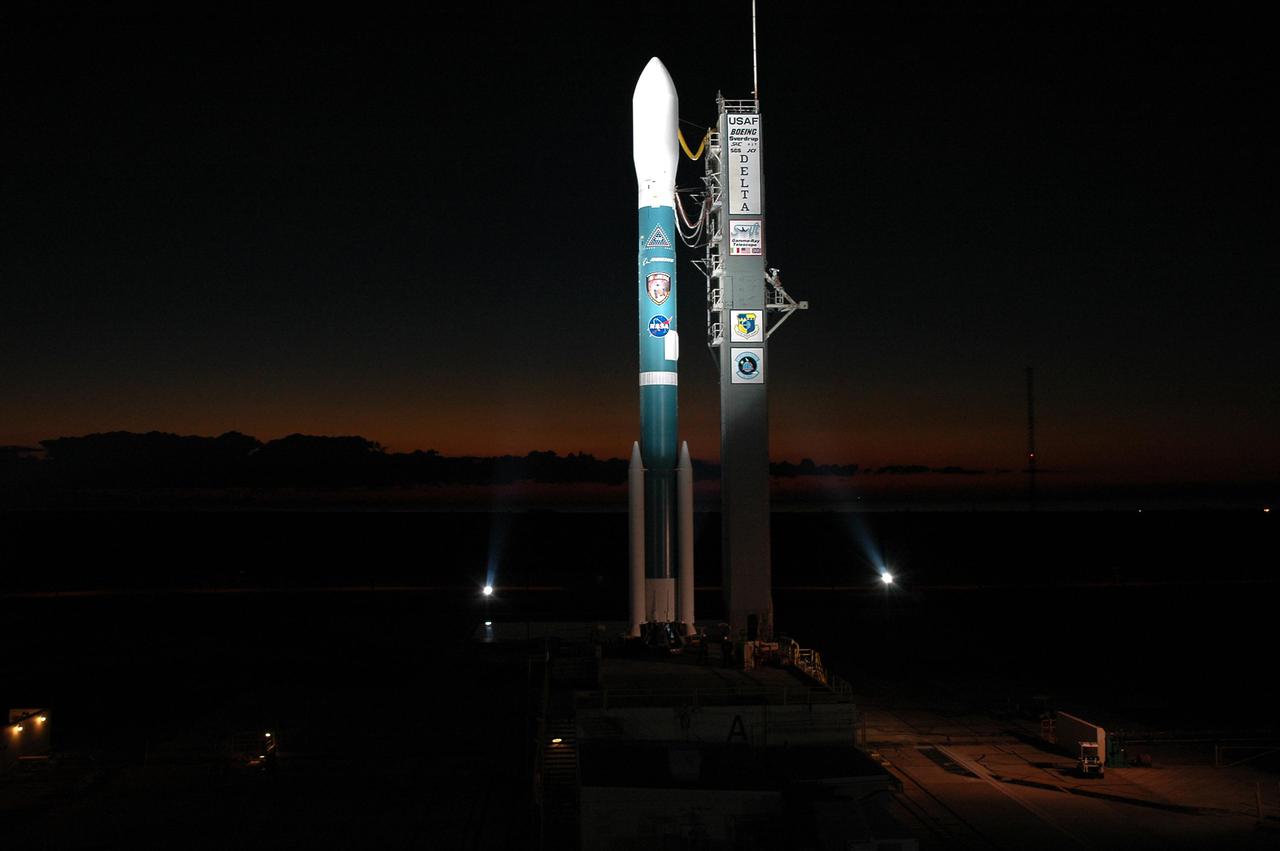

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A Boeing Delta II expendable launch vehicle stands ready to launch NASA’s Swift spacecraft following tower rollback at Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. Swift is scheduled to launch Nov. 20 at 12:10 p.m. EST.
![KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for NASA’s Swift spacecraft is poised for launch at the scheduled liftoff time of 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 17-A on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/04pd2384/04pd2384~medium.jpg)
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for NASA’s Swift spacecraft is poised for launch at the scheduled liftoff time of 12:16:00.611 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 17-A on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Swift is a first-of-its-kind multi-wavelength observatory dedicated to the study of gamma-ray burst science. Its three instruments will work together to observe GRBs and afterglows in the gamma ray, X-ray, ultraviolet and optical wavebands. [Photo courtesy of Scott Andrews]

The principal theme of the STS-37 patch, designed by astronaut crewmembers, is the primary payload -- Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO) -- and its relationship to the Space Shuttle. The Shuttle and the GRO are both depicted on the patch and are connected by a large gamma. The gamma symbolizes both the quest for gamma rays by GRO as well as the importance of the relationship between the manned and unmanned elements of the United States space program. The Earth background shows the southern portion of the United States under a partial cloud cover while the two fields of three and seven stars, respectively, refer to the STS-37 mission designation.
