
Hot Jupiters are exoplanets that orbit their stars so tightly that their temperatures are extremely high, reaching over 2,400 degrees Fahrenheit (1600 Kelvin). They are also tidally locked, so one side of the planet always faces the sun and the other is in permanent darkness. Research suggests that the "dayside" is largely free of clouds, while the "nightside" is heavily clouded. This illustration represents how hot Jupiters of different temperatures and different cloud compositions might appear to a person flying over the dayside of these planets on a spaceship, based on computer modeling. Cooler planets are entirely cloudy, whereas hotter planets have morning clouds only. Clouds of different composition have different colors, whereas the clear sky is bluer than on Earth. For the hottest planets, the atmosphere is hot enough on the evening side to glow like a charcoal. Figure 1 shows an approximation of what various hot Jupiters might look like based on a combination of computer modeling and data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope. From left to right it shows: sodium sulfide clouds (1000 to 1200 Kelvin), manganese sulfide clouds (1200 to 1600 Kelvin), magnesium silicate clouds (1600 to 1800 Kelvin), magnesium silicate and aluminum oxide clouds (1800 Kelvin) and clouds composed of magnesium silicate, aluminum oxide, iron and calcium titanate (1900 to 2200 Kelvin). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21074
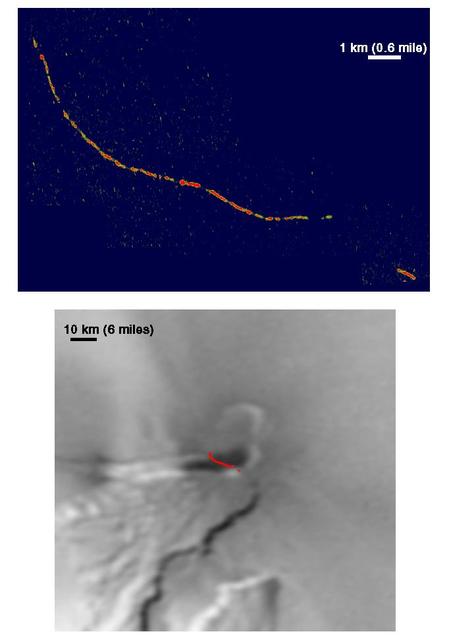
Pele Hot Caldera Margin
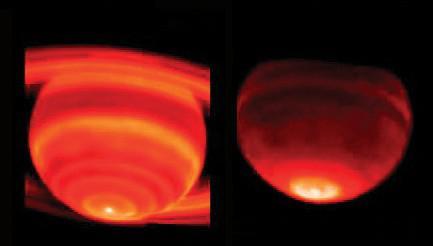
Red-Hot Saturn

Saturn Hot Spot
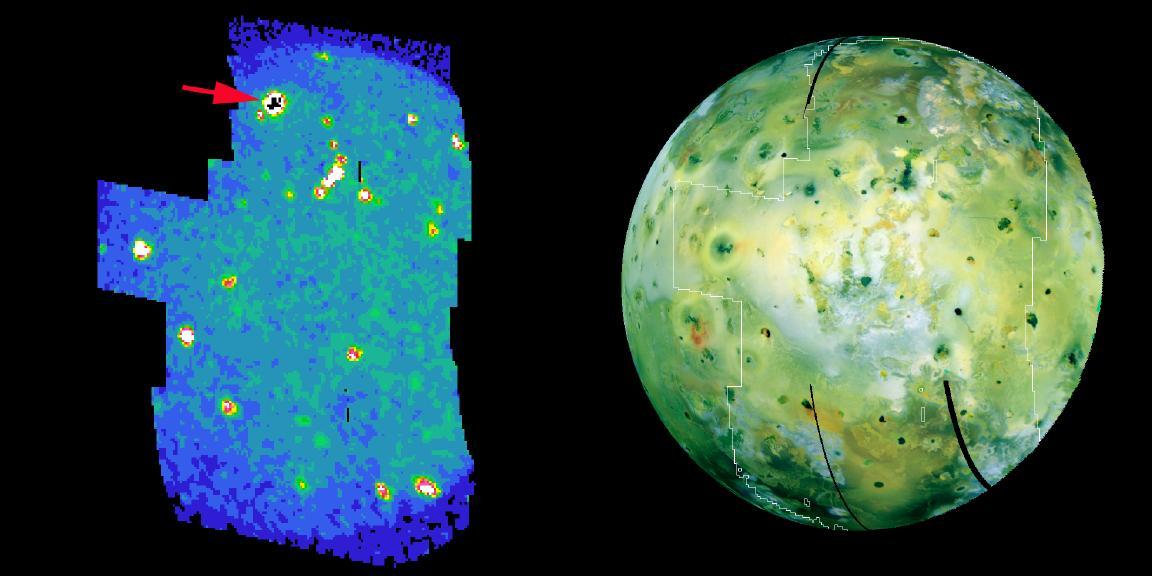
Hot Spots on Io
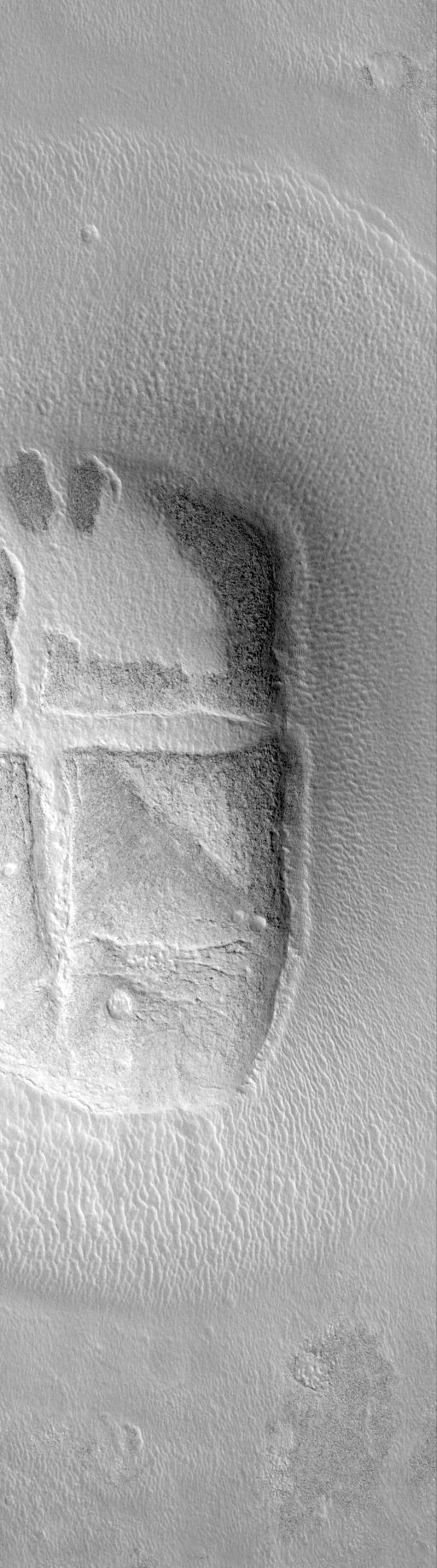

Hot-Cross-Bun on the Northern Plains
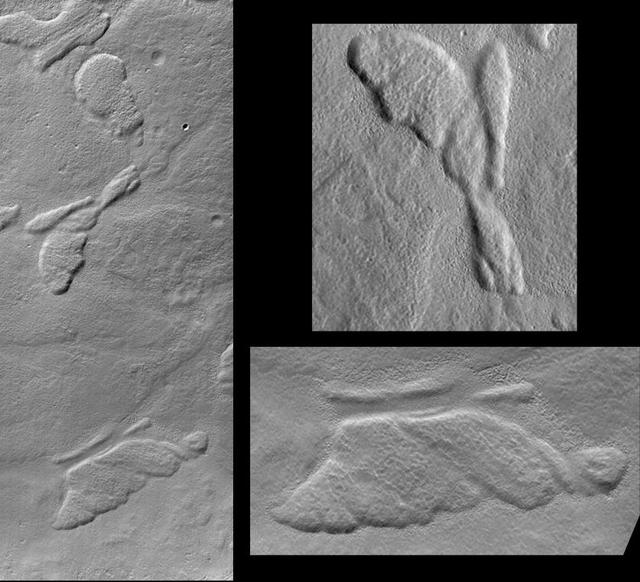
Hot Dog and Butterfly, Nereidum Montes

This composite image shows a hot spot in Jupiter's atmosphere. In the image on the left, taken on Sept. 16, 2020, by the Gemini North telescope on the island of Hawaii, the hot spot appears bright in the infrared at a wavelength of 5 microns. In the inset image on the right, taken by Juno's JunoCam visible-light imager, also on Sept. 16 during Juno's 29th perijove pass, the hot spot appears dark. Scientists have known of Jupiter's hot spots for a long time. On Dec. 7, 1995, the Galileo probe likely descended into a similar hot spot. To the naked eye, Jupiter's hot spots appear as dark, cloud-free areas in Jupiter's equatorial belt, but at infrared wavelengths, which are invisible to the human eye, they are extremely bright, revealing the warm, deep atmosphere below the clouds. High-resolution images of hot spots such as these are key both to understanding the role of storms and waves in Jupiter's atmosphere. Citizen scientist Brian Swift processed the images to enhance the color and contrast, with further processing by Tom Momary to map the JunoCam image to the Gemini data. The international Gemini North telescope is a 26.6-foot-diameter (8.1-meter-diameter) optical/infrared telescope optimized for infrared observations, and is managed for the NSF by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24299
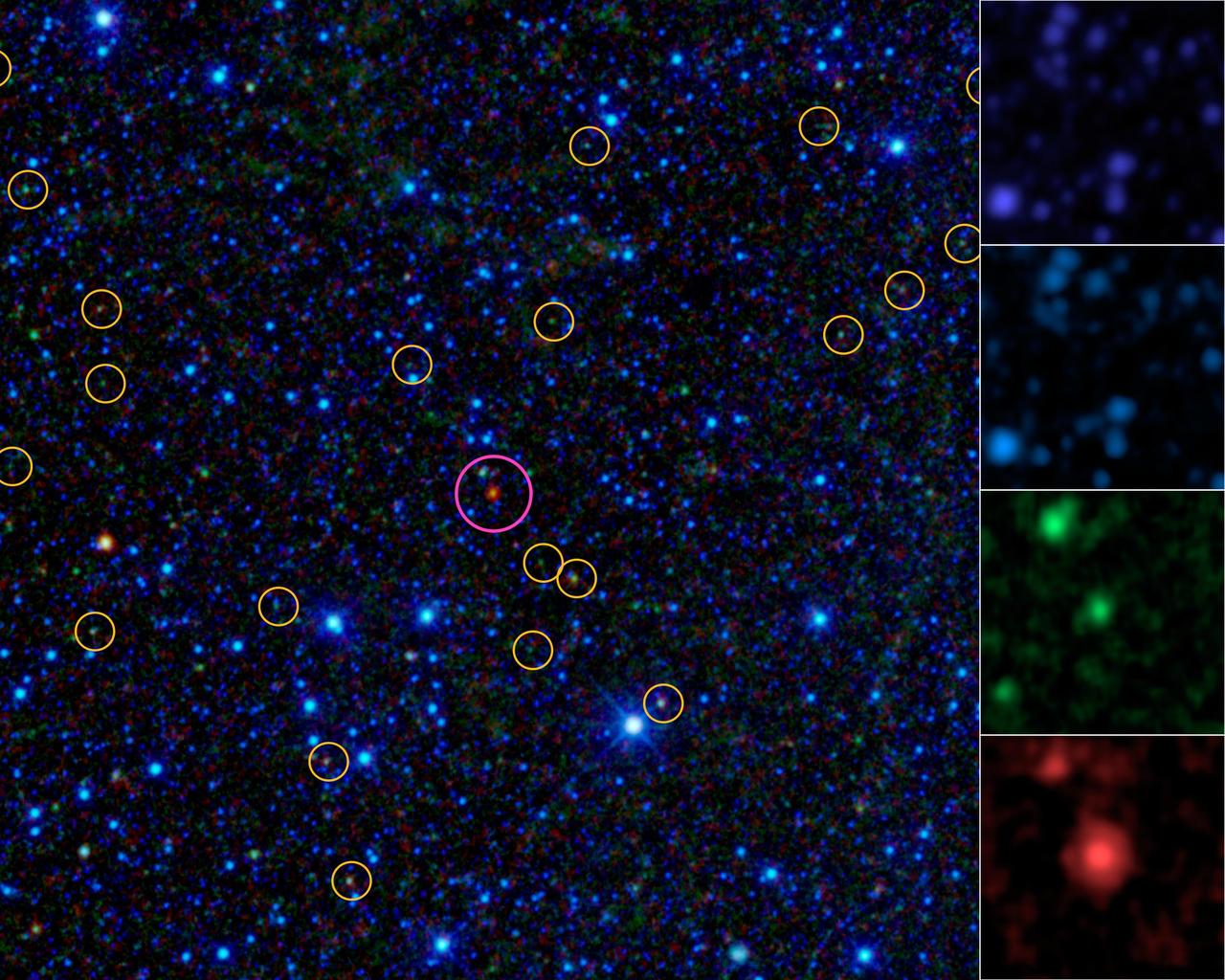
This image is a portion of the all-sky survey from NASA WISE. It highlights the first of about 1,000 hot DOGs found by the mission magenta circle. Hot DOGs are hot dust-obscured galaxies and are among the most powerful galaxies known.
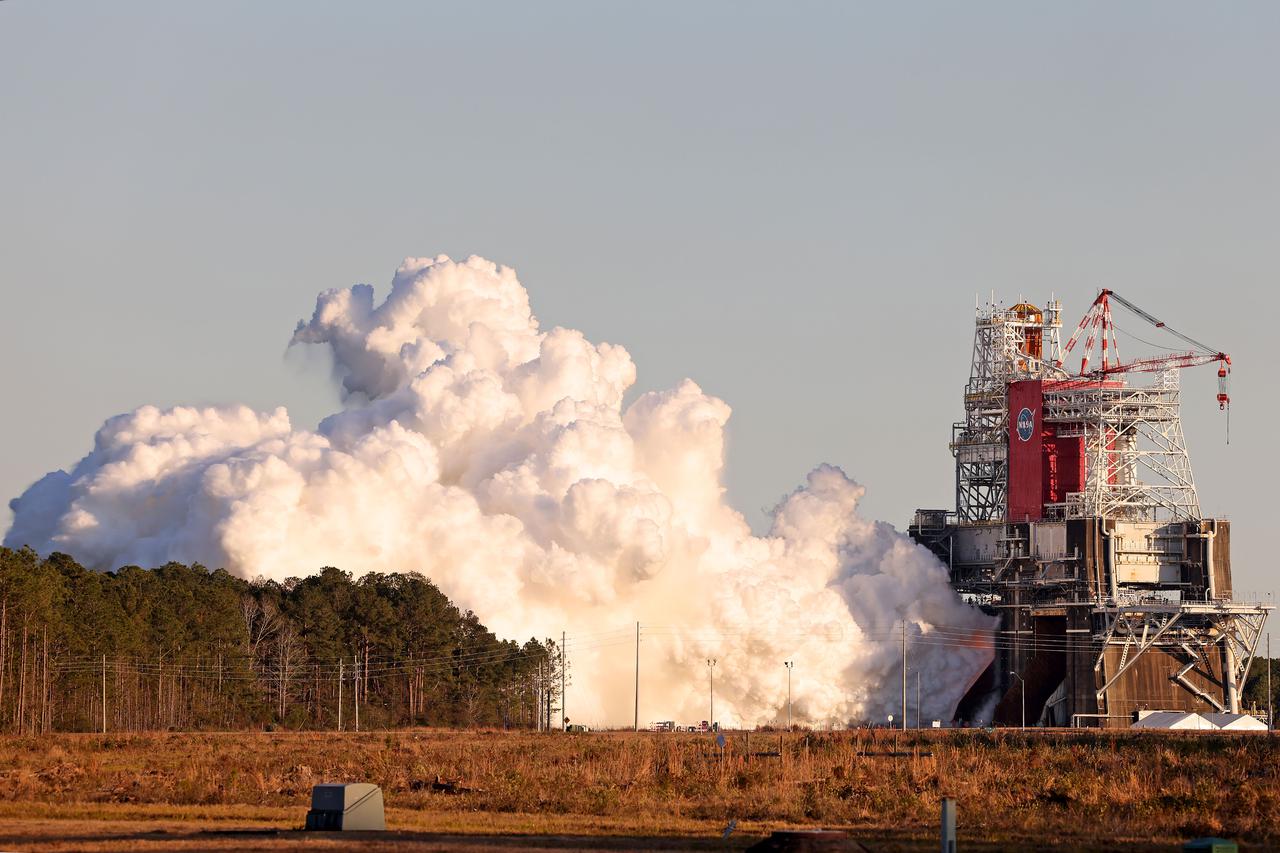

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
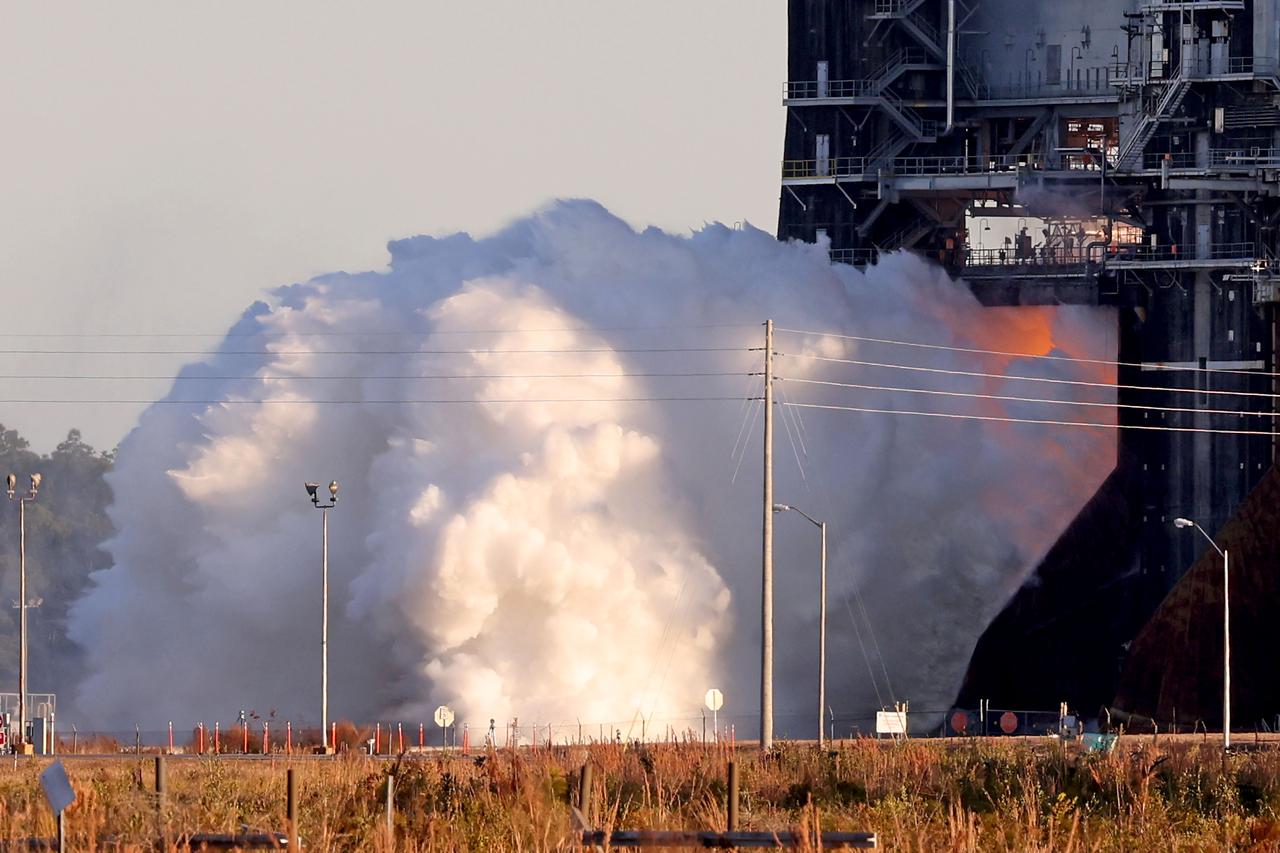

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
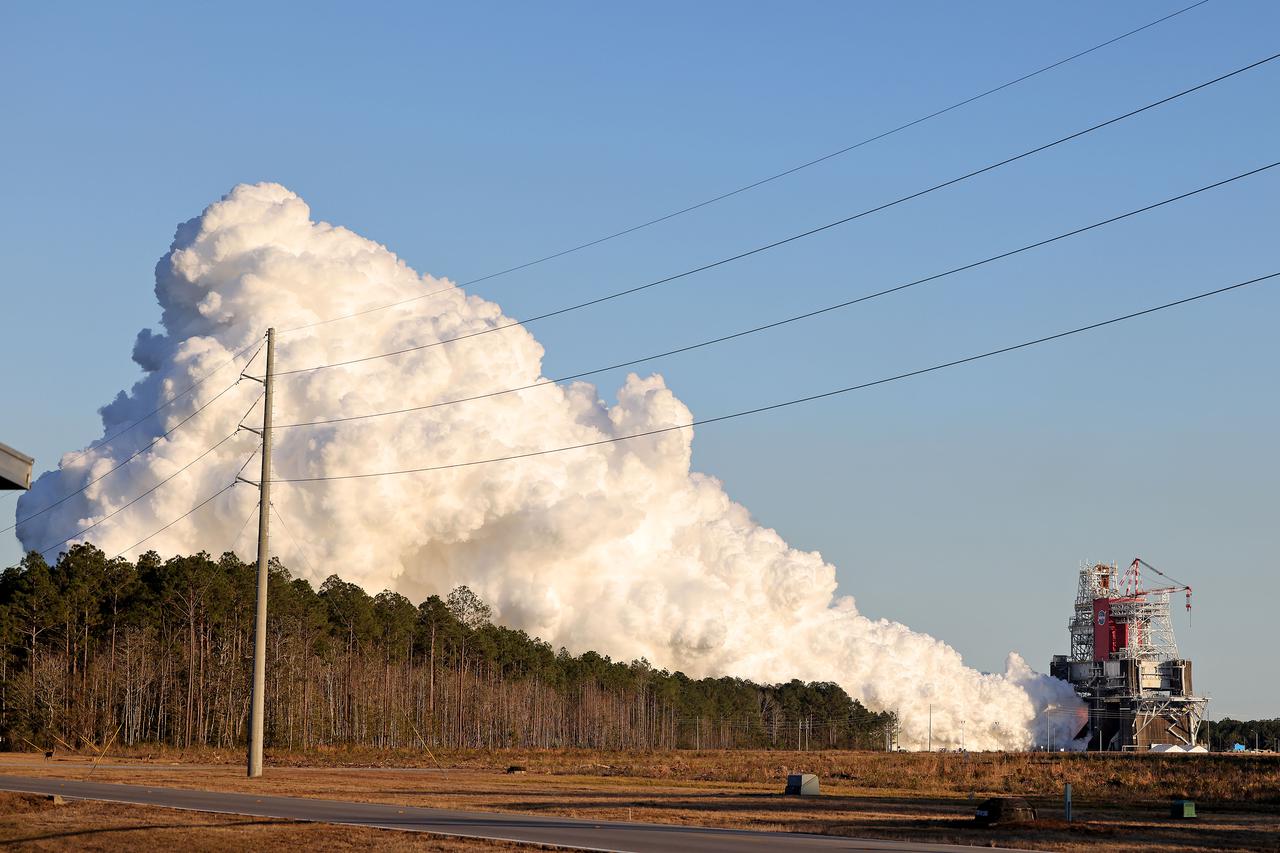

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
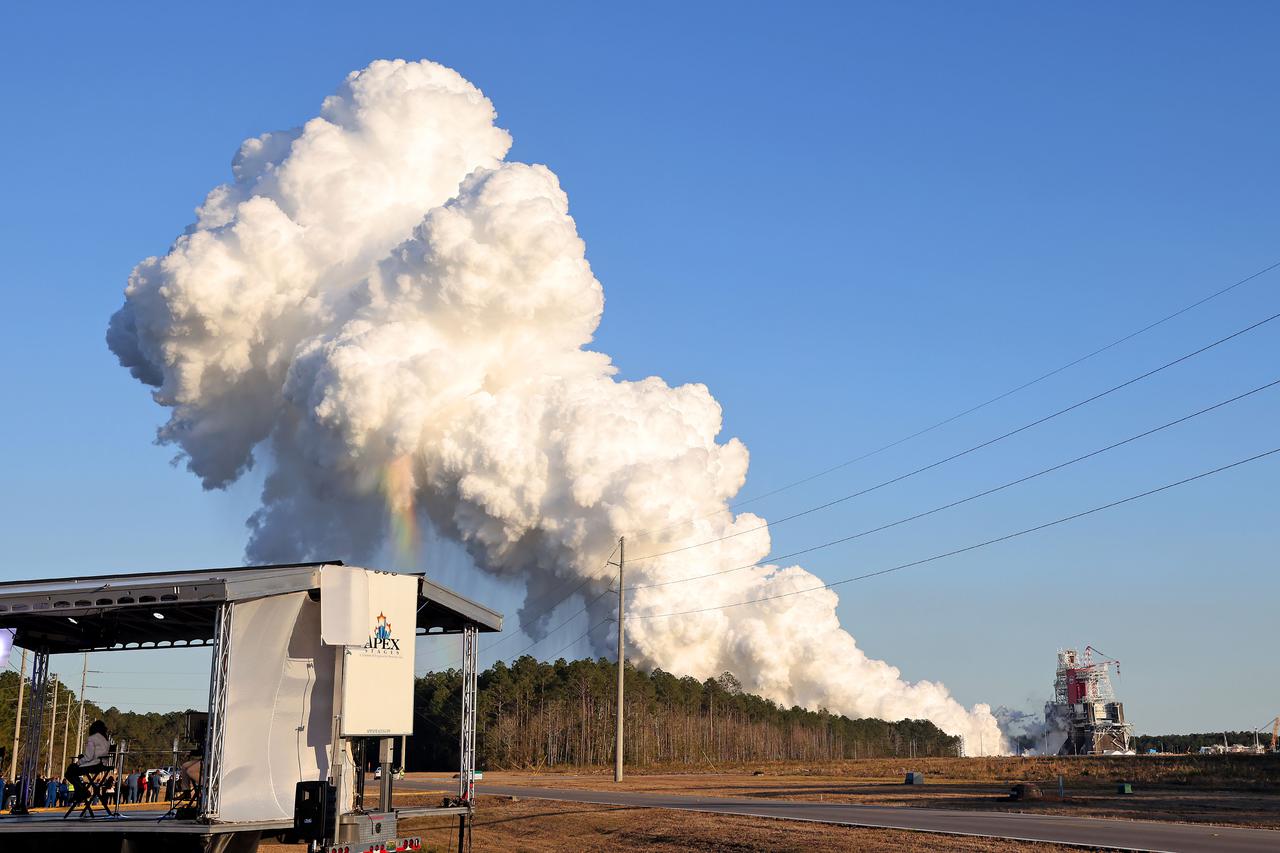

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
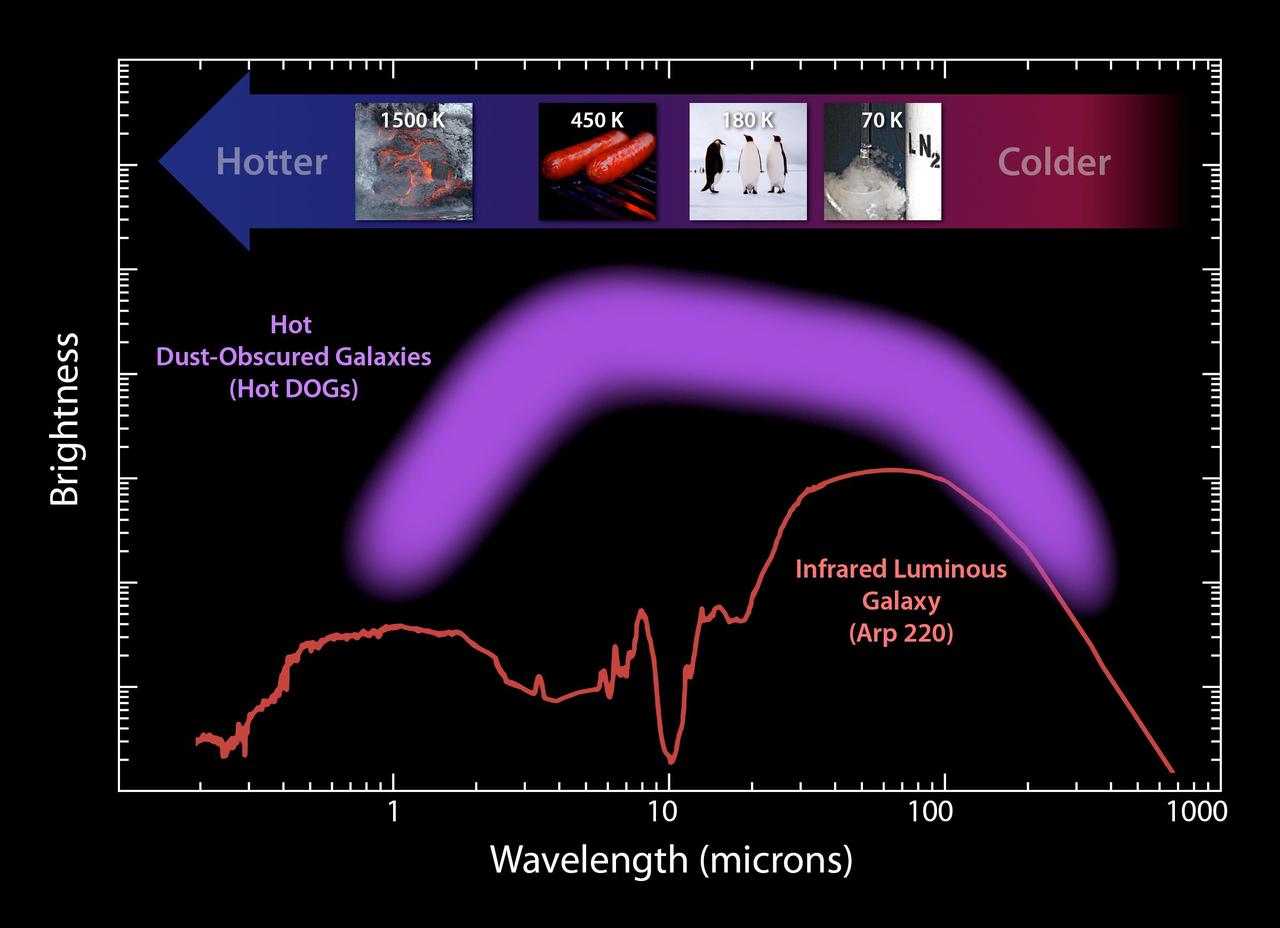
This plot illustrates the new population of hot DOGs, or hot dust-obscured objects, found by WISE. The purple band represents the range of brightness observed for the extremely dusty objects.
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
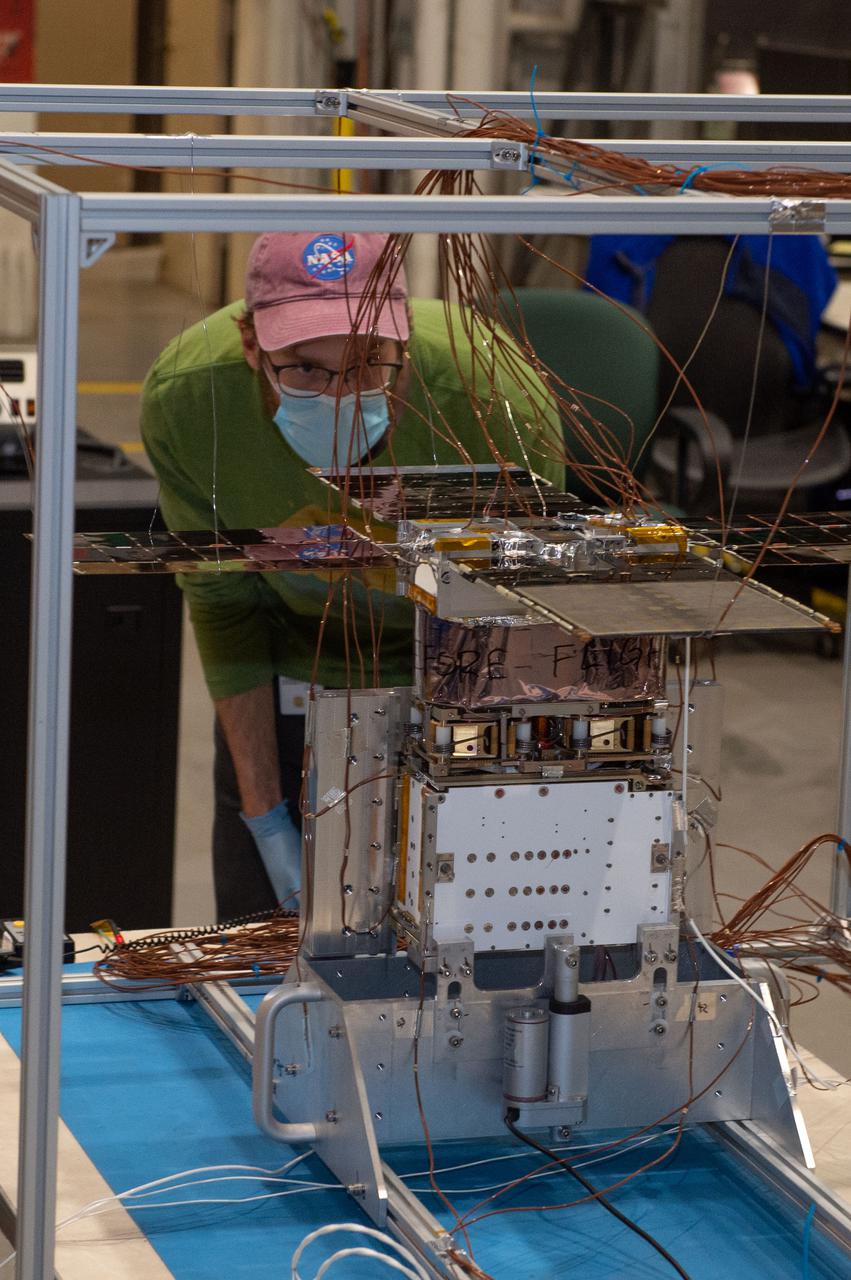
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
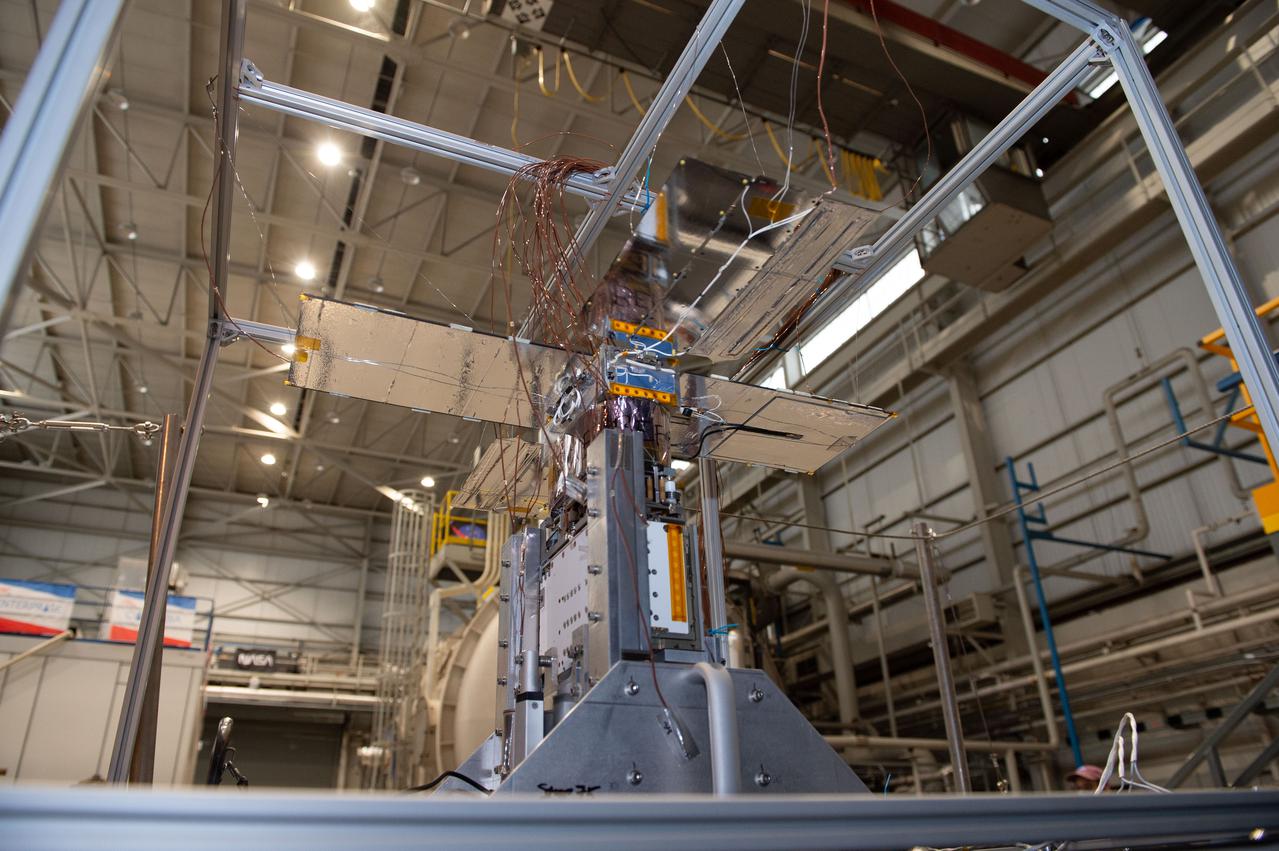

NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
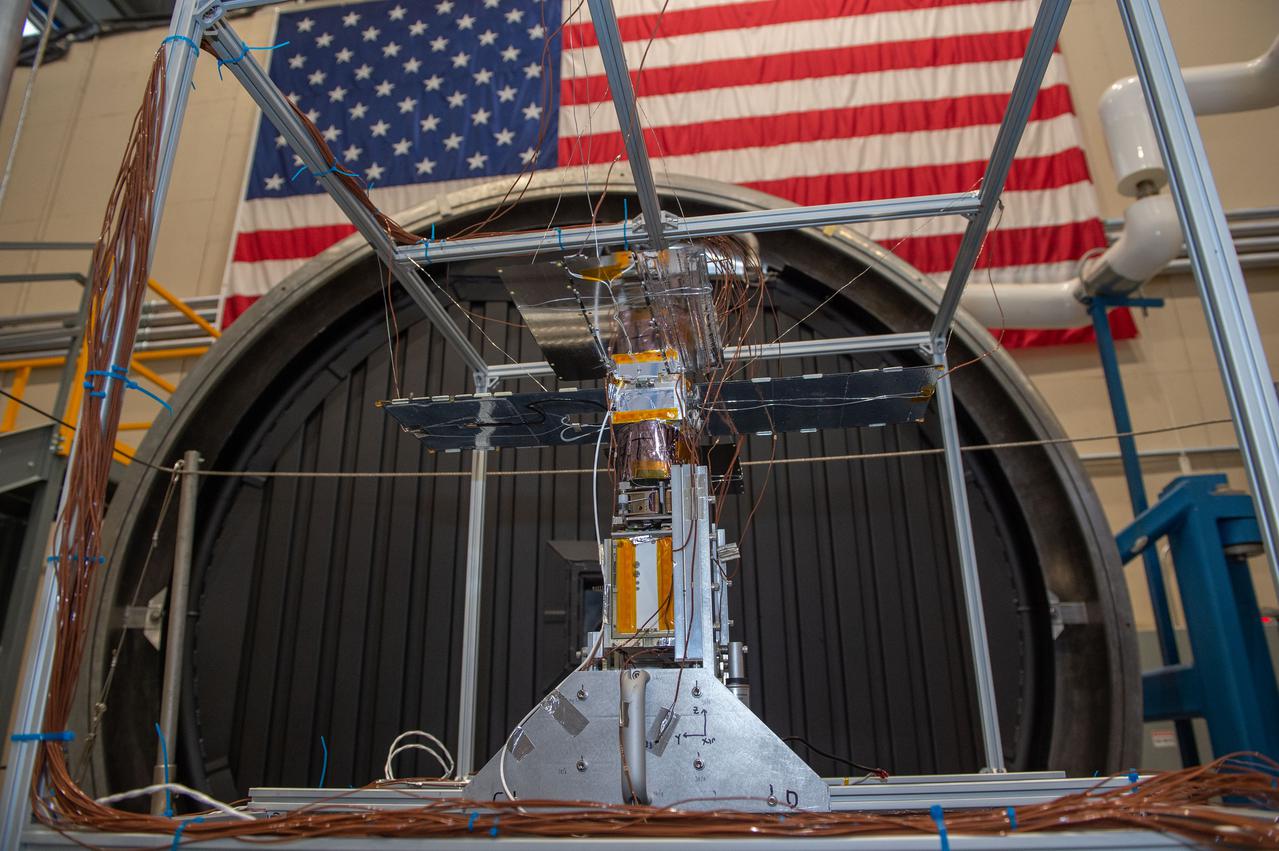
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box
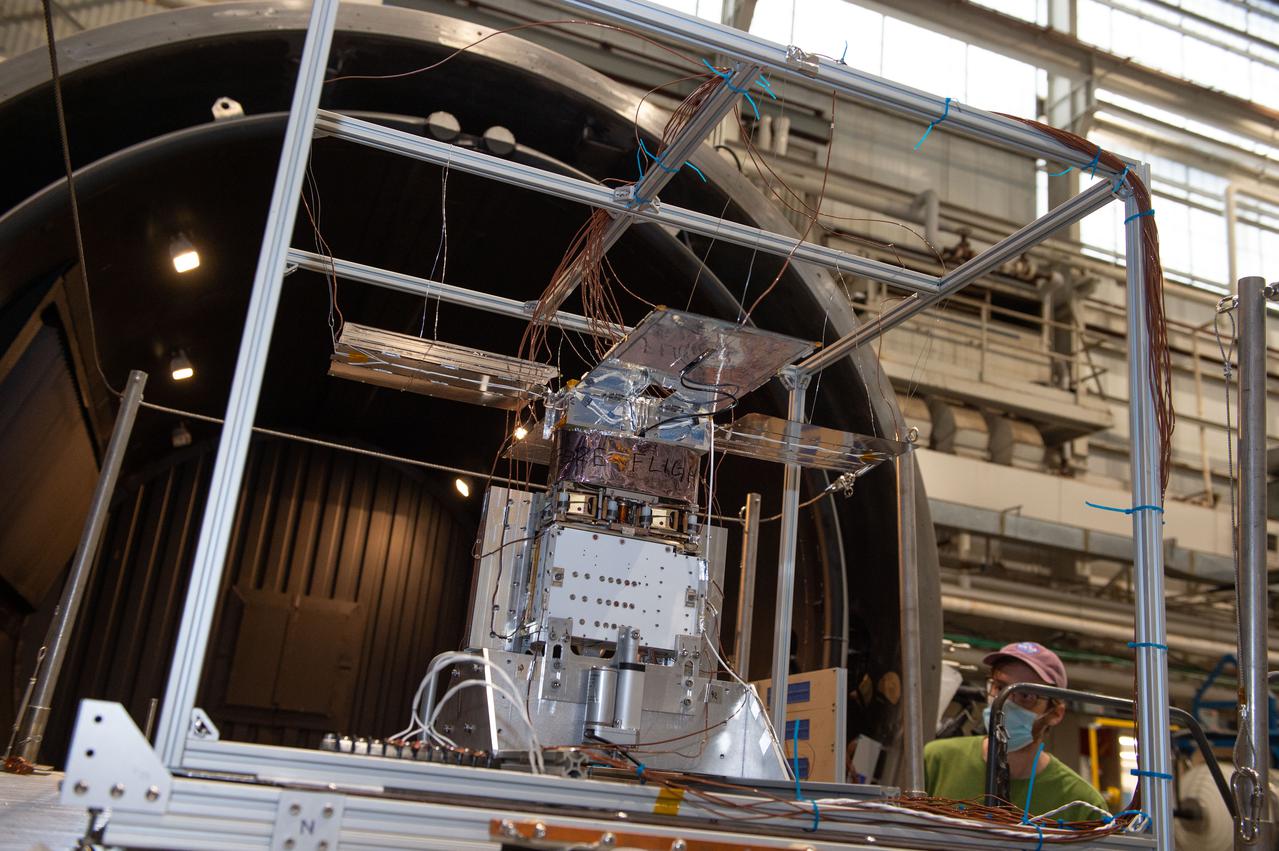
NEA Scout spacecraft after de-integration from hot box

This composite image shows a hot spot in Jupiter's atmosphere. In the image on the left, taken on Nov. 8, 2020, by NASA's Infrared Telescope Facility (IRTF) on the island of Hawaii, the hot spot appears bright in the infrared. The inset image on the right, taken by the JunoCam visible-light imager (also on Nov. 8, during Juno's 30th perijove pass), the hot spot appears dark and is flanked by high light-colored clouds to the south and a bright white storm to the west. Jupiter's hot spots have been known for a long time. On Dec. 7, 1995, the Galileo probe likely descended into a similar hot spot. To the naked eye, Jupiter's hot spots appear as dark, cloud-free spots in Jupiter's equatorial belt, but at infrared wavelengths, they are extremely bright, revealing the warm, deep atmosphere below the clouds. High-resolution images of hot spots such as these are key to understanding the role of storms and waves in Jupiter's atmosphere and to solving the mystery of Jupiter's elusive water. Citizen scientist Kevin Gill processed the image to enhance the color and contrast, with further processing by Tom Momary to map the JunoCam image to the IRTF data. The NASA IRTF is a 10.5-foot-diameter (3.2-meter-diameter) telescope optimized for infrared observations and is managed for NASA by the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Hawai'i. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24300
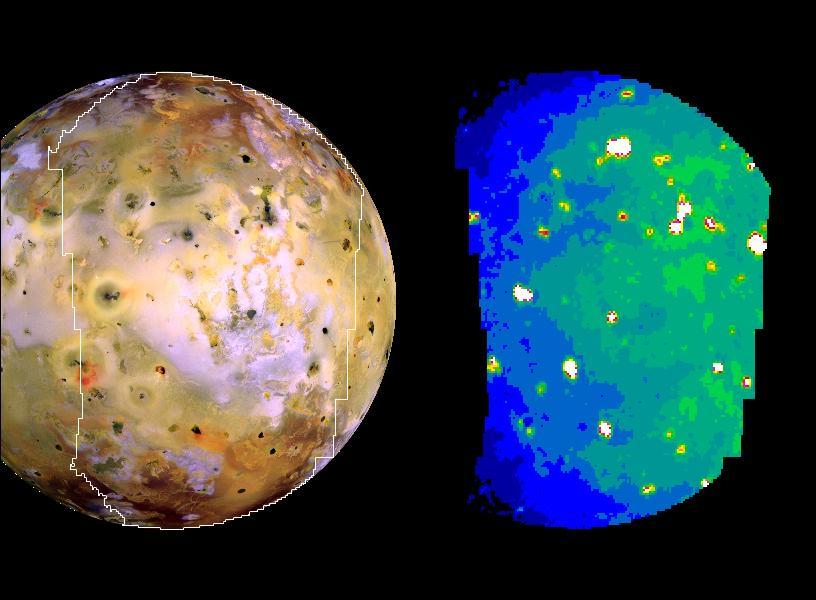
Io in Infrared with Giant Plume New Hot Spot
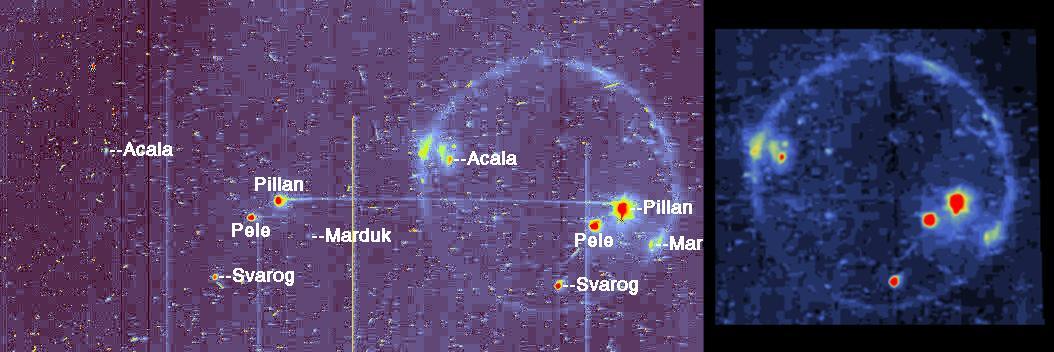
Io in Eclipse reveals High Temperature Hot Spots

Saturn North Pole Hot Spot and Hexagon
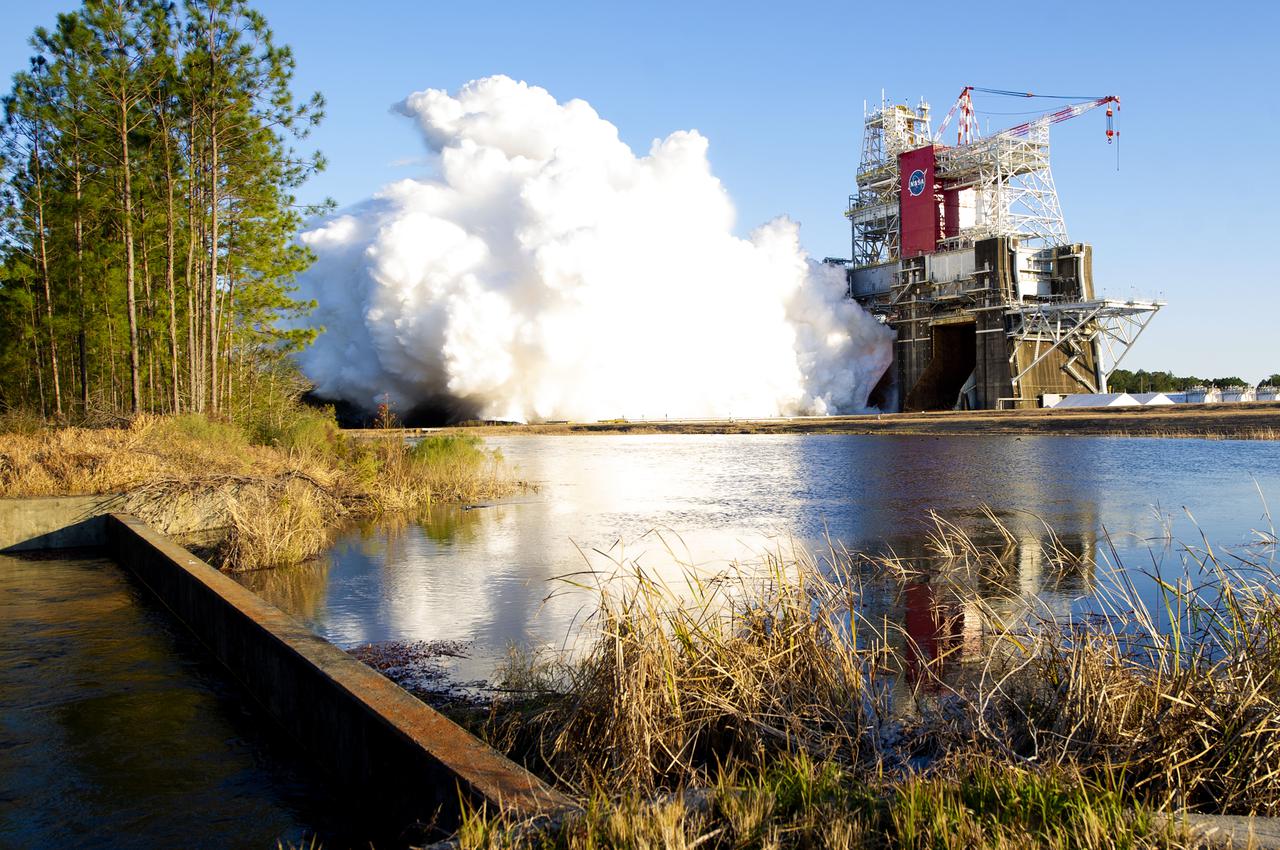

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
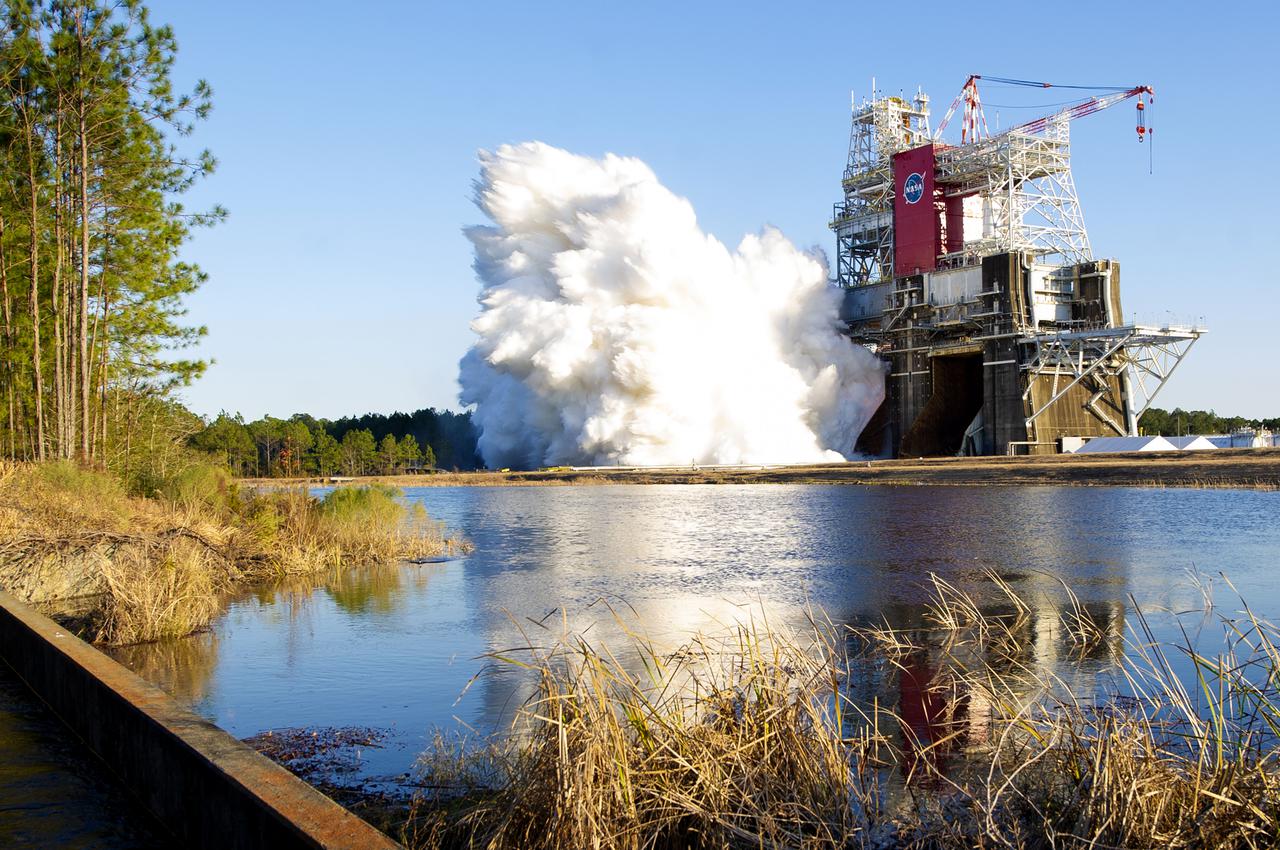

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
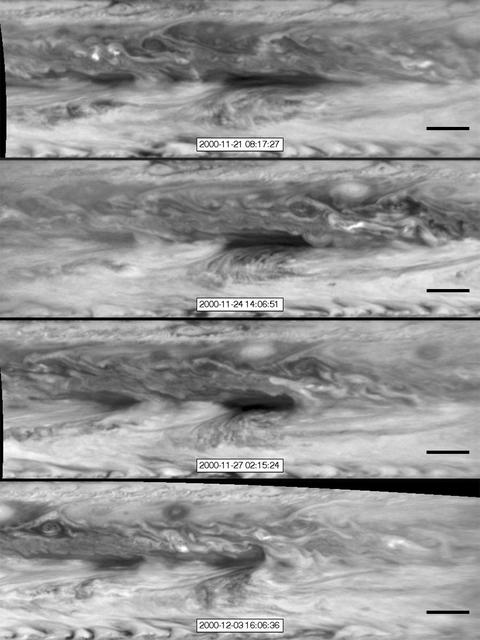
In this series of images from NASA Cassini spacecraft, a dark, rectangular hot spot interacts with a line of vortices that approaches from on the upper-right side. The interaction distorts the shape of the hot spot, leaving it diminished.

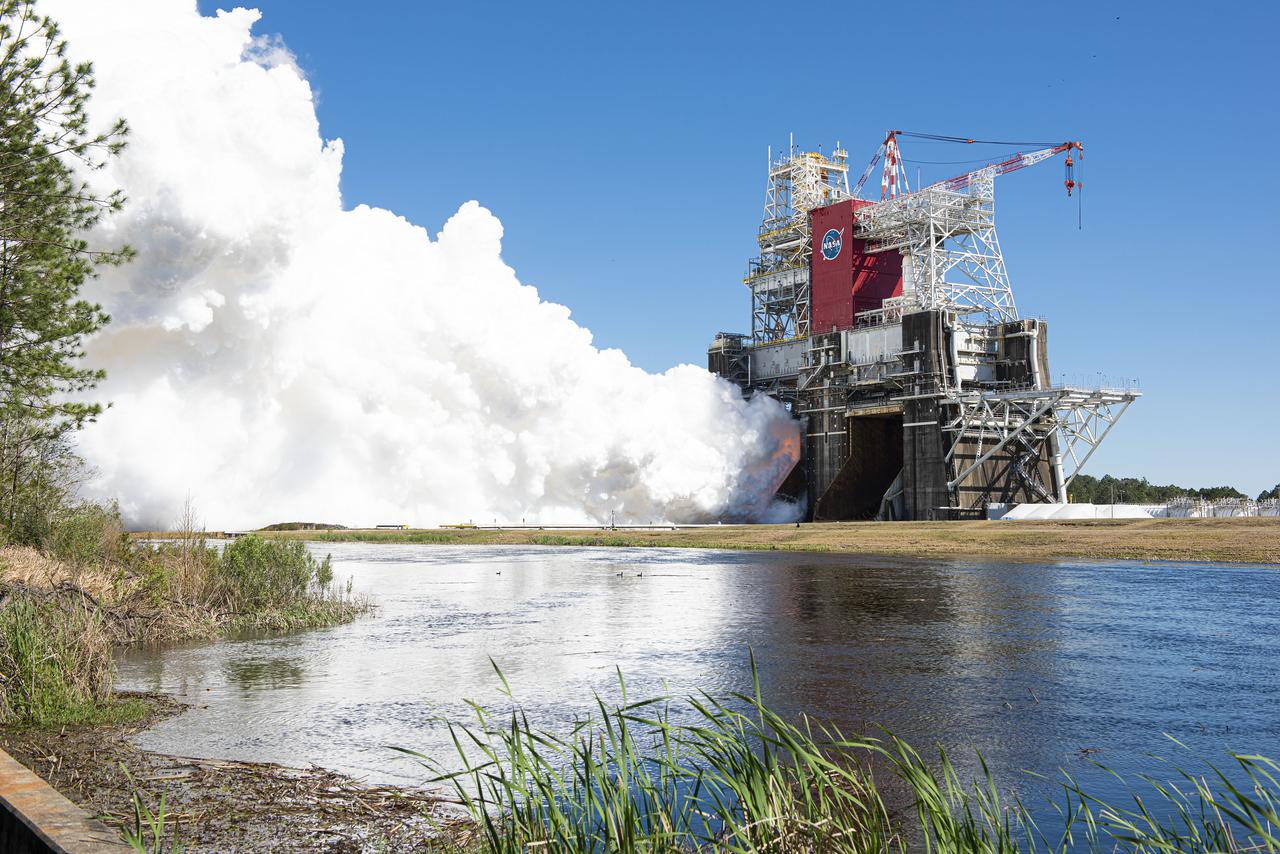
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

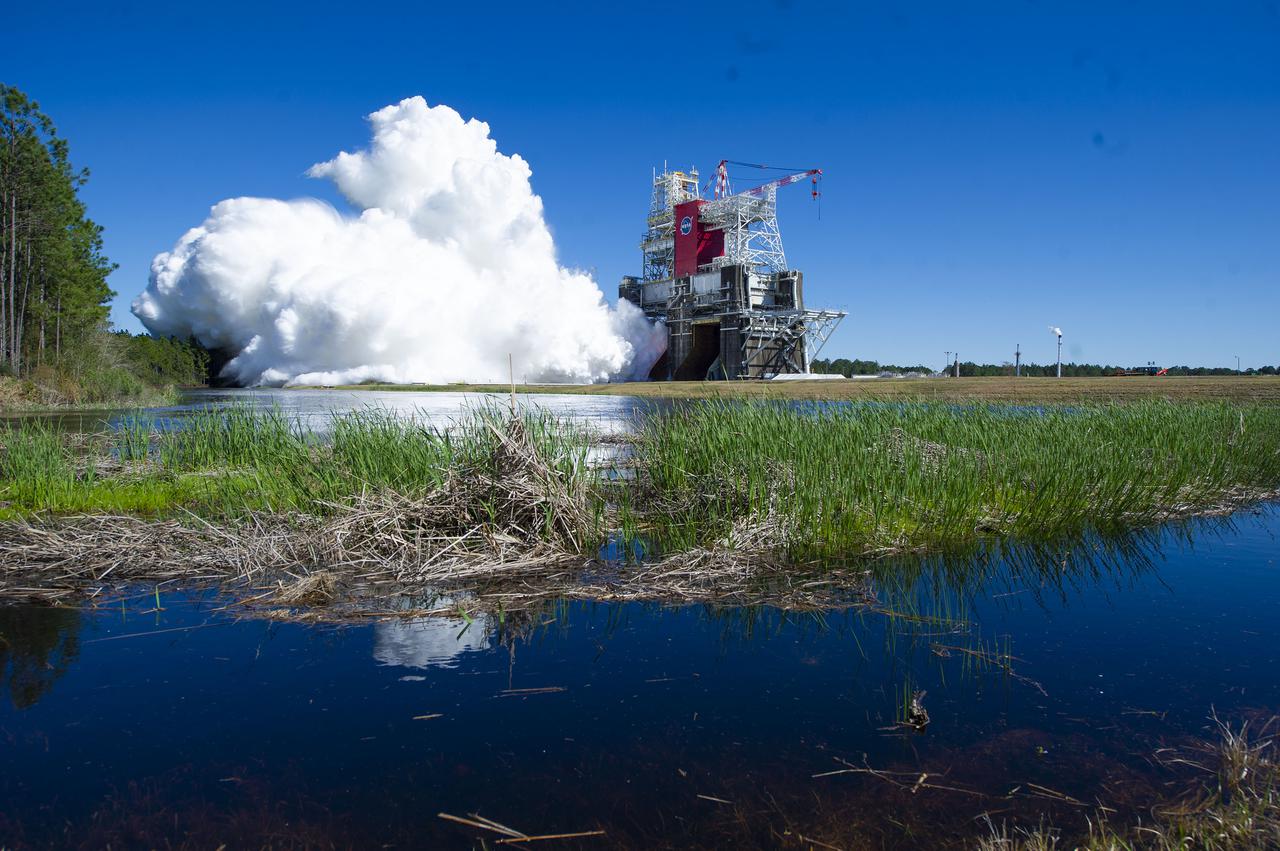
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

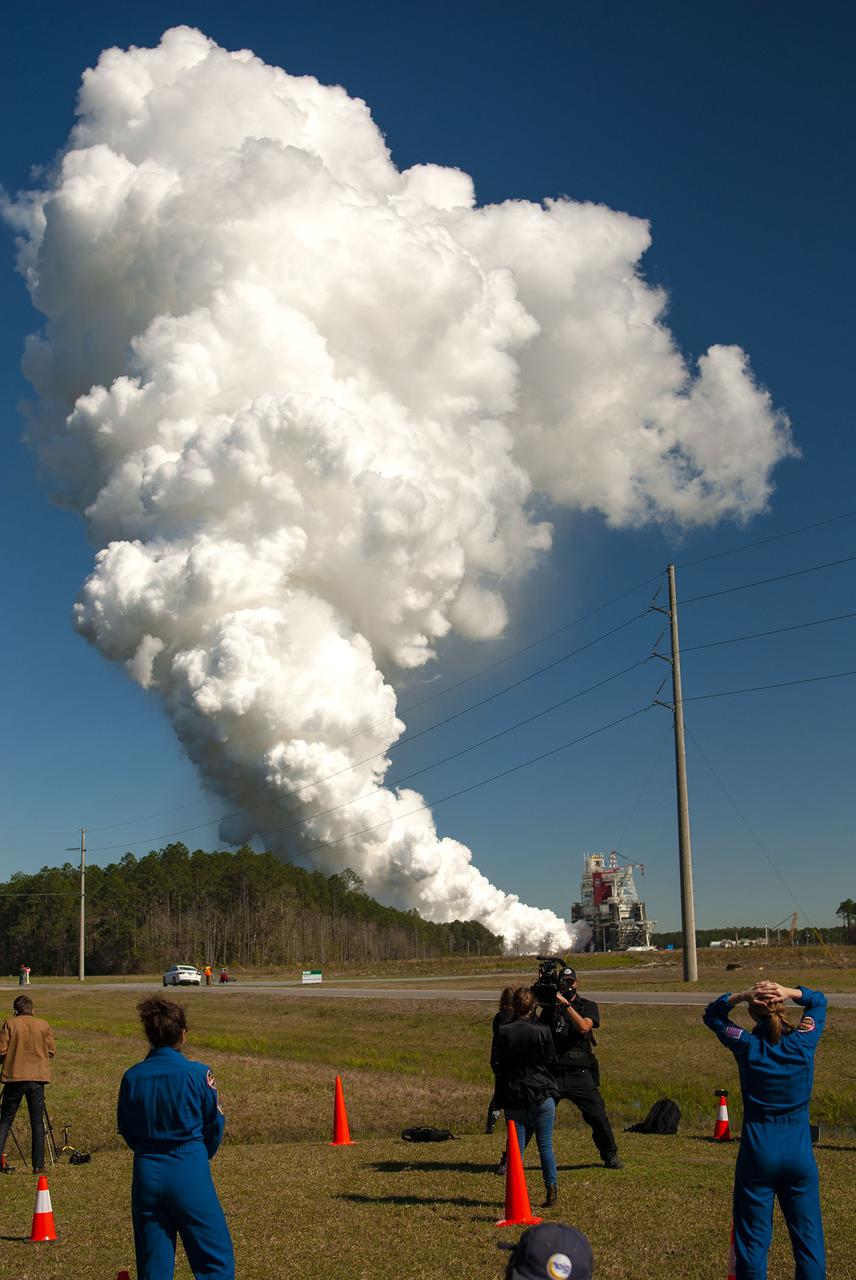
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
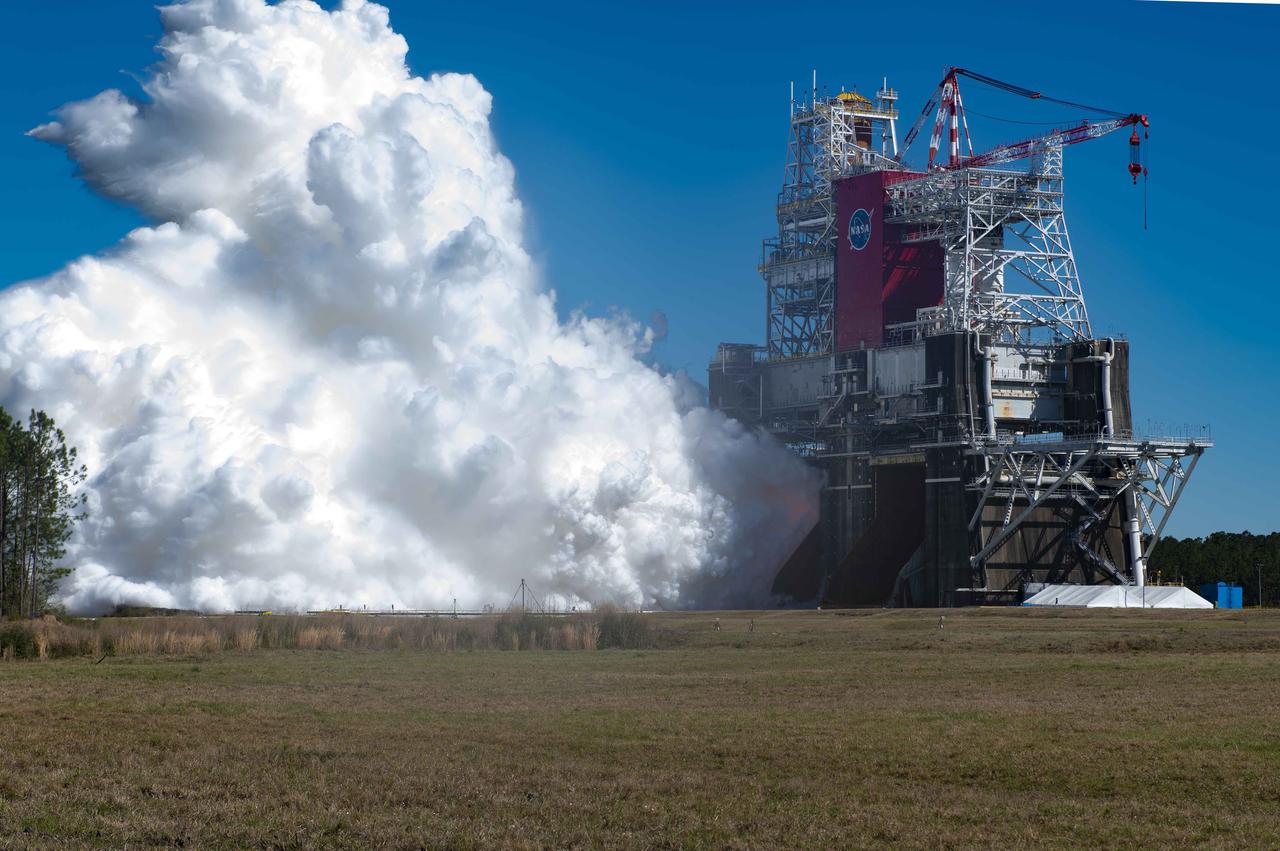

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
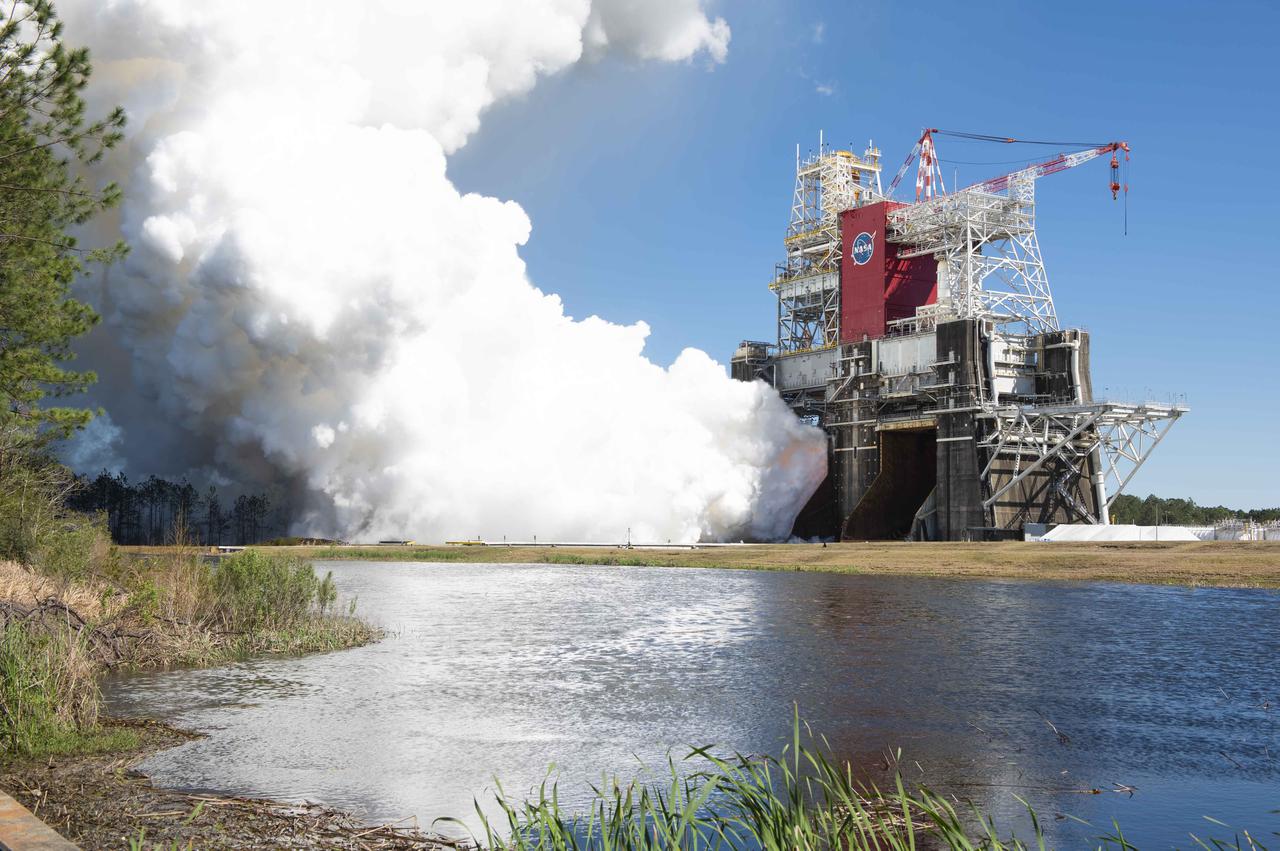

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
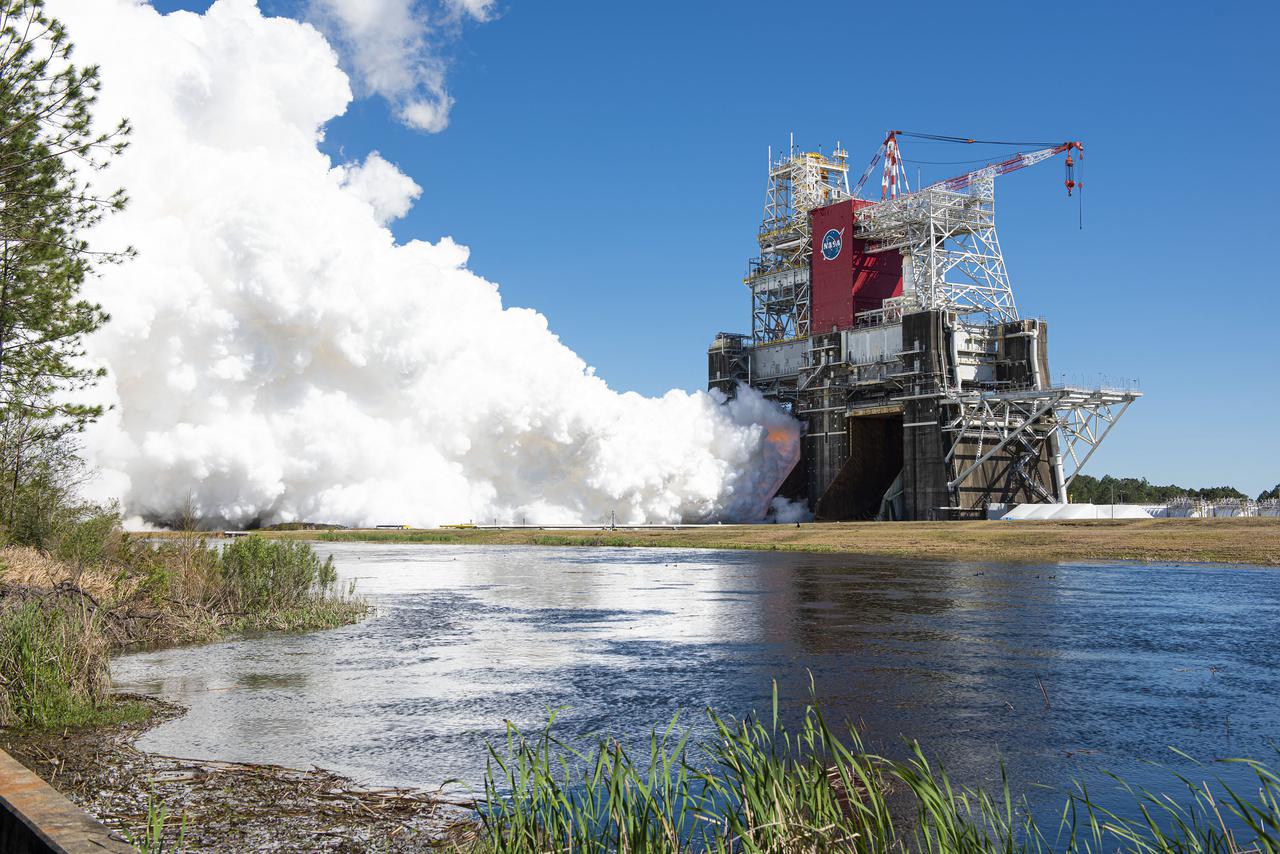

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
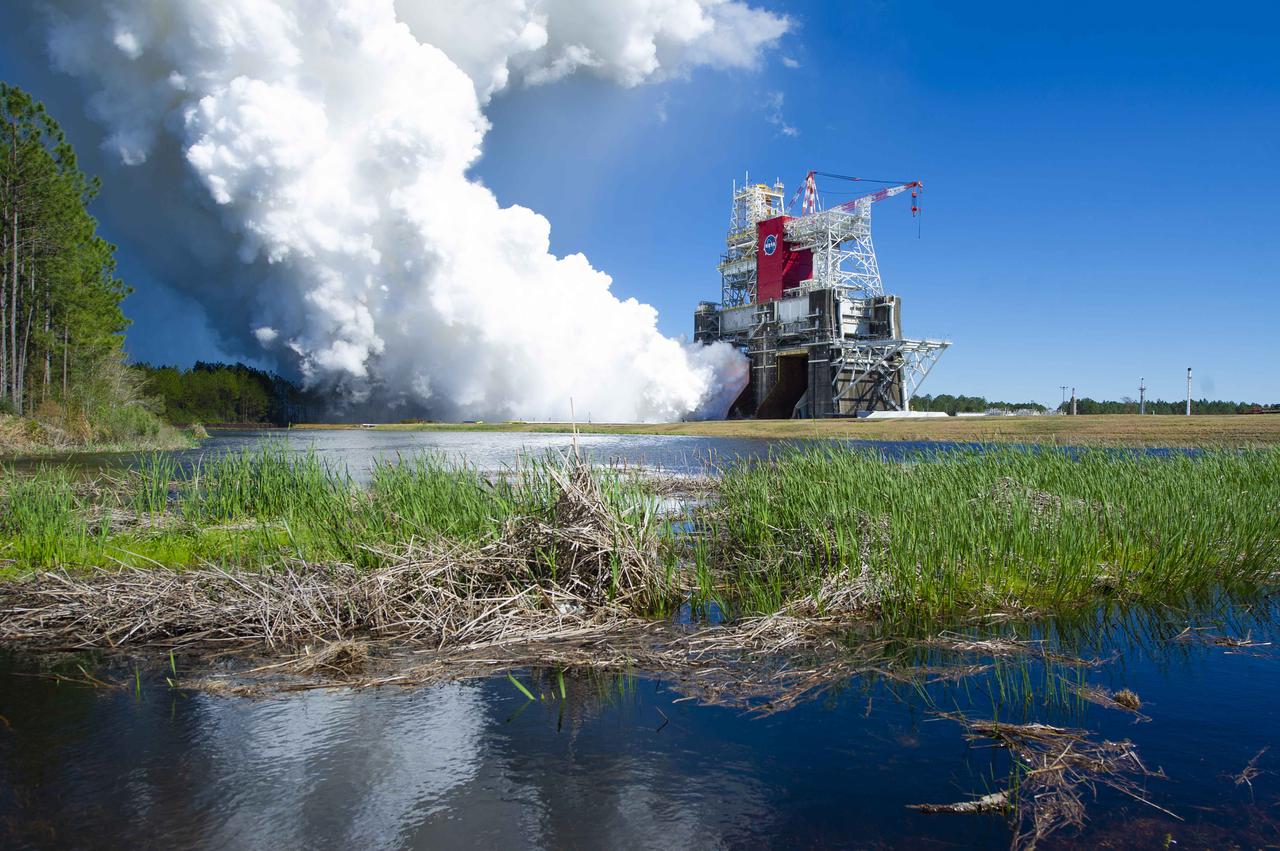

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
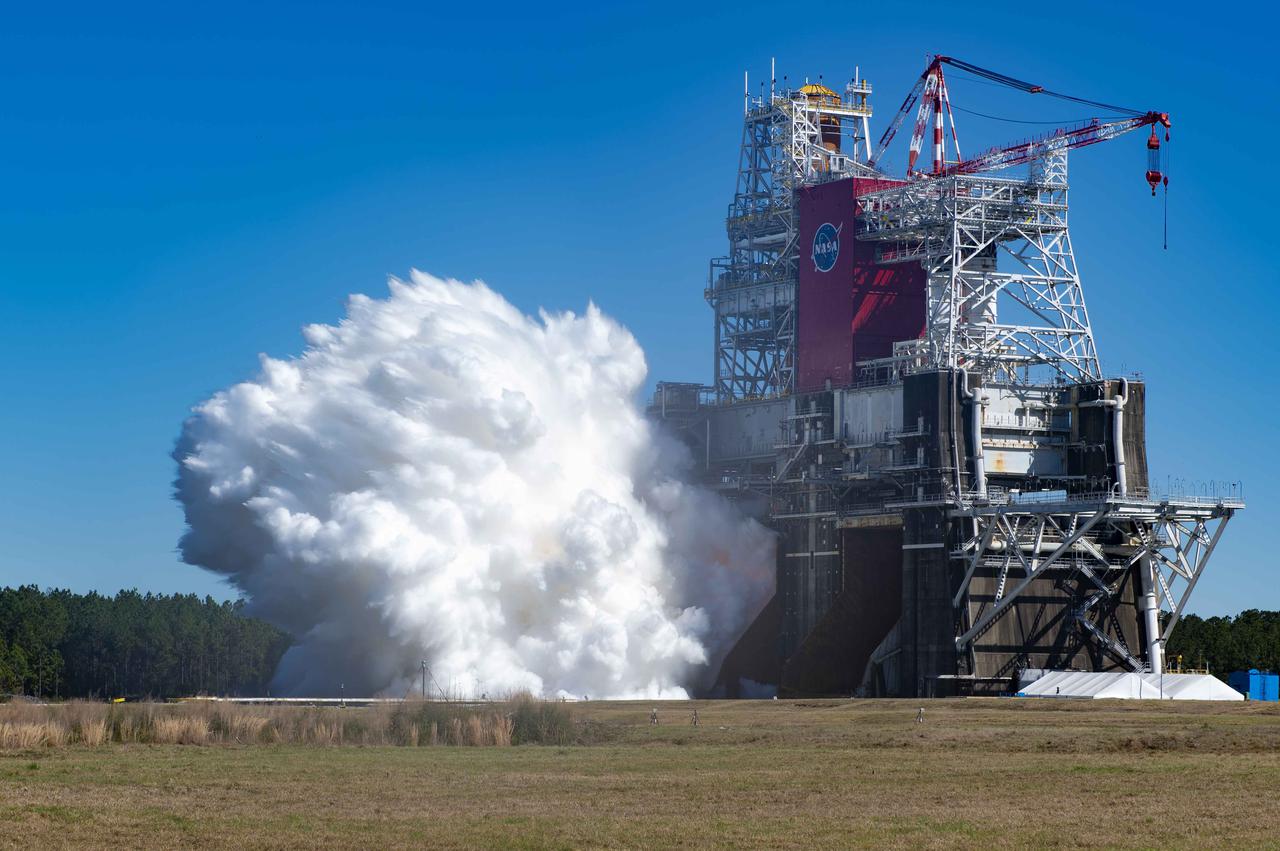

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
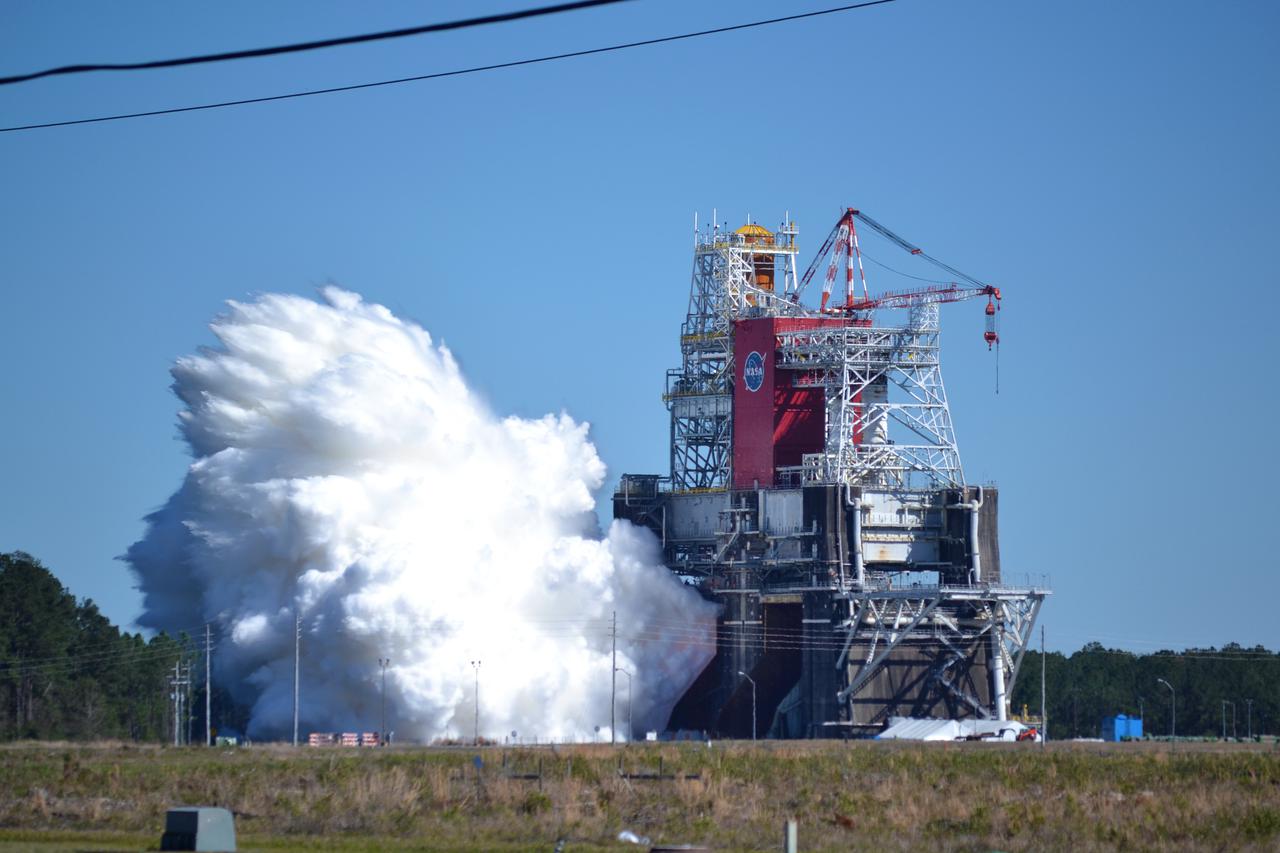

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
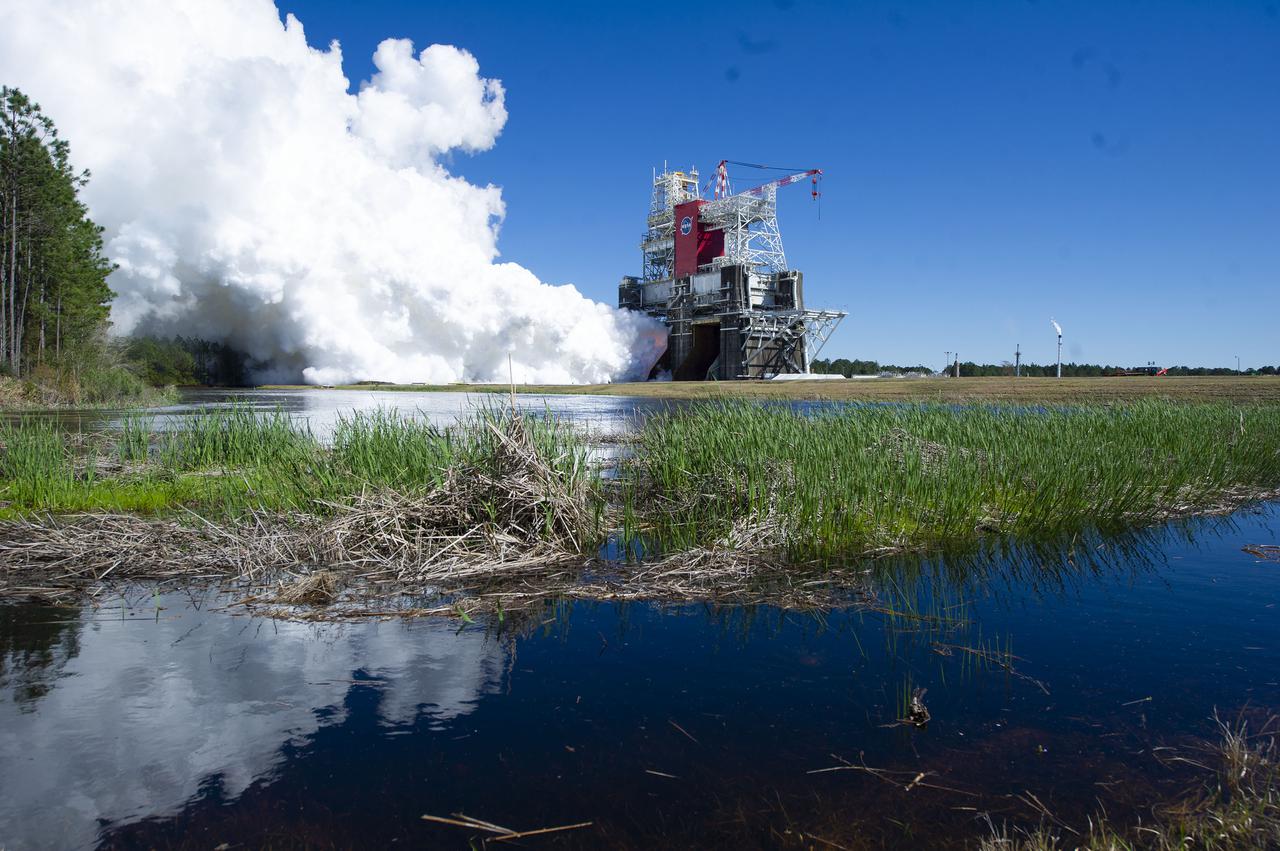

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
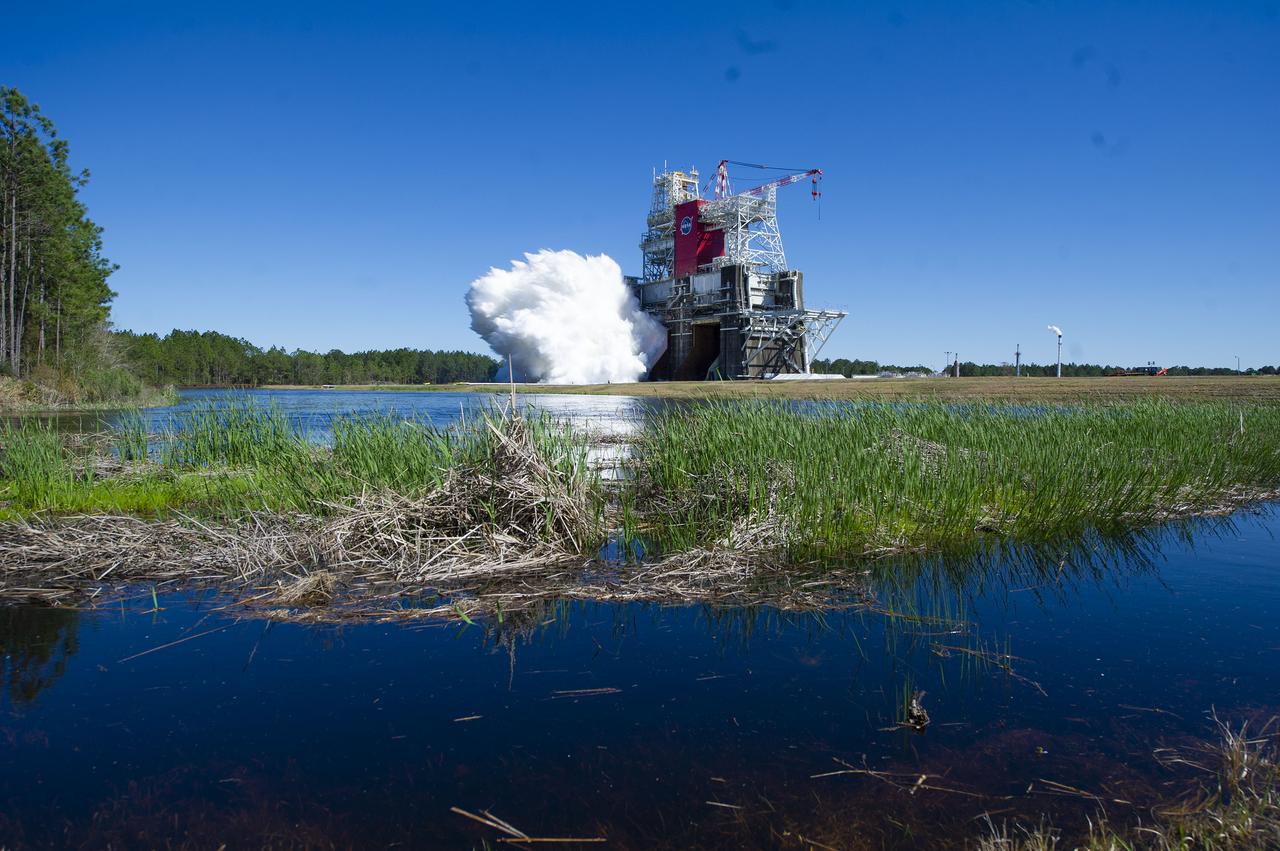

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
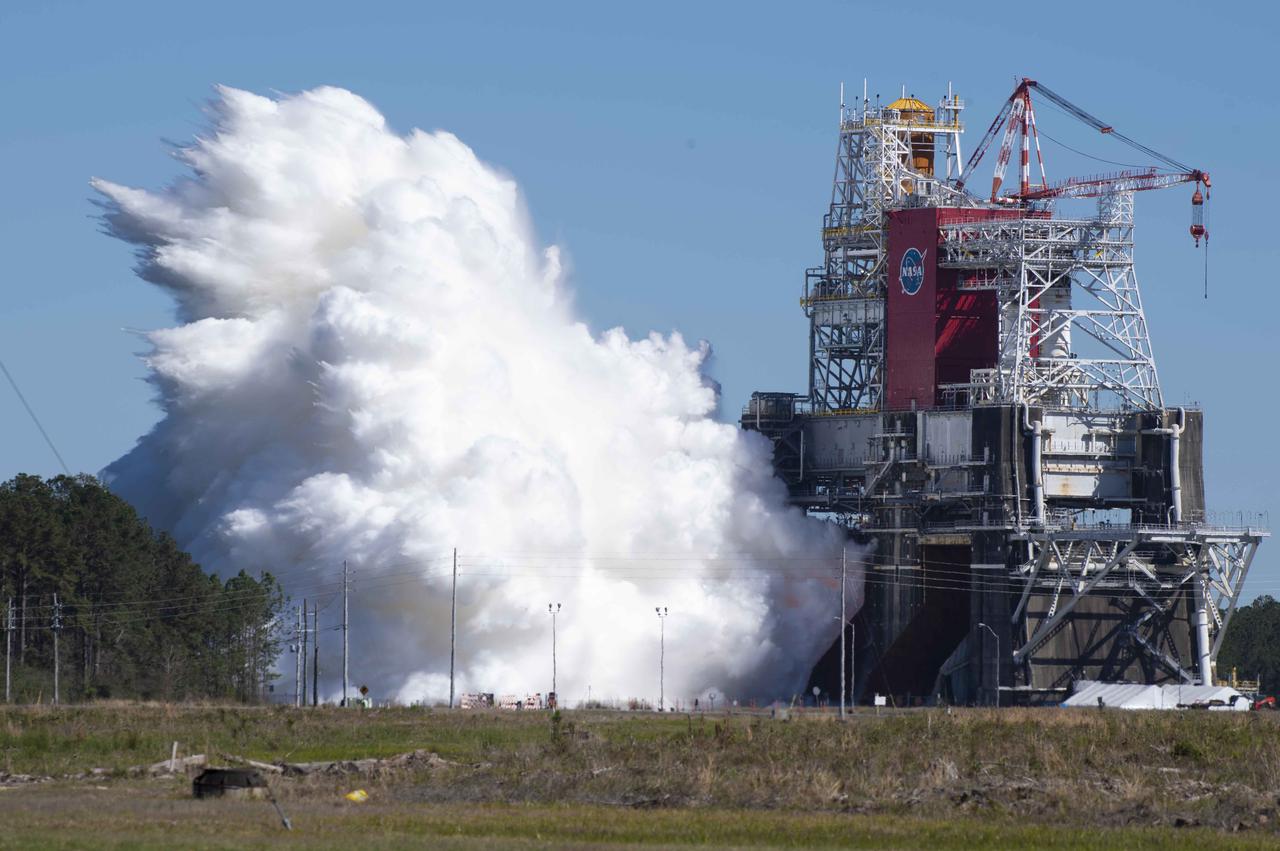

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
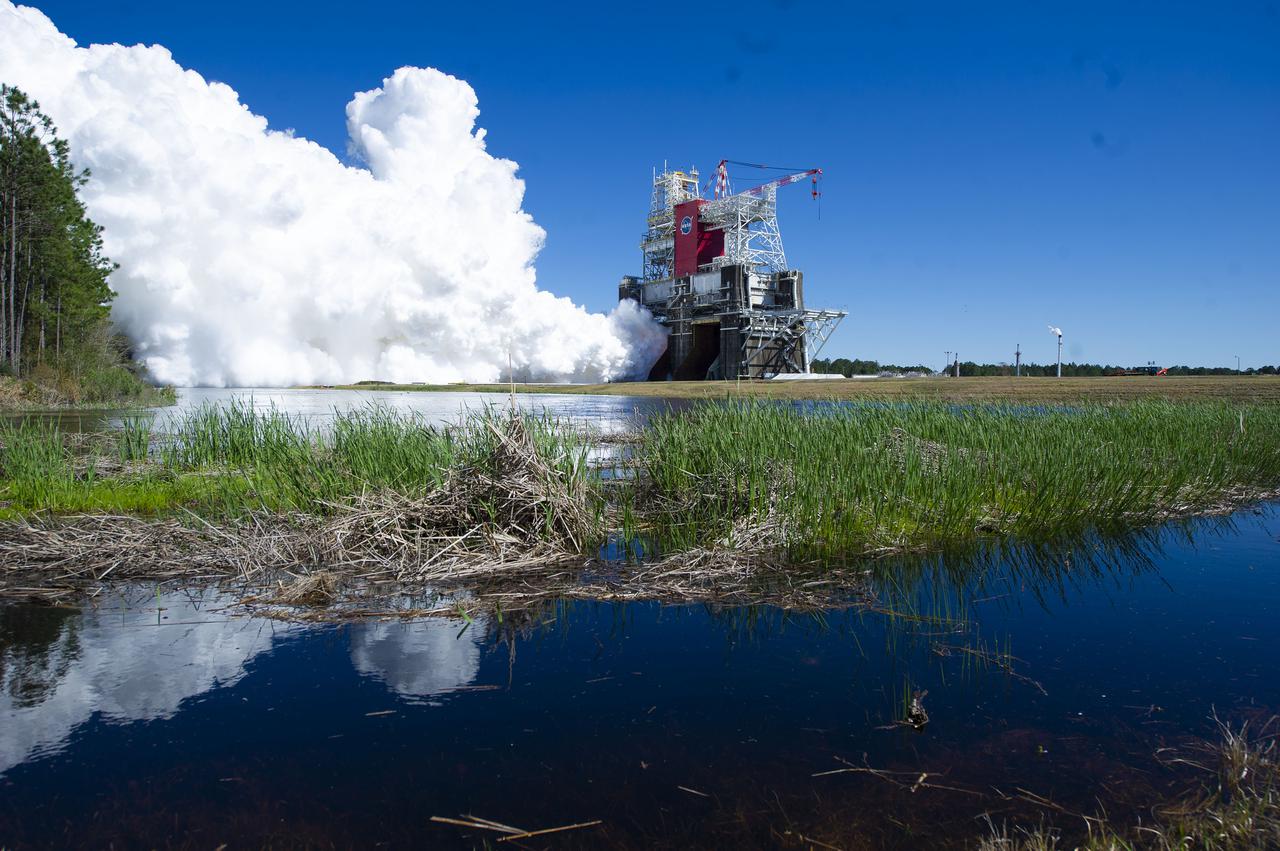

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

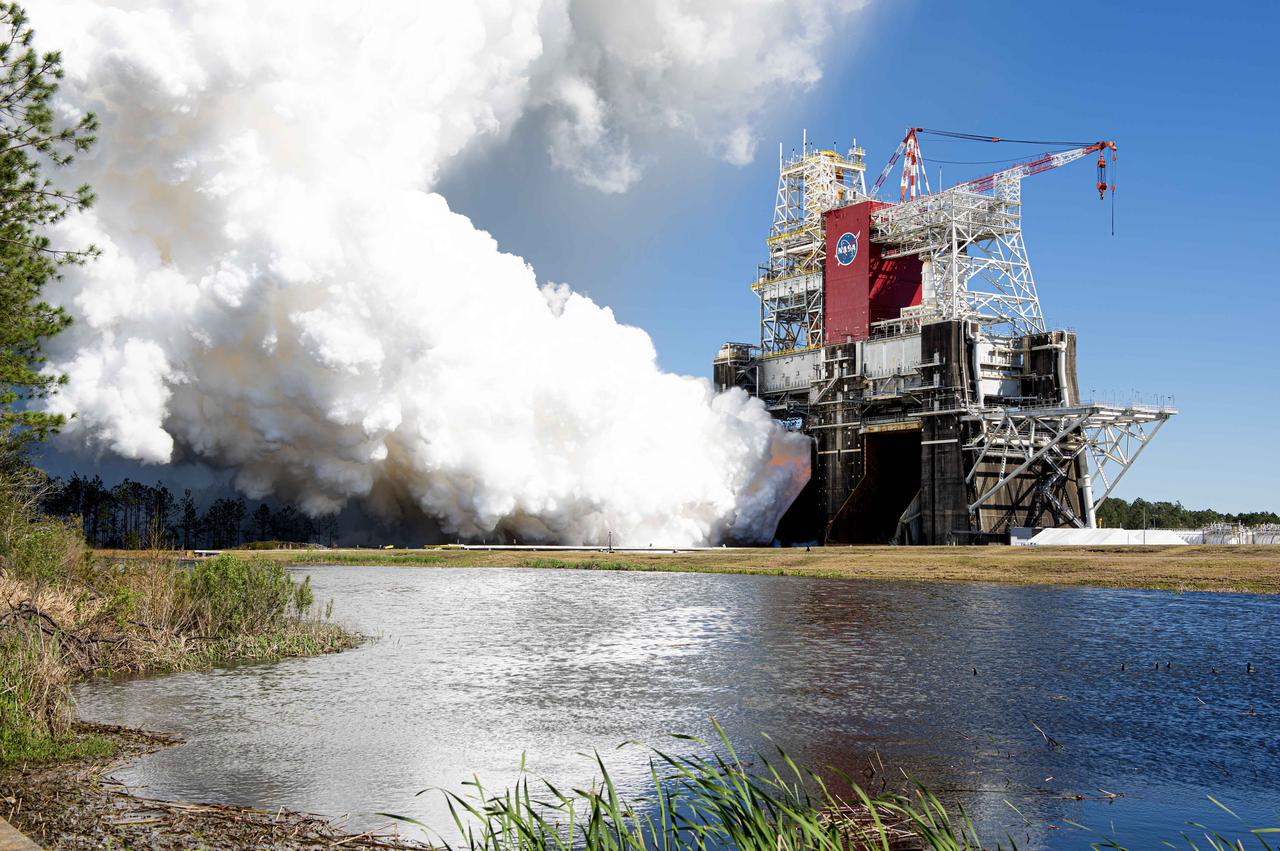
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
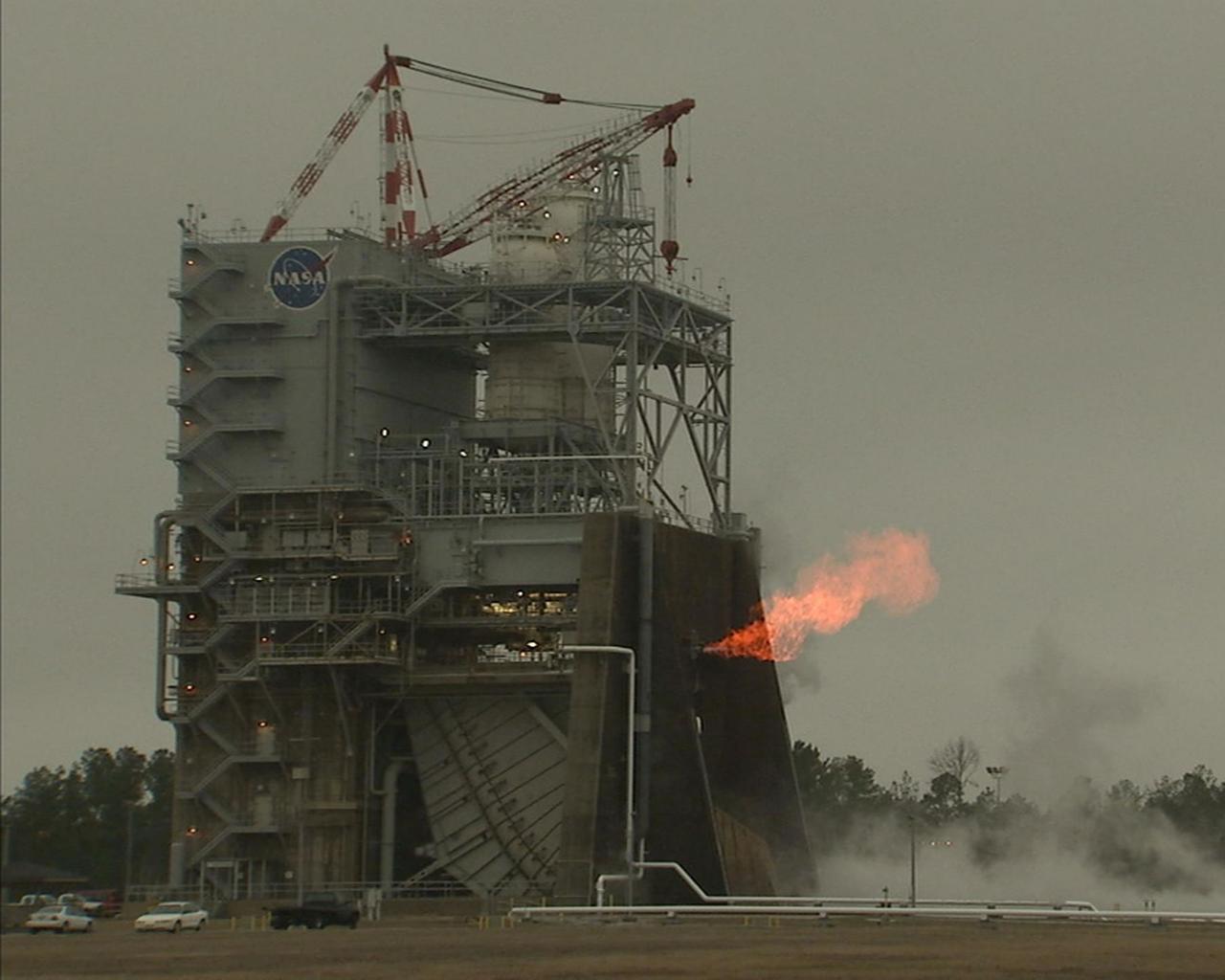
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

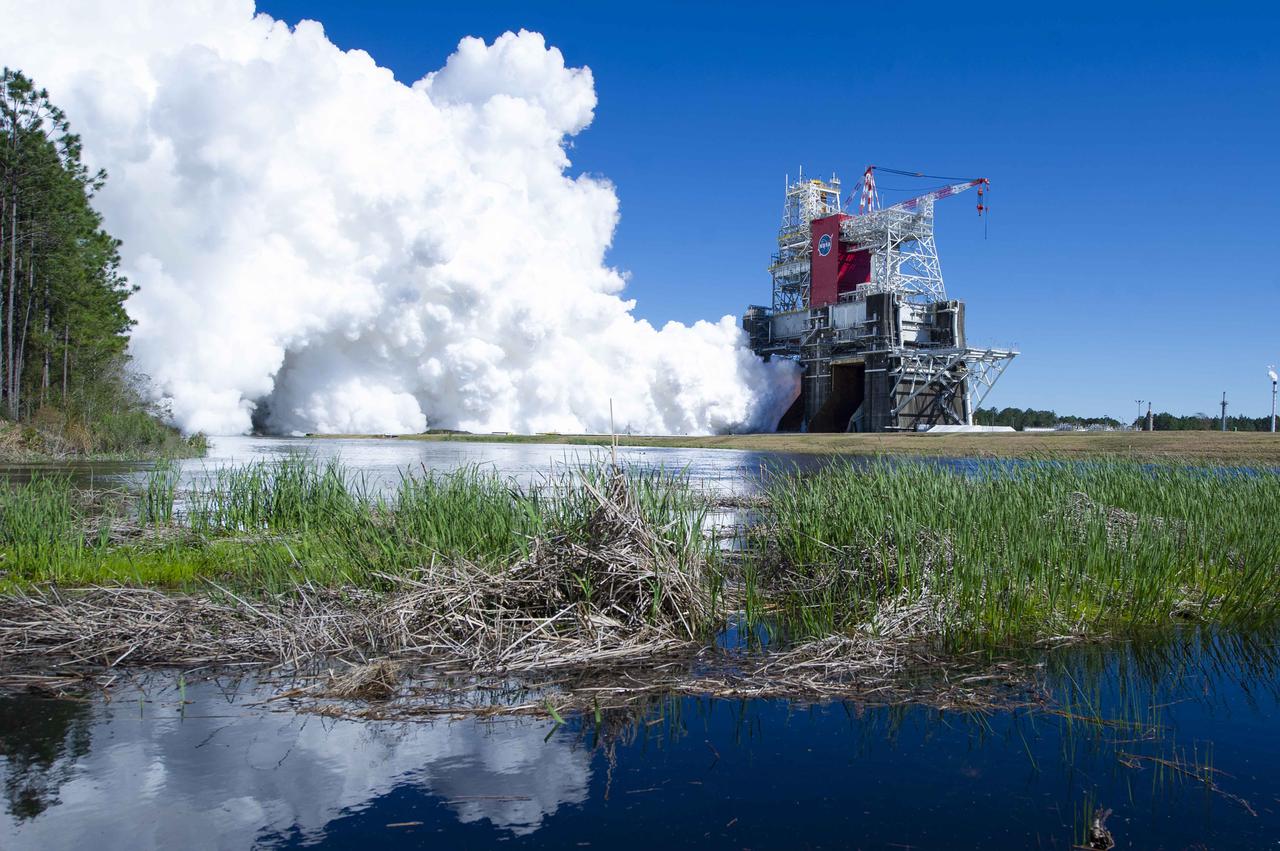
NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
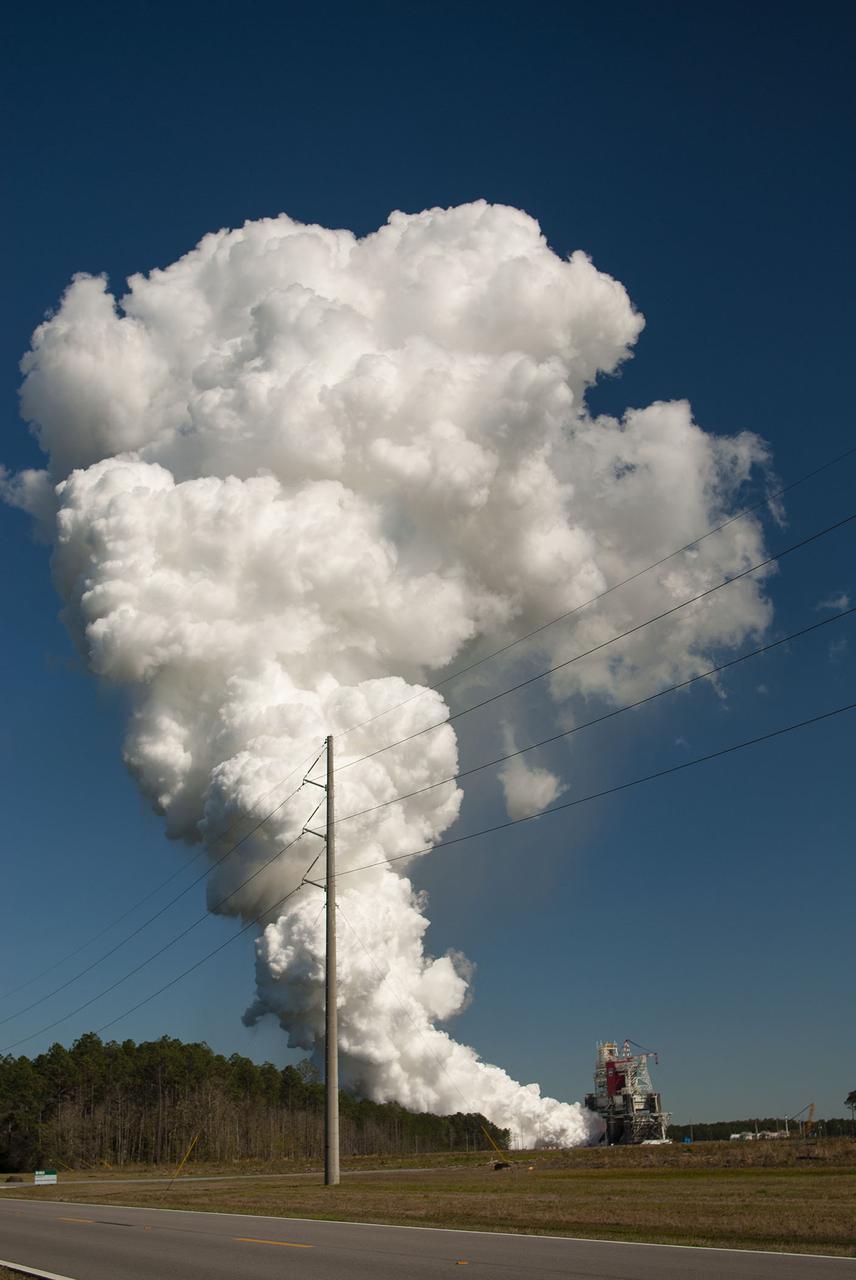

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
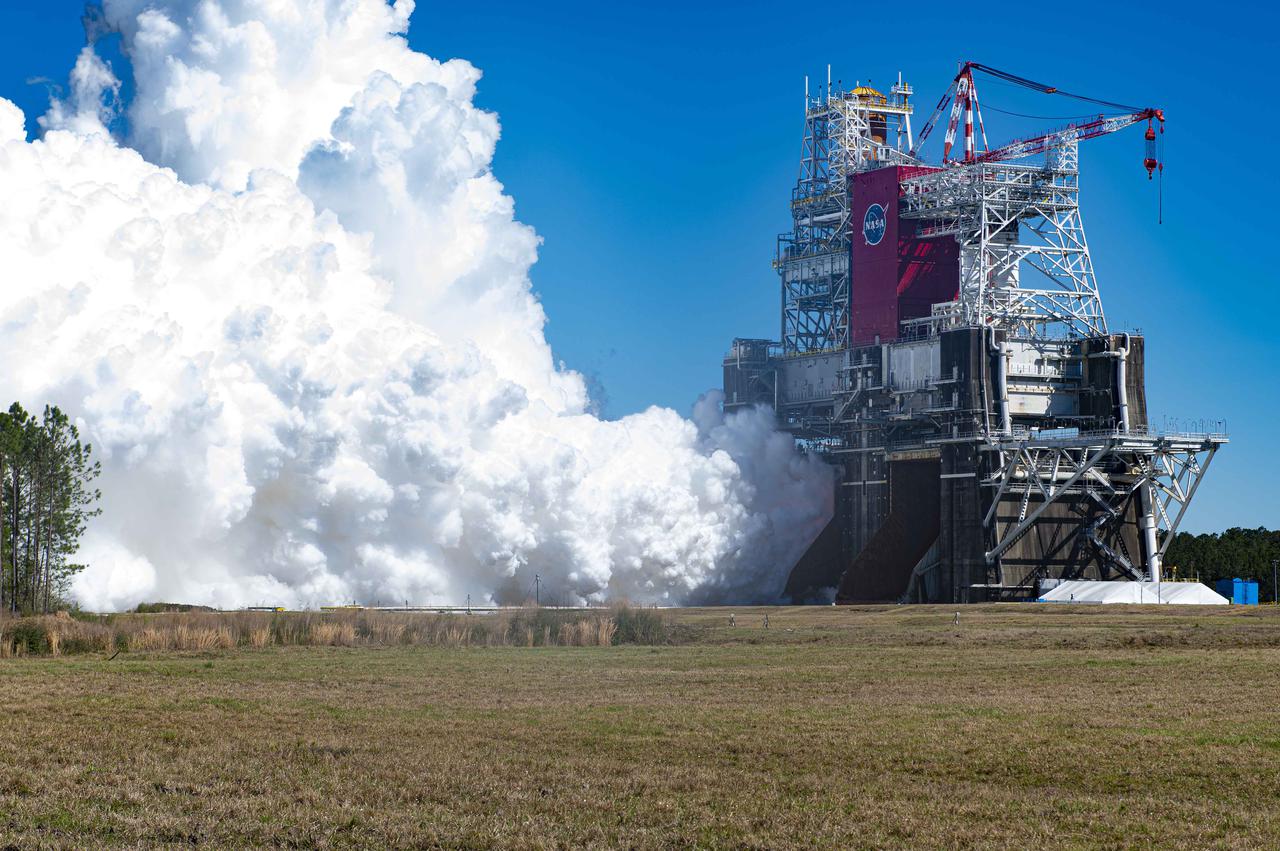

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
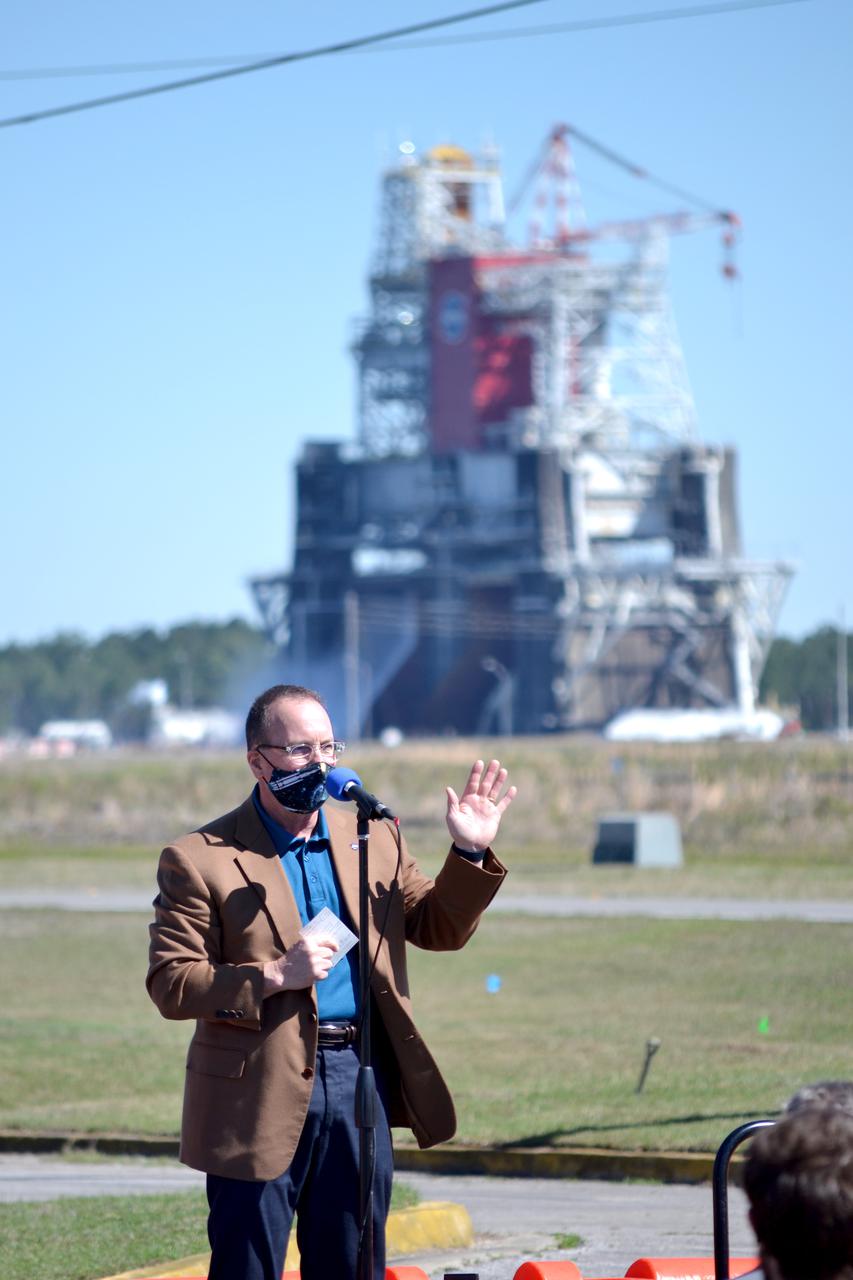

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
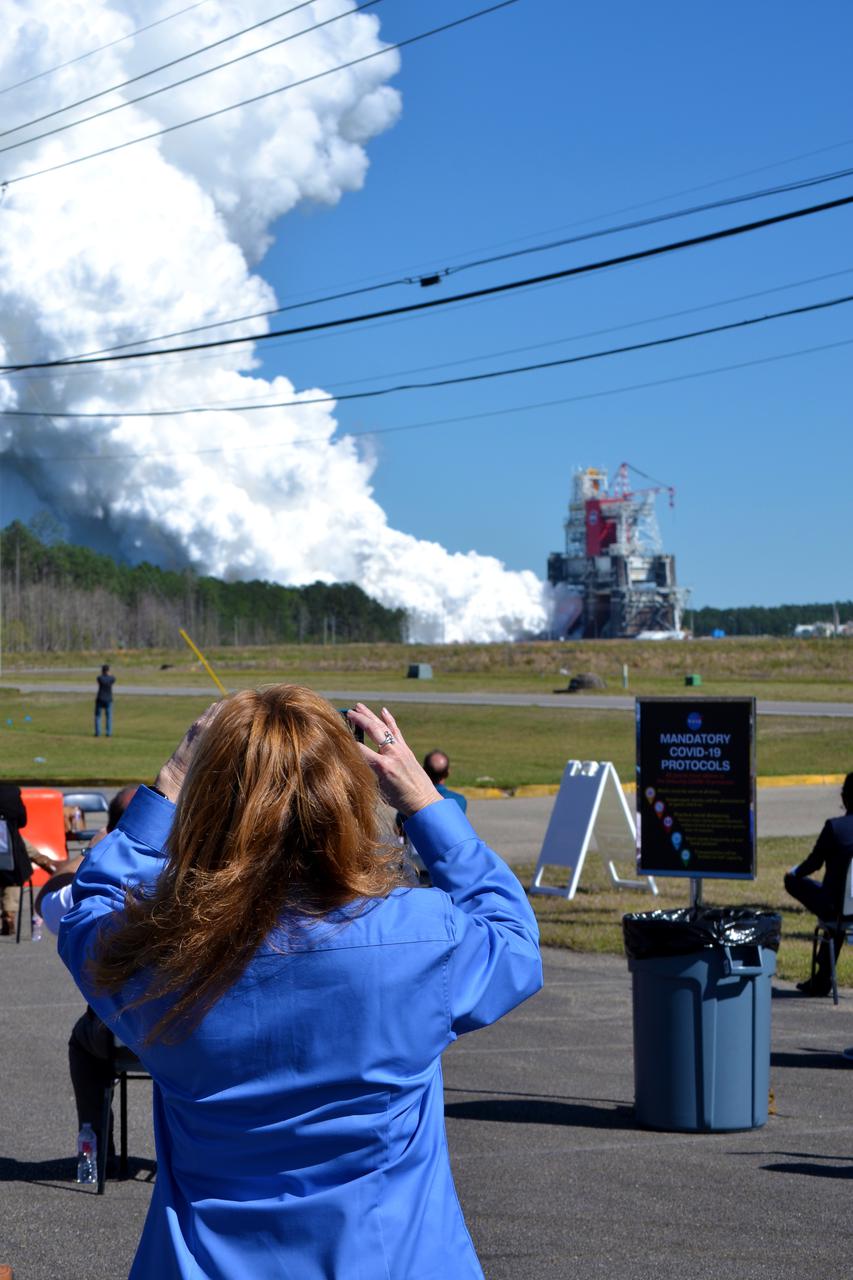

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
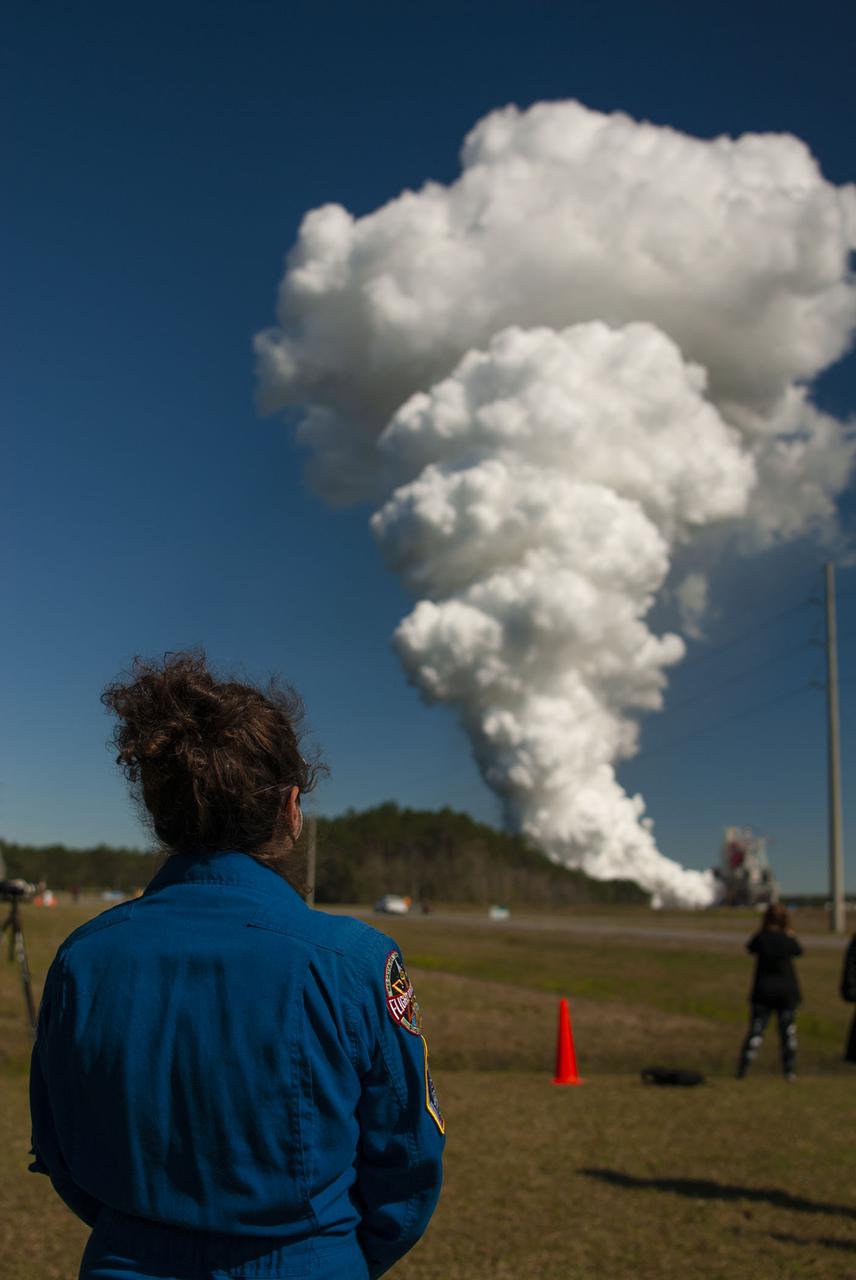

NASA conducts a hot fire test March 18, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, which represents a comprehensive assessment of the core stage and its integrated systems prior to its launch on the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
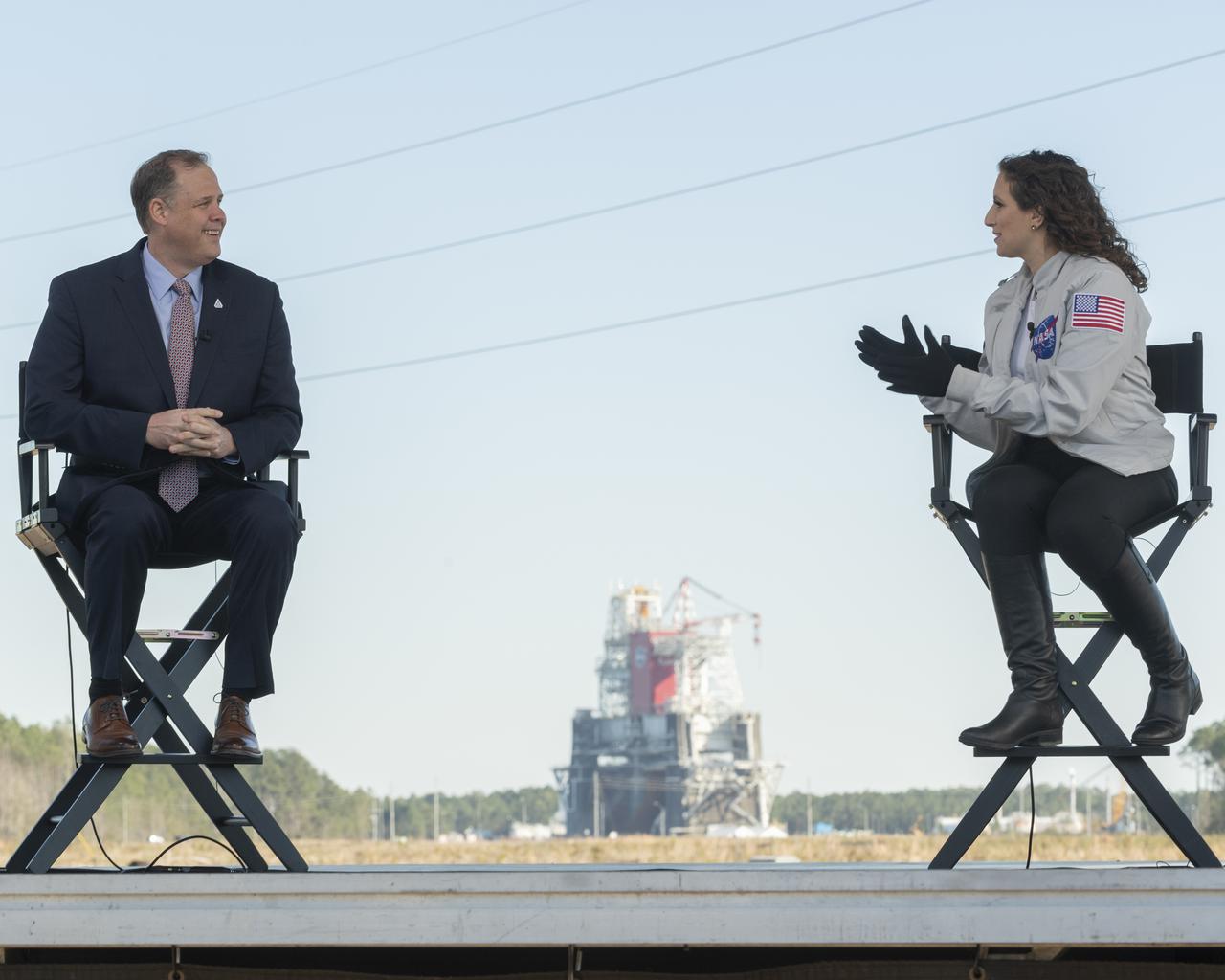

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television with Leigh D’Angelo of NASA, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
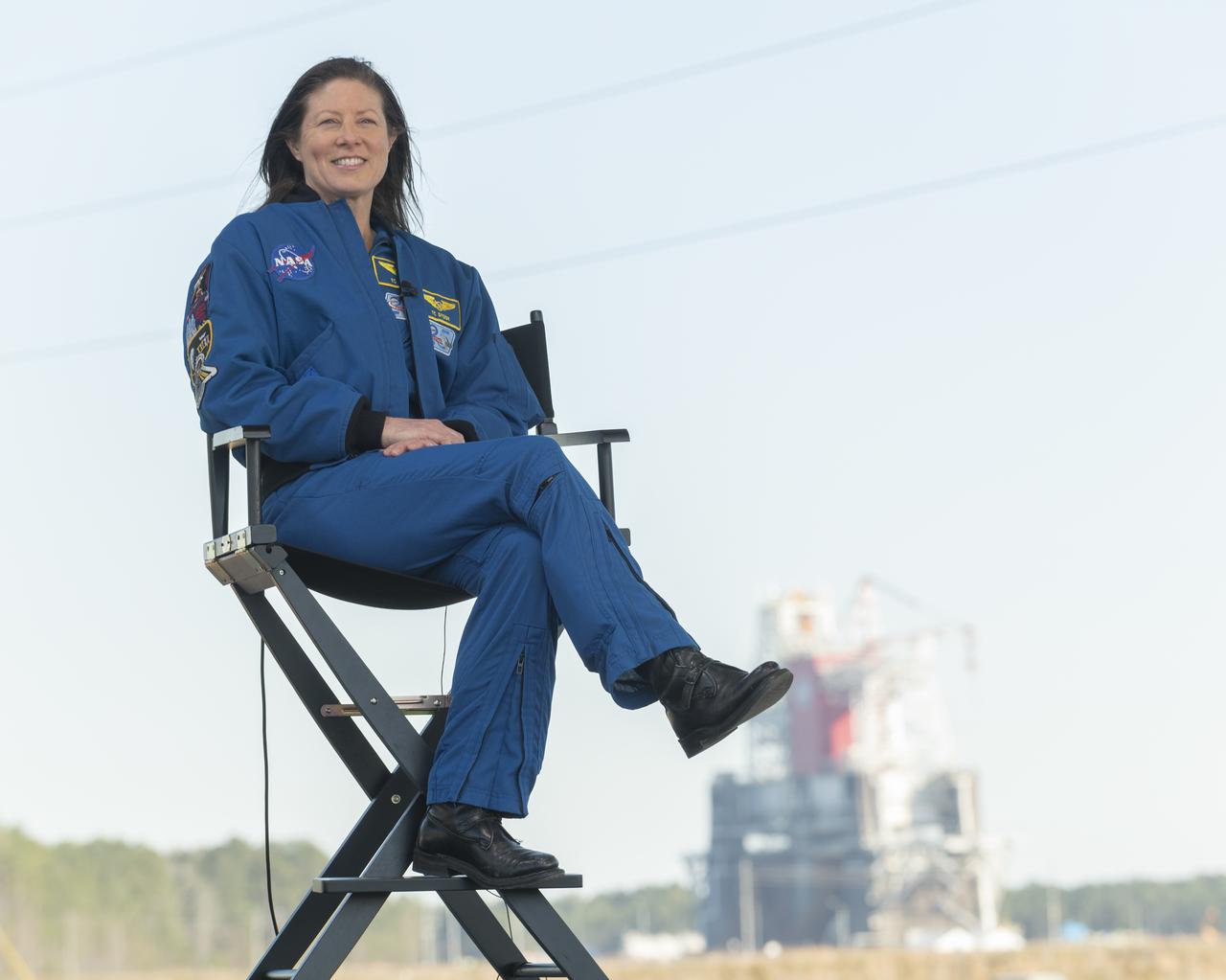

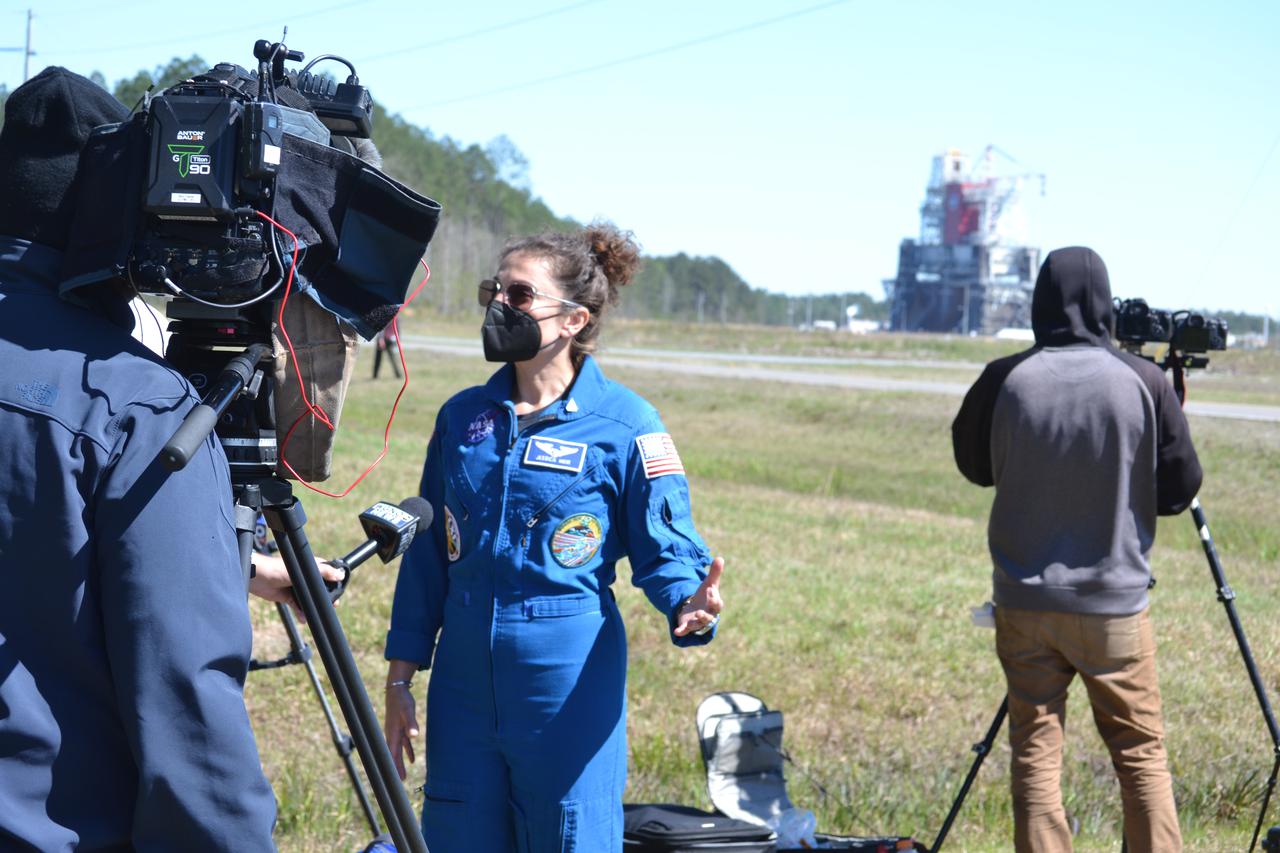
NASA astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
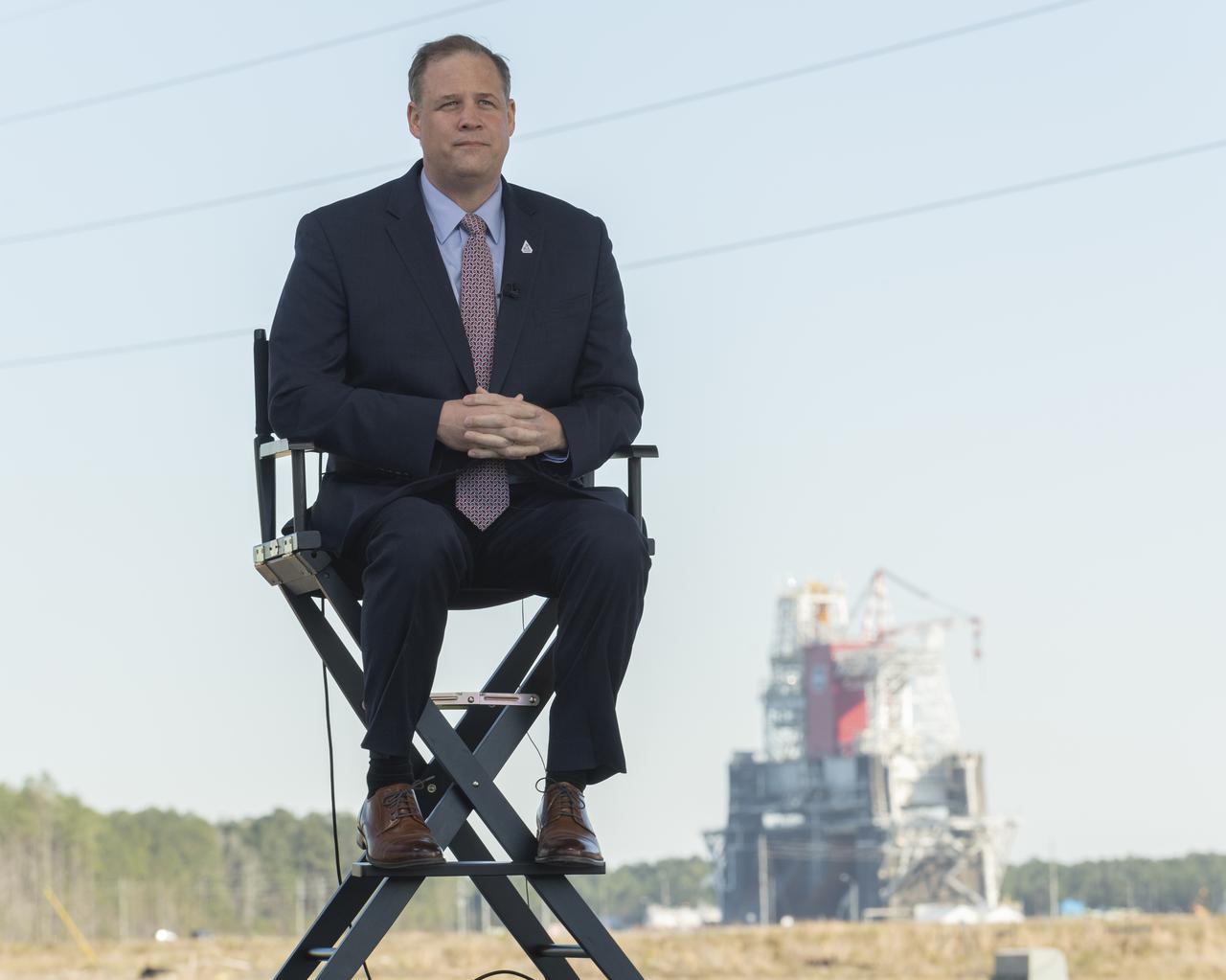

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine discusses the upcoming Green Run hot fire test on NASA television, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. In the background, the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
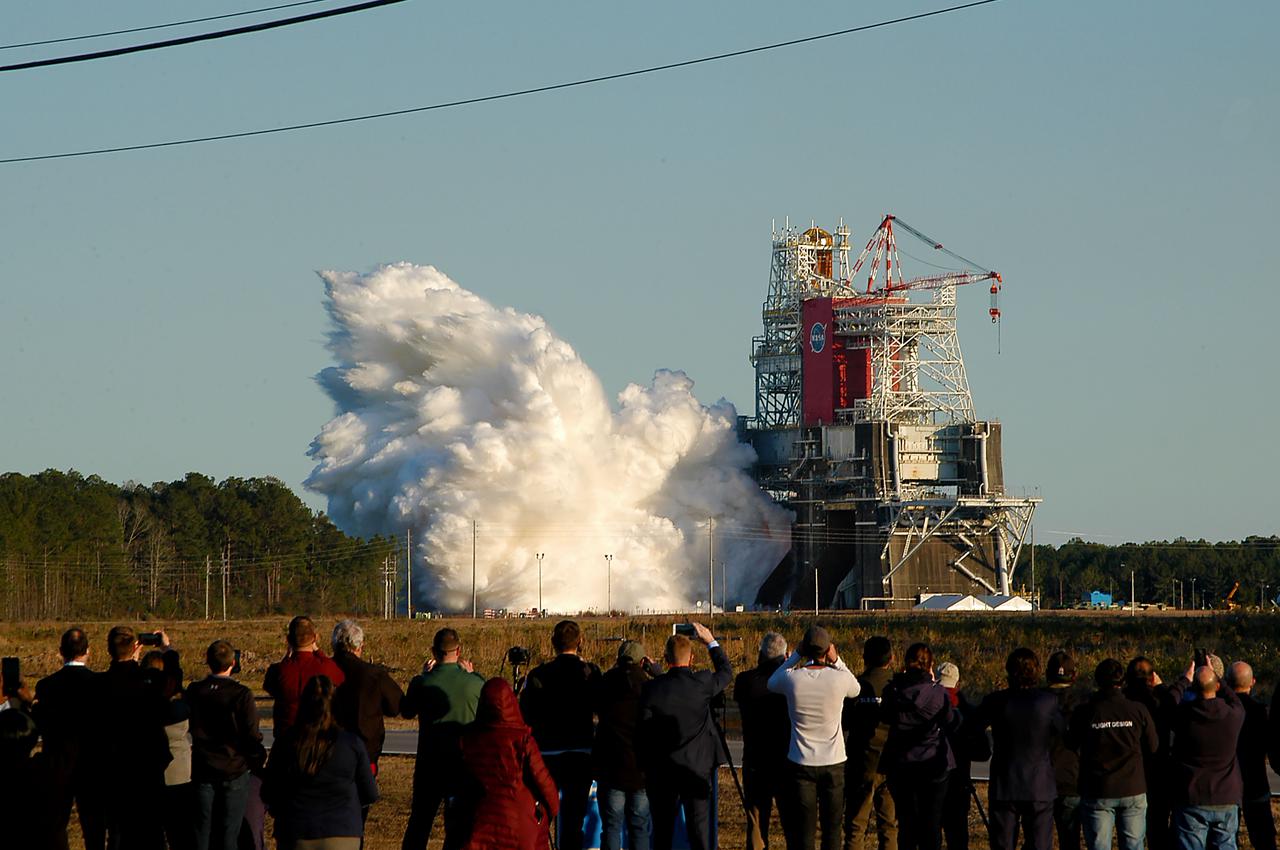

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
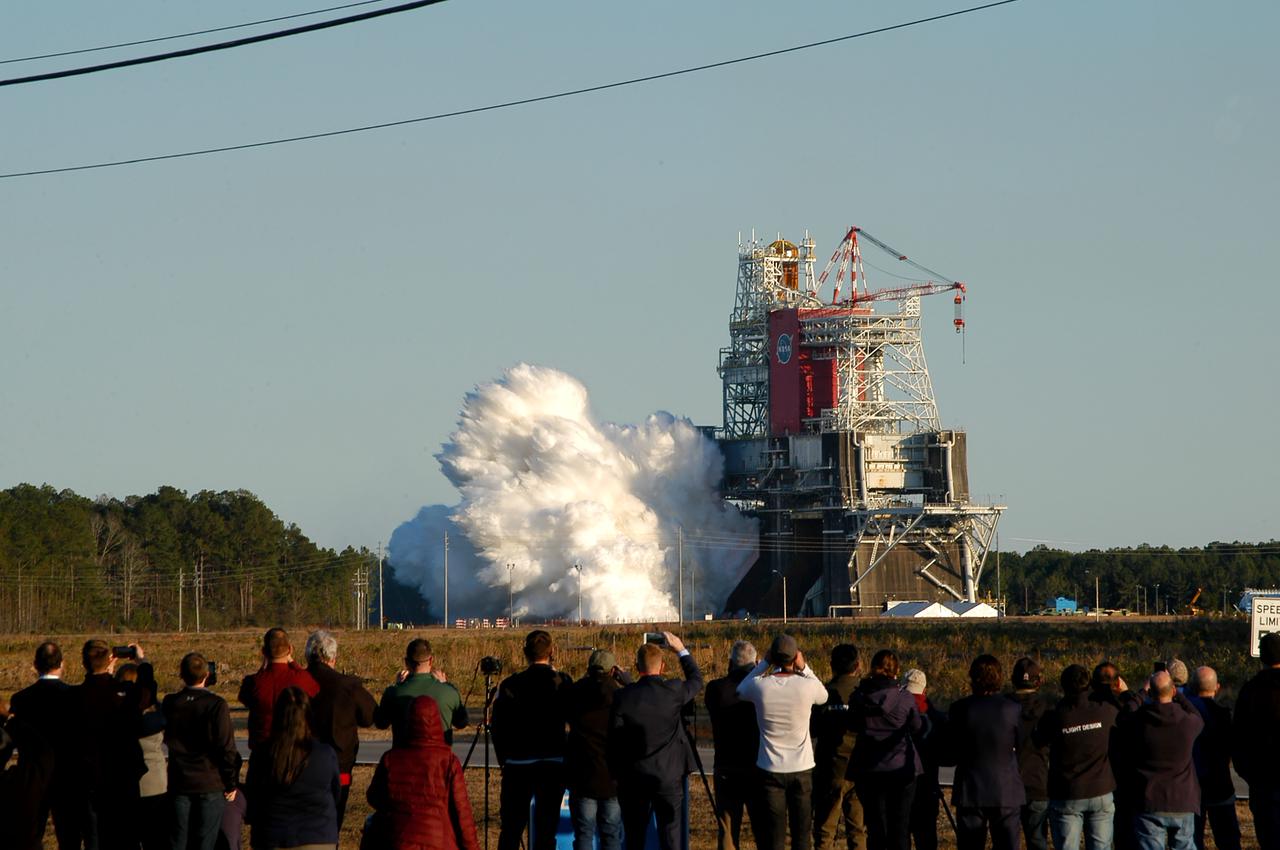

NASA conducts a hot fire test Jan. 16, 2021, of the core stage for the agency’s Space Launch System rocket on the B-2 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis. The hot fire test of the stage’s four RS-25 engines generated a combined 1.6 million pounds of thrust, just as will occur during an actual launch. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the SLS core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon.
The first hot-fire test of the J-2X power pack 1A gas generator was performed Jan. 31 on the A-1 Test Stand at Stennis Space Center. Initial indications are that all test objectives were met. The test was designed as a 3.42-second helium spin start with gas generator ignition and it went the full scheduled duration. Test conductors reported a smooth start with normal shutdown and described the event as a 'good test.' The test was part of the early component testing for the new J-2X engine being built by NASA to power the Ares I and Ares V rockets that will carry humans back to the moon and on to Mars. It was performed as one in a series of 12 scheduled tests. Those tests began last November at Stennis, but the January 31 event represented the first hot-fire test. The Stennis tests are a critical step in the successful development of the J-2X engine.
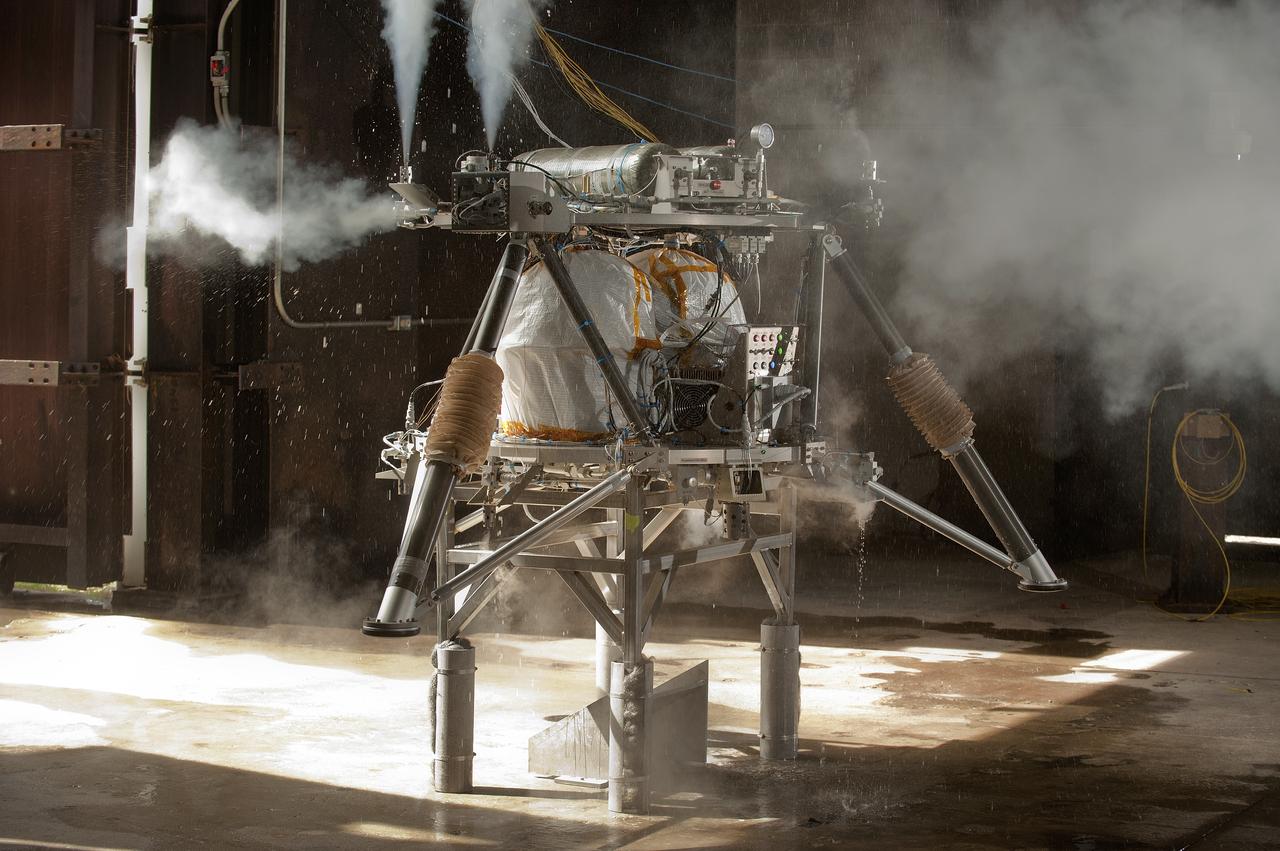

THE FIRST STAP DOWN TEST OF THE HOT FIRE ROBOTIC LANDER
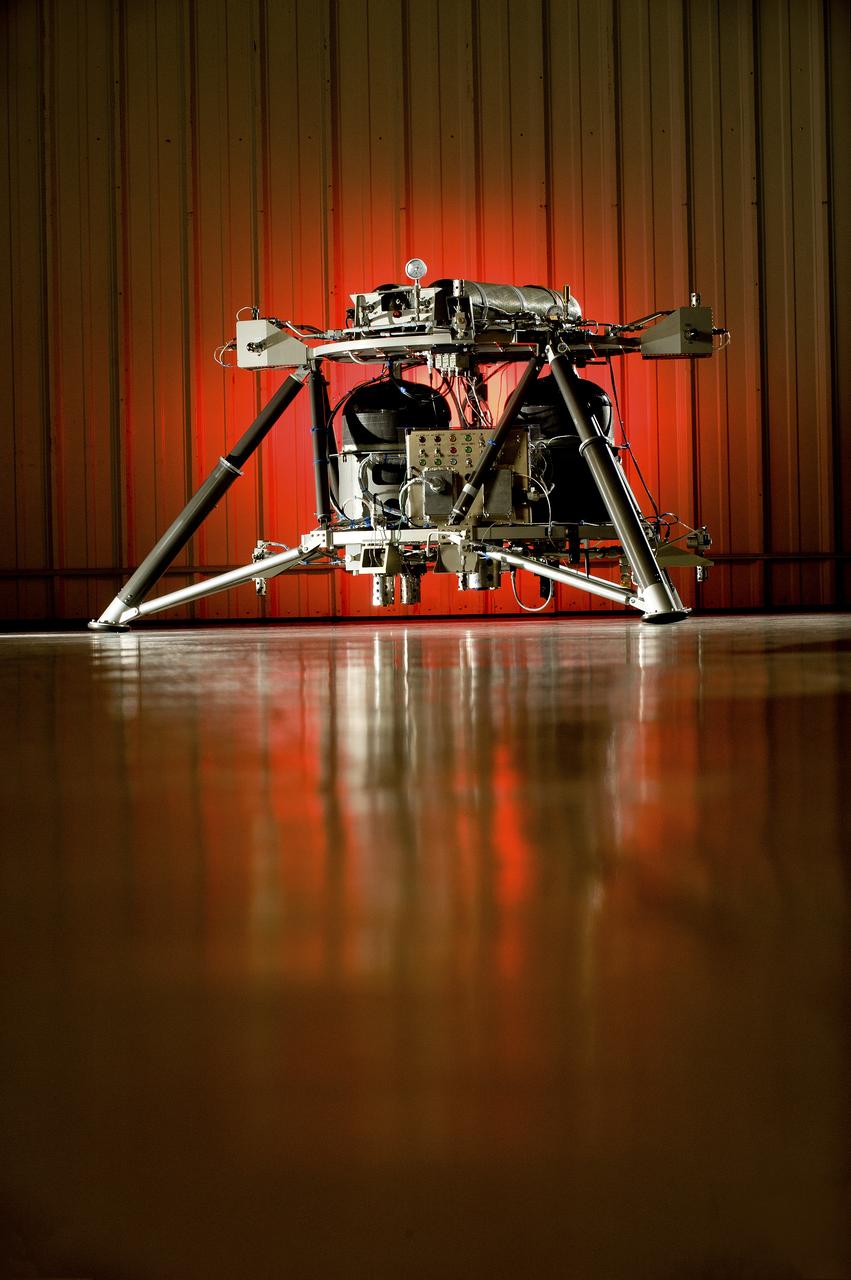

THE HOT FIRE ROBOTIC LANDER PROTOTYPE AT TELEDYNE BROWN ENGINEERING.

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Friday, Jan. 15, 2021 at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

The turbulent atmosphere of a hot, gaseous planet known as HD 80606b is shown in this simulation based on data from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.

These thermal images show a hot south pole on the planet Neptune. These warmer temperatures provide an avenue for methane to escape out of the deep atmosphere. The images were obtained with the Very Large Telescope in Chile Sept. 1 and 2, 2006.
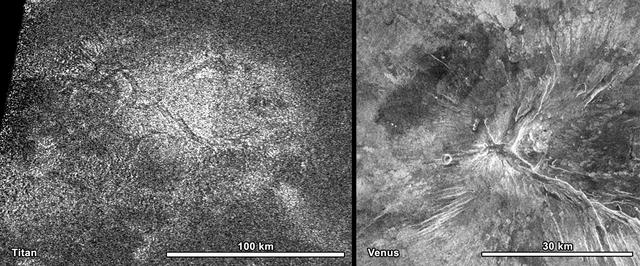
NASA Cassini spacecraft obtained this image of a feature shaped like a hot cross bun in the northern region of Titan left that bears a striking resemblance to a similar feature on Venus right.
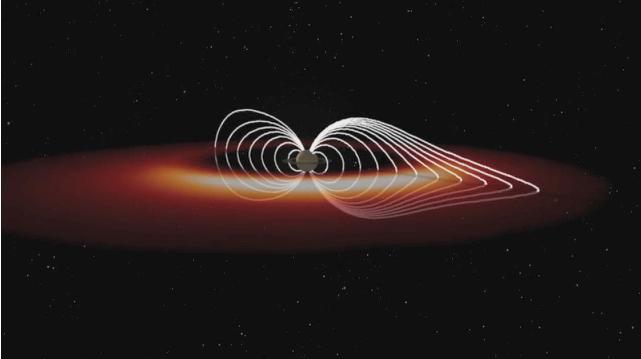
This frame from an animation based on data obtained by NASA Cassini spacecraft shows how the explosions of hot plasma on the night side orange and white periodically inflate Saturn magnetic field white lines.

This infrared image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope shows a galaxy that appears to be sizzling hot, with huge plumes of smoke swirling around it. The galaxy is known as Messier 82 or the Cigar galaxy.
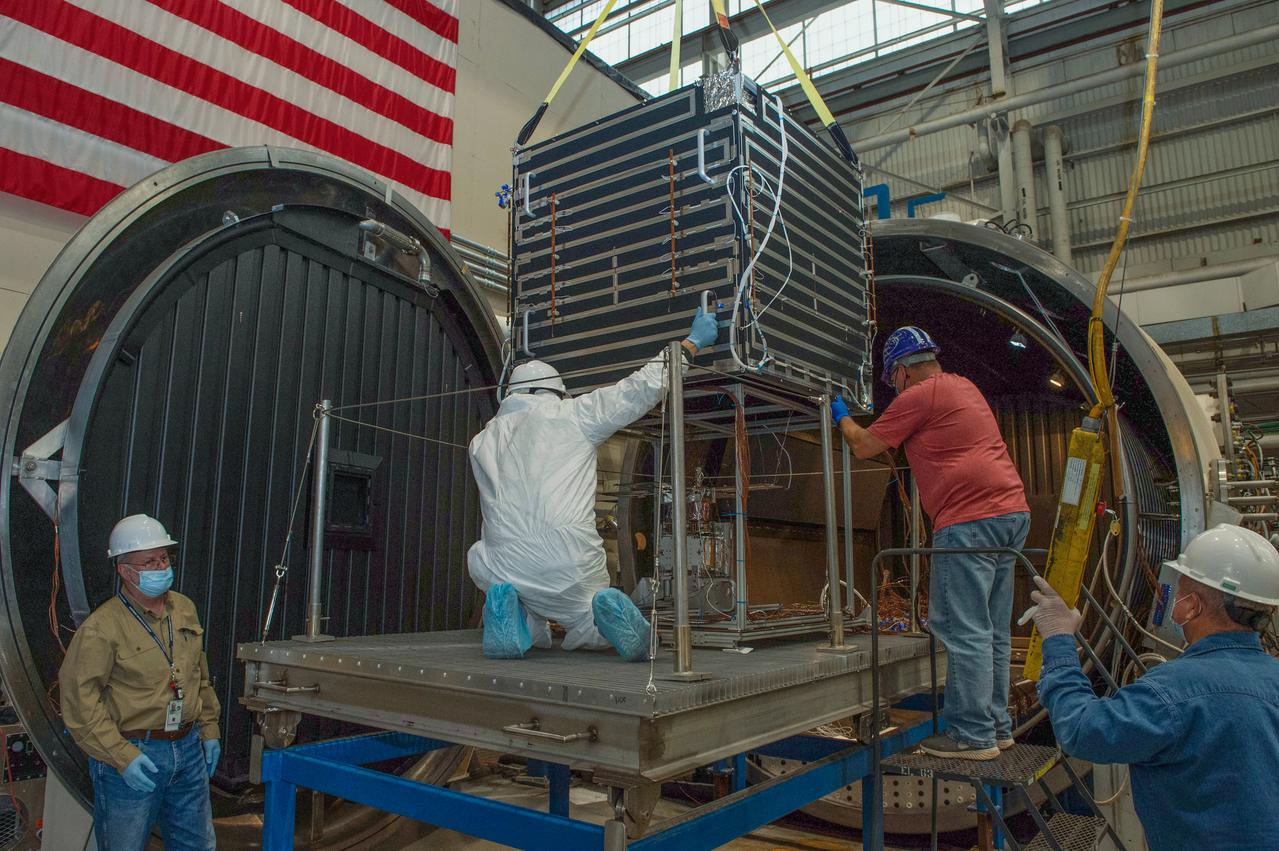

Opening Thermal Vacuum Chamber V15 to extract hot box containing NEA Scout spacecraft 2 of 2
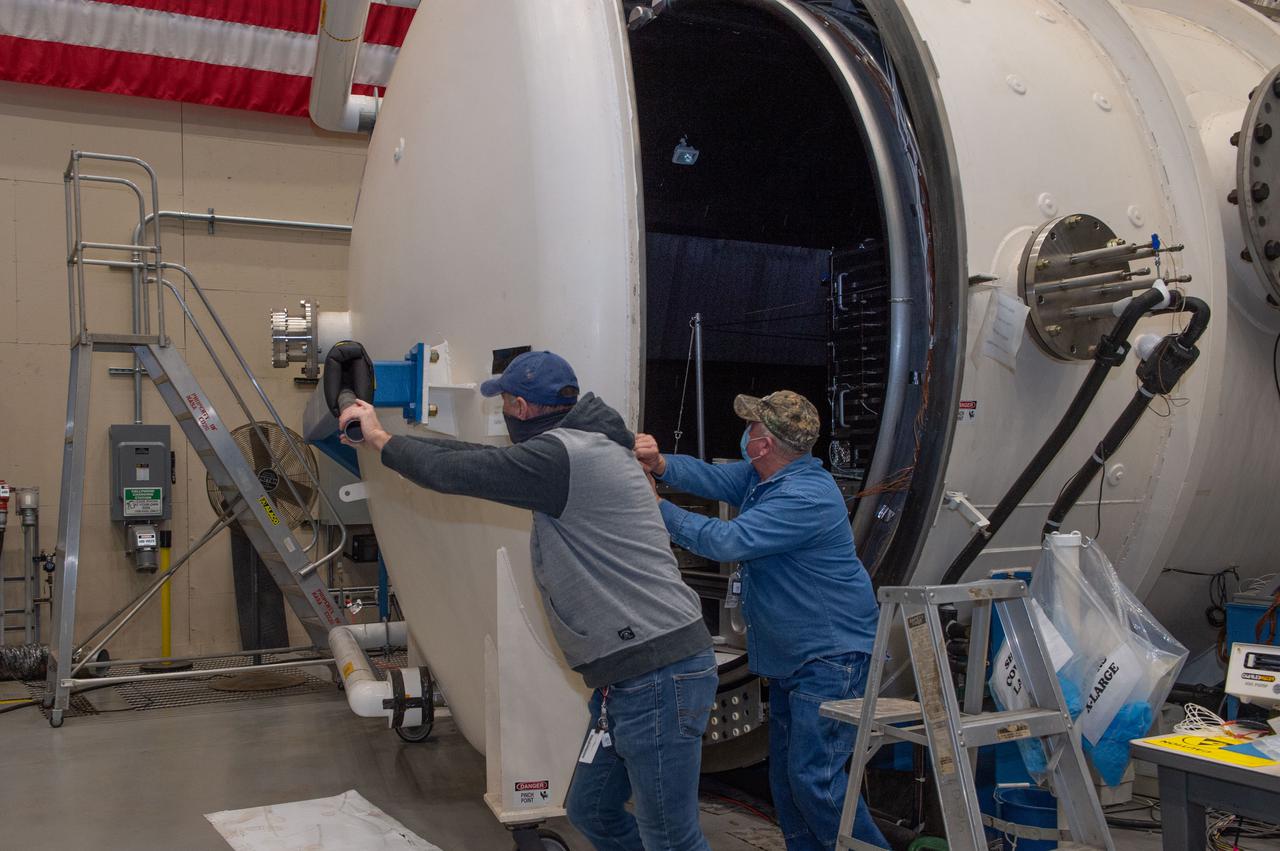

Opening Thermal Vacuum Chamber V15 to extract hot box containing NEA Scout spacecraft.
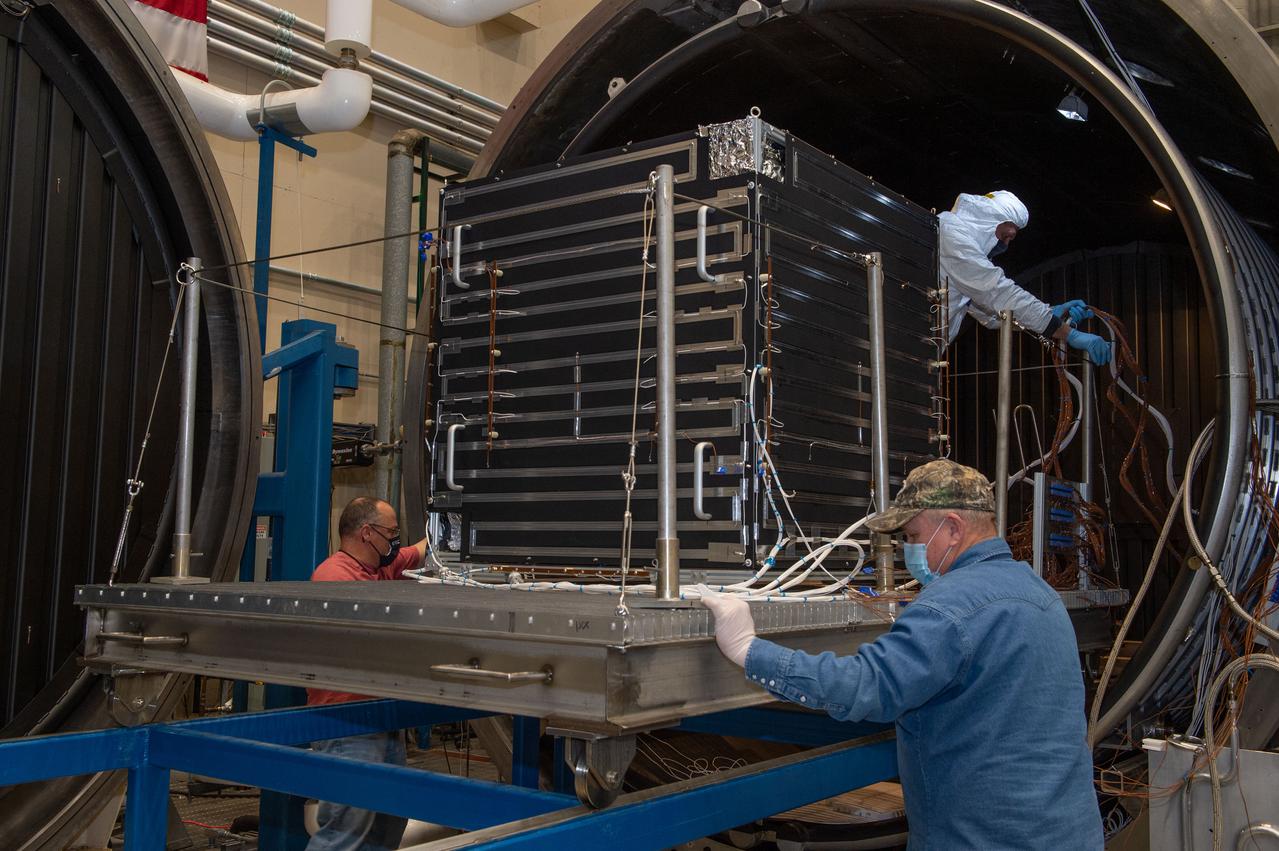

Removal of hot box containing NEA Scout spacecraft from Thermal Vacuum Chamber V15 1 of 2
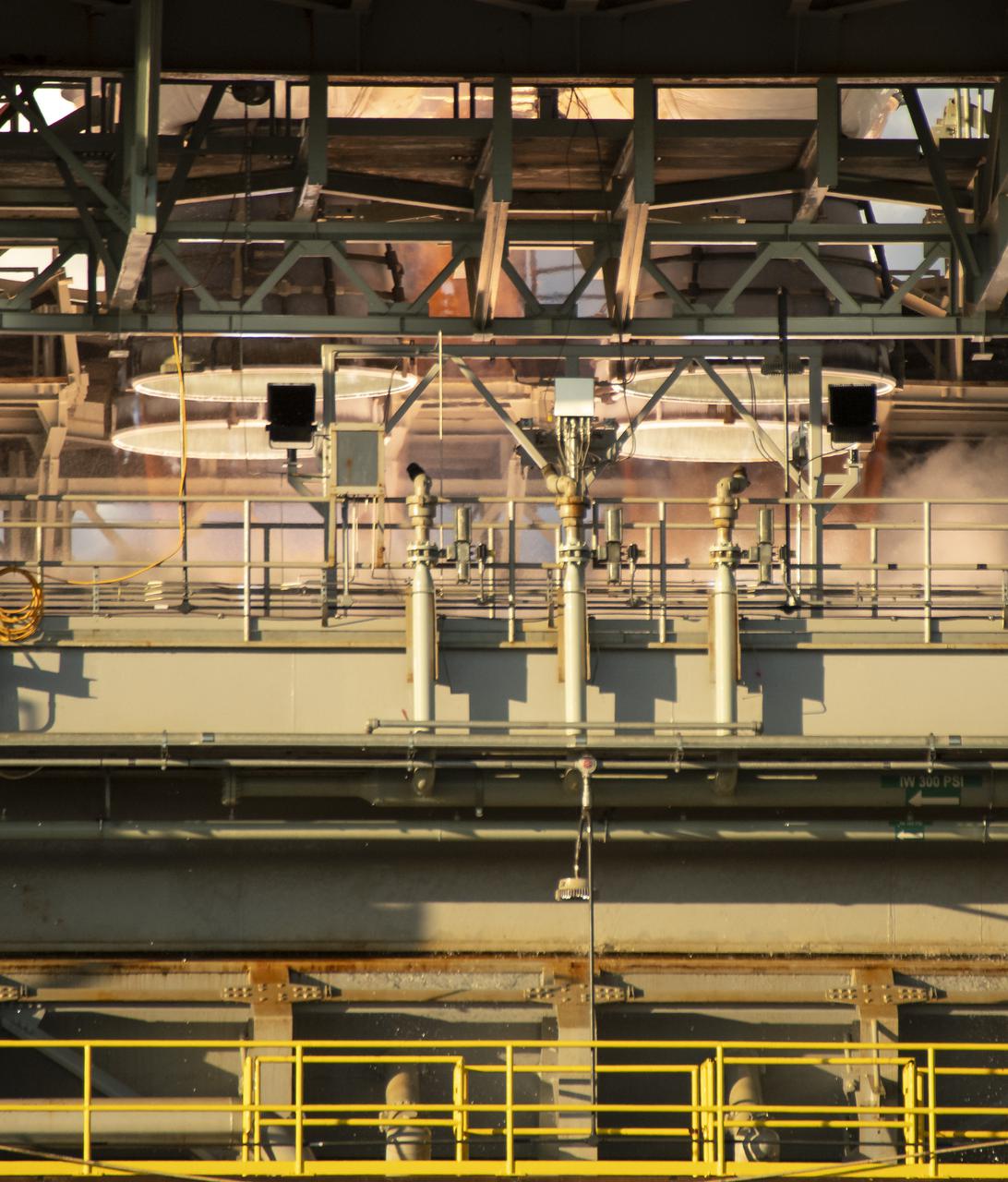

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
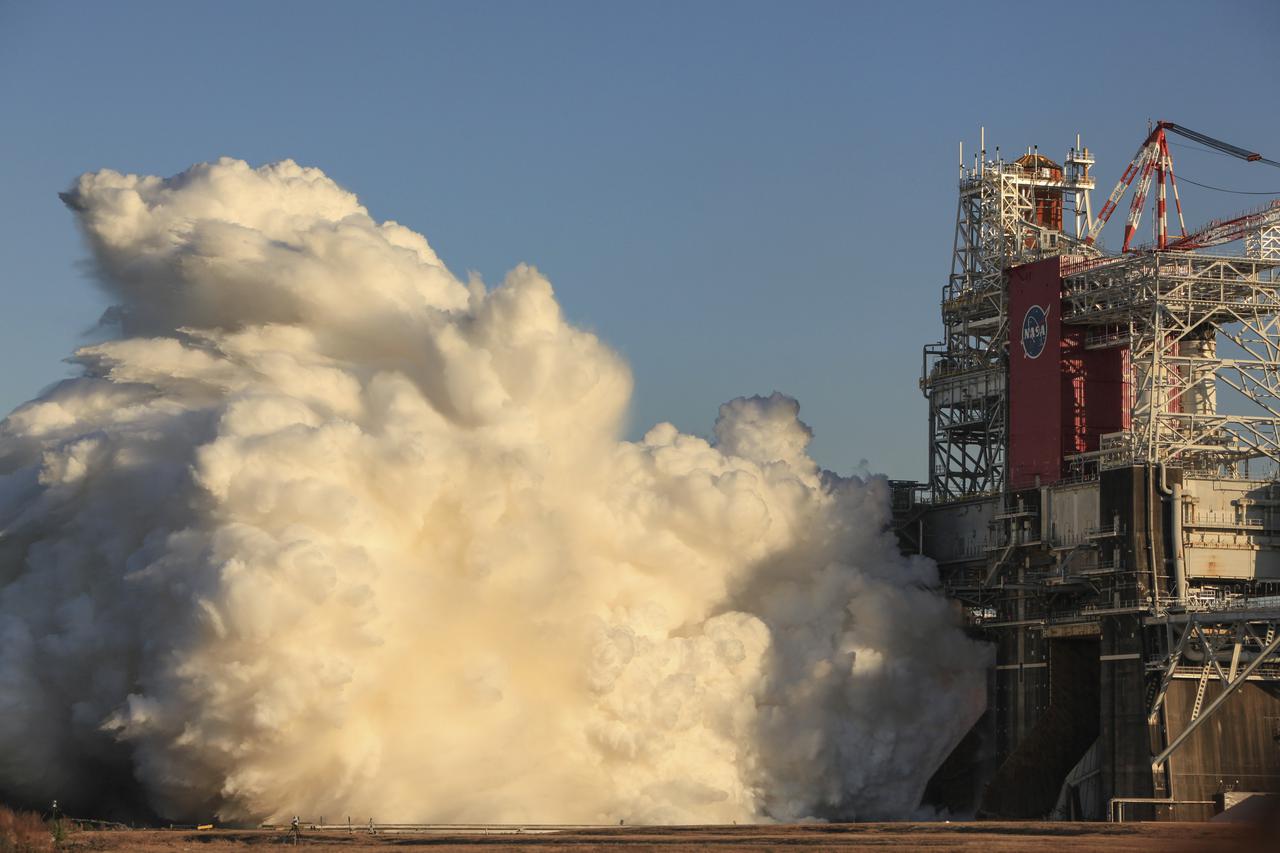

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
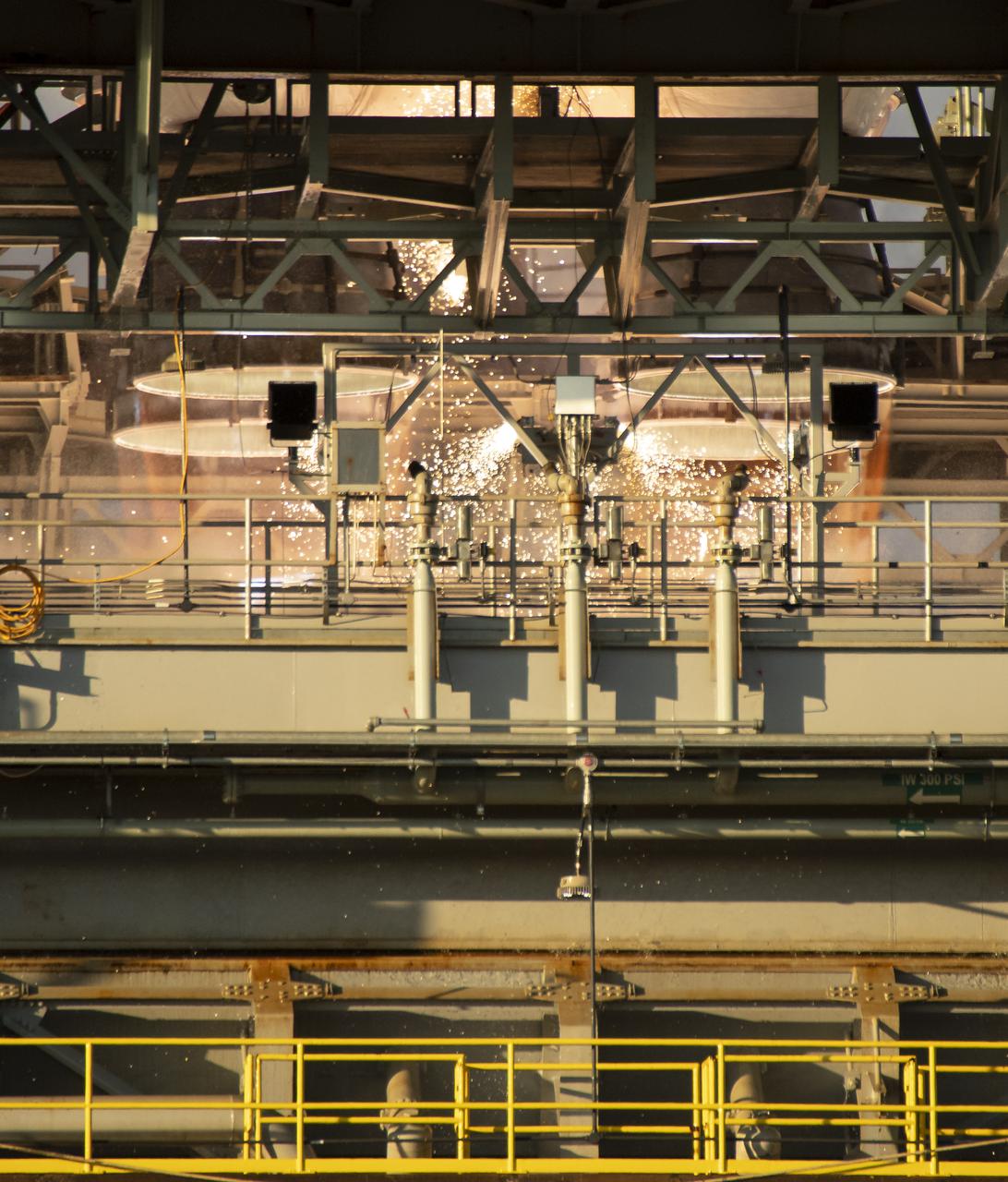

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
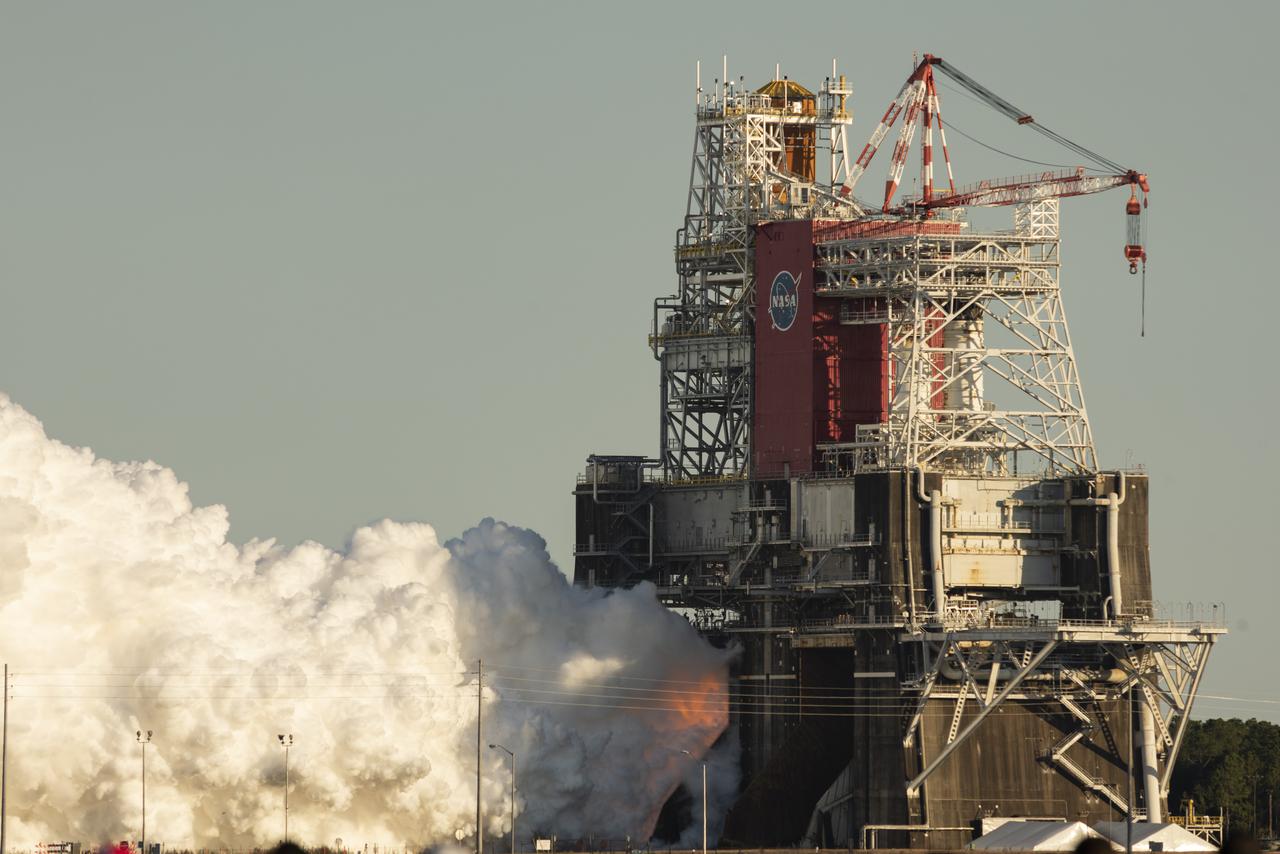

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
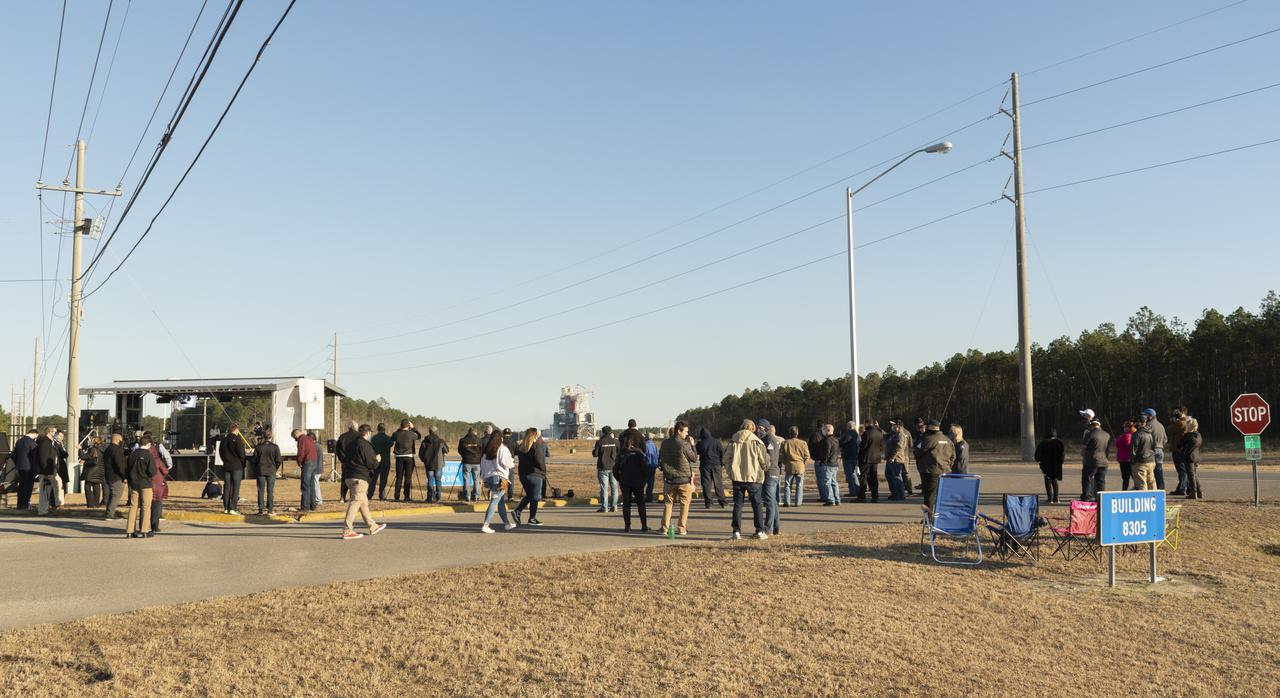

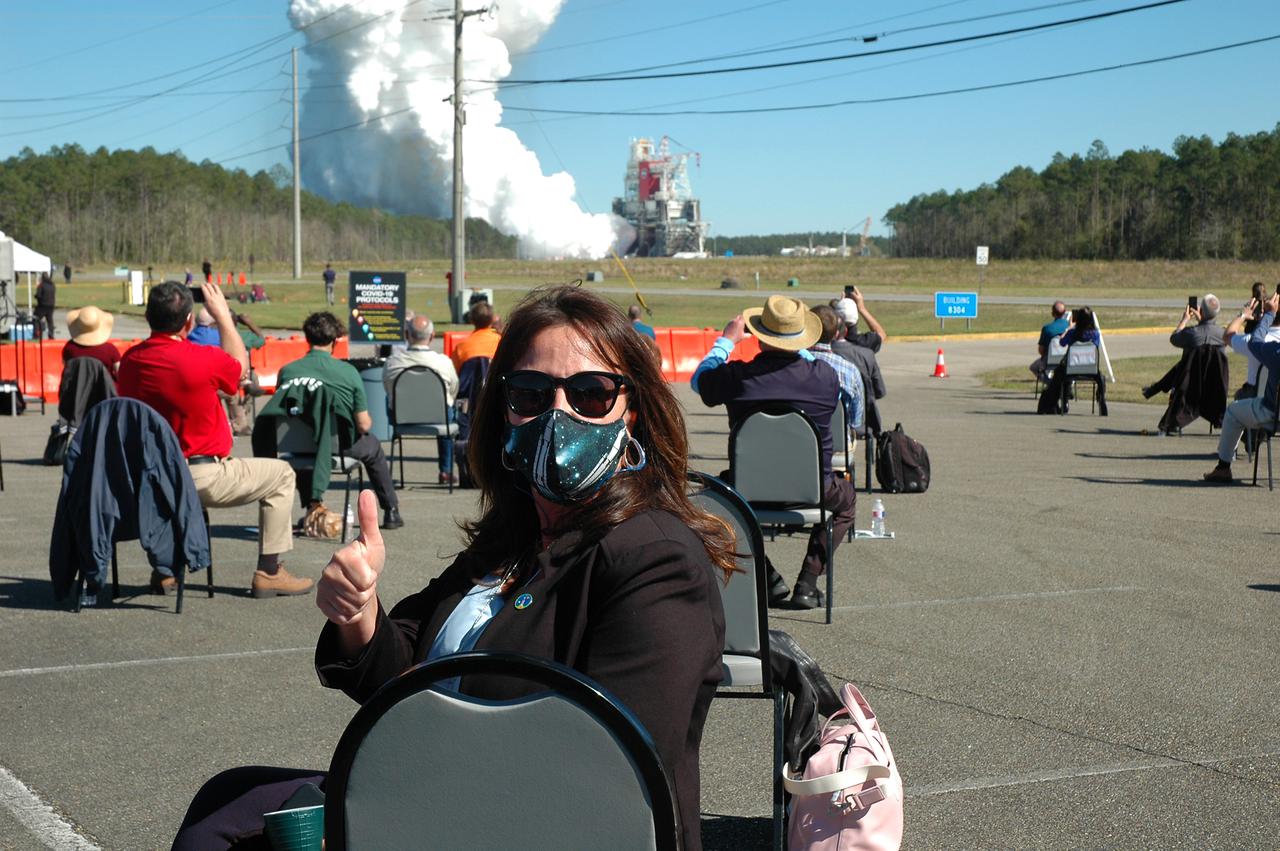
NASA guests gather to watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket undergoes a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

Invited media gather to report as the core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket undergoes a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Saturday, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
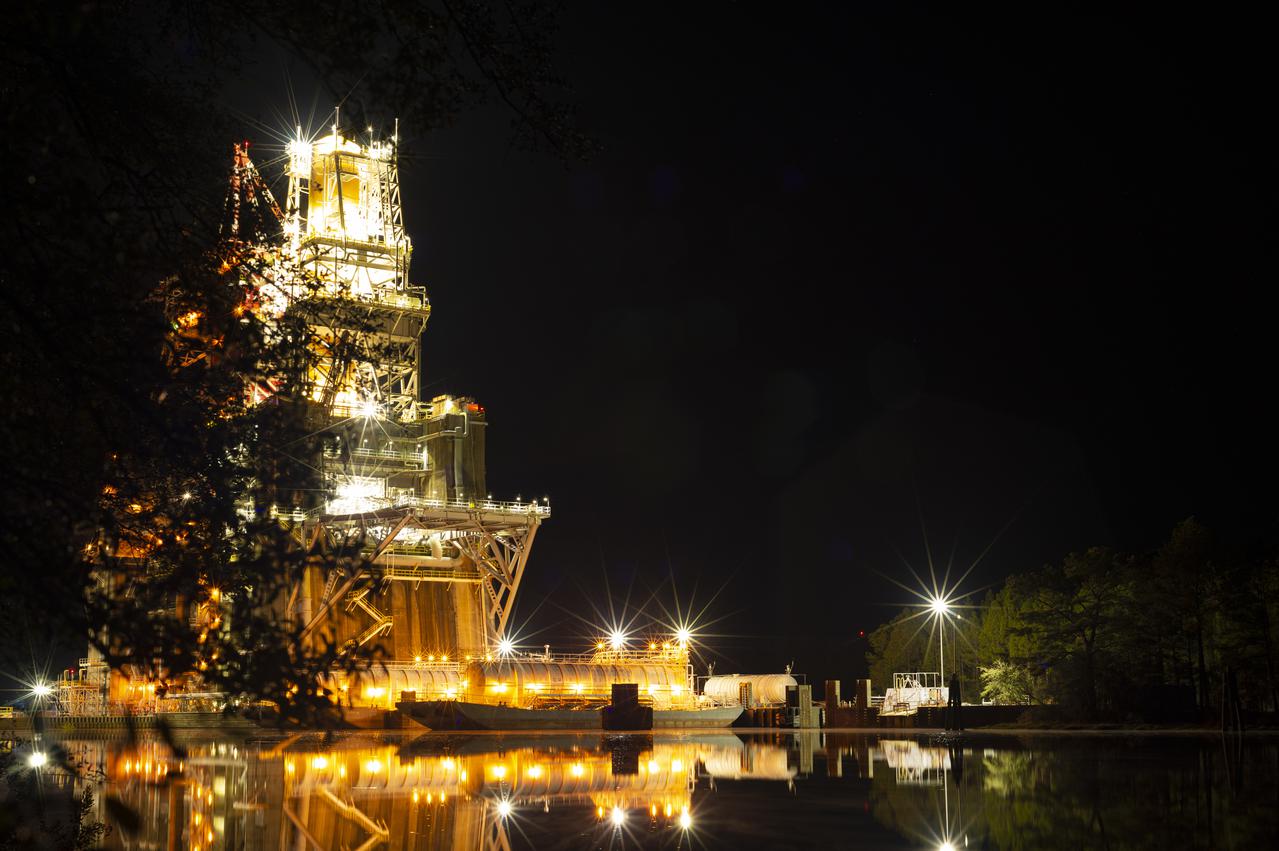

The B-2 Test Stand with the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in later in the evening after a hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
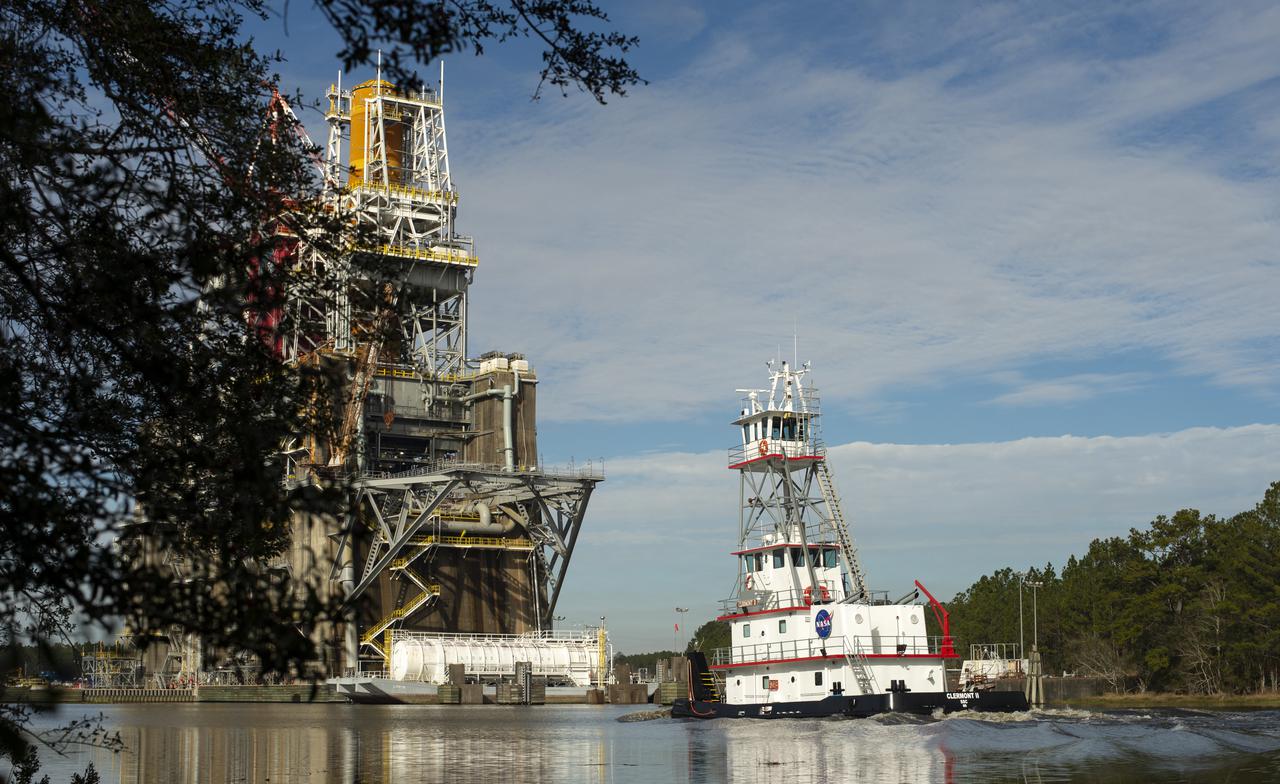

NASA tugboat Clermont II arrives at the B-2 Test Stand the day after a hot fire test of the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. During the test the four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
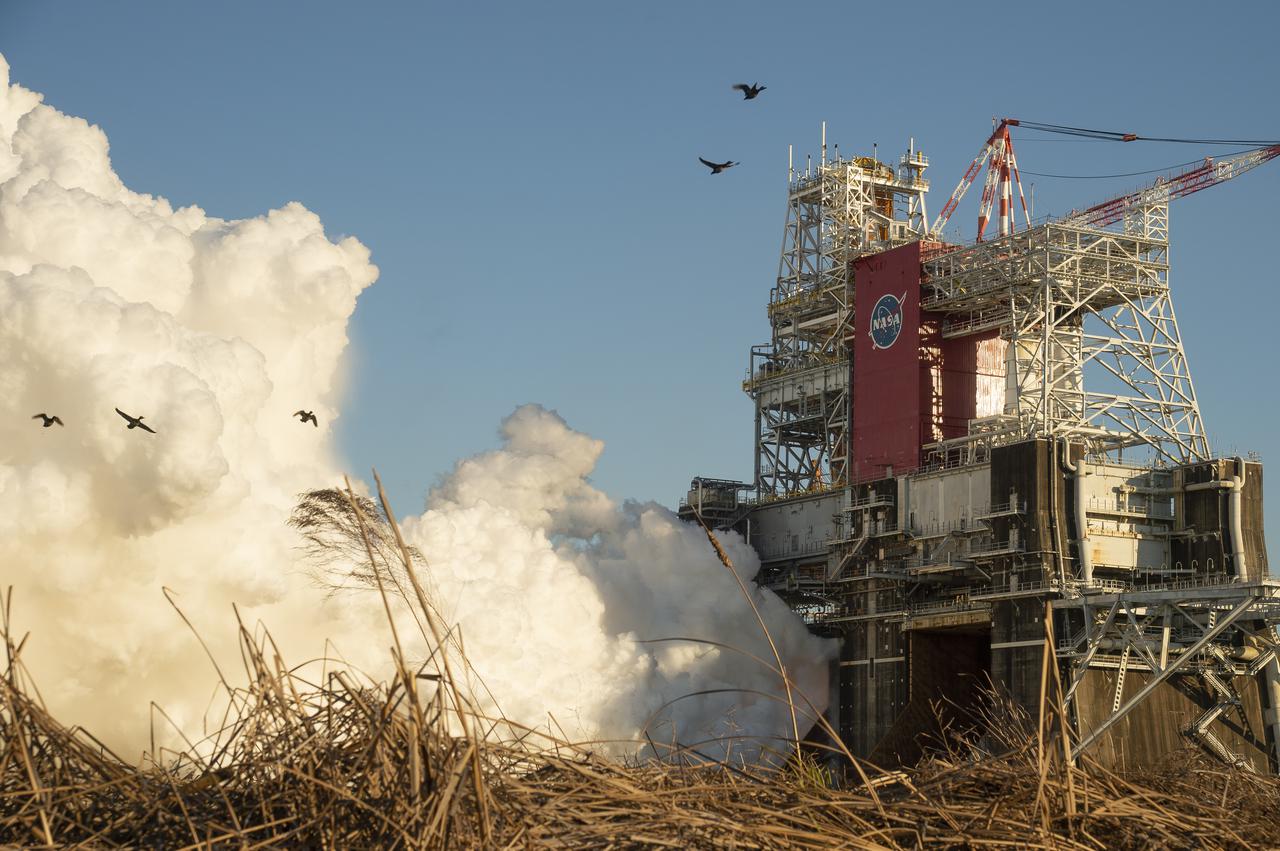

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
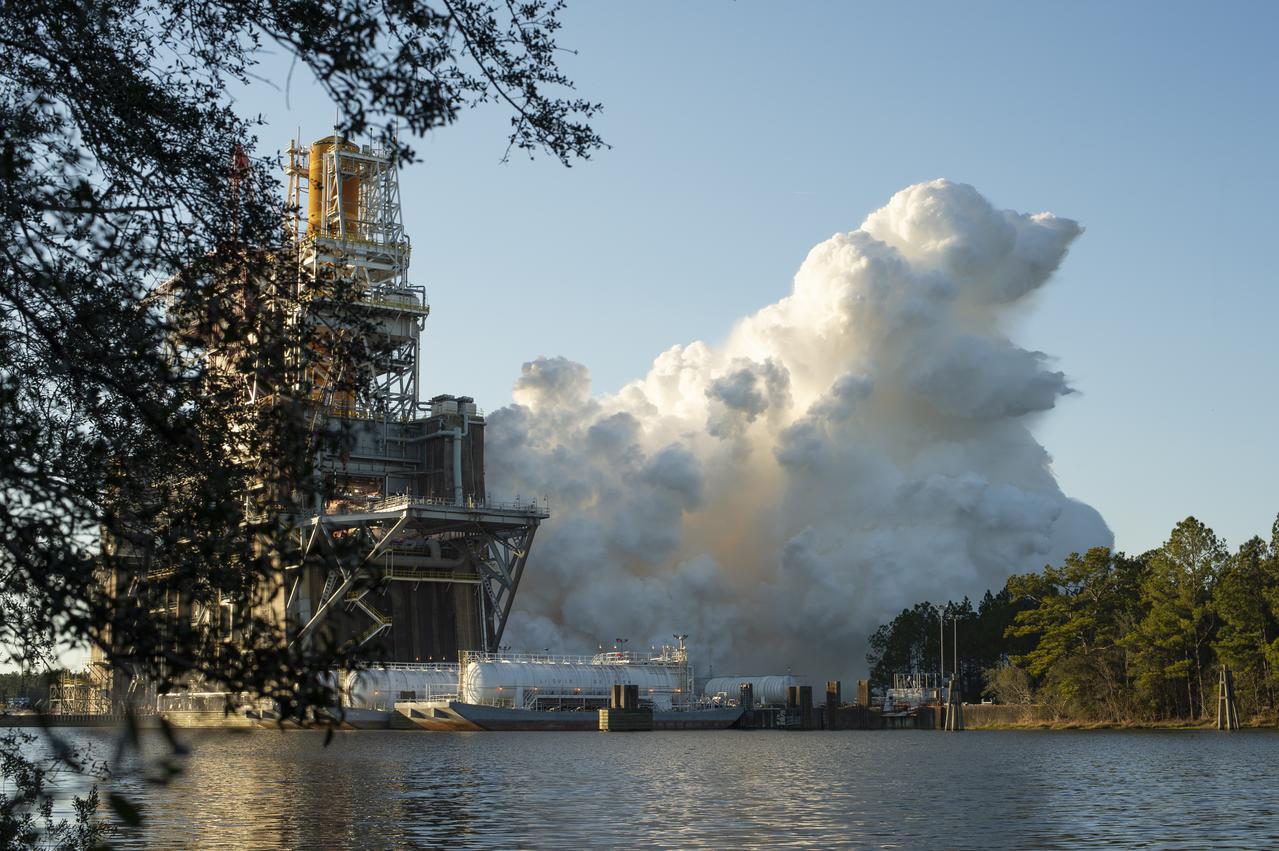

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
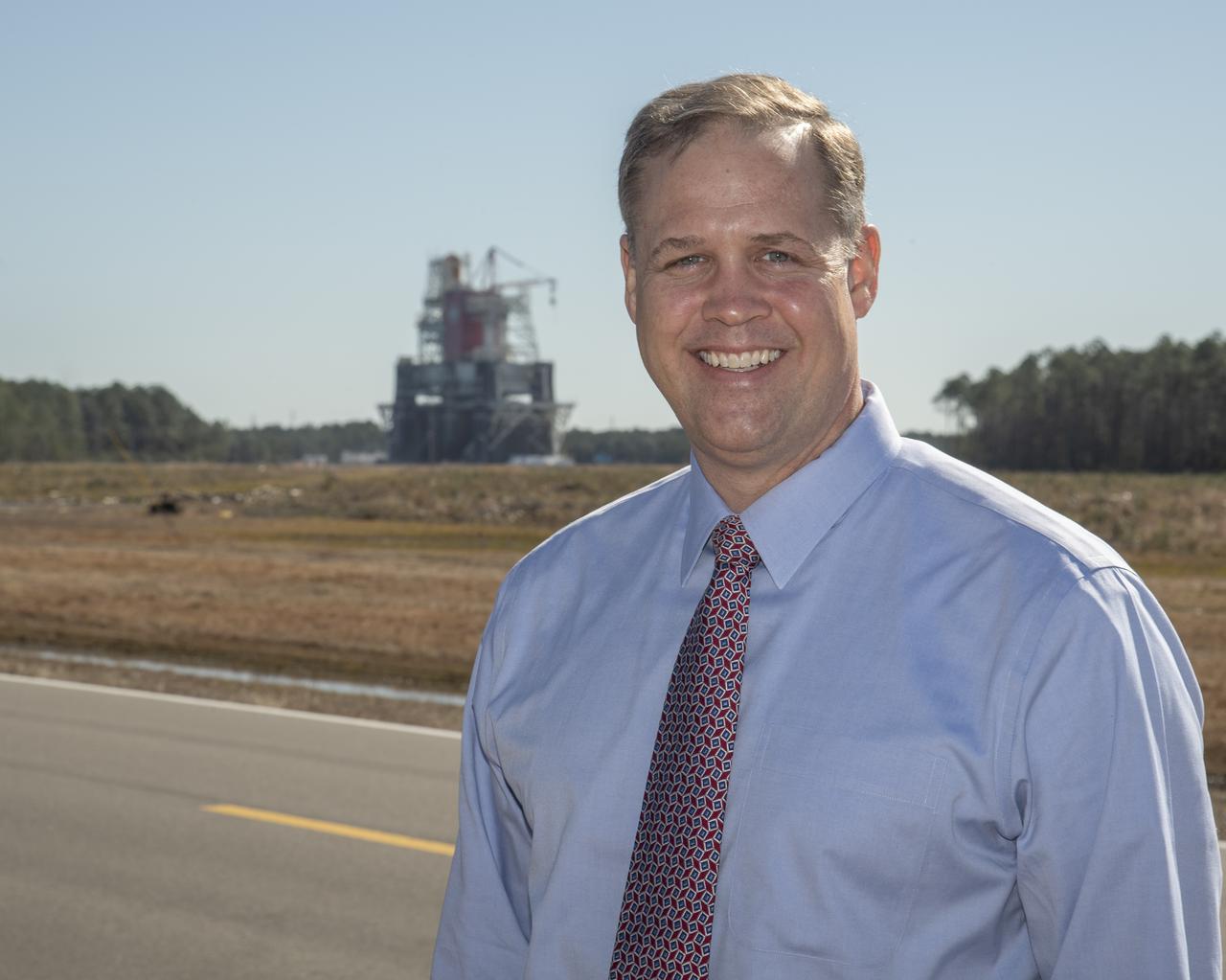

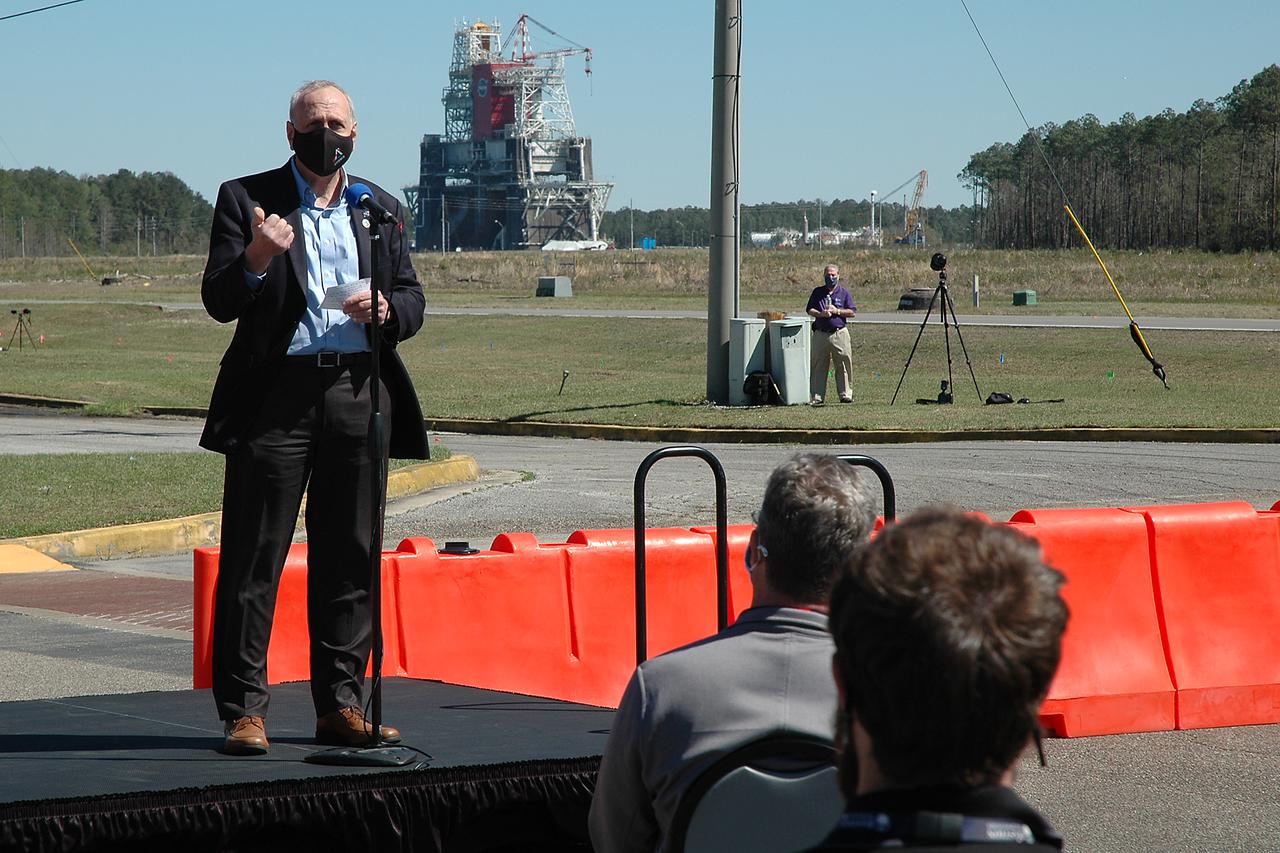
The core stage for the first flight of NASA's Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand behind NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine ahead of a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, January 16, 2021, at NASA's Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System's core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
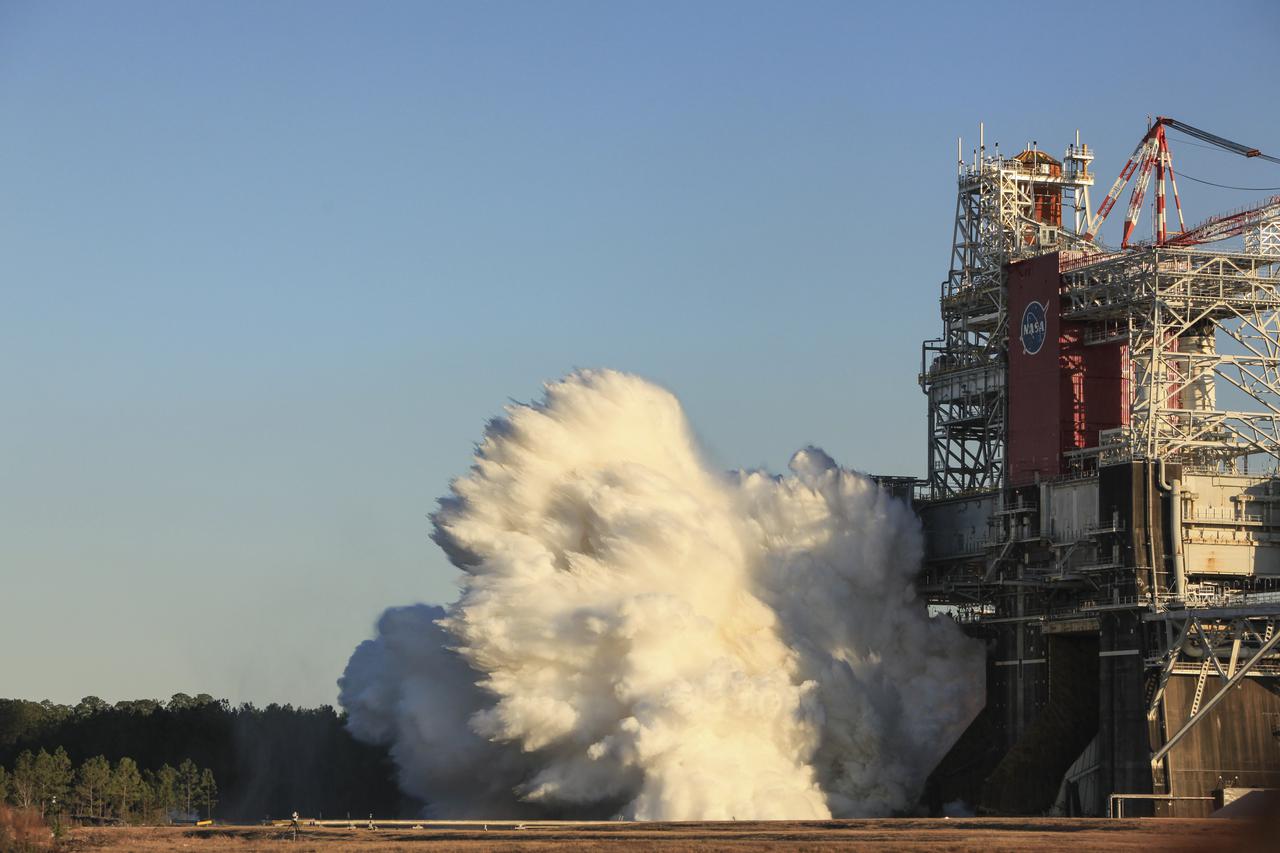

The core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket is seen in the B-2 Test Stand during a scheduled eight minute duration hot fire test, Saturday, Jan. 16, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for a little more than one minute and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire is the final test of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)
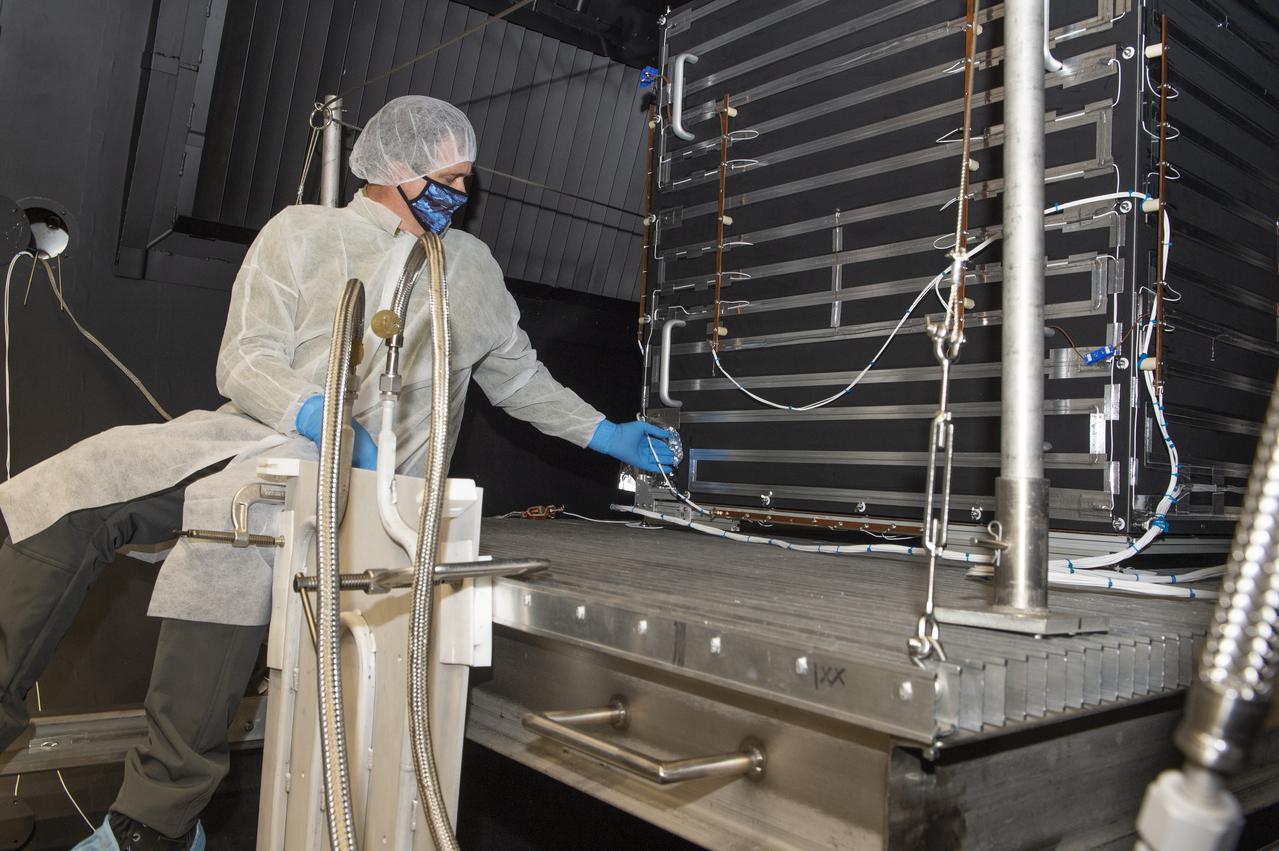

NEA (Near Earth Asteroid) Scout Hot Box – Repress Chamber V-15 and removal of Optical Witness Samples, (OWS), for analysis
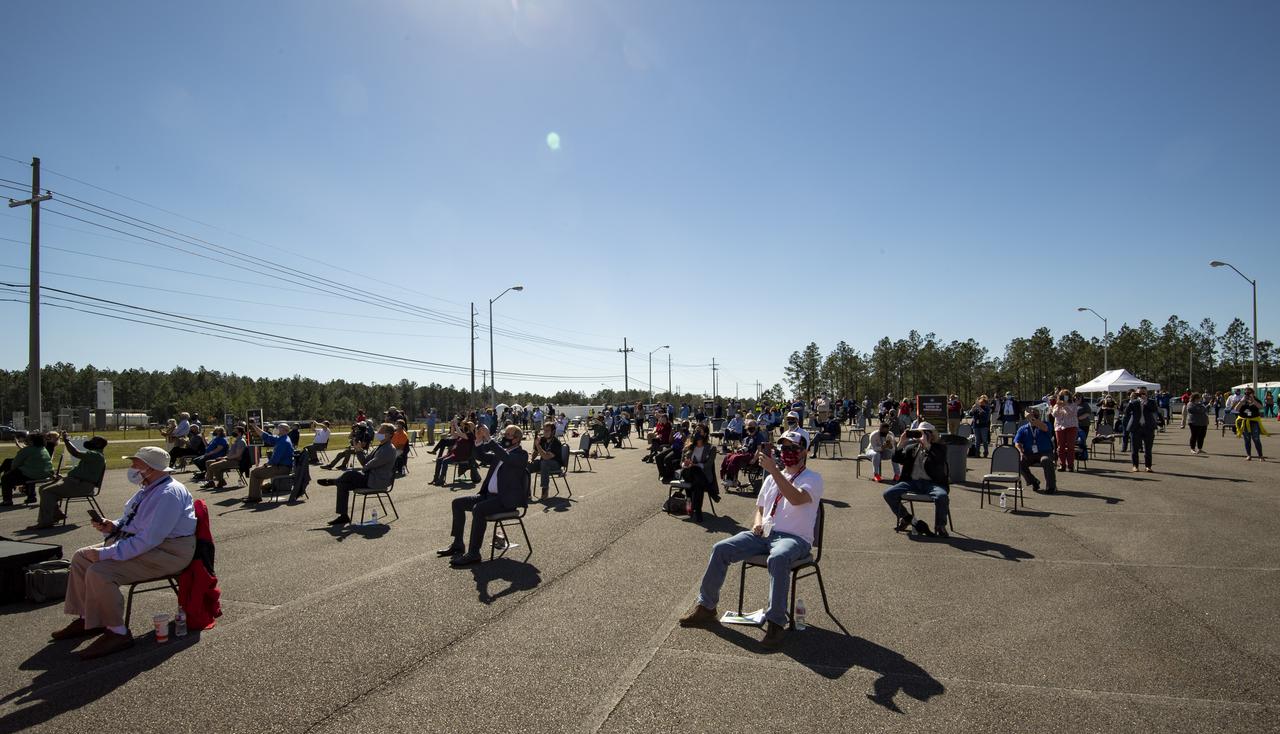

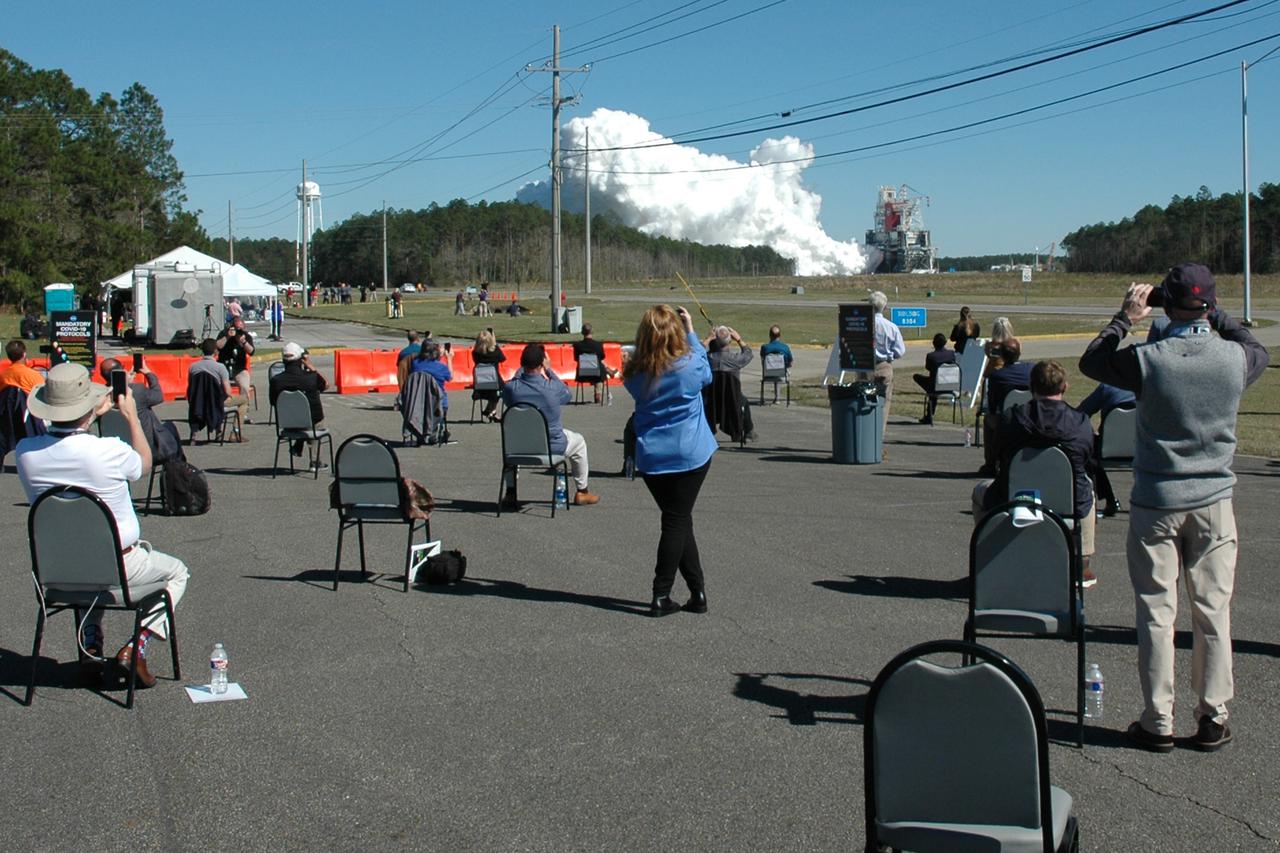
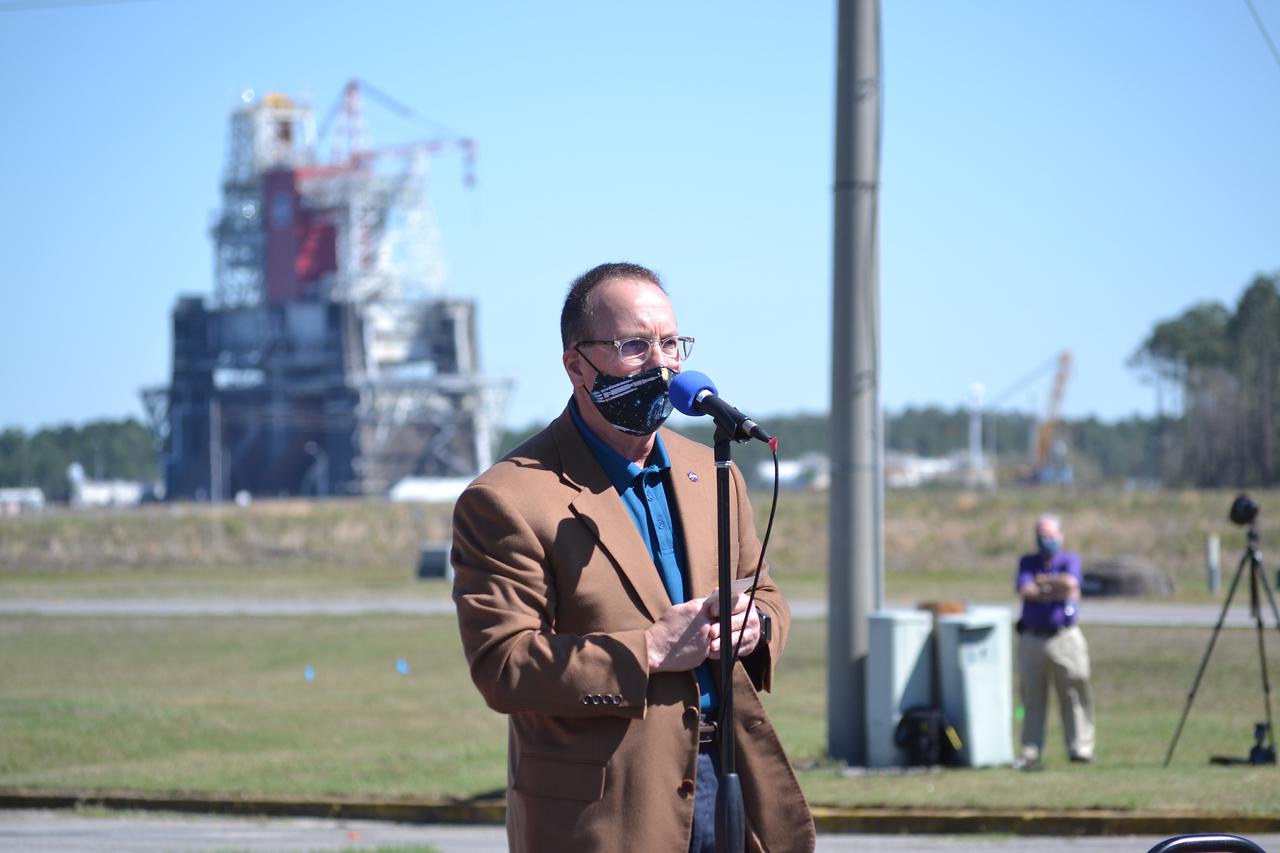
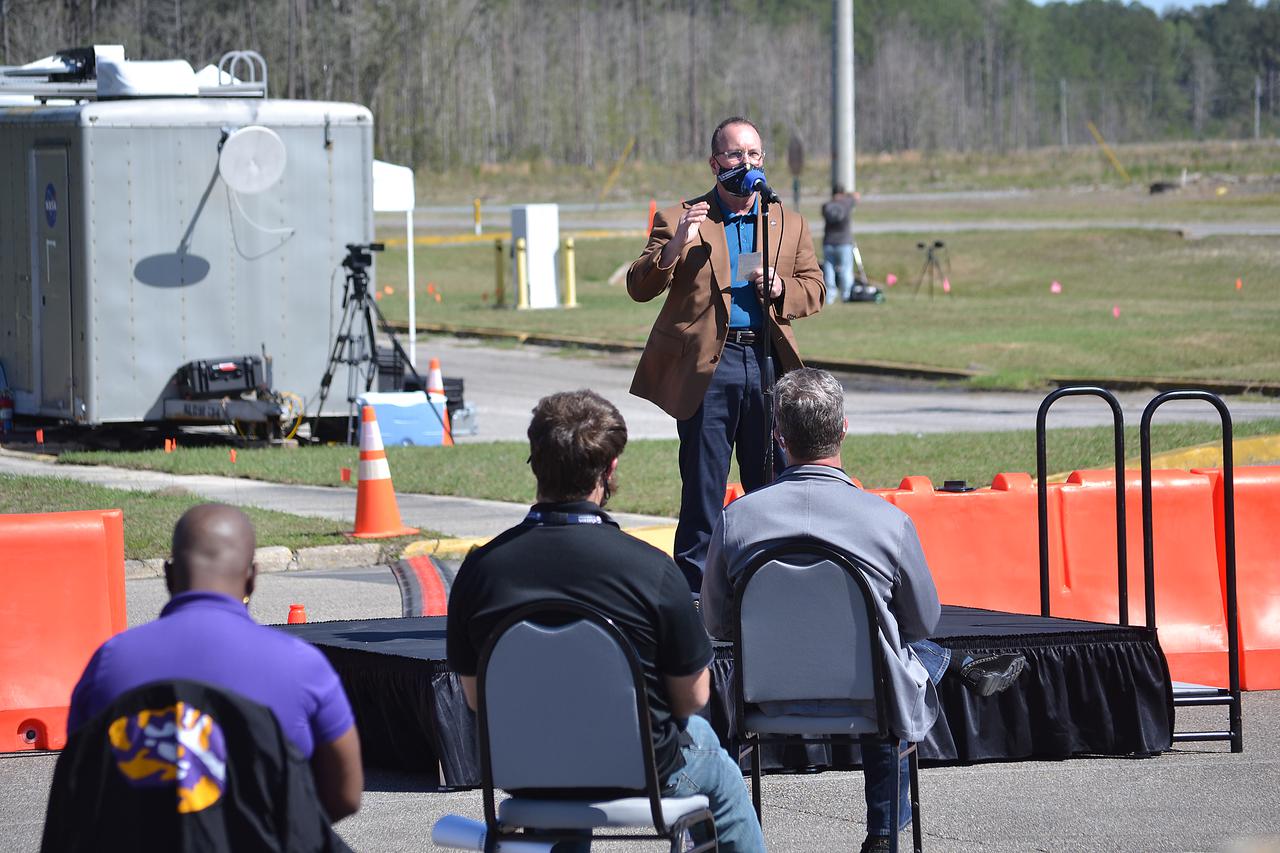
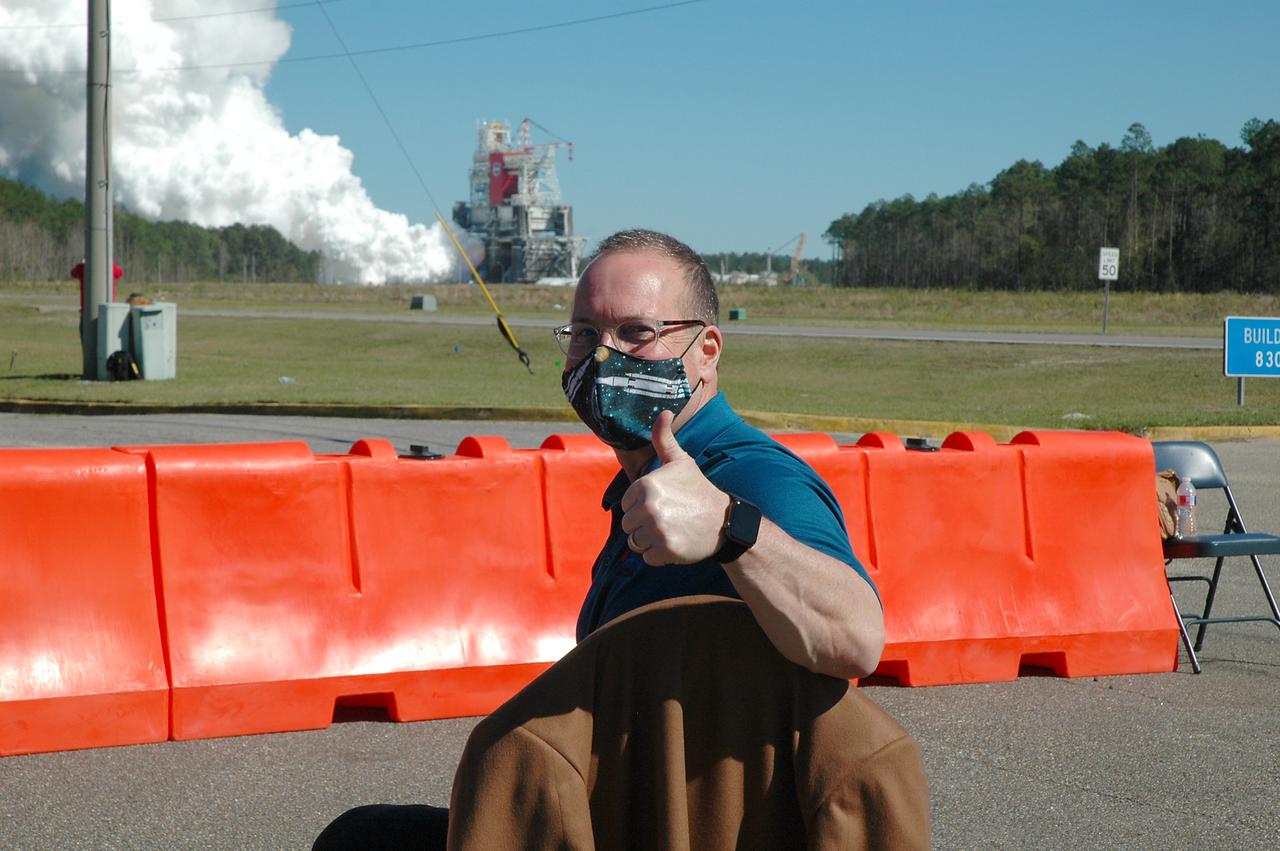
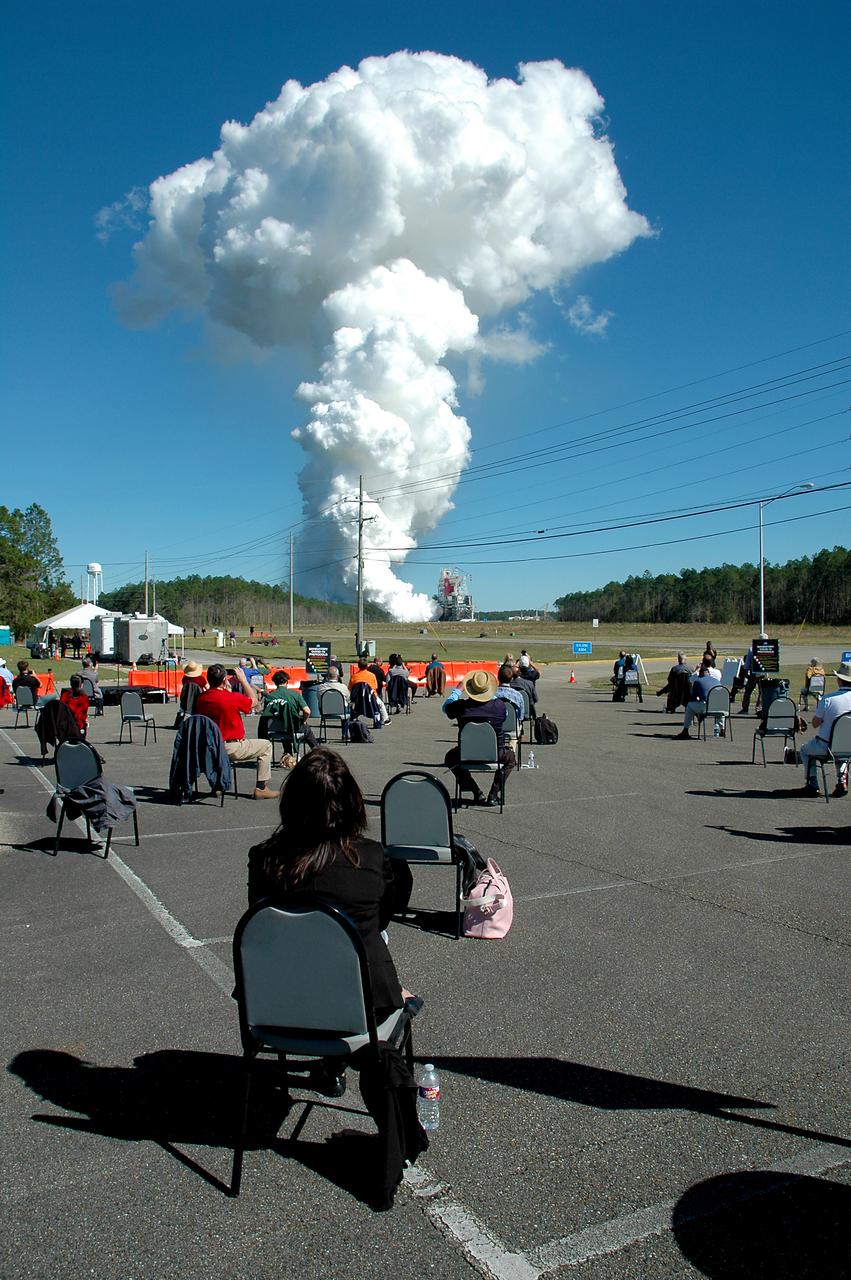
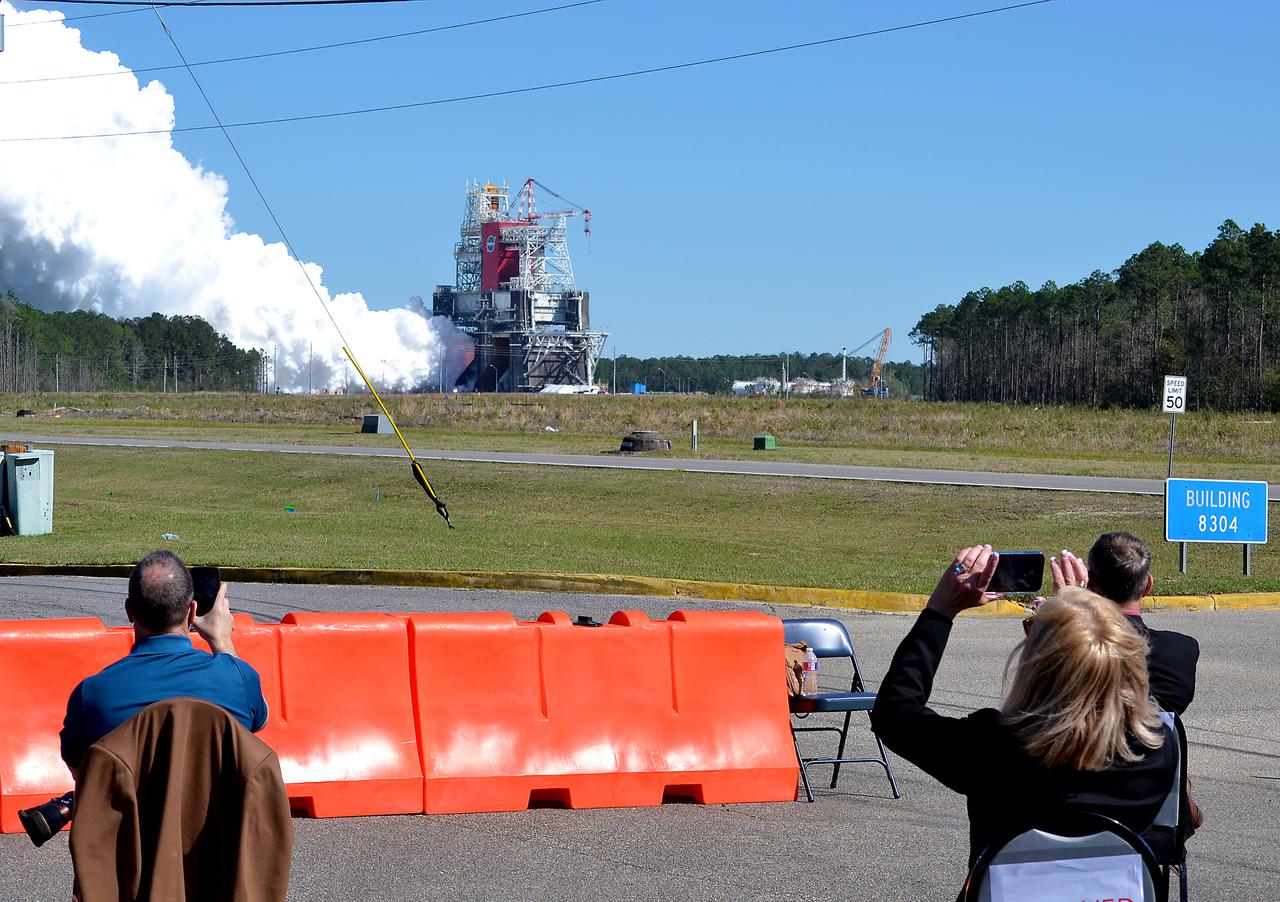
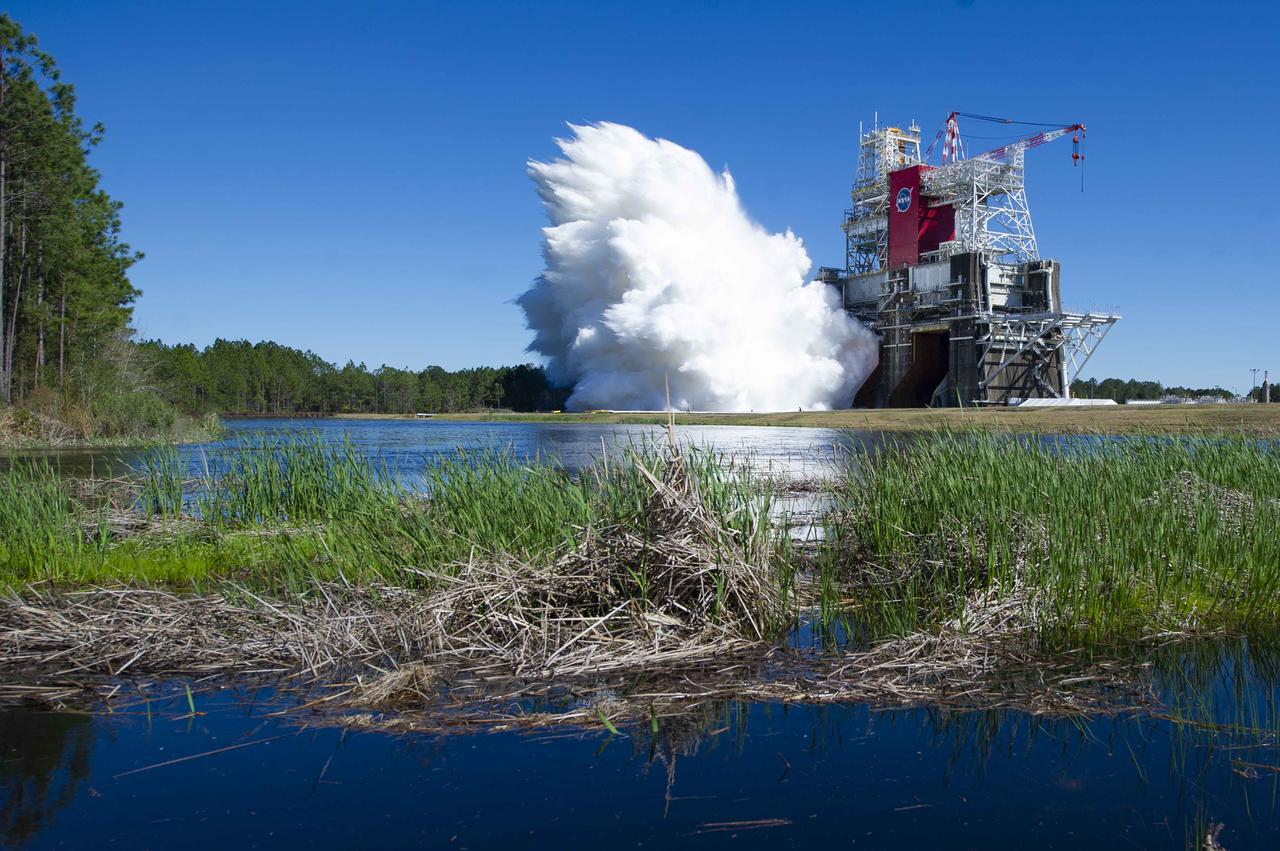
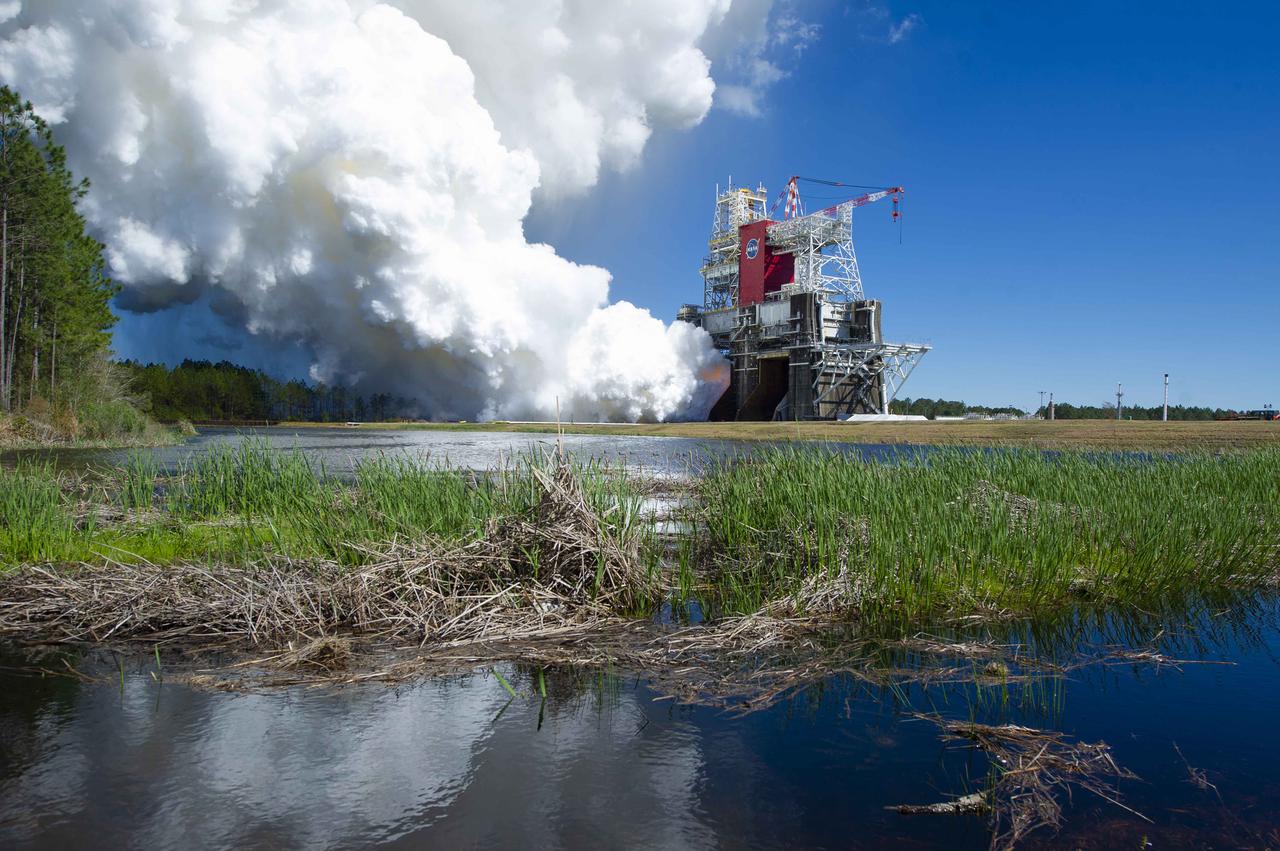
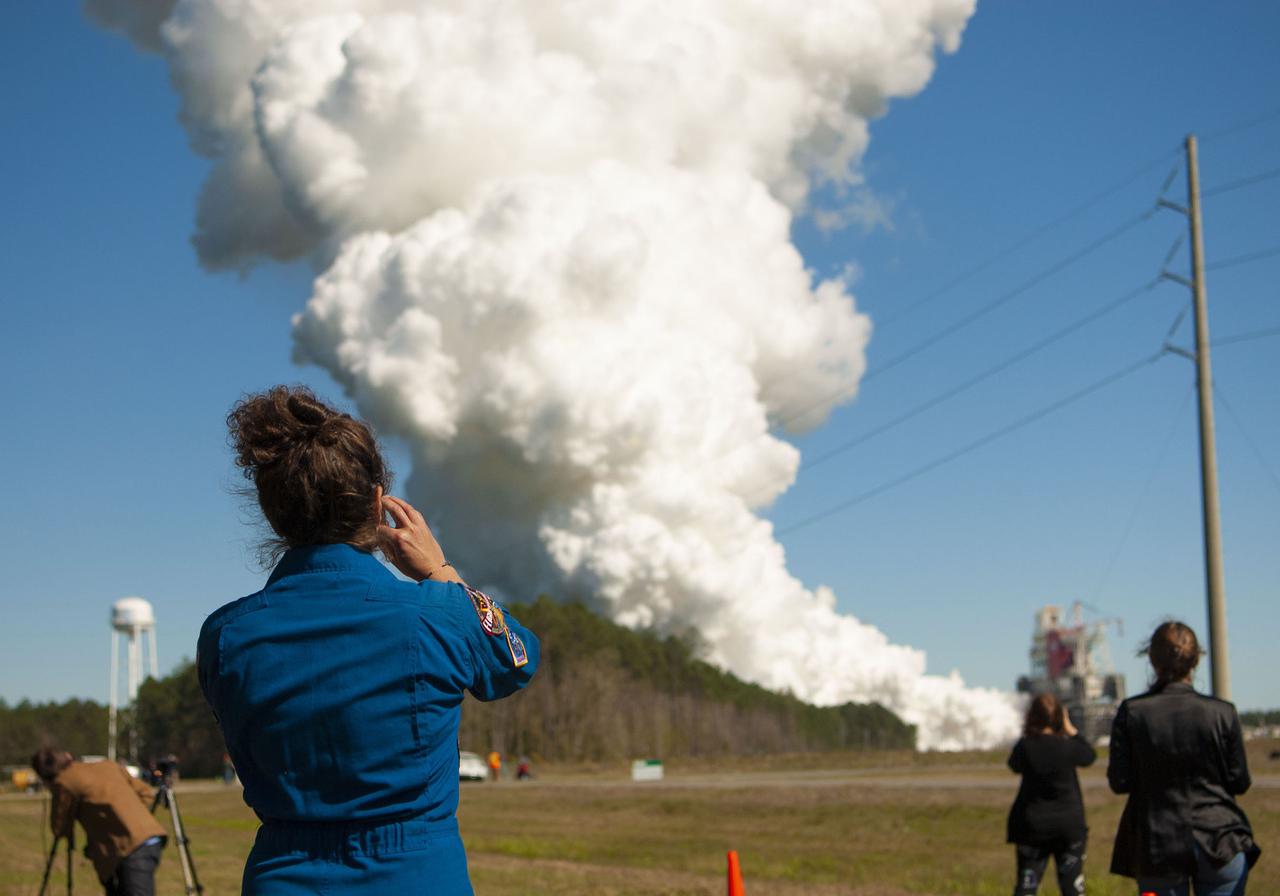
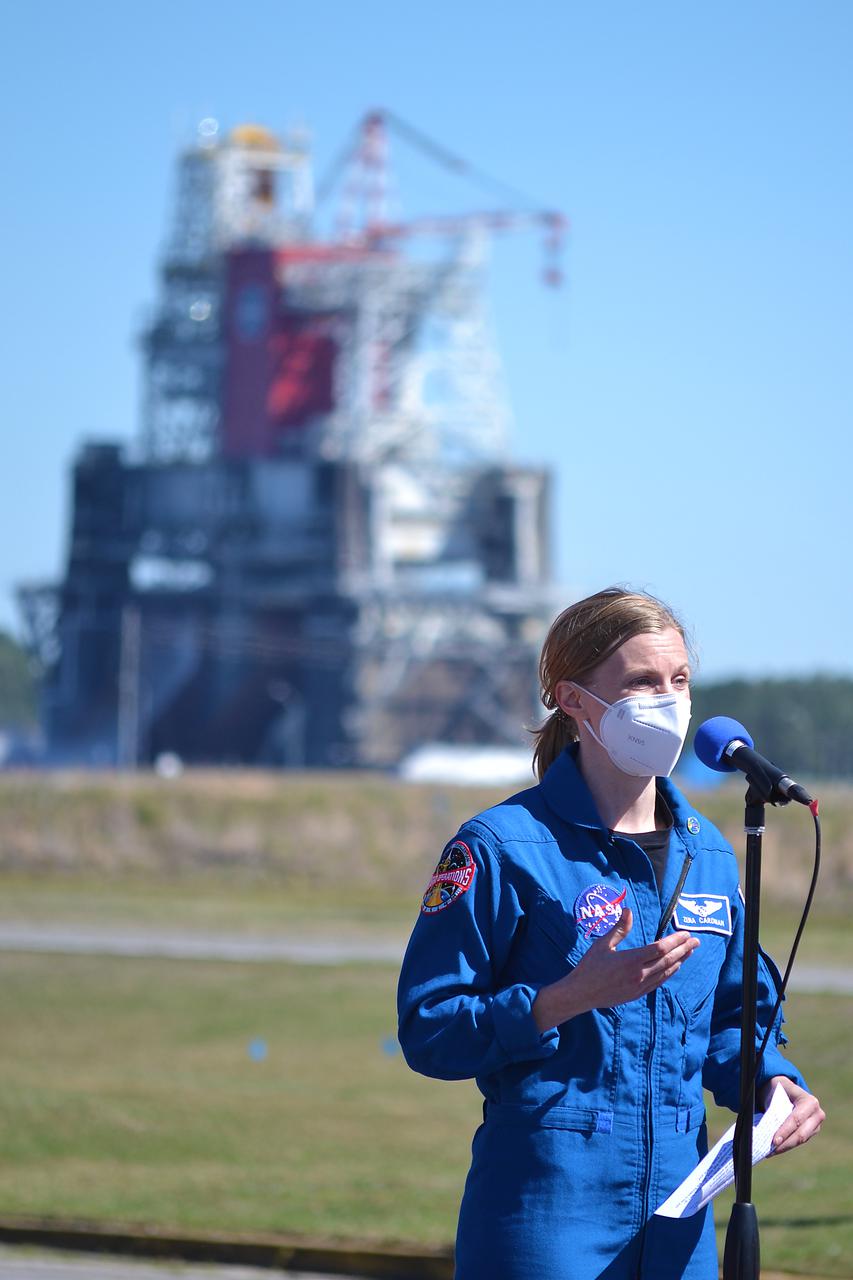
Invited guests watch as the core stage for the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket undergoes a second hot fire test in the B-2 Test Stand, Thursday, March 18, 2021, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four RS-25 engines fired for the full-duration of 8 minutes during the test and generated 1.6 million pounds of thrust. The hot fire test is the final stage of the Green Run test series, a comprehensive assessment of the Space Launch System’s core stage prior to launching the Artemis I mission to the Moon. Photo Credit: (NASA/Robert Markowitz)