
NASA’s fifth core value – inclusion – is installed in the Central Campus lobby at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 1, 2020. On July 23, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announced the addition of this fifth core value to the existing values embraced by NASA: safety, integrity, teamwork, and excellence. In his announcement, Bridenstine stated “Incorporating inclusion as a NASA core value is an important step to ensuring this principle remains a long-term focus for our agency and becomes ingrained in the NASA family DNA.”

NASA’s fifth core value – inclusion – is installed in the Central Campus lobby at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 1, 2020. On July 23, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announced the addition of this fifth core value to the existing values embraced by NASA: safety, integrity, teamwork, and excellence. In his announcement, Bridenstine stated “Incorporating inclusion as a NASA core value is an important step to ensuring this principle remains a long-term focus for our agency and becomes ingrained in the NASA family DNA.”

NASA’s core values are shown in the Central Campus lobby at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the installation of NASA’s fifth core value – inclusion – on Sept. 1, 2020. On July 23, NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announced the addition of this fifth core value to the existing values embraced by NASA: safety, integrity, teamwork, and excellence. In his announcement, Bridenstine stated “Incorporating inclusion as a NASA core value is an important step to ensuring this principle remains a long-term focus for our agency and becomes ingrained in the NASA family DNA.”
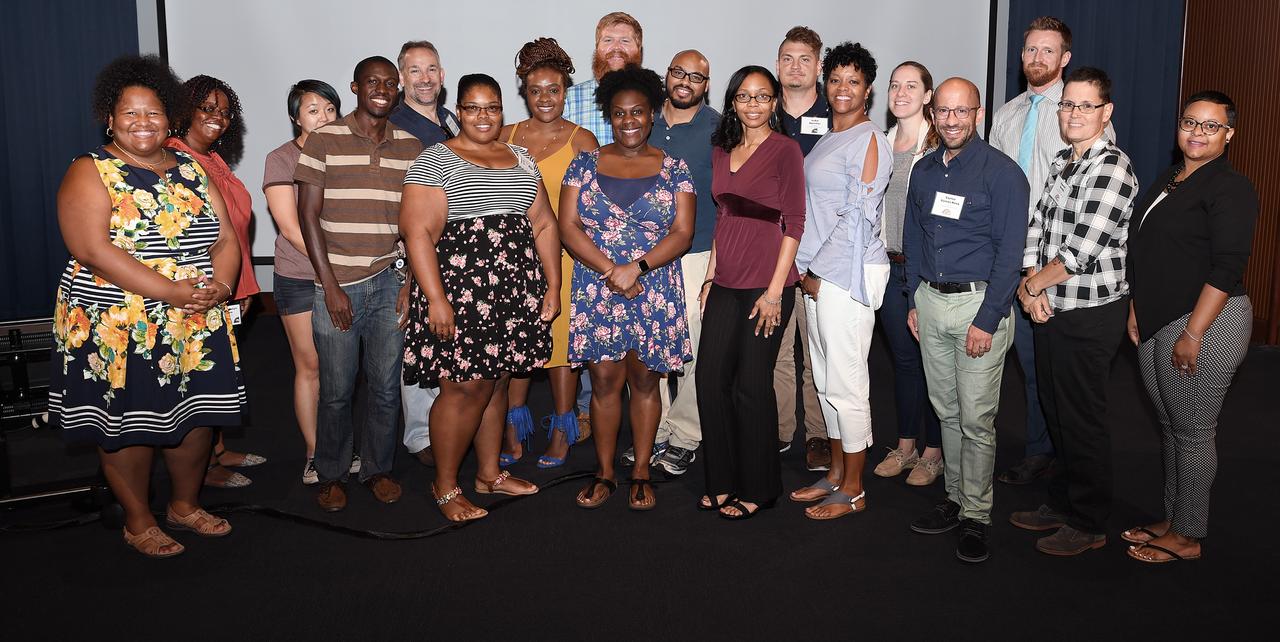

Diversity and Inclusion Program D&IP Advisory Committee Orientation was held August 9, 2018 Group shot
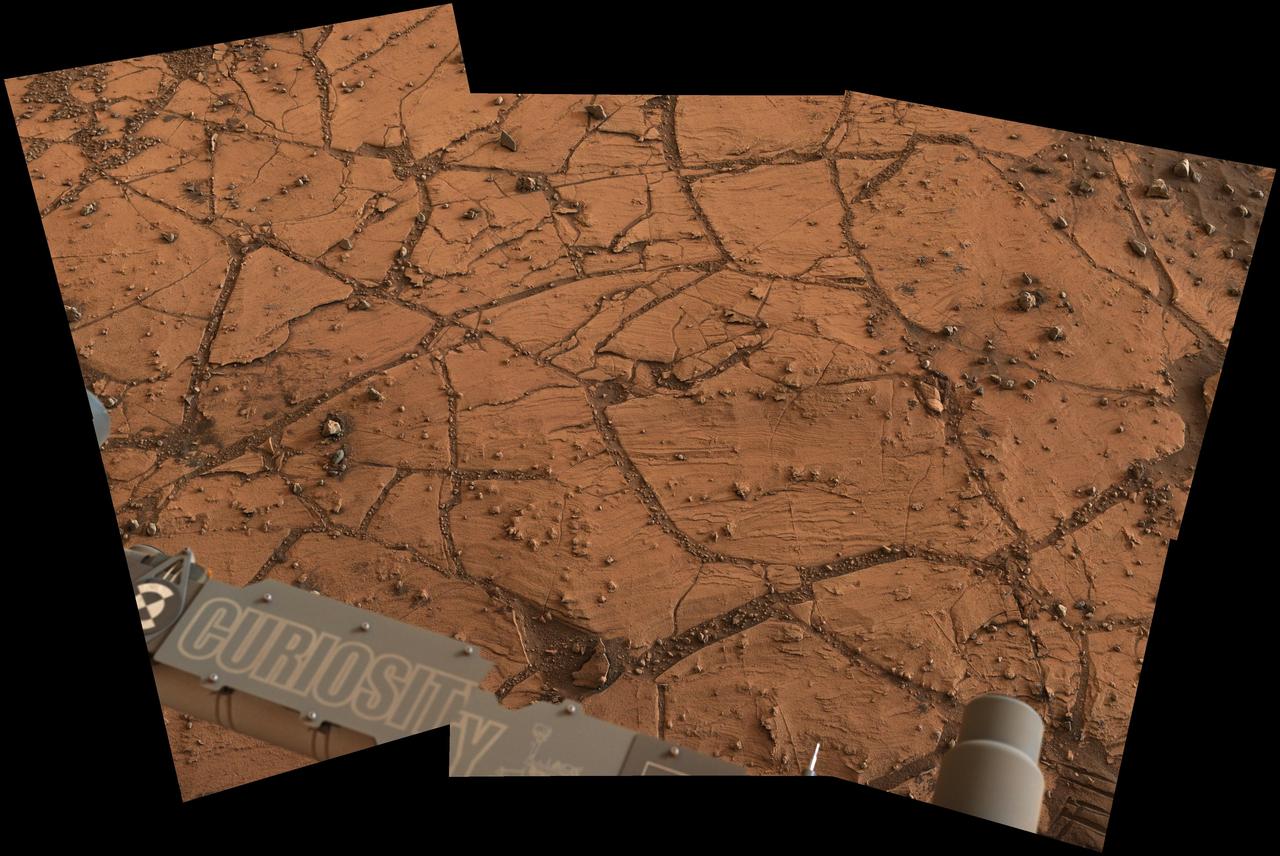

This patch of Martian bedrock, about 2 feet 70 centimeters across, is finely layered rock with some pea-size inclusions. It lies near the lowest point of the Pahrump Hills outcrop, which forms part of the basal layer of Mount Sharp.
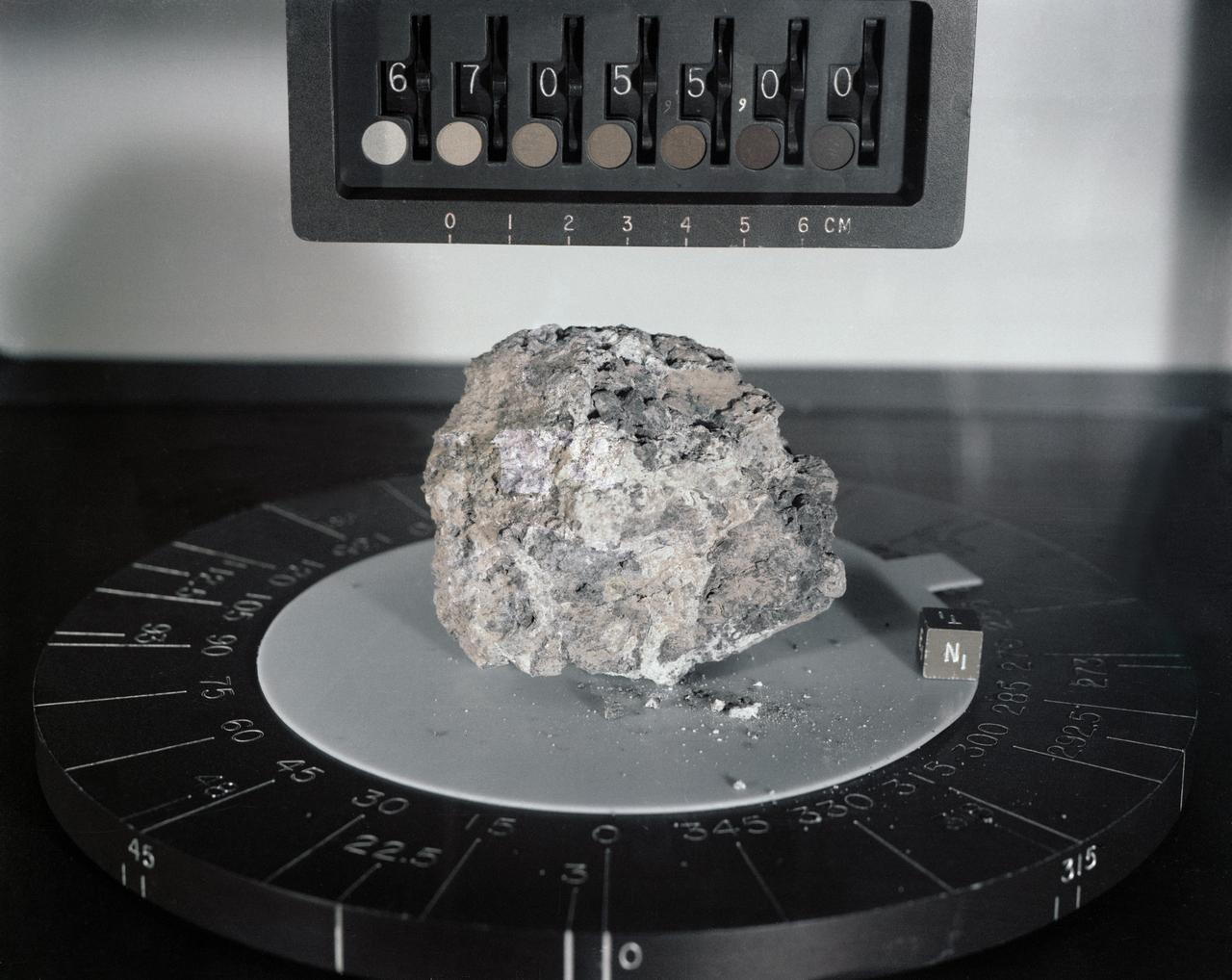

S72-36949 (April 1972) --- A black and white breccia from the rim of North Ray Crater. Its white, feldspar-rich, fine grained matrix is very friable. A variety of different rock types are observed as inclusions. They range in size from several centimeters to less than 1mm. Note also the presence white, feldspar-rich inclusions.

Guest speaker Sinead Burke, in front, from Ireland, gave a presentation on “Breaking the Mould – A Lesson in Equity,” to Kennedy Space Center employees on Nov. 30, 2022, and to employees at other NASA centers via live stream on YouTube. Members of the Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Accessibility Roundtable and the Disability Awareness Action Working Group (DAAWG), standing from left are Nicole Delvesco, Lisa Williams, Willie Gainey, Annie Williams, and Glenn Semmel. The event was sponsored by Kennedy’s DAAWG and the Spaceport Integration Directorate. Burke, who is an advocate for the inclusion of all, amplifies the voices who are often not considered.
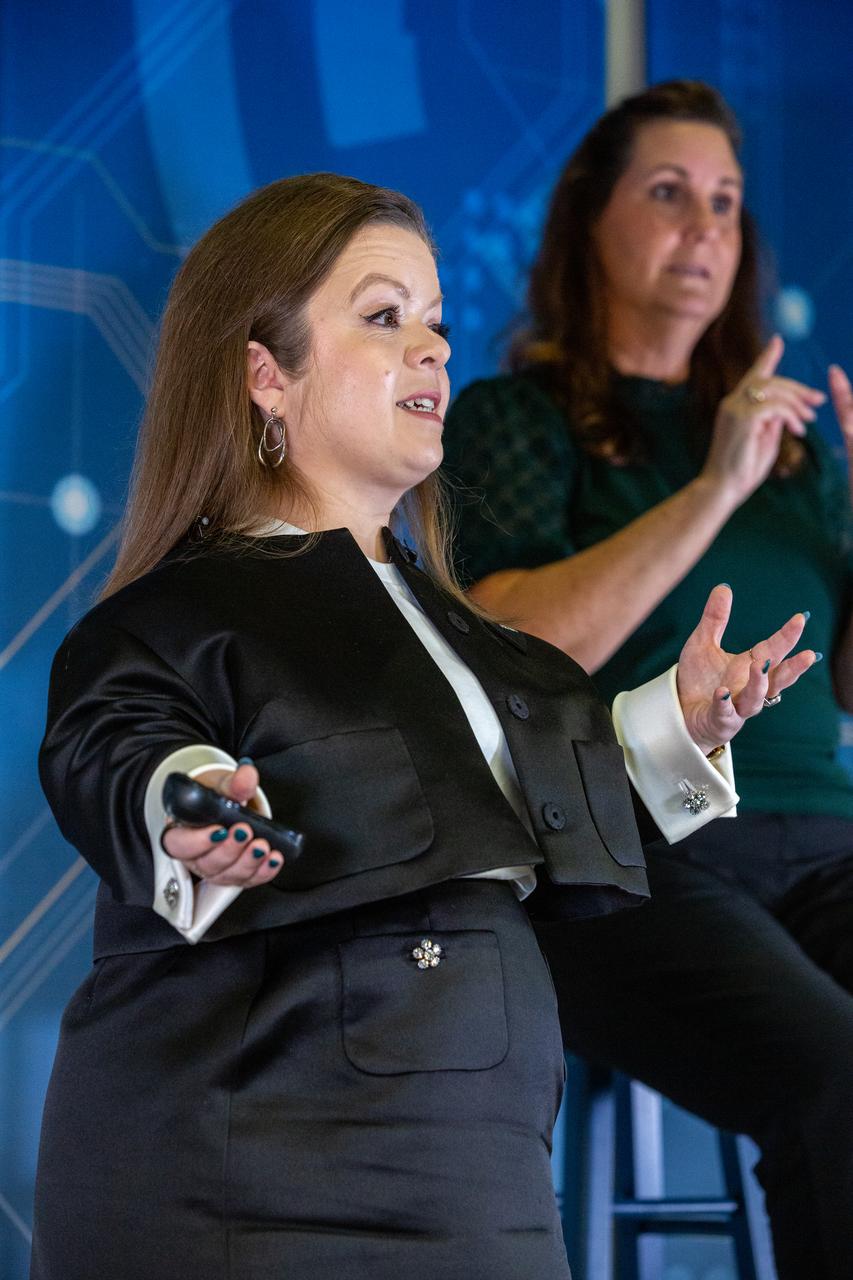

Guest speaker Sinead Burke, from Ireland, gave a presentation on “Breaking the Mould – A Lesson in Equity,” to Kennedy Space Center employees on Nov. 30, 2022, and to employees at other NASA centers via live stream on YouTube. The event was sponsored by the center’s Disability Awareness and Action Working Group (DAAWG) and the Spaceport Integration Directorate. Burke, who is an advocate for the inclusion of all, amplifies the voices who are often not considered.
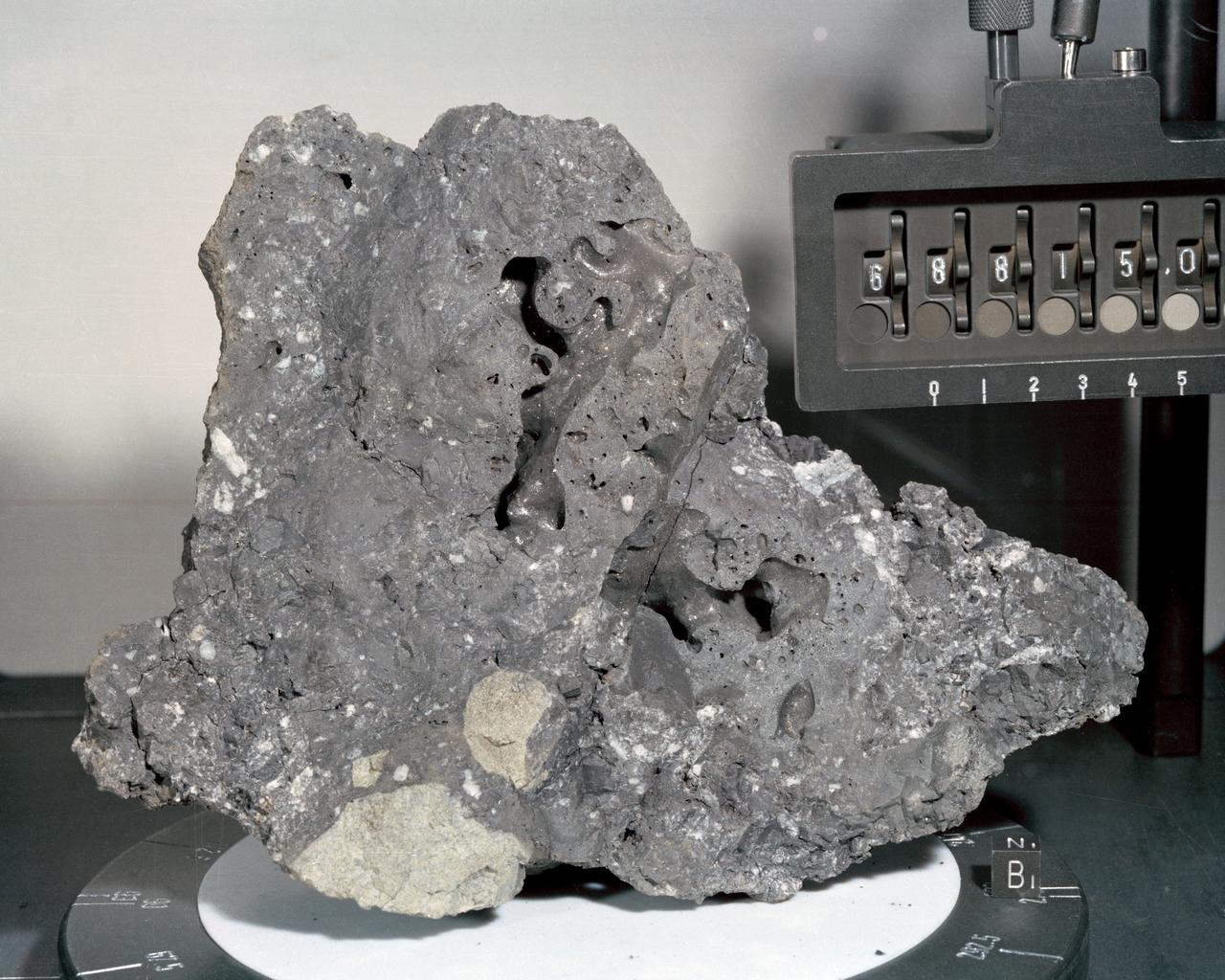

A closeup view or "mug shot" of Apollo 16 lunar sample no. 68815, a dislodged fragment from a parent boulder roughly four feet high and five feet long encountered at Station 8. The crew tried in vain to overturn the parent boulder. A fillet-soil sample was taken close to the boulder, allowing for study of the type and rate of erosion acting on lunar rocks. The fragment itself is very hard, has many veticles and a variety of inclusions. In addition, numerous metallic particles were observed in the black matrix.
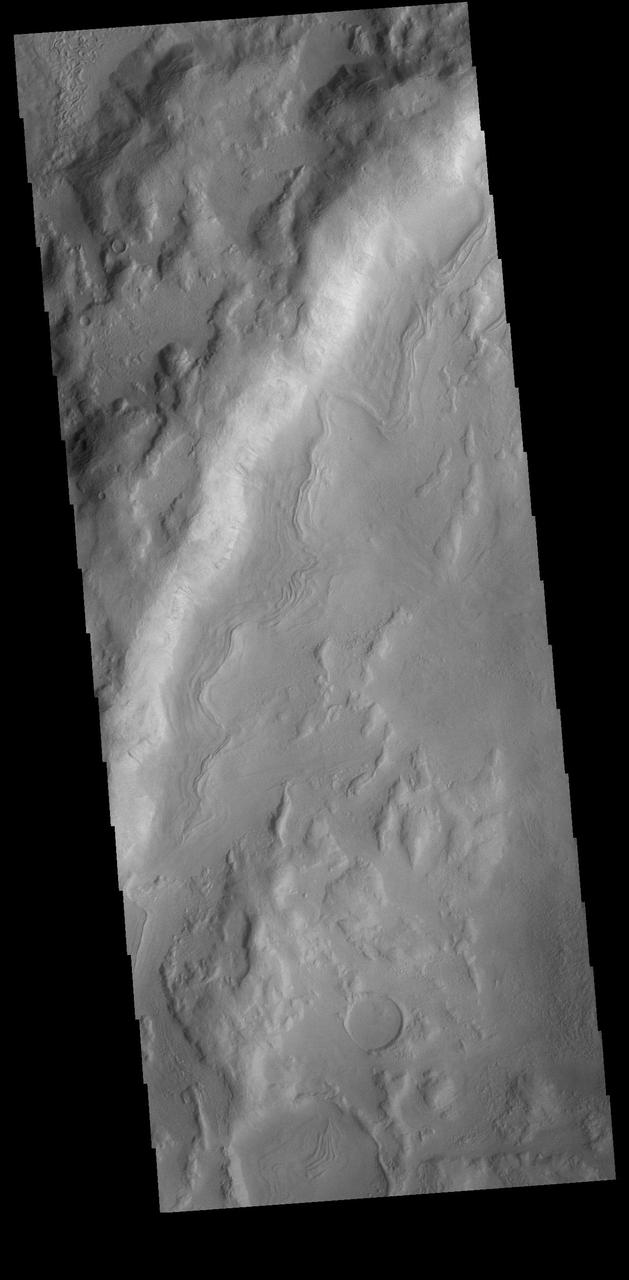

This VIS image is located in an unnamed crater in Noachis Terra. The sinuous feature near the bottom of the crater rim appears to have been caused by down slope movement of materials. The sinuous nature may have been created by inclusion of a volatile material such as ice. Orbit Number: 74447 Latitude: -39.937 Longitude: 11.1296 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2018-09-26 05:13 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22844
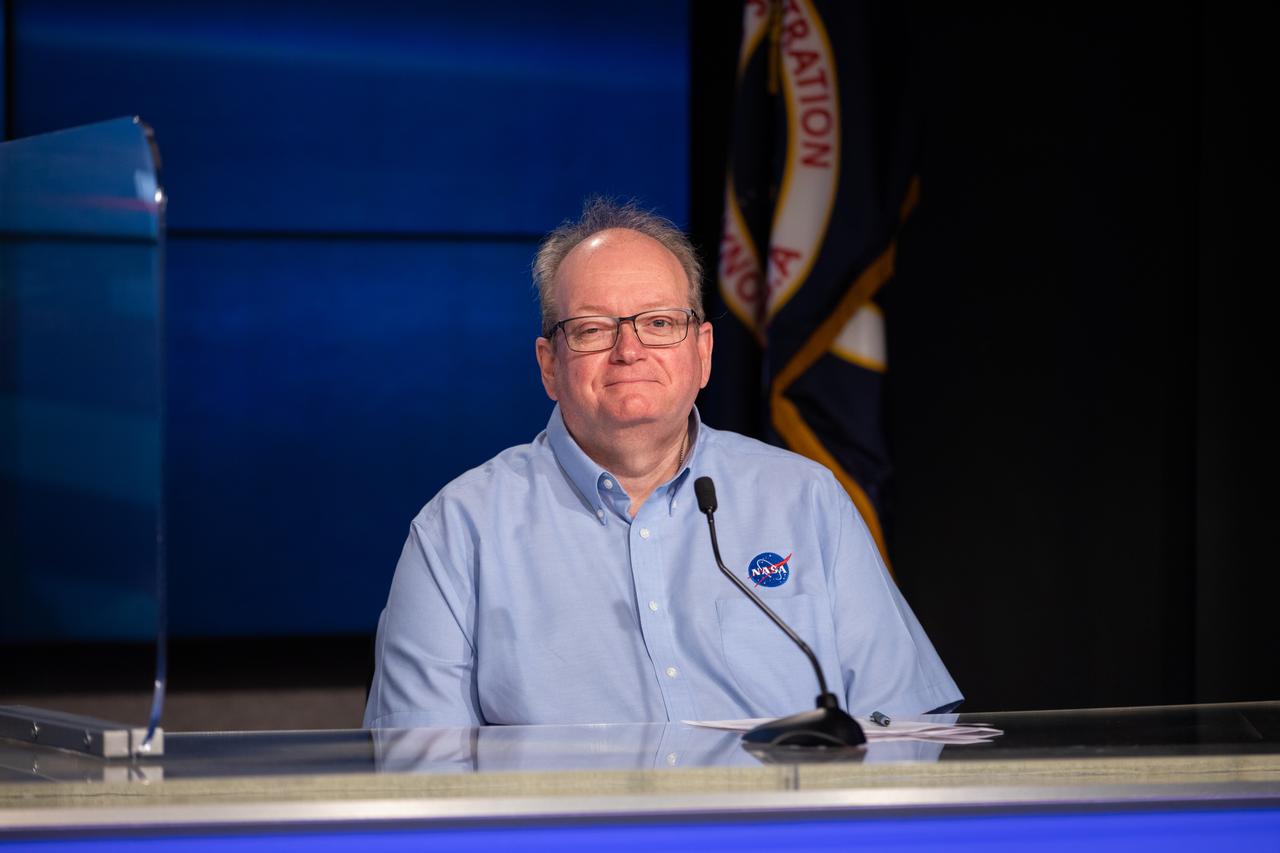

NASA Kennedy Space Center Associate Director, Management Burt Summerfield participates in a virtual town hall meeting on Aug. 20, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium. During the town hall, Kennedy’s senior leaders answered questions submitted by the workforce and discussed a wide range of topics, including upcoming milestones, updates on the criteria for returning to onsite work, and diversity and inclusion at the multi-user spaceport.
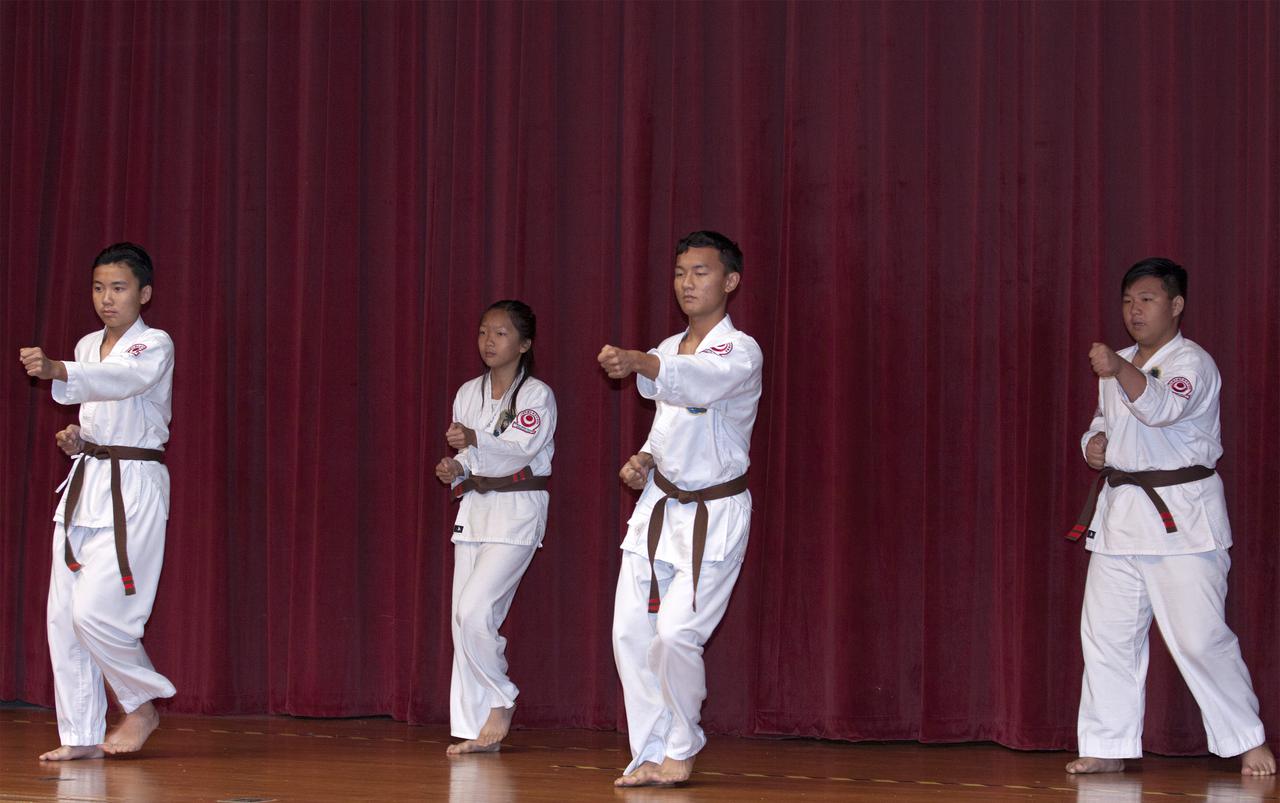

Students of the Taka Shin Kai Isshinryu Karate Dojo in Melbourne, Fla., perform karate during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The style of karate they performed is called Isshinryu Karate. The theme of the event, hosted by the Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, was 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

Veronica Villalobos, Director, Office of Diversity and Inclusion, Office of Personnel Management, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
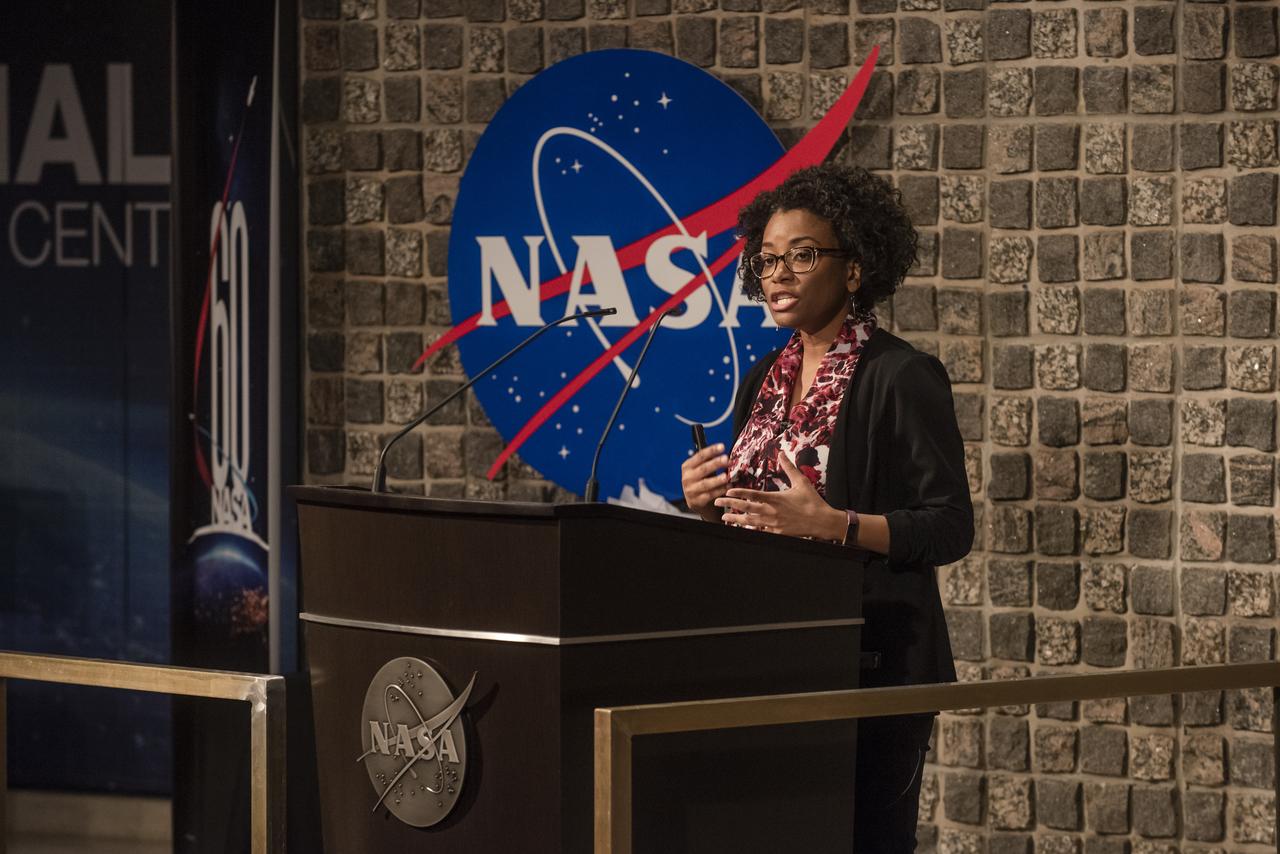

Dr. Shanique Brown, an assistant professor of industrial-organizational psychology at Wayne State University in Detroit, Michigan, delivers the Black History Month keynote address to team members at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center Feb. 28. Participants mingled with Brown and Marshall leaders after the speech and a panel discussion on diversity and inclusion, and sampled a variety of ethnic foods. The 2019 commemoration, themed "Migrations From Here to There," was organized by Marshall's Office of Diversity and Equal Opportunity
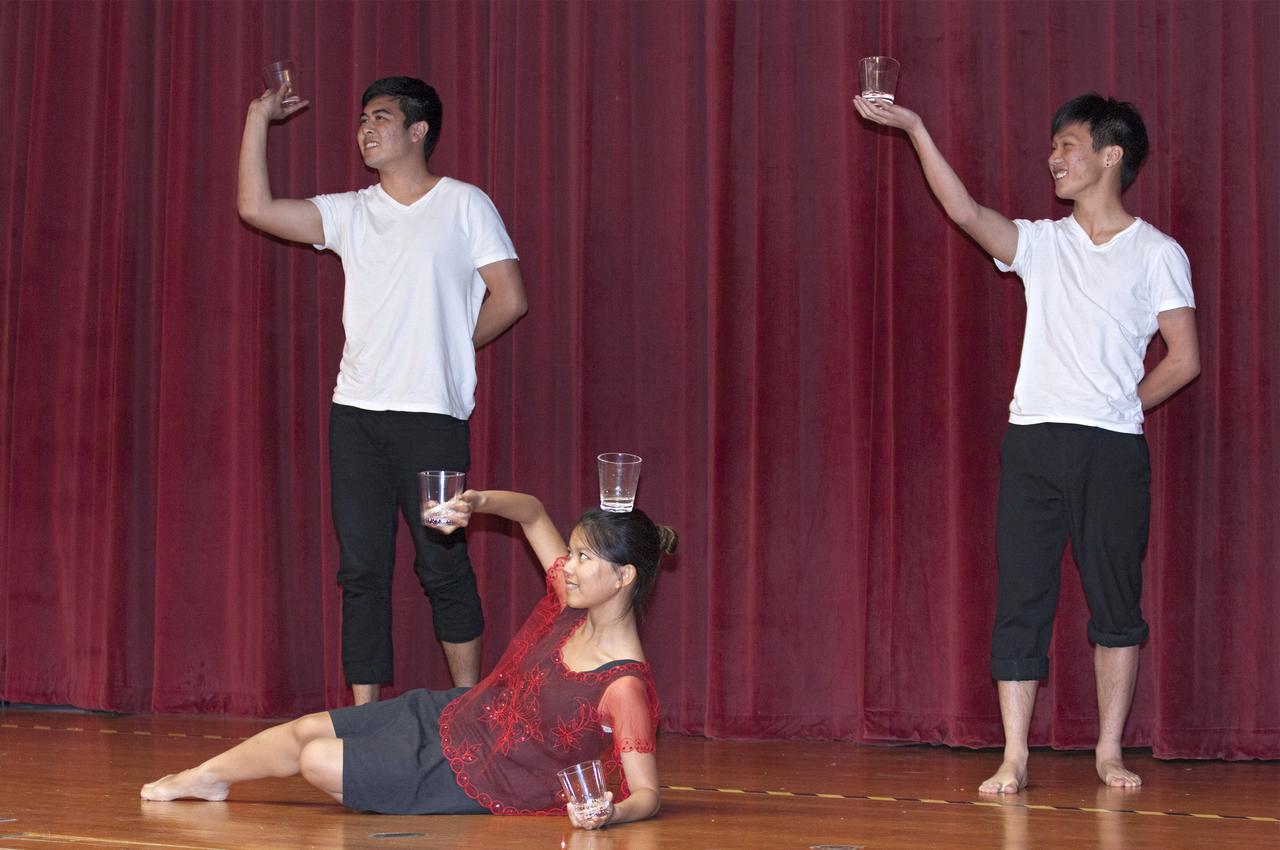

The Filipino Student Association FSA at the University of Central Florida UCF perform a traditional Filipino cultural dance during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The theme of the event, hosted by the Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, was 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

From left, NASA Kennedy Space Center Associate Director, Technical Kelvin Manning; Director Bob Cabana; Deputy Director Janet Petro; and Associate Director, Management Burt Summerfield participate in a virtual town hall meeting on Aug. 20, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium. During the town hall, Kennedy’s senior leaders answered questions submitted by the workforce and discussed a wide range of topics, including upcoming milestones, updates on the criteria for returning to onsite work, and diversity and inclusion at the multi-user spaceport.
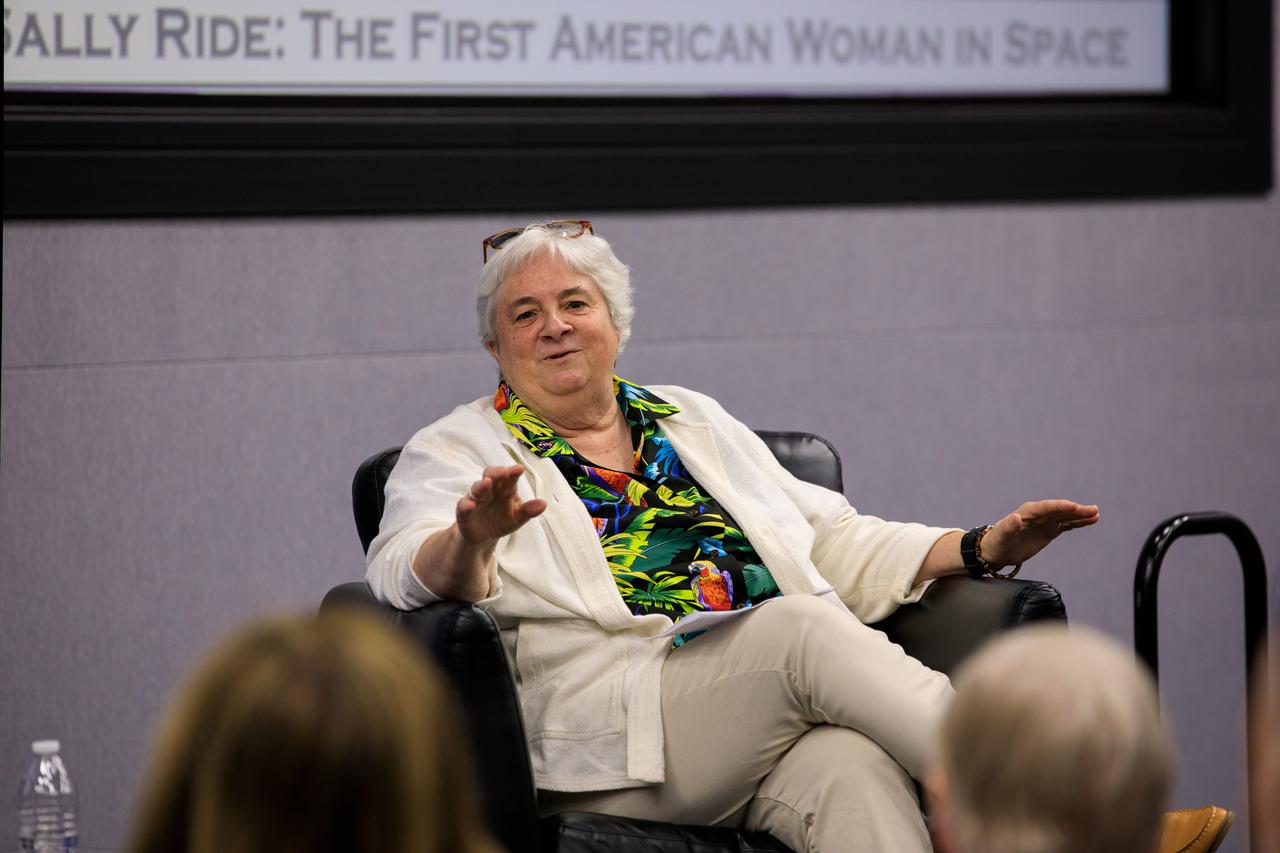

Bear Ride, the sister of pioneering astronaut Sally Ride, speaks during “The Legacy of Sally Ride: The First American Woman in Space” event at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2023. Forty years ago, Ride made her trailblazing flight into space. A hero to millions, Ride was a steadfast advocate for inclusion in STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) – especially for girls and young women – until her death in 2012 from pancreatic cancer.

NASA Chief Historian Brian Odom moderates “The Legacy of Sally Ride: The First American Woman in Space” event at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2023. Forty years ago, Ride made her trailblazing flight into space. A hero to millions, Ride was a steadfast advocate for inclusion in STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) – especially for girls and young women – until her death in 2012 from pancreatic cancer. Appearing on the monitor in the background is Sally Ride’s life partner of 27 years, Tam O’Shaughnessy.
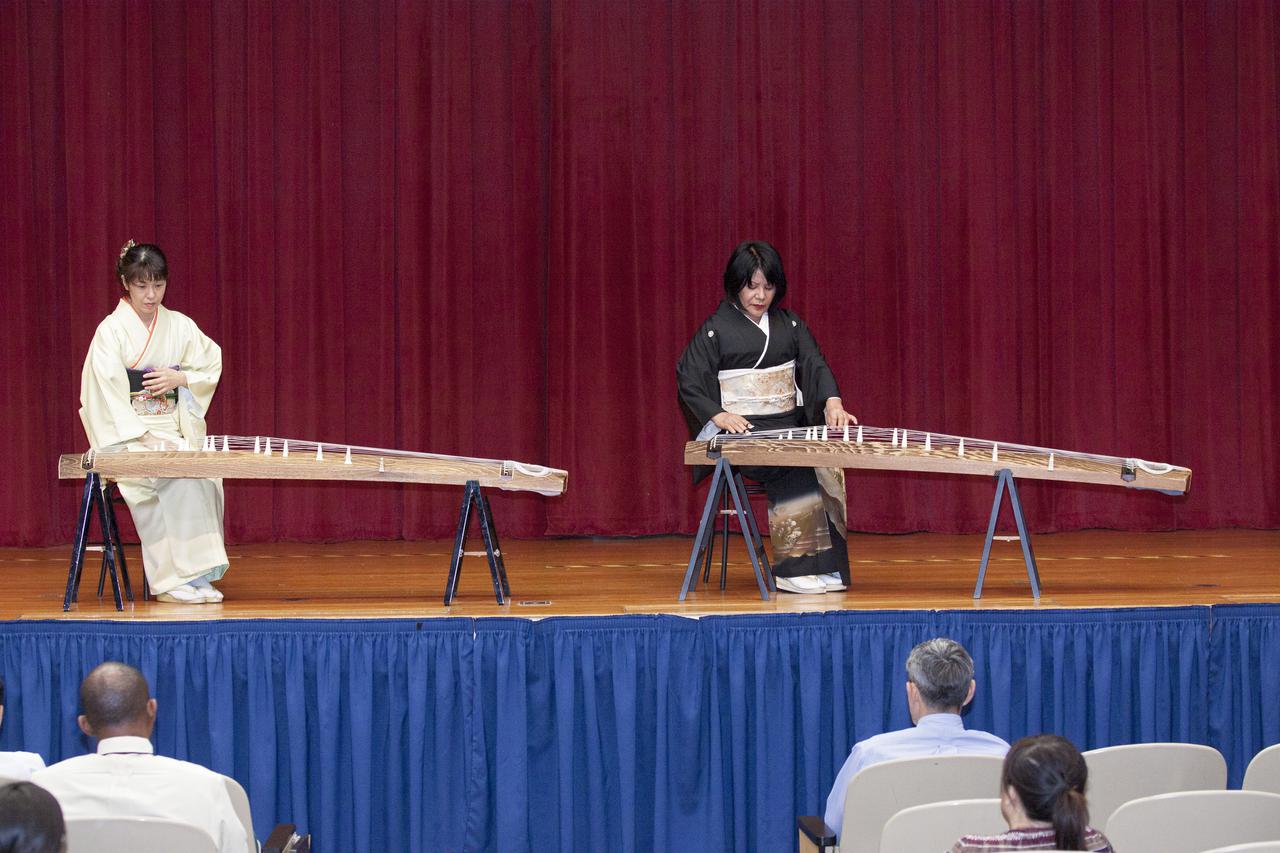

Japanese Traditional Koto Music is performed by Yoshino-kai during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The theme of the event, hosted by the Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, was 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
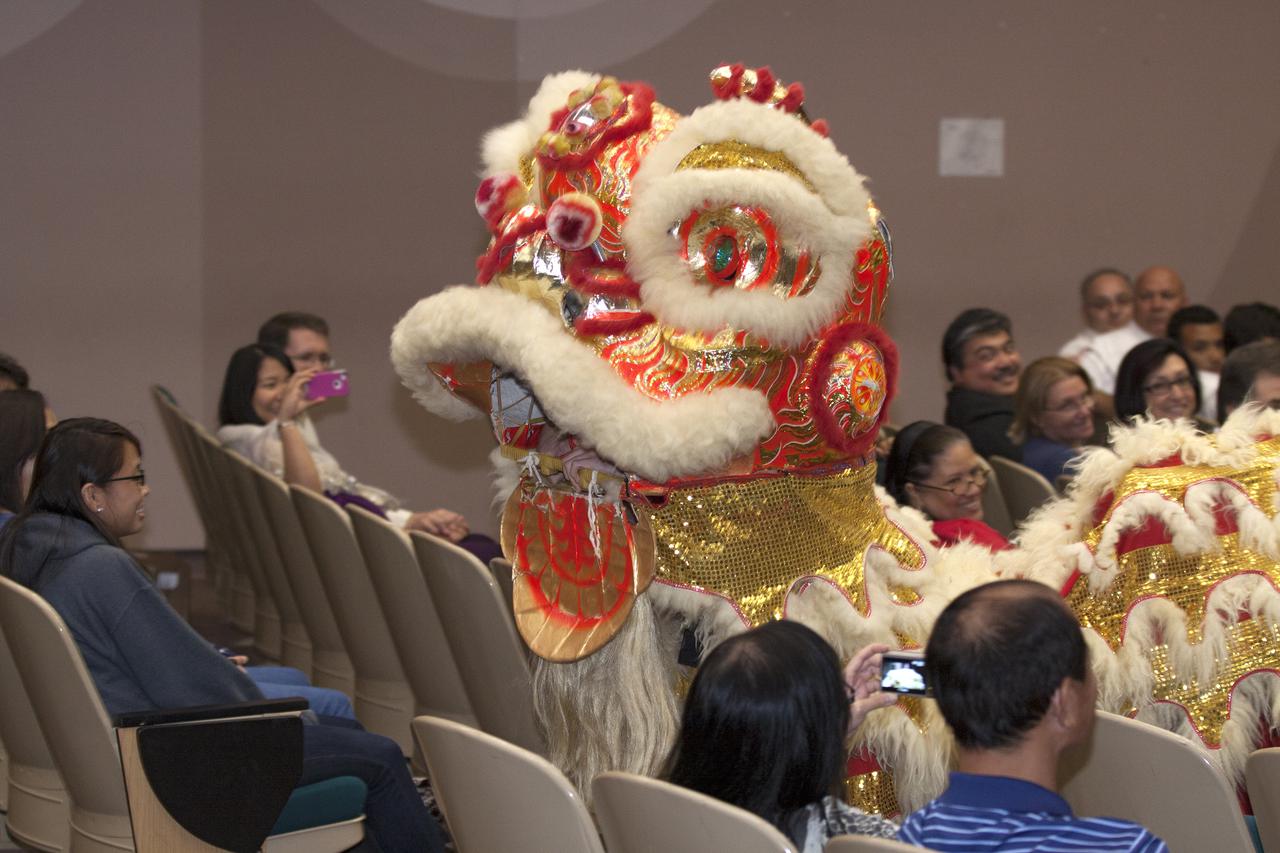

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students of the Asian Pacific American Coalition APAC of the University of Central Florida UCF perform a lion dance during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The theme of the event, hosted by the Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, was 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

Kennedy Space Center employees attend “The Legacy of Sally Ride: The First American Woman in Space” event at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2023. Forty years ago, Ride made her trailblazing flight into space. A hero to millions, Ride was a steadfast advocate for inclusion in STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) – especially for girls and young women – until her death in 2012 from pancreatic cancer.

Wayne State University professor Shanique Brown, far right, takes part in a panel discussion on diversity and building strong, inclusive teams. She was joined by, from right, Lewis Wooten, associate program manager for the Space Launch System Program Office at Marshall; moderator Lisa Watson-Morgan, deputy director of Marshall's Engineering Directorate; Rick Burt, director of Marshall's Safety & Mission Assurance Directorate; and Bobby Watkins, director of the Human Exploration Development and Operations Office.
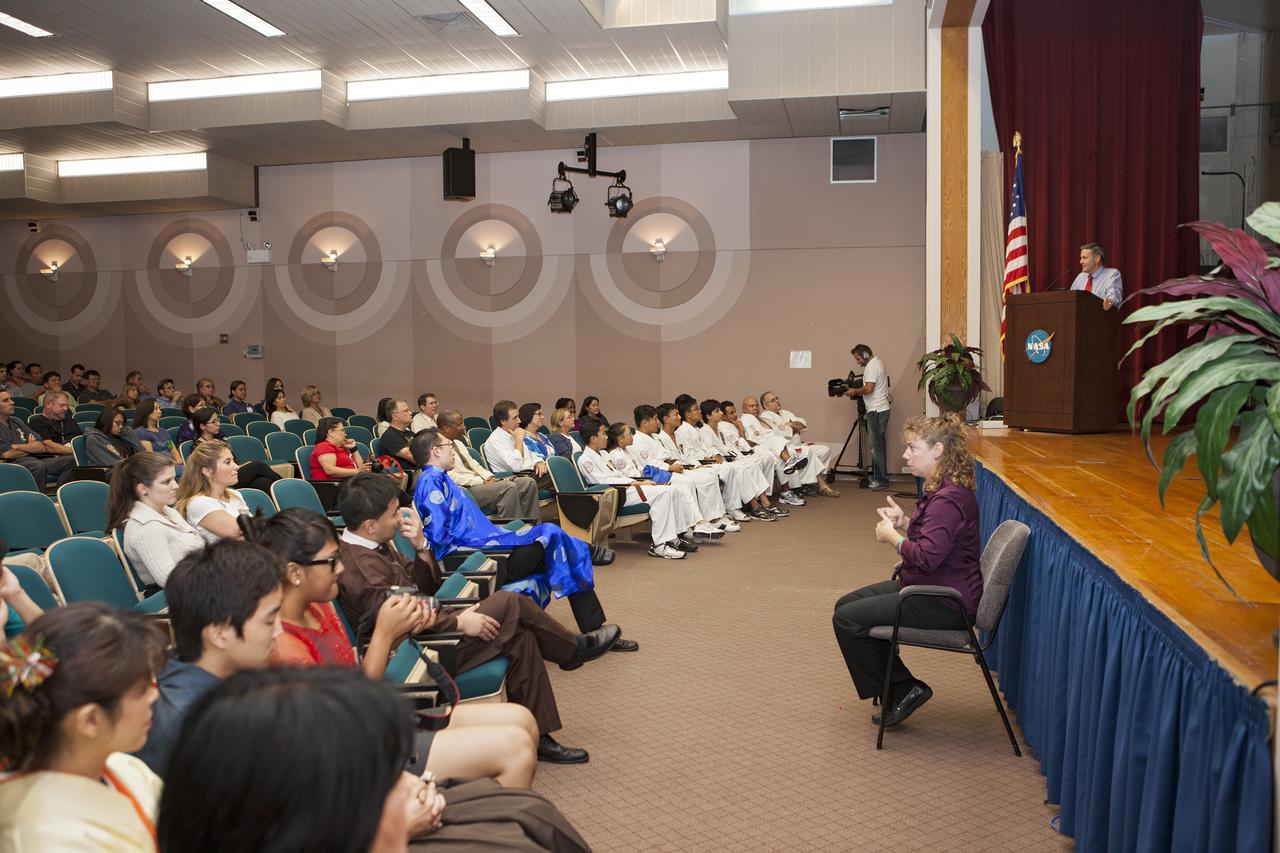

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana addresses workers during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, an employee resource group at KSC, hosted an Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration, 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett

NASA Kennedy Space Center Associate Director, Technical Kelvin Manning participates in a virtual town hall meeting on Aug. 20, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium. During the town hall, Kennedy’s senior leaders answered questions submitted by the workforce and discussed a wide range of topics, including upcoming milestones, updates on the criteria for returning to onsite work, and diversity and inclusion at the multi-user spaceport.
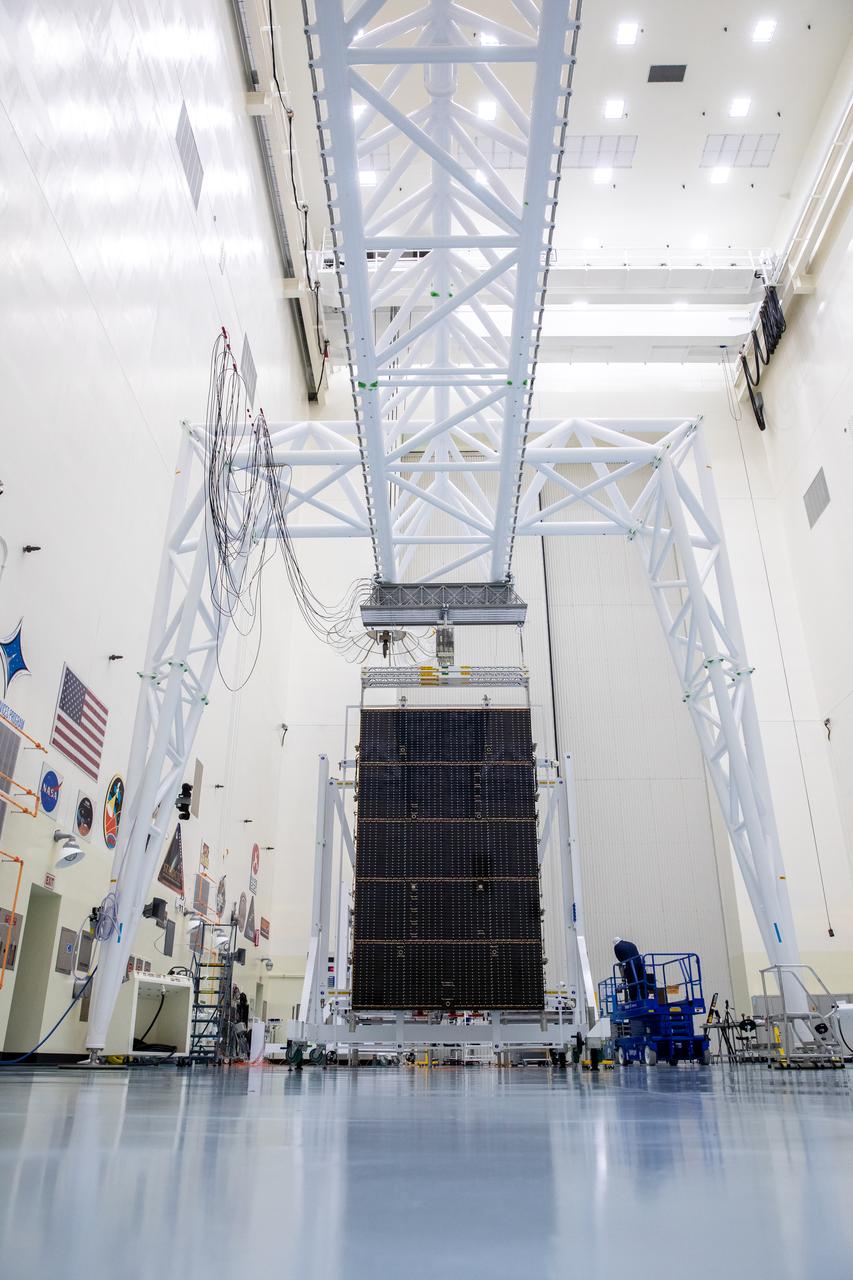

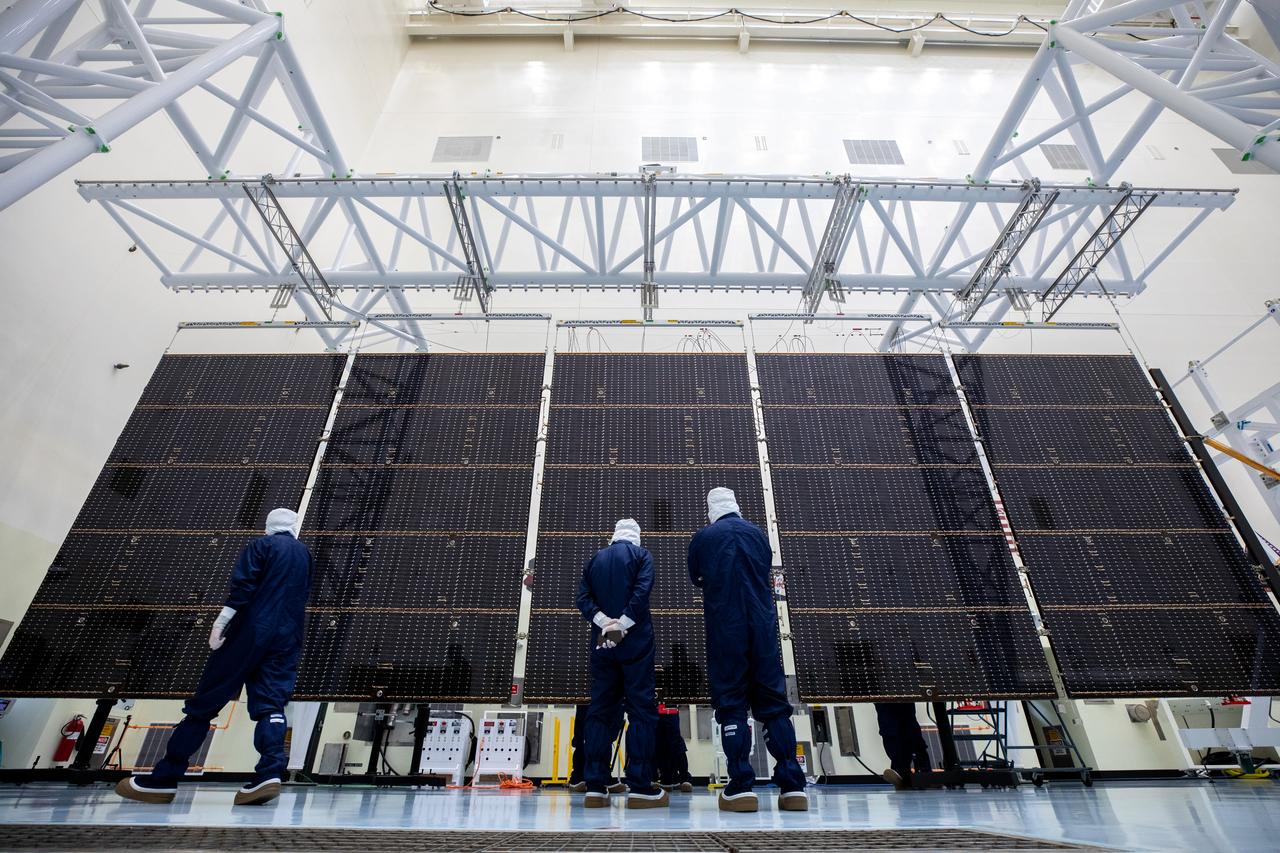
The first of two five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper stands inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
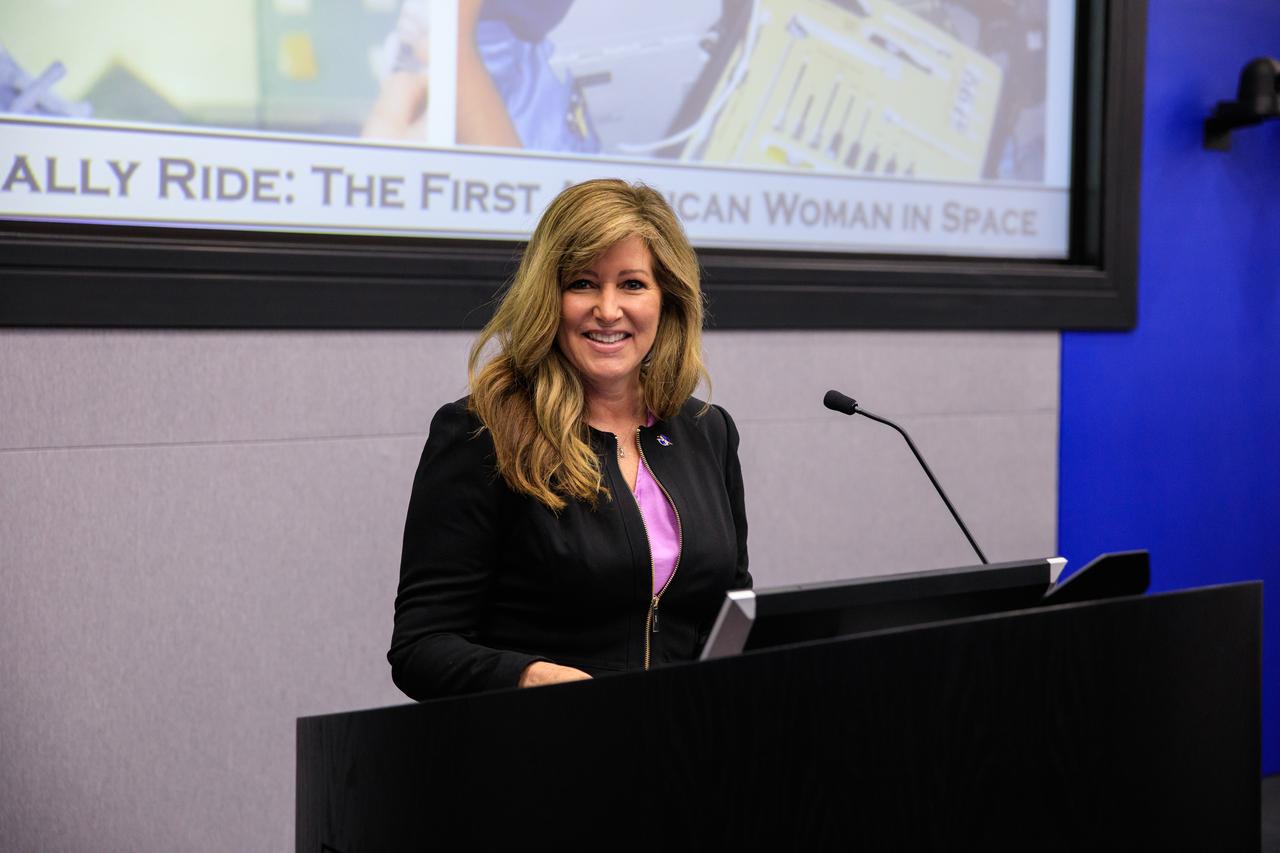

Jennifer Kunz, associate director, technical, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, addresses the audience at “The Legacy of Sally Ride: The First American Woman in Space” event at the Florida spaceport on June 15, 2023. Forty years ago, Ride made her trailblazing flight into space. A hero to millions, Ride was a steadfast advocate for inclusion in STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) – especially for girls and young women – until her death in 2012 from pancreatic cancer.
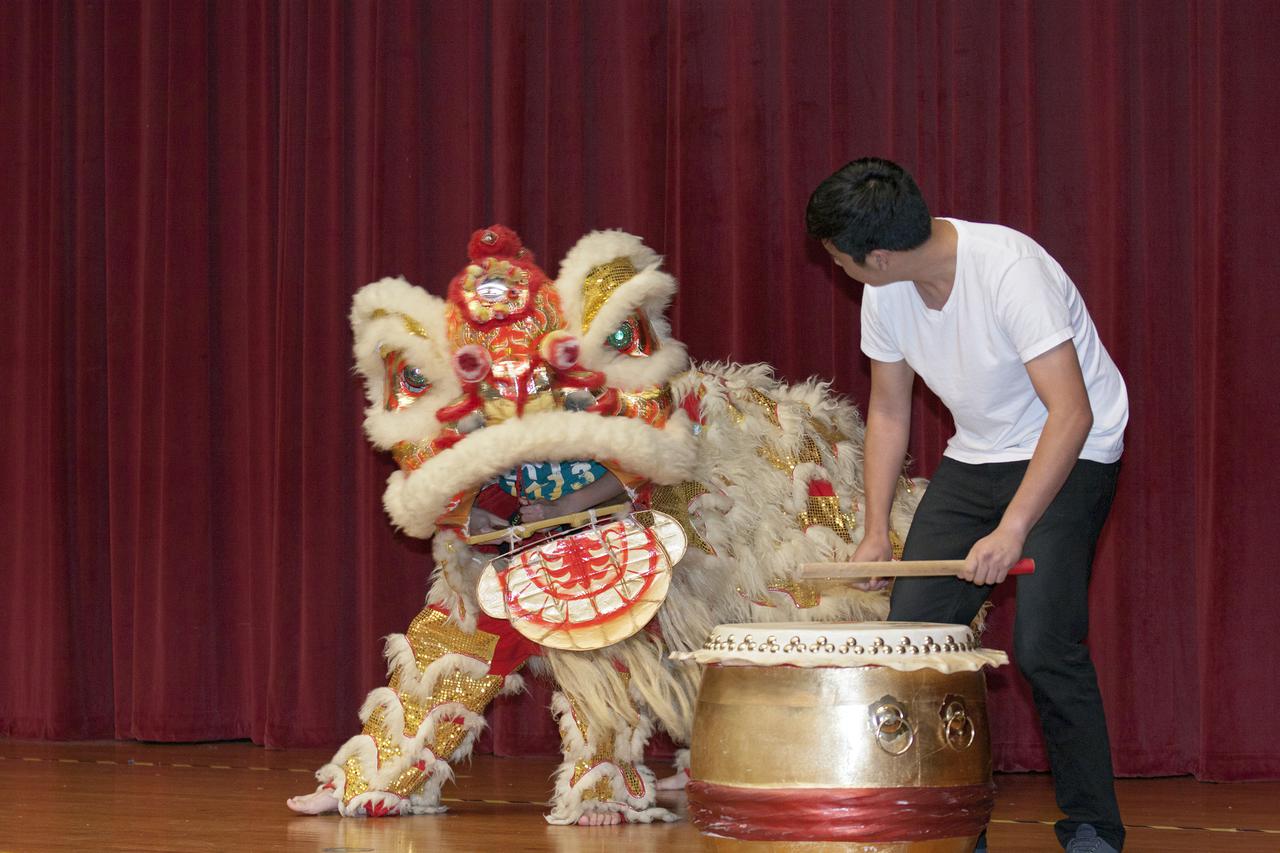

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Students of the Asian Pacific American Coalition APAC of the University of Central Florida UCF perform a lion dance during the Asian-Pacific American Heritage Month celebration on May 23 at the KSC Training Auditorium. The theme of the event, hosted by the Asian-Pacific American Connection APAC, was 'Building Leadership: Embracing Cultural Values and Inclusion.' APAC is an employee resource group at KSC. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
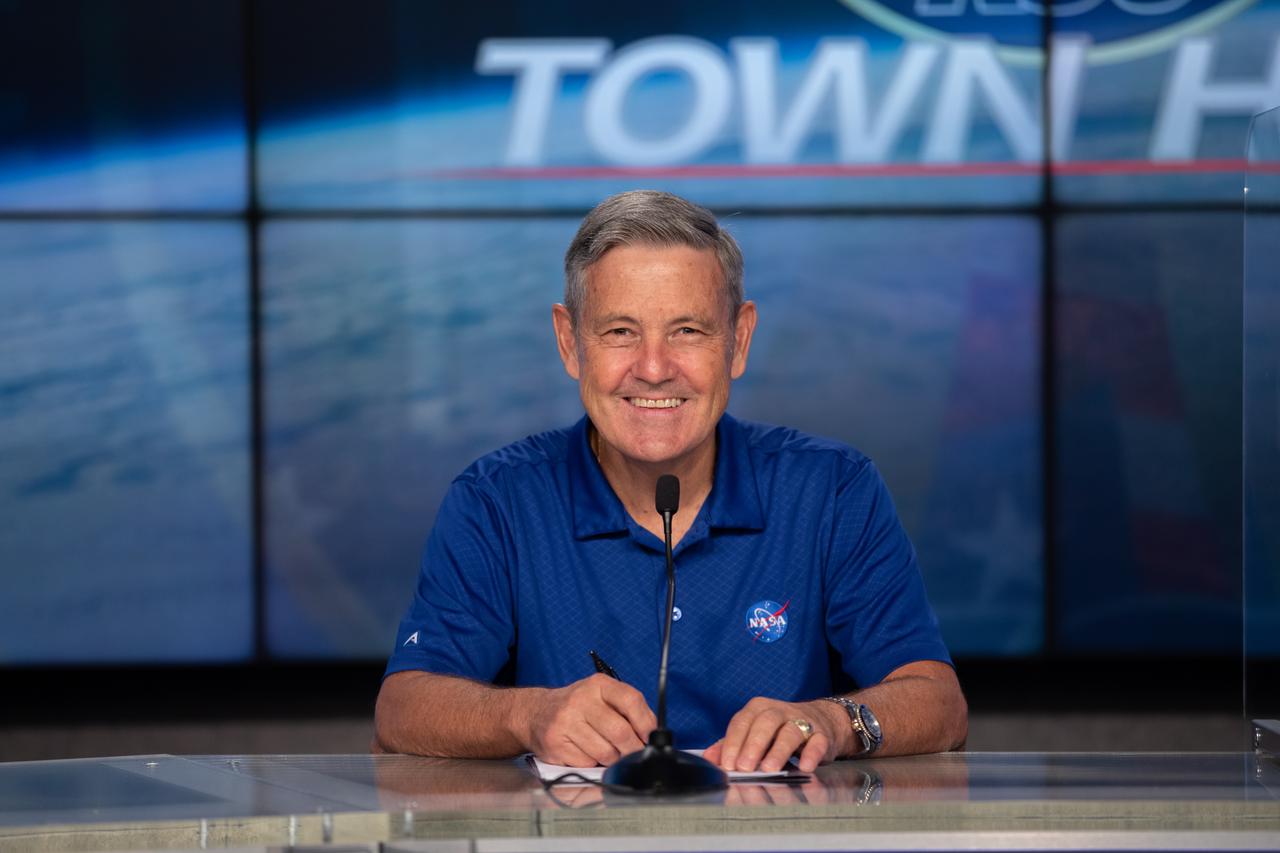

NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana participates in a virtual town hall meeting on Aug. 20, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium. During the town hall, Kennedy’s senior leaders answered questions submitted by the workforce and discussed a wide range of topics, including upcoming milestones, updates on the criteria for returning to onsite work, and diversity and inclusion at the multi-user spaceport.

Guest speaker Sinead Burke, from Ireland, gave a presentation on “Breaking the Mould – A Lesson in Equity,” to Kennedy Space Center employees on Nov. 30, 2022, and to employees at other NASA centers via live stream on YouTube. The event was sponsored by the center’s Disability Awareness and Action Working Group (DAAWG) and the Spaceport Integration Directorate. Burke, who is an advocate for the inclusion of all, amplifies the voices who are often not considered.
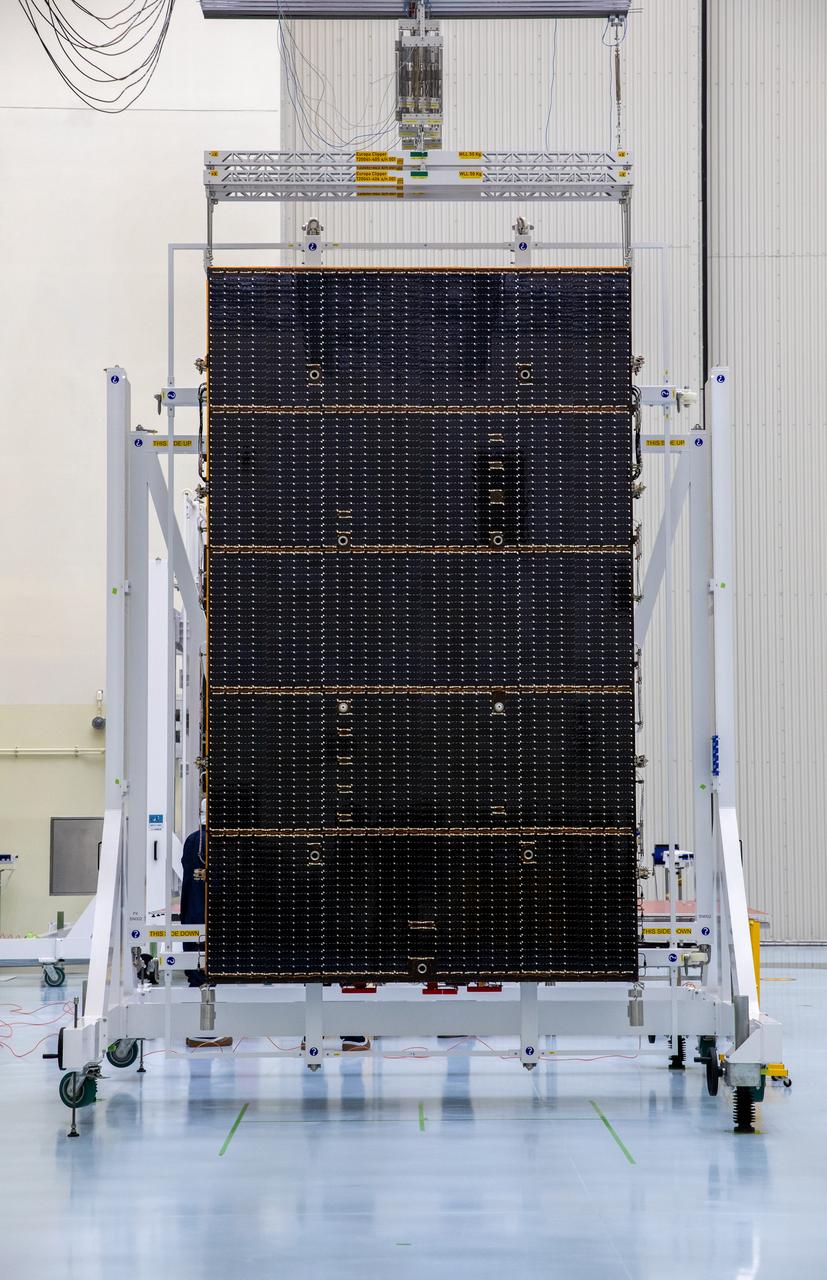

The first of two five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper stands inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
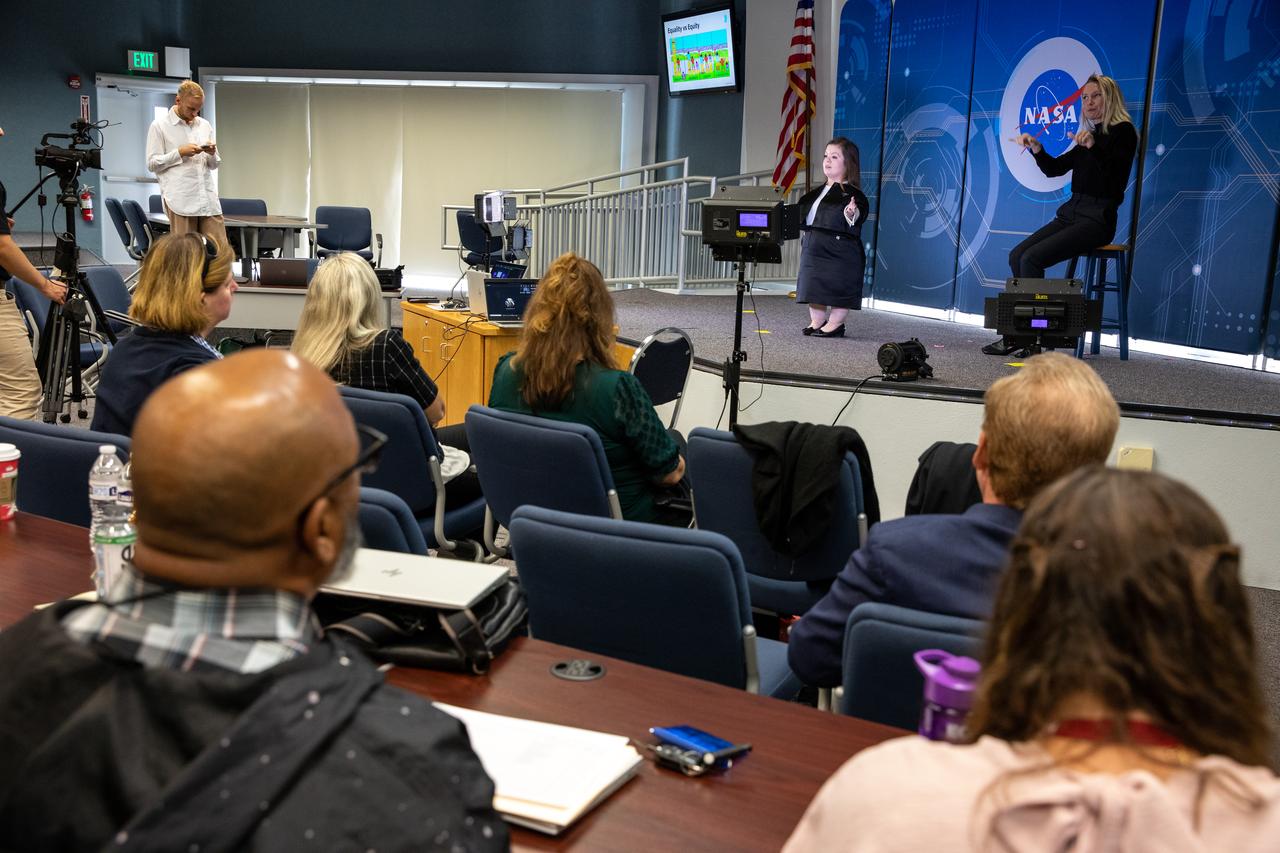

Guest speaker Sinead Burke, from Ireland, gave a presentation on “Breaking the Mould – A Lesson in Equity,” to Kennedy Space Center employees on Nov. 30, 2022, and to employees at other NASA centers via live stream on YouTube. The event was sponsored by the center’s Disability Awareness and Action Working Group (DAAWG) and the Spaceport Integration Directorate. Burke, who is an advocate for the inclusion of all, amplifies the voices who are often not considered.
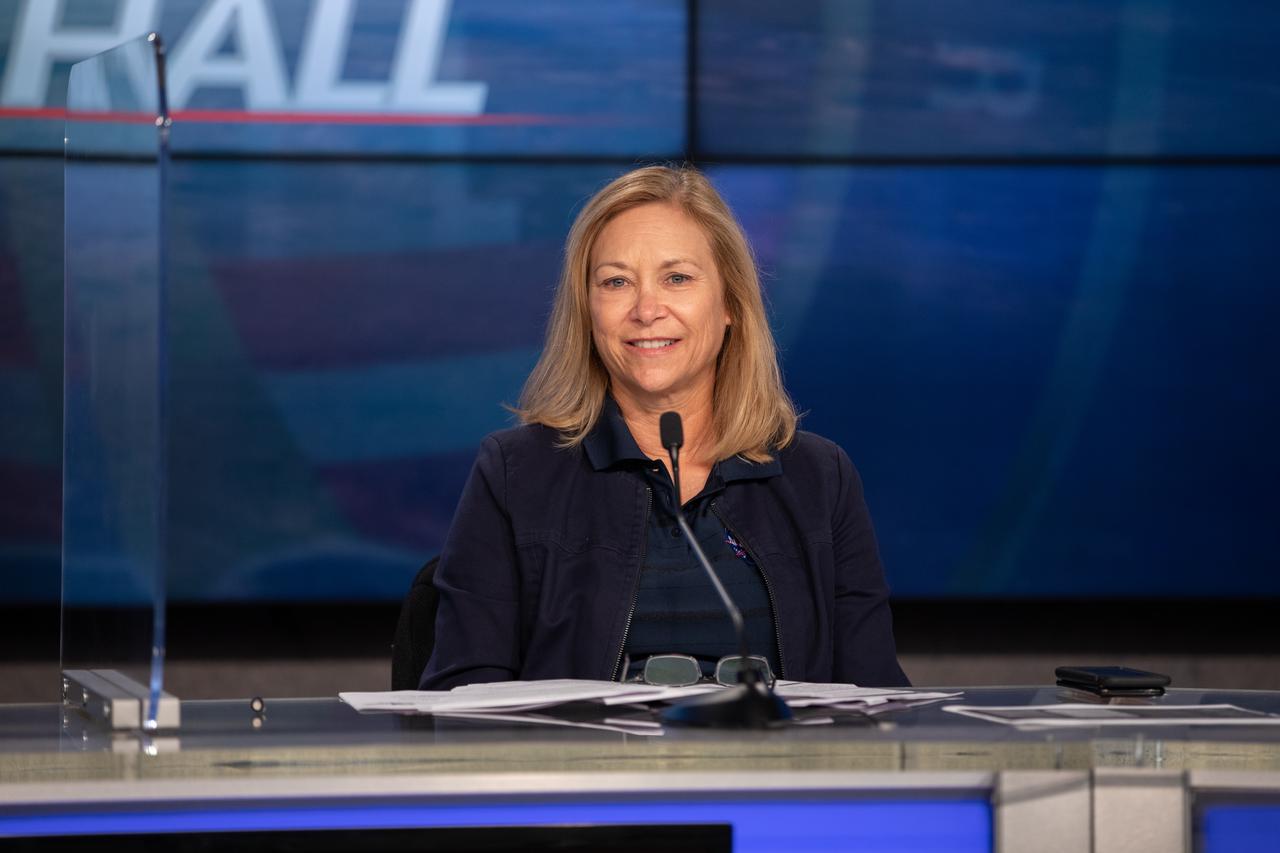

NASA Kennedy Space Center Deputy Director Janet Petro participates in a virtual town hall meeting on Aug. 20, 2020, inside the Florida spaceport’s Press Site auditorium. During the town hall, Kennedy’s senior leaders answered questions submitted by the workforce and discussed a wide range of topics, including upcoming milestones, updates on the criteria for returning to onsite work, and diversity and inclusion at the multi-user spaceport.
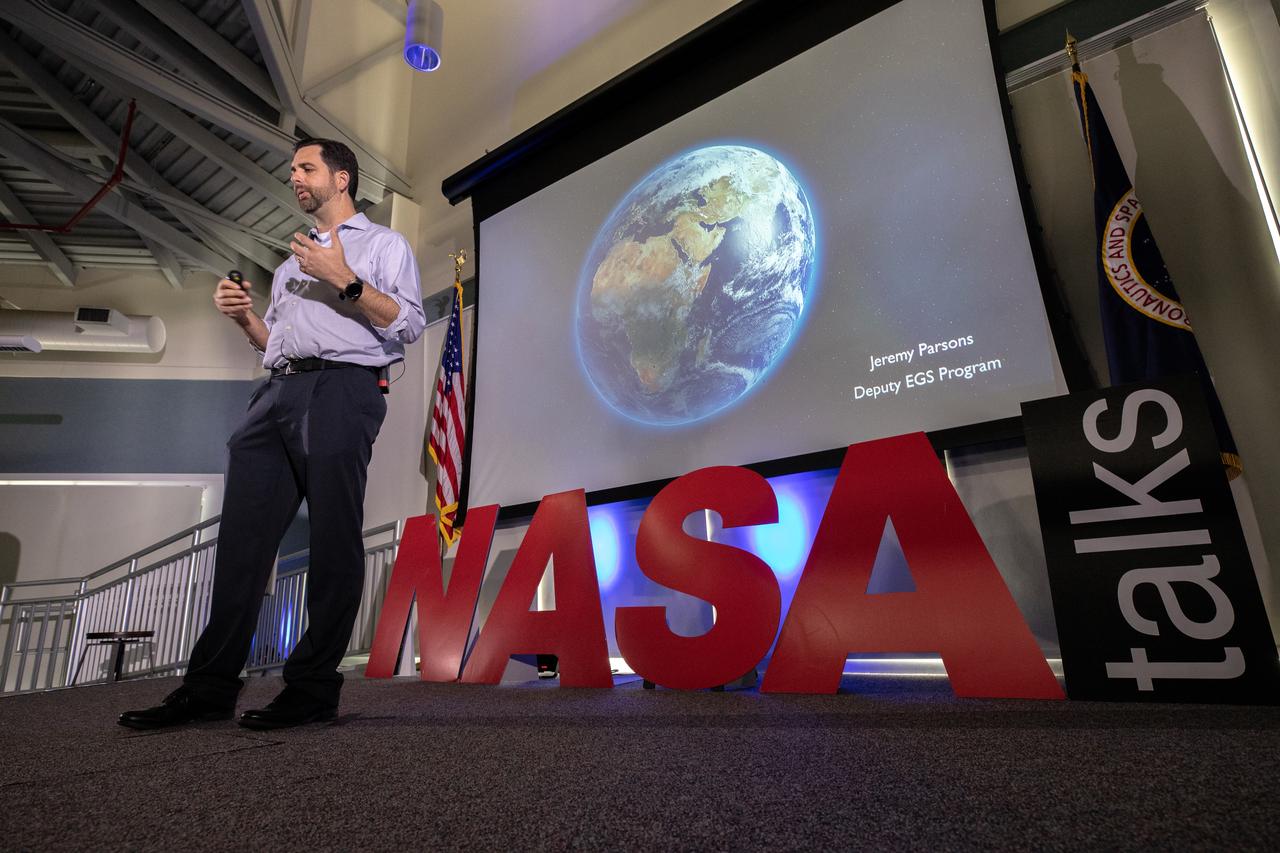

Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Tony Derbyshire, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
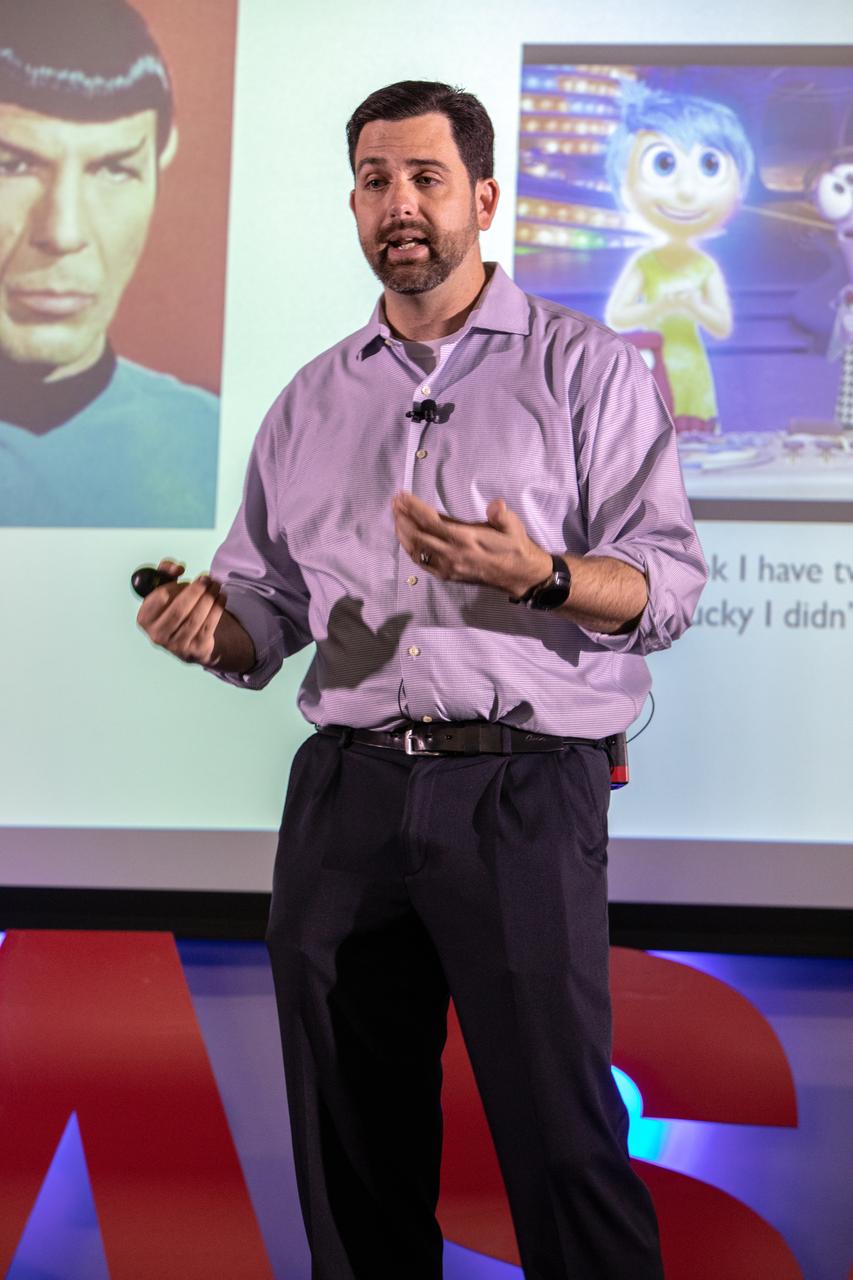

Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Tony Derbyshire, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
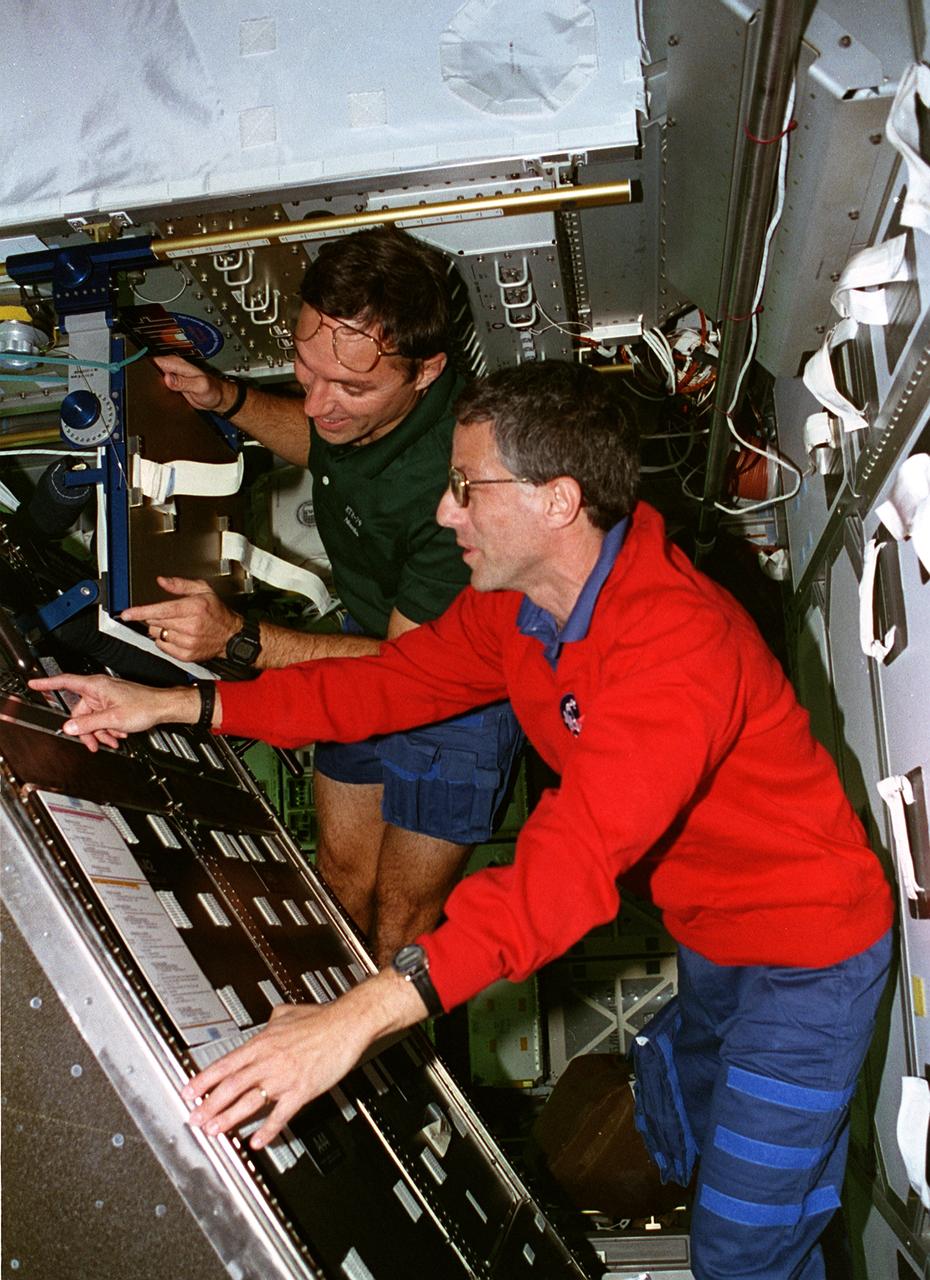

STS079-302-006 (16-26 Sept. 1996) --- Astronauts Jerome (Jay) Apt (right) and Carl E. Walz, both mission specialists, tilt the Active Rack Isolation System (ARIS) hardware which was included on this flight to evaluate conditions and hardware requirements for the International Space Station (ISS). The ARIS is designed to isolate certain experiments from major disturbances that are expected to be found on the ISS, such as vibrations caused by the movement of mechanisms and crew members and the operation of equipment. STS-79 was chosen for the inclusion of the experiment because the Shuttle-Mir complex more closely approximates the acceleration environment of the ISS.

Kennedy Space Center’s Tony Derbyshire speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 31, 2019, during the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Scott Colloredo, deputy director of Engineering at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen, Tony Derbyshire and Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
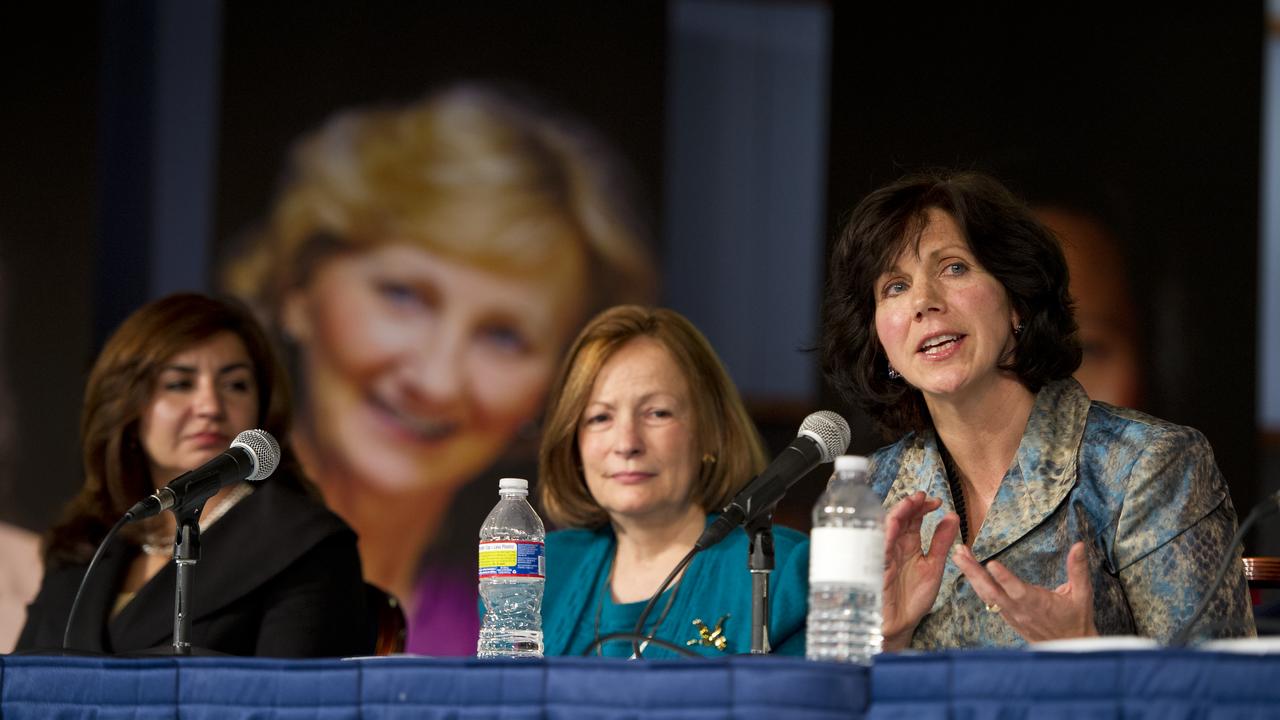

Catherine Didion, far right, Senior Fellow, National Academy of Engineering, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. Didion is joined by Marcia Smith, President, Space Policy Online.com, and Veronica Villalobos, Director, Office of Diversity and Inclusion, Office of Personnel Management, far left. The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
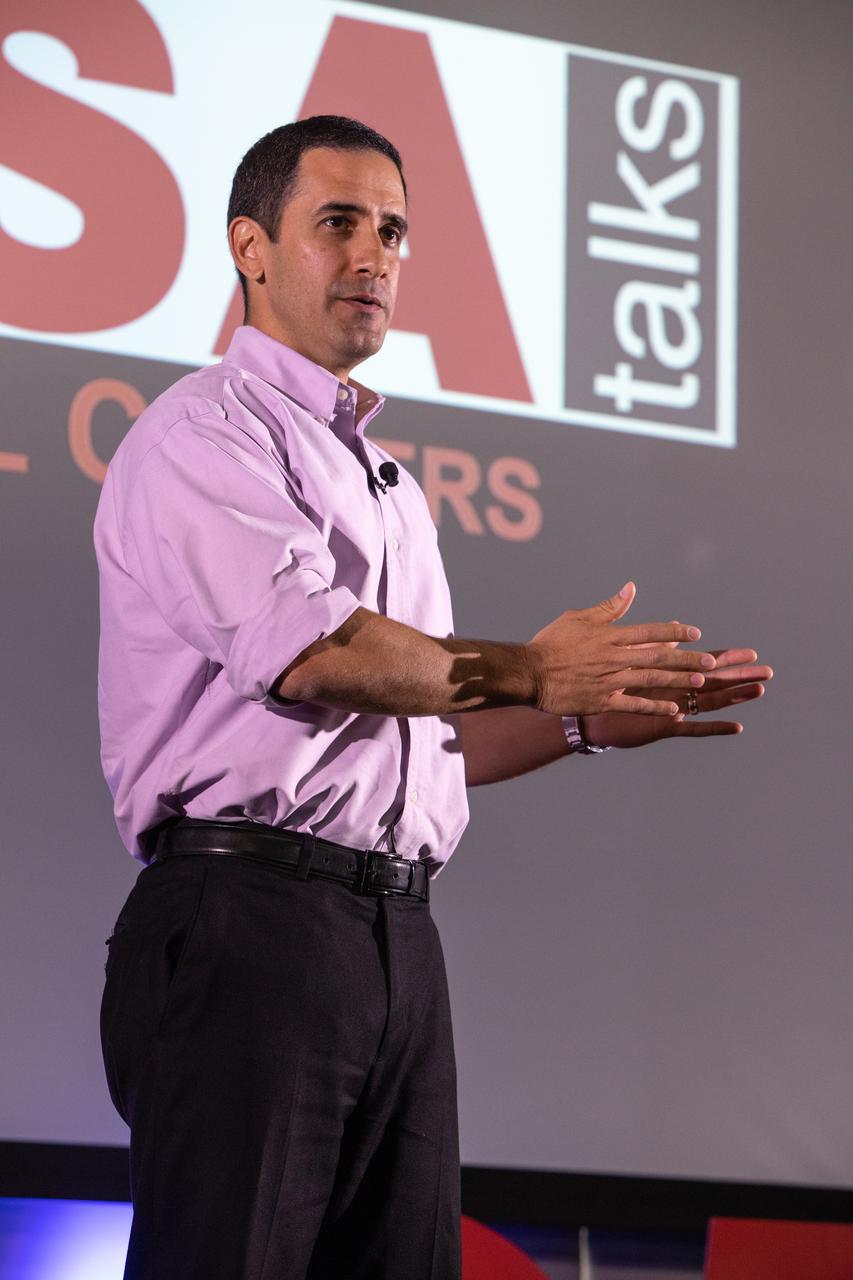

Kennedy Space Center’s Tony Derbyshire speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
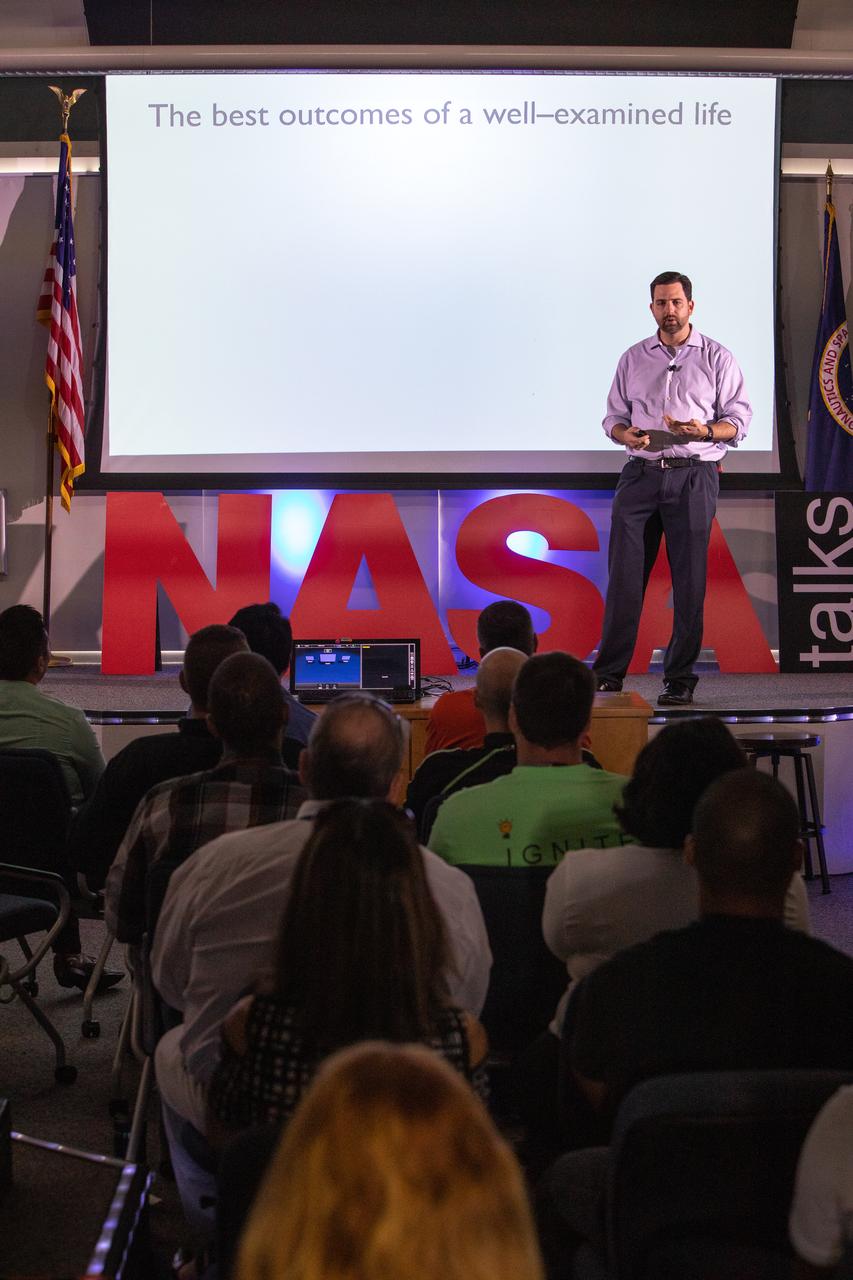

Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to Kennedy employees on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Kennedy Learning Institute during the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Tony Derbyshire, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
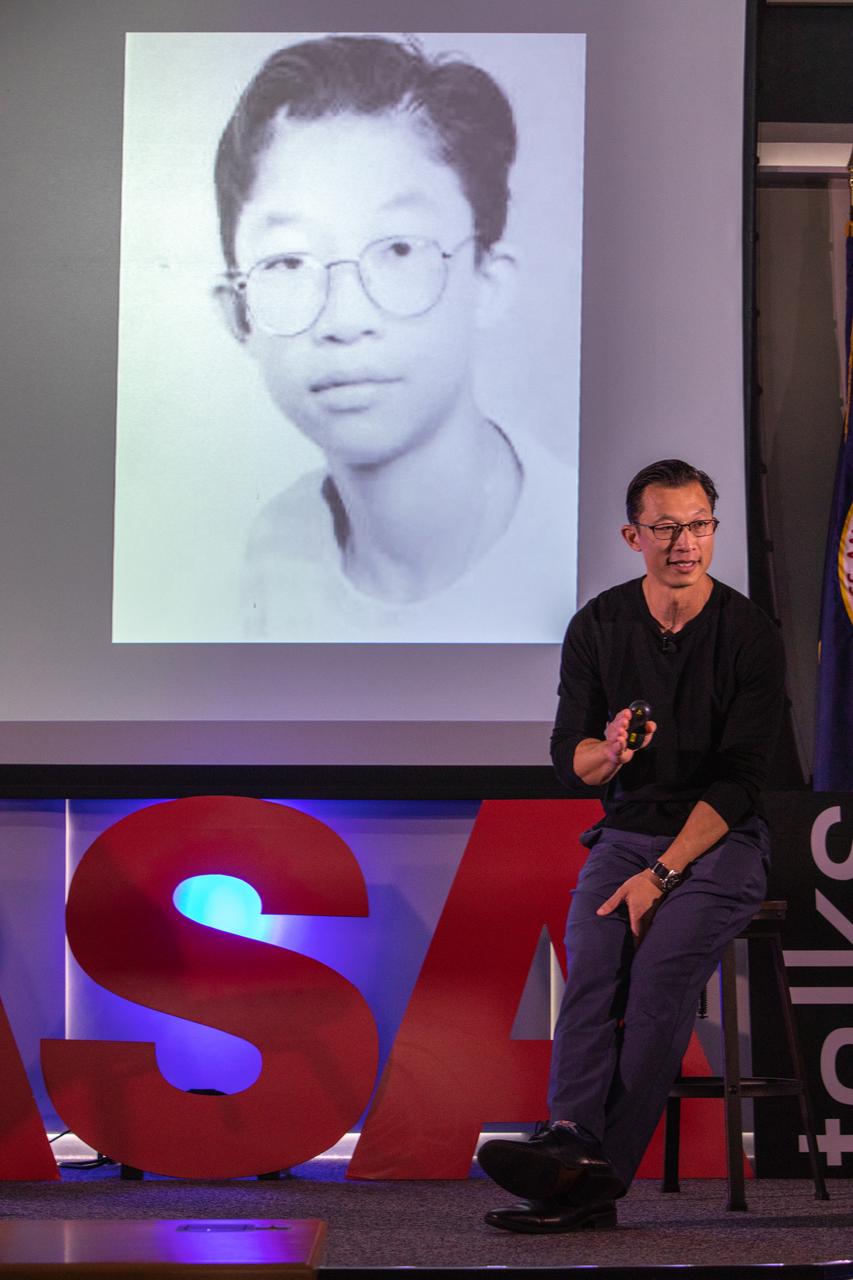

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Lori Garver (far right) NASA Deputy Administrator, participates in a panel discussion at the Women, Innovation and Aerospace event celebrating Women's History Month at the George Washington University Jack Morton Auditorium, Thursday, March 8, 2012 in Washington. Garver is seen with Kathy Sullivan, NOAA Deputy Administrator; Catherine Didion, Senior Fellow, National Academy of Engineering; Marcia Smith, President, spacepolicyonline.com and Veronica Villalobos, Director, Office of Diversity and Inclusion, Office of Personnel Management (far left). The WIA day-long event will help to foster a discussion for students and early career professionals about how to continue to encourage women to enter and succeed in the field of aerospace. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
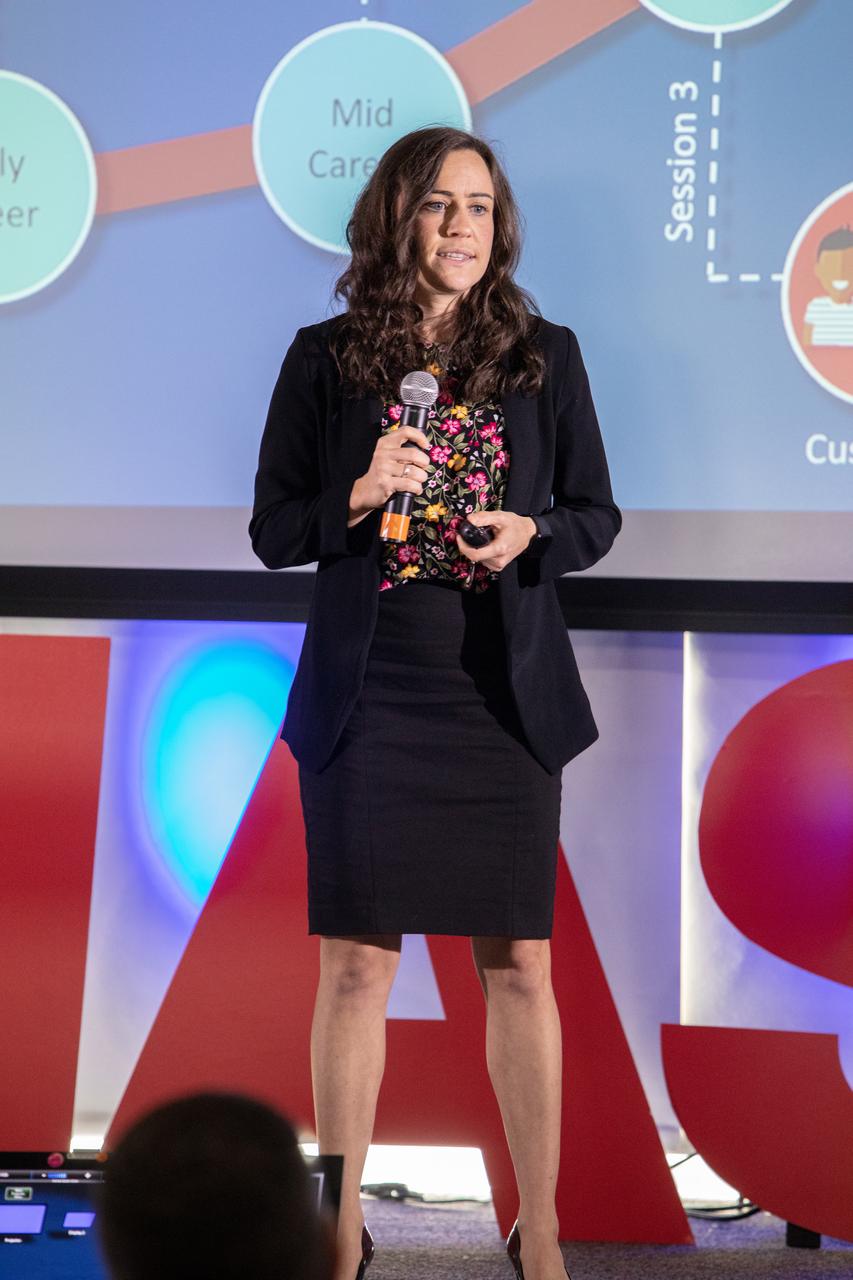

Kennedy Space Center’s Jennifer Lane participates the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen, Tony Derbyshire and Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
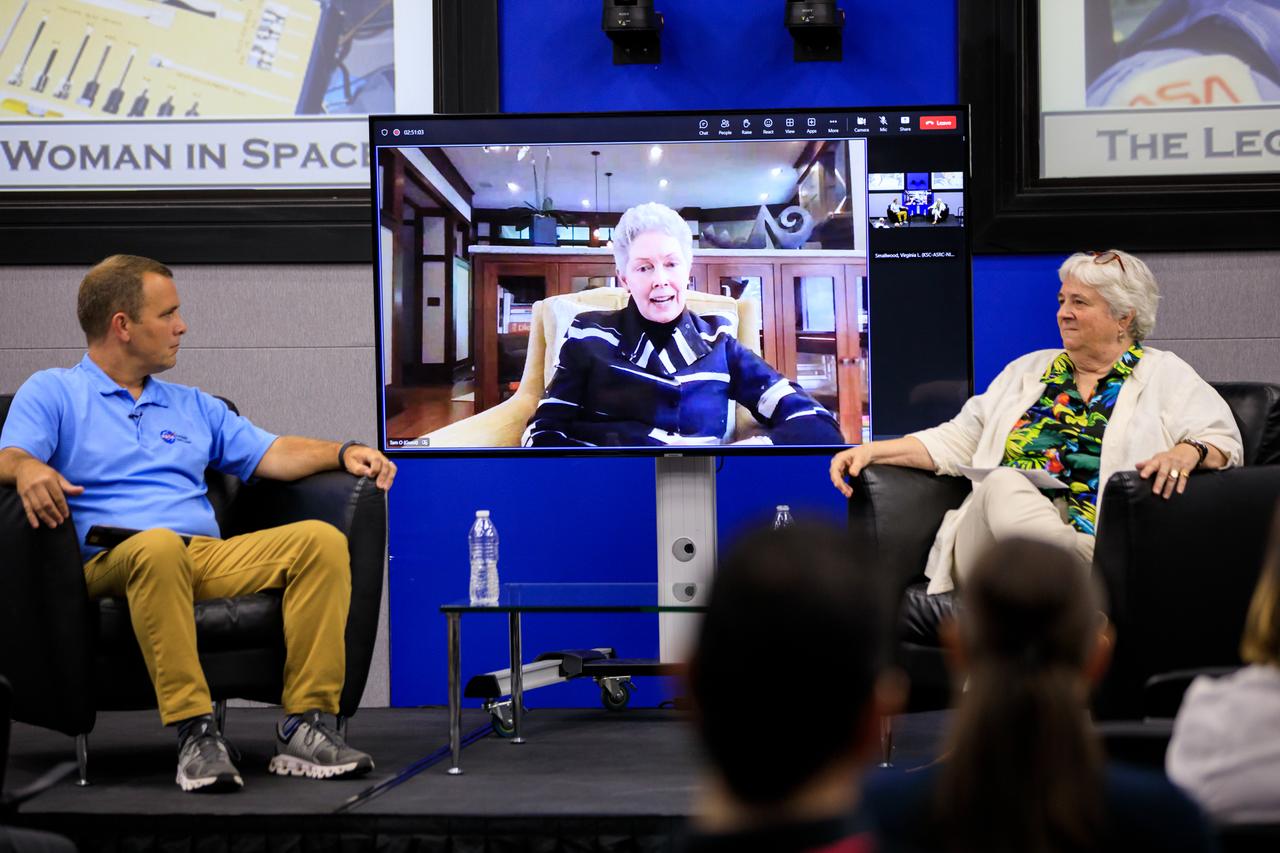

Tam O’Shaughnessy, center (on the monitor), speaks during “The Legacy of Sally Ride: The First American Woman in Space” event at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 15, 2023. O’Shaughnessy was Ride’s lifetime partner for 27 years, until the pioneering astronaut died in 2012 at age 61 from pancreatic cancer. NASA Chief Historian Brian Odom, left, and Bear Ride, Sally Ride’s sister, also participated in the event. Forty years ago, Ride made her trailblazing flight into space. She also was a physicist and a steadfast advocate for inclusion in STEM (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) – especially for girls and young women.
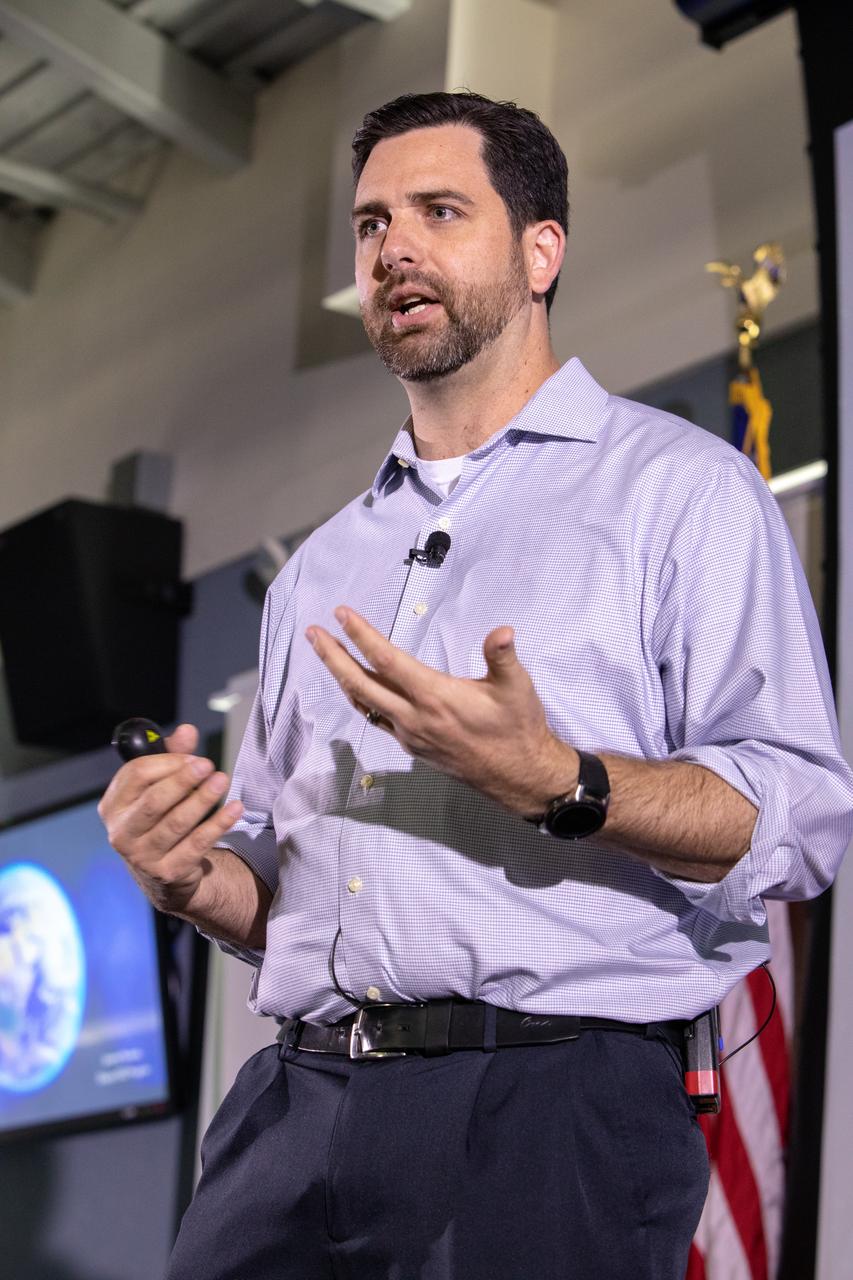

Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks at the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions on Oct. 31, 2019, in the Kennedy Learning Institute. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Tony Derbyshire, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.

Kennedy Space Center’s Jennifer Lane addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 31, 2019, during the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen, Tony Derbyshire and Jeremy Parsons, deputy manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
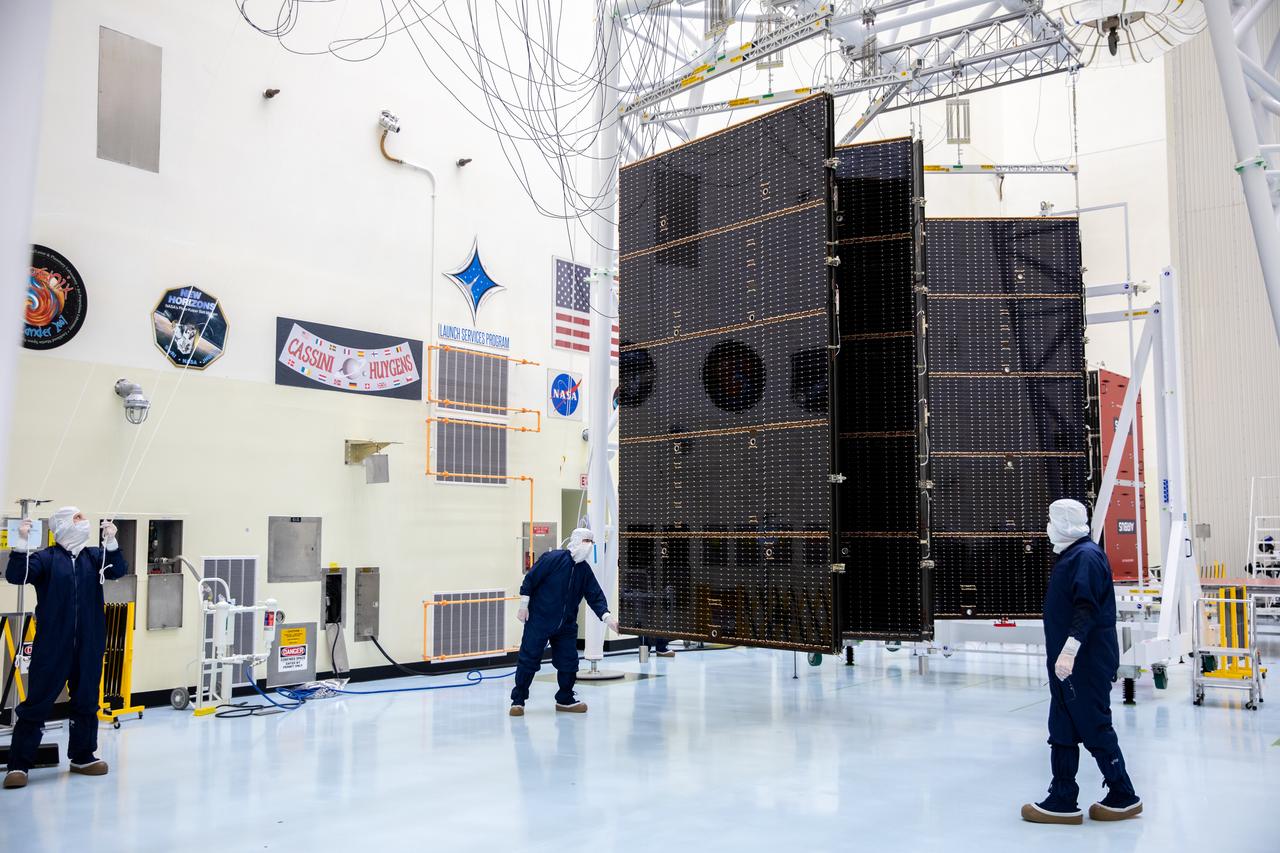

Technicians working inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida unfolded and fully extended the first of two five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper in preparation for inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
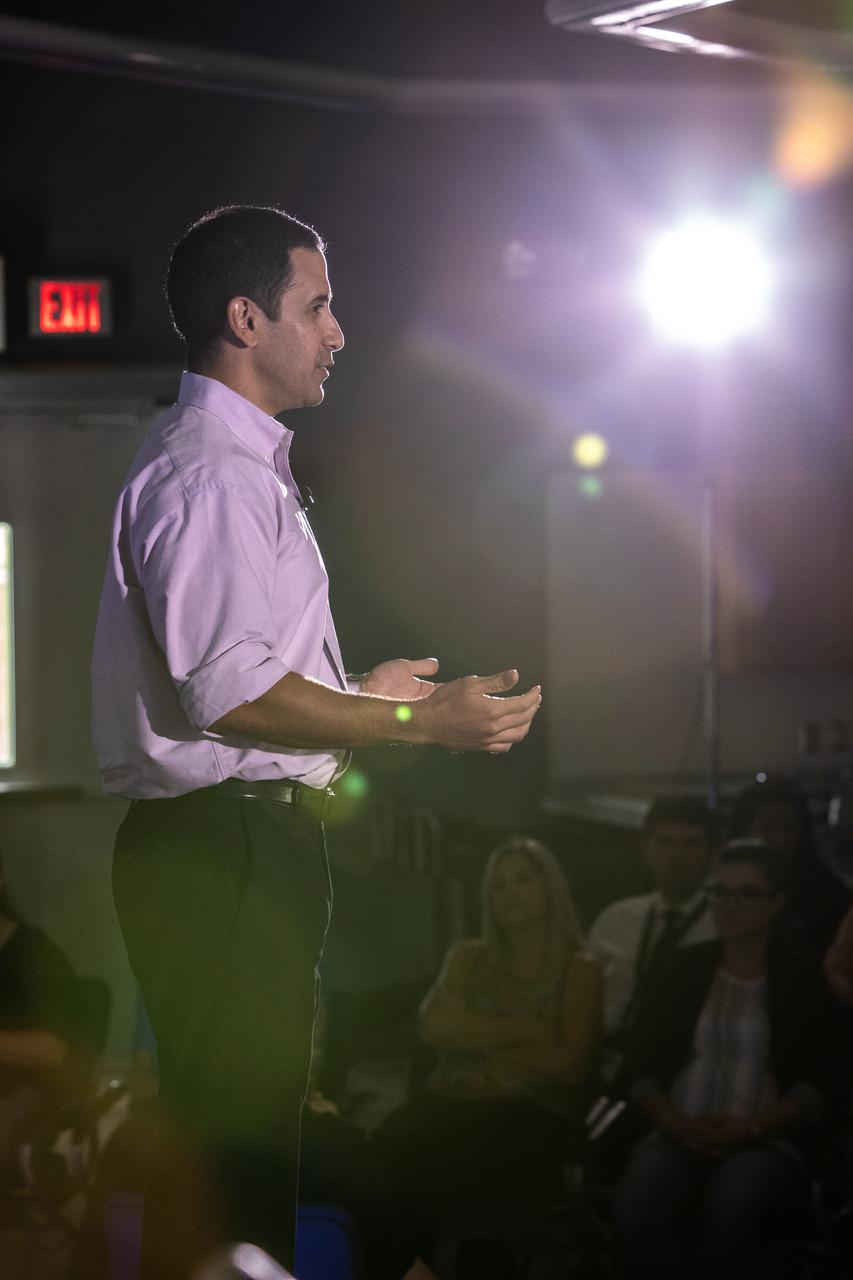

Kennedy Space Center’s Tony Derbyshire addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 31, 2019, during the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Johnny Nguyen and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
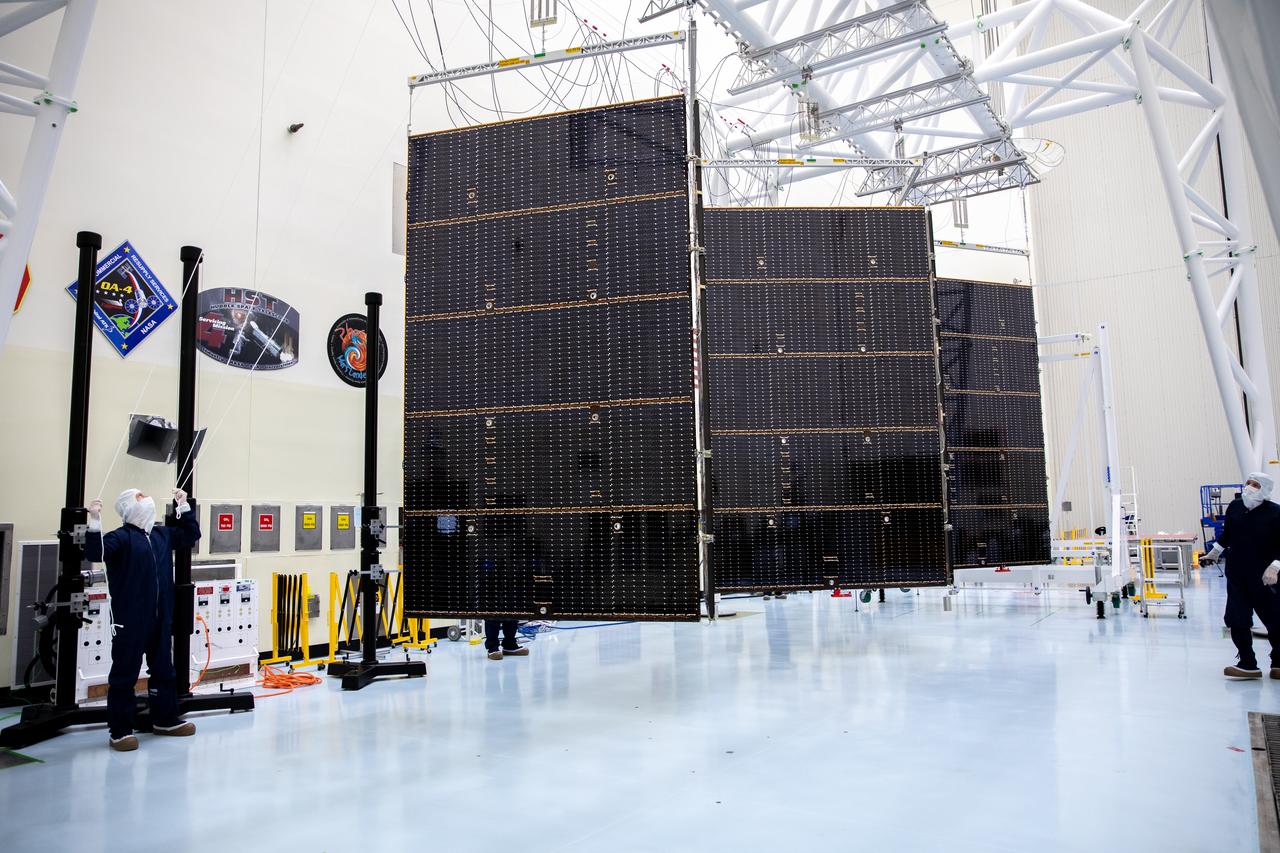

Technicians working inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida unfolded and fully extended the first of two five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper in preparation for inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
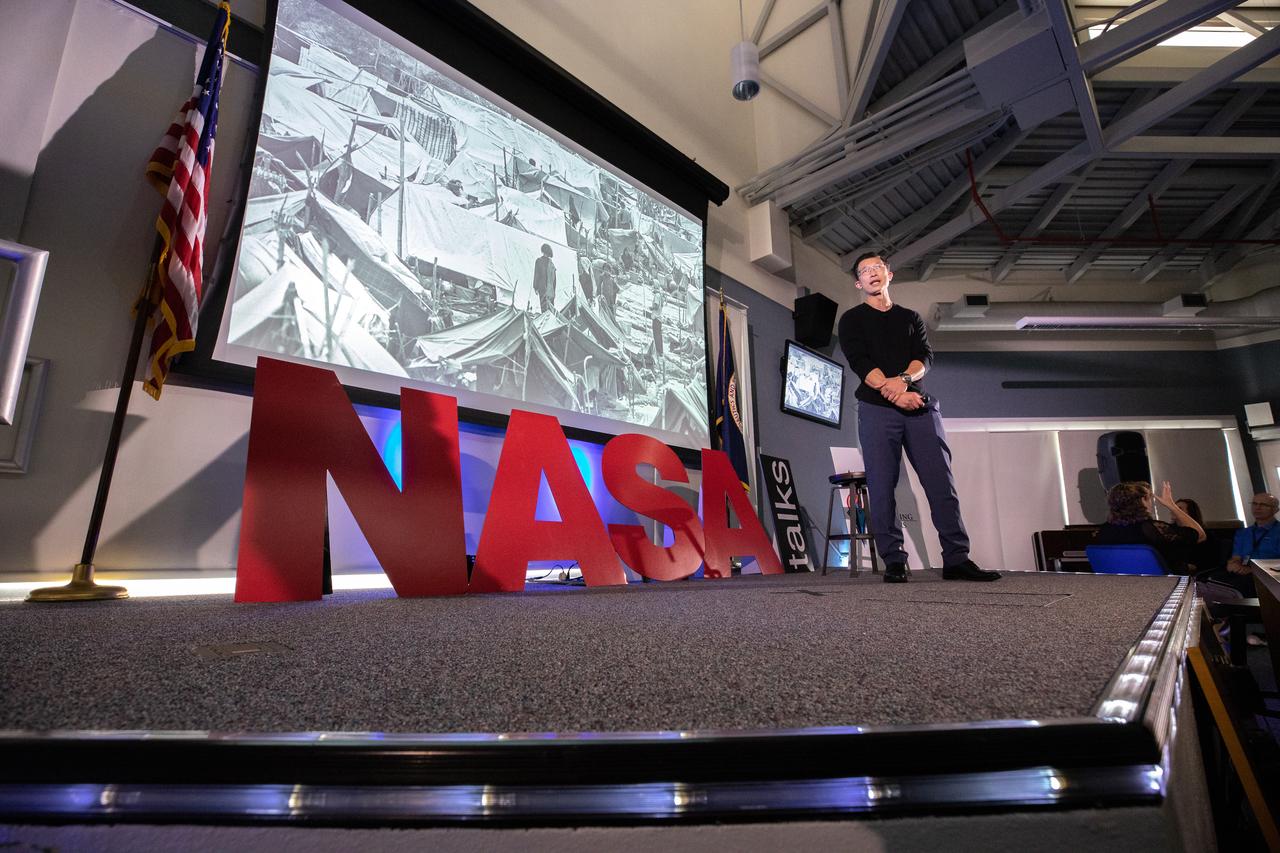

Kennedy Space Center’s Johnny Nguyen addresses co-workers inside the Florida spaceport’s Kennedy Learning Institute on Oct. 31, 2019, during the fourth in a series of five TED Talk-style informational sessions. Sponsored by Kennedy’s Launching Leaders and Leadership for the Future, NASAtalks focuses on the topic of intentional careers and aims to provide employees with tools and knowledge that can be utilized for career growth. The theme of this fourth session was employees, and additional speakers included Kennedy’s Tony Derbyshire and Deputy Manager of NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Jeremy Parsons, with a skill-building section on vulnerability, authentic self and diverse inclusion by Ronnie Rodriguez.
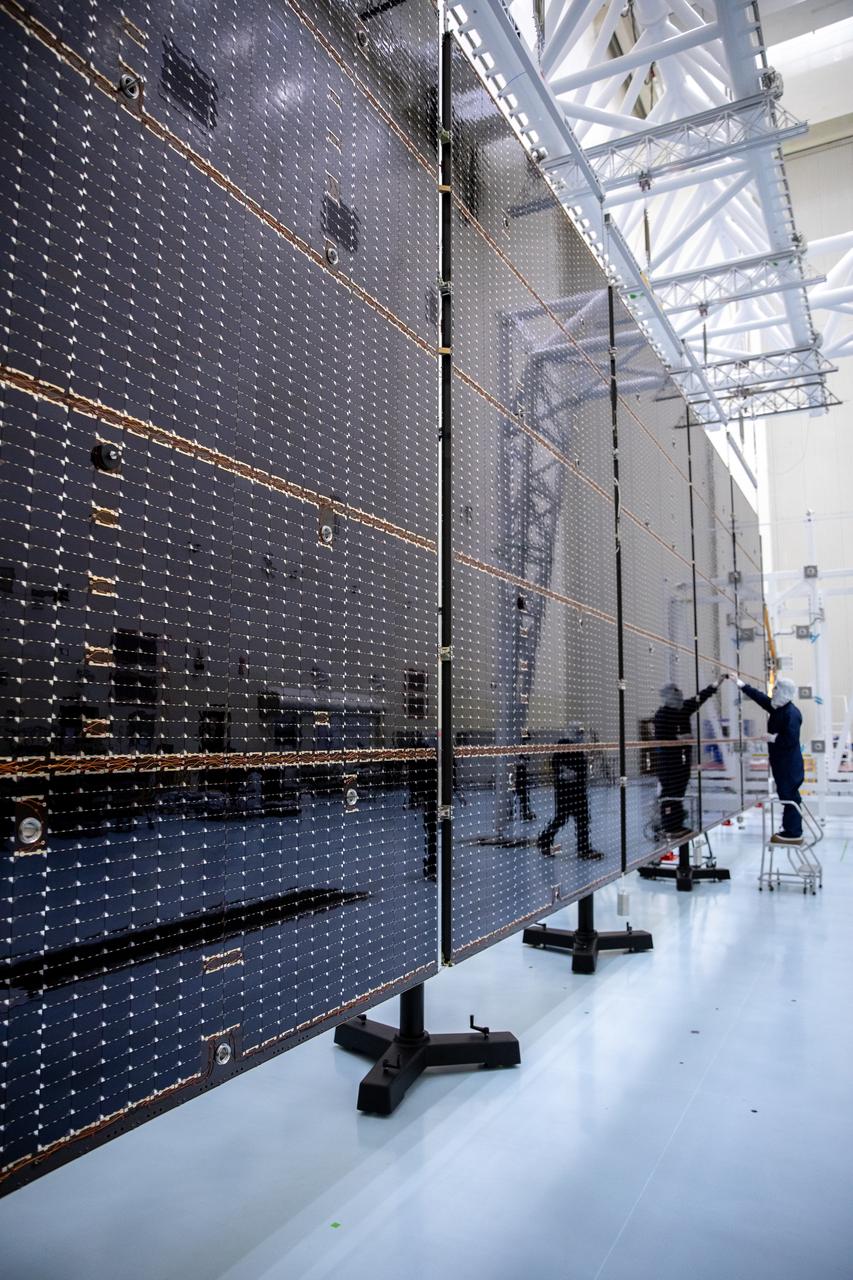

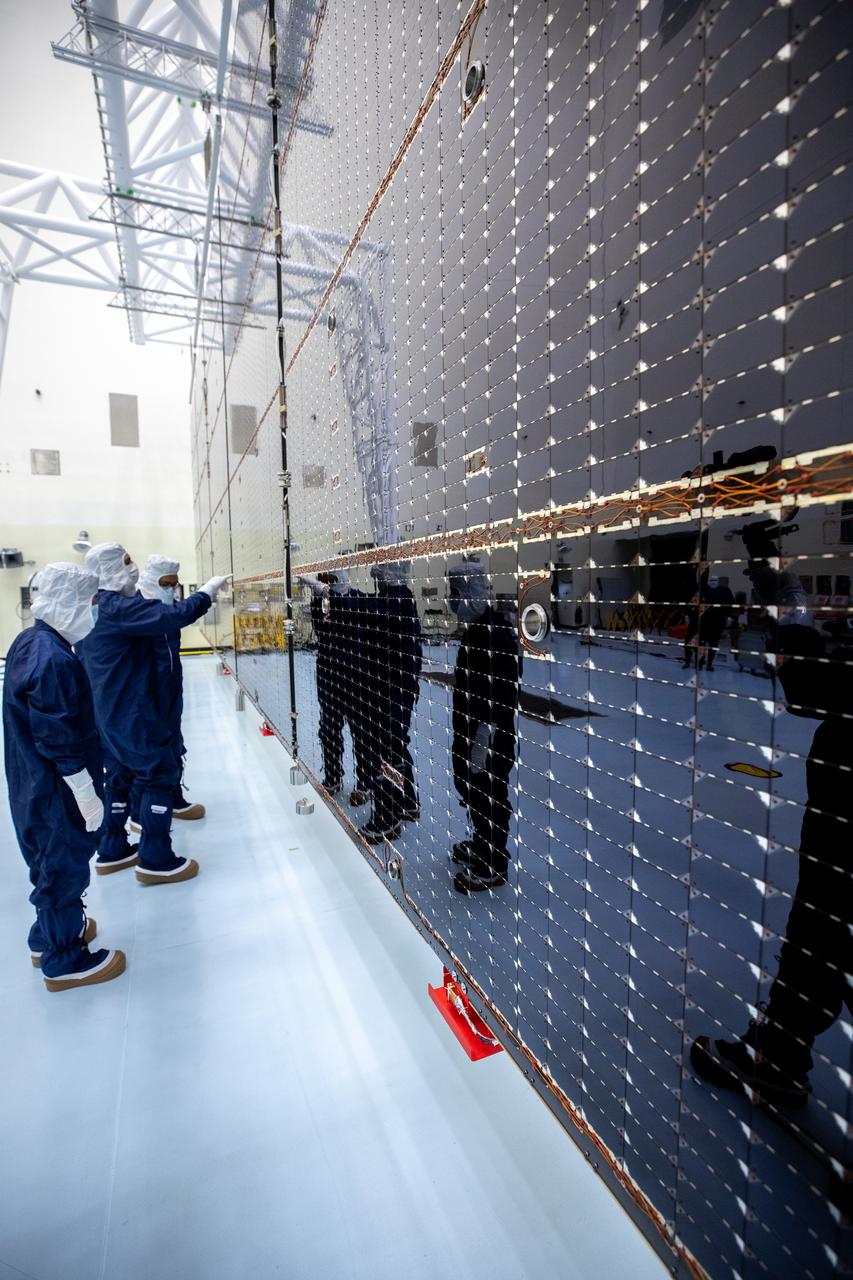
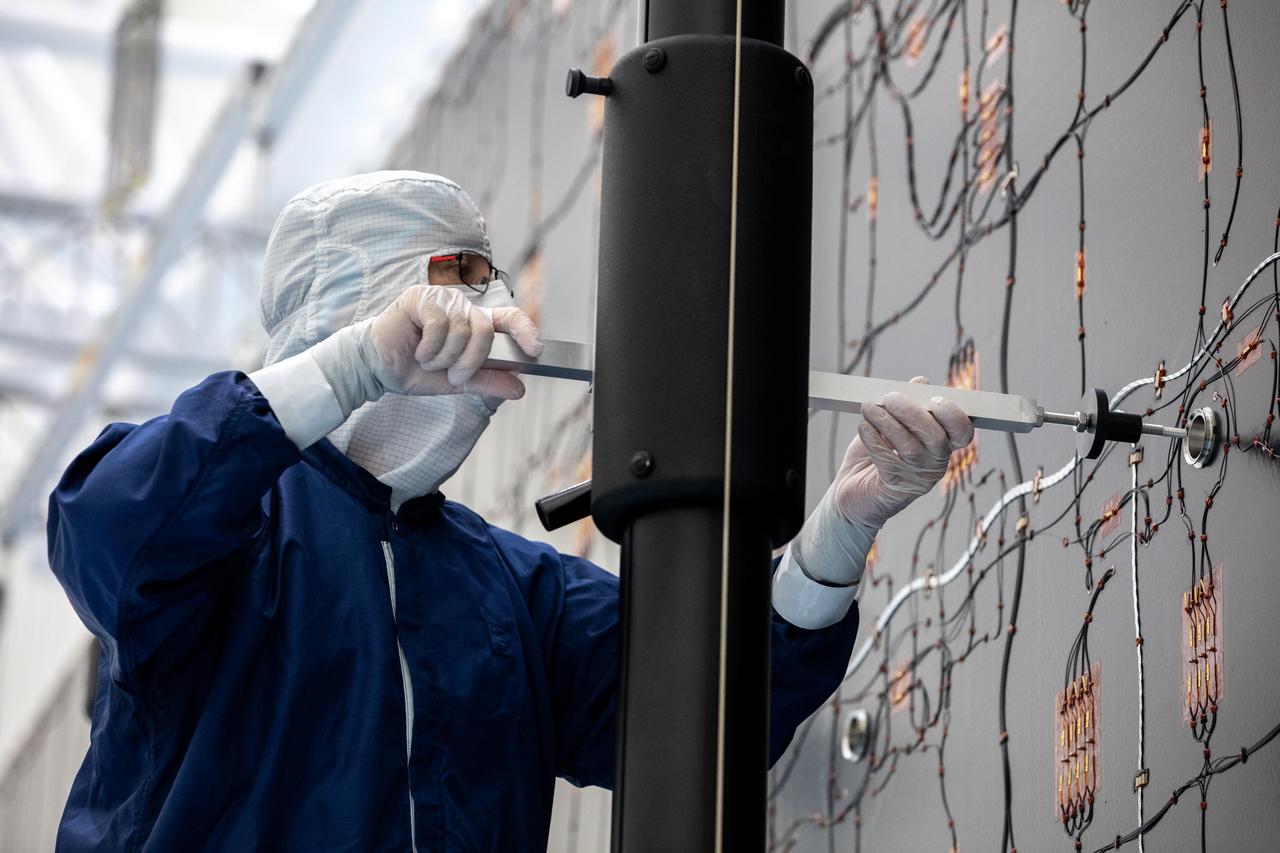
Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
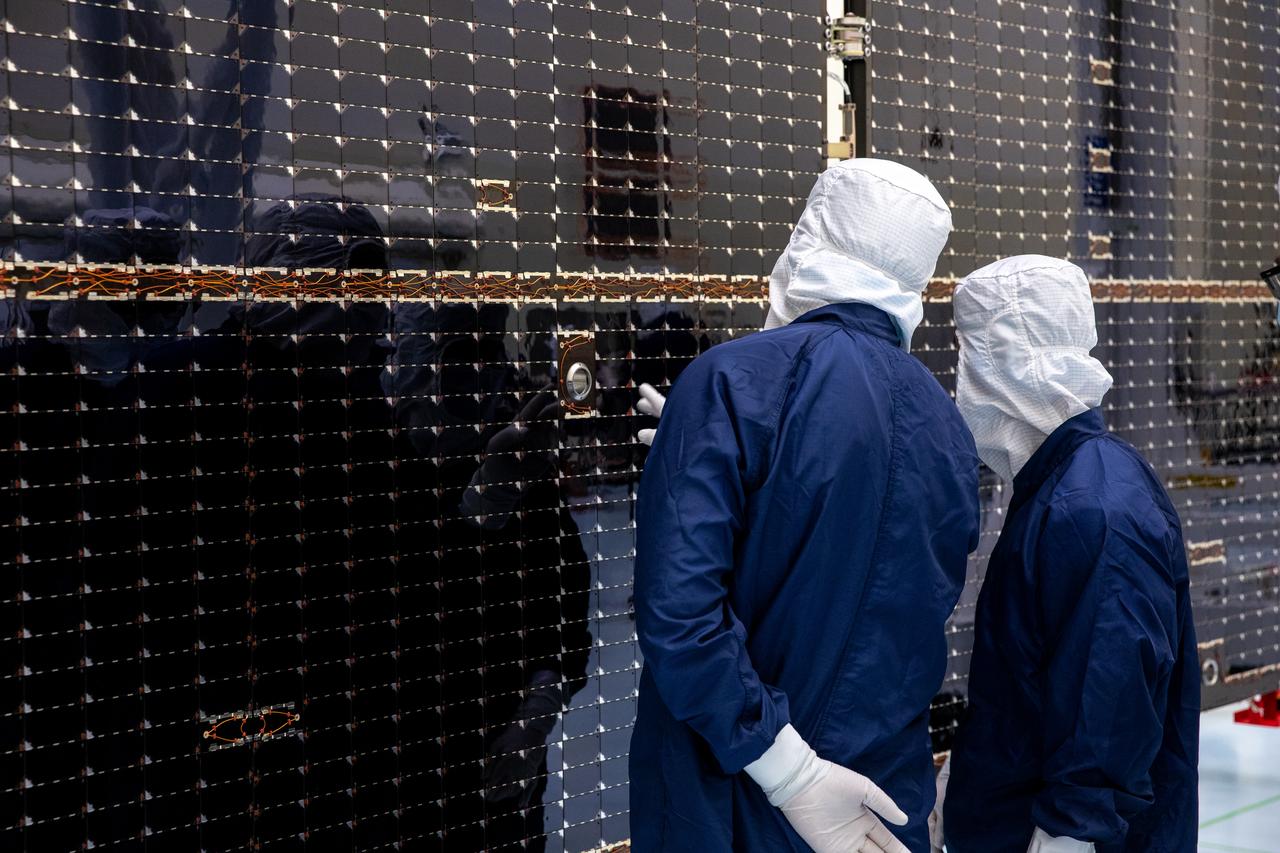

Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
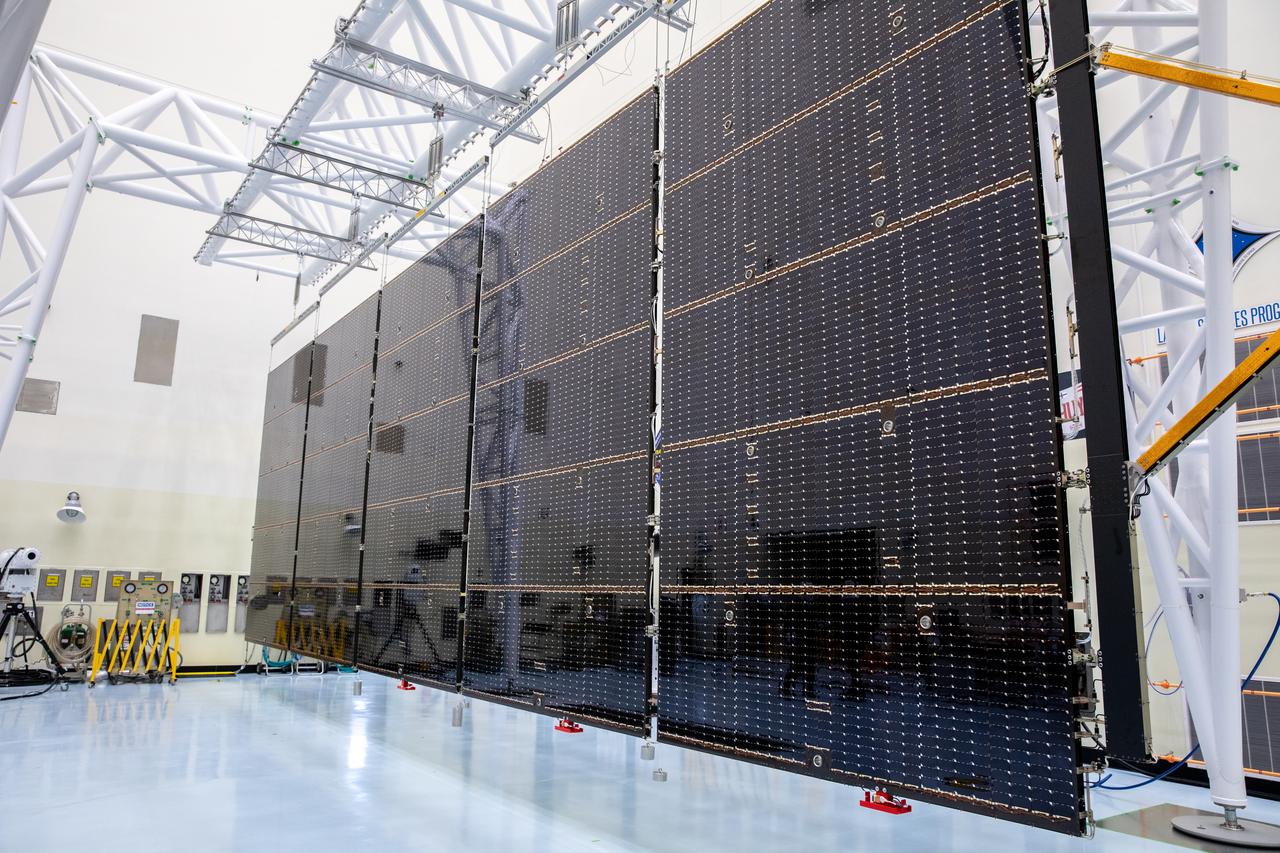

The first of two five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper is fully extended from a shipping configuration and suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture to begin inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.

Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.
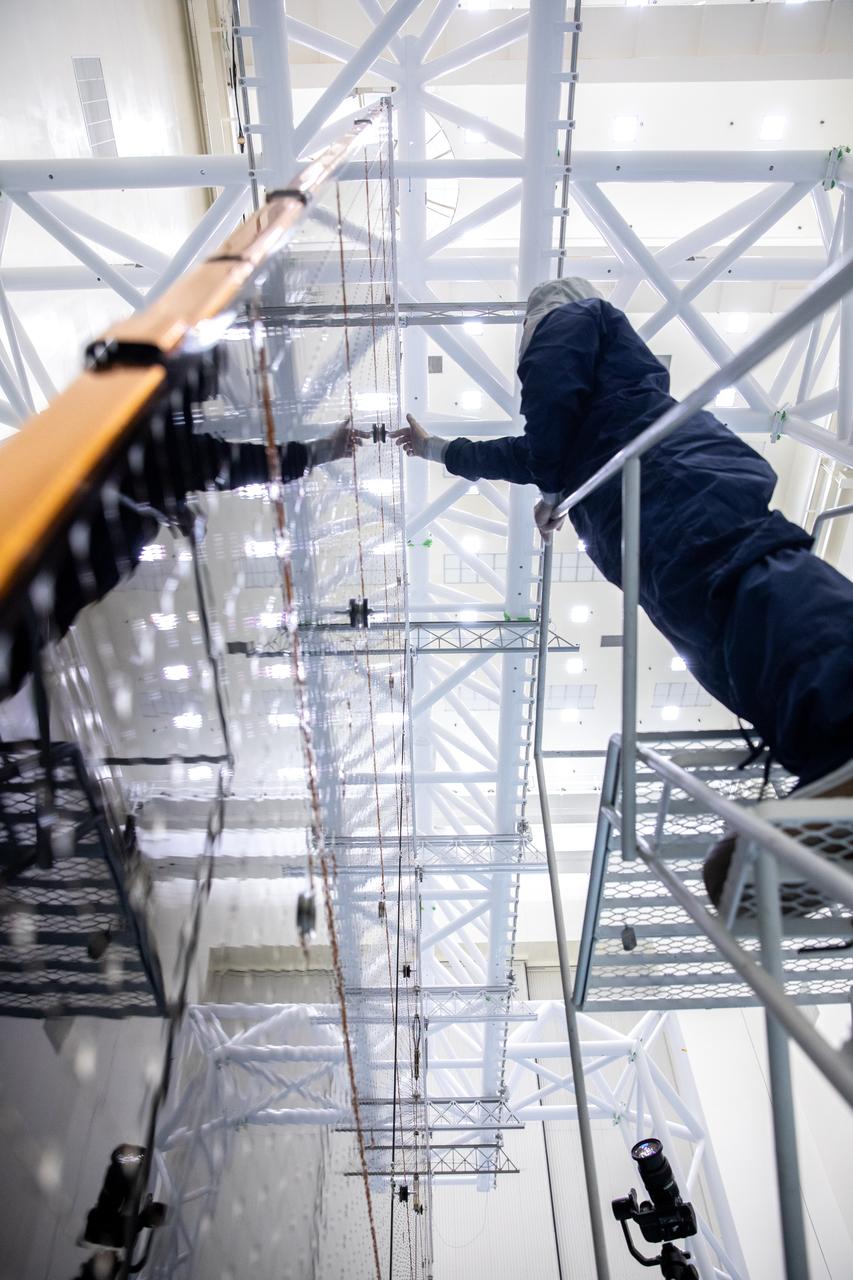

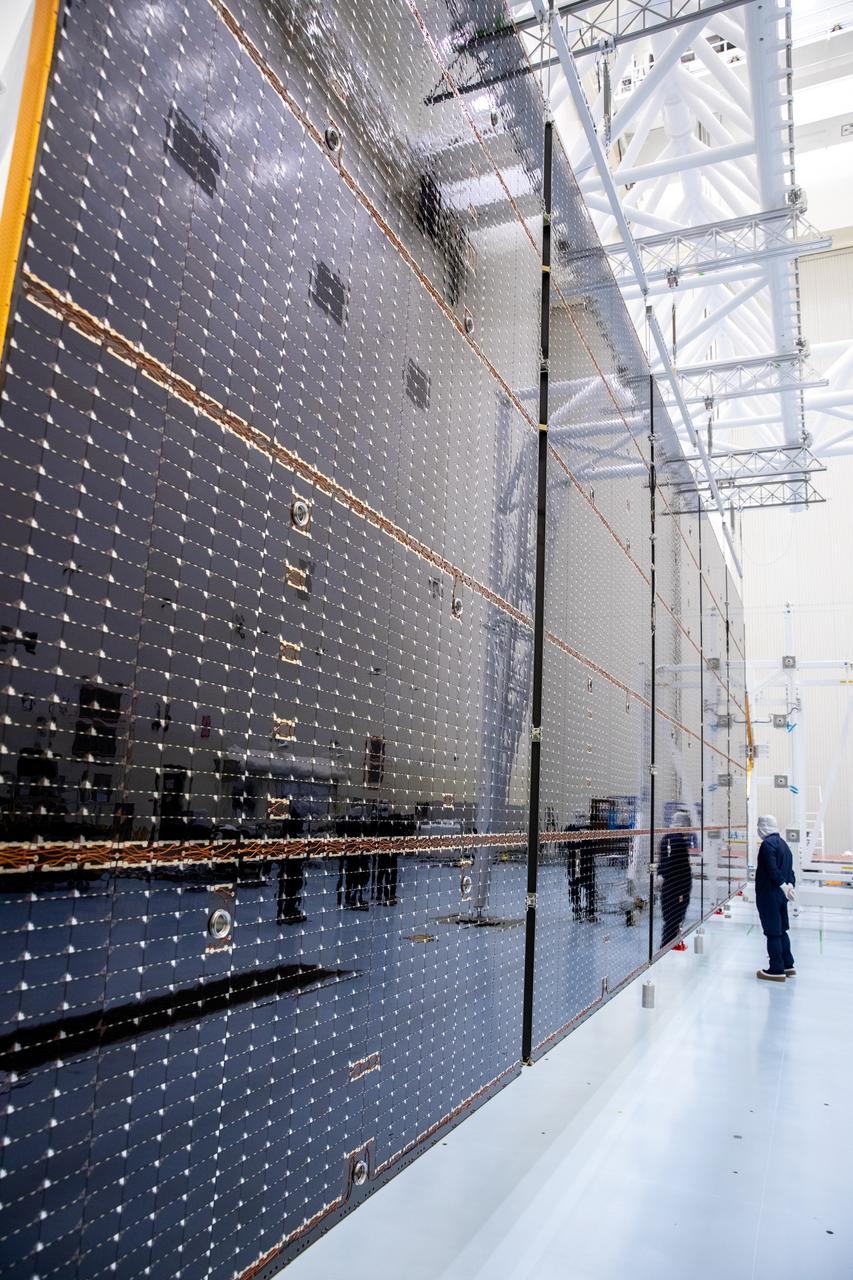
Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.

Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.

Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.

Technicians examine the first of two fully extended five-panel solar arrays built for NASA’s Europa Clipper suspended on a support system called a gravity offload fixture during inspection and cleaning as part of assembly, test, and launch operations inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, March 6, 2024. Another name for the gravity offload fixture is the Transportable Large Envelope Deployment Facility (T-LEDF). When both solar arrays are installed and deployed on Europa Clipper – the agency’s largest spacecraft ever developed for a planetary mission – the spacecraft will span a total length of more than 100 feet and weigh 7,145 pounds without the inclusion of propellants.

This perspective view shows the Strait of Gibraltar, which is the entrance to the Mediterranean Sea from the Atlantic Ocean. Europe (Spain) is on the left. Africa (Morocco) is on the right. The Rock of Gibraltar, administered by Great Britain, is the peninsula in the back left. The Strait of Gibraltar is the only natural gap in the topographic barriers that separate the Mediterranean Sea from the world's oceans. The Sea is about 3700 kilometers (2300 miles) long and covers about 2.5 million square kilometers (one million square miles), while the Strait is only about 13 kilometers (8 miles) wide. Sediment samples from the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea that include evaporite minerals, soils, and fossil plants show that about five million years ago the Strait was topographically blocked and the Sea had evaporated into a deep basin far lower in elevation than the oceans. Consequent changes in the world's hydrologic cycle, including effects upon ocean salinity, likely led to more ice formation in polar regions and more reflection of sunlight back to space, resulting in a cooler global climate at that time. Today, topography plays a key role in our regional climate patterns. But through Earth history, topographic change, even perhaps over areas as small as 13 kilometers across, has also affected the global climate. This image was generated from a Landsat satellite image draped over an elevation model produced by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). The view is eastward with a 3-times vertical exaggeration to enhance topographic expression. Natural colors of the scene (green vegetation, blue water, brown soil, white beaches) are enhanced by image processing, inclusion of some infrared reflectance (as green) to highlight the vegetation pattern, and inclusion of shading of the elevation model to further highlight the topographic features. Landsat has been providing visible and infrared views of the Earth since 1972. SRTM elevation data matches the 30-meter (99-feet) resolution of most Landsat images and will substantially help in analyses of the large Landsat image archive. Elevation data used in this image was acquired by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on February 11, 2000. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA03397
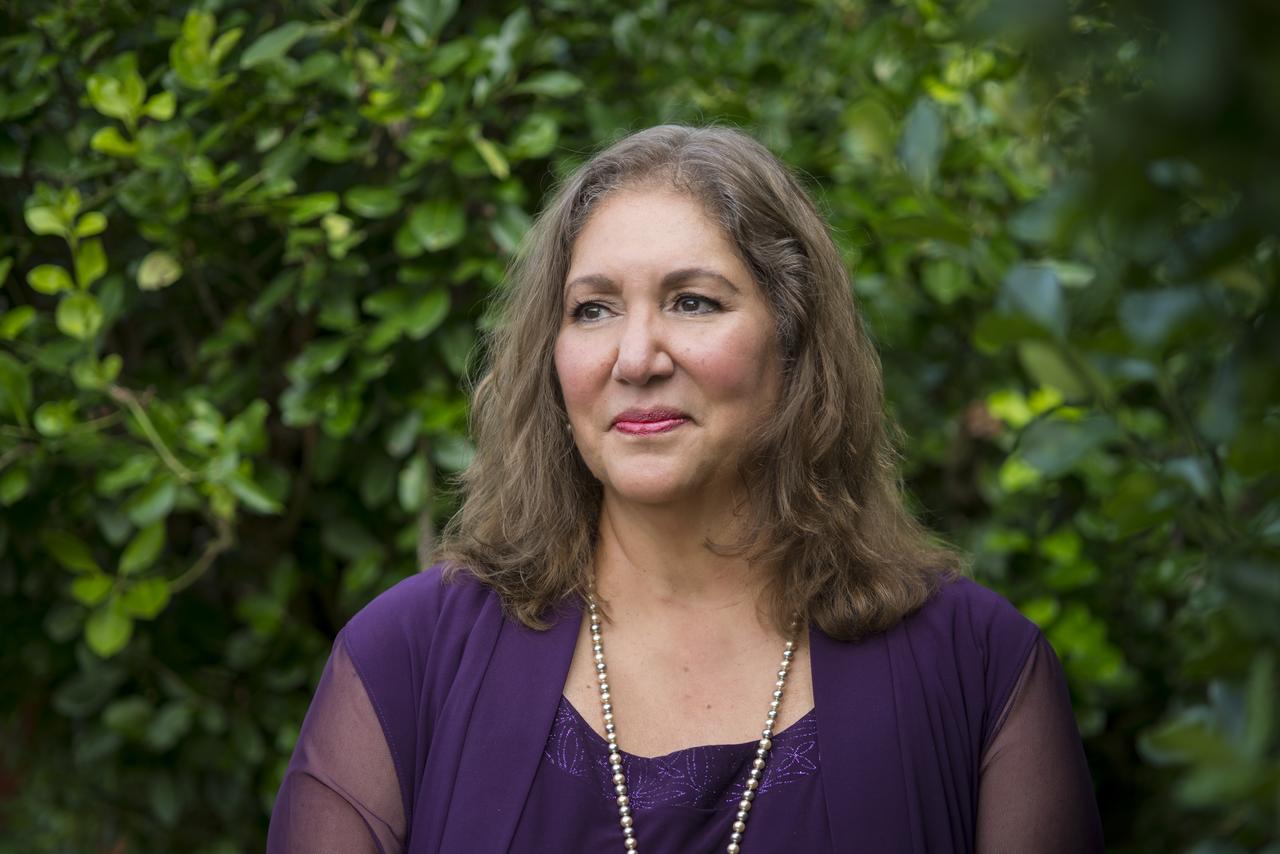

“I grew up in Venezuela and studied in the military high school Gran Mariscal de Ayacucho. They would frequently bring in speakers, usually professional that were doing important work. Here comes Dr. Humberto Fernandez-Moran, a Venezuelan scientist working at NASA He was speaking to us about teamwork and he told an anecdote about this janitor that was mopping the floors in one of the NASA installations, when someone asked the man what he was doing. The janitor turned around and said “I’m sending people to the Moon.” In that moment I thought, “Wow, NASA is a really inclusive place to work because they value all the contributions of the people that work for them.” When I immigrated to the United States, I didn’t start my career at NASA. I worked in various positions in the private and public sector. When I saw this position open and applied, I was reminded of that story. Later on, I worked for NASA as part of the new employee orientation team for a little over a year I would share that story with the new hires to let them know that NASA was extremely inclusive and that their work would matter. Regardless of the scope of their contribution you were part of a team working toward the same goal. When someone asks me about my job? I respond with immense pride I am part of the Office of the General Counsel – International Law Practice Group and I send astronauts into space." NASA Legal Administrative Specialist, Linda Perozo, poses for a portrait outside her home in Maryland, Wednesday, Sept. 16, 2020. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
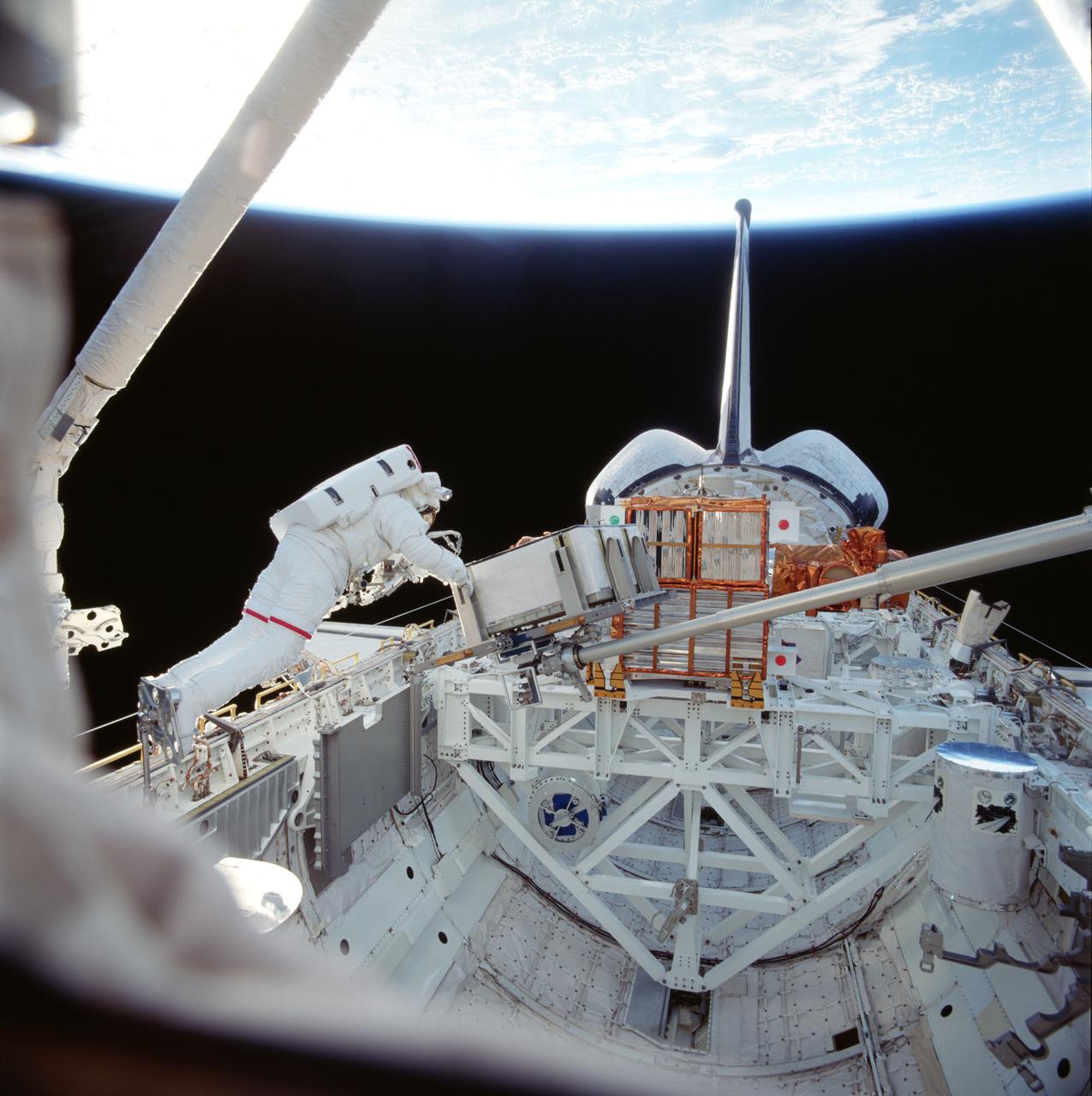

STS087-718-073 (19 November ? 5 December 1997) --- On the Space Shuttle Columbia's first ever spacewalk (EVA), astronaut Winston E. Scott works with a simulated battery and 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time this trip of Columbia. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the ISS. This crane device is designed to aid future spacewalkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier, astronauts Takao Doi (at the base of the crane, out of frame at right), an international mission specialist representing Japan, and Winston E. Scott had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations, long ago manifest for this mission, after completing a contingency spacewalk to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).
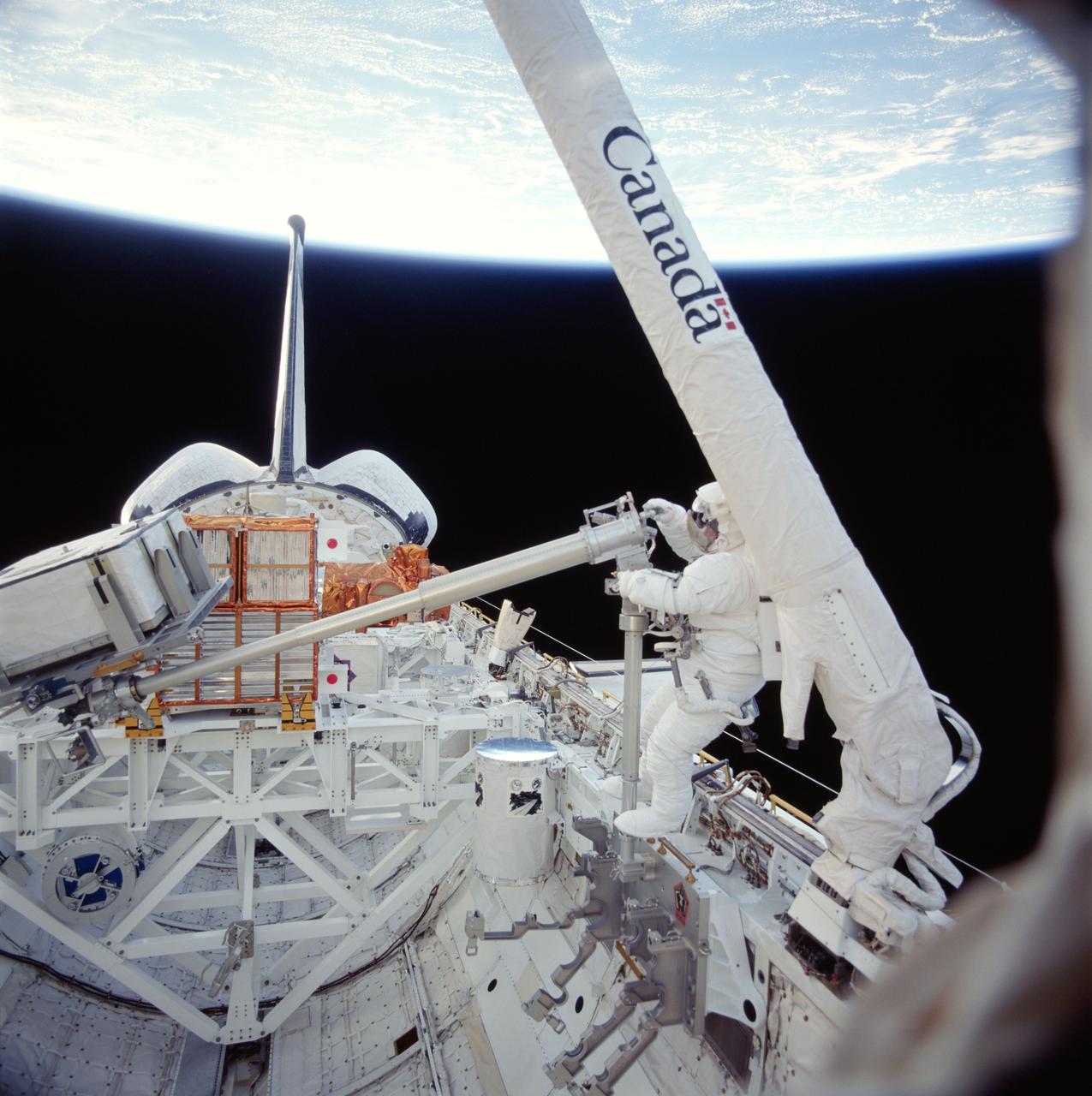

STS087-718-069 (19 November ? 5 December 1997) --- On the Space Shuttle Columbia's first ever spacewalk (EVA), astronaut Takao Doi works with a 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time this trip of Columbia. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the Space Station. This crane device is designed to aid future spacewalkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan, and astronaut Winston E. Scott had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations, long ago manifest for this mission, after completing a contingency spacewalk to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).
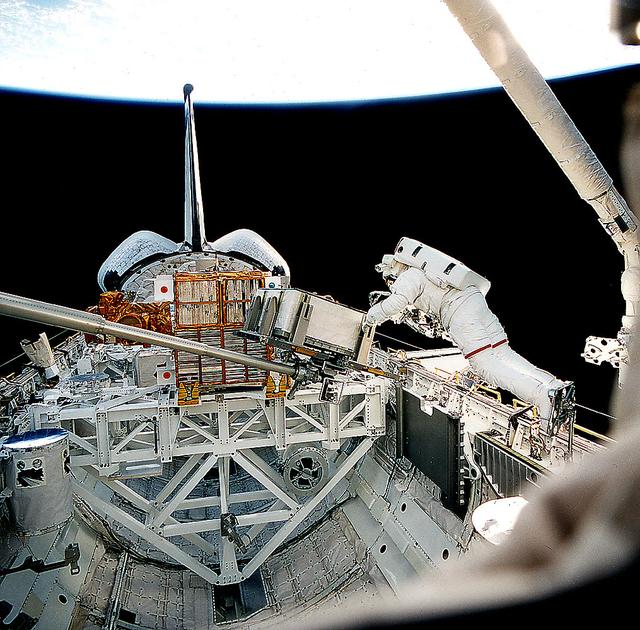

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia's (STS-87) first ever Extravehicular Activity (EVA), astronaut Takao Doi works with a 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the Space Station. This crane device is designed to aid future space walkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan, and astronaut Winston E. Scott, mission specialist, had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations after completing a contingency EVA to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).
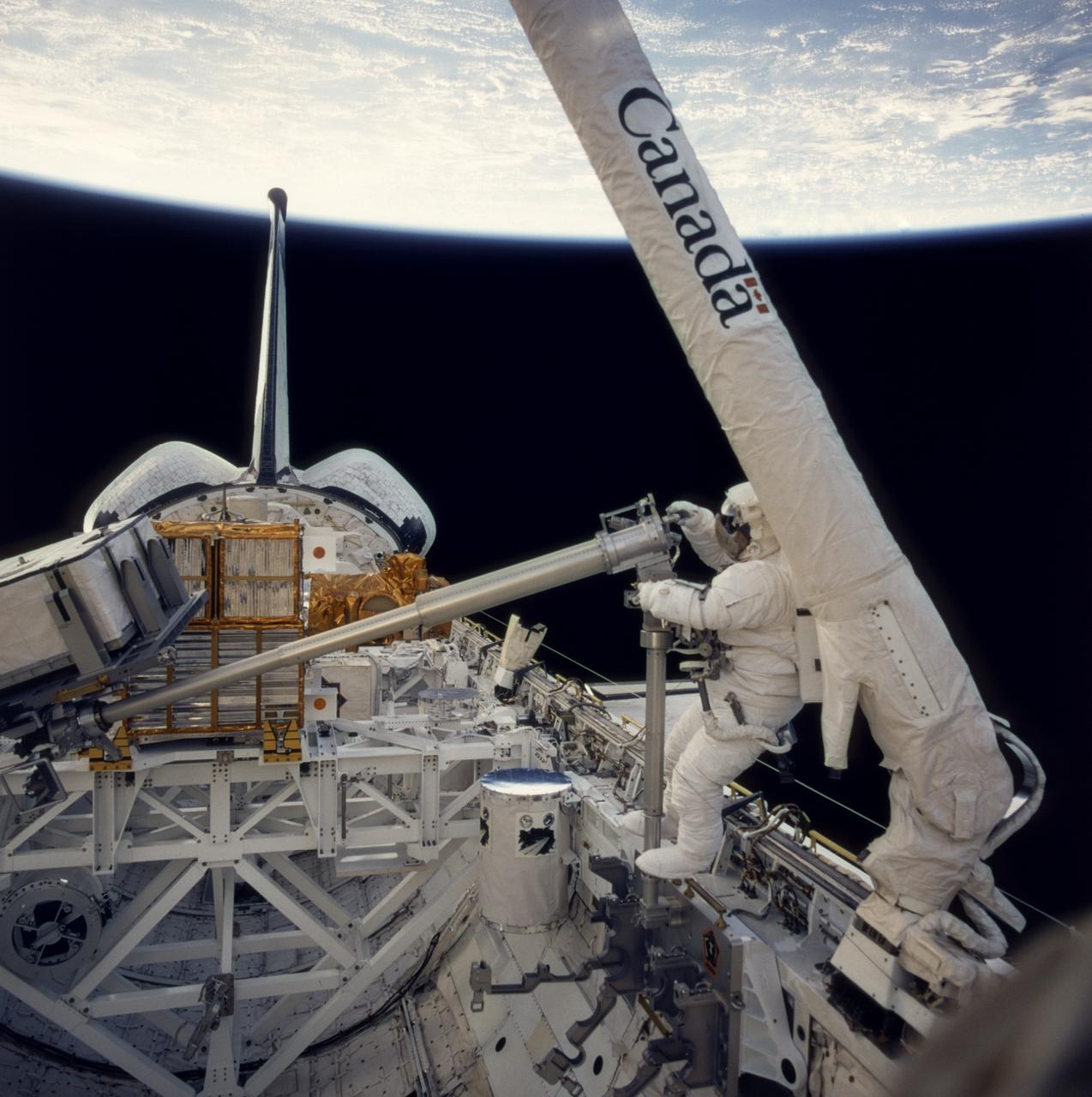

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia's (STS-87) first ever Extravehicular Activity (EVA), astronaut Takao Doi works with a 156-pound crane carried onboard for the first time. The crane's inclusion and the work with it are part of a continuing preparation effort for future work on the International Space Station (ISS). The ongoing project allows for evaluation of tools and operating methods to be applied to the construction of the Space Station. This crane device is designed to aid future space walkers in transporting Orbital Replacement Units (ORU), with a mass up to 600 pounds (like the simulated battery pictured here), from translating carts on the exterior of ISS to various worksites on the truss structure. Earlier Doi, an international mission specialist representing Japan, and astronaut Winston E. Scott, mission specialist, had installed the crane in a socket along the middle port side of Columbia's cargo bay for the evaluation. The two began the crane operations after completing a contingency EVA to snag the free-flying Spartan 201 and berth it in the payload bay (visible in the background).

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Nili Fossae. Nili Fossae is a collection of curved faults and down-dropped blocks of crust between the faults called graben. The graben lie northeast of the large volcano Syrtis Major and northwest of the ancient impact basin Isidis Planitia. The linear ridge in the center of the image is one side of a very large graben. When large amounts of pressure or tension are applied to rocks on timescales that are fast enough that the rock cannot respond by deforming, the rock breaks along faults. In the case of a graben, two parallel faults are formed by extension of the crust and the rock in between the faults drops downward into the space created by the extension. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85787 Latitude: 19.3564 Longitude: 73.5306 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-04-17 00:20 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25093
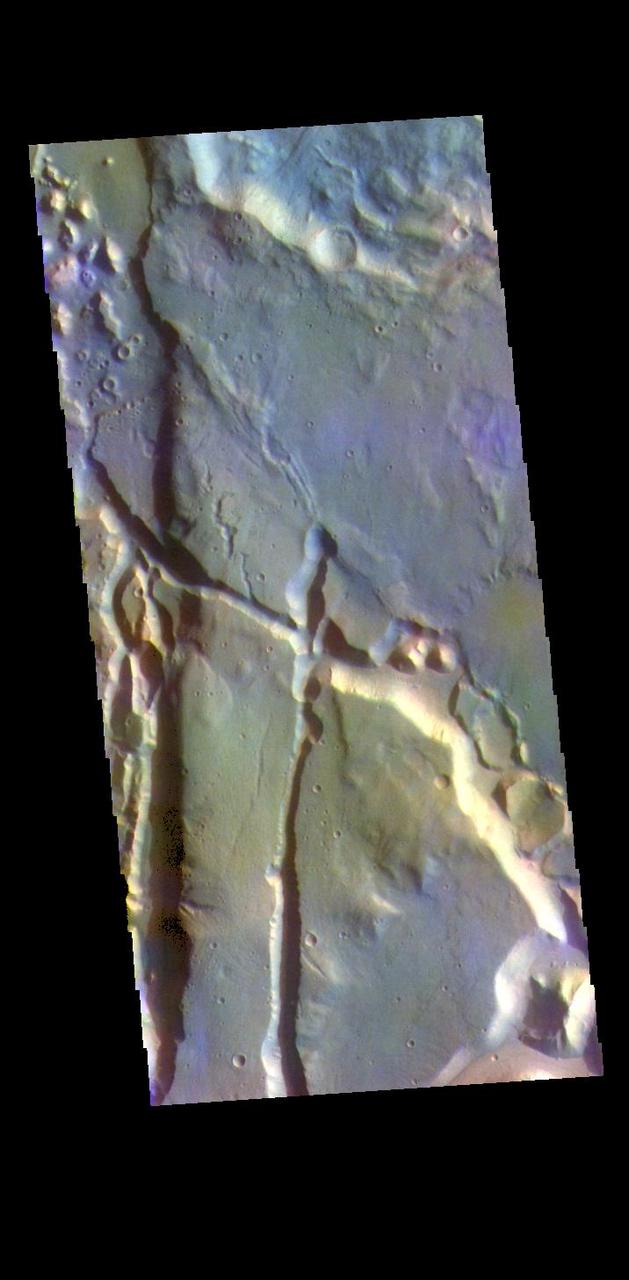

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Cydonia Mensae. Cydonia Mensae is located in the region between the cratered highlands of northwestern Arabia Terra and the southern lowlands of Acidalia Planitia. This area contains many different landforms, including tectonic features, chaos terrain and impact craters. This VIS image shows a portion of chaos in the top left of the frame, and several tectonic depressions. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 95074 Latitude: 35.0203 Longitude: 347.284 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-05-21 16:54 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26152

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Argentea Planum. The edge of the south polar cap is visible at the bottom of the image. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85035 Latitude: -82.5422 Longitude: 335.069 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-14 01:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25051

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Oyama Crater. Located in Arabia Terra near Mawrth Vallis, Oyama Crater is 101km (63 miles) in diameter. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 94363 Latitude: 23.2241 Longitude: 340.695 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-03-24 03:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26128

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Ariadnes Colles. The term colles means hills or knobs. In this false color combination the hills stand out against the darker surrounding plains. This difference is due to the amount of dust covering the hills versus the plains. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 92641 Latitude: -34.2832 Longitude: 171.529 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-11-02 07:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26090

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sabaea. Dark blue in this filter combination is usually basalt sand. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 94160 Latitude: 18.2445 Longitude: 77.6595 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-03-07 10:37 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26127

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sabaea. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 87197 Latitude: 18.0891 Longitude: 77.0112 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-08-11 02:38 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25380

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Oenotria Scopuli, which is the bright cliff in the center of the image. Oenotria Scopuli is located in Terra Sabaea. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85962 Latitude: -5.59203 Longitude: 68.4149 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-05-01 10:01 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25099

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows a cross section of Hebes Chasma, including Hebes Mensa (middle of image). Hebes Chasma is an inclosed basin not connected to Valles Marineris. It is 319 km long (east/west, 198 miles), 130 km wide (north/south, 81miles) and up to 8km (5 miles) deep. Hebes Mensa is a large deposit of layered material within the chasma. Extensive erosion has created gullies in the mensa and distributed fine sand size materials to create dunes and sand drifts. Hebes Mensa is 7.5 km (4.7 miles) high, 120 km (75 miles) long and 43 km (27 miles) wide. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85967 Latitude: -1.25893 Longitude: 283.562 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-05-01 19:55 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25100

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of northern Arabia Terra. Arabia Terra is one of the oldest surface regions on Mars and contains a large variety of surface features. The region is dissected with numerous unnamed channels of all sizes and complexities, as well as numerous pits of unknown origin. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 87213 Latitude: 18.2378 Longitude: 335.439 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-08-12 10:16 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25381

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of northwestern Arabia Terra. The channels in the top part of the image are all unnamed. They are draining from the highlands of Arabia Terra into the lowlands of Acidalia Planitia. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85453 Latitude: 32.3047 Longitude: 347.214 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-03-20 12:23 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25057

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Australe Montes. This region of highlands is located near the south polar cap. The pale blue surface at the bottom of the image is likely surface frost. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 84934 Latitude: -81.7965 Longitude: 10.5697 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-02-05 18:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25008

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows a cross section of Gale Crater, including the large layered deposit in the center of the crater. The Curiosity Rover is located on the floor of Gale Crater. Gale Crater is 154 km (95 miles) in diameter and is located near Terra Cimmeria. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85710 Latitude: -5.28449 Longitude: 138.202 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-04-10 16:02 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25092

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Lunae Planum. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 95001 Latitude: 18.596 Longitude: 295.651 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-05-15 16:32 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26137
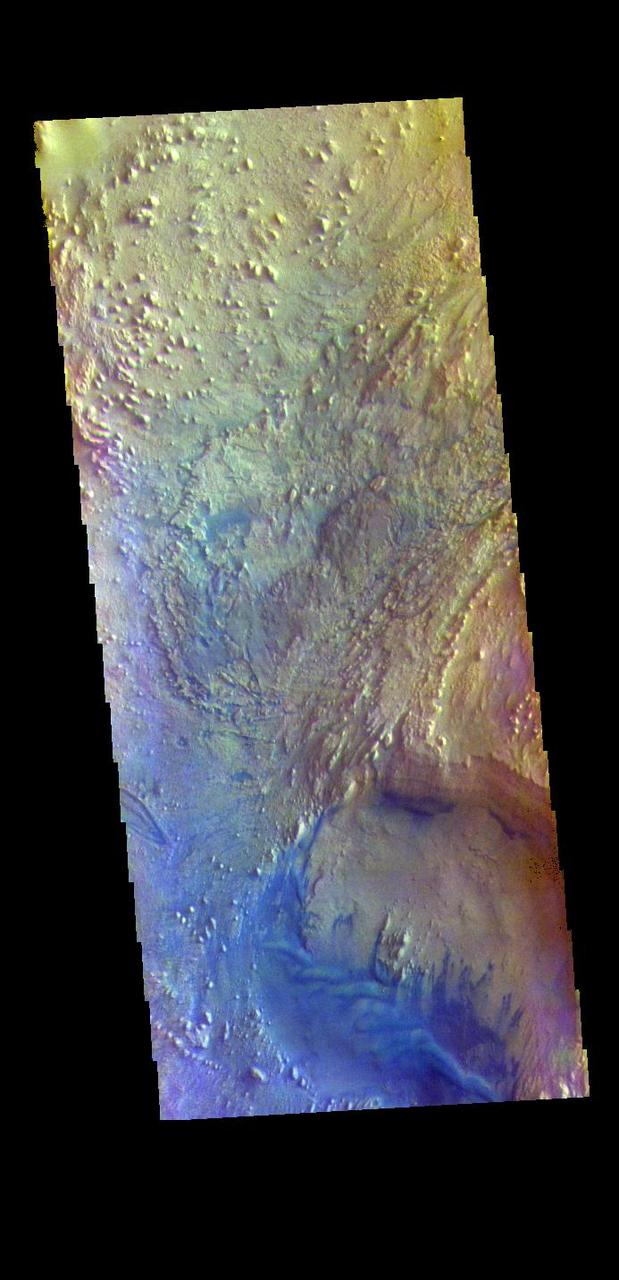
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the floor of Firsoff Crater. Located in southern Arabia Terra, Firsoff Crater, and the neighboring Crommelin Crater, have large layered deposits on the crater floor. The circular feature at the bottom of the image is a smaller crater within Firsoff Crater. The layering of the interior deposit can be seen in the northern side of this smaller crater. Wind action has modified the large deposit. In this color combination dark blue typically indicates basaltic sand. Firsoff Crater is 90 km (56 miles) in diameter. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 94812 Latitude: 2.77617 Longitude: 350.268 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-04-30 02:58 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26134
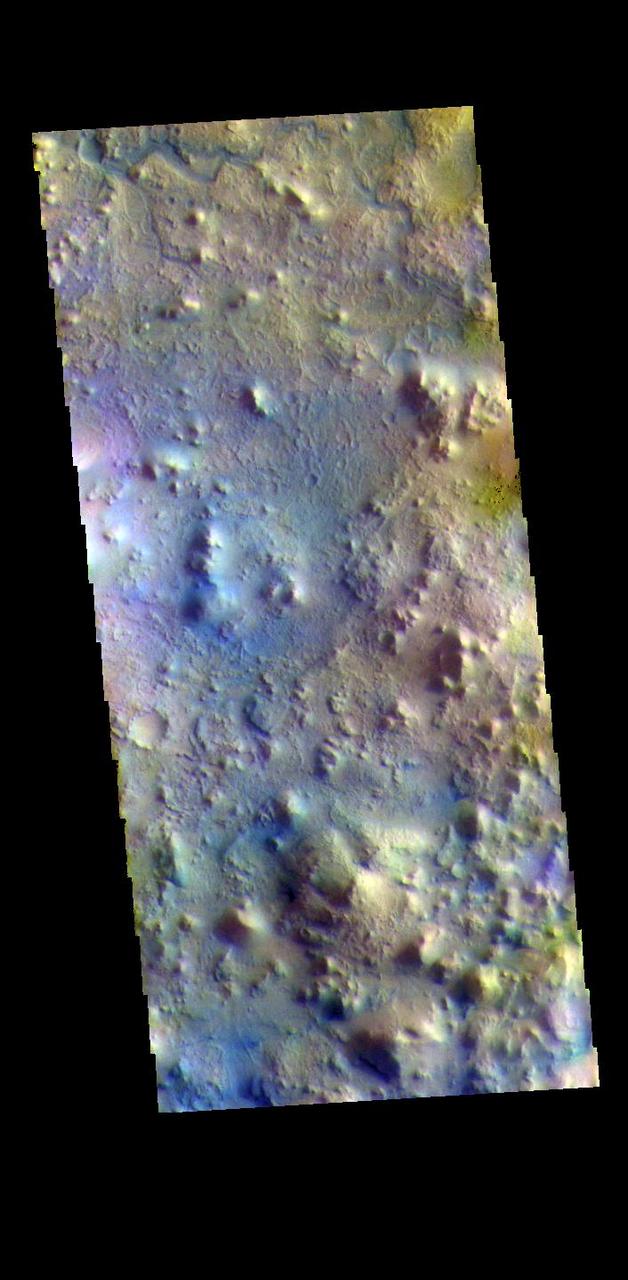

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sabaea, in the region between Nili Fossae and Isidis Planitia. This image is located just east of Jezero Crater, the home of the Mars 2020 rover (Perserverance) and its little helicopter buddy (Ingenuity). The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 95021 Latitude: 18.3774 Longitude: 78.6869 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-05-17 08:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26138
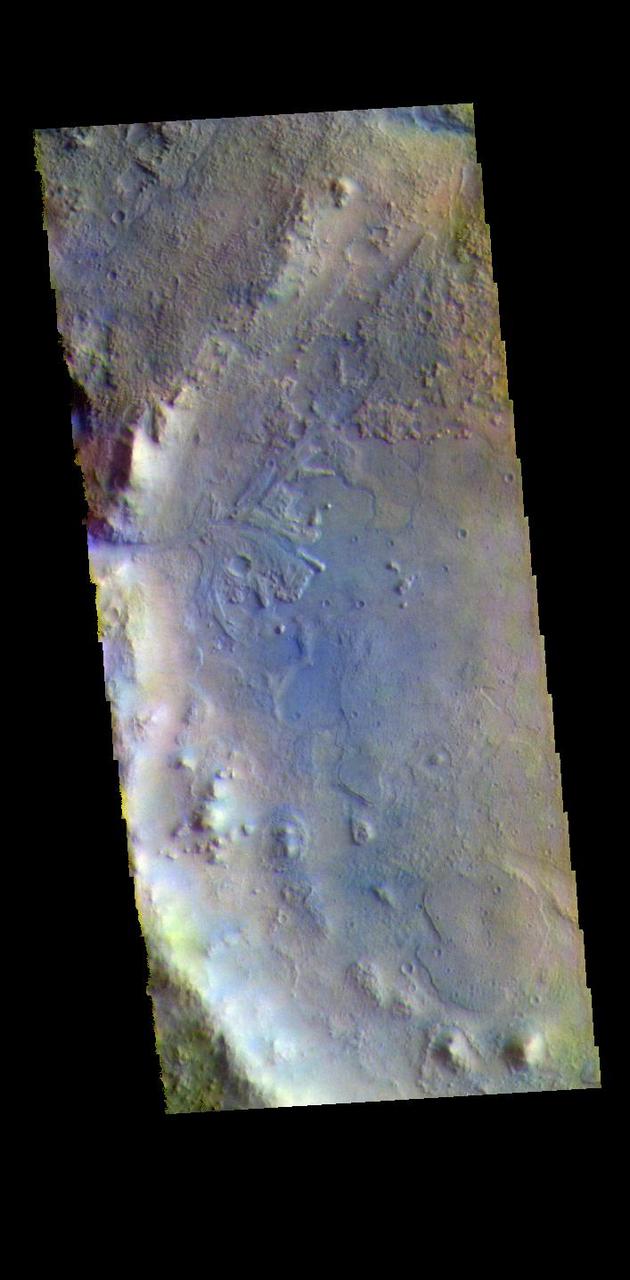

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows the western half of Jezero Crater. The Perserverance Rover is located in this part of the crater – near the delta deposit formed by the influx of silt laden water into the crater at a time during Mars' past that was wetter. The crater most likely hosted a lake for a period of time. Jezero Crater is 47km (29 miles) in diameter. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 95046 Latitude: 18.449 Longitude: 77.436 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-05-19 09:28 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26140
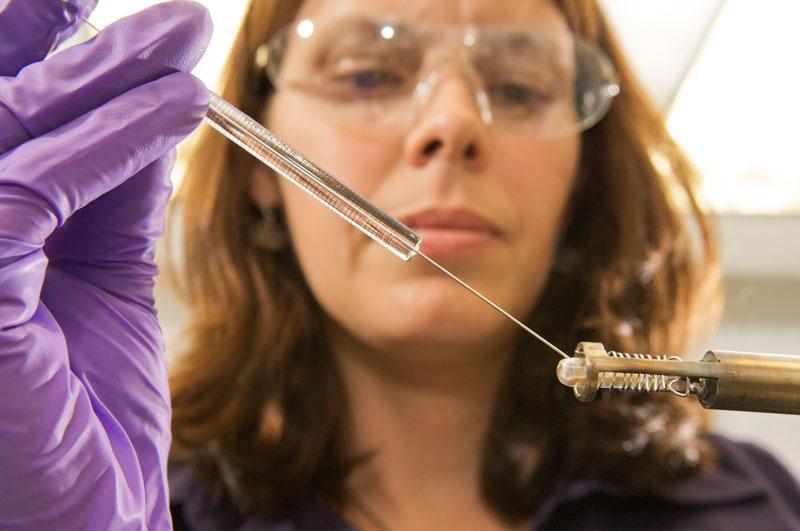

On Saturday, November 26, NASA is scheduled to launch the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission featuring Curiosity, the largest and most advanced rover ever sent to the Red Planet. The Curiosity rover bristles with multiple cameras and instruments, including Goddard's Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) instrument suite. By looking for evidence of water, carbon, and other important building blocks of life in the Martian soil and atmosphere, SAM will help discover whether Mars ever had the potential to support life. Curiosity will be delivered to Gale crater, a 96-mile-wide crater that contains a record of environmental changes in its sedimentary rock, in August 2012. ----- Goddard scientist Jennifer Eigenbrode injected a chemical into a rock sample and then heated the test tube to determine whether the sample-preparation method preserved the sample's molecular structure. Her testing proved successful, ultimately leading to the experiment's inclusion on the Sample Analysis at Mars instrument. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of the northern rim of Huygens Crater (bright feature in center of image). Huygens Crater is 467 km (290 miles) in diameter and is located in Terra Sabaea. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 86000 Latitude: -11.048 Longitude: 52.8798 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-05-04 13:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25101

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of northern Syrtis Major Planum. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85463 Latitude: 17.4847 Longitude: 60.8084 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-03-21 08:04 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25058

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sirenum. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 92415 Latitude: -38.6129 Longitude: 210.798 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-10-14 17:24 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26121

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows the floor of Matara Crater. A large sand sheet dominates the floor of this crater located in Noachis Terra. The top of the sand sheet has been sculpted by the wind, creating dune forms. Matara Crater is 48km (30 miles) in diameter. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 83817 Latitude: -49.4554 Longitude: 34.8949 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-11-05 19:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25002

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows several craters in Terra Cimmeria. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 83681 Latitude: -31.6763 Longitude: 180.725 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-10-25 13:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24999

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Lomonosov Crater. Lomonosov Crater is 130km (81 miles) in diameter and is located in northern Acidalia Planitia. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85534 Latitude: 64.7689 Longitude: 351.857 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-03-27 04:54 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25060

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Arabia Terra. Arabia Terra is one of the oldest surface regions on Mars and contains a large variety of surface features. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 85578 Latitude: 20.3273 Longitude: 342.869 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-03-30 19:20 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25055
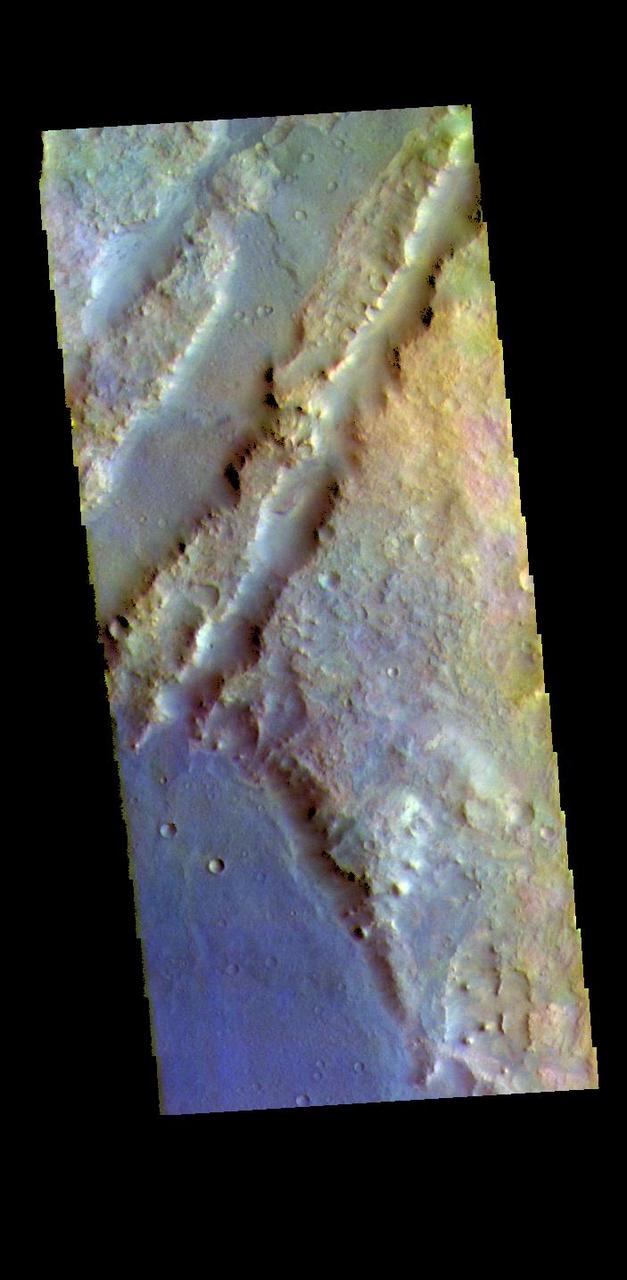
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The linear depressions in today's false color image are part of Nili Fossae. Nili Fossae is a collection of curved faults and down-dropped blocks of crust between the faults. The "fossae," or graben, lie northeast of the large volcano Syrtis Major and northwest of the ancient impact basin Isidis Planitia. The troughs, which can be almost 500 meters (1,600 feet) deep , make concentric curves that follow the outline of Isidis Planitia. The graben likely formed as the crust sagged under the weight of lava flows filling the Isidis Planitia impact basin. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 88158 Latitude: 20.507 Longitude: 72.6076 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-10-29 05:43 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25388
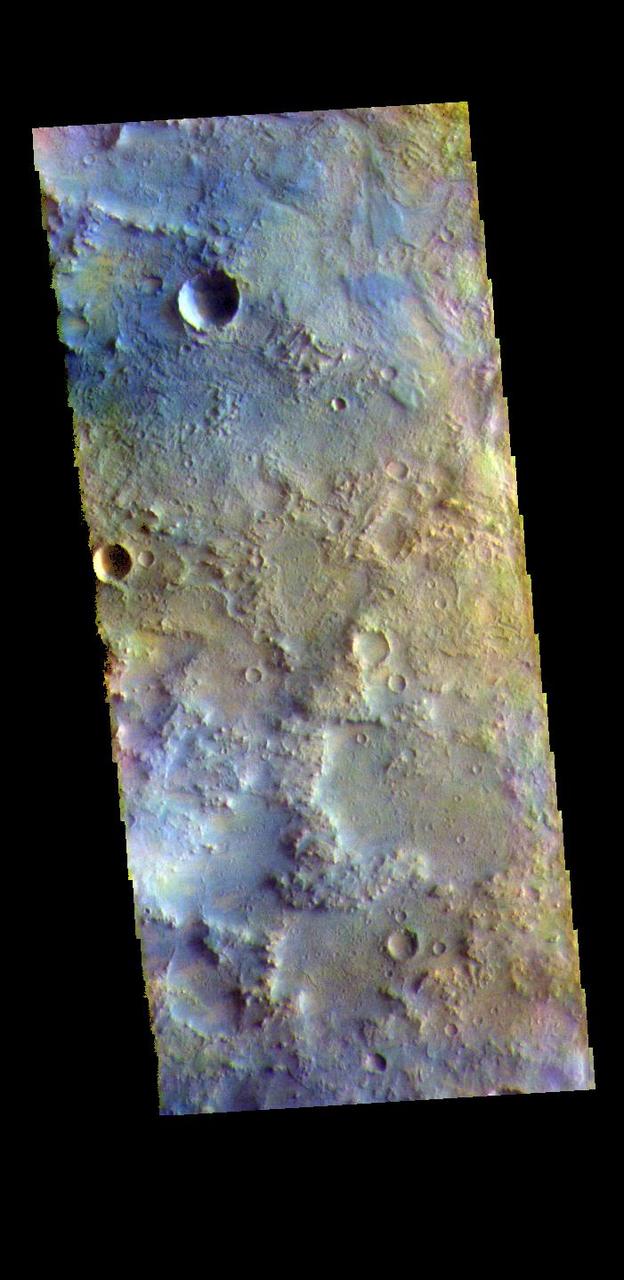
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sabaea. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 94472 Latitude: 18.2986 Longitude: 76.7725 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-04-02 03:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26131

“My background and experience have been unique. I didn't grow up in space. I didn't grow up in a family of people who watched the Moon landing. I came to discover space at a much later age. That and the fact that I come from the cultural background I come from (being born and raised in Puerto Rico), has always made me question some of the assumptions about why we do what we do in space and how we go about it. “In my experience and in my career that has proven effective because people want the challenge, and they want to engage everyone and make sure that the best of the best are participating. I have found myself in settings where my point of view has been valued because I was asking some of the questions that some folks took for granted. “I think it’s also that I came at a good time when we are having these important discussions about diversity and inclusion, and people do want these different kinds of views. Space is so international now that this diversity is such an important aspect of it too. Even as an adult starting to learn about these topics, it was natural for me to be having these discussions with other colleagues from Latin America and South Africa and Australia. It’s a key feature of my own experience but also, I think, the time that we’re living right now, which is really exciting.” Laura M. Delgado López, Policy Analyst for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, poses for a portrait on Monday, Sept. 21, 2020 in Virginia. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Today's VIS image shows part of Karzok Crater. This crater is one of two located on the flanks of Olympus Mons. Karzok Crater is 15.6km (9.7 mi) in diameter. Olympus Mons is the largest volcano in the solar system, reaching heights over 40 km (25 miles) tall from base to summit, with the base covering an area as large as the state of Arizona. For comparison, Mauna Loa is 9 km (5.5 miles) tall measured from its base on the sea floor. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 86755 Latitude: 18.2292 Longitude: 228.192 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2021-07-05 17:12 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24993

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Cimmeria. Soffen Crater is at the top of the image, and is 58 km (36 miles) in diameter. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 91831 Latitude: -24.6619 Longitude: 141.019 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-08-27 15:15 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26085
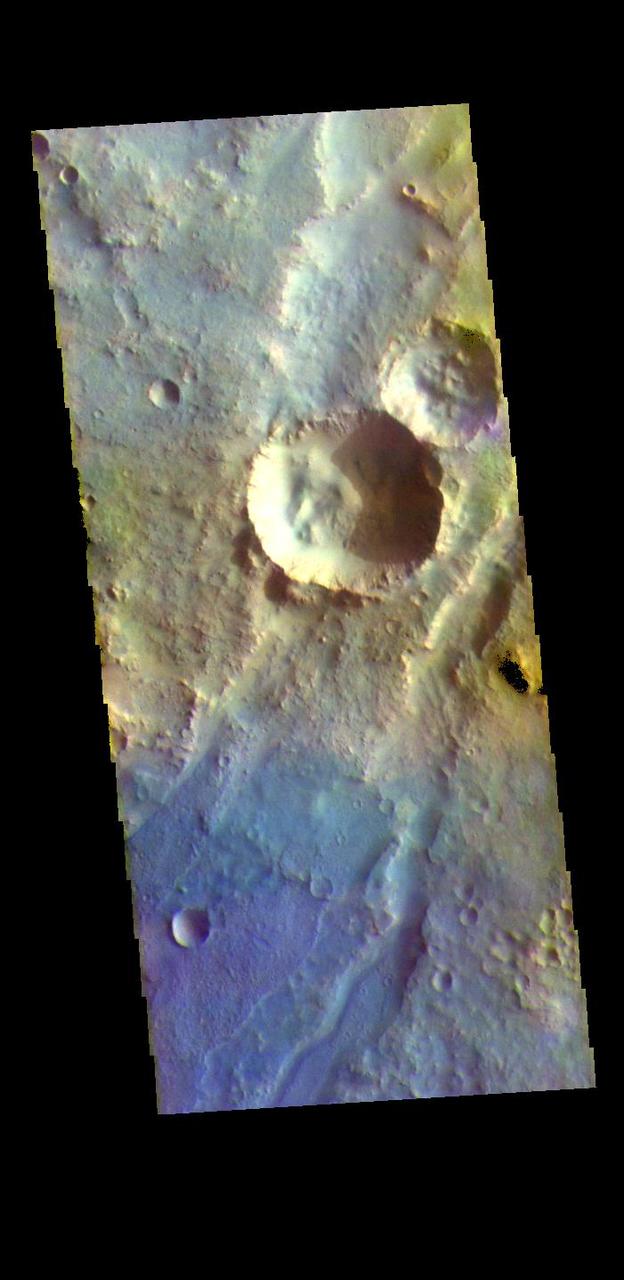
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The linear depressions in today's false color image are part of Nili Fossae. Nili Fossae is a collection of curved faults and down-dropped blocks of crust between the faults. The "fossae," or graben, lie northeast of the large volcano Syrtis Major and northwest of the ancient impact basin Isidis Planitia. The troughs, which can be almost 500 meters (1,600 feet) deep , make concentric curves that follow the outline of Isidis Planitia. The graben likely formed as the crust sagged under the weight of lava flows filling the Isidis Planitia impact basin. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 94834 Latitude: 21.5829 Longitude: 73.0022 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2023-05-01 22:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26136
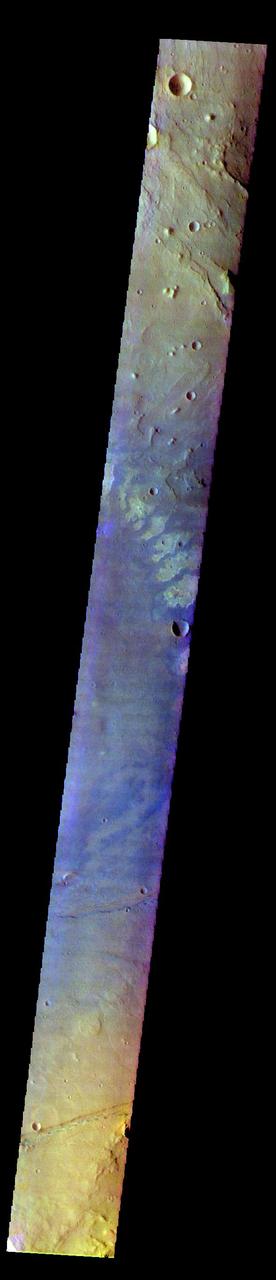
The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Terra Sirenum. The THEMIS VIS camera is capable of capturing color images of the Martian surface using five different color filters. In this mode of operation, the spatial resolution and coverage of the image must be reduced to accommodate the additional data volume produced from using multiple filters. To make a color image, three of the five filter images (each in grayscale) are selected. Each is contrast enhanced and then converted to a red, green, or blue intensity image. These three images are then combined to produce a full color, single image. Because the THEMIS color filters don't span the full range of colors seen by the human eye, a color THEMIS image does not represent true color. Also, because each single-filter image is contrast enhanced before inclusion in the three-color image, the apparent color variation of the scene is exaggerated. Nevertheless, the color variation that does appear is representative of some change in color, however subtle, in the actual scene. Note that the long edges of THEMIS color images typically contain color artifacts that do not represent surface variation. Orbit Number: 92366 Latitude: -37.8538 Longitude: 184.585 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-10-10 16:34 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26089