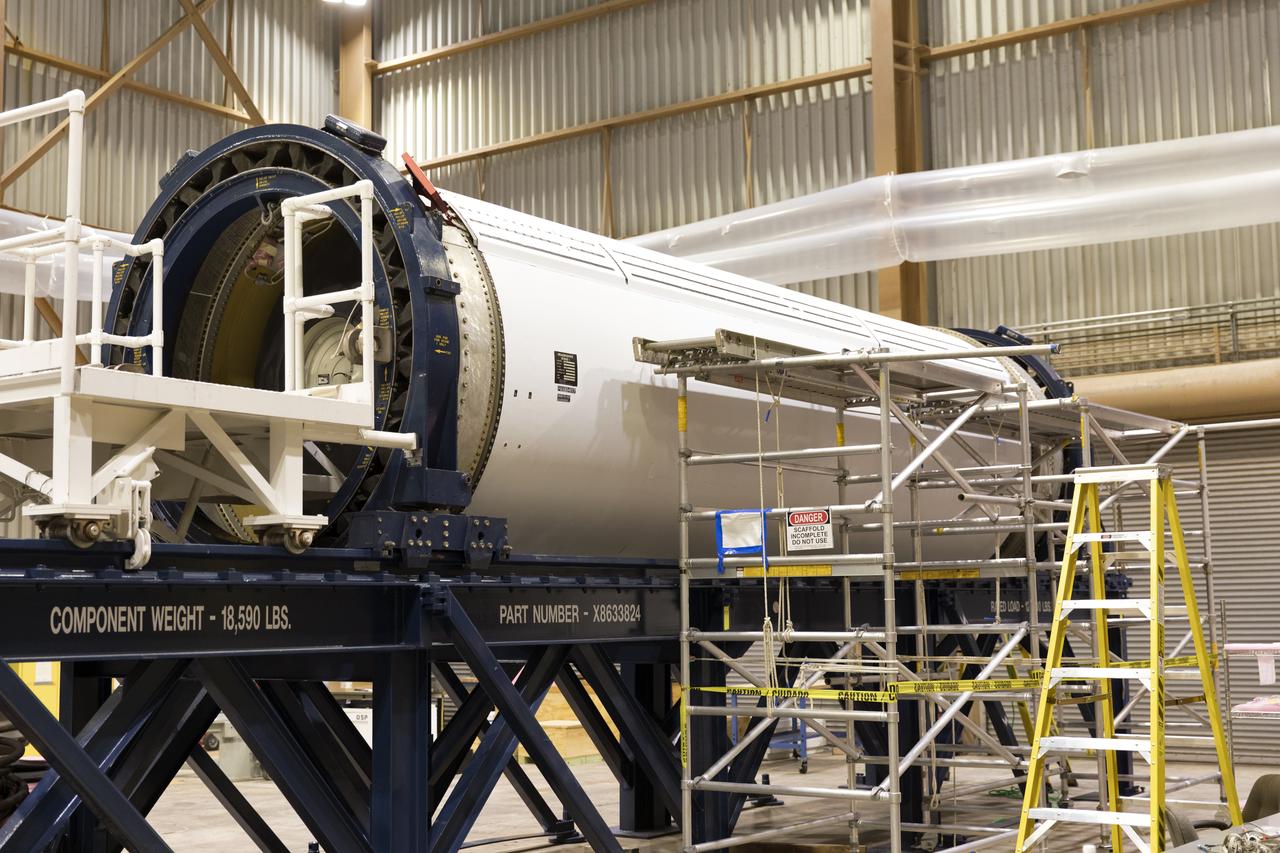

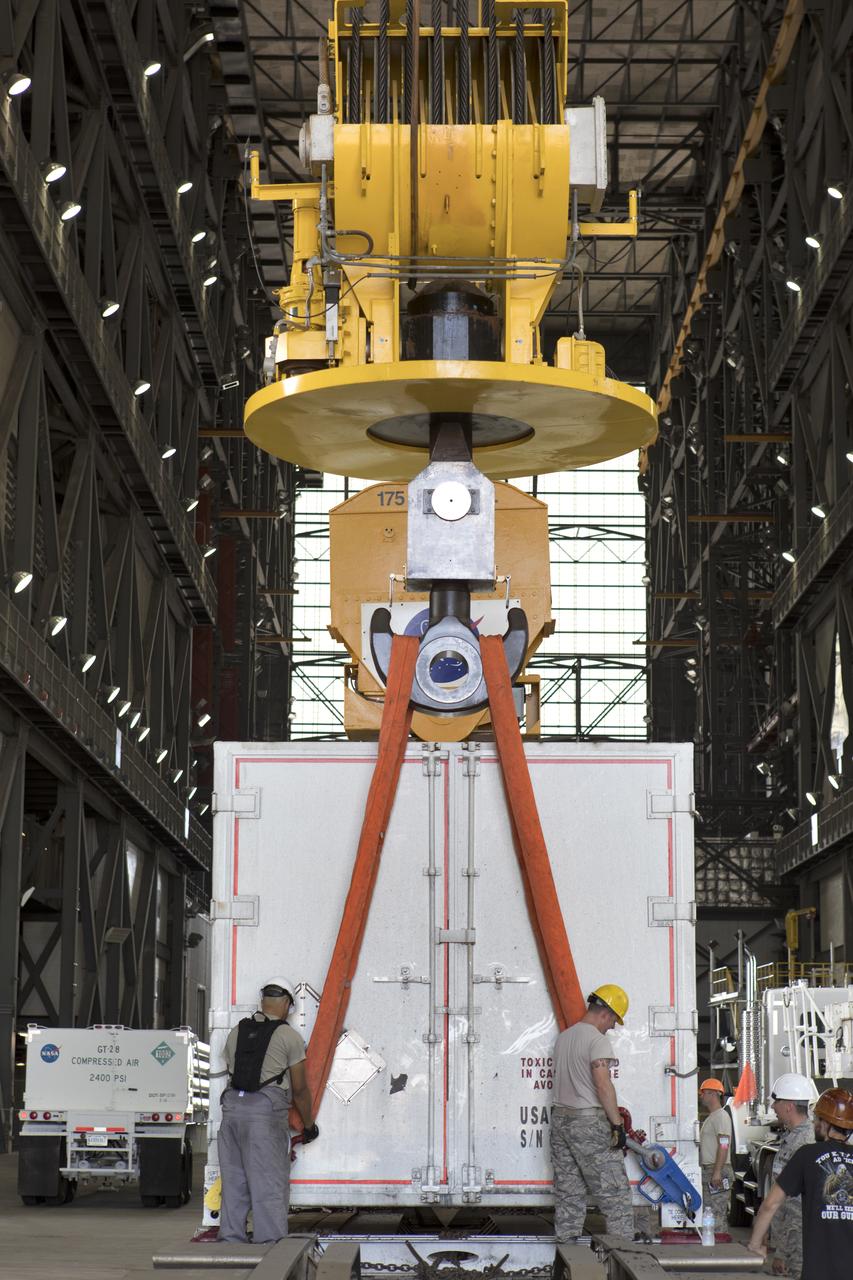
The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
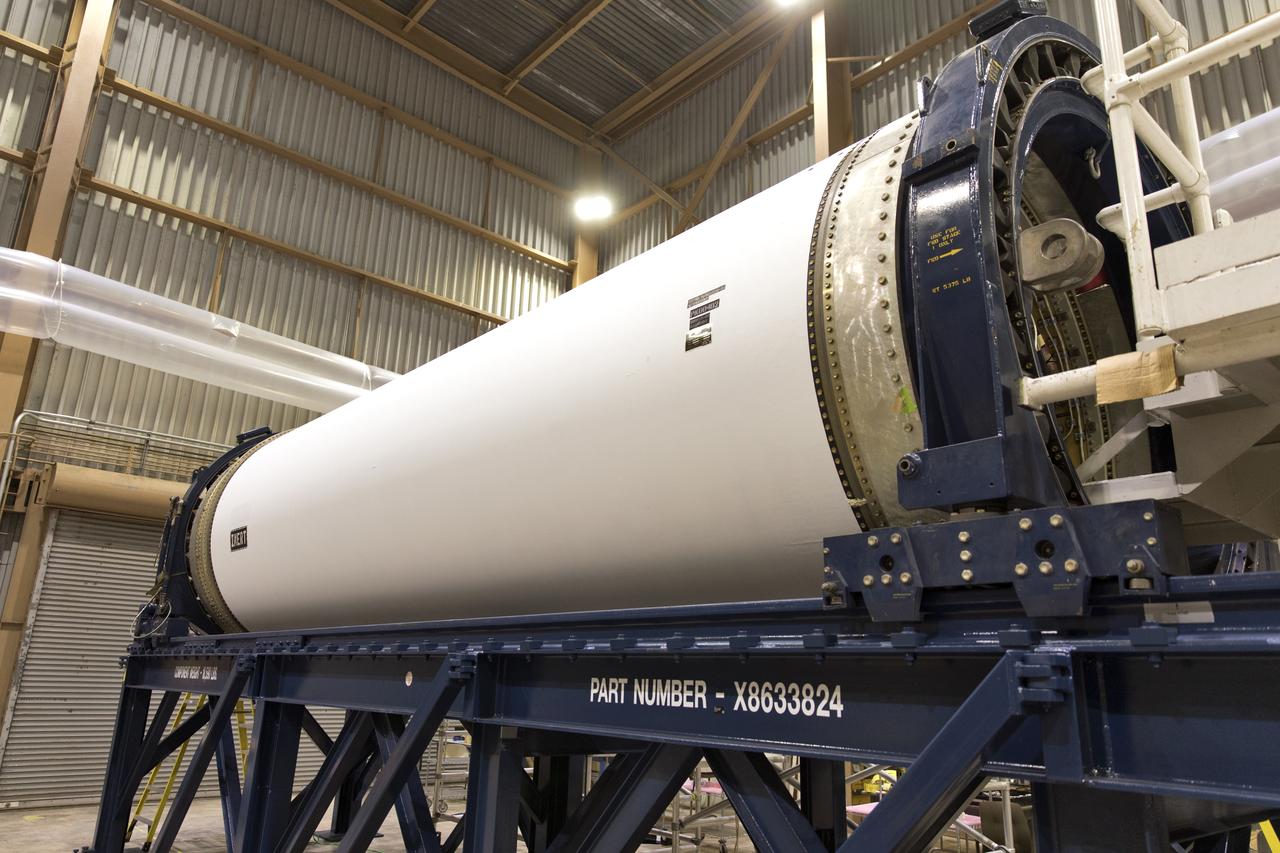

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
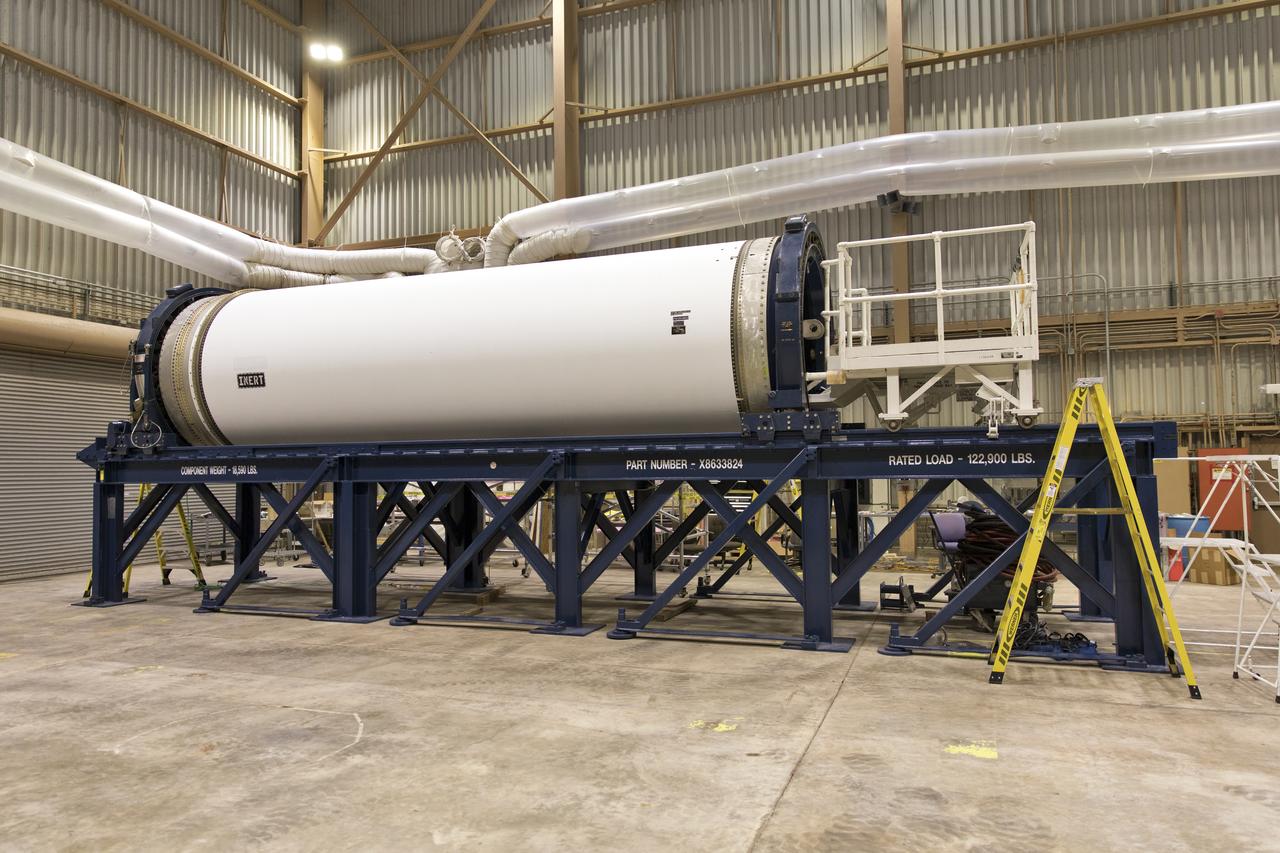

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
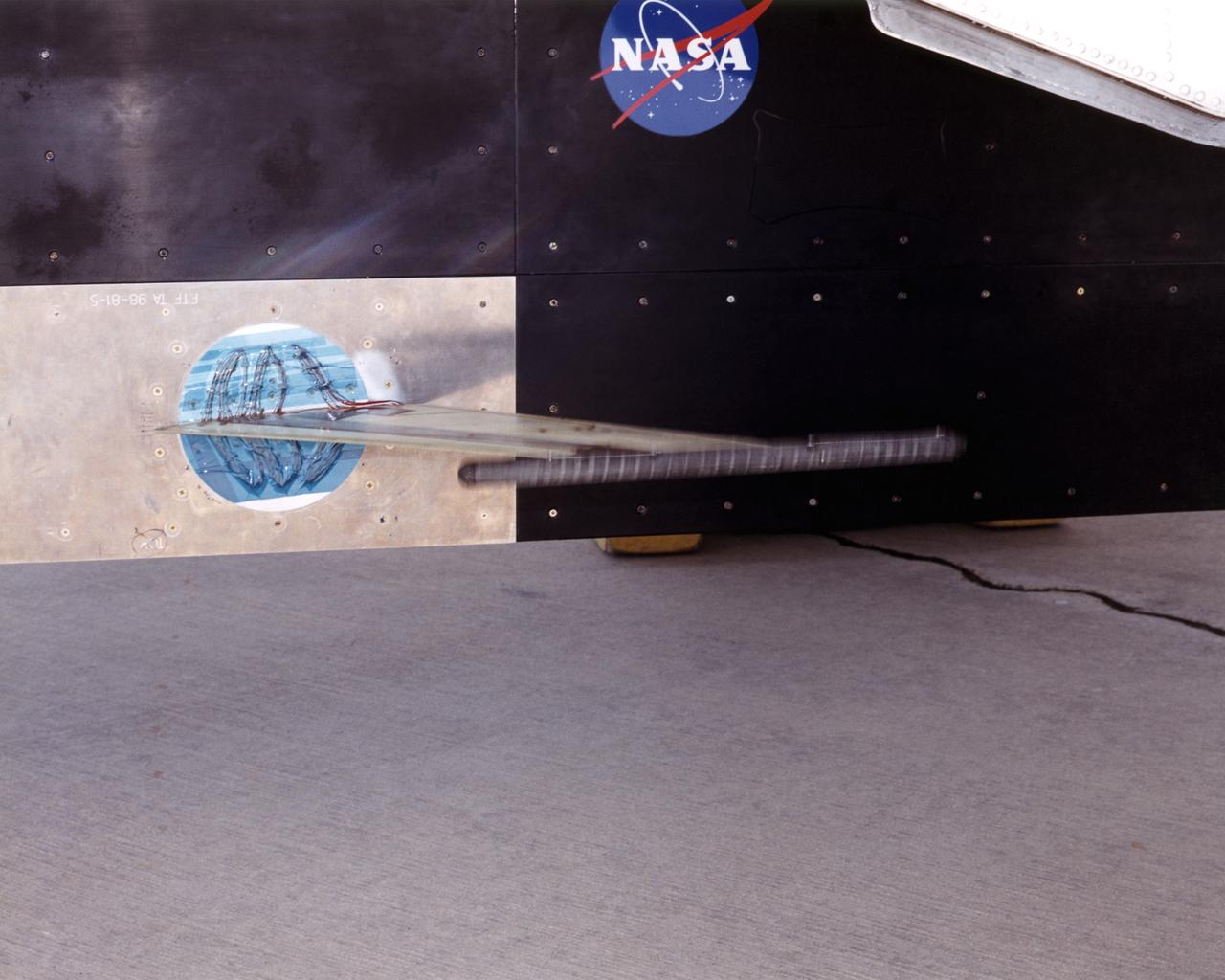
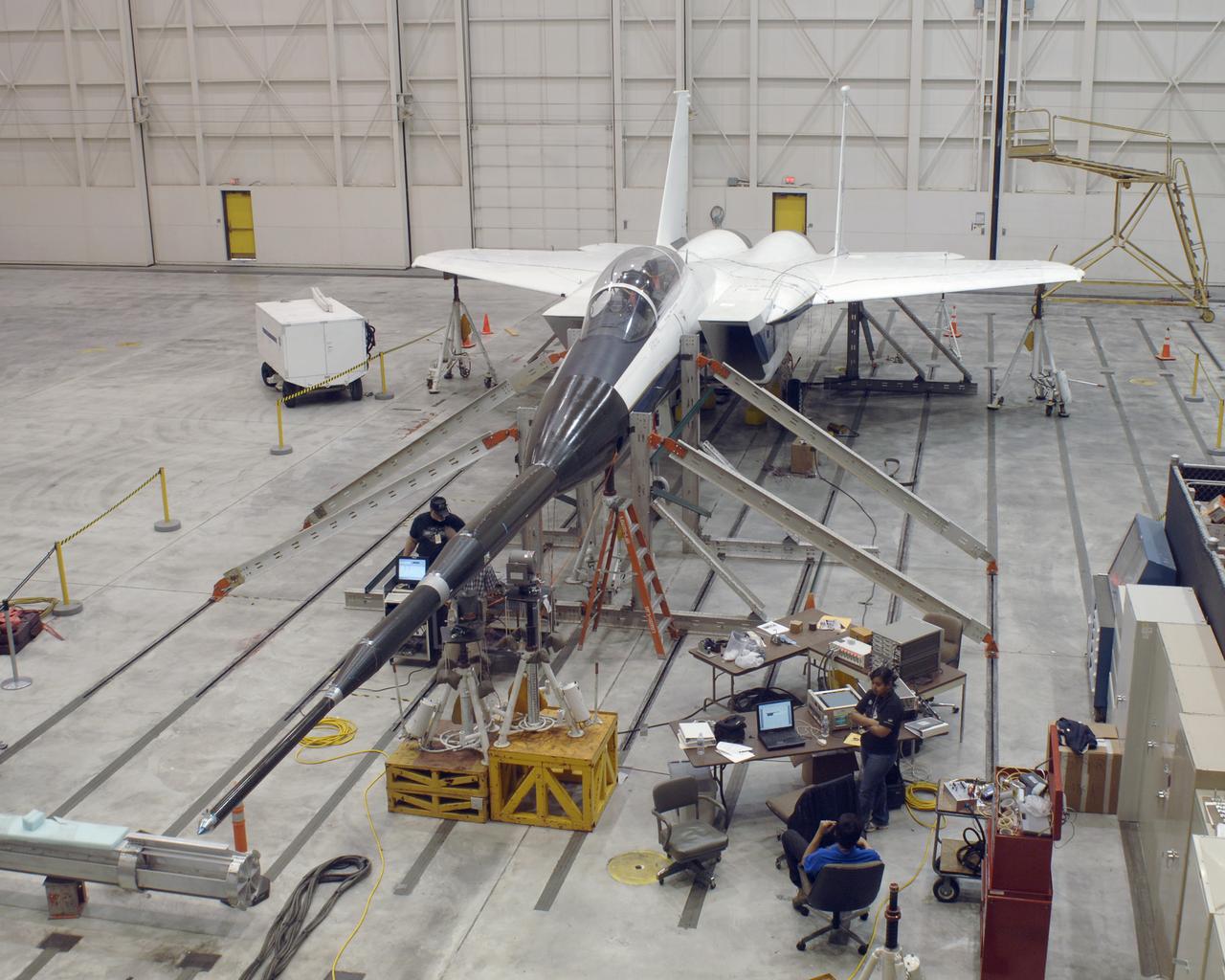
The Aerostructures Test Wing (ATW) experiment, which consisted of an 18-inch carbon fiber test wing with surface-mounted piezoelectric strain actuators, undergoing ground testing prior to flight on Dryden's F-15B Research Testbed aircraft
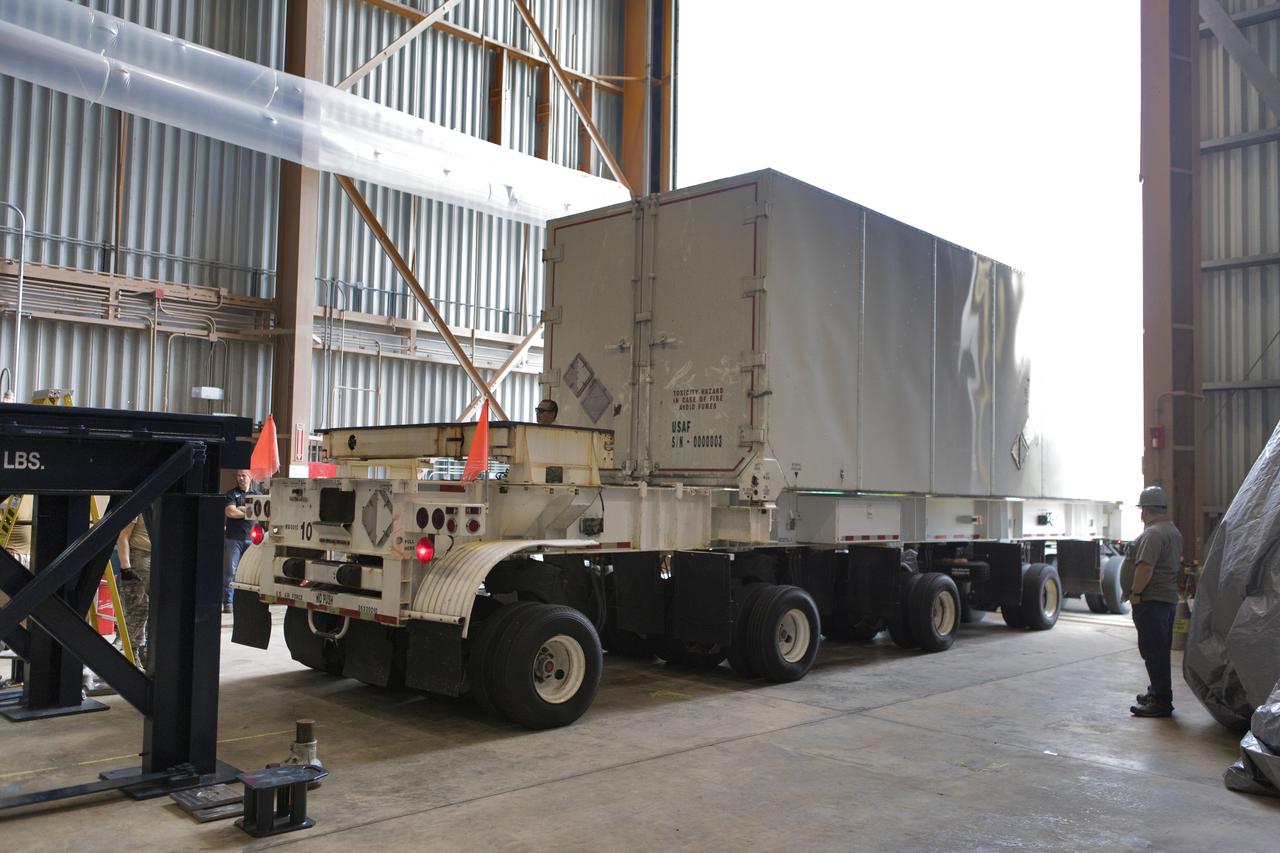

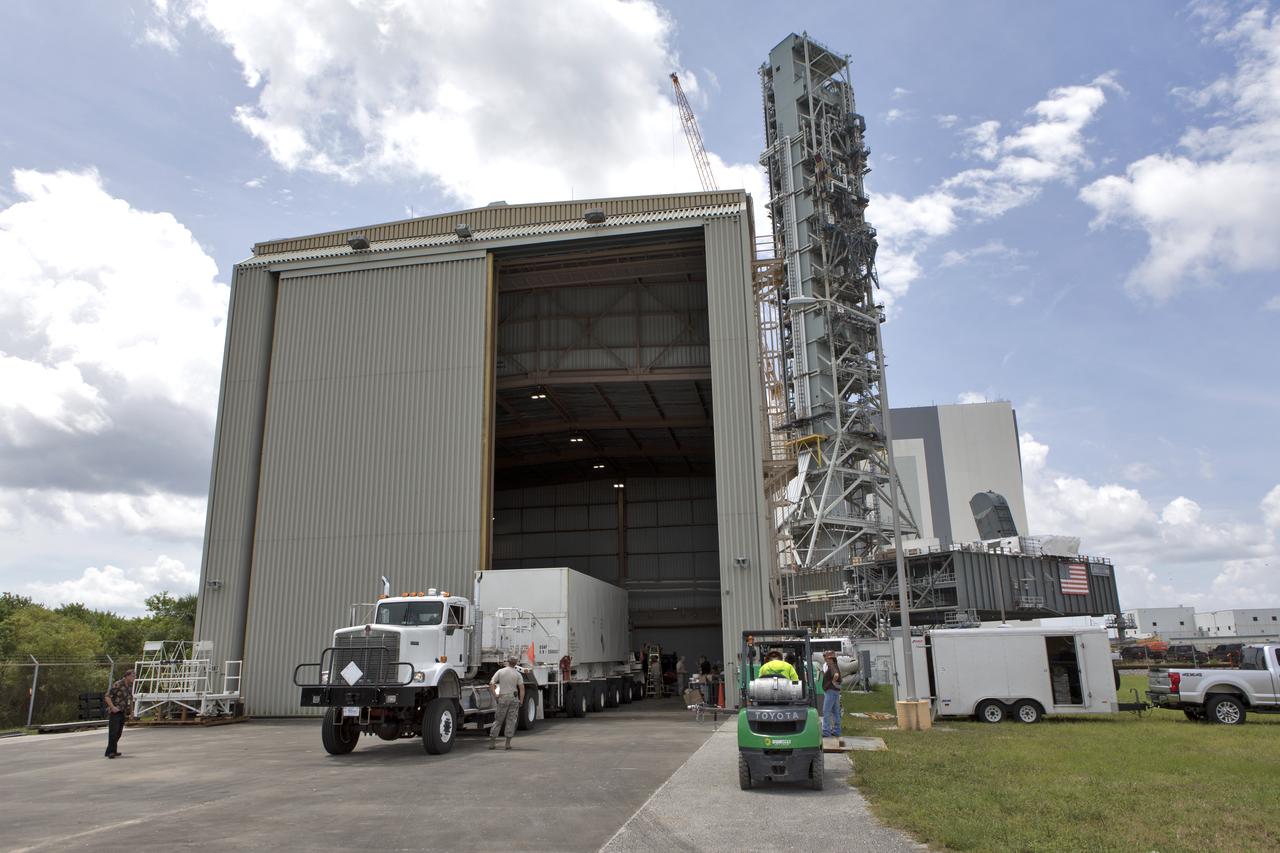
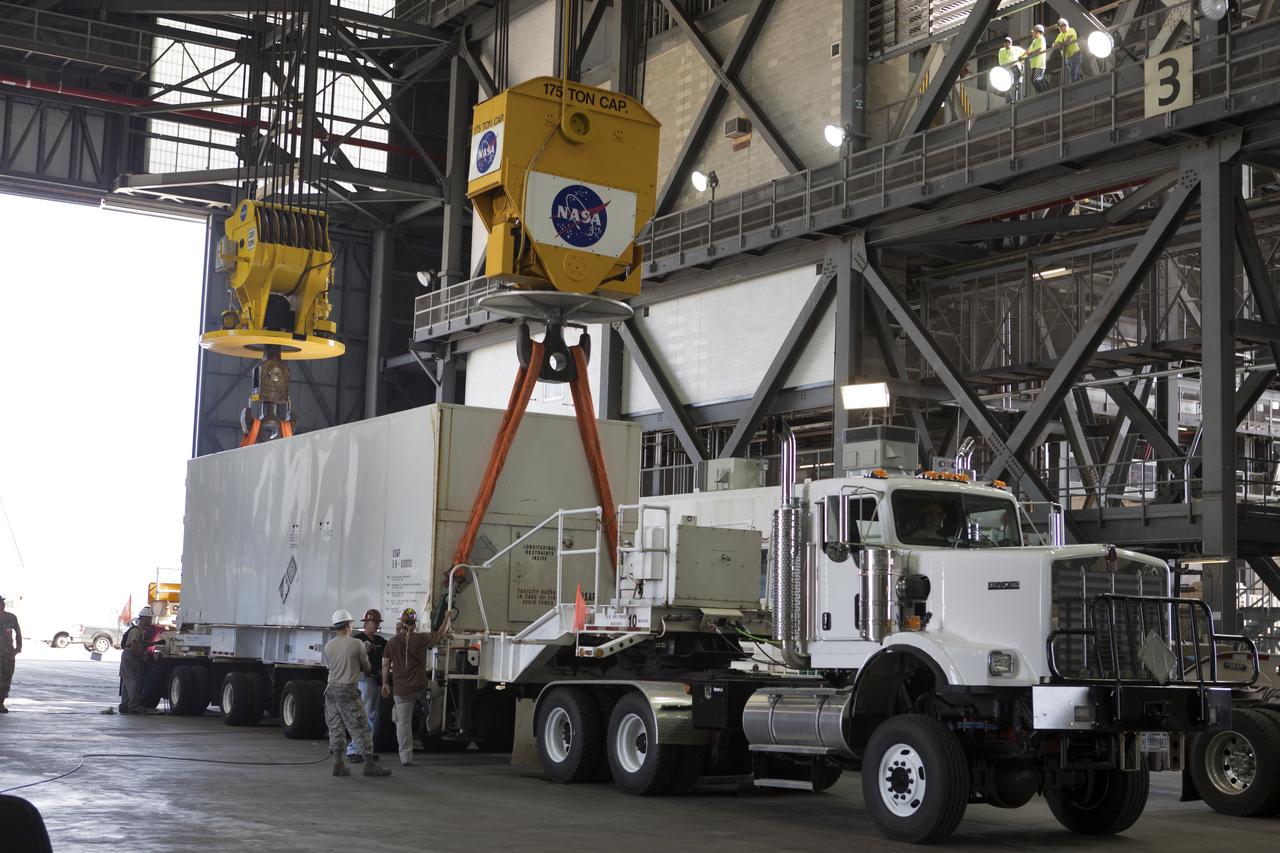
Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
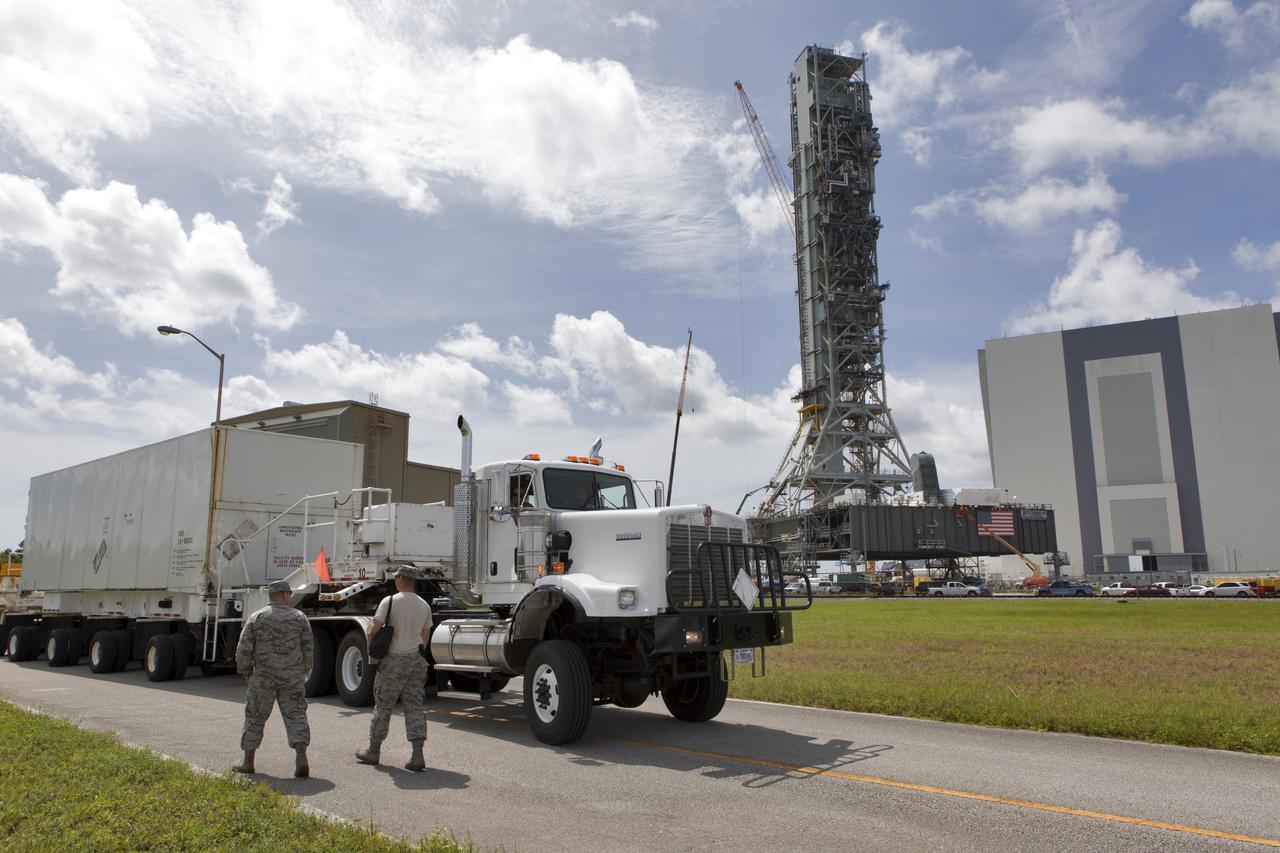

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
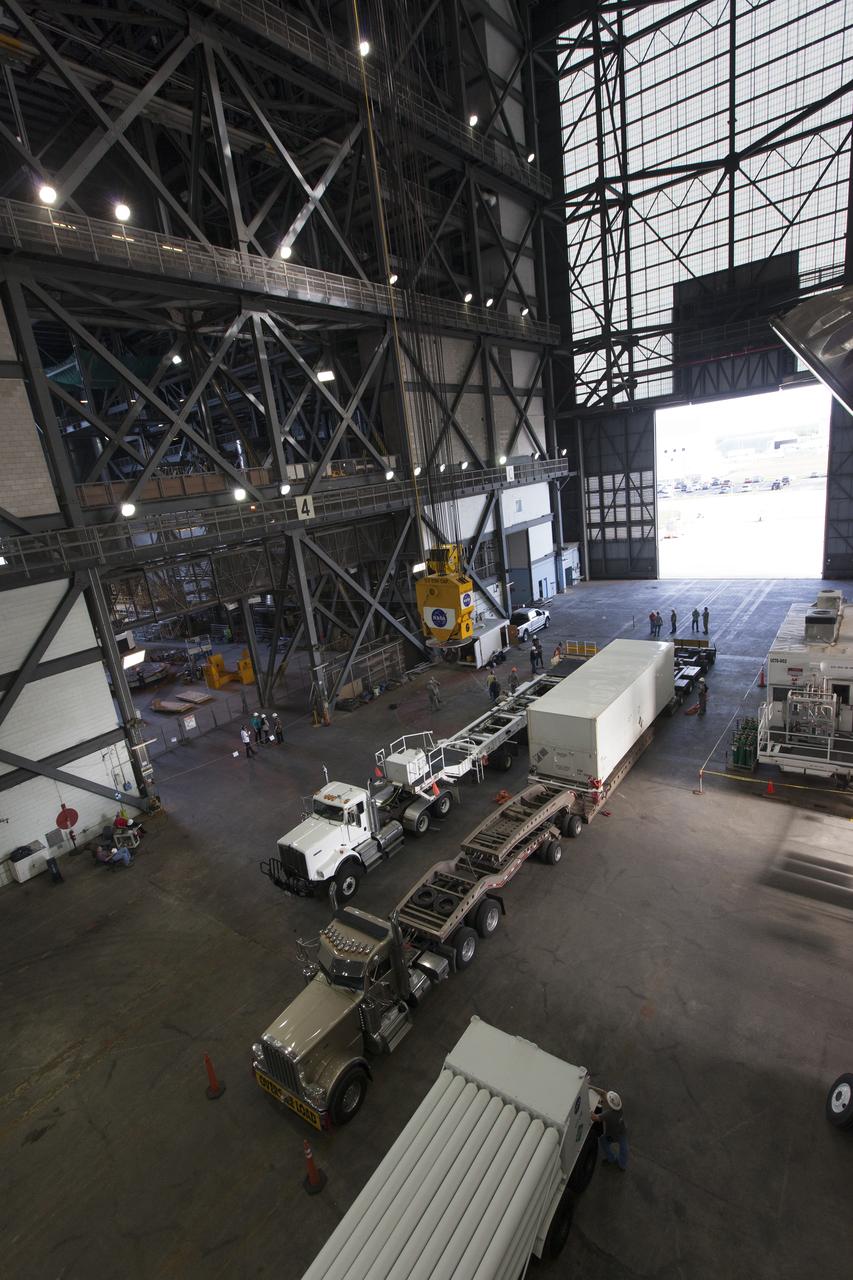

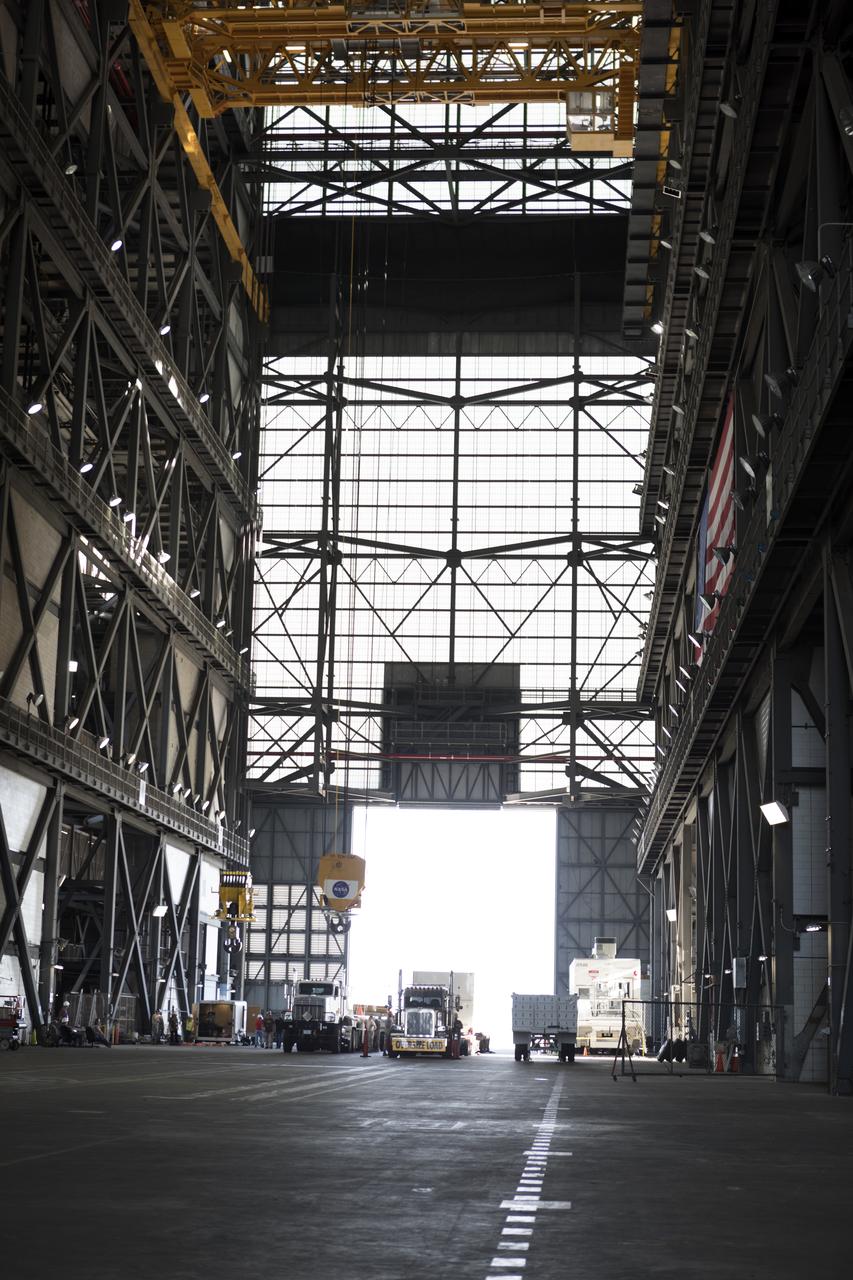
The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
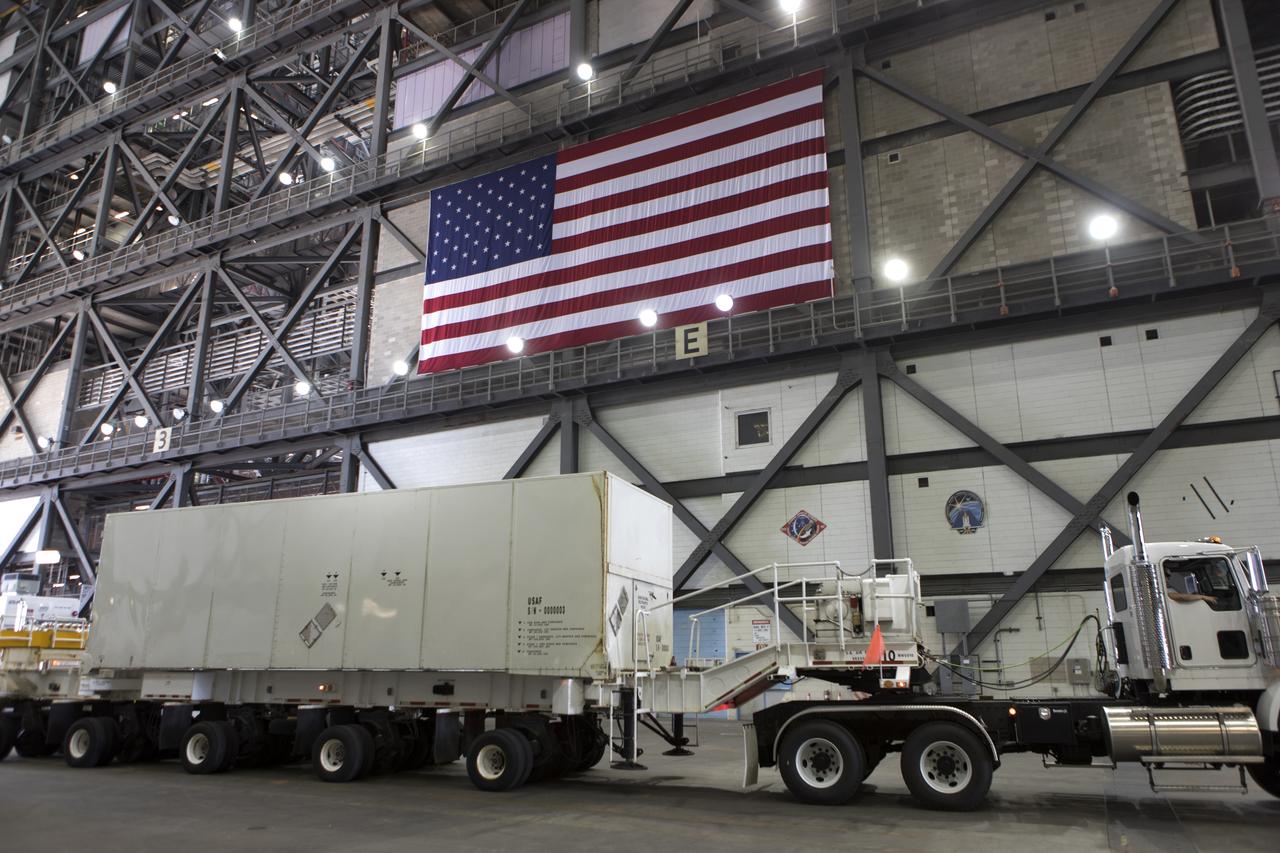

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) will be moved from the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
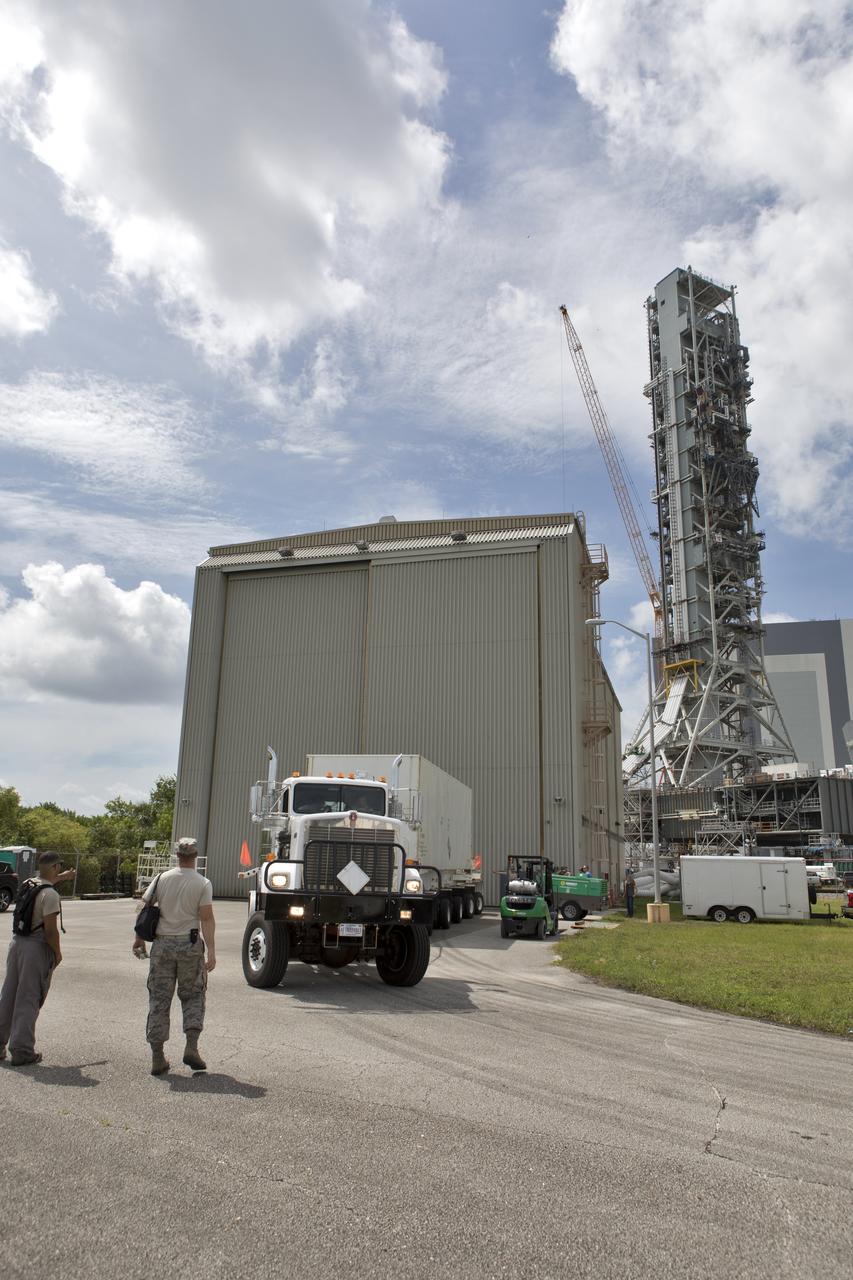

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
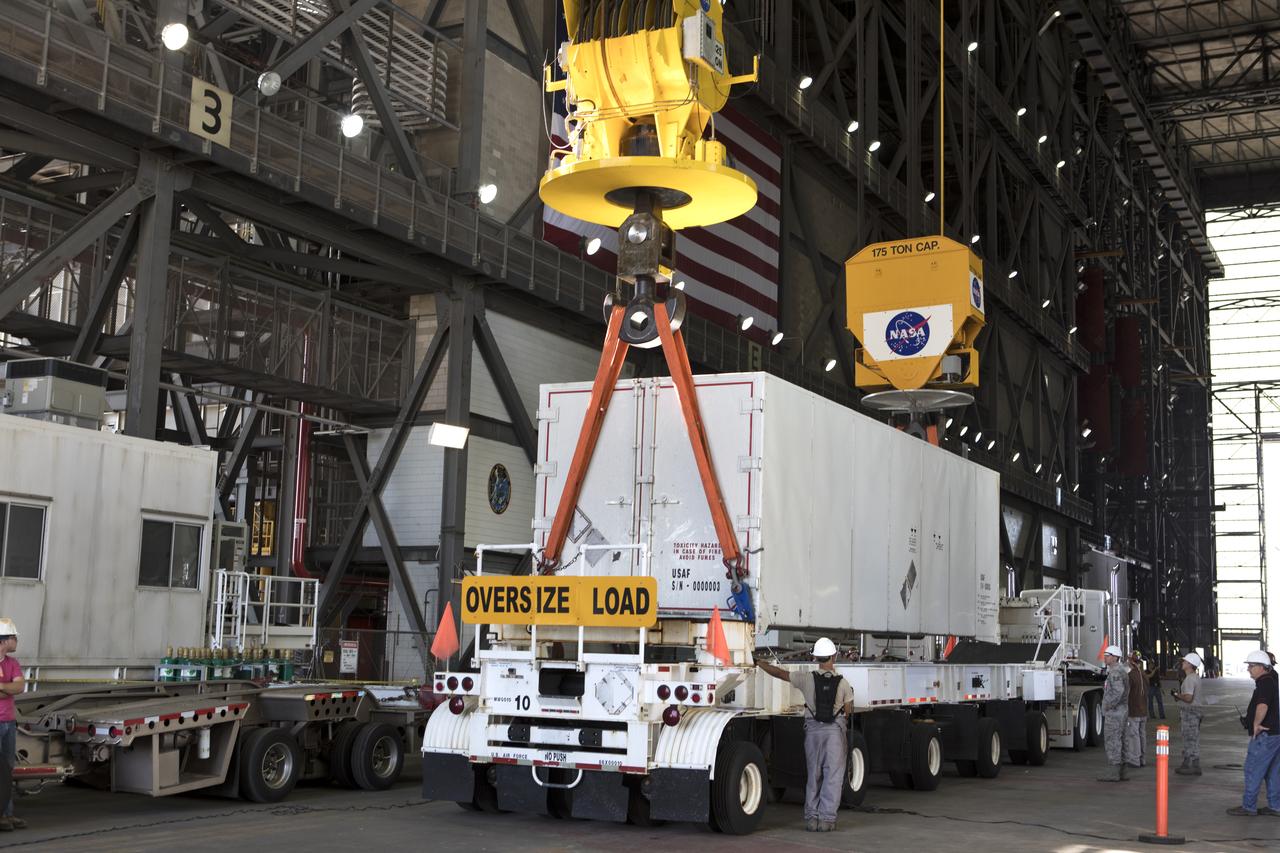

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians on the Test Operations Support Contract attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
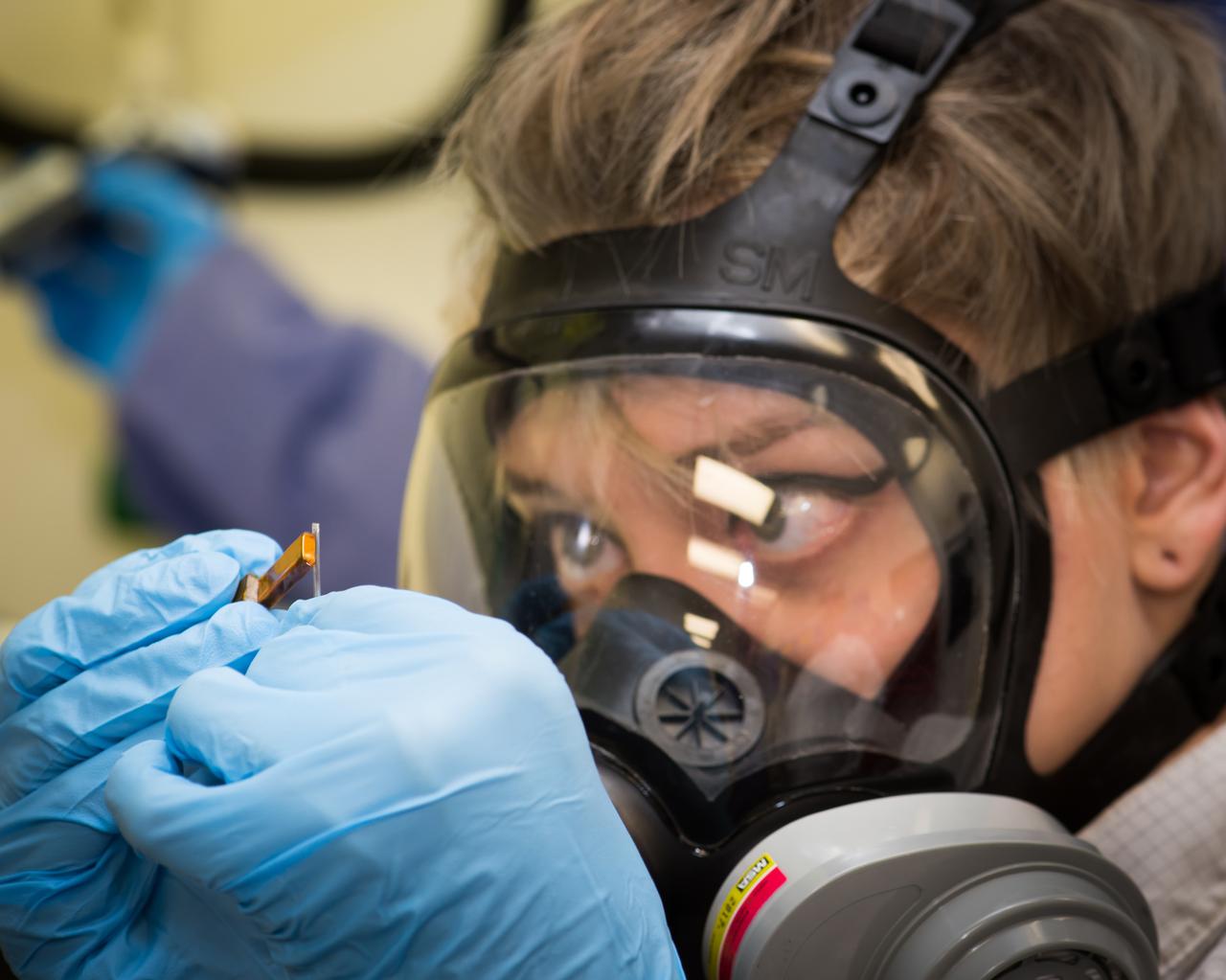

Light Microscopy Modle, LMM, Ground Unit Testing, GU. Control Systems Engineer using a small magnet to maneuver a 1mm metal stir-bar into a colloid sample fluid-filled capillary. The capillary tubes of sample fluid will be filled and sealed. The sample fluid supplied by a Principal Investigator typically contains some hazardous/toxic chemicals that she must ensure will not leak and put the astronauts at risk. On-orbit on the LMM, ‘insitu mixing’ is used, which uses electromagnetic inductors to stimulate the metal stir-bar to mix the fluid within the sealed capillary.
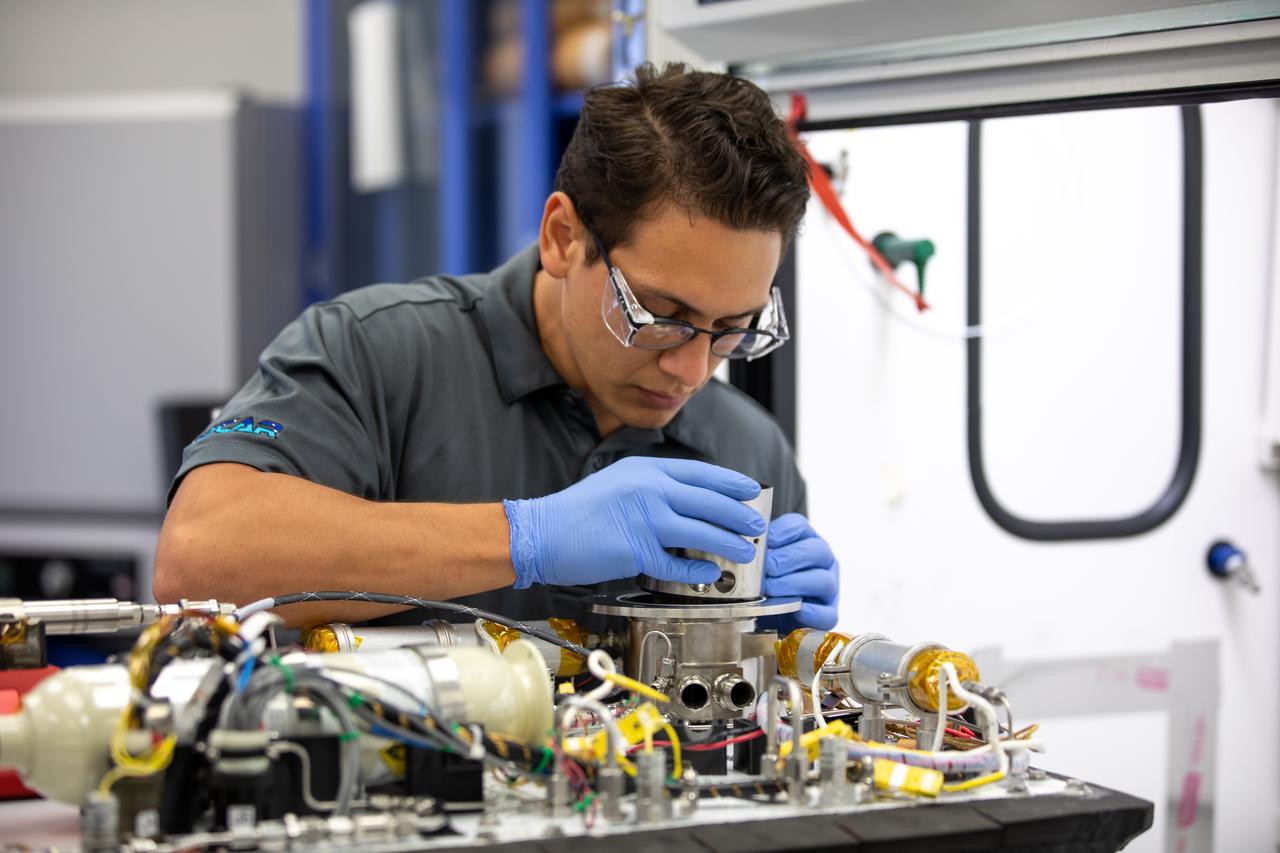

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
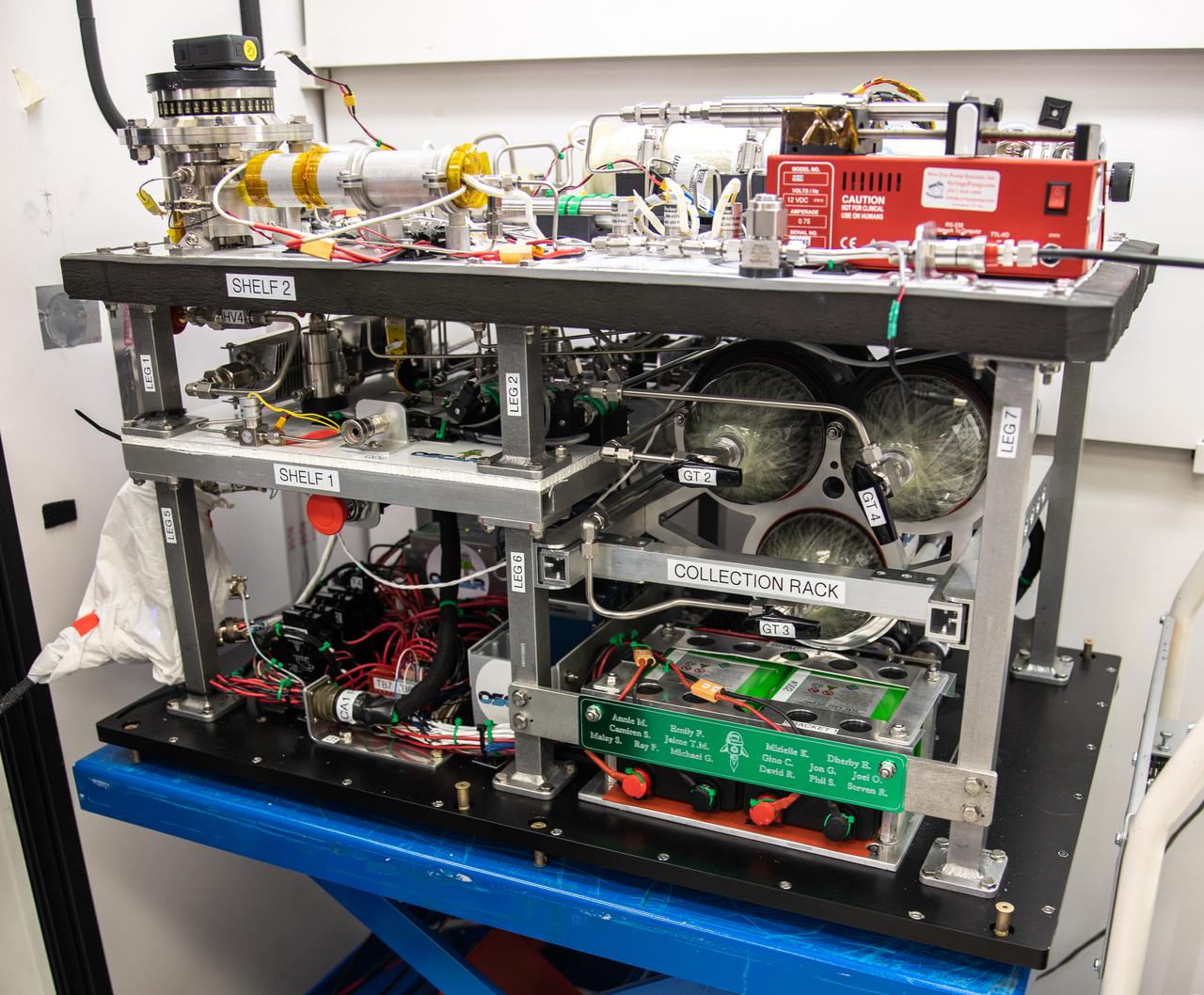
Members of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team perform ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
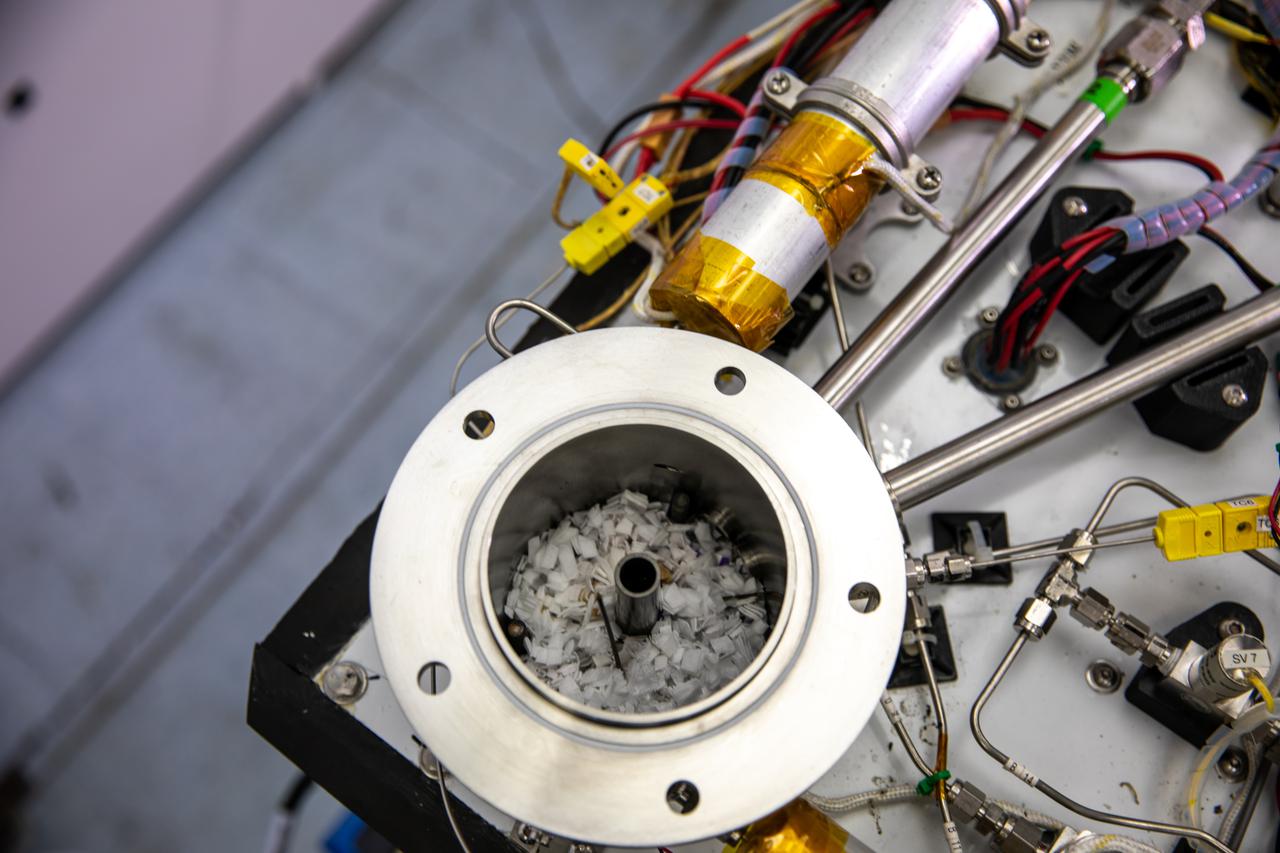
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
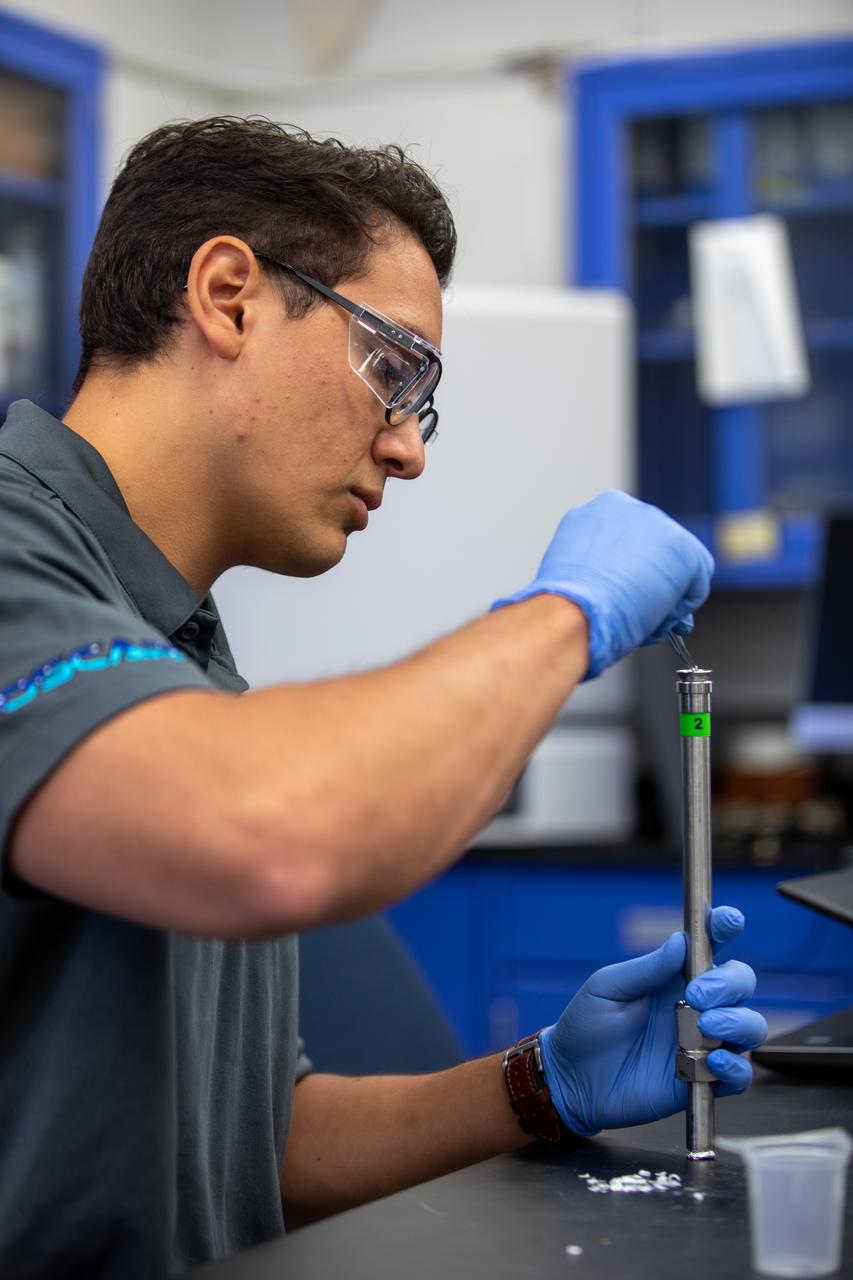

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
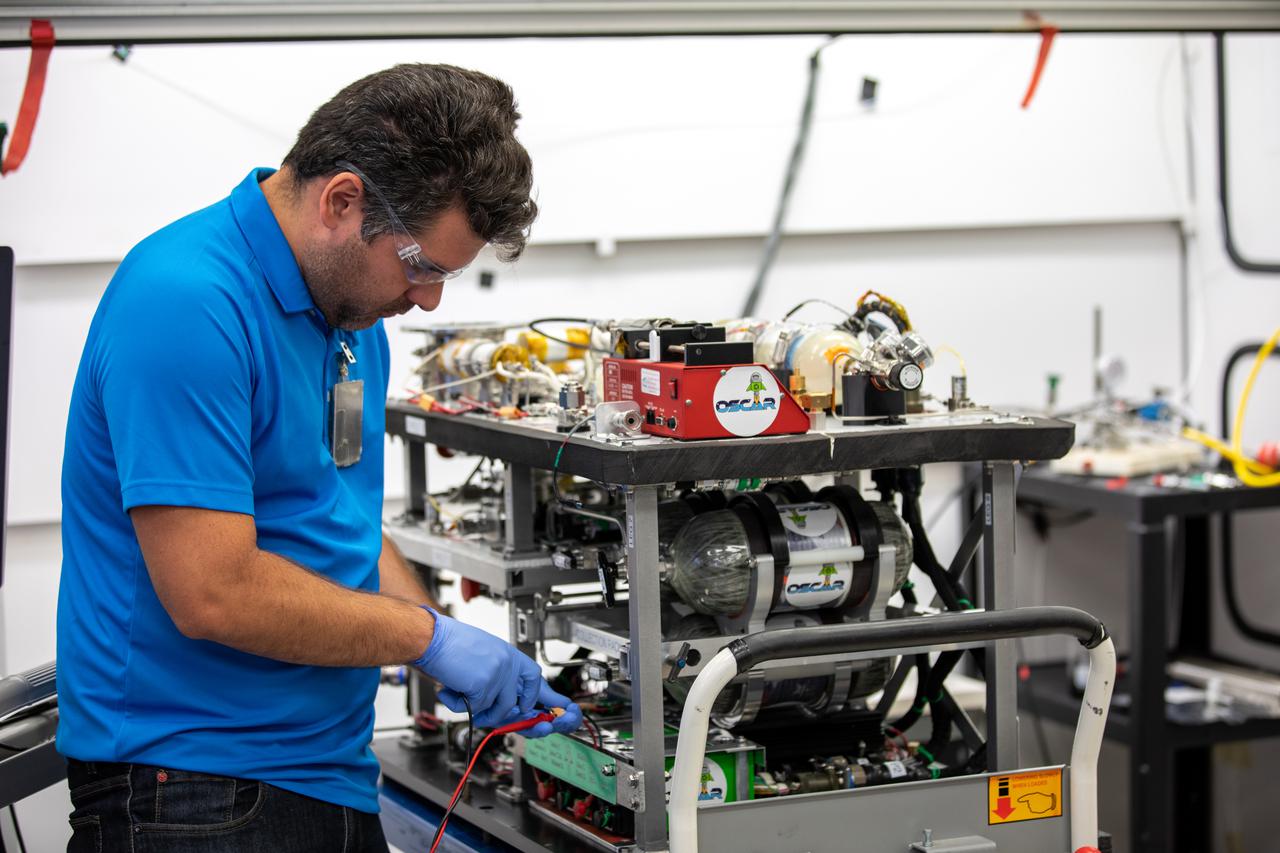

Jaime Toro, an aerospace/mechanical engineer and member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team, performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
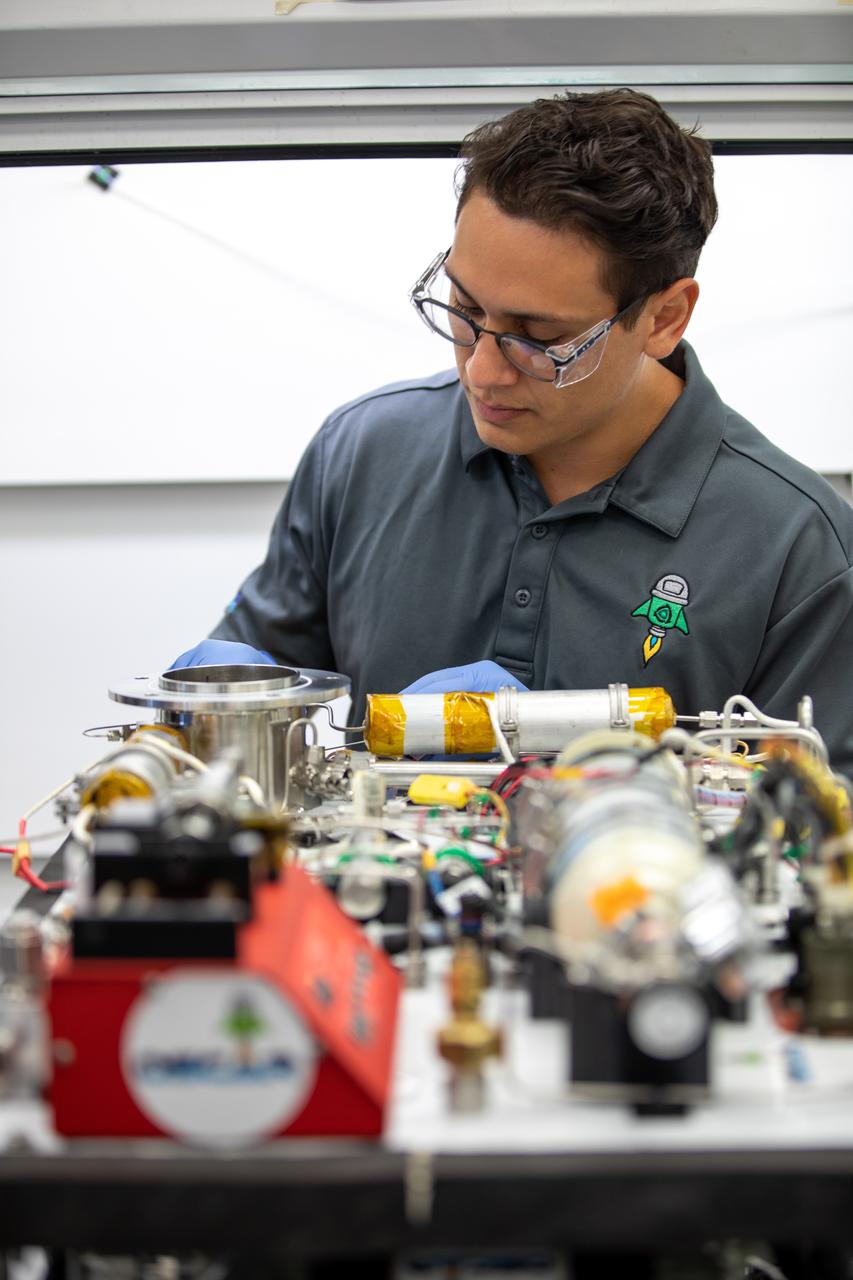

Ray Pitts, co-principal investigator for the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR), performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.
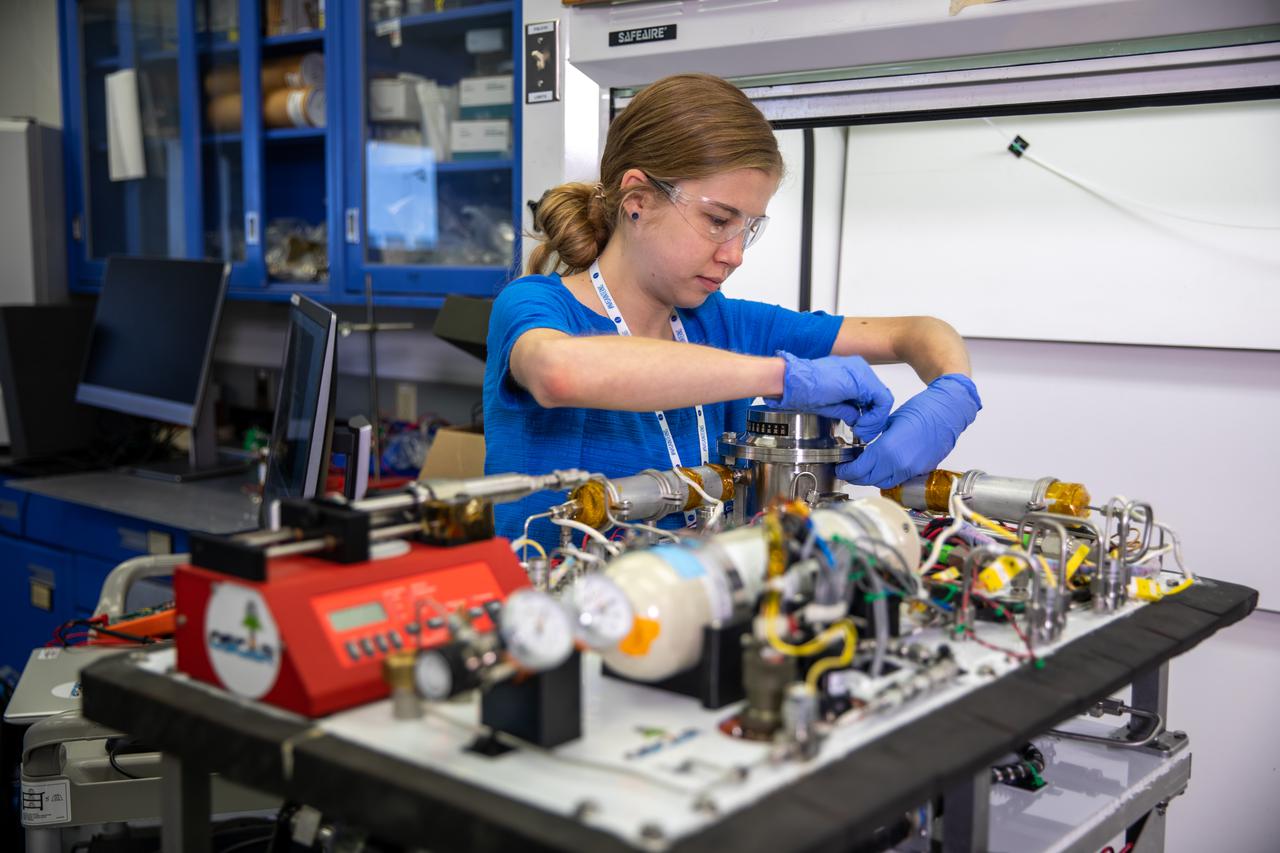
A member of the Orbital Syngas Commodity Augmentation Reactor (OSCAR) team performs ground testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests are in preparation for a scheduled suborbital flight test later this year, facilitated by NASA’s Flight Opportunities program. Begun as an Early Career Initiative project, OSCAR evaluates technology to make use of trash and human waste generated during long-duration spaceflight.

