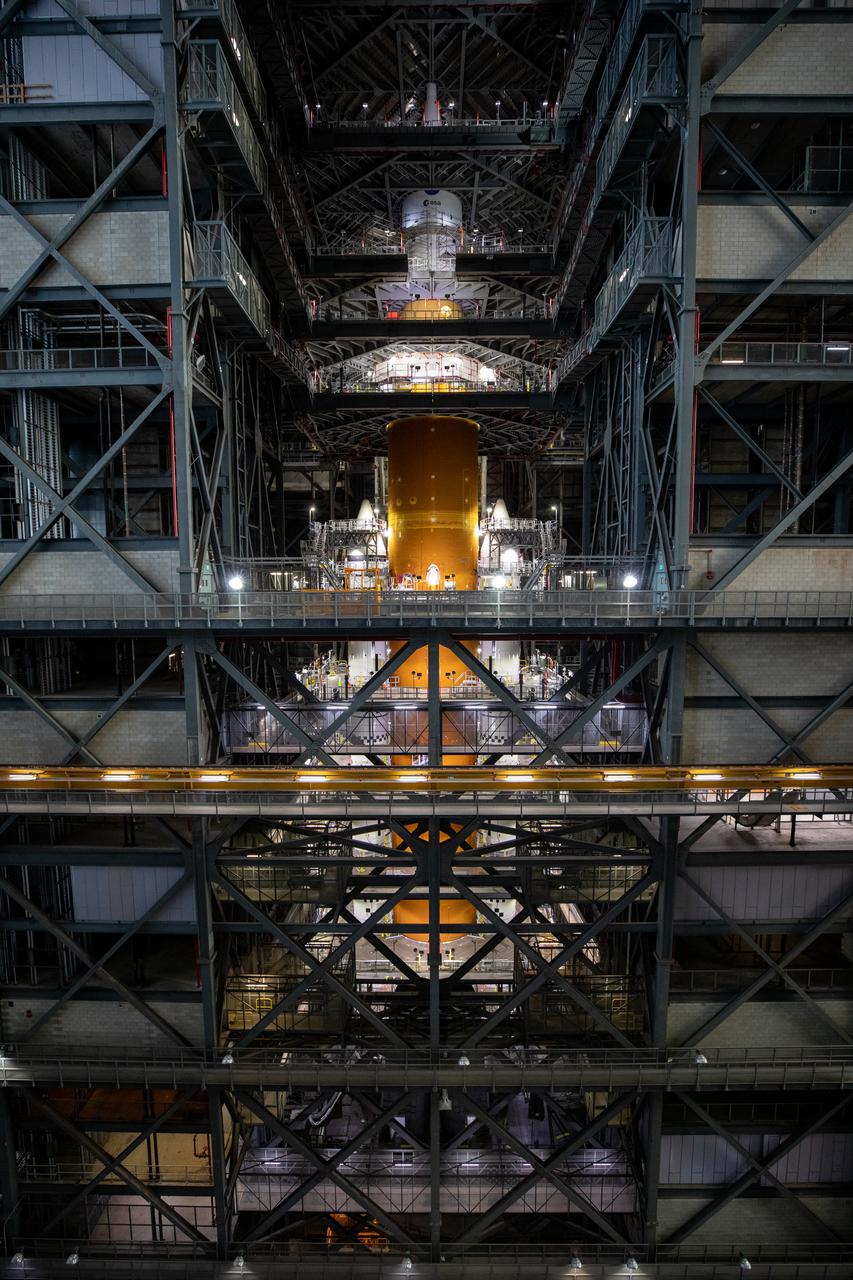

Artemis I Orion Lift and Mate - Fully Stacked
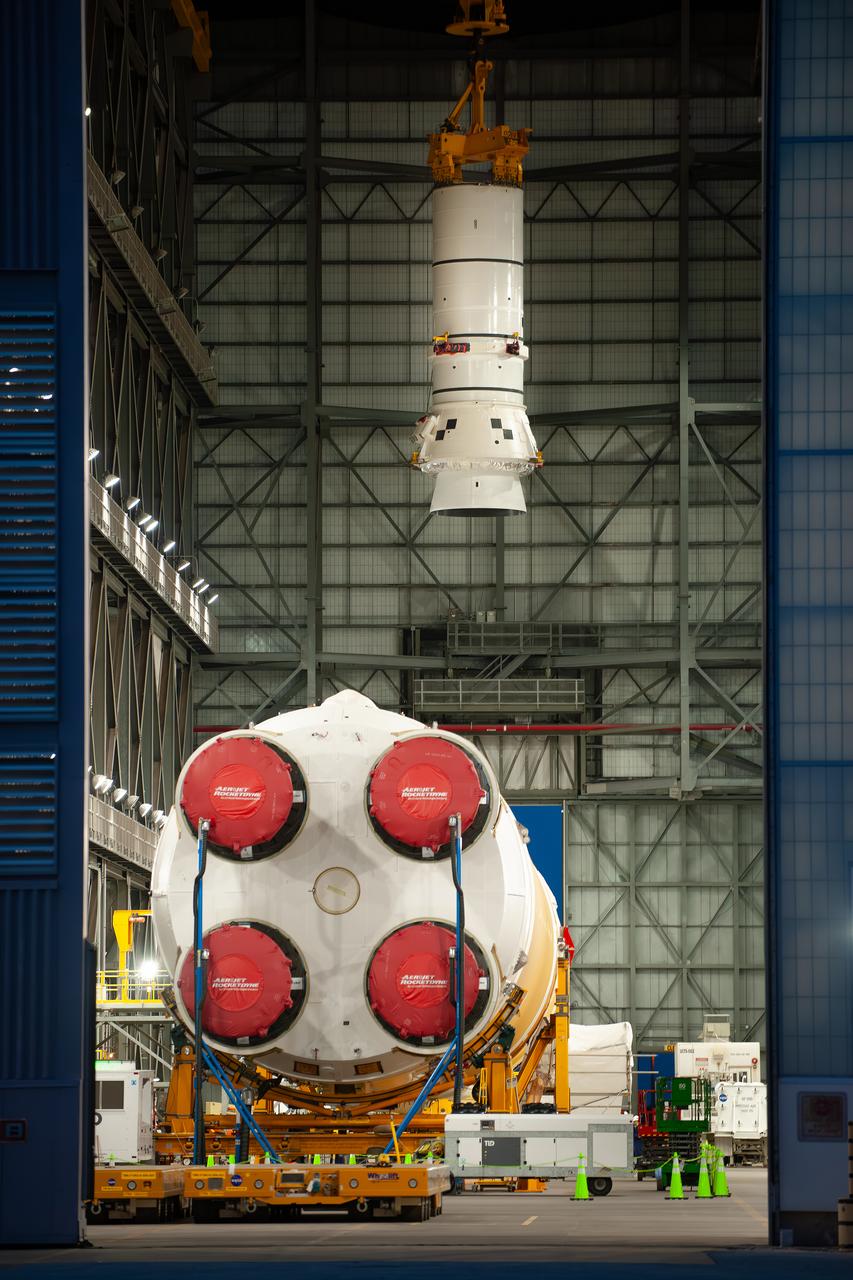

Down the transfer aisle from the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, an overhead crane hoists the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS Moon rocket inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of the mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.

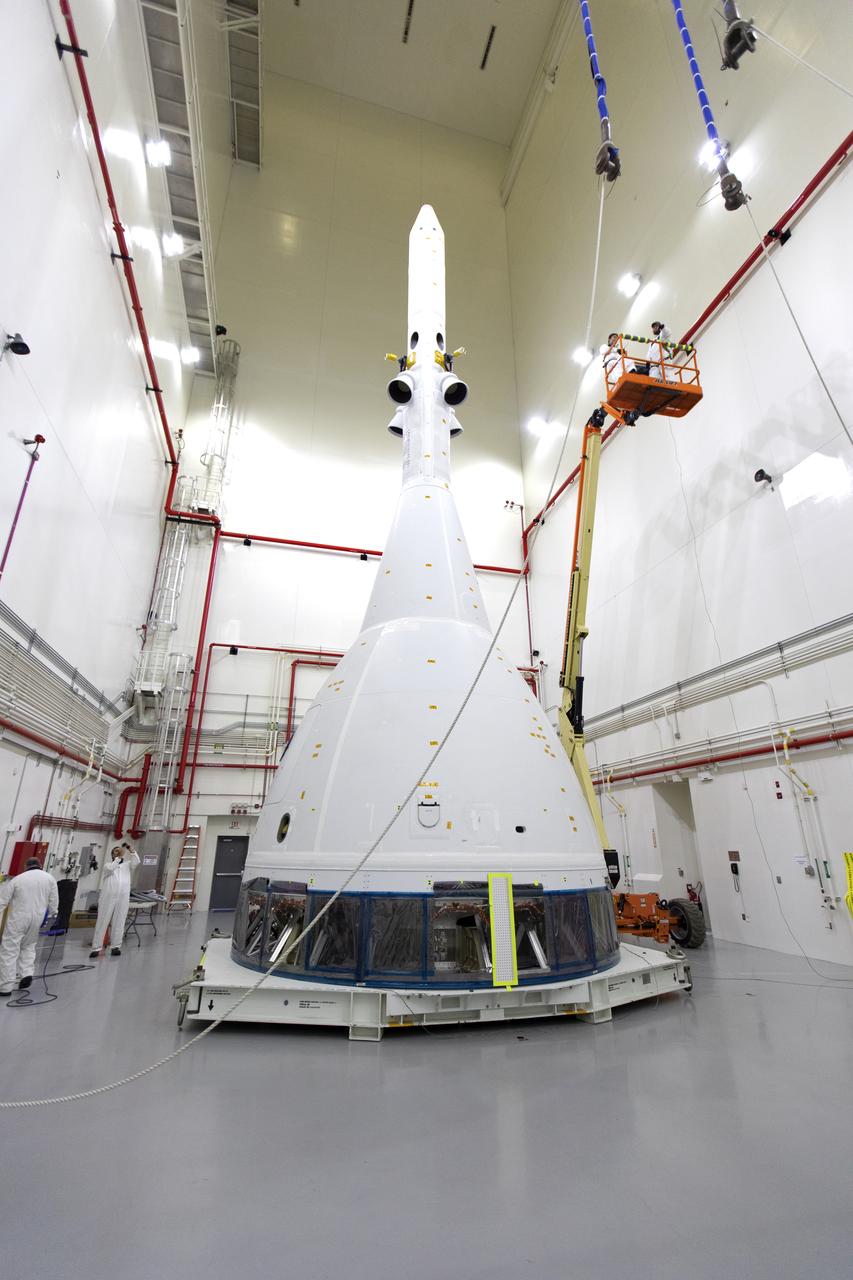
Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
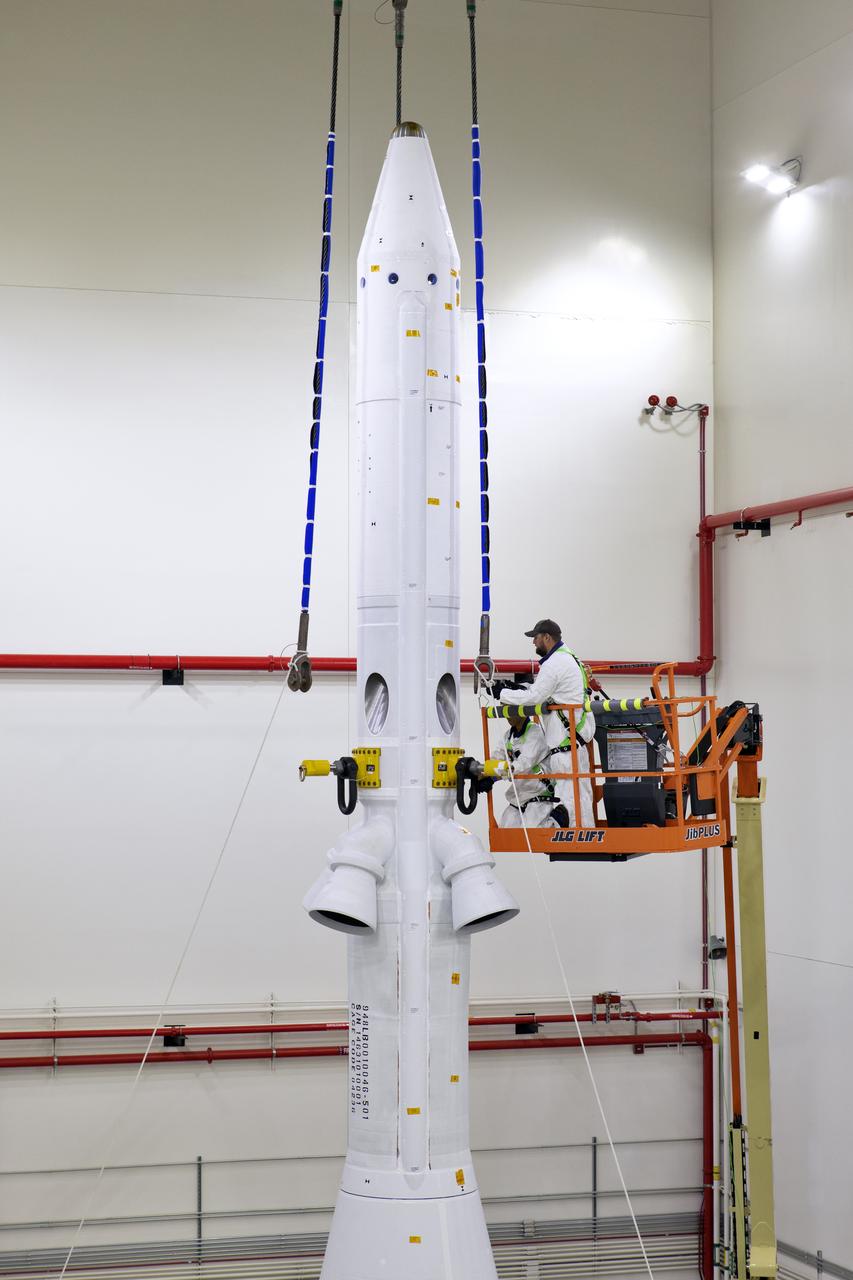

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. In view are the LAS attitude control motor, jettison motor and abort motor. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
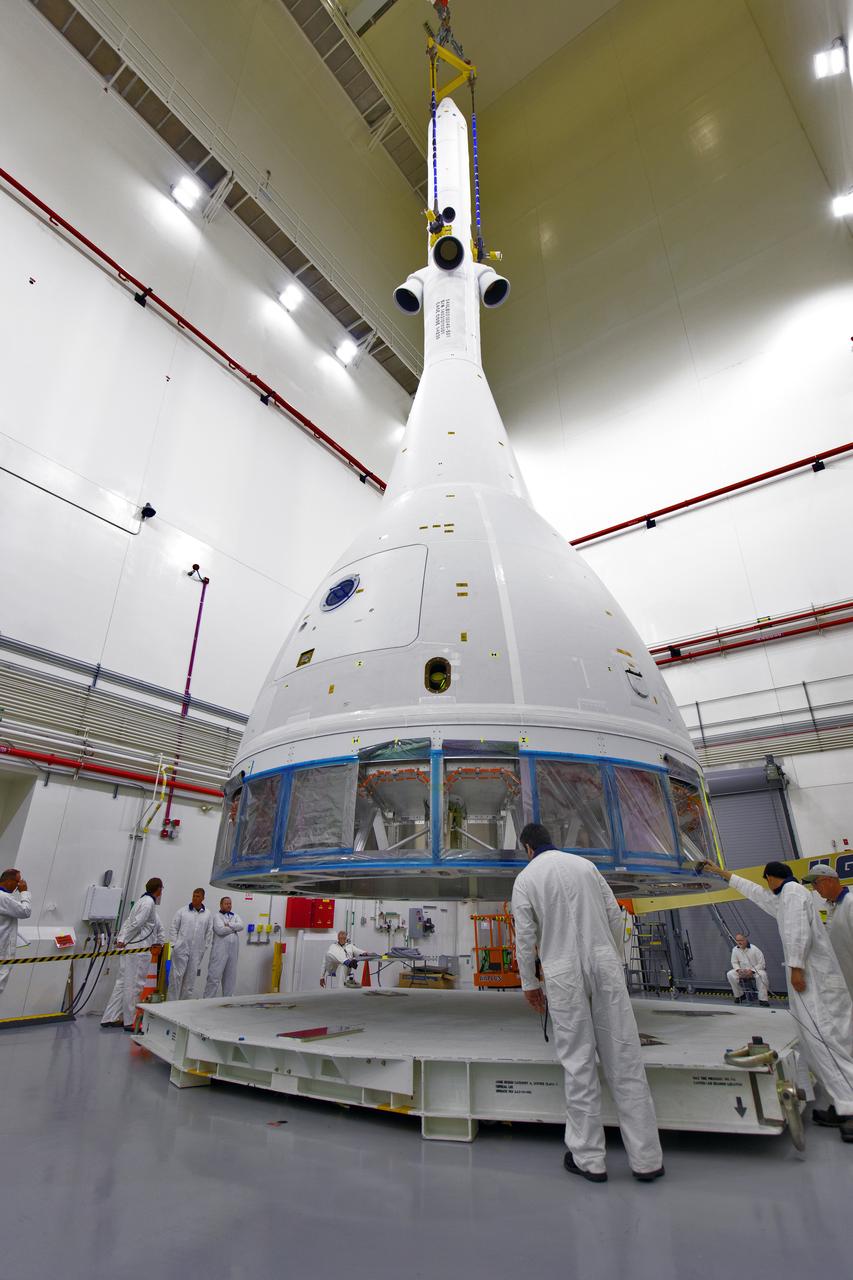

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
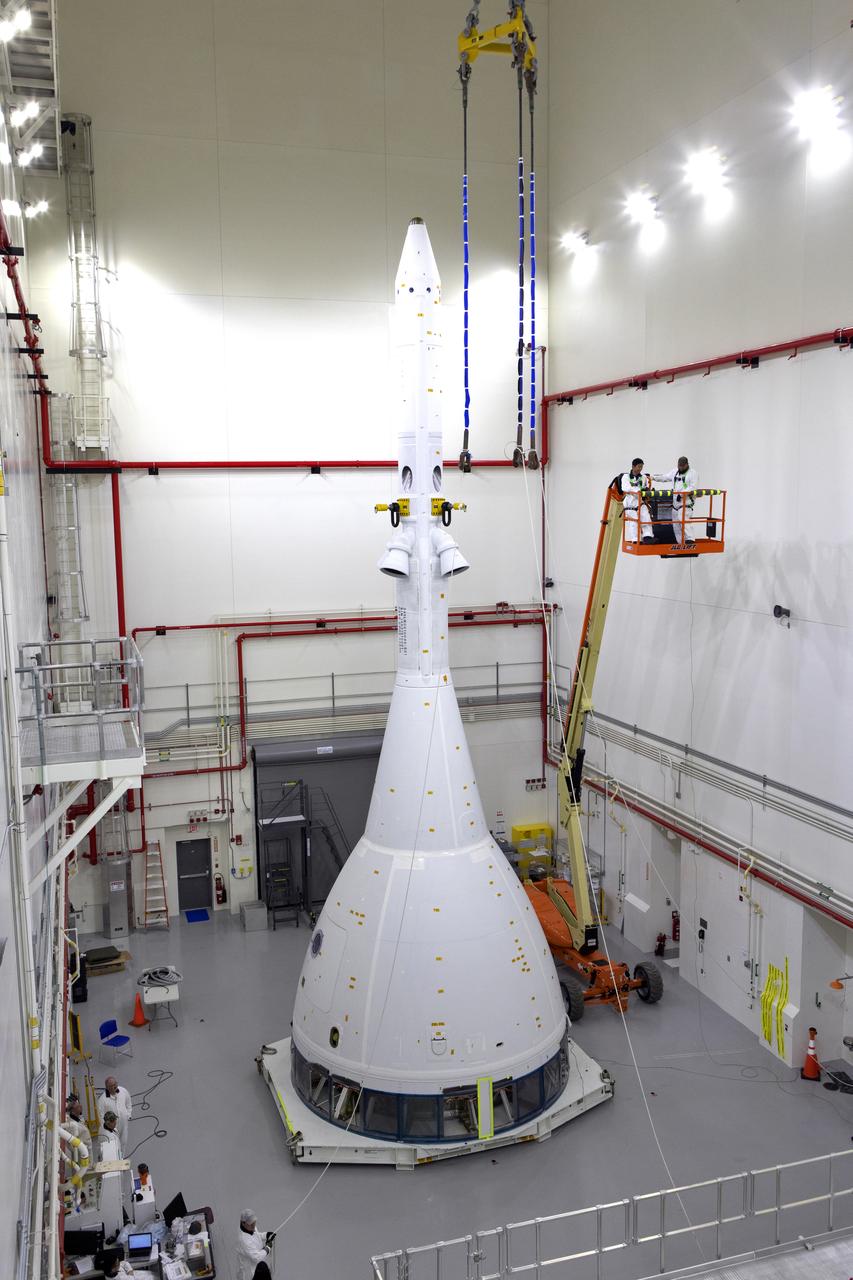

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
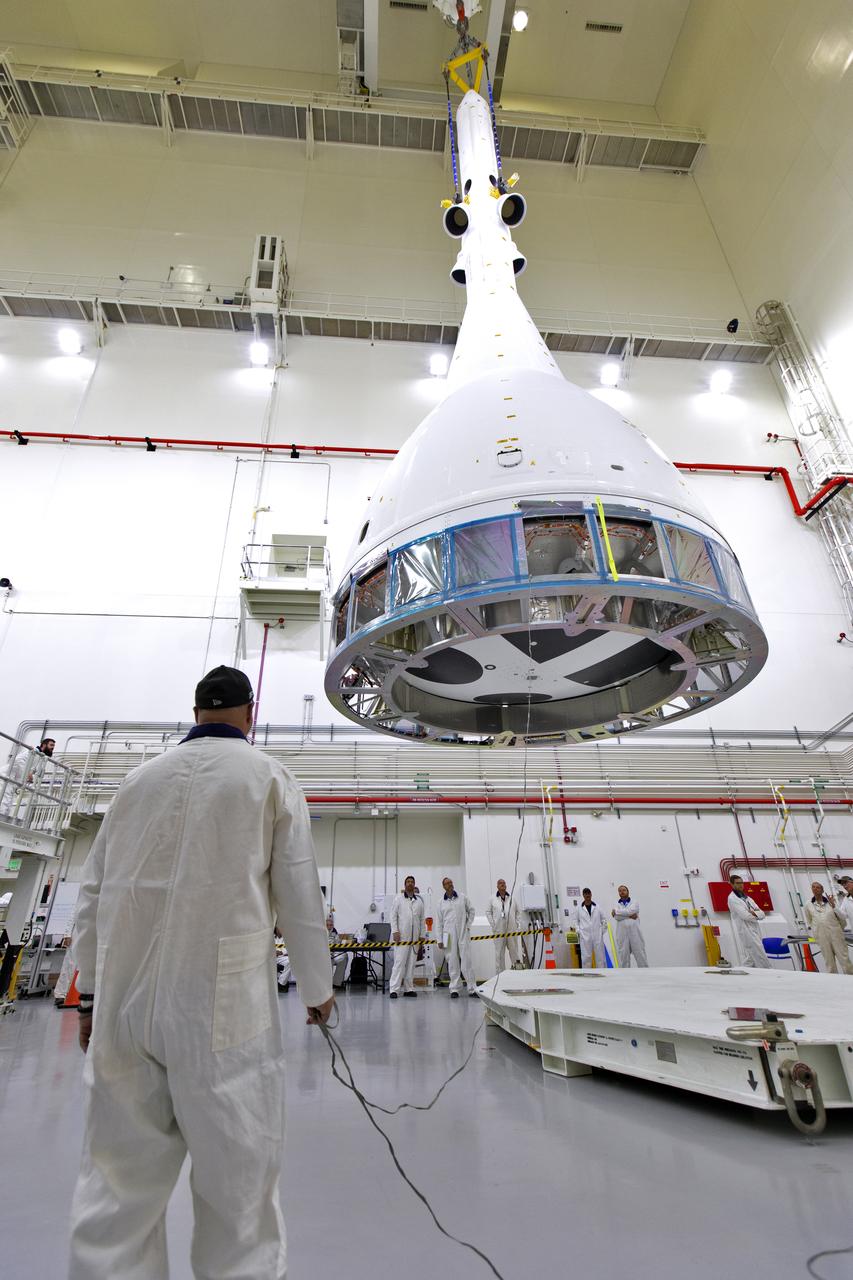

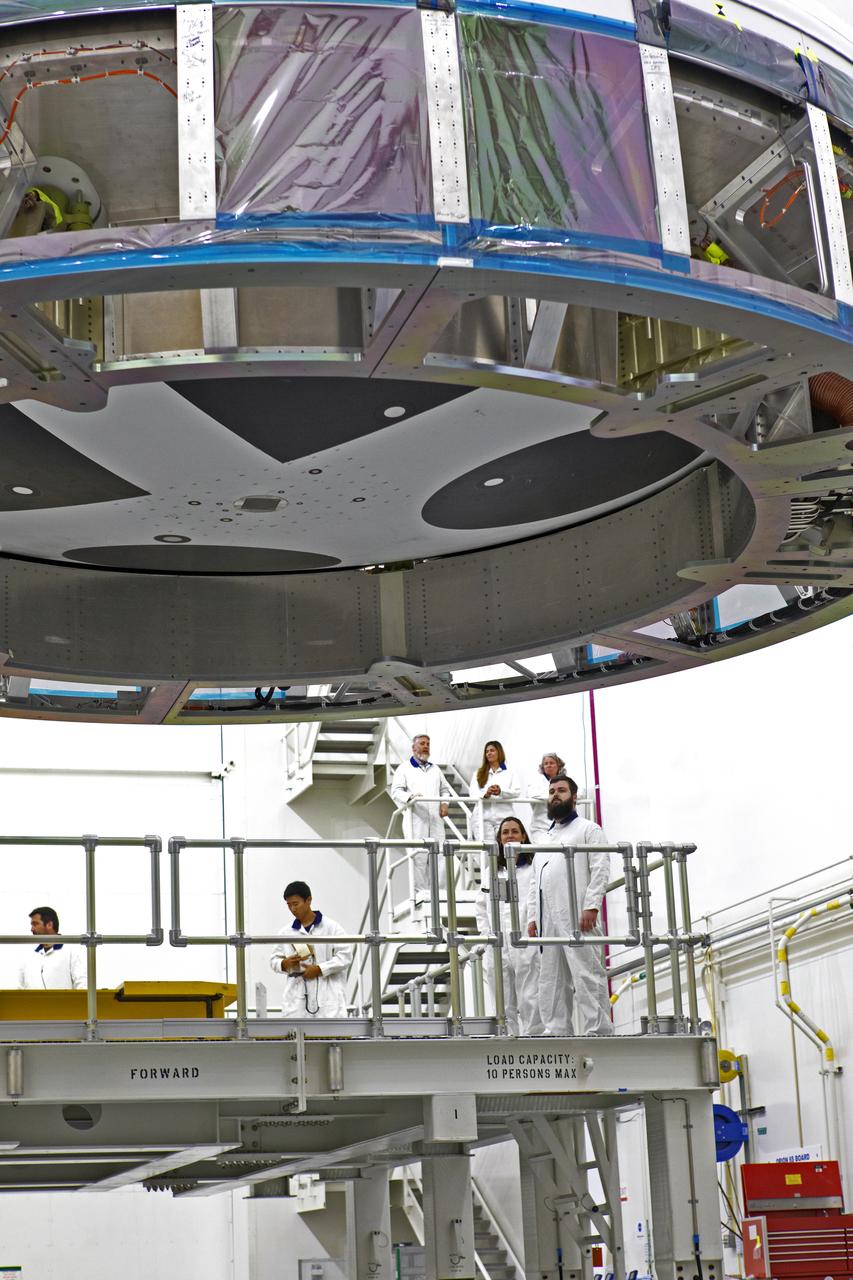
Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. It is being lifted by crane for transfer to a KAMAG transporter. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
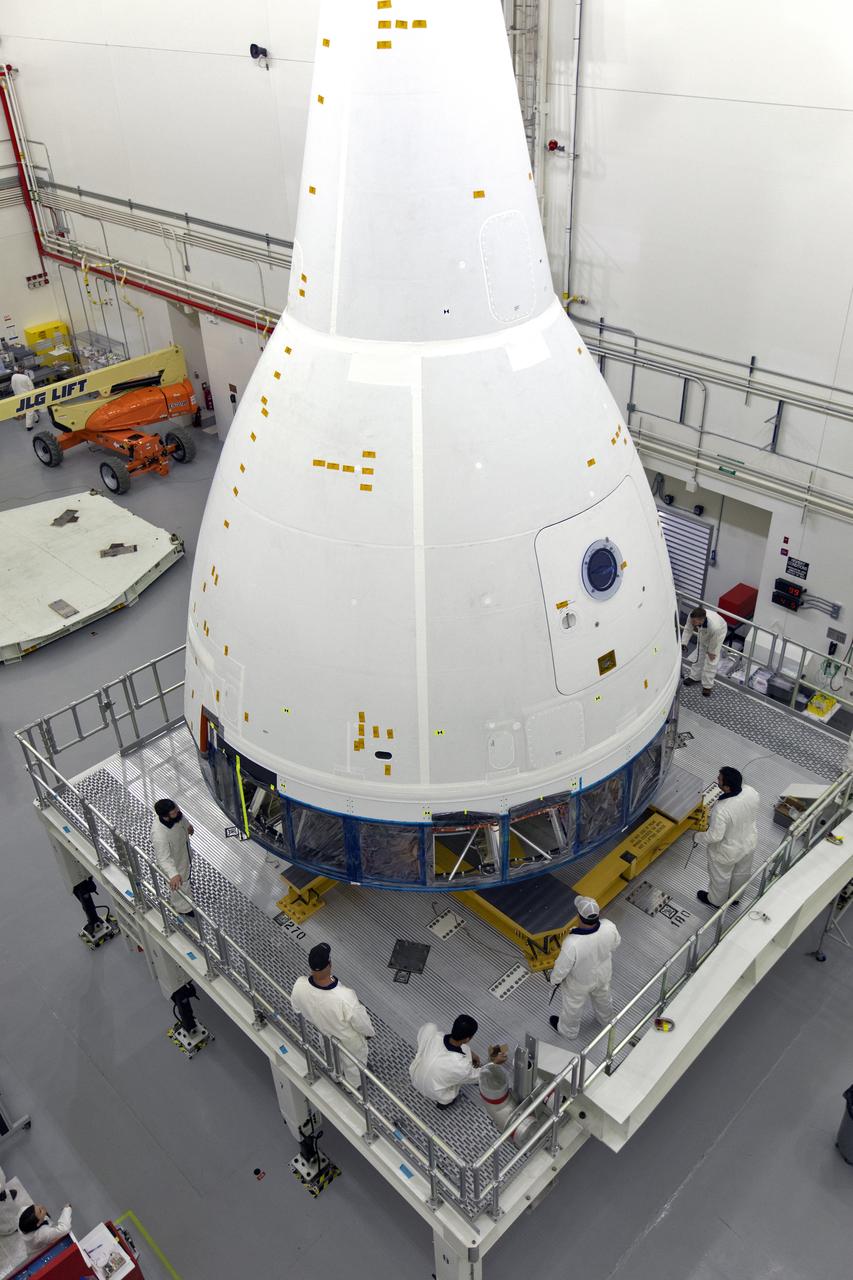

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
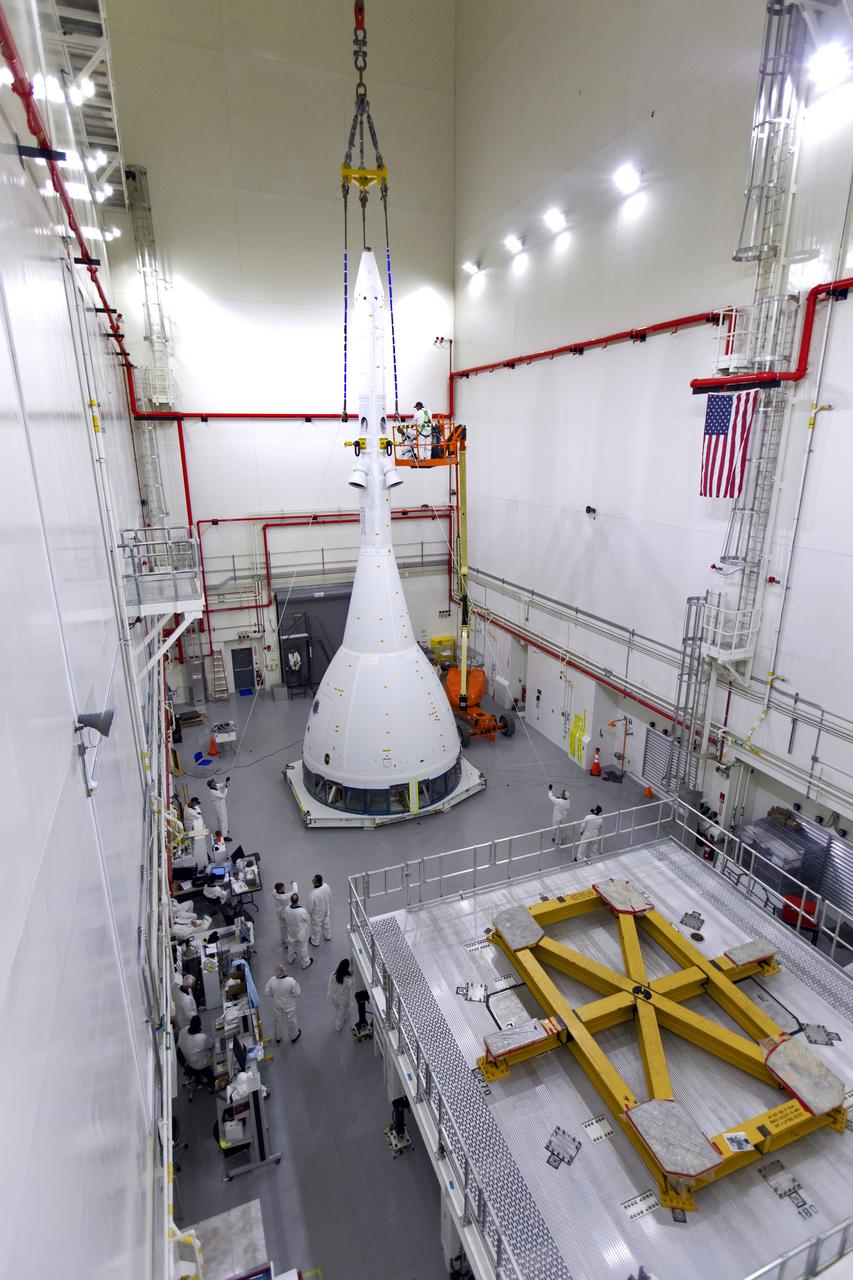

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
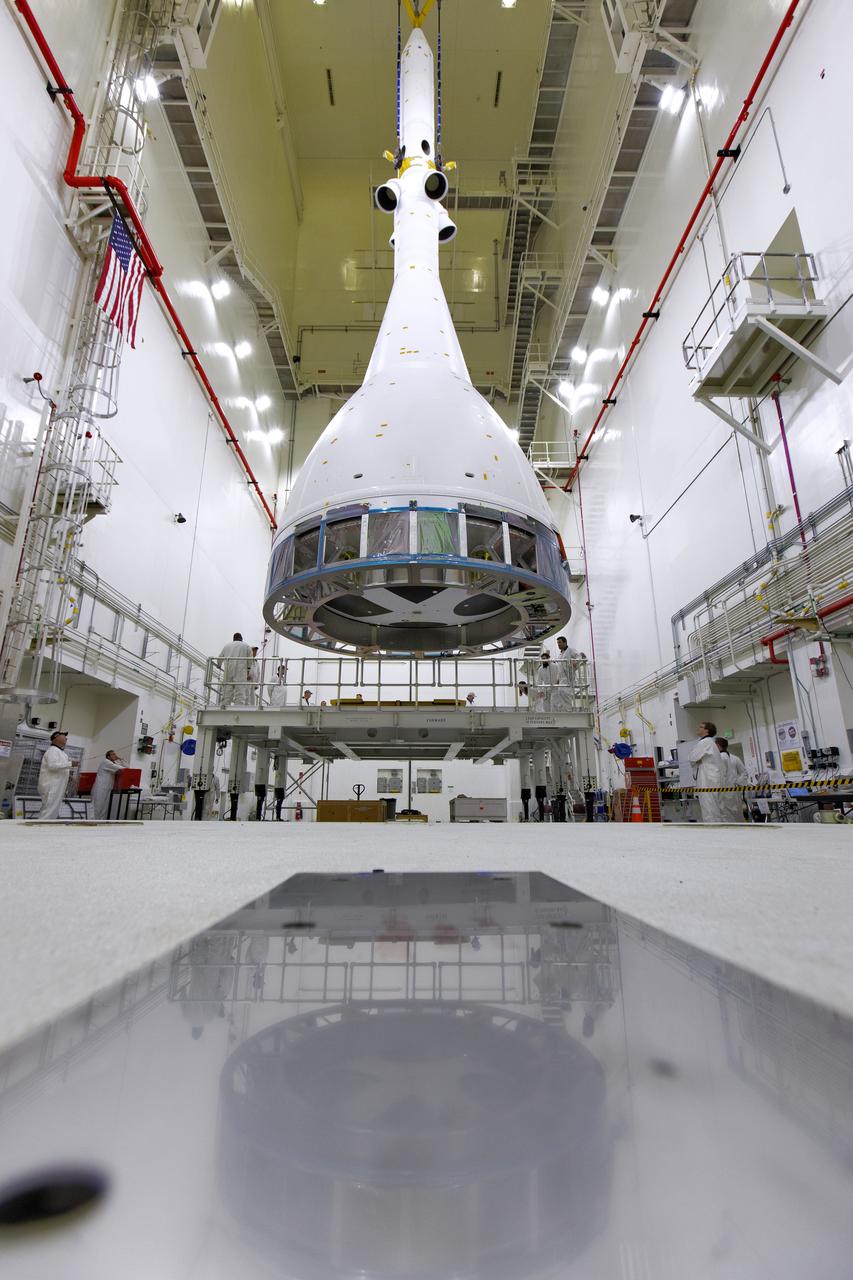

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. It is being lifted by crane for transfer to a KAMAG transporter. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
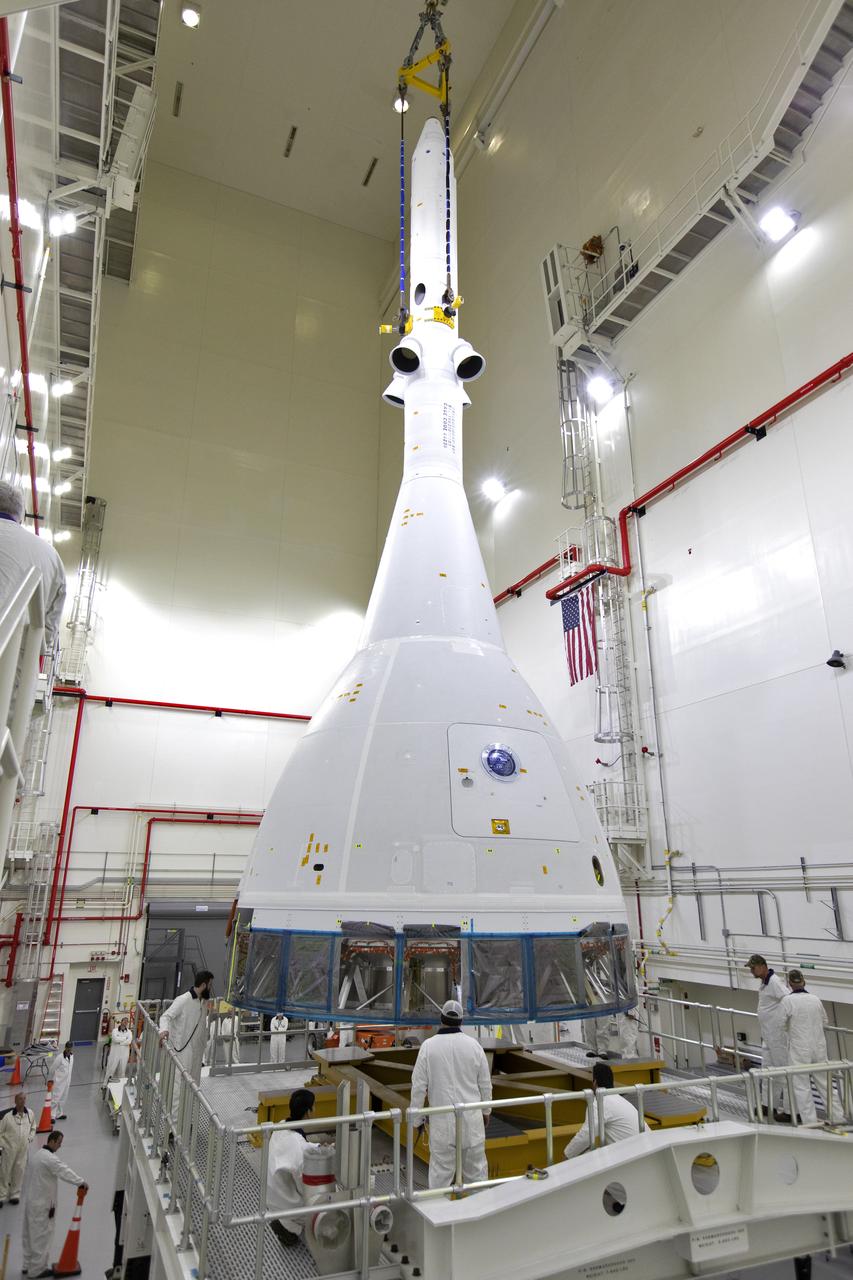

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
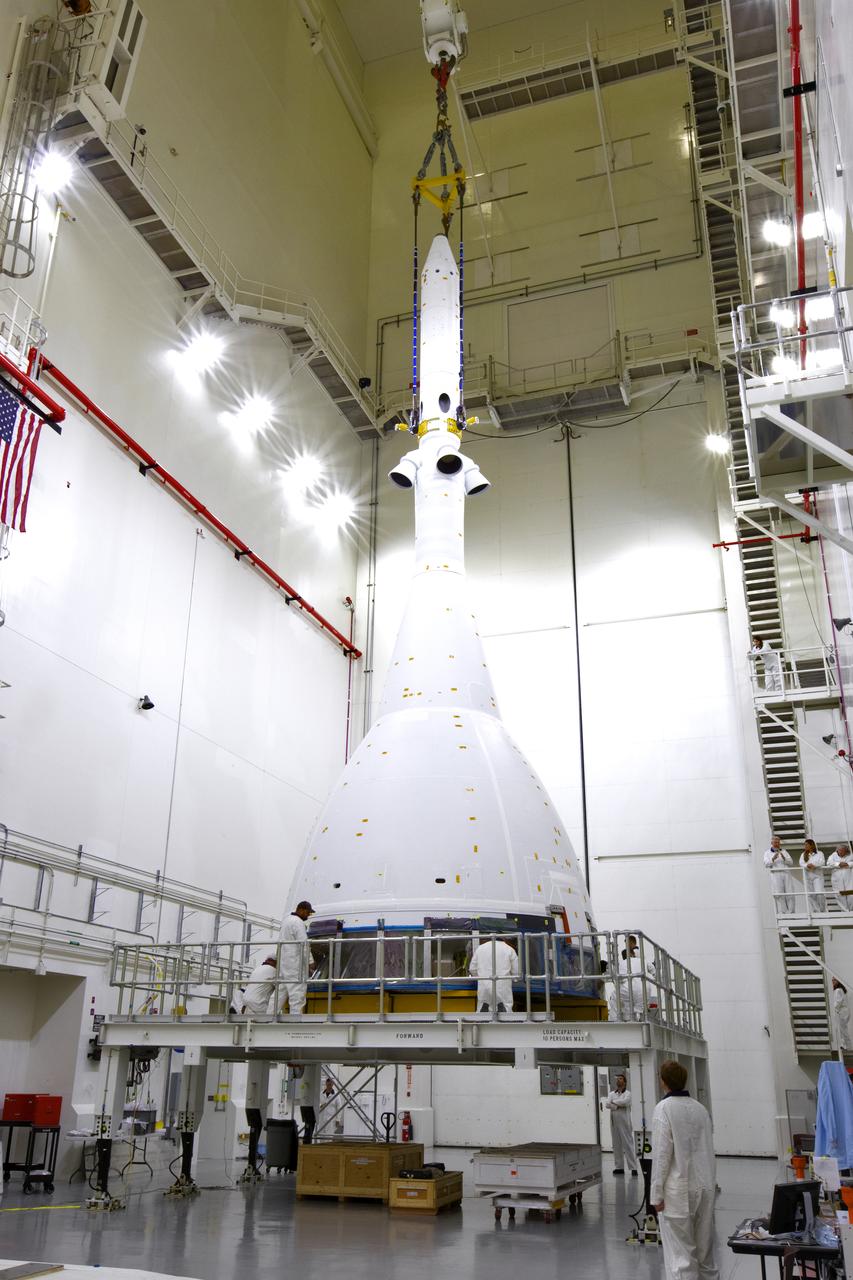

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
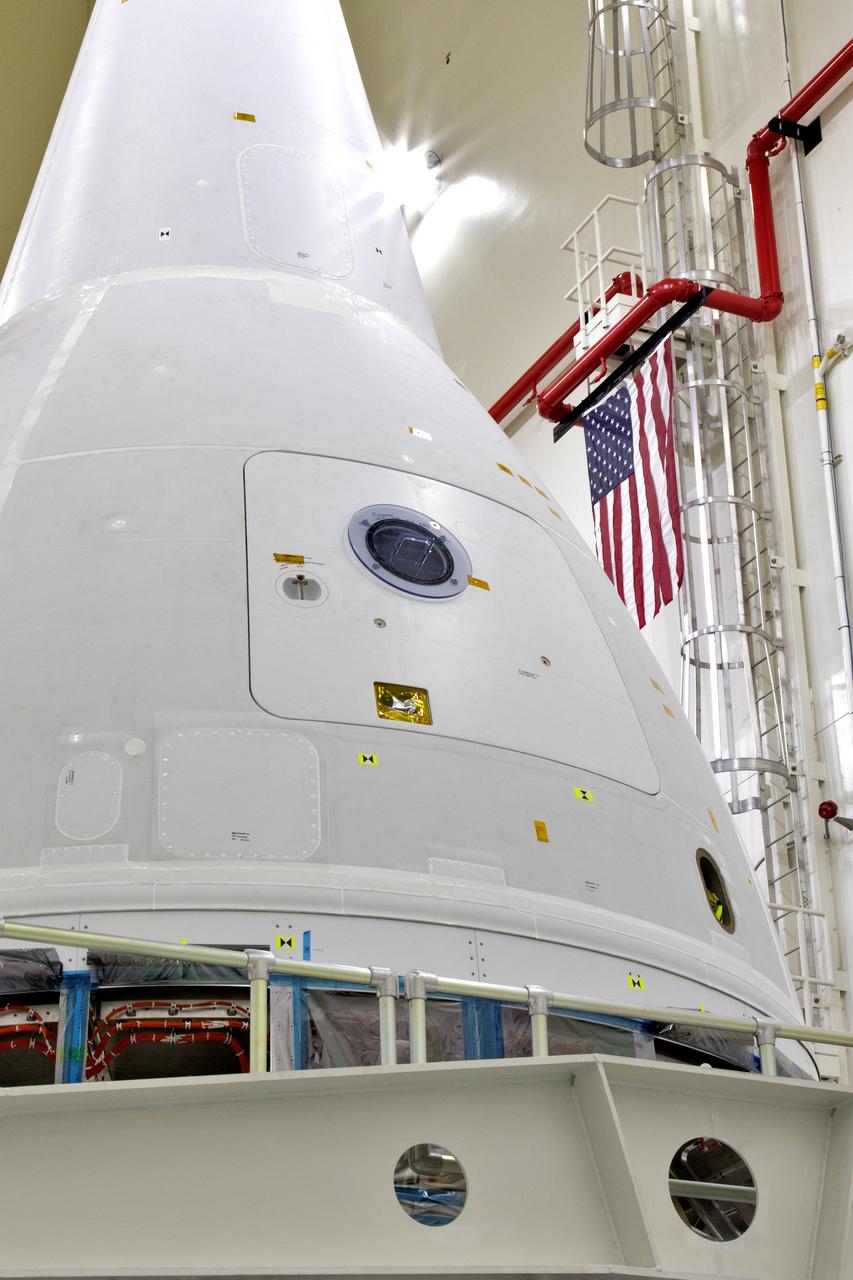

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
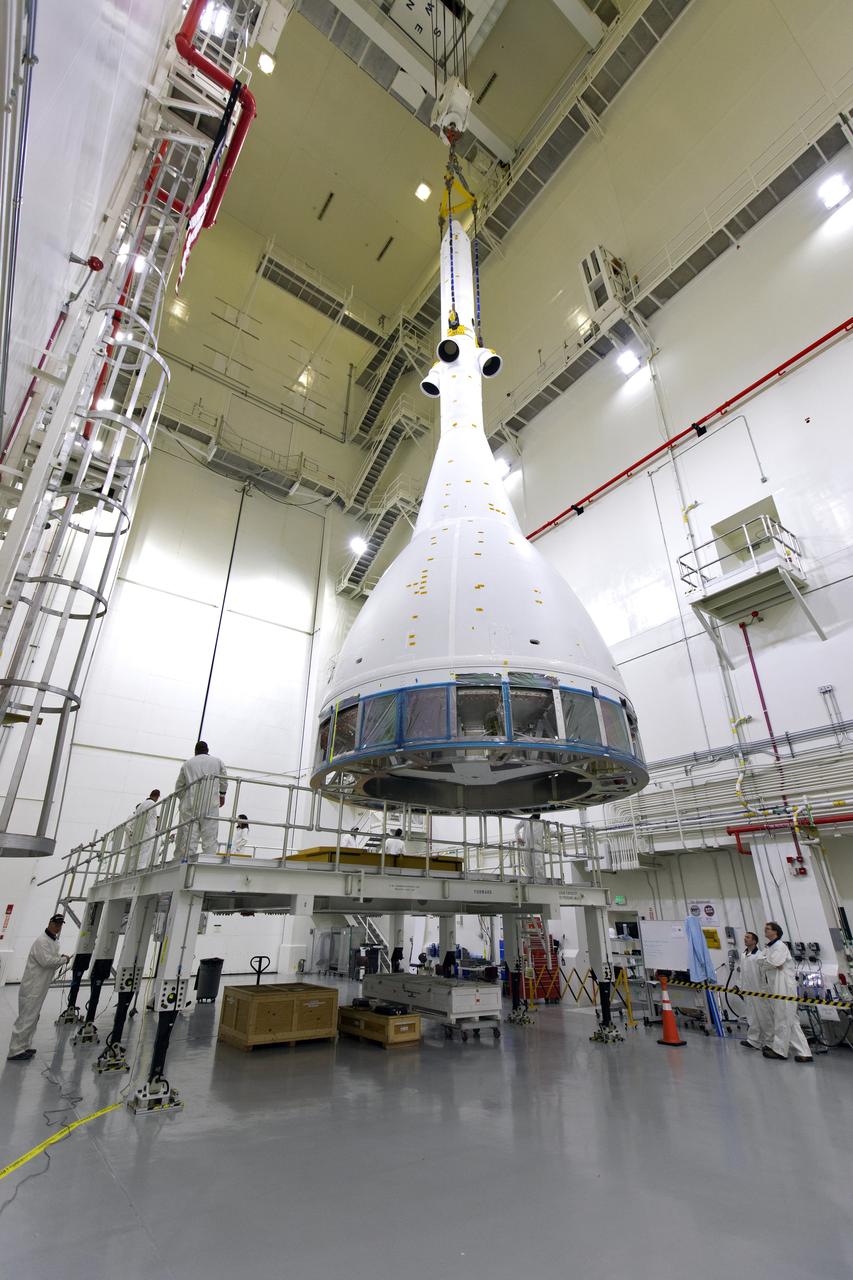

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. It is being lifted by crane for transfer to a KAMAG transporter. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
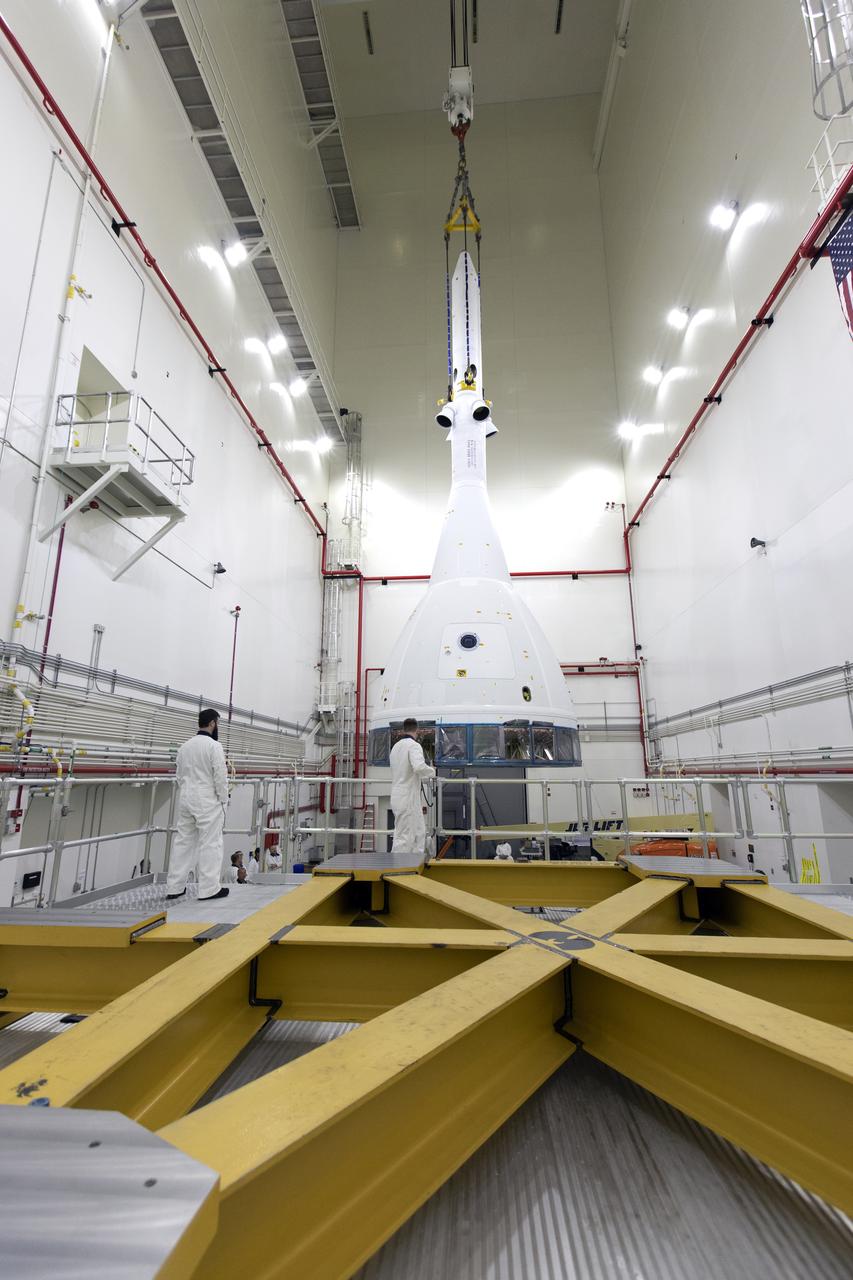