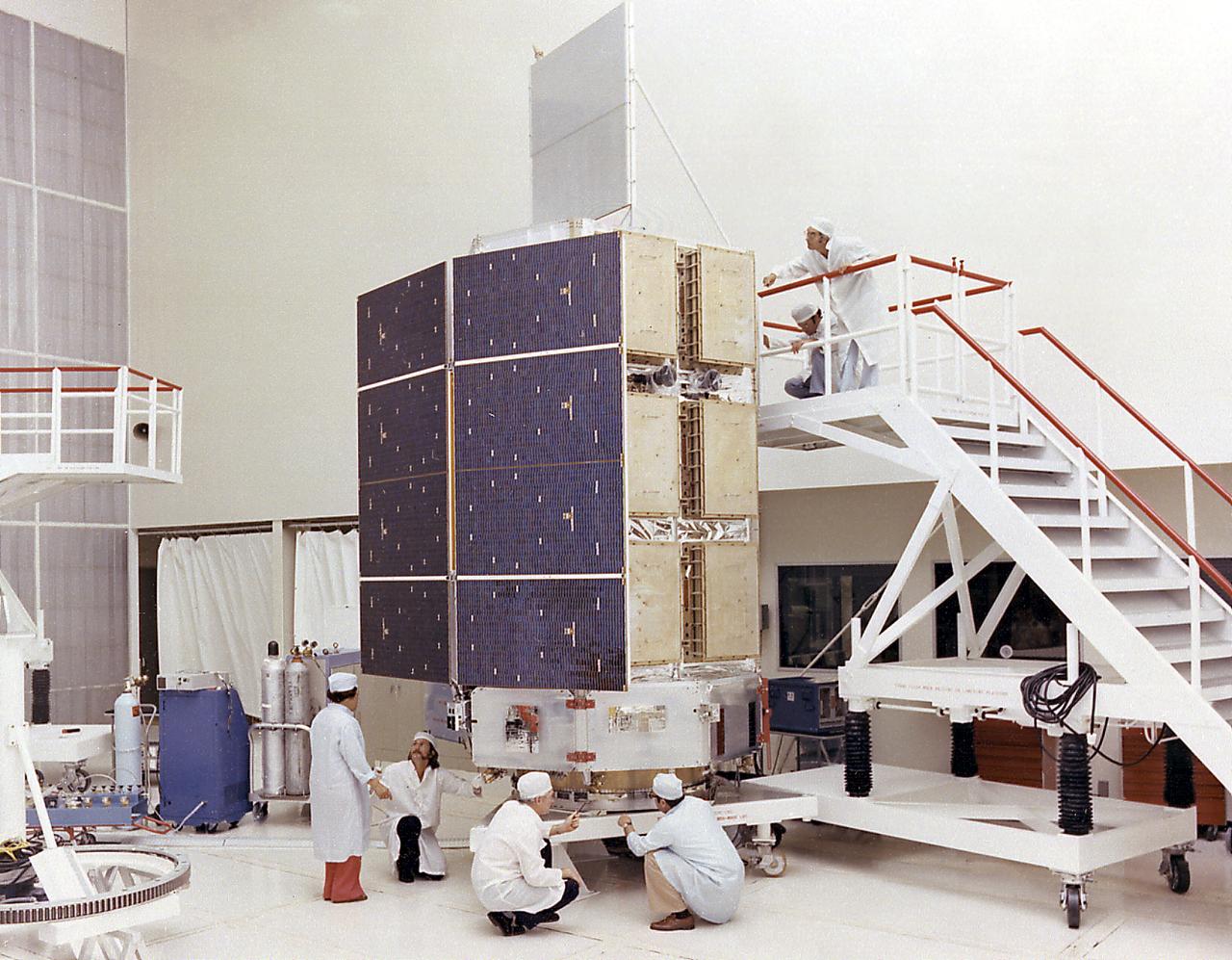

This photograph shows the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3 being assembled at TRW, Inc. Designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the objectives of the HEAO-3 were to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the project management responsibilities for the HEAO missions.
