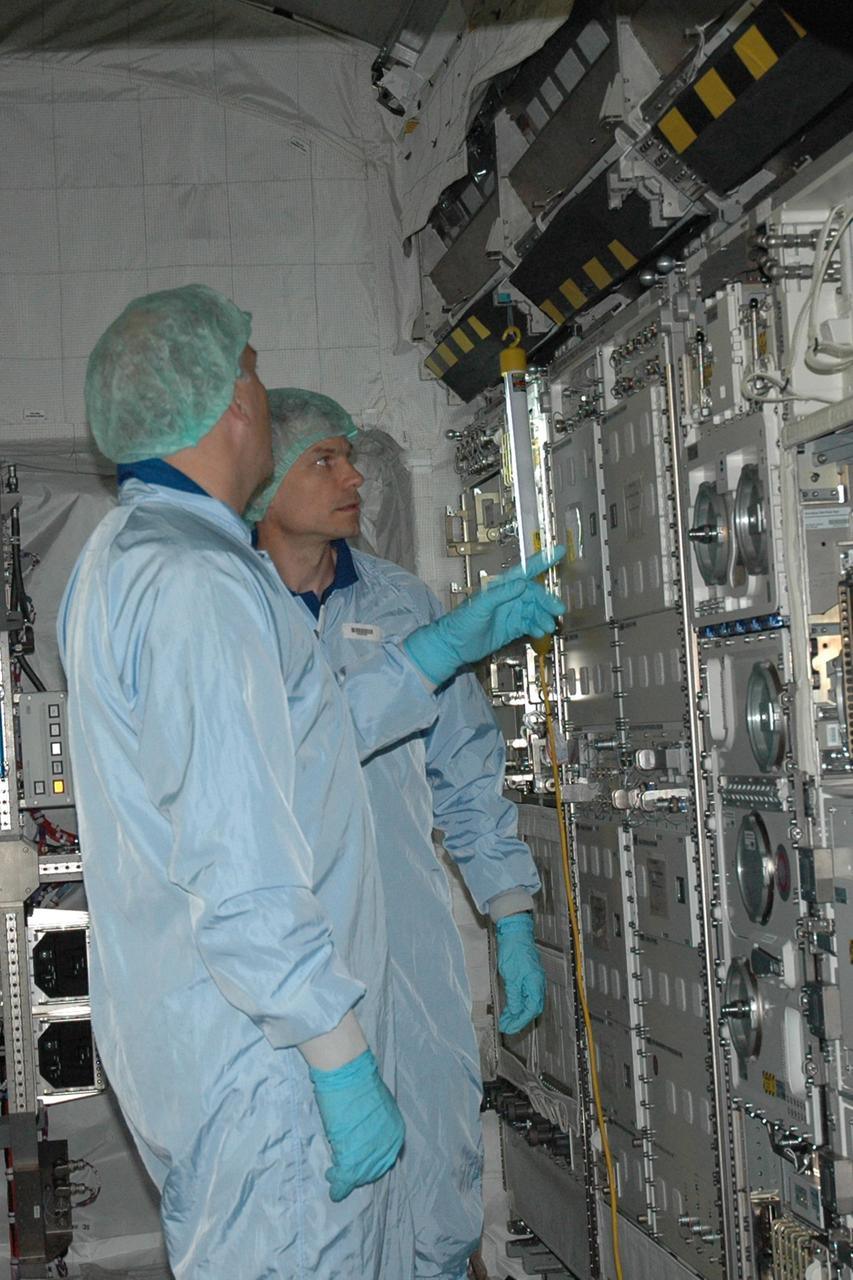

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-122 Mission Specialist Stanley Love looks at the experiment racks inside the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. He and other crew members are at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The crew comprises Commander Stephen Frick, Pilot Alan Poindexter, and Mission Specialists Rex Walheim, Stanley Love, Leland Melvin and Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

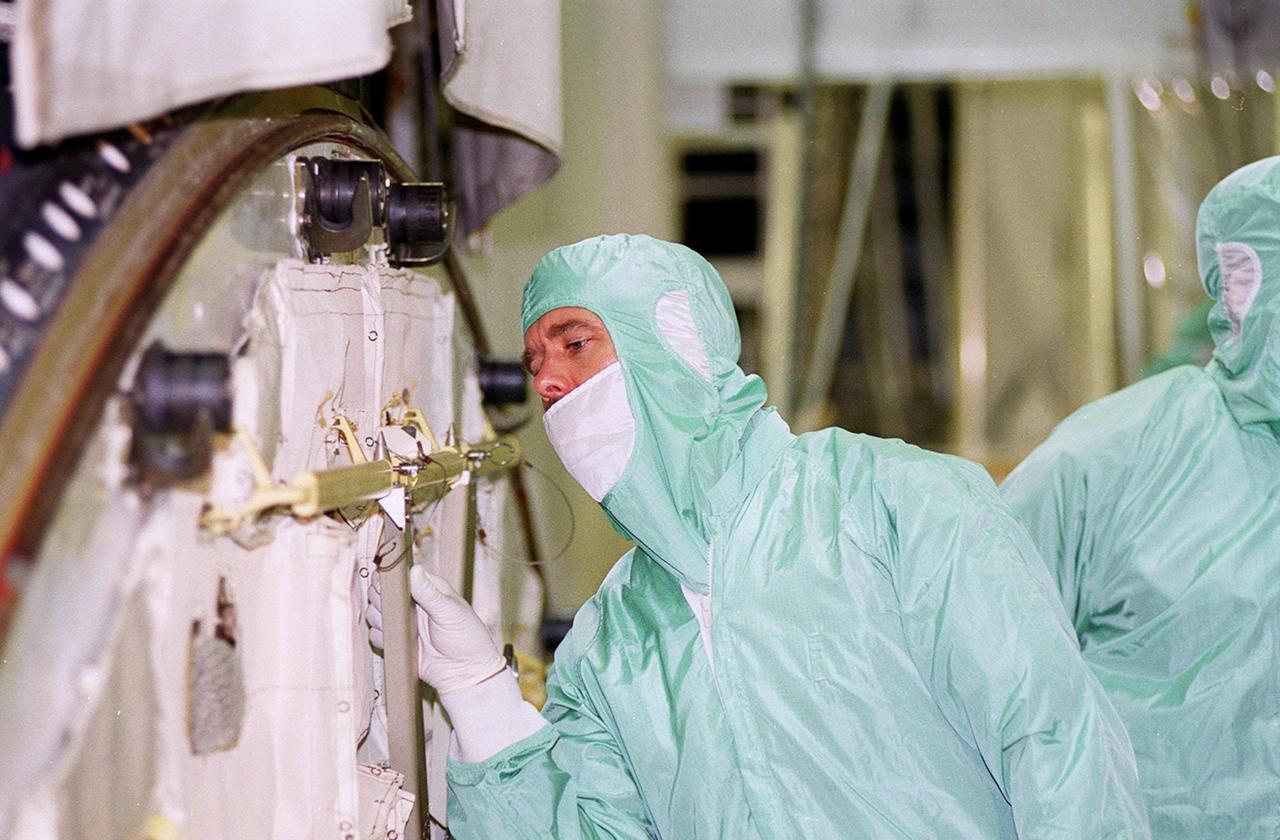
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-122 Mission Specialist Rex Walheim points at part of the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. He and other crew members are at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The crew comprises Commander Stephen Frick, Pilot Alan Poindexter, and Mission Specialists Rex Walheim, Stanley Love, Leland Melvin and Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

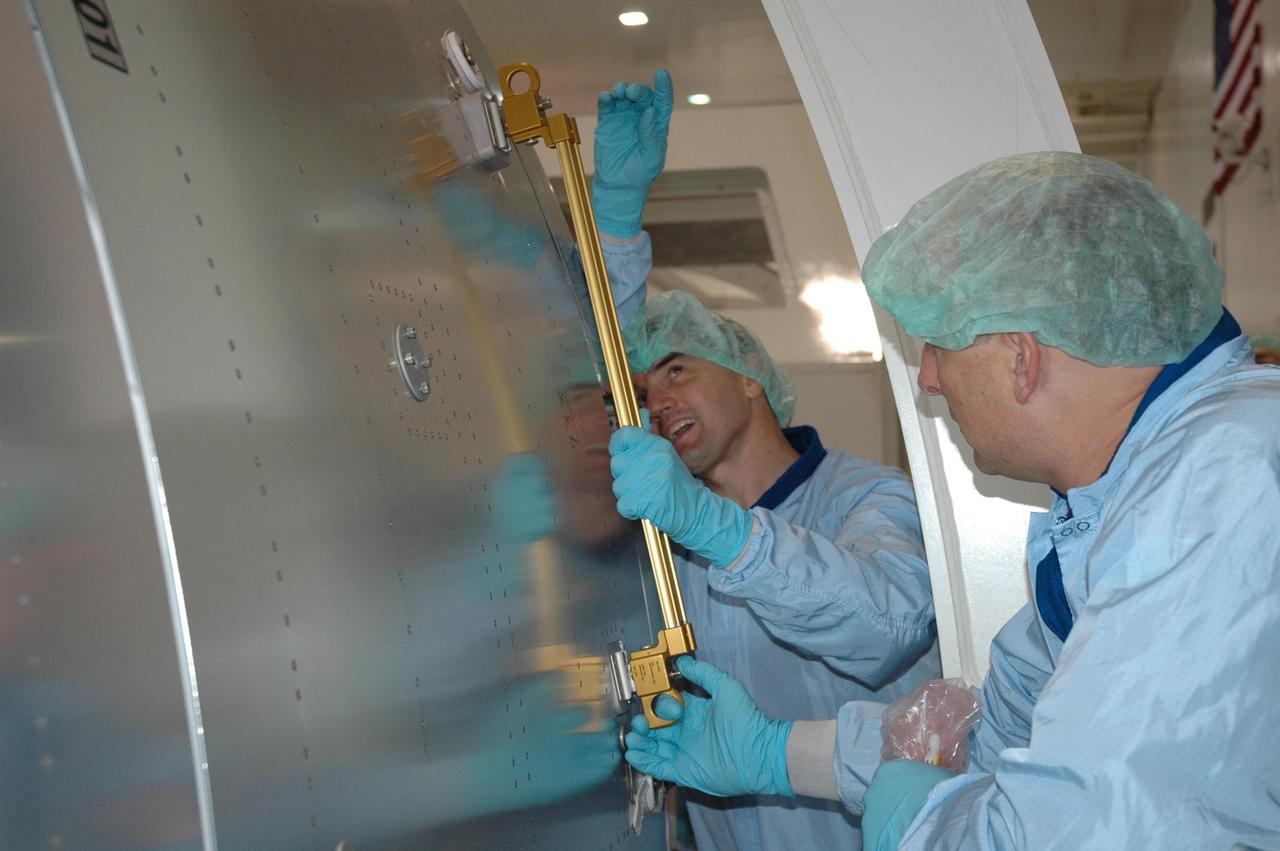
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-122 Mission Specialist Leland Melvin gets a close look at the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. The crew is at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The crew comprises Commander Stephen Frick, Pilot Alan Poindexter, and Mission Specialists Rex Walheim, Stanley Love, Leland Melvin and Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-122 crew look over the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. The crew is at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The crew comprises Commander Stephen Frick, Pilot Alan Poindexter, and Mission Specialists Rex Walheim, Stanley Love, Leland Melvin and Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
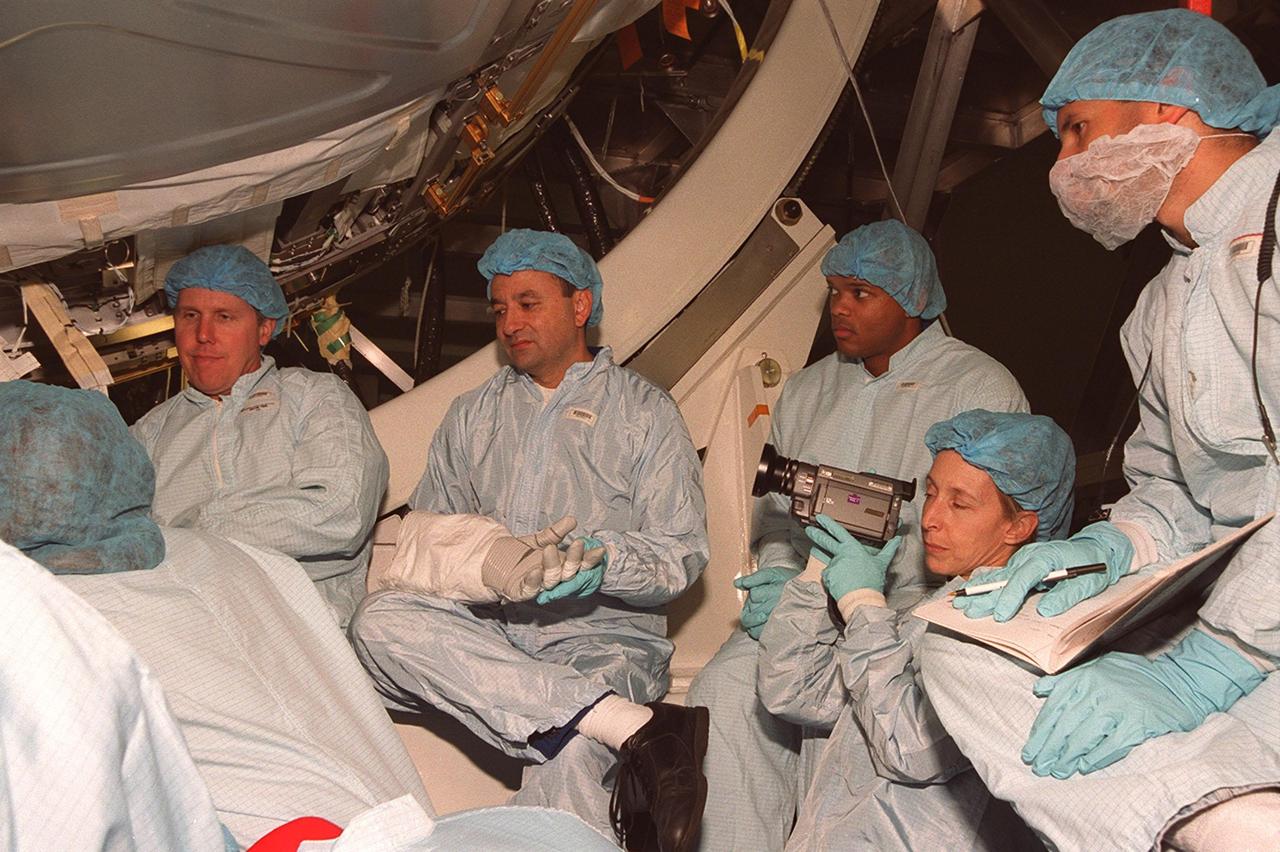

In the Space Station Processing Facility, members of the STS-98 crew, sitting in front of the U.S. Lab, Destiny, listen to a trainer during Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) activities. Seen, left to right, are Mission Specialist Thomas Jones, Pilot Mark Polansky and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Marsha Ivins (with camera). The CEIT allows a crew to become familiar with equipment they will be handling during the mission. With launch scheduled for Jan. 18, 2001, the STS-98 mission will be transporting the Lab to the International Space Station with five system racks already installed inside of the module. After delivery of electronics in the lab, electrically powered attitude control for Control Moment Gyroscopes will be activated
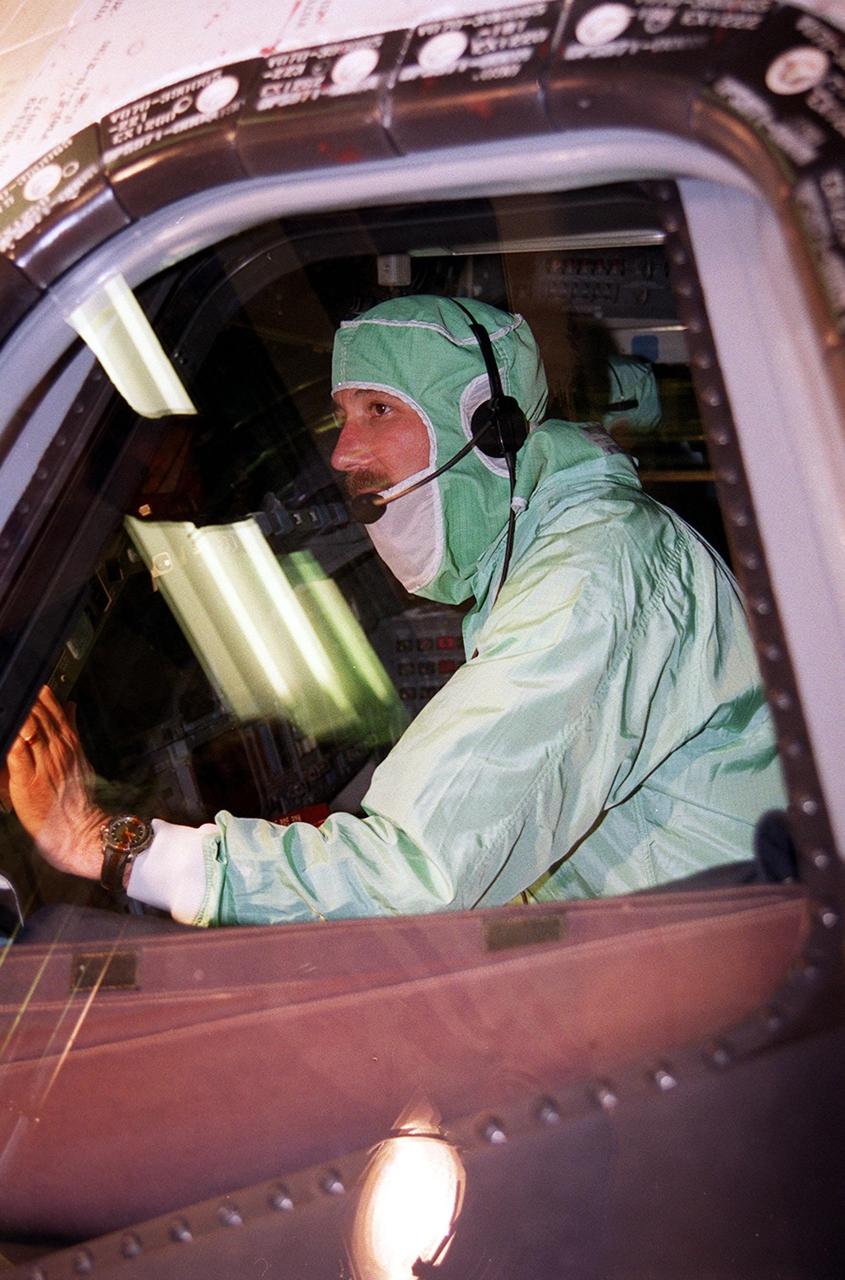

During a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, STS-100 Commander Kent V. Rominger checks out the windshield in orbiter Endeavour. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
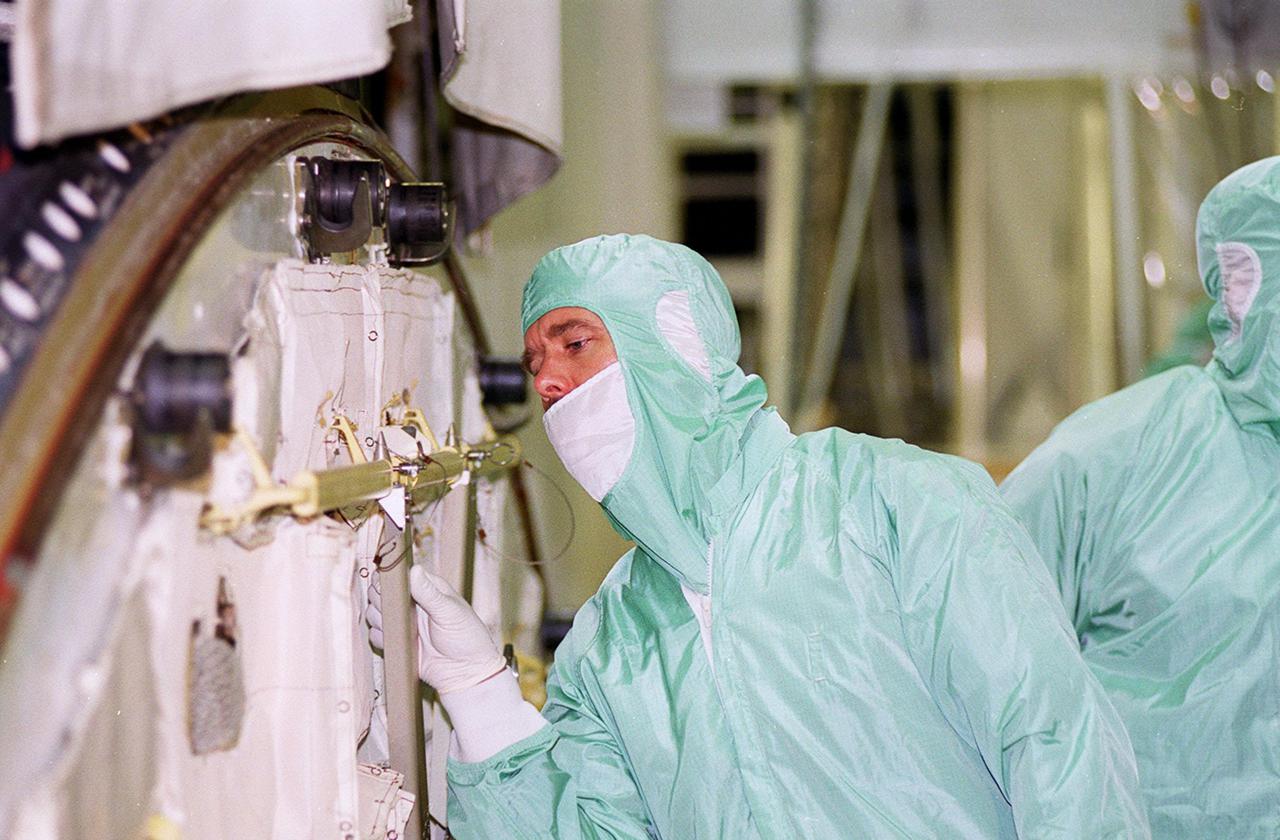

Dressed in protective clothing, STS-100 Mission Specialist Chris Hadfield looks at equipment in the payload bay of orbiter Endeavour during a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Hadfield is with the Canadian Space Agency. Endeavour is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
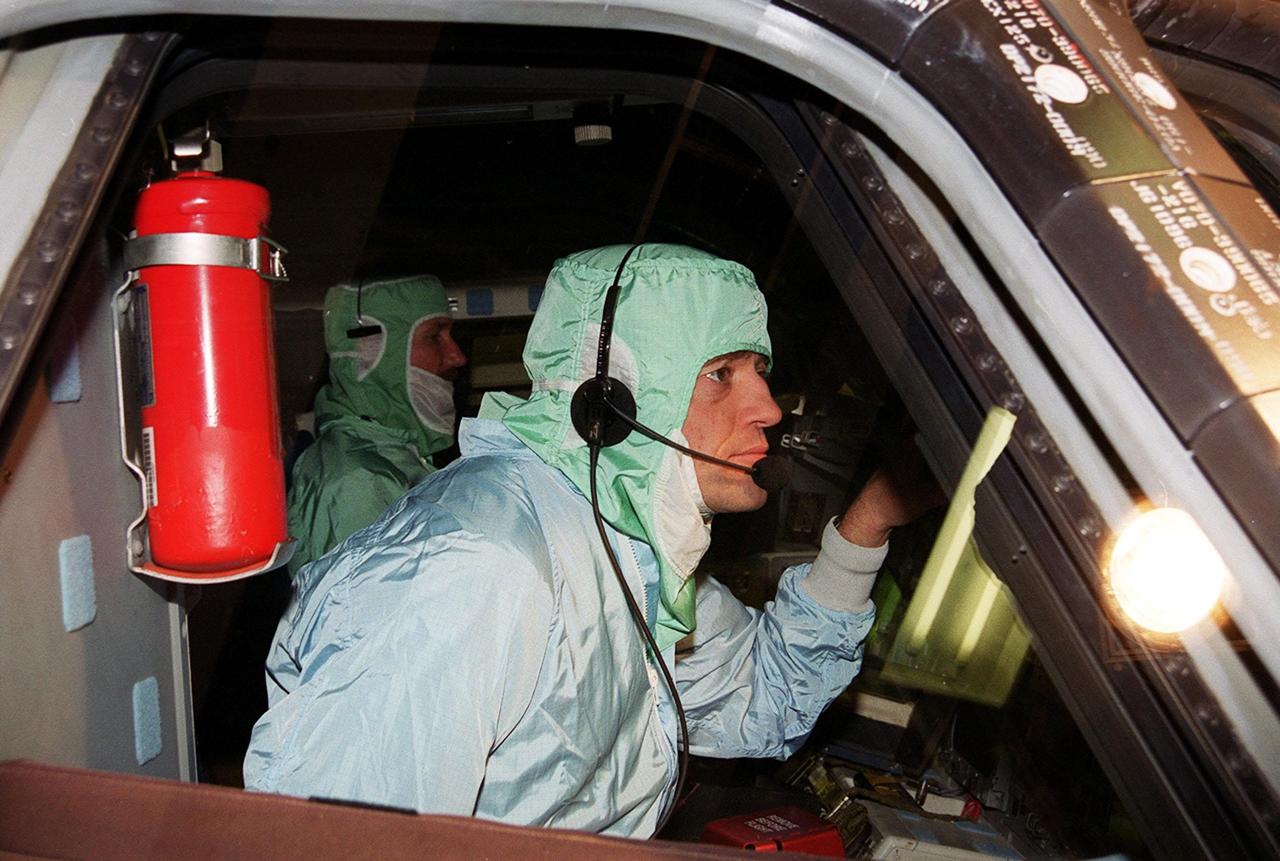

During a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, STS-100 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby checks out the windshield in orbiter Endeavour. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Commander Kent V. Rominger and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
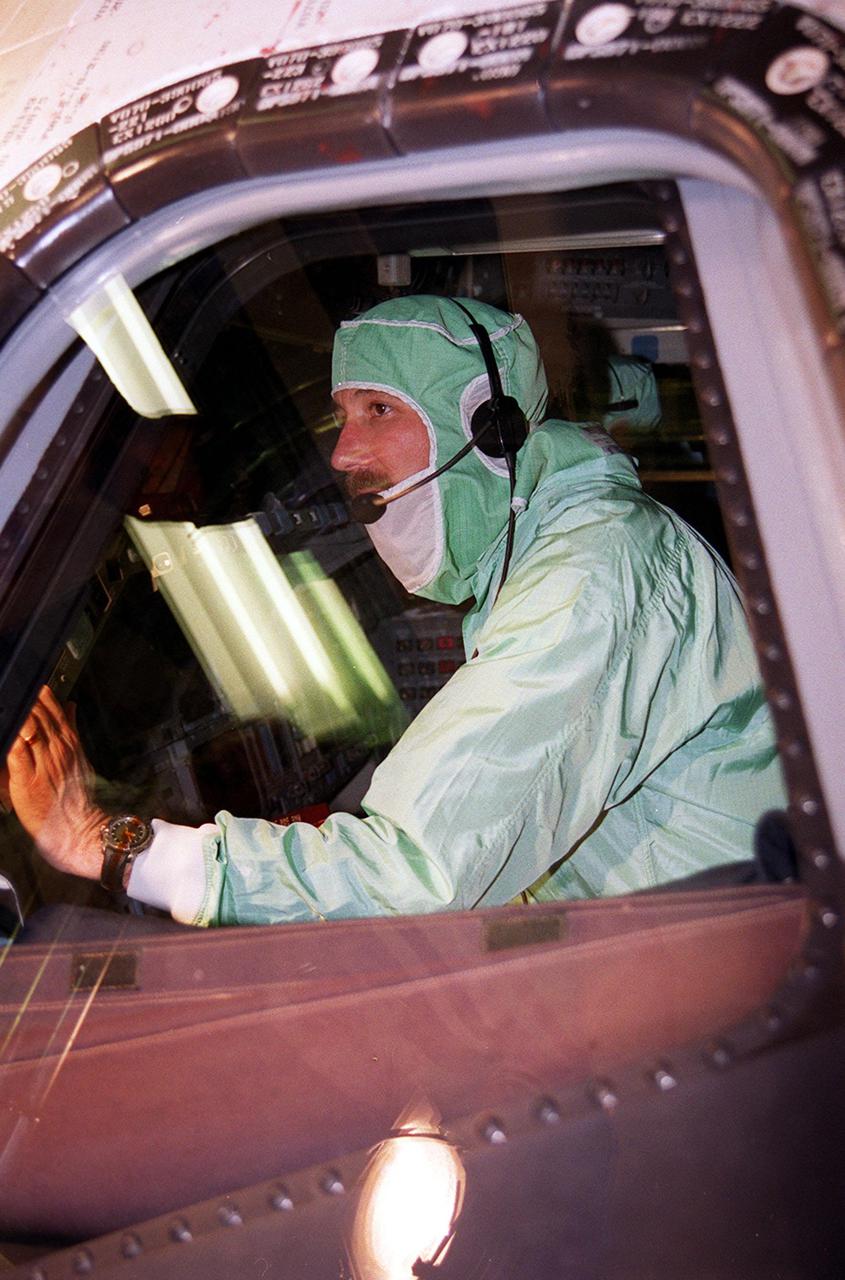

During a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, STS-100 Commander Kent V. Rominger checks out the windshield in orbiter Endeavour. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

Dressed in protective clothing, STS-100 Mission Specialist Chris Hadfield looks at equipment in the payload bay of orbiter Endeavour during a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Hadfield is with the Canadian Space Agency. Endeavour is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

During a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, STS-100 Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby checks out the windshield in orbiter Endeavour. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Commander Kent V. Rominger and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
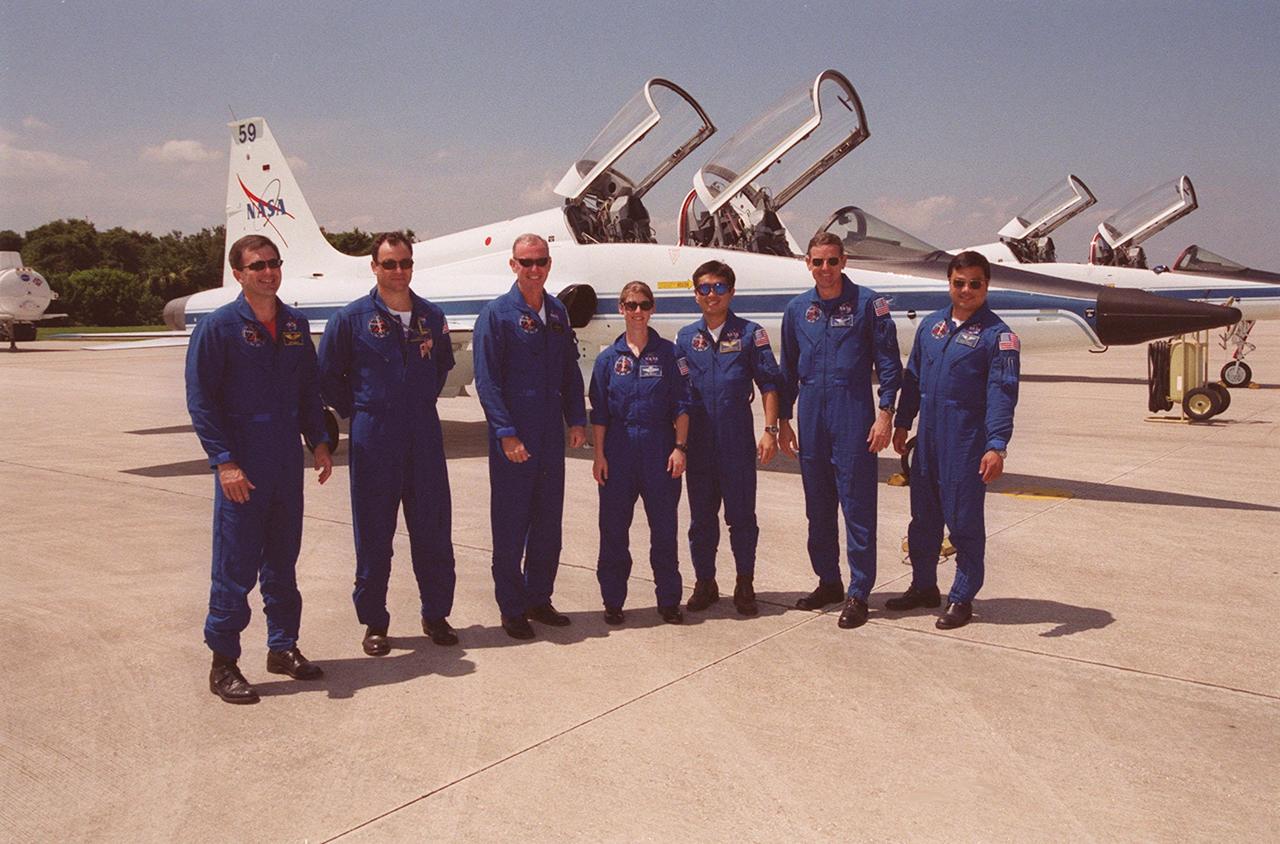

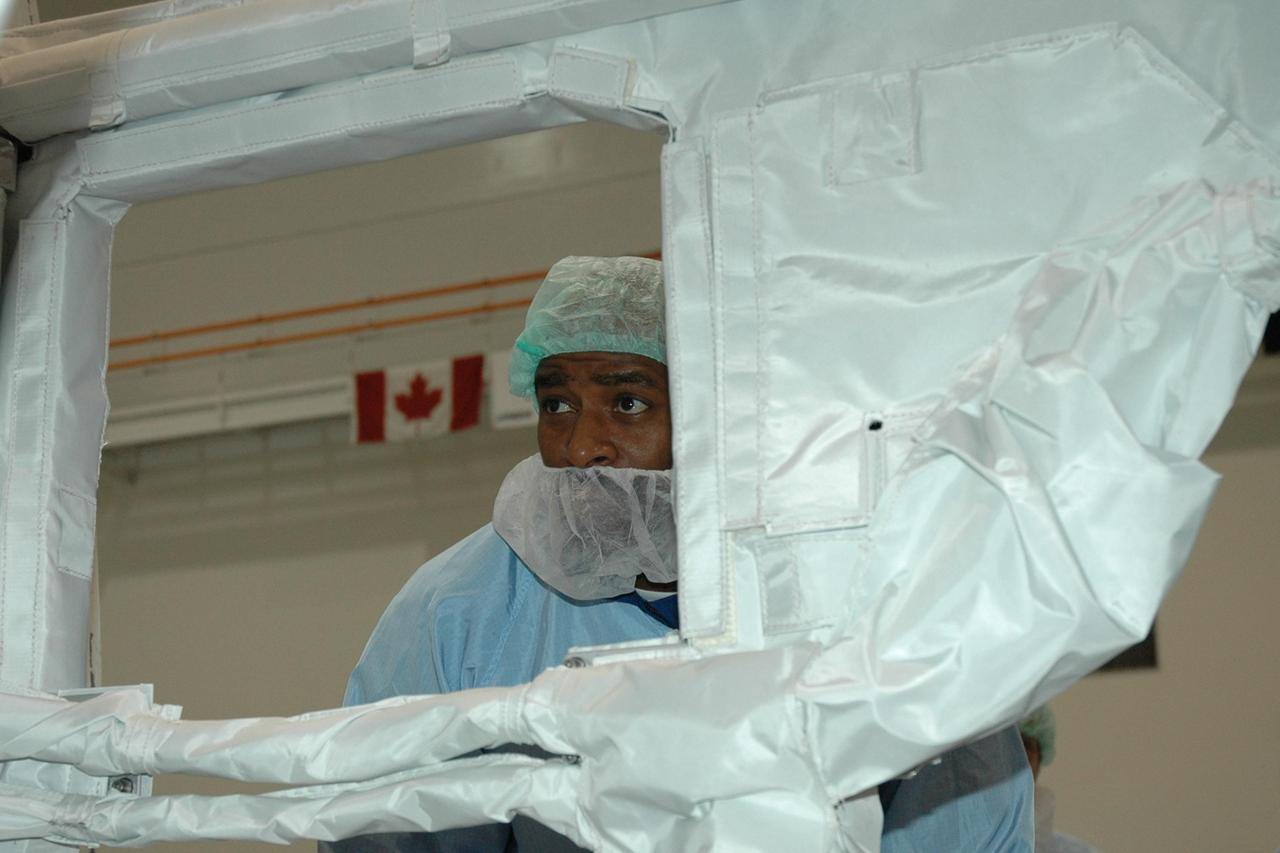
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew line up on the runway at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). From left are Mission Specialists Jeff Wisoff and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pam Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao. Wakata is with the Japanese space agency. During the CEIT, the crew will spend time at SPACEHAB becoming familiar with the payload and equipment they will use on their mission to the International Space Station. The mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
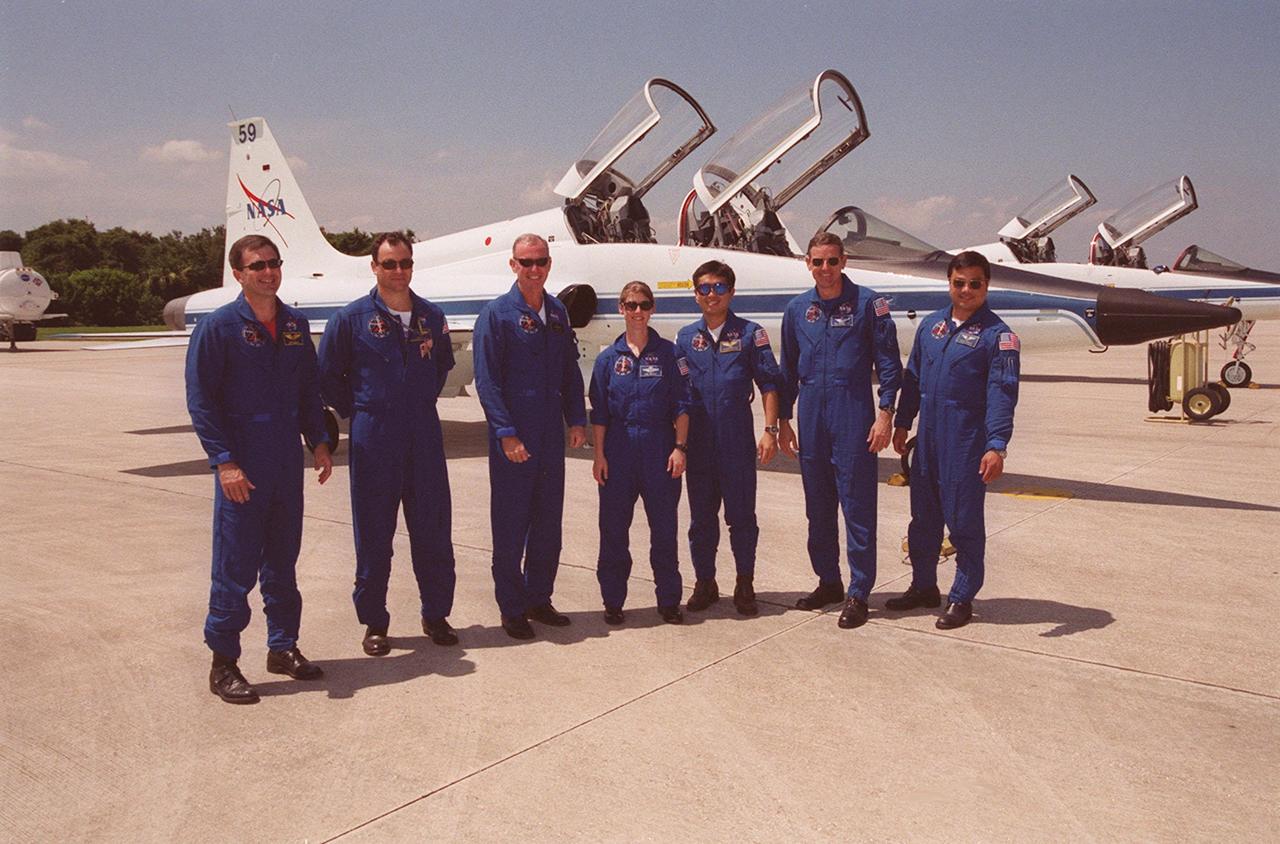

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-92 crew line up on the runway at KSC’s Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving to take part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT). From left are Mission Specialists Jeff Wisoff and Michael Lopez-Alegria, Commander Brian Duffy, Pilot Pam Melroy, and Mission Specialists Koichi Wakata, Bill McArthur and Leroy Chiao. Wakata is with the Japanese space agency. During the CEIT, the crew will spend time at SPACEHAB becoming familiar with the payload and equipment they will use on their mission to the International Space Station. The mission payload includes the Integrated Truss Structure Z1, an early exterior framework to allow the first U.S. solar arrays on a future flight to be temporarily installed on Unity for early power; Ku-band communication to support early science capability and U.S. television; and PMA-3 to provide a Shuttle docking port for solar array installation on the sixth ISS flight and Lab installation on the seventh ISS flight. STS-92 is scheduled to launch Oct. 5 from launch Pad 39A
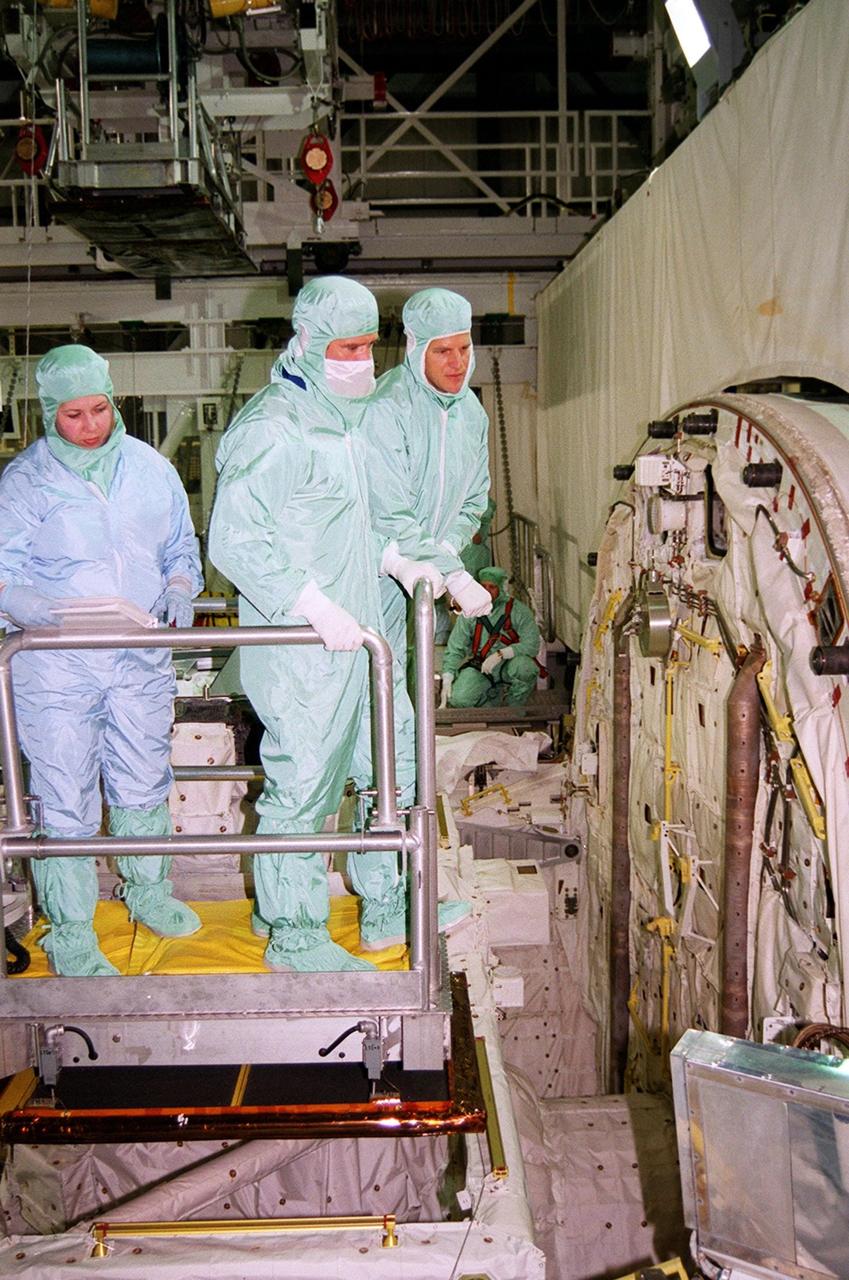

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski and Chris Hadfield look at the reel tether on the crew compartment hatch. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Endeavour is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
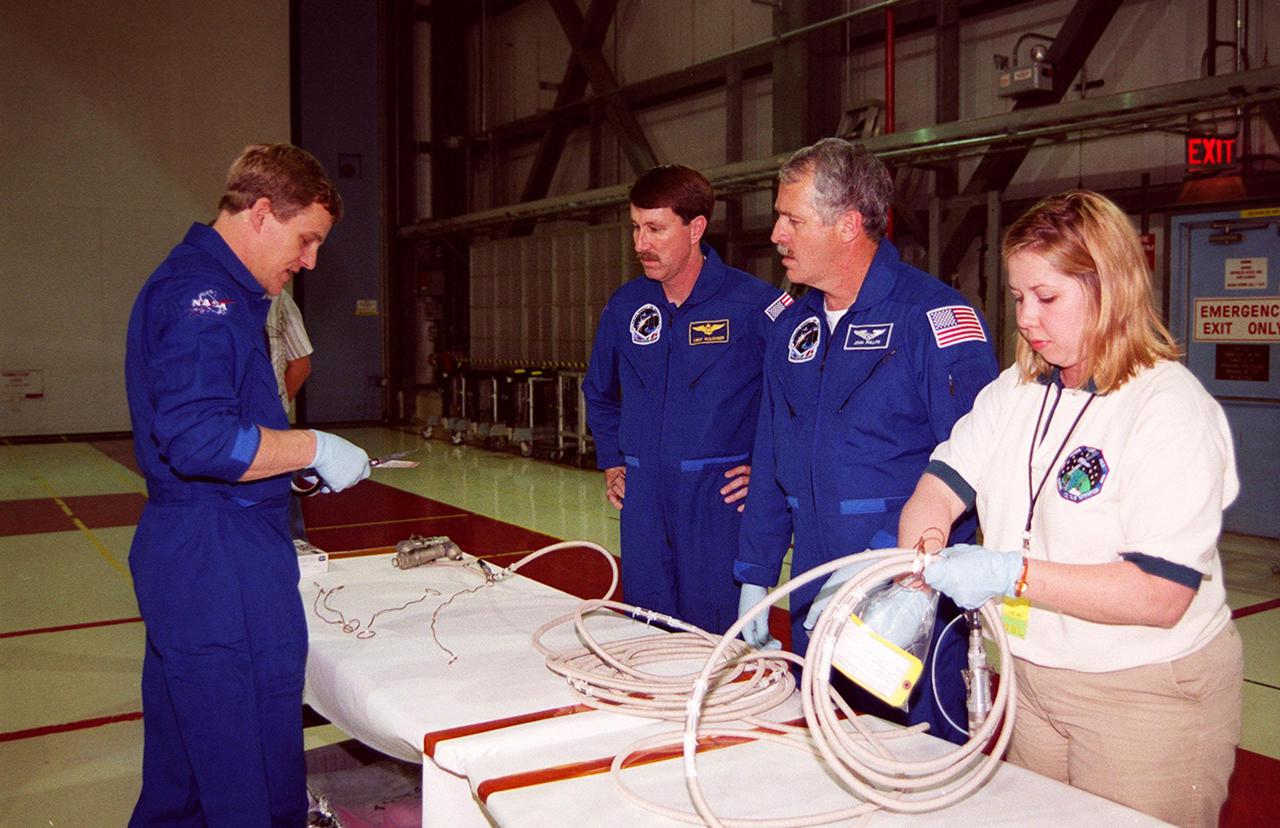

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left), Chris Hadfield (center), who is with the Canadian Space Agency, and John L. Phillips look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
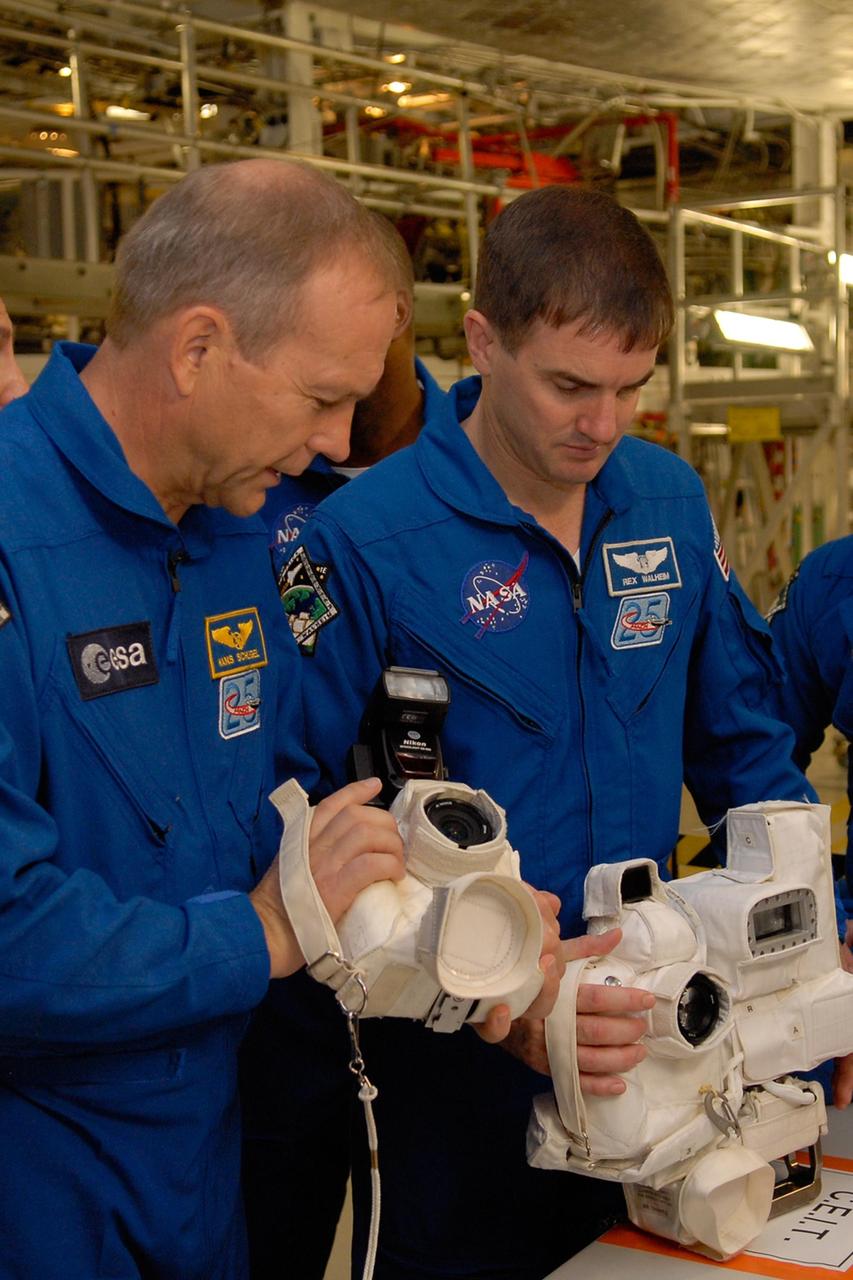

