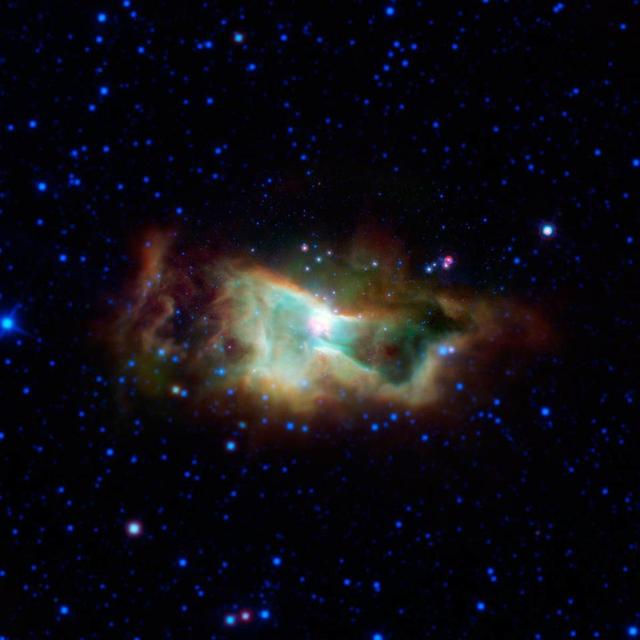

This cloud of glowing gas is the Iris nebula, also called NGC 7023.as seen in infrared light by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope. It lies 1,300 light-years away in the Cepheus constellation.
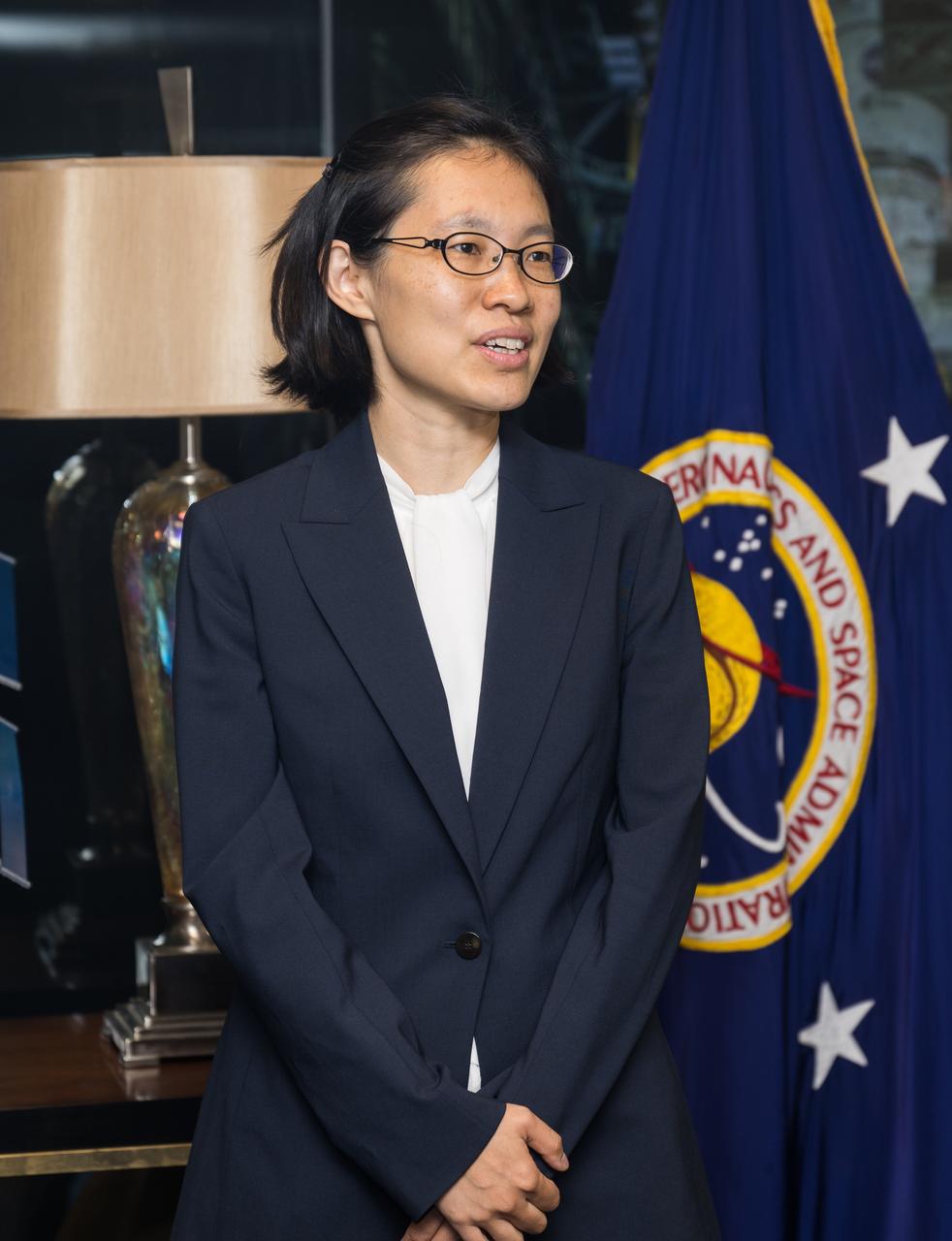

Iris Lan gives remarks after she was ceremonially sworn in as NASA’s General Counsel by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
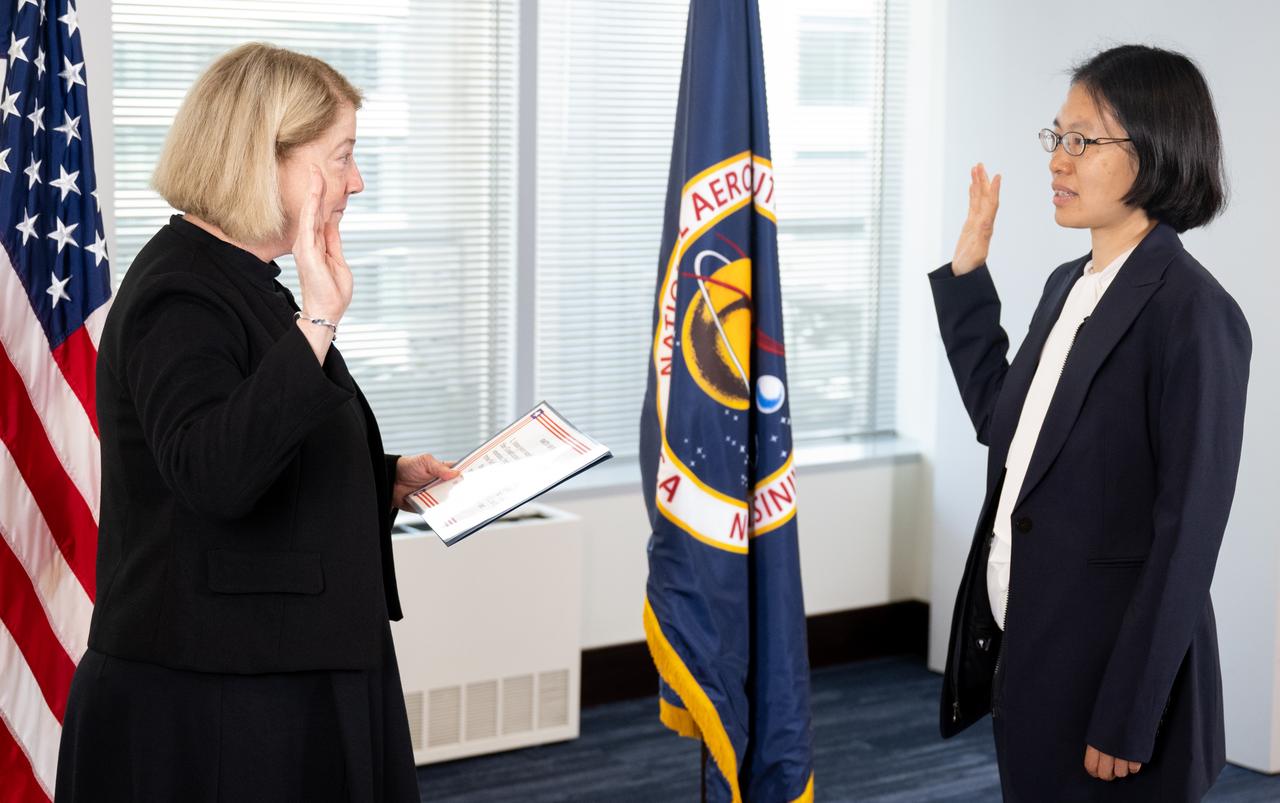

Iris Lan, right, is sworn in as NASA’s General Counsel by NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Monday, June 5, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
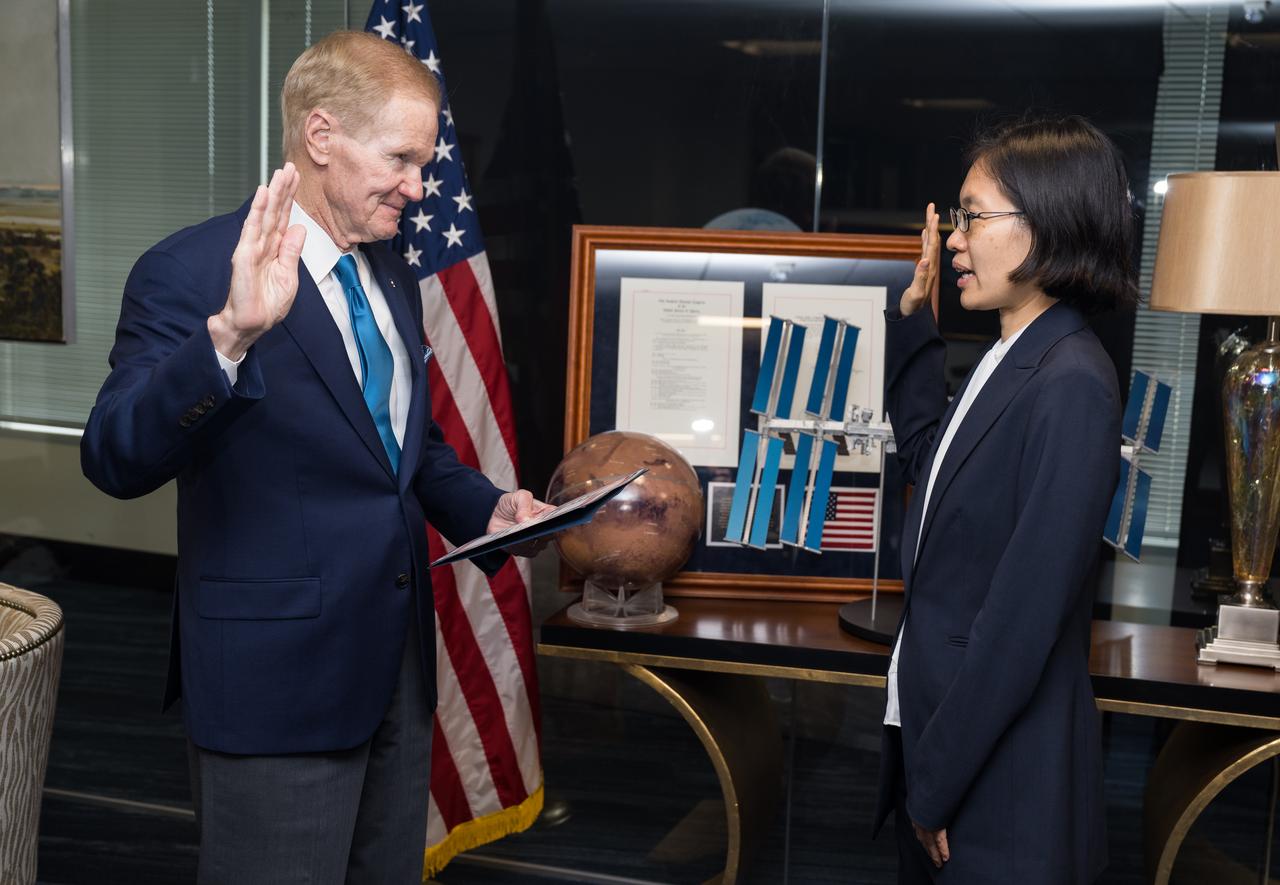

Iris Lan is ceremonially sworn in as NASA’s General Counsel by NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers carry half of a payload fairing into a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California where it will be processed and used for NASA's IRIS mission. The fairing will be fitted to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket and will protect the IRIS spacecraft from atmospheric heating and stress during launch. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
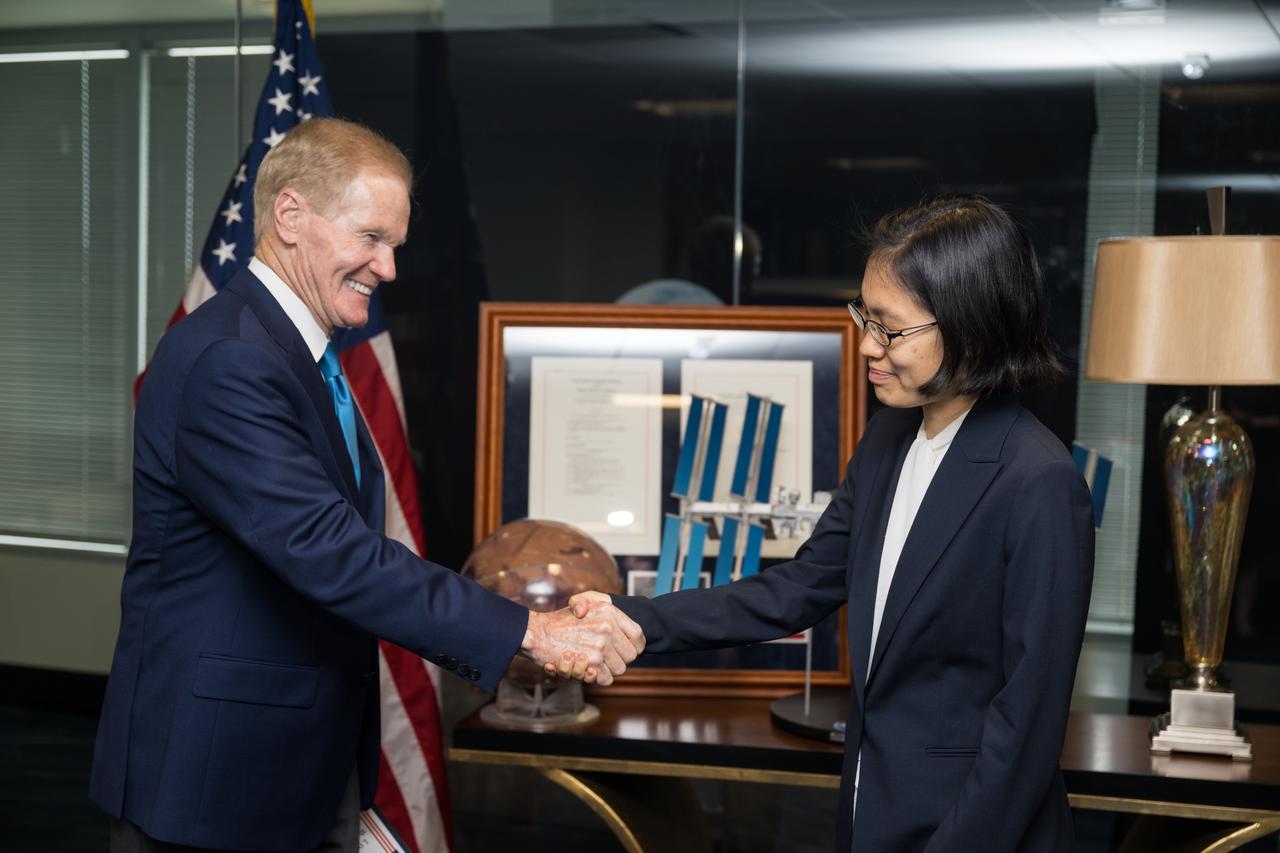

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson shakes hands with NASA General Counsel Iris Lan after she was ceremonially sworn in as the General Counsel, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
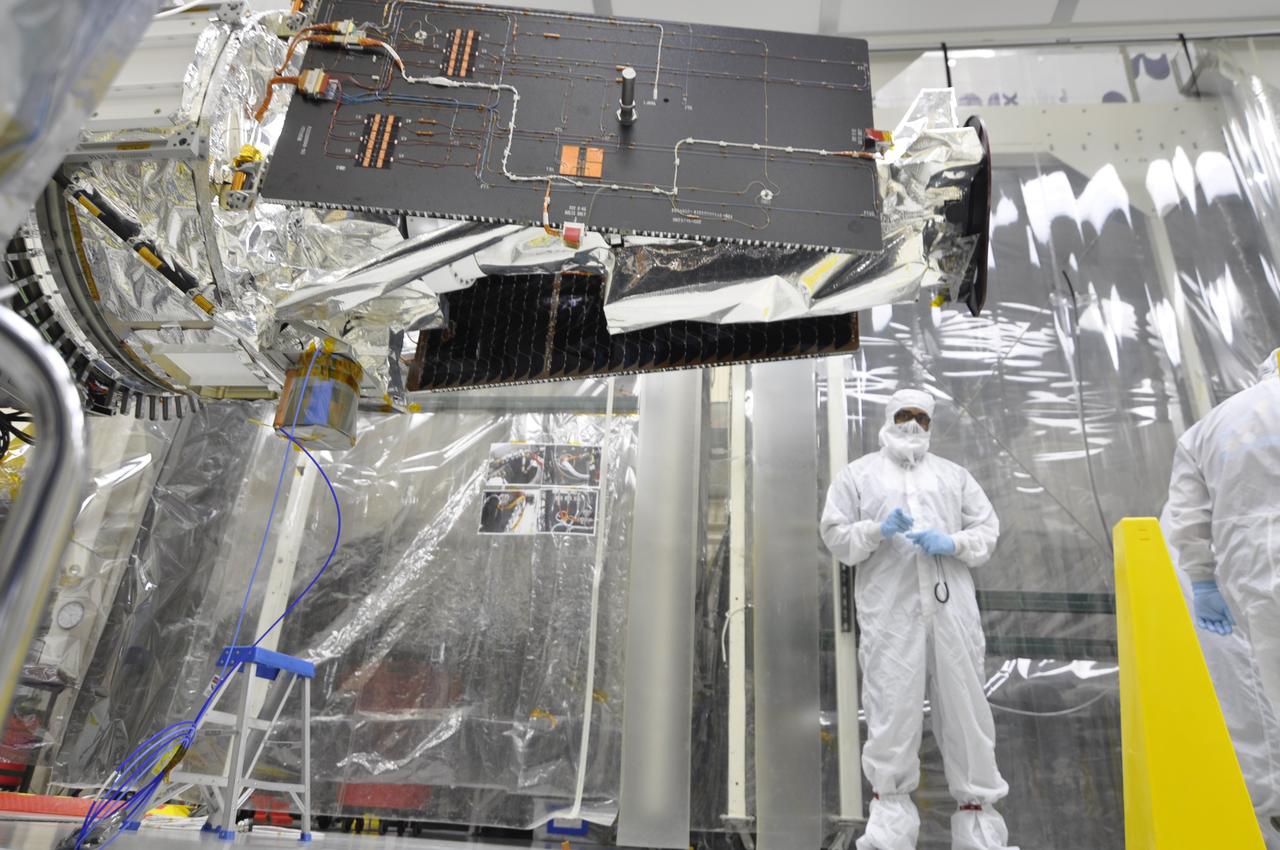

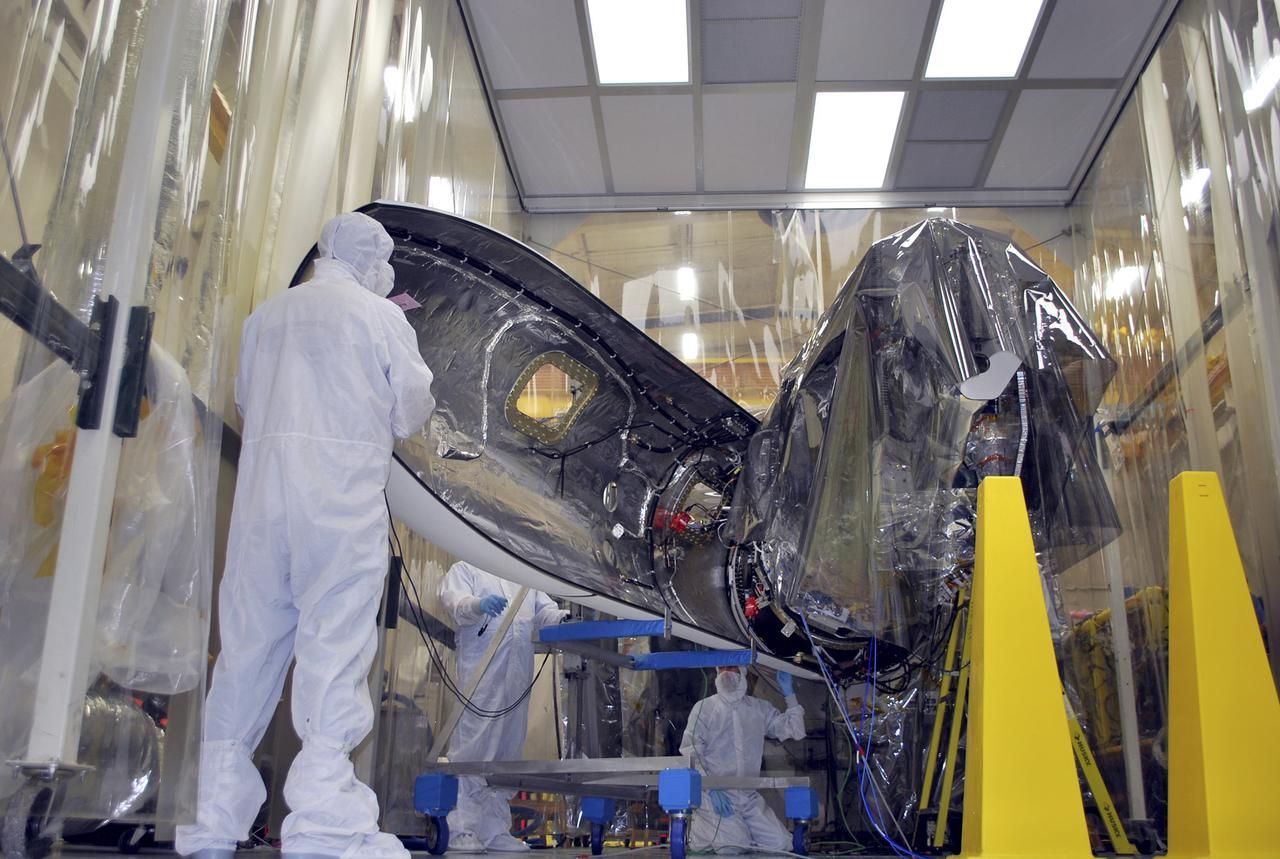
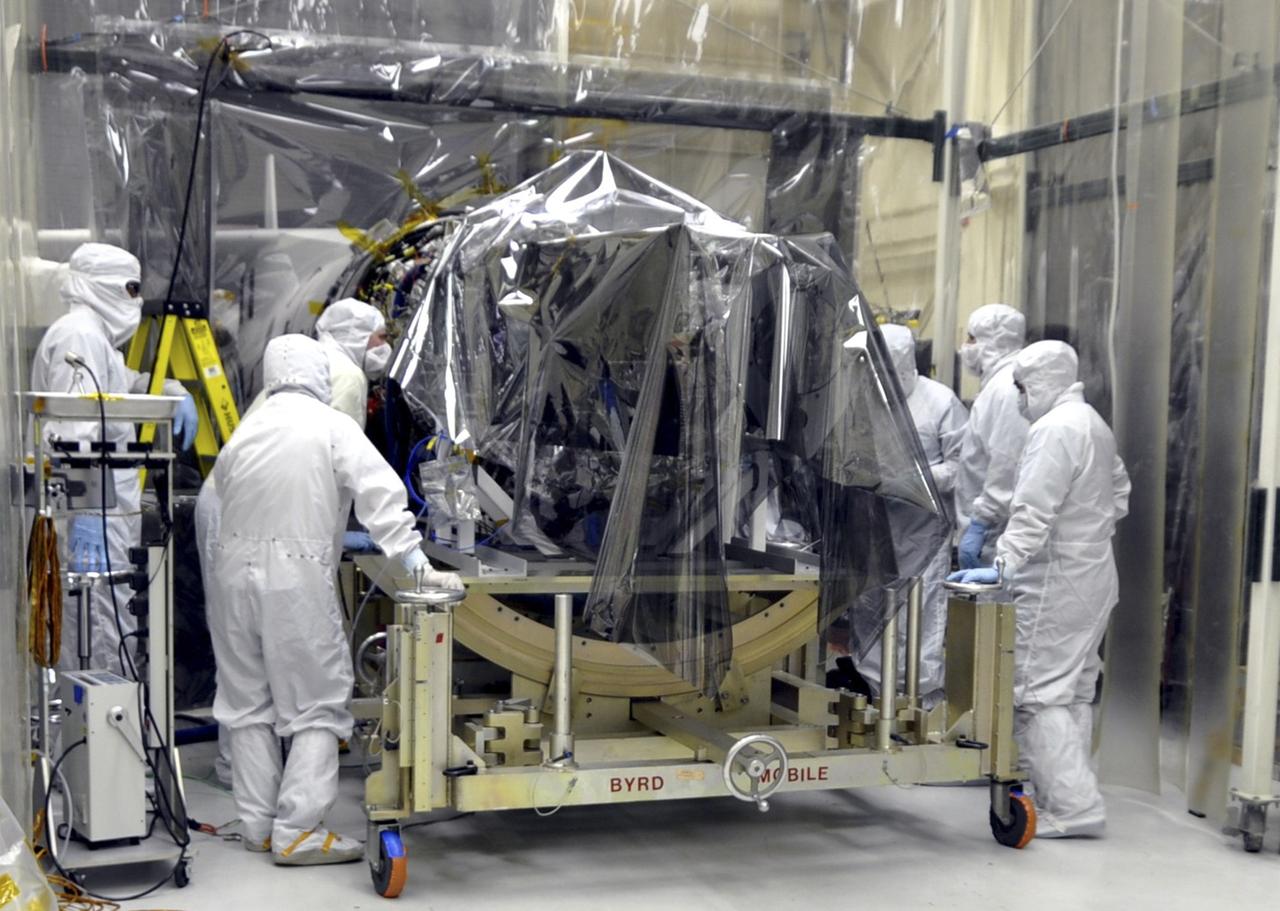
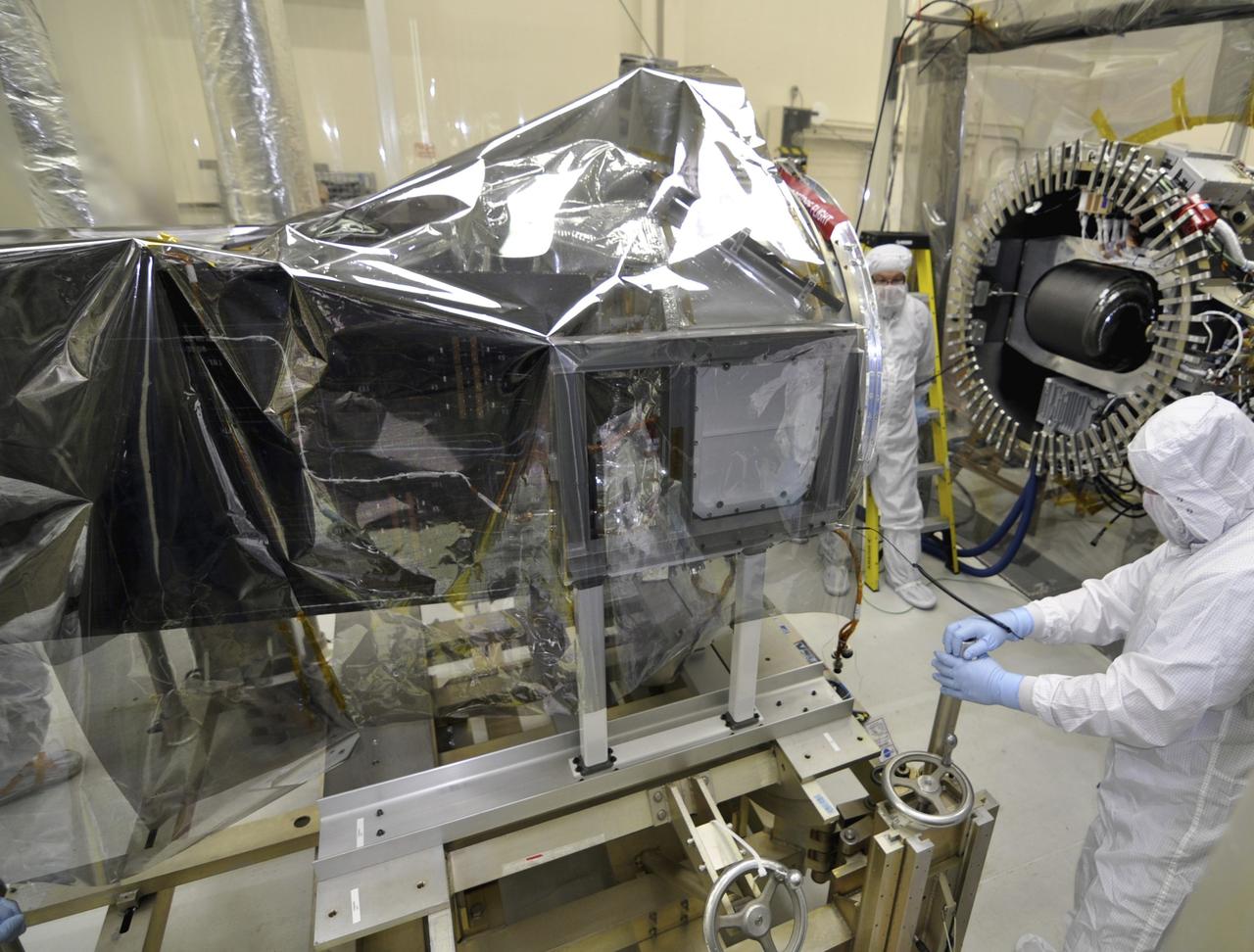
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
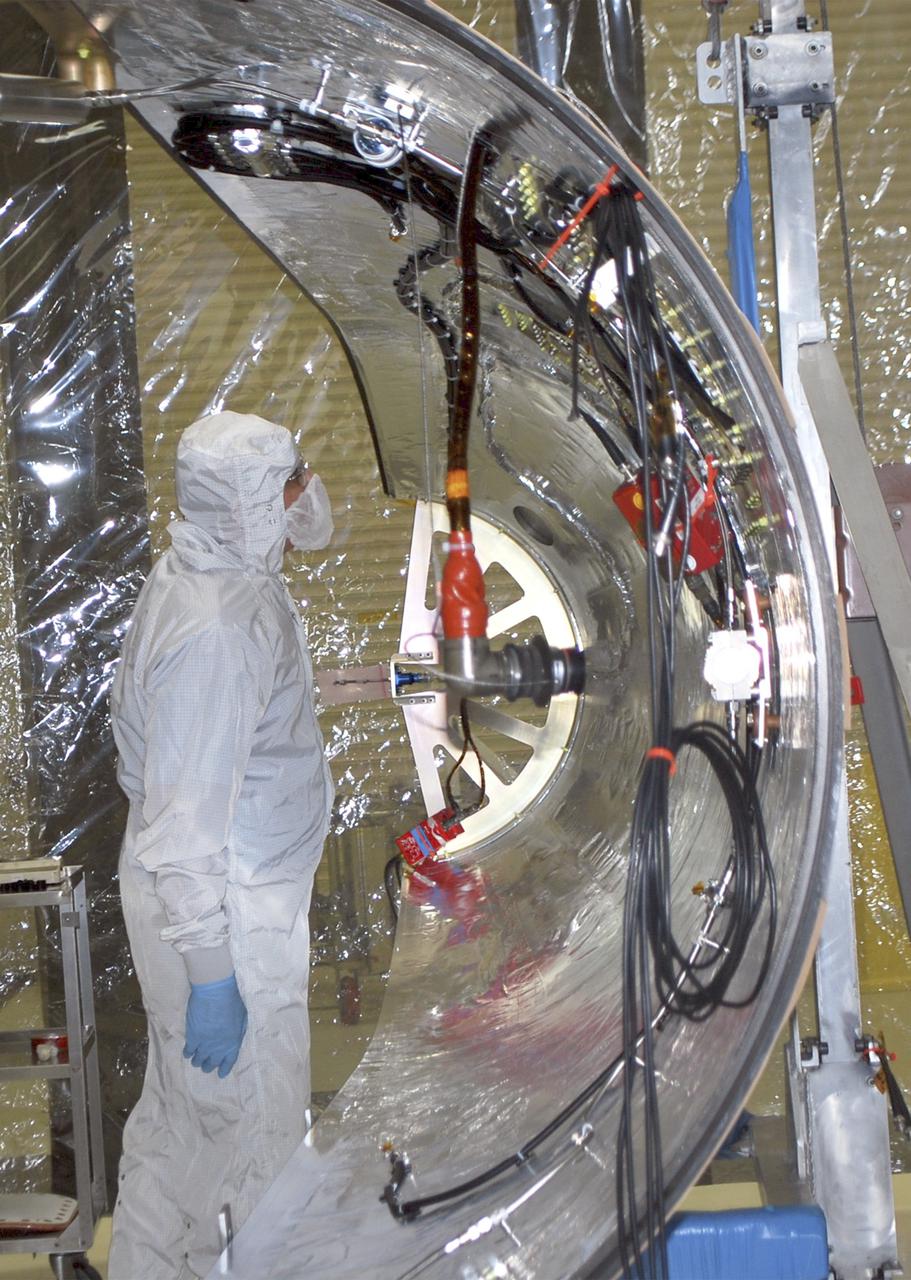

