
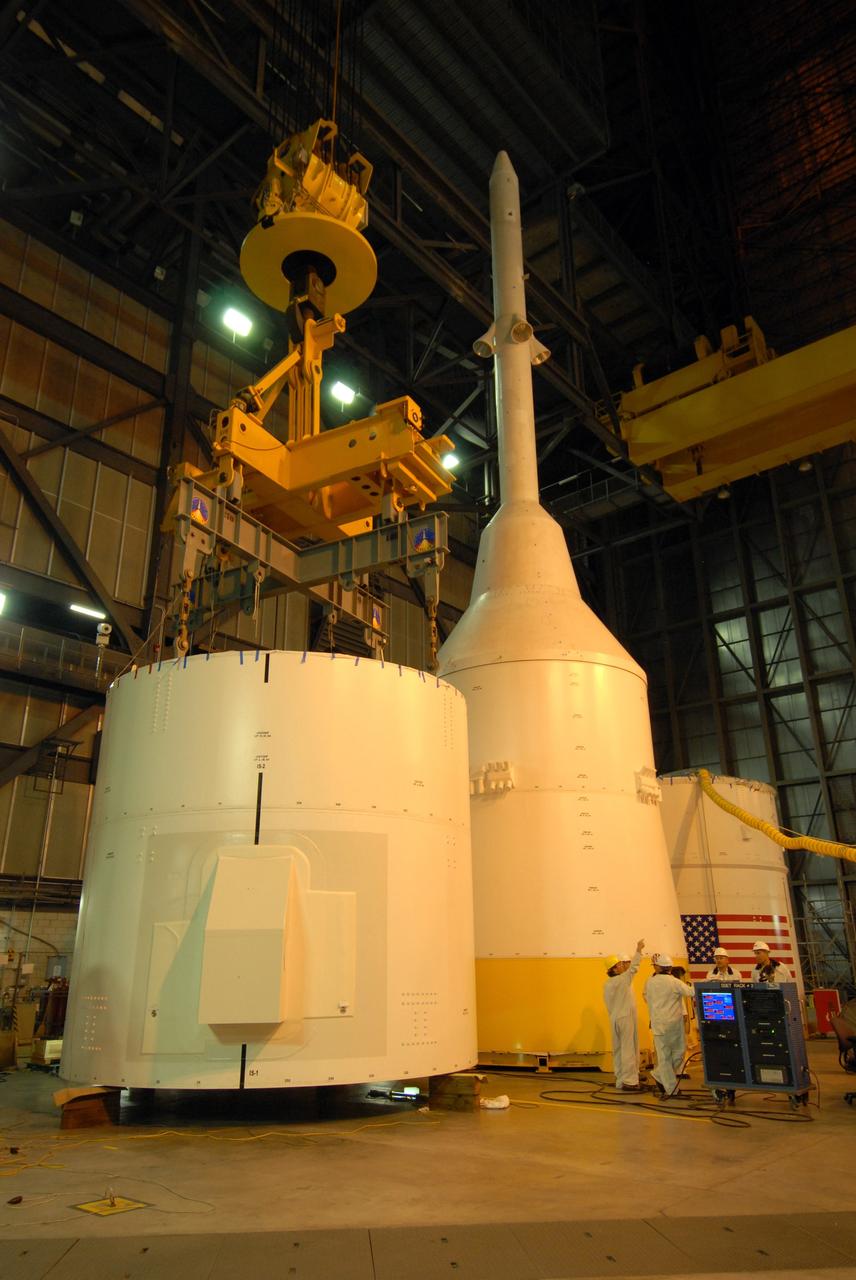
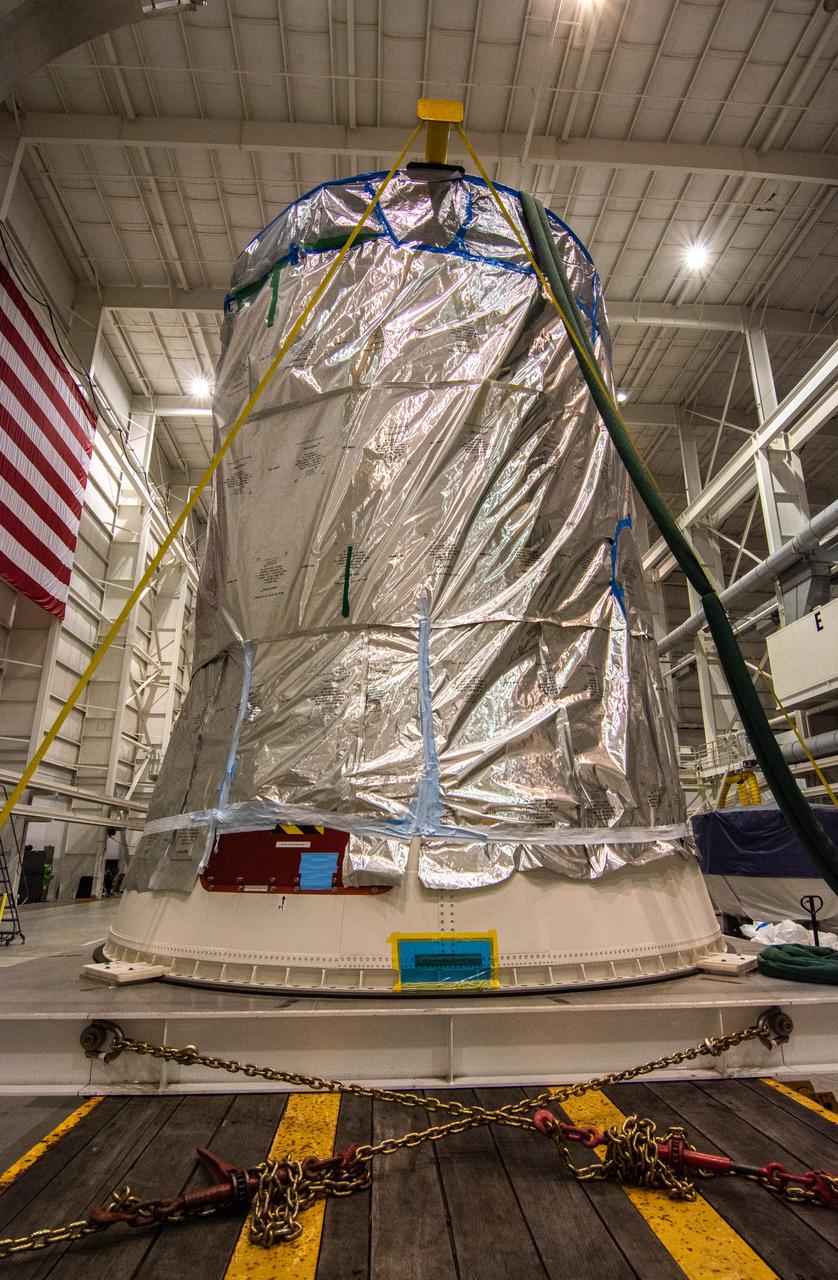
Inside Building B7525 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the aft stub adapter (ASA) is installed to the interstage adapter (ISA) for a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The launch vehicle will send NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
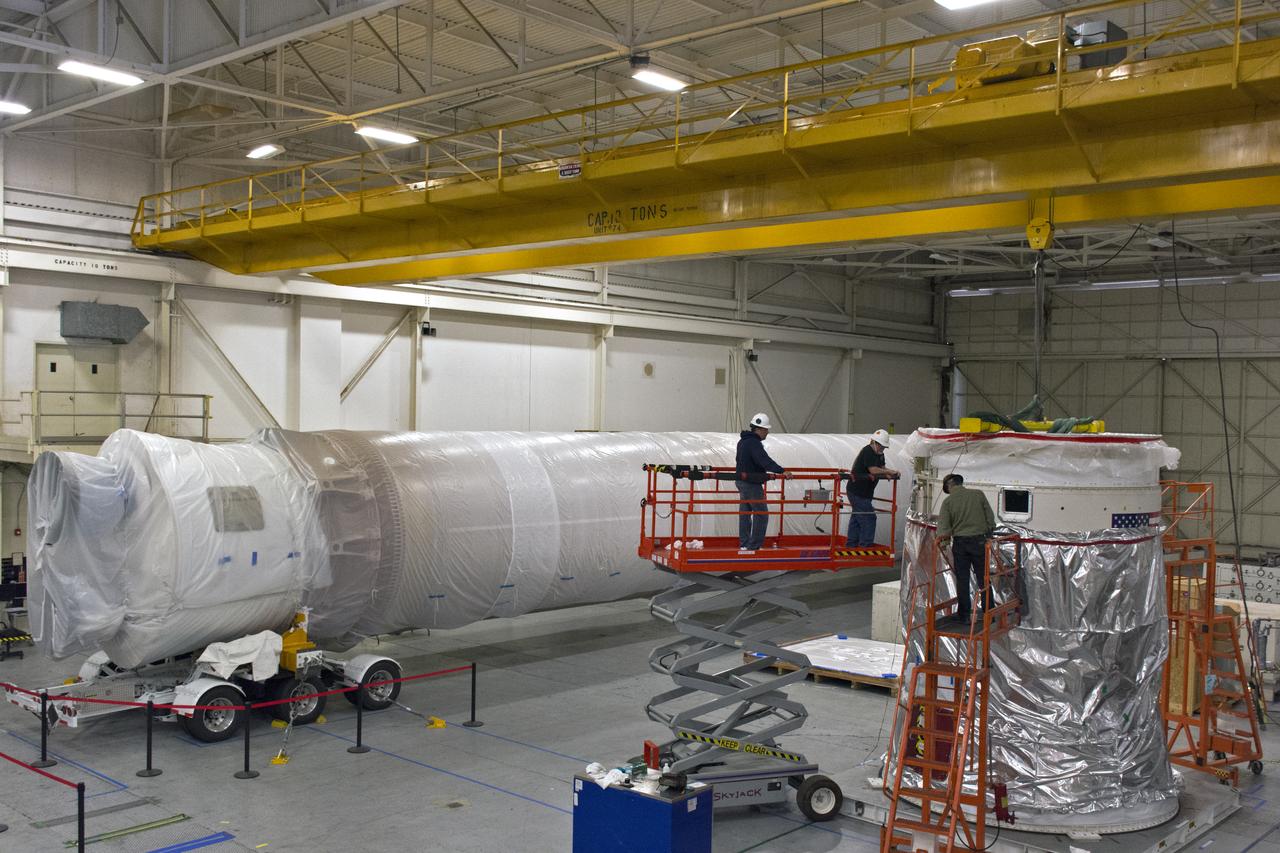

Inside Building B7525 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the aft stub adapter (ASA) is installed to the interstage adapter (ISA) for a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket. The launch vehicle will send NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
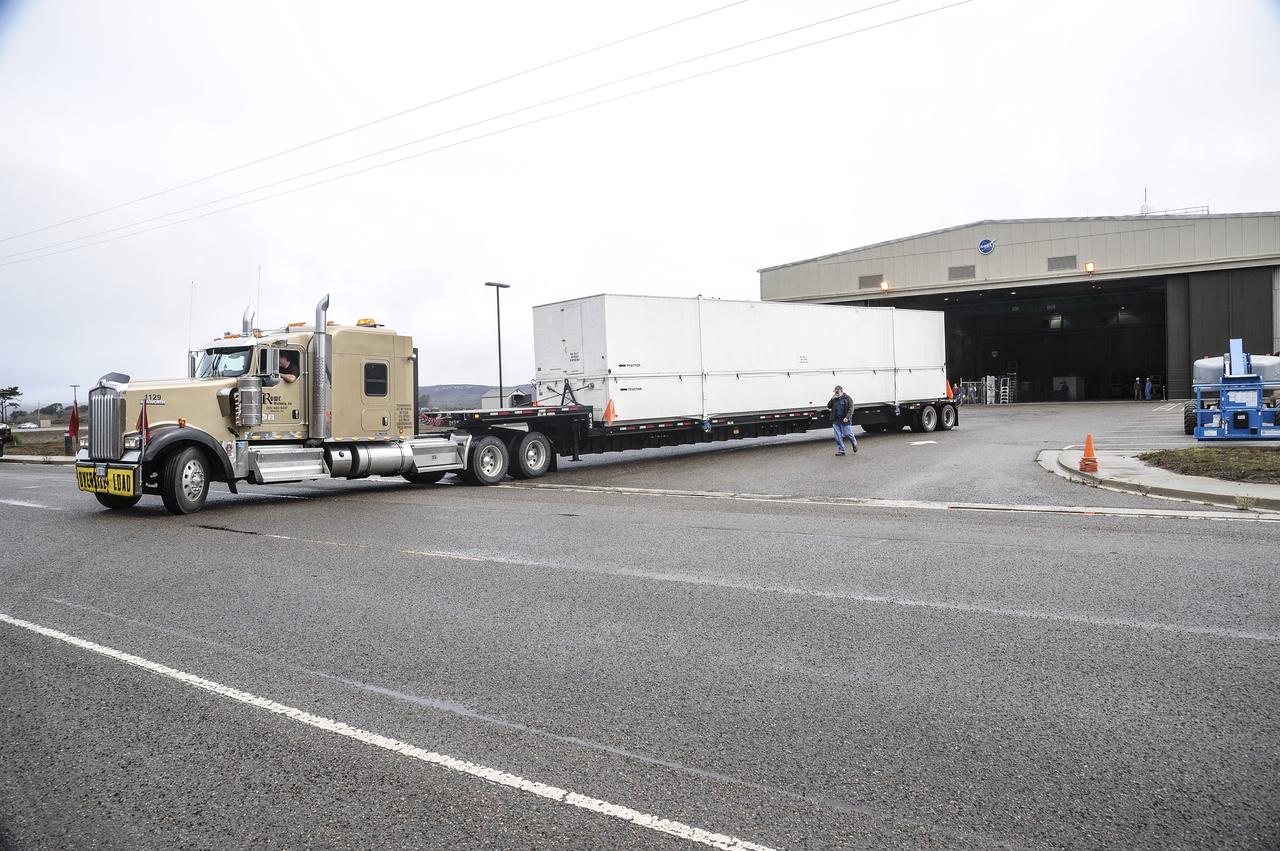

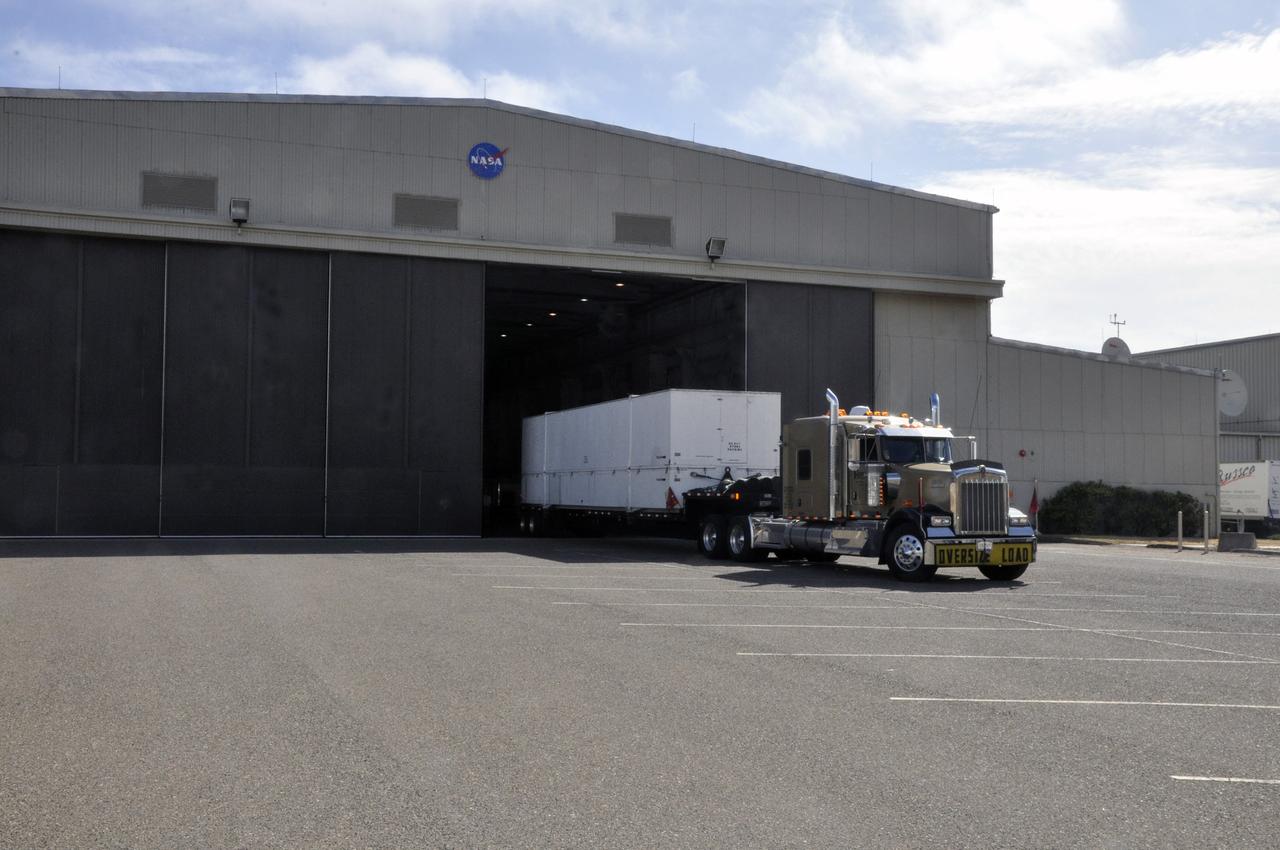
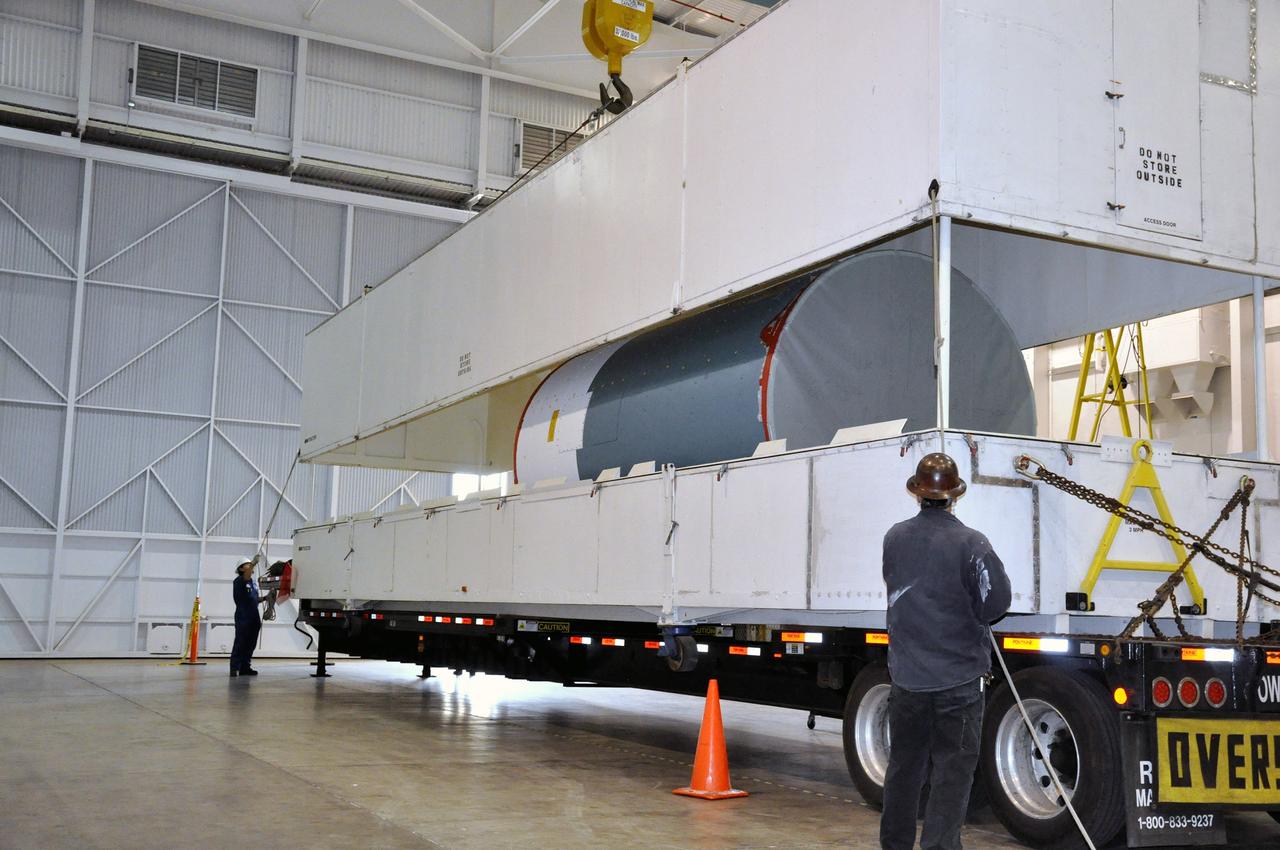
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
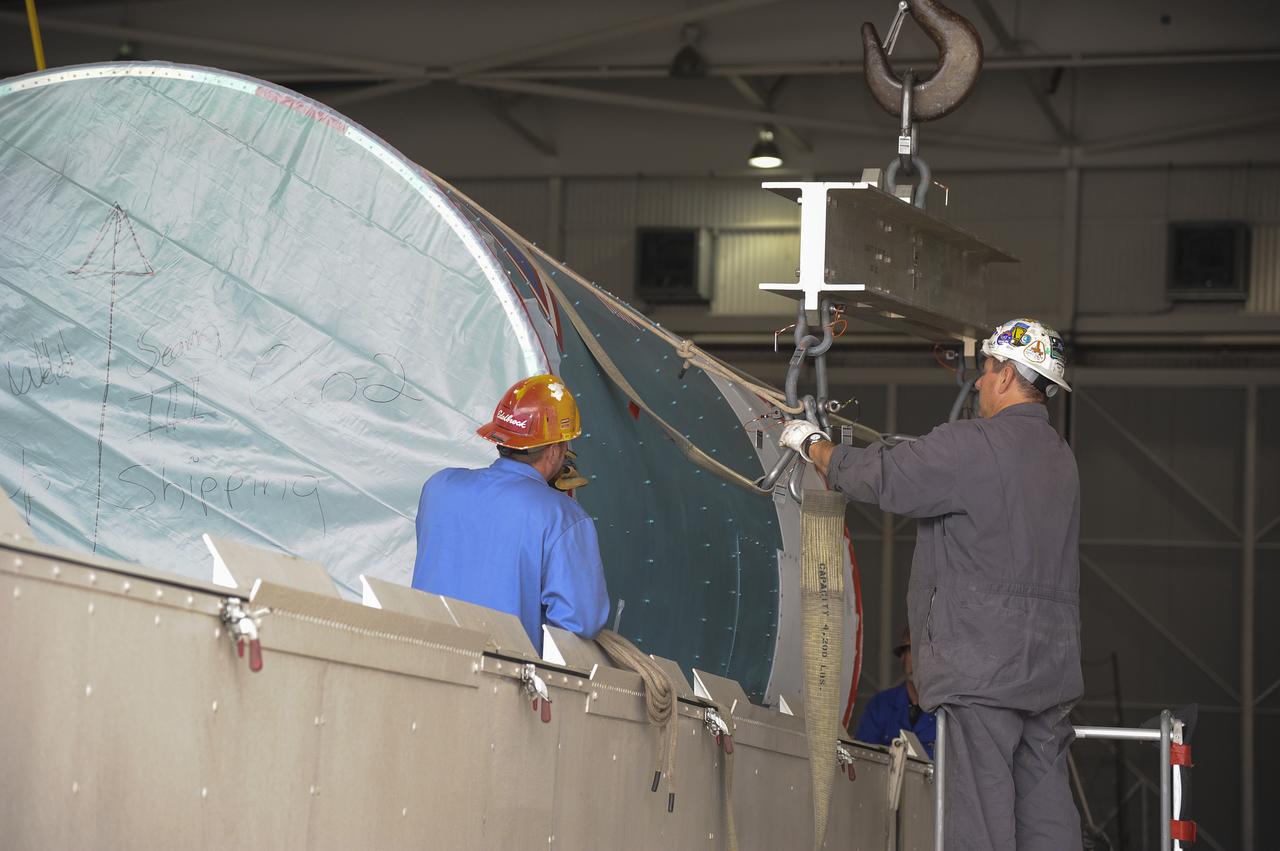

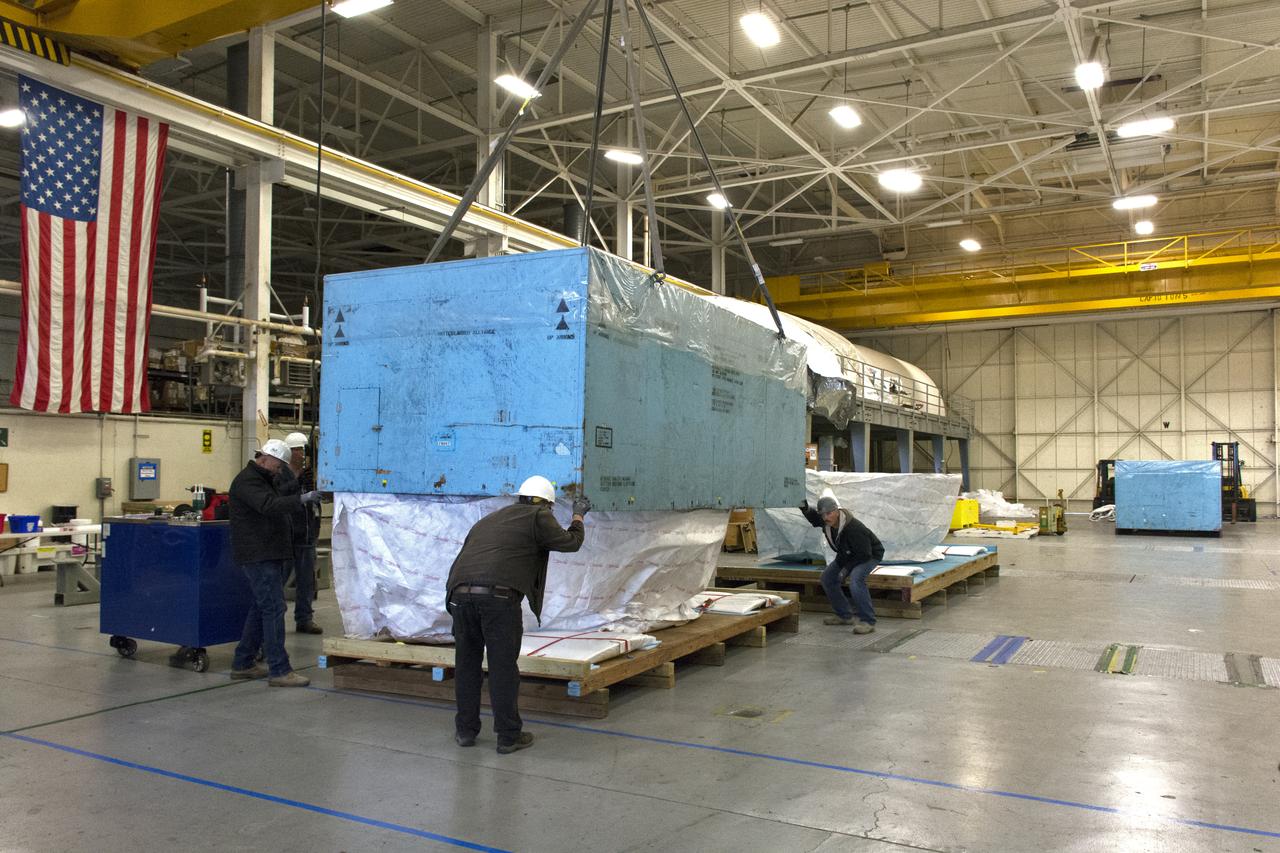
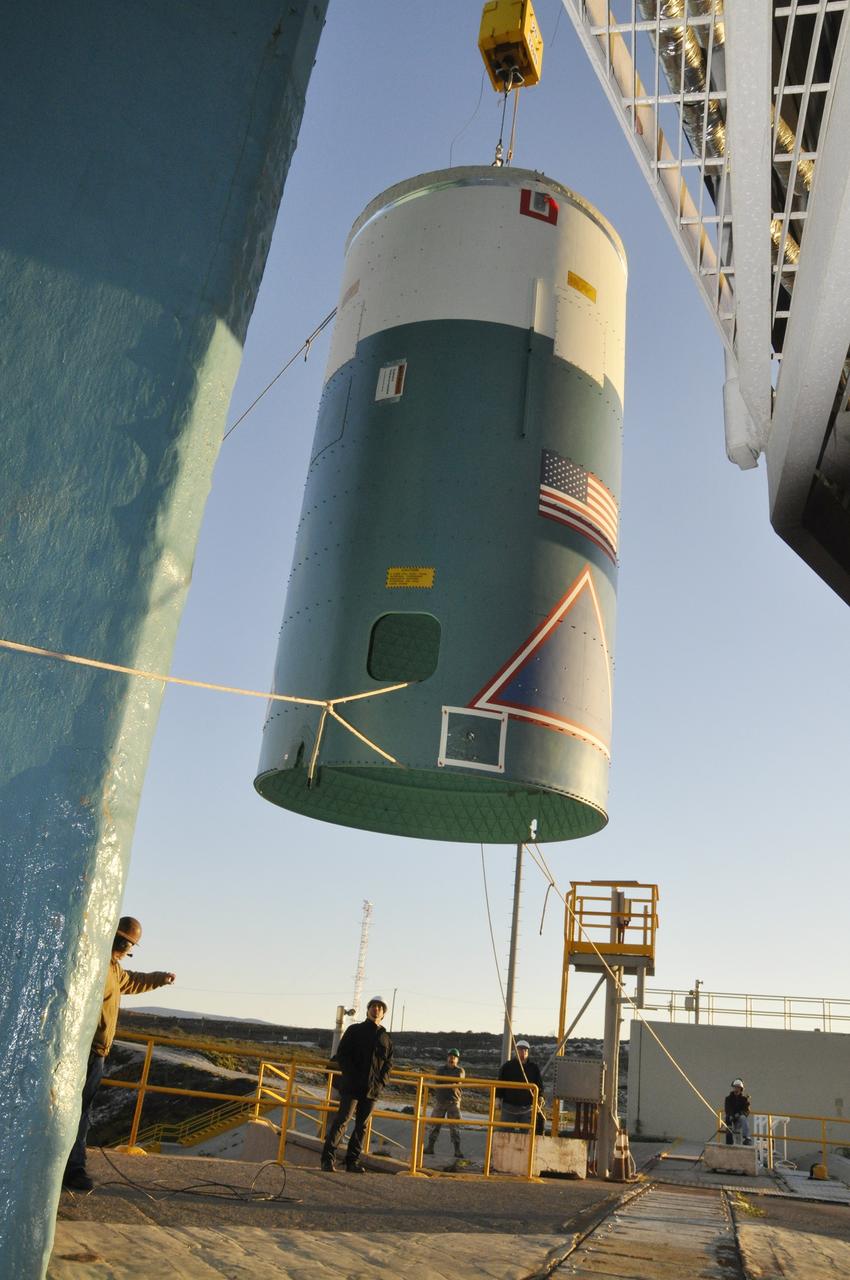
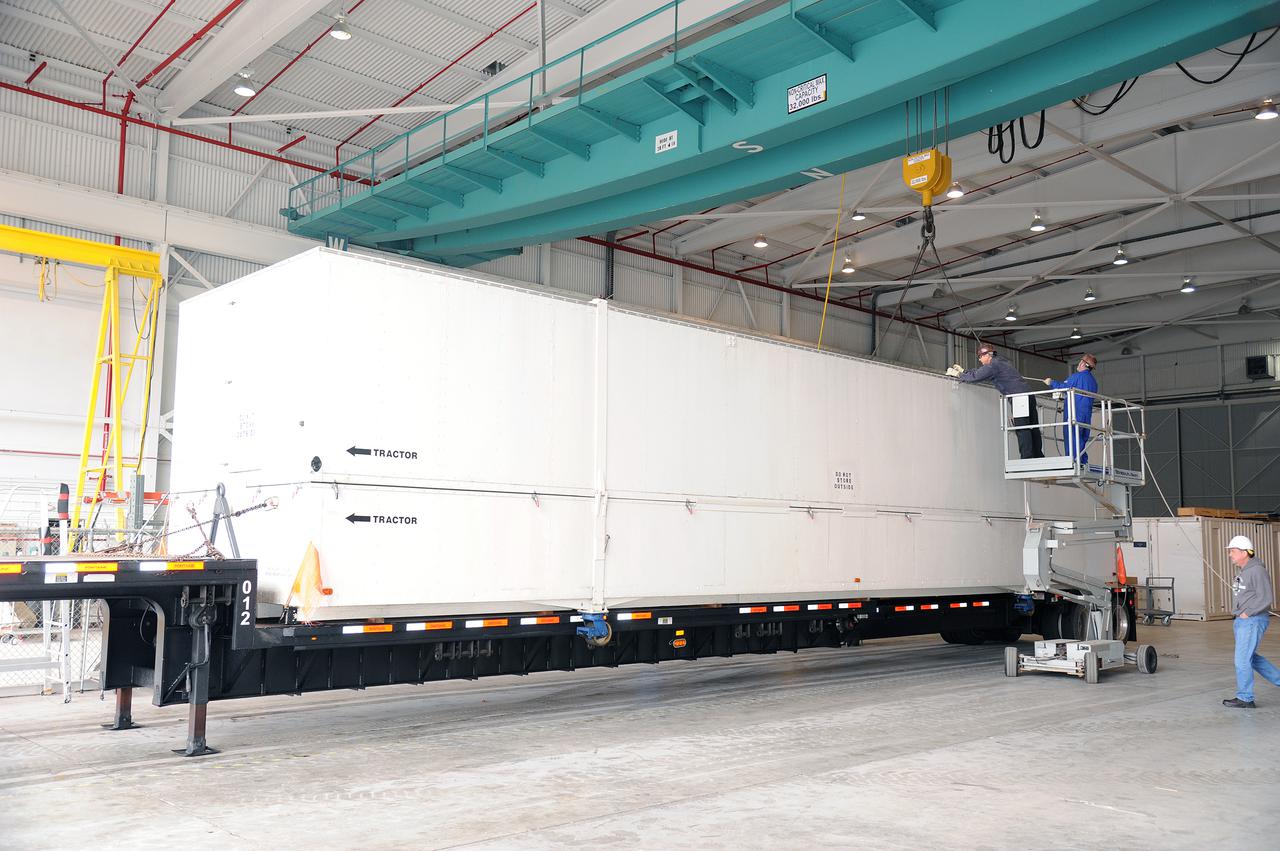
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to a lifting device in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
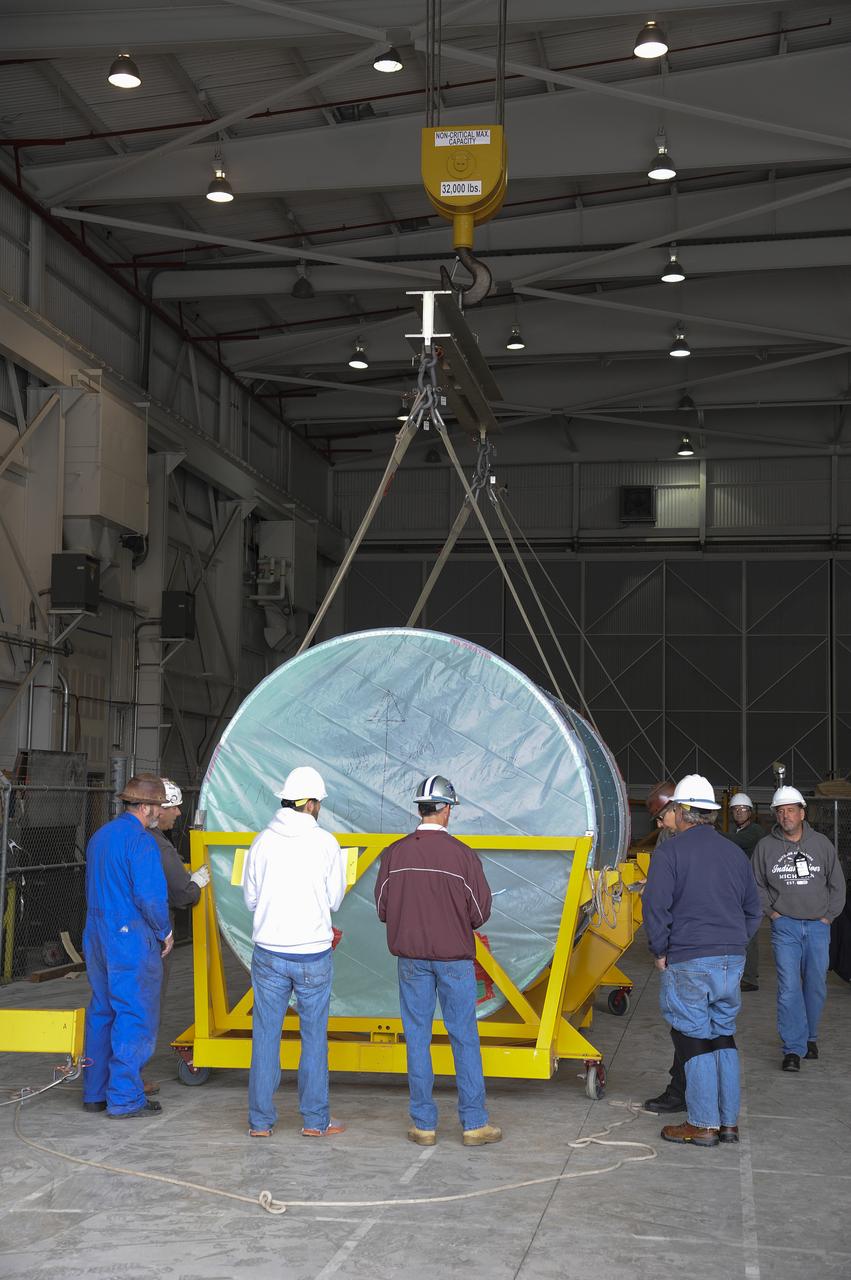

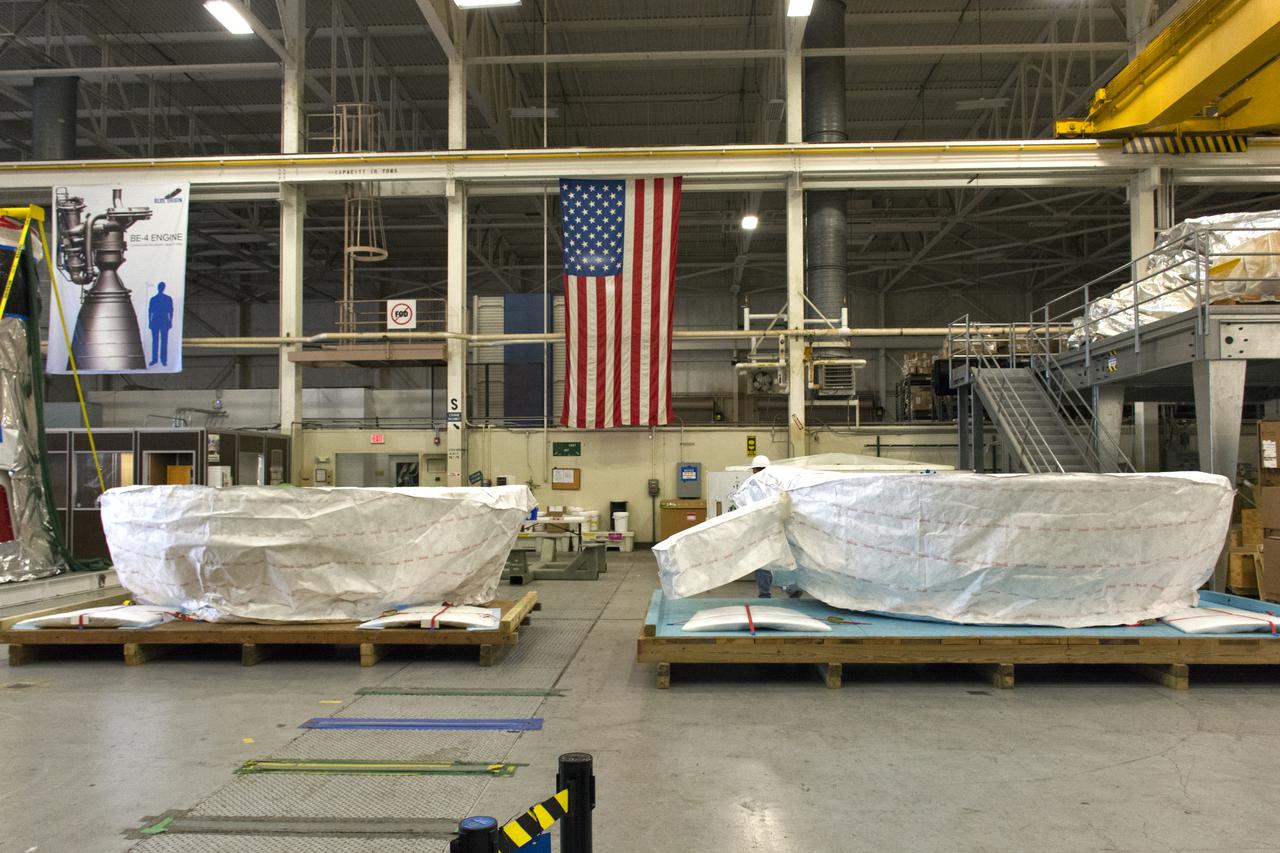
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lower the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a transportation hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
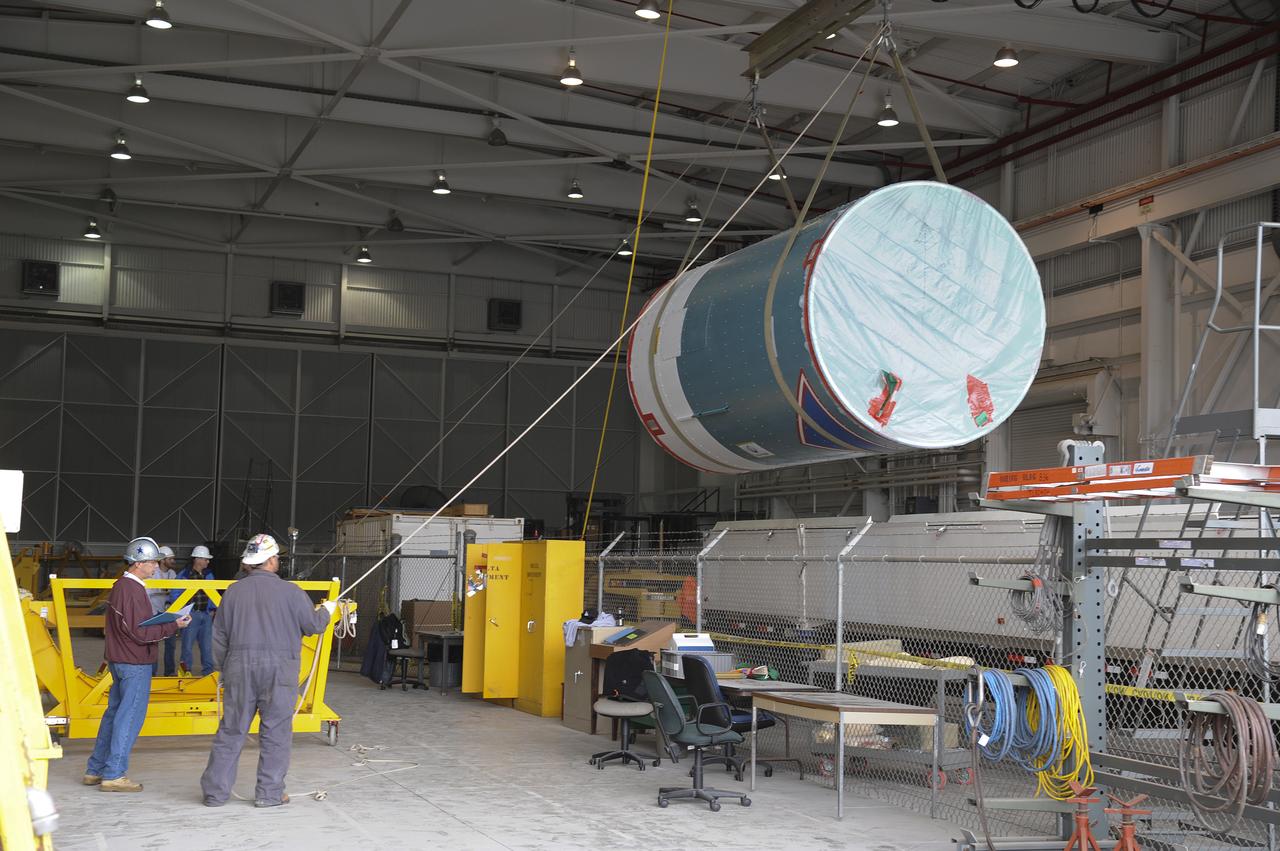

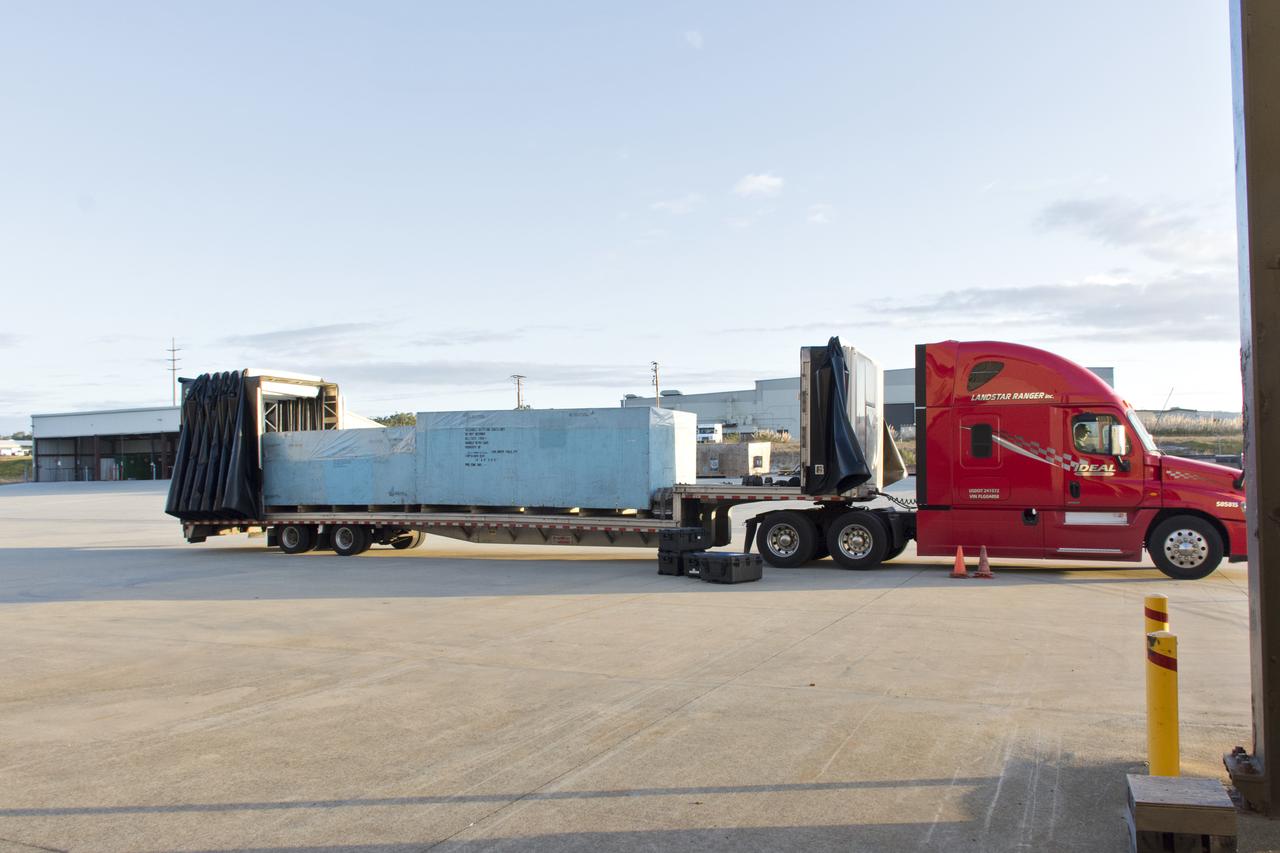
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lift the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from its transportation trailer in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
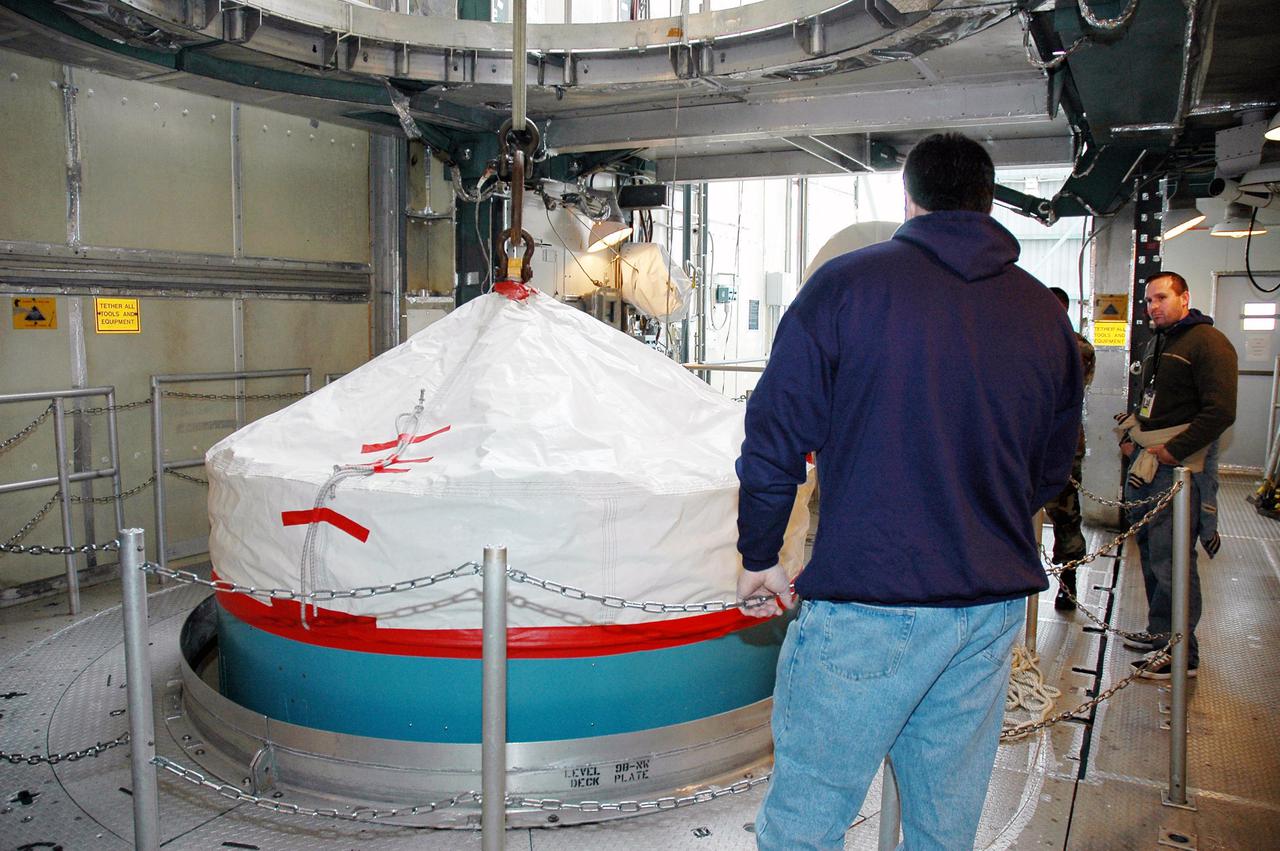

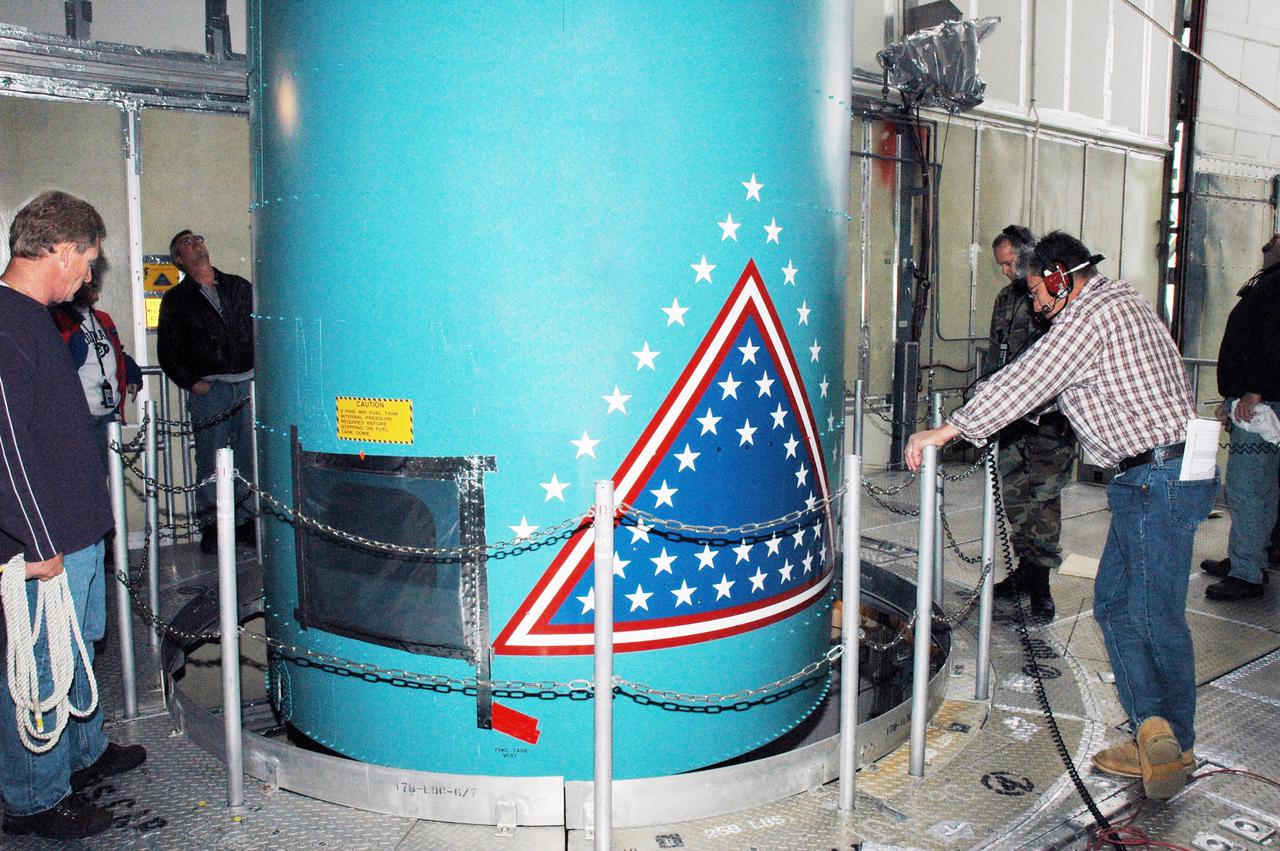
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is being lifted away from the center body section. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
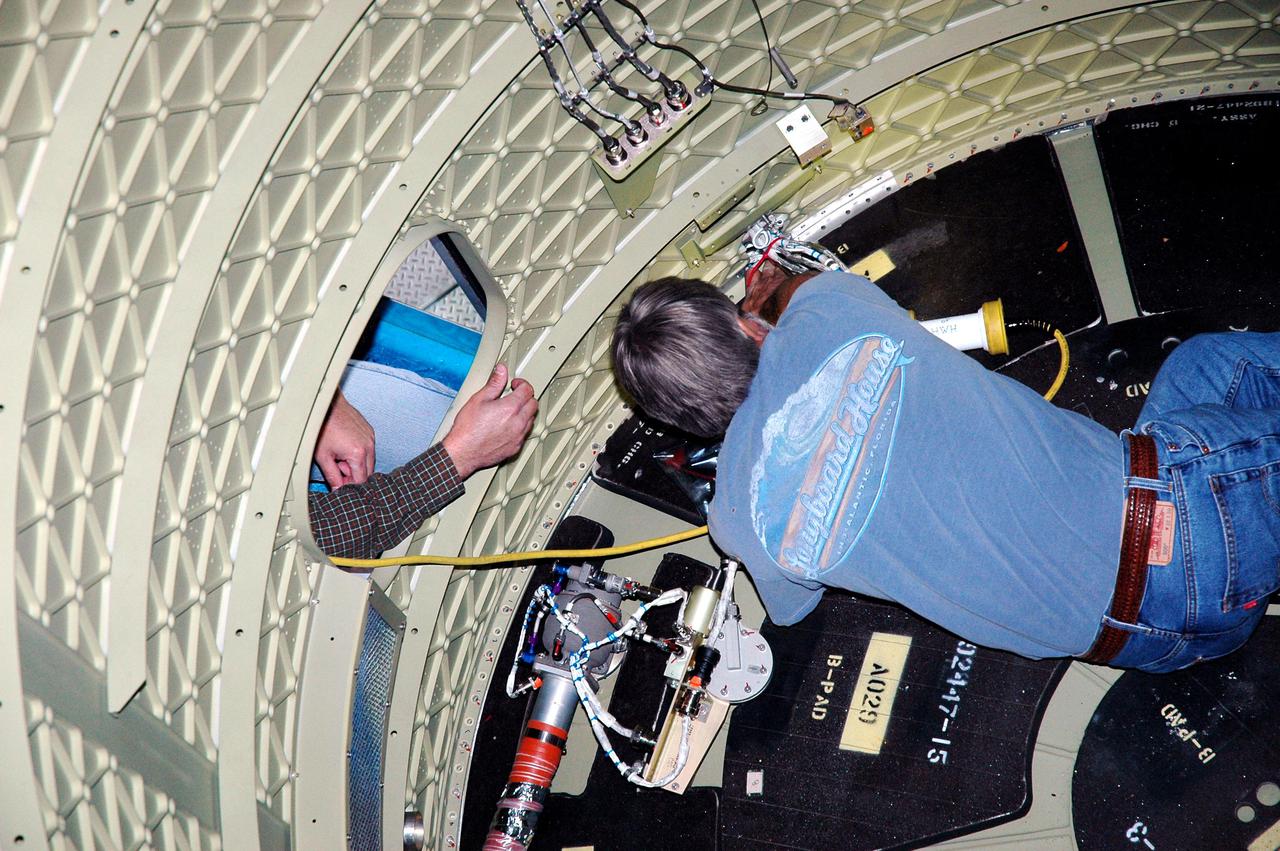

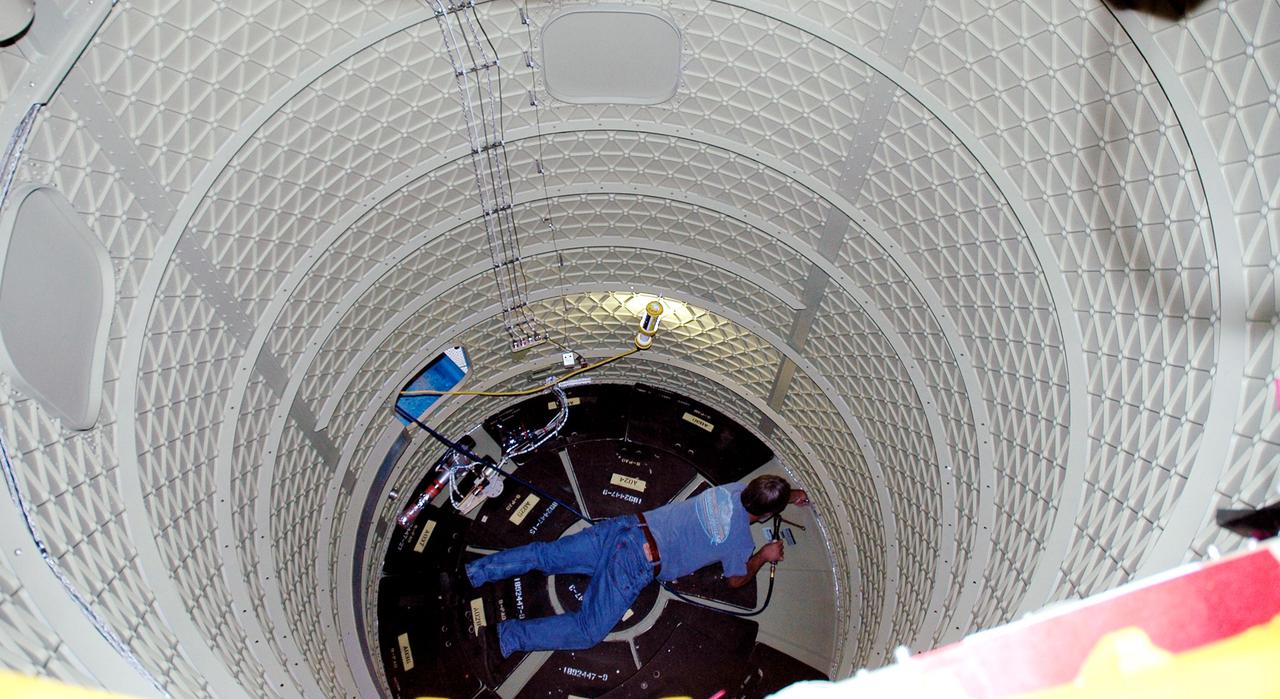
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., a technician works inside the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter, which is being removed. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
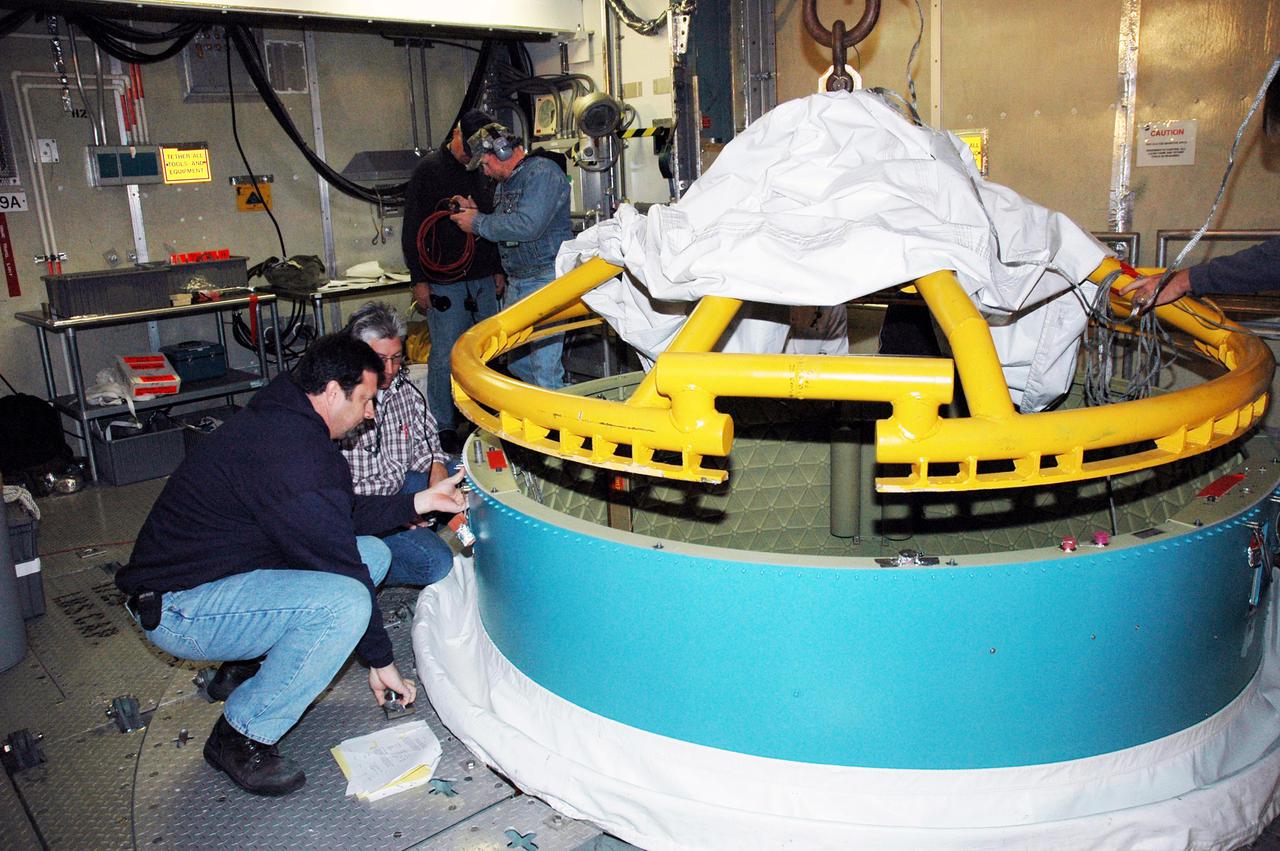

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is being removed. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.

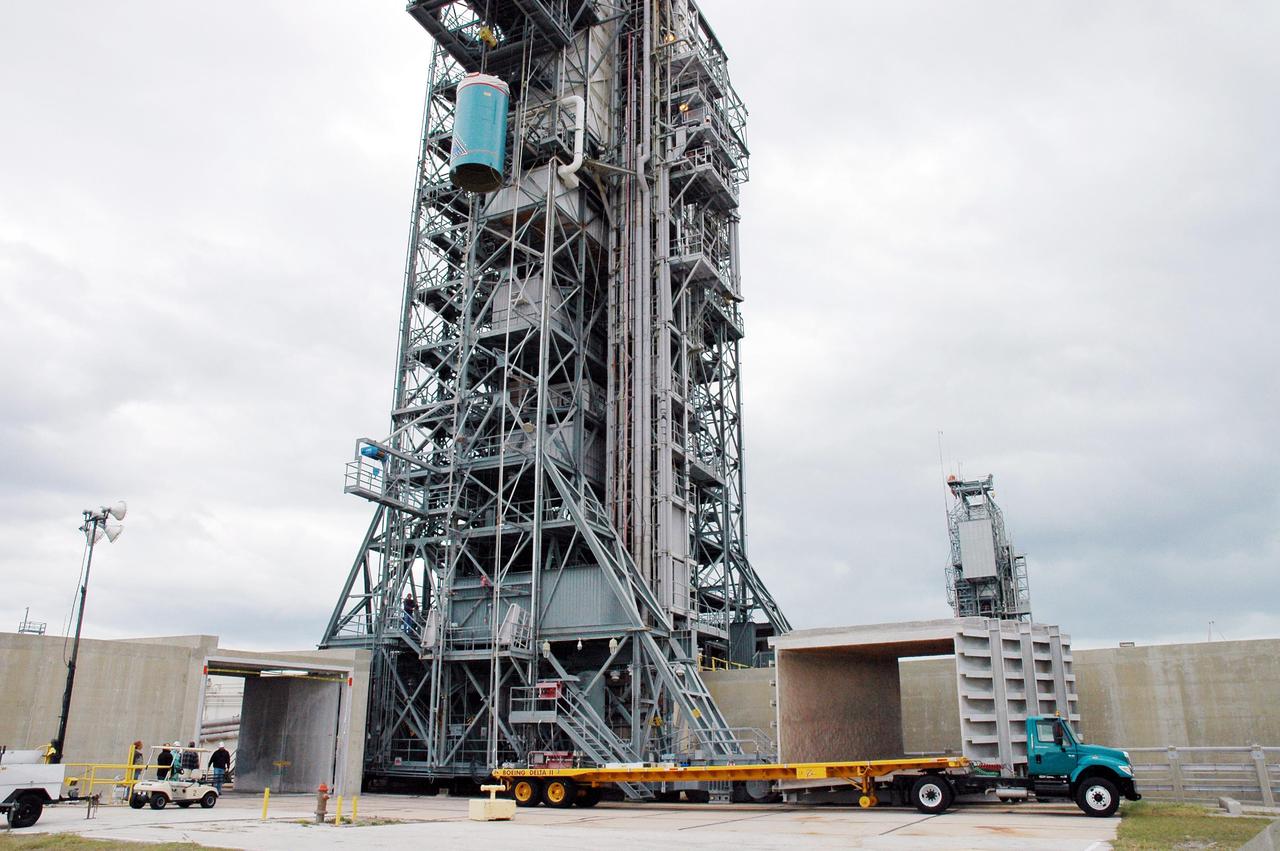
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is being lowered out of the tower. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is seen being lowered toward the pad. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.

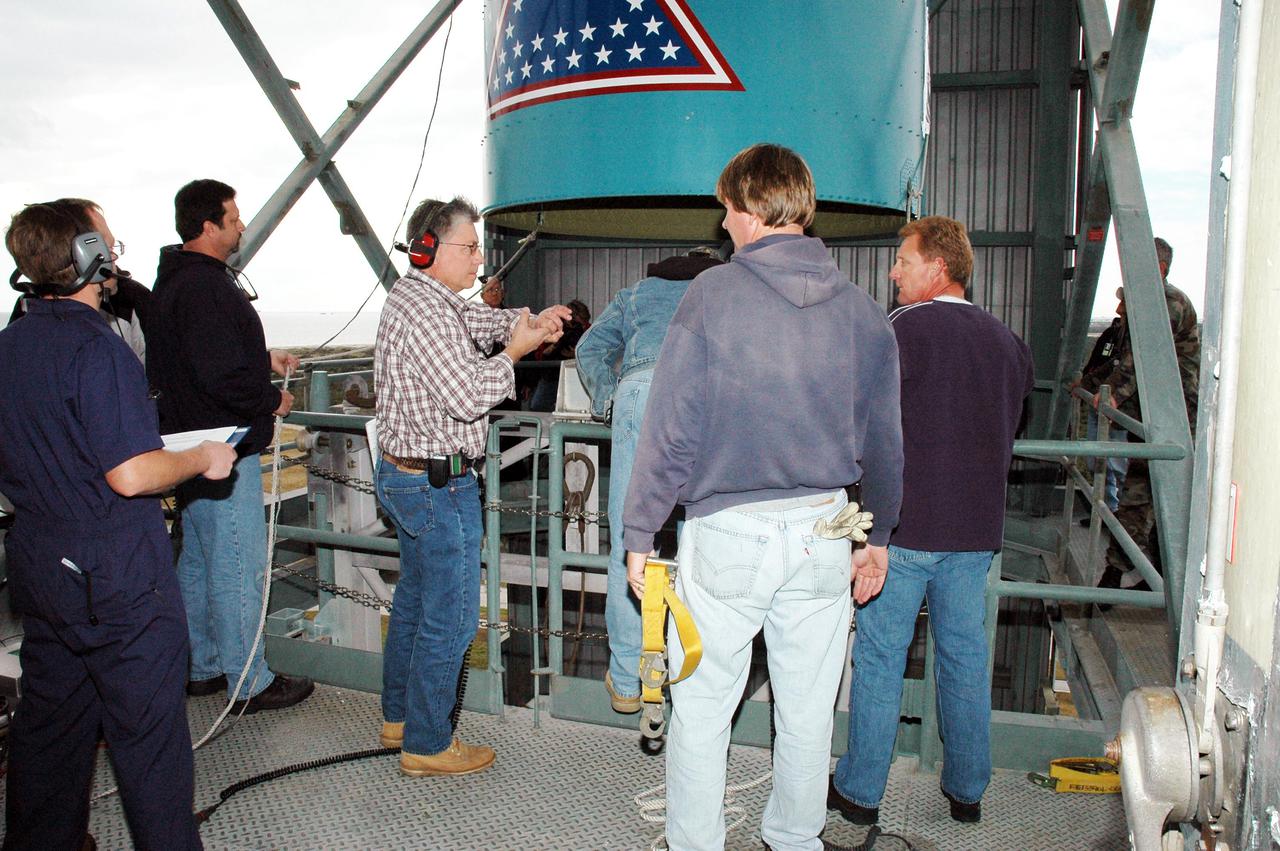
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., a technician works inside the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter, which is being removed. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., Boeing Delta II interstage adapter reaches the pad after being removed from the center body section. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is being lowered out of the tower. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
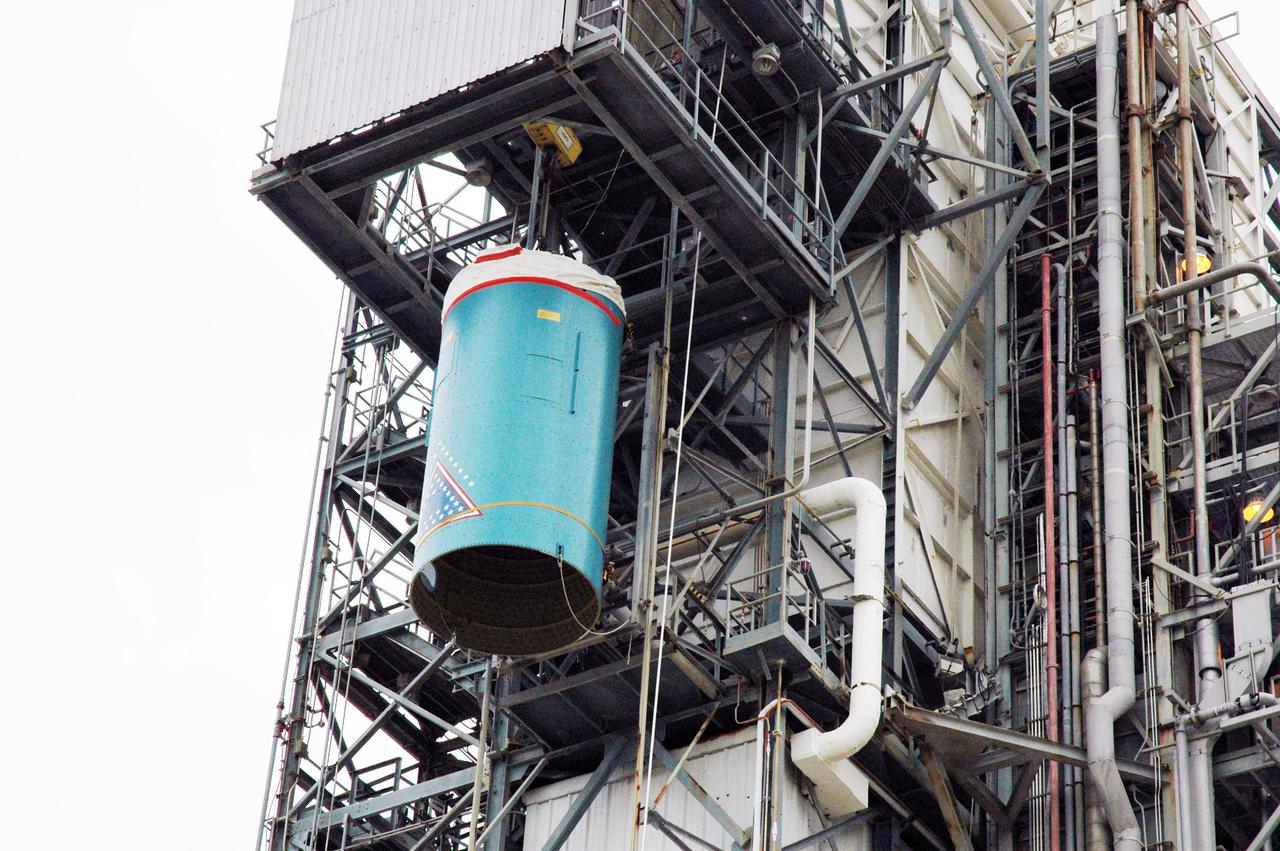

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is seen being lowered toward the pad. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
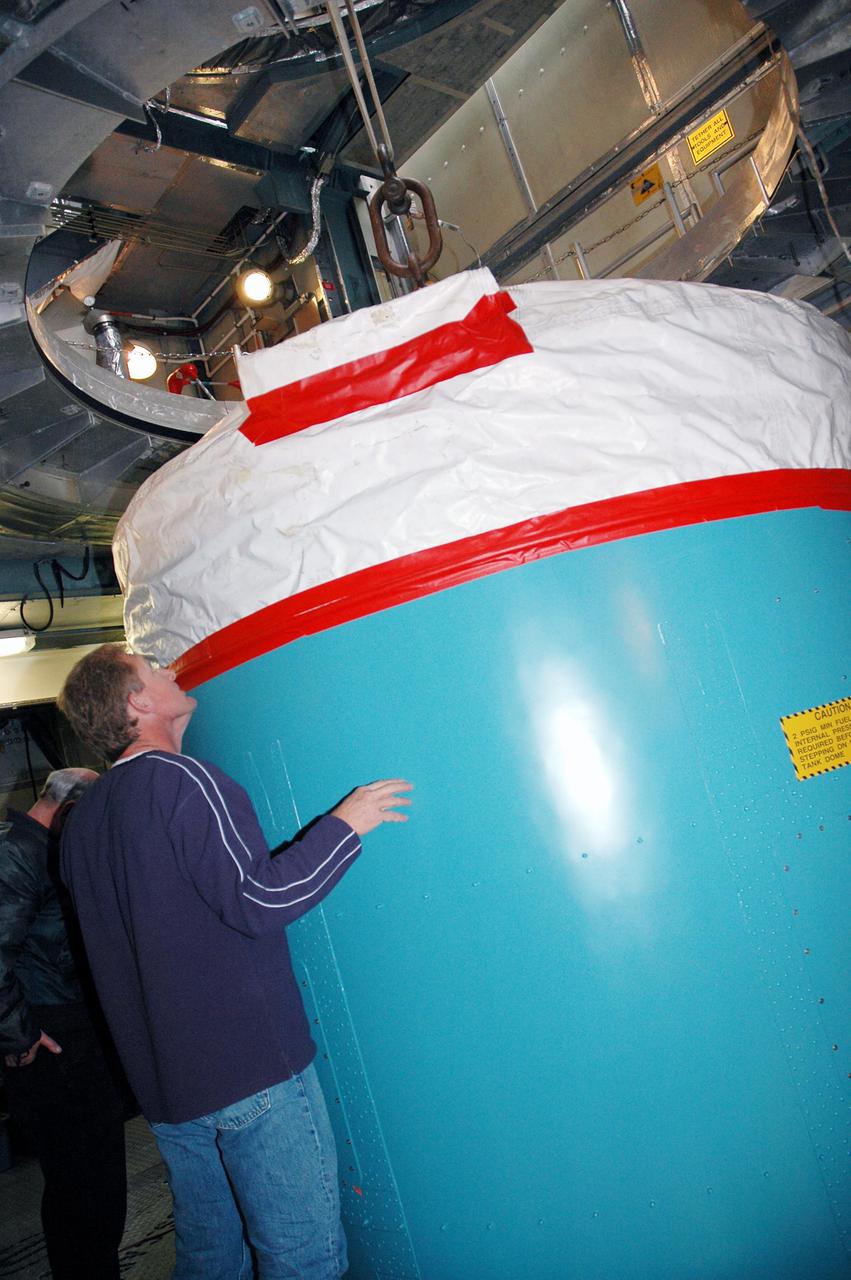

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the mobile service tower on Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station , Fla., the Boeing Delta II interstage adapter is lifted away from the center body section. The interstage adapter was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. It will be replaced, and the second stage previously removed will be re-installed within a few days. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
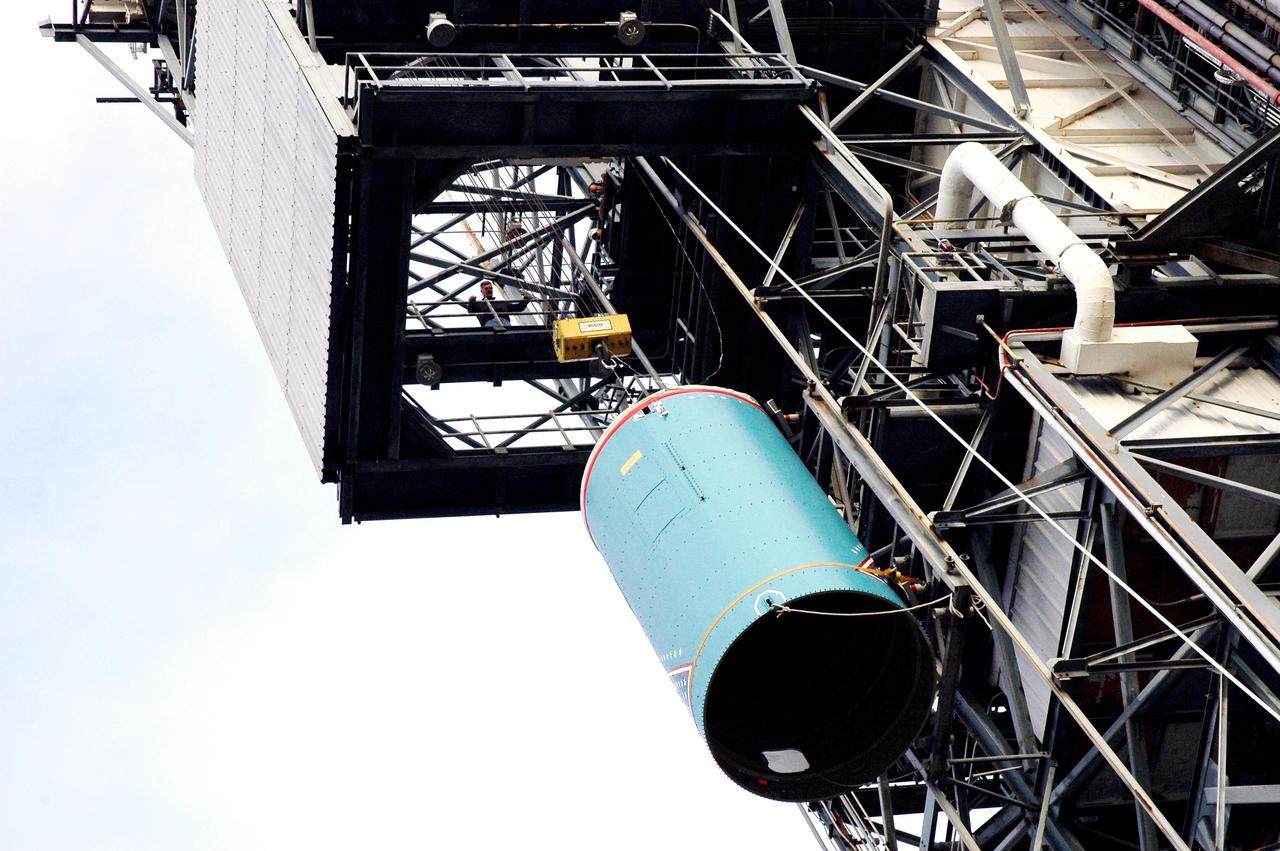
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The replacement interstage adapter for the Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft is lifted up the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
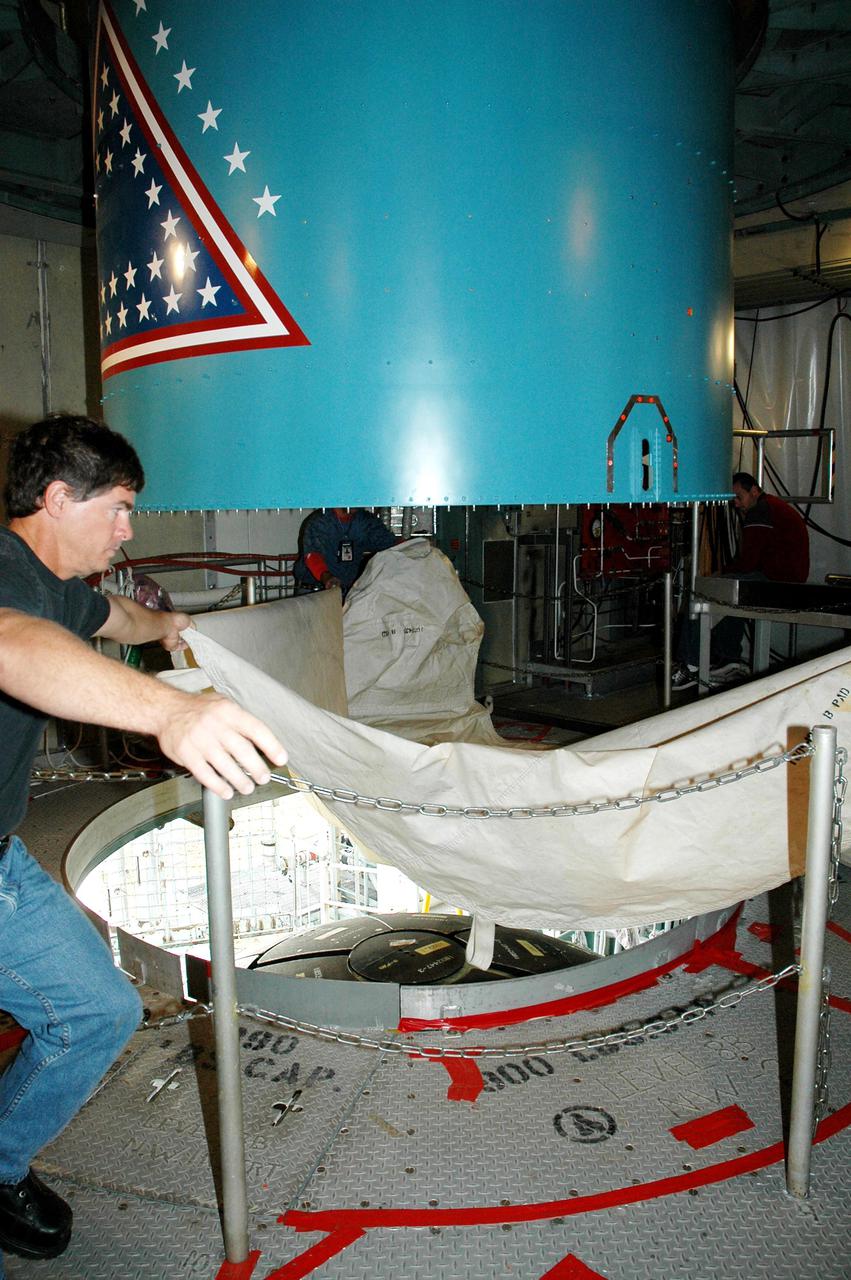

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., a Boeing worker removes a protective cover before the replacement interstage adapter is lowered toward the Boeing Delta II below. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
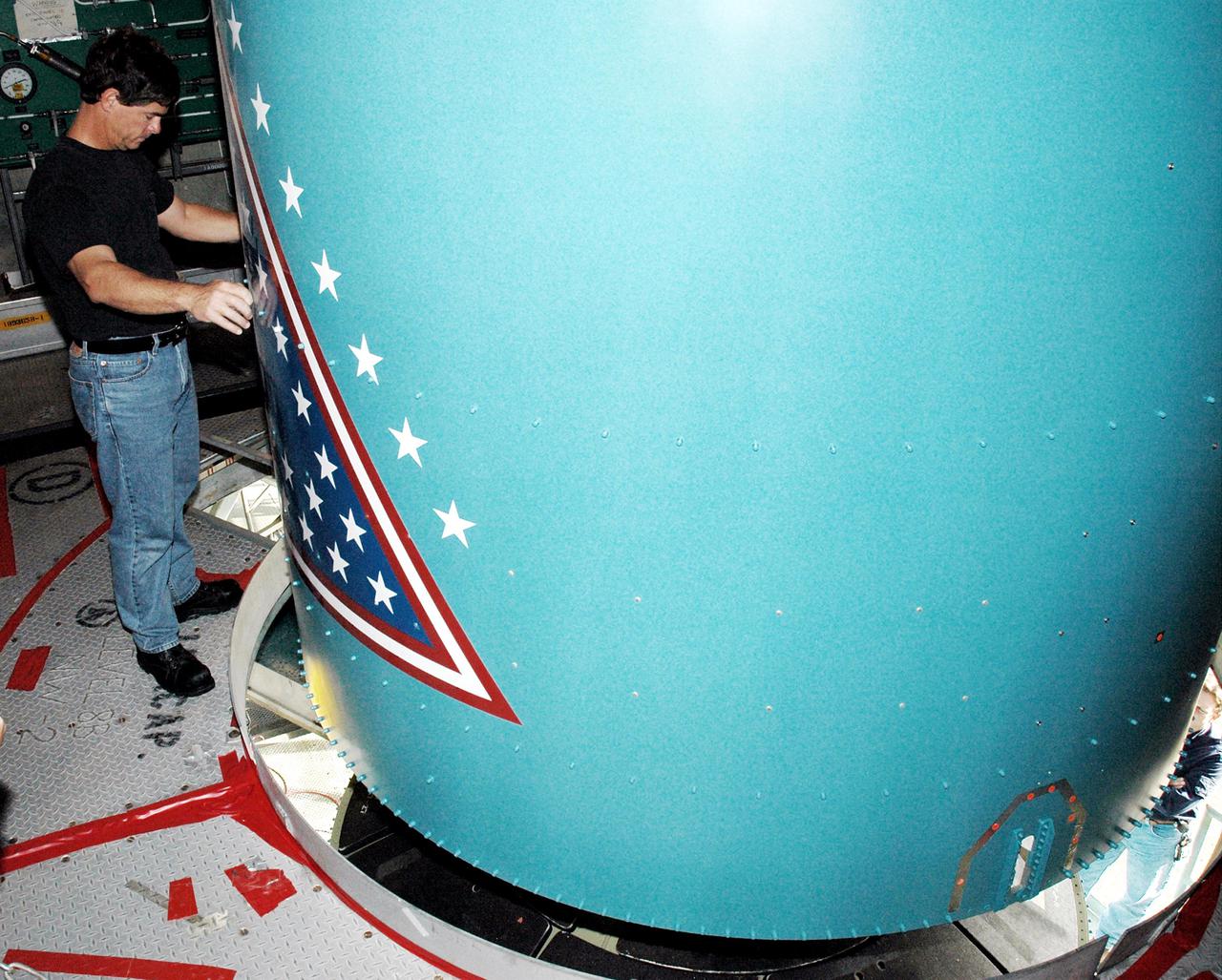
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., a Boeing worker aids in lowering the replacement interstage adapter toward the Boeing Delta II below. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
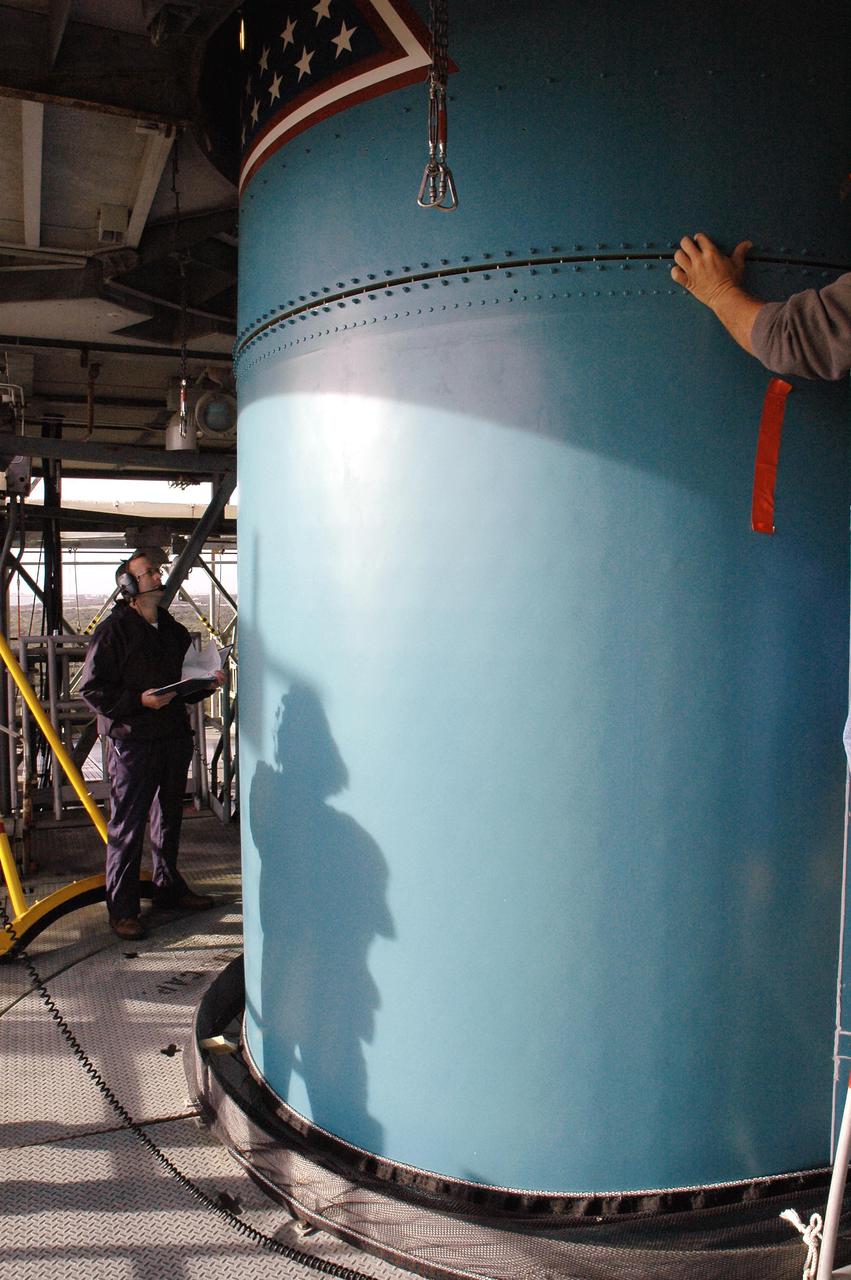

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Boeing workers aid in lowering the replacement interstage adapter toward the Boeing Delta II below. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
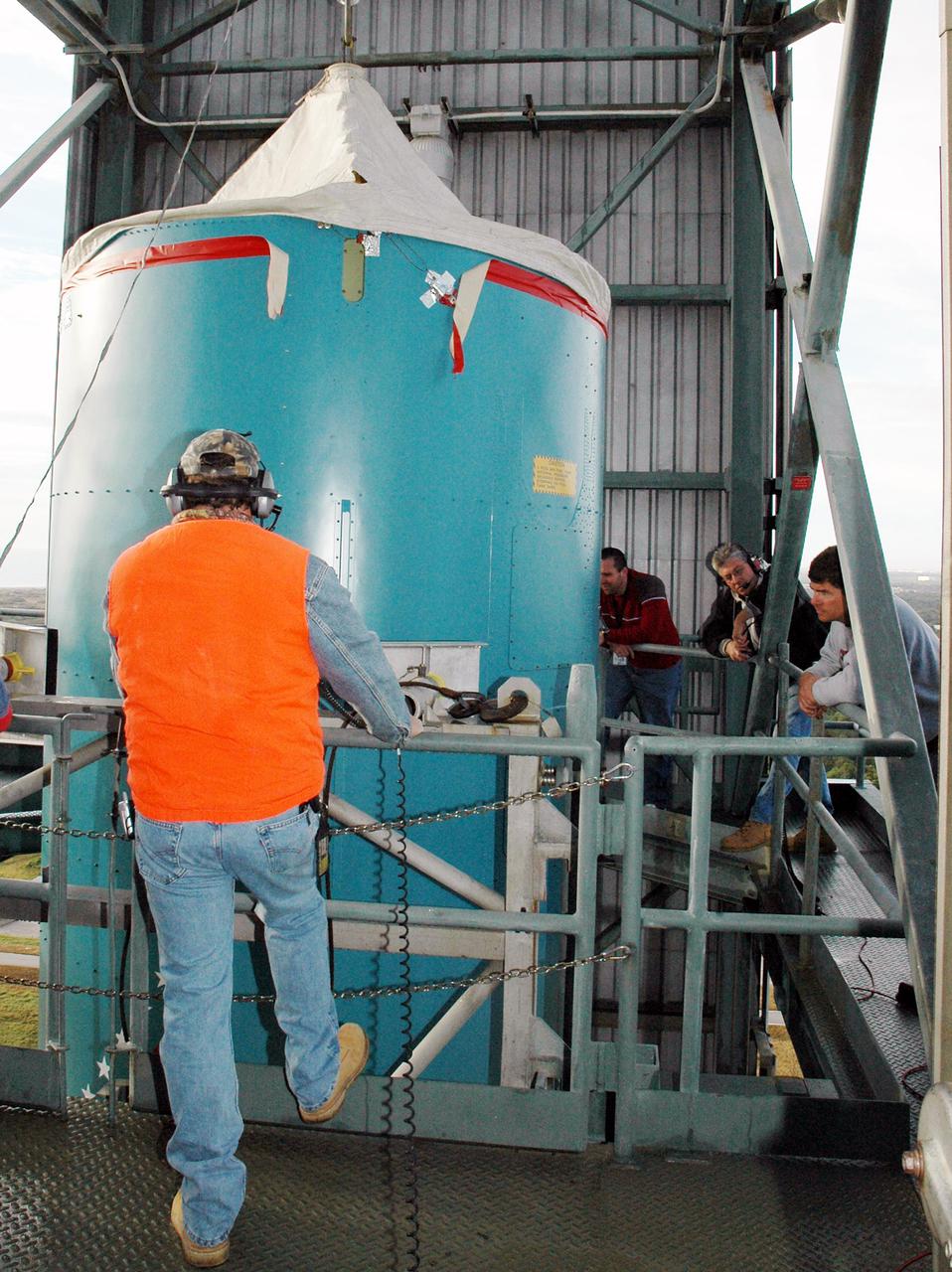

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - On the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Boeing workers stand by as the replacement interstage adapter for the Boeing Delta II is lowered. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
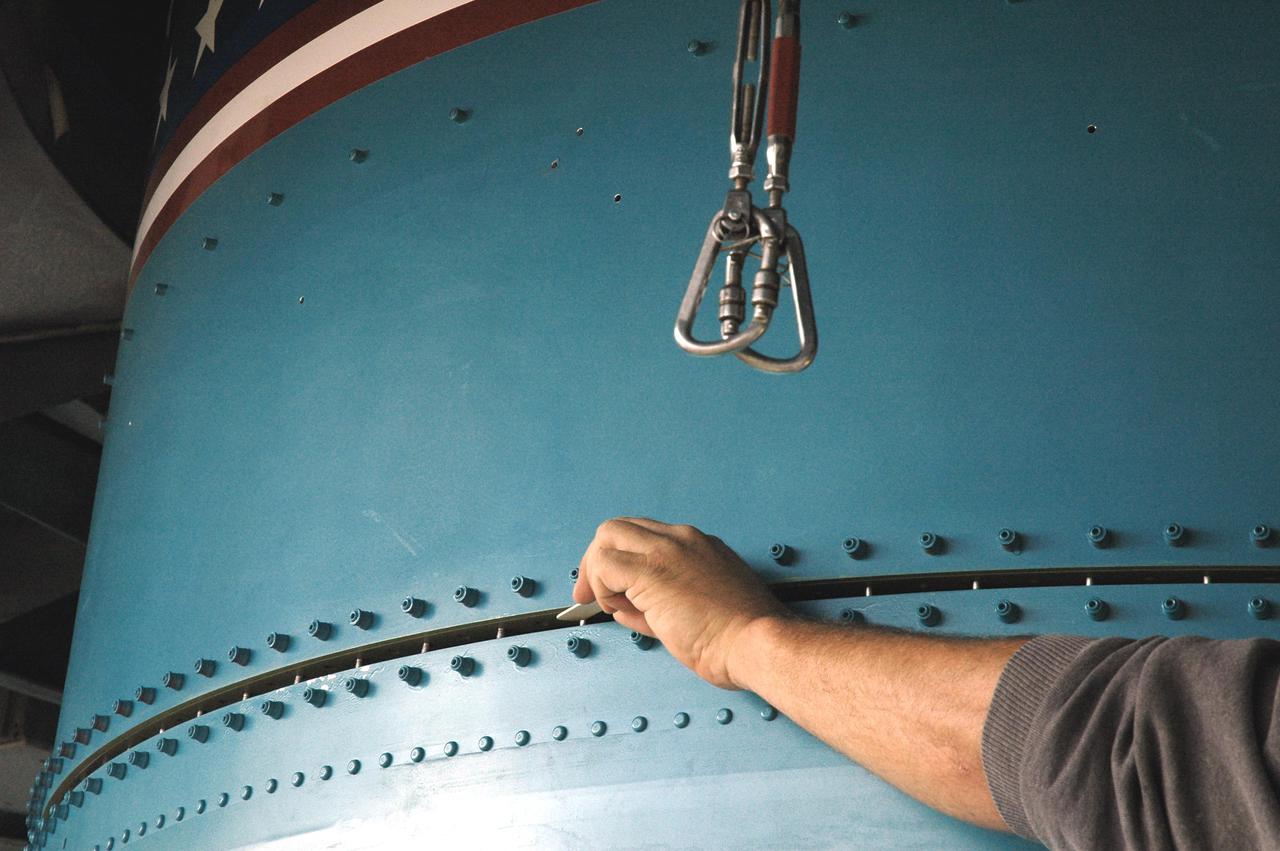

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla., Boeing technicians work at attaching the replacement interstage adapter to the center body section of the Boeing Delta II rocket. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
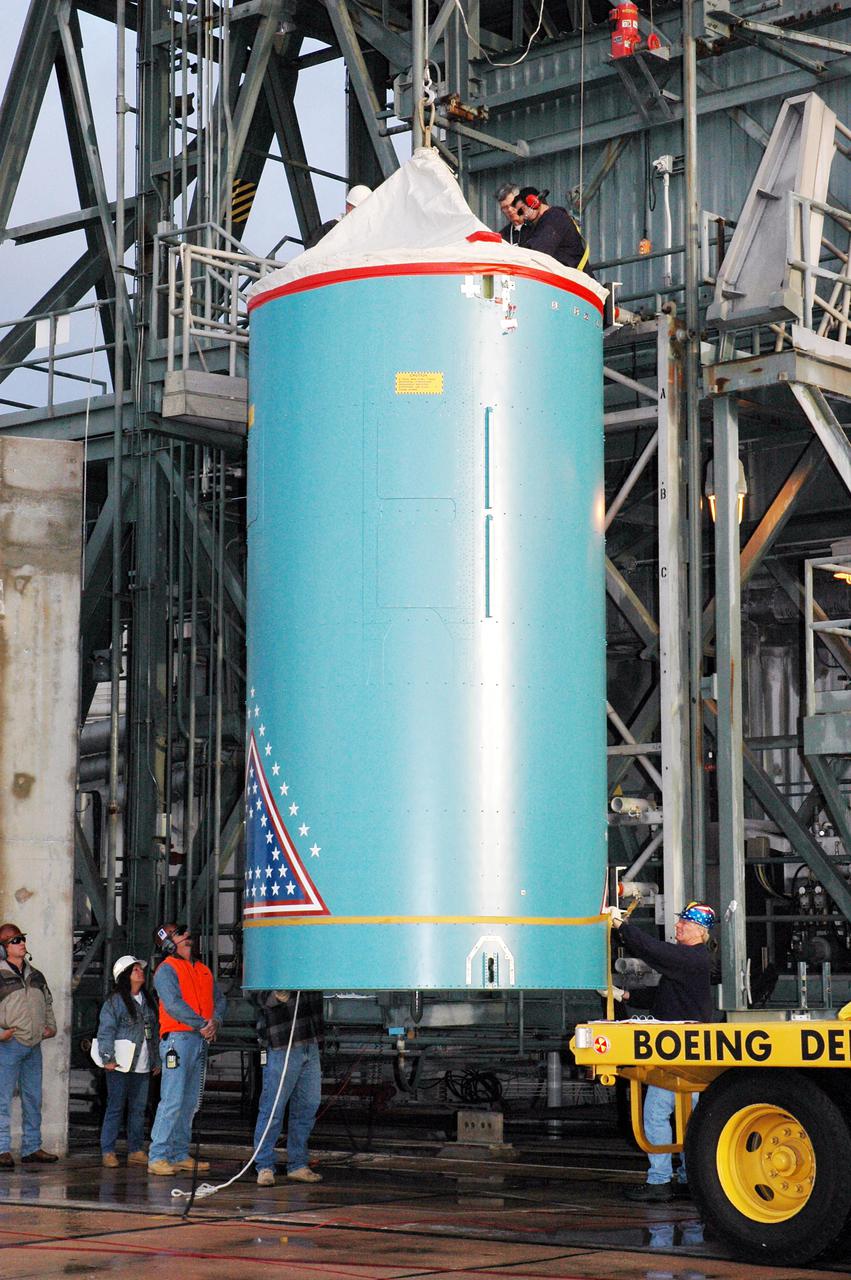
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The replacement interstage adapter for the Boeing Delta II launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft is ready to be lifted up the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. Boeing workers will attach the adapter to the rocket’s center body section. Later the second stage, which was removed to allow access to the previous adapter, will be reattached. The first adapter was removed after it was found to be faulty during a review of launch vehicle hardware. Launch of Deep Impact is now scheduled no earlier than Jan. 12.
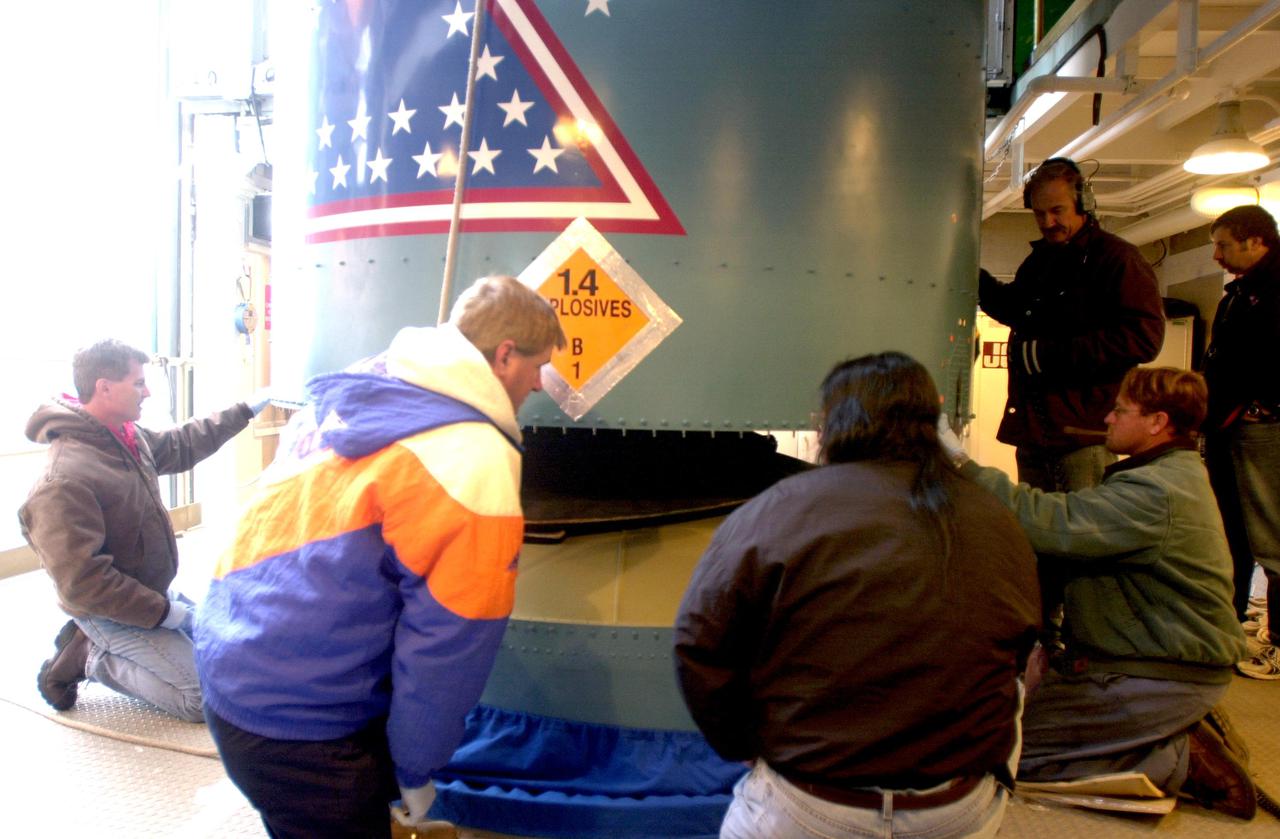

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - The interstage of a Boeing Delta 2 rocket is mated with the interstage adapter below it in the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The Delta 2 is the launch vehicle for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-N) spacecraft. NOAA-N is the fourth in the series of support dedicated microwave instruments for the generation of temperature, moisture, surface, and hydrological products in cloudy regions where visible and infrared (IR) instruments have decreased capability. Launch aboard a Boeing Delta II rocket is currently scheduled for no earlier than May 11, 2005.
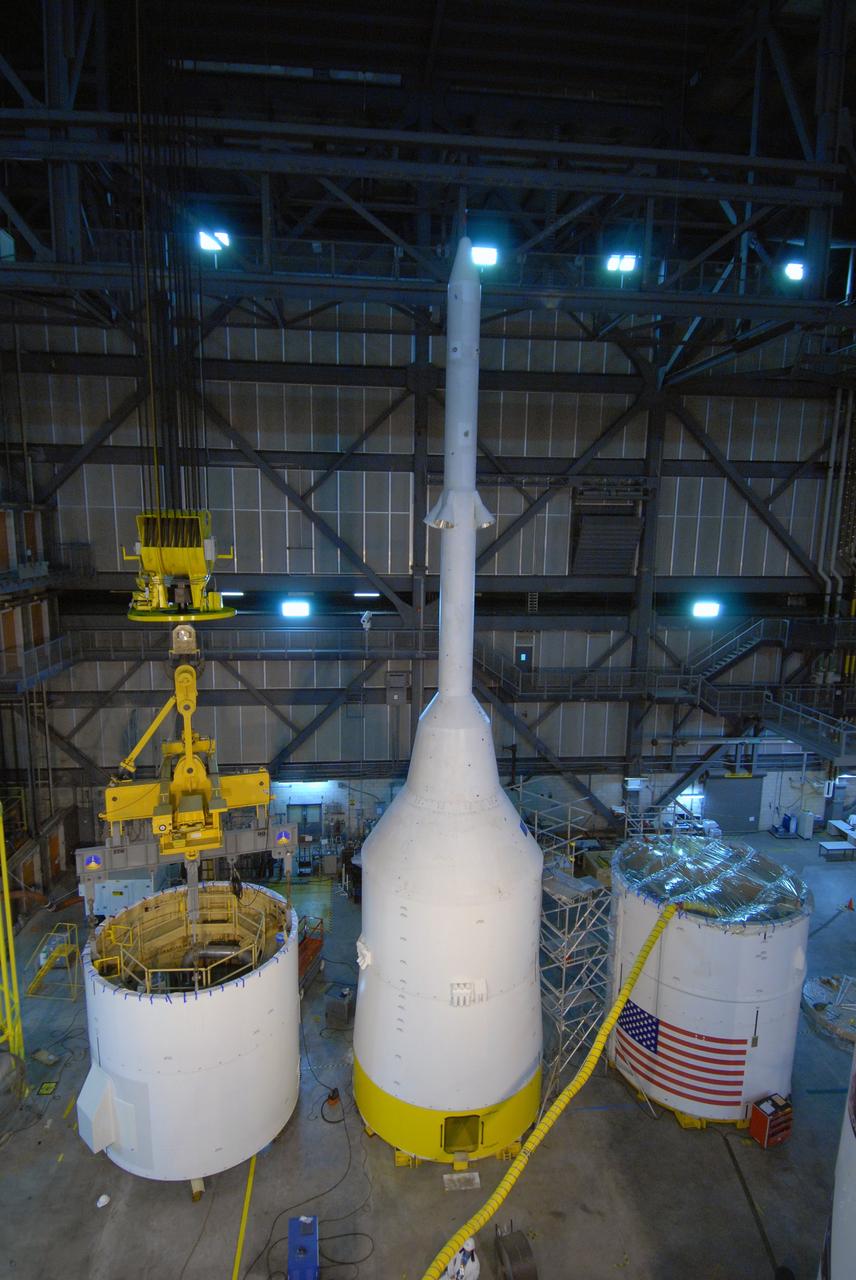

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator (left) is being lifted to move it to the forward assembly. The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. At center is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
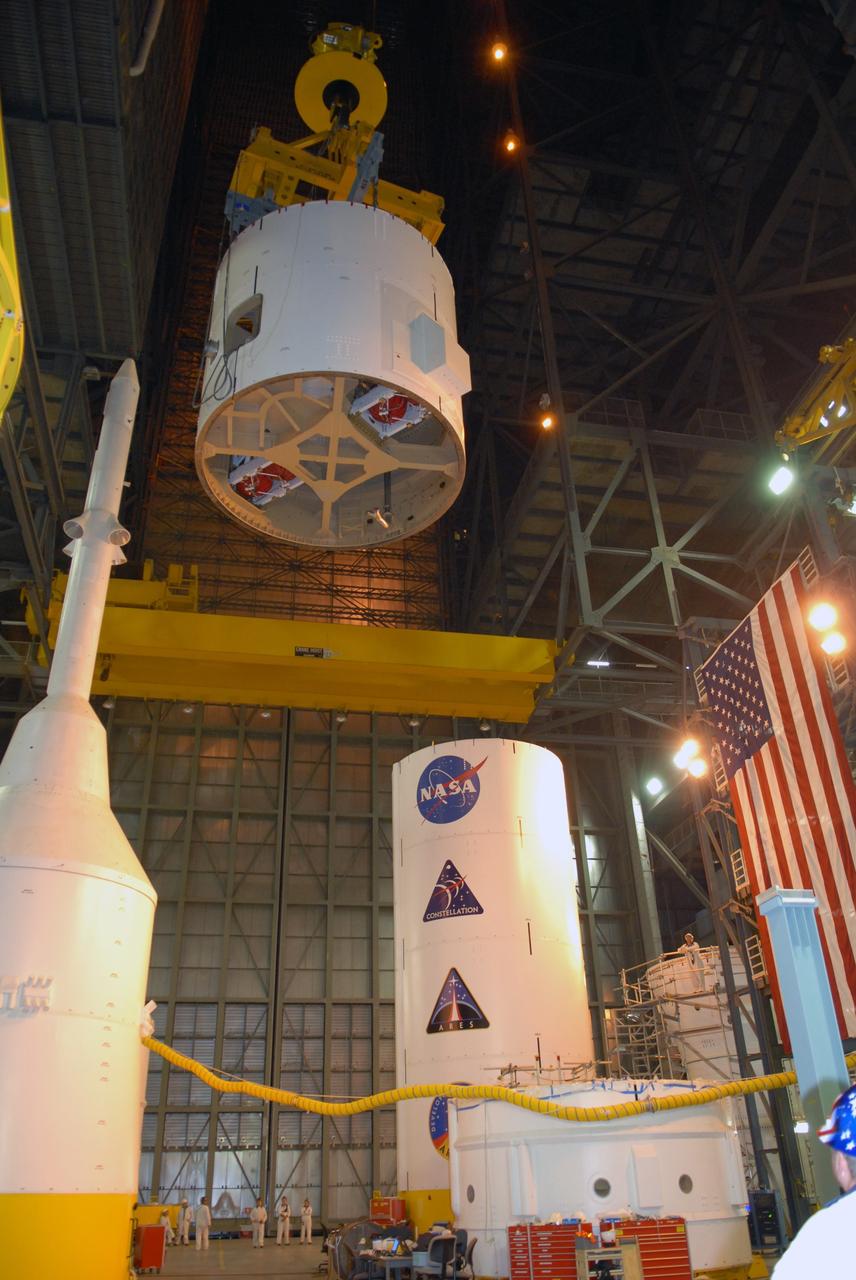

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator is being moved to the forward assembly. The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. To the left is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
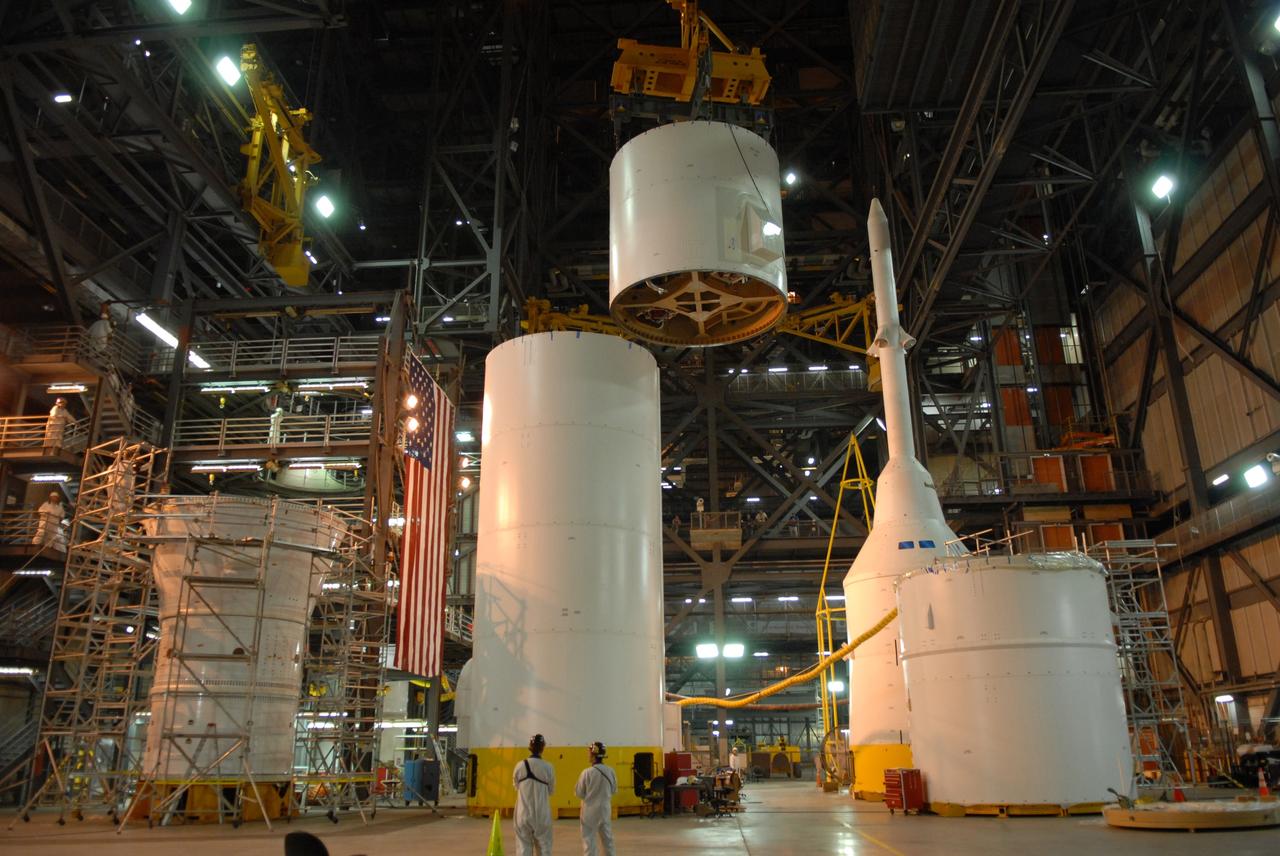

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator is being moved to the forward assembly (far left). The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. To the right is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
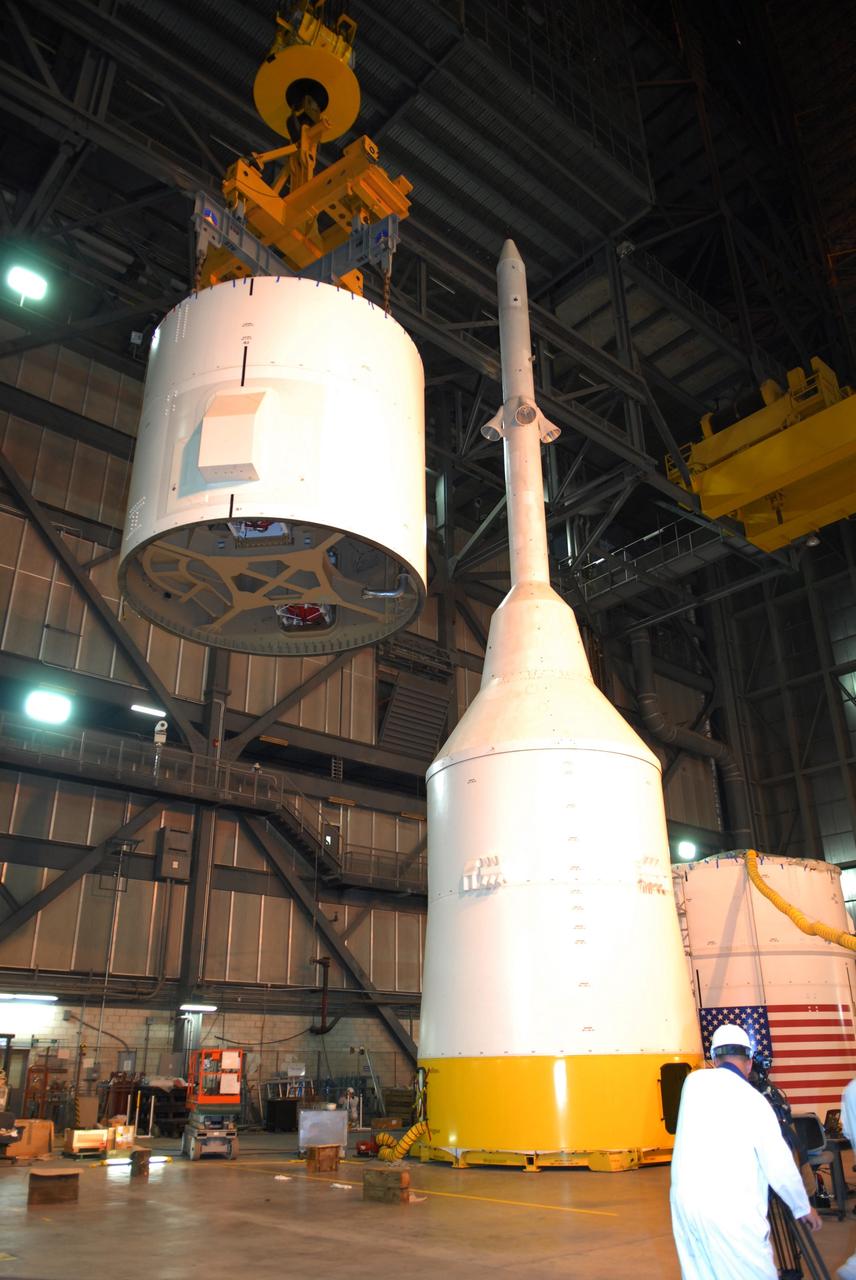

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator is being moved to the forward assembly. The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. To the right is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Ares I-X interstage 1 for the upper stage simulator is lifted to move it to the forward assembly. The interstage will be mated with the frustum on the forward assembly. To the right is the crew module-launch abort system, or CM-LAS, and simulator service module-service adapter stack. Ares I-X is the flight test vehicle for the Ares I, a component of the Constellation Program. Ares I is the essential core of a safe, reliable, cost-effective space transportation system that eventually will carry crewed missions back to the moon, on to Mars and out into the solar system. Ares I-X is targeted for launch in August 2009. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs

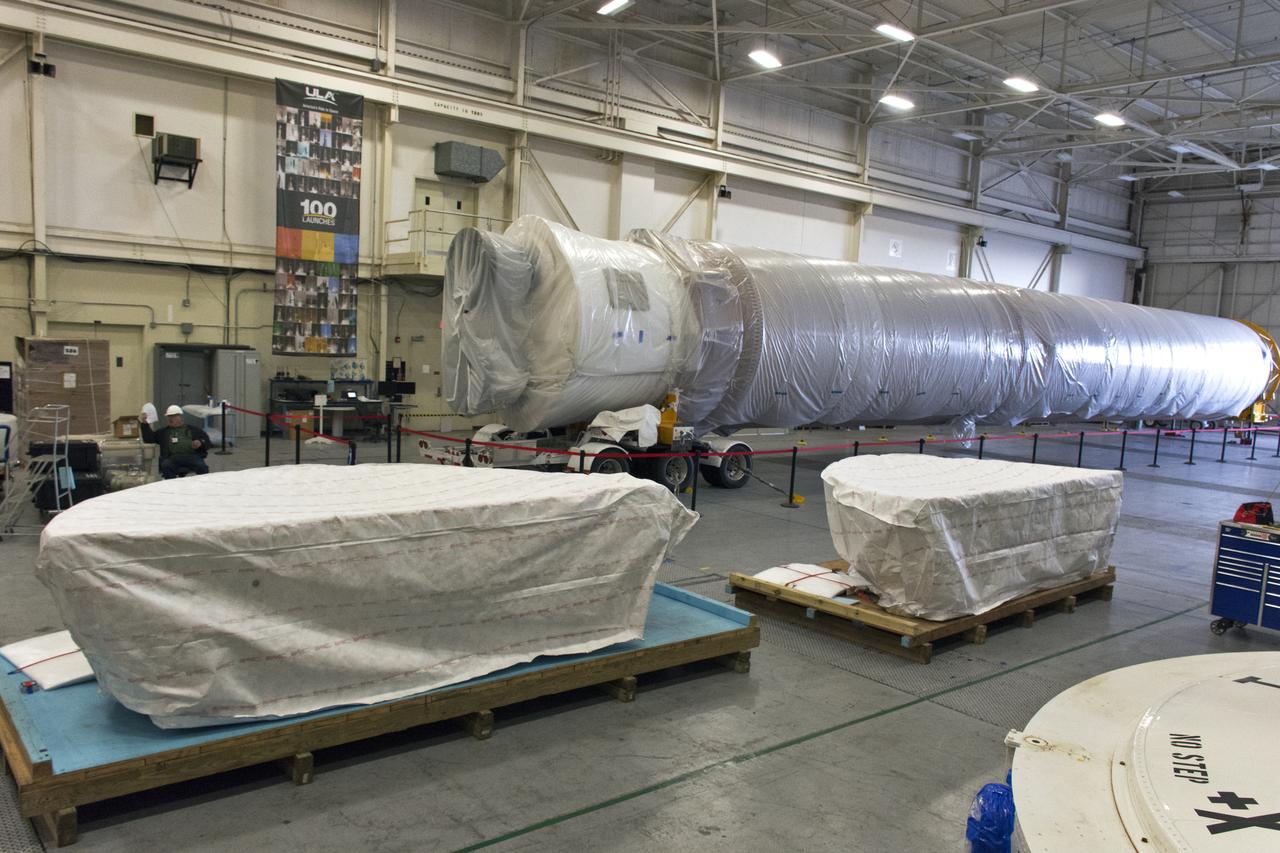
At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing is offloaded for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing arrives for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing has been offloaded for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
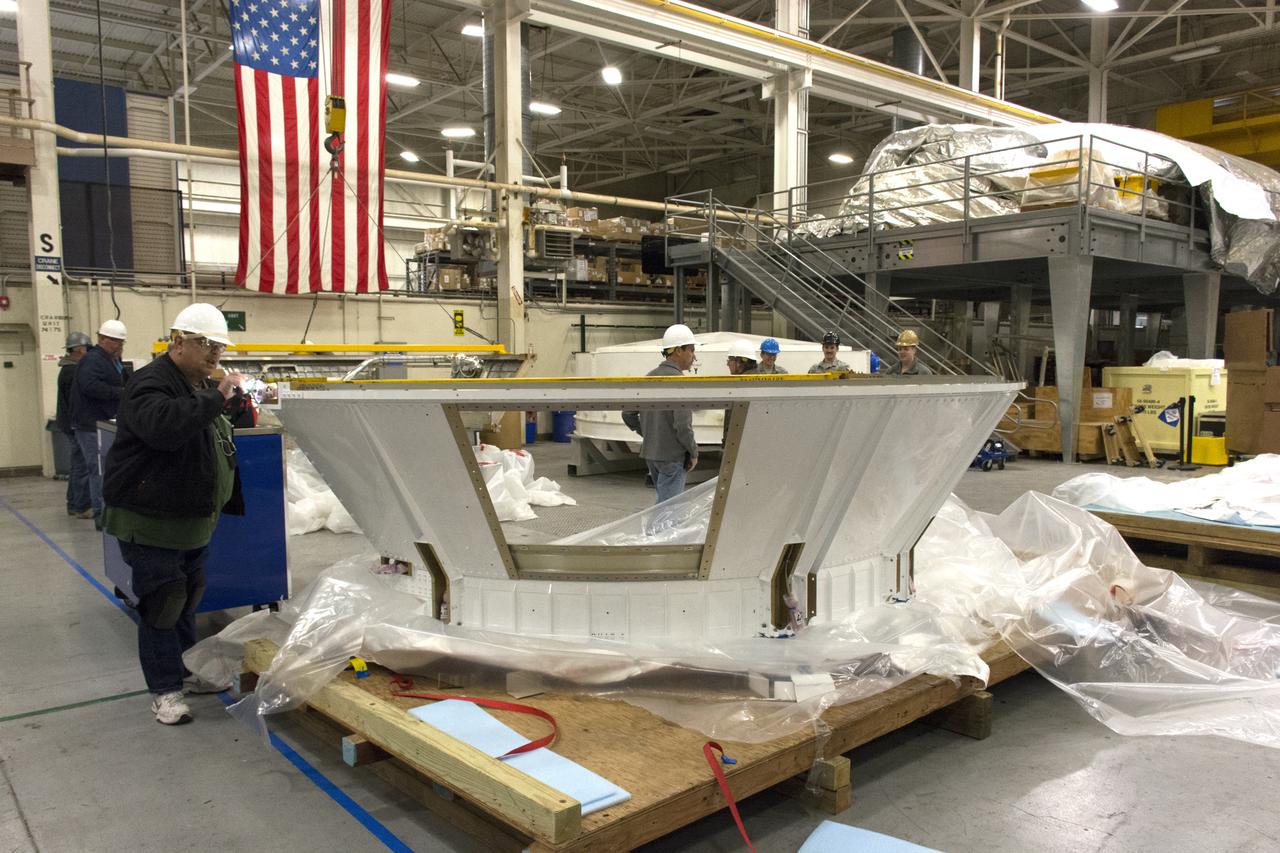

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
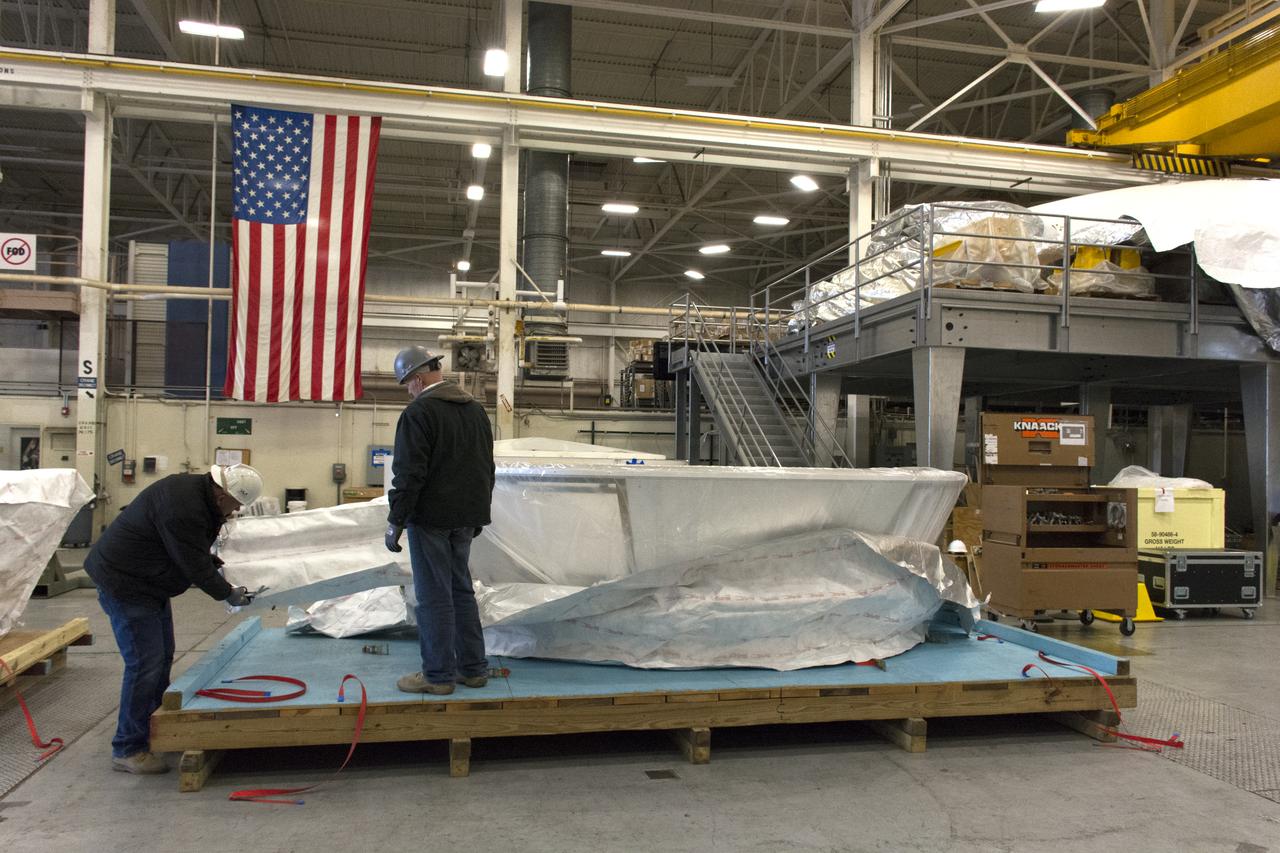

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
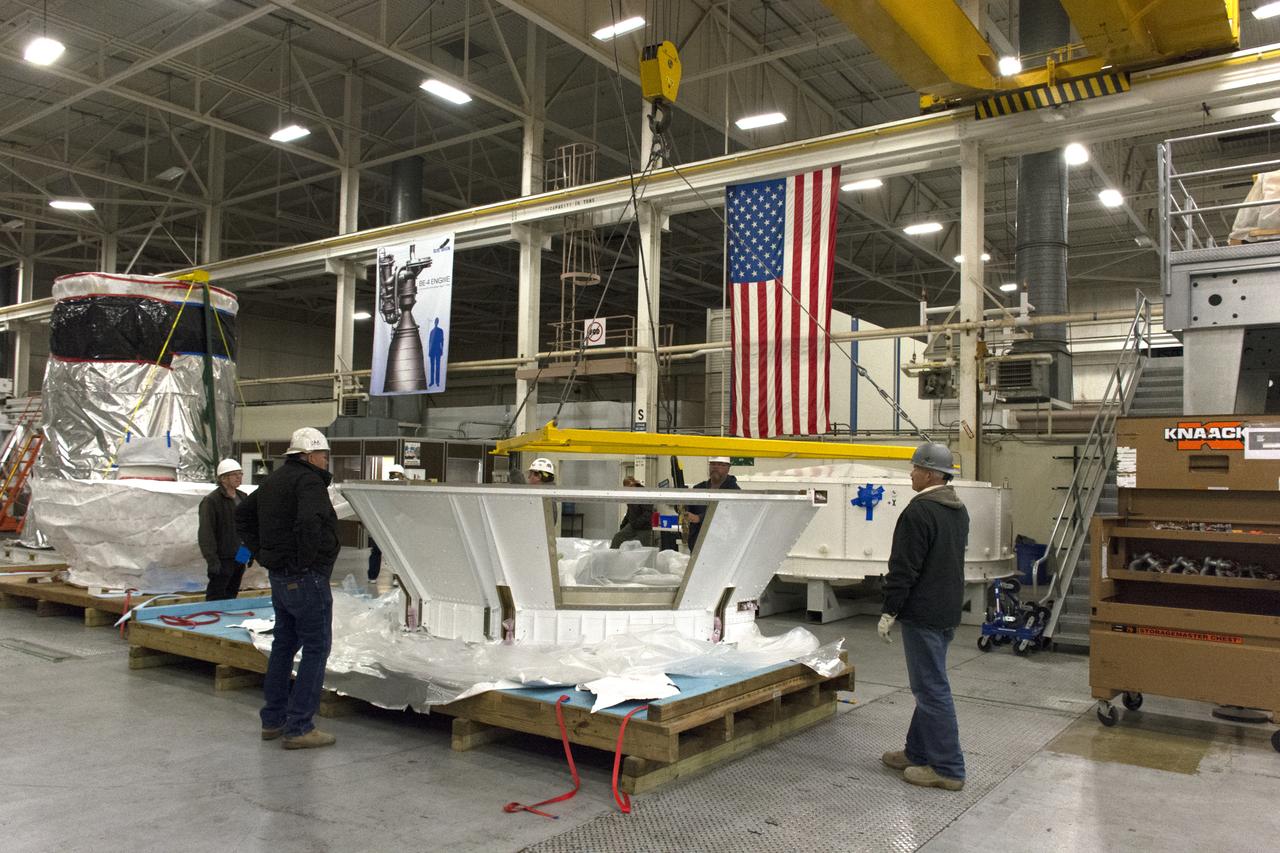

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians inspect the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
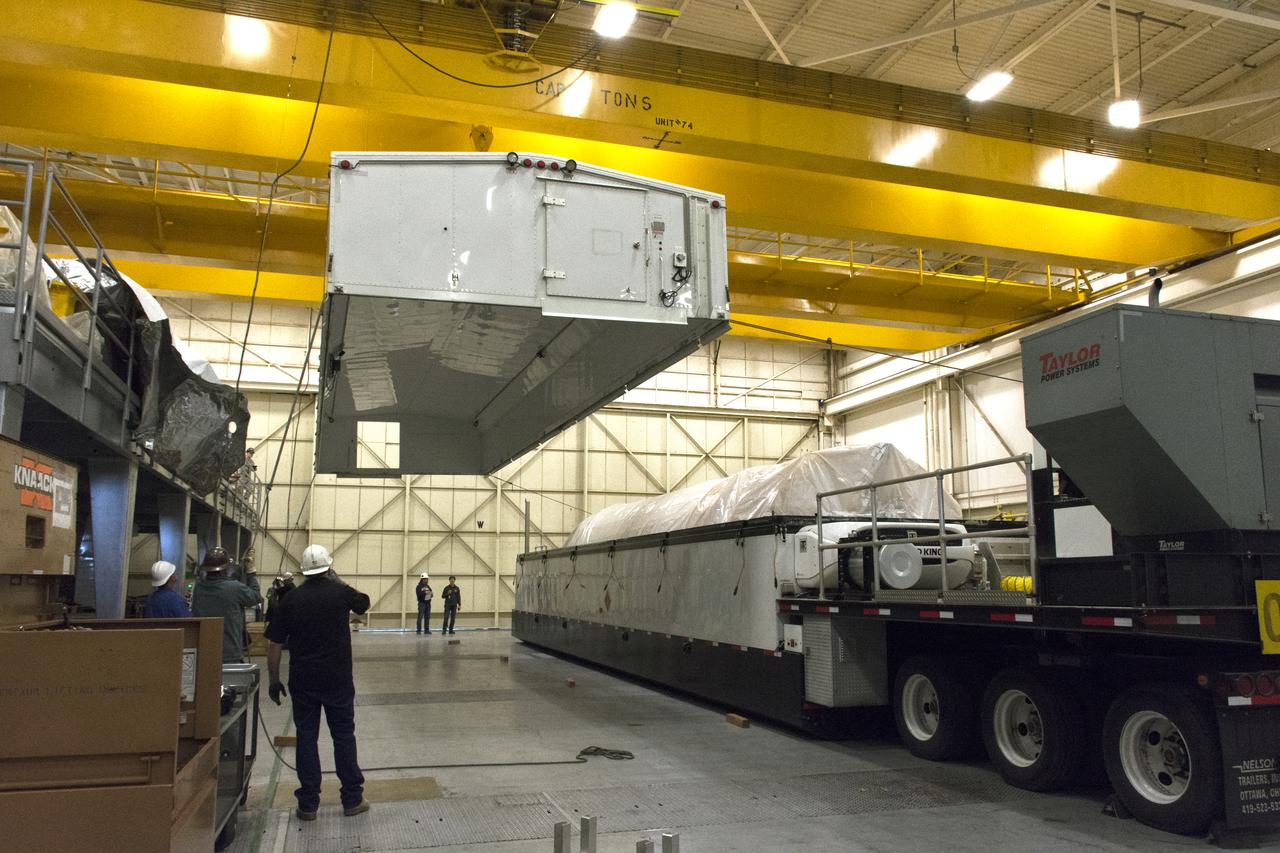

Inside Building B7525 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Centaur upper stage for a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is offloaded from a transport truck. The launch vehicle will send NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
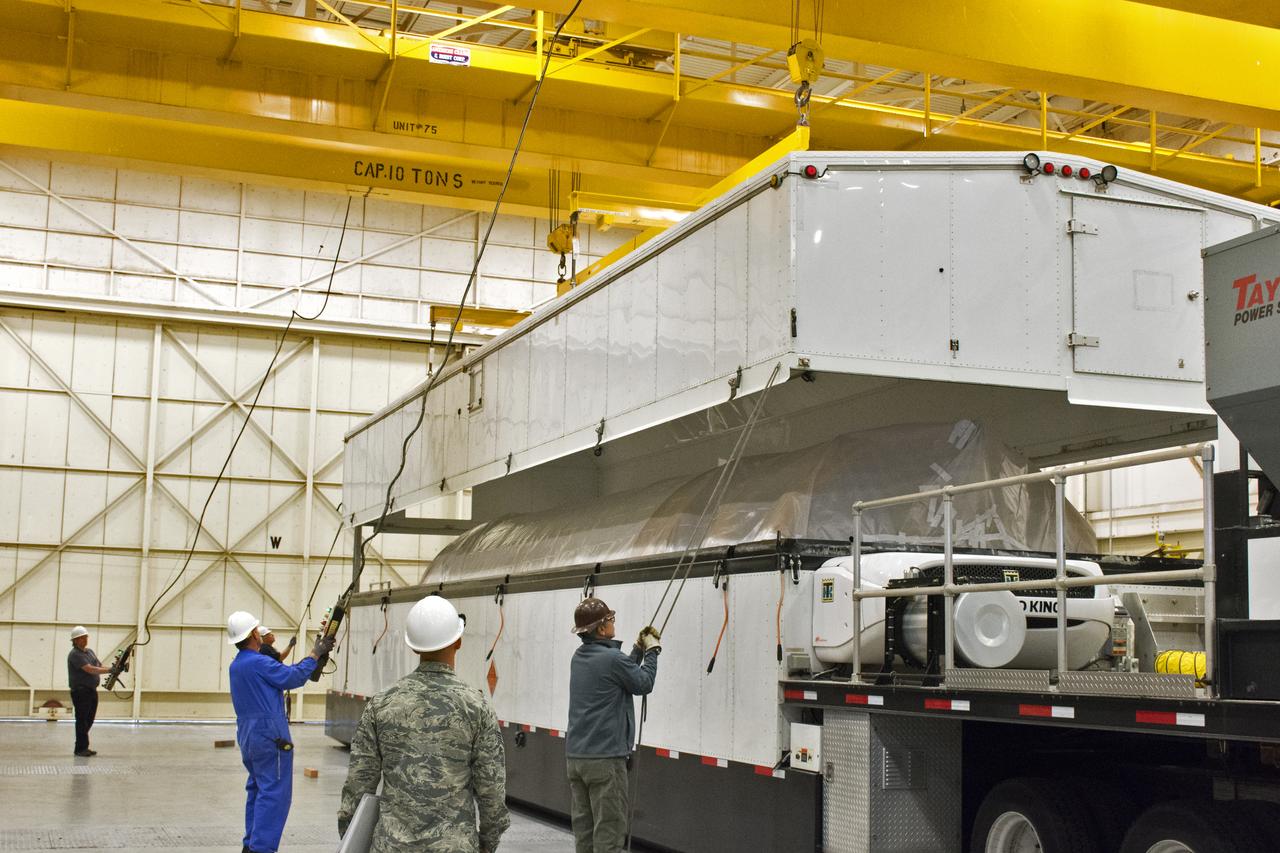

Inside Building B7525 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Centaur upper stage for a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is offloaded from a transport truck. The launch vehicle will send NASA's Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, spacecraft to land on Mars. InSight is the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
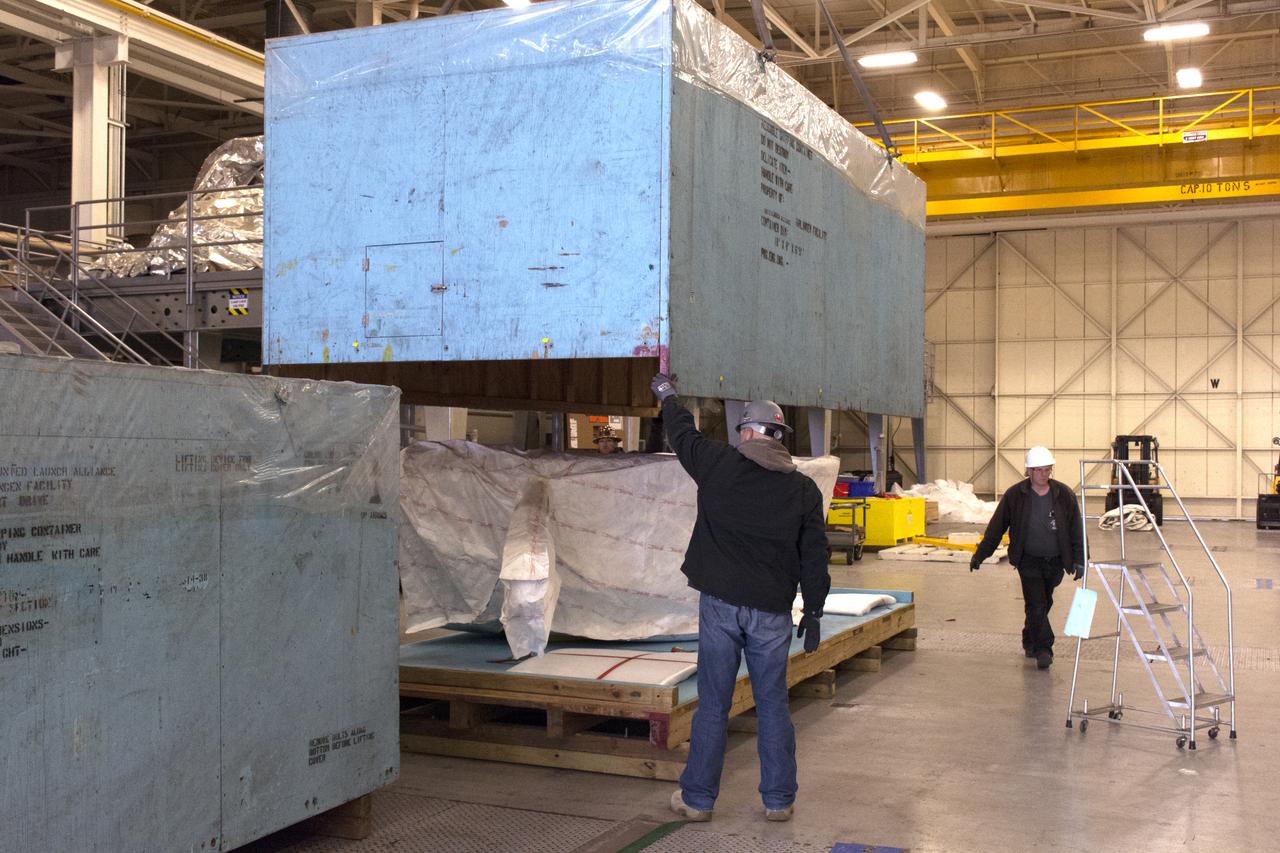

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing is offloaded for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the boattail adaptor interface that will connect the Centaur upper stage to the payload fairing has been offloaded for NASA's upcoming Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport, or InSight, mission to land on Mars. InSight will liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket to send the spacecraft on the first mission to explore the Red Planet's deep interior. It will investigate processes that shaped the rocky planets of the inner solar system including Earth. Liftoff from Vandenberg is scheduled for May 5, 2018.
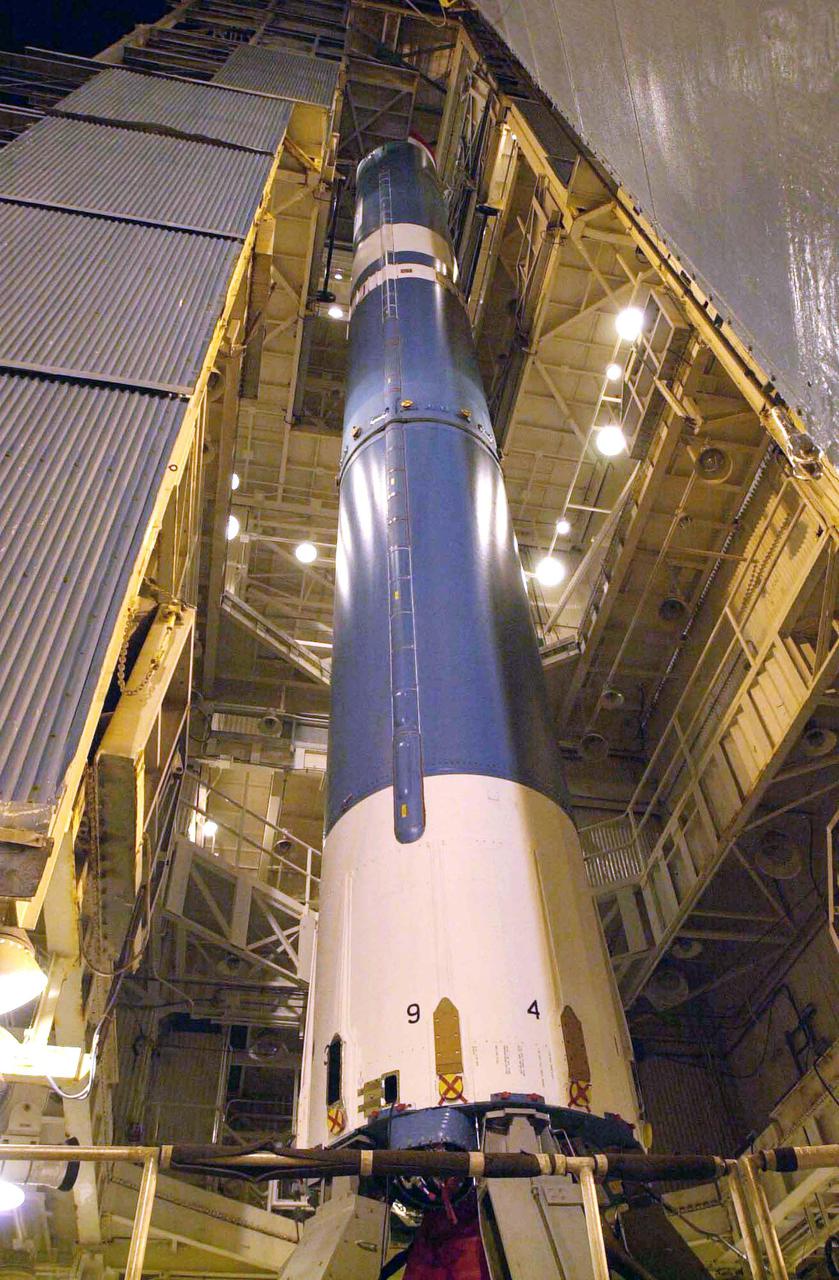

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - The first stage of a Boeing Delta II rocket is in the launch service tower of Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. It will be mated with an interstage adapter and Solid Rocket Boosters for the launch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-N) spacecraft. Launch of NOAA-N aboard the Boeing Delta II rocket is currently scheduled for May 11, 2005. NOAA-N is the fourth in the series of support dedicated microwave instruments for the generation of temperature, moisture, surface, and hydrological products in cloudy regions where visible and infrared (IR) instruments have decreased capability.
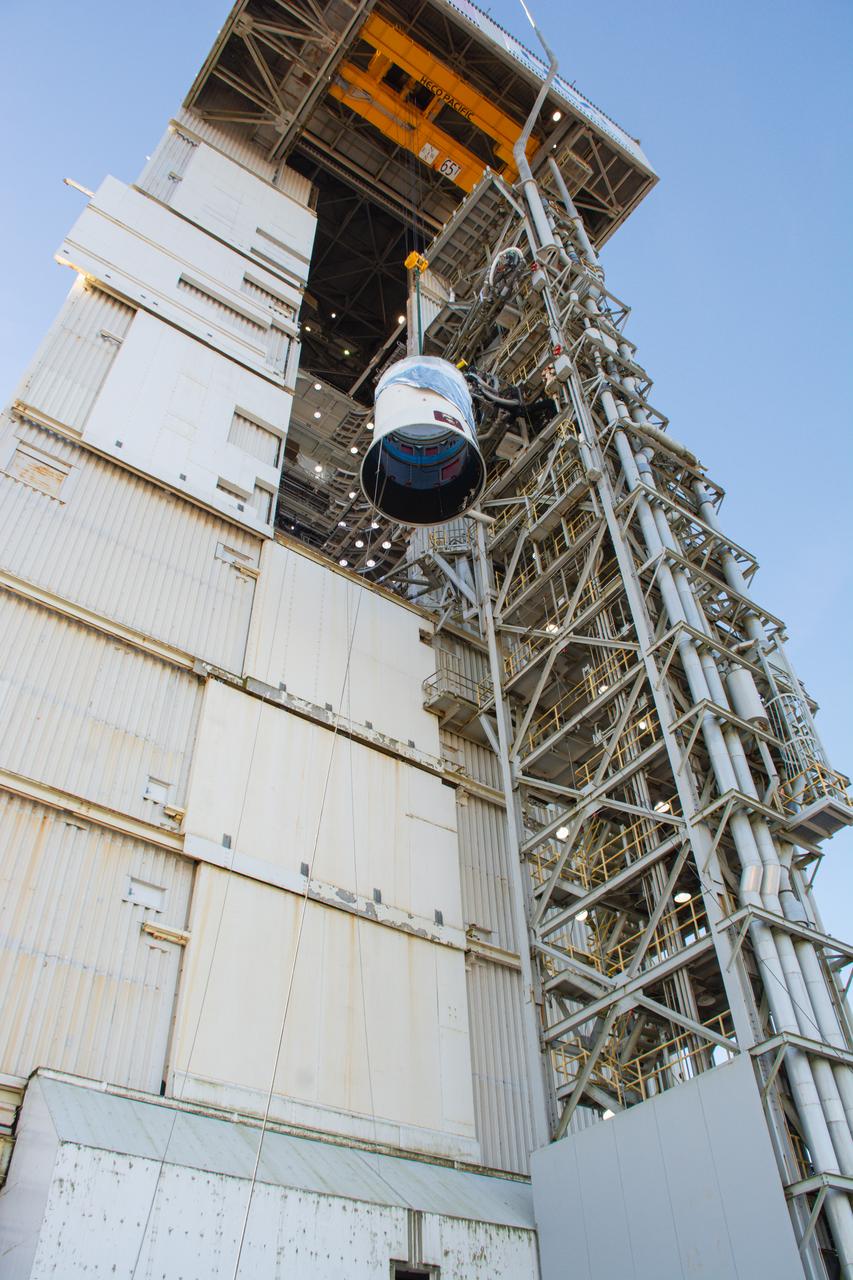

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V interstage adapter and aft stub adapter are hoisted up at the vertical integration facility at Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 29, 2022. The adapter will be moved into the integration facility and secured atop the ULA Atlas V in preparation for the launch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2). JPSS-2 and NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) secondary payload are scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from SLC-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite, and NOAA-20, previously known as JPSS-1, are both already in orbit. Each satellite carries at least four advanced instruments to measure weather and climate conditions on Earth. LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

The United Launch Alliance Atlas V interstage adapter and aft stub adapter are hoisted up at the vertical integration facility at Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 29, 2022. The adapter will be moved into the integration facility and secured atop the ULA Atlas V in preparation for the launch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2). JPSS-2 and NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) secondary payload are scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from SLC-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite, and NOAA-20, previously known as JPSS-1, are both already in orbit. Each satellite carries at least four advanced instruments to measure weather and climate conditions on Earth. LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
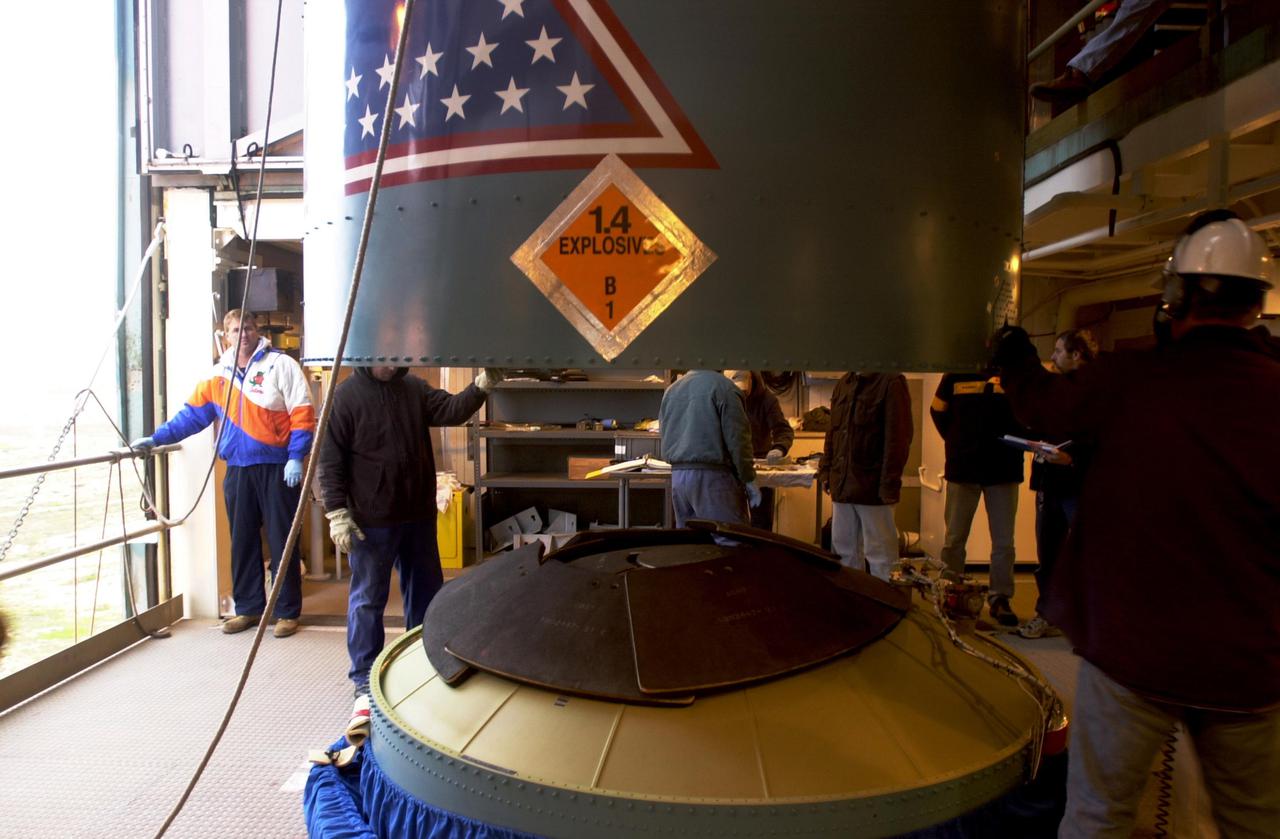

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - In the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the interstage of a Boeing Delta 2 rocket is lowered toward the interstage adapter. The two stages will be mated for launch of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-N) spacecraft. The NOAA-N satellite will be placed into a polar orbit aboard a Boeing Delta 2 rocket. The spacecraft will continue to provide a polar-orbiting platform to support (1) environmental monitoring instruments for imaging and measuring the Earth's atmosphere, its surface, and cloud cover, including Earth radiation, atmospheric ozone, aerosol distribution, sea surface temperature, and vertical temperature and water profiles in the troposphere and stratosphere; (2) measurement of proton and electron flux at orbit altitude; (3) data collection from remote platforms; and (4) the Search and Rescue Satellite-Aided Tracking (SARSAT) system. Additionally, NOAA-N is the fourth in the series of support dedicated microwave instruments for the generation of temperature, moisture, surface, and hydrological products in cloudy regions where visible and infrared (IR) instruments have decreased capability. Launch is currently scheduled for no earlier than May 11, 2005.
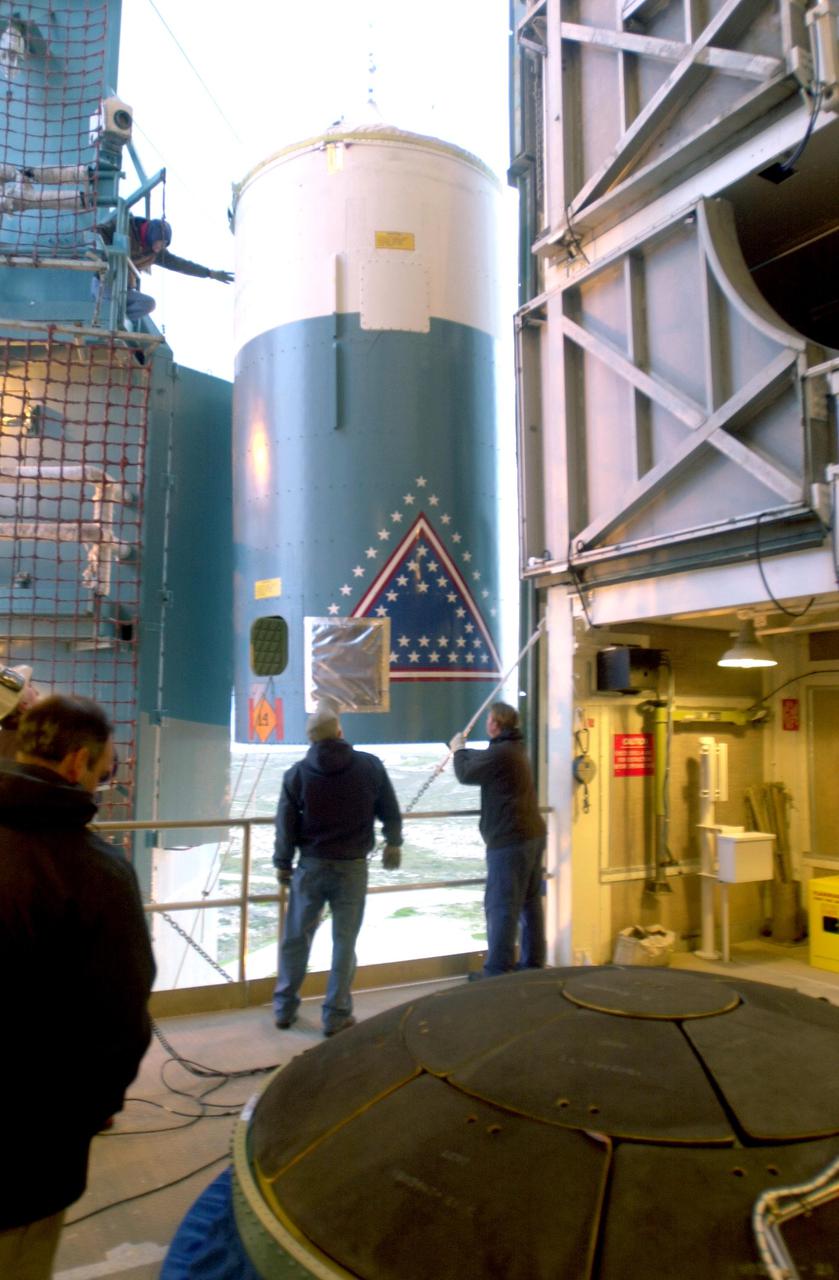

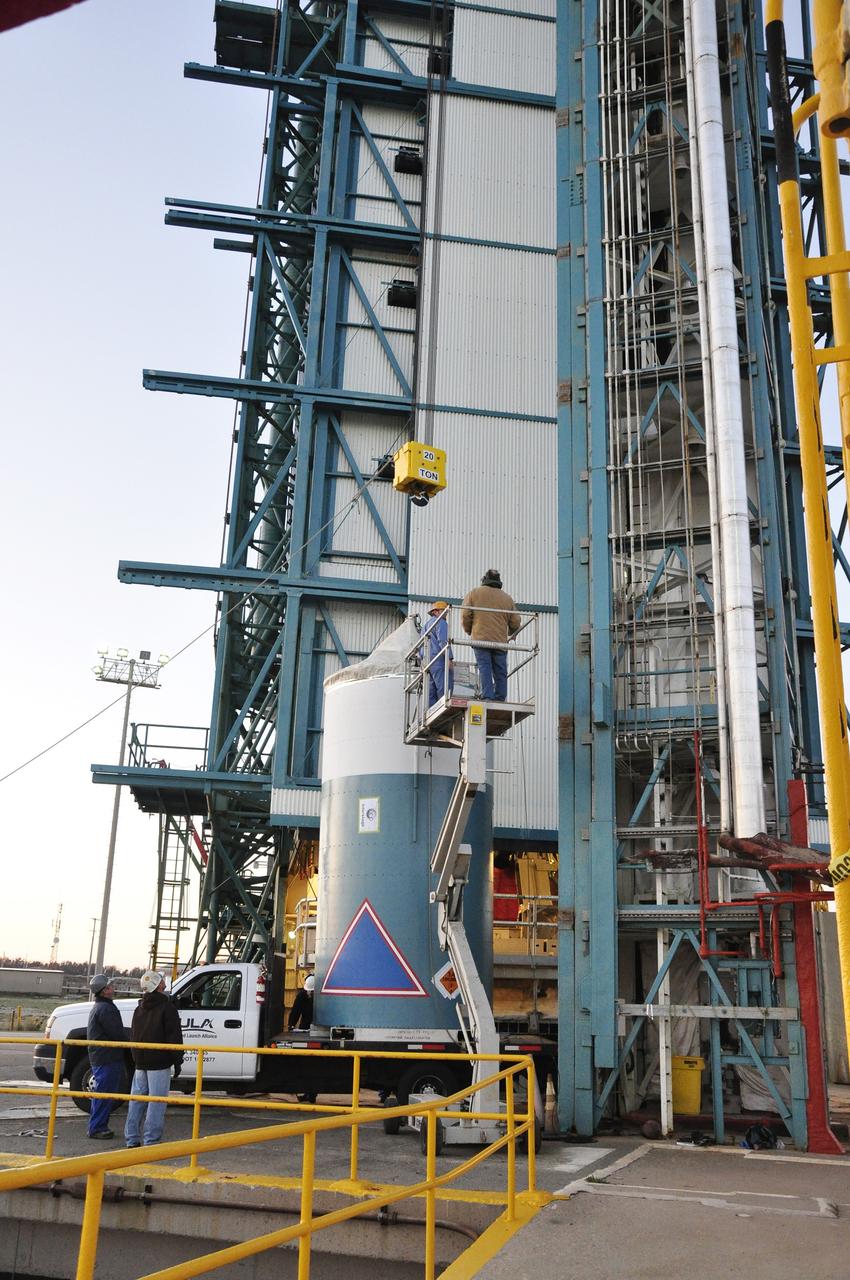
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, CALIF. - The interstage of a Boeing Delta 2 rocket is lifted to an upper level on the launch service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. It will be mated with the first stage in the launch service tower. In the foreground is the interstage adapter. The Delta 2 is the launch vehicle for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA-N) spacecraft. The NOAA-N satellite will be placed into a polar orbit aboard a Boeing Delta 2 rocket. The spacecraft will continue to provide a polar-orbiting platform to support (1) environmental monitoring instruments for imaging and measuring the Earth's atmosphere, its surface, and cloud cover, including Earth radiation, atmospheric ozone, aerosol distribution, sea surface temperature, and vertical temperature and water profiles in the troposphere and stratosphere; (2) measurement of proton and electron flux at orbit altitude; (3) data collection from remote platforms; and (4) the Search and Rescue Satellite-Aided Tracking (SARSAT) system. Additionally, NOAA-N is the fourth in the series of support dedicated microwave instruments for the generation of temperature, moisture, surface, and hydrological products in cloudy regions where visible and infrared (IR) instruments have decreased capability. Launch is currently scheduled for no earlier than May 11, 2005.
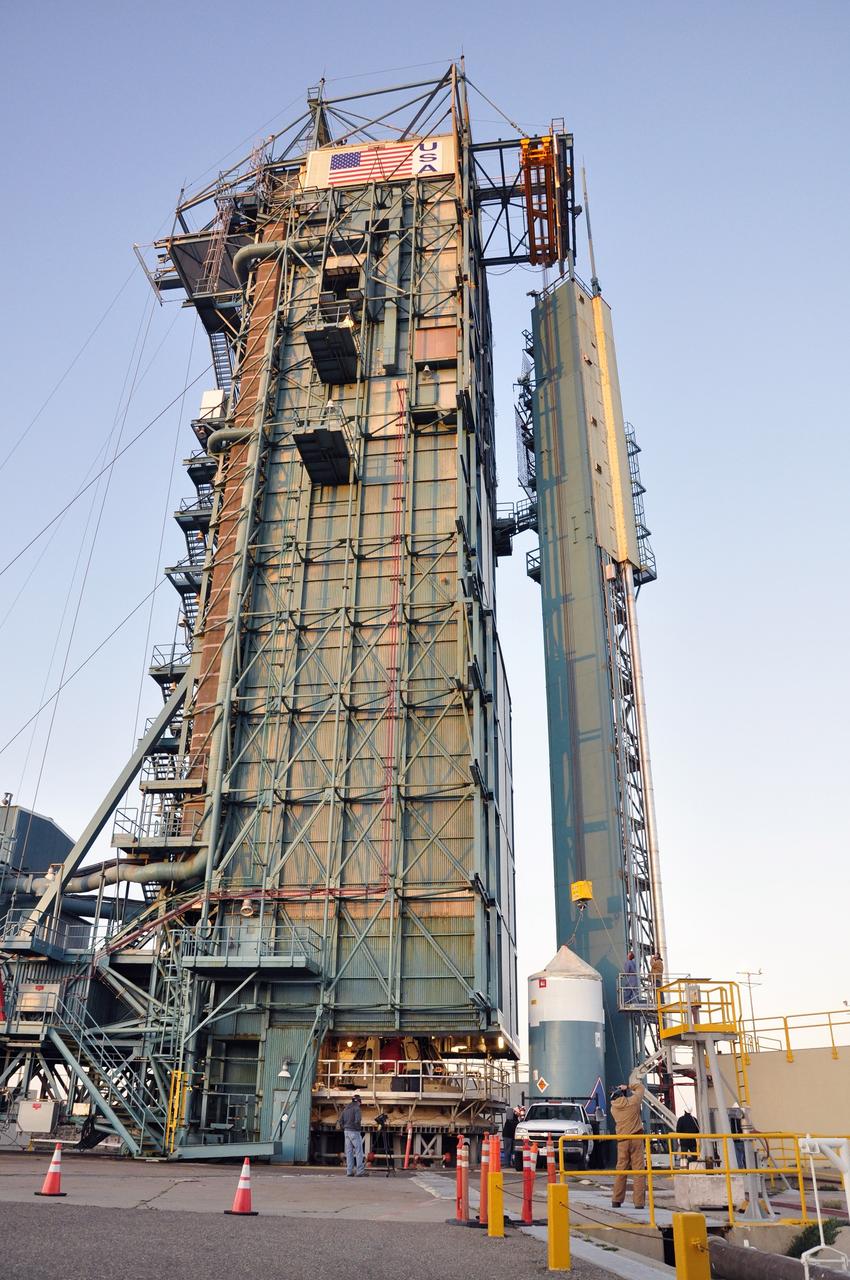

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to lift the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
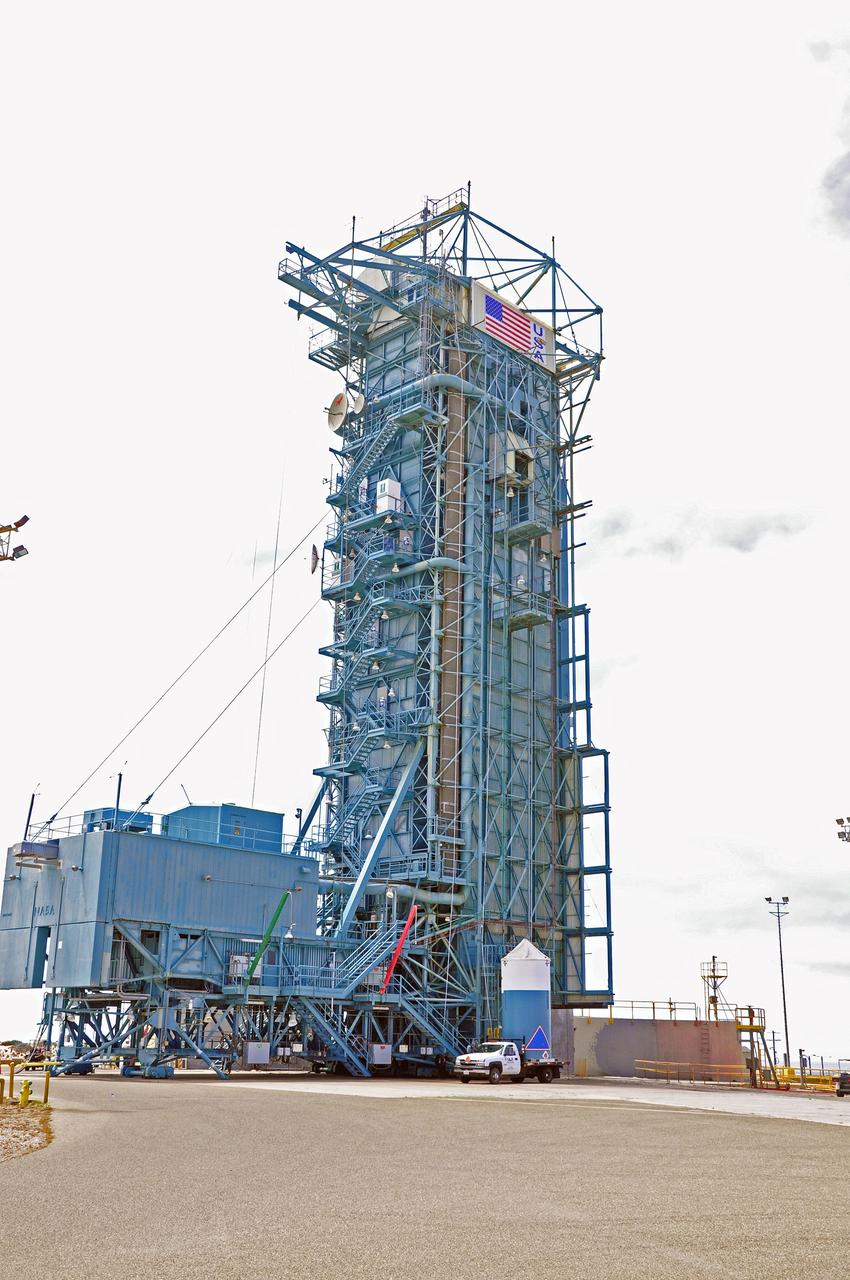

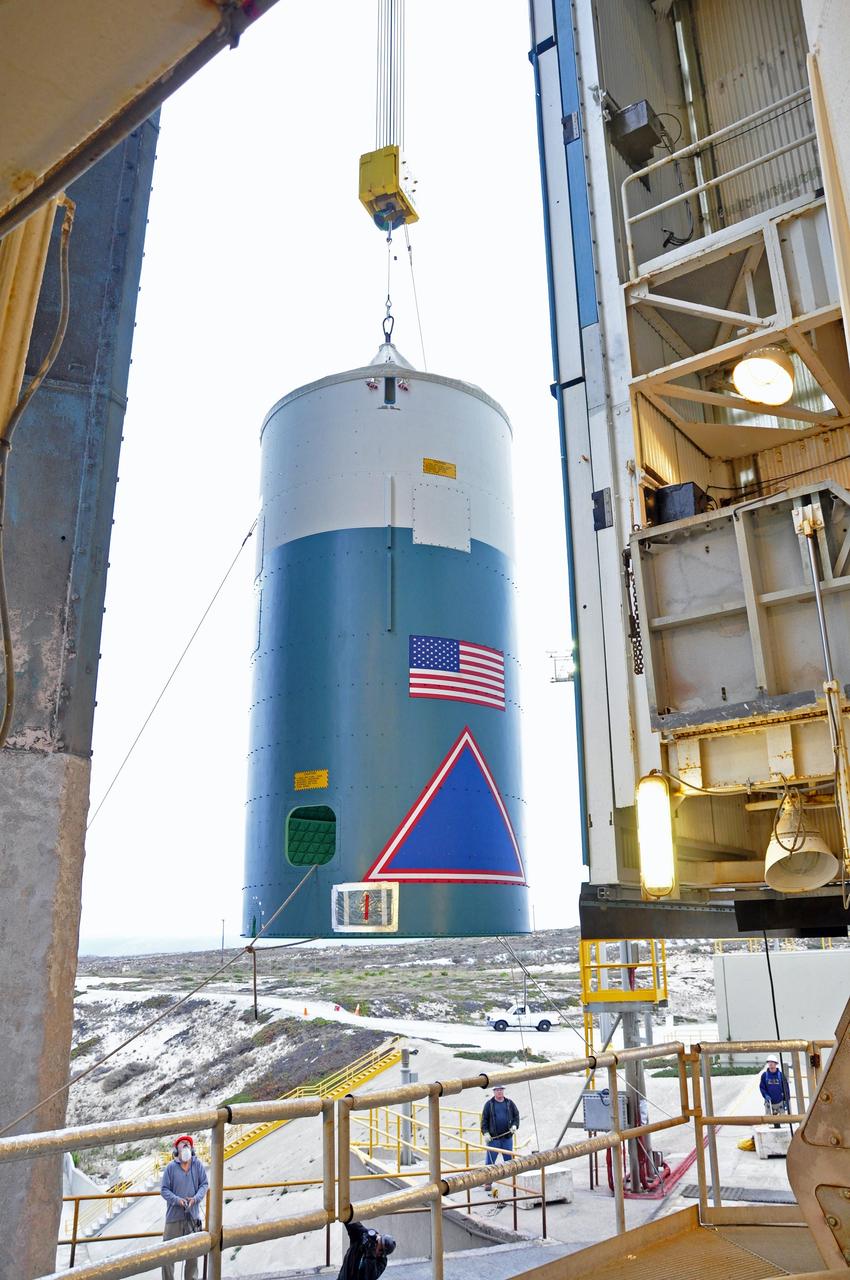
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is ready to be lifted into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
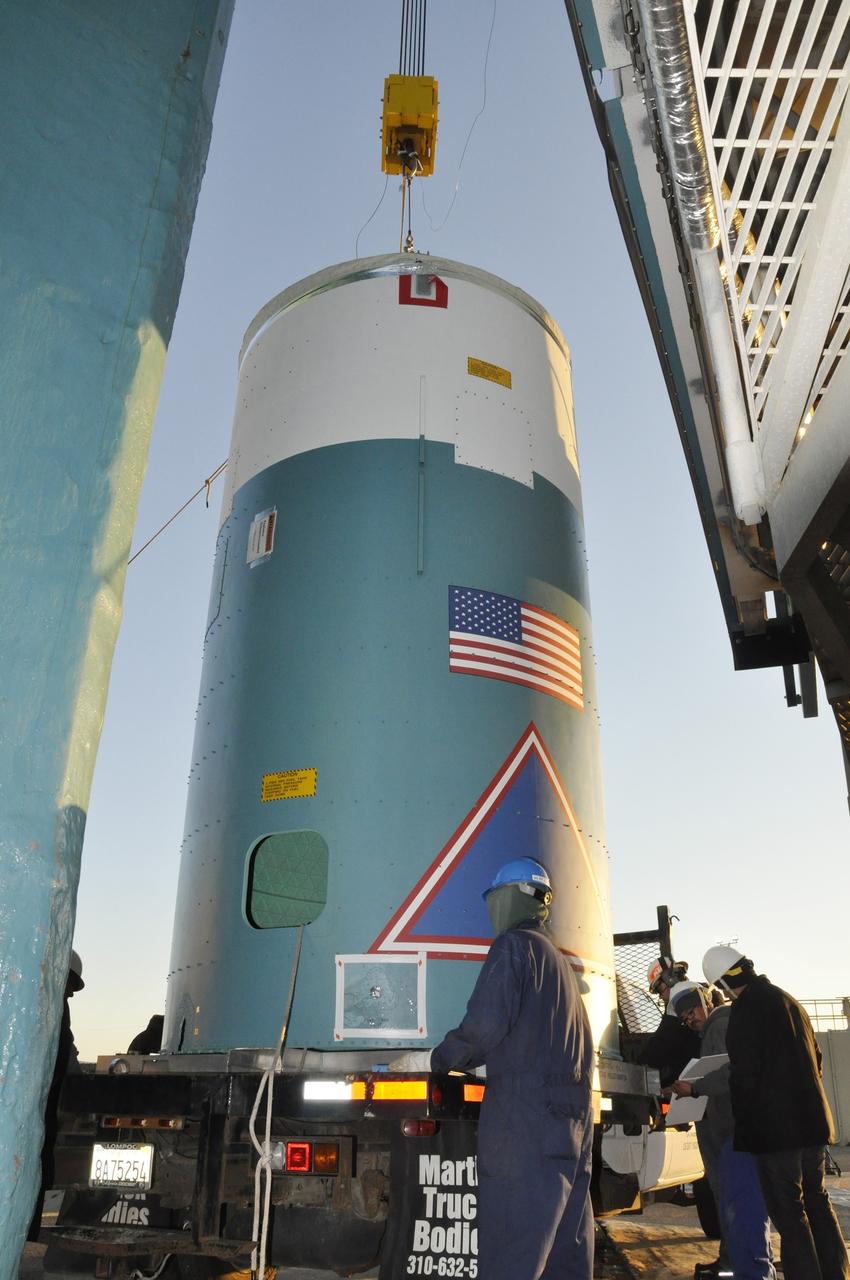

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare to lift the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, by crane into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
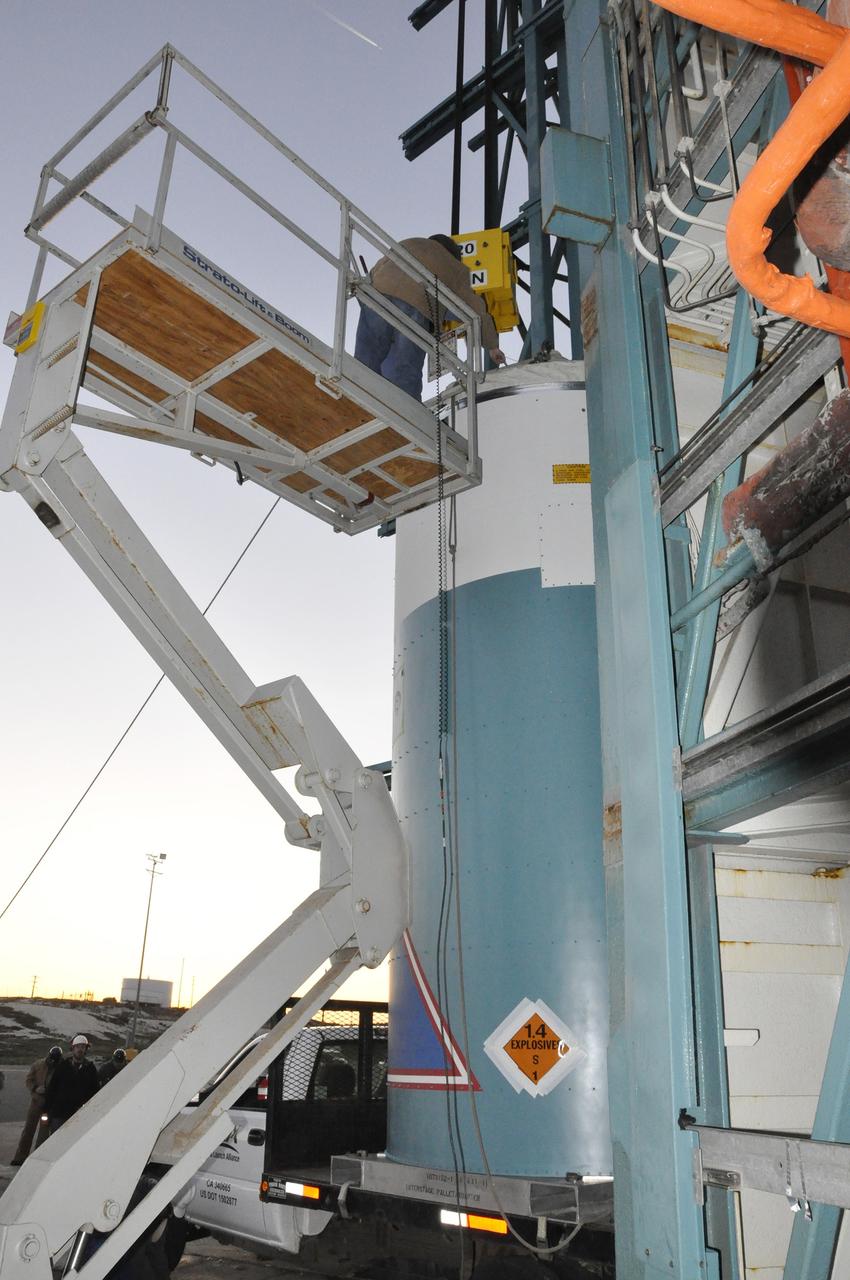

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker connects a crane to the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, at the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
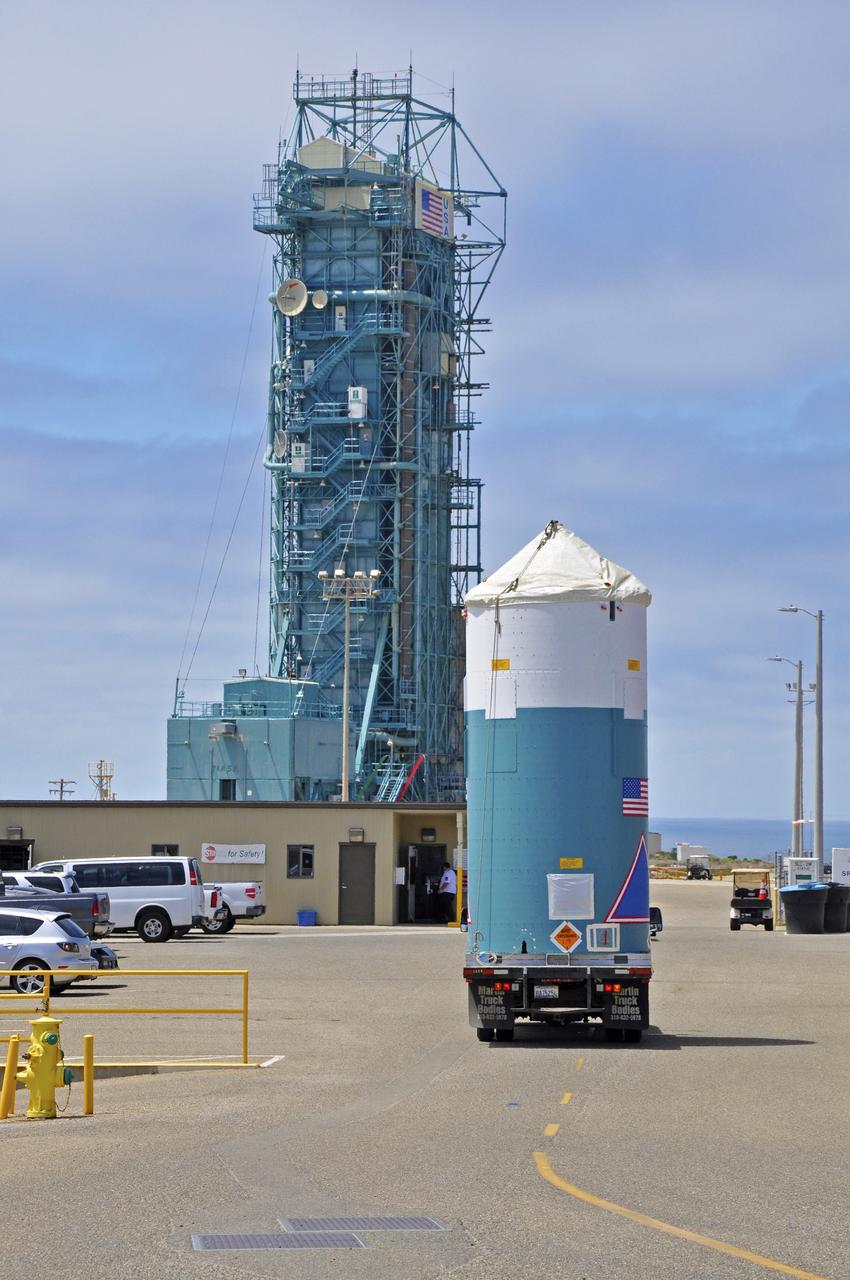

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, approaches the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to hoist the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
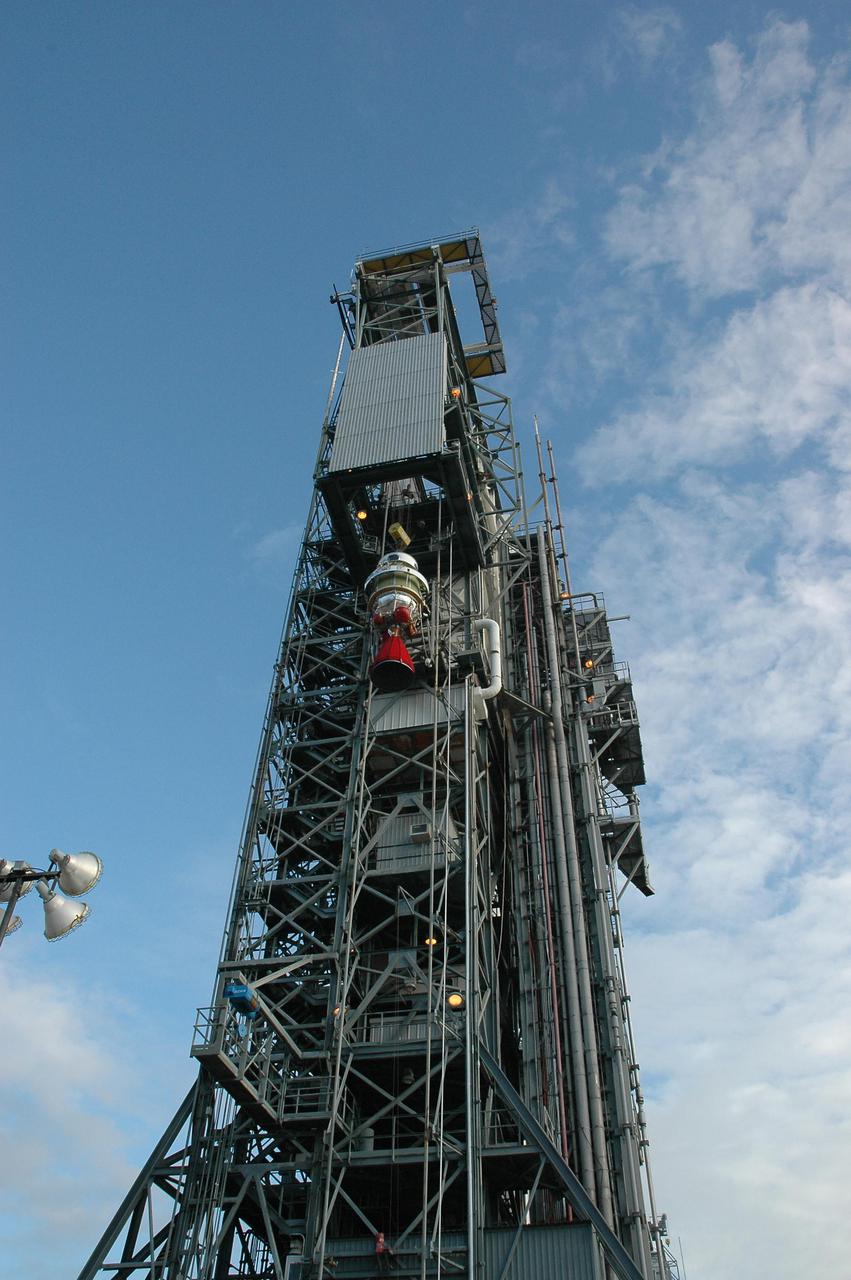

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Boeing Delta II second stage reaches the top of the mobile service tower. The component will be reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.

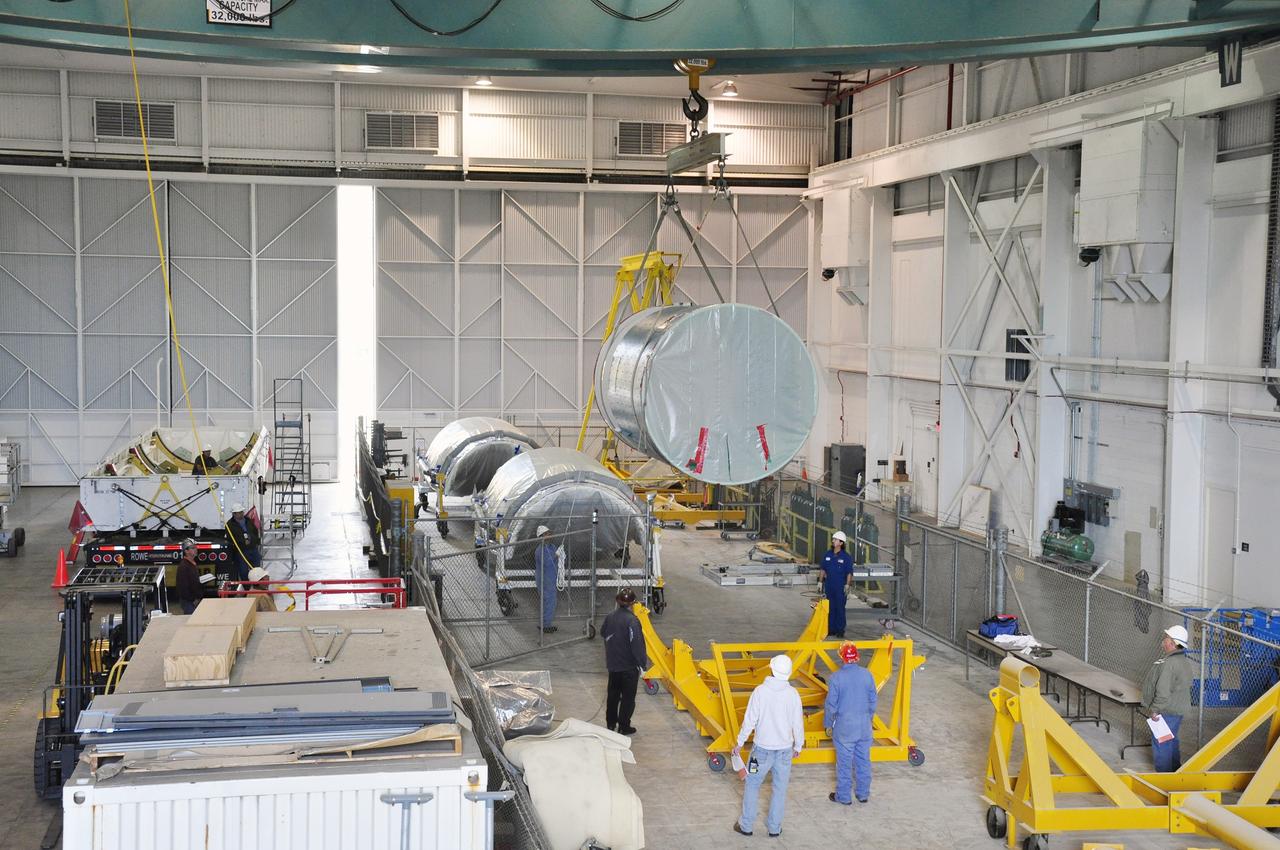
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane lifts the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

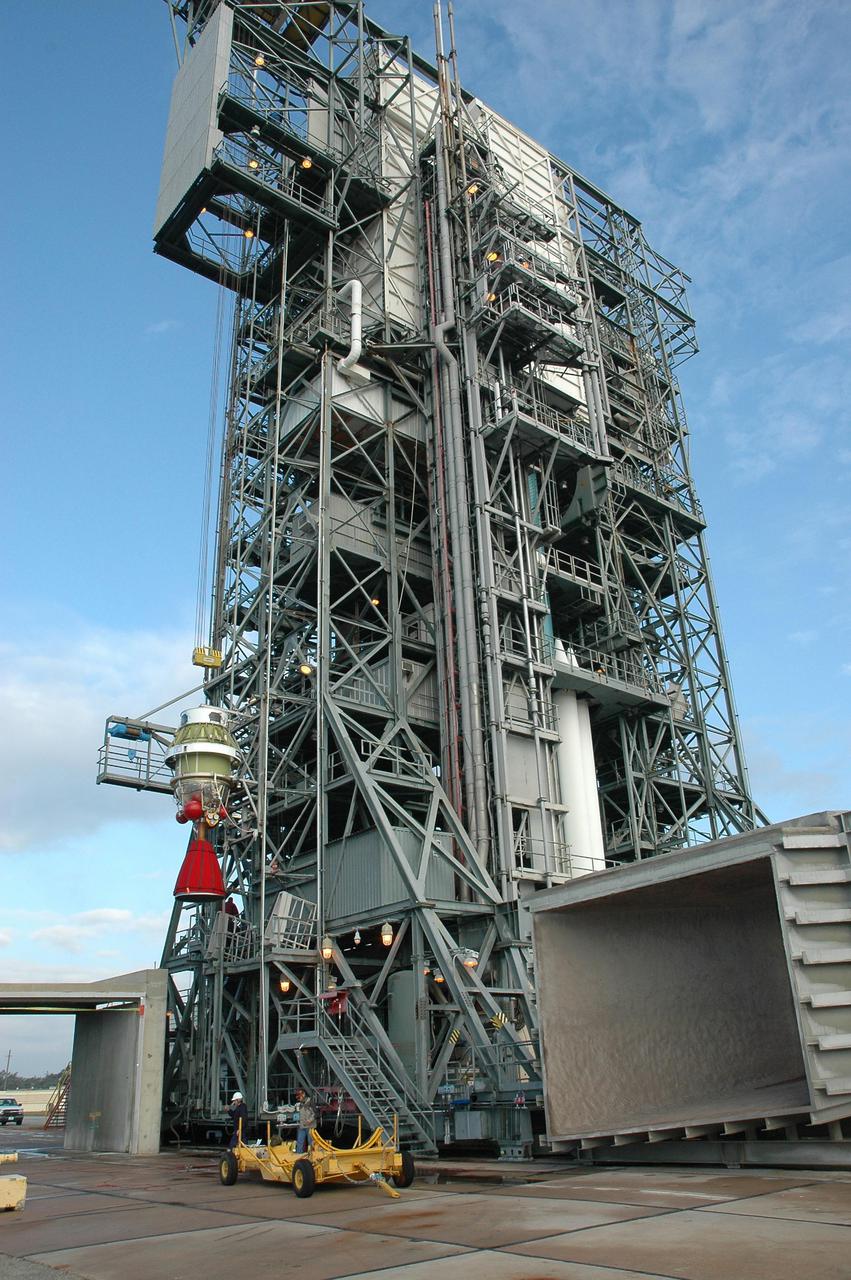
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Boeing workers attach the Delta II second stage to the interstage adapter on the rocket below. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, the Boeing Delta II second stage is lifted up the mobile service tower. The component will be reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.

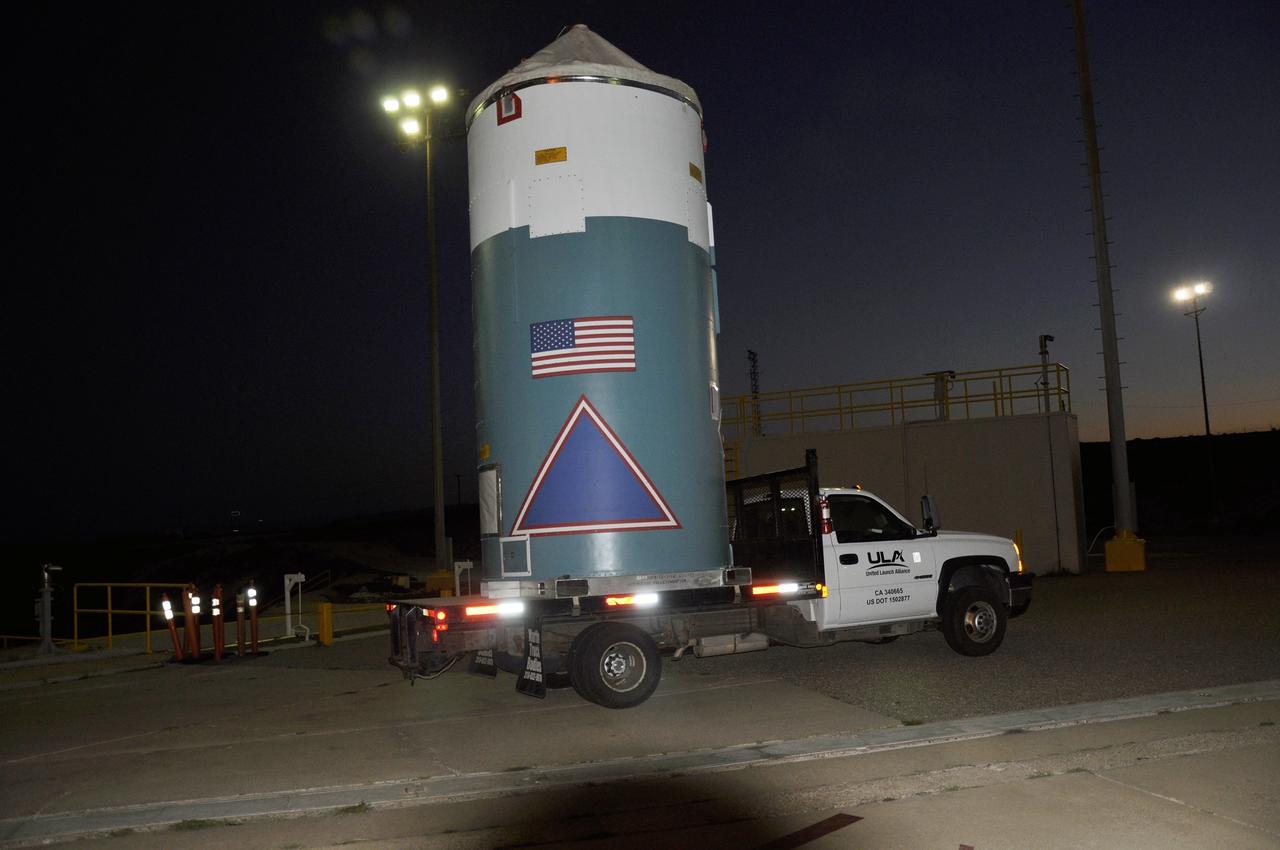
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A truck transporting the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, backs into the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http:__oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA_Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is delivered to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. –The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, arrives at the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker prepares to connect a crane to the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, at the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
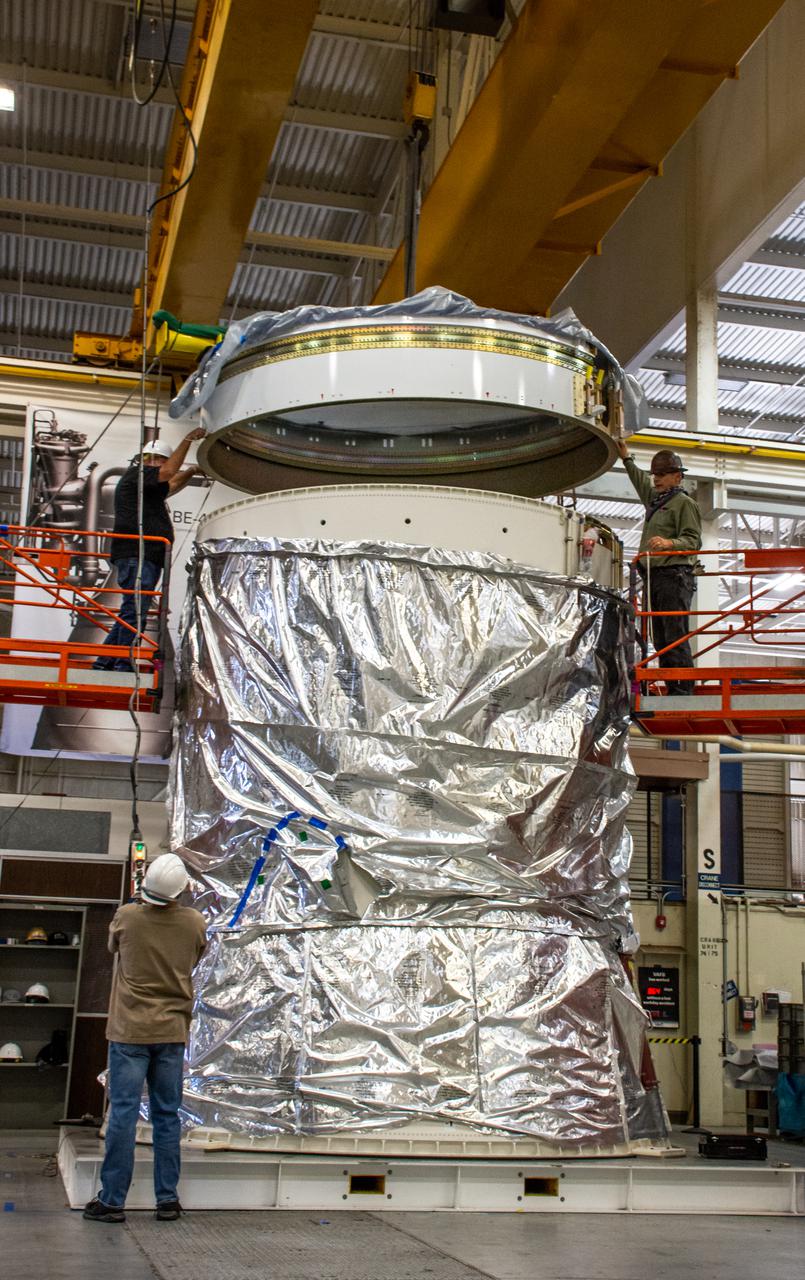

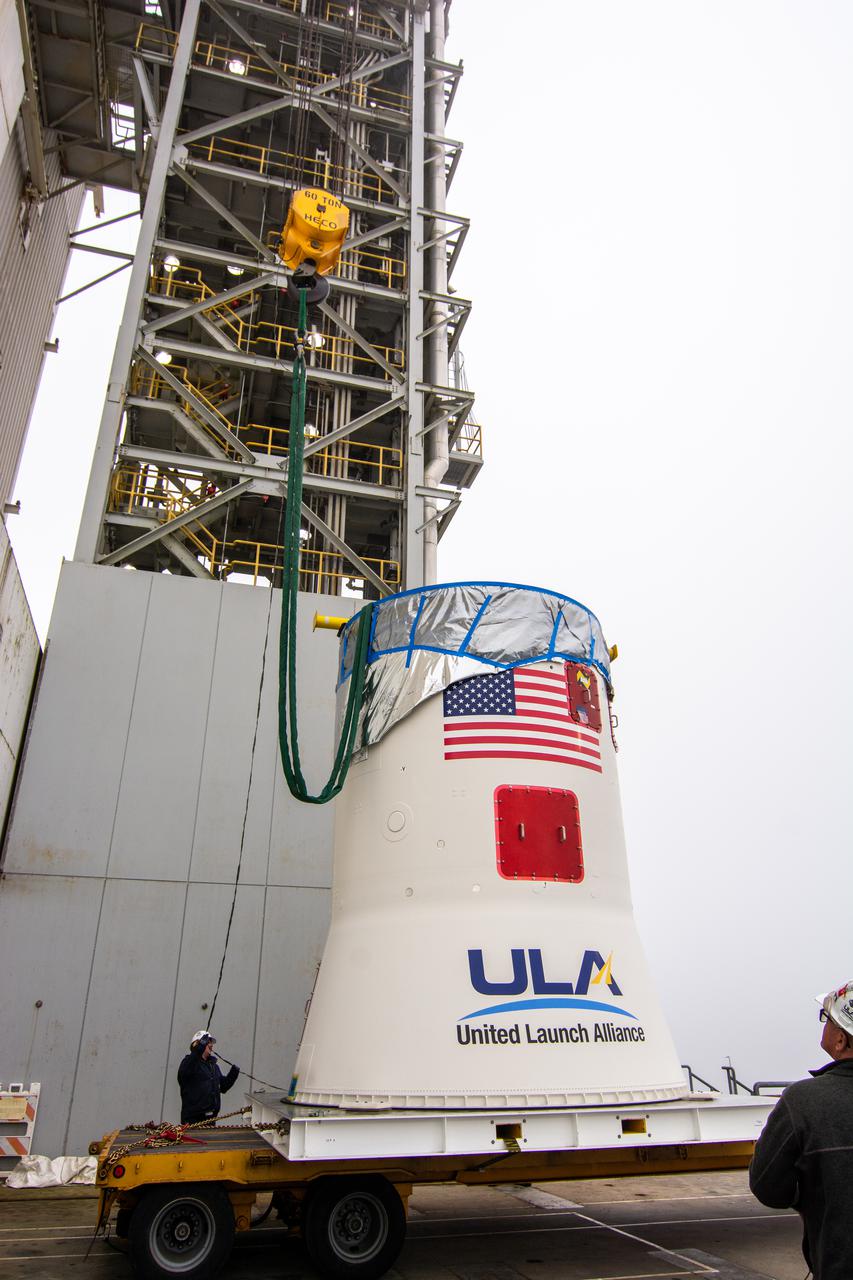
Inside Building 7525, a processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, workers assist as the aft stub adapter is lowered onto the interstage adapter for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Nov. 4, 2020. The Atlas V will launch NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

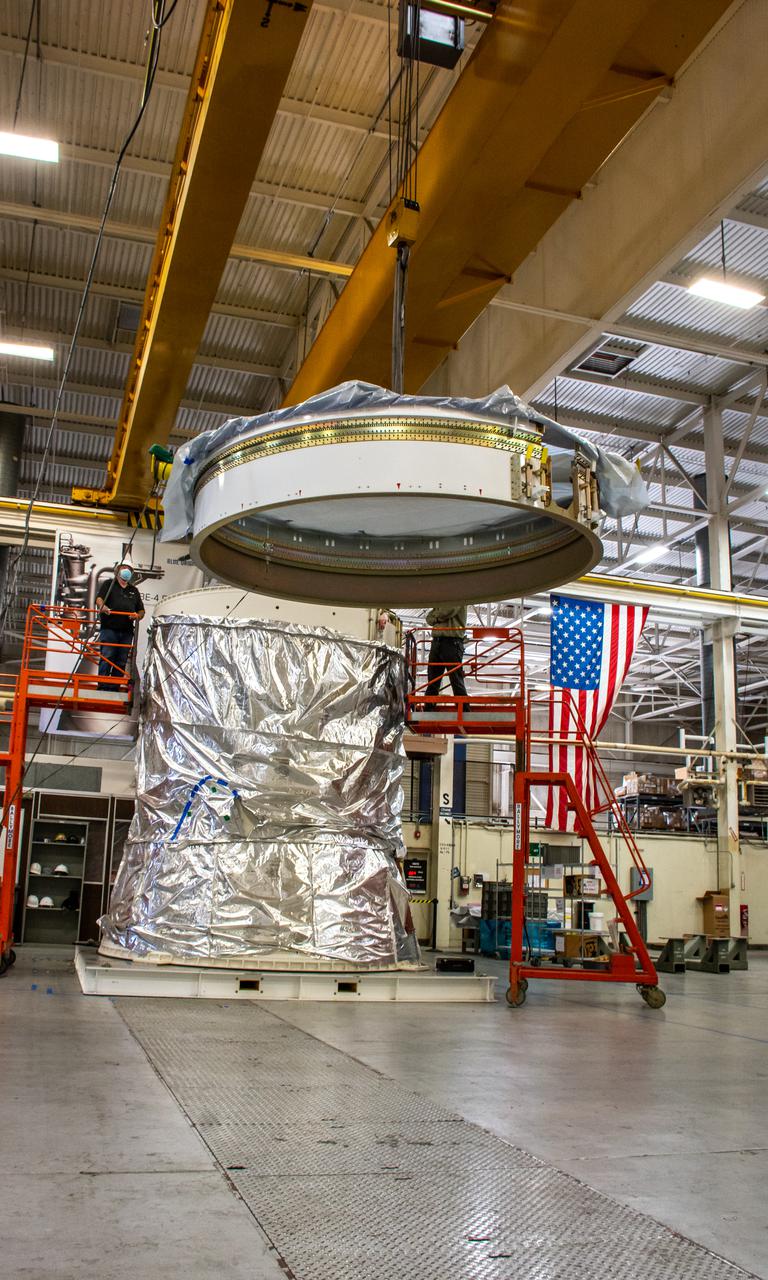
Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

Preparations are underway to lift the interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
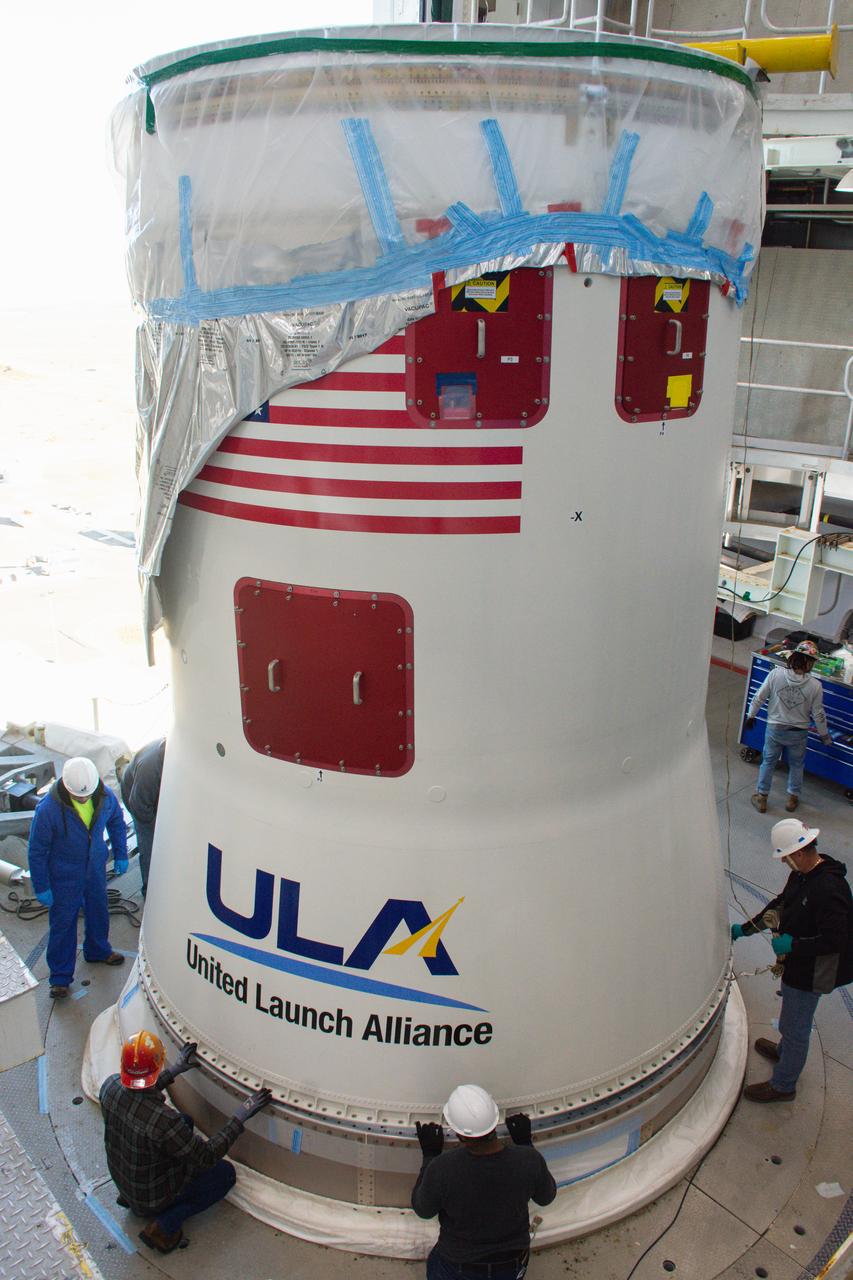

Technicians help secure the United Launch Alliance Atlas V interstage adapter and aft stub adapter to the Atlas V rocket inside the vertical integration facility at Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Sept. 29, 2022. The rocket is being prepared to launch the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2). JPSS-2 and NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) secondary payload. The launch is scheduled for Nov. 1 from SLC-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The NOAA/NASA Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership (Suomi NPP) satellite, and NOAA-20, previously known as JPSS-1, are both already in orbit. Each satellite carries at least four advanced instruments to measure weather and climate conditions on Earth. LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

Inside Building 7525, a processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the aft stub adapter is lifted for mating to the interstage adapter for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Nov. 4, 2020. The Atlas V will launch NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.

The interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Centaur Atlas V for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission are lifted by crane from a flatbed truck at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
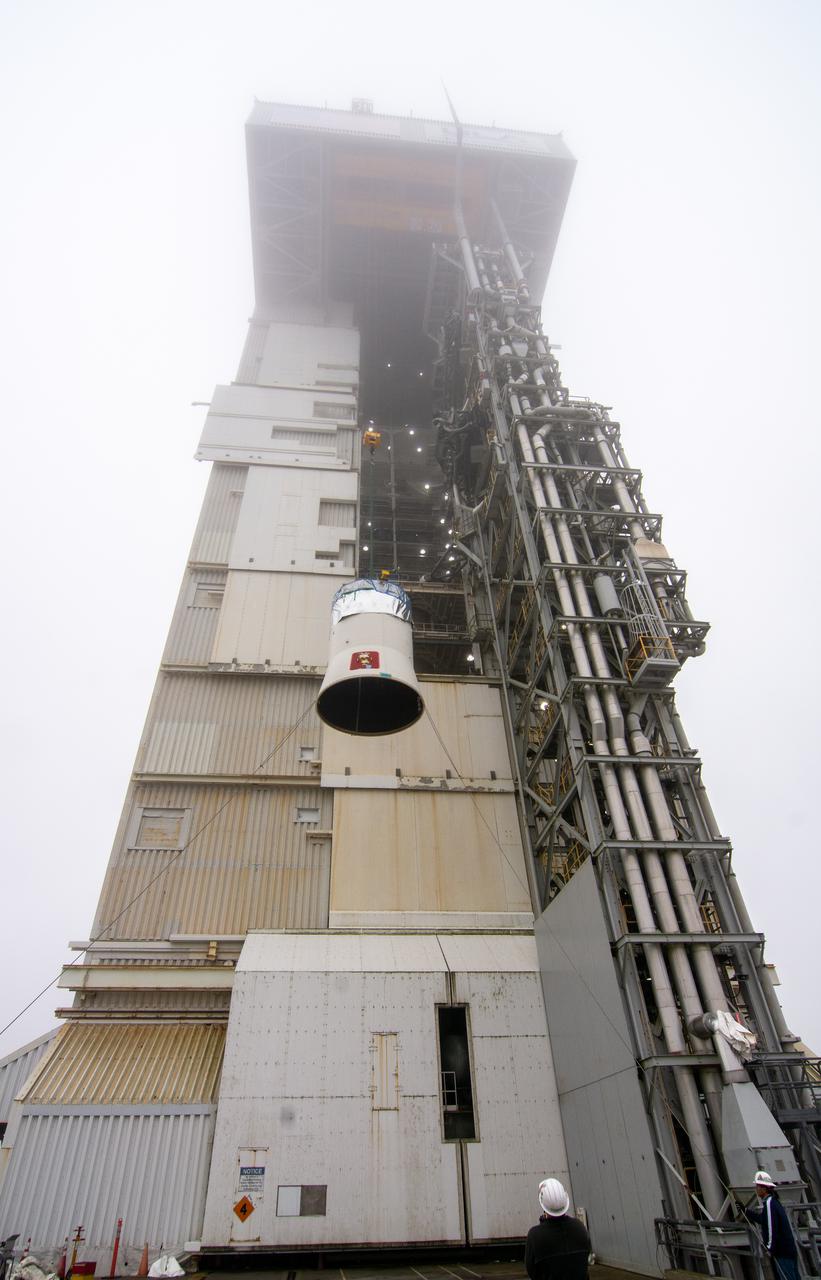

The interstage and assembly second stage adapters for the United Alliance Atlas V Centaur second stage for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission are lifted by crane at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, on July 14, 2021. The adapters will be stacked atop the Centaur second stage in the Vertical Integration Facility near the launch pad. The Landsat 9 mission will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
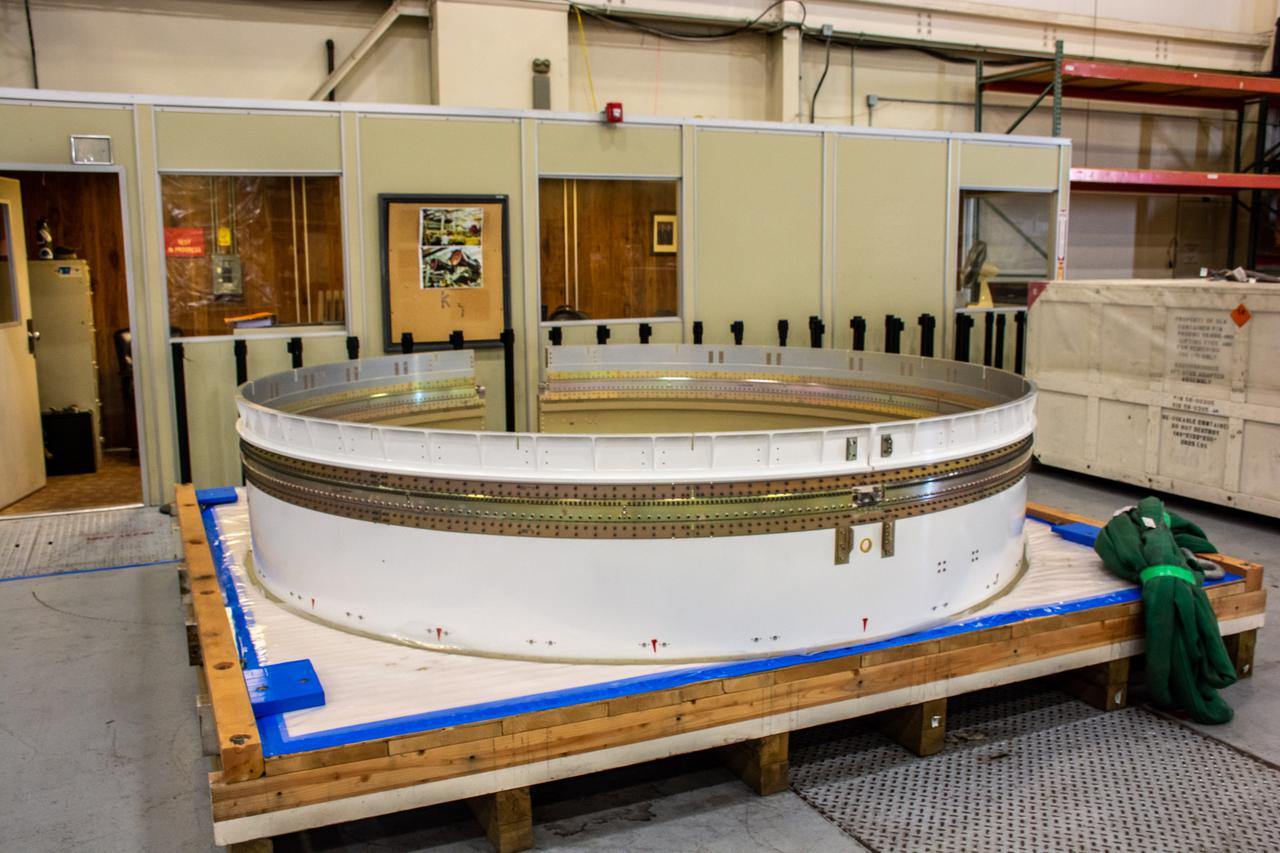

Inside Building 7525, a processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, the aft stub adapter is being prepared for mating to the interstage adapter for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Nov. 4, 2020. The Atlas V will launch NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near-infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
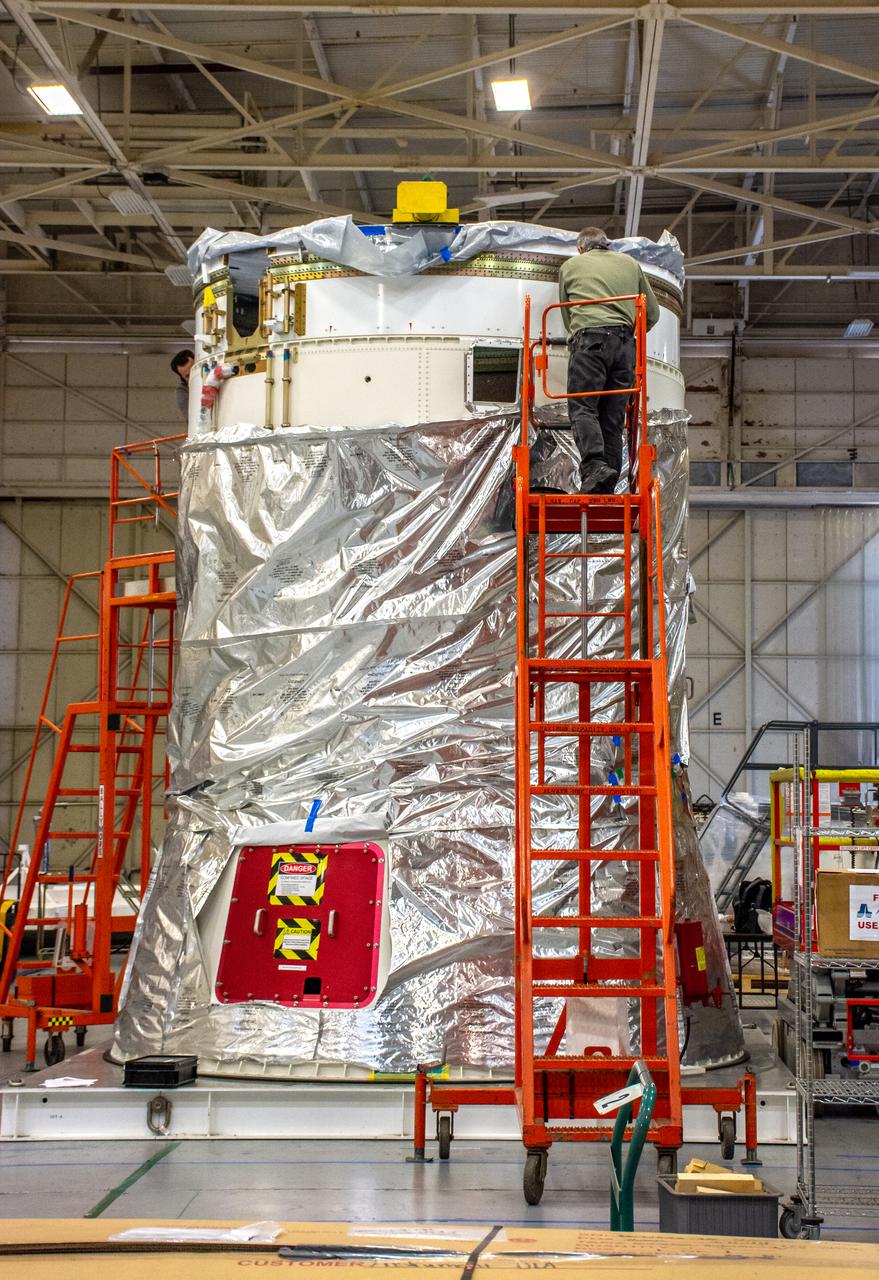

Inside Building 7525, a processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a worker secures the aft stub adapter onto the interstage adapter for the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on Nov. 4, 2020. The Atlas V will launch NASA’s Landsat 9 satellite from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center. Landsat 9 will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. It will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
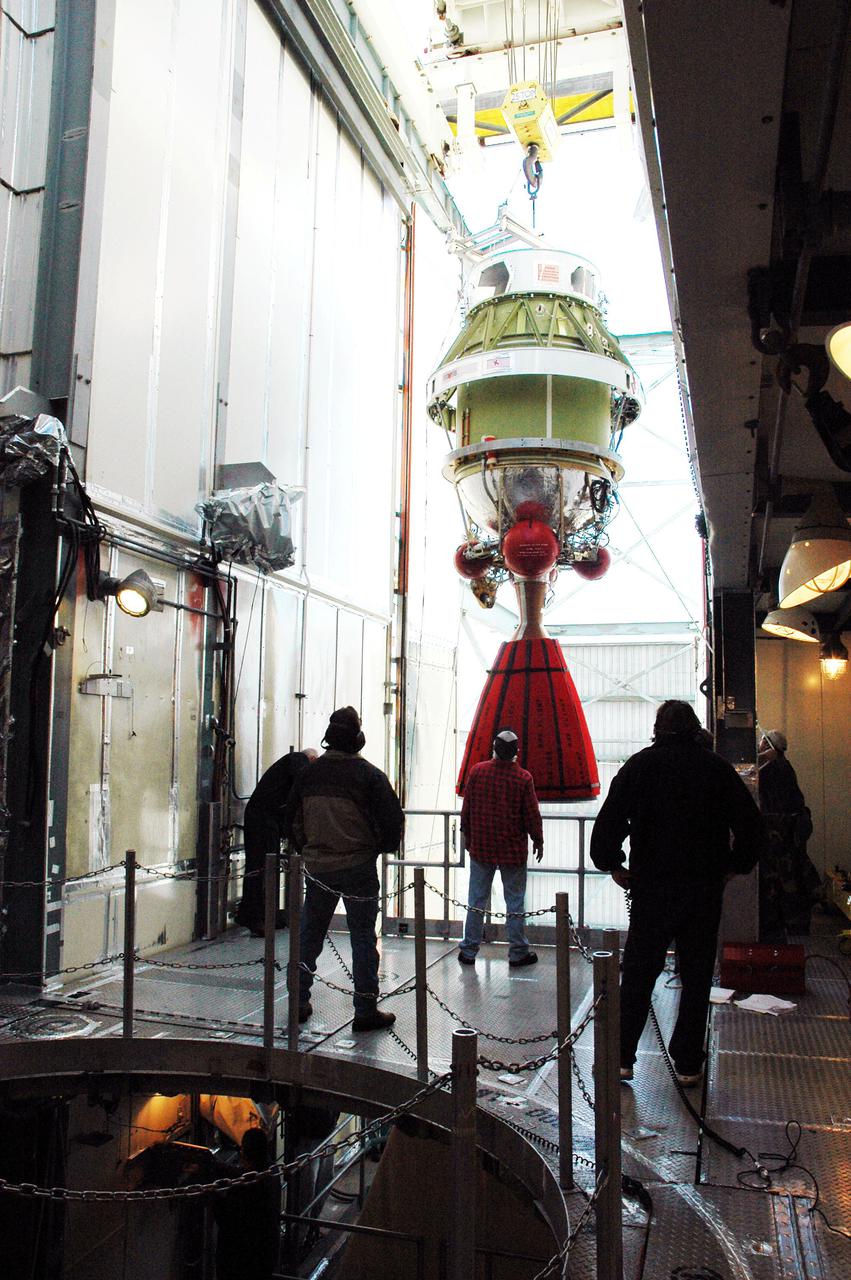

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view from inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, shows the Boeing Delta II second stage as it reaches the top. The component will be reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.
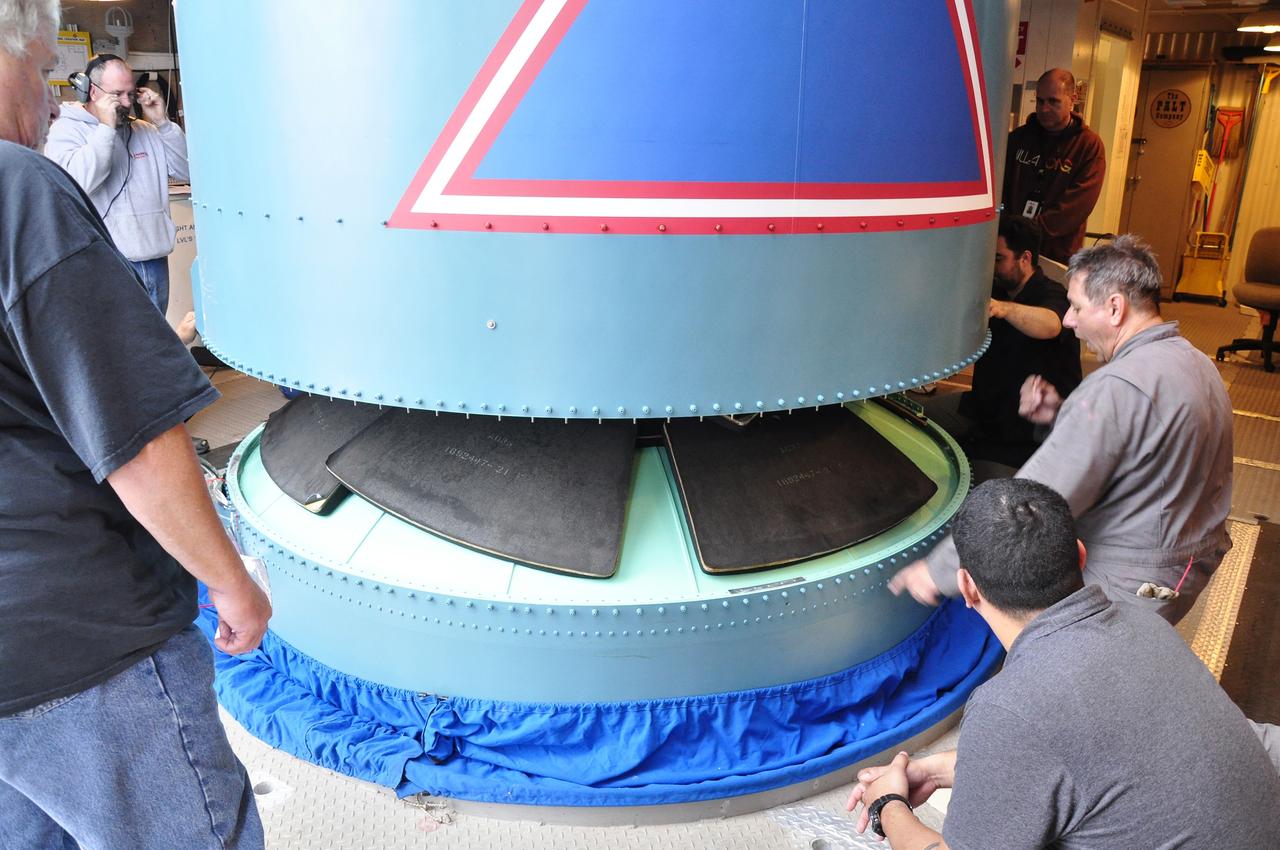

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is lowered into place on the rocket's first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Processing of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft SMAP into orbit is underway at the pad. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
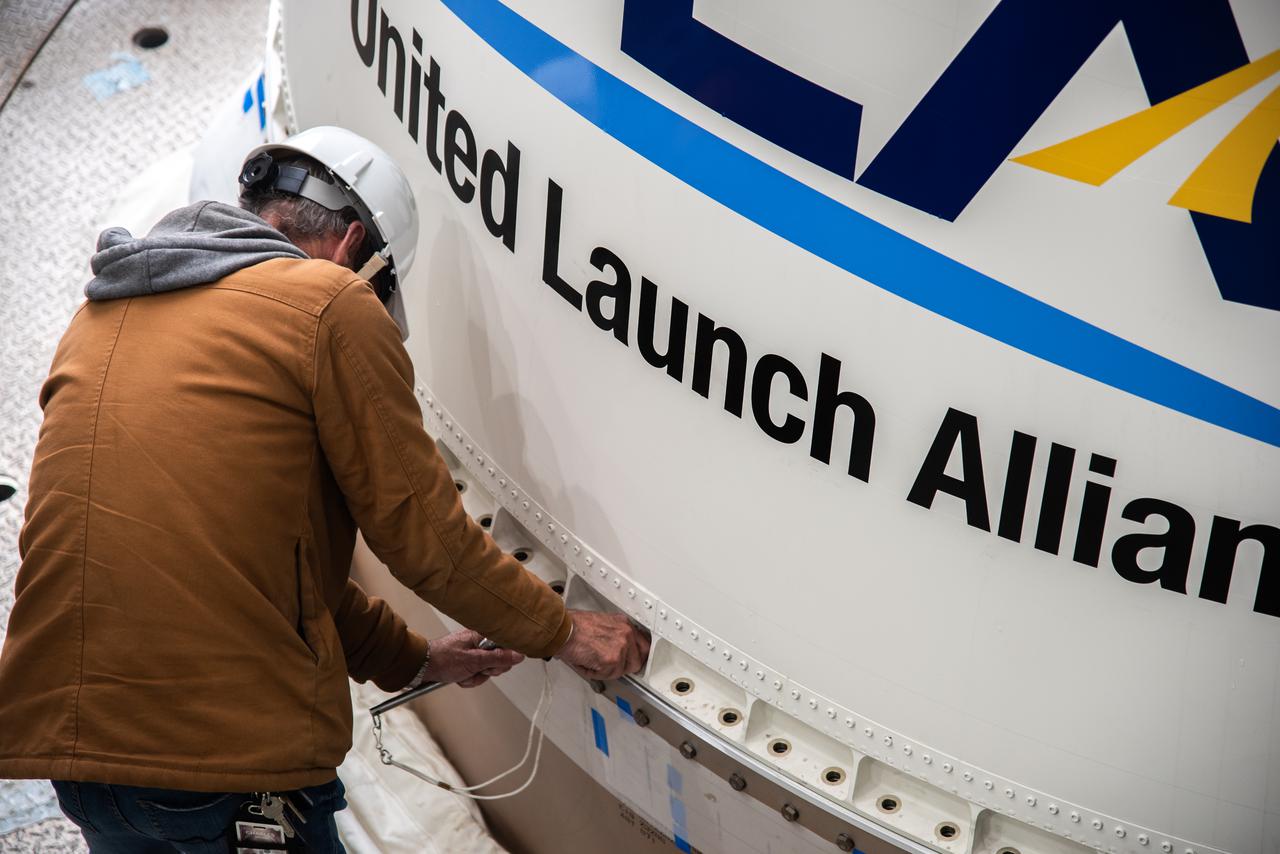

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Source Base in California, workers help secure the interstage and assembly second stage adapters to the Centaur second stage of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission on July 14, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
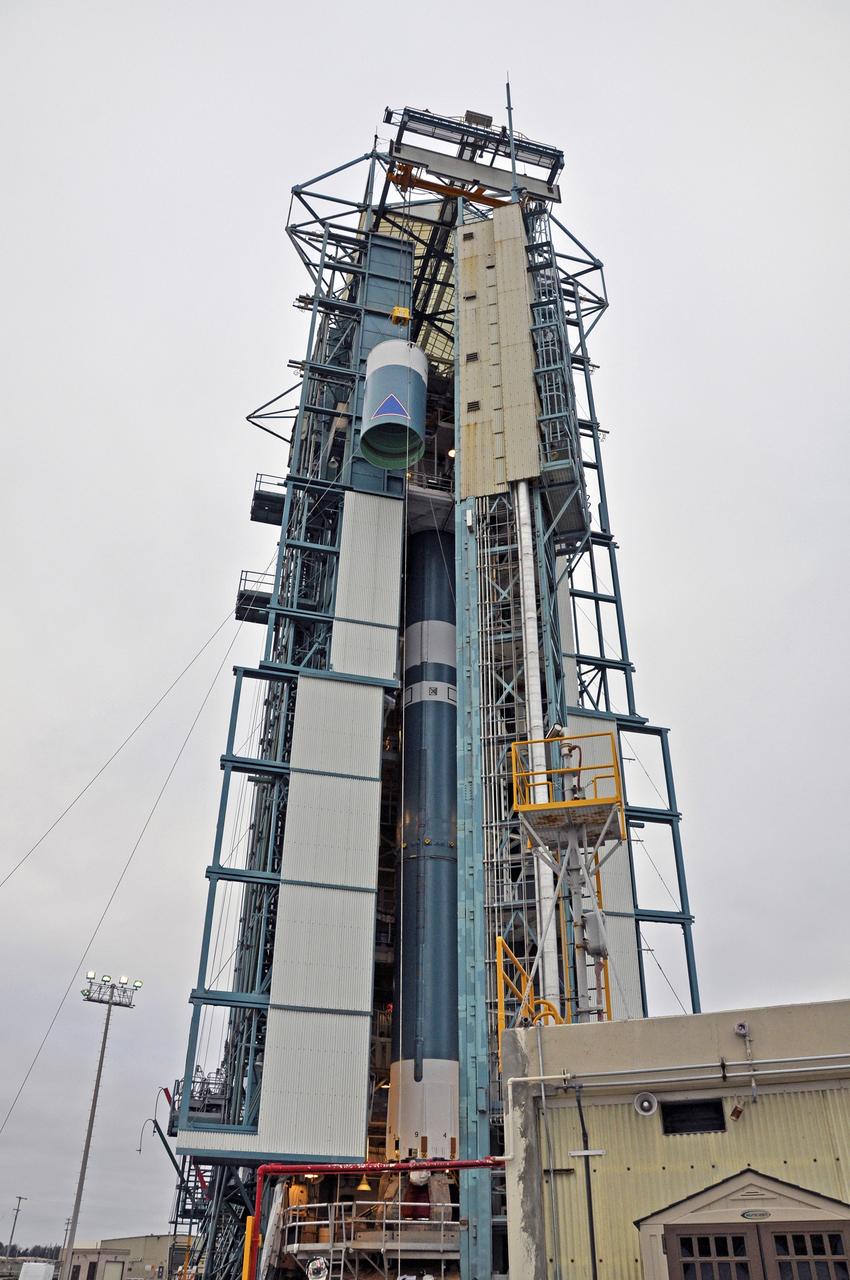

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is lifted up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, higher than the rocket's first stage already in position in the tower. Processing of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft SMAP into orbit is underway at the pad. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
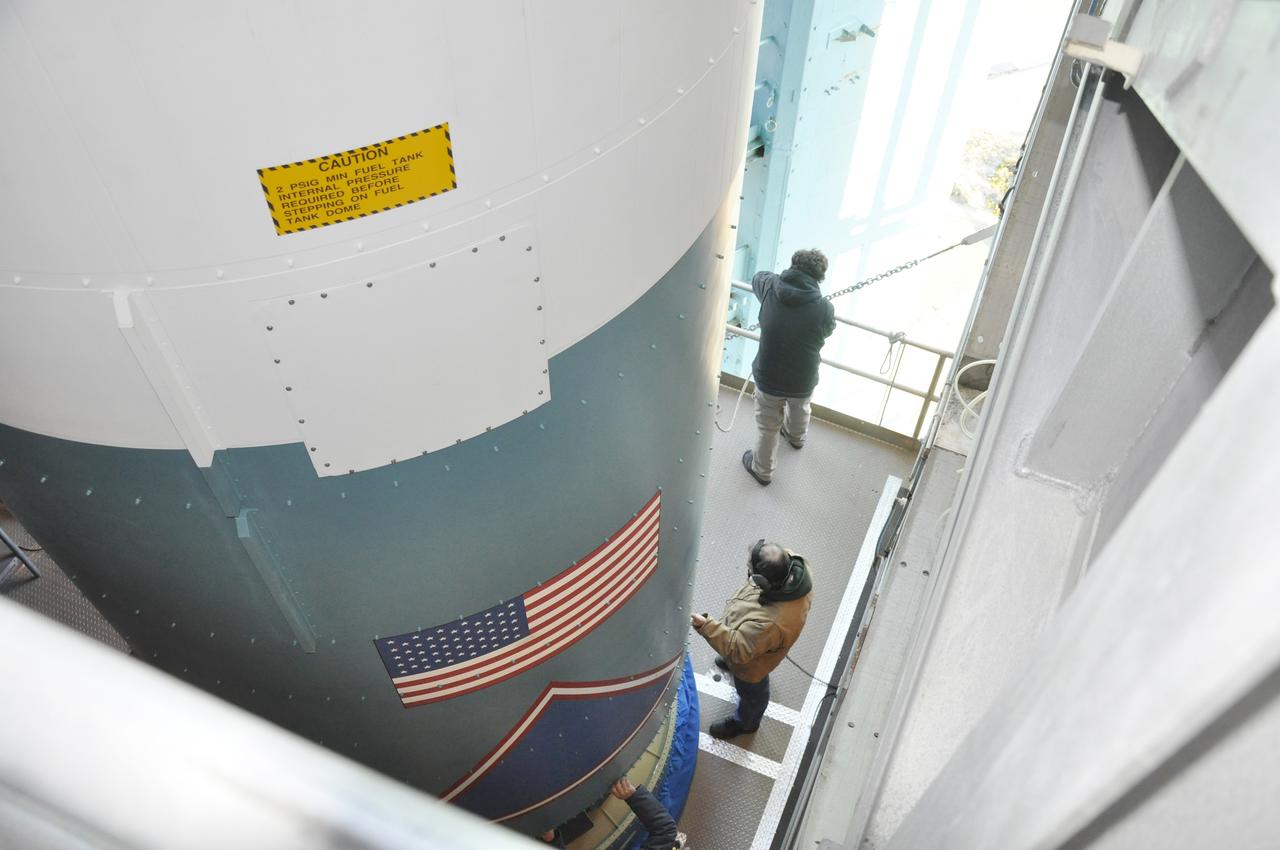

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to connect the Delta II first stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the interstage adapter, or ISA, newly delivered to the environmental enclosure, or clean room, near the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
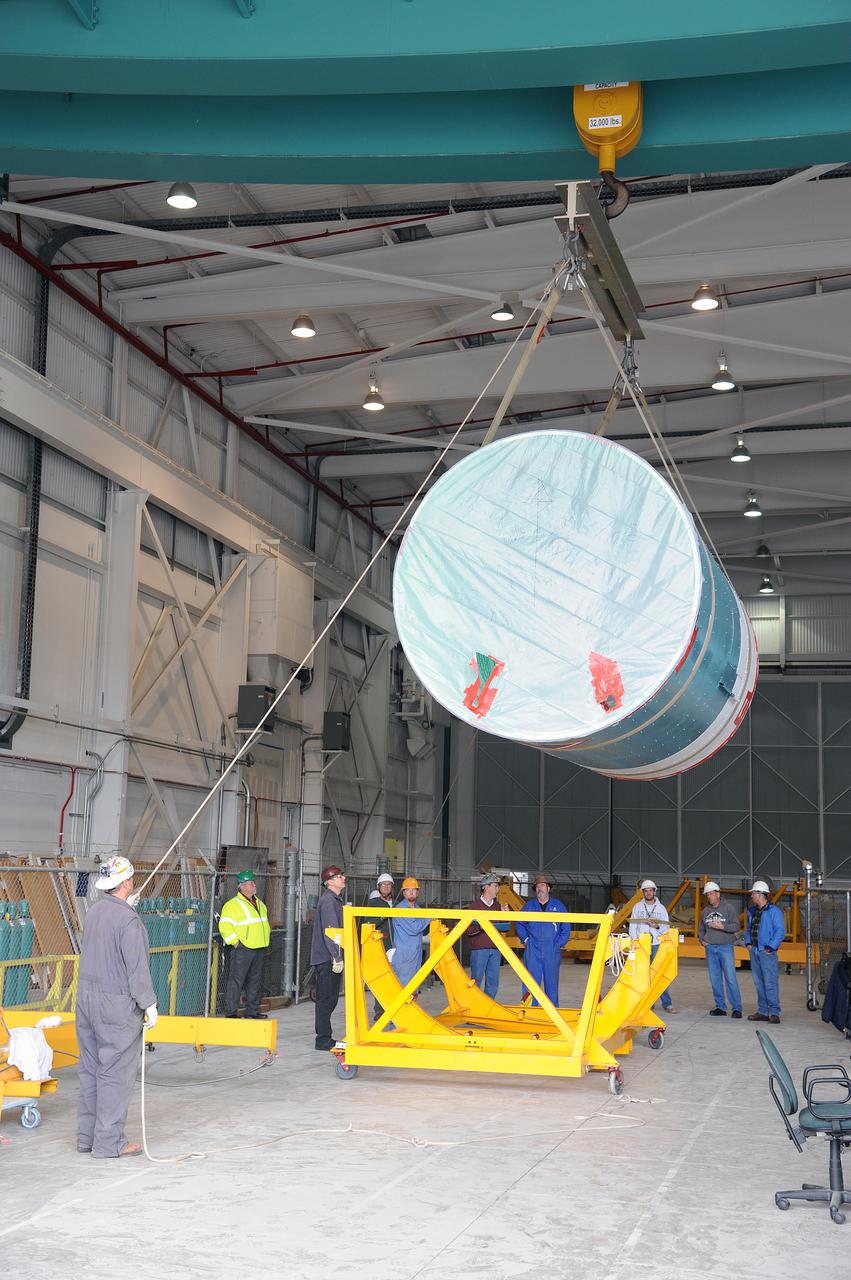

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lower the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, toward a transportation hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http:__oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA_Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – As the cover of the transportation trailer is lifted in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the canister containing the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, comes into view. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is hoisted up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Processing of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft SMAP into orbit is underway at the pad. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The canister containing the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, glides toward a flight hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
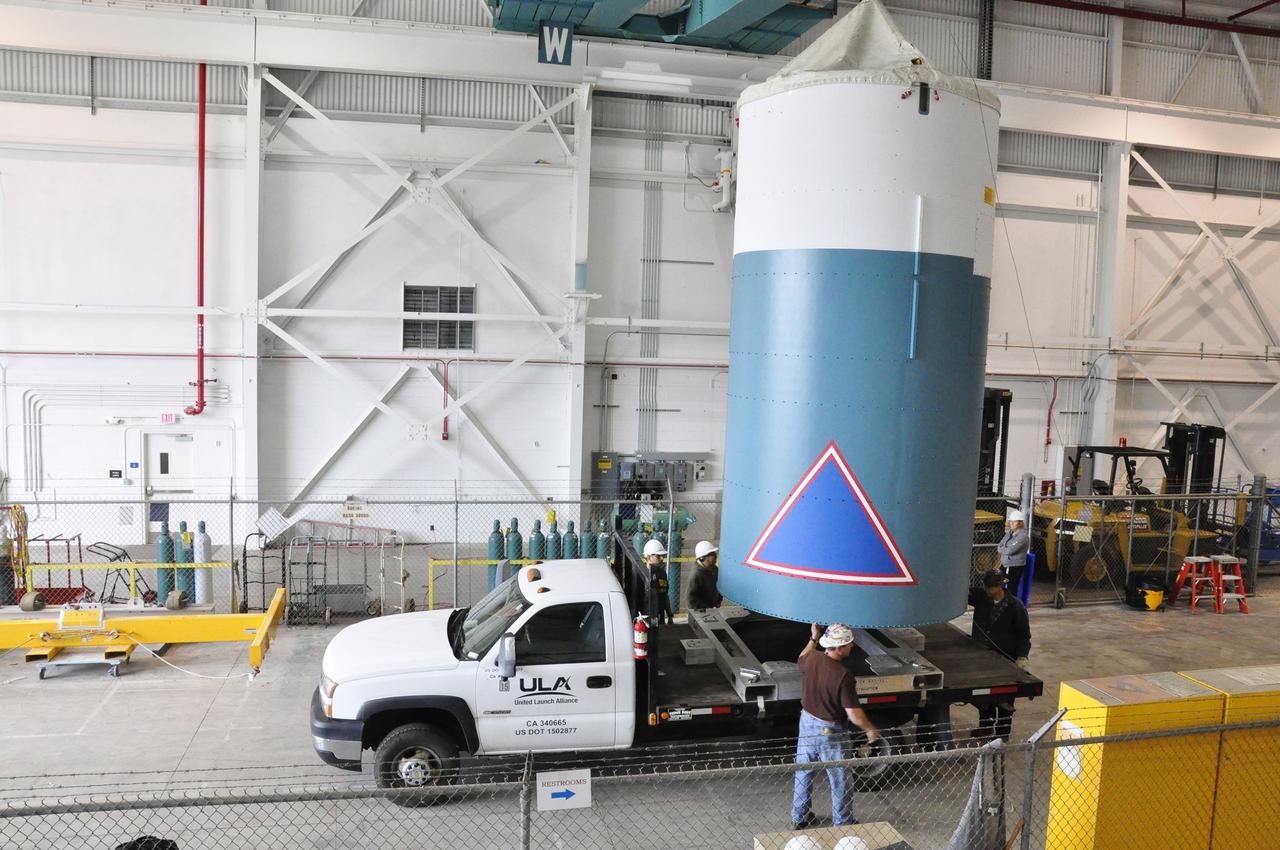

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is lowered onto the flatbed of the truck that will transport it from the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to the pad. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
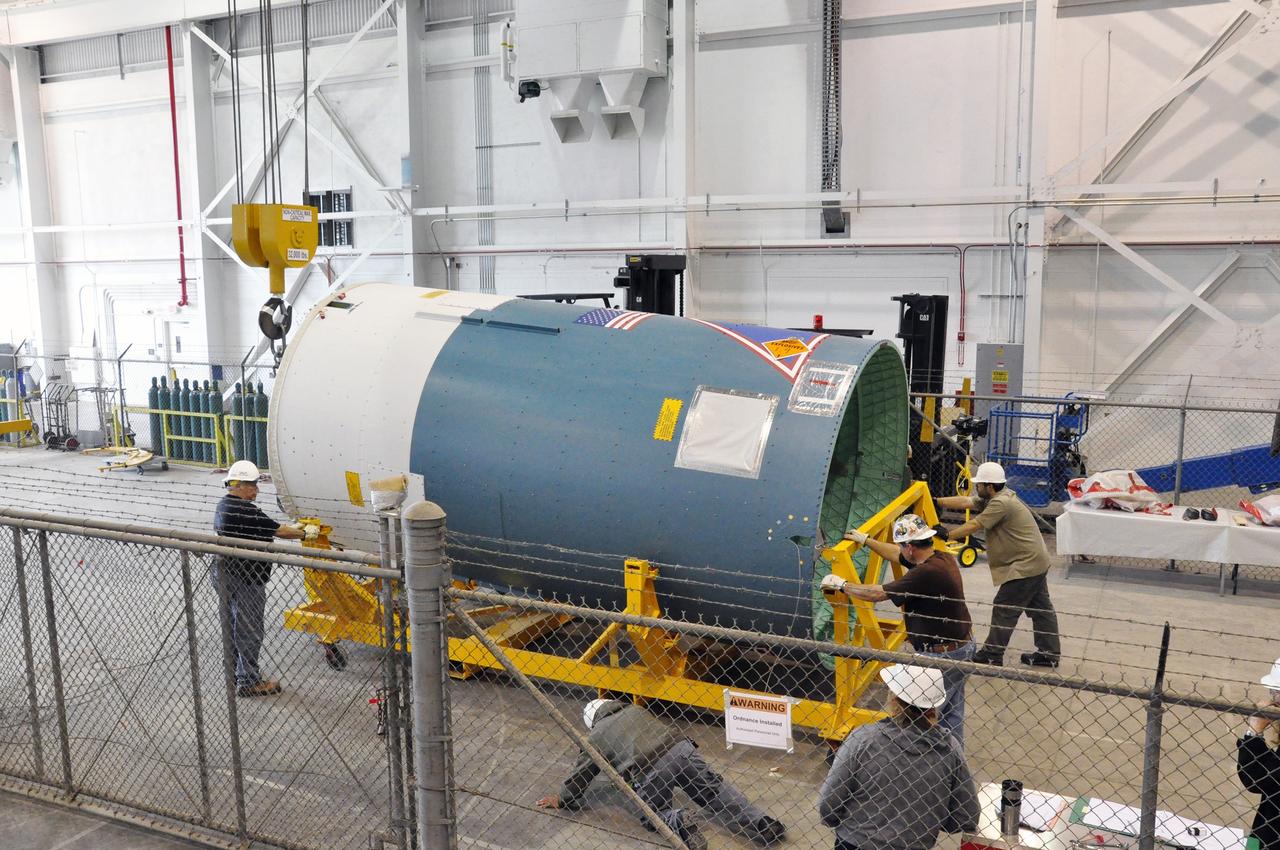

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare to raise the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into a vertical position in the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during preparations for its move to the pad. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
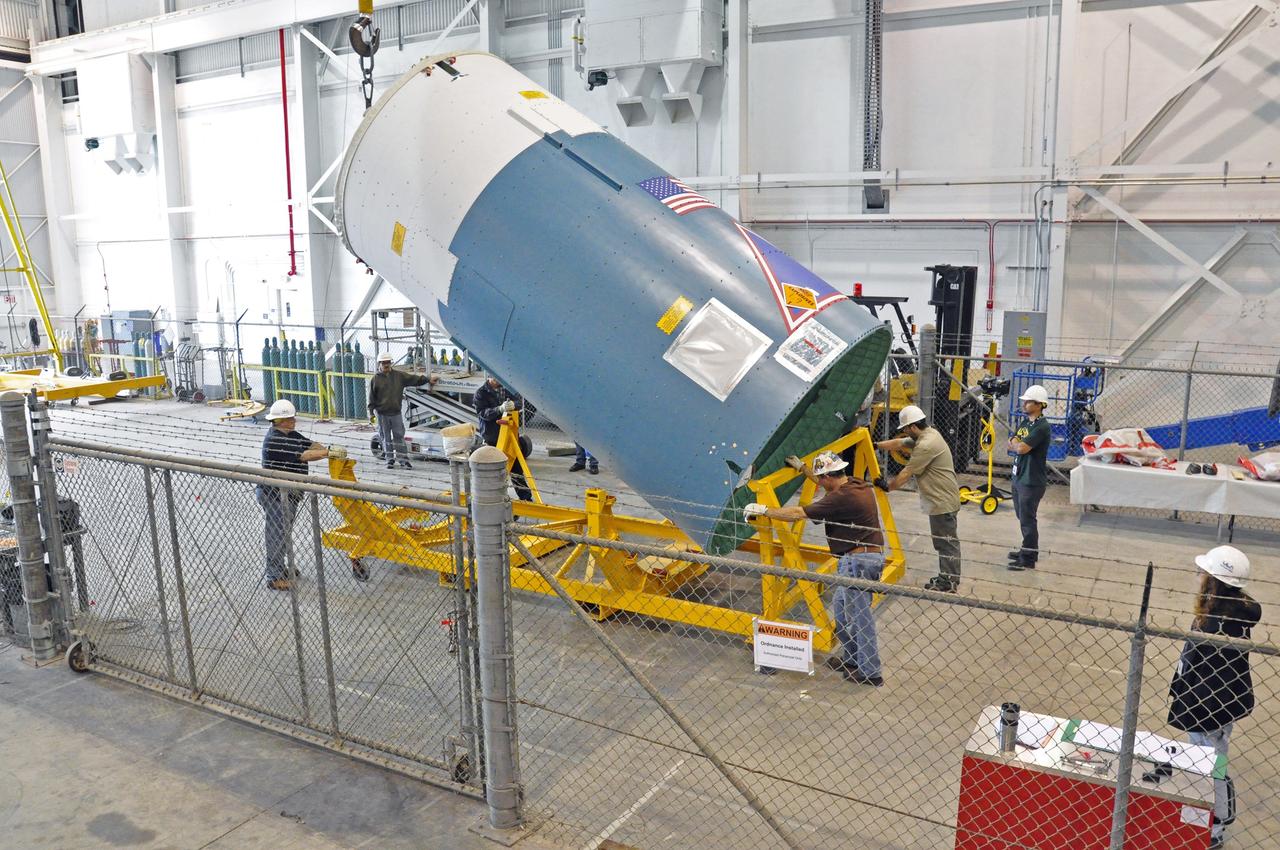

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers raise the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into a vertical position in the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during preparations for its move to the pad. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
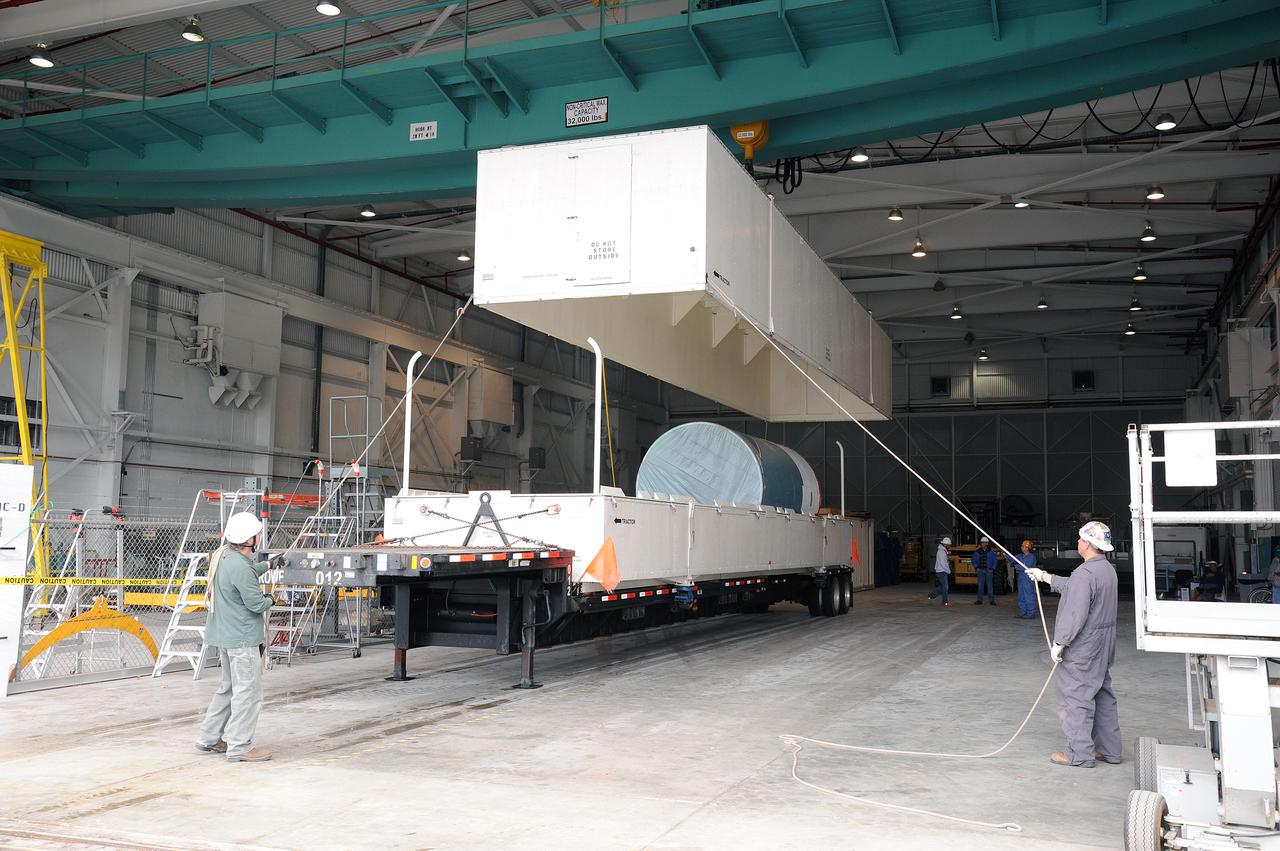

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – As the cover of the transportation trailer is lifted in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, comes into view. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http:__oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA_Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
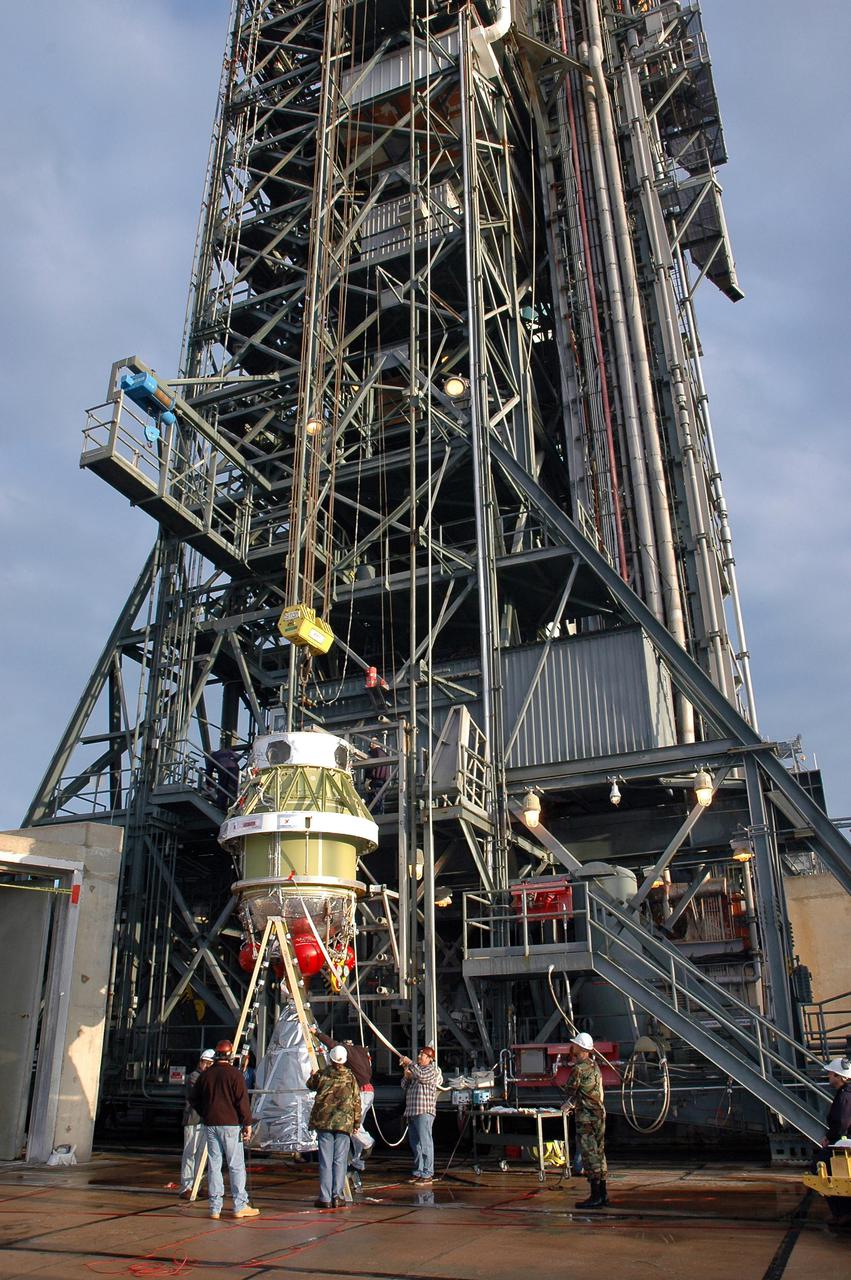

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers remove a protective wrap from the Boeing Delta II second stage. The component will be lifted up the mobile service tower and reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.
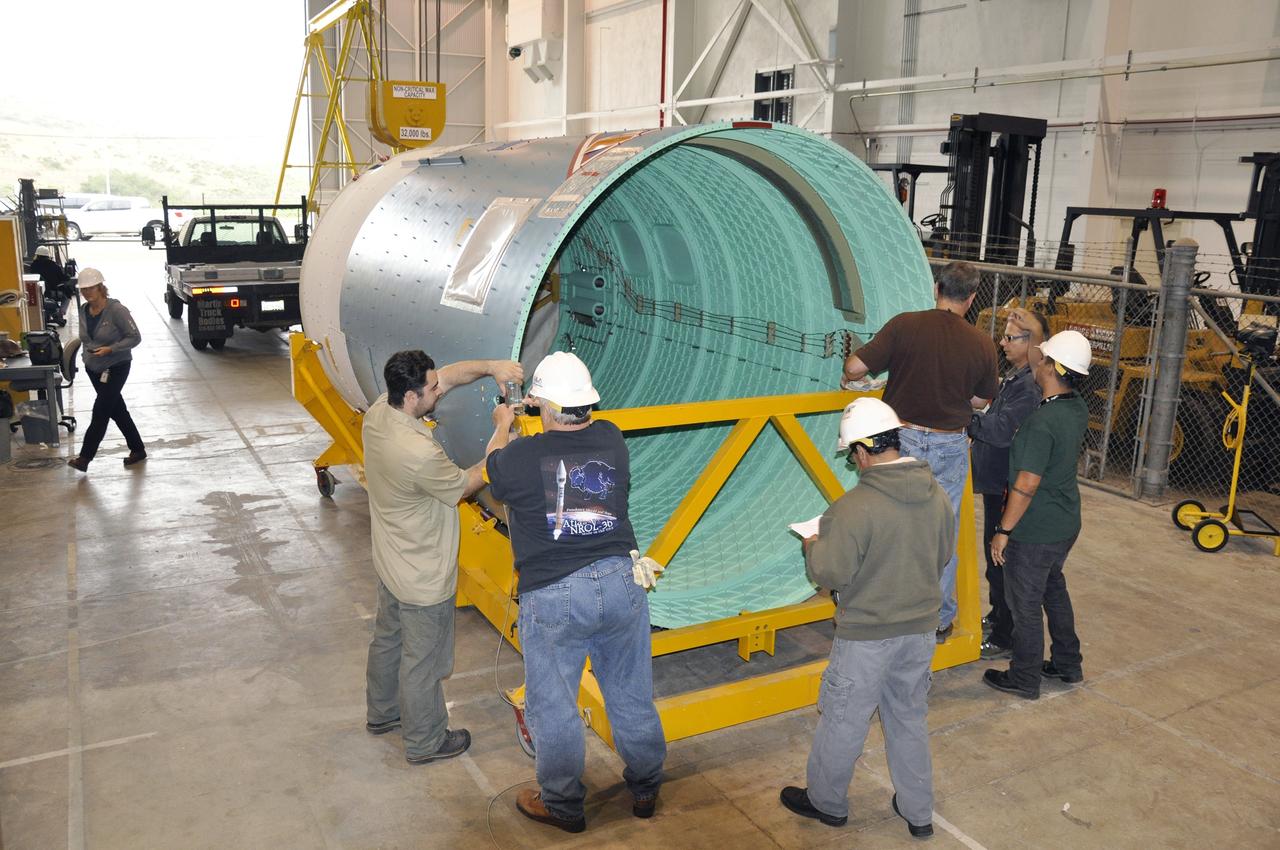

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is attached to a lifting device in the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during preparations for its move to the pad. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
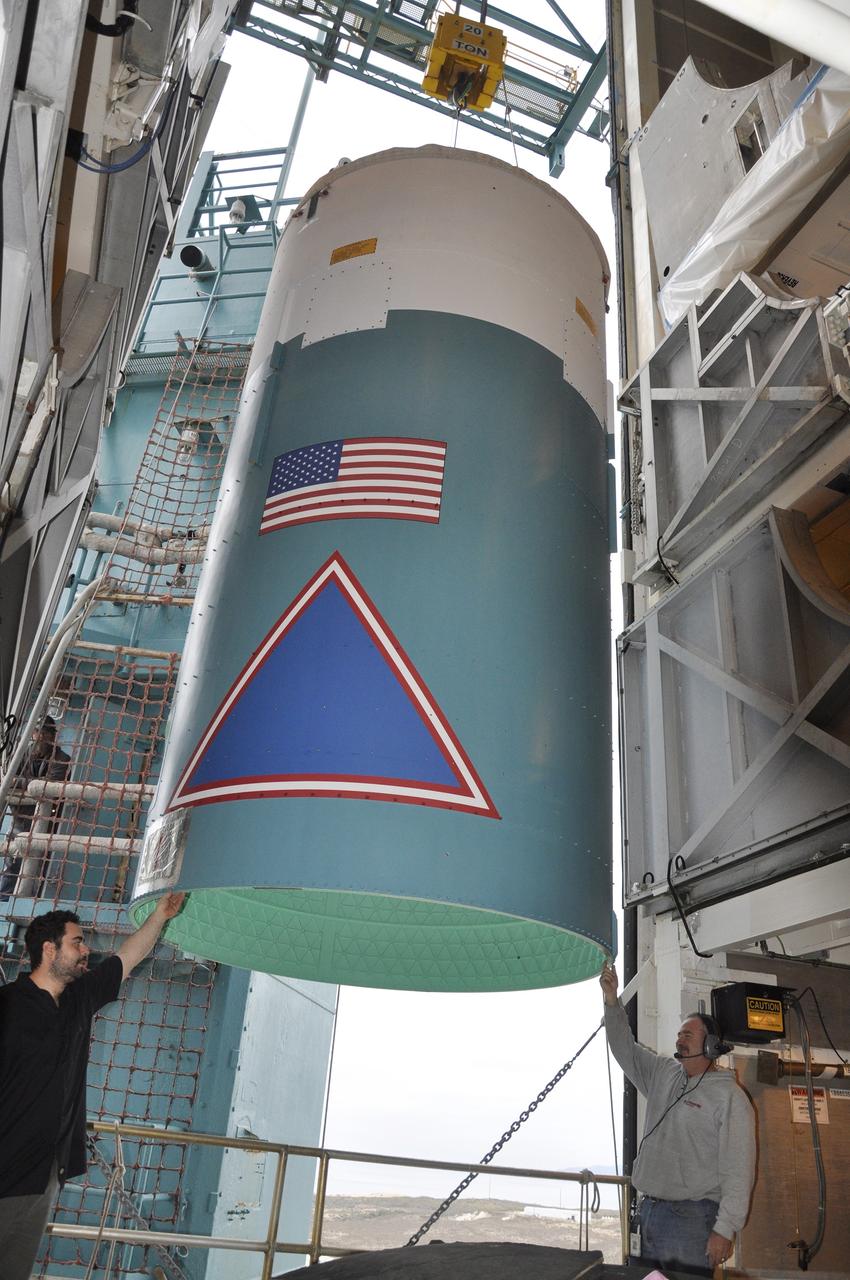
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is transferred into the environmental enclosure in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Processing of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft SMAP into orbit is underway at the pad. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
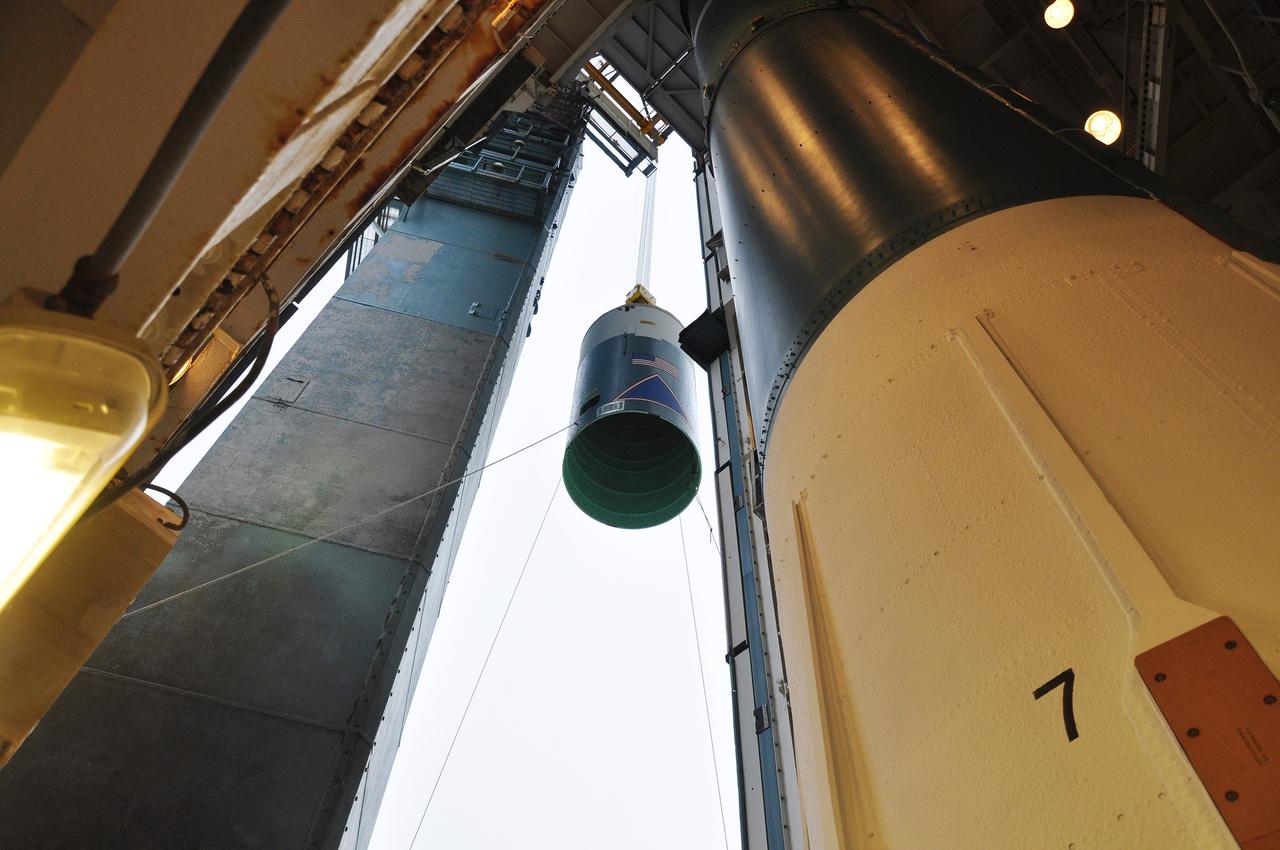

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The view from inside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California shows the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, as it rises past the rocket's first stage already in position in the tower. Processing of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket that will loft SMAP into orbit is underway at the pad. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
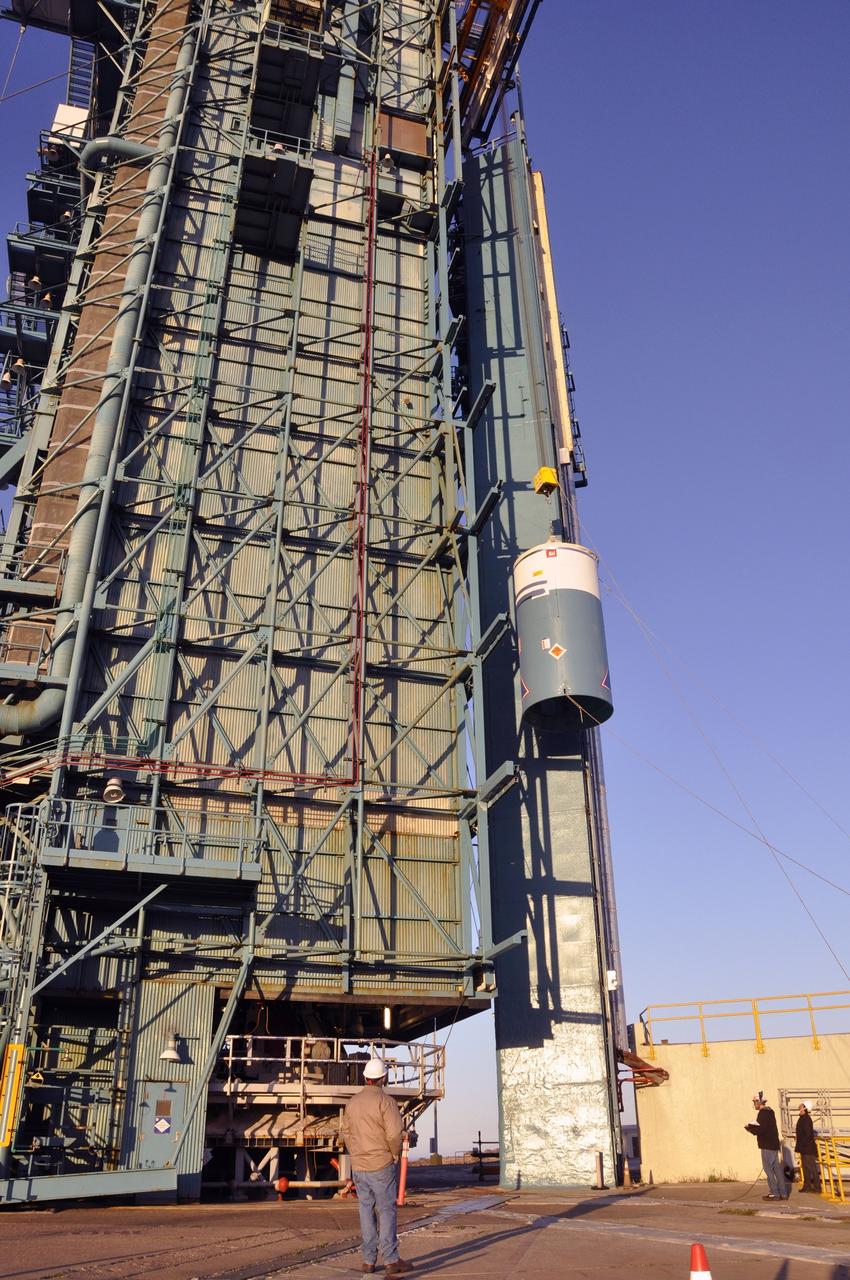

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers stand watch as a crane pulls the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
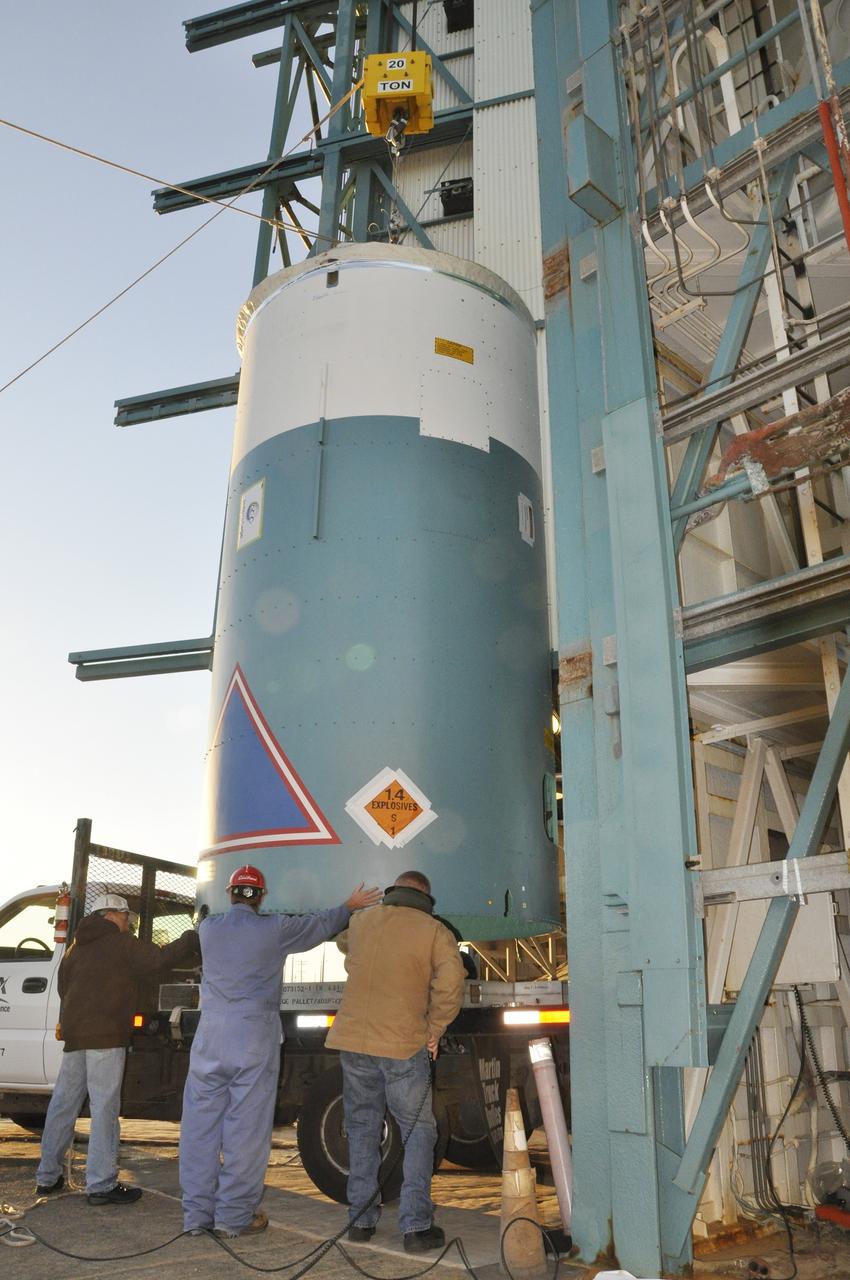

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers steady the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as a crane lifts it from its transporter next to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
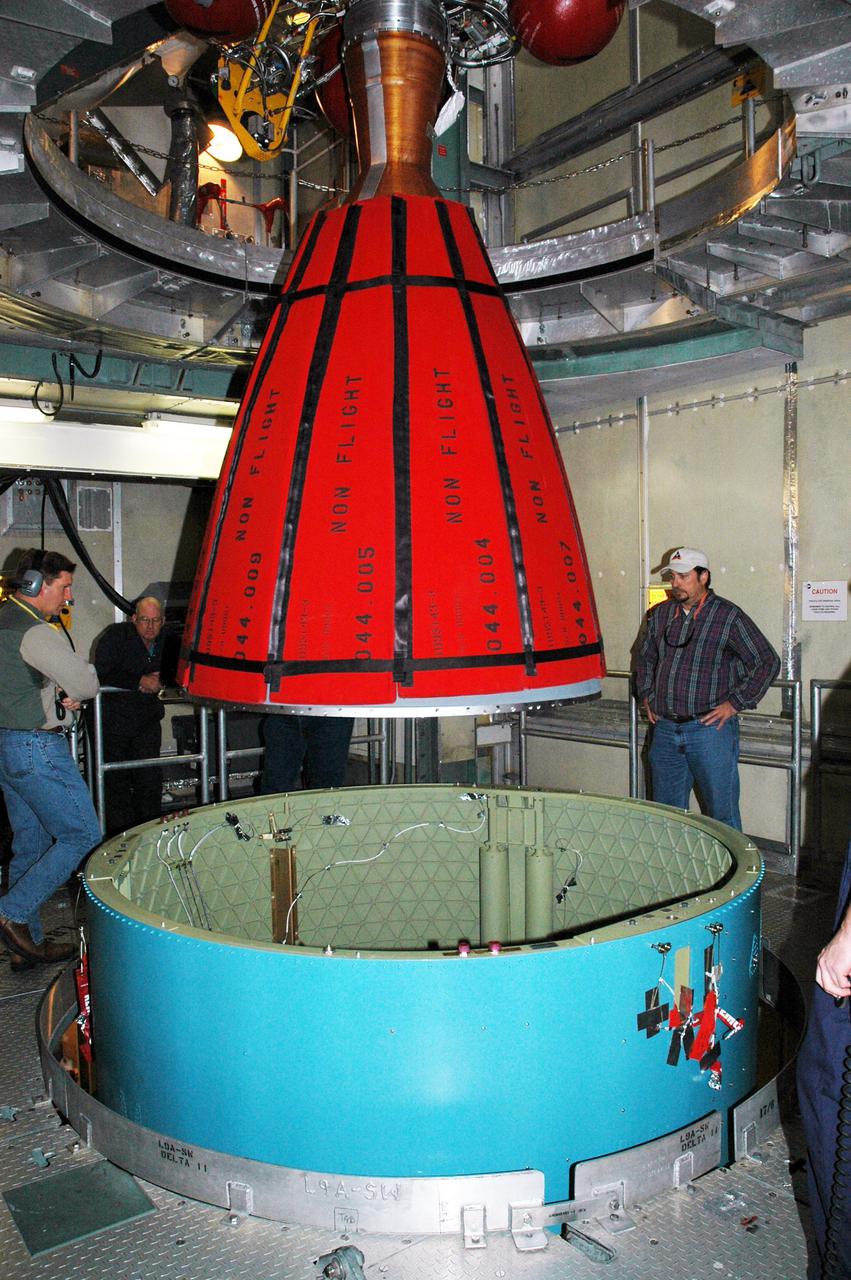

