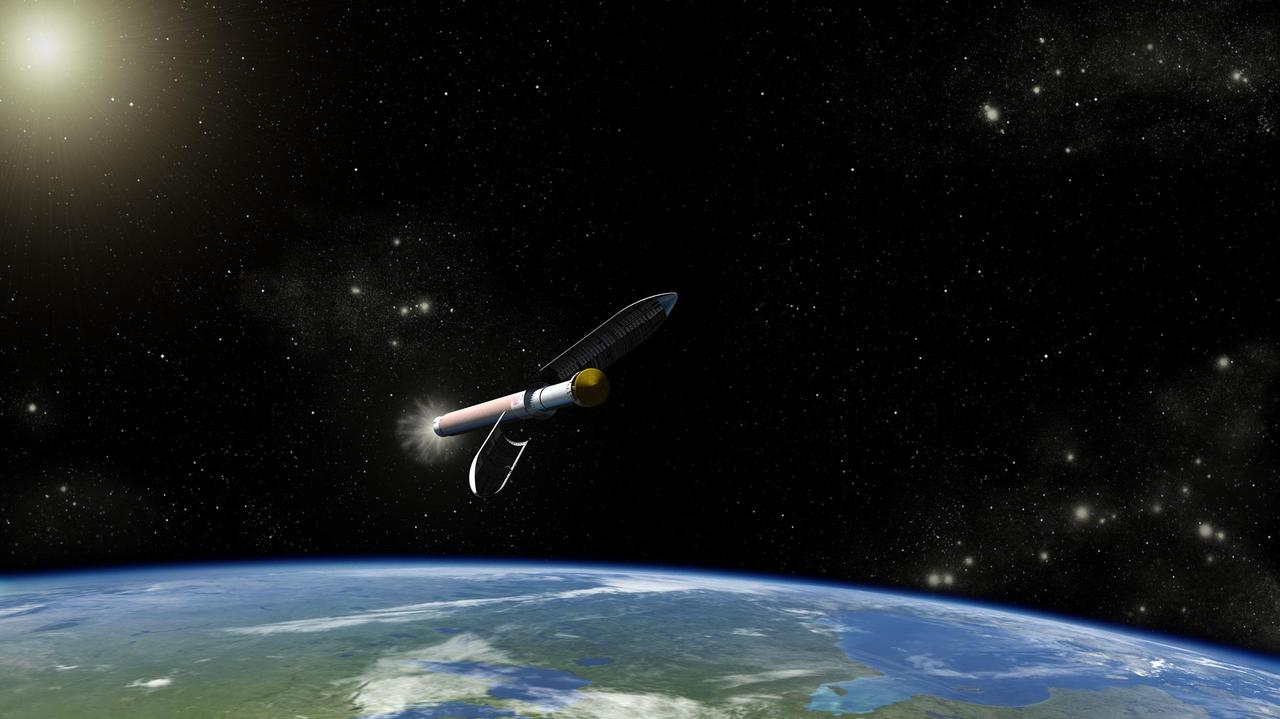

This artist concept is of the Atlas V541 launch vehicle that will carry NASA Curiosity rover on its way to Mars. The Atlas V 541 vehicle was selected as it has the right liftoff capability for heavy weight requirements of the rover and its spacecraft.
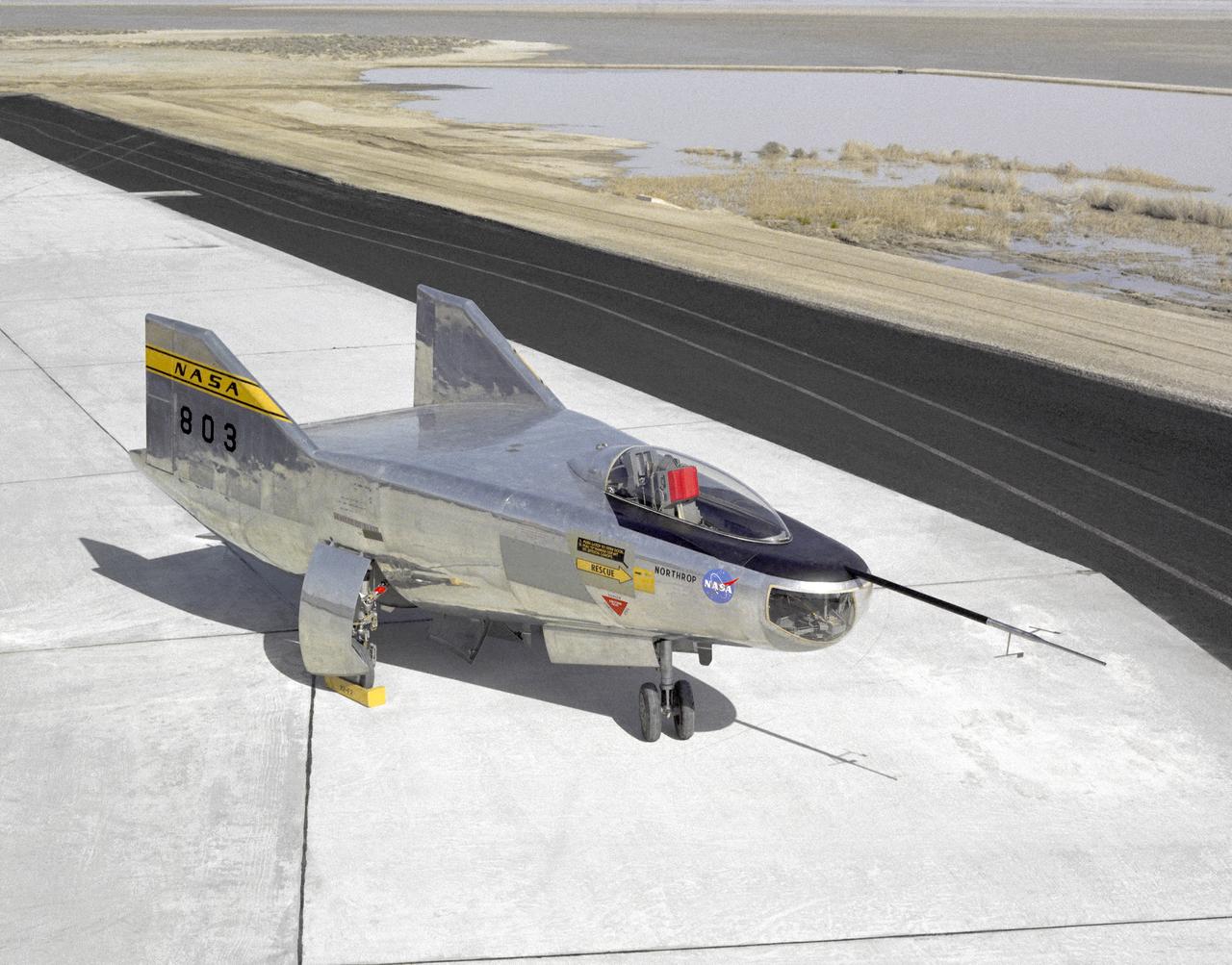

The M2-F2 Lifting Body is seen here on the ramp at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.

JSC2002-E-31360 (23 July 2002) --- Astronaut Jeffrey S. Ashby (left), STS-112 mission commander, and instructor David L. Mumme are pictured near a KC-135 aircraft at Ellington Field near the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Although used primarily for the Zero Gravity program at JSC, the large aircraft also fits the bill for heavy aircraft familiarization. Most training for Shuttle landings takes place in the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA), which is much lighter in gross weight than the Shuttle. It does a superb job of flying like the Shuttle while on final, but in the flare (right at landing) there are some subtleties to the dynamics of heavy aircraft that only a vehicle of similar weight can demonstrate. Astronauts practice landings in the KC-135 since it is more similar in gross weight to a Shuttle.
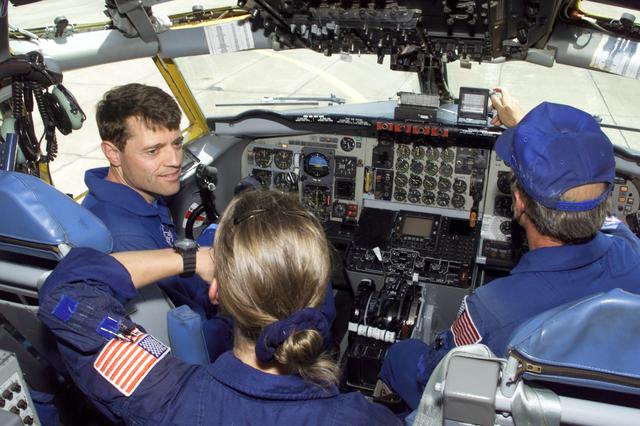

JSC2002-E-31362 (23 July 2002) --- Astronauts Jeffrey S. Ashby (left) and Pamela A. Melroy, STS-112 mission commander and pilot, respectively; along with instructor David L. Mumme, are photographed in the cockpit of a KC-135 aircraft at Ellington Field near the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Although used primarily for the Zero Gravity program at JSC, the large aircraft also fits the bill for heavy aircraft familiarization. Most training for Shuttle landings takes place in the Shuttle Training Aircraft (STA), which is much lighter in gross weight than the Shuttle. It does a superb job of flying like the Shuttle while on final, but in the flare (right at landing) there are some subtleties to the dynamics of heavy aircraft that only a vehicle of similar weight can demonstrate. Astronauts practice landings in the KC-135 since it is more similar in gross weight to a Shuttle.
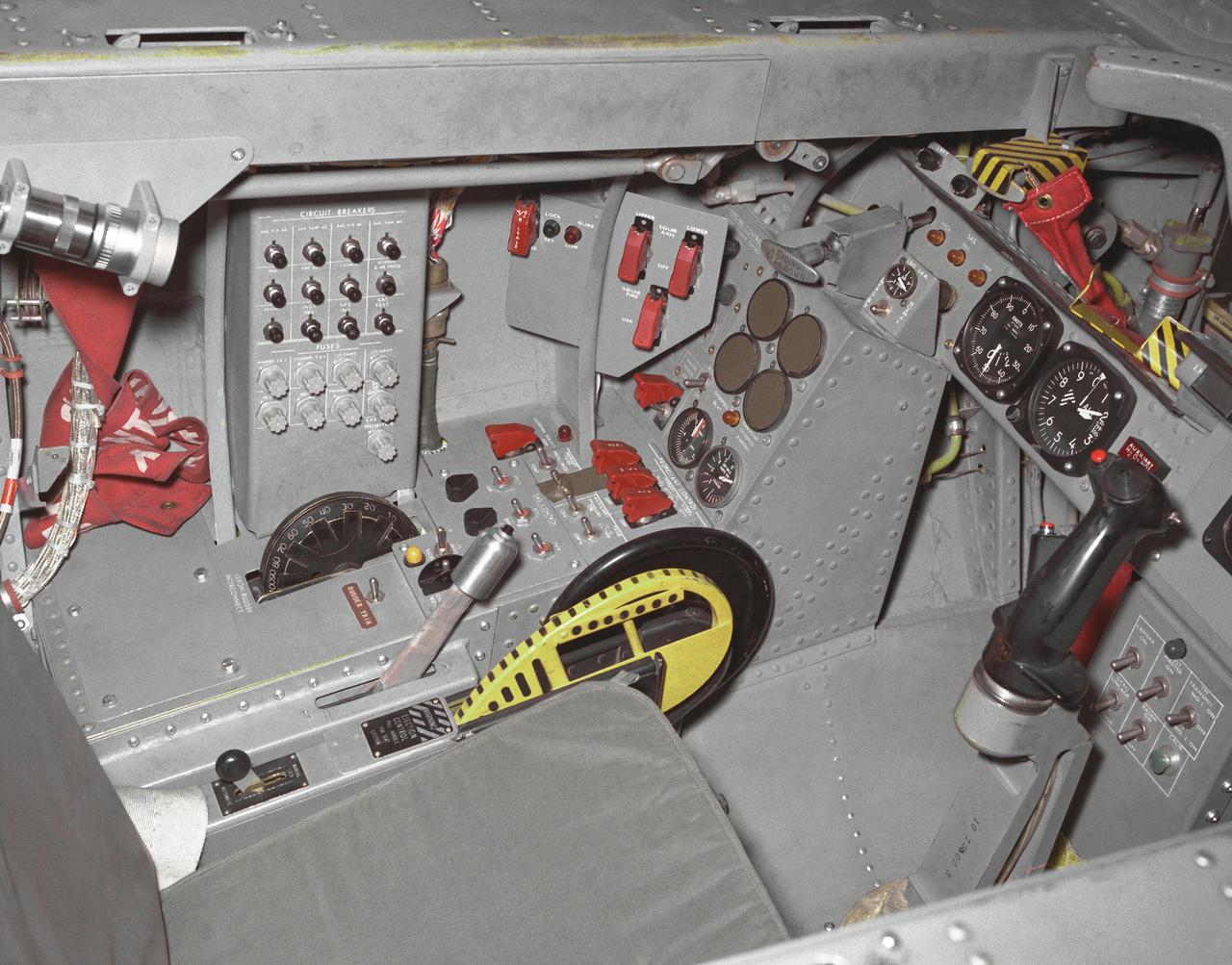

This photo shows the left side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
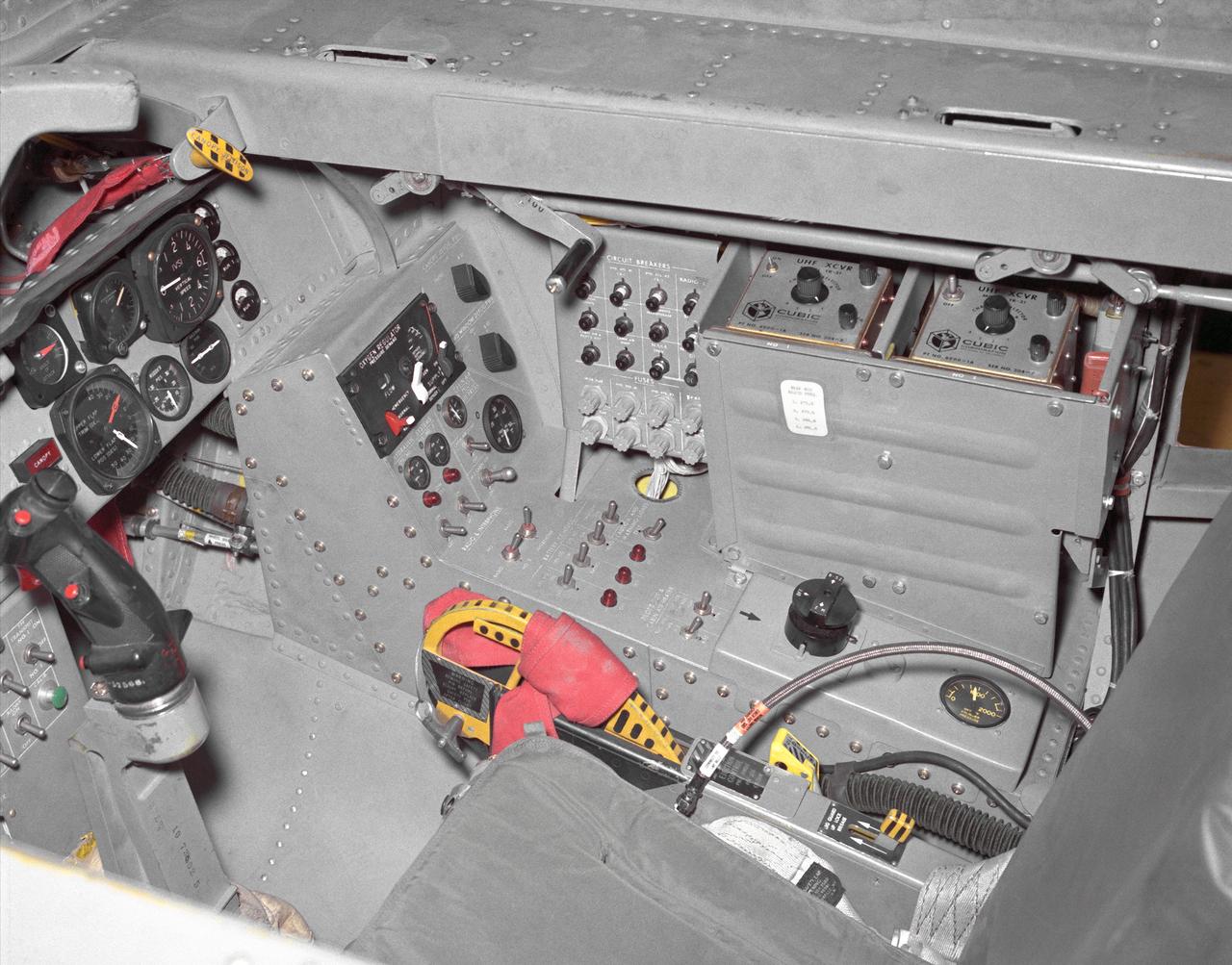

This photo shows the right side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
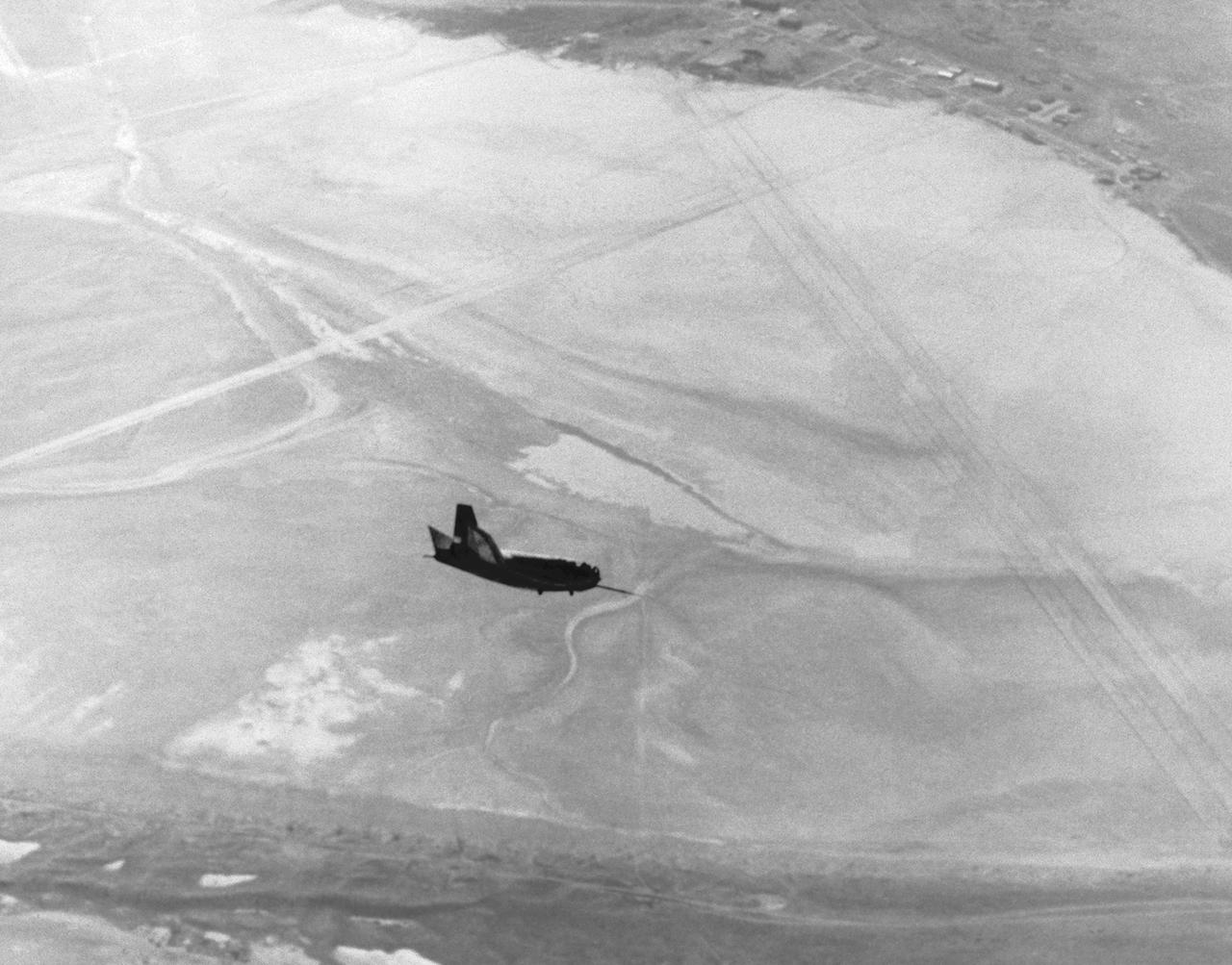

The HL-10 lifting body is seen here in flight over Rogers Dry Lake at Edwards AFB. After the vehicle's fins were modified following its first flight, the HL-10 proved to be the best handling of the heavy-weight lifting bodies flown at Edwards Air Force Base. The HL-10 flew much better than the M2-F2, and pilots were eager to fly it.
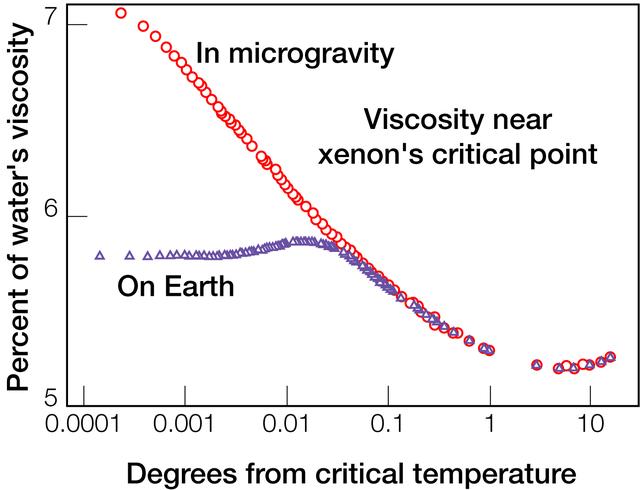
The Critical Viscosity of Xenon Experiment (CVX-2) on the STS-107 Research 1 mission in 2002 will measure the viscous behavior of xenon, a heavy inert gas used in flash lamps and ion rocket engines, at its critical point. Because xenon near the critical point will collapse under its own weight, experiments on Earth (green line) are limited as they get closer (toward the left) to the critical point. CVX in the microgravity of space (red line) moved into unmeasured territory that scientists had not been able to reach.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Members of the crawlerway system evaluation team pose for a group portrait in front of the Headquarters Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The team received the Florida Project of the Year award from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). The Cape Canaveral branch of the ASCE nominated the team for its project, the Crawlerway Evaluation to Support a Heavy-Lift Program. The crawlerway is a 130-foot-wide, specialty-built roadway between Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), where rockets and spacecraft are prepared for flight, and Launch Pad 39A and 39B. The team's more than two-year evaluation confirmed the crawlerway system would be able to support the weight of moving the agency's future heavy-lift rockets and potential commercial vehicles from the VAB to the launch pads. The award honors the team's outstanding engineering efforts in research, design, construction and management, recognizing the complexity of multi-agency coordination and cost-effective engineering advances. For more information on the American Society of Civil Engineers, visit: http://www.asce.org. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA managers at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida show off the Florida Project of the Year trophies that the crawlerway system evaluation team received from the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). From left are Michael Benik, director of Center Operations; Pepper Phillips, manager of the 21st Century Ground Systems Program Office; and Russell Romanella, associate director for Engineering and Technical Operations. The Cape Canaveral branch of the ASCE nominated the team for its project, the Crawlerway Evaluation to Support a Heavy-Lift Program. The crawlerway is a 130-foot-wide, specialty-built roadway between Kennedy's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), where rockets and spacecraft are prepared for flight, and Launch Pad 39A and 39B. The team's more than two-year evaluation confirmed the crawlerway system would be able to support the weight of moving the agency's future heavy-lift rockets and potential commercial vehicles from the VAB to the launch pads. The award honors the team's outstanding engineering efforts in research, design, construction and management, recognizing the complexity of multi-agency coordination and cost-effective engineering advances. For more information on the American Society of Civil Engineers, visit: http://www.asce.org. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
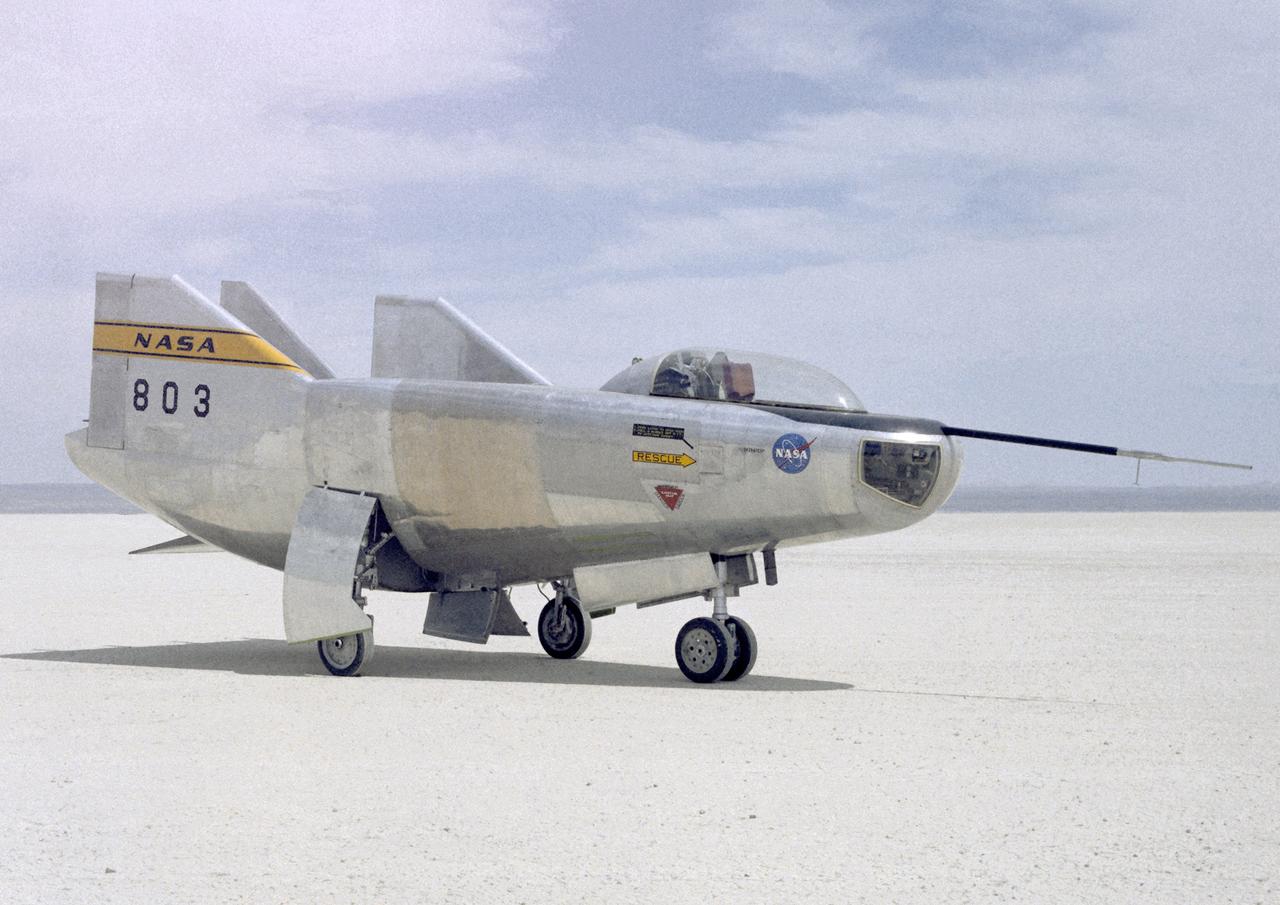

The M2-F3 Lifting Body is seen here on the lakebed next to the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC--later Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. The May 1967 crash of the M2-F2 had torn off the left fin and landing gear. It had also damaged the external skin and internal structure. Flight Research Center engineers worked with Ames Research Center and the Air Force in redesigning the vehicle with a center fin to provide greater stability. Then Northrop Corporation cooperated with the FRC in rebuilding the vehicle. The entire process took three years.
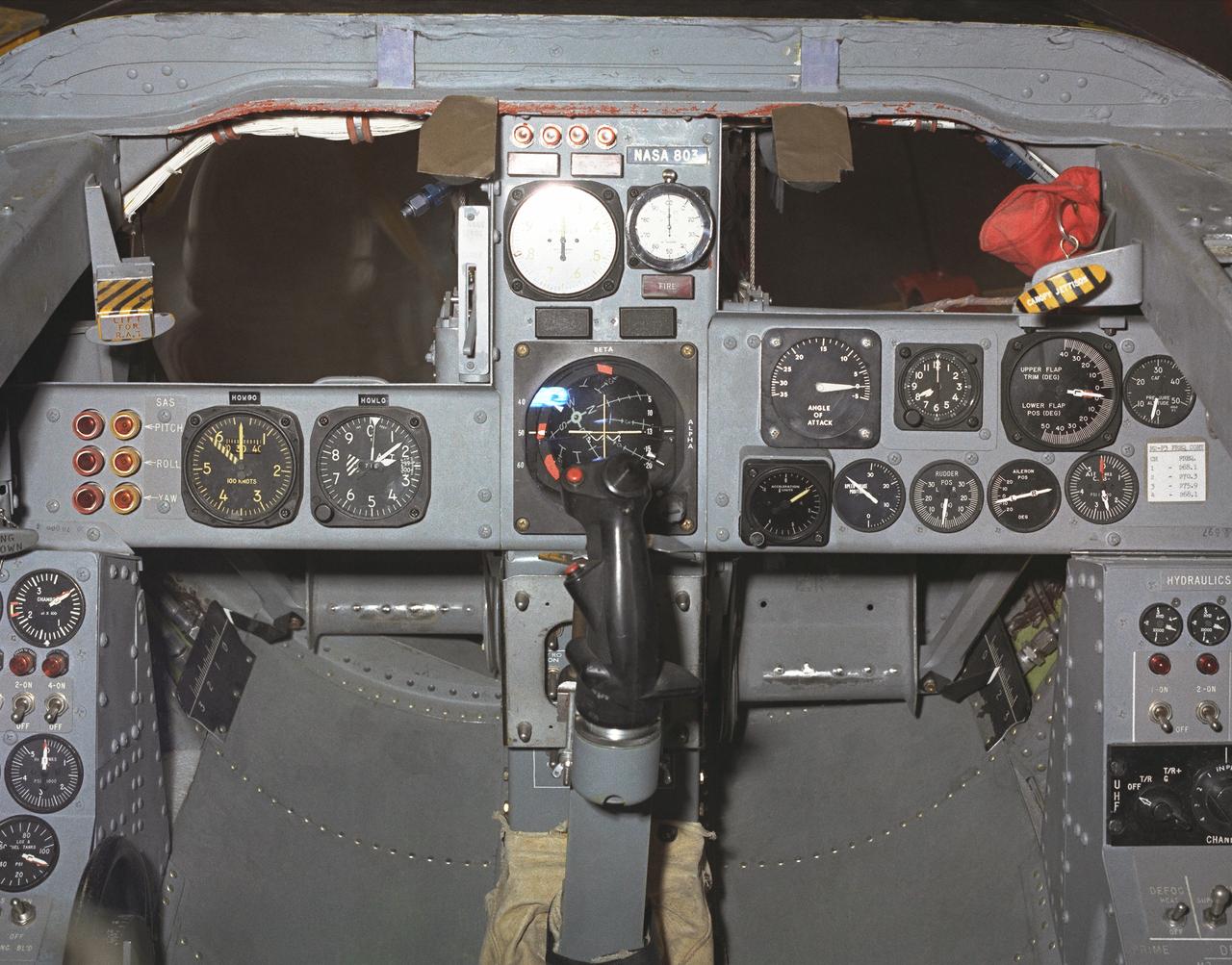

This photo shows the cockpit instrument panel of the M2-F3 Lifting Body.
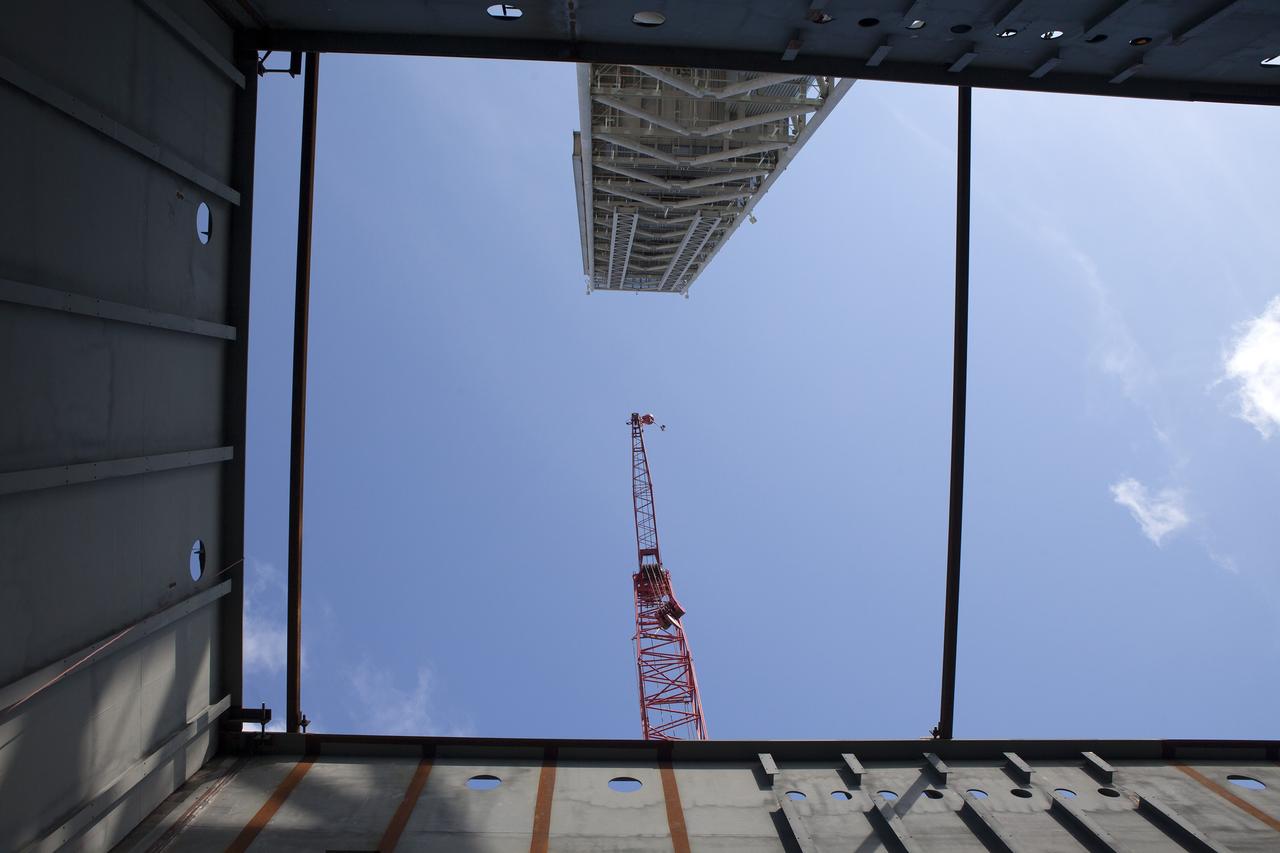

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In this view looking up from beneath the ML, the tower and a large crane are visible. The crane is situated near the ML for lifting of heavy metal beams and other construction materials. Sections of the ML are being modified and strengthened to accommodate the weight, size and thrust at launch of NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The existing 24-foot exhaust hole is being enlarged and strengthened for the larger, heavier SLS rocket. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission-1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
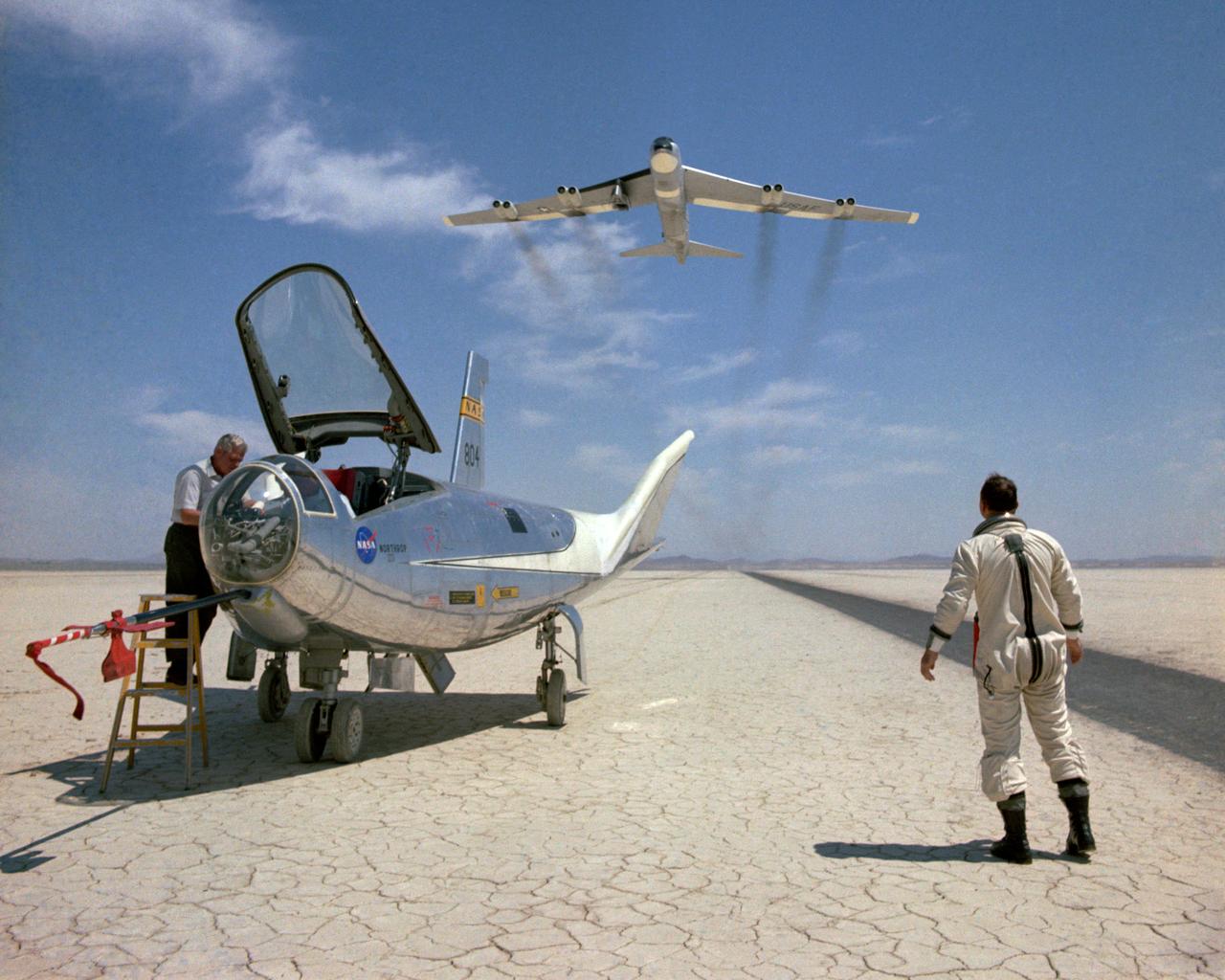

The HL-10 was one of five heavyweight lifting-body designs flown at NASA's Flight Research Center (FRC--later Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, from July 1966 to November 1975 to study and validate the concept of safely maneuvering and landing a low lift-over-drag vehicle designed for reentry from space. Northrop Corporation built the HL-10 and M2-F2, the first two of the fleet of "heavy" lifting bodies flown by the NASA Flight Research Center. The contract for construction of the HL-10 and the M2-F2 was $1.8 million. "HL" stands for horizontal landing, and "10" refers to the tenth design studied by engineers at NASA's Langley Research Center, Hampton, Va. After delivery to NASA in January 1966, the HL-10 made its first flight on Dec. 22, 1966, with research pilot Bruce Peterson in the cockpit. Although an XLR-11 rocket engine was installed in the vehicle, the first 11 drop flights from the B-52 launch aircraft were powerless glide flights to assess handling qualities, stability, and control. In the end, the HL-10 was judged to be the best handling of the three original heavy-weight lifting bodies (M2-F2/F3, HL-10, X-24A). The HL-10 was flown 37 times during the lifting body research program and logged the highest altitude and fastest speed in the Lifting Body program. On Feb. 18, 1970, Air Force test pilot Peter Hoag piloted the HL-10 to Mach 1.86 (1,228 mph). Nine days later, NASA pilot Bill Dana flew the vehicle to 90,030 feet, which became the highest altitude reached in the program. Some new and different lessons were learned through the successful flight testing of the HL-10. These lessons, when combined with information from it's sister ship, the M2-F2/F3, provided an excellent starting point for designers of future entry vehicles, including the Space Shuttle.
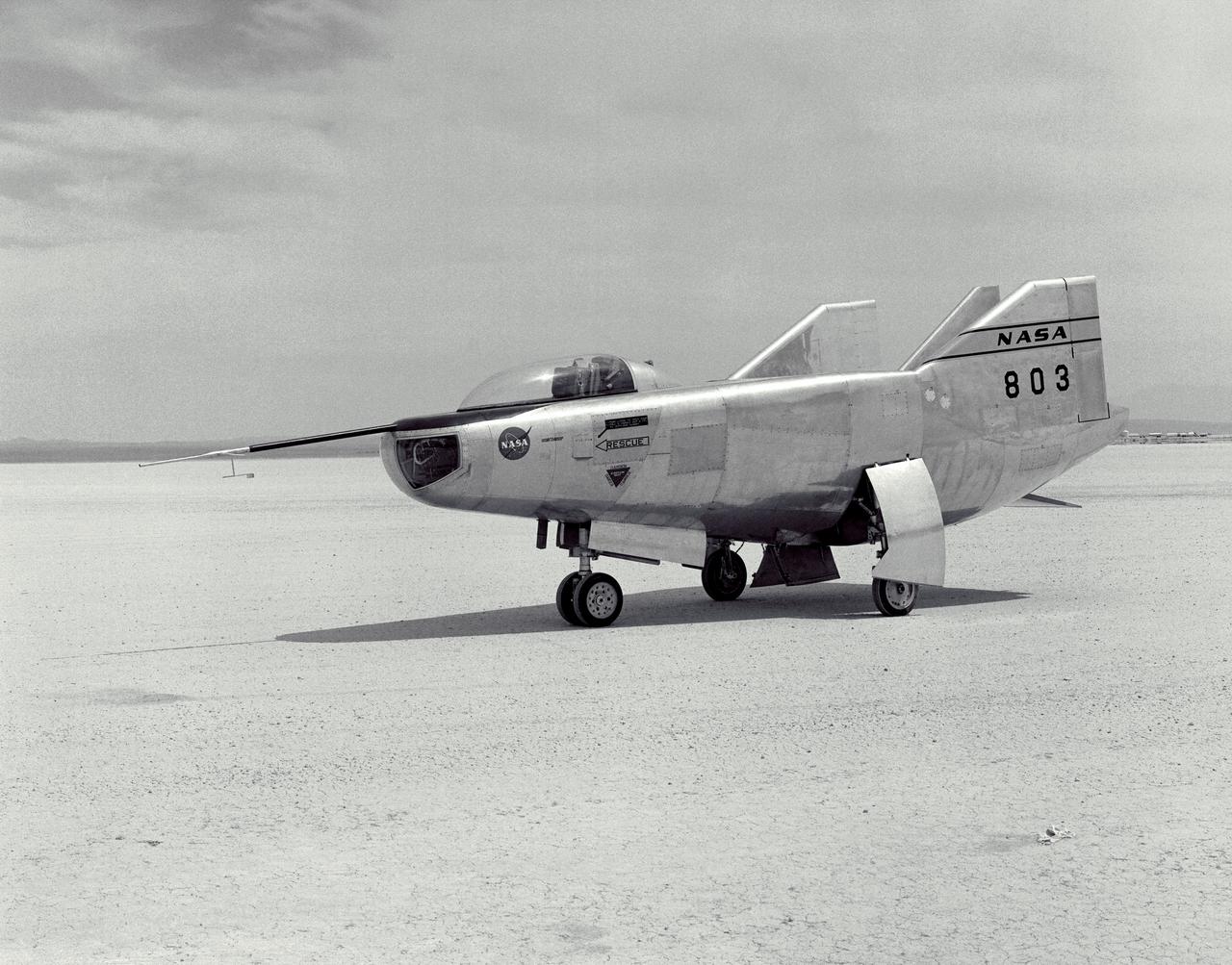

The M2-F3 Lifting Body is seen here on the lakebed at the NASA Flight Research Center (FRC--later the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. After a three-year-long redesign and rebuilding effort, the M2-F3 was ready to fly. The May 1967 crash of the M2-F2 had damaged both the external skin and the internal structure of the lifting body. At first, it seemed that the vehicle had been irreparably damaged, but the original manufacturer, Northrop, did the repair work and returned the redesigned M2-F3 with a center fin for stability to the FRC.
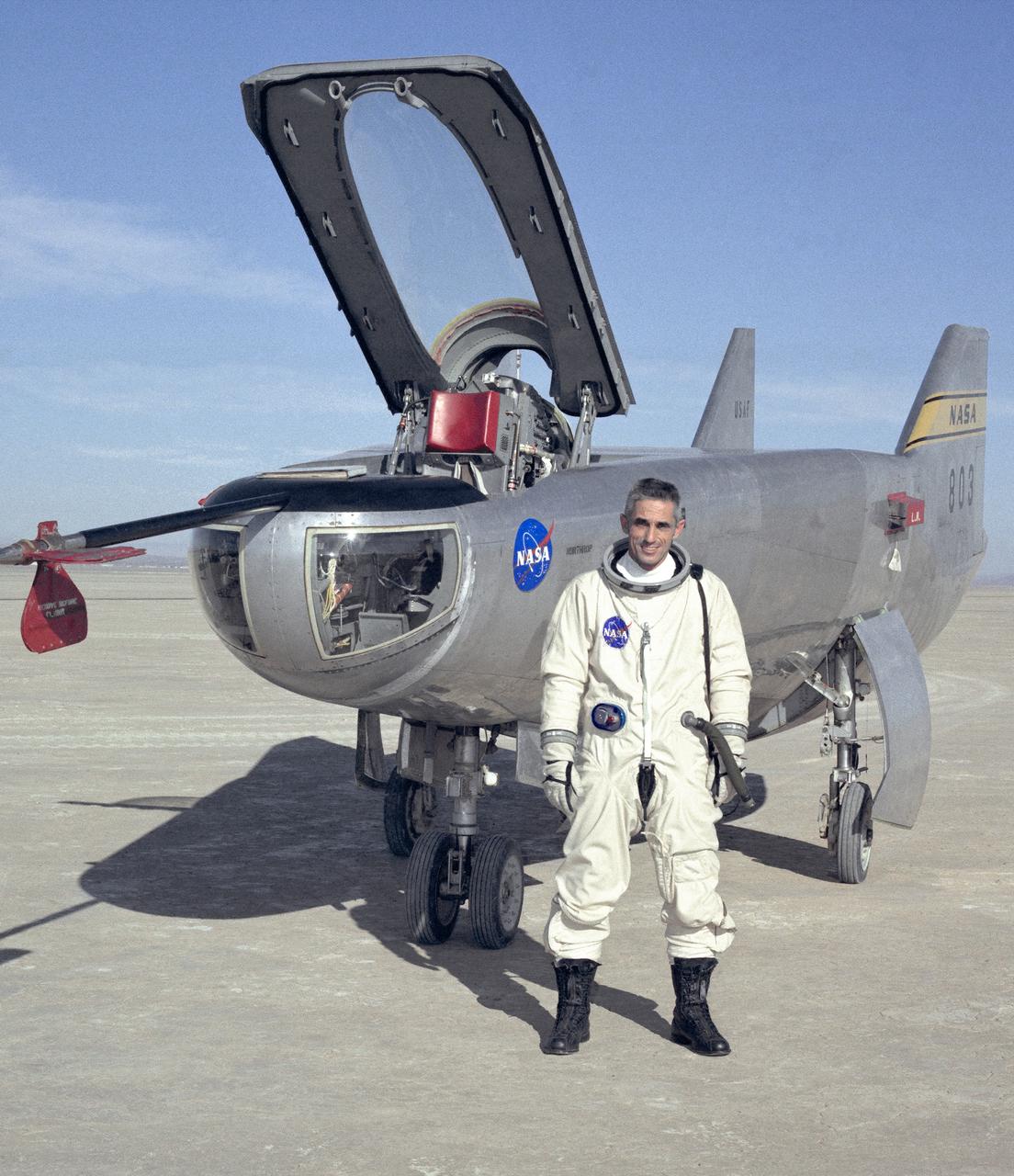

NASA research pilot John A. Manke is seen here in front of the M2-F3 Lifting Body. Manke was hired by NASA on May 25, 1962, as a flight research engineer. He was later assigned to the pilot's office and flew various support aircraft including the F-104, F5D, F-111 and C-47. After leaving the Marine Corps in 1960, Manke worked for Honeywell Corporation as a test engineer for two years before coming to NASA. He was project pilot on the X-24B and also flew the HL-10, M2-F3, and X-24A lifting bodies. John made the first supersonic flight of a lifting body and the first landing of a lifting body on a hard surface runway. Manke served as Director of the Flight Operations and Support Directorate at the Dryden Flight Research Center prior to its integration with Ames Research Center in October 1981. After this date John was named to head the joint Ames-Dryden Directorate of Flight Operations. He also served as site manager of the NASA Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility. John is a member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots. He retired on April 27, 1984.
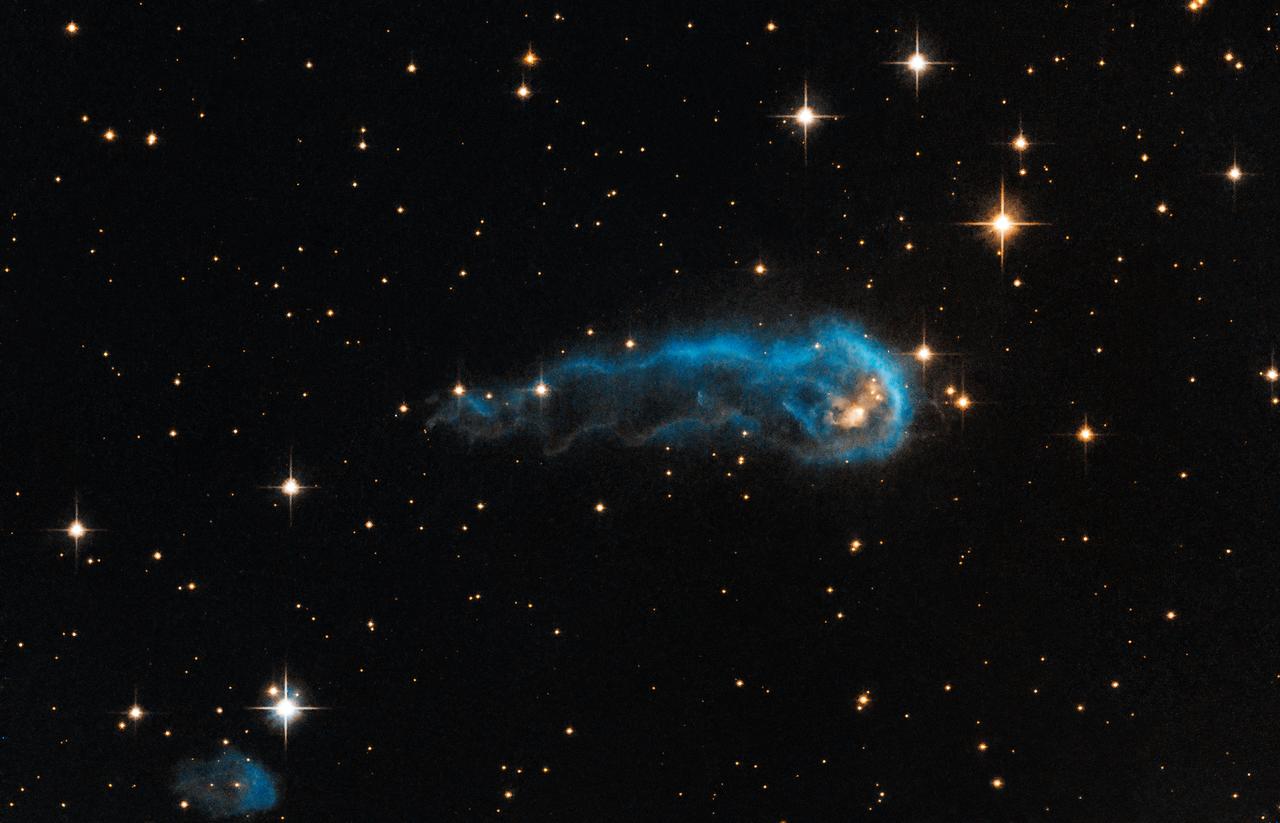
This light-year-long knot of interstellar gas and dust resembles a caterpillar on its way to a feast. But the meat of the story is not only what this cosmic caterpillar eats for lunch, but also what's eating it. Harsh winds from extremely bright stars are blasting ultraviolet radiation at this "wanna-be" star and sculpting the gas and dust into its long shape. The culprits are 65 of the hottest, brightest known stars, classified as O-type stars, located 15 light-years away from the knot, towards the right edge of the image. These stars, along with 500 less bright, but still highly luminous B-type stars make up what is called the Cygnus OB2 association. Collectively, the association is thought to have a mass more than 30,000 times that of our sun. The caterpillar-shaped knot, called IRAS 20324+4057, is a protostar in a very early evolutionary stage. It is still in the process of collecting material from an envelope of gas surrounding it. However, that envelope is being eroded by the radiation from Cygnus OB2. Protostars in this region should eventually become young stars with final masses about one to ten times that of our sun, but if the eroding radiation from the nearby bright stars destroys the gas envelope before the protostars finish collecting mass, their final masses may be reduced. Spectroscopic observations of the central star within IRAS 20324+4057 show that it is still collecting material quite heavily from its outer envelope, hoping to bulk up in mass. Only time will tell if the formed star will be a "heavy-weight" or a "light-weight" with respect to its mass. This image of IRAS 20324+4057 is a composite of Hubble Advanced Camera for Surveys data taken in green and infrared light in 2006, and ground-based hydrogen data from the Isaac Newton Telescope in 2003. The object lies 4,500 light-years away in the constellation Cygnus. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
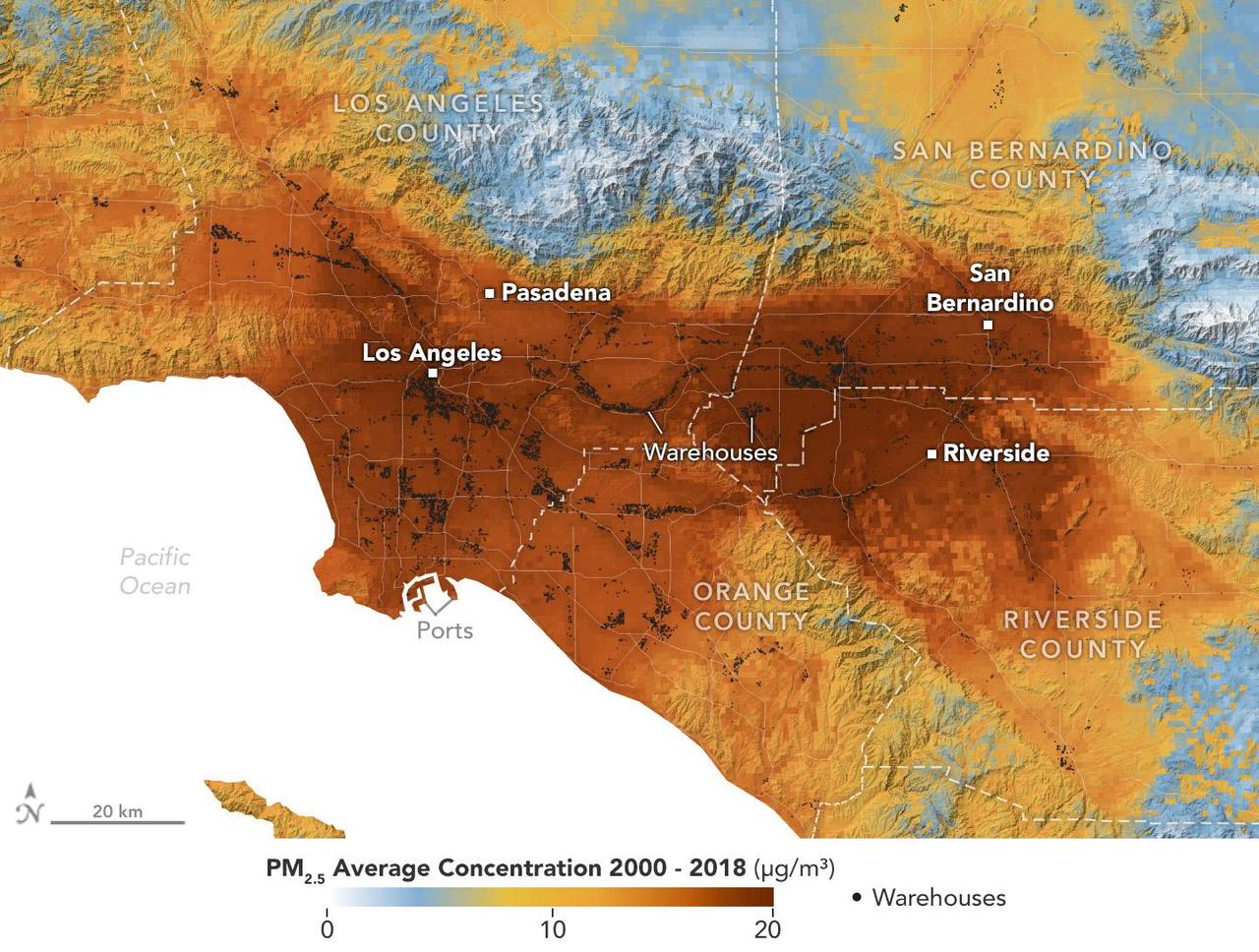
A data visualization shows the average concentration of PM2.5 particulate pollution in the Los Angeles region from 2000 to 2018, along with the locations of nearly 11,000 warehouses over the same time period. Particles measuring 2.5 micrometers or less, PM2.5 are pollutants that can be inhaled into the lungs and absorbed into the bloodstream. A NASA-funded study published in September 2024 in GeoHealth analyzed patterns and trends of atmospheric PM2.5 concentration and found that ZIP codes with more or larger warehouses had higher levels of PM2.5 and elemental carbon over time than those with fewer warehouses. Elemental carbon is a type of PM2.5 that is produced by heavy-duty diesel engines. In the visualization, areas with higher concentrations of PM2.5 are shown in darker red, and locations of warehouses are indicated by small black circles (many of them clustered closely together). The PM2.5 data came from models based on satellite observations, including from NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instruments. The PM2.5 warehouse locations were derived from a commercial real estate database. Particulate pollution has been linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, some cancers, and adverse birth outcomes, including premature birth and low infant birth weight. As the e-commerce boom of recent decades has spurred warehouse construction, pollution in nearby neighborhoods has become a growing area for research. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26415
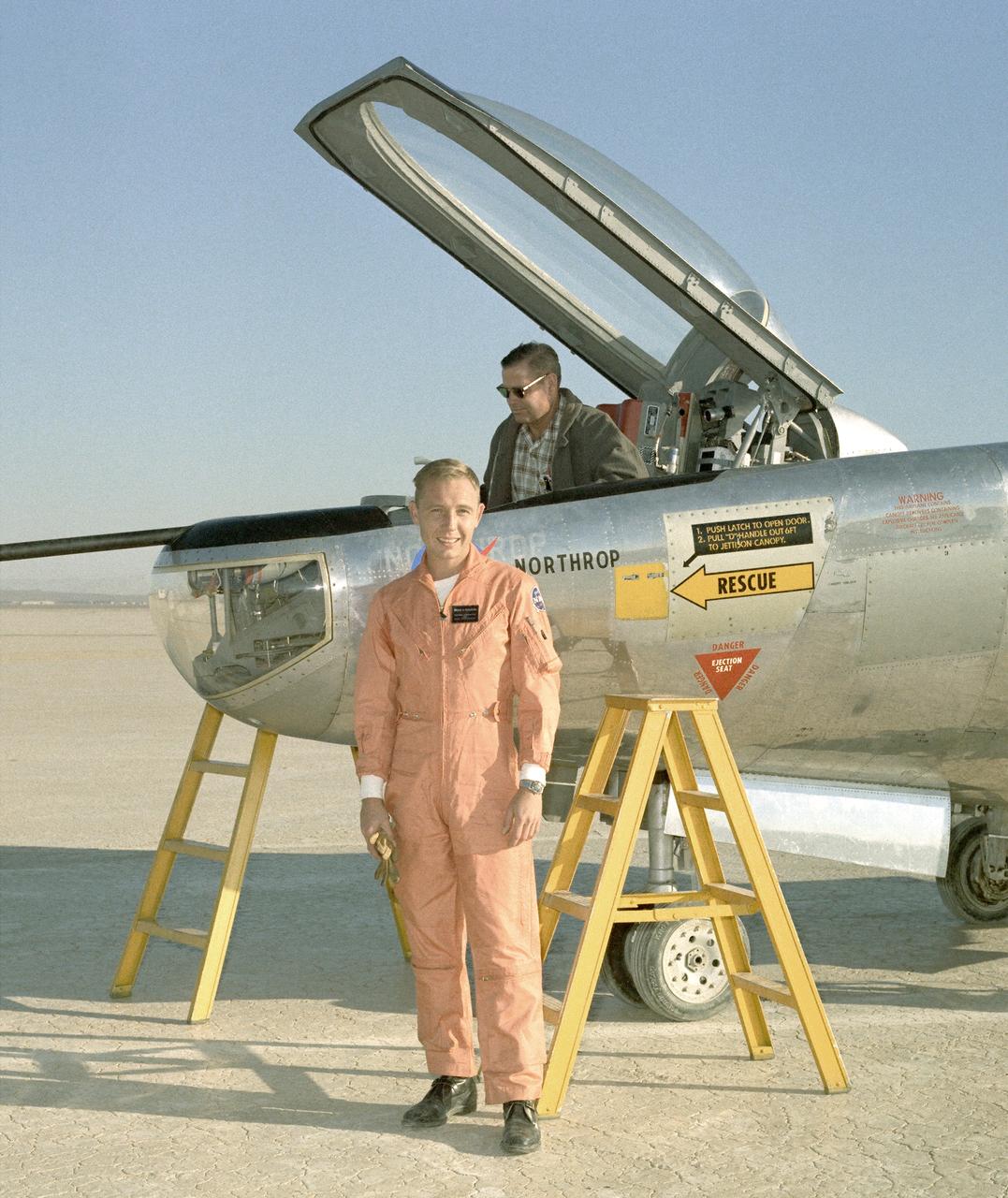

Bruce A. Peterson standing beside the M2-F2 lifting body on Rogers Dry Lake. Peterson became the NASA project pilot for the lifting body program after Milt Thompson retired from flying in late 1966. Peterson had flown the M2-F1, and made the first glide flight of the HL-10 heavy-weight lifting body in December 1966. On May 10, 1967, Peterson made his fourth glide flight in the M2-F2. This was also the M2-F2's 16th glide flight, scheduled to be the last one before the powered flights began. However, as pilot Bruce Peterson neared the lakebed, the M2-F2 suffered a pilot induced oscillation (PIO). The vehicle rolled from side to side in flight as he tried to bring it under control. Peterson recovered, but then observed a rescue helicopter that seemed to pose a collision threat. Distracted, Peterson drifted in a cross-wind to an unmarked area of the lakebed where it was very difficult to judge the height over the lakebed because of a lack of the guidance the markers provided on the lakebed runway. Peterson fired the landing rockets to provide additional lift, but he hit the lakebed before the landing gear was fully down and locked. The M2-F2 rolled over six times, coming to rest upside down. Pulled from the vehicle by Jay King and Joseph Huxman, Peterson was rushed to the base hospital, transferred to March Air Force Base and then the UCLA Hospital. He recovered but lost vision in his right eye due to a staph infection.
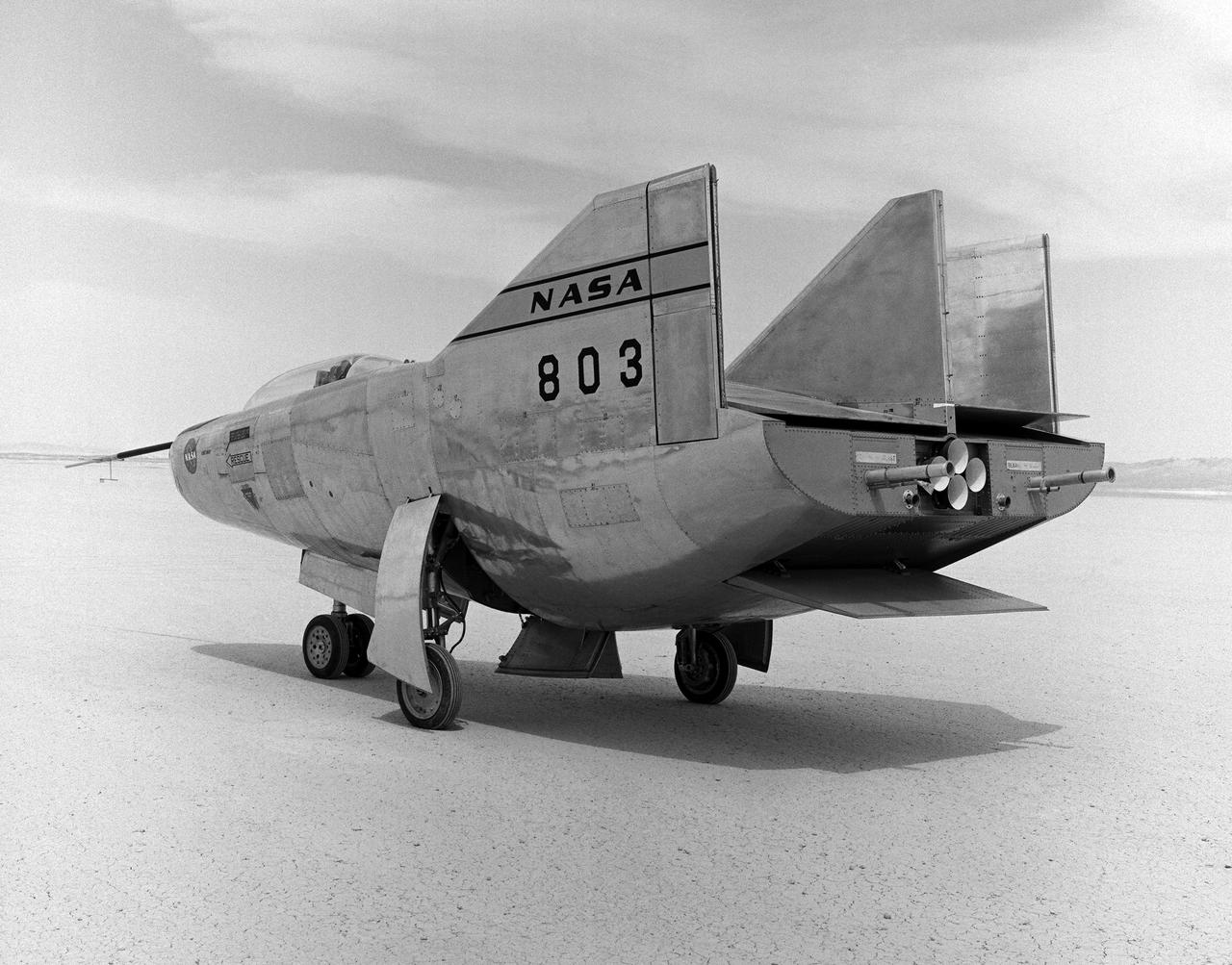

The M2-F3 Lifting Body is seen here on the lakebed next to the NASA Flight Research Center (later the Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California. Redesigned and rebuilt from the M2-F2, the M2-F3 featured as its most visible change a center fin for greater stability. While the M2-F3 was still demanding to fly, the center fin eliminated the high risk of pilot induced oscillation (PIO) that was characteristic of the M2-F2.