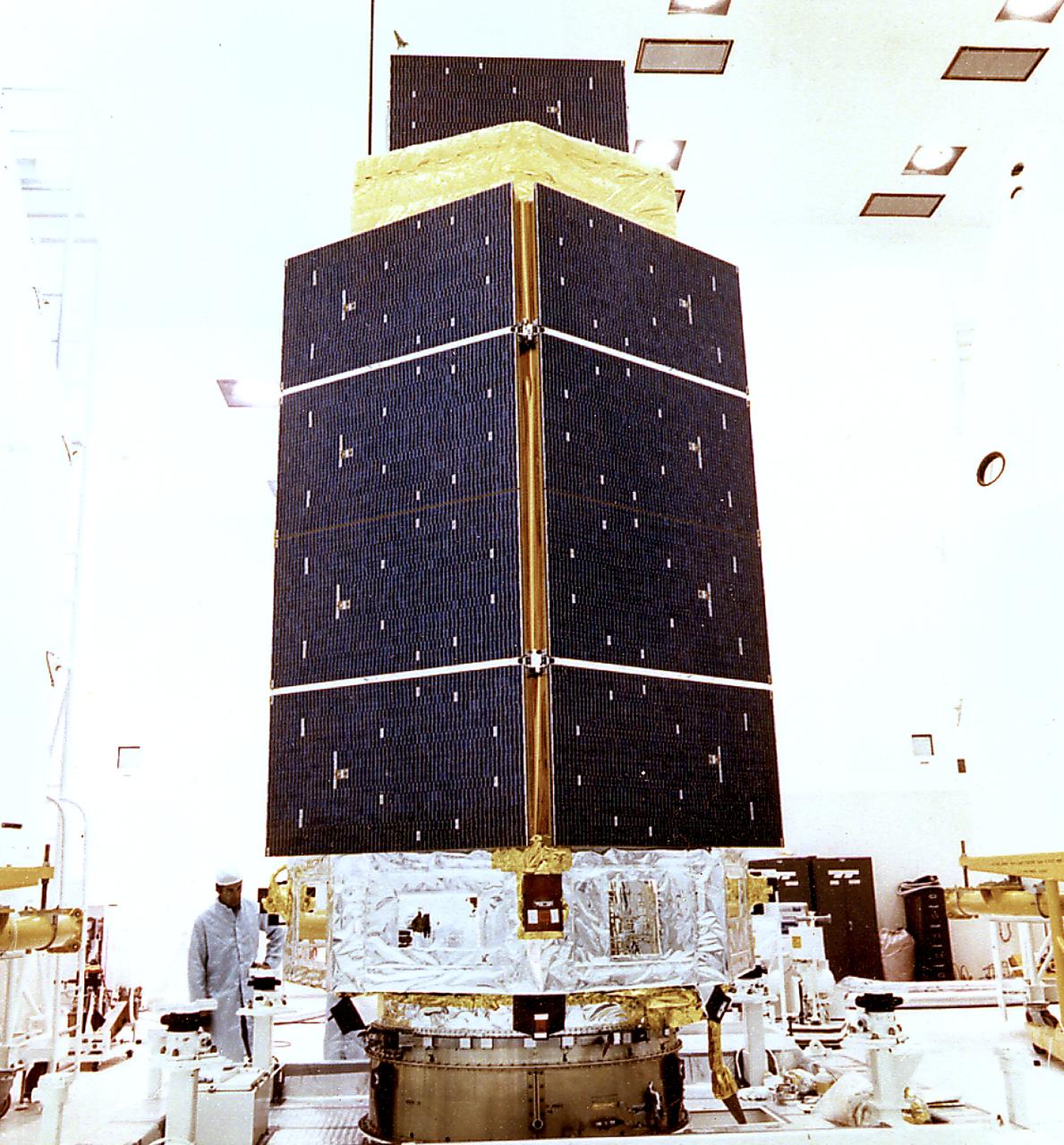

This photograph shows the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3 being prepared for encapsulation. Designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the objectives of the HEAO-3 were to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the project management responsibilities for the HEAO missions.

This artist's concept depicts the third observatory, the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3 in orbit. Designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the HEAO-3's mission was to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit.
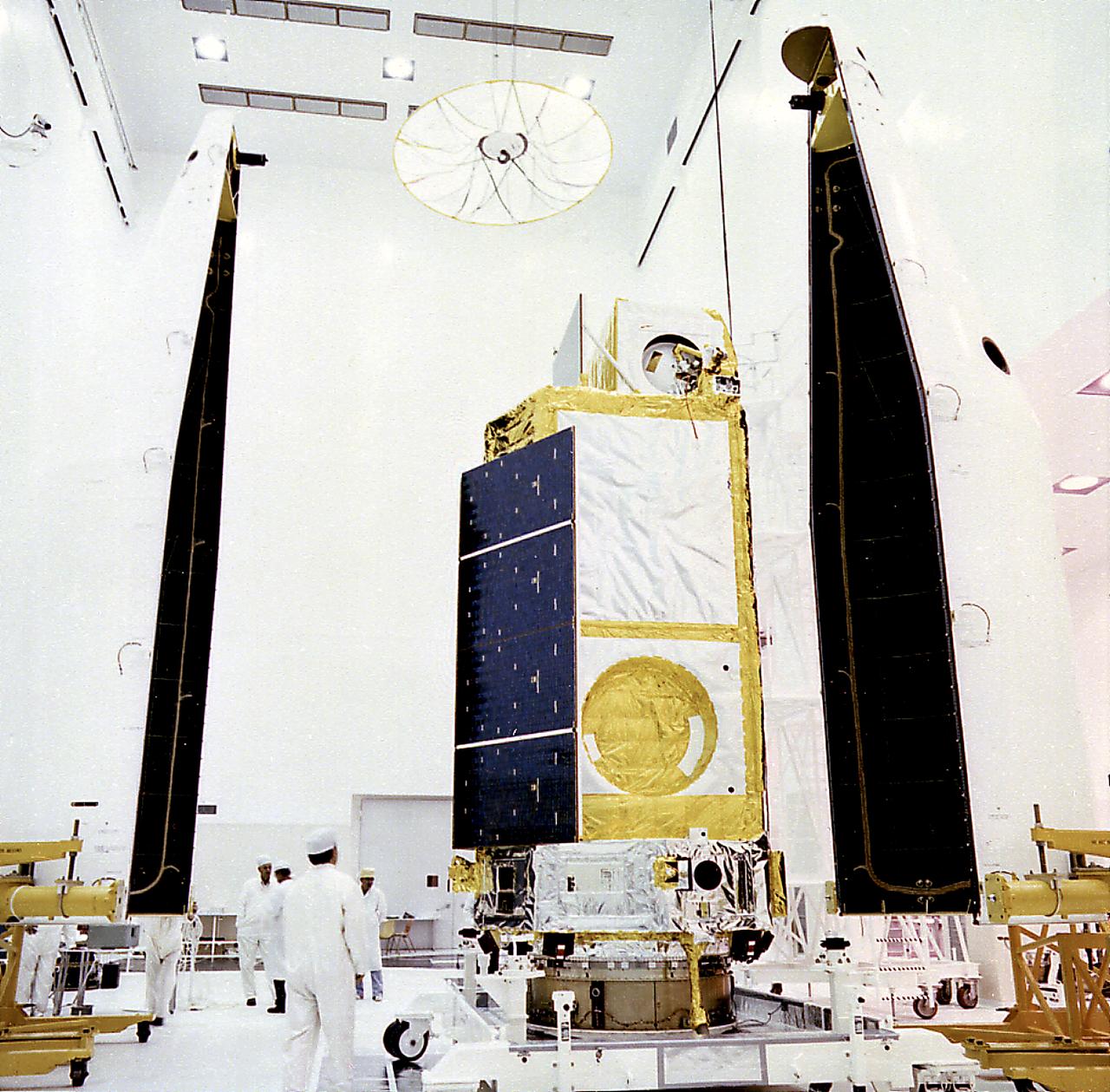
This photograph was taken during encapsulation of the High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO)-3. Designed and developed by TRW, Inc. under the direction of the Marshall Space Flight Center, the objectives of the HEAO-3 were to survey and map the celestial sphere for gamma-ray flux and make detailed measurements of cosmic-ray particles. It carried three scientific experiments: a gamma-ray spectrometer, a cosmic-ray isotope experiment, and a heavy cosmic-ray nuclei experiment. The HEAO-3 was originally identified as HEAO-C but the designation was changed once the spacecraft achieved orbit. The Marshall Space Flight Center had the project management responsibilities for the HEAO missions.