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Boeing workers watch as the Delta II second stage is lowered toward the rocket below. The component will be reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.
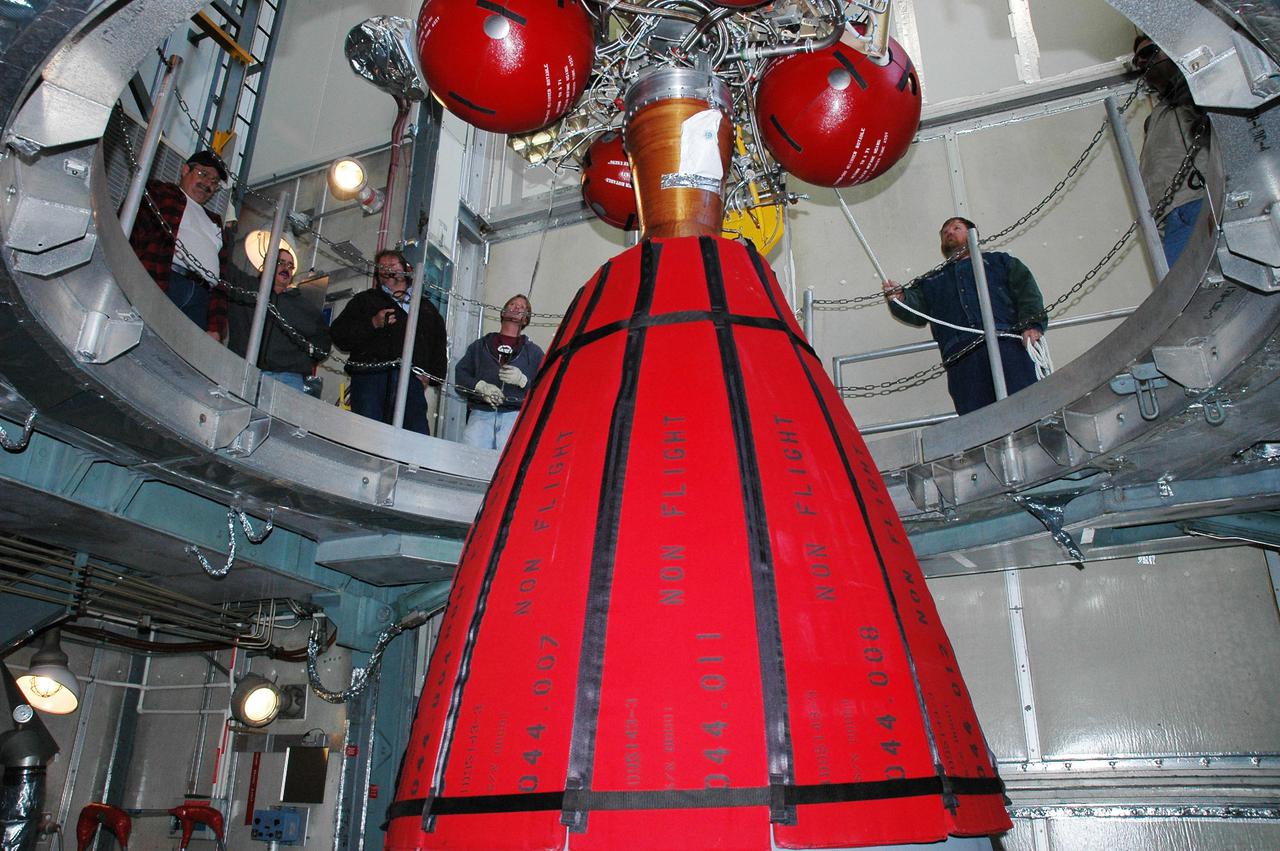
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Boeing workers watch as the Delta II second stage is lowered toward the rocket below. The component will be reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.
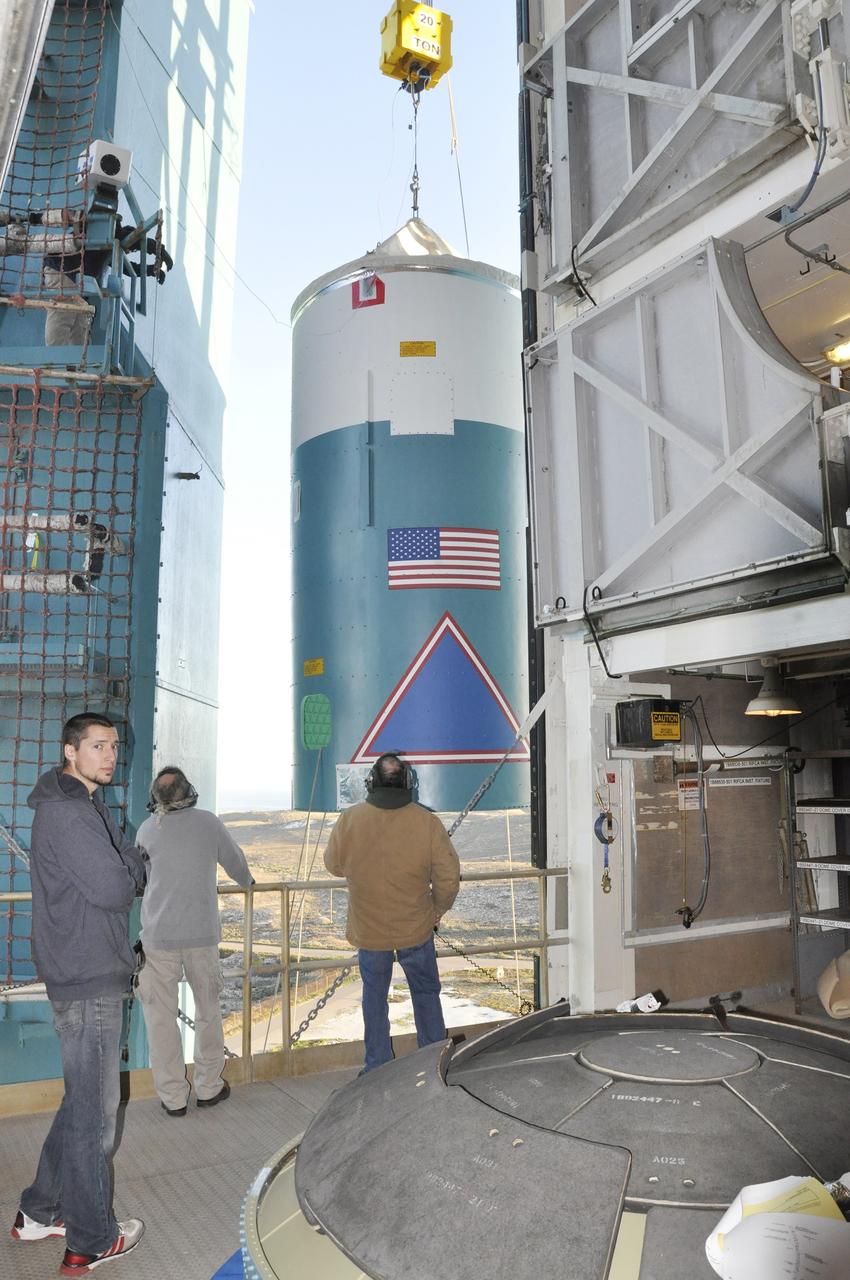

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, near the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
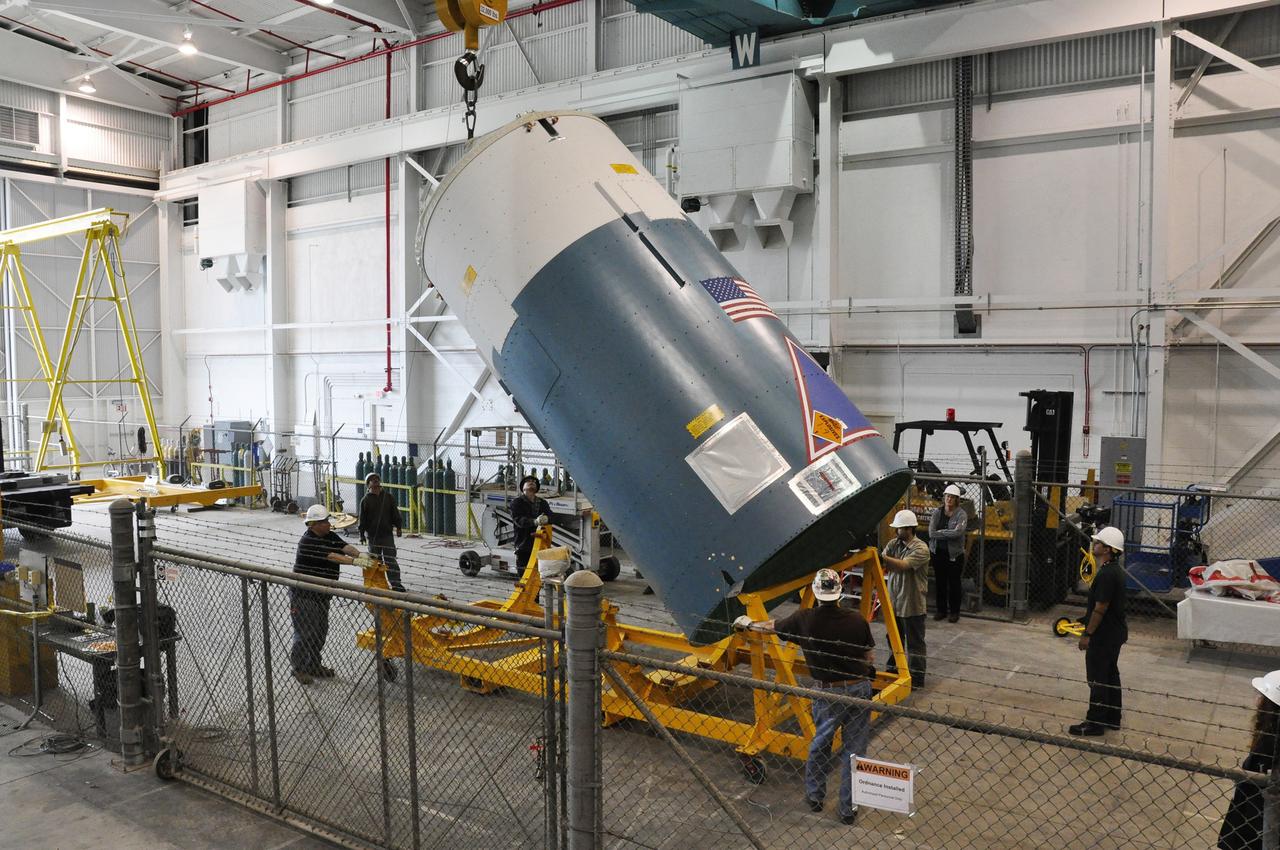

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Slowly and carefully, the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, is raised into a vertical position in the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California during preparations for its move to the pad. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
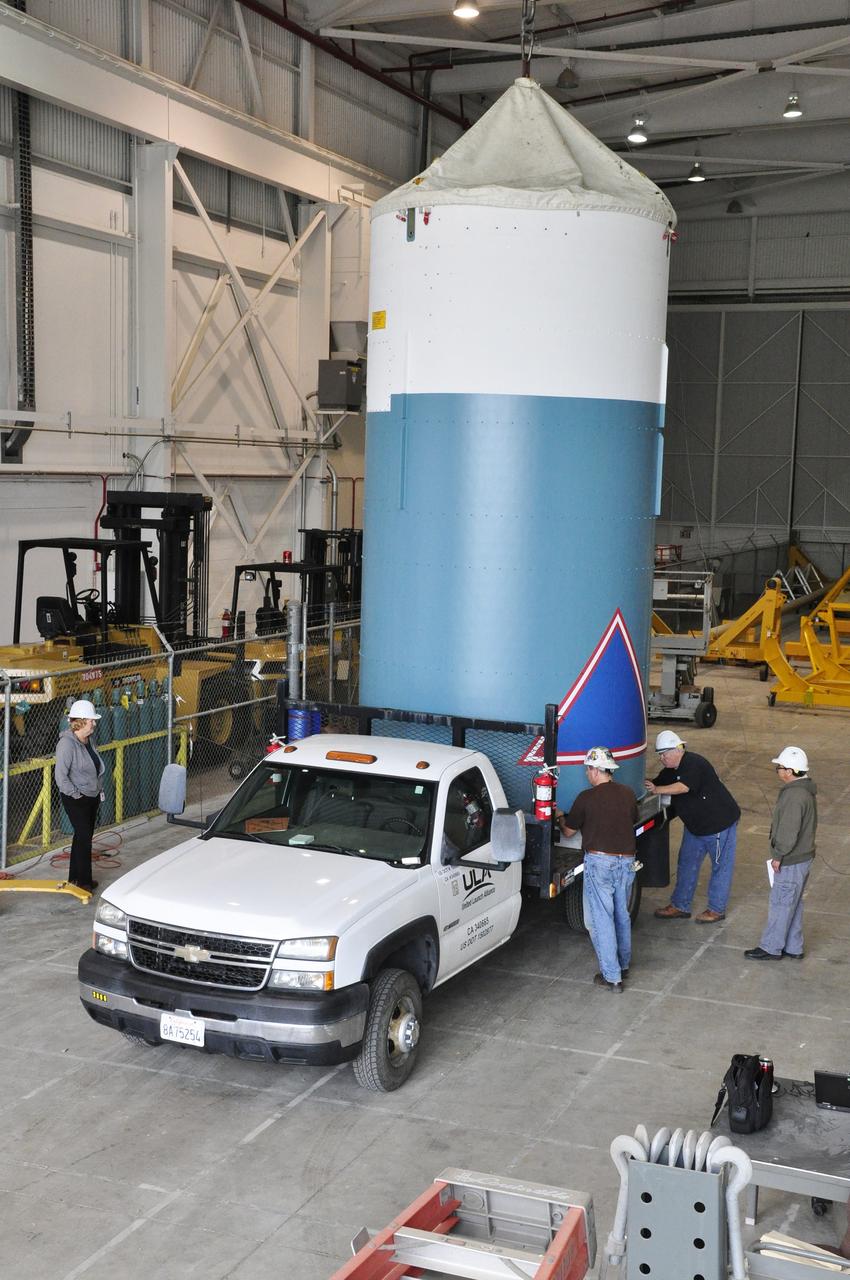

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers secure the Delta II interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, onto the flatbed of the truck that will transport it to the pad from the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
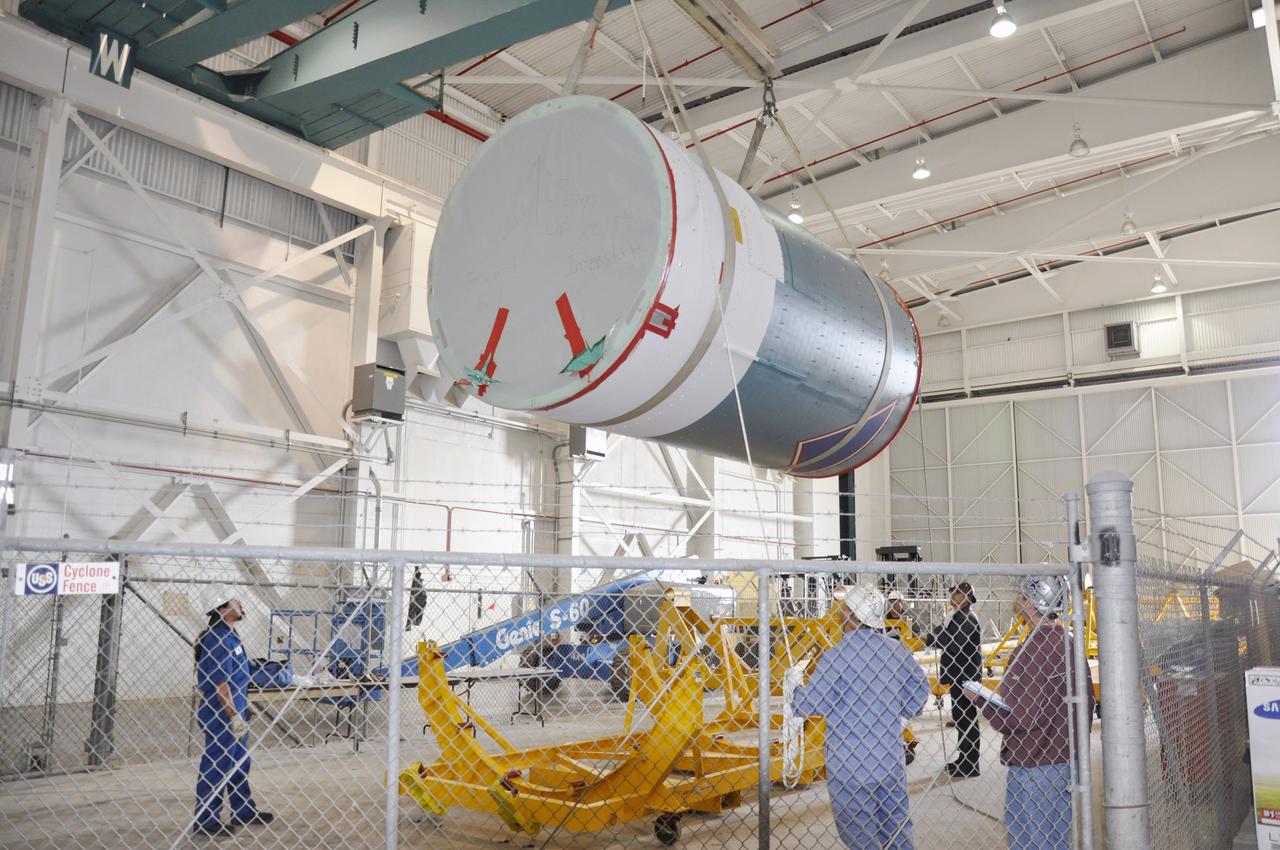

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lower the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, toward a flight hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
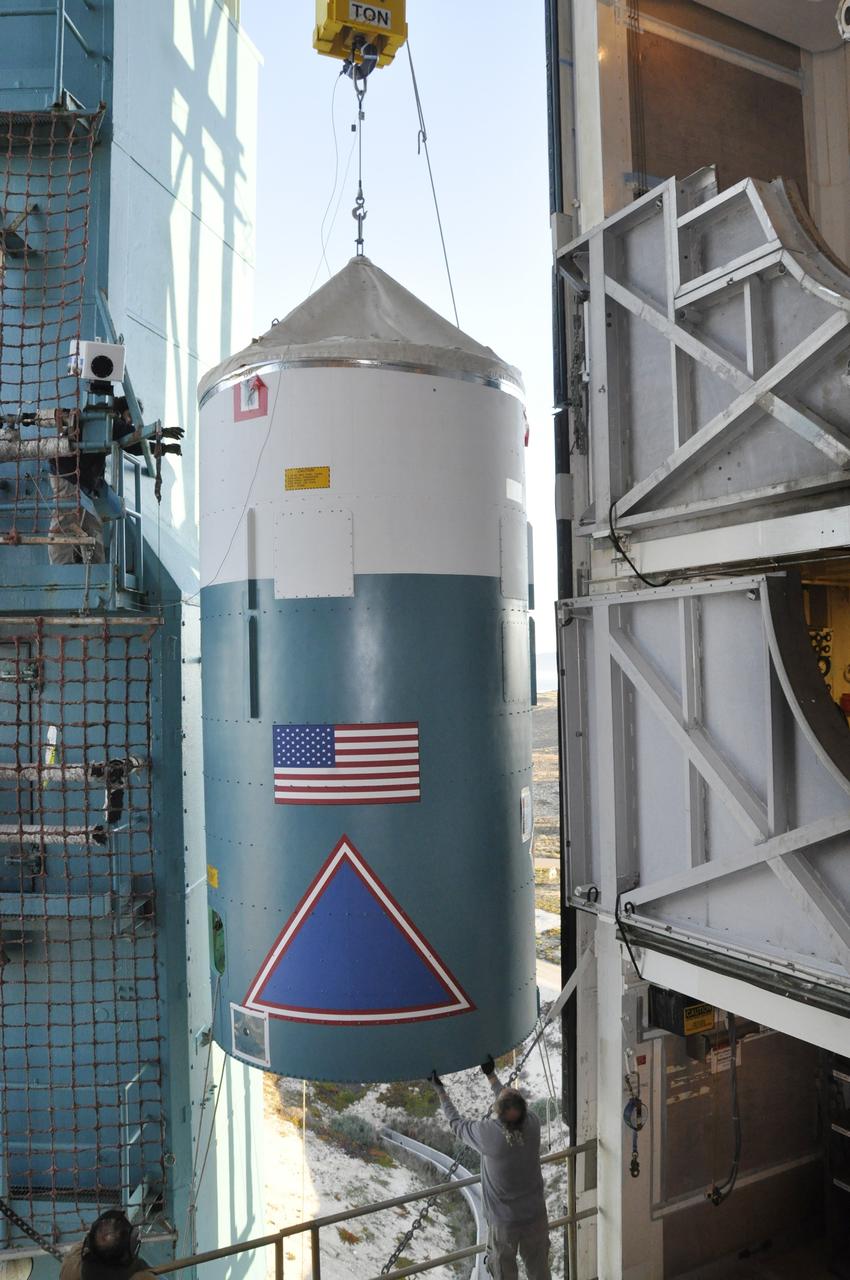

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker steadies the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, upon its arrival in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, near the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
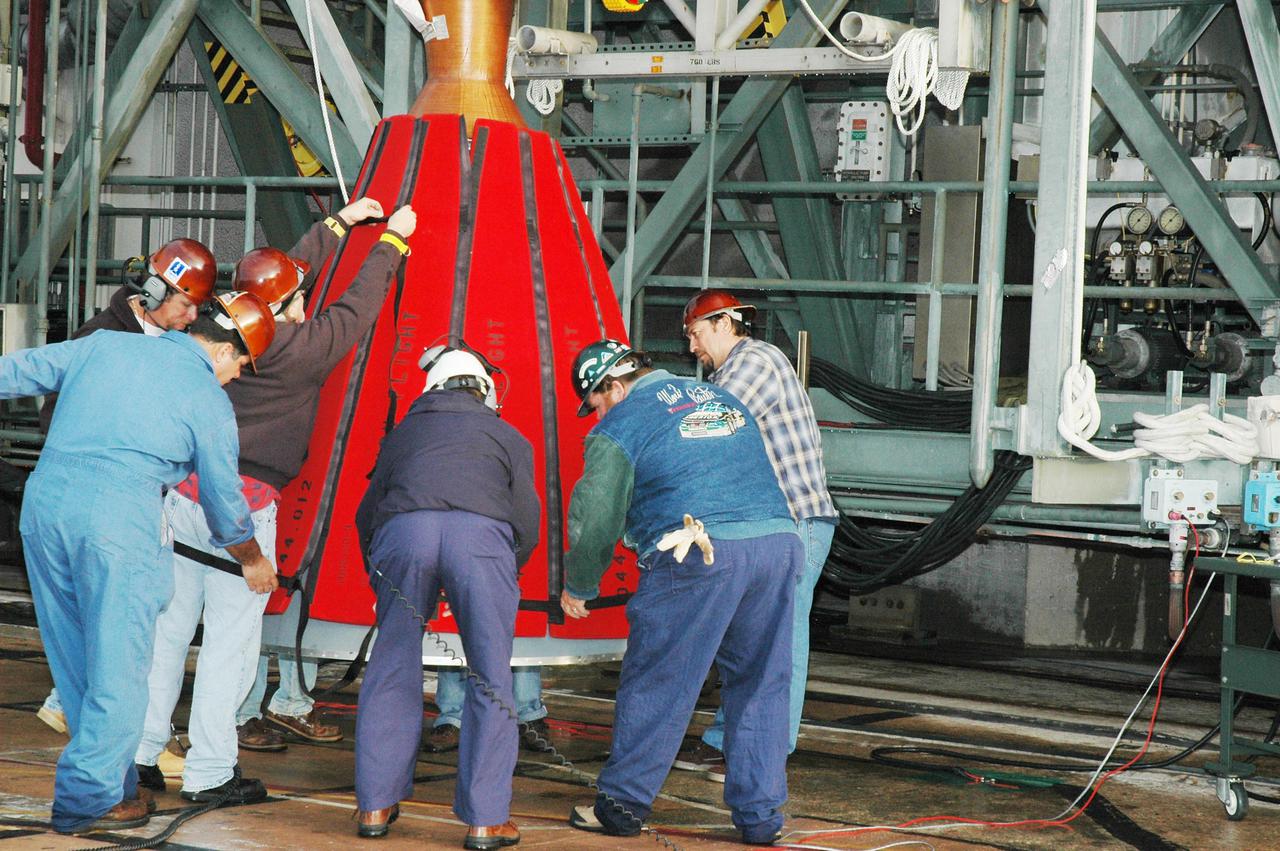

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Launch Pad 17-B, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, workers install a protective wrap on the Boeing Delta II second stage. The component will be lifted up the mobile service tower and reattached to the interstage adapter on the Delta II. The rocket is the launch vehicle for the Deep Impact spacecraft, scheduled for liftoff no earlier than Jan. 12. A NASA Discovery mission, Deep Impact will probe beneath the surface of Comet Tempel 1 on July 4, 2005, when the comet is 83 million miles from Earth, and reveal the secrets of its interior. After releasing a 3- by 3-foot projectile to crash onto the surface, Deep Impact’s flyby spacecraft will collect pictures and data of how the crater forms, measuring the crater’s depth and diameter, as well as the composition of the interior of the crater and any material thrown out, and determining the changes in natural outgassing produced by the impact. It will send the data back to Earth through the antennas of the Deep Space Network.

Inside the Vertical Integration Facility at Space Launch Complex 3 at Vandenberg Space Source Base in California, workers help secure the interstage and assembly second stage adapters to the Centaur second stage of the United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for NASA’s Landsat 9 mission on July 14, 2021. Landsat 9 will launch atop the Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg in September 2021. The launch is being managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy Space Center, America’s multiuser spaceport. The Landsat 9 satellite will continue the nearly 50-year legacy of previous Landsat missions. It will monitor key natural and economic resources from orbit. Landsat 9 is managed by the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The satellite will carry two instruments: the Operational Land Imager 2, which collects images of Earth’s landscapes in visible, near infrared and shortwave infrared light, and the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2, which measures the temperature of land surfaces. Like its predecessors, Landsat 9 is a joint mission between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
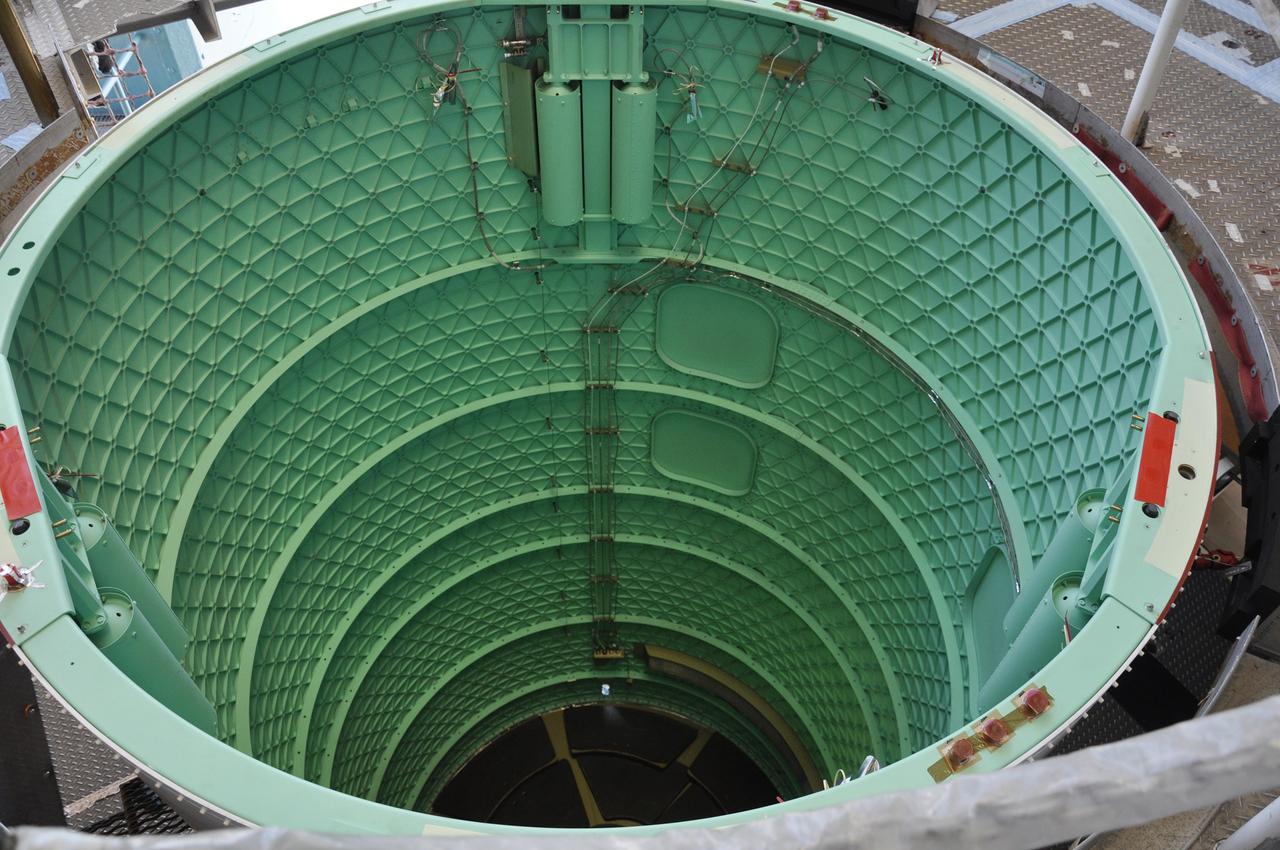

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is connected to the Delta II first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California and ready for delivery of the rocket's second stage. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
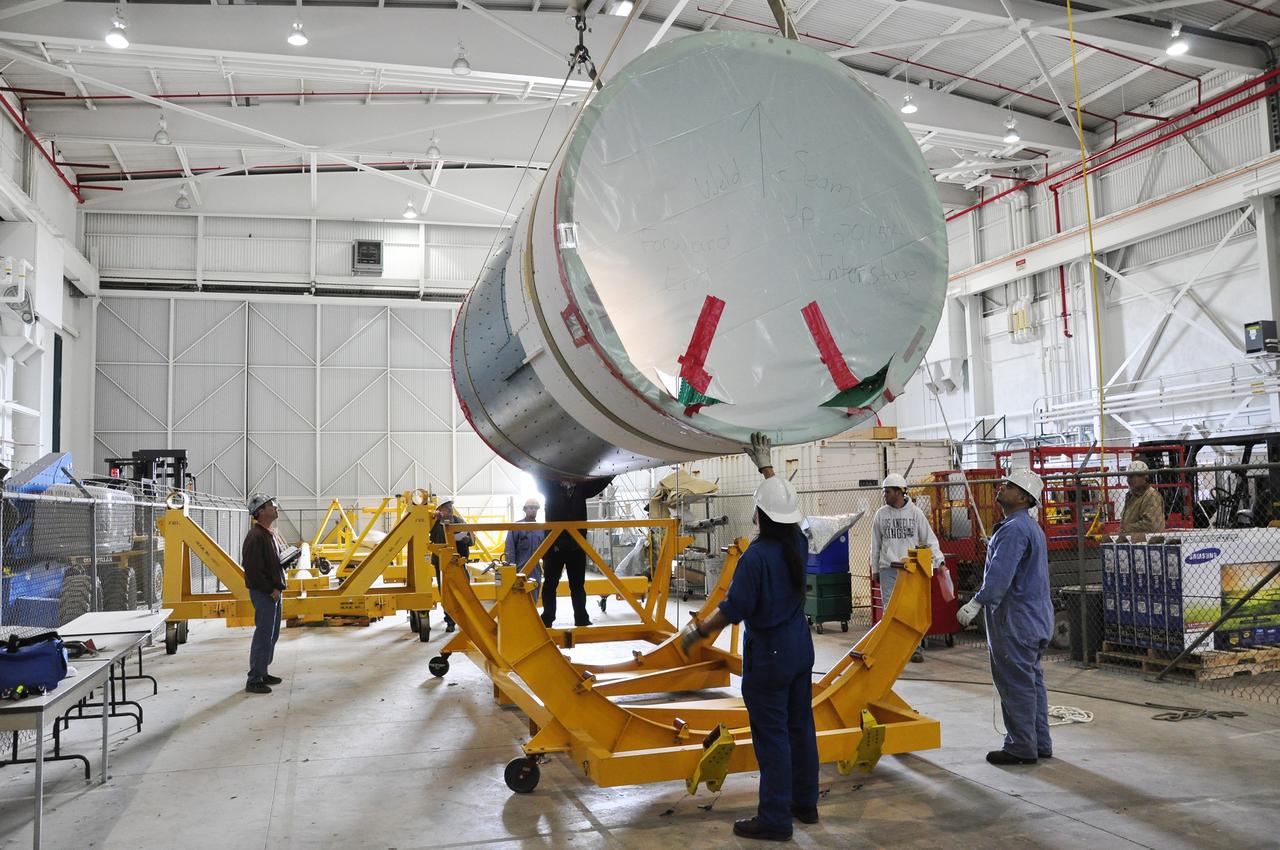

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lower the canister containing the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Soil Moisture Active Passive mission, or SMAP, into a flight hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on south Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket will loft SMAP into orbit from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2. The ISA connects the Delta II first and second stages and encloses the second stage engine and thrust section. The spacecraft will provide global measurements of soil moisture and its freeze/thaw state. These measurements will be used to enhance understanding of processes that link the water, energy and carbon cycles, and to extend the capabilities of weather and climate prediction models. The data returned also will be used to quantify net carbon flux in boreal landscapes and to develop improved flood prediction and drought monitoring capabilities. Launch is scheduled for November 2014. To learn more about SMAP, visit http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
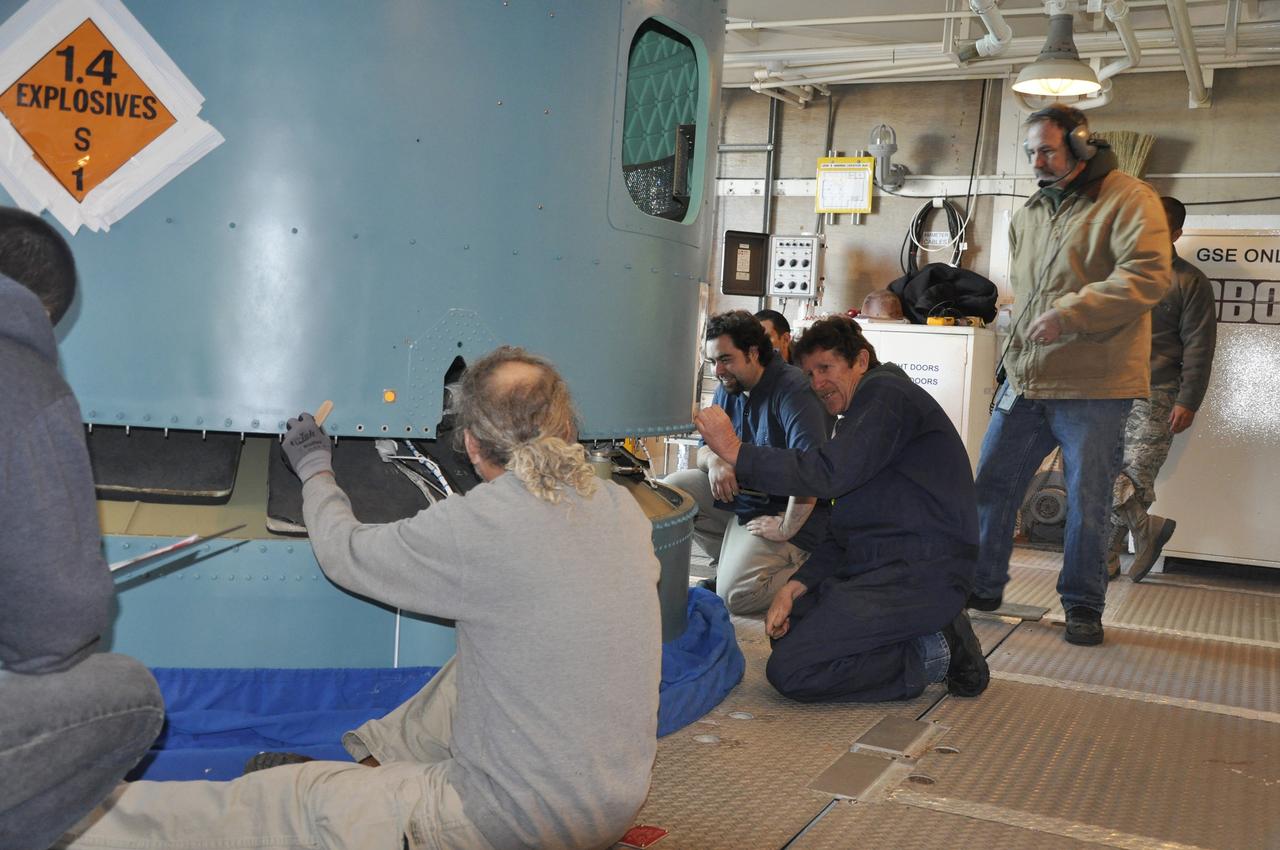

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers connect the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Delta II first stage in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, near the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch into a polar Earth orbit aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II 7320-10C rocket in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. Once in orbit, OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
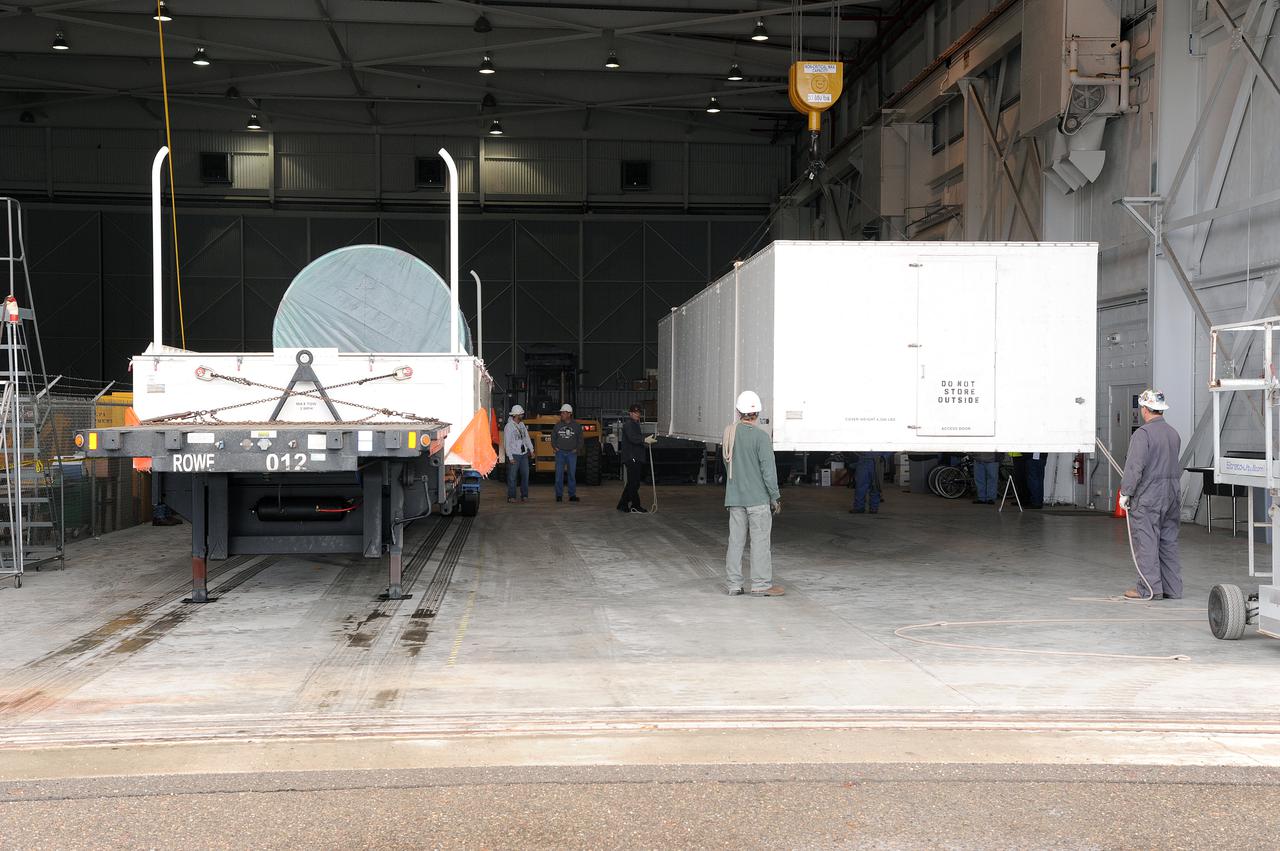

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers remove the cover of the transportation trailer protecting the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http:__oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA_Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB