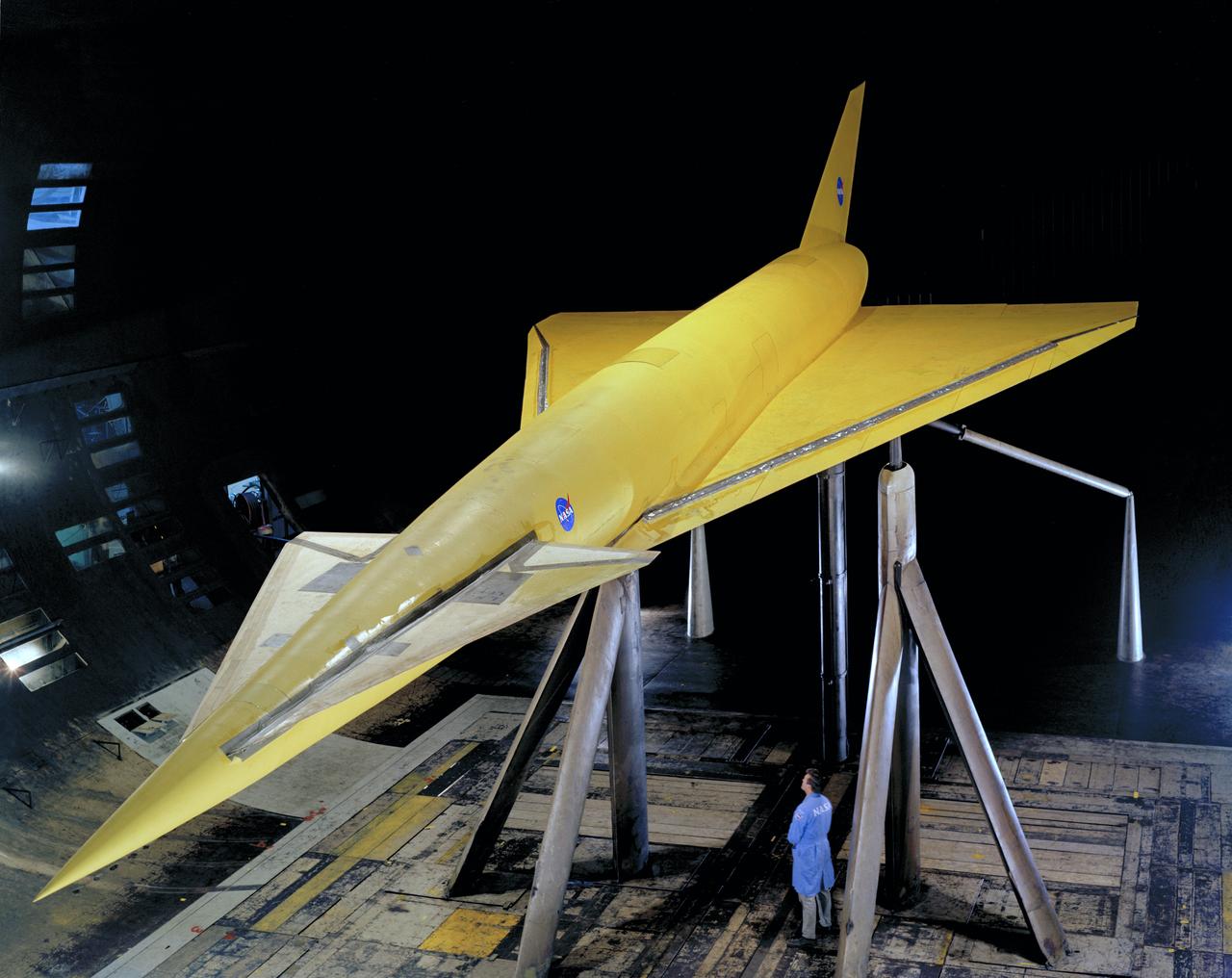
High 3/4 top front view of model in Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel. Bob Bishop in lower right. Delta Wing with Conard.

An artist's rendering of the air-breathing, hypersonic X-43B, the third and largest of NASA's Hyper-X series flight demonstrators, which could fly later this decade. Revolutionizing the way we gain access to space is NASA's primary goal for the Hypersonic Investment Area, managed for NASA by the Advanced Space Transportation Program at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The Hypersonic Investment area, which includes leading-edge partners in industry and academia, will support future generation reusable vehicles and improved access to space. These technology demonstrators, intended for flight testing by decade's end, are expected to yield a new generation of vehicles that routinely fly about 100,000 feet above Earth's surface and reach sustained speeds in excess of Mach 5 (3,750 mph), the point at which "supersonic" flight becomes "hypersonic" flight. The flight demonstrators, the Hyper-X series, will be powered by air-breathing rocket or turbine-based engines, and ram/scramjets. Air-breathing engines, known as combined-cycle systems, achieve their efficiency gains over rocket systems by getting their oxygen for combustion from the atmosphere, as opposed to a rocket that must carry its oxygen. Once a hypersonic vehicle has accelerated to more than twice the speed of sound, the turbine or rockets are turned off, and the engine relies solely on oxygen in the atmosphere to burn fuel. When the vehicle has accelerated to more than 10 to 15 times the speed of sound, the engine converts to a conventional rocket-powered system to propel the craft into orbit or sustain it to suborbital flight speed. NASA's series of hypersonic flight demonstrators includes three air-breathing vehicles: the X-43A, X-43B and X-43C.
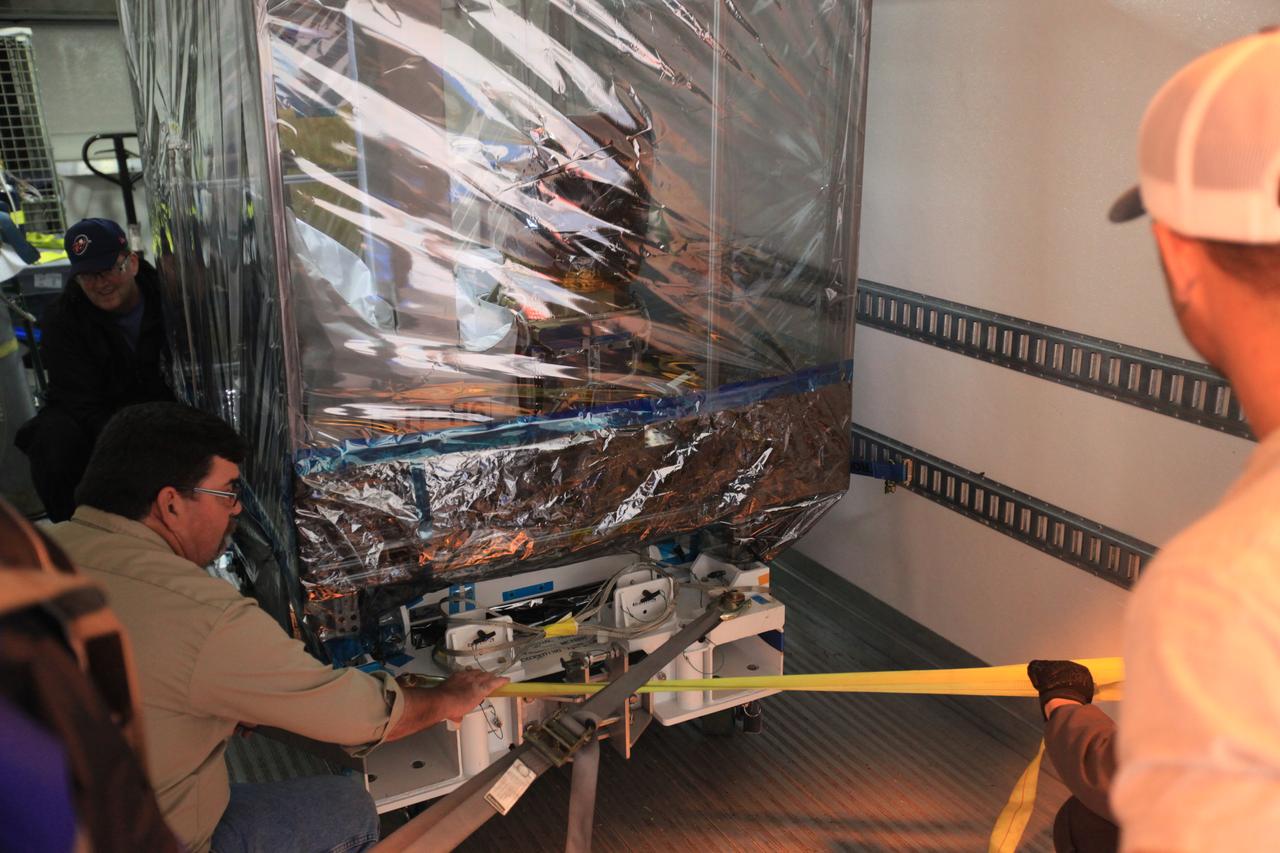

Technicians secure the Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) inside a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
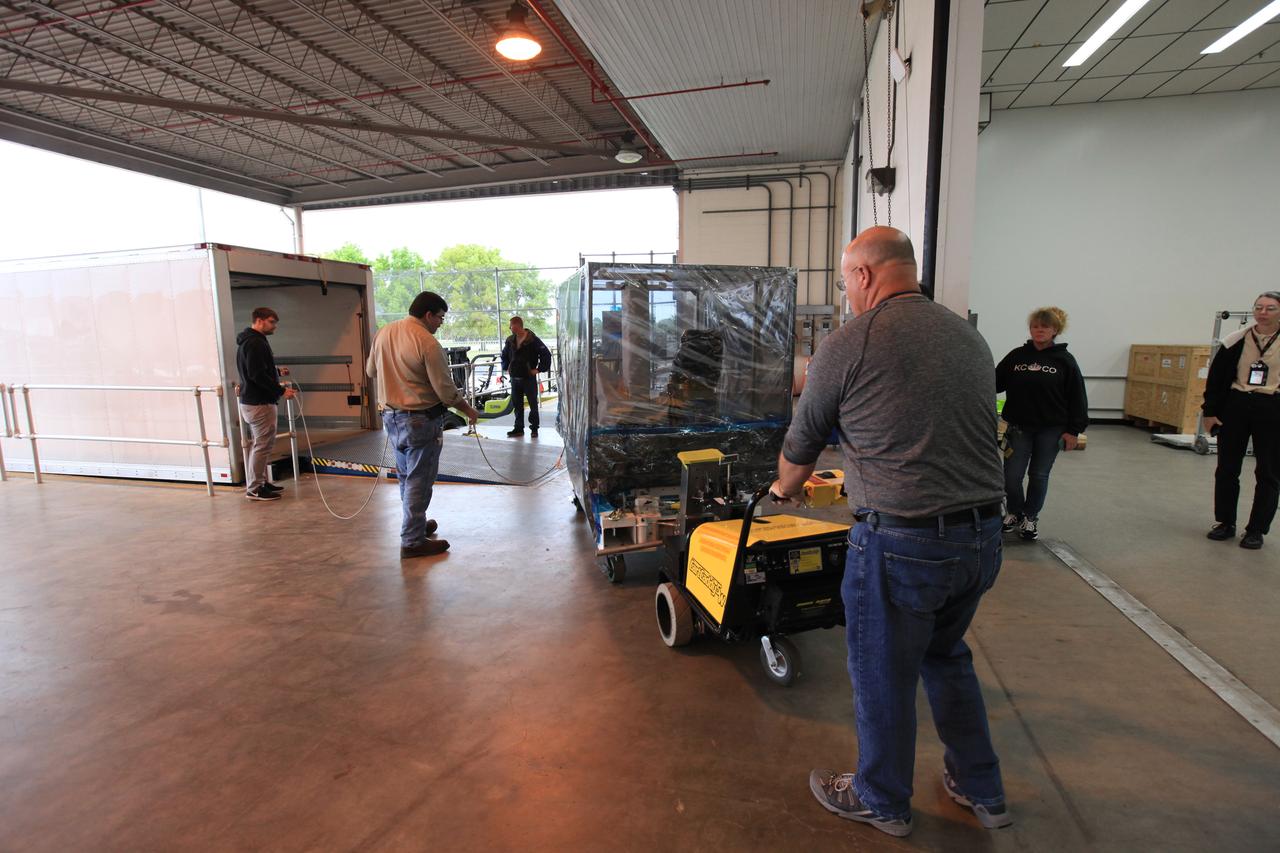

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is moved to a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
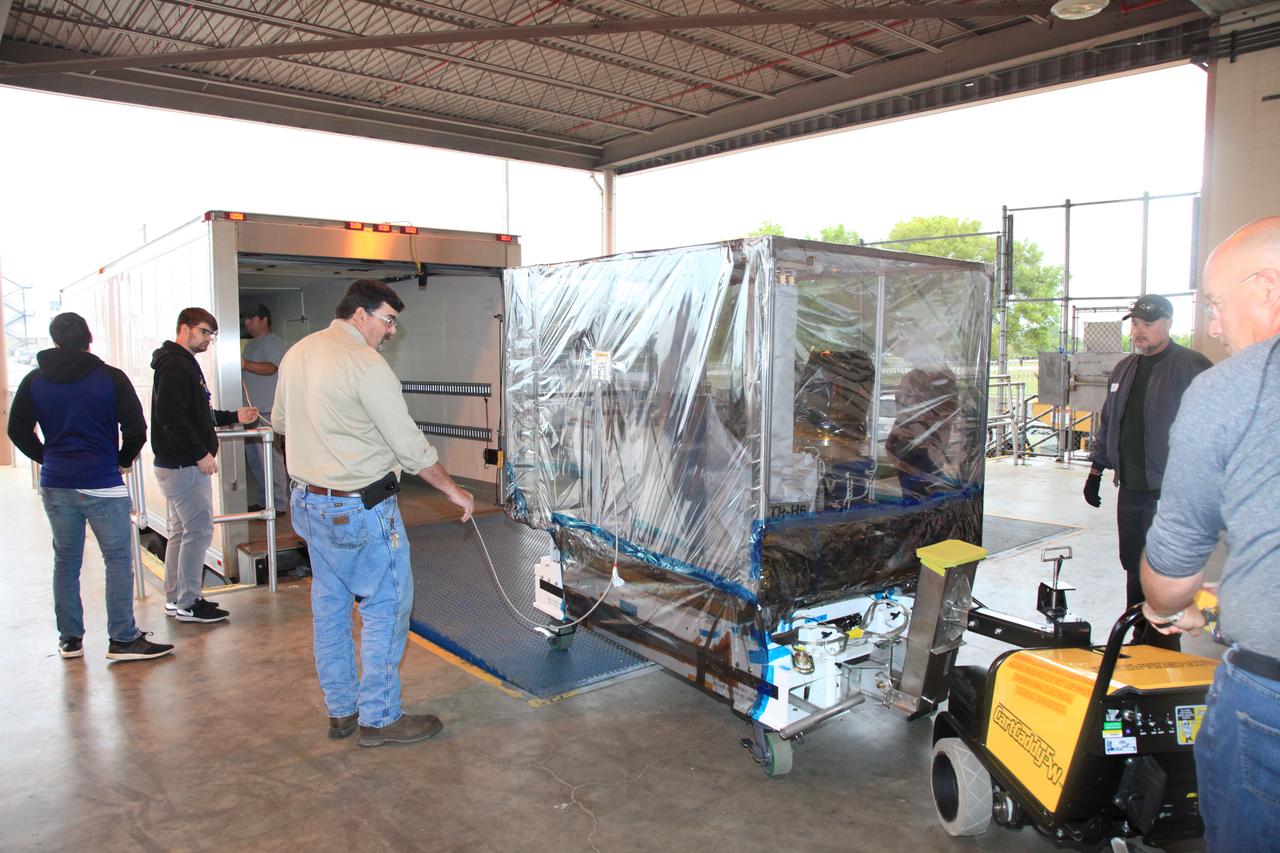

The Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) payload is being loaded into a transport truck at the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 19, 2019. The payload will be moved to the SpaceX facility where it will be stowed in the trunk of the Dragon spacecraft for delivery to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.

This photograph depicts an air-breathing rocket engine prototype in the test bay at the General Applied Science Lab facility in Ronkonkoma, New York. Air-breathing engines, known as rocket based, combined-cycle engines, get their initial take-off power from specially designed rockets, called air-augmented rockets, that boost performance about 15 percent over conventional rockets. When the vehicle's velocity reaches twice the speed of sound, the rockets are turned off and the engine relies totally on oxygen in the atmosphere to burn hydrogen fuel, as opposed to a rocket that must carry its own oxygen, thus reducing weight and flight costs. Once the vehicle has accelerated to about 10 times the speed of sound, the engine converts to a conventional rocket-powered system to propel the craft into orbit or sustain it to suborbital flight speed. NASA's Advanced Space Transportation Program at Marshall Space Flight Center, along with several industry partners and collegiate forces, is developing this technology to make space transportation affordable for everyone from business travelers to tourists. The goal is to reduce launch costs from today's price tag of $10,000 per pound to only hundreds of dollars per pound. NASA's series of hypersonic flight demonstrators currently include three air-breathing vehicles: the X-43A, X-43B and X-43C.
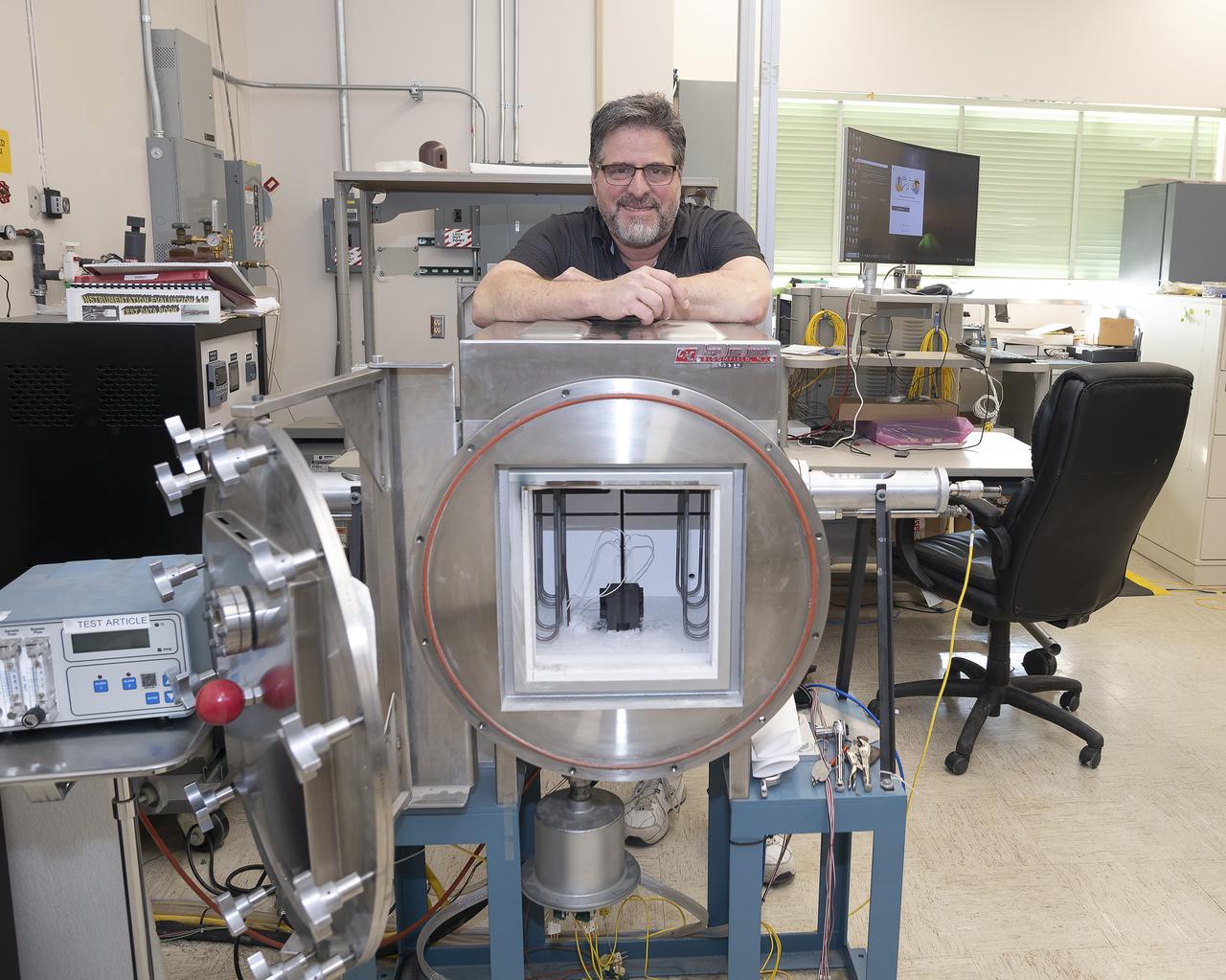

Anthony piazza, a researcher at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research center in Edwards, California, works with high-temperature strain sensors. This test article is a bending load bar, which enables high-temperature optical strain sensor research up to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
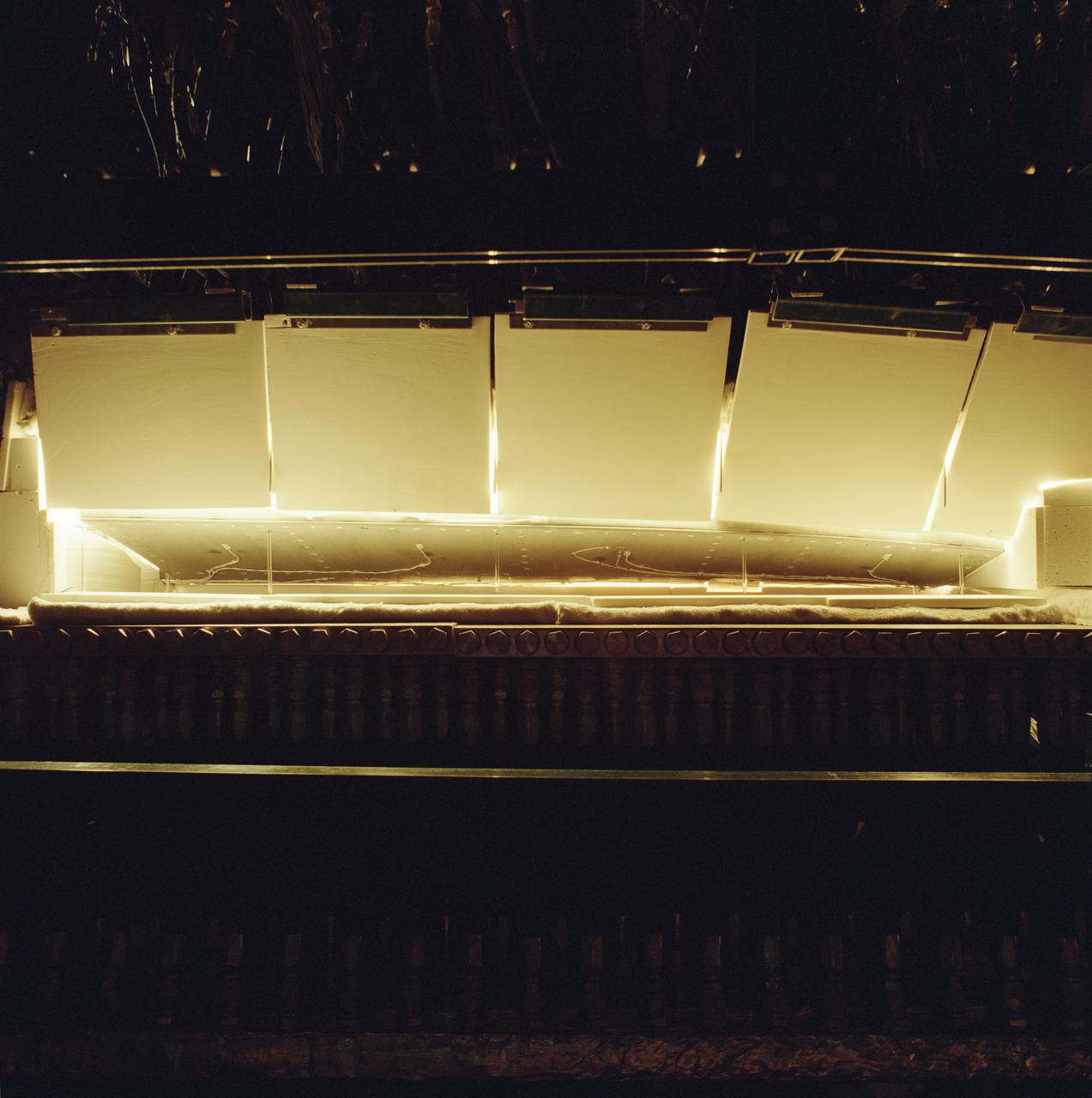

The X-37 advanced technology demonstrator flaperon unit was one of the first ever thermal and mechanical qualification tests of a carbon-carbon control surface designed for space flight. The test also featured extensive use of high-temperature fiber optic strain sensors. Peak temperatures reached 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
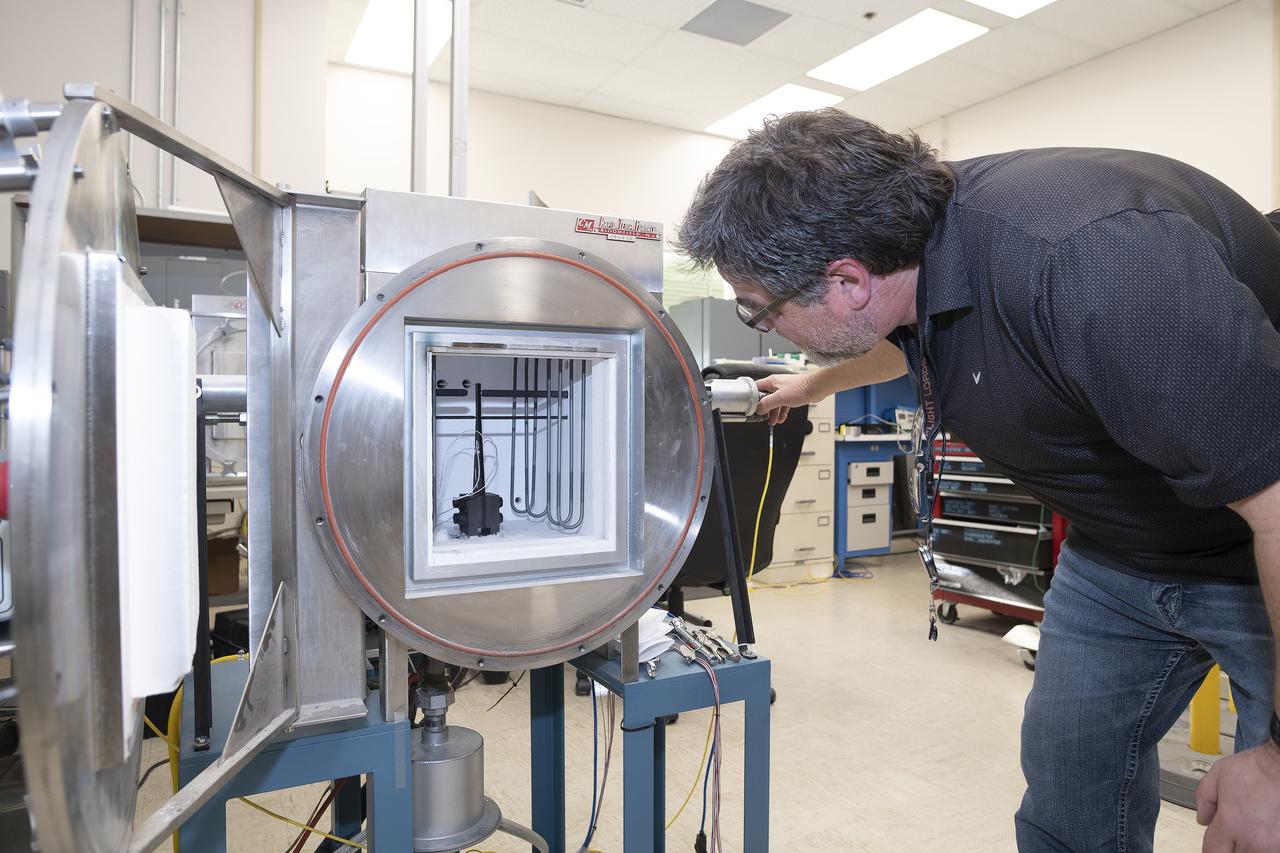

Anthony piazza, a researcher at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research center in Edwards, California, works with high-temperature strain sensors. This test article is a bending load bar, which enables high-temperature optical strain sensor research up to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit.
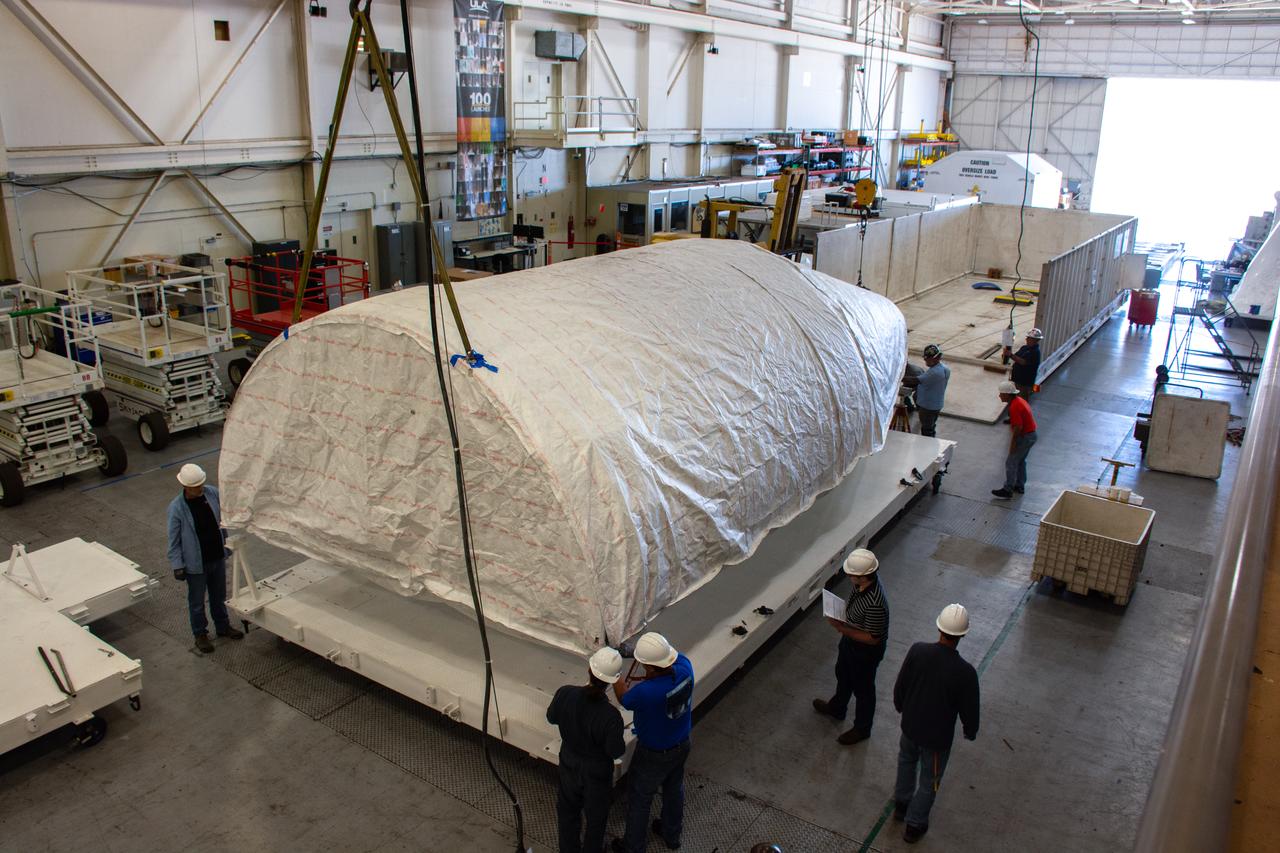

A crew offloaded the United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V payload fairing from its transport container in building B7525 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Aug. 8, 2022, for NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3 East. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.
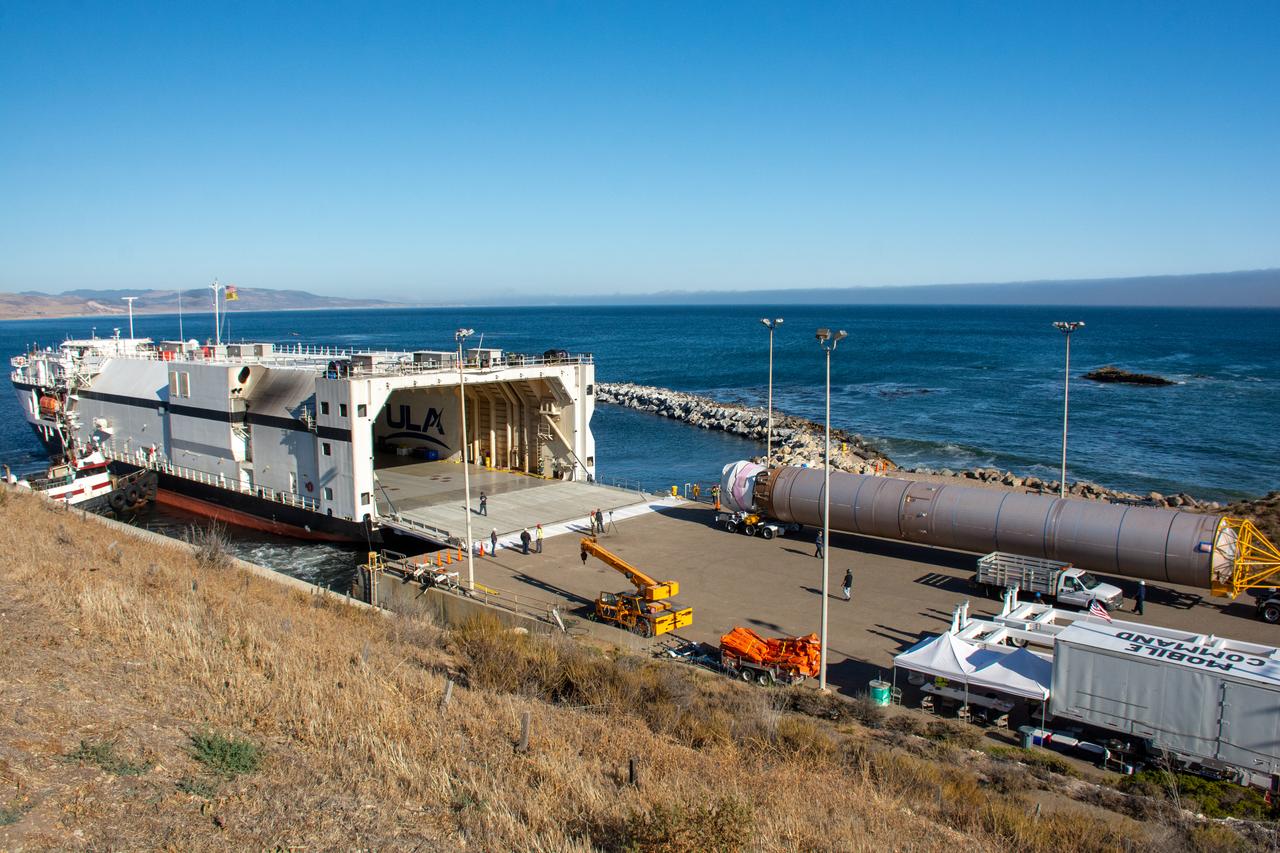

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is offloaded from its water transport at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on July 11, 2022, for NASA and NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on the final ULA Atlas V rocket to launch from Vandenberg. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is offloaded from its water transport at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on July 11, 2022, for NASA and NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on the final ULA Atlas V rocket to launch from Vandenberg. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.
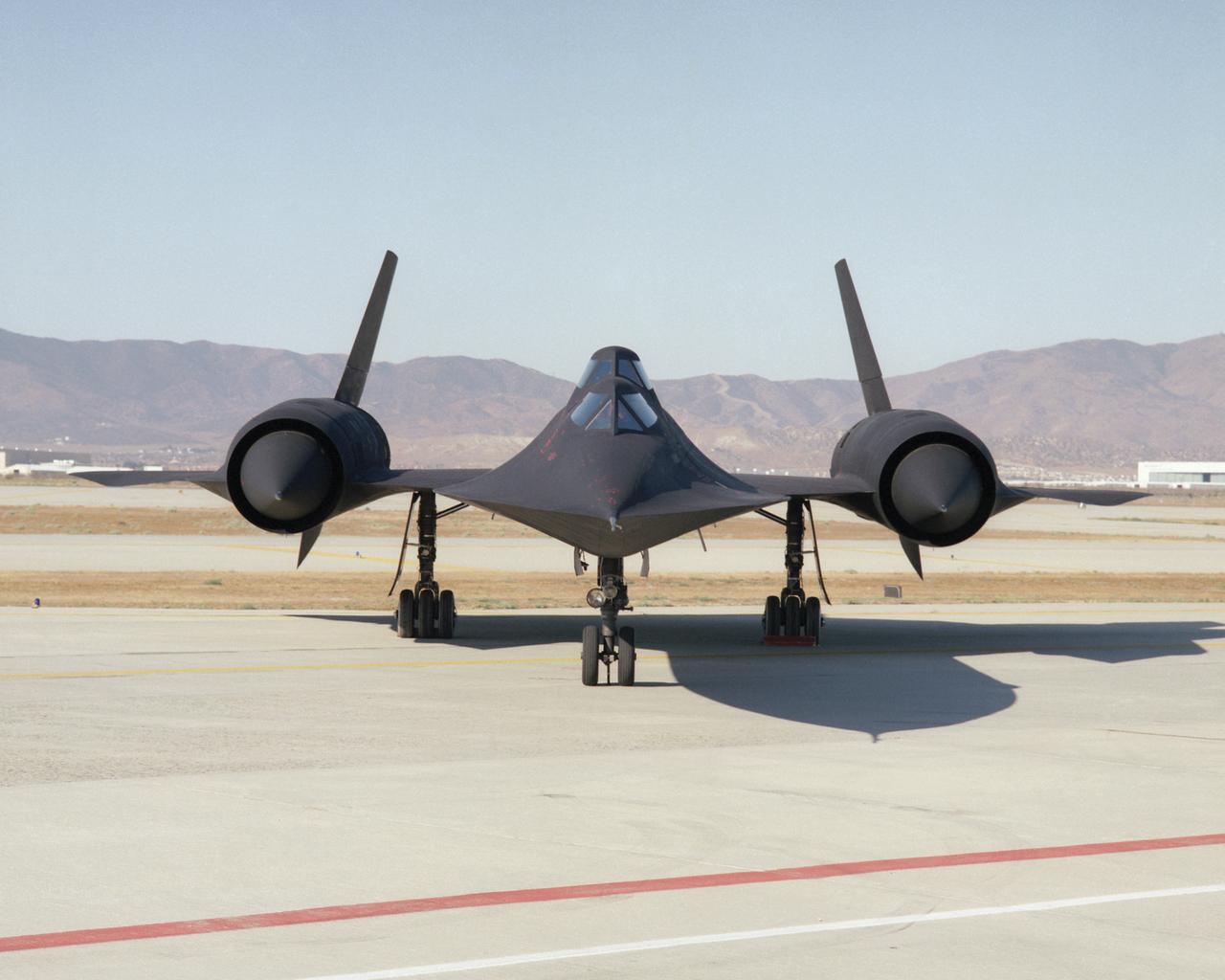

This photo shows a head-on view of NASA's SR-71B, used for pilot proficiency and training, on the ramp at the Air Force's Plant 42 in Palmdale, California, shortly before delivery to the Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility (later, Dryden Flight Research Center) at Edwards, California. NASA operated two of these unique aircraft, an SR-71A, for high-speed, high altitude research, and this SR- 71B pilot trainer for most of the decade of the 1990s. The "B" model is special because of its raised rear cockpit, which provided a second pilot position so a trainer and an experienced pilot could both see what was going on during flights. The SR-71 was designed and built by the Lockheed Skunk Works, now the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. Studies have shown that less than 20 percent of the total thrust used to fly at Mach 3 is produced by the basic engine itself. The balance of the total thrust is produced by the unique design of the engine inlet and "moveable spike" system at the front of the engine nacelles, and by the ejector nozzles at the exhaust which burn air compressed in the engine bypass system. Data from the SR-71 high speed research program will be used to aid designers of future supersonic/hypersonic aircraft and propulsion systems, including a high speed civil transport.
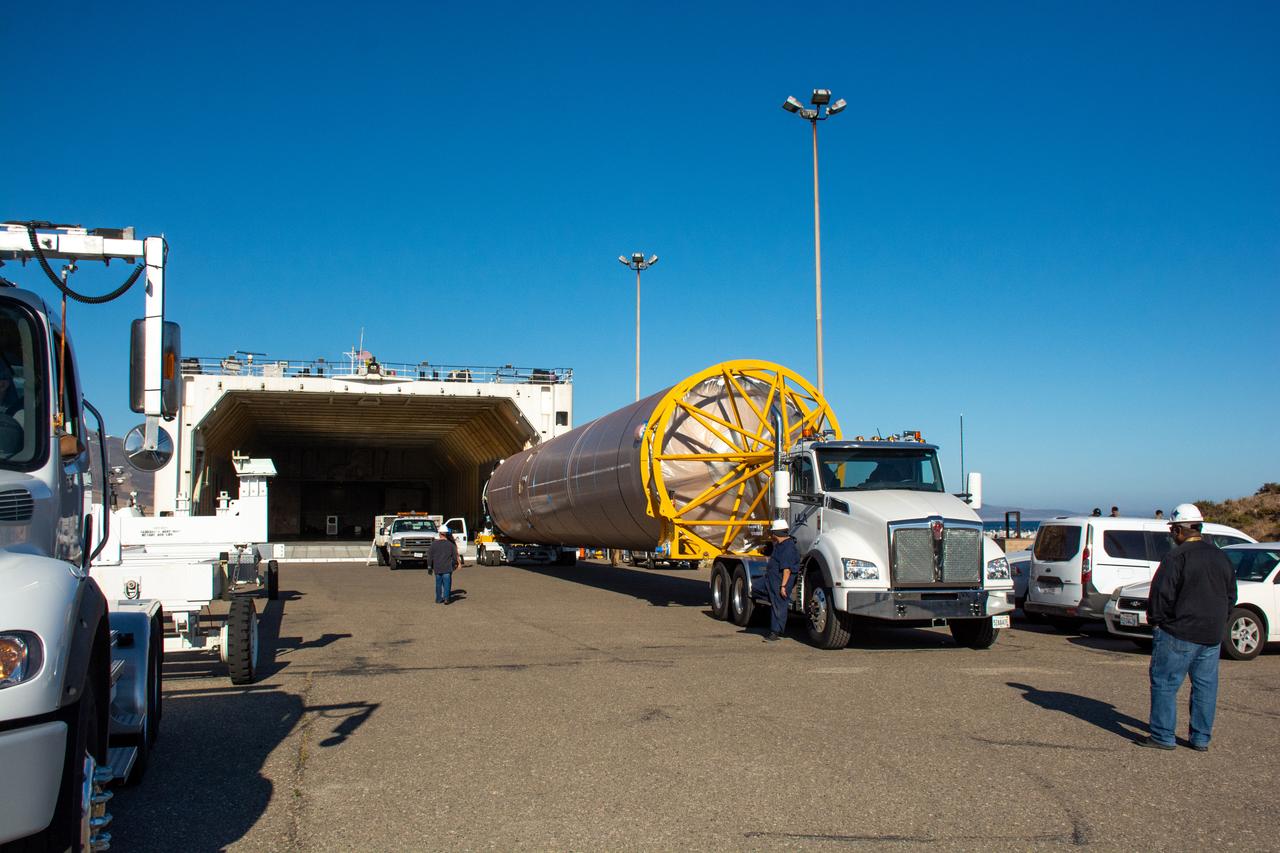

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is offloaded from its water transport at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on July 11, 2022, for NASA and NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on the final ULA Atlas V rocket to launch from Vandenberg. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.
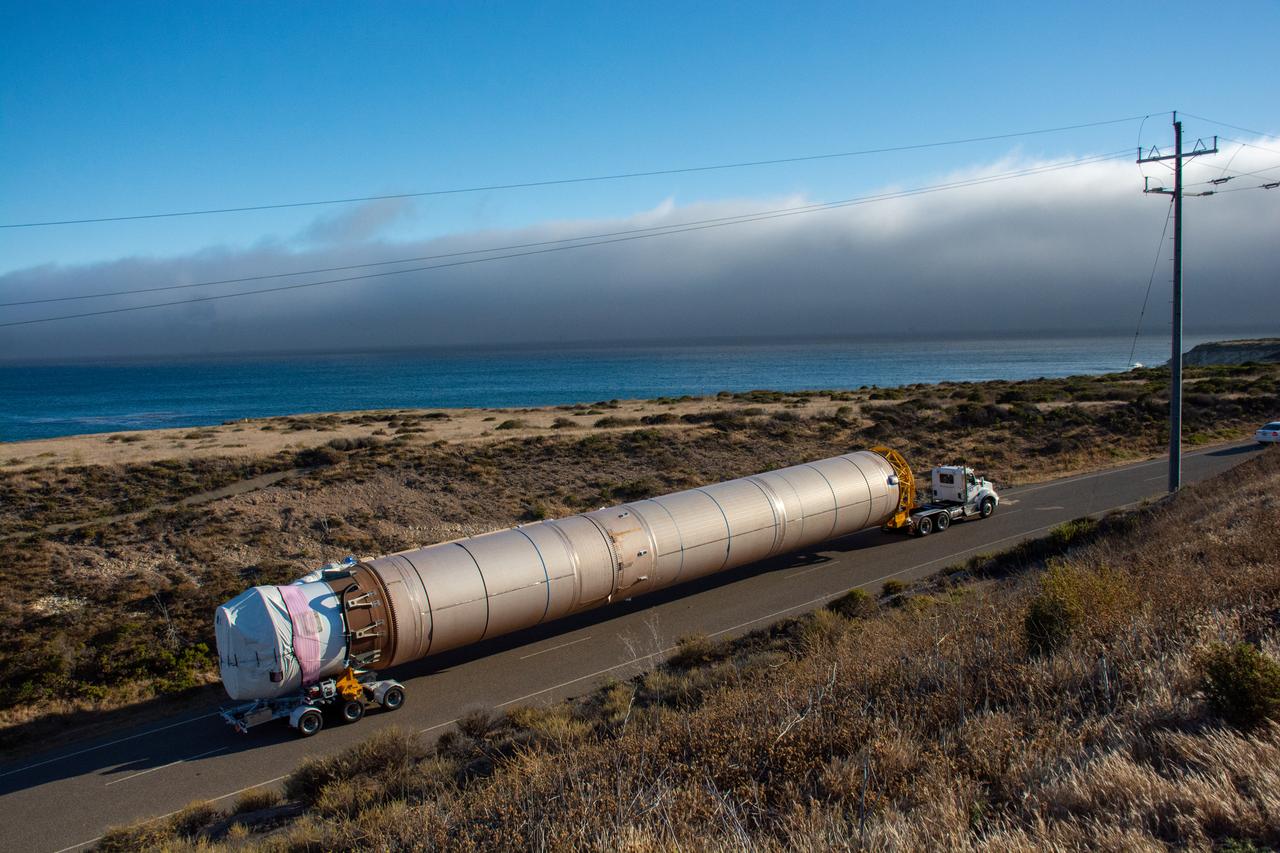

The United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V booster is transported to the Horizontal Integration Facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on July 11, 2022, for NASA and NOAA’s Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on the final ULA Atlas V rocket to launch from Vandenberg. JPSS-2 will scan the globe as it orbits from the North to the South Pole, crossing the equator 14 times a day. From 512 miles above Earth, it will capture data that inform weather forecasts, extreme weather events, and climate change. The Visible Infrared Radiometer Suite instrument will collect imagery for global observations of the land, atmosphere, cryosphere, and oceans. Launching as a secondary payload to JPSS-2 is NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID), dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID is a demonstration of a hypersonic inflatable aerodynamic decelerator, or aeroshell, technology that could one day help land humans on Mars.
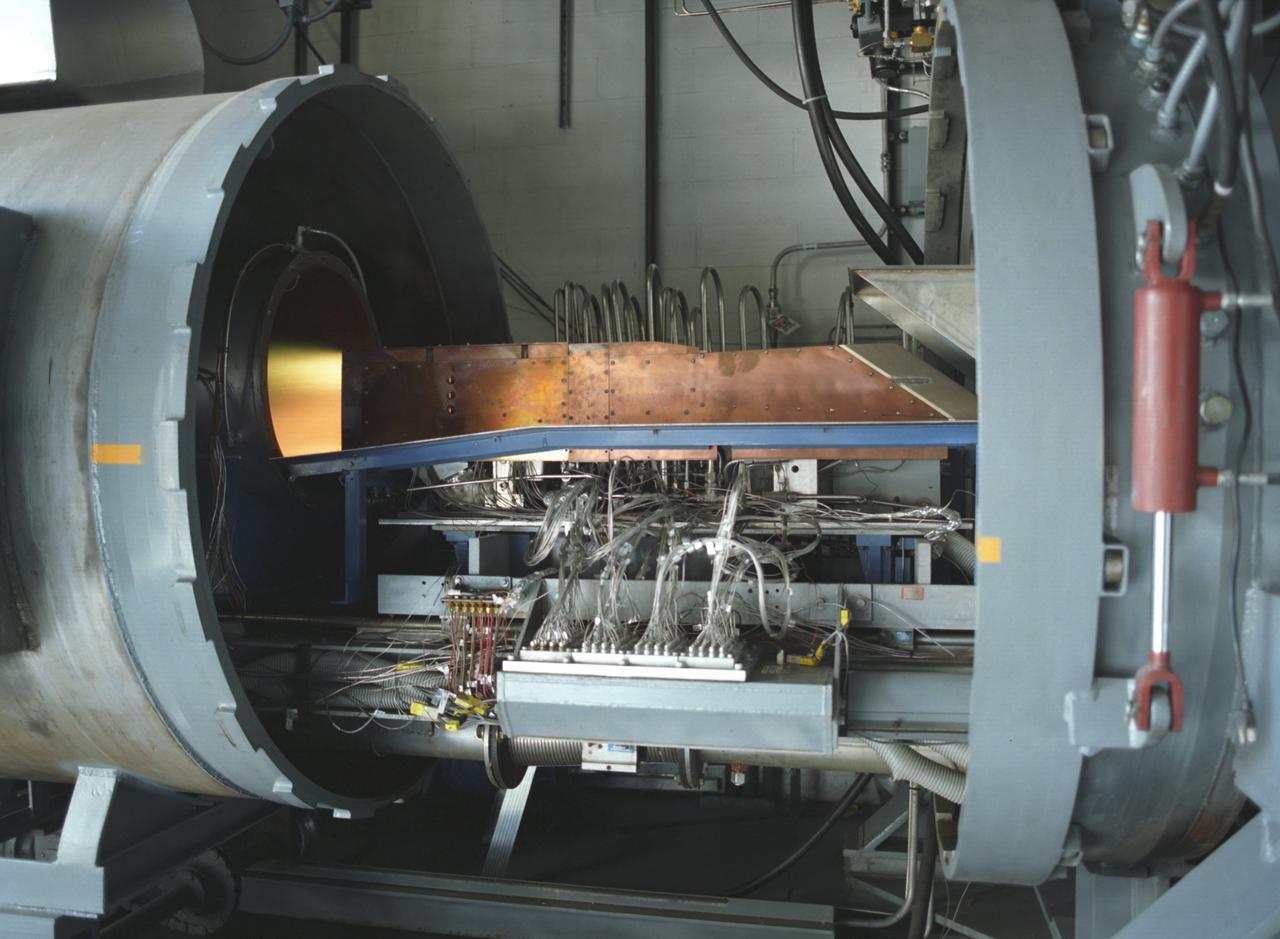
This photograph depicts an air-breathing rocket engine that completed an hour or 3,600 seconds of testing at the General Applied Sciences Laboratory in Ronkonkoma, New York. Referred to as ARGO by its design team, the engine is named after the mythological Greek ship that bore Jason and the Argonauts on their epic voyage of discovery. Air-breathing engines, known as rocket based, combined-cycle engines, get their initial take-off power from specially designed rockets, called air-augmented rockets, that boost performance about 15 percent over conventional rockets. When the vehicle's velocity reaches twice the speed of sound, the rockets are turned off and the engine relies totally on oxygen in the atmosphere to burn hydrogen fuel, as opposed to a rocket that must carry its own oxygen, thus reducing weight and flight costs. Once the vehicle has accelerated to about 10 times the speed of sound, the engine converts to a conventional rocket-powered system to propel the craft into orbit or sustain it to suborbital flight speed. NASA's Advanced SpaceTransportation Program at Marshall Space Flight Center, along with several industry partners and collegiate forces, is developing this technology to make space transportation affordable for everyone from business travelers to tourists. The goal is to reduce launch costs from today's price tag of $10,000 per pound to only hundreds of dollars per pound. NASA's series of hypersonic flight demonstrators currently include three air-breathing vehicles: the X-43A, X-43B and X-43C.