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew look over cameras that will be used during the mission. From left are Mission Specialists Hans Schlegel and Rex Walheim. Schlegel represents the European Space Agency. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
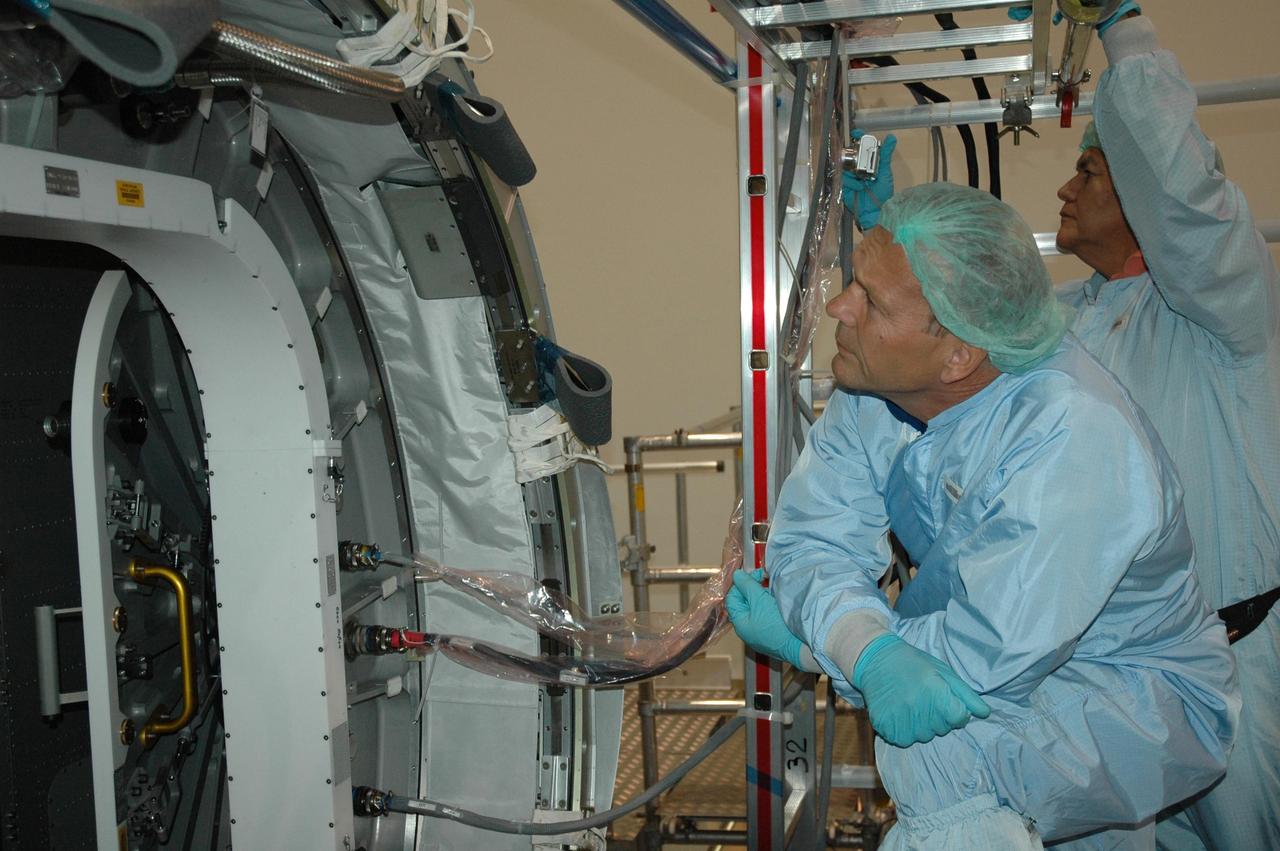

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. STS-122 Mission Specialist Hans Schlegel looks closely at the hatch on the Columbus Research Laboratory in the Space Station Processing Facility. Schegel represents the European Space Agency. The crew is at Kennedy to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The Columbus Lab is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station. It will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. Columbus, a program of ESA, is a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
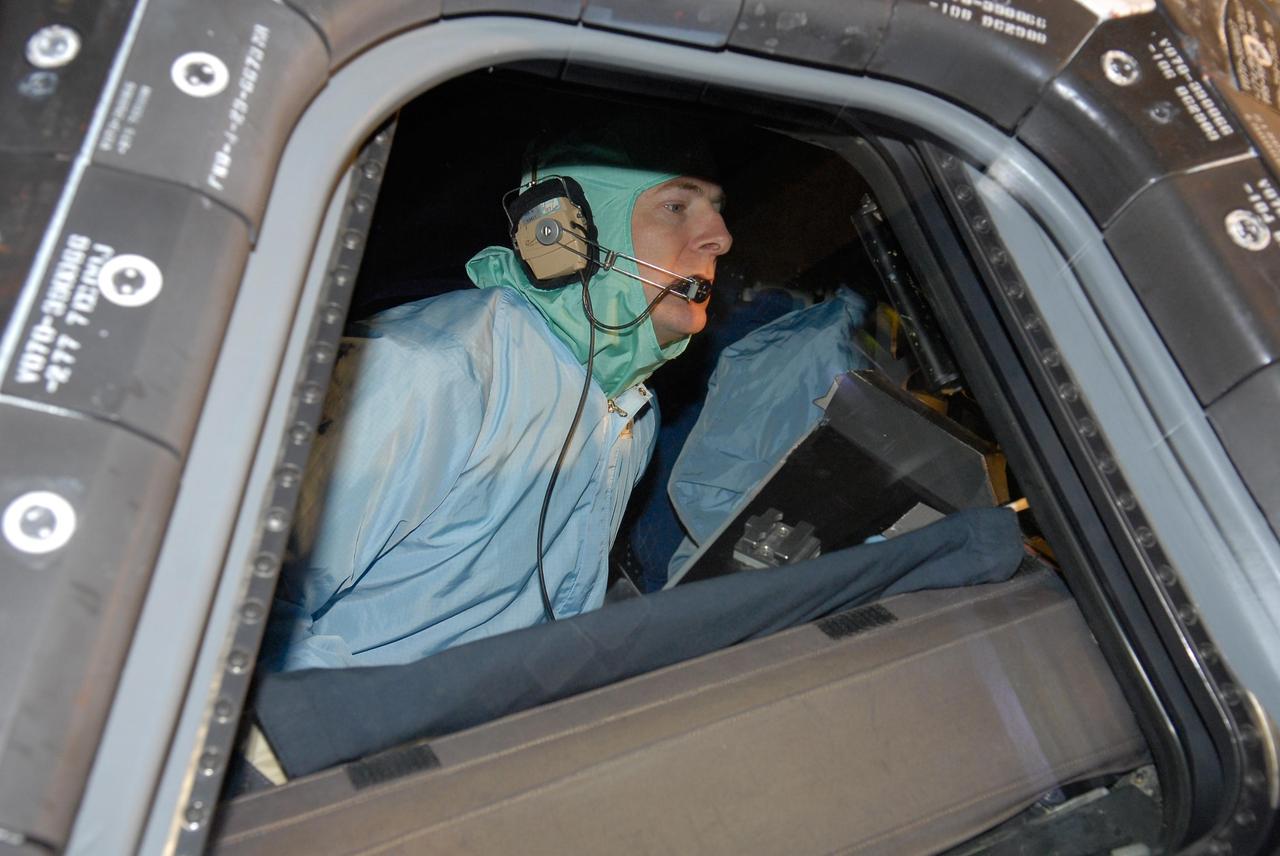

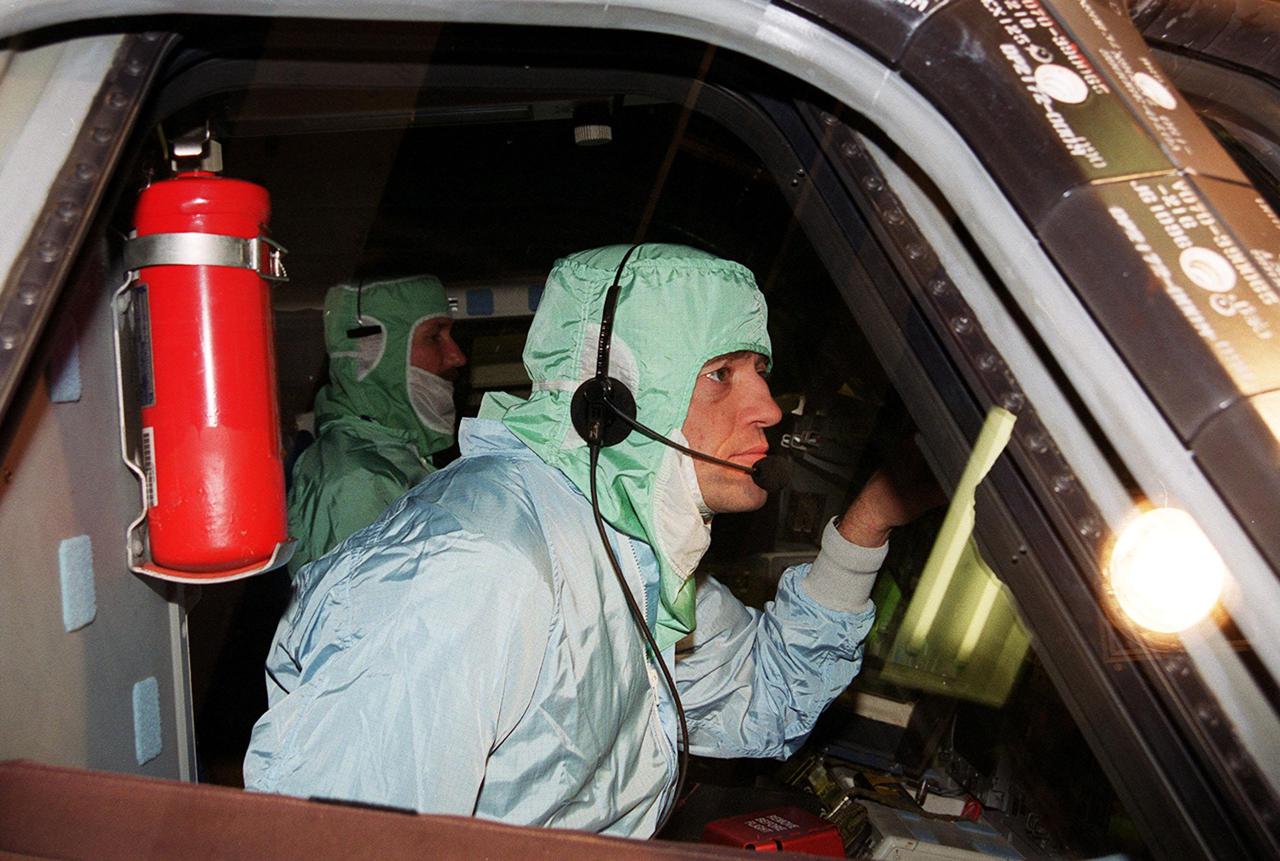
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-122 Pilot Alan Poindexter checks out the cockpit on space shuttle Atlantis. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
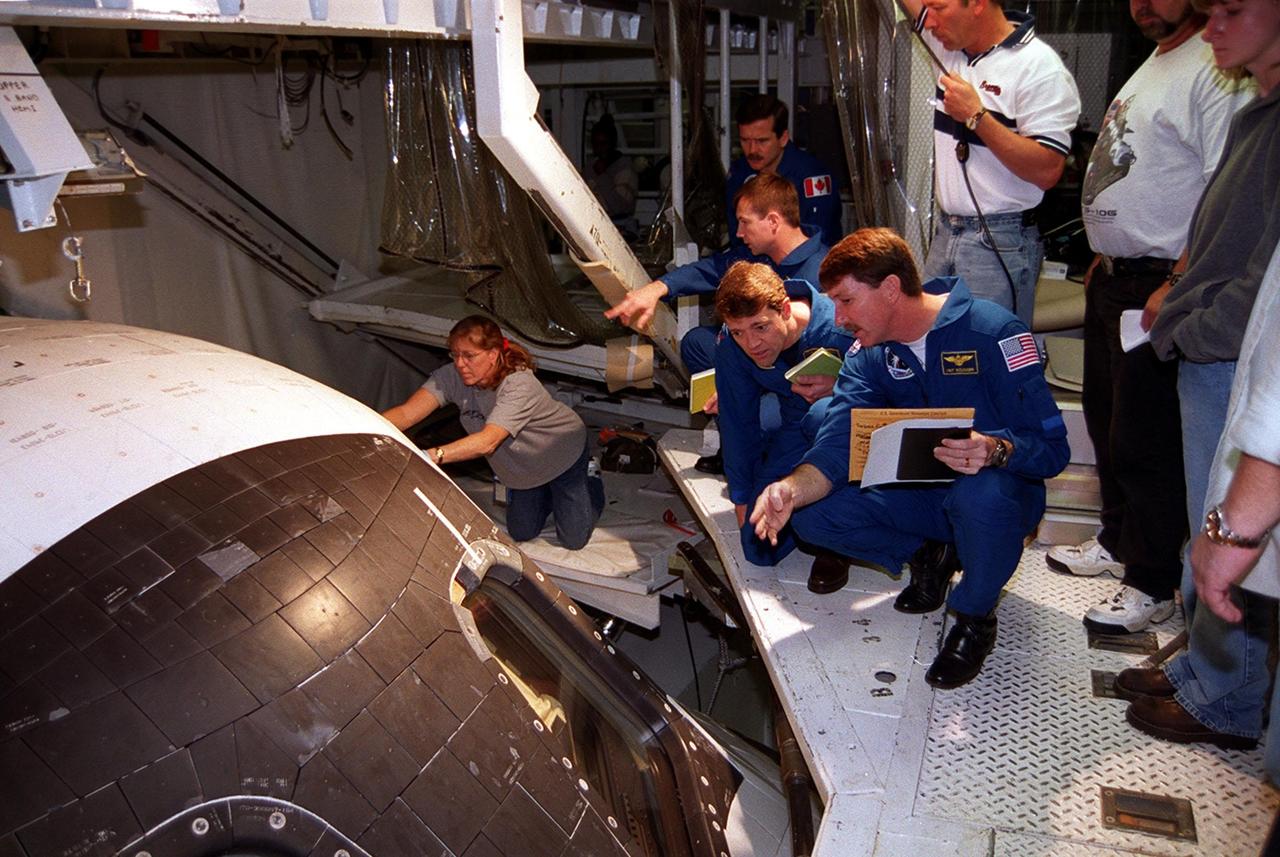
Members of the STS-100 crew check out Endeavour inside the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2. In their blue uniforms, they are (front to back) Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeff rey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, and Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski and Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency. Endeavour is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
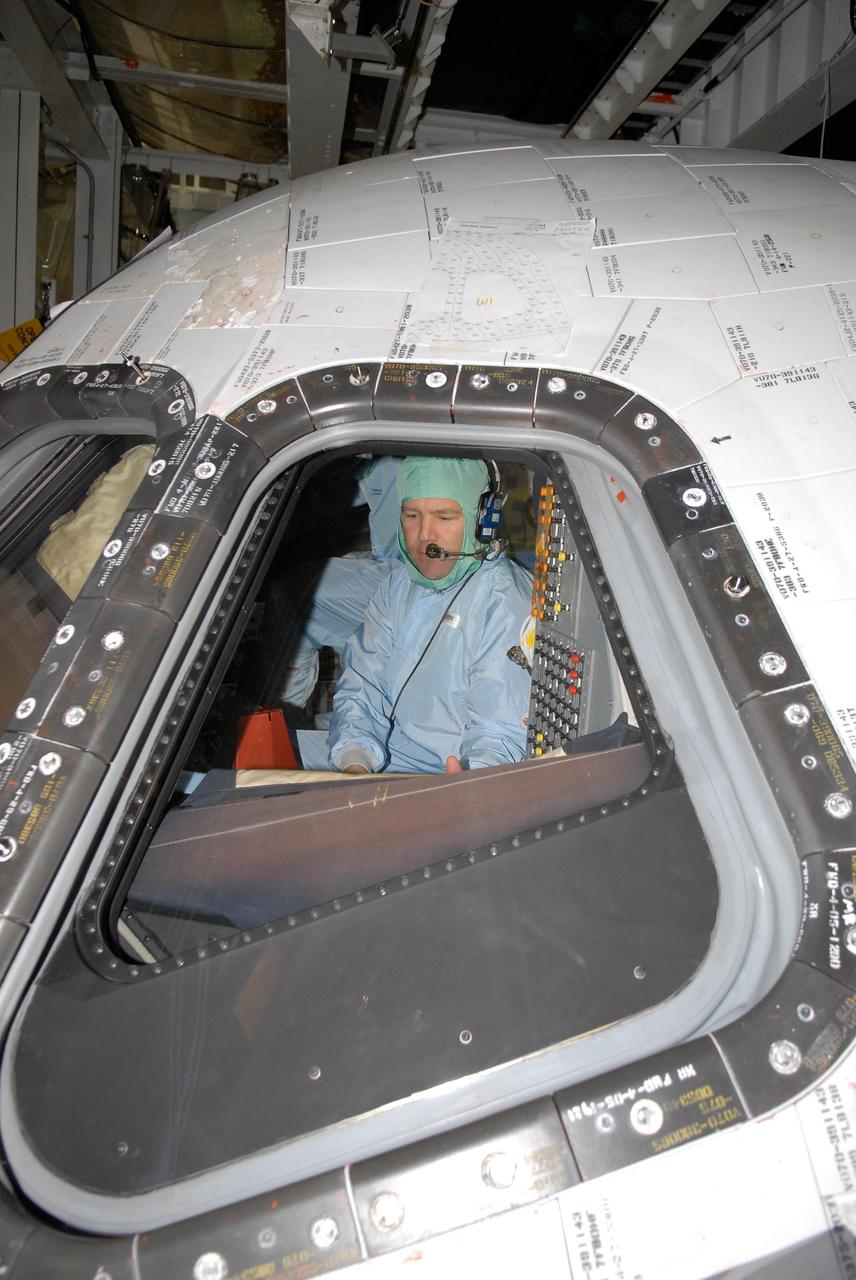

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-122 Commander Stephen Frick checks out the cockpit on space shuttle Atlantis. He and other crew members are at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
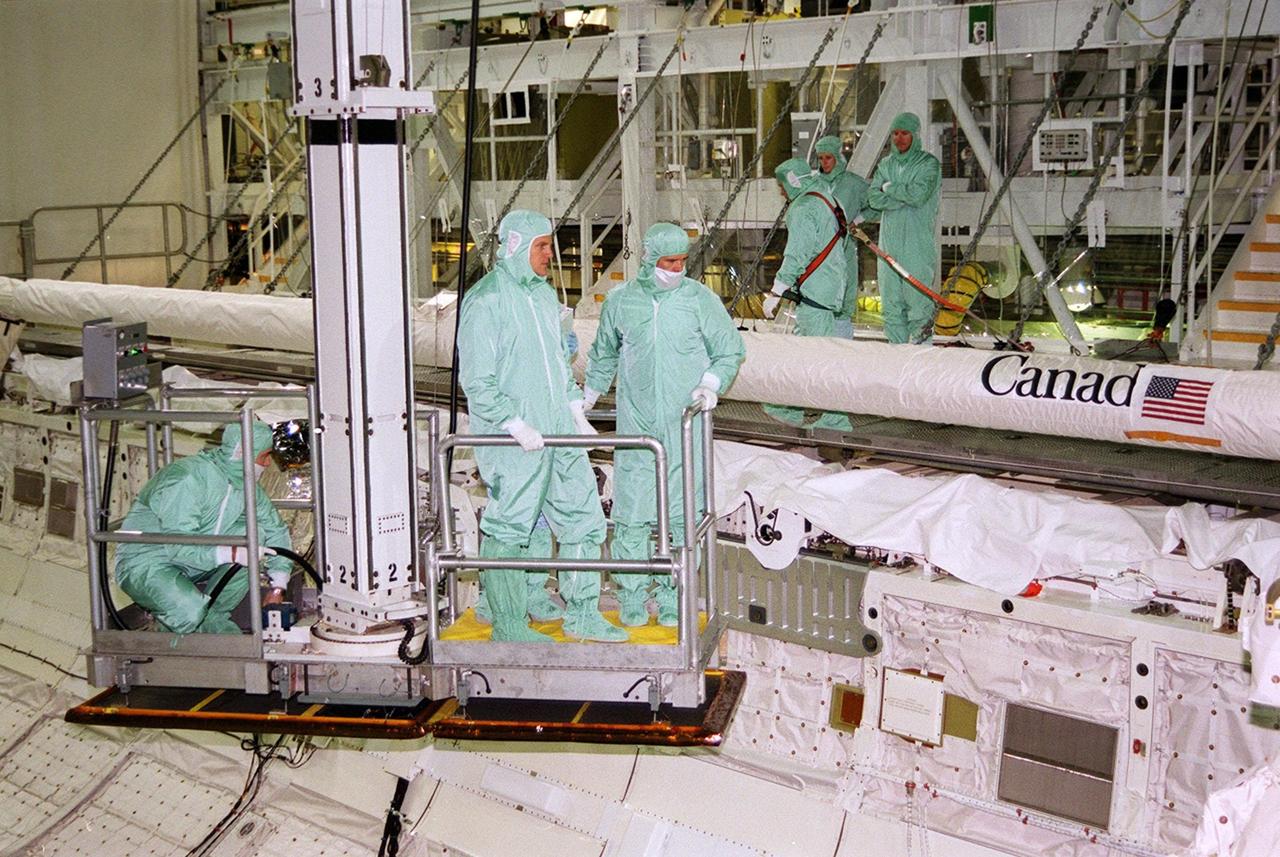

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, members of the STS-100 crew get a look at the payload inside Endeavour. Stretching the length of the payload bay is the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, that they will be attaching to the Space Station for use in assembling future components. . The crew, who are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), comprises Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Endeavour is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left) and Chris Hadfield (right), who is with the Canadian Space Agency, look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
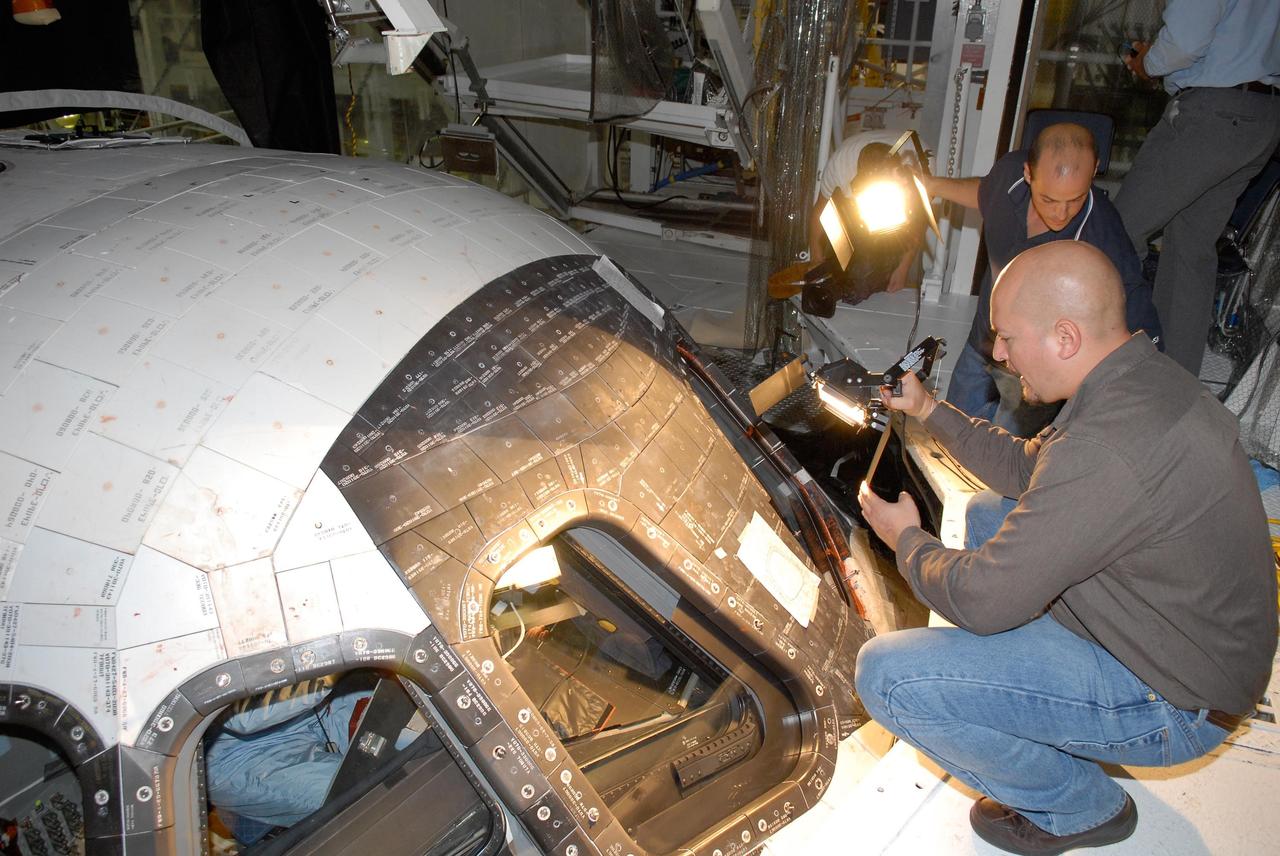

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, United Space Alliance technicians provide lights over the space shuttle Atlantis' cockpit. STS-122 Commander Stephen Frick is inside checking the cockpit for launch readiness. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-122 Commander Stephen Frick checks out the cockpit on space shuttle Atlantis. He and other crew members are at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
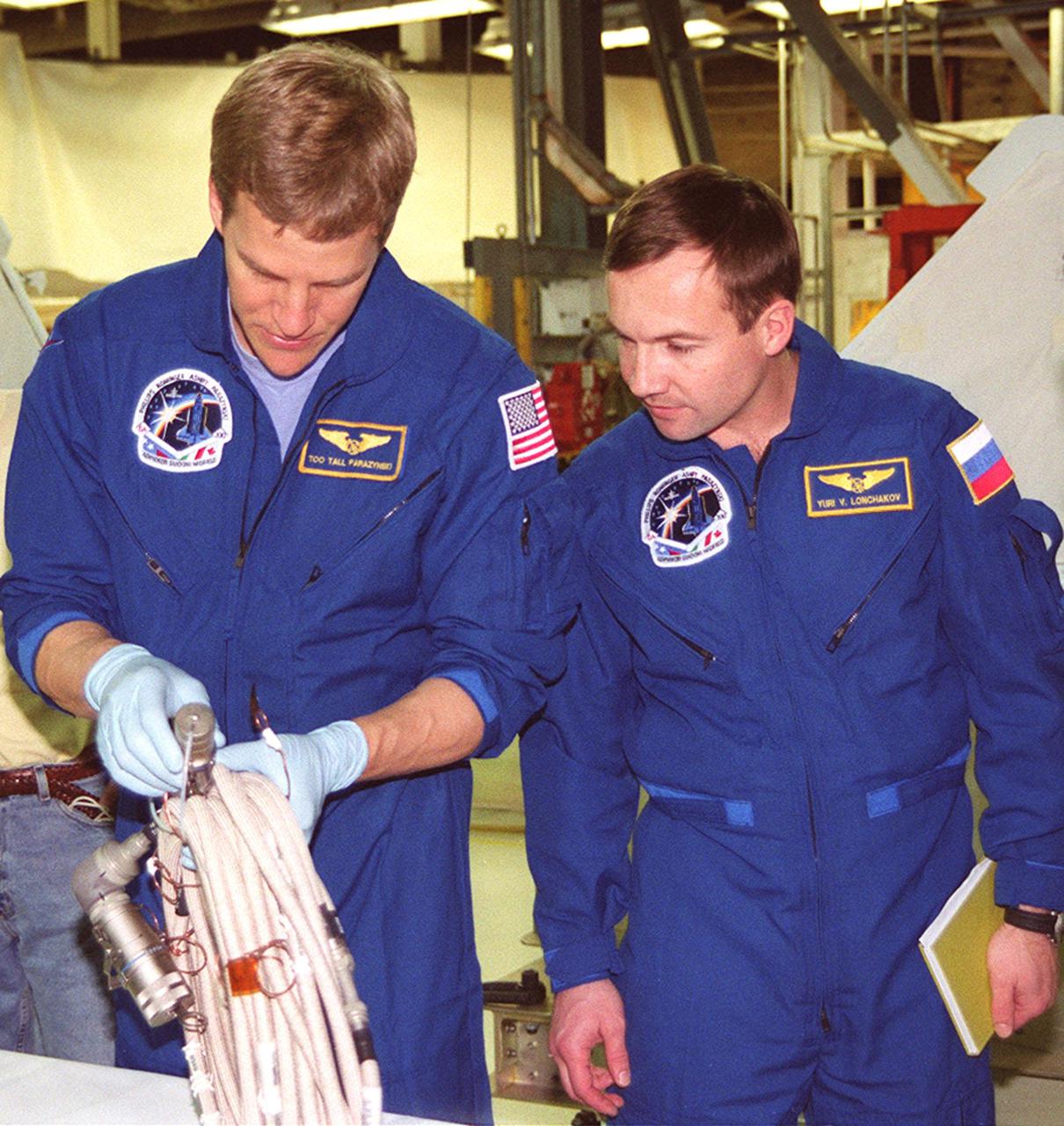

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left) and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, John L. Phillips and Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
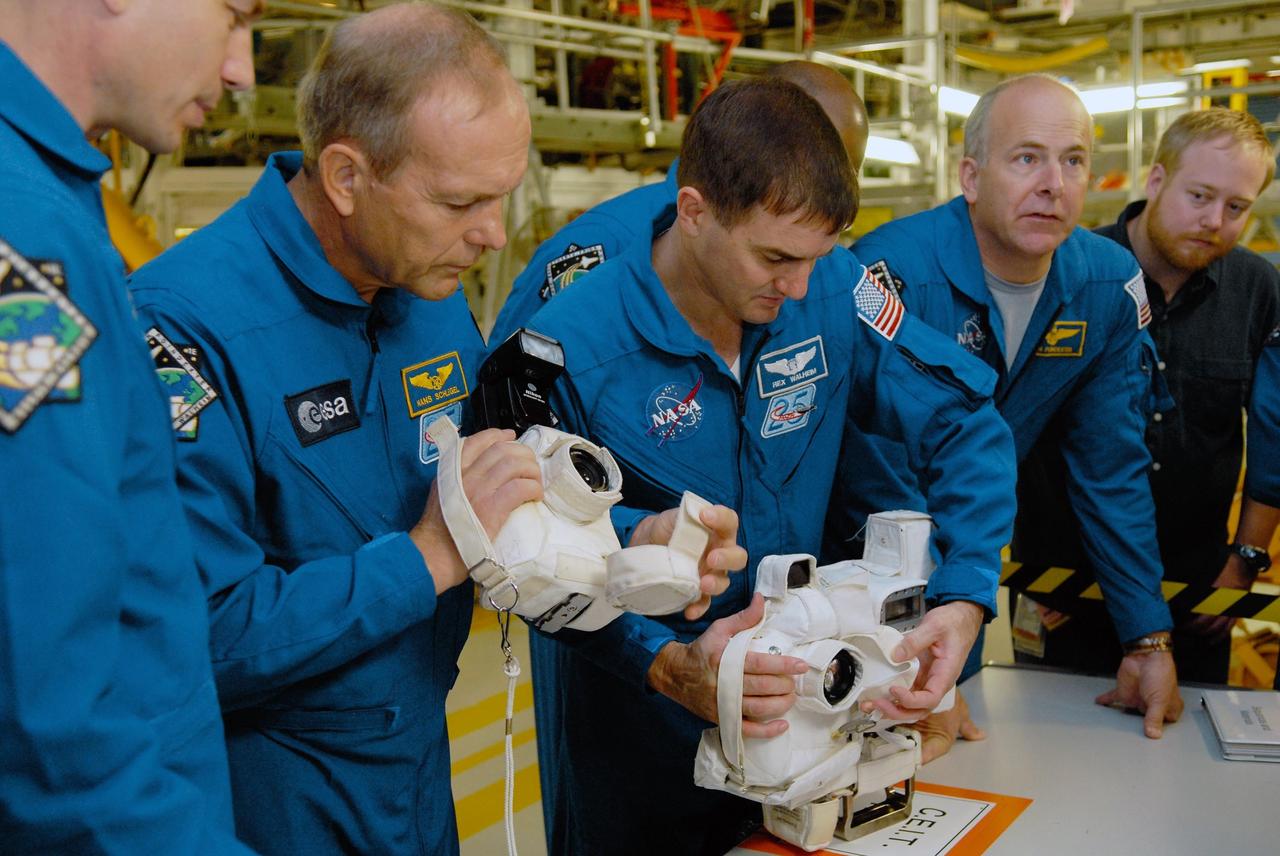

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew look over cameras that will be used during the mission. From left are Mission Specialists Stanley Love, Hans Schlegel and Rex Walheim and Pilot Alan Poindexter. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
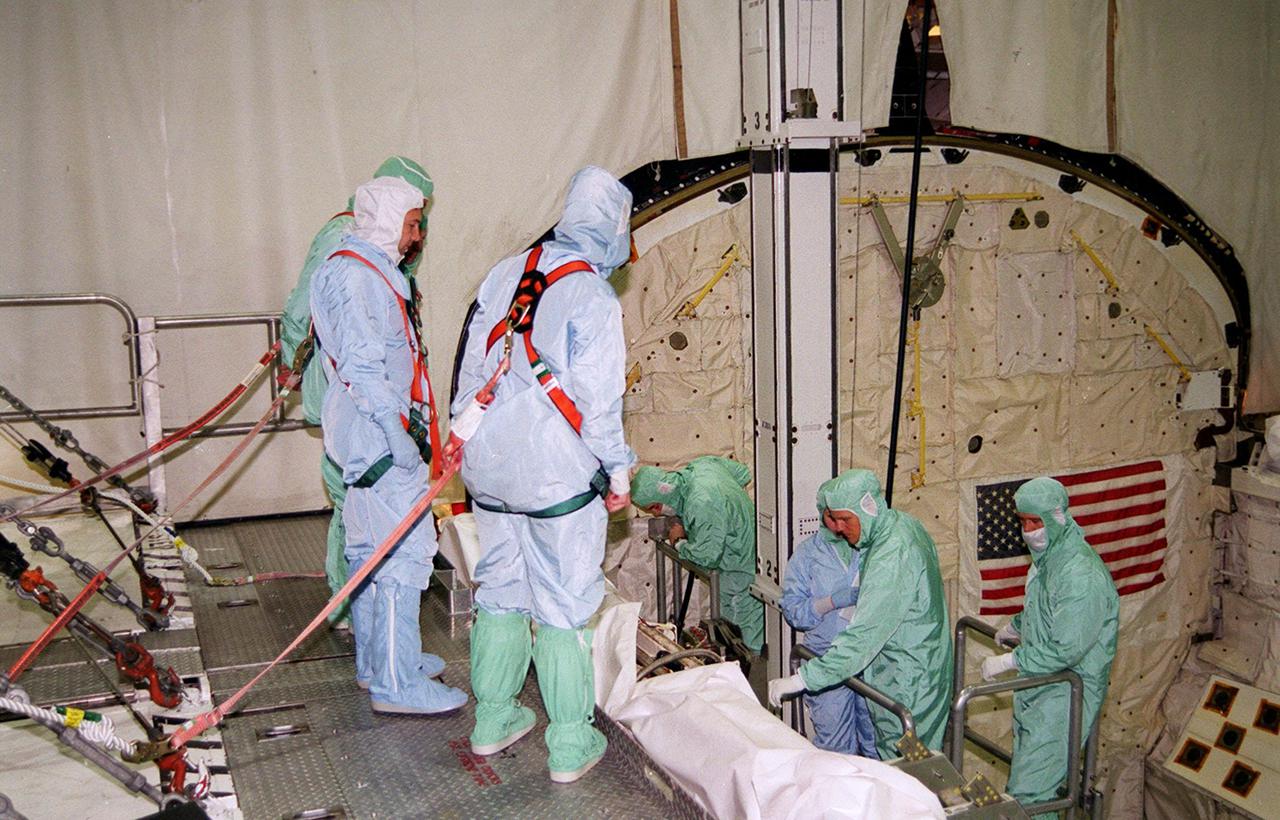

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, members of the STS-100 crew look over the payload in Endeavour during a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC. Lowered into the payload bay, they are looking at the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS. The crew comprises Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS will be attached to the Space Station to aid in assembling future components. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
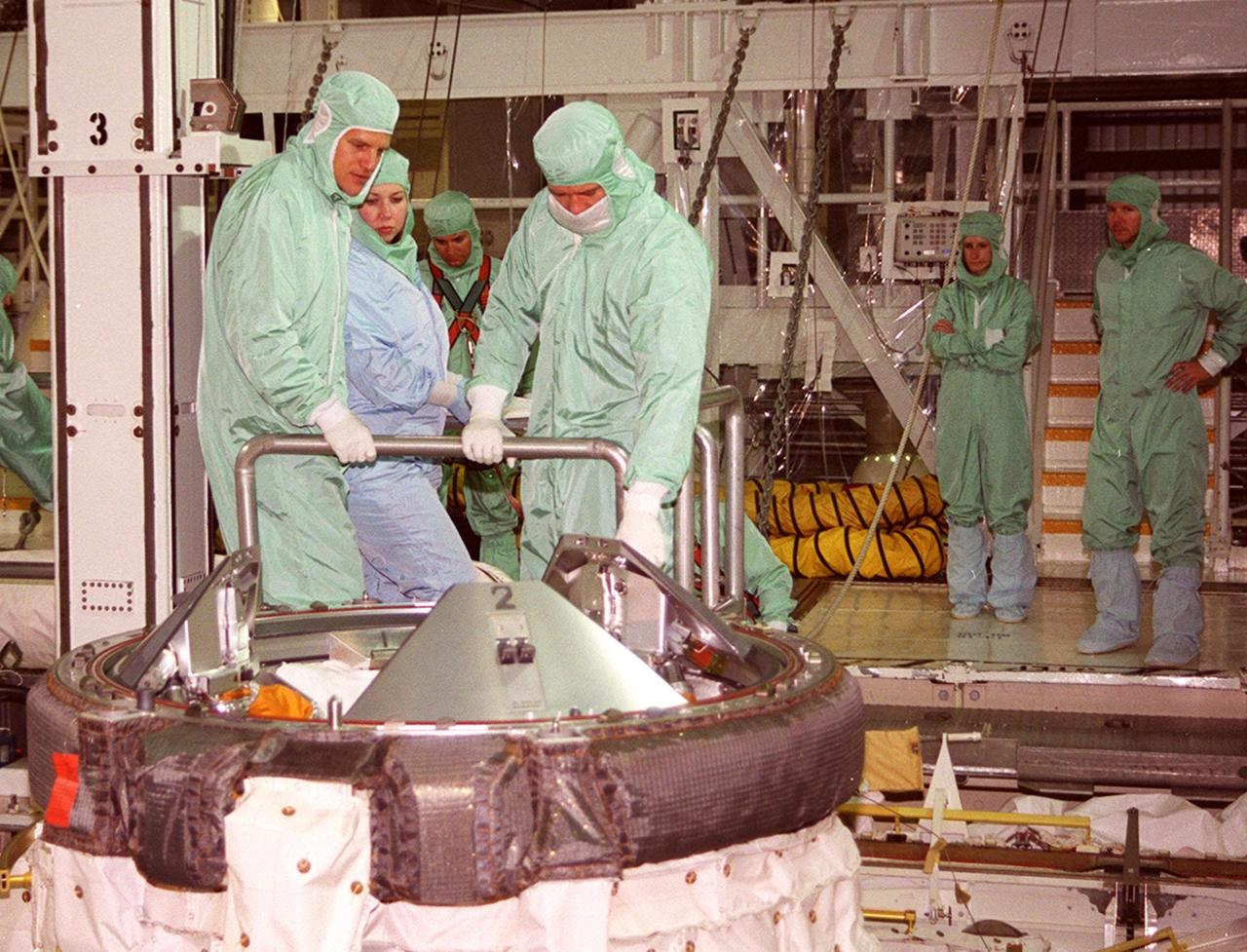

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, STS-100 Mission Specialist Scott Parazynski (left, foreground) and Chris Hadfield (right, foreground) look over the docking mechanism in payload bay of Endeavour. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. Endeavour is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
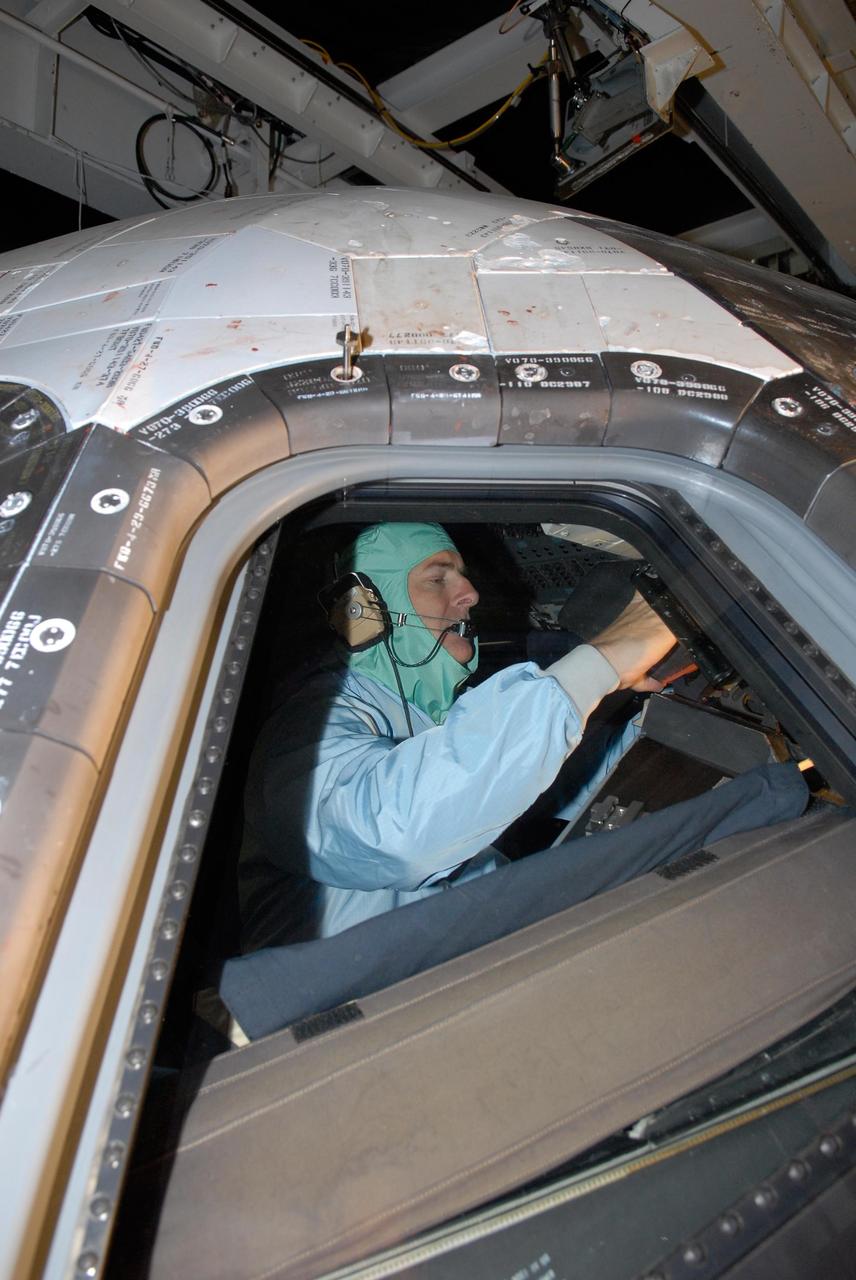

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-122 Pilot Alan Poindexter checks out the cockpit on space shuttle Atlantis. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
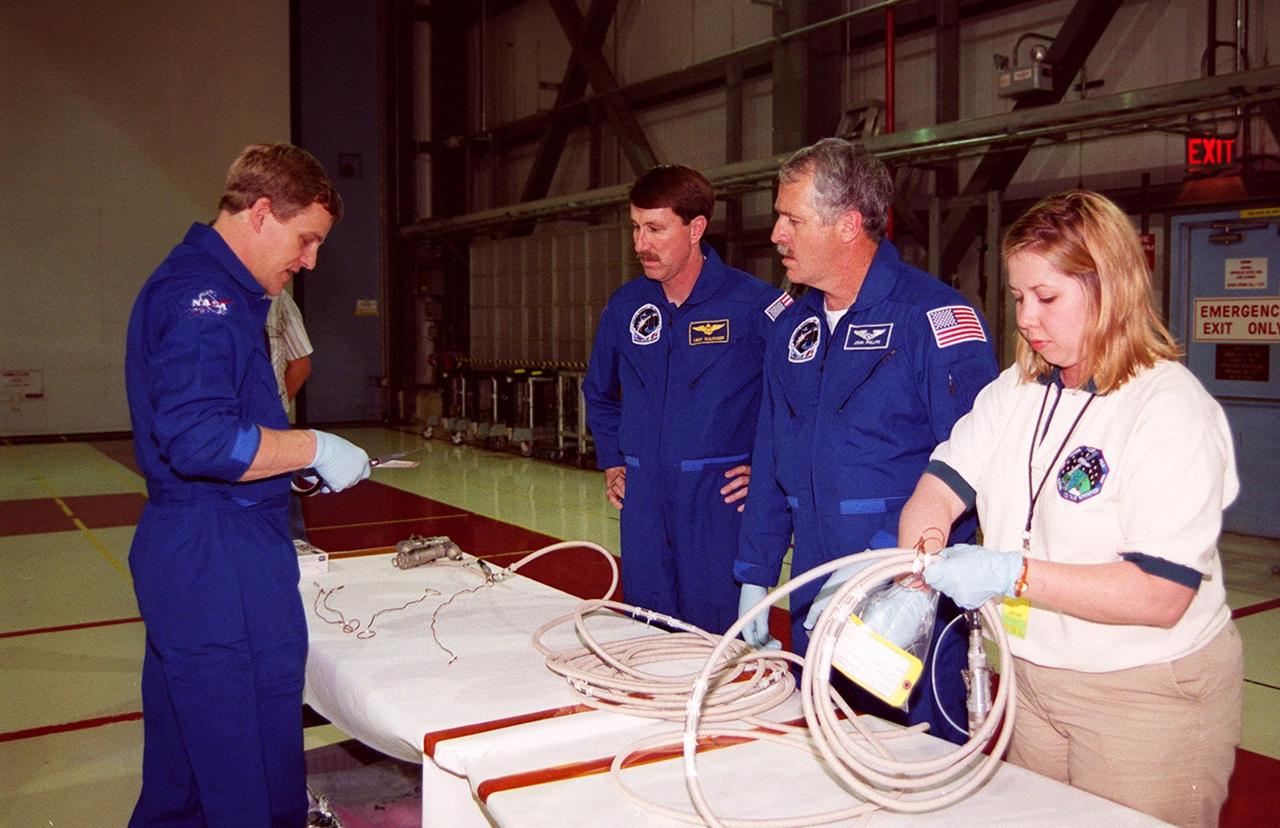

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left), Chris Hadfield (center), who is with the Canadian Space Agency, and John L. Phillips look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
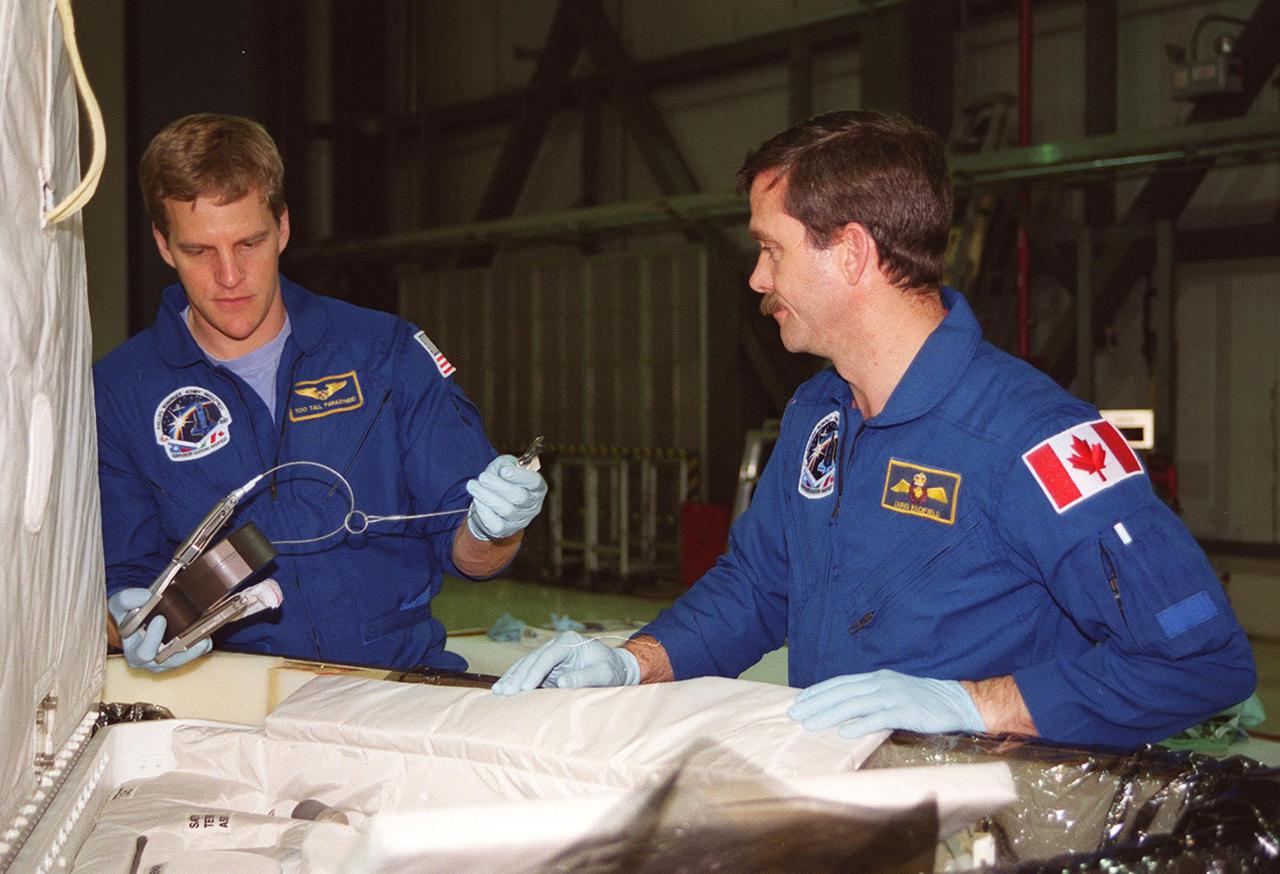

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left) and Chris Hadfield (right), who is with the Canadian Space Agency, look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
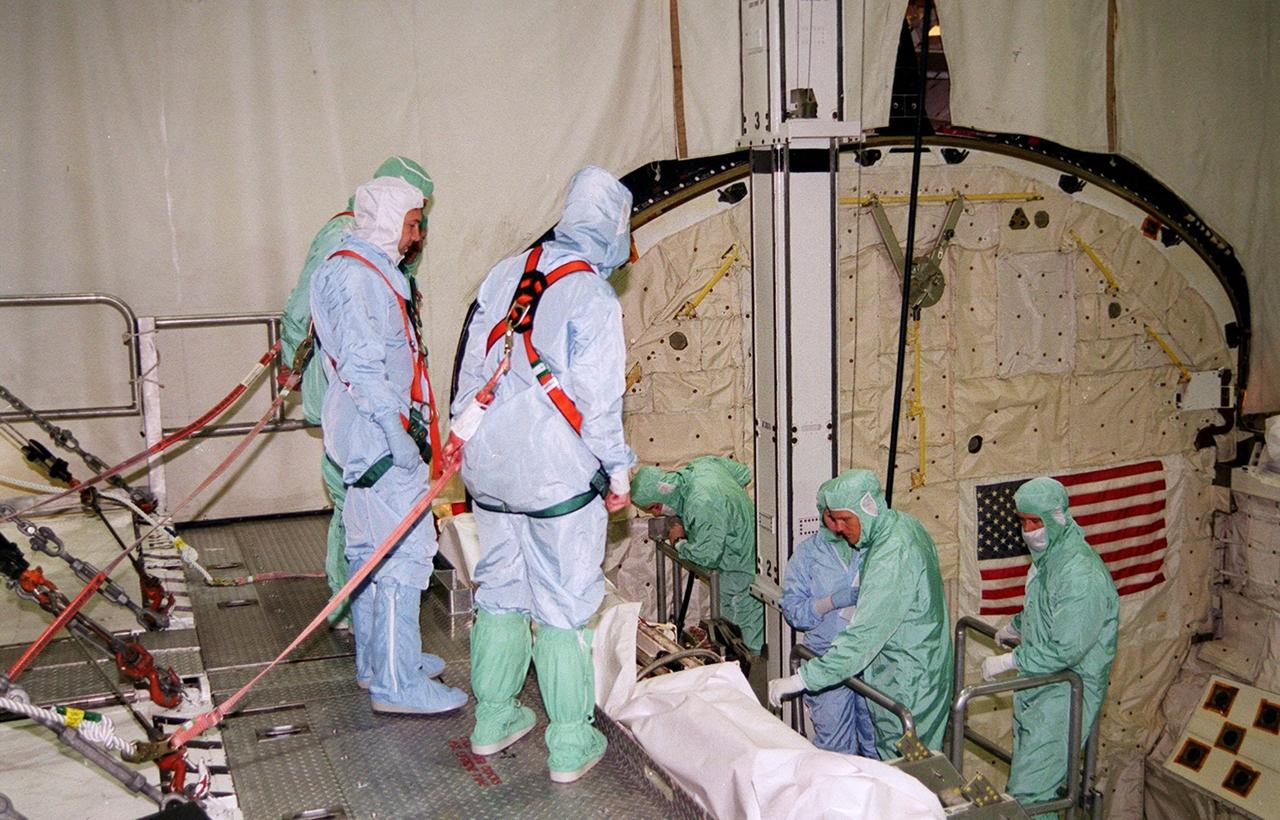

In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, members of the STS-100 crew look over the payload in Endeavour during a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC. Lowered into the payload bay, they are looking at the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS. The crew comprises Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, Scott Parazynski, John L. Phillips, Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency, and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. The SSRMS will be attached to the Space Station to aid in assembling future components. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
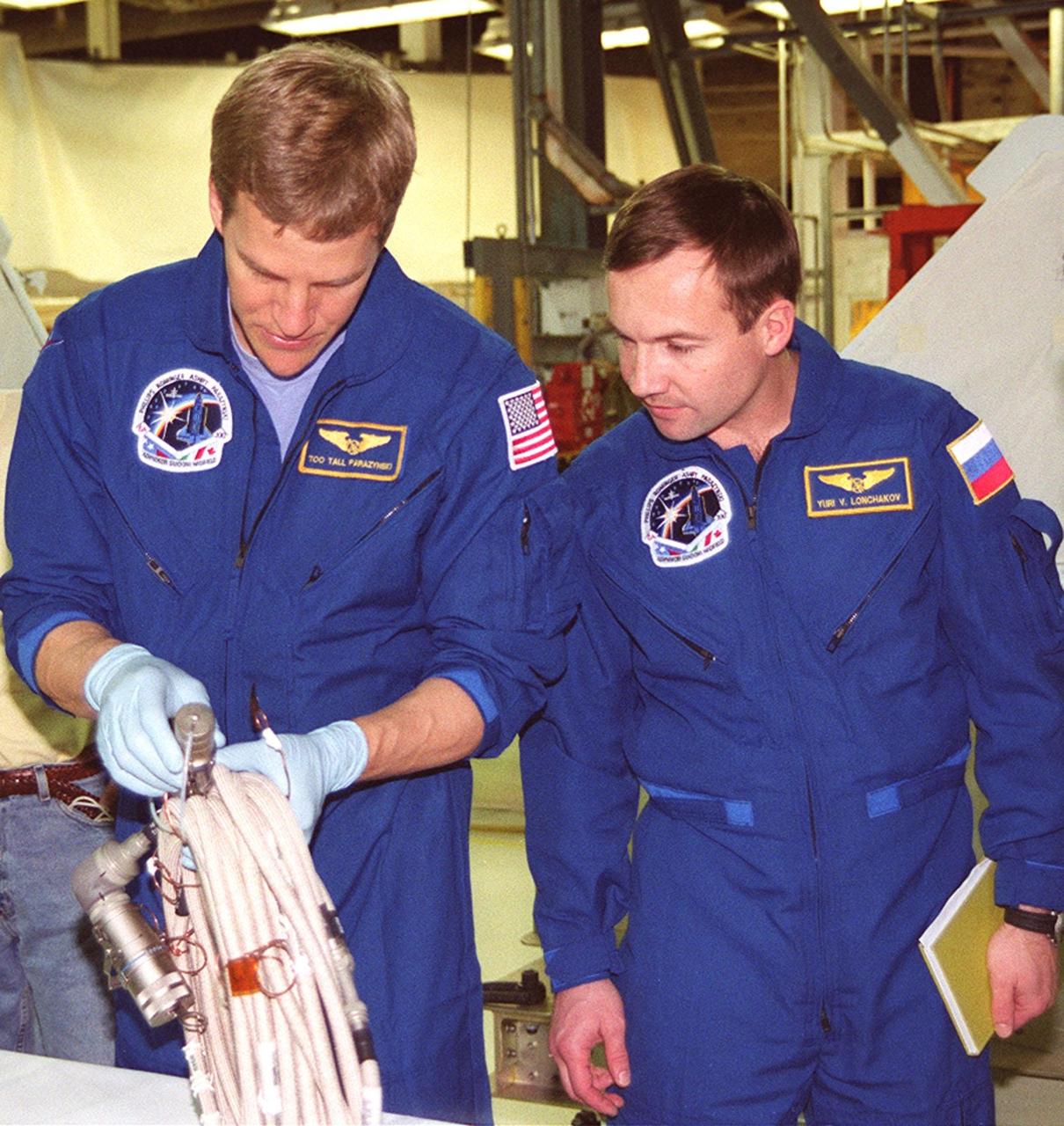

STS-100 Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski (left) and Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, look over equipment that will be used during their mission. They are taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) at KSC, along with other crew members Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby and Mission Specialists Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency, John L. Phillips and Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency. The orbiter is also carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
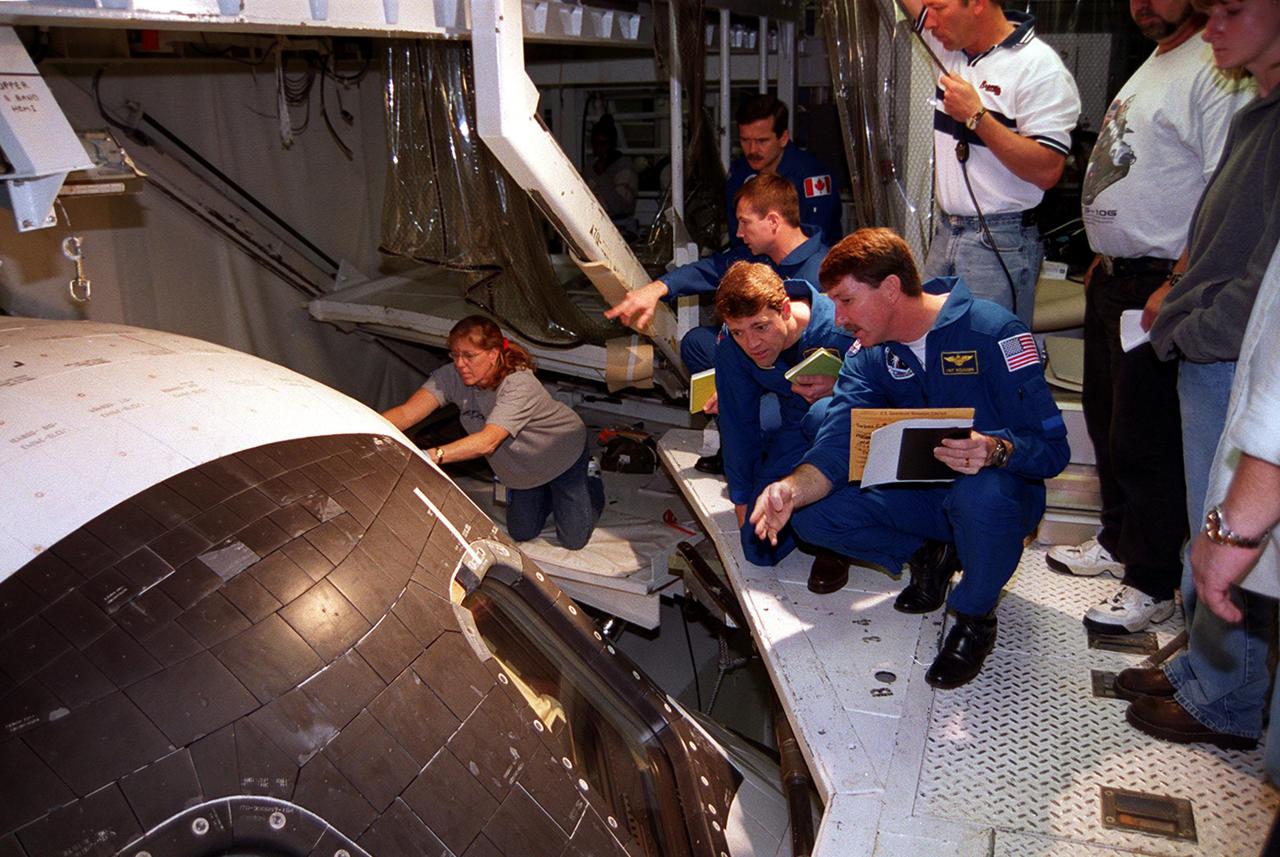
Members of the STS-100 crew check out Endeavour inside the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2. In their blue uniforms, they are (front to back) Commander Kent V. Rominger, Pilot Jeff rey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Yuri Lonchakov, who is with the Russian Aviation and Space Agency, and Chris Hadfield, who is with the Canadian Space Agency. Other crew members at KSC for the CEIT are Mission Specialists Scott Parazynski and Umberto Guidoni, who is with the European Space Agency. Endeavour is carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello and the Canadian robotic arm, SSRMS, to the International Space Station. Raffaello carries six system racks and two storage racks for the U.S. Lab. Launch of mission STS-100 is scheduled for April 19 at 2:41 p.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39A
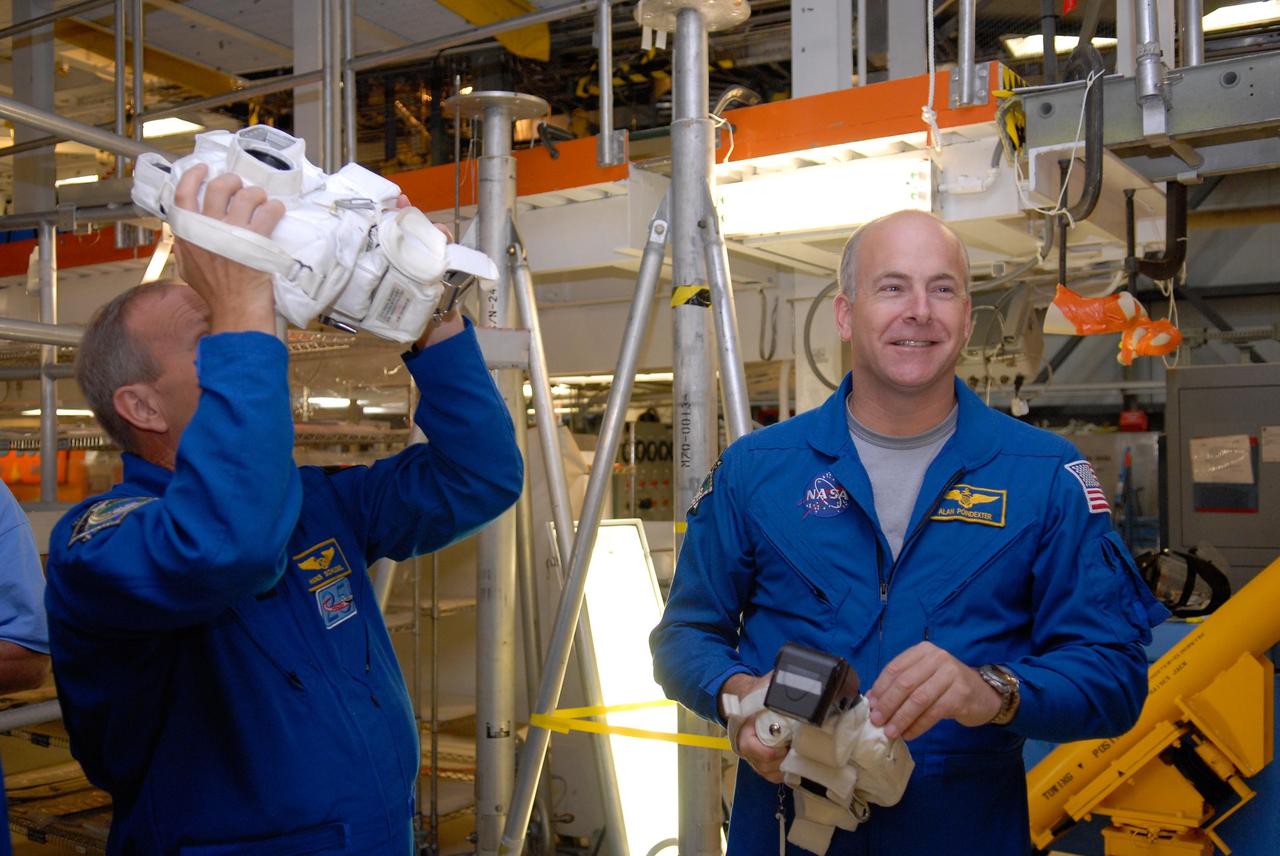

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew practice handling cameras that will be used during the mission. At left is Mission Specialist Hans Schlegel. At right is Pilot Alan Poindexter. Schlegel represents the European Space Agency. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
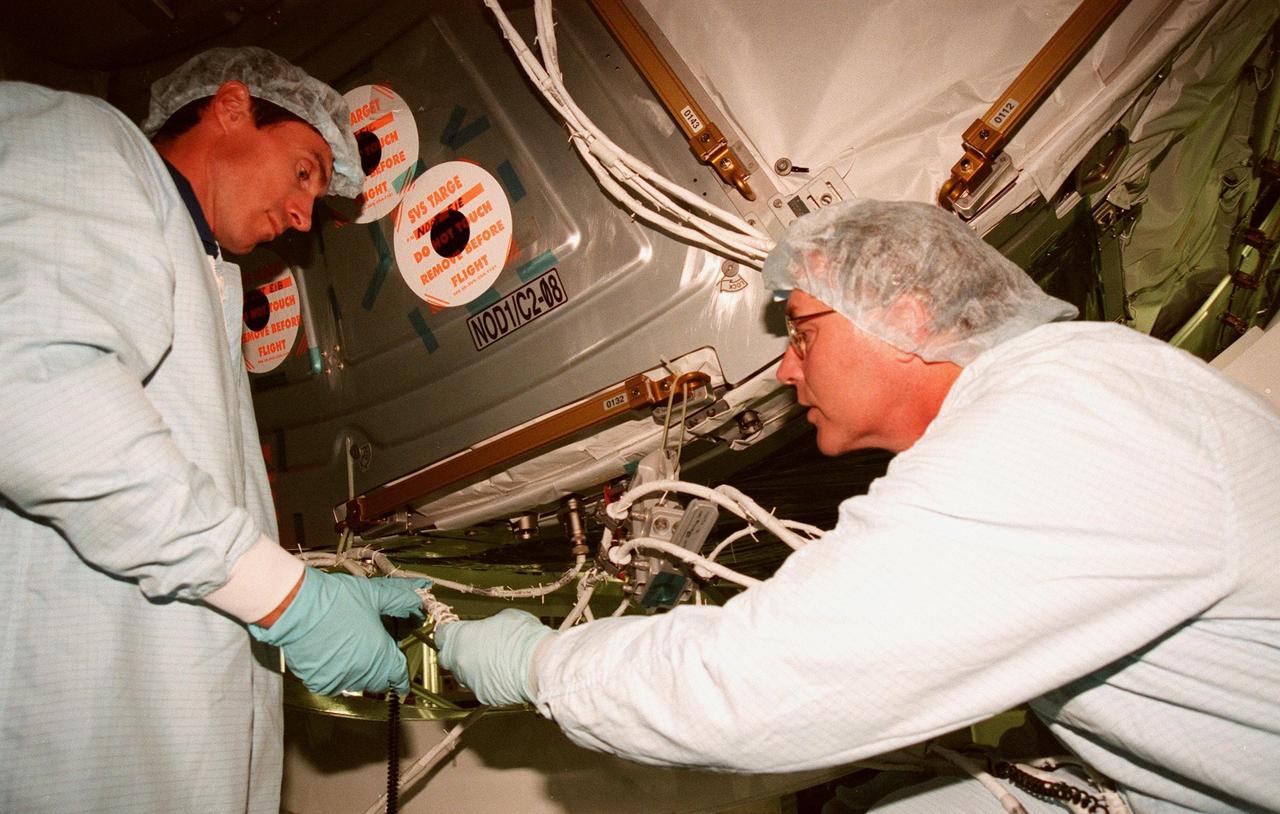
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-88 Mission Specialists Sergei Krikalev, a Russian cosmonaut, and Jerry L. Ross check out equipment on the Unity connecting module, primary payload on the mission. The STS-88 crew members are participating in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), familiarizing themselves with the orbiter's midbody and crew compartments. Scheduled for launch on Dec. 3, 1998, STS-88 will be the first Space Shuttle launch for the International Space Station. The Unity connecting module will be mated to the Russian-built Zarya control module, already on orbit after a November launch. Unity will have two Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) attached and 1 stowage rack installed inside. PMA-1 will connect U.S. and Russian elements; PMA-2 will provide a Shuttle docking location. Eventually, Unity's six ports will provide connecting points for the Z1 truss exterior framework, U.S. lab, airlock, cupola, Node 3, and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, as well as the control module. Zarya is a self-supporting active vehicle, providing propulsive control capability and power through the early assembly stages. It provides fuel storage capability and a rendezvous and docking capability to the Service Module
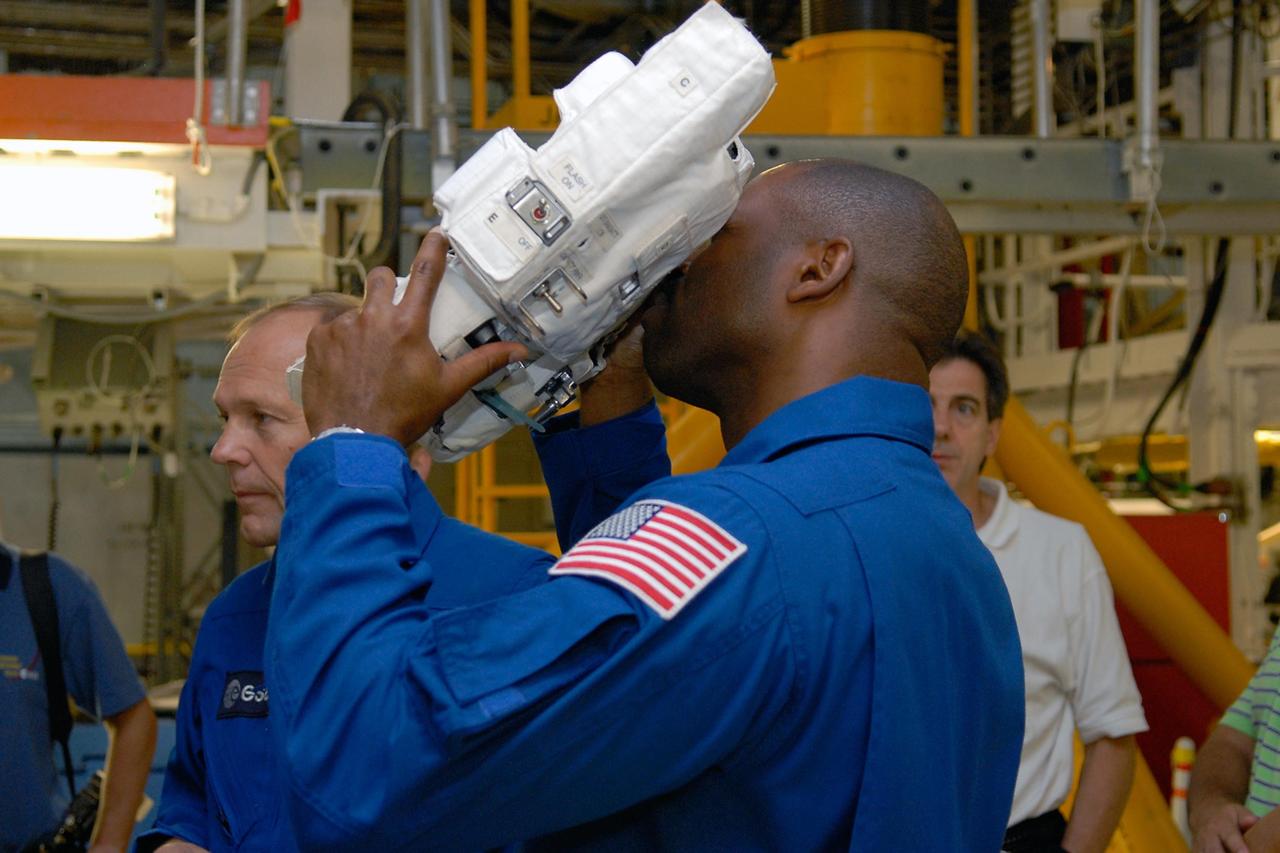

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew practice handling cameras that will be used during the mission. With the camera is Mission Specialist Leland Melvin. At left is Mission Specialist Hans Schlegel, who represents the European Space Agency. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew practice handling cameras that will be used during the mission. Holding the camera at left is Mission Specialist Hans Schlegel. Next to him, from left, are Mission Specialists Leland Melvin, Rex Walheim and Stanley Love. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
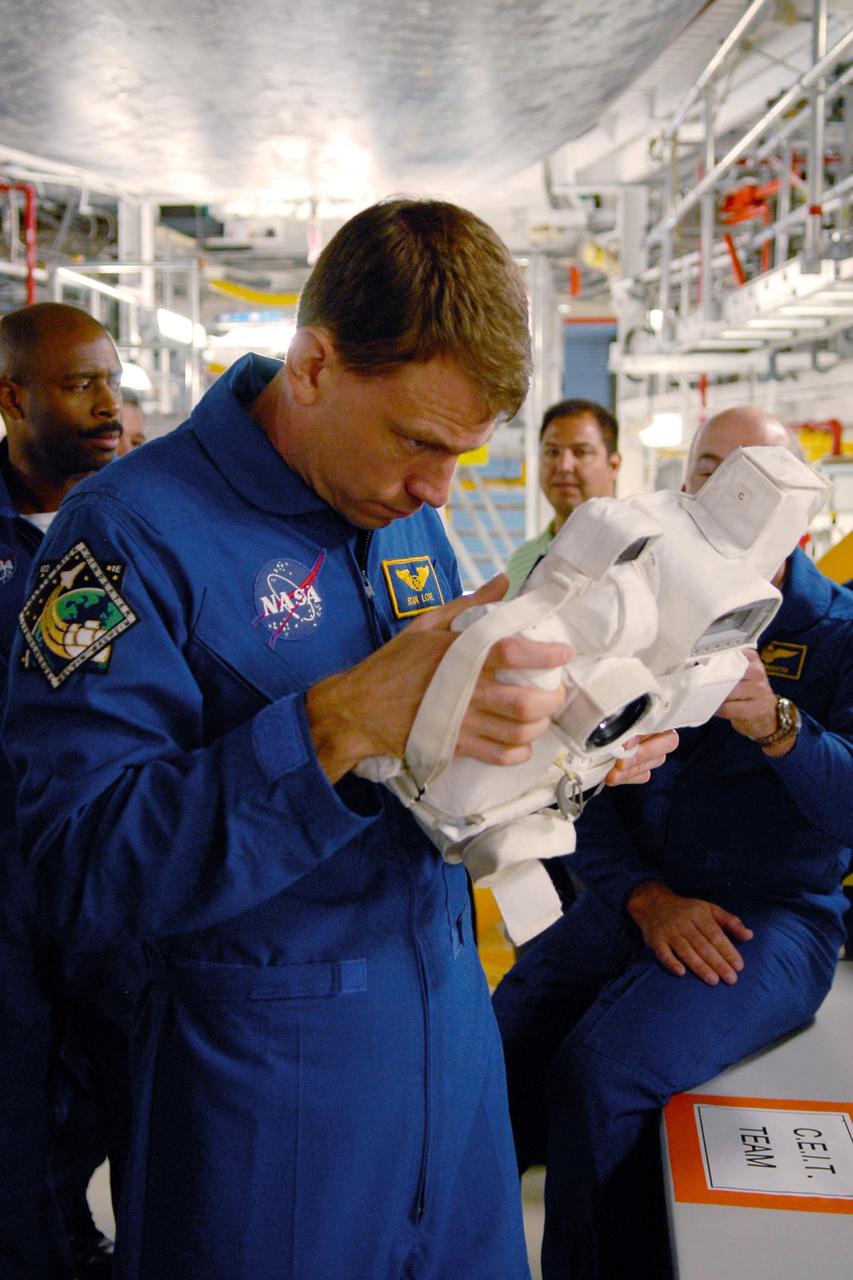

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew practice handling cameras that will be used during the mission. In the foreground is Mission Specialist Stanley Love. Behind him at left is Mission Specialist Leland Melvin; at right is Pilot Alan Poindexter. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
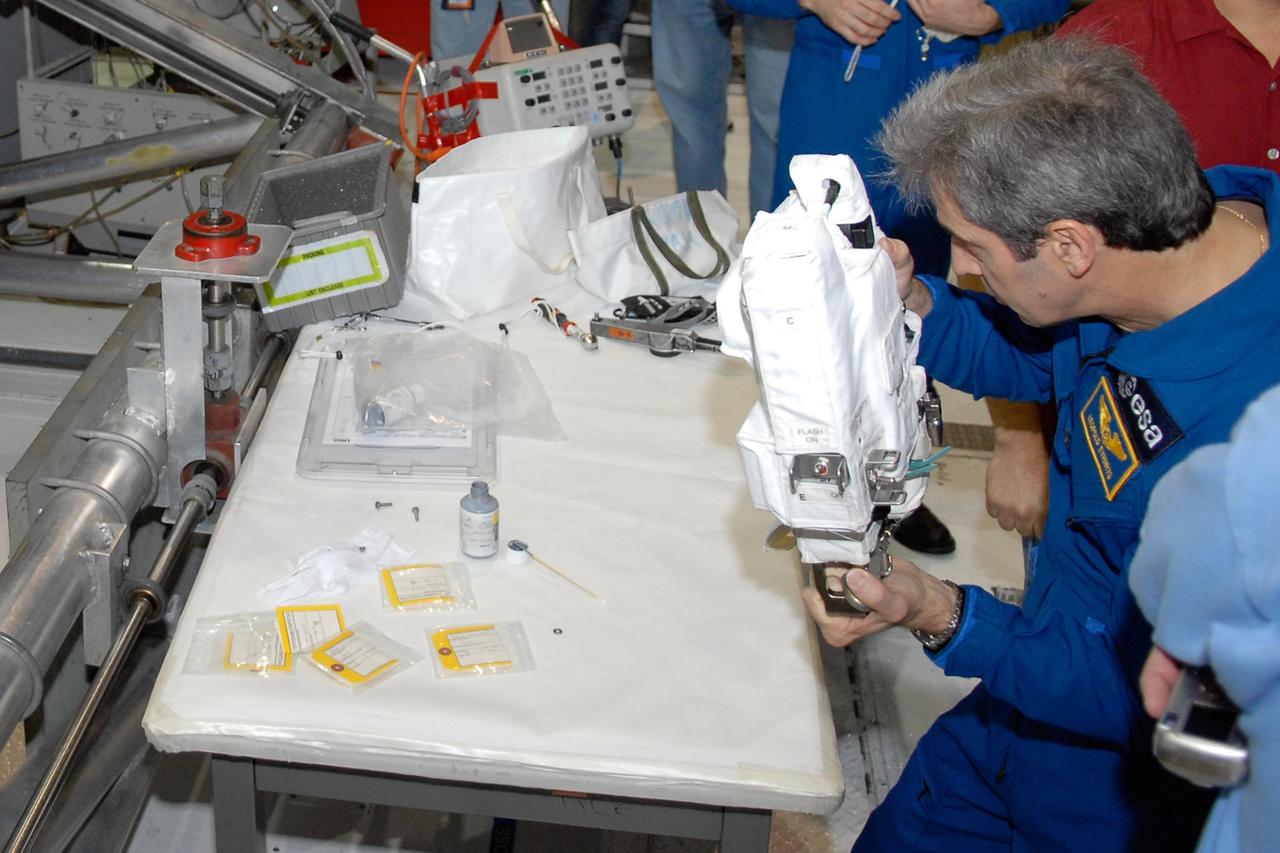

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, members of the STS-122 crew practice handling cameras that will be used during the mission. Holding the camera is astronaut Leopold Eyharts, with the European Space Agency. He will be joining the Expedition 15 crew on the International Space Station. The crew is at Kennedy Space Center to take part in a crew equipment interface test, which helps familiarize them with equipment and payloads for the mission. Among the activities standard to a CEIT are harness training, inspection of the thermal protection system and camera operation for planned extravehicular activities, or EVAs. The mission will carry and install the Columbus Lab, a multifunctional, pressurized laboratory that will be permanently attached to Node 2 of the space station to carry out experiments in materials science, fluid physics and biosciences, as well as to perform a number of technological applications. It is Europe’s largest contribution to the construction of the International Space Station and will support scientific and technological research in a microgravity environment. STS-122 is targeted for launch in December. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett