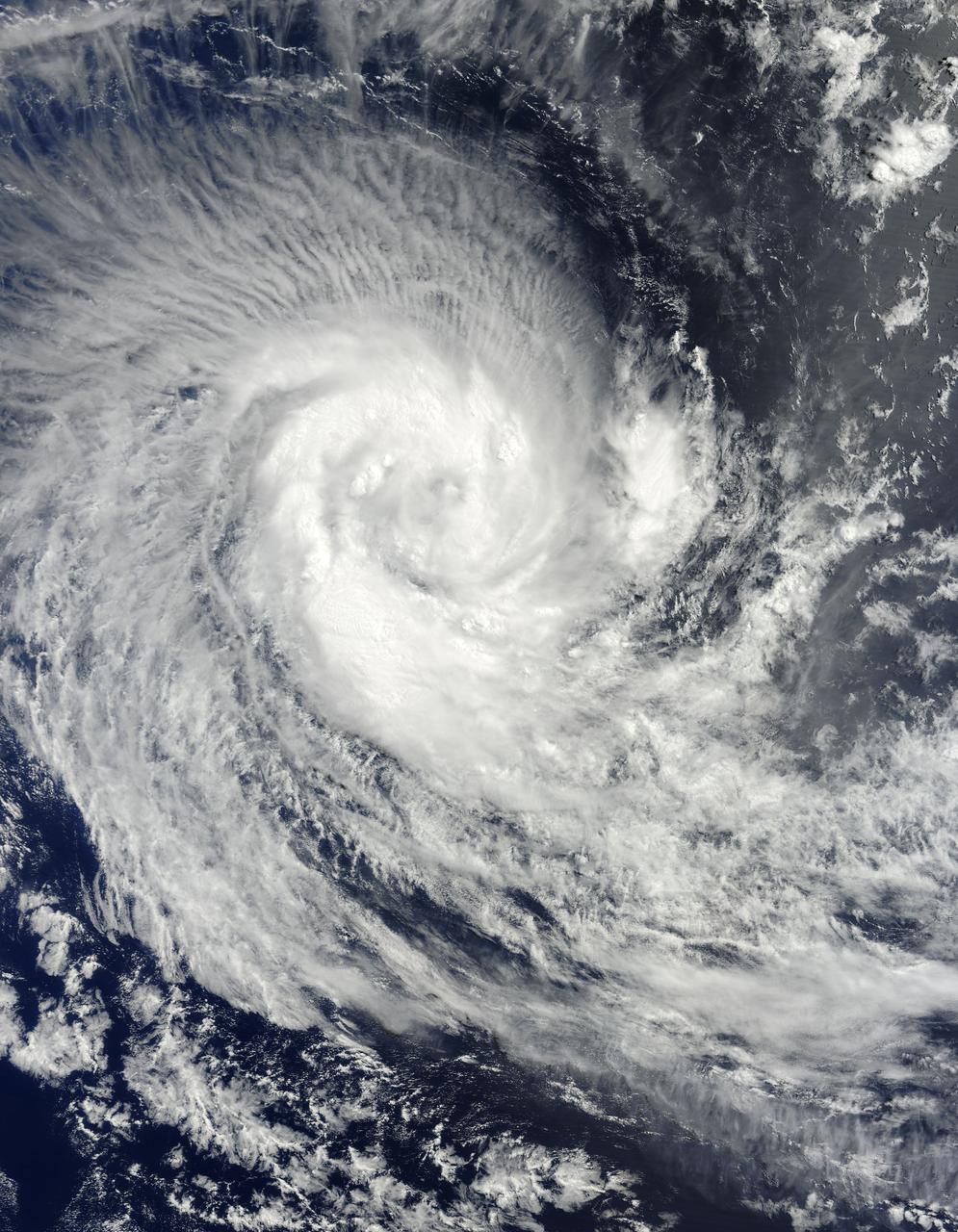
NASA image acquired March 24, 2010. Tropical Cyclone Imani swirled over the Southern Indian Ocean on March 24, 2010. The same day, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that the storm had maximum sustained winds of 55 knots (100 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 70 knots (130 kilometers per hour). The storm was located roughly 745 nautical miles (1,380 kilometers) west-southwest of Cocos Island, having traveled toward the south-southwest for several hours. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image of the storm on March 24, 2010. Imani spans several hundred kilometers over the Southern Indian Ocean, producing thin, radial clouds on its northern margin. The storm occurs far from any major landmass. The JTWC forecast that Imani would continue traveling toward the south-southwest until reaching mid-latitude. The storm was expected to eventually turn southward and weaken. NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Terra - MODIS To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=43225" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=43225</a> For more information about Goddard Space Flight Center go here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html</a>

Tropical Cyclone Mahasen is moving north through the Indian Ocean along a track that places landfall along the Bangladesh coast on May 16th around 1200Z. On May 13, 2013 the Suomi NPP satellite caught an interesting glimpse of the storm as it moved off the eastern coast of India. The VIIRS Day-Night Band was able to resolve lightning flashes towards the center of the storm, along with mesopheric gravity waves emanating outwards like ripples in a pond. These gravity waves are of particular interest to air traffic controllers so assist in identifying areas of turbulence. Since the moon was in a new phase, the lights and other surface features of India and Sri Lanka are clearly visible, though the clouds of TC Mahasen are not - a tradeoff that occurs as the amount of moonlight cycles throughout the month. Credit: NASA/NOAA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>