
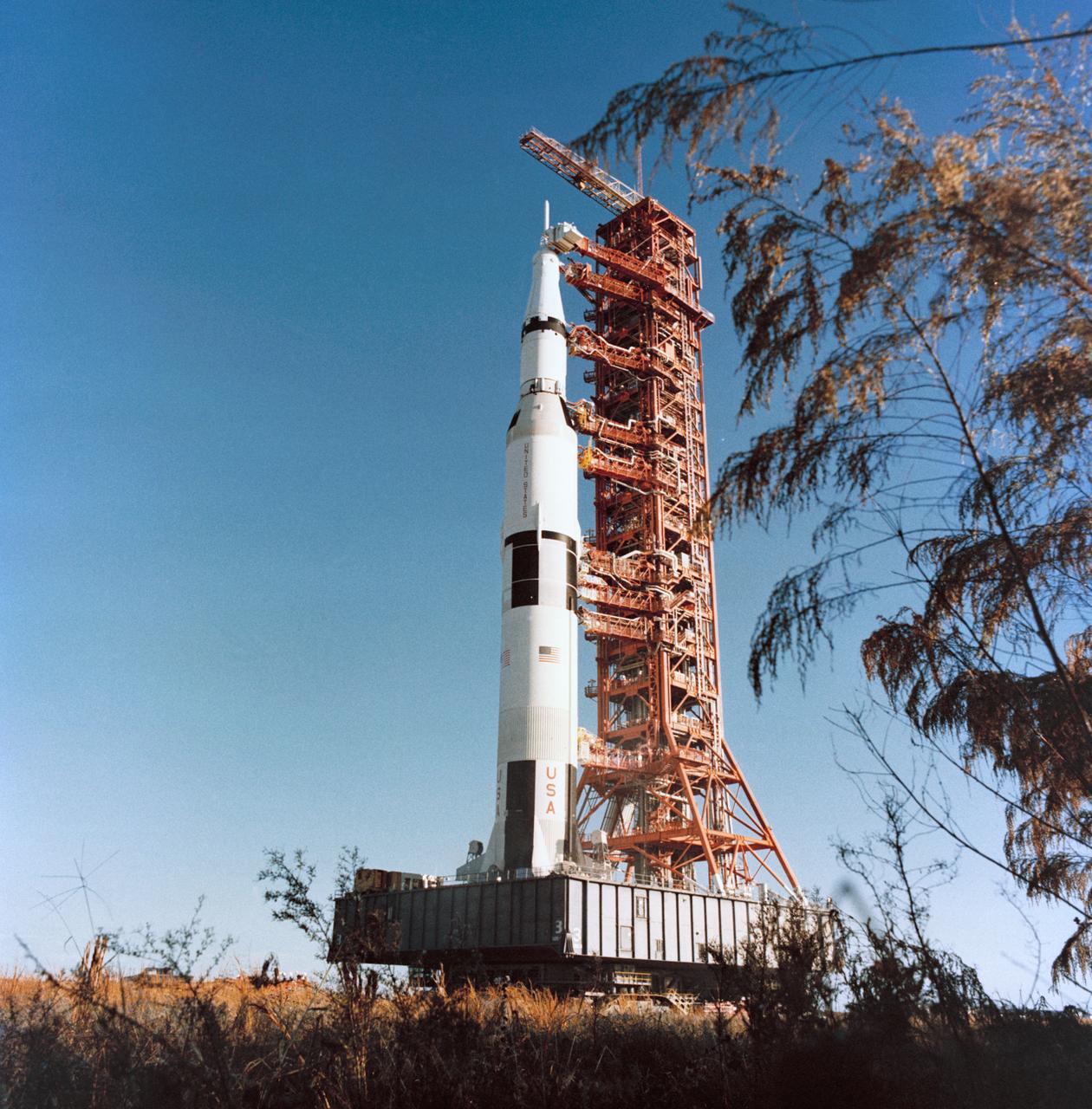
S73-34367 (16 Nov. 1973) --- A view at the Kennedy Space Center showing in the near distance the Skylab 4/Saturn 1B space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, on the morning of the launch. Photo credit: NASA
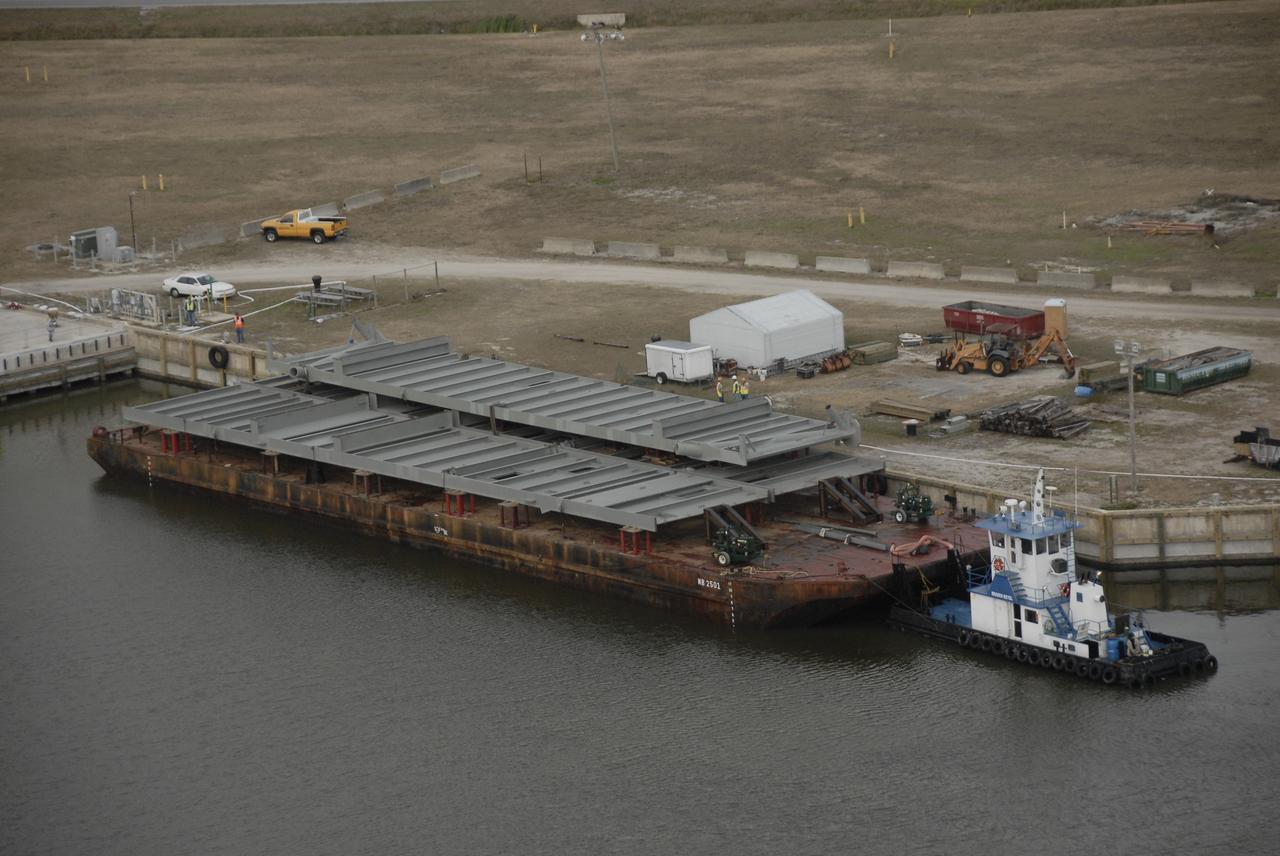

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Trestles and girders for a new mobile launcher arrive by barge at the turn basin in the Launch Complex 39 Area of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new launcher will be the base for the Constellation Program's Ares rockets to launch the Orion crew exploration vehicle and the cargo vehicle. The base is being made lighter than space shuttle mobile launcher platforms so the crawler-transporter can pick up the added load of the 345-foot tower and taller rocket. When the structural portion of the new mobile launcher is complete, umbilicals, access arms, communications equipment and command/control equipment will be installed. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
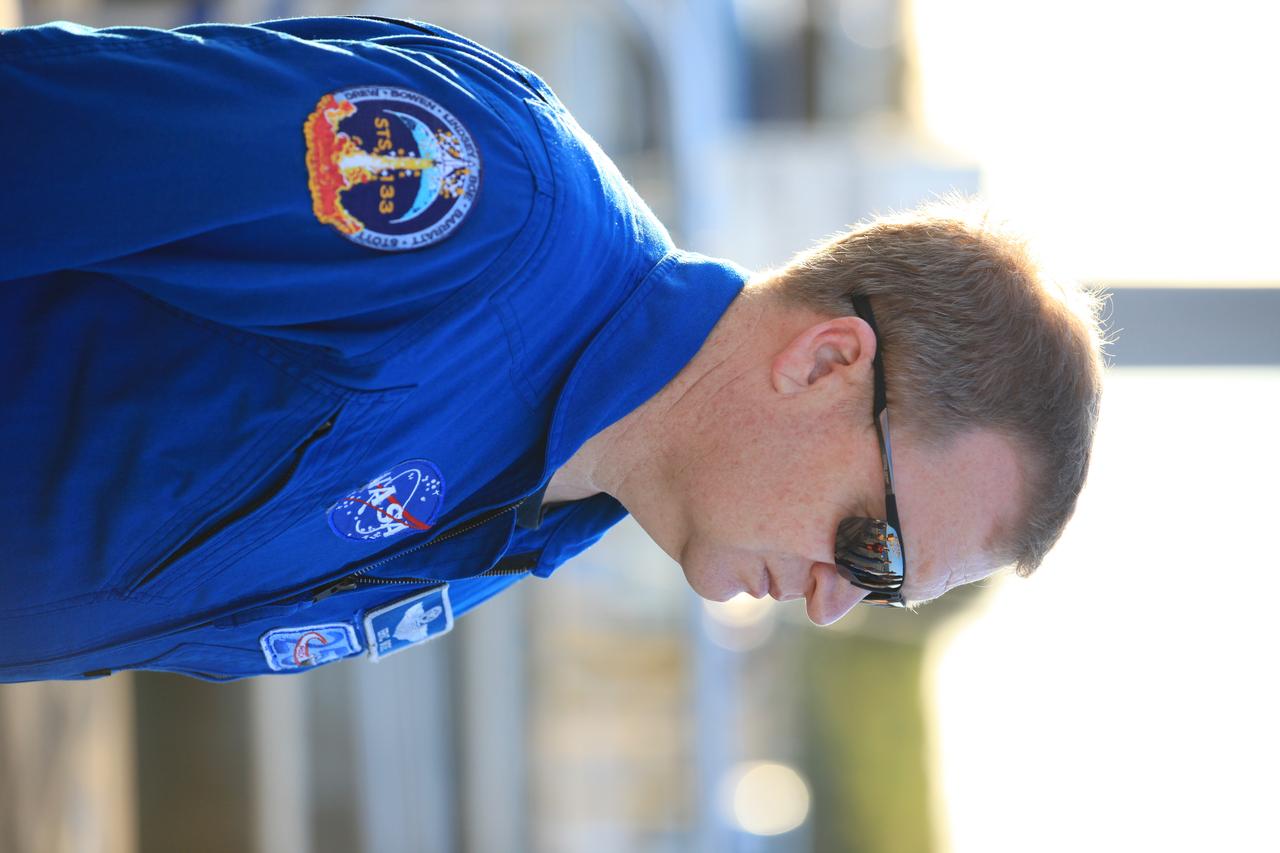

Commercial Crew Astronauts Bob Behnken , Eric Boe, Doug Hurley, and Suni Williams survey SpaceX's progress at Launch Complex 39 A. The survey helped ensure the was familiar with the launch complex and recovery ship prior to missions to station.
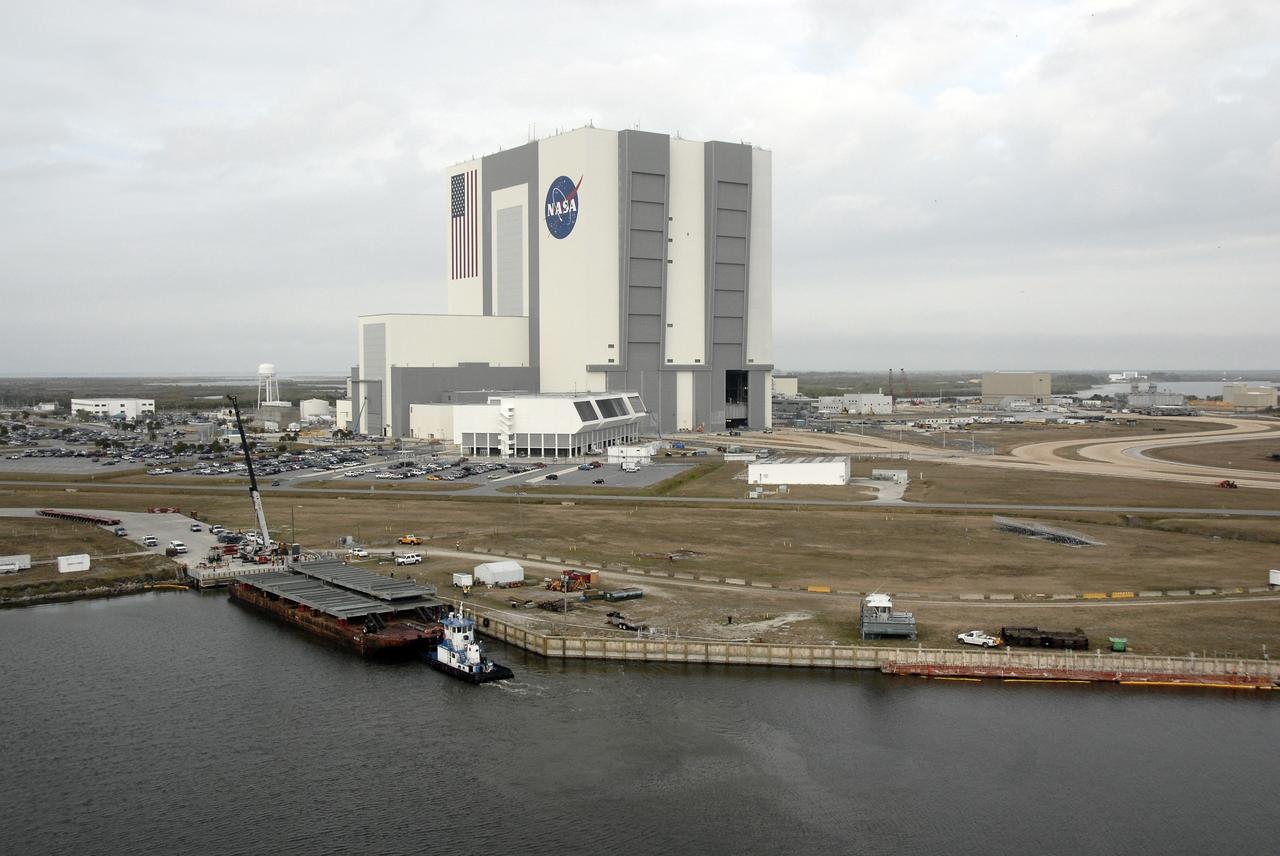

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An aerial view of the Launch Complex 39 Area NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida shows the 525-foot-tall Vehicle Assembly Building looming over the landscape. In the foreground is the turn basin, where a barge holds trestles and girders for the new mobile launcher. The new launcher will be the base for the Constellation Program's Ares rockets to launch the Orion crew exploration vehicle and the cargo vehicle. The base is being made lighter than space shuttle mobile launcher platforms so the crawler-transporter can pick up the added load of the 345-foot tower and taller rocket. When the structural portion of the new mobile launcher is complete, umbilicals, access arms, communications equipment and command/control equipment will be installed. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
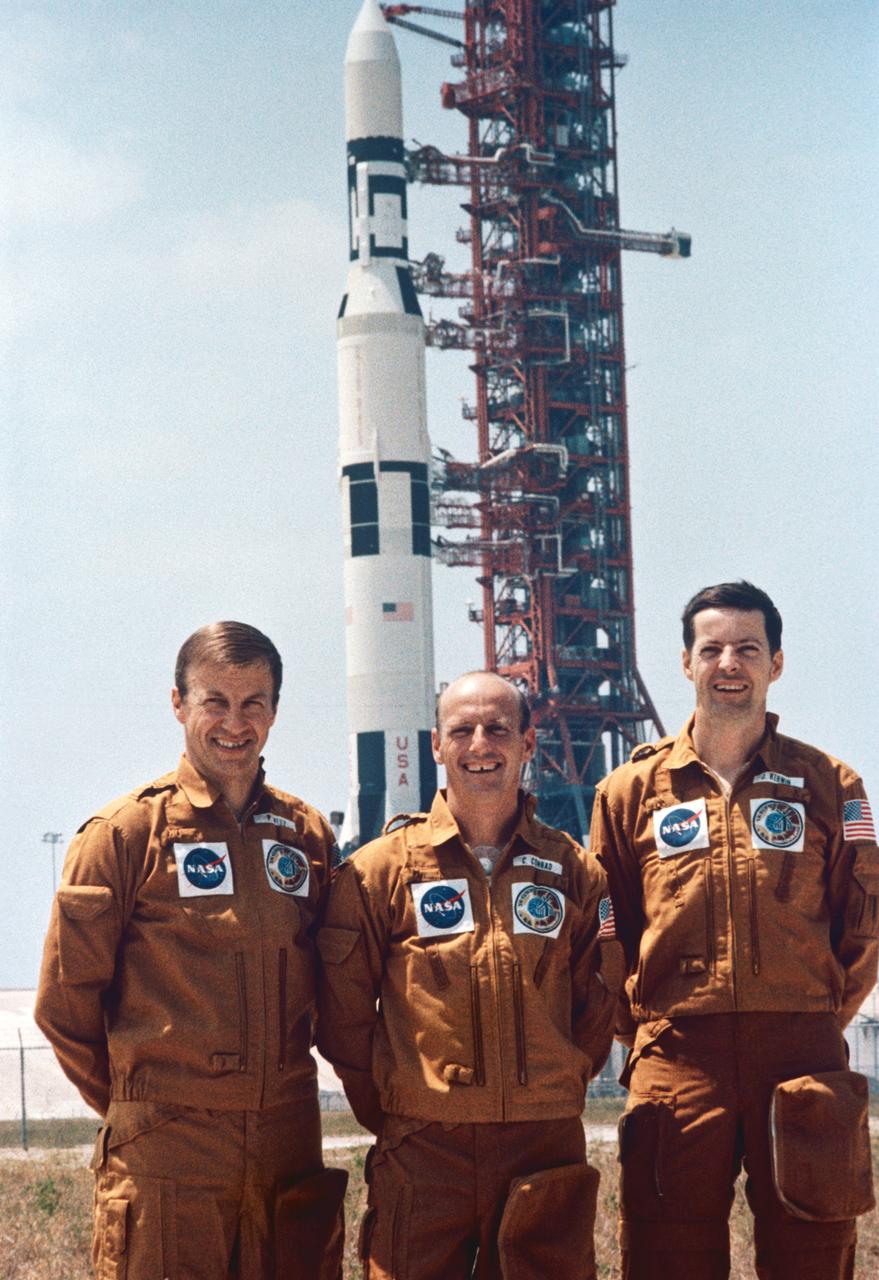

S73-25902 (4 May 1973) --- The three prime crew members of the first manned Skylab mission (Skylab 2) are photographed at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during preflight activity. They are, left to right, astronaut Paul J. Weitz, pilot; astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and scientist-astronaut Joseph P. Kerwin, science pilot. In the background is the Skylab 1/Saturn V space vehicle with its Skylab space station payload on Pad A. Photo credit: NASA
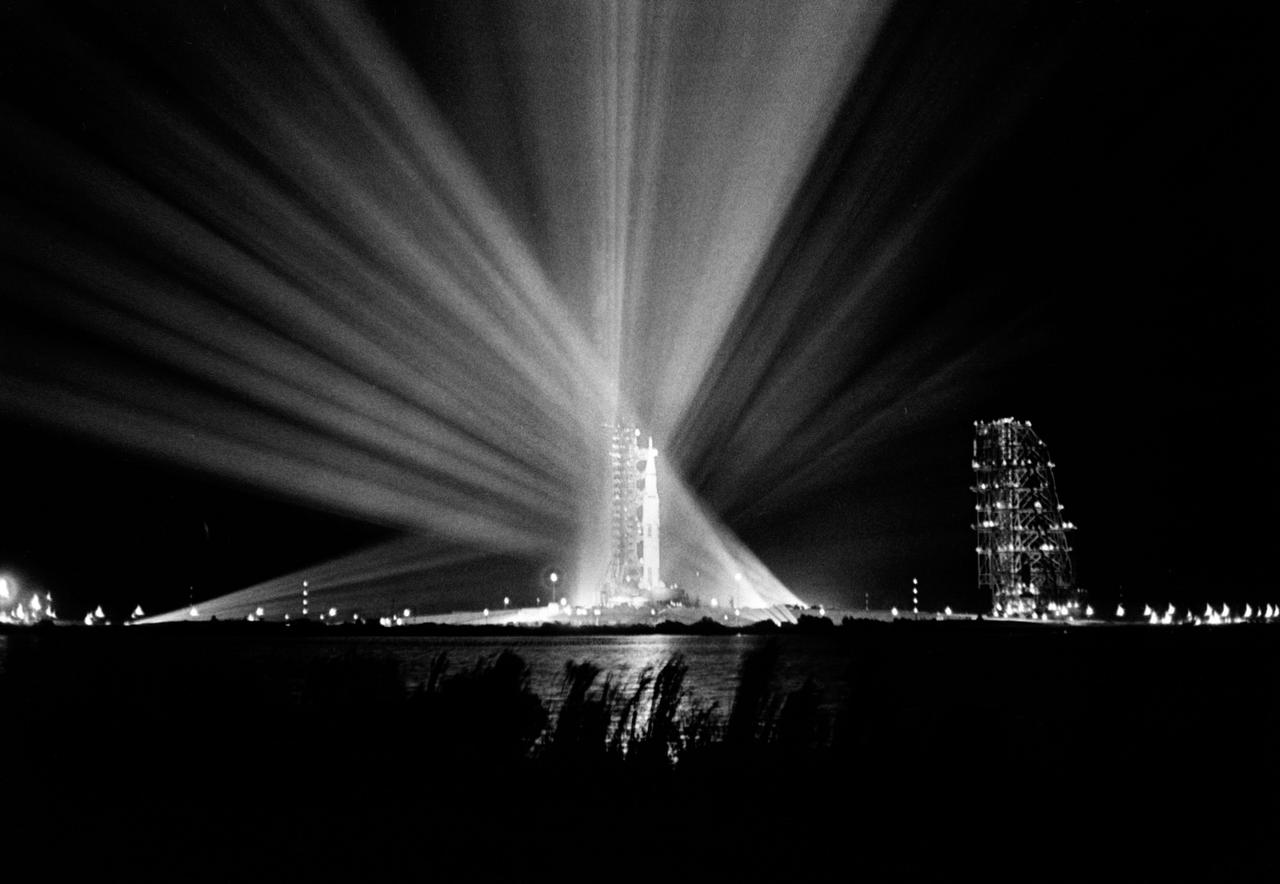

S69-25879 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Nighttime view of the 363-feet-high Apollo 9 space vehicle at Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, during preparations for the scheduled 10-day Earth-orbital space mission. The crew of the Apollo 9 (Spacecraft 104/Lunar Module 3/Saturn 504) space flight will be astronauts James A. McDivitt, David R. Scott, and Russell L. Schweickart.
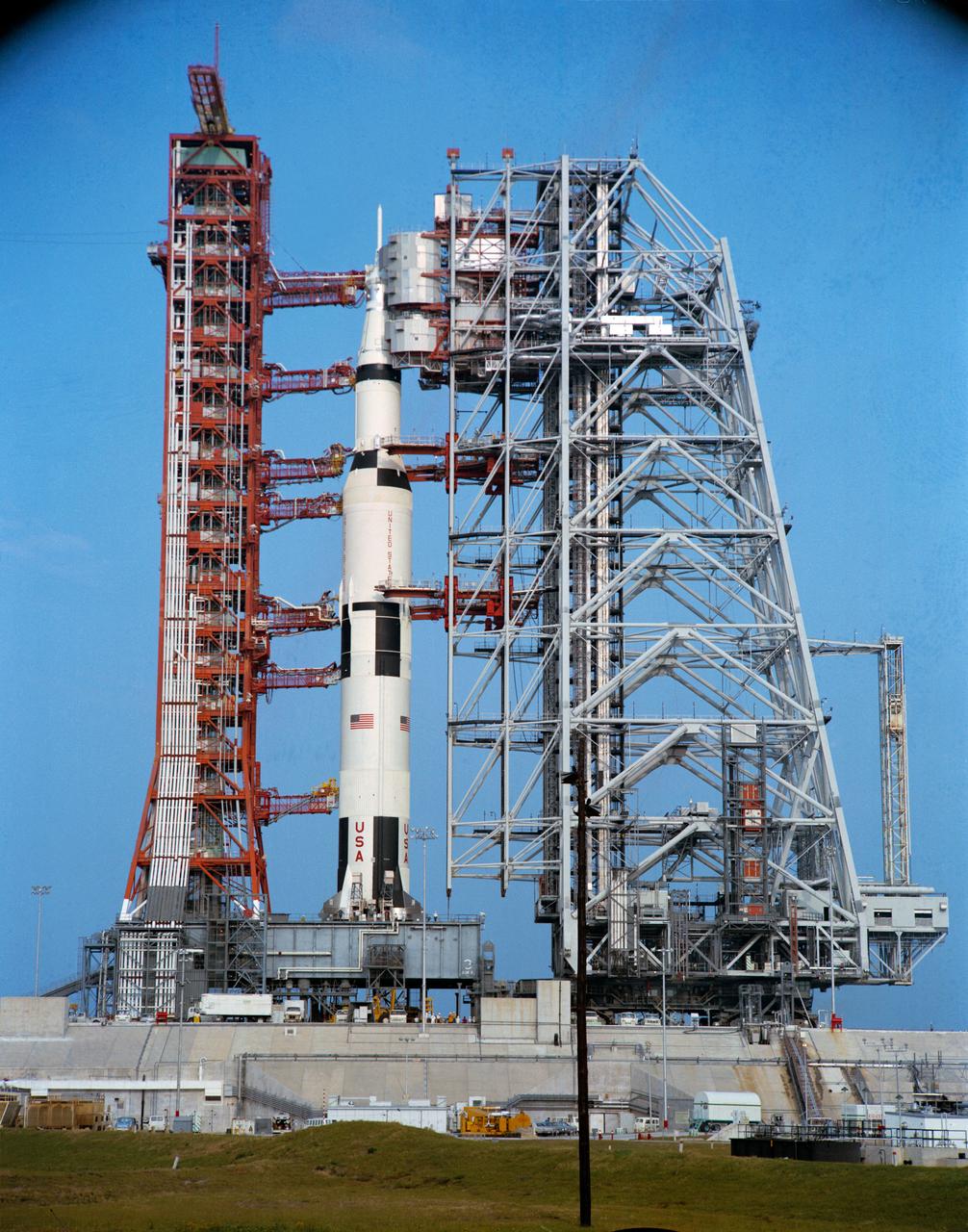

S72-34473 (29 March 1972) --- A ground-level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC), showing the 363-feet tall Apollo 16 (Spacecraft 113/Lunar Module 11/Saturn 511) space vehicle during a Countdown Demonstration Test (CDDT). The CDDT was part of the preflight preparations for the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission. The crew of Apollo 16, scheduled for launch on April 16, 1972, are astronauts John W. Young, commander; Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot.
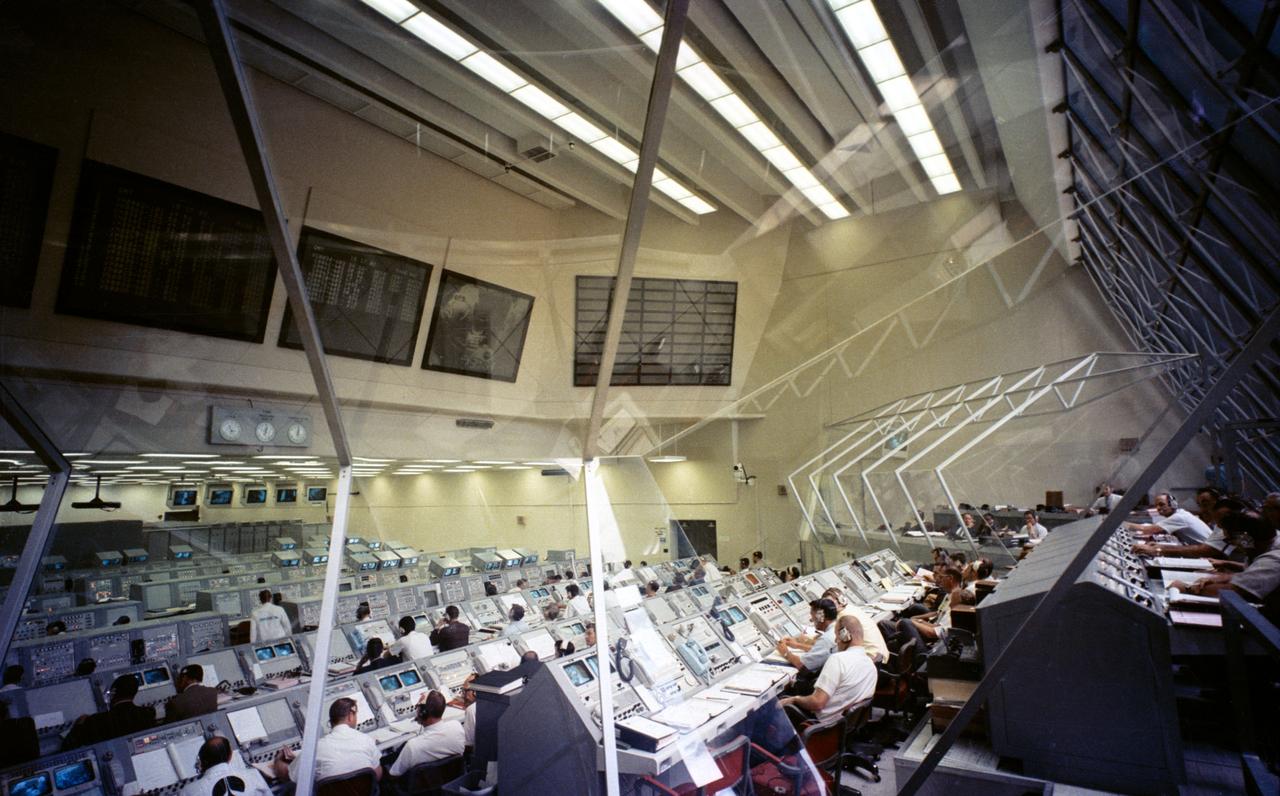

S69-34332 (13 May 1969) --- Overall view of Firing Room 3 of the Launch Control Center, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, during an Apollo 10 Countdown Demonstration Test. The crew of the scheduled Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot. The Launch Control Center is at the Vehicle Assembly Building. The Apollo 10 space vehicle will be launched from Pad 39B.
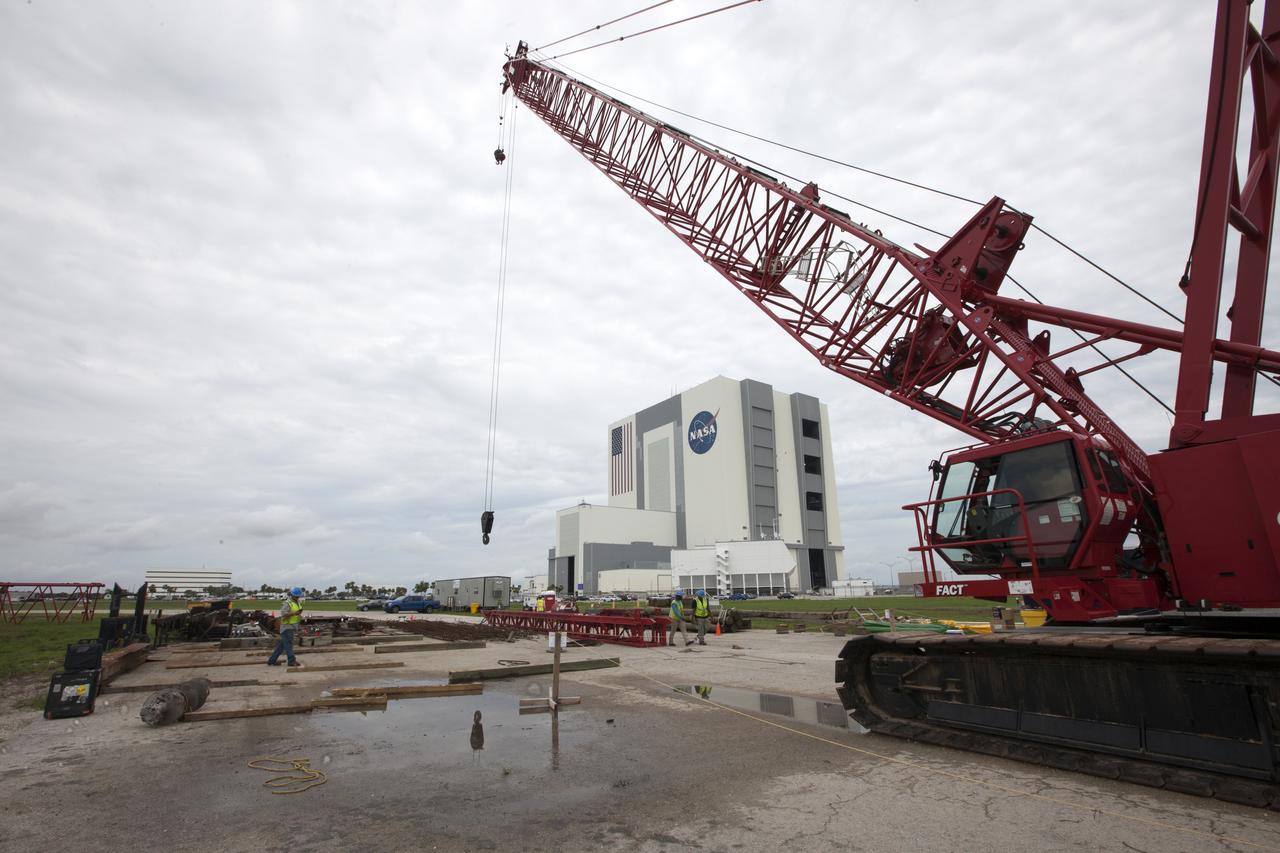

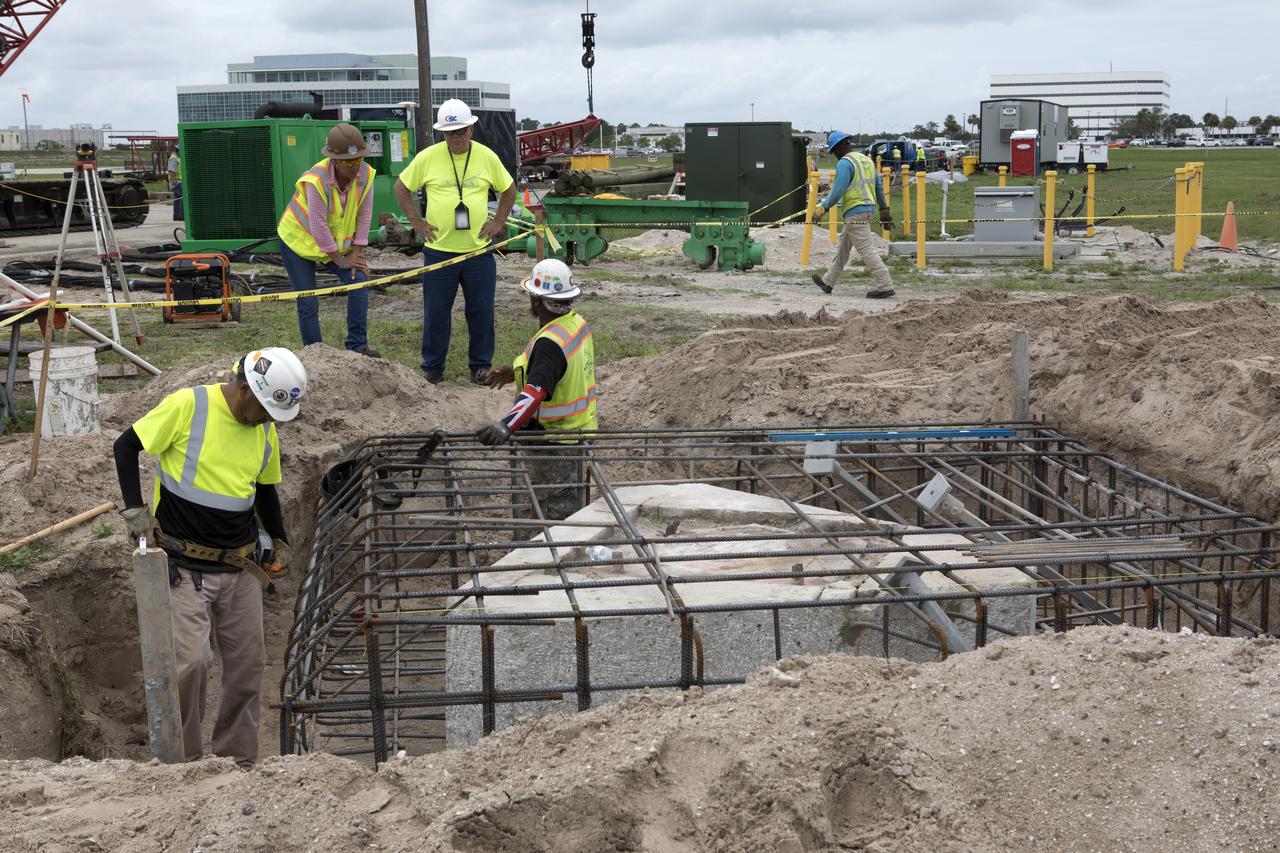
Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
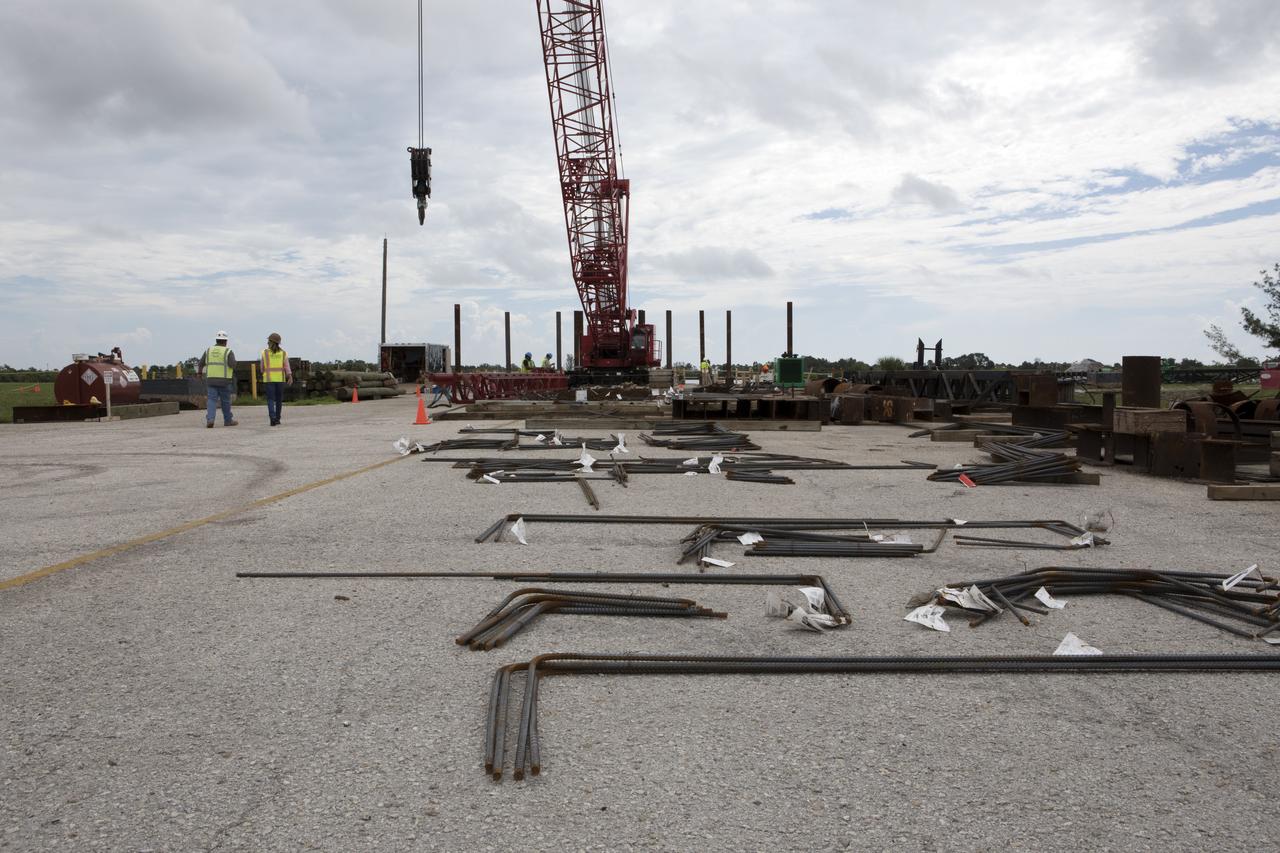

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the 300,000-pound core booster aboard the modified Pegasus barge. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
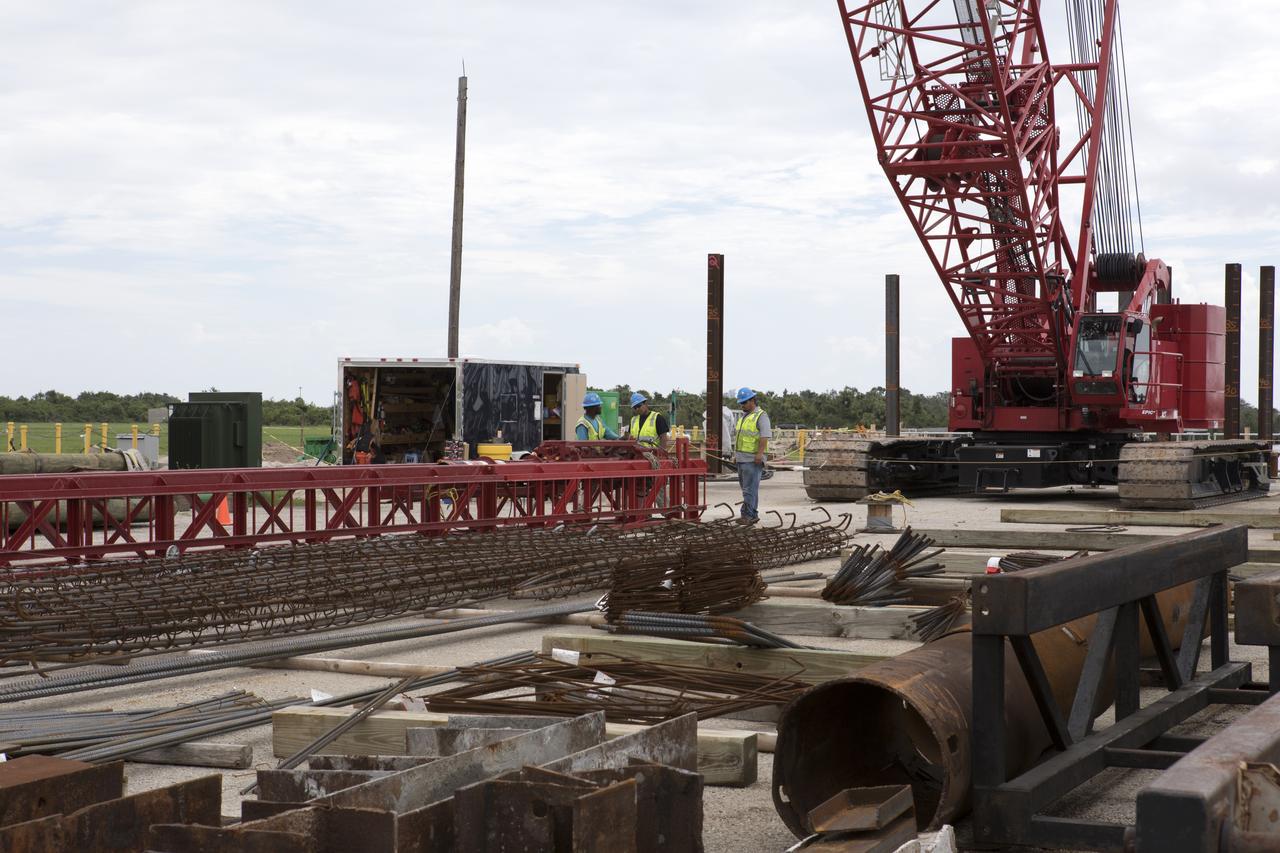

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Equipment is staged and a crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
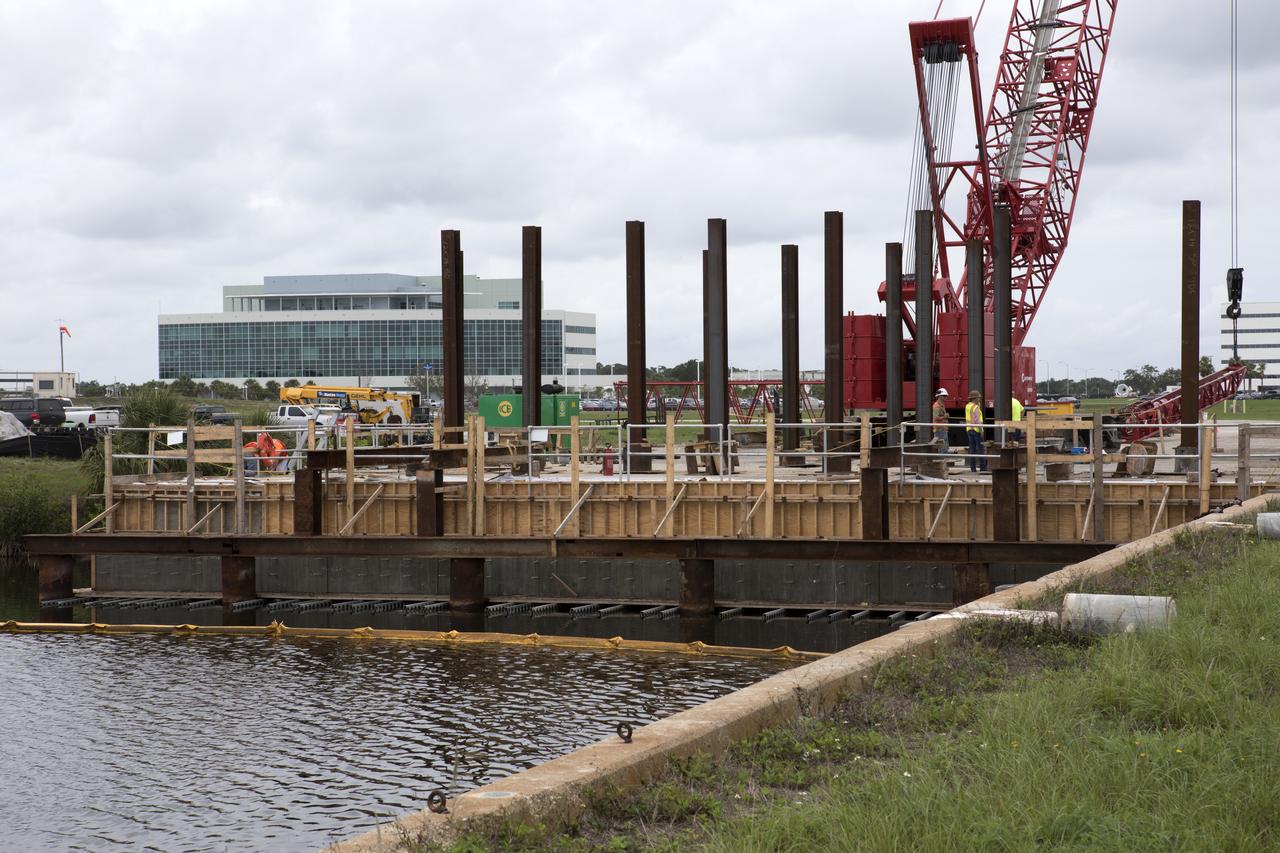

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Precast concrete poles are being driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core booster aboard the barge Pegasus. Construction workers with Southeast Cherokee Construction Inc. work to shore up the turn basin area. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the 300,000-pound core booster aboard the modified Pegasus barge. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
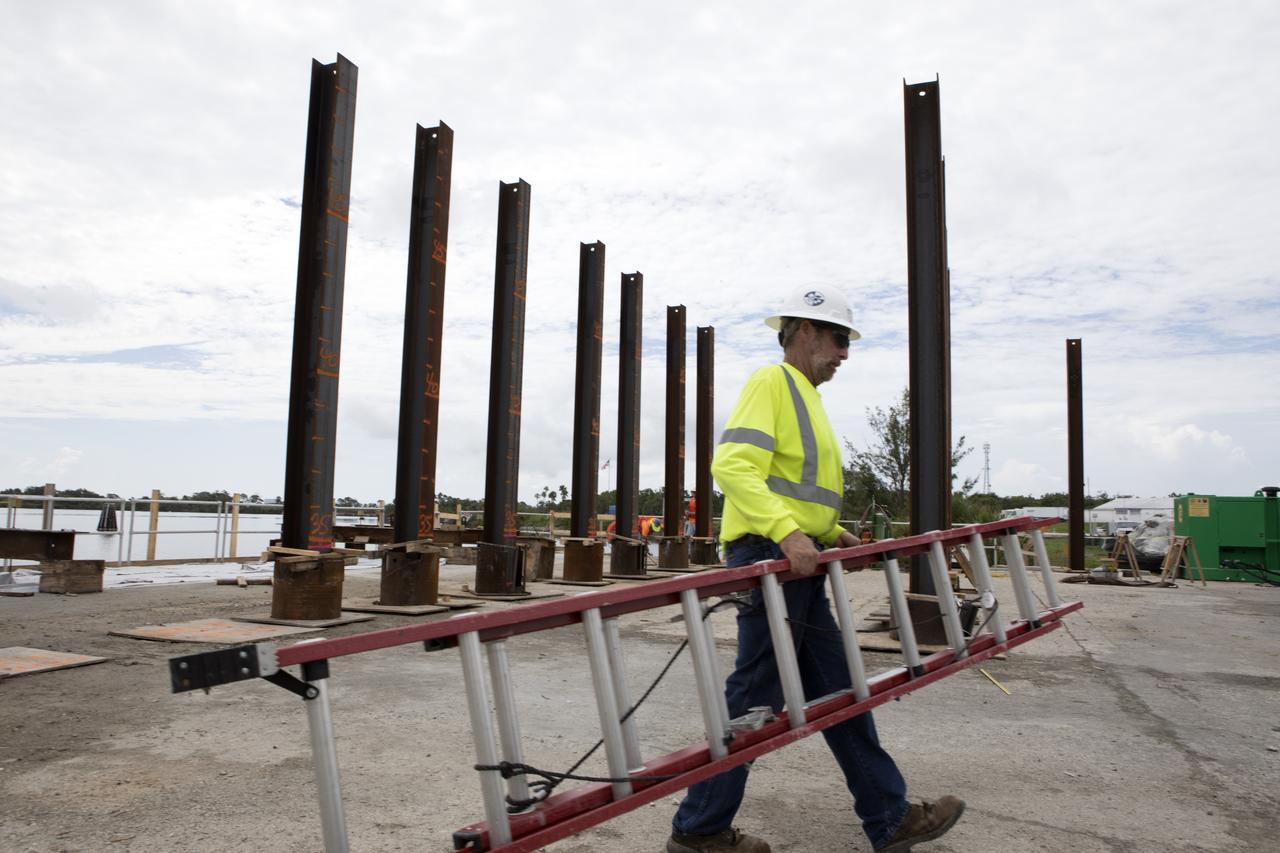

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Precast concrete poles are being driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
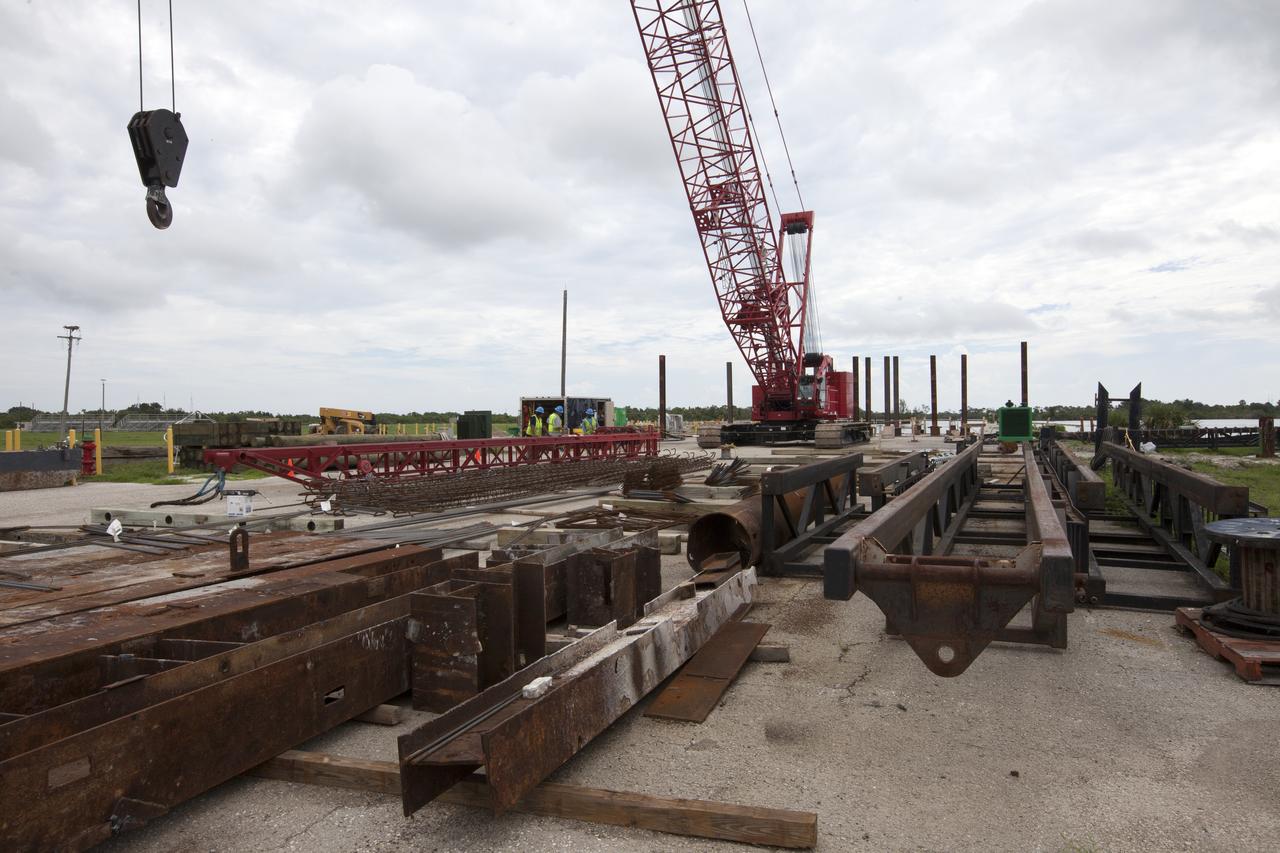

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Equipment is staged and a crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
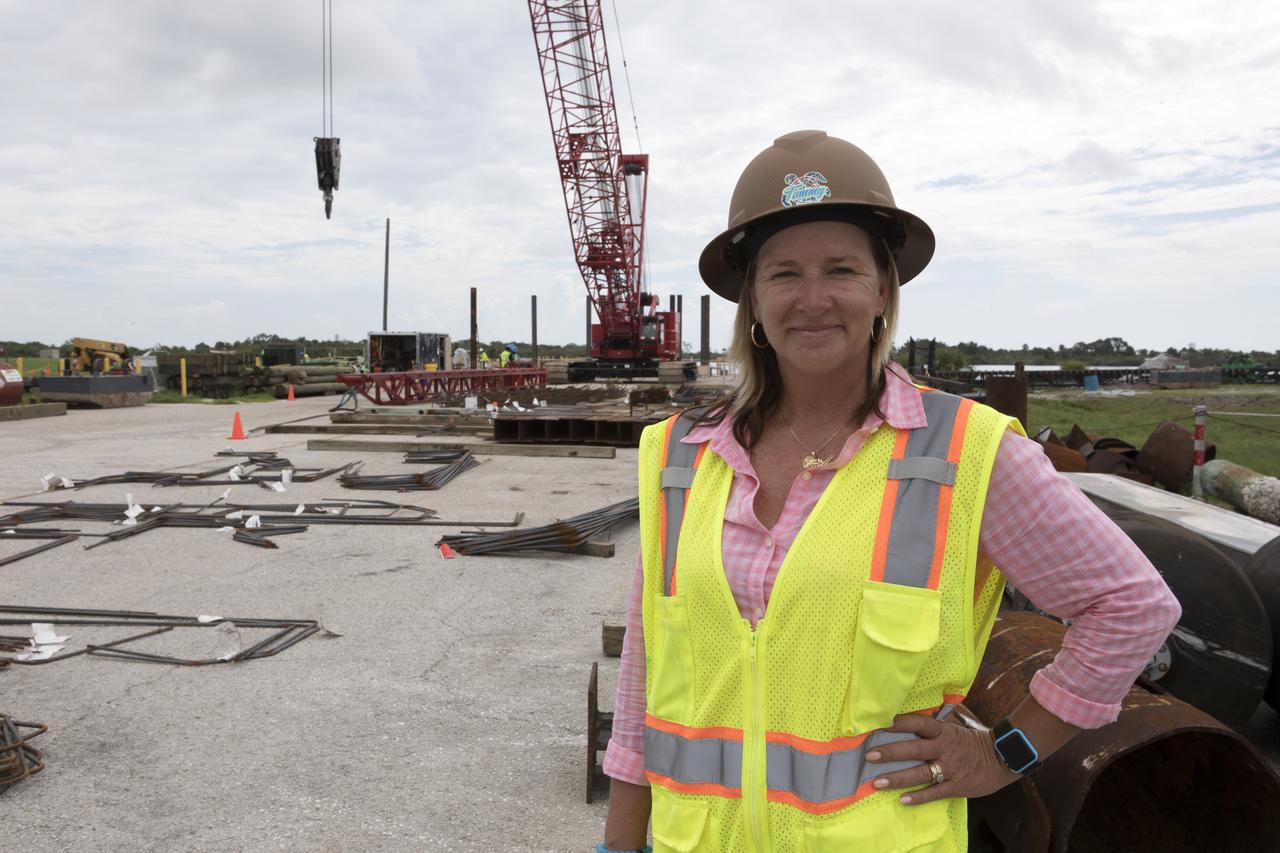

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. In the foreground is Tammy Kelly, site manager, with Southeast Cherokee Construction Inc. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
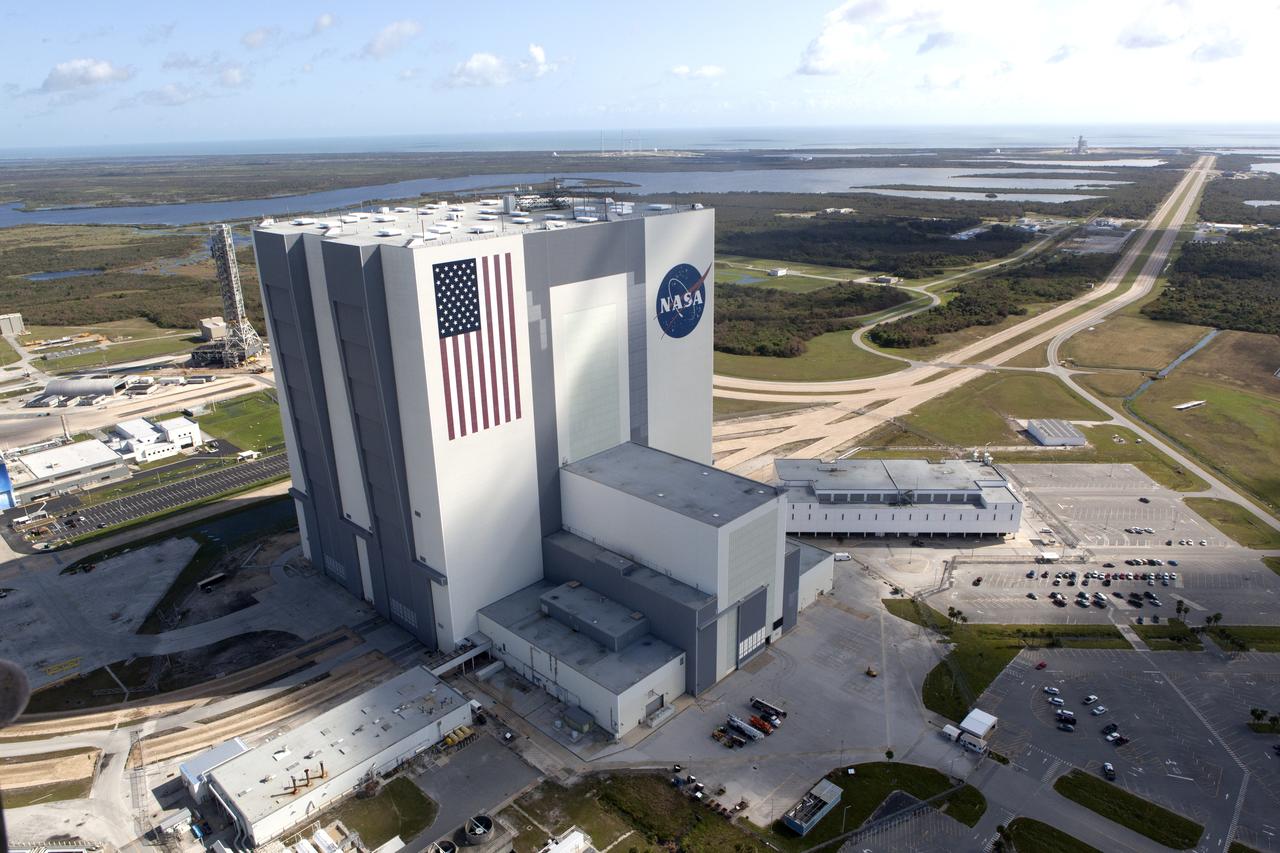

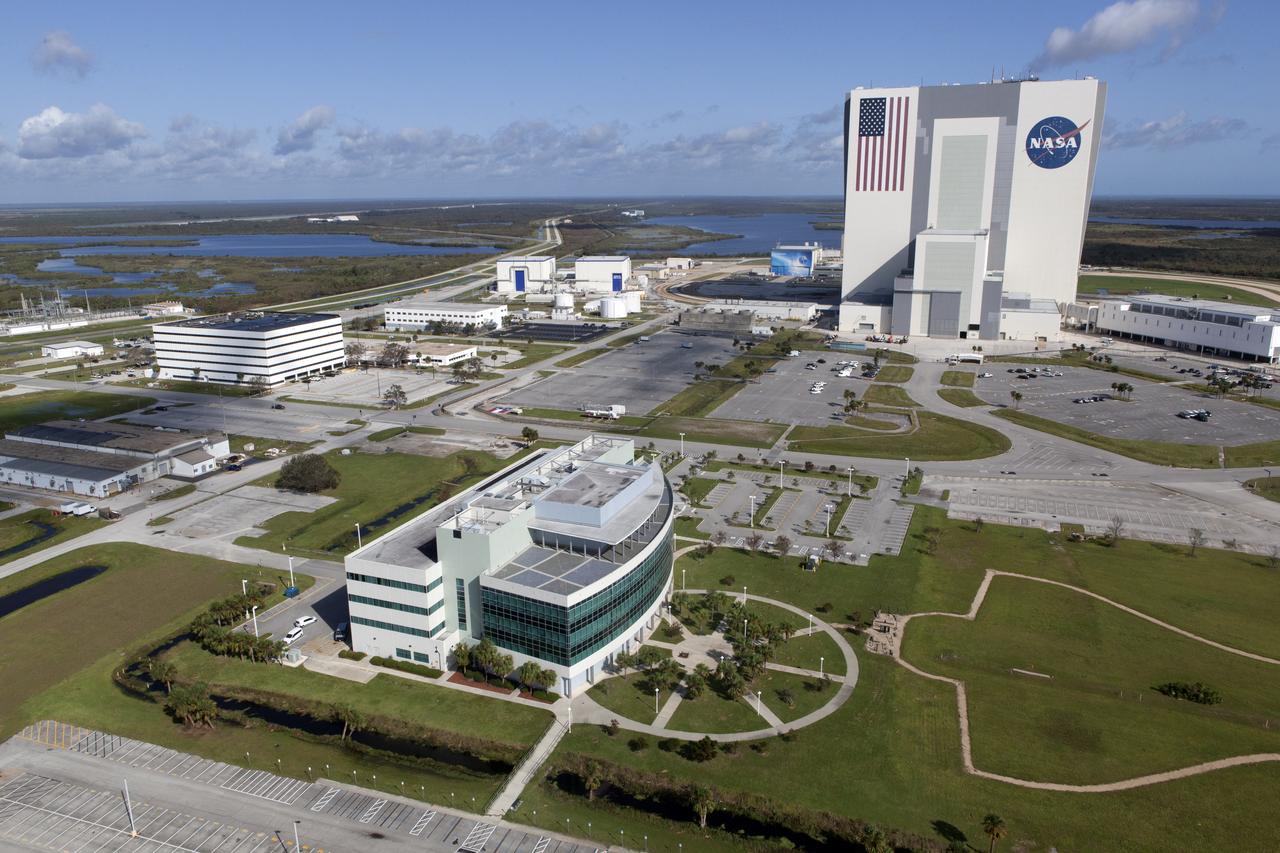
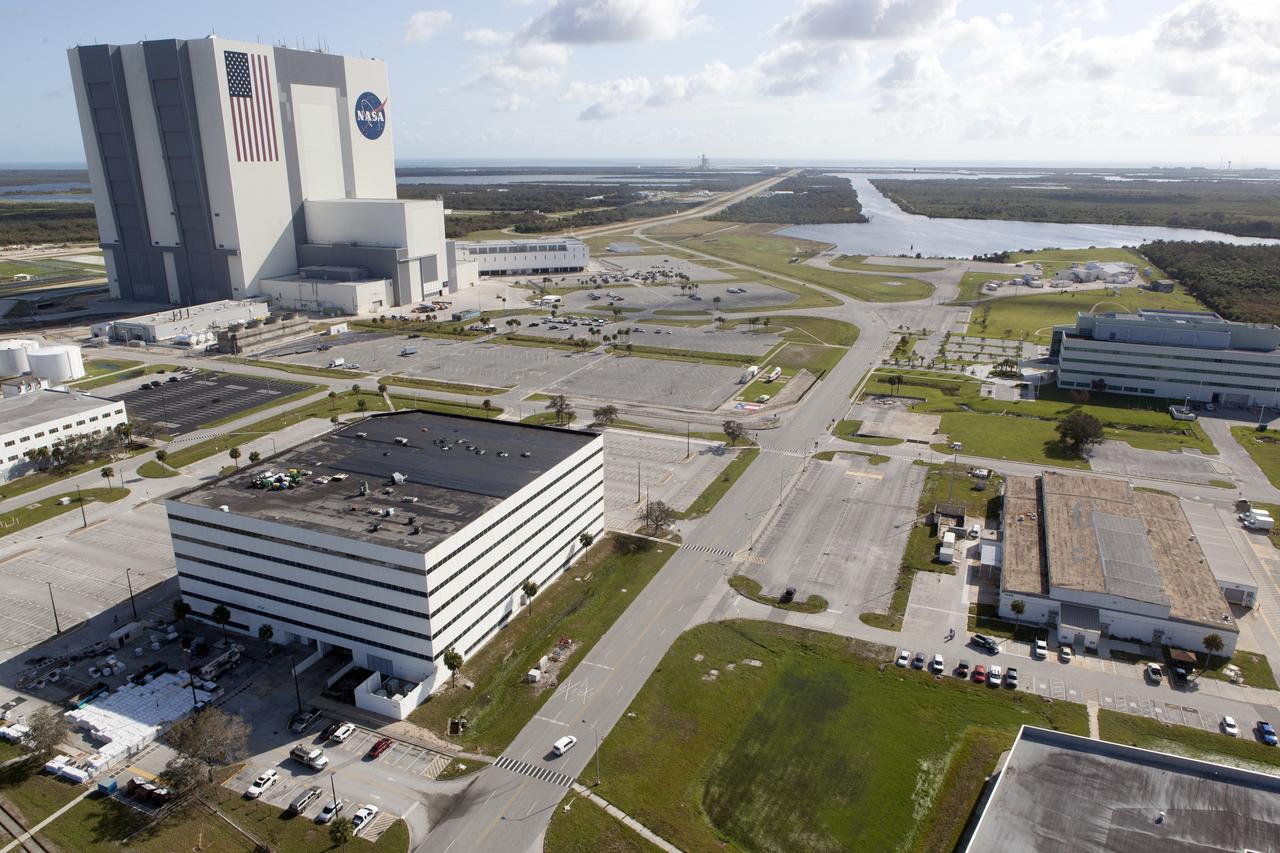
The Mobile Launcher (ML), Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), Launch Control Center (LCC), and Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
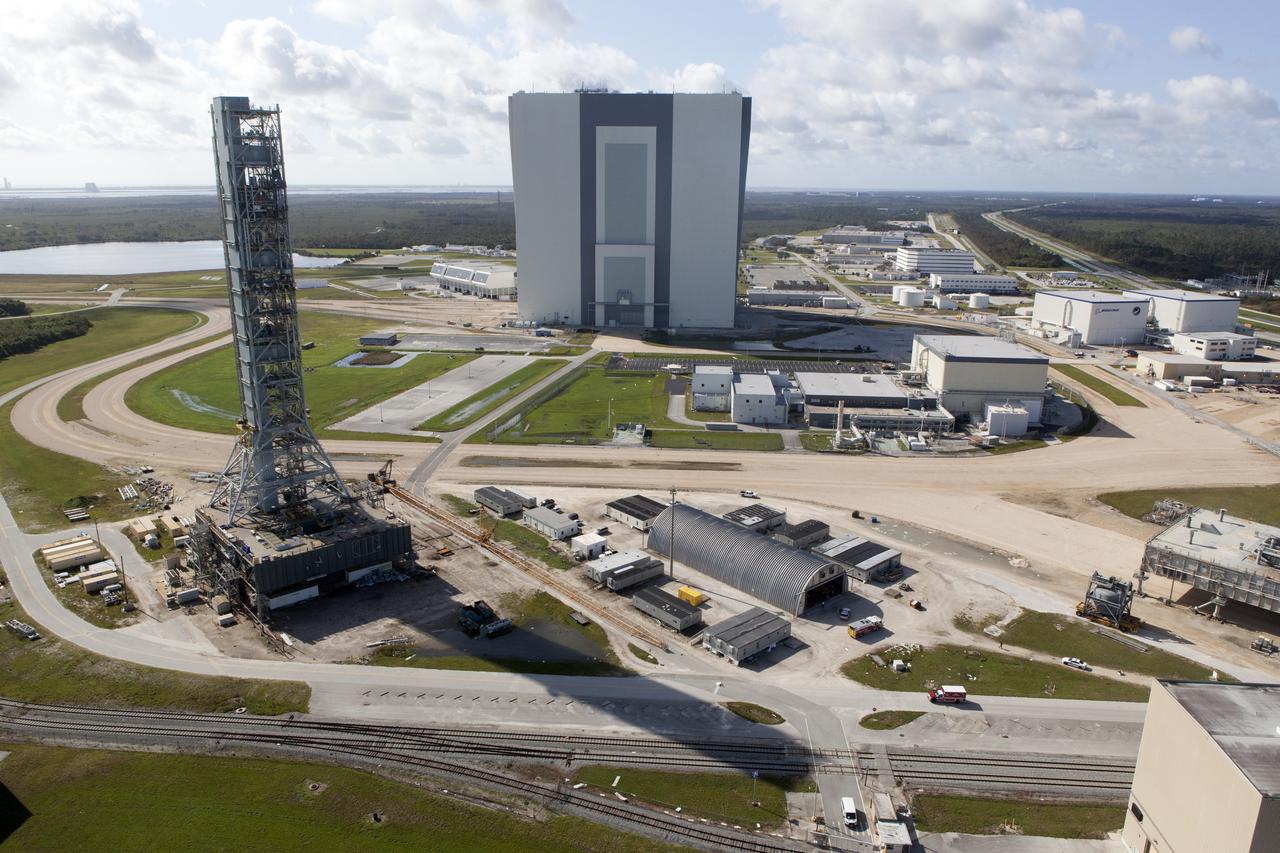

The Mobile Launcher (ML), Launch Control Center (LCC), Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), and Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
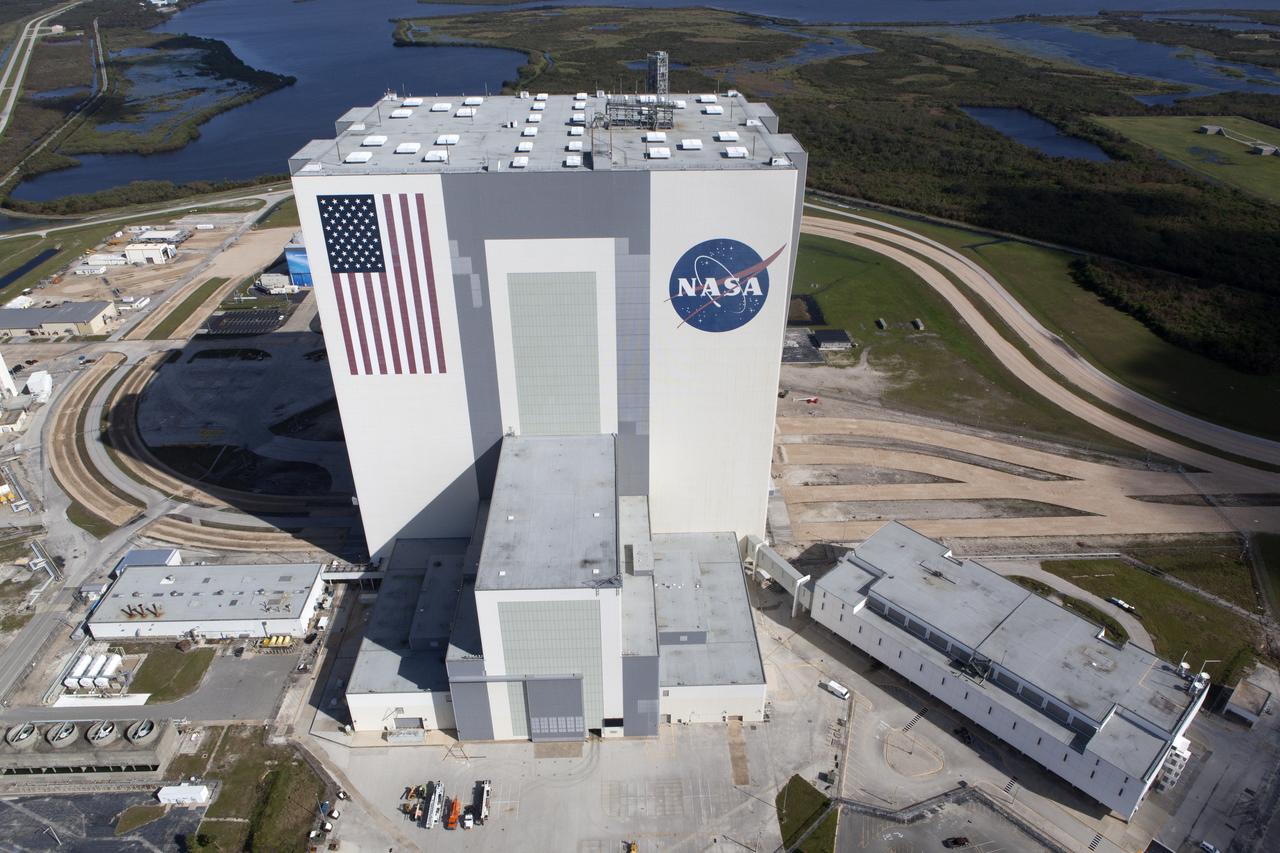

The Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), Launch Control Center (LCC), and Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
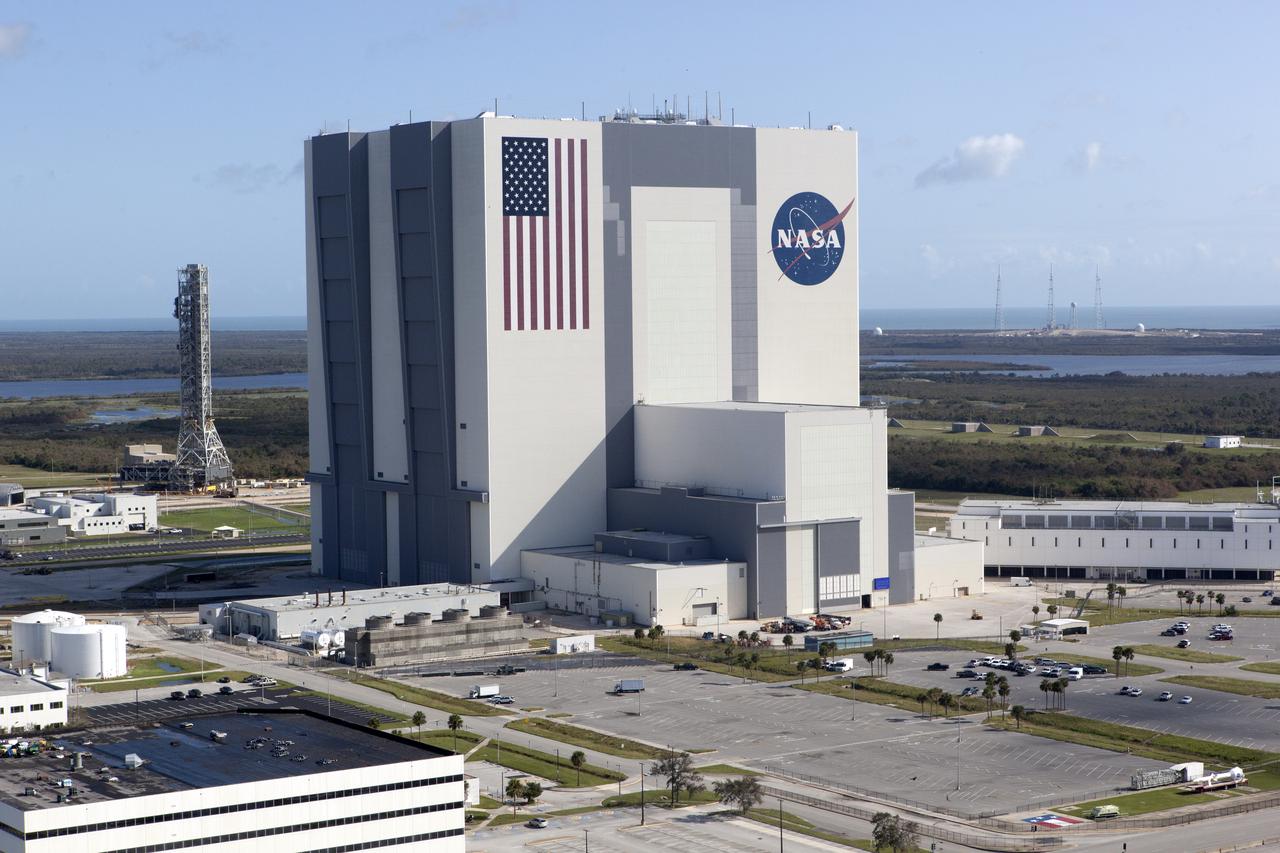

The Mobile Launcher (ML), Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB), Launch Control Center (LCC), and Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
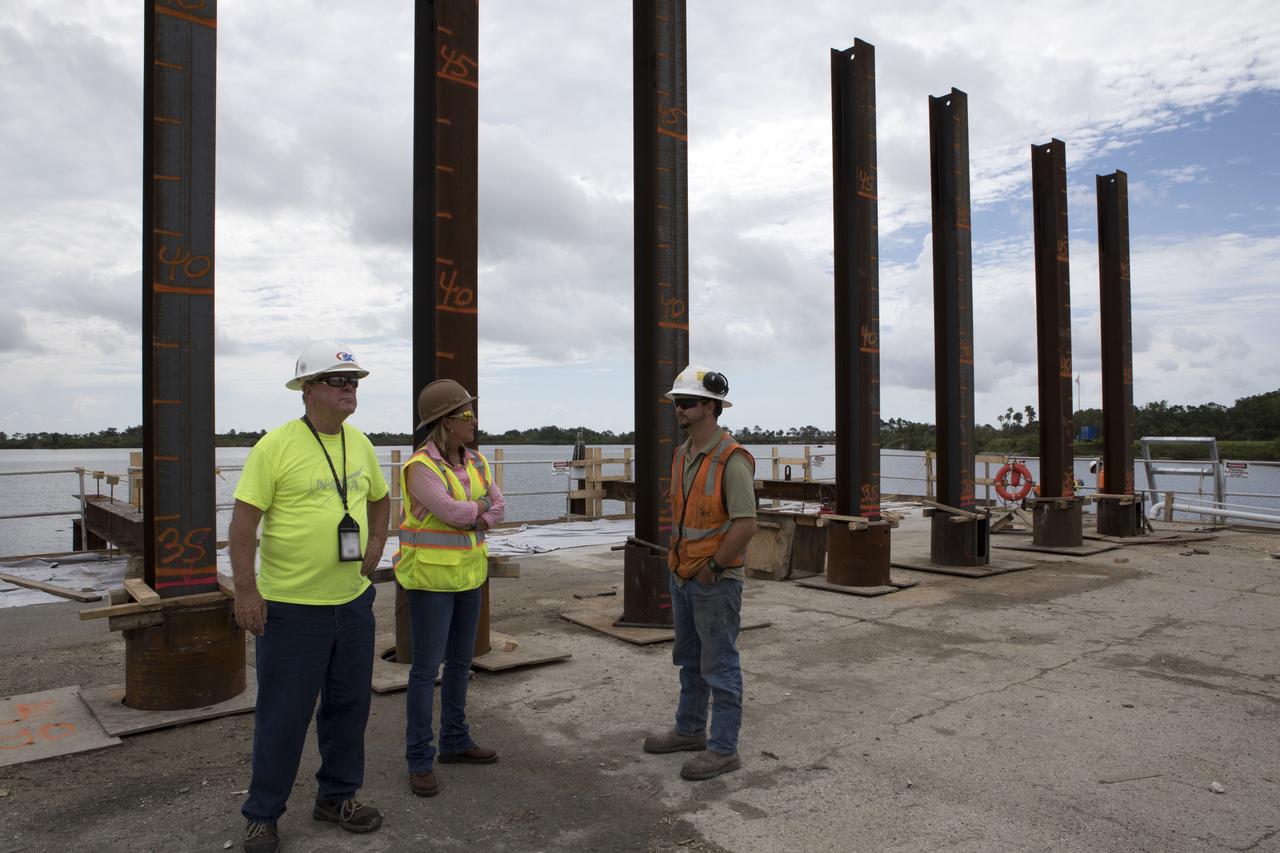

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Tammy Kelly, in the center, site manager, with Southeast Cherokee Construction Inc. talks with construction workers. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.

Modifications are underway at the Launch Complex 39 turn basin wharf at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to prepare for the arrival of the agency's massive Space Launch System (SLS) core stage aboard the barge Pegasus. Tammy Kelly, in the center, site manager, with Southeast Cherokee Construction Inc. talks with construction workers. A crane will be used to lift up precast concrete poles and position them to be driven to a depth of about 70 feet into the bedrock below the water around the turn basin. The upgrades are necessary to accommodate the increased weight of the core stage along with ground support and transportation equipment aboard the modified barge Pegasus. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing the upgrades to the turn basin wharf.
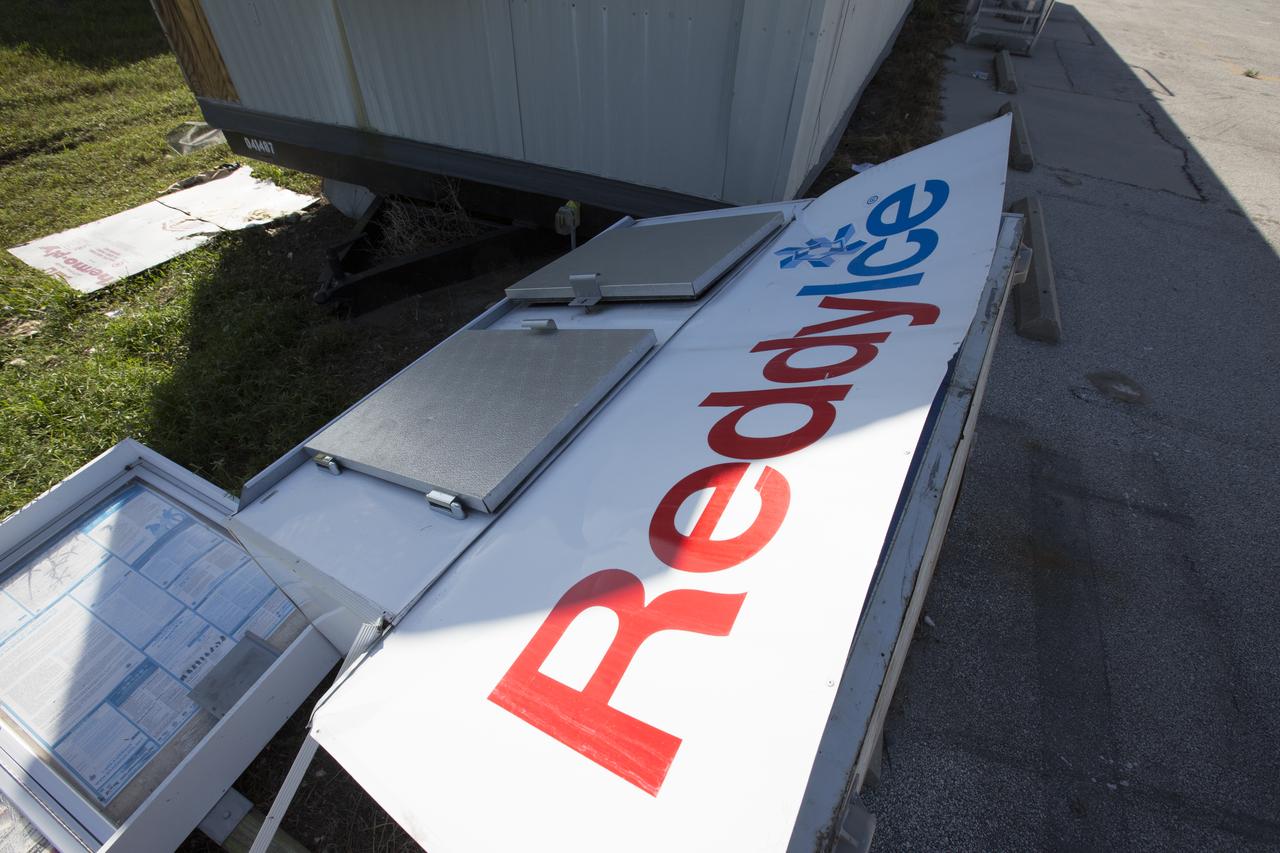

An ice dispenser damaged by Hurricane Matthew is seen in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.

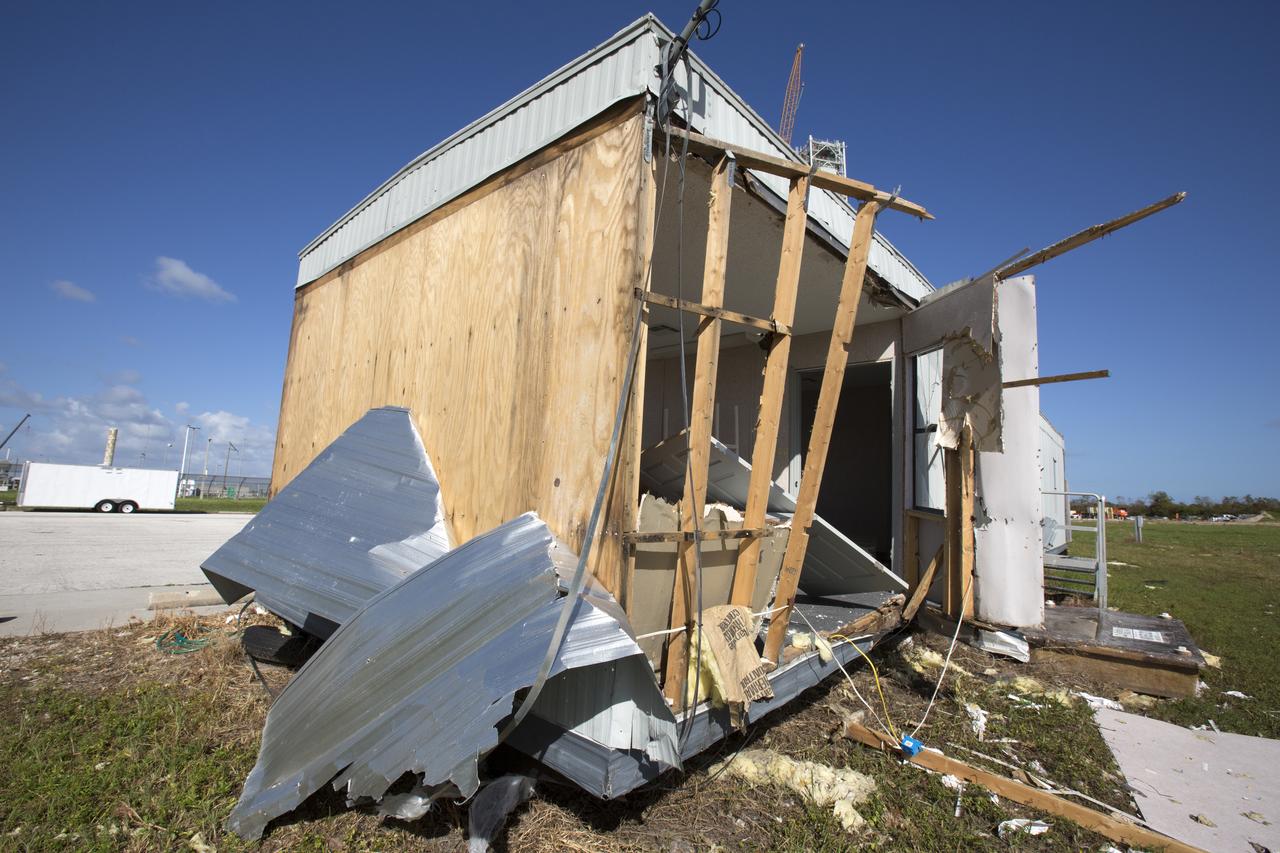
A construction trailer damaged by Hurricane Matthew is seen in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
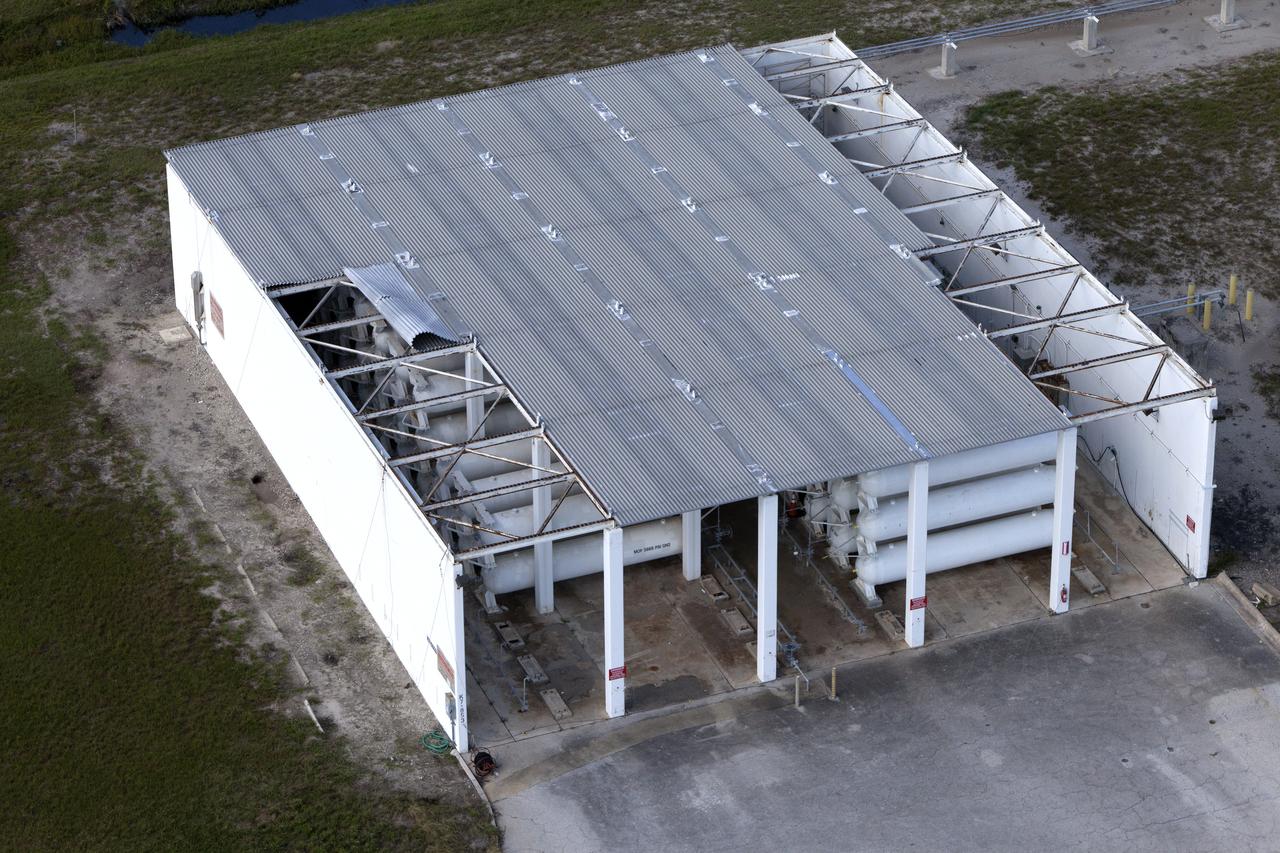

A tank stroage unit near Launch Complex 39 is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.

Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.

Launch Complex 39 surrounding areas are seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.
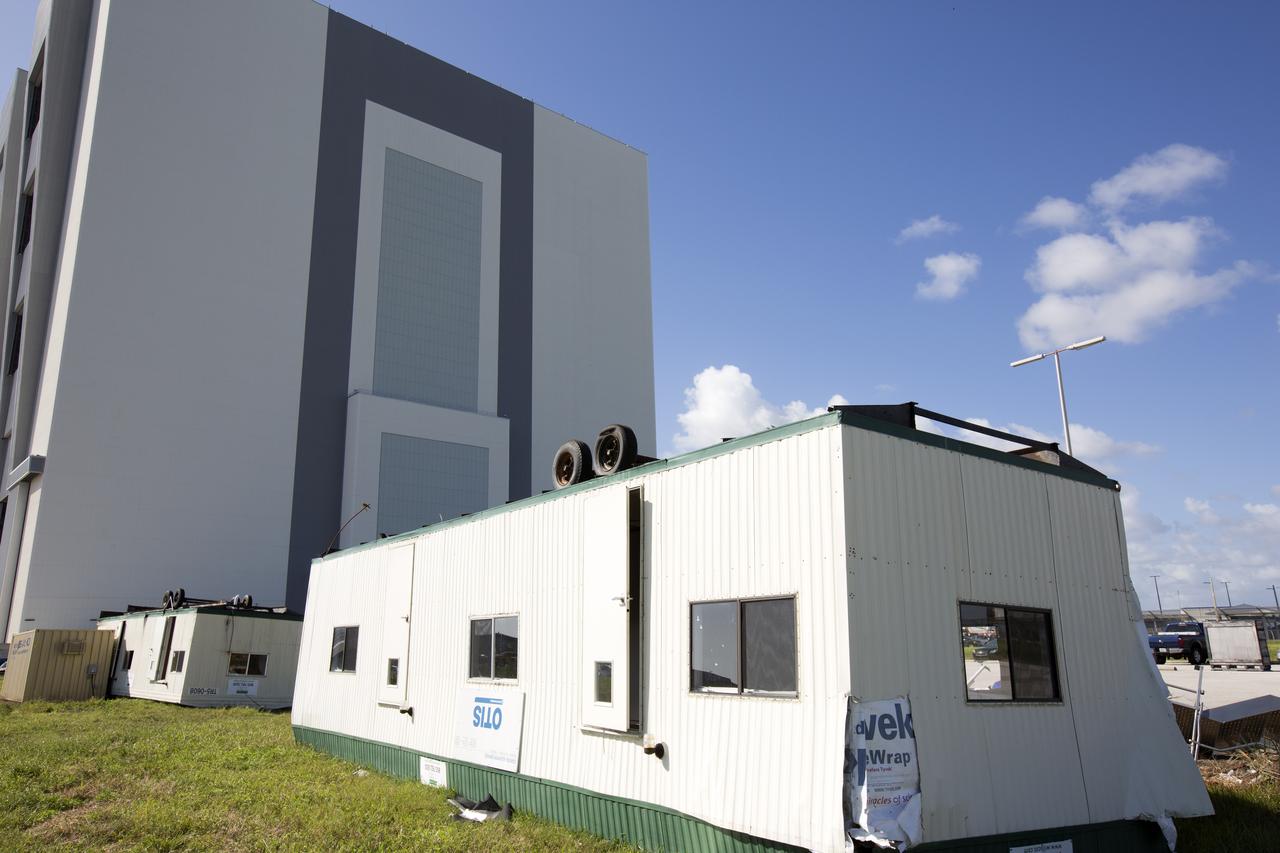

A construction trailer damaged by Hurricane Matthew is seen in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.

A construction trailer damaged by Hurricane Matthew is seen in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
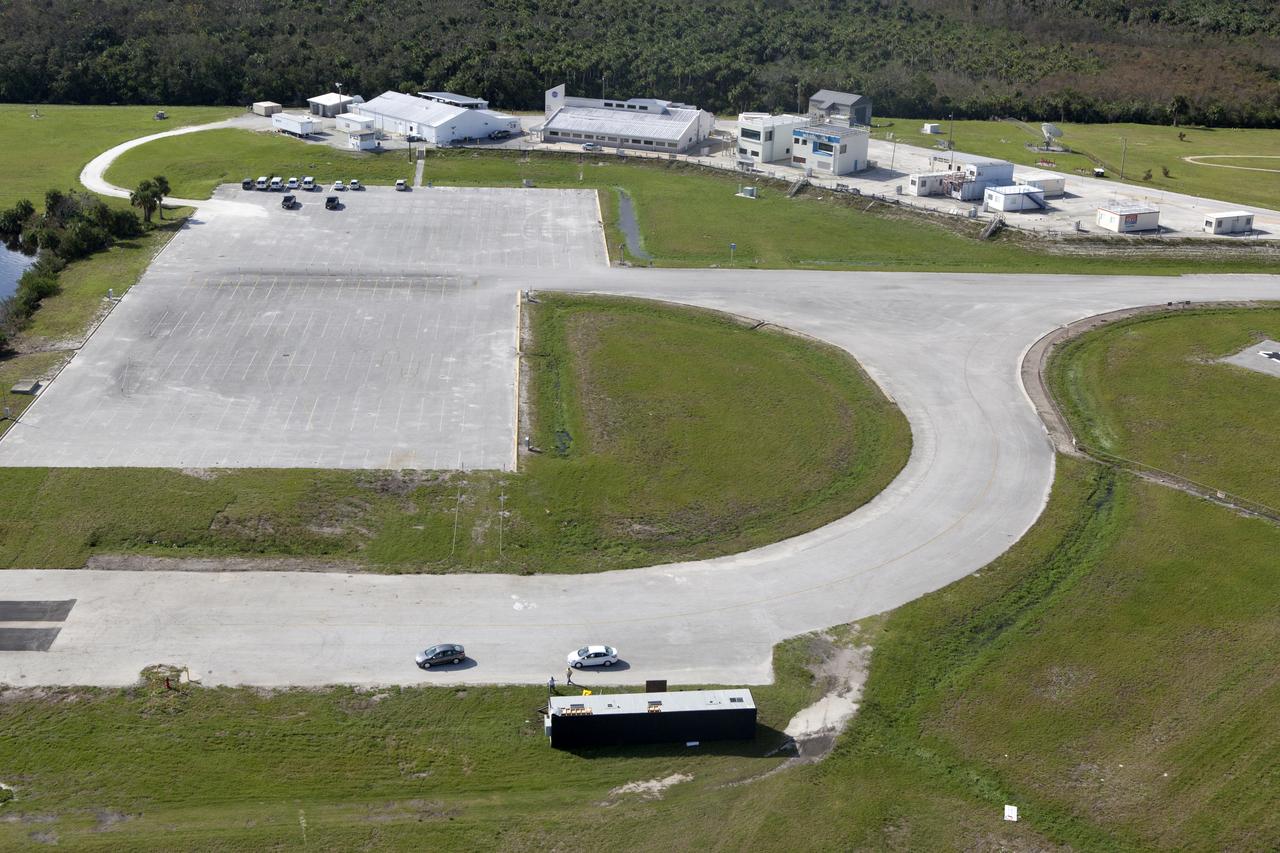

The Launch Complex 39 Press Site is seen during an aerial survey of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on September 12, 2017. The survey was performed to identify structures and facilities that may have sustained damage from Hurricane Irma as the storm passed Kennedy on September 10, 2017. NASA closed the center ahead of the storm's onset and only a small team of specialists known as the Rideout Team was on the center as the storm approached and passed.

S73-25140 (16 April 1973) --- A ground-level view of Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, showing the 341-feet tall Skylab 1/Saturn V space vehicle on the pad soon after being rolled out from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The vehicle is composed of the Saturn V first (S-1C) stage, the Apollo Telescope Mount (ATM), the Multiple Docking Adapter (MDA), the Airlock Module (AM), and the Orbital Workshop (OWS). Photo credit: NASA
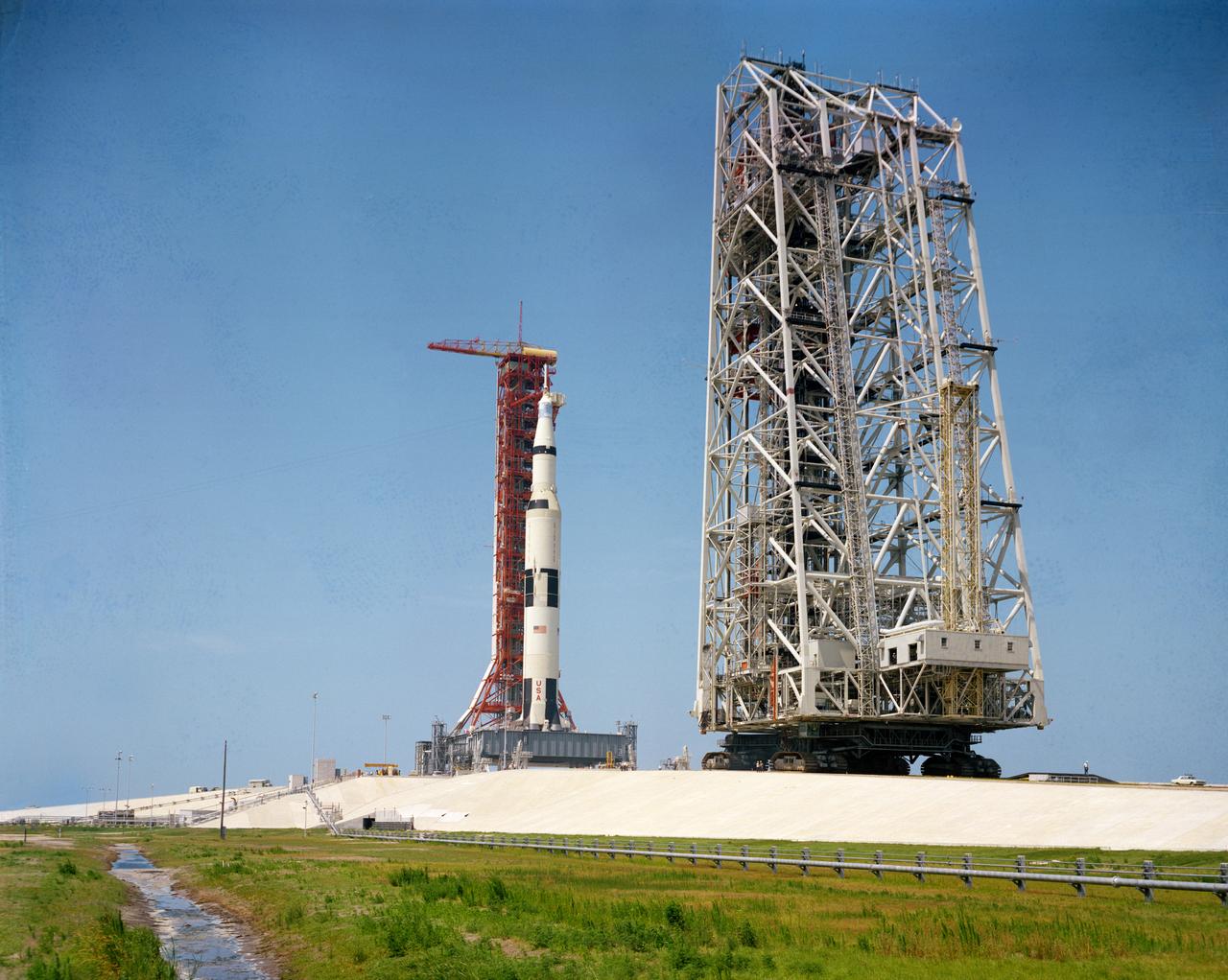

S69-34320 (17 May 1969) --- Ground level view of the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. The service structure is in the right foreground. The crew of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
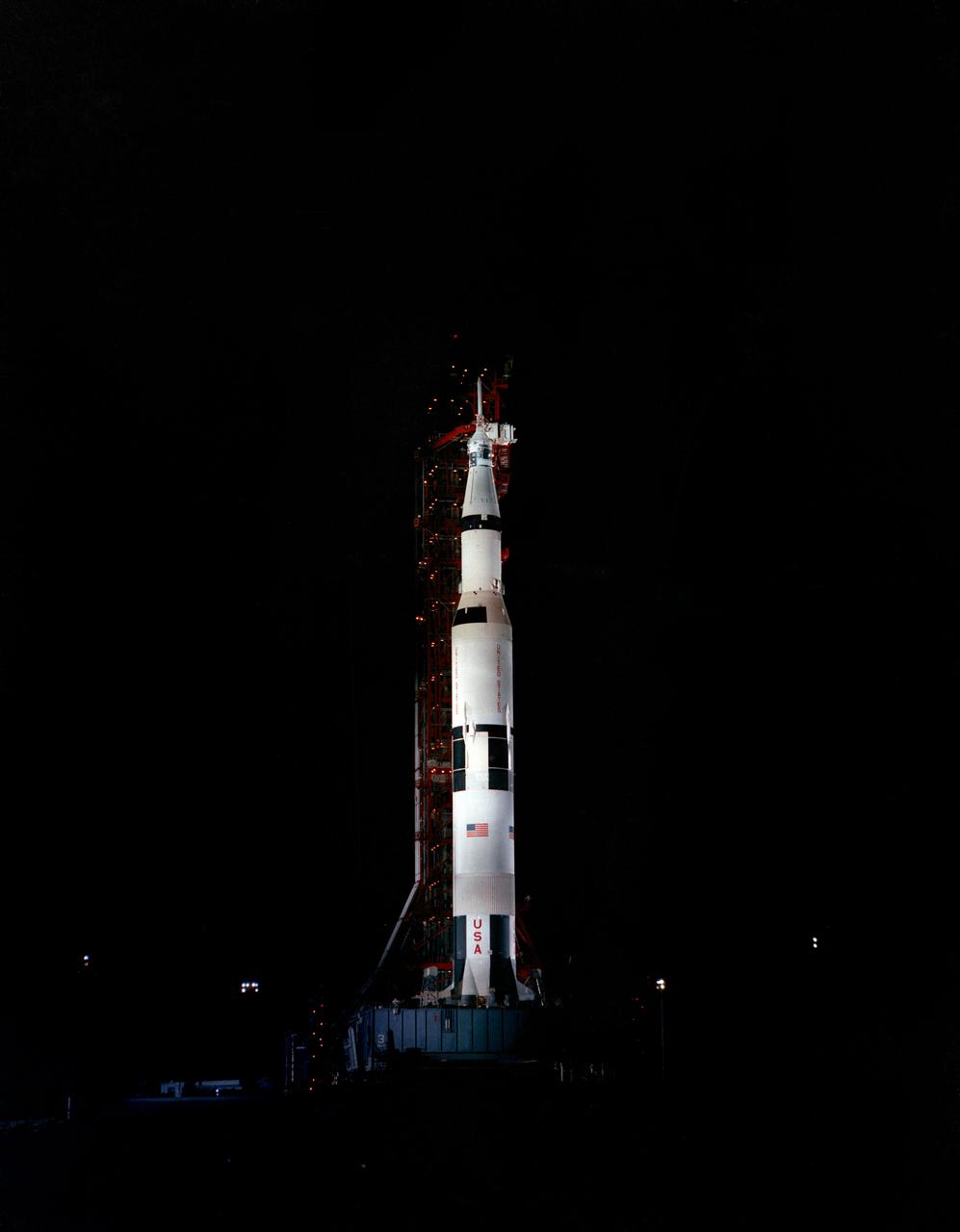

S69-33855 (4 May 1969) --- Nighttime, ground-level view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. This photograph of the 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V stack was taken during pull back of the mobile service structure. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan.
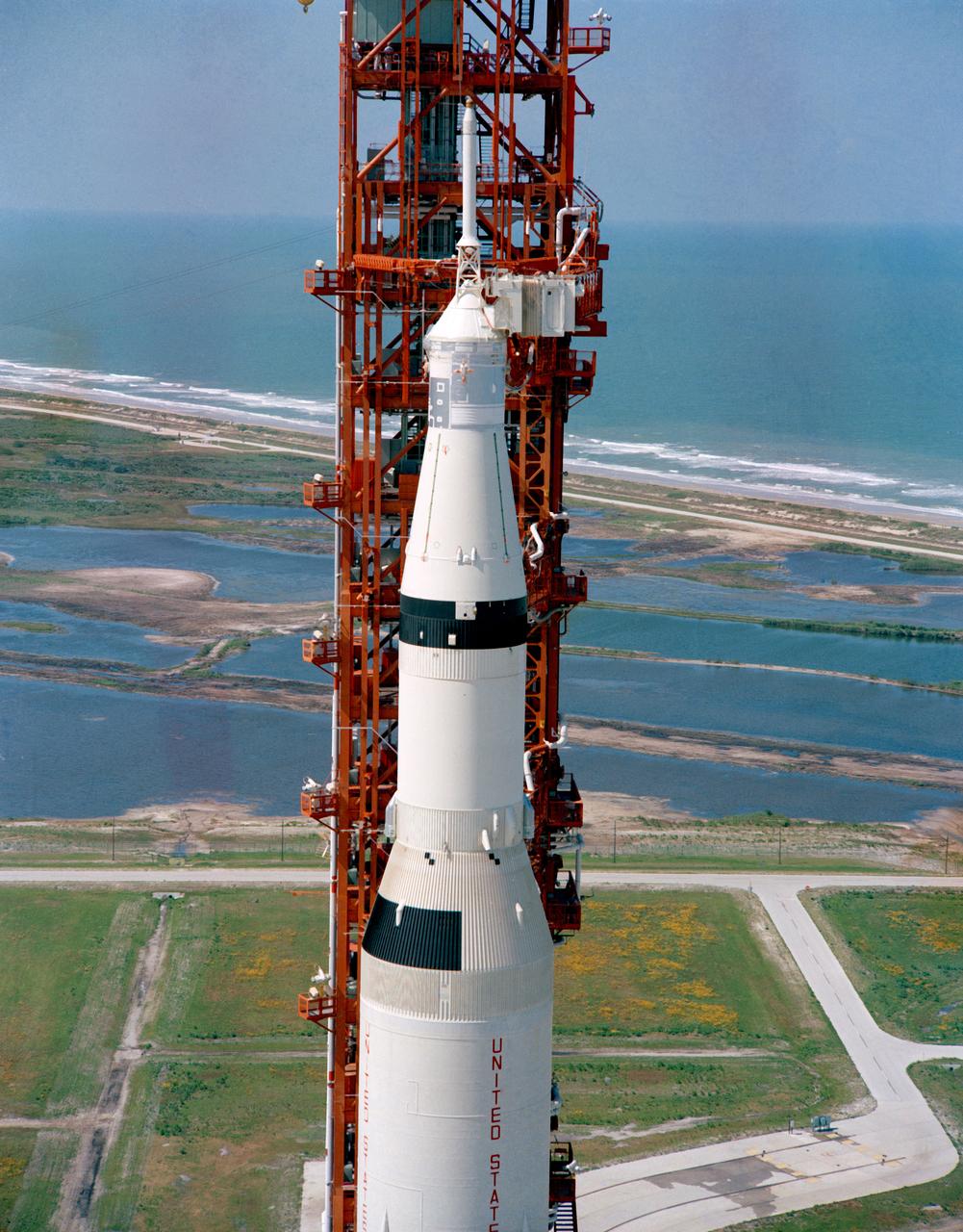

S69-33854 (4 May 1969) --- Aerial (high-angle, clasp) view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. This photograph of the 363-feet tall Apollo/Saturn V stack was taken during pull back of the mobile service structure. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, John W. Young, and Eugene A. Cernan.

S69-34328 (17 May 1969) --- Ground level view of the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
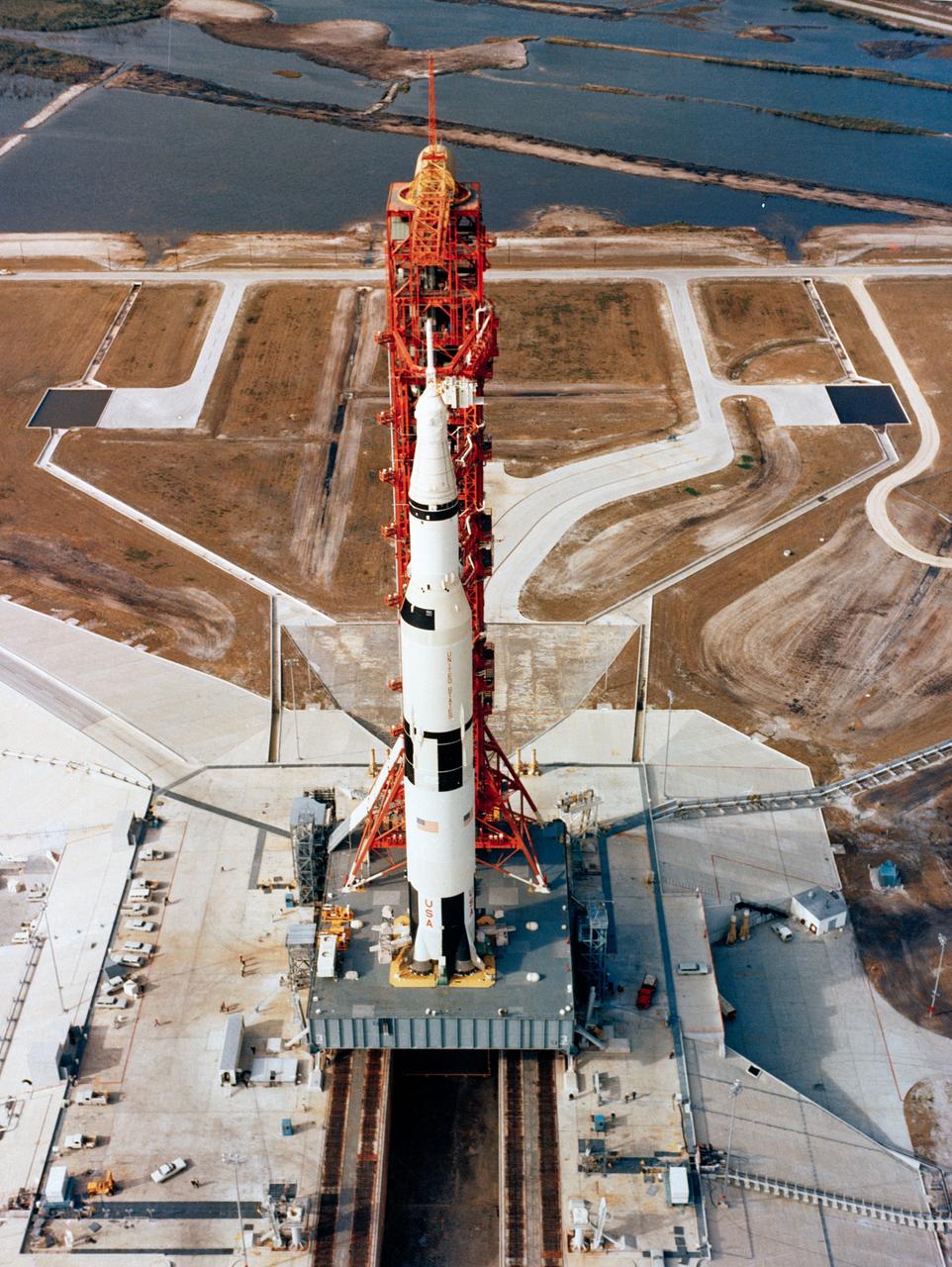

S69-34327 (13 May 1969) --- Aerial, high-angle, view of the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module 4/Saturn 505) space vehicle at Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The crew of the Apollo 10 lunar orbit mission will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
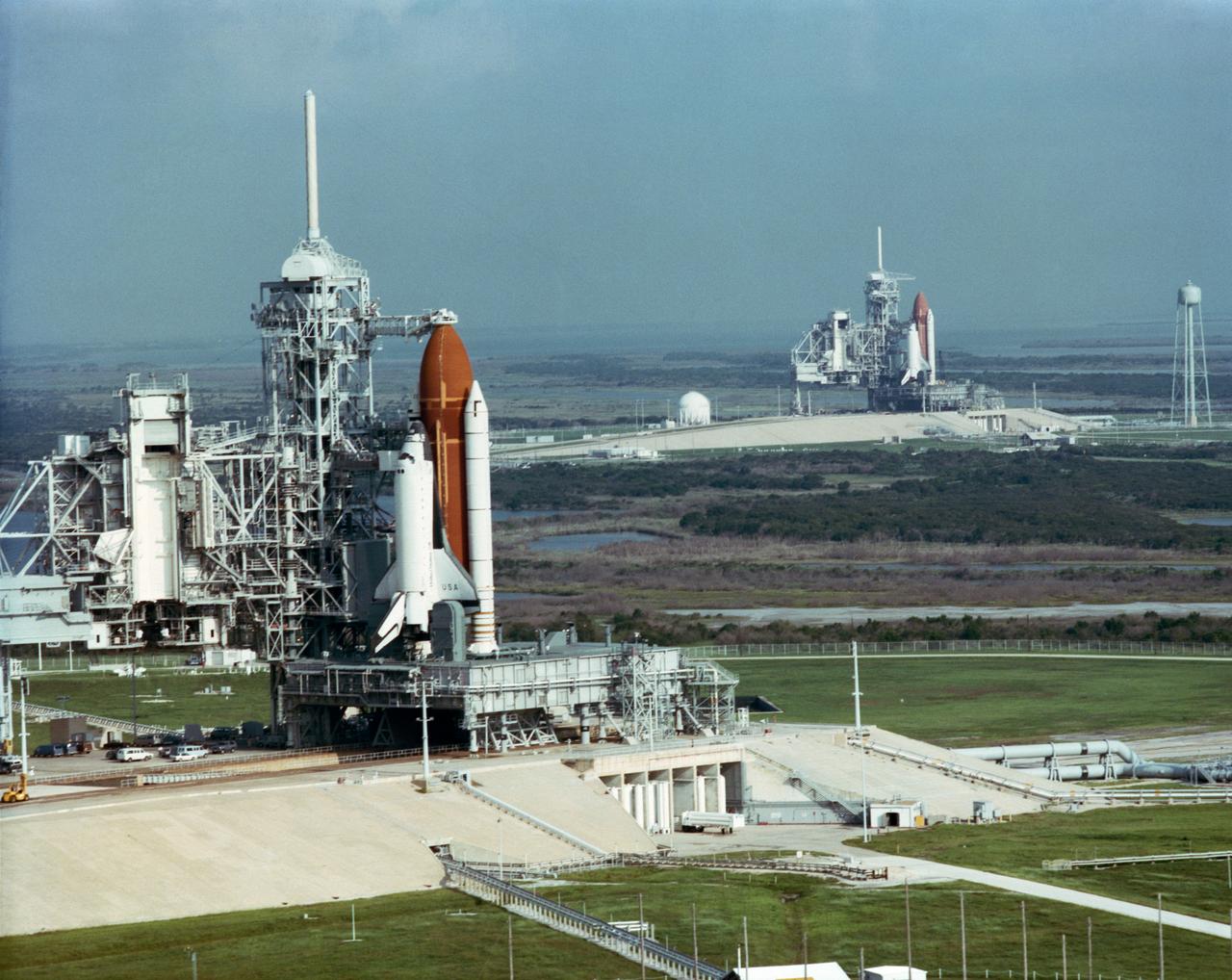

S90-48650 (5 Sept 1990) --- This rare view shows two space shuttles on adjacent pads at Launch Complex 39 with the Rotating Service Structures (RSR) retracted. Space Shuttle Columbia (foreground) is on Pad A where it awaits further processing for a September 6 early morning launch on STS-35. Discovery, its sister spacecraft, is set to begin preparations for an October liftoff on STS-41 when the Ulysses spacecraft is scheudled to be taxied into space. PLEASE NOTE: Following the taking of this photograph, STS-35 was postponed and STS-41's Discovery was successfully launched on Oct. 6.

S69-27916 (11 March 1969) --- Aerial view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module-4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on its way to Pad B. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 10 flight is scheduled as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
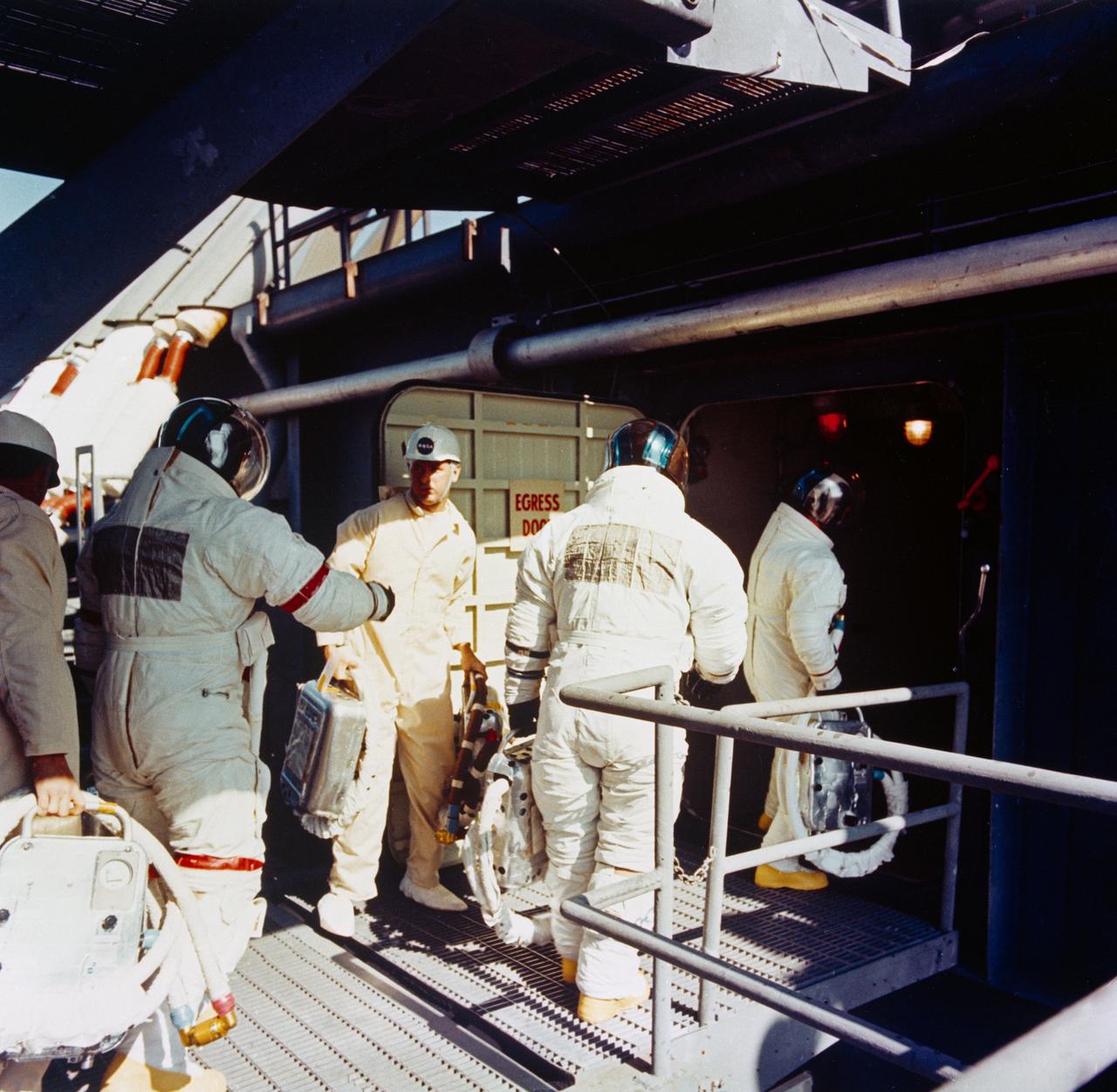

S71-16635 (31 Jan. 1971) --- The three Apollo 14 astronauts arrive at the White Room atop Pad A, Launch Complex 39, during the Apollo 14 prelaunch countdown. Apollo 14, with Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, aboard was launched at 4:03:02 p.m. (EST), Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar landing mission. Note identifying bands on the sleeve and leg of Shepard. Standing in the center foreground is astronaut Thomas P. Stafford, chief of the MSC Astronaut Office.
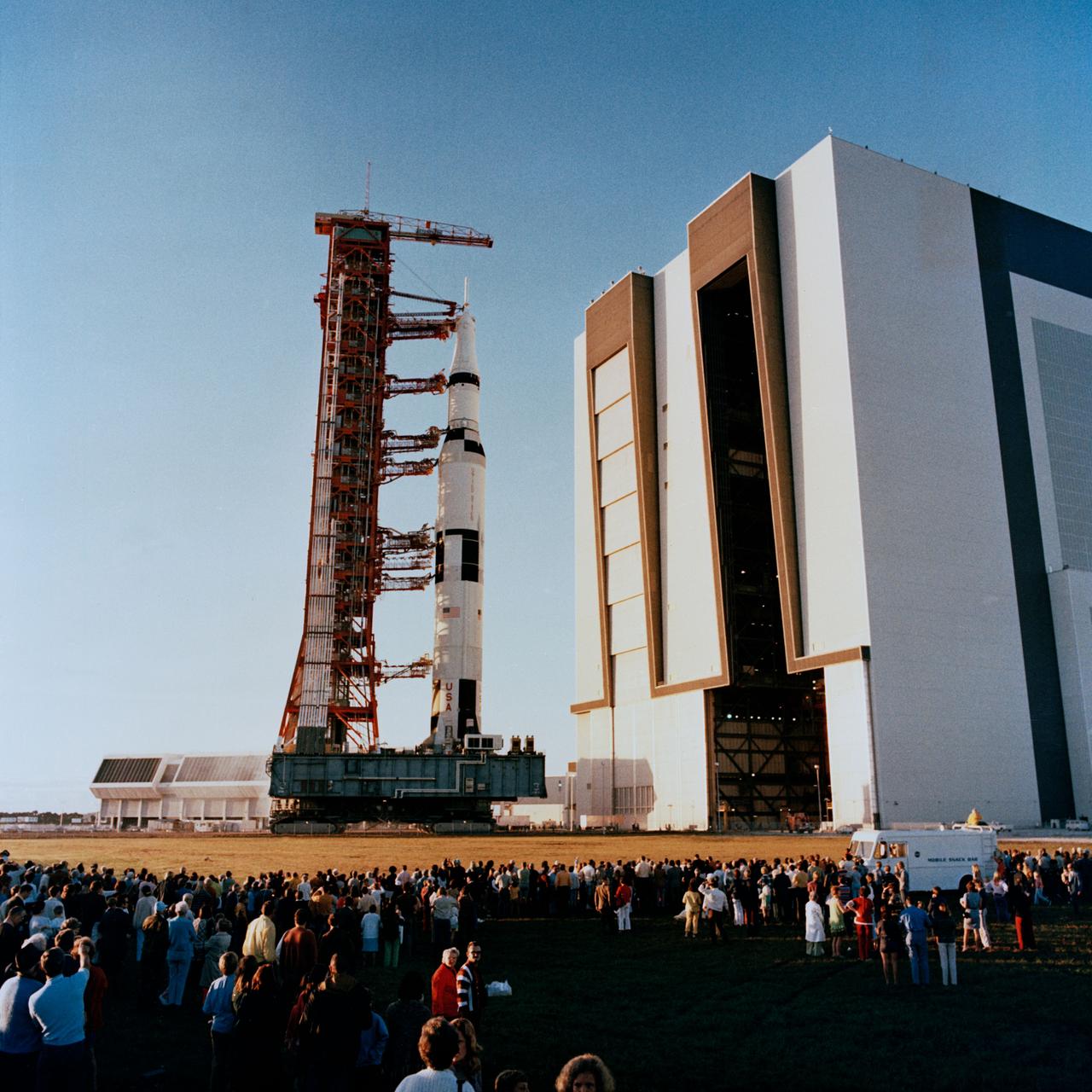

S72-19795 (13 Dec. 1971) --- A large crowd of spectators look on as the 363-feet tall Apollo 16 (Spacecraft 113/Lunar Module 11/Saturn 511) space vehicle moves out of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Complex 39 toward Pad A. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The prime crew men of the scheduled Apollo 16 lunar landing mission are astronauts John W. Young, commander; Thomas K. Mattingly, command module pilot; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot.
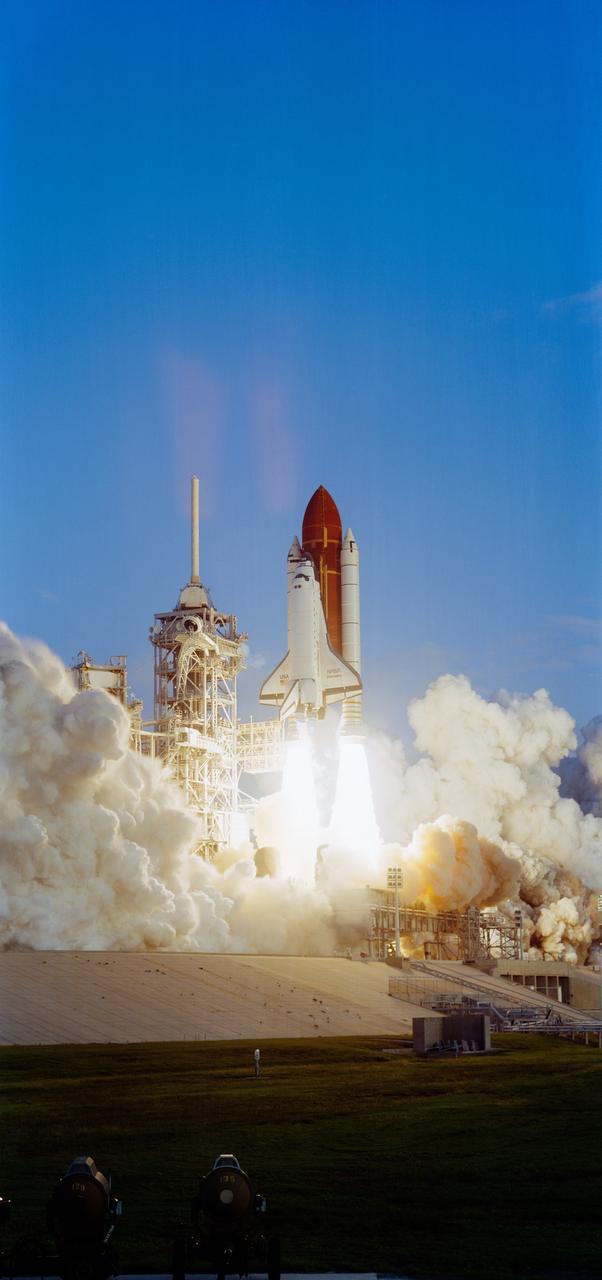

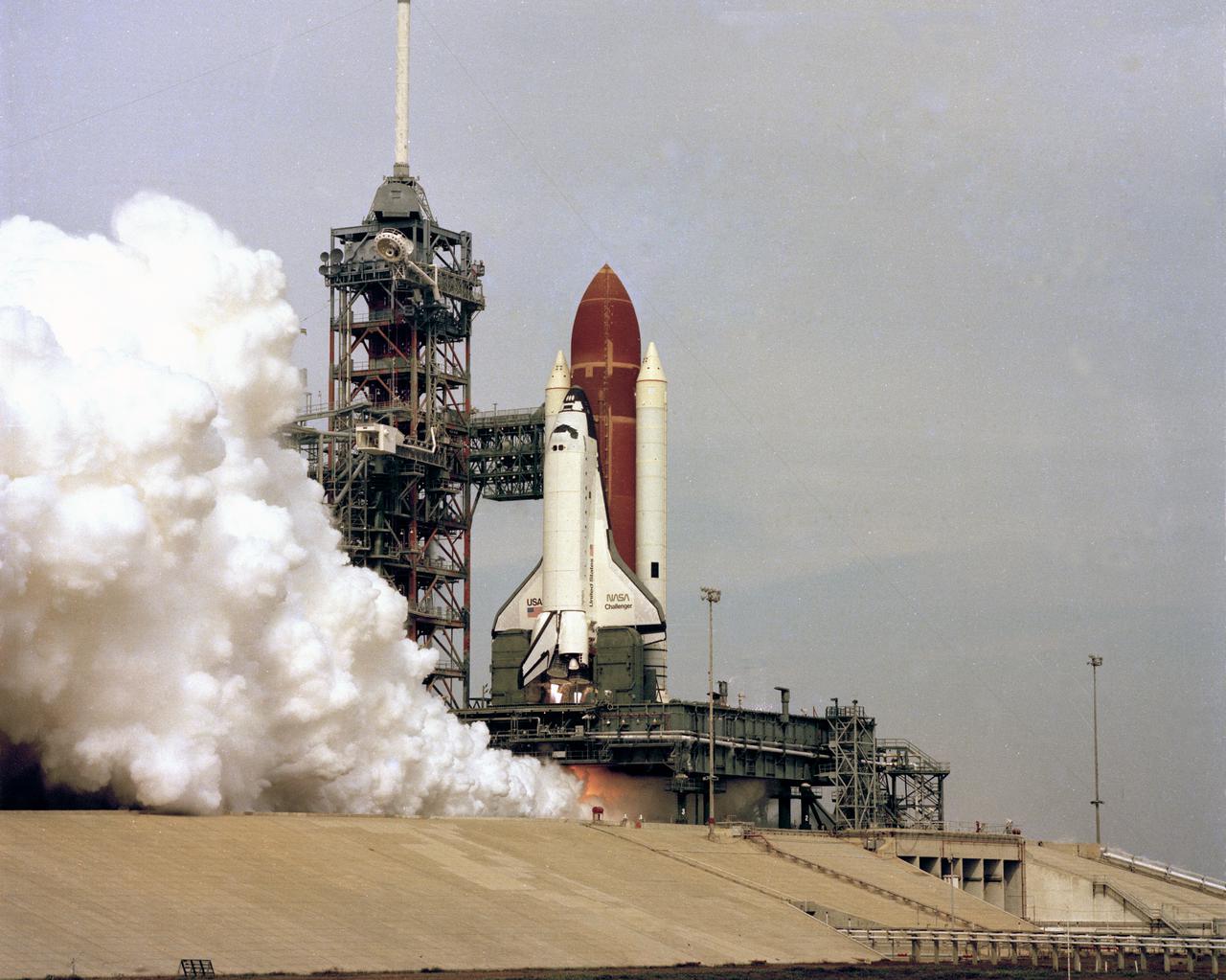
STS-41 Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, lifts off from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Launch Complex (LC) Pad 39 mobile launcher platform at 7:47 am (Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)). OV-103 riding atop the external tank (ET) and flanked by two solid rocket boosters (SRBs), is captured just moments after liftoff. Not yet clear of the fixed service structure (FSS) tower, OV-103 is highlighted against the cloudless morning sky. Exhaust smoke billows from the SRBs and the space shuttle main engines (SSMEs) creating a cloud over the launch pad area.
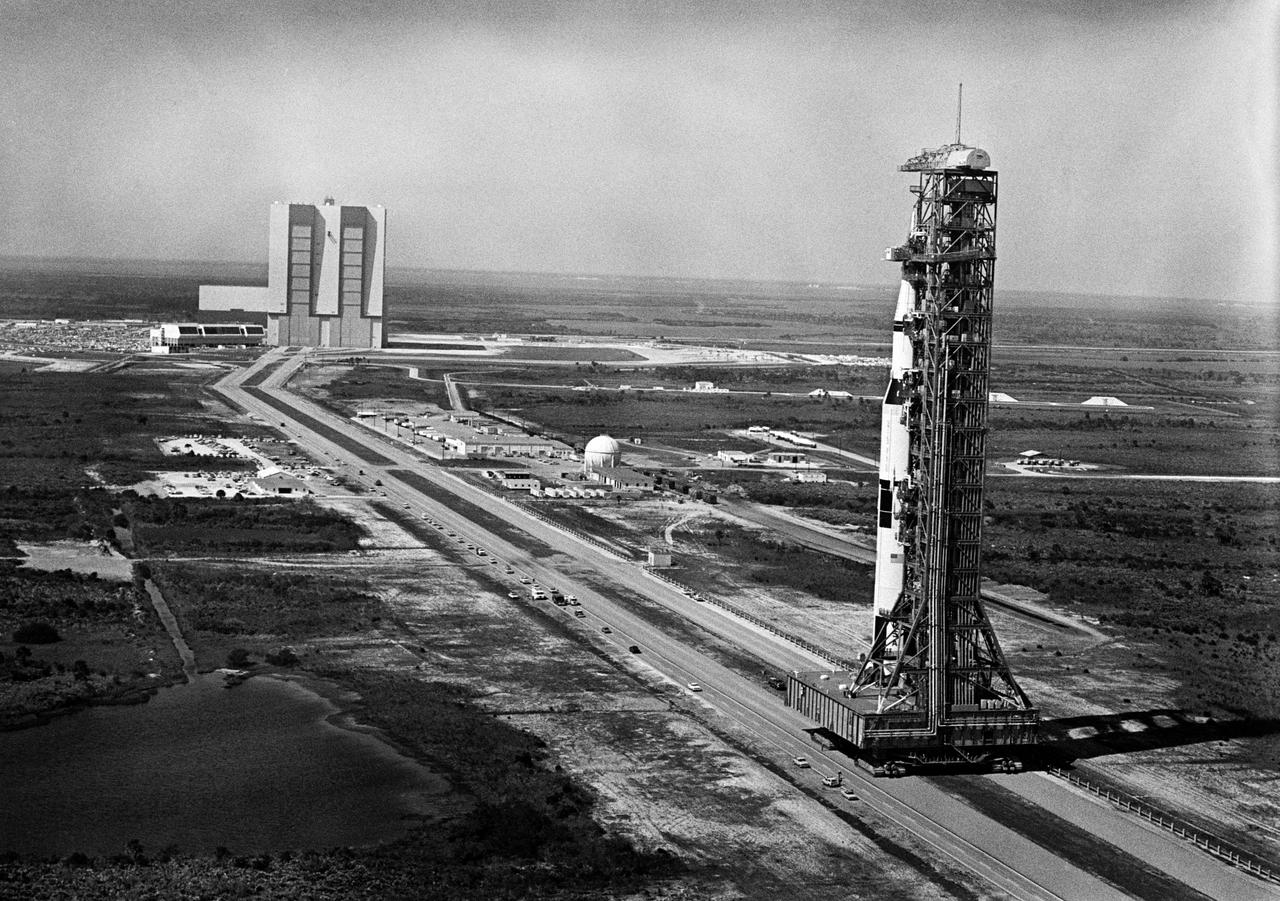

S69-27741 (11 March 1969) --- Aerial view at Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, showing the 363-feet tall Apollo 10 (Spacecraft 106/Lunar Module-4/Saturn 505) space vehicle on its way to Pad B. The Vehicle Assembly Building is in the background. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The Apollo 10 flight is schedule as a lunar orbit mission. The Apollo 10 crew will be astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; John W. Young, command module pilot; and Eugene A. Cernan, lunar module pilot.
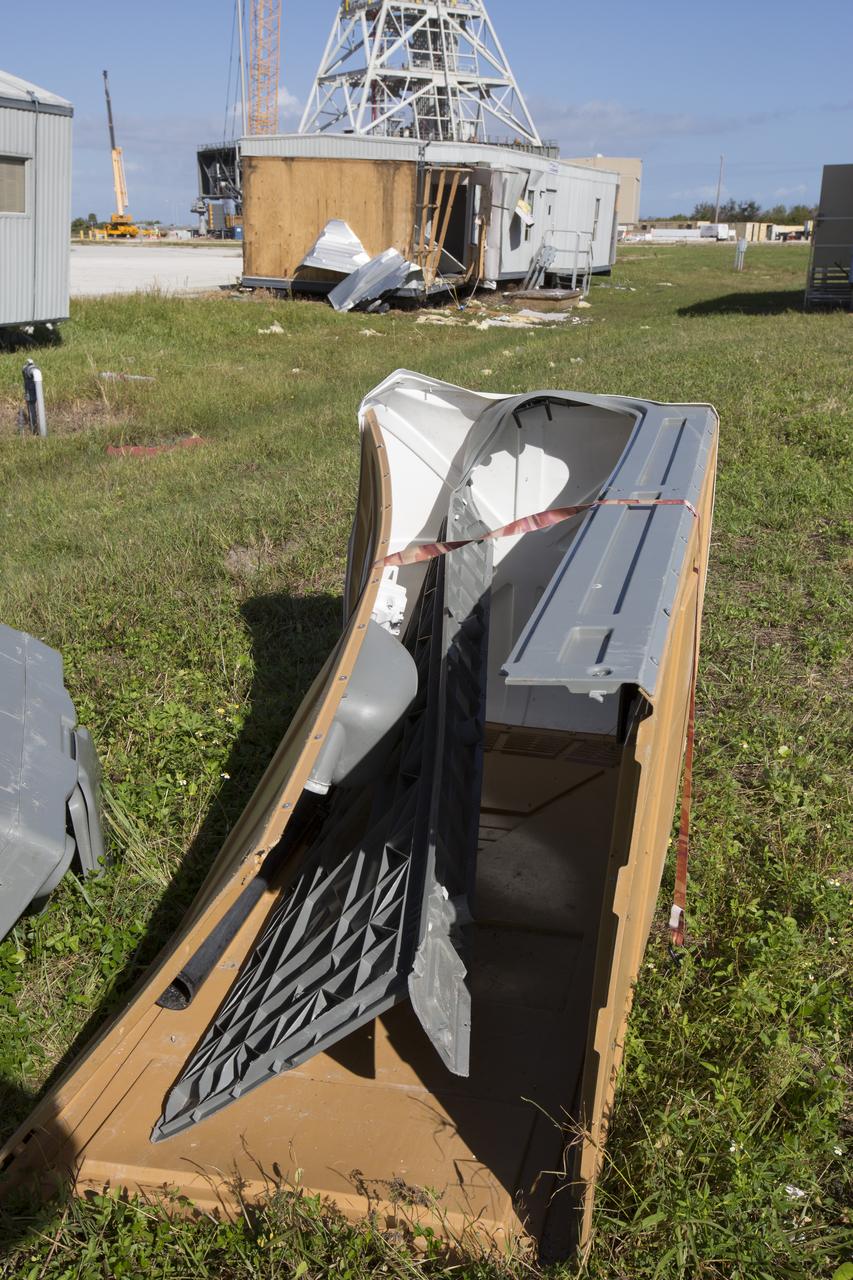

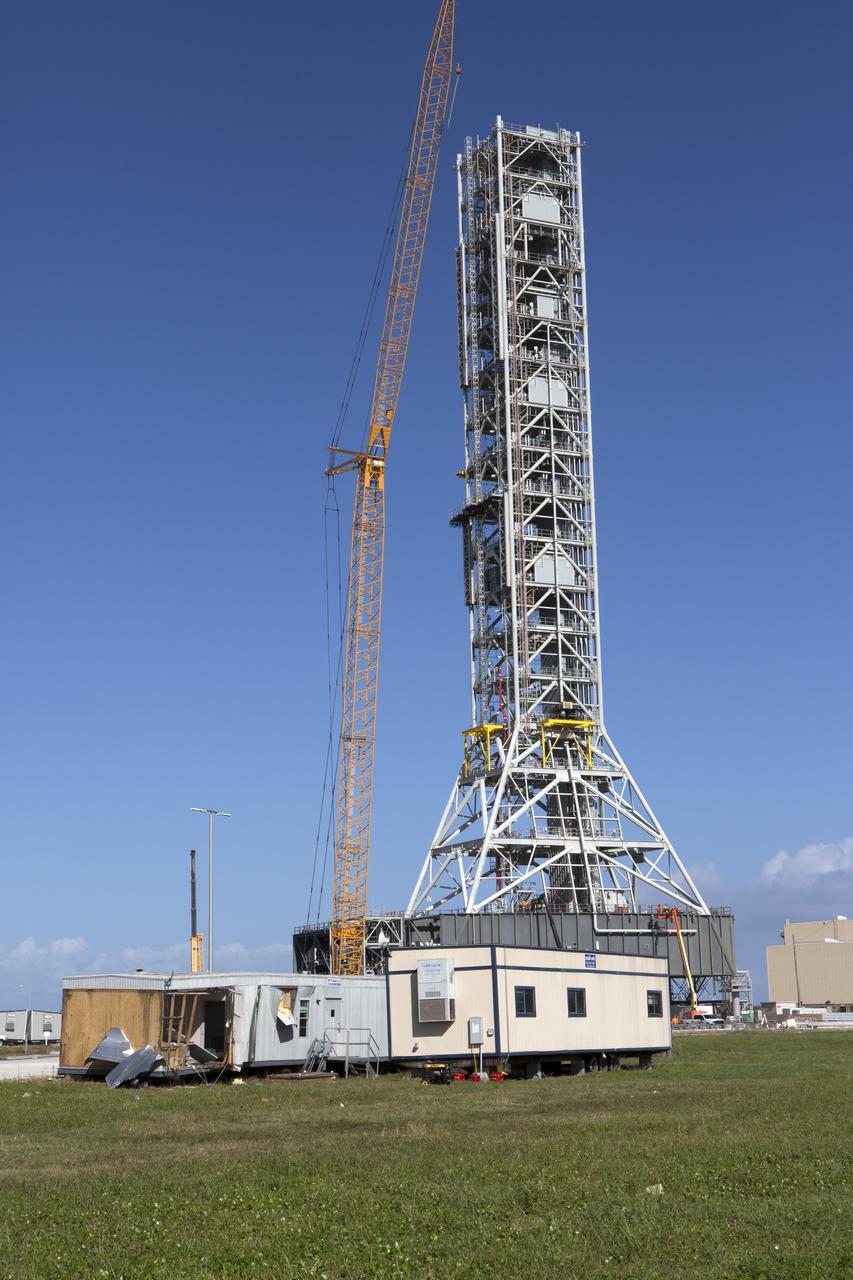
A damaged construction trailer and several pieces of associated debris, aftermath of Hurricane Matthew, are seen near the Mobile Launcher in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
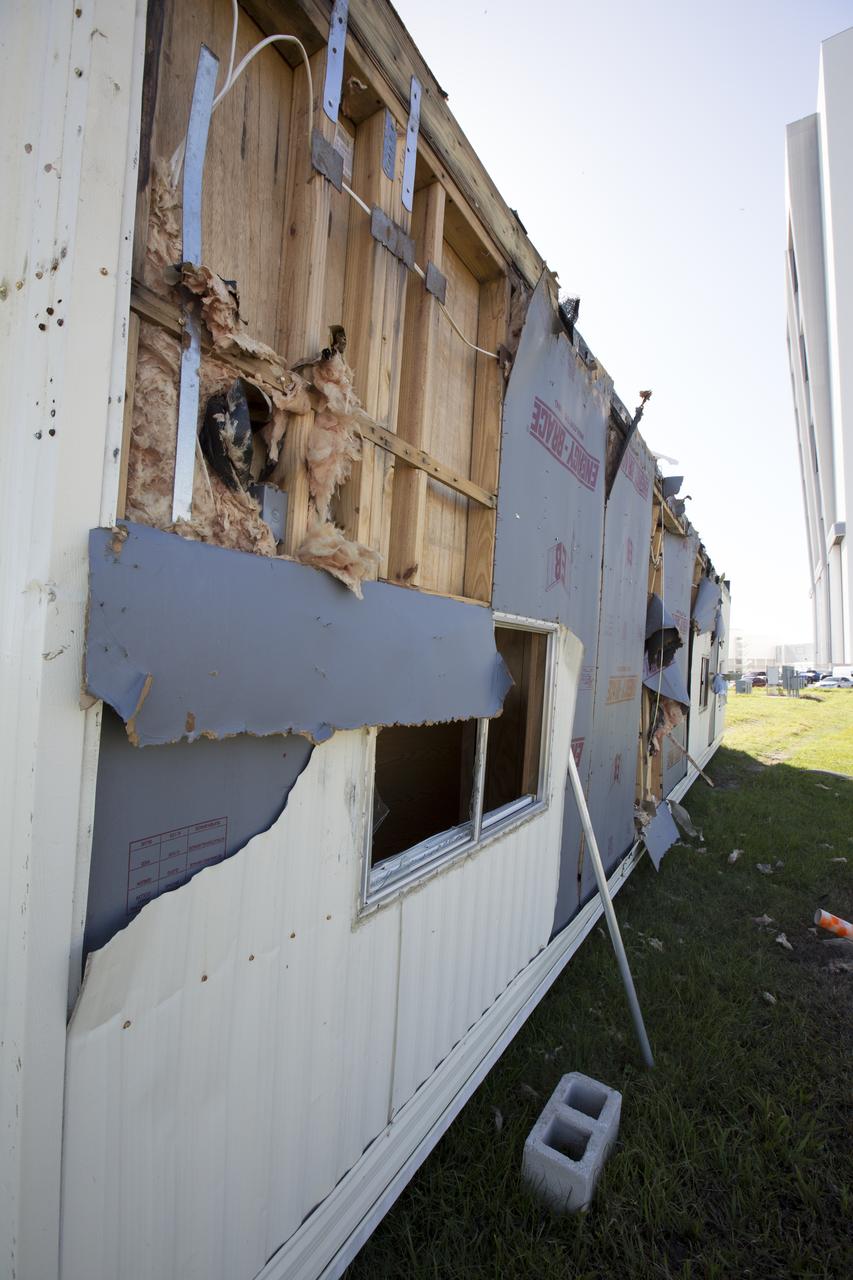

Siding damage caused by Hurricane Matthew is seen inside a support building in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
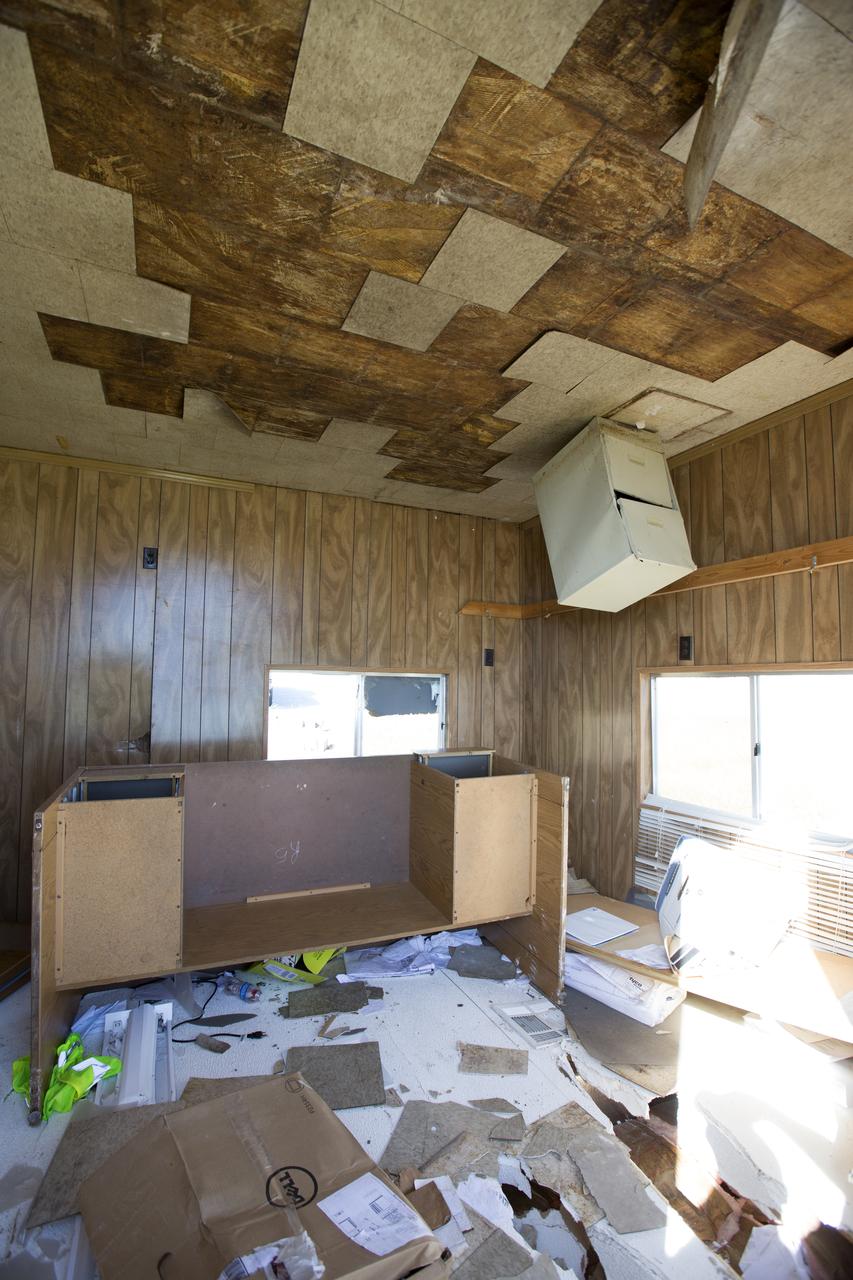

Ceiling and furniture damage caused by Hurricane Matthew is seen inside a support building in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
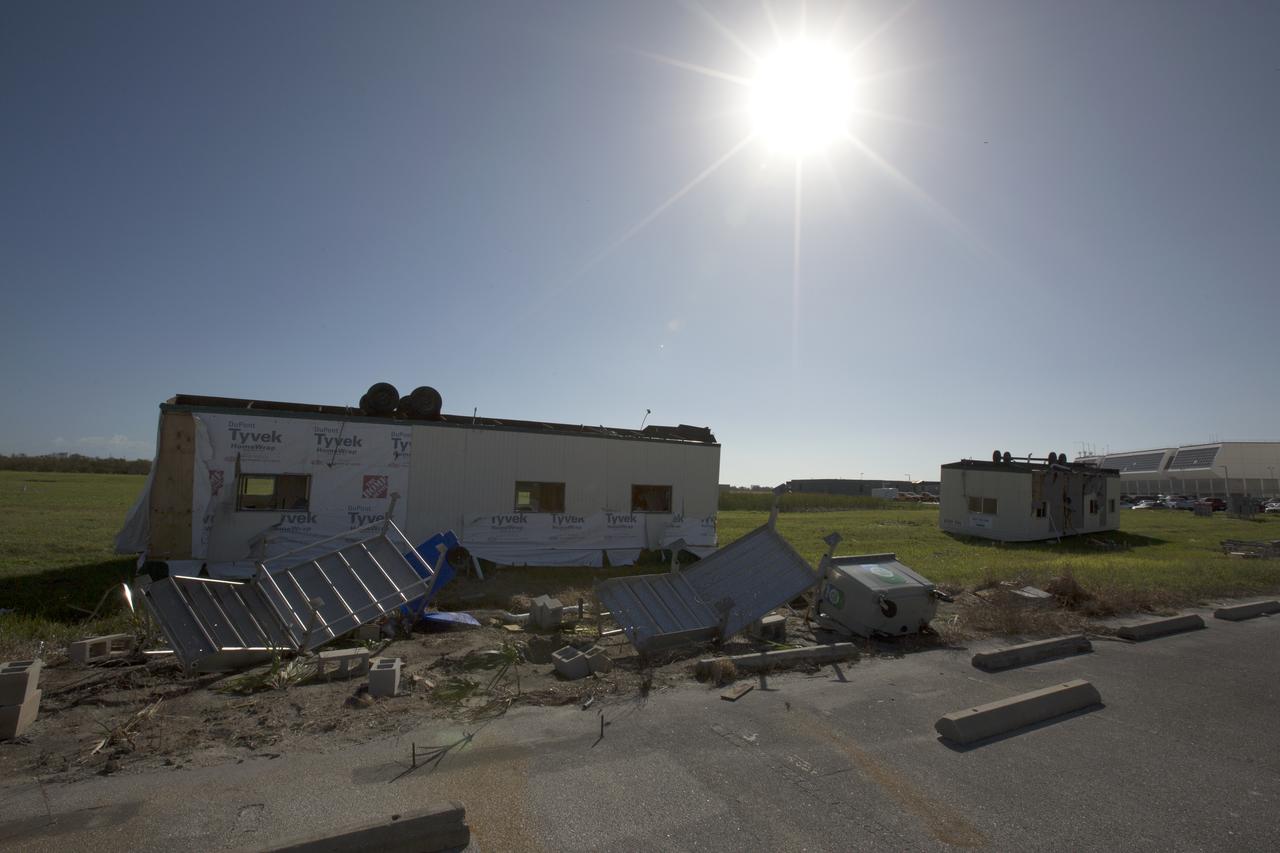

Damaged construction trailers and several pieces of associated debris, aftermath of Hurricane Matthew, are seen in front of the Mobile Launcher in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
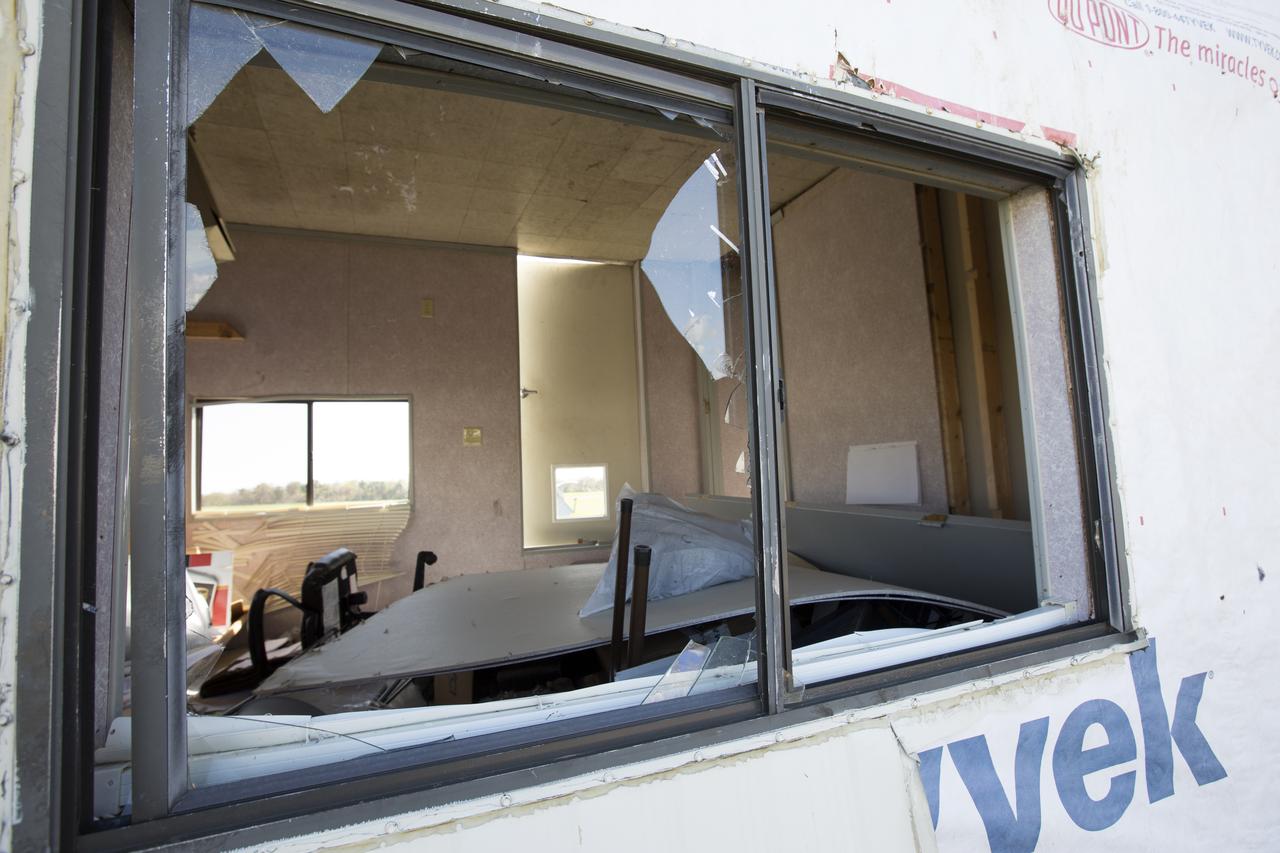

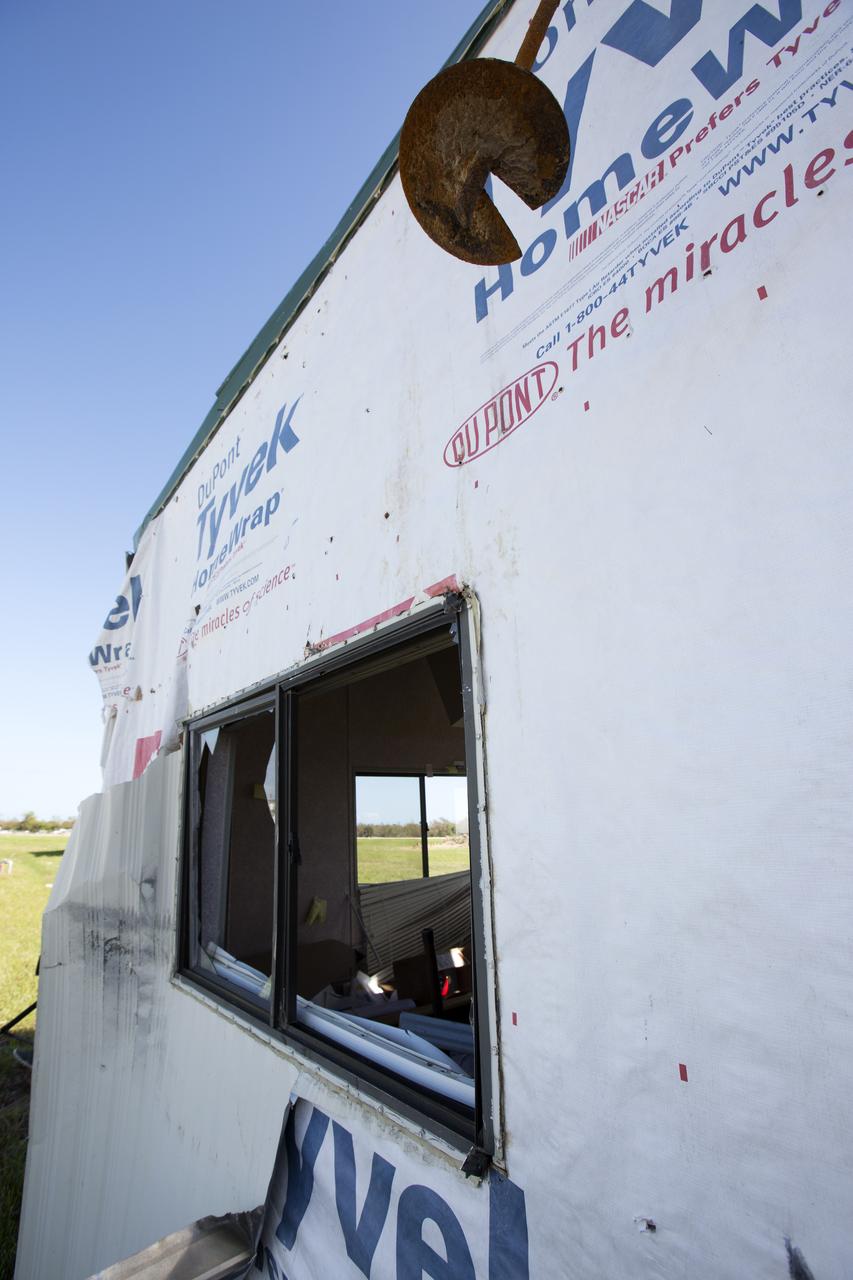
A broken window caused by Hurricane Matthew is seen inside a support building in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
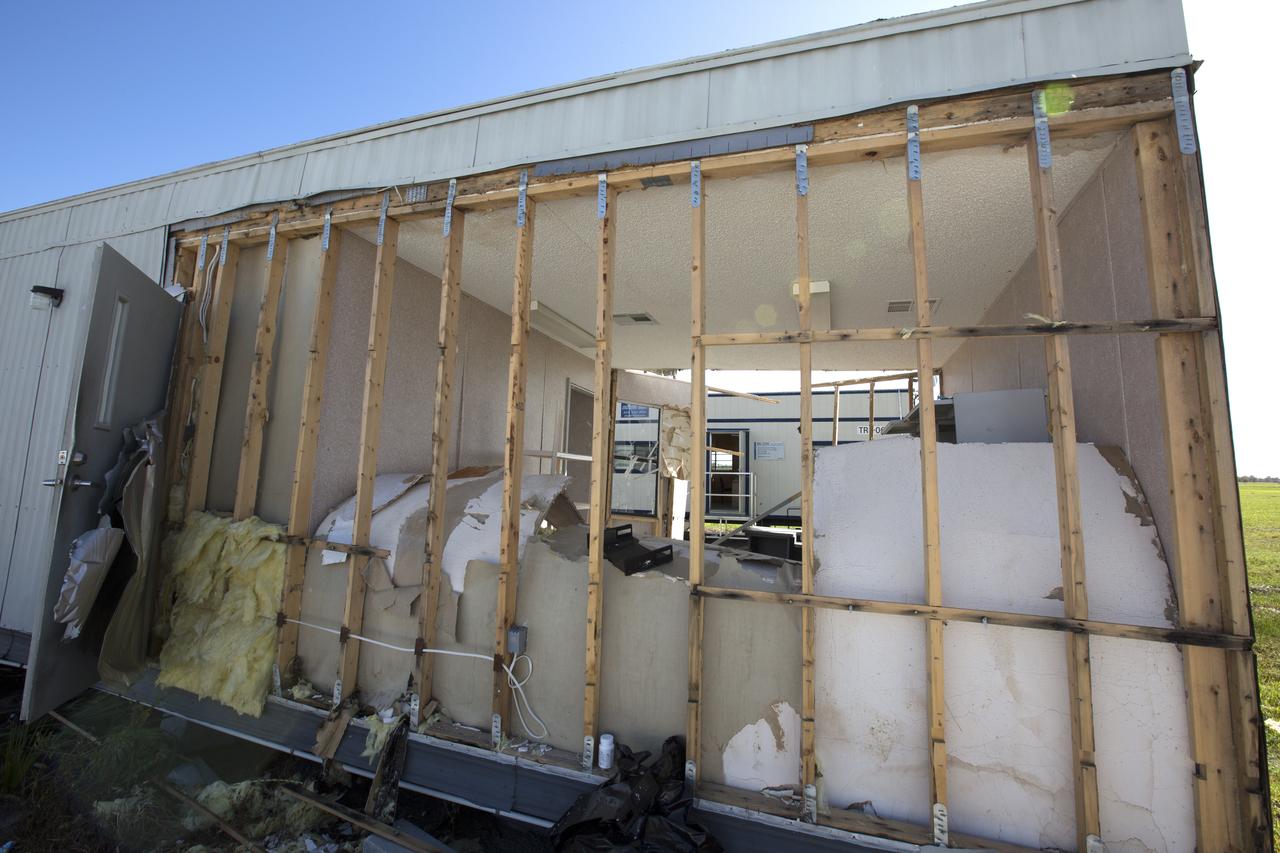

Hurricane Matthew tore away a section of wall on a support building in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
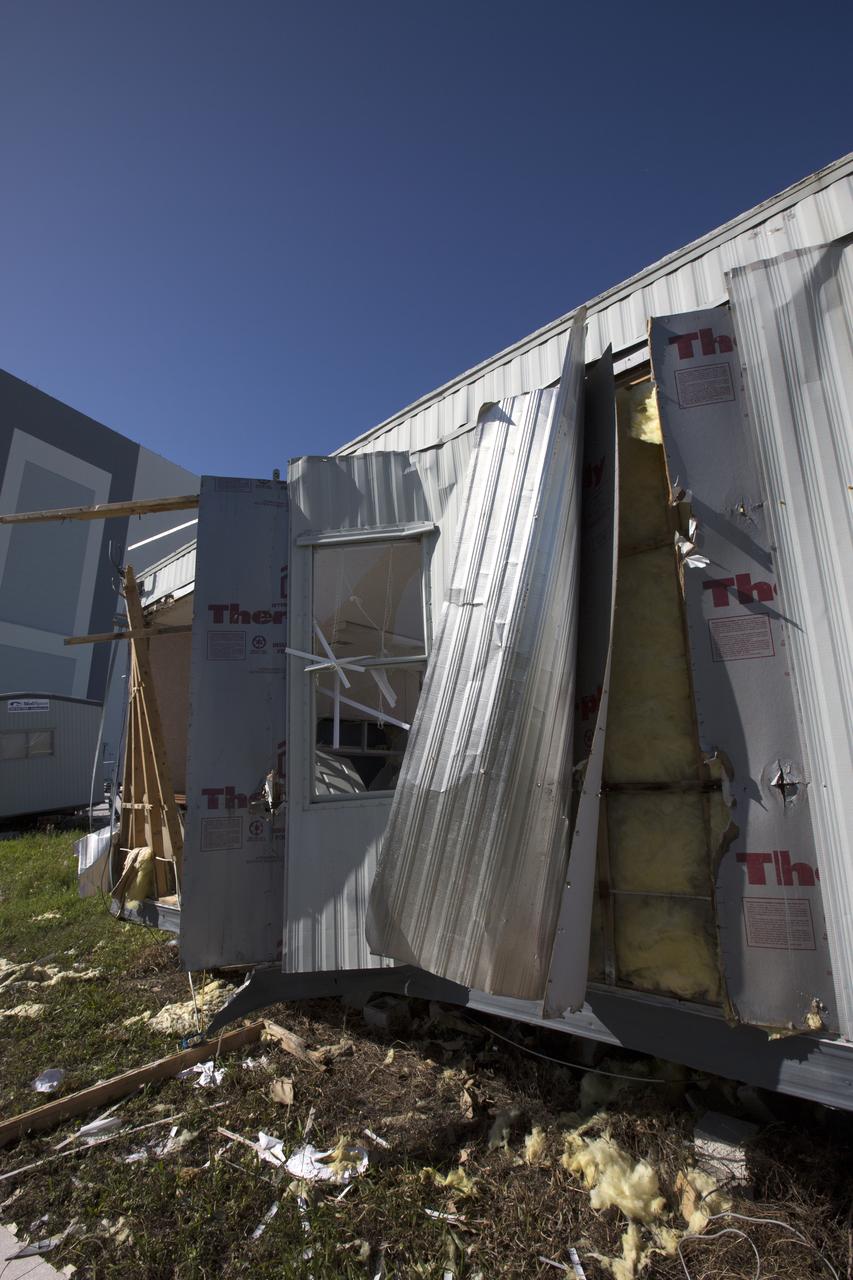

Siding damage caused by Hurricane Matthew is seen inside a support building in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
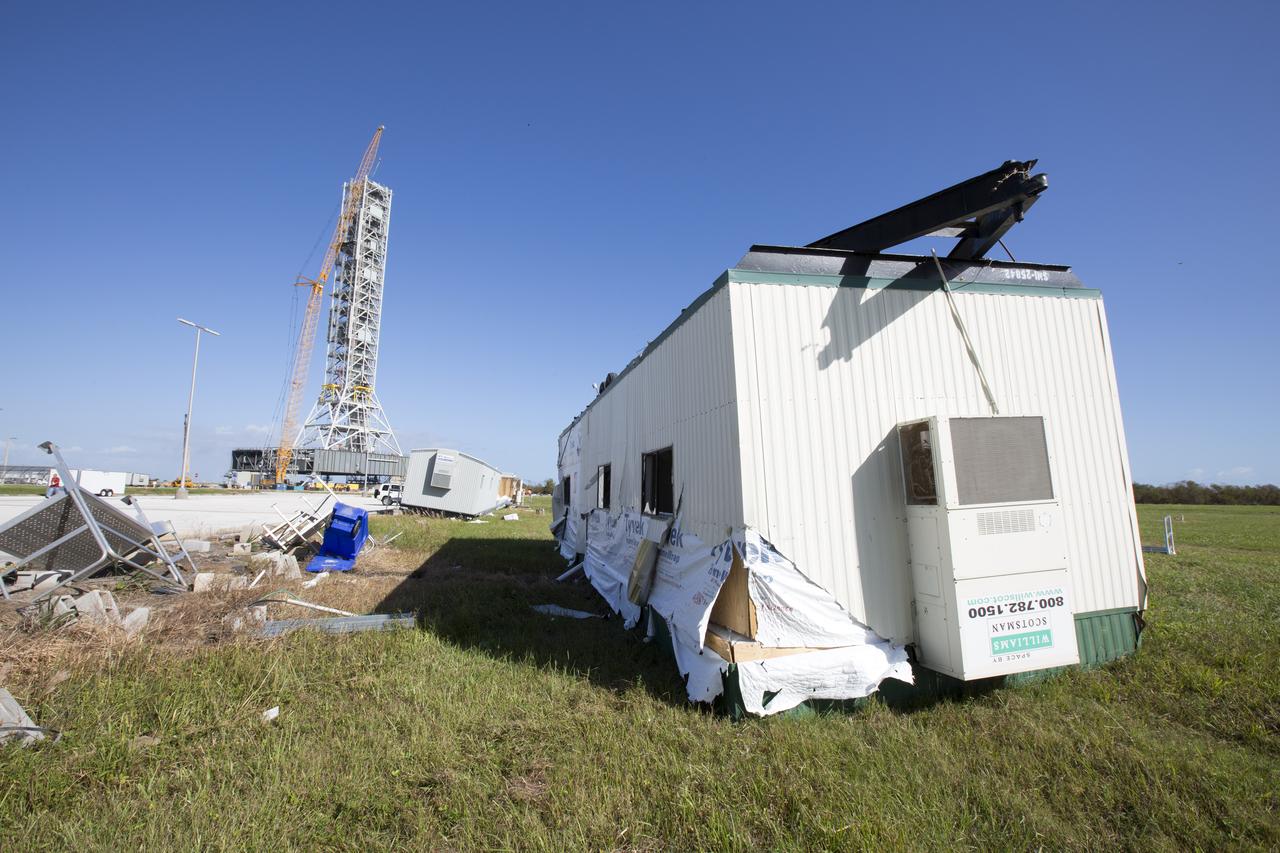

A damaged construction trailer and several pieces of associated debris, aftermath of Hurricane Matthew, are seen in front of the Mobile Launcher in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.

A damaged construction trailer and several pieces of associated debris, aftermath of Hurricane Matthew, are seen in front of the Mobile Launcher in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.

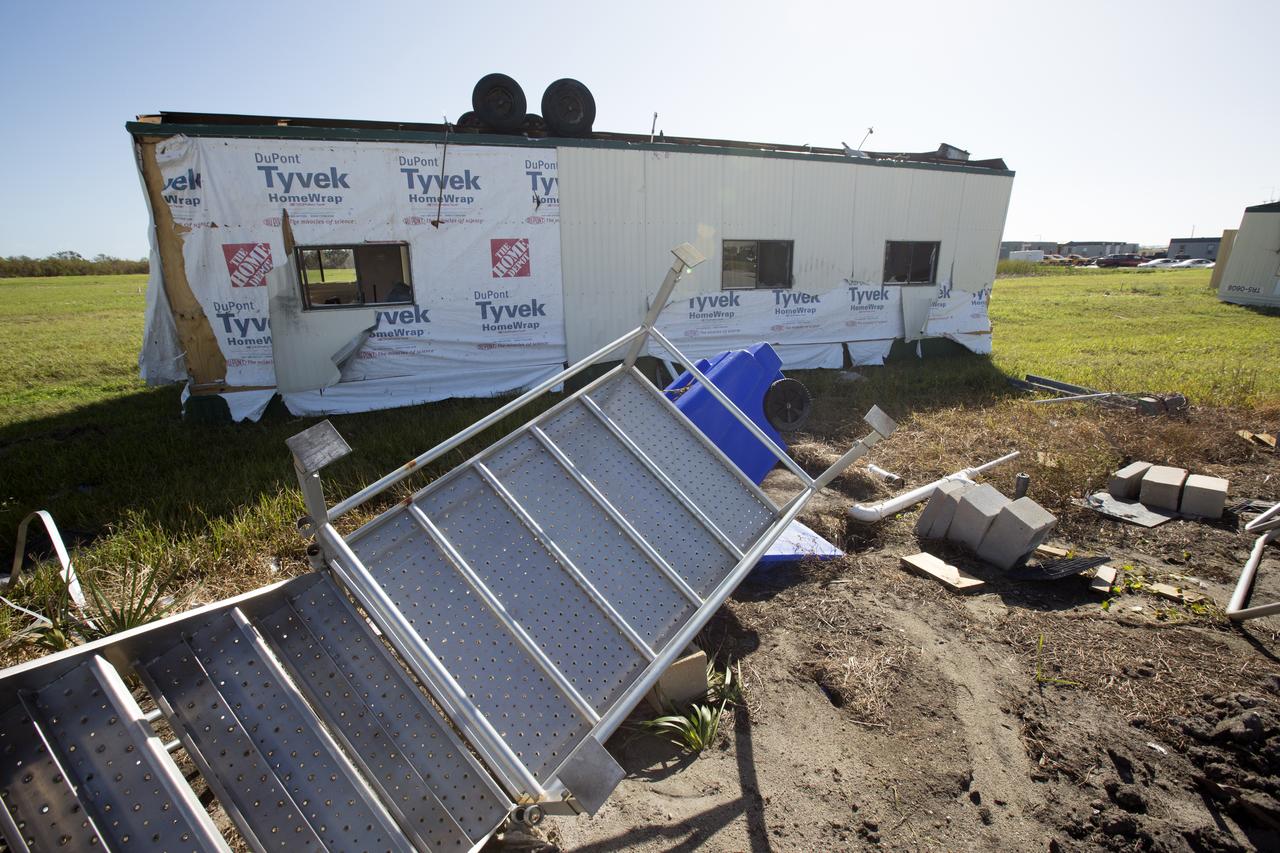
A construction trailer damaged by Hurricane Matthew is seen in front of the Mobile Launcher within the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assessments and repairs are in progress at various structures and facilities across the spaceport, part of the ongoing recovery from Hurricane Matthew, which passed to the east of Kennedy on Oct. 6 and 7, 2016. The center received some isolated roof damage, damaged support buildings, a few downed power lines, and limited water intrusion. Beach erosion also occurred, although the storm surge was less than expected.
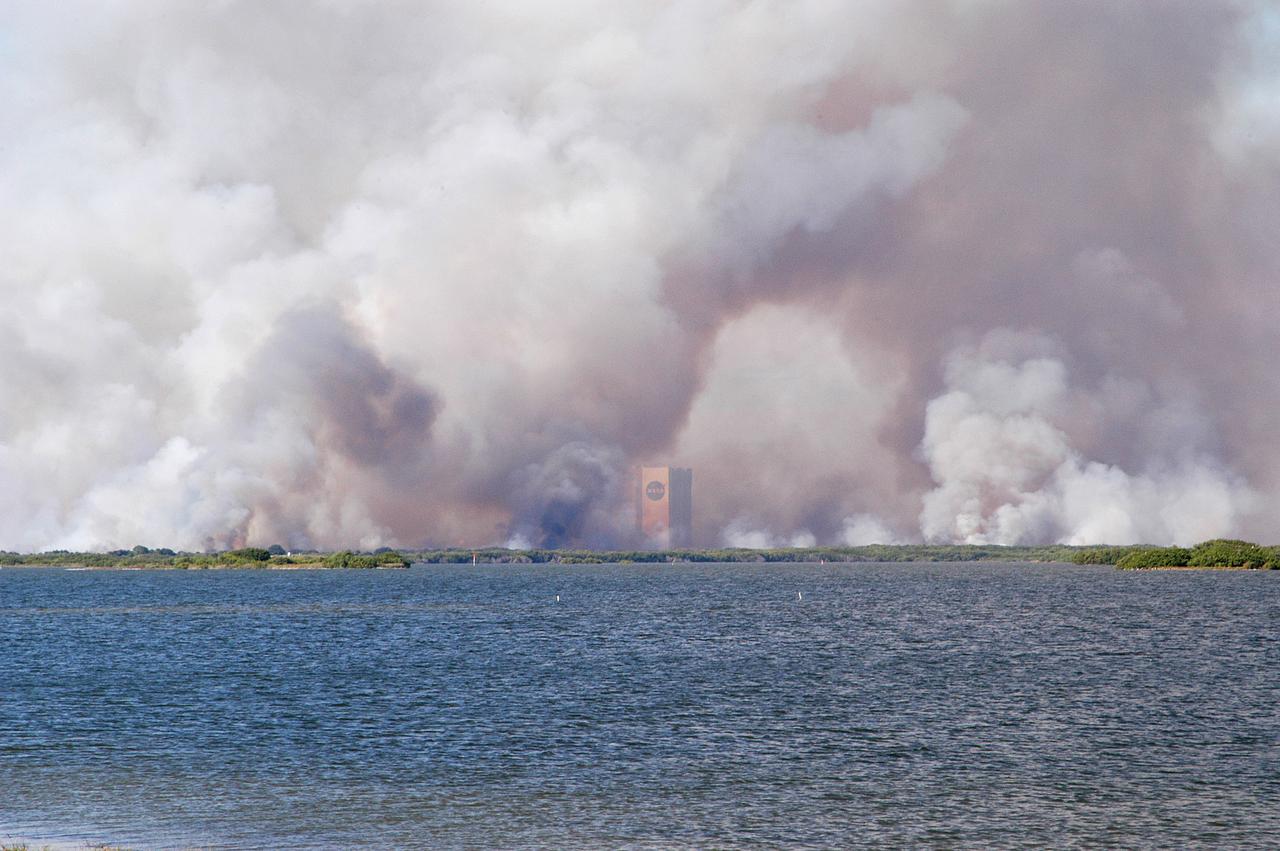

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Smoke from a successful controlled burn near KSC’s Launch Complex 39 surrounds the Vehicle Assembly Building and spreads across the horizon. The water in the foreground is the Banana River.
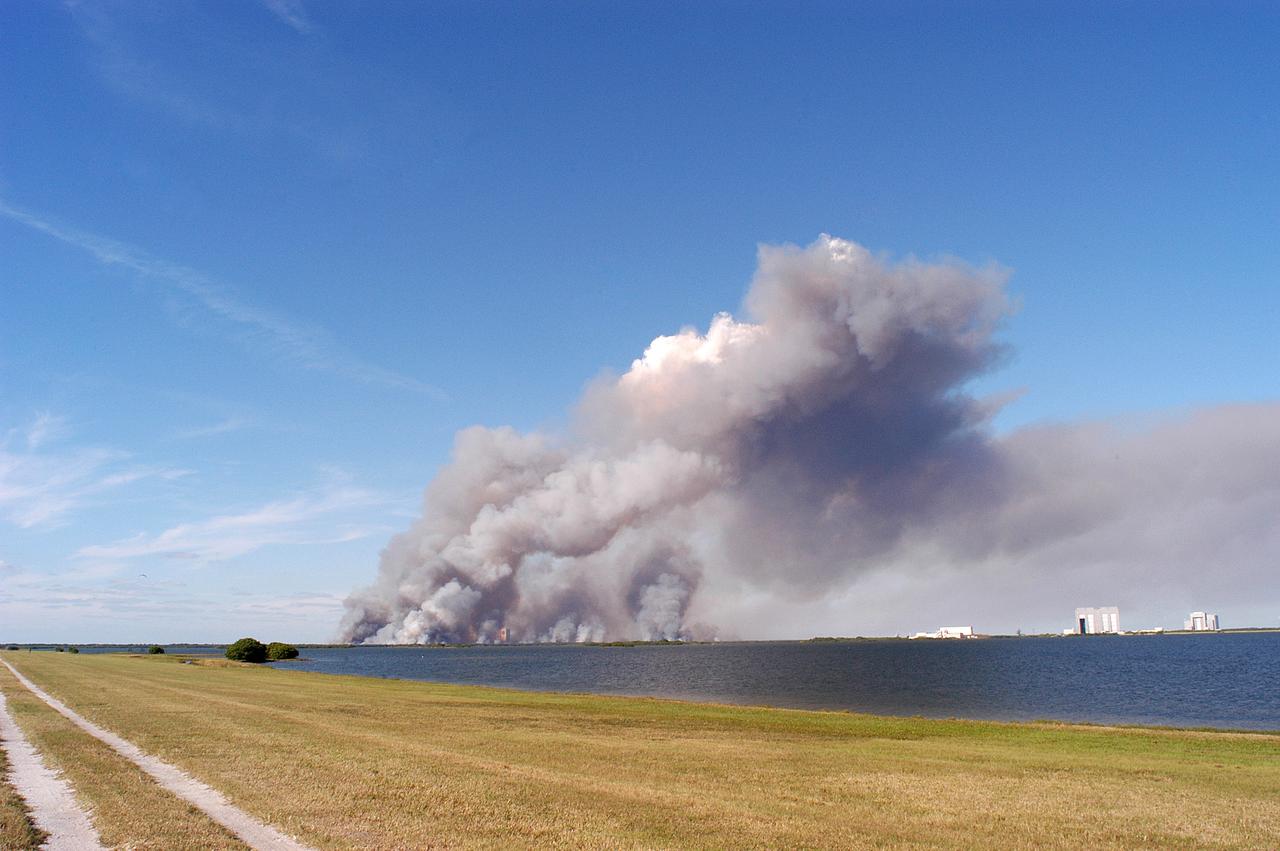

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A successful controlled burn near KSC’s Launch Complex 39 area creates clouds of smoke in a clear blue sky. The water seen is the Banana River.
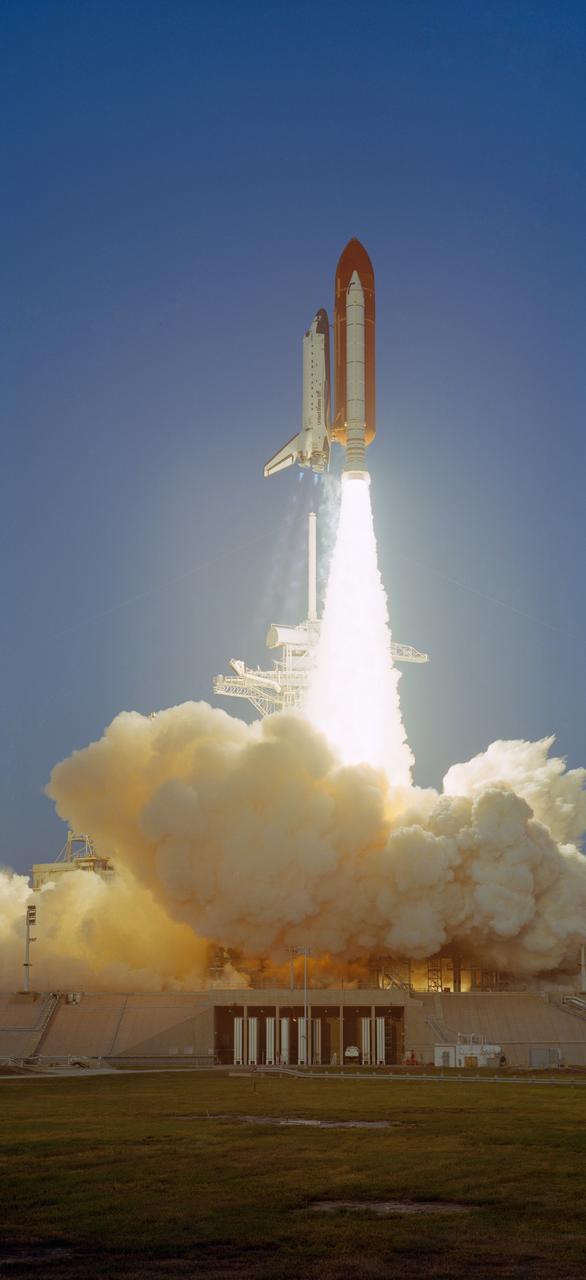

STS041-S-101 (6 Oct 1990) --- Discovery lifts off from Launch Complex 39 at the Kennedy Space Center to begin a four-day mission in space for its five-man crew. Onboard the spacecraft are Astronauts Richard N. Richards, Robert D. Cabana, William M. Shepherd, Bruce E. Melnick and Thomas D. Akers. Discovery lifted off at 7:47 a.m. EDT on Oct. 6, 1990. A few hours after this photo was made, the crewmembers released the Ulysses spacecraft on its way to a long-awaited mission.

S73-32568 (20 July 1973) --- Floodlights illuminate this nighttime view of the Skylab 3/Saturn 1B space vehicle at Pad B, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center, Florida, during prelaunch preparations. The reflection is the water adds to the scene. In addition to the Command/Service Module and its launch escapte system, the Skylab 3 space vehicle consists of the Saturn 1B first (S-1B) stage and the Saturn 1B second (S-IVB) stage. The crew for the scheduled 59-day Skylab 3 mission in Earth orbit will be astronauts Alan L. Bean, Owen K. Garriott and Jack R. Lousma. Skylab 3 was launched on July 28, 1973. Photo credit: NASA
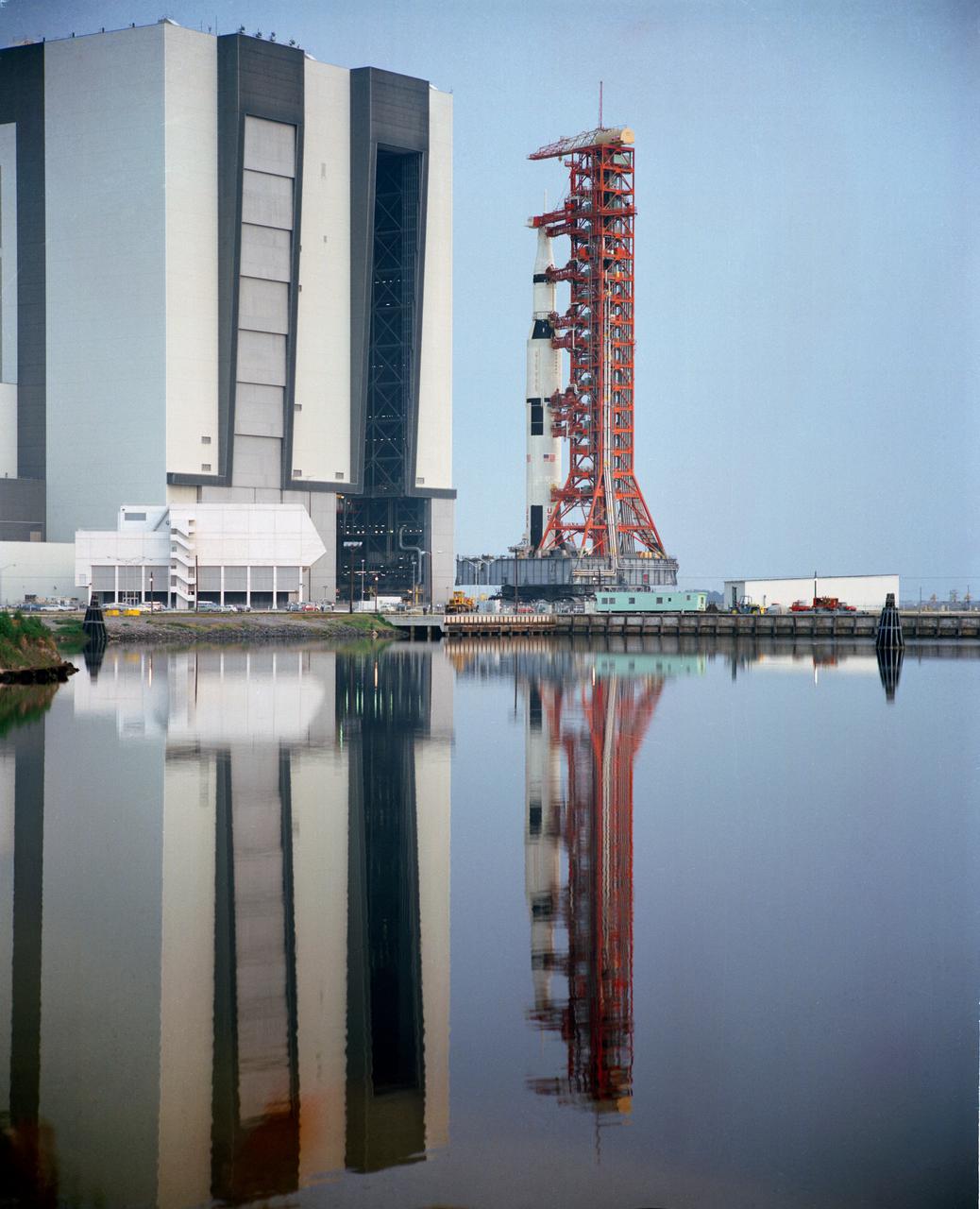

S71-33786 (11 May 1971) --- The 363-feet tall Apollo (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle which leaves the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. Apollo 15 is scheduled as the fourth manned lunar landing mission by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and is scheduled to lift off on July 26, 1971. The crew men will be astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While astronaut Scott and Irwin will descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
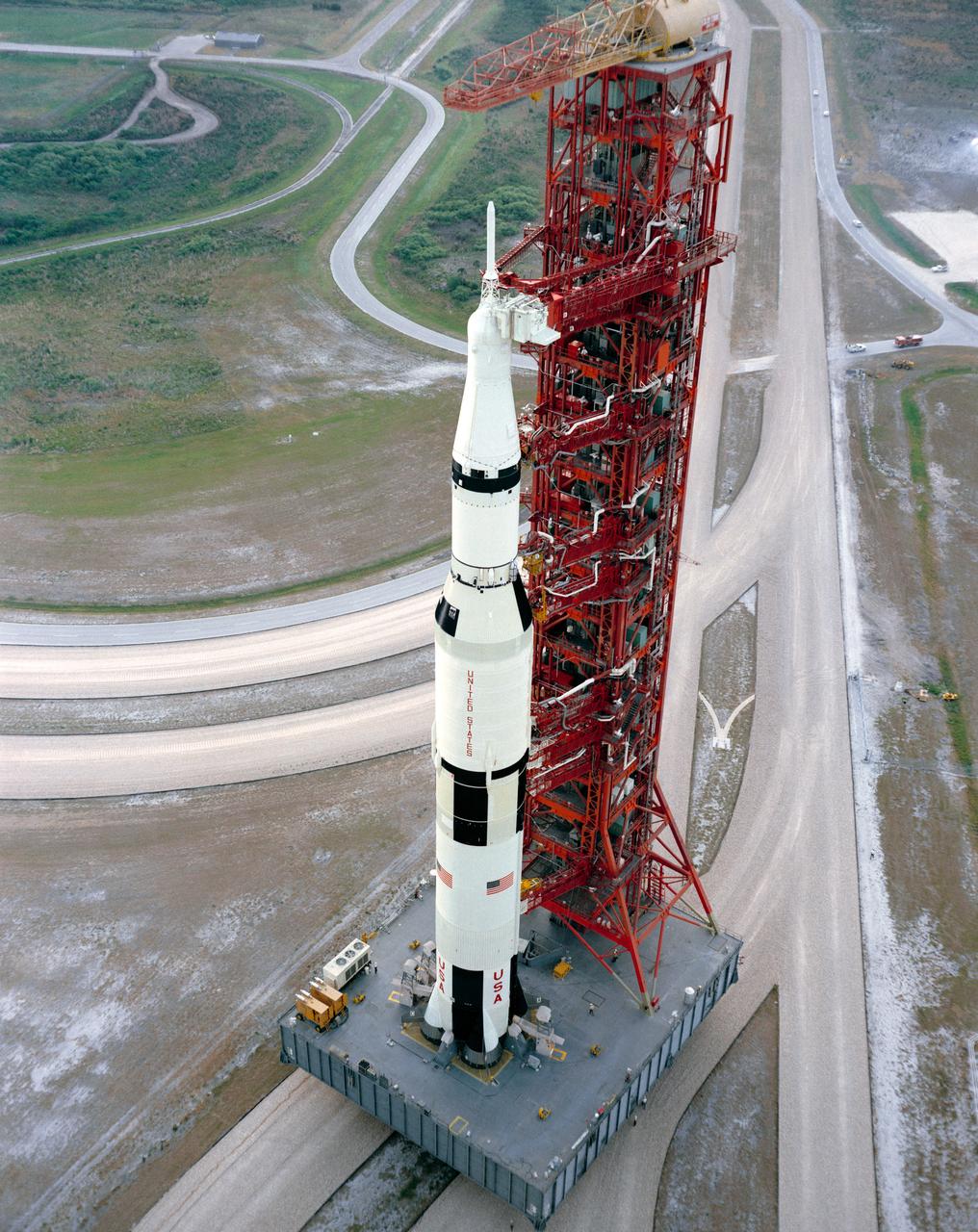

S71-33781 (11 May 1971) --- High angle view showing the Apollo 15 (Spacecraft 112/Lunar Module 10/Saturn 510) space vehicle on the way from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) to Pad A, Launch Complex 39, Kennedy Space Center (KSC). The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. Apollo 15 is scheduled as the fourth manned lunar landing mission by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The crew men will be astronauts David R. Scott, commander; Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descend in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Worden will remain with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

S72-19794 (13 Dec. 1971) --- A ground-level view showing the tall Apollo 16 (Spacecraft 113/Lunar Module 11/Saturn 511) space vehicle at the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) Launch Complex 39 being moved from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) toward Pad A. The Saturn V stack and its mobile launch tower are atop a huge crawler-transporter. The prime crew men of the scheduled Apollo 16 lunar landing mission are astronauts John W. Young, Apollo 16 lunar landing mission are astronauts John W. Young, commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot.
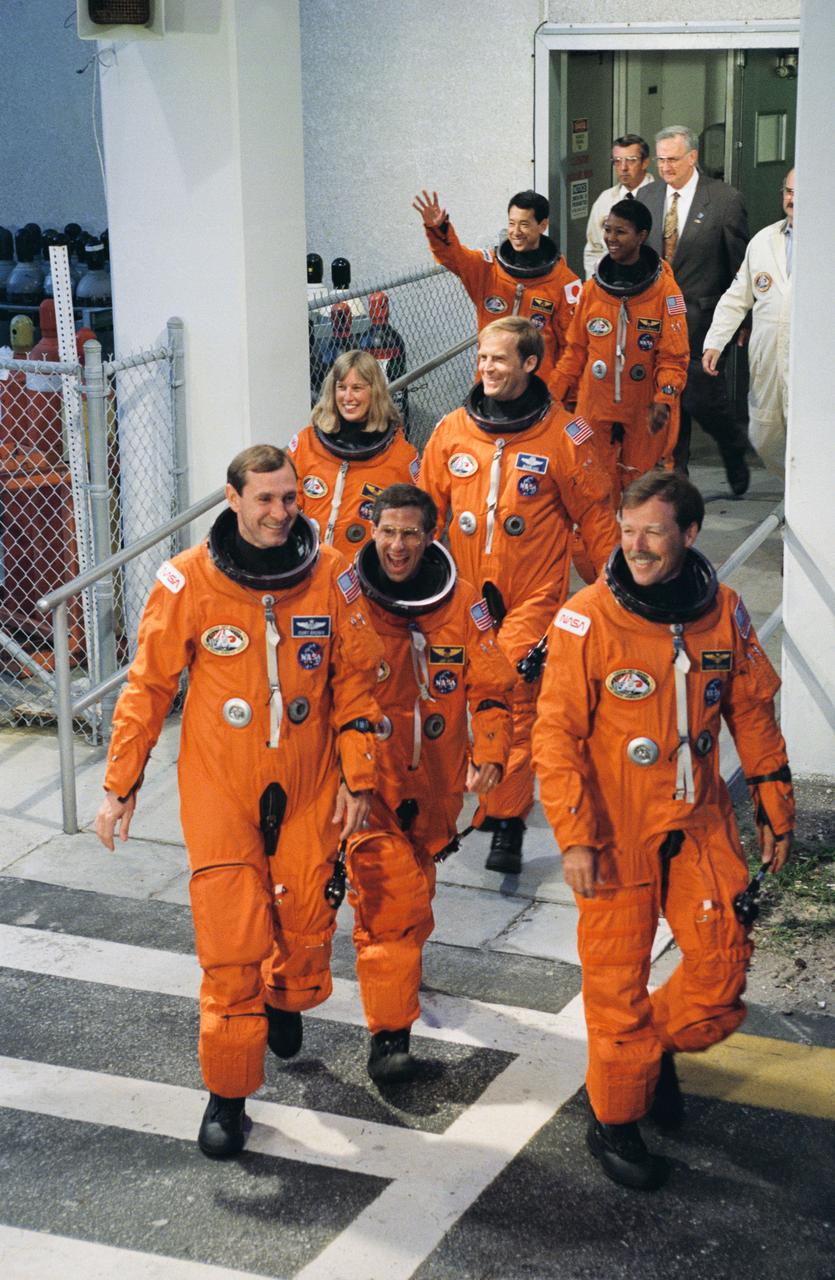

STS047-S-038 (12 Sept 1992) --- The seven crewmembers who will be aboard for Endeavour's second trip into space leave the Operations and Checkout Building to board a van headed for Launch Complex 39. This mission will be devoted to support of the Spacelab-J mission, a joint effort between Japan and the United States. Launch occurred at 10:23:00:0680 a.m. (EDT), September 12, 1992. Onboard were astronauts Robert L. Gibson, mission commander; Curtis L. Brown Jr., pilot; Mark C. Lee, payload commander; and Jerome (Jay) Apt, Mae C. Jemison and N. Jan Davis, mission specialists; along with payload specialist Mamoru Mohri, representing the National Space Development Agency (NASDA) of Japan.
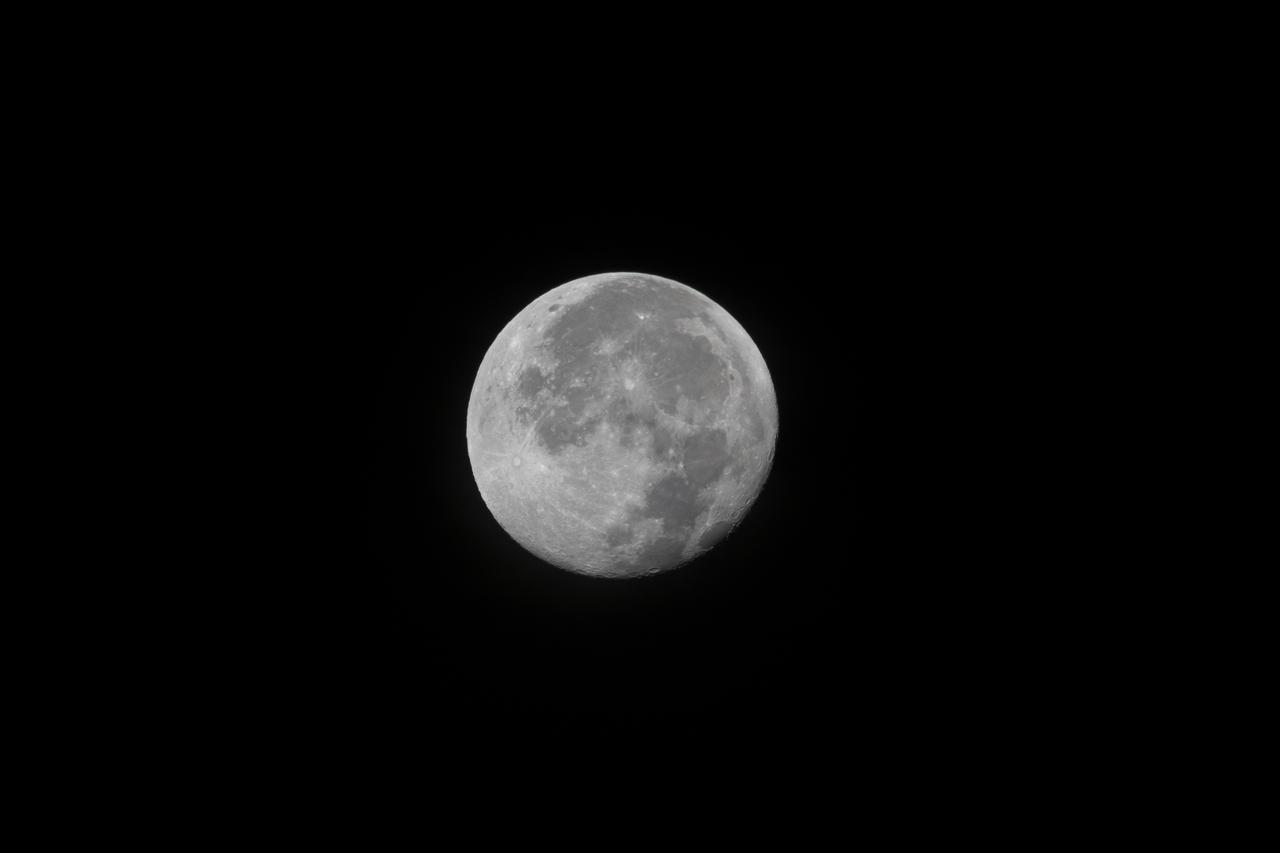

A brilliant full moon rises over the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A brilliant full moon rises over the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Launch Complex 39 Construction: Launch Complex 39 LC-39 was originally designed and built to launch American astronauts toward the moon. The complex stretches inland from the Atlantic Ocean across four miles of what, until 1963, was a land of intermittent marshes and sandy scrub growth. In less than four years, starting with 1963 and ending with 1966, it was transformed into an operational spaceport embodying a mobile concept: rockets and spacecraft are erected in one area and transported to a separate location for launch. A total of 153 vehicles have been launched from LC-39. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
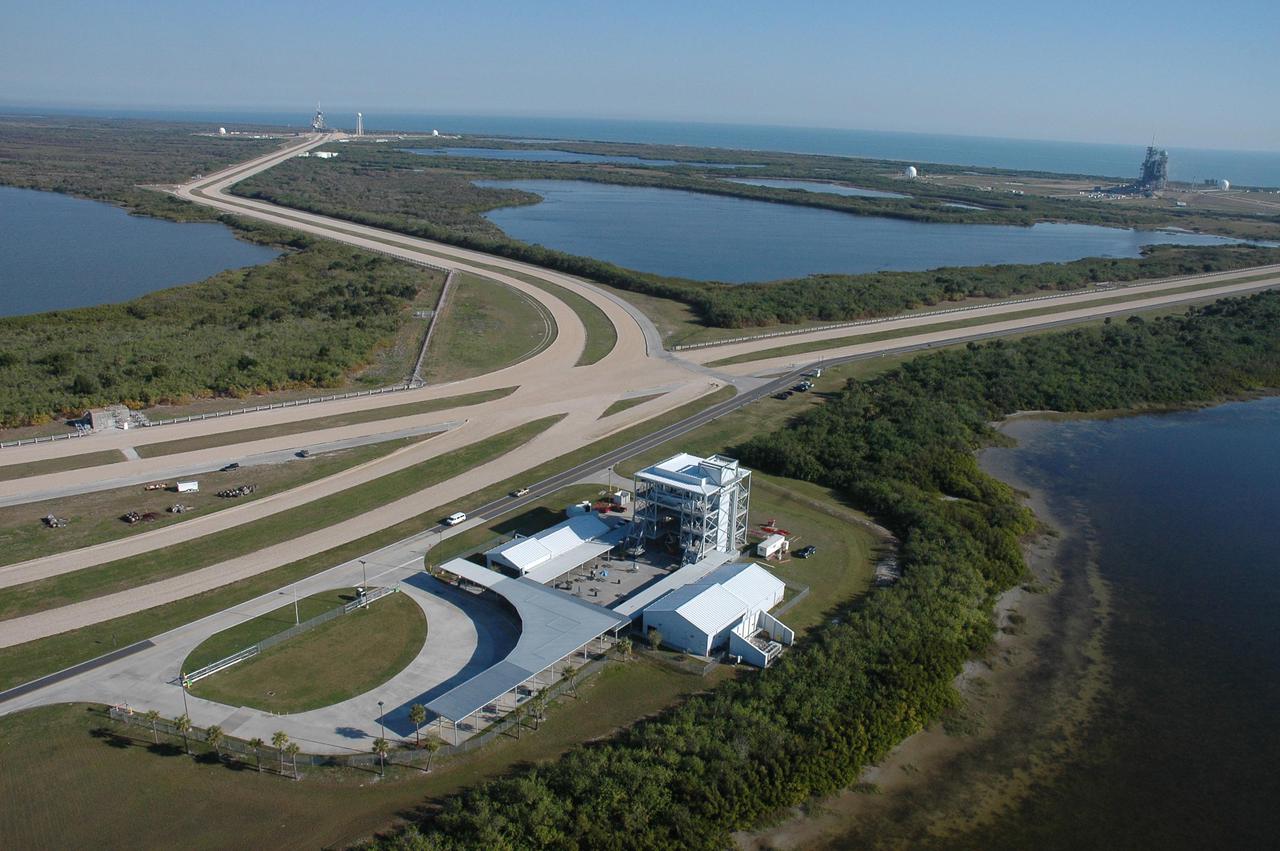

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This aerial view on NASA's Kennedy Space Center shows the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry in the foreground, the crawlerways leading to the launch pads, and space shuttle Launch Complex 39 Pad A (left) and Pad B in the background, silhouetted by the Atlantic Ocean. Photo credit: Cory Huston
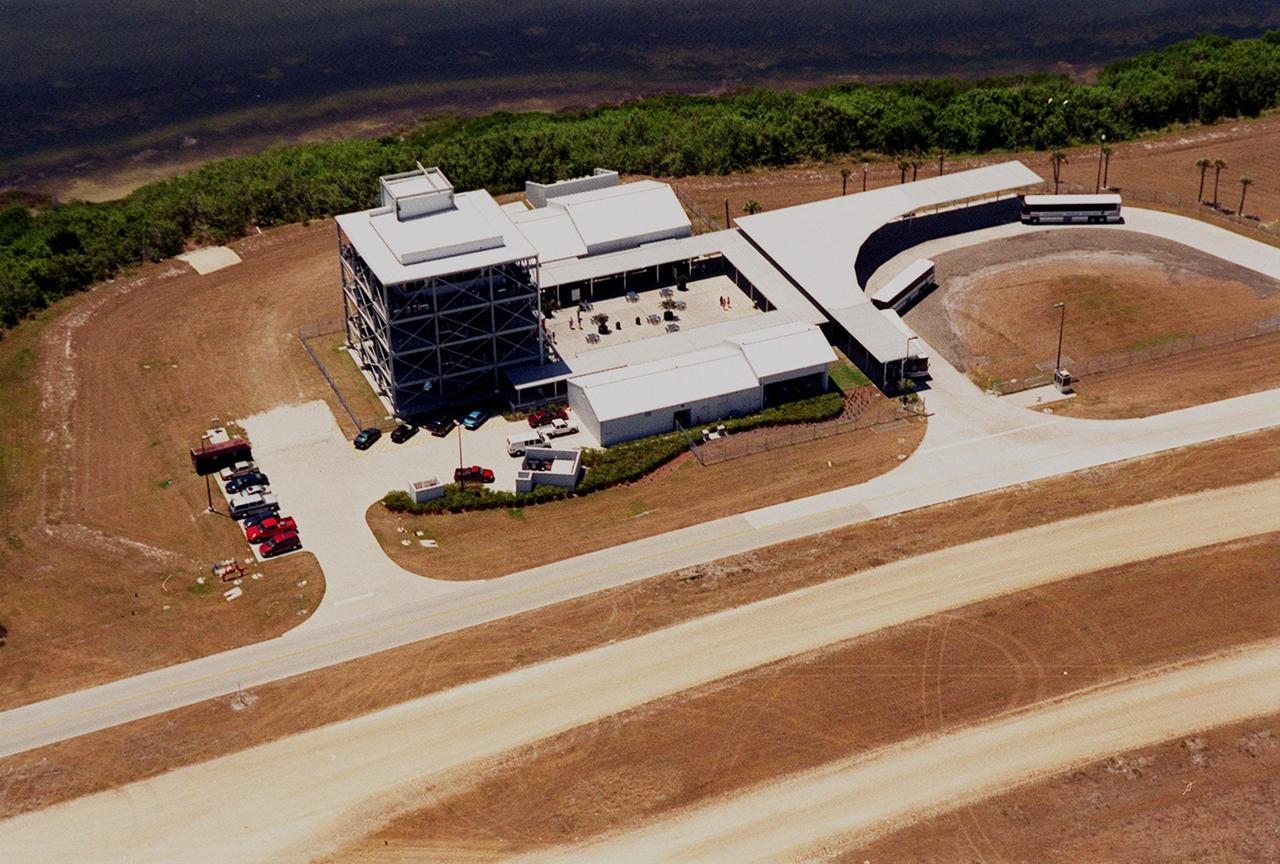

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (foreground) which is used to transport Space Shuttles to the pads
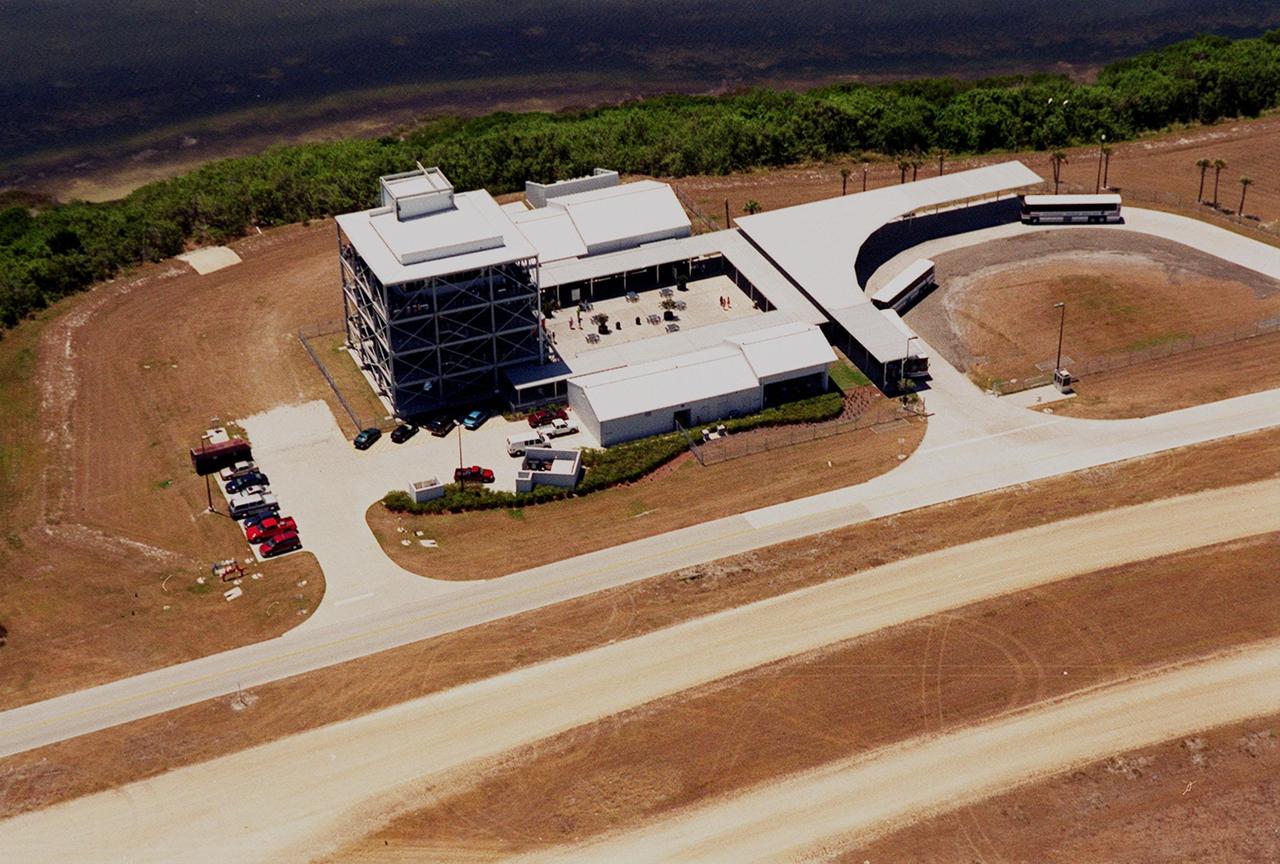

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (foreground) which is used to transport Space Shuttles to the pads

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
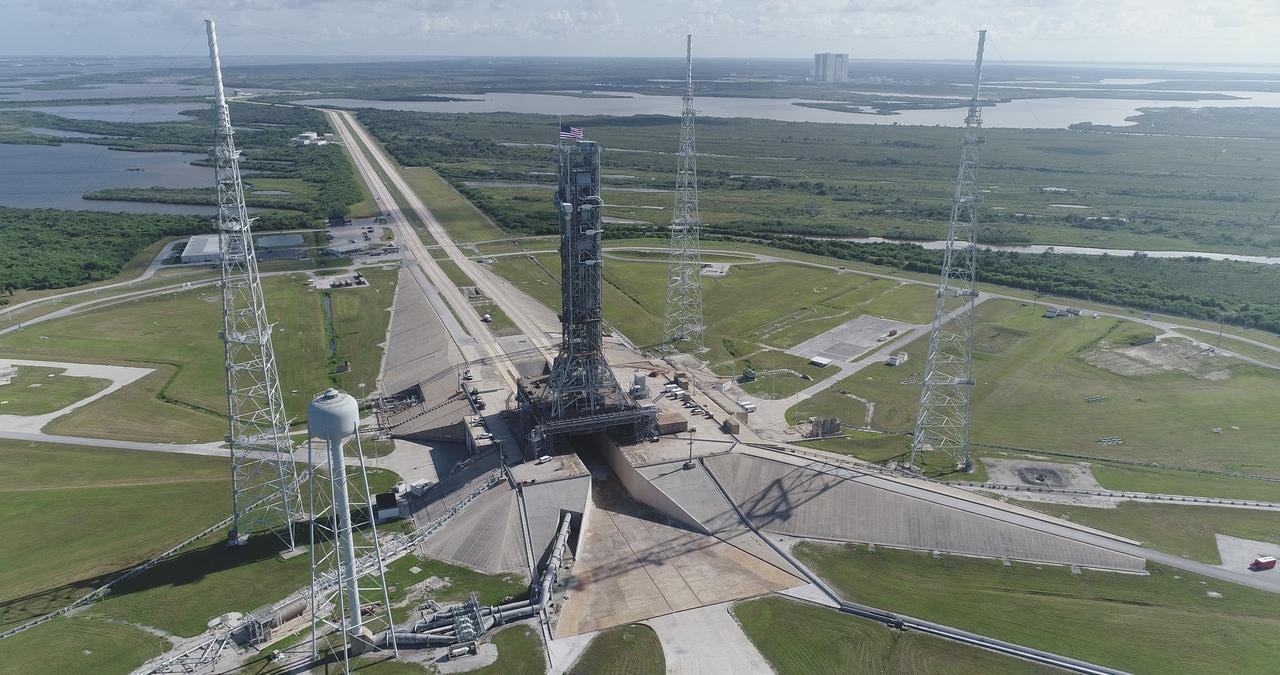

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
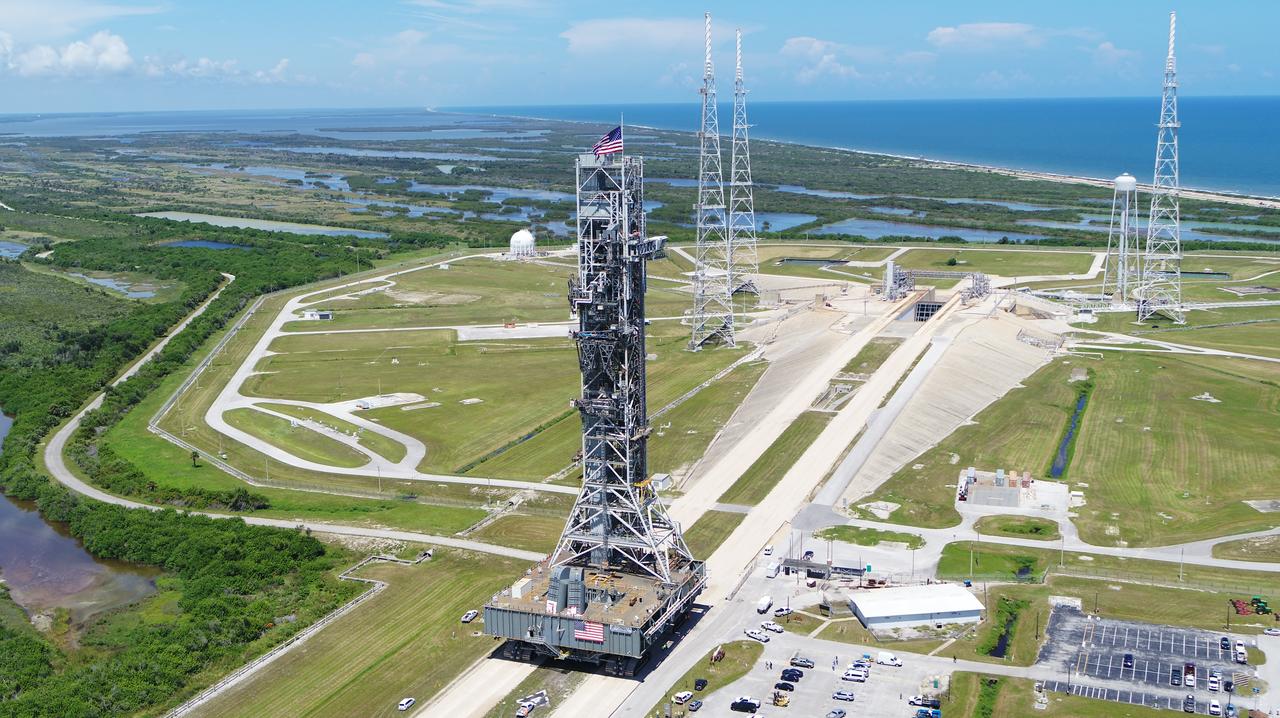

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
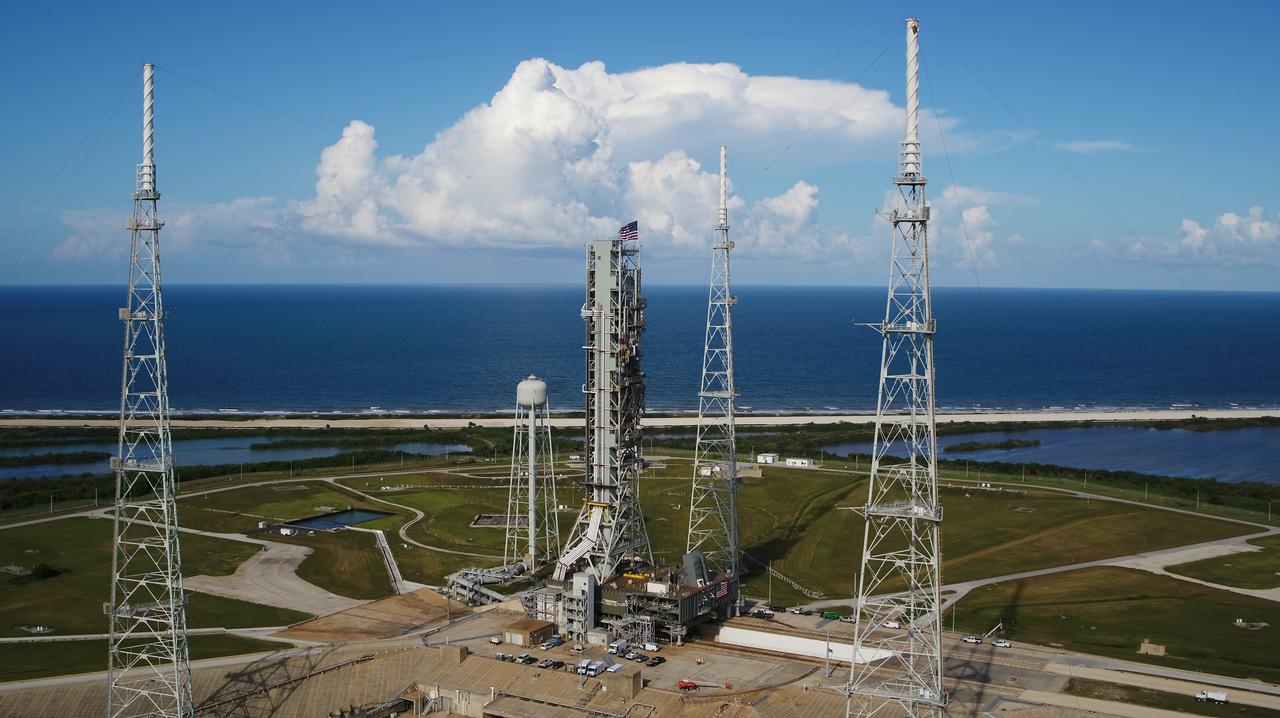

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
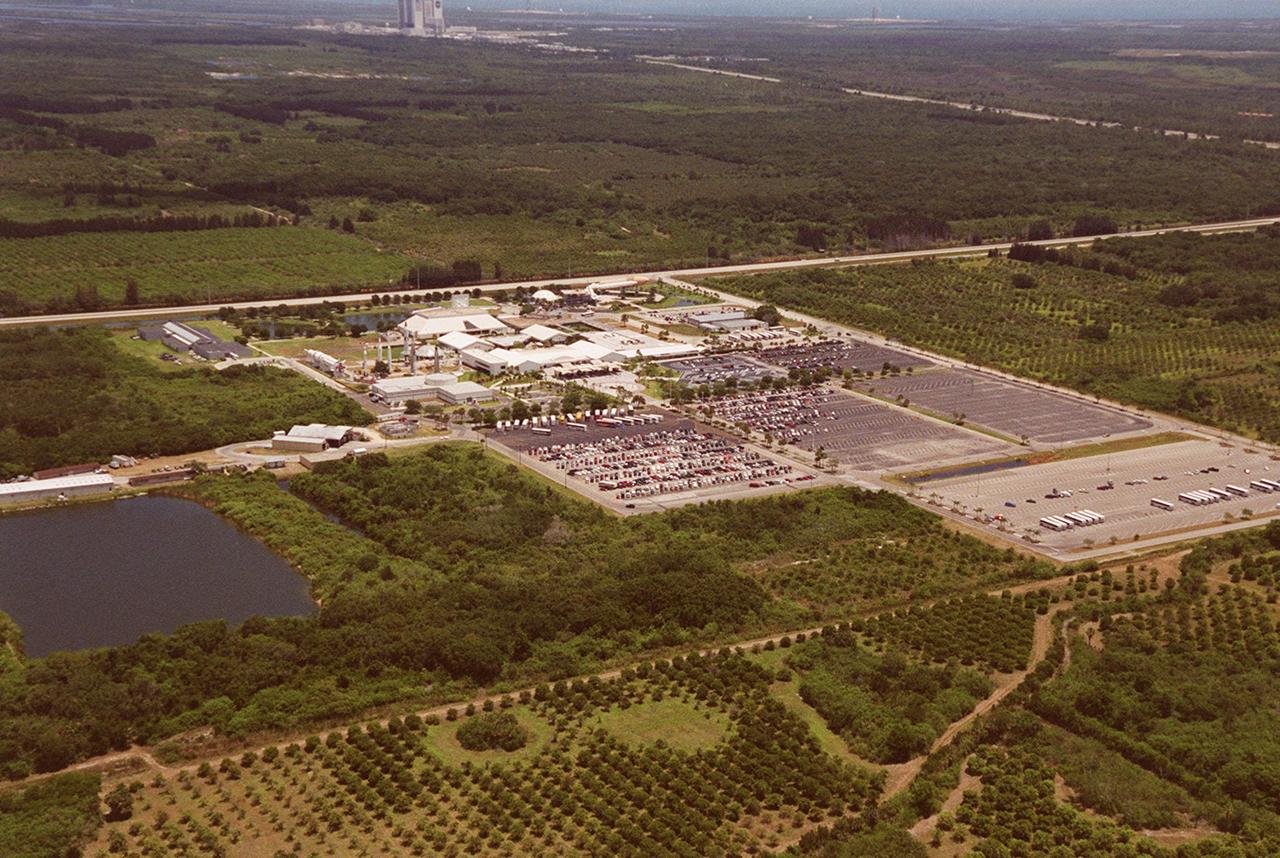

This aerial view is of Kennedy Space Center's Visitor Complex. The Vehicle Assembly Building, located in the Launch Complex 39 area, can be seen in the background
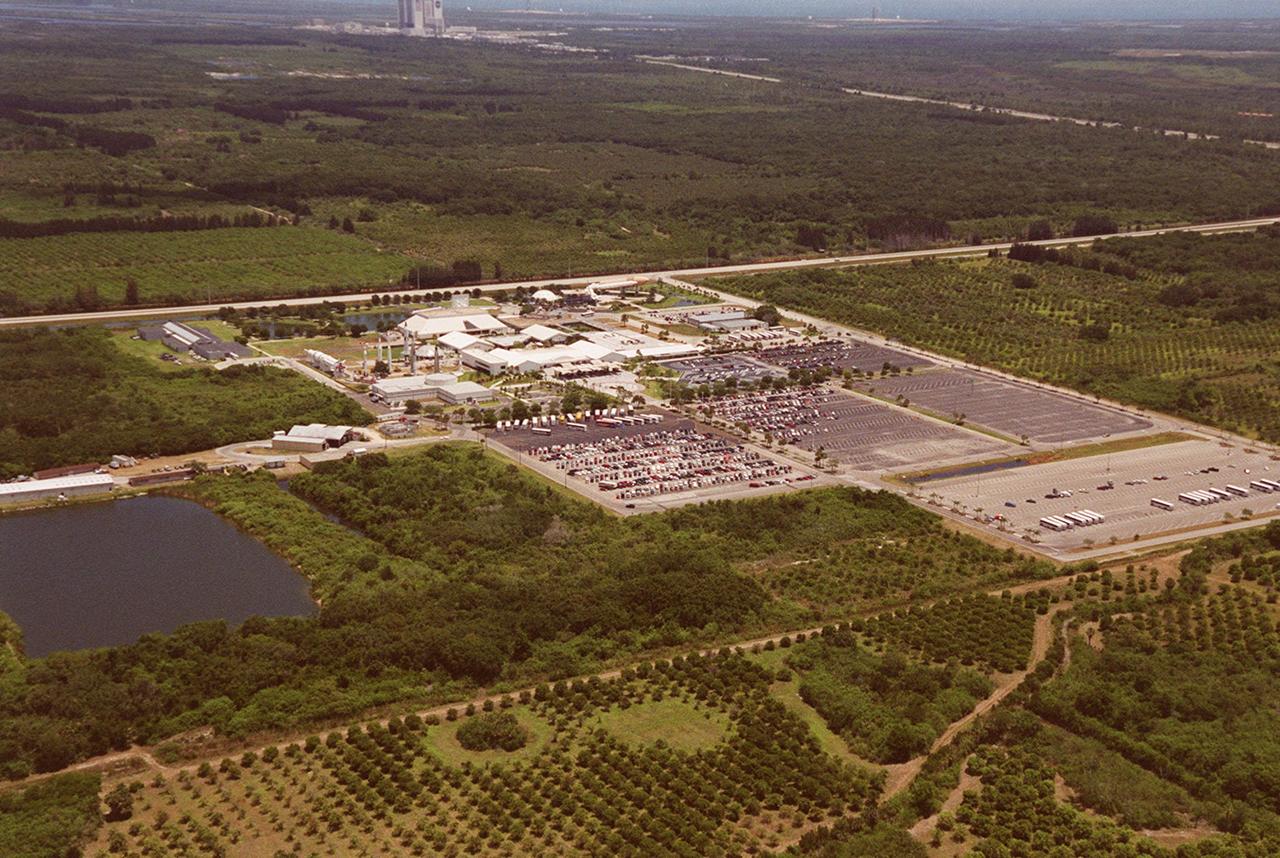

This aerial view is of Kennedy Space Center's Visitor Complex. The Vehicle Assembly Building, located in the Launch Complex 39 area, can be seen in the background
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- STS-6 second Flight Readiness Firing test, Launch Complex 39. Photo credit: NASA
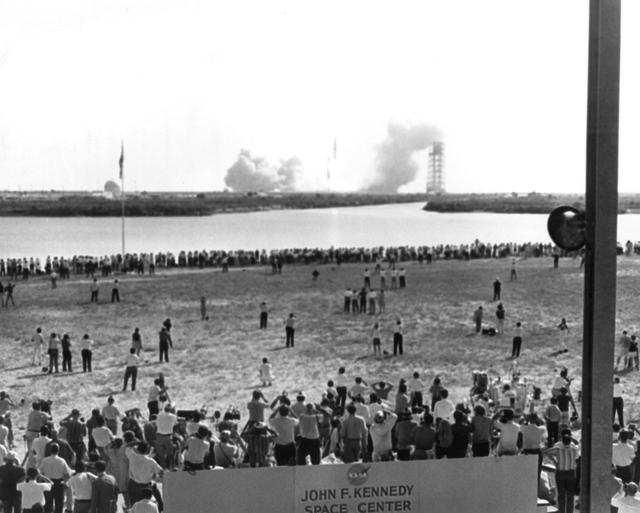

View of Complex 39 Press Site during Apollo 11 launch, July 16, 1969
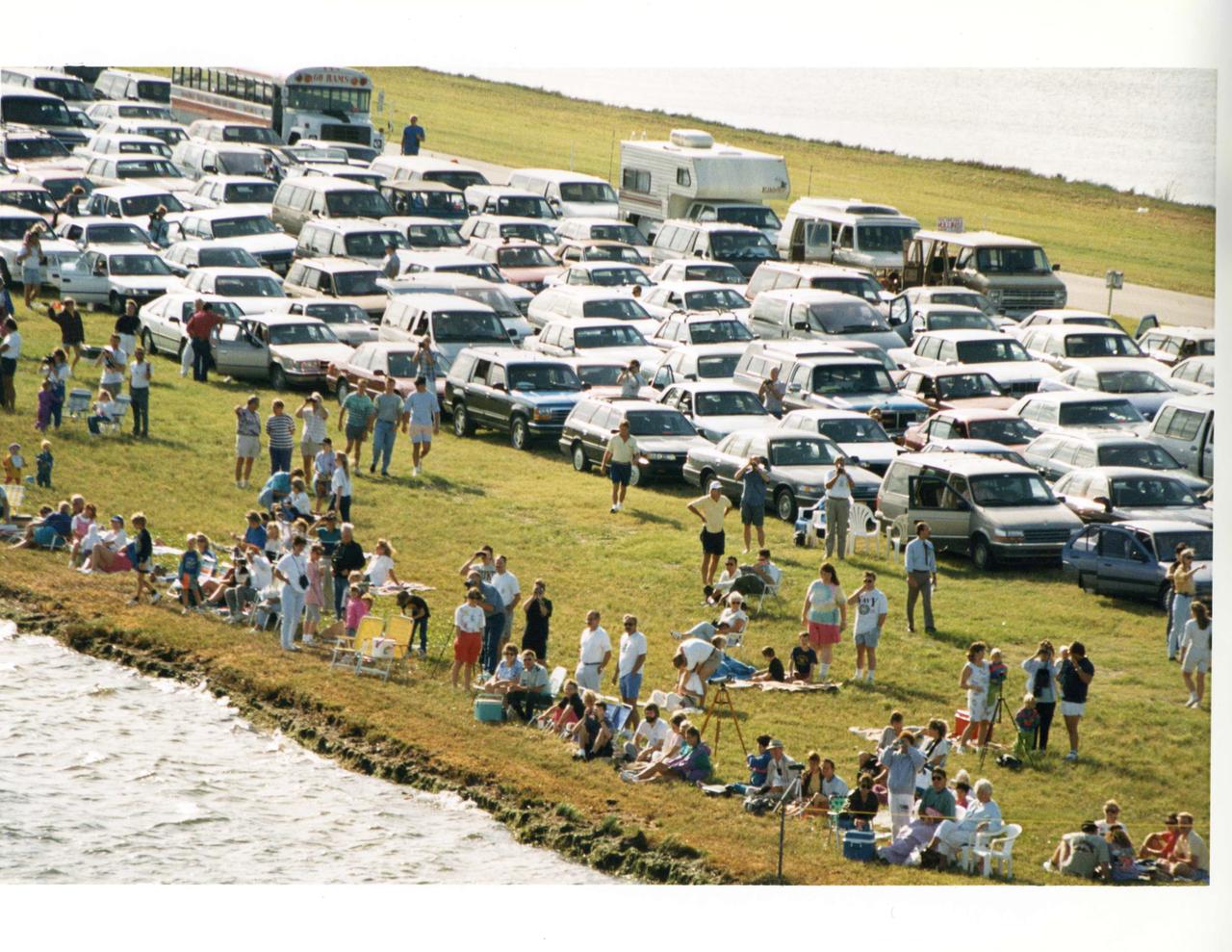

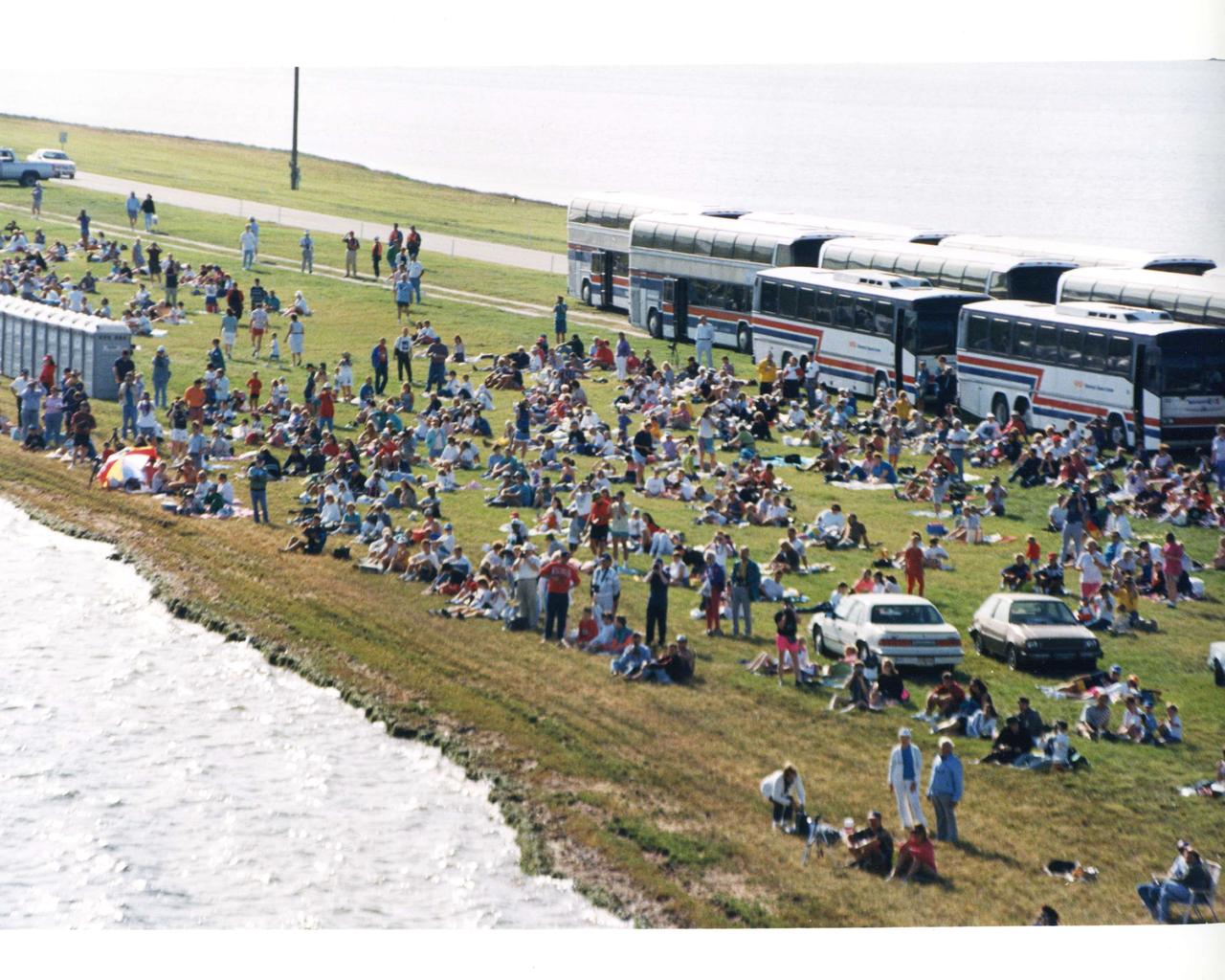
Aerial of the NASA Causeway East showing the viewing area set up for space shuttle launch viewers with car passes. Launch Complex 39 is to the north.
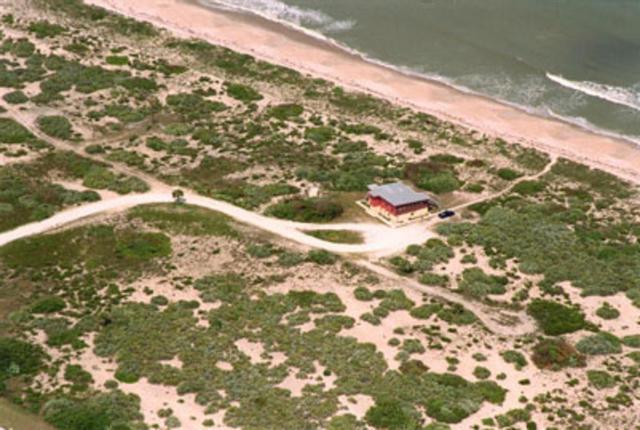

An aerial view focuses on the Beach House, a site for meetings on the Center. It sits south of Launch Complex 39 and Complex 41, near Phillips Parkway, which runs parallel to the Atlantic Ocean.
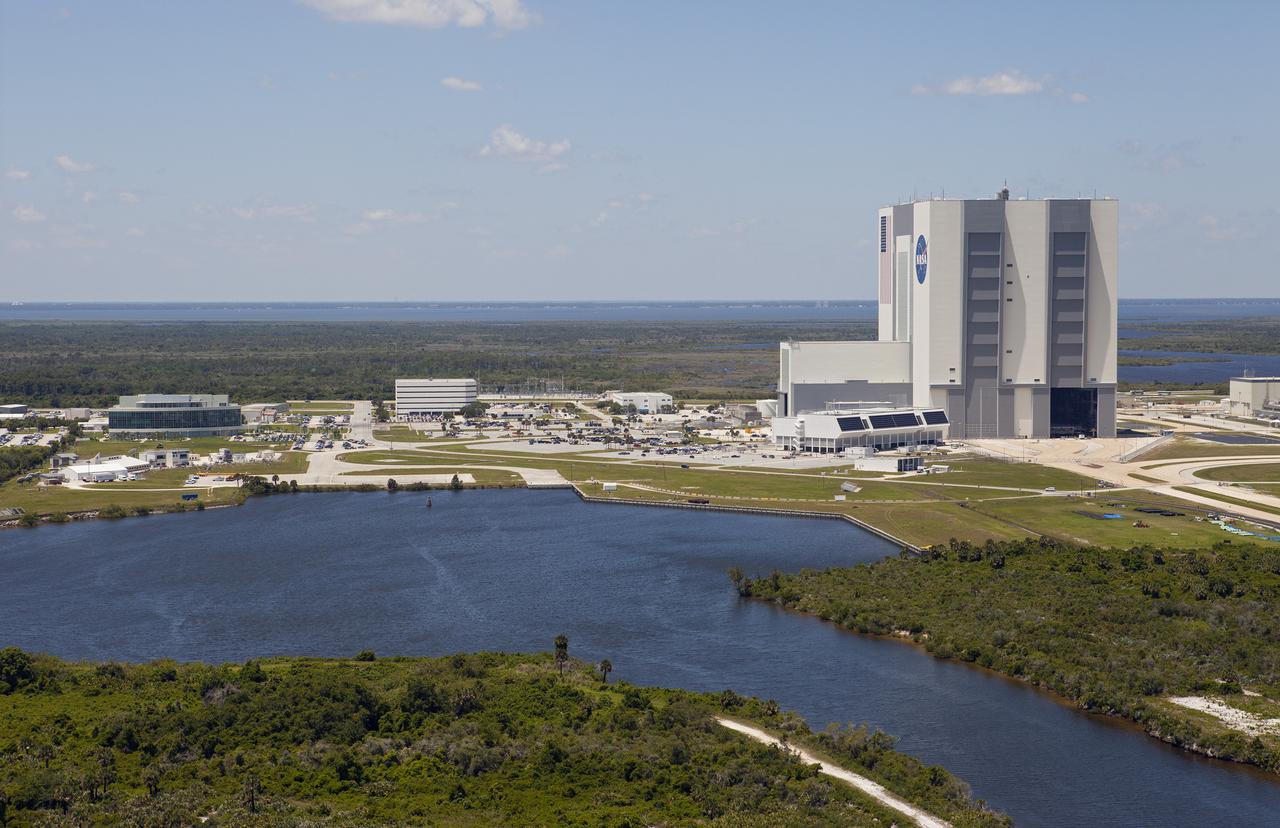

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An up close aerial view of the Vehicle Assembly Building and other facilities in the Launch Complex 39 area at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In front of the VAB is the Launch Control Center. To the left are the Operations Support Buildings I and II. Upgrades are underway at Pad B and other facilities in the Launch Complex 39 area. The Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, Program office at Kennedy is leading the center’s transformation from a historically government-only launch complex to a spaceport that can safely handle a variety of rockets and spacecraft, including NASA’s Space Launch System. For more information about GSDO, visit: http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Kim Shiflett
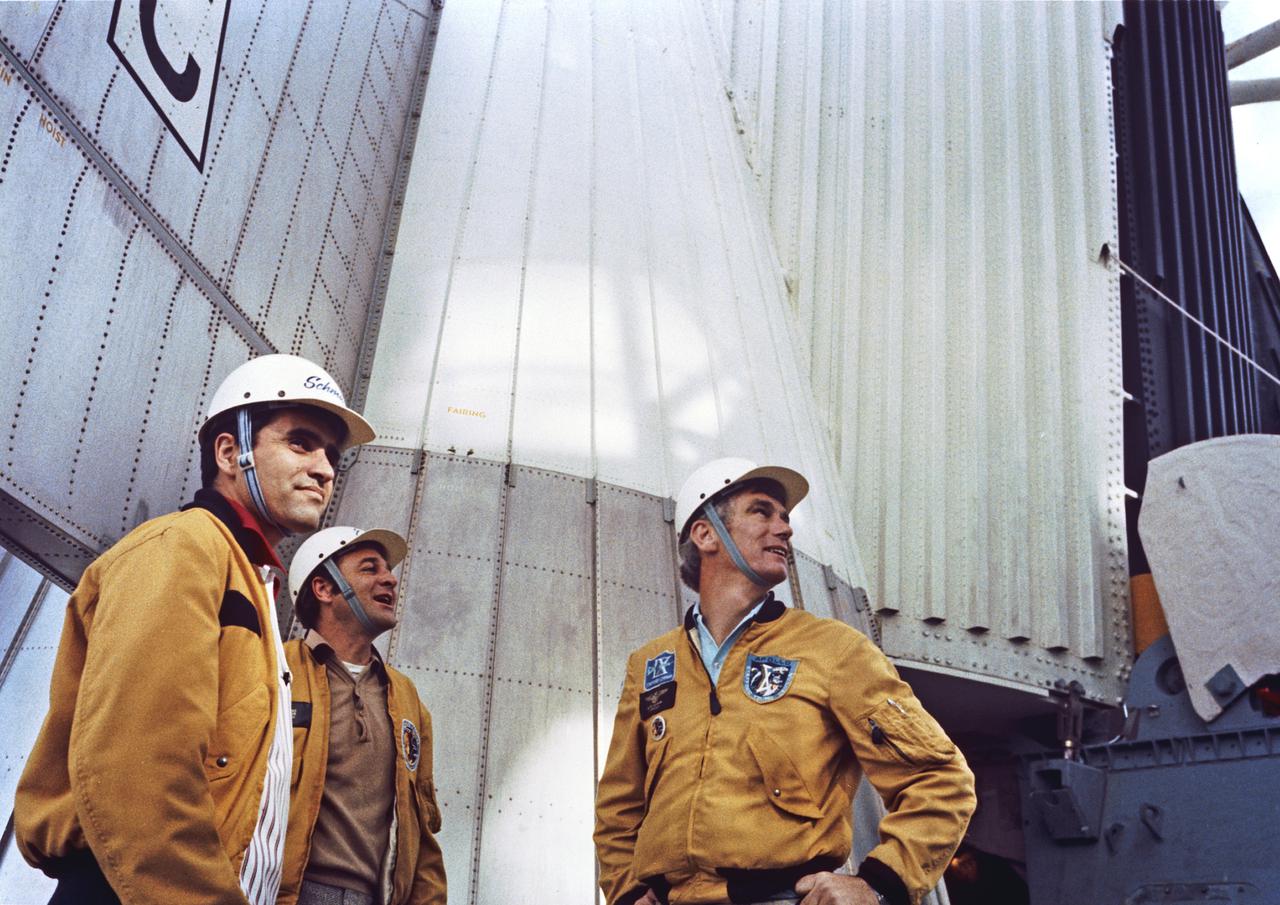

The Apollo 17 prime crew pauses on the access arm leading to their spacecraft, mated to the Saturn V launch vehicle at Complex 39, during Emergency Egress Test.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Launch Complex 39 facilities are now visible through the openings left by missing panels from the exterior walls of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB)following Hurricane Frances. The storm's path over Florida took it through Cape Canaveral and KSC property during Labor Day weekend. Located in the heart of Launch Complex 39, the VAB is used for the integration and stacking of Space Shuttle elements and for the checkout and storage of Space Shuttle External Tanks.
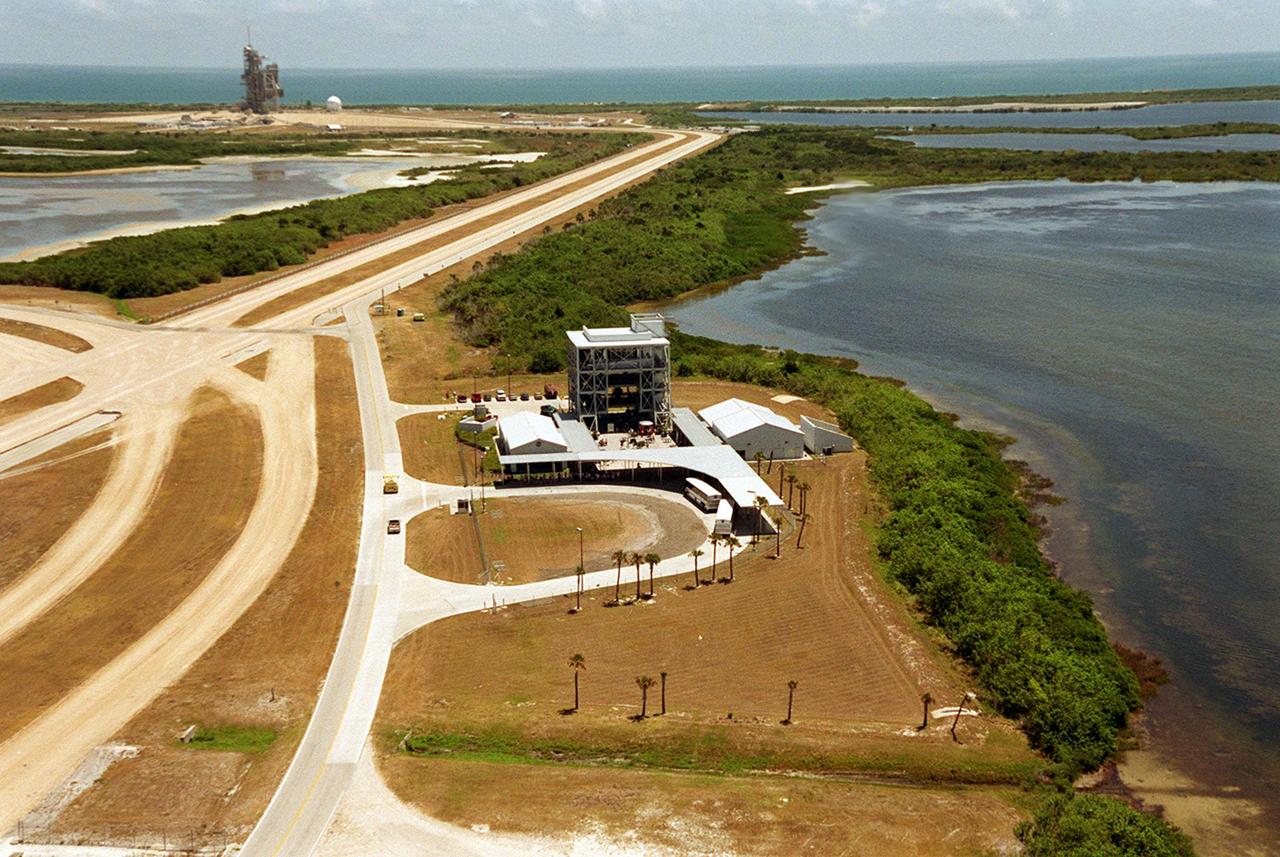

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (left) which is used to transport Space Shuttles from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pads. Pad A can be seen in the background.
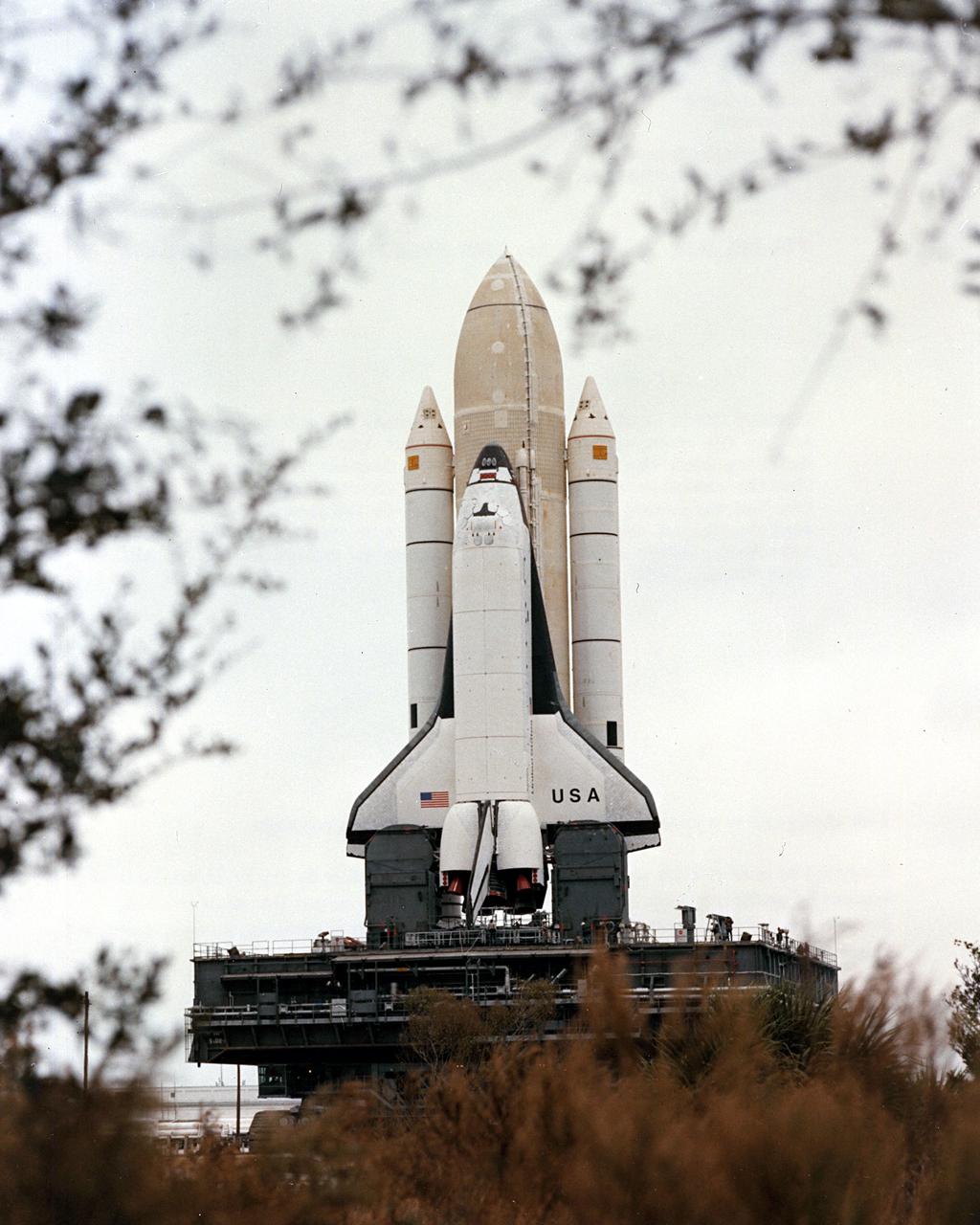

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-1 stands framed in vegetation lining the superhighay-wide crawlerway linking the Vehicle Assembly Building with the twin pads of Launch Complex 39. The first Space Shuttle assembly emerged from the VAB shortly after 8 a.m. today for the 3.5-mile journey to Complex 39's Pad A. The Shuttle was on the hardstand at Pad A approximately seven and a half hours after rollout began. Launch is scheduled for no eariler than March 1981.
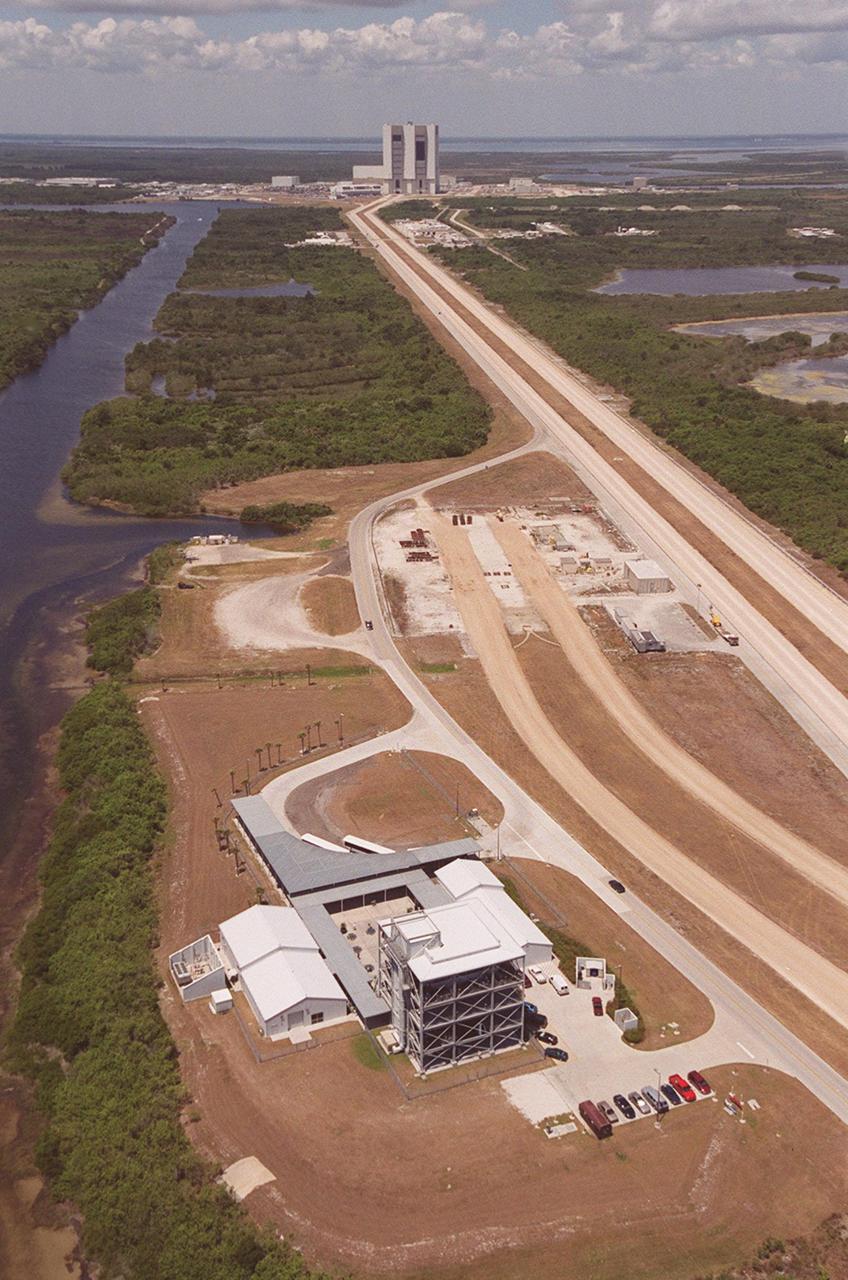

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (right) which is used to transport Space Shuttles from the Vehicle Assembly Building (background) to the pads
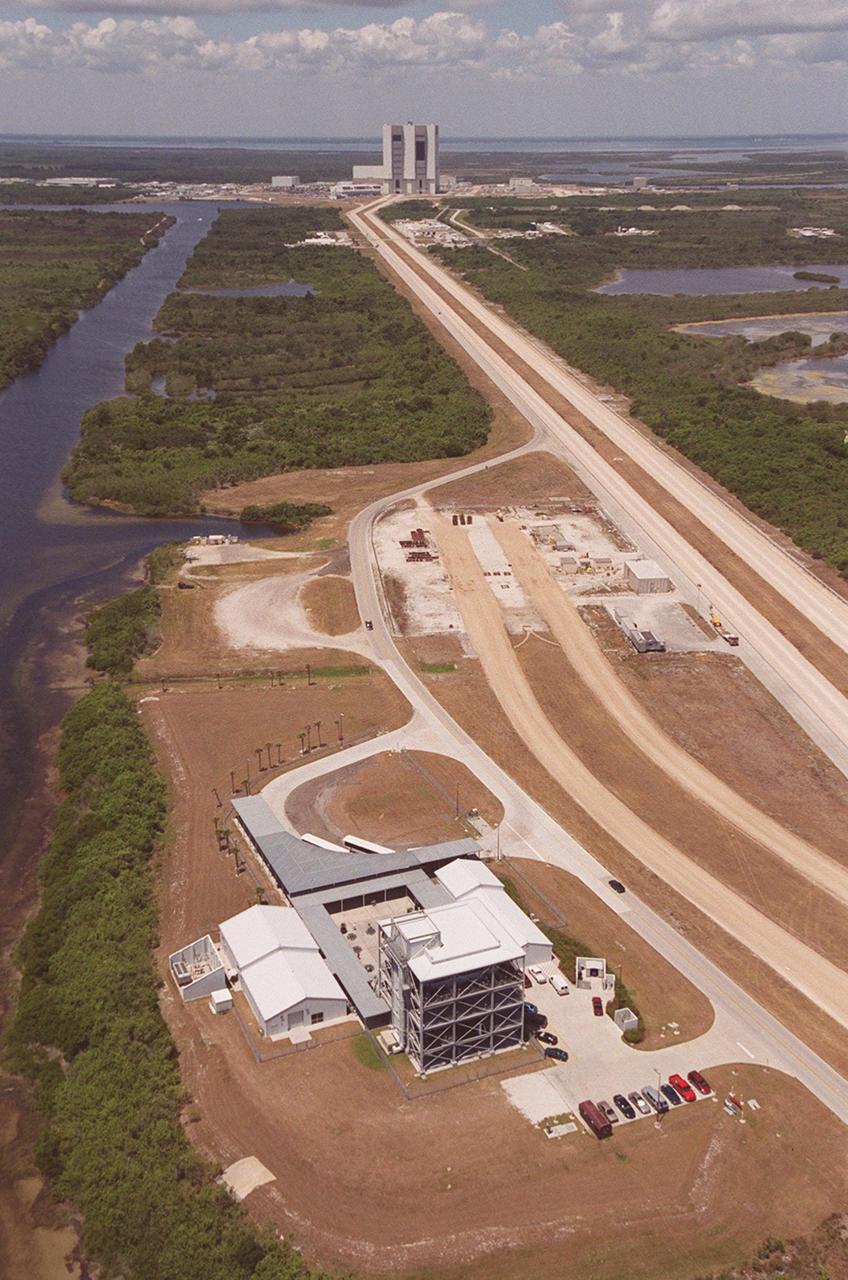

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (right) which is used to transport Space Shuttles from the Vehicle Assembly Building (background) to the pads

This aerial view is of a tour stop on the KSC bus tour, the Launch Complex 39 Observation Gantry. This stop allows visitors to view and photograph Pads A and B in Launch Complex 39 from an elevated vantage point. The roadway leading to the tour stop runs next to the crawlerway (left) which is used to transport Space Shuttles from the Vehicle Assembly Building to the pads. Pad A can be seen in the background.

A sunrise panoramic view of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and surrounding waterways at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in VAB High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
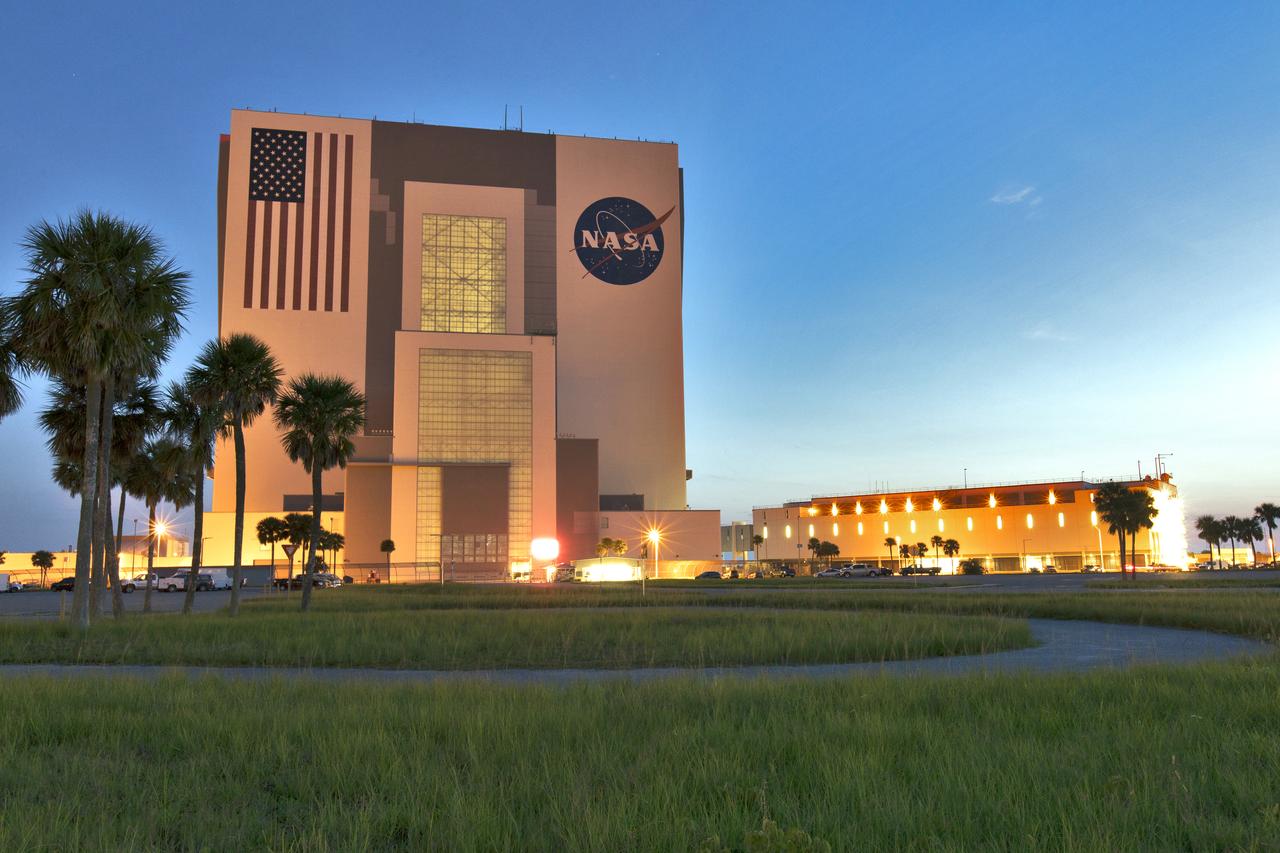

A sunrise panoramic view of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of work platforms have been installed in High Bay 3 of the VAB. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

A dragonfly perches on a tree branch with the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) in view in the background at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in VAB High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
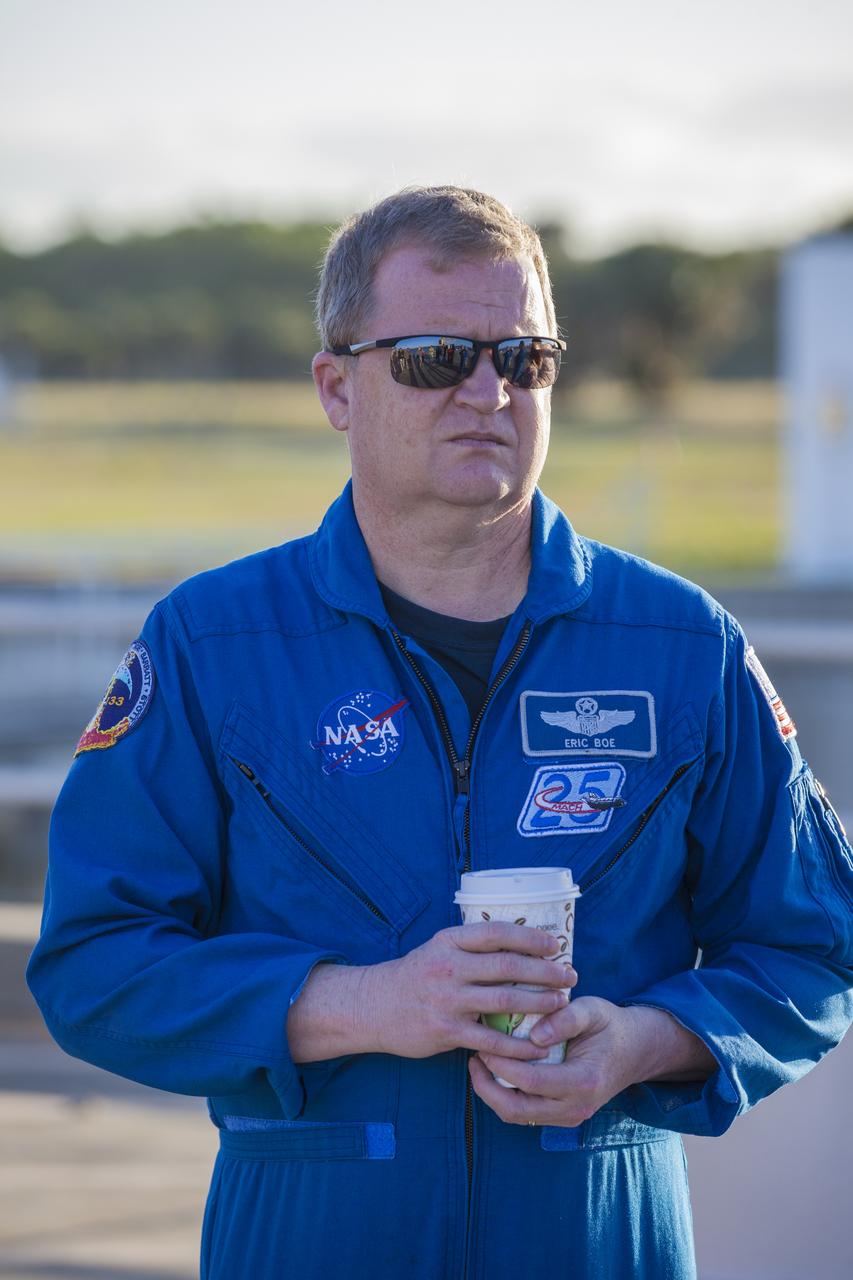

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Naval Ordnance Test Unit basin in Florida, Commercial Crew Program astronaut Eric Boe observes operation of the SpaceX recovery ship. During a recent visit to the Kennedy Space Center, the crew members were given an up-close look at preparations for the SpaceX Crew Dragon flight tests.

A brilliant blue sky forms the backdrop for a fish-eye panoramic view of the south side of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in VAB High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) and deep space missions. At left is the Launch Control Center, where Firing Room 1 has been upgraded to support EM-1.
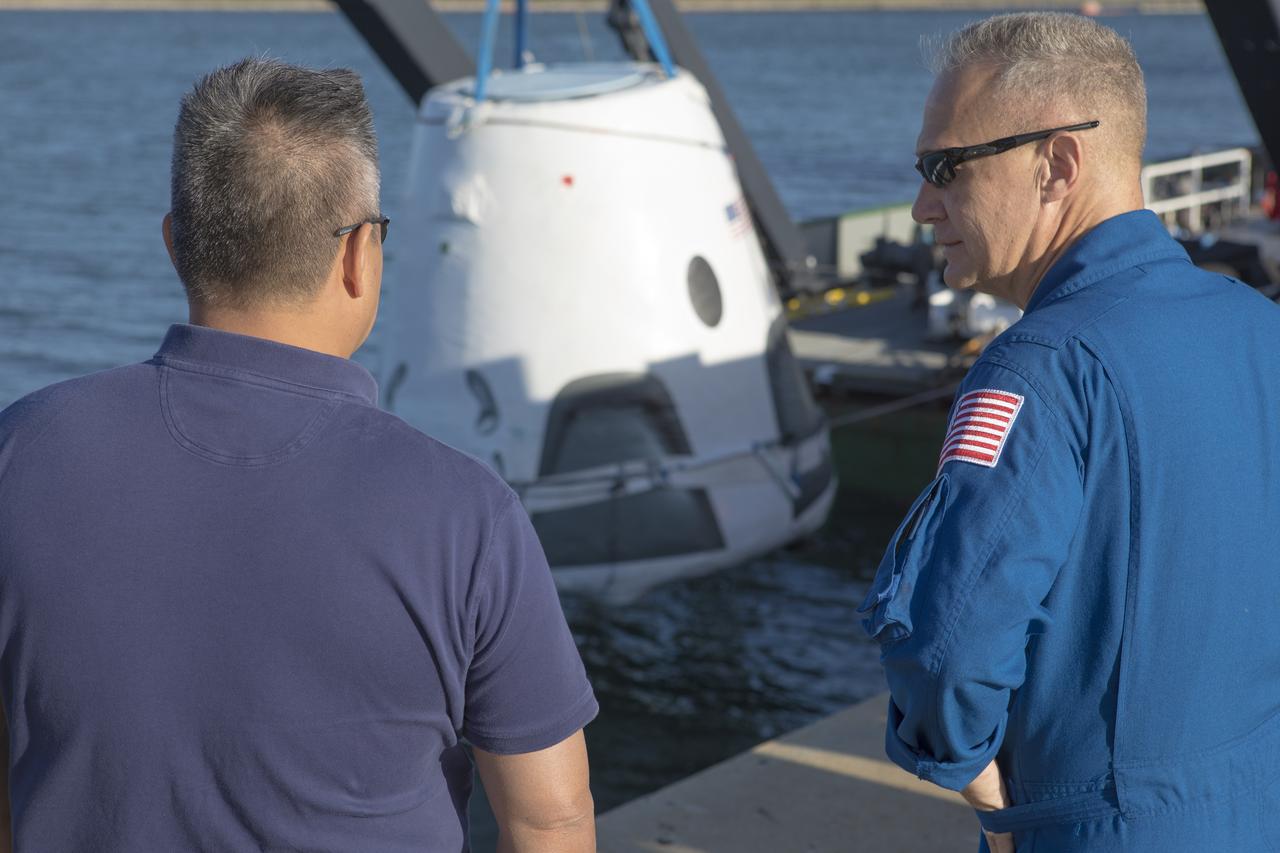

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Naval Ordnance Test Unit basin in Florida, Commercial Crew Program astronaut Doug Hurley, right, observes operation of the SpaceX recovery ship. During a recent visit to the Kennedy Space Center, the crew members were given an up-close look at preparations for the SpaceX Crew Dragon flight tests.

A sunrise time-lapse panoramic view of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of work platforms have been installed in High Bay 3 of the VAB. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

A brilliant blue sky forms the background for a panoramic view of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) and Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Ten levels of work platforms have been installed in High Bay 3 of the VAB. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
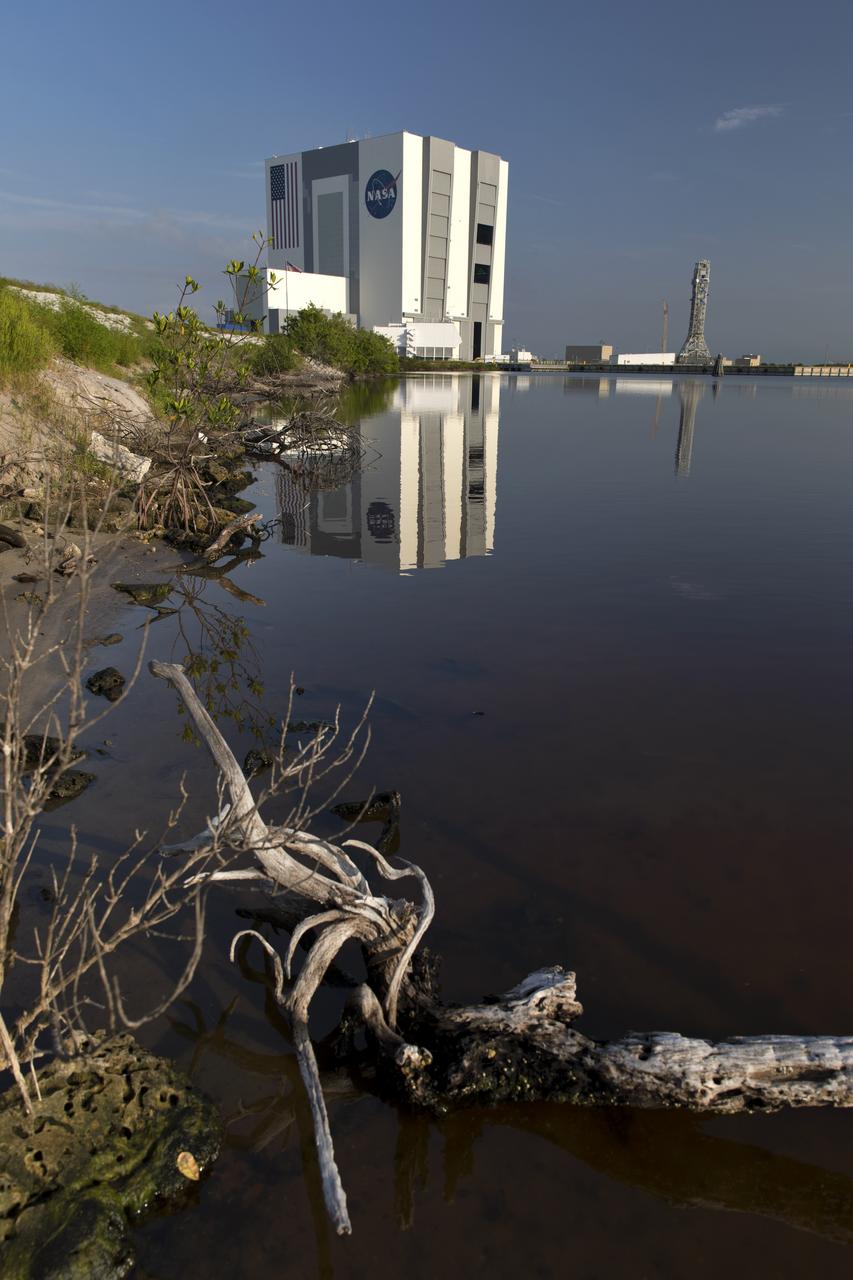

The iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) casts a reflection in a surrounding waterway at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view are the south and east sides of the building. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in VAB High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
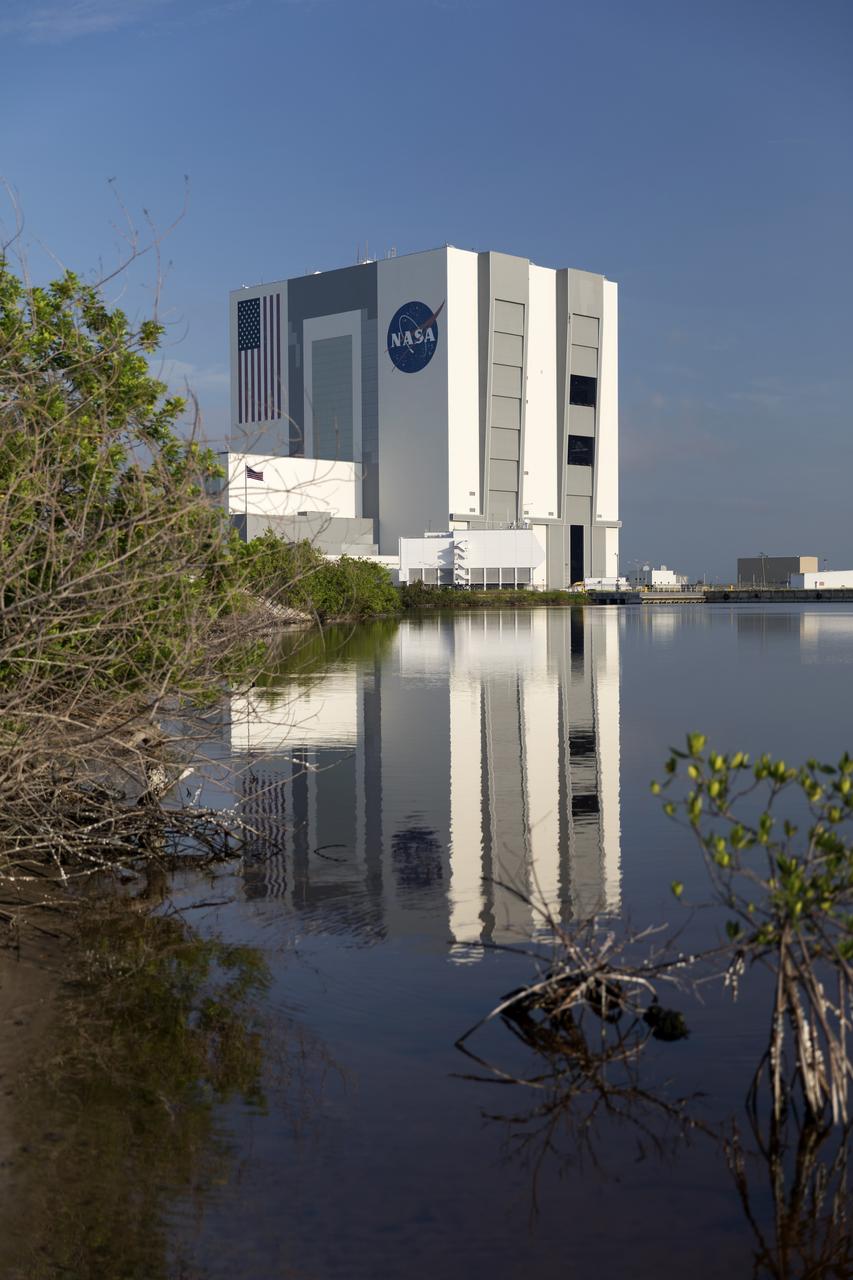

A brilliant blue sky forms the backdrop for a view of the south and east sides of the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades. The building casts a reflection in a surrounding waterway. Ten levels of new work platforms have been installed in VAB High Bay 3. They will surround and provide access for service and processing of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades and installation of the new work platforms to support the launch of the SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
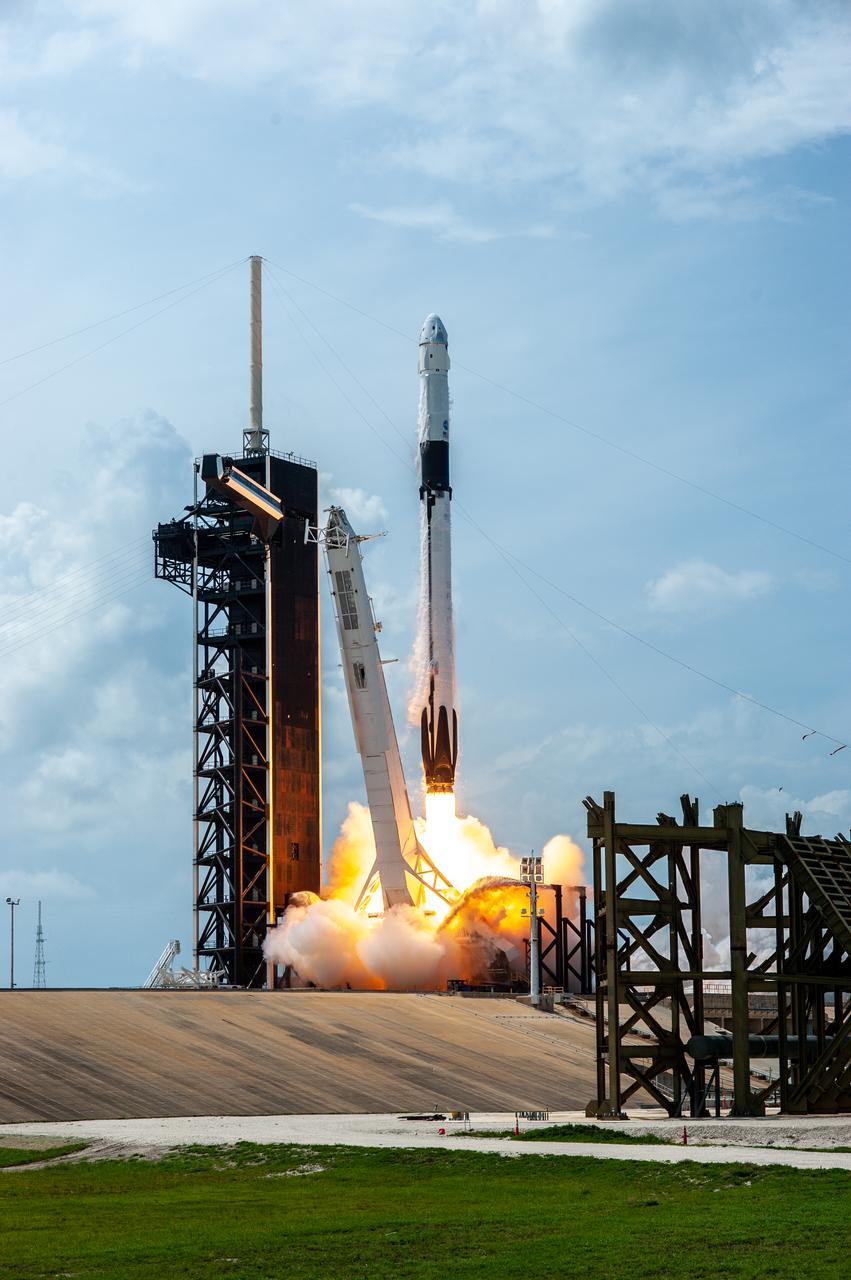

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.

A brilliant blue sky forms the backdrop for a fish-eye panoramic view of the south side of the Launch Control Center (LCC) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Firing Room 1 inside the LCC has been completely upgraded and modernized to support the testing, processing, countdown and launch of NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space mission. Exploration Ground Systems oversaw the upgrades.
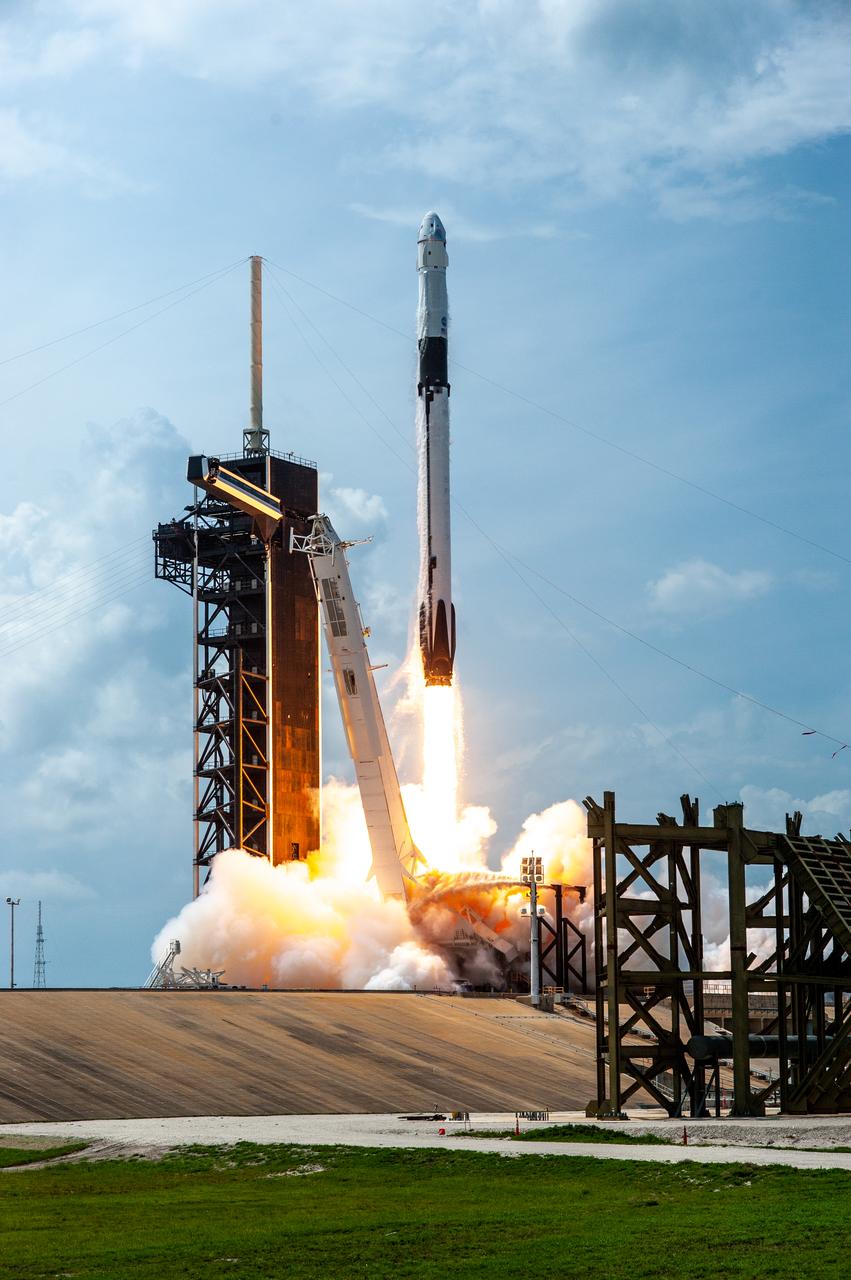

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.
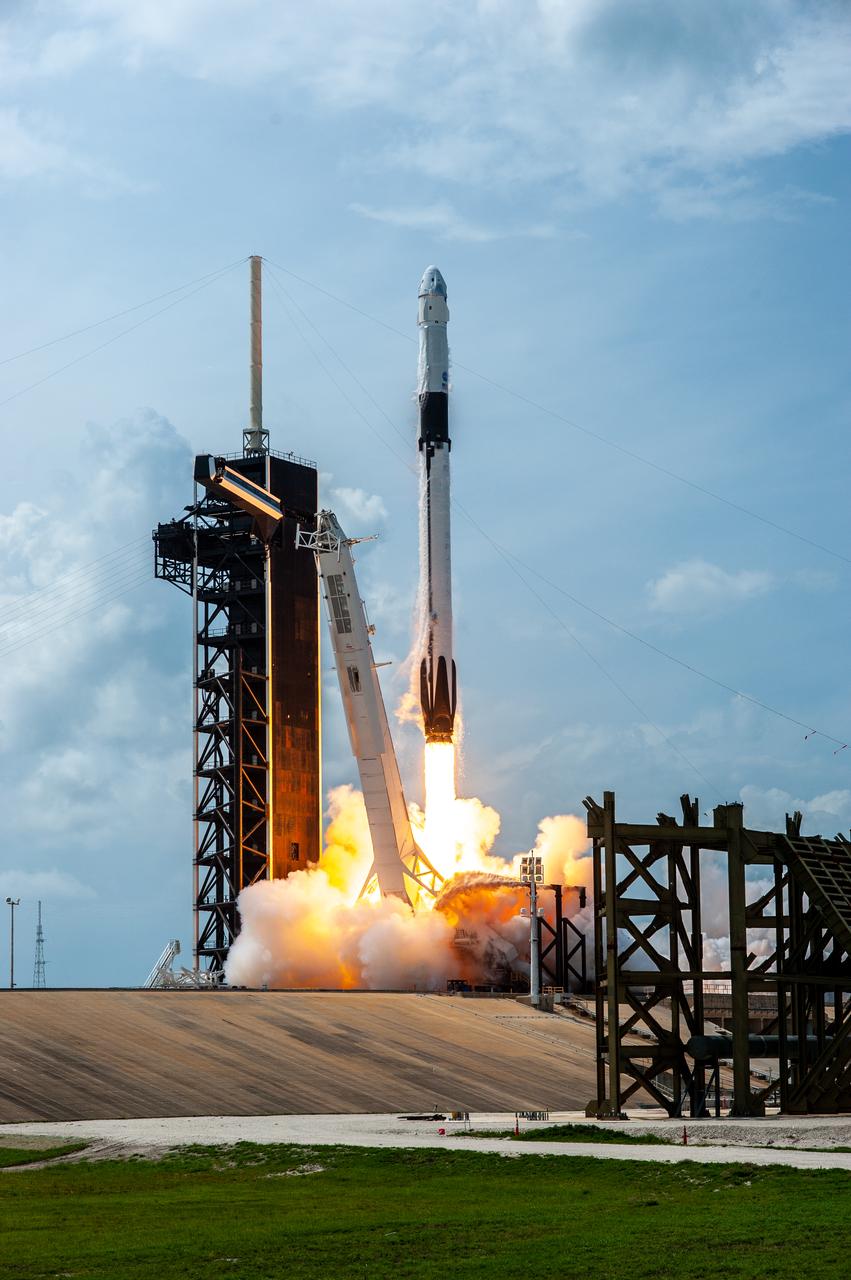

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 30, 2020, carrying NASA astronauts Robert Behnken and Douglas Hurley to the International Space Station for the agency’s SpaceX Demo-2 mission. Liftoff occurred at 3:22 p.m. EDT. Behnken and Hurley are the first astronauts to launch from U.S. soil to the space station since the end of the Space Shuttle Program in 2011. Part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, this will be SpaceX’s final flight test, paving the way for the agency to certify the crew transportation system for regular, crewed flights to the orbiting laboratory.

Teams with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program transport the 380-foot-tall mobile launcher 1 along a 4.2-mile stretch to the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Oct. 3, 2024. The crawler transporter recently reached 2,500 miles traveling to the launch pad since its construction in 1965. The mobile launcher has been at Launch Complex 39B since August 2023 undergoing upgrades and tests in preparation for NASA’s Artemis II mission. The mobile launcher will be used to assemble, process, and launch NASA’s SLS (Space Launch Systems) and Orion spacecraft to the Moon and beyond.
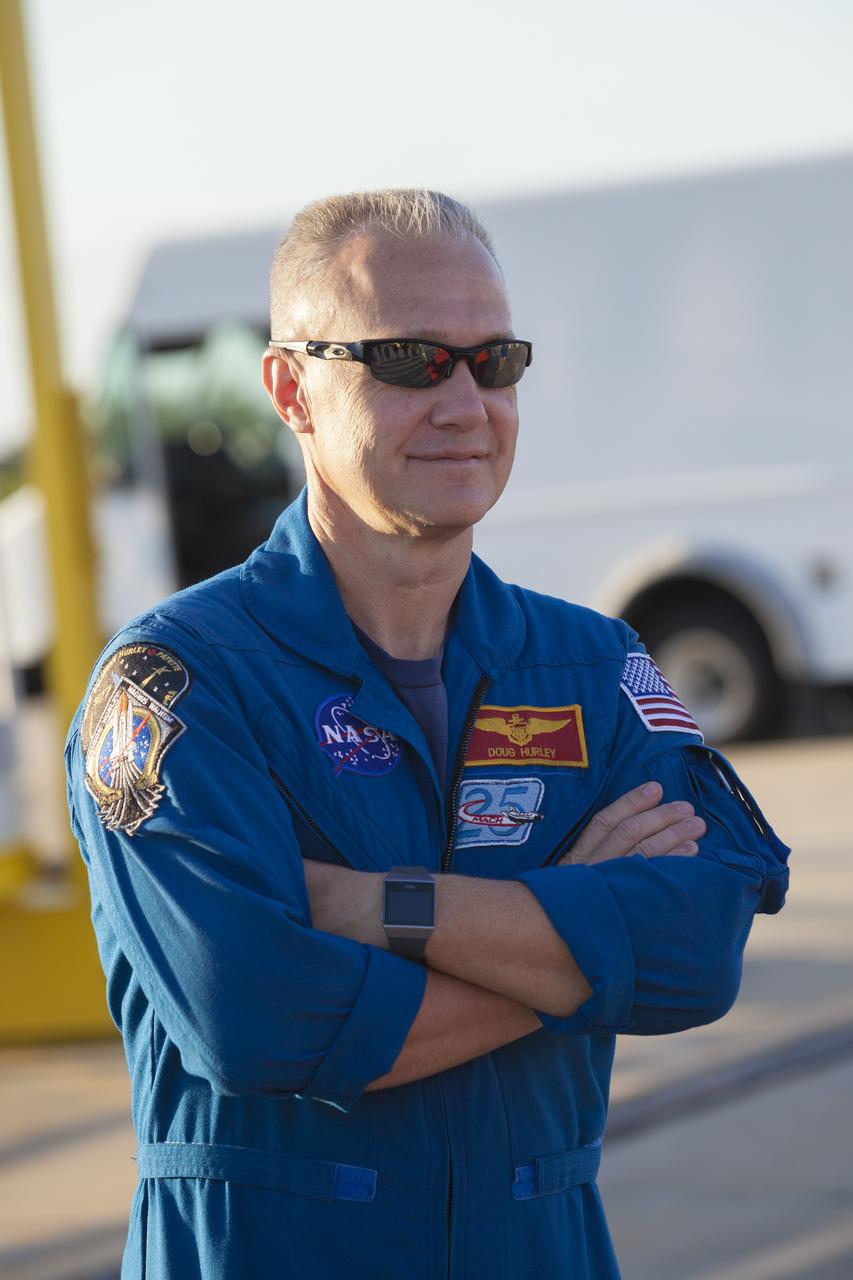

At Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Naval Ordnance Test Unit basin in Florida, Commercial Crew Program astronaut Doug Hurley observes operation of the SpaceX recovery ship. During a recent visit to the Kennedy Space Center, the crew members were given an up-close look at preparations for the SpaceX Crew Dragon flight tests.