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are completing the integration of a test version of the Orion crew module with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
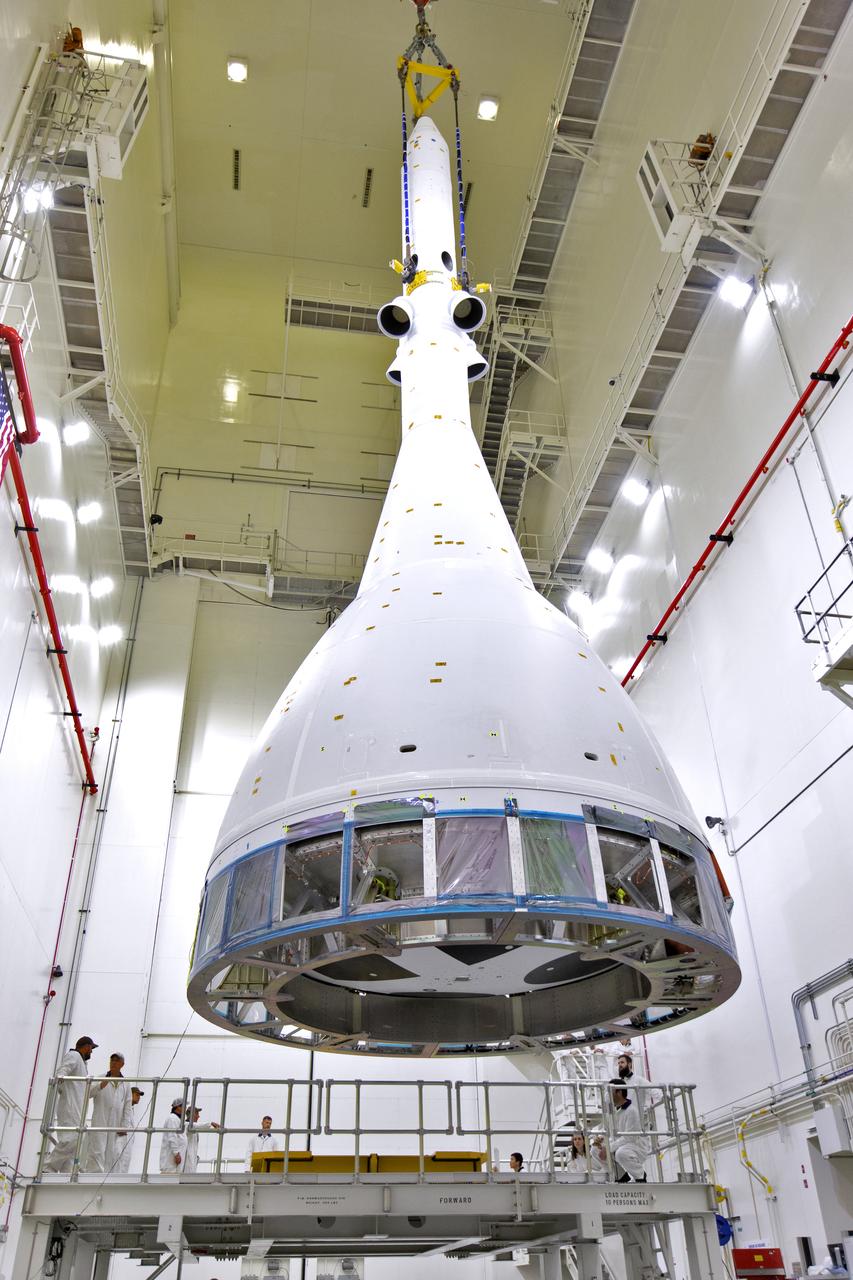

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. It is being lifted by crane for transfer to a KAMAG transporter. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
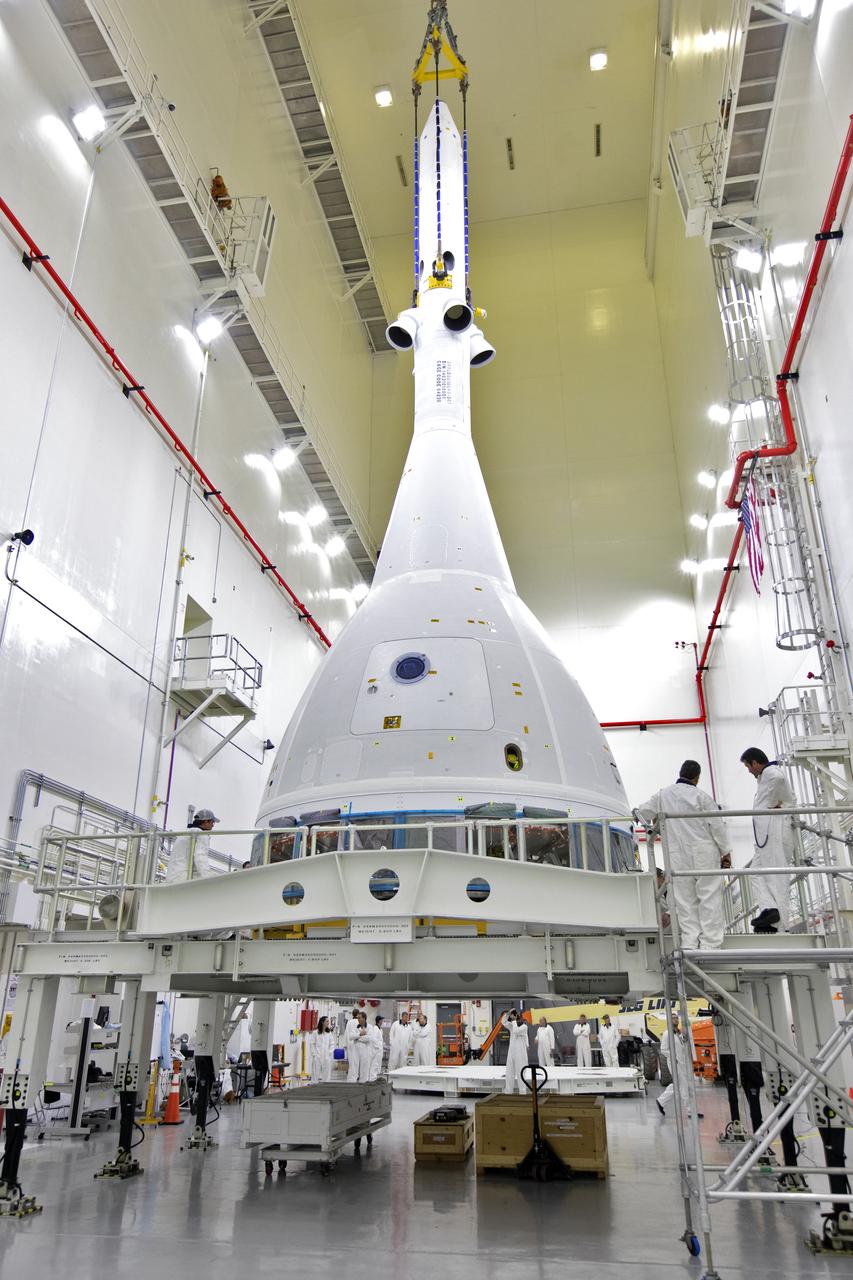

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a test version of the Orion crew module has been integrated with the Launch Abort System (LAS) on May 18, 2019. The test vehicle and the LAS will be used for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the LAS, planned for July 2. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety if an emergency occurs during ascent on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs, contractors Jacob's, Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch and the 45th Space Wing are performing flight operations for AA-2.
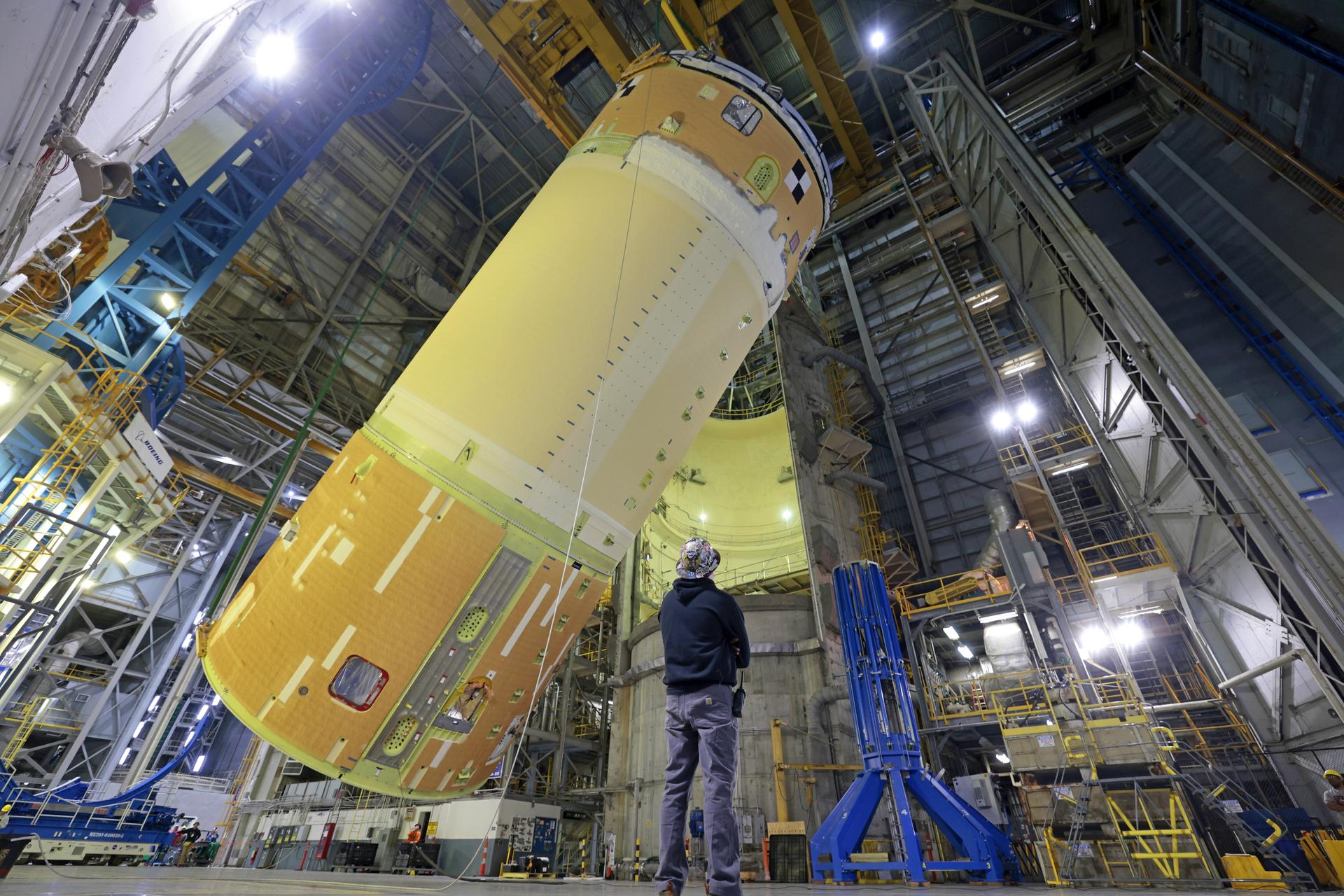

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
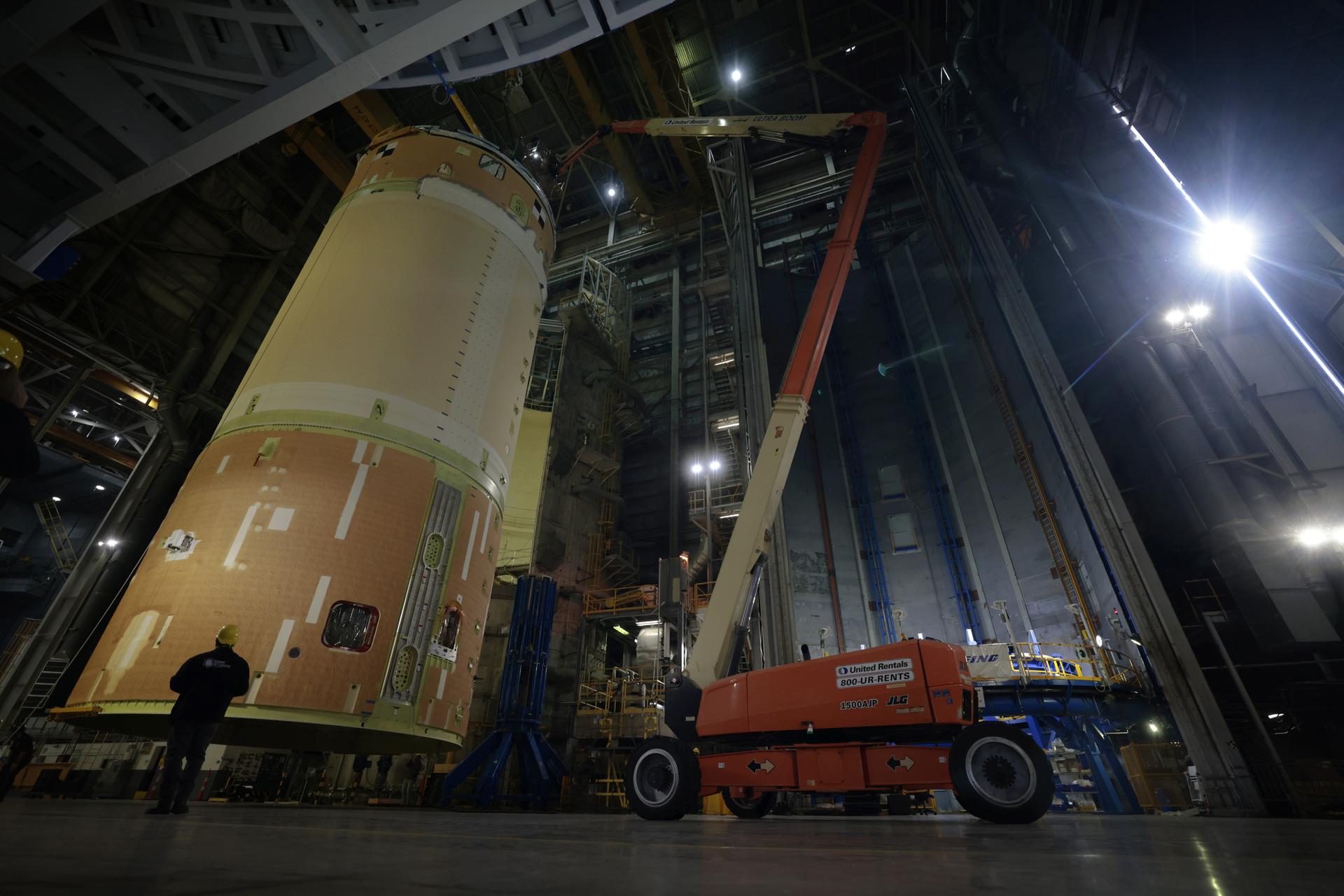

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
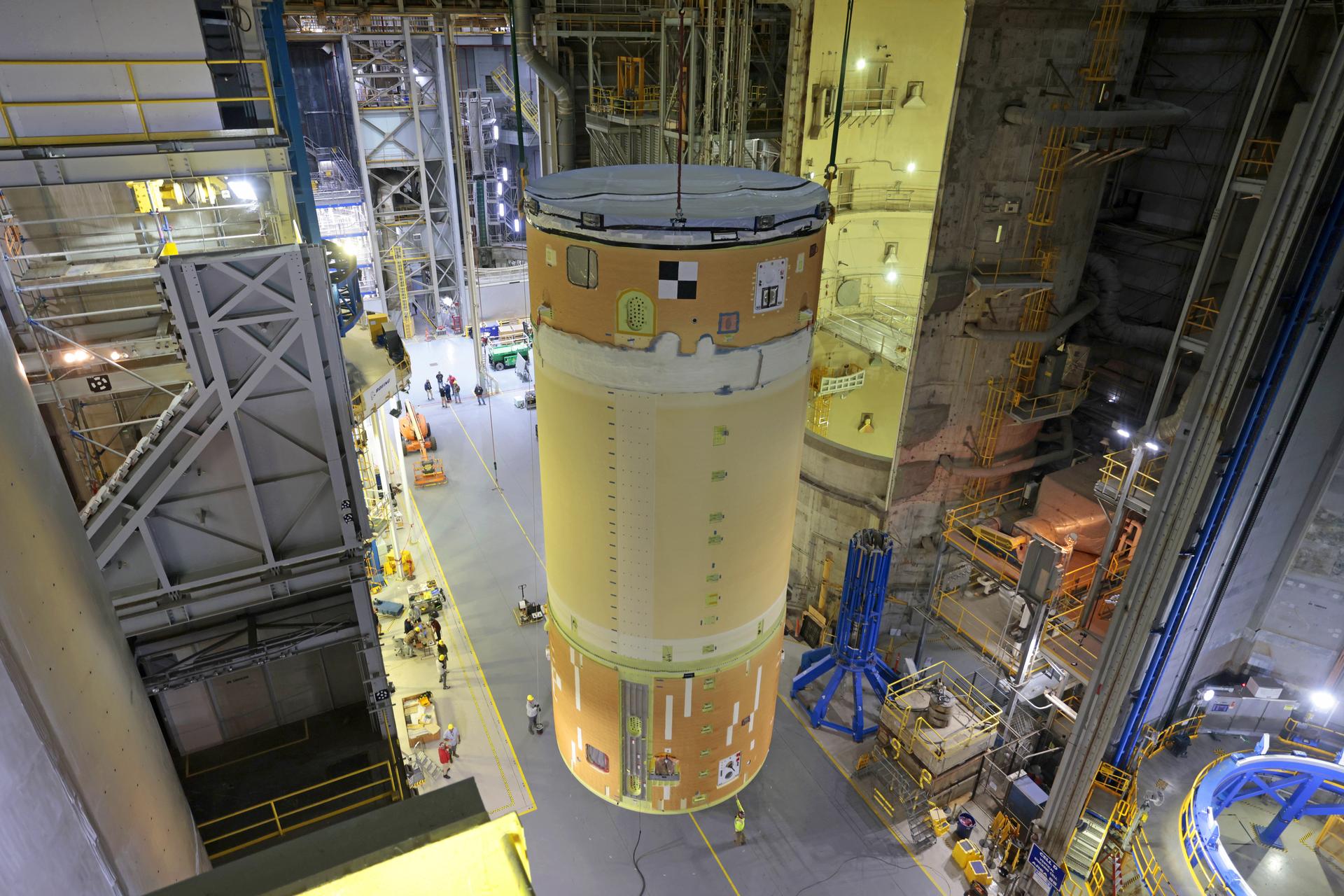

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
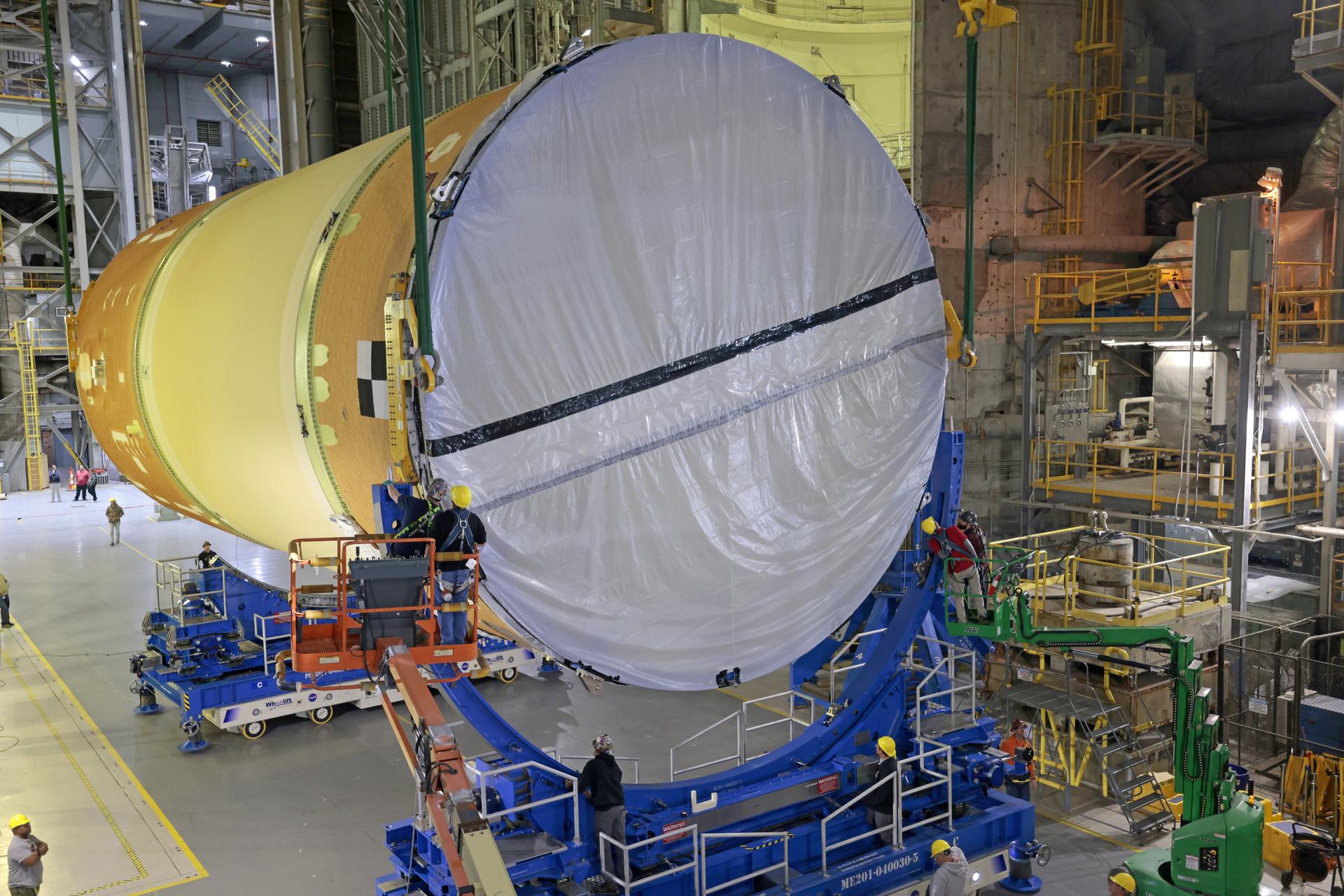

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
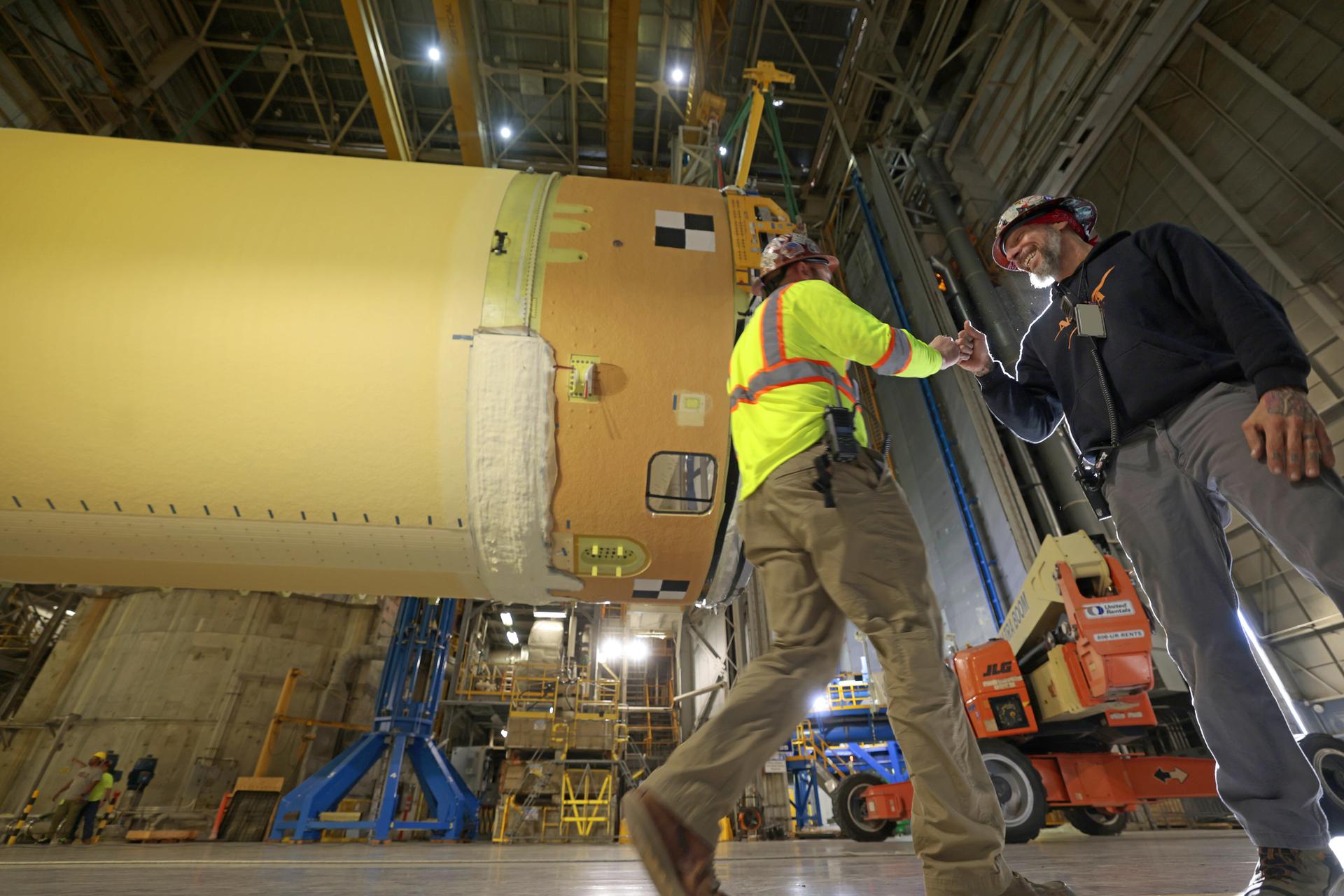

