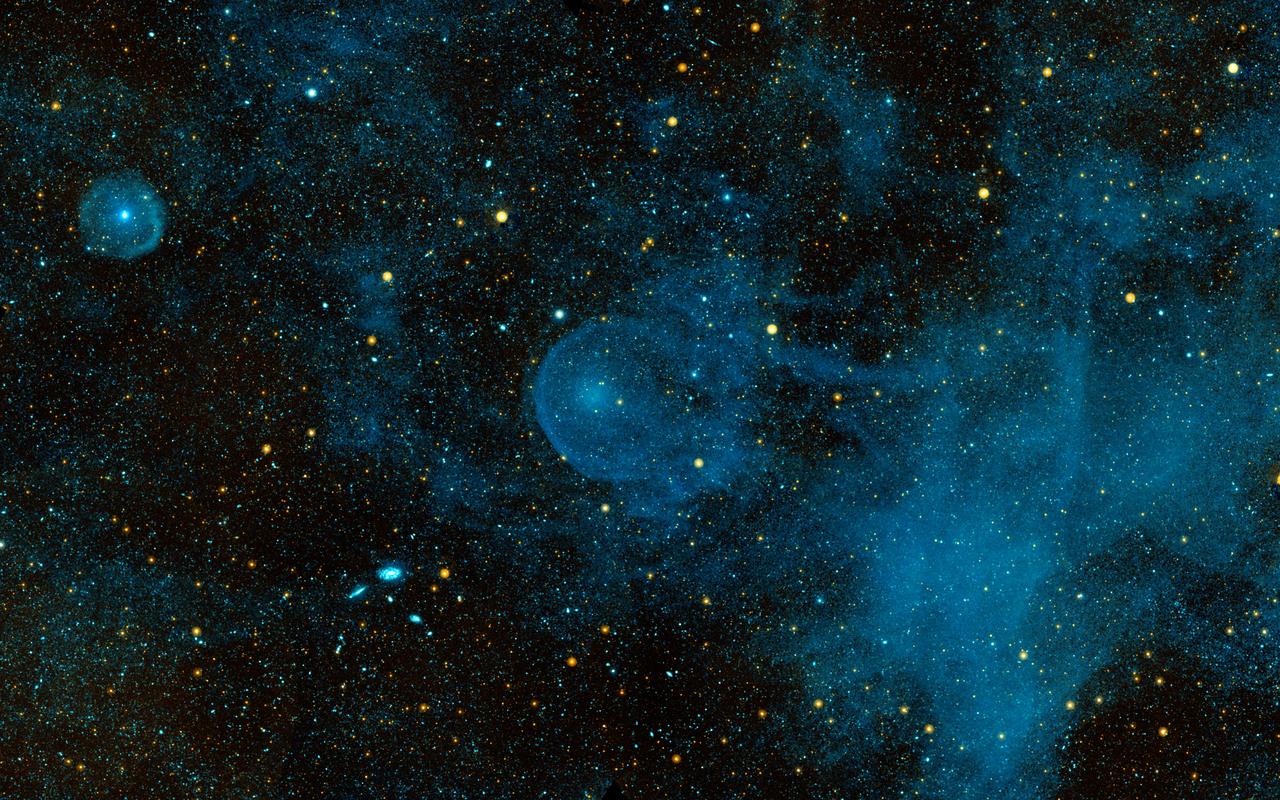

A runaway star, called CW Leo, plowing through the depths of space and piling up interstellar material before it, can be seen in this ultraviolet image from NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer.

At first glance this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image seems to show an array of different cosmic objects, but the speckling of stars shown here actually forms a single body — a nearby dwarf galaxy known as Leo A. Its few million stars are so sparsely distributed that some distant background galaxies are visible through it. Leo A itself is at a distance of about 2.5 million light-years from Earth and a member of the Local Group of galaxies; a group that includes the Milky Way and the well-known Andromeda galaxy. Astronomers study dwarf galaxies because they are very numerous and are simpler in structure than their giant cousins. However, their small size makes them difficult to study at great distances. As a result, the dwarf galaxies of the Local Group are of particular interest, as they are close enough to study in detail. As it turns out, Leo A is a rather unusual galaxy. It is one of the most isolated galaxies in the Local Group, has no obvious structural features beyond being a roughly spherical mass of stars, and shows no evidence for recent interactions with any of its few neighbours. However, the galaxy’s contents are overwhelmingly dominated by relatively young stars, something that would normally be the result of a recent interaction with another galaxy. Around 90% of the stars in Leo A are less than eight billion years old — young in cosmic terms! This raises a number of intriguing questions about why star formation in Leo A did not take place on the “usual” timescale, but instead waited until it was good and ready.

At first glance, this NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope image seems to show an array of different cosmic objects, but the speckling of stars shown here actually forms a single body — a nearby dwarf galaxy known as Leo A. Its few million stars are so sparsely distributed that some distant background galaxies are visible through it. Leo A itself is at a distance of about 2.5 million light-years from Earth and a member of the Local Group of galaxies; a group that includes the Milky Way and the well-known Andromeda galaxy. Astronomers study dwarf galaxies because they are very numerous and are simpler in structure than their giant cousins. However, their small size makes them difficult to study at great distances. As a result, the dwarf galaxies of the Local Group are of particular interest, as they are close enough to study in detail. As it turns out, Leo A is a rather unusual galaxy. It is one of the most isolated galaxies in the Local Group, has no obvious structural features beyond being a roughly spherical mass of stars, and shows no evidence for recent interactions with any of its few neighbors. However, the galaxy’s contents are overwhelmingly dominated by relatively young stars, something that would normally be the result of a recent interaction with another galaxy. Around 90% of the stars in Leo A are less than eight billion years old — young in cosmic terms! This raises a number of intriguing questions about why star formation in Leo A did not take place on the “usual” timescale, but instead waited until it was good and ready. Image credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA; Acknowledgment: Judy Schmidt
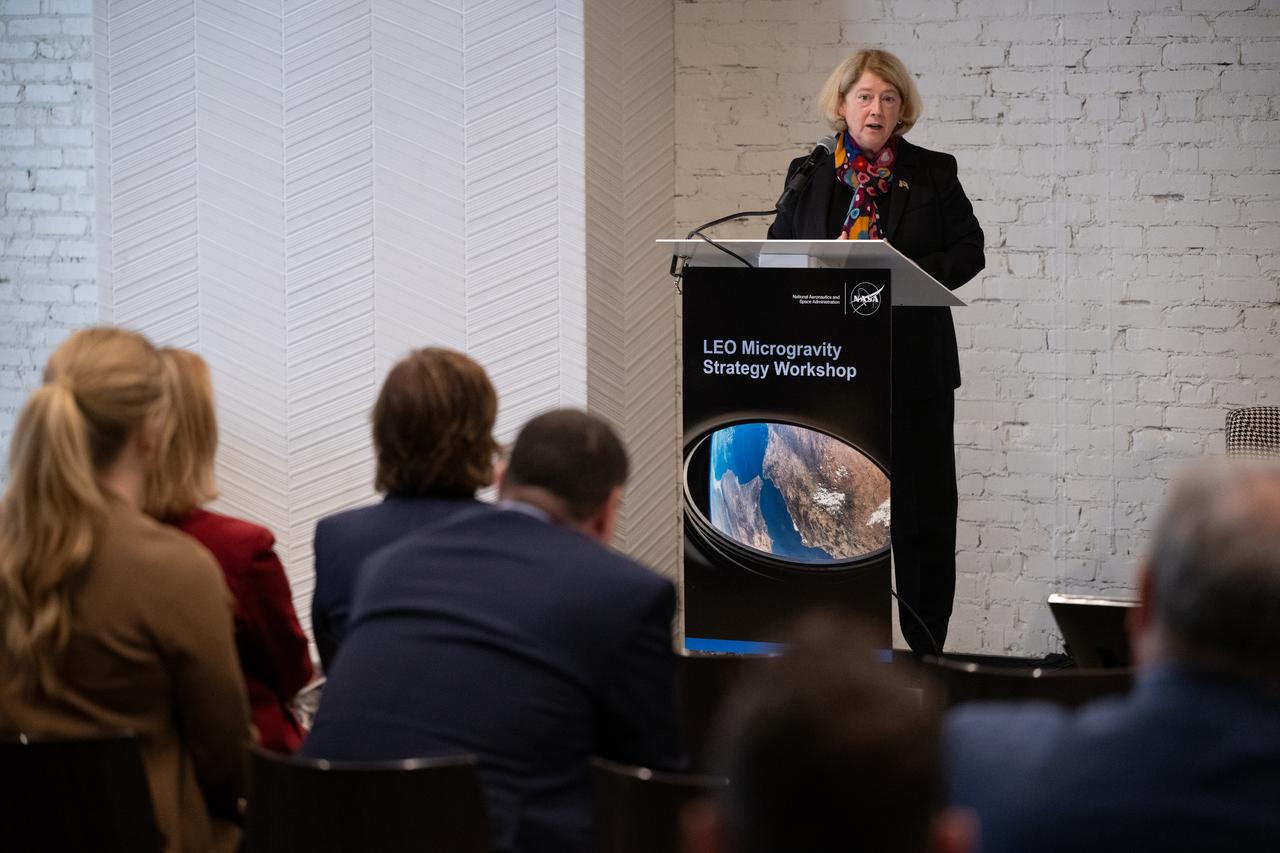

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
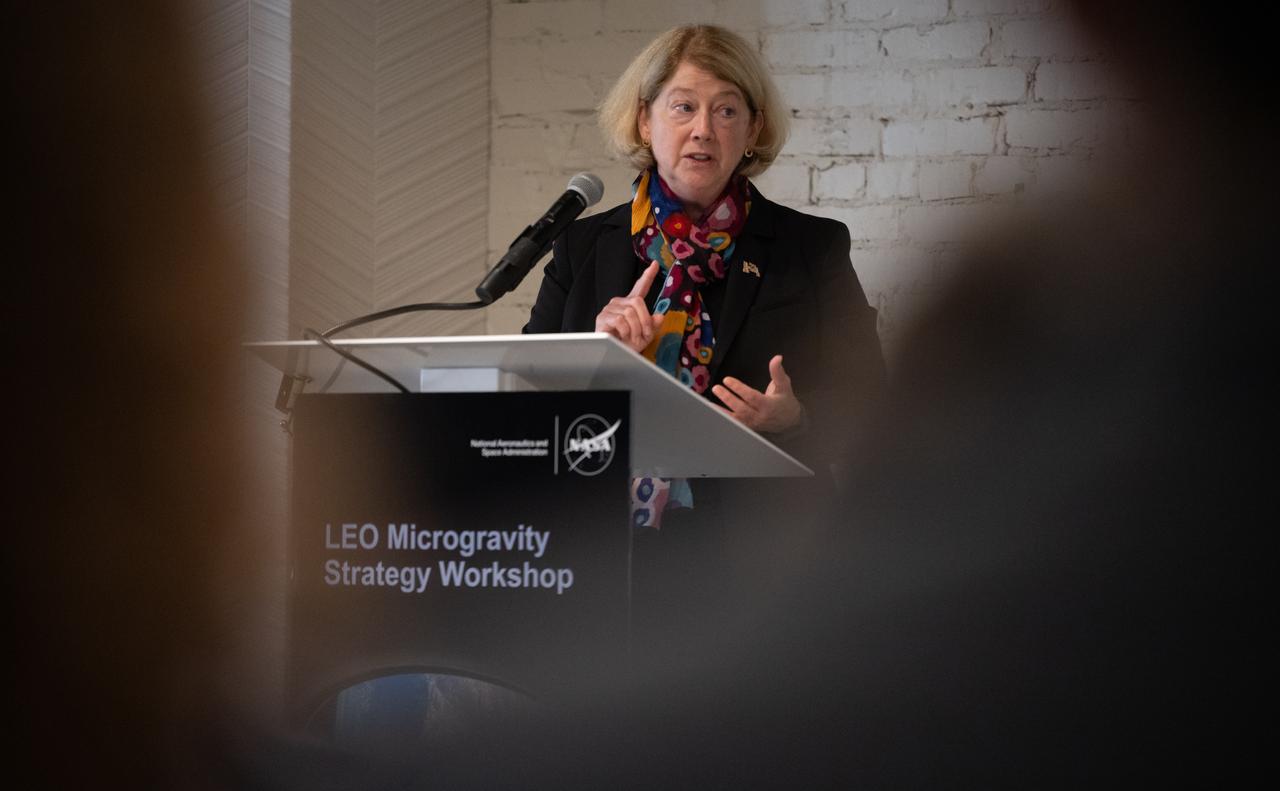

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
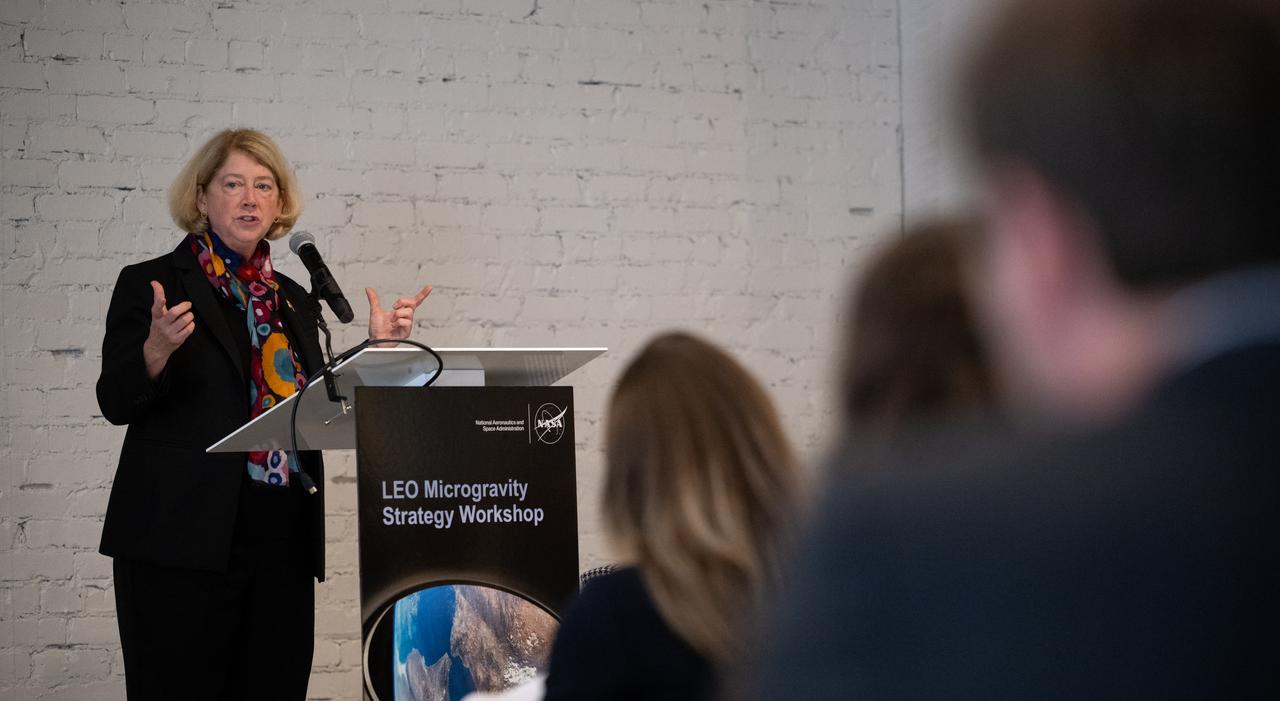

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
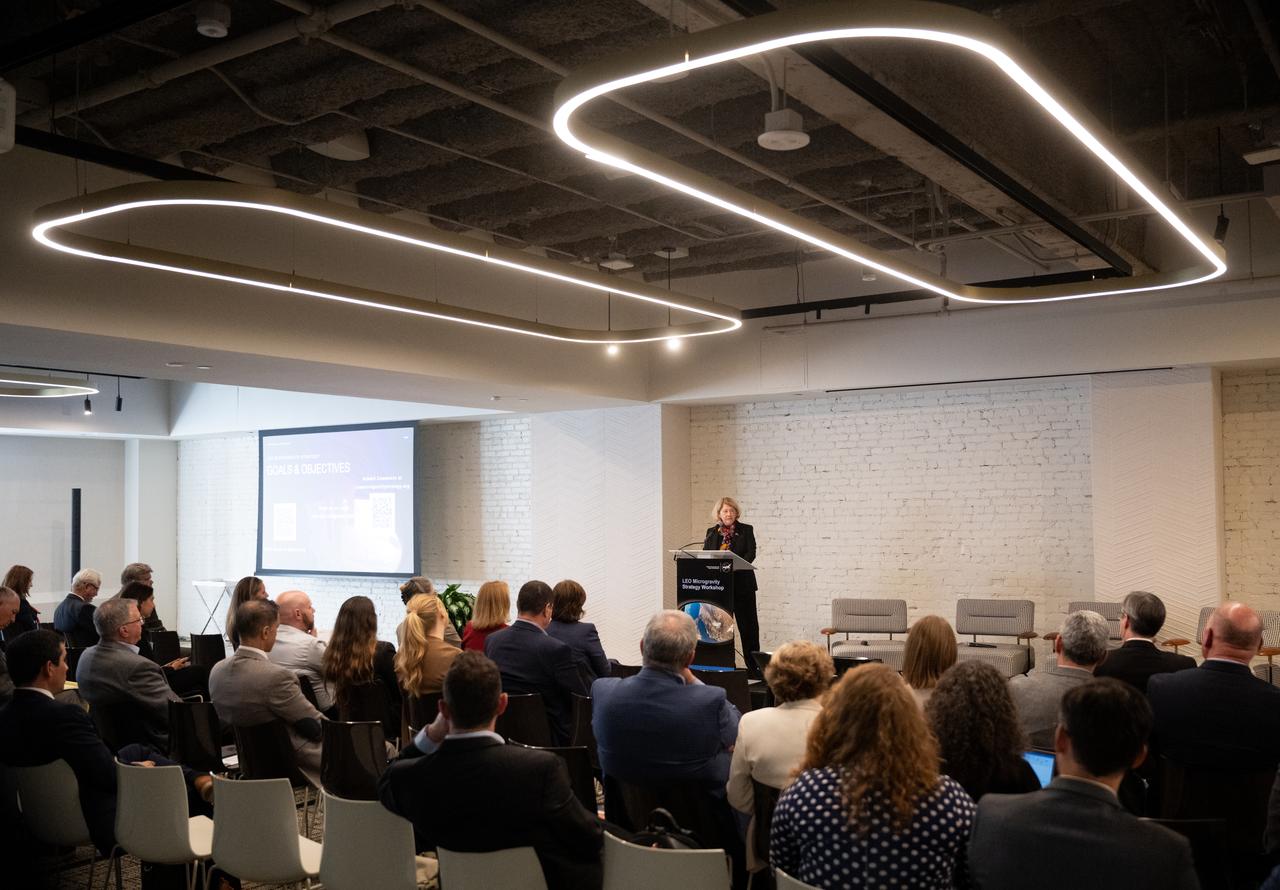

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy gives closing remarks at NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
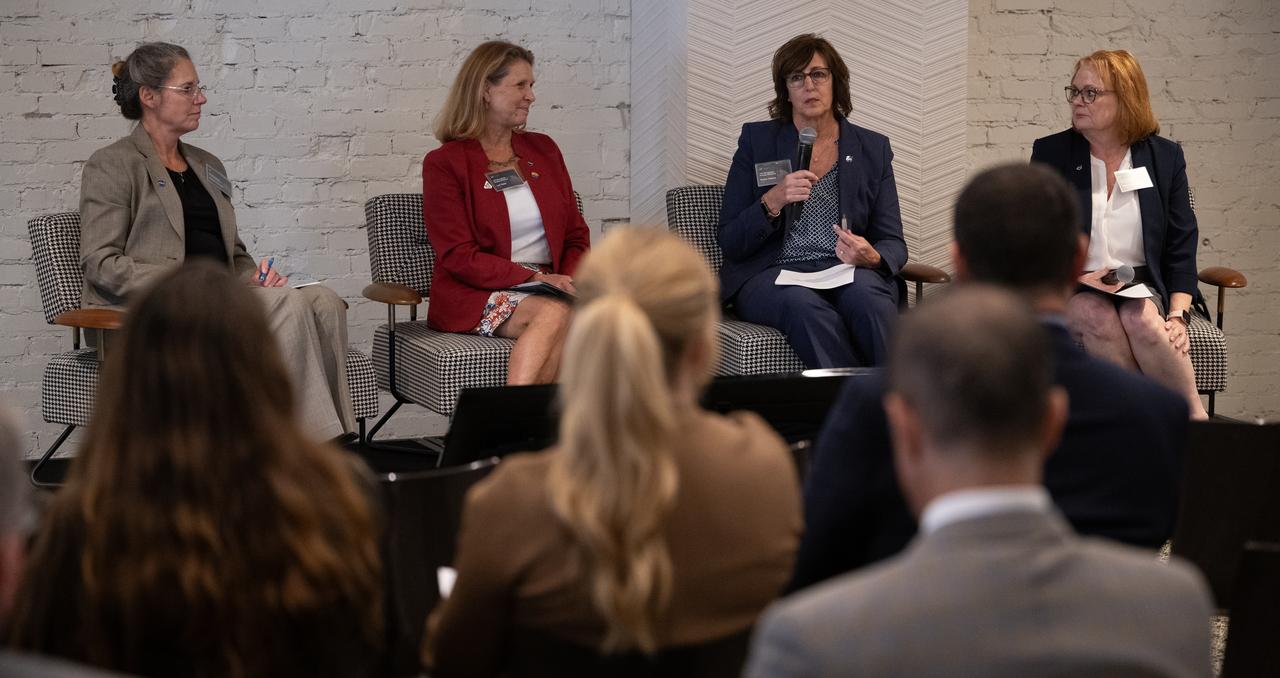

Sandra Connelly, deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, left, Lori Glaze, acting deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, Robyn Gatens, director of the International Space Station at NASA Headquarters, and Carrie Olsen, manager of the Next Gen STEM project for NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, discuss key takeaways at the conclusion of NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
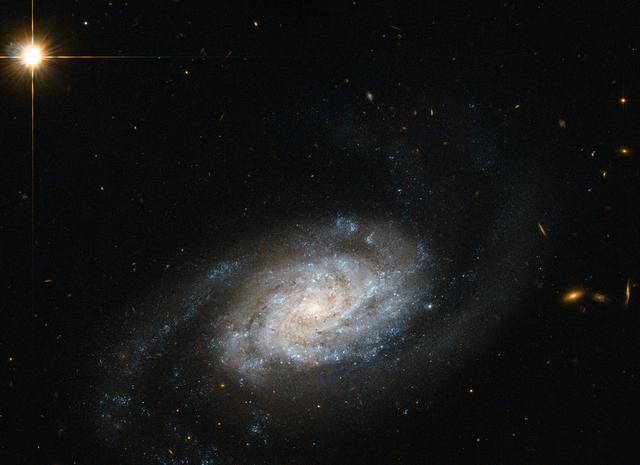

Shown here is a spiral galaxy known as NGC 3455, which lies some 65 million light-years away from us in the constellation of Leo (the Lion). Galaxies are classified into different types according to their structure and appearance. This classification system is known as the Hubble Sequence, named after its creator Edwin Hubble. In this image released 14, April, 2014, NGC 3455 is known as a type SB galaxy — a barred spiral. Barred spiral galaxies account for approximately two thirds of all spirals. Galaxies of this type appear to have a bar of stars slicing through the bulge of stars at their center. The SB classification is further sub-divided by the appearance of a galaxy's pinwheeling spiral arms; SBa types have more tightly wound arms, whereas SBc types have looser ones. SBb types, such as NGC 3455, lie in between. NGC 3455 is part of a pair of galaxies — its partner, NGC 3454, lies out of frame. This cosmic duo belong to a group known as the NGC 3370 group, which is in turn one of the Leo II groups, a large collection of galaxies scattered some 30 million light-years to the right of the Virgo cluster. This image is from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA, Acknowledgement: Nick Rose <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
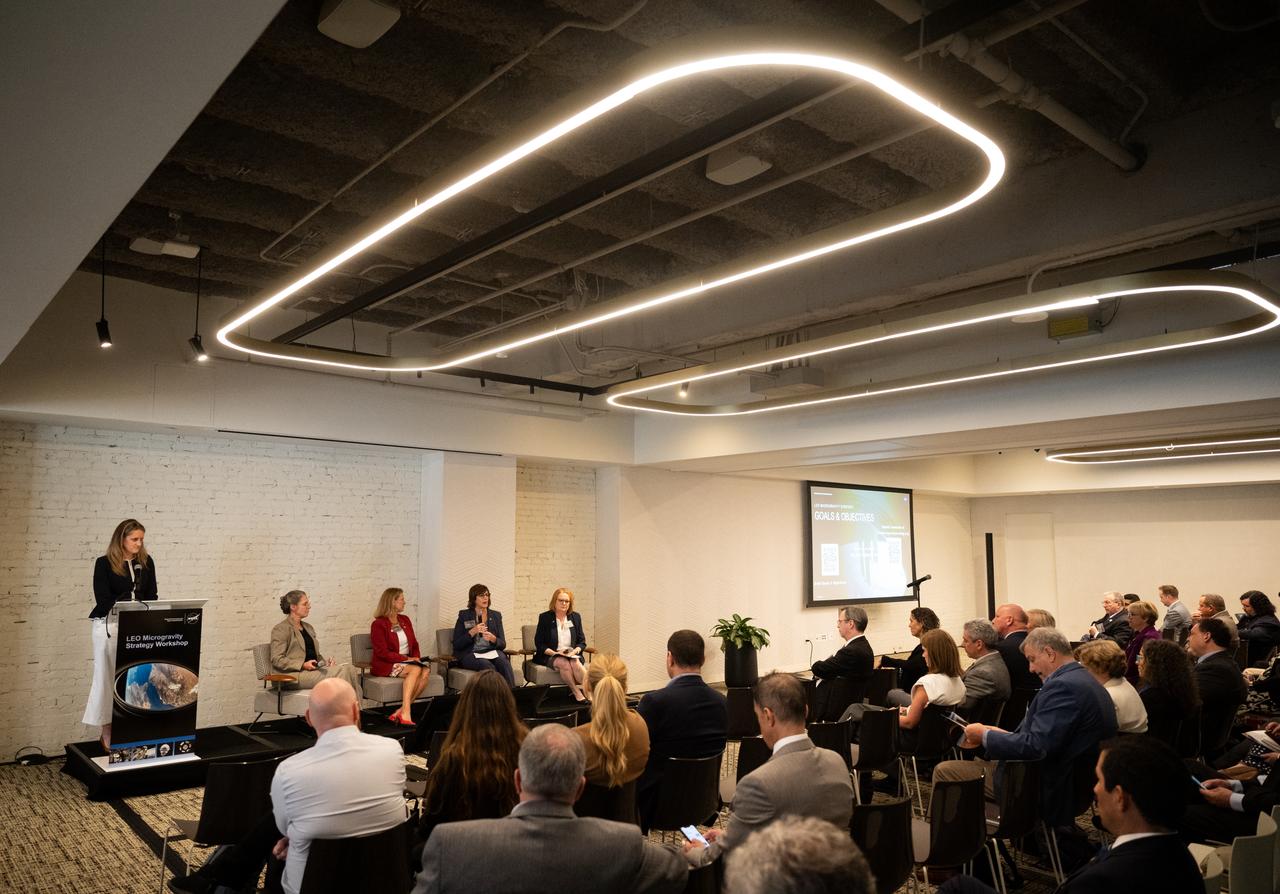

Amber Jacobson, press secretary to NASA’s Deputy Administrator, left, moderates a discussion of key takeaways with Sandra Connelly, deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, second from left, Lori Glaze, acting deputy associate administrator for NASA’s Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, Robyn Gatens, director of the International Space Station at NASA Headquarters, and Carrie Olsen, manager of the Next Gen STEM project for NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, at the conclusion of NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy Industry and Academia Workshop, Friday, Sept. 13, 2024, at Convene in Washington. NASA’s LEO Microgravity Strategy effort aims to develop and document an objectives-based approach toward the next generation of human presence in low Earth orbit to advance microgravity science, technology, and exploration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
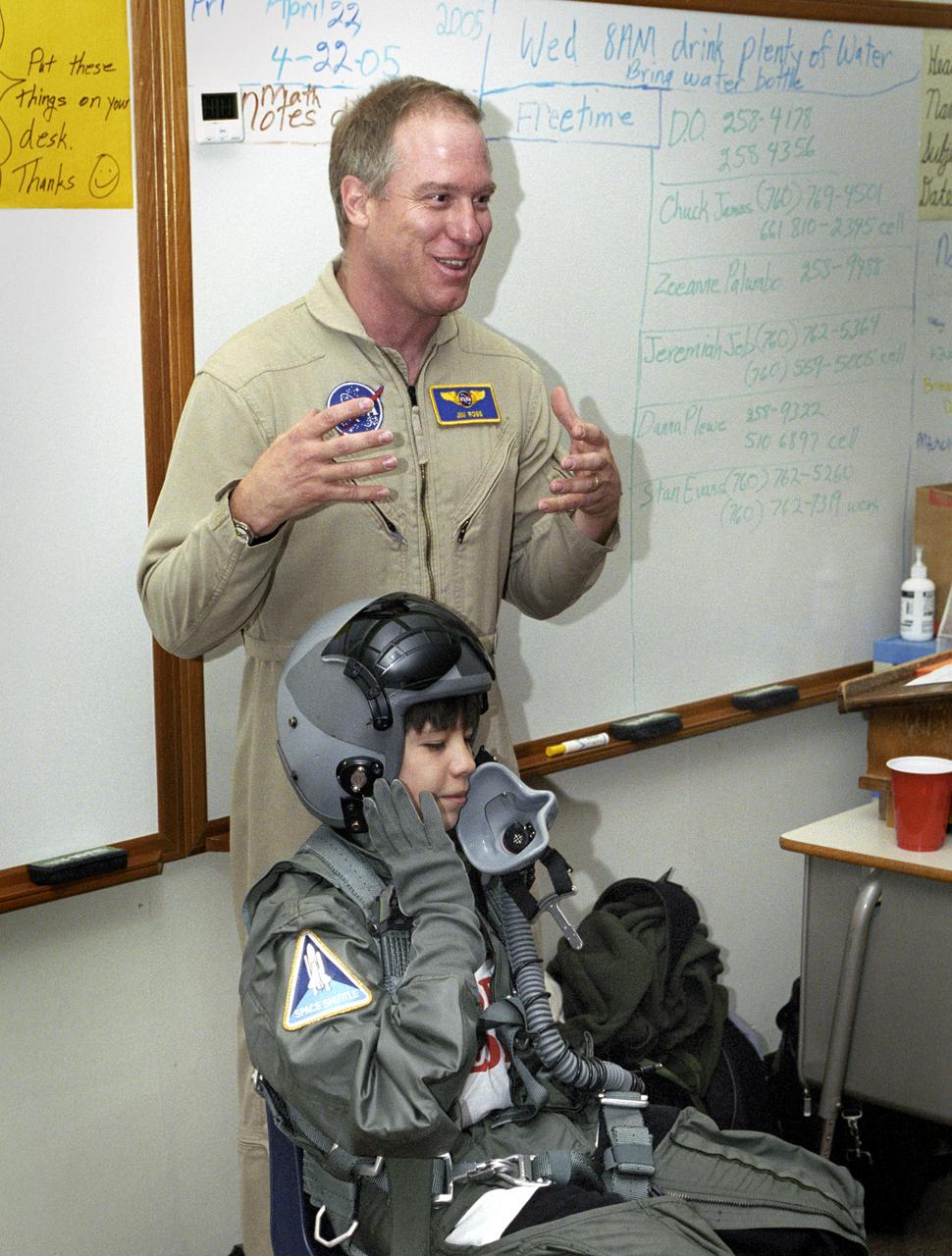

While NASA Dryden's Jim Ross outlined his job as an aerial photographer, sixth-grade student Leo Banuelos learned first-hand about the gear Ross wears in the cockpit.
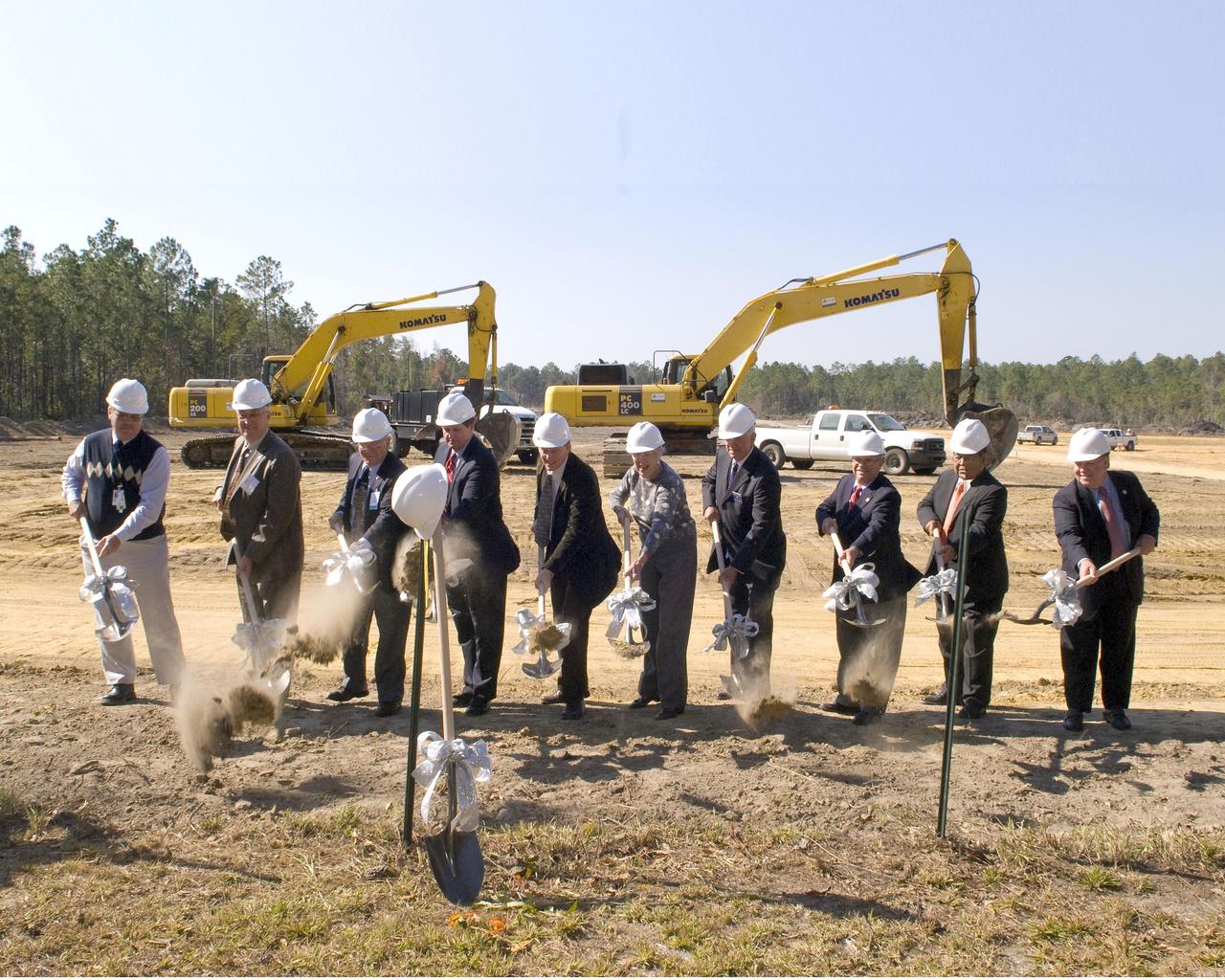

Community leaders from Mississippi and Louisiana break ground for the new INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility during a Nov. 20 ceremony. Groundbreaking participants included (l to r): Gottfried Construction representative John Smith, Mississippi Highway Commissioner Wayne Brown, INFINITY board member and Apollo 13 astronaut Fred Haise, Stennis Director Gene Goldman, Studio South representative David Hardy, Leo Seal Jr. family representative Virginia Wagner, Hancock Bank President George Schloegel, Mississippi Rep. J.P. Compretta, Mississippi Band of Choctaw Indians representative Charlie Benn and Louisiana Sen. A.G. Crowe.
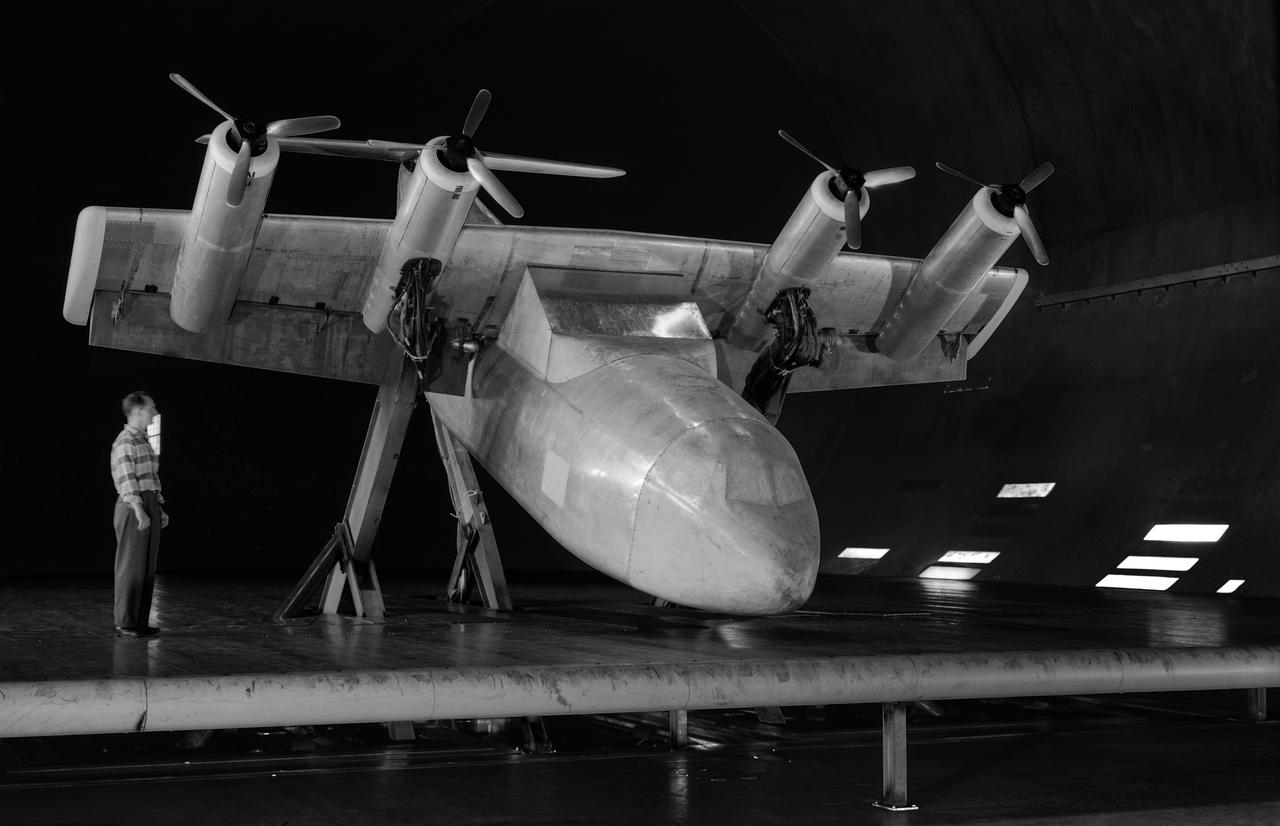

Tilt wing propeller model. 3/4 front view. 4 prop tilt wing nose down variable struts on ground board. Leo Holl, NASA Ames Engineer.

BioSentinel spacecraft enters a lunar flyby trajectory into a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.

The BioSentinel spacecraft enters a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.
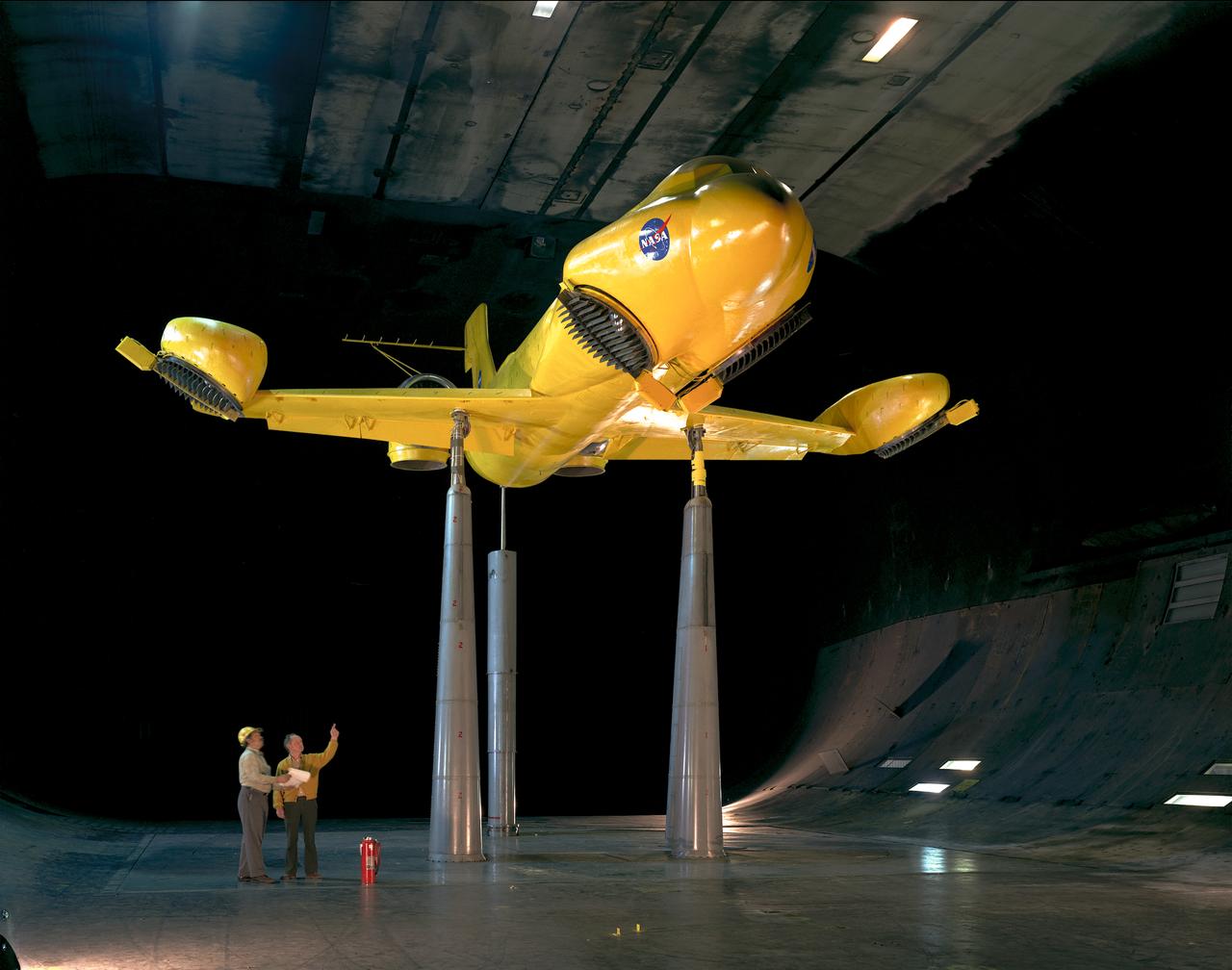

3/4 lower front view of DC-9 lift/cruz fan transport model. Pictured with Eloy Martinez (left, mechanic) Leo Hall (right, engineer).
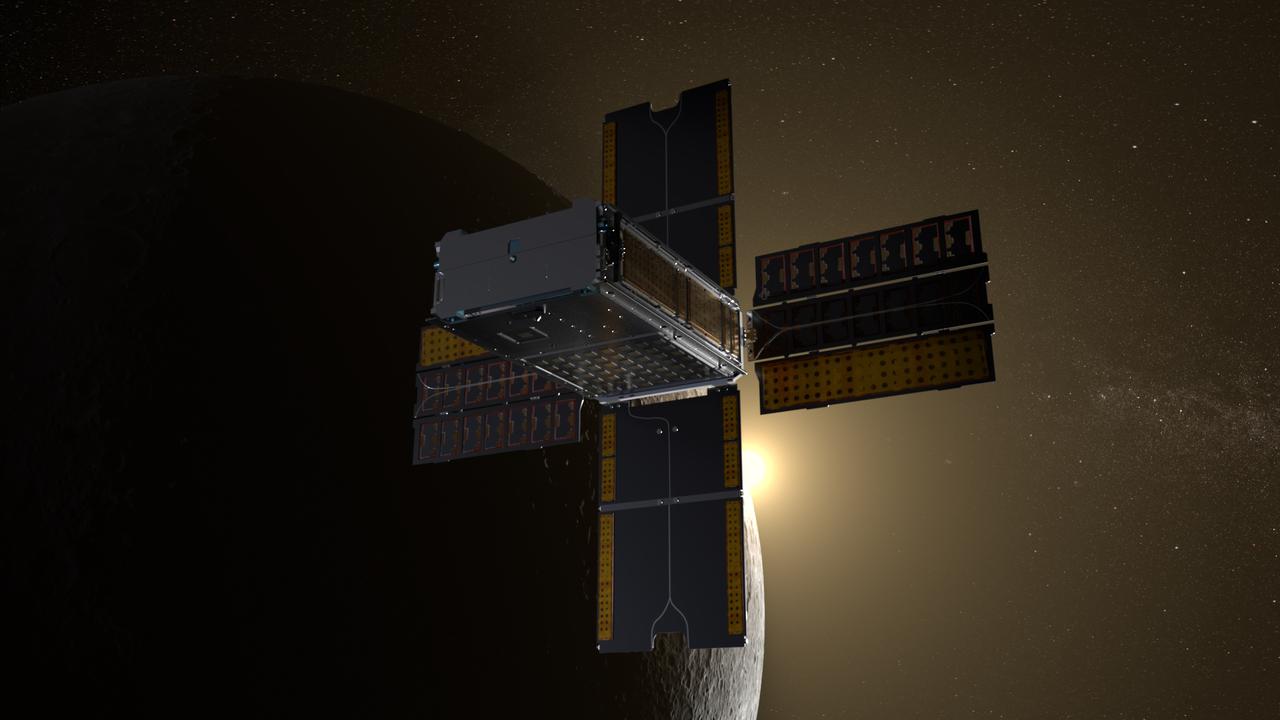

BioSentinel spacecraft enters a lunar flyby trajectory into a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.
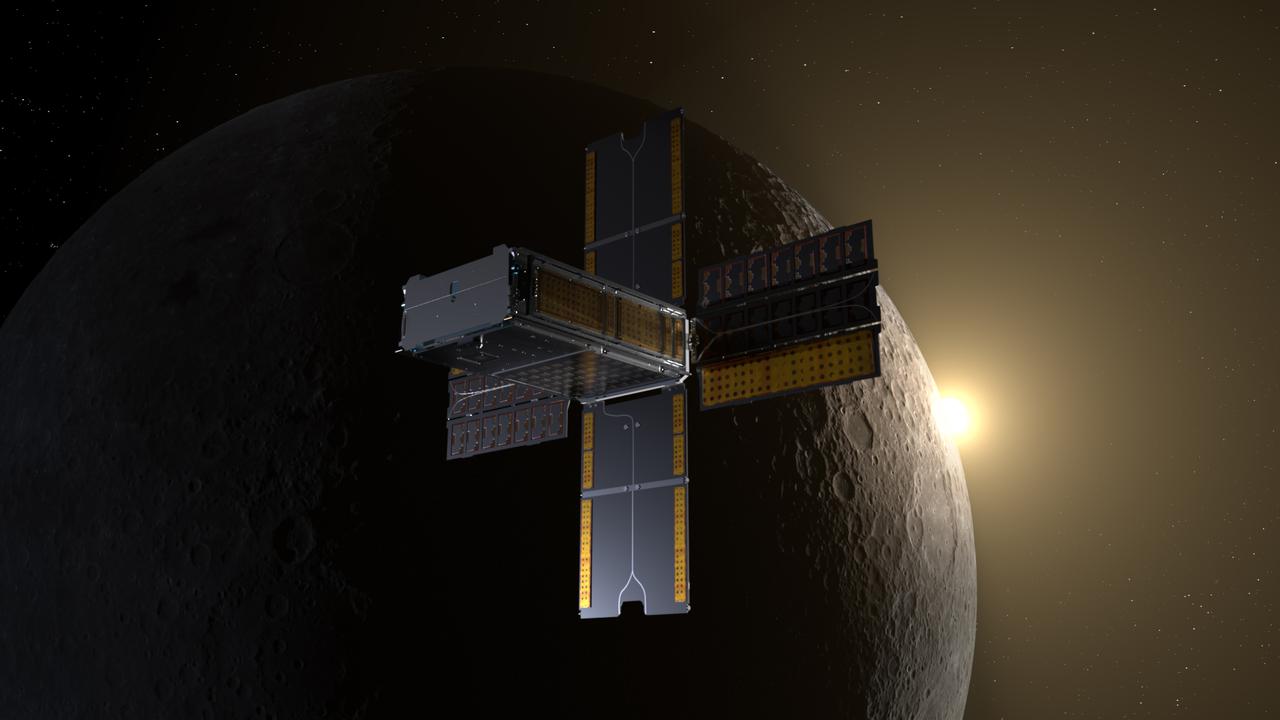

BioSentinel spacecraft enters a lunar flyby trajectory into a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.
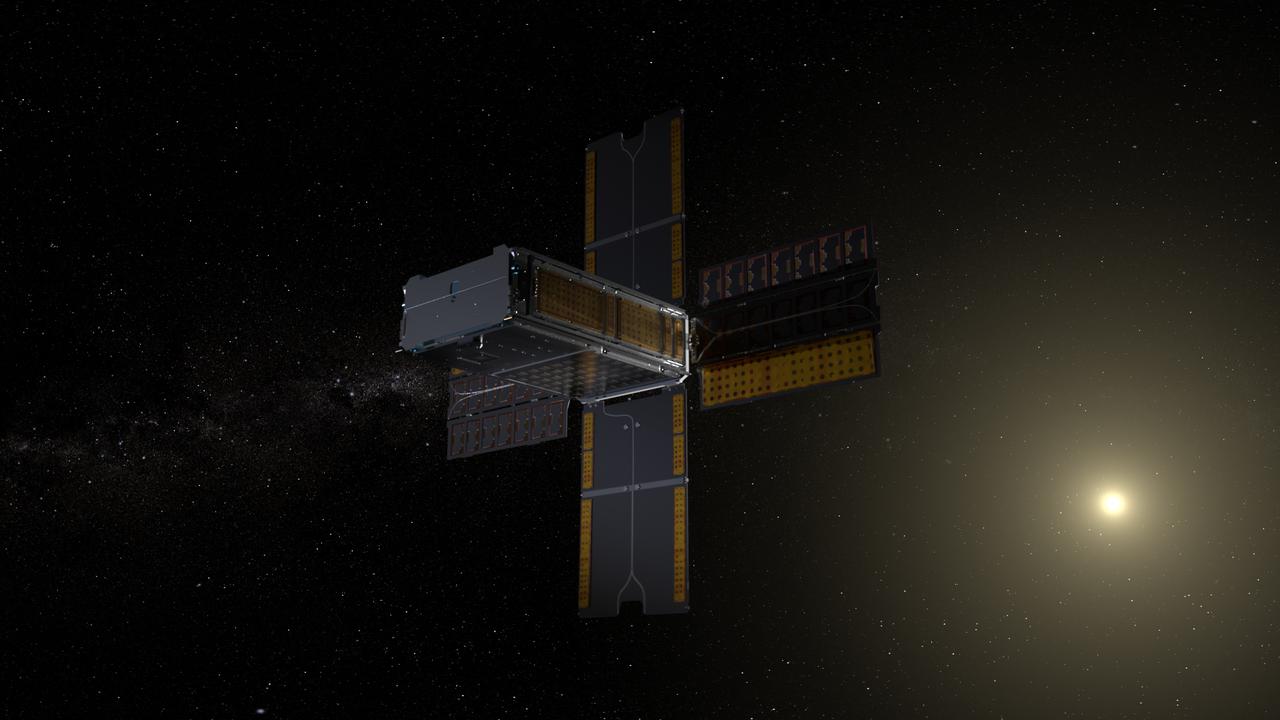

The BioSentinel spacecraft enters a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.
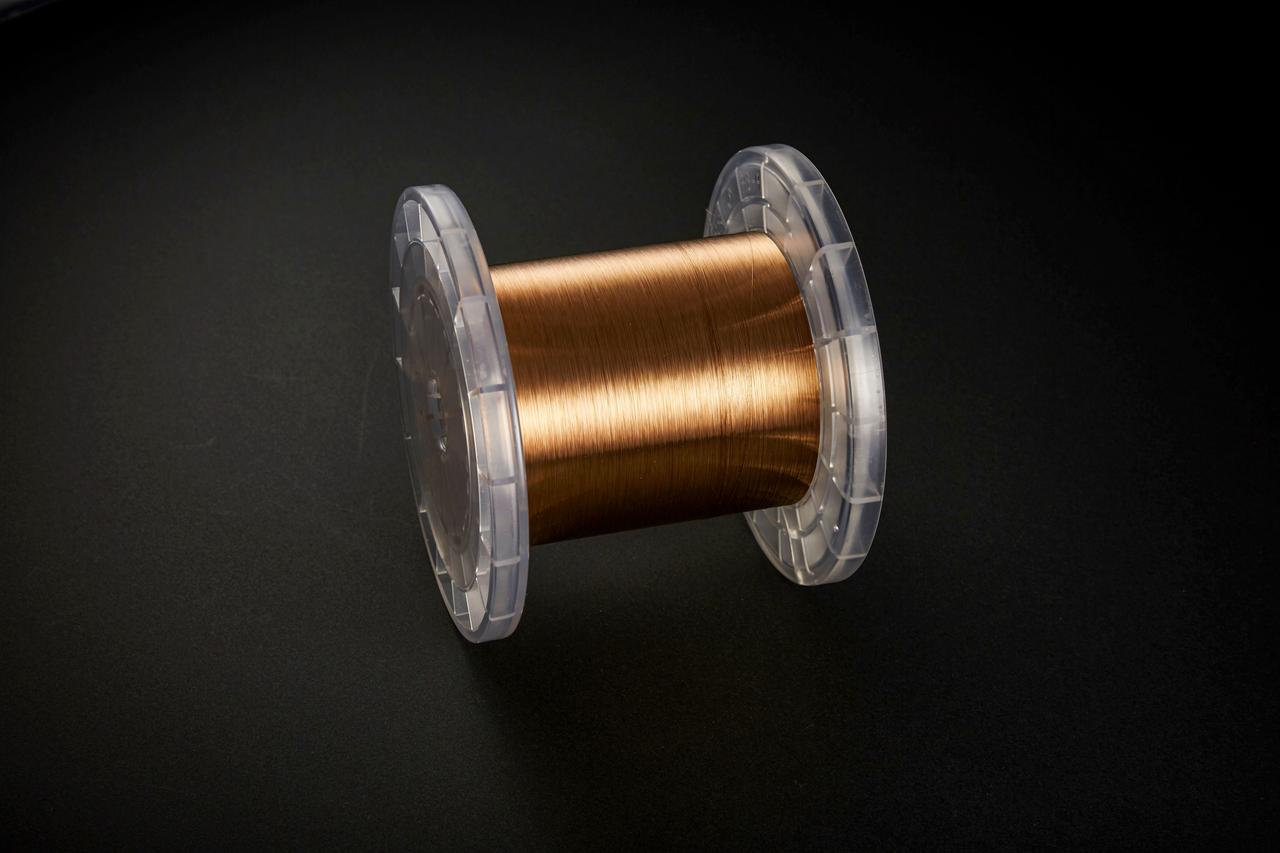

jsc2020e040942 (4/18/2015) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
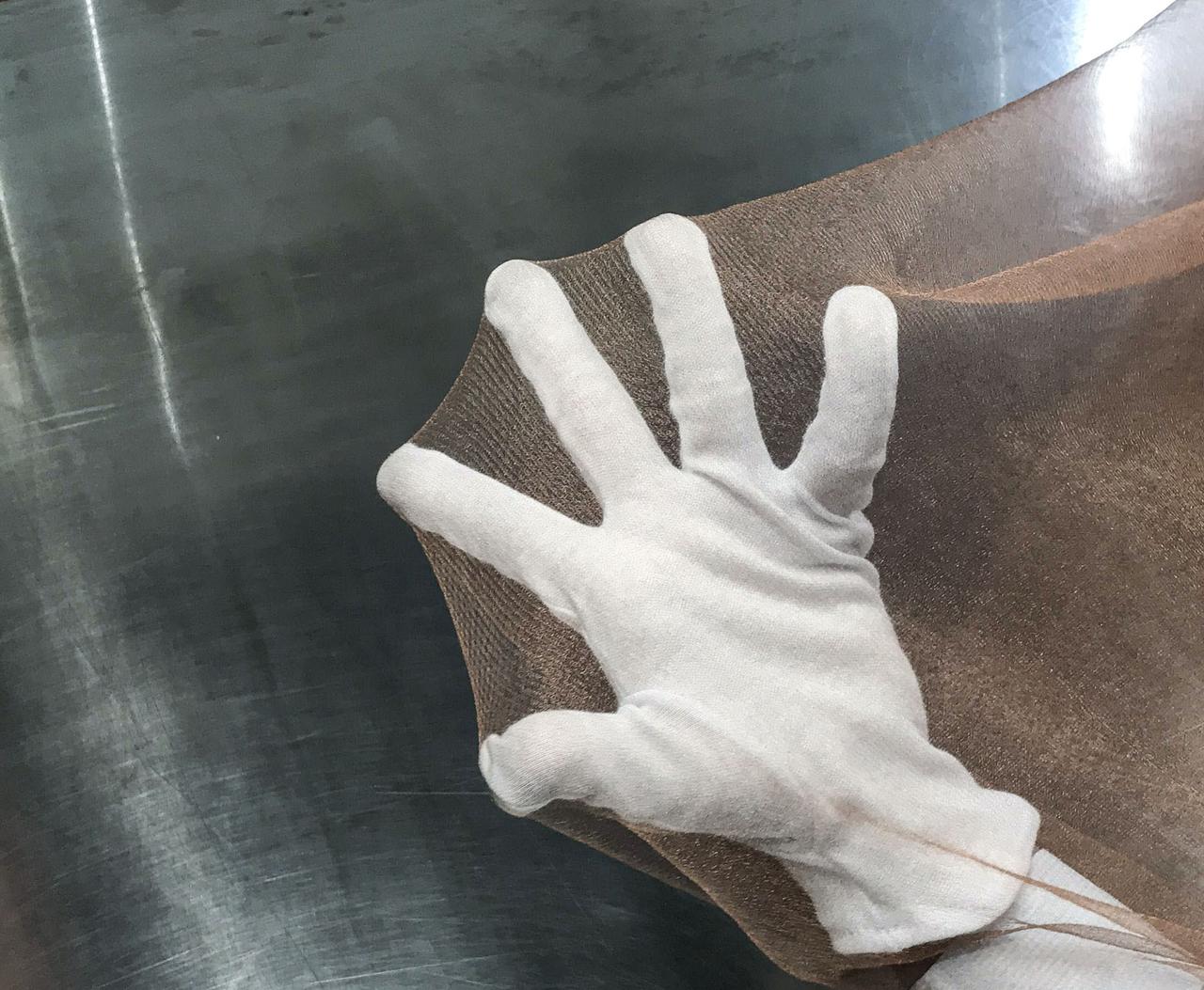

jsc2020e040945 (7/10/2020) --- Copper zirconium antenna metal mesh. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
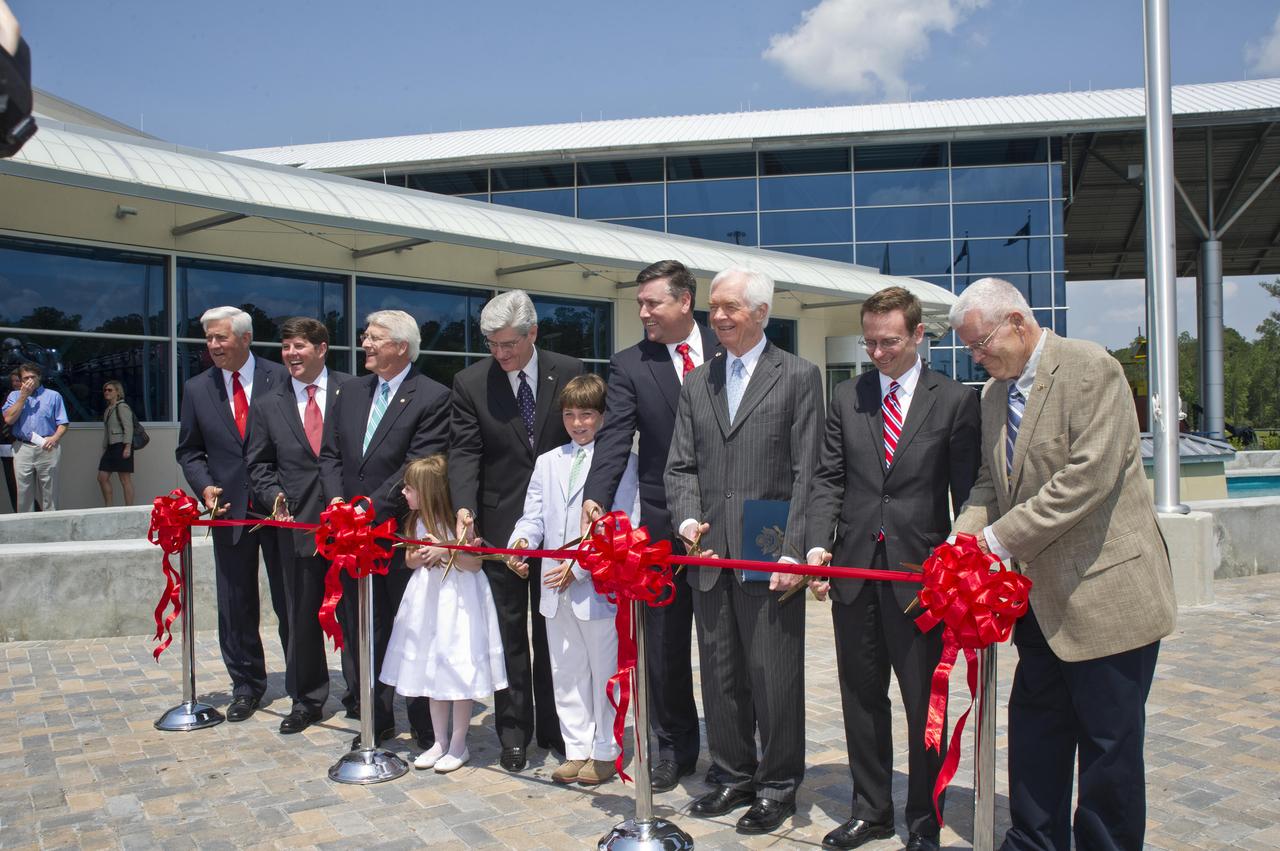

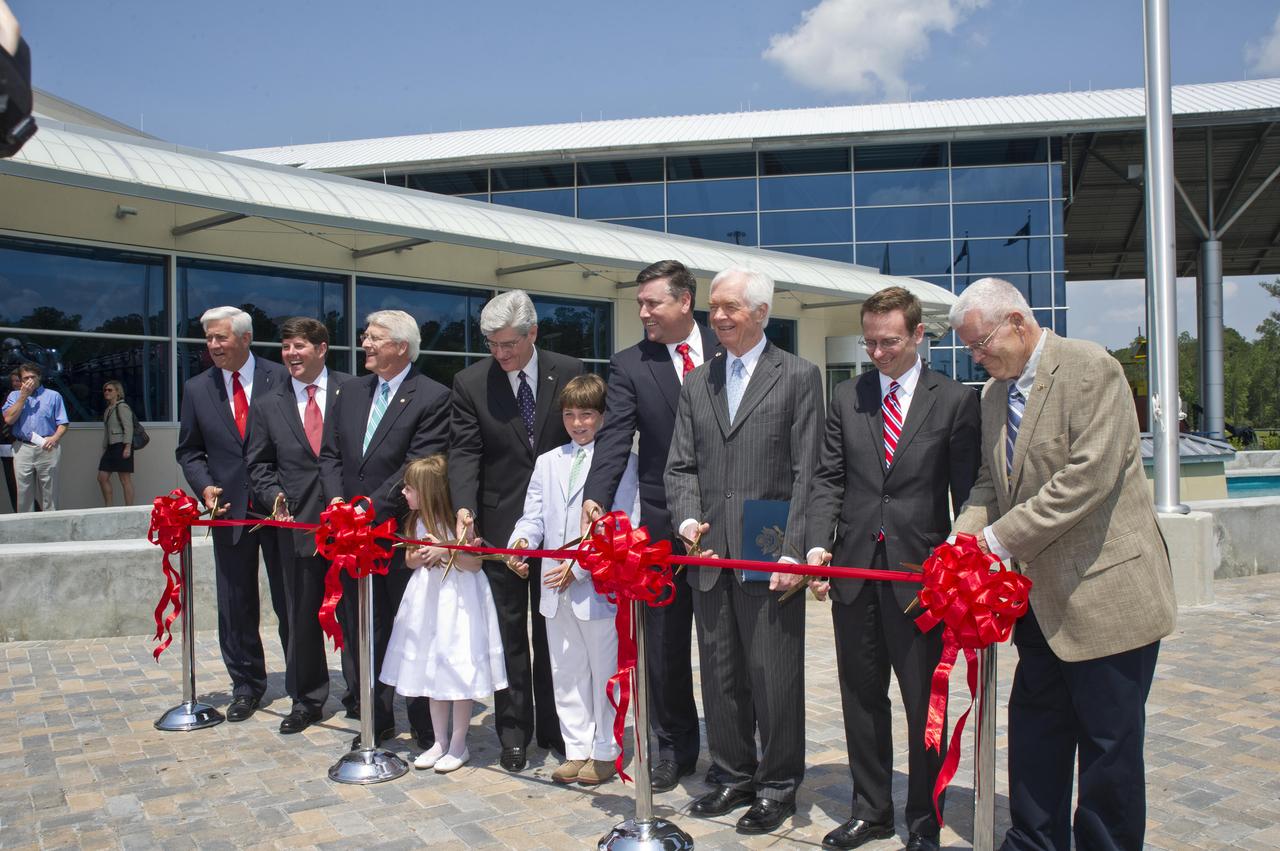
Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
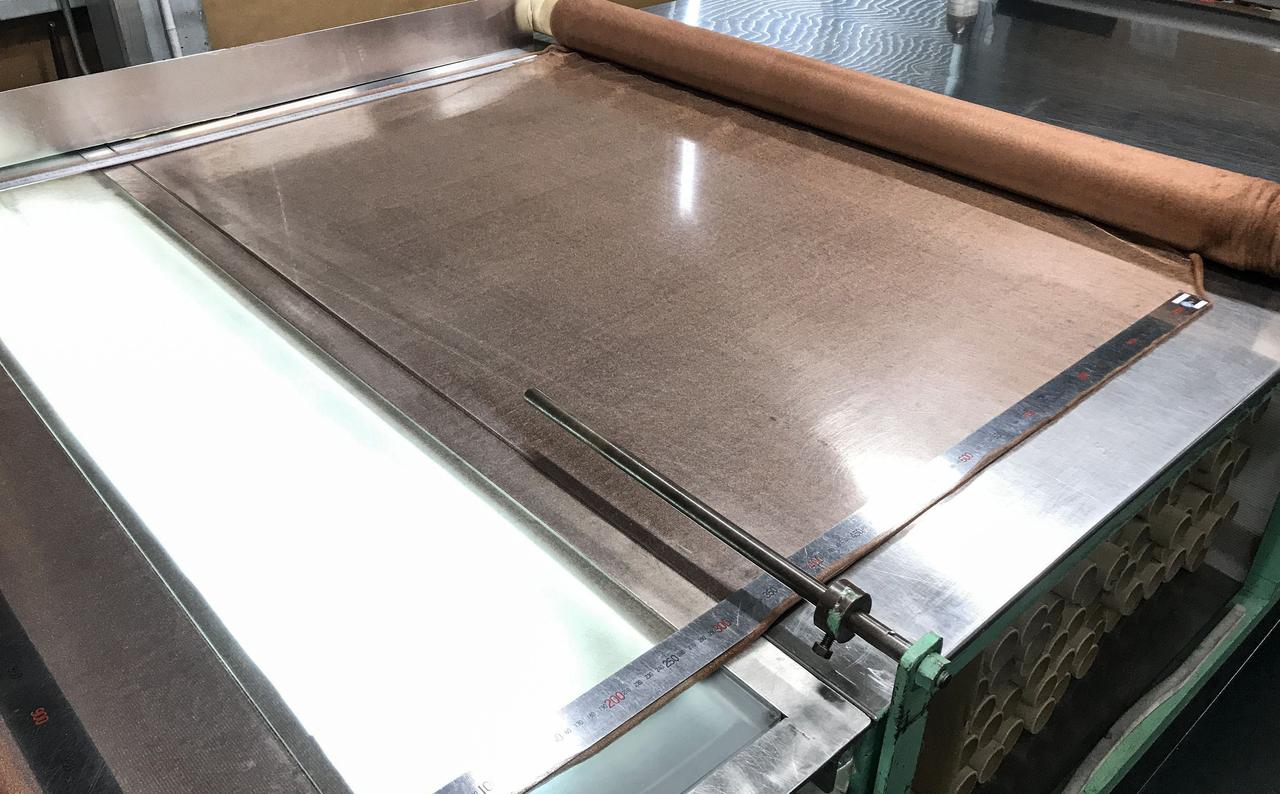

jsc2020e040944 (7/8/2020) --- Copper zirconium antenna metal mesh. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040941 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040940 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
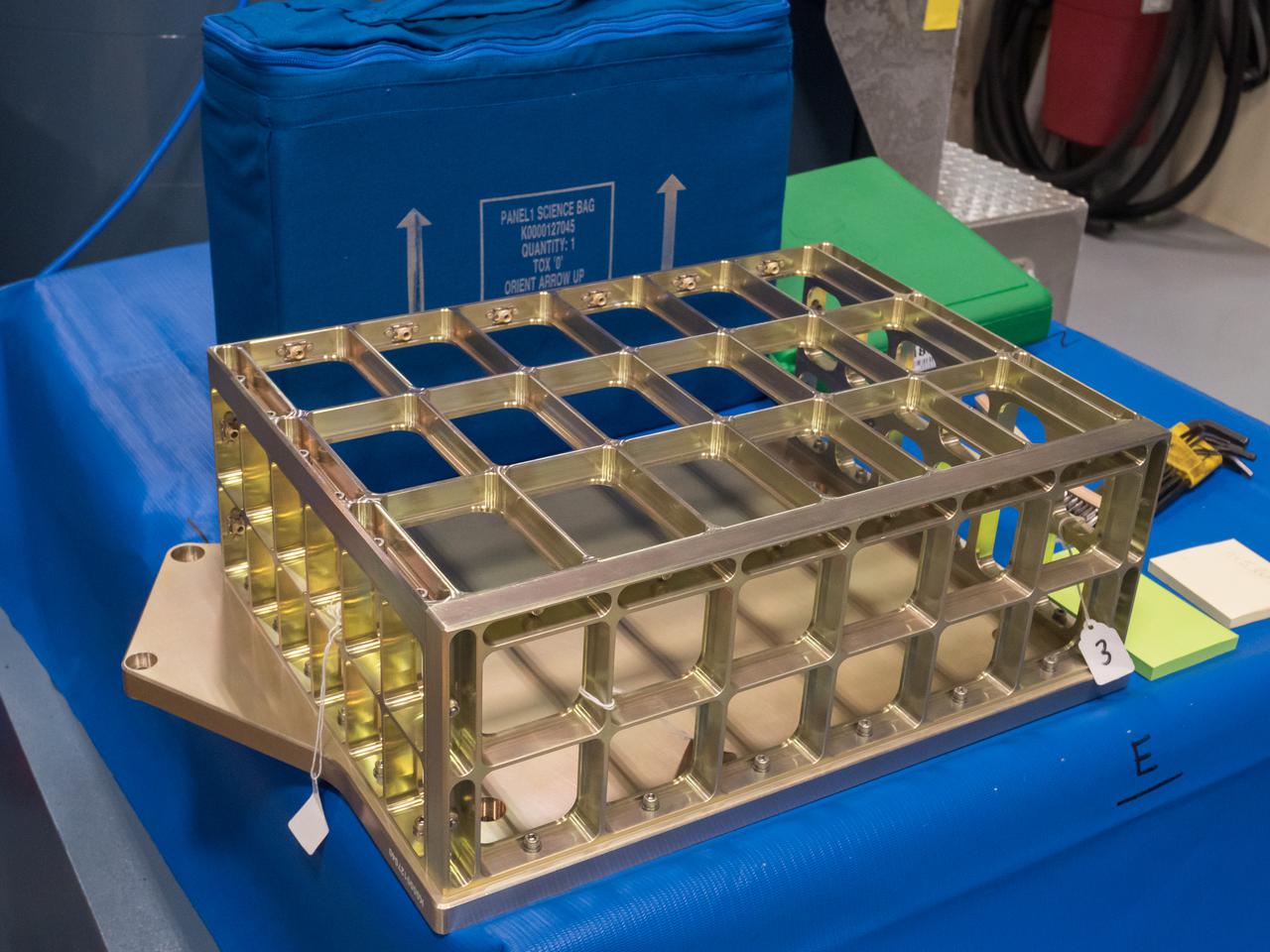
NASA’s BioExperiment-1 is being prepared for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plant, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
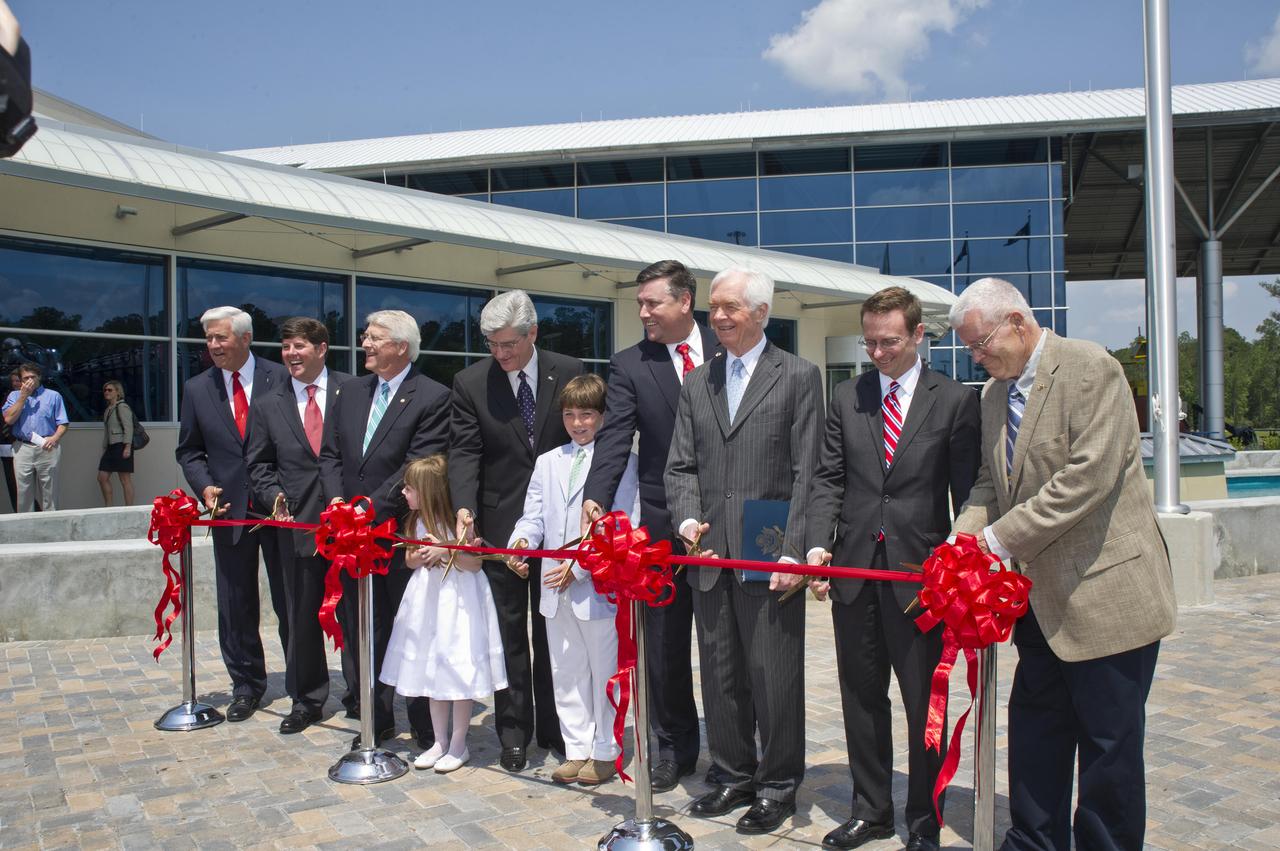

Ceremony participants prepare to cut the ribbon on the INFINITY at NASA Stennis Space Center facility April 11, 2012. Participating in the ceremony were (l to r): Gulfport Mayor and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Chairman George Schloegel; U.S. Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss.; U.S. Sen. Roger Wicker, R-Miss.; Roy S. Estess granddaughter Lauren McKay; Mississippi Gov. Phil Bryant; Leo Seal Jr. grandson Leo Seal IV; Stennis Director Patrick Scheuermann; U.S. Sen. Thad Cochran, R-Miss.; NASA Chief of Staff David Radzanowski; and Apollo 13 astronaut and INFINITY Science Center Inc. Vice Chairman Fred Haise.
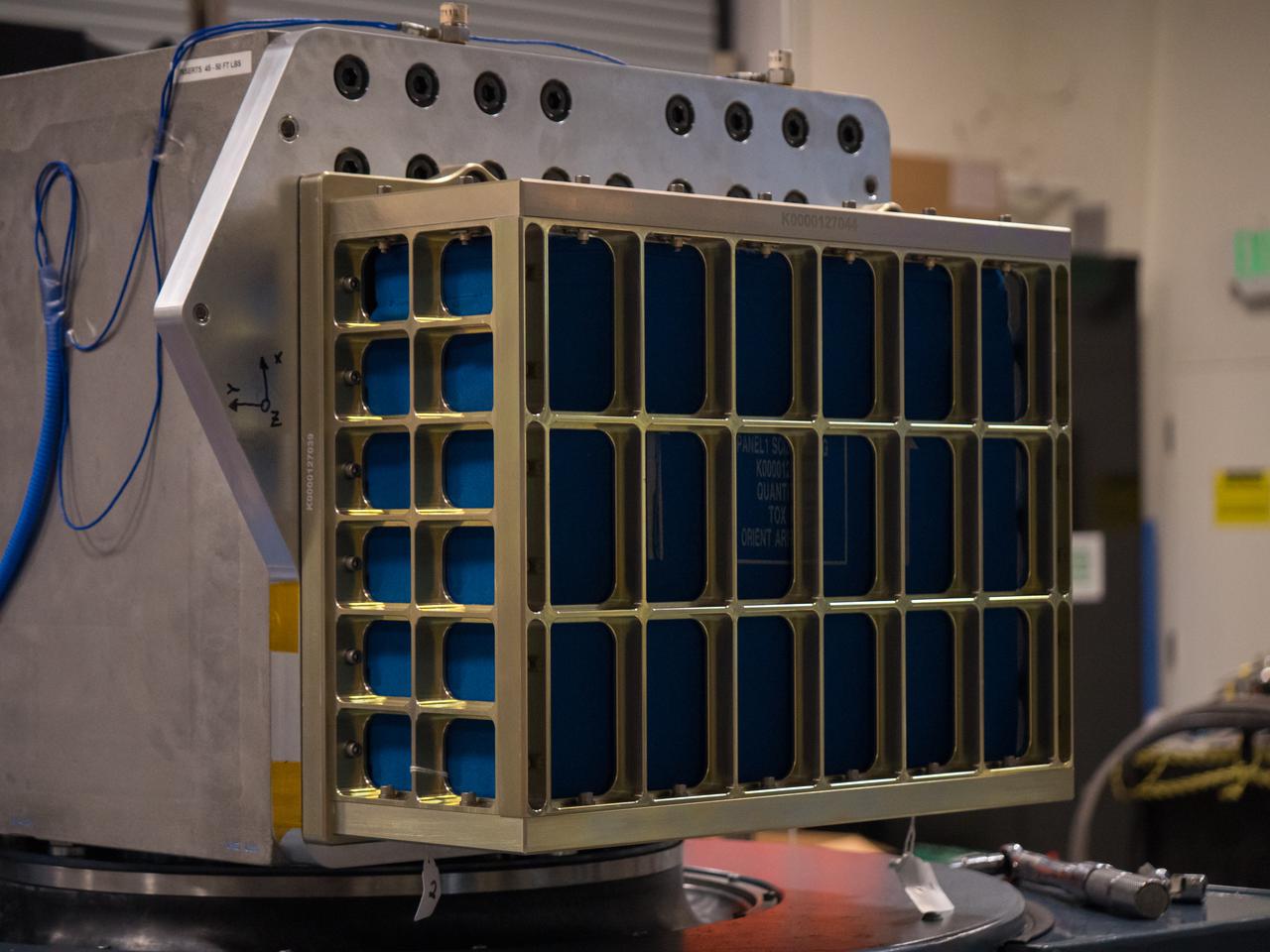
NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) undergoes testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
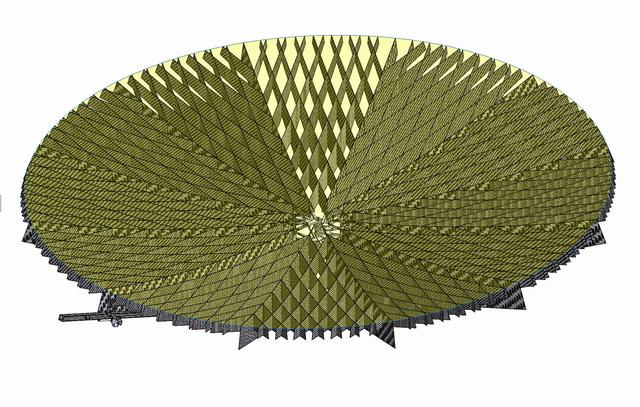
jsc2020e040943 (9/10/2020) --- An example of a copper zirconium antenna metal mesh on a deployable reflector. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: Technosolver Corporation, JAXA.
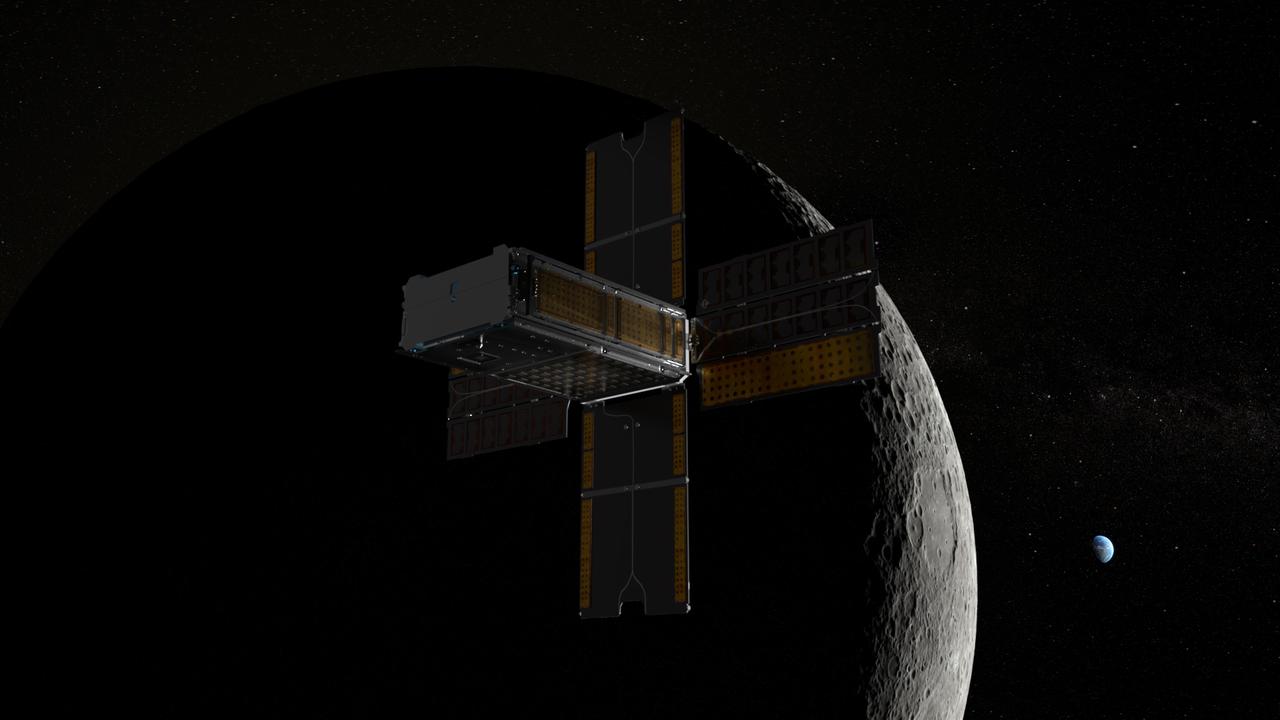

BioSentinel spacecraft leaves Earth and enters a lunar flyby trajectory into a heliocentric orbit. BioSentinel will detect and measure the impact of space radiation on living organisms over long durations beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Illustration by Daniel Rutter.
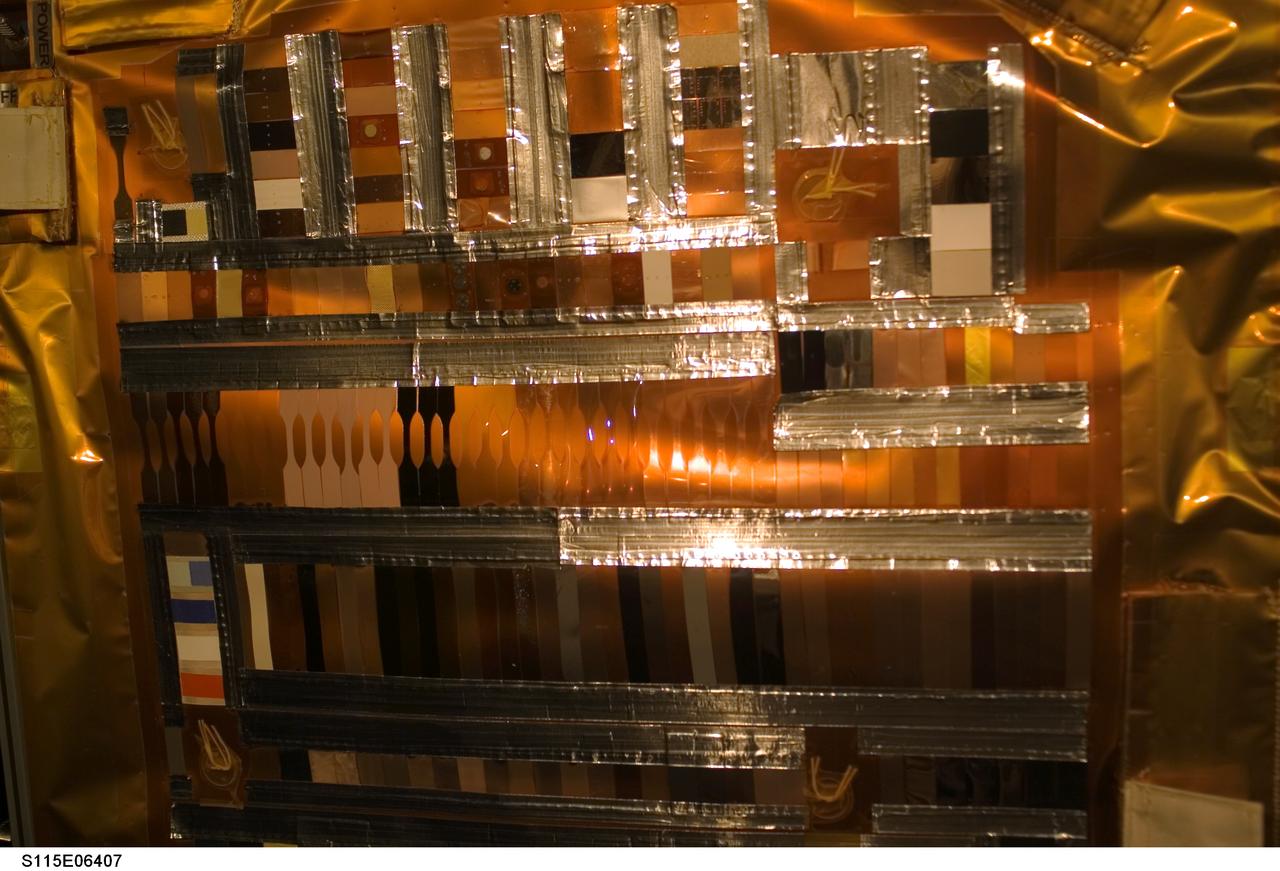

s115e06407 (9/17/2006) --- The Materials International Space Station Experiment-5 (MISSE-5) was an external payload that flew on-board the ISS from August 2005 until September 2006. MISSE-5 provided an opportunity for researchers to test a wide range of samples in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) environment.

Dave Flowers, the project manager for NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) in Exploration Research and Technology Programs, prepares it for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
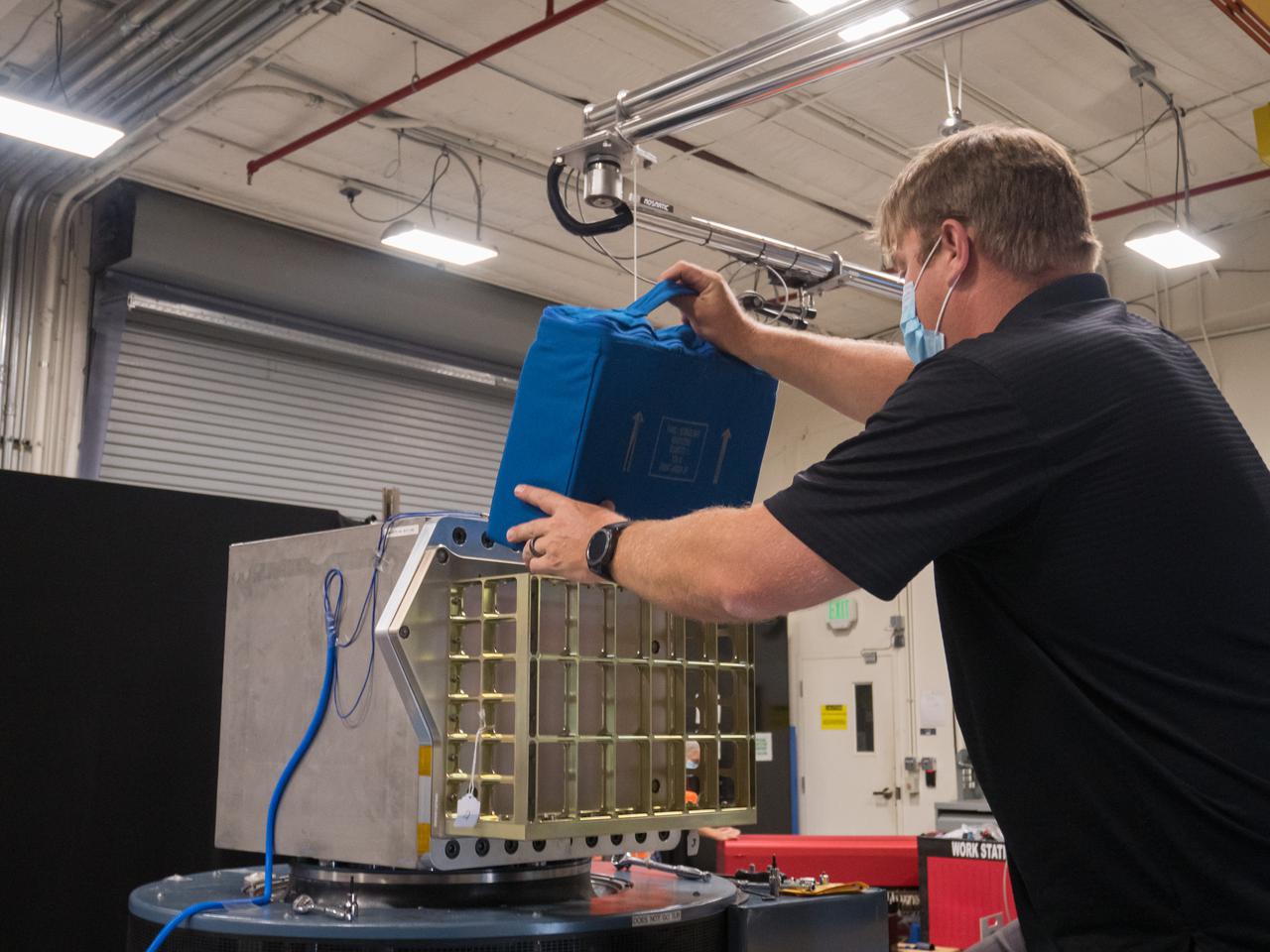

Adam Chaney, a mechanical engineer with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares NASA’s Biology Experiment-1 (BioExpt-1) for testing in the Vibration Laboratory at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 13, 2021. BioExpt-1 is a space biology pathfinder, which will carry plants, algae, yeast, and fungi for biology research beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). NASA will install the BioExpt-1 payload container assembles onto panels inside the Orion capsule. BioExpt-1 will return these science payloads to Earth to provide critical and unique data about life beyond LEO for the first time in more than 40 years. Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration of the Moon and eventually on to Mars.
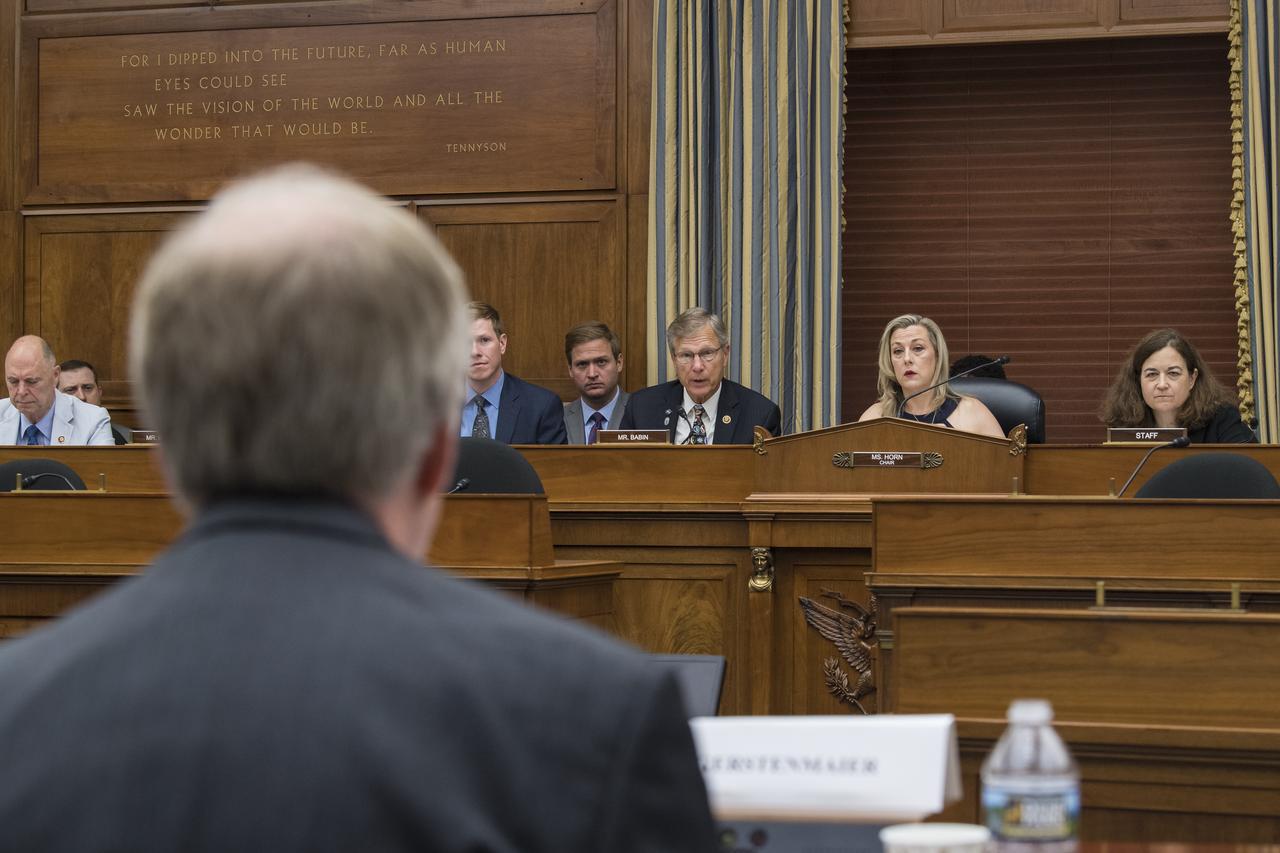

Congressman Brian Babin, R-Texas, asks NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, a question during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

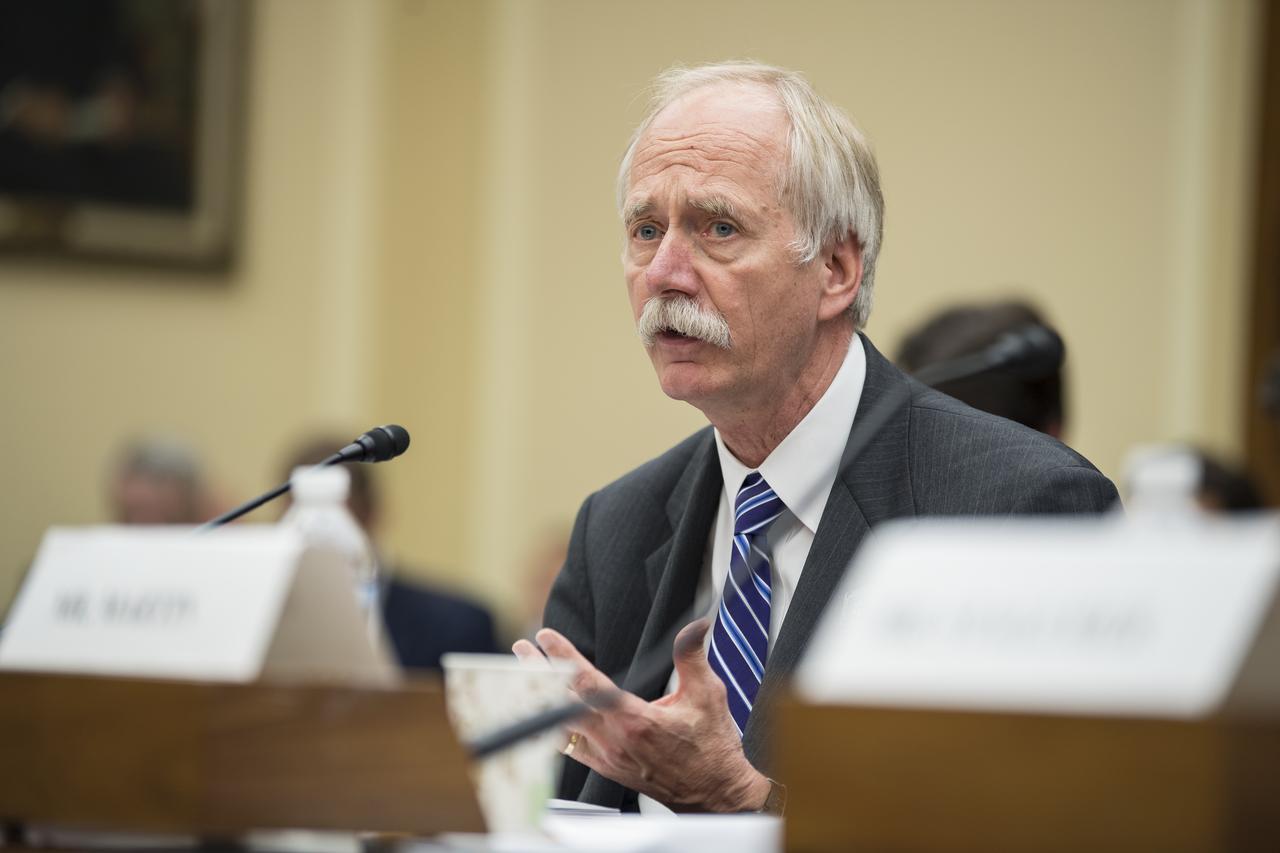
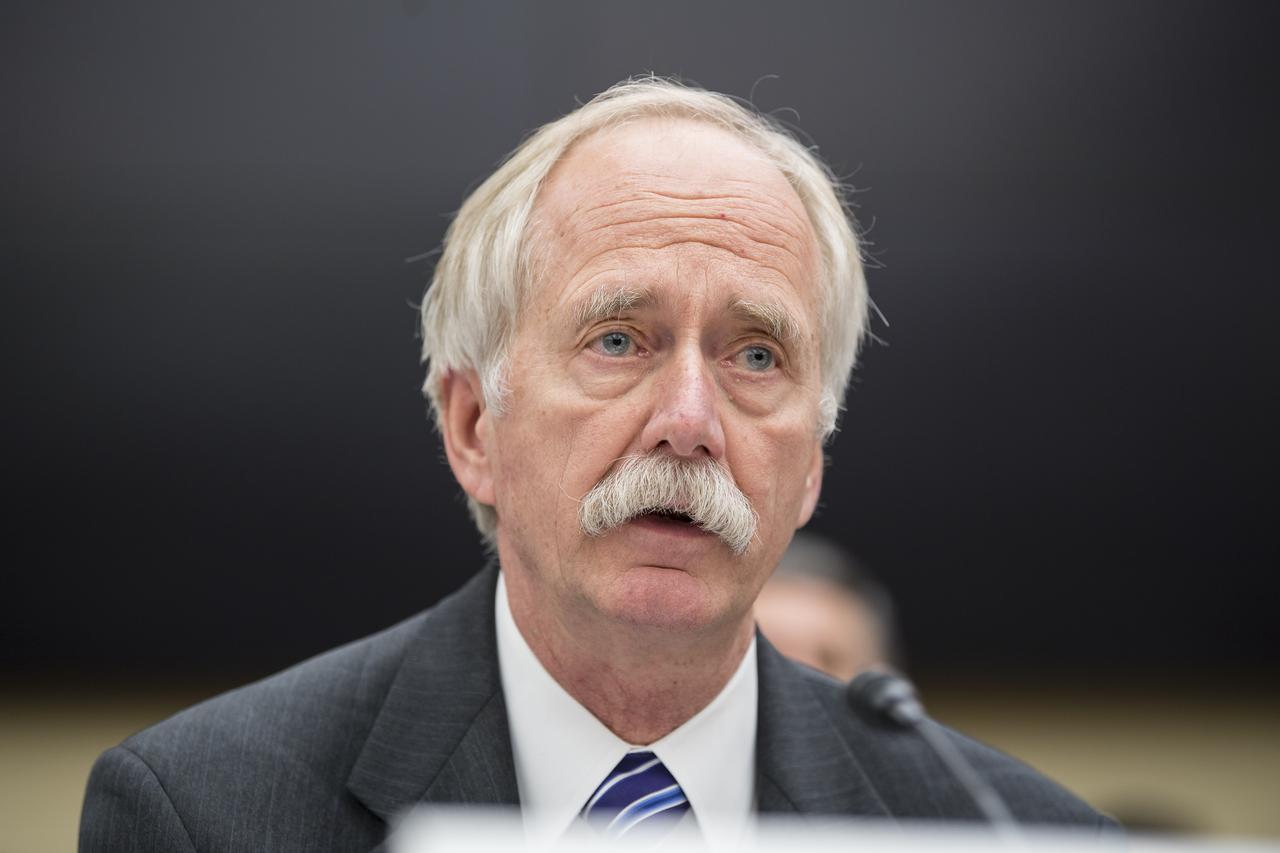
The Honorable Paul Martin, inspector general, NASA, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
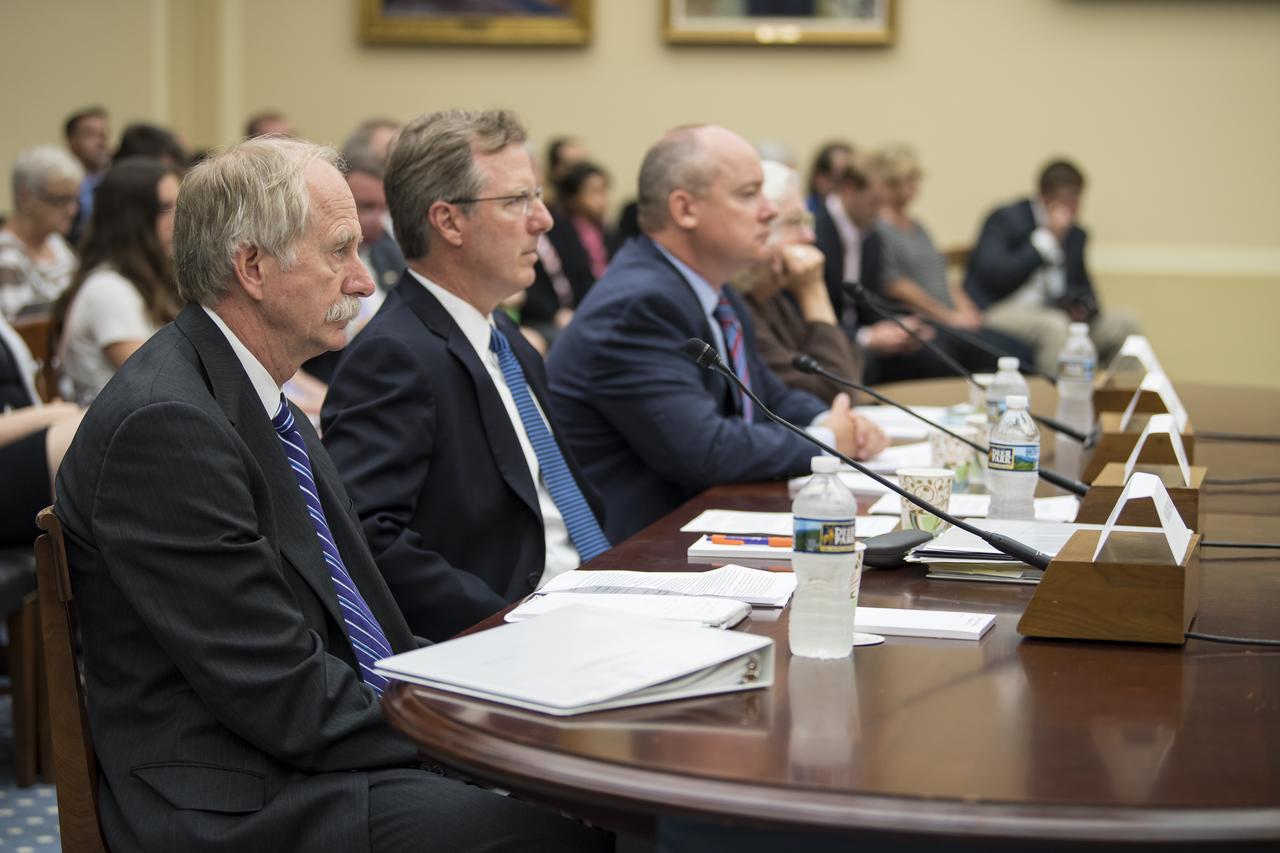

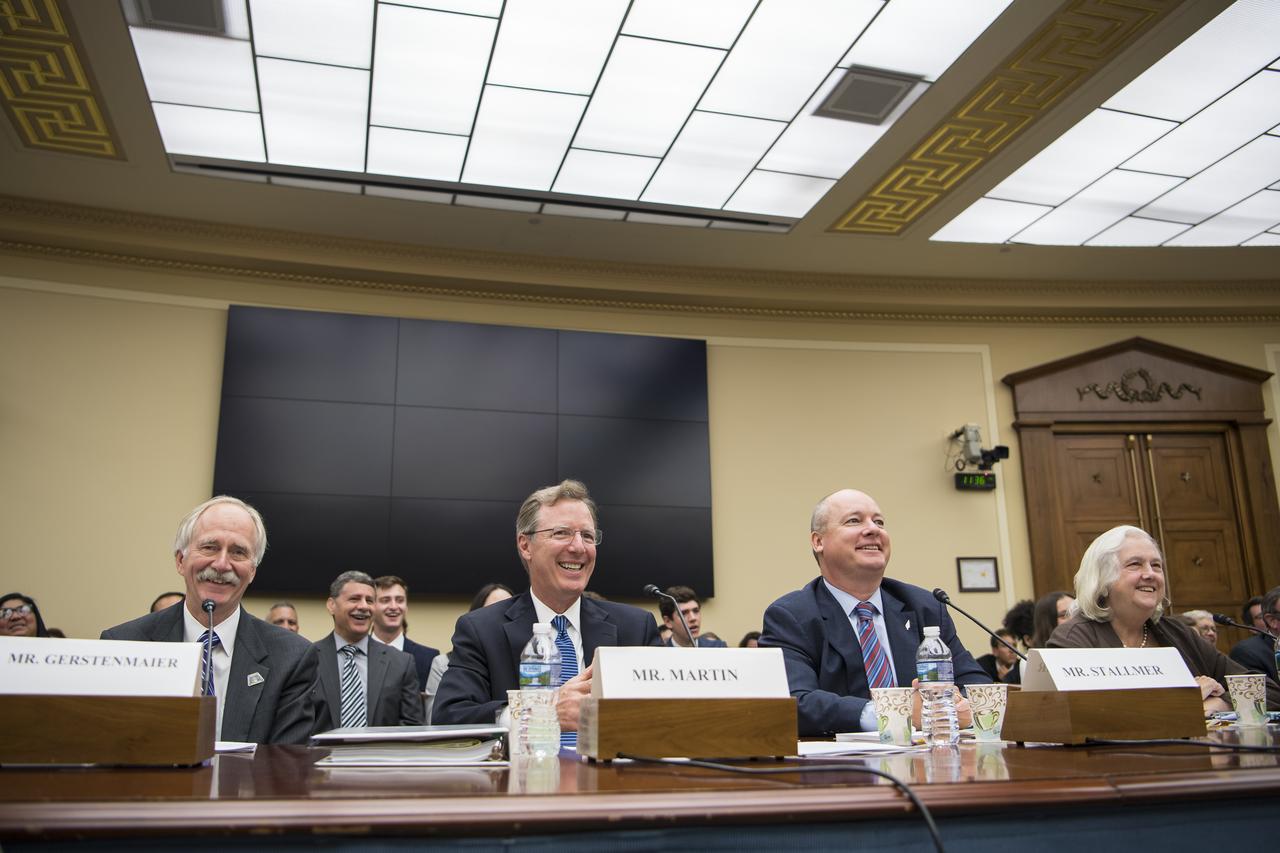
From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier; NASA Inspector General, Paul Martin; Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer; and University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz testify during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
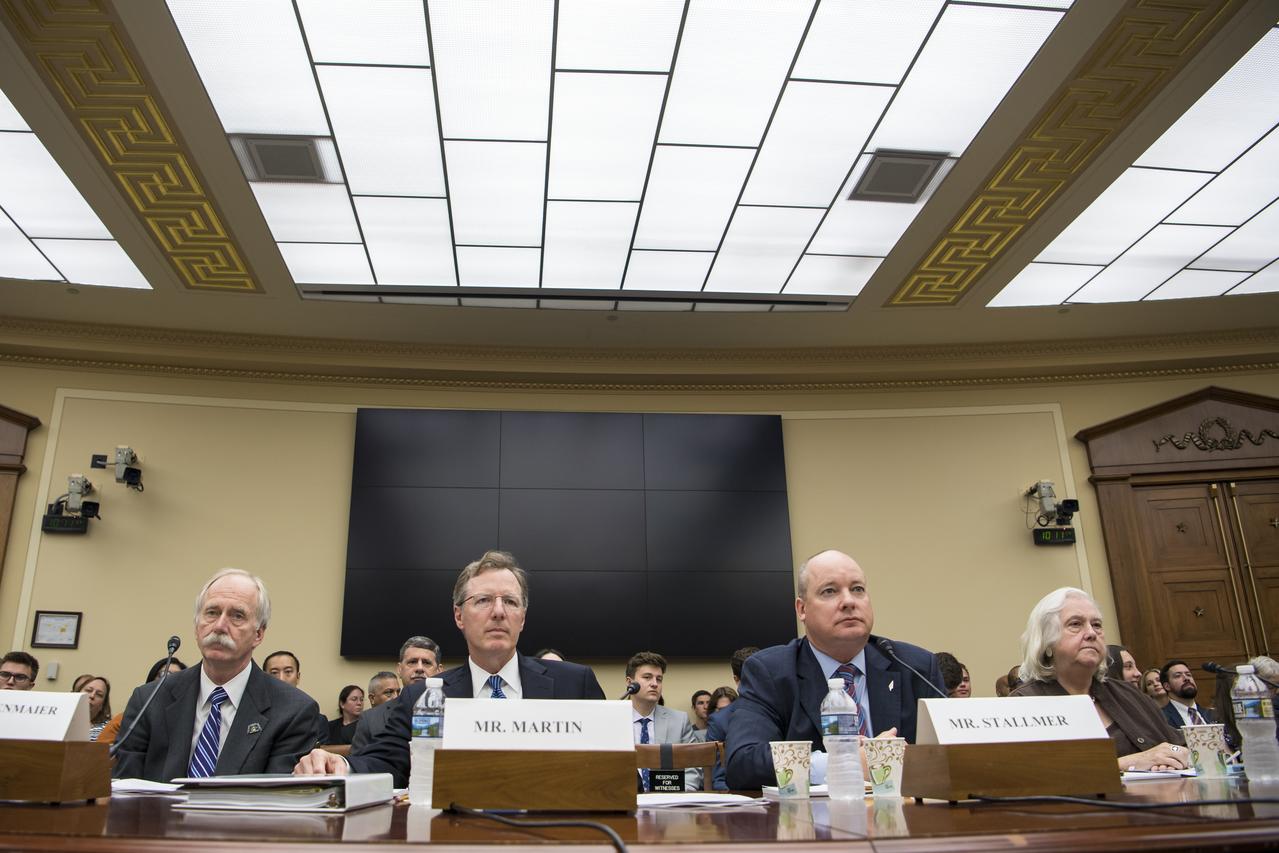

From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier; NASA Inspector General, Paul Martin; Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer; and University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz testify during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

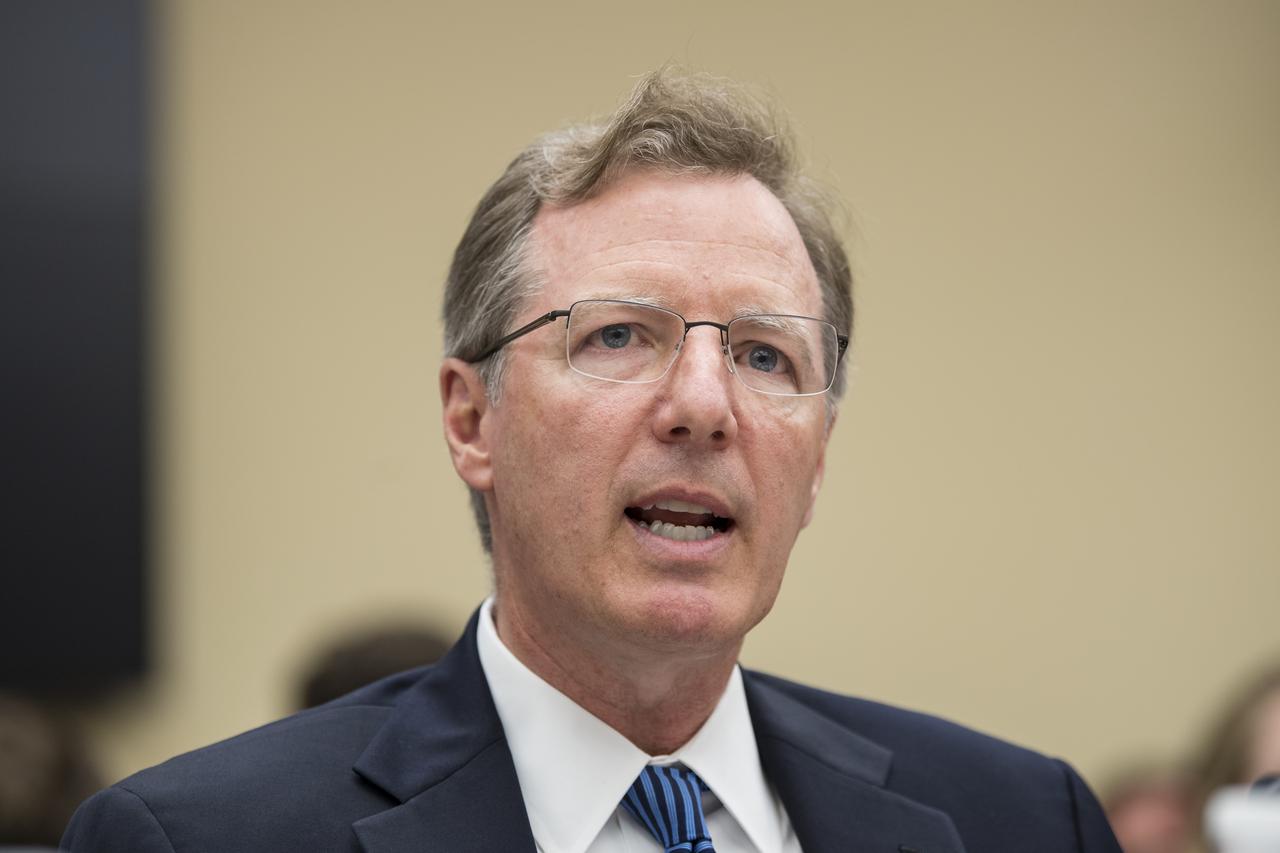
NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The Honorable Paul Martin, inspector general, NASA, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
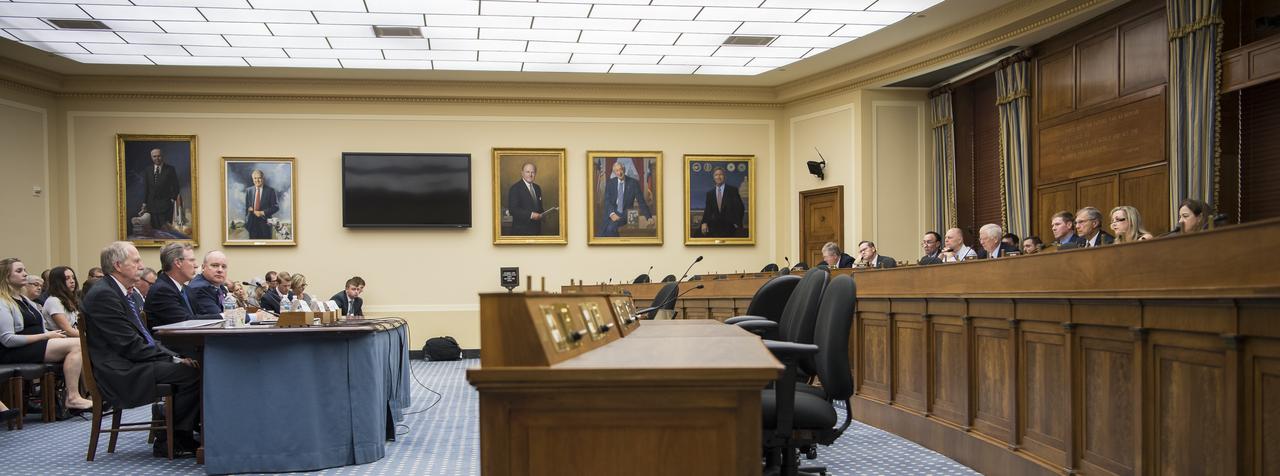

From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier; NASA Inspector General, Paul Martin; Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer; and University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz testify during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Chair of the Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee, Kendra Horn, D-Okla., speaks during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," where NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, and NASA Inspector General, Paul Martin testified, Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, right, speaks with Chair of the Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee, Congresswoman Kendra Horn, D-Okla., second from left, after he testified during a House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
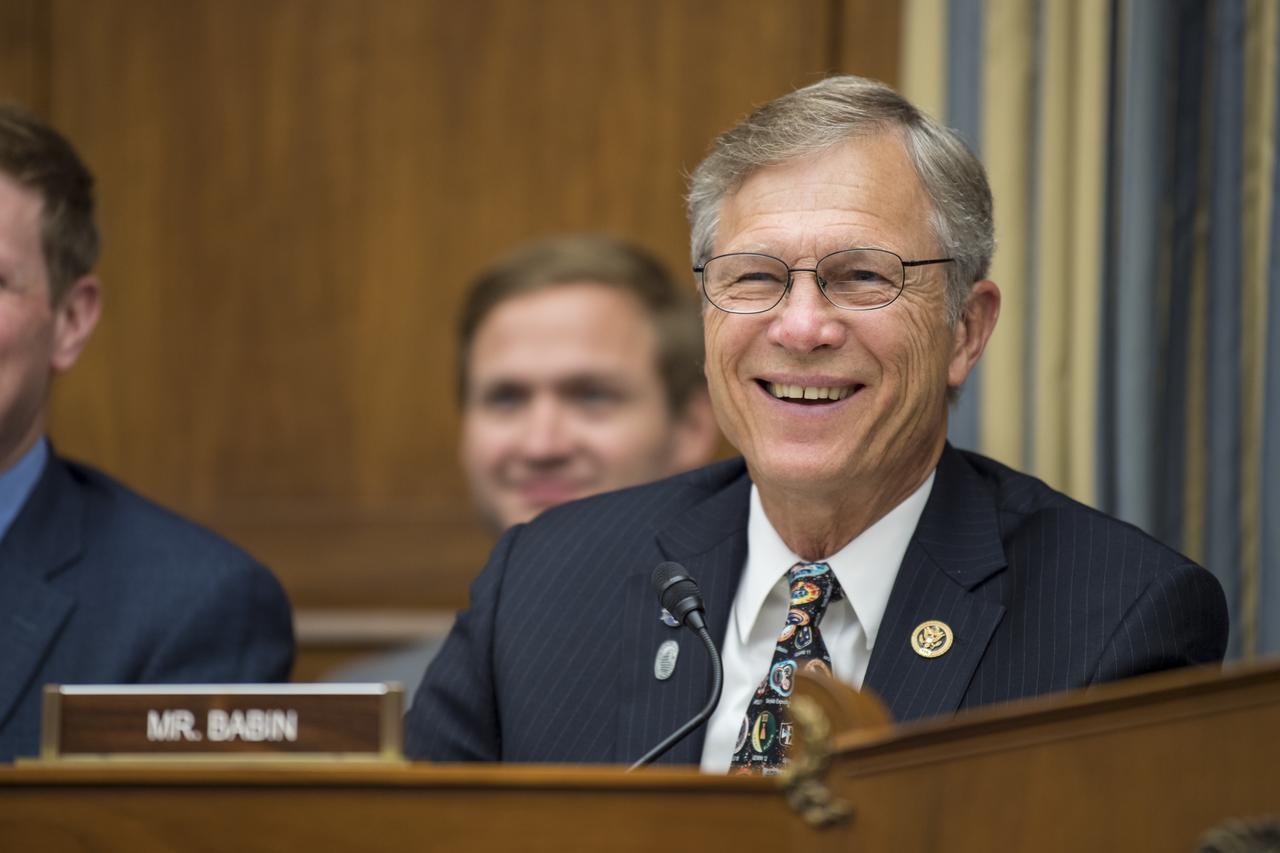

Congressman Brian Babin, R-Texas, reacts during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
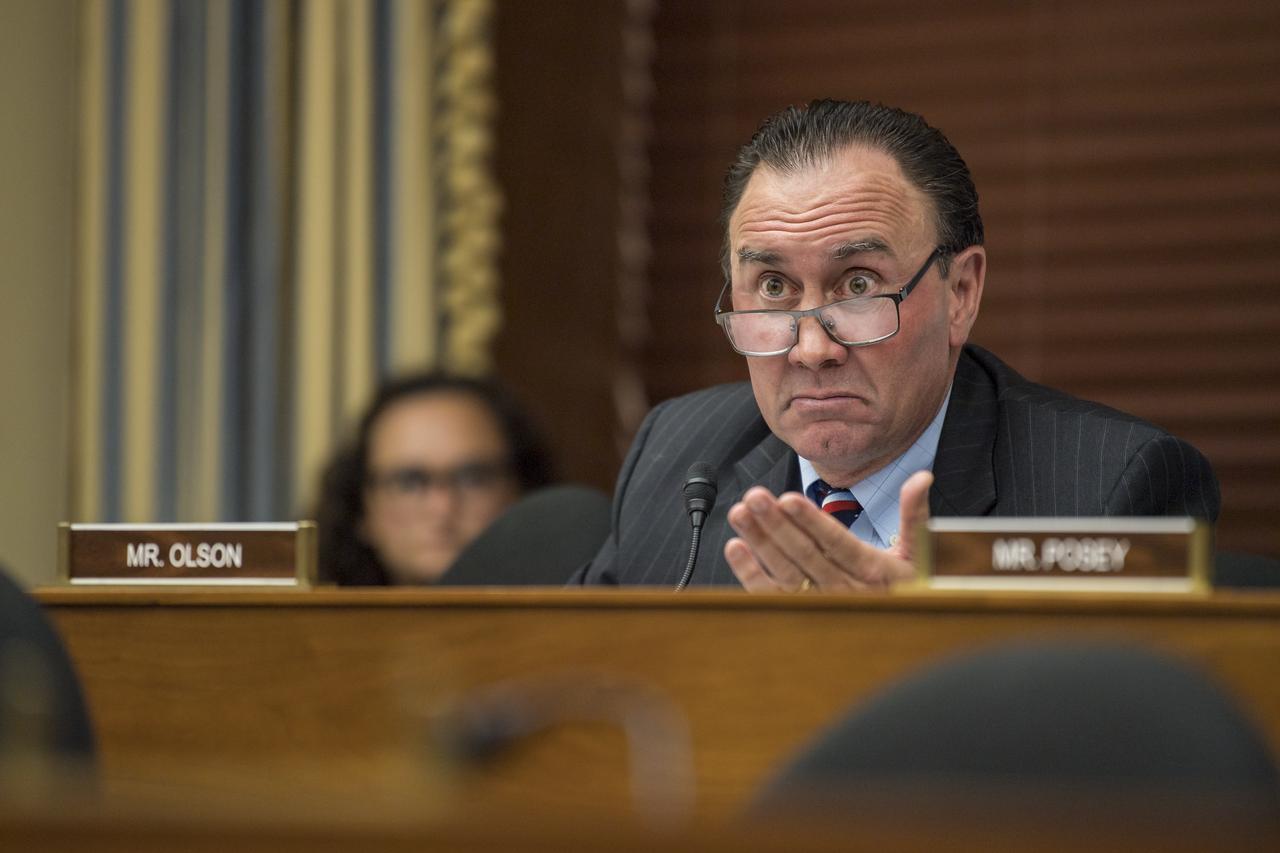

Congressman Pete Olson, R-Texas, asks NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, a question during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
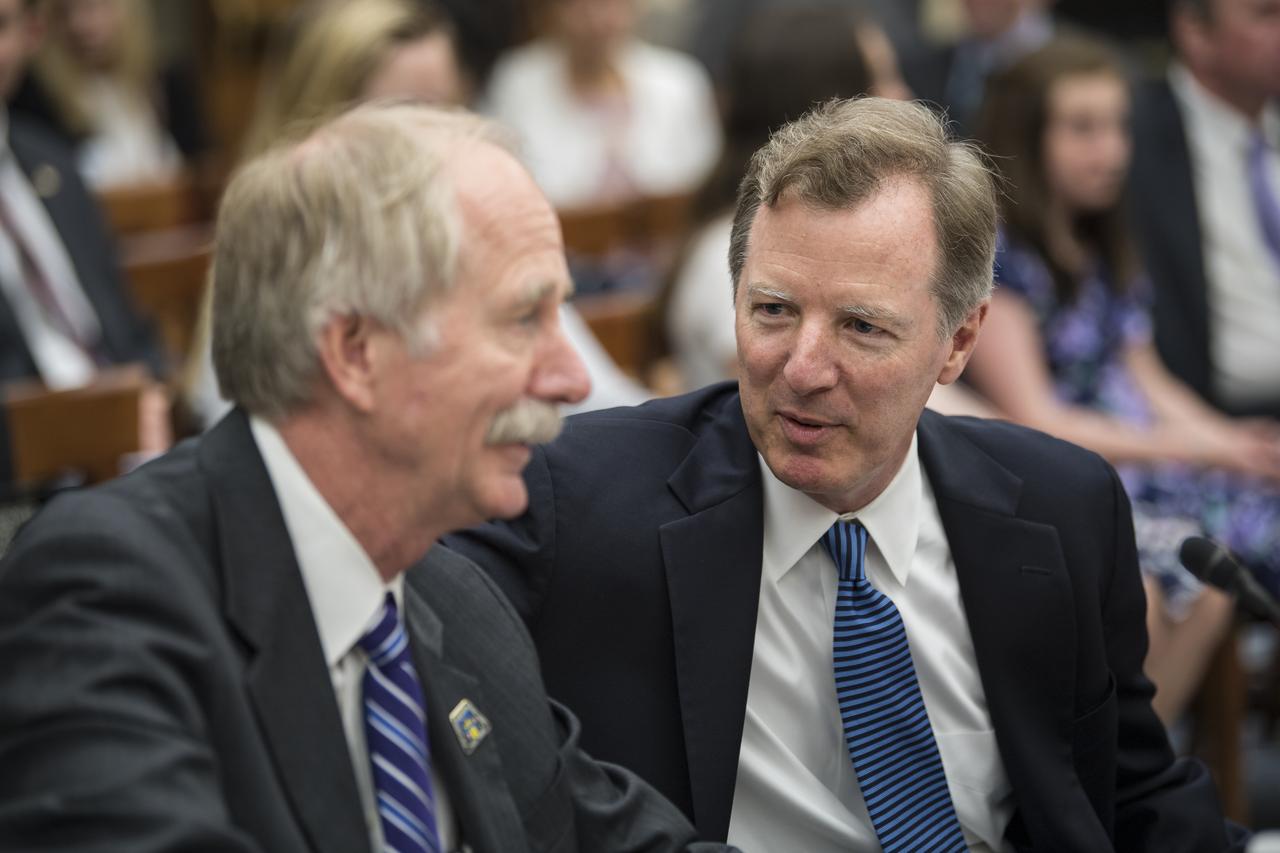
The Honorable Paul Martin, inspector general, NASA, speaks to Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, NASA, before they testify during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
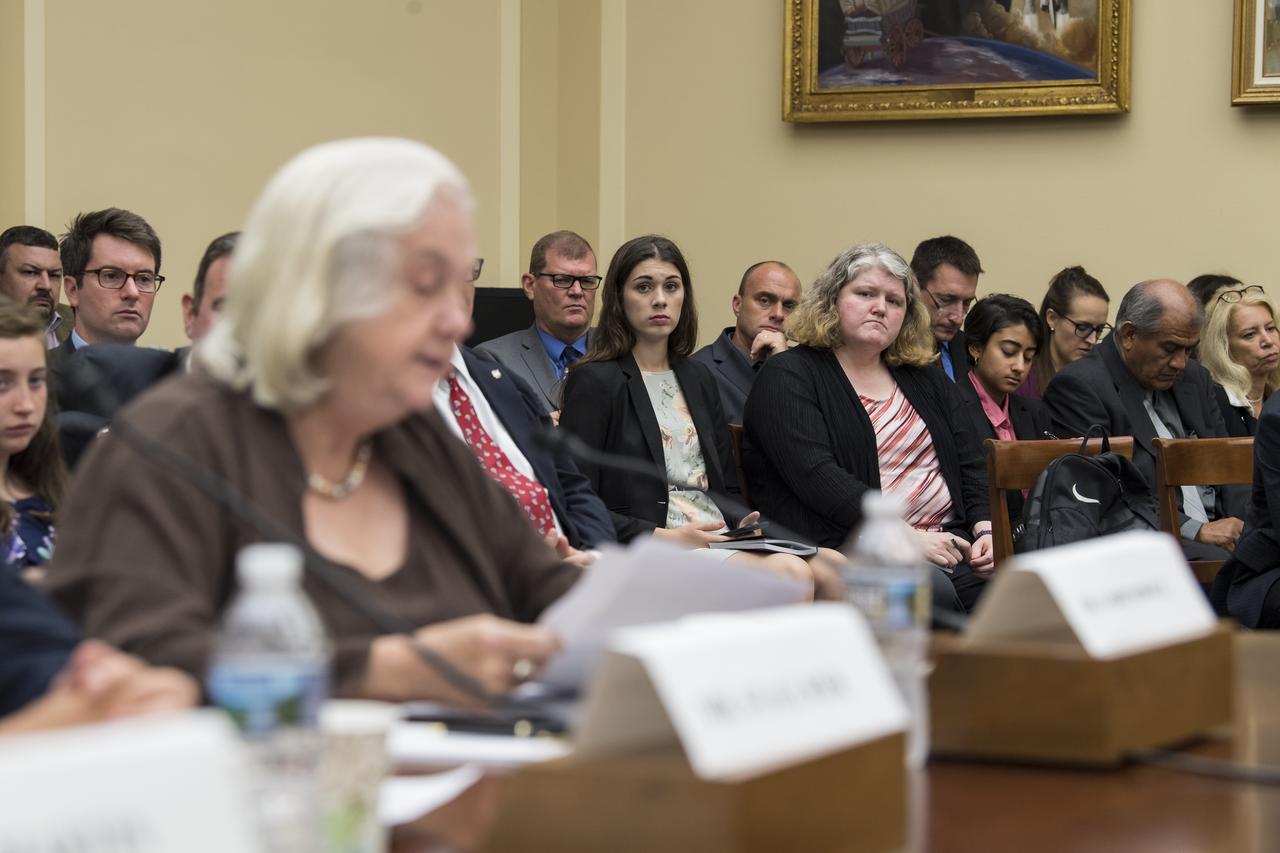
Audience members listen as University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
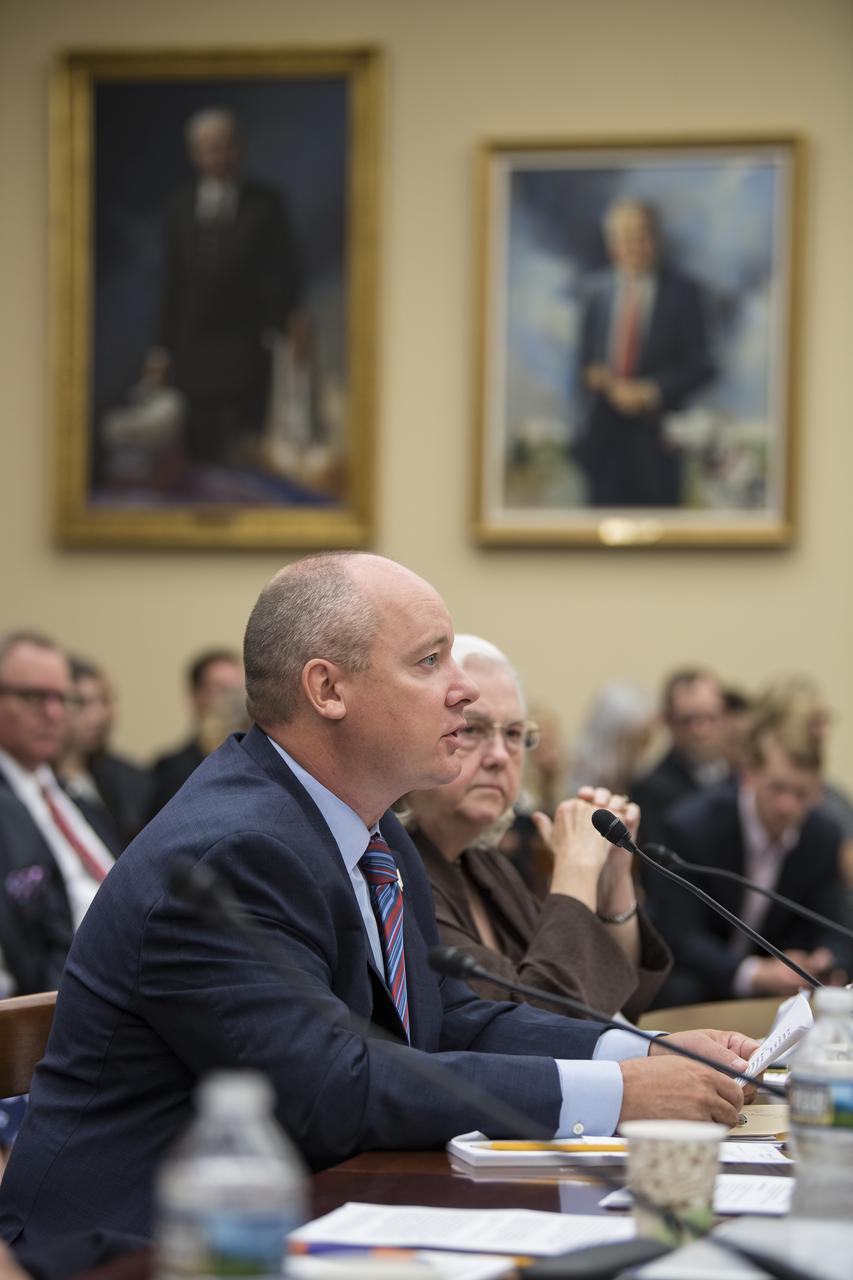

Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
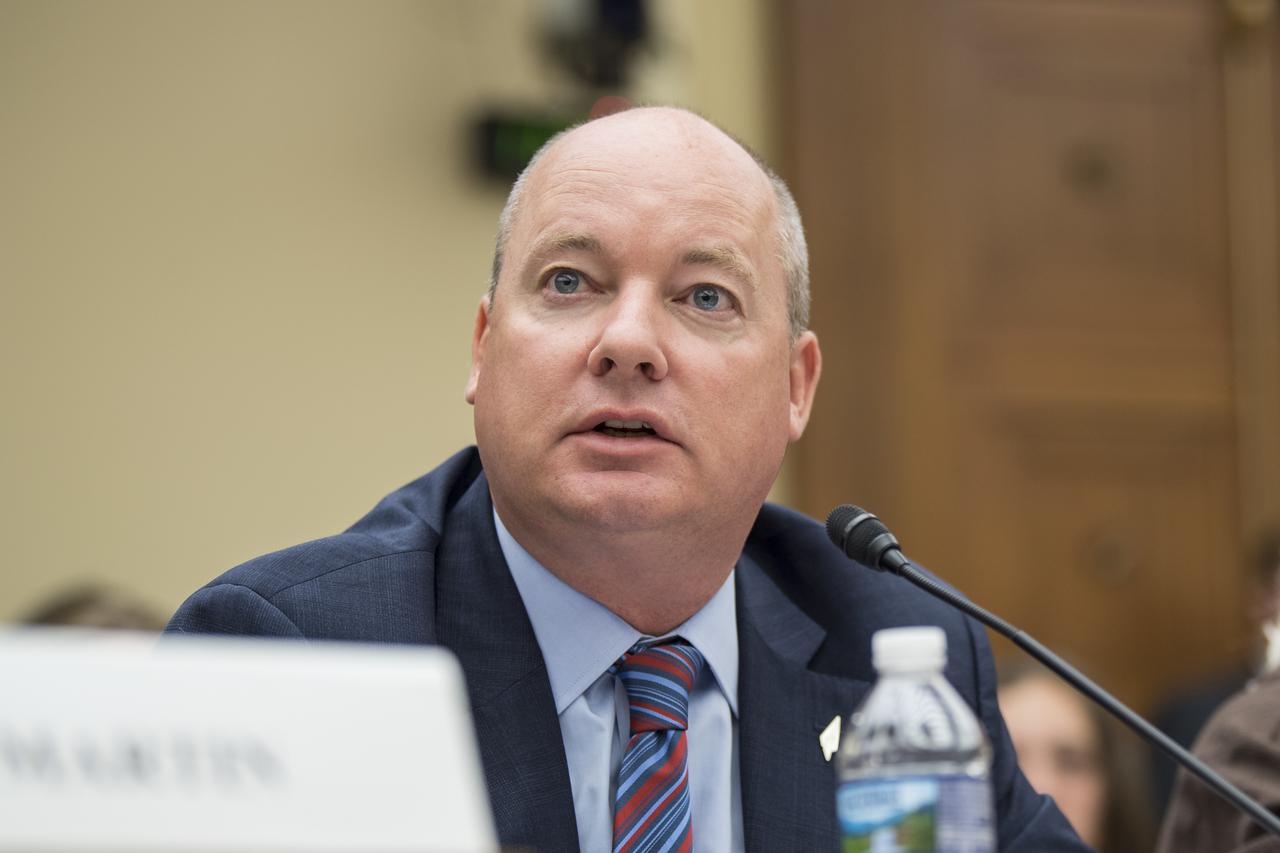

Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, testifies during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
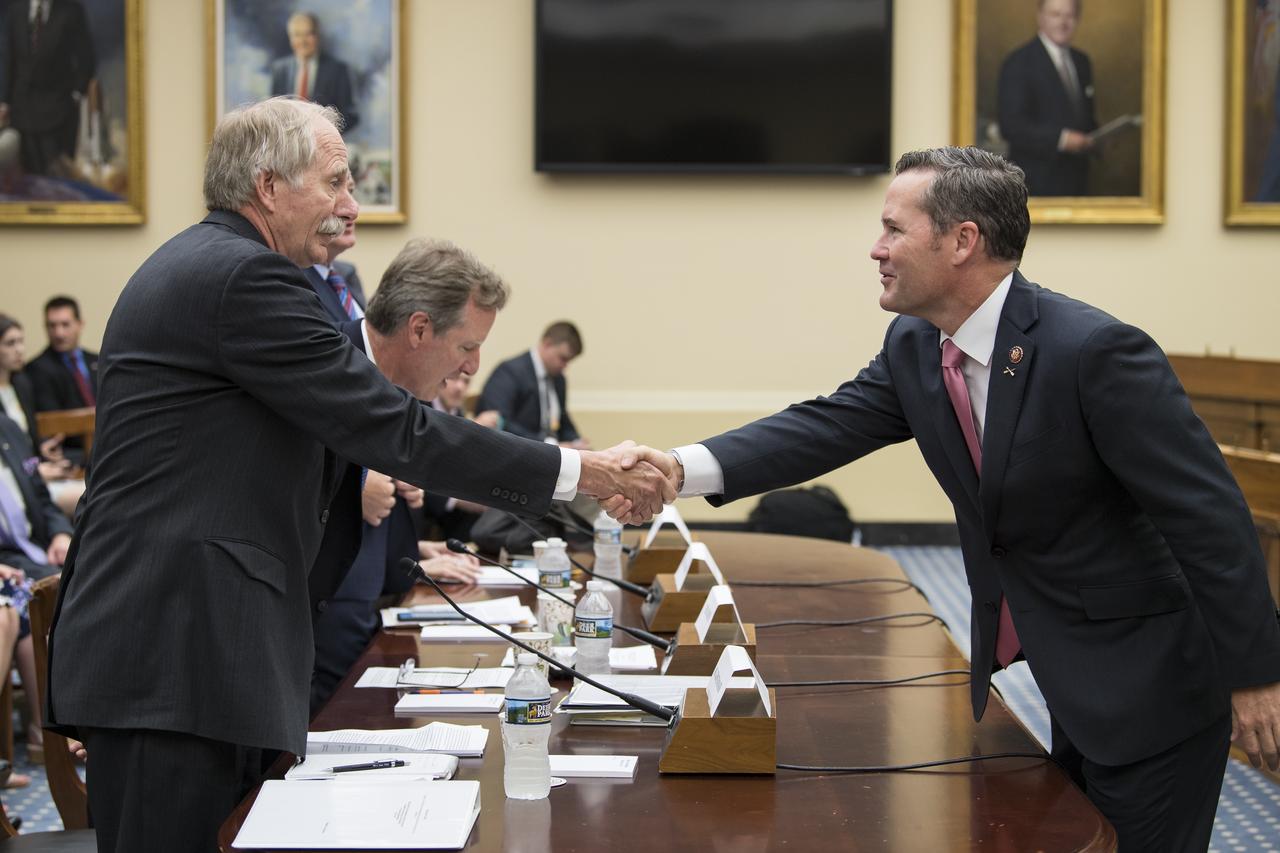

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier, left, shakes hands with Congressman Michael Waltz, R-Fla., before testifying during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

U.S. Representative Eddie Johnson, D-Texas, asks a question during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations, Bill Gerstenmaier; NASA Inspector General, Paul Martin; Commercial Spaceflight Federation President, Eric Stallmer; and University of Mississippi Professor Emerita and Editor in Chief of the Journal of Space Law, Joanne Gabrynowicz react to a comment by Congressman Pete Olson (R-TX) during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “A Review of NASA’s Plans for the International Space Station and Future Activities in Low Earth Orbit," Wednesday, July 10, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
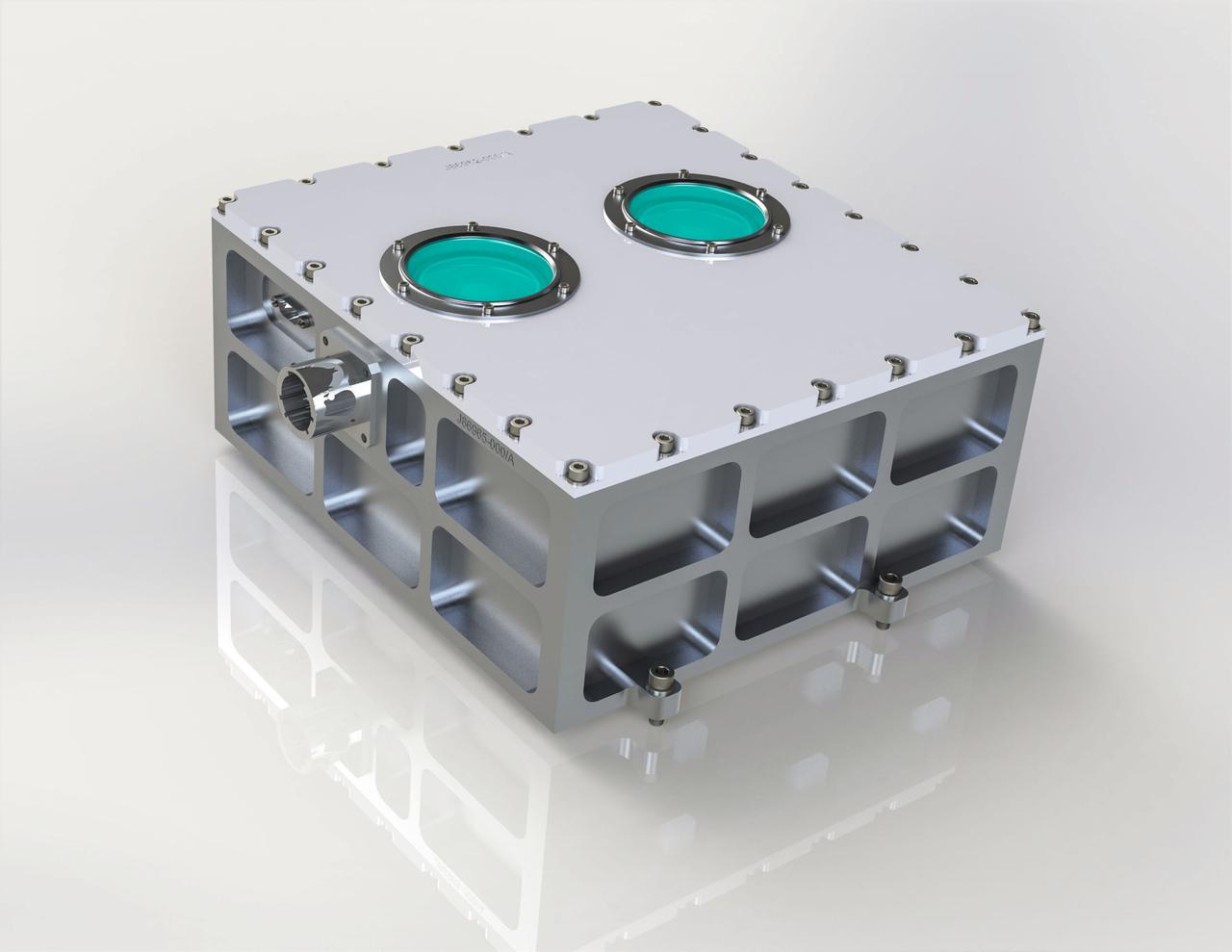
jsc2022e031221 (4/26/2022) --- An external view of the LEONIDAS payload displaying the NREP interface connection and viewing windows for the standard optical sensor and event based sensor. LEO-TM N-REP ISS Demonstration Advanced Sensor (Nanoracks-LEONIDAS) explores design of low-Earth orbit satellites to perform portions of the Department of Energy mission. The investigation collects data on various backgrounds (local time of day, glint, clouds, etc.) to support development of a machine learning algorithm. Imagery courtesy of Sandia National Laboratory.
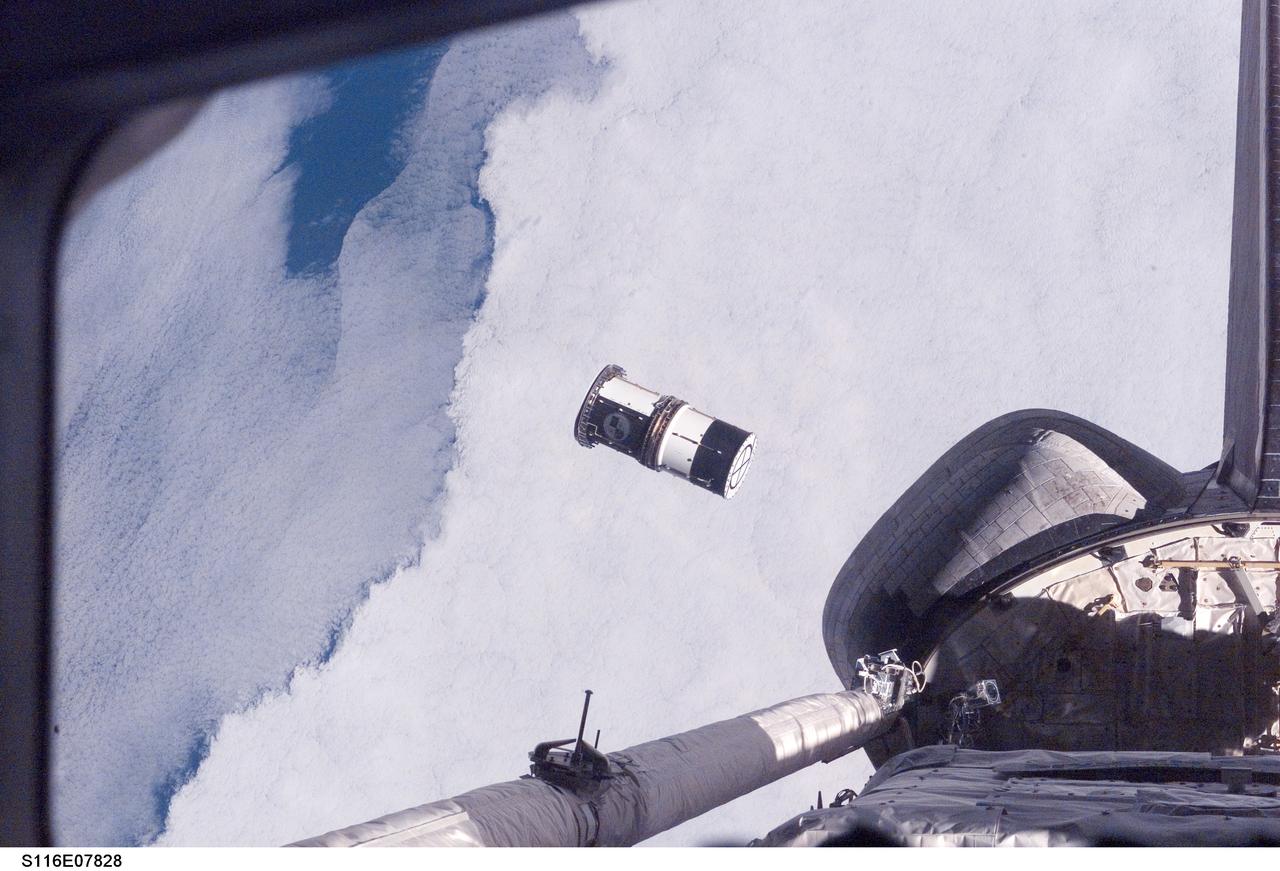

S116-E-07828 (21 Dec. 2006) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Discovery, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment (ANDE) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-116 crewmembers. ANDE consists of two micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
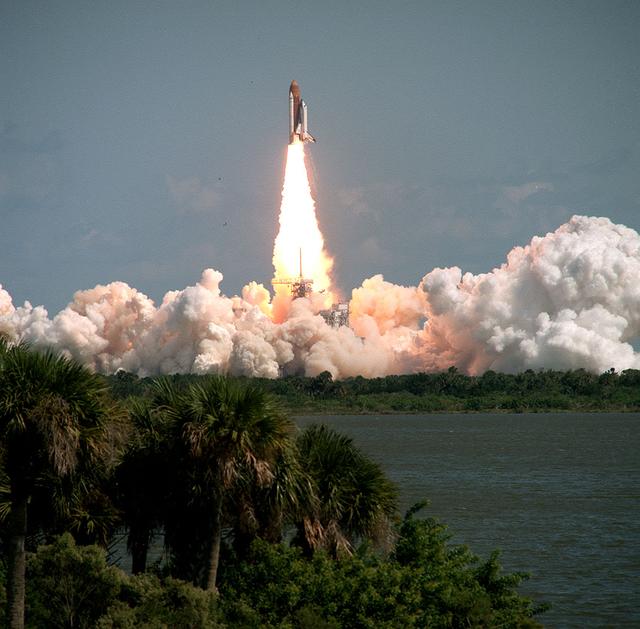

The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-52) thunders off Launch Pad 39B, embarking on a 10-day flight and carrying a crew of six who will deploy the Laser Geodynamic Satellite II (LAGEOS). LAGEOS is a spherical passive satellite covered with reflectors which are illuminated by ground-based lasers to determine precise measurements of the Earth's crustal movements. The other major payload on this mission is the United States Microgravity Payload 1 (USMP-1), where experiments will be conducted by crew members while in low earth orbit (LEO).

Kathleen Boggs, Systems and Technology Demonstration Manager in the International Space Station Division of NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, is seen a keynote titled “From LEO to the Moon, Mars, and Beyond: Shaping Capability Development Strategies for NASA’s Human Exploration Campaign” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Thursday, Oct. 24, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
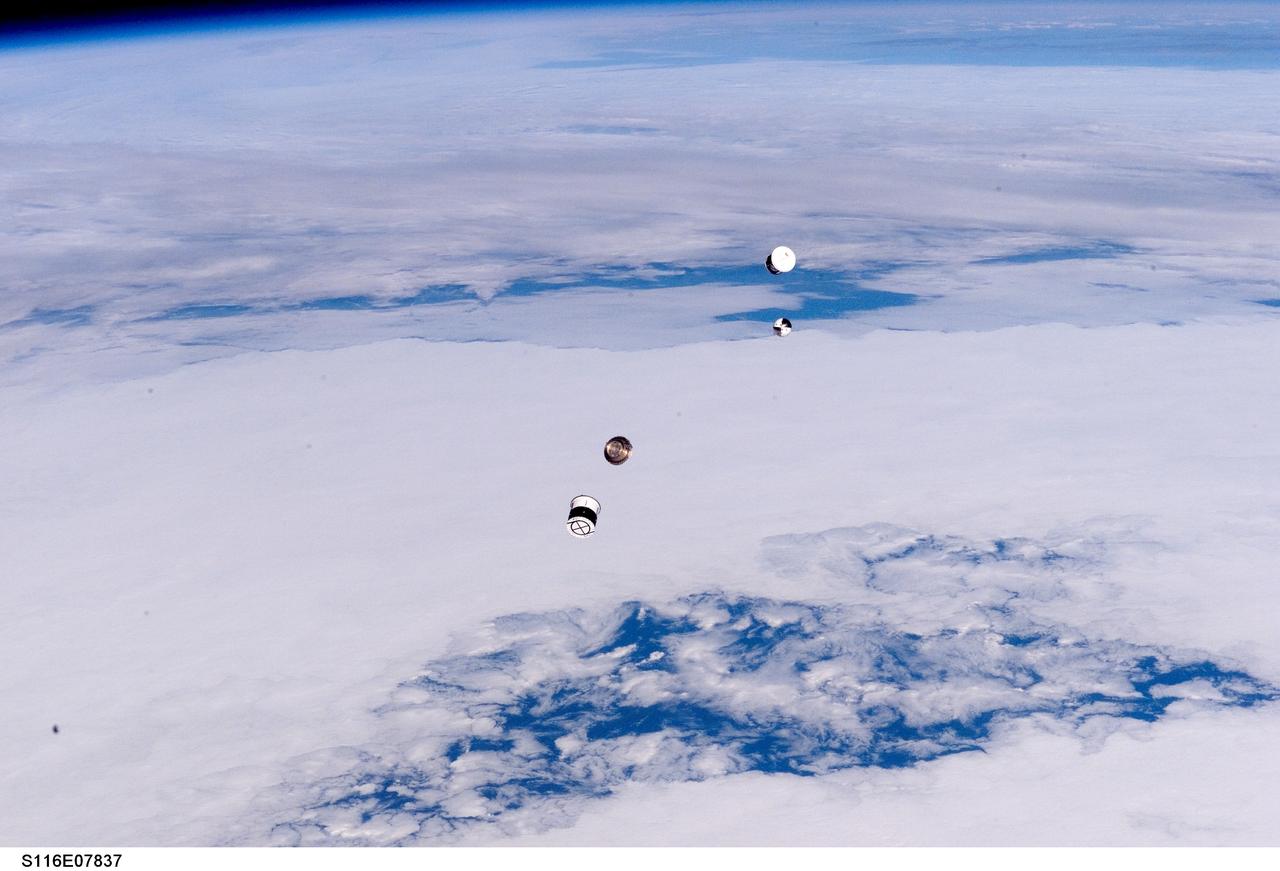

S116-E-07837 (21 Dec. 2006) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Discovery, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment (ANDE) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-116 crewmembers. ANDE consists of two micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
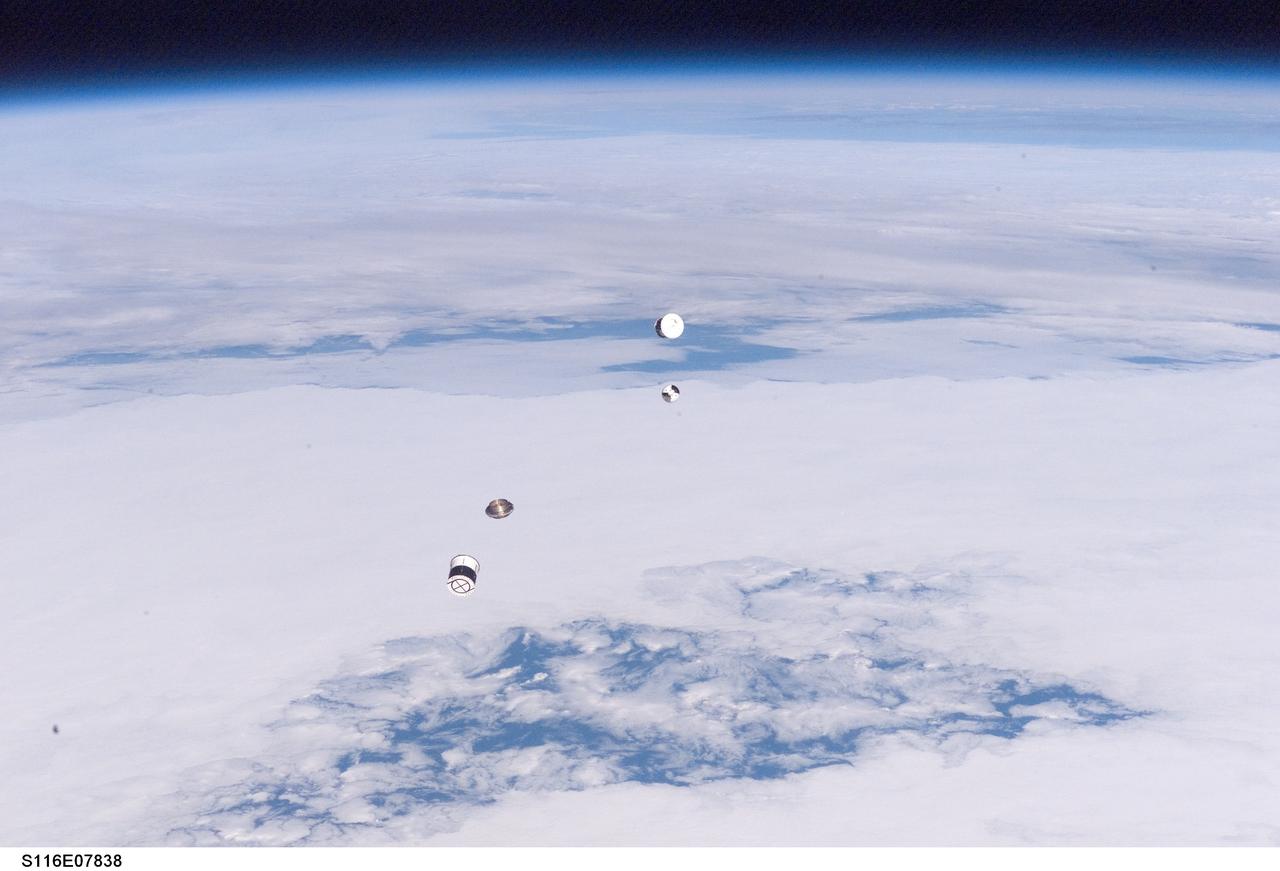

S116-E-07838 (21 Dec. 2006) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Discovery, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment (ANDE) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-116 crewmembers. ANDE consists of two micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
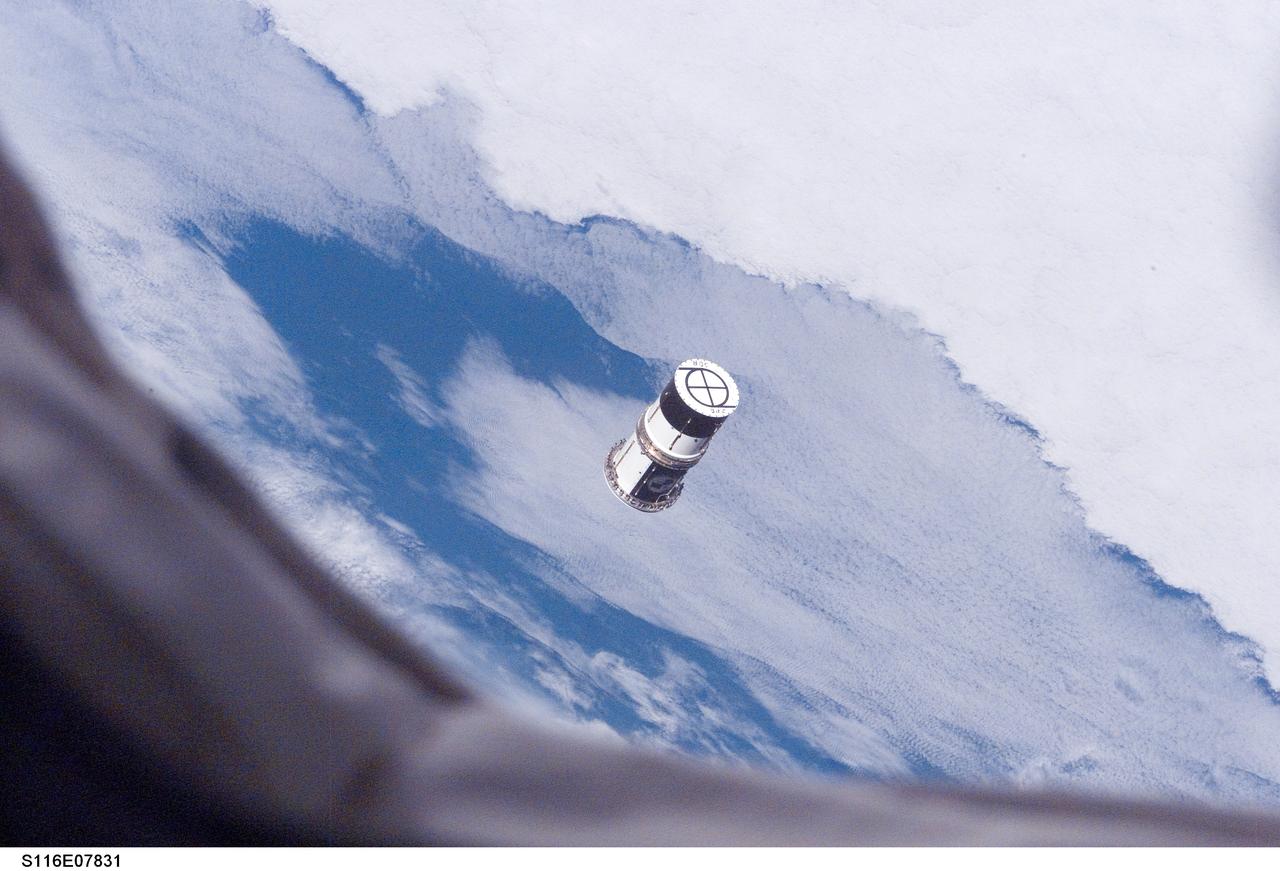

S116-E-07831 (21 Dec. 2006) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Discovery, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment (ANDE) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-116 crewmembers. ANDE consists of two micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
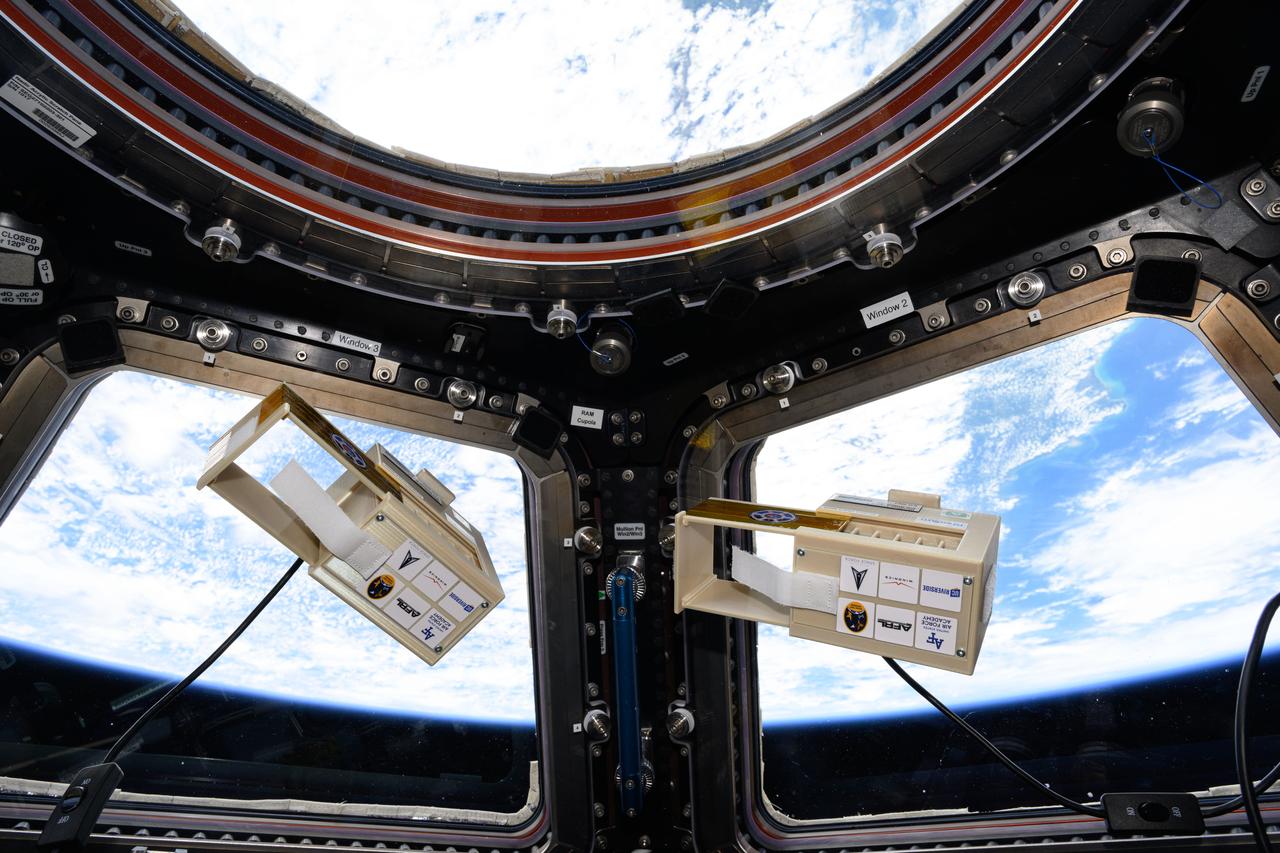

iss073e0076872 (5/21/2025) --- The LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) hardware seen aboard the International Space Station. Rhodium Plant LIFE studies how radiation and gravitational forces at different orbital altitudes affect plant growth. Results could provide a better understanding of plant growth in space and reveal how changes in gene expression influence root development, contributing to improved production of plants in space and on Earth.
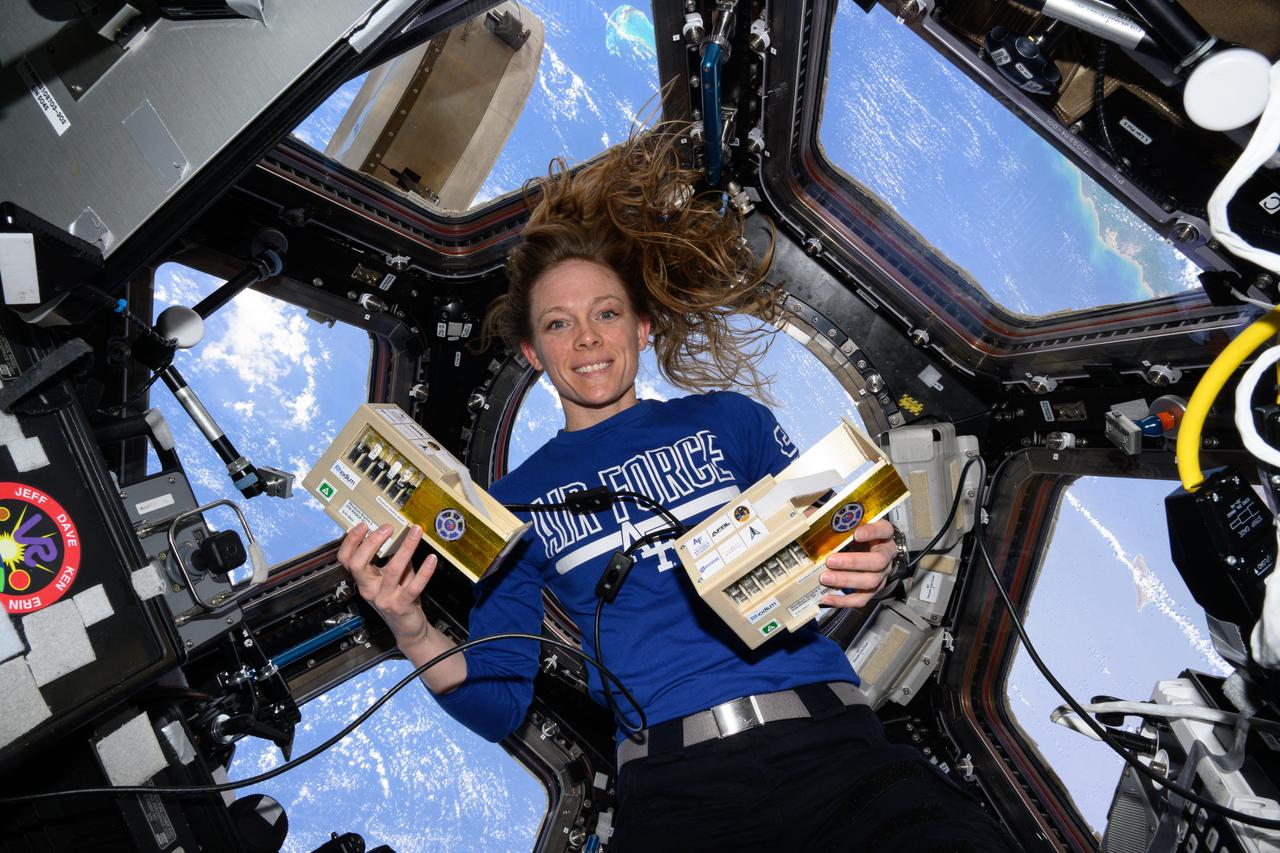

iss073e0076885 (5/21/2025) --- NASA astronaut Nichole Ayers is pictured inside the cupola with space botany hardware that supports the LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) investigation. The investigation studies the affects of radiation and microgravity on plant growth to promote self-sustainable long-term human missions and increase crop production on Earth.

s114e7235 (8/6/2005) --- Backdropped by a colorful Earth, this aft view of the International Space Station was photographed during the flyaround by the Space Shuttle Discovery following the undocking of the two spacecraft. Visible in the frame are the P6 Truss / Photovoltaic Solar Arrays and MISSE-5. The Materials International Space Station Experiment-5 (MISSE-5) was an external payload that flew on-board the ISS from August 2005 until September 2006. MISSE-5 provided an opportunity for researchers to test a wide range of samples in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) environment.
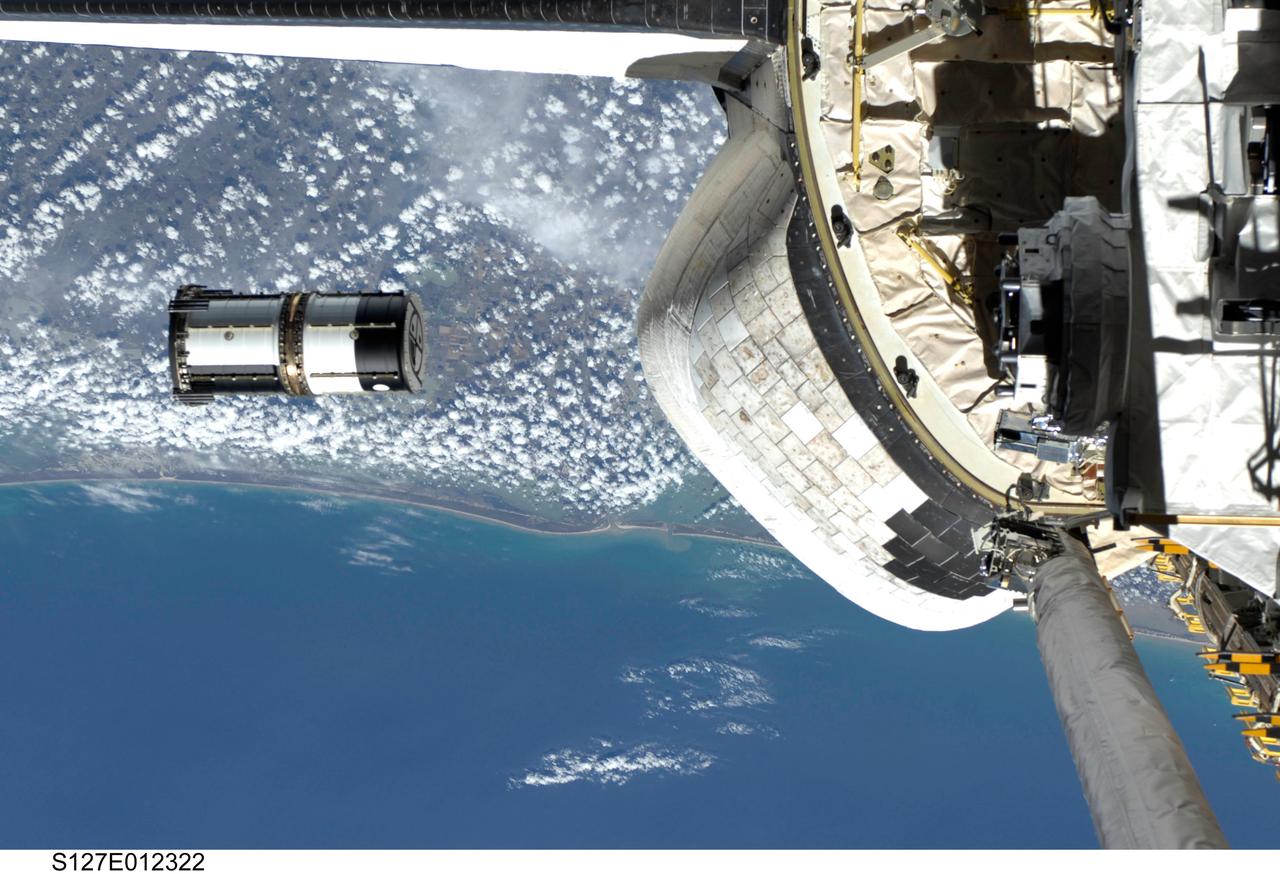

S127-E-012322 (30 July 2009) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment 2 (ANDE-2) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-127 crew members. ANDE-2 consists of two spherical micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low-Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
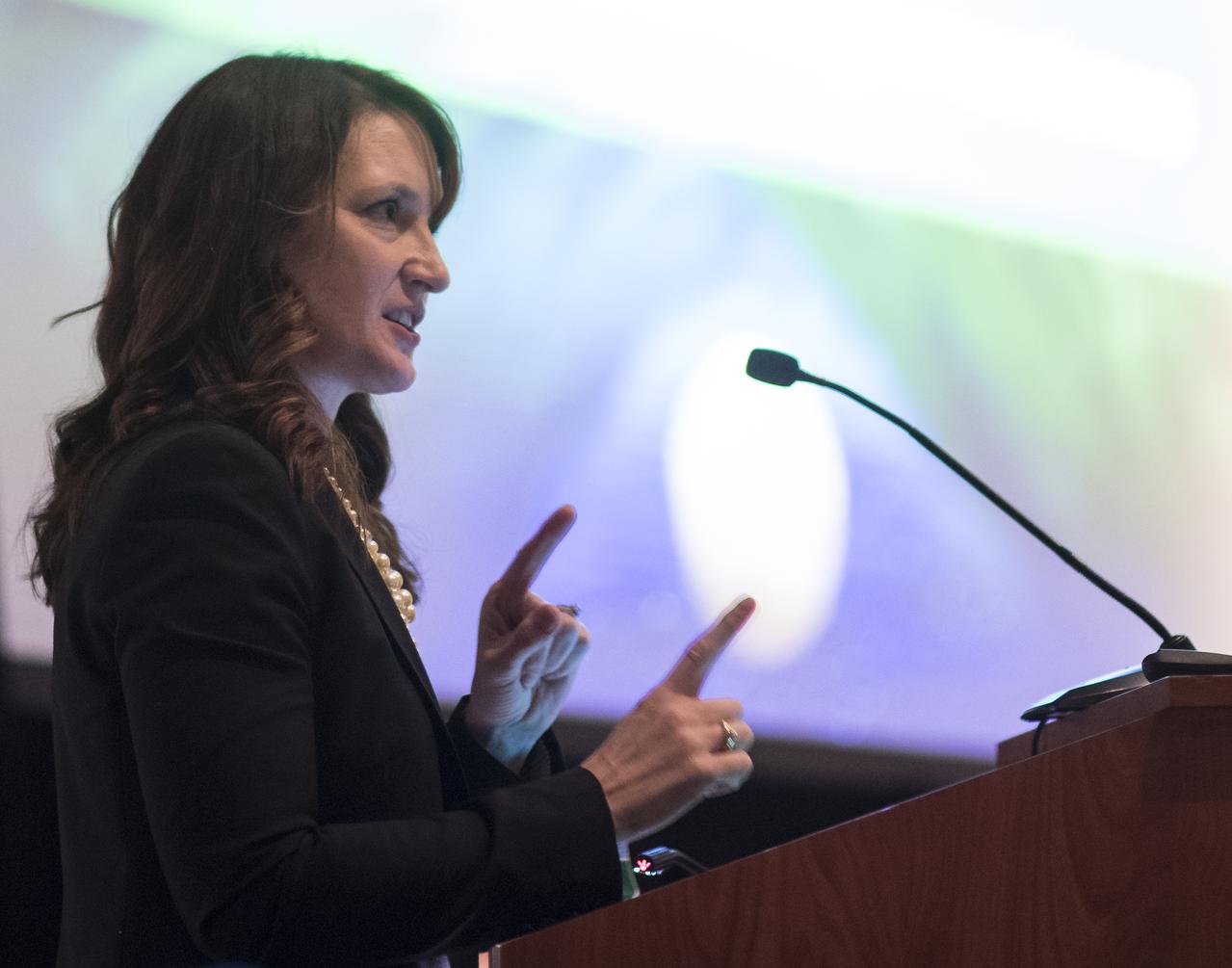

Kathleen Boggs, Systems and Technology Demonstration Manager in the International Space Station Division of NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, is seen a keynote titled “From LEO to the Moon, Mars, and Beyond: Shaping Capability Development Strategies for NASA’s Human Exploration Campaign” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Thursday, Oct. 24, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

ISS072E034796 (10/10/2024) --- The LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) hardware seen aboard the International Space Station. Rhodium Plant LIFE studies how radiation and gravitational forces at different orbital altitudes affect plant growth. Results could provide a better understanding of plant growth in space and reveal how changes in gene expression influence root development, contributing to improved production of plants in space and on Earth.
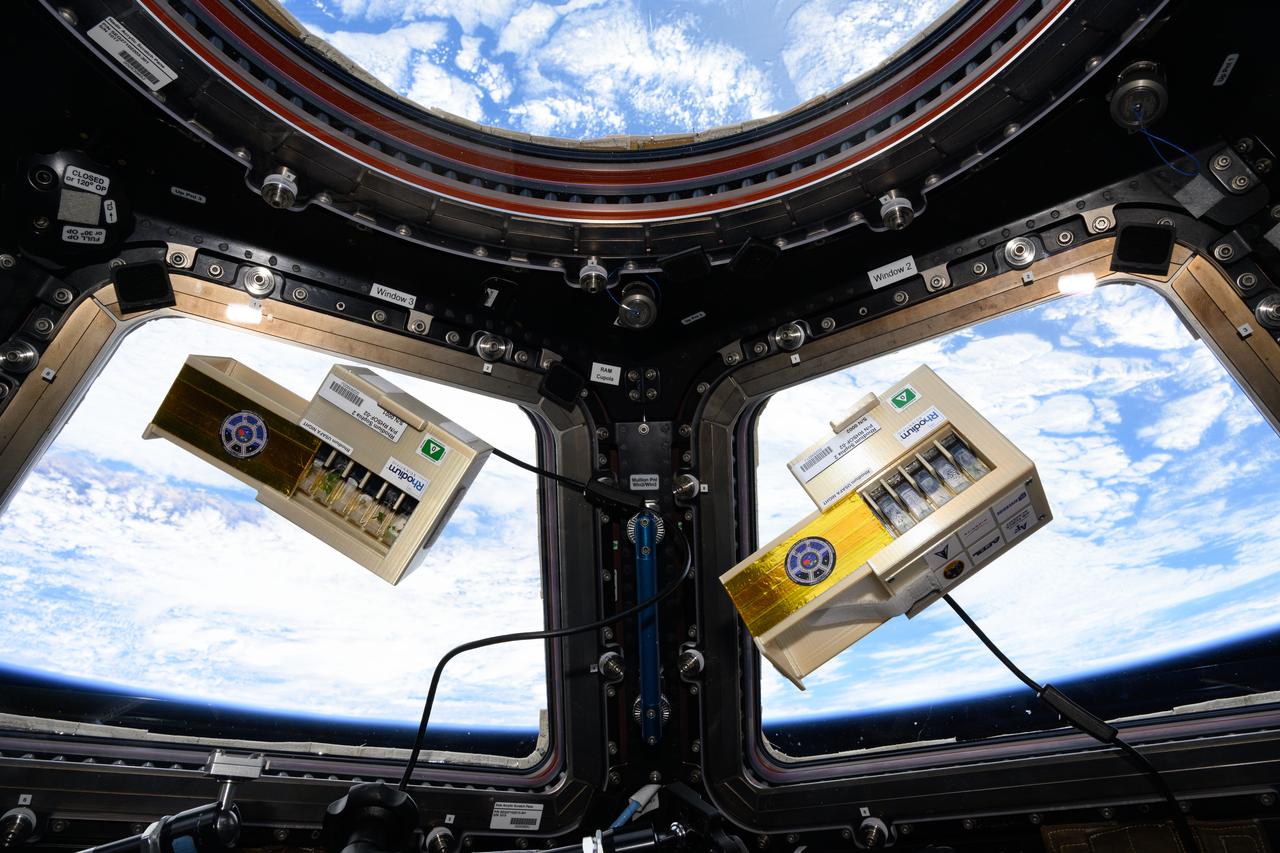

iss073e0076866 (5/21/2025) --- The LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) hardware seen aboard the International Space Station. Rhodium Plant LIFE studies how radiation and gravitational forces at different orbital altitudes affect plant growth. Results could provide a better understanding of plant growth in space and reveal how changes in gene expression influence root development, contributing to improved production of plants in space and on Earth.

S127-E-012308 (30 July 2009) --- As seen through windows on the aft flight deck of Space Shuttle Endeavour, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment 2 (ANDE-2) is released from the shuttle's payload bay by STS-127 crew members. ANDE-2 consists of two spherical micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low-Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
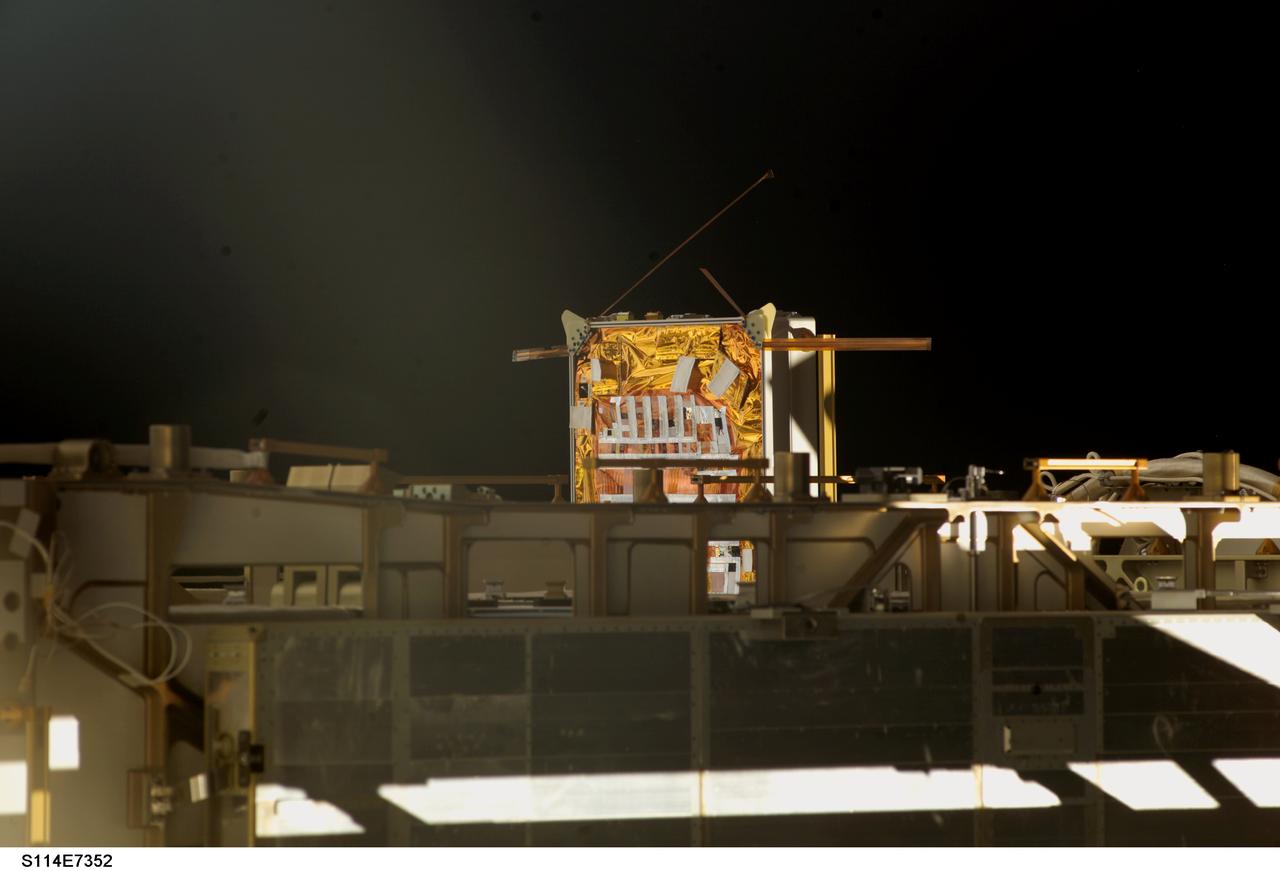

s114e7352 (8/6/2005) --- A view of the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) 5 Passive Experiment Containter (PEC) mounted on the P6 Truss during one of the STS-114 missions Extravehicular Activities (EVAs). The Materials International Space Station Experiment-5 (MISSE-5) was an external payload that flew on-board the ISS from August 2005 until September 2006. MISSE-5 provided an opportunity for researchers to test a wide range of samples in the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) environment.

The crewmembers of Space Shuttle mission 51-F have chosen as their insignia this design by Houston artist Skip Bradley. The Space Shuttle Challenger is depicted ascending toward the heavens in search of new knowledge in the field of solar and steallar astronomy, with its Spacelab 2 payload. The constellations Leo and Orion are in the positions they will be in, relative to the sun during the flight. The nineteen stars signify that this will be the 19th STS flight.
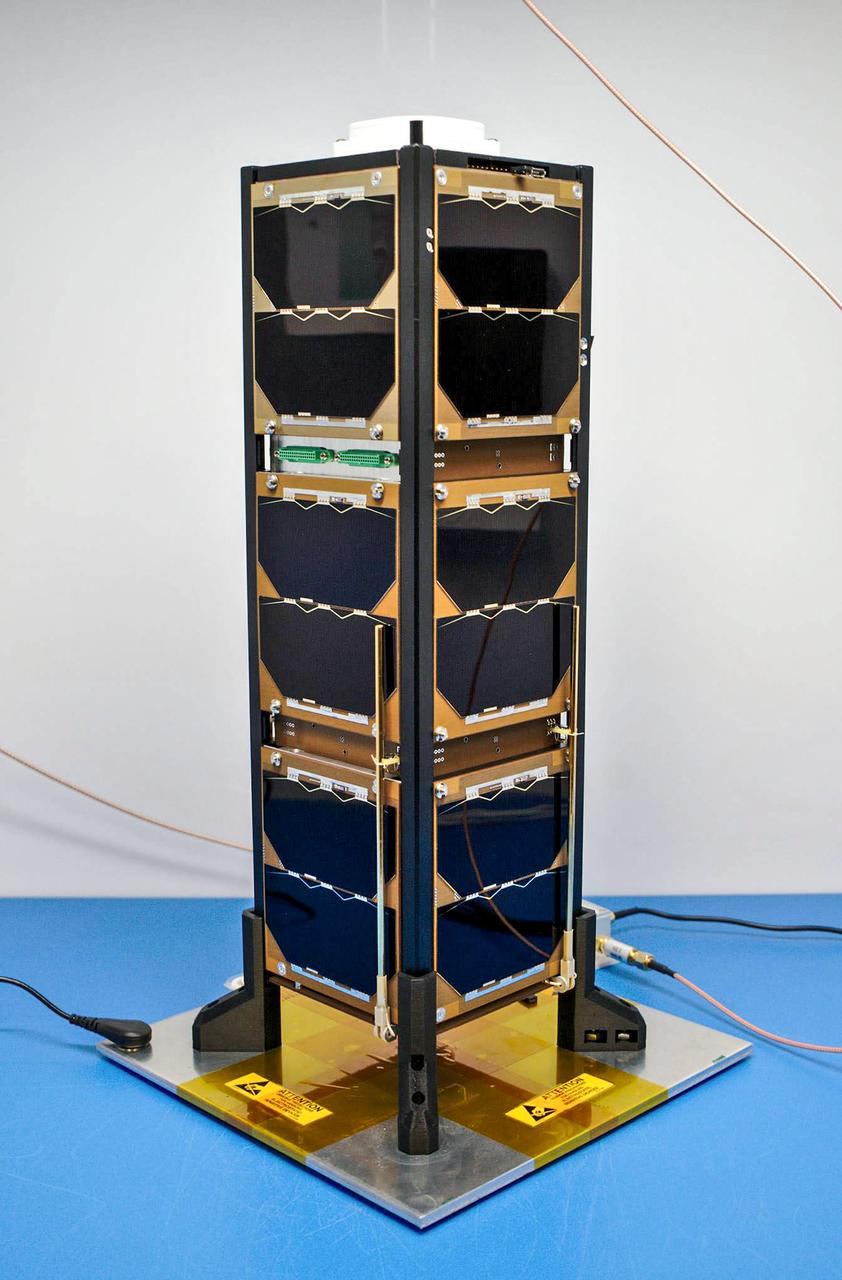

jsc2020e016862 (3/26/2020) --- Bobcat-1 with its deployable communication antenna stowed. Bobcat-1 is the Ohio University CubeSat, which has, together with the educational purpose, the objective of experimenting the GNSS inter-constellation time-offset estimate from LEO orbit. GNSS inter-constellation time-offset estimate is critical for users with a limited visibility of GNSS satellites, such as users in the high altitude Space Service Volume (as GEO or HEO).
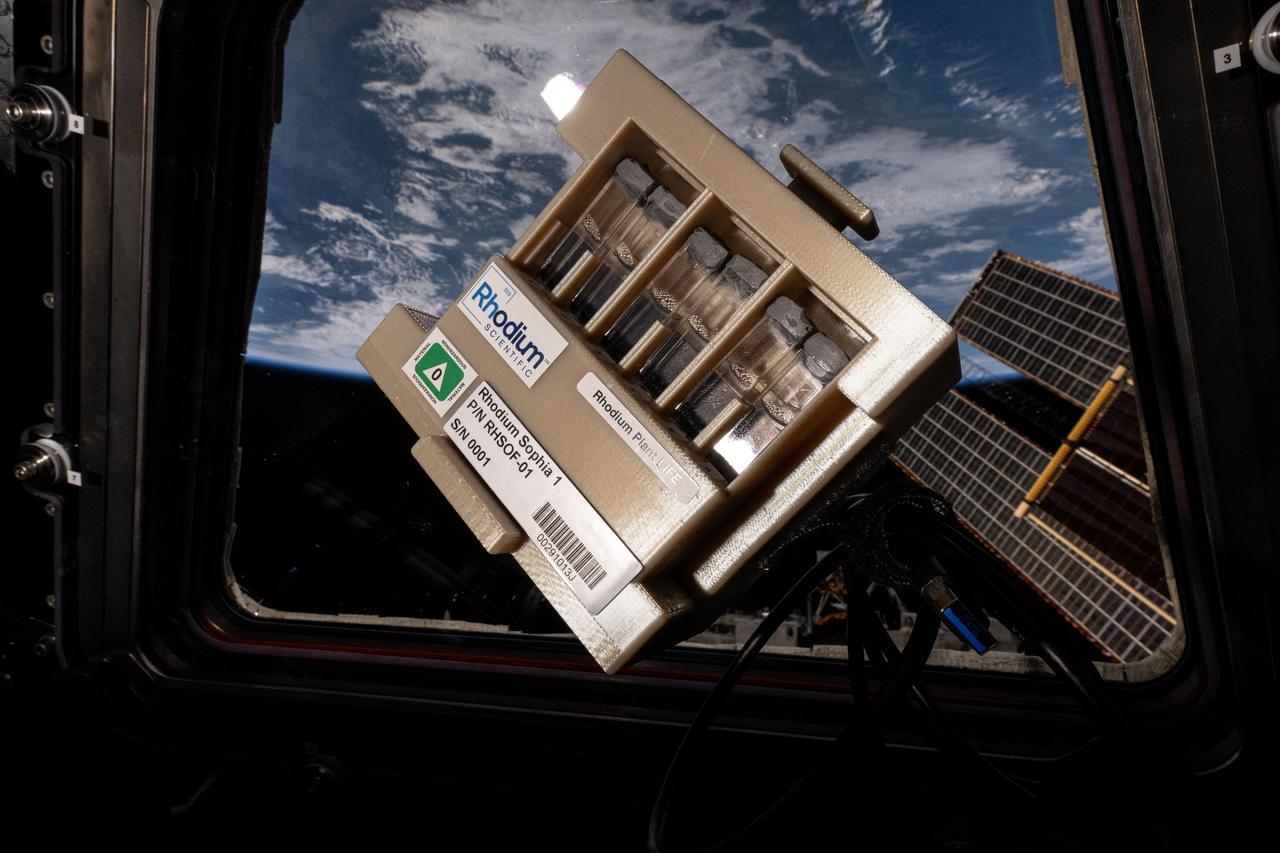

iss072e034773 (10/11/2024) --- The LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) hardware seen aboard the International Space Station. Rhodium Plant LIFE studies how radiation and gravitational forces at different orbital altitudes affect plant growth. Results could provide a better understanding of plant growth in space and reveal how changes in gene expression influence root development, contributing to improved production of plants in space and on Earth.
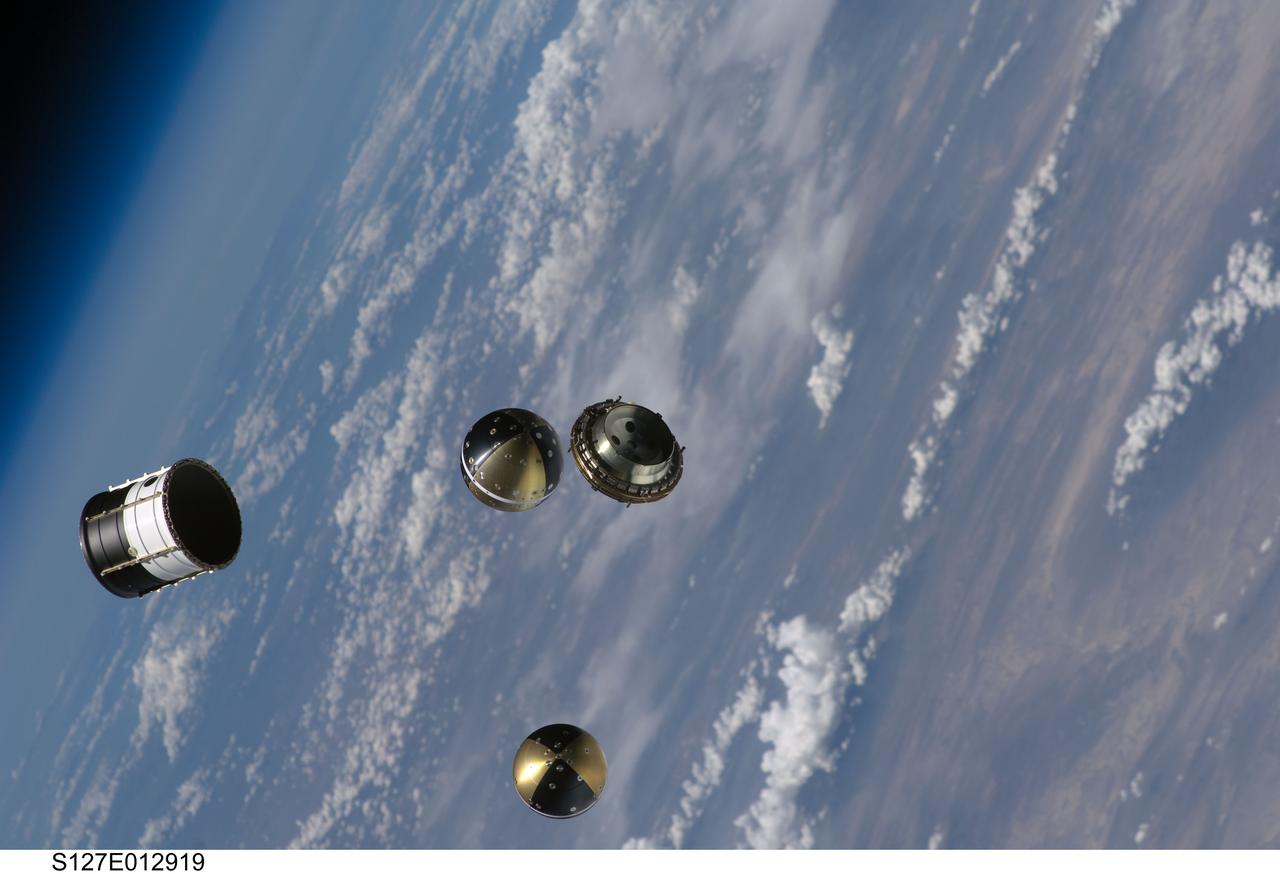

S127-E-012919 (30 July 2009) --- Backdropped by a blue and white Earth, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment 2 (ANDE-2) is photographed after its release from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay by STS-127 crew members. ANDE-2 consists of two spherical micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low-Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
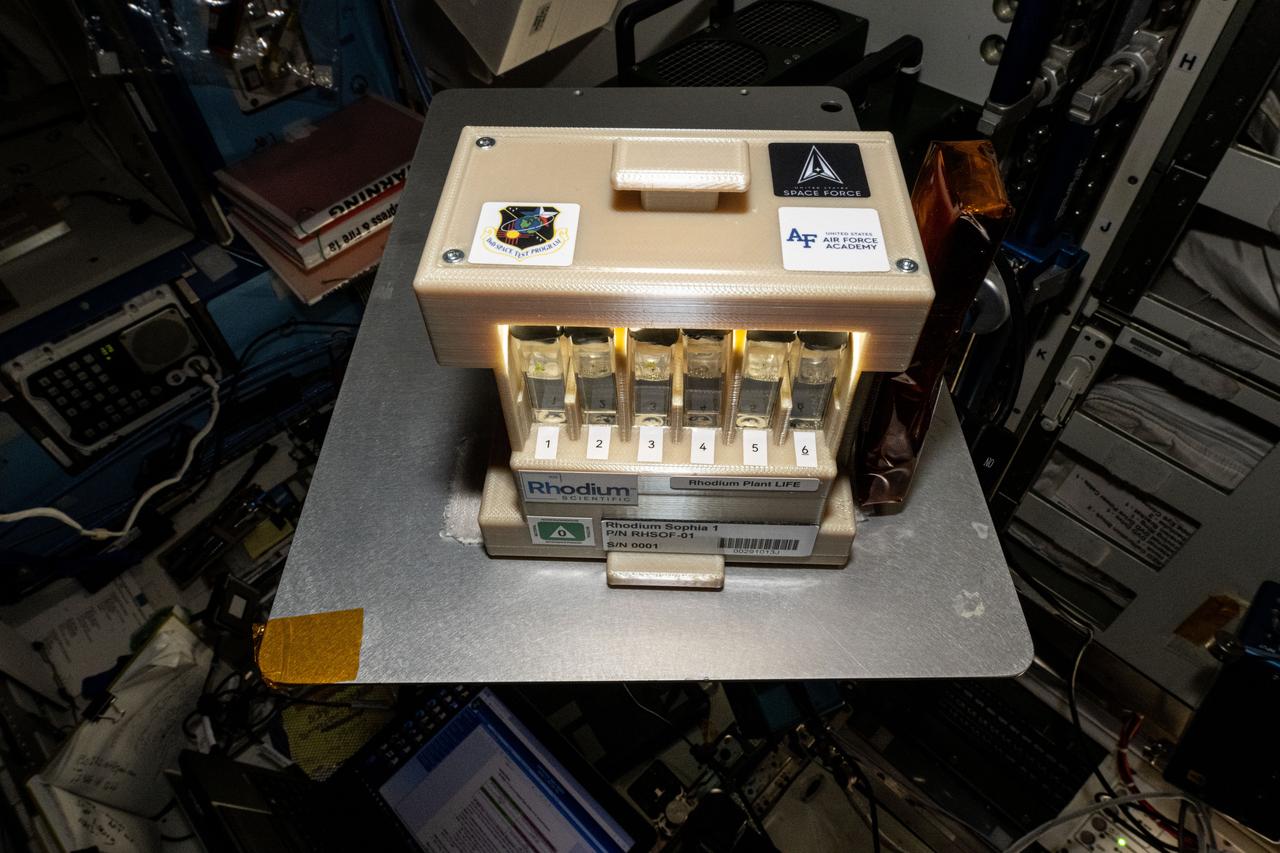

ISS072E034769 (10/11/2024) --- The LEO Integrated Flori-culture Experiment (LIFE) 01 (Rhodium Plant LIFE) hardware seen aboard the International Space Station. Rhodium Plant LIFE studies how radiation and gravitational forces at different orbital altitudes affect plant growth. Results could provide a better understanding of plant growth in space and reveal how changes in gene expression influence root development, contributing to improved production of plants in space and on Earth.

Kathleen Boggs, Systems and Technology Demonstration Manager in the International Space Station Division of NASA’s Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate, is seen a keynote titled “From LEO to the Moon, Mars, and Beyond: Shaping Capability Development Strategies for NASA’s Human Exploration Campaign” at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Thursday, Oct. 24, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
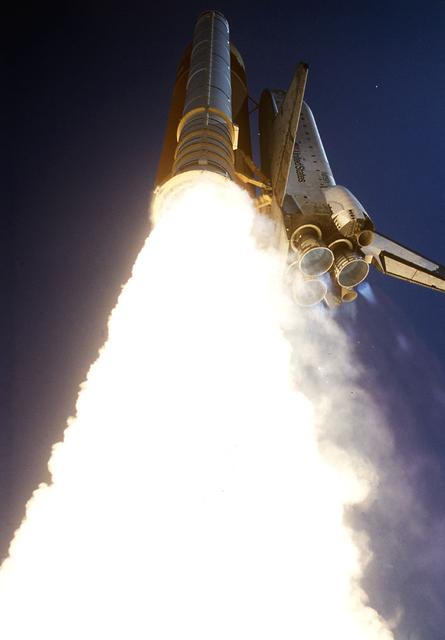

The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-52) thunders off Launch Pad 39B, embarking on a 10-day flight and carrying a crew of six who will deploy the Laser Geodynamic Satellite II (LAGEOS). LAGEOS is a spherical passive satellite covered with reflectors which are illuminated by ground-based lasers to determine precise measurements of the Earth's crustal movements. The other major payload on this mission is the United States Microgravity Payload 1 (USMP-1), where experiments will be conducted by crew members while in low earth orbit (LEO).

ISS006-E-40537 (March 2003) --- The Coma Cluster, a collection of stars which are visible to the naked eye in the constellation Coma Berenices, is visible in this view photographed by astronaut Donald R. Pettit, Expedition Six NASA ISS science officer, on board the International Space Station (ISS). The Coma Cluster is visible as a faint fuzzy patch between the constellations Leo and Virgo. The naked eye cannot resolve the individual stars, but collectively, they merge into a fuzzy flow in this part of the sky.
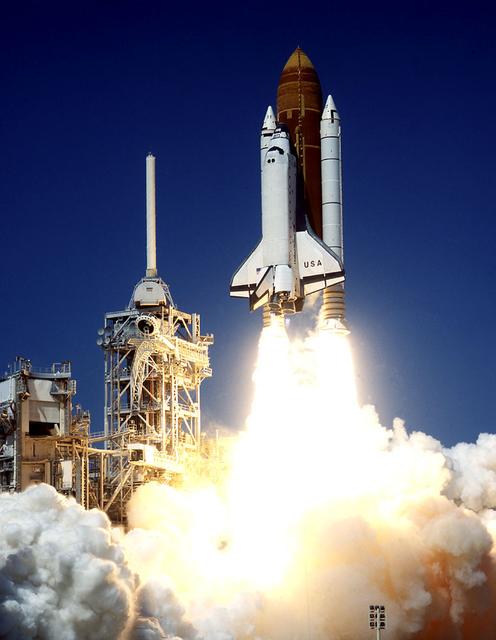

The Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-52) thunders off Launch Pad 39B, embarking on a 10-day flight and carrying a crew of six who will deploy the Laser Geodynamic Satellite II (LAGEOS). LAGEOS is a spherical passive satellite covered with reflectors which are illuminated by ground-based lasers to determine precise measurements of the Earth's crustal movements. The other major payload on this mission is the United States Microgravity Payload 1 (USMP-1), where experiments will be conducted by crew members while in low earth orbit (LEO).
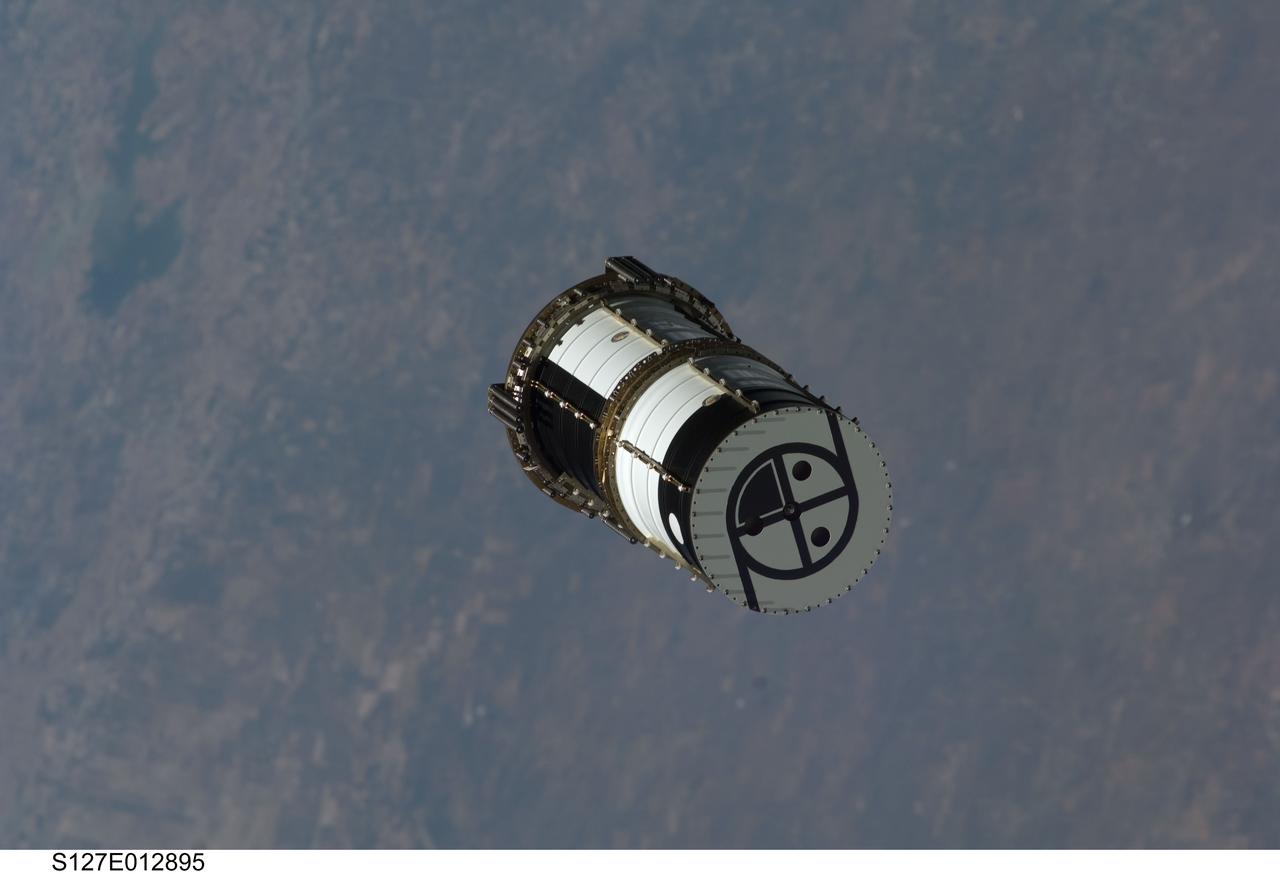

S127-E-012895 (30 July 2009) --- A Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment 2 (ANDE-2) is photographed after its release from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay by STS-127 crew members. ANDE-2 consists of two spherical micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low-Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.
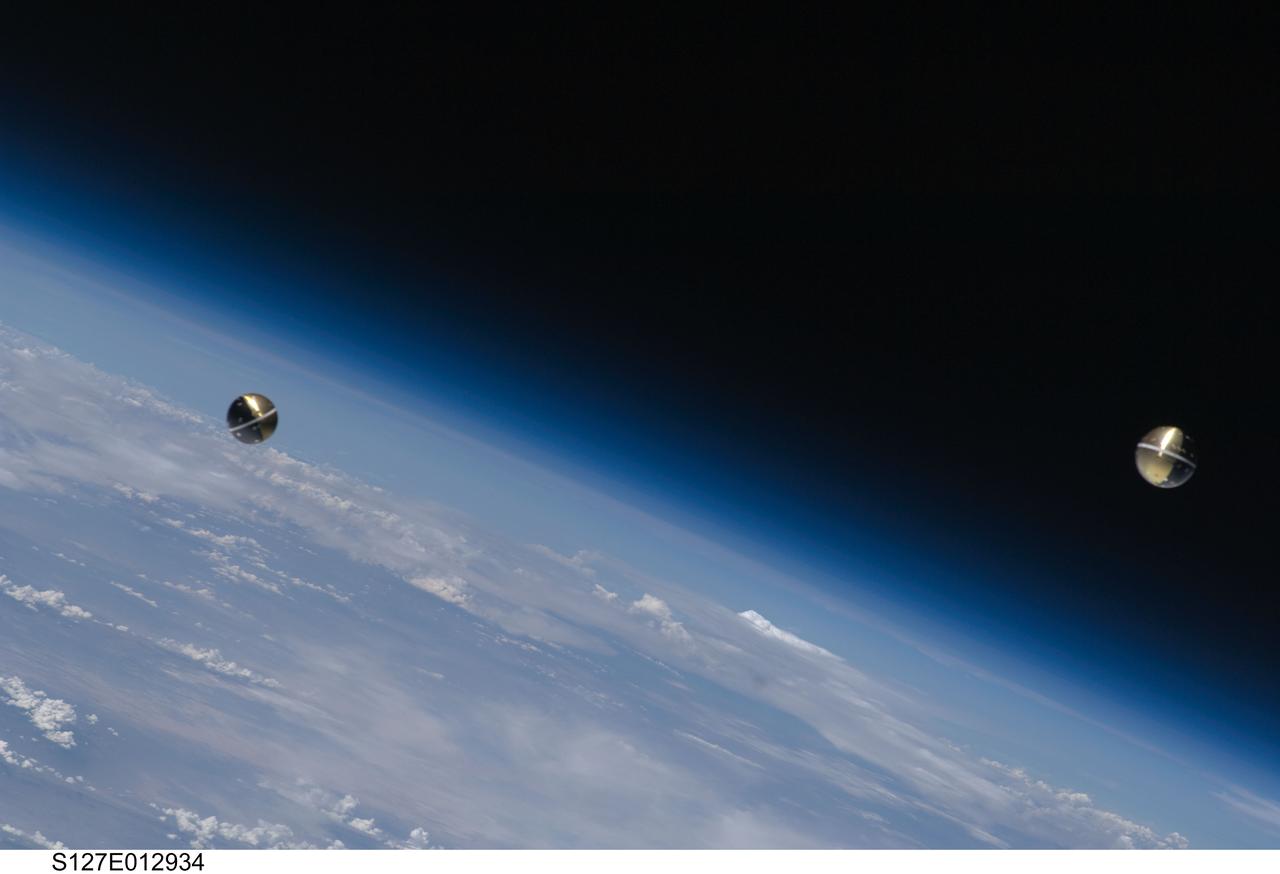

S127-E-012934 (30 July 2009) --- Backdropped by Earth’s horizon and the blackness of space, a Department of Defense pico-satellite known as Atmospheric Neutral Density Experiment 2 (ANDE-2) is photographed after its release from Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay by STS-127 crew members. ANDE-2 consists of two spherical micro-satellites which will measure the density and composition of the low-Earth orbit (LEO) atmosphere while being tracked from the ground. The data will be used to better predict the movement of objects in orbit.

Members of the NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center Ascent Abort-2 management and engineering team contributed to the AA-2 launch at Cape Canaveral in Florida July 2, 2019. From left are Gary Martin, Rose Blomquist, Ernest Mwajagu, Lucas Moxey, Leo Gross, Jeff Sutherland, Chuck Rogers, Joe Hernandez, David Dowdell, Jeri Myers and Dan Nolan. Additional engineering team members include Paul Aristo, Bob Clark and Nikki Martin. Team members hold elements of the stack that was launched to show how the separation ring, crew module and Launch Abort System fit together.

Key state and community leaders celebrated April 6 with the signing of a construction contract for the state-of-the-art INFINITY Science Center planned near John C. Stennis Space Center in south Mississippi. Gulfport Mayor George Schloegel (l to r), chair of non-profit INFINITY Science Center Inc., was joined for the signing ceremony at the Hancock Bank in Gulfport by Virginia Wagner, sister of late Hancock Bank President Leo Seal Jr.; and Roy Anderson III, president and CEO of Roy Anderson Corp. Seal was the first chair of INFINITY Science Center Inc., which has led in development of the project. Roy Anderson Corp. plans to begin construction on the 72,000-square-foot, $28 million science and education center in May. The Mississippi Department of Transportation (MDOT) also is set to begin construction of a $2 million access road to the new center. The April 6 ceremony was attended by numerous officials, including former Stennis Space Center Directors Jerry Hlass and Roy Estess; Mississippi Senate President Pro Tempore Billy Hewes, R-Gulfport; Mississippi Rep. Diane Peranich, D-Pass Christian; and MDOT Southern District Commissioner Wayne Brown.

S85-29498 (June 1985) --- The crew members of space shuttle mission STS-51F have chosen as their insignia this design by Houston artist Skip Bradley. The space shuttle Challenger is depicted ascending toward the heavens in search of new knowledge in the field of solar and stellar astronomy, with its Spacelab 2 payload. The constellations Leo and Orion are in the positions they will be in, relative to the sun during the flight. The nineteen stars signify that this will be the 19th STS flight. Crew members for the mission are astronauts C. Gordon Fullerton, commander; Roy D. Bridges, pilot; F. Story Musgrave, Anthony W. England and Karl J. Henize, mission specialist; and payload specialists Loren W. Acton and John David Bartoe. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA
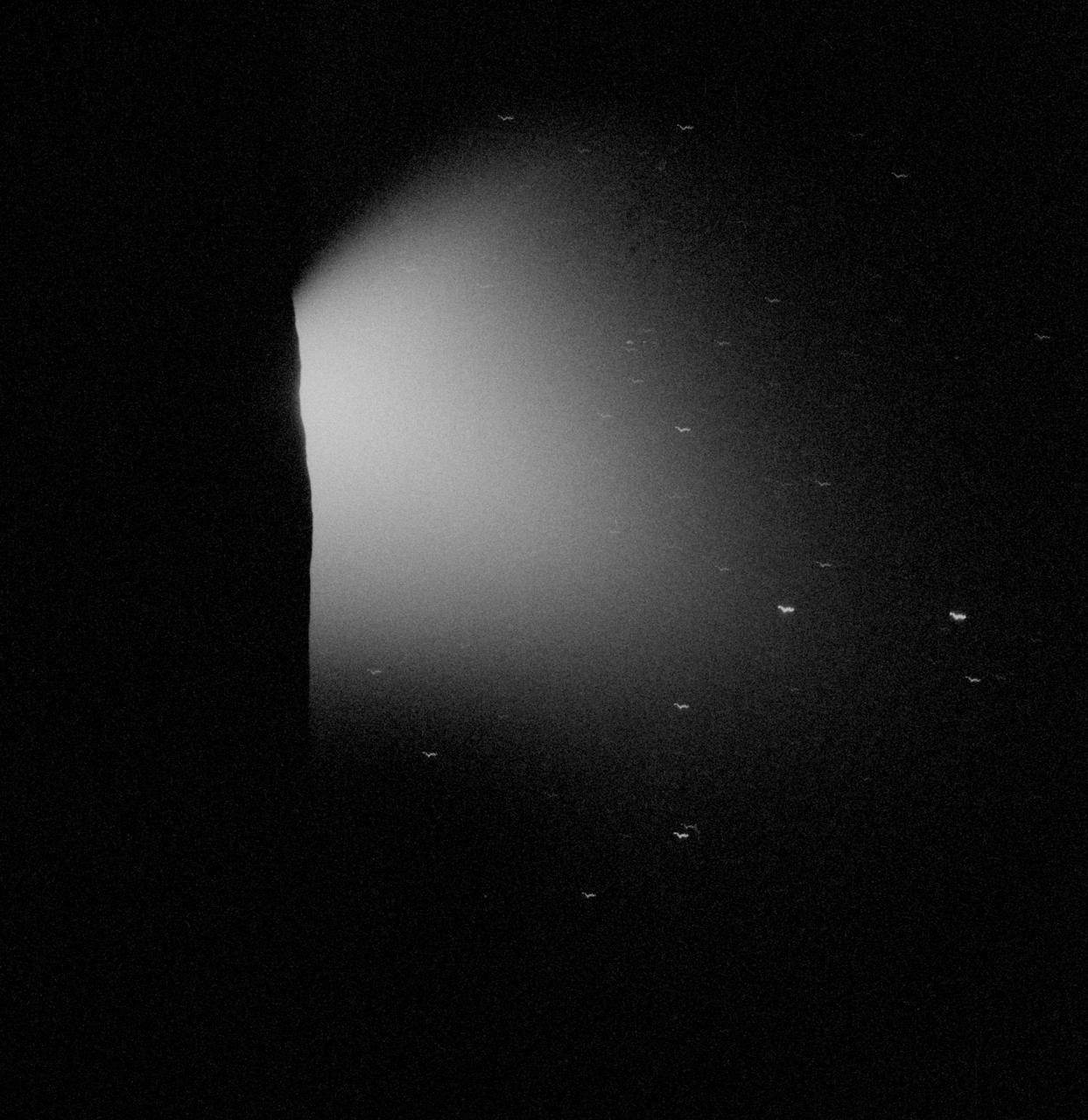

AS15-98-13311 (31 July 1971) --- The solar corona, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft about one minute prior to sunrise on July 31, 1971, is seen just beyond the lunar horizon. The bright object on the opposite of the frame is the planet Mercury. The bright star near the frame center is Regulus, and the lesser stars form the head of the constellation Leo. Mercury is approximately 28 degrees from the center of the sun. The solar coronal streamers, therefore, appear to extend about eight degrees from the sun's center. This solar corona photograph was the second in a series of seven. Three such series were obtained by astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, during the solo part of his lunar orbital flight. They represent man's first view of this part of the sun's light. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the Hadley-Apennine area of the moon, astronaut Worden remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
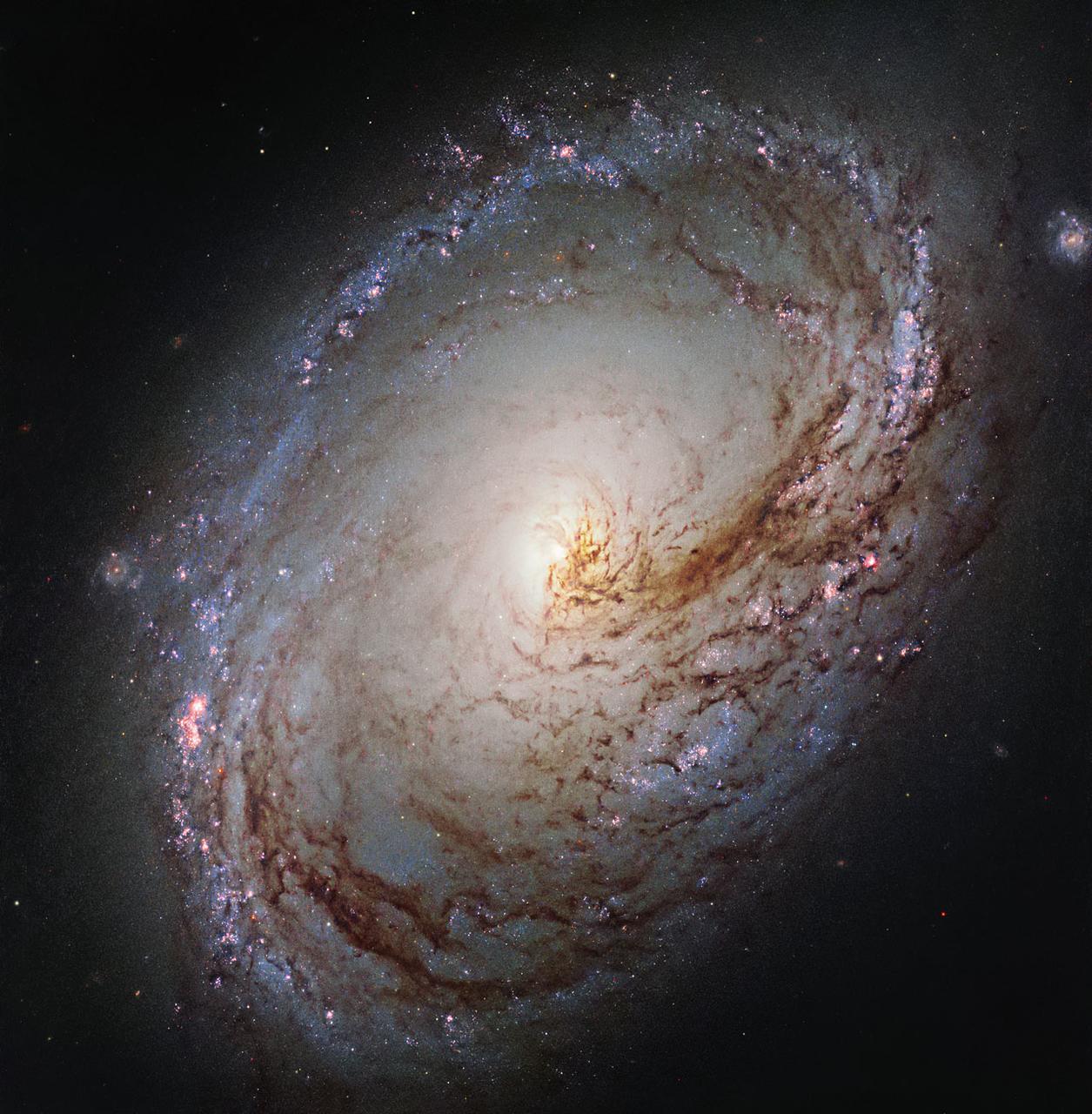

This new NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows Messier 96, a spiral galaxy just over 35 million light-years away in the constellation of Leo (The Lion). It is of about the same mass and size as the Milky Way. It was first discovered by astronomer Pierre Méchain in 1781, and added to Charles Messier’s famous catalogue of astronomical objects just four days later. The galaxy resembles a giant maelstrom of glowing gas, rippled with dark dust that swirls inwards towards the nucleus. Messier 96 is a very asymmetric galaxy; its dust and gas is unevenly spread throughout its weak spiral arms, and its core is not exactly at the galactic centre. Its arms are also asymmetrical, thought to have been influenced by the gravitational pull of other galaxies within the same group as Messier 96. This group, named the M96 Group, also includes the bright galaxies Messier 105 and Messier 95, as well as a number of smaller and fainter galaxies. It is the nearest group containing both bright spirals and a bright elliptical galaxy (Messier 105).
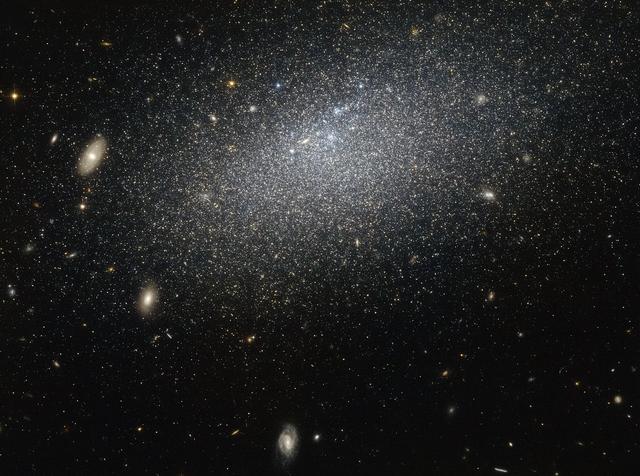

The drizzle of stars scattered across this image forms a galaxy known as UGC 4879. UGC 4879 is an irregular dwarf galaxy — as the name suggests, galaxies of this type are a little smaller and messier than their cosmic cousins, lacking the majestic swirl of a spiral or the coherence of an elliptical. This galaxy is also very isolated. There are about 2.3 million light years between UGC 4879 and its closest neighbour, Leo A, which is about the same distance as that between the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way. This galaxy’s isolation means that it has not interacted with any surrounding galaxies, making it an ideal laboratory for studying star formation uncomplicated by interactions with other galaxies. Studies of UGC 4879 have revealed a significant amount of star formation in the first 4-billion-years after the Big Bang, followed by a strange nine-billion-year lull in star formation, ended 1-billion-years ago by a more recent reignition. The reason for this behaviour, however, remains mysterious, and the solitary galaxy continues to provide ample study material for astronomers looking to understand the complex mysteries of starbirth throughout the Universe.

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076054 -- NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, left, talks to The Boeing Company's Vice President and Program Manager of Commercial Programs John Mulholland, center, and Director of Crew and Mission Operations Chris Ferguson at the company's Houston Product Support Center near Johnson Space Center. Boeing showcased its work on a fully outfitted test version of the CST-100 spacecraft to Bolden and Johnson management. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair
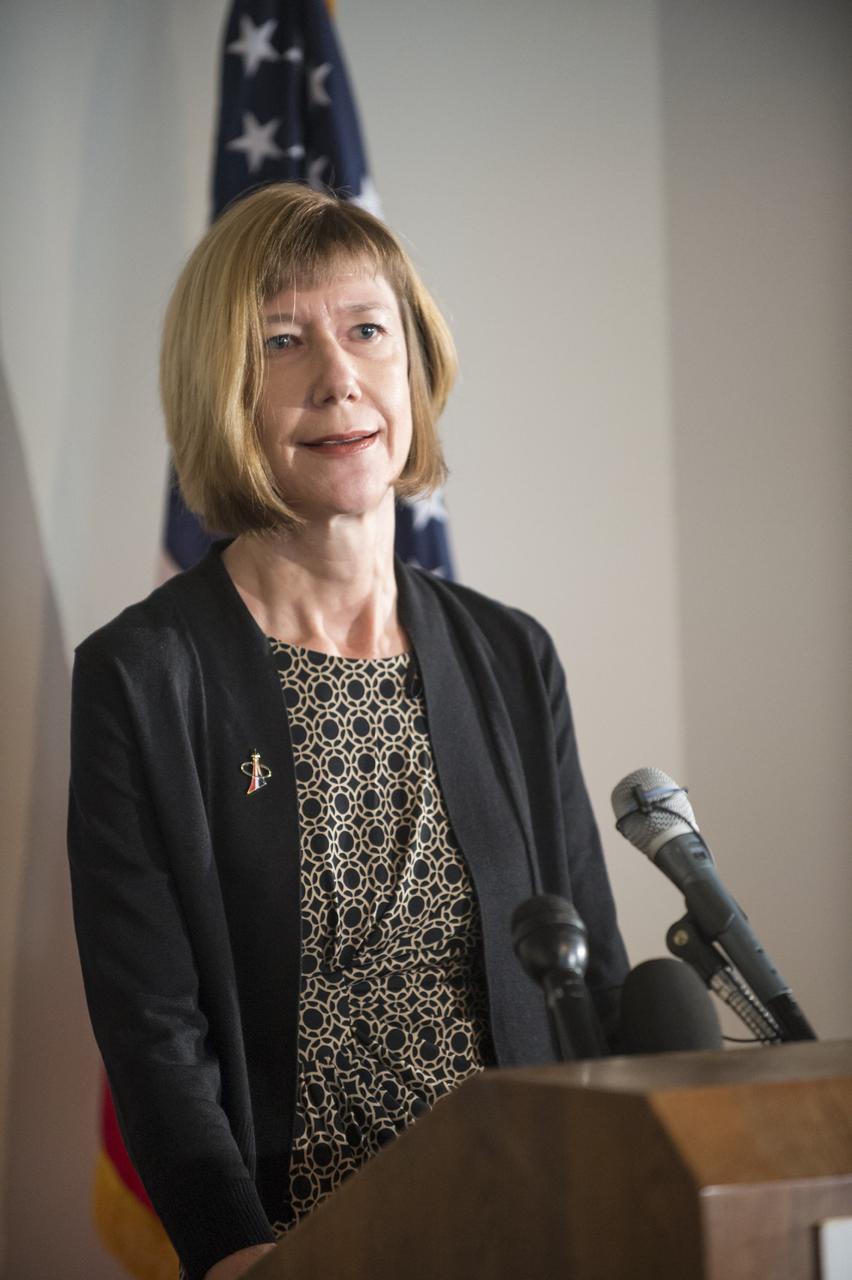

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068290 - Kathy Lueders, NASA deputy manager for the Commercial Crew Program, addresses the media before the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
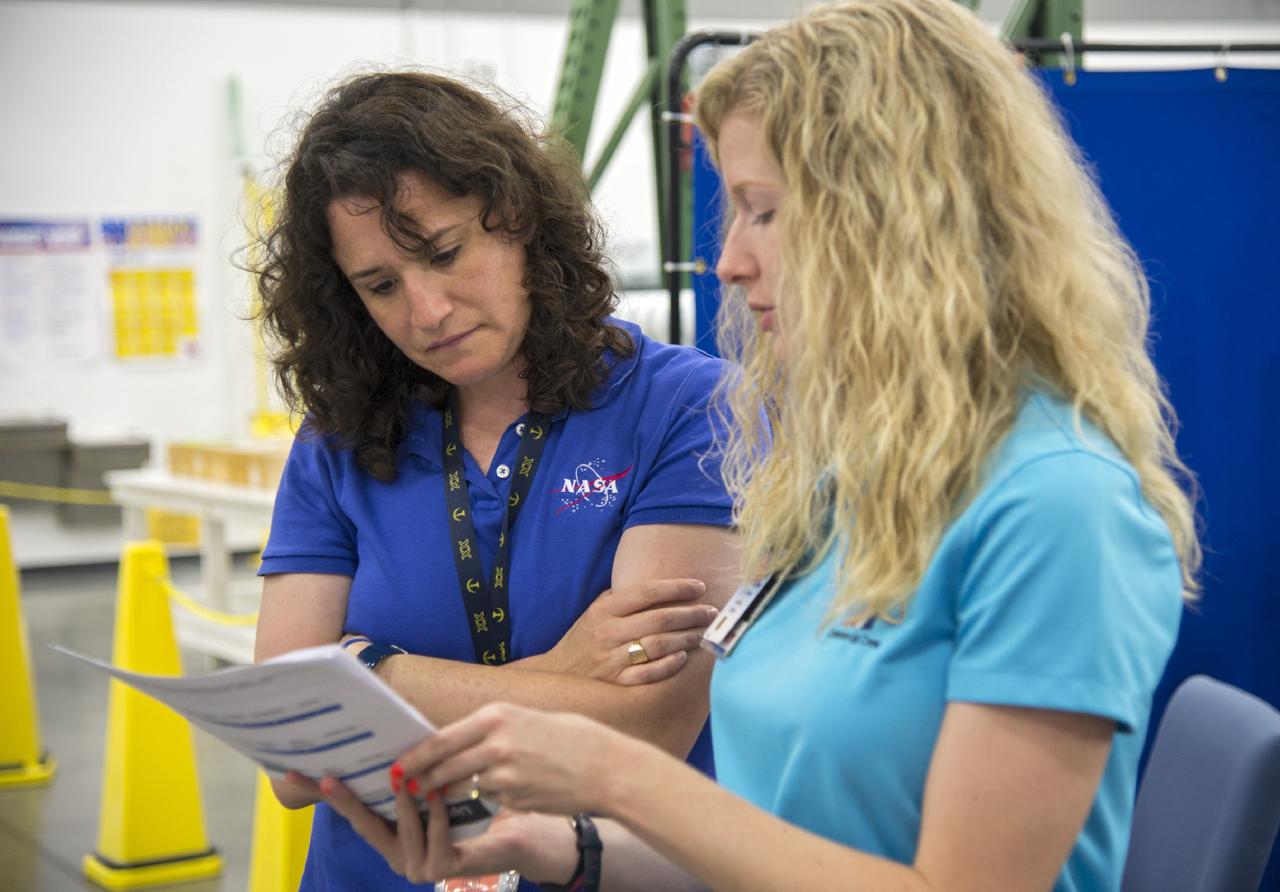

HOUSTON - NASA astronaut Serena Aunon and Andrea Gilkey, a human factors engineer with The Boeing Company, tag up before Aunon puts on her orange launch-and-entry suit for a fit check evaluation of the CST-100 spacecraft at the company's Houston Product Support Center. Aunon's fit check will help evaluate a crew's maneuverability in the spacecraft and test communications. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations, including the International Space Station. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
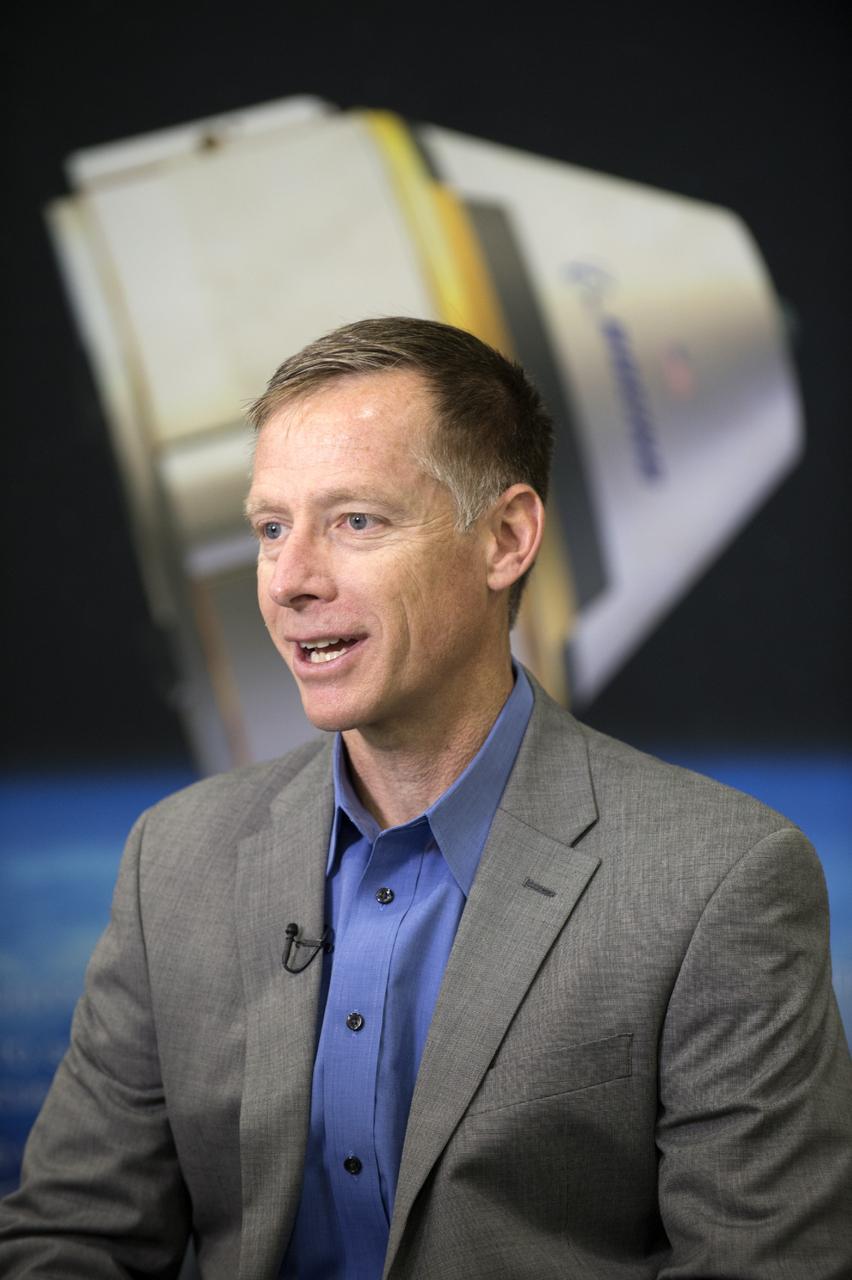

HOUSTON - Chris Ferguson, director of Crew and Mission Operations for The Boeing Company, is interviewed by the media during the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations, including the International Space Station. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during its Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
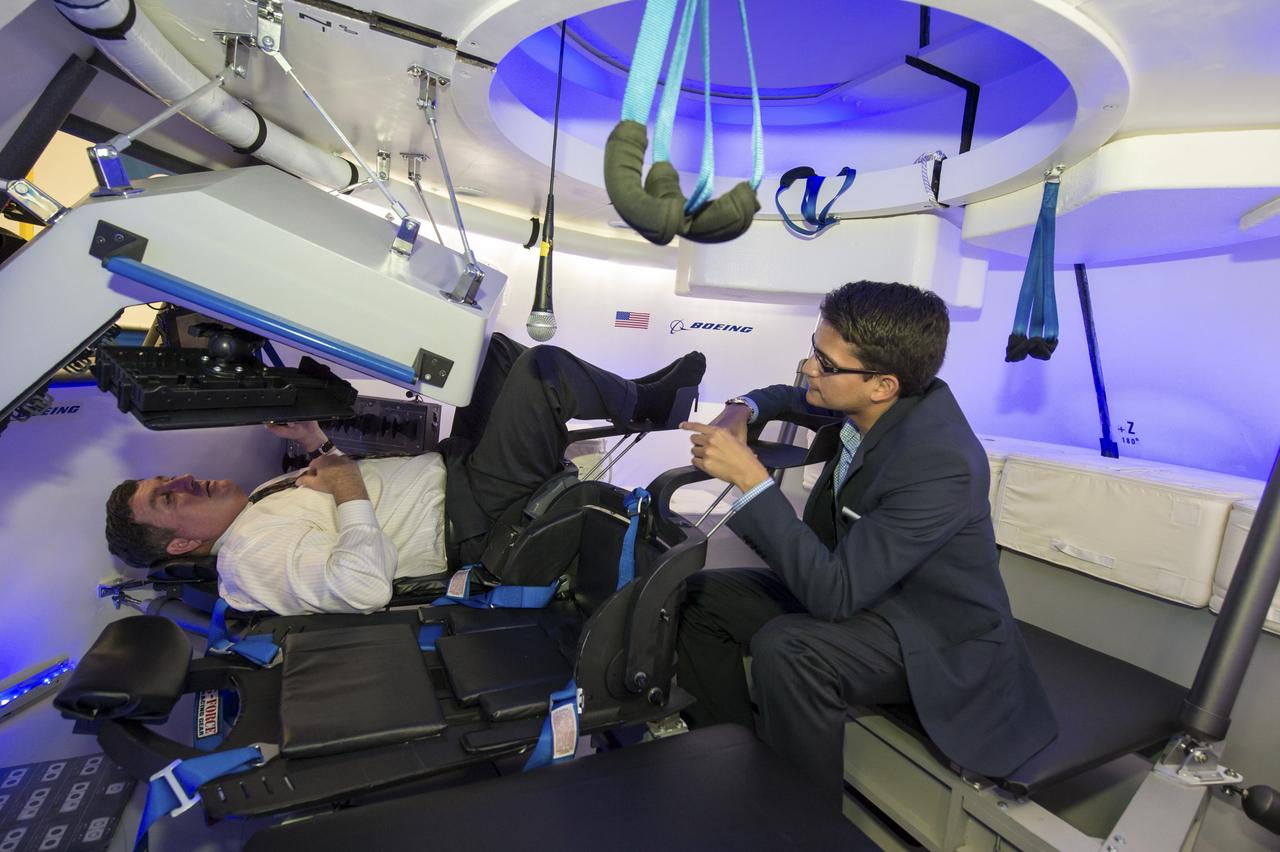

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076056 -- Kirk Shireman, deputy director of NASA's Johnson Space Center, takes the controls of The Boeing Company's mock-up CST-100 spacecraft at the company's Houston Product Support Center. Helping Shireman inside the fully outfitted test version of the CST-100 is Tony Castilleja, a mechanical engineer working on the Boeing project. Boeing showcased its work on a fully outfitted test version of the spacecraft to Bolden and Johnson management. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair

HOUSTON -- JSC-2013-E076046 -- Tony Castilleja, a mechanical engineer working on The Boeing Company's CST-100 endeavor, right, shows off a mock-up seat made from 3-D printing technology at the company's Houston Product Support Center near Johnson Space Center. Boeing showcased its work on a fully outfitted test version of the CST-100 spacecraft to NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden, not pictured, and Johnson management. Boeing's CST-100 is designed to transport a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/James Blair
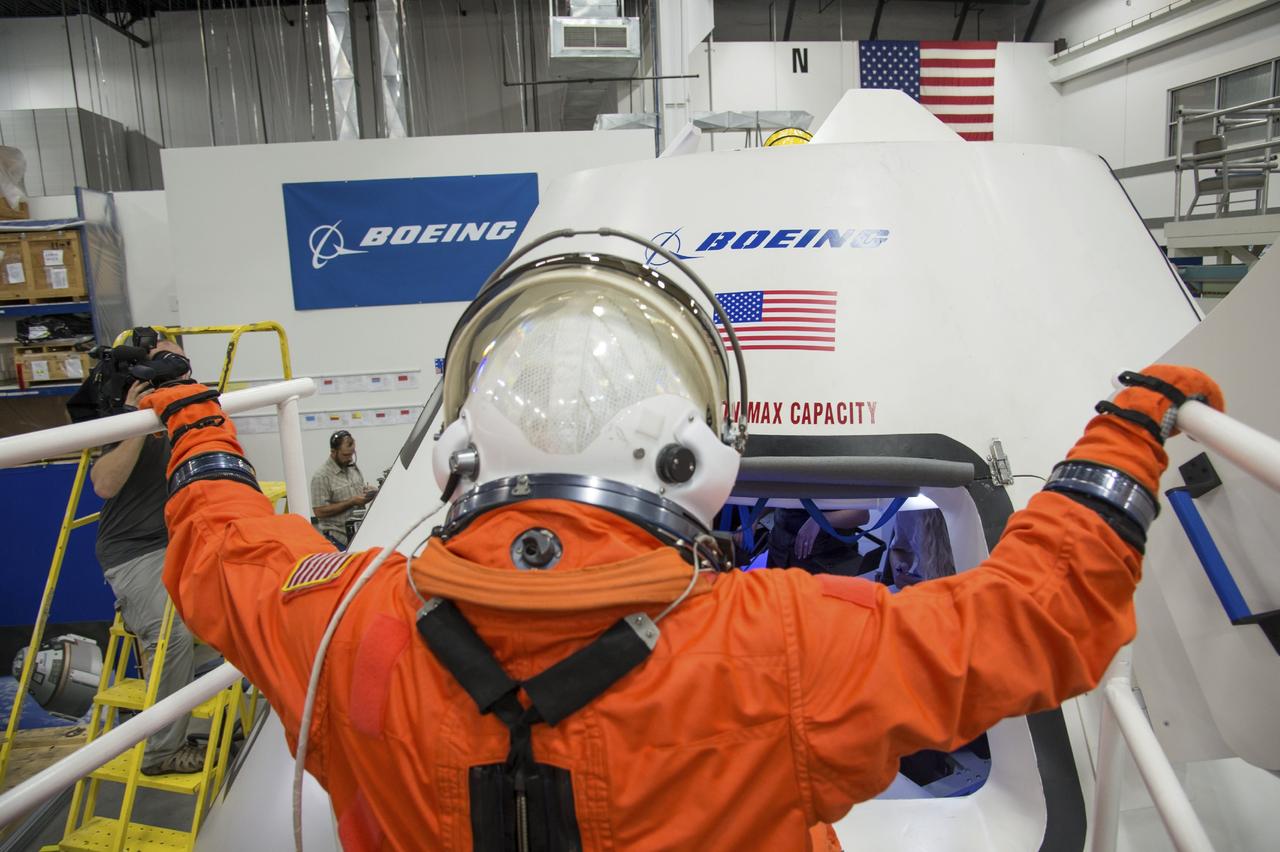

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068269 - NASA astronaut Serena Aunon prepares to enter The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft for a fit check evaluation at the company's Houston Product Support Center. Aunon's fit check will help evaluate a crew's maneuverability in the spacecraft and test communications. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
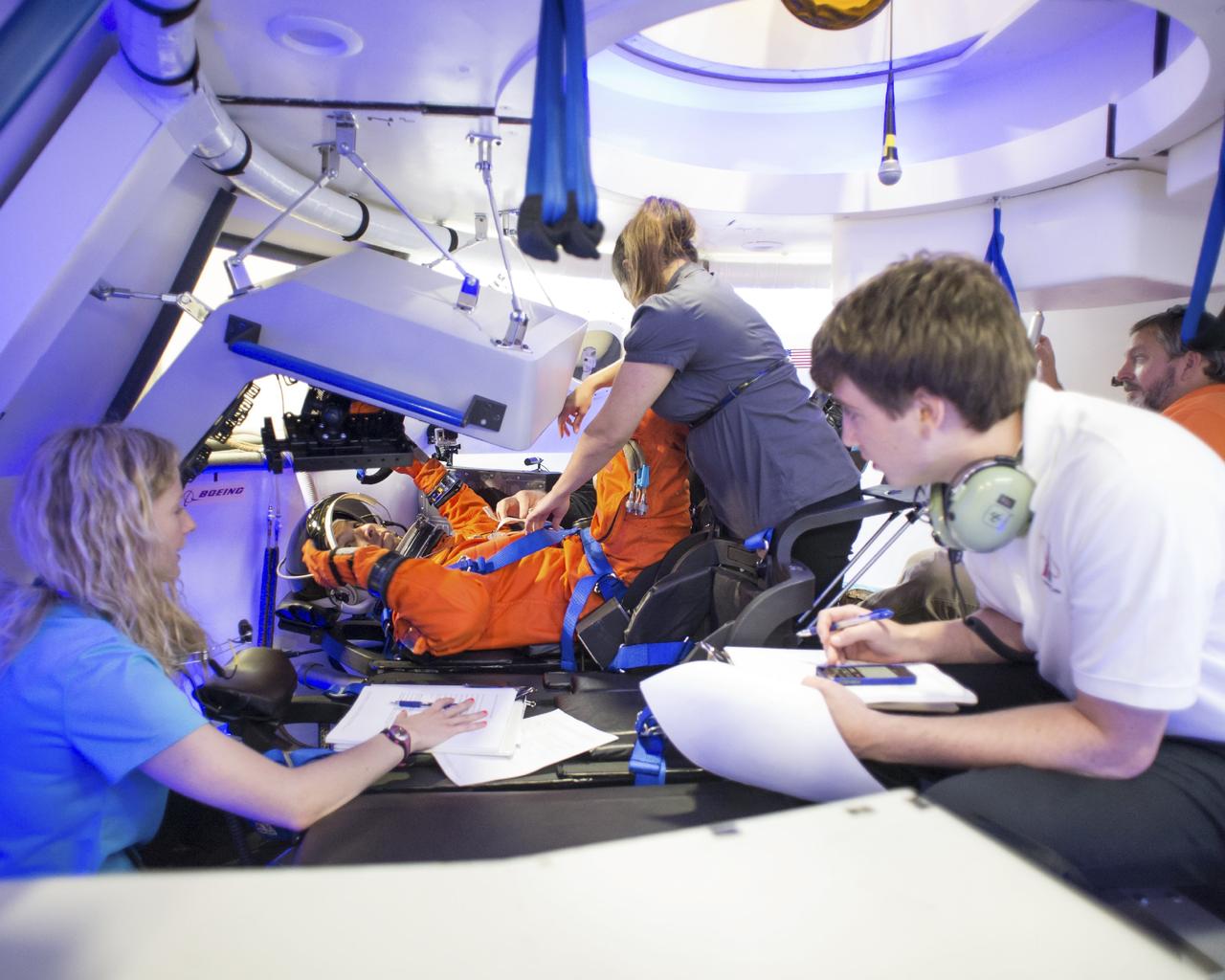

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068344 - NASA astronaut Randy Bresnik gets into position in The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft for a fit check evaluation at the company's Houston Product Support Center. Bresnik's fit check will help evaluate a crew's maneuverability in the spacecraft and test communications. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
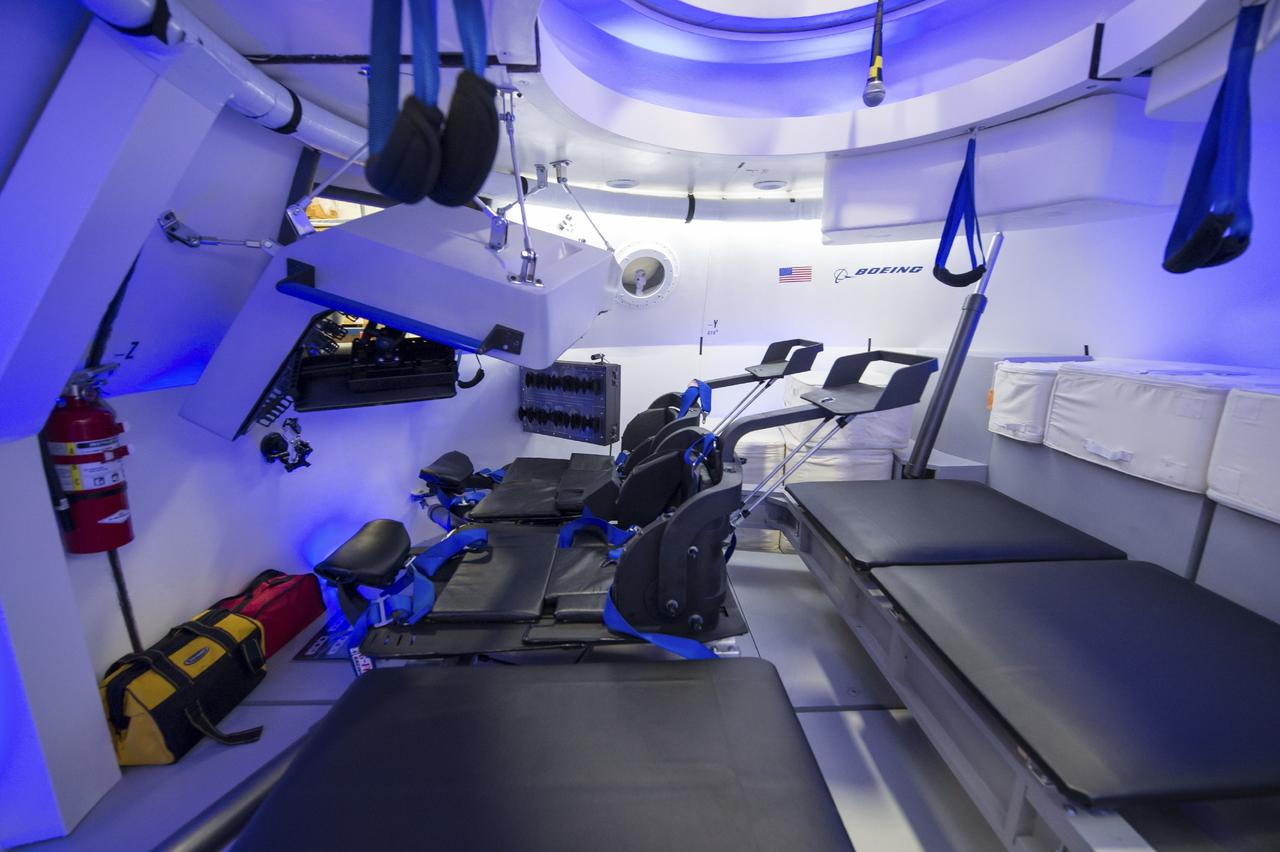

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068245 - The Boeing Company unveils the interior its fully outfitted CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center in Texas. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations, including the International Space Station. Boeing is one of three aerospace industry partners working with CCP during its Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative, which is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
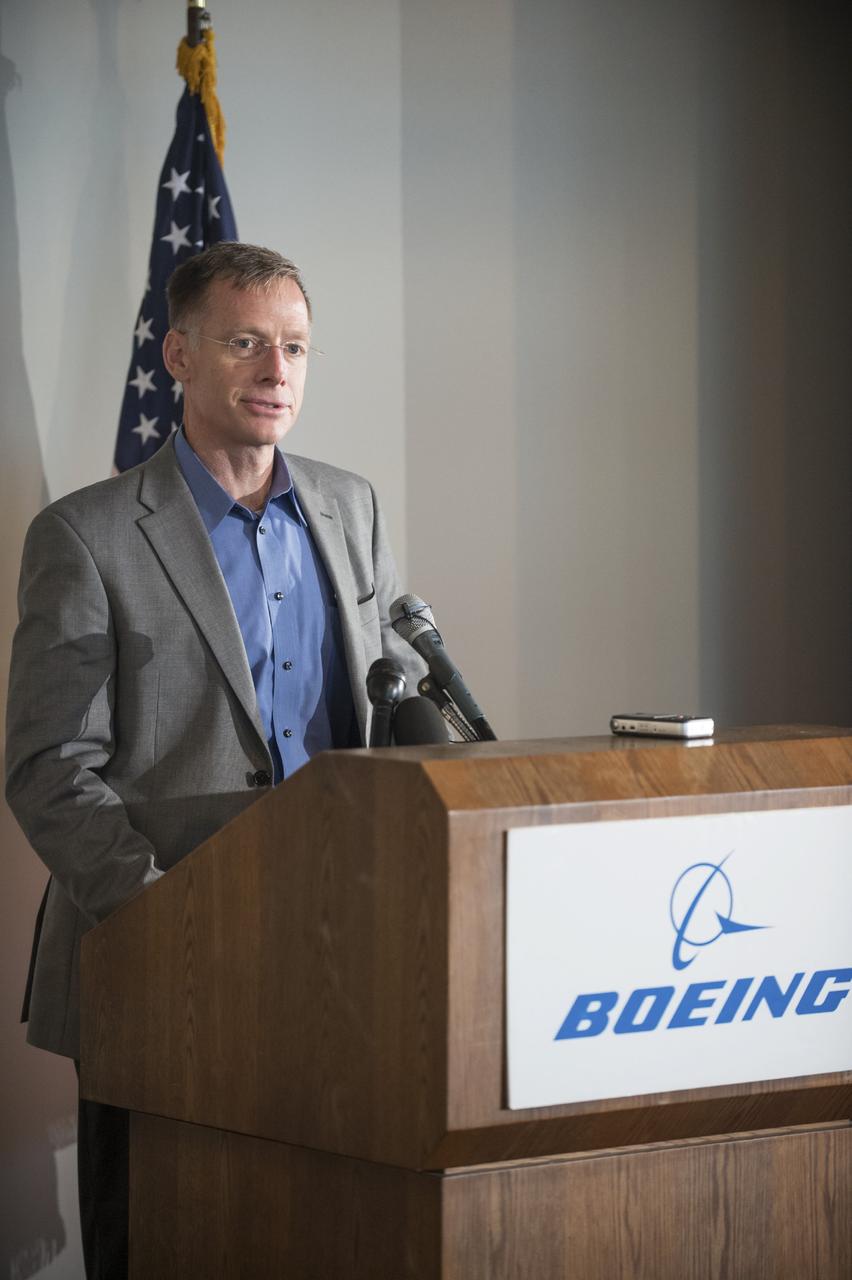

HOUSTON - JSC2013e068300 - Chris Ferguson, director of Crew and Mission Operations for The Boeing Company and former NASA astronaut, addresses the media before the unveiling of a CST-100 mock-up at the company's Houston Product Support Center. This test version is optimized to support five crew members and will allow the company to evaluate crew safety, interfaces, communications, maneuverability and ergonomics. Boeing's CST-100 is being designed to transport crew members or a mix of crew and cargo to low-Earth-orbit destinations. The evaluation is part of the ongoing work supporting Boeing's funded Space Act Agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the agency's Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCiCap is intended to make commercial human spaceflight services available for government and commercial customers. To learn more about CCP, visit http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz