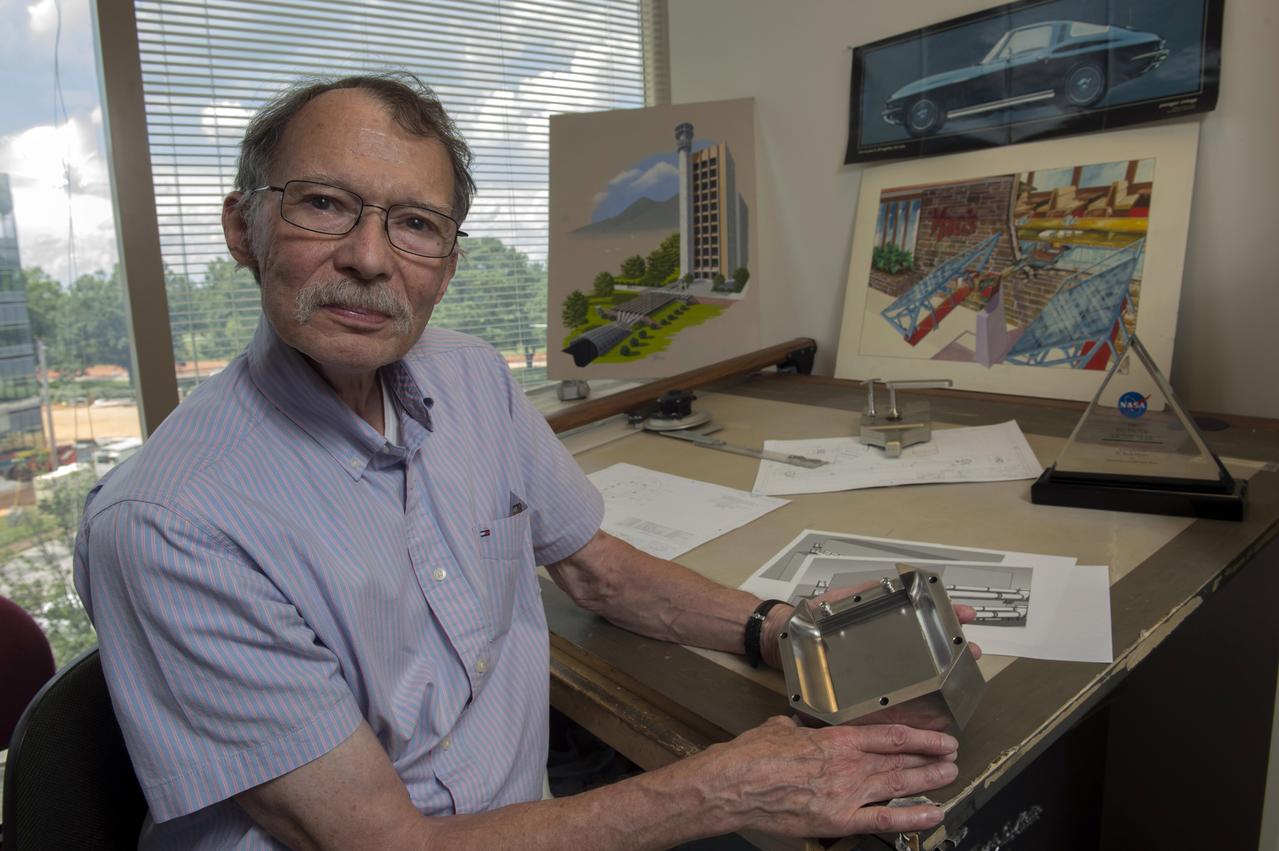

Neill Myers, Marshall’s most patented inventor, demonstrates the Variable-Aperture Reciprocating Reed Valve, an invention that won him his fourth Marshall Invention of the Year award.
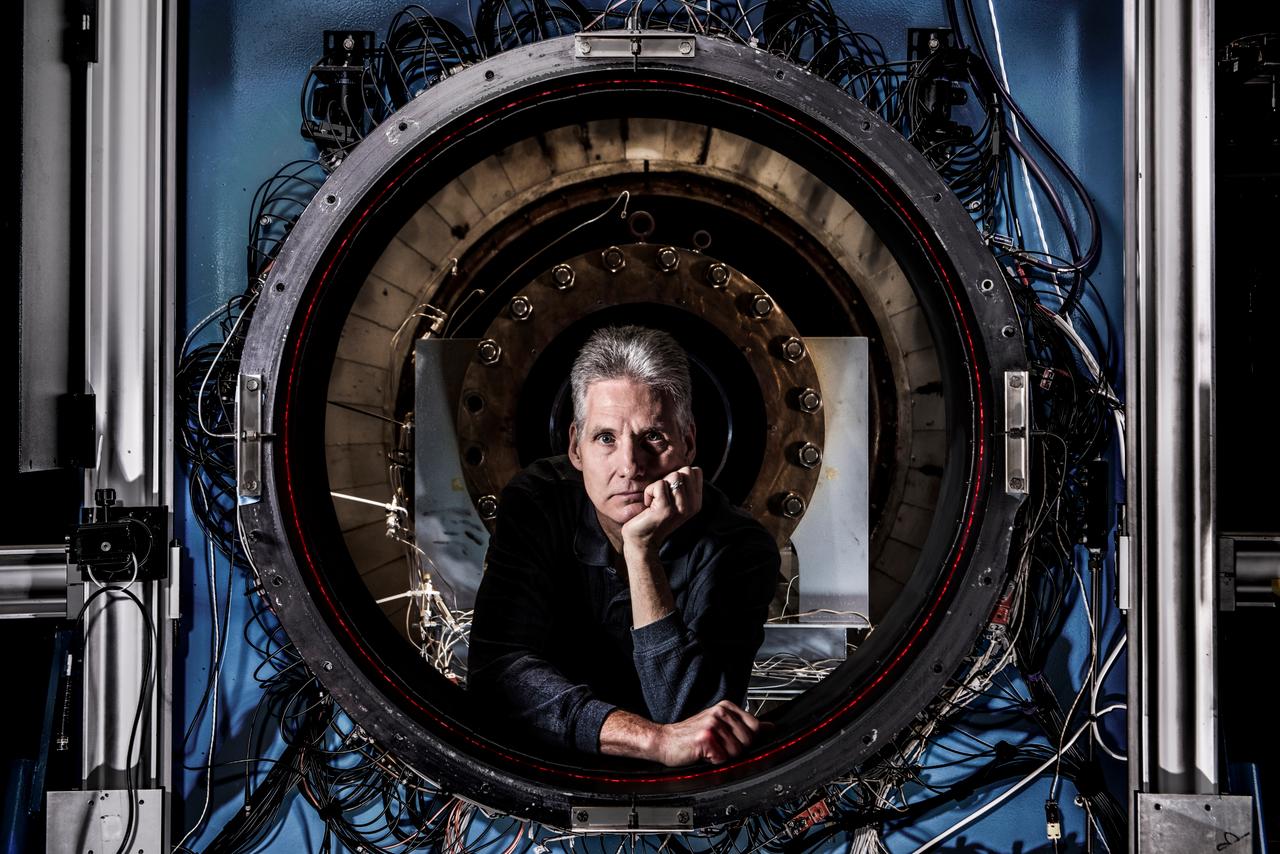

How do you measure a cloud? Tim Bencic does it with lasers. The NASA Glenn engineer invented a tomography system for our Propulsion Systems Lab to help understand the dangers of ice crystal icing on airplanes. Bencic’s system, affectionally called “Tim-ography” is like a CAT Scan. The laser light within its circular geometry bounces off the surface of ice particles in the cloud and fiber optic detectors map out its properties. This tool is helping NASA’s researchers make aircraft safer in challenging weather conditions.
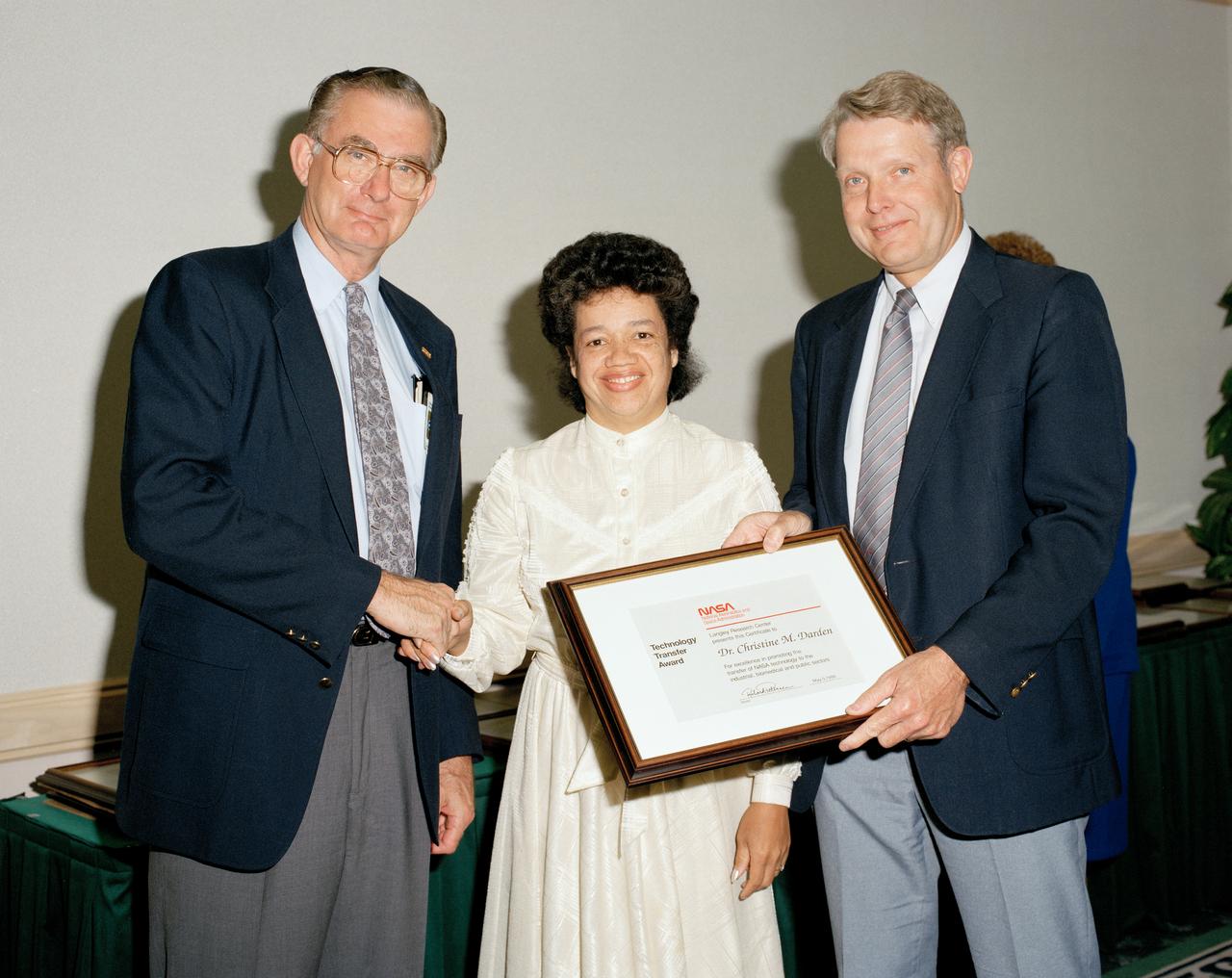

Technology Transfer Awards, Dr. Christine M. Darden, with Center Director Richard W. Peterson on the right.
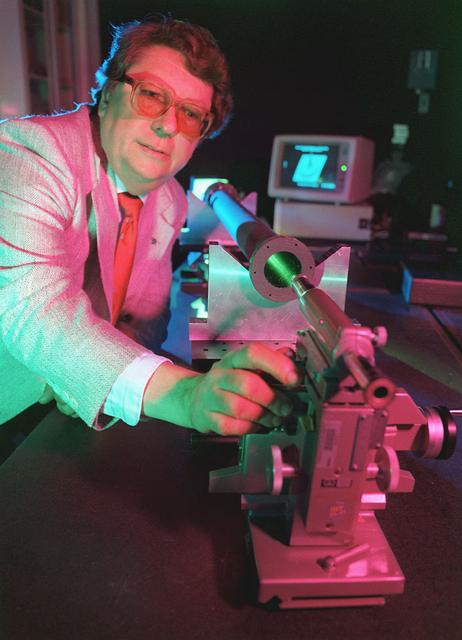

Marshall's 1992 Inventor of the Year demonstrates his multi-layer water window imaging x-ray microscope.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Independent inventor Peter Homer, left, founder of Flagsuit LLC, inserts a glove which he designed into a glove box for a demonstration of its dexterity and flexibility during the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Homer was the winner of the competition held in 2007. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Independent inventor Peter Homer, founder of Flagsuit LLC, submits a glove which he designed to a dexterity and flexibility test during the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Homer was the winner of the competition held in 2007. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

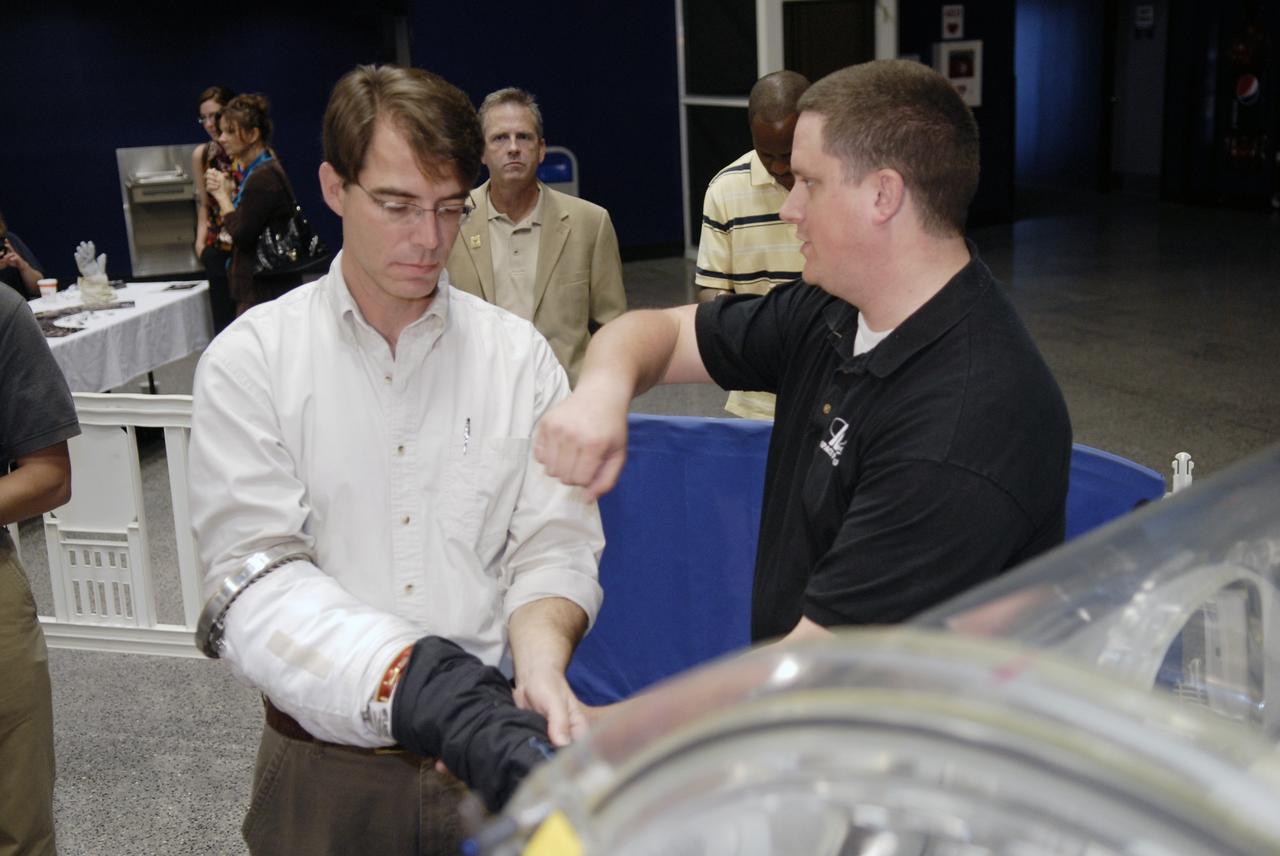
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Independent inventor Peter Homer, founder of Flagsuit LLC, inserts a glove which he designed into a glove box for a dexterity and flexibility test during the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Homer was the winner of the competition held in 2007. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

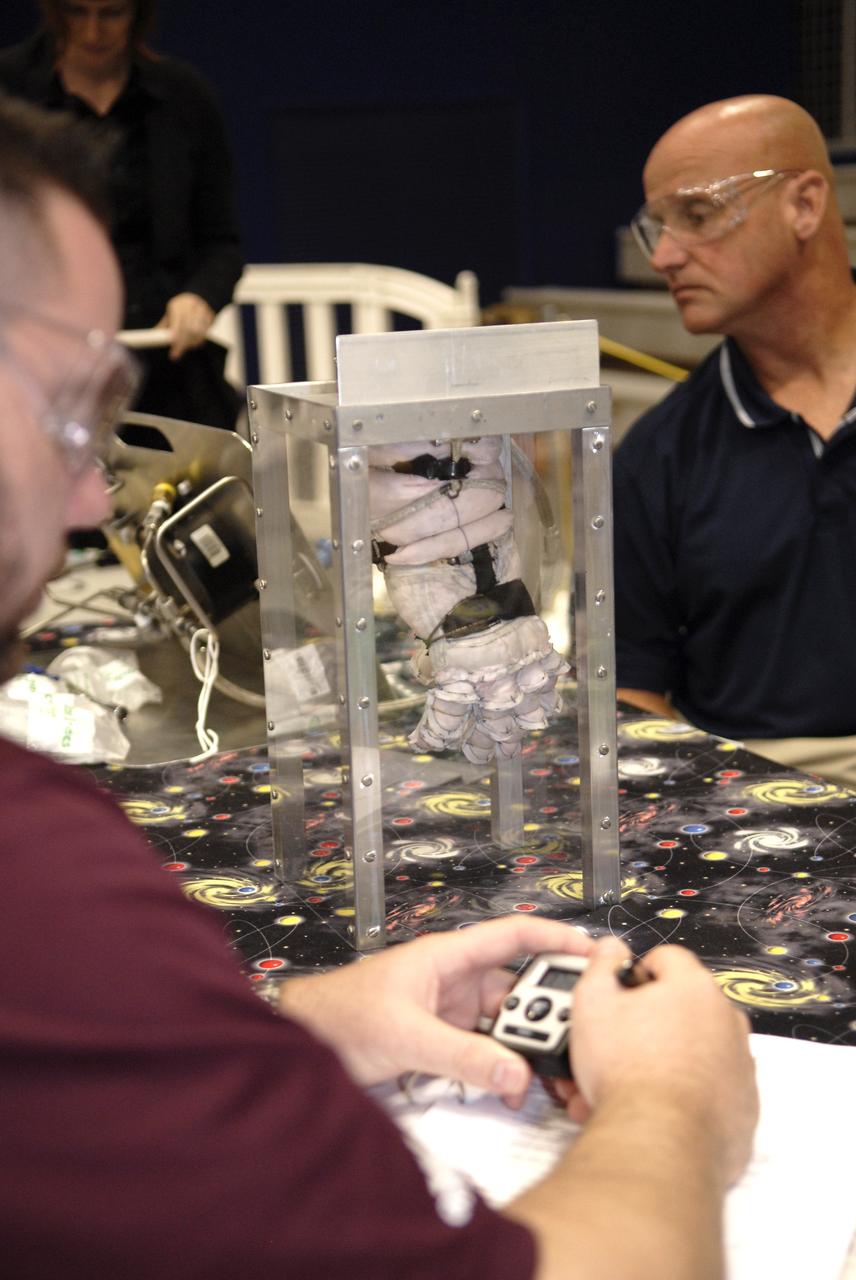
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Independent inventor Ted Southern of Brooklyn, N.Y., submits a glove which he designed to a burst test as representatives of ILC Dover monitor how much internal pressure the glove can withstand. Southern is a participant in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, being held at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

A Co-inventor of the Shape Memory Alloy, Spring Tire, shows the NASA Chief Technologist the first SMA Spring Tire Prototype during a tour of the Glenn Research Center, Simulated Lunar Operations Laboratory (SLOPE).

By 1870, American and British inventors had found other ways to use rockets. For example, the Congreve rocket was capable of carrying a line over 1,000 feet to a stranded ship. In 1914, an estimated 1,000 lives were saved by this technique.

In this photograph, Marshall Space Flight Center Director, Dr. Wernher von Braun, presents a Co-Inventor’s award to MSFC employee Martin Hall of the Mechanical Engineering Laboratory during the NASA Anniversary ceremony.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A representative of ILC Dover prepares a newly designed glove for a dexterity and flexibility test during the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
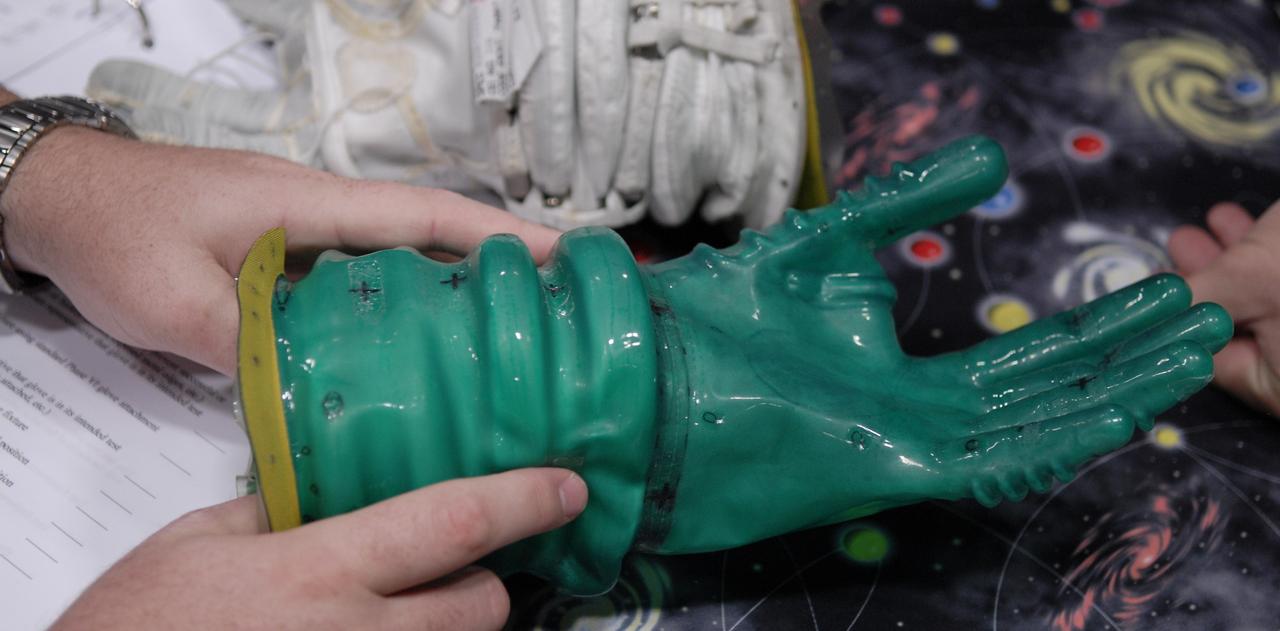

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This newly designed glove is one of the entries in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
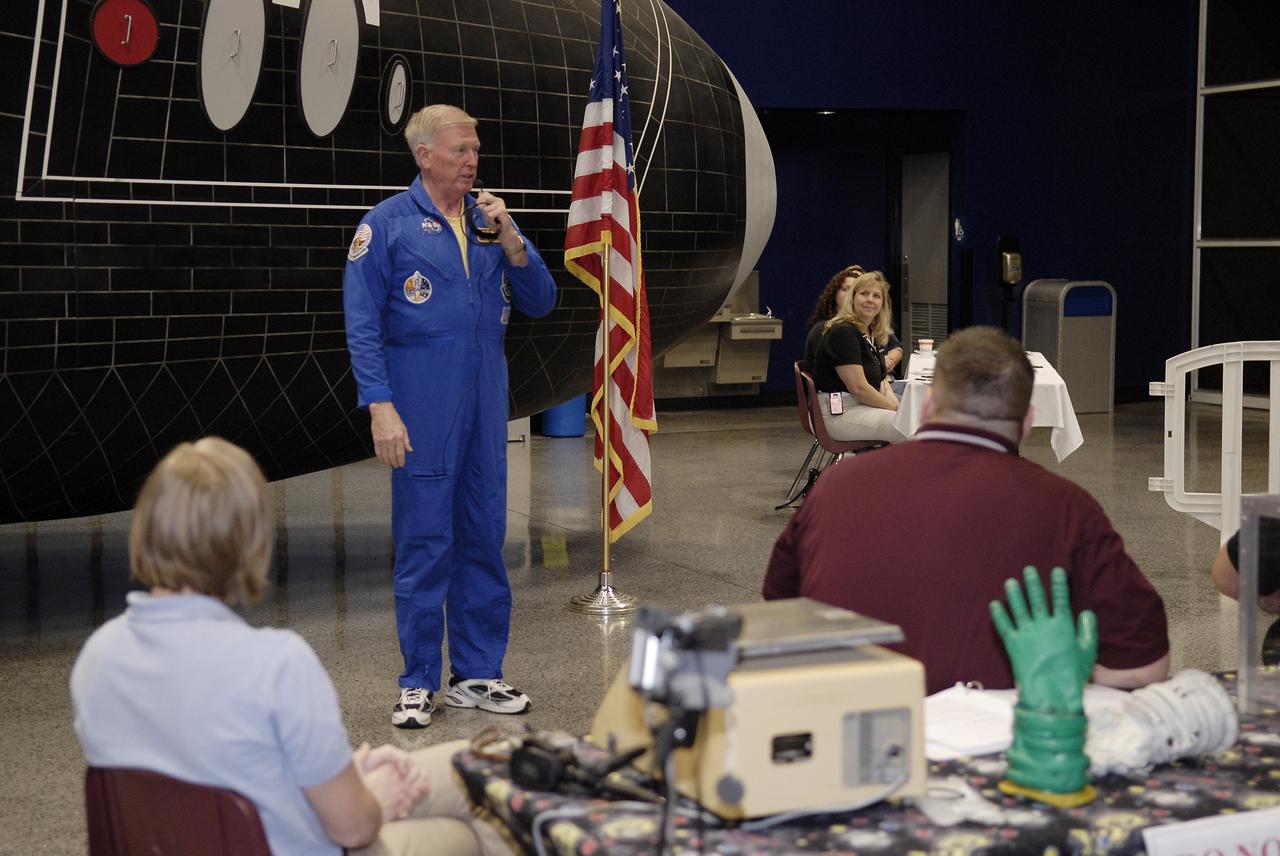

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Former NASA astronaut Jon McBride, at microphone, addresses the participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
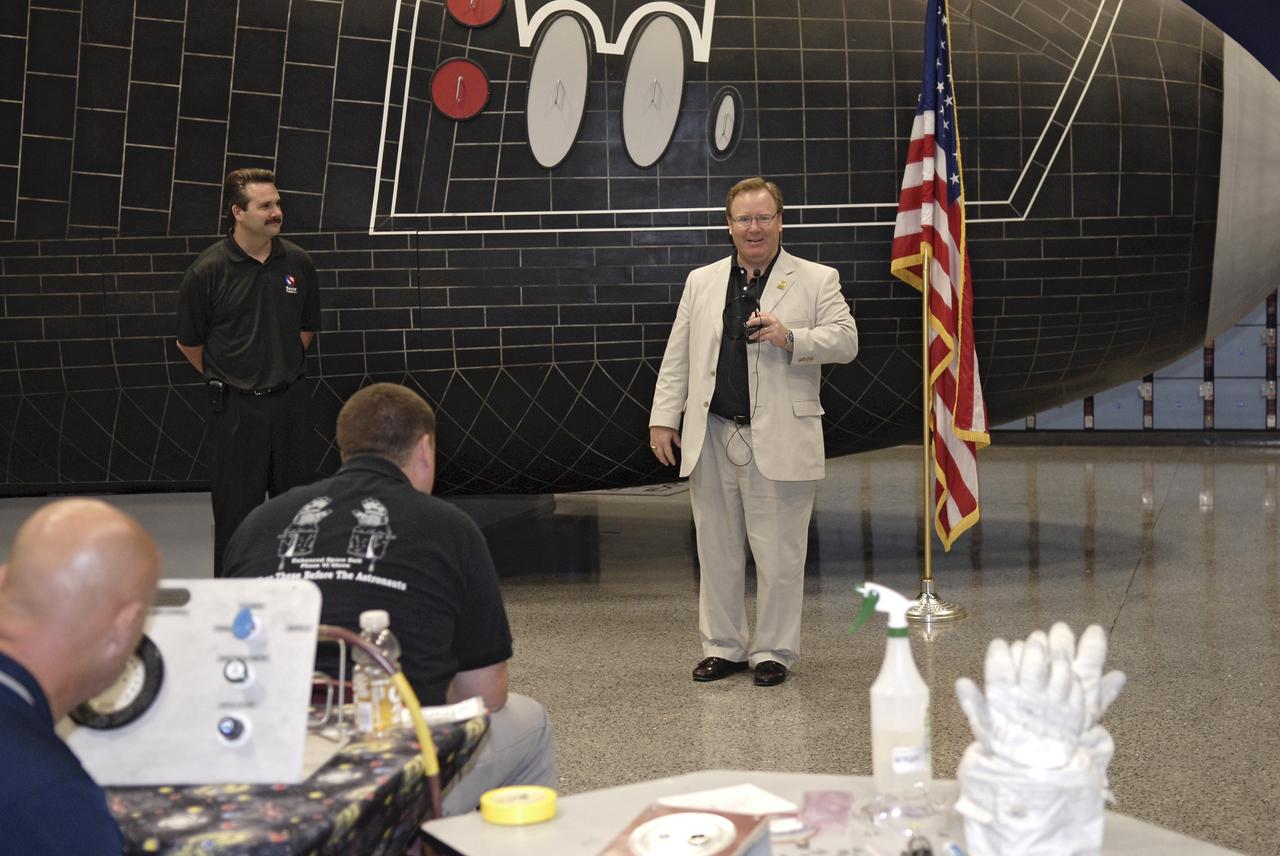

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Doug Comstock, at microphone, director of the NASA Innovative Partnerships Program, addresses the participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
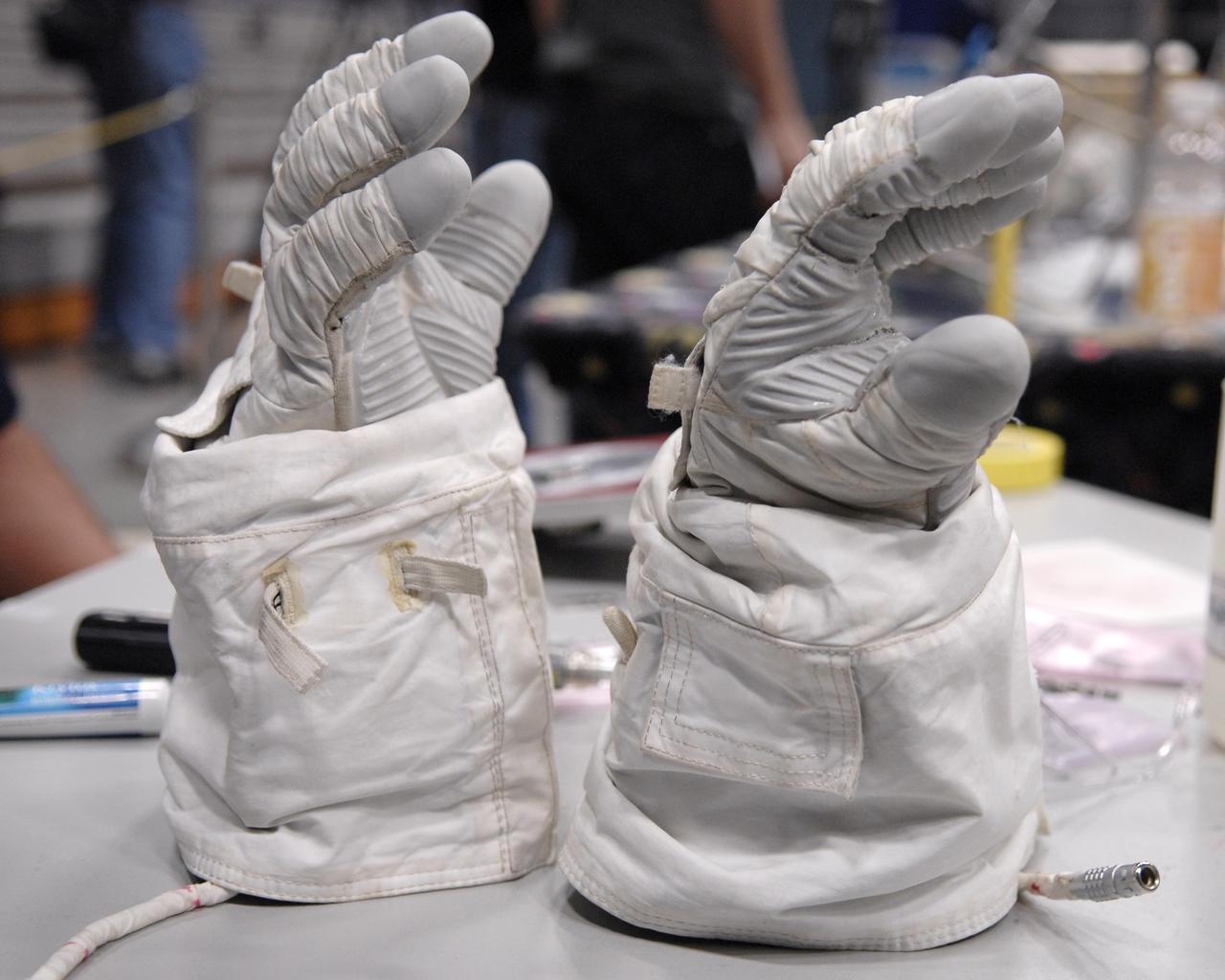

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – These newly designed gloves are entries in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
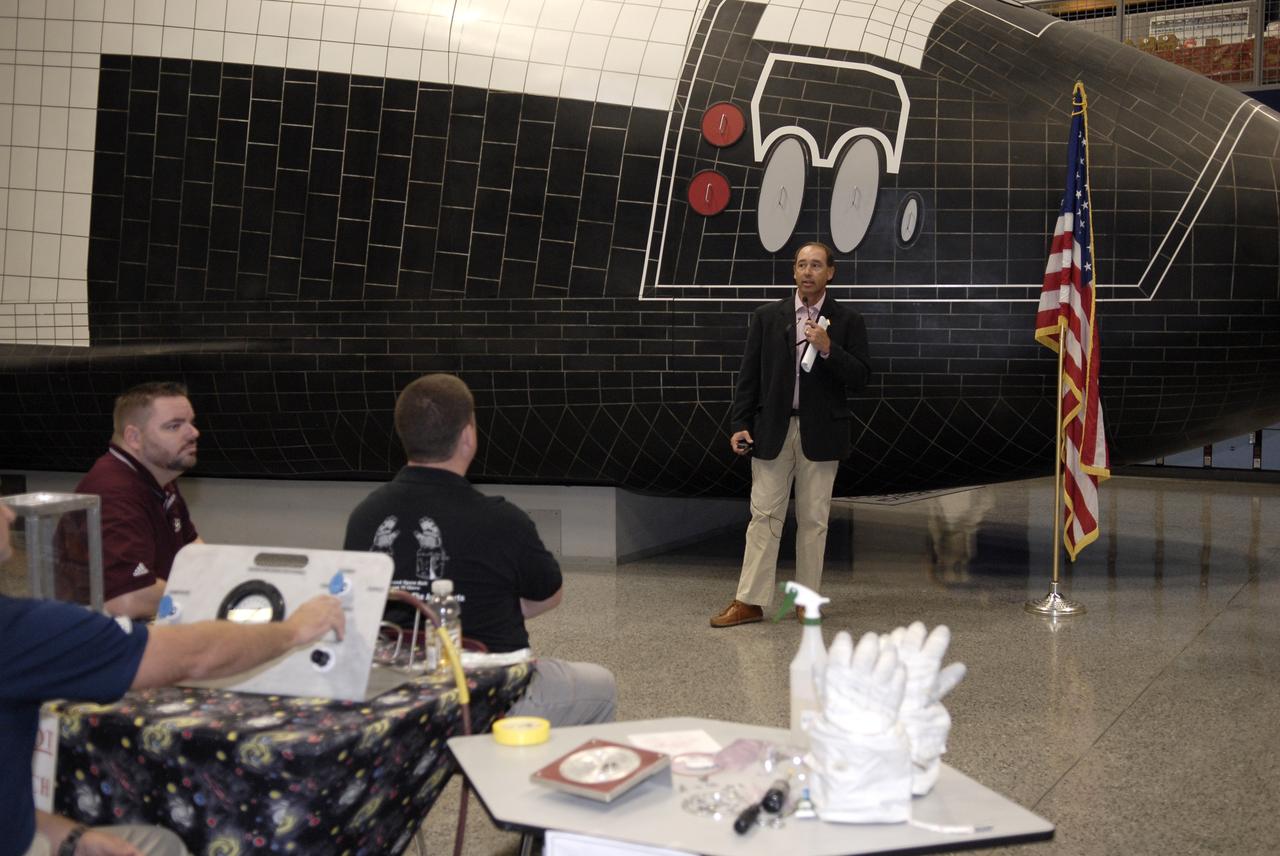

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Andy Petro, at microphone, manager of NASA Centennial Challenges, addresses the participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

By the end of the 19th century, soldiers, sailors, and practical and not-so practical inventors, had developed a stake in rocketry. Skillful theorists, like Konstantian Tsiolkovsky in Russia, were examining the fundamental scientific theories behind rocketry. They were begirning to consider the possibility of space travel
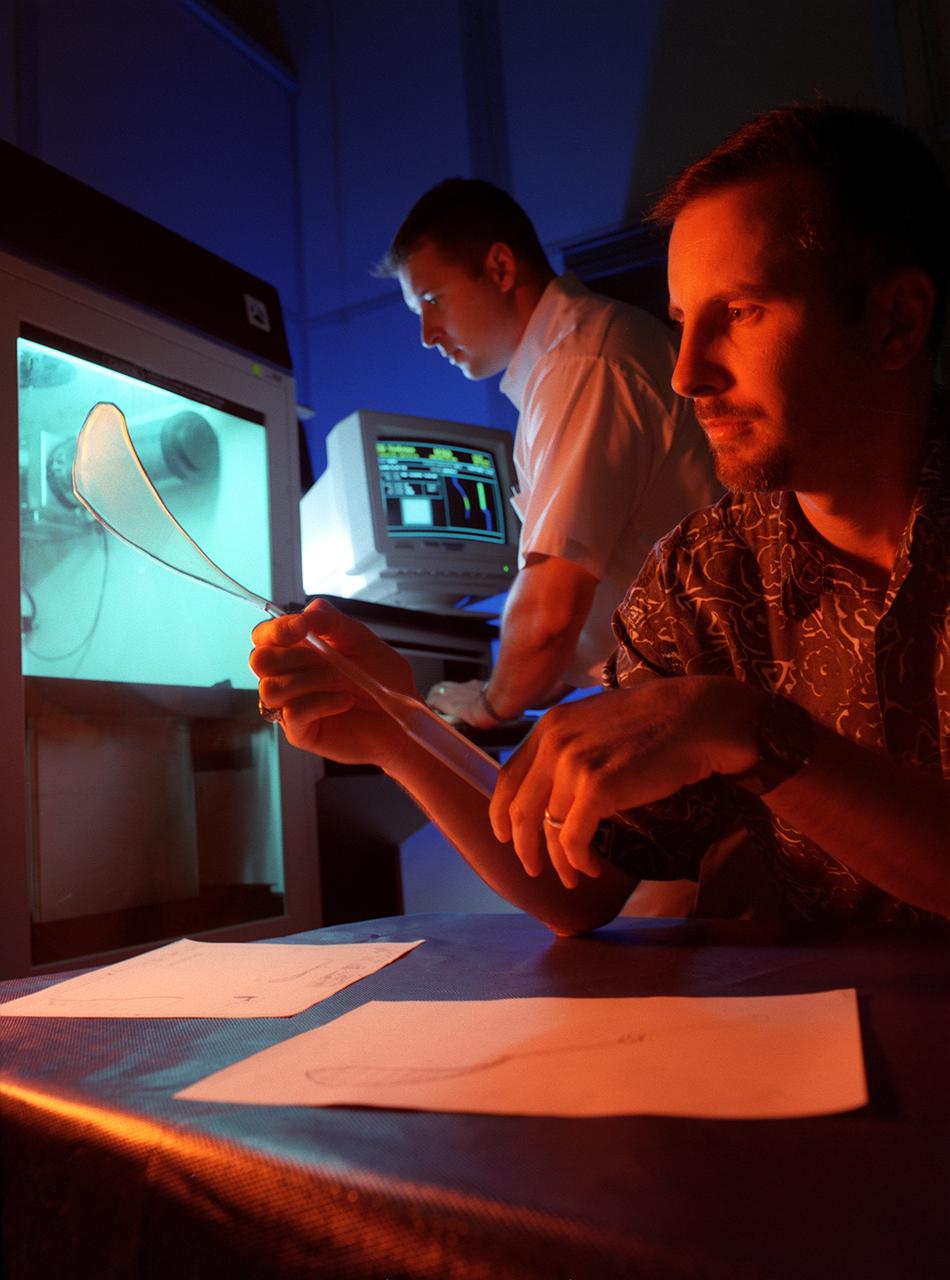
Marshall inventors Seth Lawson and Stanley Smeltzer display a pair of obstetrical forceps they designed. The forceps, made from composite space-age materials, measure the force applied during instrument-assisted delivery. The new forceps will help medical students get a feel for instrument-assisted deliveries before entering practice.
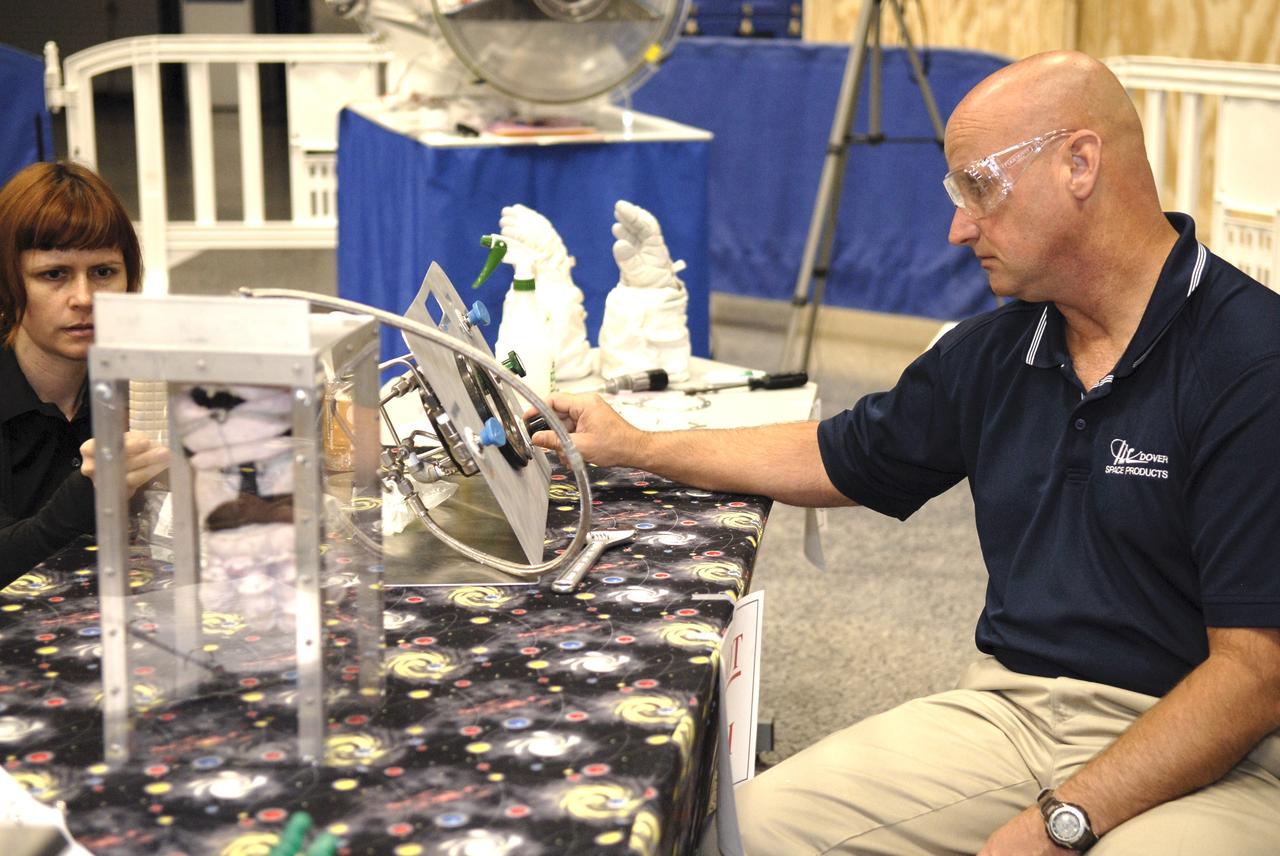

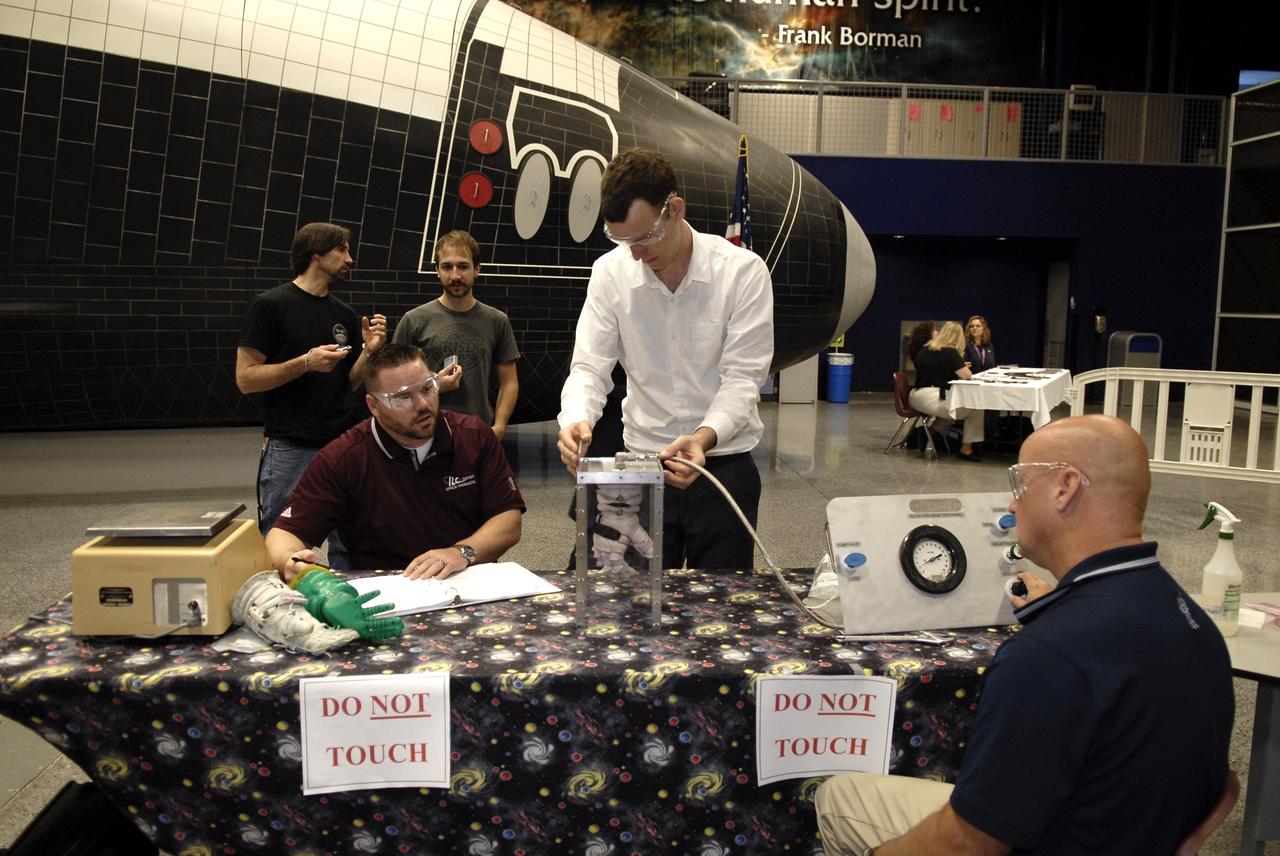
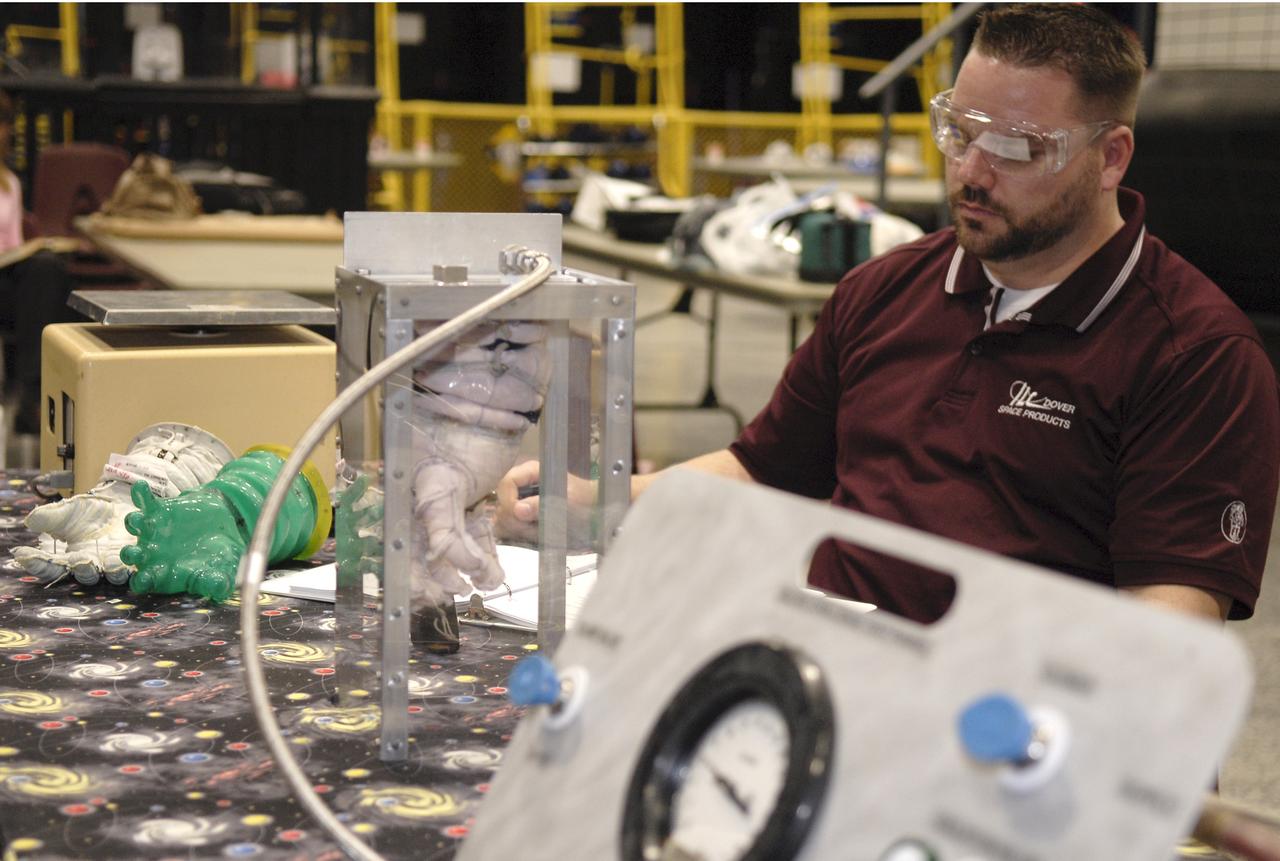
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A representative of ILC Dover monitors how much internal pressure a newly designed glove can withstand during a burst test at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
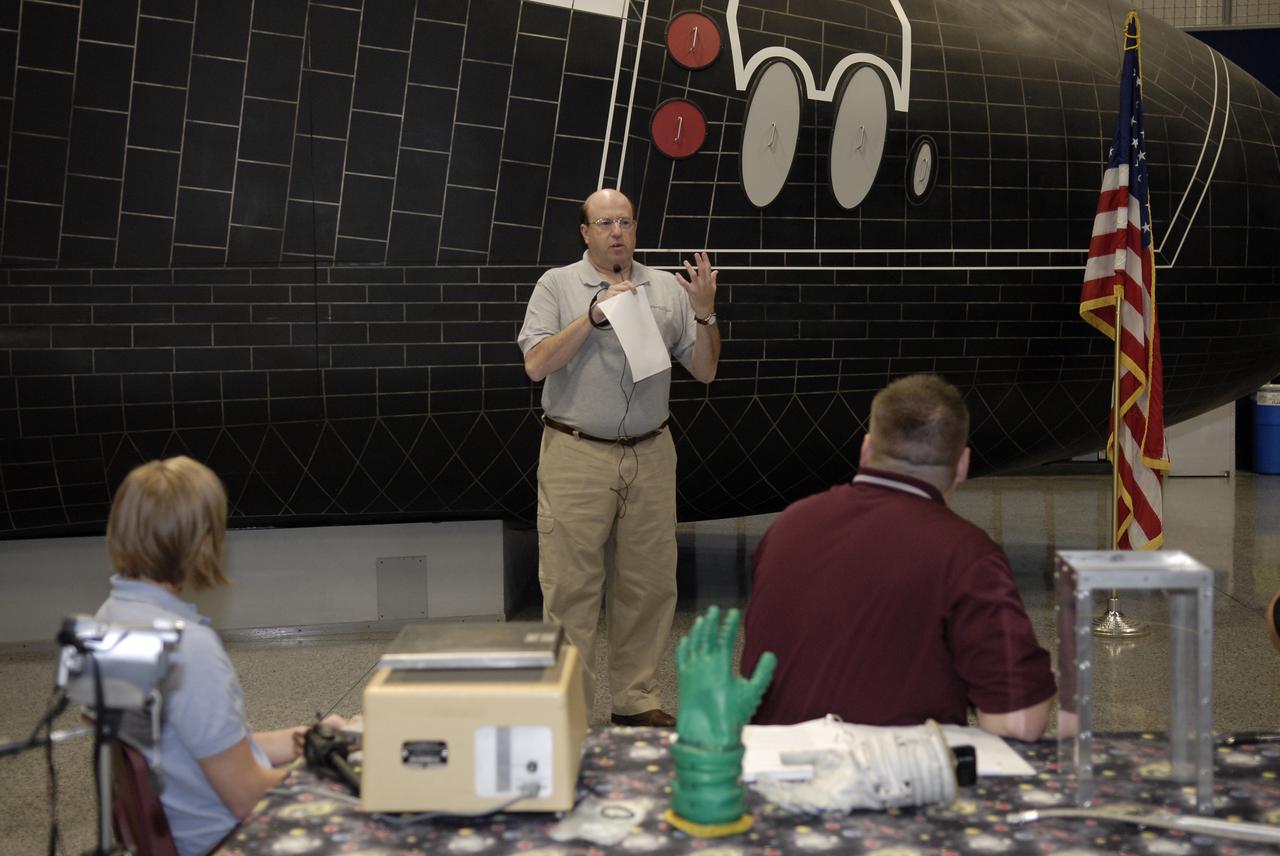

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alan Hayes, at microphone, chairman of Volanz Aerospace Inc., addresses the participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Volanz Aerospace Inc., of Owings, Md., administers the competition at no cost to NASA. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Representatives of ILC Dover monitor how much internal pressure a newly designed glove can withstand during a burst test at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A representative of ILC Dover monitors how much internal pressure a newly designed glove can withstand during a burst test at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
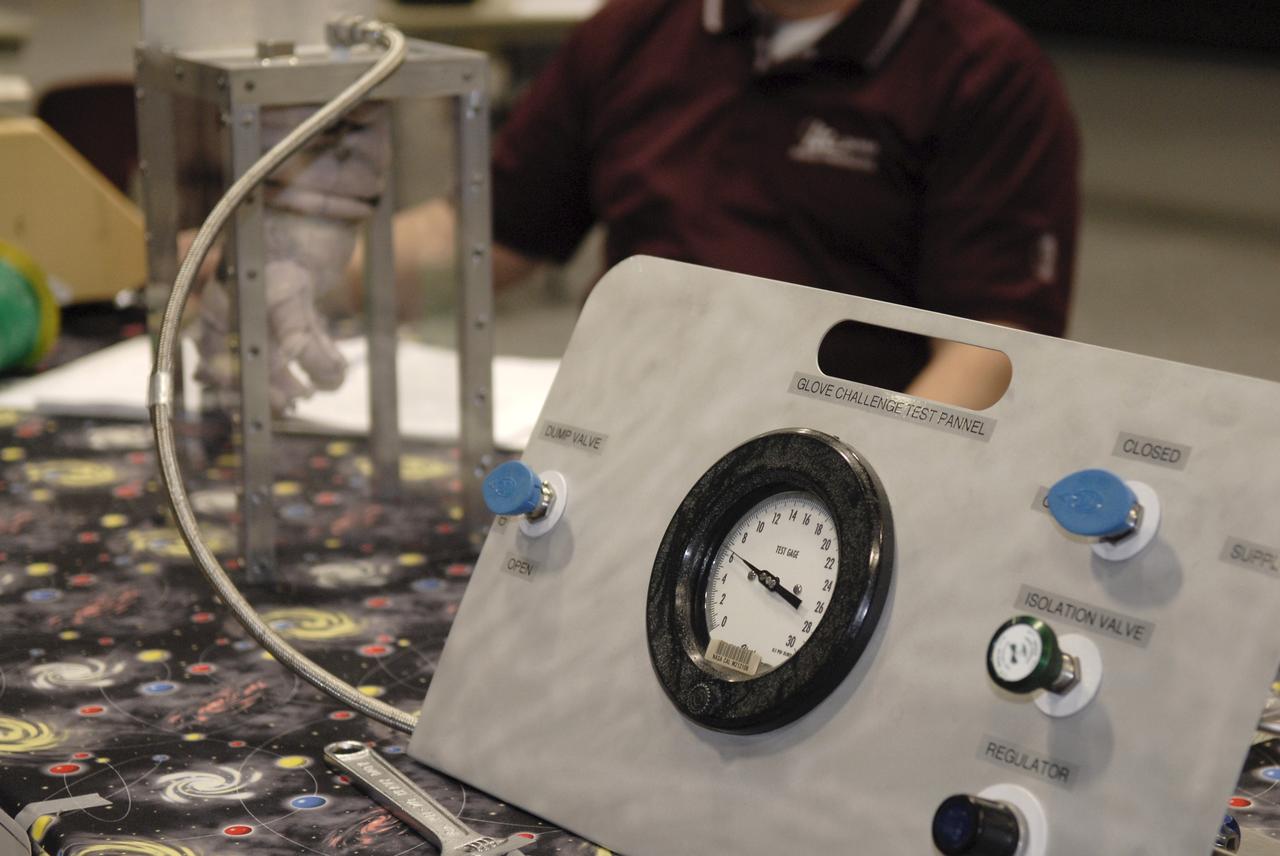

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This gauge is measuring how much internal pressure a newly designed glove can withstand during a burst test at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
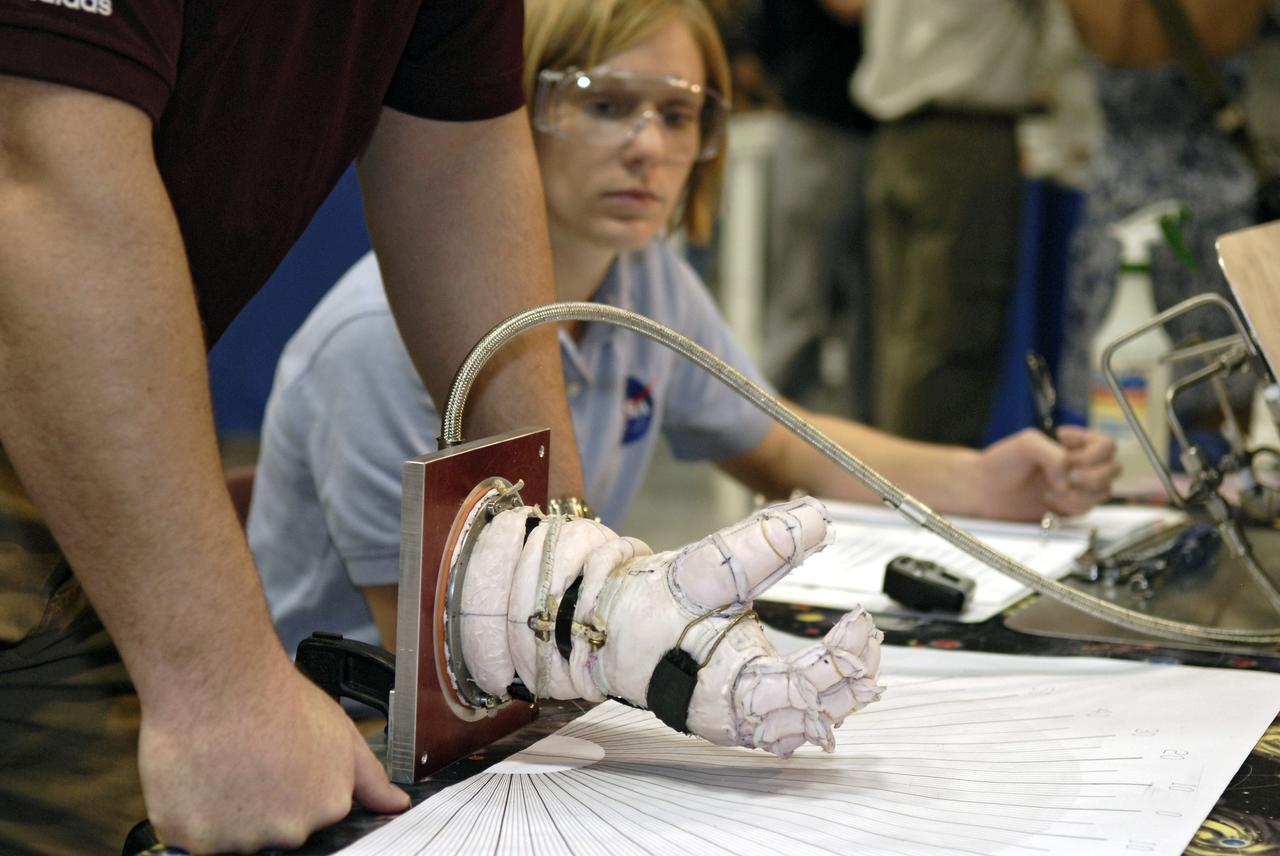

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This newly designed glove, one of the entries in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, undergoes a joint force test the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
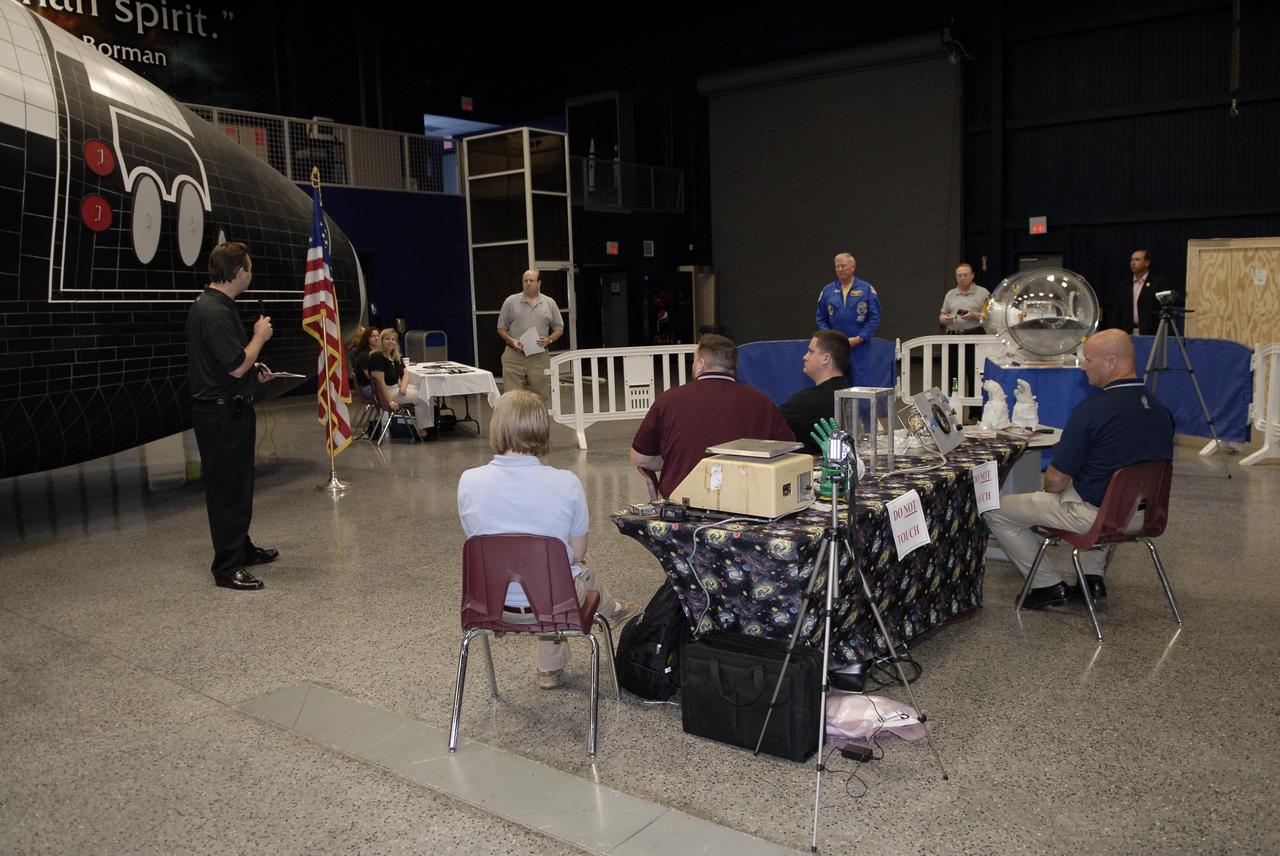

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Paul Secor, left, of Secor Strategies LLC, addresses the participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Secor Strategies LLC, of Titusville, Fla., is a sponsor of the event and provided local logistical services. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, inventors tested the gloves to measure dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
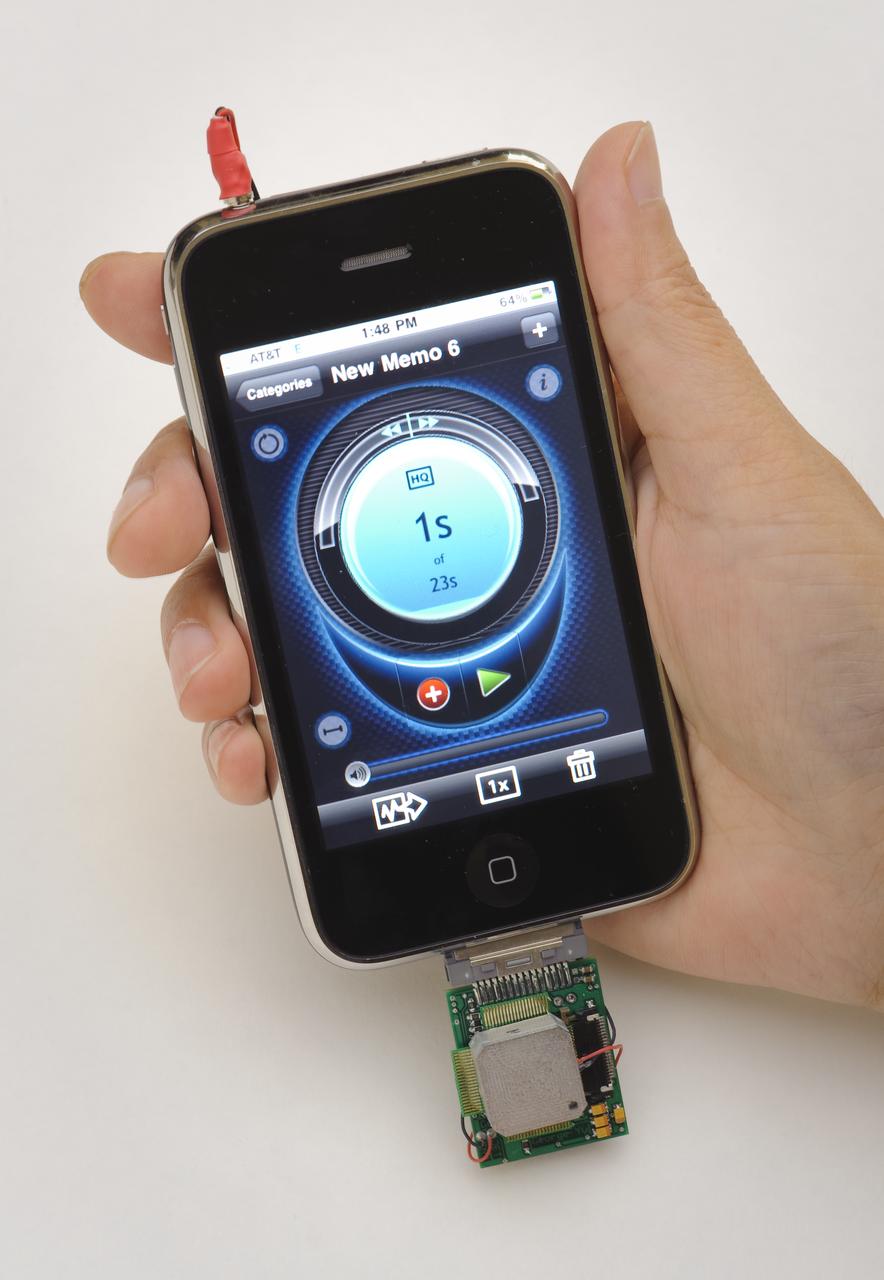

A Nanosensor Device for Cellphone Intergration and Chemical Sensing Network. iPhone with sensor chip, data aquisition board and sampling jet.(Note 4-4-2012:High Sensitive, Low Power and Compact Nano Sensors for Trache Chemical Detection' is the winner of the Government Invention of the Year Award 2012 (winning inventors Jing Li and Myya Meyyappan, NASA/ARC, and Yijiang Lu, University of California Santa Cruz. )
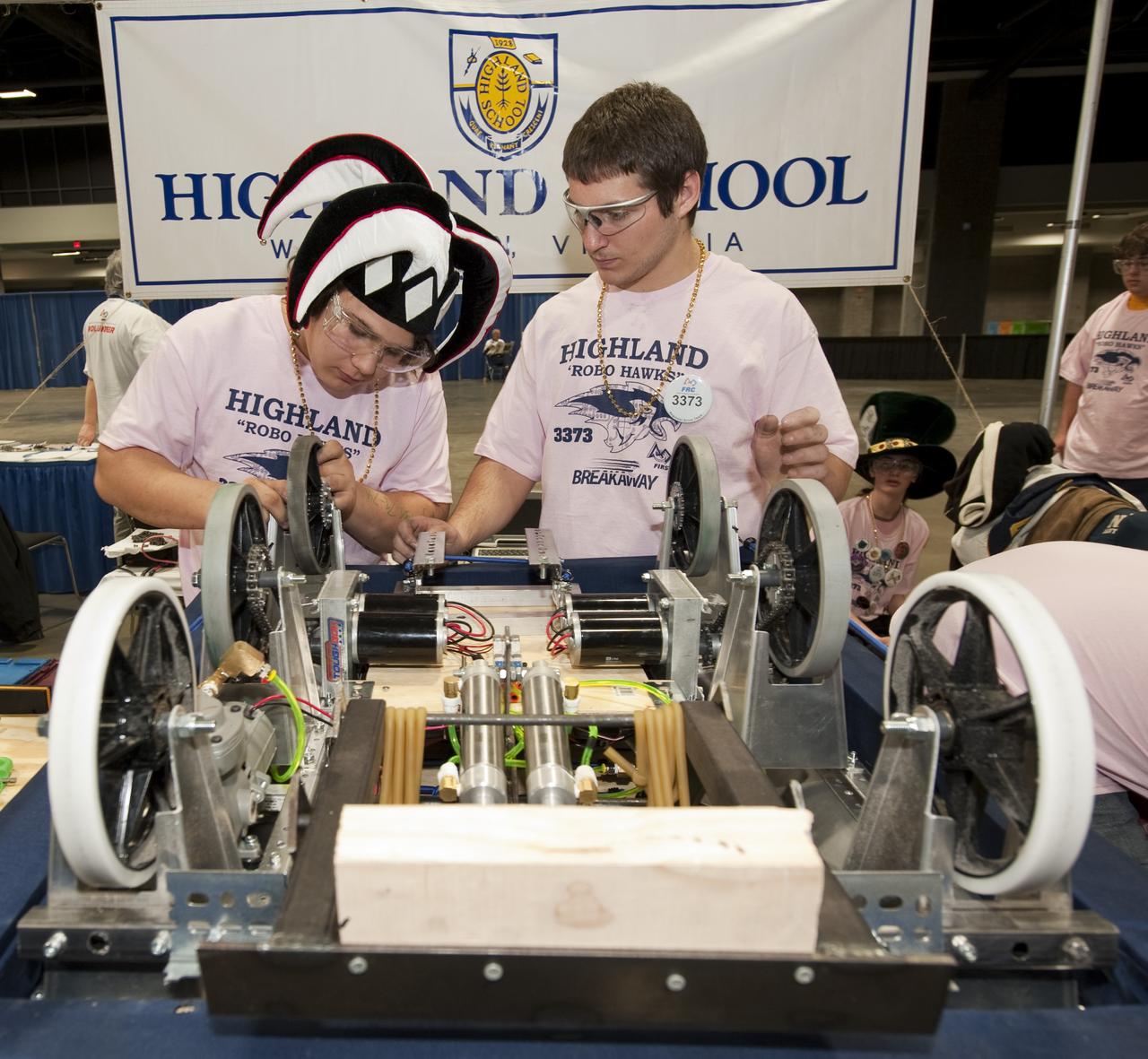

Students from the Highland School in Warrenton, Va. work on their robot in the "Pit Area" as they prepare to compete in the First Robotics Competition, Friday, March 5, 2010, in Washington. The student competition is called "For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology," or FIRST. The program was founded in 1989 by inventor Dean Kamen to inspire an appreciation of science and technology in young people, their schools and communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers) Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
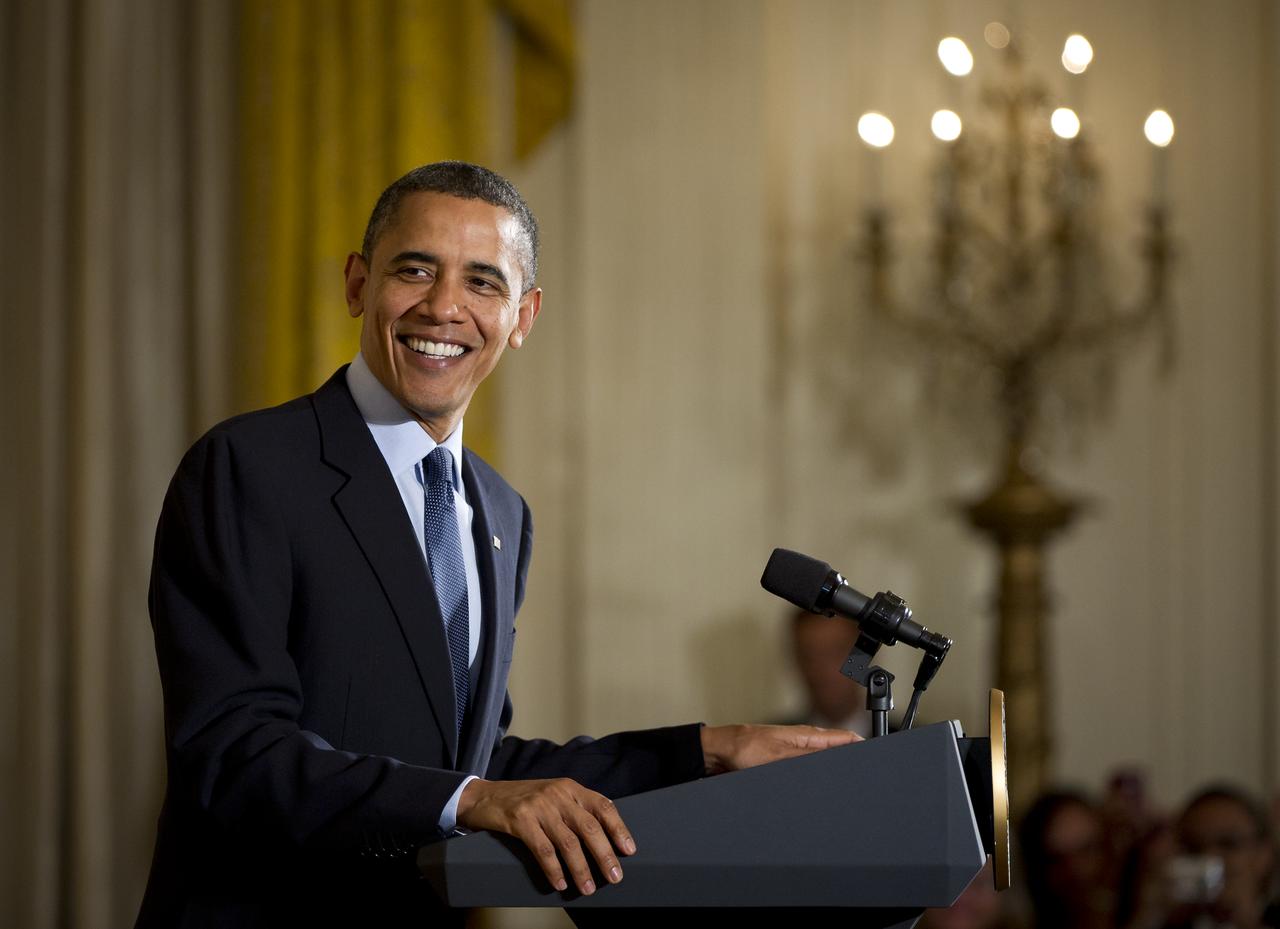

U.S. President Barack Obama smiles during a ceremony for recipients of the National Medal of Science and the National Medal of Technology and Innovation, the highest honors bestowed by the United States government on scientists, engineers, and inventors, at the White House in Washington, Wednesday, Nov. 17, 2010. Amongst those in attendance where NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
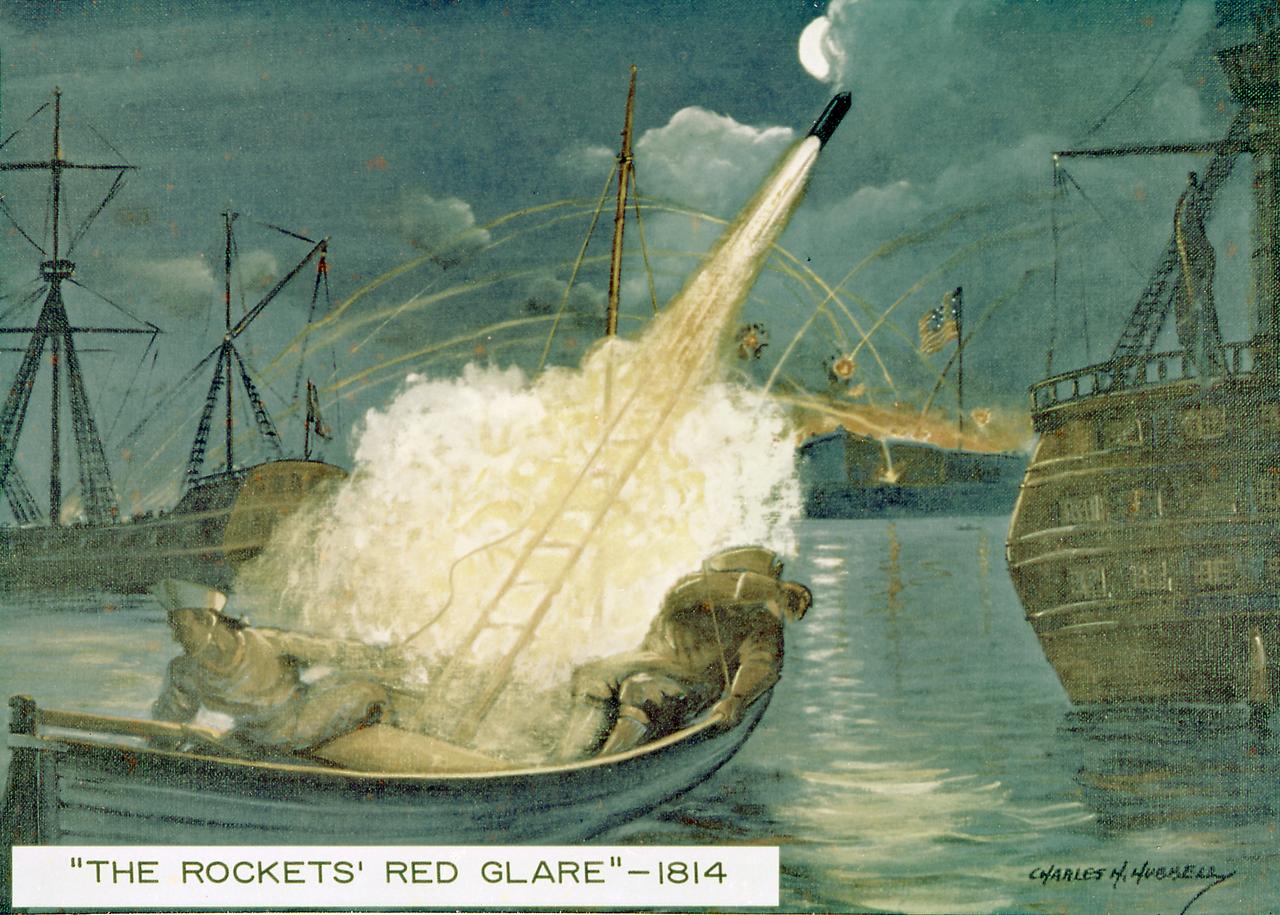

The British fired Congreve rockets against the United States in the War of 1812. As a result Francis Scott Key coined the phrase the "rocket's red glare." Congreve had used a 16-foot guide stick to help stabilize his rocket. William Hale, another British inventor, invented the stickless rocket in 1846. The U.S. Army used the Hale rocket more than 100 years ago in the war with Mexico. Rockets were also used to a limited extent by both sides in the American Civil War.
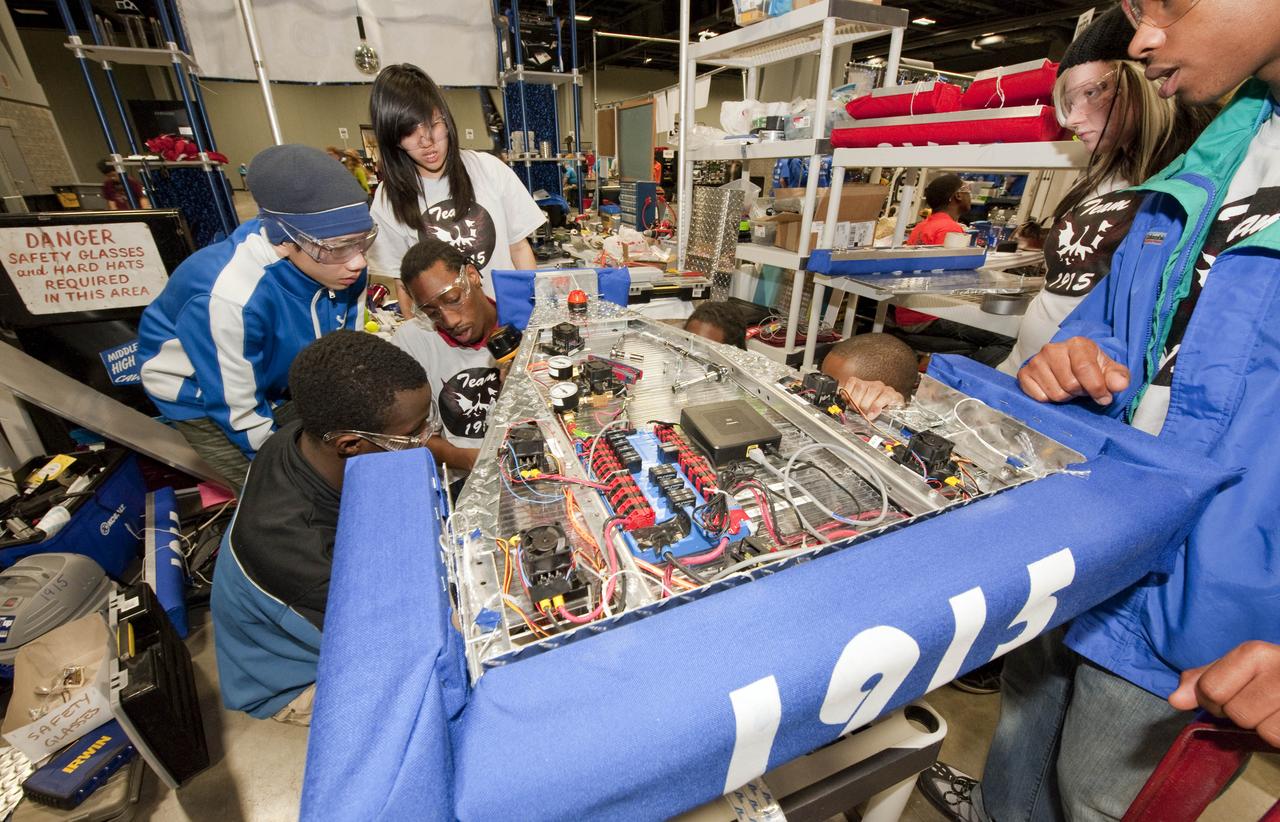

Students from McKinley Tech High School in Washington, D.C., work on their robot in the "Pit Area" as they prepare to compete in the First Robotics Competition, Friday, March 5, 2010, in Washington. The student competition is called "For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology," or FIRST. The program was founded in 1989 by inventor Dean Kamen to inspire an appreciation of science and technology in young people, their schools and communities. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
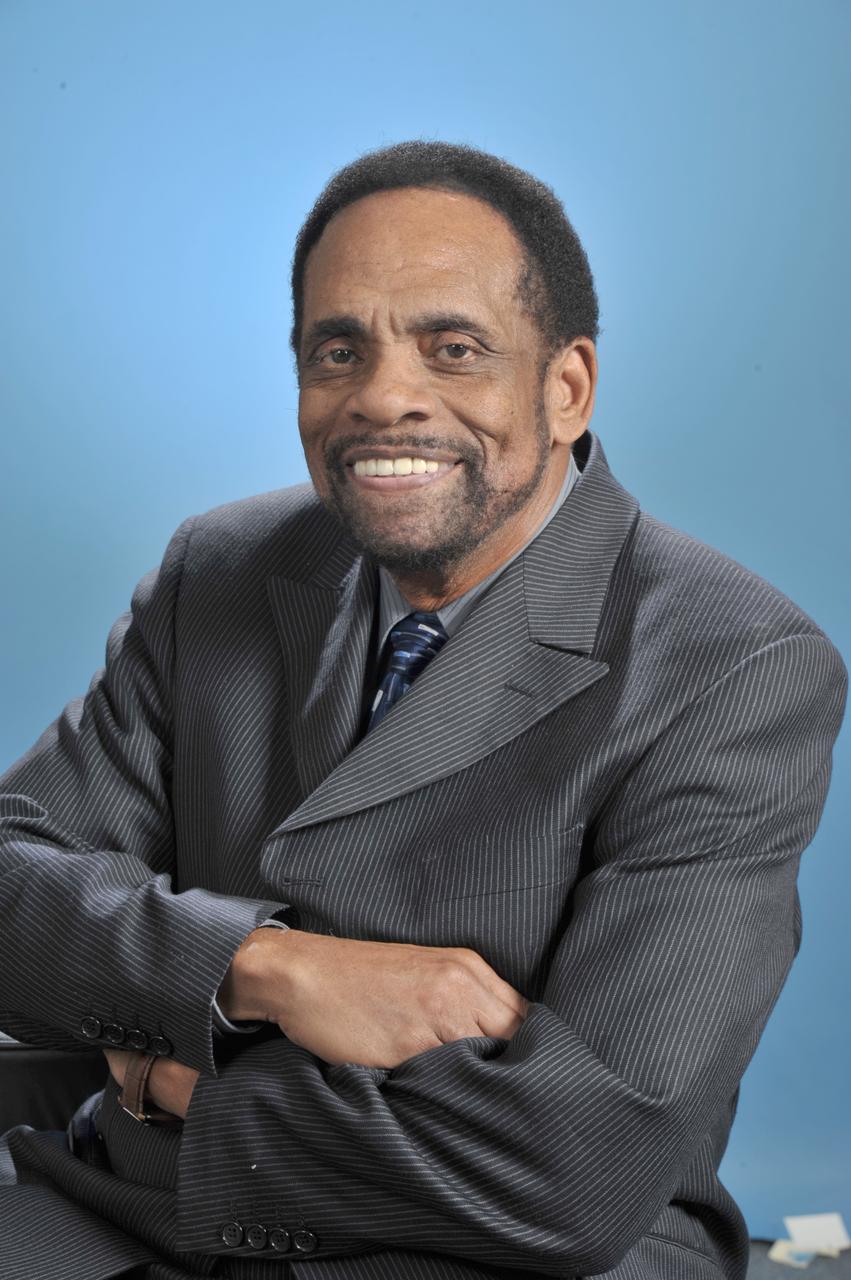

George Edward Alcorn, a pioneering African American physicist and engineer, is credited with dozens of inventions over the course of a distinguished career in private industry and at NASA, for which he earned eight patents. Alcorn joined Goddard Space Flight Center in 1978 and held numerous leadership roles in both research and administration until his retirement in 2012. One of Alcorn’s signature accomplishments at NASA was developing a smaller, more sensitive X-ray spectrometer, changing the way scientists were able to use the powerful tool in deep space exploration missions. His tool, which uses thermomigration of aluminum, can gather information about remote solar systems; for the invention, Alcorn was honored as the NASA Goddard Inventor of the Year in 1984. In addition to his groundbreaking contributions as an inventor and innovator, Alcorn also championed efforts to hire more women and minorities at Goddard, for which he was honored with the NASA Equal Opportunity Medal, and taught students at Howard University and the University of the District of Columbia. He also founded the Saturday Academy, an honors program in math and science for underserved middle school students. He earned many accolades over the years from NASA and beyond. These include, in 2010, the Robert H. Goddard Award for Merit, for his outstanding innovation and significant contributions to space science, technology, and NASA programs, as well as recognition in 1994 at Howard University’s Heritage of Greatness awards ceremony. He was also inducted into the National Inventor’s Hall of Fame in 2015. Alcorn passed away in 2024 at the age of 84.
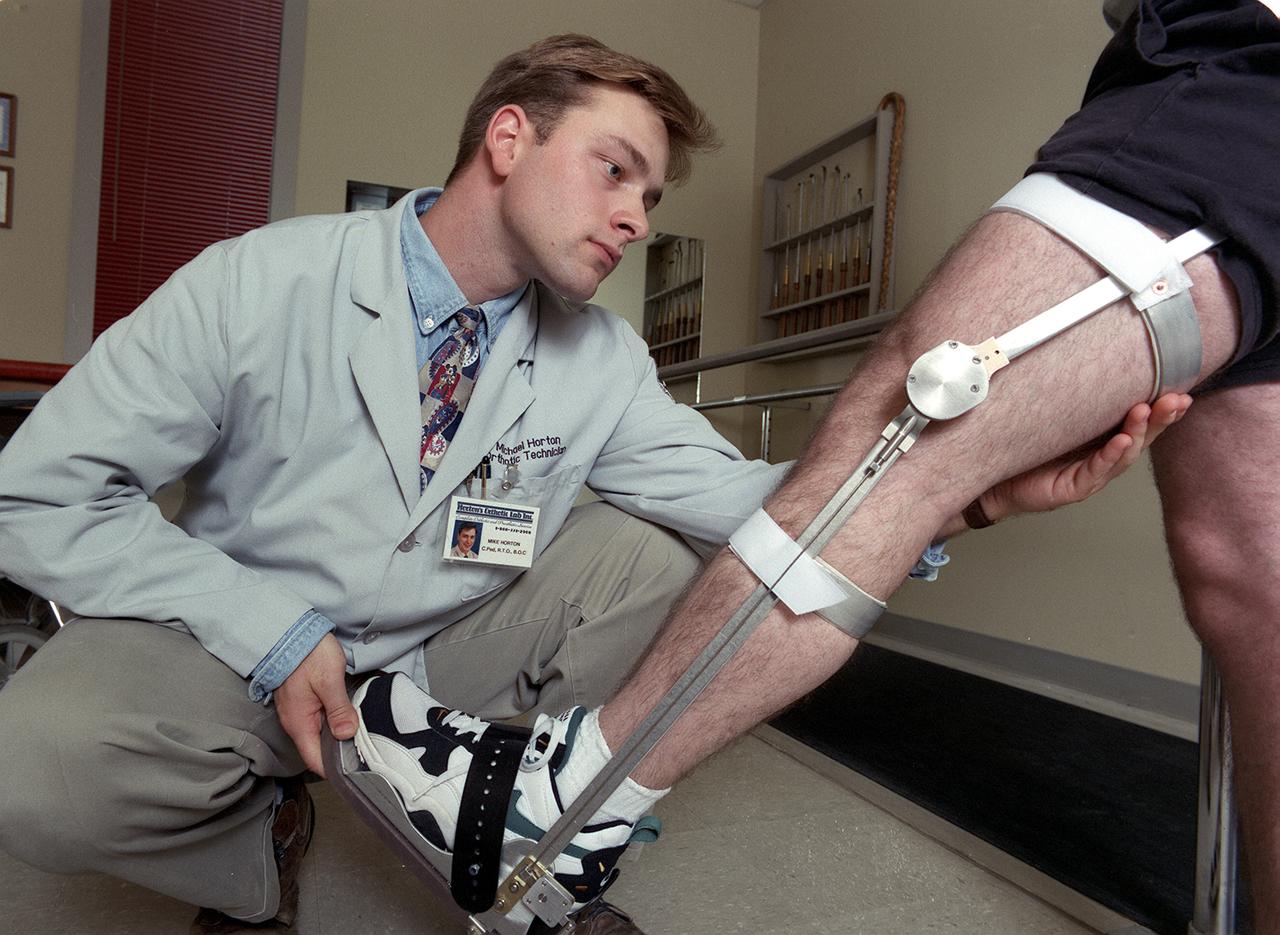
A knee brace that uses Space Shuttle propulsion technology has moved a step closer to being available to help knee injury and stroke patients and may possibly benefit patients with birth defects, spinal cord injuries, and post-polio conditions. After years of hard work, inventors at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, have turned over the final design and prototype to industry partners at Horton's Orthotic Lab in Little Rock, Arkansas for further clinical testing. The device, called the Selectively Lockable Knee Brace, may mean faster, less painful rehabilitation for patients by allowing the knee to move when weight is not on the heel. Devices currently on the market lock the knee in a rigid, straight-leg position, or allow continuous free motion. Pictured here is a knee brace prototype being tested and fitted at Horton's Orthotic Lab. The knee brace is just one example of how space technology is being used to improve the lives of people on Earth. NASA's MSFC inventors Michael Shadoan and Neill Myers are space propulsion engineers who use the same mechanisms and materials to build systems for rockets that they used to design and develop the knee brace.
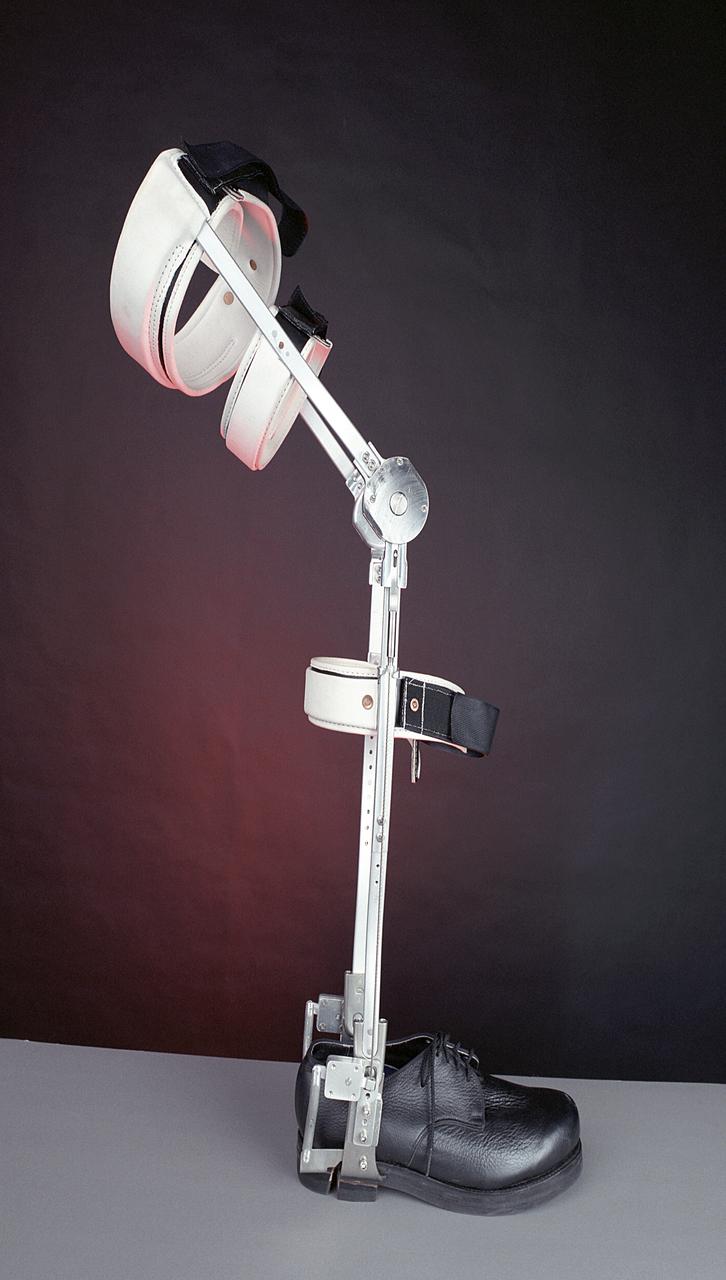

A knee brace that uses Space Shuttle propulsion technology has moved a step closer to being available to help knee injury and stroke patients and may possibly benefit patients with birth defects, spinal cord injuries, and post-polio conditions. After years of hard work, inventors at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, have turned over the final design and prototype to industry partners at Horton's Orthotic Lab in Little Rock, Arkansas for further clinical testing. The device, called the Selectively Lockable Knee Brace, may mean faster, less painful rehabilitation for patients by allowing the knee to move when weight is not on the heel. Devices currently on the market lock the knee in a rigid, straight-leg position, or allow continuous free motion. The knee brace is just one example of how space technology is being used to improve the lives of people on Earth. NASA's MSFC inventors Michael Shadoan and Neill Myers are space propulsion engineers who use the same mechanisms and materials to build systems for rockets that they used to design and develop the knee brace.
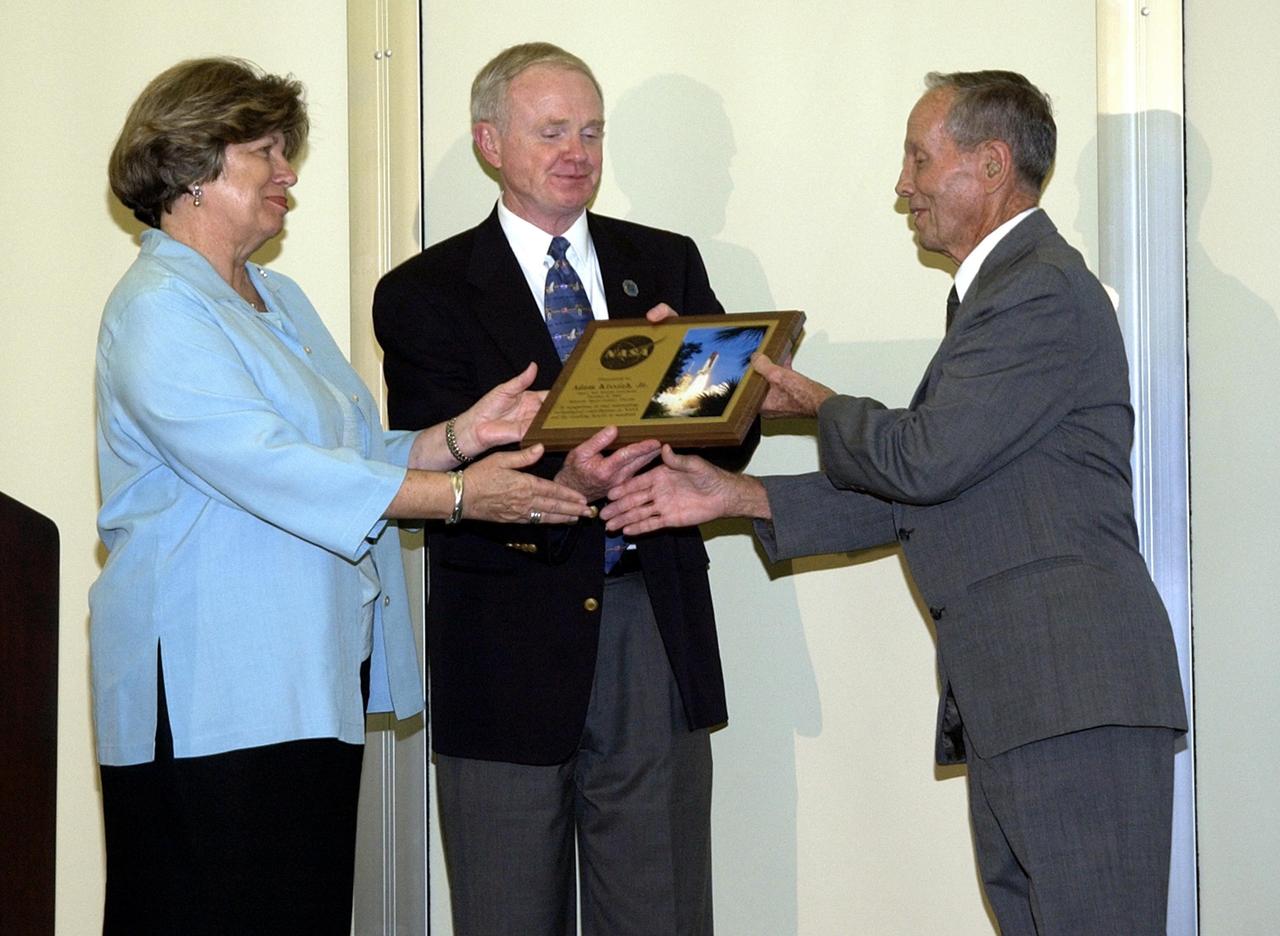

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Adam Kissiah (right), a retired NASA-KSC engineer and inventor of a cochlear implant, receives an exceptional category NASA Space Act Award for his 25-year-old technology breakthrough during a technology awards luncheon held at the KSC Visitor Complex Debus Center. Presenting the award are, from left, Acting Deputy Center Director JoAnn Morgan, Center Director Roy Bridges, and Kissiah. The award included a monetary award and a certificate signed by the NASA Administrator. Space Act Awards provide official recognition and grant equitable monetary awards for inventions and scientific and technical contributions that have helped achieve NASA's aeronautical and space goals.
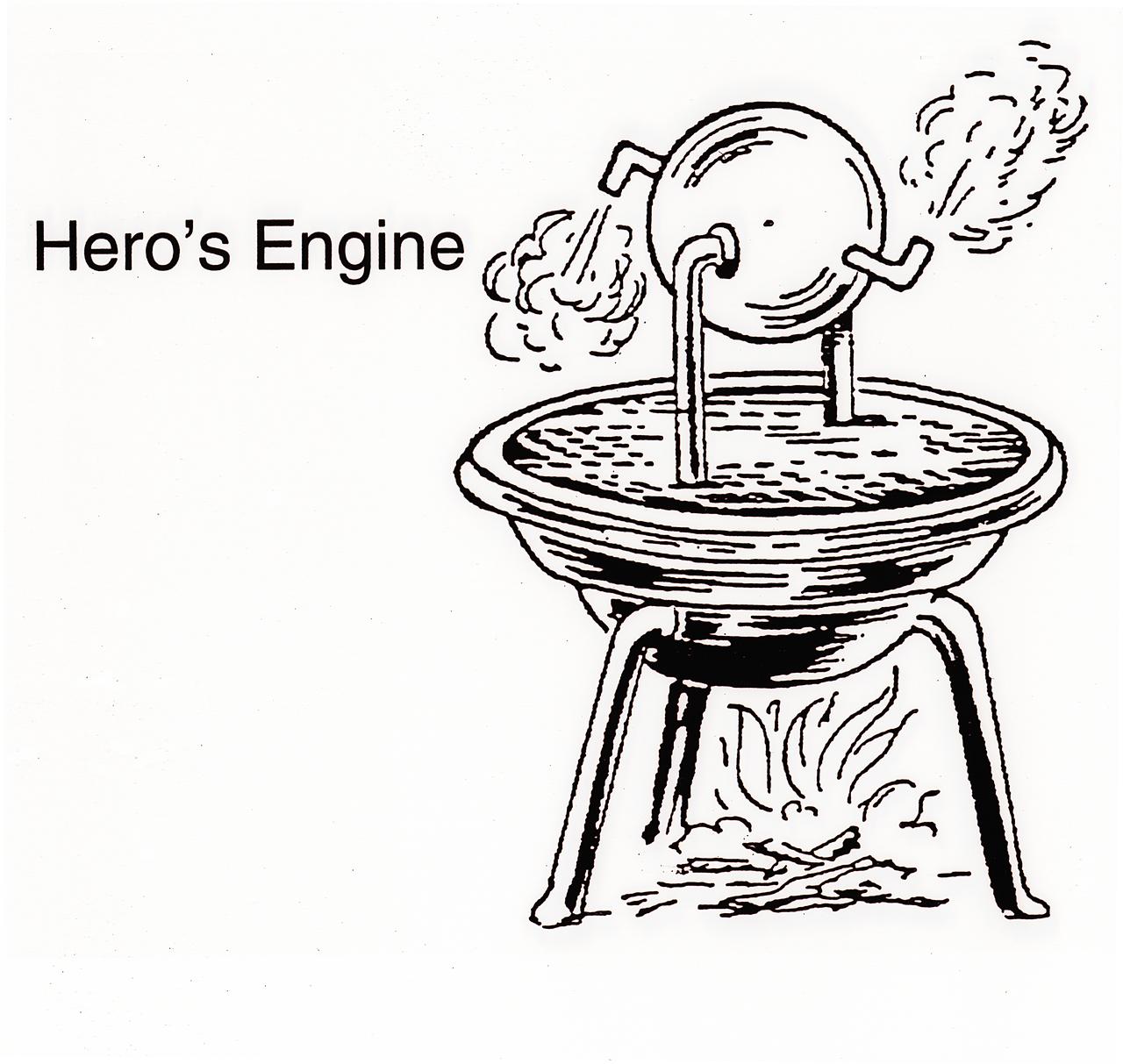
Legendary characters used the power of mythology to fly through the heavens. About 200 BC, a Greek inventor known as Hero of Alexandria came up with a new invention that depended on the mechanical interaction of heat and water. He invented a rocket-like device called an aeolipile. It used steam for propulsion. Hero mounted a sphere on top of a water kettle. A fire below the kettle turned the water into steam, and the gas traveled through the pipes to the sphere. Two L-shaped tubes on opposite sides of the sphere allowed the gas to escape, and in doing so gave a thrust to the sphere that caused it to rotate.
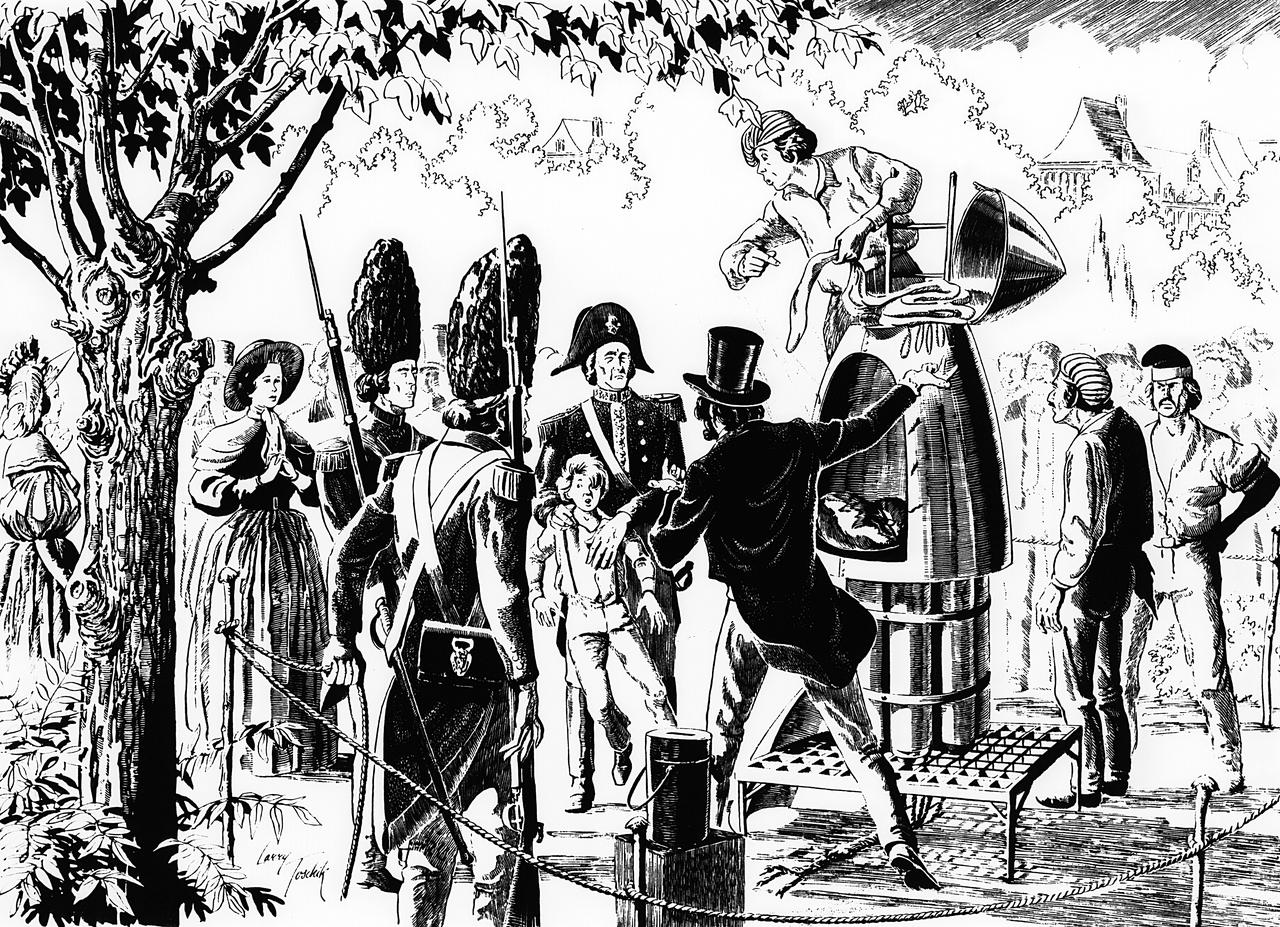

During the 19th century, rocket enthusiasts and inventors began to appear in almost every country. Some people thought these early rocket pioneers were geniuses, and others thought they were crazy. Claude Ruggieri, an Italian living in Paris, apparently rocketed small animals into space as early as 1806. The payloads were recovered by parachute. As depicted here by artist Larry Toschik, French authorities were not always impressed with rocket research. They halted Ruggieri's plans to launch a small boy using a rocket cluster. (Reproduced from a drawing by Larry Toschik and presented here courtesy of the artist and Motorola Inc.)
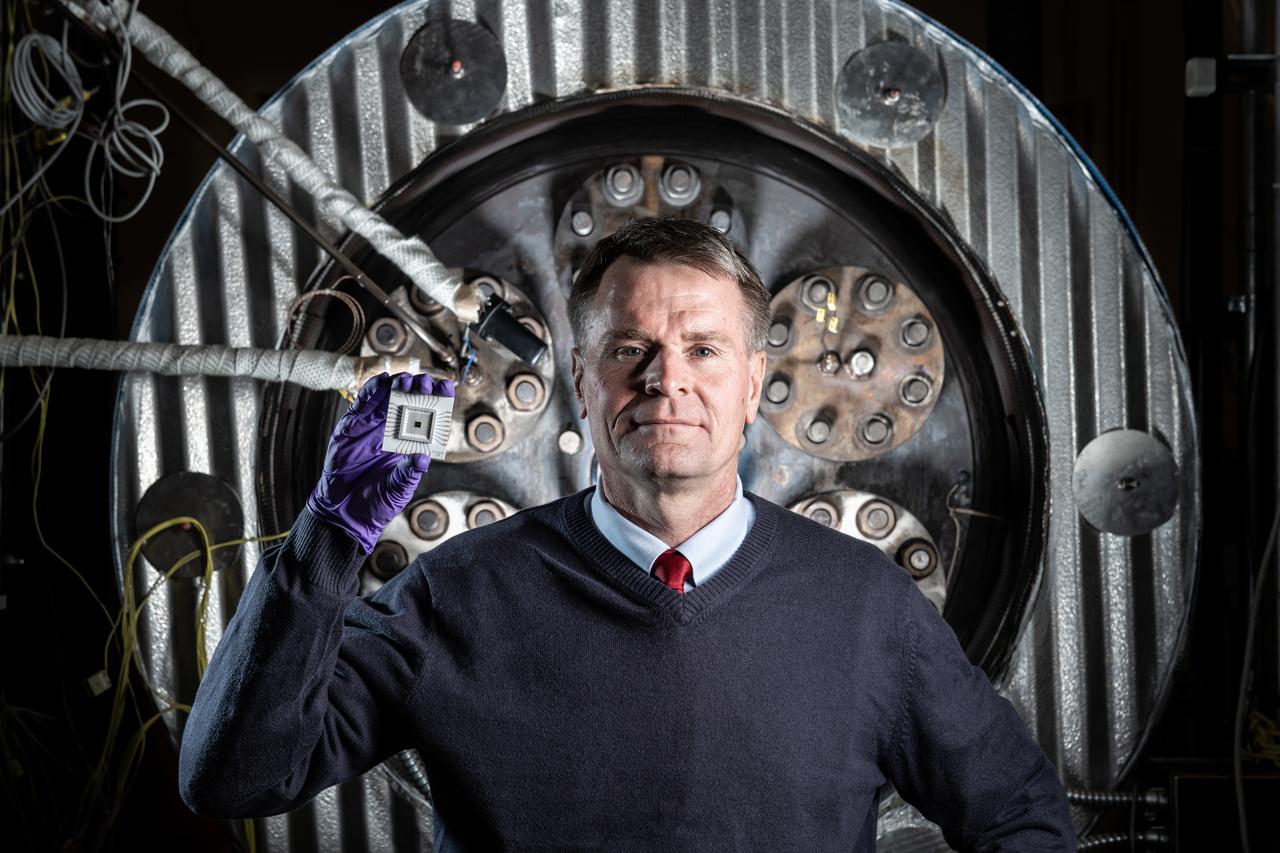

Phil Neudeck- Can Take the Heat When it comes to the heat of extreme environments like Venus, electronics can get fried within a few minutes of arrival. But NASA Researcher Phil Neudeck and his team have developed extremely durable silicon carbide semiconductor integrated circuits to survive those harsh conditions. After successfully testing the electronics in our high-pressure, high-temperature extreme environments chamber, there is now a path forward for Venus landers to survive and operate scientific experiments on the planet’s surface for longer durations.
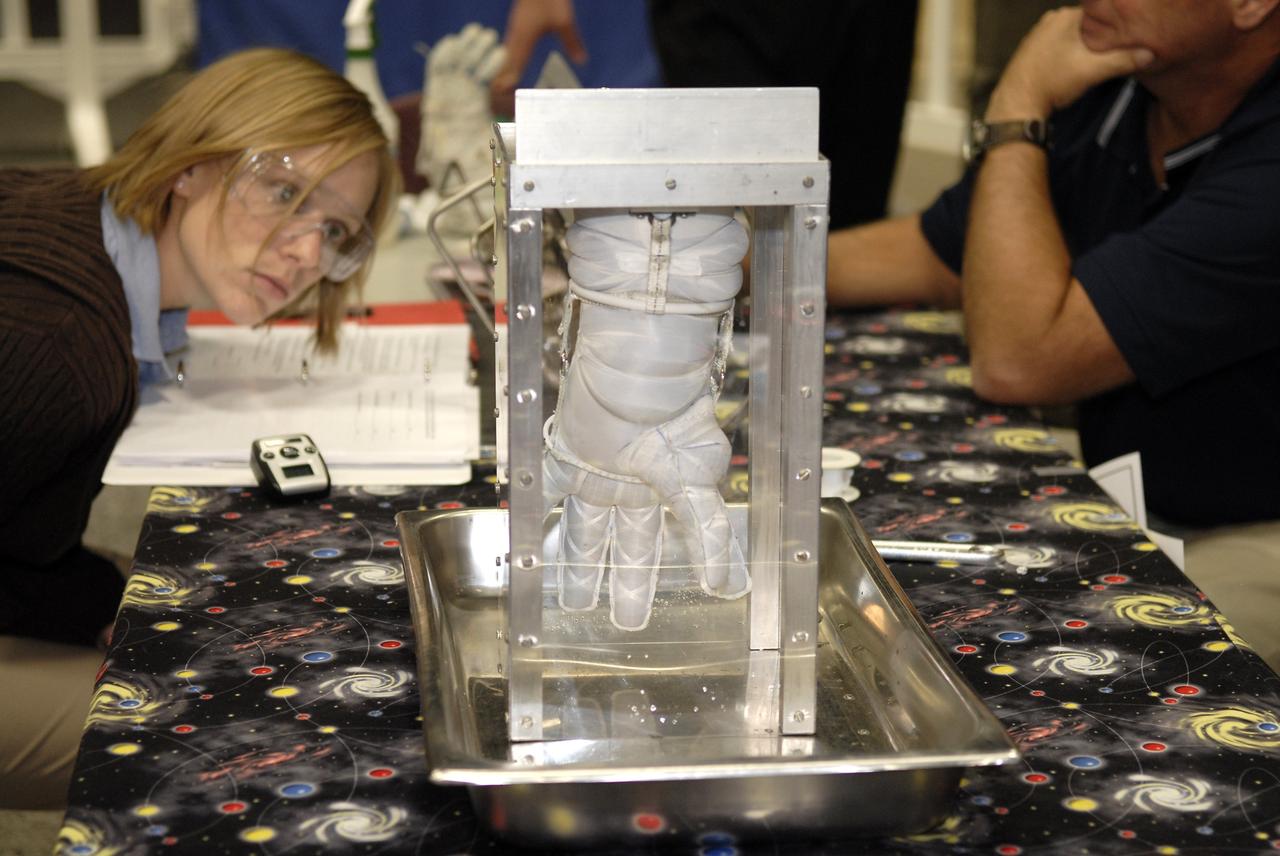

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A newly designed glove is submitted to a burst test to determine how much internal pressure it can withstand at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
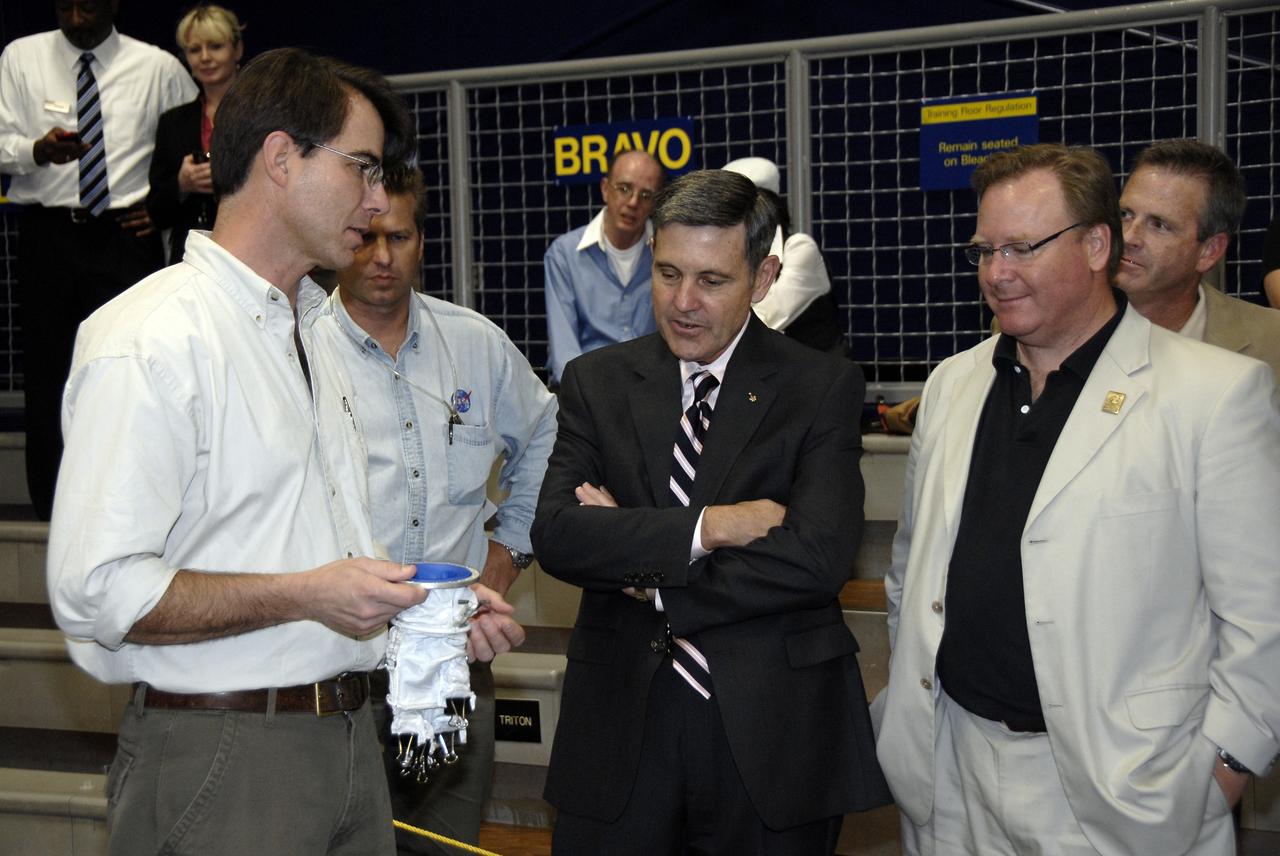

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, first-prize winner Peter Homer, left, of Southwest Harbor, Maine, talks with Kennedy Director Bob Cabana and Doug Comstock, director of the NASA Innovative Partnerships Program, about his winning glove design in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
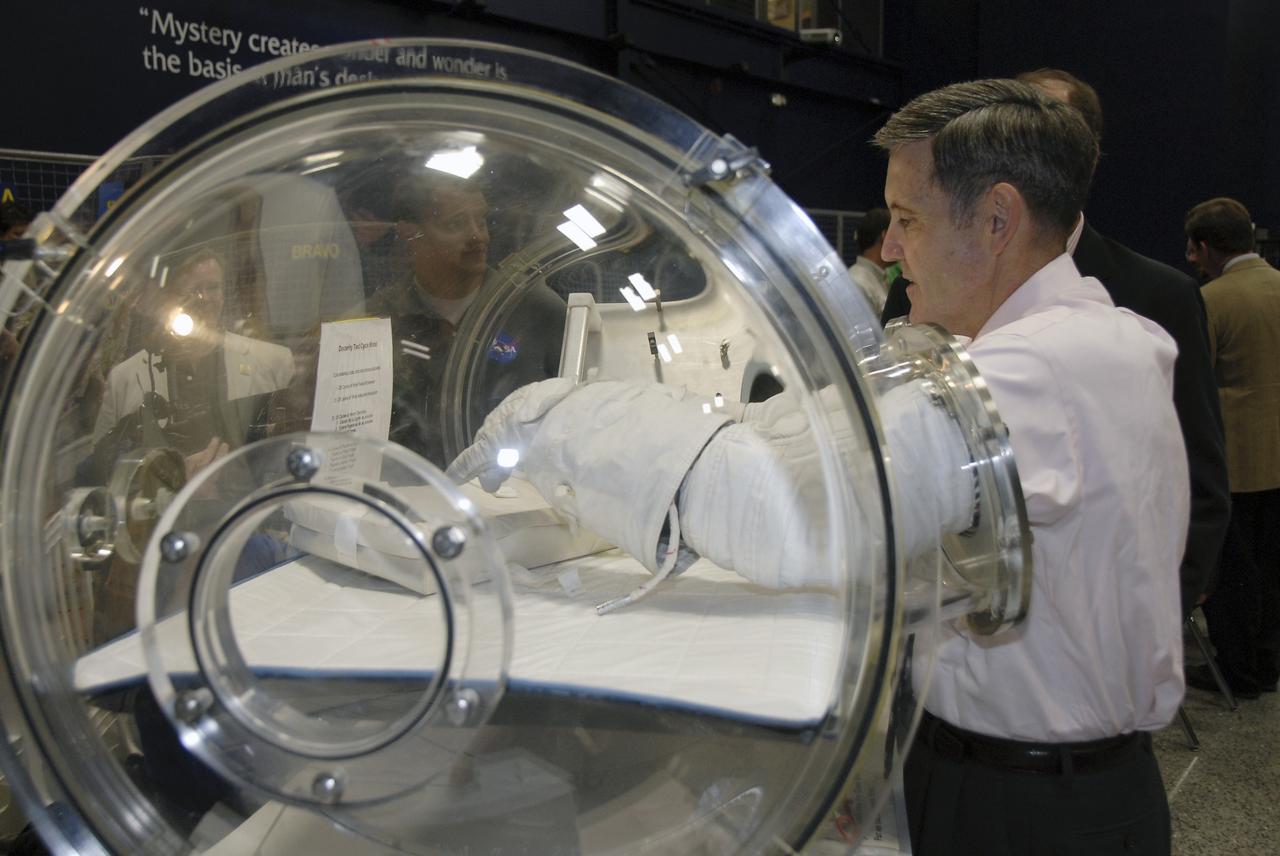

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, a former astronaut, tests a pair of space gloves for their dexterity and flexibility in a glove box at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
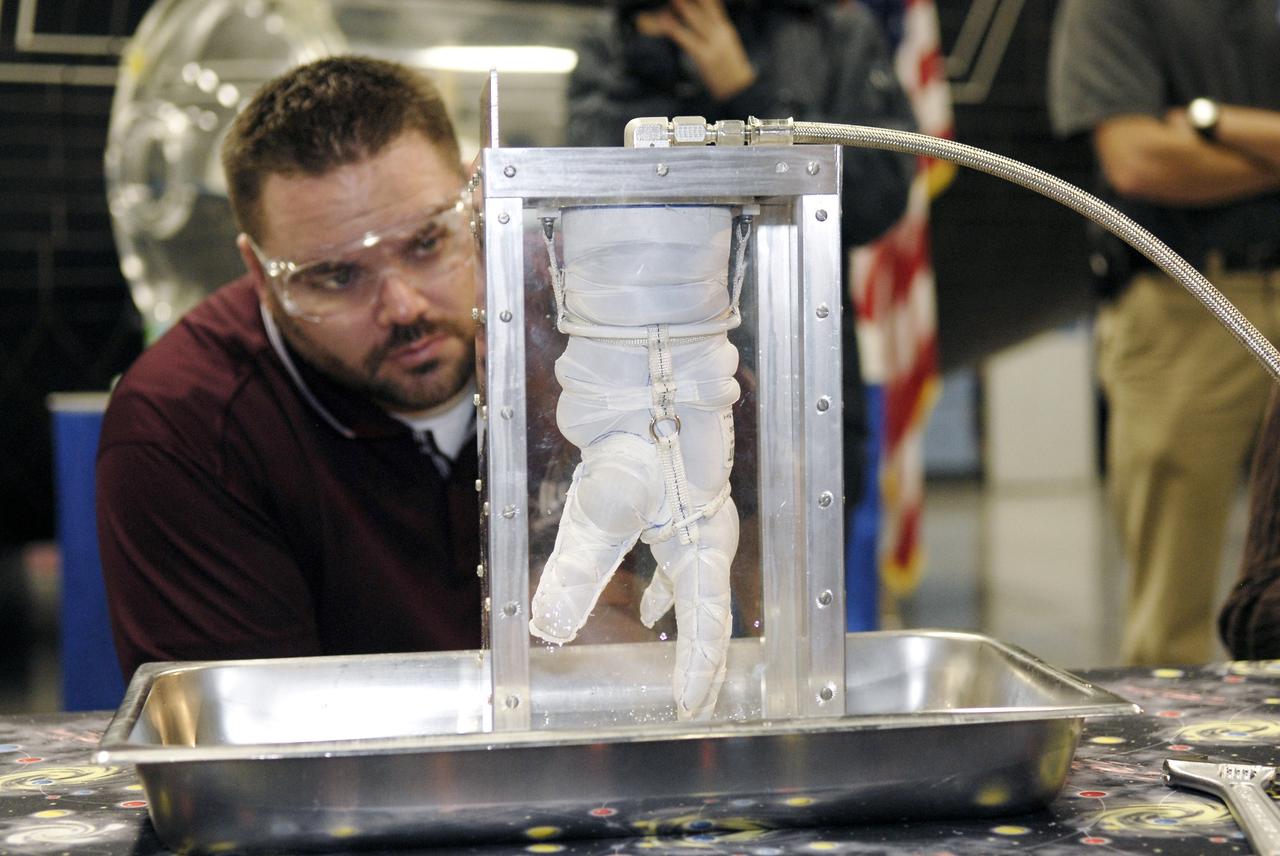

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A representative of ILC Dover monitors how much internal pressure a newly designed glove can withstand during a burst test at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
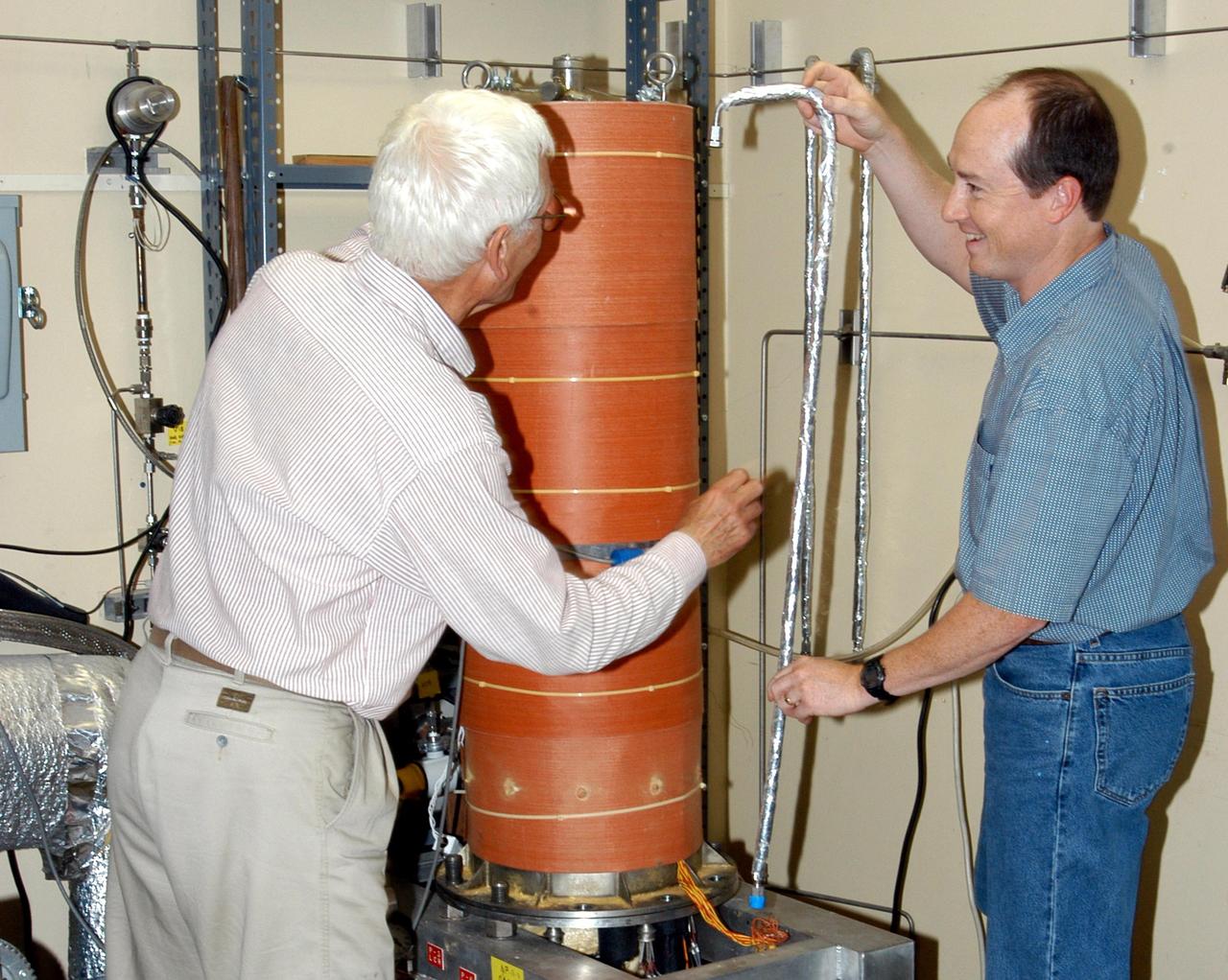

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - James E. Fesmire (right), NASA lead engineer for the KSC Cryogenics Testbed, works on Cryostat-1, the Methods of Testing Thermal Insulation and Association Test Apparatus, which he developed. At left is co-inventor Dr. Stan Augustynowicz, chief scientist with Sierra Lobo Inc. in Milan, Ohio. Cryostat-1 provides absolute thermal performance values of cryogenic insulation systems under real-world conditions. Cryogenic liquid is supplied to a test chamber and two guard chambers, and temperatures are sensed within the vacuum chamber to test aerogels, foams or other materials. The Cryostat-1 machine can detect the absolute heat leakage rates through materials under the full range of vacuum conditions. Fesmire recently acquired three patents for testing thermal insulation materials for cryogenic systems. The research team of the Cryogenics Testbed offers testing and support for a number of programs and initiatives for NASA and commercial customers.
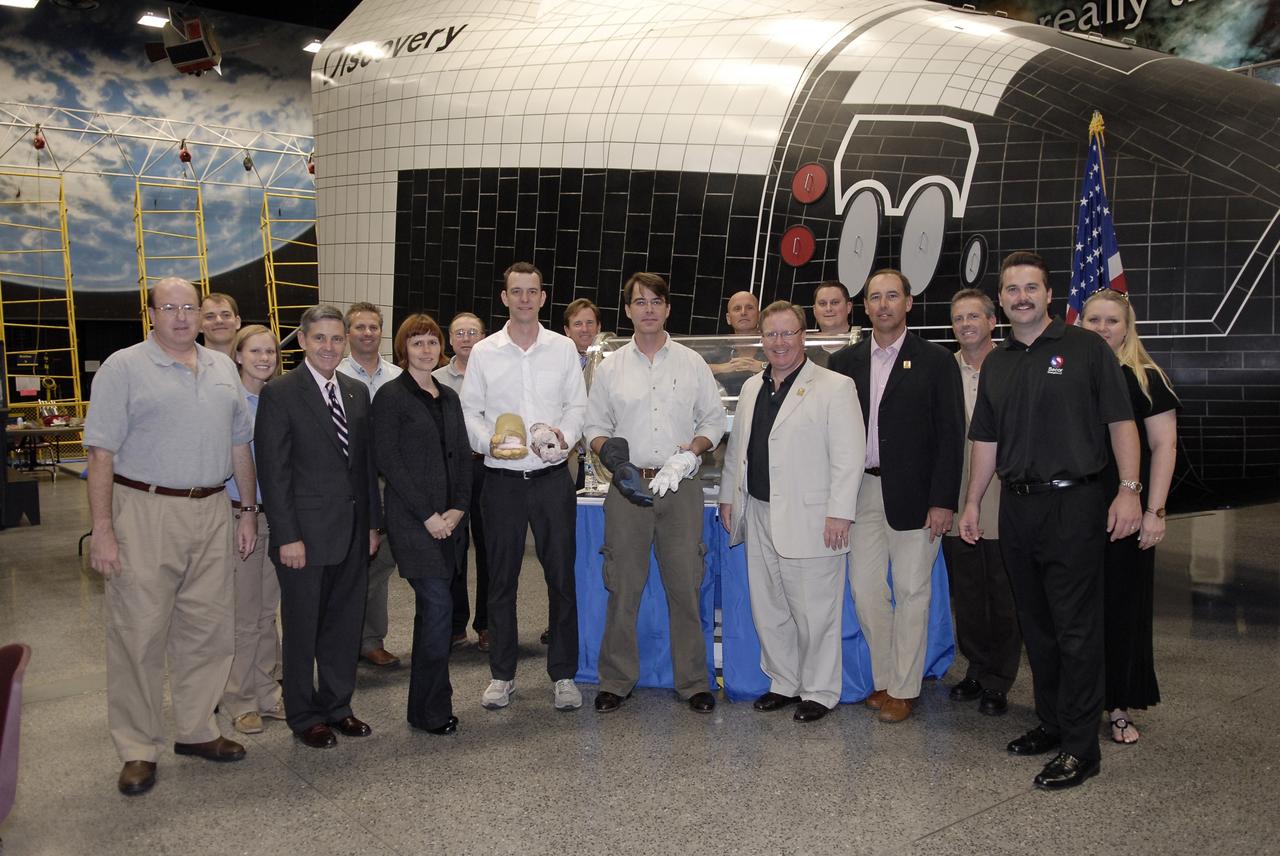

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, participants in the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, pose for a group portrait. In the center of the front row are the winners, Ted Southern of Brooklyn, N.Y., at left, and Peter Homer of Southwest Harbor, Maine. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
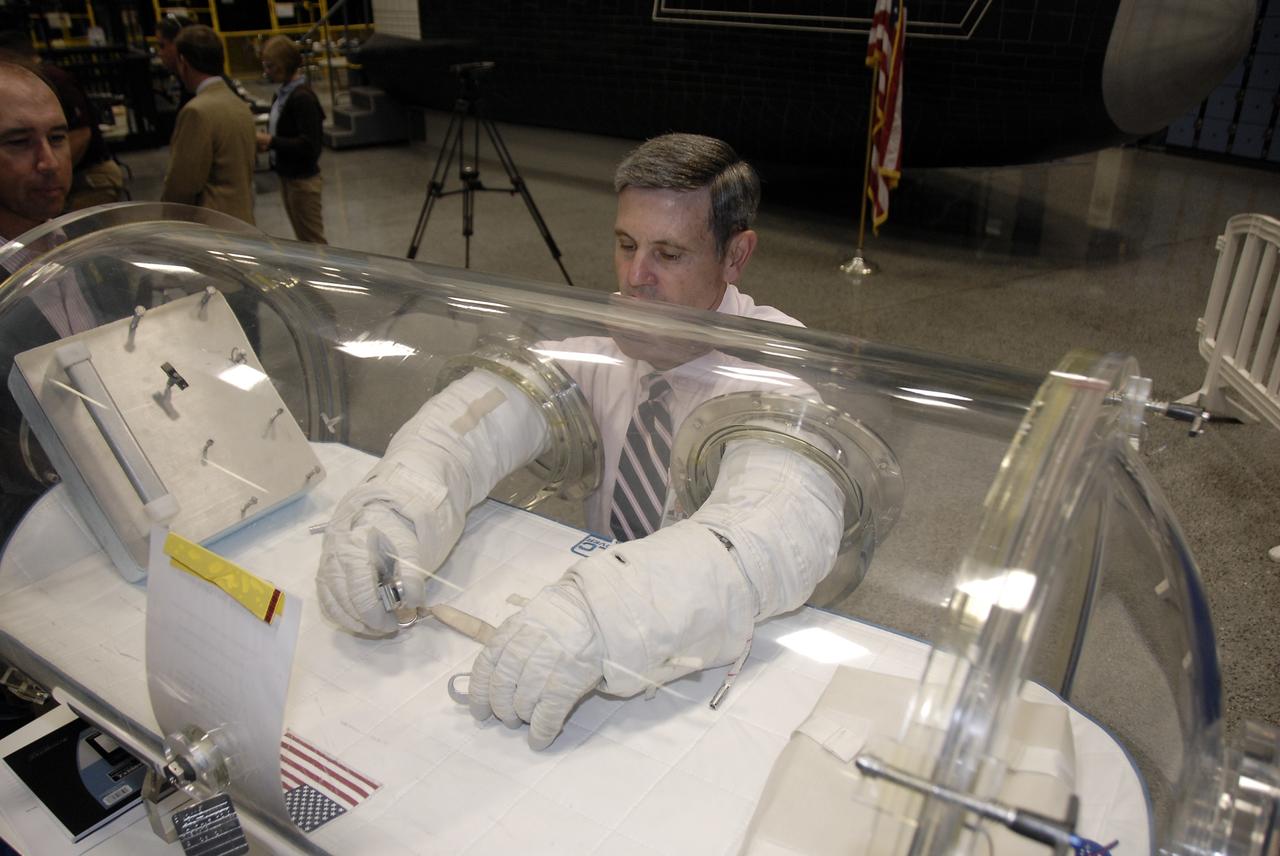

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, a former astronaut, tries out a pair of space gloves for their dexterity and flexibility in a glove box at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
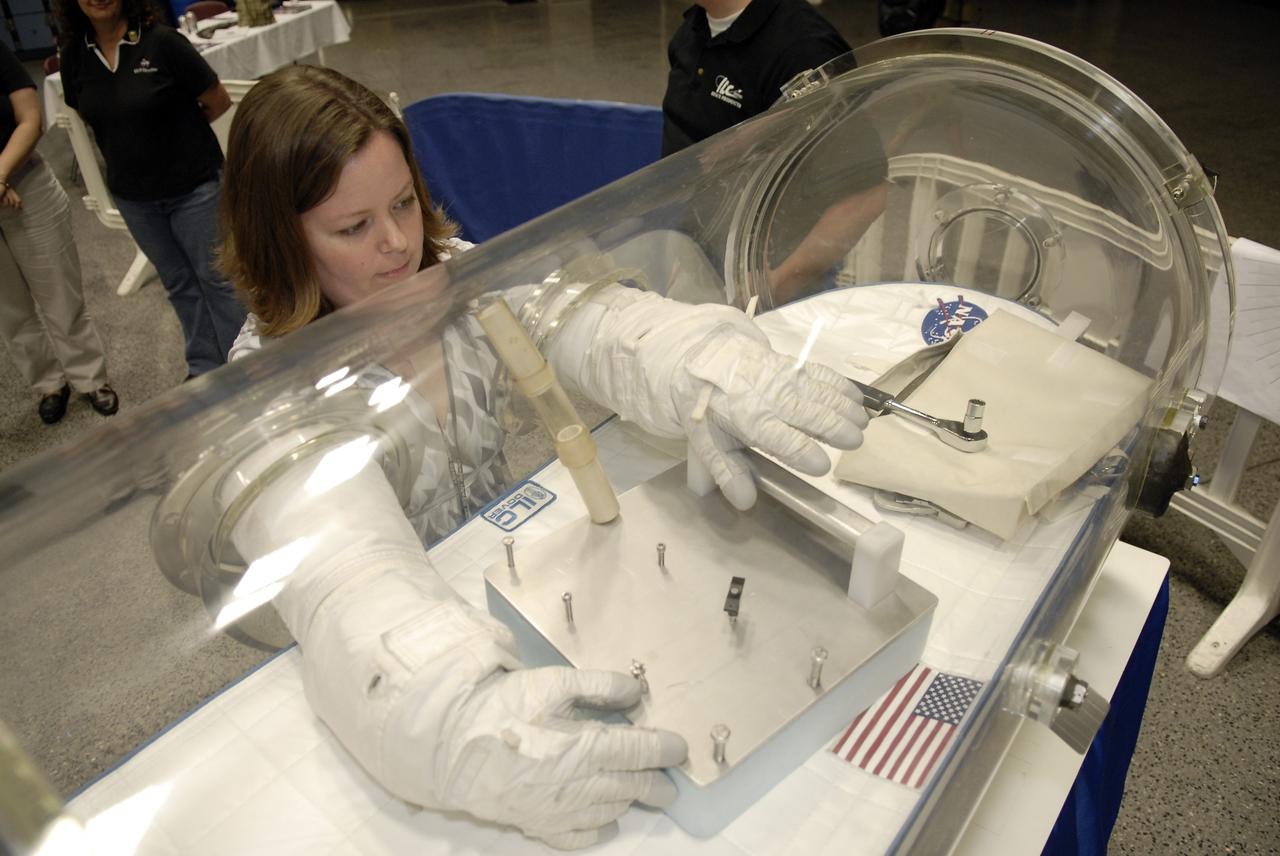

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Anna Heiney, a Public Affairs support writer with Abacus Technology at Kennedy, tries out a pair of space gloves for their dexterity and flexibility in a glove box at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. Looking over his shoulder is Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
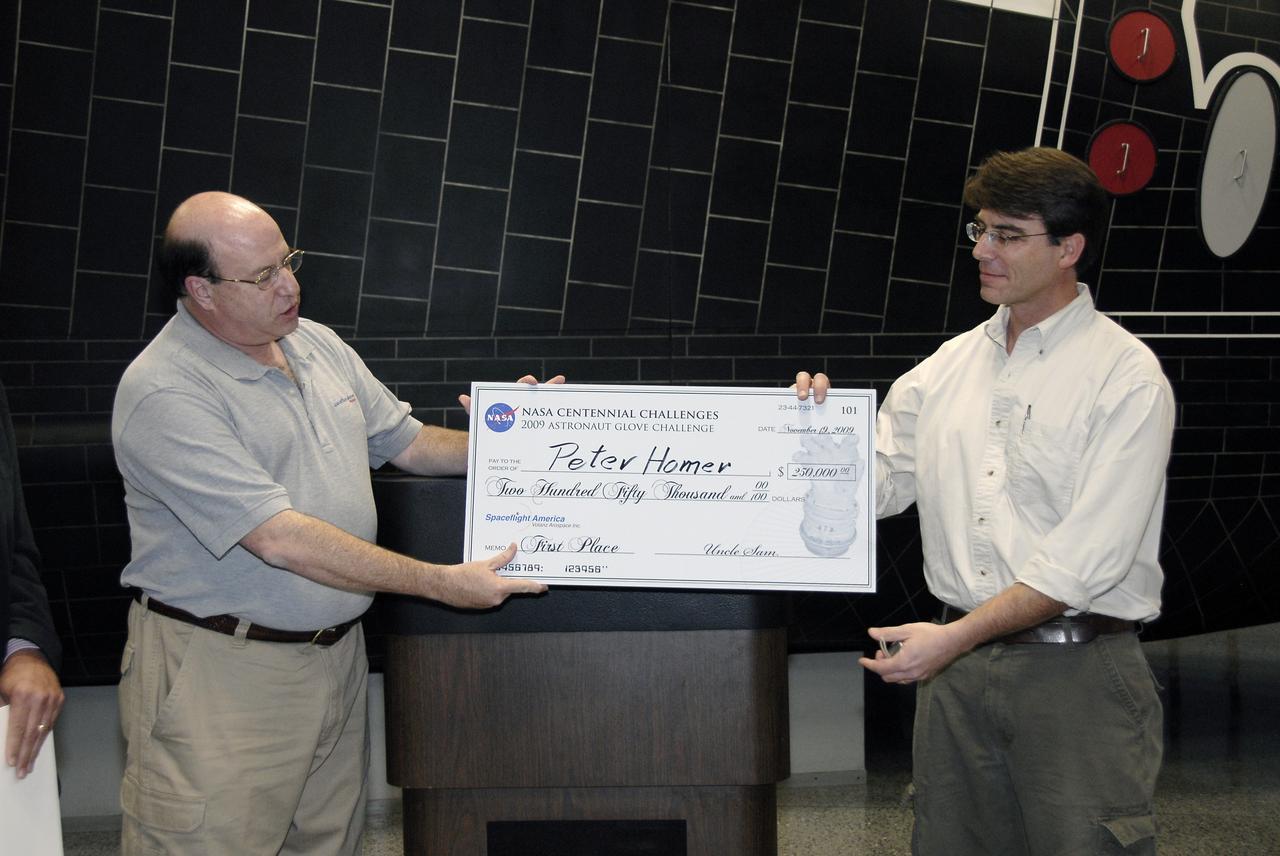

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alan Hayes, left, chairman of Volanz Aerospace Inc., presents Peter Homer of Southwest Harbor, Maine, with the first place prize of $250,000 at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
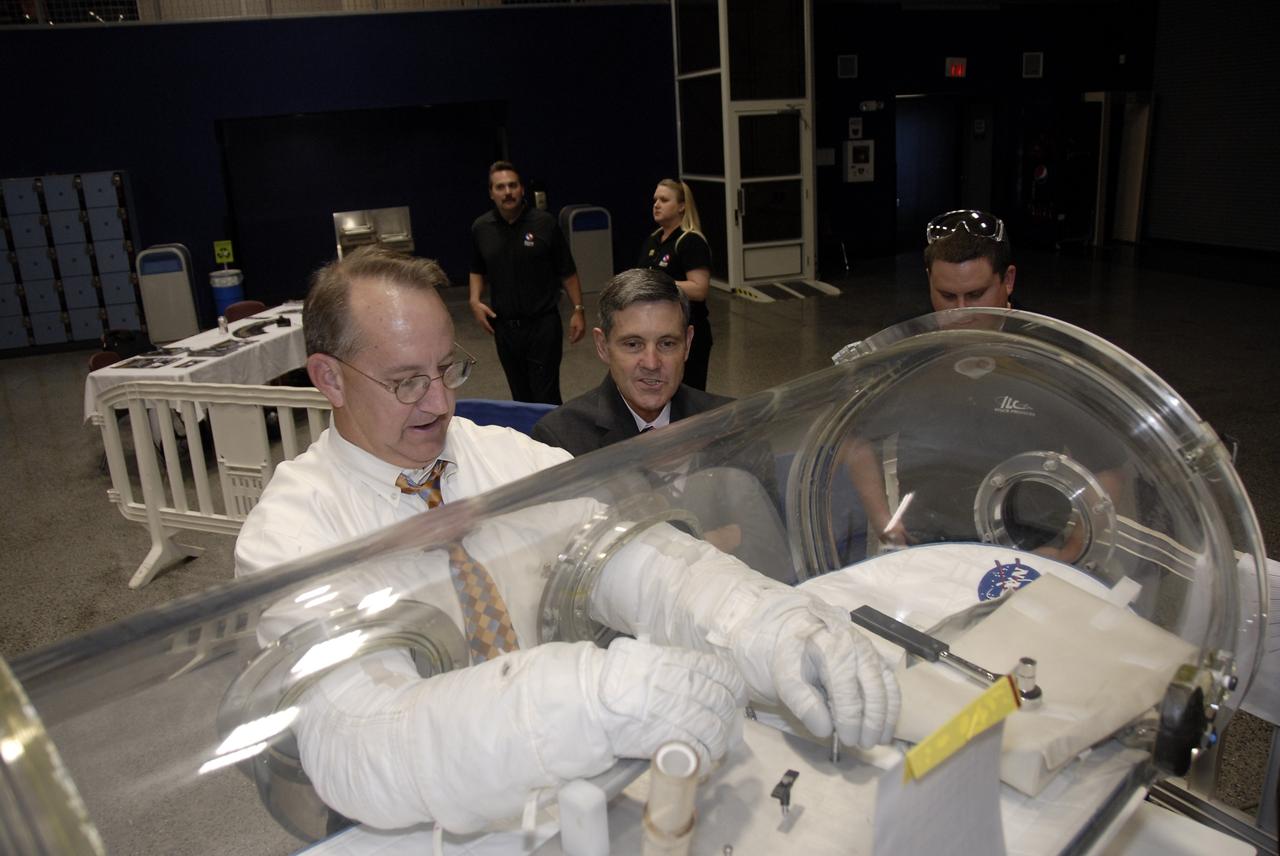

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Patrick Simpkins, director of Engineering at Kennedy, tries out a pair of space gloves for their dexterity and flexibility in a glove box at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. Looking over his shoulder is Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
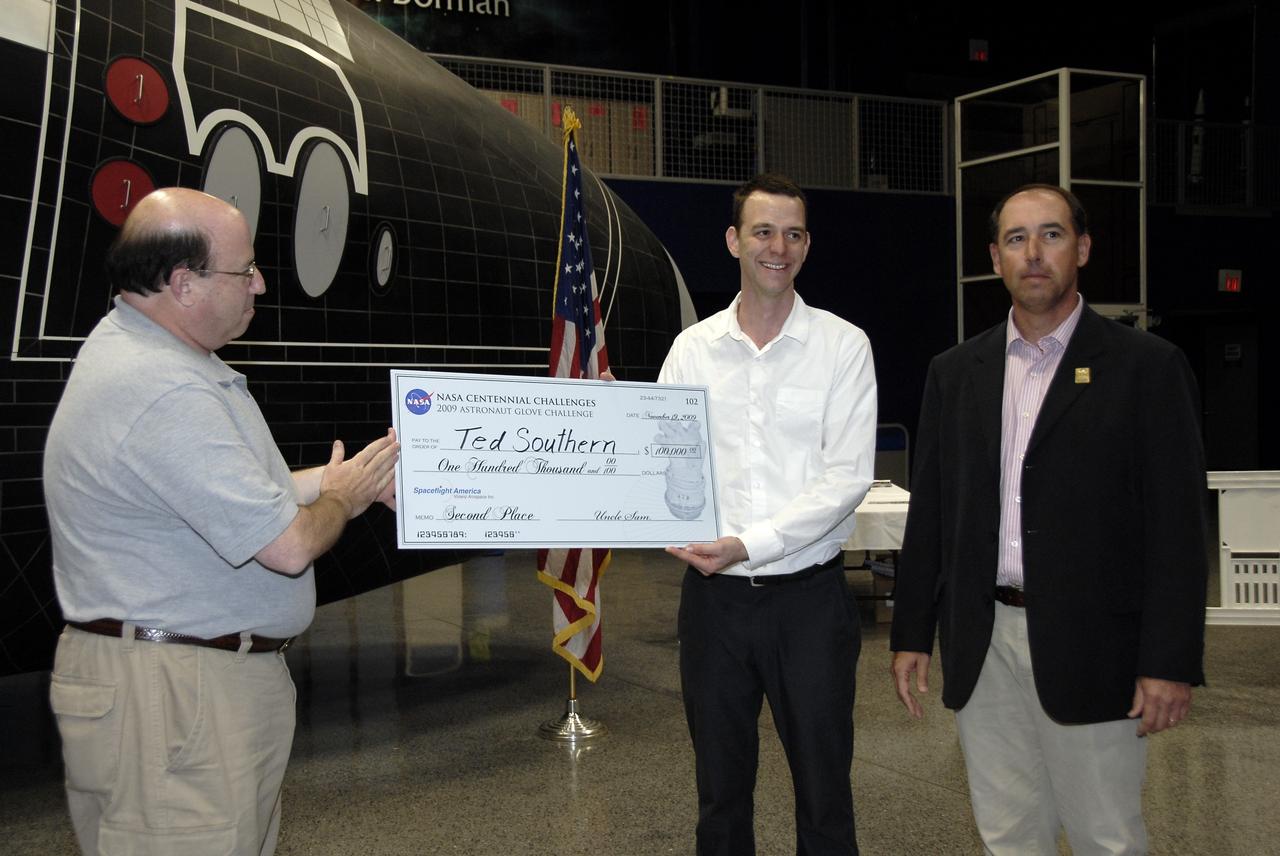

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Alan Hayes, left, chairman of Volanz Aerospace Inc., presents Ted Southern of Brooklyn, N.Y., with the second place prize of $100,000 at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, as Andy Petro, manager of NASA Centennial Challenges, stands by at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
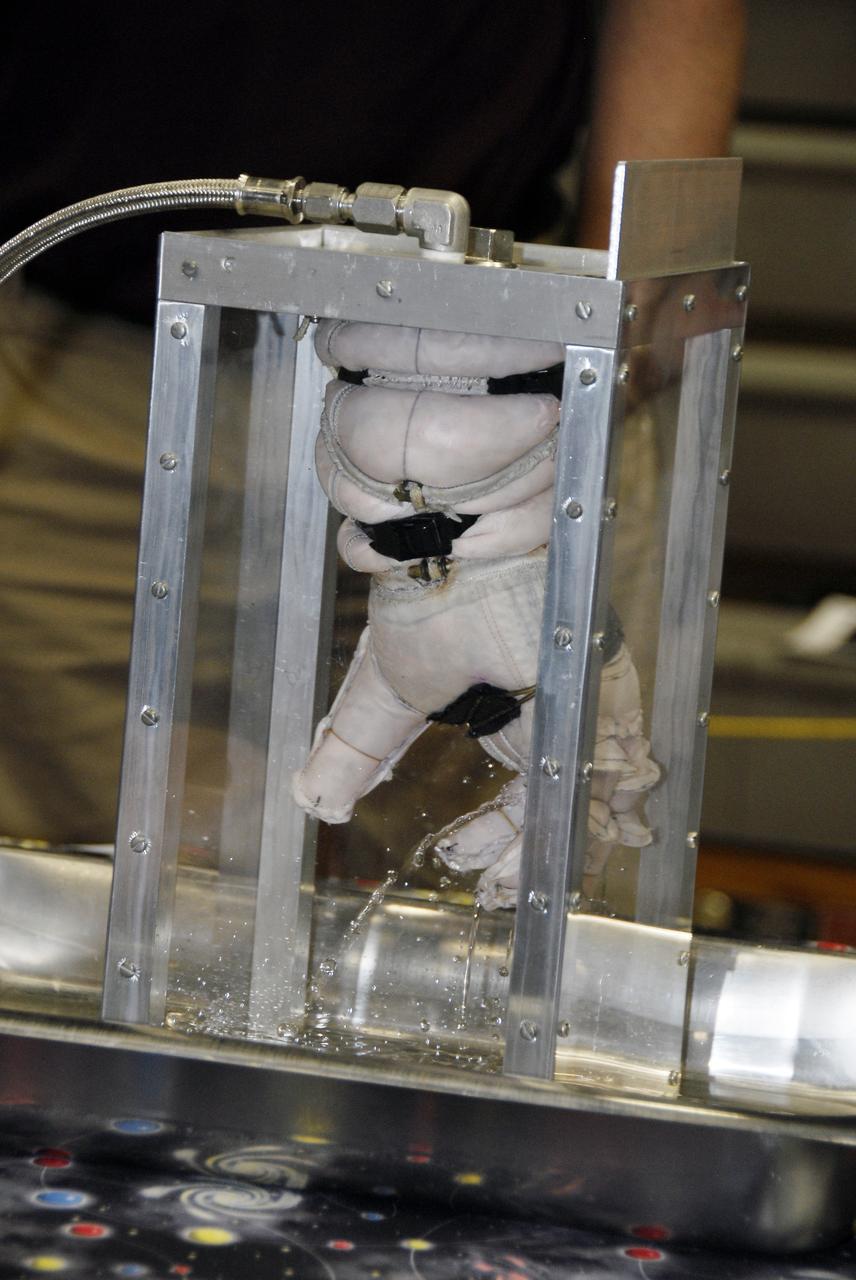

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A newly designed glove is submitted to a burst test to determine how much internal pressure it can withstand at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, at the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
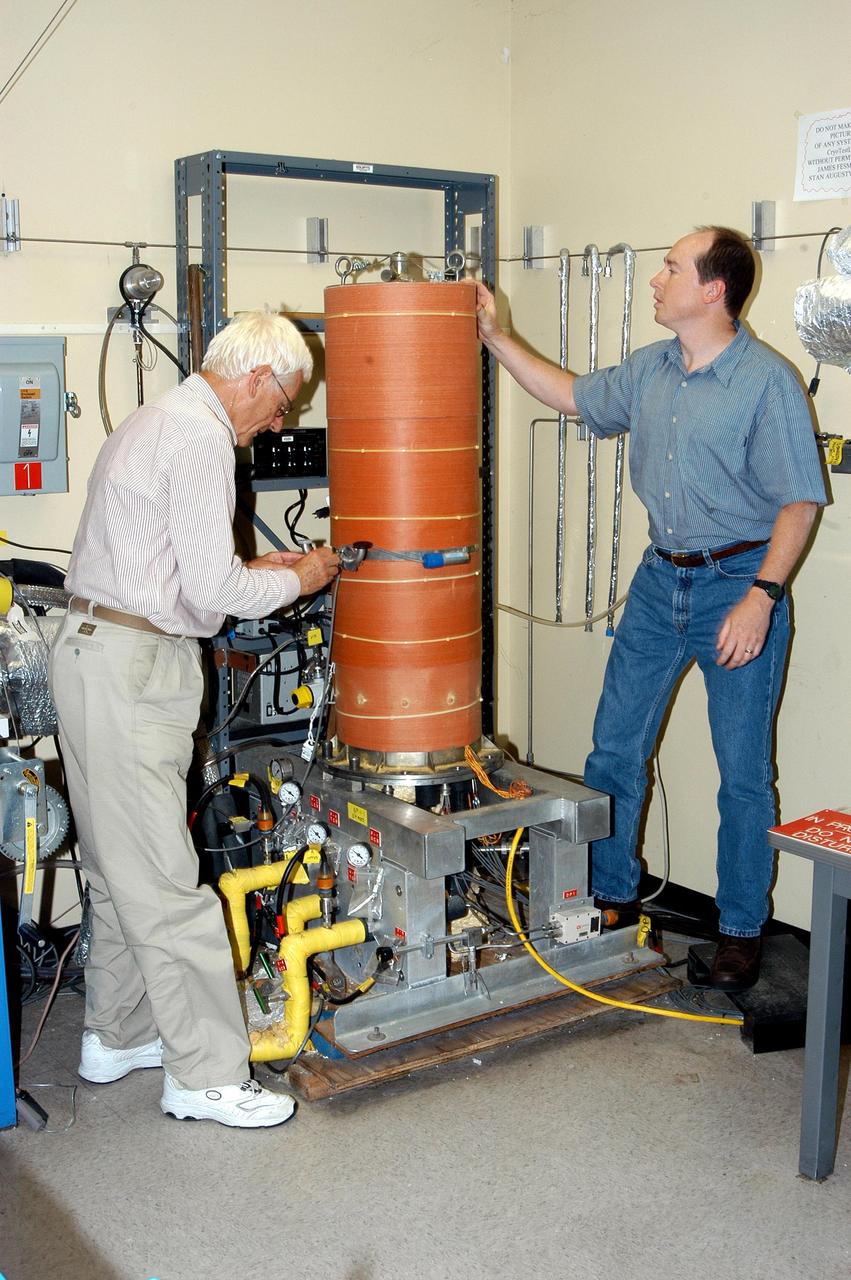

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - James E. Fesmire (right), NASA lead engineer for the KSC Cryogenics Testbed, works on Cryostat-1, the Methods of Testing Thermal Insulation and Association Test Apparatus, which he developed. At left is co-inventor Dr. Stan Augustynowicz, chief scientist with Sierra Lobo Inc. in Milan, Ohio. Cryostat-1 provides absolute thermal performance values of cryogenic insulation systems under real-world conditions. Cryogenic liquid is supplied to a test chamber and two guard chambers, and temperatures are sensed within the vacuum chamber to test aerogels, foams or other materials. The Cryostat-1 machine can detect the absolute heat leakage rates through materials under the full range of vacuum conditions. Fesmire recently acquired three patents for testing thermal insulation materials for cryogenic systems. The research team of the Cryogenics Testbed offers testing and support for a number of programs and initiatives for NASA and commercial customers.
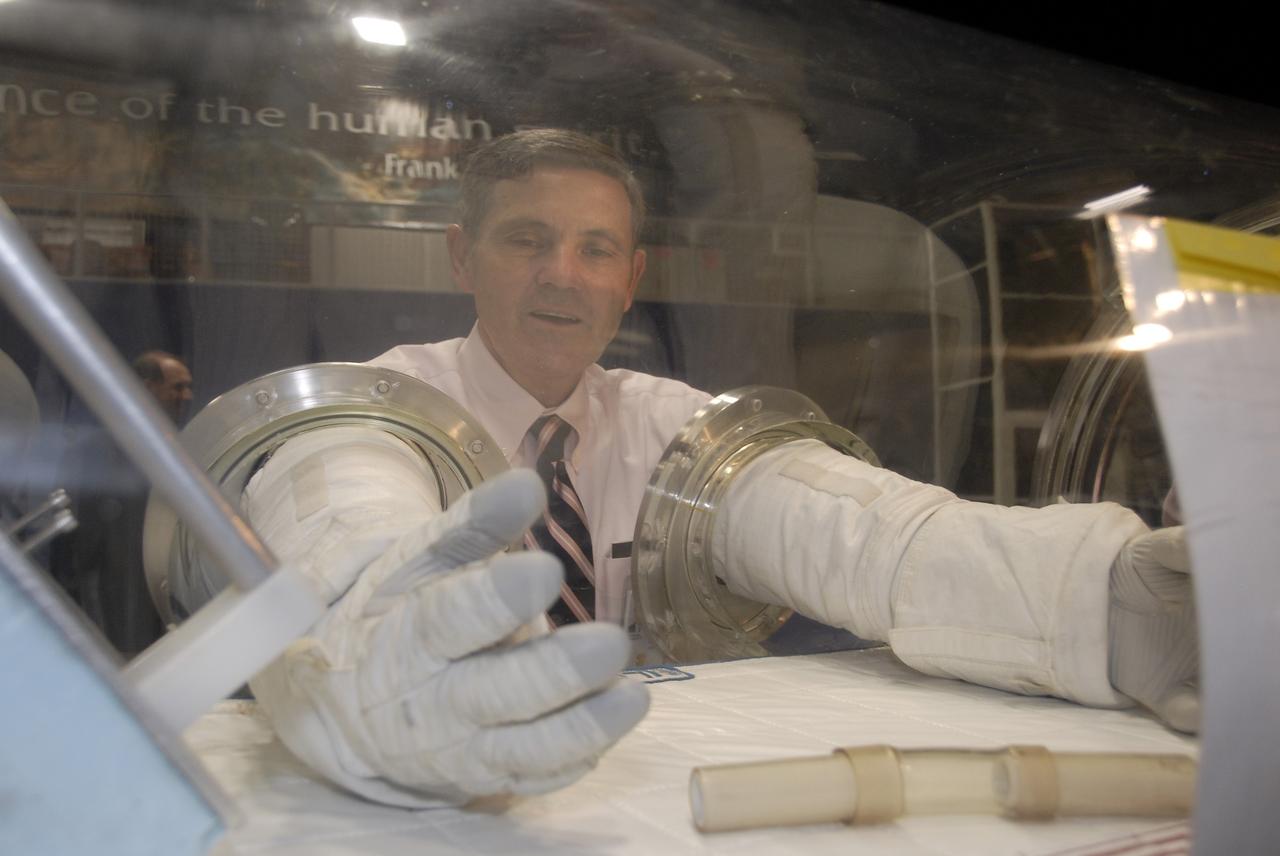

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, a former astronaut, tries out a pair of space gloves for their dexterity and flexibility in a glove box at the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
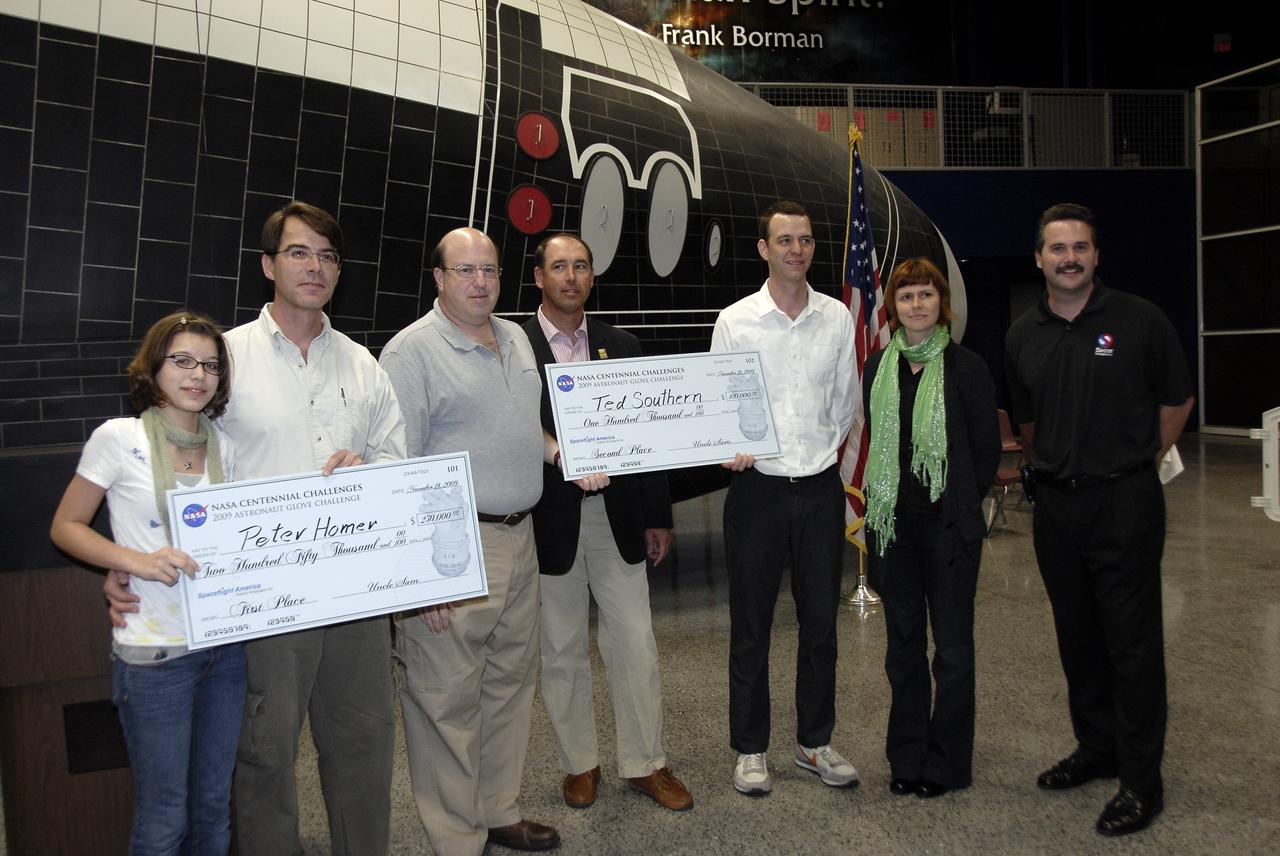

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the Astronaut Hall of Fame near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the winners of the 2009 Astronaut Glove Challenge, part of NASA’s Centennial Challenges Program, pose for a group photograph with their friends, family and the event organizers. From left are Caroline Homer and her father, Peter Homer, winner of the $250,000 first prize; Alan Hayes, chairman of Volanz Aerospace Inc.; Andy Petro, manager of NASA Centennial Challenges; Ted Southern, winner of the $100,000 second prize; his friend and glove tester Amy Miller; and Paul Secor, Secor Strategies LLC. The nationwide competition focused on developing improved pressure suit gloves for astronauts to use while working in space. During the challenge, the gloves were submitted to burst tests, joint force tests and tests to measure their dexterity and strength during operation in a glove box which simulates the vacuum of space. Centennial Challenges is NASA’s program of technology prizes for the citizen-inventor. The winning prize for the Glove Challenge is $250,000 provided by the Centennial Challenges Program. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
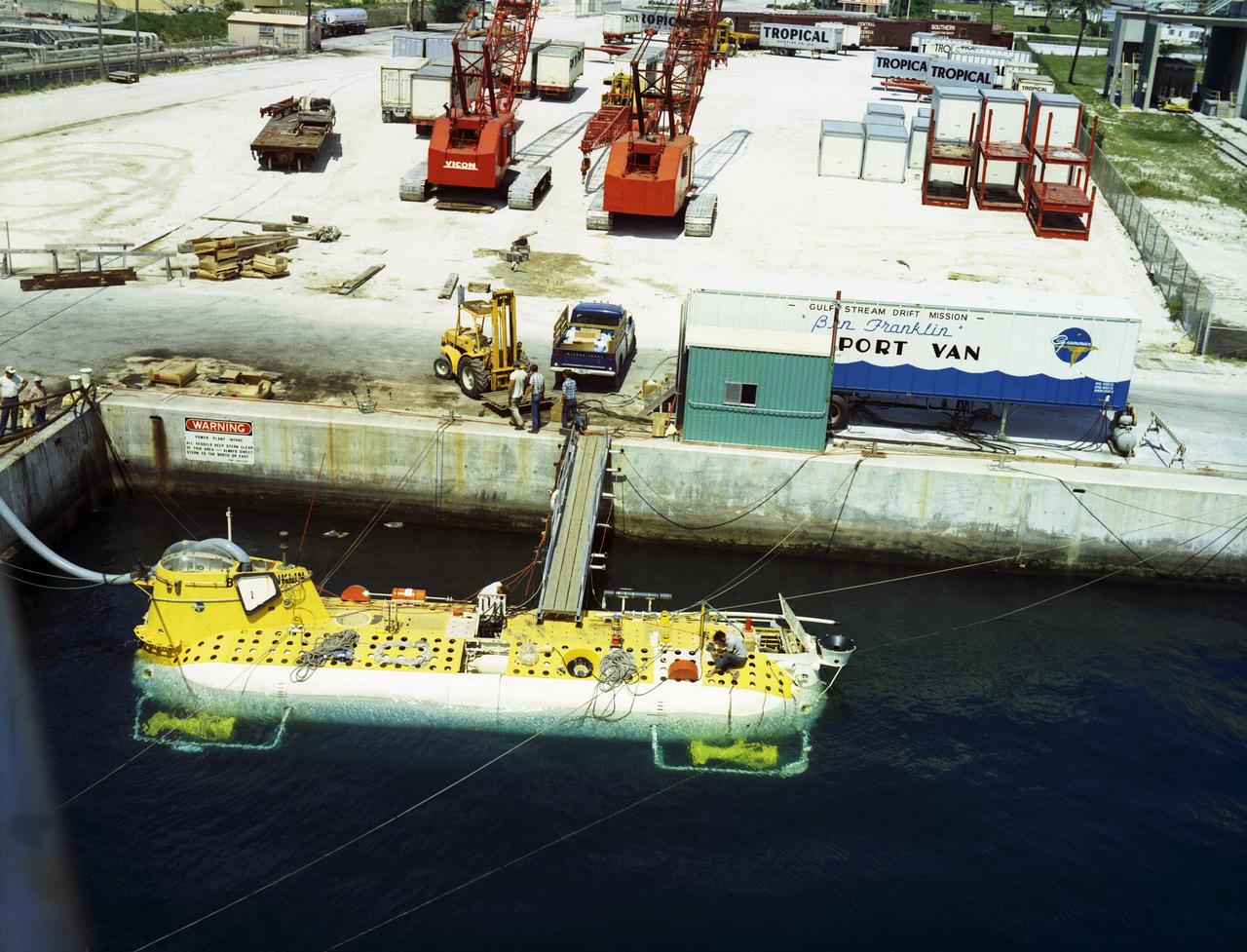

This is an aerial view of the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin" at dock. Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
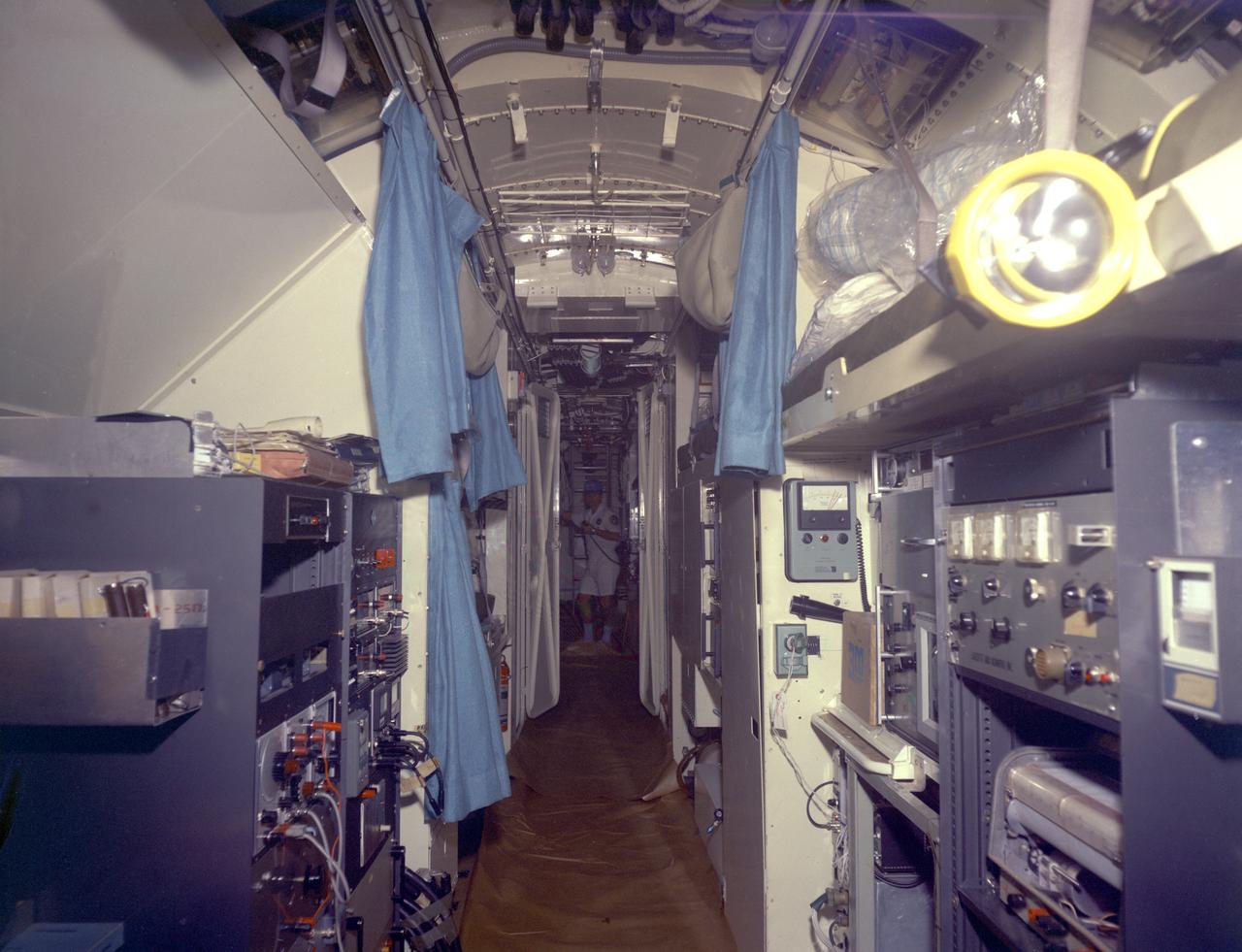
This is an interior view of the living quarters of the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep- ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effect of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
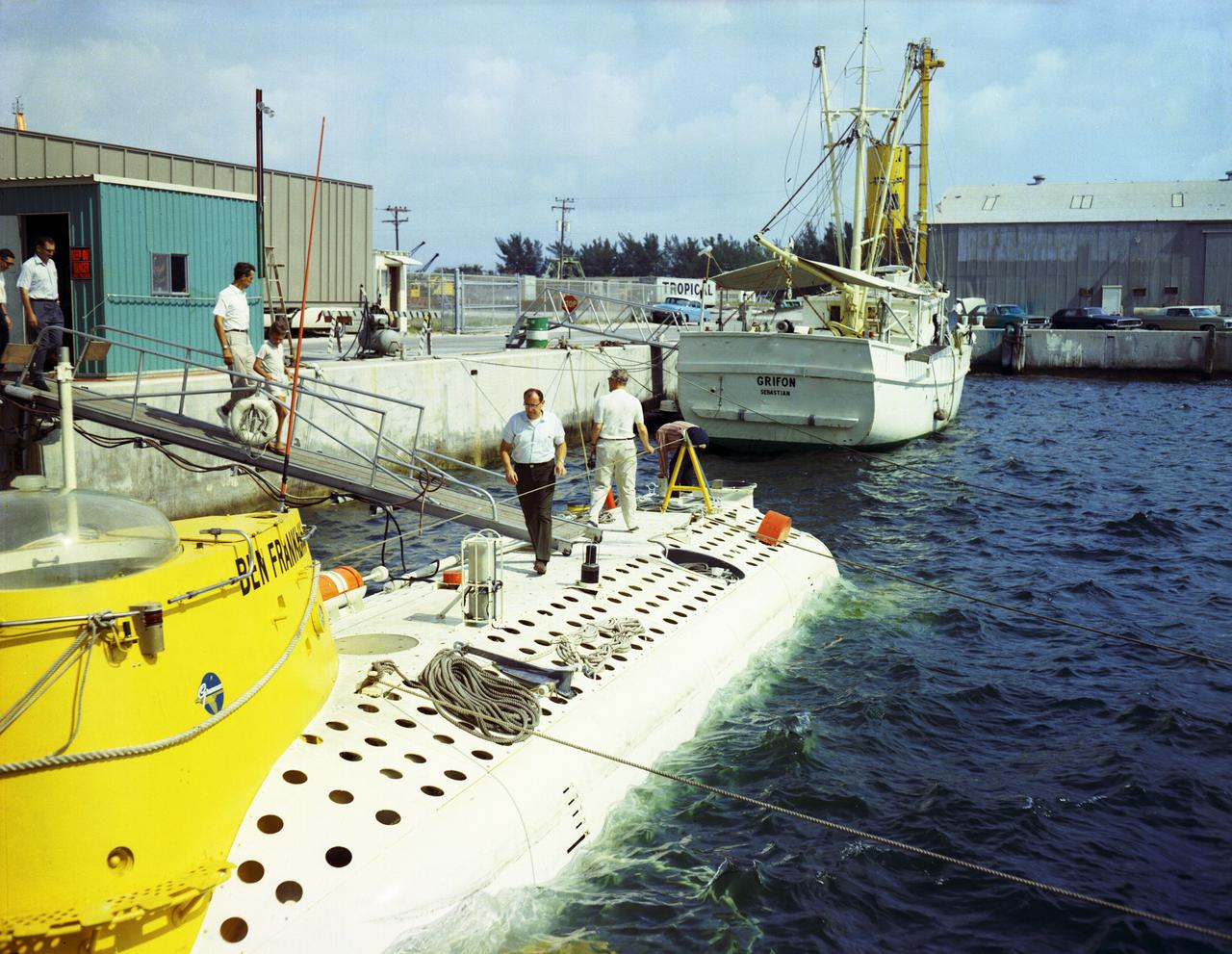

This photograph depicts Dr. von Braun (at right, showing his back) and other NASA officials surveying the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
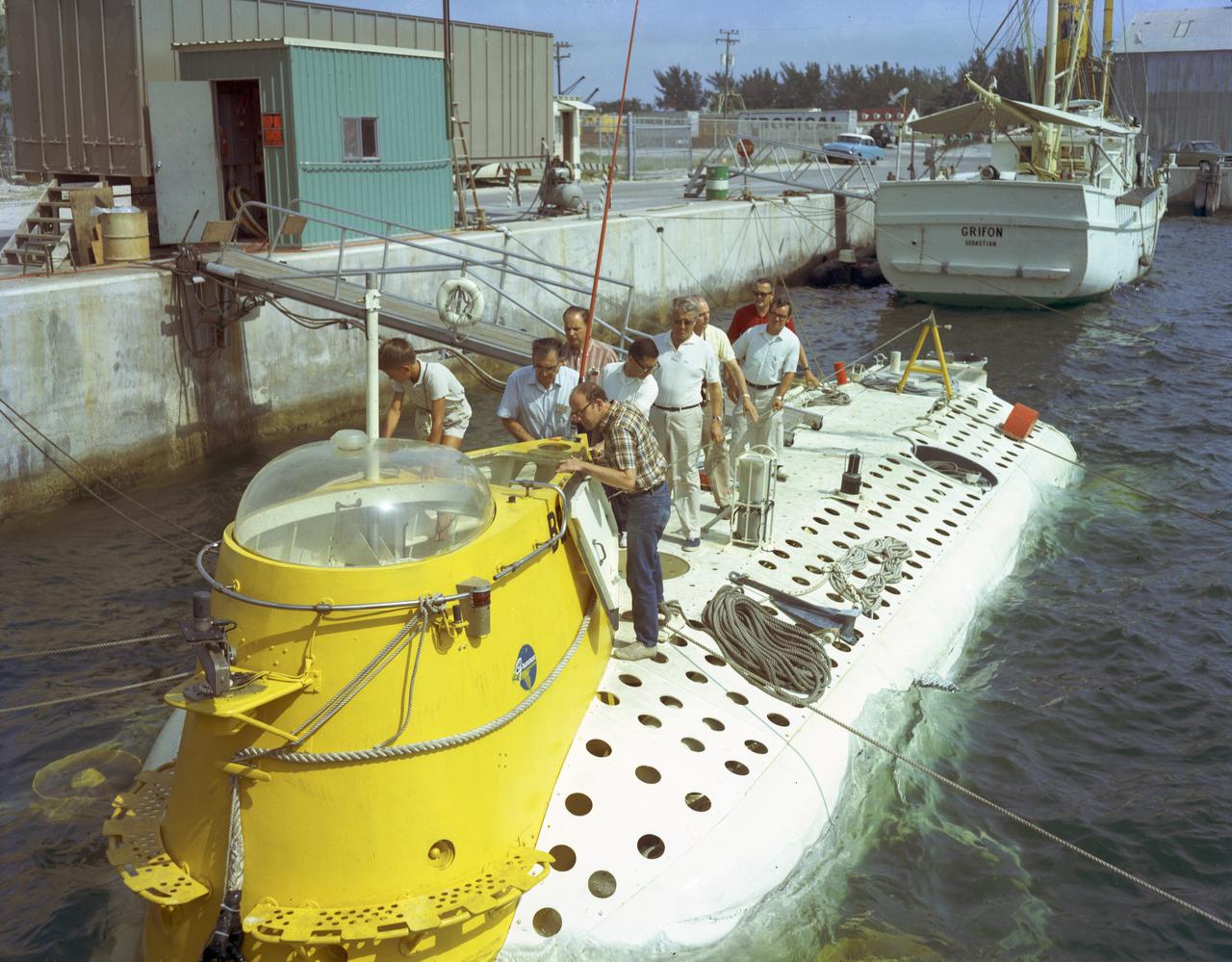

This photograph depicts Dr. von Braun (fourth from far right) and other NASA officials surveying the deep-sea research submarine "Ben Franklin." Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.
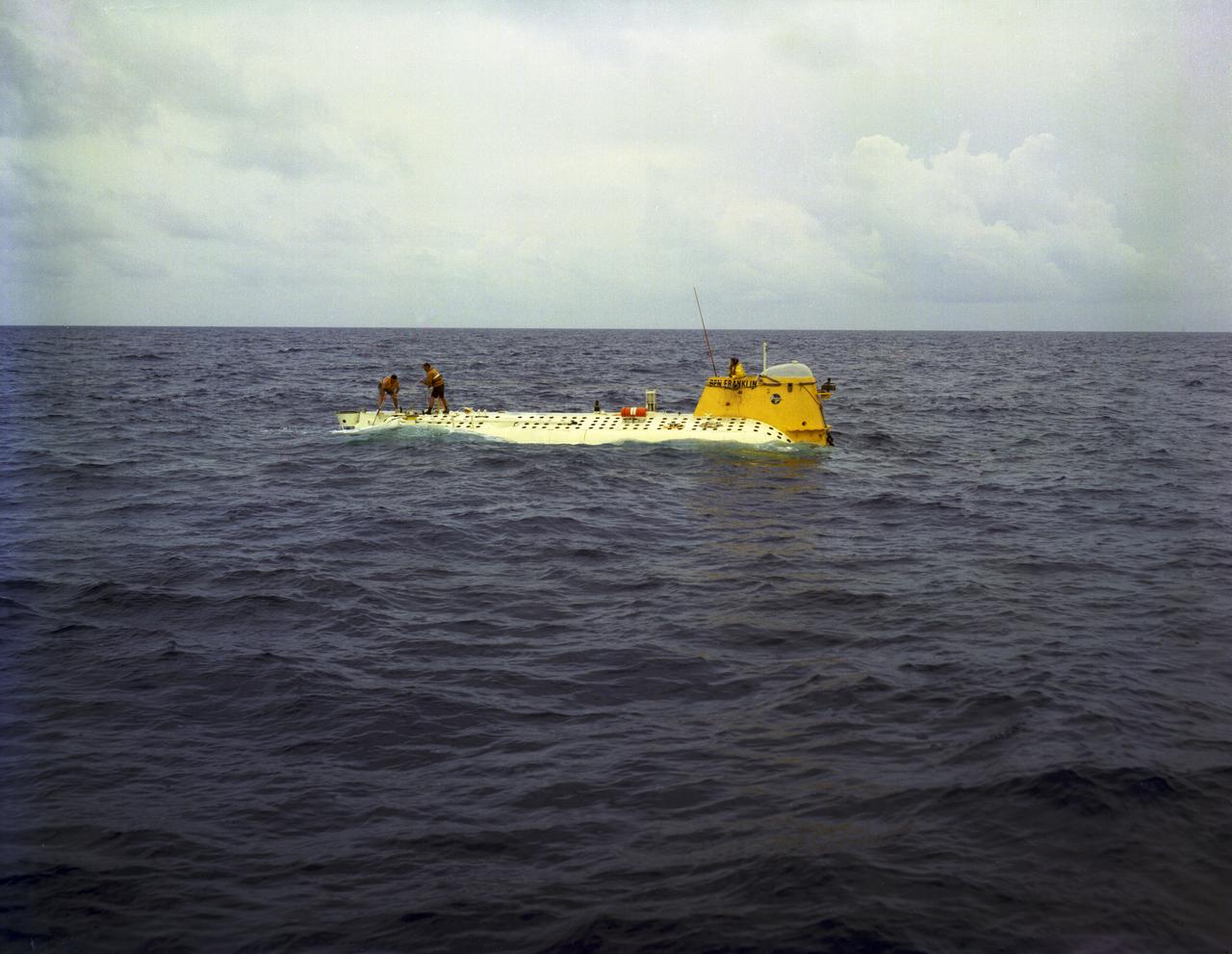

In this photograph, the deep-sea Research Submarine "Ben Franklin" drifts off the East Coast of the United States (U.S.) prior to submerging into the ocean. Named for American patriot and inventor Ben Franklin, who discovered the Gulf Steam, the 50-foot Ben Franklin was built between 1966 and 1968 in Switzerland for deep-ocean explorer Jacques Piccard and the Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation. The submersible made a famous 30-day drift dive off the East Coast of the United States and Canada in 1969 mapping the Gulf Stream's currents and sea life, and also made space exploration history by studying the behavior of aquanauts in a sealed, self-contained, self-sufficient capsule for NASA. On July 14, 1969, the Ben Franklin was towed to the high-velocity center of the Stream off the coast of Palm Beach, Florida. With a NASA observer on board, the sub descended to 1,000 feet off of Riviera Beach, Florida and drifted 1,400 miles north with the current for more than four weeks, reemerging near Maine. During the course of the dive, NASA conducted exhaustive analyses of virtually every aspect of onboard life. They measured sleep quality and patterns, sense of humor and behavioral shifts, physical reflexes, and the effects of a long-term routine on the crew. The submarine's record-shattering dive influenced the design of Apollo and Skylab missions and continued to guide NASA scientists as they devised future marned space-flight missions.

NASA images acquired October 15, 2012 The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured these nighttime views of the Persian Gulf region on September 30, October 5, October 10, and October 15, 2012. The images are from the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. Each image includes an inset of the Moon in four different phases. September 30 shows the Persian Gulf by the light of the full Moon; October 15 shows the effects of a new Moon. As the amount of moonlight decreases, some land surface features become harder to detect, but the lights from cities and ships become more obvious. Urbanization is most apparent along the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, in Qatar, and in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). In Qatar and UAE, major highways can even be discerned by nighttime lights. In eighteenth-century England, a small group of entrepreneurs, inventors and free thinkers—James Watt and Charles Darwin’s grandfathers among them—started a club. They named it the Lunar Society, and the “lunaticks” scheduled their dinner meetings on evenings of the full Moon. The timing wasn’t based on any kind of superstition, it was based on practicality. In the days before electricity, seeing one’s way home after dark was far easier by the light of a full Moon. In the early twenty-first century, electricity has banished the need for such careful scheduling, but the light of the full Moon still makes a difference. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS day-night band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79834" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>