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. Orion is being prepared for its first integrated uncrewed flight atop the SLS on Exploration Mission-1. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
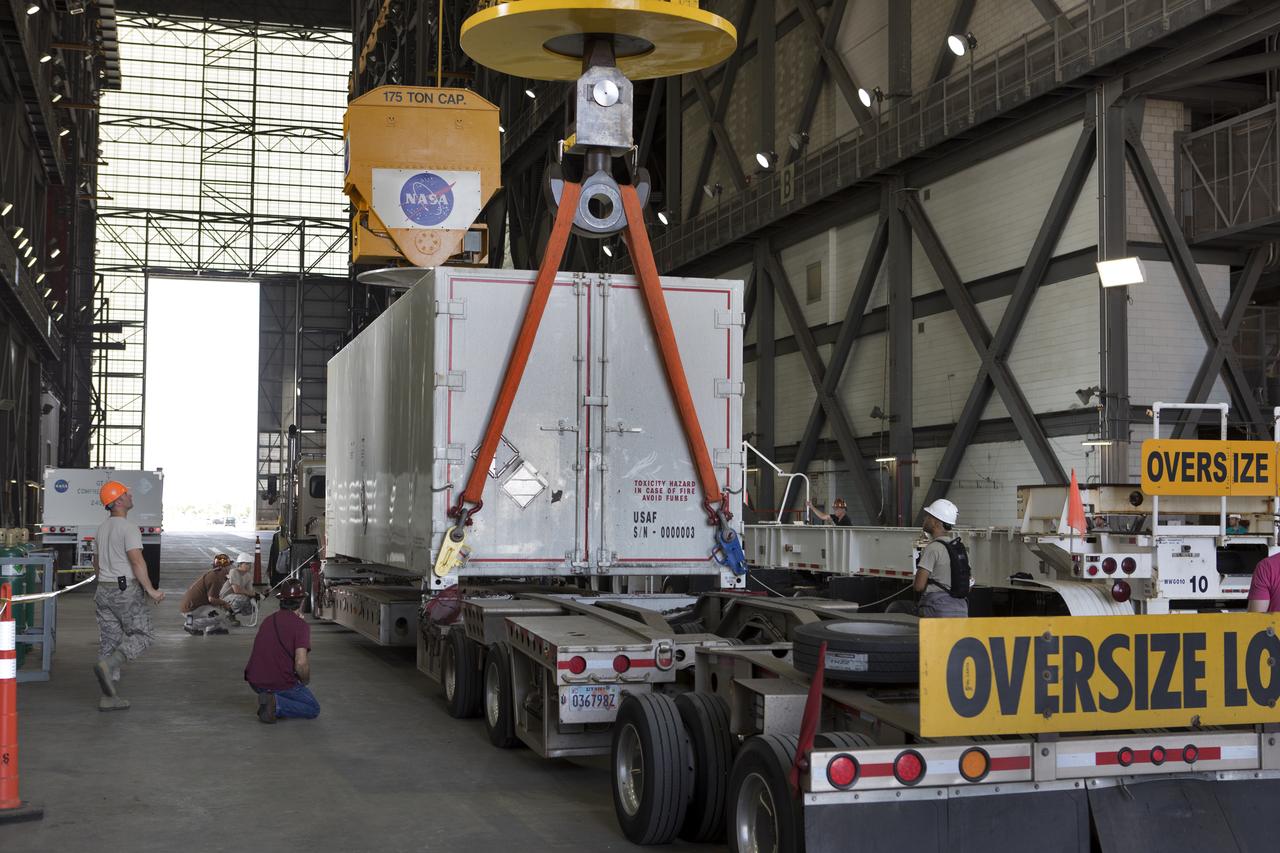

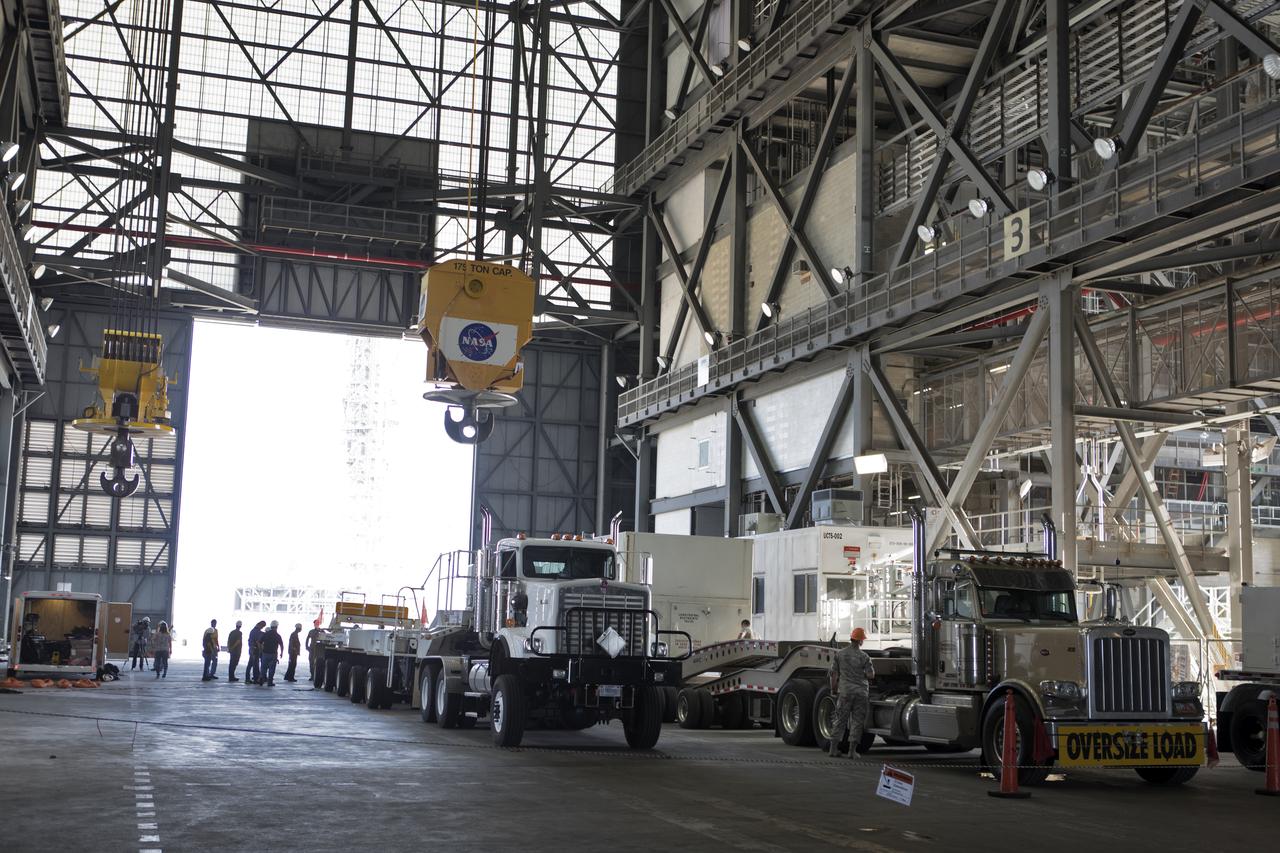
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jacob’s technicians attach a crane to a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
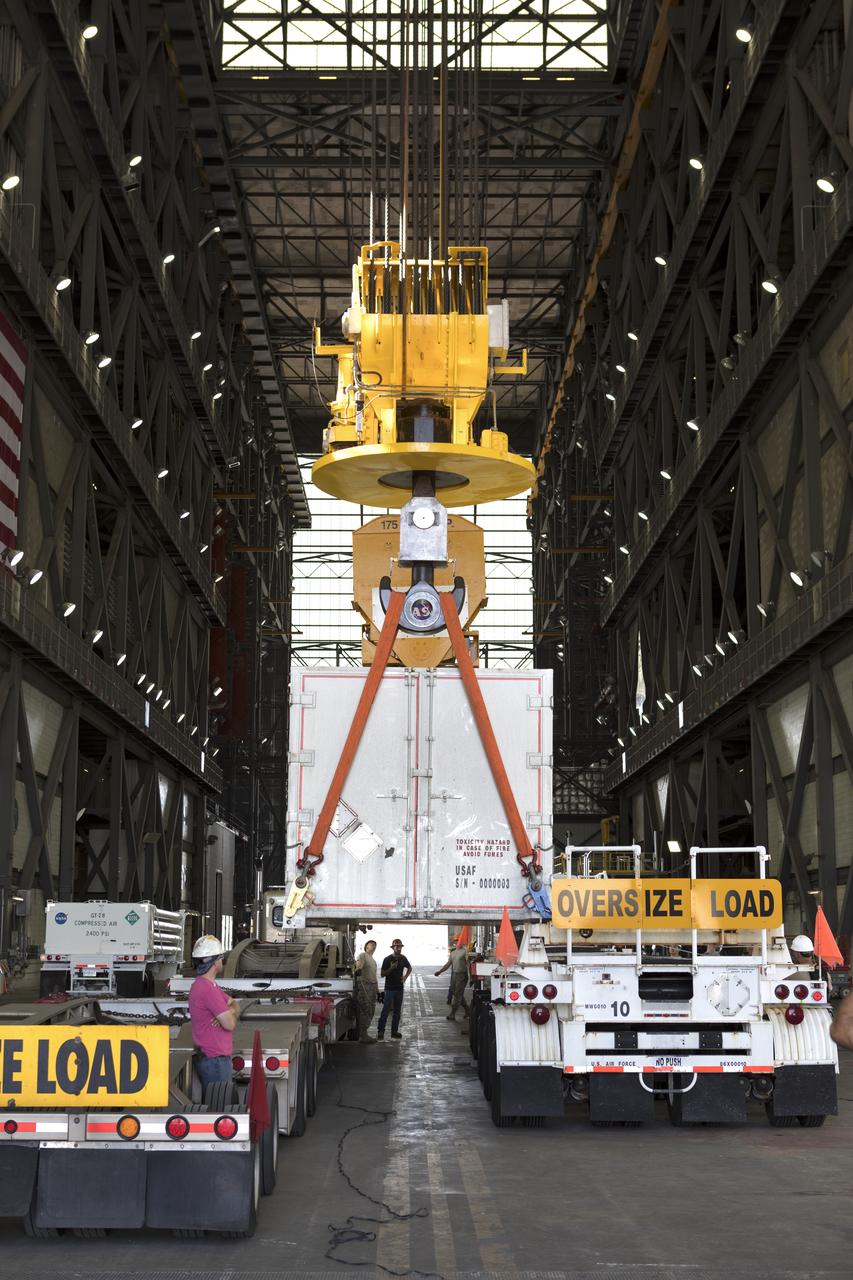

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
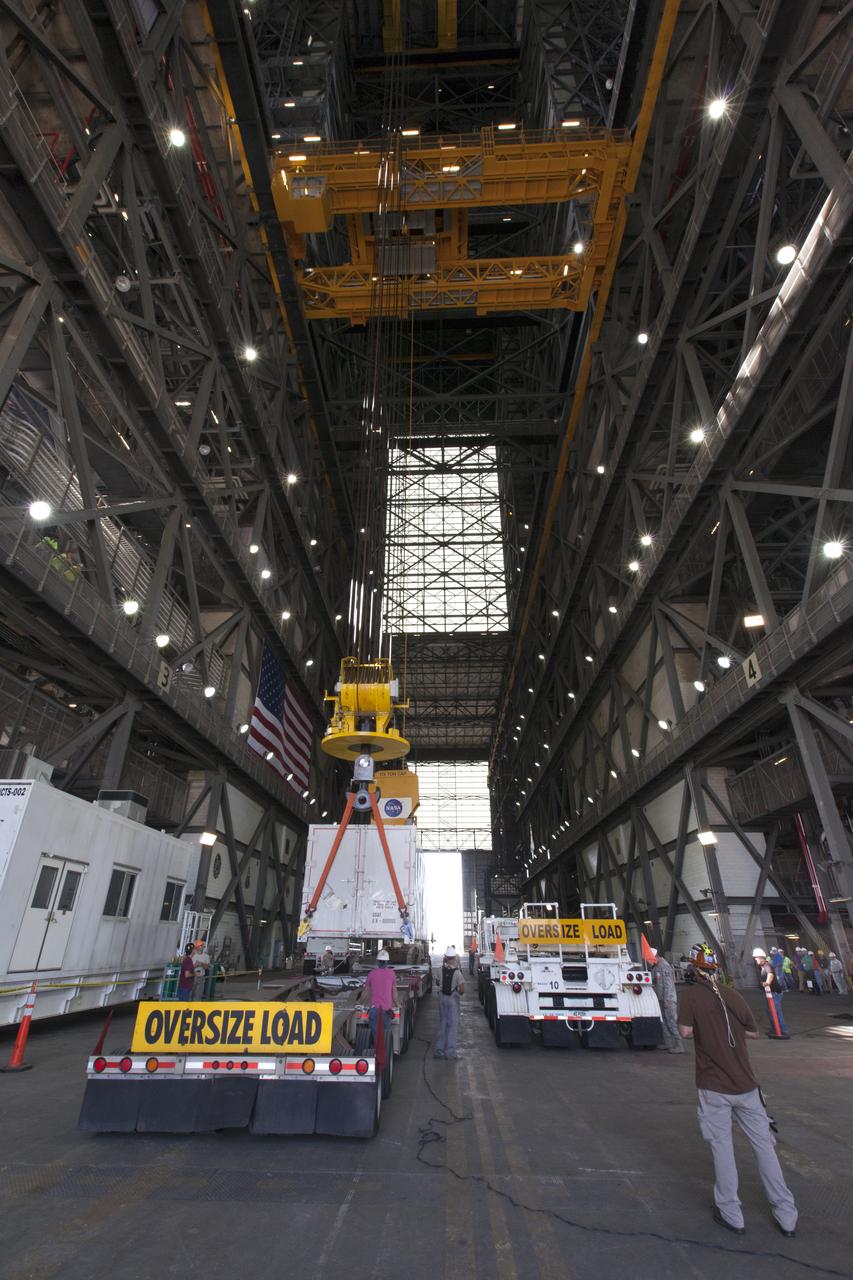

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up a shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lifted and transferred to another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

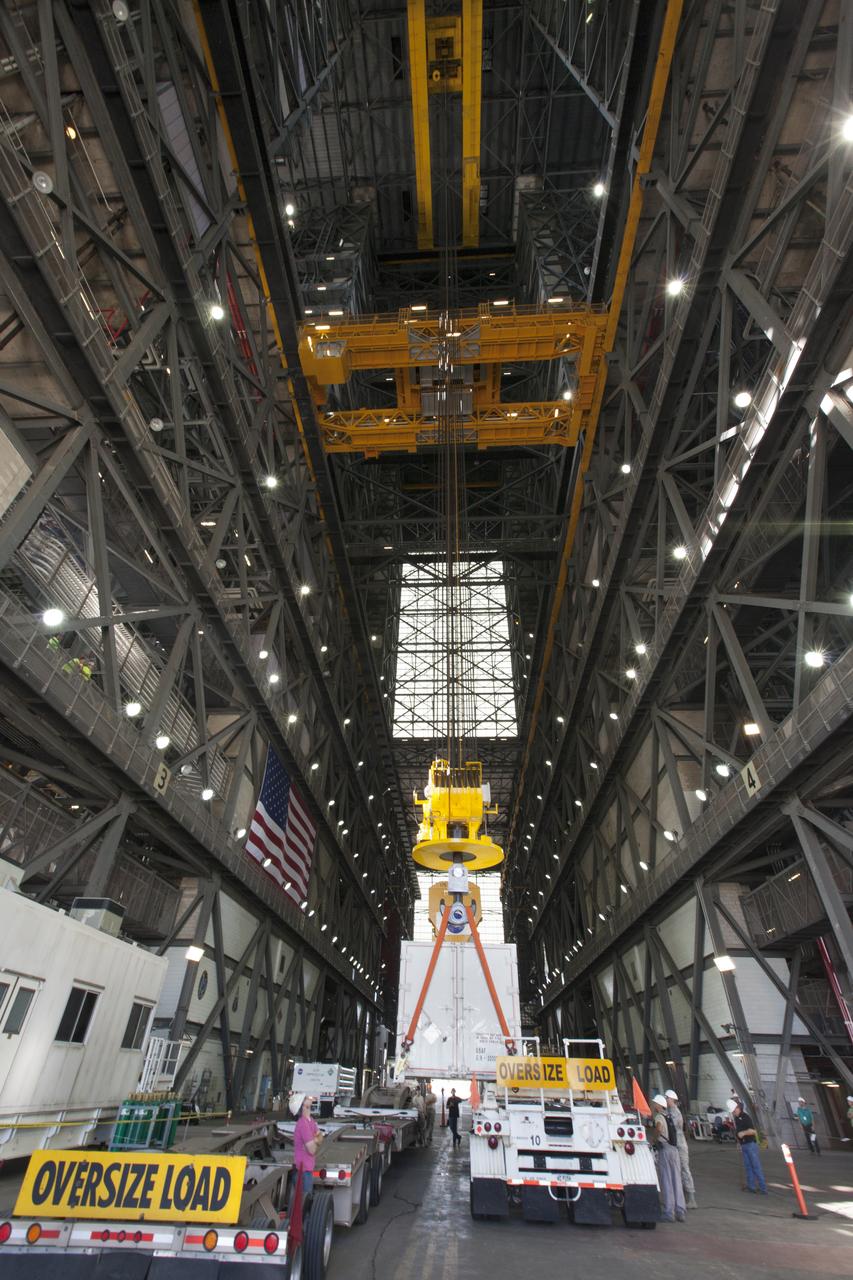
In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane operated by Jacob’s technicians lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is used to lift up the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside on July 20, 2018. The container will be lowered onto another transporter and moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.

NASA Dryden's F-15B testbed aircraft with the Gulfstream Quiet Spike sonic boom mitigator attached undergoes ground vibration testing in preparation for test flights. The project seeks to verify the structural integrity of the multi-segmented, articulating spike attachment designed to reduce and control a sonic boom.
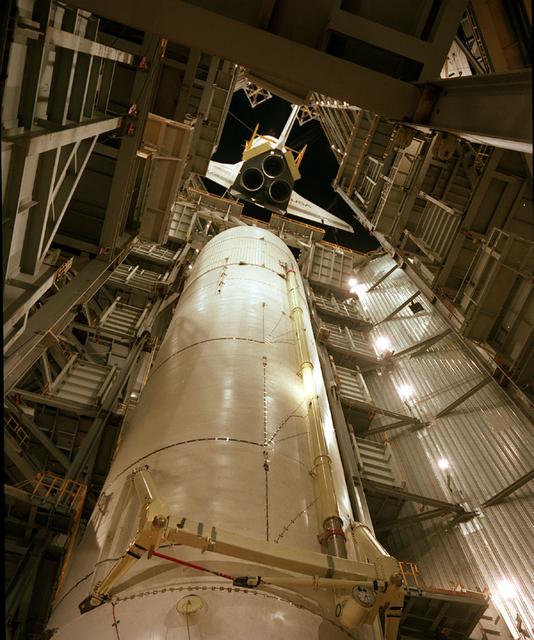

This is an interior ground level view of the Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise being lowered for mating to External Tank (ET) inside Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
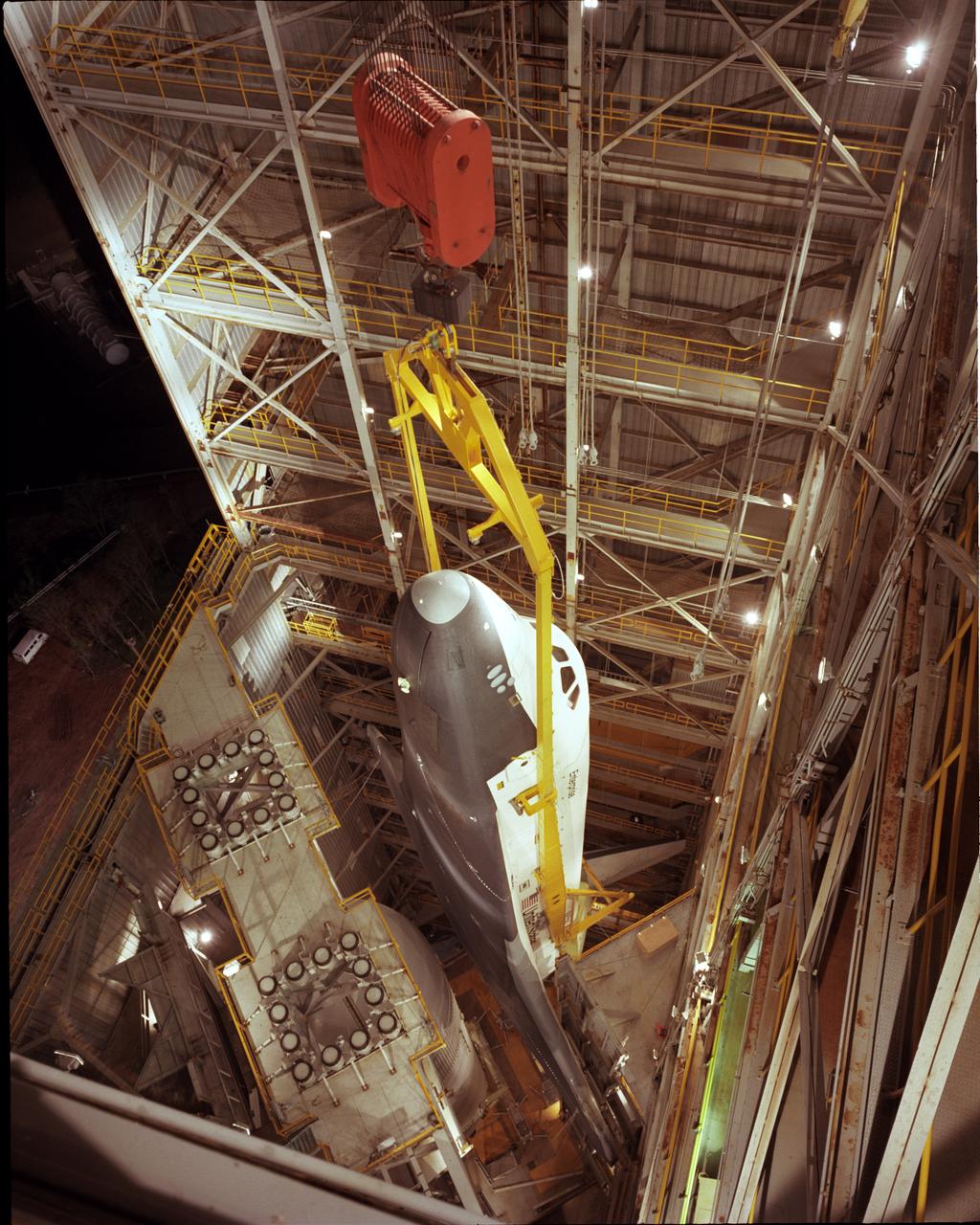

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is lowered into the Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT) at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
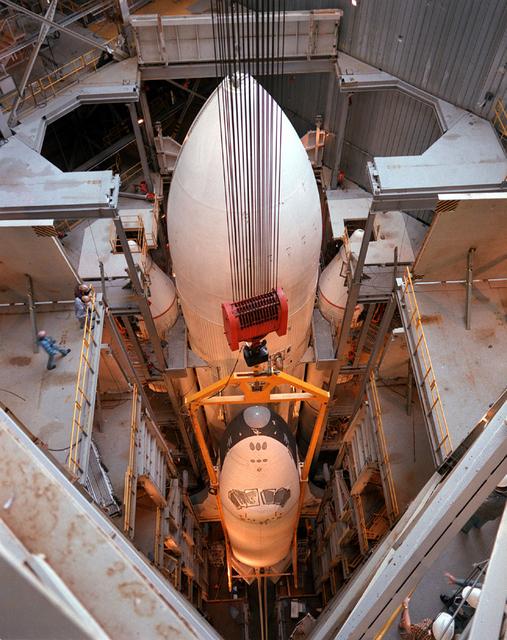

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise inside of Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters were vertically mated.
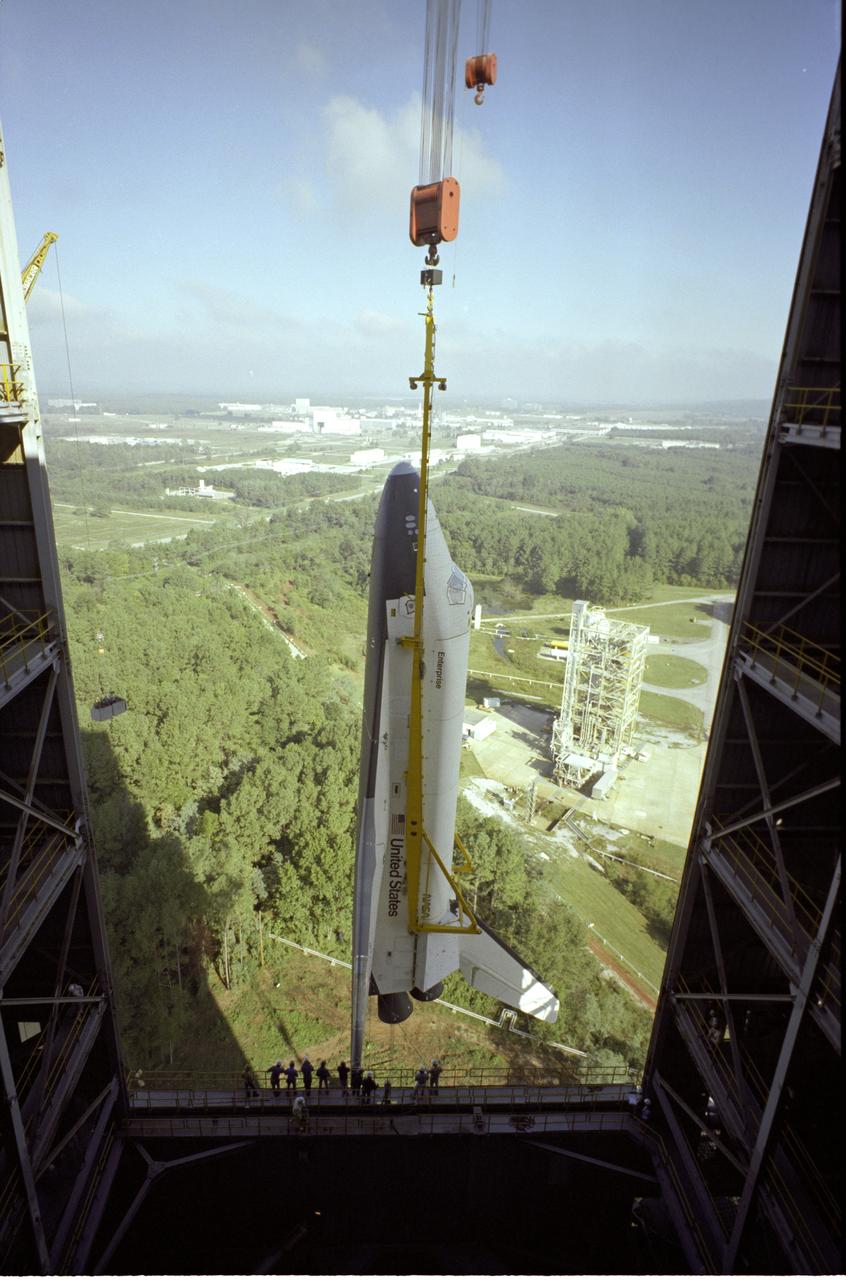

The Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is being installed into liftoff configuration at Marshall Space Flight Center's Dynamic Test Stand for Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT). The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.
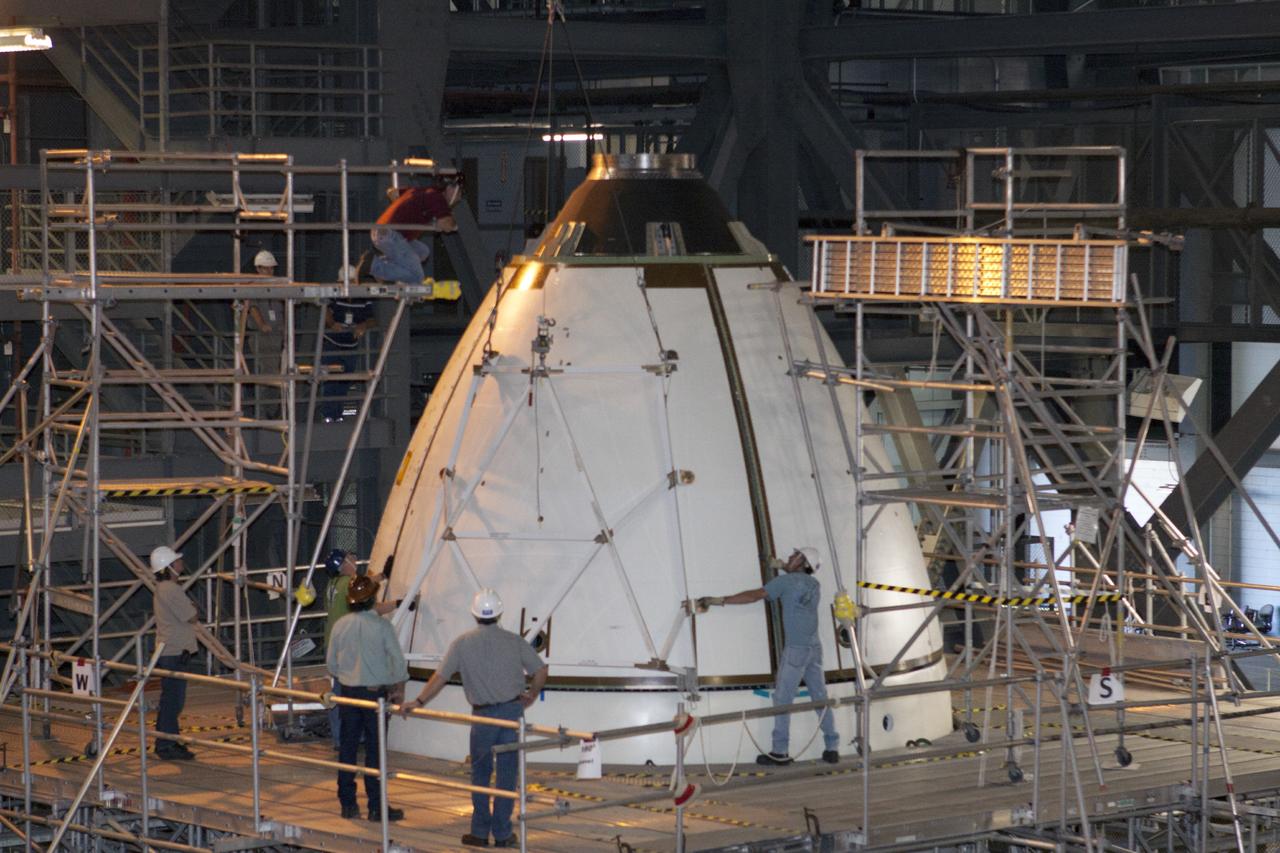

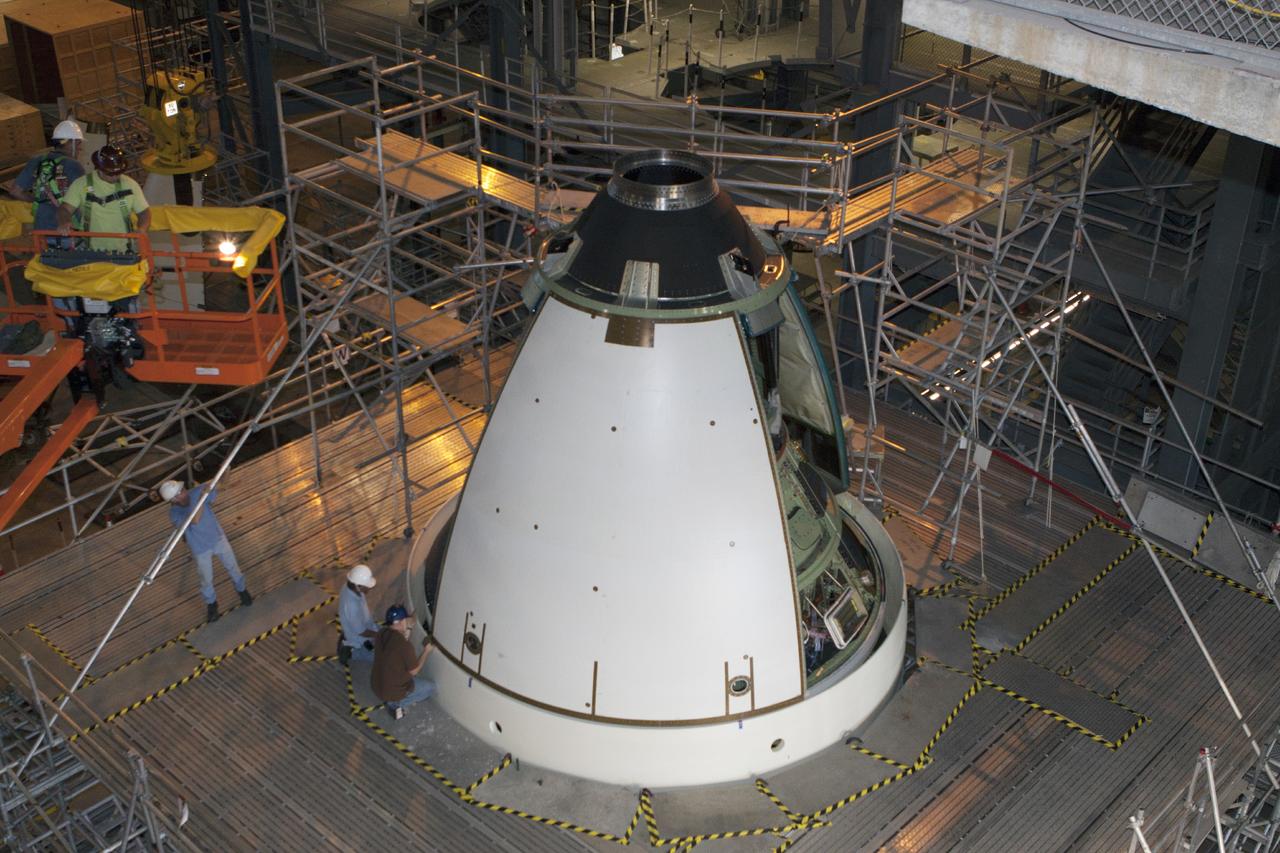
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians complete the installation of ogive panels on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians attach an ogive panel on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians attach an ogive panel on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

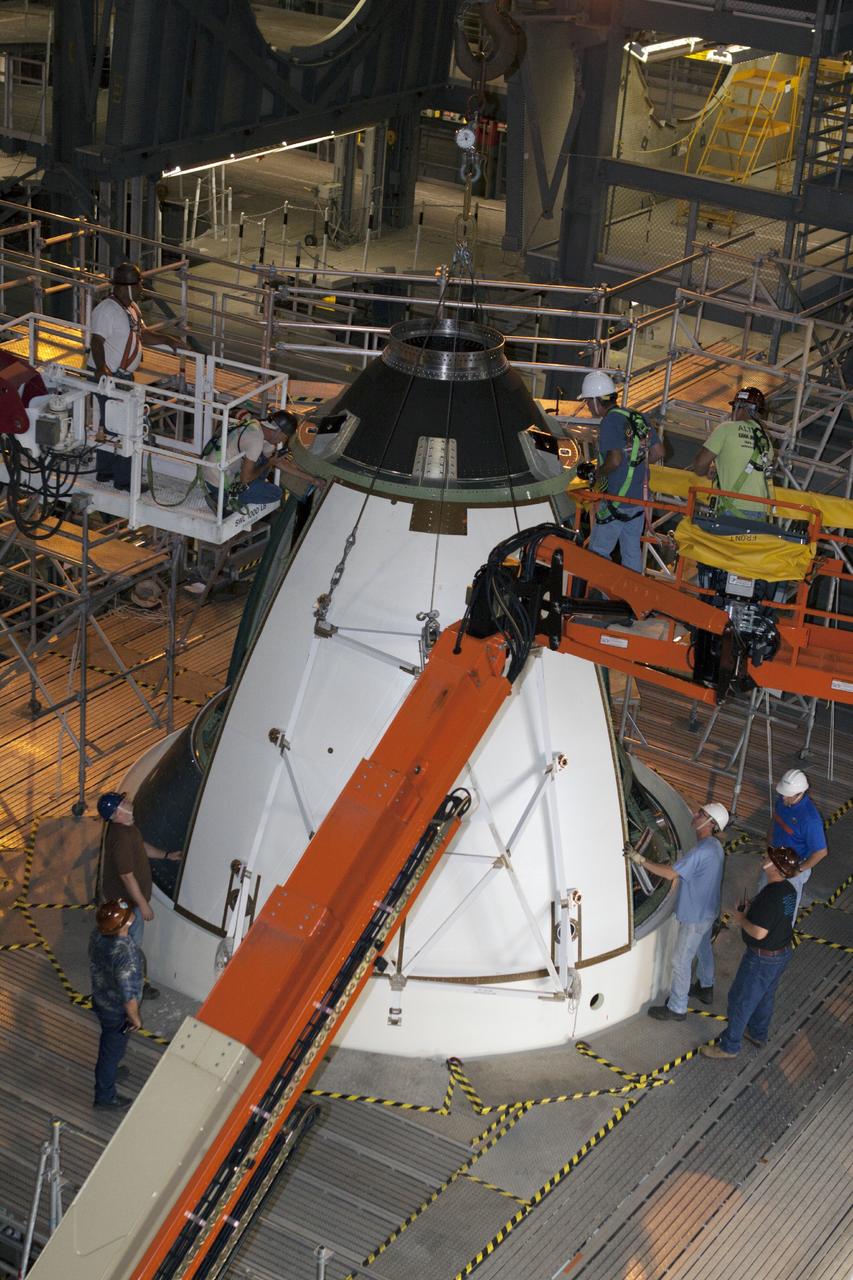
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians complete the installation of ogive panels on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

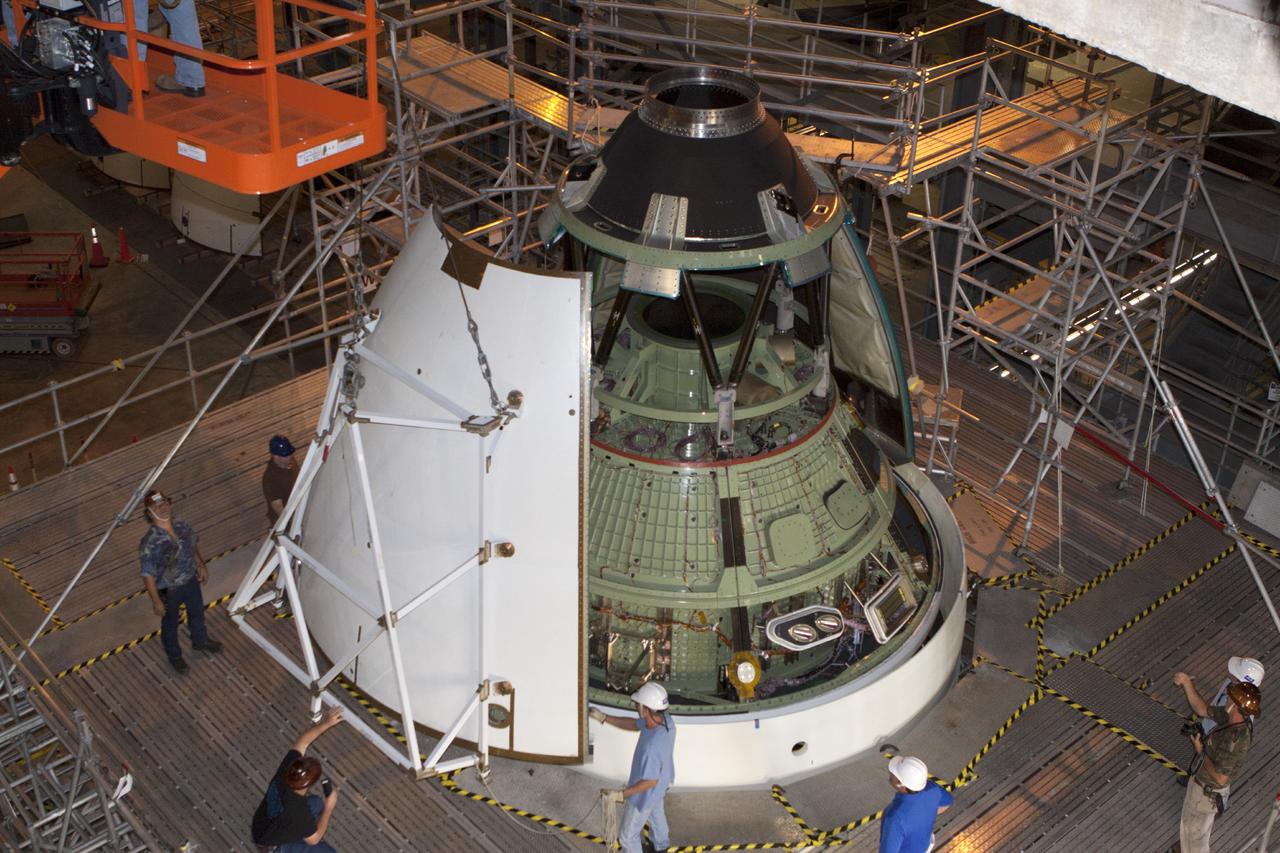
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare an ogive panel for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
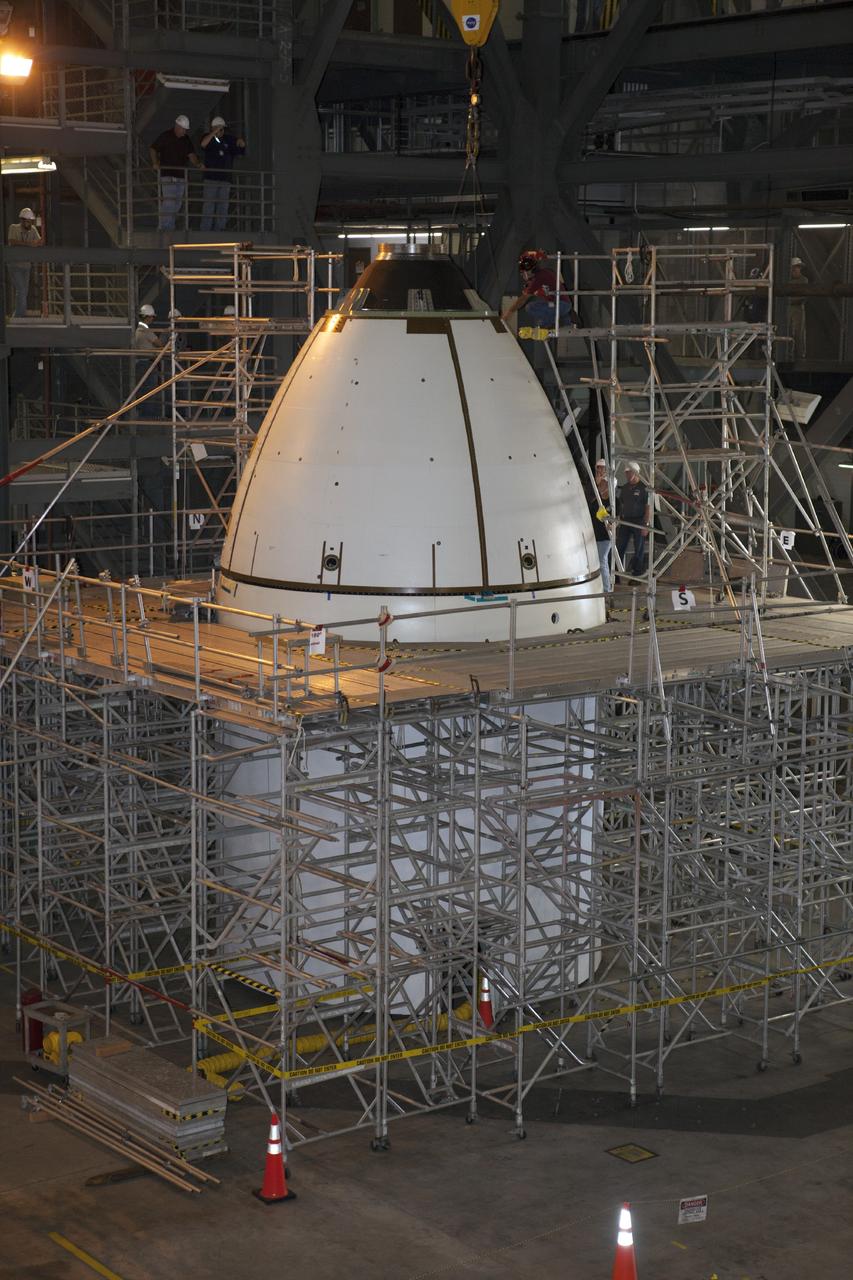

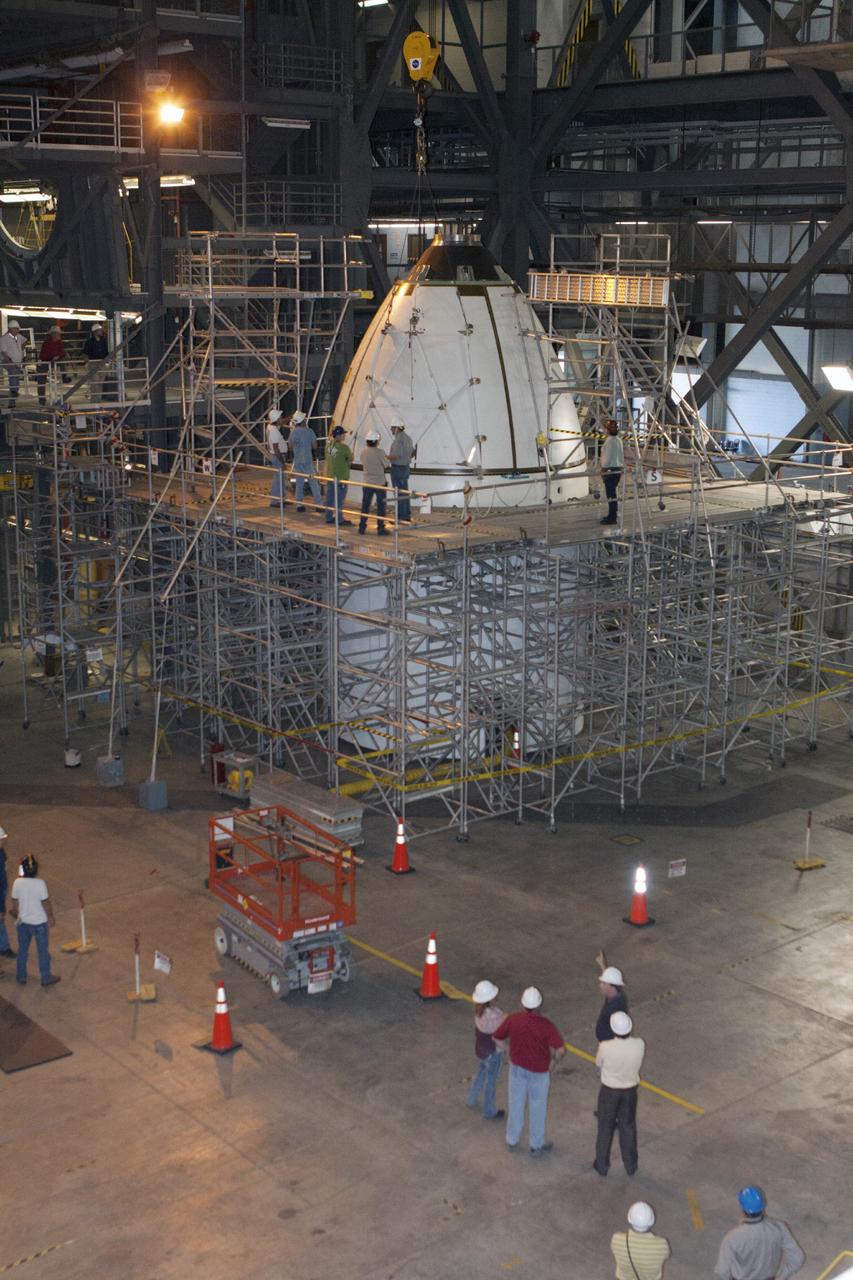
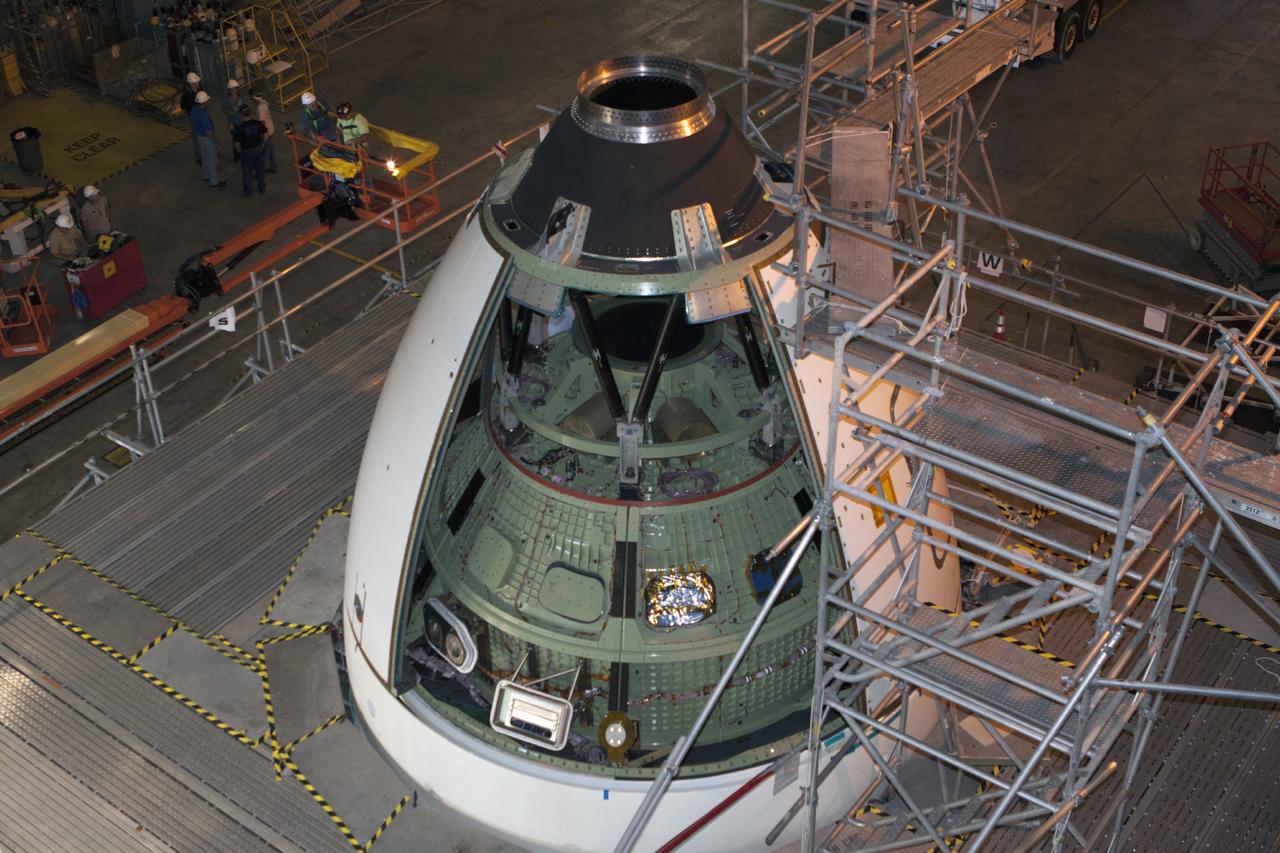
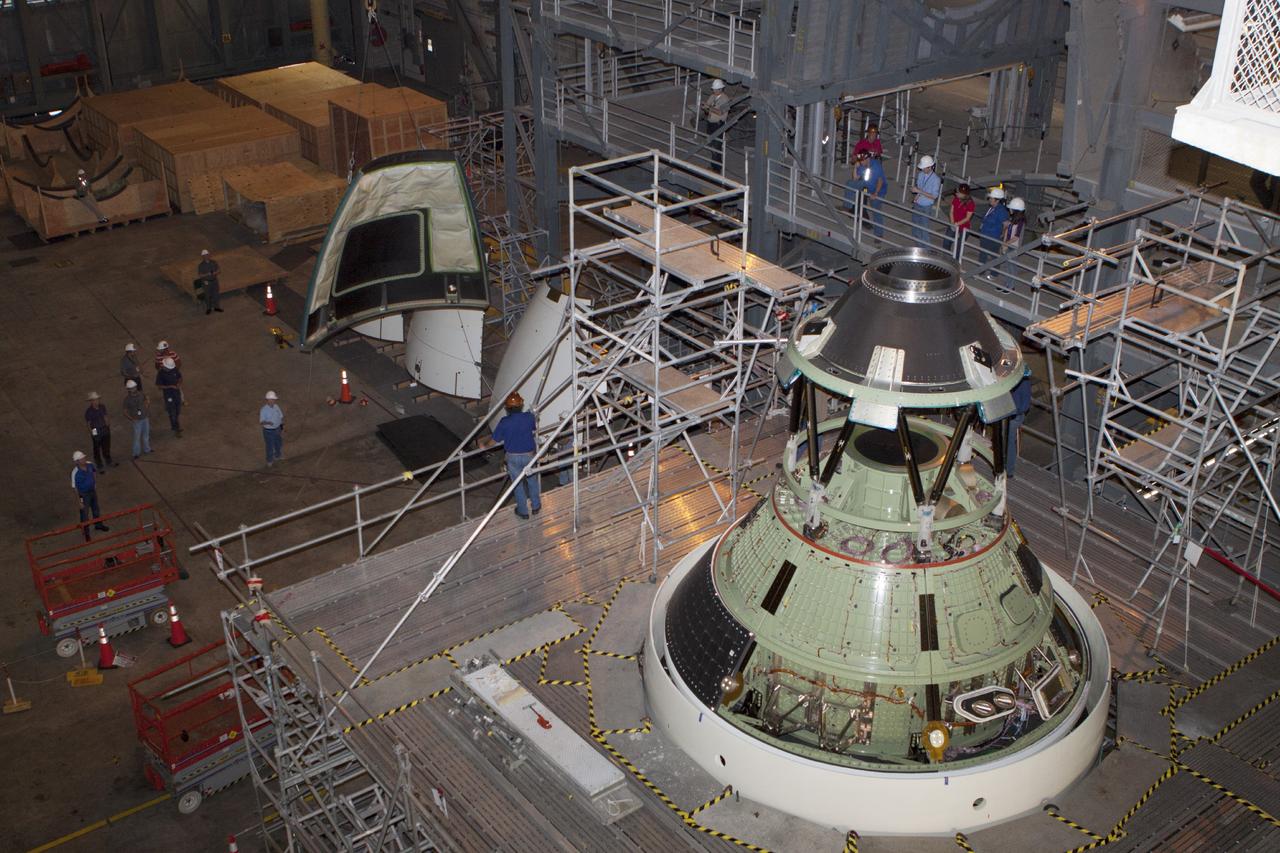
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, all four ogive panels have been installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
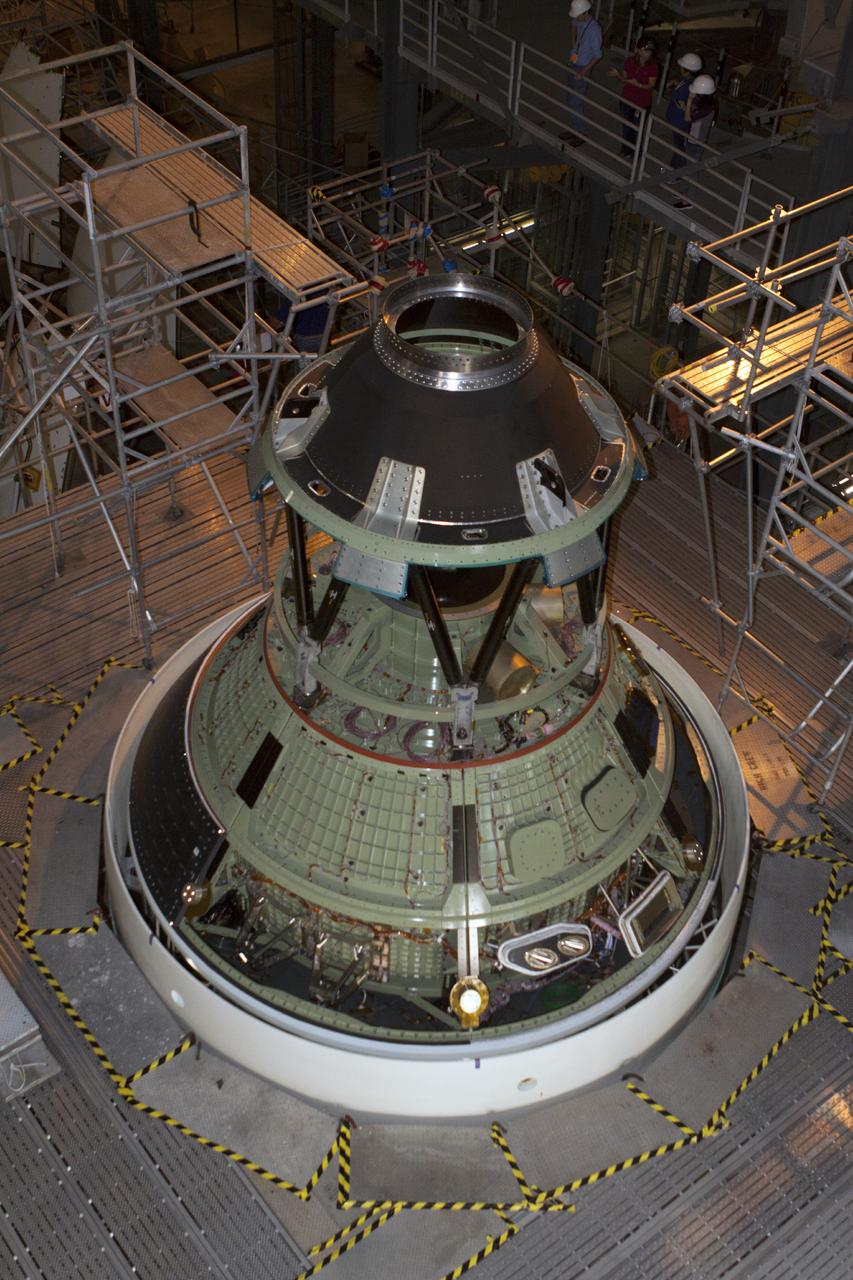

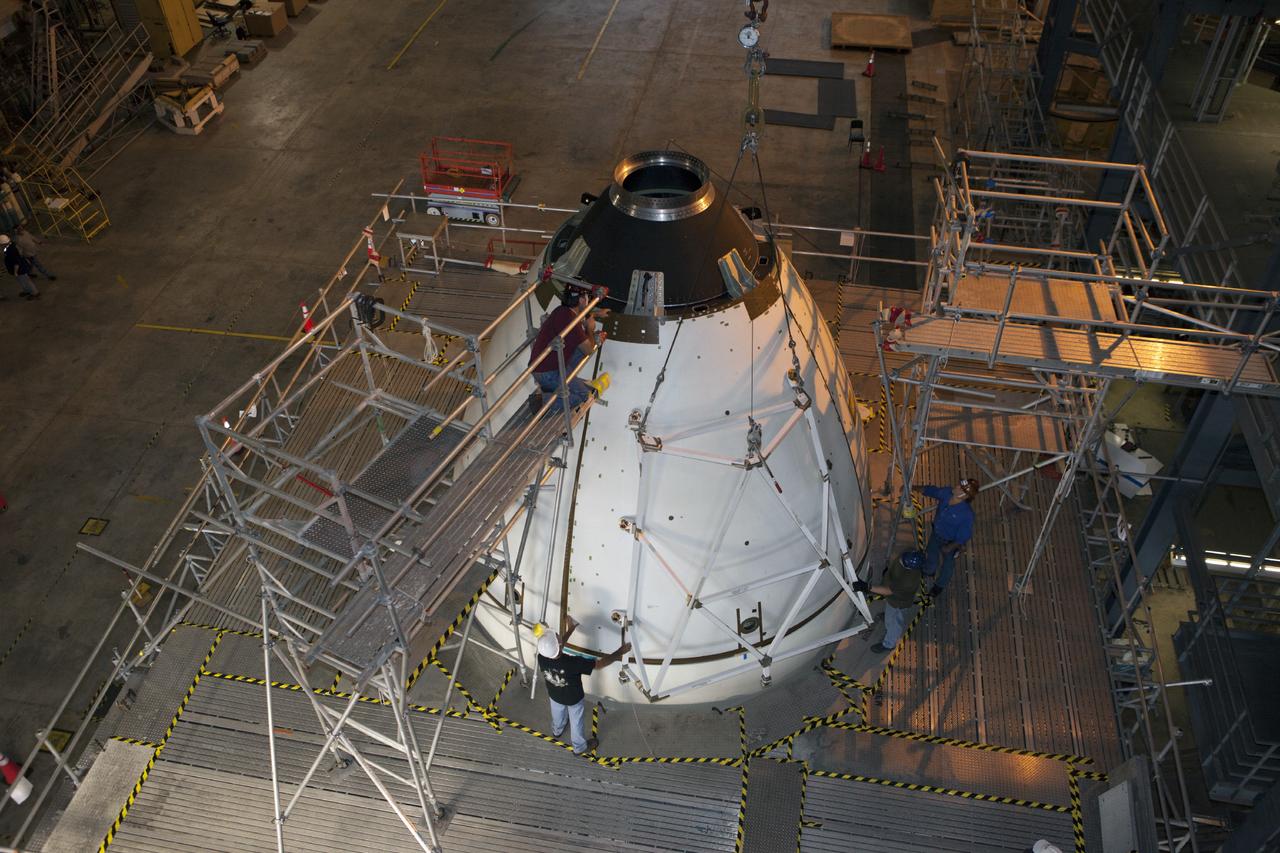
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle is being prepared for installation of the ogive panels in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
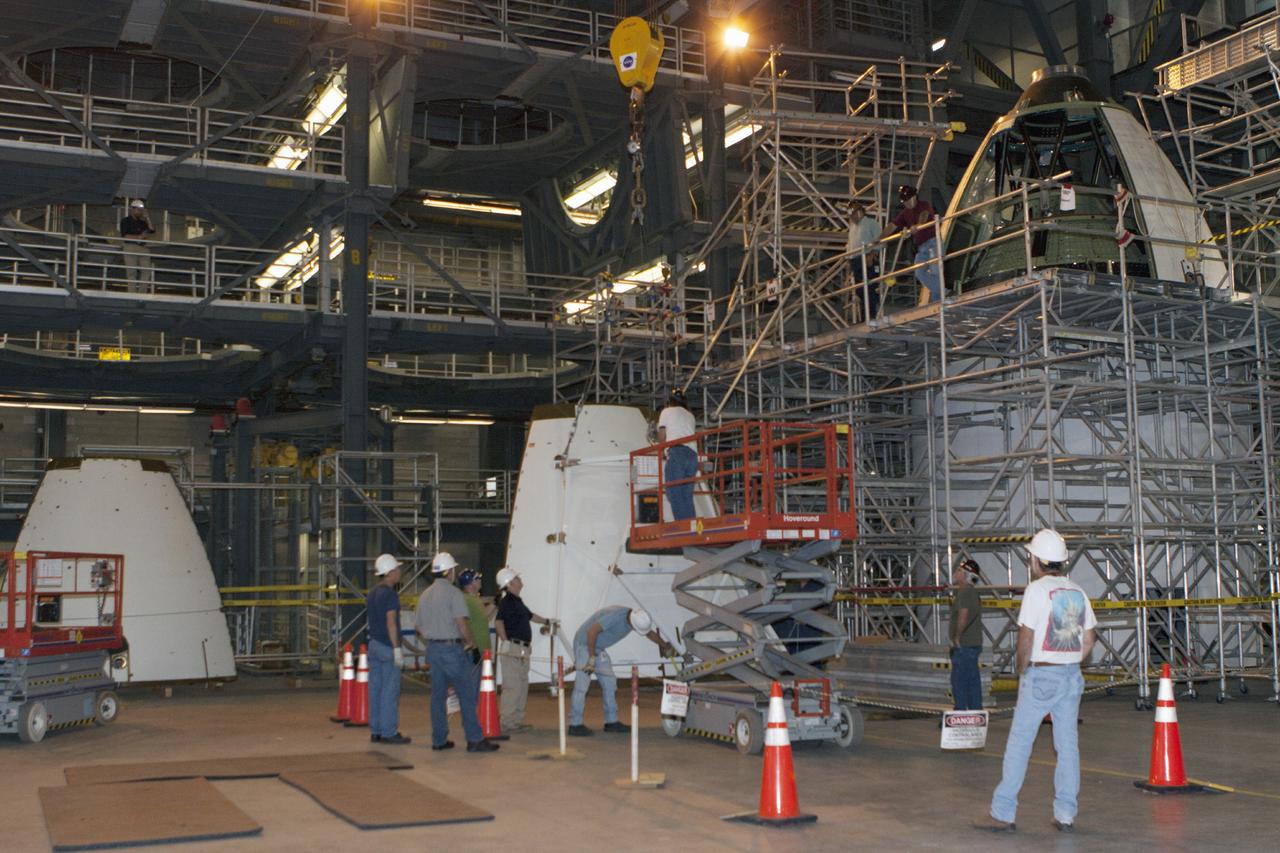

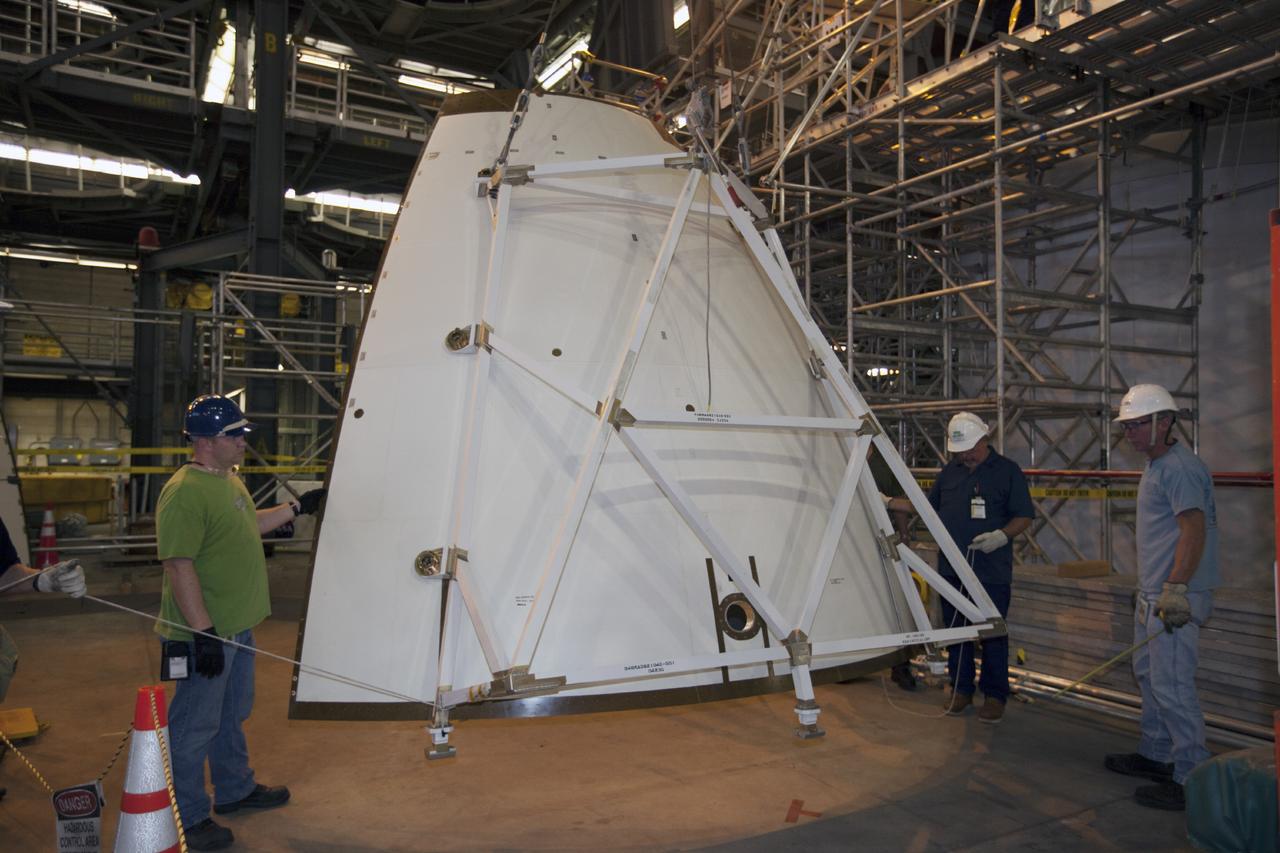
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare an ogive panel for lifting by crane so that it can be installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
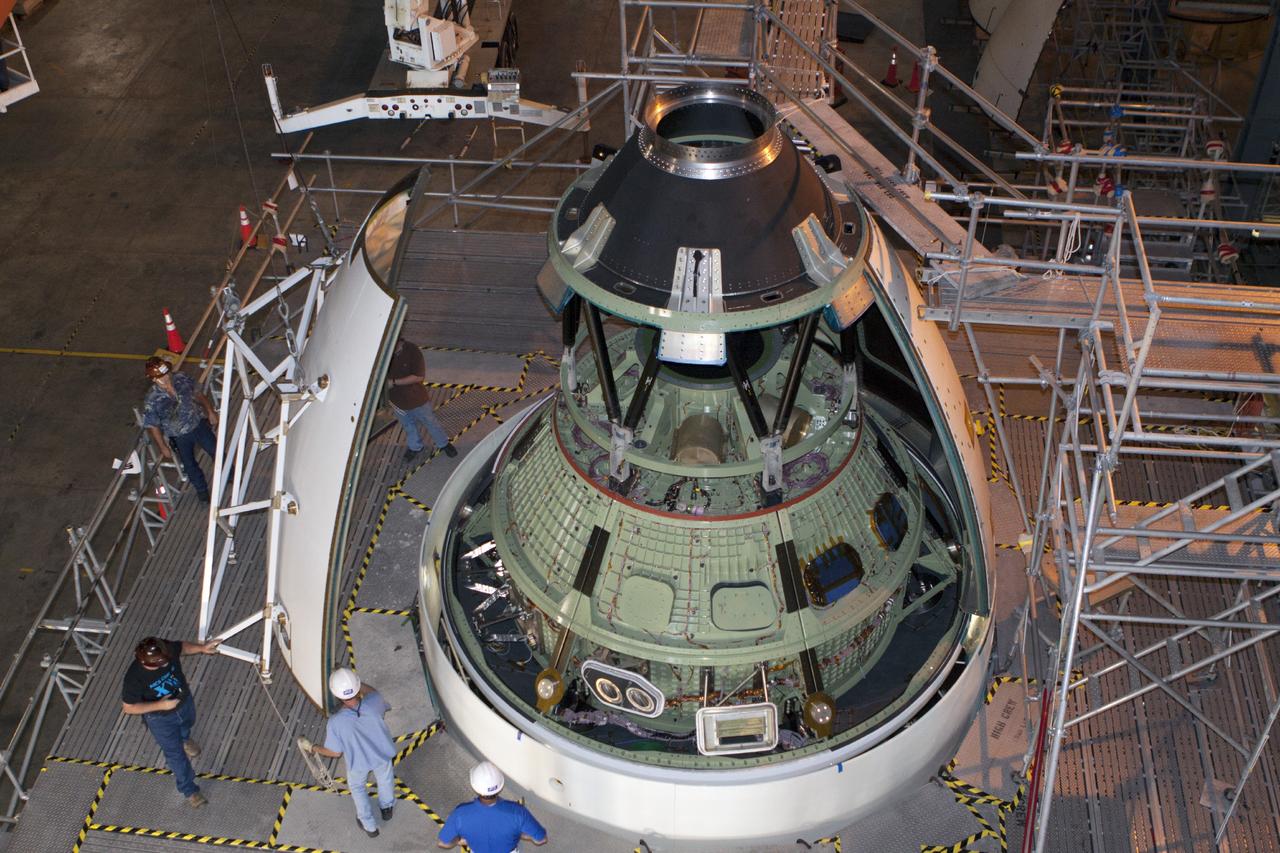

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians use a special handling device to bring an ogive panel closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, several ogive panels have been installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians attach the fourth ogive panel on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians complete the installation of an ogive panel on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to attach an ogive panel around the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
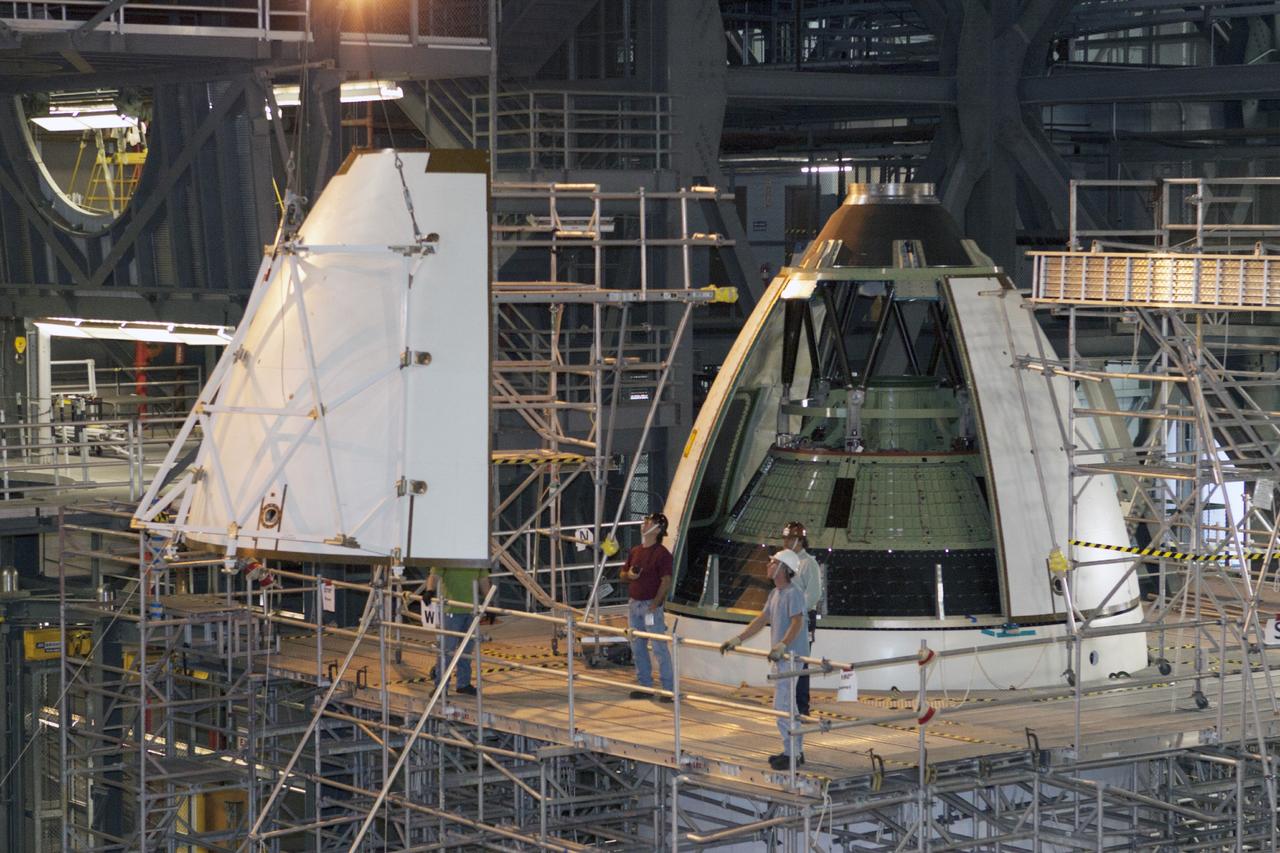

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to move an ogive panel closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
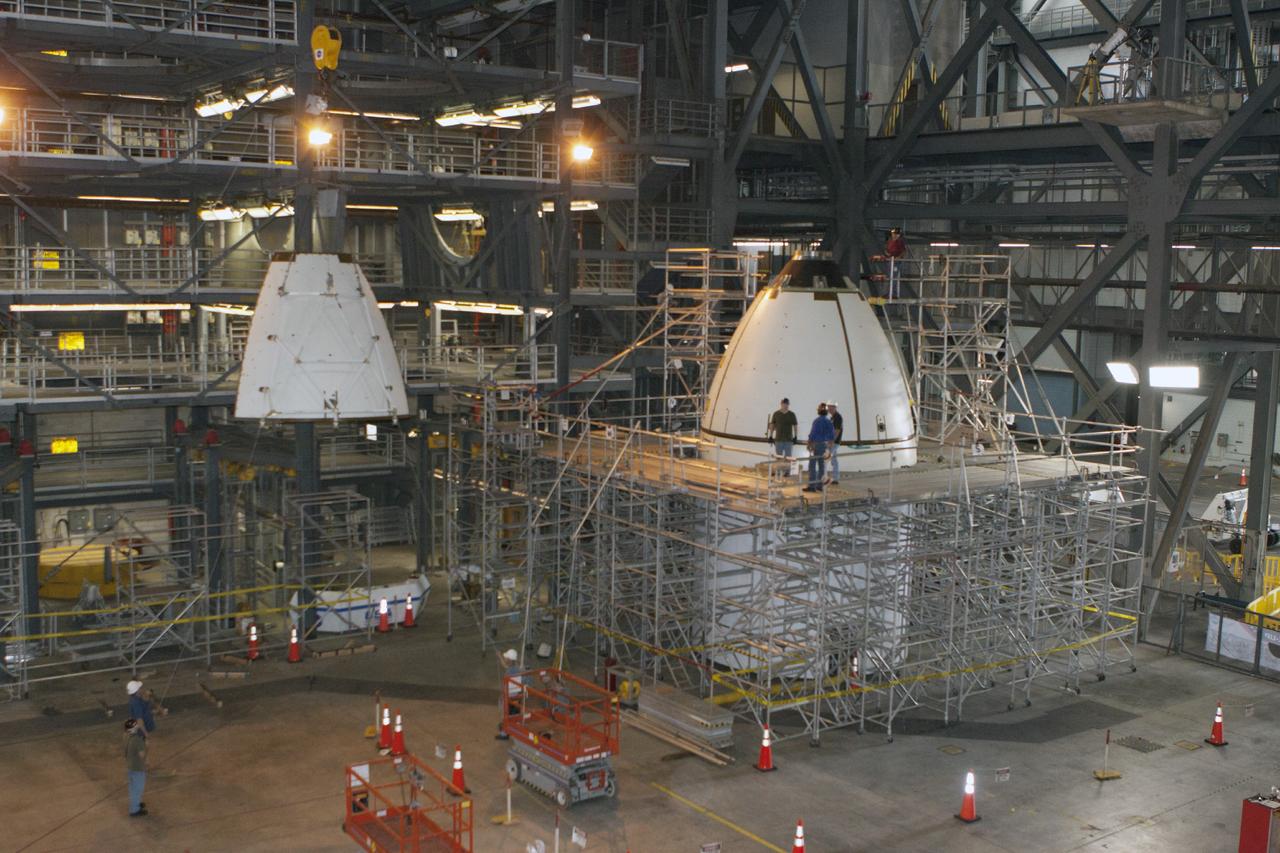

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the fourth ogive panel is lifted by crane so that they can be installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. Three of the panels have already been installed on the test vehicle. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
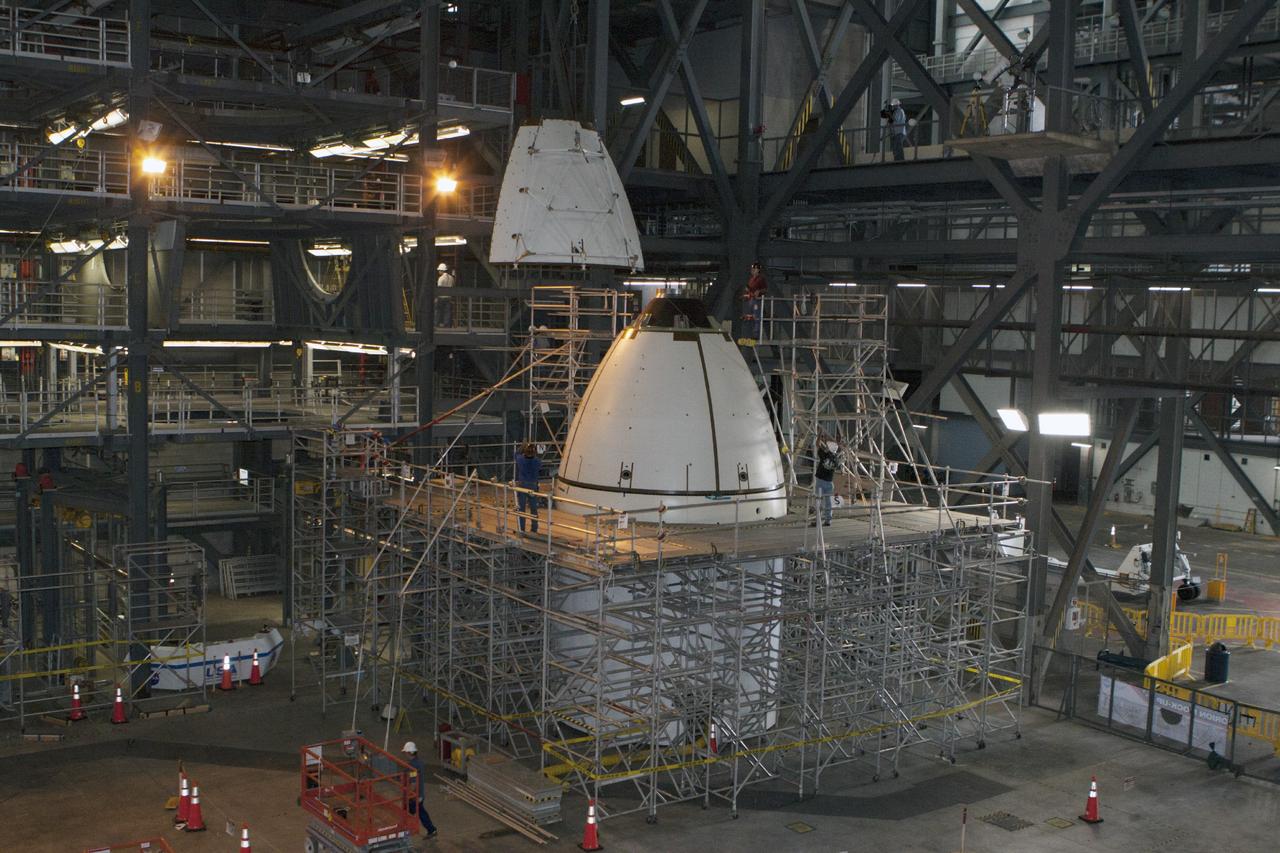

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the fourth ogive panel is lifted by crane so that they can be installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. Three of the panels have already been installed on the test vehicle. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
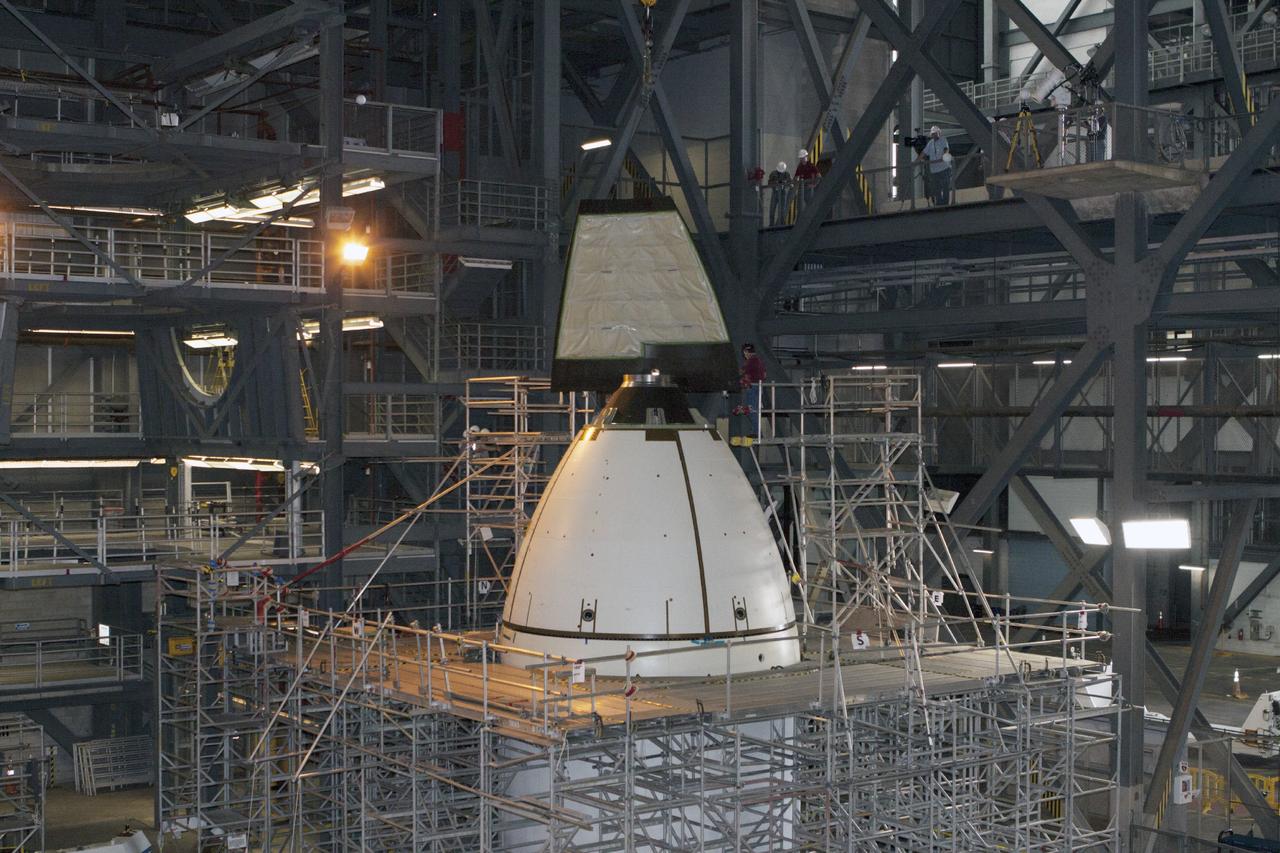

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as the fourth ogive panel is lifted by crane so that they can be installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. Three of the panels have already been installed on the test vehicle. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
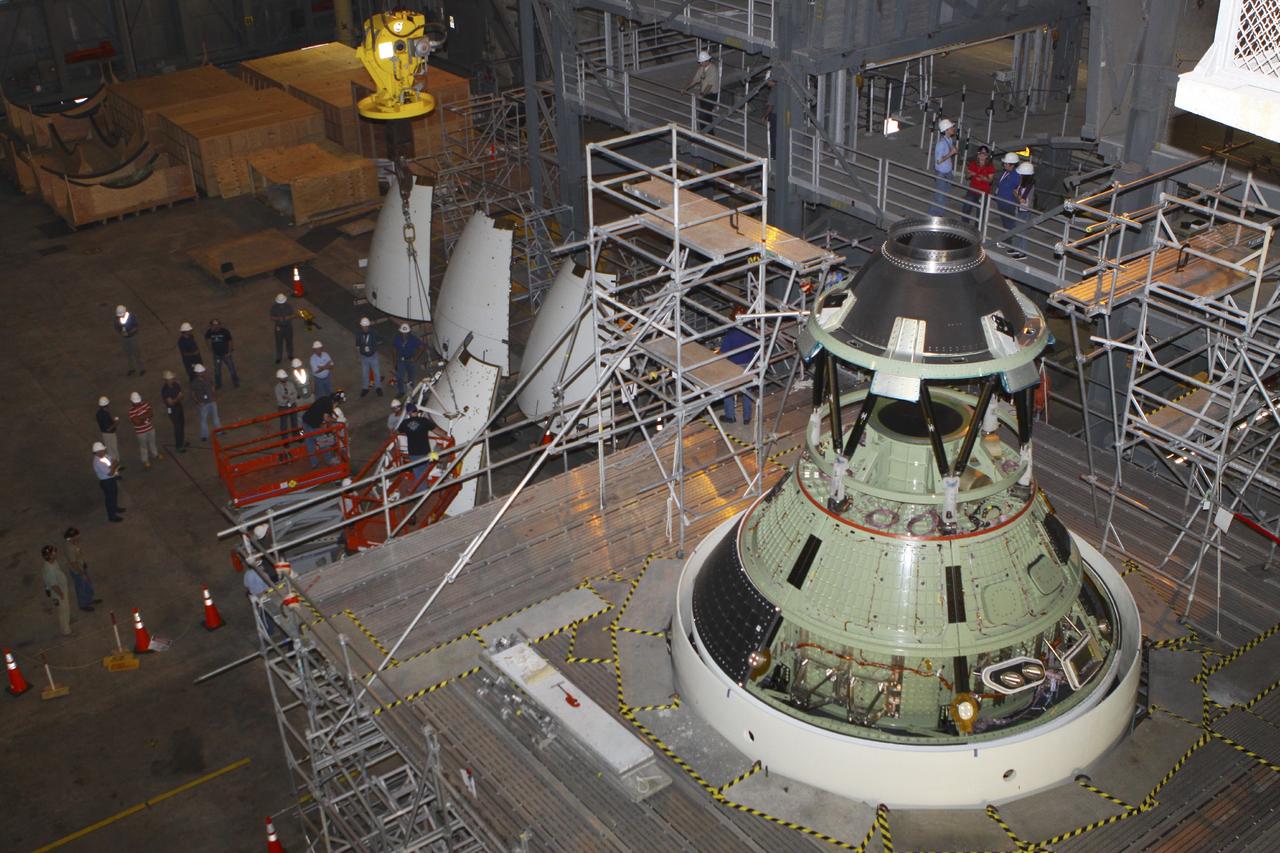

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare the four ogive panels for lifting by crane so that they can be installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is used to move one of four ogive panels closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is used to move one of four ogive panels closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to move one of four ogive panels closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
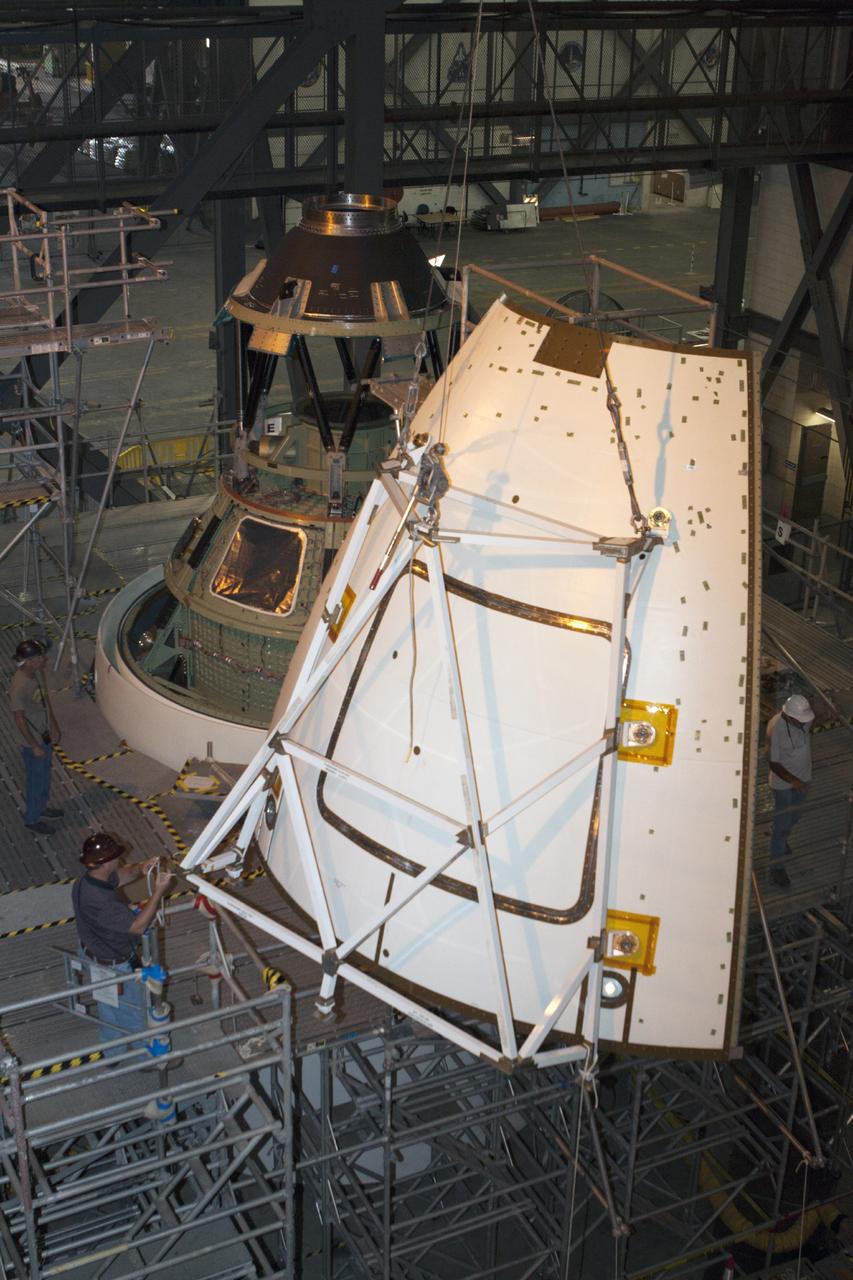

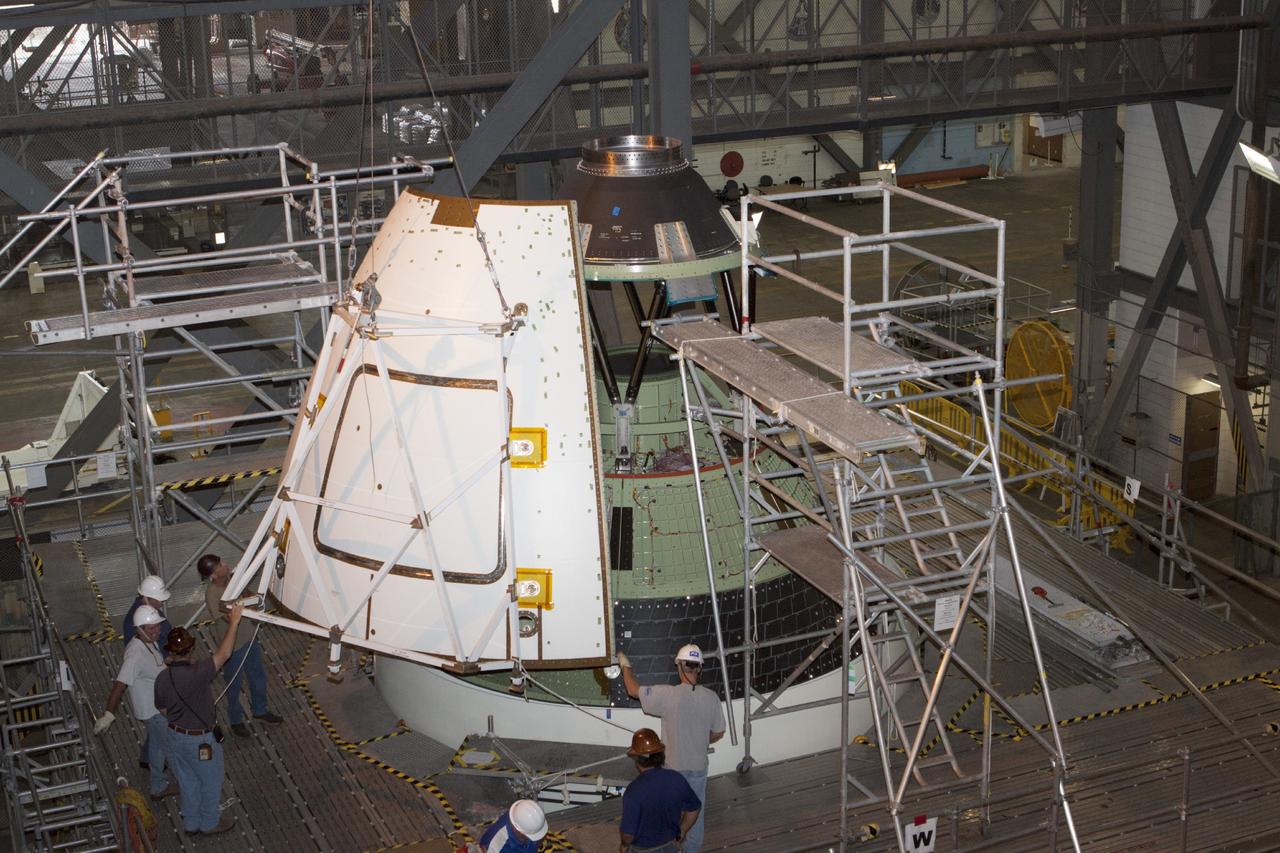
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to move one of four ogive panels closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
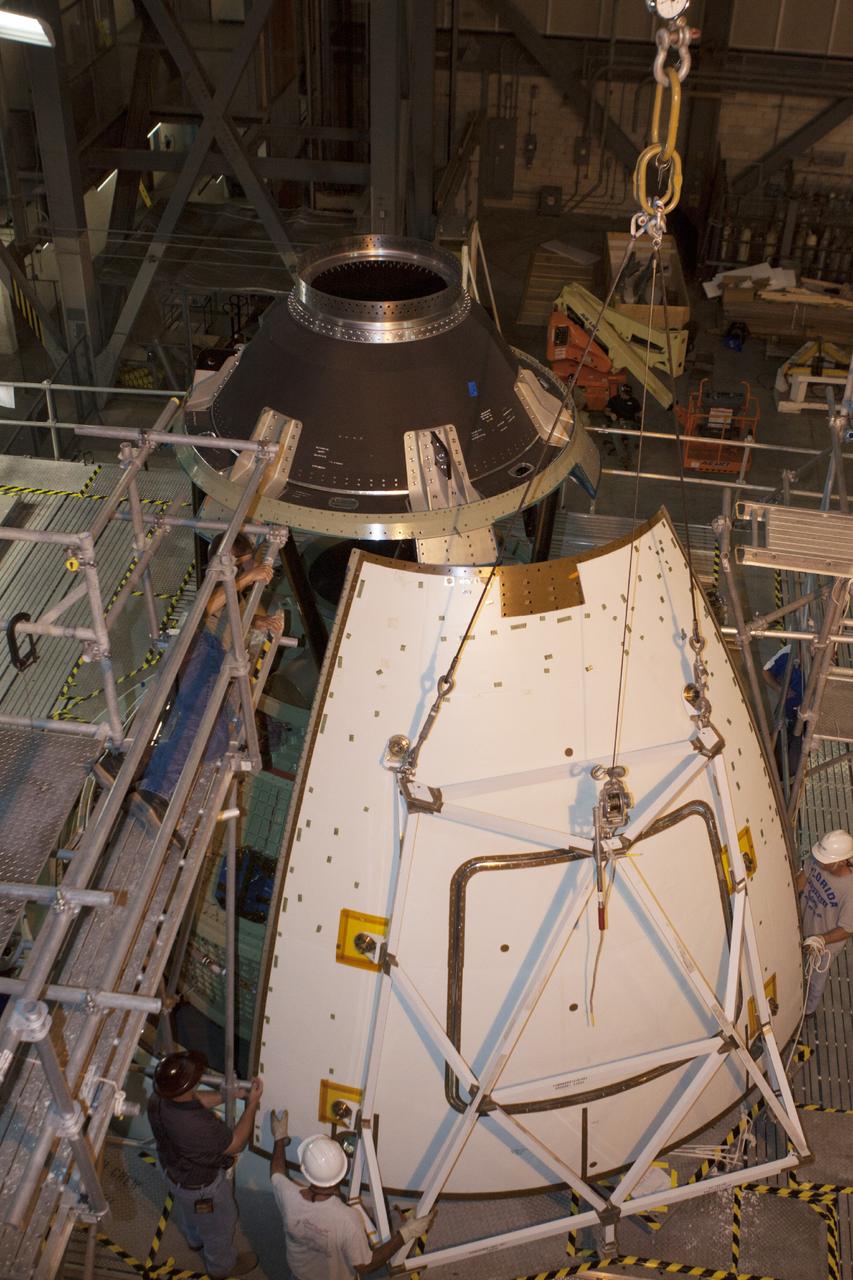

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is used to move one of four ogive panels closer for installation on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
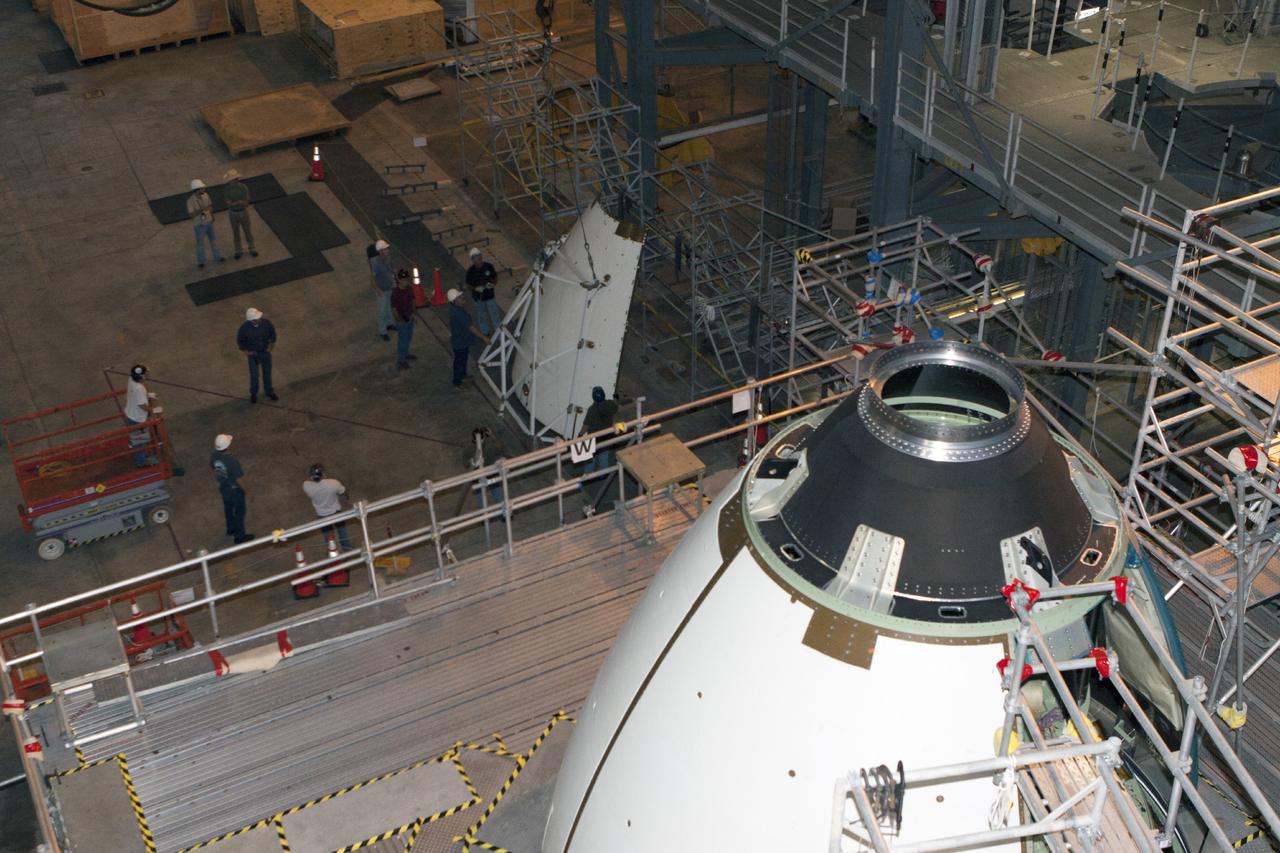

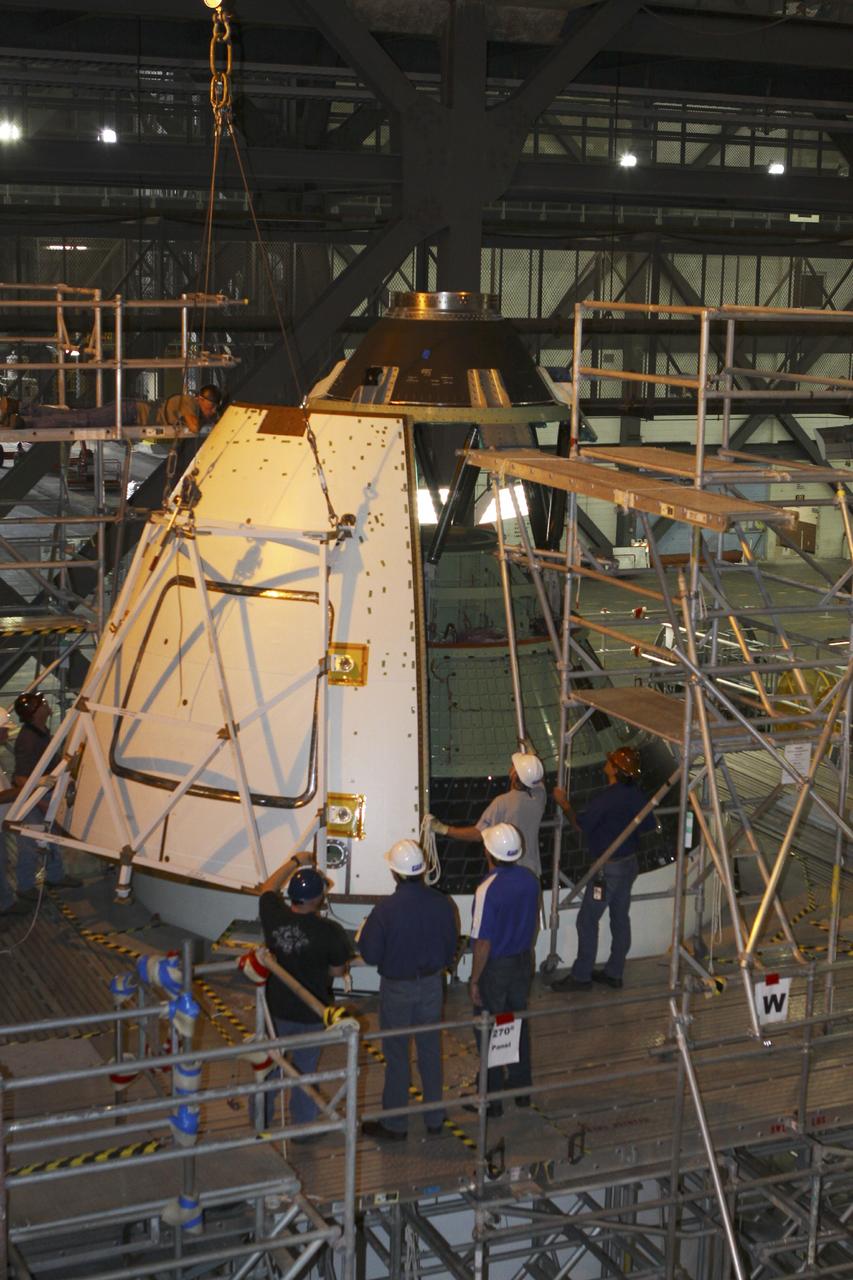
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, three ogive panels have been installed on the Orion ground test vehicle in Vehicle Assembly Building high bay 4. The fourth ogive panel is being lifted by crane for installation. The ogive panels enclose and protect the Orion spacecraft and attach to the Launch Abort System. The test vehicle is being used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for path finding operations, including simulated manufacturing, assembly and stacking procedures. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Kim Shiflett
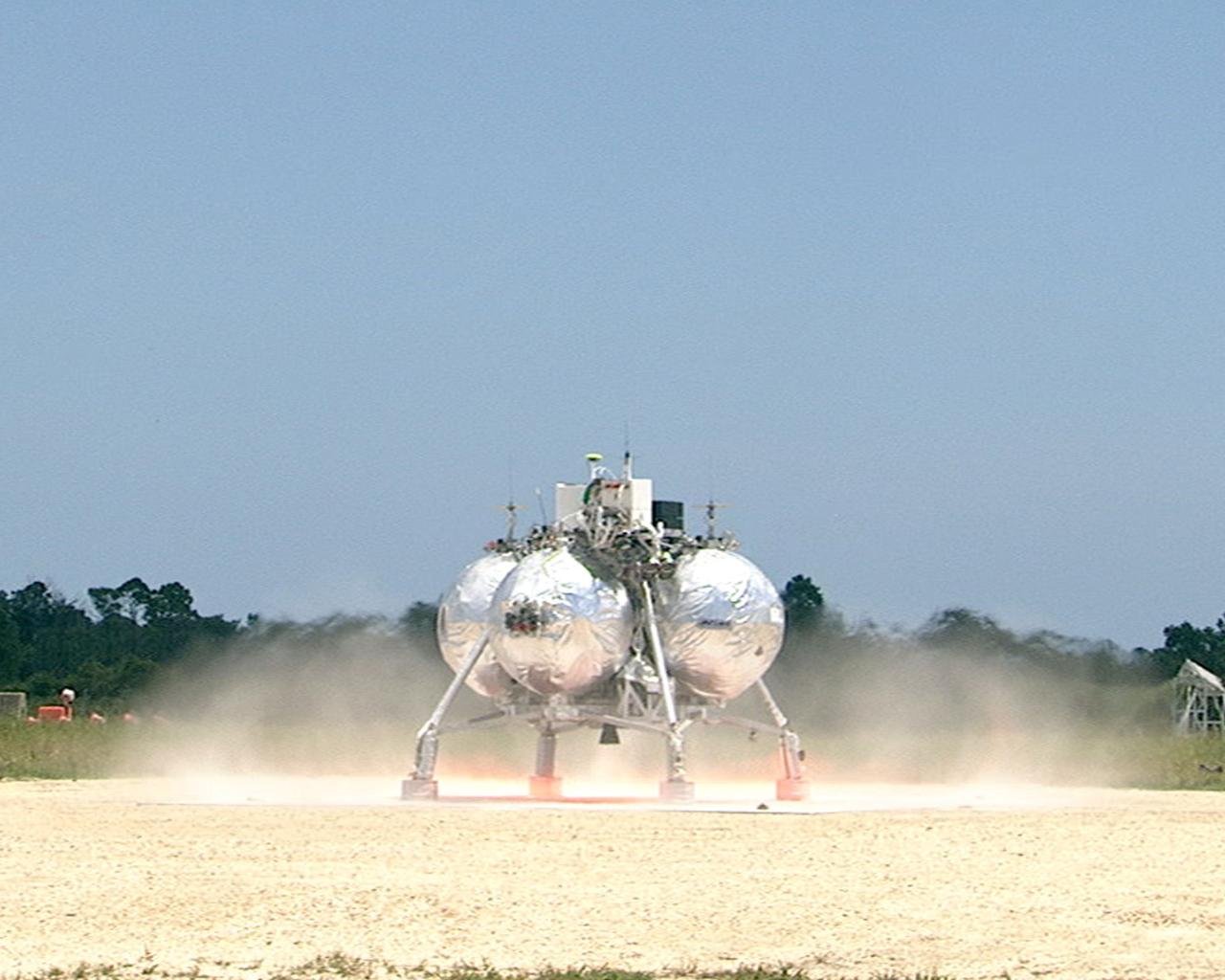

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Morpheus prototype lander begins to lift off of the ground during a free-flight test. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
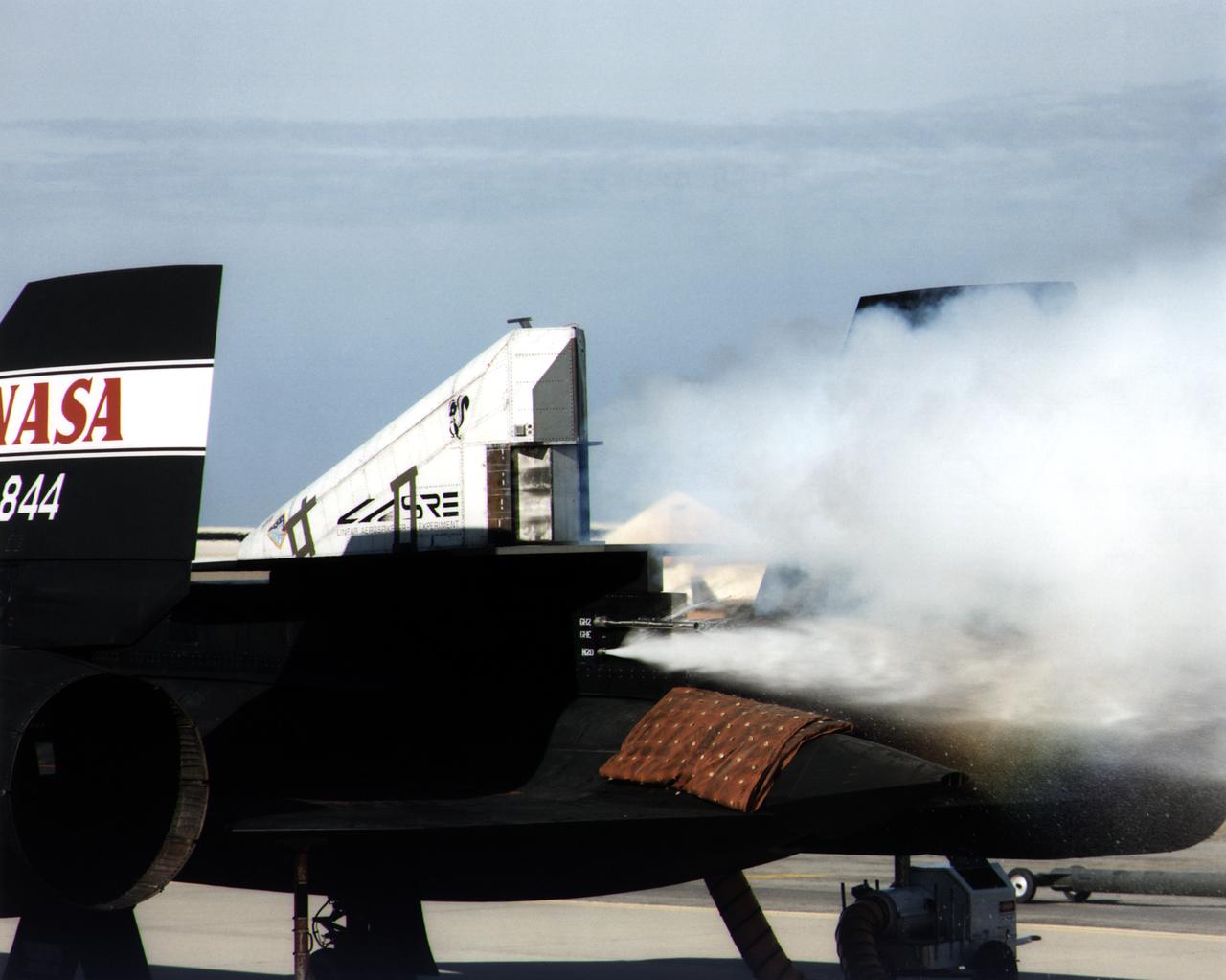

This photograph shows a ground cold flow test of the linear aerospike rocket engine mounted on the rear fuselage of an SR-71.
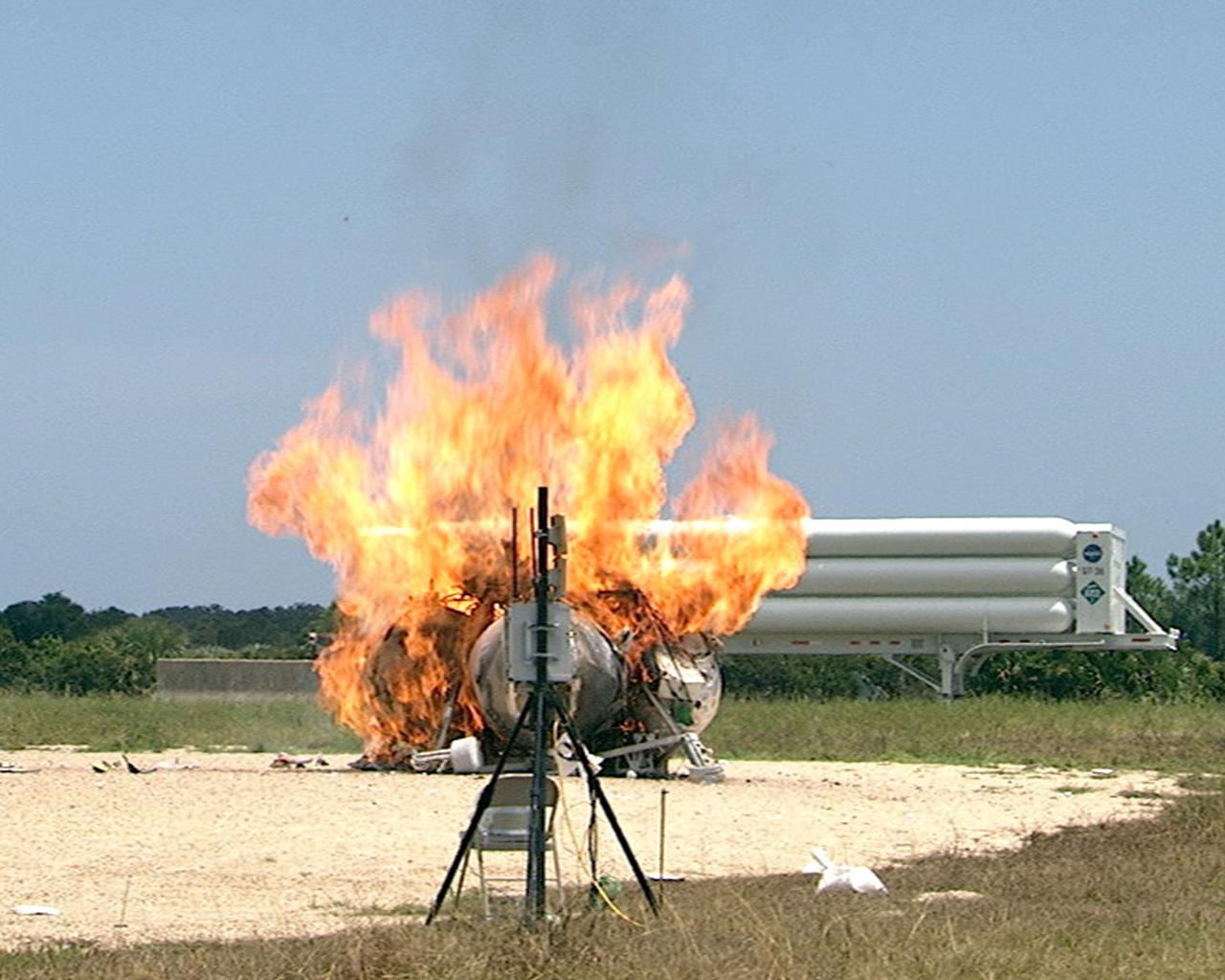

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. No one was injured and the resulting fire was extinguished by Kennedy fire personnel. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
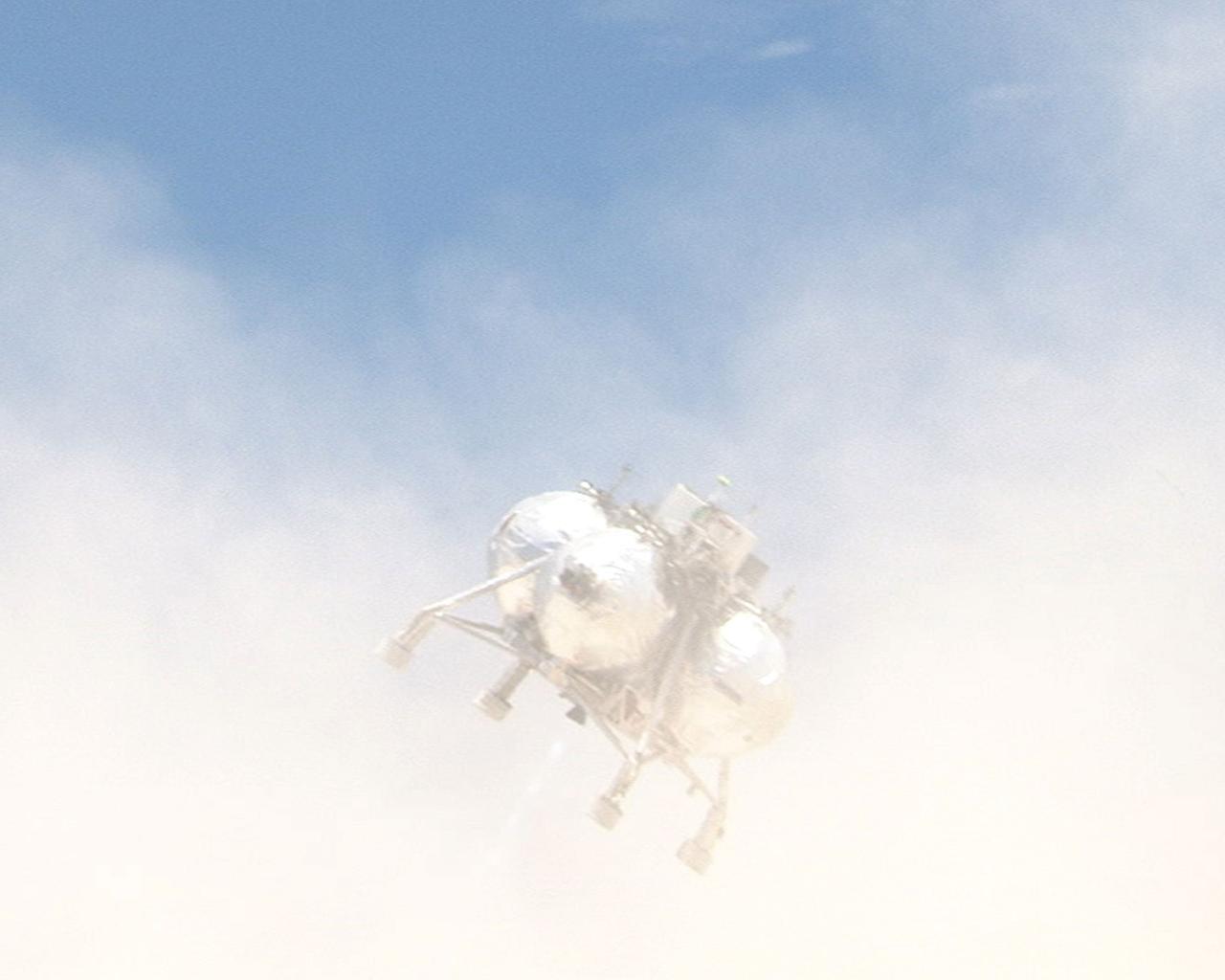

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
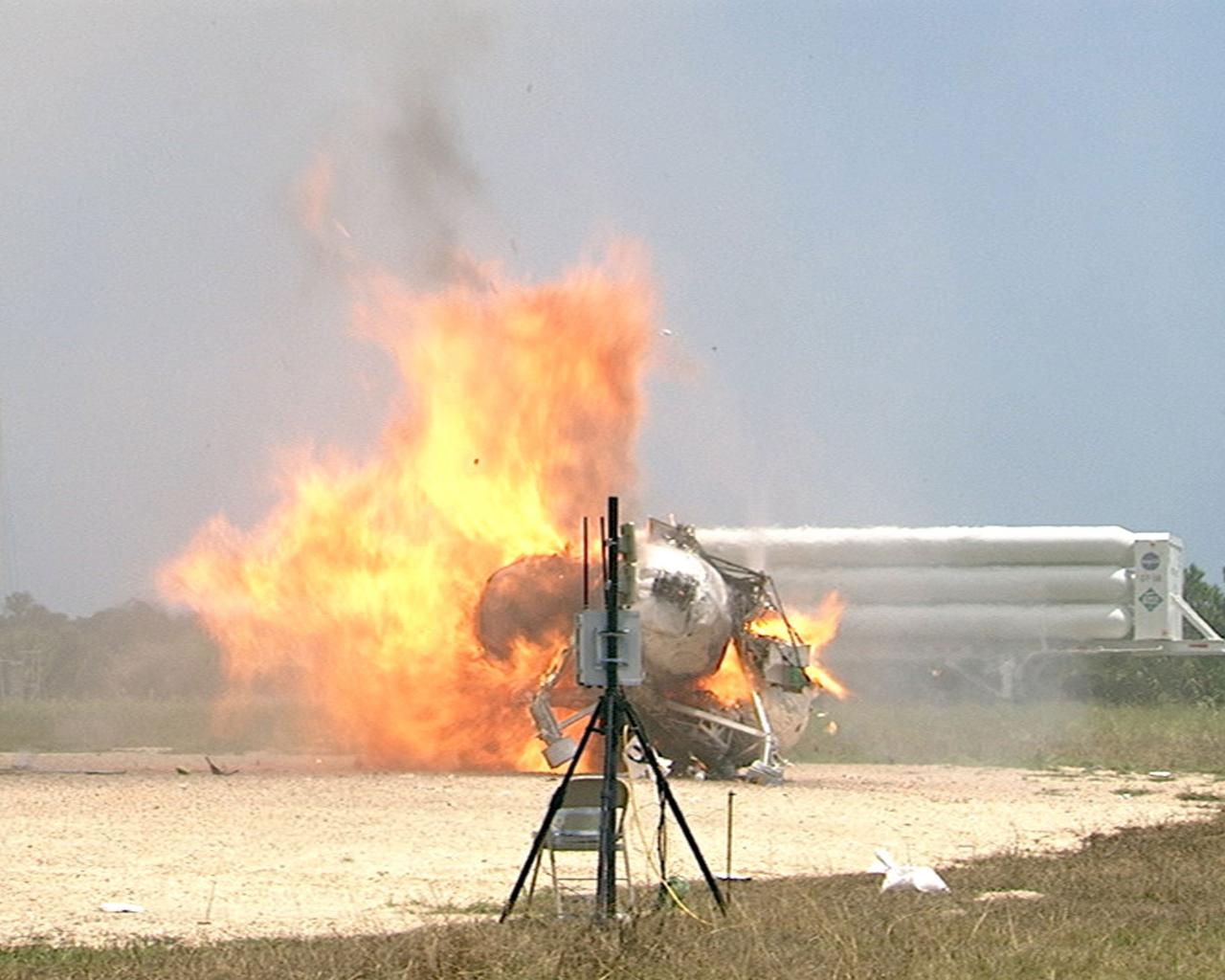

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a free-flight test of the Project Morpheus vehicle at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the vehicle lifted off the ground and then experienced a hardware component failure, which prevented it from maintaining stable flight. No one was injured and the resulting fire was extinguished by Kennedy fire personnel. Engineers are looking into the test data and the agency will release information as it becomes available. Failures such as these were anticipated prior to the test, and are part of the development process for any complex spaceflight hardware. Testing of the prototype lander had been ongoing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston in preparation for its first free-flight test at Kennedy Space Center. Morpheus was manufactured and assembled at JSC and Armadillo Aerospace. Morpheus is large enough to carry 1,100 pounds of cargo to the moon – for example, a humanoid robot, a small rover, or a small laboratory to convert moon dust into oxygen. The primary focus of the test is to demonstrate an integrated propulsion and guidance, navigation and control system that can fly a lunar descent profile to exercise the Autonomous Landing and Hazard Avoidance Technology, or ALHAT, safe landing sensors and closed-loop flight control. For more information on Project Morpheus, visit http://morpheuslander.jsc.nasa.gov/. Photo credit: NASA
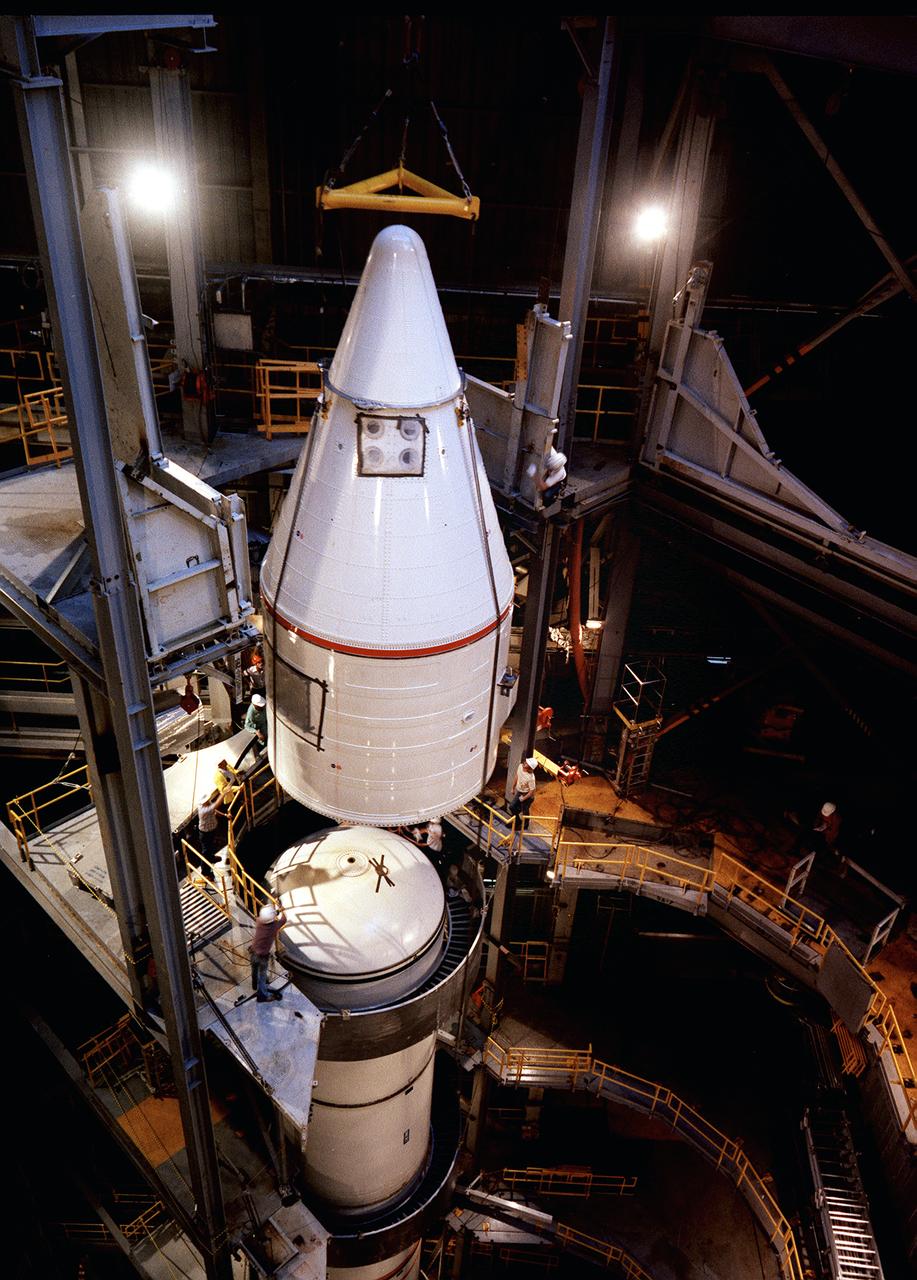

Workmen in the Dynamic Test Stand lowered the nose cone into place to complete stacking of the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The SRB would be attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT was to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB'S to which the ET was attached.
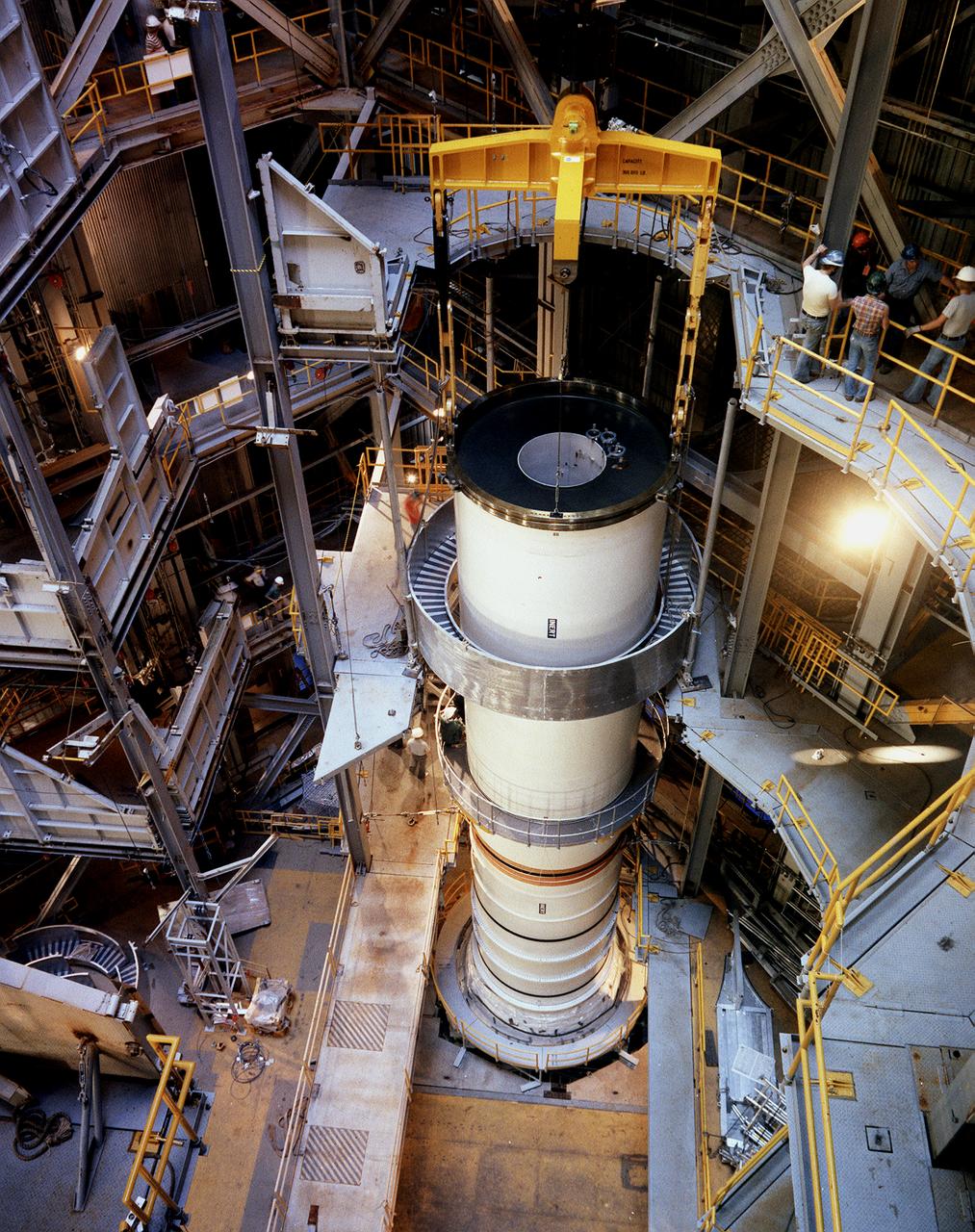

This photograph shows stacking of the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) segments in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Staging shown here are the aft skirt, aft segment, and aft center segment. The SRB was attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT is to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB's to which the ET was attached.
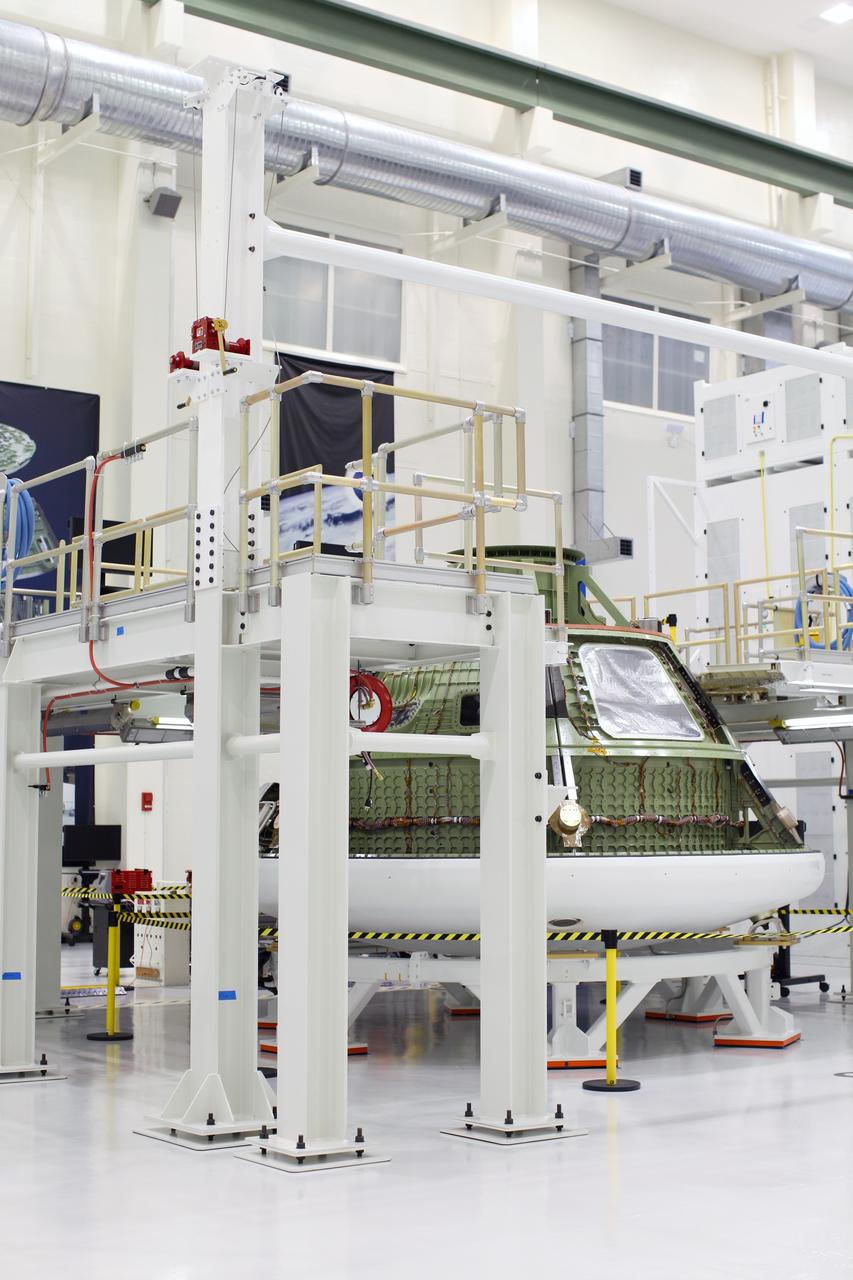

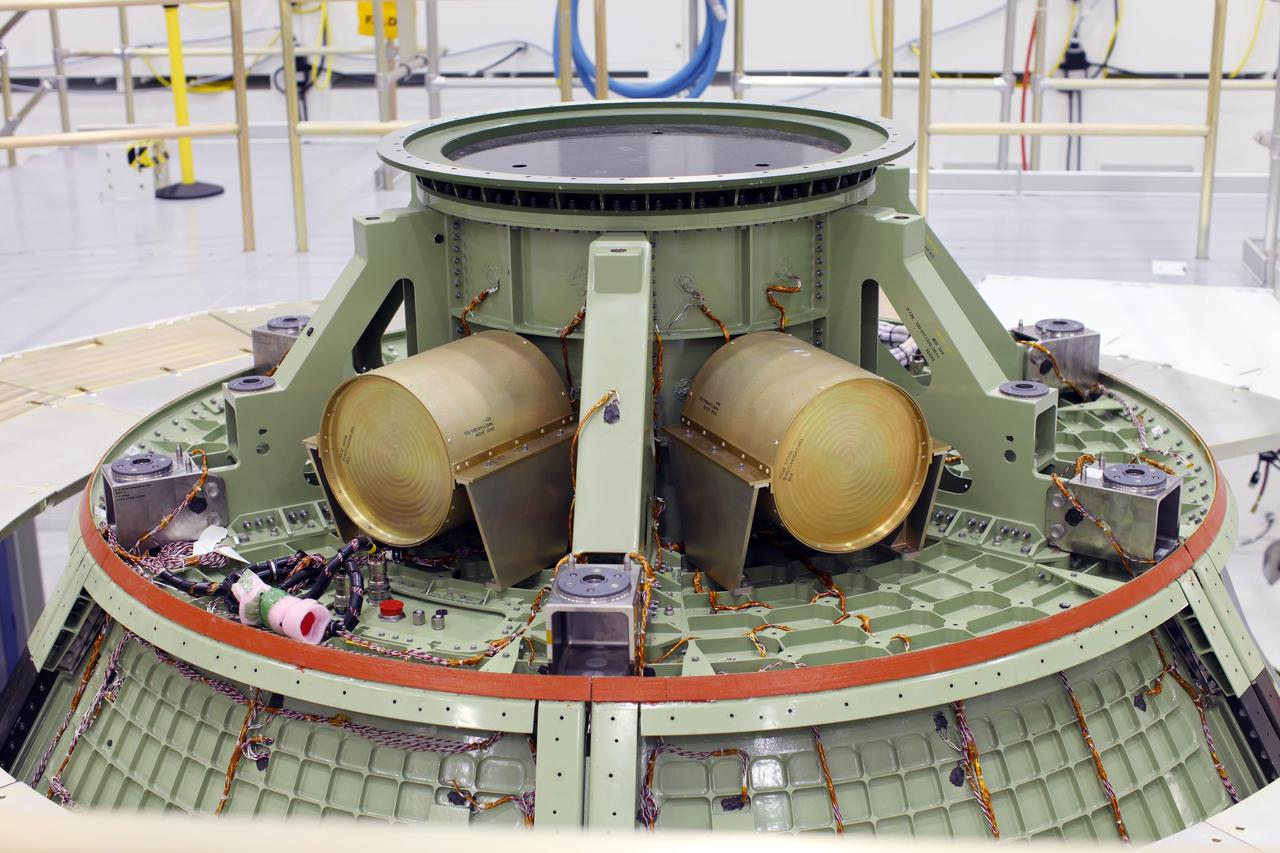
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
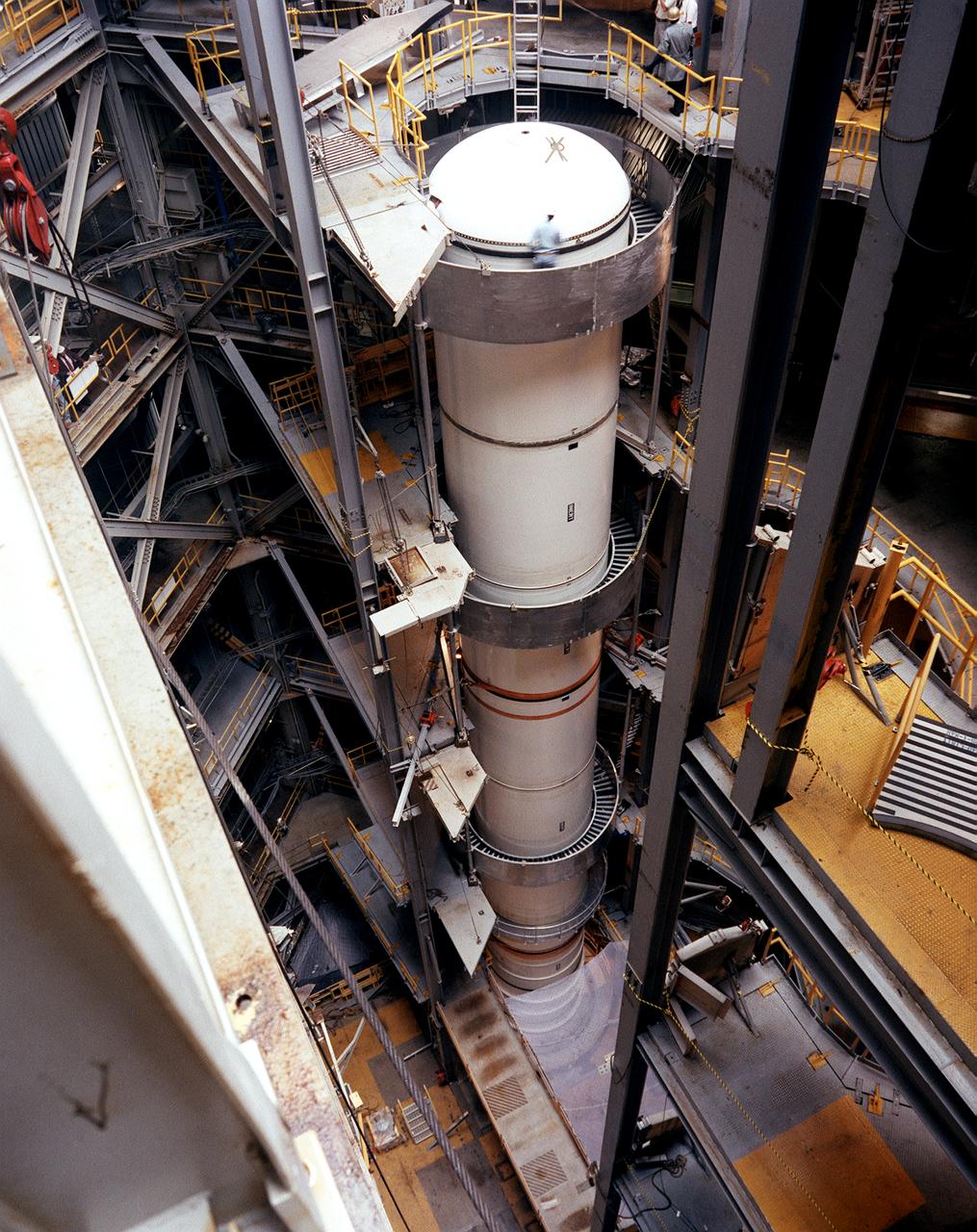
This photograph shows the left side of the solid rocket booster (SRB) segment as it awaits being mated to the nose cone and forward skirt in the Dynamic Test Stand at the east test area of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The SRB would be attached to the external tank (ET) and then the orbiter later for the Mated Vertical Ground Vibration Test (MVGVT), that resumed in October 1978. The stacking of a complete Shuttle in the Dynamic Test Stand allowed test engineers to perform ground vibration testing on the Shuttle in its liftoff configuration. The purpose of the MVGVT was to verify that the Space Shuttle would perform as predicted during launch. The platforms inside the Dynamic Test Stand were modified to accommodate two SRB's to which the ET was attached.
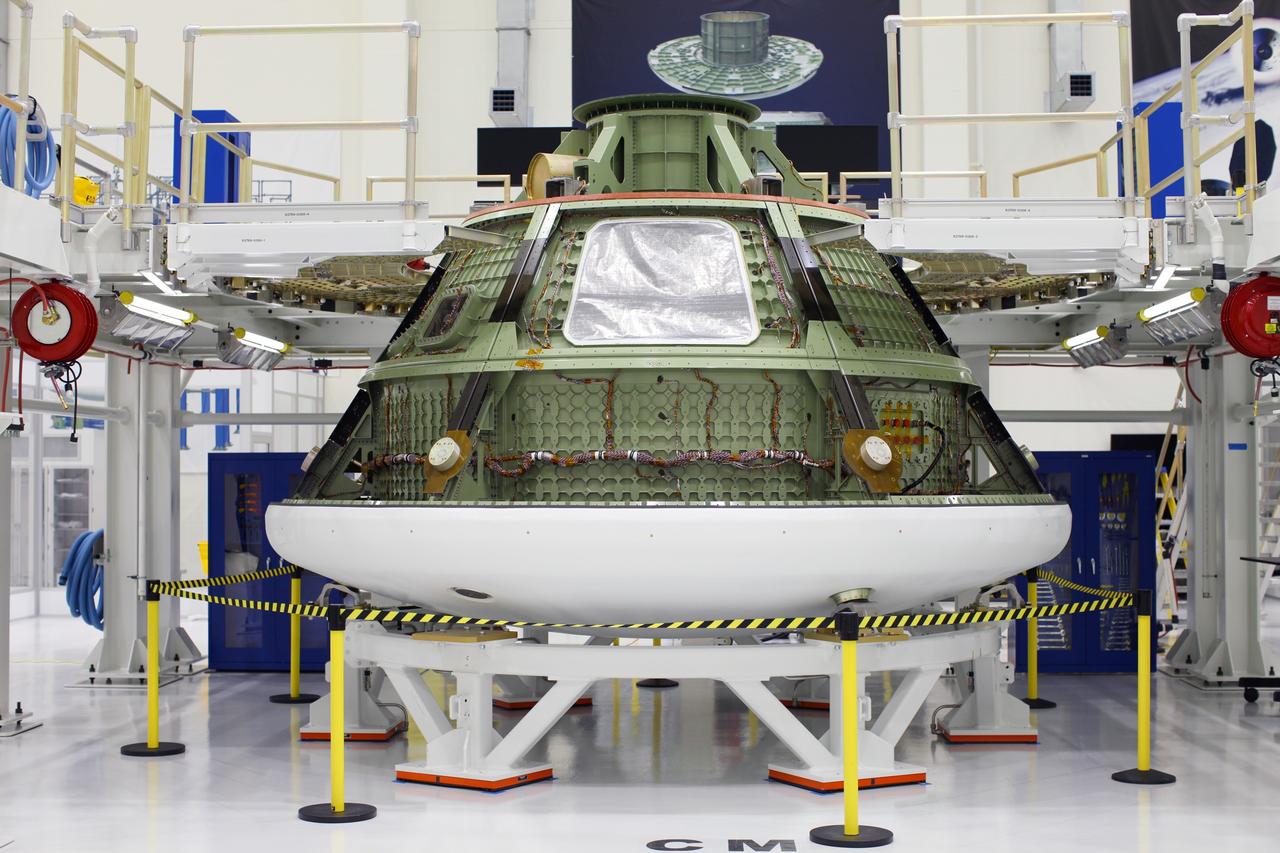

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion ground test vehicle sits in a work stand. The heat panels have been removed. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
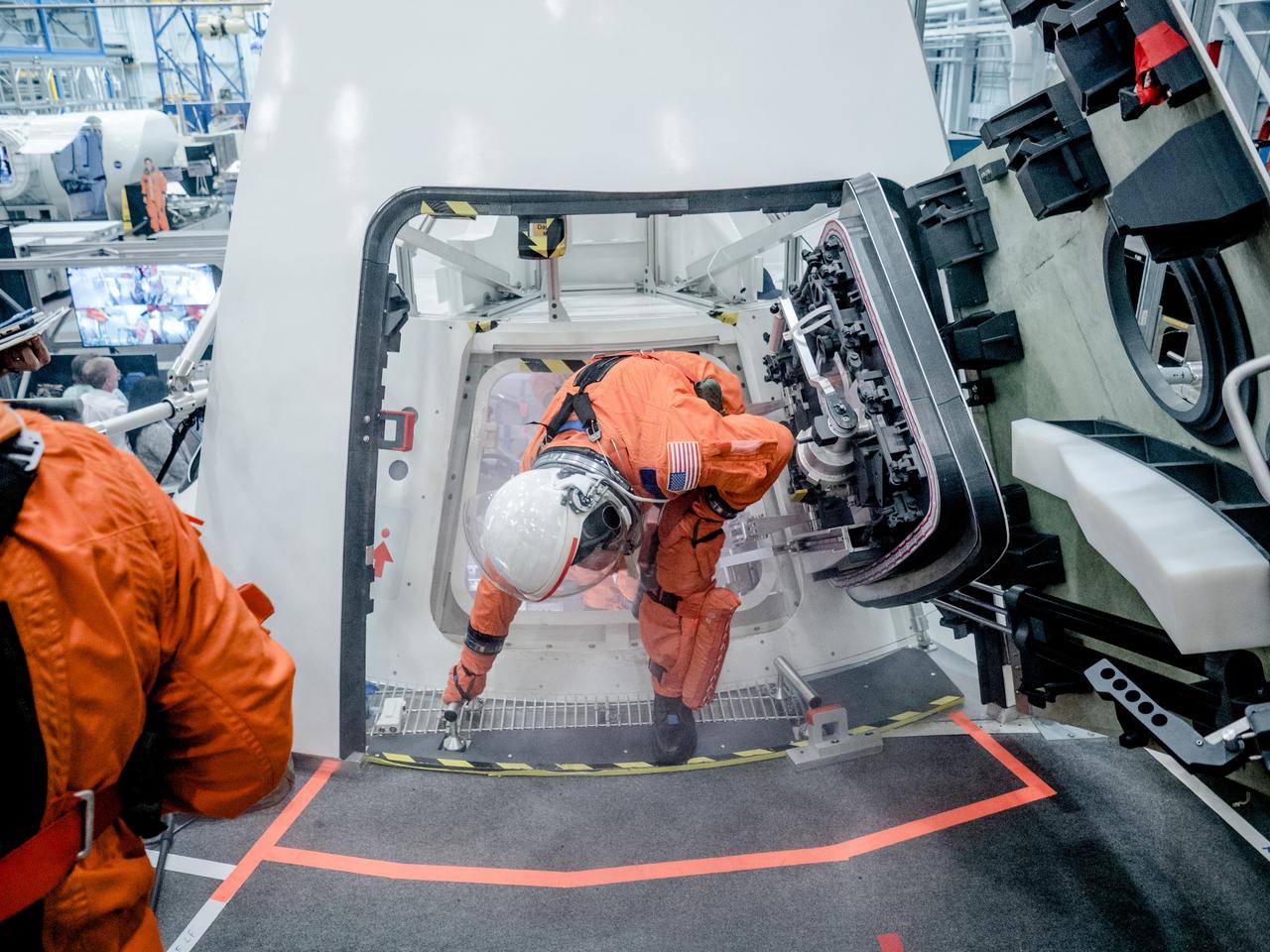

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..
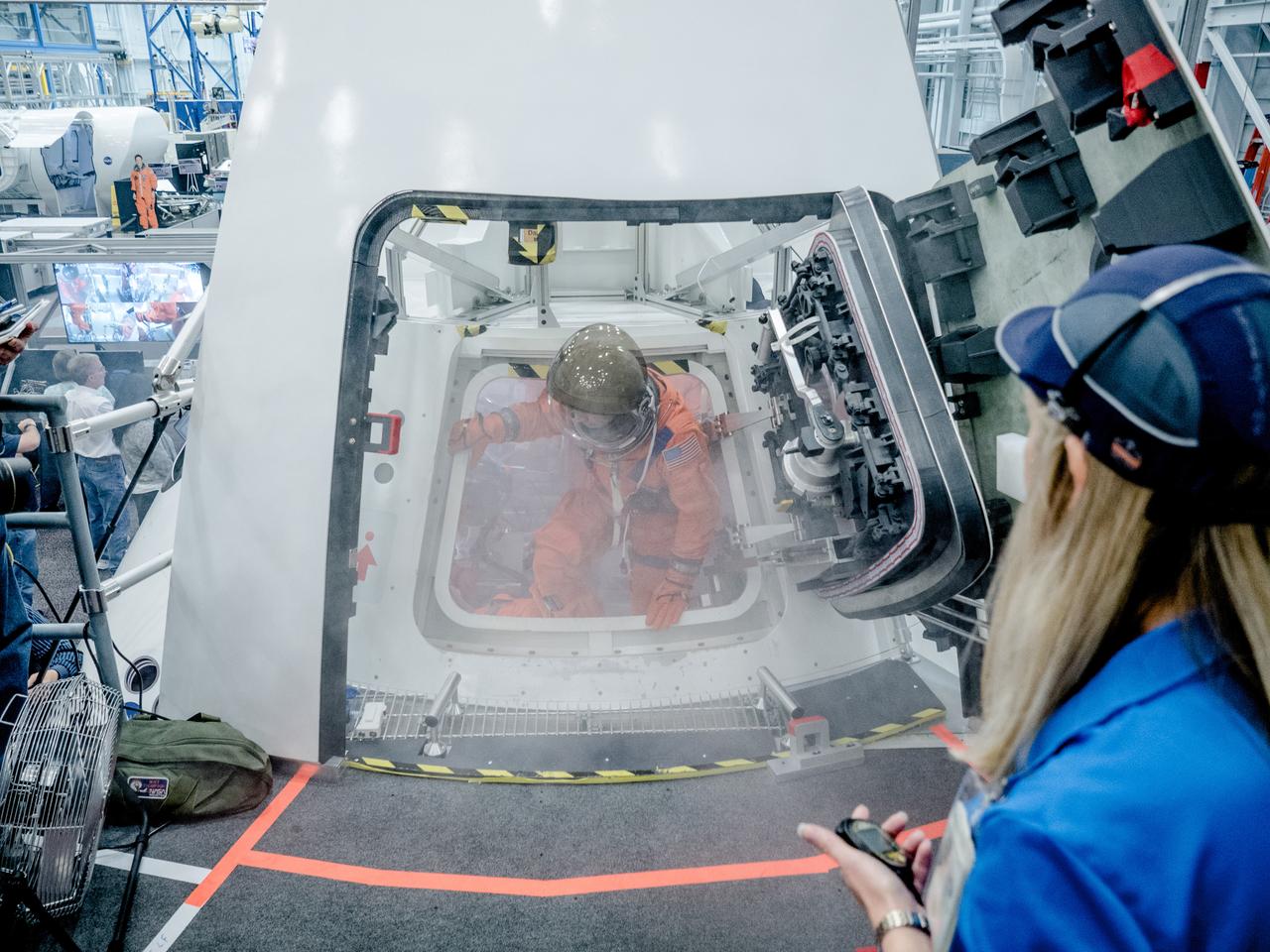

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..
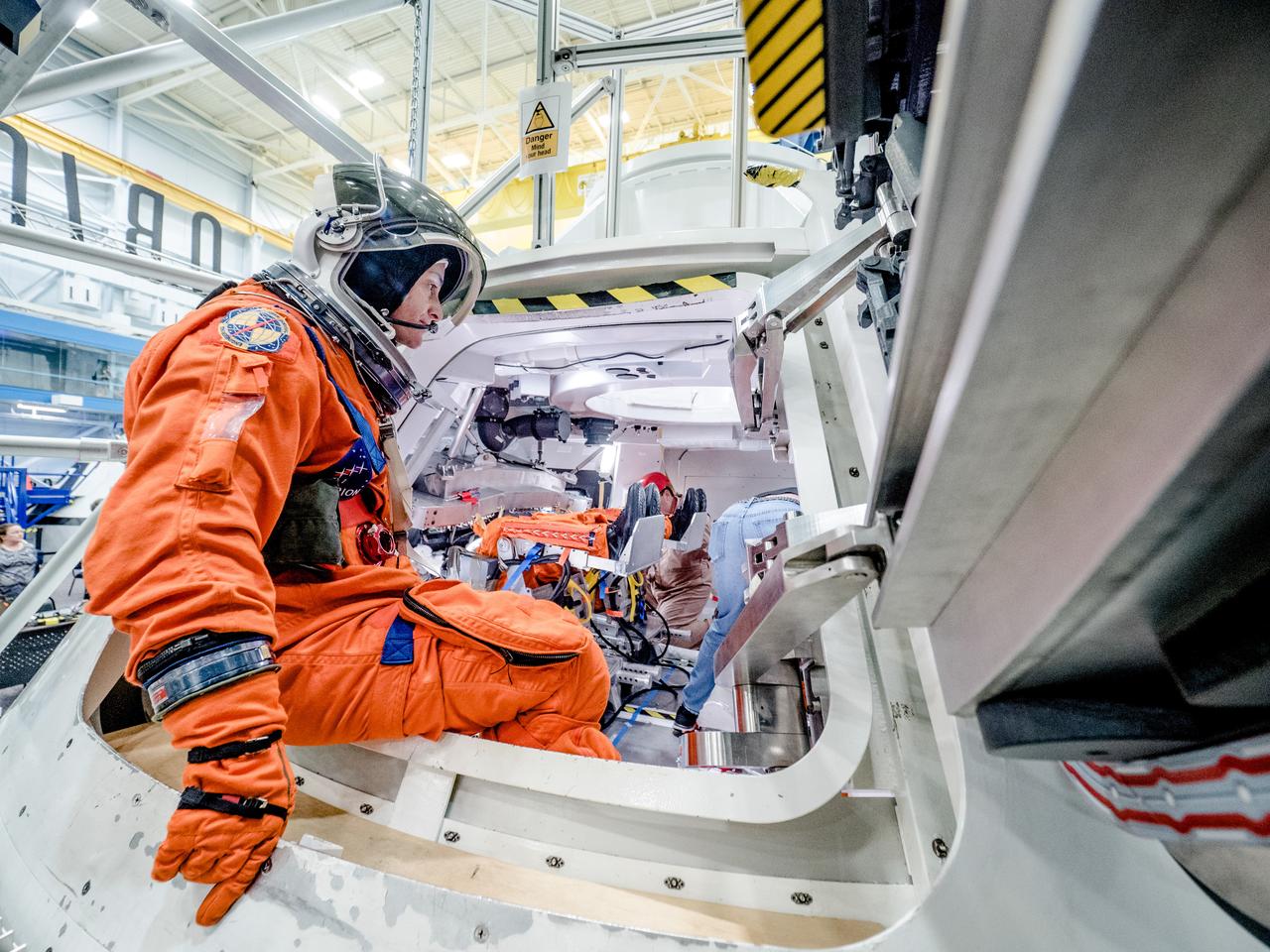

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..
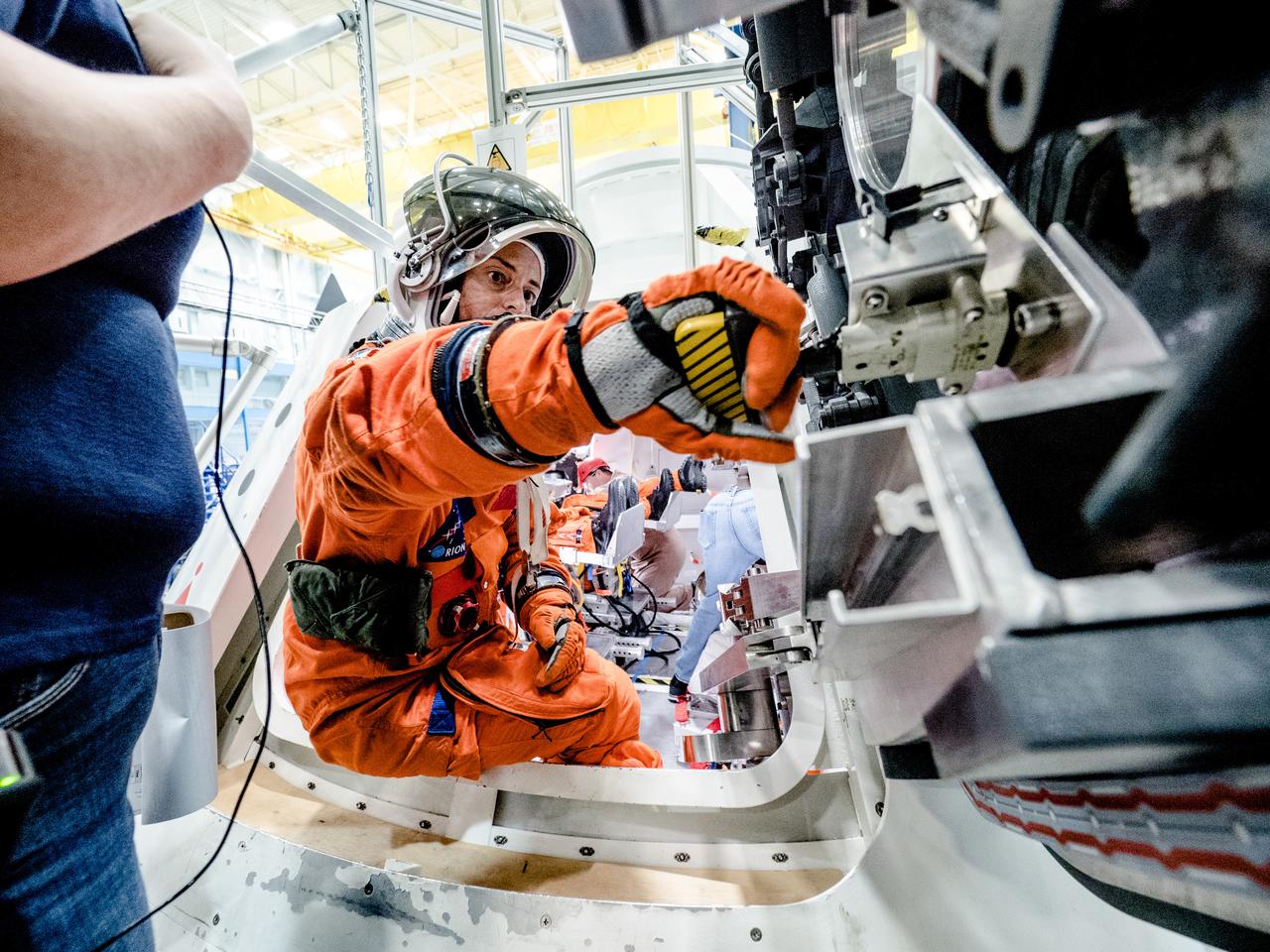

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..

NASA is performing a series of tests to evaluate how astronauts and ground crew involved in final preparations before Orion missions will quickly get out of the spacecraft if an emergency were to occur on the pad prior to launch. In the hours before astronauts launch to space in Orion from NASA’s modernized spaceport in Florida in on the agency’s Space Launch System rocket, they will cross the Crew Access Arm 300 feet above the ground and climb inside the crew module with the assistance of ground personnel trained to help them strap into their seats and take care of last-minute needs. The testing is helping engineers evaluate hardware designs and establish procedures that would be used to get astronauts and ground crew out of the capsule as quickly as possible. Flight and ground crew are required to get out of Orion within two minutes to protect for a variety of failure scenarios that do not require the launch abort system to be activated, such as crew incapacitation, fire or the presence of toxins in the cabin. This testing took place the week of Oct. 30, 2017 using the Orion mockup in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. In this photo, engineers used fake smoke to imitate a scenario in which astronauts must exit the capsule when their vision is obscured. Markings on the ground indicate where the Crew Access Arm would be located and help guide the crew. This testing is a collaborative effort between the Orion and Ground Systems Development and Operations programs. Previous egress testing at Johnson and in the Gulf of Mexico has evaluated how crew will exit the spacecraft at the end of their missions..
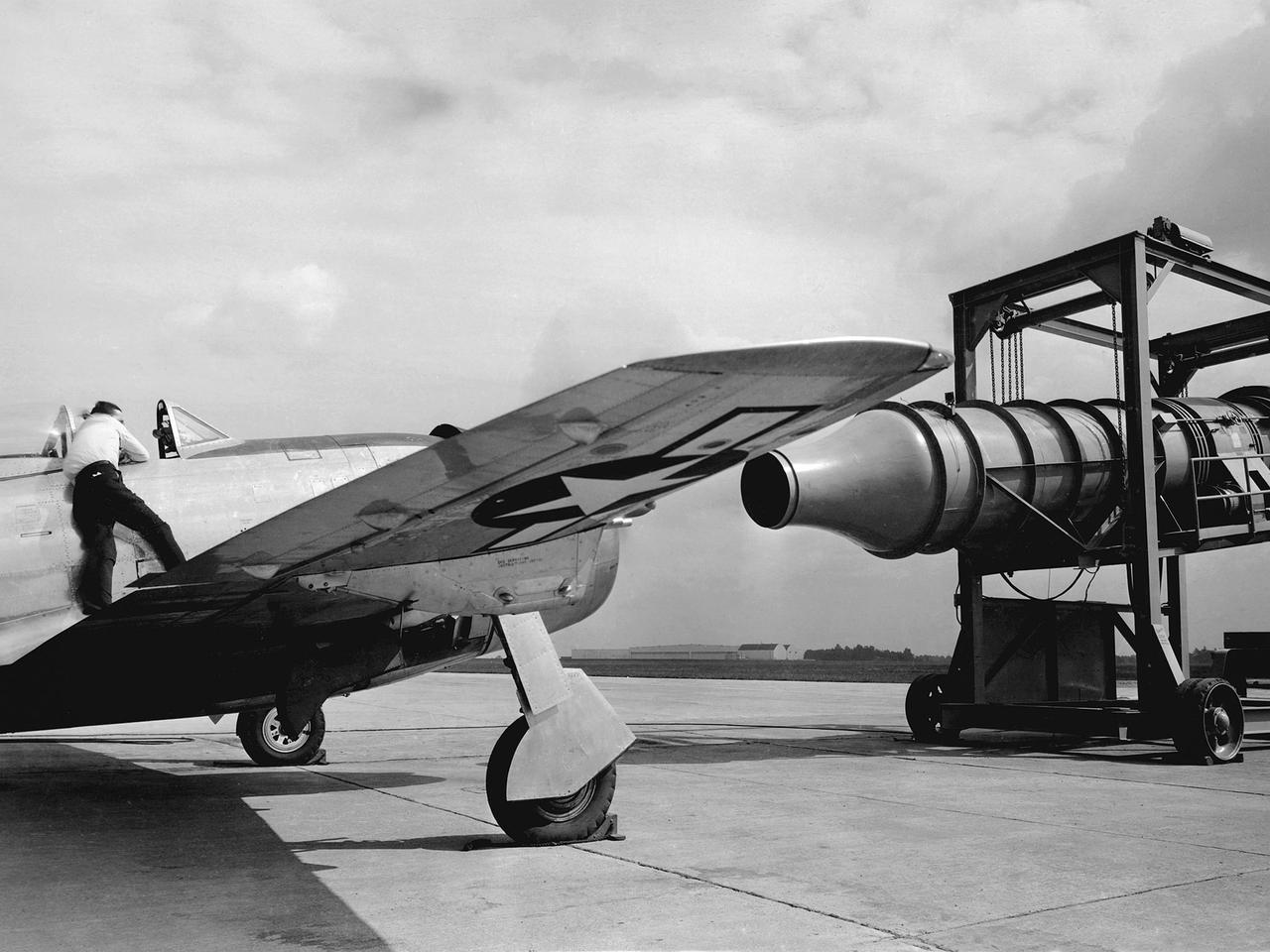

A Republic P-47G Thunderbolt is tested with a large blower on the hangar apron at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The blower could produce air velocities up to 250 miles per hour. This was strong enough to simulate take-off power and eliminated the need to risk flights with untried engines. The Republic P-47G was loaned to the laboratory to test NACA modifications to the Wright R-2800 engine’s cooling system at higher altitudes. The ground-based tests, seen here, were used to map the engine’s normal operating parameters. The P-47G then underwent an extensive flight test program to study temperature distribution among the engine’s 18 cylinders and develop methods to improve that distribution.
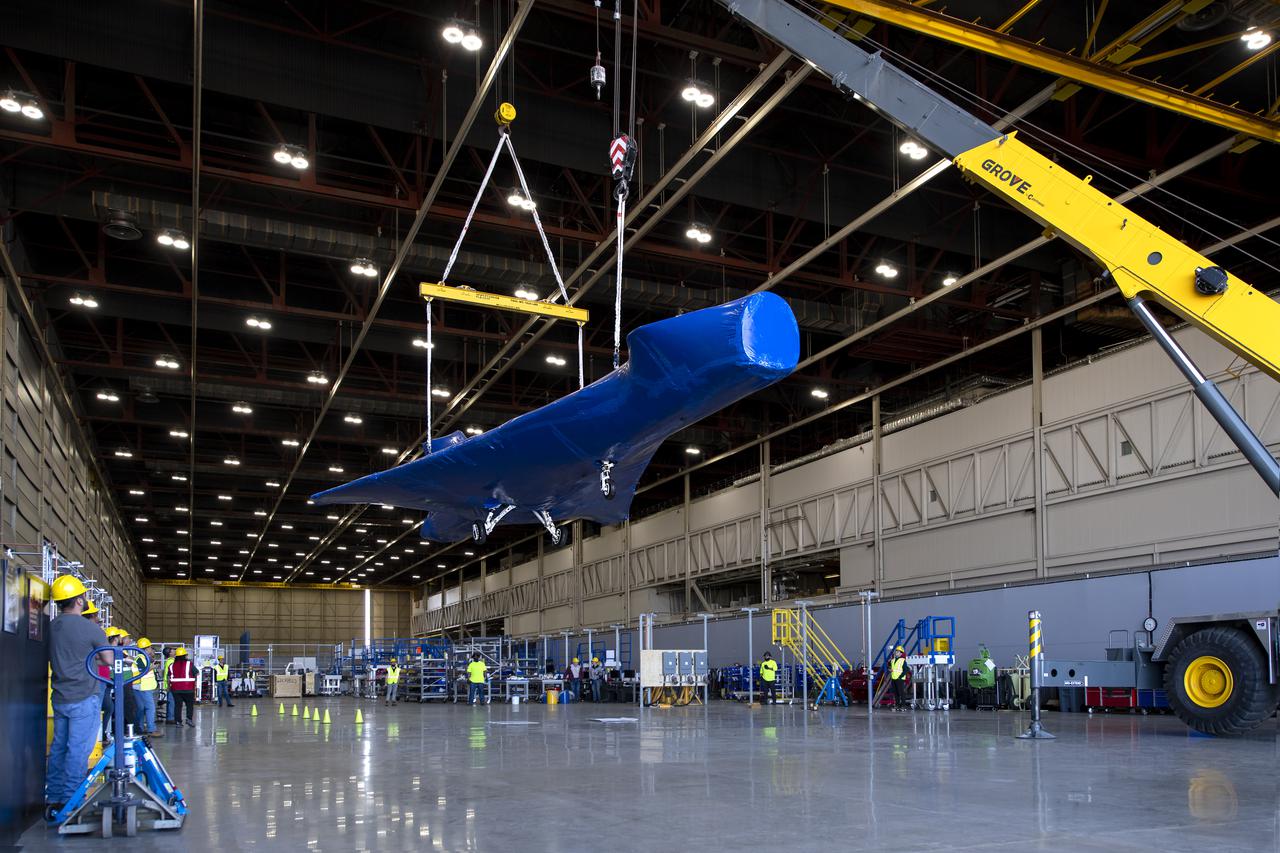

The X-59, NASA’s quiet supersonic technology experimental aircraft, is suspended in the air at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, following several months of critical ground testing in Ft. Worth, Texas
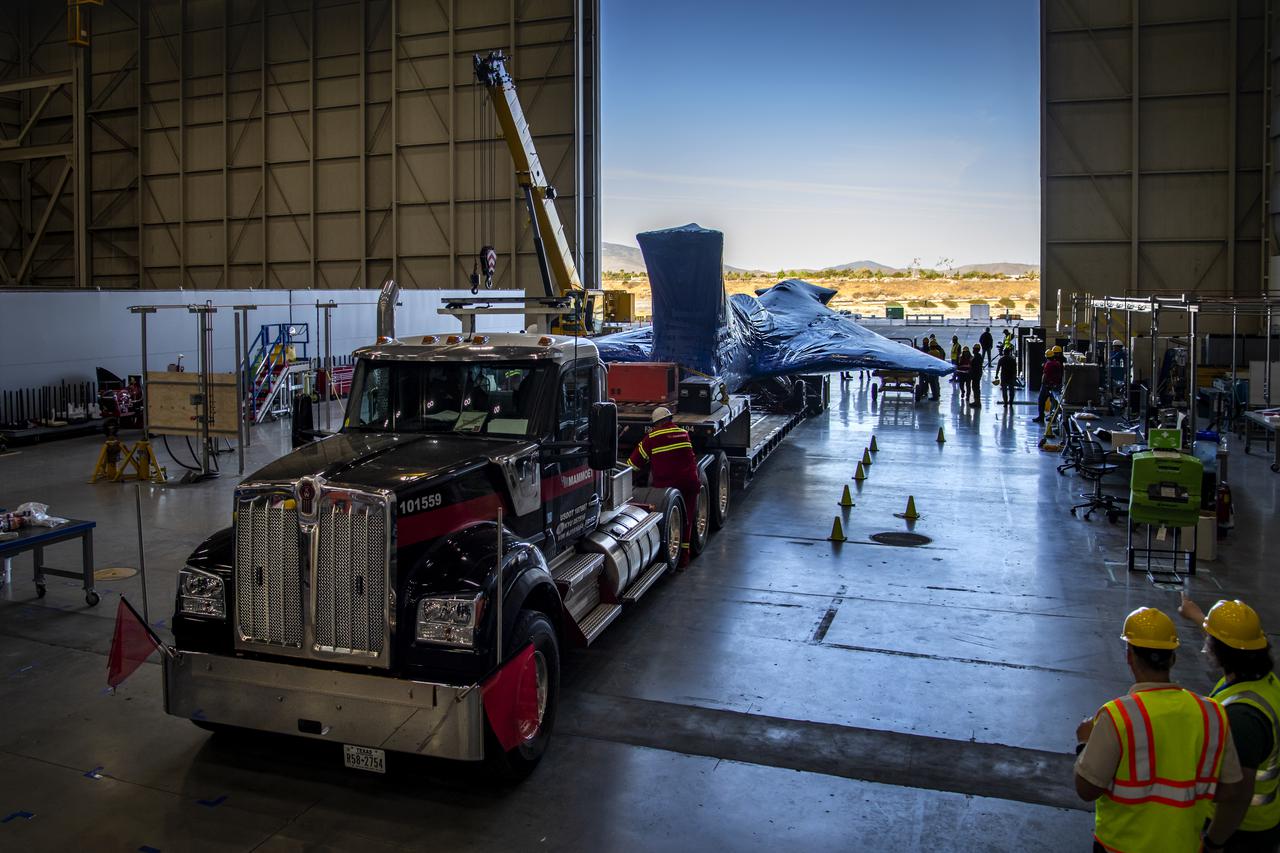

The X-59, NASA’s quiet supersonic technology experimental aircraft, arrives back at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, following several months of critical ground testing in Ft. Worth, Texas
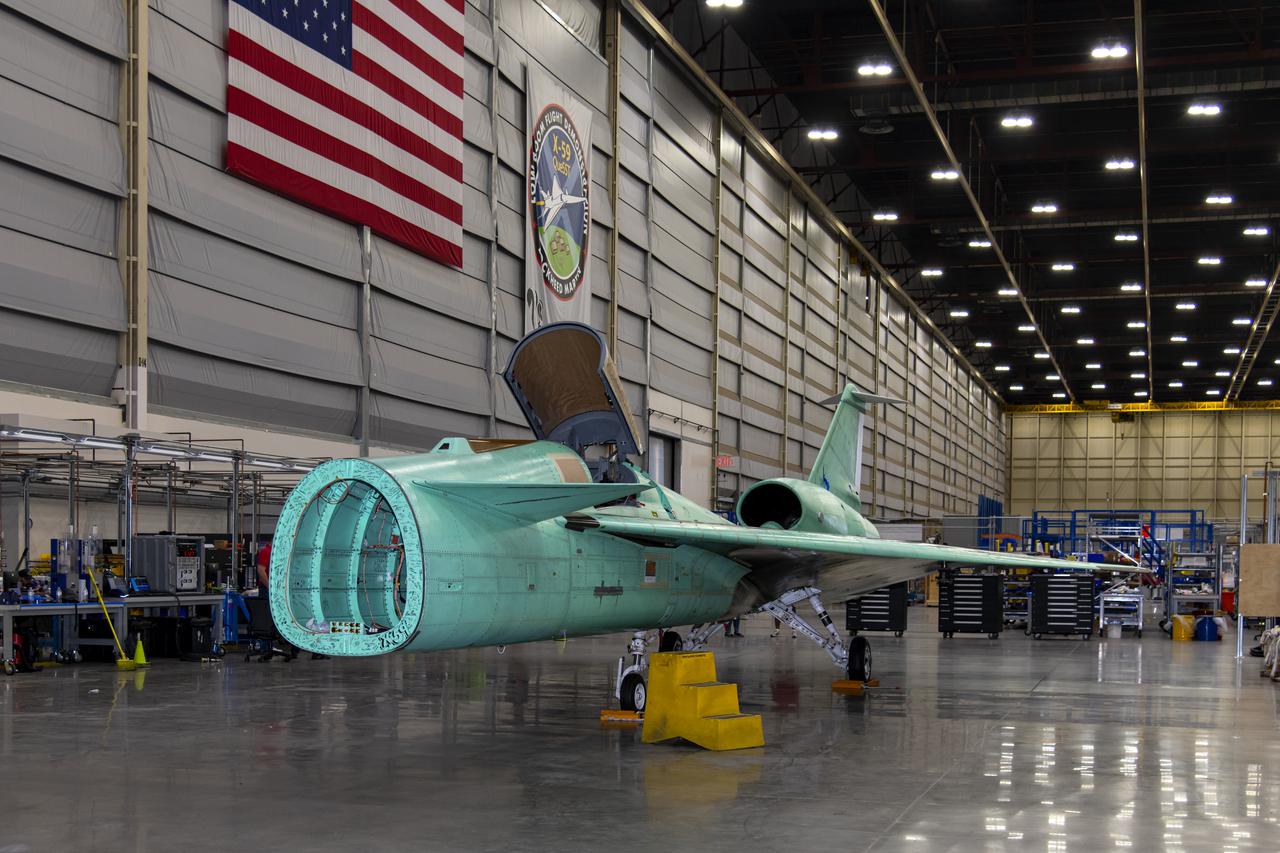

The X-59, NASA's quiet supersonic technology experimental aircraft, sits in Lockheed Martin's Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California, following its return from several months of critical ground testing in Ft. Worth, Texas
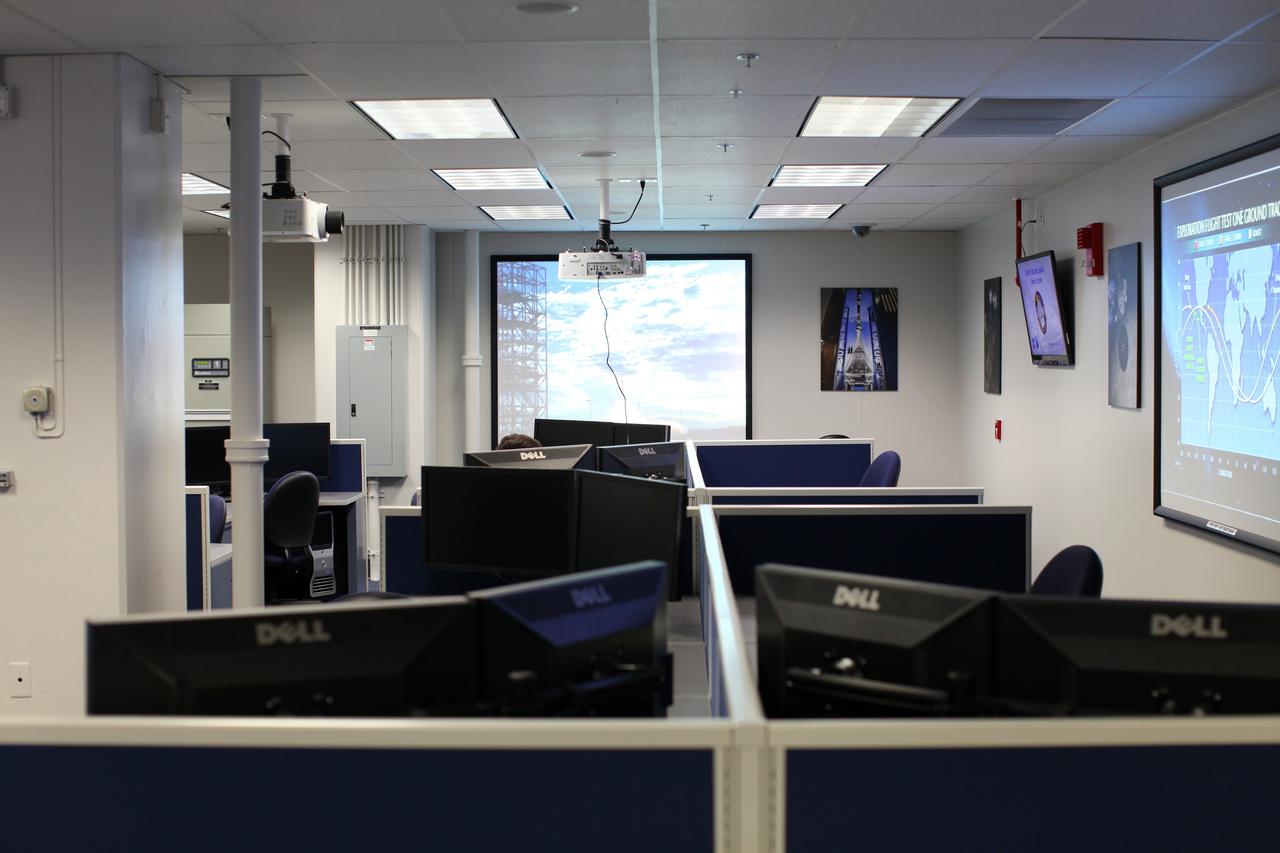

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
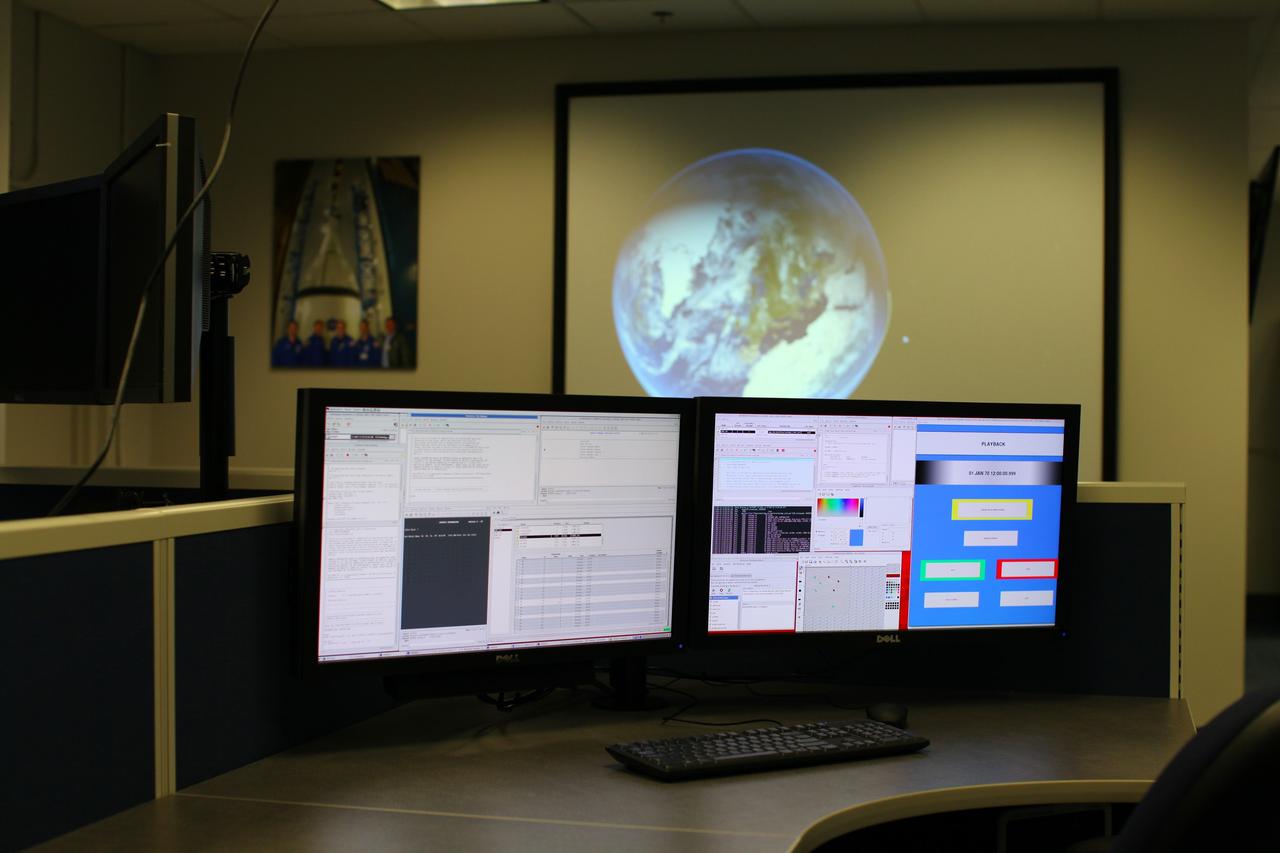
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, media tour the new Orion Test and Launch Control Center. During a tour of the facility, media representatives viewed Orion, several processing stations, and the Orion Test and Launch Control Center. The ground test vehicle will remain at Kennedy for acoustic and modal testing. The heat shield on the bottom of the module will be removed and replaced with a more flight-like heat shield that was built by Lockheed Martin in Denver and will be shipped to Kennedy for installation. The test vehicle will then be in its vehicle configuration for the splashdown test at Langley as NASA prepares for Exploration Flight Test-1. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

The team that tested the umbilical lines and accessories that will connect from the mobile launcher to NASA's Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 hold a banner signing event July 24, 2018, to mark completion of testing at the Launch Equipment Test Facility (LETF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Attending the event is Mike Bolger, center, Exploration Ground Systems manager. A total of 21 umbilicals and launch accessories were tested on various simulators at the LETF before they were transferred to the mobile launcher for installation.
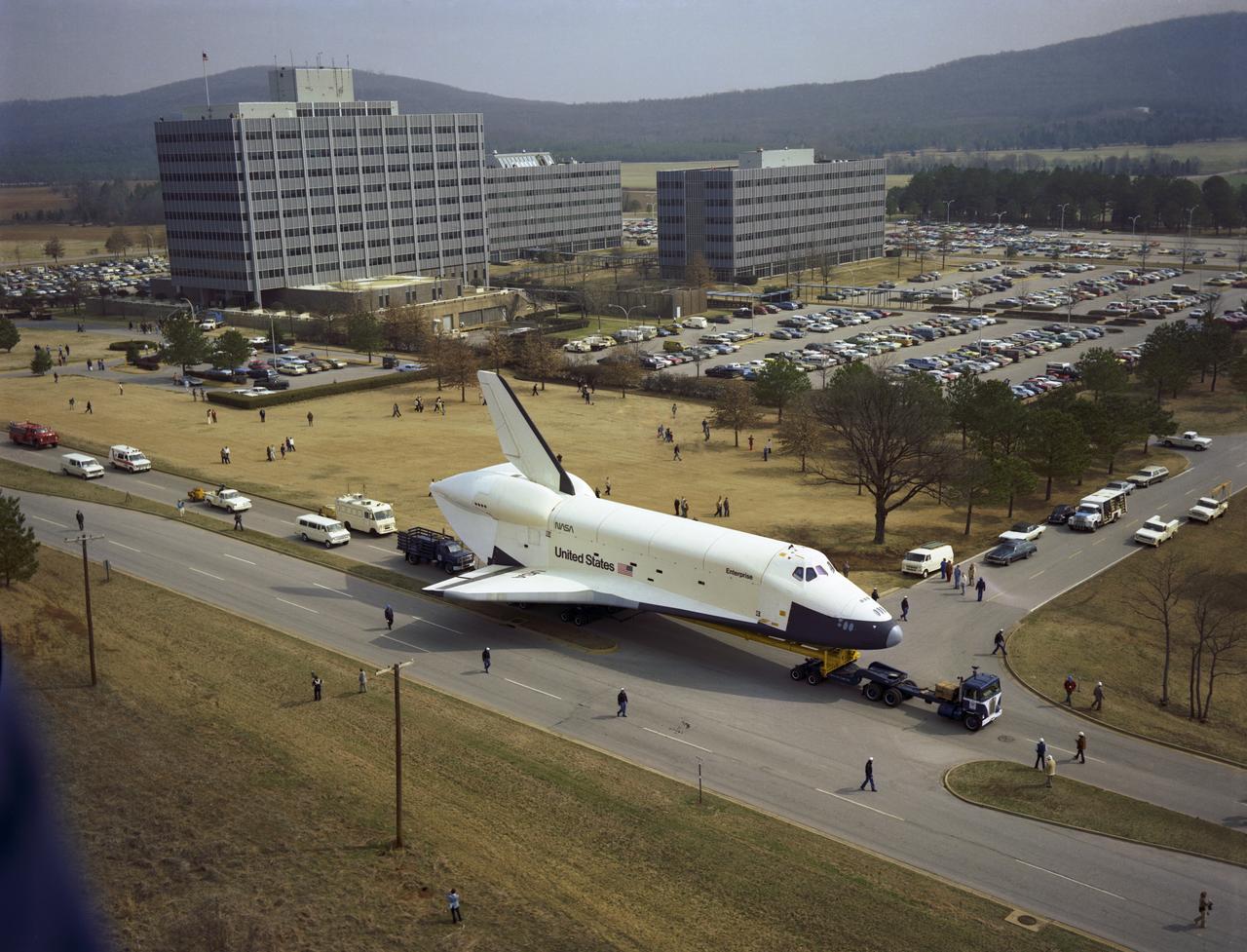

In this view, the Shuttle Orbiter Enterprise is seen heading South on Rideout Road with Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC'S) administrative 4200 Complex in the background, as it is being transported to MSFC's building 4755 for later Mated Vertical Ground Vibration tests (MVGVT) at MSFC's Dynamic Test Stand. The tests marked the first time ever that the entire shuttle complement (including Orbiter, external tank, and solid rocket boosters) were mated vertically.

NASA’s all-electric X-57 Maxwell prepares for ground vibration testing, or GVT, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Done in parallel with cruise motor controller testing, the GVT tested the vehicle at various vibration levels, helping engineers to examine and validate the integrity of the vehicle for flight conditions. A goal of X-57 is to help the Federal Aviation Administration set certification standards for emerging electric aircraft markets.

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. In this photo, taken July 10, 1961, actual ground breaking has occurred for the S-IC test stand site.

At its founding, the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) inherited the Army’s Jupiter and Redstone test stands, but much larger facilities were needed for the giant stages of the Saturn V. From 1960 to 1964, the existing stands were remodeled and a sizable new test area was developed. The new comprehensive test complex for propulsion and structural dynamics was unique within the nation and the free world, and they remain so today because they were constructed with foresight to meet the future as well as on going needs. Construction of the S-IC Static test stand complex began in 1961 in the west test area of MSFC, and was completed in 1964. The S-IC static test stand was designed to develop and test the 138-ft long and 33-ft diameter Saturn V S-IC first stage, or booster stage, weighing in at 280,000 pounds. Required to hold down the brute force of a 7,500,000-pound thrust produced by 5 F-1 engines, the S-IC static test stand was designed and constructed with the strength of hundreds of tons of steel and 12,000,000 pounds of cement, planted down to bedrock 40 feet below ground level. The foundation walls, constructed with concrete and steel, are 4 feet thick. The base structure consists of four towers with 40-foot-thick walls extending upward 144 feet above ground level. The structure was topped by a crane with a 135-foot boom. With the boom in the upright position, the stand was given an overall height of 405 feet, placing it among the highest structures in Alabama at the time. In this photo, taken July 10, 1961, actual ground breaking has occurred for the S-IC test stand site.
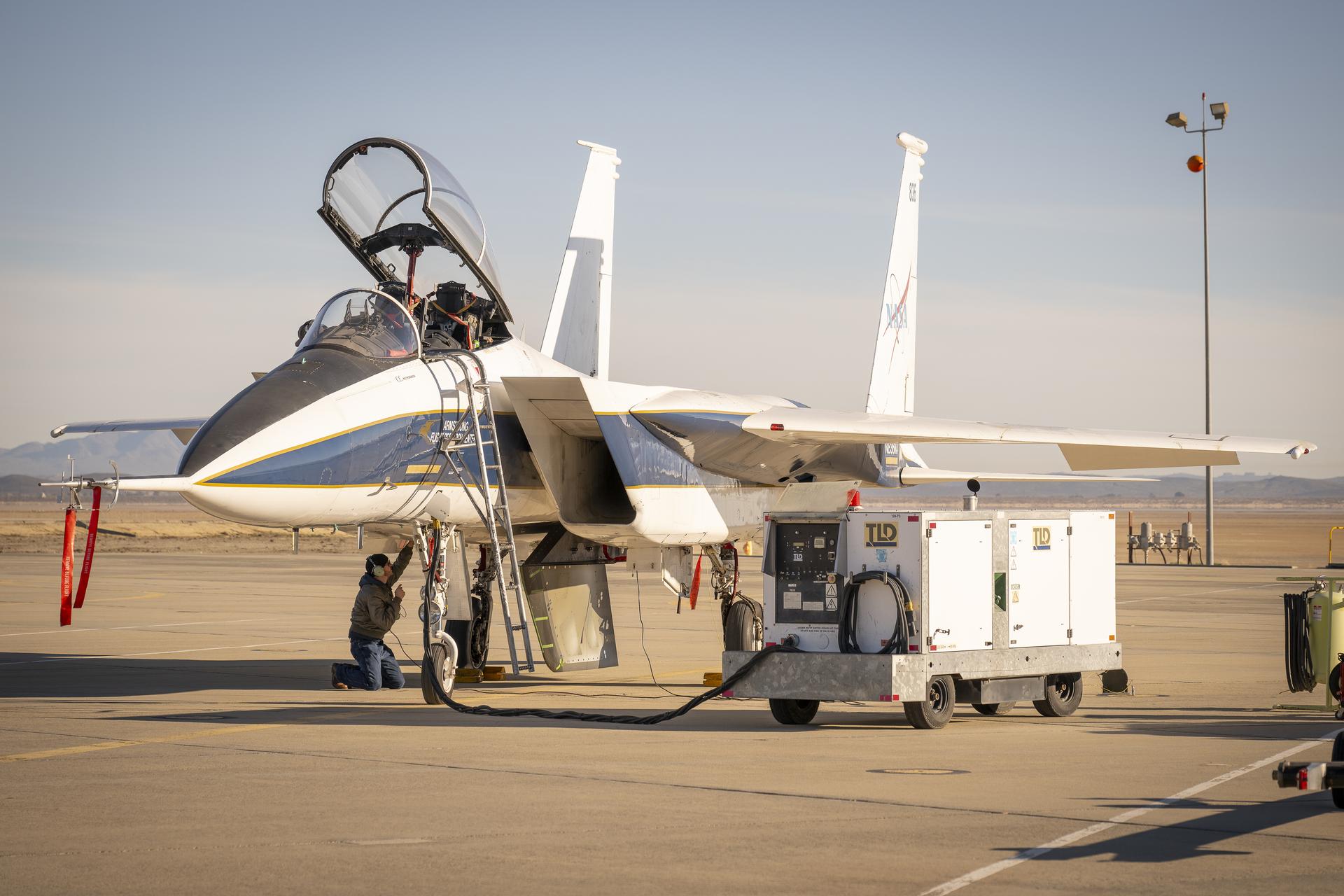

NASA ground crew prepares the agency’s F-15 research aircraft and Cross Flow Attenuated Natural Laminar Flow (CATNLF) test article ahead of its first high-speed taxi test on Tuesday, Jan. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The CATNLF design aims to reduce drag on wing surfaces to improve efficiency and, in turn, reduce fuel burn.
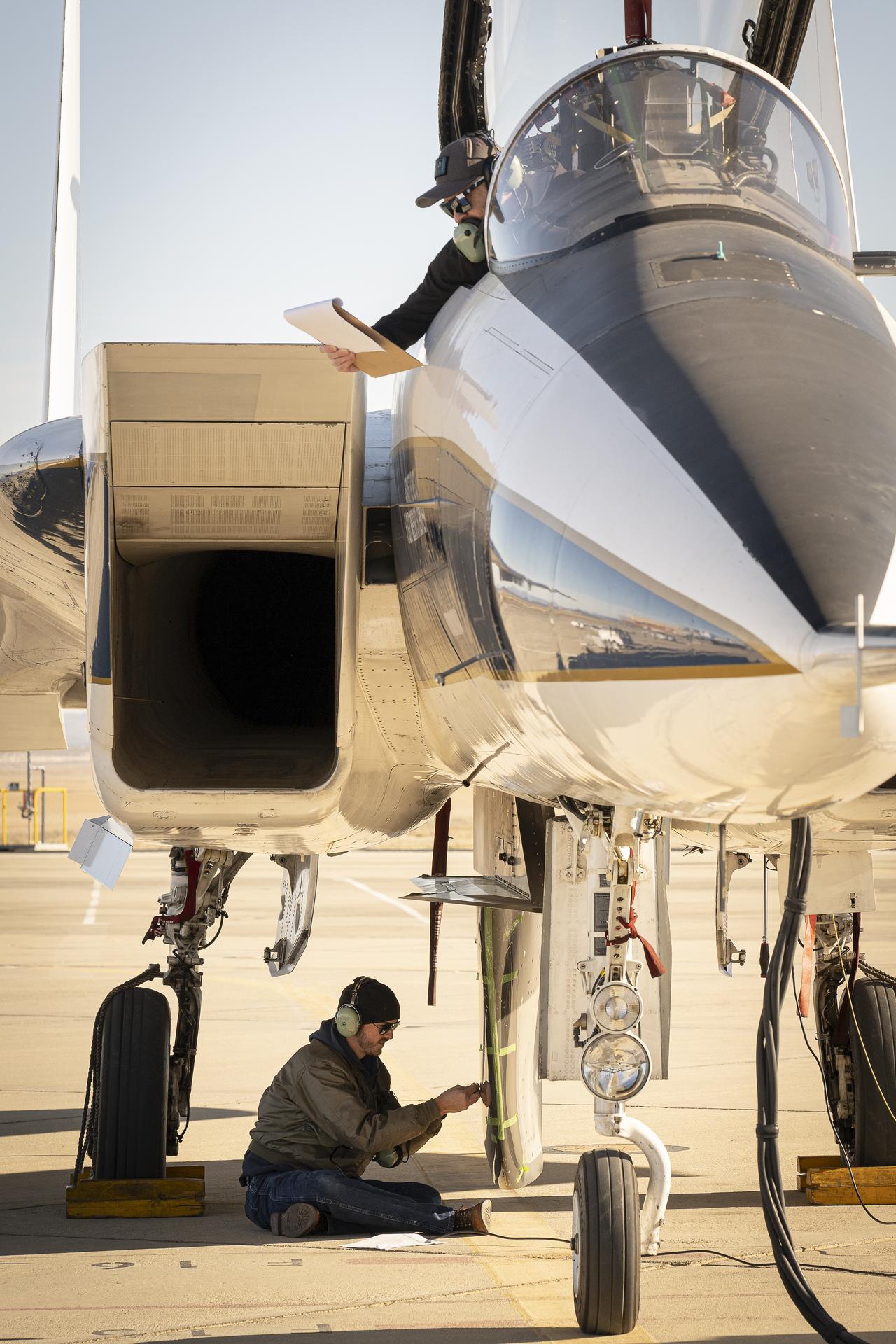

NASA ground crew prepares the agency’s F-15 research aircraft and Cross Flow Attenuated Natural Laminar Flow (CATNLF) test article ahead of its first high-speed taxi test on Tuesday, Jan. 12, 2026, at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The CATNLF design aims to reduce drag on wing surfaces to improve efficiency and, in turn, reduce fuel burn.
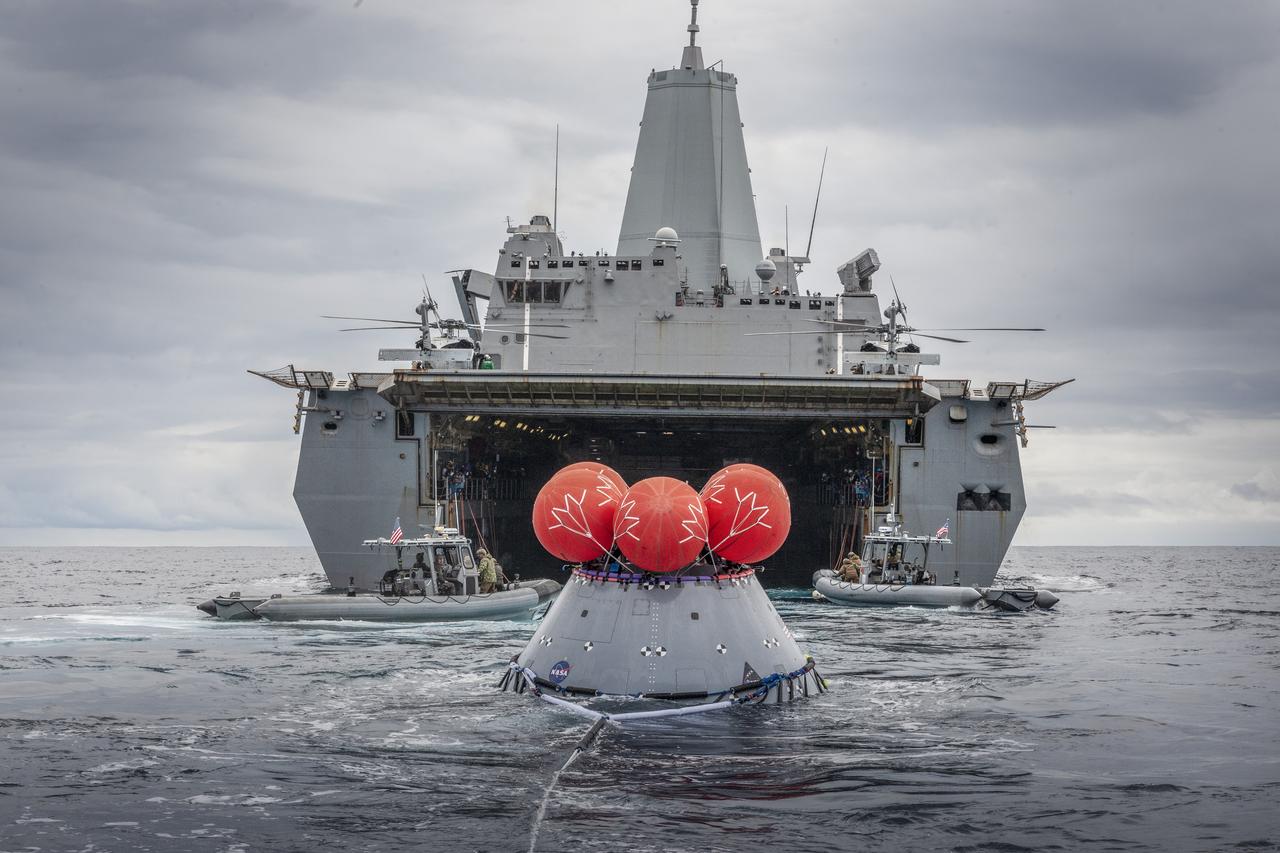

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
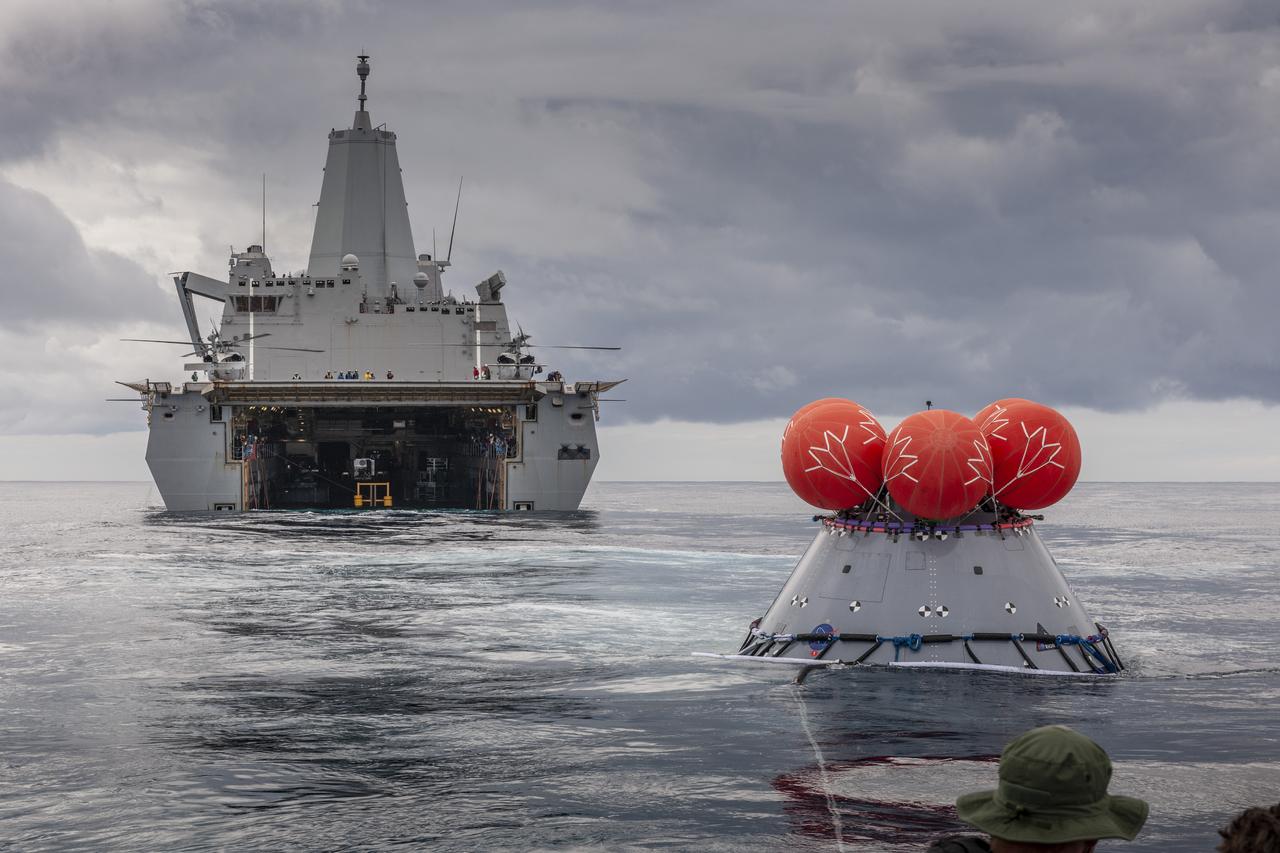

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
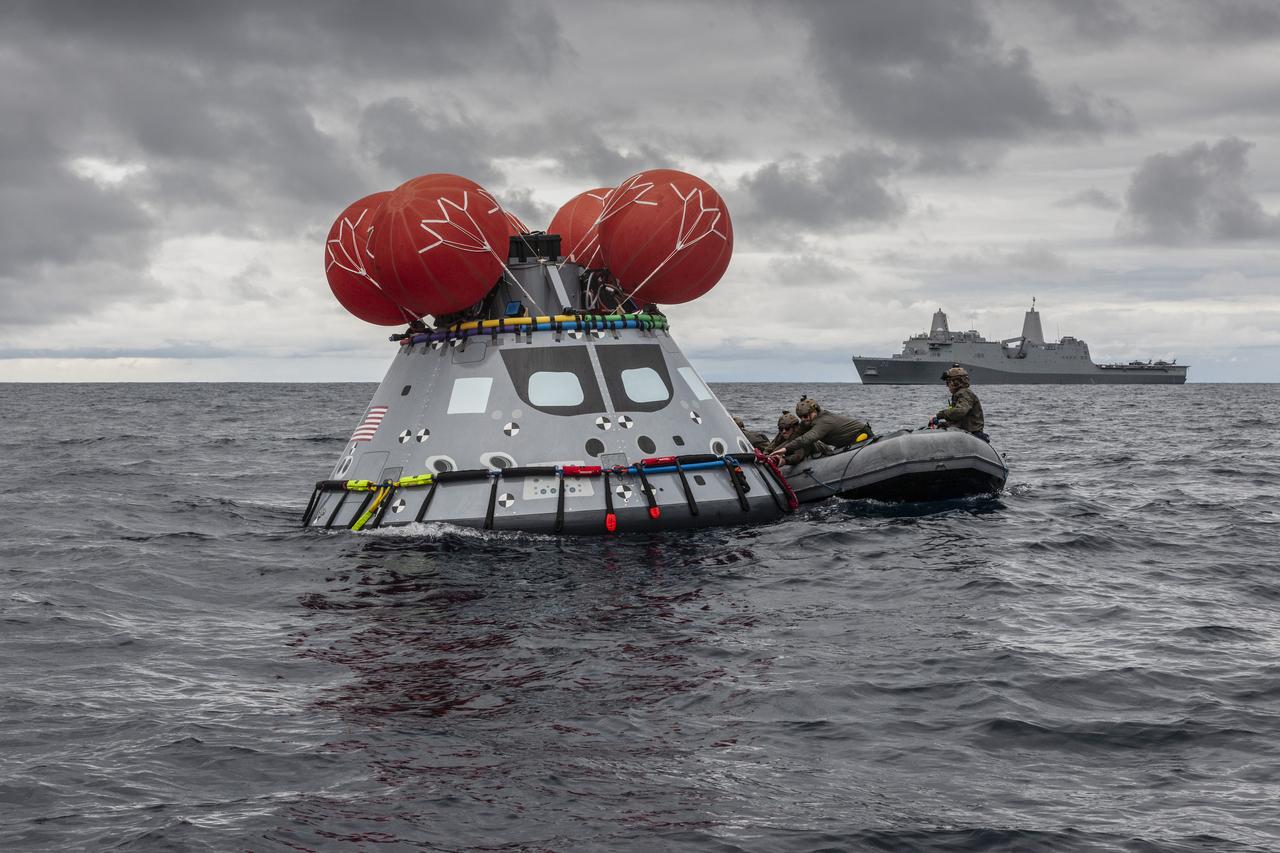

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
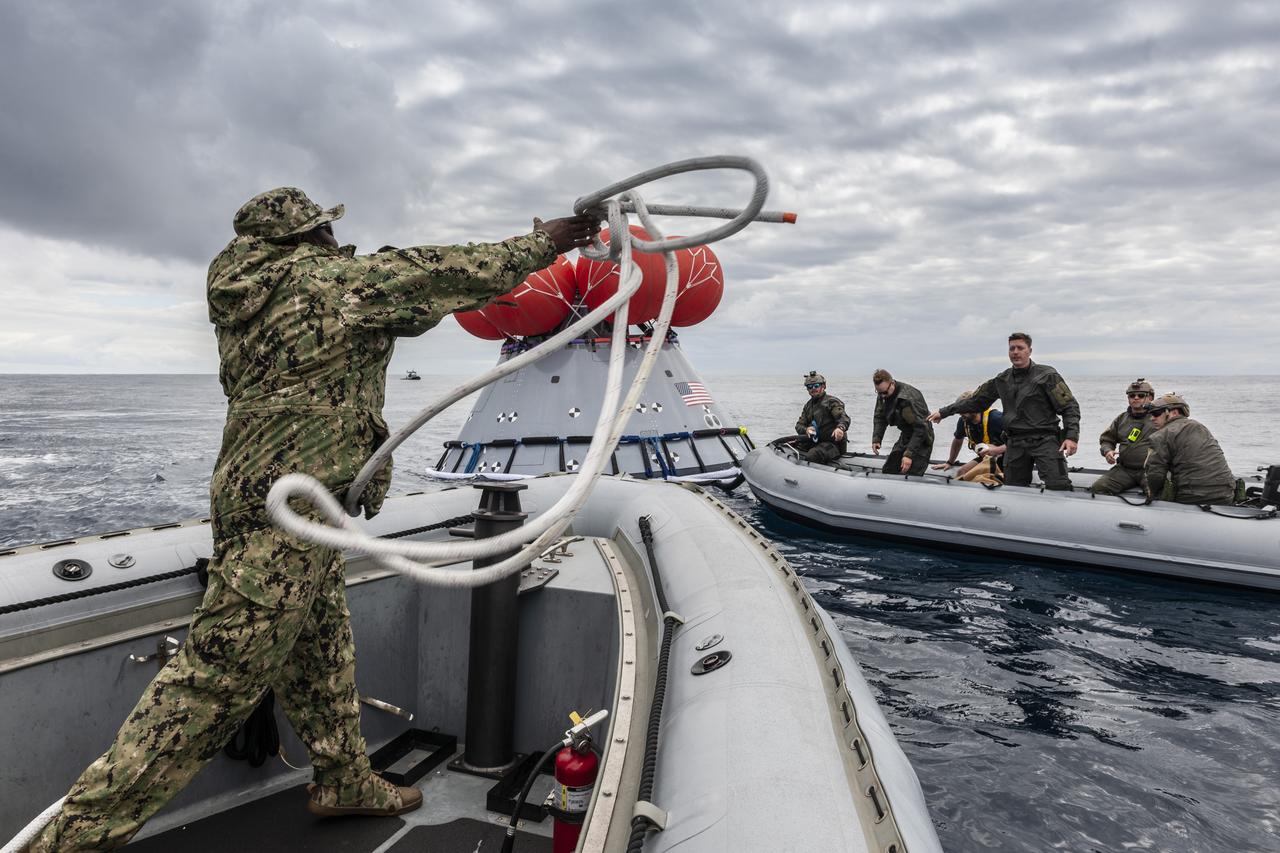

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
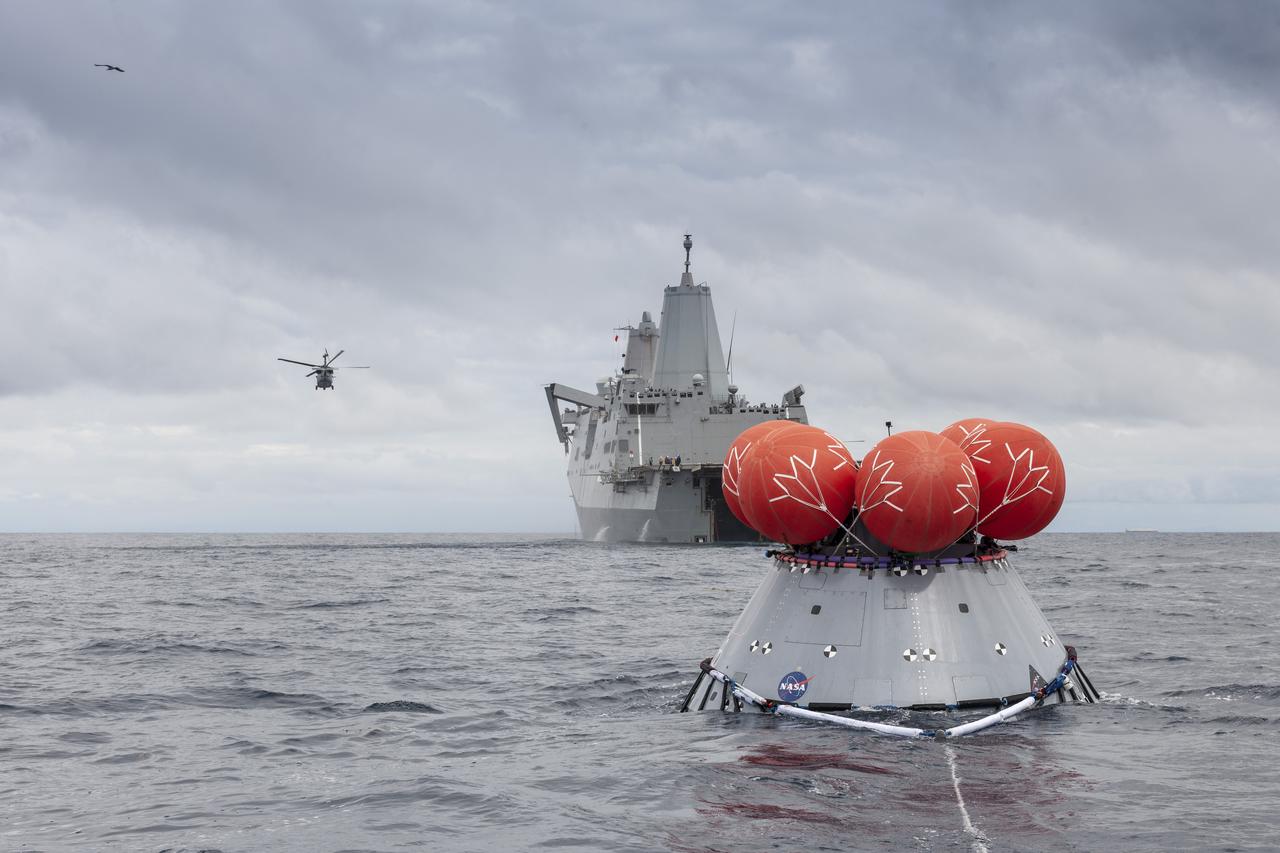

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
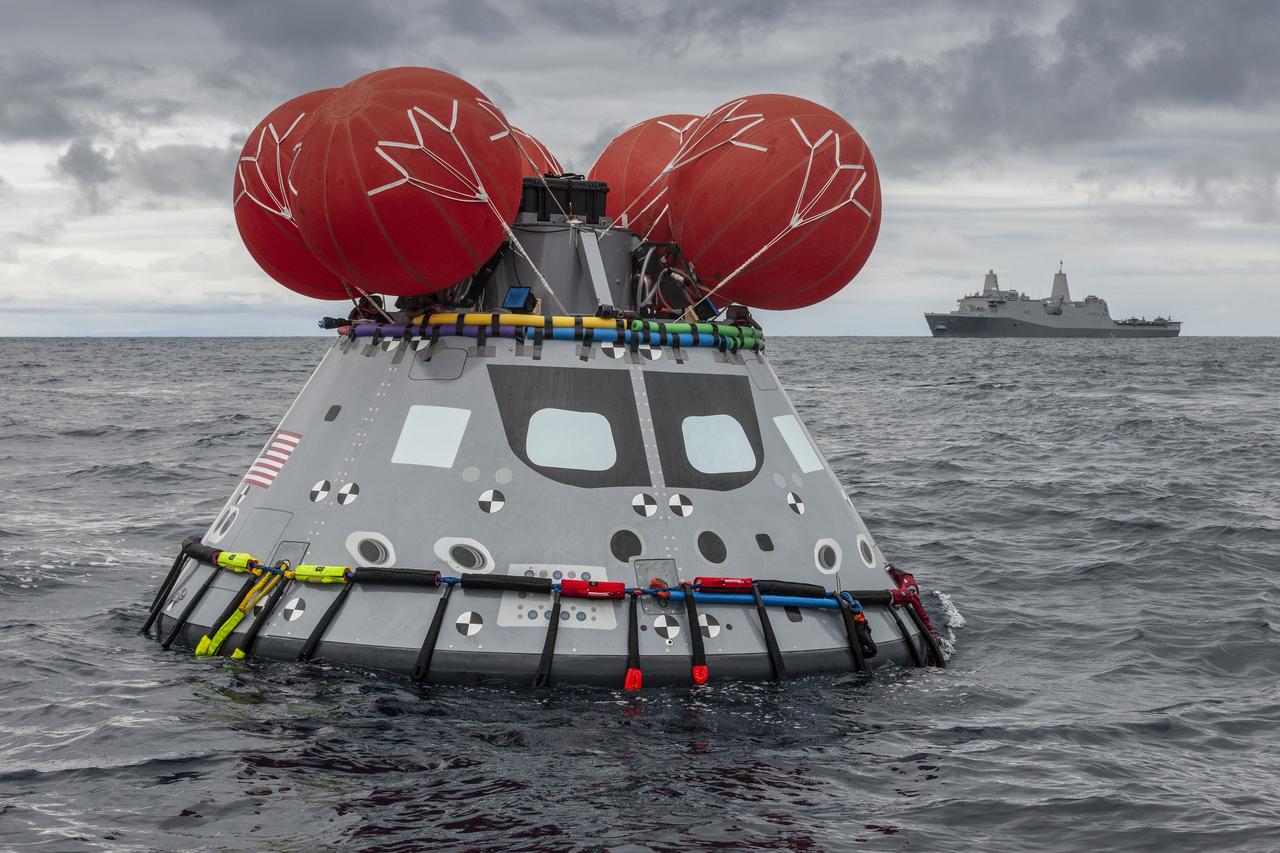

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
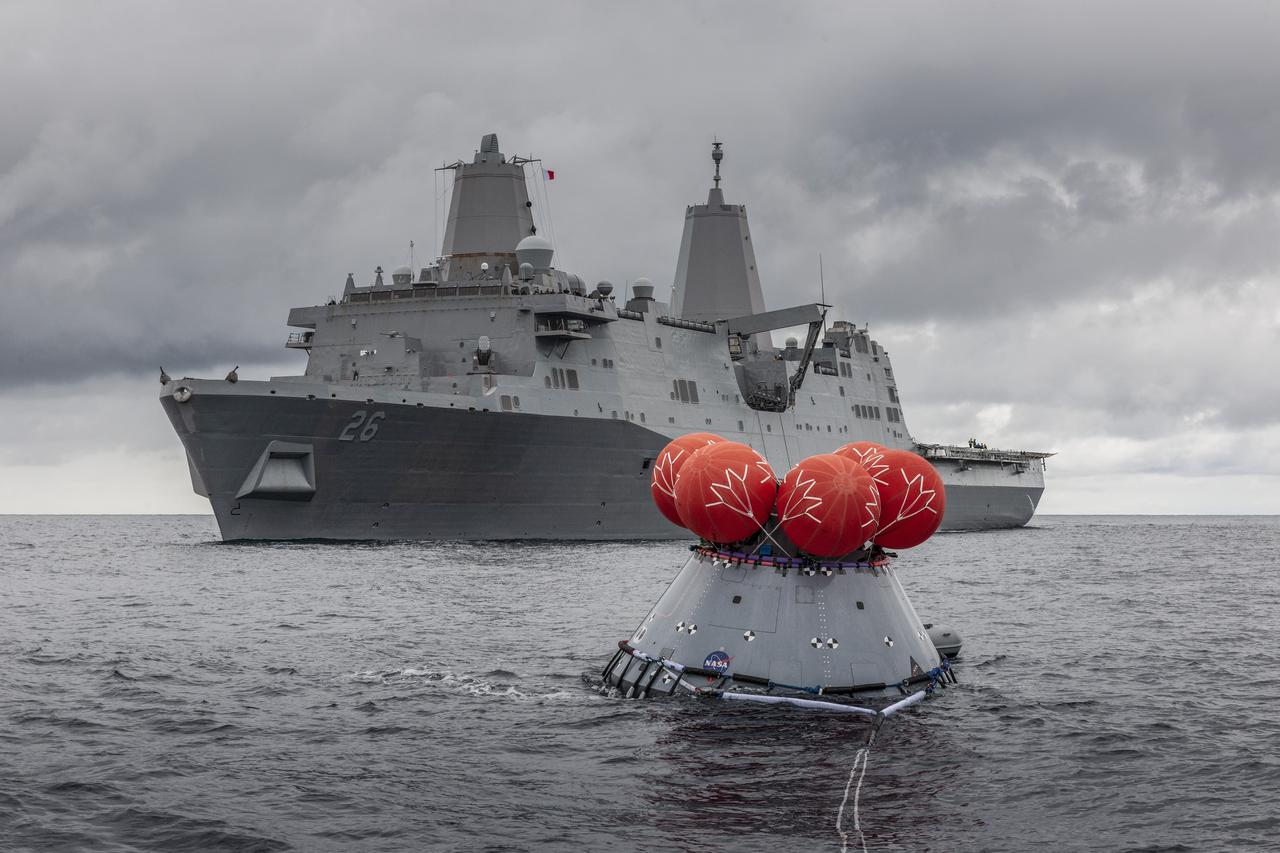

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
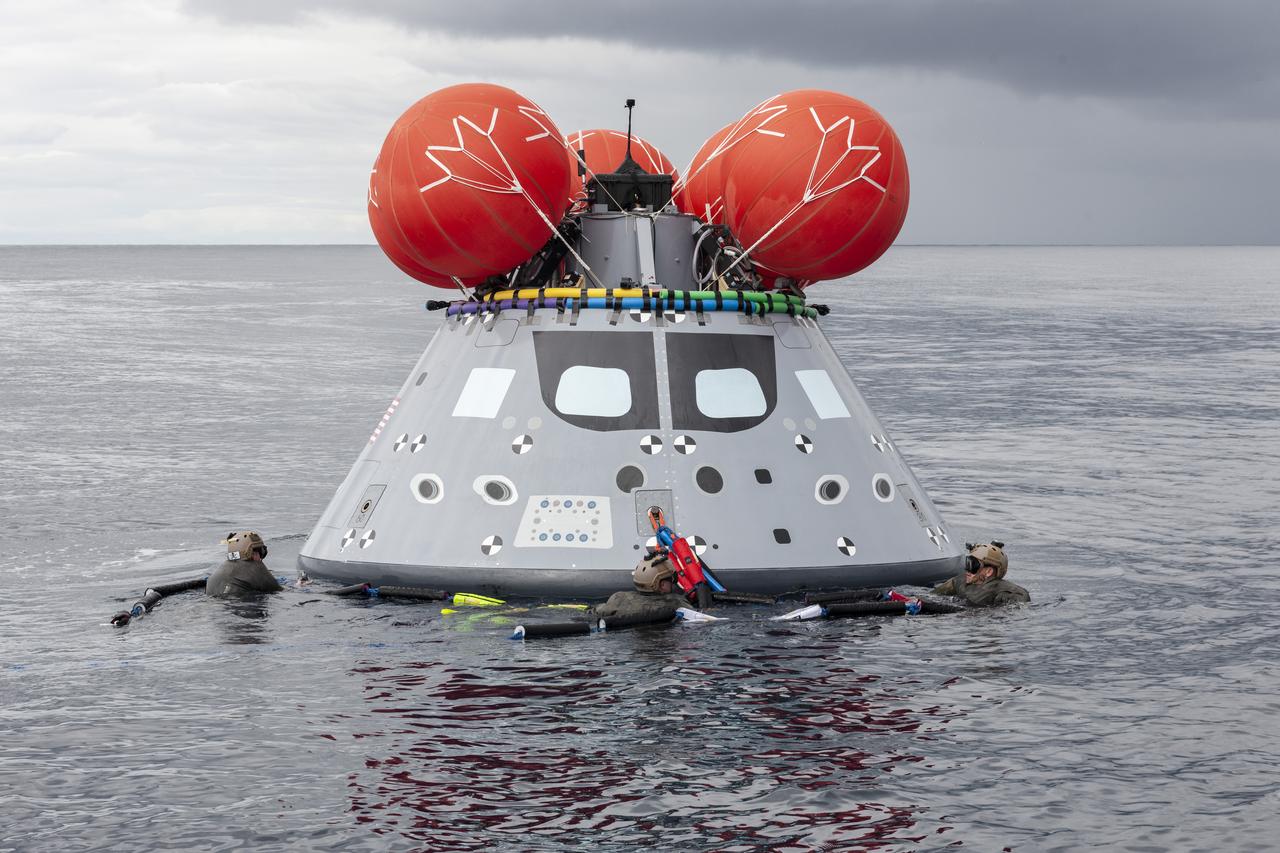

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
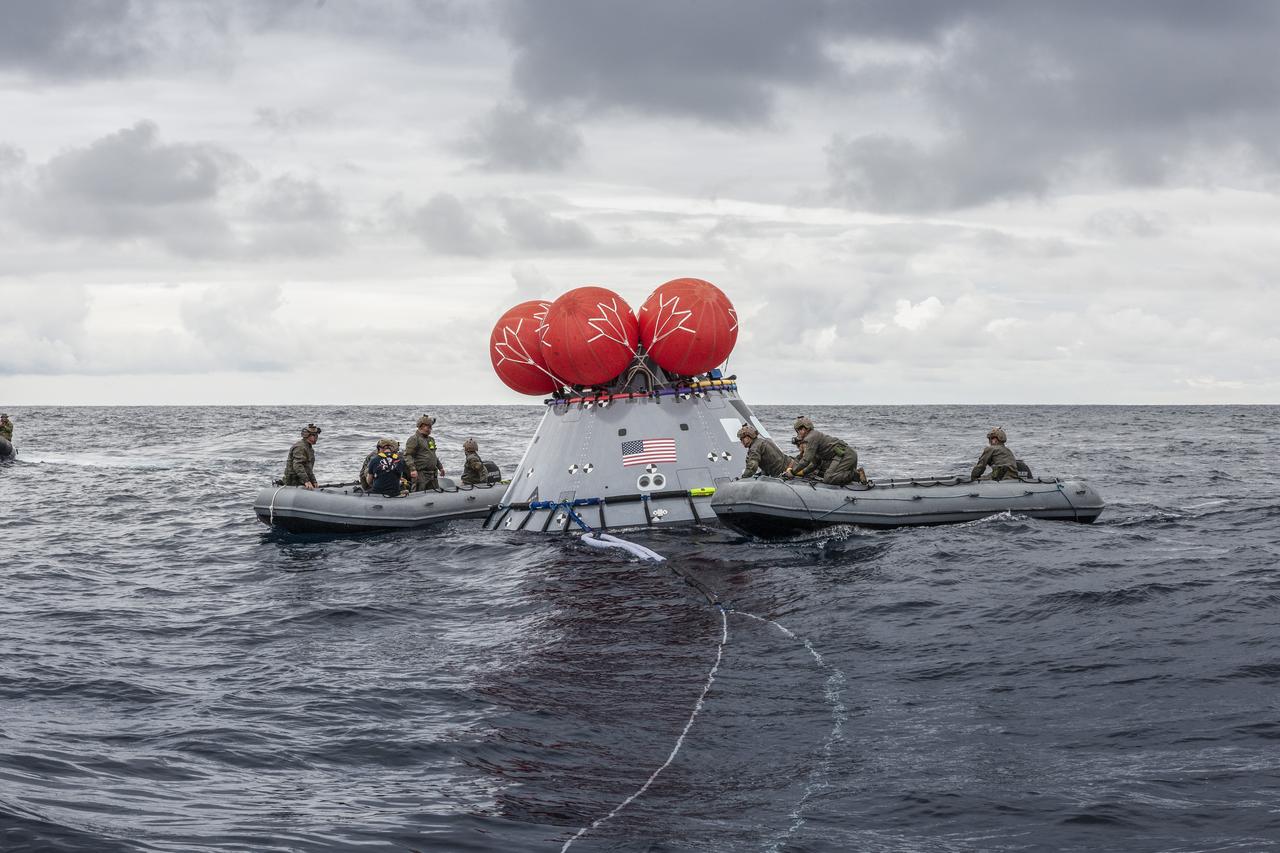

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
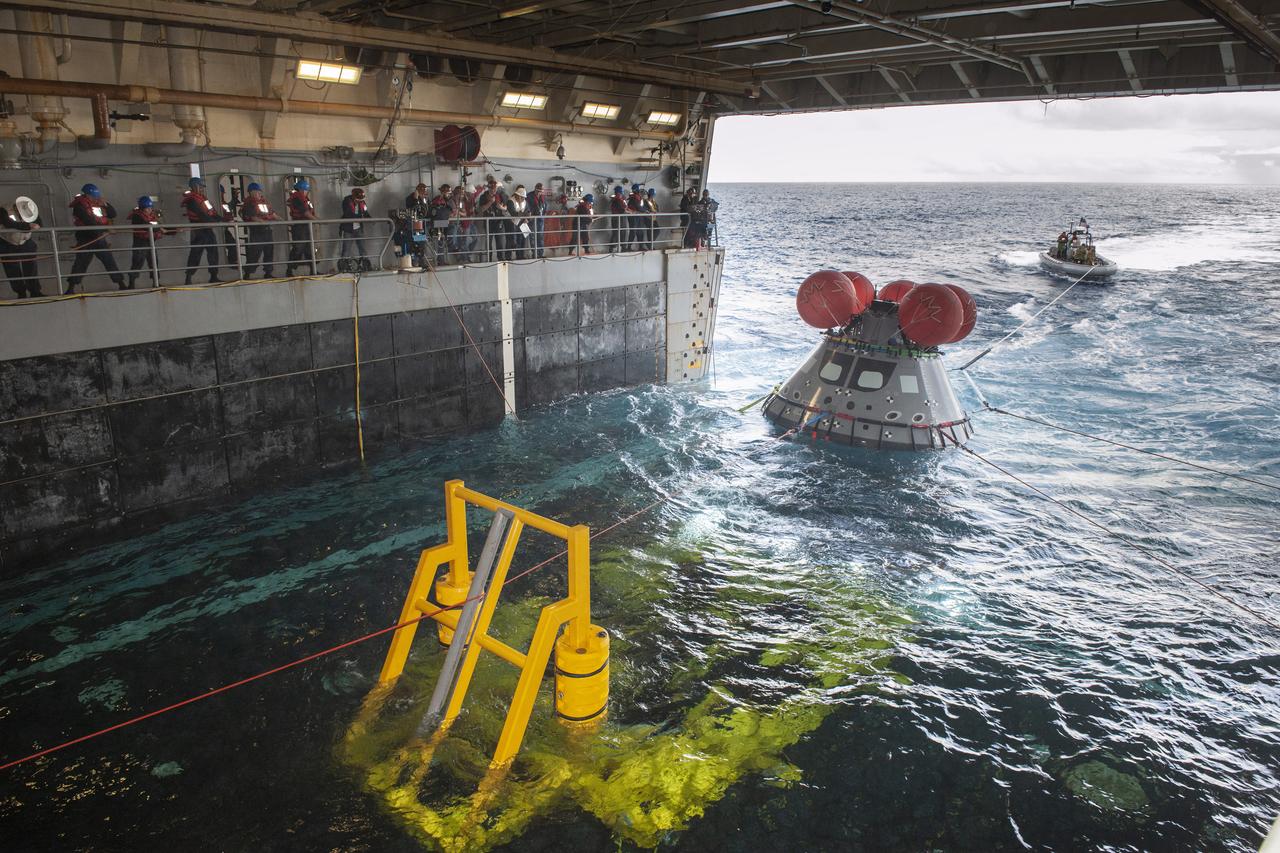

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
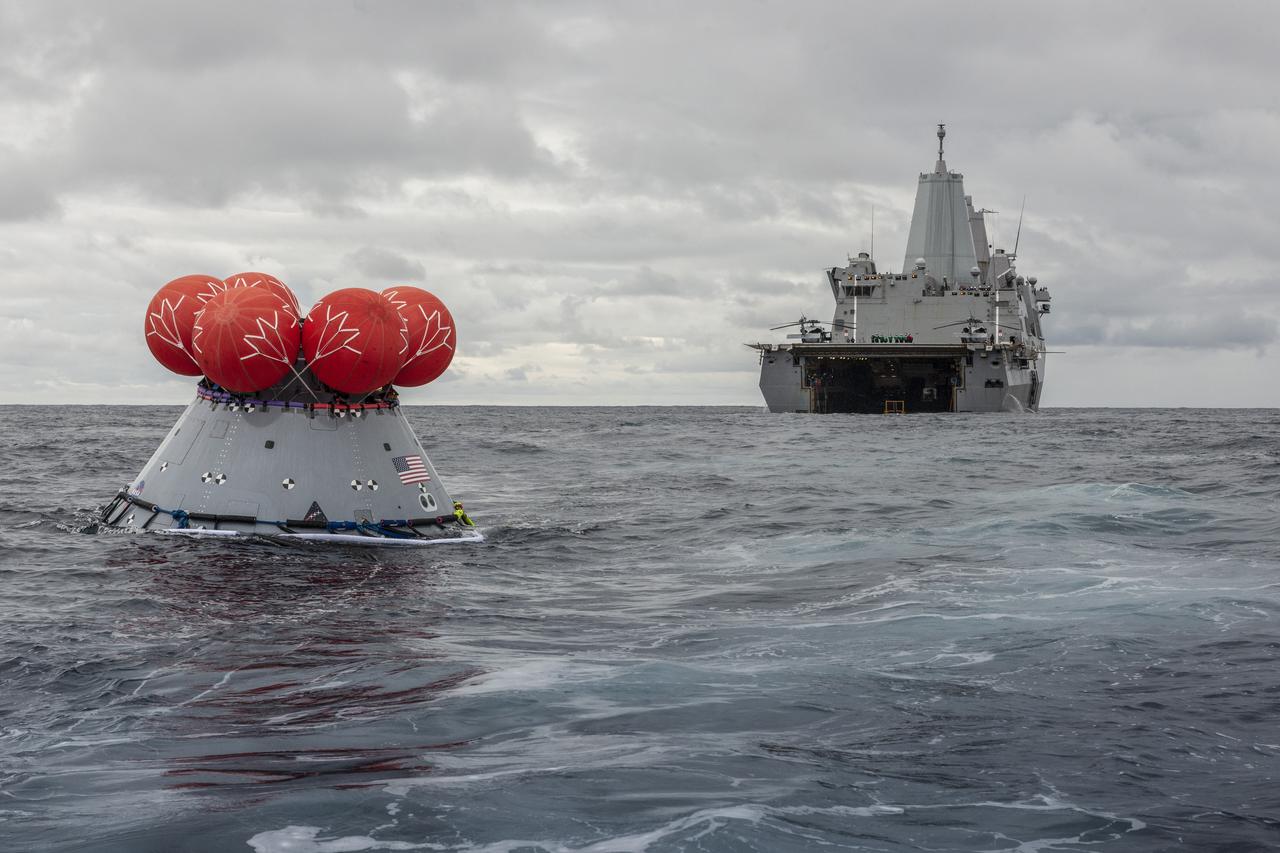

During Underway Recovery Test-8, NASA's Landing and Recovery team from Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center performed their first full mission profile test of the recovery procedures for Artemis I aboard the USS John P. Murtha in the Pacific Ocean. Artemis I will be the first integrated flight test of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Systems: the Orion spacecraft, Space Launch System rocket, with the newly upgraded Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy Space Center.
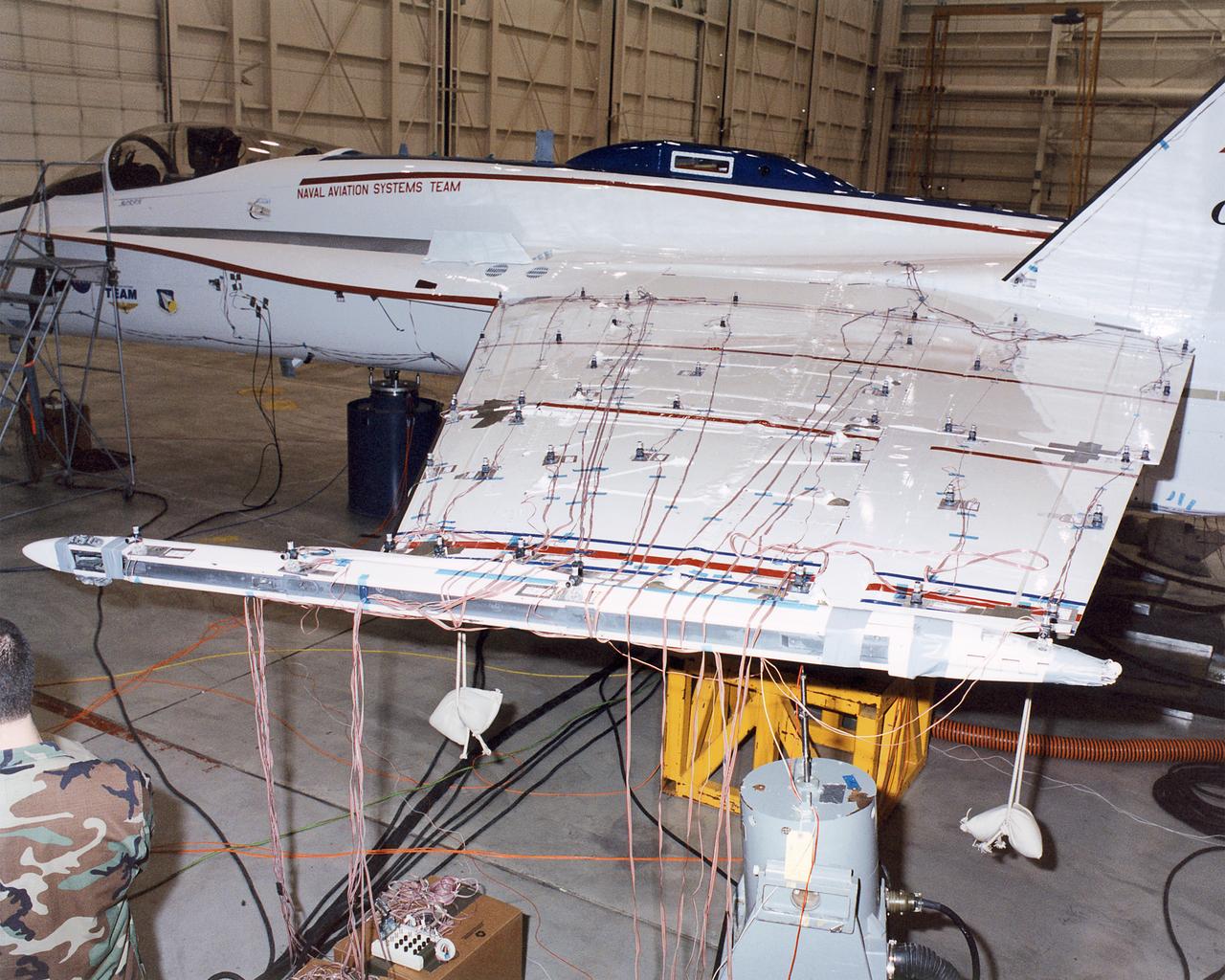

The upper wing surfaces of the Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 test aircraft are covered with accelerometers and other sensors during ground vibration tests at NASA Dryden Flight Research Center.