VANDENBERG AFB – An engineer examines the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
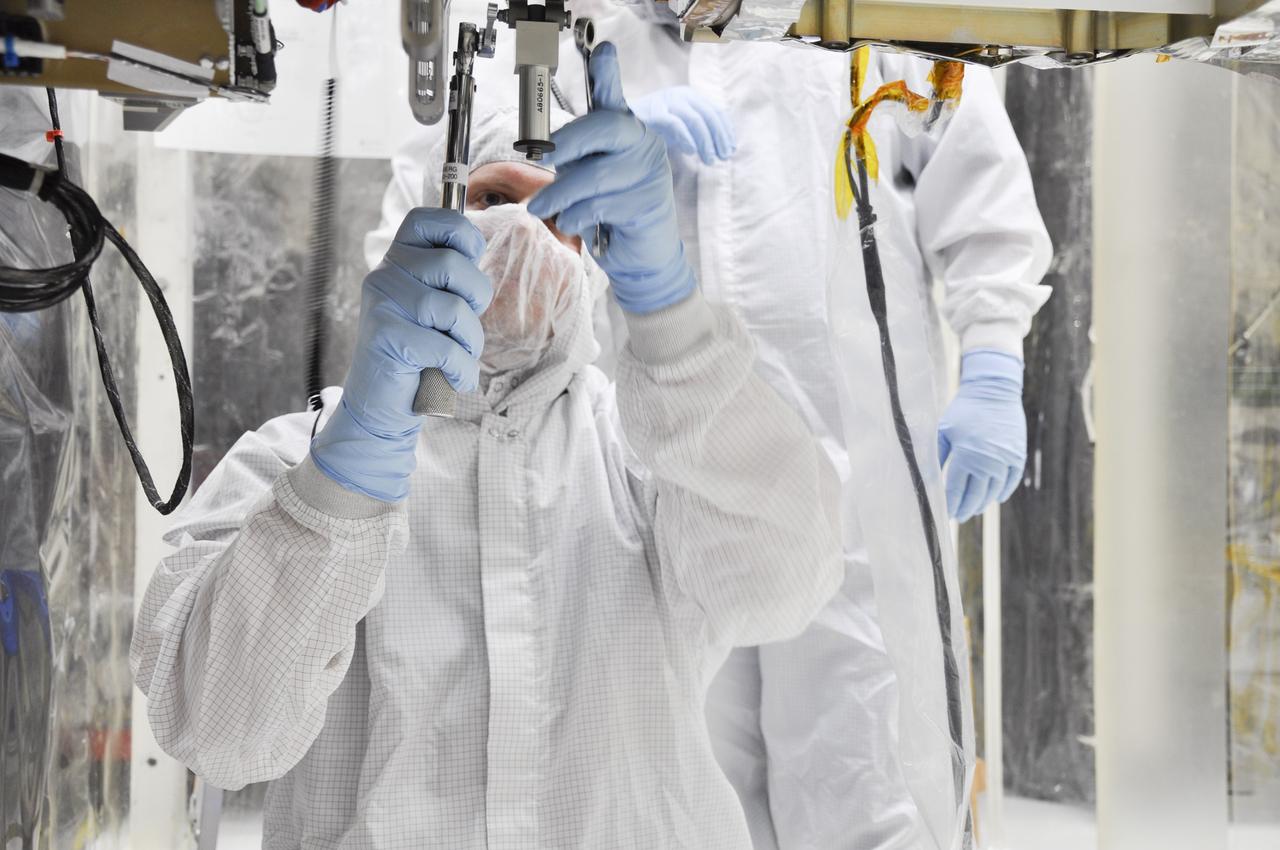

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers install a radial retraction system on NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
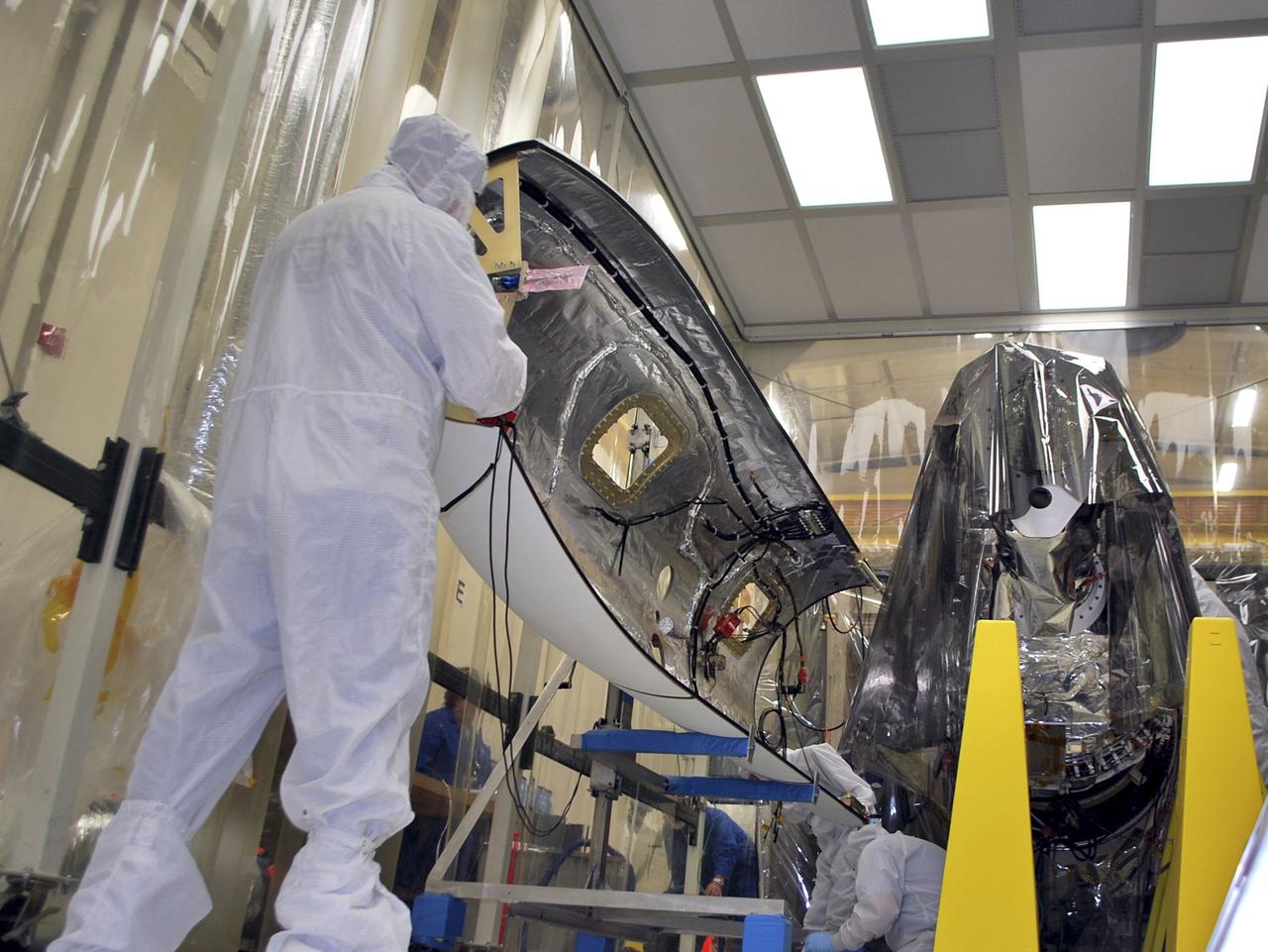

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
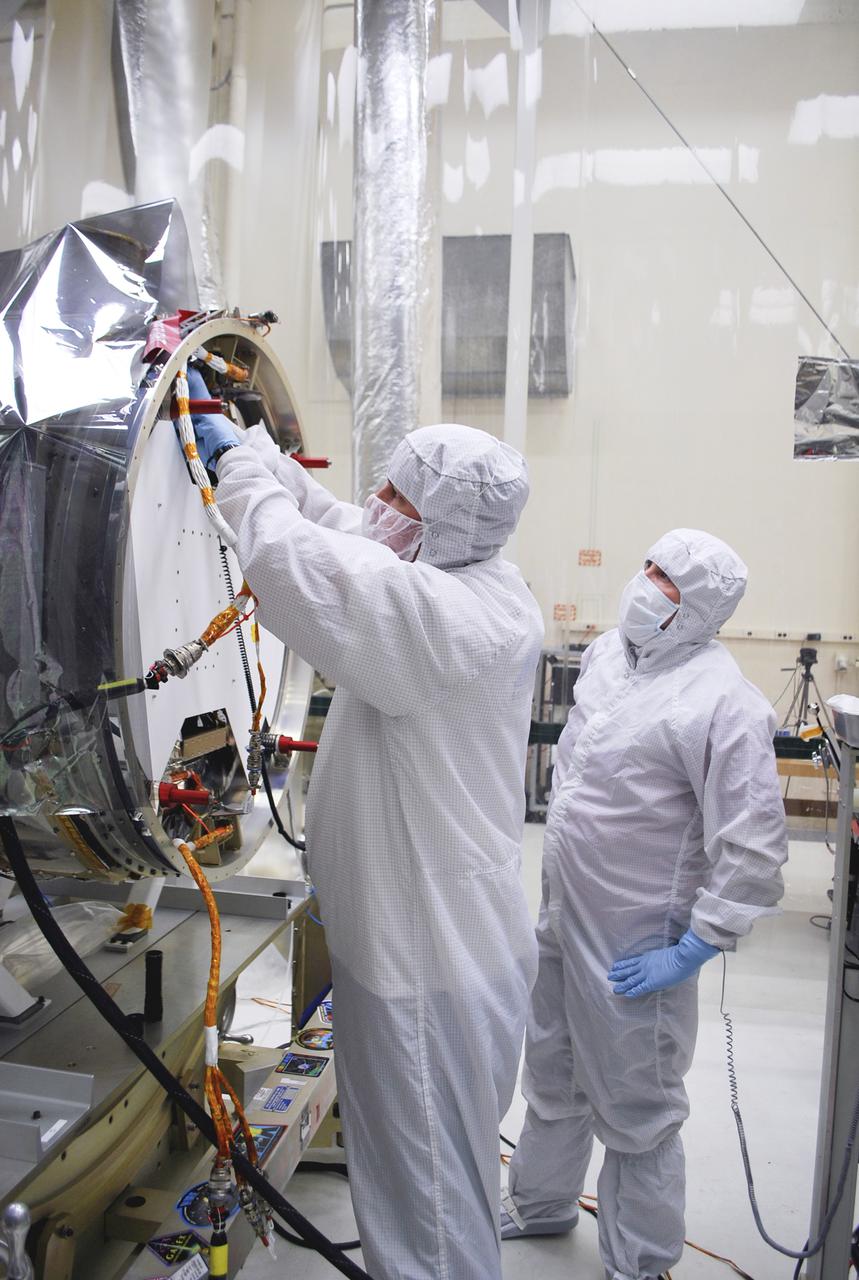

VANDENBERG, AFB - Engineers and members of the IRIS-Pegasus launch team re-verify the spacecraft ahead of the next flight simulation for the mission. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg where NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
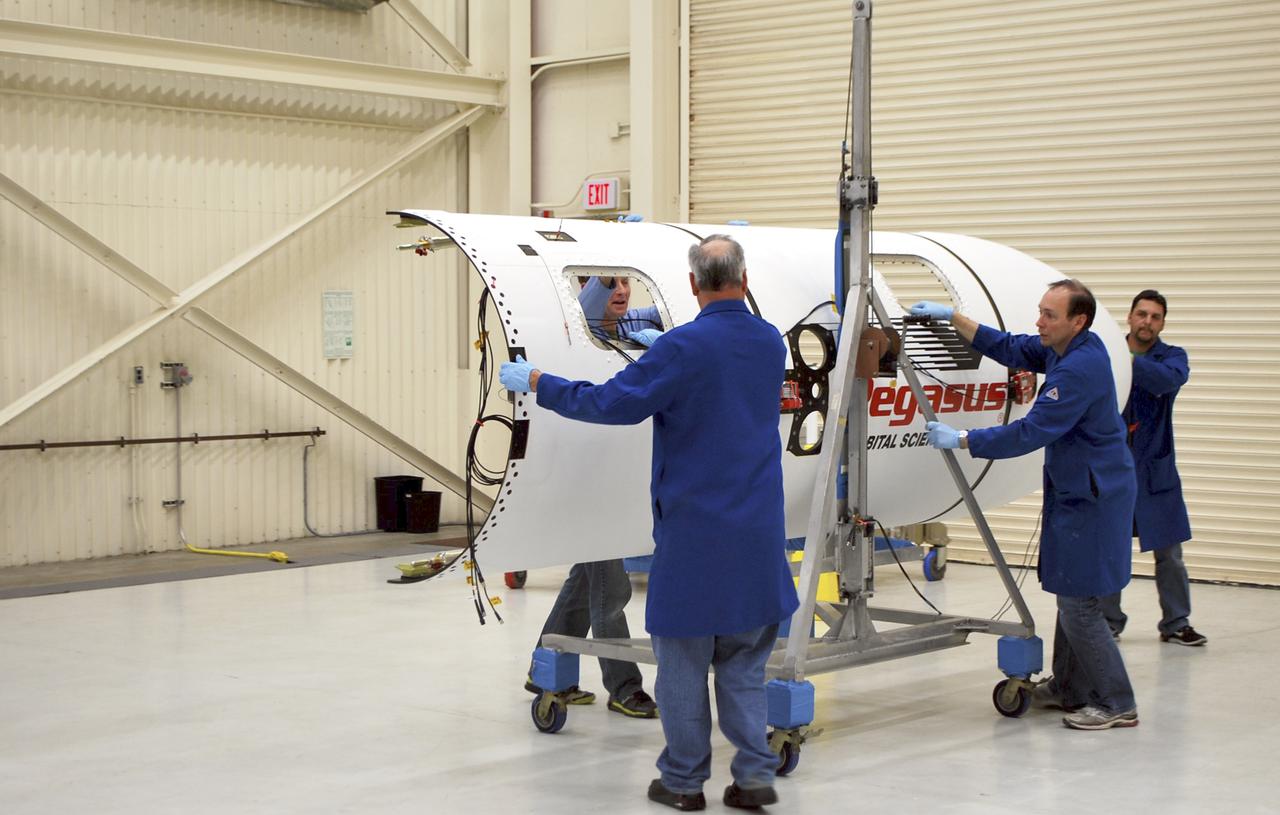

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG, AFB - Engineers and members of the IRIS-Pegasus launch team re-verify the spacecraft ahead of the next flight simulation for the mission. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg where NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
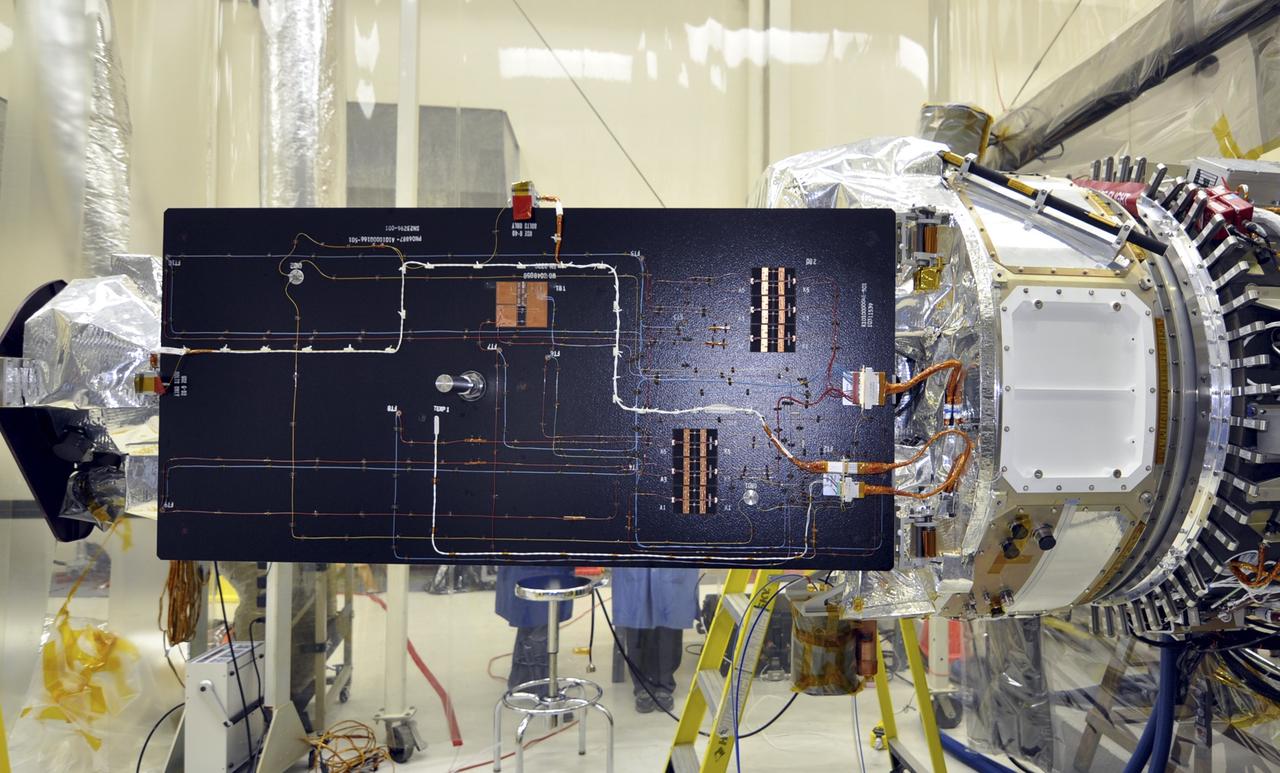
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers install a radial retraction system on NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

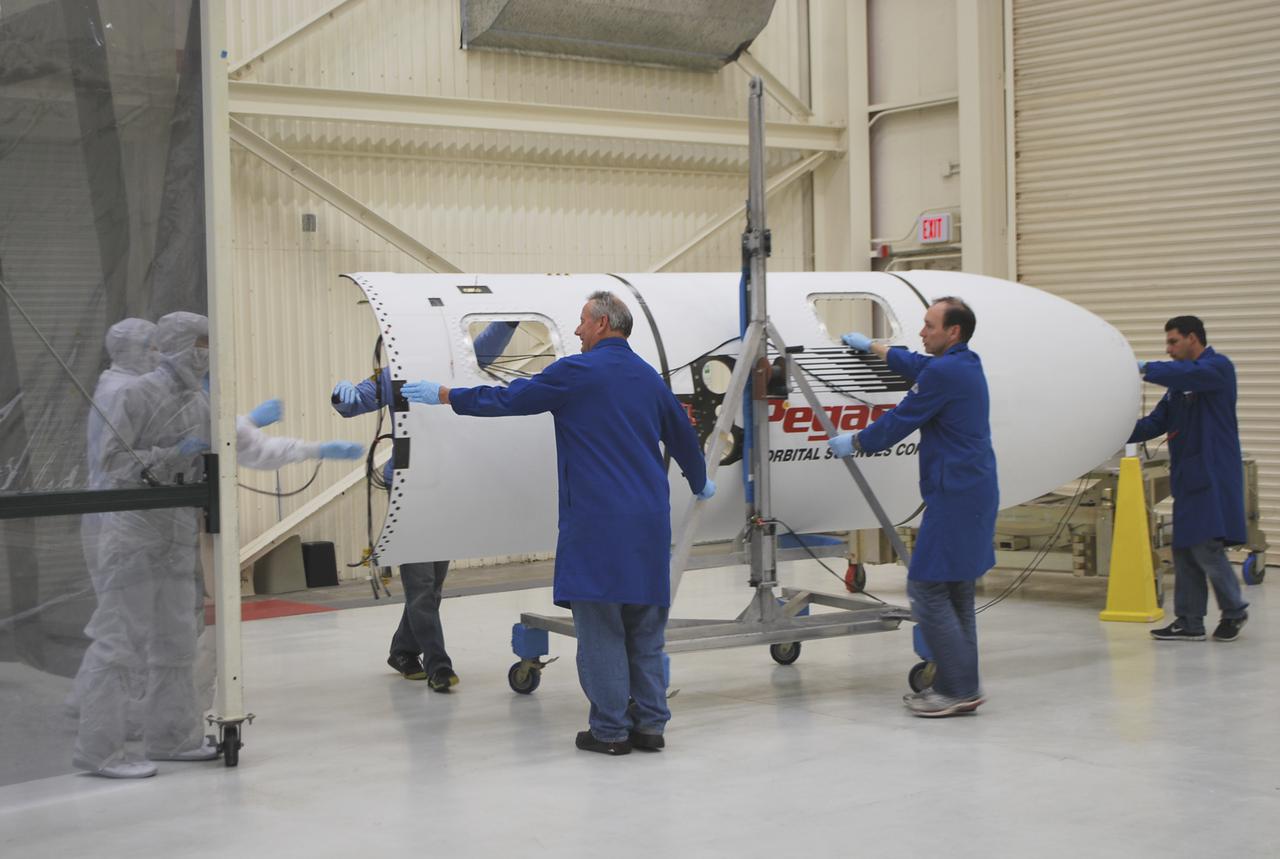
VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
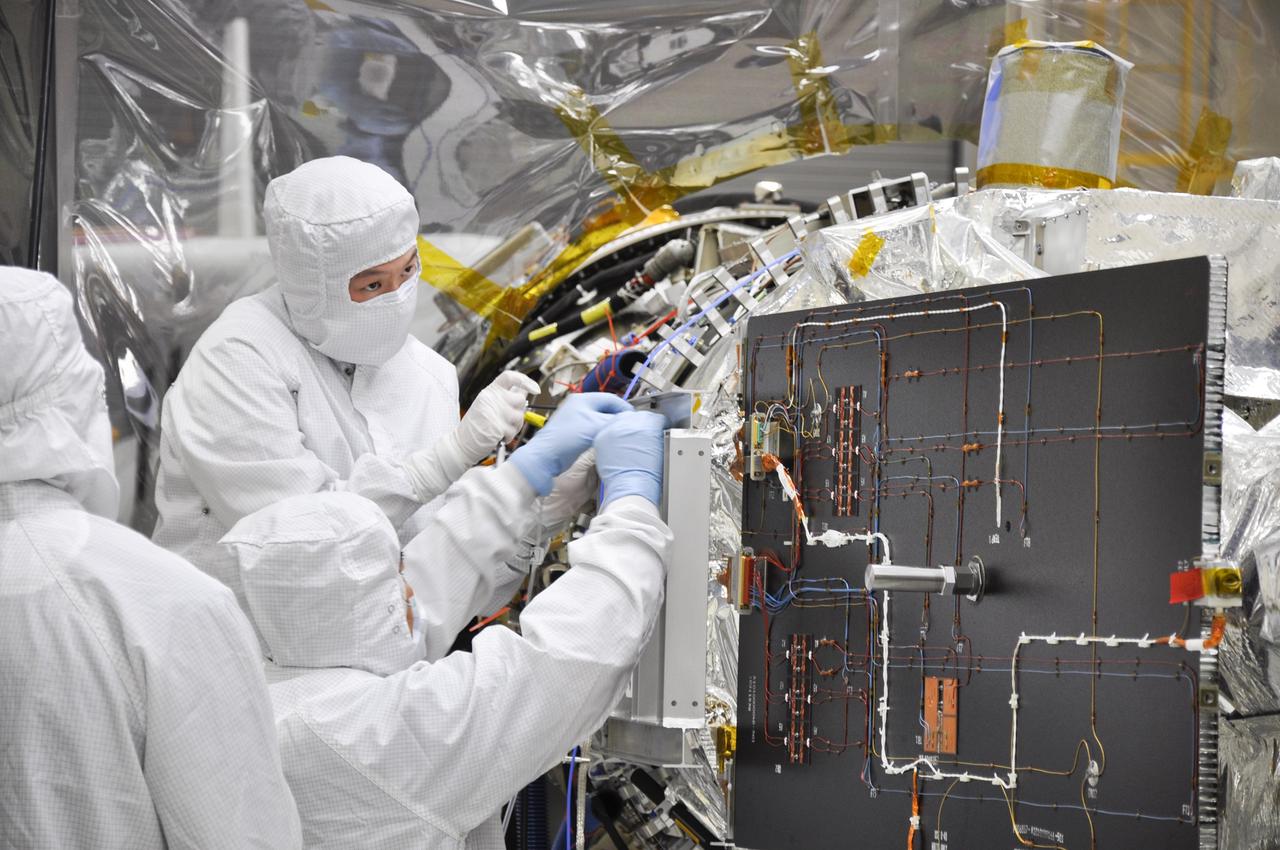

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. - A mission logo decal for the launch of NASA's IRIS solar observatory aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. The decal is on the side of the Pegasus. Engineers are working inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
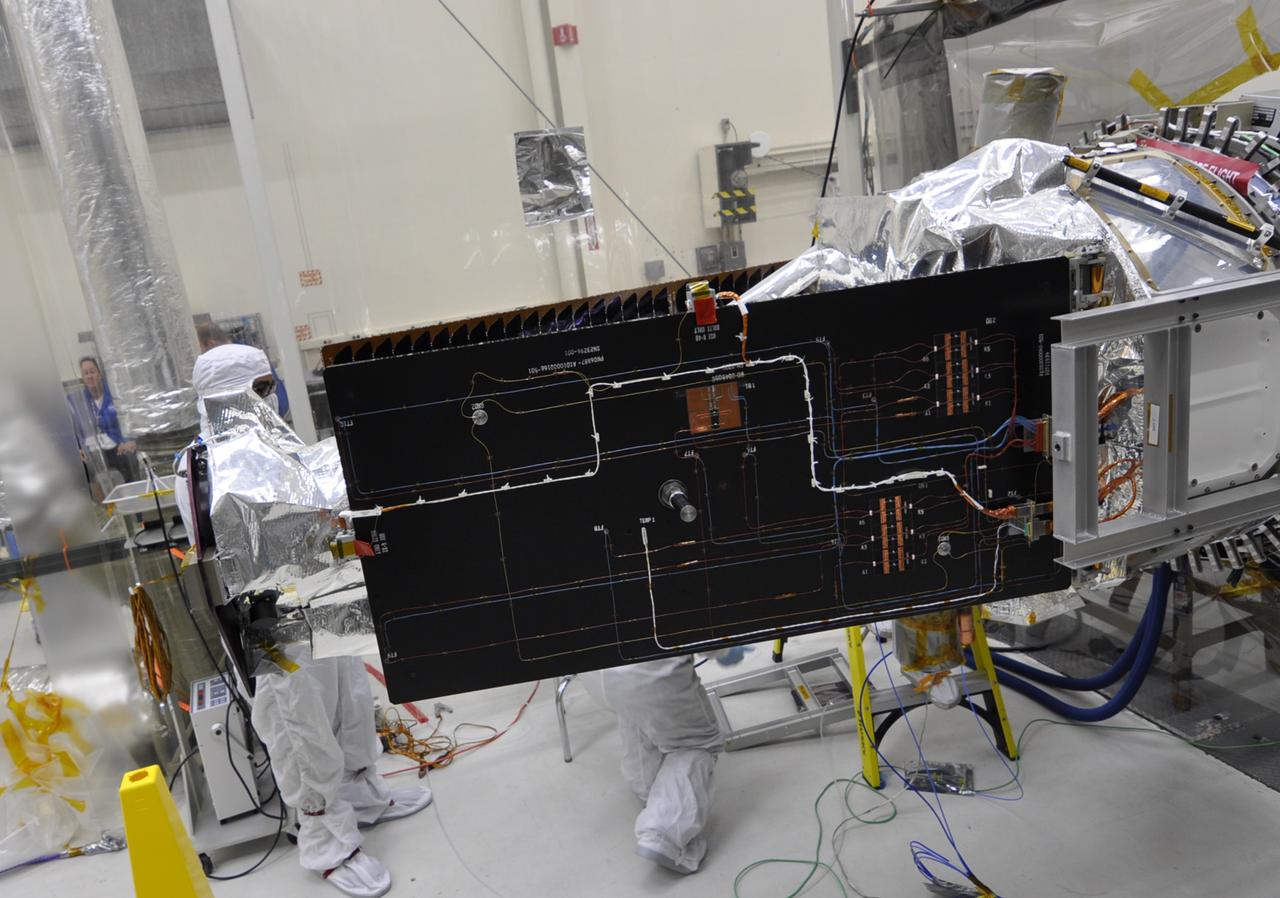

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
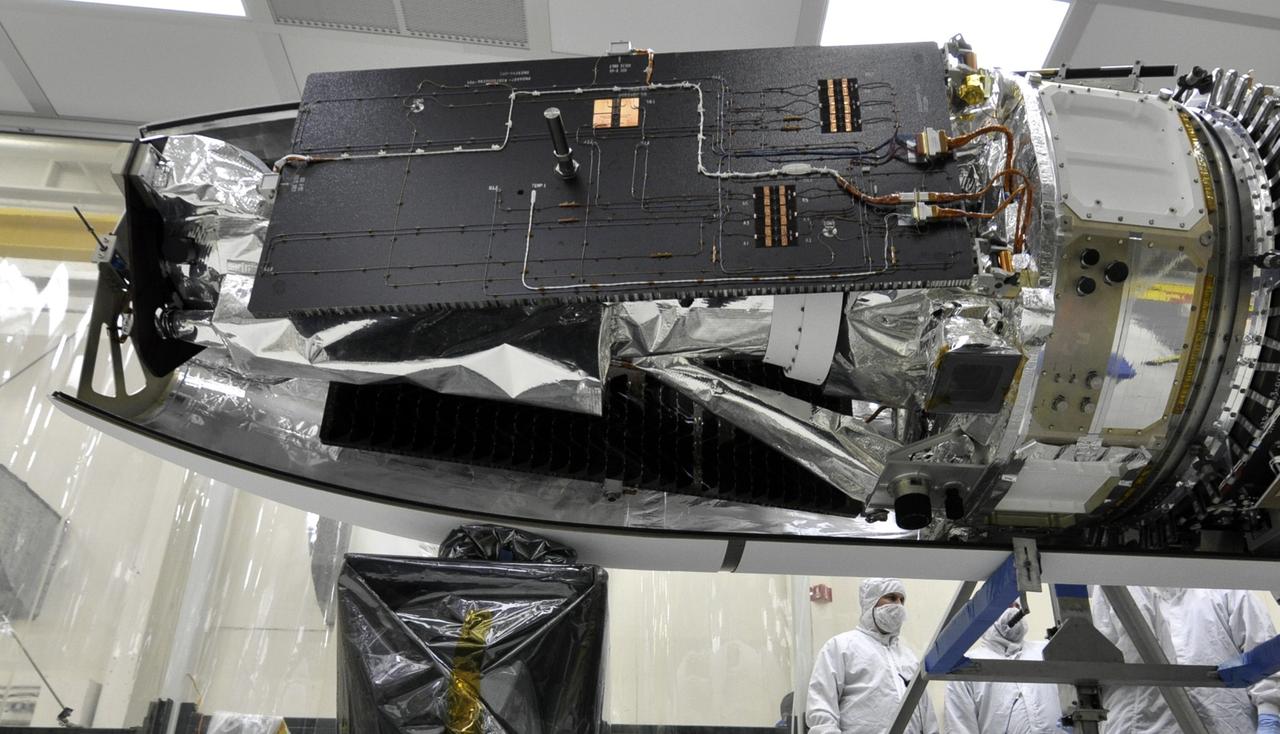

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers attach the starboard side of the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
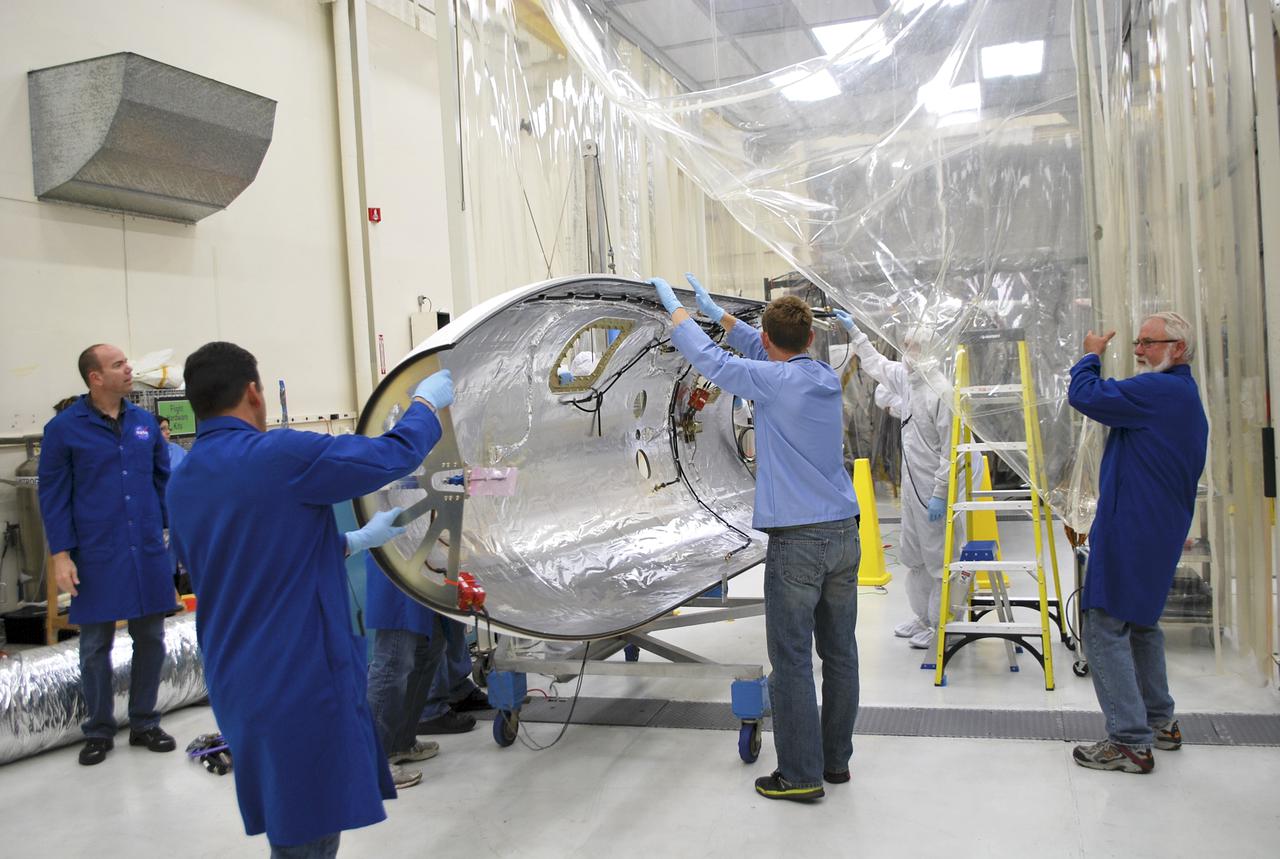

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
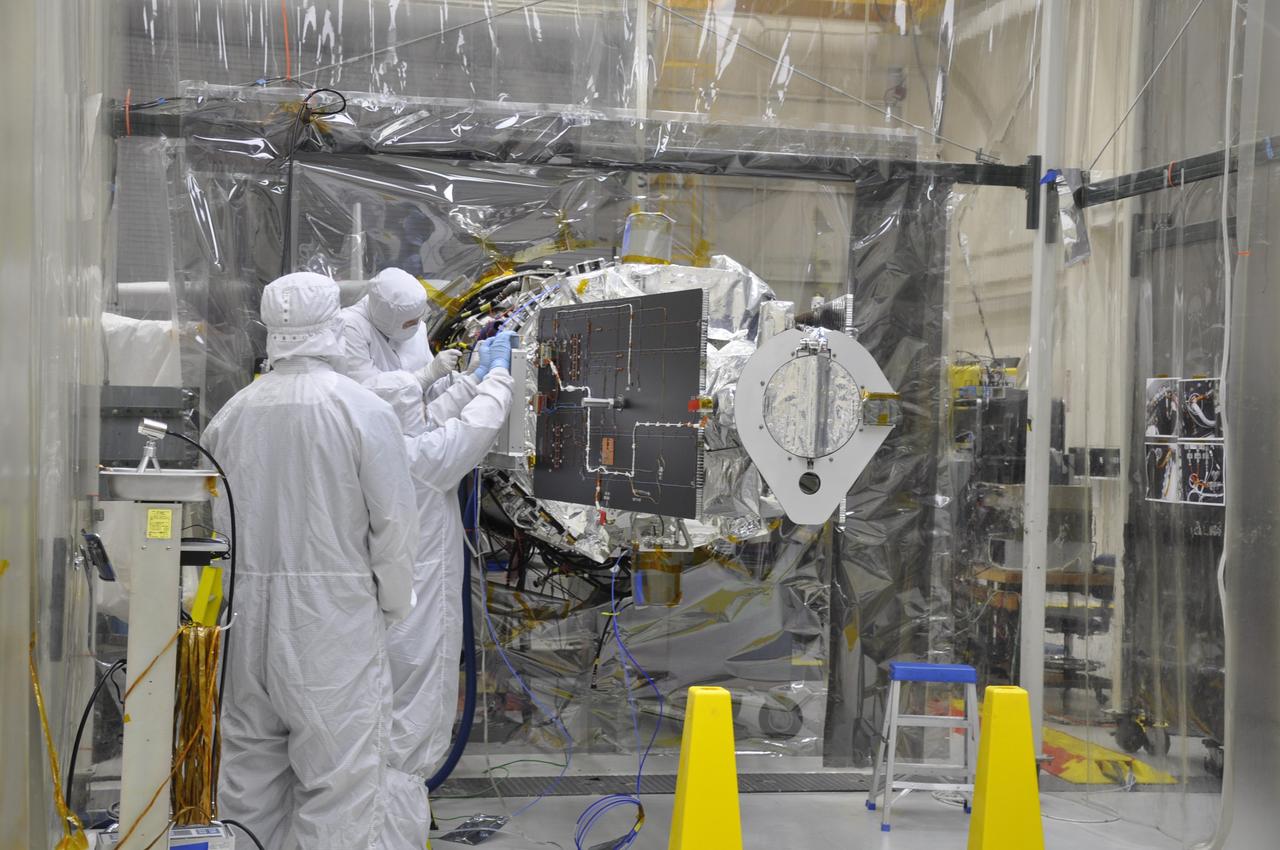

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. - A mission logo decal for the launch of NASA's IRIS solar observatory aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. The decal is on the side of the Pegasus. Engineers are working inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
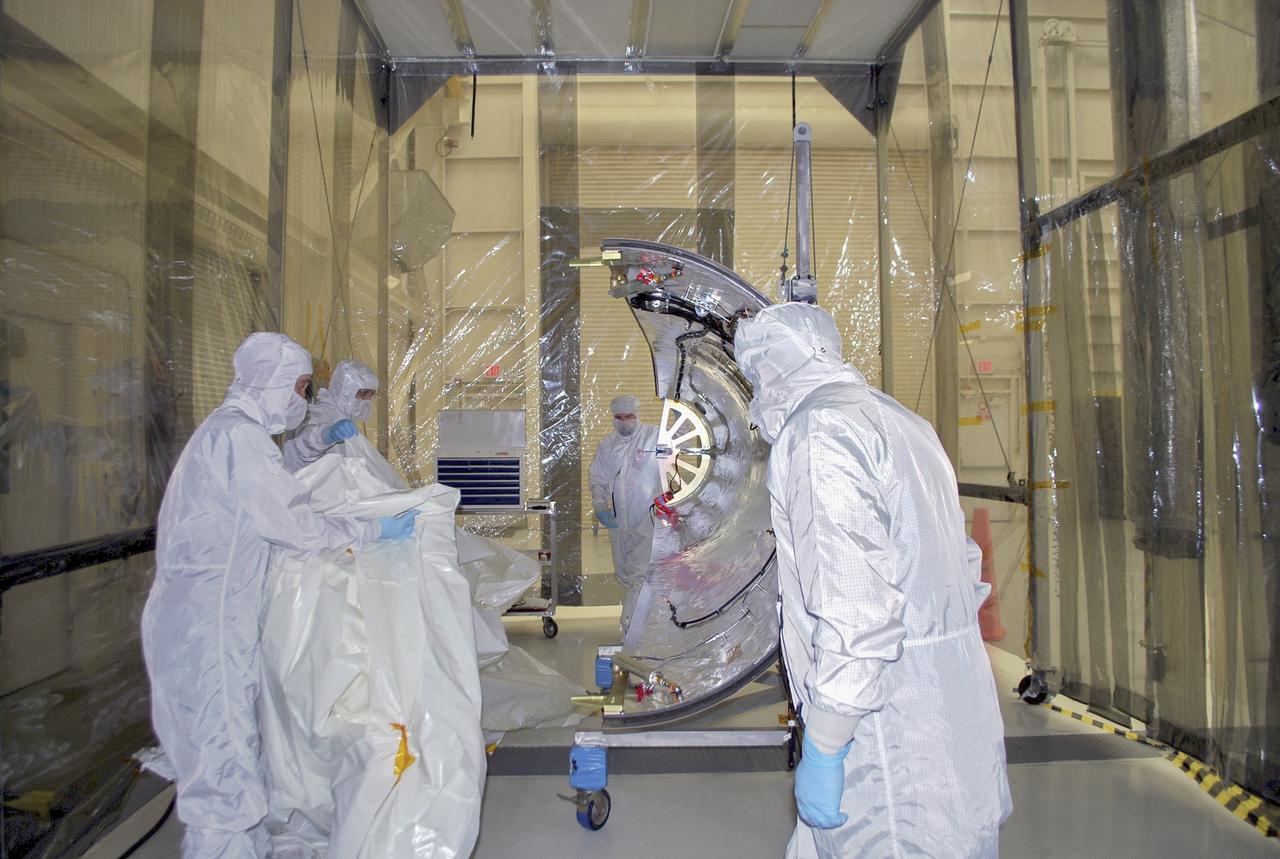

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
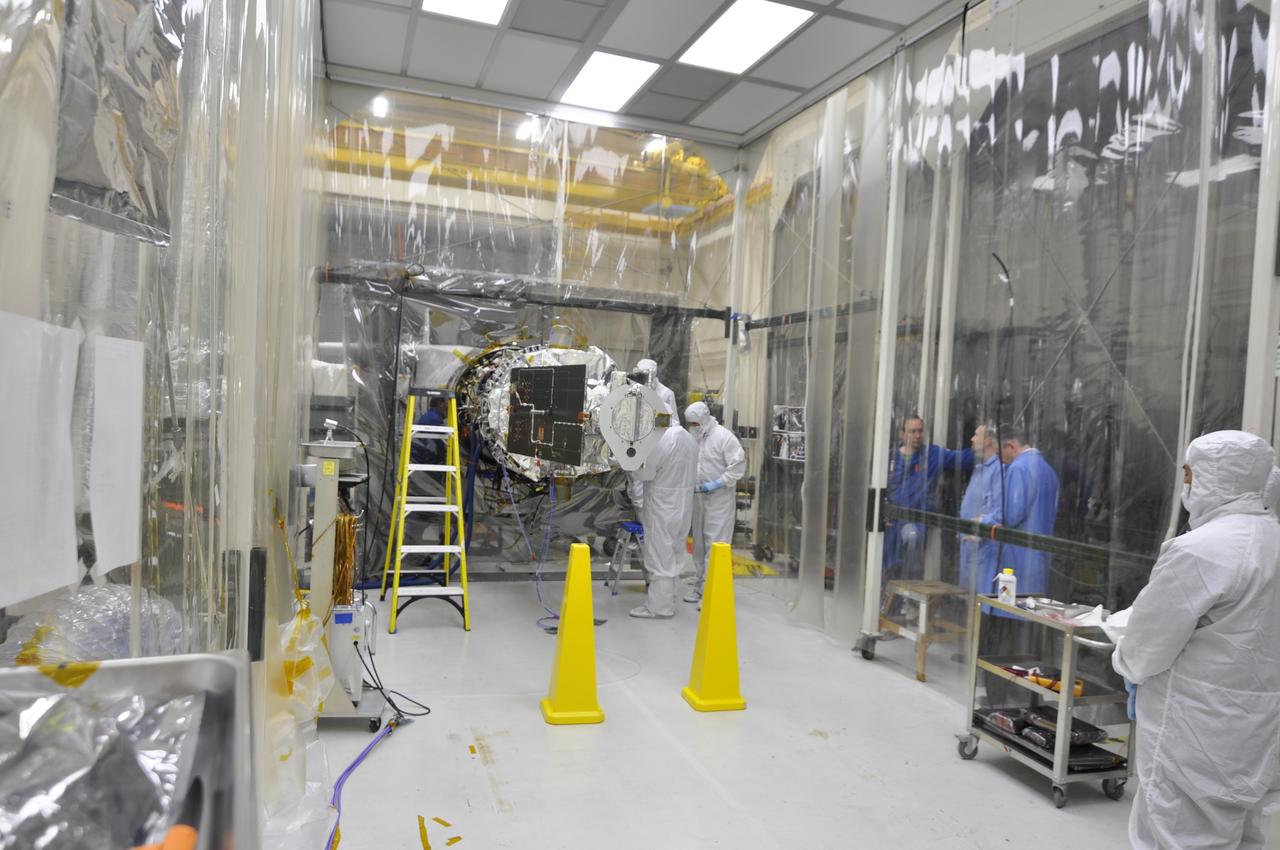

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
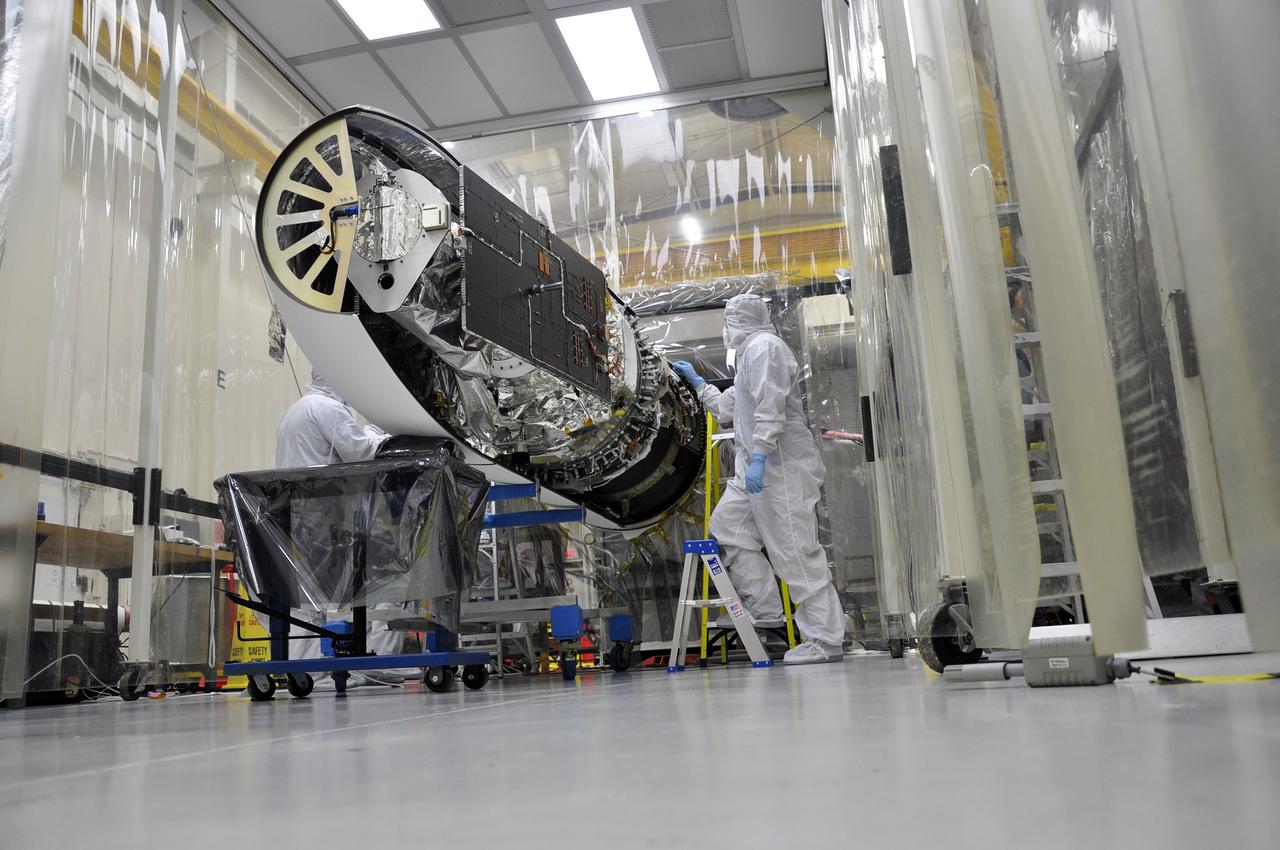

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers attach the starboard side of the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers unwrap NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers install a radial retraction system on NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
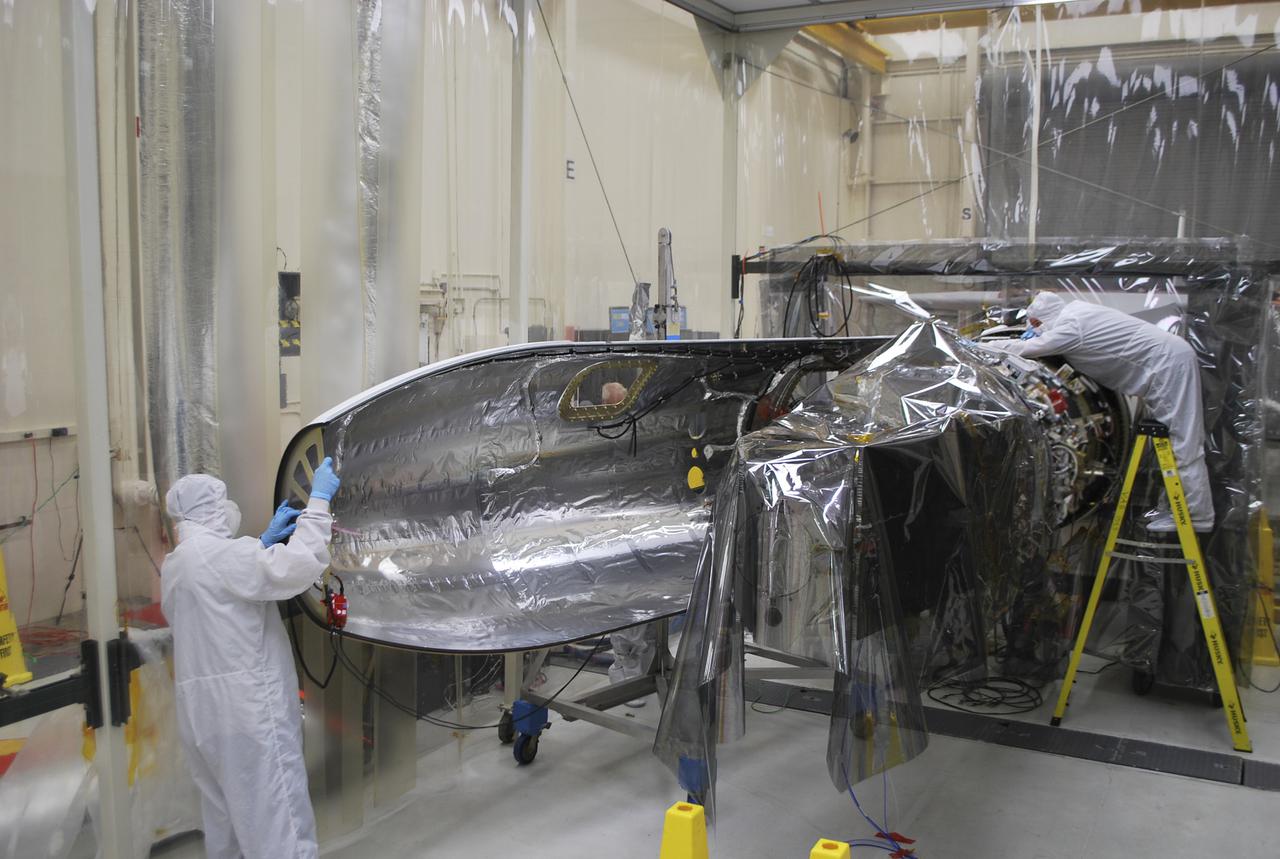

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the payload fairing into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
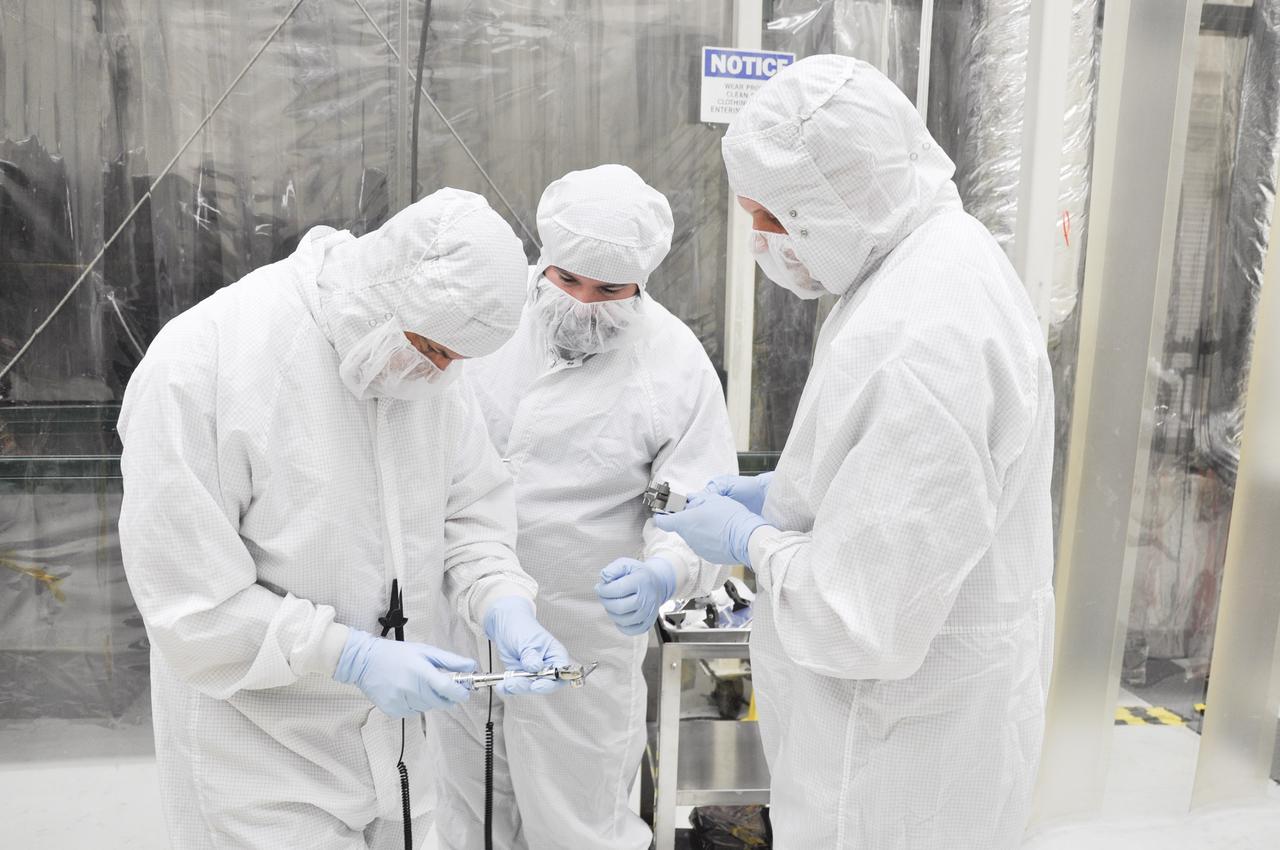

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to install a radial retraction system on NASA's IRIS spacecraft after its connection to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
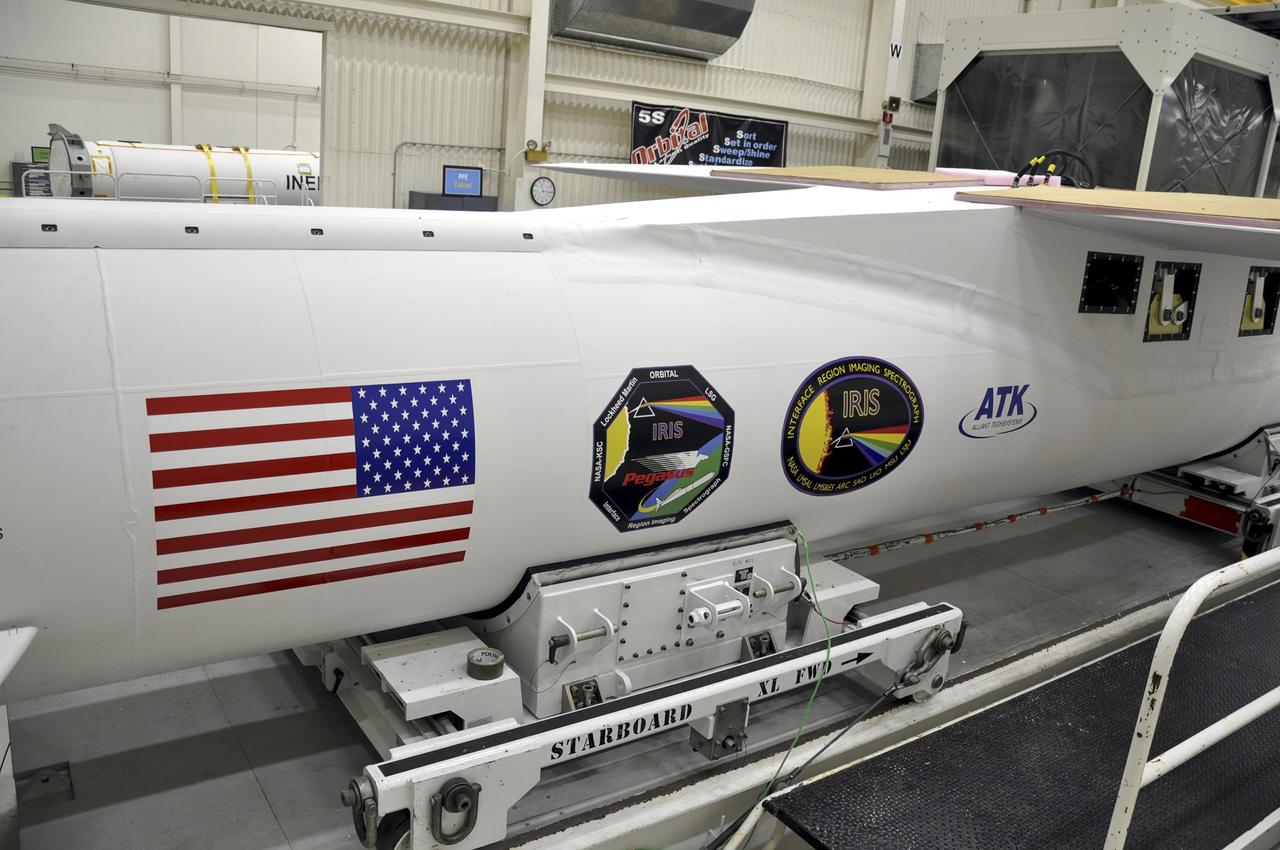

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. - An Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket undergoes launch preparations inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base for NASA's IRIS mission, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
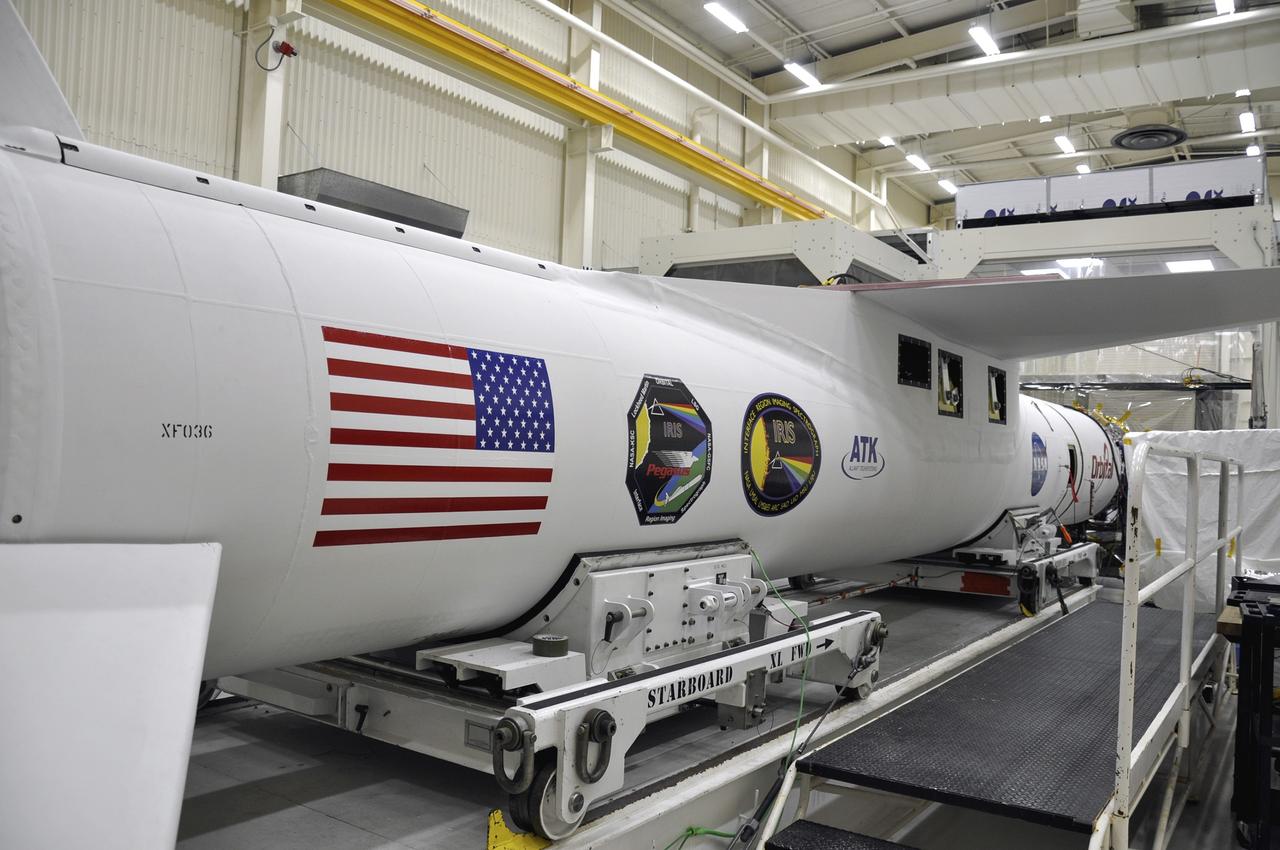

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. - An Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket undergoes launch preparations inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base for NASA's IRIS mission, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
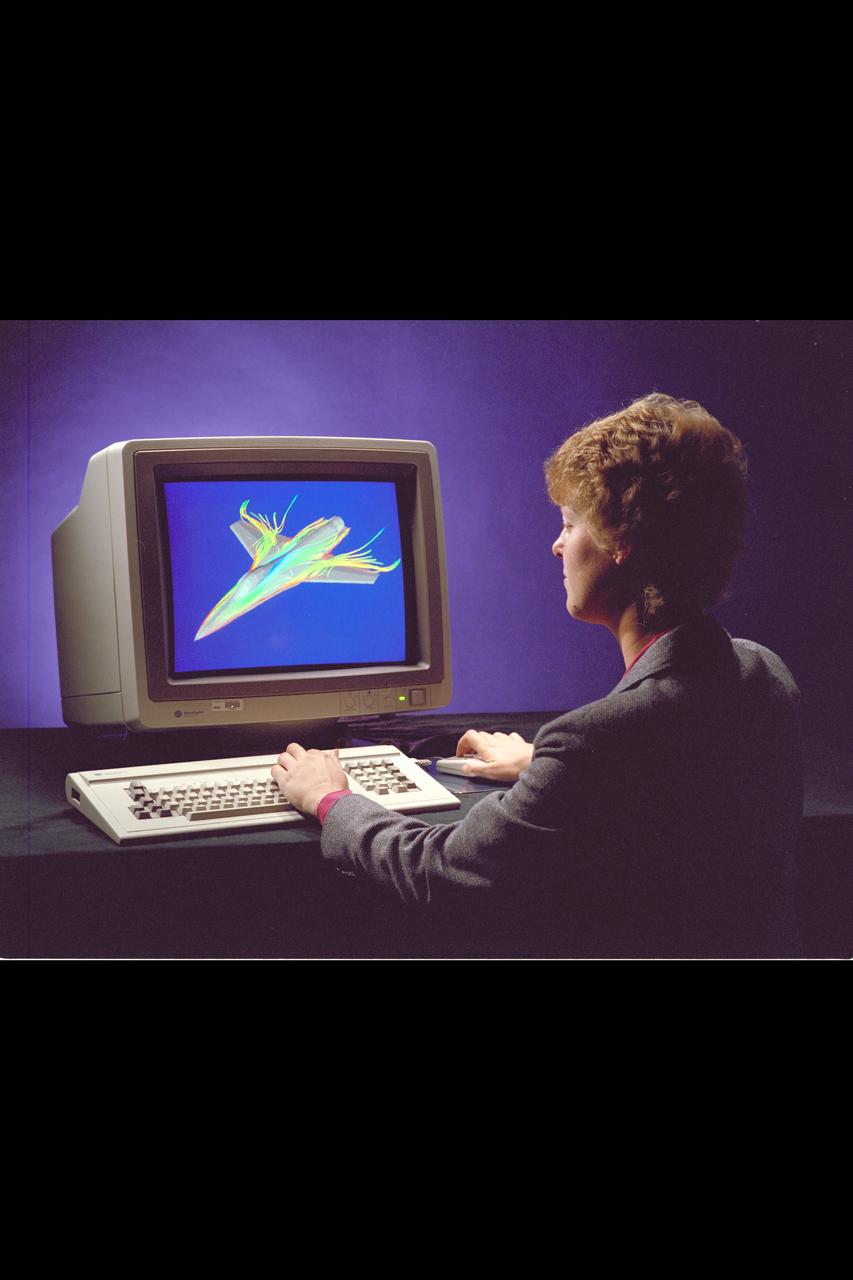

Iris Workstation with CFD CGI airfoil
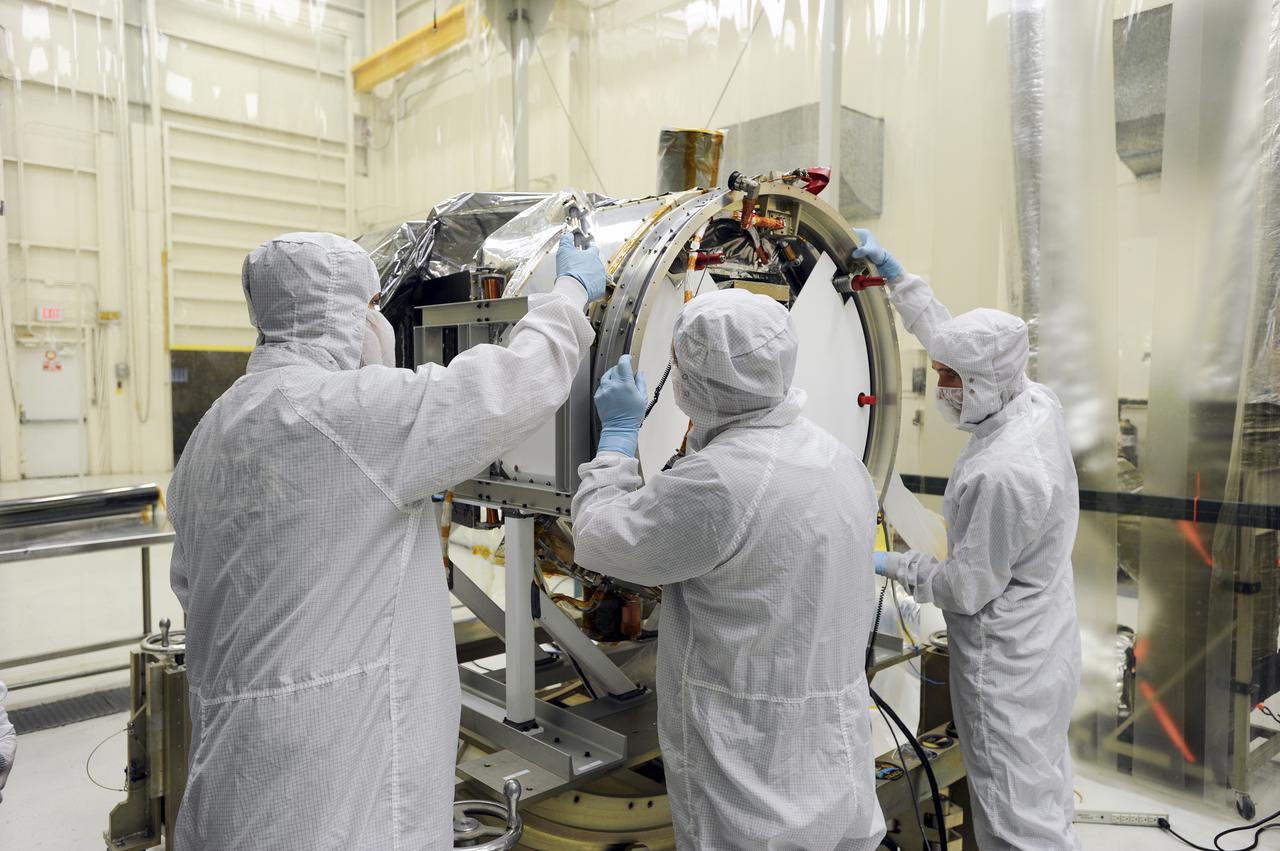

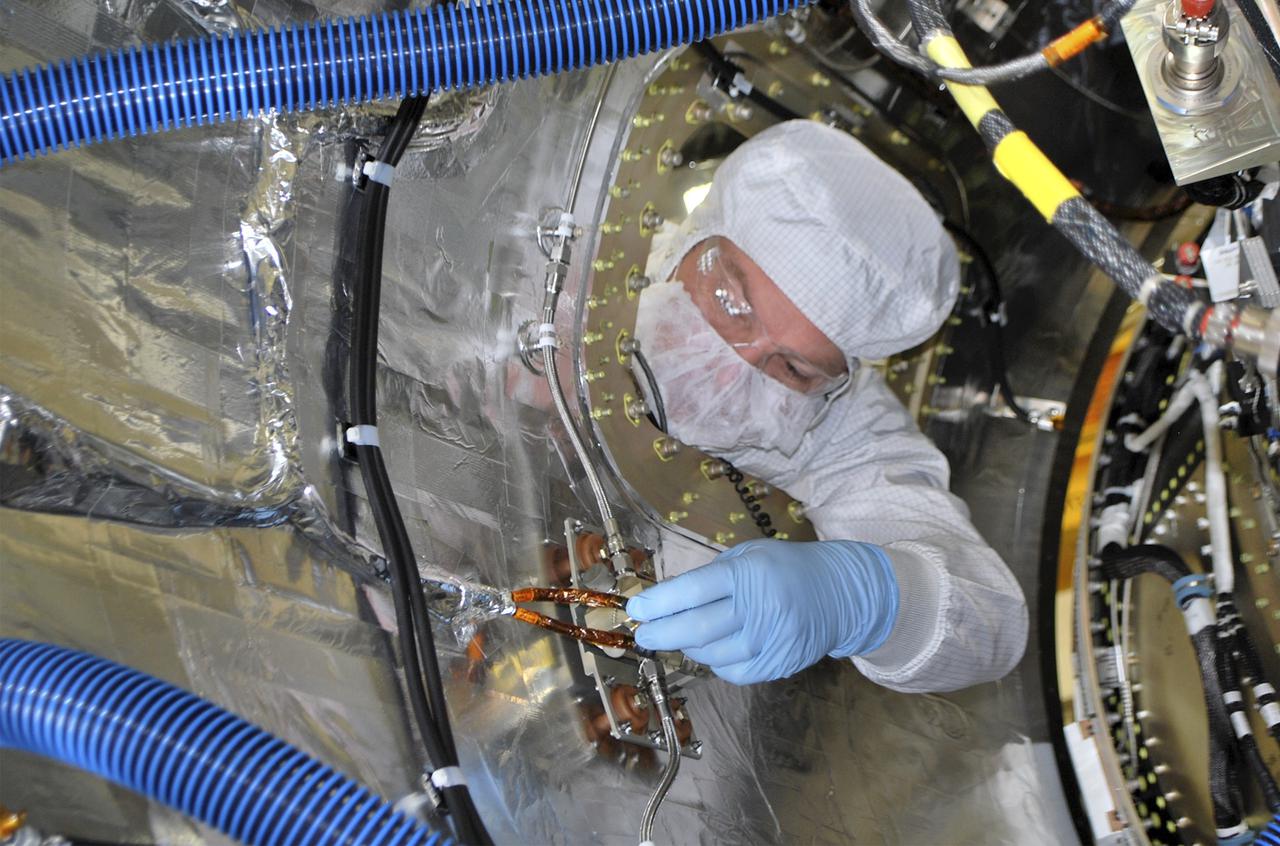
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Members of the IRIS and Pegasus launch teams working in a hangar at Vandenberg connect the separation ring for NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Doug Gruben

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Members of the IRIS and Pegasus launch teams working in a hangar at Vandenberg work connect the separation ring for NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Doug Gruben

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Members of the IRIS and Pegasus launch teams working in a hangar at Vandenberg prepare the separation ring for connection to NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Doug Gruben
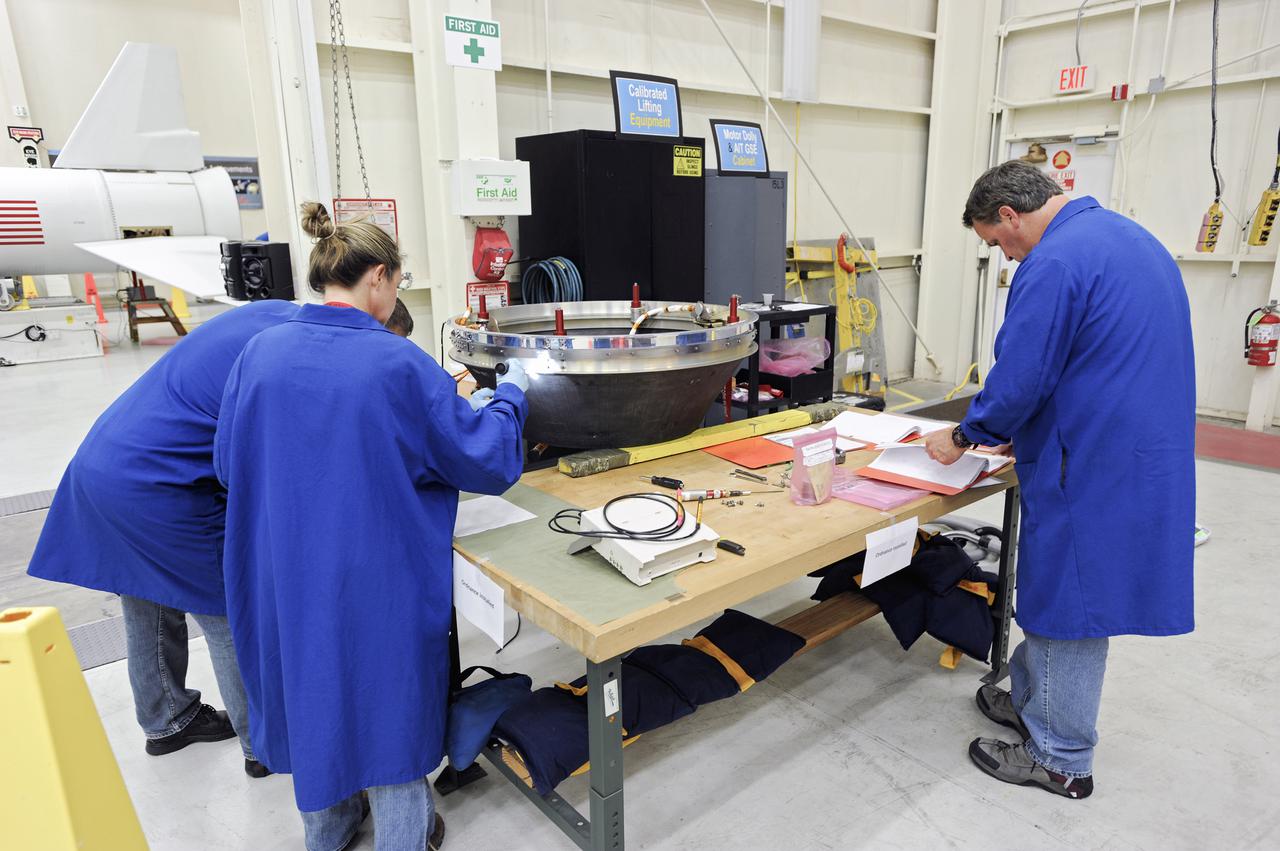

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Members of the IRIS and Pegasus launch teams working in a hangar at Vandenberg prepare the separation ring for connection to NASA's IRIS spacecraft, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Doug Gruben
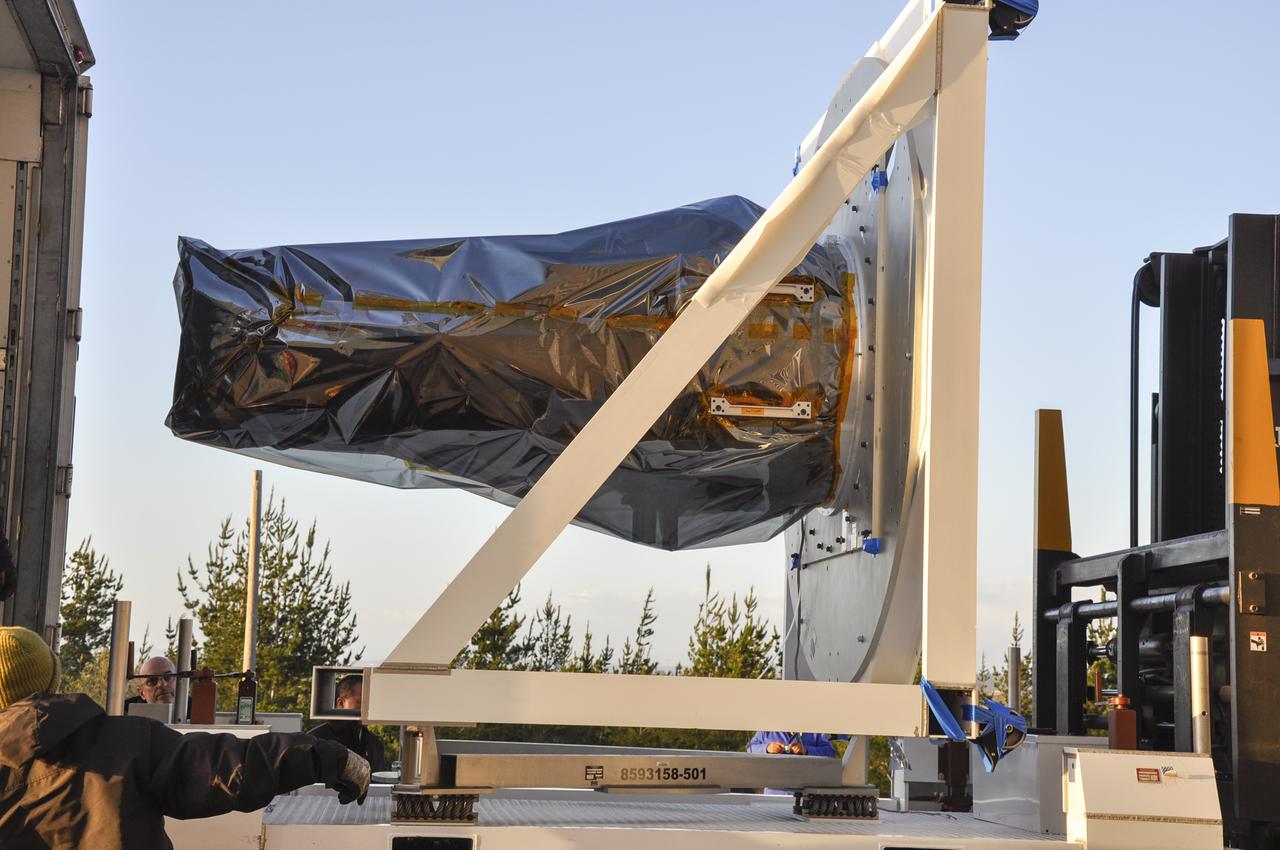

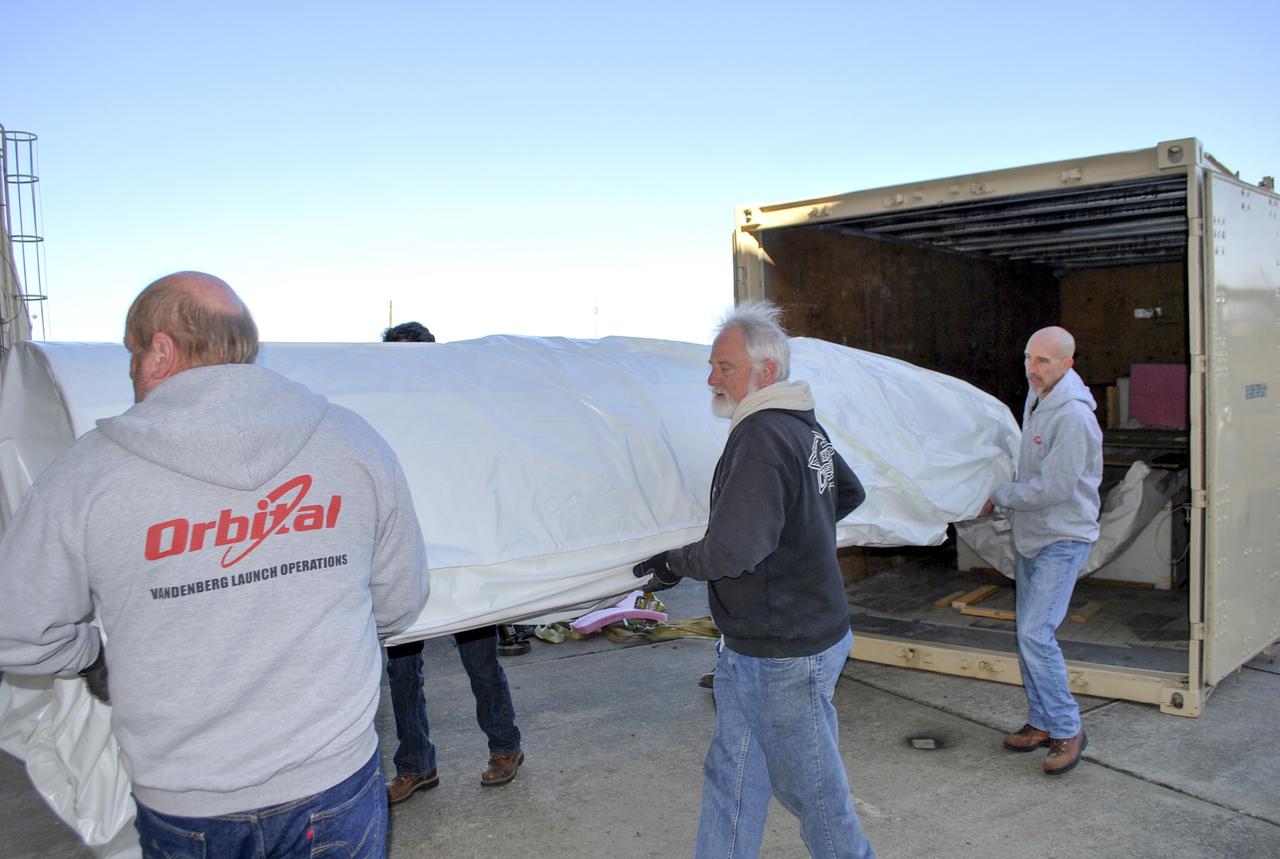
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers unload NASA's IRIS spacecraft from a truck at the processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
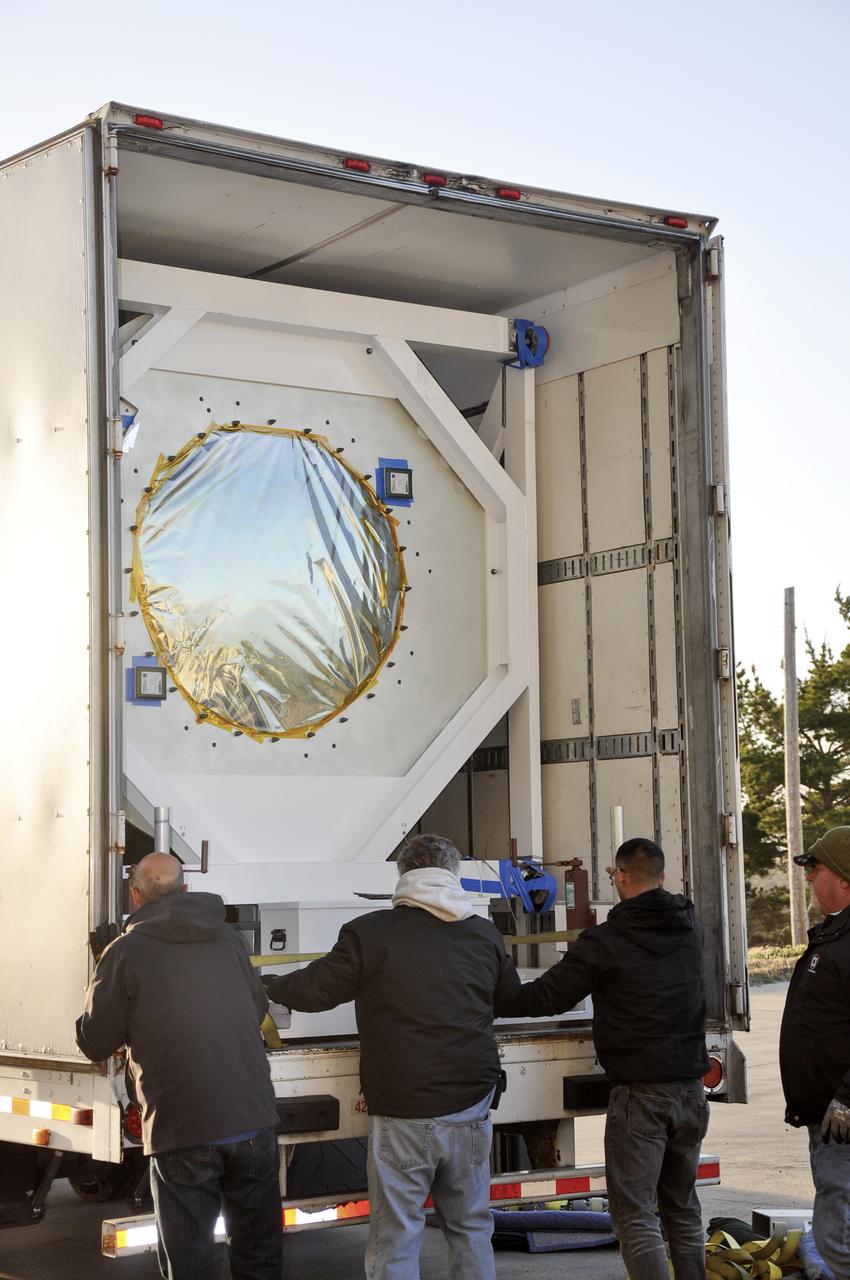

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers prepare to unload NASA's IRIS spacecraft from a truck at the processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
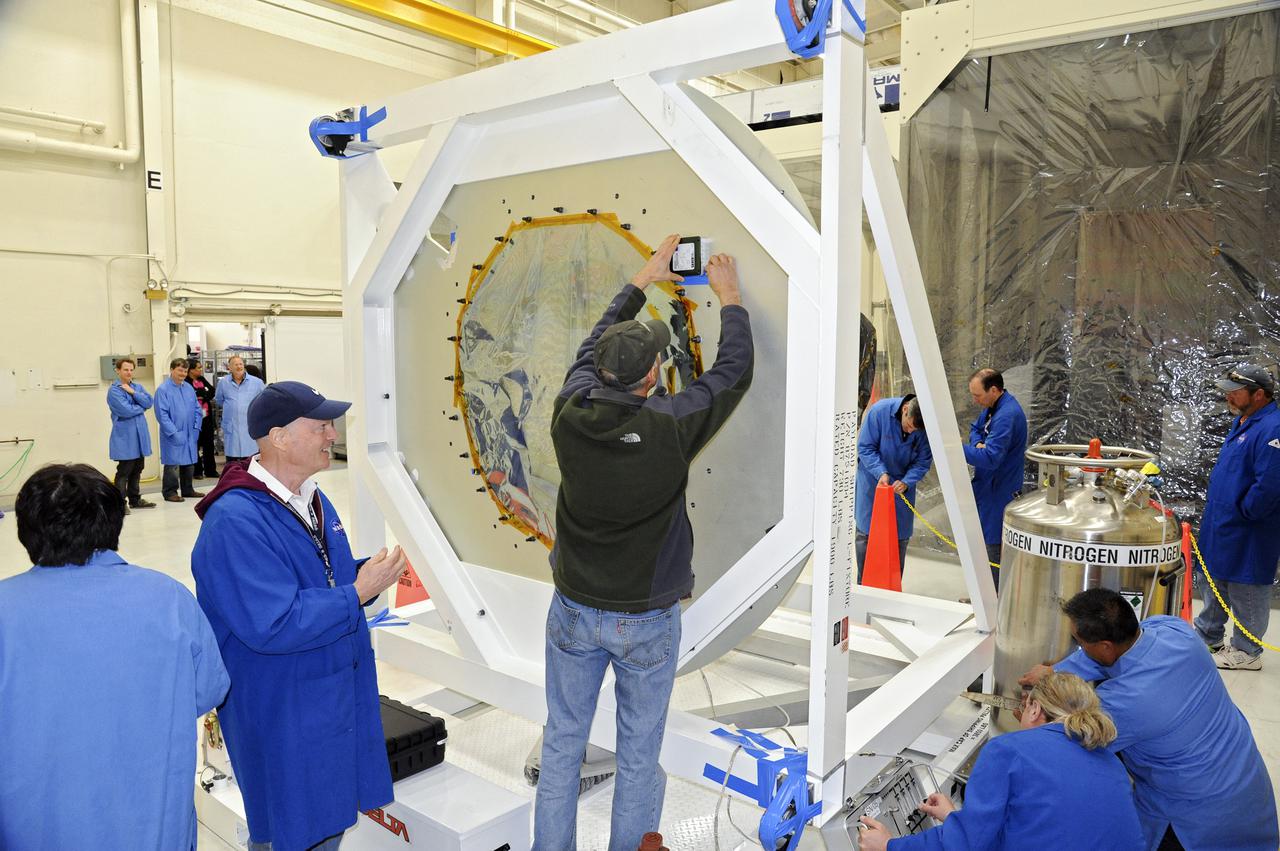

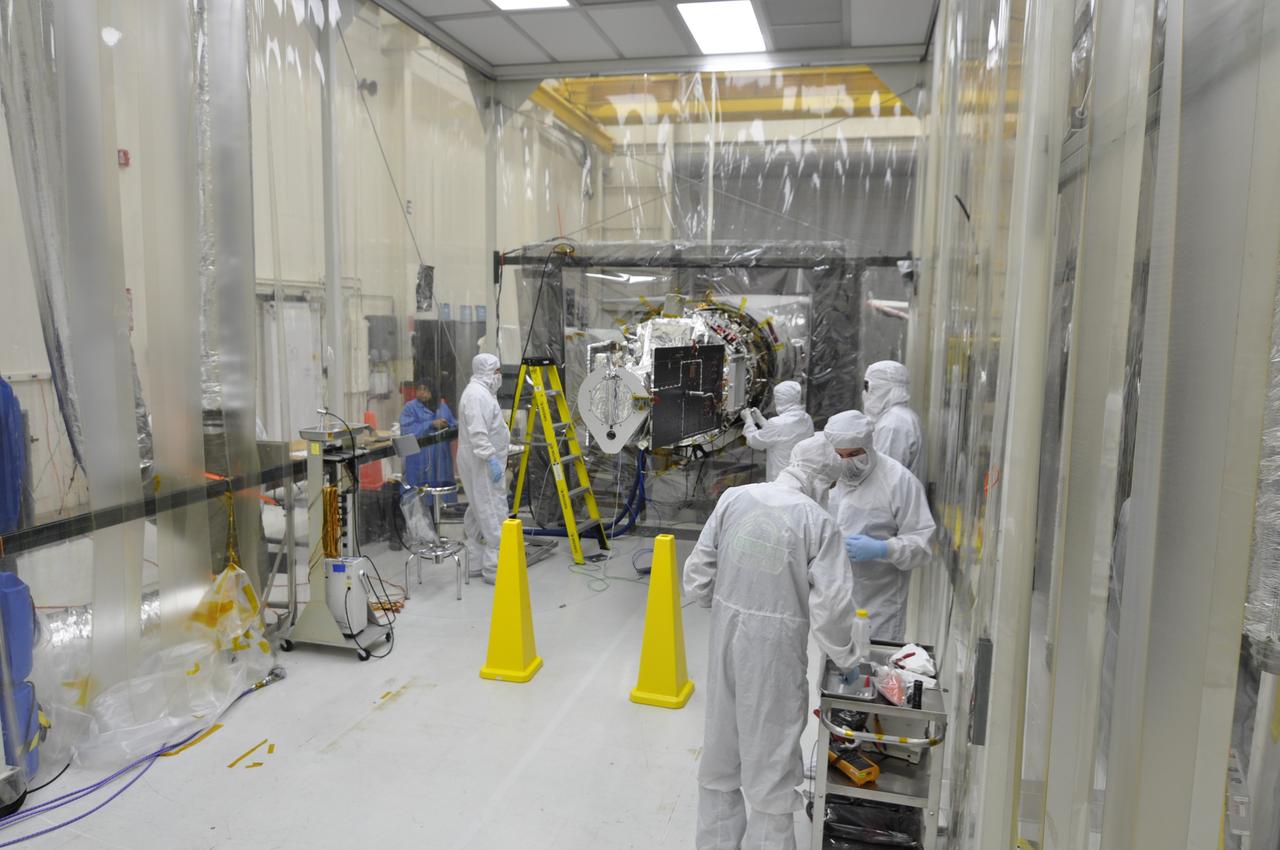
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians begin processing NASA's IRIS spacecraft at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Tony Vauelin
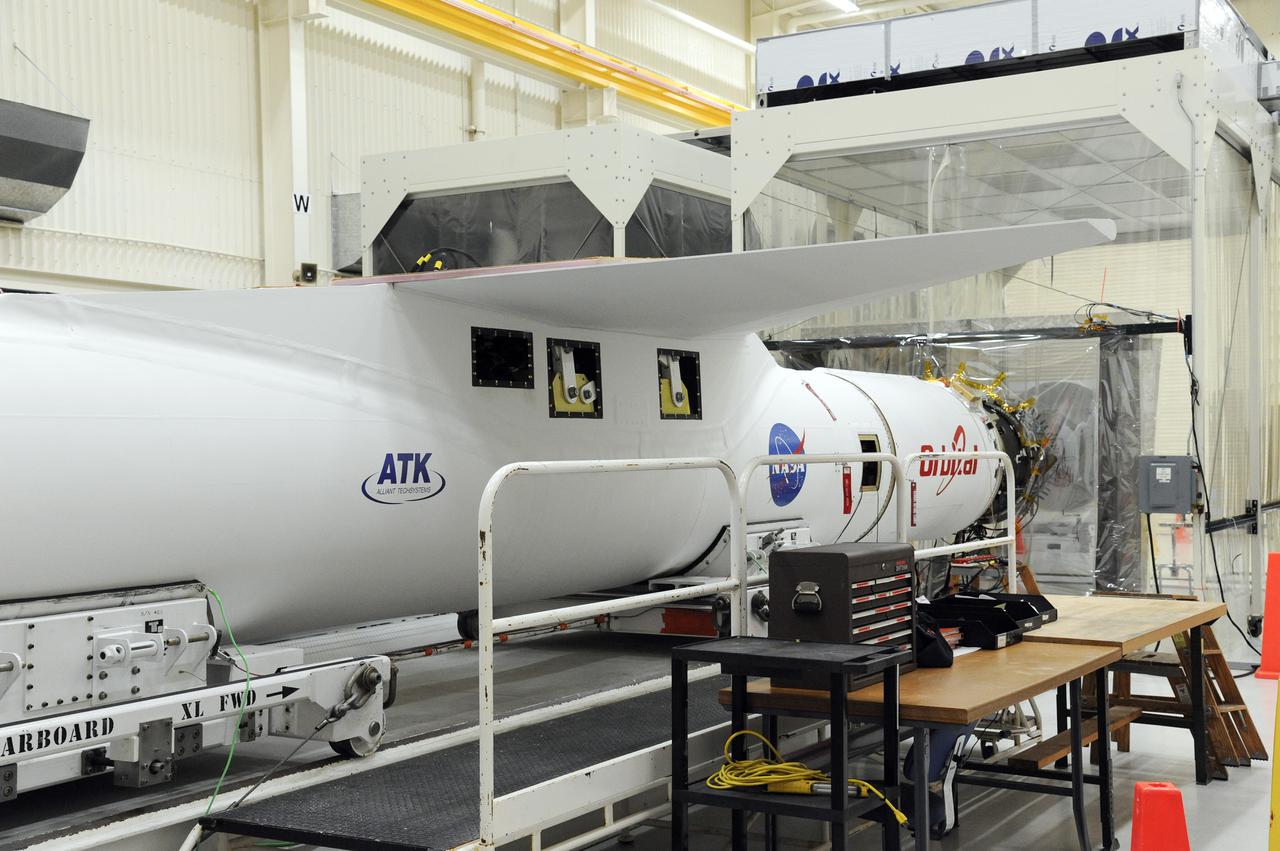

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will carry NASA's IRIS spacecraft is positioned for processing at Vandenberg. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Tony Vauelin
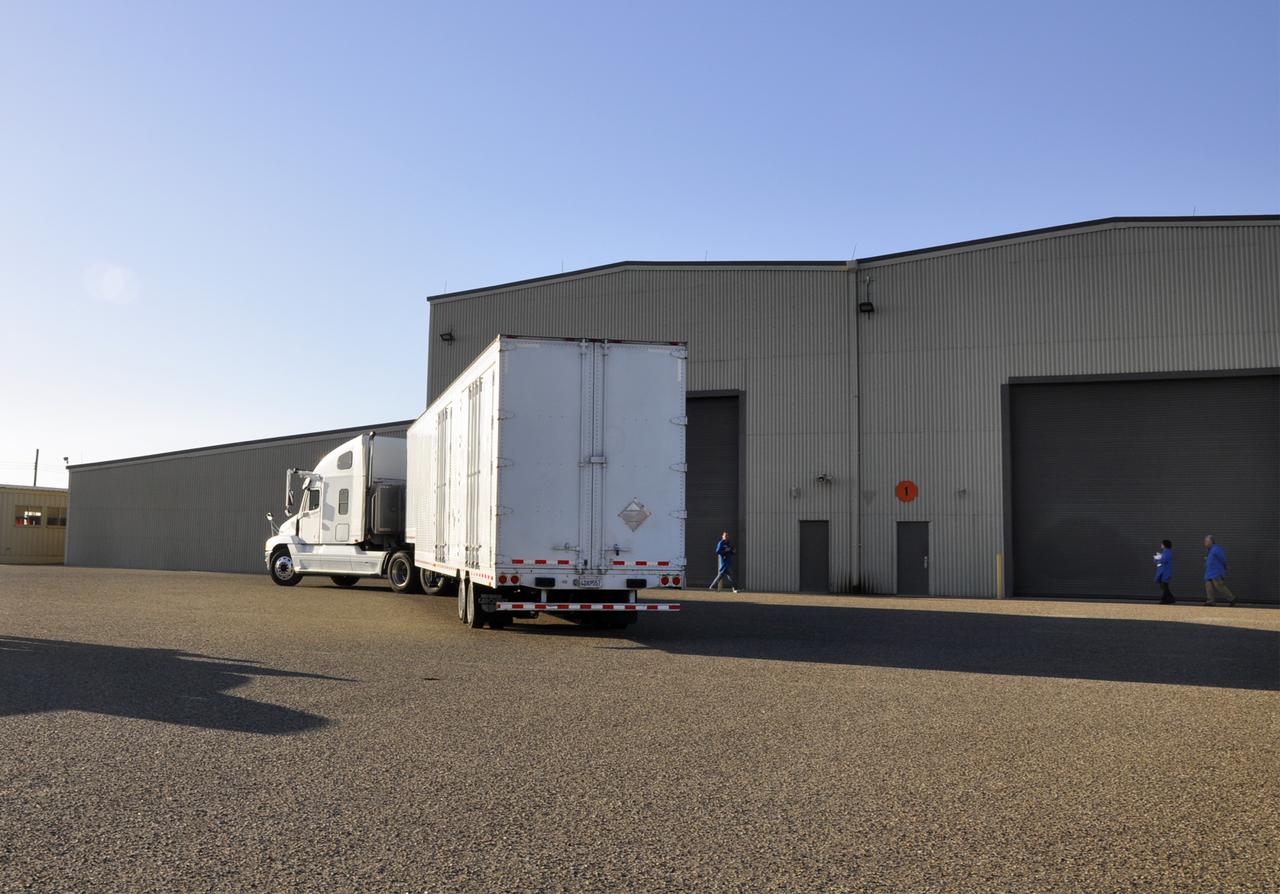

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck carrying NASA's IRIS spacecraft nears the processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
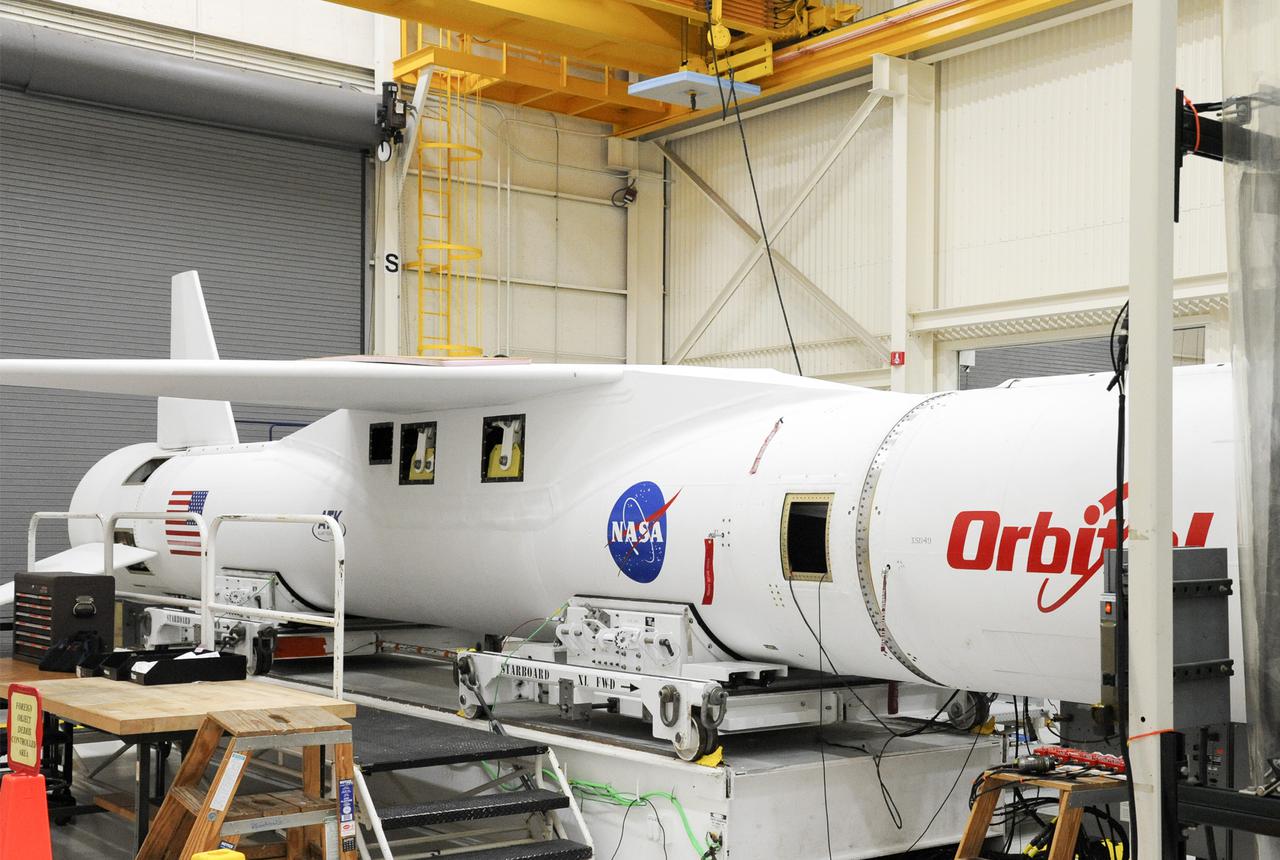

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will carry NASA's IRIS spacecraft is positioned for processing at Vandenberg. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Tony Vauelin
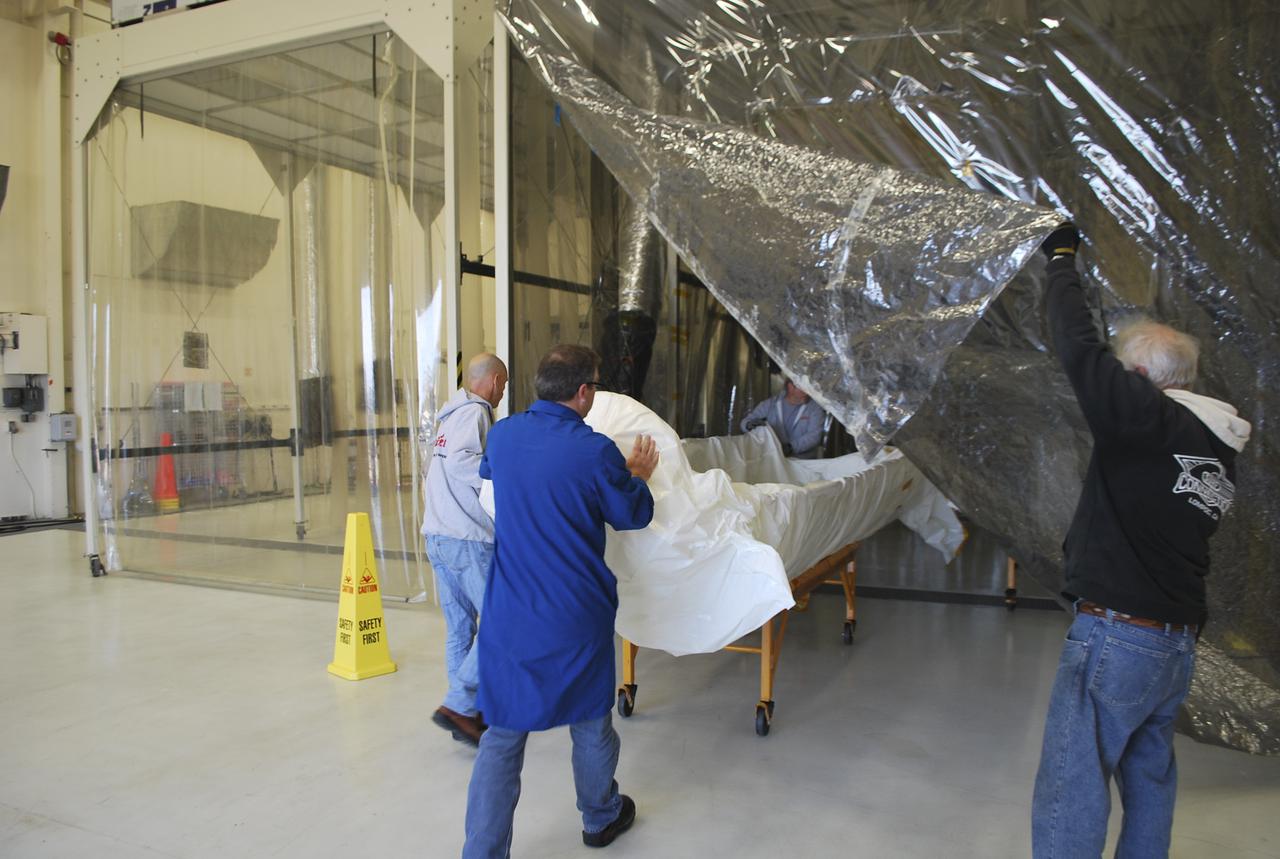

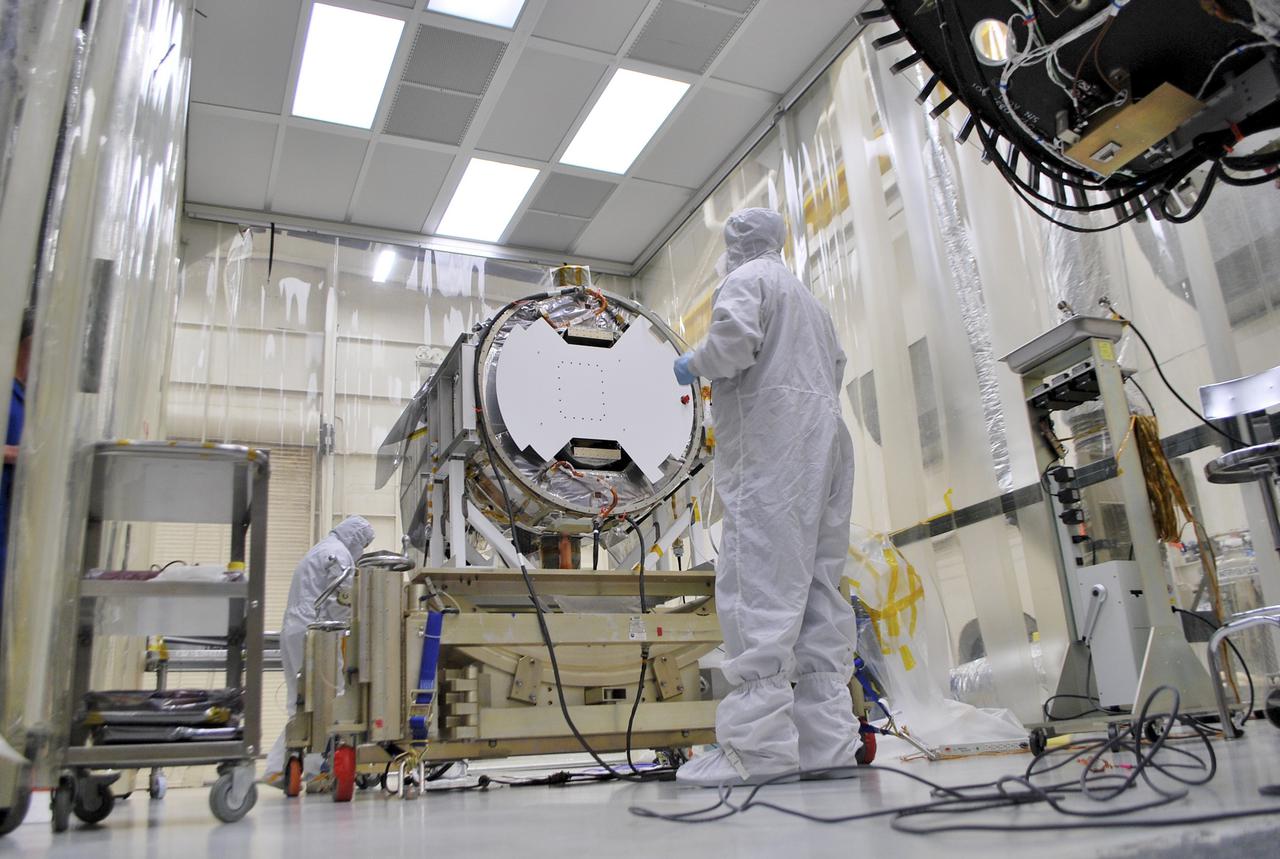
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers load half of a payload fairing inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California where it will be processed and used for NASA's IRIS mission. The fairing will be fitted to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket and will protect the IRIS spacecraft from atmospheric heating and stress during launch. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – An Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will carry NASA's IRIS spacecraft is positioned for processing at Vandenberg. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Tony Vauelin
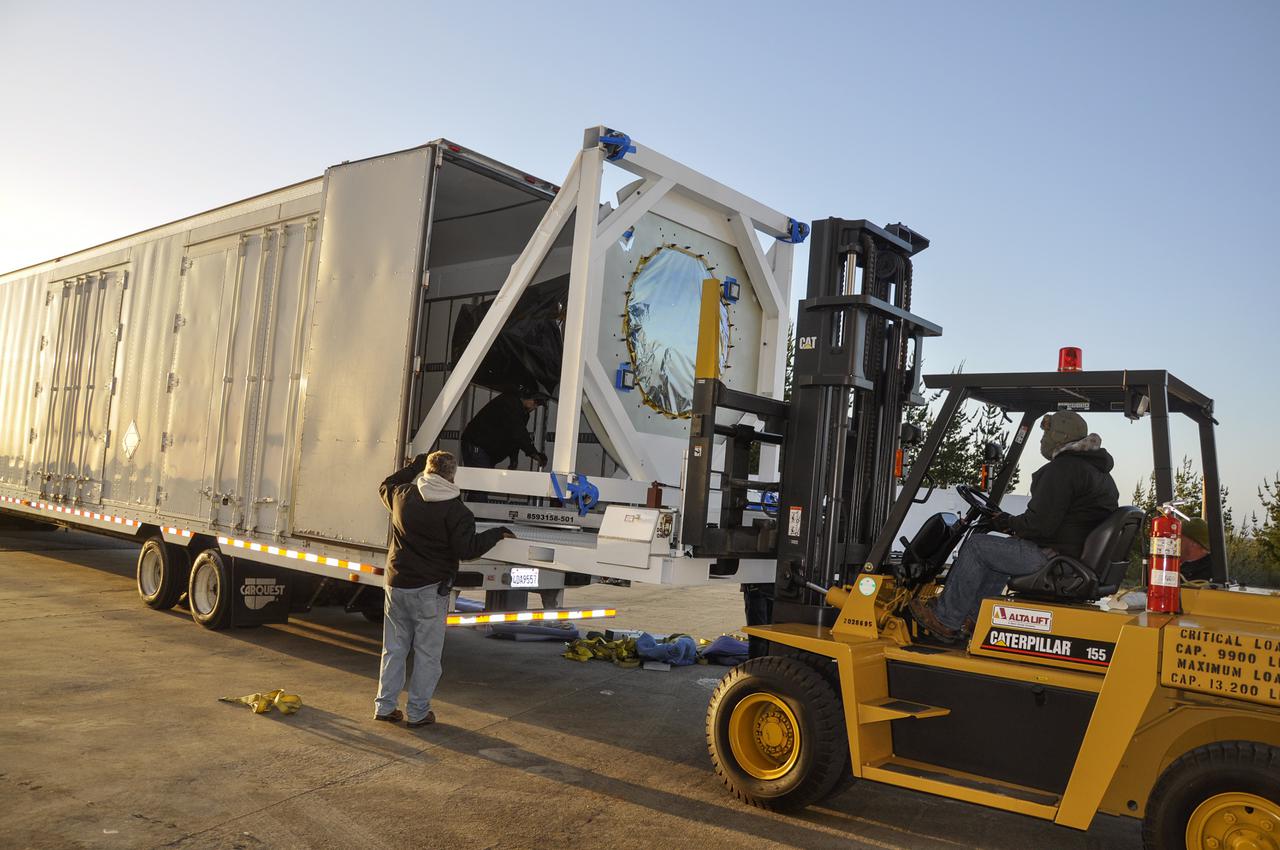

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers unload NASA's IRIS spacecraft from a truck at the processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
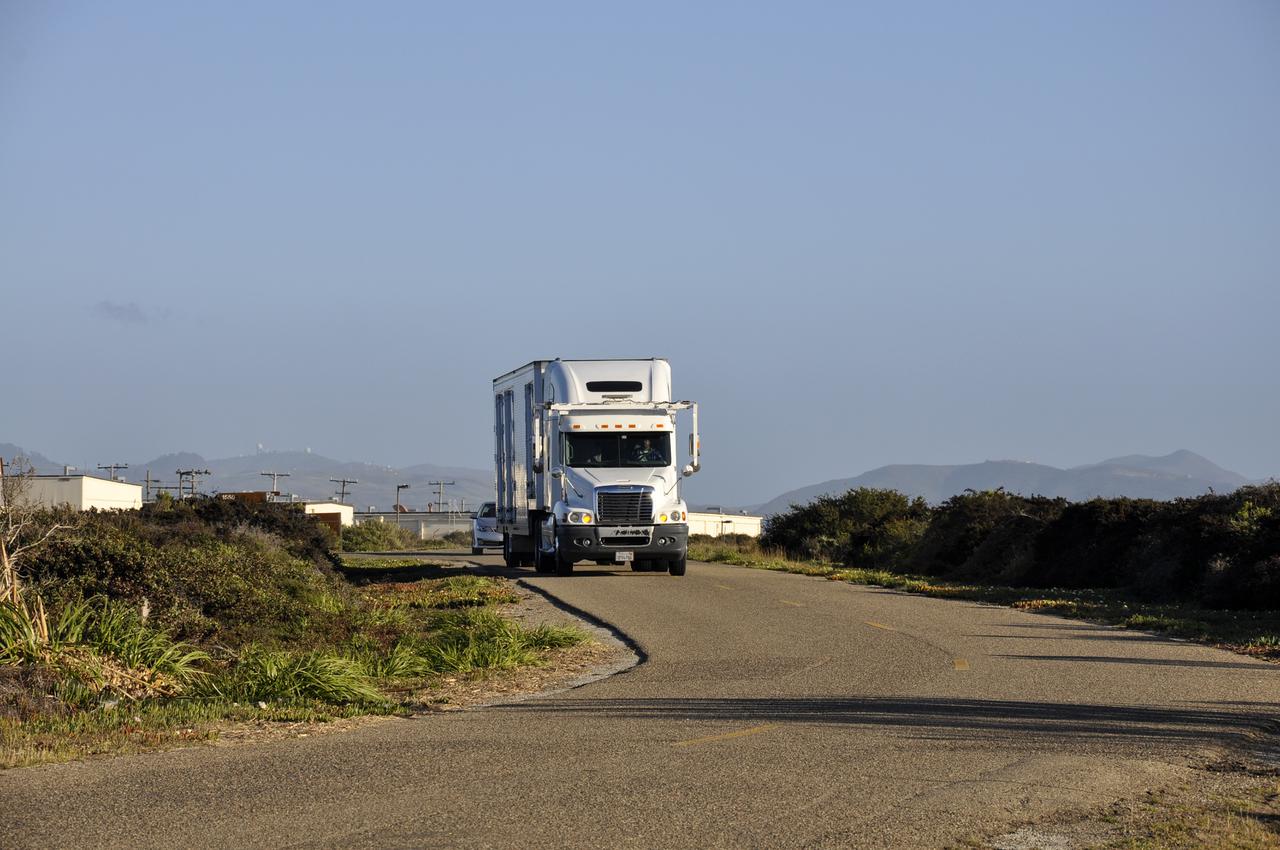

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – A truck carrying NASA's IRIS spacecraft nears the processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
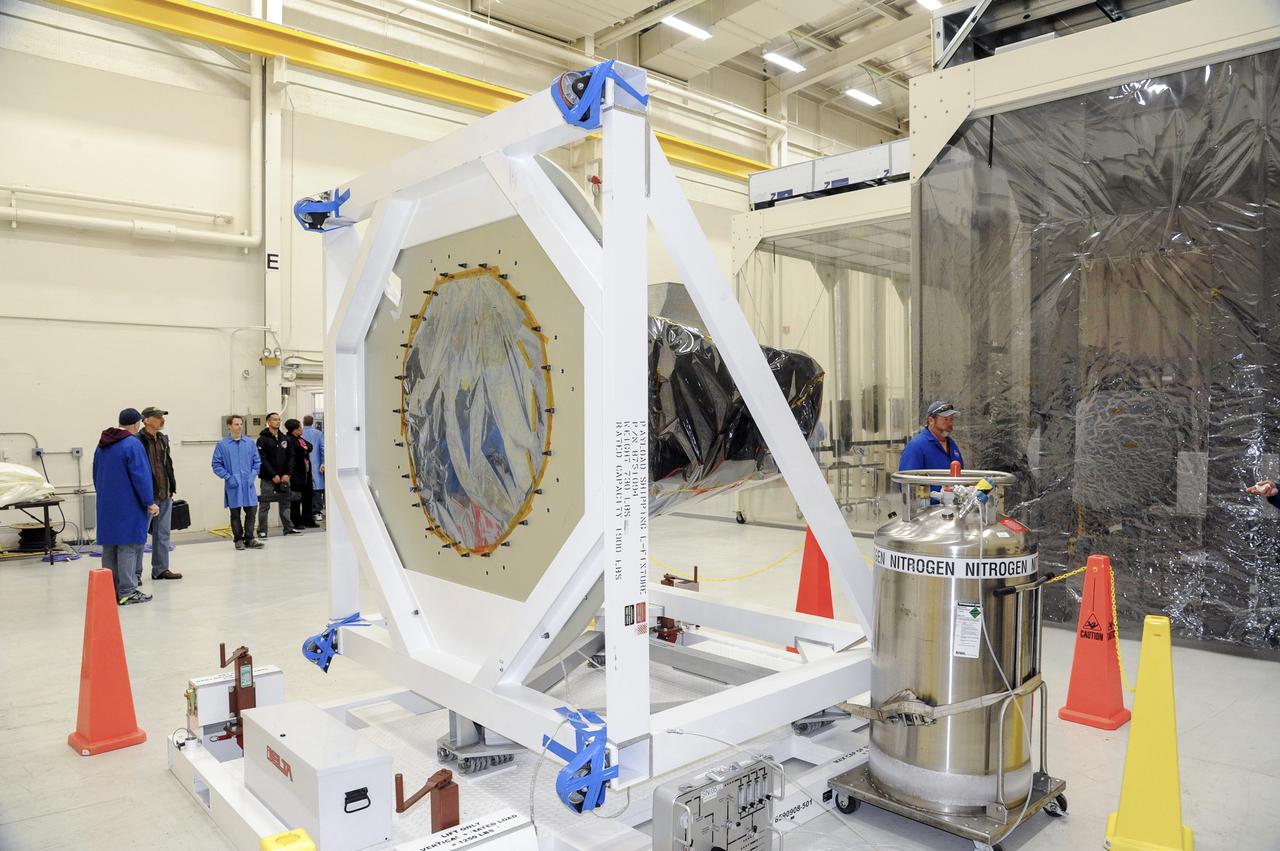

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Technicians begin processing NASA's IRIS spacecraft at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Tony Vauelin
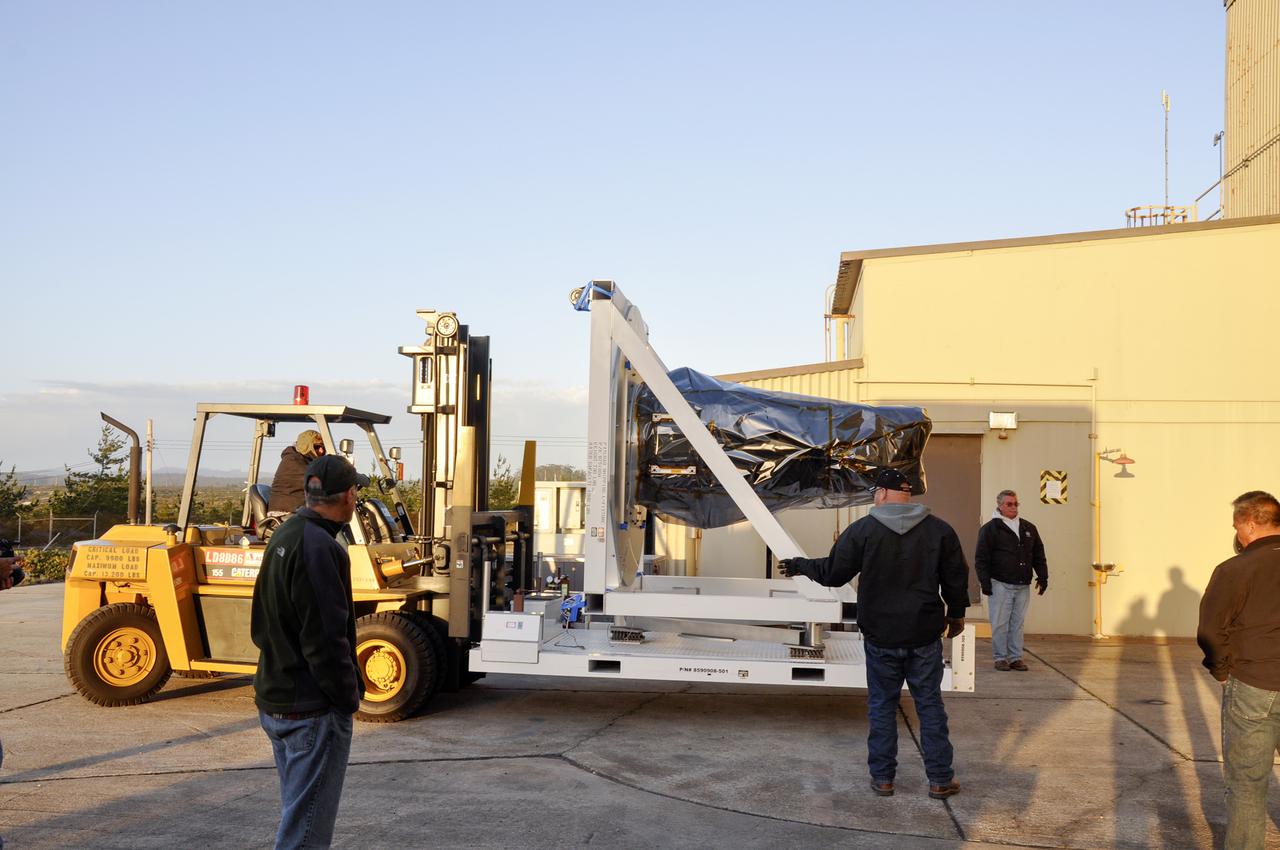

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers move NASA's IRIS spacecraft into a processing facility at Vandenberg where the spacecraft will be readied for launch aboard an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket. IRIS is short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph and the spacecraft's mission will improve our understanding of how heat and energy move through the deepest levels of the sun’s atmosphere, thereby increasing our ability to forecast space weather. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
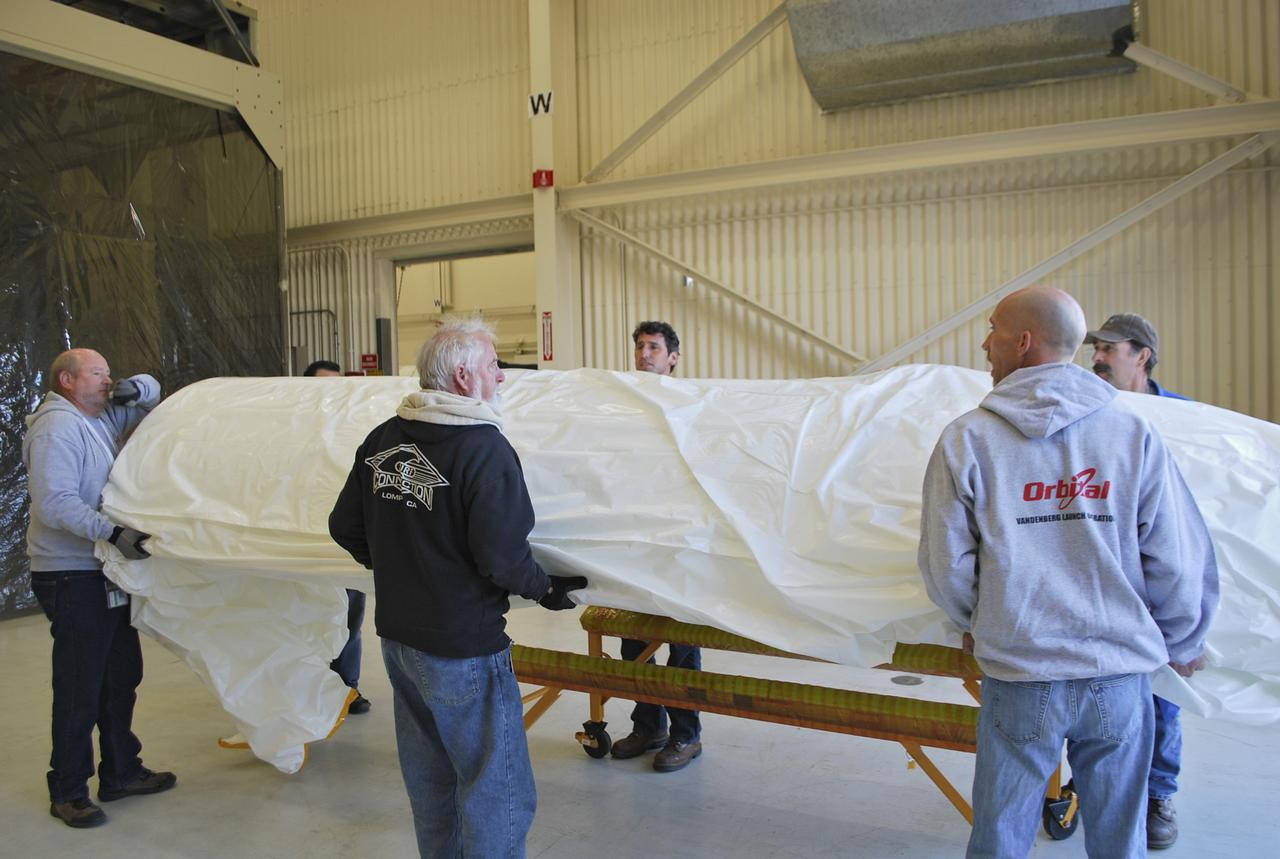

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers load half of a payload fairing inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California where it will be processed and used for NASA's IRIS mission. The fairing will be fitted to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket and will protect the IRIS spacecraft from atmospheric heating and stress during launch. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
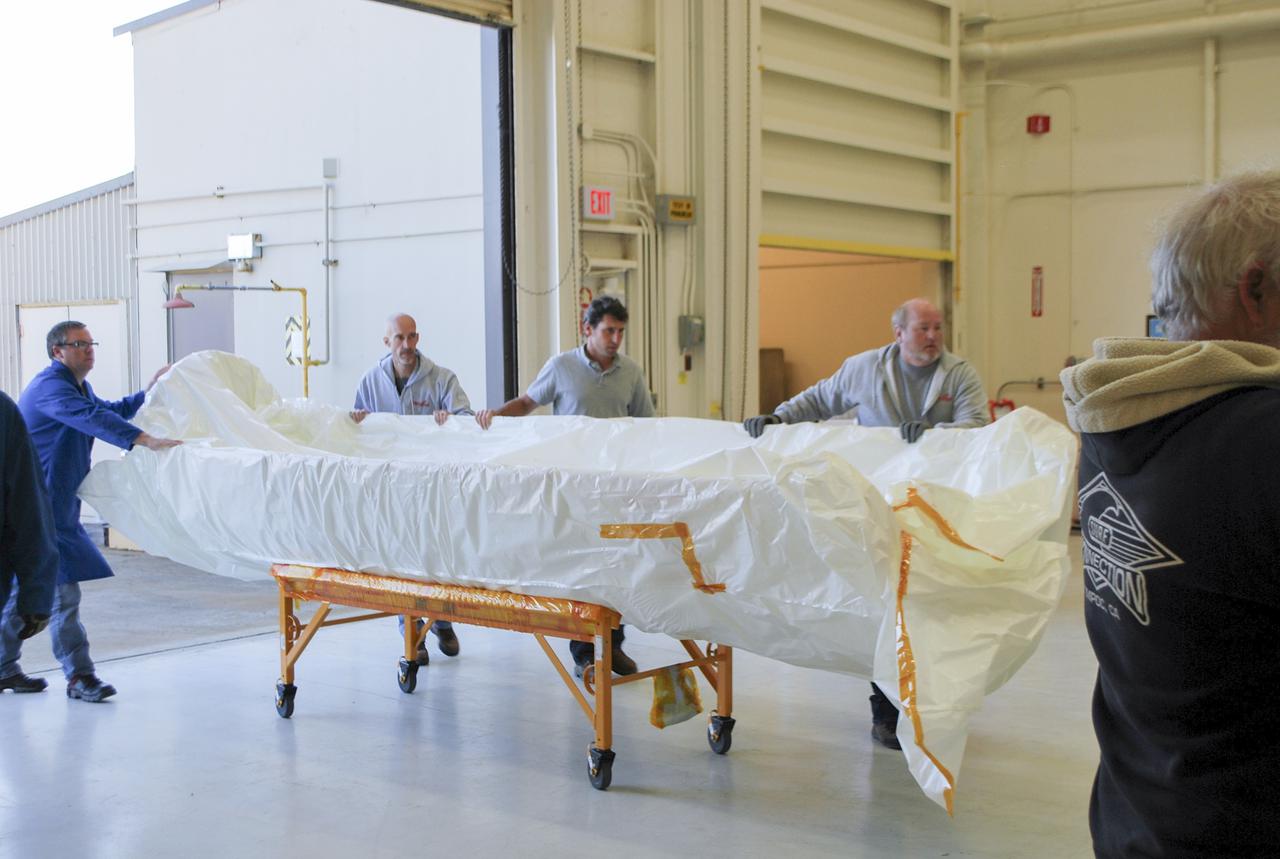

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Workers load half of a payload fairing inside a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California where it will be processed and used for NASA's IRIS mission. The fairing will be fitted to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus rocket and will protect the IRIS spacecraft from atmospheric heating and stress during launch. Photo credit: VAFB_Randy Beaudoin
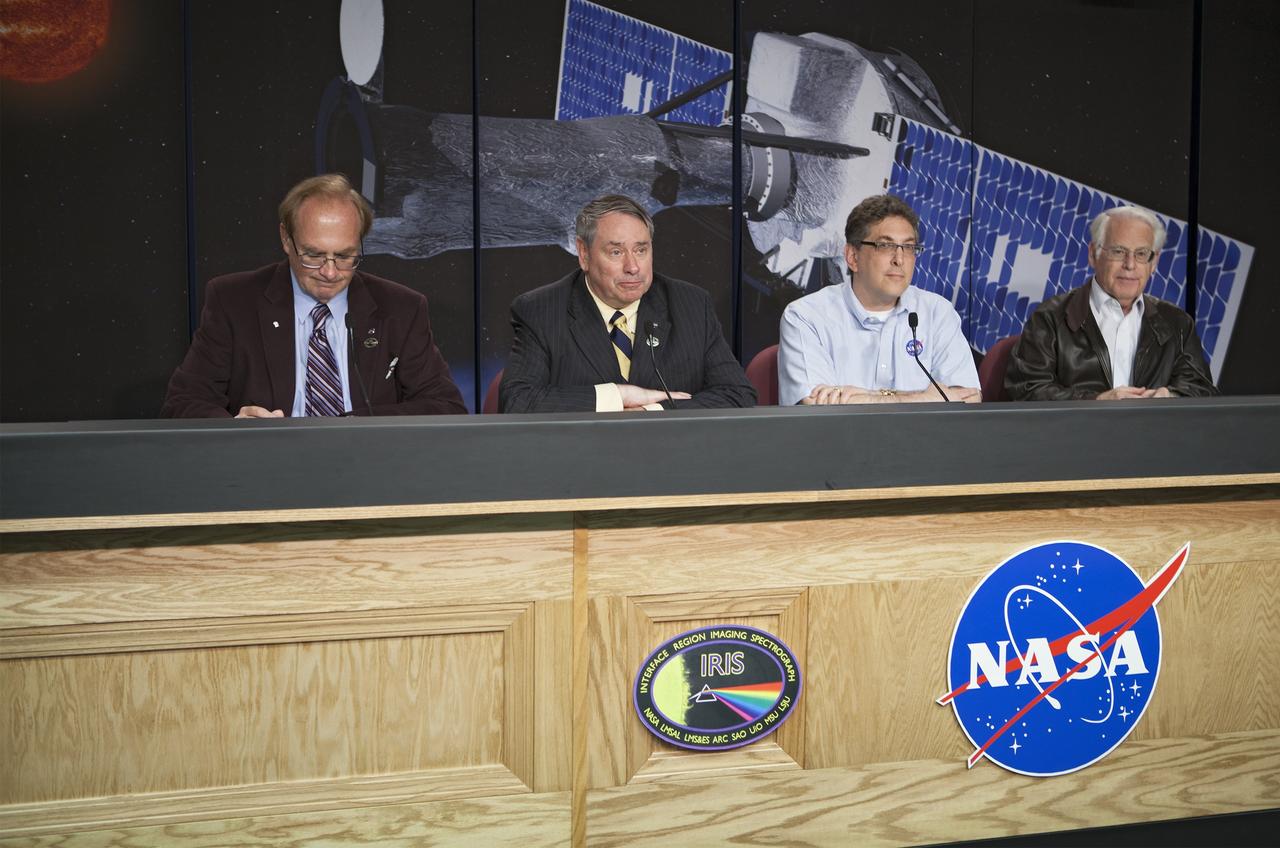

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA hosted a prelaunch mission briefing on the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory scheduled to launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Participating in the news conference are George Diller, NASA Public Affairs, Dr. S. Pete Worden, director of NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif., Jeffrey Newmark, IRIS Program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., and Alan Title, IRIS principal investigator with Lockheed Martin. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper
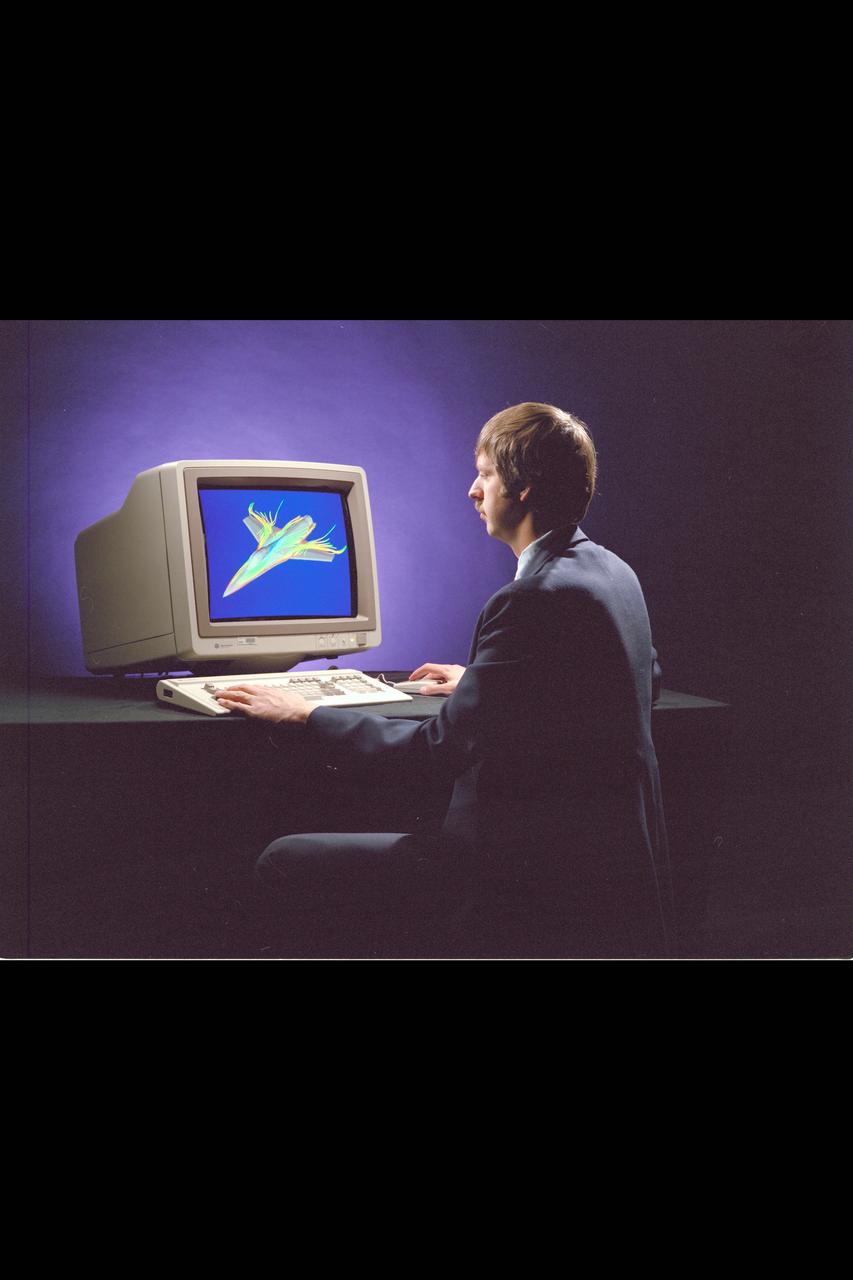

Iris Workstation with J. Flores computes F-16 CFD CGI

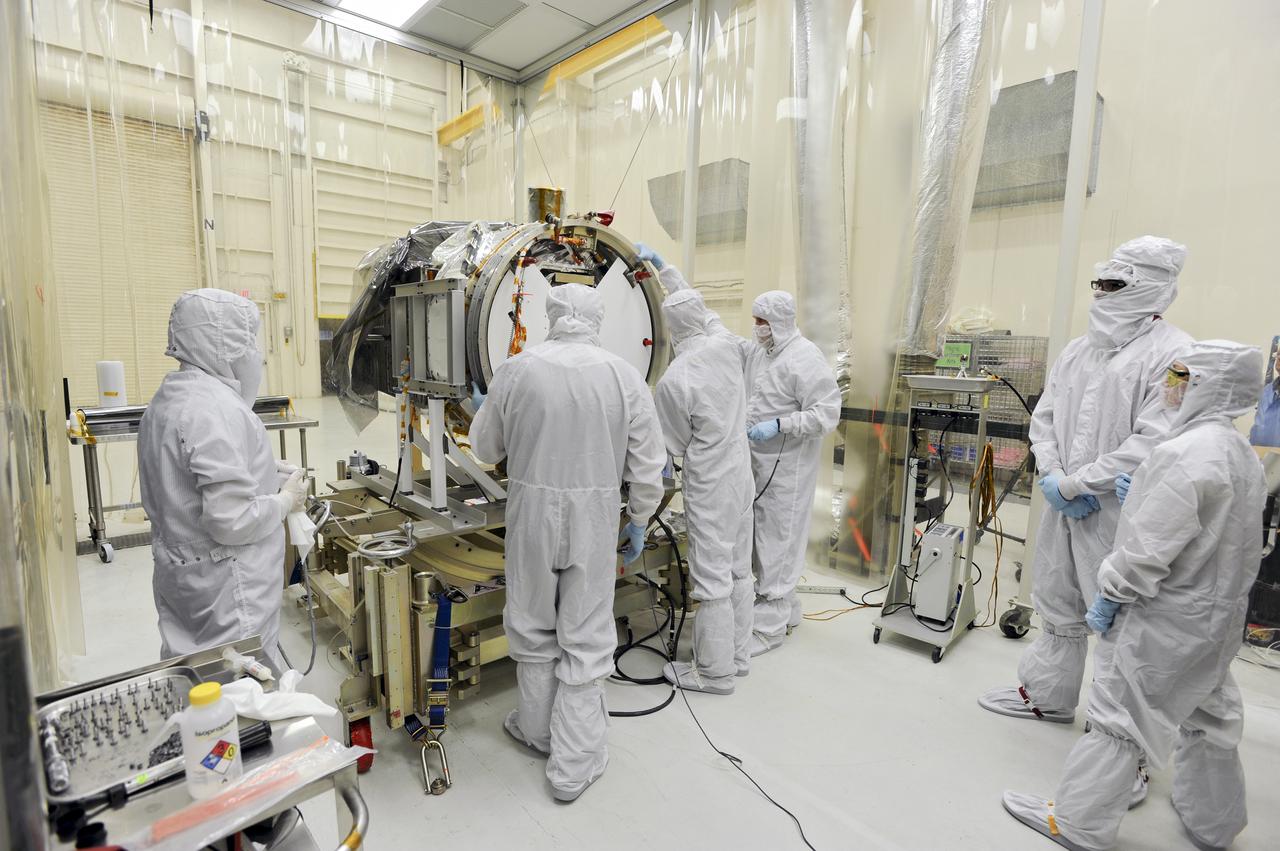
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
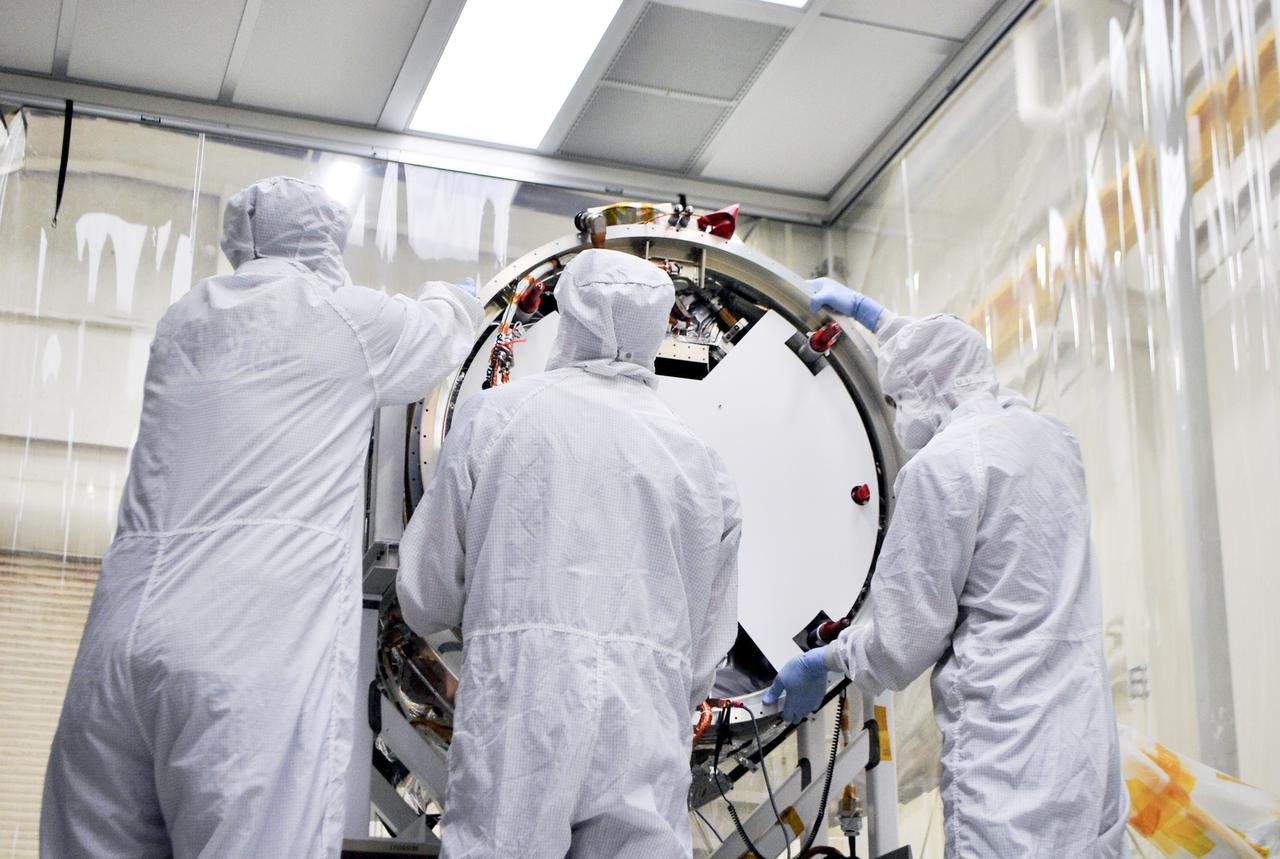

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers install a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

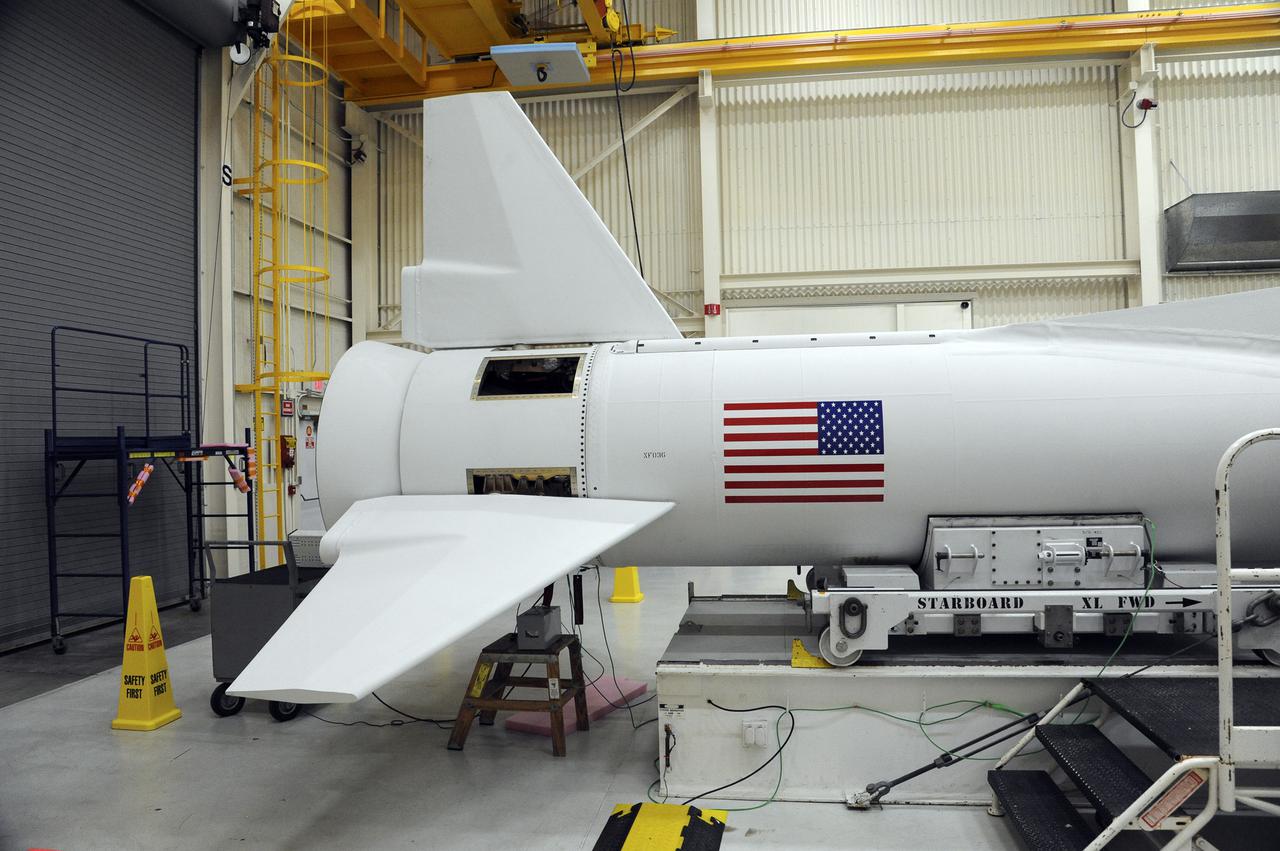
VANDENBERG AFB – An engineer makes preparations on the starboard side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
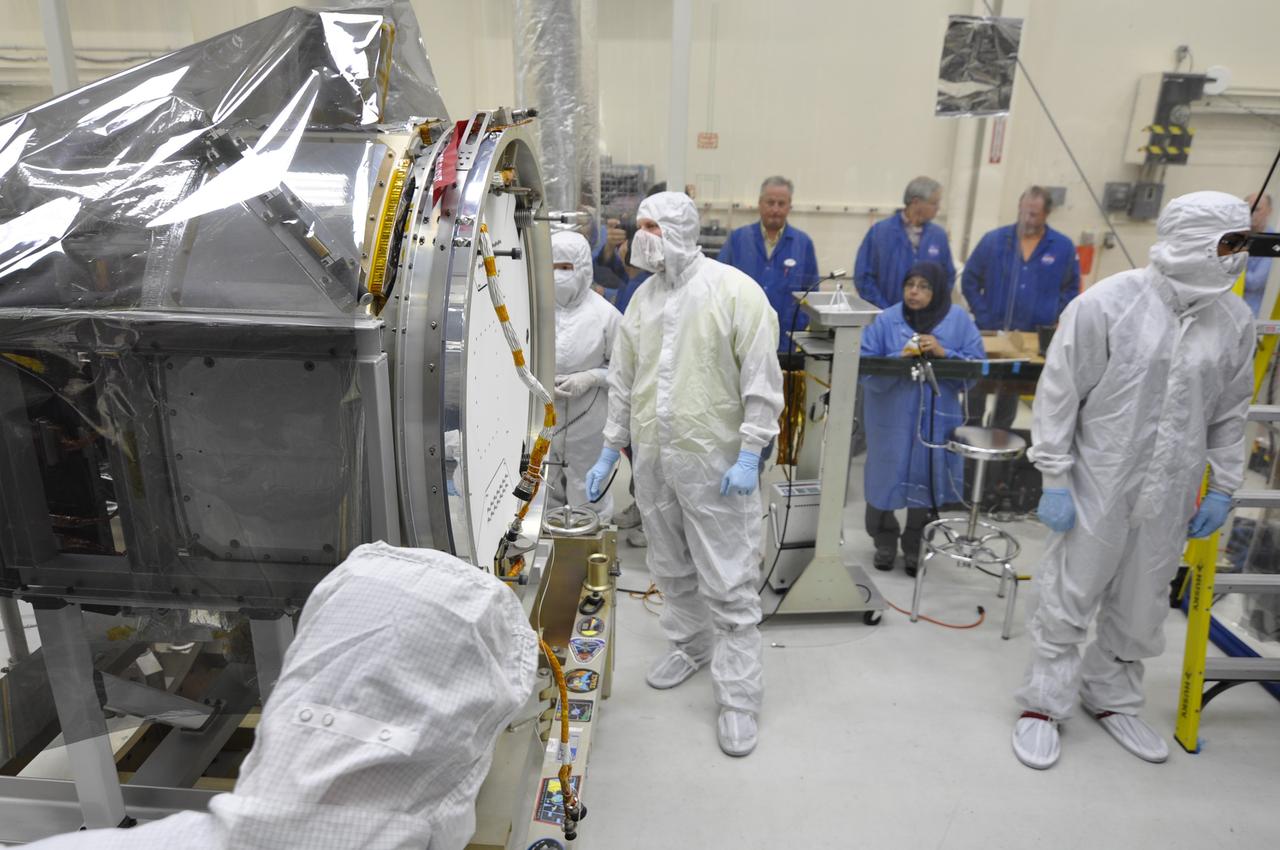

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers install a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
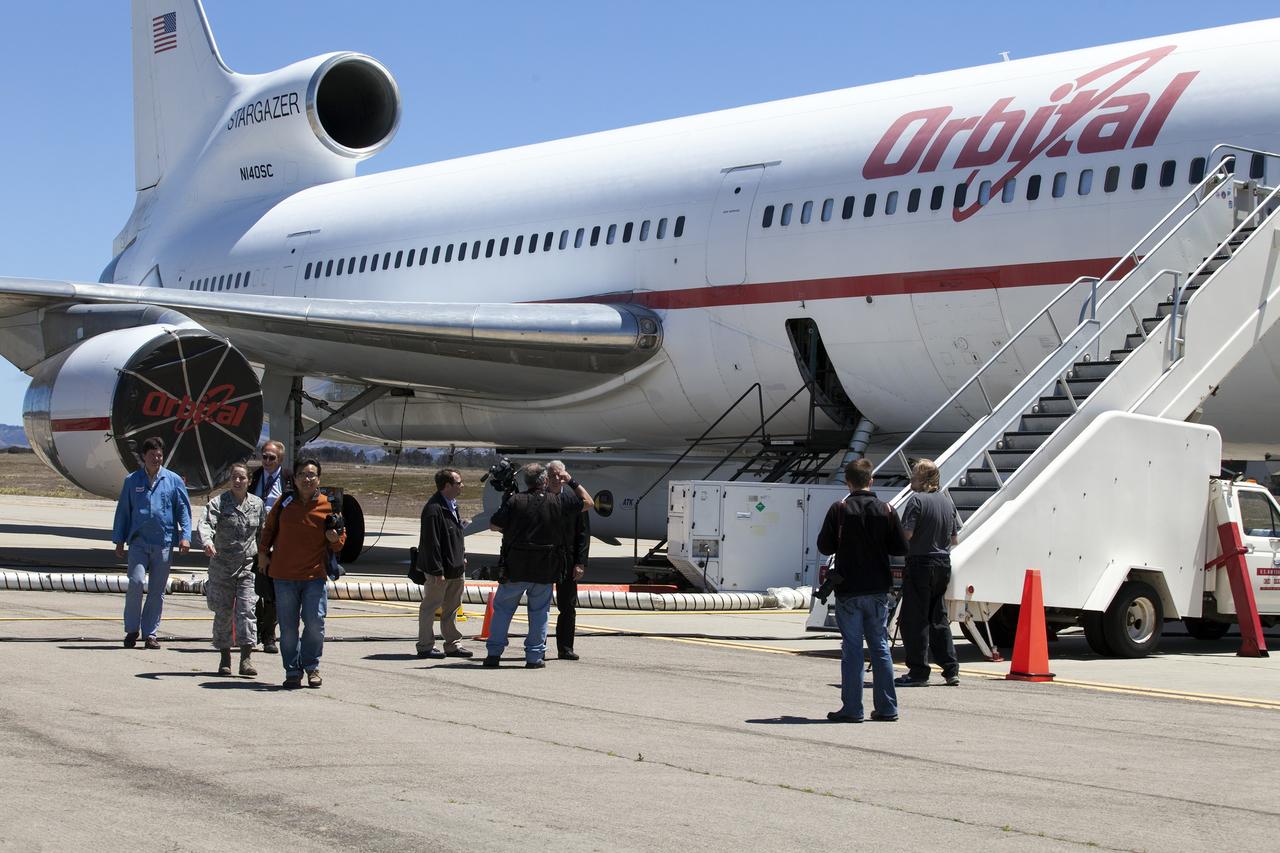

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Final checkouts are being completed at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California as preparations continue for the launch from the L-1011 carrier aircraft of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
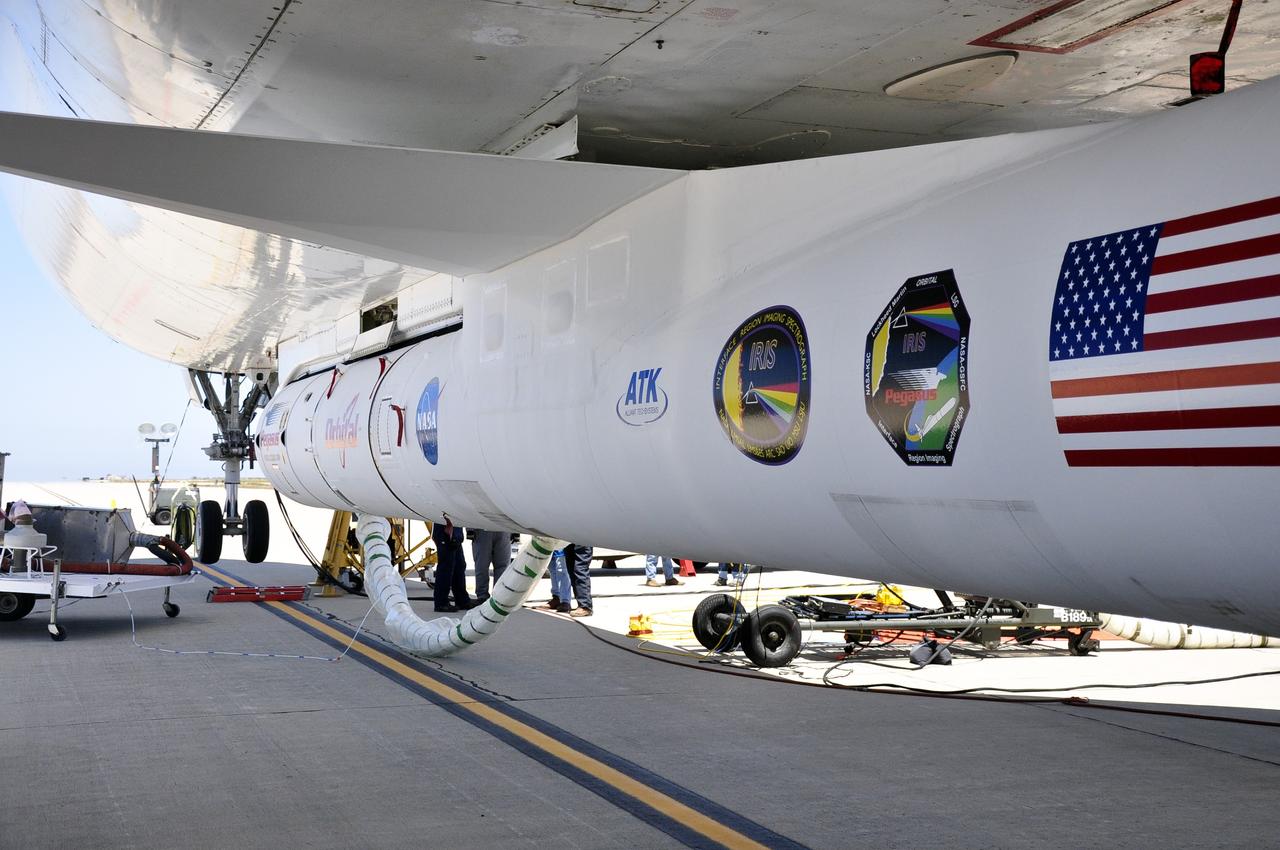

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
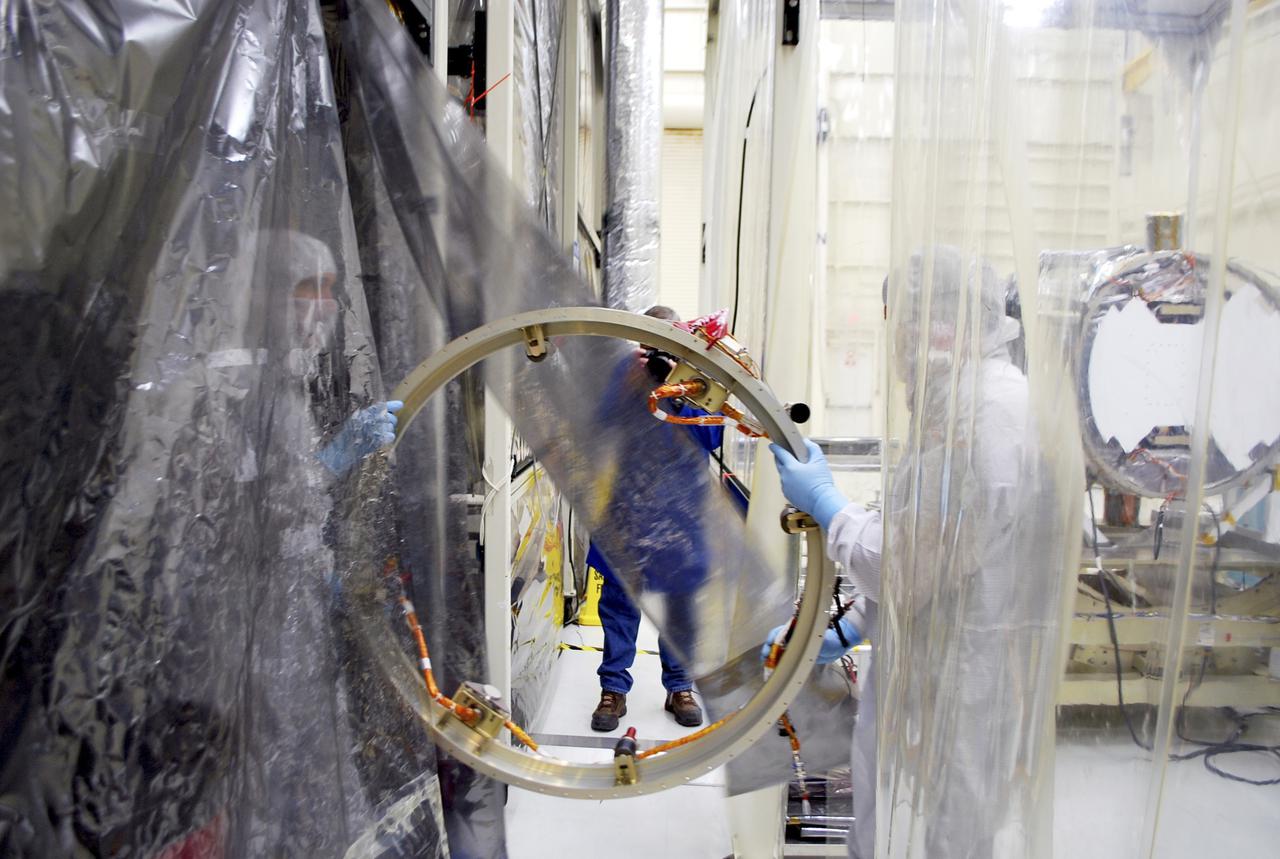

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
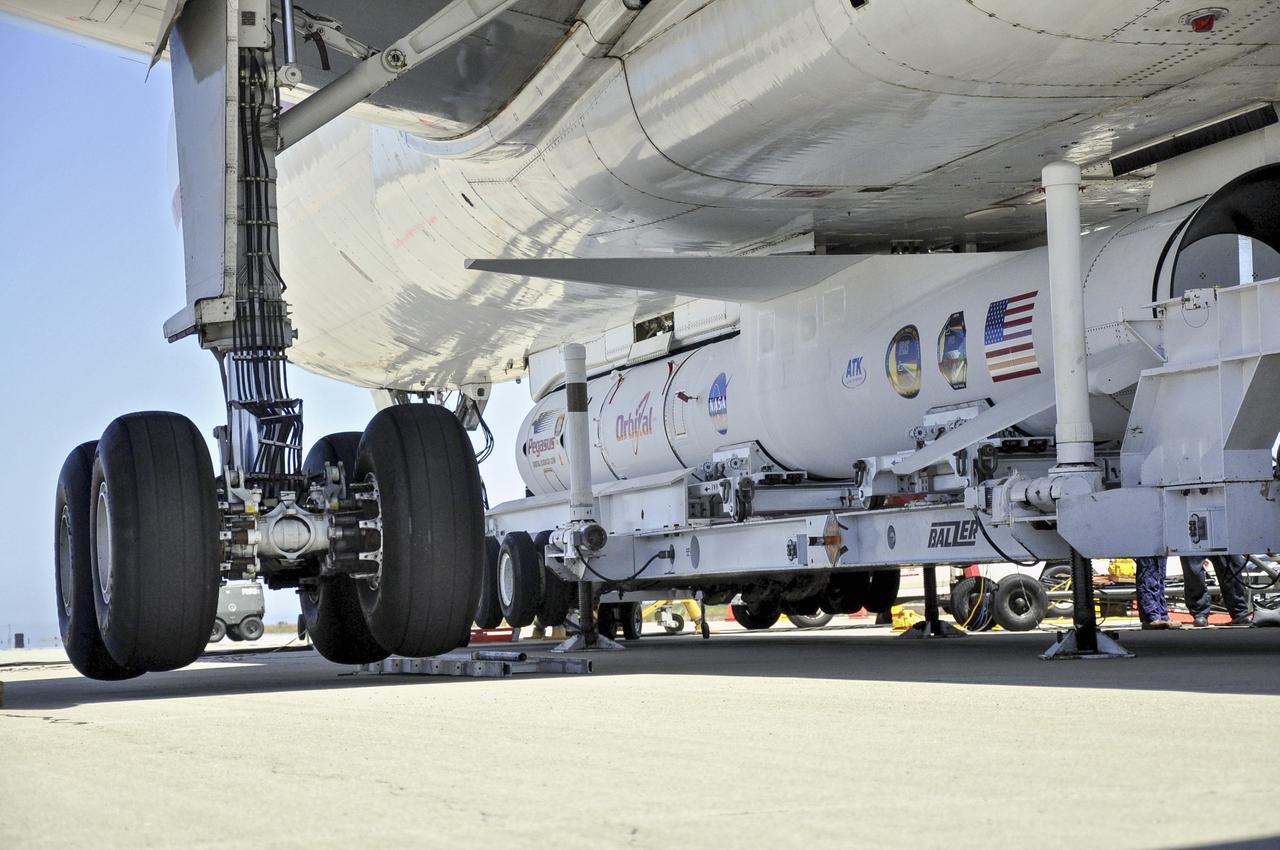

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
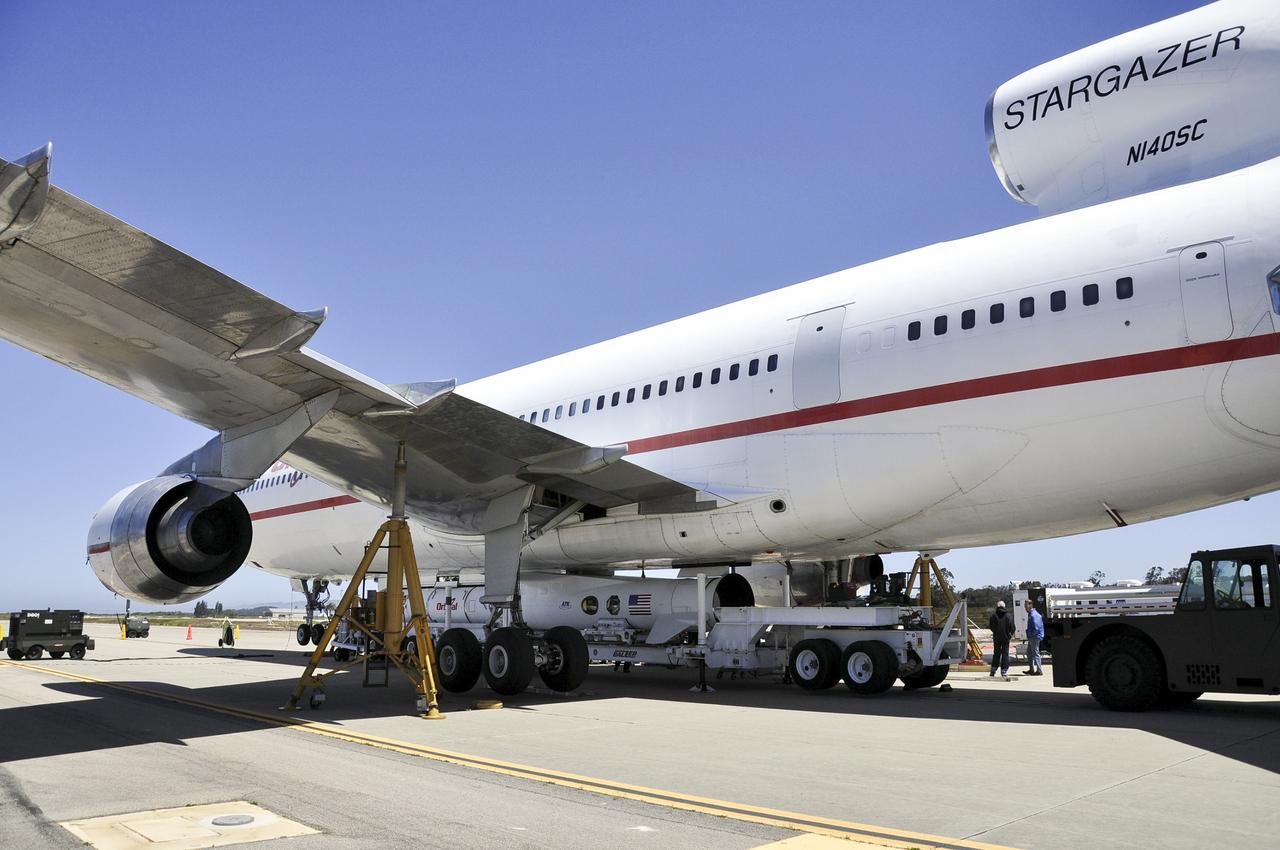

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
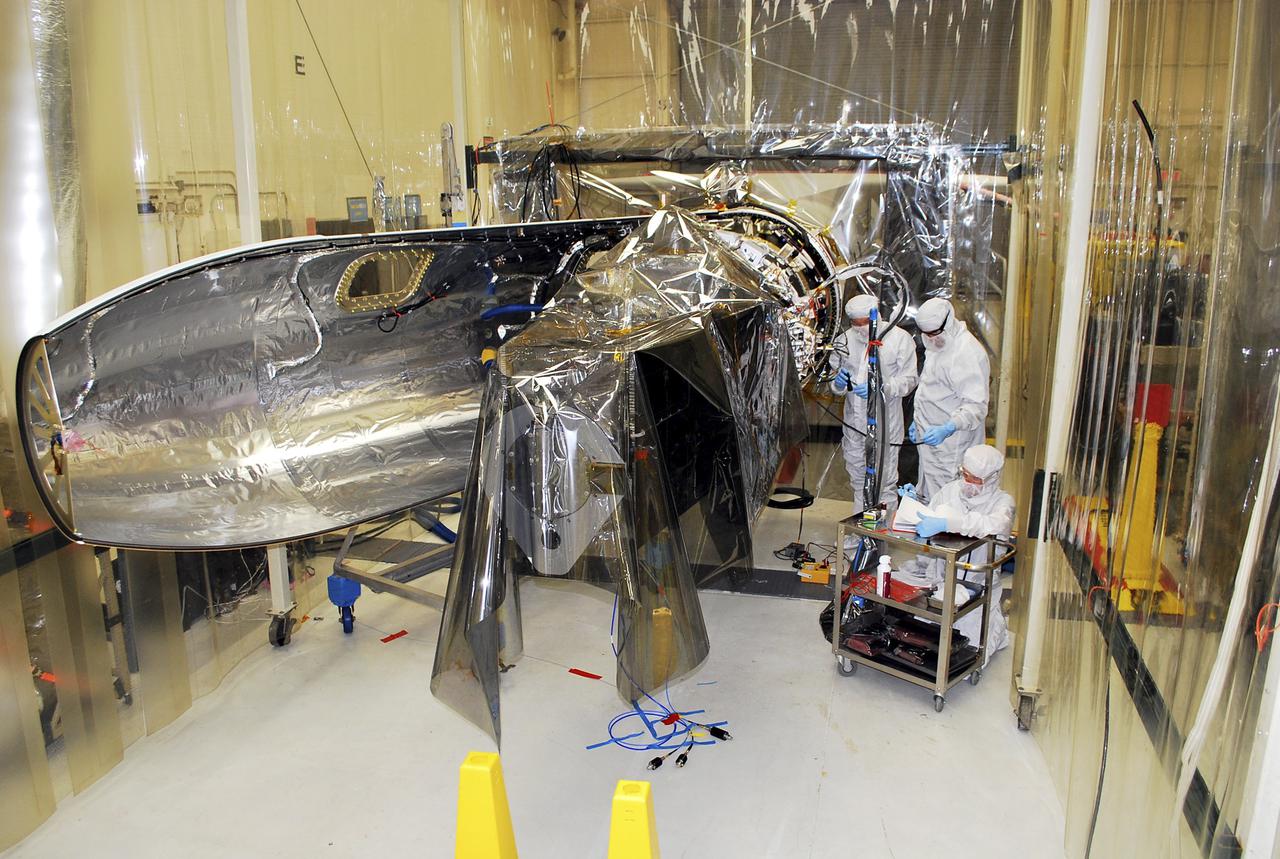

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers make preparations on the starboard side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
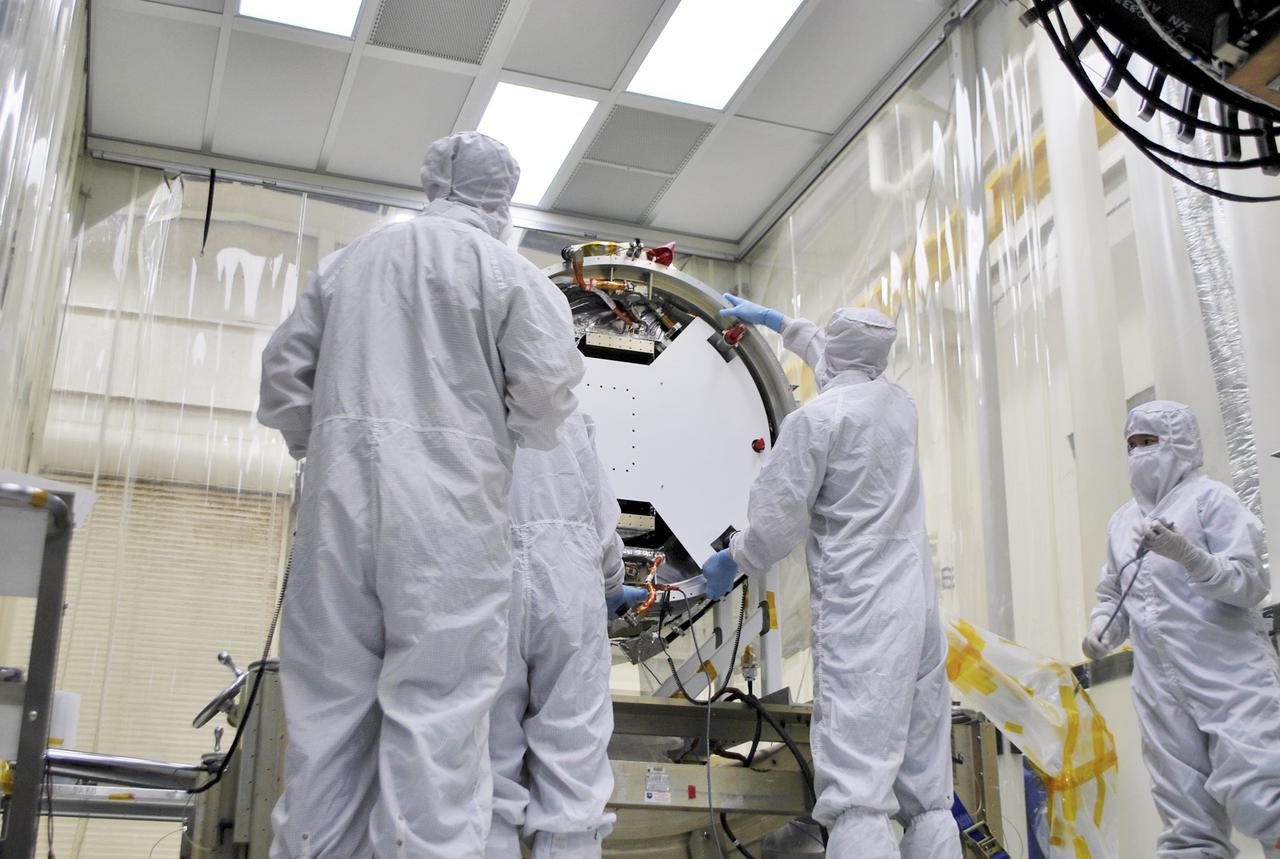

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers install a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
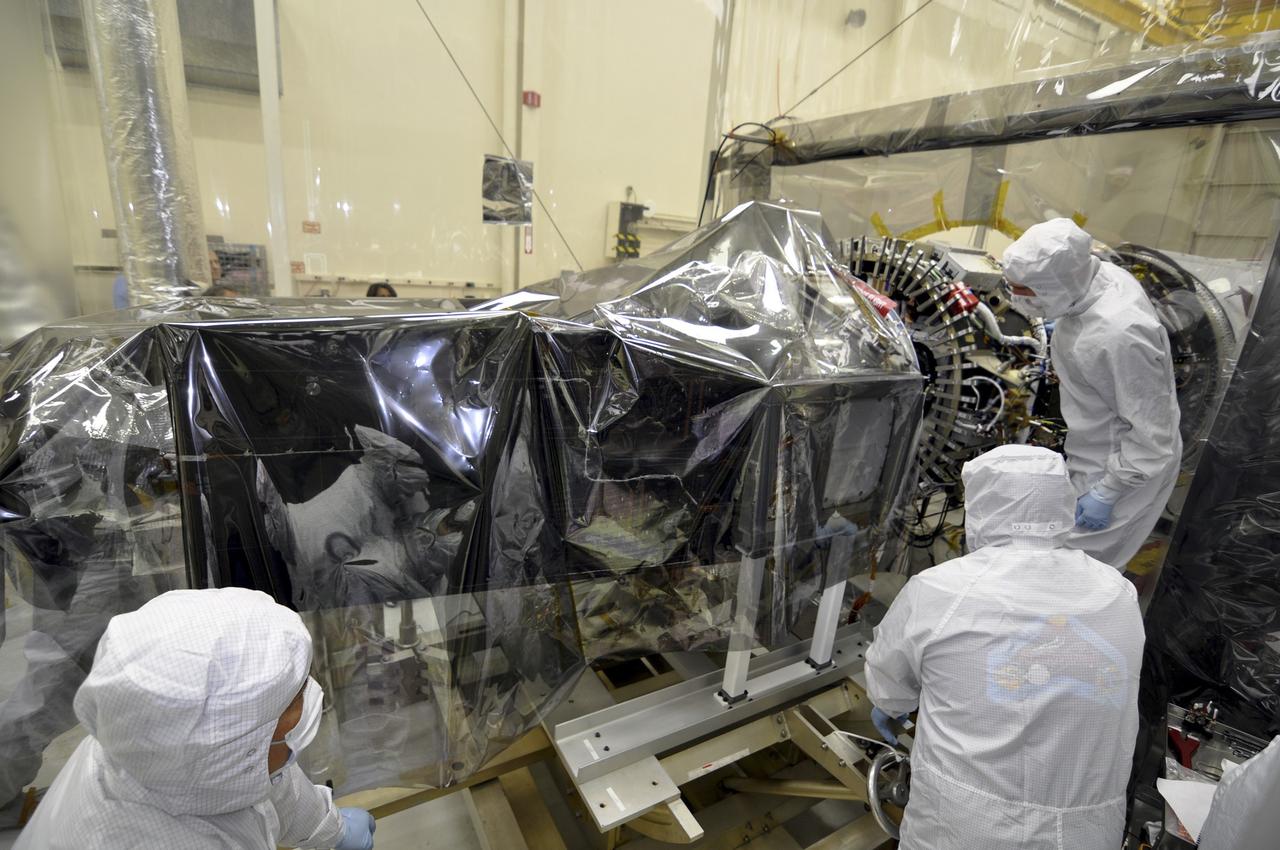

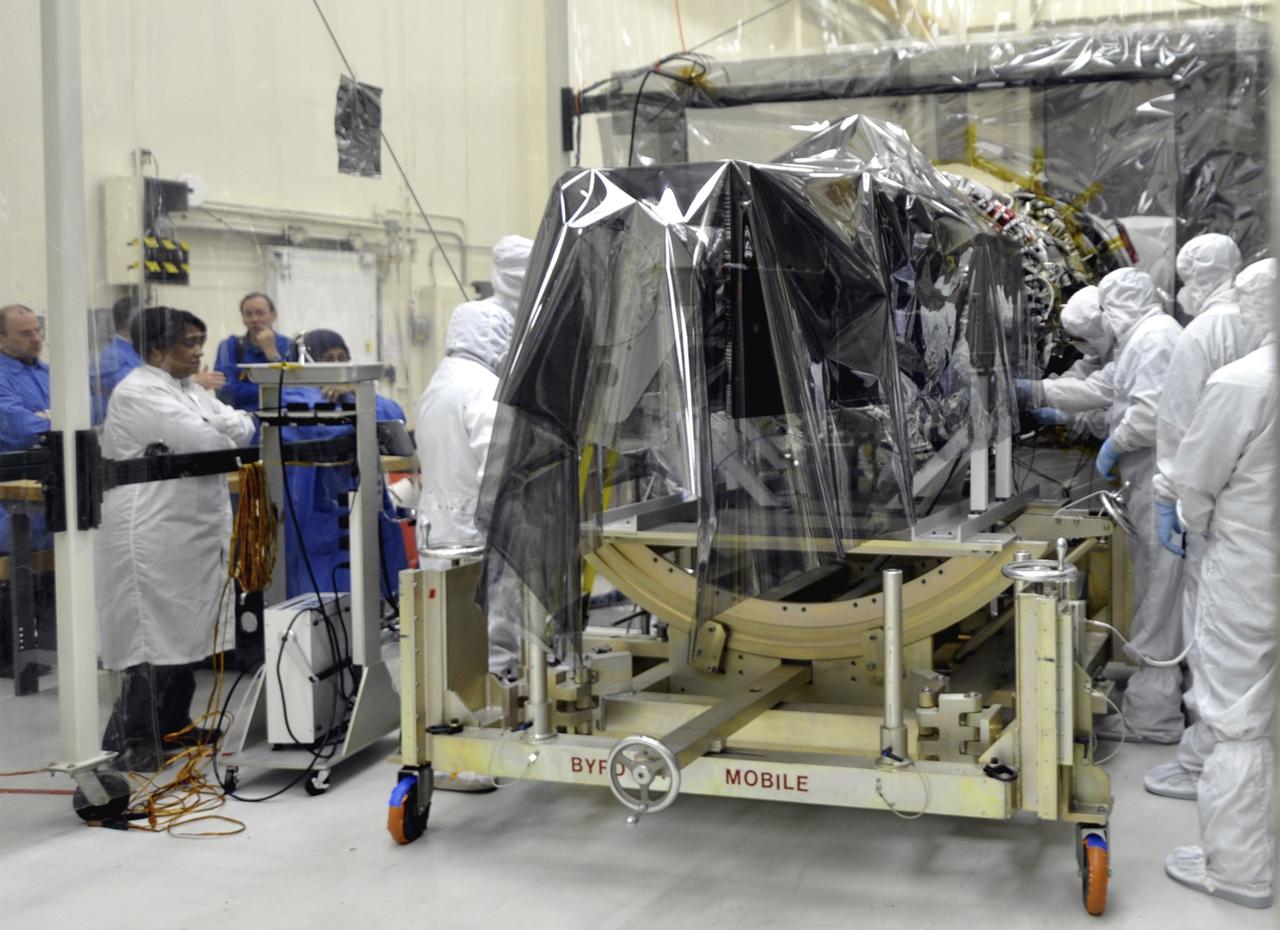
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
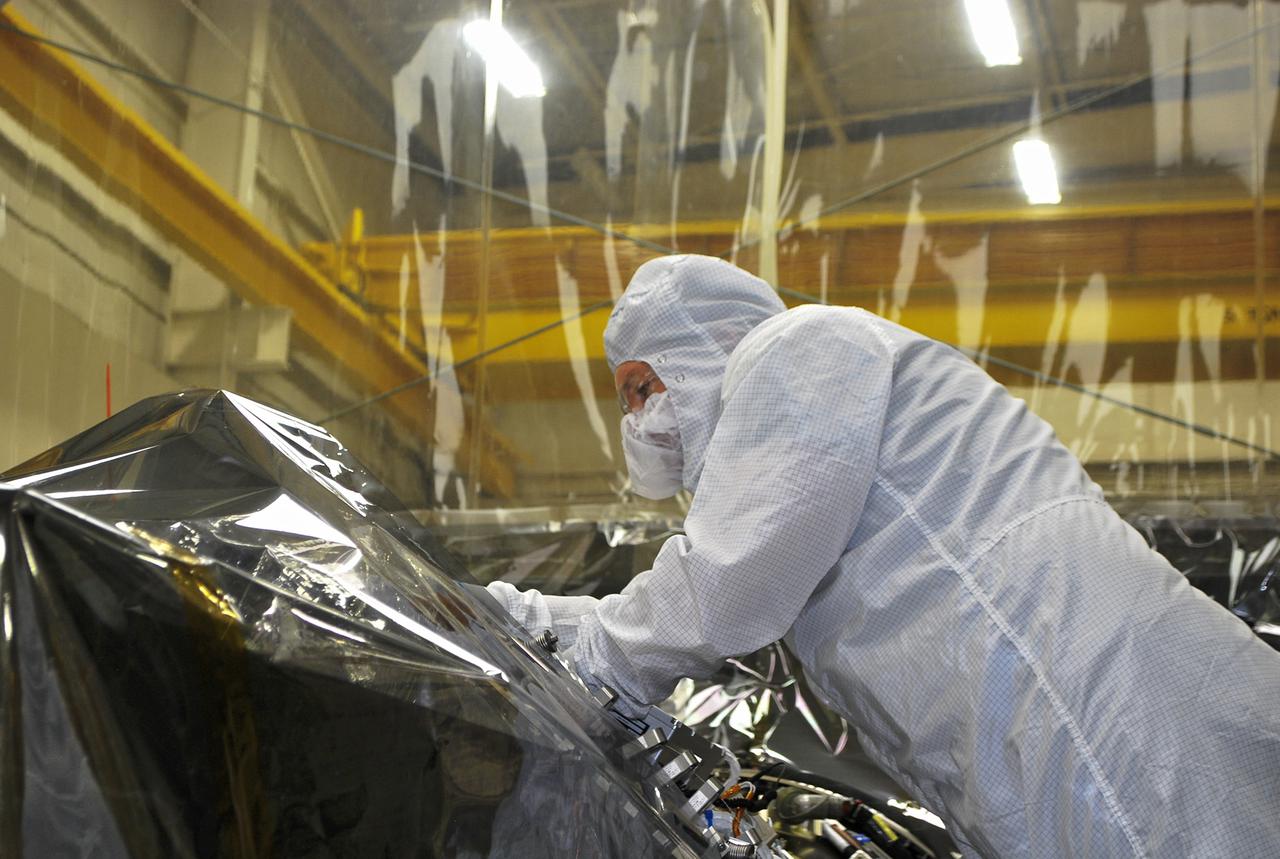

VANDENBERG AFB – An engineer makes preparations on the starboard side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
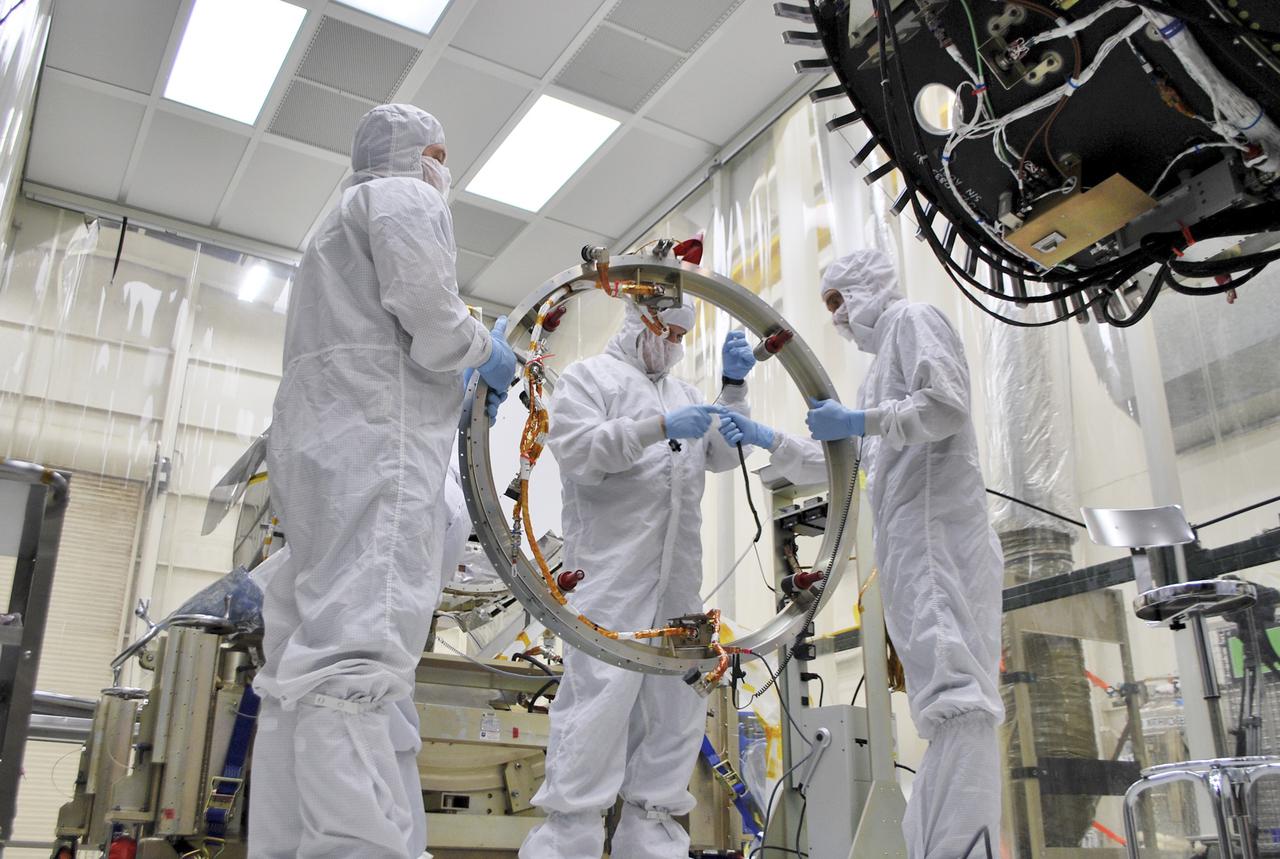

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
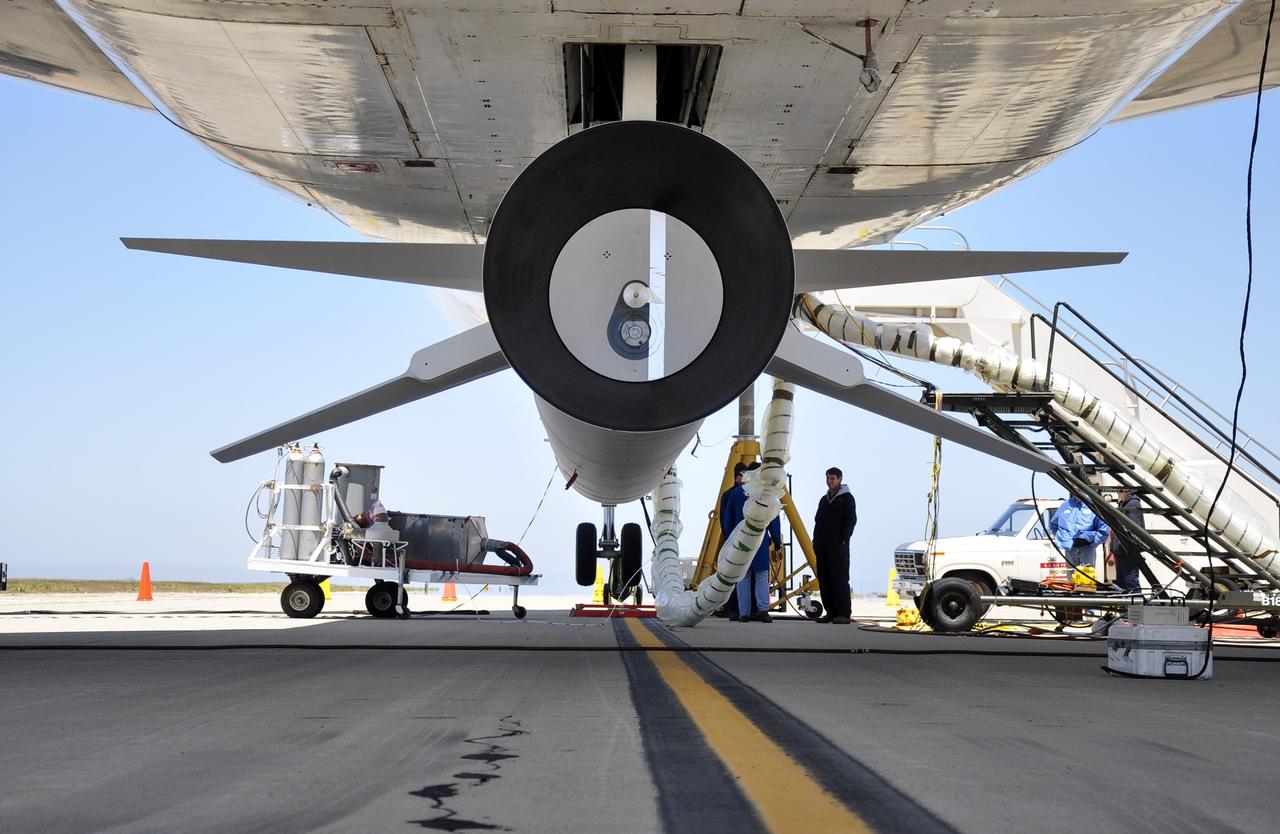

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

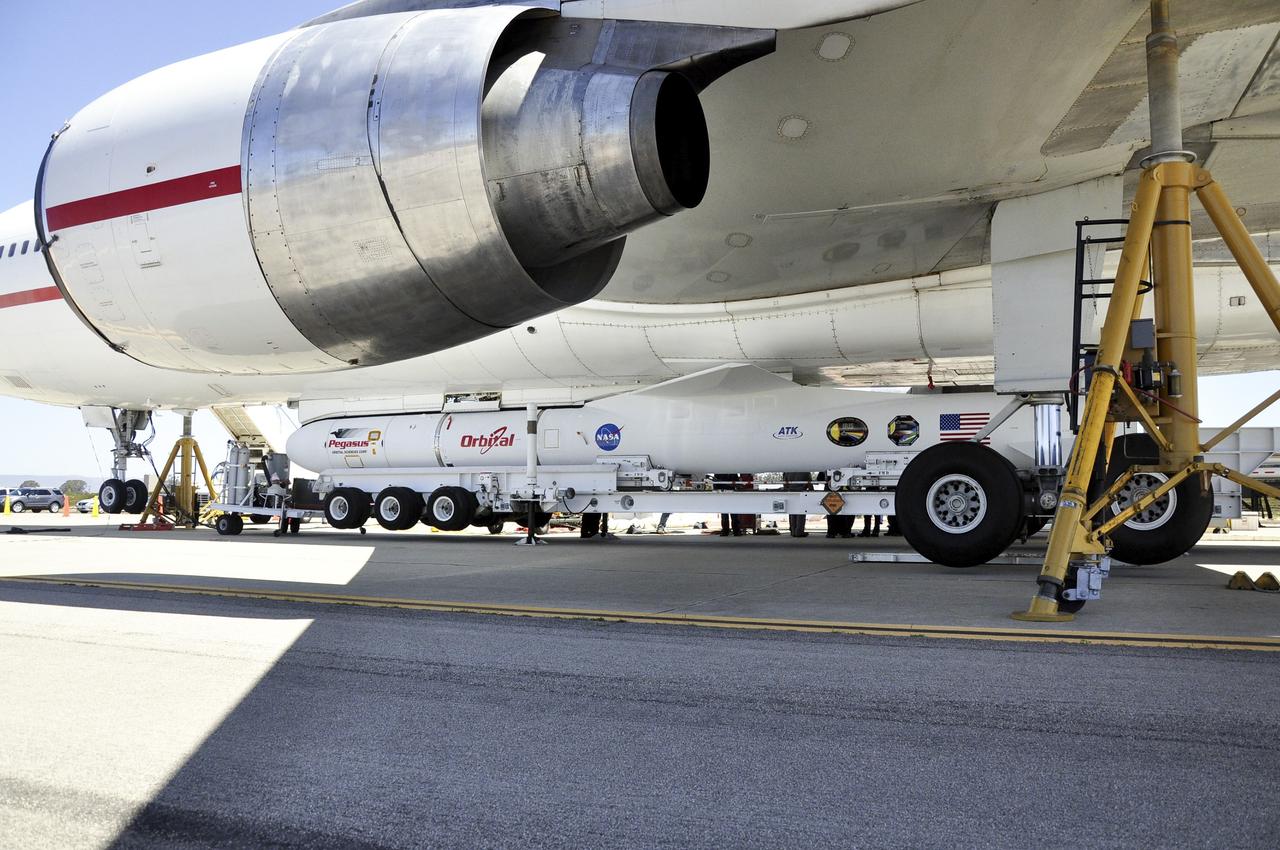
VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
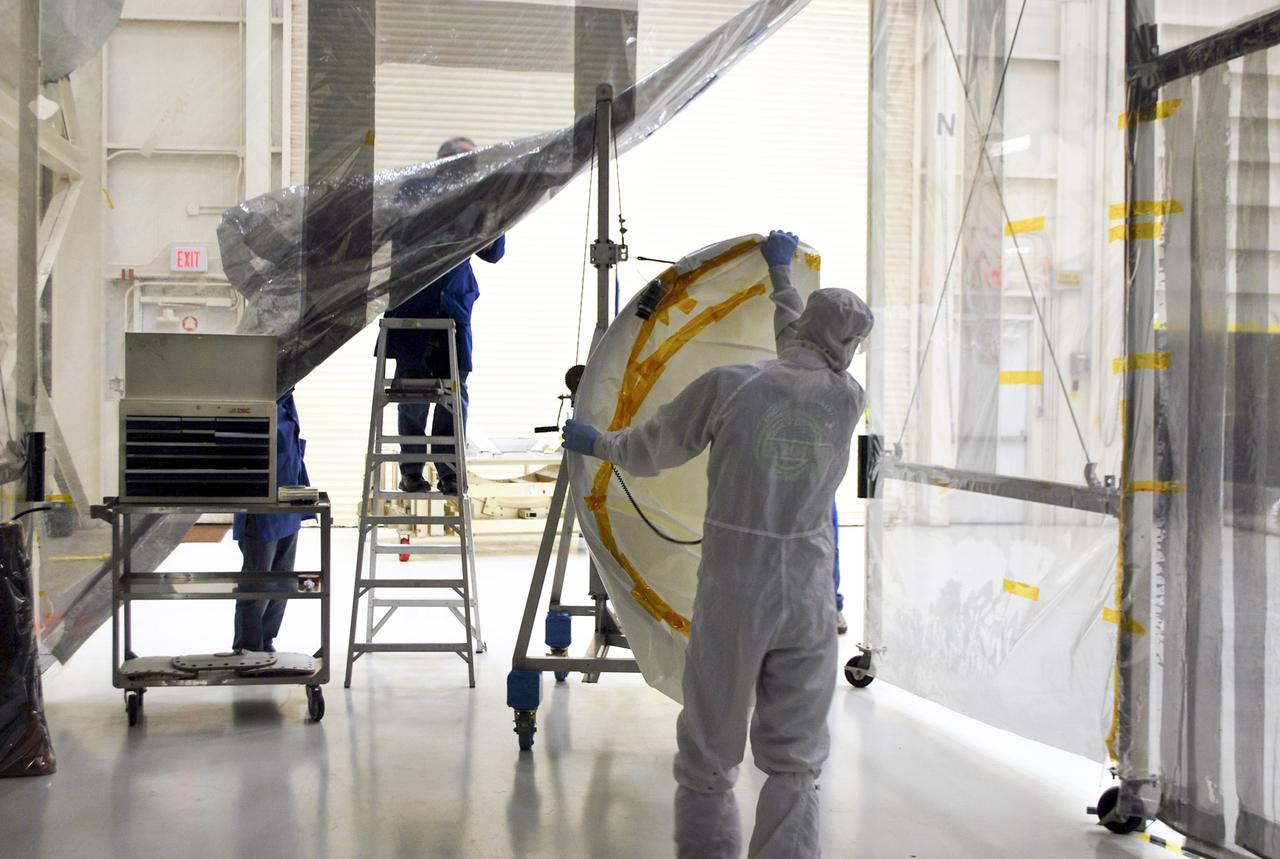

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the port side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
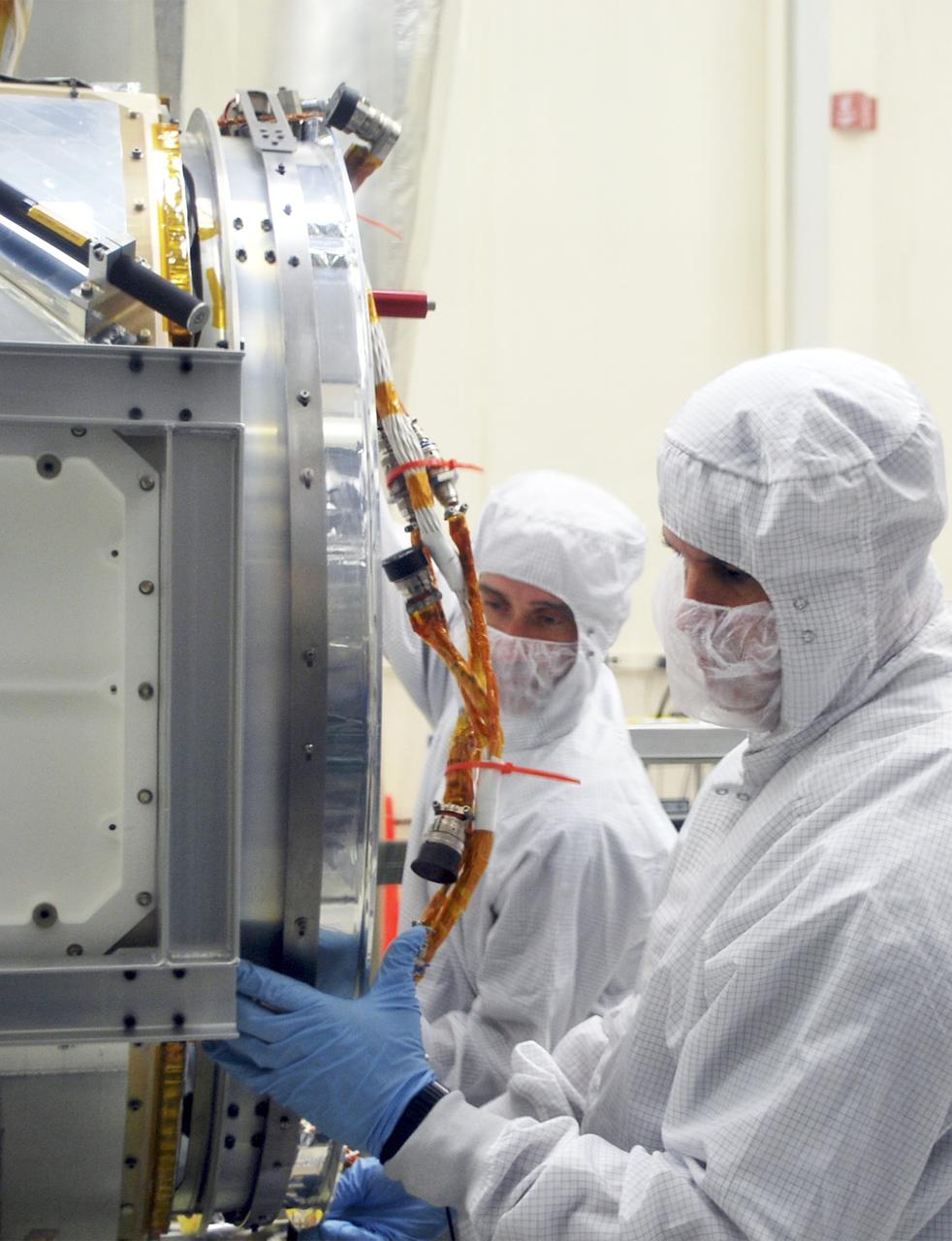

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers install a separation system ring that will be attached to NASA's Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, spacecraft. The separation system will push IRIS away from an Orbital Pegasus XL rocket when the spacecraft reaches its proper orbit after launch. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. For more information, visit http:__iris.gsfc.nasa.gov Photo credit: NASA_Randy Beaudoin
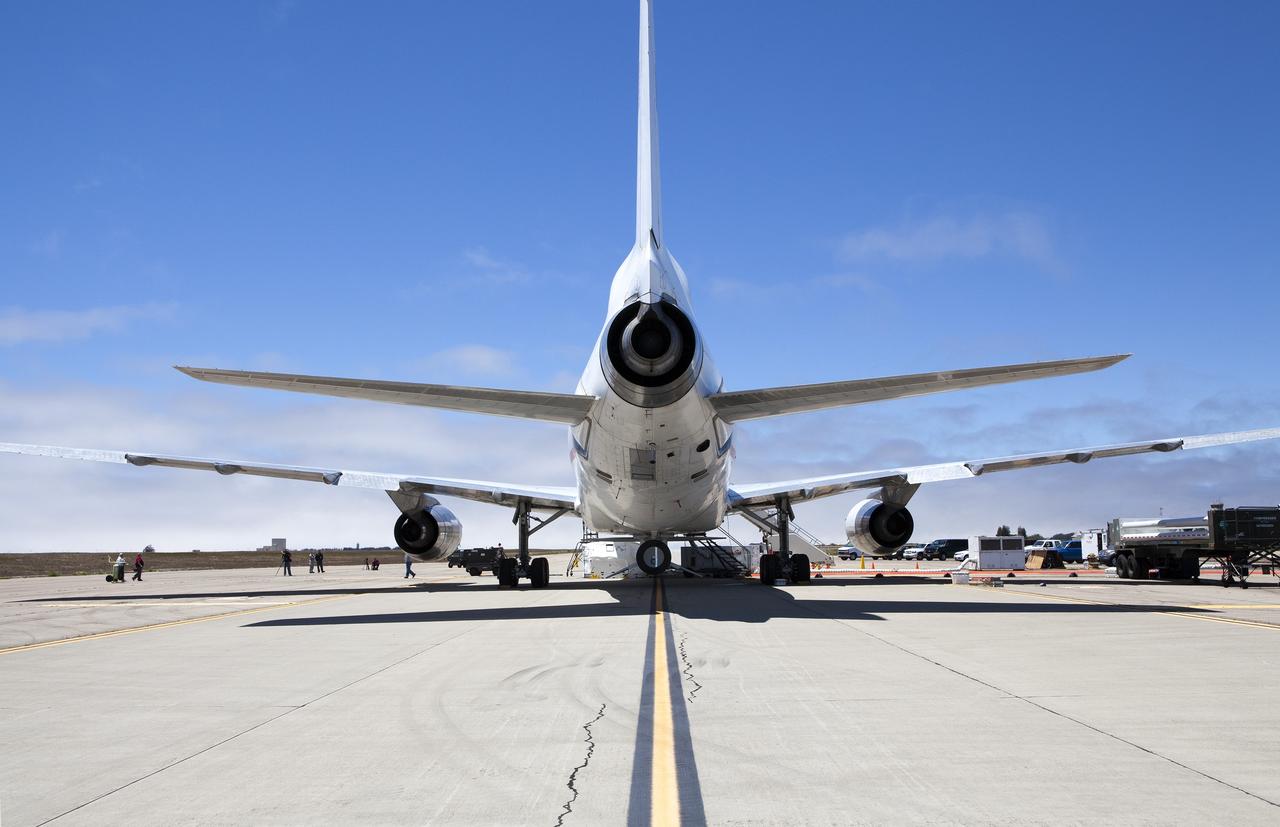

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Final checkouts are being completed at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California as preparations continue for the launch from the L-1011 carrier aircraft of the Orbital Sciences Corp. Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper
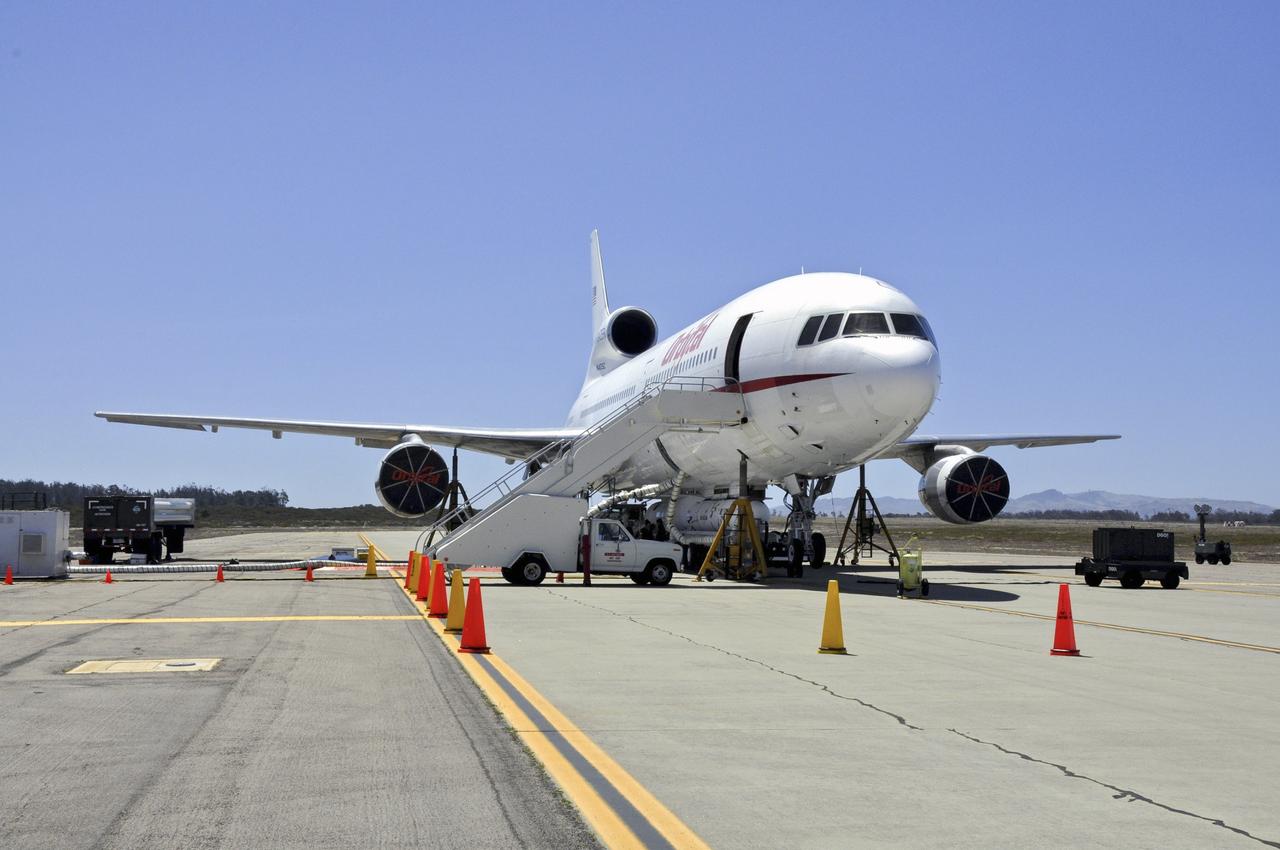

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
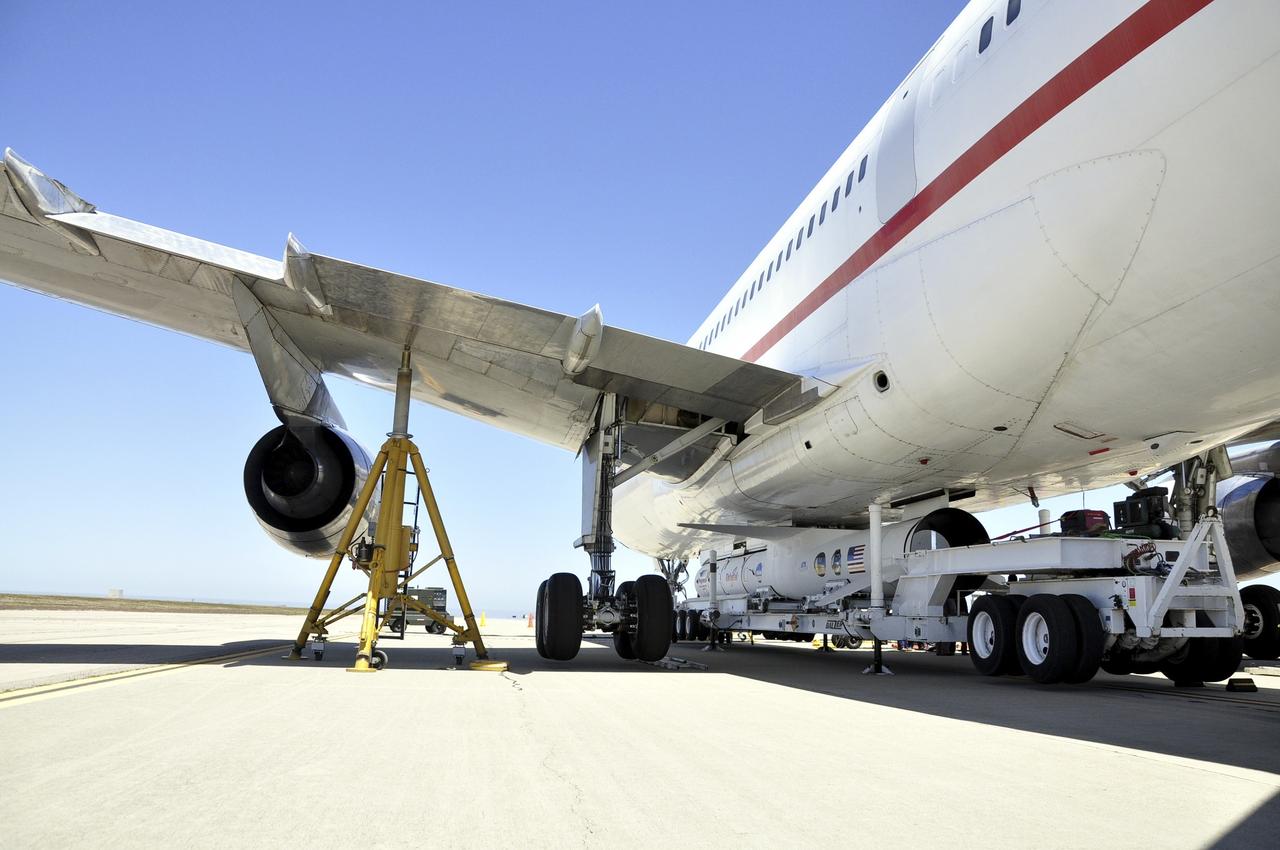

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers prepare to connect NASA's IRIS spacecraft to the nose of an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg no earlier than June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
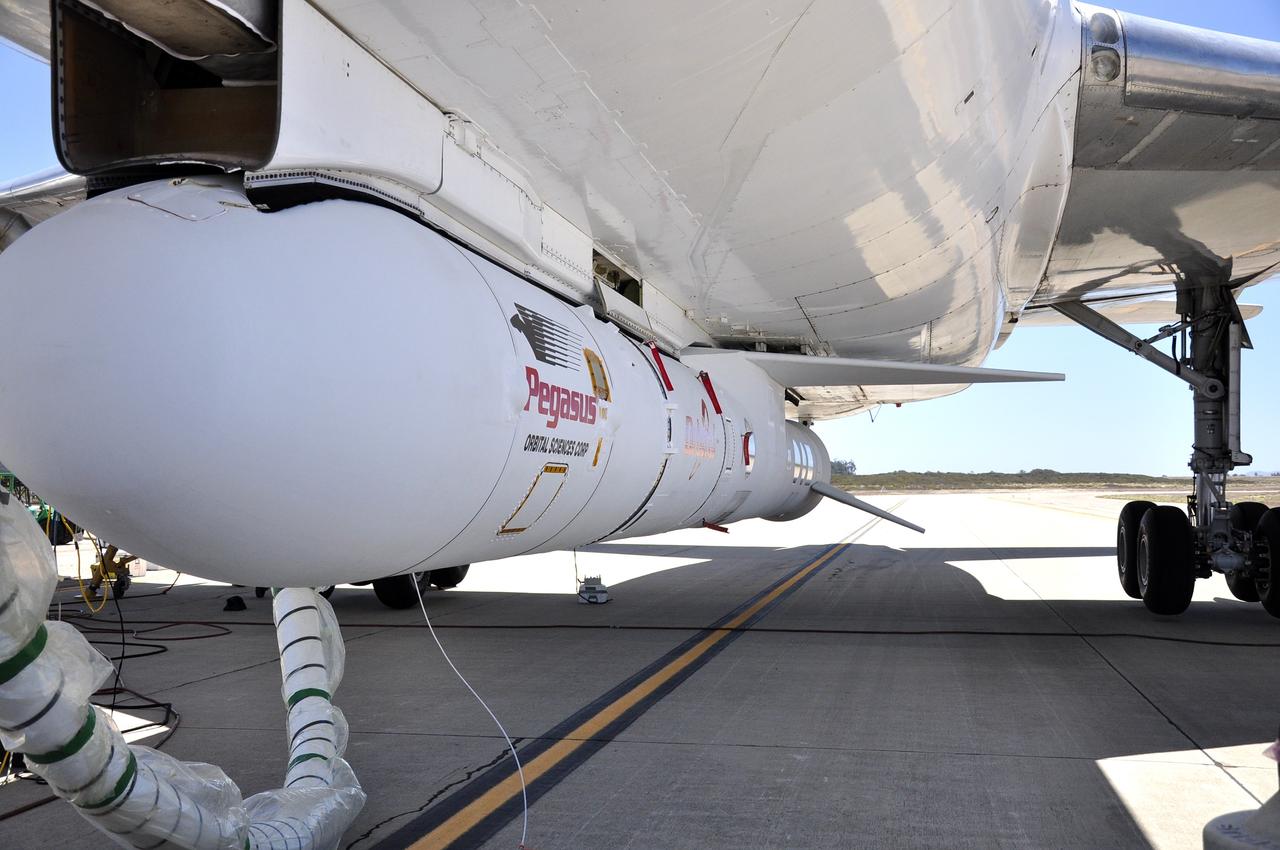

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Technicians and engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California mate the Pegasus XL rocket with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory to the Orbital Sciences L-1011 carrier aircraft. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
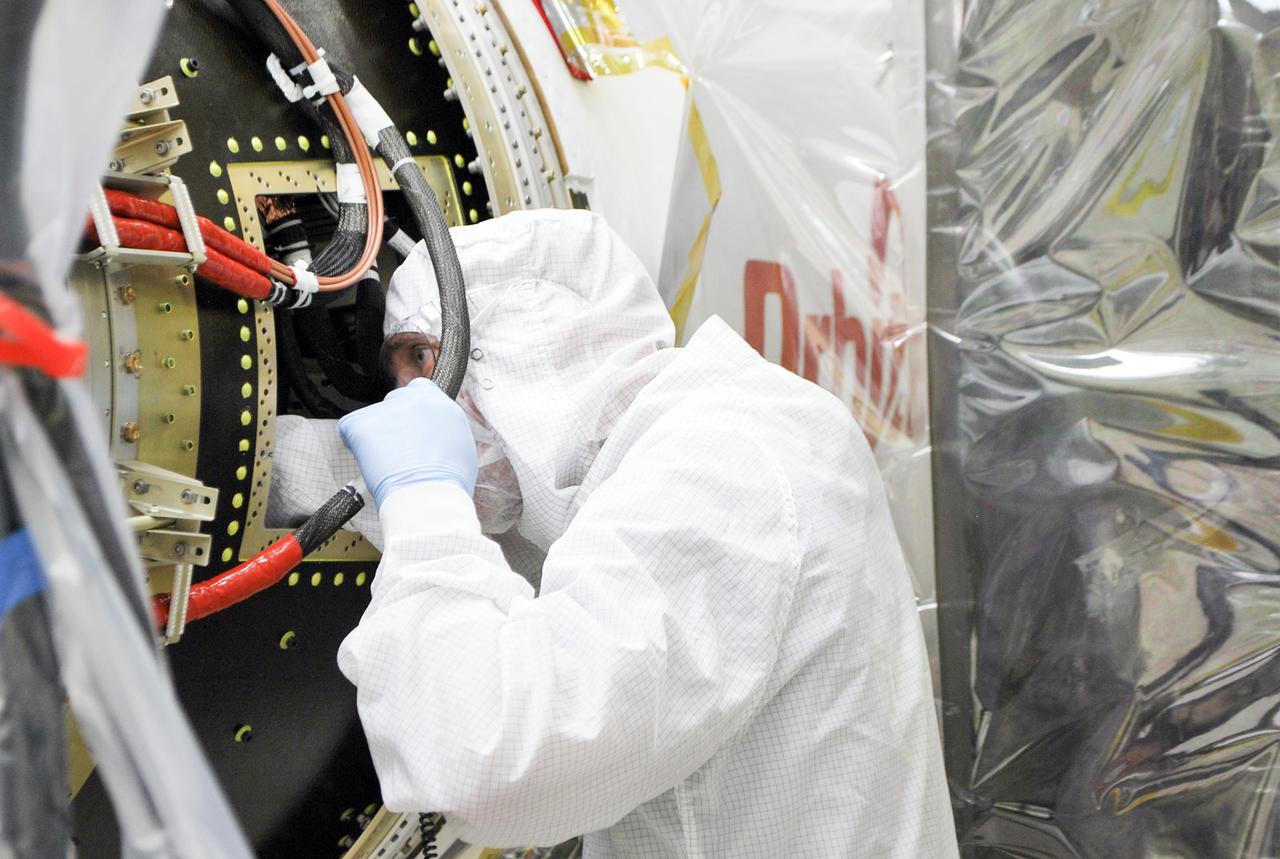

- VANDENBERG AFB – An engineer makes preparations on the starboard side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AFB – Detail of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
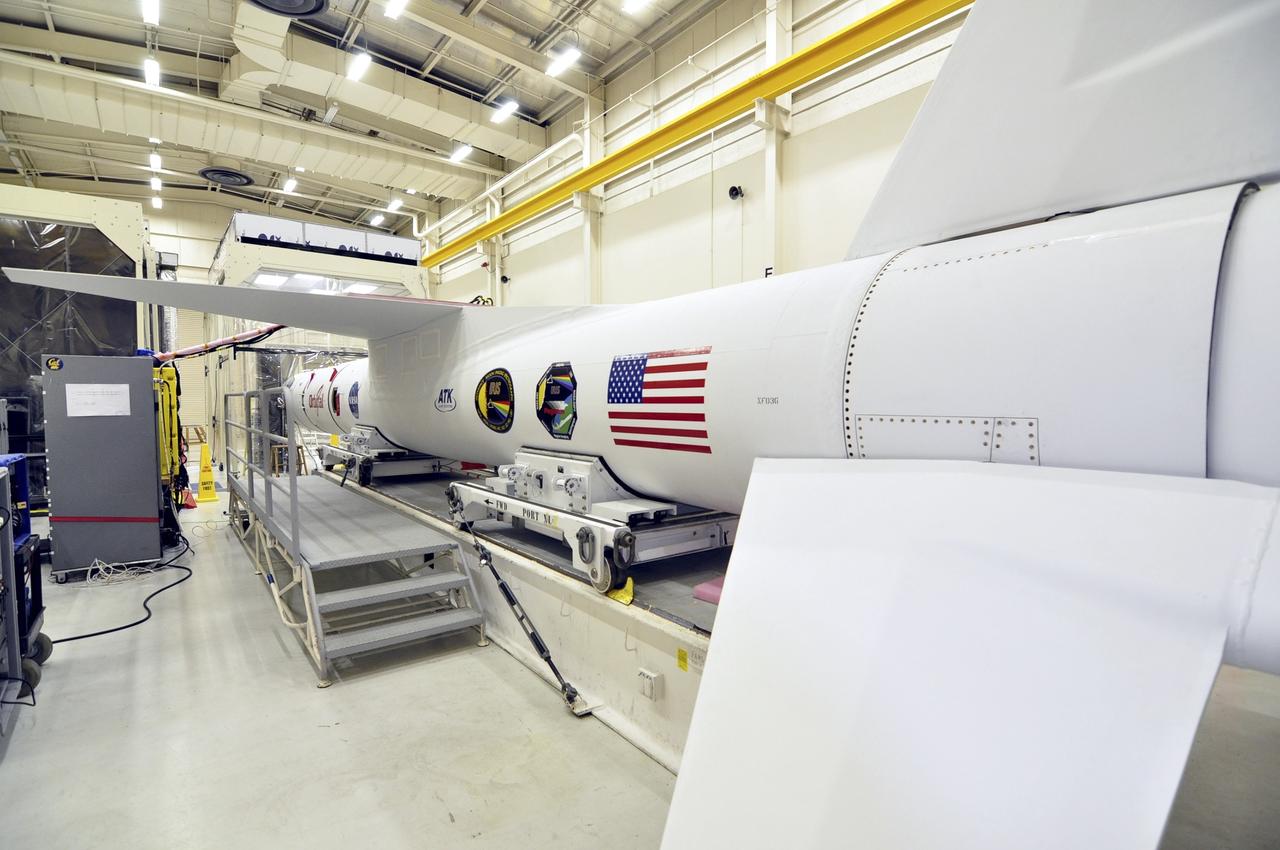

VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June is seen in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
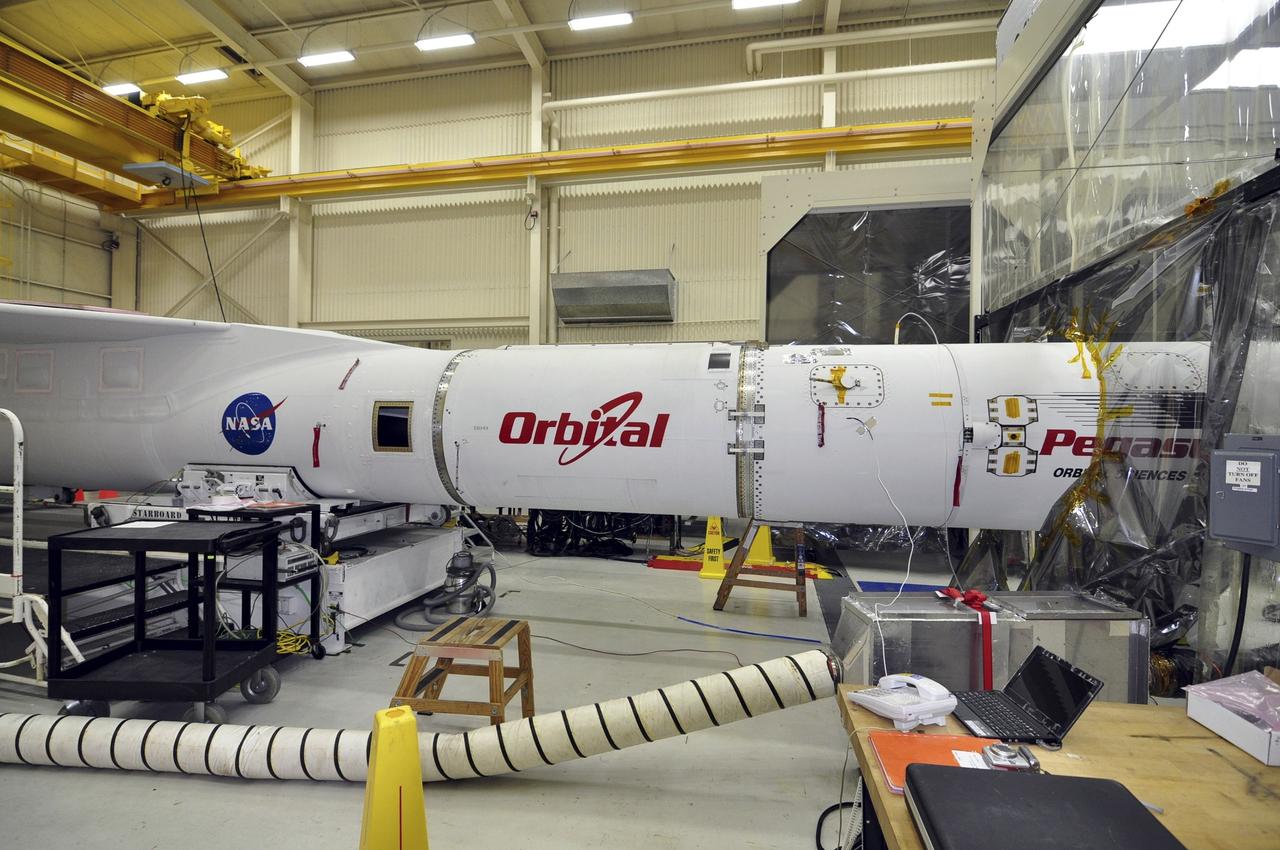

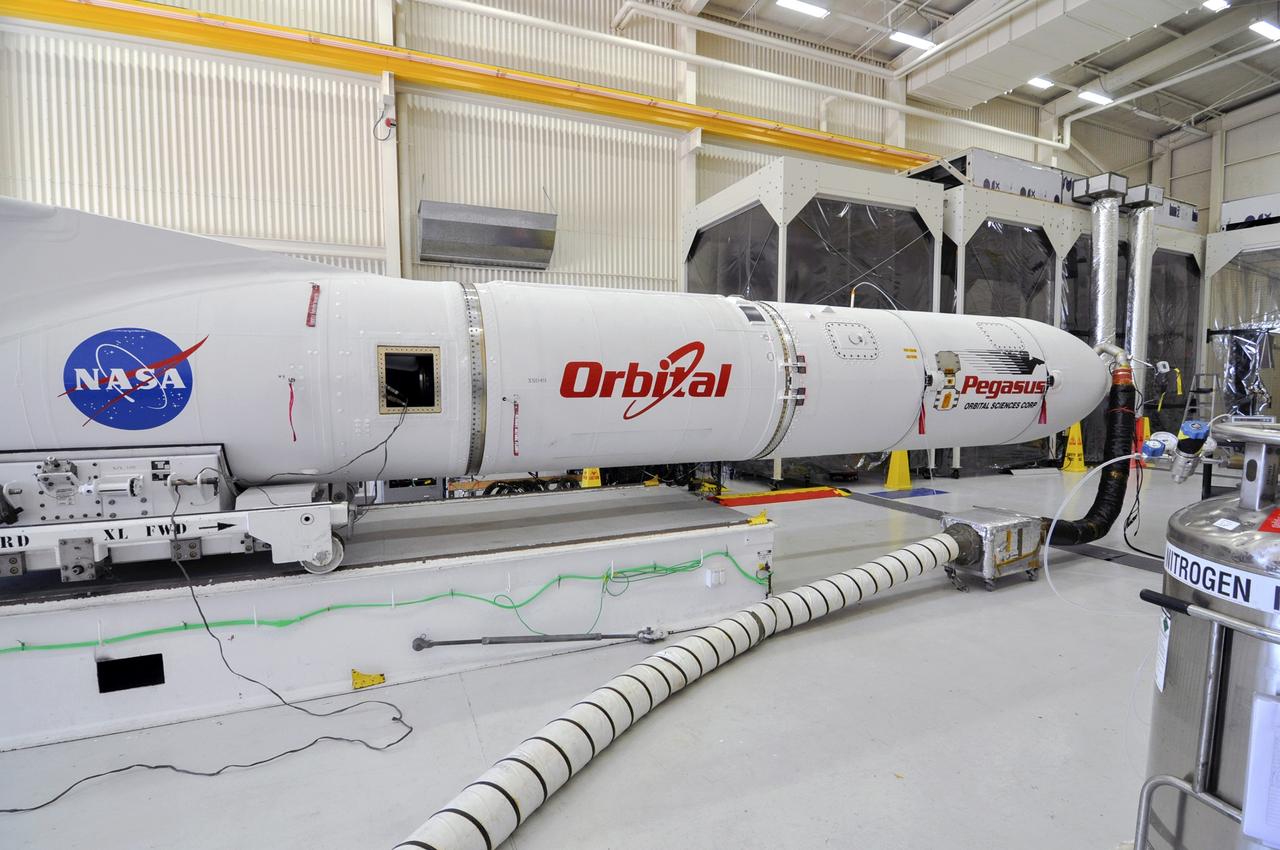
VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June is seen in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
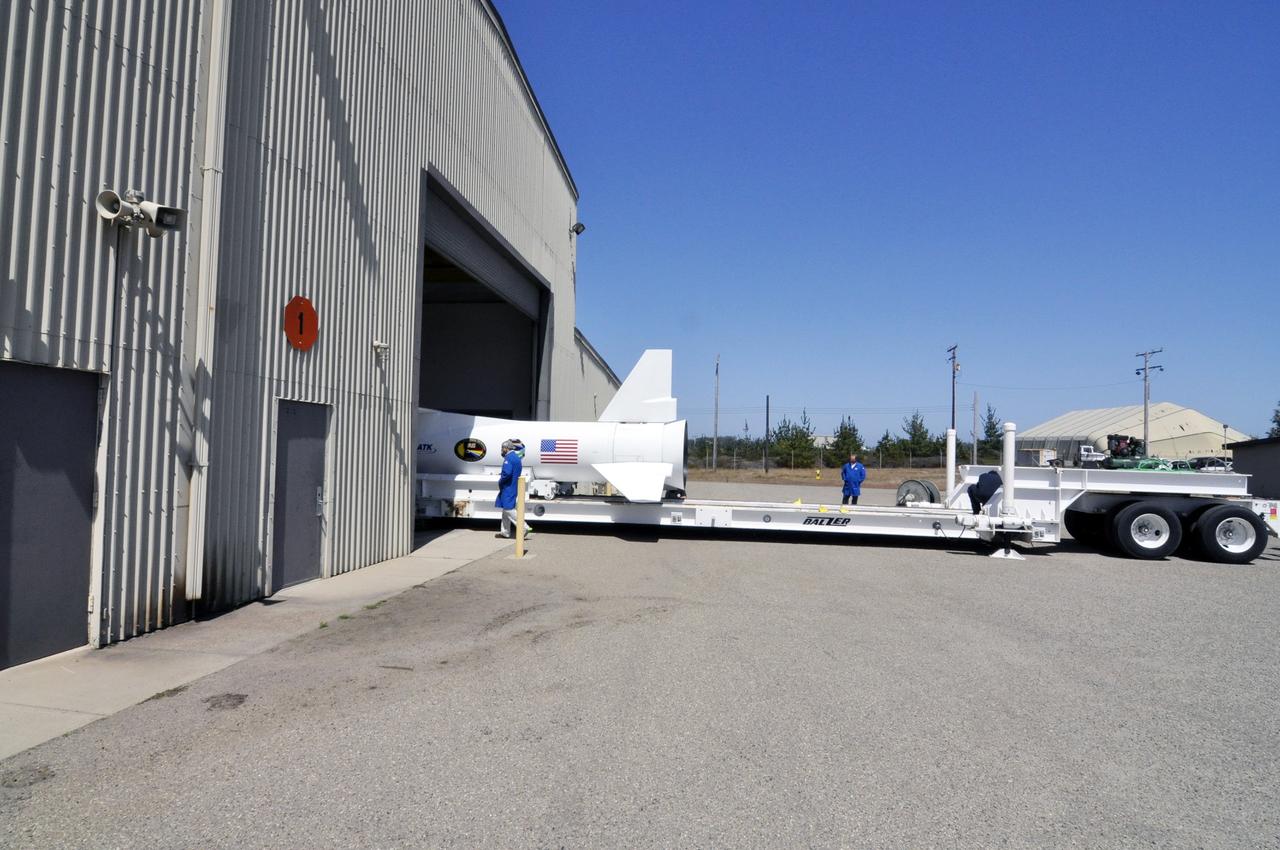

VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit is moved from a hangar onto a transporter at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit is moved from a hangar onto a transporter at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
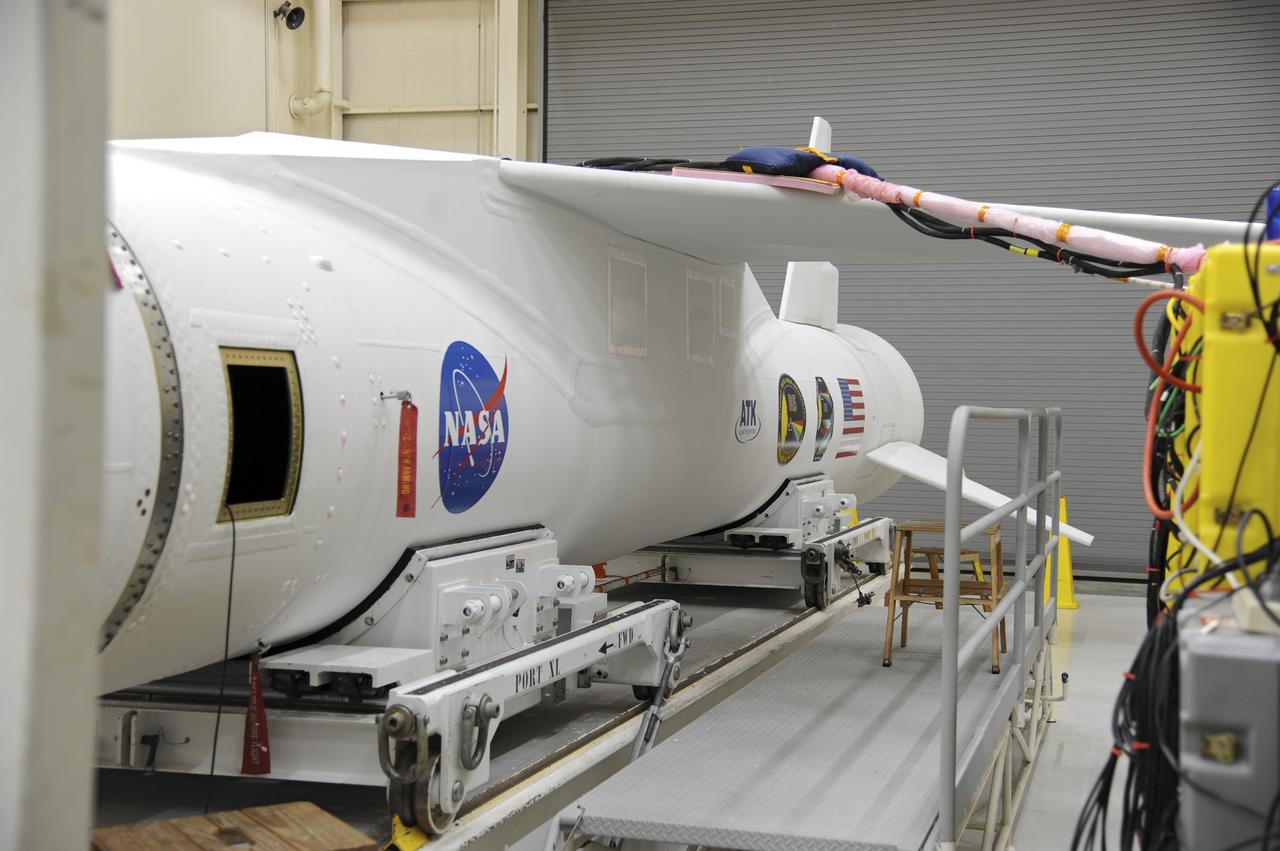

VANDENBERG AFB – Detail of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin

VANDENBERG AFB – Detail of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
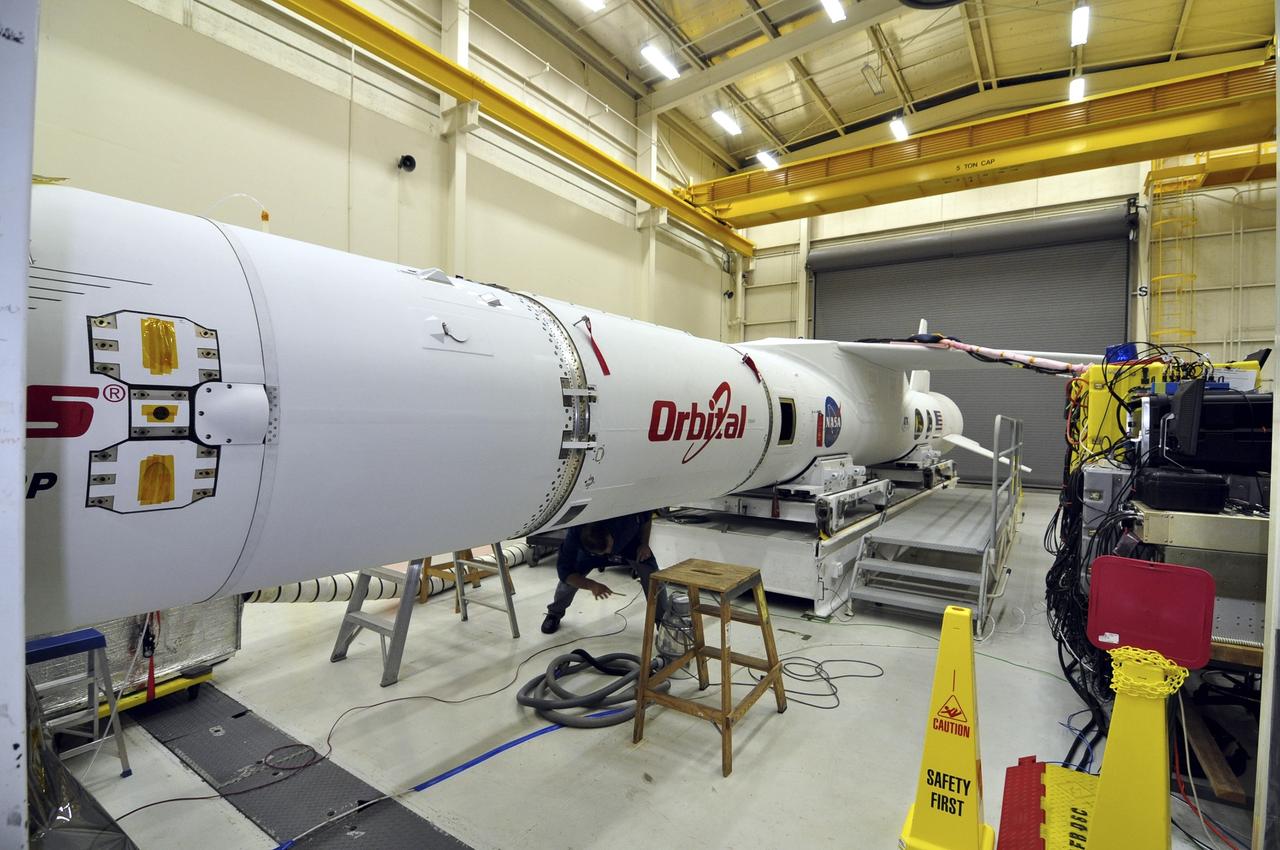

VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit in June is seen in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin
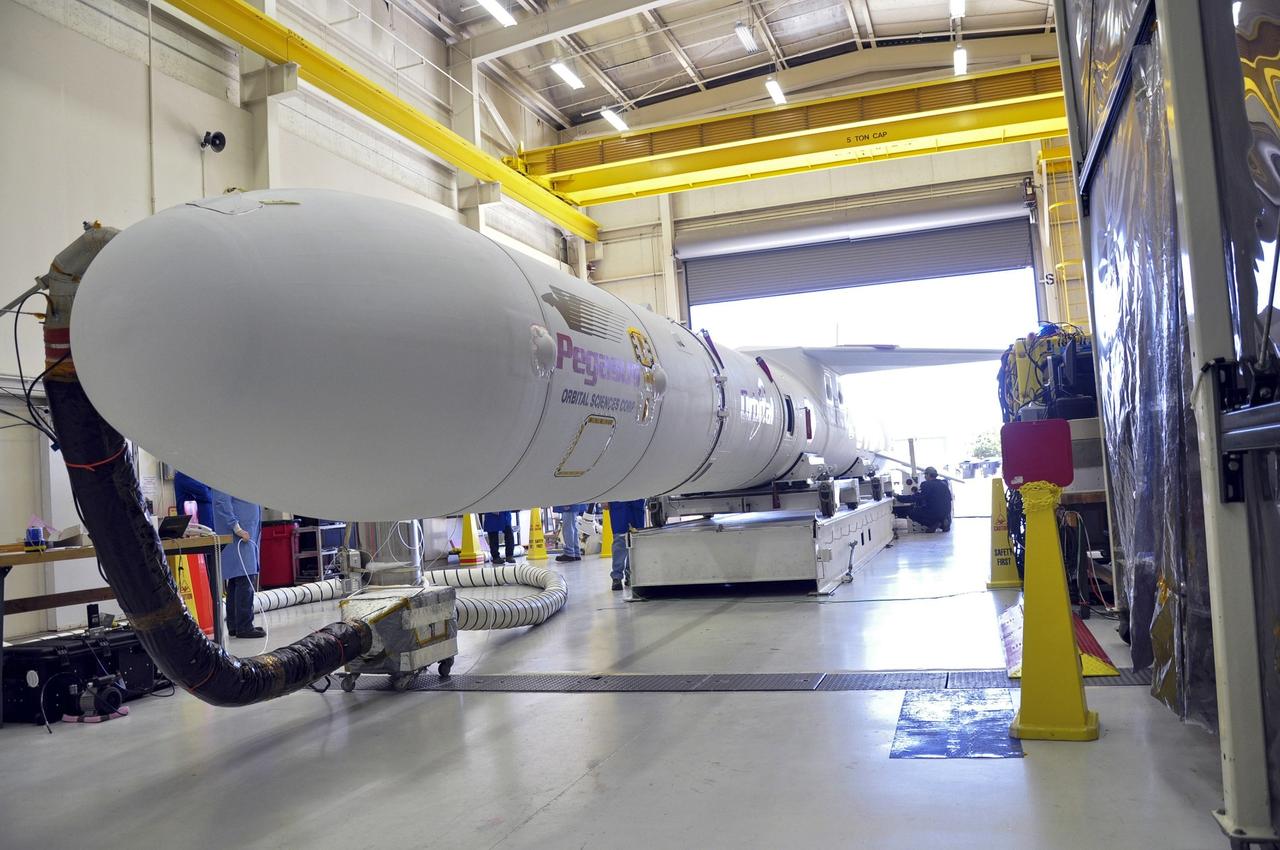

VANDENBERG ABF, Calif. - The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift NASA's IRIS solar observatory into orbit is moved from a hangar onto a transporter at Vandenberg Air Force Base. IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch from Vandenberg June 26. IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: VAFB/Randy Beaudoin