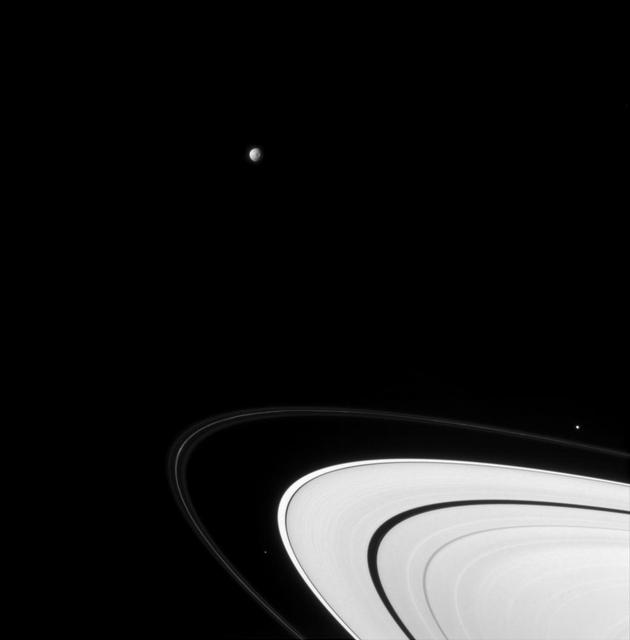

Moon Harvest
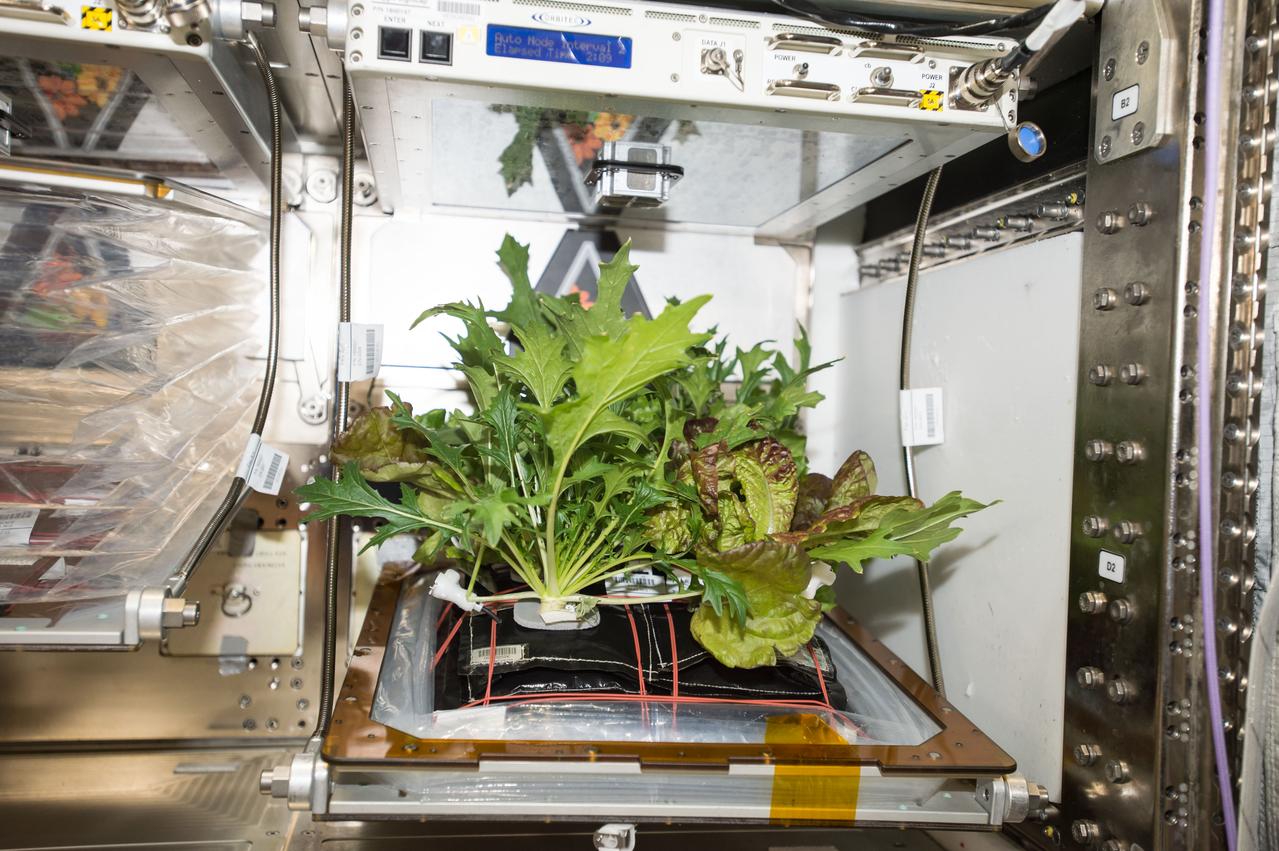

Three different varieties of plants growing in the Veggie plant growth chamber on the International Space Station were harvested this morning.
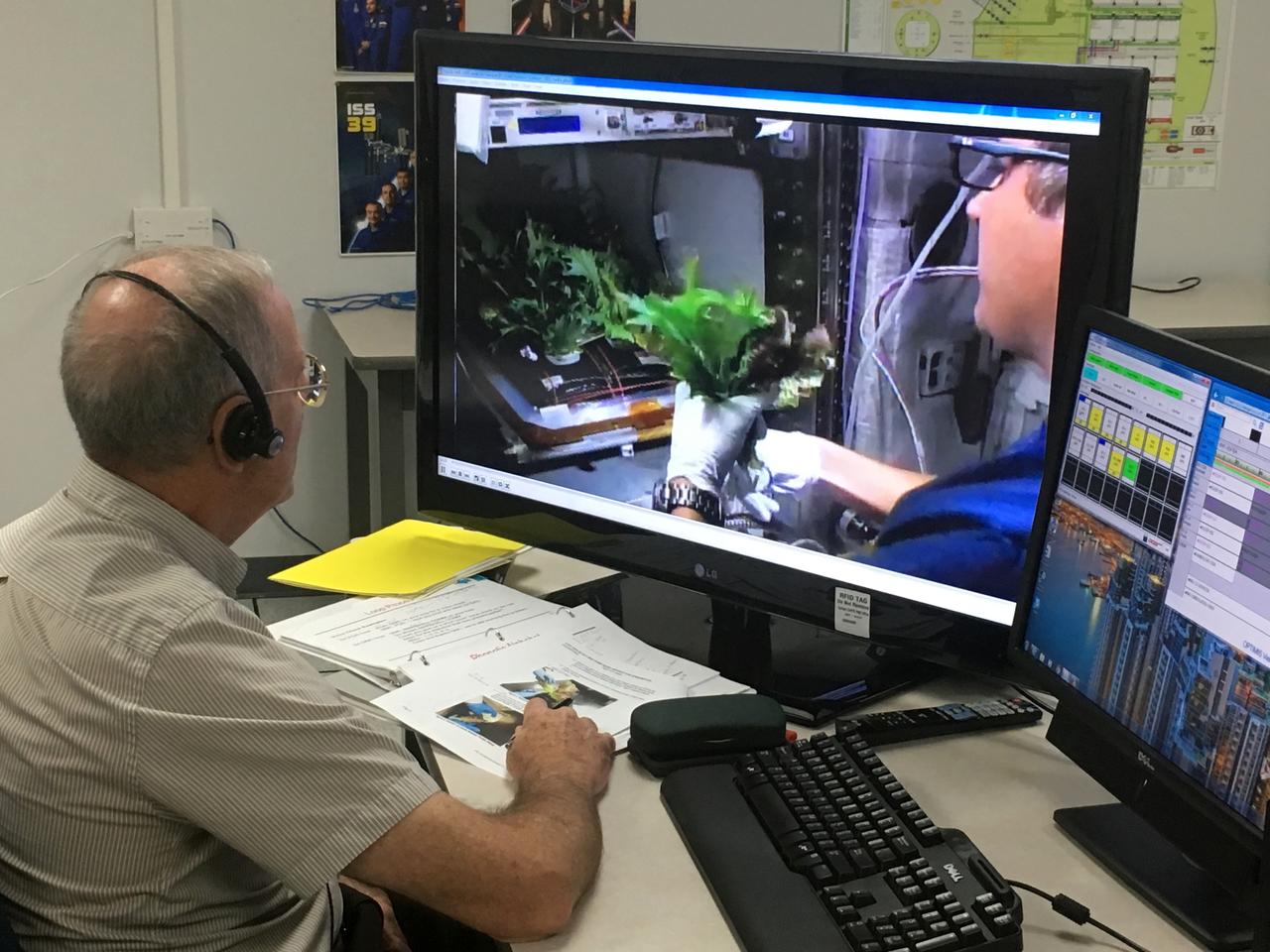

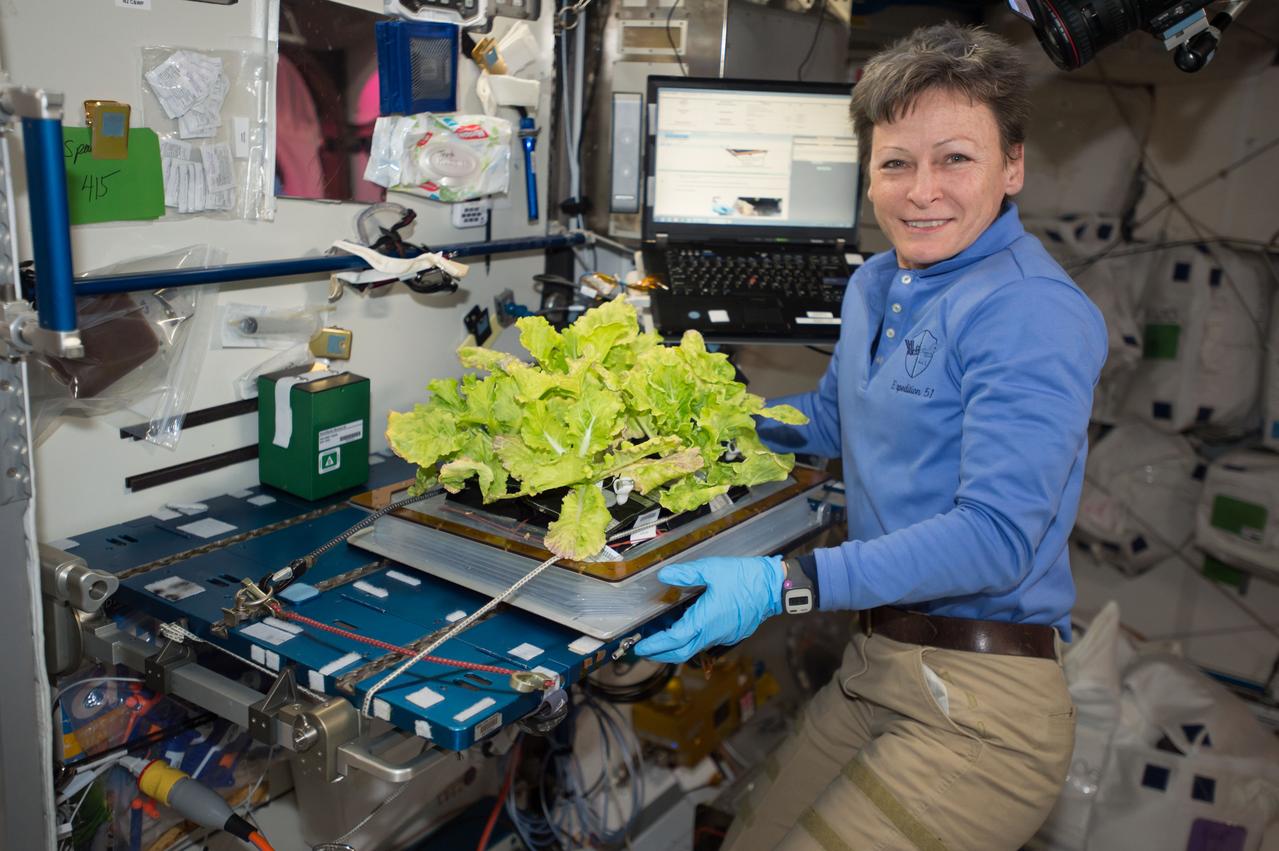
Charles Spern, project manager on the Engineering Services Contract, communicates instructions for the Veggie system to astronaut Joe Acaba on the International Space Station. Spern is in the Experiment Monitoring Room in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three different varieties of plants from the Veg-03D plant experiment were harvested.
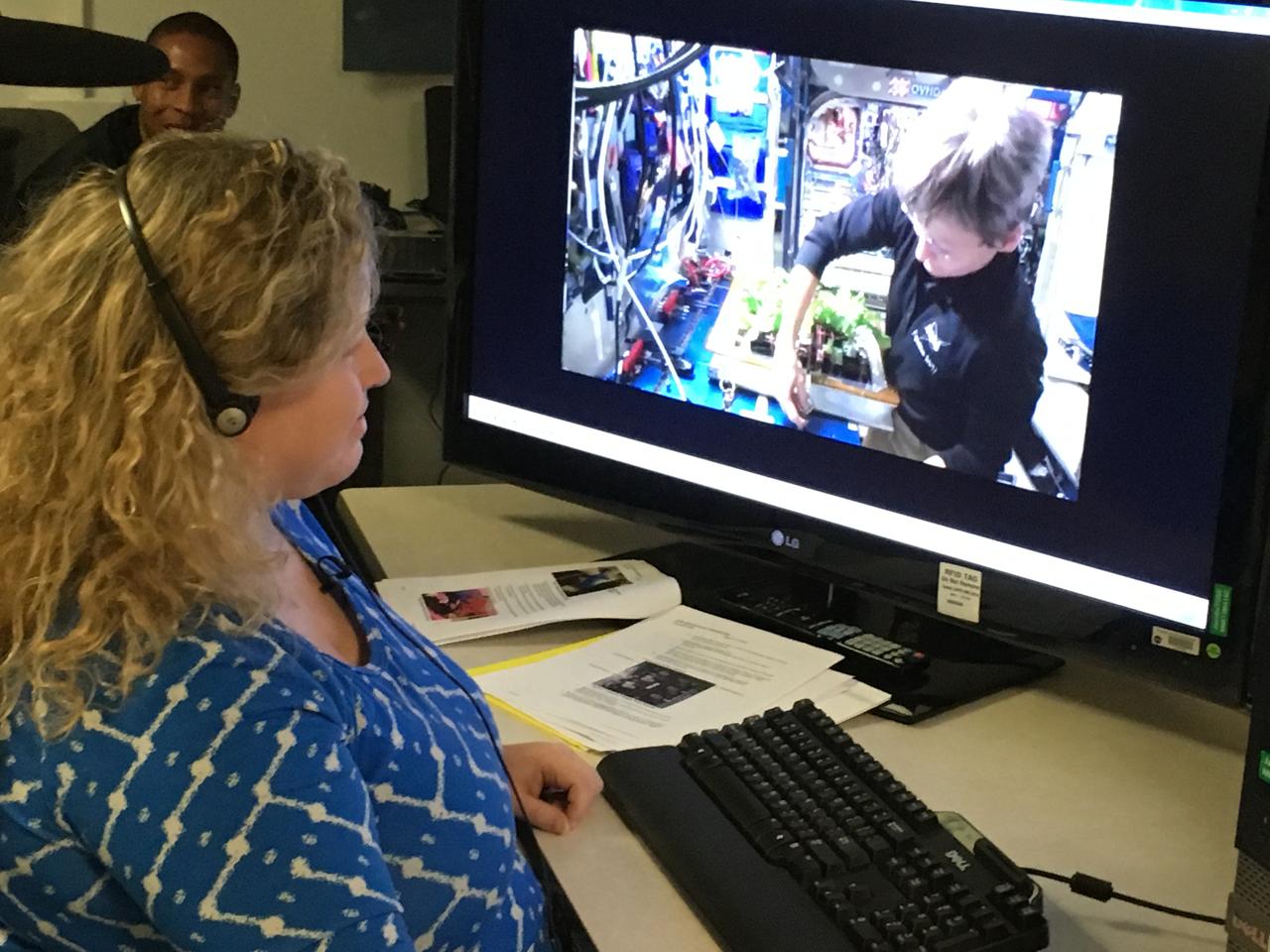

At Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Veggie Project Manager Nicole Dufour instructs astronaut Peggy Whitson during the harvest of Chinese cabbage aboard the International Space Station. While the space station crew will get to eat some of the Chinese cabbage, the rest is being saved for scientific study back at Kennedy Space Center. This is the fifth crop grown aboard the station, and the first Chinese cabbage.

Arabidopsis thaliana plants are seen inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 prior to harvest of half the plants. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, harvests half the Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.
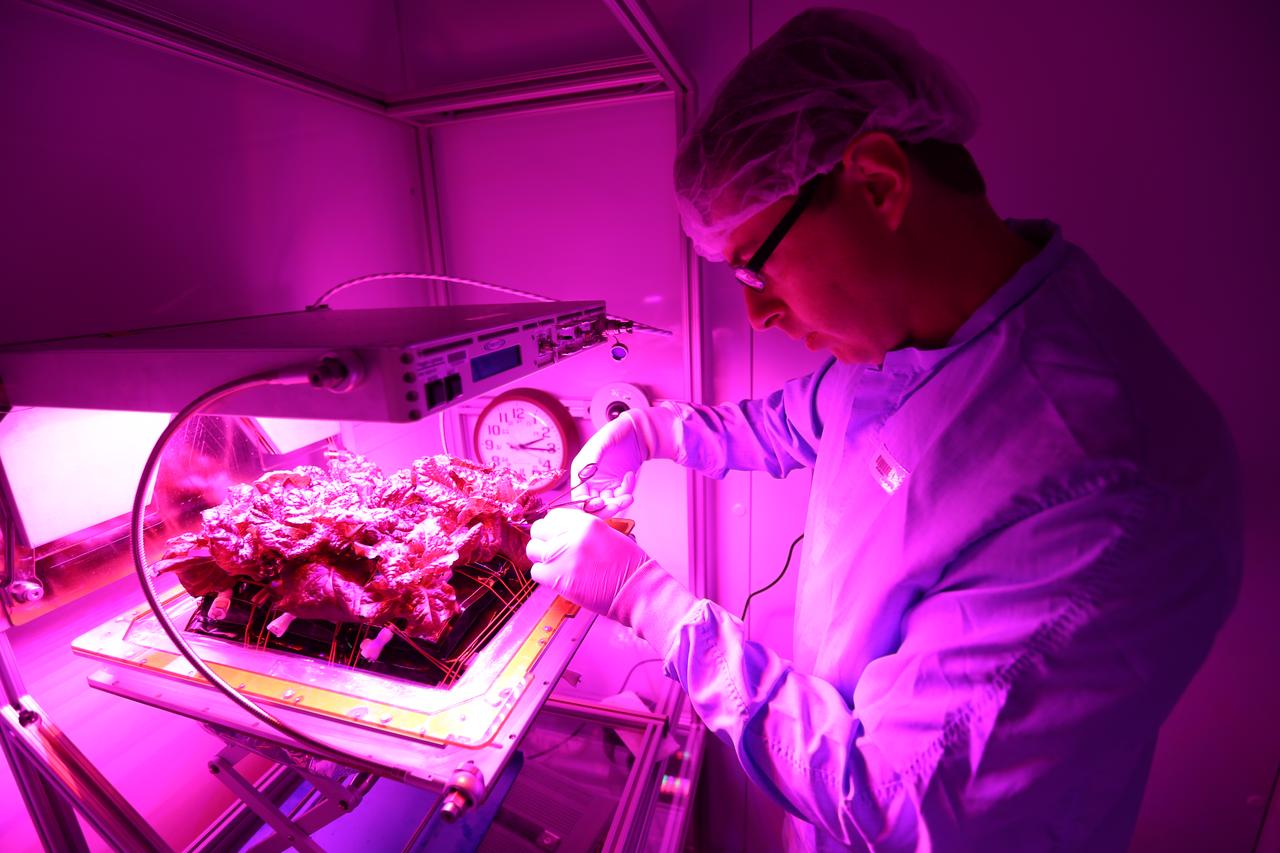

Inside the Veggie flight laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Matthew Romeyn, a NASA Pathways intern from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, harvests a portion of the 'Outredgeous' red romaine lettuce from the Veg-03 ground control unit. The purpose of the ground Veggie system is to provide a control group to compare against the lettuce grown in orbit on the International Space Station. Veg-03 will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.
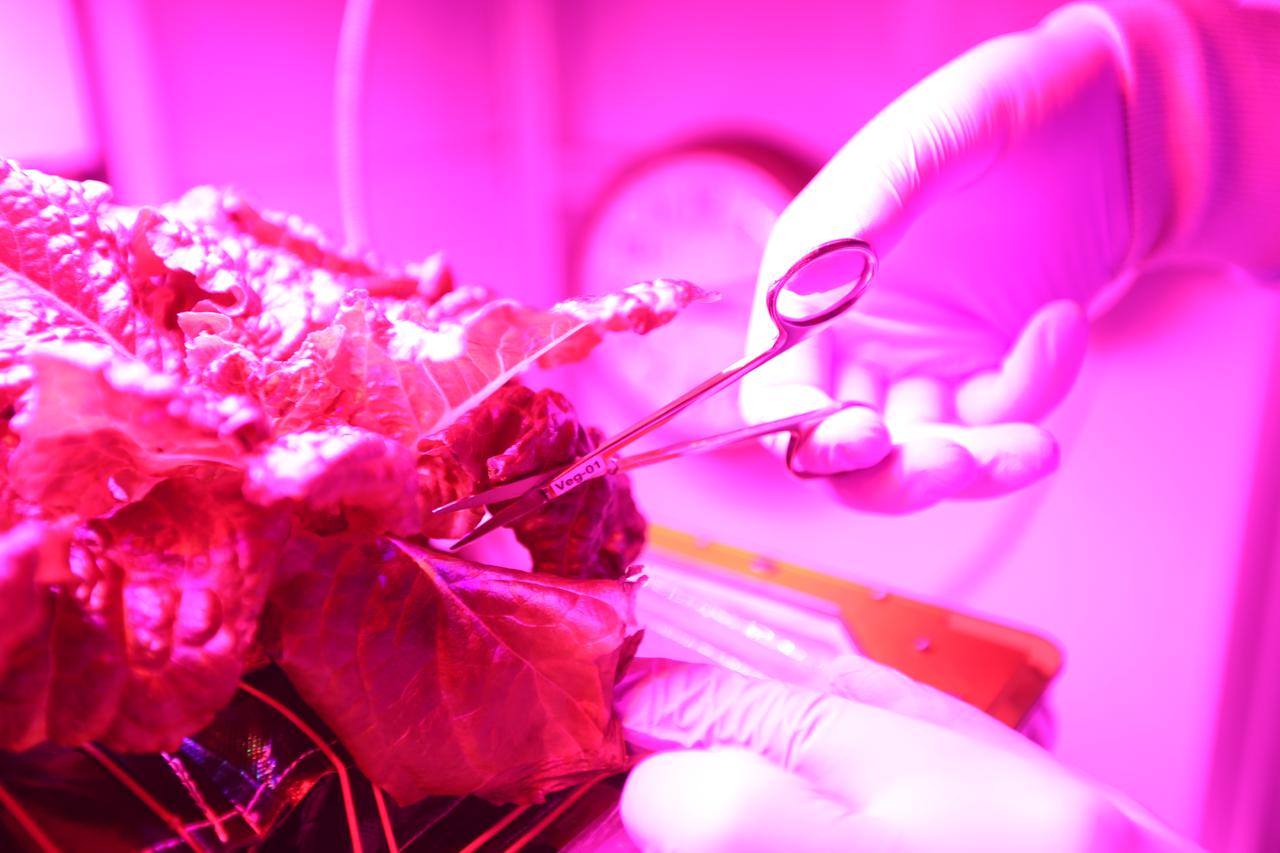
Inside the Veggie flight laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a research scientist harvests a portion of the 'Outredgeous' red romaine lettuce from the Veg-03 ground control unit. The purpose of the ground Veggie system is to provide a control group to compare against the lettuce grown in orbit on the International Space Station. Veg-03 will continue NASA’s deep space plant growth research to benefit the Earth and the agency’s journey to Mars.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, uses a FluorPen to measure the chlorophyll fluorescence of Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. Half the plants were then harvested. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

Team members pause for a photo after the successful harvest of half the Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. From right to left are Jeff Richards with Stinger-Ghaffarian Technologies; David Hanson, part of the principal investigator's team; Oscar Monje with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Engineering Services Contract; and John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with Kennedy's Test and Operations Support Contract. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, places Arabidopsis thaliana plants harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 into an Ultra-low Freezer chilled to -150 degrees Celsius. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, places Arabidopsis thaliana plants harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 into a Mini ColdBag that quickly freezes the plants. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, opens the door to the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 for a test harvest of half of the Arabidopsis thaliana plants growing within. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, uses a FluorPen to measure the chlorophyll fluorescence of Arabidopsis thaliana plants inside the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1. Half the plants were then harvested. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.

John "JC" Carver, a payload integration engineer with NASA Kennedy Space Center's Test and Operations Support Contract, opens the door to the growth chamber of the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) Flight Unit No. 1 for a test harvest of half of the Arabidopsis thaliana plants growing within. The harvest is part of an ongoing verification test of the APH unit, which is located inside the International Space Station Environmental Simulator in Kennedy's Space Station Processing Facility. The APH undergoing testing at Kennedy is identical to one on the station and uses red, green and broad-spectrum white LED lights to grow plants in an environmentally controlled chamber. The seeds grown during the verification test will be grown on the station to help scientists understand how these plants adapt to spaceflight.
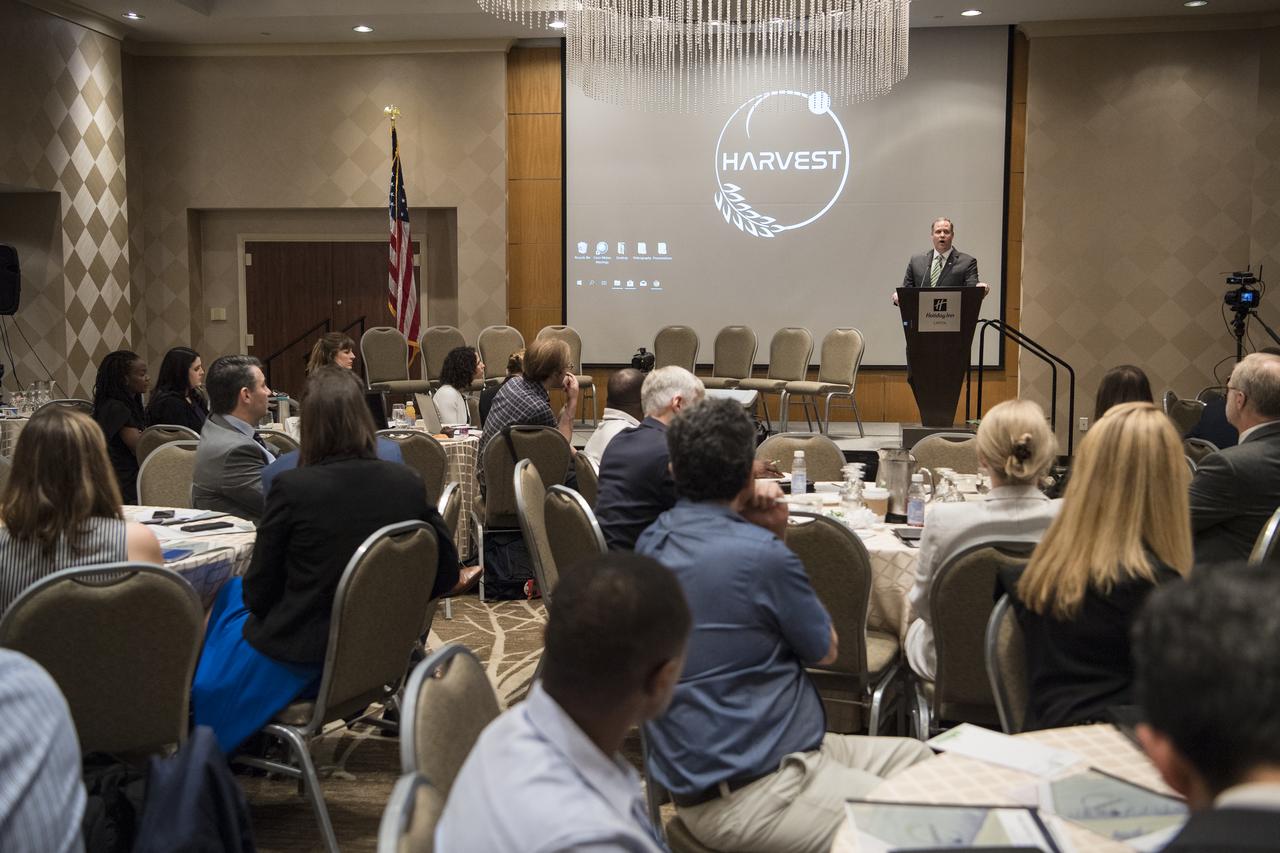

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks at the Harvest Outreach and Stakeholder Interaction Day, Tuesday, June 25, 2019, at the Holiday Inn in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks at the Harvest Outreach and Stakeholder Interaction Day, Tuesday, June 25, 2019, at the Holiday Inn in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
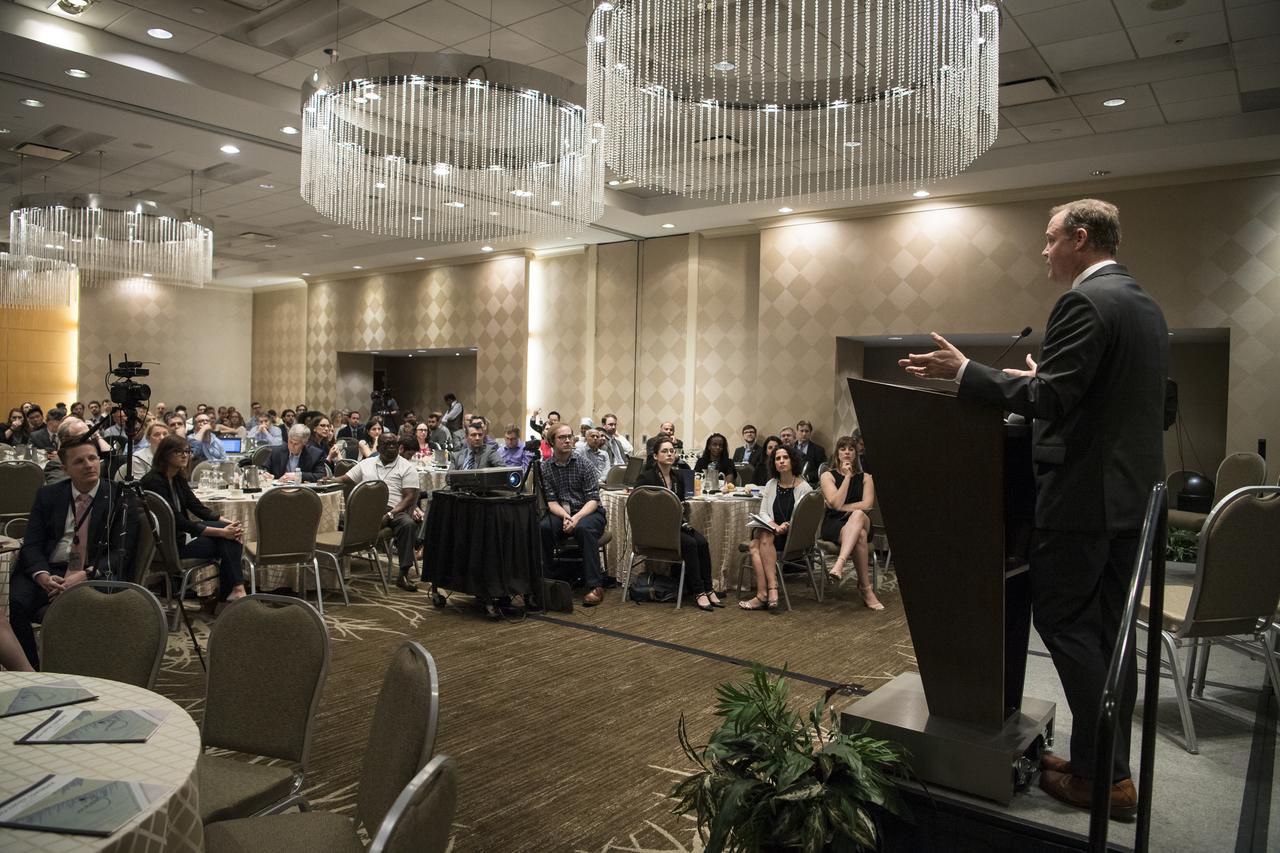

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks at the Harvest Outreach and Stakeholder Interaction Day, Tuesday, June 25, 2019, at the Holiday Inn in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
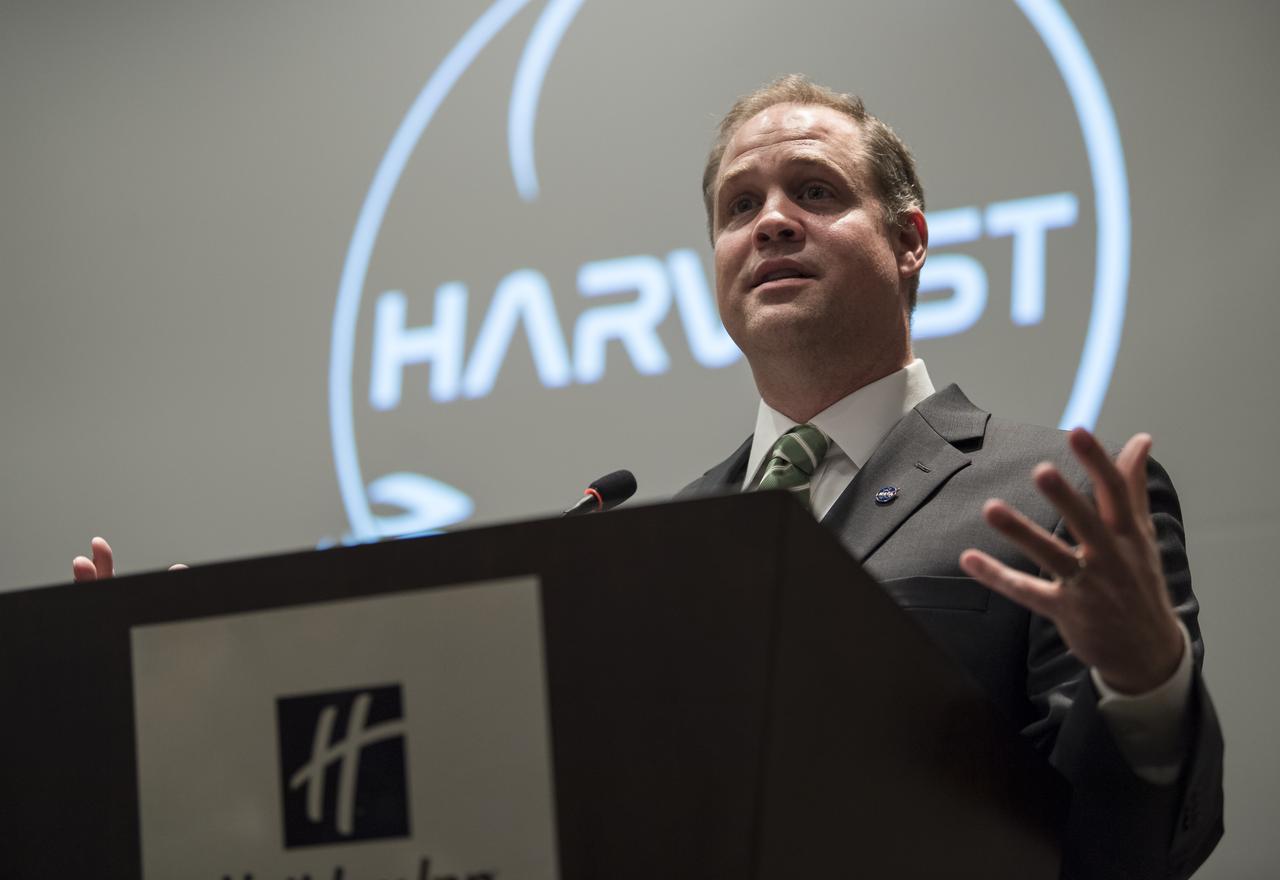

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks at the Harvest Outreach and Stakeholder Interaction Day, Tuesday, June 25, 2019, at the Holiday Inn in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
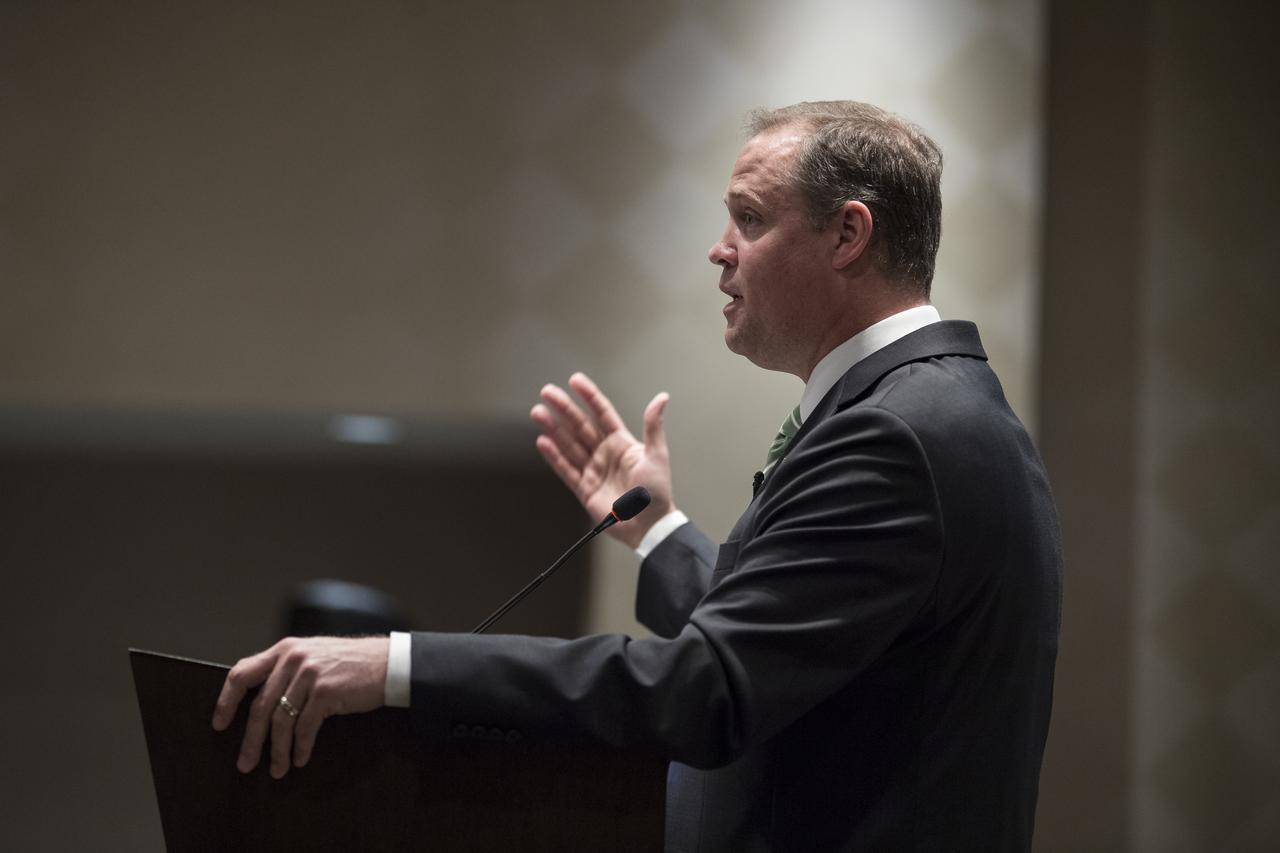

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine gives keynote remarks at the Harvest Outreach and Stakeholder Interaction Day, Tuesday, June 25, 2019, at the Holiday Inn in Washington. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
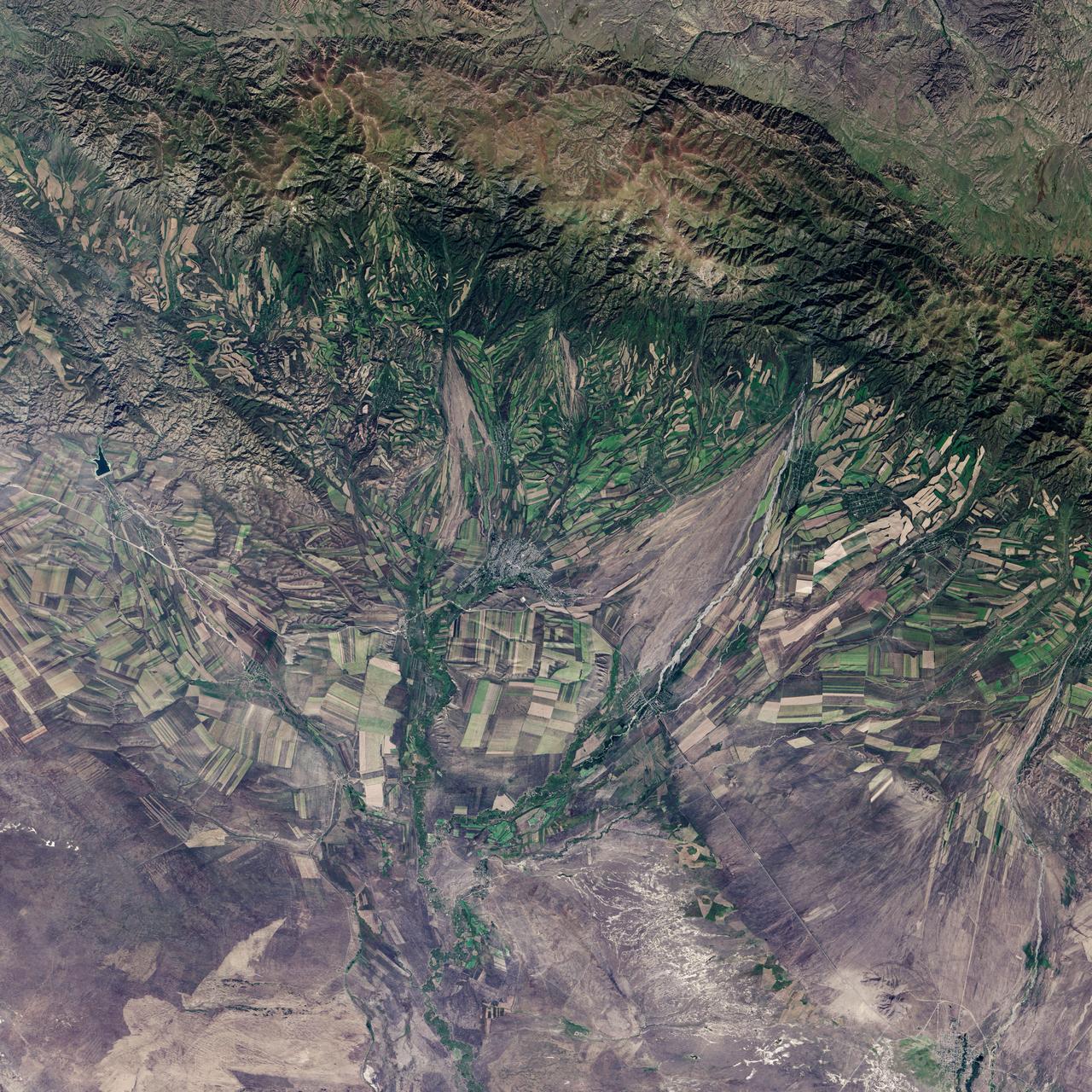

September 22, the autumnal equinox, marks the beginning of fall in the Northern Hemisphere, but the fall harvest begins early in the harsh continental climate of eastern Kazakhstan. By September 9, 2013, when the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on the Landsat 8 satellite acquired this image, several fields were already harvested and bare. Others were dark green with pasture grasses or ripening crops. The fields fill the contours of the land, running long and narrow down mountain valleys and spreading in large squares over the plains. Agriculture is an important segment of the economy in Kazakhstan: the country’s dry climate is ideal for producing high quality wheat for export. However, 61 percent of the country’s agricultural land is pasture for livestock. The area shown in this image, far eastern Kazakhstan near the Chinese border, is a minor wheat-growing region and may also produce sunflowers, barley, and other food crops. An artifact of Soviet-era collective farms, most of the farms in Kazakhstan are large, covering more than 5,000 hectares (12,500 acres). Some of the larger fields in the image reflect the big business side of agriculture. However, family farms and small agriculture businesses account for 35 percent of the country’s agricultural production, and some of these are visible as well, particularly in the uneven hills and mountains. Nearly all agriculture in Kazakhstan is rain fed. Farmers in this region have designed their fields to take advantage of rain flowing down hills, allowing the natural shape of the land to channel water to crops. The effect is a mosaic of green and tan with tones matching the natural vegetation in the mountains to the north. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey. Caption by Holli Riebeek. Instrument: Landsat 8 - OLI More info: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/16IZ047" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/16IZ047</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
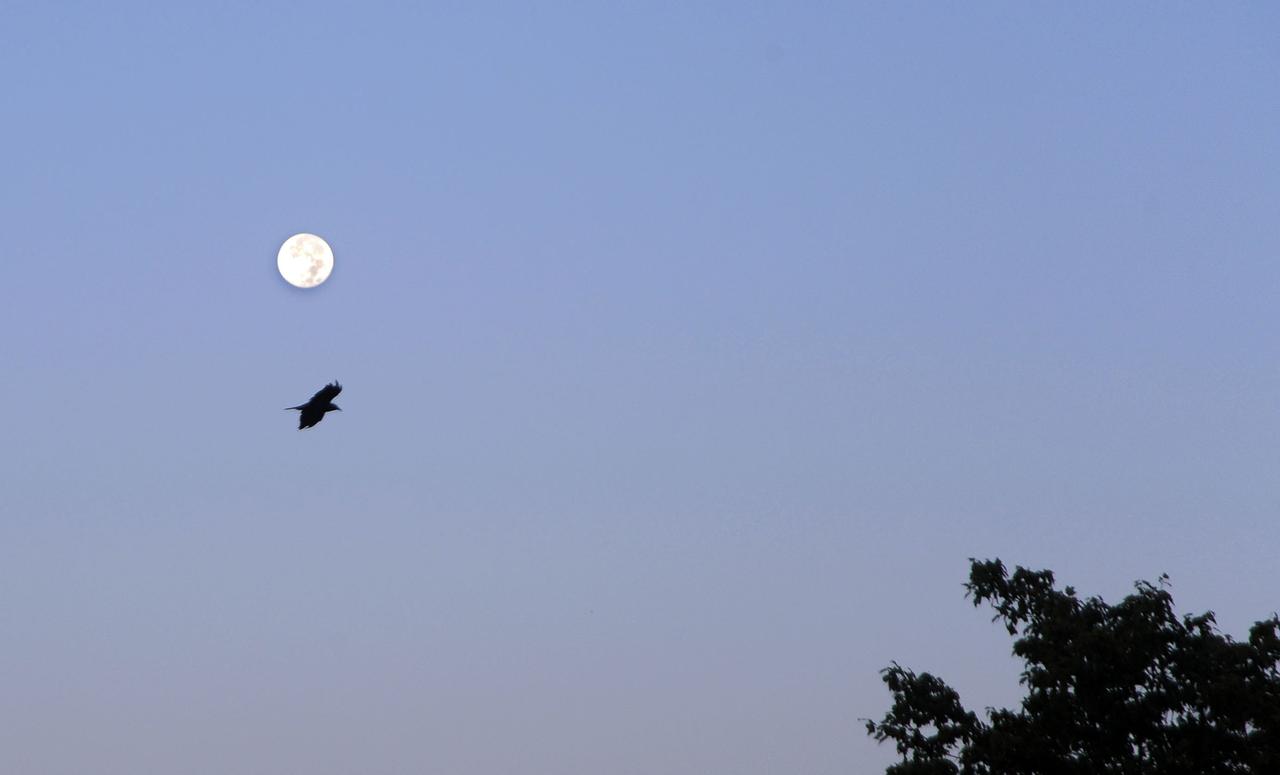

September's Harvest Moon as seen around NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. According to folklore, every full Moon has a special name. There's the Wolf Moon, the Snow Moon, the Worm Moon, the Sprouting Grass Moon, the Flower Moon, the Strawberry Moon, the Thunder Moon, the Sturgeon Moon, the Harvest Moon, the Hunter's Moon, the Beaver Moon, and the Long Night's Moon. Each name tells us something about the season or month in which the full Moon appears. This month's full Moon is the Harvest Moon. More about the Harvest Moon from NASA: Science <a href="http://1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Debbie Mccallum <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
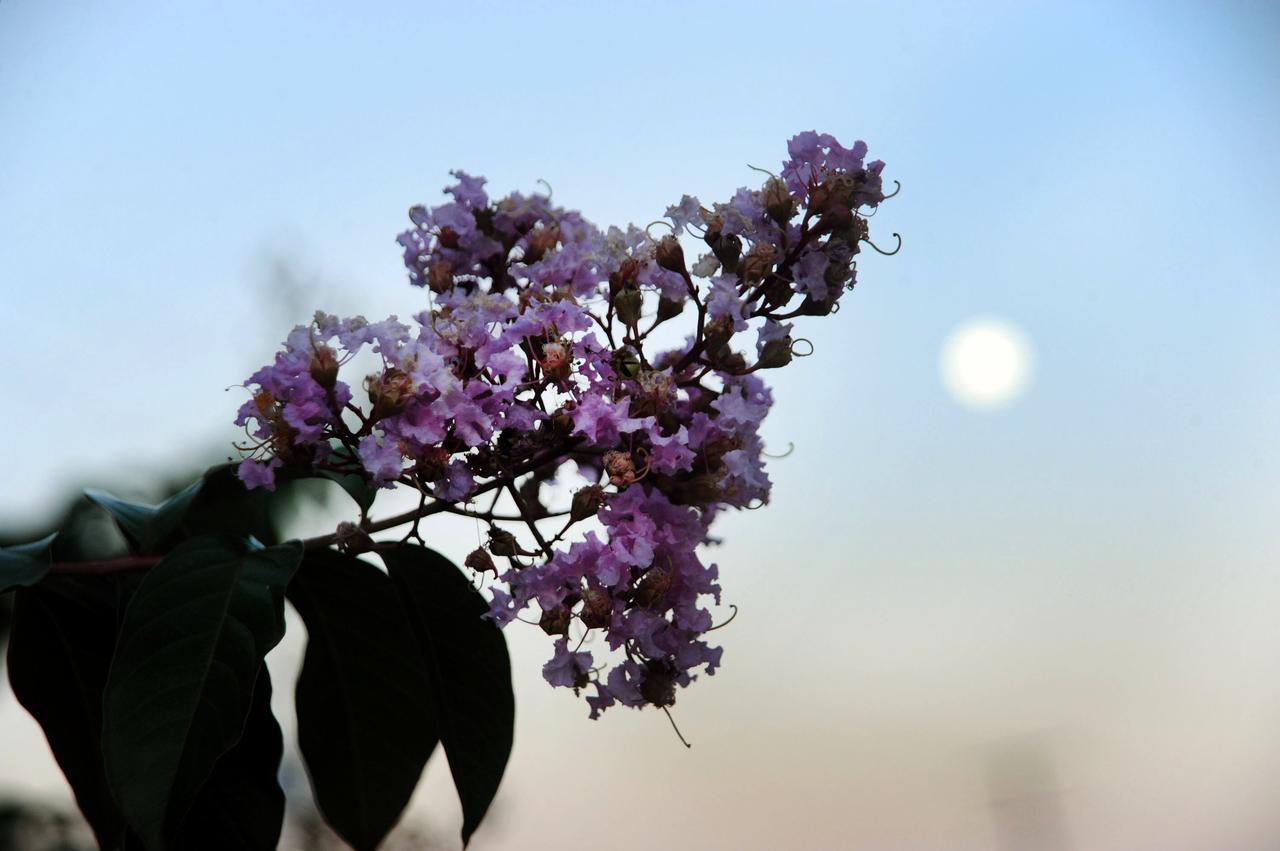

September's Harvest Moon as seen around NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. According to folklore, every full Moon has a special name. There's the Wolf Moon, the Snow Moon, the Worm Moon, the Sprouting Grass Moon, the Flower Moon, the Strawberry Moon, the Thunder Moon, the Sturgeon Moon, the Harvest Moon, the Hunter's Moon, the Beaver Moon, and the Long Night's Moon. Each name tells us something about the season or month in which the full Moon appears. This month's full Moon is the Harvest Moon. More about the Harvest Moon from NASA: Science <a href="http://1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Debbie Mccallum <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
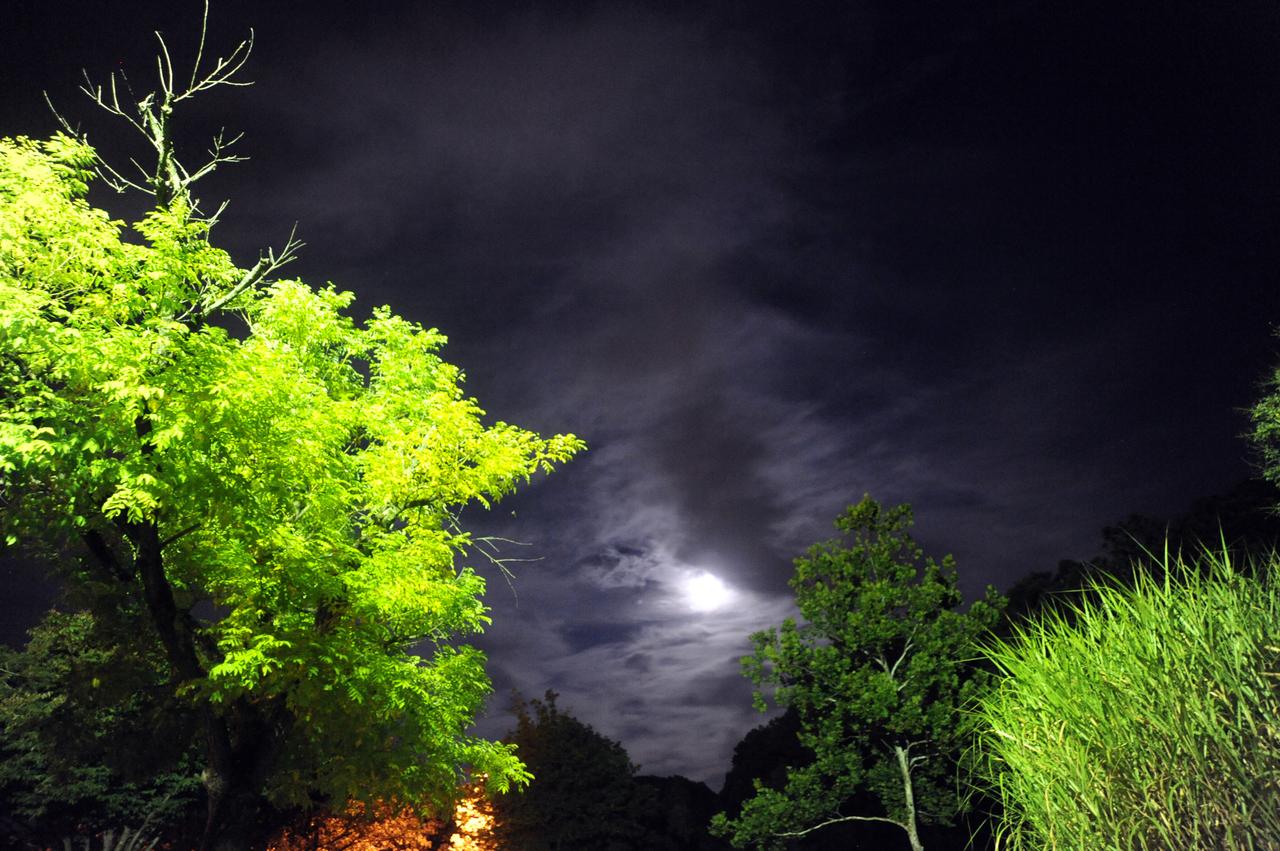

September's Harvest Moon as seen around NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. According to folklore, every full Moon has a special name. There's the Wolf Moon, the Snow Moon, the Worm Moon, the Sprouting Grass Moon, the Flower Moon, the Strawberry Moon, the Thunder Moon, the Sturgeon Moon, the Harvest Moon, the Hunter's Moon, the Beaver Moon, and the Long Night's Moon. Each name tells us something about the season or month in which the full Moon appears. This month's full Moon is the Harvest Moon. More about the Harvest Moon from NASA: Science <a href="http://1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/16lb1eZ</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Debbie Mccallum <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
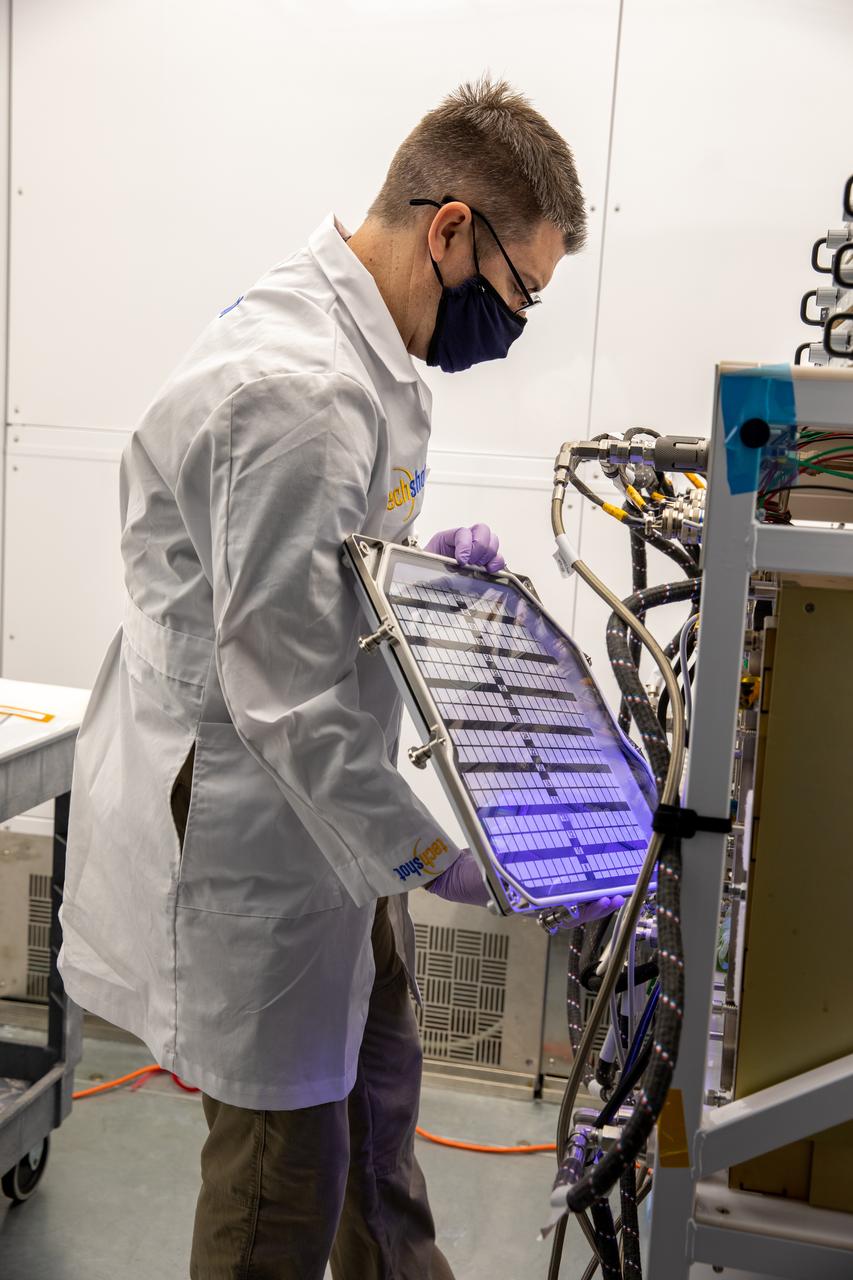

A researcher prepares to harvest radishes grown in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, which also involves growing two radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
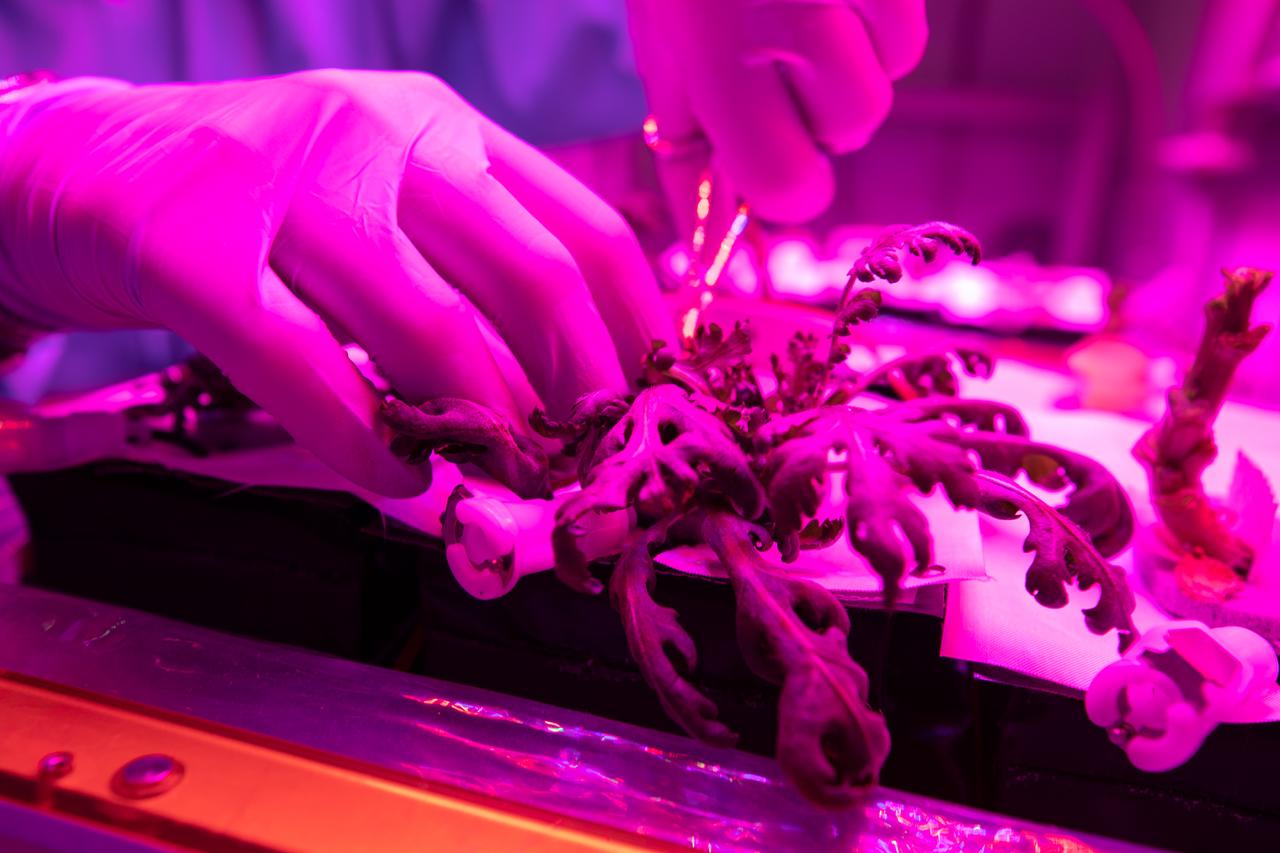

Test crops are harvested inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT) to study their potential to grow in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
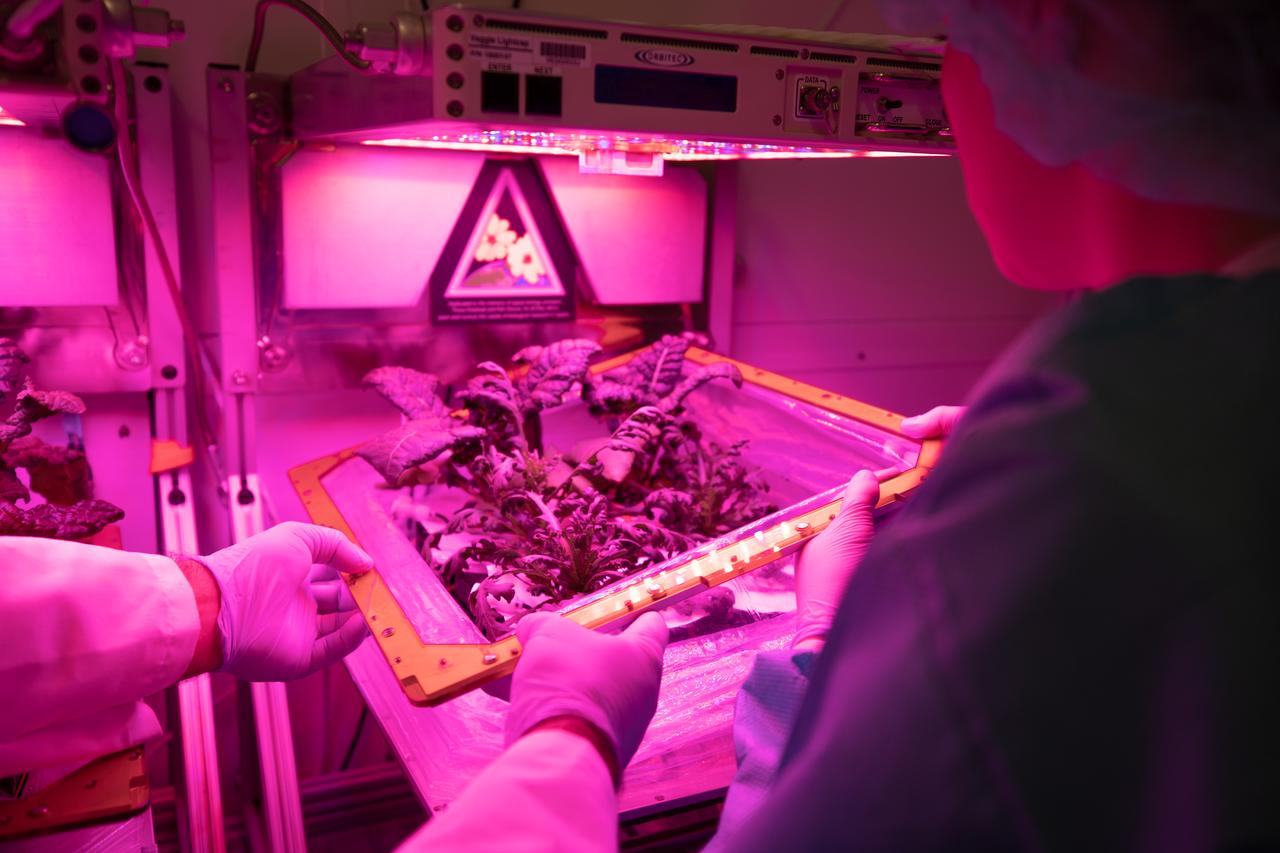

Kennedy Space Center employees harvest test crops inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT) to study their potential to grown in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
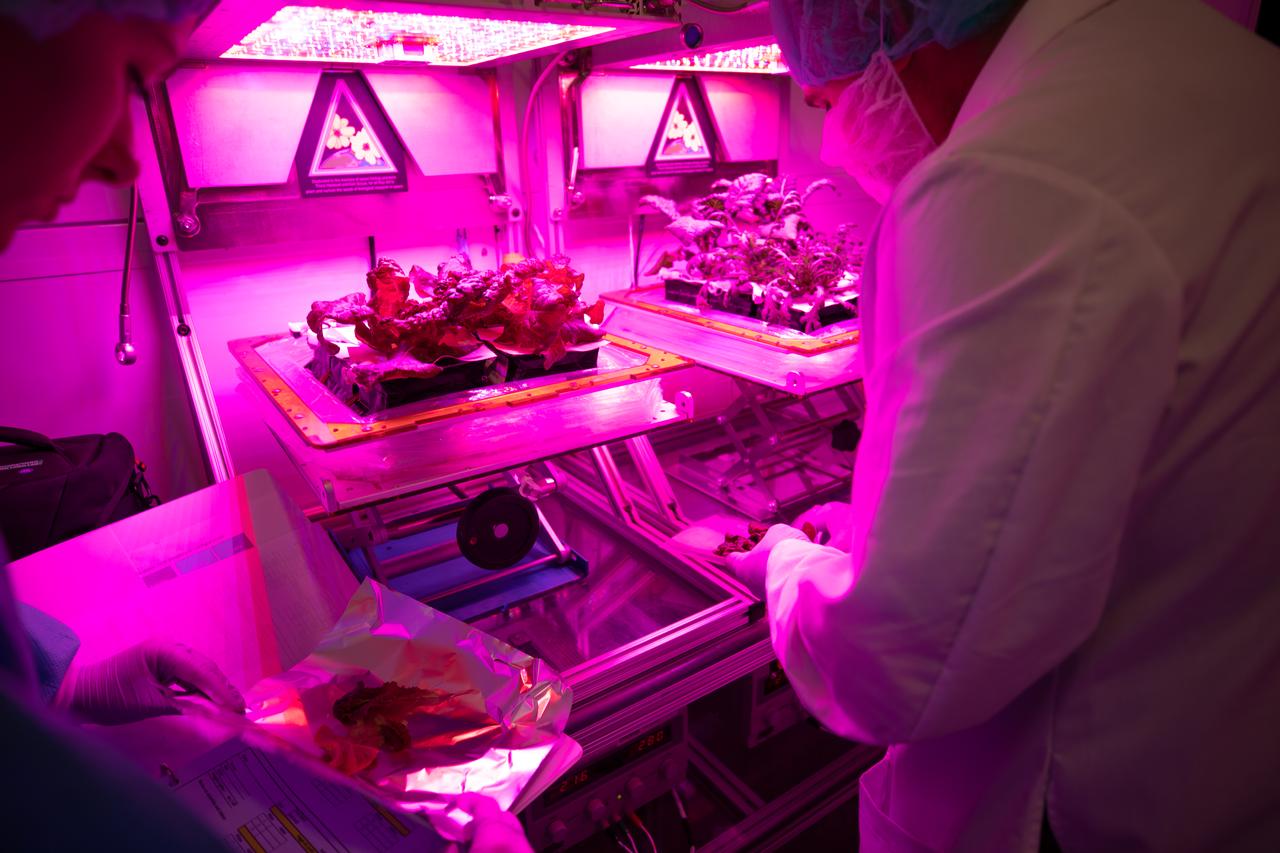

Kennedy Space Center Veggie Project Manager Trent Smith harvests test crops inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Florida spaceport’s Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT) to study their potential to grown in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
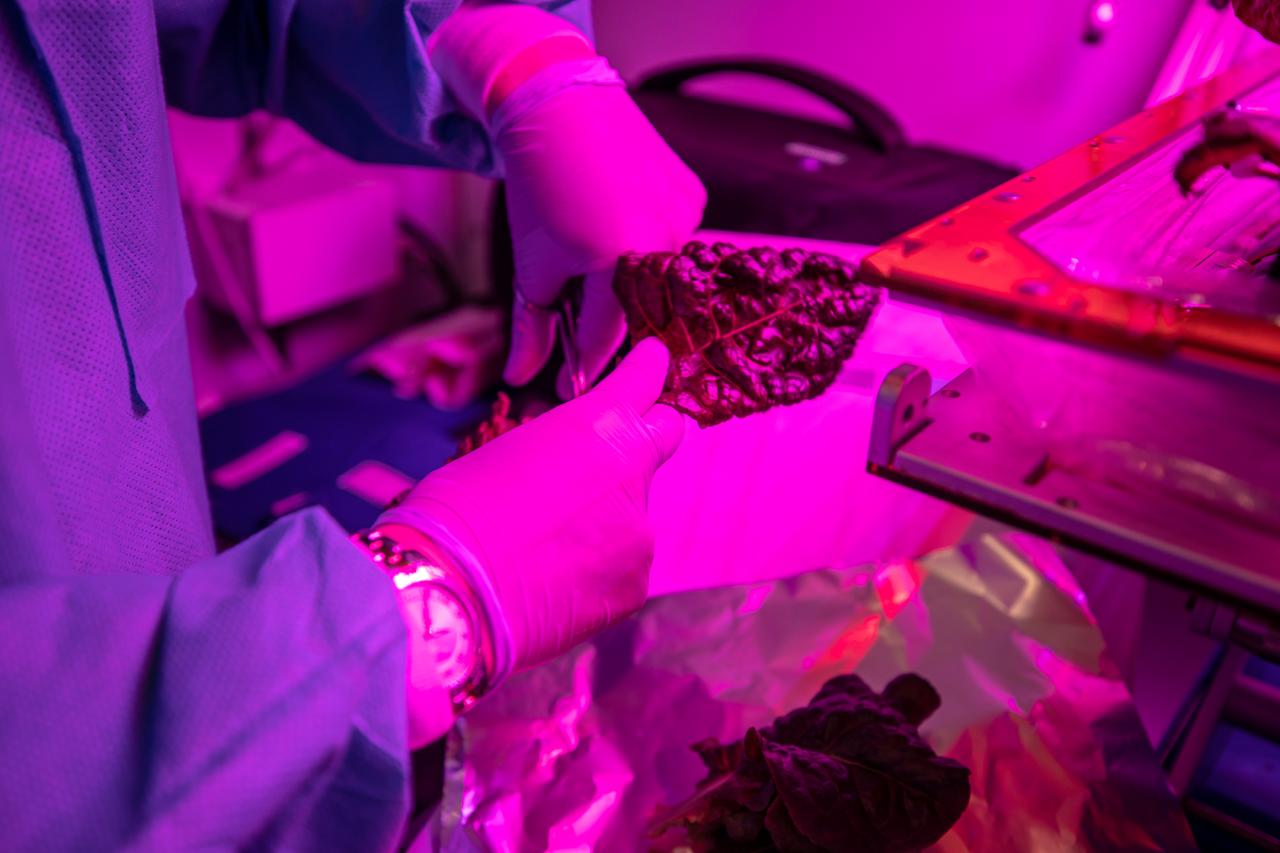

Test crops are harvested inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT) to study their potential to grow in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
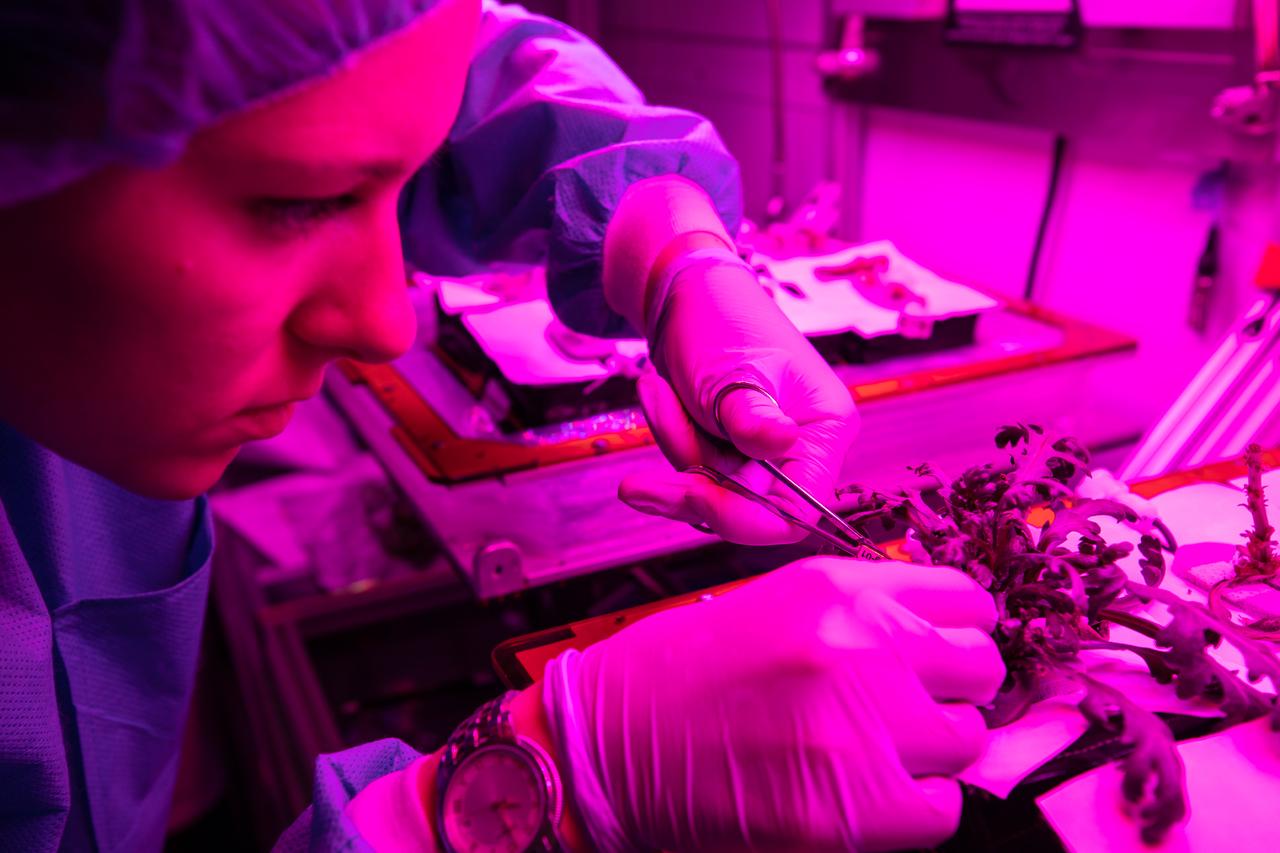

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests shungiku – an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). The SVT included the harvest of two other plant cultivars – amara mustard and ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce – and will study their potential to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
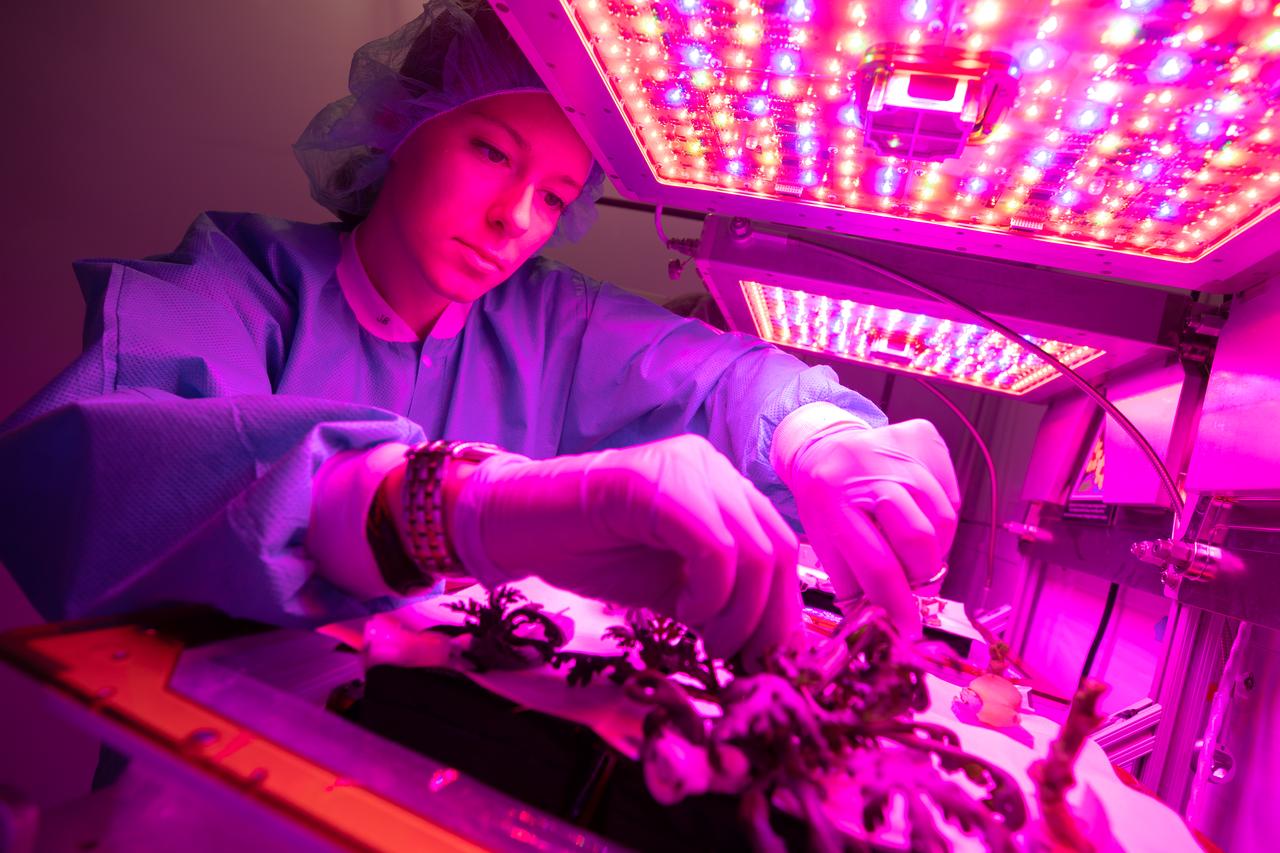

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests shungiku – an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). The SVT included the harvest of two other plant cultivars – amara mustard and ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce – and will study their potential to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
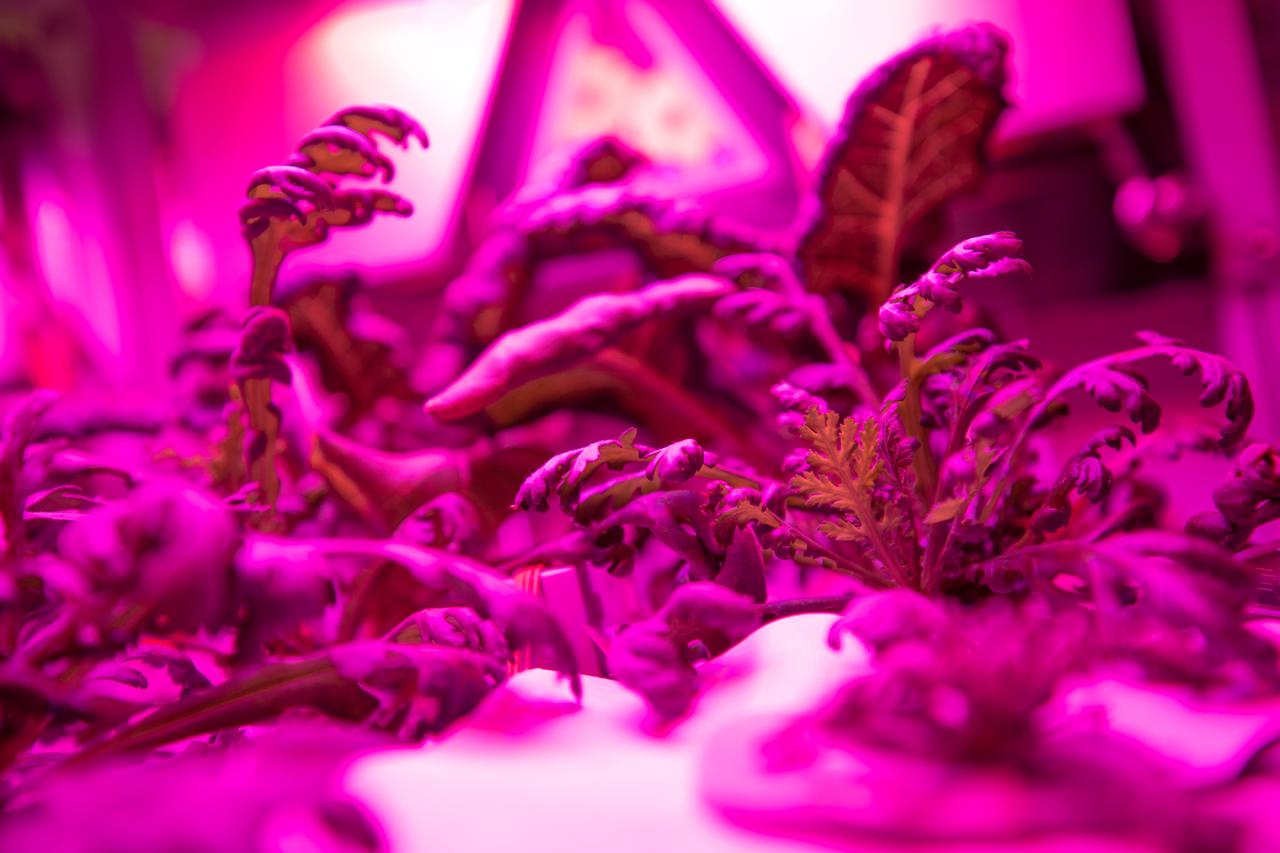

Three crops grown under a test condition representative of the International Space Station are photographed moments before harvest for a science verification test (SVT) in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2019. The SVT will study the potential of the three plant cultivars to grow in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
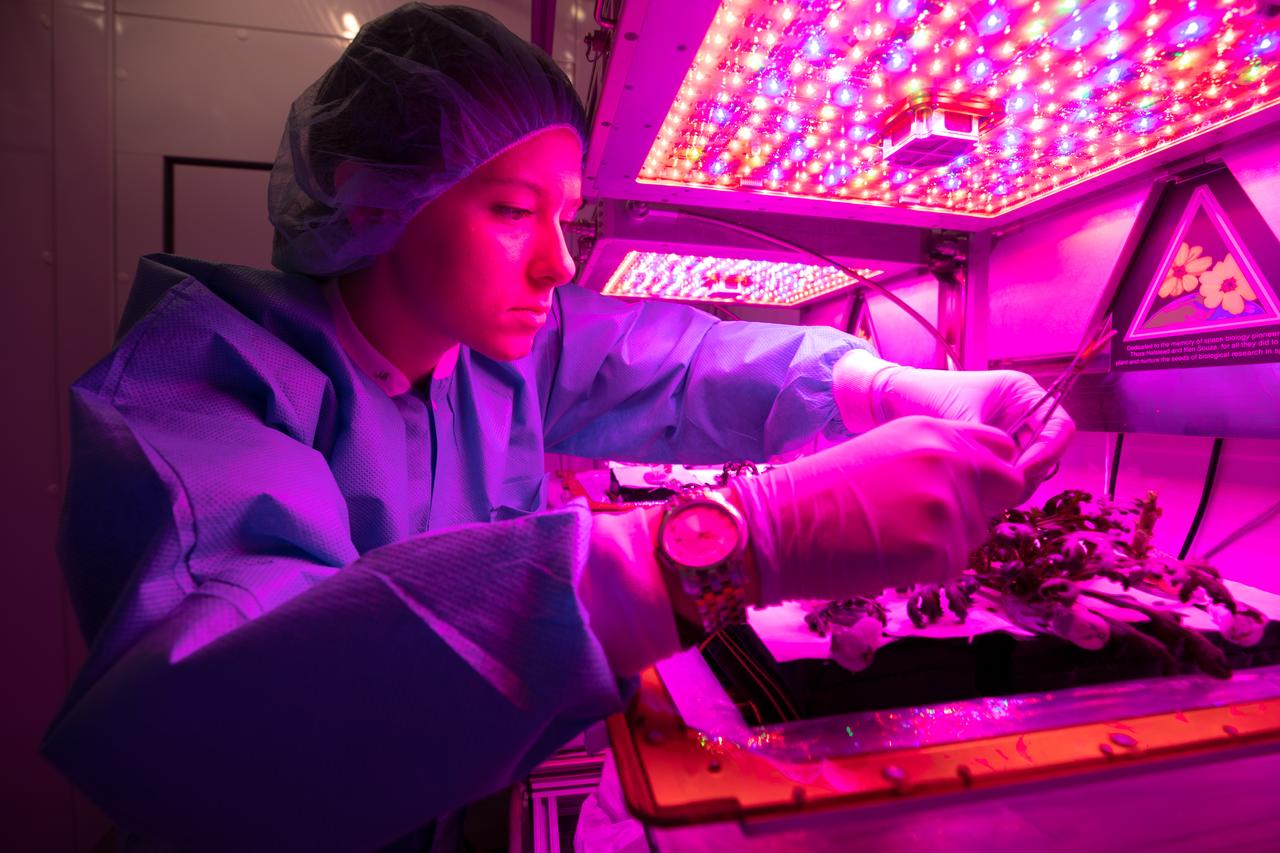

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests shungiku – an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). The SVT included the harvest of two other plant cultivars – amara mustard and ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce – and will study their potential to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
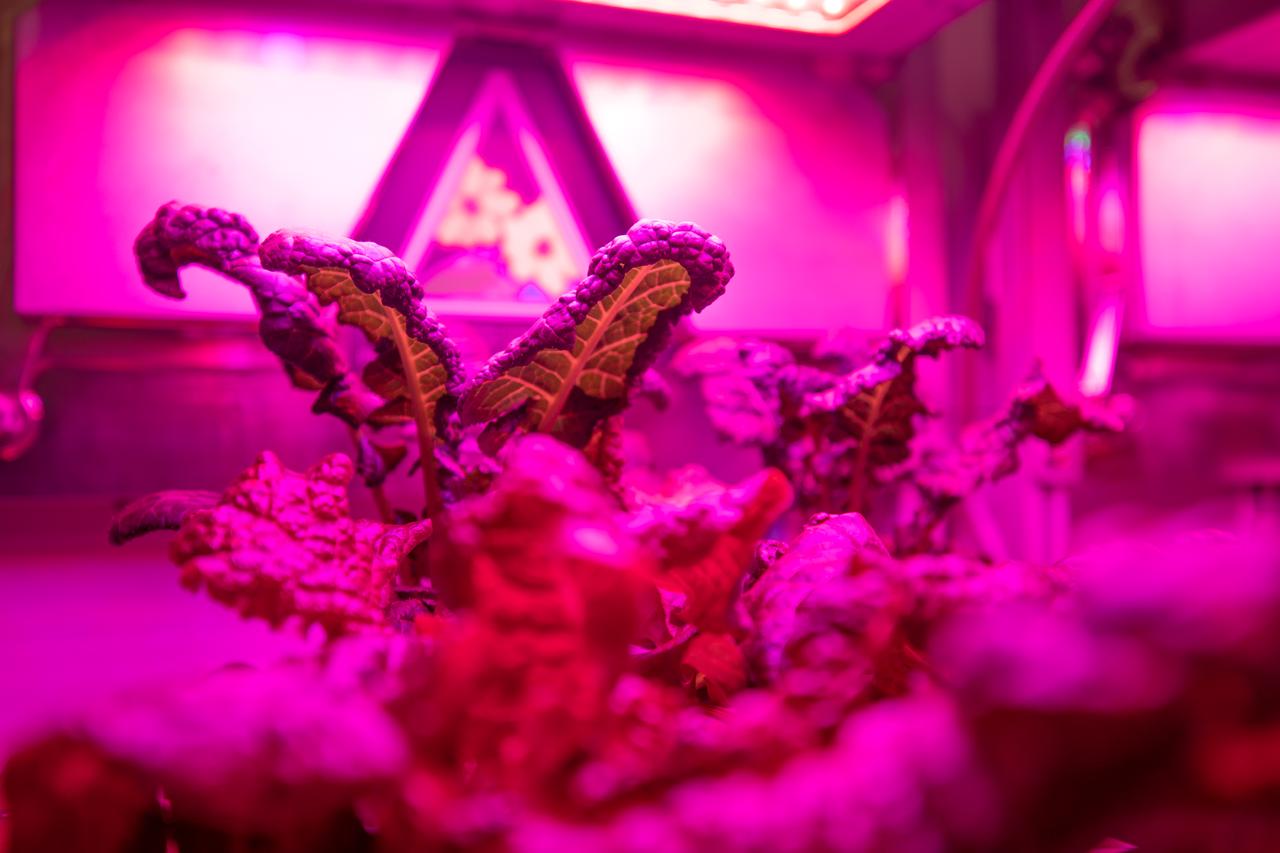

Three crops grown under a test condition representative of the International Space Station are photographed moments before harvest for a science verification test (SVT) in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2019. The SVT will study the potential of the three plant cultivars to grow in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
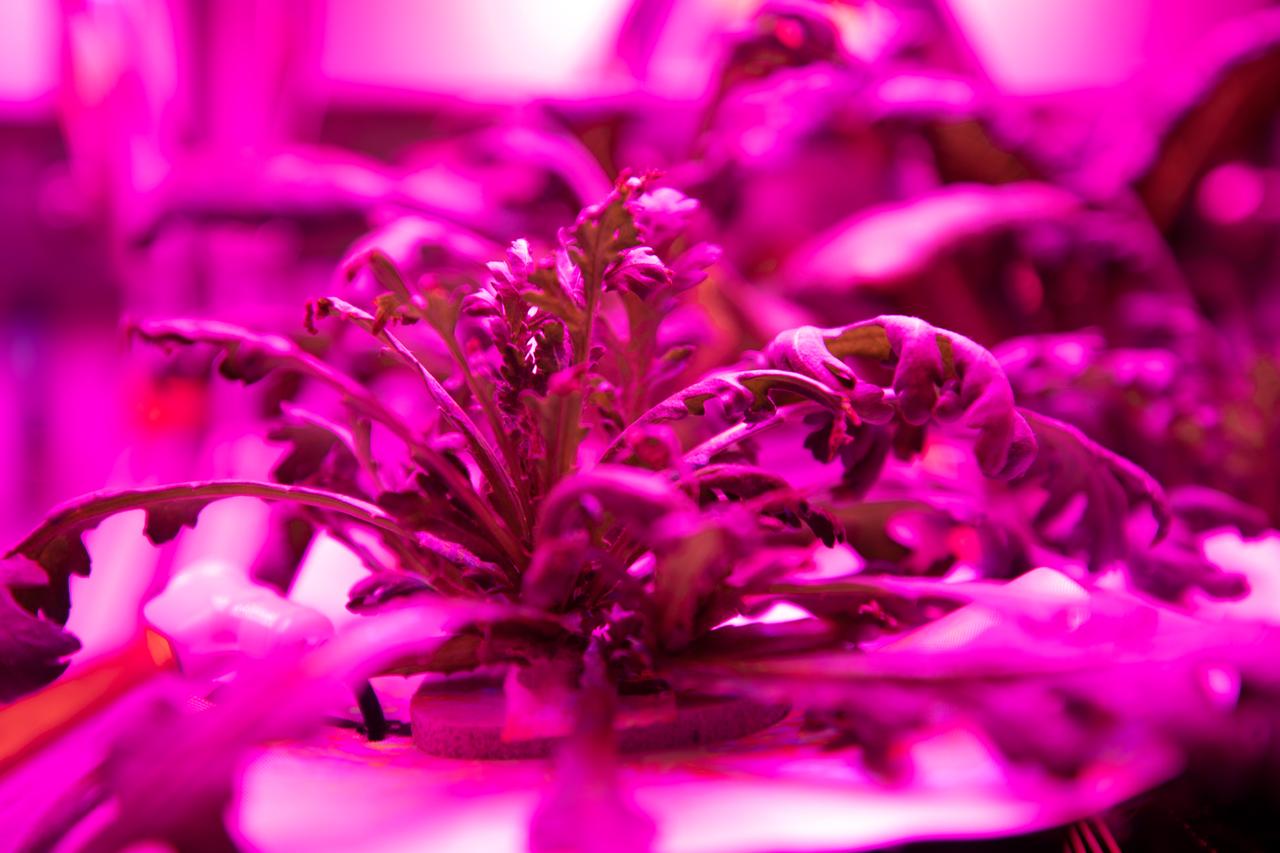

Three crops grown under a test condition representative of the International Space Station are photographed moments before harvest for a science verification test (SVT) in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 30, 2019. The SVT will study the potential of the three plant cultivars to grow in space. The harvest included ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce, which has been grown in space before, and two new plant cultivars – amara mustard and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
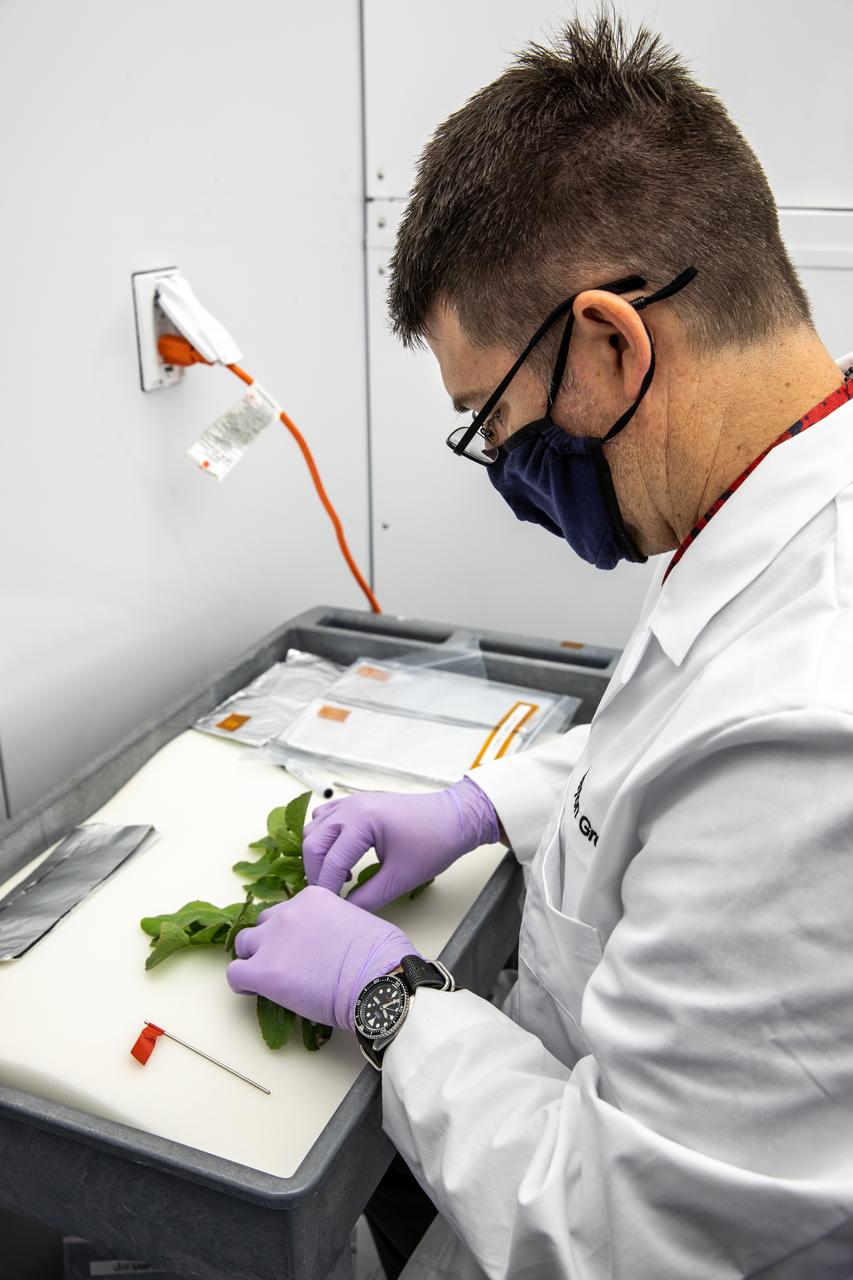

A research scientist collects measurements of radishes harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, which also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
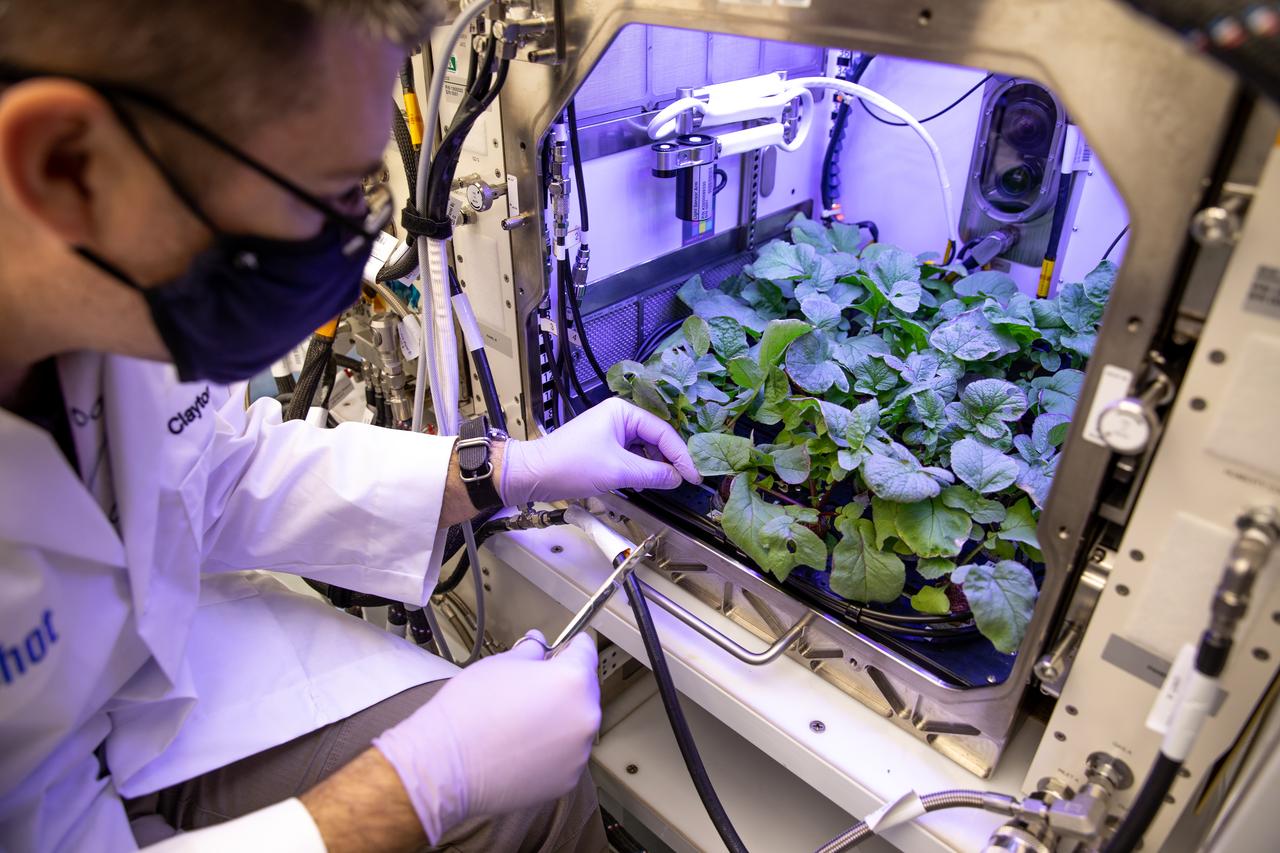

A research scientist harvests radishes grown in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.

A researcher takes measurements of a radish crop harvested from the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, which also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
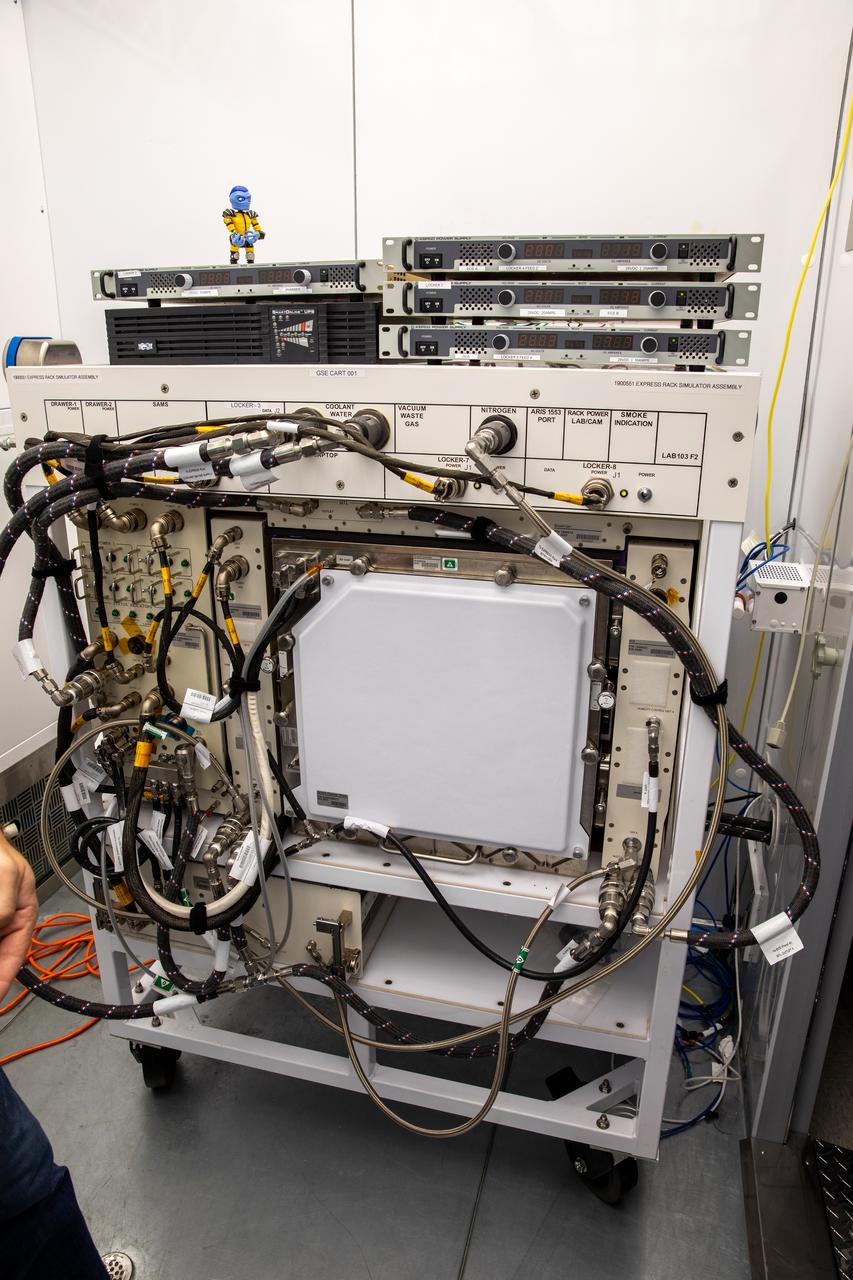

In view is the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. Part of the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, a ground control crop of radishes was grown at Kennedy and harvested on Dec. 14. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
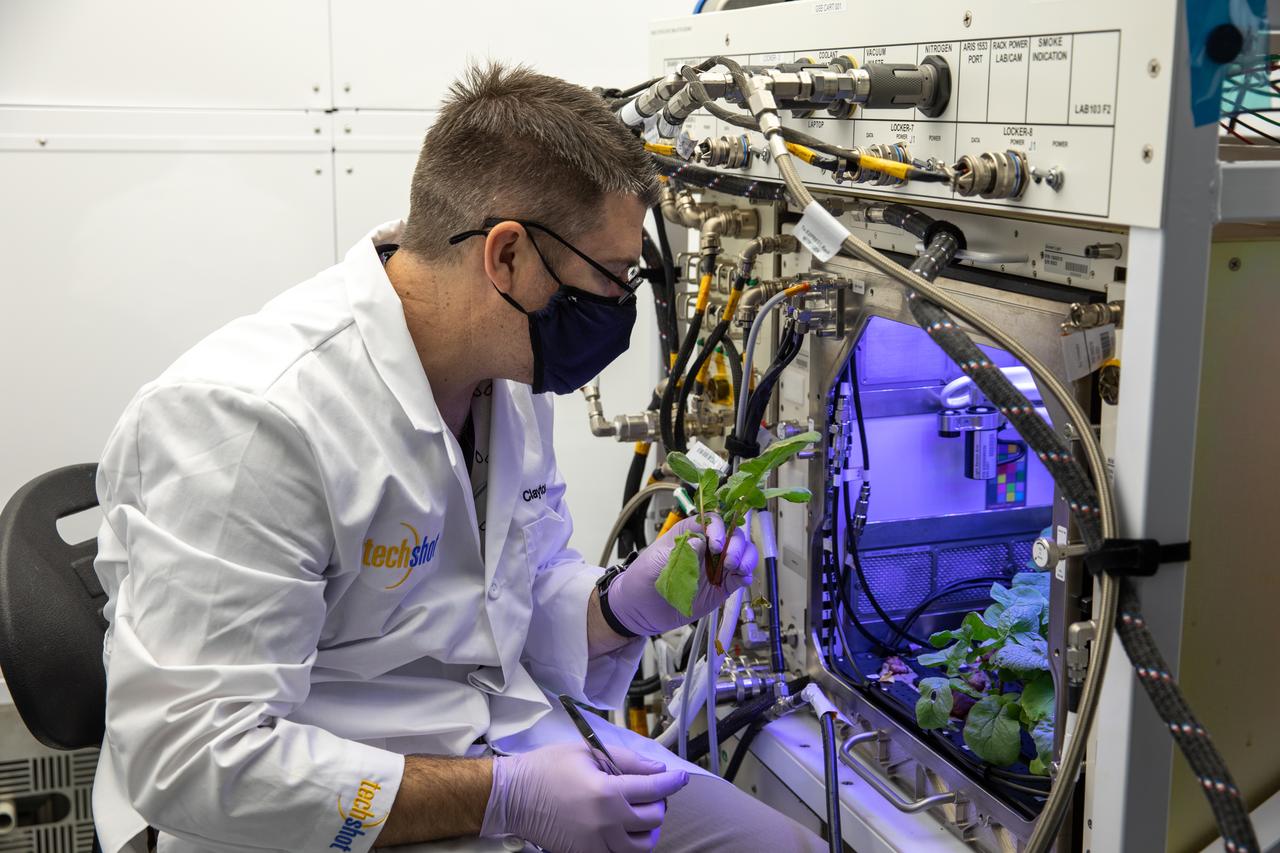

A research scientist harvests radishes grown in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
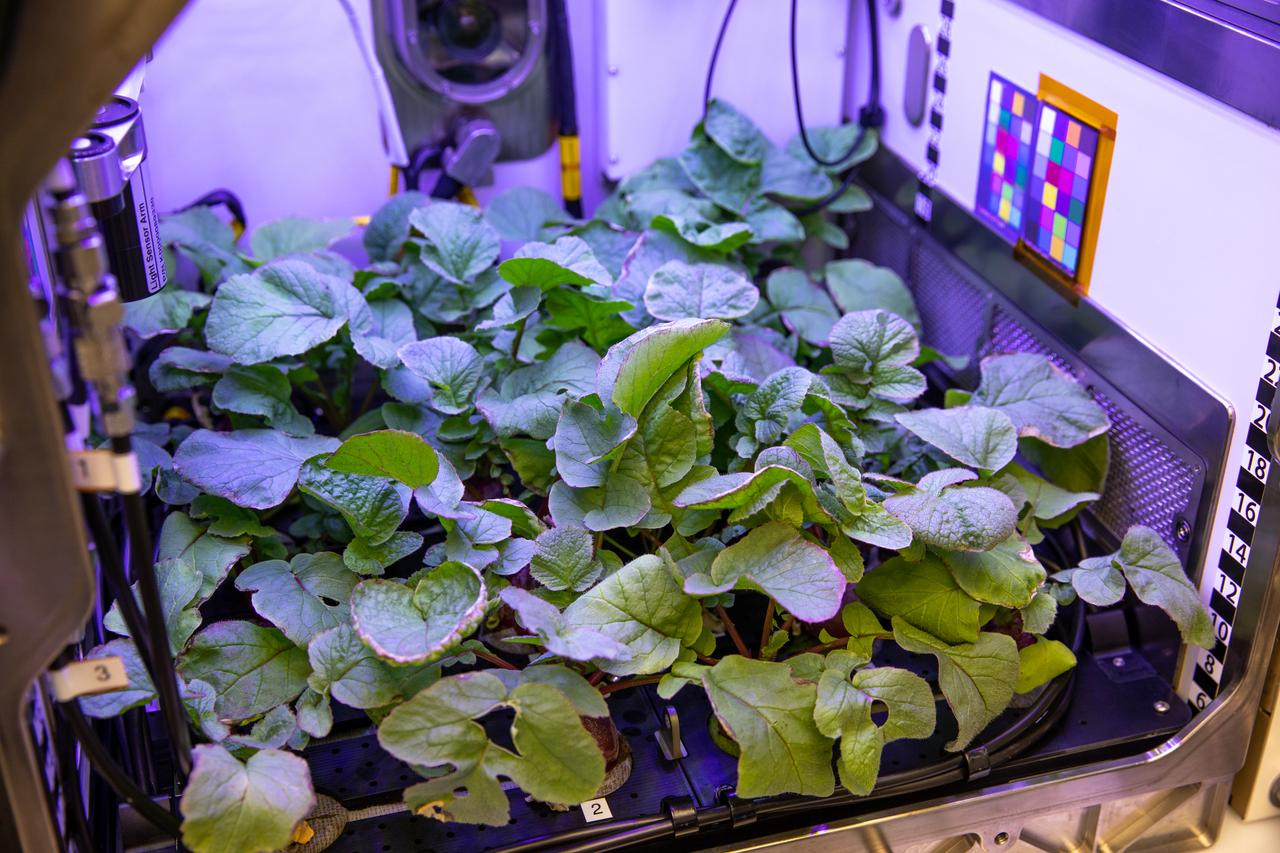

A view of radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
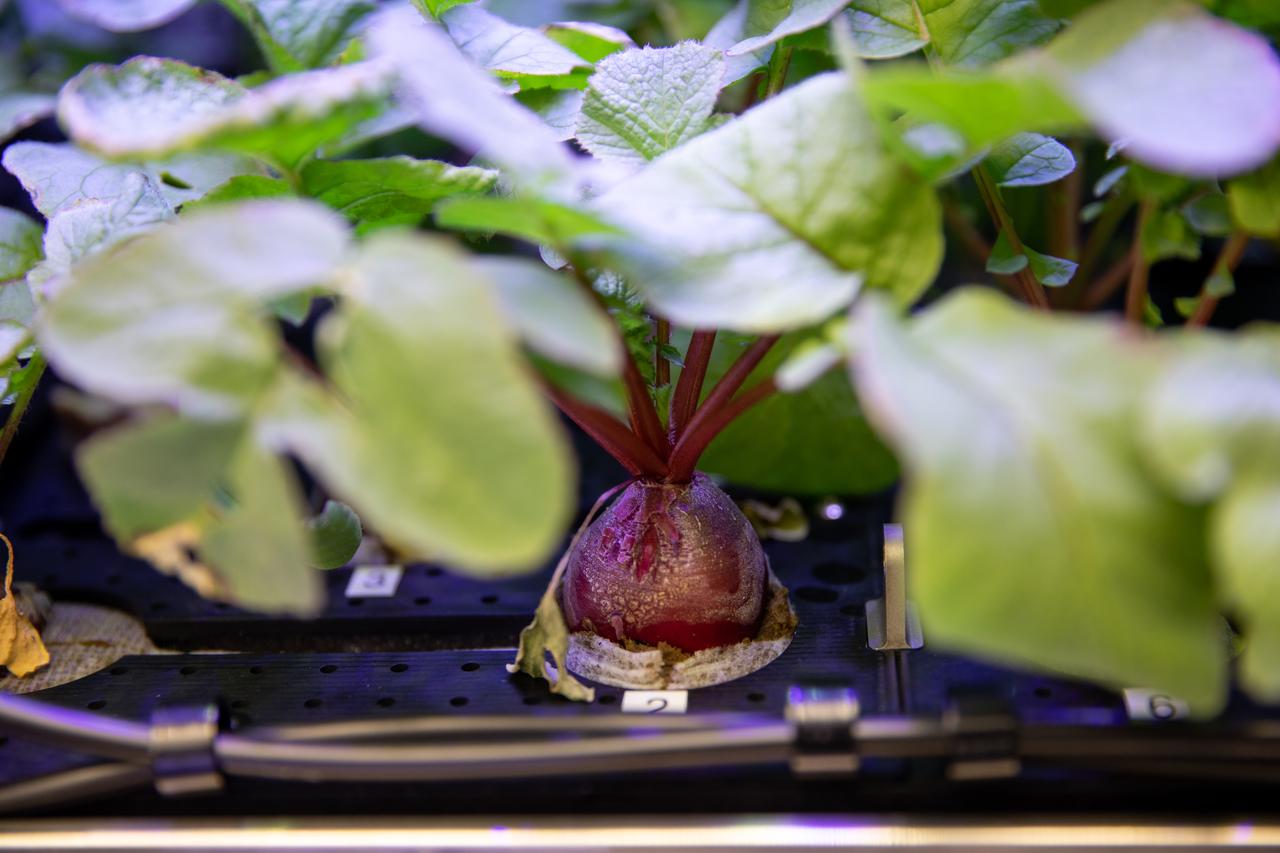

A view of radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
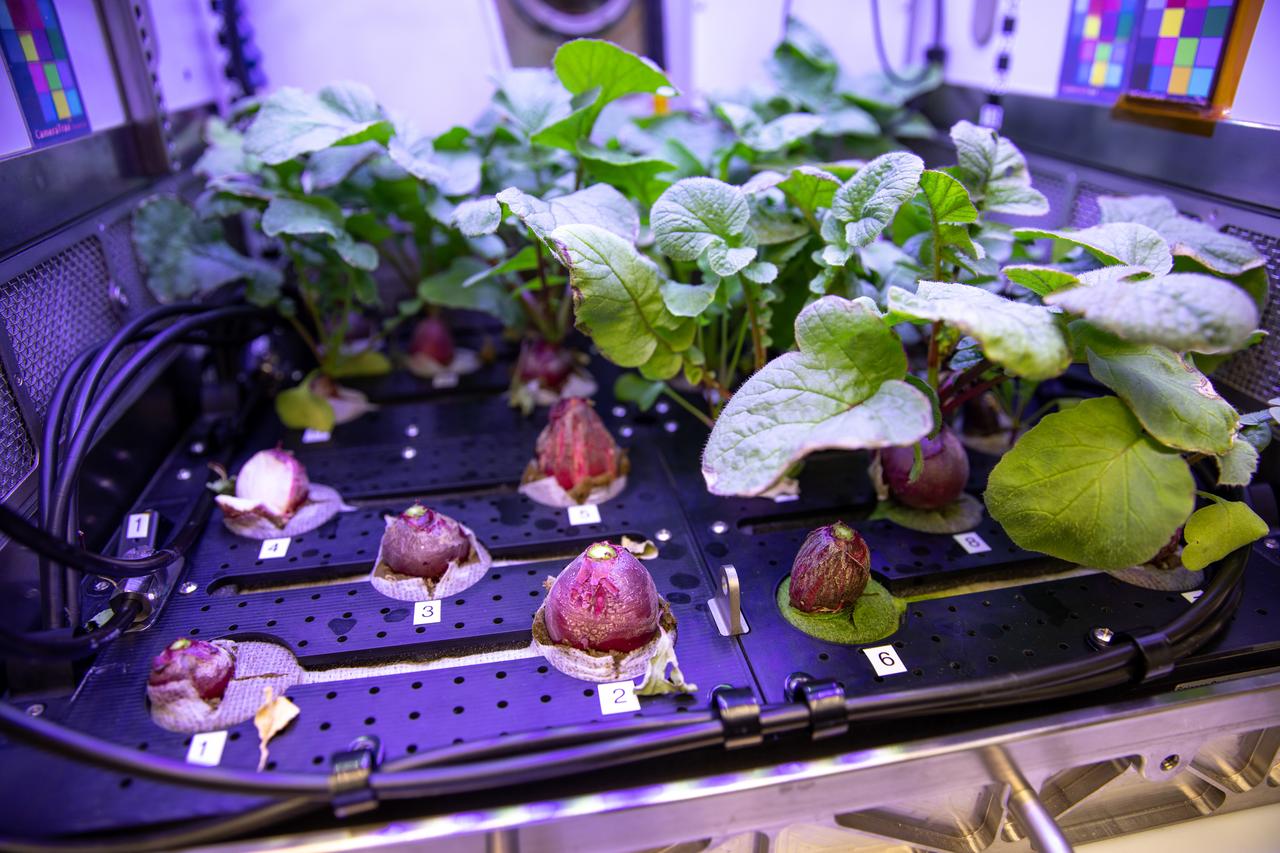

A view of radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
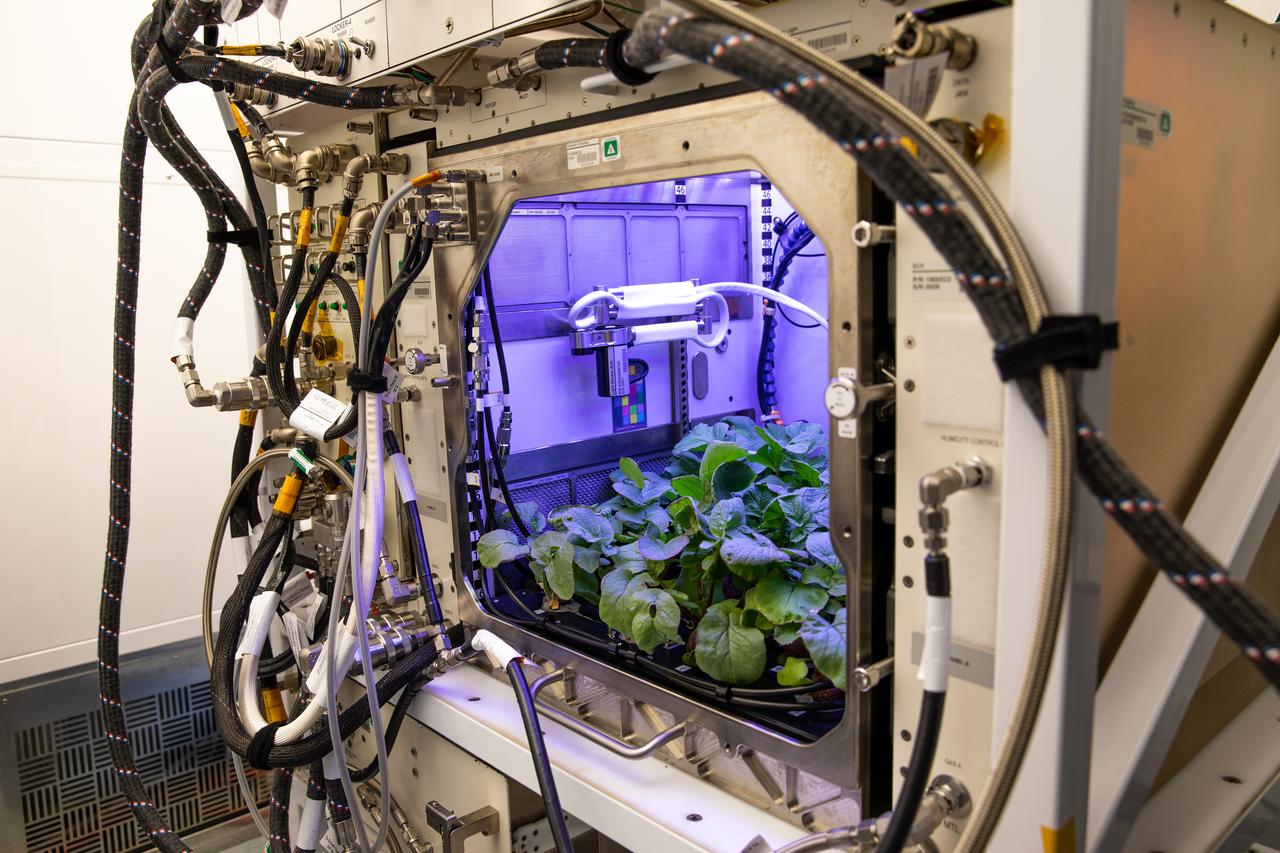

A view of radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, which also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
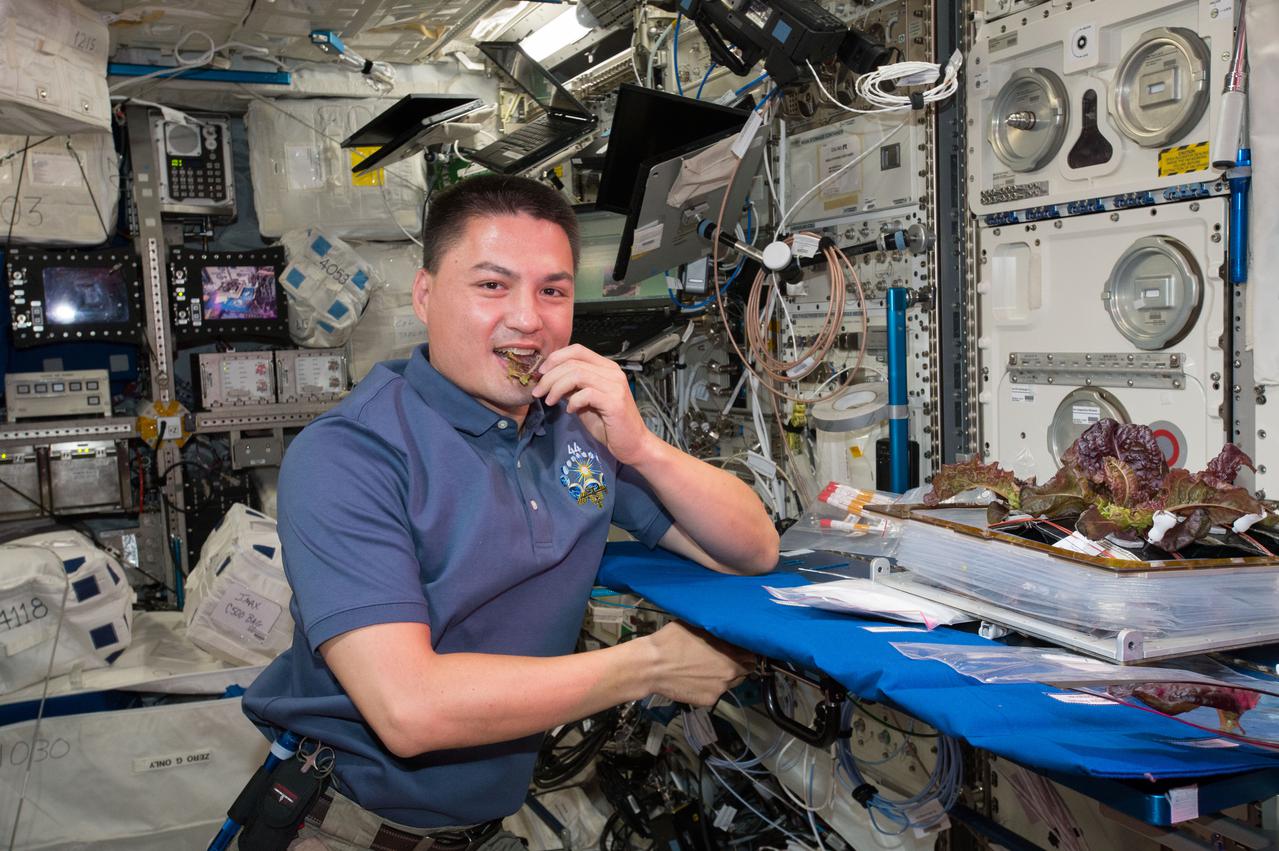

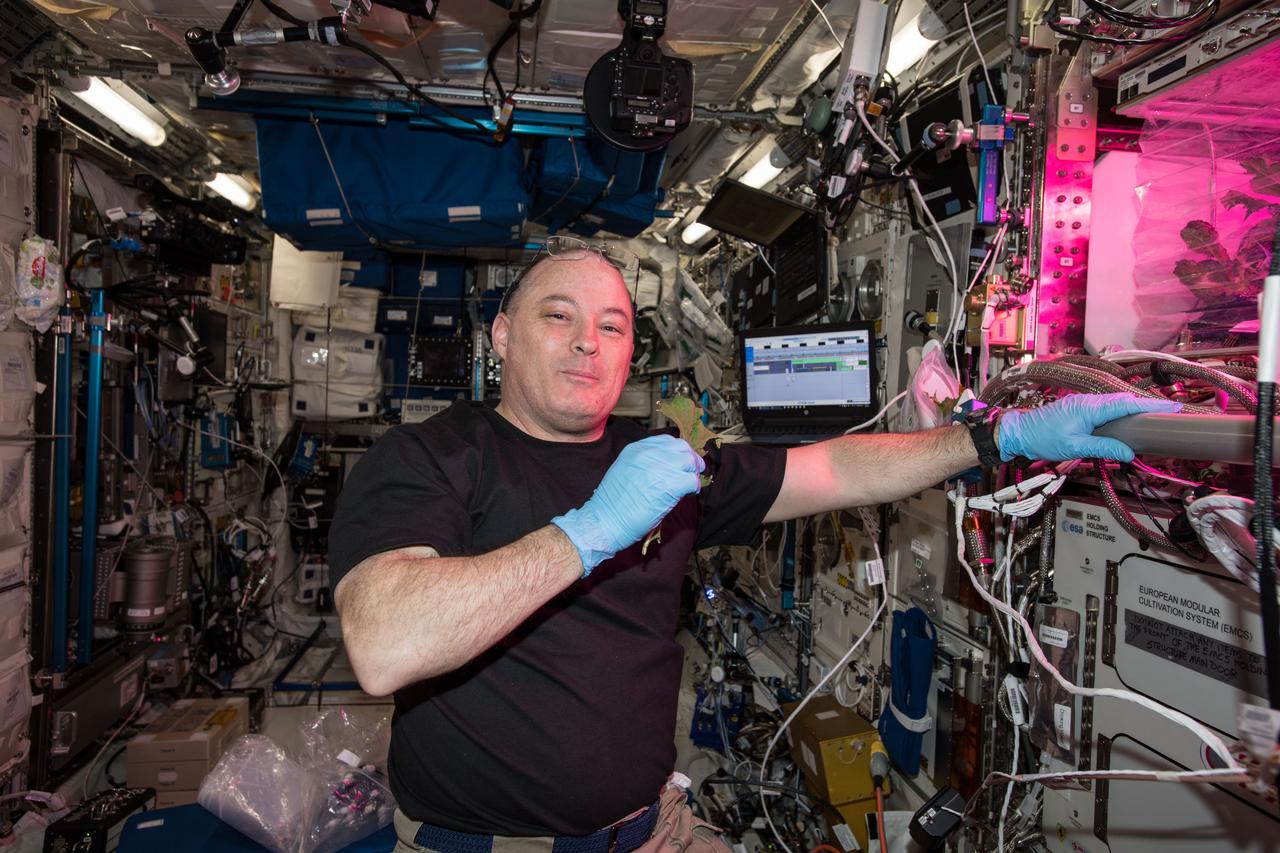
NASA Astronaut Kjell Lindgren takes a bite of plants harvested for the VEG-01 investigation. He harvested them on the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) in the Node 2/Harmony.
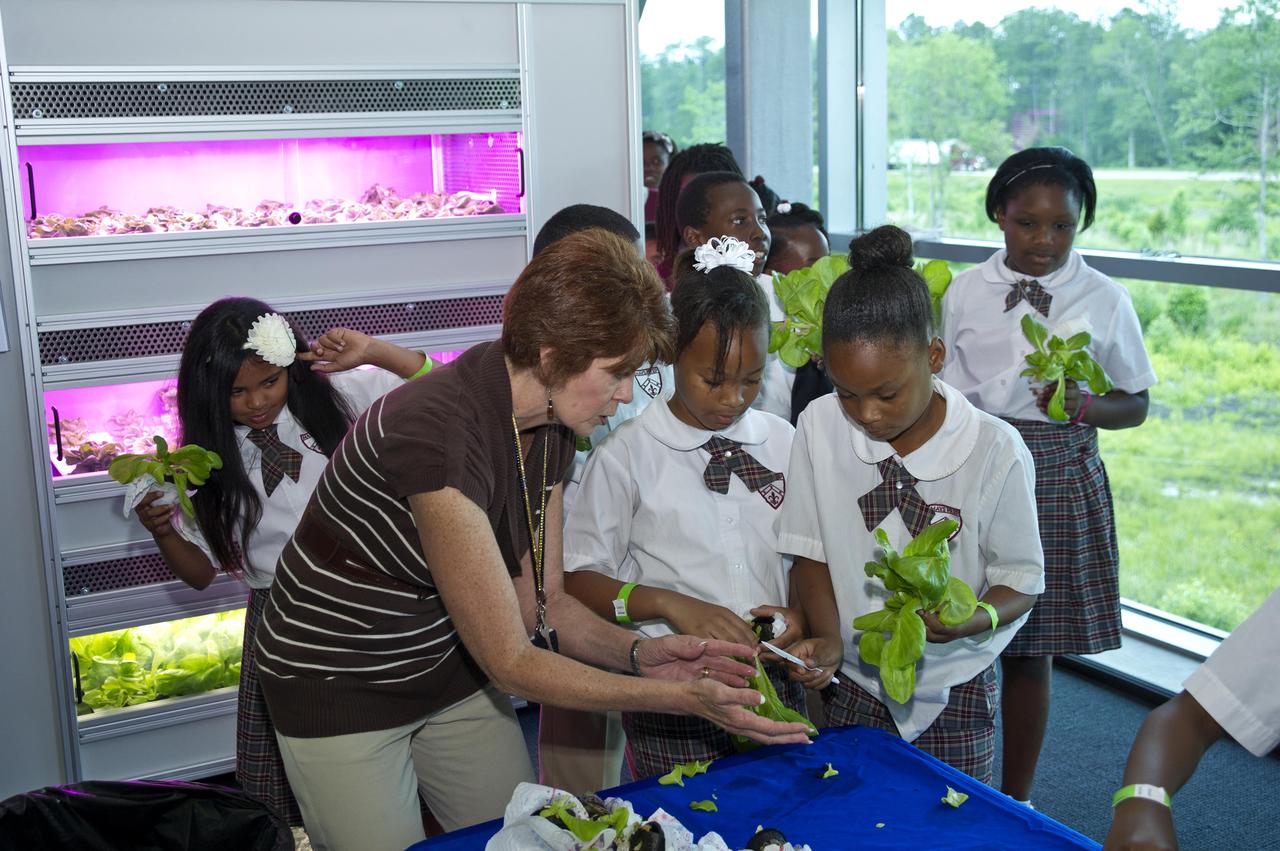

Janice Hueschen of Innovative Imaging & Research Corp. at Stennis Space Center helps students from Benjamin E. Mays Preparatory School in New Orleans harvest lettuce at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility May 7, 2012. The Louisiana students assisted in the first harvest of lettuce from the Controlled Environment Agriculture unit, which uses an aeroponic process that involves no soil and advance LED lighting techniques.

Shania Etheridge from Benjamin E. Mays Preparatory School in New Orleans shows off the head of lettuce she harvested at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility May 7, 2012. The Louisiana students assisted in the first harvest of lettuce from the Controlled Environment Agriculture unit, which uses an aeroponic process that involves no soil and advance LED lighting techniques.

Lauren Lombard from Benjamin E. Mays Preparatory School in New Orleans enjoys lettuce she helped to harvest at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility May 7, 2012. The Louisiana students assisted in the first harvest of lettuce from the Controlled Environment Agriculture unit, which uses an aeroponic process that involves no soil and advance LED lighting techniques
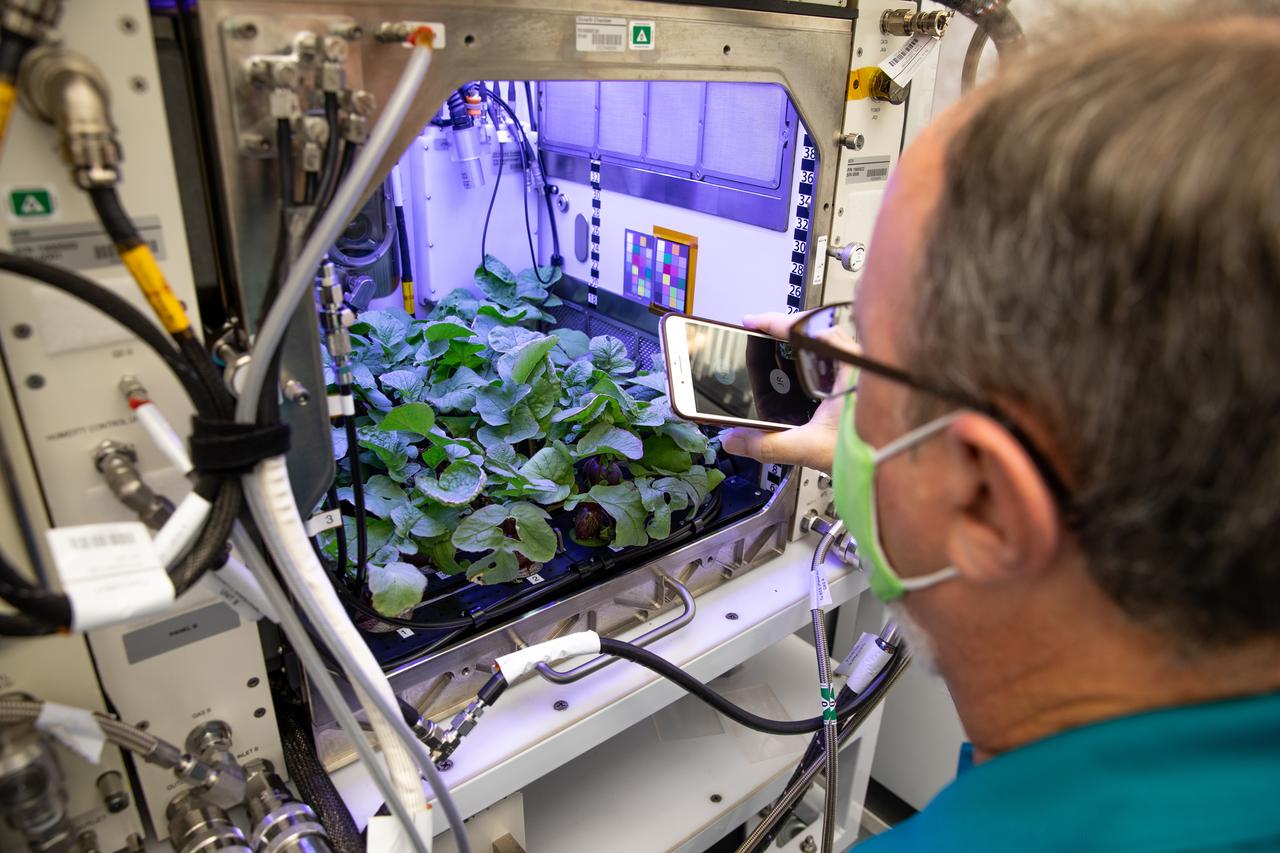

Dave Reed, Florida operations director for Techshot, Inc., observes radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment. The experiment also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
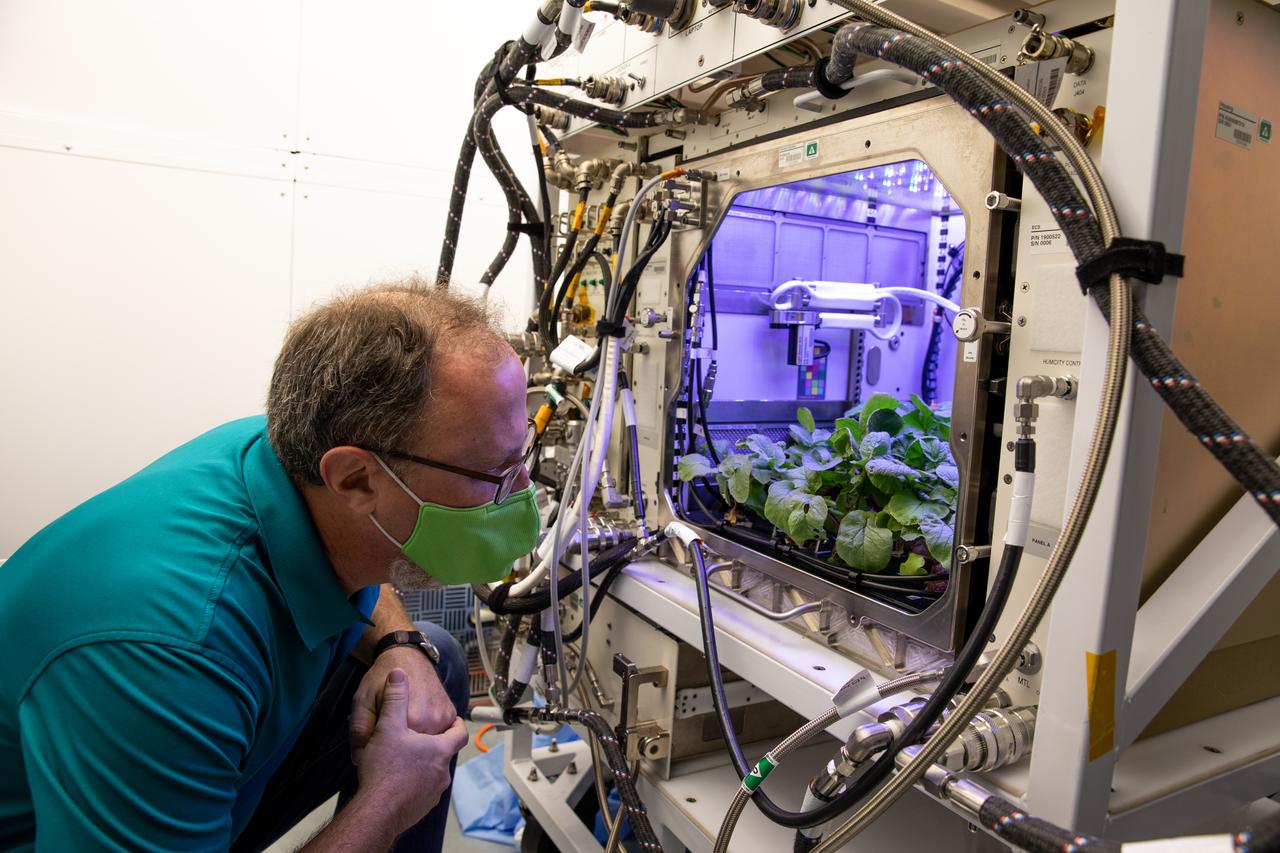

Dave Reed, Florida operations director for Techshot, Inc., observes radishes growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat (APH) ground unit inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Dec. 14, 2020. The radishes are a ground control crop for the Plant Habitat-02 (PH-02) experiment, which also involves growing two similar radish crops inside the International Space Station’s APH. NASA astronaut Kate Rubins harvested the first crop on Nov. 30, and the second harvest aboard the orbiting laboratory is planned for Dec. 30. Once samples return to Earth, researchers will compare those grown in space to the radishes grown here on Earth to better understand how microgravity affects plant growth.
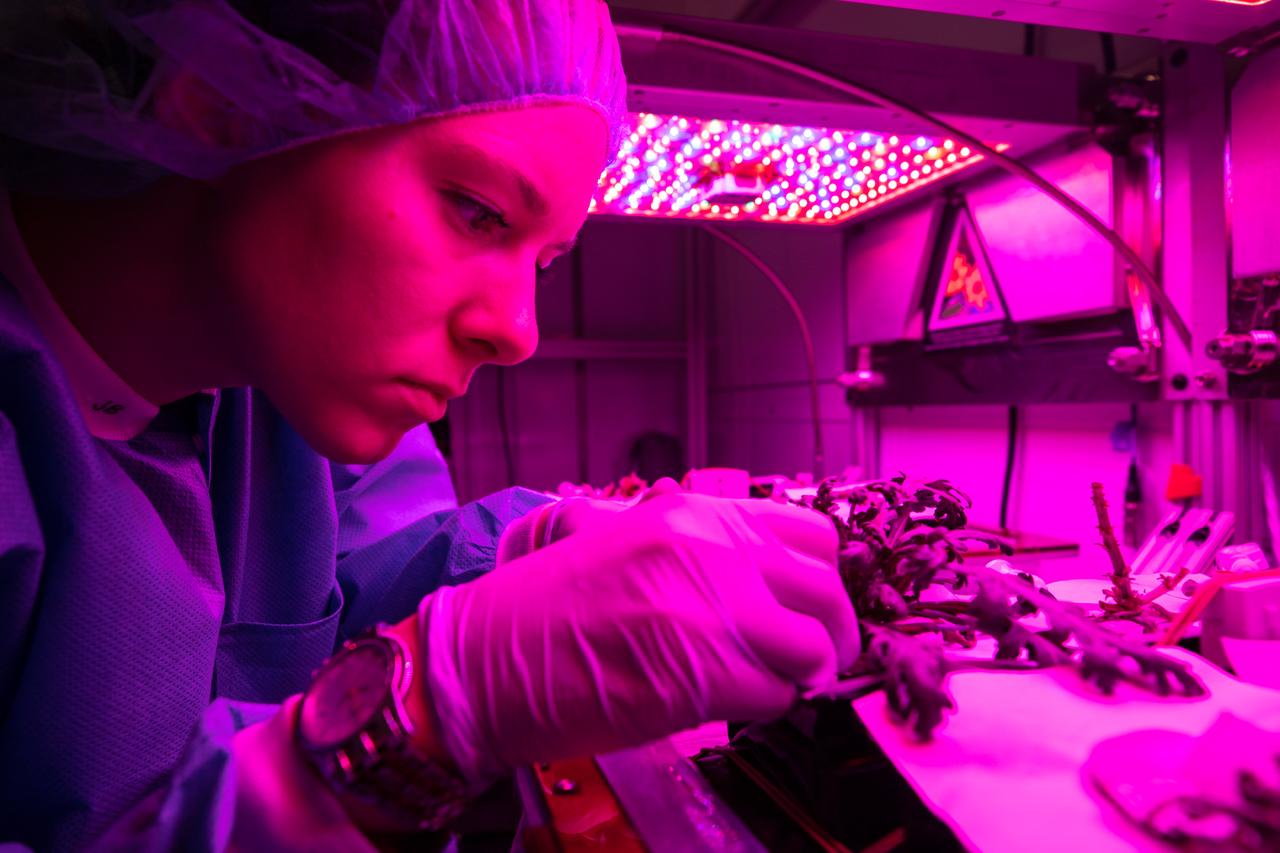

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
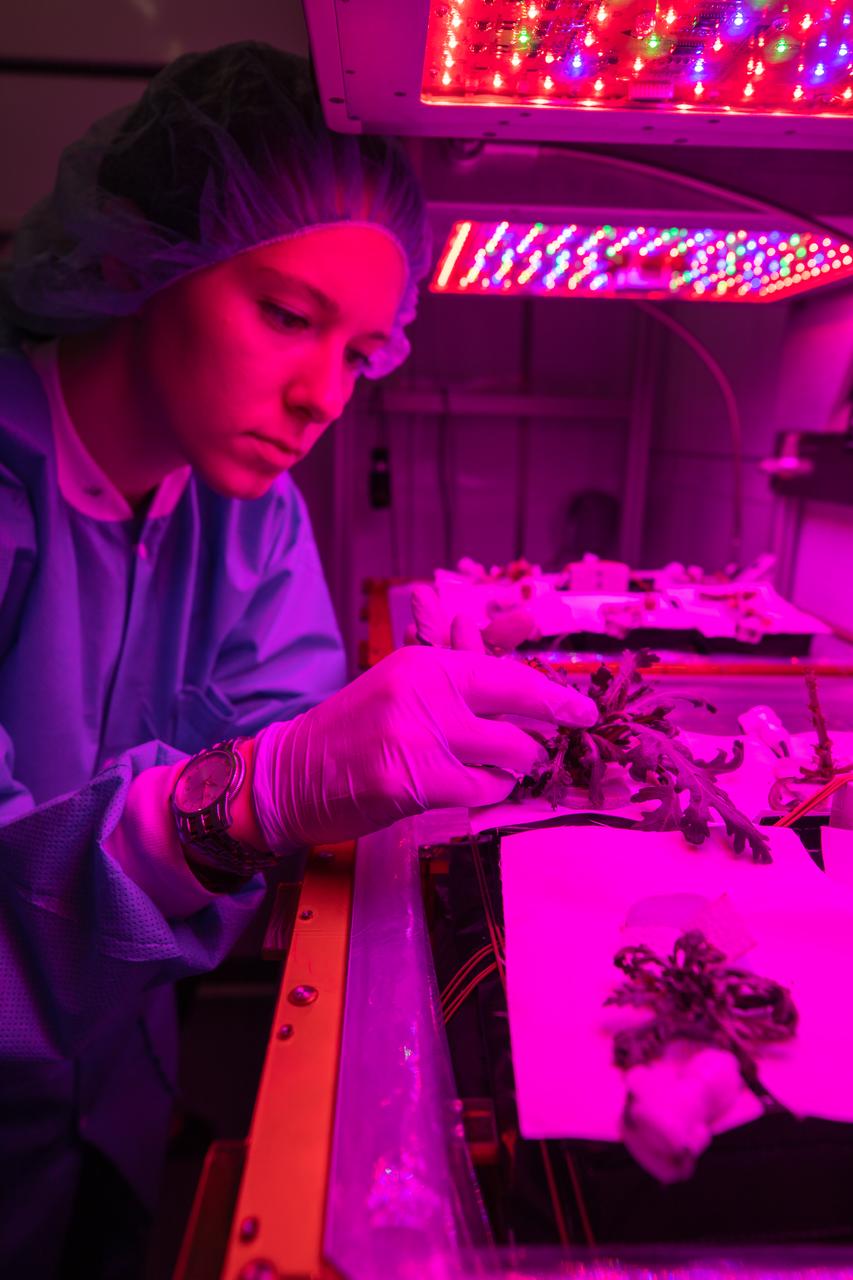

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
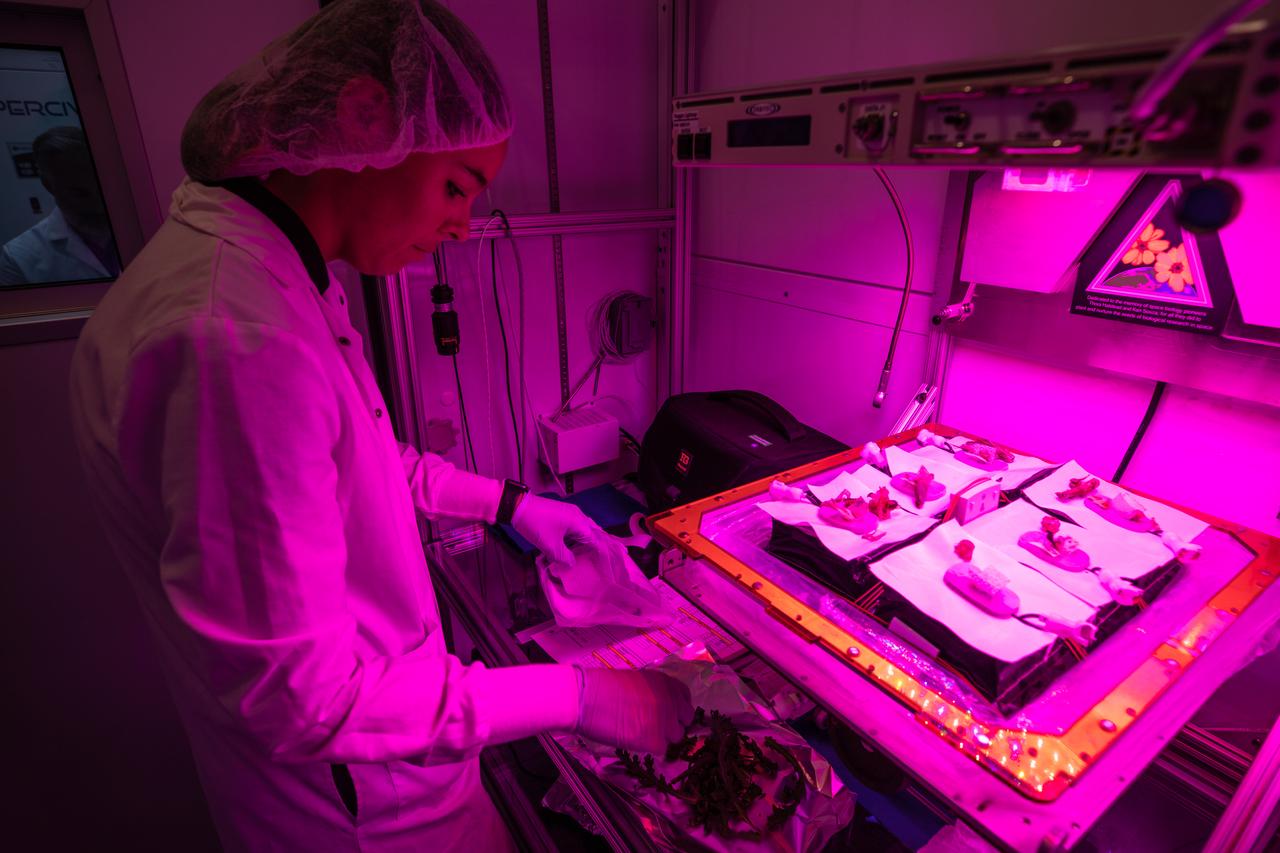

Kennedy Space Center employee Anna Maria Ruby harvests plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
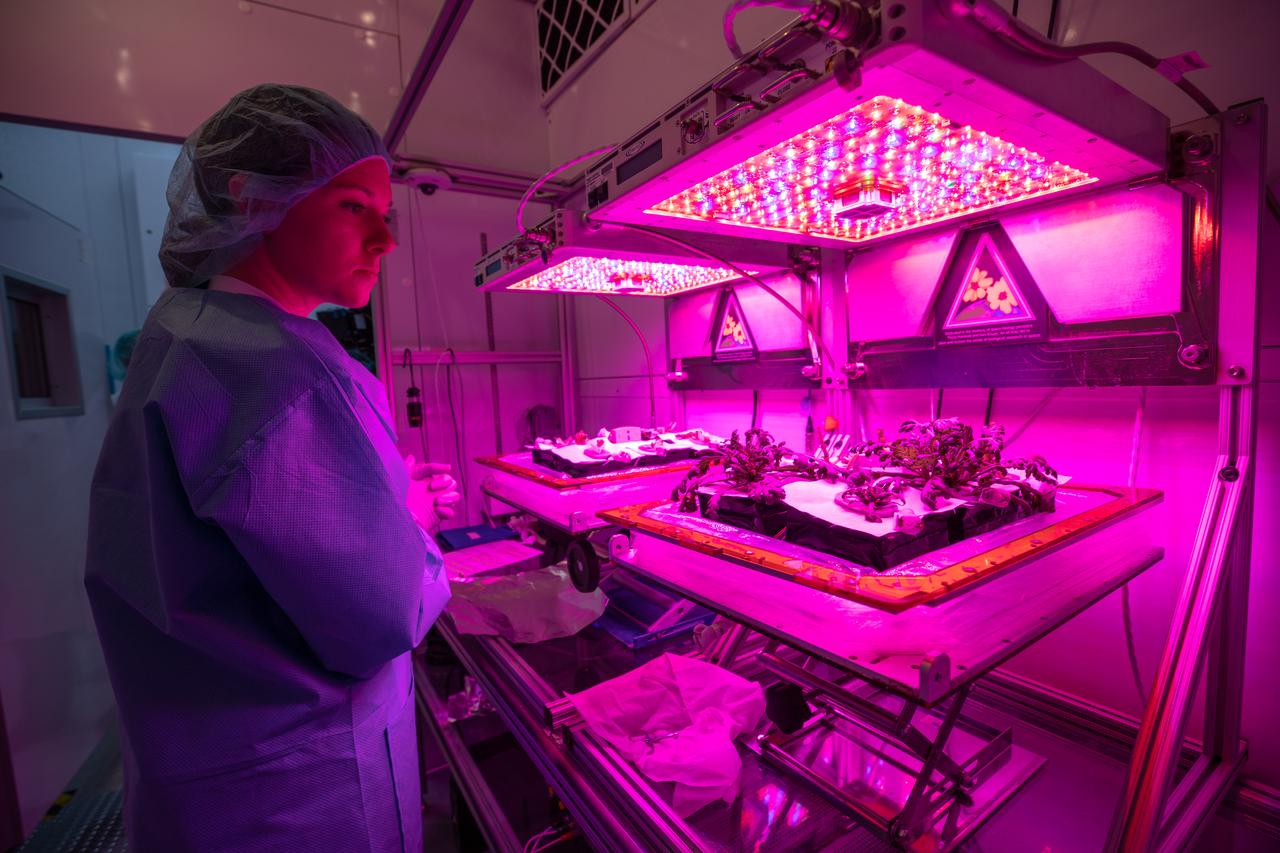

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, observes plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility prior to harvesting them on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
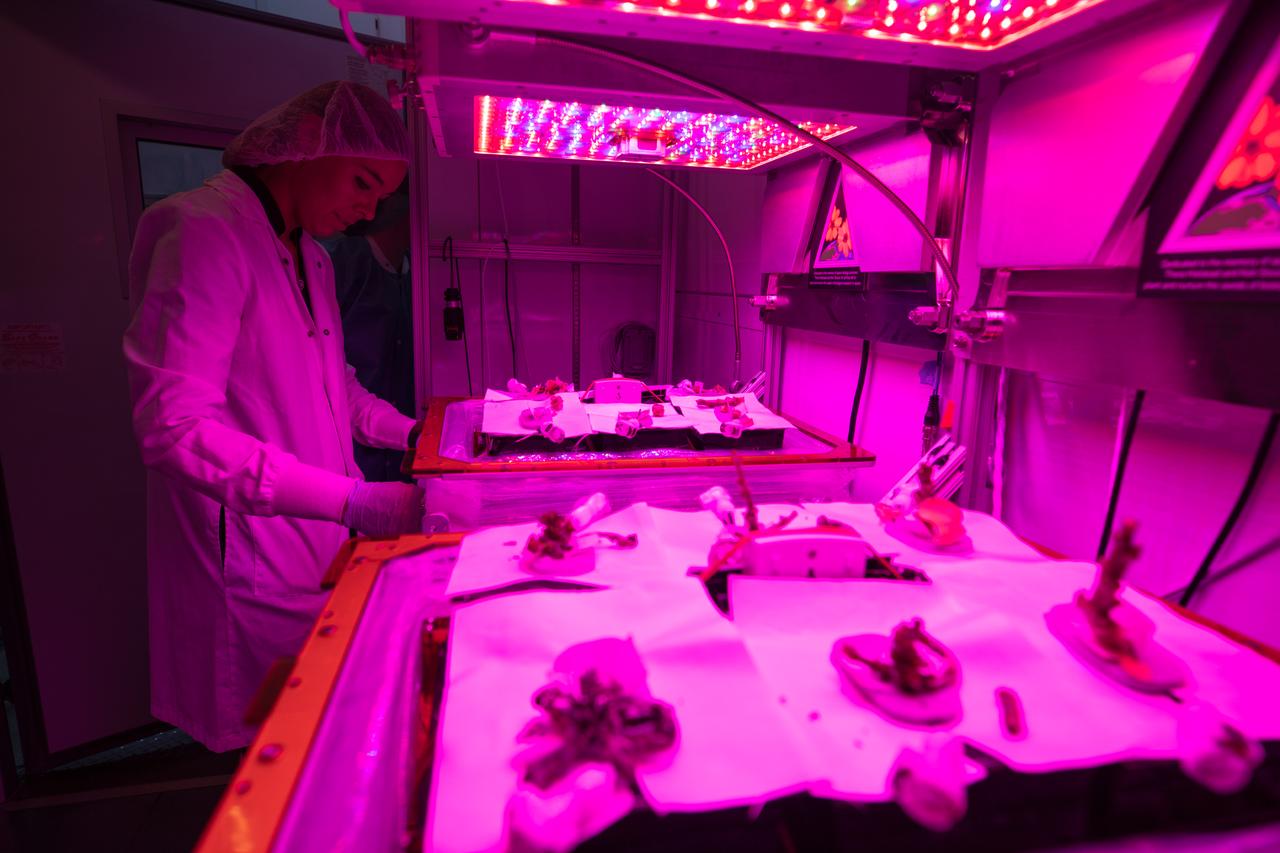

Kennedy Space Center employee Anna Maria Ruby observes plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility prior to harvesting them on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.
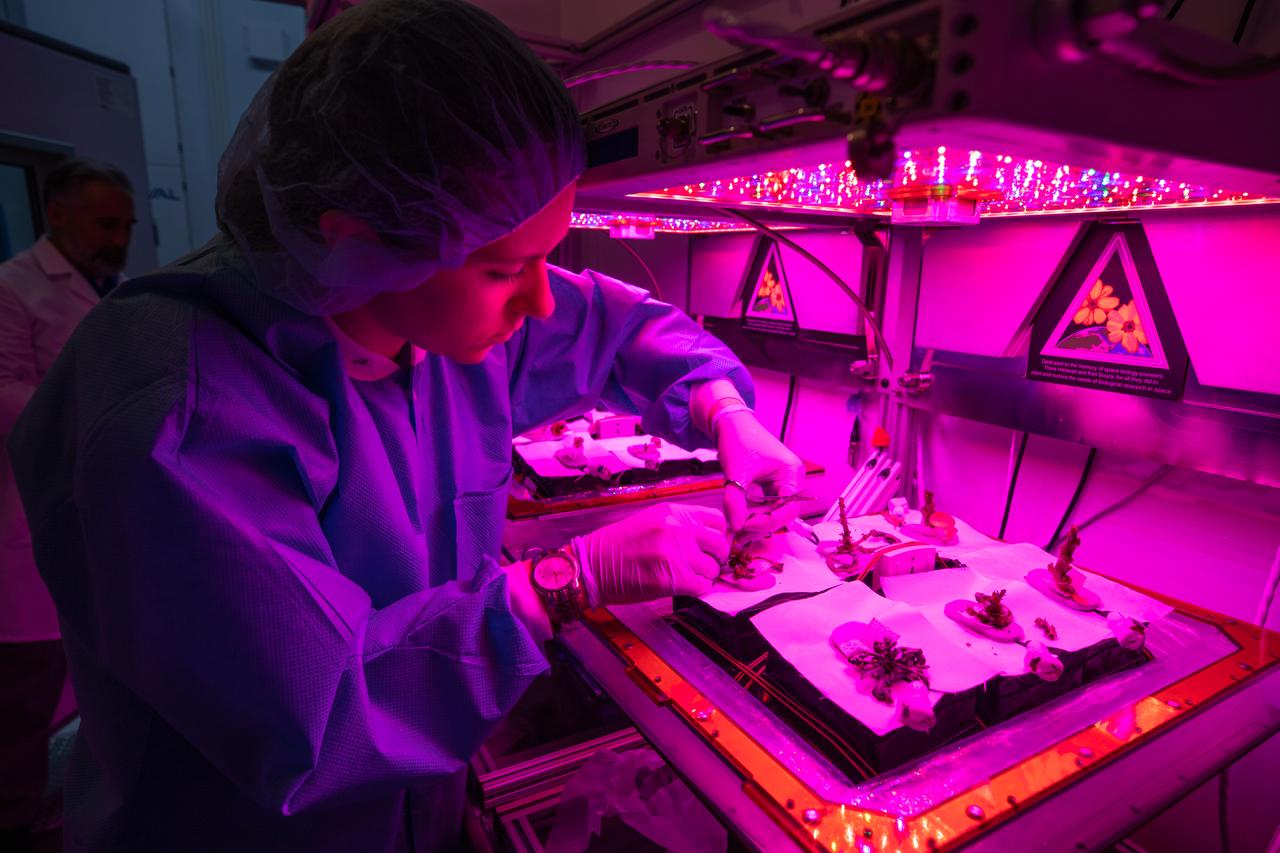

Jess Bunchek, an associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, harvests plant cultivars inside the Veggie growth chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 30, 2019, for a science verification test (SVT). This SVT will study the potential of three plants – amara mustard, ‘outredgeous’ red romaine lettuce and shungiku, an Asian green comparable to an edible chrysanthemum – to grow in space. All three lettuce plants were grown from seed film, making this the first SVT with this new plant growth material. Earlier this year, the amara mustard and shungiku plants were grown for the first time using seed bags – referred to as pillows – during the Sustained Veggie project, a study funded by the Human Research Program.

iss071e675220 (Sept. 18, 2024) -- September's full moon, known as the "Harvest Moon," is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above Beijing.

Commander Steve Swanson harvests plants for the VEG-01 investigation. He is harvesting them on the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) in the Node 2/Harmony. The Veg-01 hardware validation test investigation utilizes the Veggie facility on ISS. This investigation will assess on-orbit function and performance of the Veggie,and focus on the growth and development of Outredgeous Lettuce (Lactuca sativa ) seedlings in the spaceflight environment and the effects of the spaceflight environment on composition of microbial flora on the Veggie-grown plants and the Veggie facility. Lettuce plants are harvested on-orbit, frozen at <-80oC and returned to the ground for post-flight evaluation. Microbial sampling swabs will be taken of the Veggie facility and plant material, frozen and returned to the ground for environmental microbiological examination. Rooting pillows and water sample syringes will also be returned for microbial sampling and root analysis.
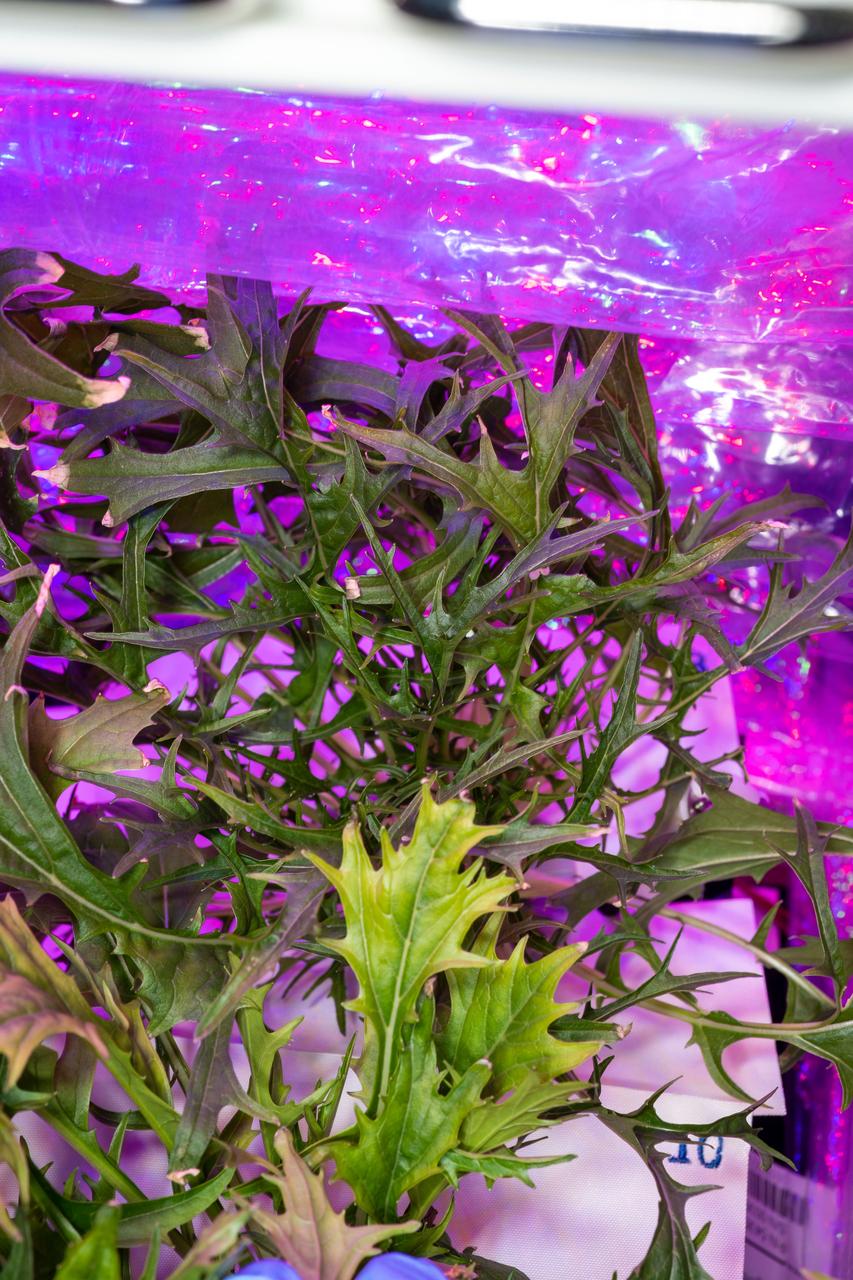

Documentation of a Mizuna mustard plant growing in Plant Pillow 8 in the Vegetable Production System (Veggie). Photo was taken prior to plant harvesting operations (OPS) for the Veg-04B experiment.
iss055e001193 (March 8, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Scott Tingle eats a piece of lettuce harvested as part of the ongoing space crop study VEG-03. The botany experiment uses the Veggie plant growth facility to cultivate a type of cabbage, lettuce and mizuna which are harvested on-orbit with some samples consumed by astronauts and others returned to Earth for testing.
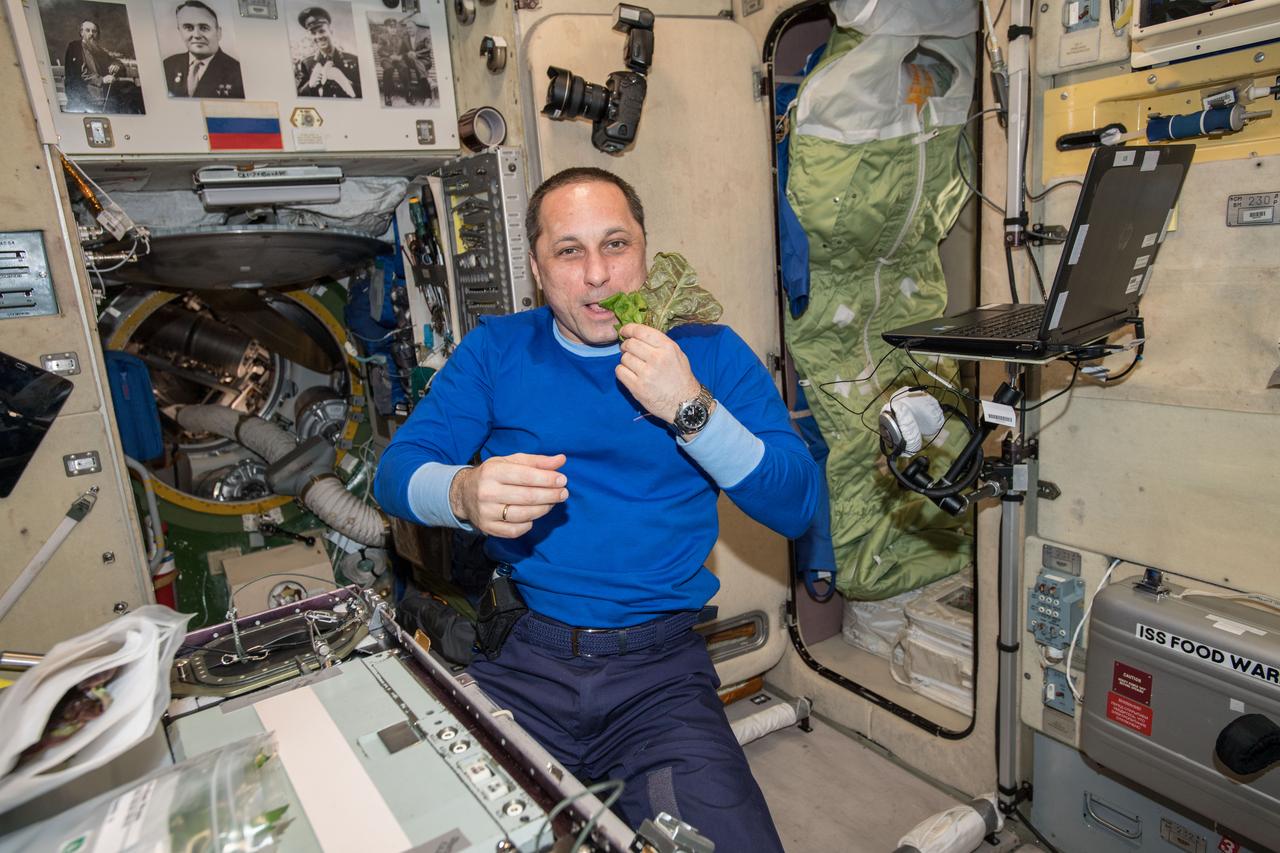

iss055e001536 (March 8, 2018) --- Expedition 55 Commander Anton Shkaplerov eats a piece of lettuce harvested as part of the ongoing space crop study VEG-03. The botany experiment uses the Veggie plant growth facility to cultivate a type of cabbage, lettuce and mizuna which are harvested on-orbit with some samples consumed by astronauts and others returned to Earth for testing.
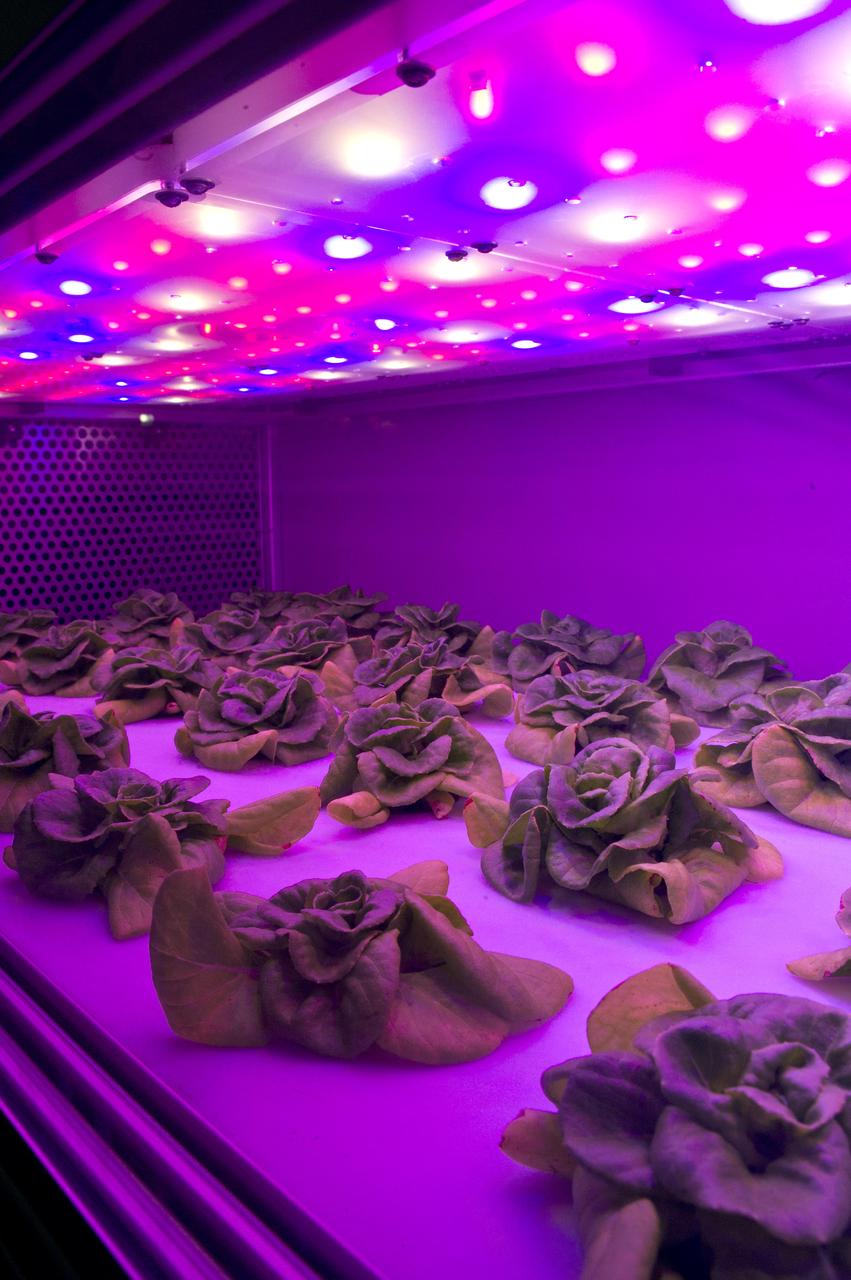

The Controlled Environment Agriculture unit at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center visitor center and museum grows butterhead lettuce using an aeroponic process that involves no soil and advance LED lighting techniques. Students from Benjamin E. Mays Preparatory School in New Orleans helped to harvest the first crop of lettuce during a visit to the facility May 7, 2012.
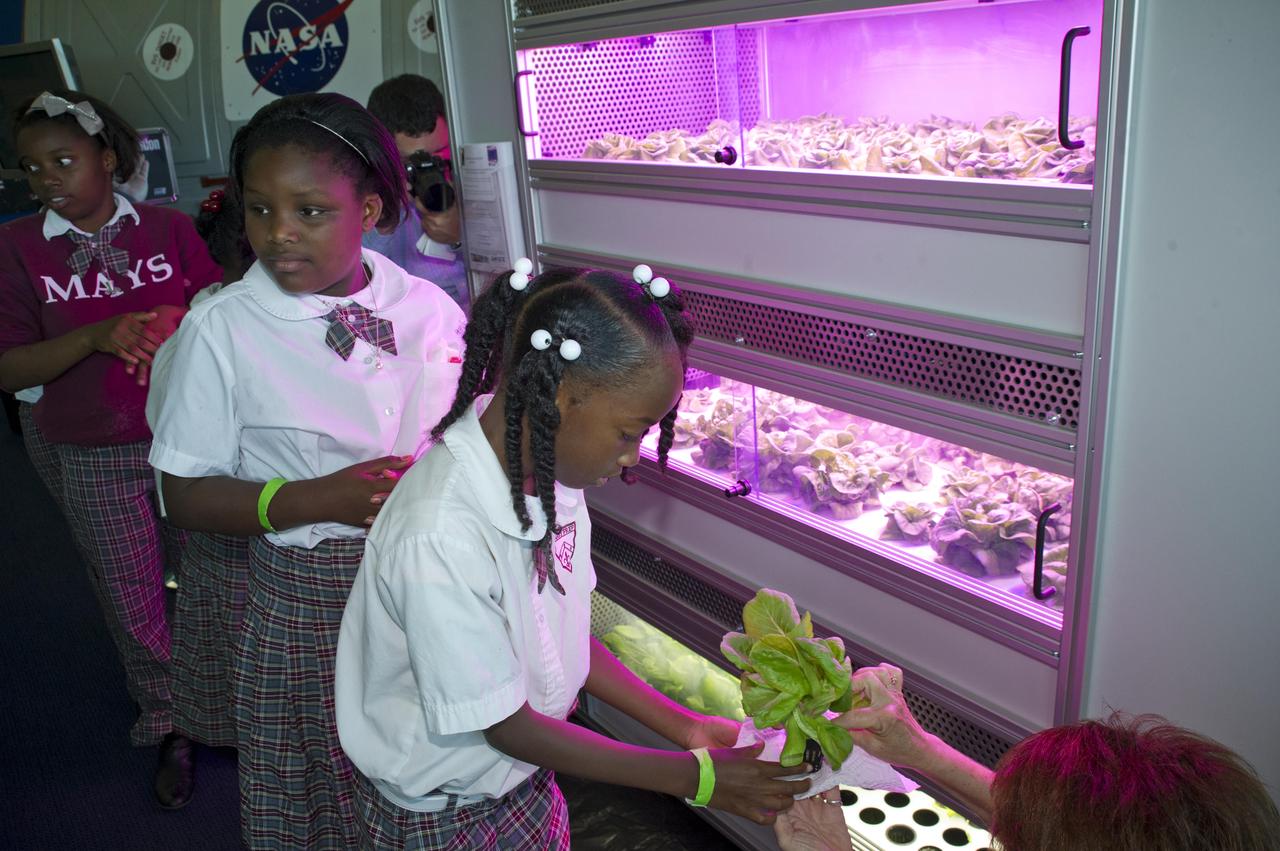

Students from Benjamin E. Mays Preparatory School in New Orleans enjoyed a hands-on experience at the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility May 7, 2012. The Louisiana students assisted in the first harvest of lettuce from the Controlled Environment Agriculture unit, which uses an aeroponic process that involves no soil and advance LED lighting techniques.
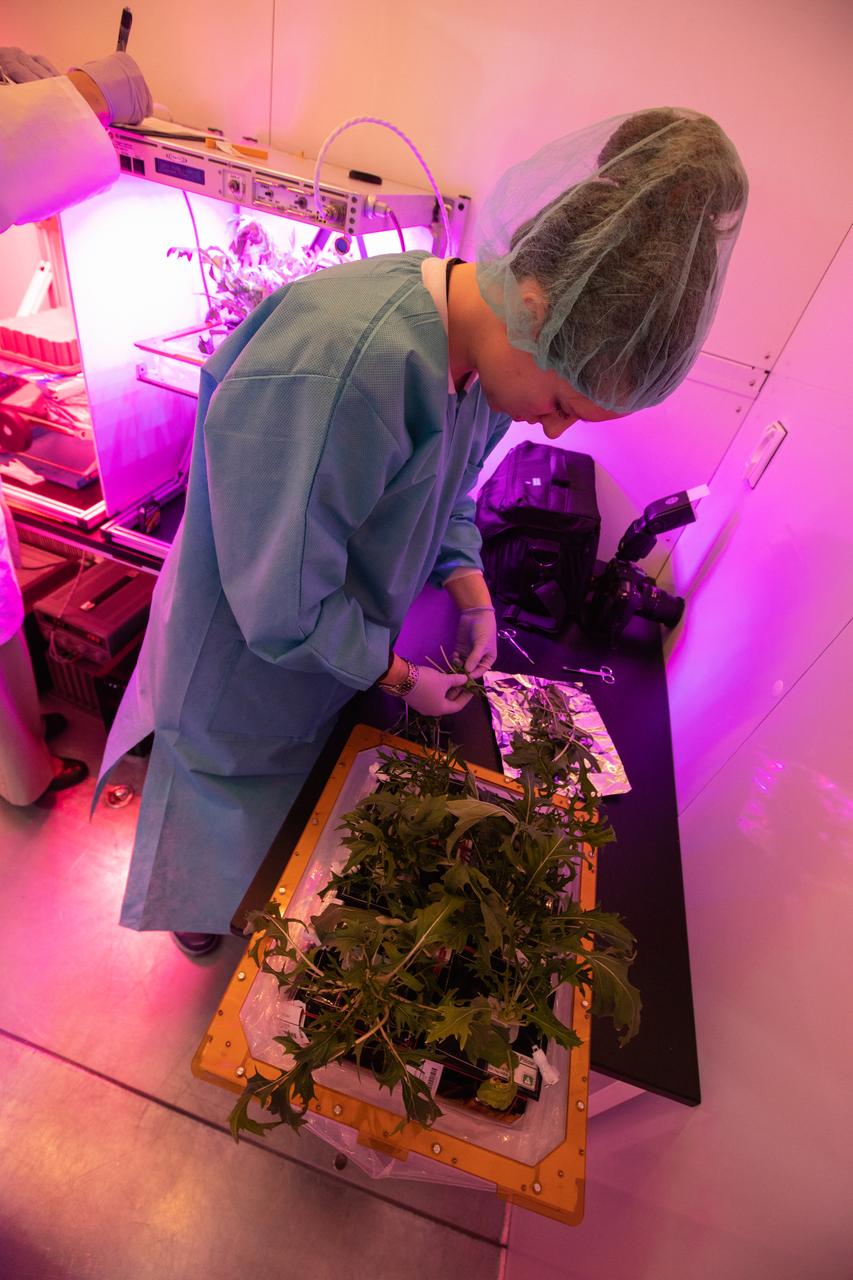

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.

Gretchen Maldonado Vazquez, a microbiologist, weighs the harvest of mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, from the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions, and a similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
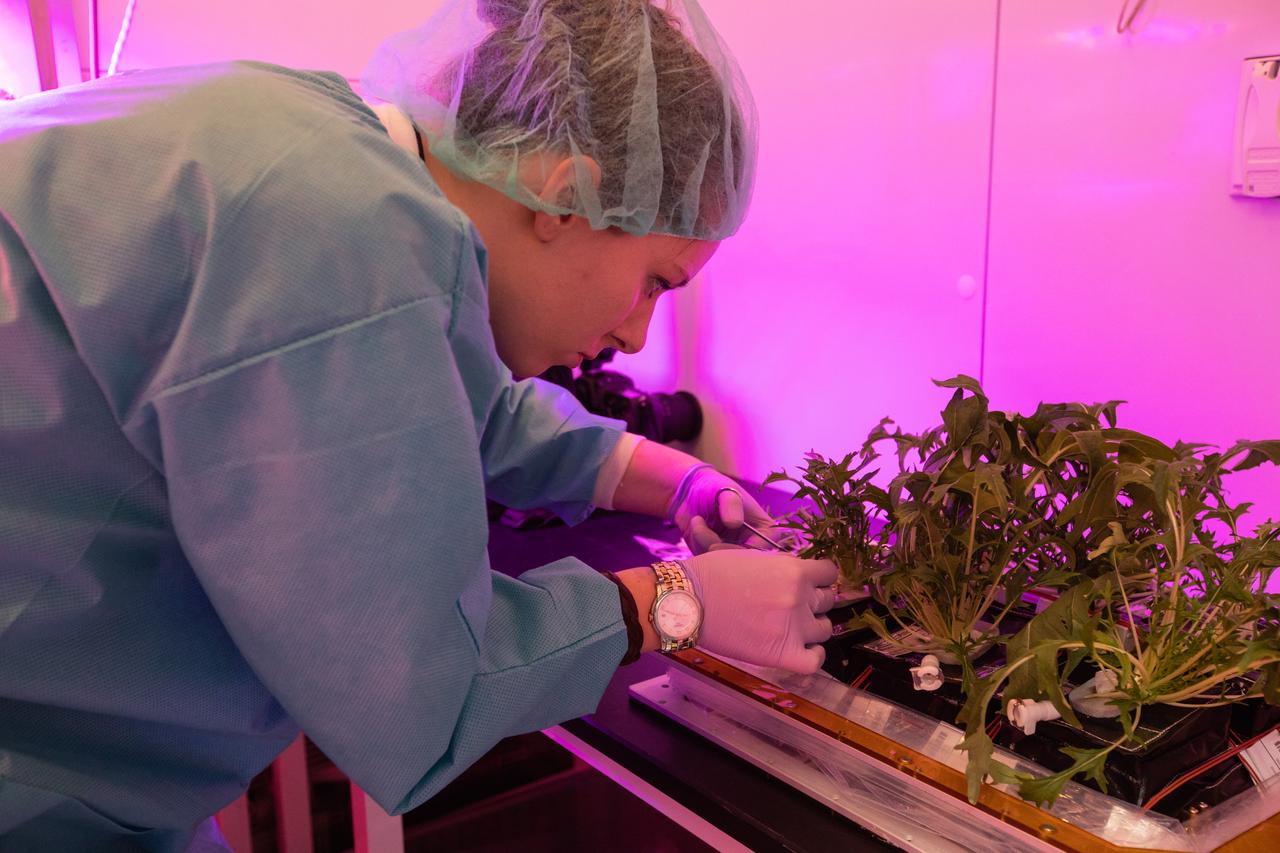

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
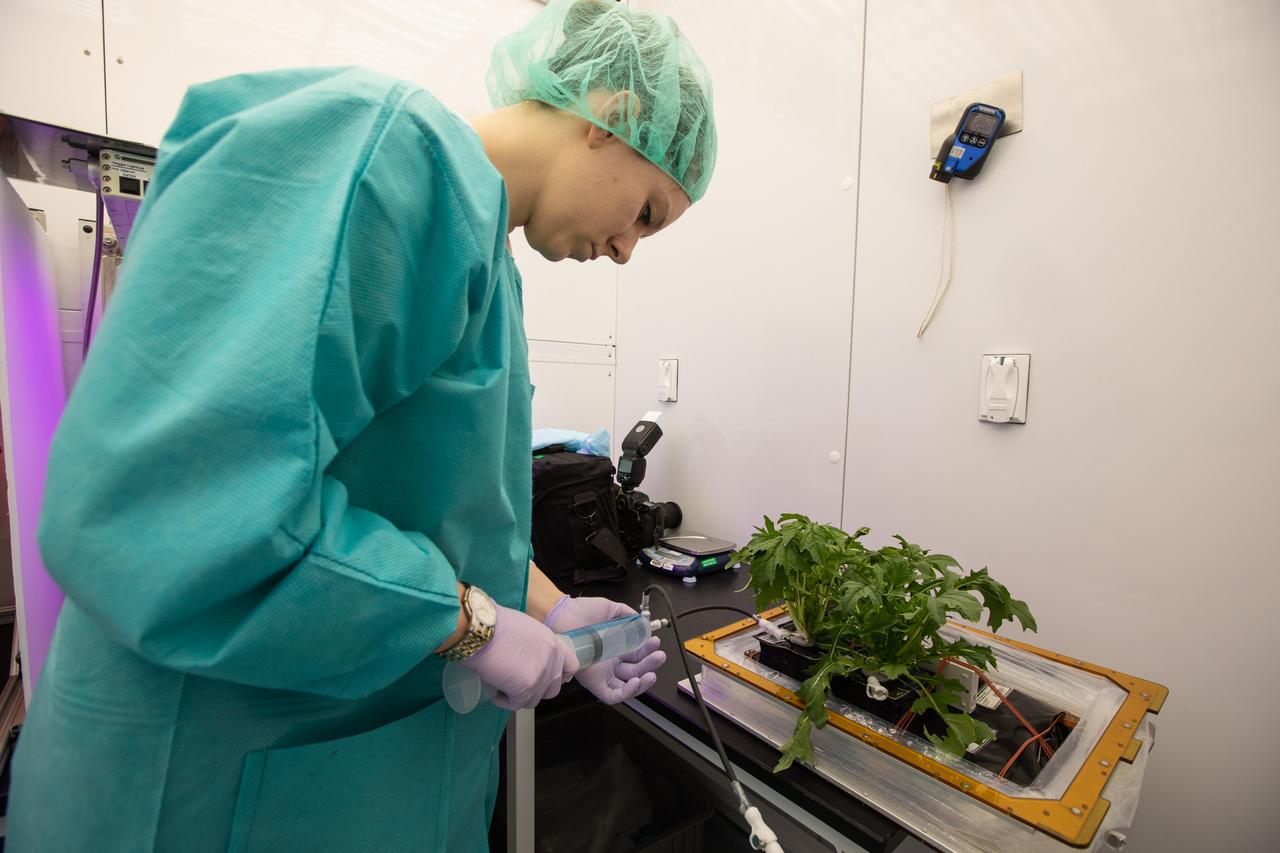

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
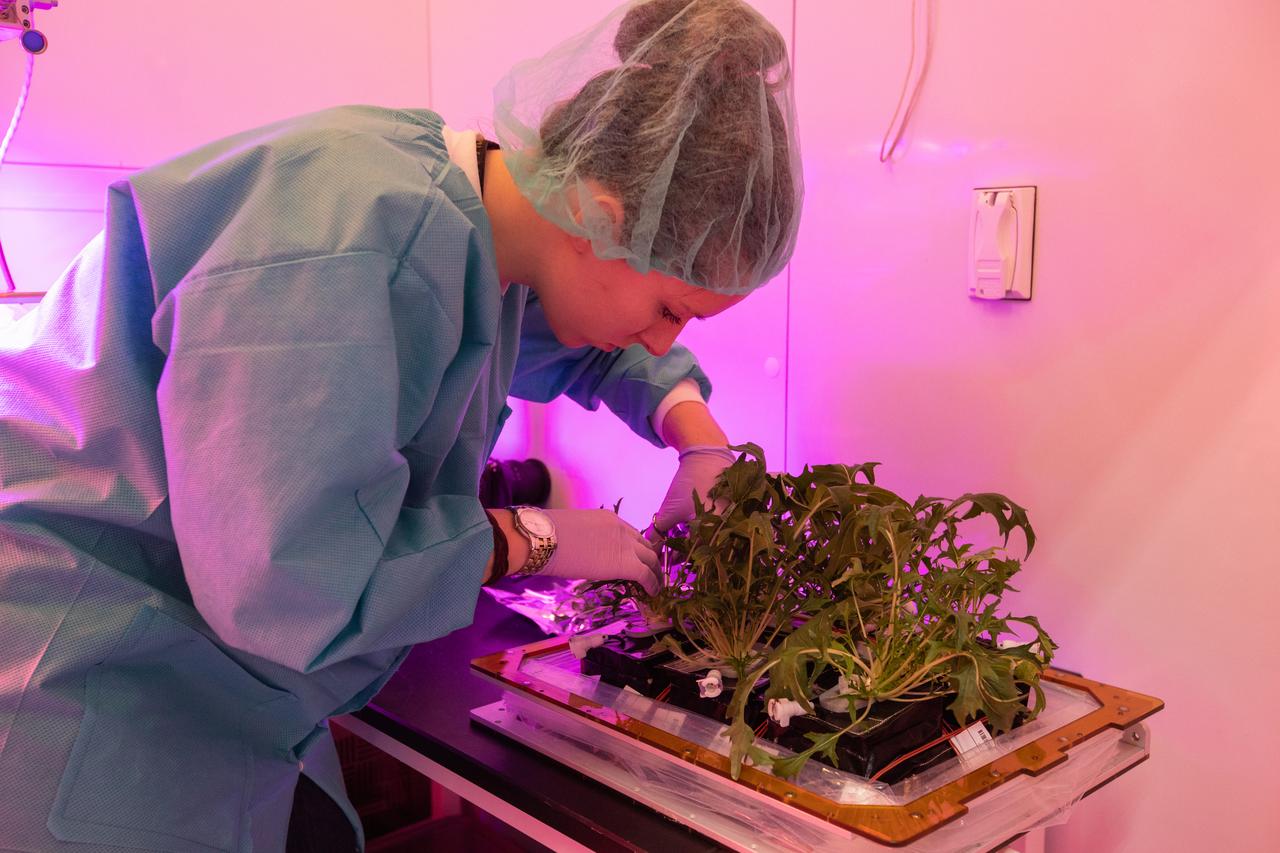

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
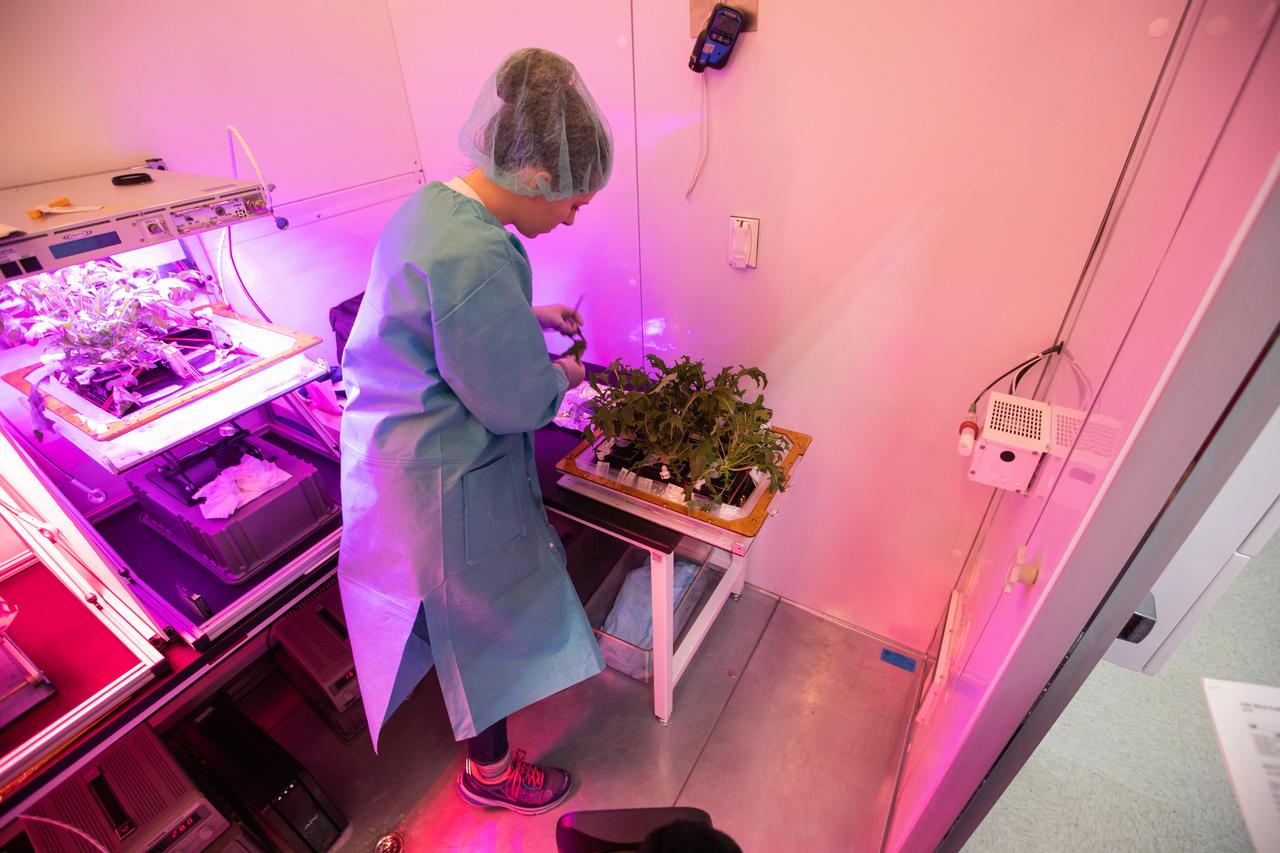

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
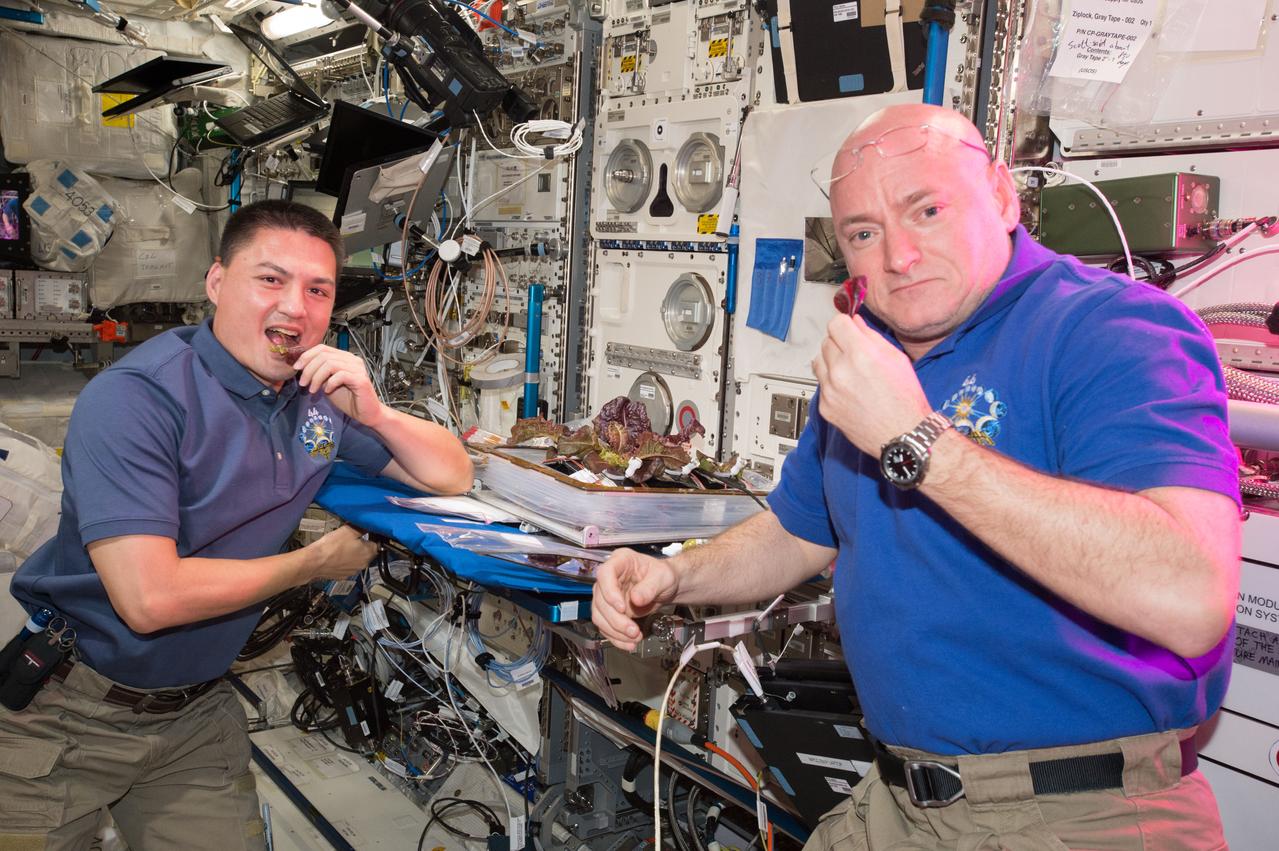
ISS044E045825 (08/11/2015) --- NASA astronauts Scott Kelly and Kjell Lindgren on the International Space Station are getting their taste buds ready for the first taste of food that's grown, harvested and eaten in space, a critical step on the path to Mars. The crew took their first bites on Aug. 10, 2015.
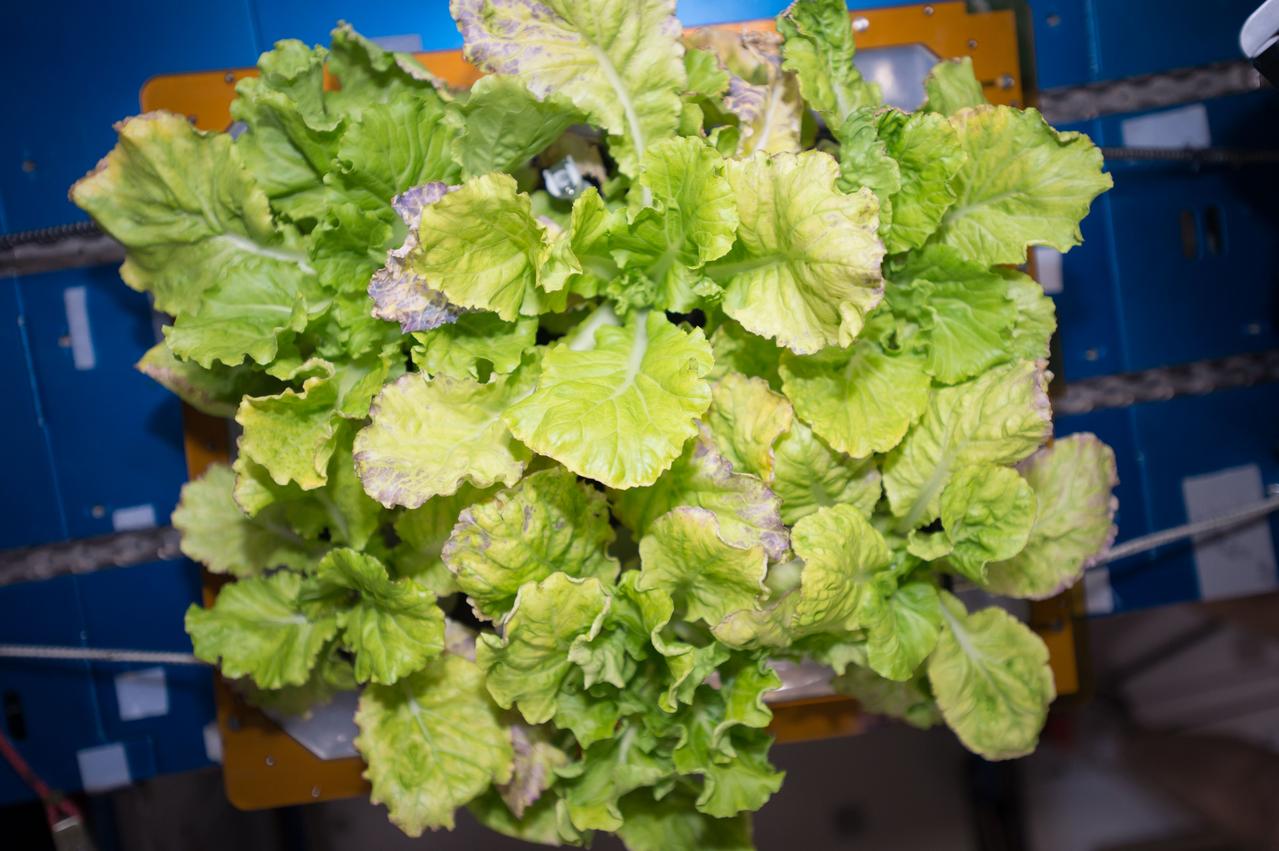

View of cabbage plants in the Vegetable Production System (Veggie) bellows, with the bellows secured to the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) in the Harmony Node 2. Image was taken during final harvesting operations (OPS) for the Veg-03 experiment.
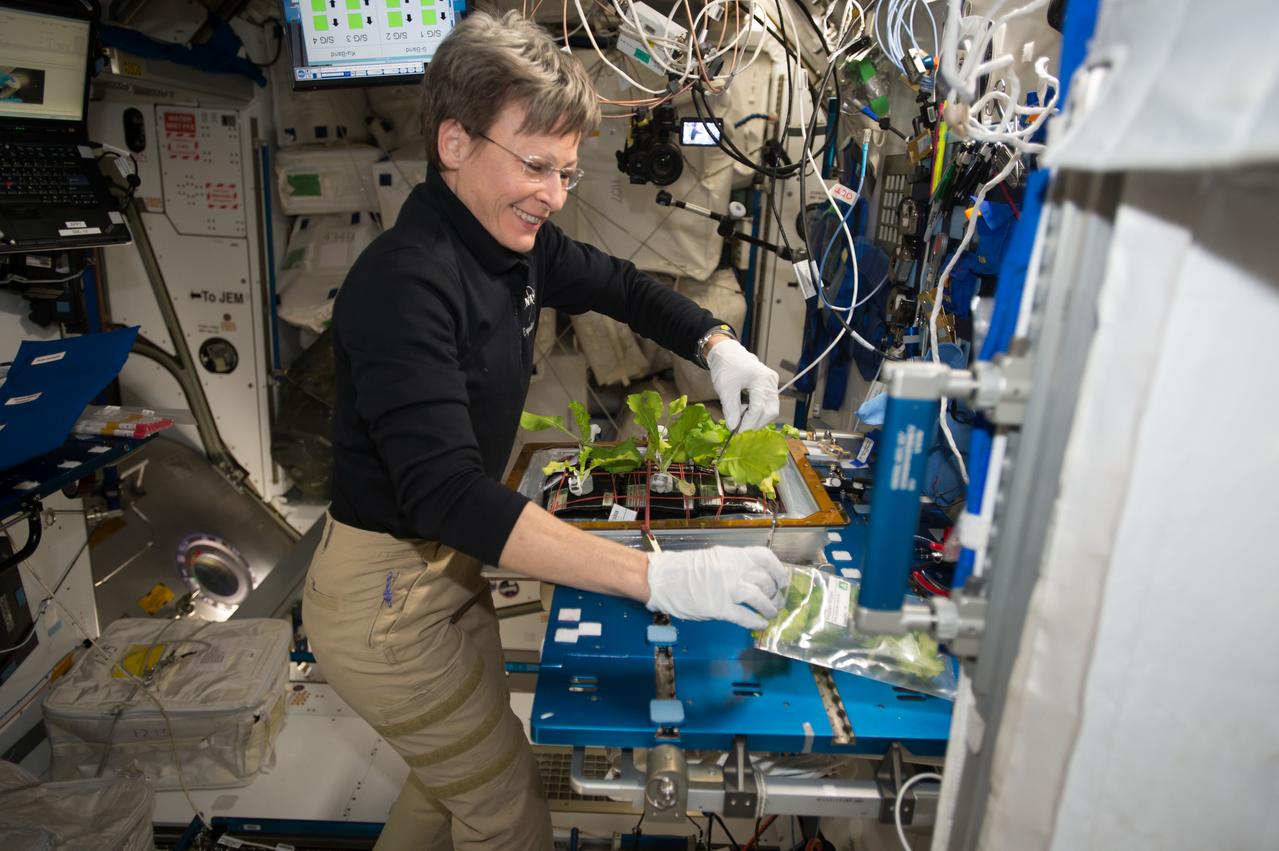

iss050e050335 (2/17/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson during harvesting and cleaning of VEG-03, in the Node 2. Organisms grow differently in space, from single-celled bacteria to plants and humans. But future long-duration space missions will require crew members to grow their own food, so understanding how plants respond to microgravity is an important step toward that goal. Veg-03 uses the Veggie plant growth facility to cultivate a type of cabbage, which is harvested in orbit with samples returned to Earth for testing.
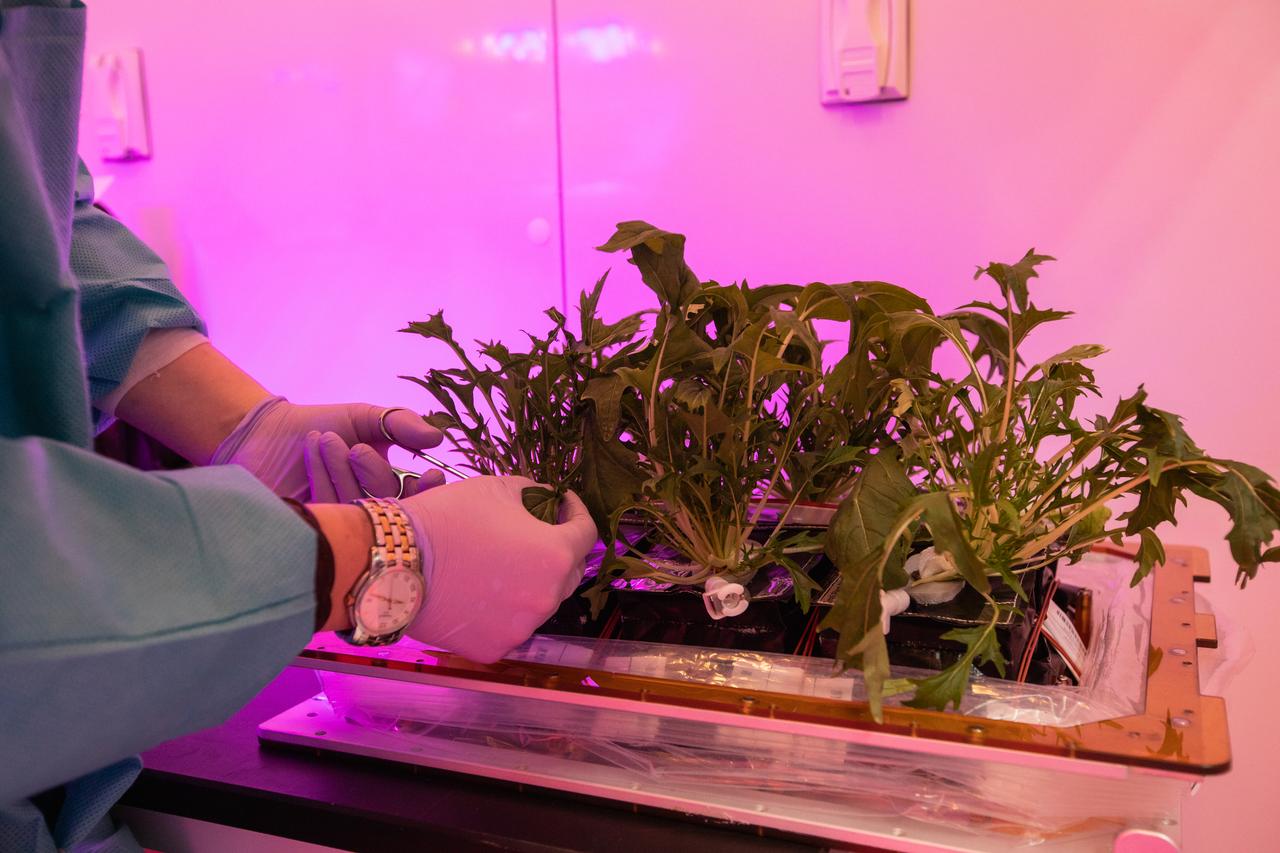

Mizuna mustard is harvested inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. The VEG-04B mission is expected to provide sensory stimulation and help mark the passage of time in the confined and isolated environment of the space station. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
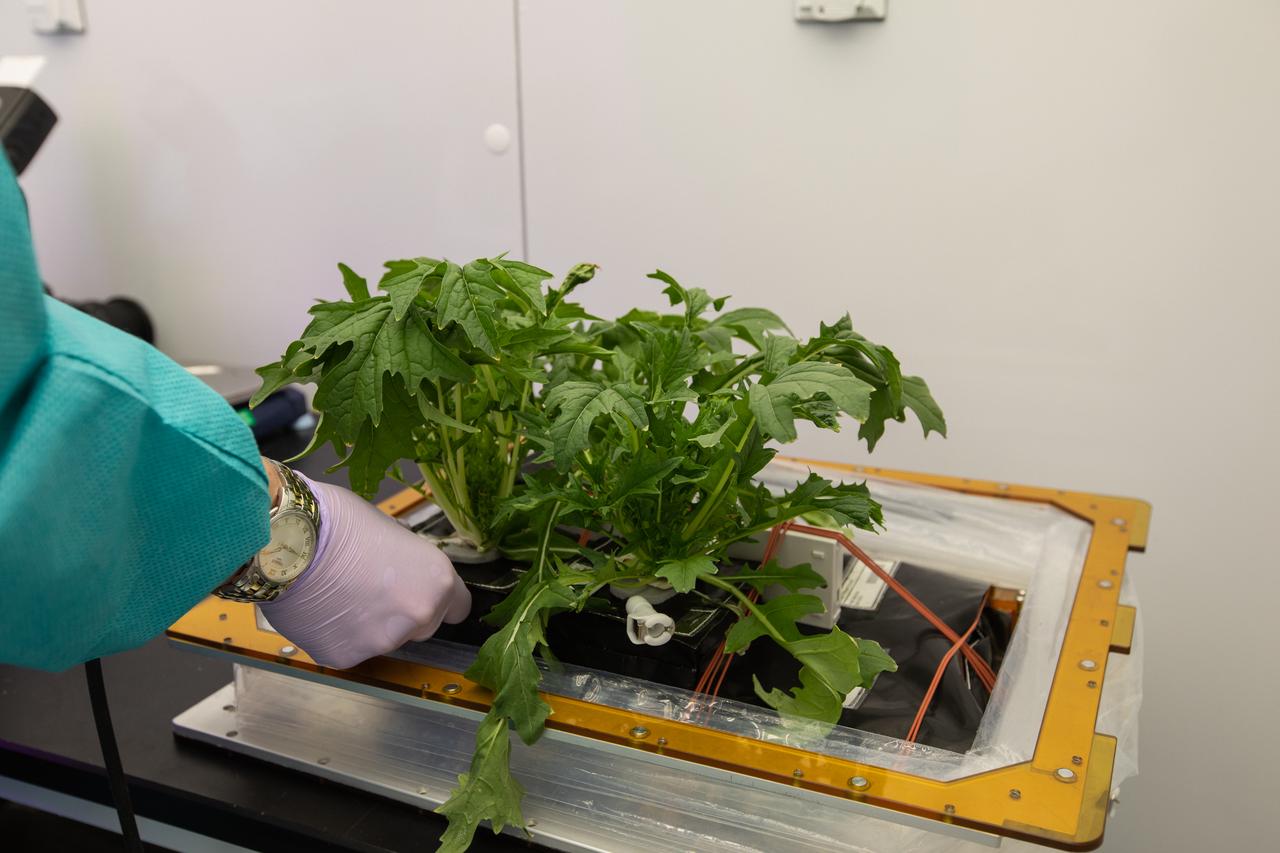

Jess Bunchek, a veggie plant scientist and pseudonaut, harvests mizuna mustard inside the Veggie harvest chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 19, 2019, as part of the Experiment Verification Test for the VEG-04B mission that will launch to the International Space Station later this year. VEG-04B examines the interactions between light and spaceflight by growing plants under two different LED lighting conditions. A similar harvest will be conducted on the space station after a grow-out duration of 56 days. The VEG-04B mission is expected to provide fresh food, sensory stimulation and help mark the passage of time in the confined and isolated environment of the space station. Ultimately, fresh vegetables grown in space will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet, prepping them for long-duration space exploration.
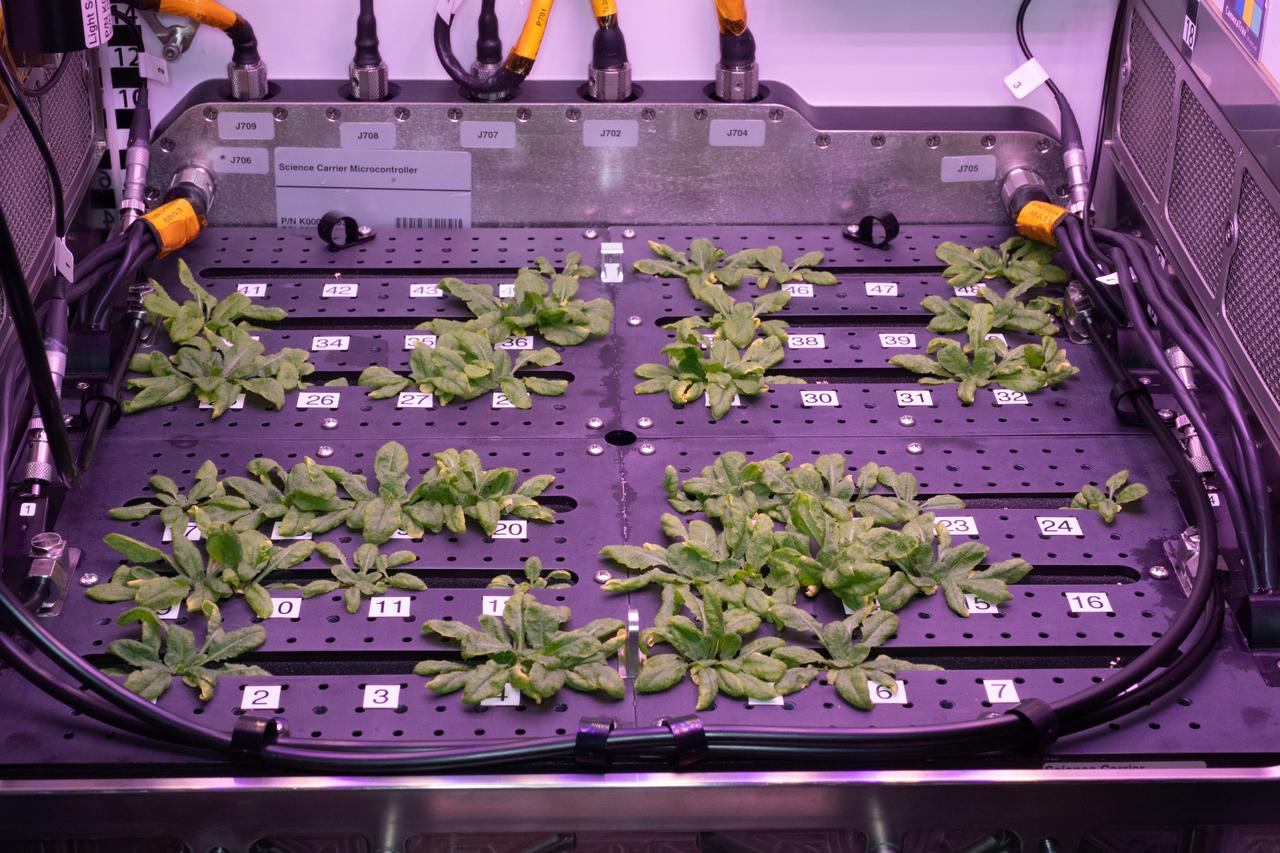

View during harvest of Arabidopsis plants. Photo was taken by Expedition 56 crew.
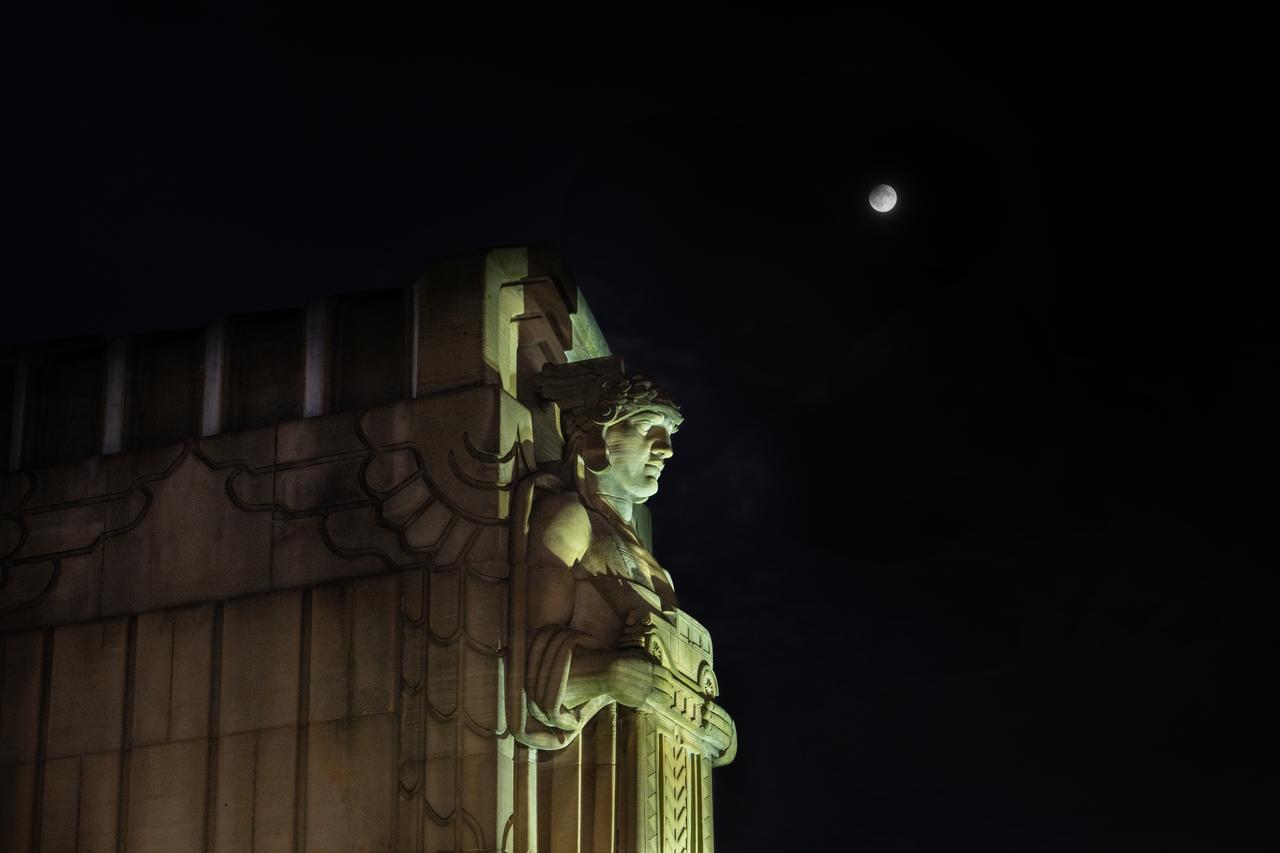

Guardians of Traffic Statue in Cleveland, OH in front of the Supermoon that was visible on September 17th, 2024. On this day, the full moon was a partial lunar eclipse; a supermoon; and a harvest moon.

iss051e051923 (5/03/2017) --- NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson poses with cabbage plants in the Vegetable Production System (Veggie) bellows in the Harmony Node 2. Image was taken during final harvesting operations (OPS) for the Veg-03 experiment.
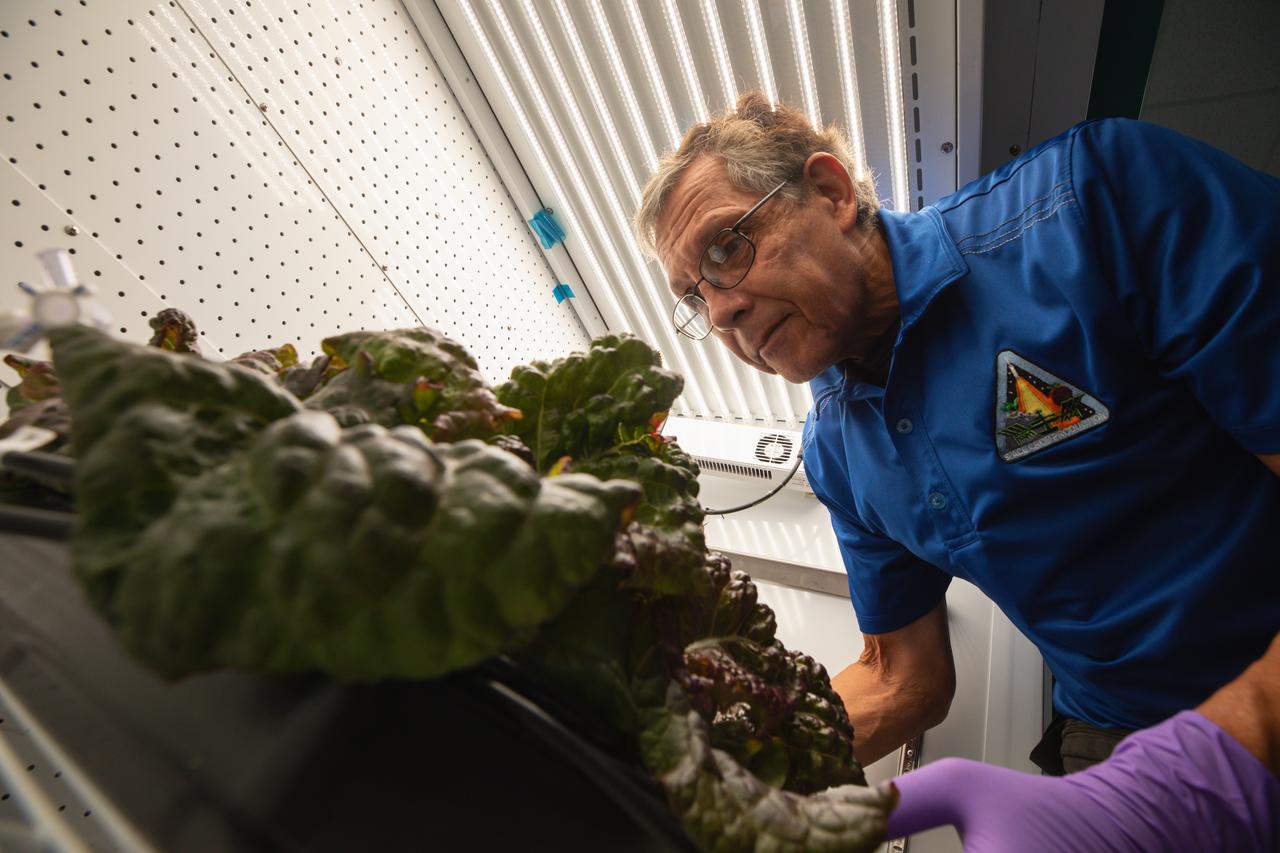

Space crop production scientist Oscar Monje harvests Outredgeous romaine lettuce for preflight testing of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 29, 2024. PH-07 will be sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
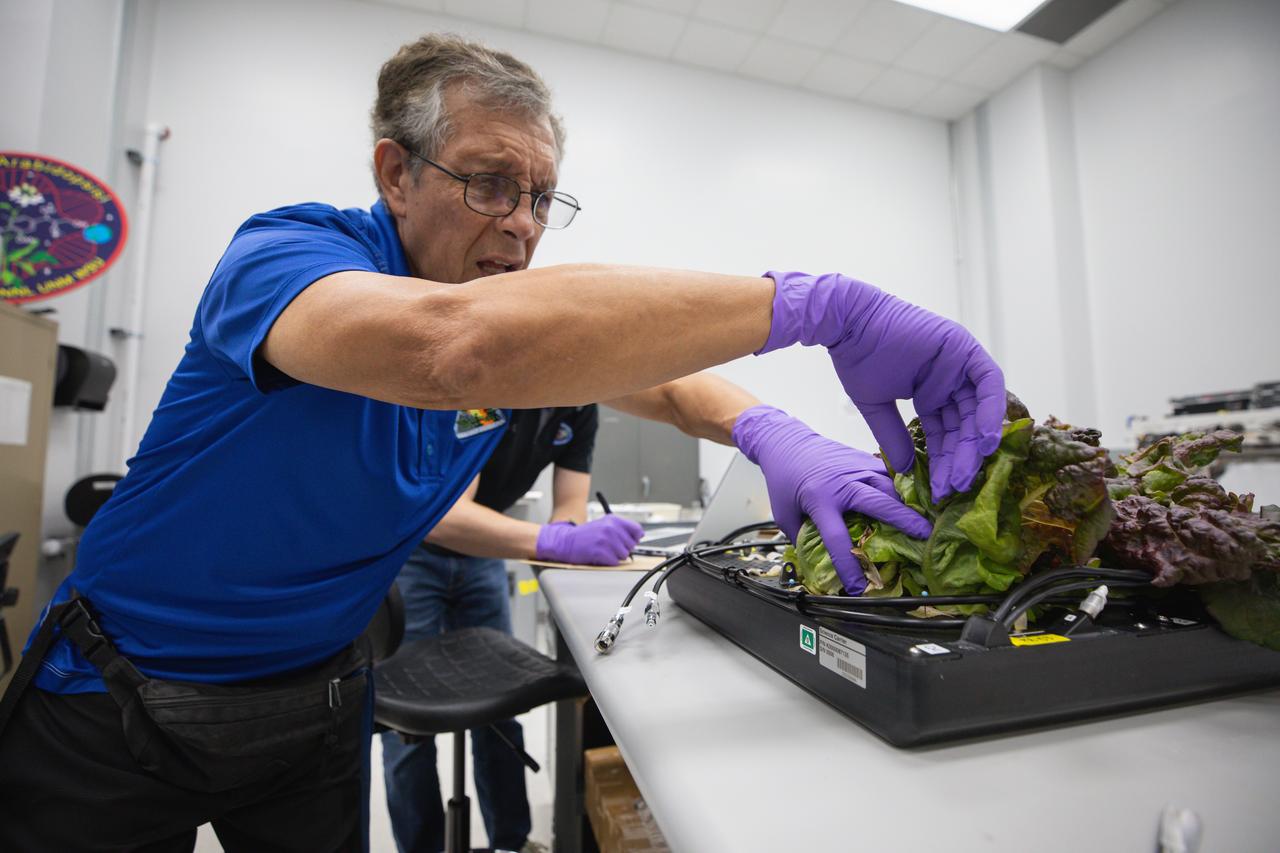

Space crop production scientist Oscar Monje harvests Outredgeous romaine lettuce for preflight testing of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 29, 2024. PH-07 will be sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
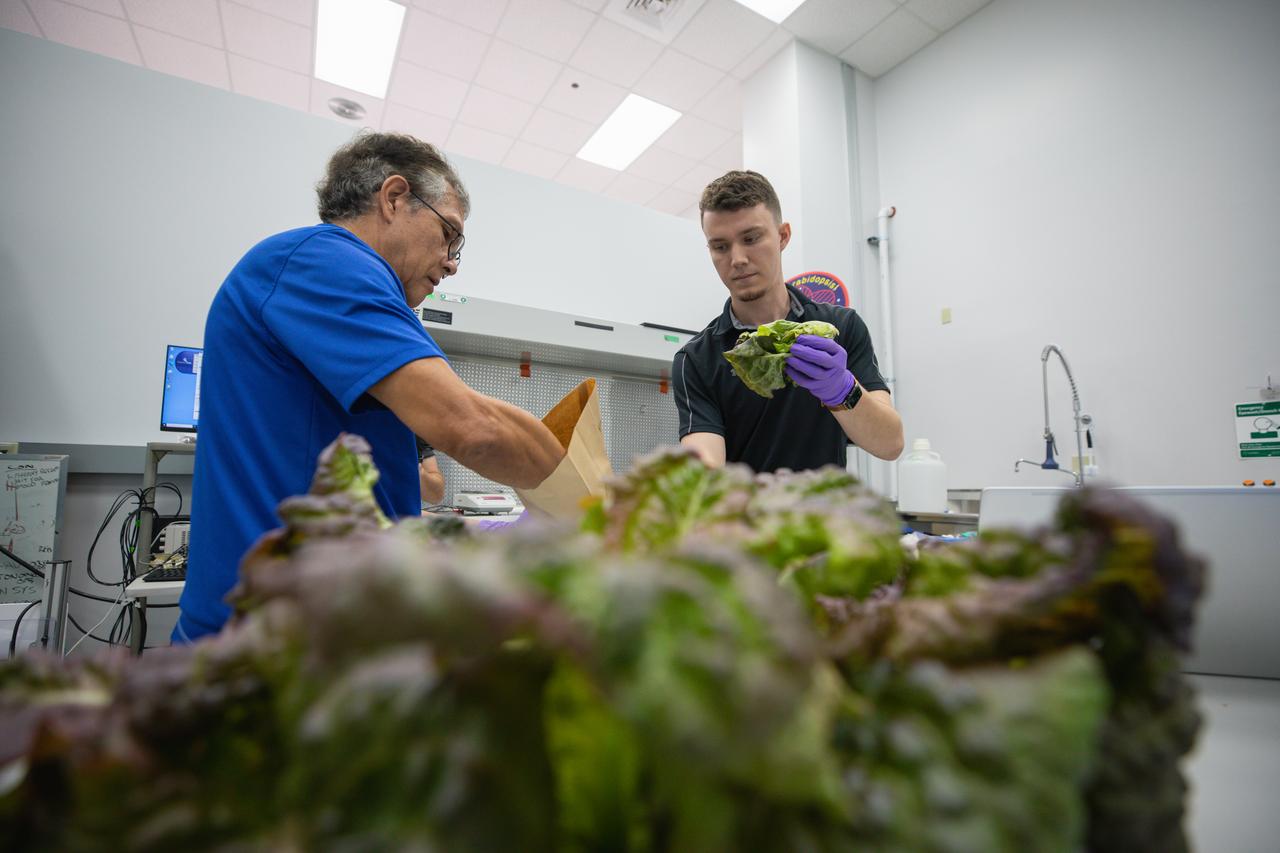

Space crop production scientists Oscar Monje (left) and Blake Costine harvest Outredgeous romaine lettuce for preflight testing of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 29, 2024. PH-07 will be sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.

Space crop production scientists Oscar Monje (left) and Blake Costine harvest Outredgeous romaine lettuce for preflight testing of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment inside a laboratory at the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 29, 2024. PH-07 will be sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.

ISS040-E-009116 (10 June 2014) --- In the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, harvests a crop of red romaine lettuce plants that were grown from seed inside the station?s Veggie facility, a low-cost plant growth chamber that uses a flat-panel light bank for plant growth and crew observation. For the Veg-01 experiment, researchers are testing and validating the Veggie hardware, and the plants will be returned to Earth to determine food safety.
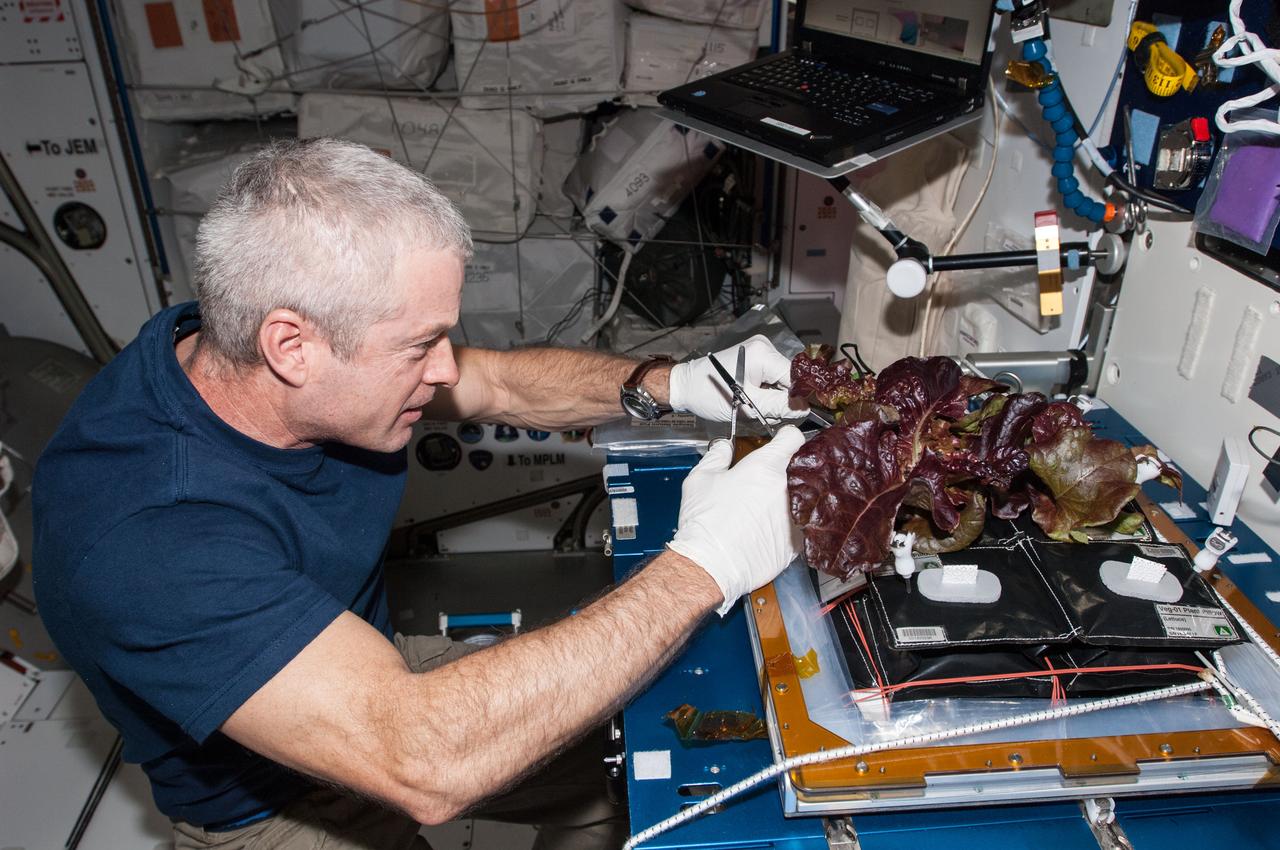

ISS040-E-009125 (10 June 2014) --- In the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, harvests a crop of red romaine lettuce plants that were grown from seed inside the station?s Veggie facility, a low-cost plant growth chamber that uses a flat-panel light bank for plant growth and crew observation. For the Veg-01 experiment, researchers are testing and validating the Veggie hardware, and the plants will be returned to Earth to determine food safety.
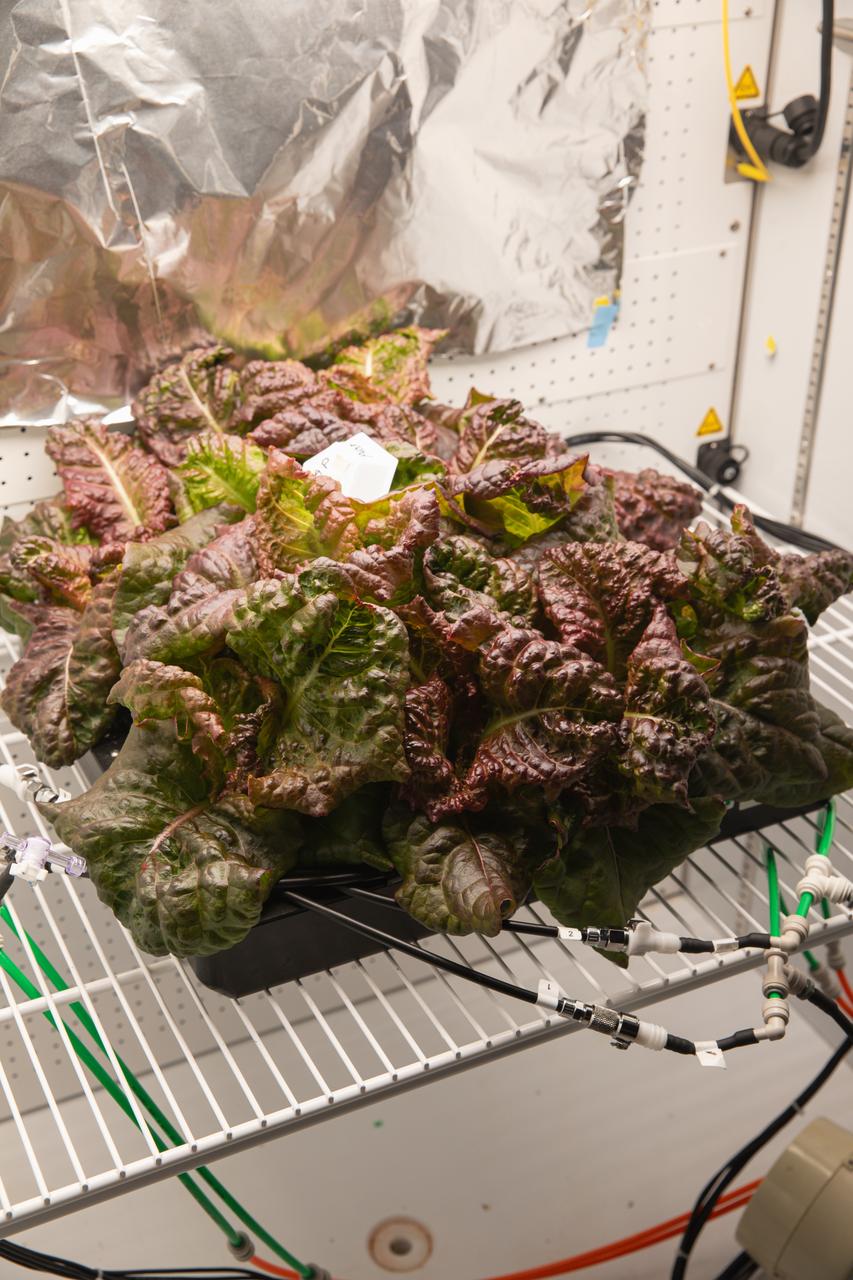

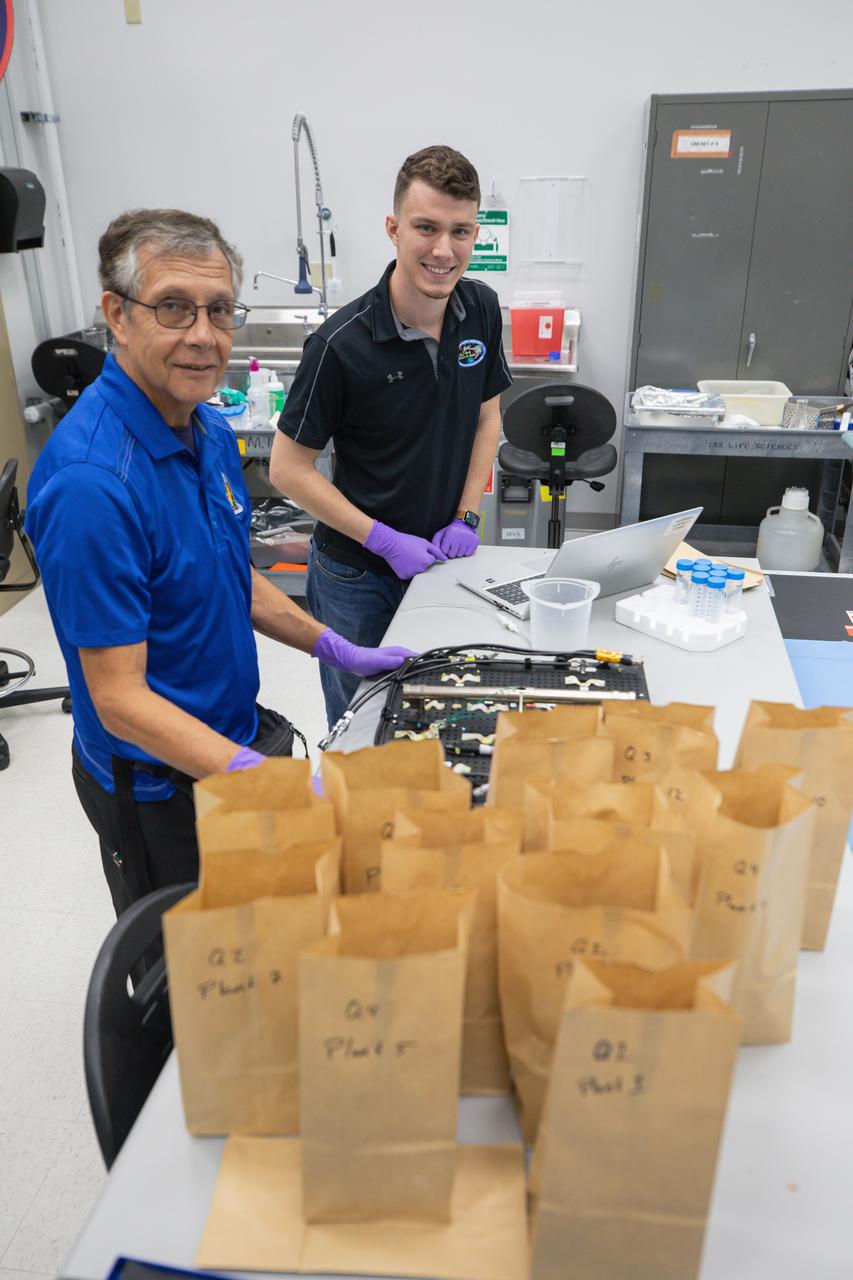
Space crop production scientists inside a laboratory at the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida harvest Outredgeous romaine lettuce for preflight testing of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, Aug. 29, 2024. PH-07 will be sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
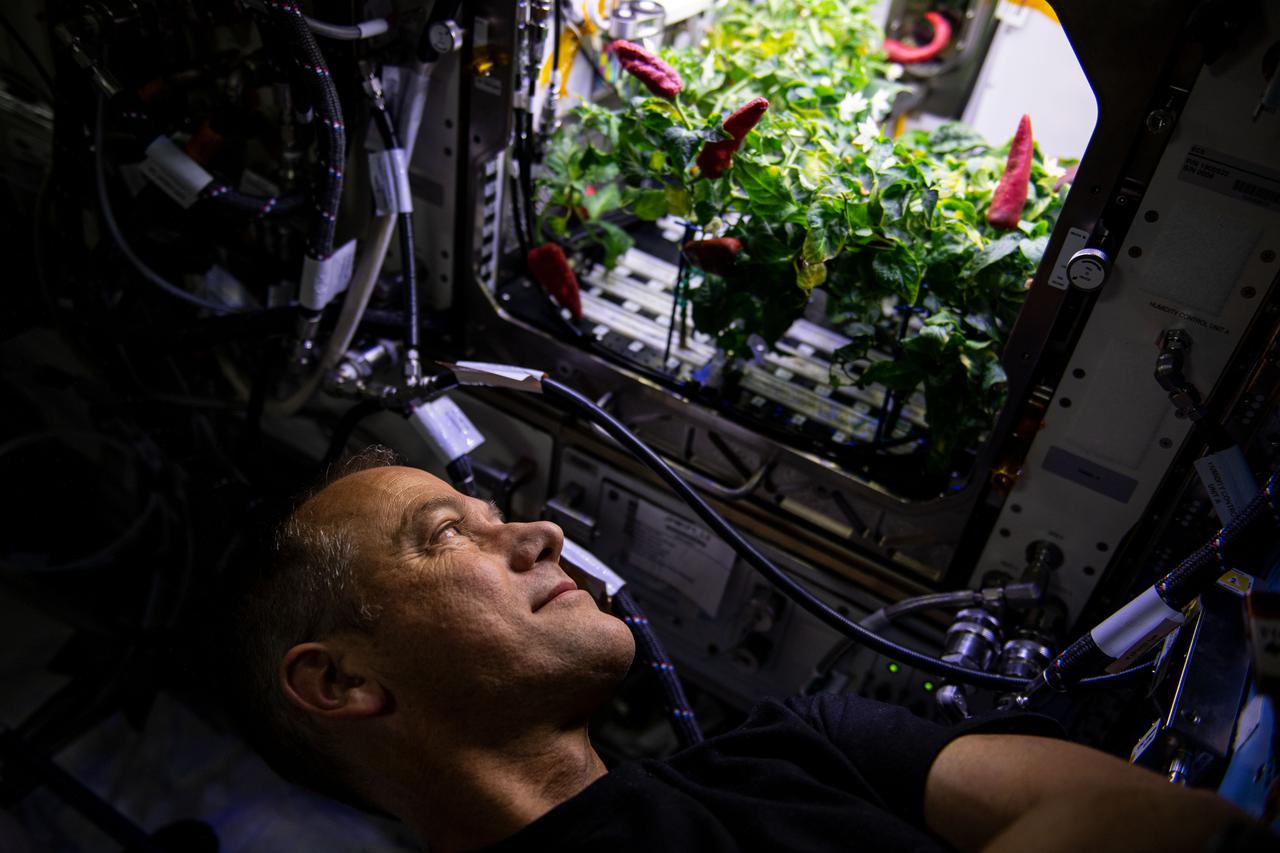

iss066e084304 (November 26, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Crew-3 member Tom Marshburn looks at chiles growing inside of the Advanced Plant Habitat. Crew-3 performed the second harvest of chiles aboard the International Space Station for the Plant Habitat-04 experiment. This plant experiment, one of the station’s most complex to date because of the long germination and growing times, will add to NASA’s knowledge of growing food crops for long-duration space missions.
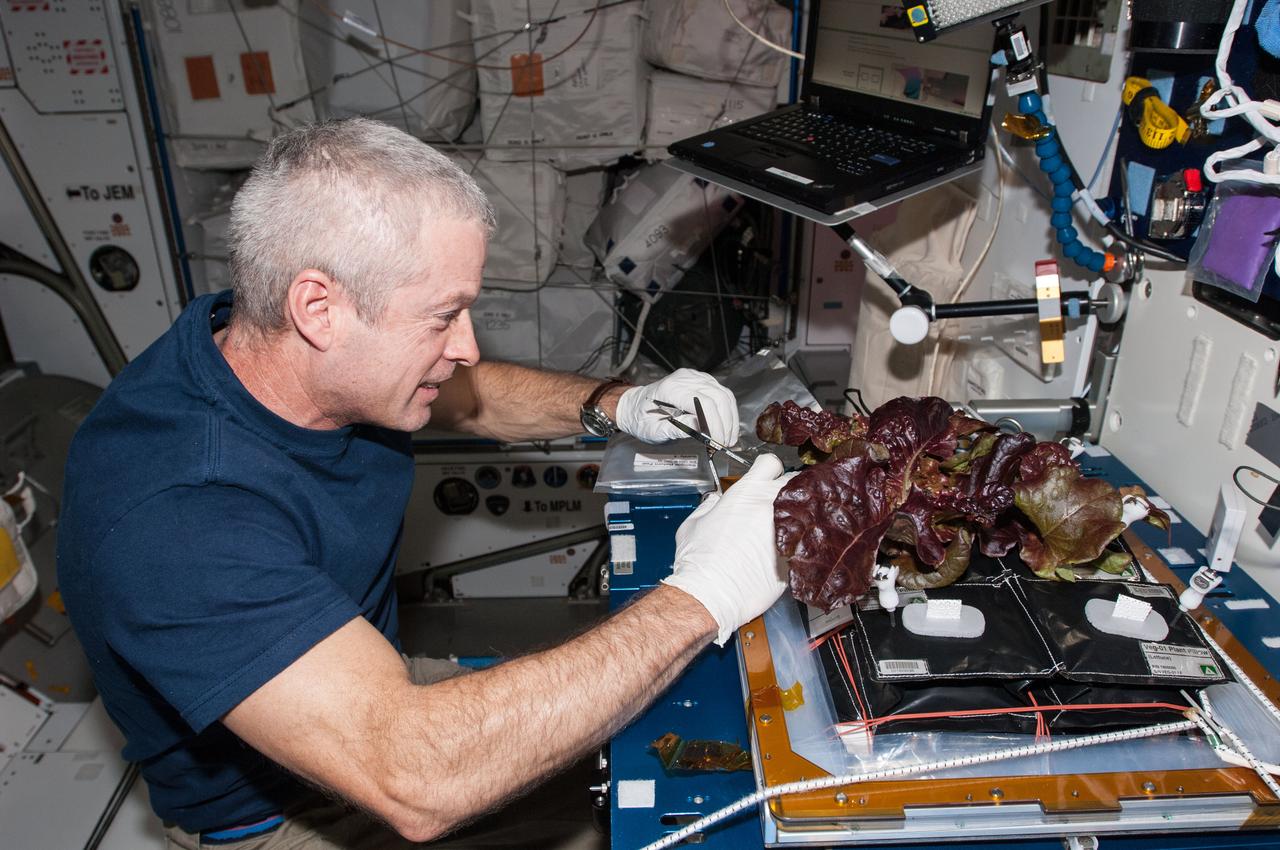

ISS040-E-009124 (10 June 2014) --- In the International Space Station?s Harmony node, NASA astronaut Steve Swanson, Expedition 40 commander, harvests a crop of red romaine lettuce plants that were grown from seed inside the station?s Veggie facility, a low-cost plant growth chamber that uses a flat-panel light bank for plant growth and crew observation. For the Veg-01 experiment, researchers are testing and validating the Veggie hardware, and the plants will be returned to Earth to determine food safety.

This Full Moon that occurred on September 17, 2024 in Cleveland, OH was a Partial Lunar Eclipse; a Supermoon; the Corn Moon; and a harvest moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
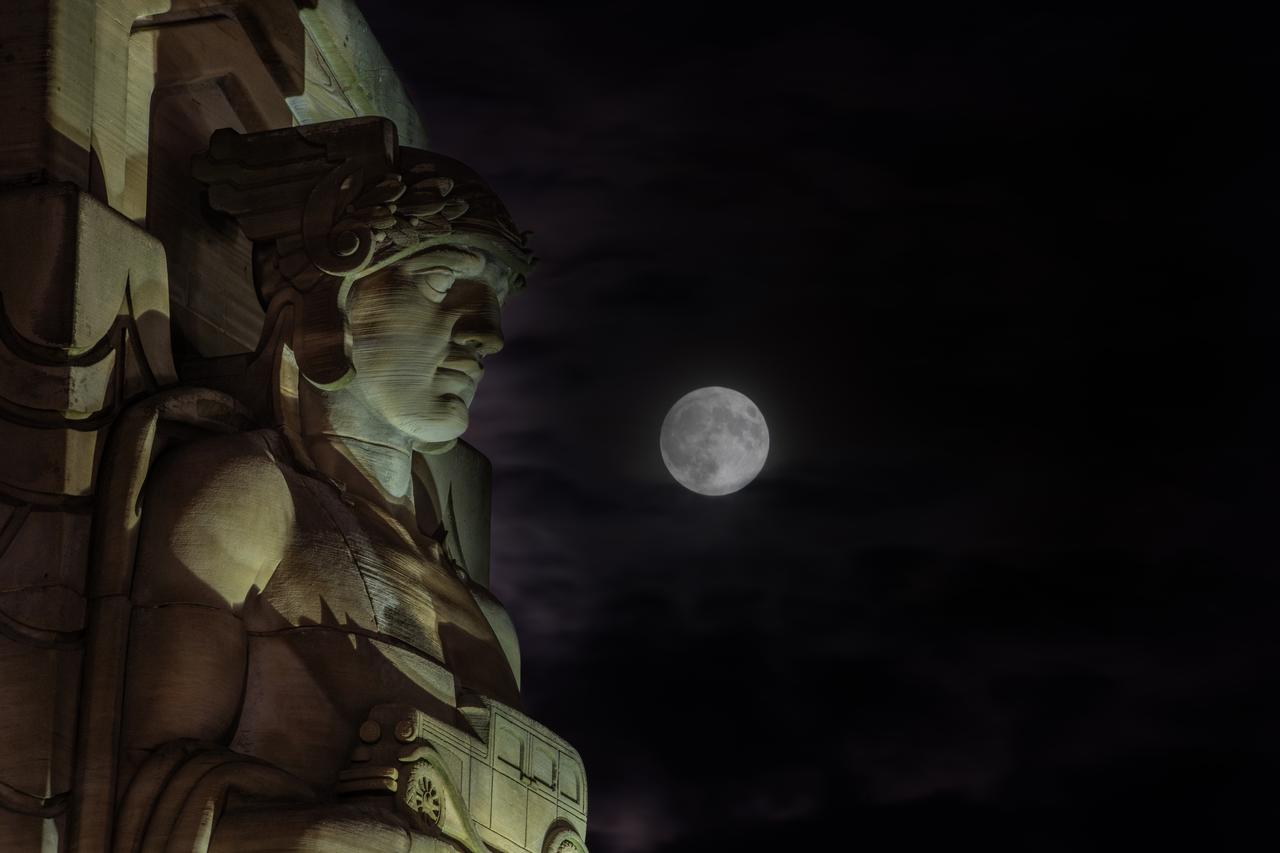

Guardians of Traffic Statue in Cleveland, OH in front of the Supermoon that was visible on September 17th, 2024. On this day, the full moon was a partial lunar eclipse; a supermoon; and a harvest moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
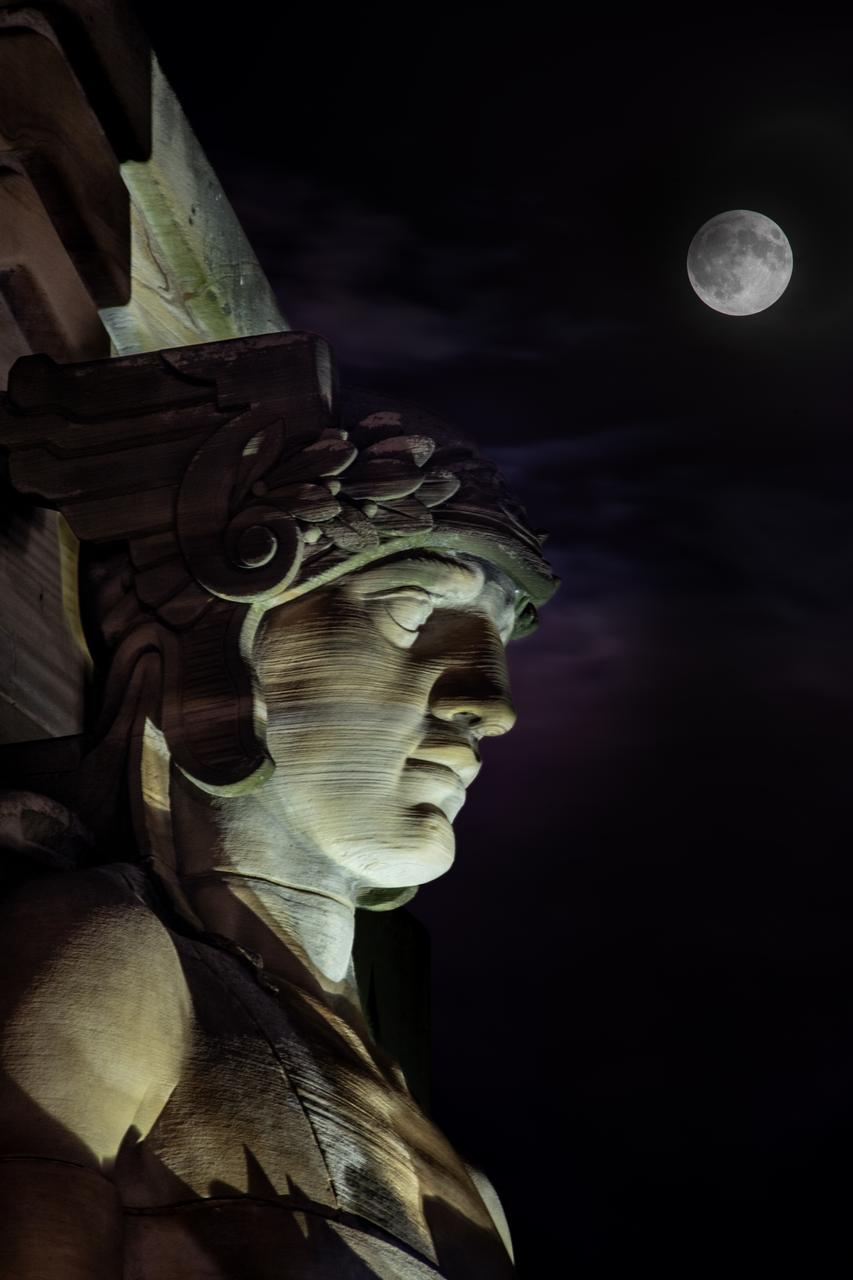

Guardians of Traffic Statue in Cleveland, OH watches over the Supermoon that was visible on September 17th, 2024. On this day, the full moon was a partial Lunar Eclipse; a Supermoon; and a Harvest Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
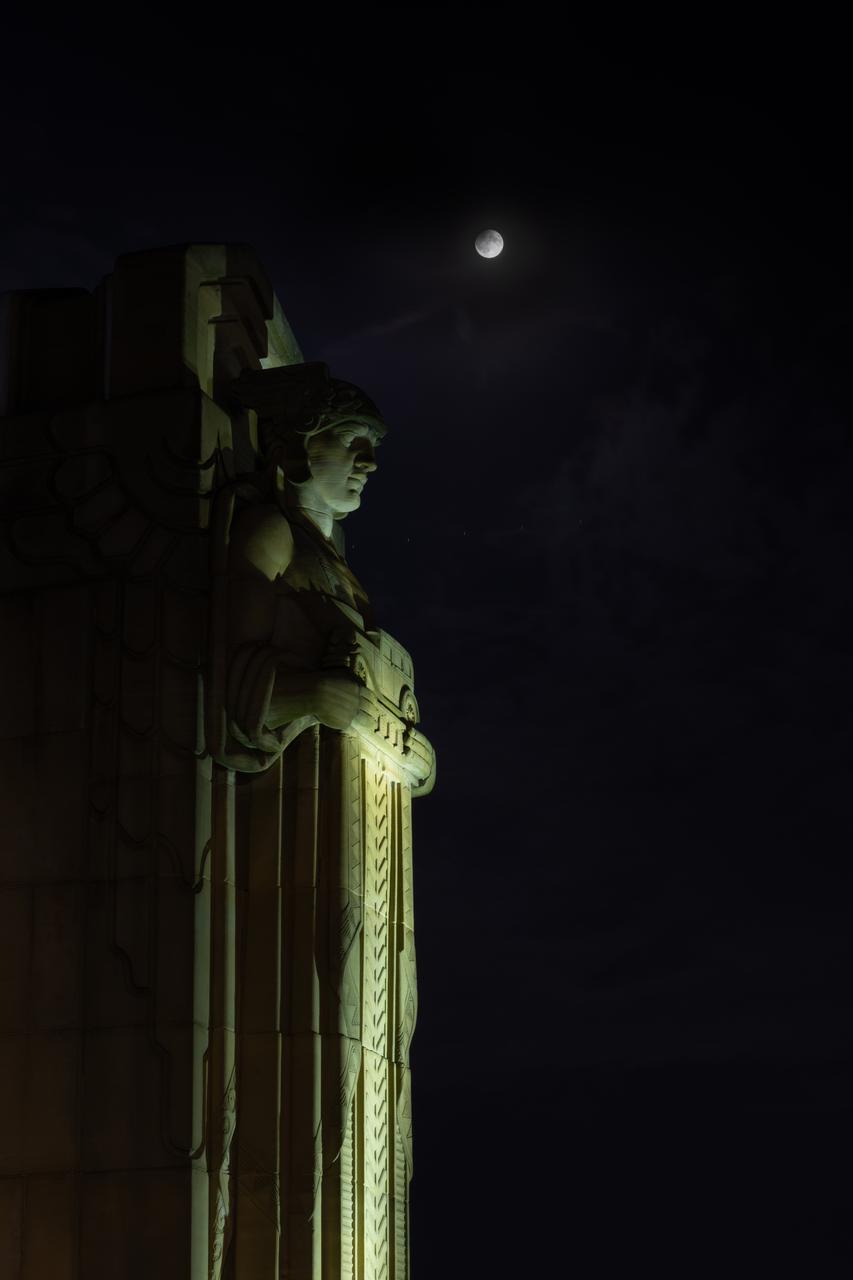

Guardians of Traffic Statue in Cleveland, OH in front of the Supermoon that was visible on September 17th, 2024. On this day, the full moon was a partial lunar eclipse; a supermoon; and a harvest moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
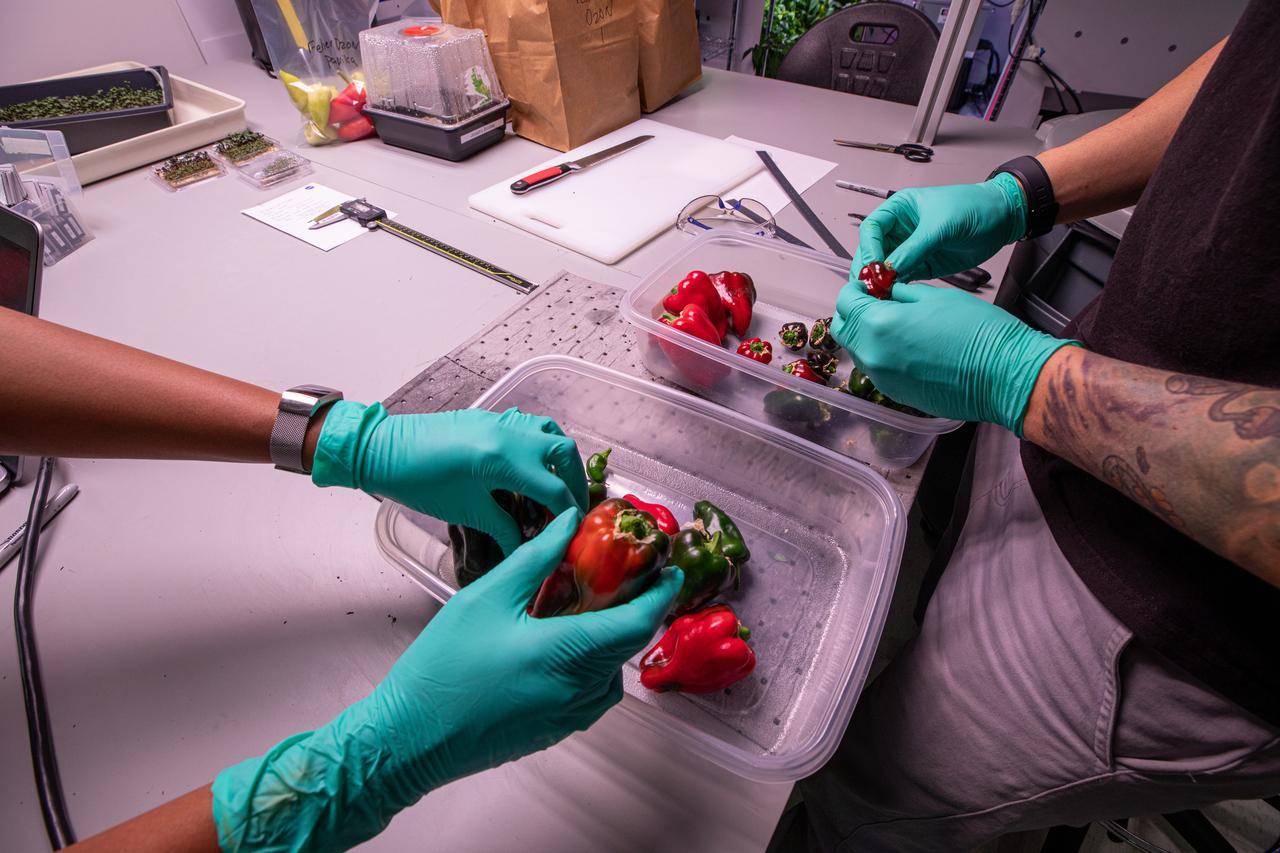

Research scientists at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing to weigh peppers grown inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020, during a growth assessment in preparation for sending them to space. Scientists waited until the peppers were red, or nearly all red, before harvesting them. Fresh produce will be an essential supplement to the pre-packaged diet for astronauts during long-duration space exploration when they are away from Earth for extended periods of time.
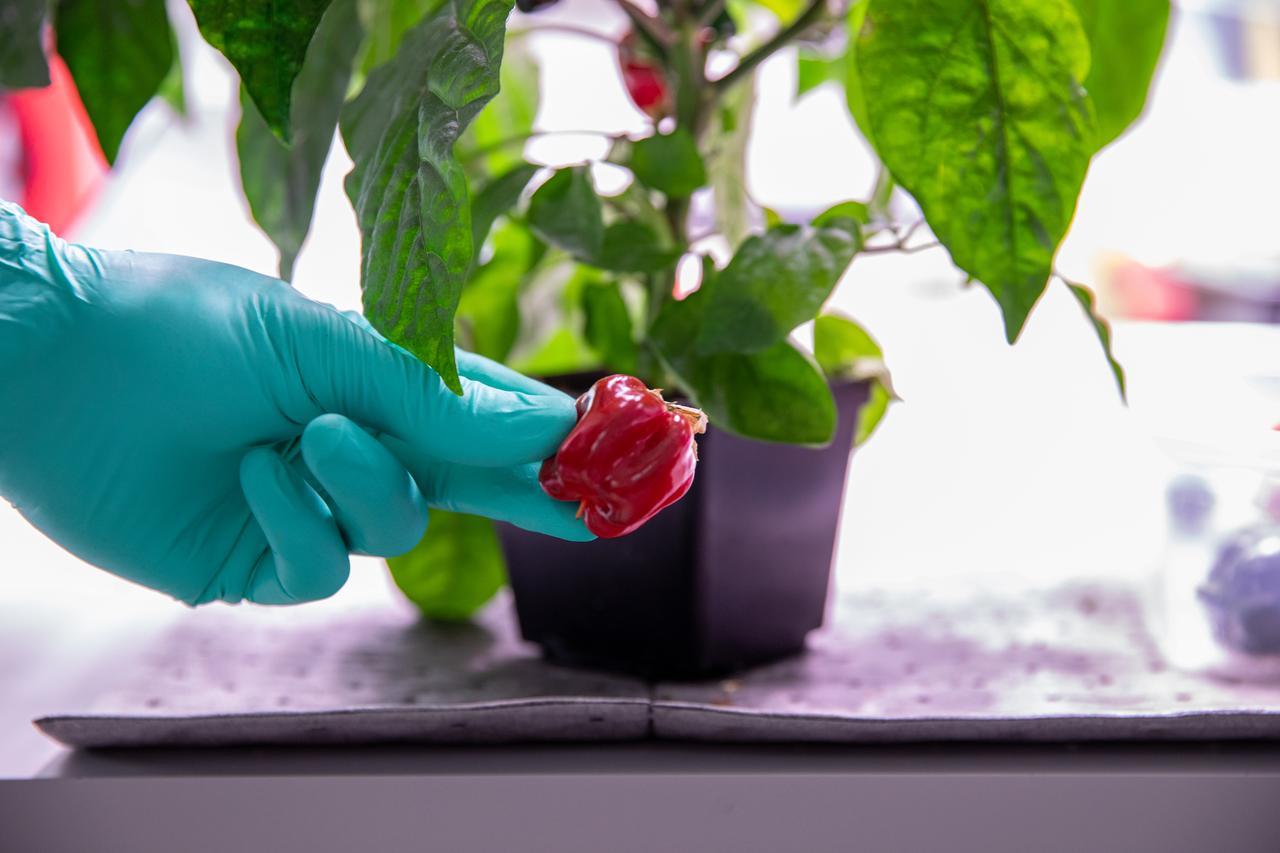

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, peppers are harvested on Jan. 15, 2020, for a growth assessment in preparation for sending them to space. As NASA prepares to send humans beyond low-Earth orbit, the ability for astronauts to grow a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables in space will be critical. Fresh produce will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet during long-duration space exploration when they are away from Earth for extended periods of time.
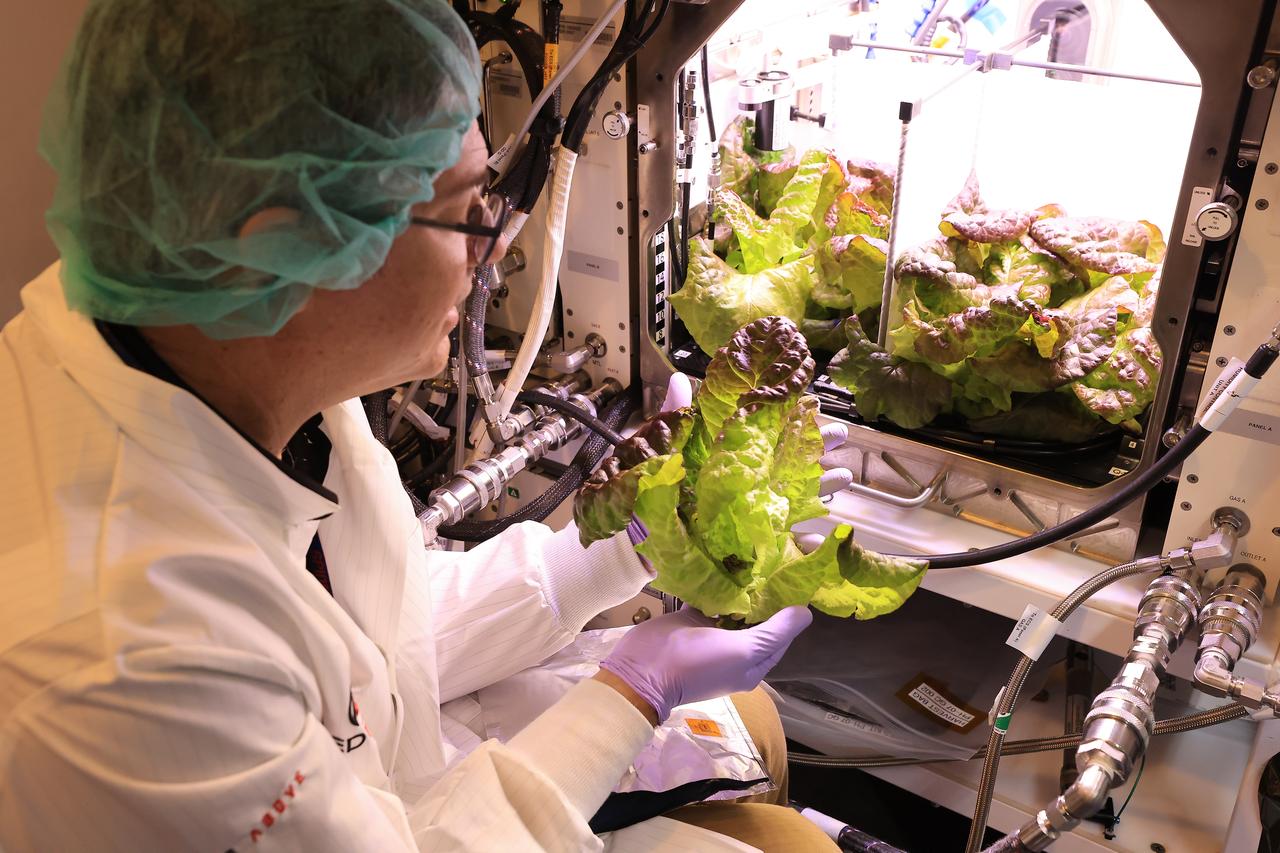

Inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a plant biologist harvests Outredgeous romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit as the ground control portion of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, April 24, 2025. PH-07 was sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
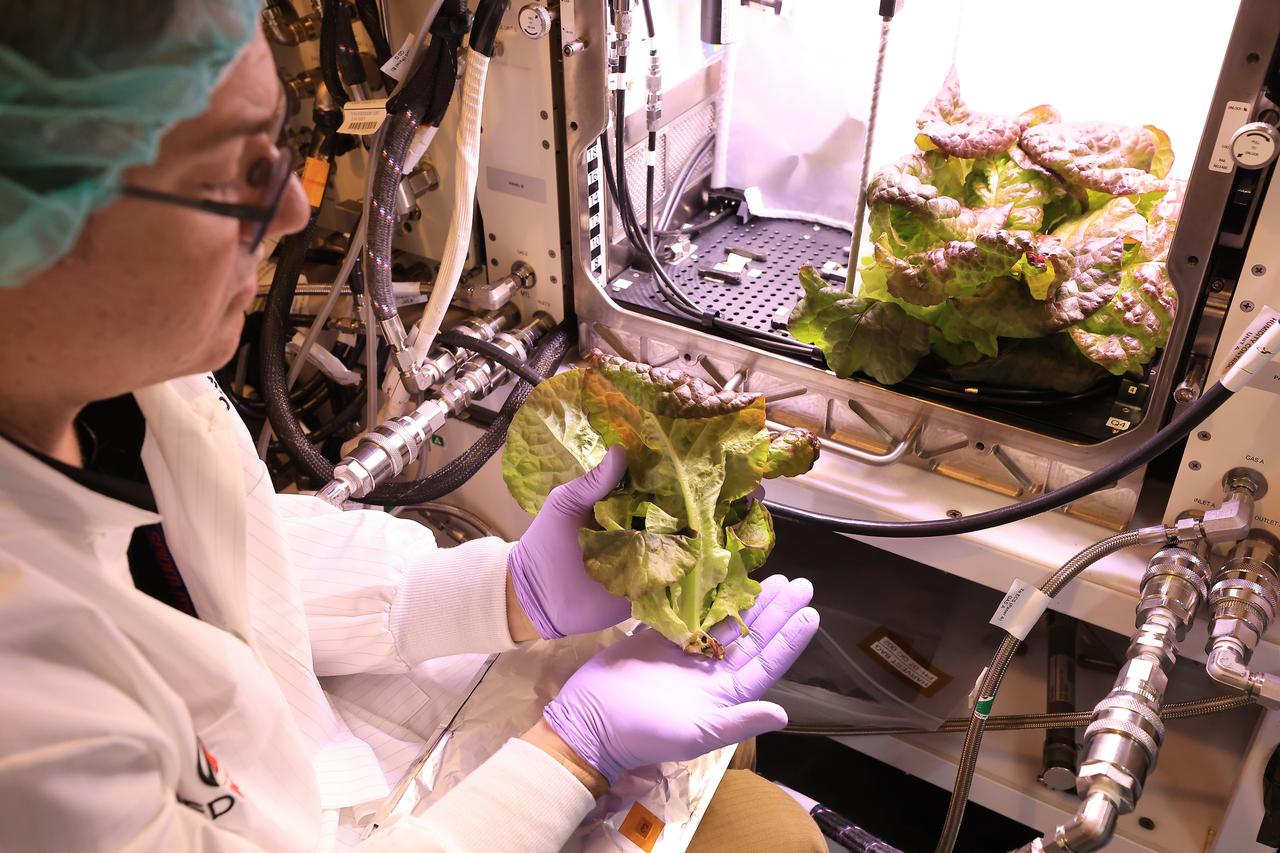

Inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a plant biologist harvests Outredgeous romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit as the ground control portion of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, April 24, 2025. PH-07 was sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
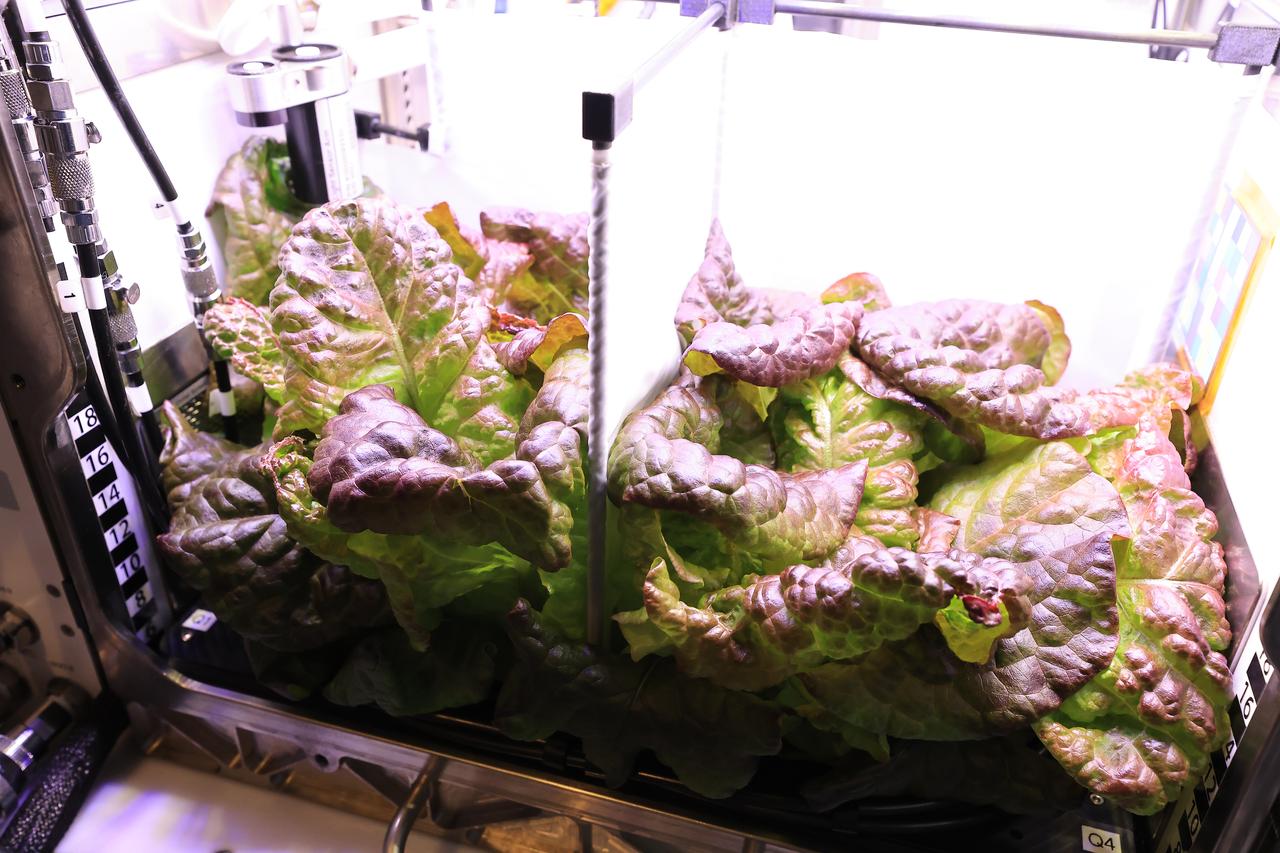

Plant biologists inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepare to harvest Outredgeous romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit as the ground control portion of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, April 24, 2025. PH-07 was sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
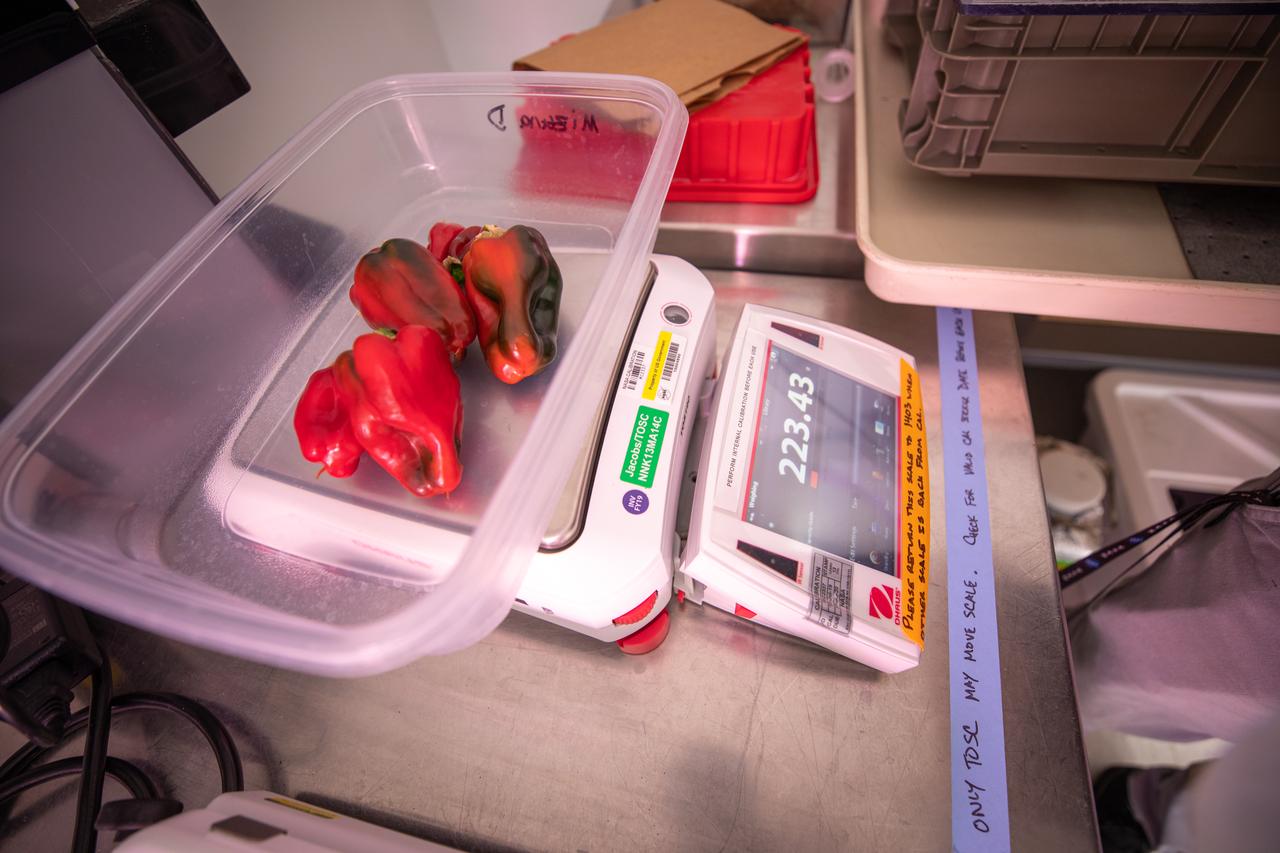

Peppers that were grown and harvested inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are weighed on Jan. 15, 2020, in preparation for sending them to space. As NASA prepares to send humans beyond low-Earth orbit, the ability for astronauts to grow a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables in space will be critical. Fresh produce will be an essential supplement to the crew’s pre-packaged diet during long-duration space exploration when they are away from Earth for extended periods of time.
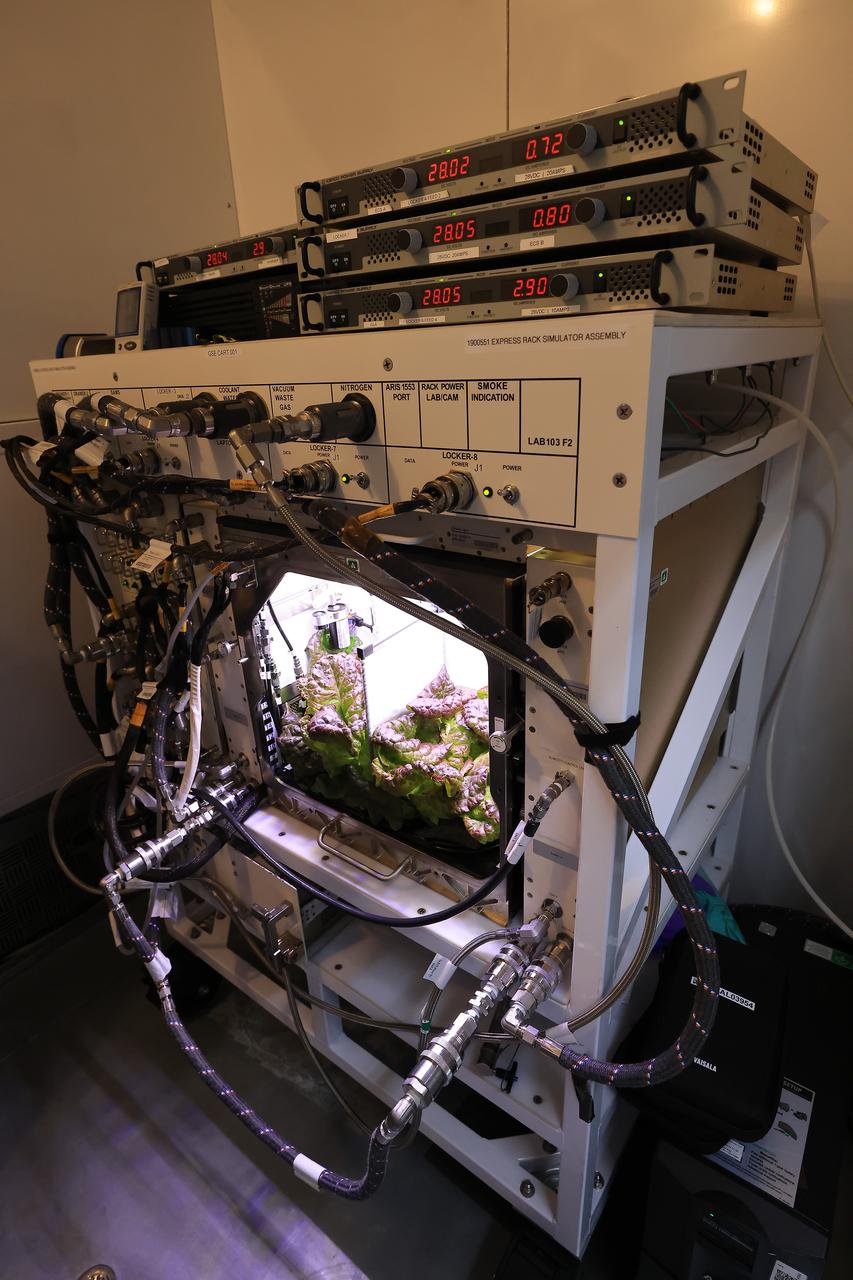

Plant biologists inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepare to harvest Outredgeous romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit as the ground control portion of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, April 24, 2025. PH-07 was sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.
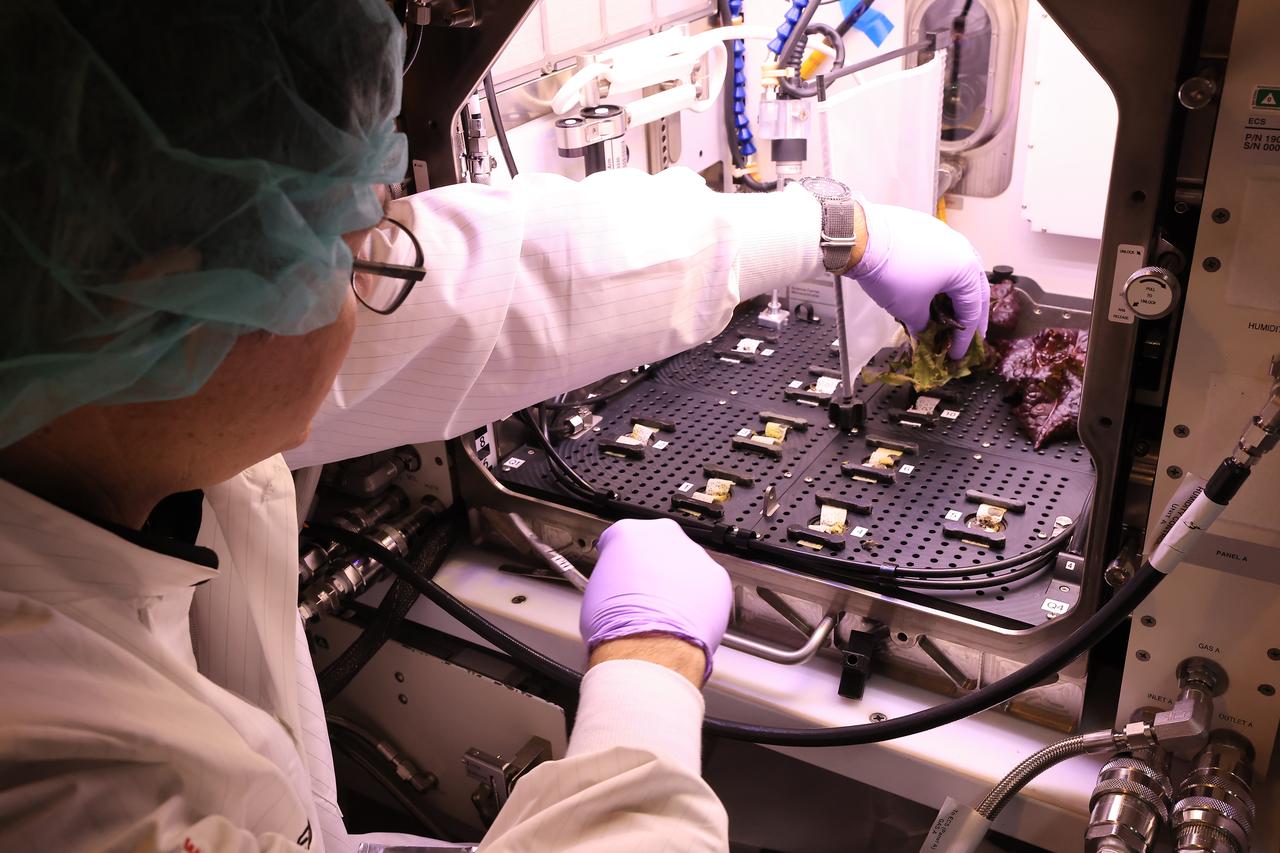

Inside a laboratory in the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a plant biologist harvests Outredgeous romaine lettuce growing in the Advanced Plant Habitat ground unit as the ground control portion of the Plant Habitat-07 (PH-07) experiment on Thursday, April 24, 2025. PH-07 was sent to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX 31st commercial resupply services mission to study how optimal and suboptimal moisture conditions impact plant growth, nutrient content, and the plant microbiome.

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.
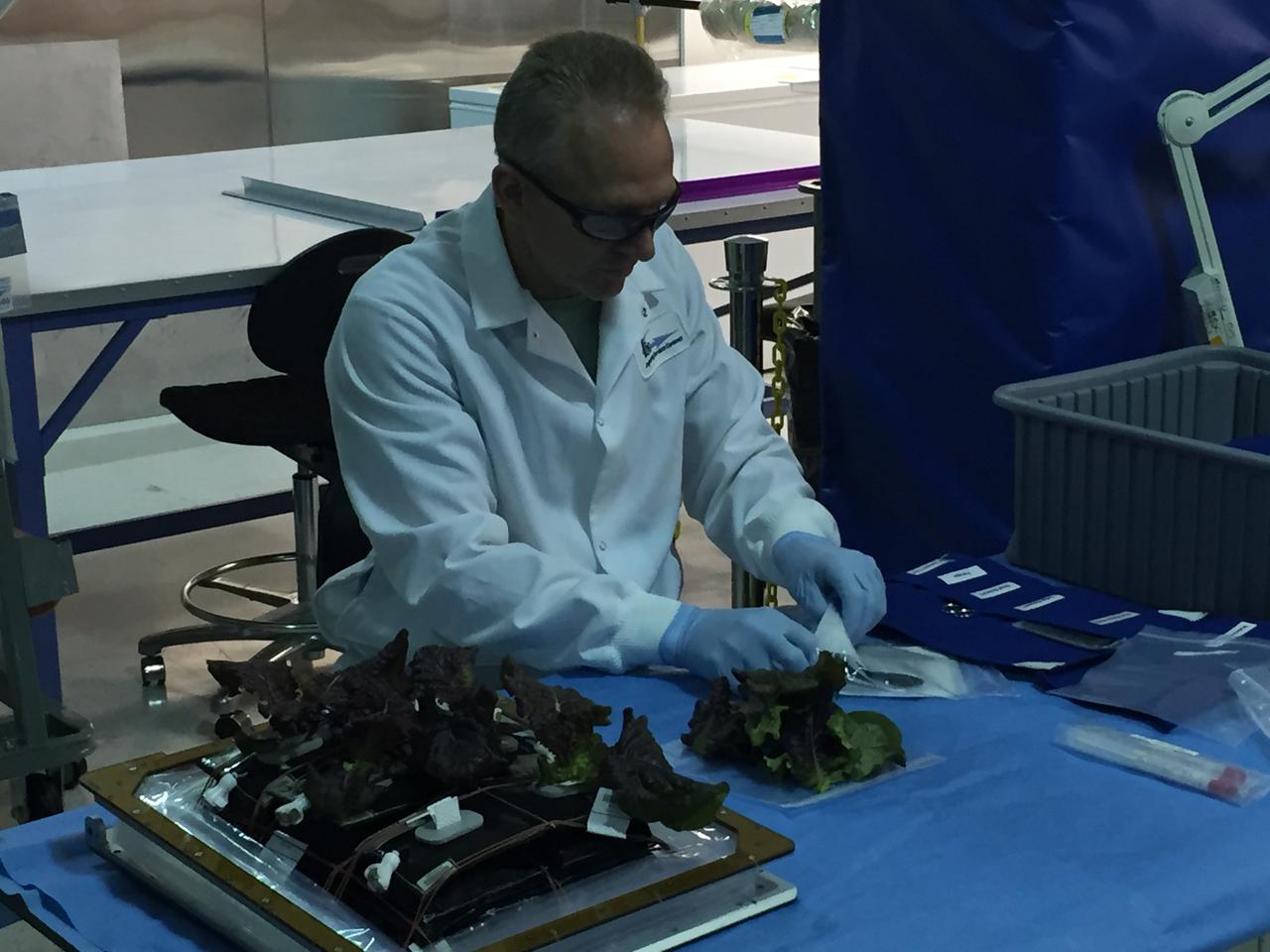

Astronaut Scott Kelly initiated VEG-01 B, the second crop of lettuce, on July, 8, 2015, and both Kelly and Astronaut Kjell Lindgren cared for the plants. The crop grew for 33 days. VEG-01 B included one set of six plant pillows planted with red romaine lettuce seeds. On Aug. 10, 2015, the crew harvested and consumed leaves from each plant. This was the first crop grown and consumed in NASA hardware. They harvested the rest of the plant tissue and froze it in the station’s Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI) for return to Earth for further study including microbial analysis, antioxidant capacity, mineral analysis and anthocyanin concentration.