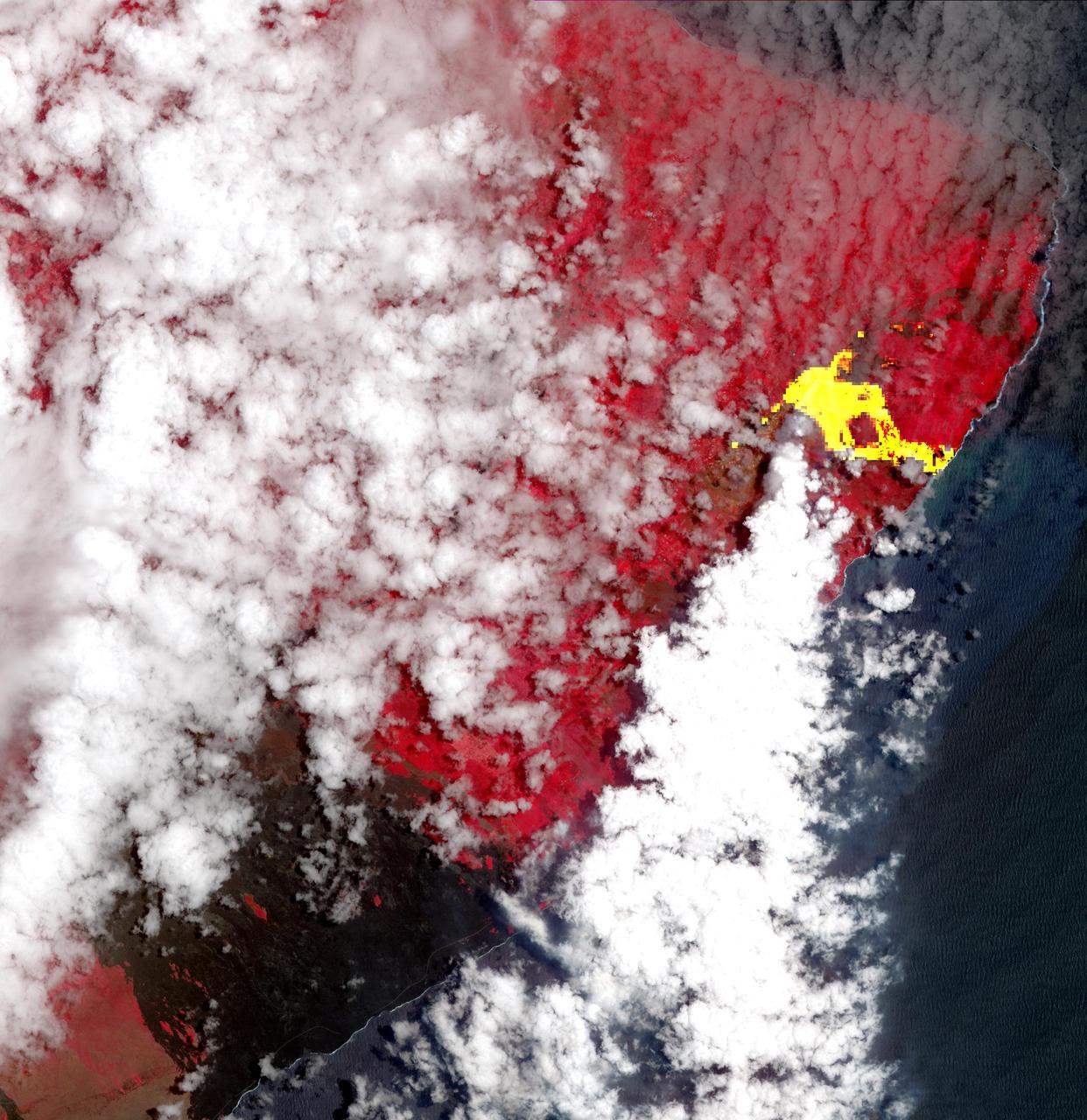
Hawaii's Kilauea's eruption, which began three weeks ago, has produced new lava flows that reached the ocean. The combination of molten lava and sea water produced clouds of noxious gases, such as hydrogen sulfide. In this image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection (ASTER) radiometer instrument on NASA's Terra satellite, vegetation is displayed in red, clouds are white and the hot lava flows, detected by ASTER's thermal infrared channels, are overlaid in yellow. The image was acquired May 22, 2018, covers an area of 20.3 by 20.9 miles (32.6 by 33.6 kilometers), and is located at 19.6 degrees north, 154.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22459

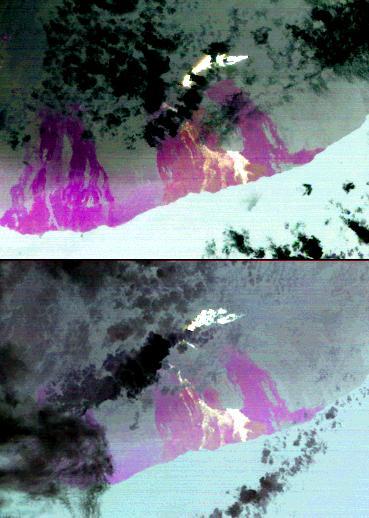
On the night of March 25, 2008, the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer instrument on NASA Terra satellite captured these thermal infrared images of Kilauea volcano on Hawaii Big Island. Kilauea was active at two locations.
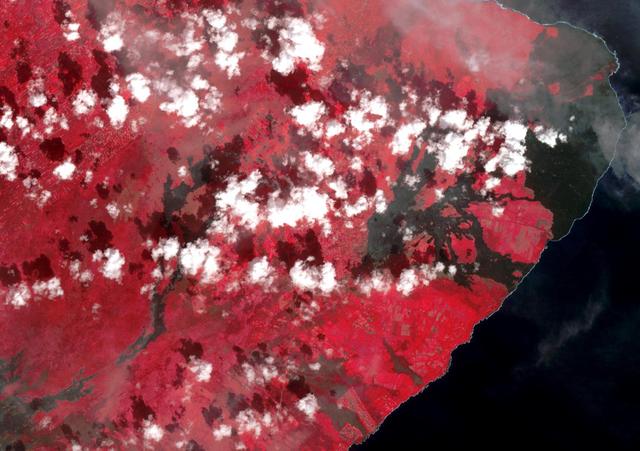

The 2018 Kilauea, Hawaii eruption began in May on Kilauea's East Rift Zone. Lava fountains up to 100 meters high, lava flows, and volcanic gas continued until August. By the time the eruption ended, over 700 houses had been destroyed, and 35 square kilometers of land had been covered by lava flows. About 3.5 square kilometers (875 acres) of new land has been created in the ocean. The before image was acquired by Landsat 8 on September 5, 2013; the ASTER image was acquired November 14, 2018. The images cover an area of 18 by 25.5 kilometers, and are located at 19.5 degrees north, 154.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22899
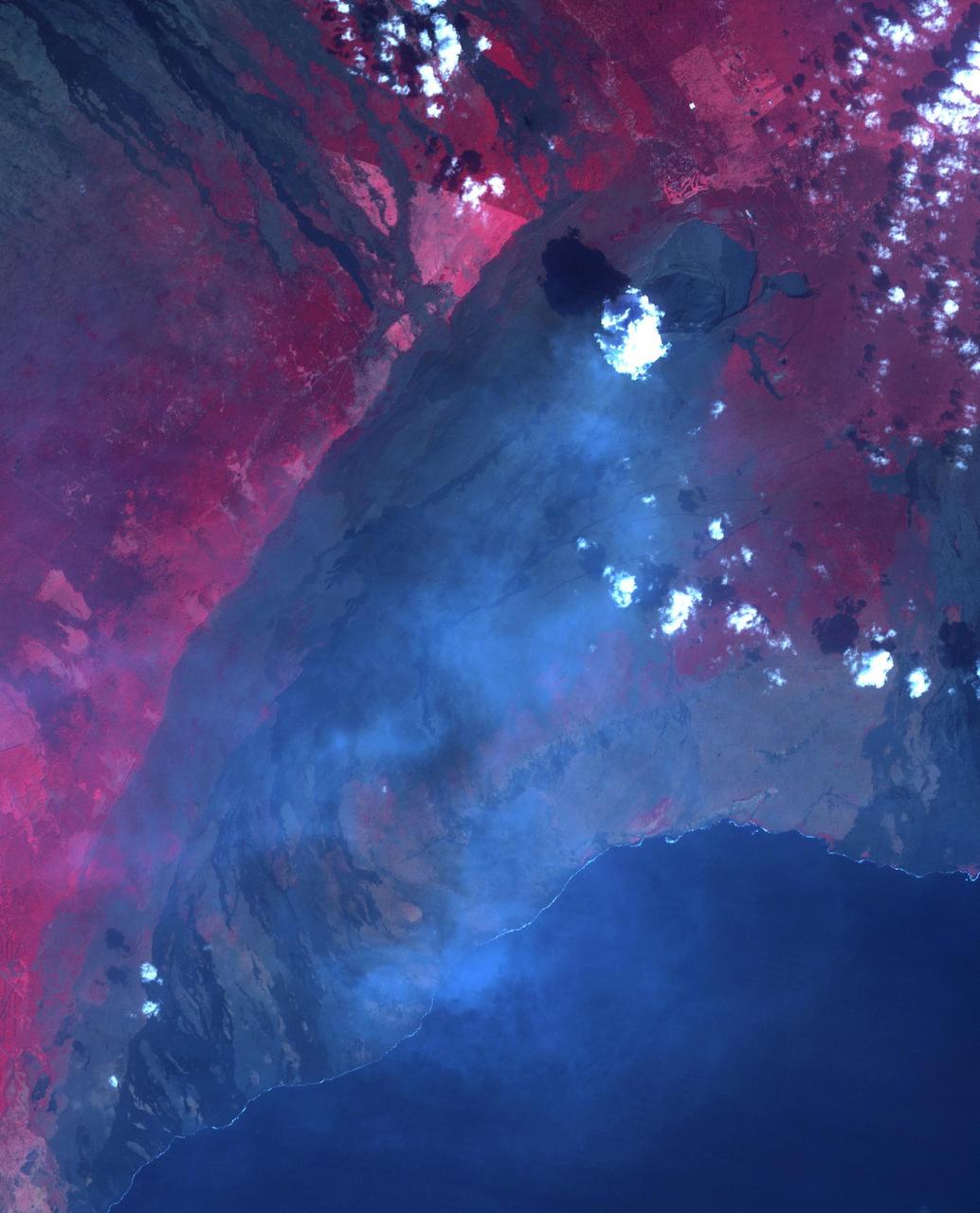

On January 18, ASTER captured this image of the continuing eruption of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii. Lava fountains in Halemaumau crater (top center of image) reached 50 m high, with a nearly vertical eruption plume. Winds carried the blue-gray plume to the south to the ocean. The TROPOMI satellite instrument detected this as a huge SO2 plume the day before. Vegetation is displayed in shades of red. The image covers an area of 38.7 by 45.8 km, and is located at 19.4 degrees north, 155.3 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26504
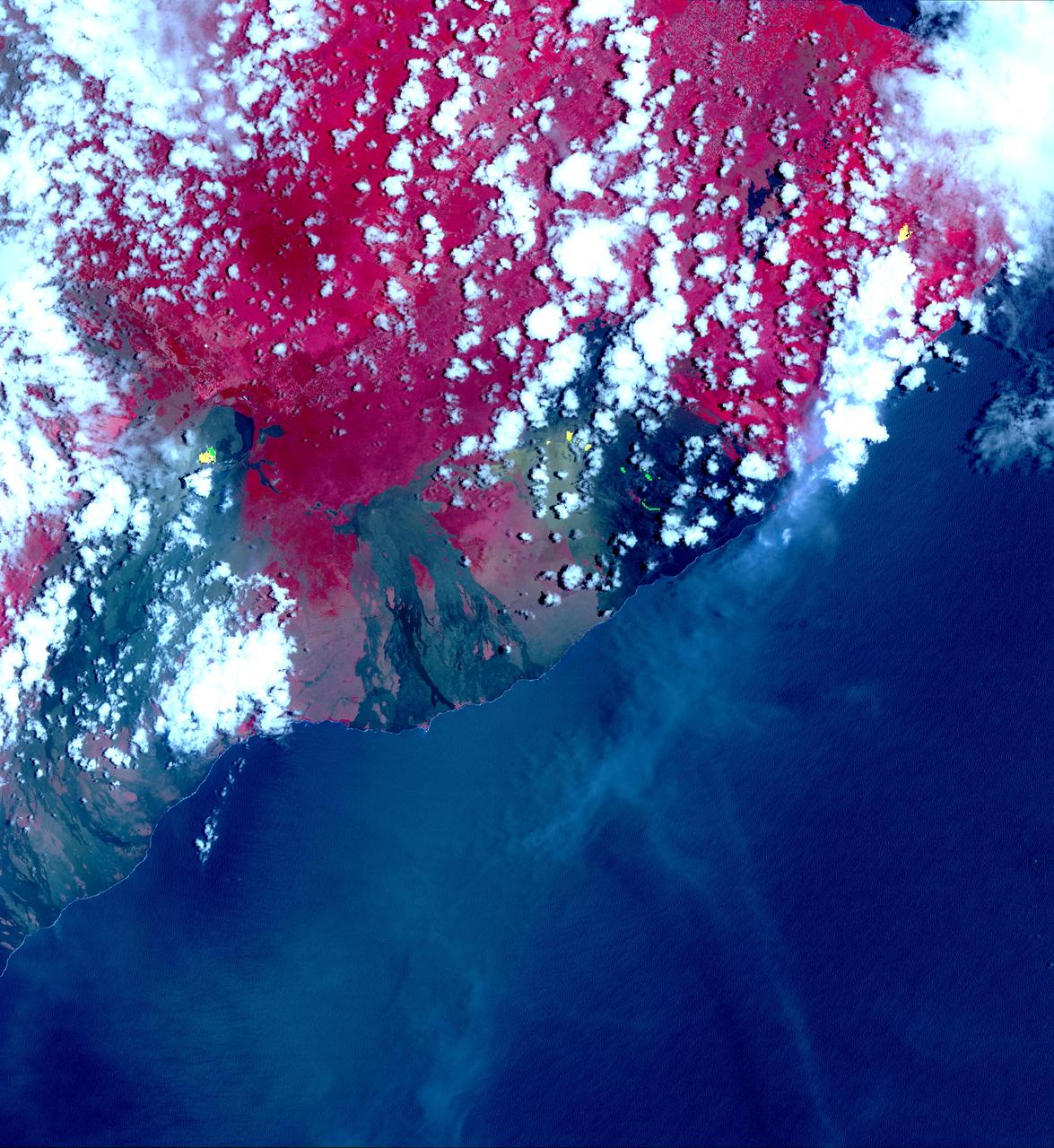

This image from NASA's Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instrument on NASA's Terra spacecraft show recent eruptions of Kilauea volcano on the island of Hawaii (the Big Island). Following days of increased seismic activity, Kilauea erupted May 3, 2018, and triggered a number of additional fissure eruptions along the East Rift Zone. The eruptions and high level of sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) prompted evacuations in the area, including the Leilani Estates subdivision near the town of Pahoa. The ASTER images, acquired on May 6, 2018, show different aspects of the eruption. A color composite depicts vegetation in red, and old lava flows in black and gray. Superimposed on the image in yellow are hotspots detected on the thermal infrared bands. The easternmost hot spots show the newly formed fissures and the lava flow spilling to the northwest. The middle spots are Pu'u O'o crater, and lava flows descending the slopes to the southeast. The westernmost area is the crater and lava lake on Kilauea's summit. The greenish area southwest of Pu'u O'o is ash deposits from its short eruption on Friday. The inset shows the massive sulfur dioxide plume is shown in yellow and yellow-green, extracted from ASTER's multiple thermal bands. A smaller, but thicker, sulfur dioxide gas plume can be seen coming from Kilauea. The prevailing trade winds blow the plumes to the southwest, out over the ocean. The images cover an area of 57.8 by 63 kilometers, and are located at 19.3 degrees North, 155.1 degrees West. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22450
On July 21, 2007, the world most active volcano, Kilauea on Hawaii Big Island, produced a fissure eruption from the Puu Oo vent, which fed an open lava channel and lava flows toward the east. This image is from NASA Terra satellite.

Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, began erupting on December 20, 2020, when a lava flow within Halema'uma'u crater interacted with a pool of water, triggering a vigorous eruption, emitting steam, ash, and sulfur dioxide gas. Since then, lava continues to enter the crater, and the lava lake appears to be stable. In the image, the lava feeder is bright red within the crater, gas is coming from the lava; the lava lake is a lighter gray donut, with a cooler lava island in the middle. The image was acquired December 28, 2020, covers an area of 29.7 by 37.2 km, and is located at 19.4 degrees north, 155.3 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24284

This satellite interferometric synthetic aperture radar image using COSMO-SkyMed radar data, depicts the relative deformation of Earth surface at Kilauea between Feb. 11, 2011 and March 7, 2011 two days following the start of the current eruption.
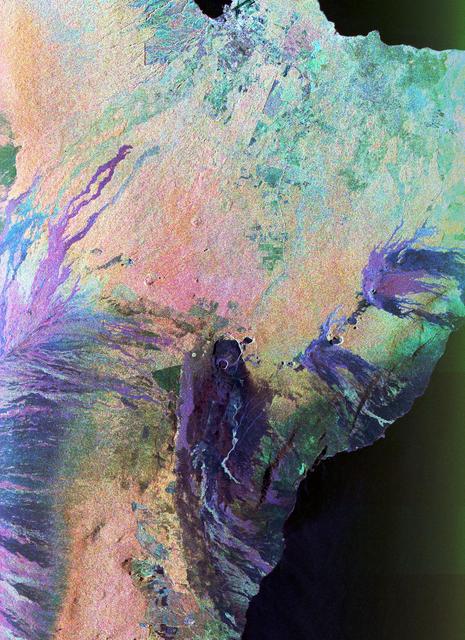

This color composite C-band and L-band image of the Kilauea volcano on the Big Island of Hawaii was acquired by NASA Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar SIR-C/X-SAR flying on space shuttle Endeavour.

This is a deformation map of the south flank of Kilauea volcano on the big island of Hawaii, centered at 19.5 degrees north latitude and 155.25 degrees west longitude. The map was created by combining interferometric radar data -- that is data acquired on different passes of the space shuttle which are then overlayed to obtain elevation information -- acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar during its first flight in April 1994 and its second flight in October 1994. The area shown is approximately 40 kilometers by 80 kilometers (25 miles by 50 miles). North is toward the upper left of the image. The colors indicate the displacement of the surface in the direction that the radar instrument was pointed (toward the right of the image) in the six months between images. The analysis of ground movement is preliminary, but appears consistent with the motions detected by the Global Positioning System ground receivers that have been used over the past five years. The south flank of the Kilauea volcano is among the most rapidly deforming terrains on Earth. Several regions show motions over the six-month time period. Most obvious is at the base of Hilina Pali, where 10 centimeters (4 inches) or more of crustal deformation can be seen in a concentrated area near the coastline. On a more localized scale, the currently active Pu'u O'o summit also shows about 10 centimeters (4 inches) of change near the vent area. Finally, there are indications of additional movement along the upper southwest rift zone, just below the Kilauea caldera in the image. Deformation of the south flank is believed to be the result of movements along faults deep beneath the surface of the volcano, as well as injections of magma, or molten rock, into the volcano's "plumbing" system. Detection of ground motions from space has proven to be a unique capability of imaging radar technology. Scientists hope to use deformation data acquired by SIR-C/X-SAR and future imaging radar missions to help in better understanding the processes responsible for volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01758
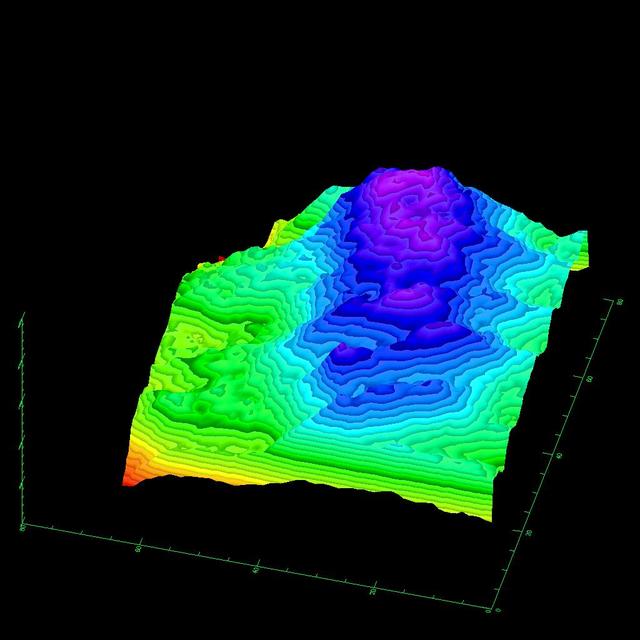
This three-dimensional image of the volcano Kilauea was generated based on interferometric fringes derived from two X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar data takes on April 13, 1994 and October 4, 1994. The altitude lines are based on quantitative interpolation of the topographic fringes. The level difference between neighboring altitude lines is 20 meters (66 feet). The ground area covers 12 kilometers by 4 kilometers (7.5 miles by 2.5 miles). The altitude difference in the image is about 500 meters (1,640 feet). The volcano is located around 19.58 degrees north latitude and 155.55 degrees west longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01761
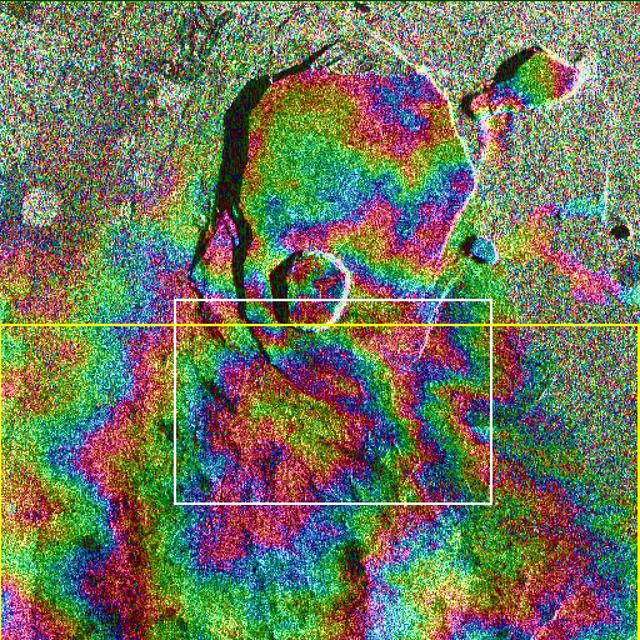
Data acquired on April 13, 1994 and on October 4, 1994 from the X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar on board the space shuttle Endeavour were used to generate interferometric fringes, which were overlaid on the X-SAR image of Kilauea. The volcano is centered in this image at 19.58 degrees north latitude and 155.55 degrees west longitude. The image covers about 9 kilometers by 13 kilometers (5.6 miles by 8 miles). The X-band fringes correspond clearly to the expected topographic image. The yellow line indicates the area below which was used for the three-dimensional image using altitude lines. The yellow rectangular frame fences the area for the final topographic image. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01762
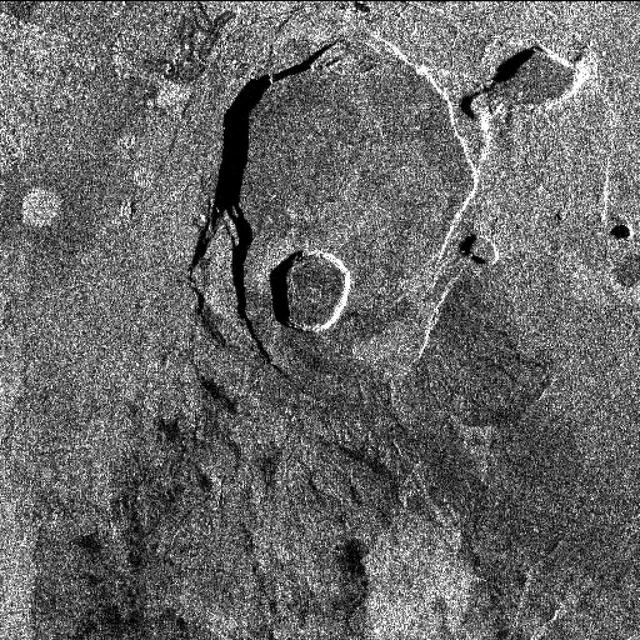
This X-band image of the volcano Kilauea was taken on October 4, 1994, by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar. The area shown is about 9 kilometers by 13 kilometers (5.5 miles by 8 miles) and is centered at about 19.58 degrees north latitude and 155.55 degrees west longitude. This image and a similar image taken during the first flight of the radar instrument on April 13, 1994 were combined to produce the topographic information by means of an interferometric process. This is a process by which radar data acquired on different passes of the space shuttle is overlaid to obtain elevation information. Three additional images are provided showing an overlay of radar data with interferometric fringes; a three-dimensional image based on altitude lines; and, finally, a topographic view of the region. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01763
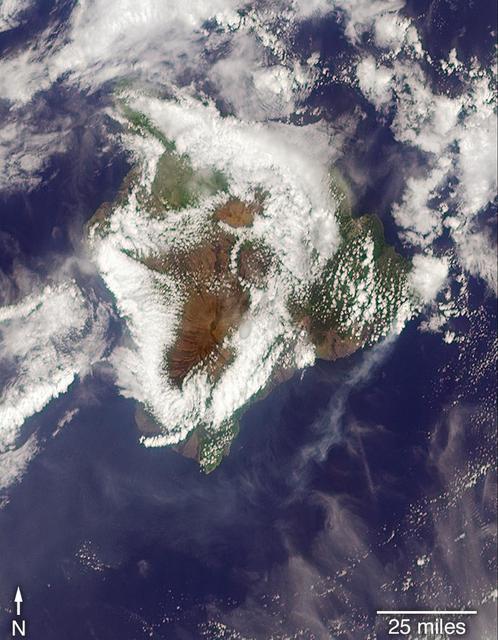

On May 3, 2018, a new eruption began at a fissure of the Kilauea volcano on the Island of Hawaii. Kilauea is the most active volcano in the world, having erupted almost continuously since 1983. Advancing lava and dangerous sulfur dioxide gas have forced thousands of residents in the neighborhood of Leilani Estates to evacuate. A number of homes have been destroyed, and no one can say how soon the eruption will abate and evacuees can return home. On May 6, 2018, at approximately 11 a.m. local time, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument on NASA's Terra satellite captured this view of the island as it passed overhead. Much of the island was shrouded by clouds, including the fissure on its eastern point. However, an eruption plume is visible streaming southwest over the ocean. The MISR instrument is unique in that it has nine cameras that view Earth at different angles: one pointing downward, four at various angles in the forward direction, and four in the backward direction. This image shows the view from one of MISR's forward-pointing cameras (60 degrees), which shows the plume more distinctly than the near-vertical views. The information from the images acquired at different view angles is used to calculate the height of the plume, results of which are superimposed on the right-hand image. The top of the plume near the fissure is at approximately 6,500 feet (2,000 meters) altitude, and the height of the plume decreases as it travels south and west. These relatively low altitudes mean that the ash and sulfur dioxide remained near the ground, which can cause health issues for people on the island downwind of the eruption. The "Ocean View" air quality monitor operated by the Clean Air Branch of the State of Hawaii Department of Health recorded a concentration of 18 μg/m3 of airborne particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter at 11 a.m. local time. This amount corresponds to an air quality rating of "moderate" and supports the MISR results indicating that ash was most likely present at ground level on this side of the island. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 97780. An annotated version is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22451

STS068-S-054 (10 October 1994) --- This is a deformation map of the south flank of Kilauea volcano on the big island of Hawaii, centered at 19.5 degrees north latitude and 155.25 degrees west longitude. The map was created by combining interferometric radar data - that is data acquired on different passes of the Space Shuttle Endeavour which are then overlaid to obtain elevation information - acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) during its first flight in April 1994 and its second flight in October 1994. The area shown is approximately 40 by 80 kilometers (25 by 50 miles). North is toward the upper left of the image. The colors indicate the displacement of the surface in that direction that the radar instrument was pointed (toward the right of the image) in the six months between images. The analysis of ground movement is preliminary, but appears consistent with the motions detected by the Global Positioning System ground receivers that have been used over the past five years. The south flank of the Kilauea volcano is among the most rapidly deforming terrain's on Earth. Several regions show motion over the six-month time period. Most obvious is at the base of Hilina Pali, where 10 centimeters (4 inches) or more of crustal deformation can be seen in a concentrated area near the coastline. On a more localized scale, the currently active Pu'u O'o summit also shows about 10 centimeters (4 inches) of change near the vent area. Finally, there are indications of additional movement along the upper southwest rift zone, just below the Kilauea caldera in the image. Deformation of the south flank is believed to be the result of movements along faults deep beneath the surface of the volcano, as well as injections of magma, or molten rock, into the volcano's "plumbing" system. Detection of ground motions from space has proven to be a unique capability of imaging radar technology. Scientists hope to use deformation data acquired by SIR-C/X-SAR and future imaging radar missions to help in better understanding the processes responsible for volcanic eruptions and earthquakes. Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth. (P-44753)
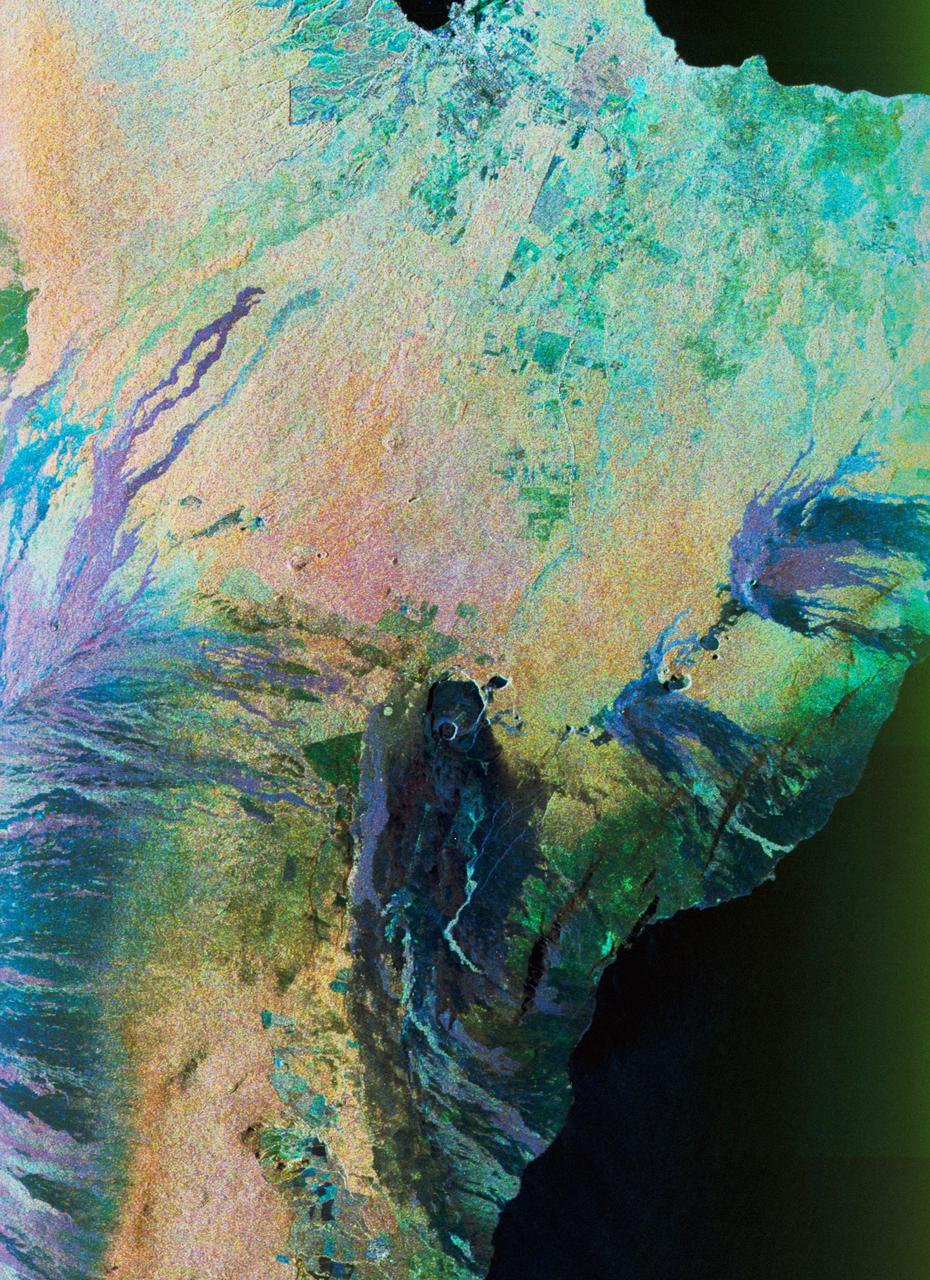

STS059-S-074 (15 April 1994) --- This color composite C-Band and L-Band image of the Kilauea volcano on the big island of Hawaii was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) flying on the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The city of Hilo can be seen at the top. The image shows the different types of lava flows around the crater Pu'u O'o. Ash deposits which erupted in 1790 from the summit of Kilauea volcano show up as dark in this image, and fine details associated with lava flows which erupted in 1919 and 1974 can be seen to the south of the summit in an area called the Ka'u Desert. In addition, the other historic lava flows created in 1881 and 1984 from Mauna Loa volcano (out of view to the left of this image) can easily be seen despite the fact that the surrounding area is covered by forest. Such information will be used to map the extent of such flows, which can pose a hazard to the subdivisions of Hilo. Highway 11 is the linear feature running from Hilo to the Kilauea volcano. The Kilauea volcano has been almost continuously active for more than the last 11 years. Field teams that were on the ground specifically to support these radar observations report that there was vigorous surface activity about 400 meters (one-quarter mile) inland from the coast. A moving lava flow about 200 meters (660 feet) in length was observed at the time of the Shuttle over flight, raising the possibility that subsequent images taken during this mission will show changes in the landscape. SIR-C/X-SAR is part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE). SIR-C/X-SAR radars illuminate Earth with microwaves allowing detailed observations at any time, regardless of weather or sunlight conditions. SIR-C/X-SAR uses three microwave wavelengths: L-Band (24 cm), C-Band (6 cm), and X-Band (3 cm). The multi-frequency data will be used by the international scientific community to better understand the global environment and how it is changing. The SIR-C/X-SAR data, complemented by aircraft and ground studies, will give scientists clearer insights into those environmental changes which are caused by nature and those changes which are induced by human activity. SIR-C was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). X-SAR was developed by the Dornire and Alenia Spazio Companies for the German Space Agency, Deutsche Agentur fuer Raumfahrtangelegenheiten (DARA), and the Italian Space Agency, Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (ASI). JPL Photo ID: P-43918

Briefing Hiking a lava field demands good preparation. Here, the team leaders brief the crew, scientists and student journalists on the route they’ll take down a scarp to the site of Kilauea’s December 1974 eruption. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Lora Bleacher In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
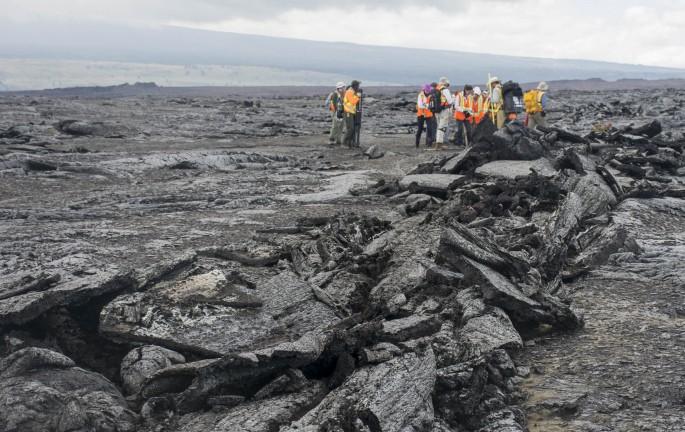

March across pahoehoe The team hikes across Kilauea’s lava fields to reach designated test sites. Several types of lava make up the fields, primarily smooth pahoehoe, which can harden into a ropy, shelly or slabby (pictured here) texture. Some of the most dangerous lava to walk on is a’a – unstable piles of jagged rock. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jasmine Blennau In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
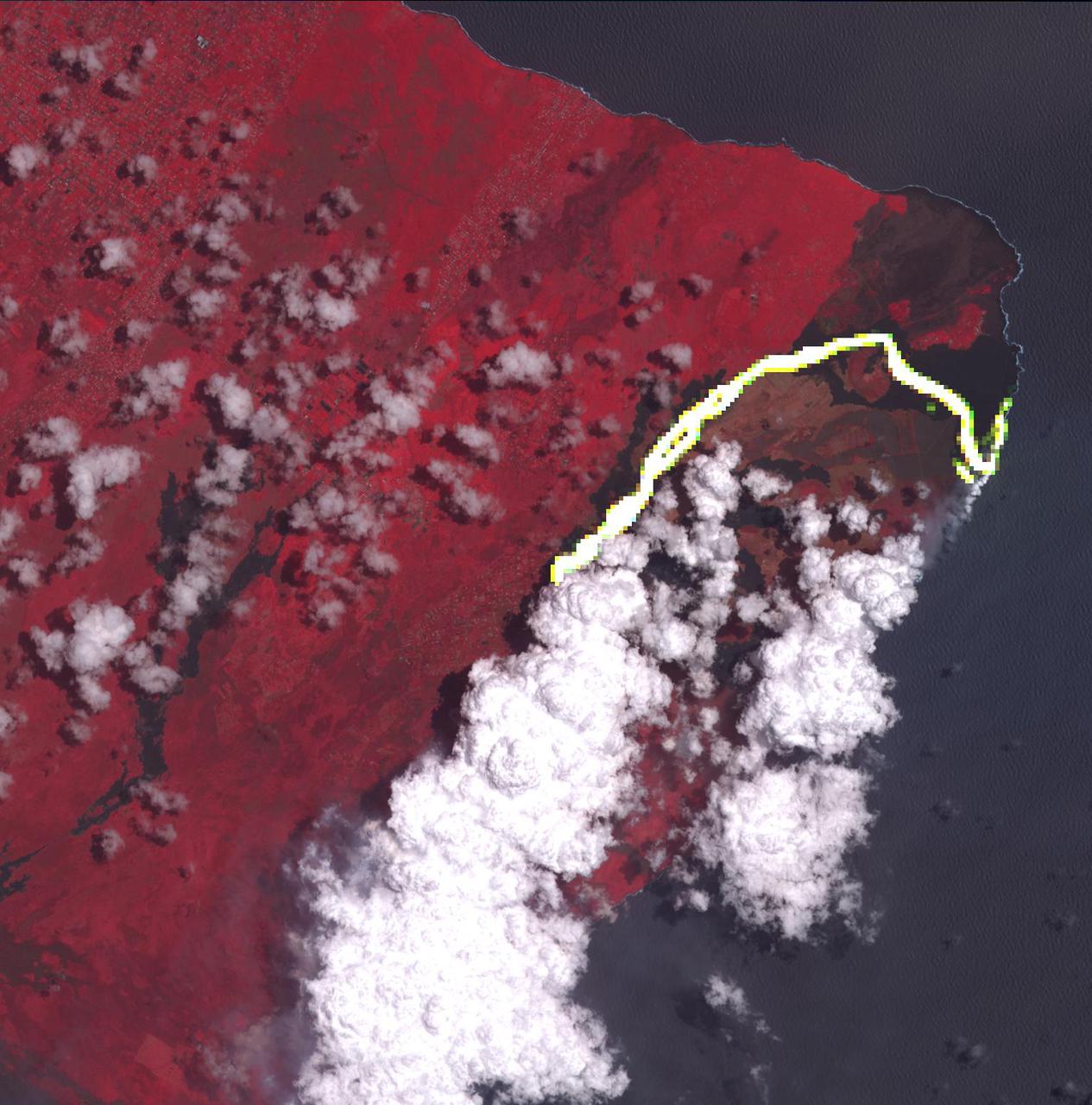
Hawaii's Kilauea volcanic eruption continues after seven weeks of continuous outpouring of lava over the northeastern part of the island. More than 6,100 acres of the Big Island have been covered with new lava, destroying hundreds of homes. At the same time, new land has been created as lava filled Kapoho Bay at the ocean. For some time, the activity has been confined to a leveed channel flow, that starts from the active-most vent, and makes it way 8 miles (13 kilometers) to the ocean. In this image from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection (ASTER) radiometer instrument on NASA's Terra satellite, vegetation is displayed in red, clouds are white and the hot lava flows, detected by ASTER's thermal infrared channels, are overlaid in yellow. The image was acquired June 23, 2018, covers an area of 14.2 by 14.6 miles (23 by 23.3 kilometers), and is located at 19.6 degrees north, 154.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22553
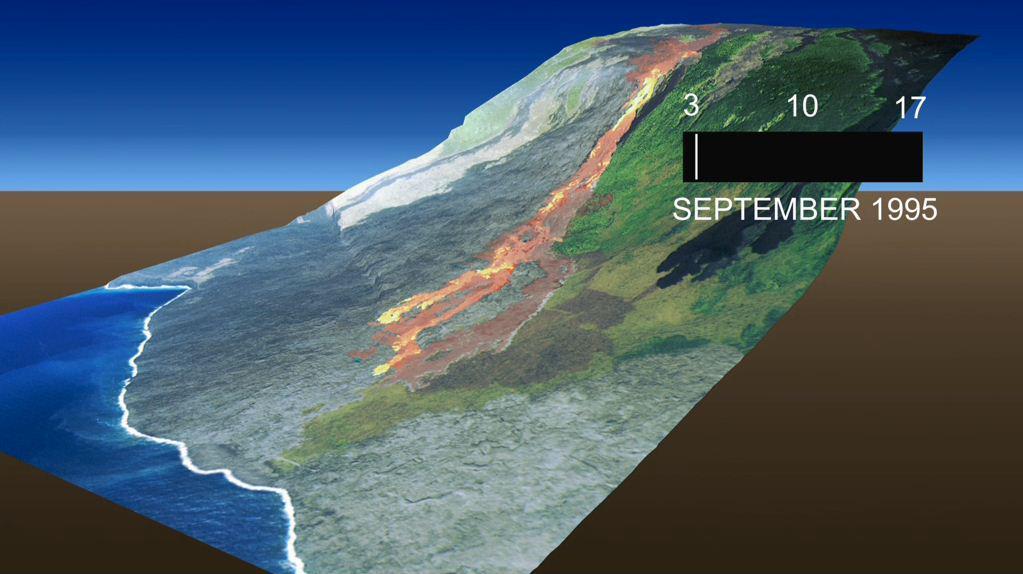
This frame from an animation, which depicts the growth of the Kamoamoa Flow Field, Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii, was generated from a sequence of ten multispectral images acquired between September 3 and 17, 1995.
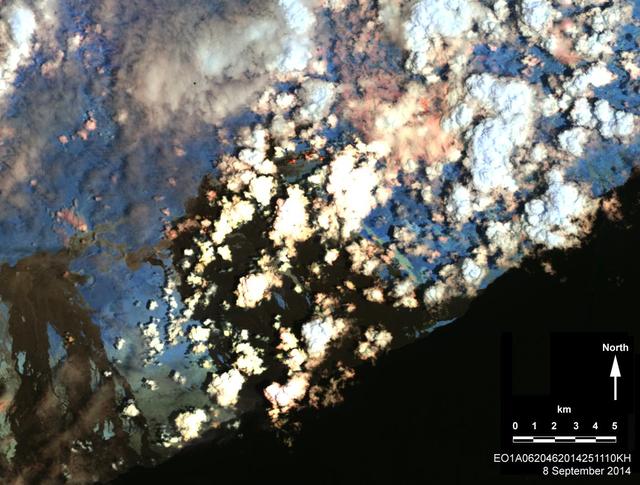

On Sept. 8, 2014, NASA Earth Observing 1 spacecraft obtained this infrared image of Kilauea volcano, Hawaii, which has been in continuous eruption since 1983. New lava flows can be seen.
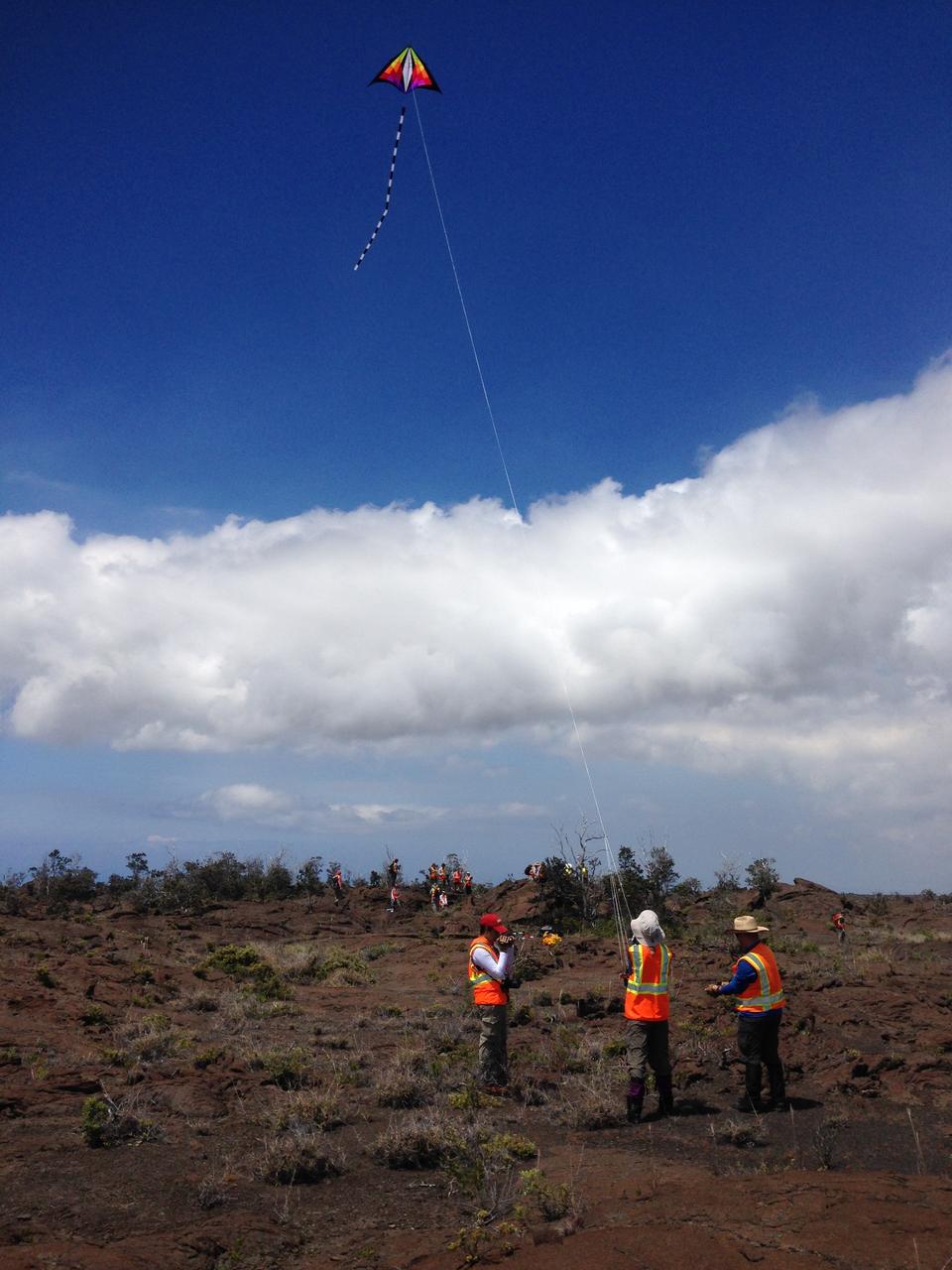

Team kite This kite was part of the scientific tool kit. It carried a camera that can be used to make high-resolution mosaics of the study site. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jacob Bleacher In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
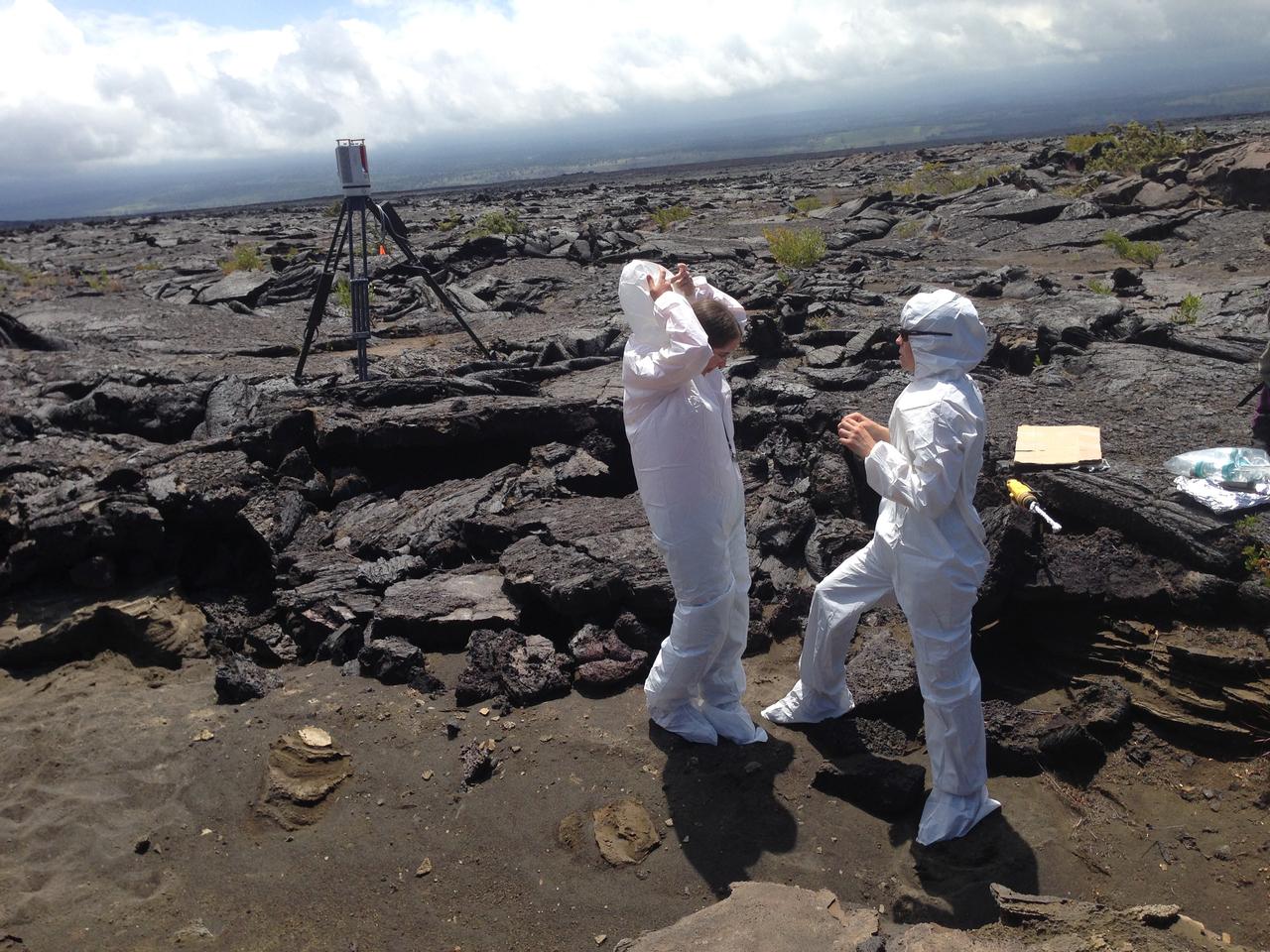

Bunny suits Scientists put on “bunny suits” before they collect samples at one of the selected sites. The suits protect the area and collected samples from contamination when investigating biological processes. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Lora Bleacher In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
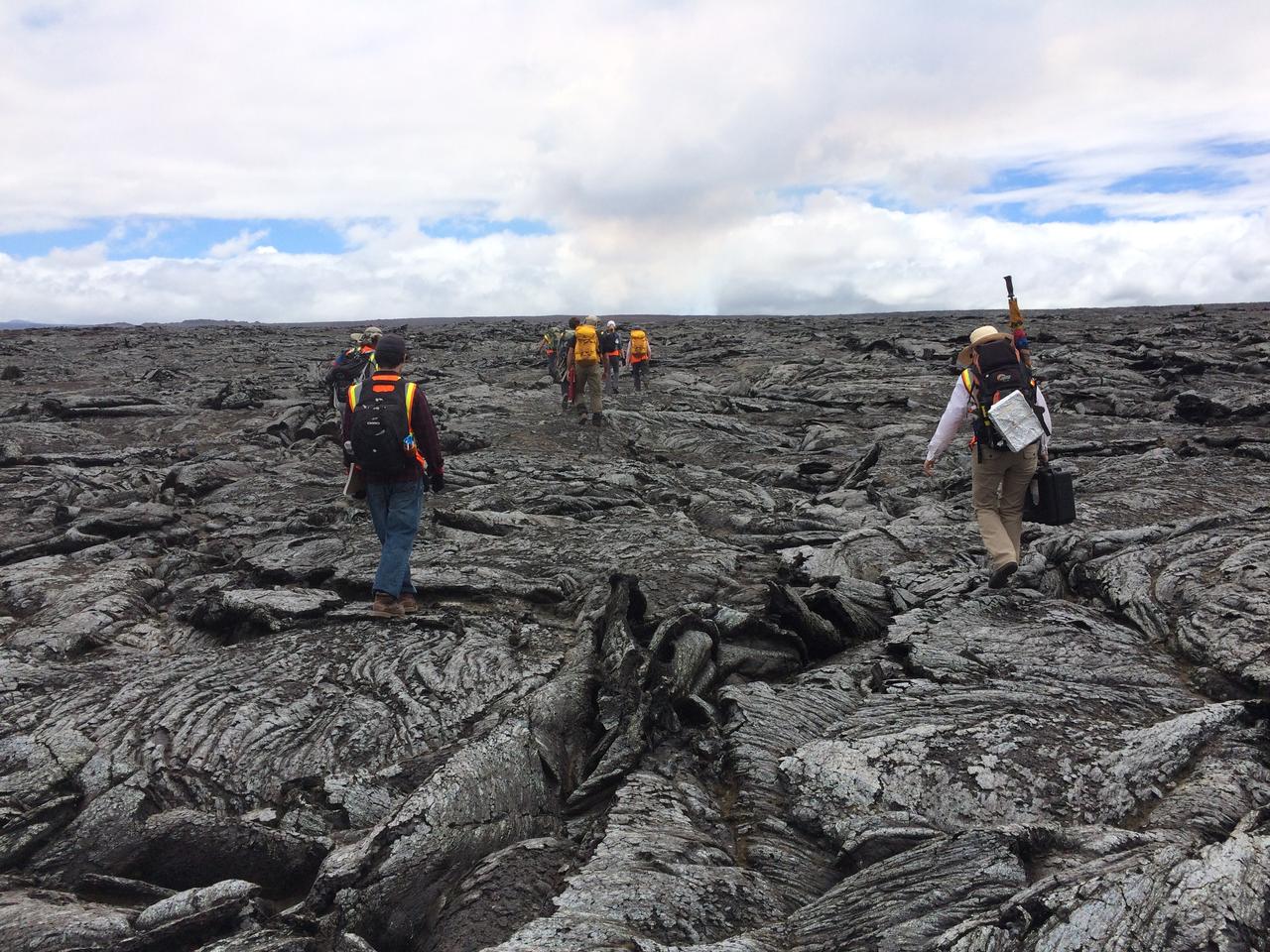

Lava formations The science and journalism teams make their way across the ropey, twisted, broken crust of the 1978 lava flow. These patterns formed as flowing lava exposed at the surface cooled and solidified, while hot lava continued to flow beneath. The dark cloud in the distance is the active volcanic plume. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Andrea Jones In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
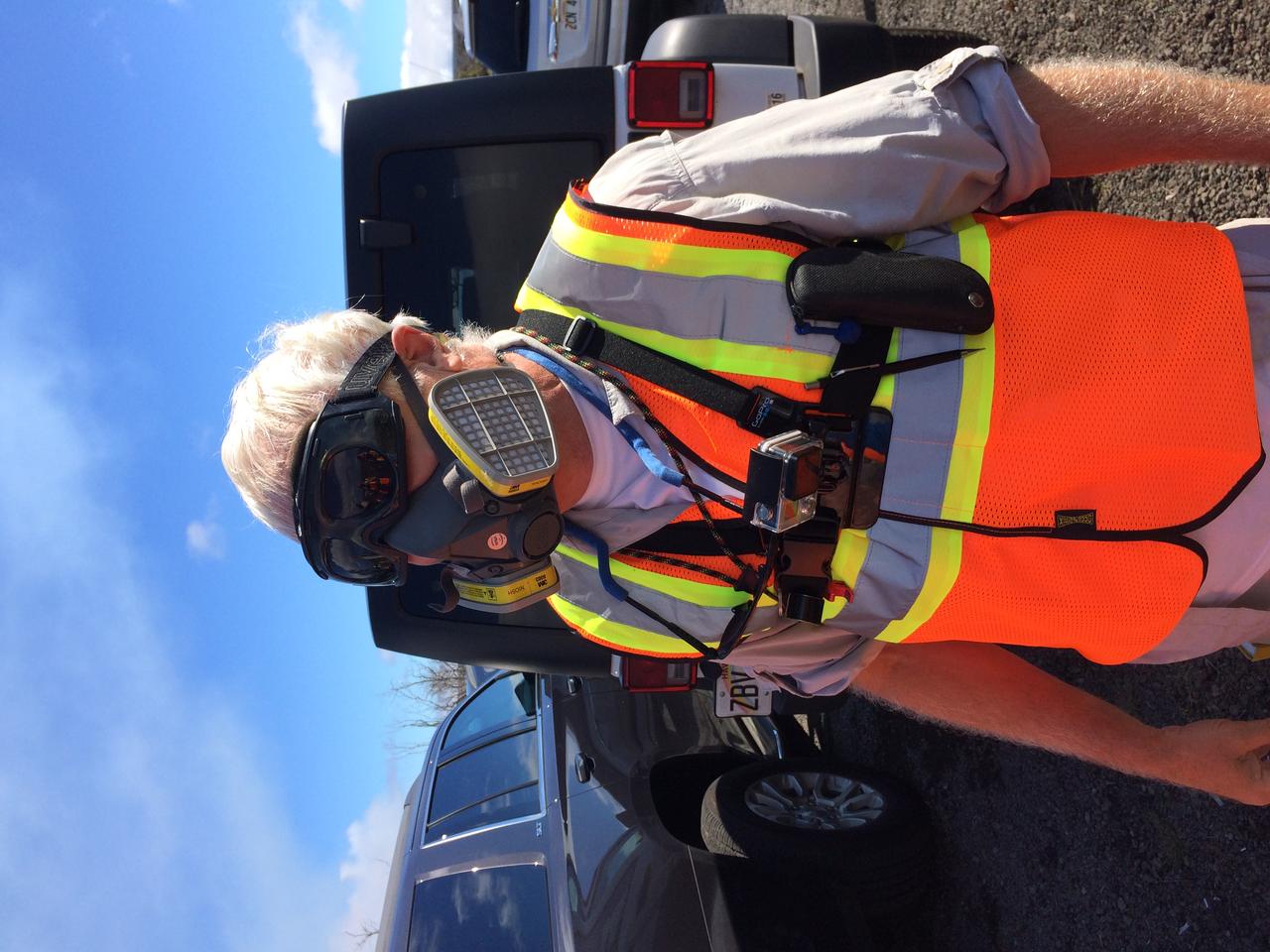

Prepared Everyone carried a respirator into the field, in case the plume from the volcano blew their way. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Andrea Jones In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
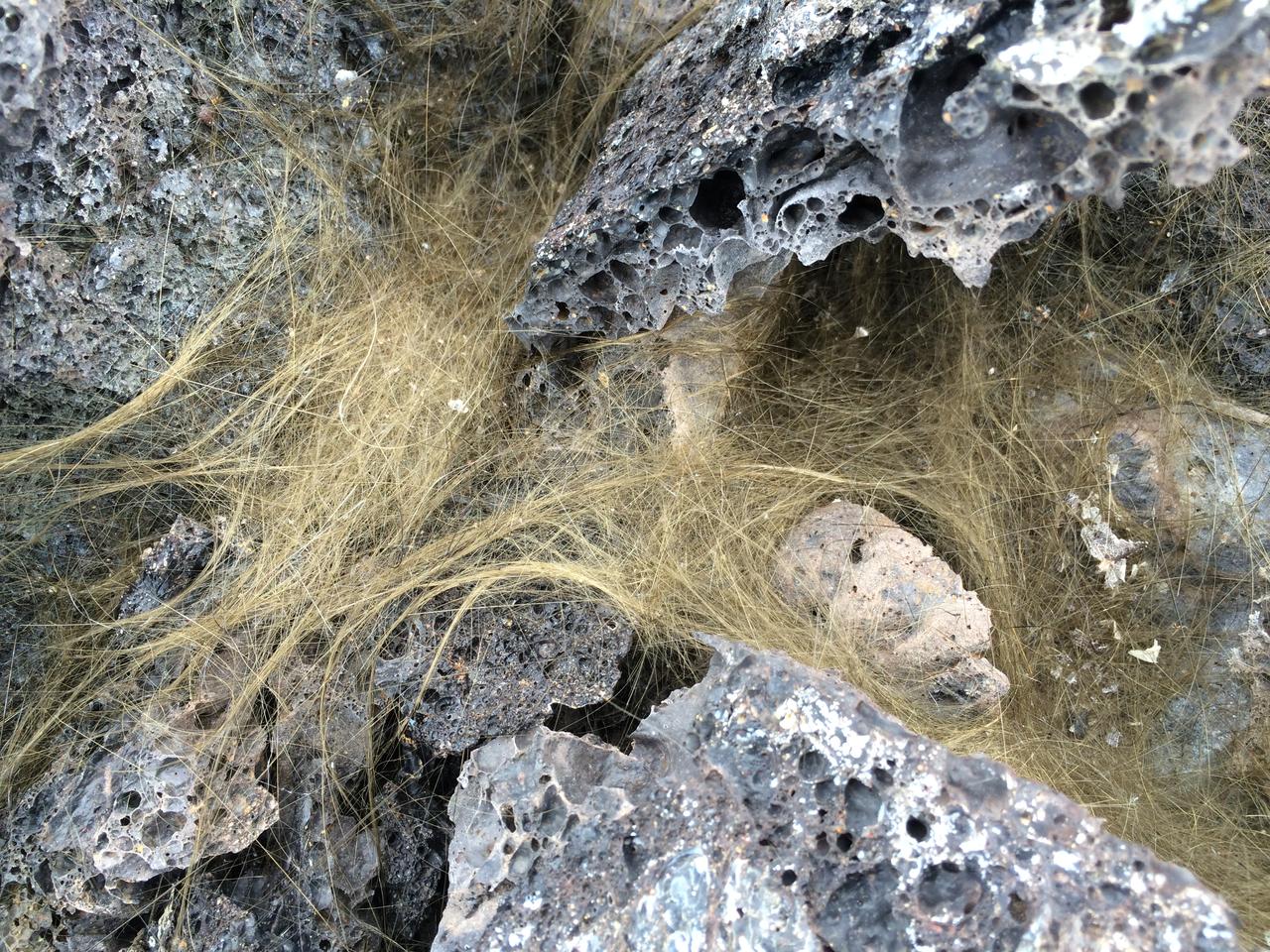

Pele’s hair Greenish-gold strands of Pele’s hair form when bubbles in hot lava pop and throw droplets into the wind. The droplets can elongate into perfectly straight, glassy strands that are as thin as human hair. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Andrea Jones In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
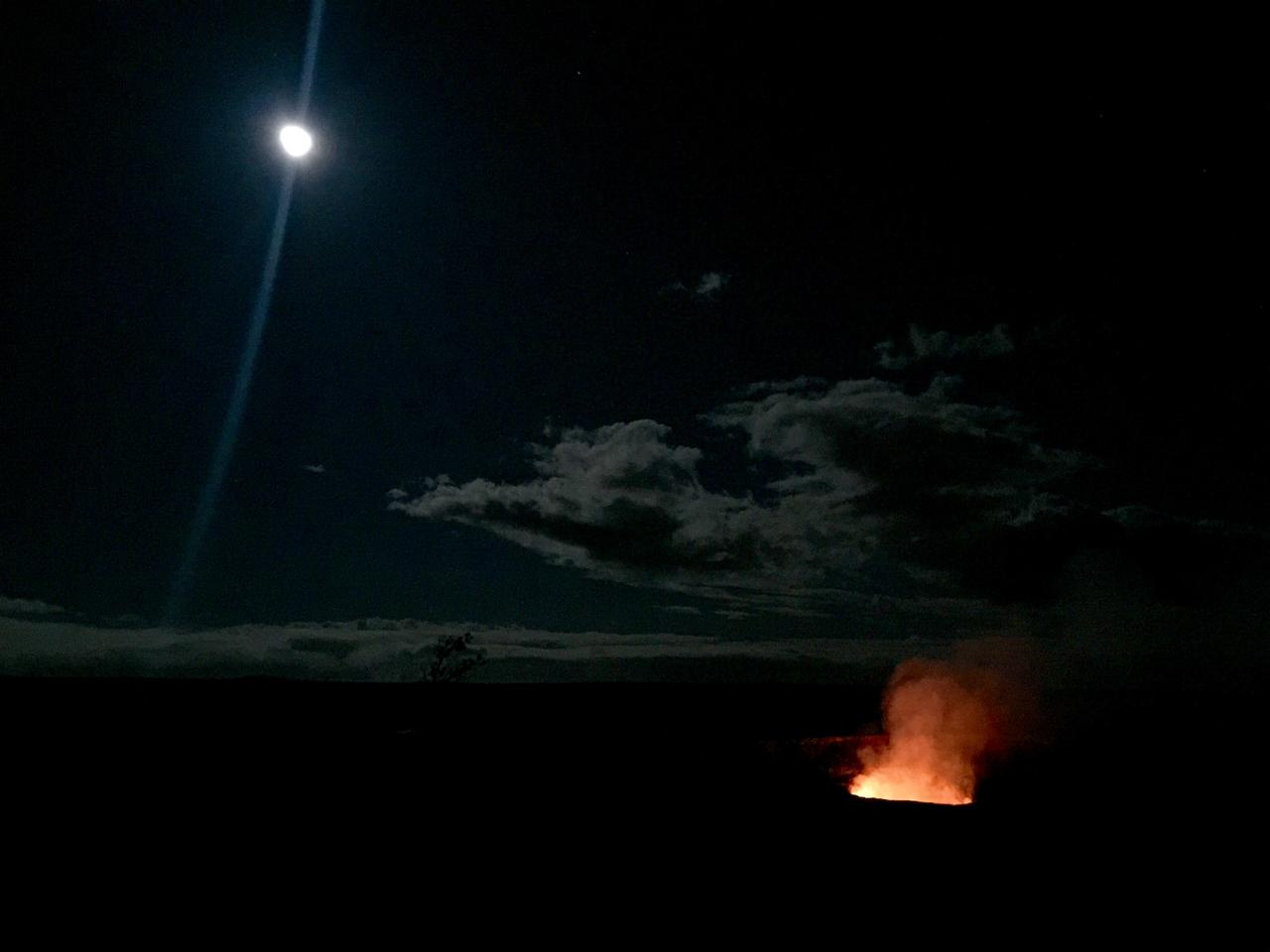

Full moon over lava lake The inspiring views at remote locations, such as Halema’uma’u Crater in Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, are an extra reward for making the trip. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Kelsey Young In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
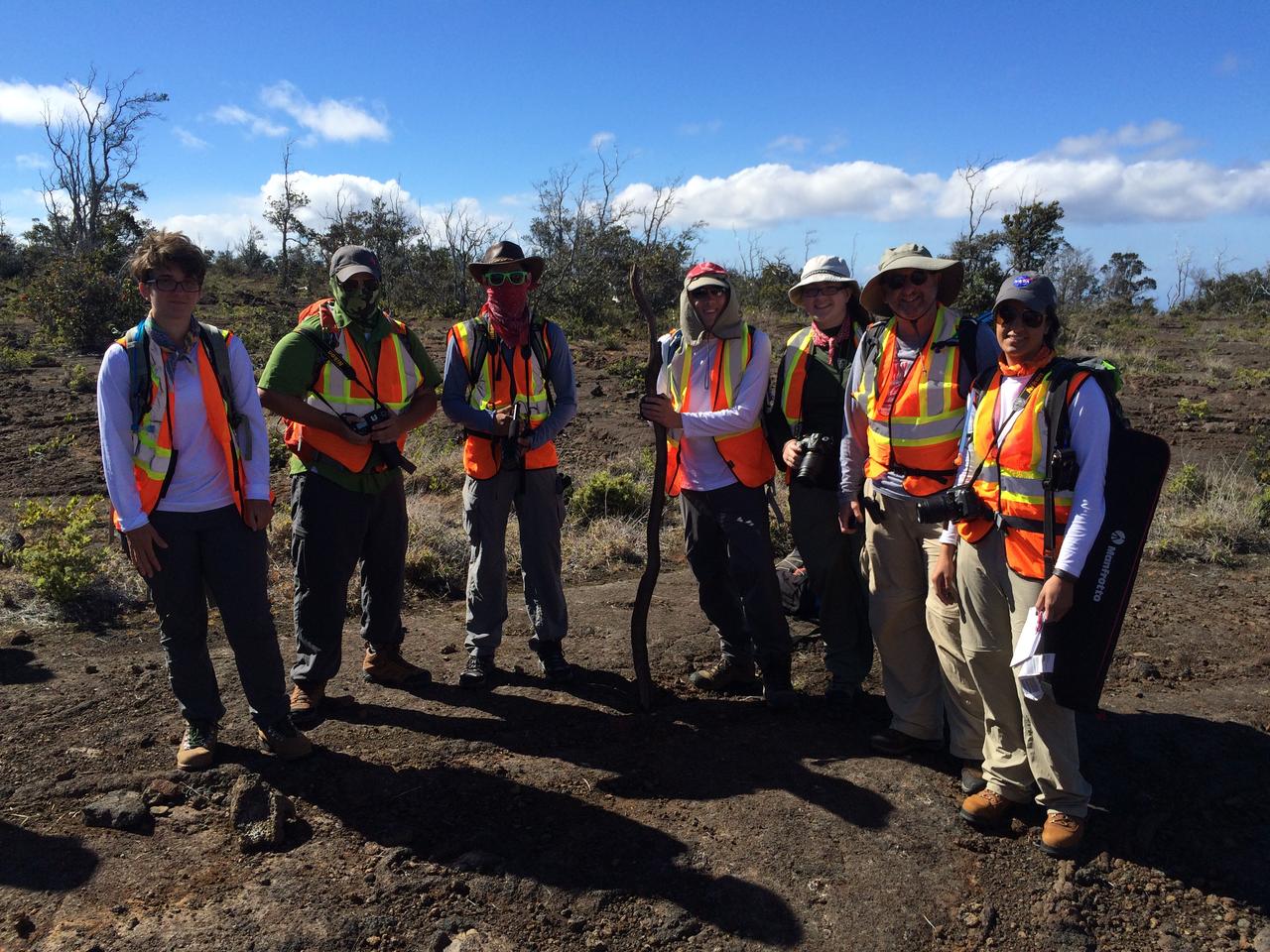

Ready to roll The five student journalists and two faculty members are ready for a day in the field. NASA/GSFC/Andrea Jones In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Smooth pahoehoe A member of the journalism team captures the alluring beauty of a pahoehoe flow. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Anthony Denicola In June, five student journalists from Stony Brook University packed their hiking boots and hydration packs and joined a NASA-funded science team for 10 days on the lava fields of Kilauea, an active Hawaiian volcano. Kilauea’s lava fields are an ideal place to test equipment designed for use on Earth’s moon or Mars, because volcanic activity shaped so much of those terrains. The trip was part of an interdisciplinary program called RIS4E – short for Remote, In Situ, and Synchrotron Studies for Science and Exploration – which is designed to prepare for future exploration of the moon, near-Earth asteroids and the moons of Mars. To read reports from the RIS4E journalism students about their experiences in Hawaii, visit <a href="http://ReportingRIS4E.com" rel="nofollow">ReportingRIS4E.com</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
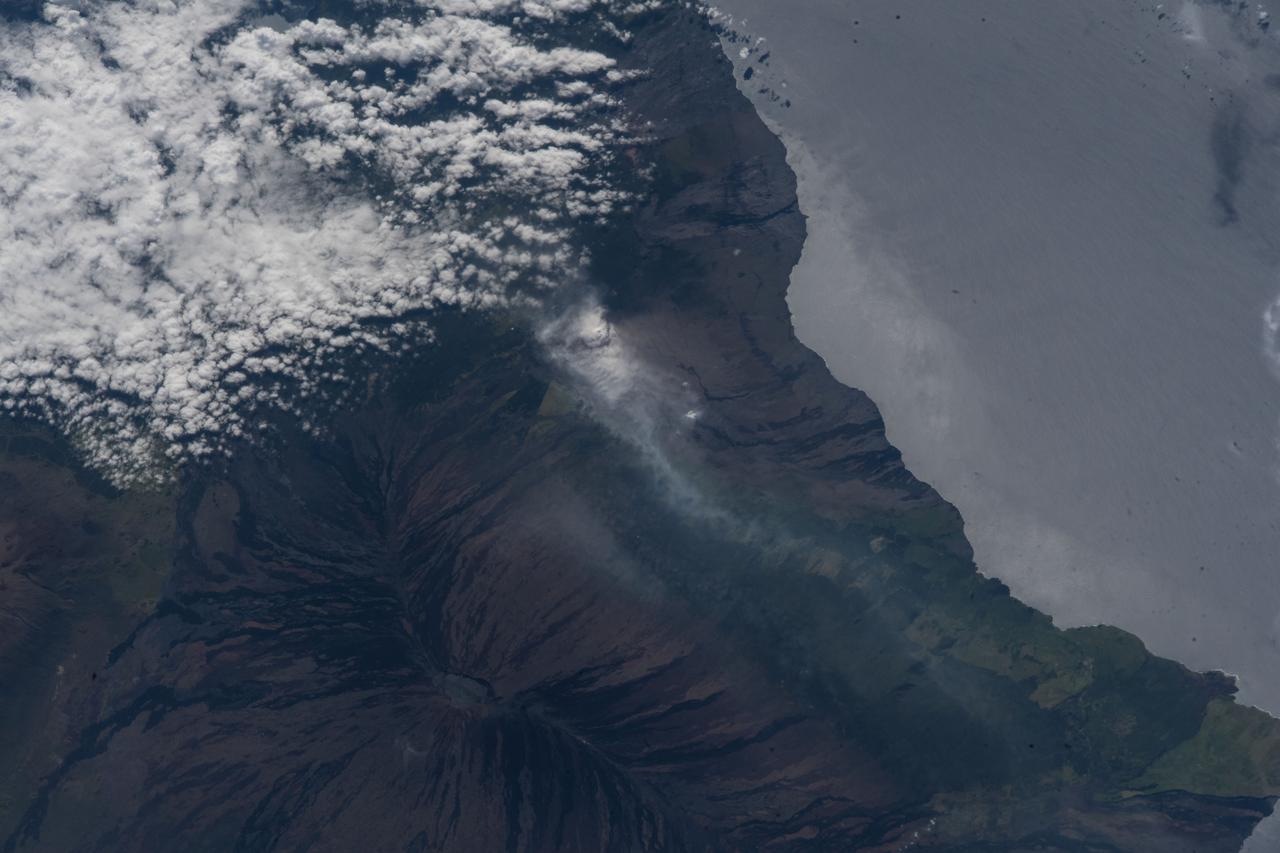

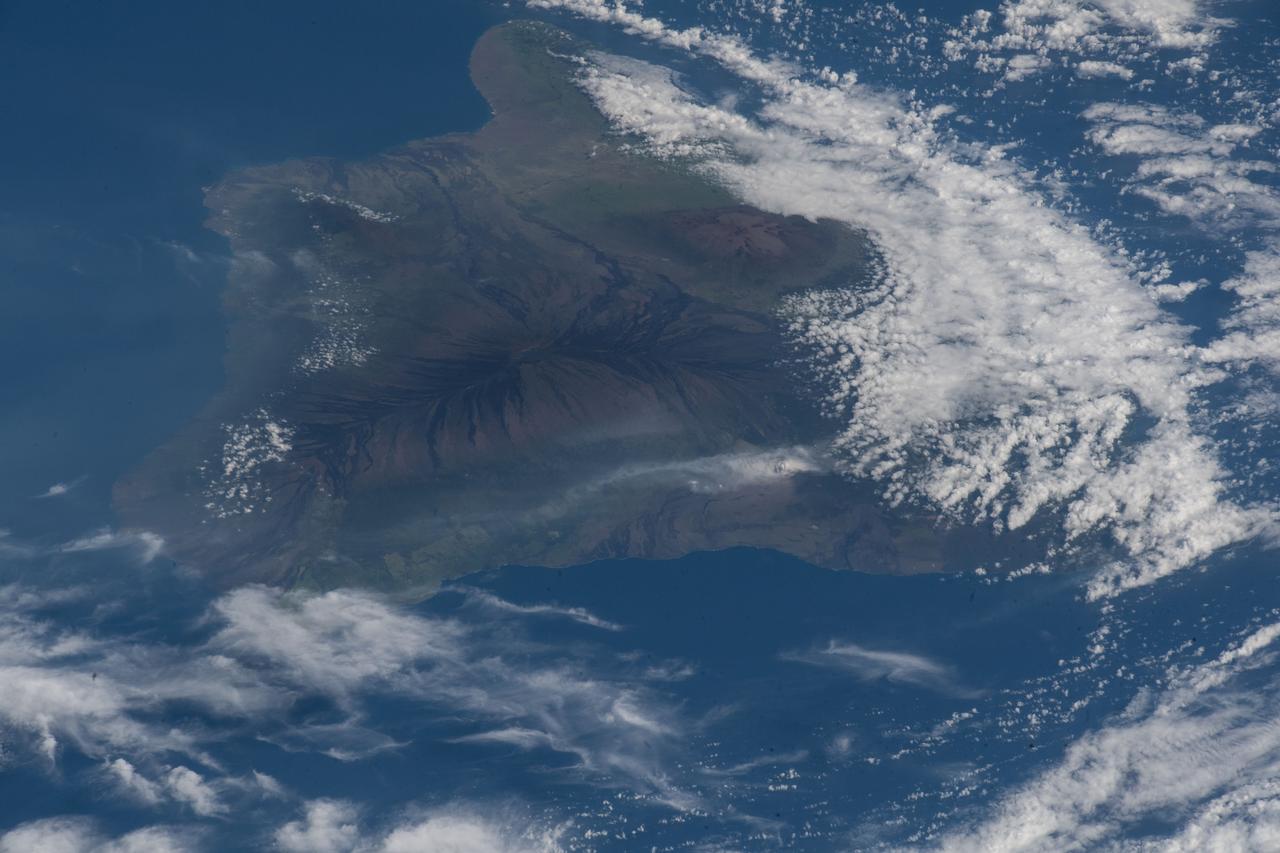
iss055e070305 (May 12, 2018) --- The volcanic ash plume from Mount Kilauea is seen just inland off the eastern coast of Hawaii's Big Island.
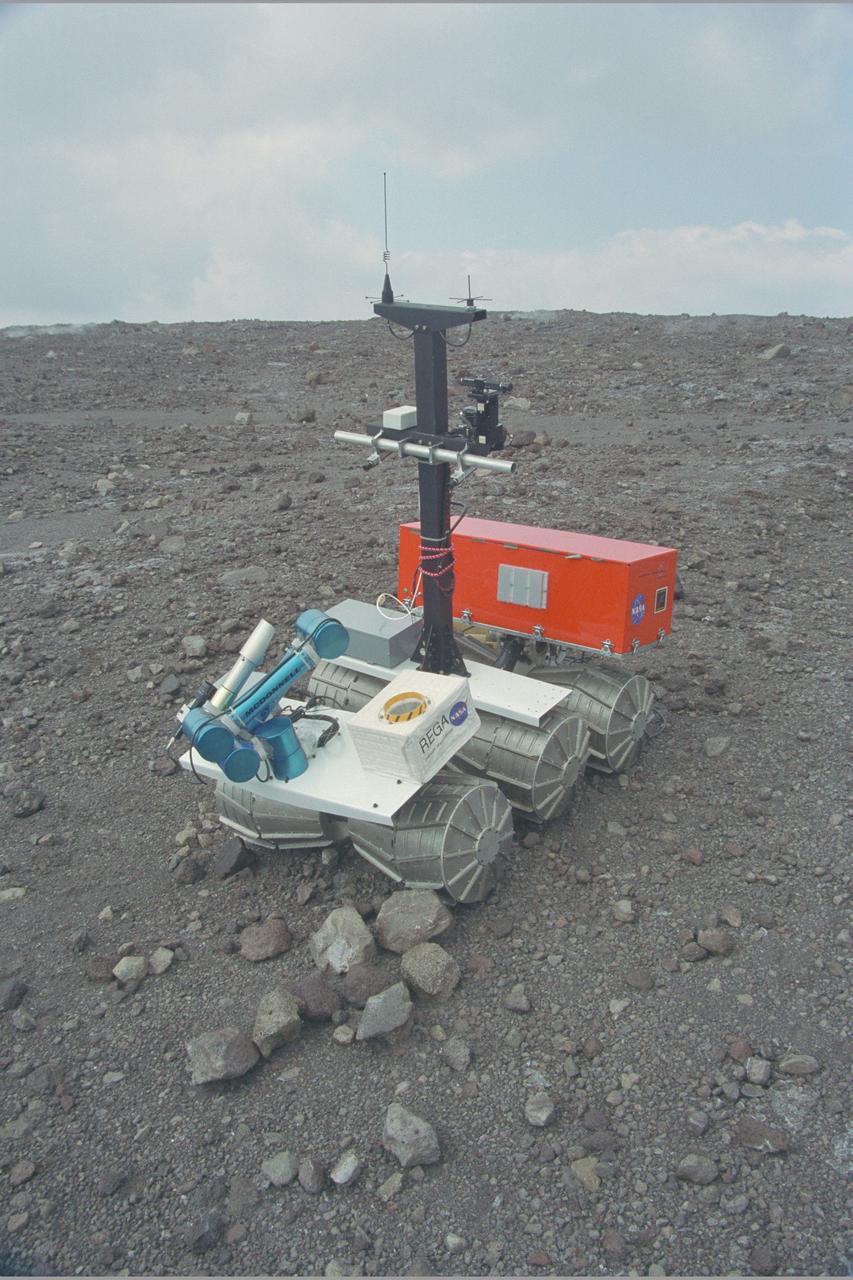

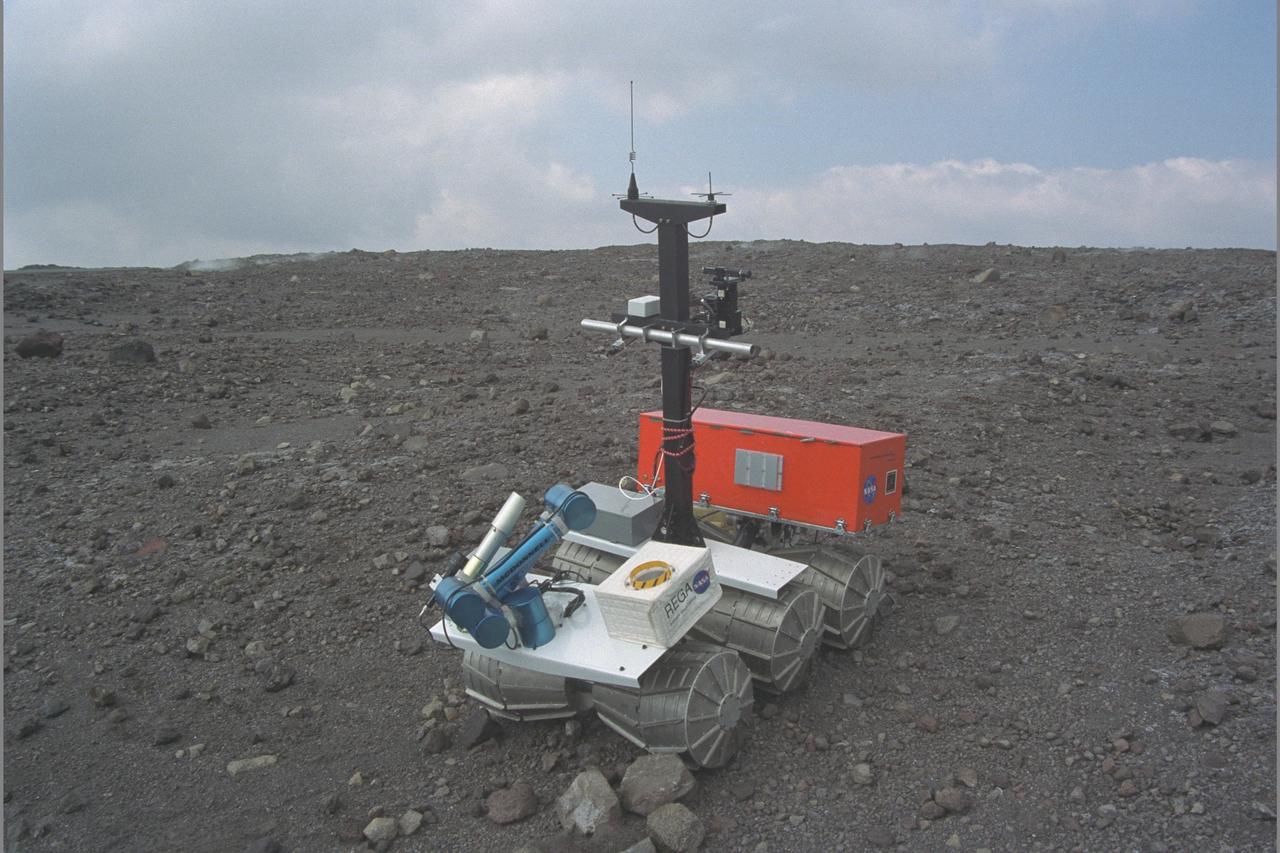
Marsokhod Russian Rover explores Kilauea, Hawaii via telepresence for Jason IV 'Island Earth' Projects (Volcano simulates Martian Terrain)
Marsokhod Russian Rover explores Kilauea, Hawaii via telepresence for Jason IV 'Island Earth' Projects (Volcano simulates Martian Terrain)
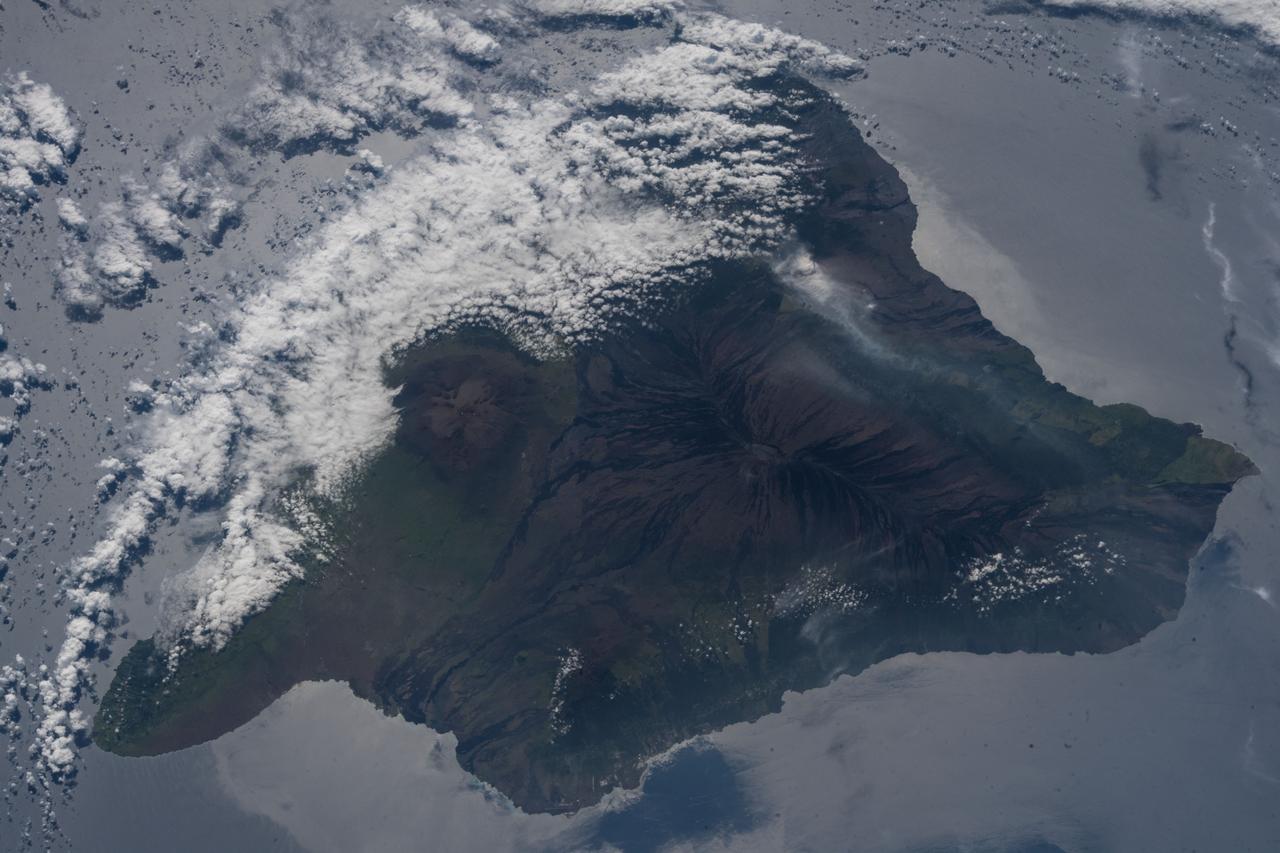

iss055e070297 (May 12, 2018) --- The volcanic ash plume from Mount Kilauea is seen just inland off the eastern coast of Hawaii's Big Island.

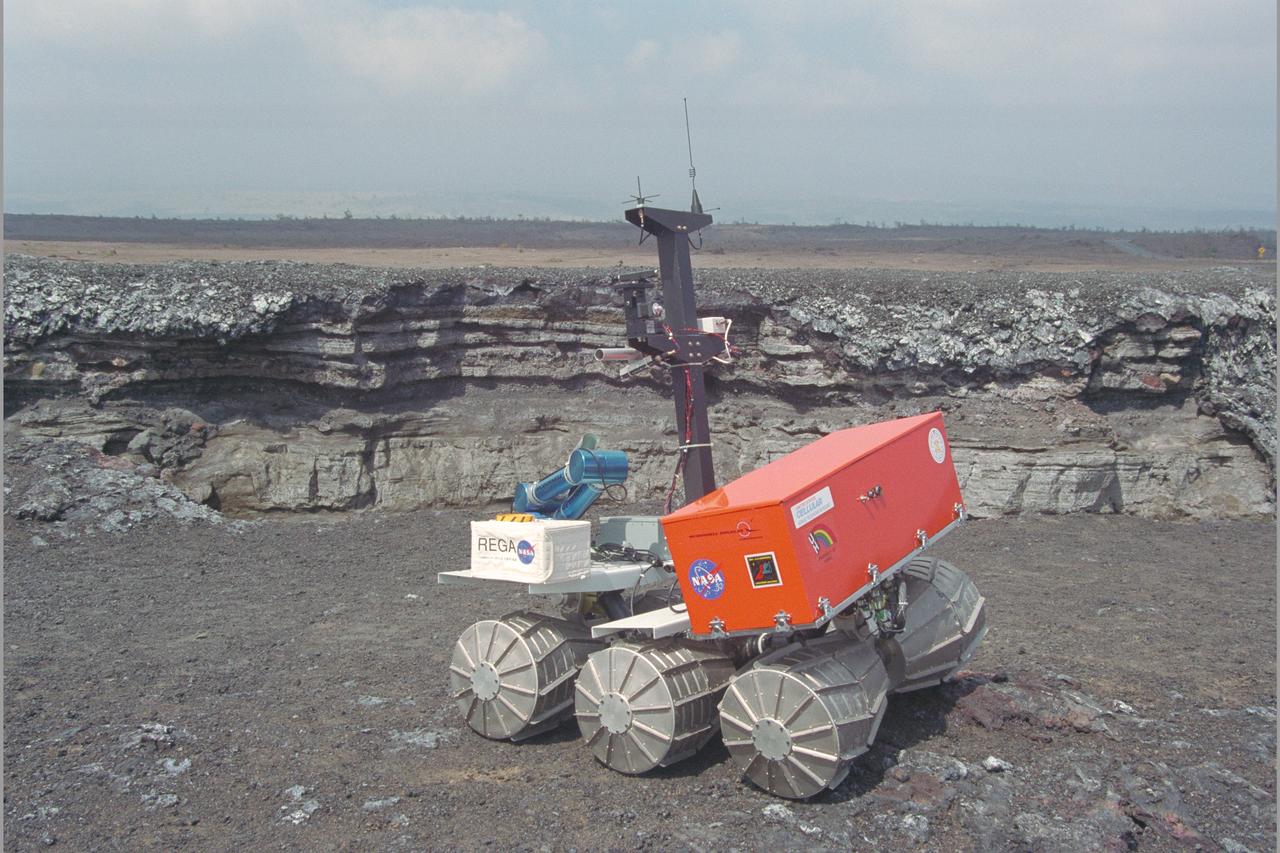
Marsokhod Russian Rover explores Kilauea, Hawaii via telepresence for Jason IV 'Island Earth' Projects (Volcano simulates Martian Terrain)

iss055e070338 (May 12, 2018) --- The ash plume from the Kilauea volcano on the big island of Hawaii was pictured May 12, 2018, from the International Space Station.

Marsokhod Russian Rover explores Kilauea, Hawaii via telepresence for Jason IV 'Island Earth' Projects (Volcano simulates Martian Terrain)

The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection (ASTER) instrument onboard NASA's Terra spacecraft obtained near-infrared data of the ongoing Kilauea volcano eruption and its impact on the Leilani Estates area on May 15, 2018 (left) and June 23, 2018 (right). The current eruption began May 3. Red areas are vegetated, while white areas are clouds or volcanic plumes. The new dark areas show where the ground has been covered with lava flows. The lava seen here, flowing a high rate of volume from a vent designated Fissure 8, flowed eastward to the coast. In early June 2018, these rapidly moving flows destroying hundreds of homes in and around the towns of Vacationland and Kapoho, and filled in Kapoho Bay. The flows are now creating a new broad delta, extending the island of Hawaii. A plume has formed where incandescent lava flows into the Pacific. In the ASTER observation obtained on June 23, a well-developed leveed and perched lava channel flowing from left to right is clearly seen. For the month of June, flow activity was mostly confined to Fissure 8 and areas fed by this lava channel. The image was acquired June 23, 2018, covers an area of about 14 by 14 miles (23 by 23 kilometers), and is located at 19.6 degrees north, 154.9 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22593

On June 27, 2014, a new vent opened on Hawaii Puu Oo vent, on the eastern flank of Kilauea volcano. NASA Terra spacecraft shows the hot lava flow in white, extending about 11 miles 17 kilometers from the vent.
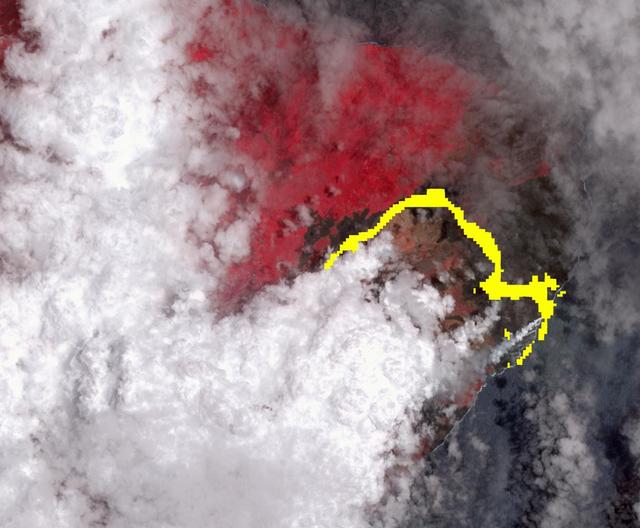

Hawaii's Kilauea volcano continues to create new land as flows from fissure 8, one of the most active to break ground since the eruption began in early May, reach the ocean. The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection (ASTER) radiometer instrument on NASA's Terra satellite detected the lava flow of fissure 8 -- which extends from Leilani Estates to the Pacific Ocean -- on July 25. In the image, vegetation is displayed in red, clouds are white and the hot lava flows, detected by ASTER's thermal infrared channels, are overlaid in yellow. The image covers an area of 9.5 by 11.5 miles (15.3 by 18.6 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22489
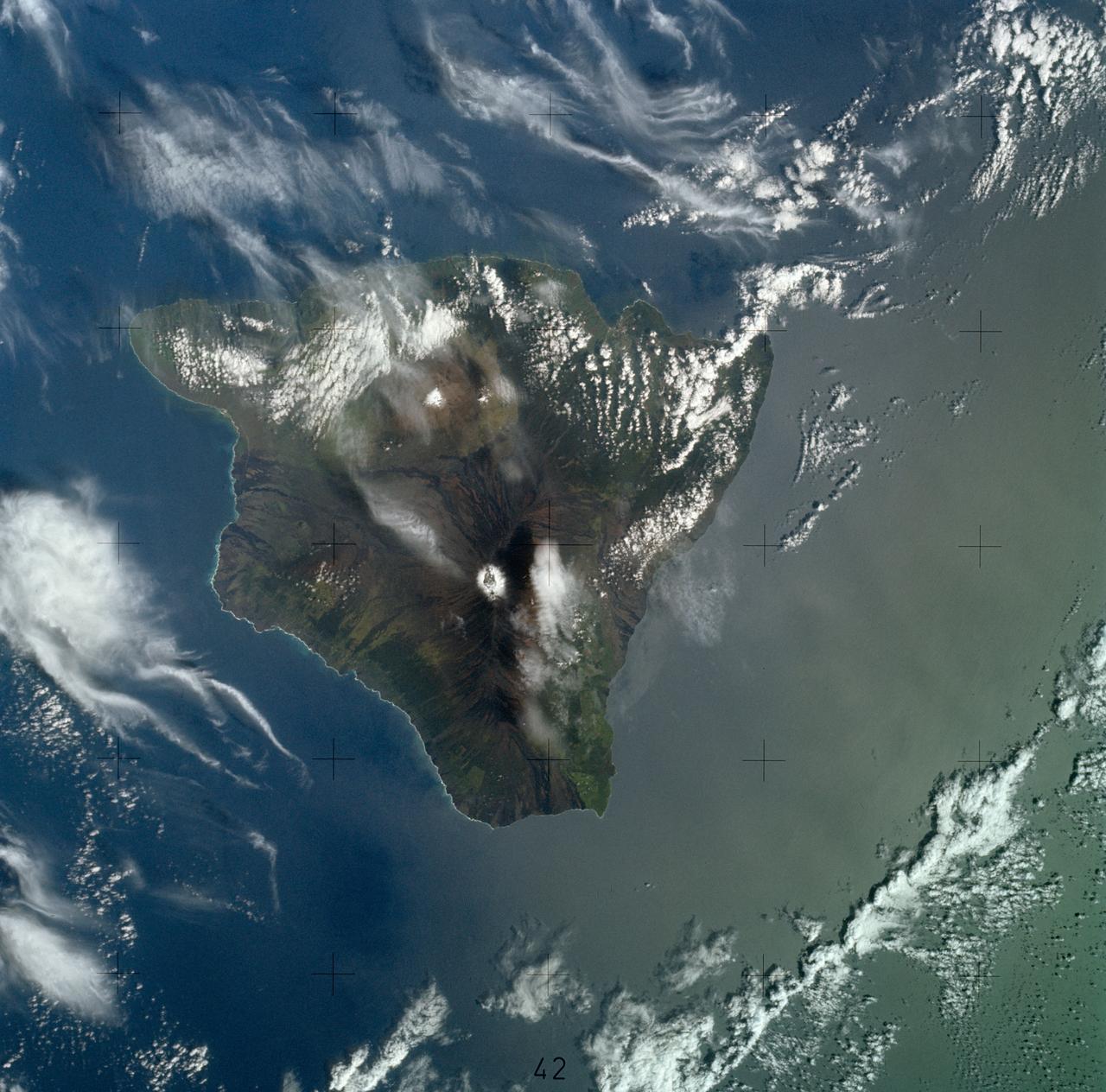

SL4-139-3997 (8 Jan. 1974) --- A vertical view of the Island of Hawaii, State of Hawaii, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by a Skylab 4 crewman. The camera used was a hand-held Hasselblad camera, with SO-368 medium-speed Ektachrome film. This photograph, taken on Jan. 8, 1974, is very useful in studies of volcanic areas. Prominent volcanic features such as the summit caldera on Mauna Loa, the extinct volcano Mauna Kea, the Kilauea caldera, and the pit crater at Halo mau mau within the caldera are easily identified. (Kilauea was undergoing frequent eruption during the mission). Detailed features such as the extent and delineation of historic lava flows on Mauna Loa can be determined and are important parameters in volcanic studies. Photo credit: NASA
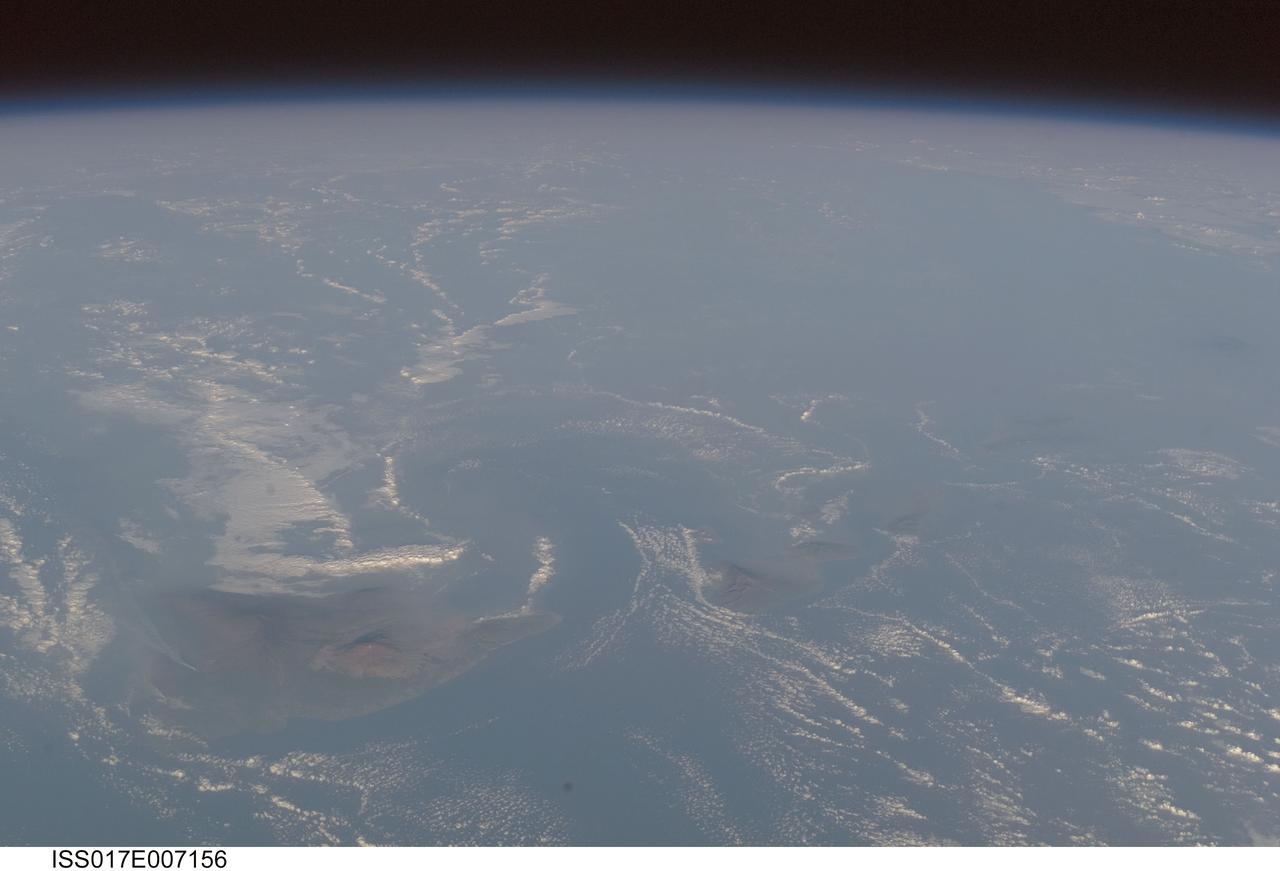

ISS017-E-007156 (17 May 2008) --- Volcanic plumes and volcanic fog in Hawaii are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 17 crewmember on the International Space Station. For 25 years, Kilauea volcano on Hawaii's Big Island has been erupting continuously. Recent explosive activity that started in March 2008 is producing increased emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2). These emissions result in a widespread caustic volcanic fog -- known as vog -- that, depending on local winds, drifts as much as 200 miles up the volcanic chain, burning throats and eyes, and inducing asthma attacks as far away as Honolulu, on the island of Oahu. An oblique view of the Hawaiian islands taken from the International Space Station -- viewed looking towards the southwest, rather than "straight down" relative to the station -- on a hazy spring day includes a regional view of three volcanic plumes from Kilauea that contribute to the vog: the plume from Halema'uma'u crater near the summit, a plume from Pu'u O'o vent along the east rift, and a plume from where lava enters the ocean on the coast outside of the park boundaries. At the time this image was taken, doctors throughout the state of Hawaii were reporting an increased caseload of people with respiratory problems. Aside from the vog, this view captures cloud formations indicative of both the large-scale air flow and the local wind patterns around the islands. The parallel lines of clouds aligned roughly northeast to southwest reveal the direction of the region's prevailing trade winds; that flow is disrupted around the islands (between Hawaii and Maui, at right), and further influenced by the local land/sea breeze which at that time had driven the cloud formations offshore and circling the islands. In addition to the Kilauea plumes, the volcanoes of Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea are also visible on the island of Hawaii (center). The uninhabited island of Kaho'olawe is just visible to the southwest of Maui.
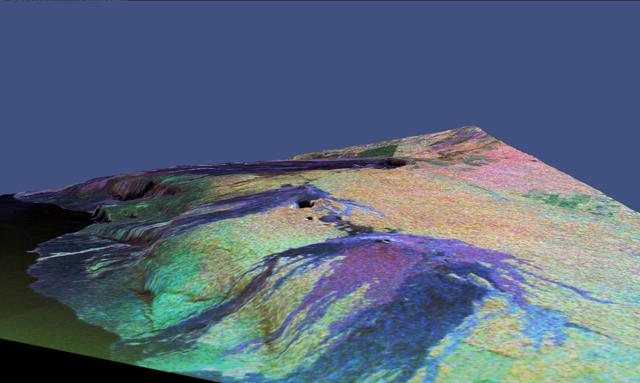
This is a three-dimensional perspective view of a false-color image of the eastern part of the Big Island of Hawaii.
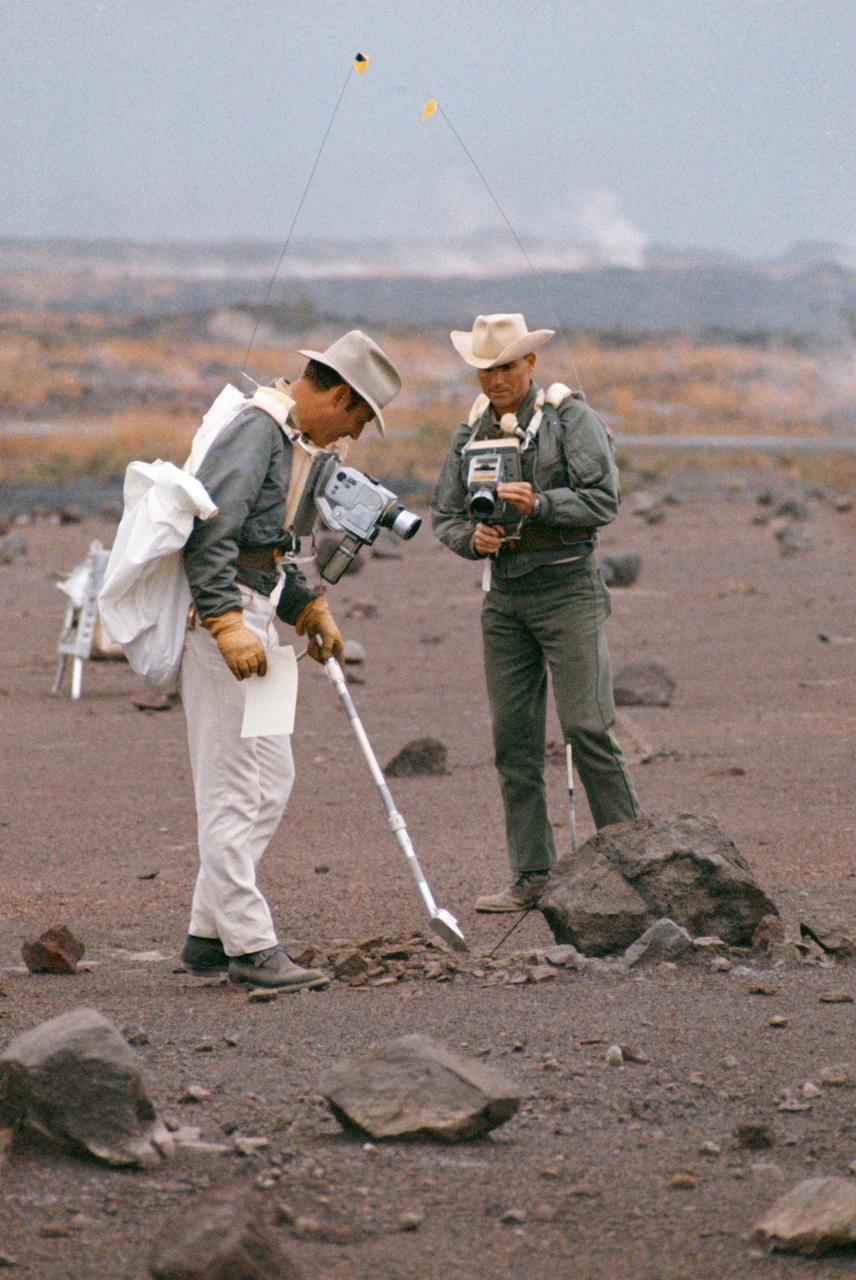

S70-20253 (December 1969) --- Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (left) commander, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, carry out a simulation of a lunar traverse at Kilauea, Hawaii, site. Both crew members of NASA's third team of moon explorers were carrying cameras and communications equipment during the simulated traverse. They maintained contact with men in the roles of spacecraft throughout the traverse. Lovell holds a scoop for the Apollo Lunar Hand Tools (ALHT) and a gnomon, also for the ALHT is deployed in front of Haise. The ALHT carrier is at left background, (almost obscured by Lovell).
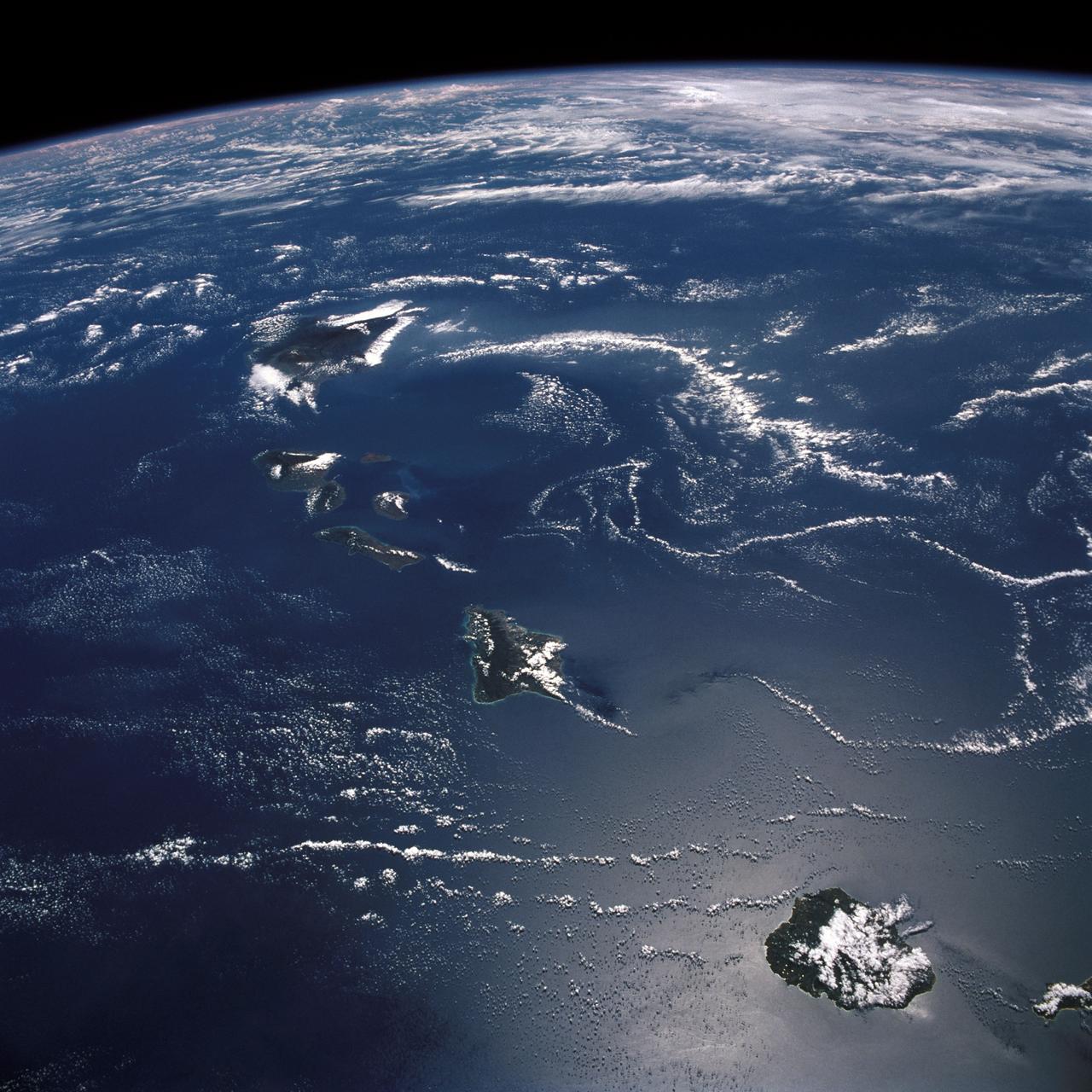

STS026-43-082 (29 Sept. - 3 Oct. 1988) --- This 70mm northerly oriented frame over the Pacific Ocean features the Hawaiian Islands chain. The islands perturb the prevailing northeasterly winds producing extensive cloud wakes in the lee of the islands. Photo experts feel that atmospheric haze in the Hawaii wake is probably a result of the continuing eruptions of Kilauea volcano on the southeast coast. From the lower right corner in a diagonal directed upward to the north are the islands of Nihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lanai, Maui, Kahoolawe, and Hawaii. This photo was shown during the post-flight press conference on October 11, 1988 by the STS-26 astronauts, who at one time during the flight wore Hawaiian attire to pay tribute to the working staff of the Hawaii tracking station.
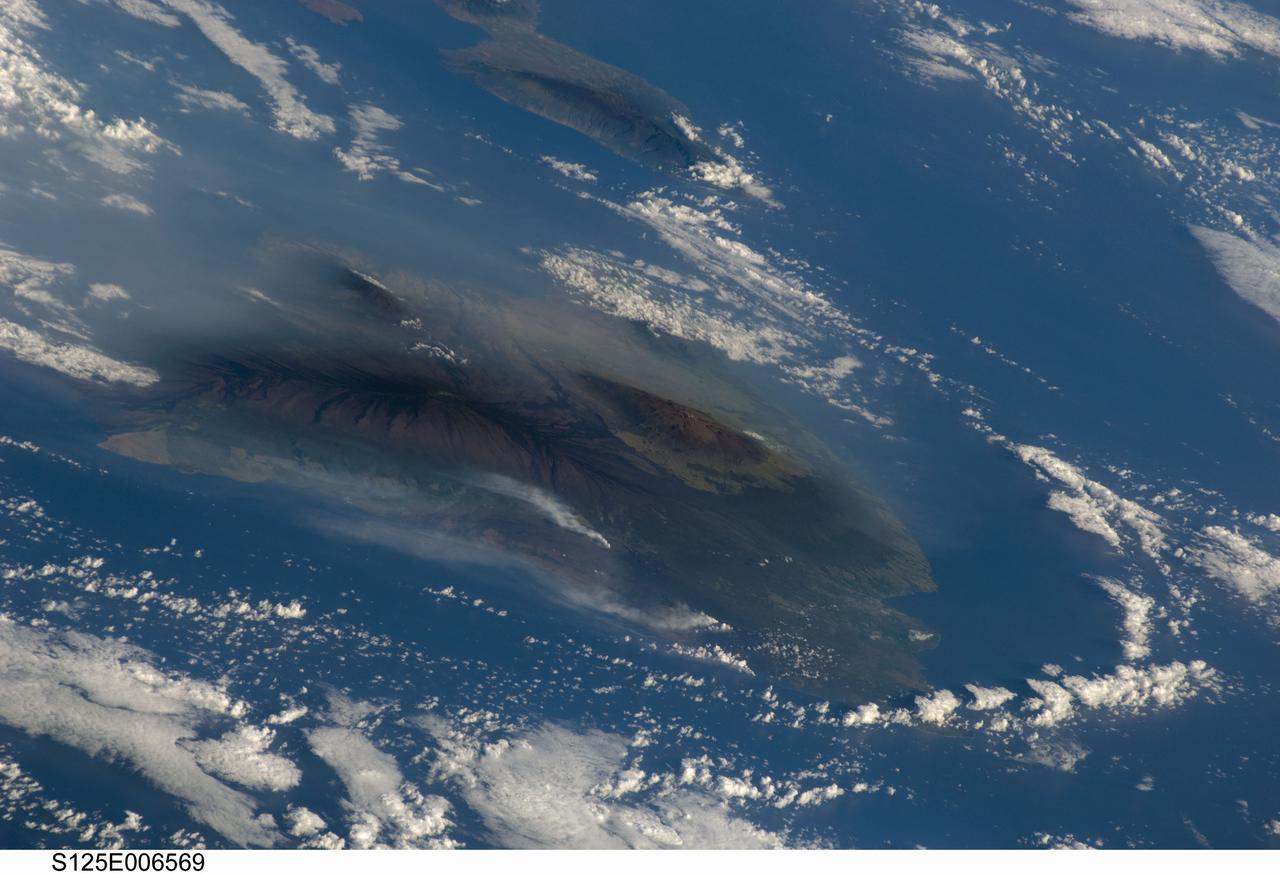

S125-E-006569 (13 May 2009) --- Hawaiian vog from Kilauea volcano, on the island of Hawaii, has been erupting continuously since 1983. This image, taken by the crew of Space Shuttle Atlantis (after completing the capture of the Hubble Space Telescope), shows the volcanic plumes from Kilauea rising up from Halema`uma`u Crater and along the coastline from lava flows entering the ocean from the East rift zone. The volcanic activity has created a blanket of volcanic fog, called vog that envelops the island. The Hawaii Volcano Observatory (HVO) maintains a website (including webcams) that continuously monitors and updates reports on the volcanic activity. Recent maps indicate expanded lava coverage along the coastal plain. In addition, Hawaii?s Department of Health maintains daily vog alerts, and publishes advisories for vog conditions around the ?big island? of Hawaii and the state. When this image was acquired, the region west of Hawaii Volcanoes National Park (downwind from the coastal plumes) had a vog advisory for people with respiratory sensitivities. The Volcano Observatory also reported that ?Lava from east rift zone vents continues to flow through tubes to the coast and is entering the ocean at two locations west of Kalapana. Sulfur dioxide emission rates from the Halema`uma`u and Pu`u `O`o vents remain elevated. Sulfur dioxide emission rates remain elevated and variable; the most recent rate measurement was 1,200 tonnes/day on May 12, compared to the 2003-2007 average rate of 140 tonnes/day. Small amounts of mostly ash-sized tephra continue to be produced consisting mostly of Pele's hair -- irregular pieces of vesicular glass -- and a few hollow spherules.?

A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse.Today's VIS image shows the summit caldera of Arsia Mons. Several small volcanic vents are visible on the caldera floor. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within the Arsia Mons caldera there was renewed activity from several small vents that occurred along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume activity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 450 km (270 miles) in diameter, almost 20 km (12 miles) high, and the summit caldera is 120 km (72 miles) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter.The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. Orbit Number: 84328 Latitude: -8.58304 Longitude: 239.166 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2020-12-17 20:11 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24393
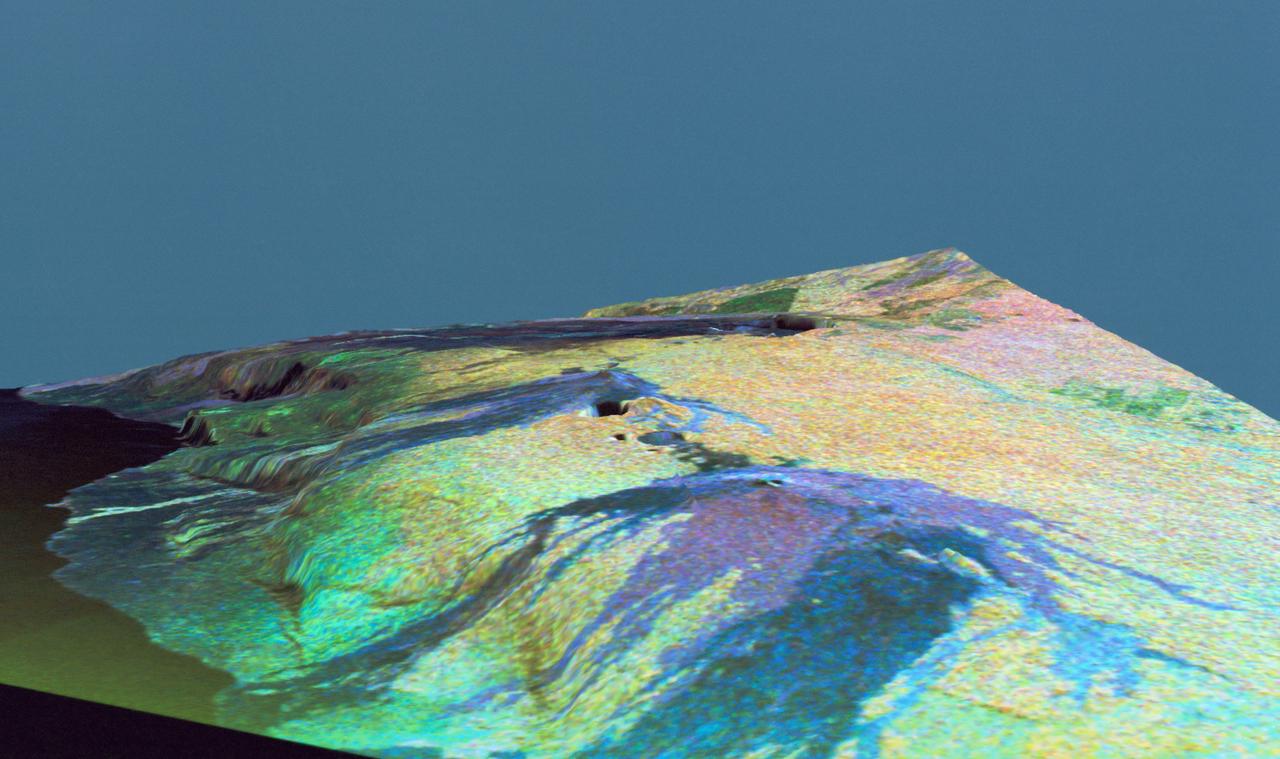
This is a three dimensional perspective view of false-color image of the eastern part of the Big Island of Hawaii. It was produced using all three radar frequencies C-Band and L-Band. This view was constructed by overlaying a SIR-C radar image on a U.S. Geological Survey digital elevation map. The image was acquired on April 12, 1994 during the 52nd orbit of the Shuttle Endeavour by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR). The area shown is approximately 34 by 57 kilomters with the top of the image pointing toward north-west. The image is centered at about 155.25 degrees west longitude and 19.5 degrees north latitude. Visible in the center of the image in blue are the summit crater (Kilauea Caidera) which contains the smaller Halemaumau Crater, and the line of collapsed craters below them that form the Chain of Craters Road. The rain forest appears bright in the image while green areas correspond to lower vegetation. The lava flows have different colors depending on their types and are easily recognizable due to their shapes. The flows at the top of the image originated from the Muana Loa volcano. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory alternative photo number is P-43932.
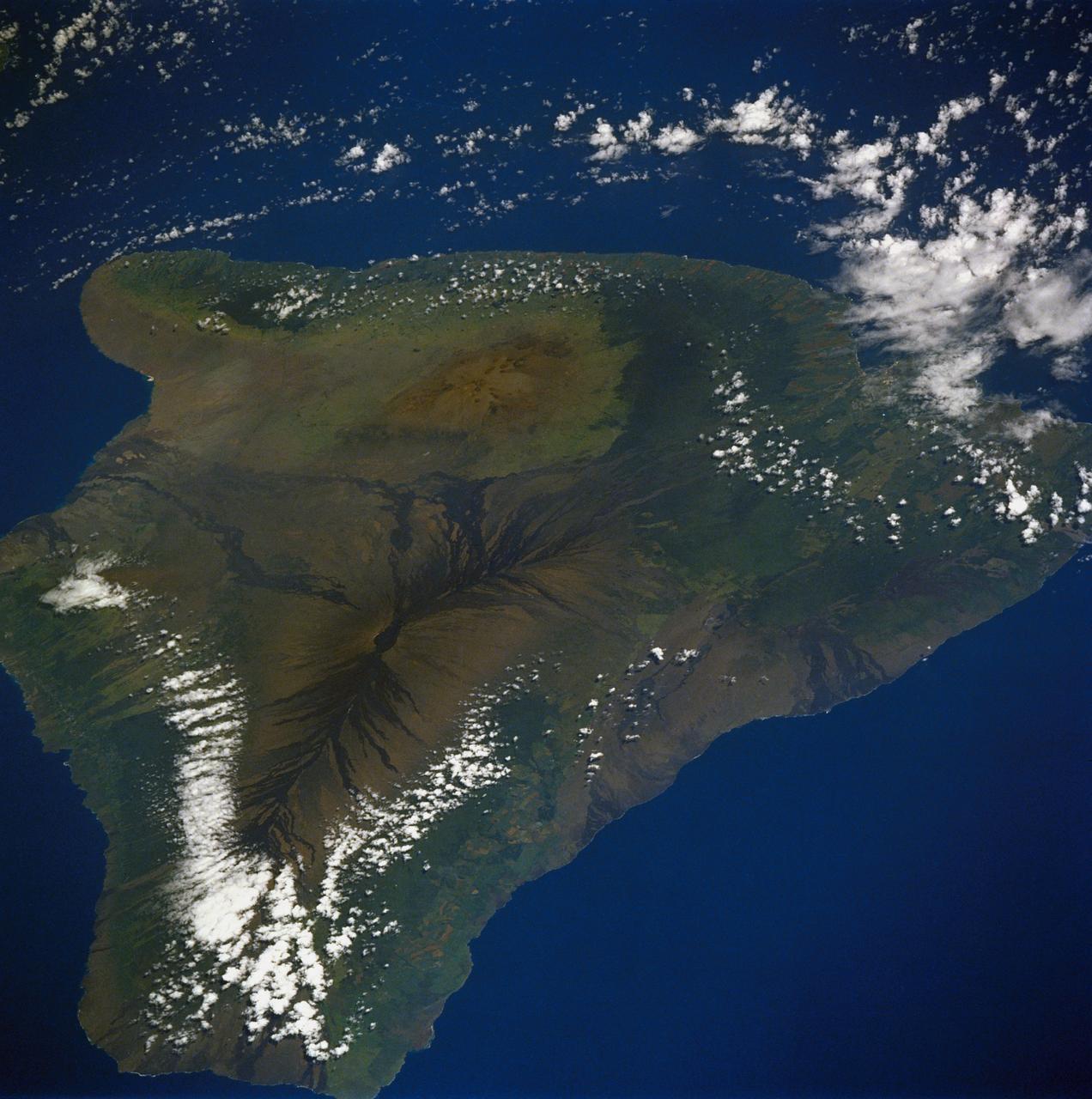
61A-50-057 (1 Nov 1985) --- An oblique view of Hawaii, the largest of the Hawaiian Island Group, as photographed by the crewmembers of Challenger on STS-61A in November of 1985. This unusual early morning view shows nearly the entire island with minimal cloud cover. Normally, these near tropical islands are obscured by heavy cloud cover except for the early morning hours. UPDATE, NOVEMBER 28, 1986 PLEASE NOTE: The Kilauea fissure, on the southeast coast, while not as prominent as ancient, neighboring Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea craters, has been spewing a molten lava flow since July 18, 1986, at a rate of six cubic yards per second. Generally flowing toward the sea, the lava mass had reached the coast by today after destroying several homes and private property along the way. The seven-mile long lava flow covered over 600 feet of coastline and extended into the ocean, creating over 12 acres of new beachfront property.

A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse.Today's VIS image shows the summit caldera of Arsia Mons. Several small volcanic vents are visible on the caldera floor. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within the Arsia Mons caldera there was renewed activity from several small vents that occurred along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume activity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 450 km (270 miles) in diameter, almost 20 km (12 miles) high, and the summit caldera is 120 km (72 miles) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter.The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. Orbit Number: 79230 Latitude: -9.4441 Longitude: 239.984 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2019-10-25 02:43 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23639

This THEMIS image shows part of the caldera floor of Arsia Mons. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption that empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within Arsia Mons there was renewed activity that occurred within the caldera along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume actitivity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Small flows are visible throughout this image. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 19588 Latitude: -9.19485 Longitude: 239.276 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-05-15 03:33 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22156

ISS019-E-011922 (28 April 2009) --- Mauna Kea Volcano in Hawaii is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 19 crewmember on the International Space Station. The island of Hawaii is home to four volcanoes monitored by volcanologists ? Mauna Loa, Hualalai, Kilauea, and Mauna Kea. Mauna Kea is depicted in this view; of the four volcanoes, it is the only one that has not erupted during historical times. The Hawaiian Islands chain, together with the submerged Emperor Chain to the northwest, form an extended line of volcanic islands and seamounts that is thought to record passage of the Pacific Plate over a ?hotspot? (or thermal plume) in the Earth?s mantle. Areas of active volcanism in the southern Hawaiian Islands today mark the general location of the hotspot. This detailed photograph illustrates why the volcano is called Mauna Kea (?white mountain? in Hawaiian). While the neighboring Mauna Loa volcano is a classic shield volcano comprised of dark basaltic lava flows, Mauna Kea experienced more explosive activity during its last eruptive phase. This covered its basalt lava flows with pyroclastic deposits that are visible as the light brown area surrounding snow on the summit (center). Numerous small red to dark gray cinder cones are another distinctive feature of Mauna Loa. The cinder cones represent the most recent type of volcanic activity at the volcano. A small area of buildings and roadways at upper right is the Pohakuloa Training Area. This is the largest US Department of Defense facility in the state of Hawaii. The site is used for U.S. Army and Marine Corps exercises.

This THEMIS image shows part of the caldera floor of Arsia Mons. It is not uncommon for calderas to have "flat" floors after the final explosive eruption the empties the subsurface magma chamber. There may still be some magma or superheated rock left after the collapse that will fill in part of the depression. Additionally, over time erosion will work to level the topography. Within Arsia Mons there was renewed activity that occurred within the caldera along the alignment of the NE/SW trend of the three large volcanoes. This ongoing, low volume actitivity is similar to the lava lake in Kilauea in Hawaii. Small flows are visible throughout this image. In the center of the image is a small "L" shaped feature. This is the summit vent for the volcanic flows around it. The flows have lapped up against the caldera wall, filling in faults left by the caldera formation and increasing the elevation of the surface in this region of the caldera. Arsia Mons is the southernmost of the Tharsis volcanoes. It is 270 miles (450km) in diameter, almost 12 miles (20km) high, and the summit caldera is 72 miles (120km) wide. For comparison, the largest volcano on Earth is Mauna Loa. From its base on the sea floor, Mauna Loa measures only 6.3 miles high and 75 miles in diameter. A large volcanic crater known as a caldera is located at the summit of all of the Tharsis volcanoes. These calderas are produced by massive volcanic explosions and collapse. The Arsia Mons summit caldera is larger than many volcanoes on Earth. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 19874 Latitude: -8.57834 Longitude: 240.452 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-06-07 18:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22157
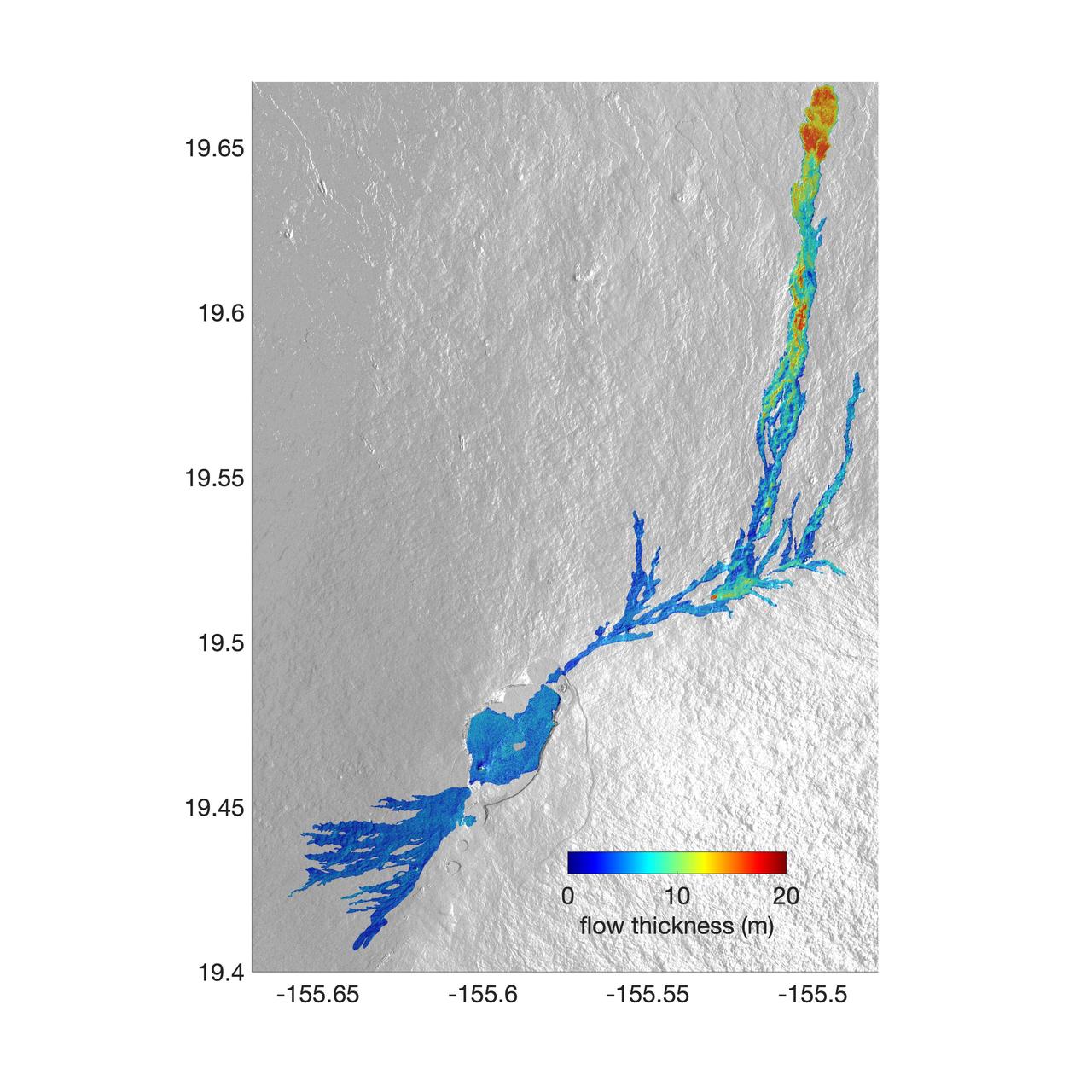
The world's largest active volcano – Hawaii's Mauna Loa – had been quiet for 38 years. But in 2022, the volcano began to stir, showing increased numbers of small earthquakes and subtle swelling of certain land surfaces in September. On November 27, fountains of lava began spurting from the mountain's Northeast Rift Zone and streams of molten rock flowed to the north. Ten days into the eruption, a NASA aircraft conducted its first flight over the erupting volcano. It carried NASA's Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar (UAVSAR) system, which was used to map the volcano's topography in fine detail with a Ka-band instrument called GLISTIN-A. Teams from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) used data from that sensor to map the thickness of those flows during a series of flights on December 7, 8, and 10. The map above shows the thickness of the lava flows during the flight on December 7, the day before USGS scientists noticed a significant decline in the pace of the eruption. A few days later, they declared the eruption had stopped. The map shows the thickness of the lava flows in the summit caldera, where the eruption began, and of lava flows on Mauna Loa's northeastern flank. The color variation from blue to orange indicates increasing lava flow thickness. A maximum thickness of roughly 25 meters (82 feet) is shown, though values exceeding 40 meters (131 feet) were observed in some areas. The thickening at the northern end of the flow is due to lava accumulating away from the vent, along with a flattening of the terrain at the saddle between the Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea volcanoes. By comparing to pre-eruption maps of this area's topography, including GLISTIN-A data collected in 2017, the USGS researchers were able to calculate the size and volume of the lava flow. Over the roughly 14-day eruption, Mauna Loa erupted more than 8.8 billion cubic feet (230 million cubic meters) along a lava flow that extended up to 16.5 miles (19.5 kilometers) from the vent, according to the USGS. The UAVSAR operates from a pod mounted beneath a crewed Gulfstream III jet from NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California. Repeated topographic maps generated with each flight reveal the progression and thickening of lava with time – important information for scientific understanding of volcano processes and for emergency response. For the Mauna Loa science flights, the instrument suite featured an additional state-of-the-art imaging tool: the synthetic aperture radar-fusion optical short-wave infrared (SAR-Fusion Optical/SWIR) camera system. SAR-Fusion collects data over the same ground swath as GLISTIN-A to map land surface changes using optical/SWIR photogrammetry methods. GLISTIN-A was designed to provide all-weather, high-resolution surface topography not available through existing lidar or radar sensors. GLISTIN-A was originally demonstrated as a new radar technique for mapping ice surfaces. Science demonstration flights began in 2013 over alpine glaciers and sea ice in Alaska, and a floodplain in California. Its applications have since expanded to other areas, such as snow accumulation and volcano dynamics. The first time the instrument was deployed for volcano response was in 2018 during the three-month eruption of Kilauea. The success of that operation paved the way for deployment to Mauna Loa. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25526