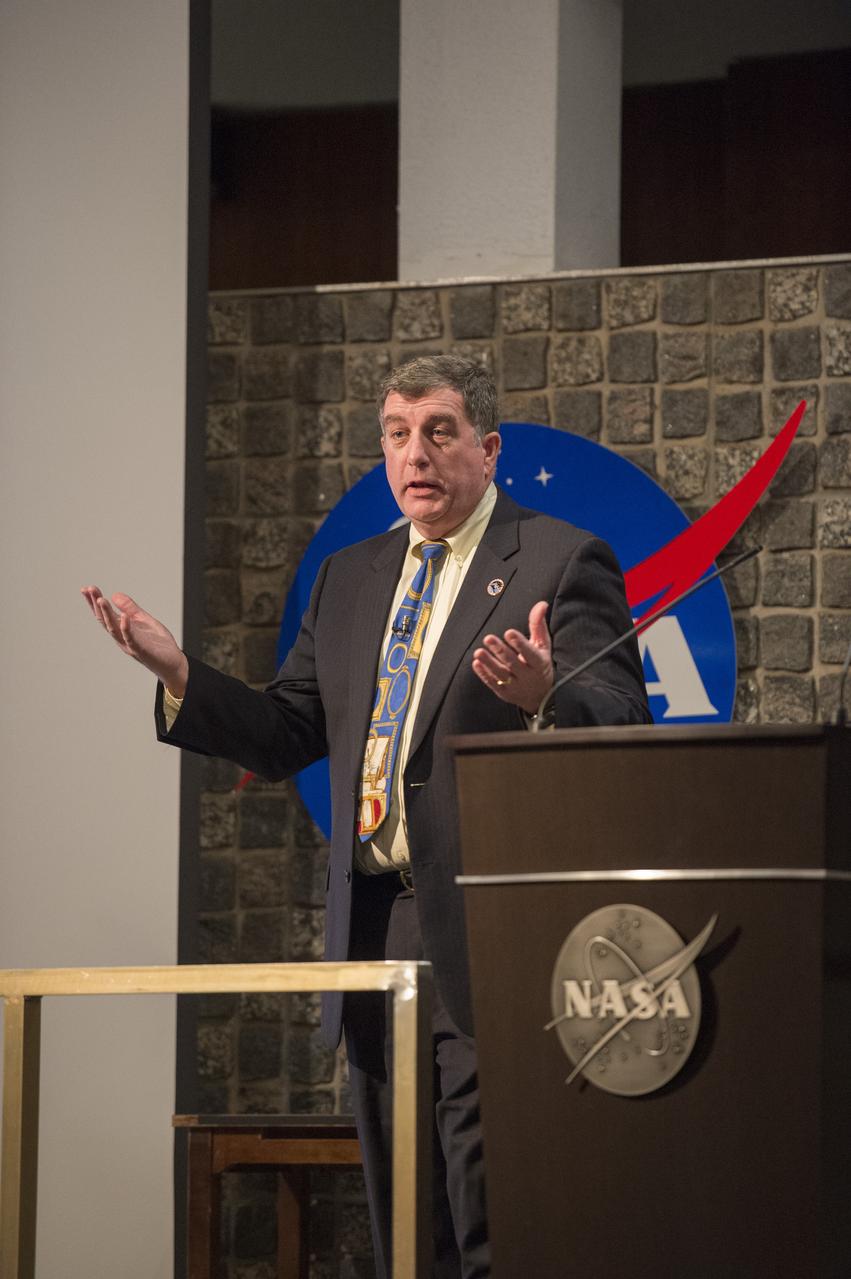

International Space Station program manager Kirk Shireman addresses station hardware and science teams at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center.

jsc2024e050835 (7/26/2024) --- Members of the STEMonstrations team at the flight configuration hardware check for the STEMonstrations: Screaming Balloon project, Seth Johnson, Michele Hooks, and Ashwin Mathews, left to right. Developed through NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement Next Gen STEM Project, STEMonstrations are short educational videos demonstrating science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) topics in microgravity for grades K through 12. STEMonstrations: Screaming Balloon examines centripetal force, whirling a penny and a hexnut inside of inflated balloons and comparing the sounds they make.
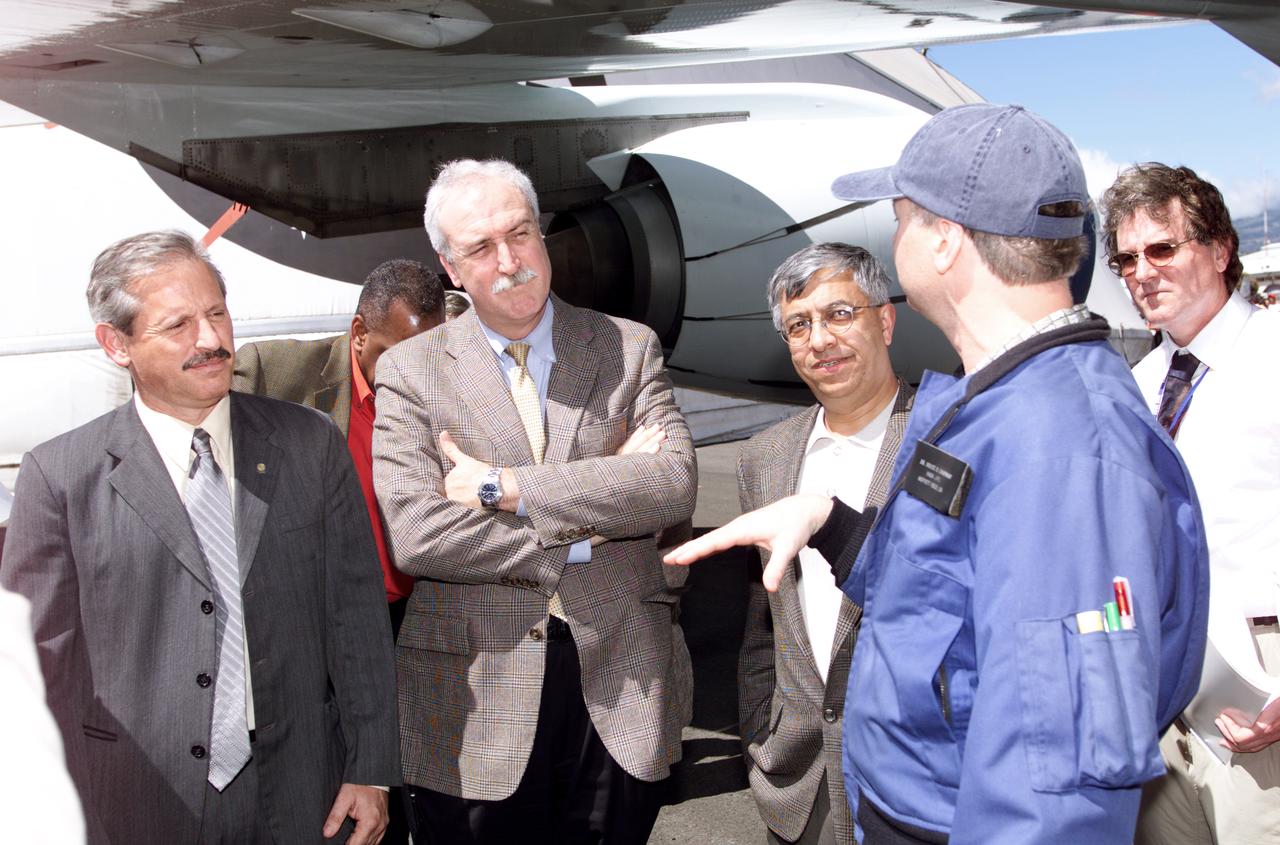

Personnel viewing AirSAR hardware while touring the outside of NASA's DC-8 during a stop-off on the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign, L-R: Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT); NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe; Dr. Gahssem Asrar, NASA Associate Administrator for Earth Science Enterprises; JPL scientist Bruce Chapman; and Craig Dobson, NASA Program Manager for AirSAR. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
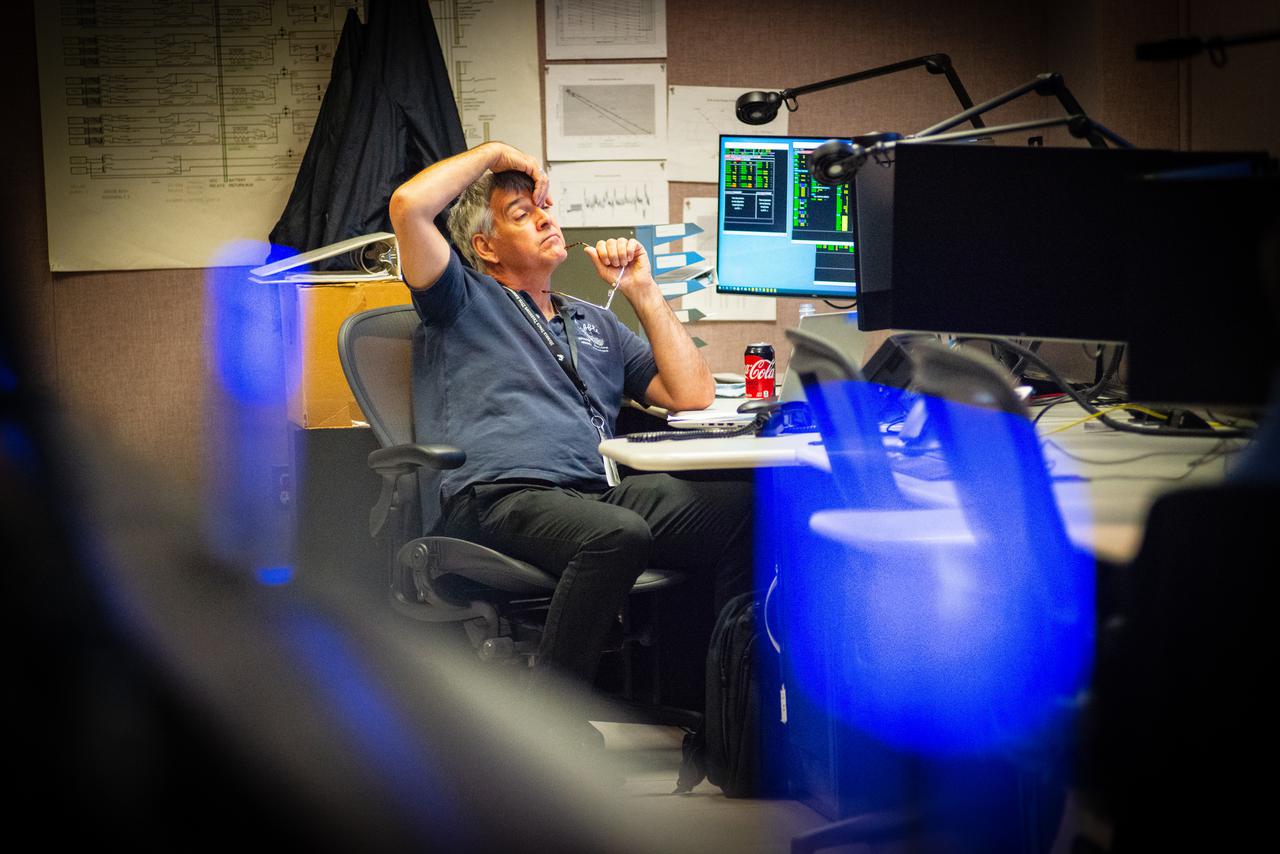

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
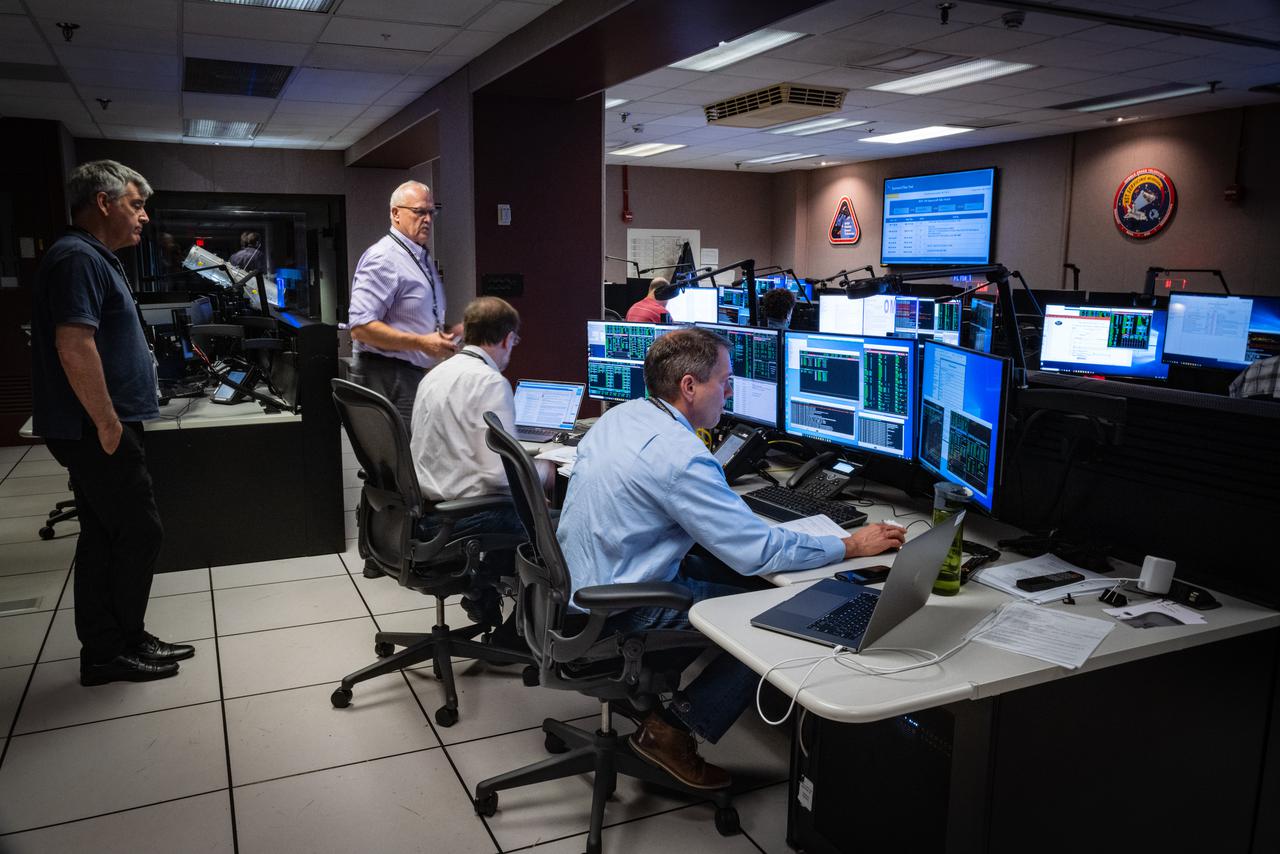

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
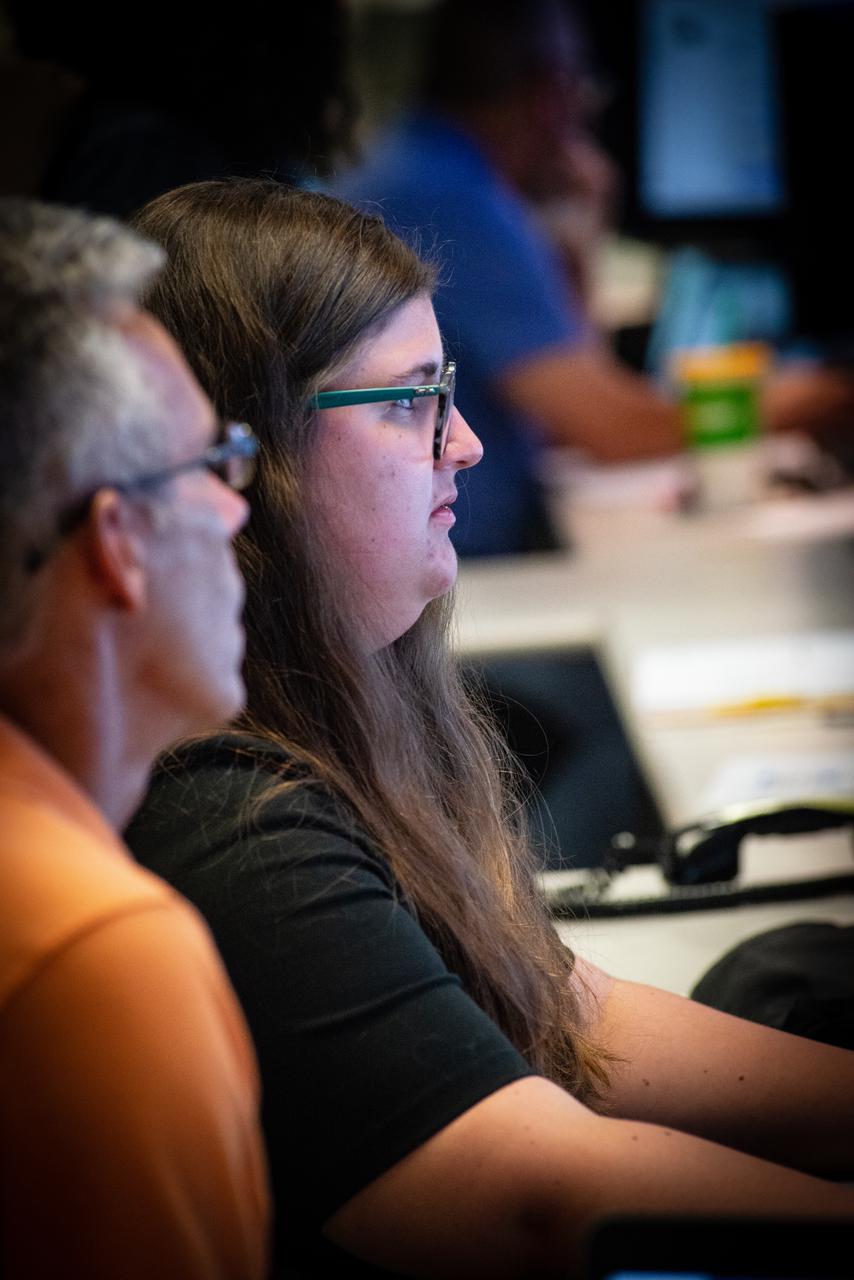

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
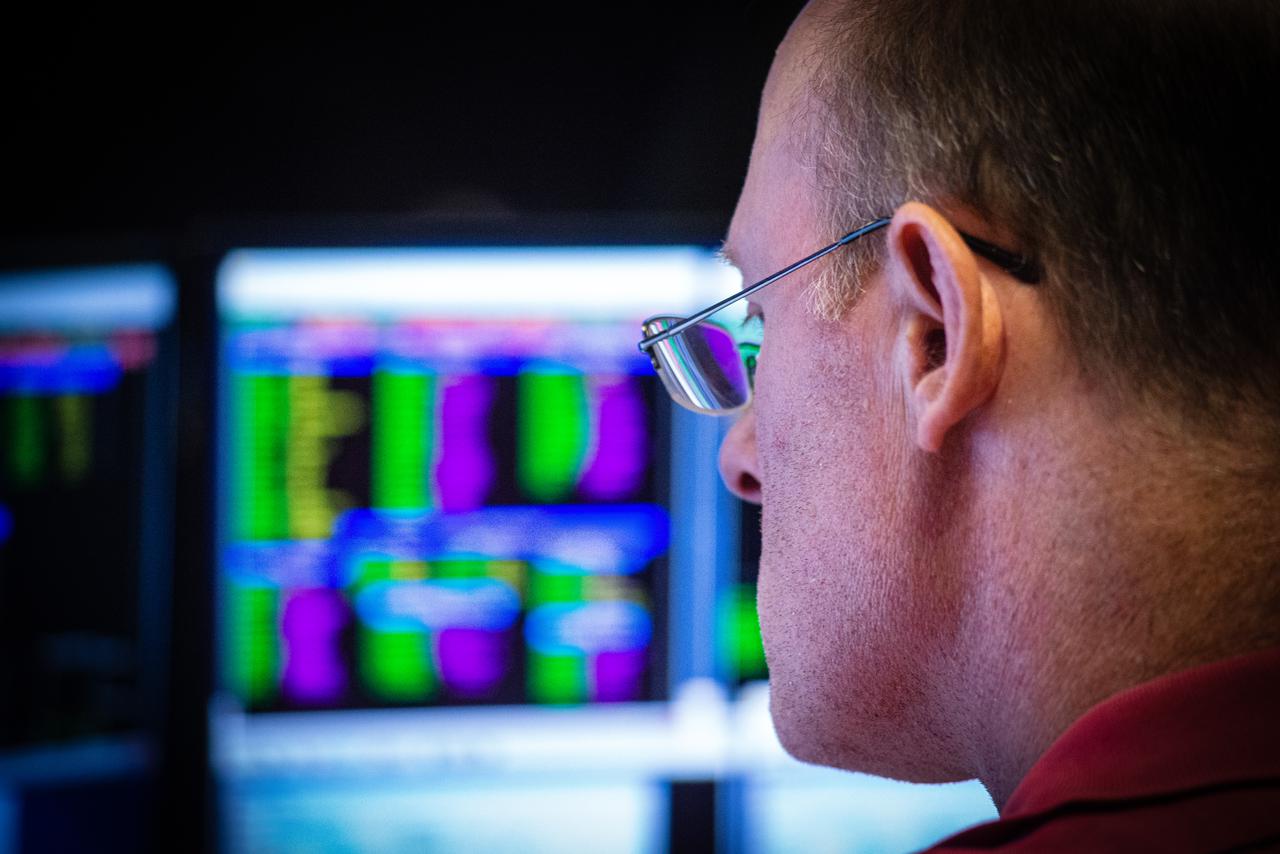

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
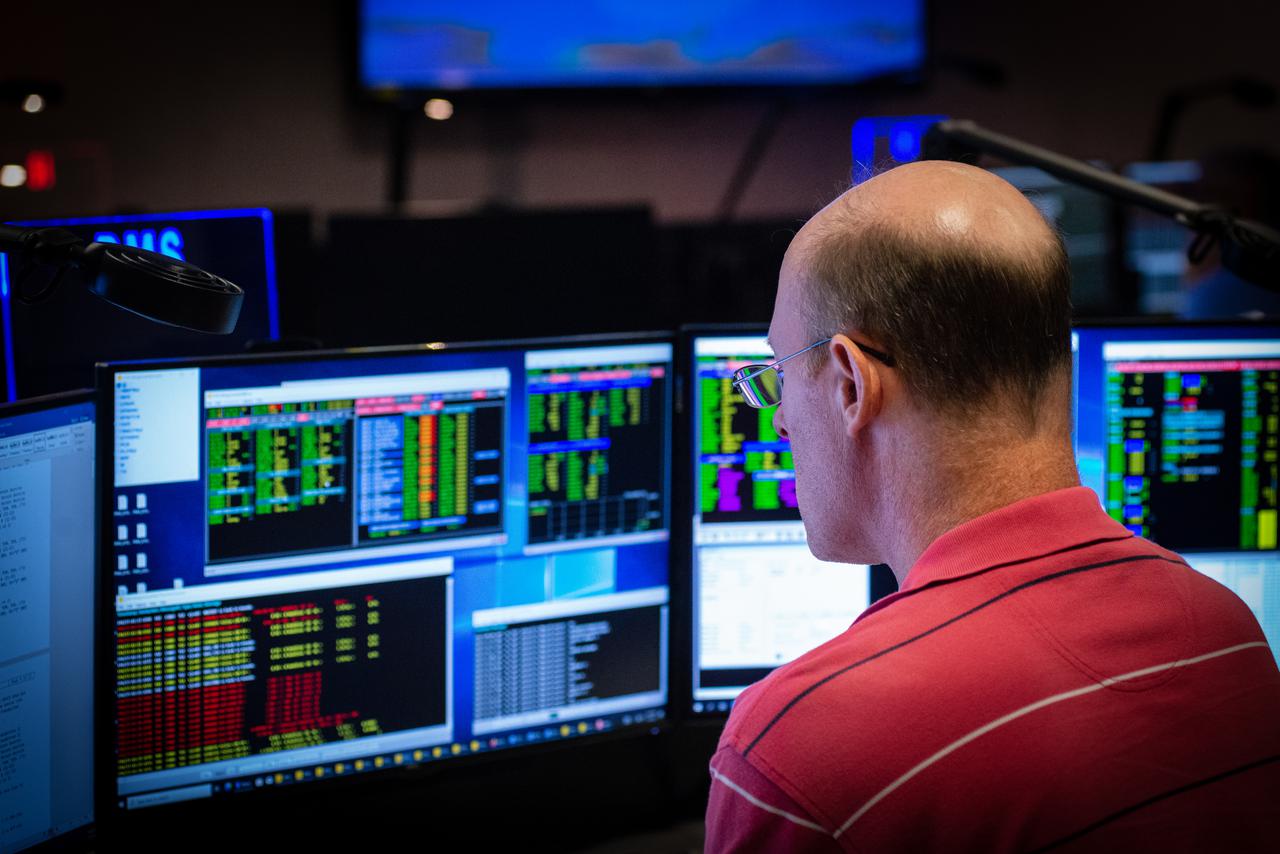

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
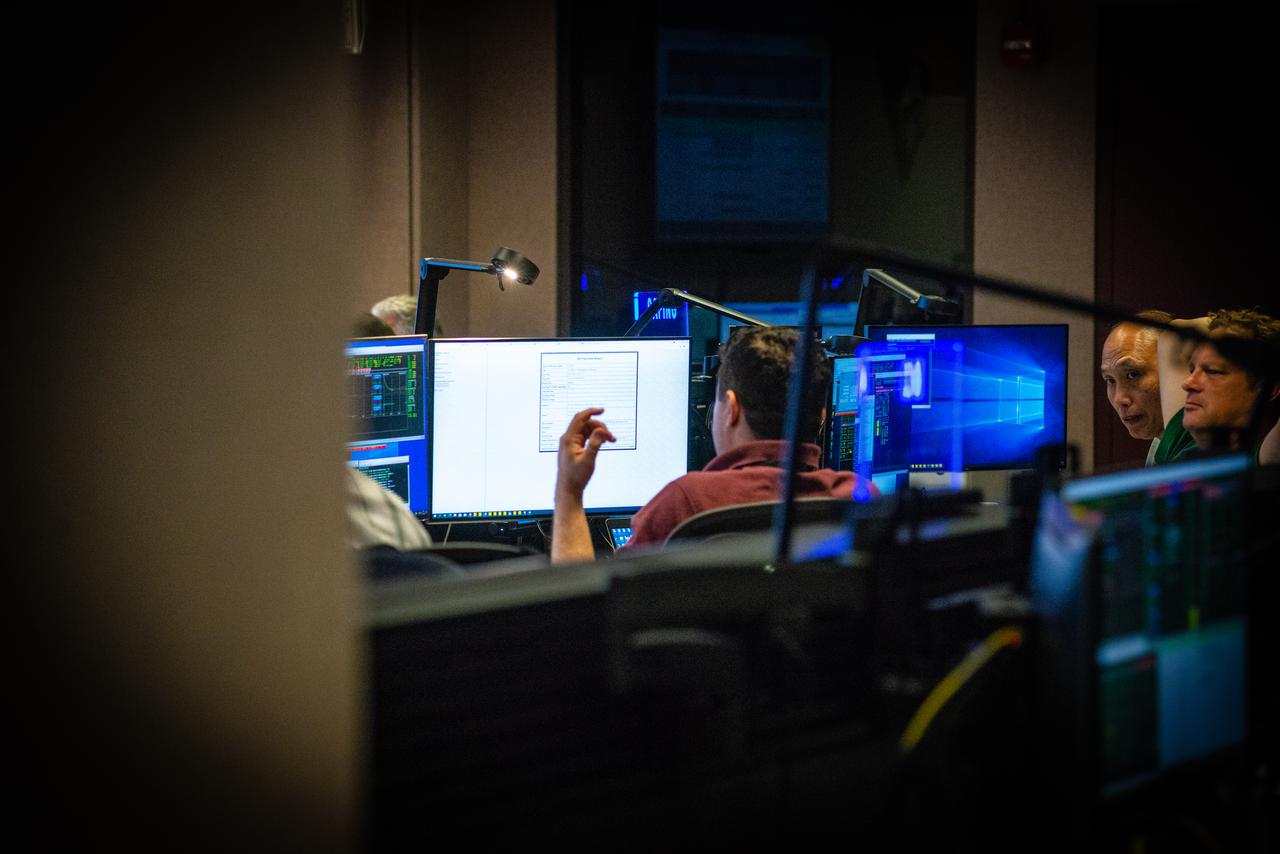

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
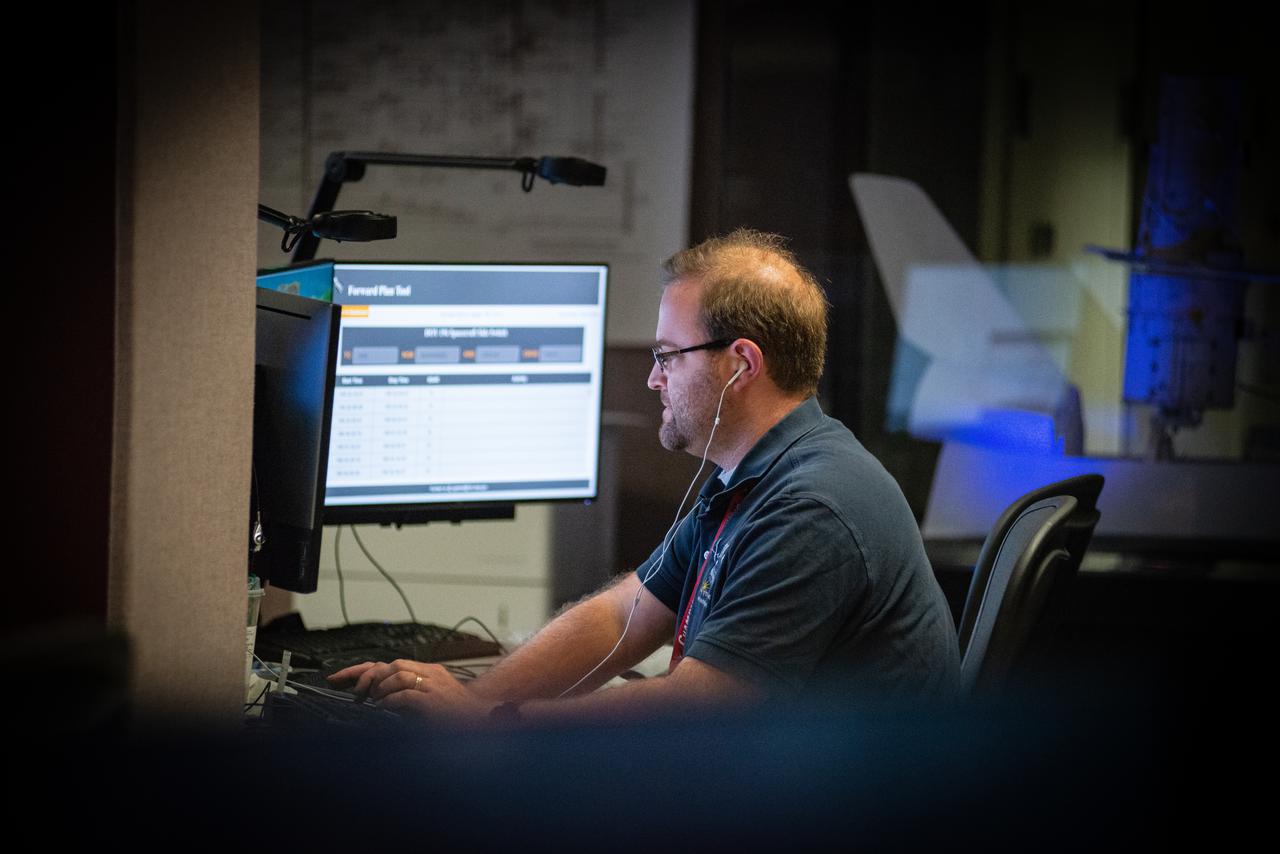

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
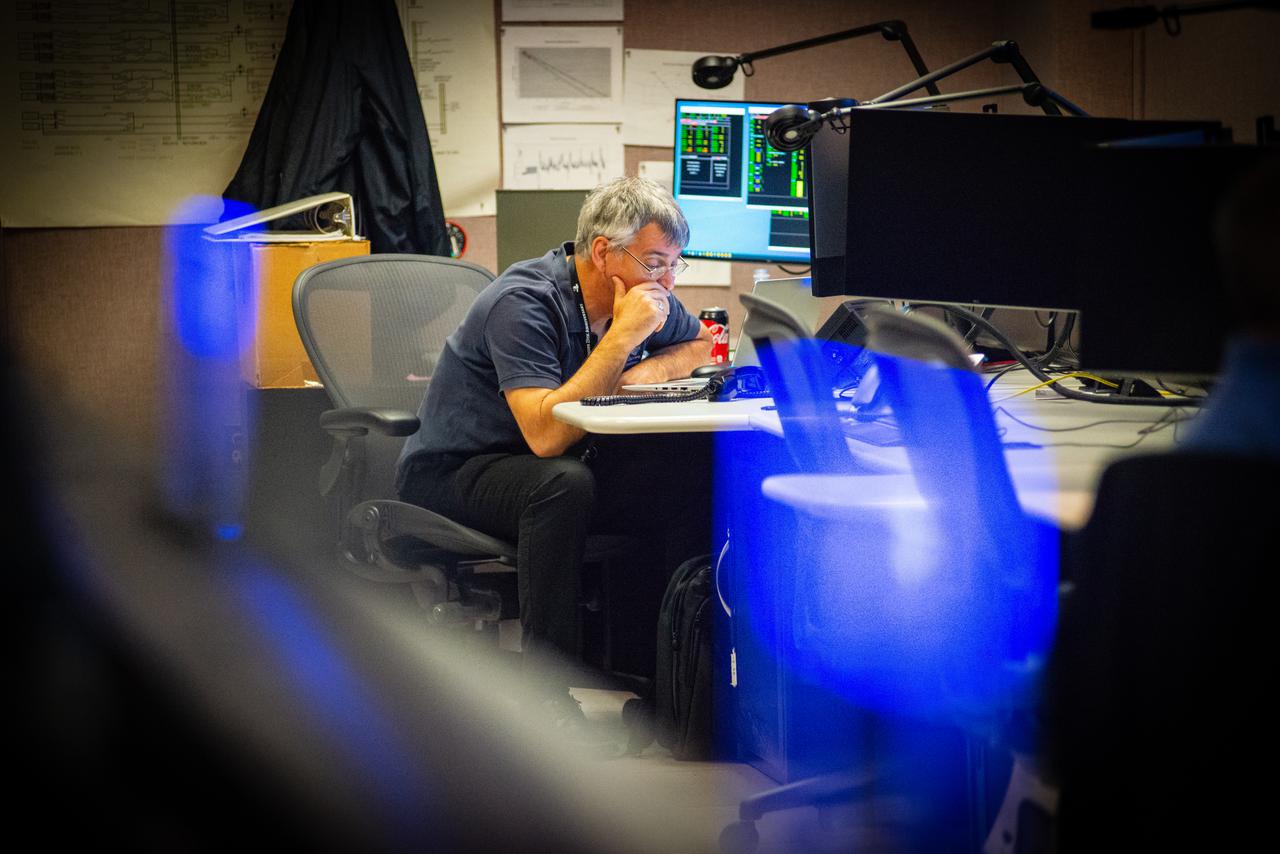

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
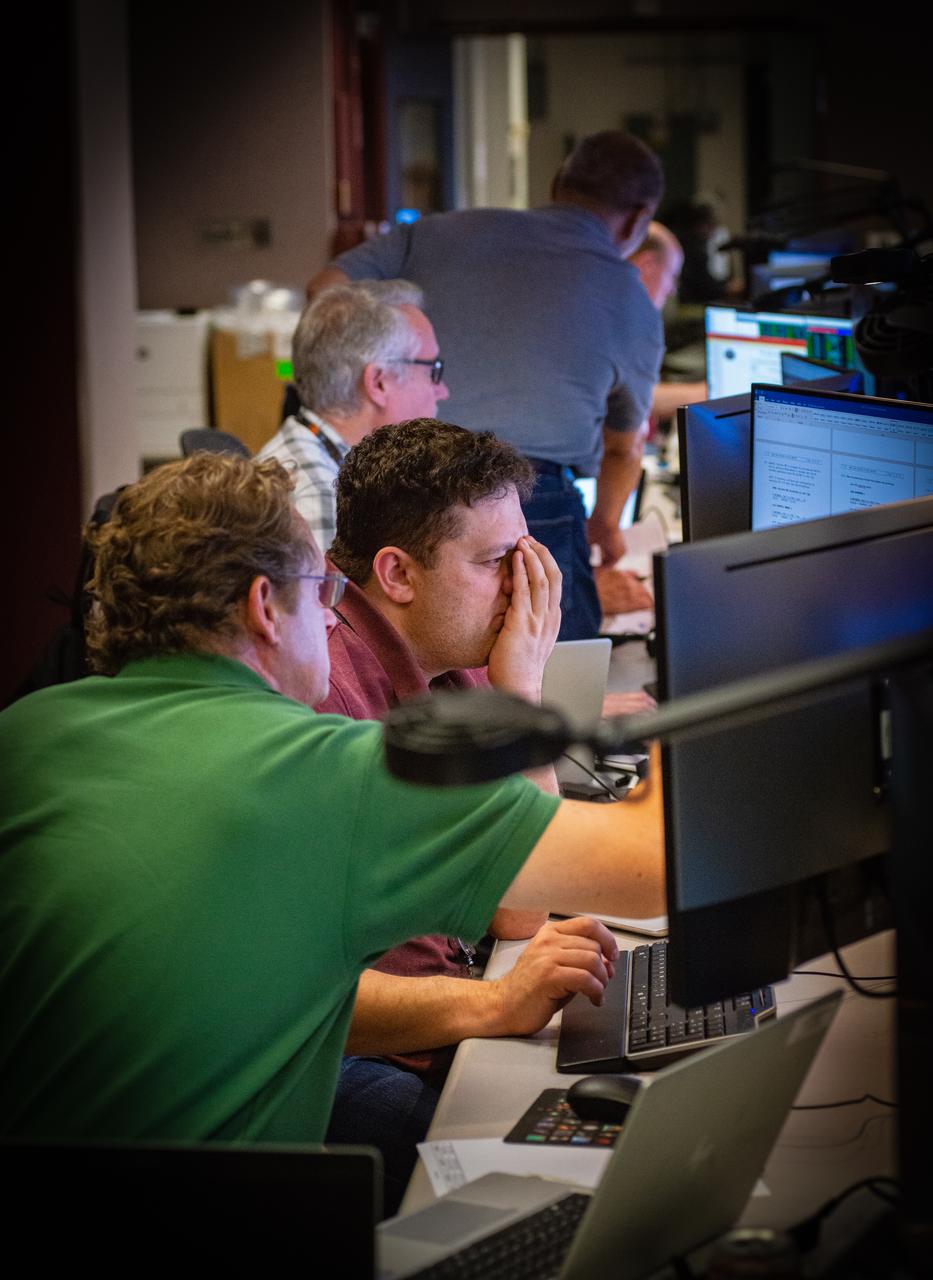

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
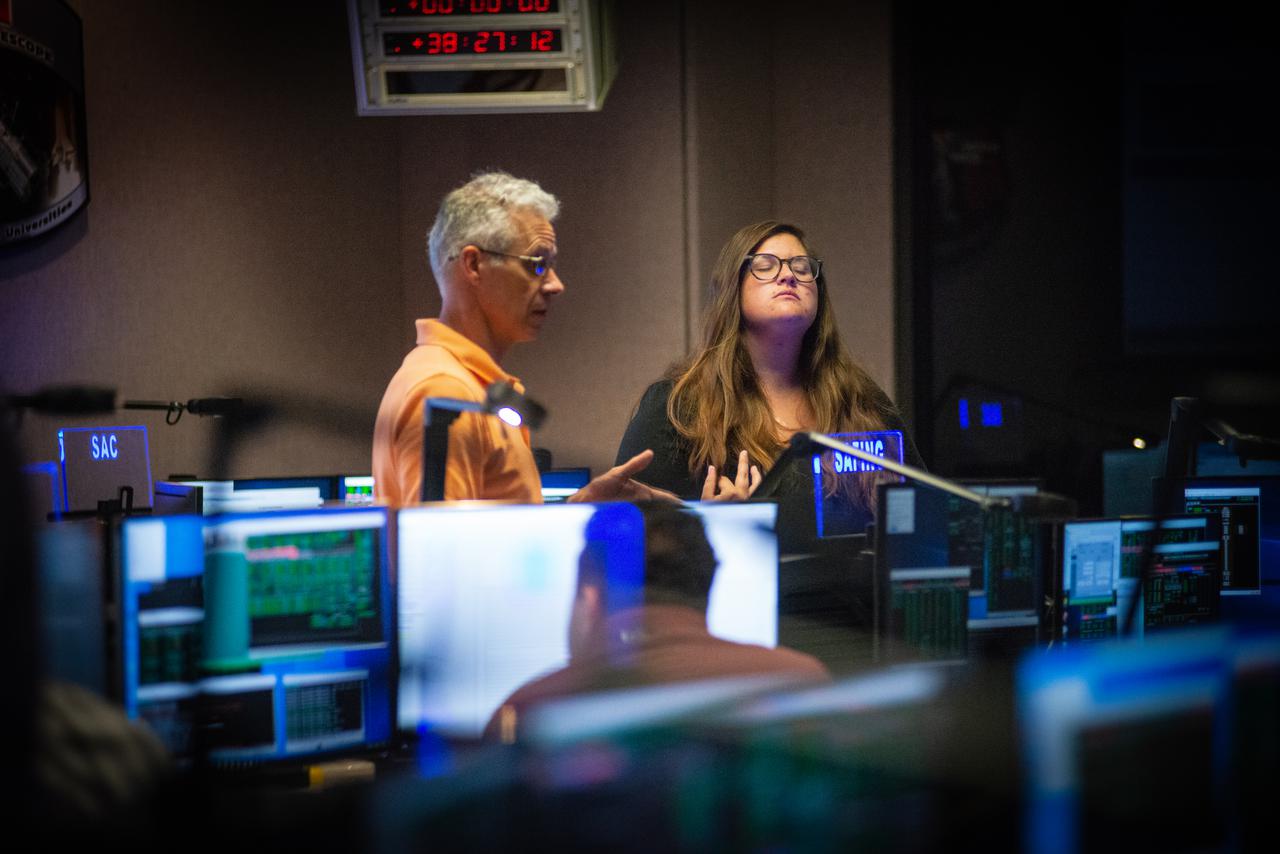

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
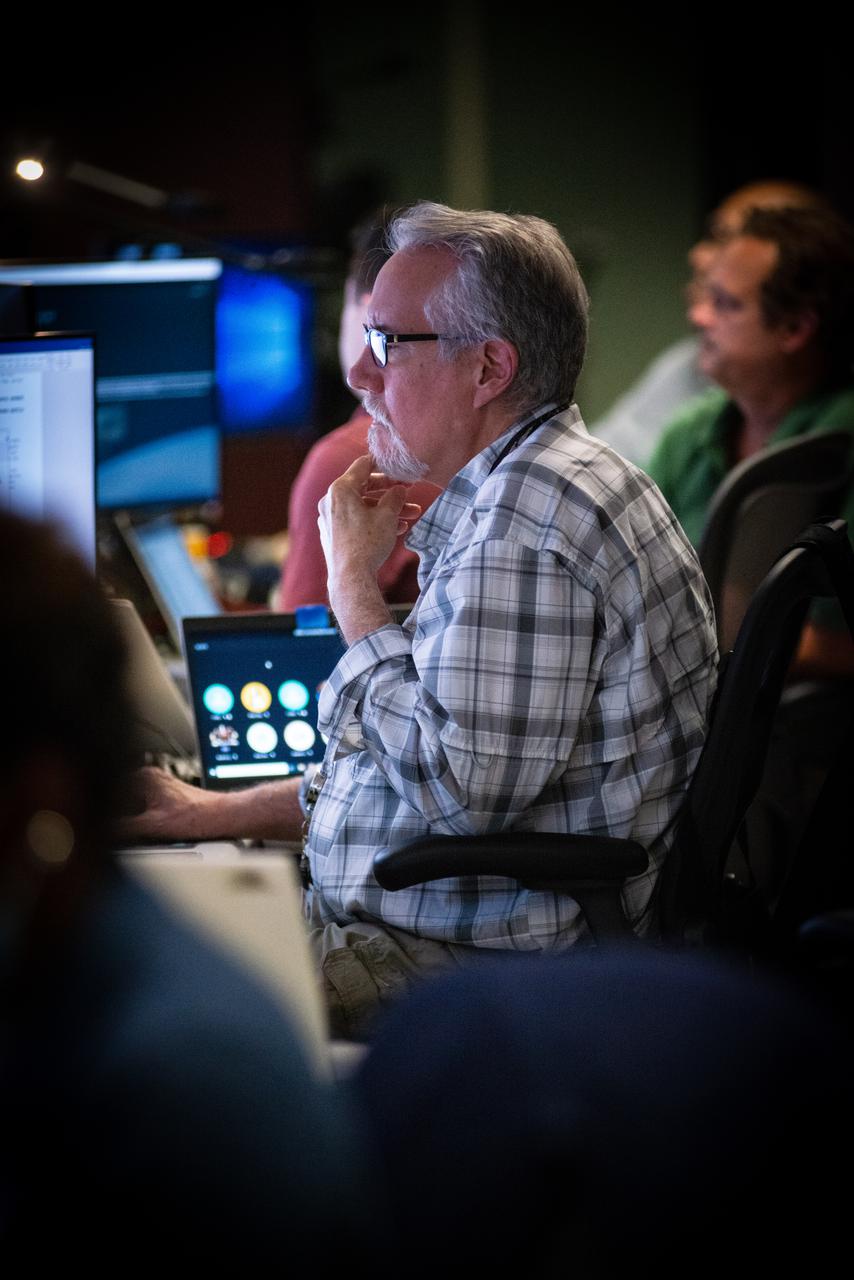

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
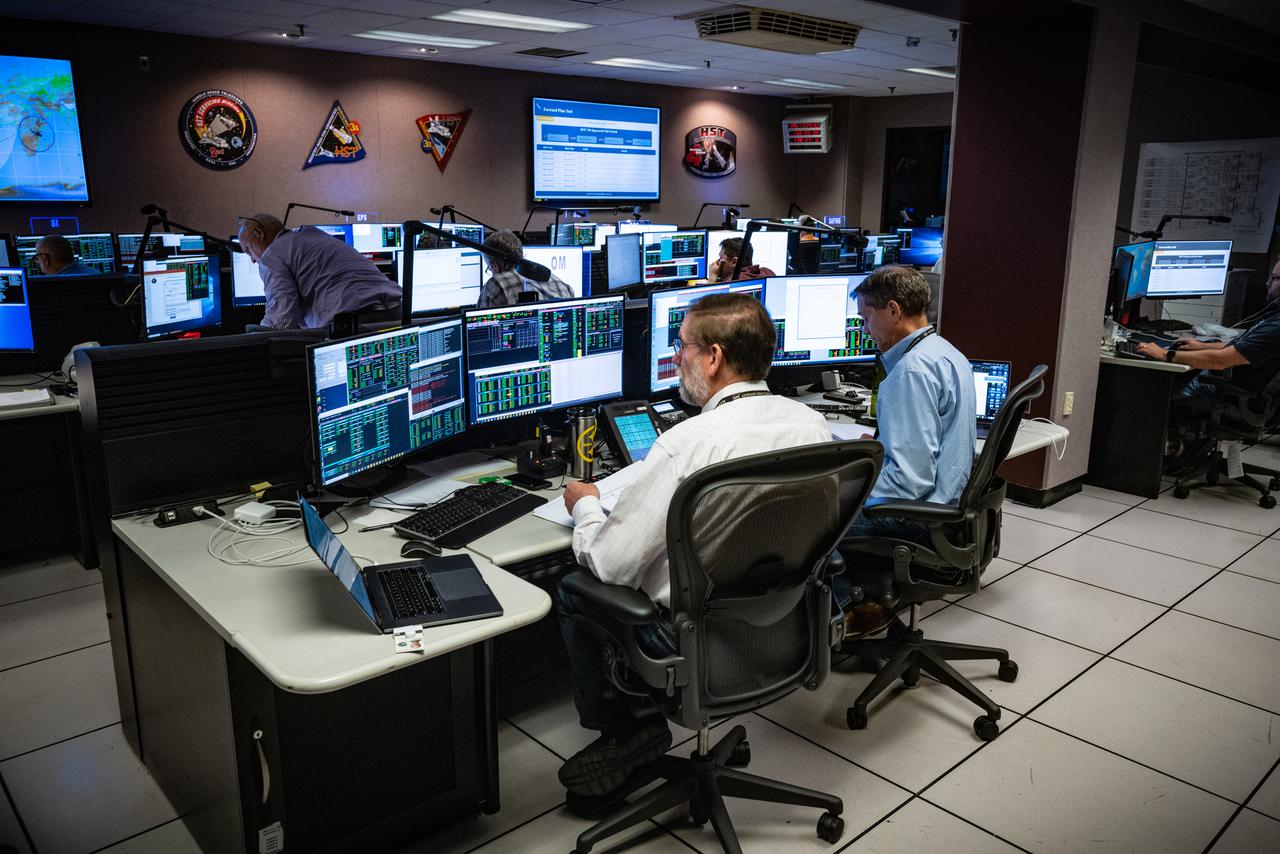

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
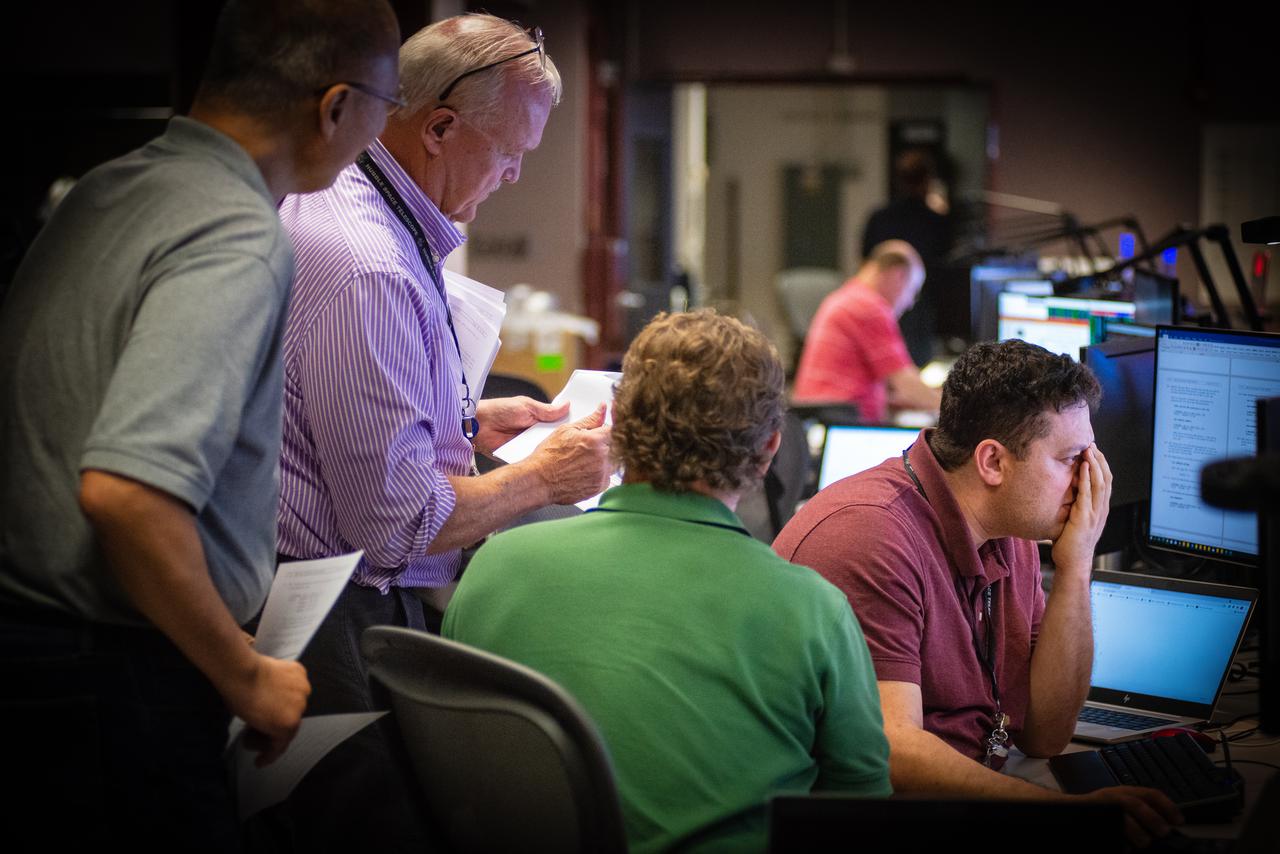

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
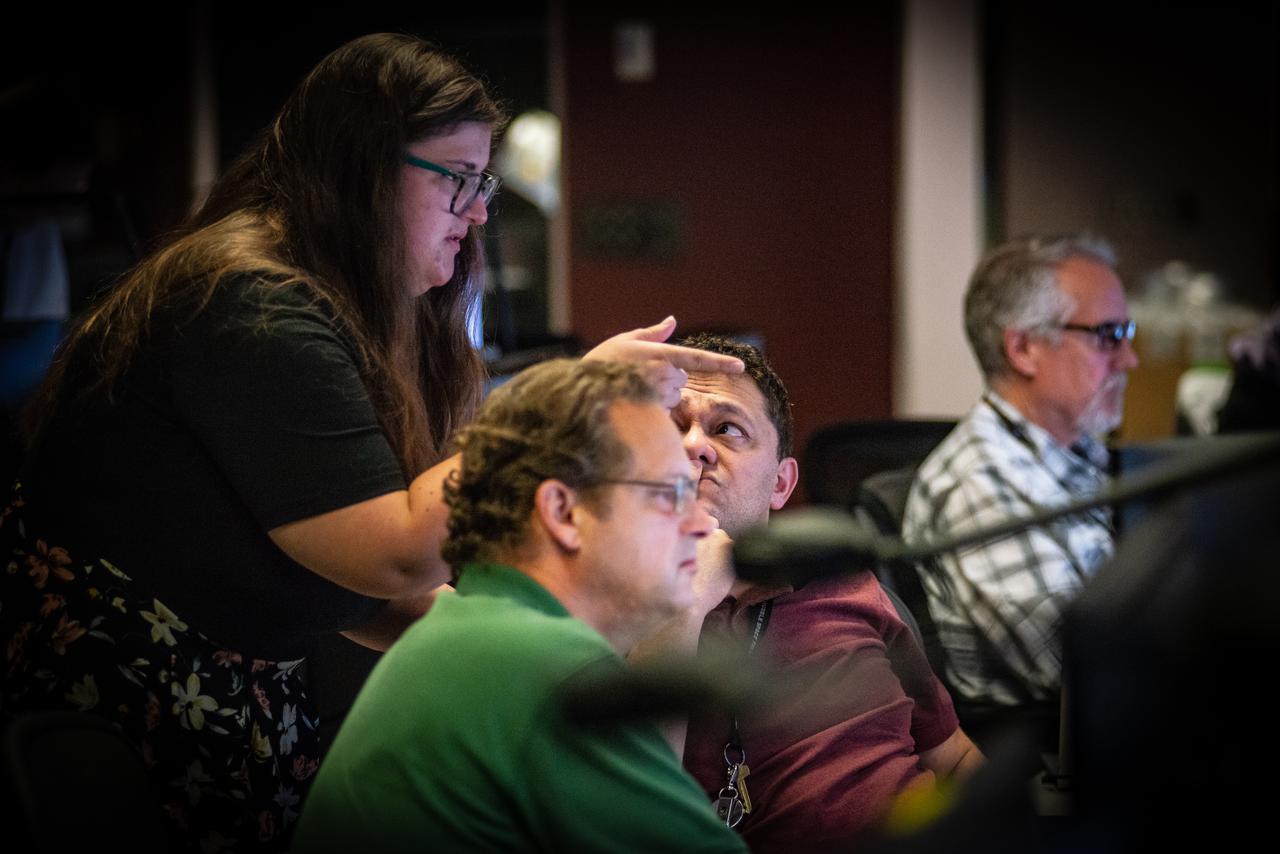

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
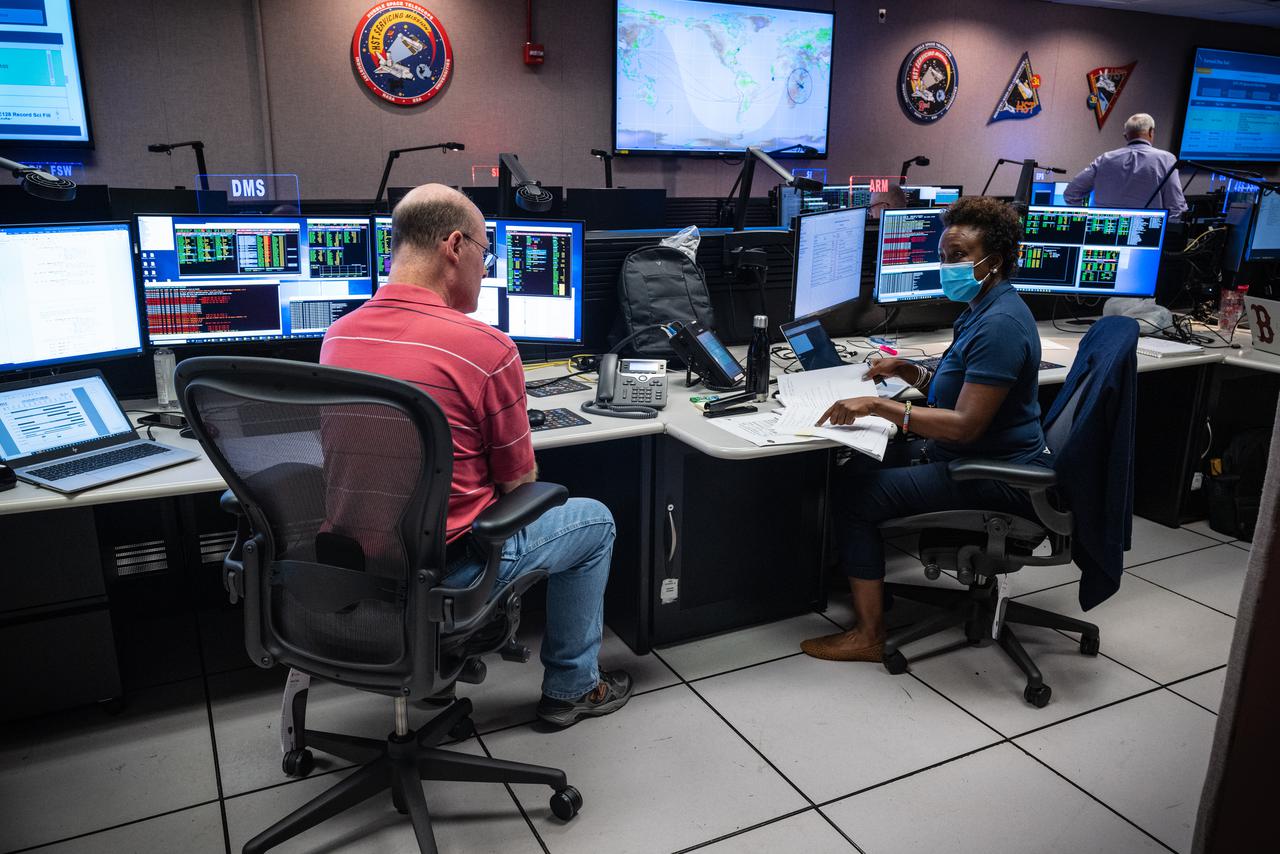

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
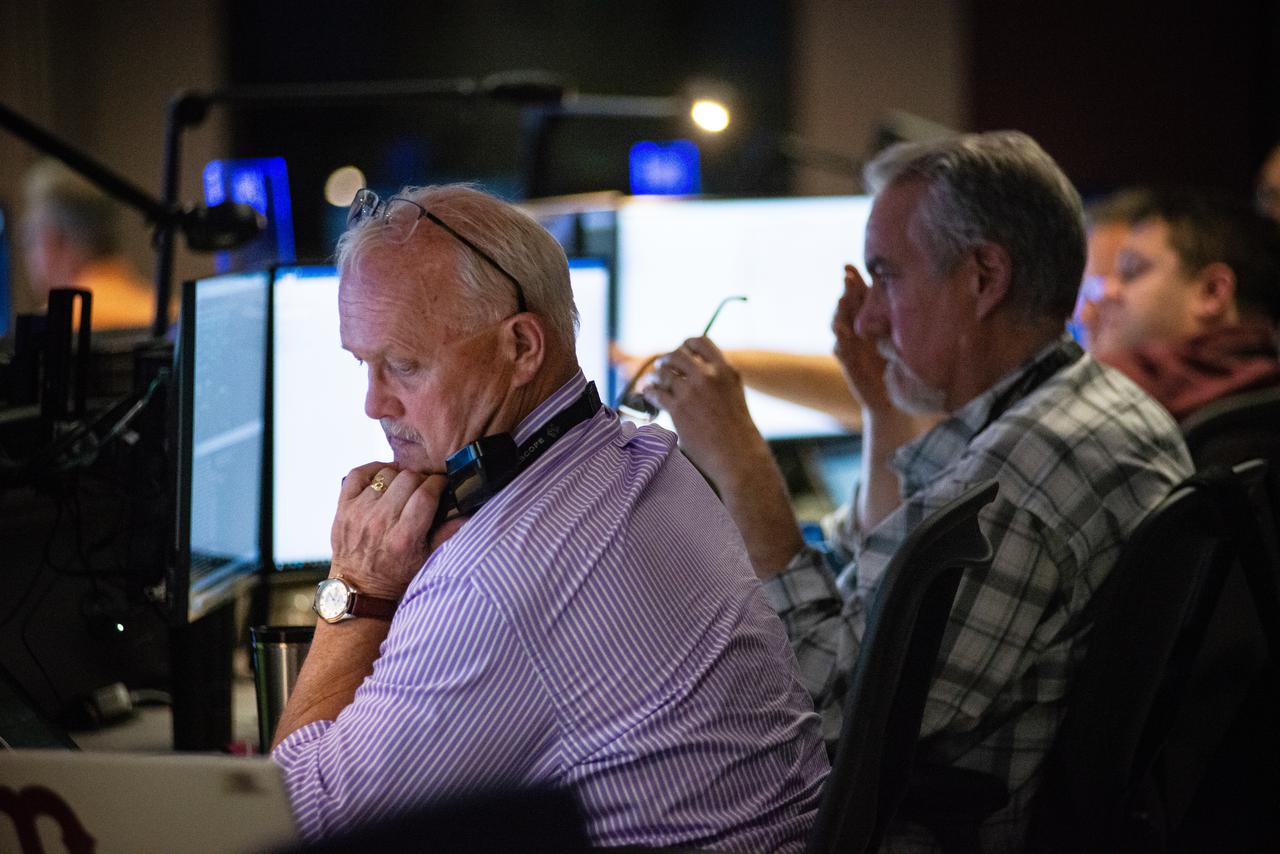

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
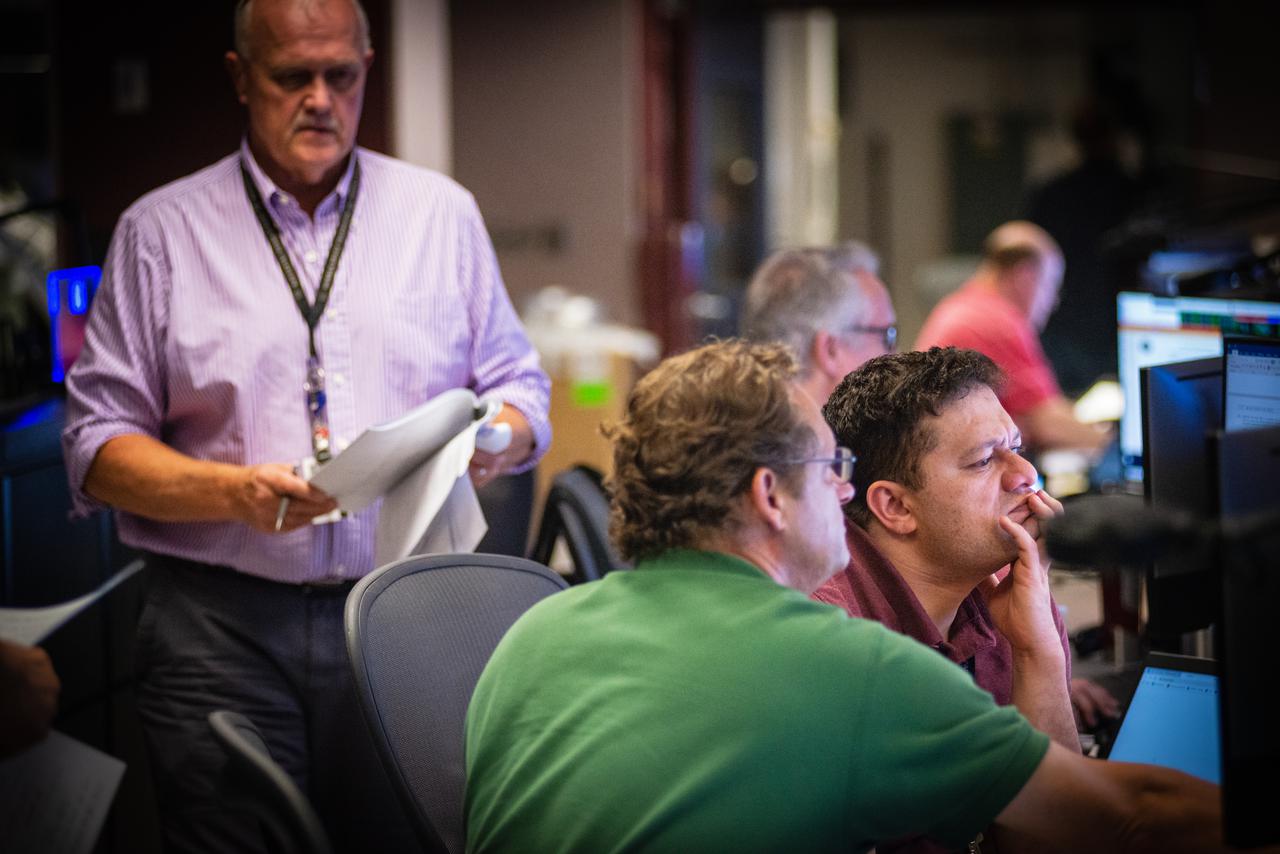

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
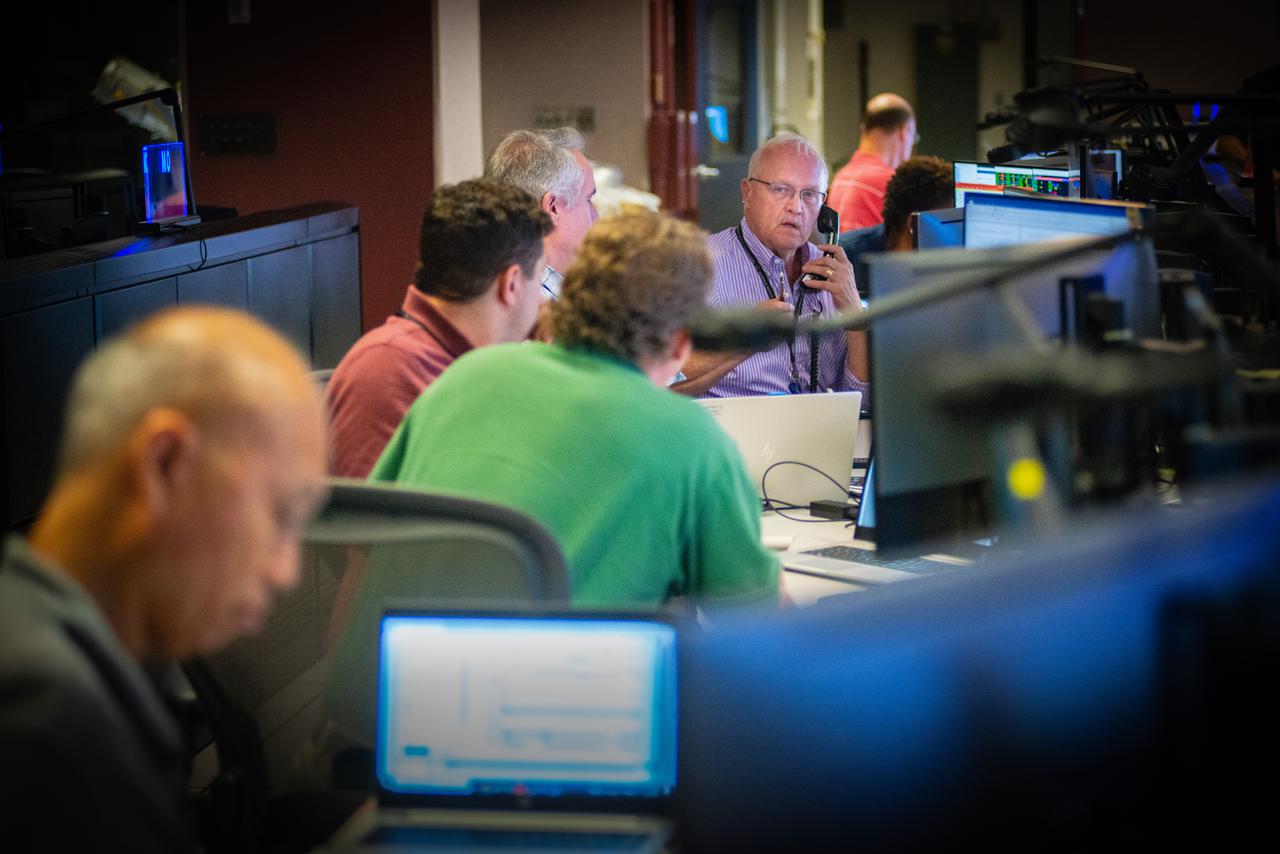

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
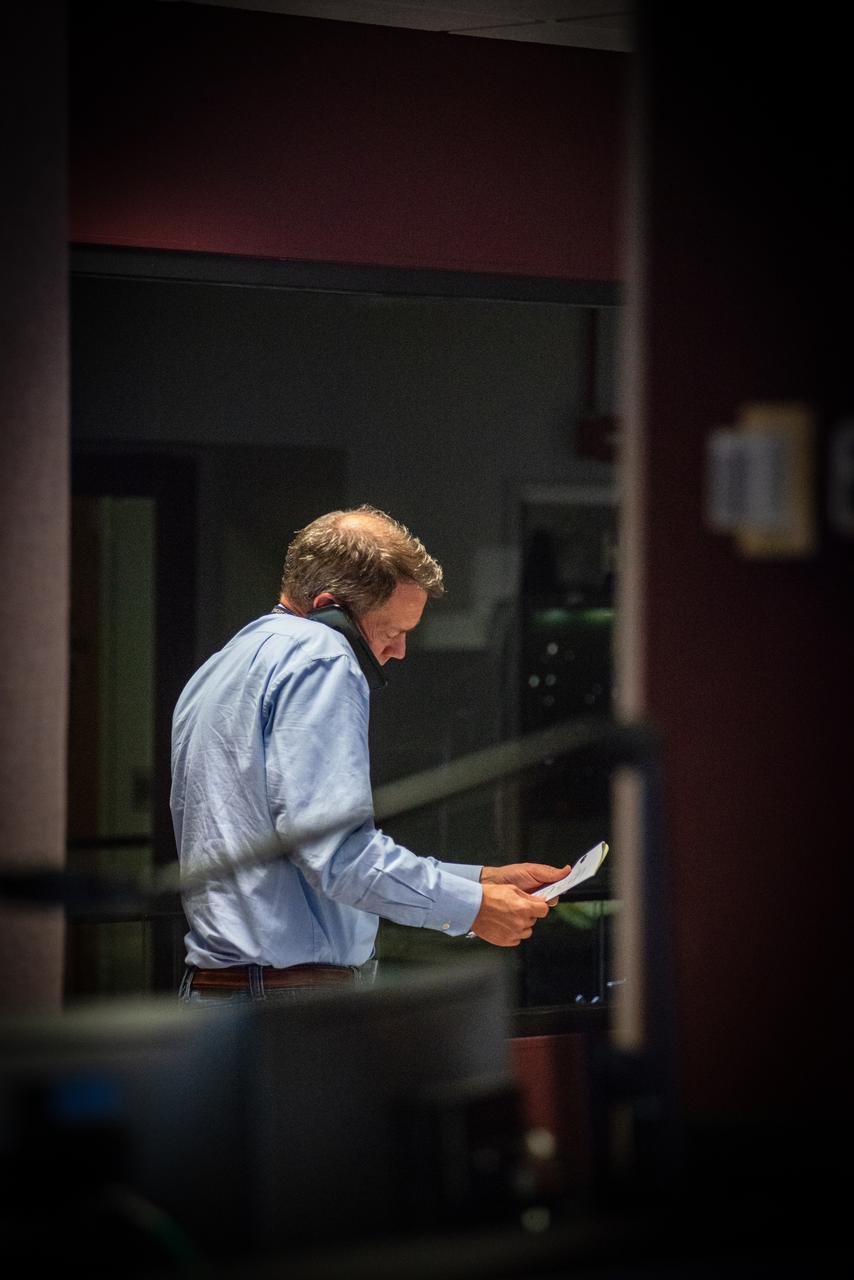

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
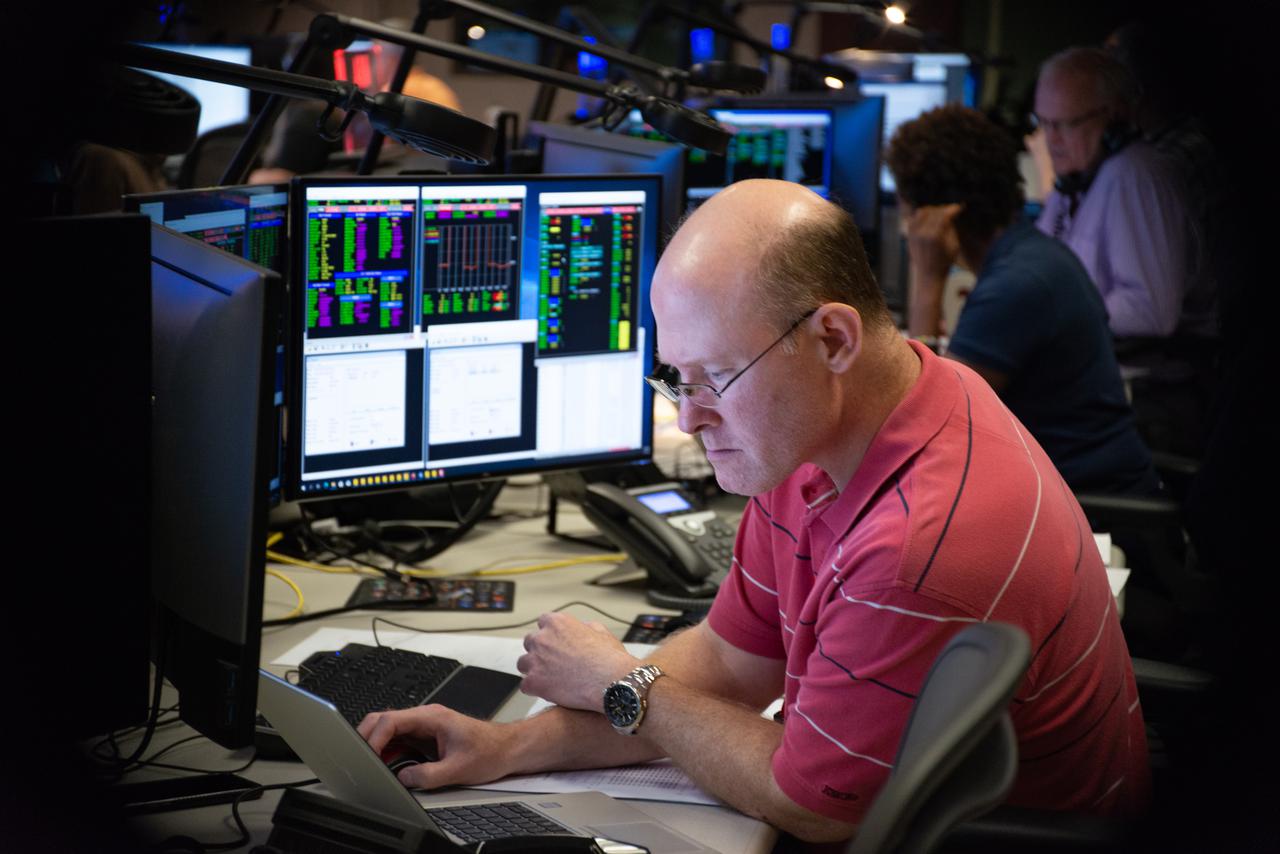

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
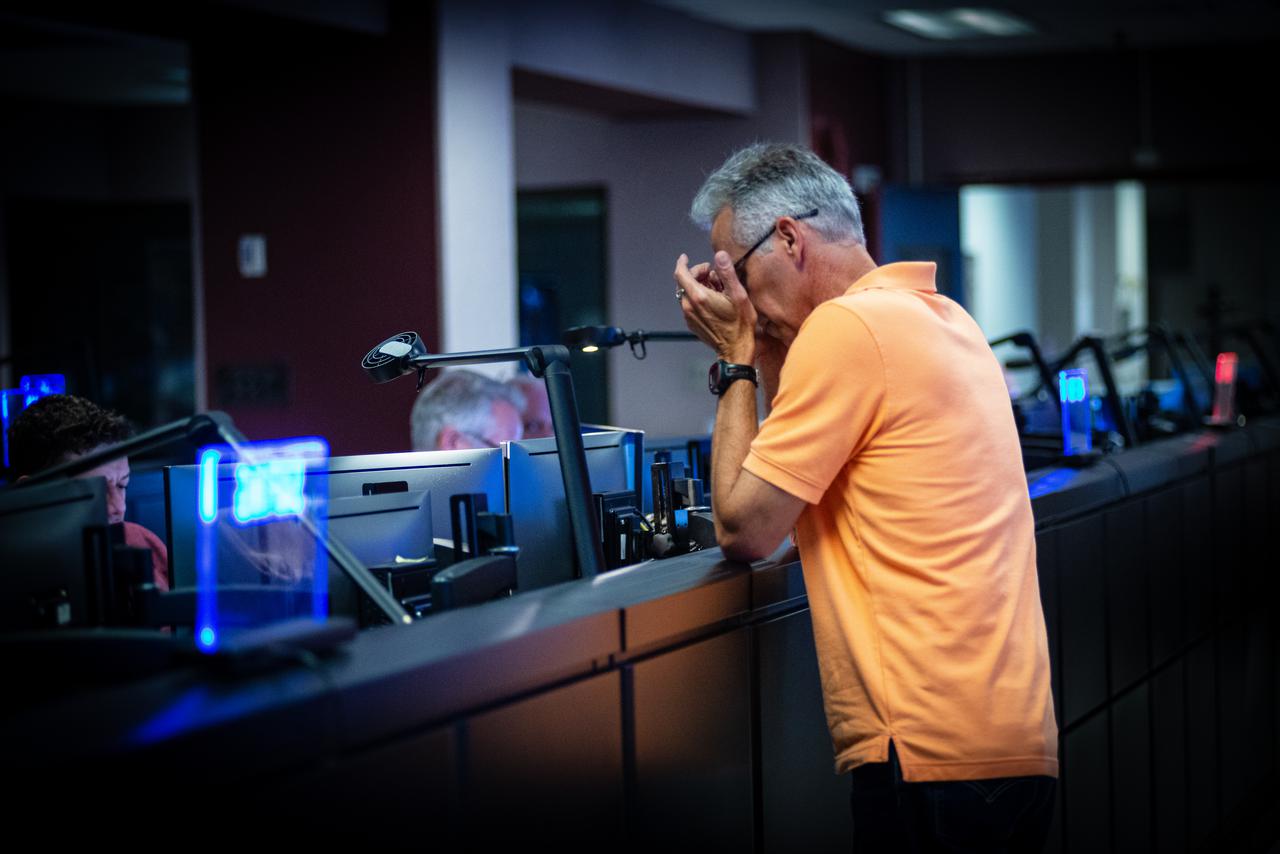

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
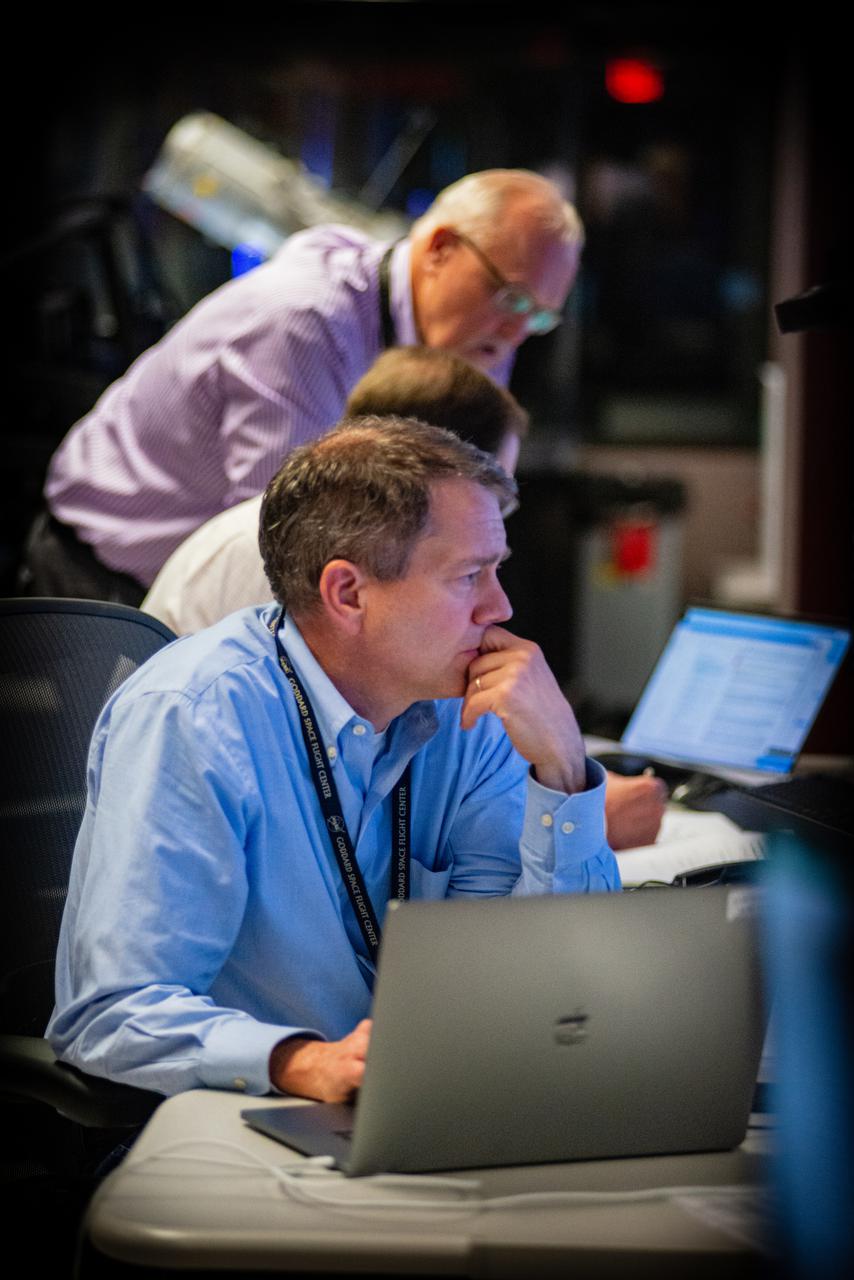

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
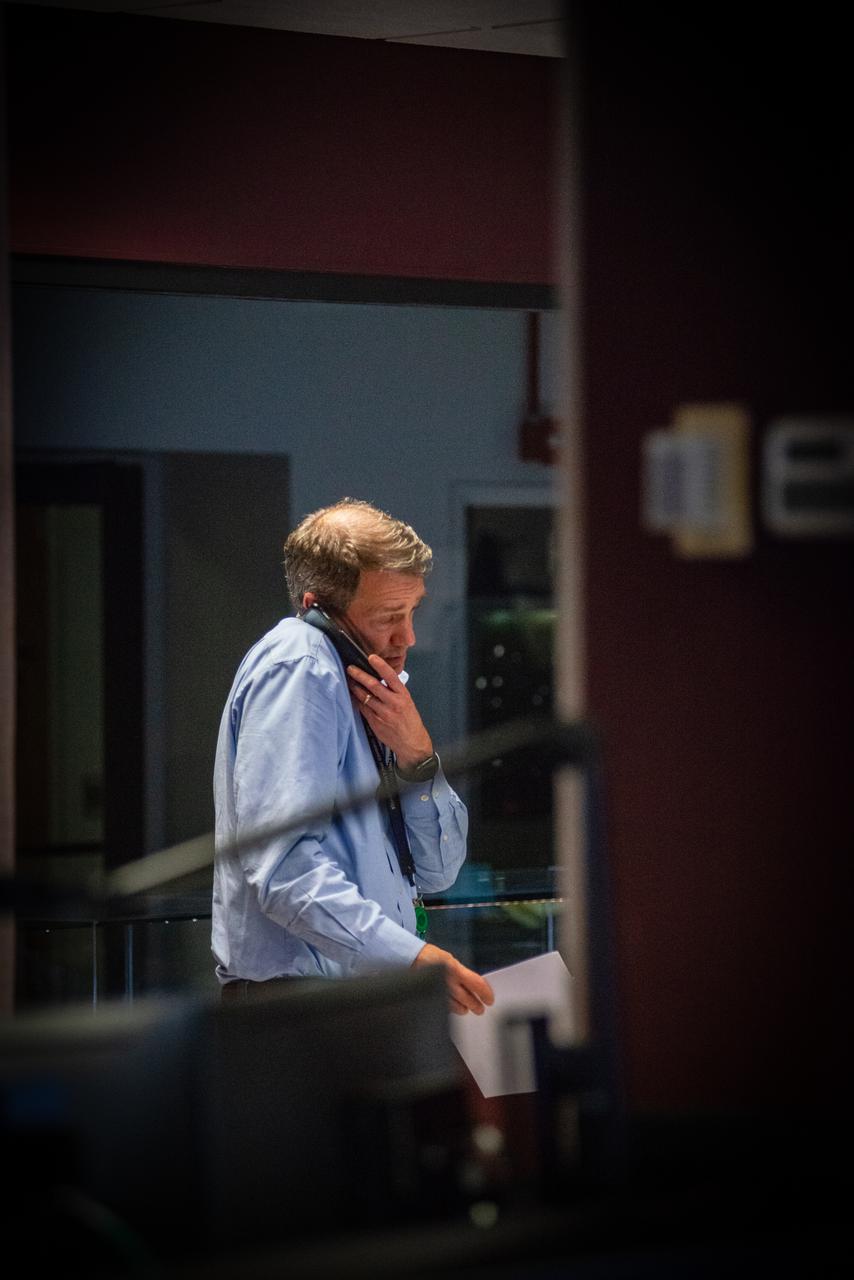

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
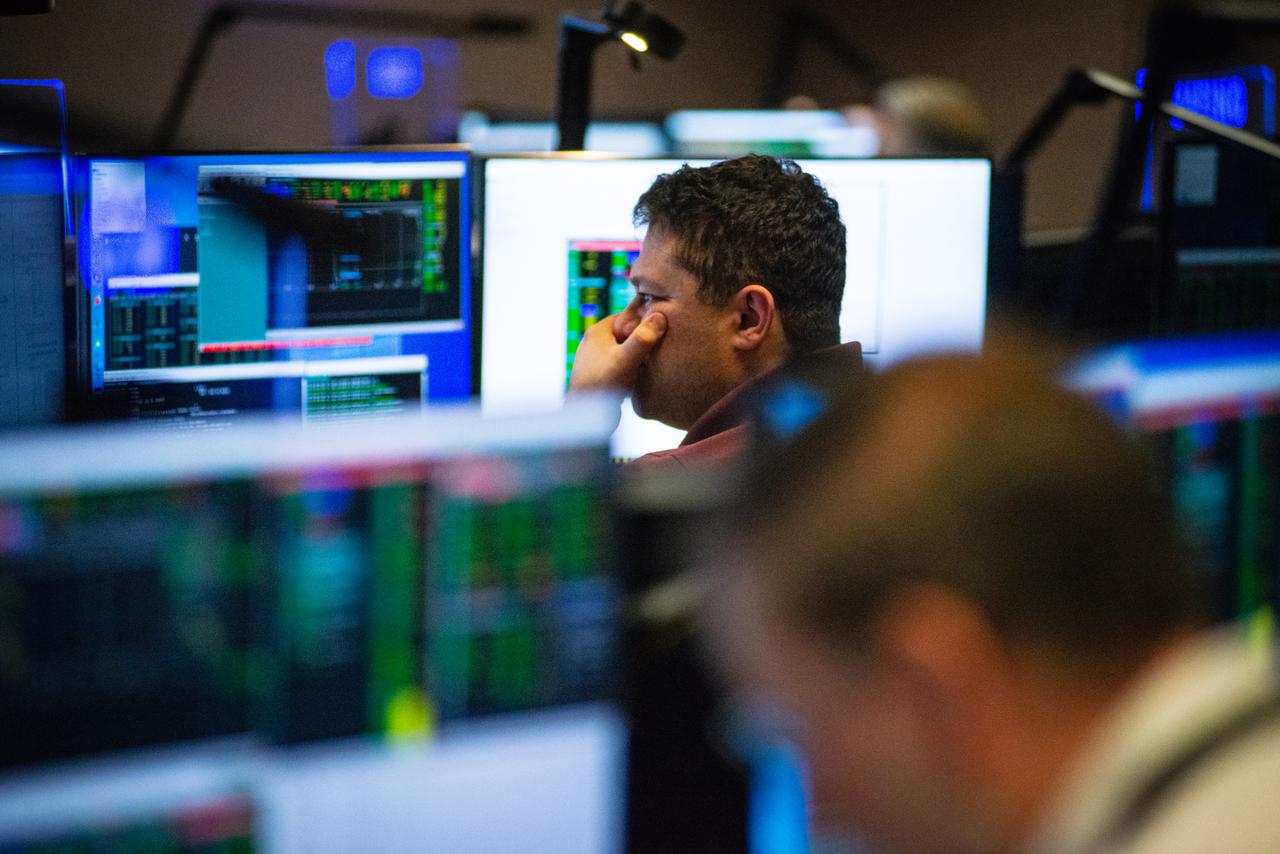

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
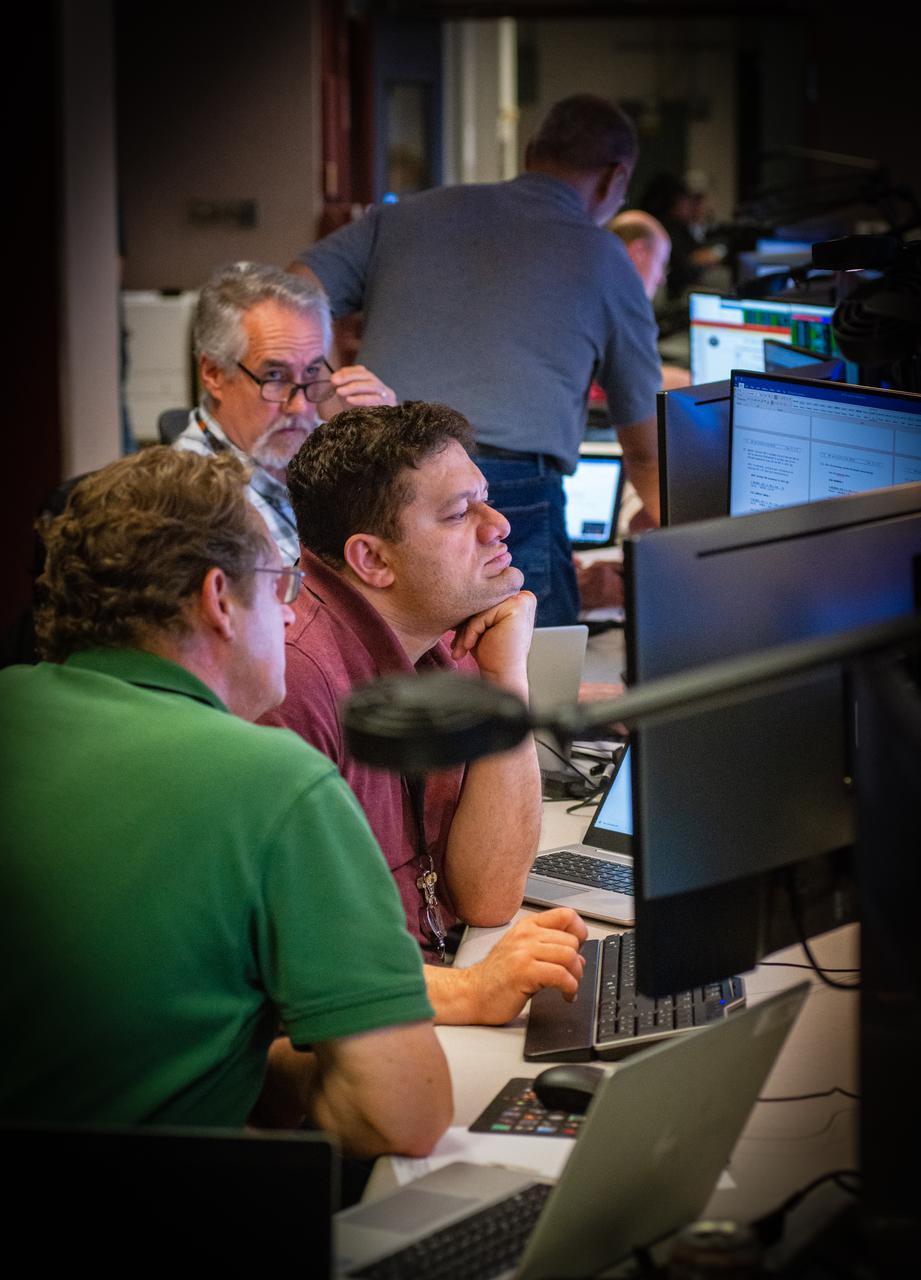

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
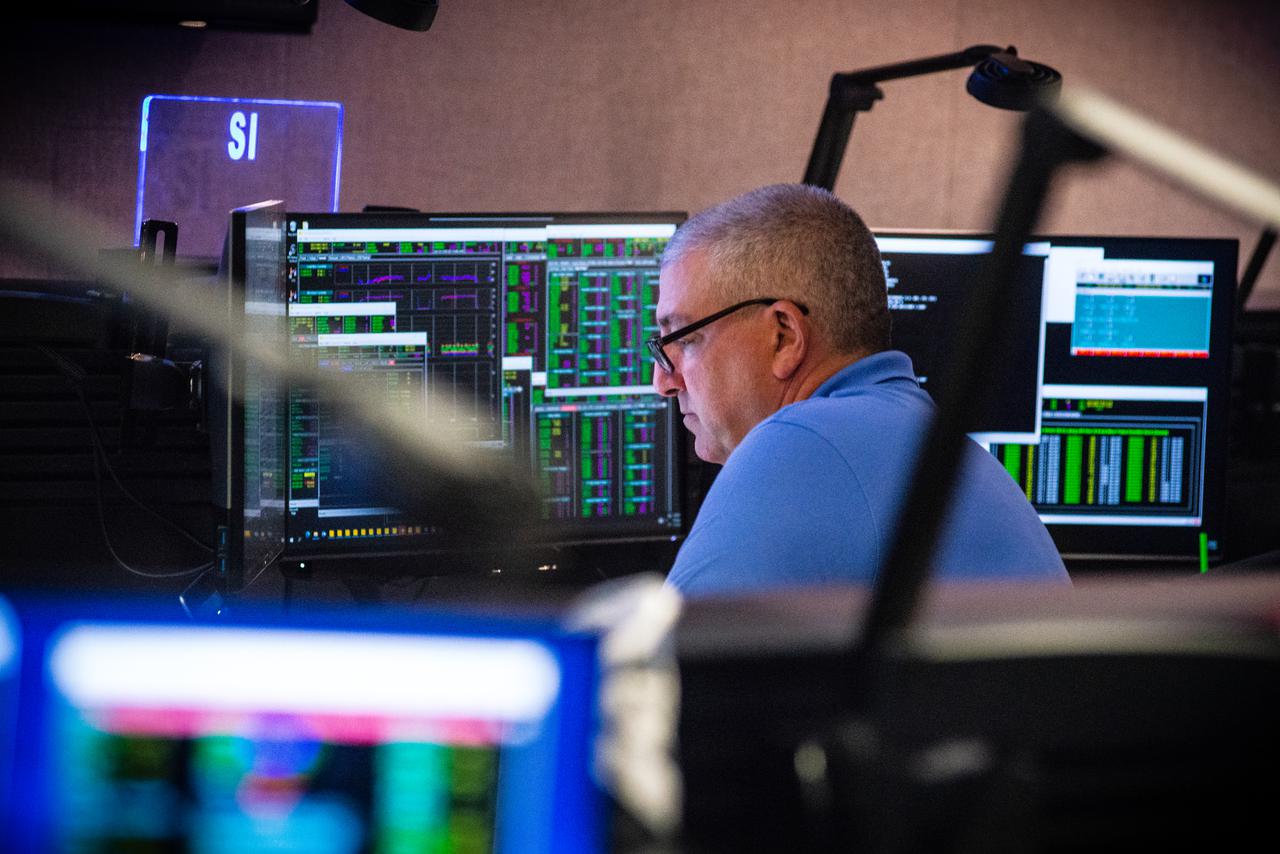

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
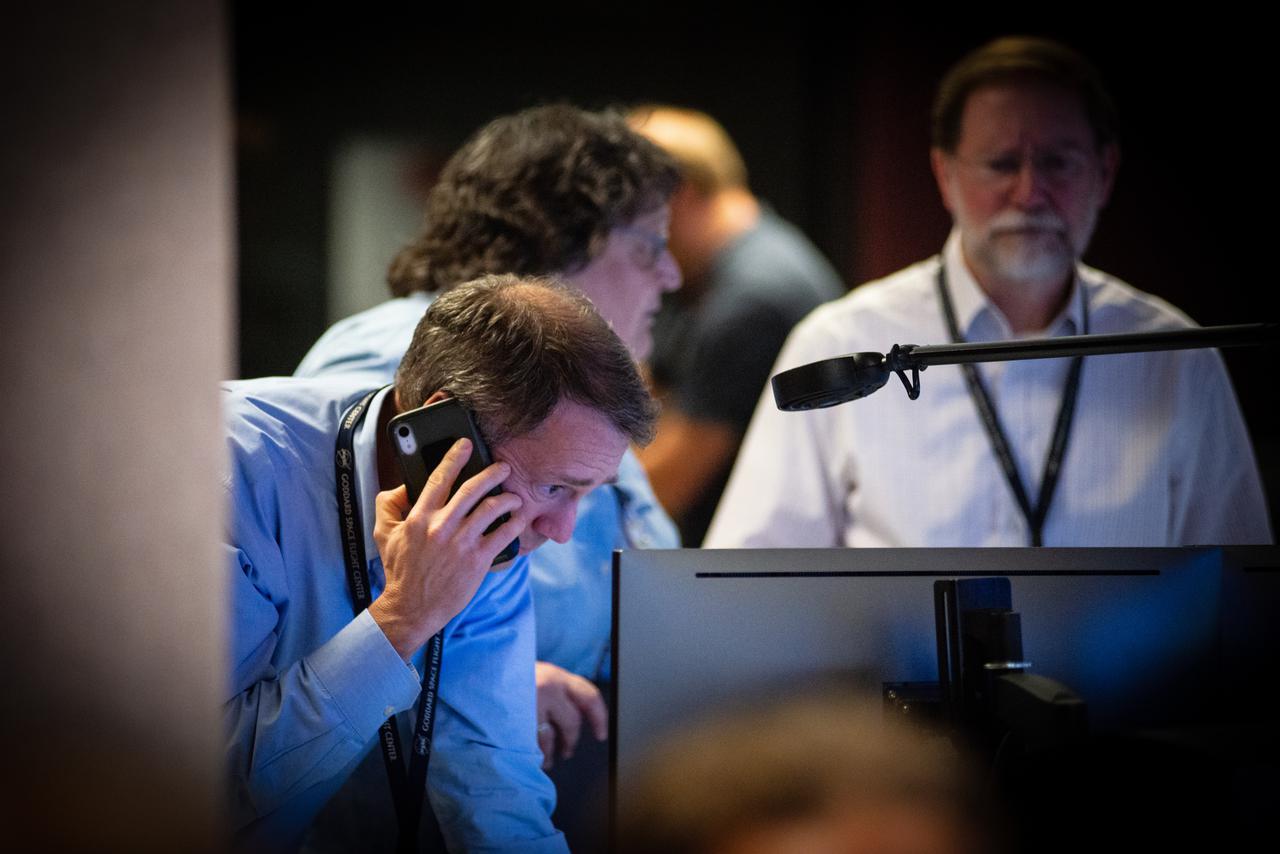

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
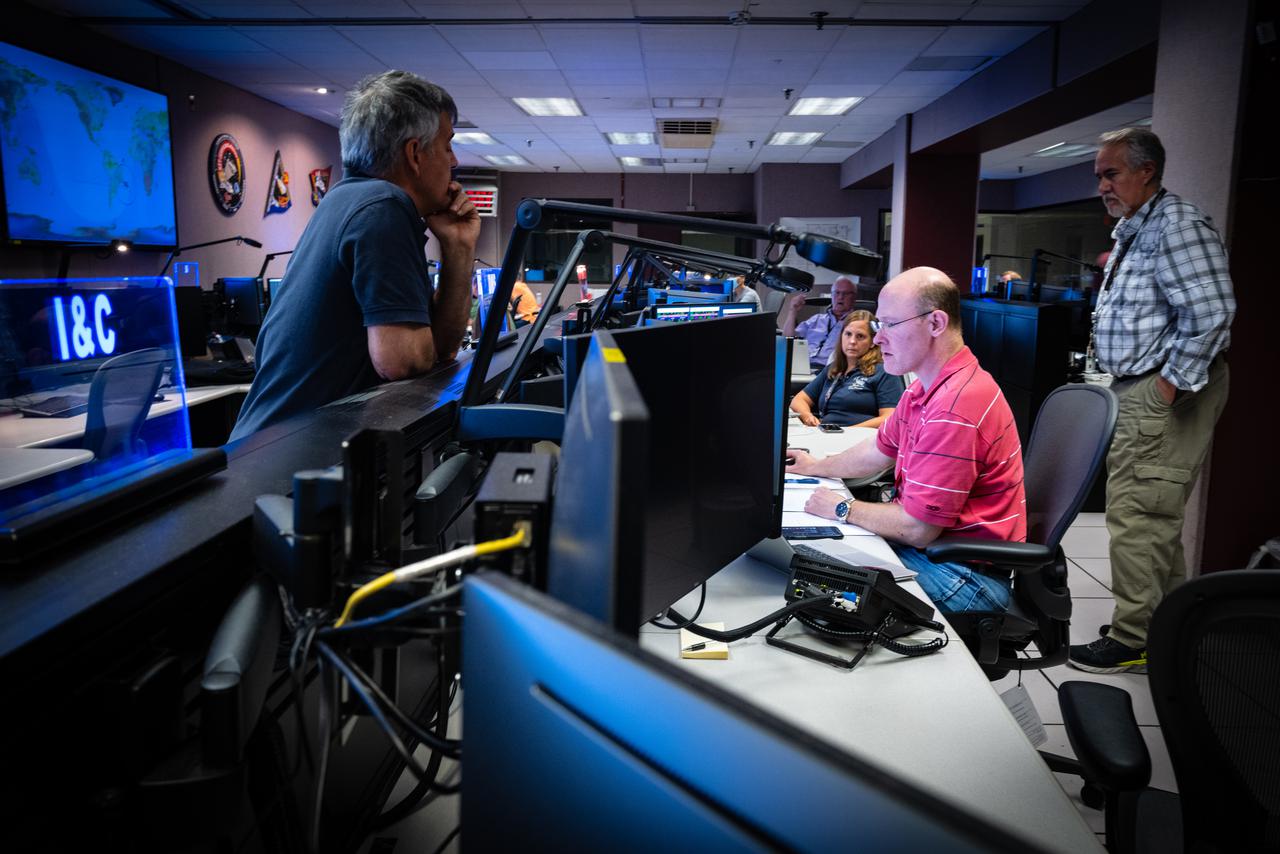

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
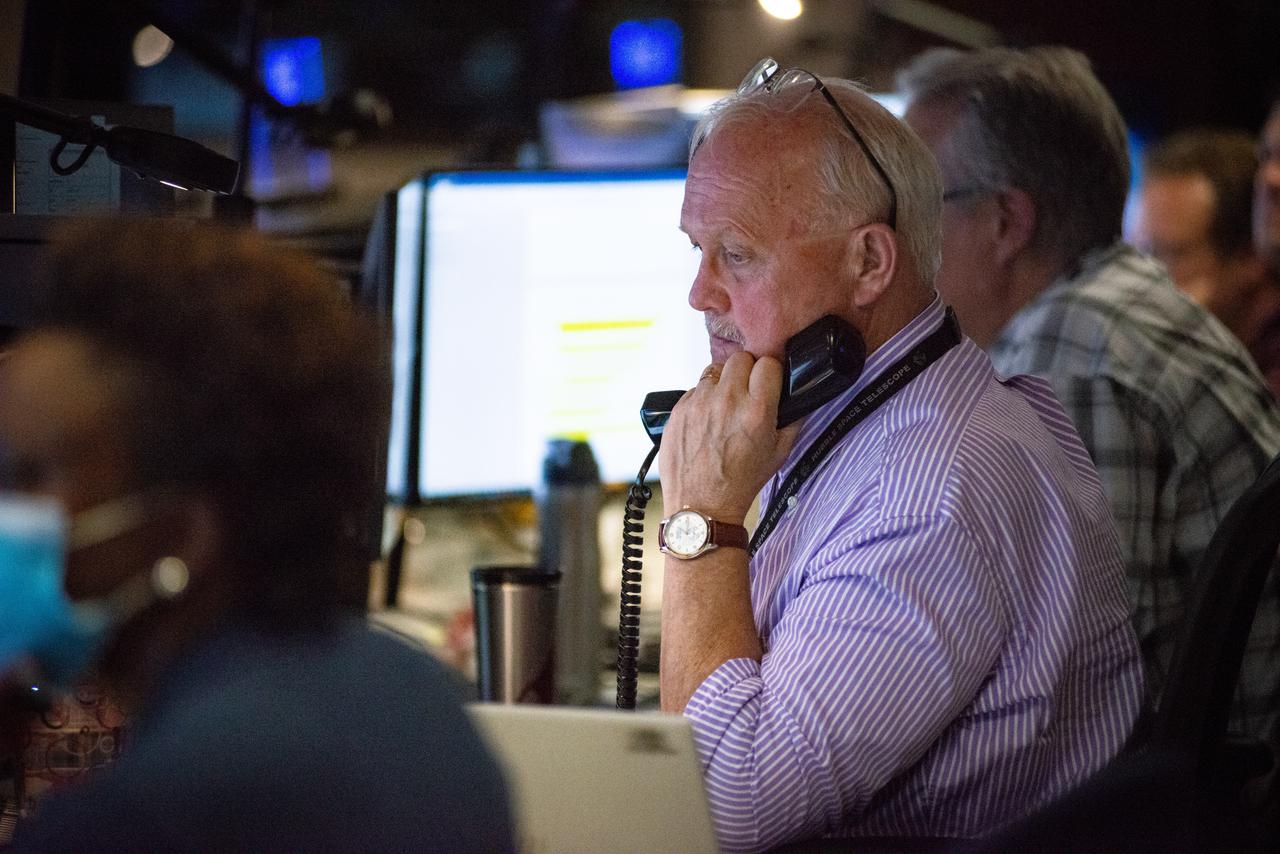

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
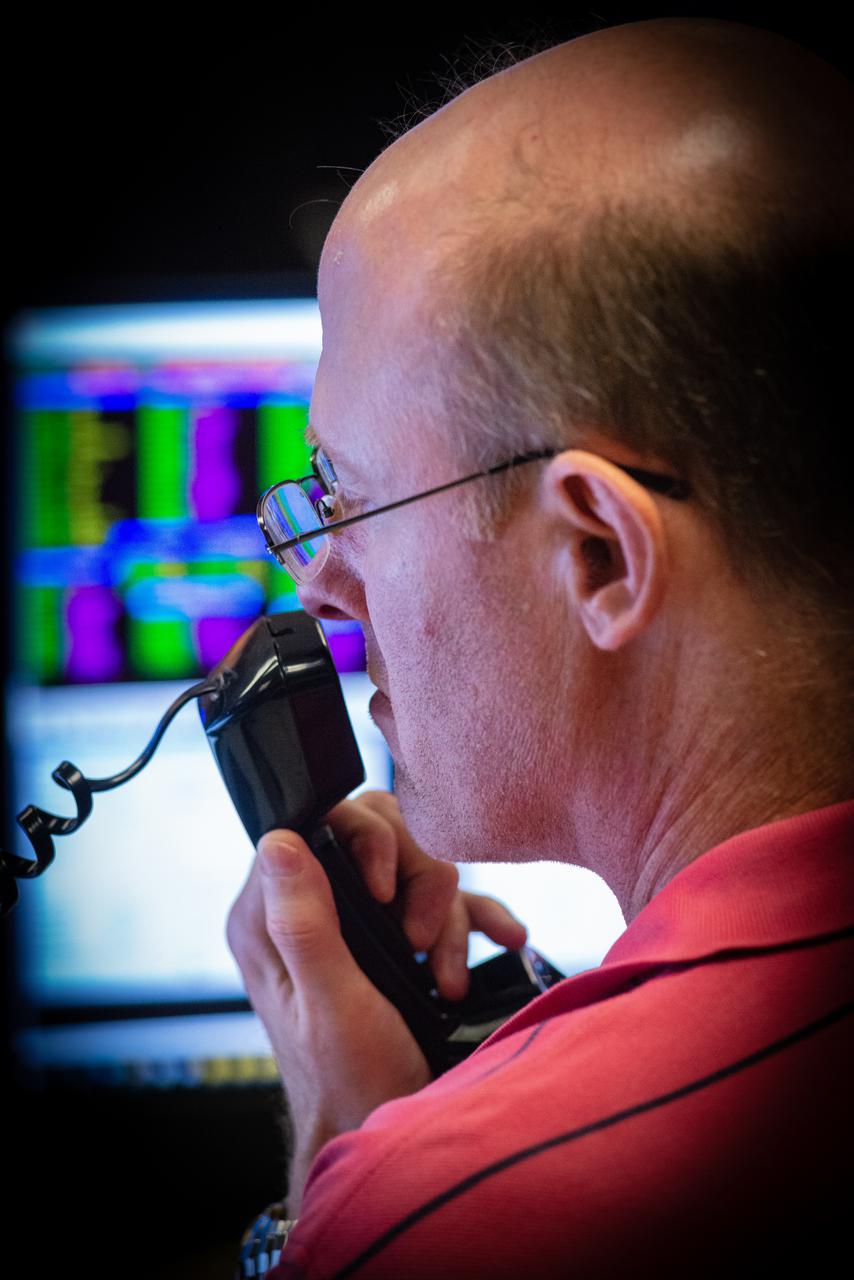

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
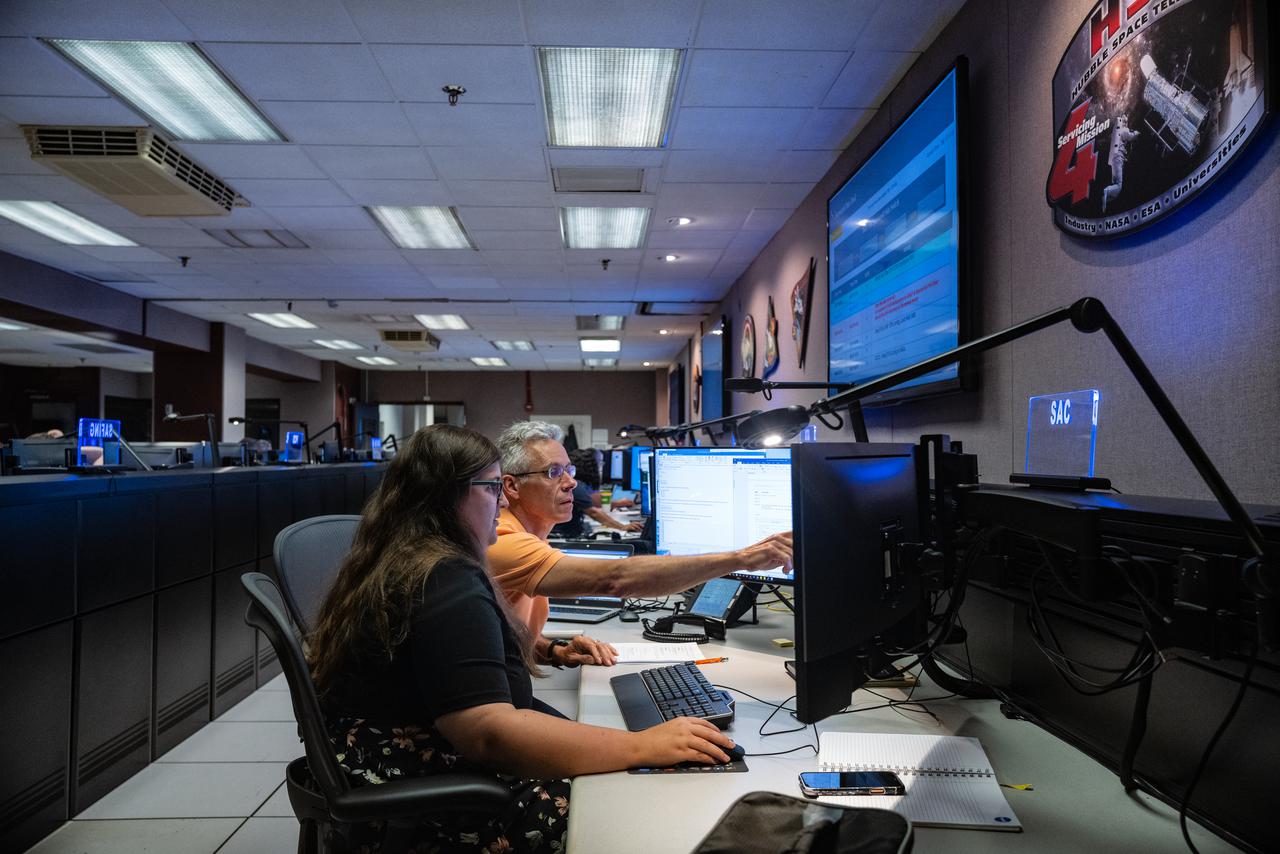

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
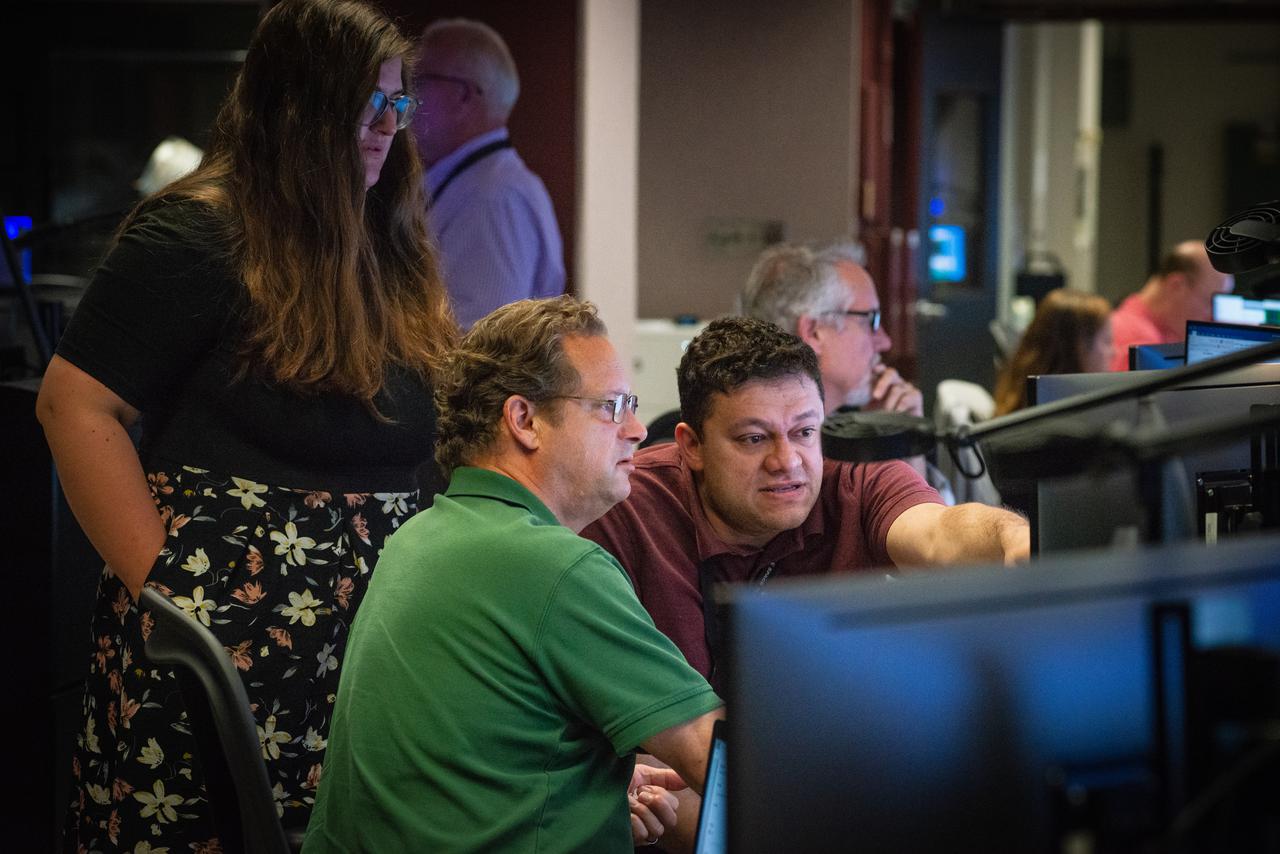

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
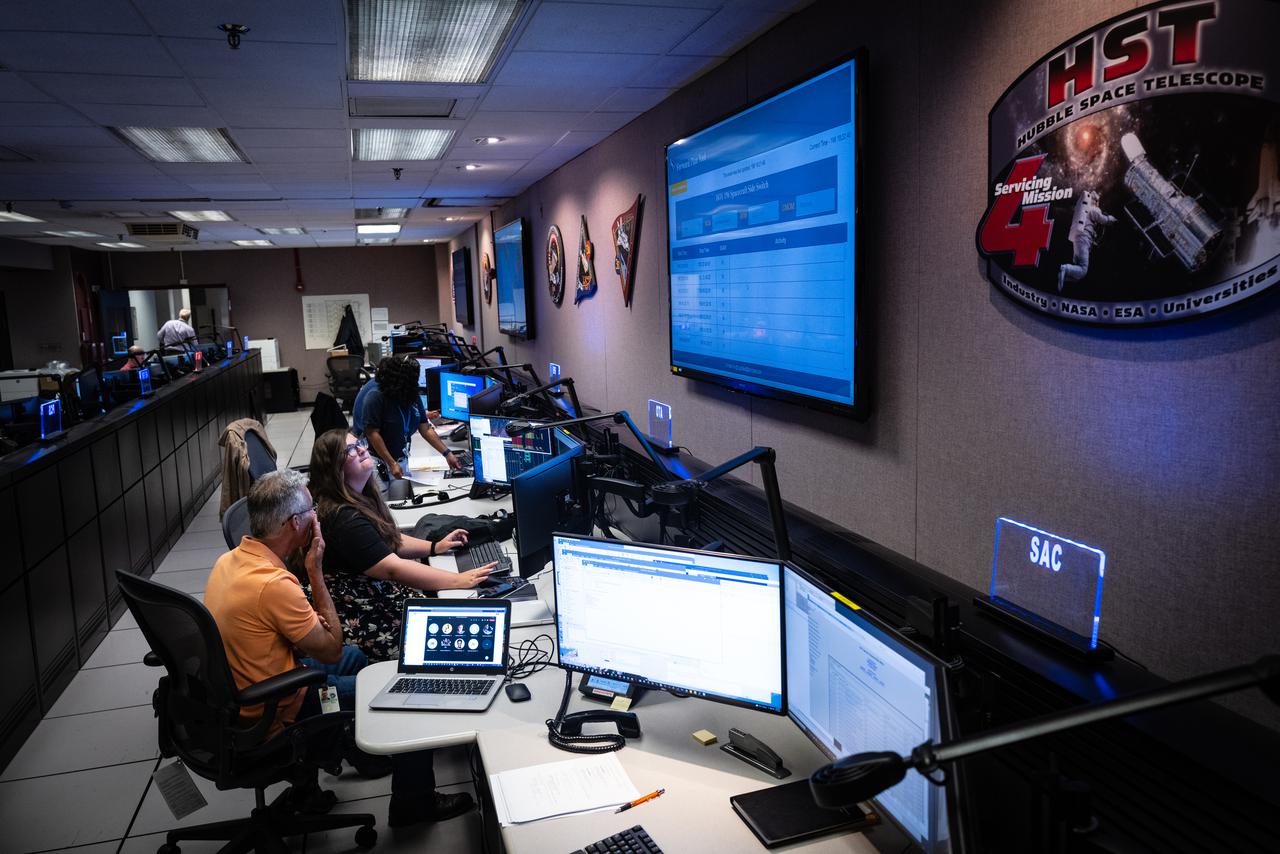

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
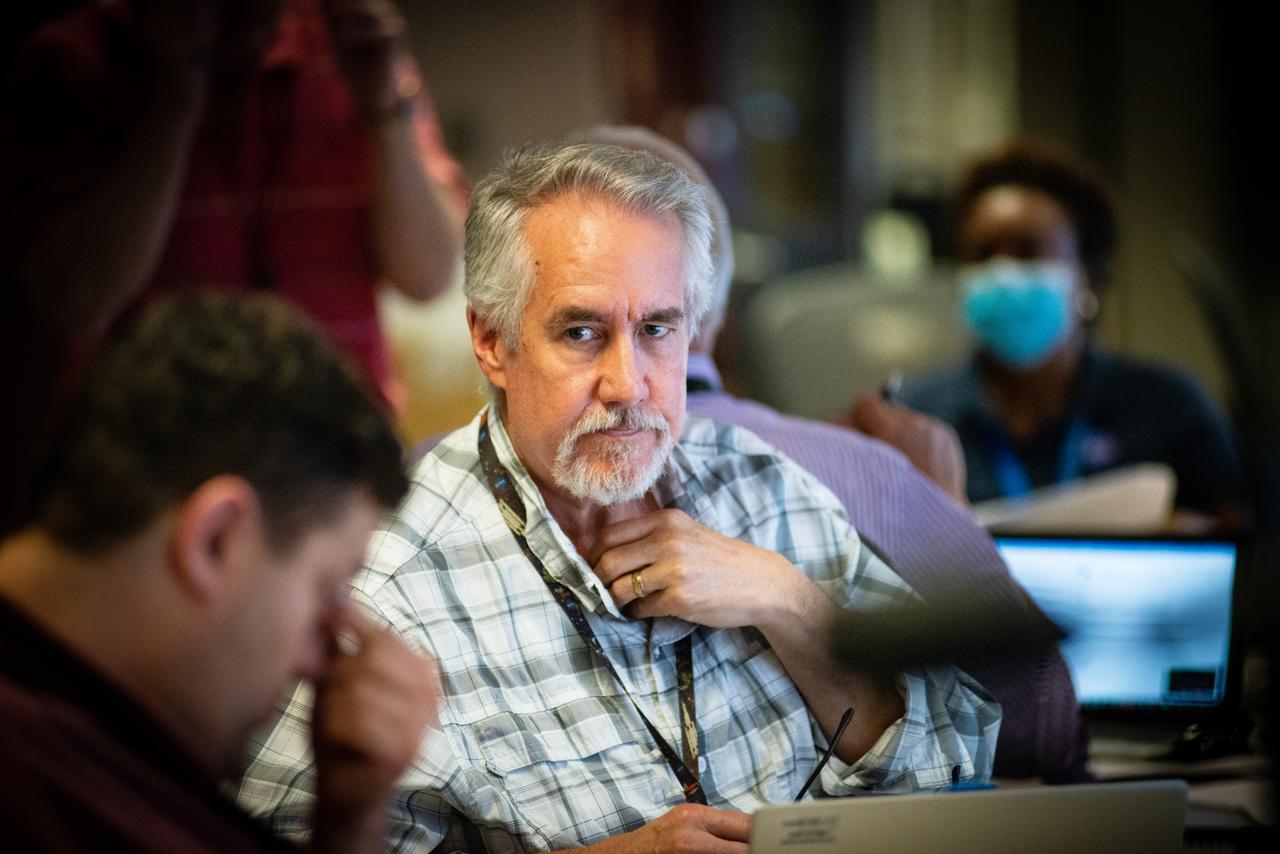

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
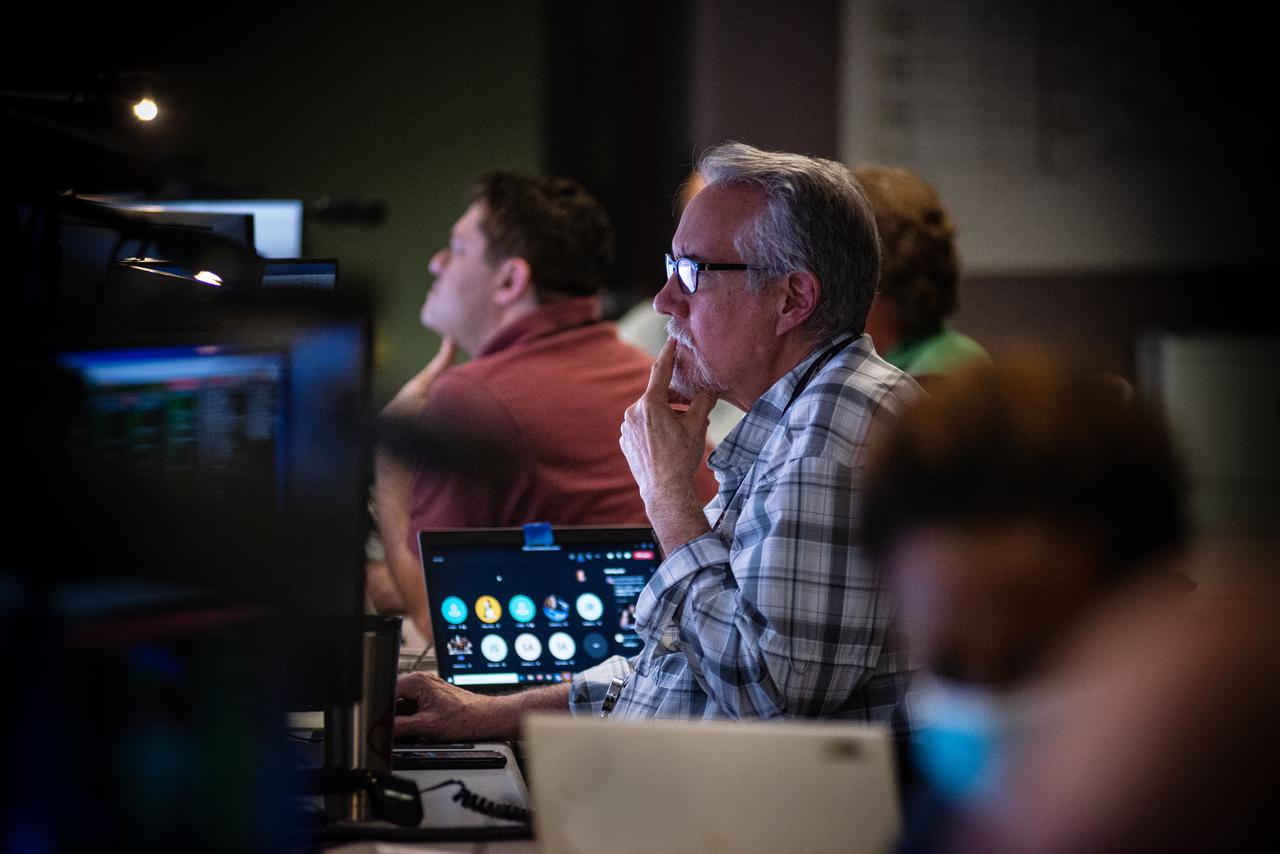

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
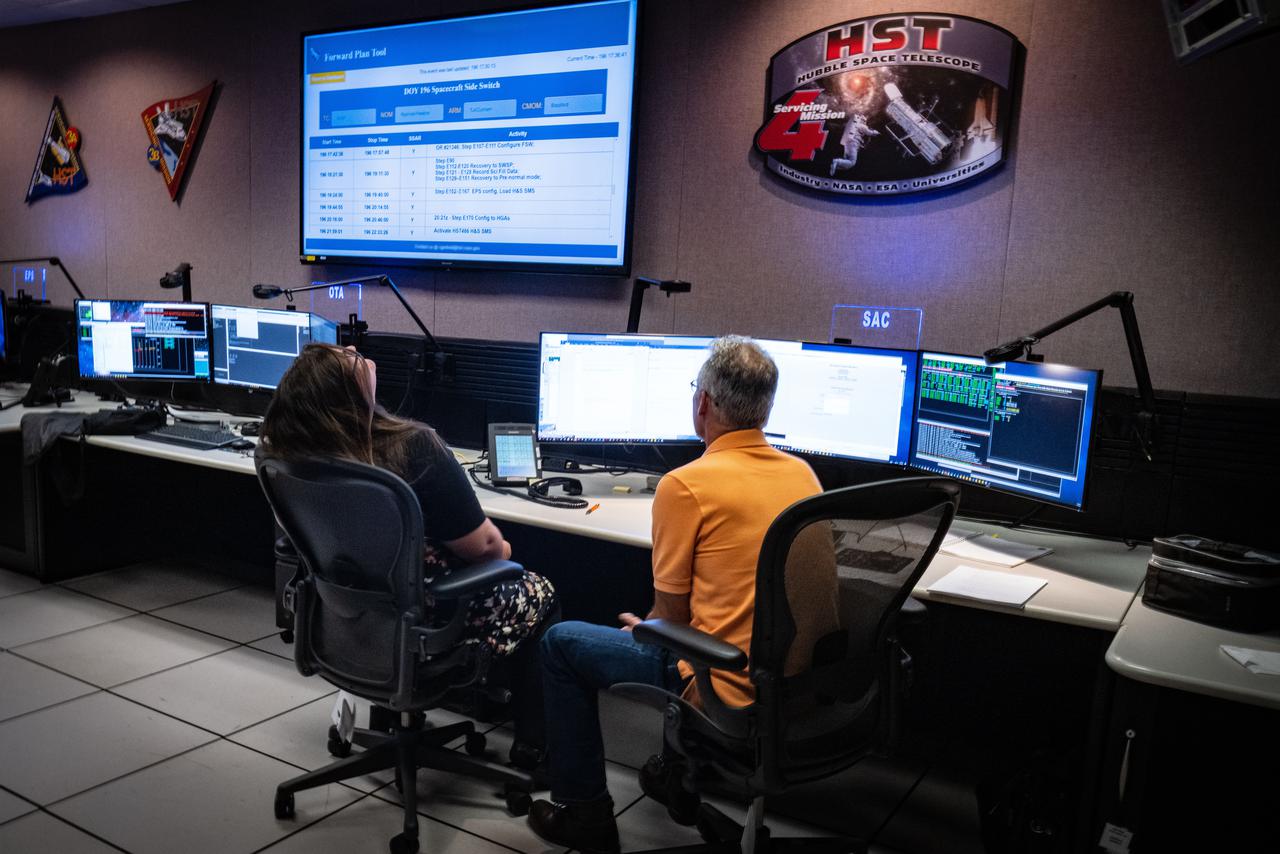

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
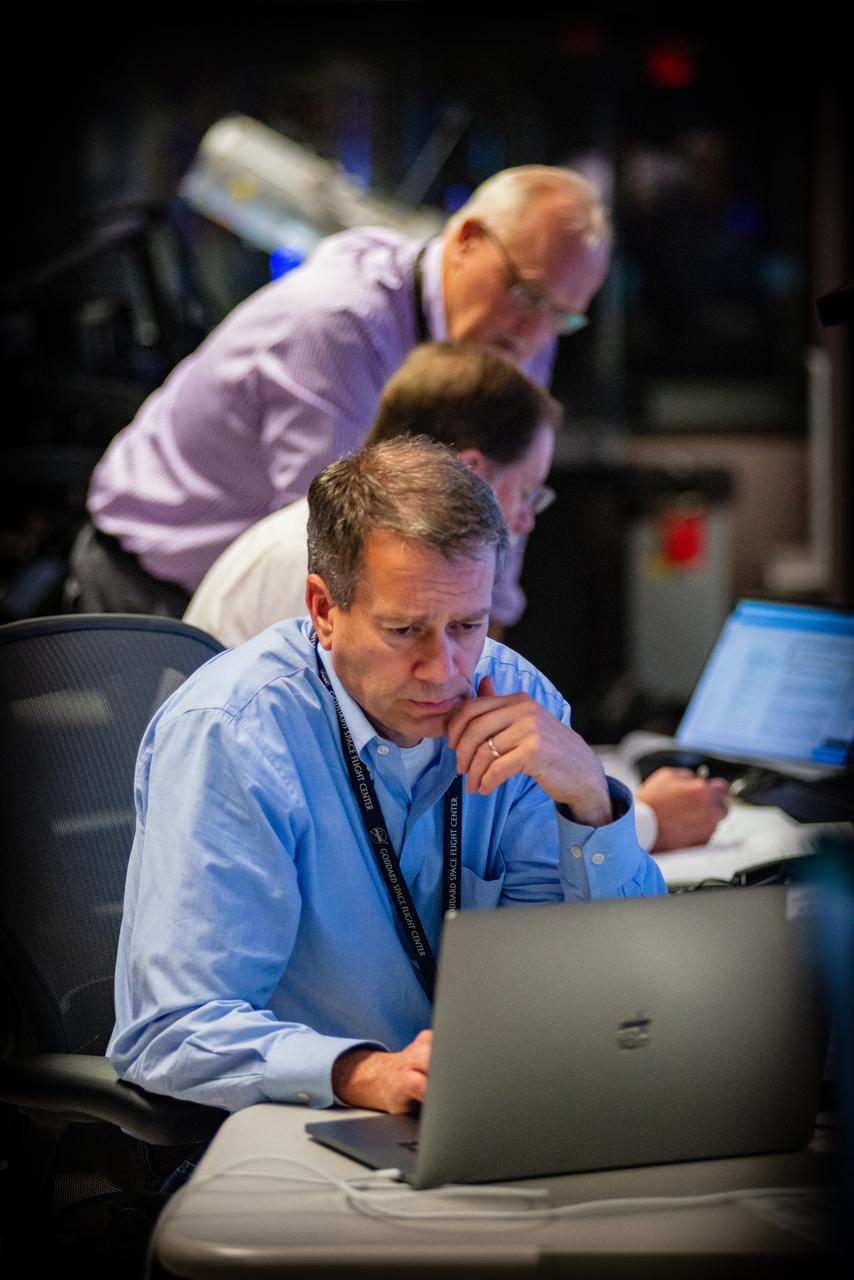

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
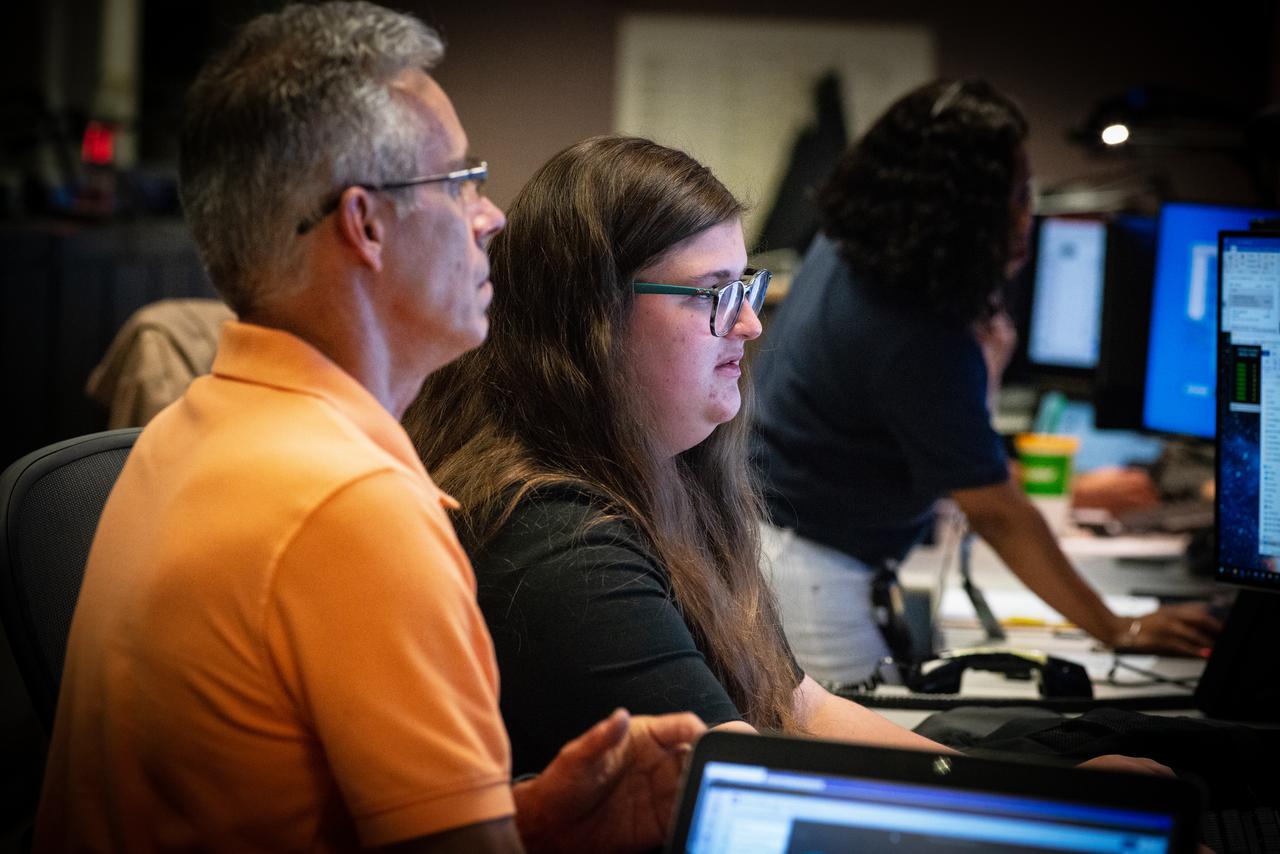

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
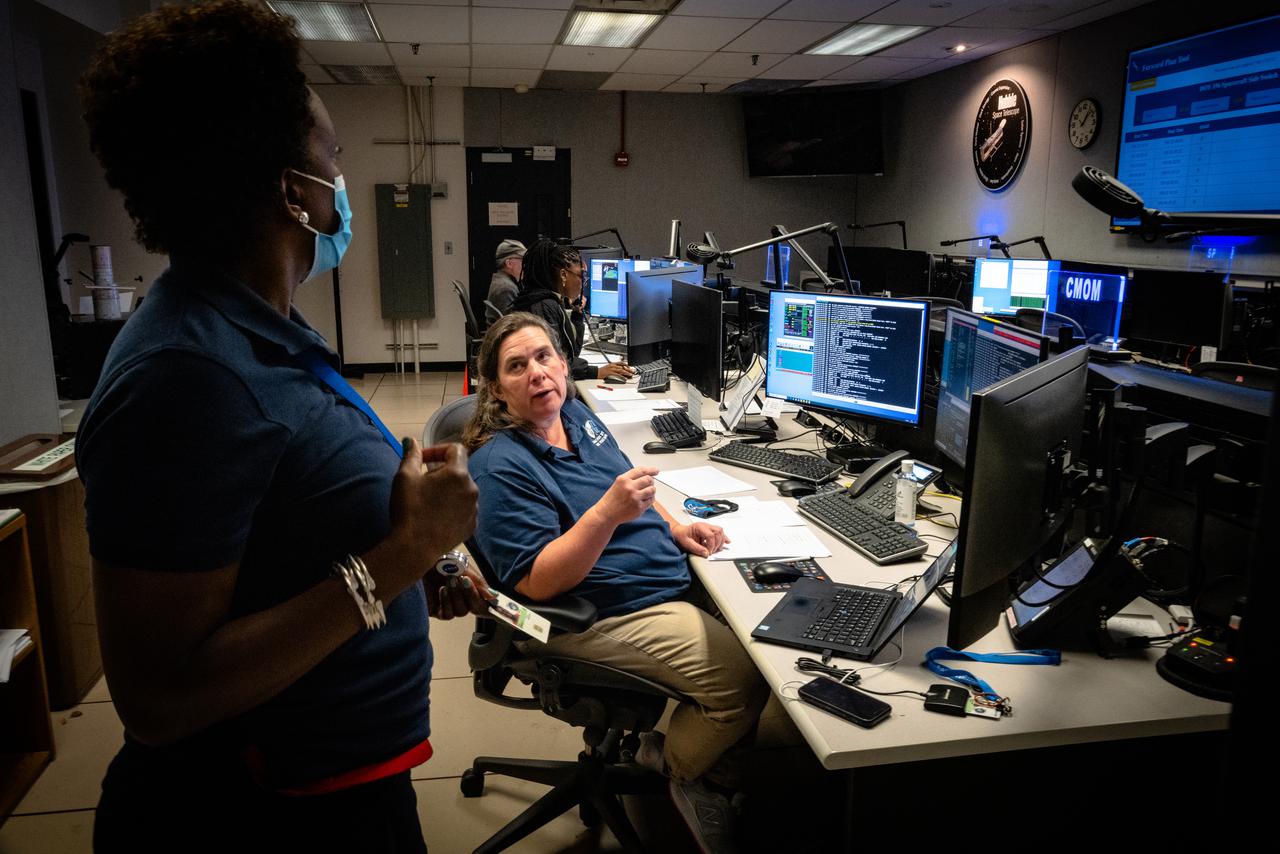

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
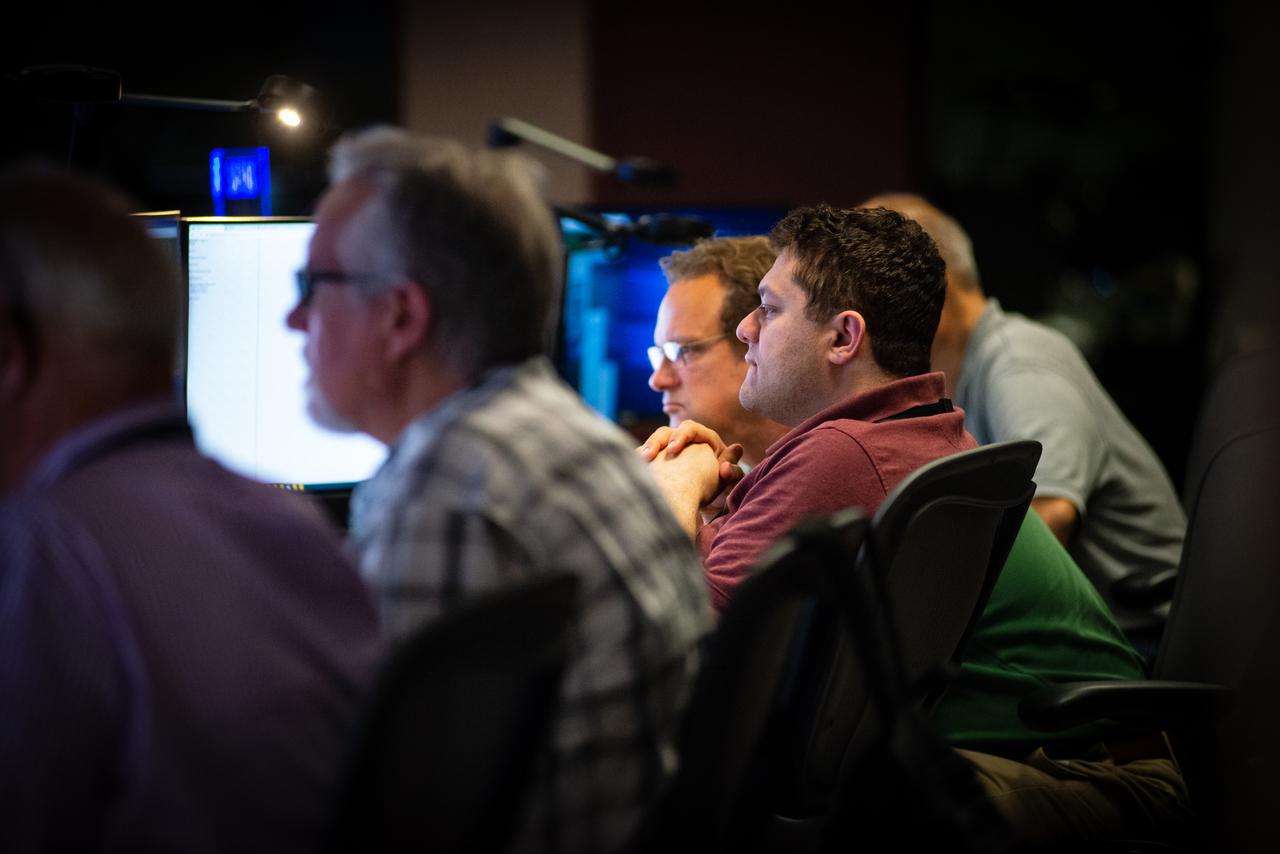

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
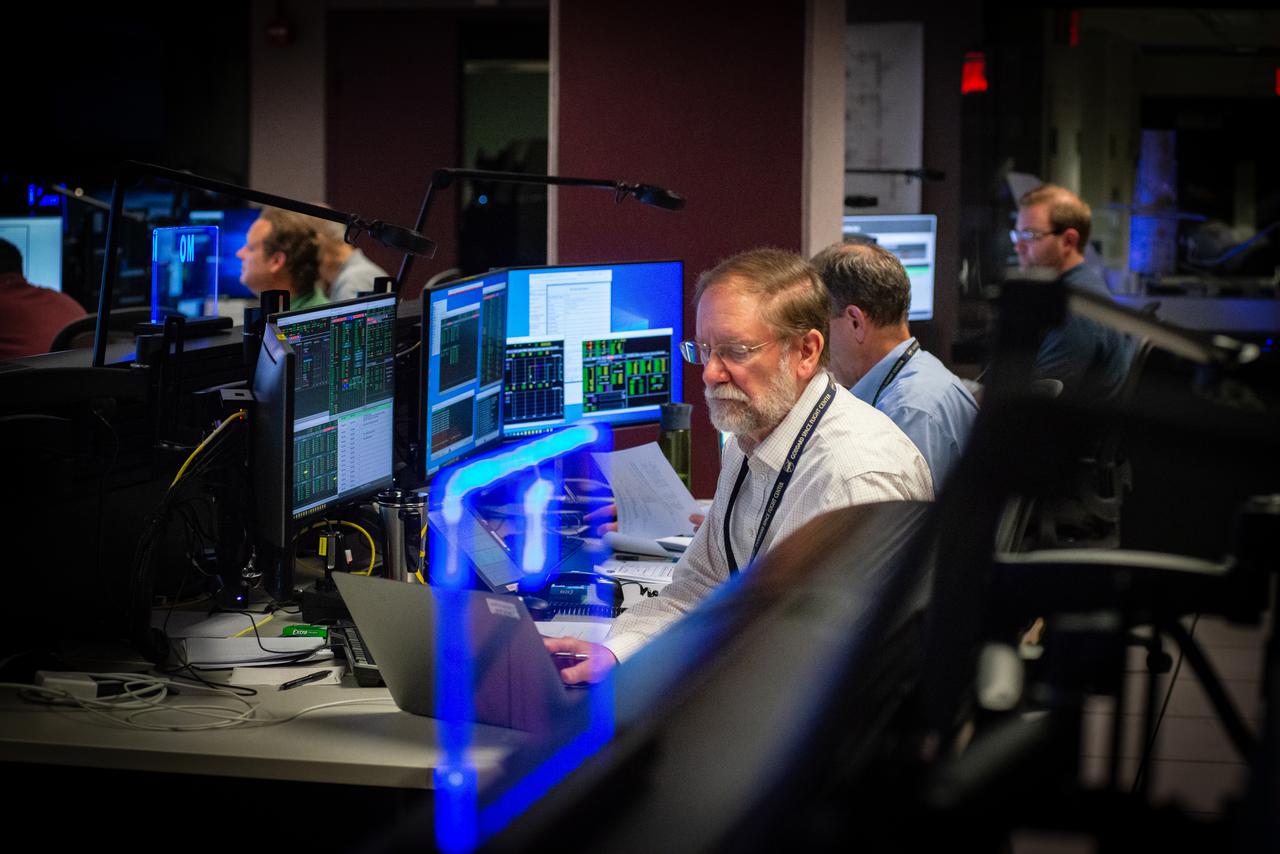

Members of the Hubble operations team work in the control room on July 15, 2021 to restore Hubble to science operations. Credits: NASA/Goddard/Rebecca Roth --- More info: Hubble’s payload computer, which controls and coordinates the observatory’s onboard science instruments, halted suddenly on June 13. When the main computer failed to receive a signal from the payload computer, it automatically placed Hubble’s science instruments into safe mode. That meant the telescope would no longer be doing science while mission specialists analyzed the situation. In response to the anomaly, NASA began a switch to backup spacecraft hardware on Hubble in response to an ongoing problem with its payload computer. This was a multi-day event. Science observations restarted the afternoon of Saturday, July 17.
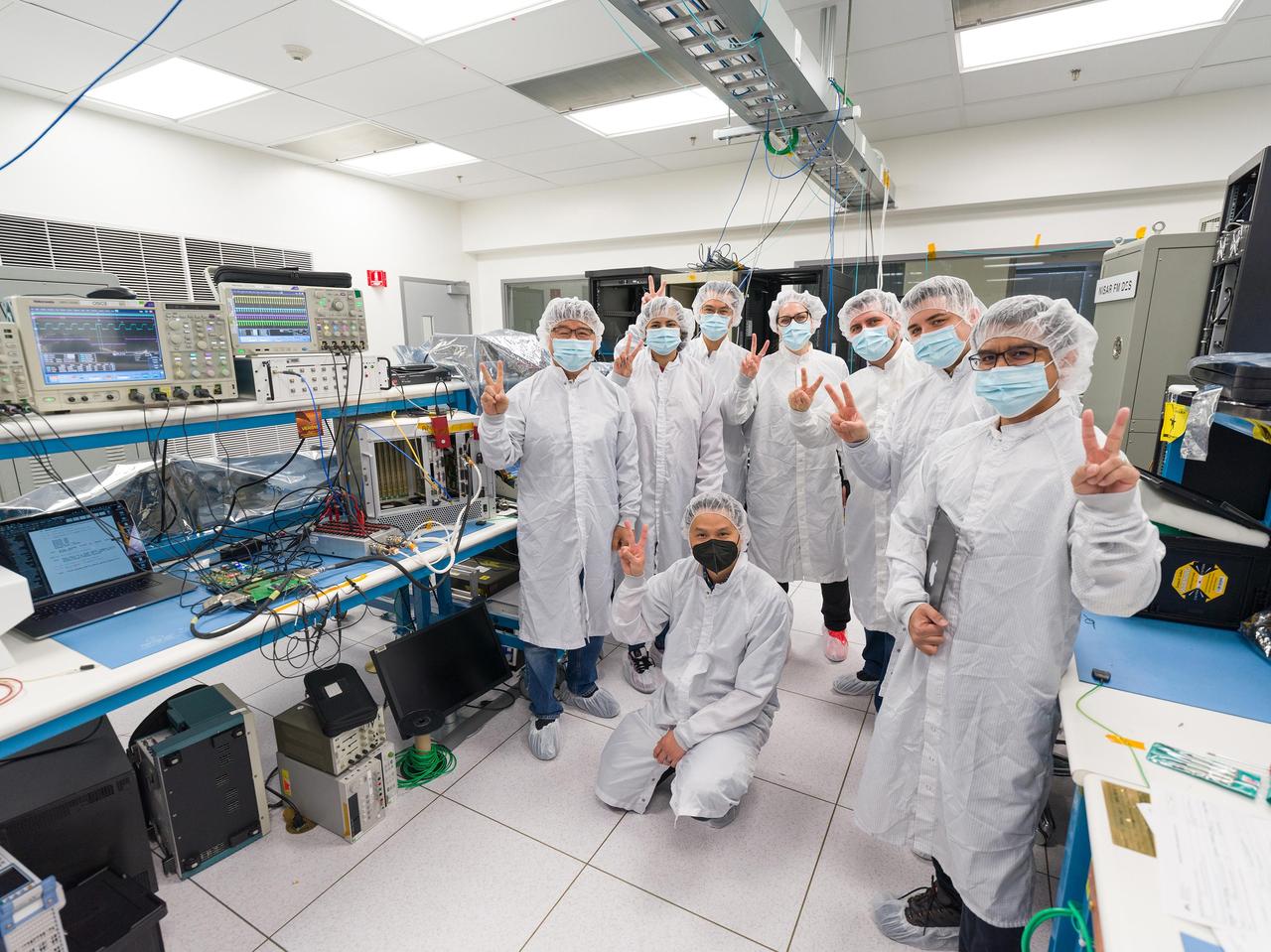

Seen here are members of the international team that participated in recent tests on prototype hardware for the Venus Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (VISAR) at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. VISAR is being developed at JPL for NASA's Venus Emissivity Radio Science, InSAR, Topography & Spectroscopy (VERITAS) mission that will launch within a decade to explore Earth's twin. In March 2023, the hardware underwent early interface tests in a JPL clean room, representing the first in a series to be run by JPL and Thales Alenia Space Italy (TASI), an international partner of the VERITAS mission that is contributing hardware to the instrument. Dressed in gowns to minimize the risk of contamination with sensitive electronics, the JPL VISAR digital team and TASI engineers pose for a photograph next to the laboratory benches where the tests took place. Figure A shows the same personnel without gowns for a team photo. From left to right: Marvin Cruz (JPL), Chester Lim (JPL), Tim Noh (JPL), Hana Haideri (JPL), Luca Di Marco Napini (TASI), Ernie Chuang (JPL), Dragana Perkovic-Martin (JPL), and Gabriel Mihu (TASI). JPL's Michael Burke, Anusha Yarlagadda, Duane Clark, and TASI's Antonio Delfino also participated in the tests but are not pictured. When VERITAS arrives in orbit, it will use VISAR to create detailed 3D global maps of Venus. The spacecraft will also carry a near-infrared spectrometer to figure out what the surface is made of. Together, the instruments will offer clues about the planet's past and present geologic processes, help reveal how the paths of Venus and Earth diverged, and how Venus lost its potential as a habitable world. VERITAS is managed by JPL. VERITAS and NASA's Deep Atmosphere Venus Investigation of Noble gases, Chemistry, and Imaging (DAVINCI) mission were selected in 2021 under NASA's Discovery Program as the agency's next missions to Venus. The Discovery Program is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, for the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate in Washington. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25833

The first NASA Dropping In a Microgravity Environment (DIME) student competition pilot project came to a conclusion at the Glenn Research Center in April 2001. The competition involved high-school student teams who developed the concept for a microgravity experiment and prepared an experiment proposal. The two student teams - COSI Academy, sponsored by the Columbus Center of Science and Industry, and another team from Cincinnati, Ohio's Sycamore High School, designed a microgravity experiment, fabricated the experimental apparatus, and visited NASA Glenn to operate their experiment in the 2.2 Second Drop Tower. Here Carol Hodanbosi of the National Center for Microgravity Research and Jose Carrion, a lab mechanic with AKAC, prepare a student experiment package (inside the silver-colored frame) inside the orange-colored drag shield that encloses all experiment hardware. This image is from a digital still camera; higher resolution is not available.
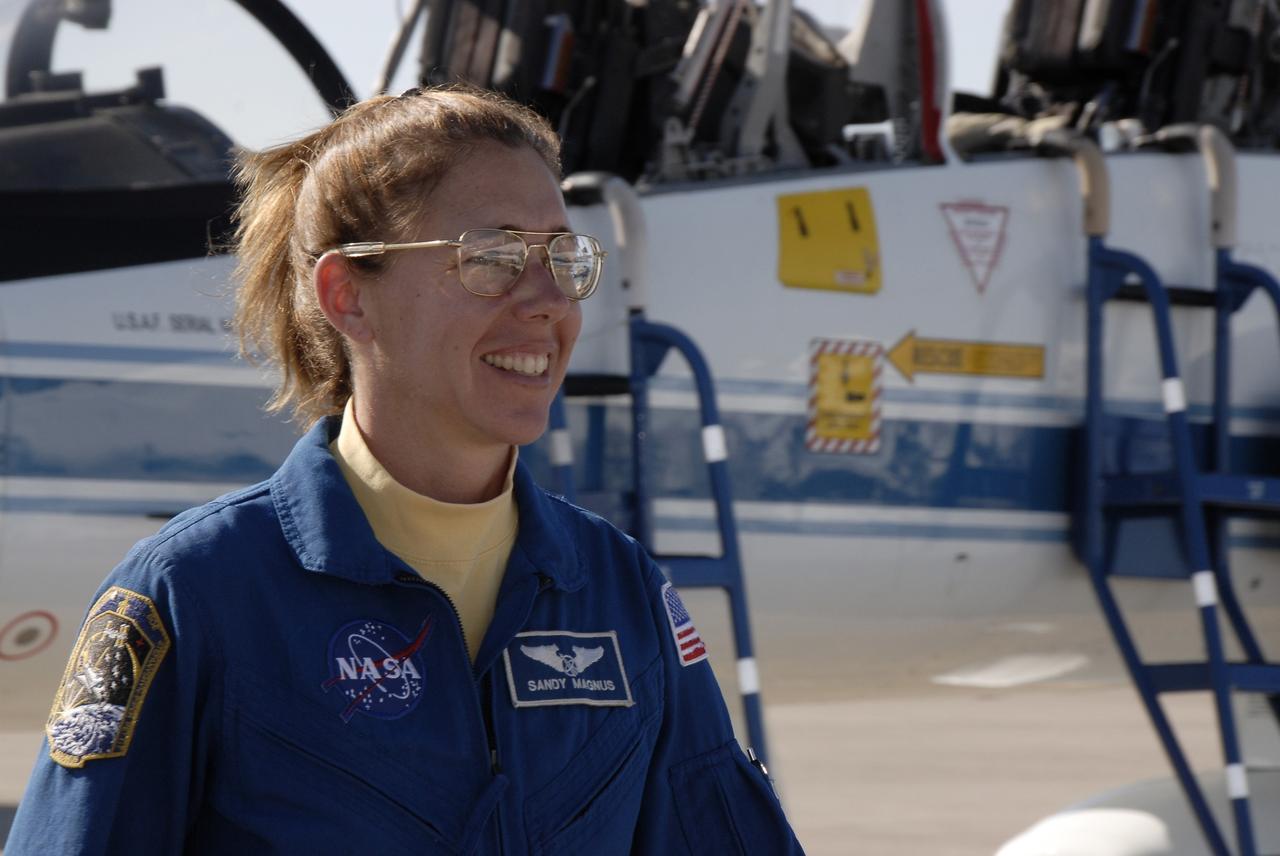

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - STS-126 Mission Specialist Sandra Magnus arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard a T-38 jet for Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test, or TCDT, activities. Magnus will remain on the International Space Station as a flight engineer and science officer for Expedition 18. During TCDT, Endeavour's astronauts and launch teams will participate in a simulated countdown, practice emergency exit procedures at the launch pad and continue to familiarize themselves with the mission payload and hardware. On this 27th mission to the International Space Station, Endeavour will carry the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo that will hold supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, additional exercise equipment, spare hardware and equipment for the regenerative life support system. Endeavour is targeted to launch at 7:55 p.m. EST on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 crew members are lowered into space shuttle Atlantis' payload bay for a close look at the hardware. Equipment familiarization is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Gregory C. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Good, Megan McArthur, John Grunsfeld, Mike Massimino and Andrew Feustel. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
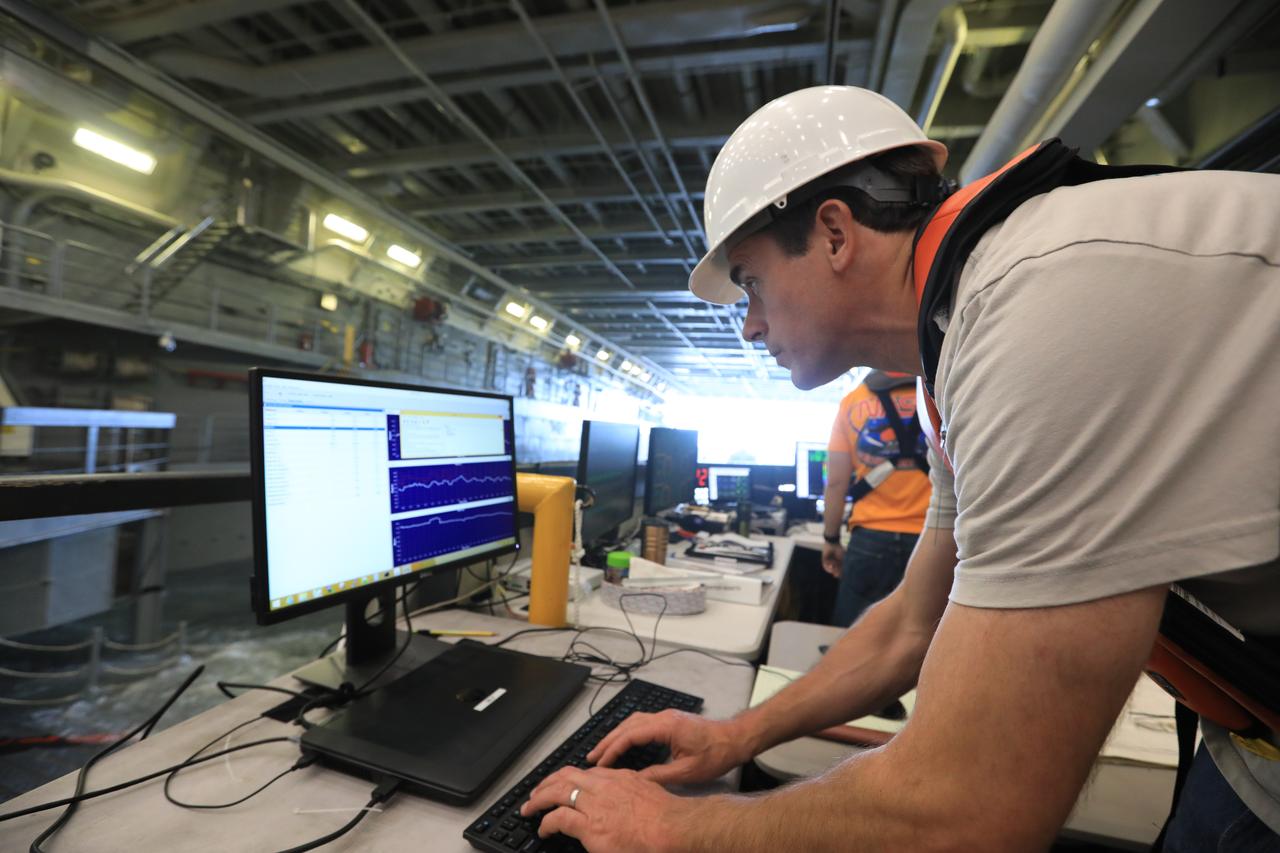

Benjamin Connell, a principal scientist with Applied Physical Sciences, monitors wave movement inside the well deck of a U.S. Navy ship during Underway Recovery Test-7 (URT-7) on Oct. 30, 2018. The Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) recovery team and the U.S. Navy will use a test version of the Orion crew module, several rigid hull inflatable boats and support equipment to verify and validate processes, procedures, hardware and personnel during recovery of Orion in open waters. The testing is one in a series of tests to verify and validate procedures and hardware that will be used to recover the Orion spacecraft after it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean following deep space exploration missions. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
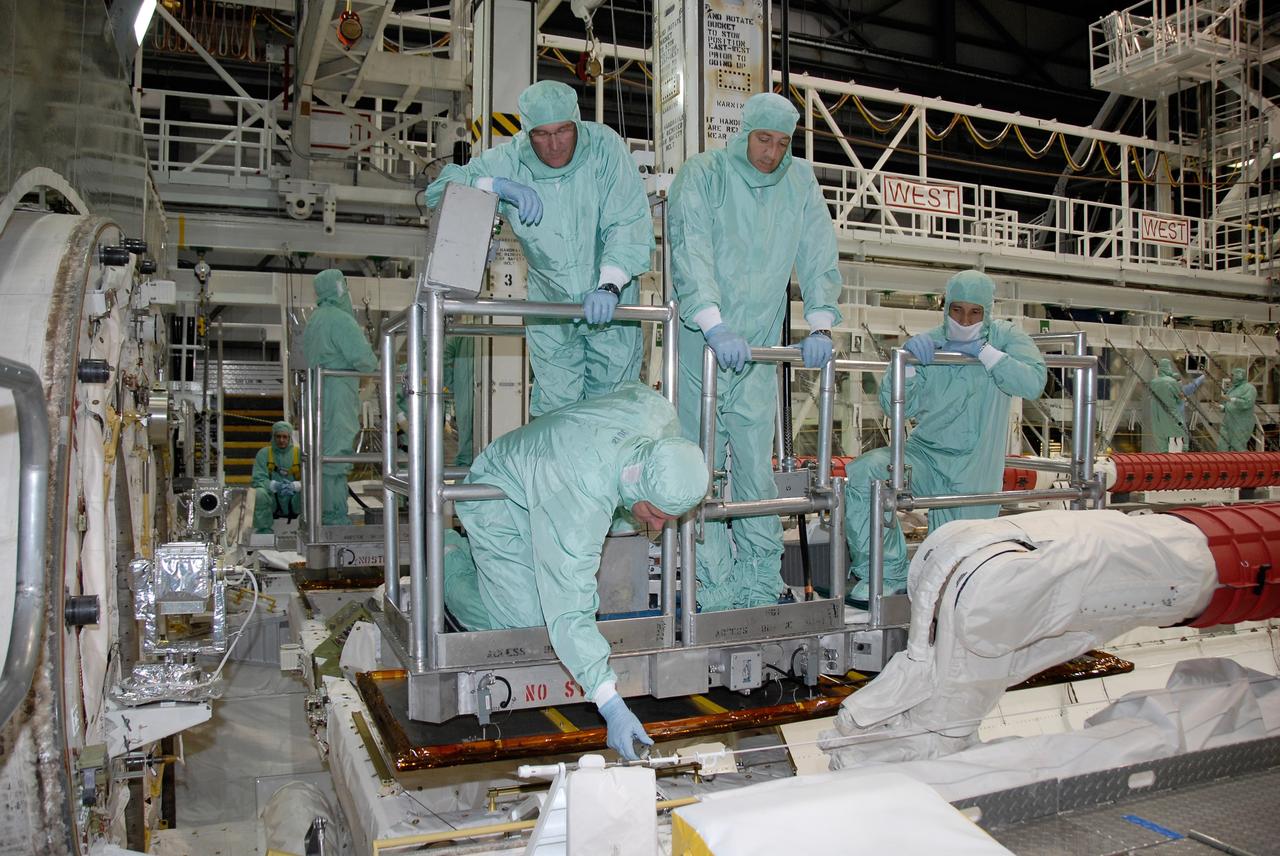

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 crew members are lowered into space shuttle Atlantis' payload bay for a close look at the hardware. Equipment familiarization is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Gregory C. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Good, Megan McArthur, John Grunsfeld, Mike Massimino and Andrew Feustel. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
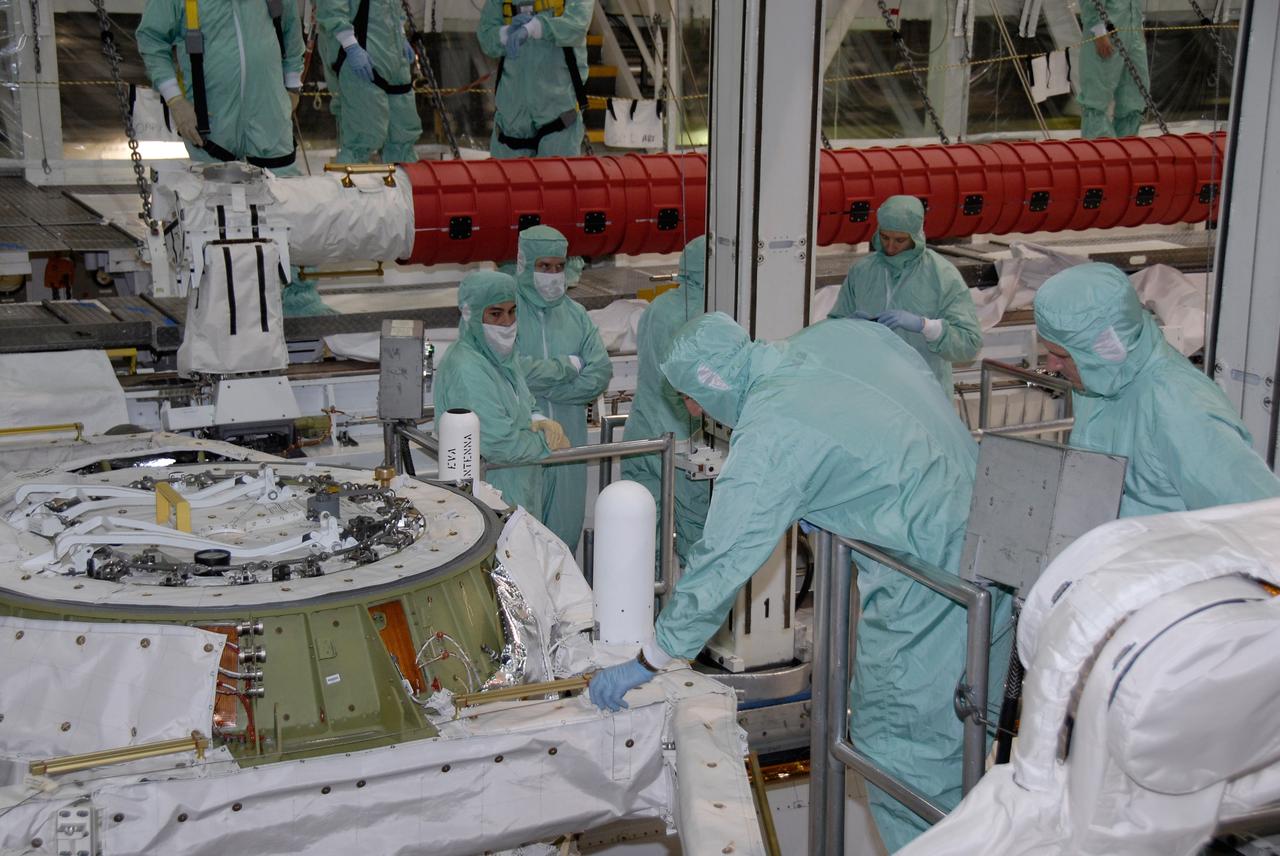

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 crew members are lowered into space shuttle Atlantis' payload bay for a close look at the hardware. Equipment familiarization is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Crew members are Commander Scott Altman, Pilot Gregory C. Johnson, and Mission Specialists Michael Good, Megan McArthur, John Grunsfeld, Mike Massimino (reaching toward the airlock) and Andrew Feustel. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
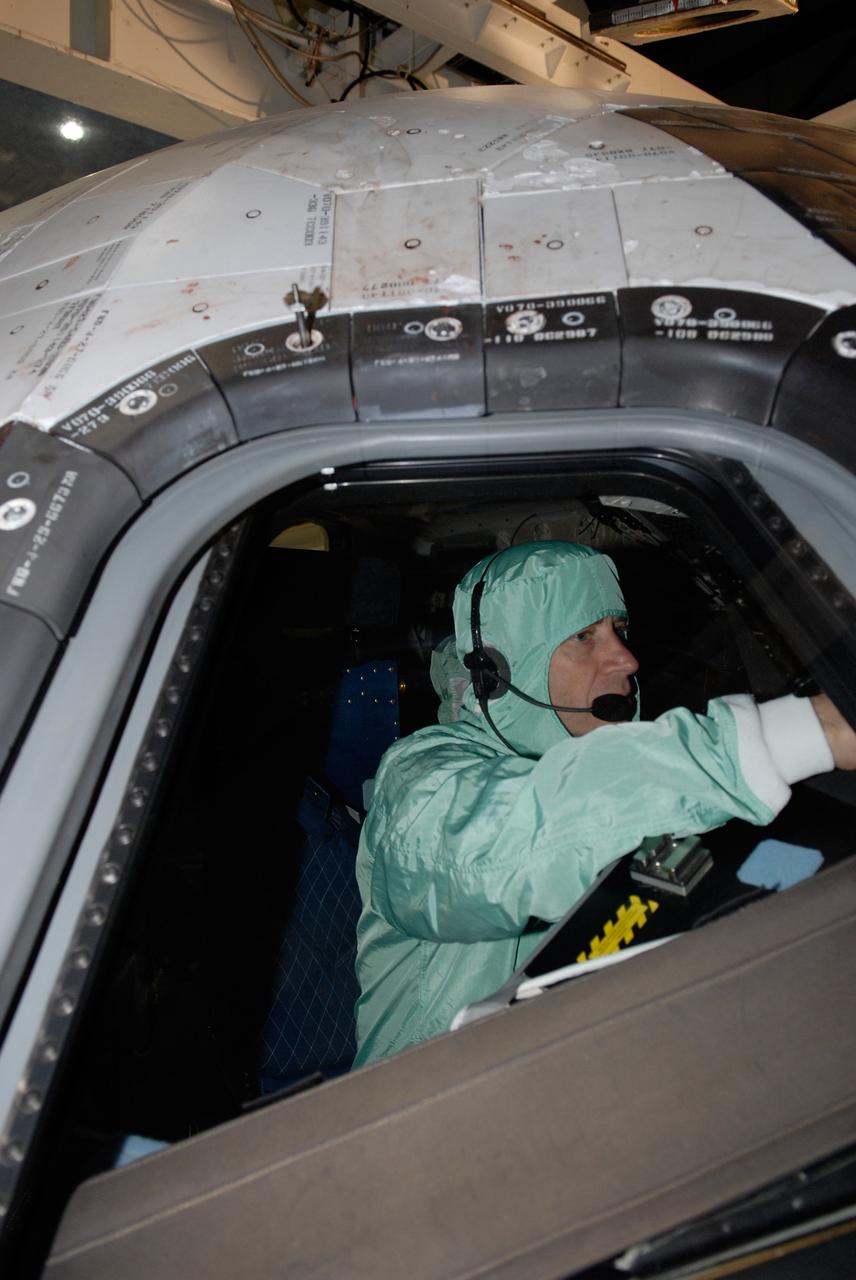

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 Pilot Gregory C. Johnson examines the cockpit window on space shuttle Atlantis, checking for sharp edges. The inspection is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
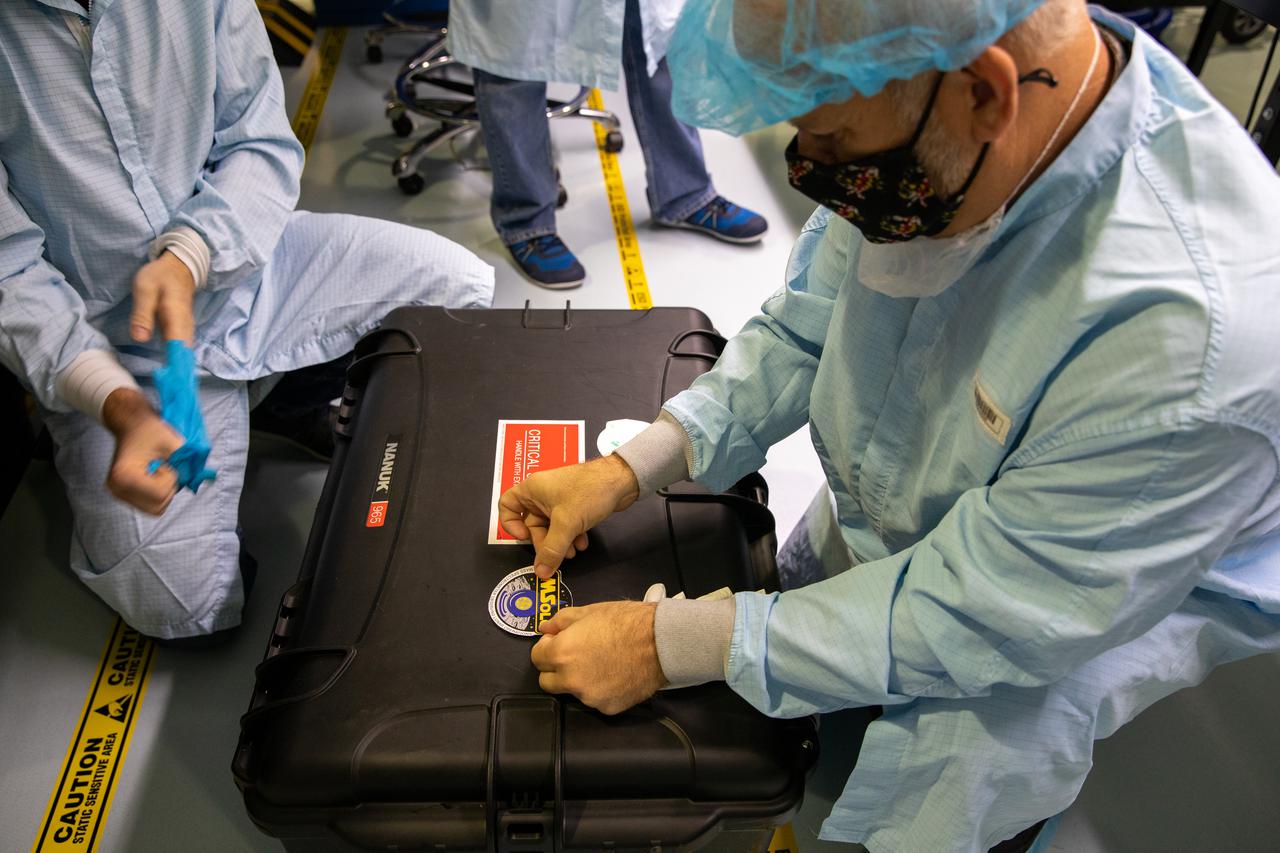

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
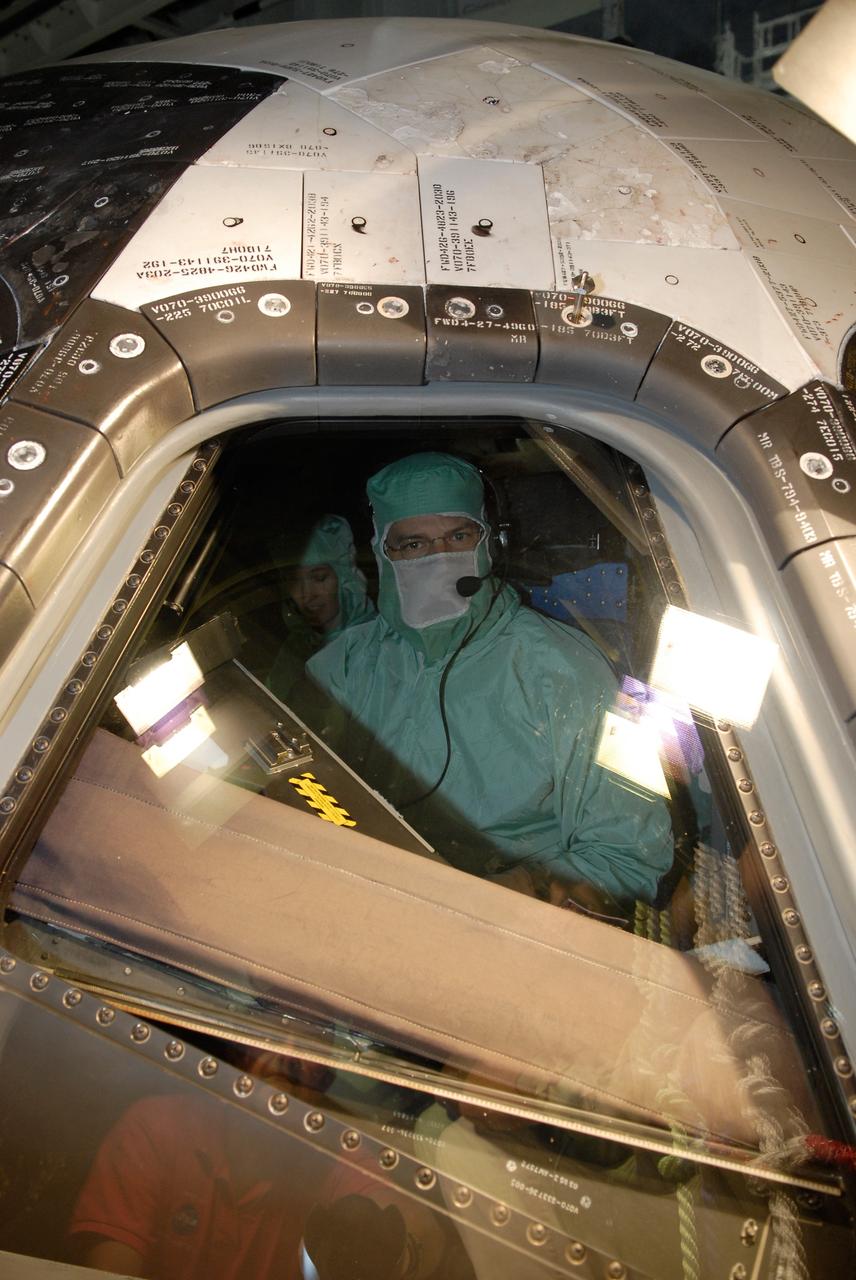
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 Commander Scott Altman examines the cockpit window on space shuttle Atlantis, checking for sharp edges. The inspection is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
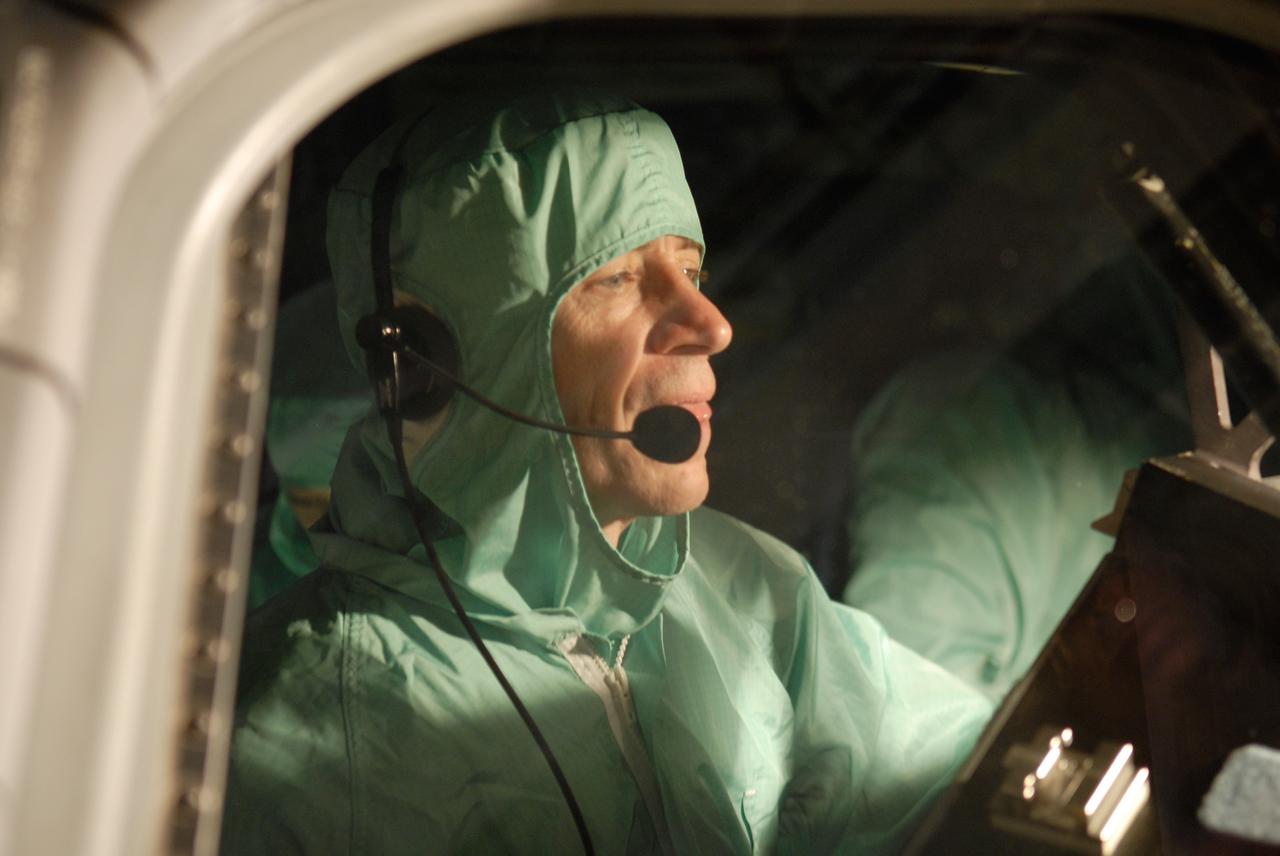

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 Pilot Gregory C. Johnson examines the cockpit window on space shuttle Atlantis, checking for sharp edges. The inspection is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
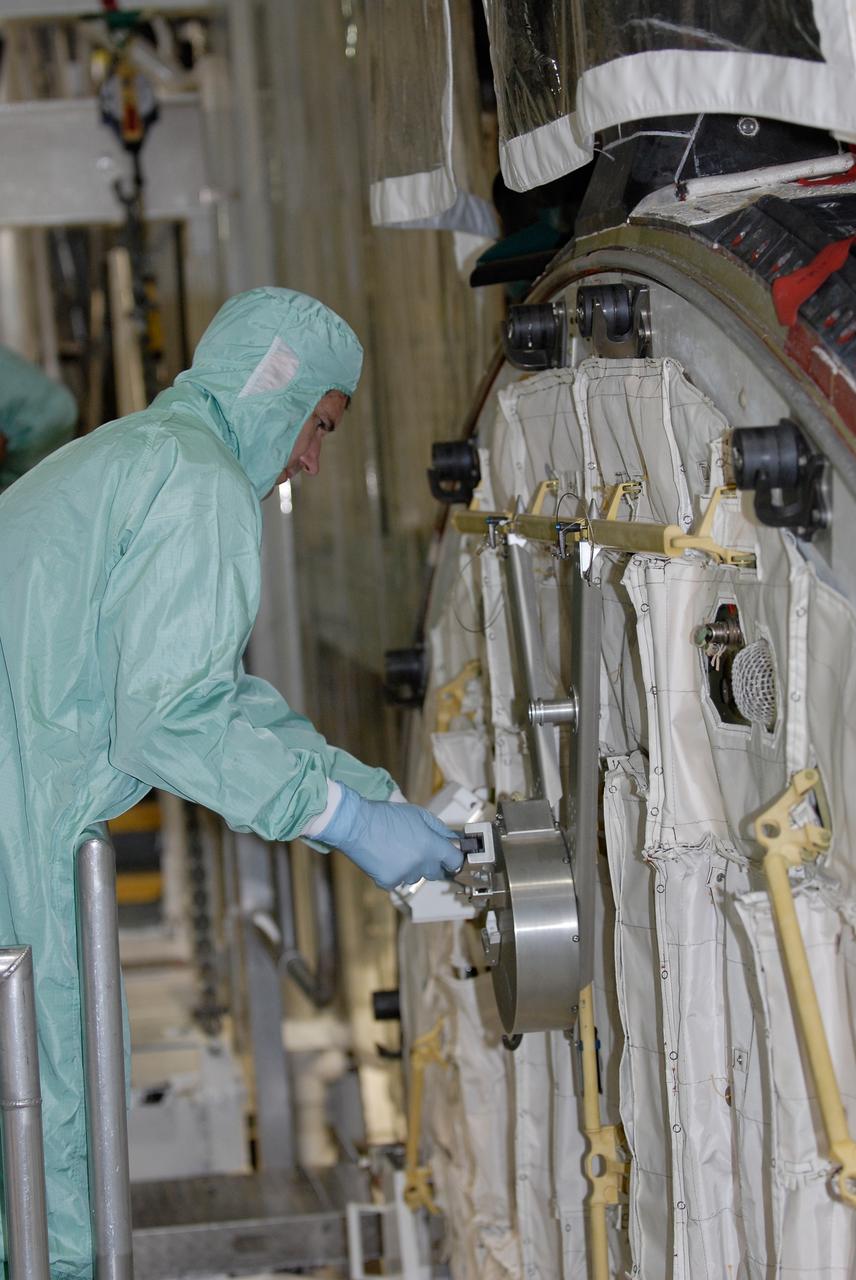

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 Mission Specialist Michael Good checks out part of the equipment in space shuttle Atlantis' payload bay. Equipment familiarization is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
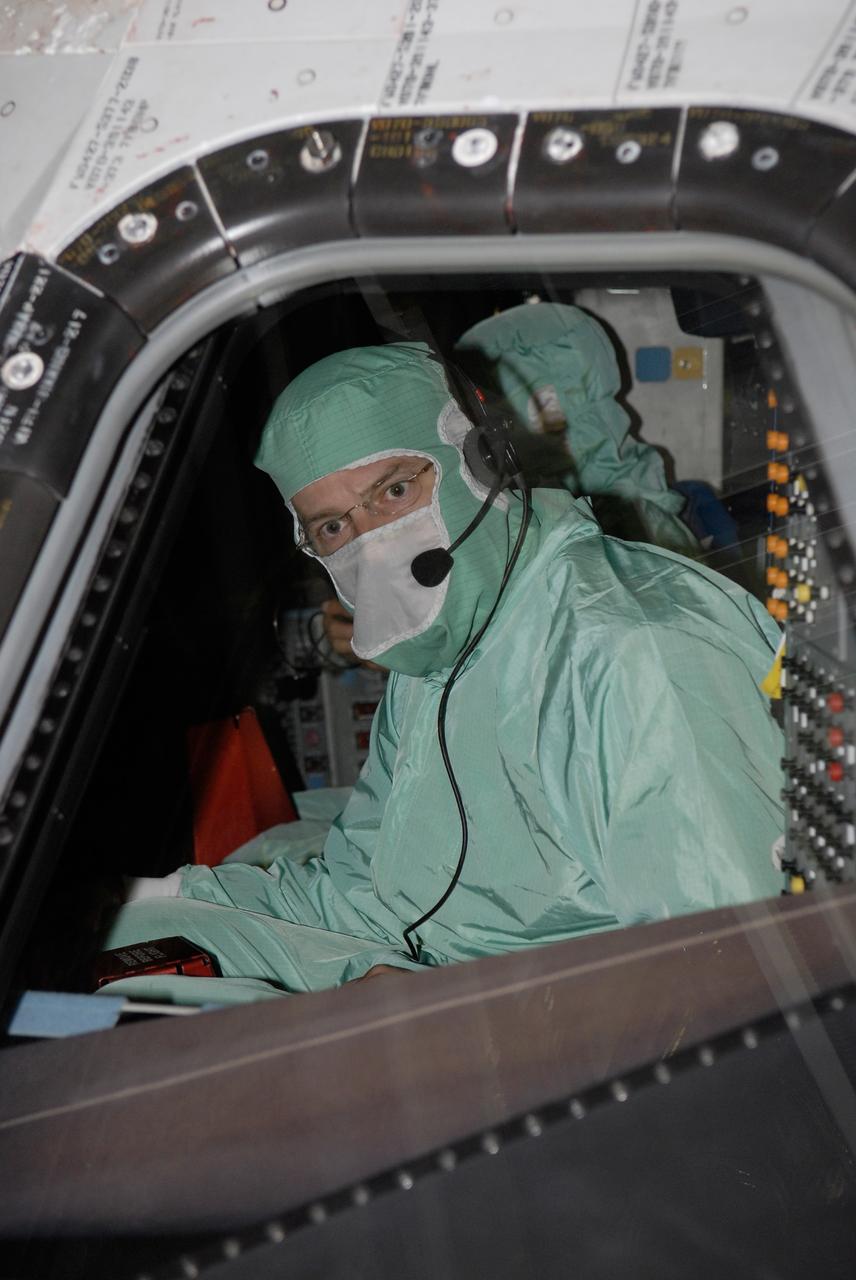

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-125 Commander Scott Altman examines the cockpit window on space shuttle Atlantis. The inspection is part of the crew equipment interface test, which provides hands-on experience with hardware and equipment for the mission. Atlantis is targeted to launch Oct. 8 on the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. The mission crew will perform history-making, on-orbit “surgery” on two important science instruments aboard the telescope. After capturing the telescope, two teams of spacewalking astronauts will perform the repairs during five planned spacewalks. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
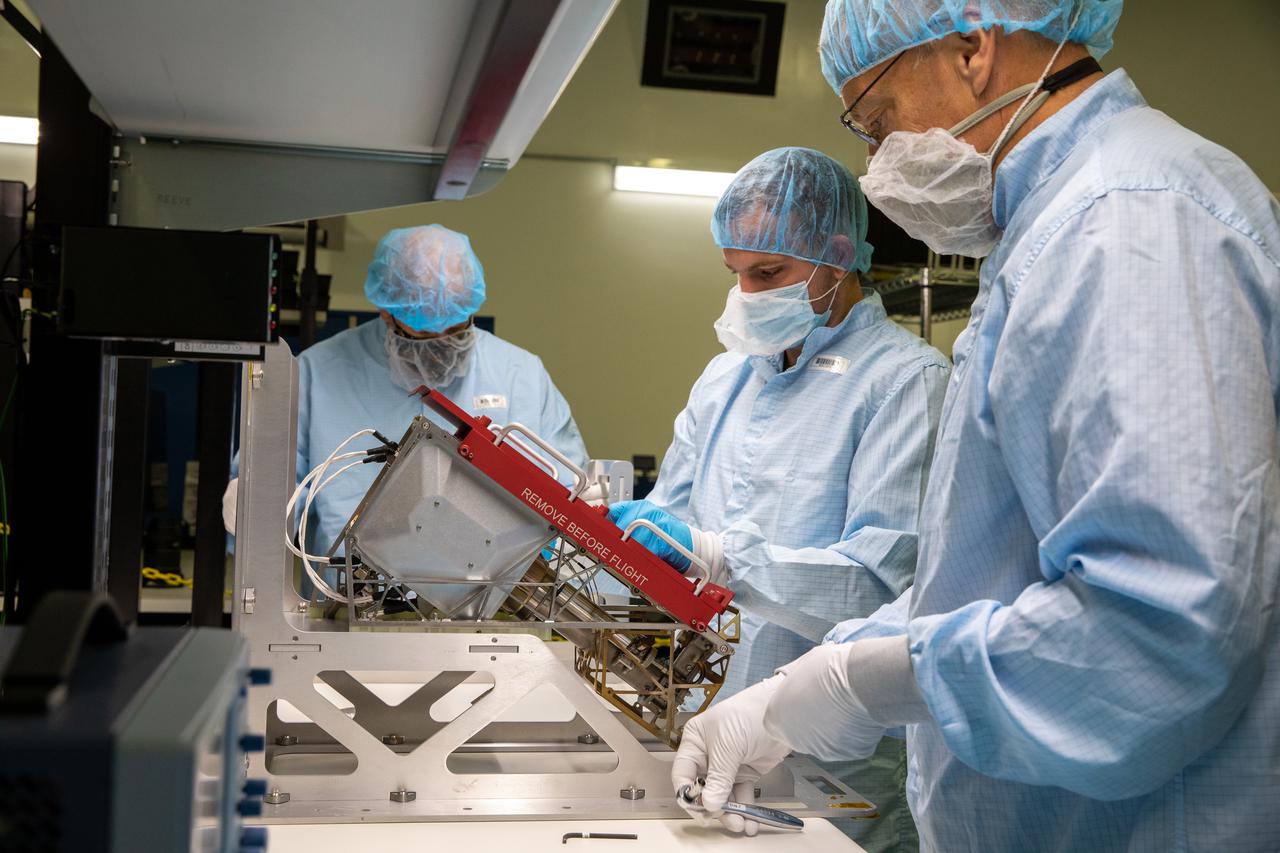

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
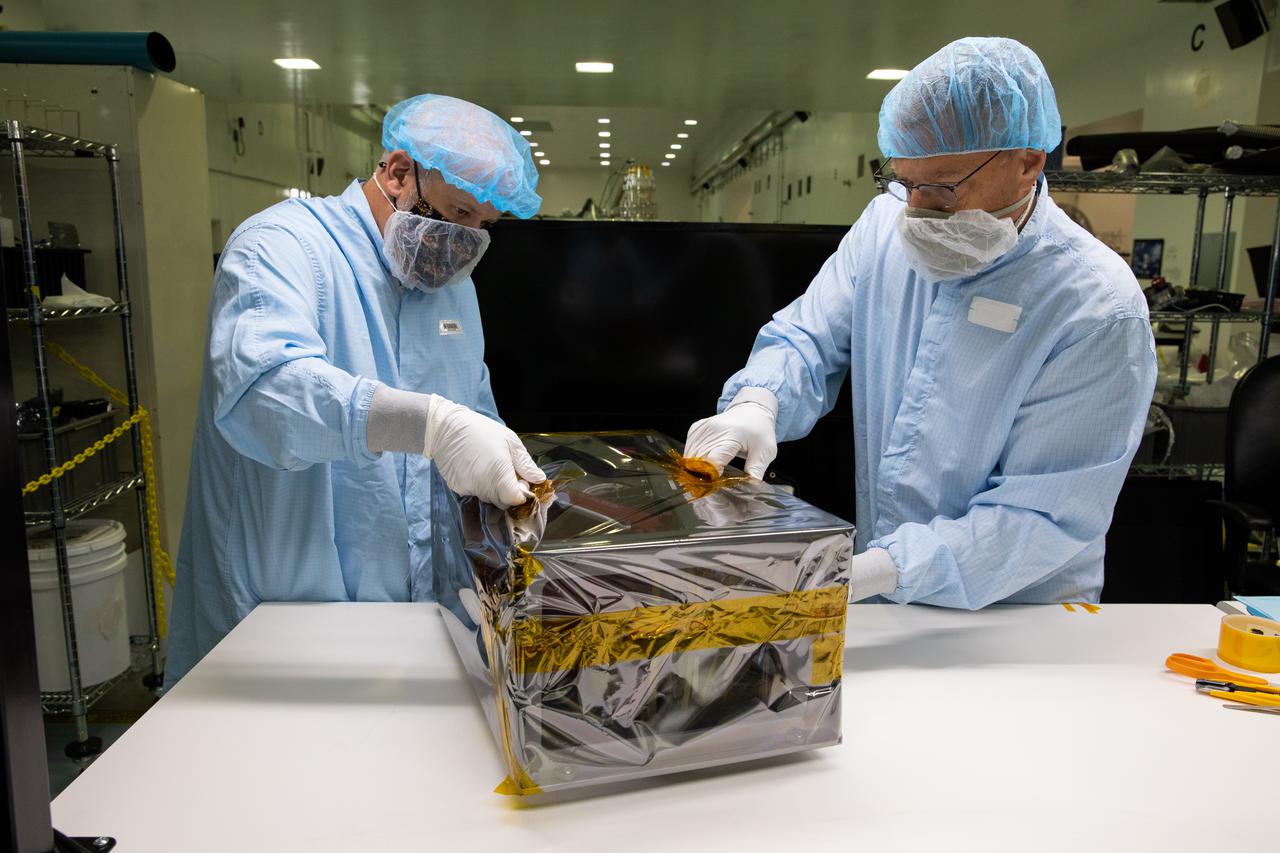

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
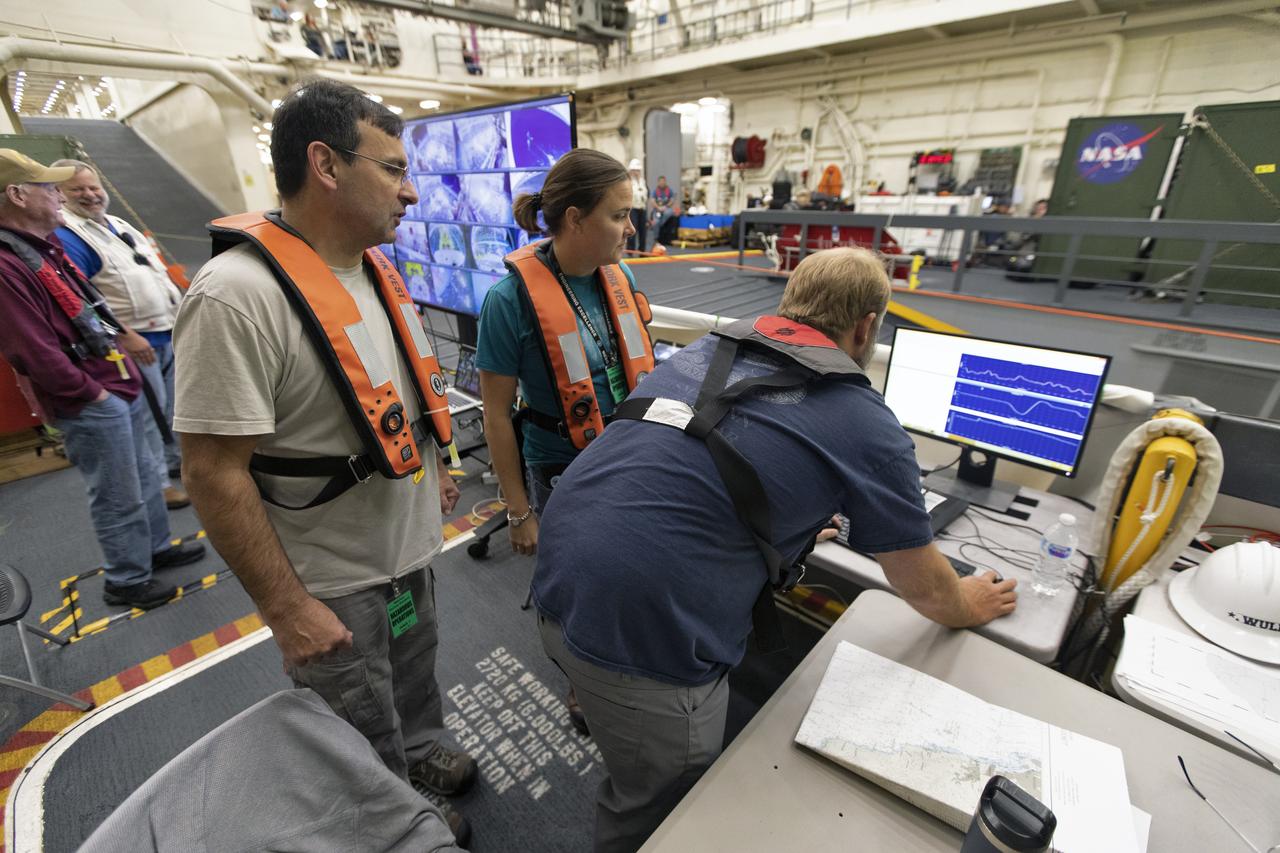

Wave trackers with Applied Physical Sciences monitor ocean wave conditions during Underway Recovery Test-7 (URT-7) aboard the USS John P. Murtha on Nov. 4, 2018. NASA's Recovery Team, along with the U.S. Navy, practice recovering a test version of the Orion capsule as part of URT-7 in the Pacific Ocean. URT-7 is one in a series of tests to verify and validate procedures and hardware that will be used to recover the Orion spacecraft after it splashes down in the Pacific Ocean following deep space exploration missions. Orion will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities.
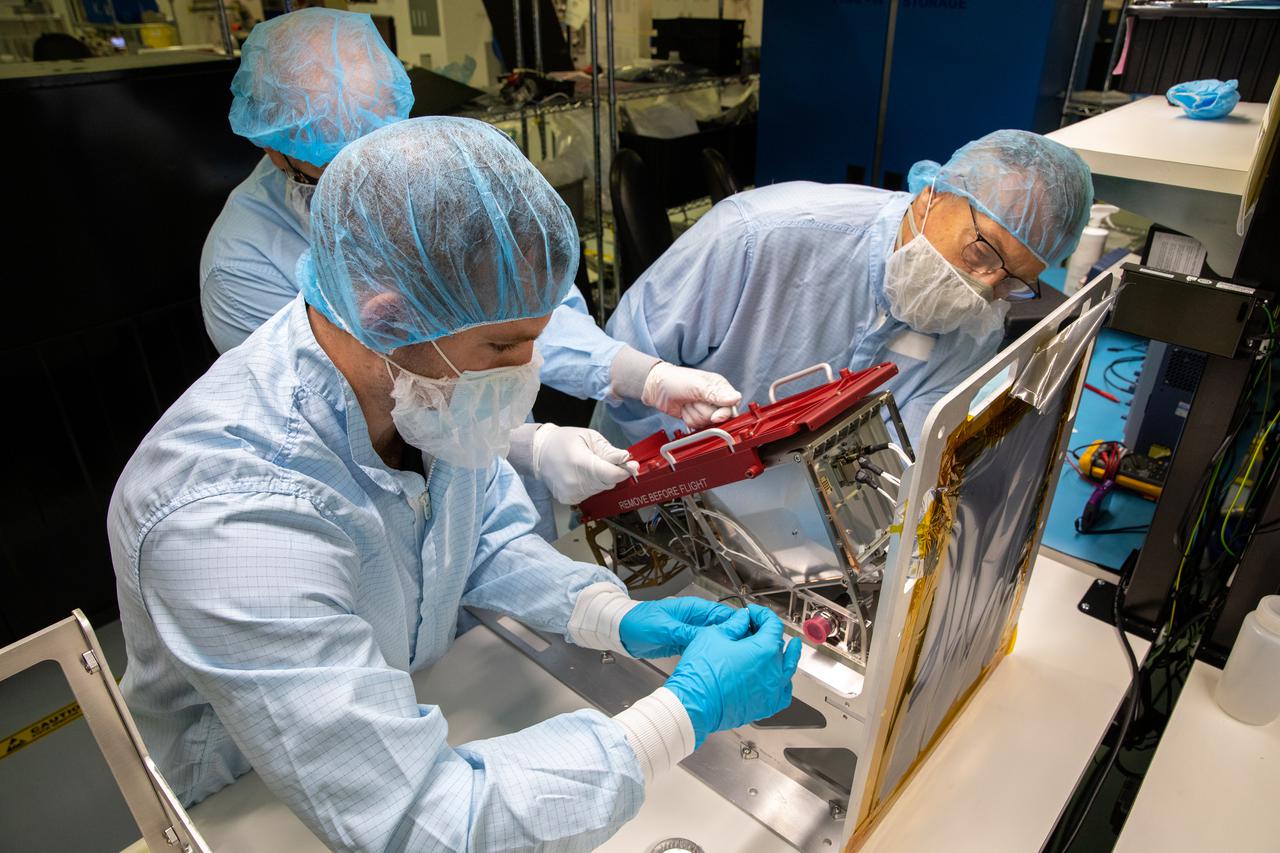

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
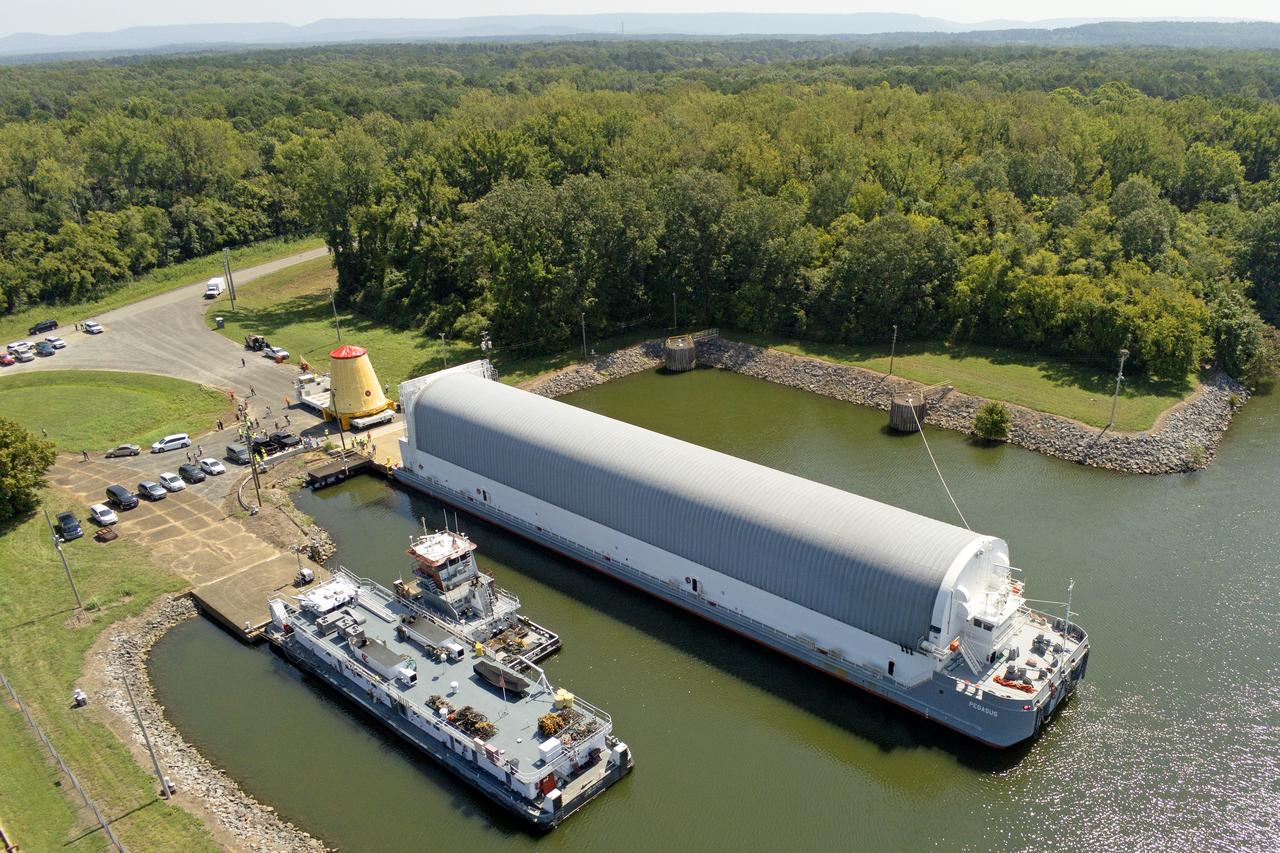

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
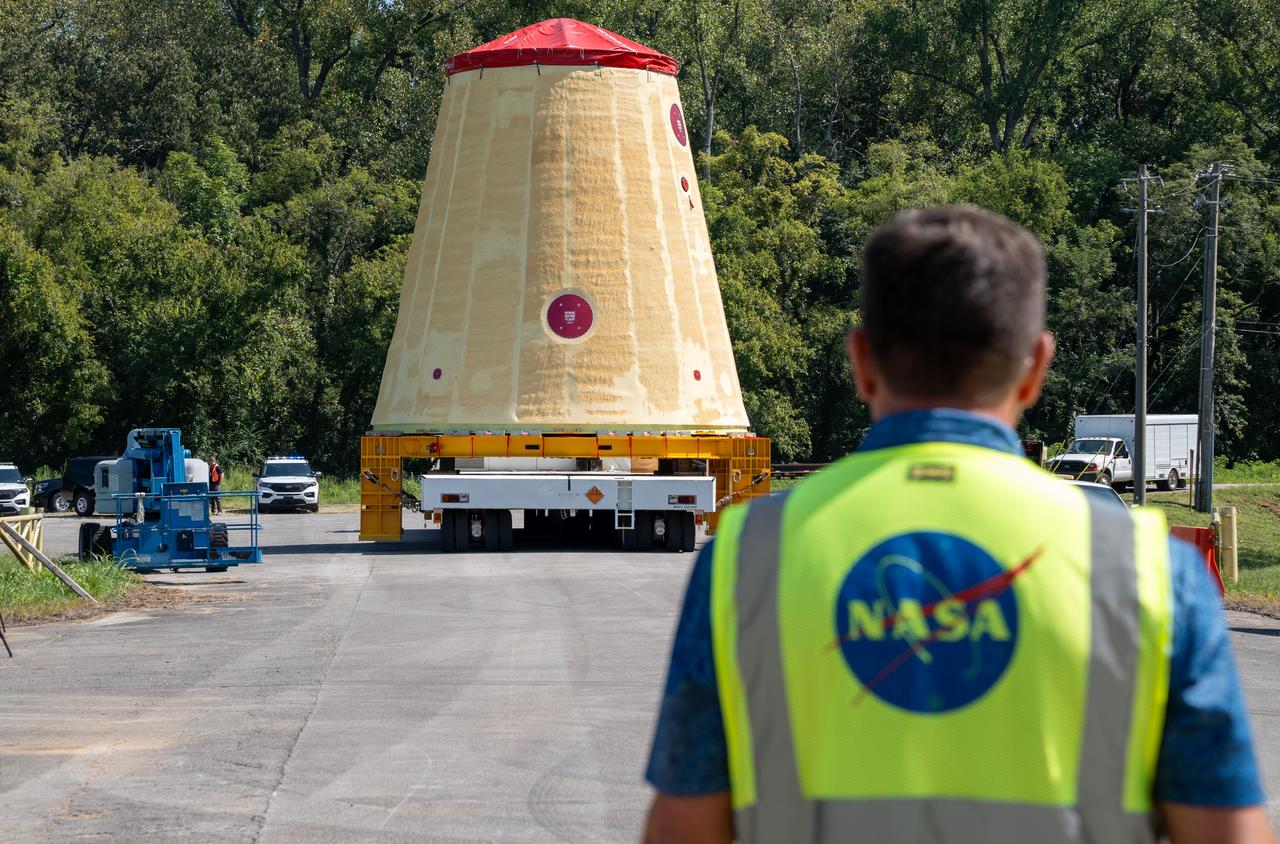

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
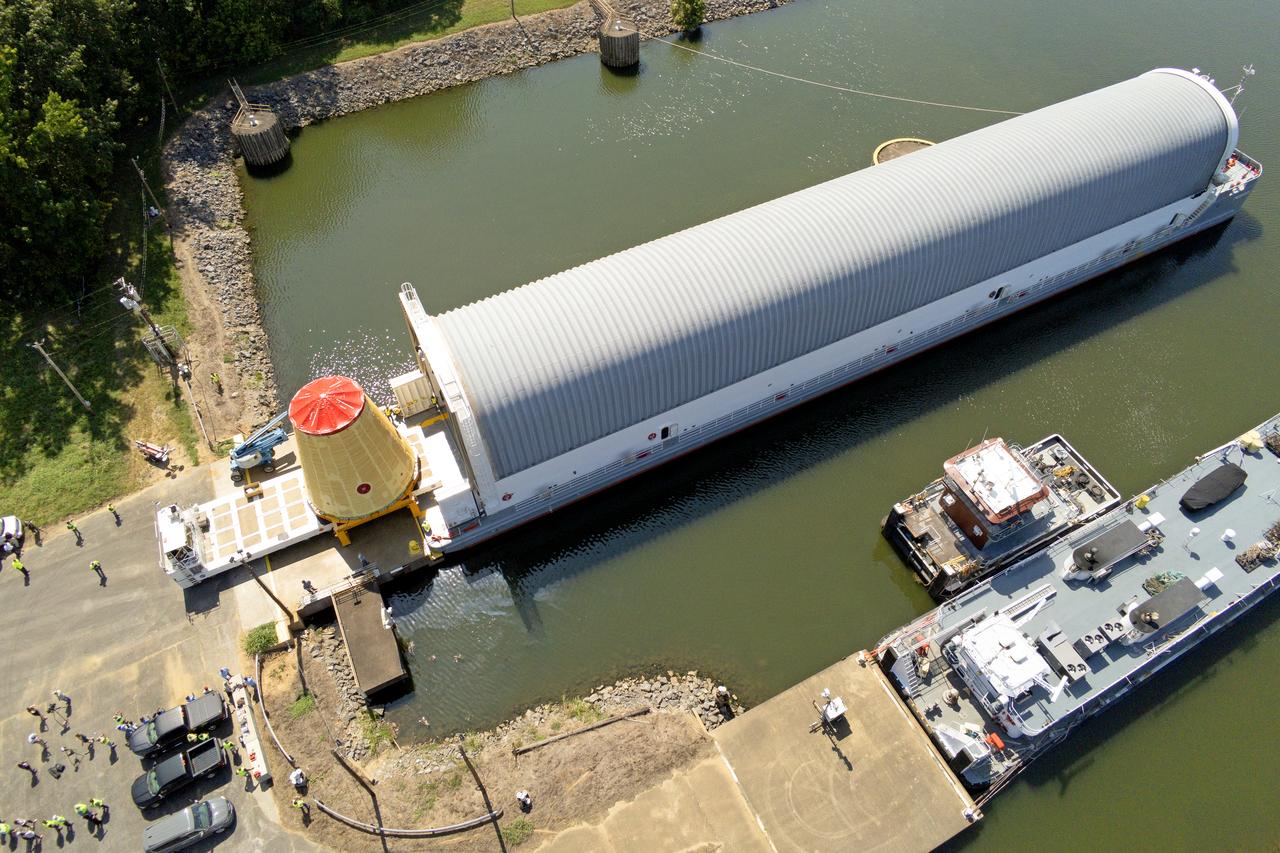

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
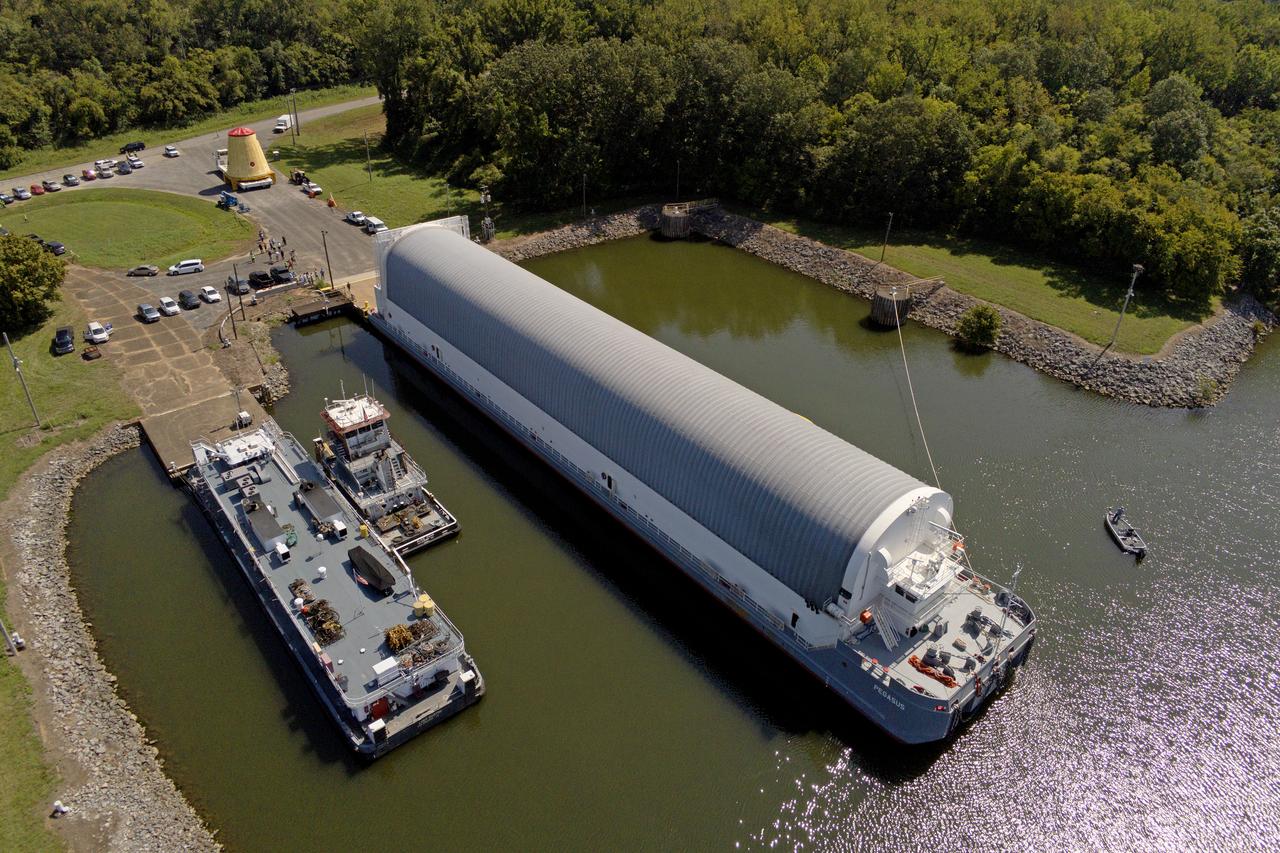

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
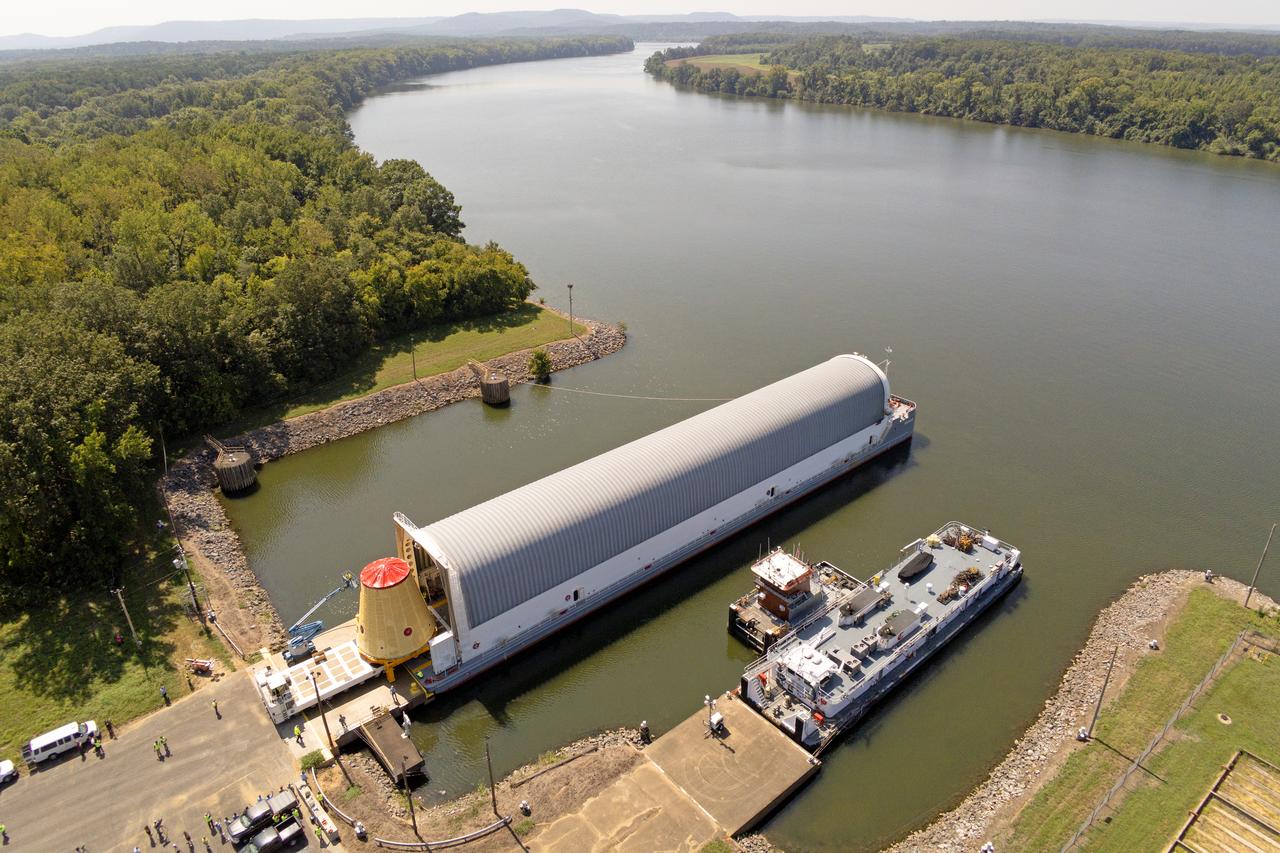

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
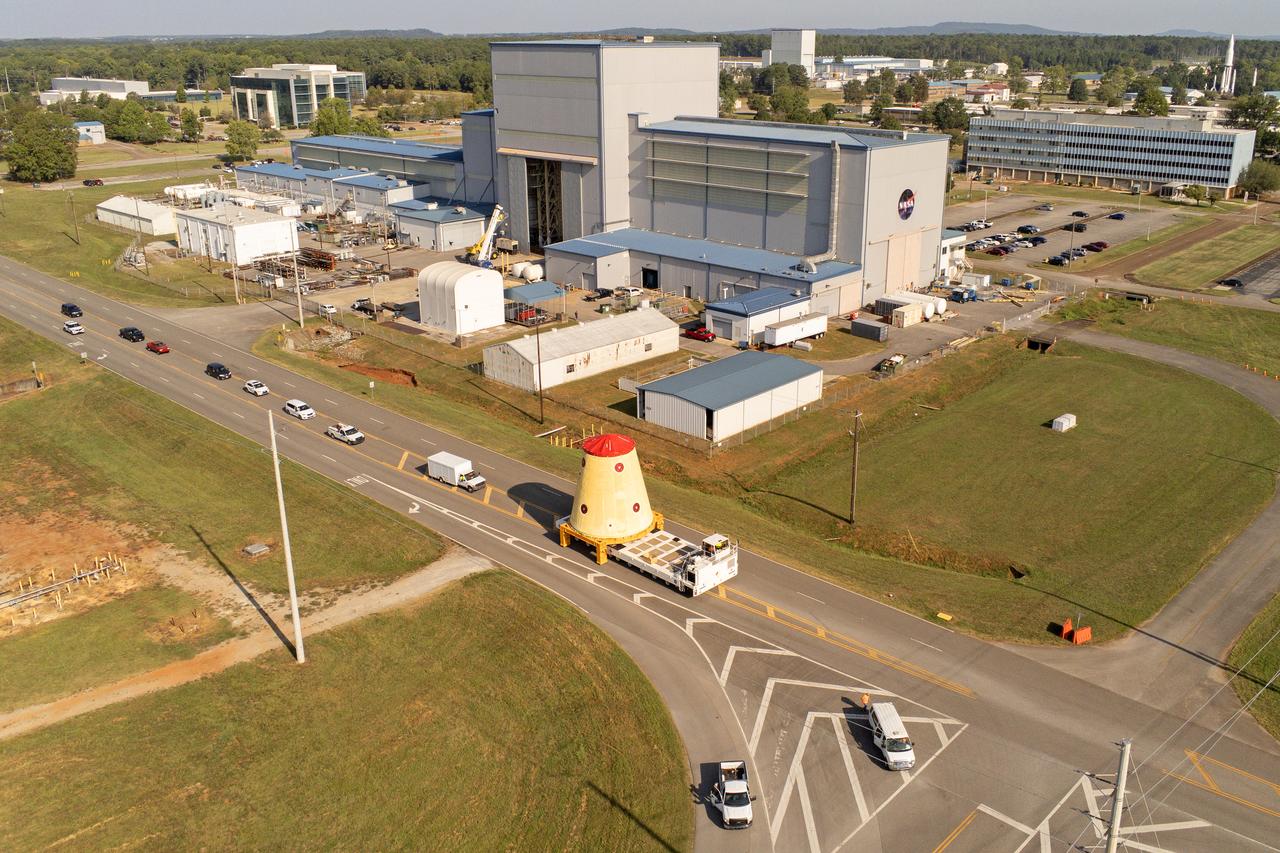

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
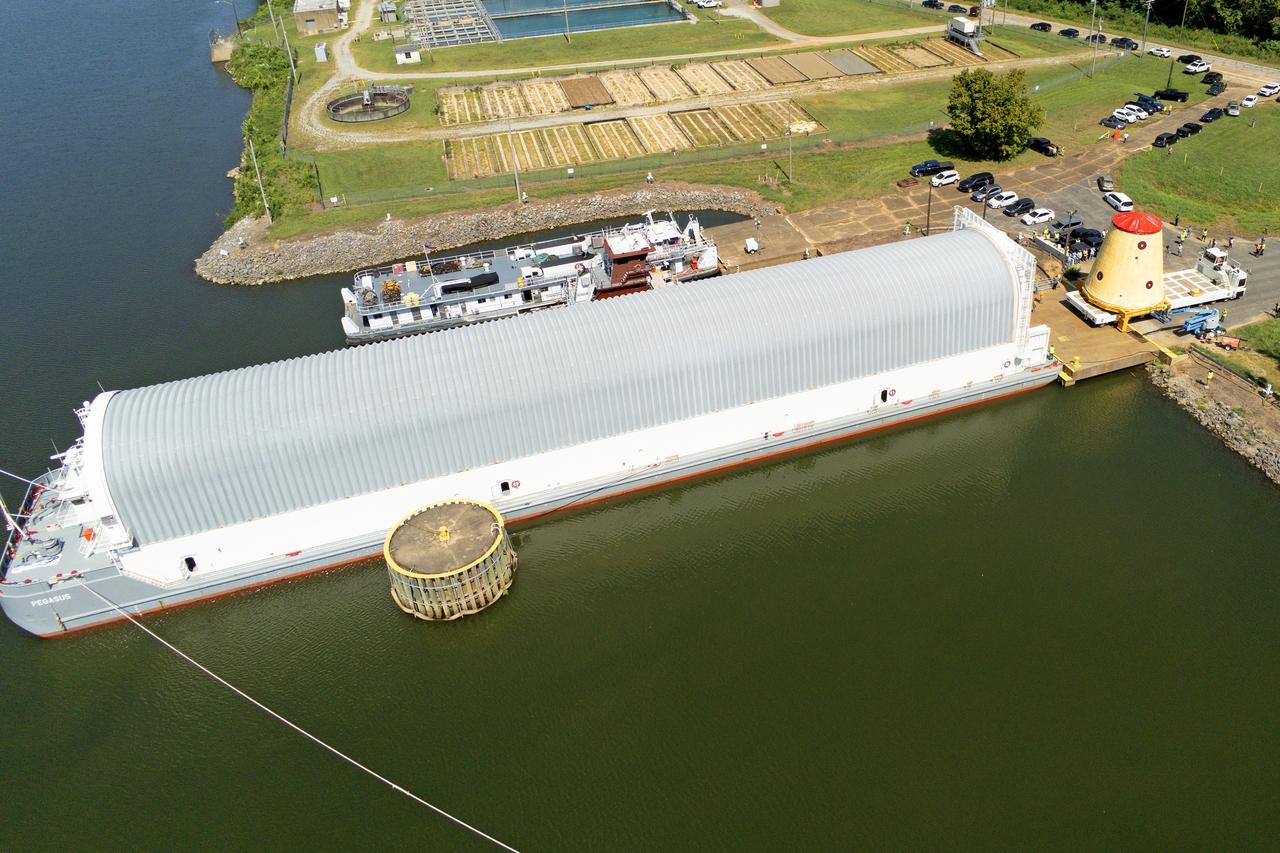

These images and videos show NASA rolling out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
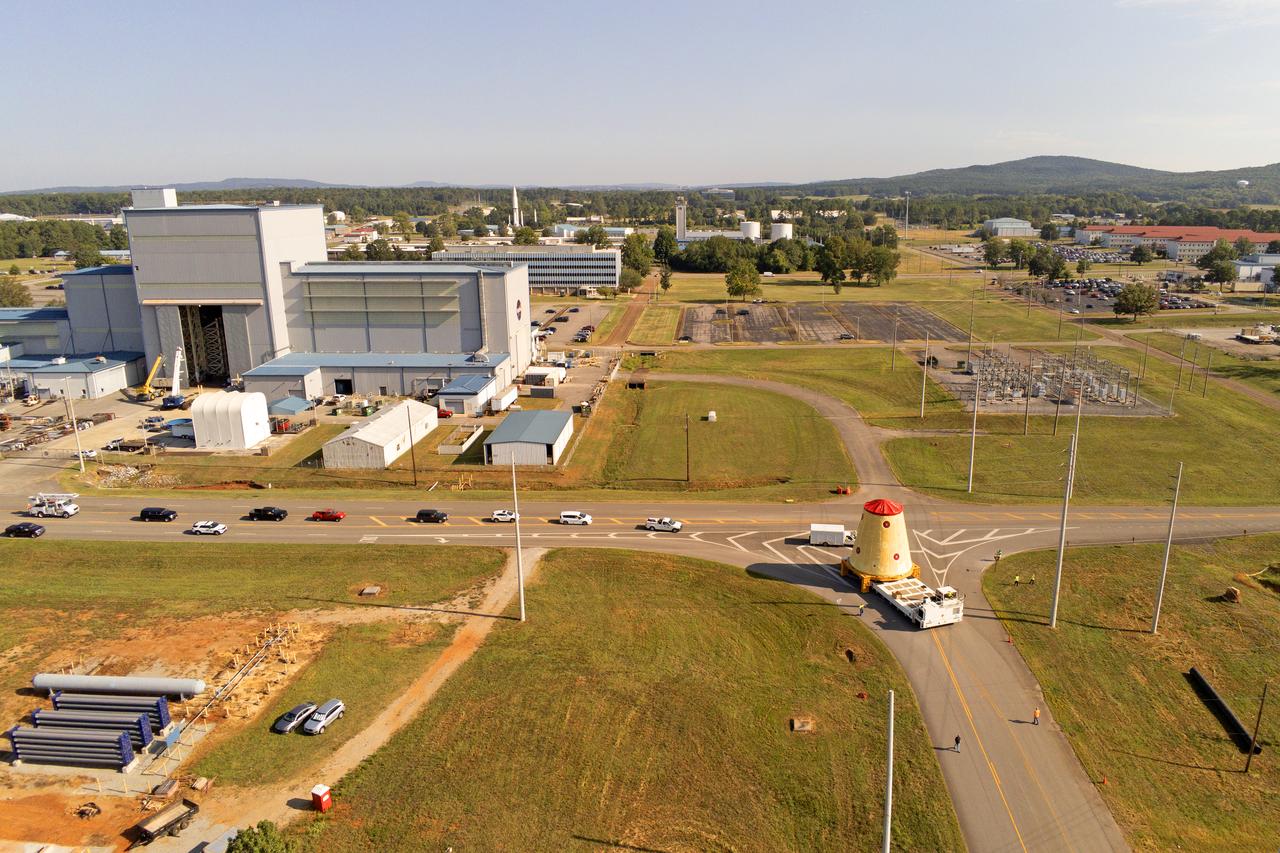

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
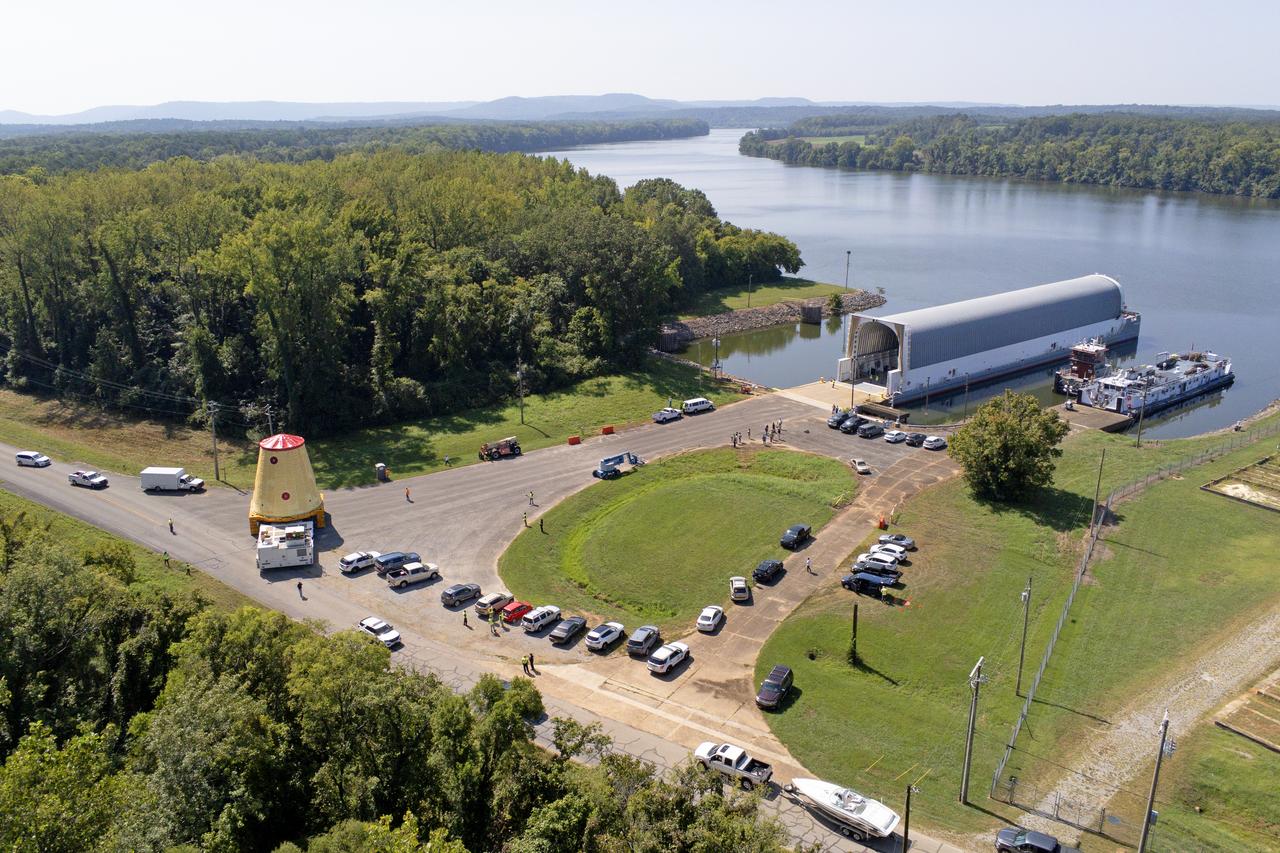

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
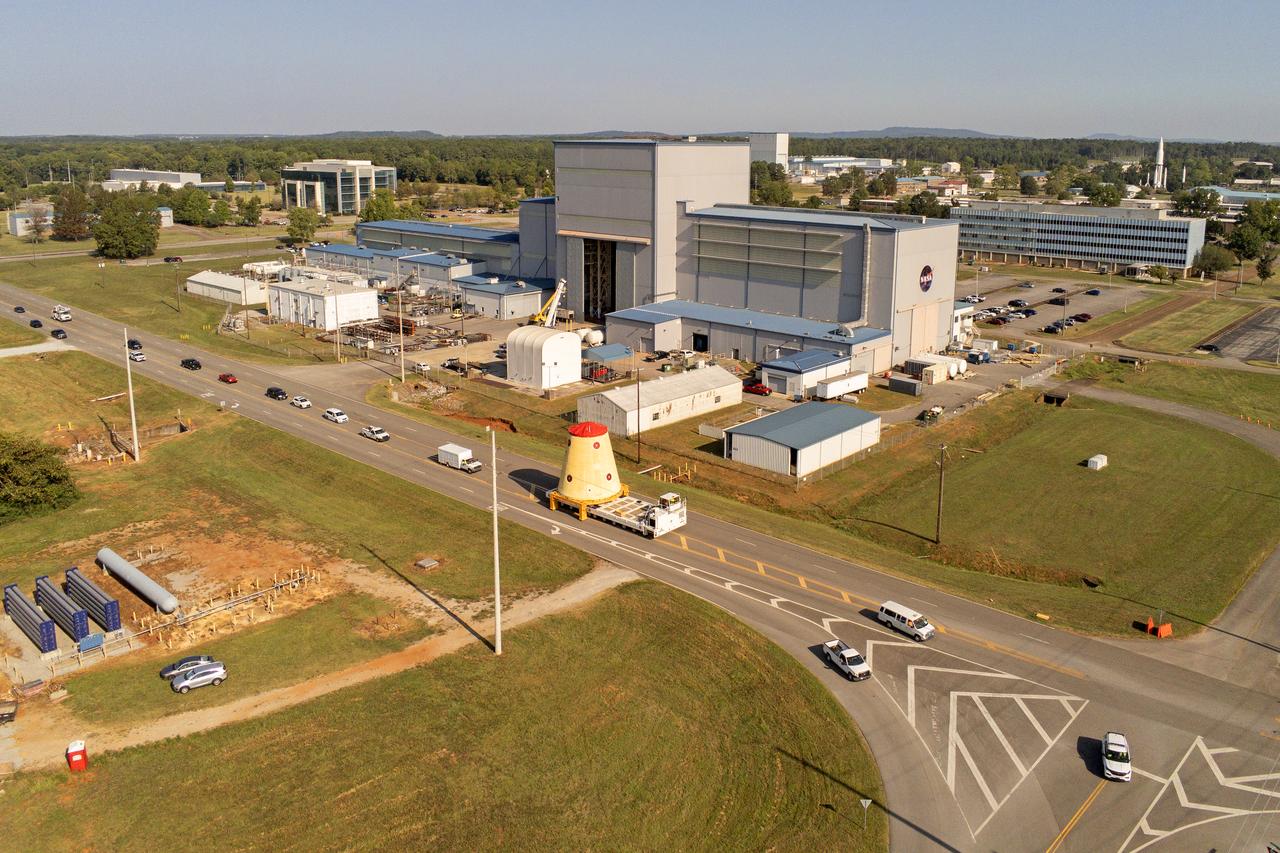

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
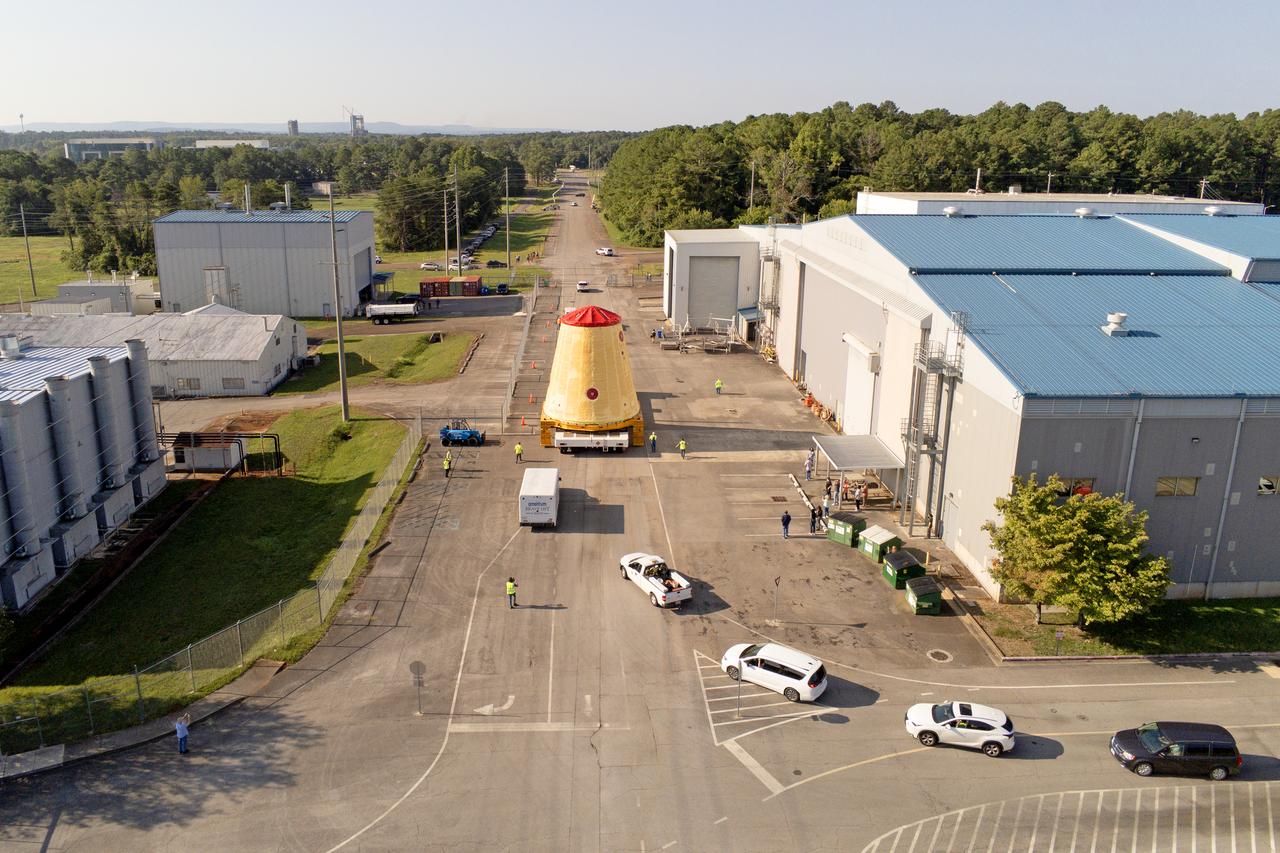

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
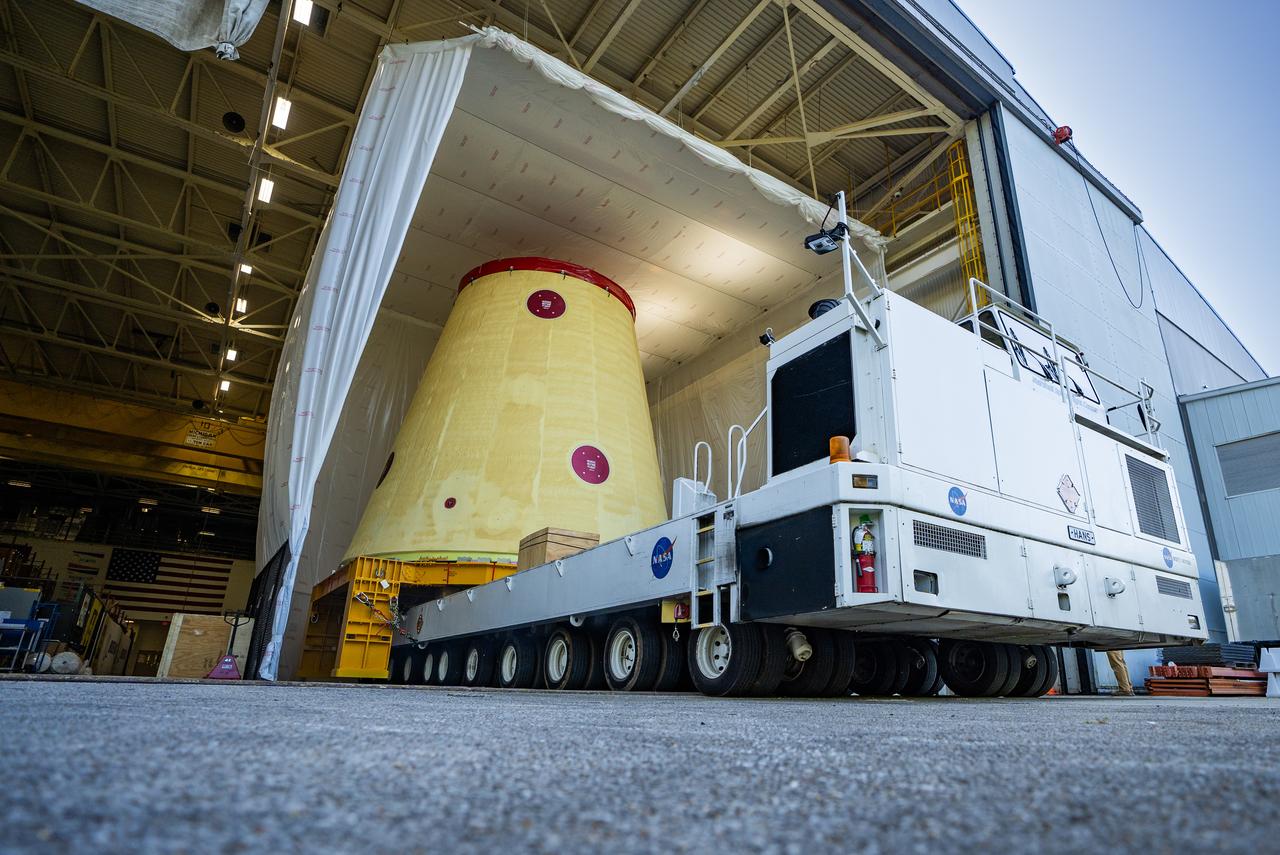

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
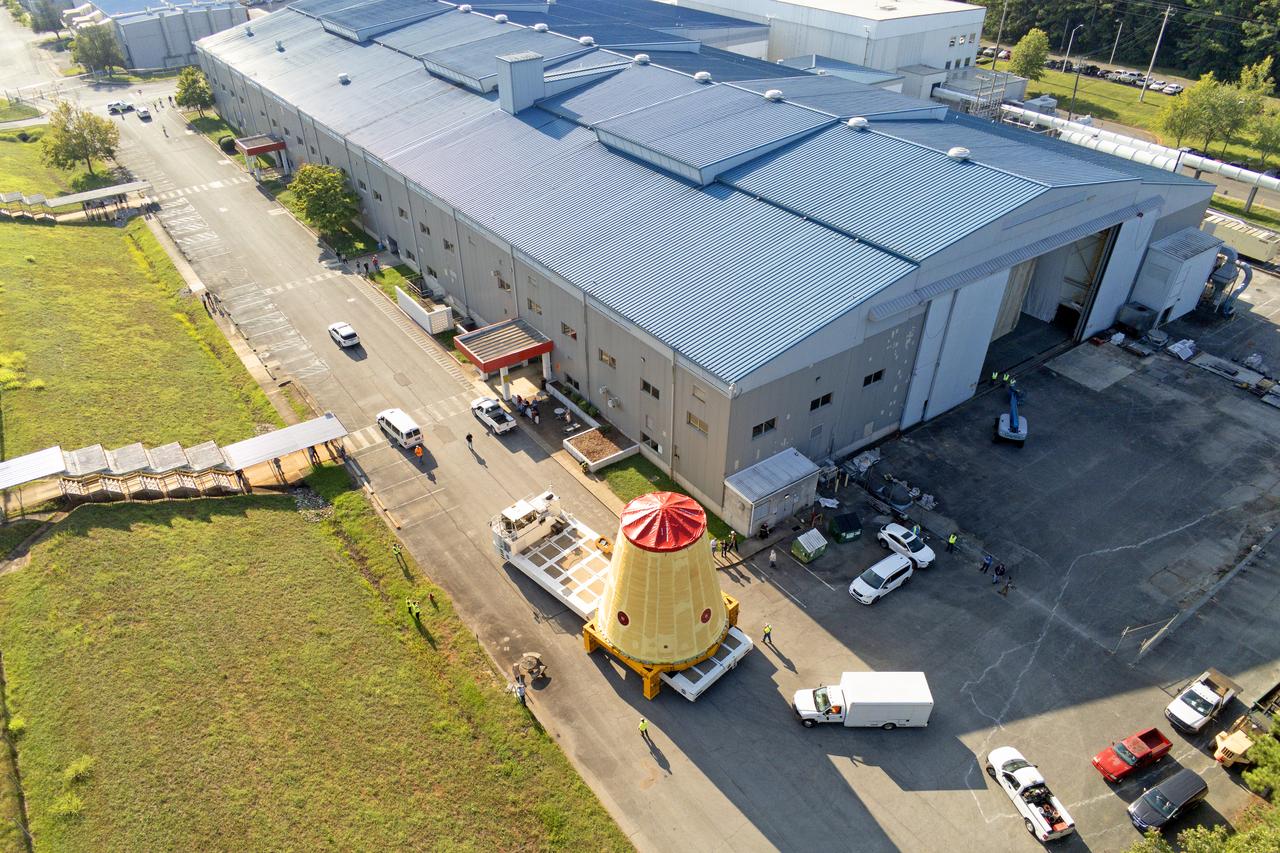

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
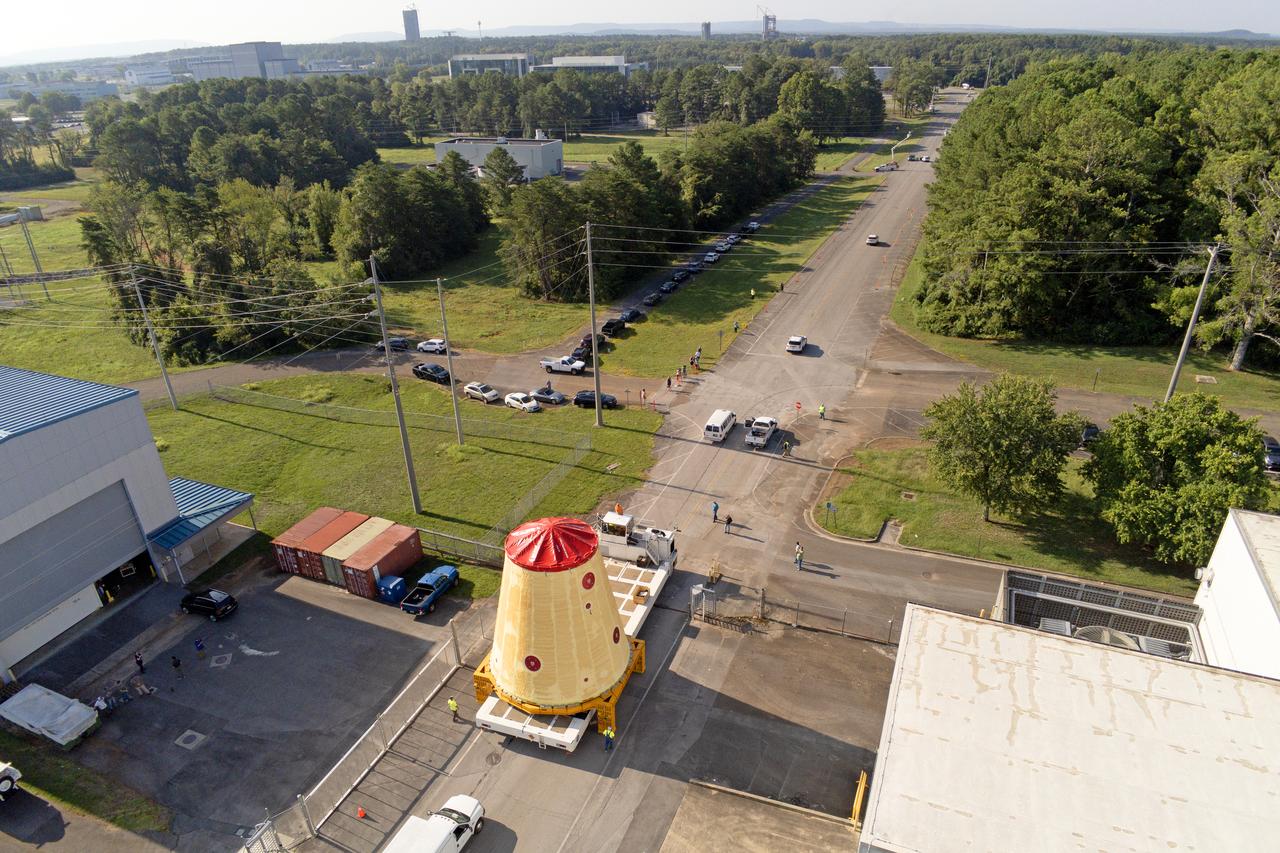

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
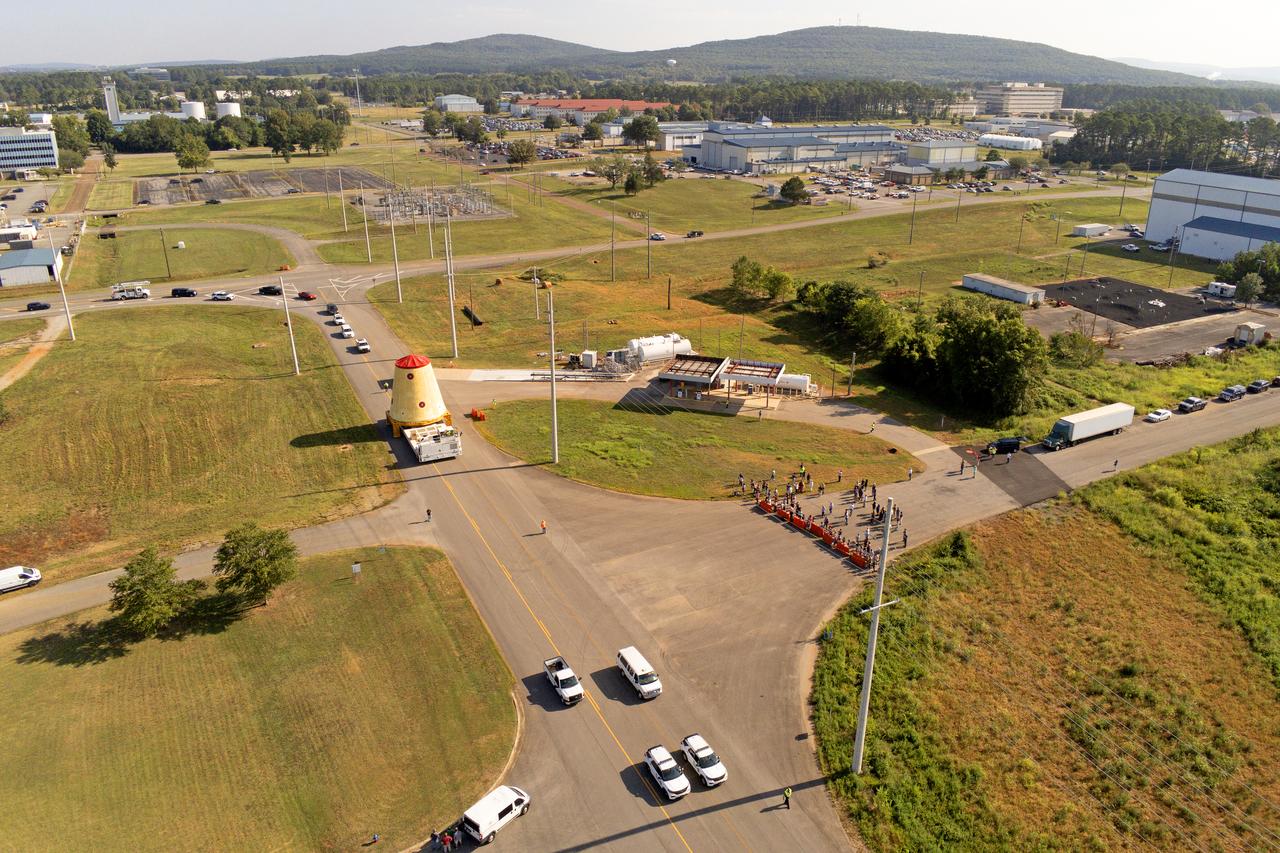

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
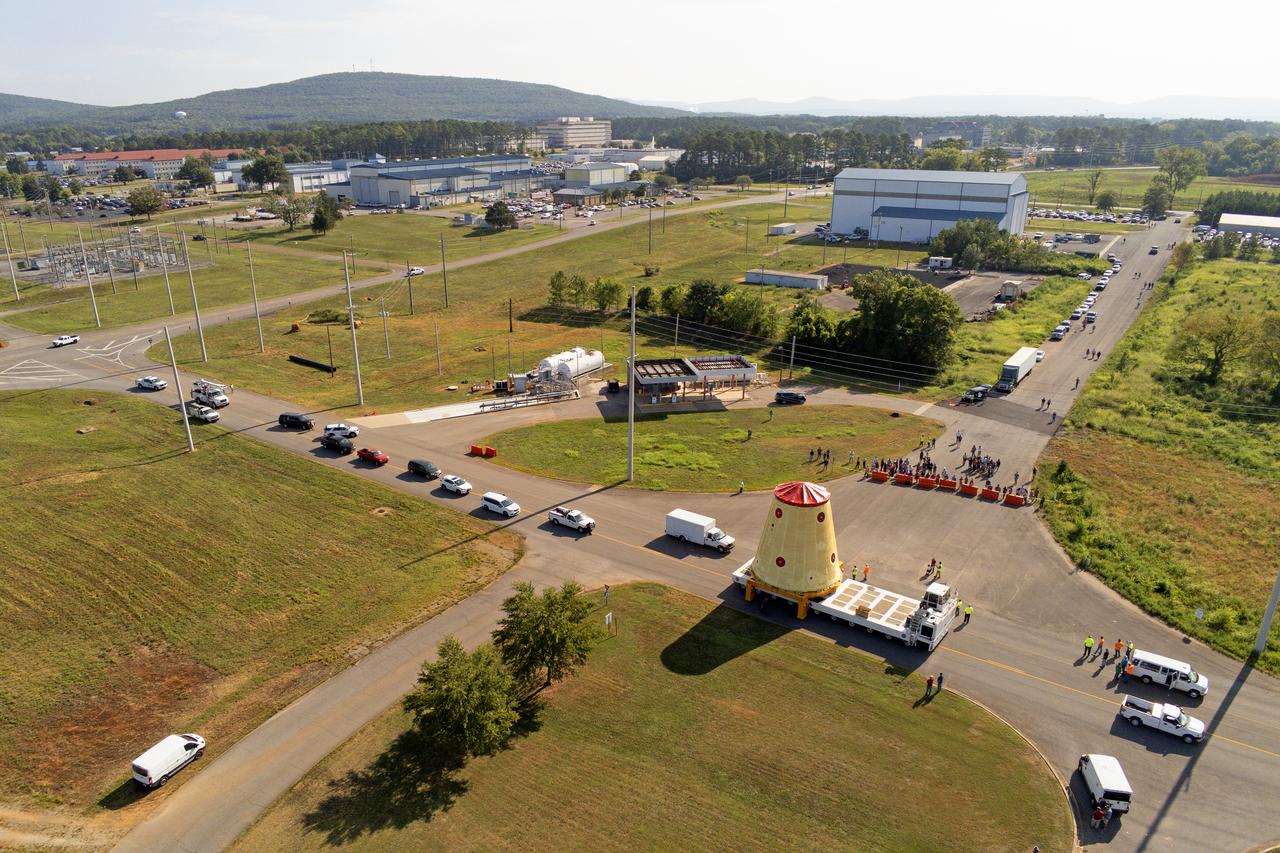

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
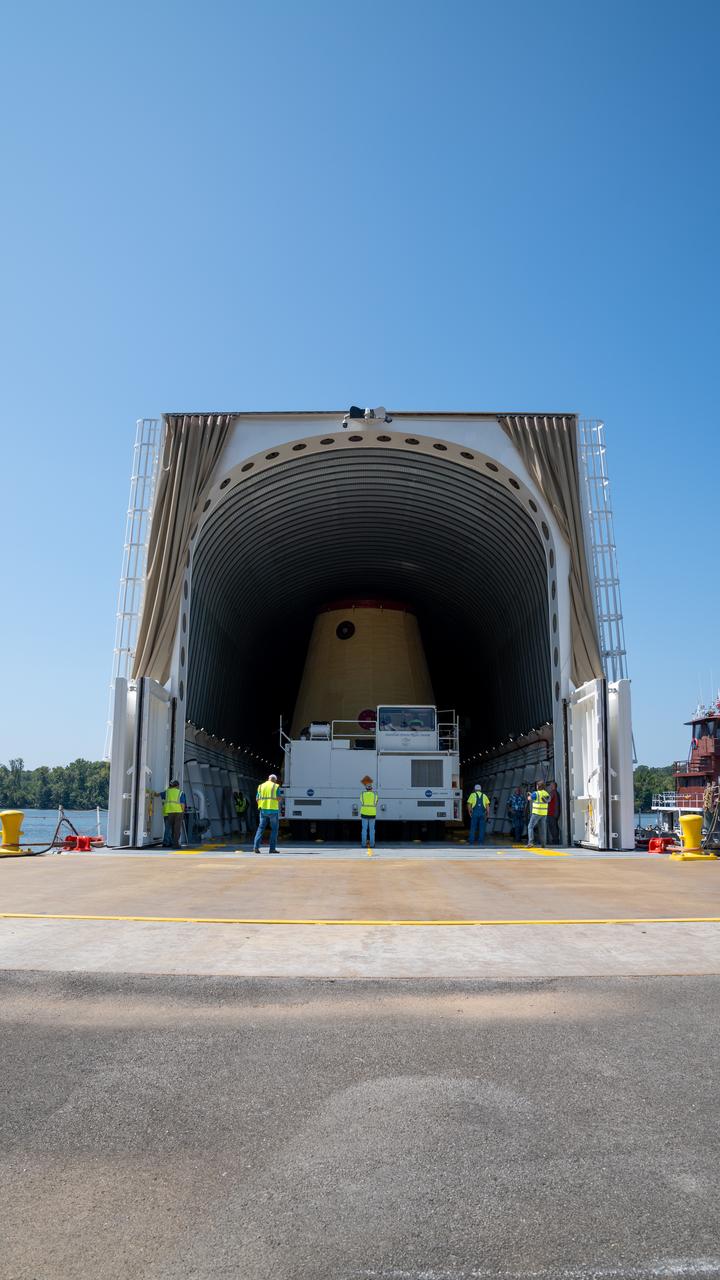

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
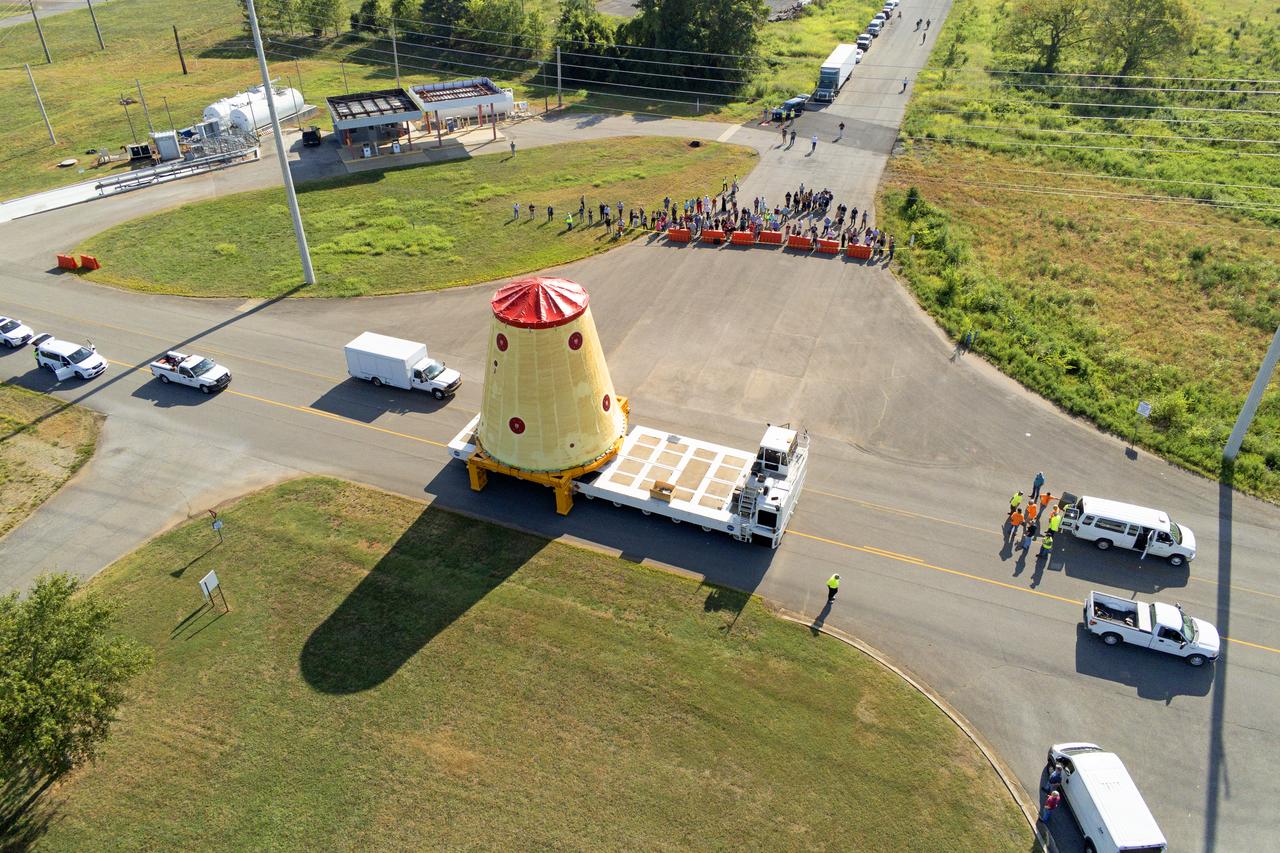

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
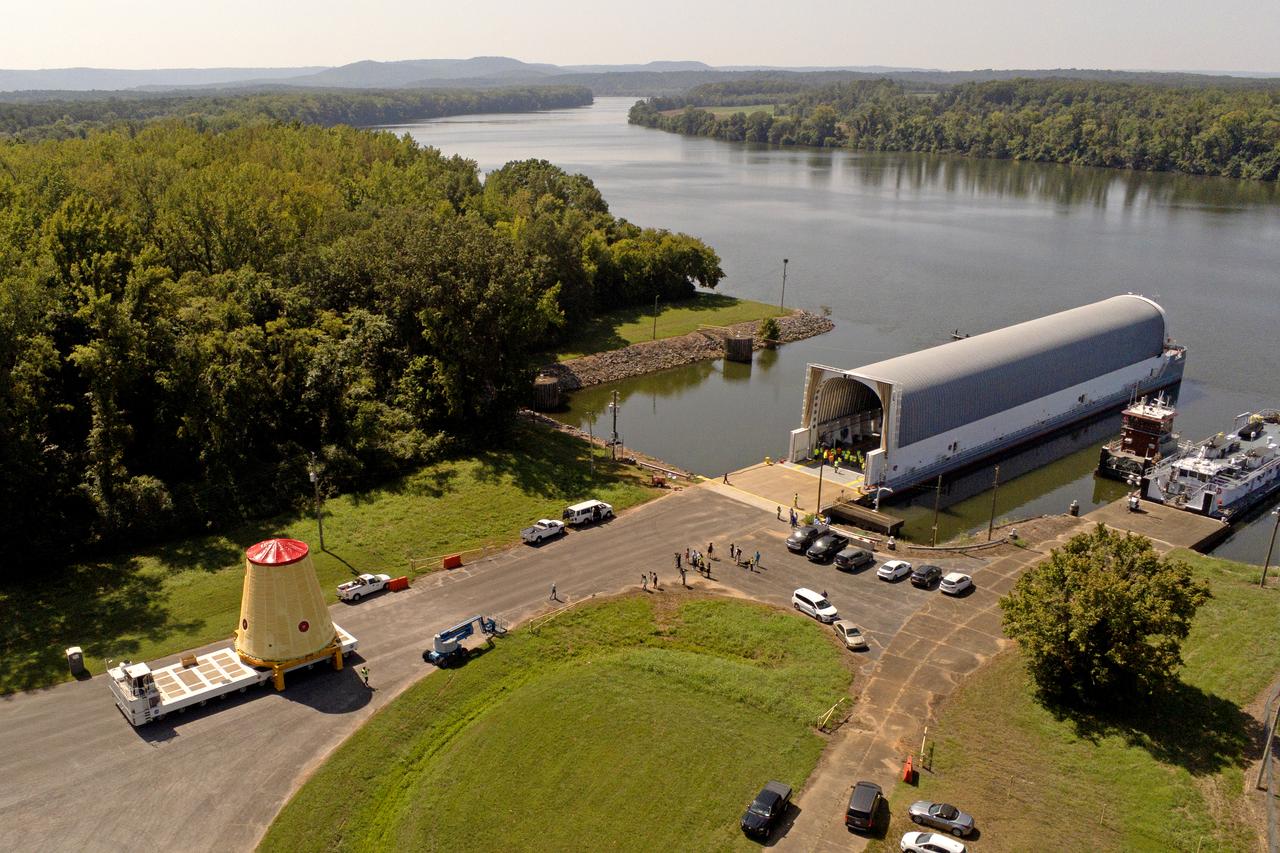

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
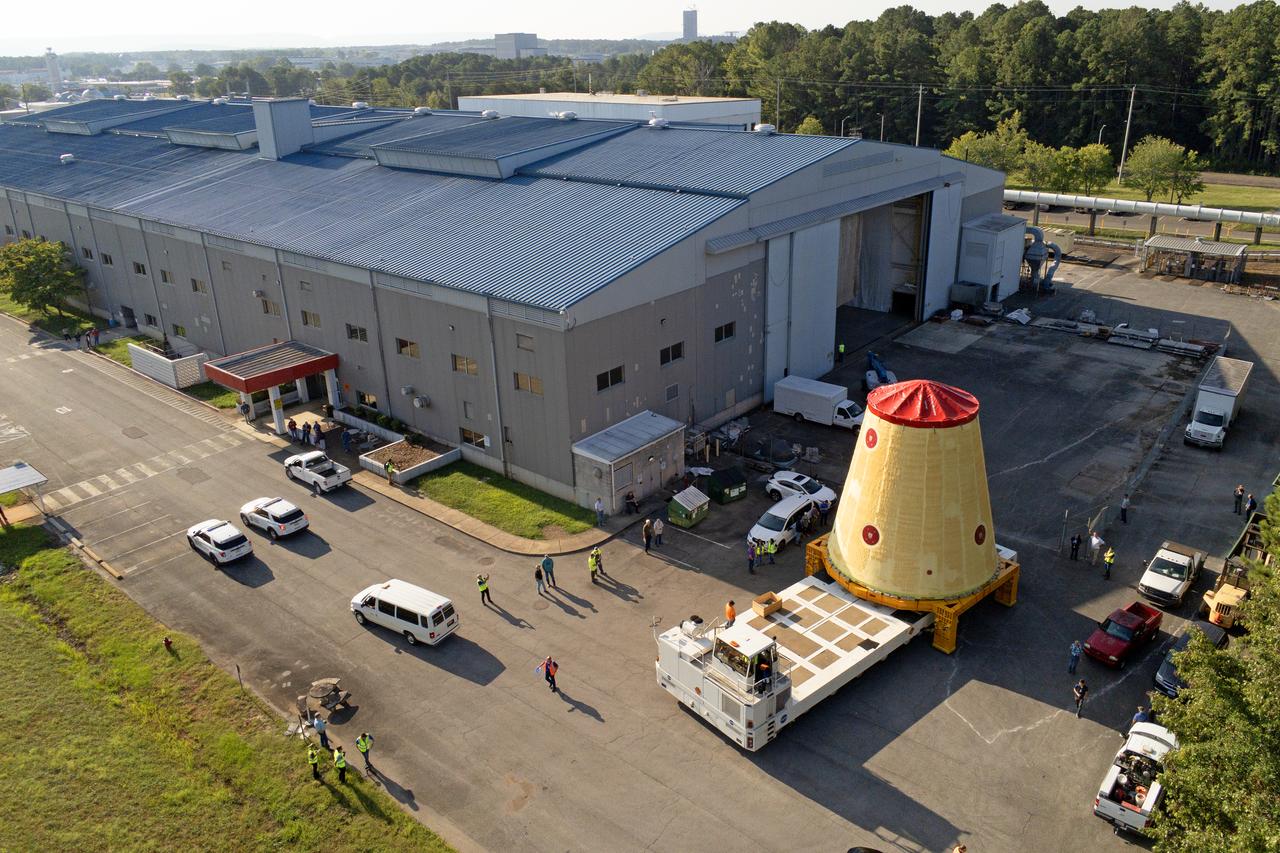

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
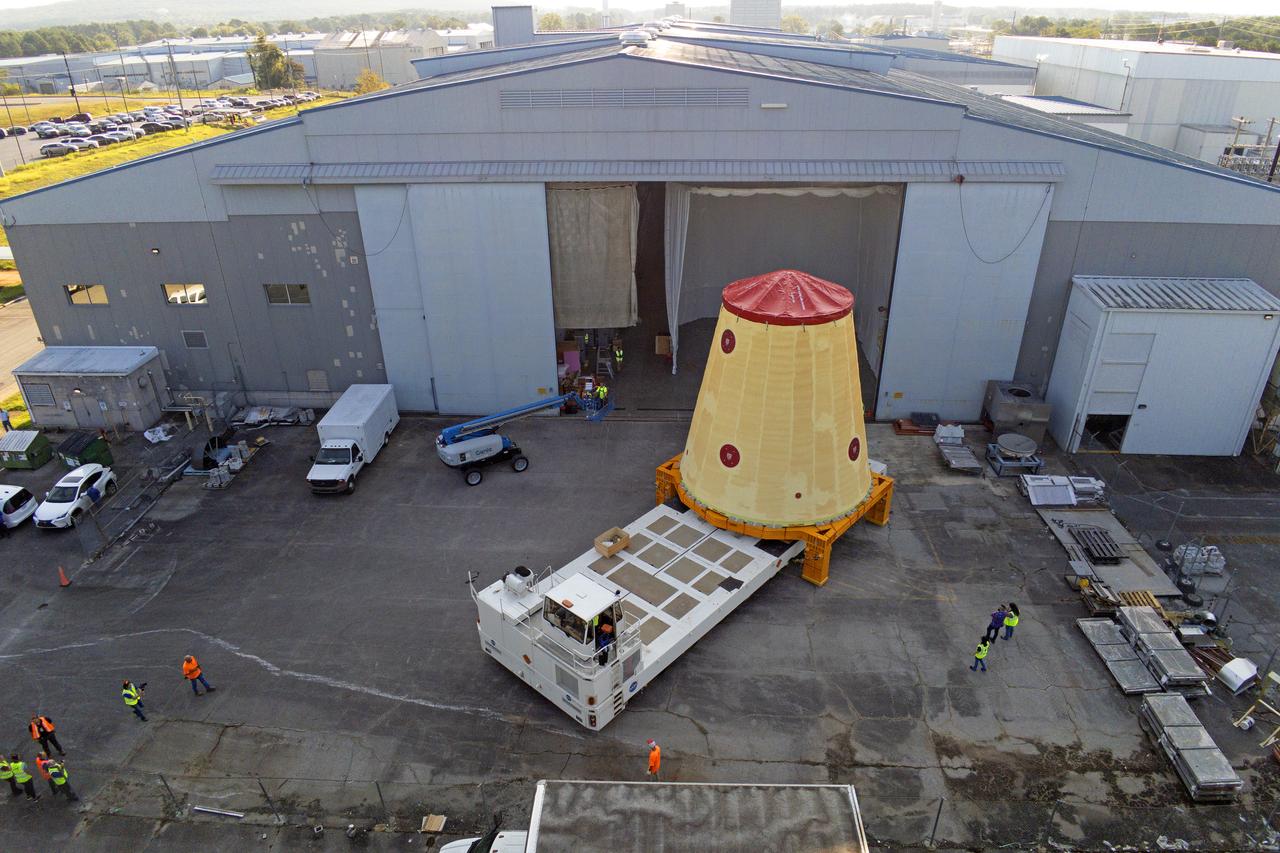

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
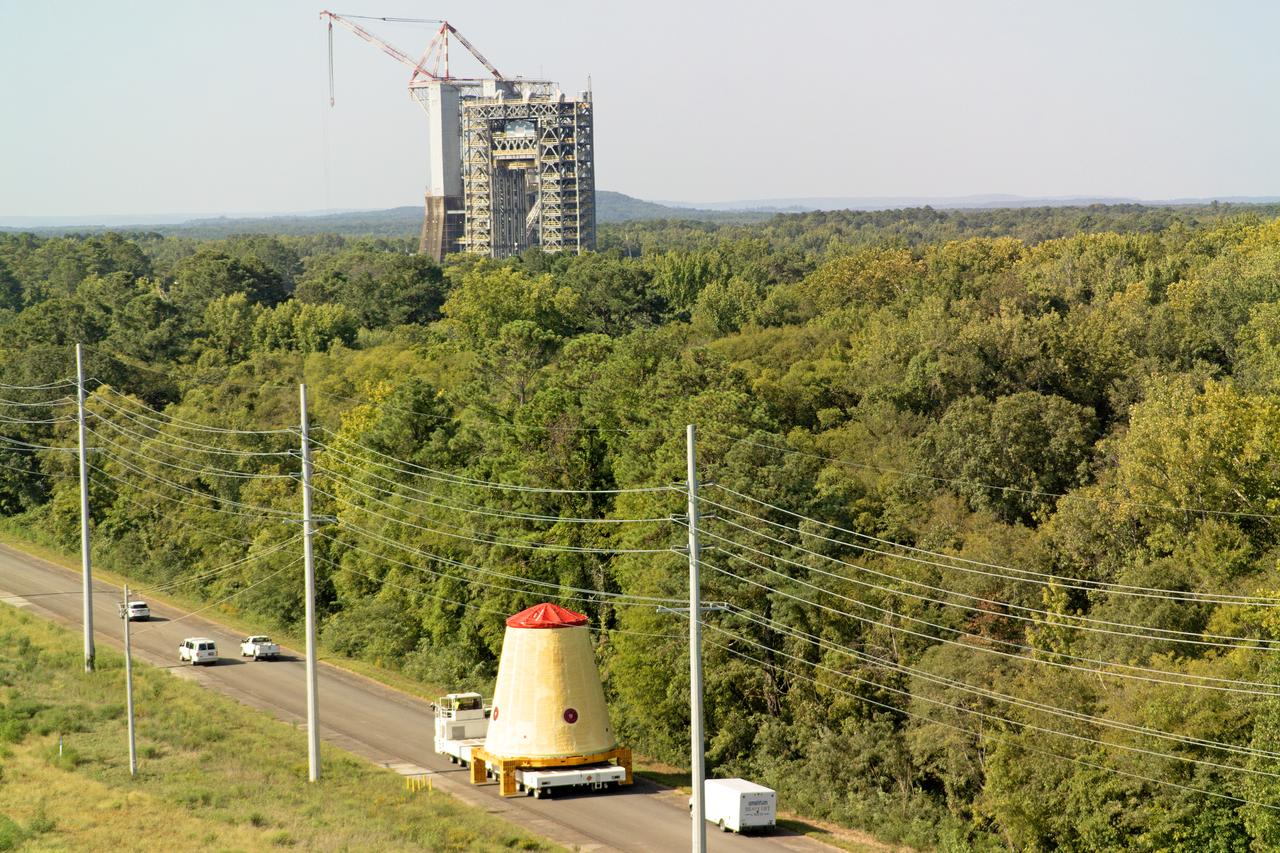

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
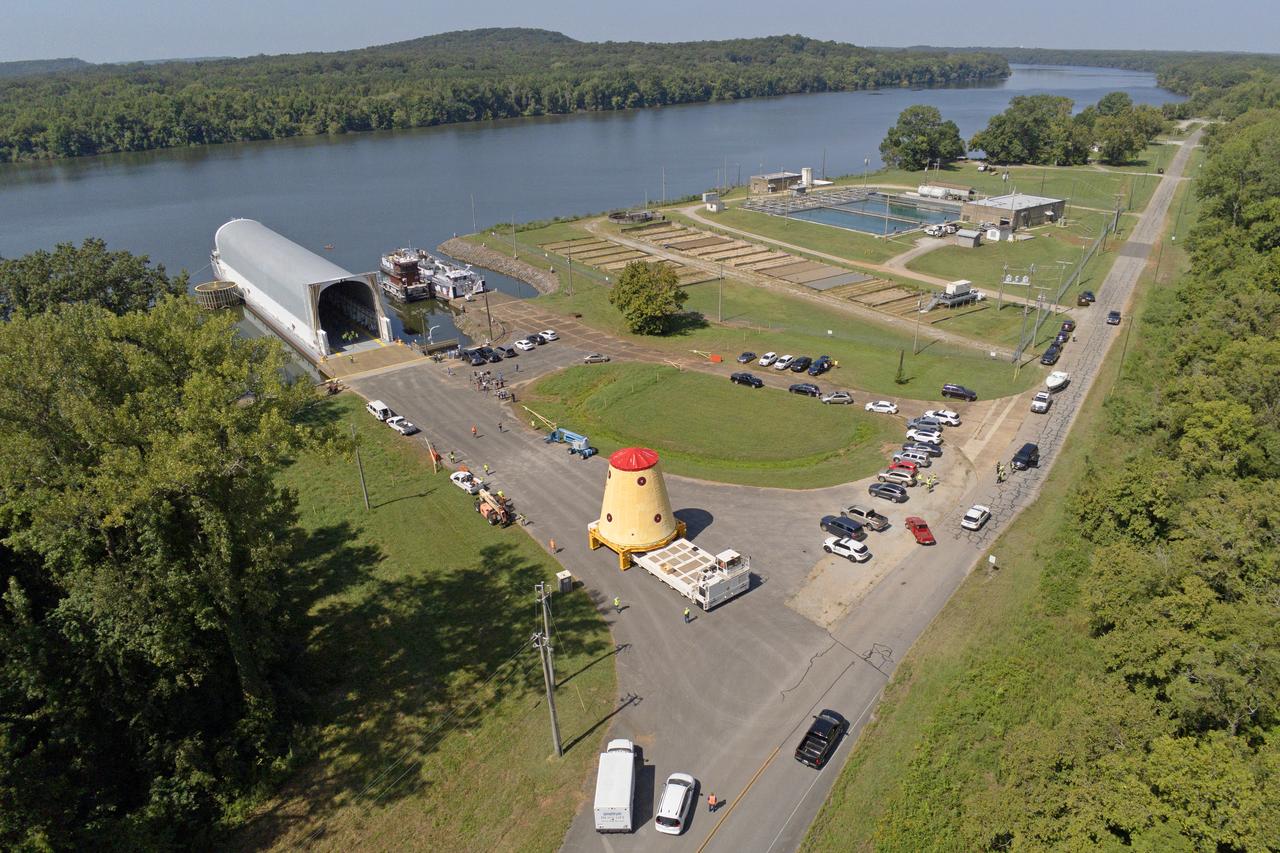

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
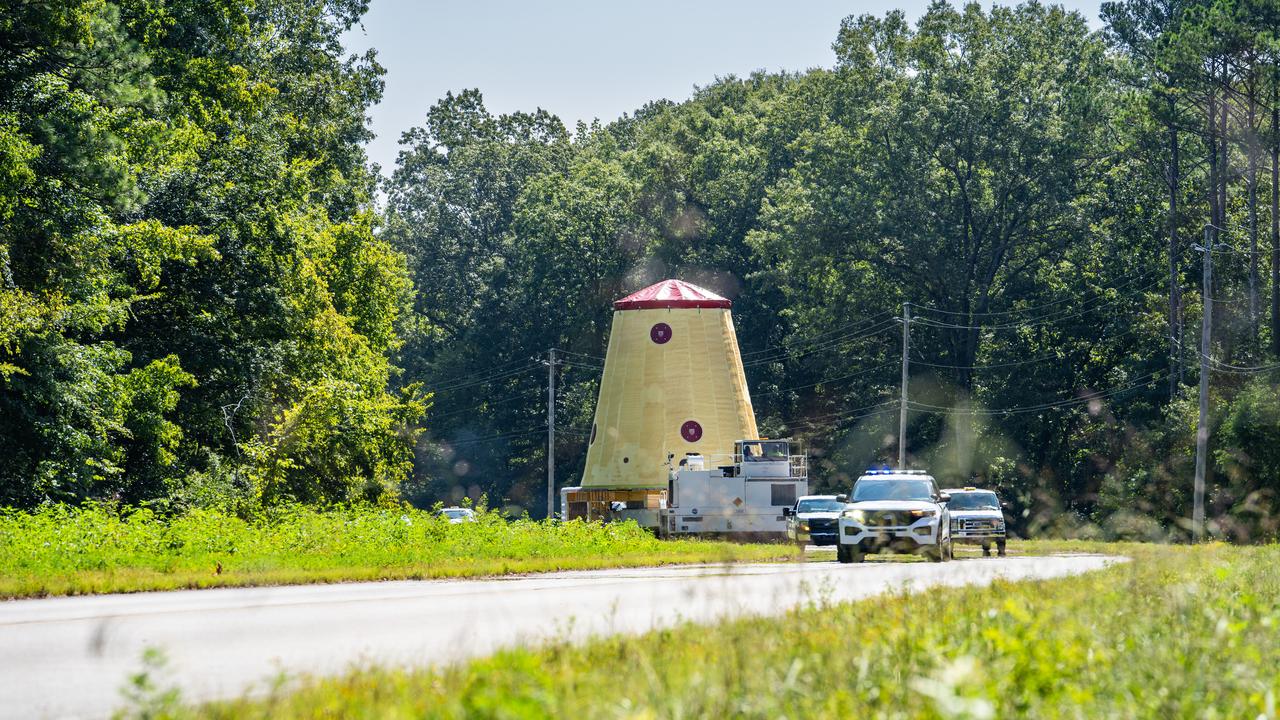

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch
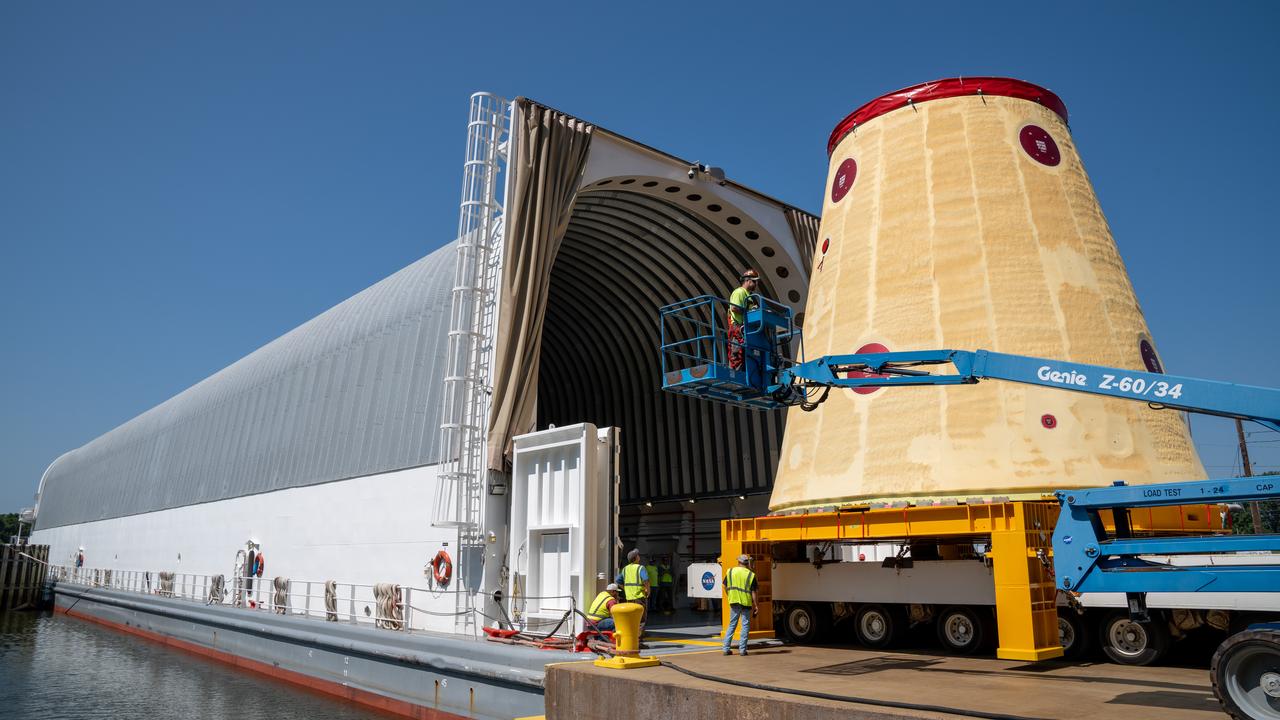

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
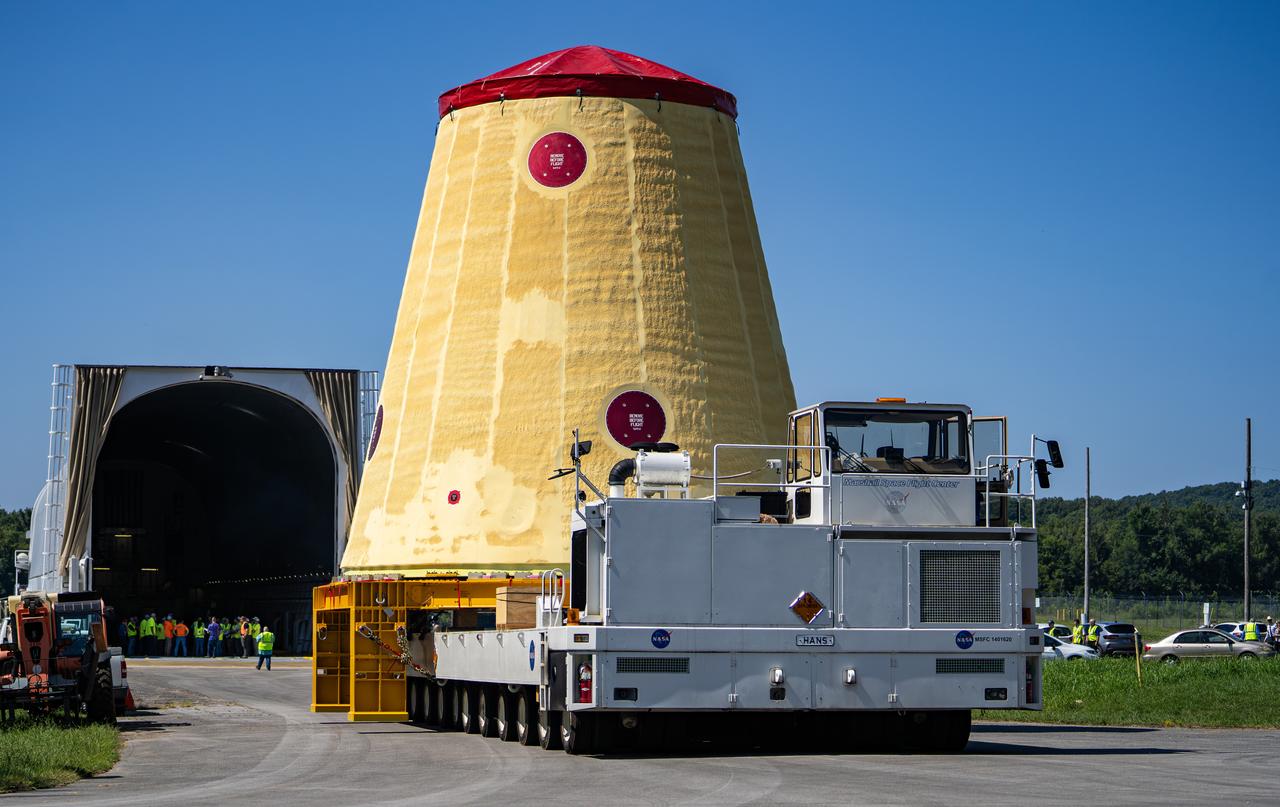

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
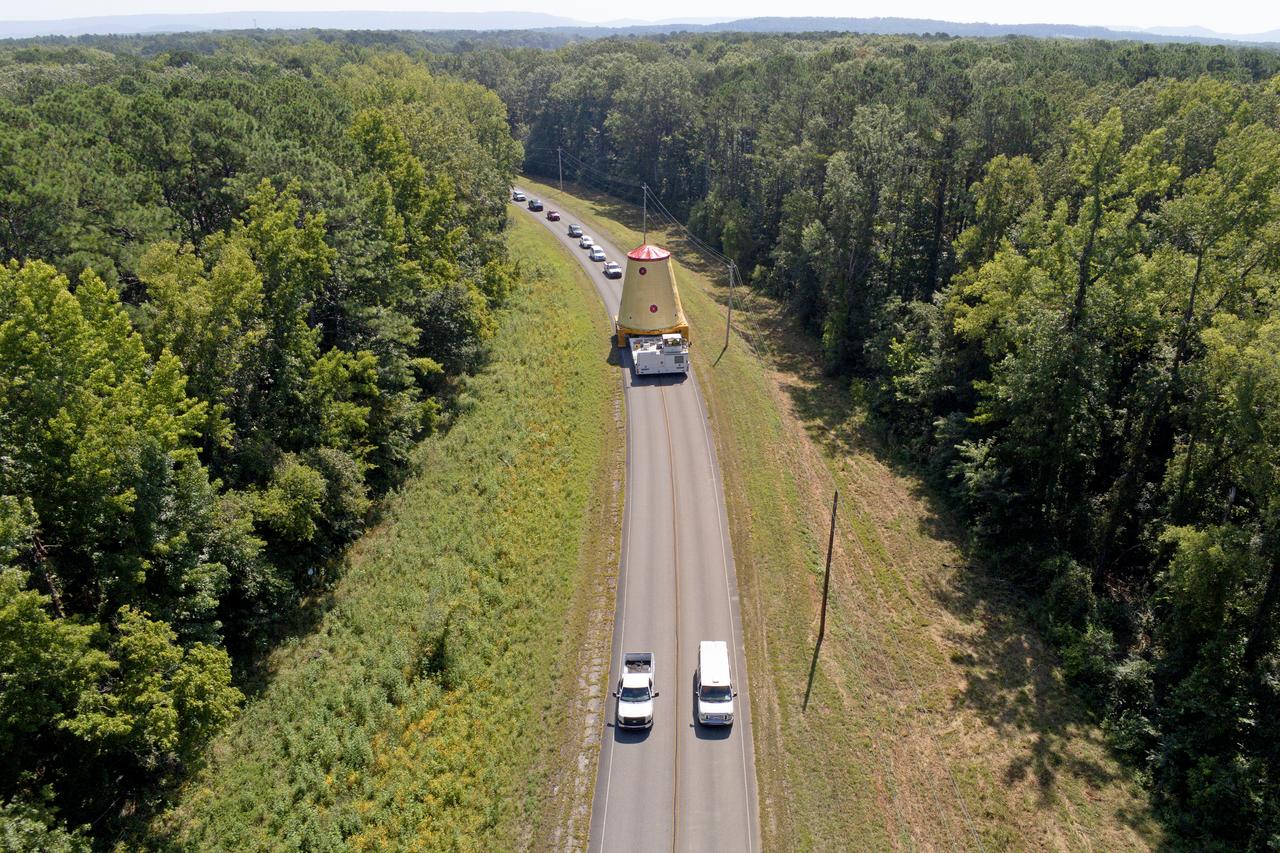

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
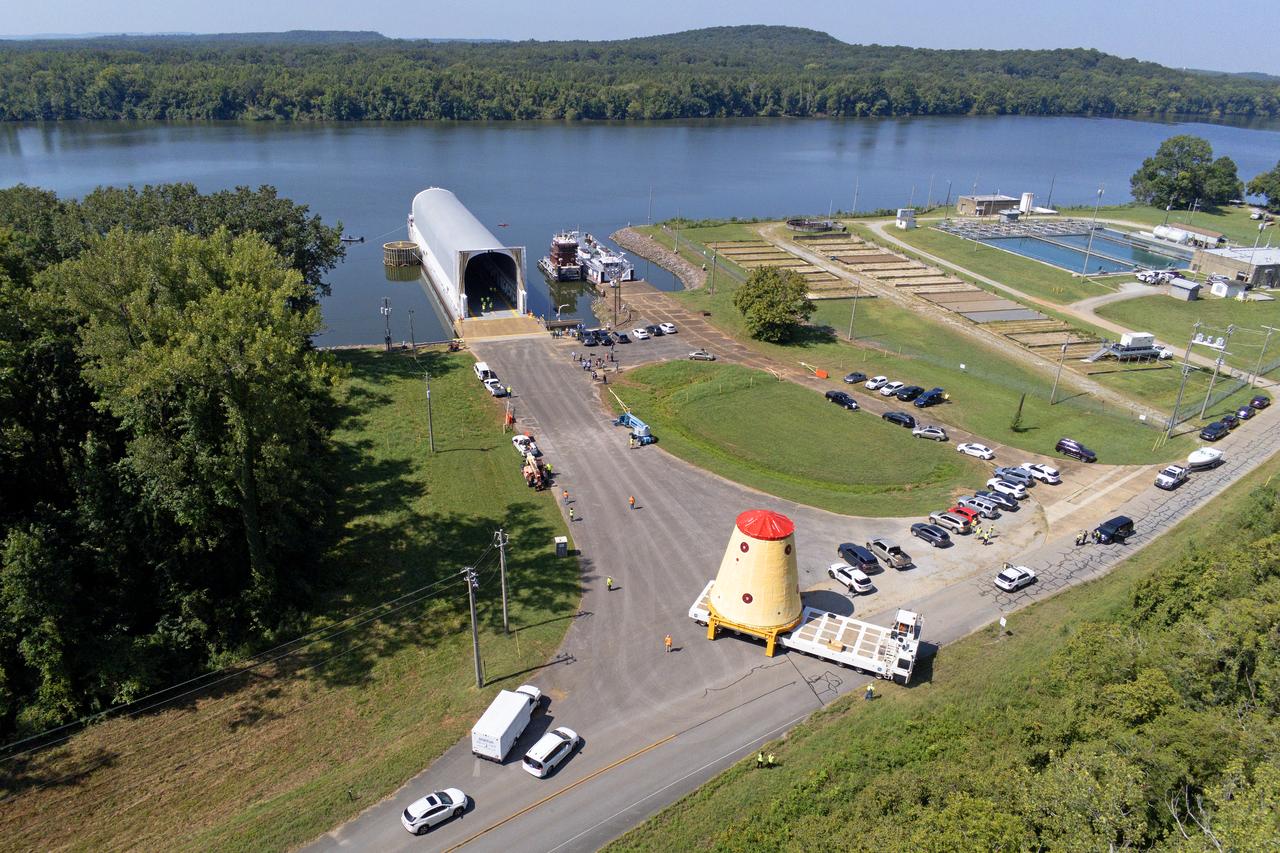

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
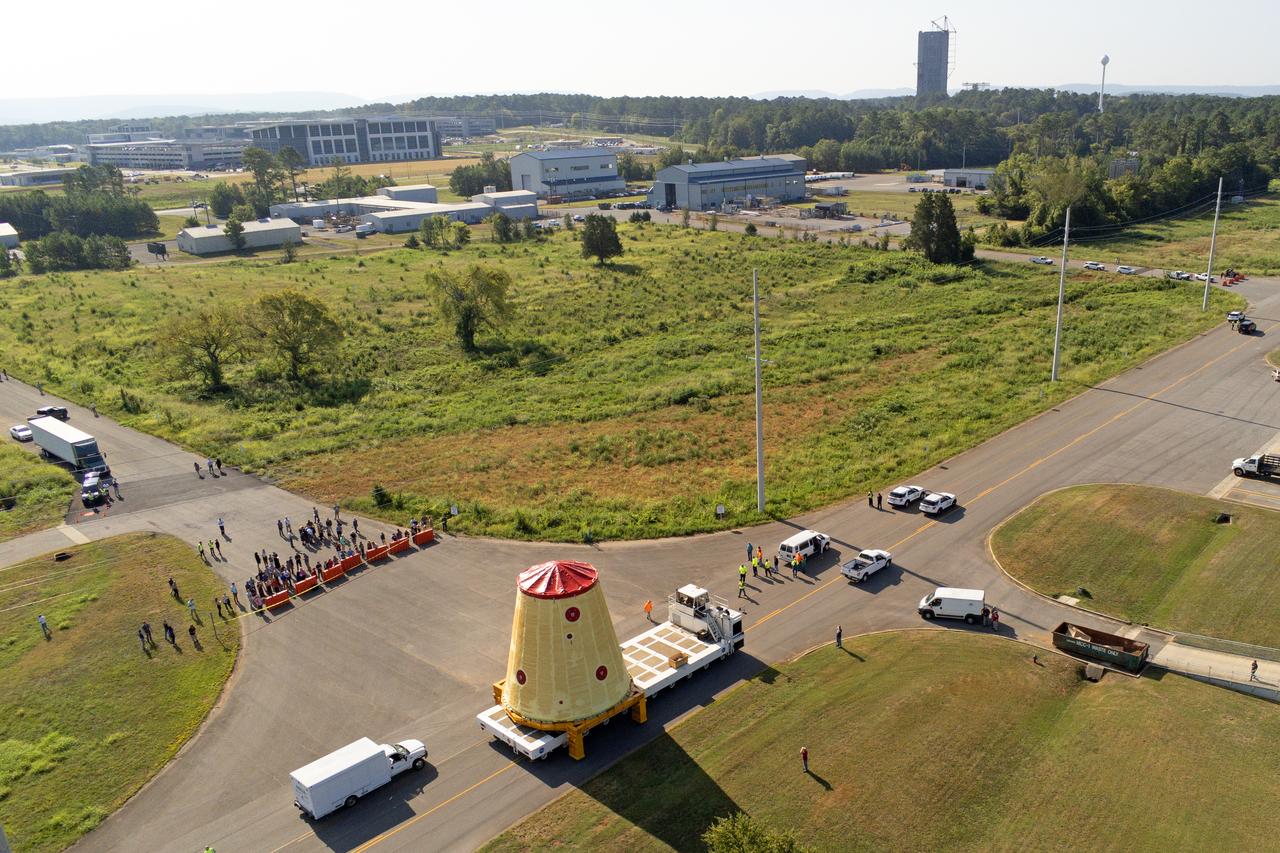

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
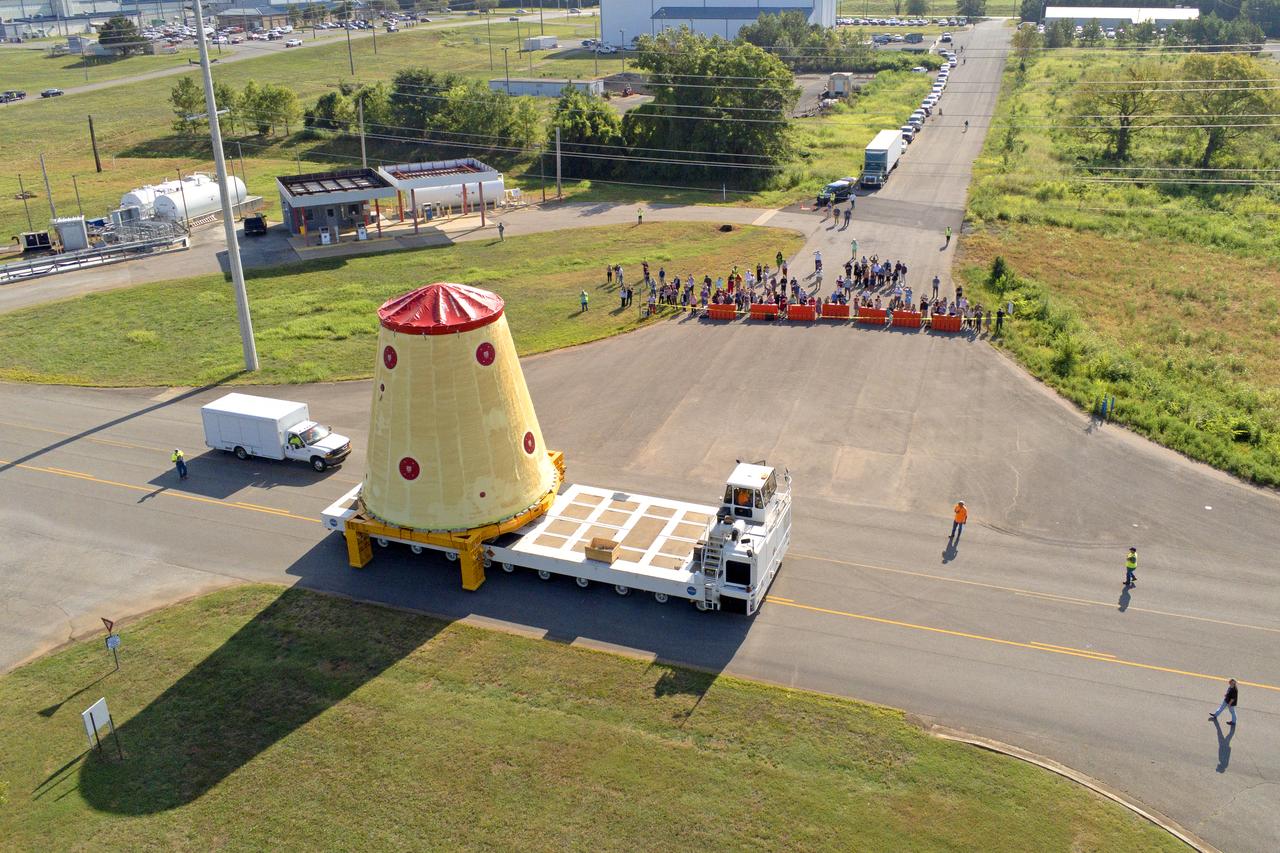

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
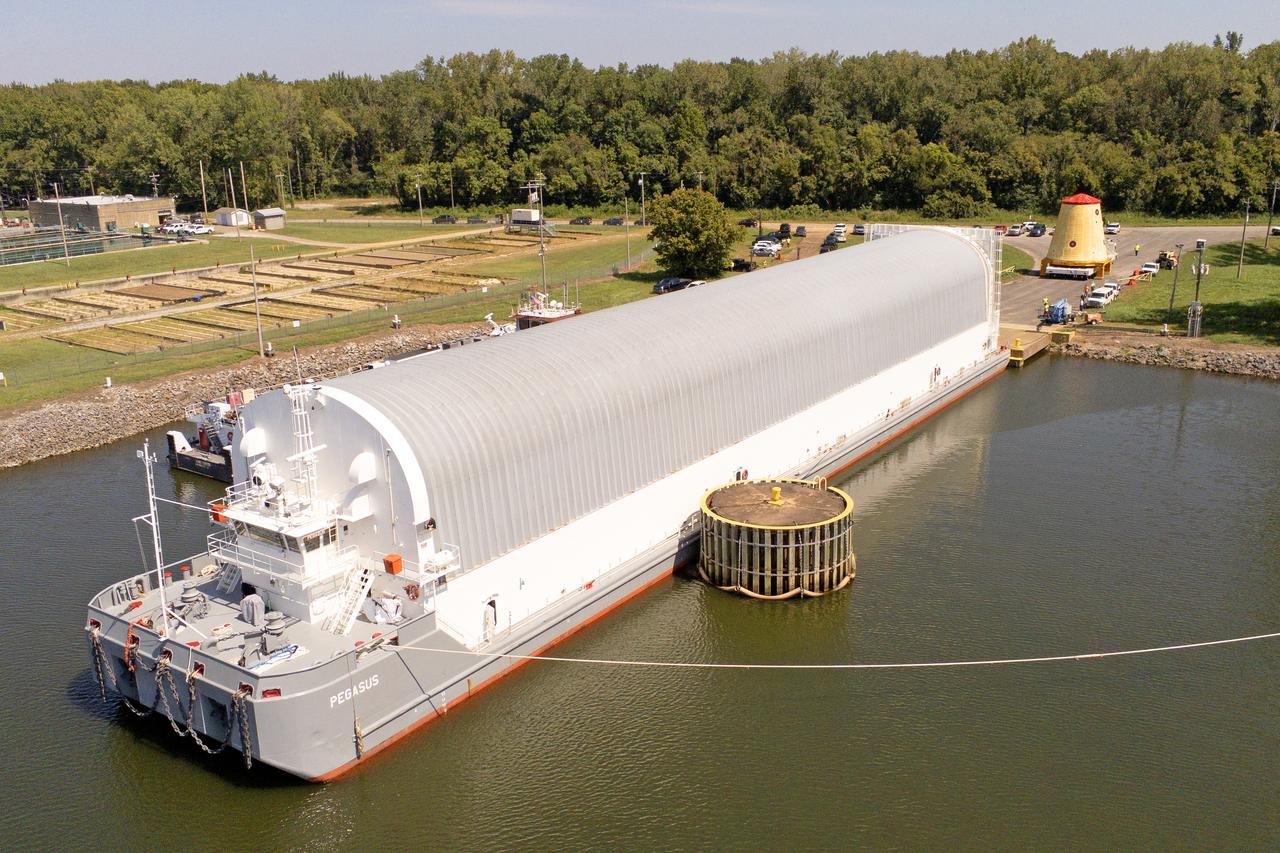

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
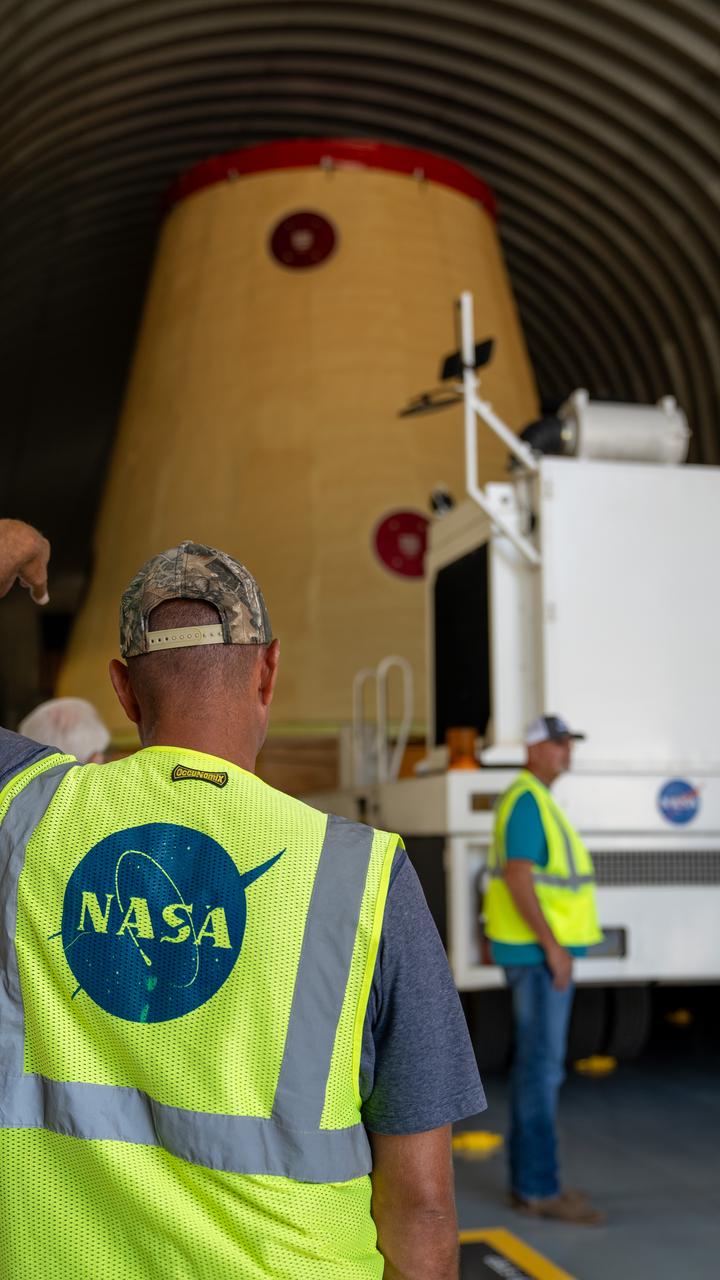

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
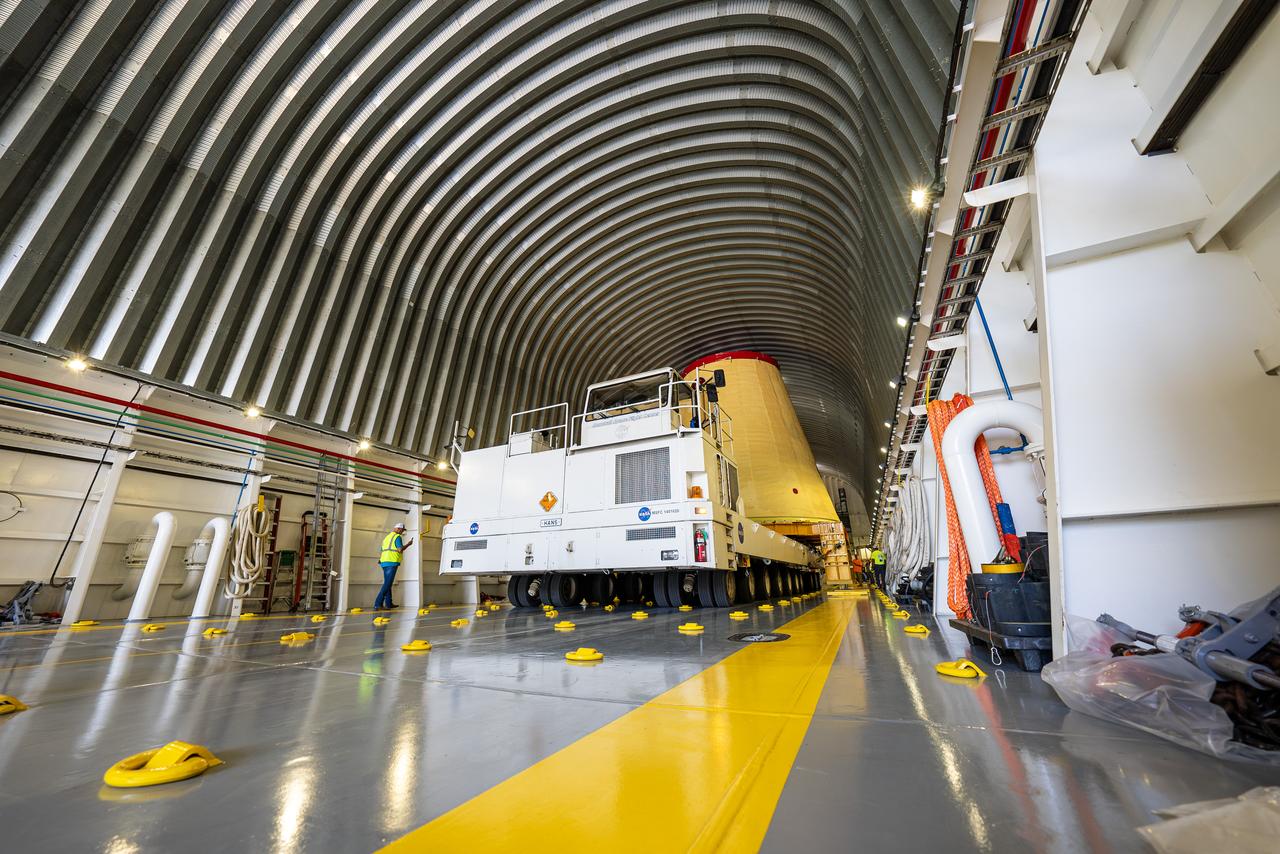

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.
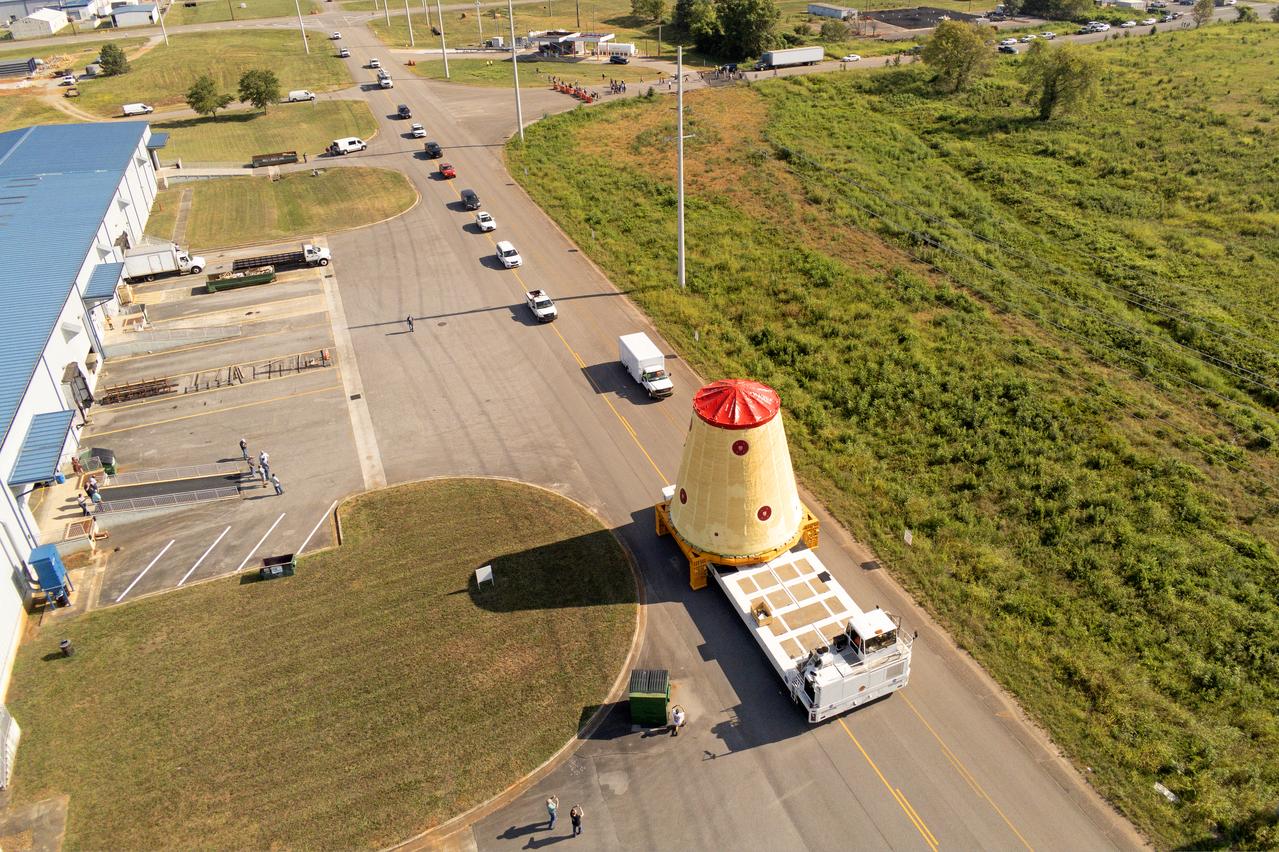

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2025. Manufactured by prime contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering and the Jacobs Space Exploration Group’s ESSCA (Engineering Services and Science Capability Augmentation) contract using NASA Marshall’s self-reacting friction-stir robotic and vertical weld tools. Crews moved the adapter out of NASA Marshall’s Building 4708 to the agency’s Pegasus barge Aug. 21. The barge will ferry the adapter first to NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, where crews will pick up additional SLS hardware for future Artemis missions, before traveling to NASA Kennedy. Once in Florida, the adapter will join the recently delivered core stage. There, teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems will prepare the adapter for stacking and launch.

REDSTONE ARSENAL GARRISON COMMANDER COL. THOMAS "DOC" HOLLIDAY, LEFT, DISCUSSES THE PROCESSES AND HARDWARE USED IN NASA IN-SPACE MANUFACTURING TECHNIQUES WITH KEN COOPER, A STRUCTURAL MATERIALS ENGINEER AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER. COOPER, PART OF THE MARSHALL ENGINEERING DIRECTORATE'S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING AND DIGITAL SOLUTIONS TEAM, WAS AMONG NUMEROUS SUBJECT-MATTER EXPERTS WHO SHARED KEY MARSHALL CAPABILITIES DURING HOLLIDAY'S MARCH 3 MARSHALL TOUR. HOLLIDAY, A DECORATED OFFICER WHOSE MILITARY CAREER BEGAN IN 1992, GAINED FIRSTHAND INSIGHT INTO MARSHALL'S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING AND 3-D PRINTING TECHNIQUES; ROUND-THE-CLOCK INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION SCIENCE AND COMMUNICATIONS SUPPORT BY THE PAYLOAD OPERATIONS INTEGRATION CENTER TEAM; AND THE LATEST UPGRADES TO MARSHALL TEST STANDS IN SUPPORT OF NEXT-GENERATION LAUNCH VEHICLE AND FLIGHT HARDWARE DEVELOPMENT. MARSHALL, A REDSTONE ARSENAL TENANT, ROUTINELY SHARES CUTTING-EDGE RESEARCH AND MANUFACTURING ADVANCES WITH ITS MILITARY AND FEDERAL AGENCY COUNTERPARTS, WORKING IN PARTNERSHIP TO ADVANCE NASA'S MISSION AND MAINTAIN THE NATION'S TECHNOLOGICAL LEADERSHIP.