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
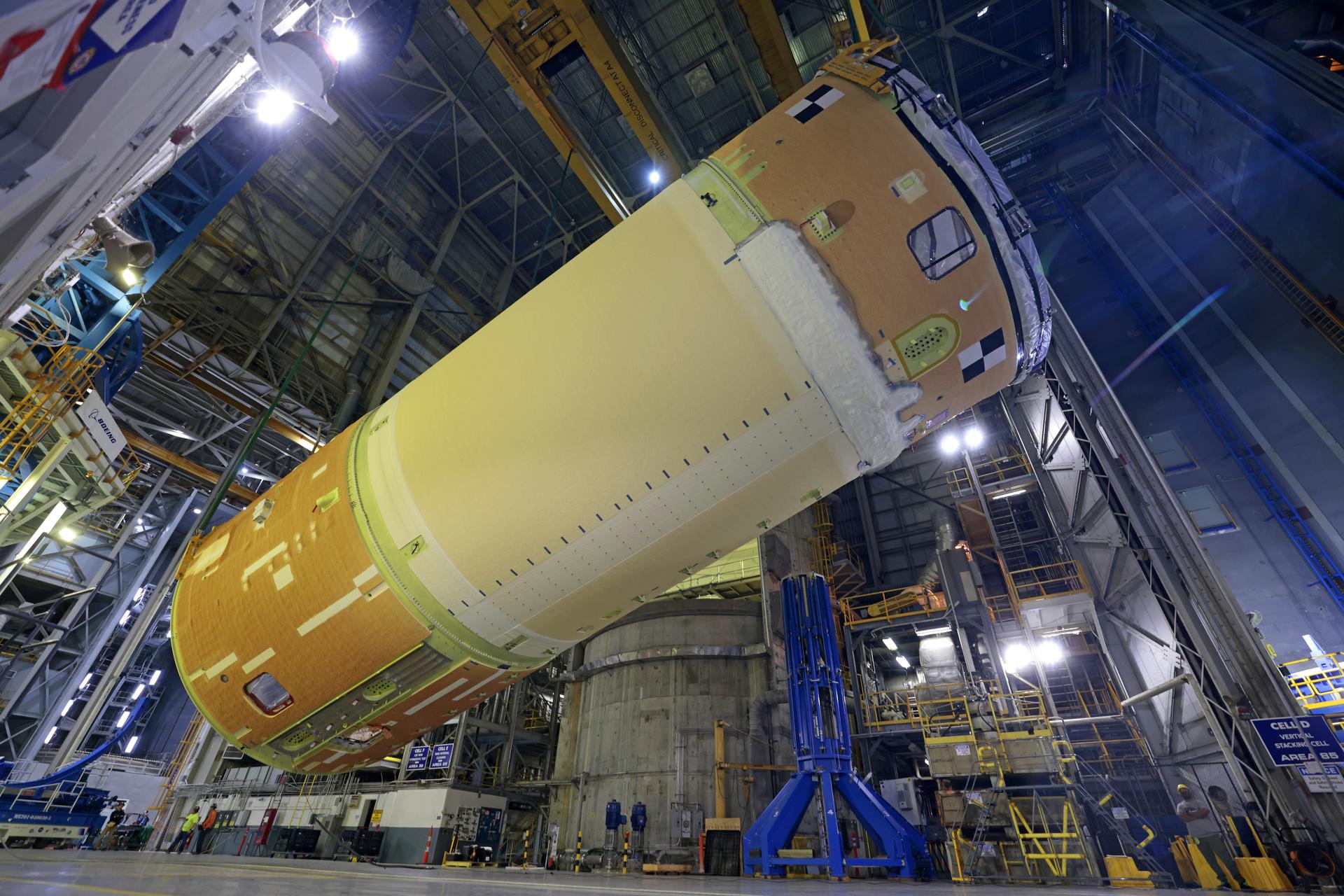

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
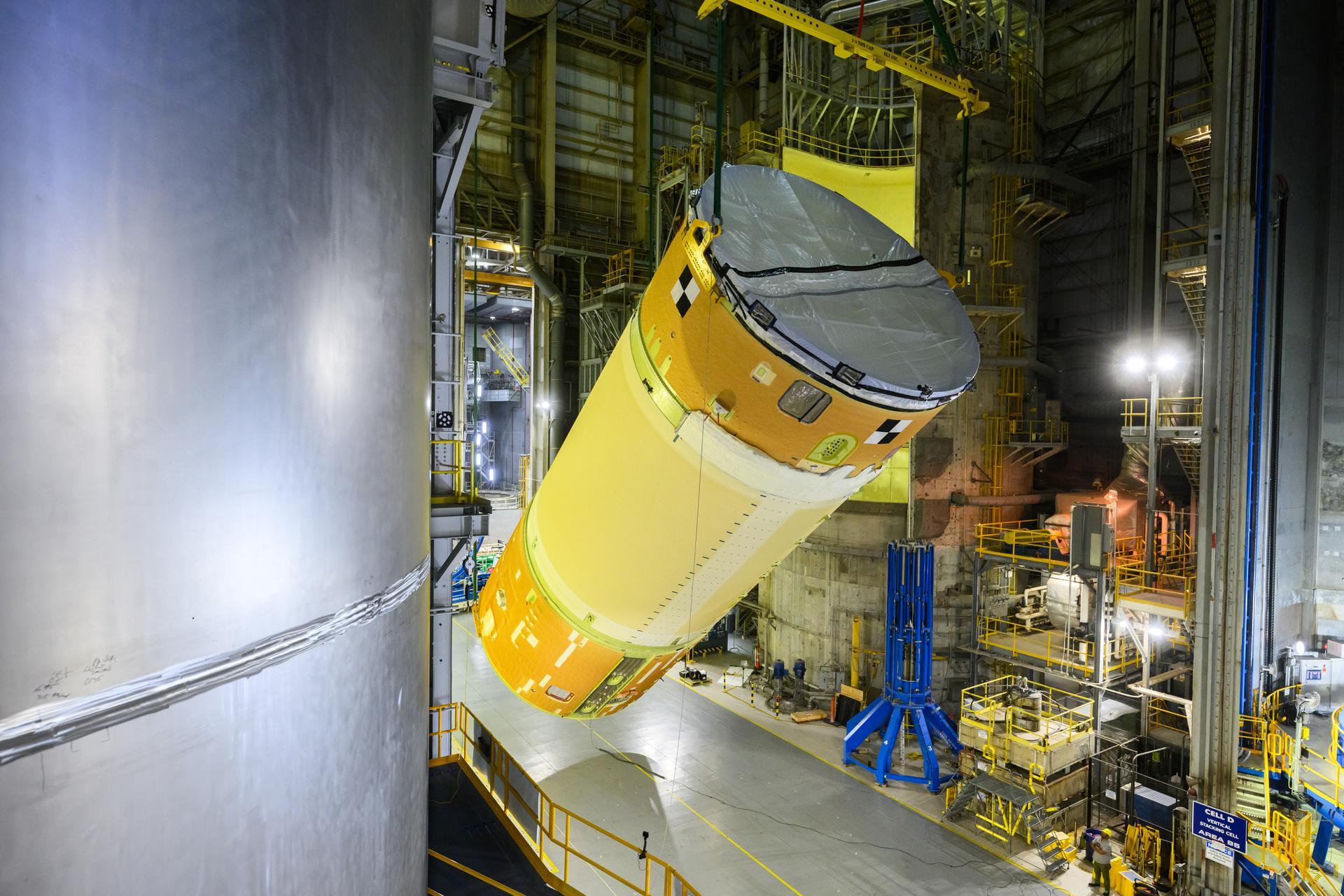

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
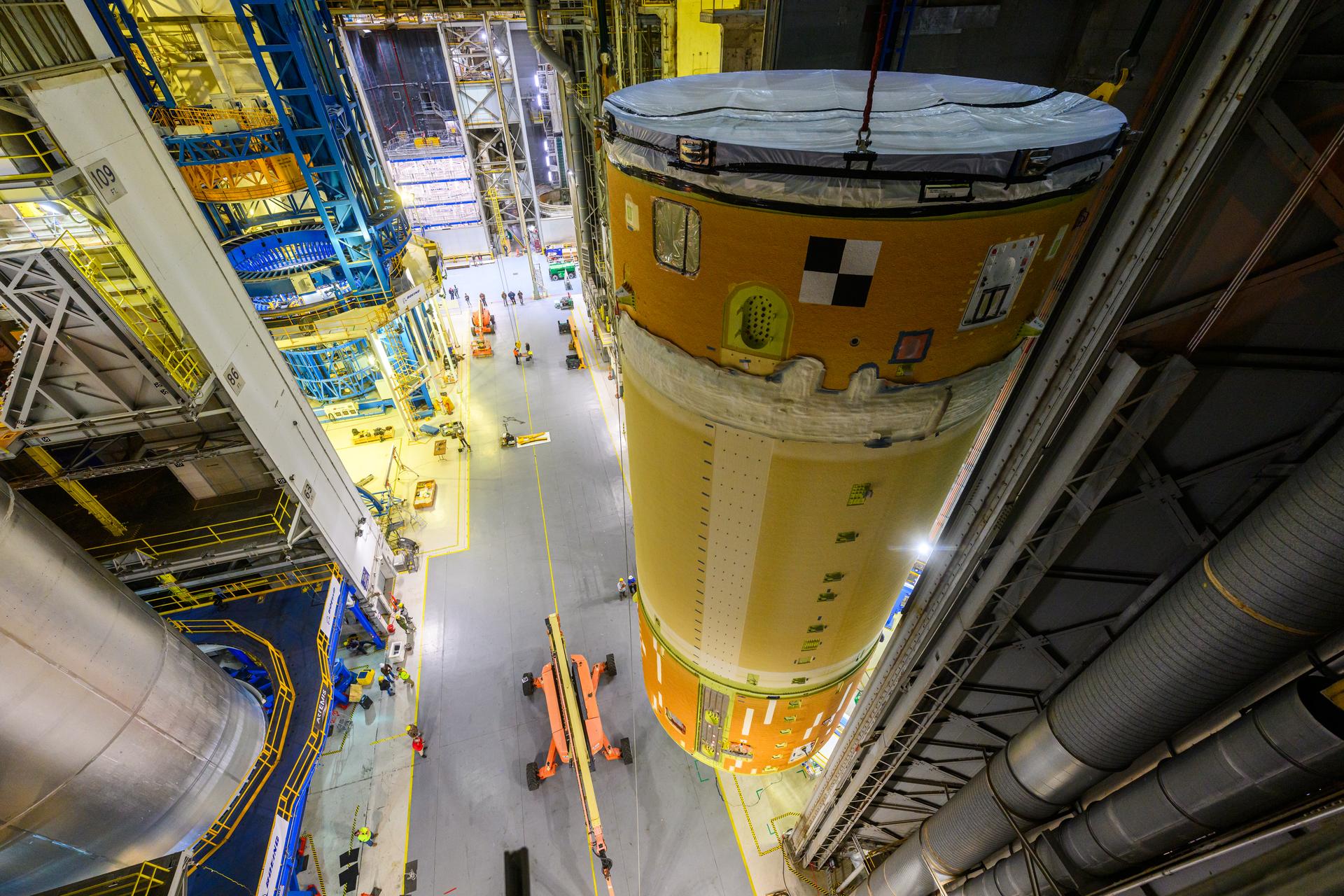

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
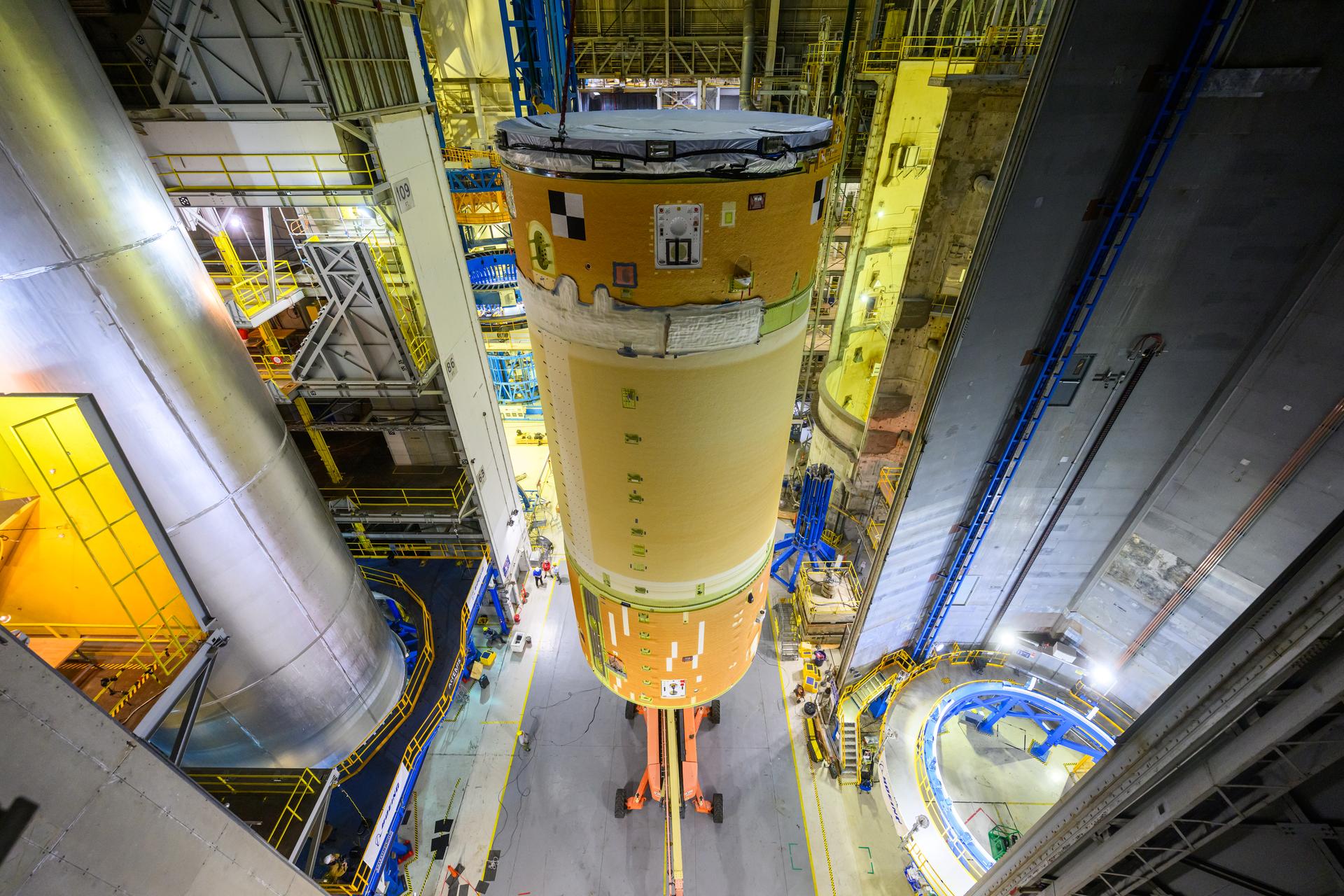

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, lift the forward-joined flight hardware for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket out of a stacking cell in the vertical assembly building on Dec. 19, 2025. The forward join, which consists of the intertank, liquid oxygen tank, and forward skirt, will be used on the core stage slated for NASA’s Artemis III mission. Teams moved the flight hardware from the cell and set it atop self-propelled mobile transporters. Soon, the article will be brought to the factory’s final assembly area where it will be mated to the core stage’s previously joined liquid hydrogen tank and undergo further integration. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
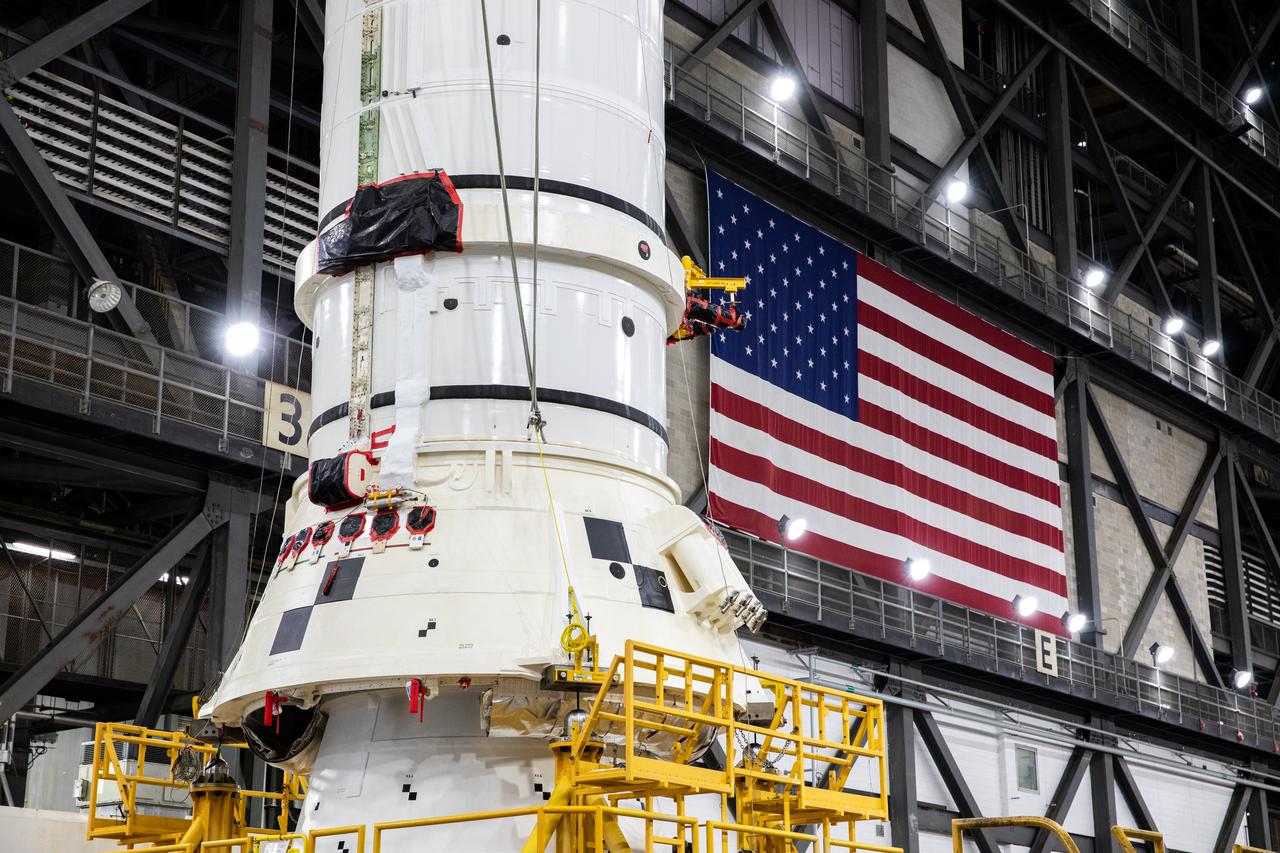
Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.
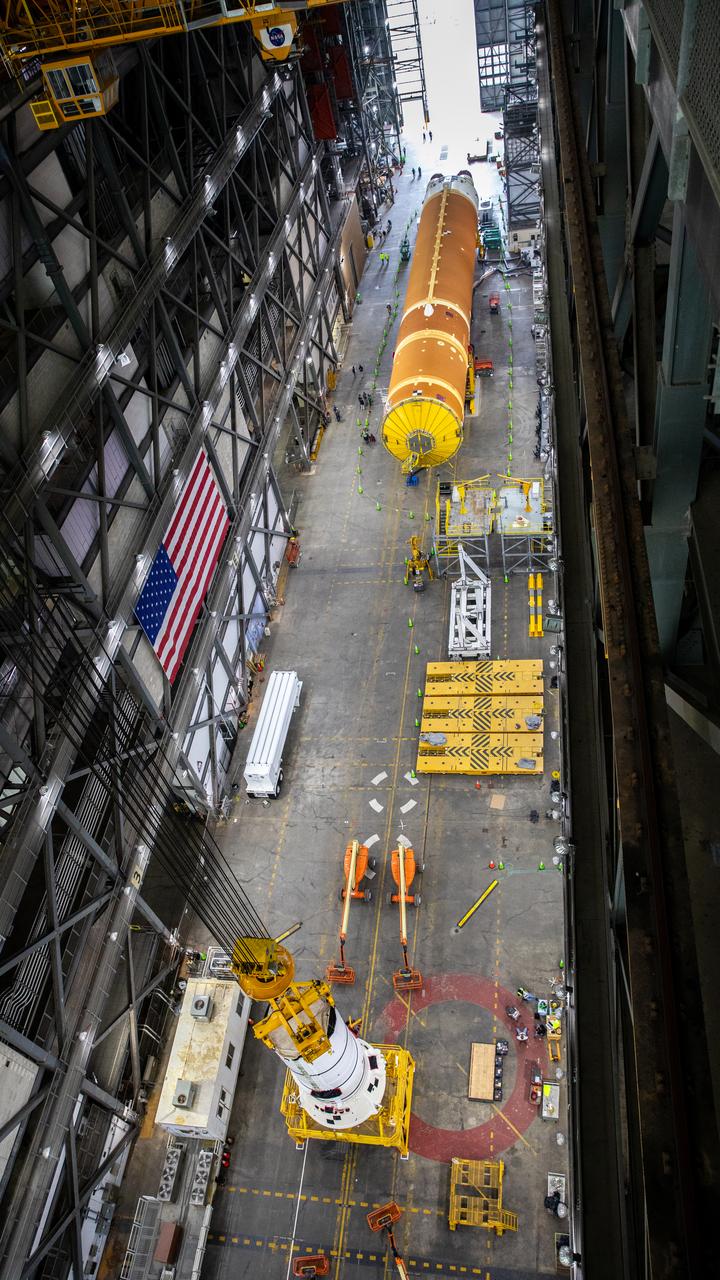

Down the transfer aisle from the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS rocket inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of the mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.

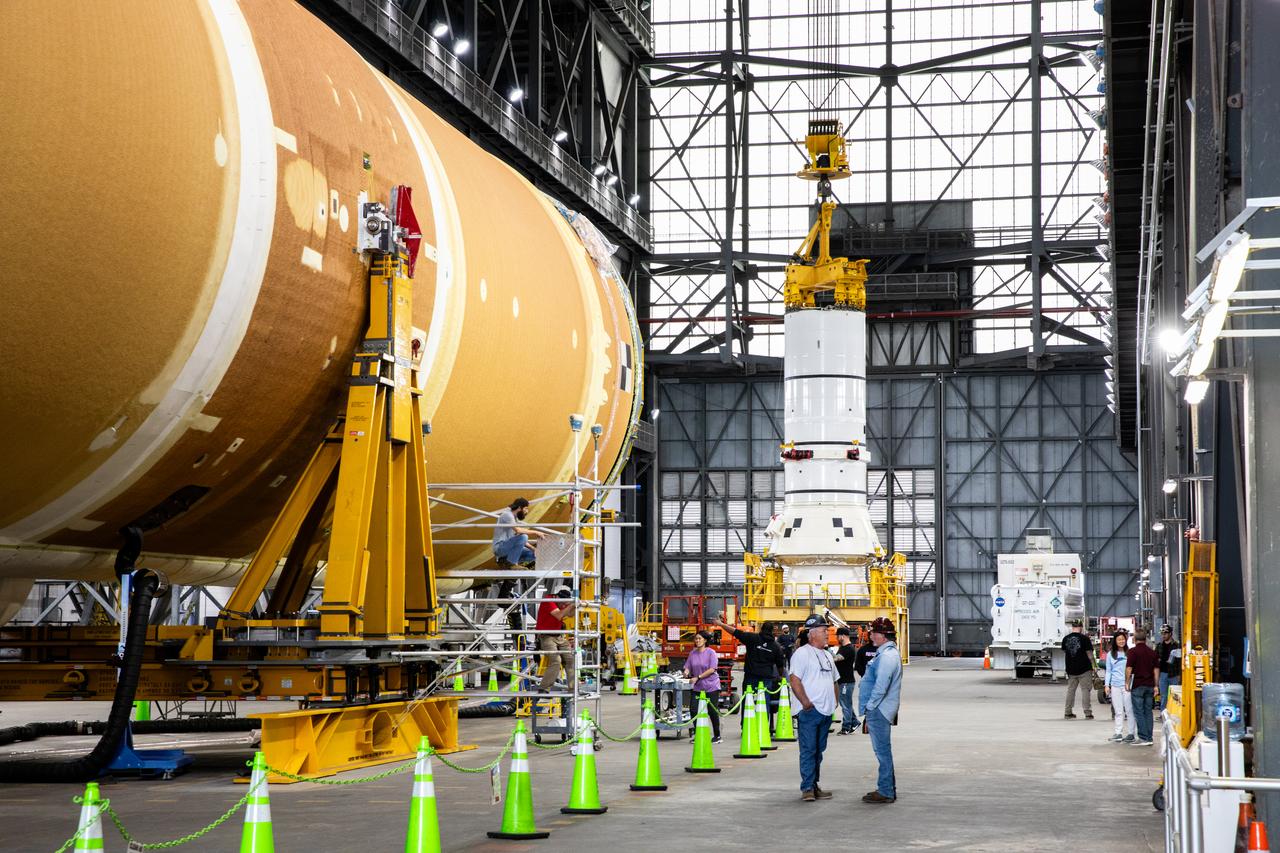
Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.

Down the transfer aisle from the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of the mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.
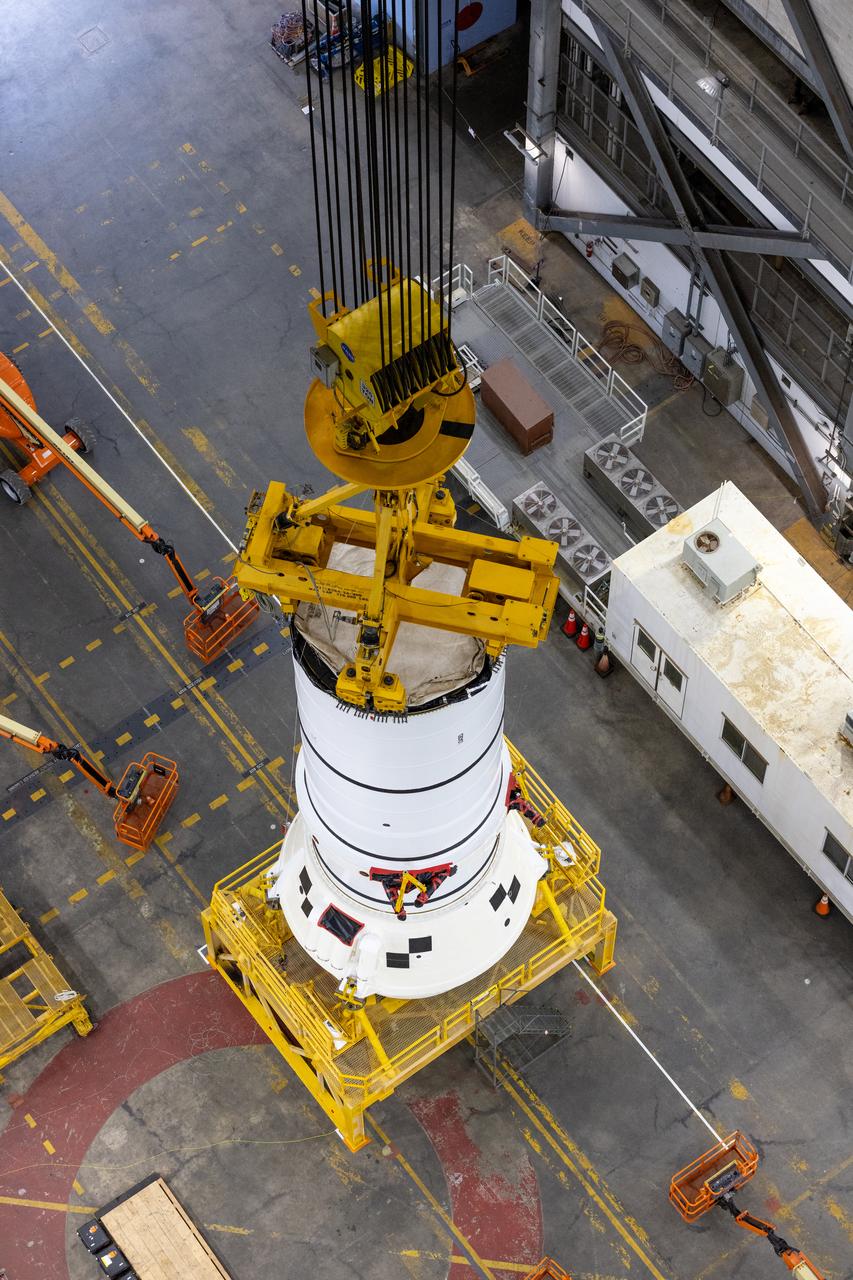

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.
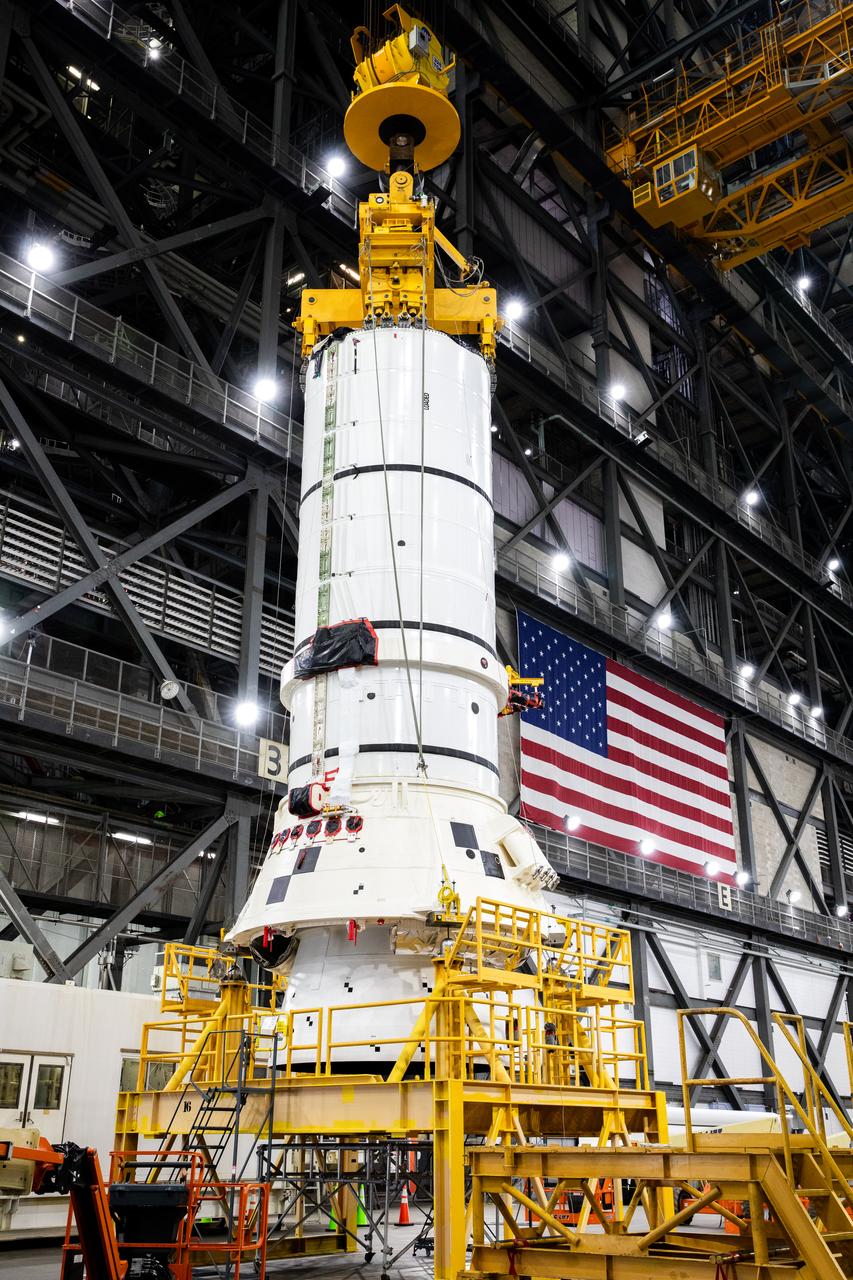

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.
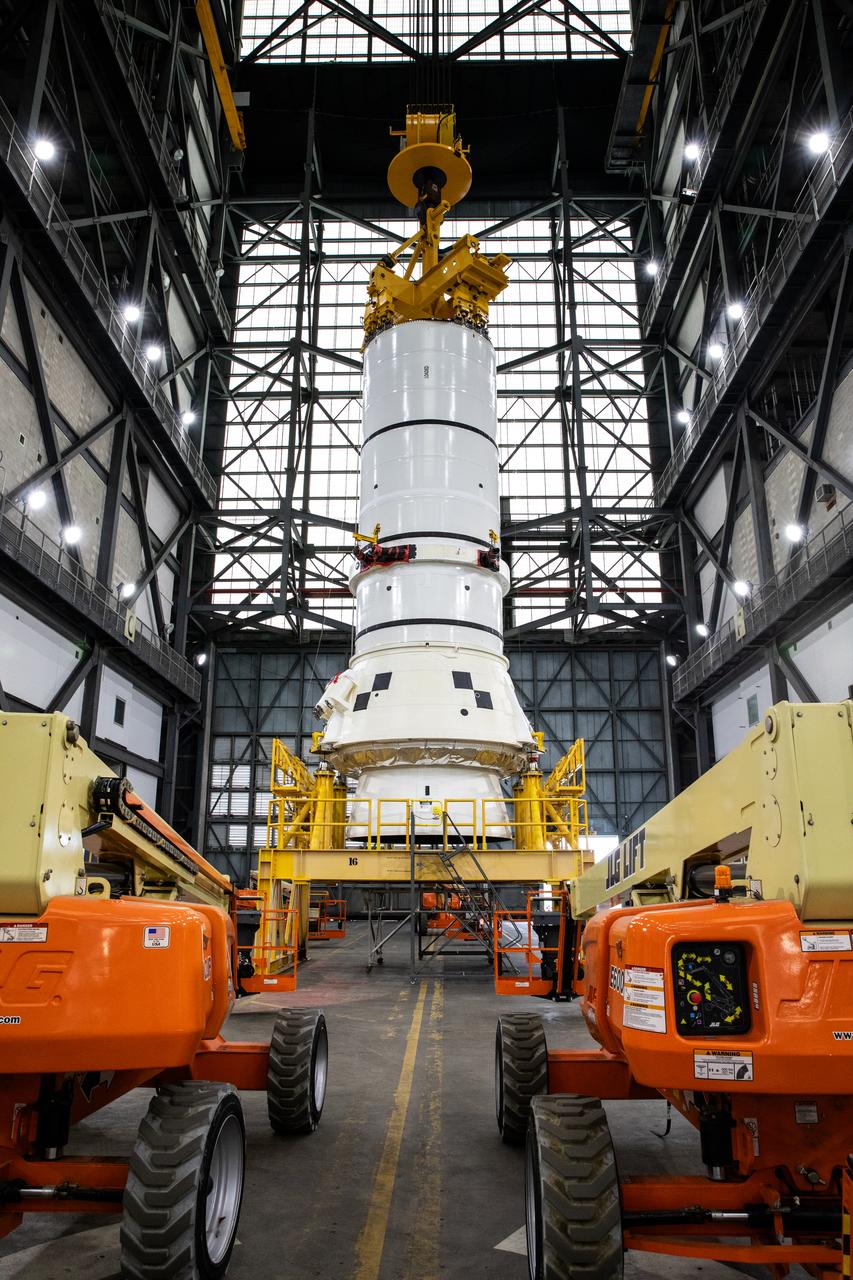

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.
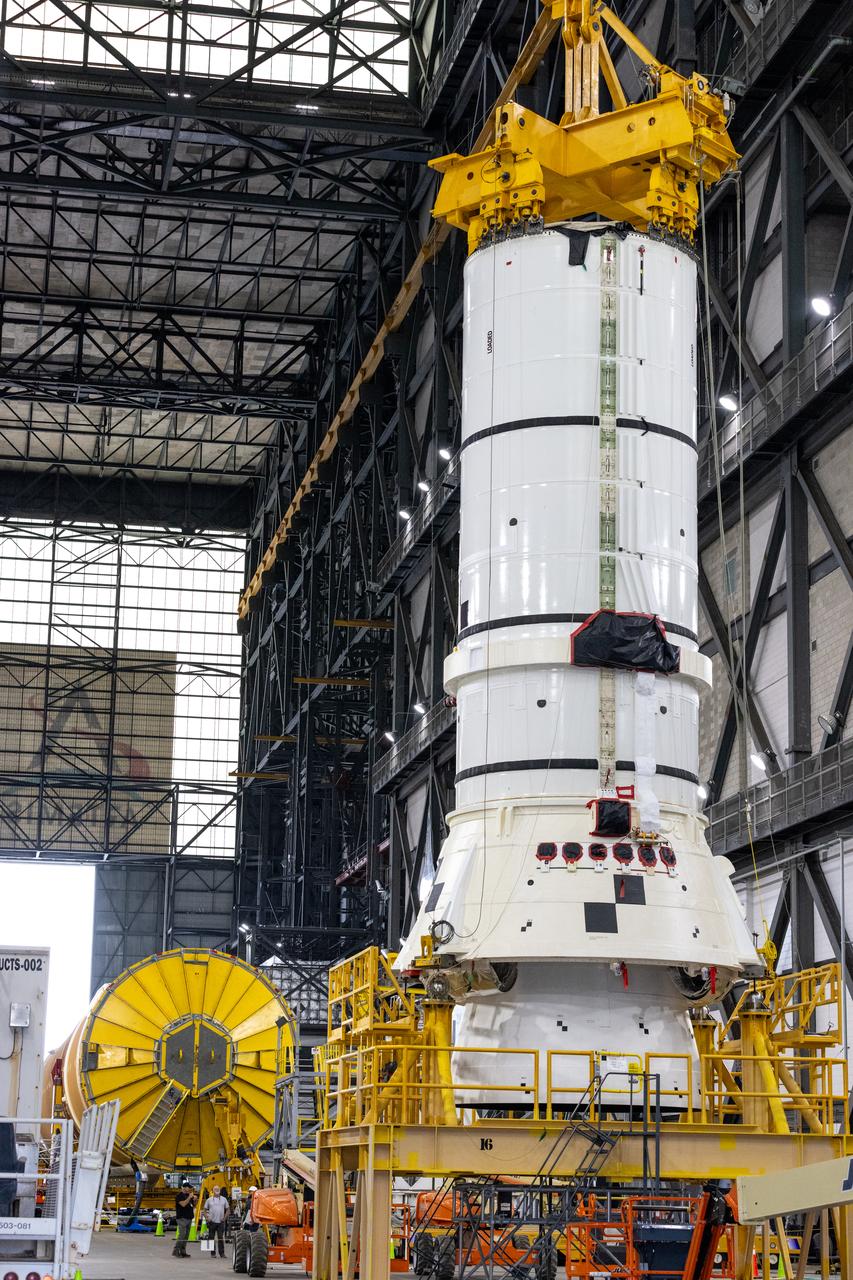

Down the transfer aisle from the Artemis II SLS (Space Launch System) core stage, engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS rocket inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of the mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.

Engineers and technicians with the Exploration Ground Systems Program attach an overhead crane to the left aft assembly, or bottom portion of the solid rocket boosters for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, inside the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Tuesday, Nov. 19, 2024. The crane will lift the aft assembly on top of mobile launcher 1 followed by the right aft assembly and stack the remaining booster segments for the Artemis II mission.

Technicians assist as a crane moves NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) stack to a ground transport vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
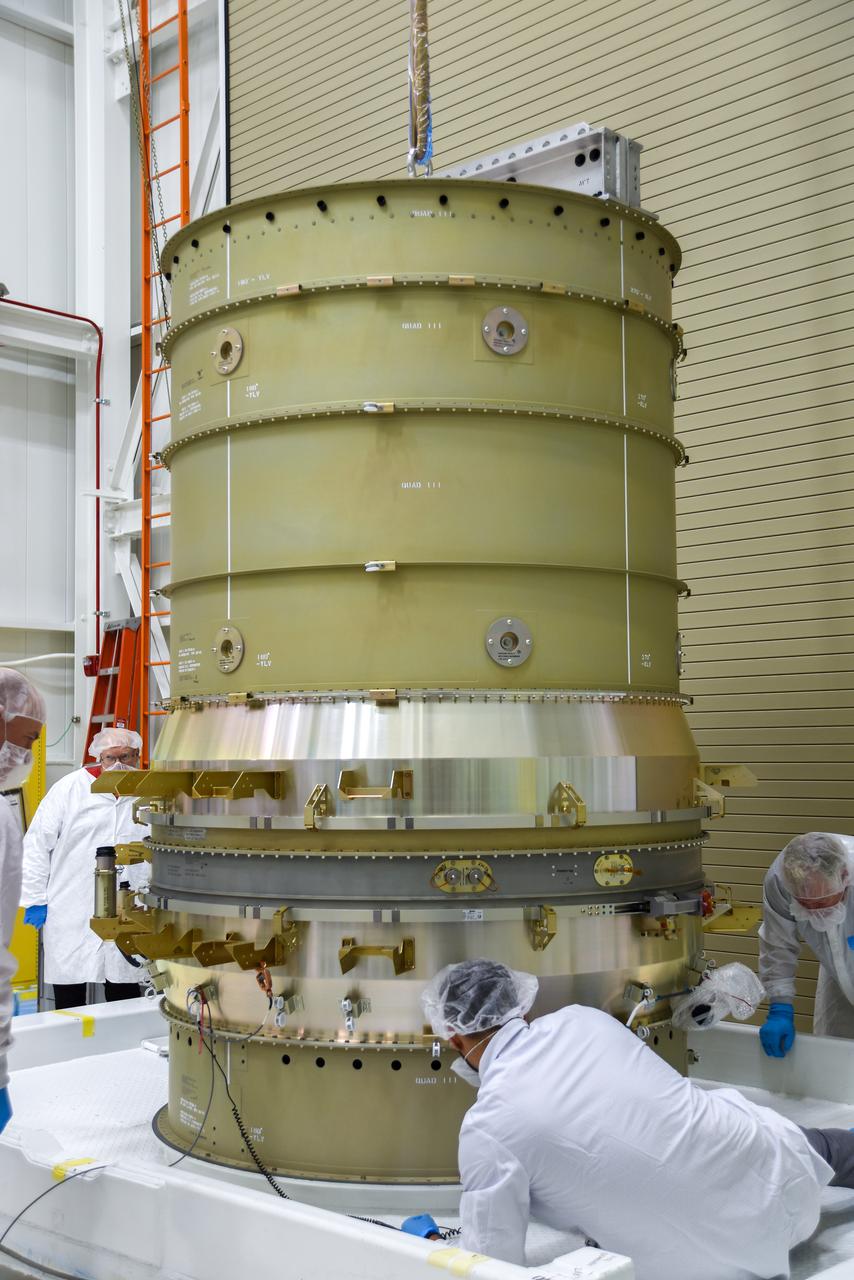

Technicians secure NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) stack onto a ground transport vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
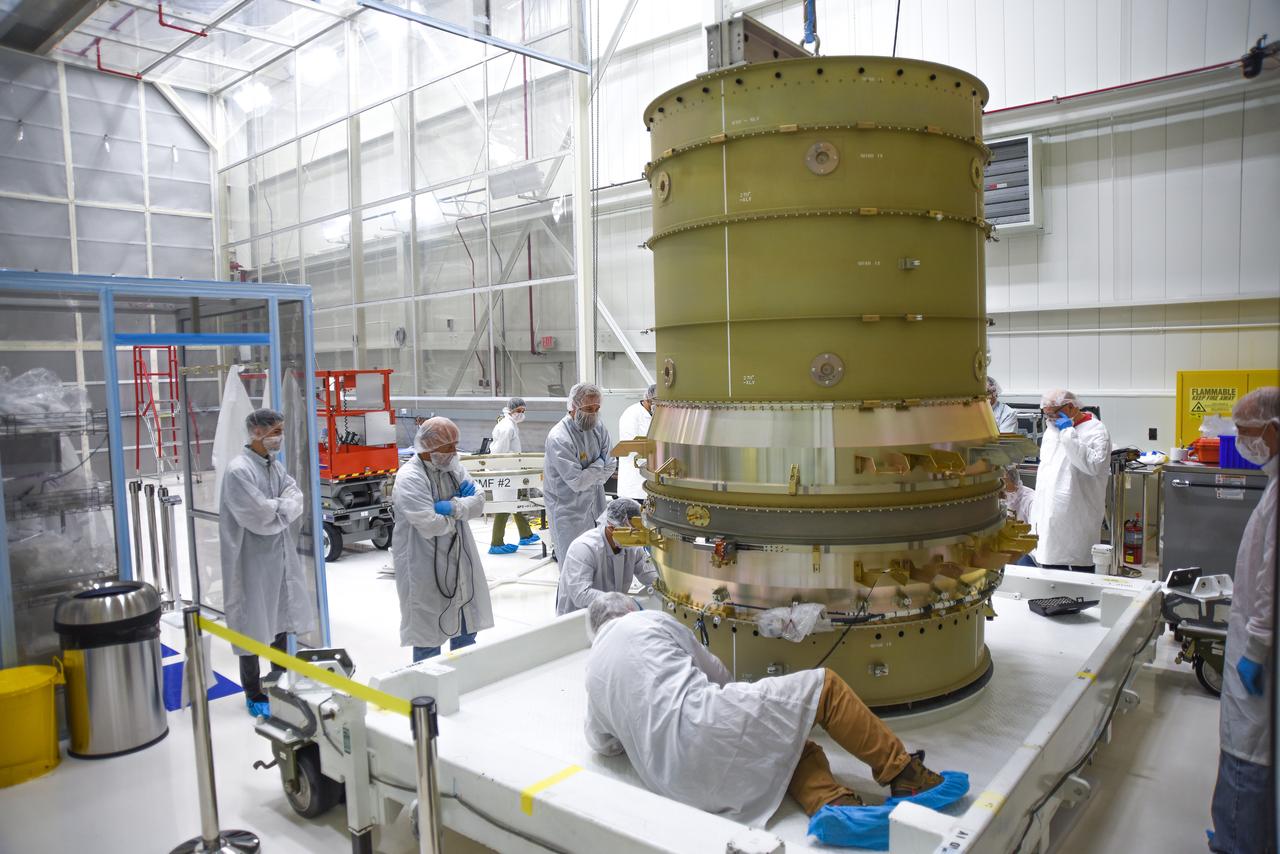

Technicians secure NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) stack onto a ground transport vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
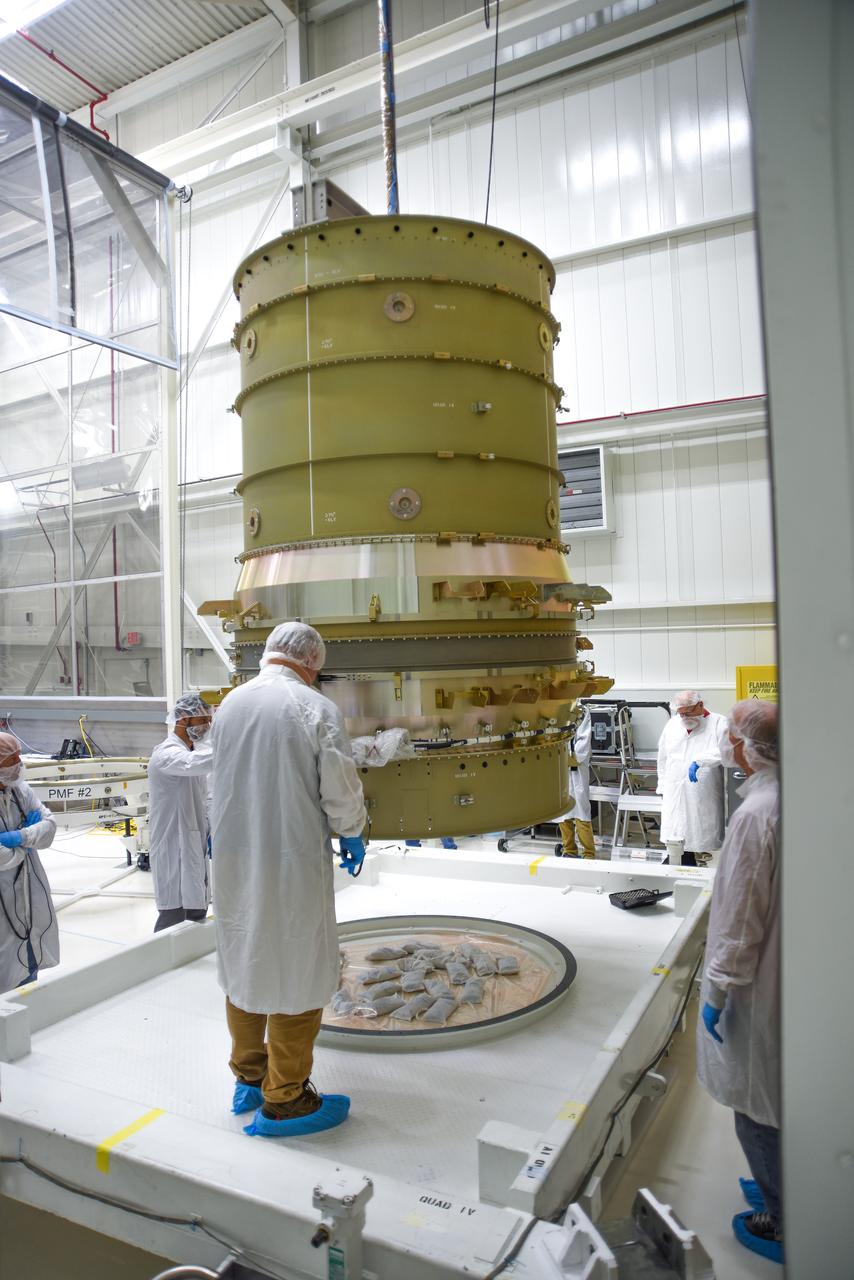

Technicians assist as a crane lowers NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) stack onto a ground transport vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
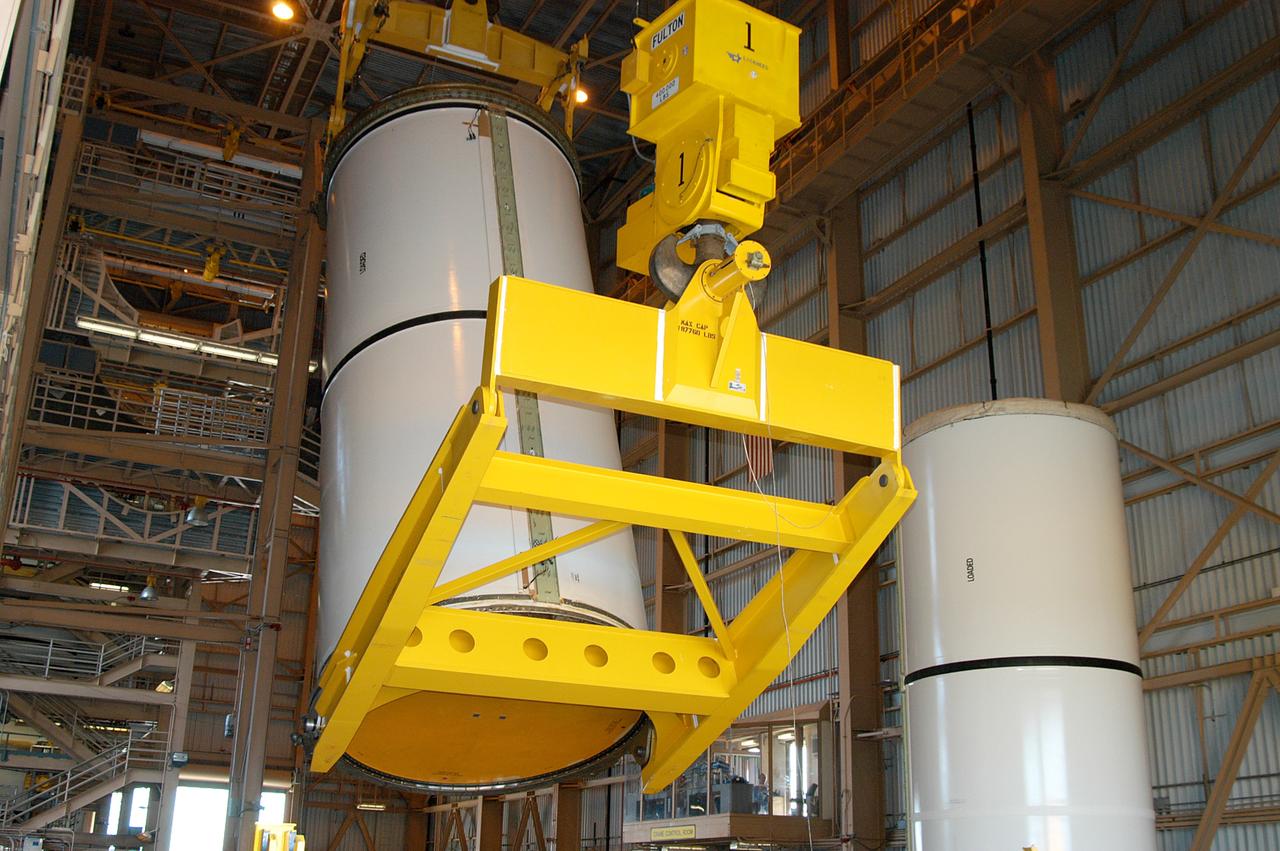

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being lifted and moved to a rail car for shipment to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.
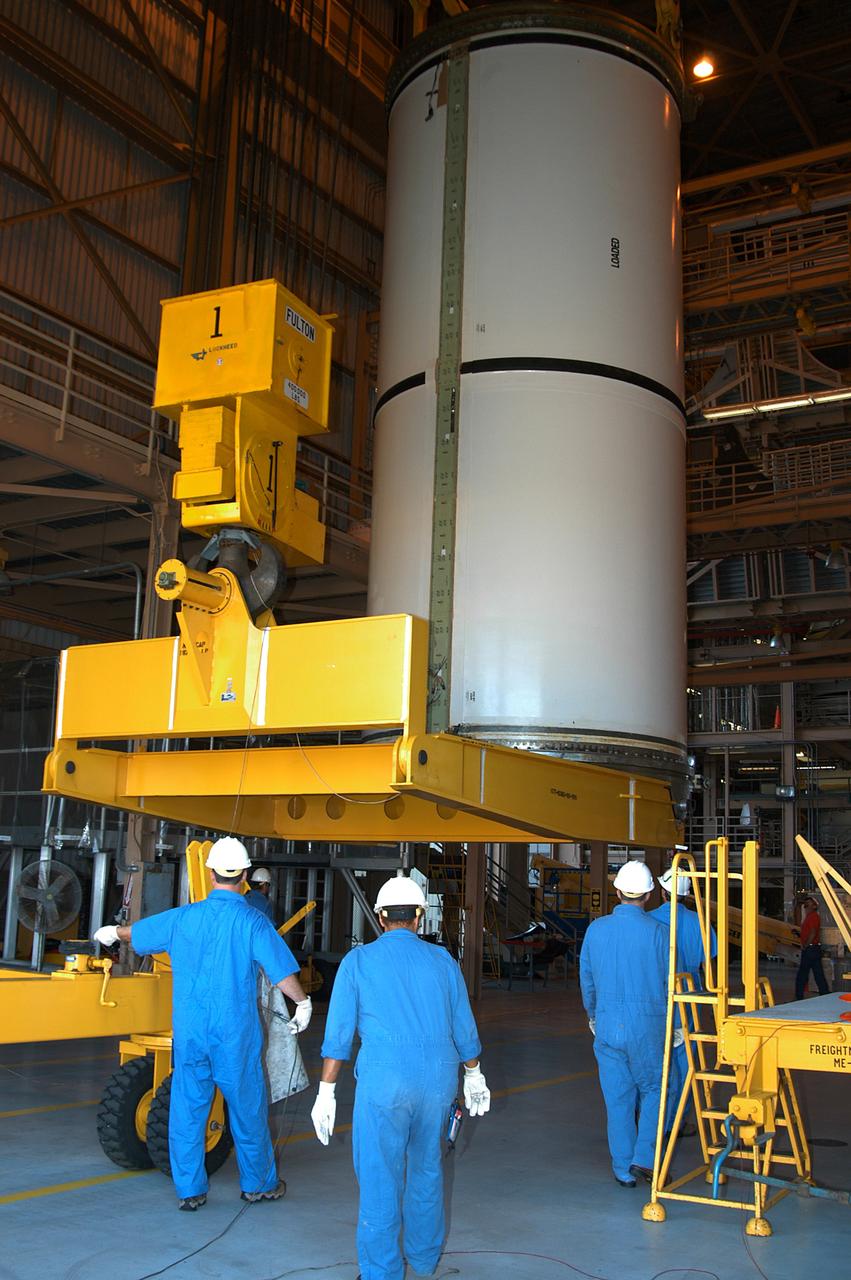

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Rotation Processing and Surge Facility, an SRB solid segment is being lifted and moved to a rail car for shipment to Utah for testing. The segment was part of the STS-114 stack. It is the first time actual flight segments that had been stacked for flight in the VAB are being returned to Utah for testing. It will undergo firing, which will enable inspectors to check the viability of the solid and verify the life expectancy for stacked segments.

Technicians use a crane to attach the payload adapter separation systems canister to NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) payload stack as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
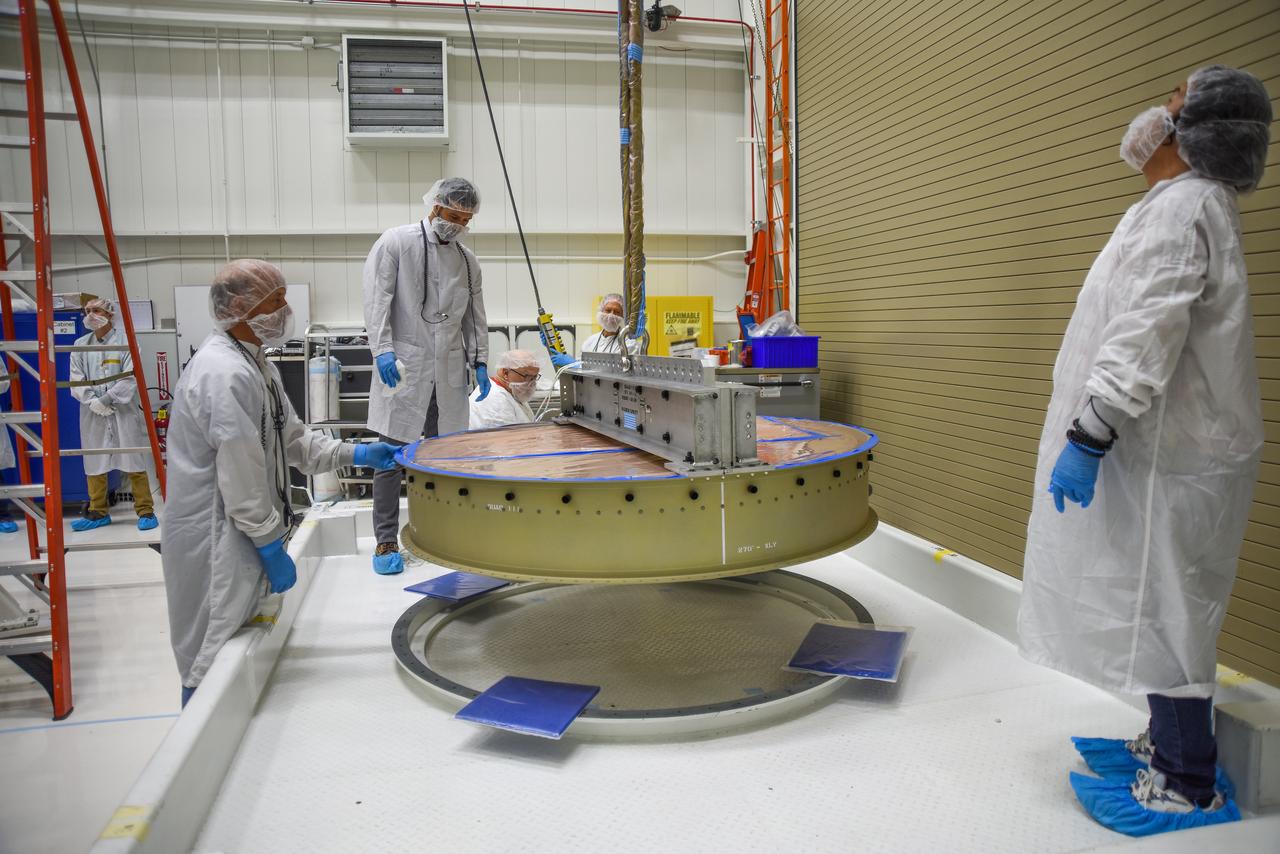

Technicians prepare the payload adapter separation systems canister to be secured onto NASA’s Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) payload stack as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 9, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking
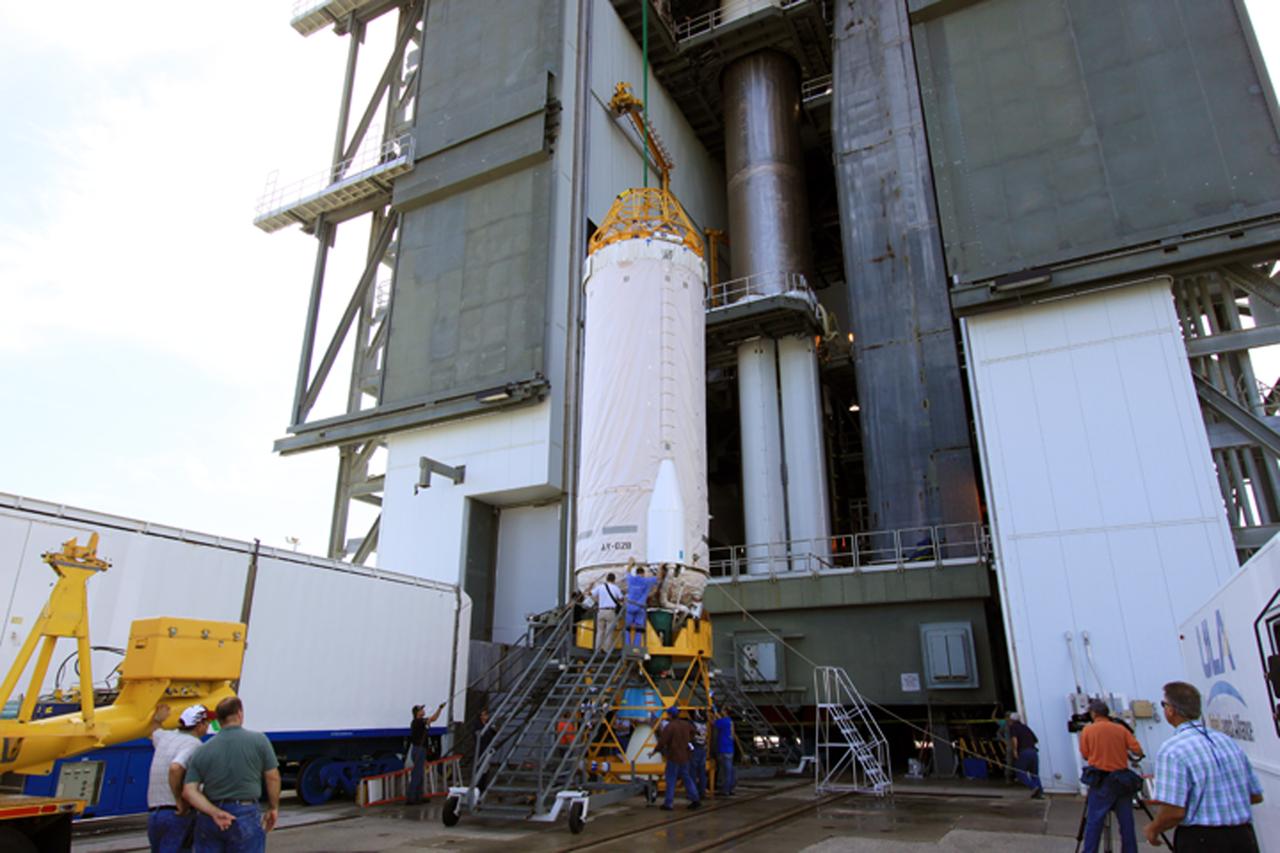

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking

MSL - Atlas 2nd Stage Move Lift & Stacking
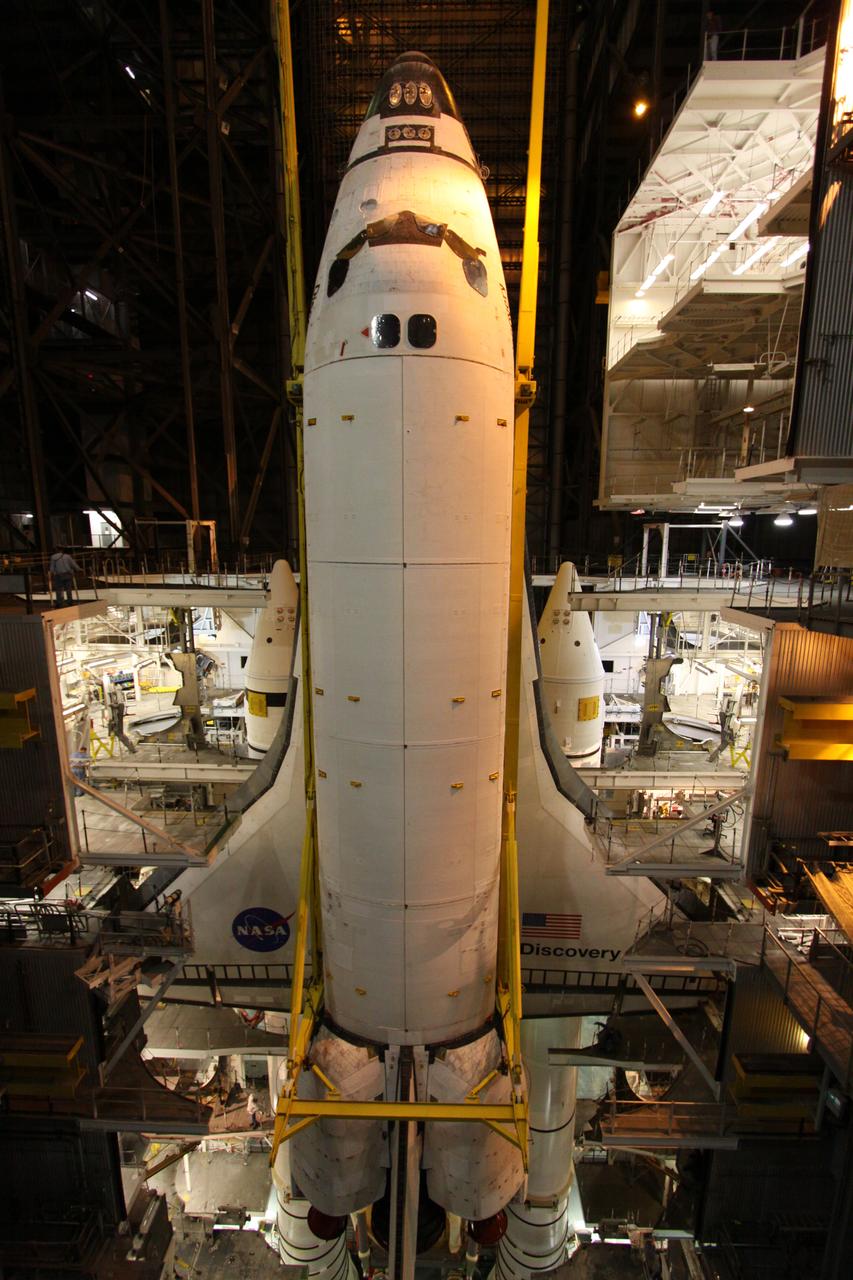

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
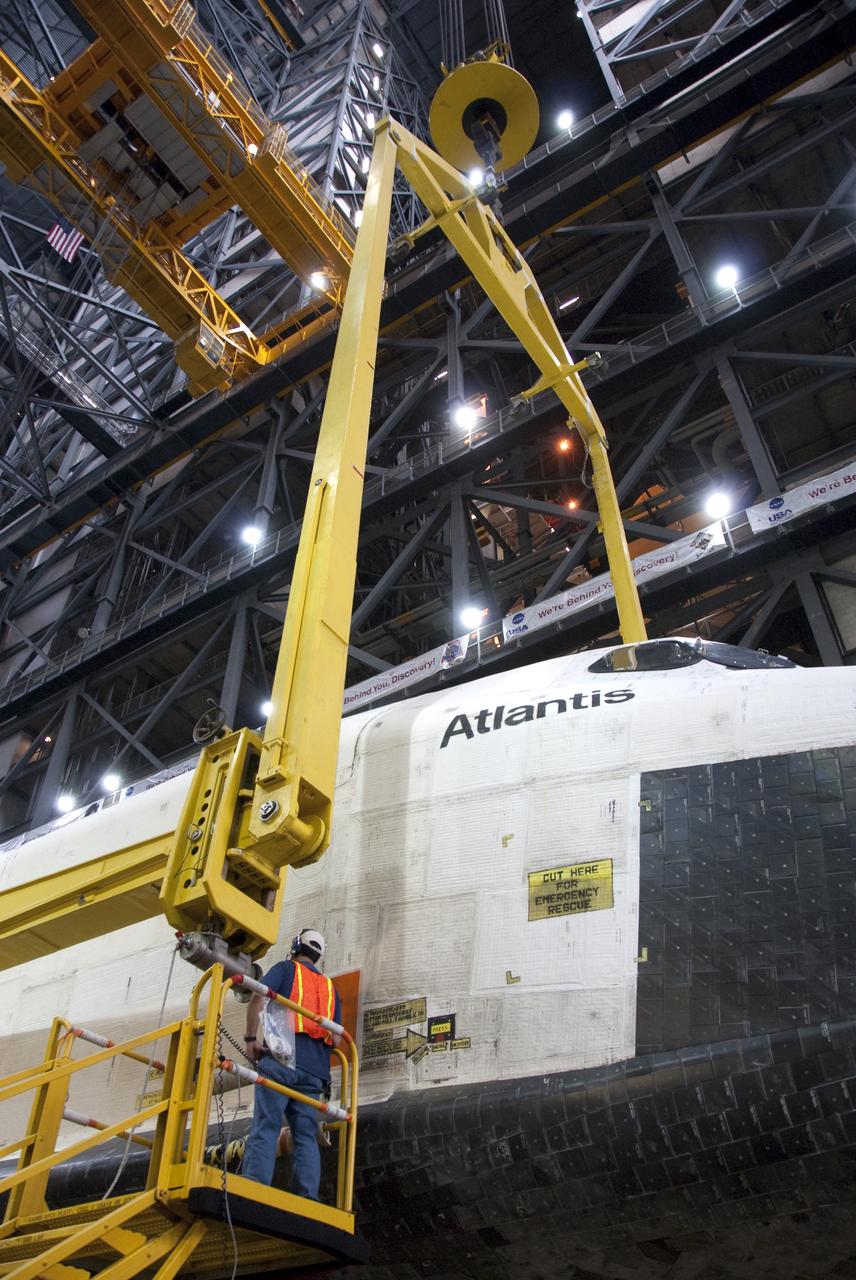

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
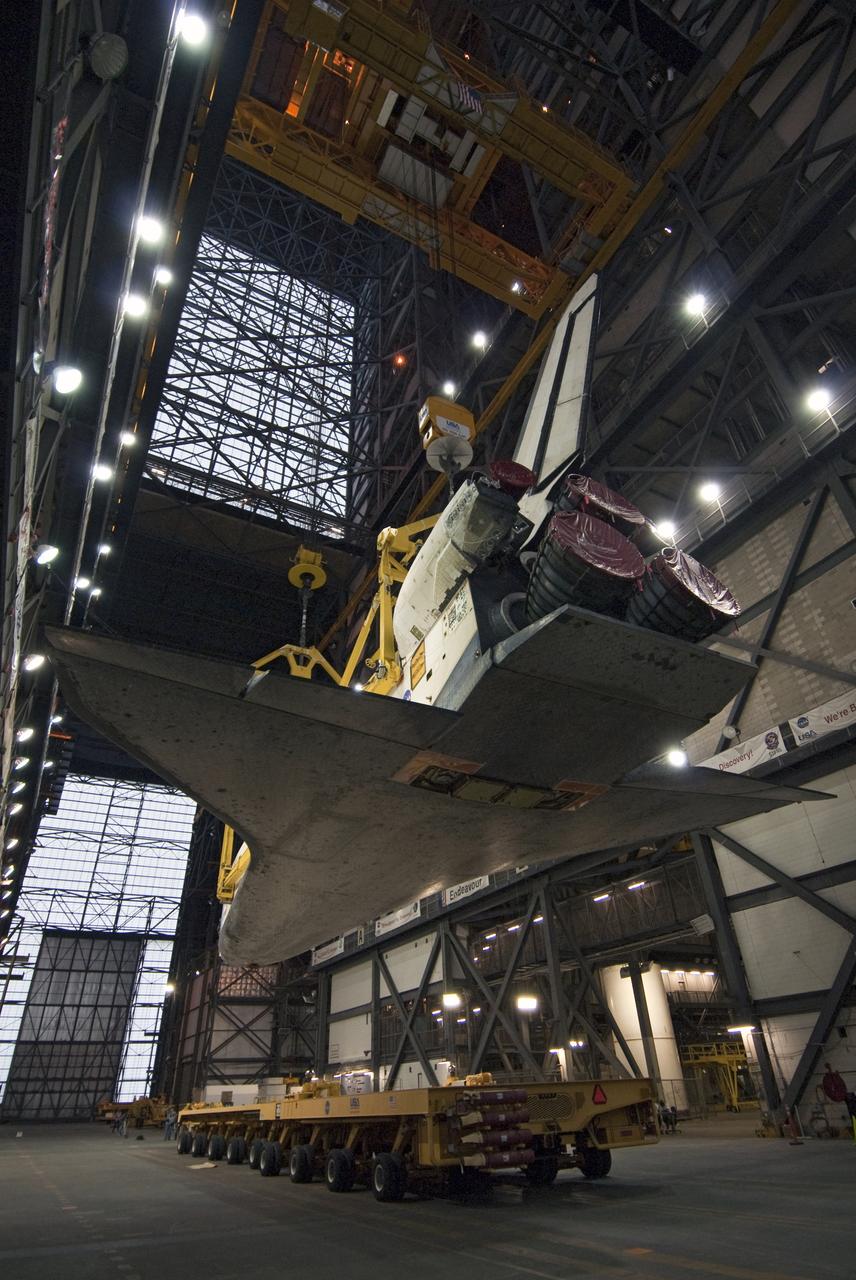

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
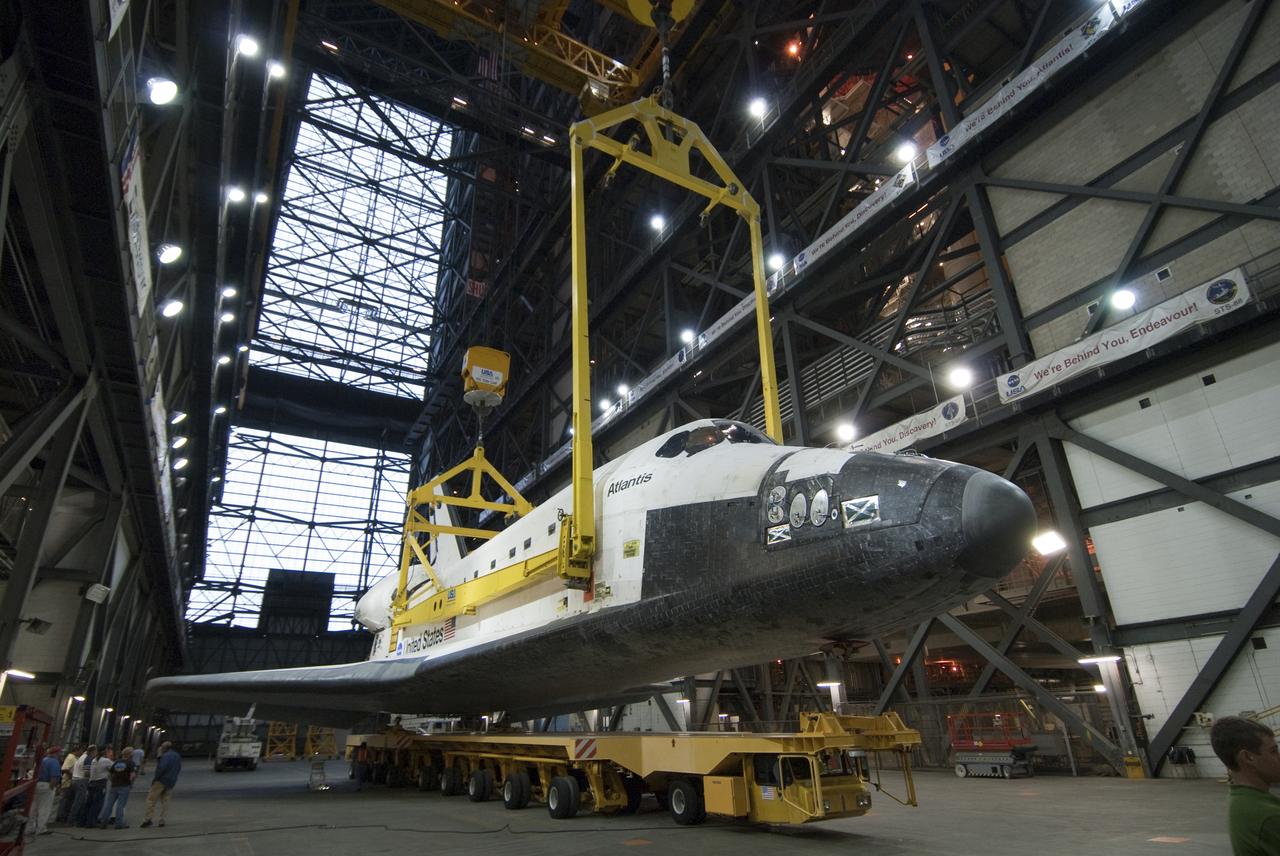

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
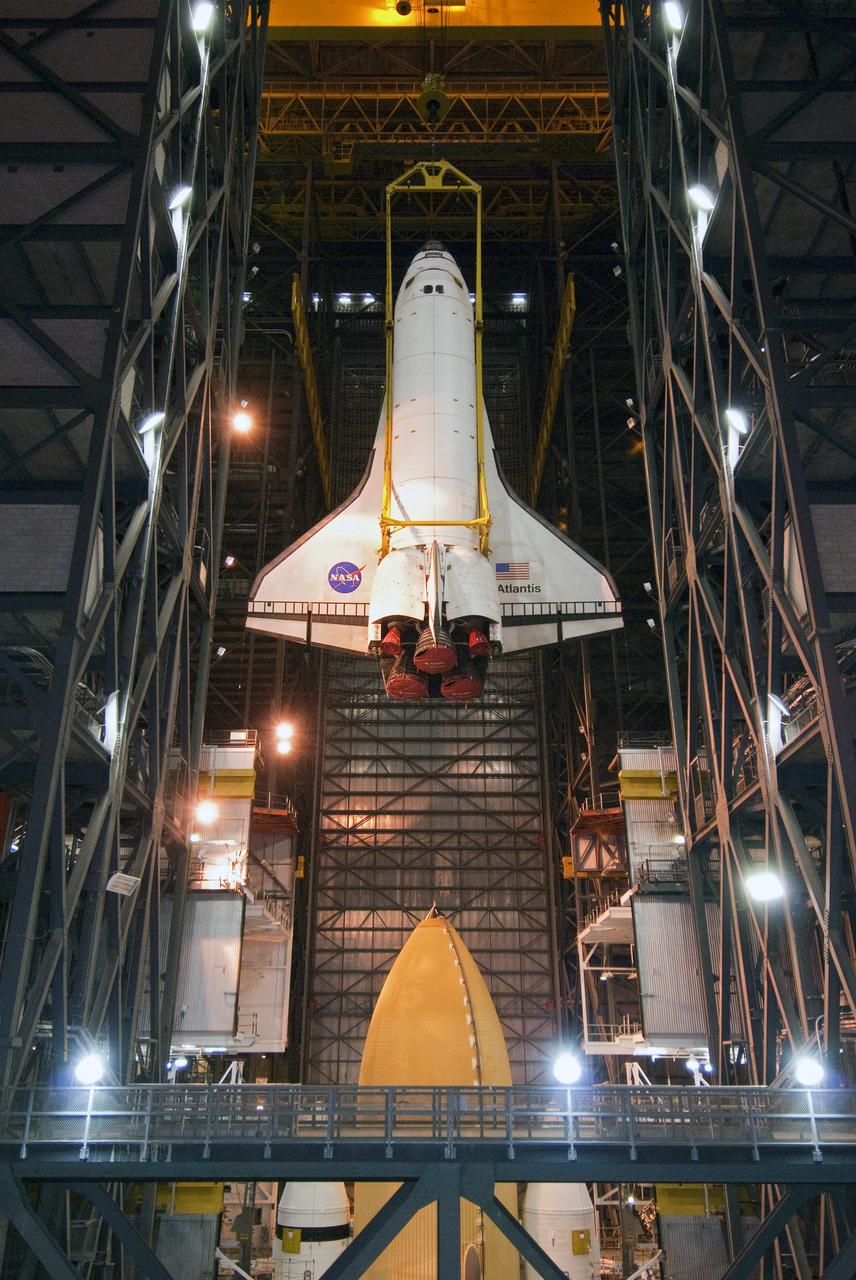

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
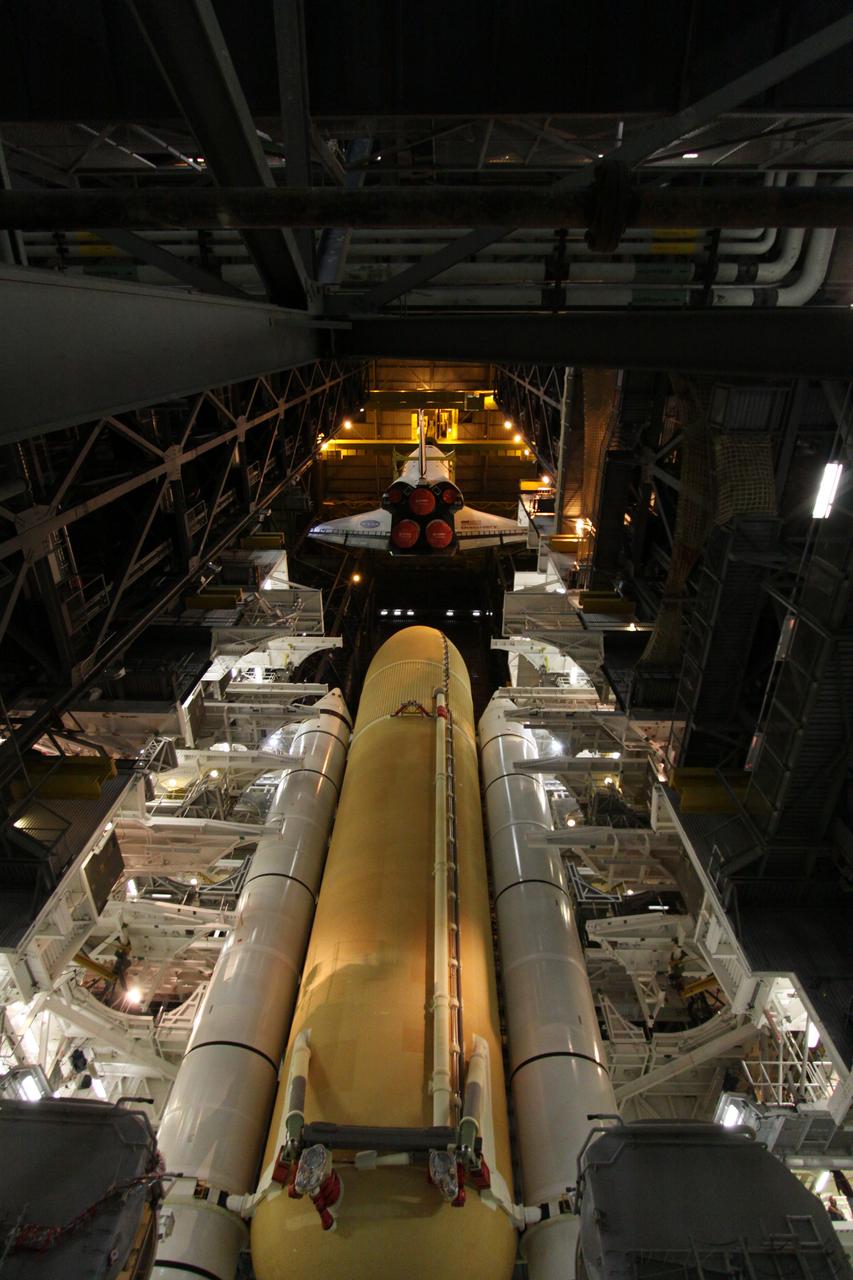

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
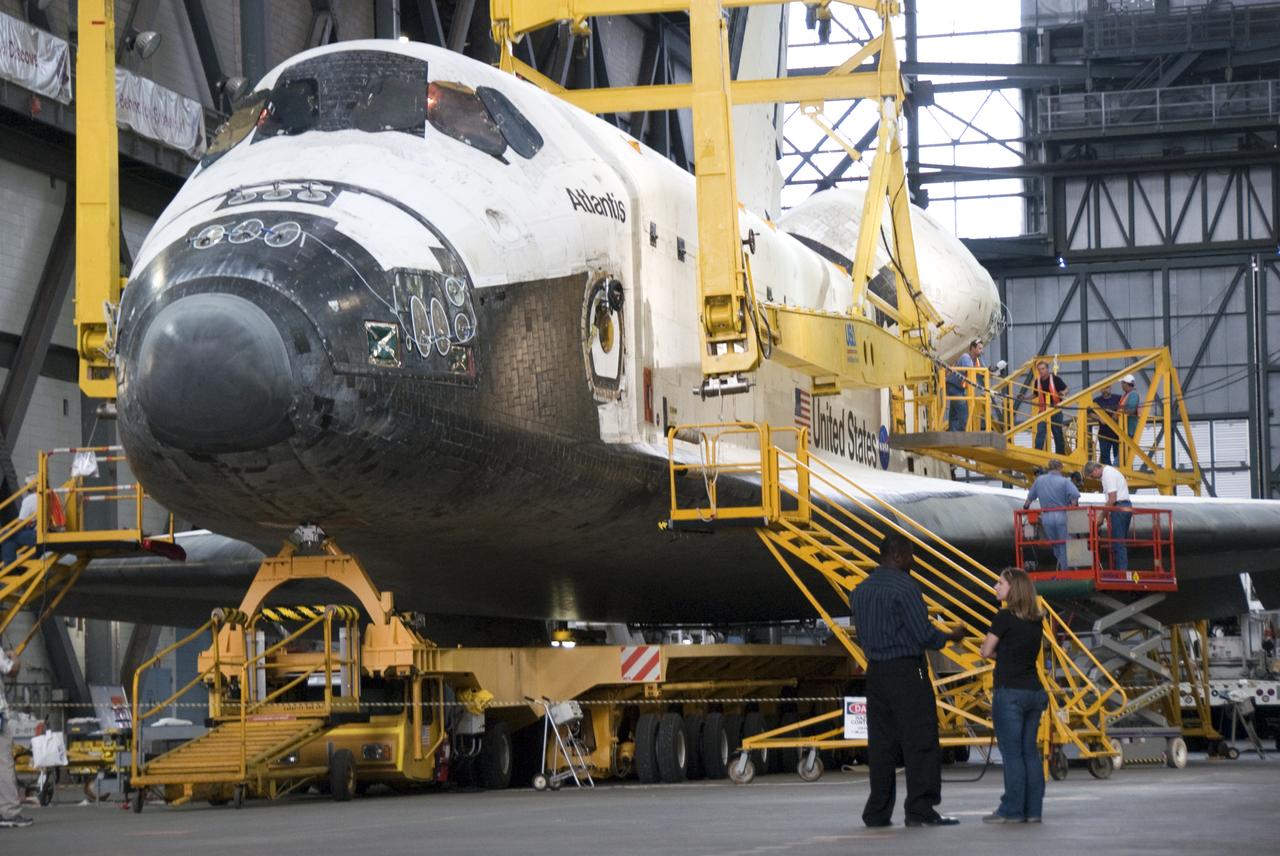

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
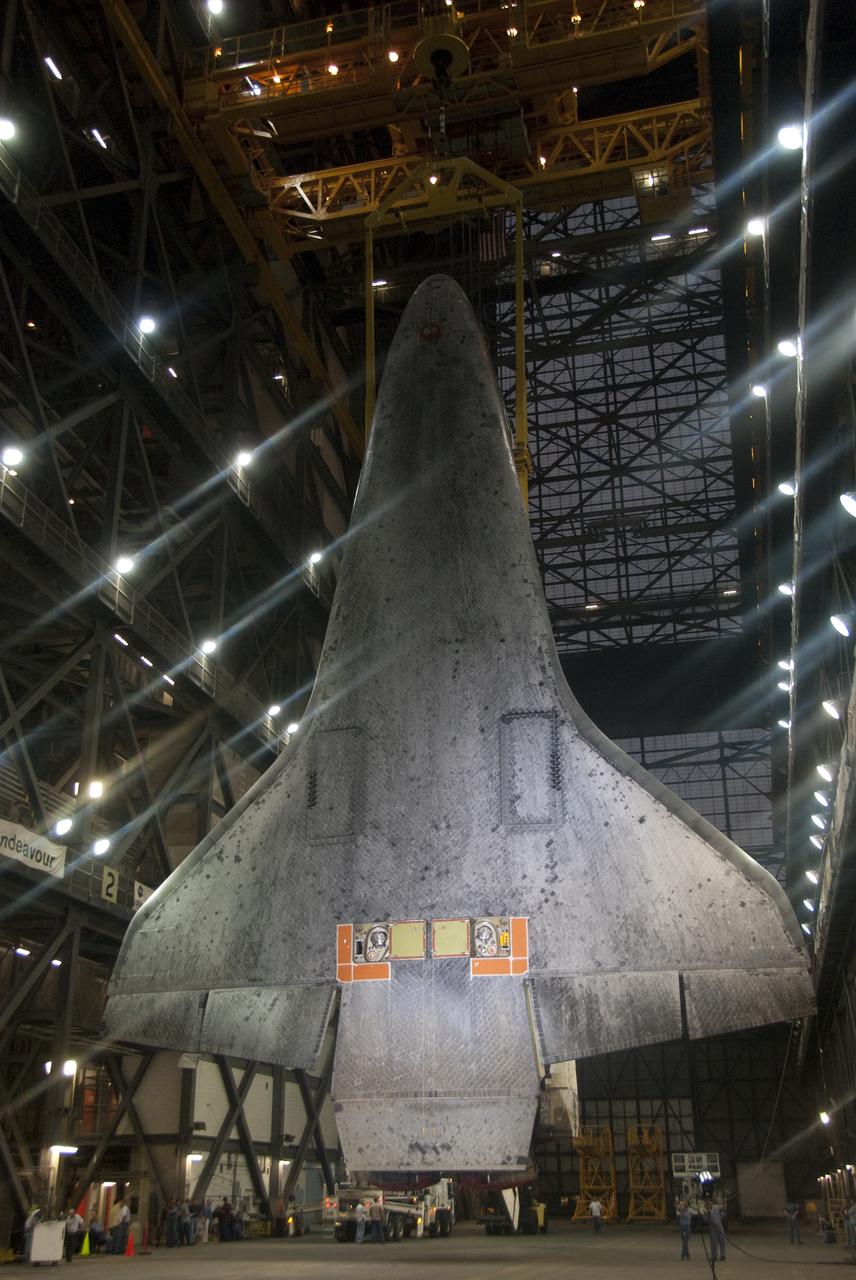

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
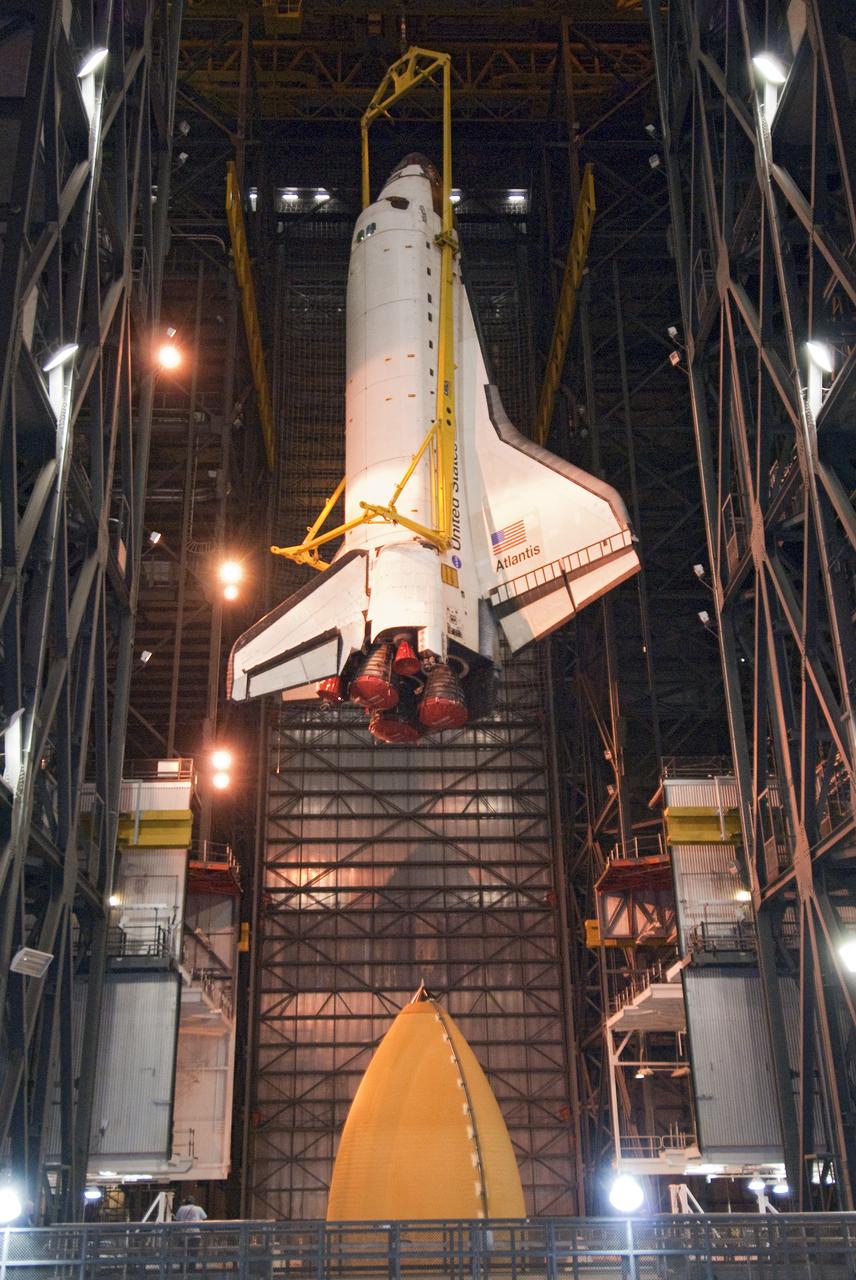

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
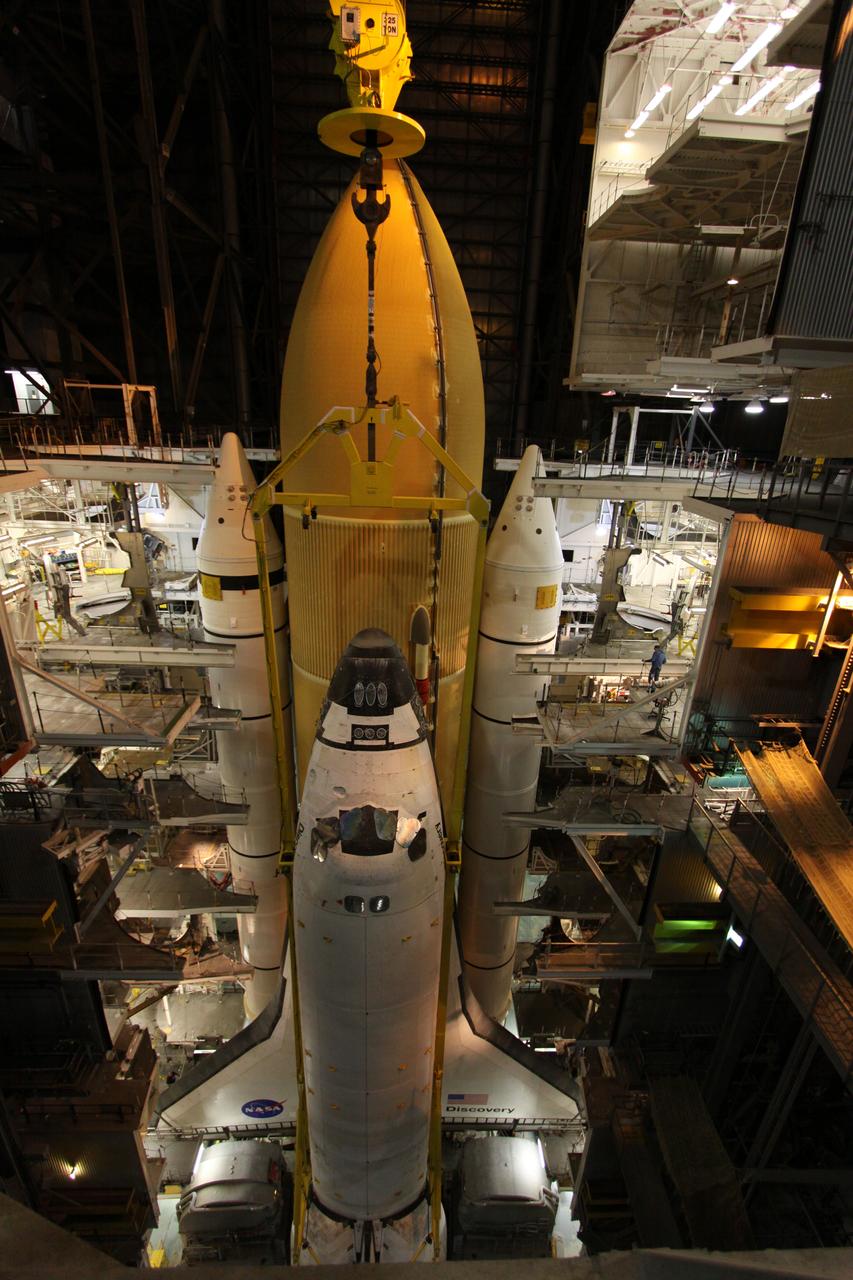

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
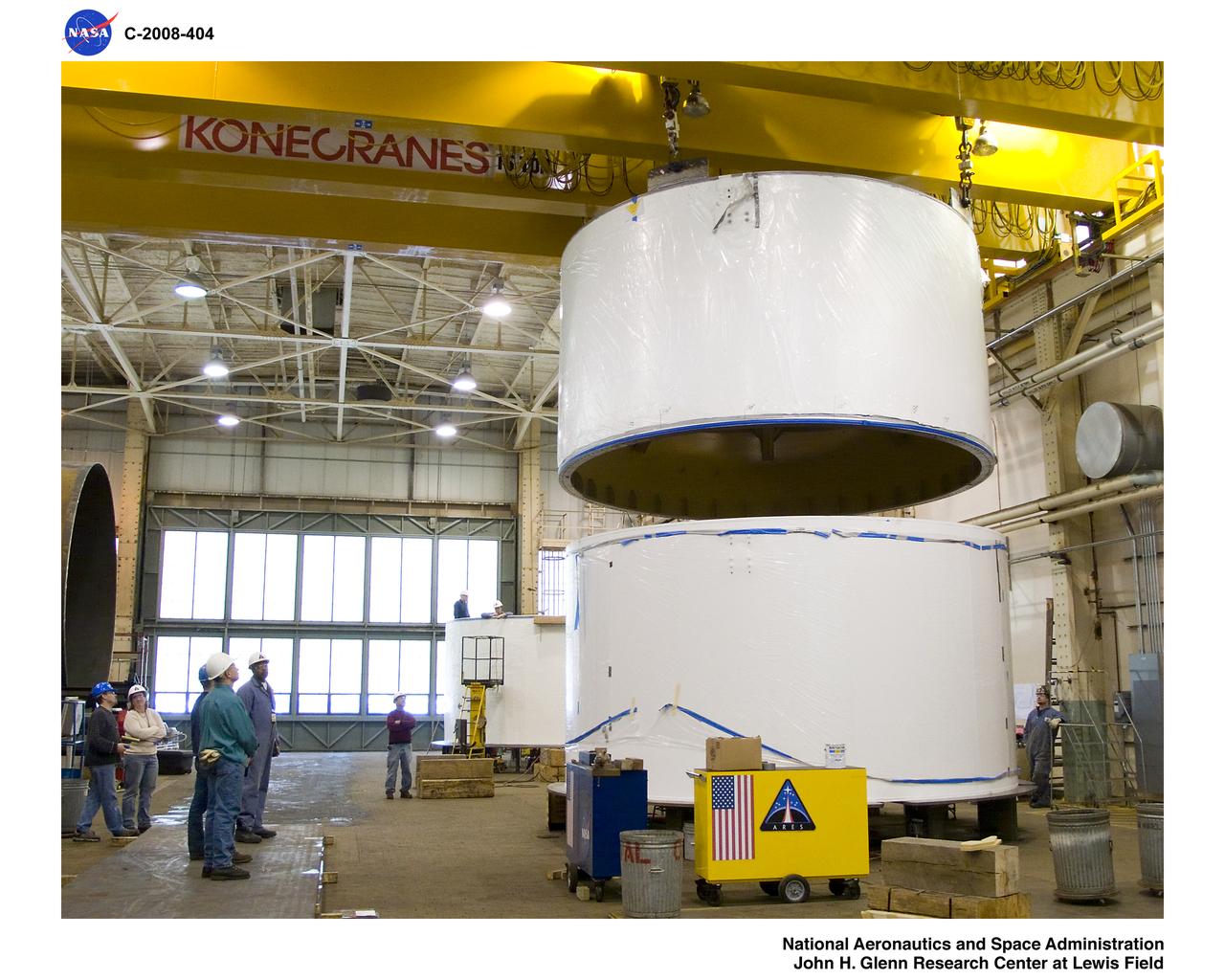

Inside BLDG.50, US4 is being lifted and will be stacked on US3.

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
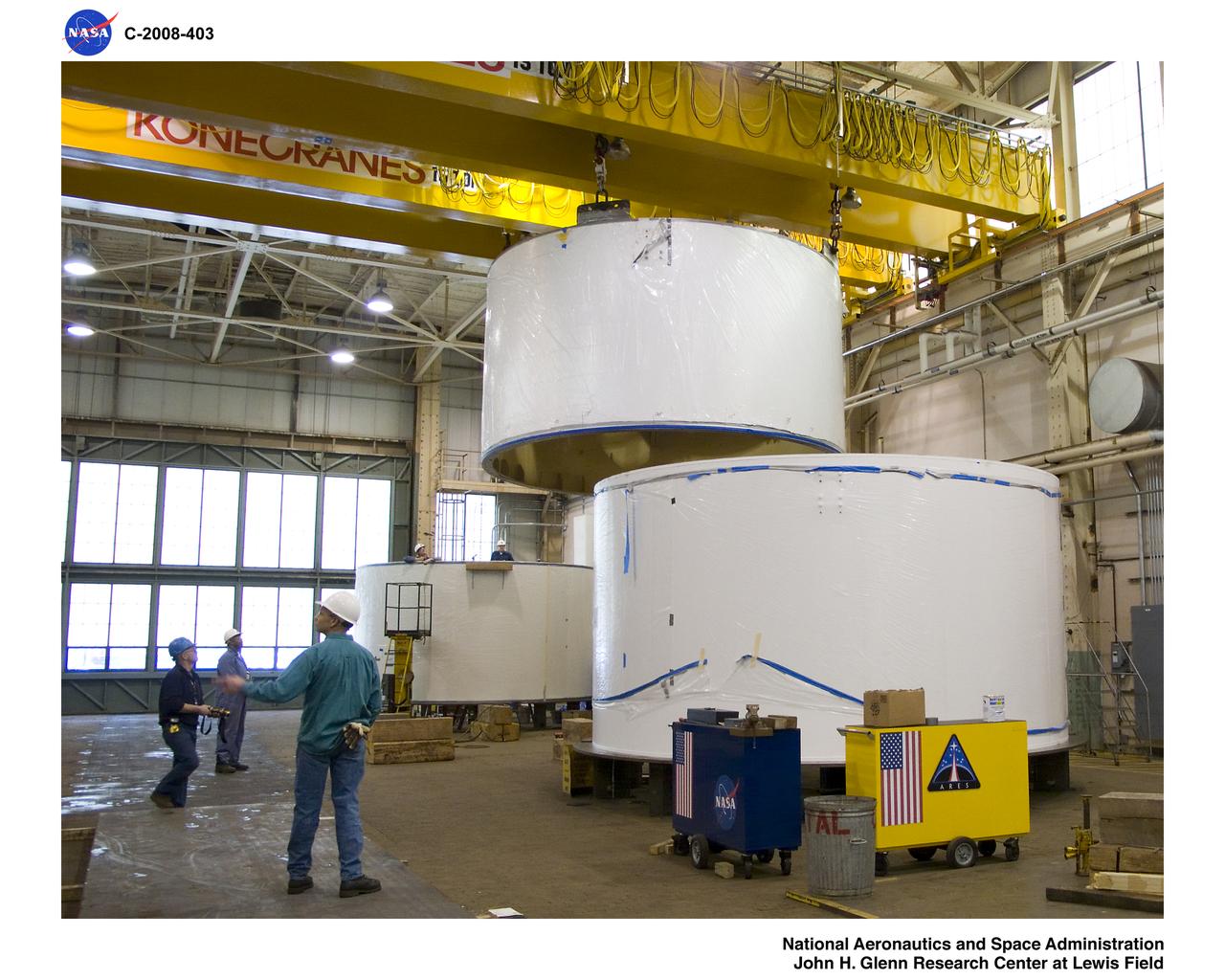

Inside BLDG.50, US4 is being lifted and will be stacked on US3.

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
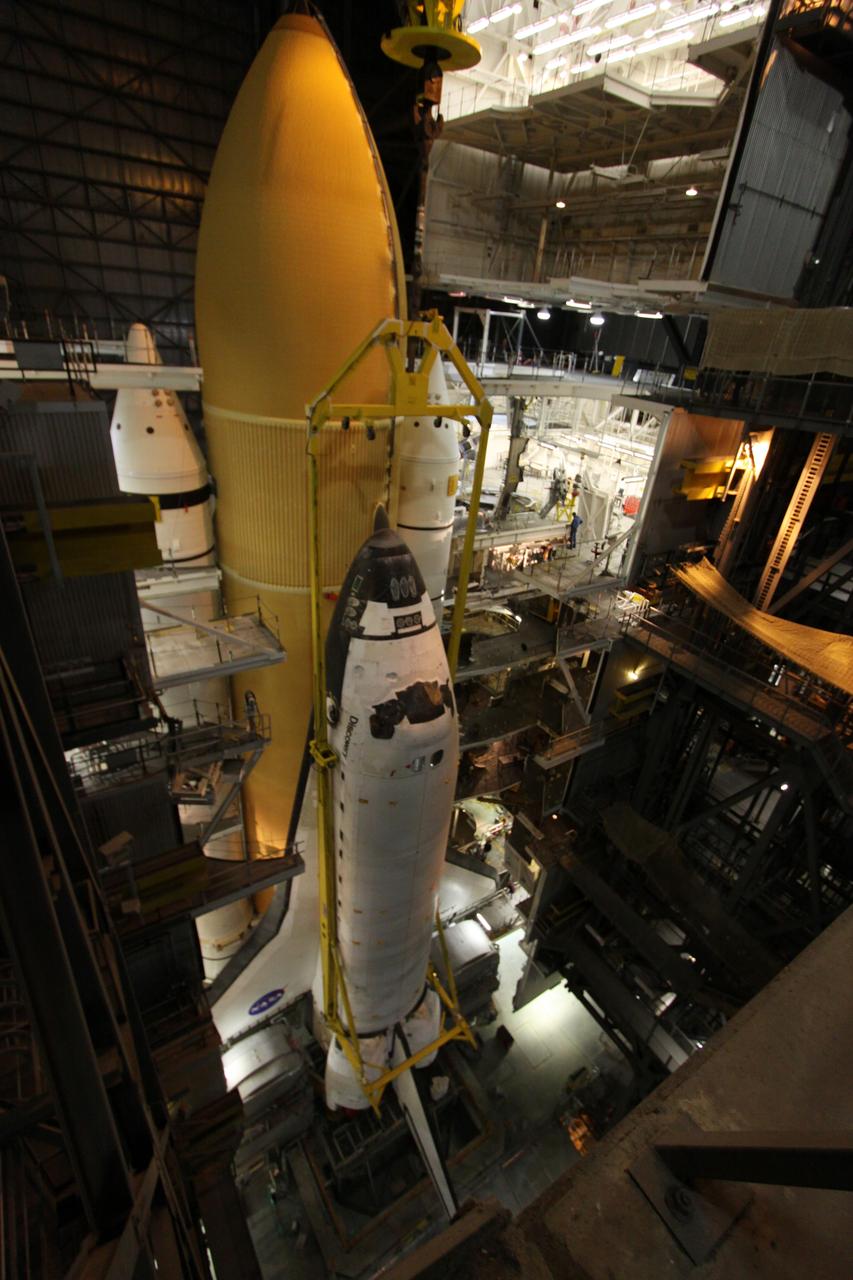

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
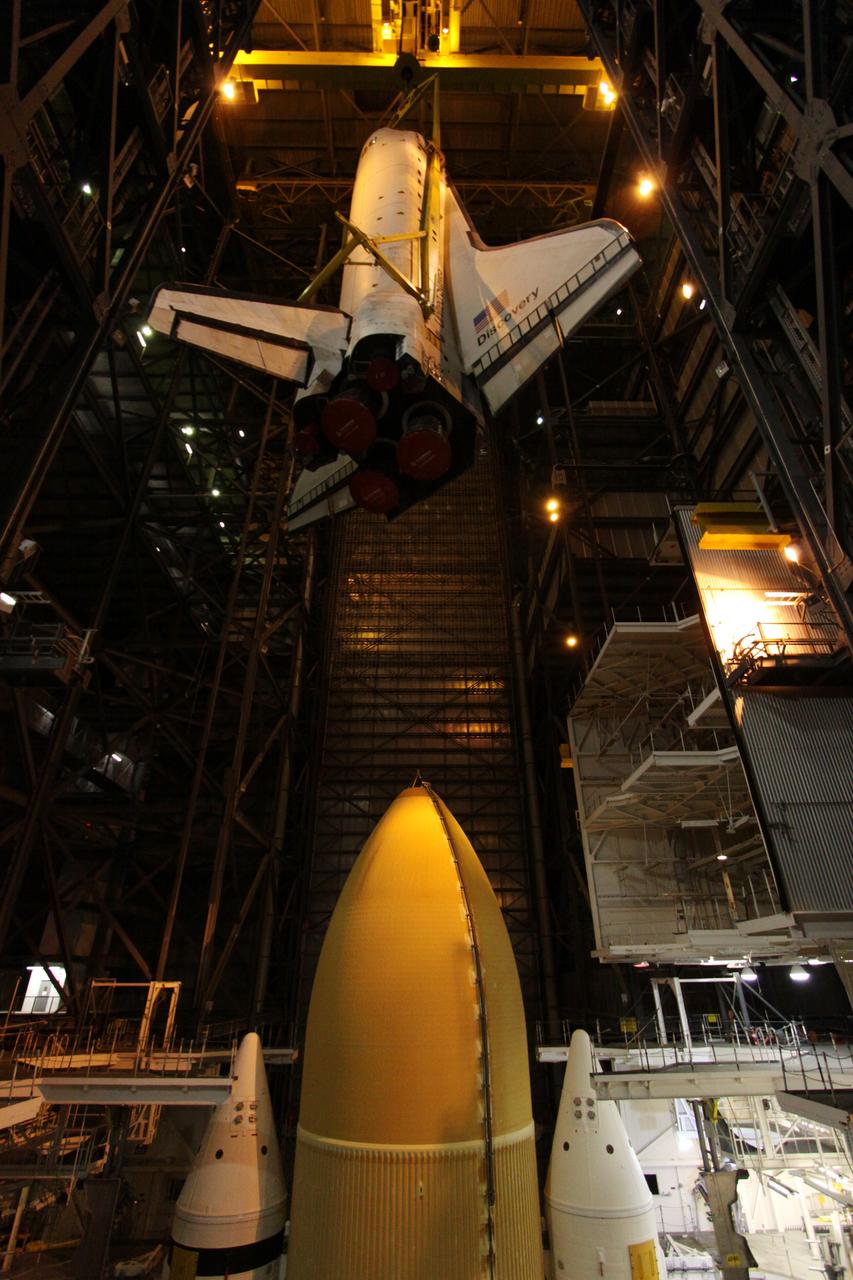

STS-131 Discovery Lift & Mate to SRB/ET Stack
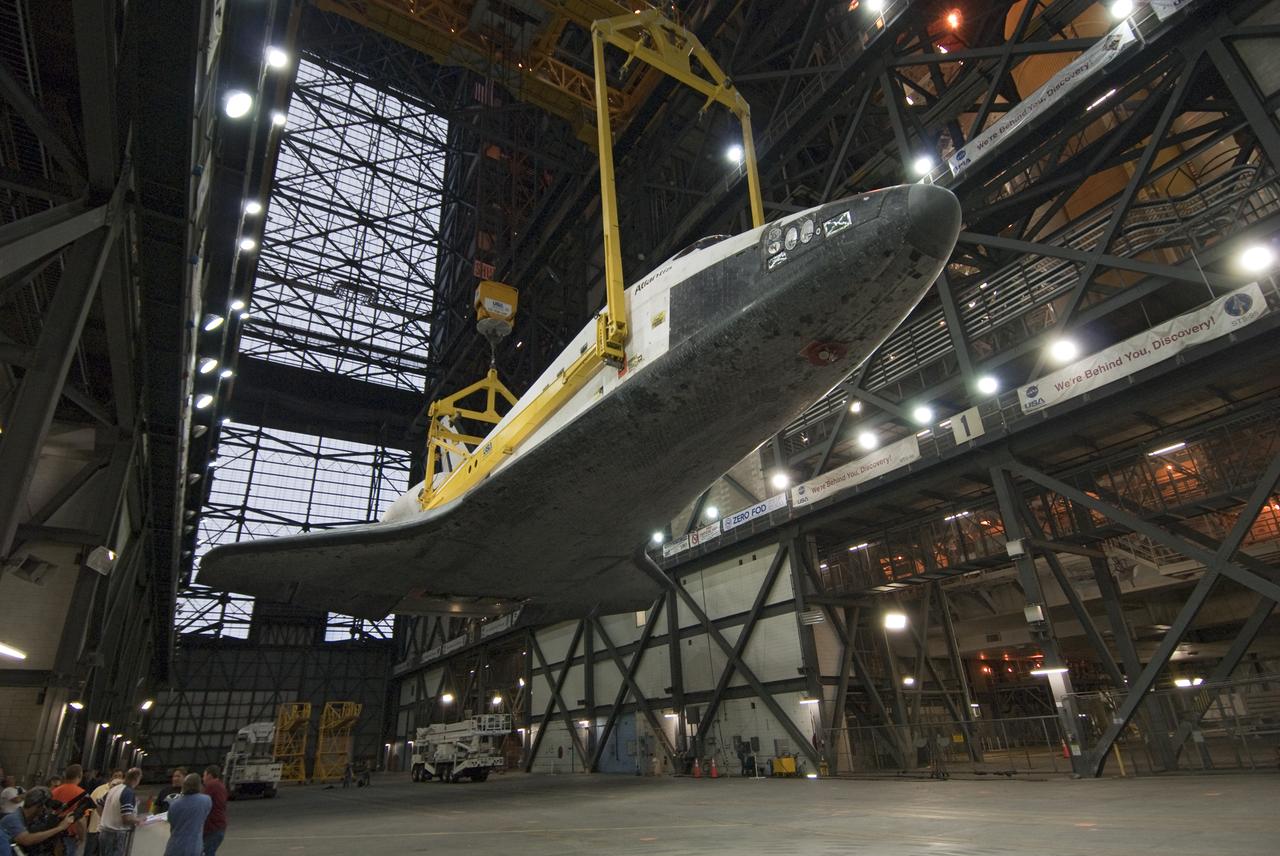

STS-132 ATLANTIS LIFT & MATE TO ET/SRB STACK
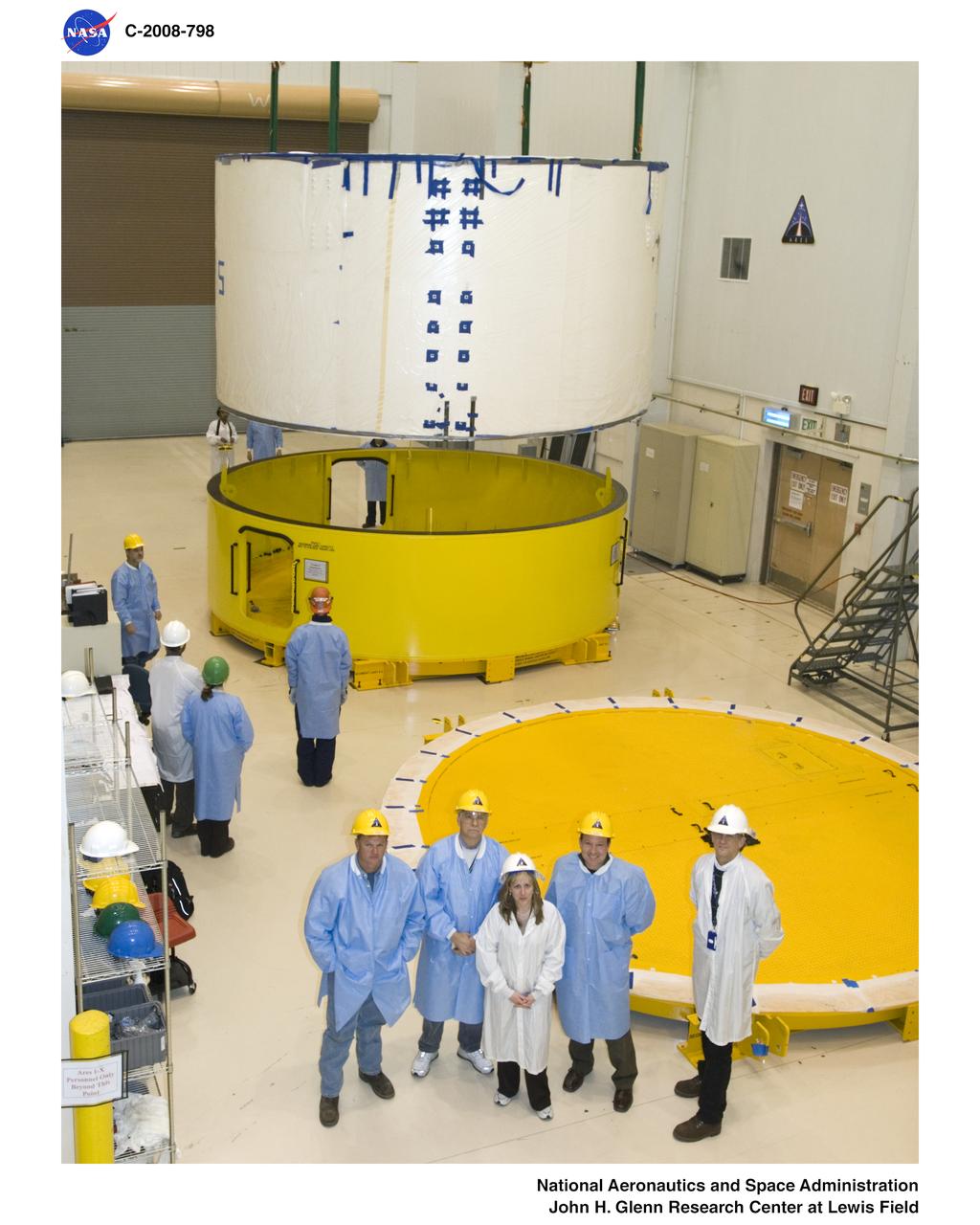

NASA Kennedy lift team observing the movement of Ares 1-X segment US-5 before its critical lift to the Super Stack
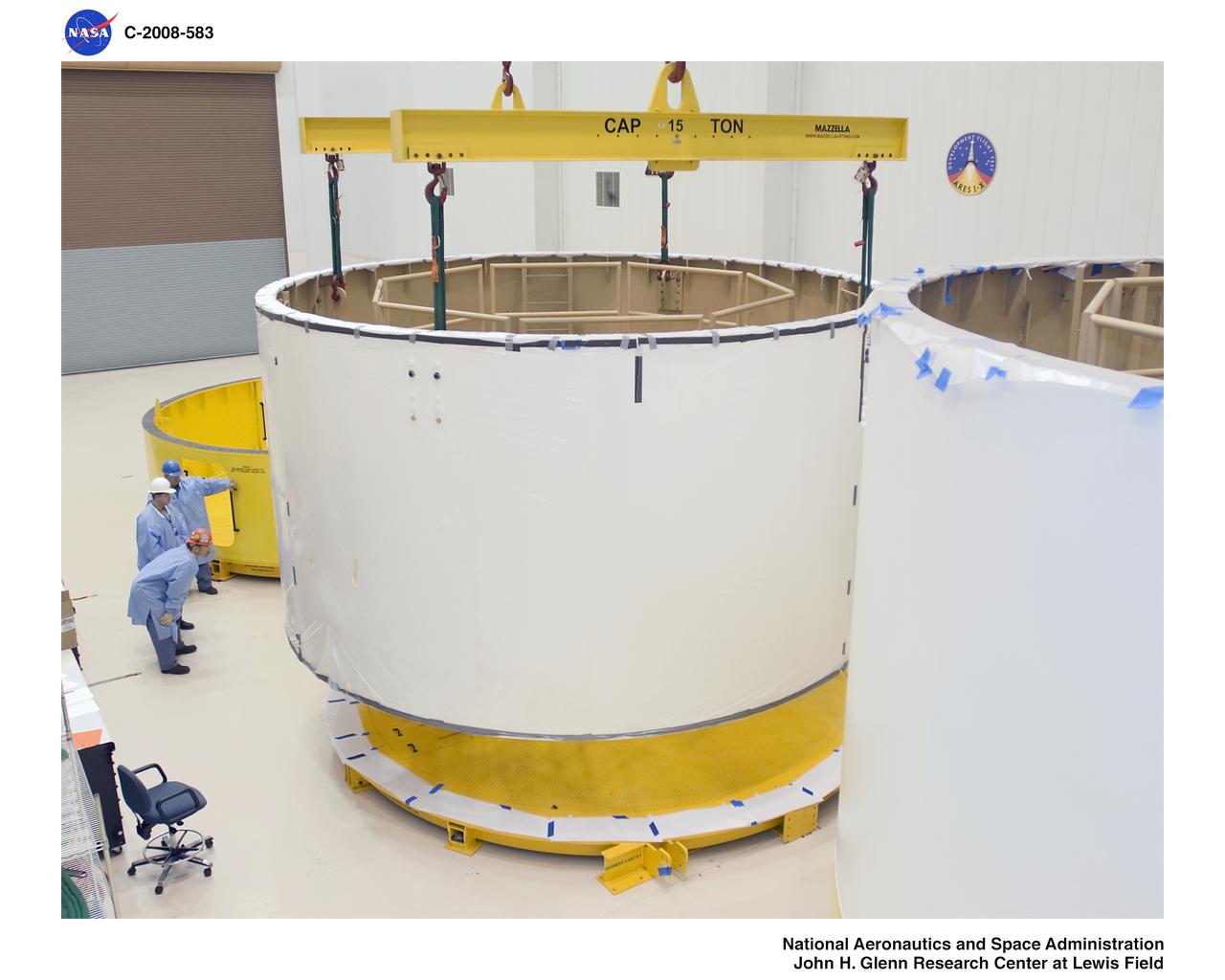

Ares 1-X segment US-3 being lifted onto the cart prior to being stacked onto US-2 to start forming the Ares 1-X USS Super Stack
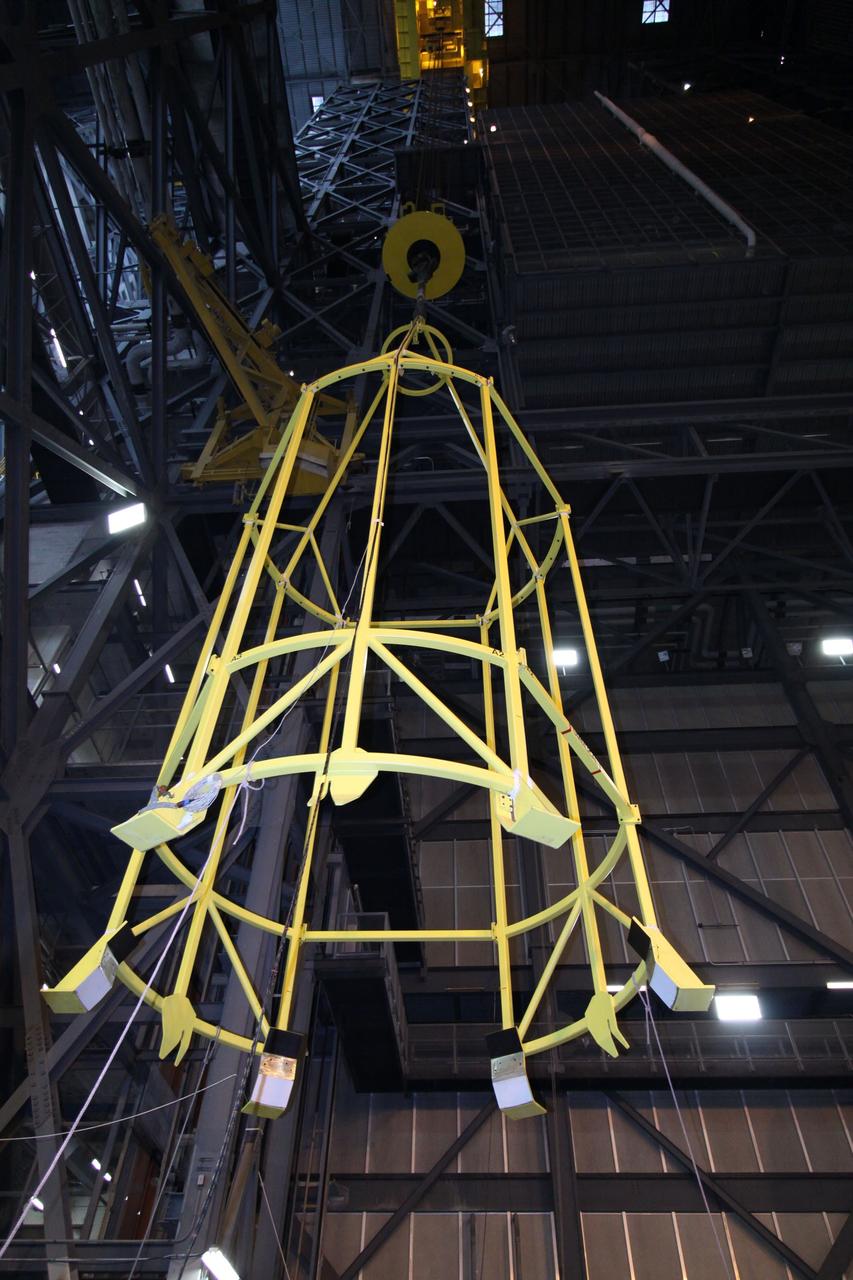

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane toward Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
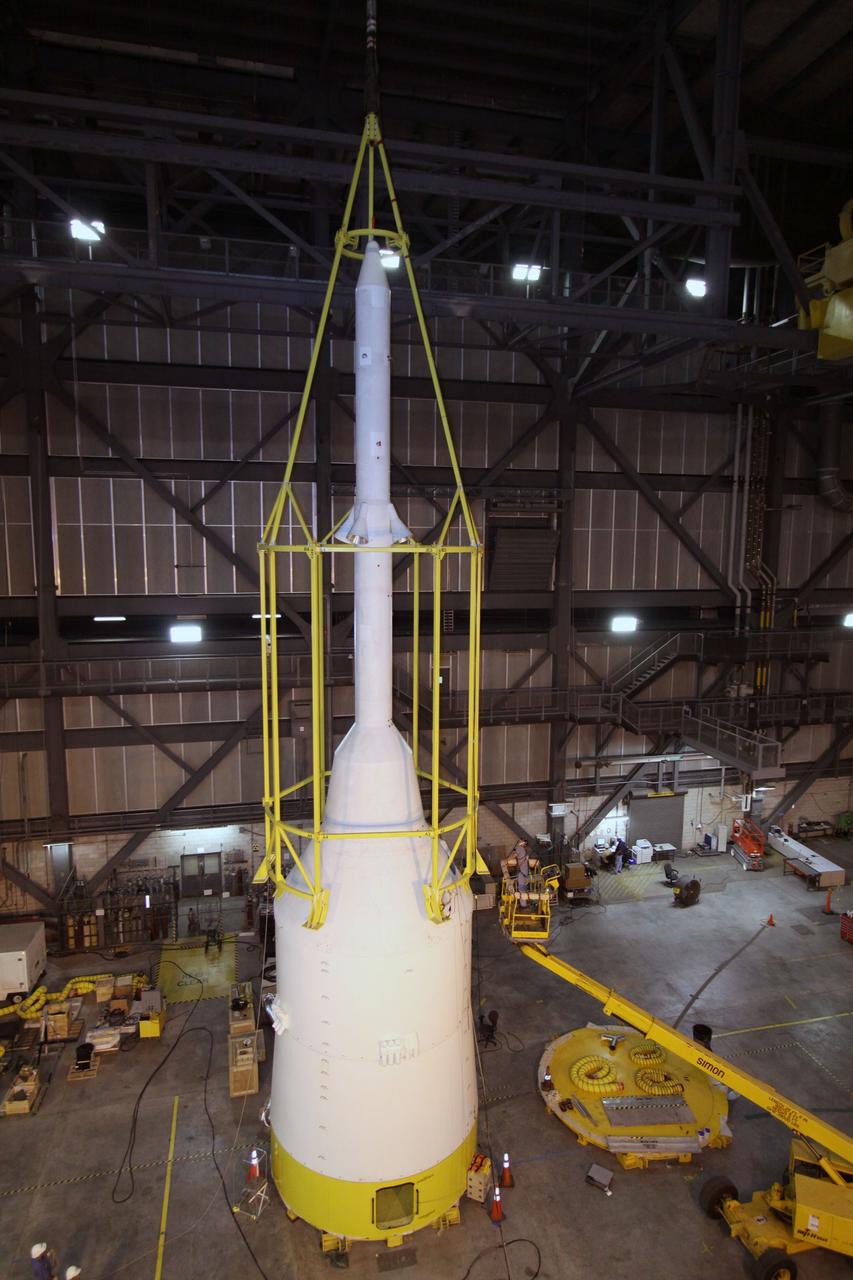

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane over Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
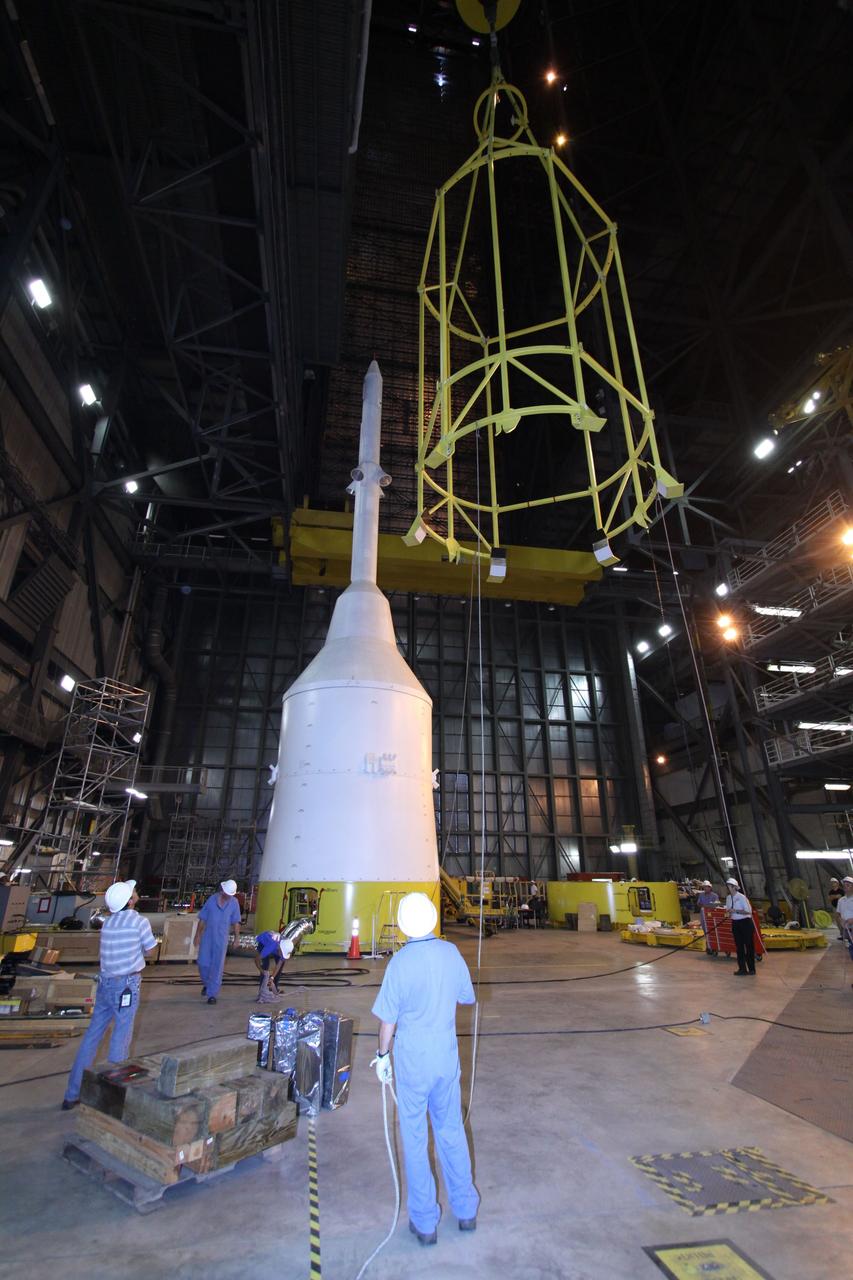

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. Technicians monitor the yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," as it is lowered by crane toward Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
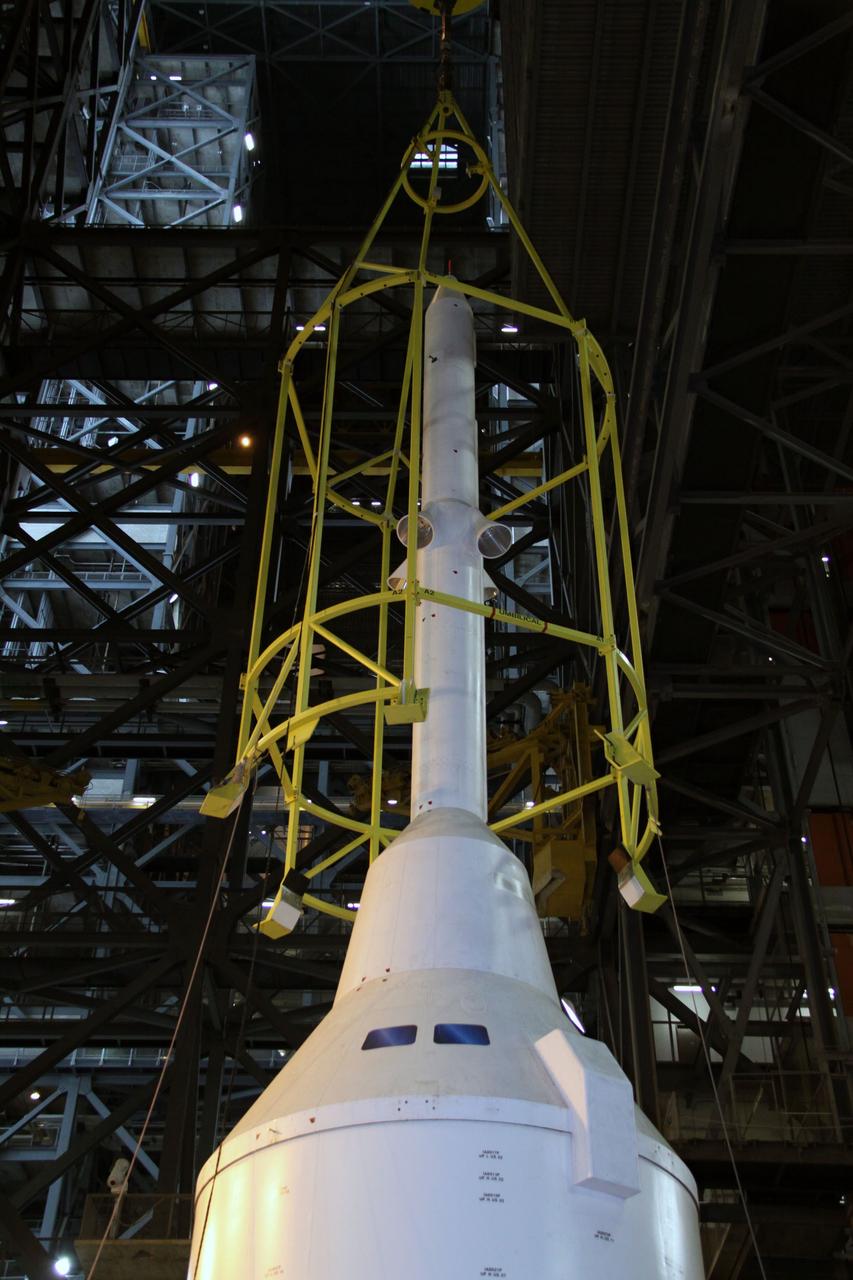

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Vehicle Assembly Building's High Bay 4, assembly of the Ares I-X rocket nears completion. The yellow framework, nicknamed the "birdcage," is lowered by crane over the Launch Abort System, or LAS, of Super Stack 5. The birdcage has the ability to lift and to stack and de-stack the Ares I-X rocket's Super Stack 5. Next, the stack will be lifted on top of the segments already in place on the mobile launcher platform, completing assembly of the rocket. Five super stacks make up the rocket's upper stage that will be integrated with the four-segment solid rocket booster first stage. Ares I-X is the test vehicle for the Ares I, which is part of the Constellation Program to return men to the moon and beyond. The Ares I-X flight test is targeted for Oct. 31, pending formal NASA Headquarters approval. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller