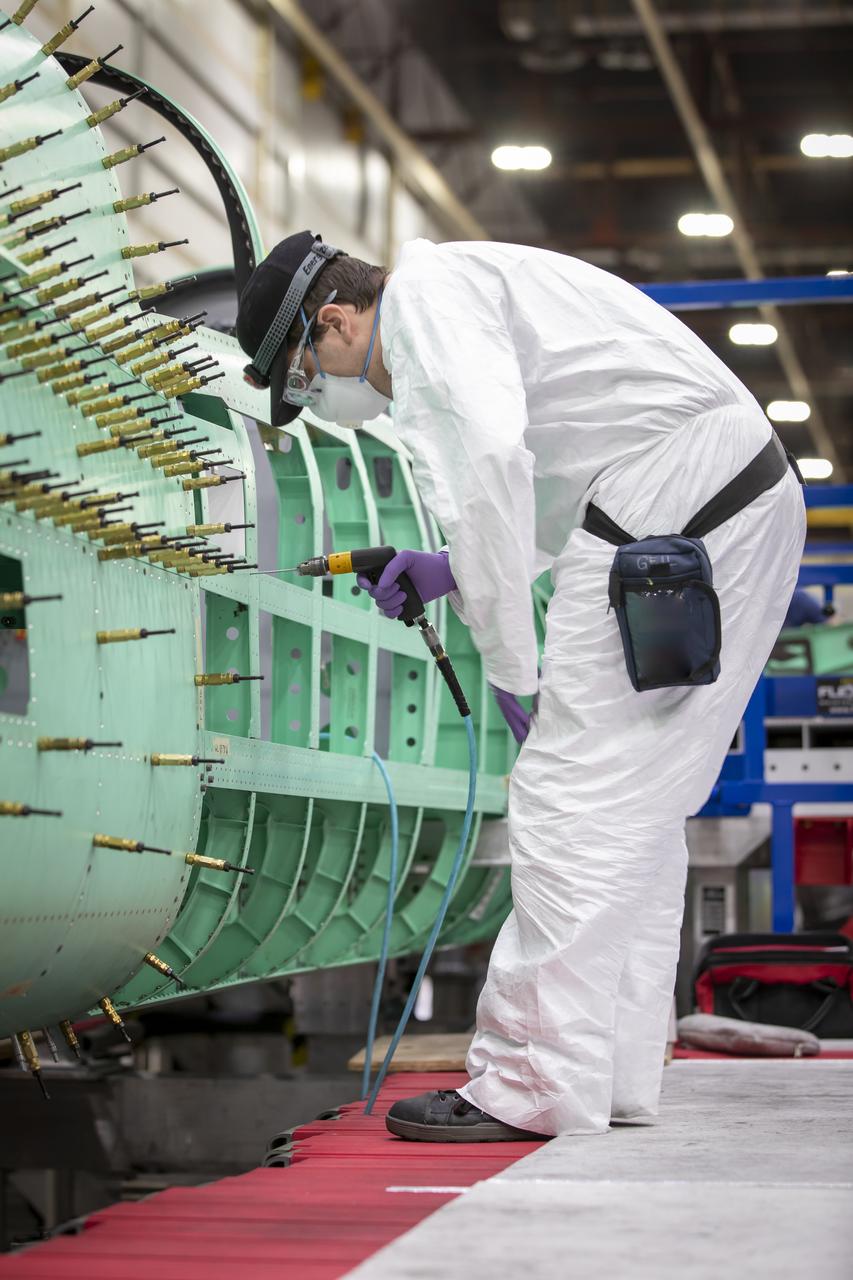

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

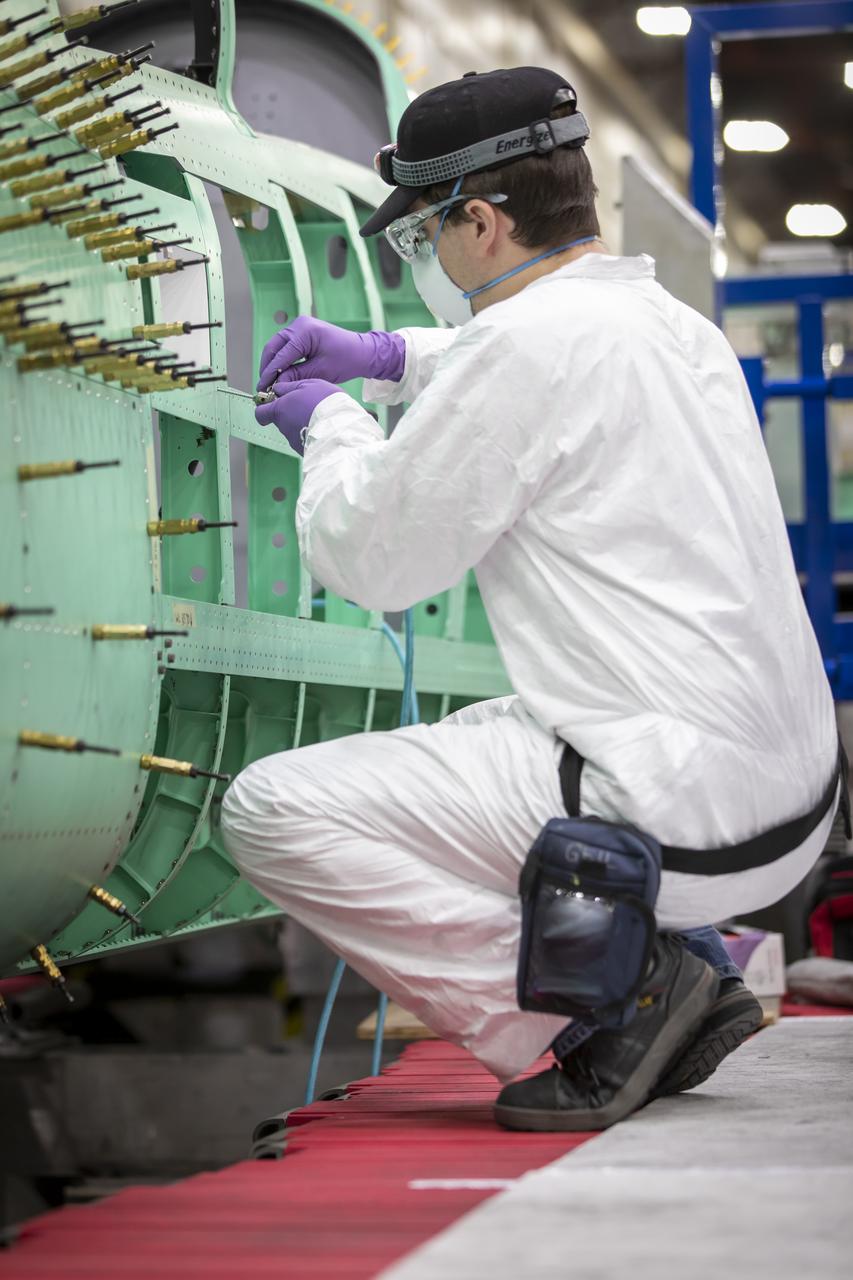
A Lockheed Martin technician prepares holes for installation of the fuselage panel on the X-59. The fuselage is the section of the aircraft that contains the cockpit. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician prepares to install the left fuselage skins onto the X-59. Once in the air, the aircraft, currently under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

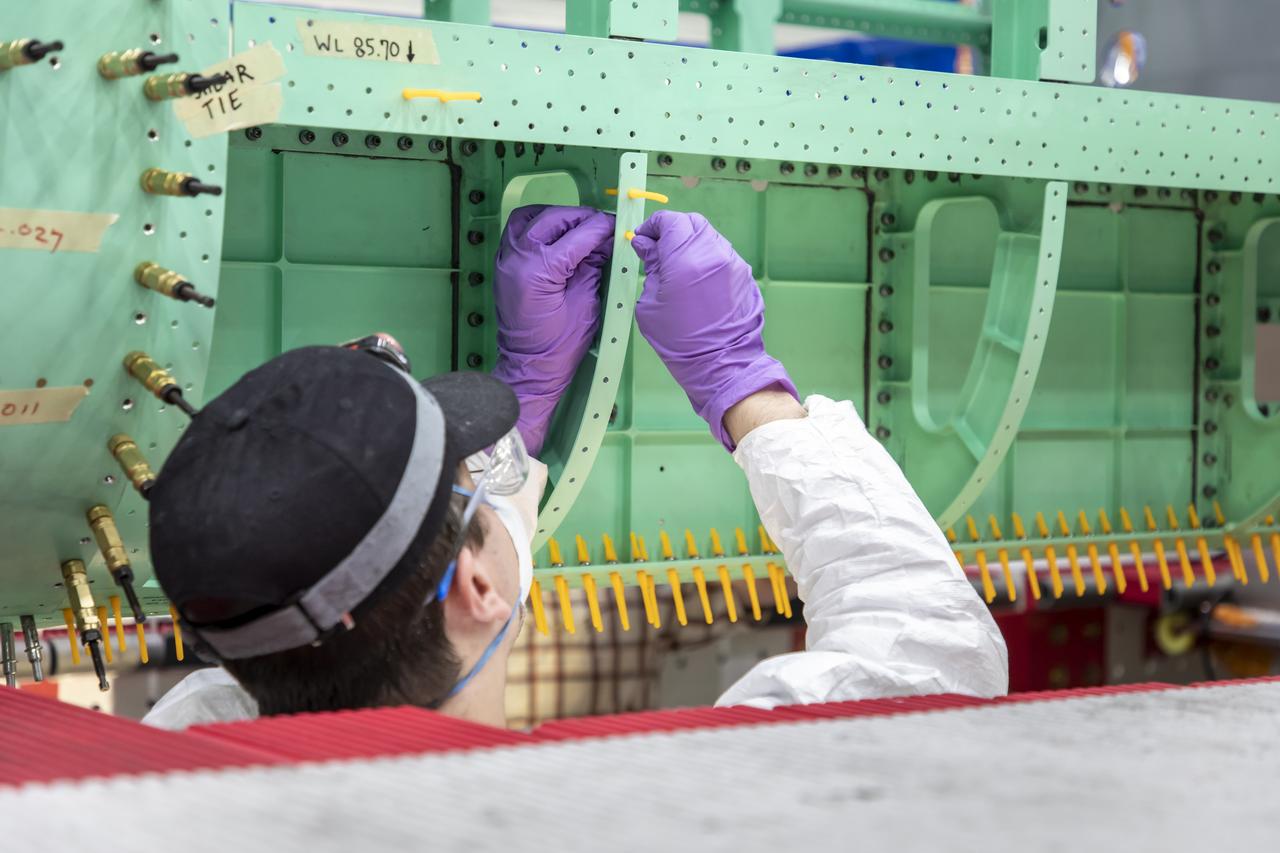
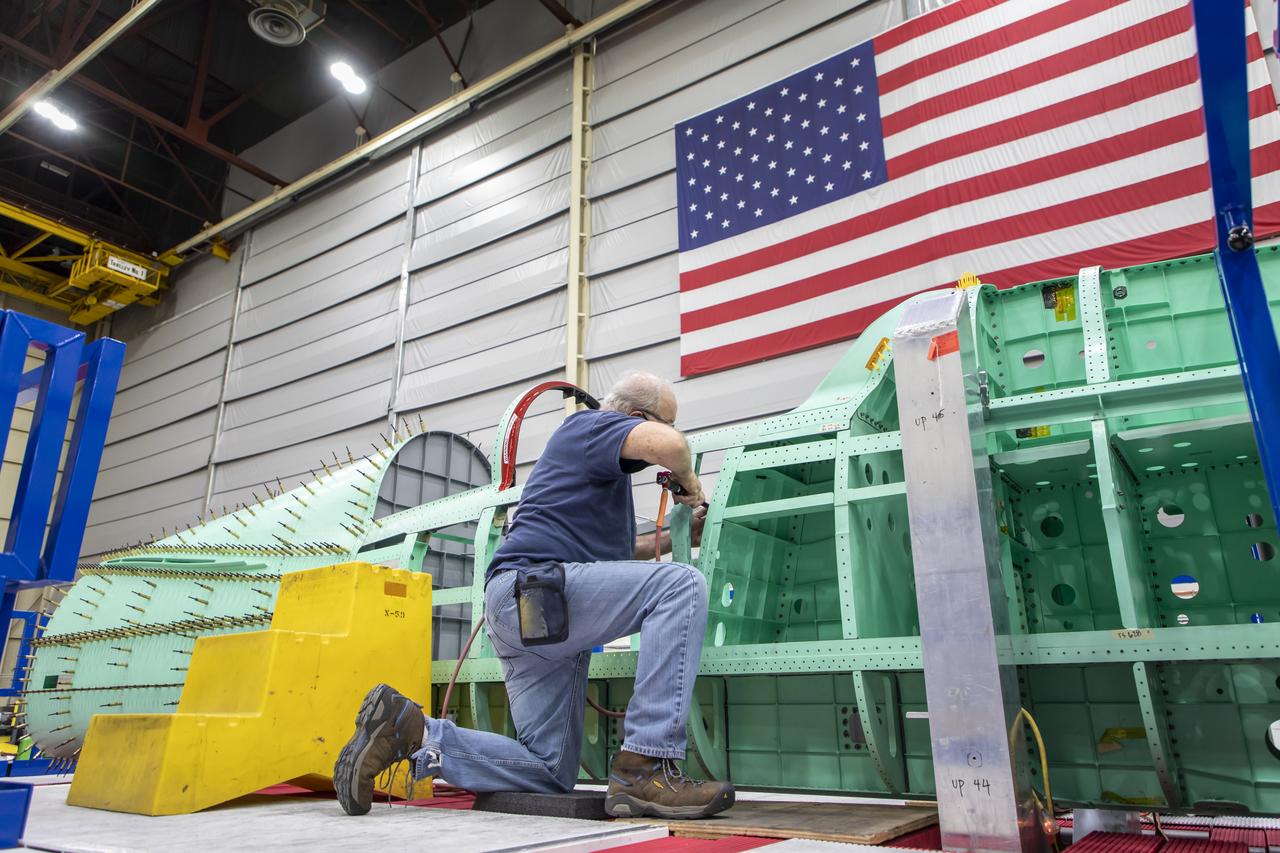
Lockheed Martin technicians work to align and check the fastener holes on the X-59’s fuselage skin. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
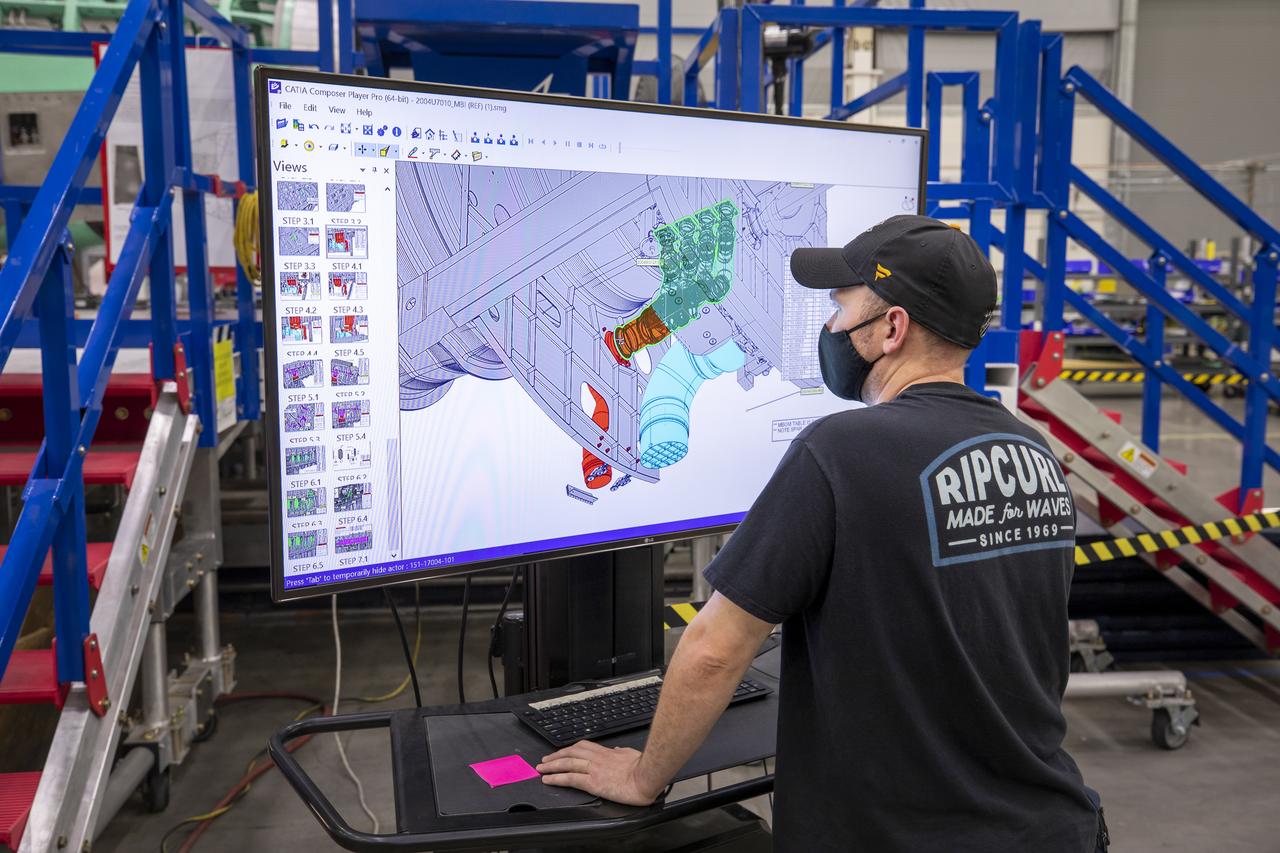

A Lockheed Martin technician looks at the connector installation on the cad model of the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
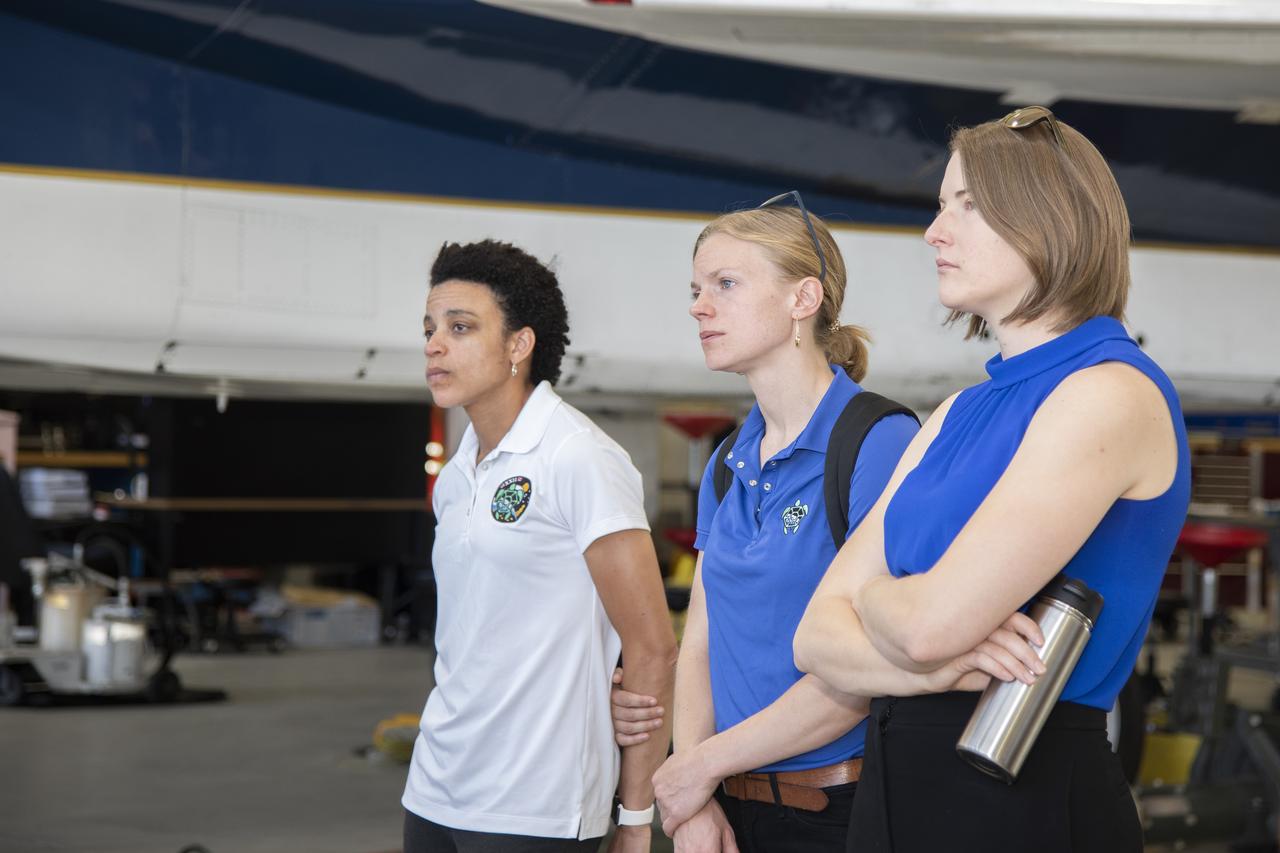

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Jessica Watkins, Zena Cardman, Kayla Barron toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California where they were briefed on the use of Armstrong's F-15 and F-18 aircraft for studying sonic booms. The aircraft will be used during the development of the low-boom X-59 aircraft that is planned to fly supersonically over land, which is not allowed at this time because of the loud noise created when flying beyond the speed of sound.
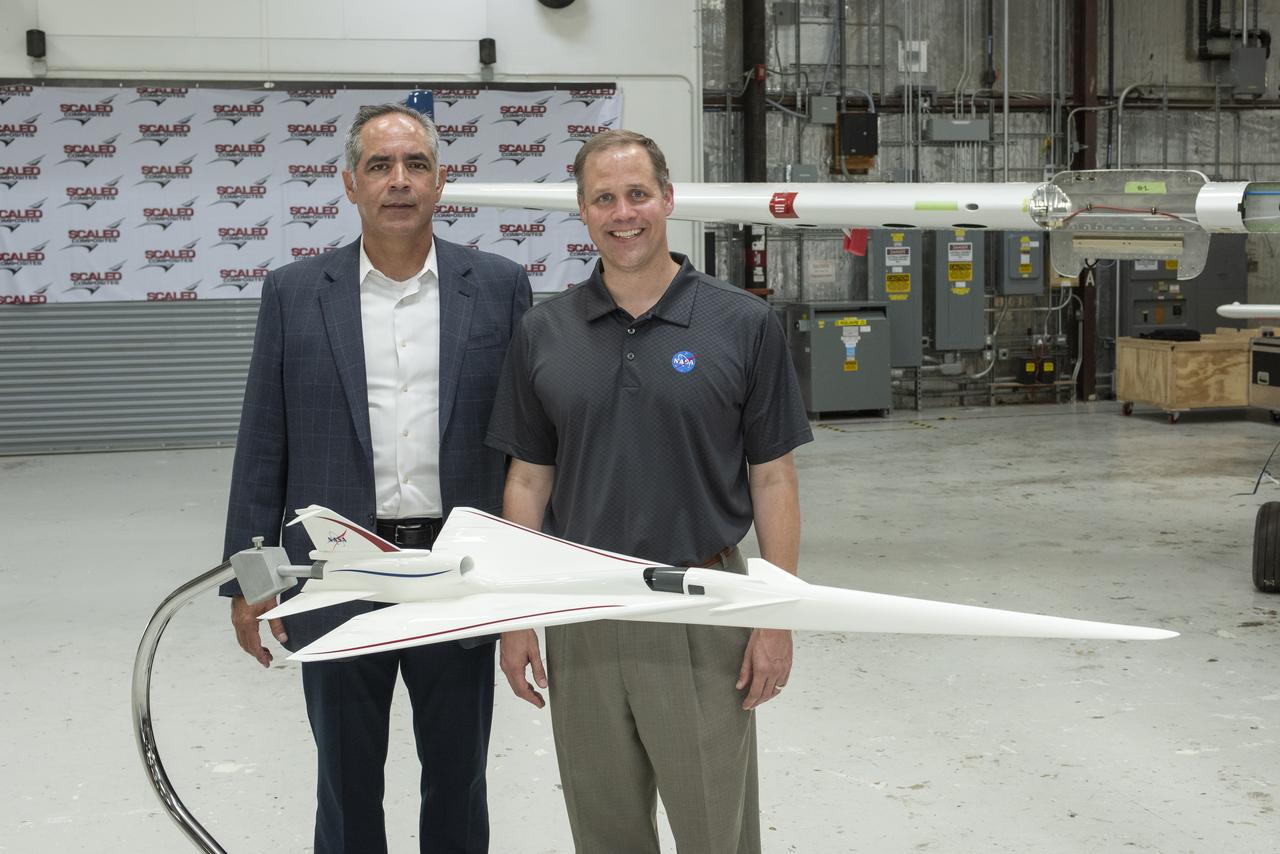

NASA Administrator Bridenstine stands with AFRC center director McBride by model NASA's Supersonic X-Plane, X-59 Quiet Supersonic Technology or QueSST. Bridenstine spoke at press event at Mojave Air and Space Port in California. The goal of X-59 is to quiet the sound when aircraft pierce the speed of sound and make a loud sonic boom on the ground.
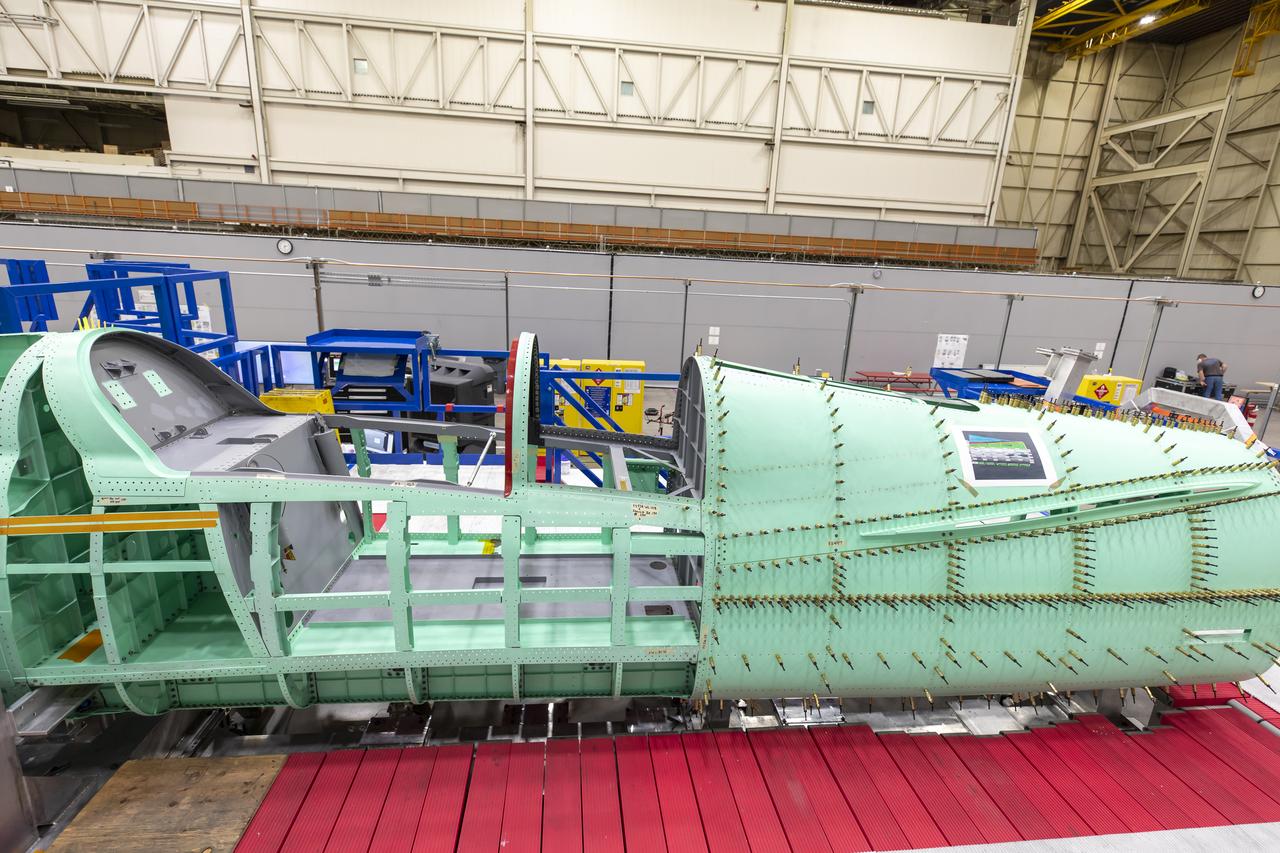
Event: SEG 210 Forebody A right side view of where the team is preparing the X-59 structure for installation of the forward fuselage, which contains the cockpit. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

Event: SEG 410 Main Wing A Lockheed Martin technician works on the installation of wiring on the trailing edge structure of the right side of the X-59’s wing. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.

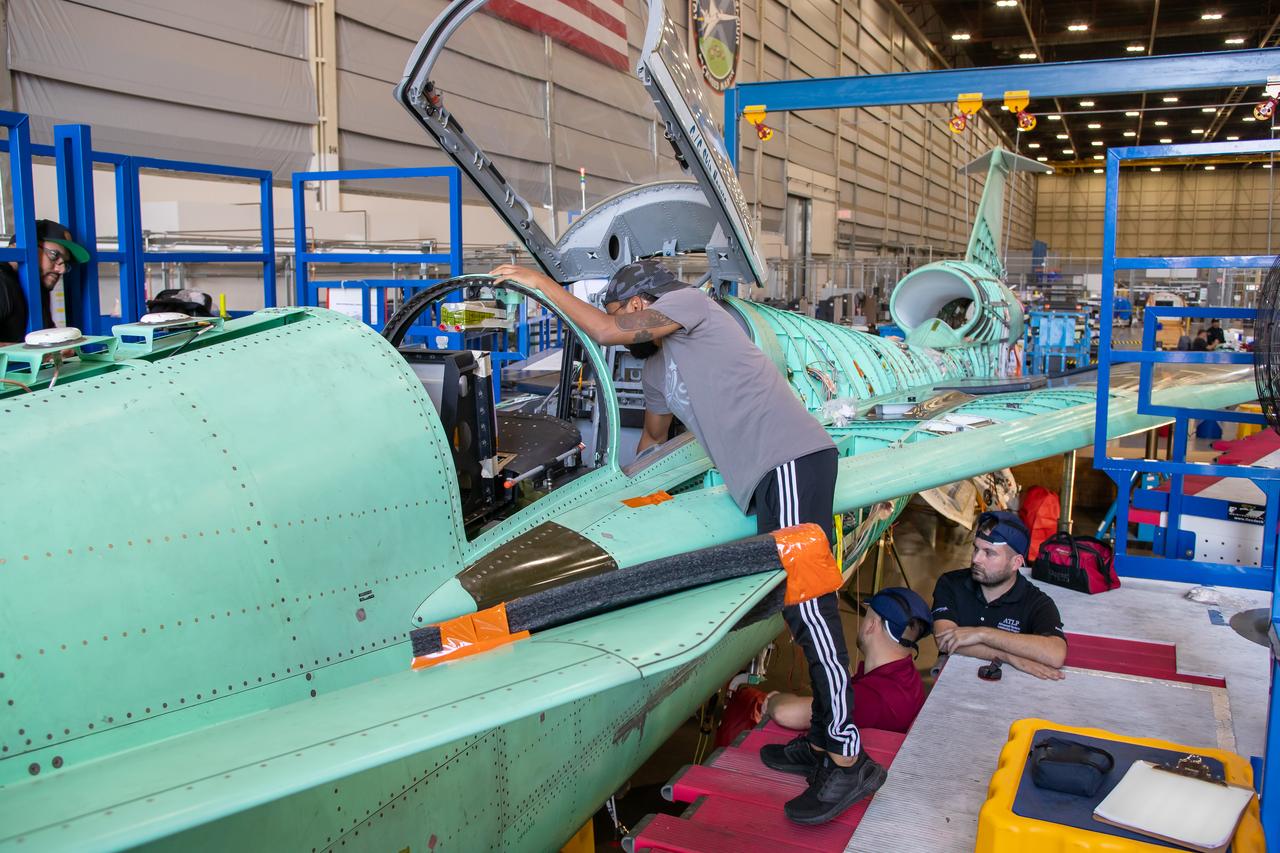
Event: SEG 210 Forebody A Lockheed Martin technician works on the ejection seat support structure and once complete, the ejection seat rails will be installed on the X-59 airplane. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
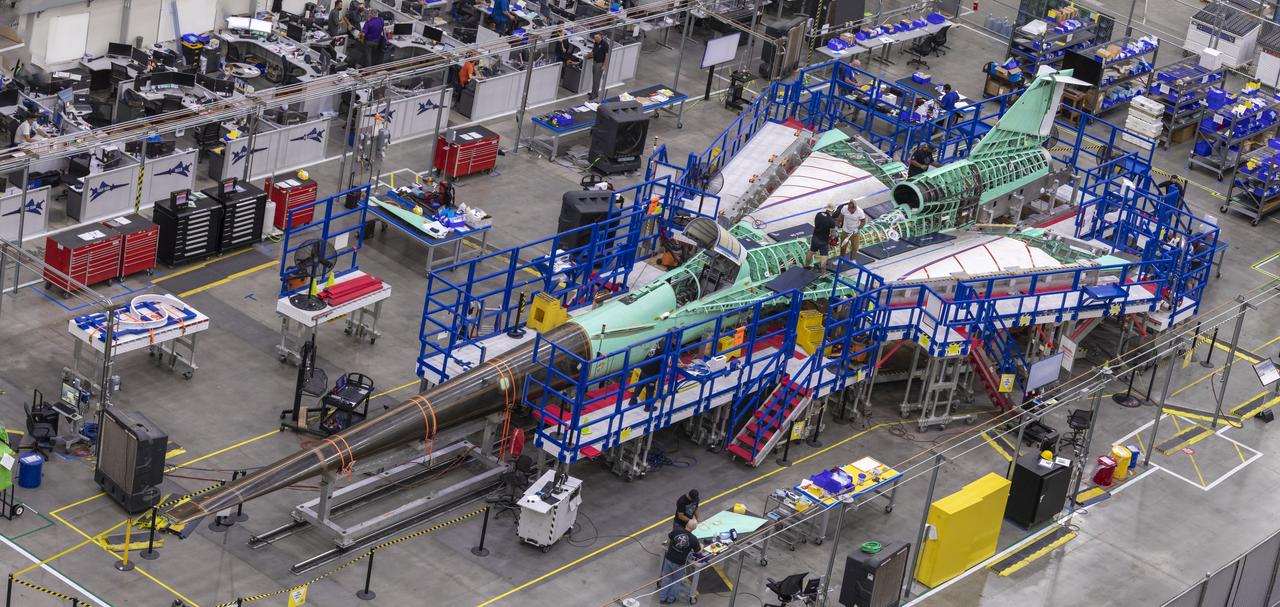

Event: Manufacturing Area From Above A overhead view of the X-59 with its nose on. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
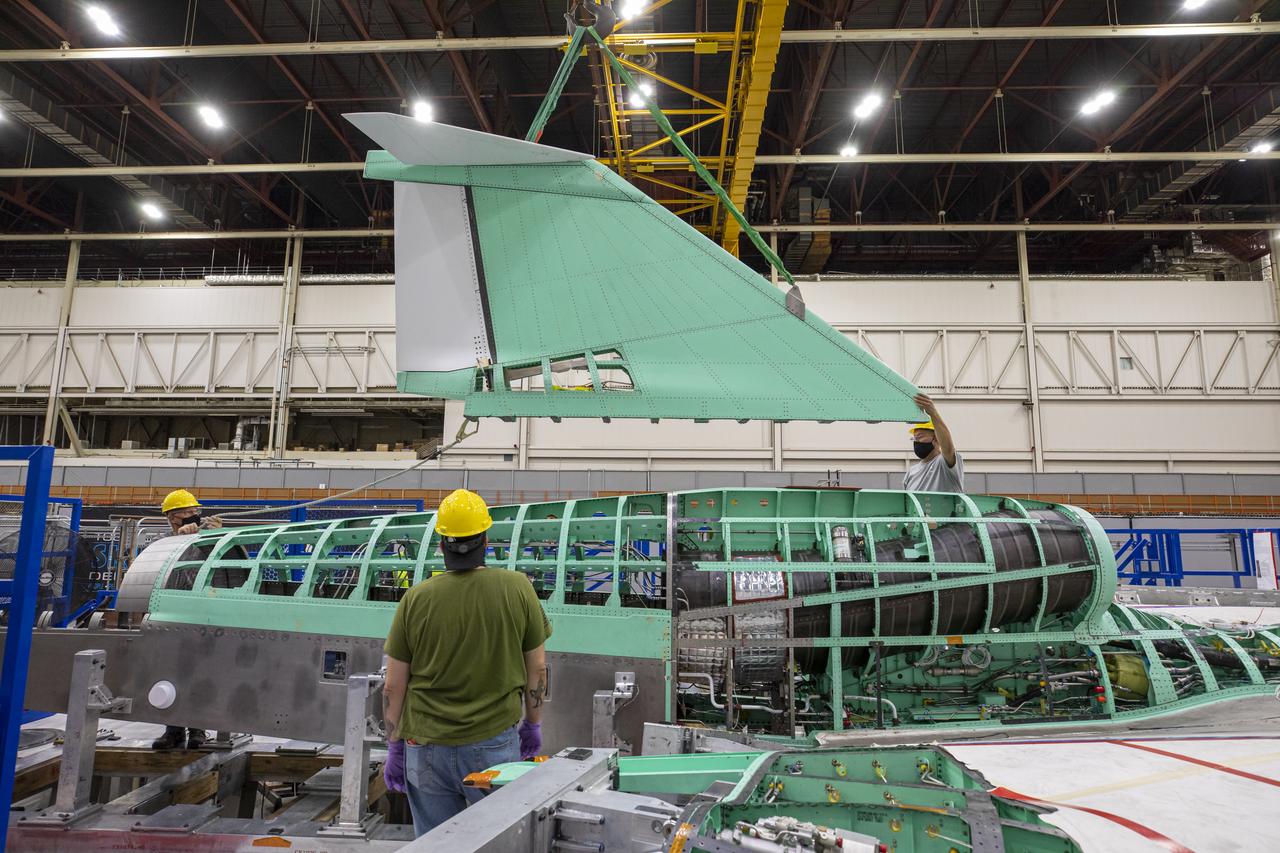

Event: SEG 570 Vertical Tail Assembly - Final Install Lockheed Martin technicians work on a fit check and installation of the vertical tail onto the X-59 aircraft. The plane is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
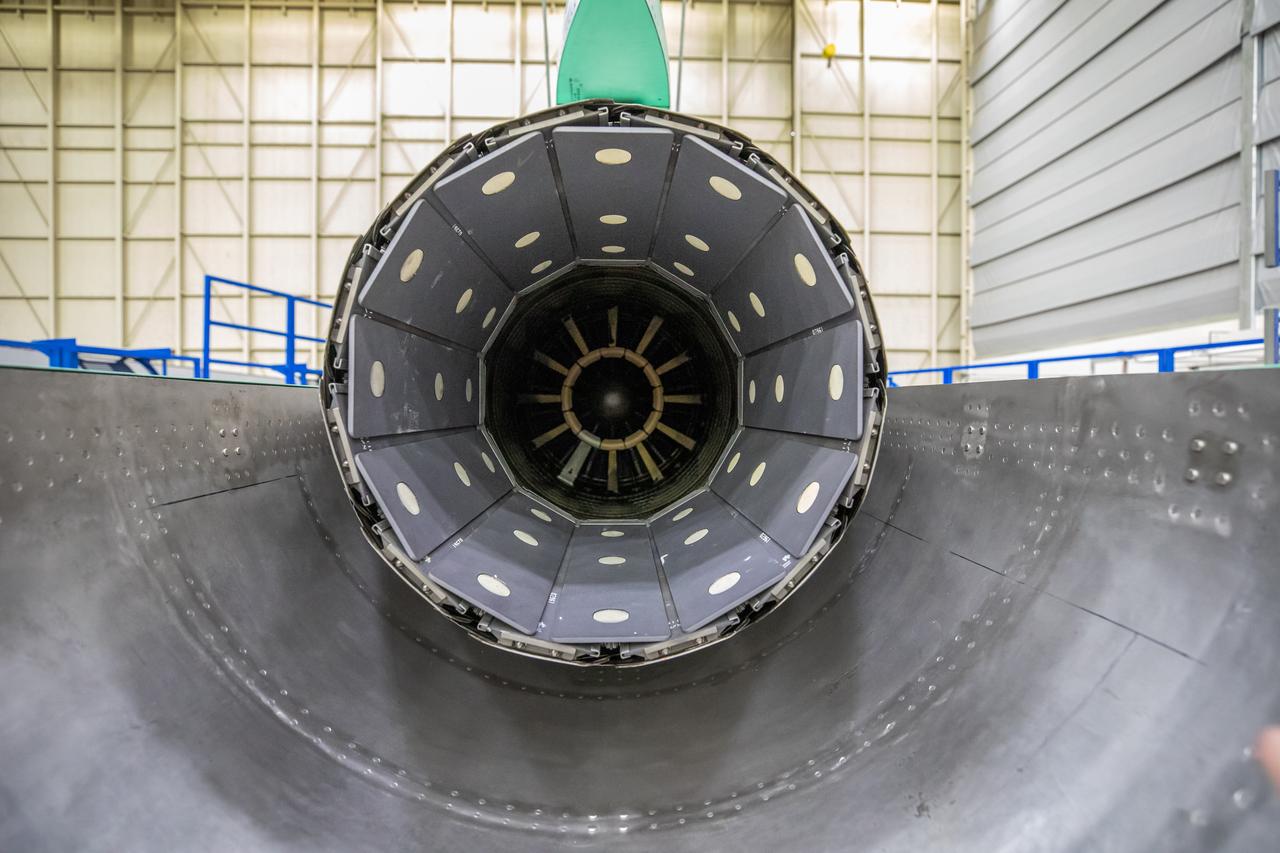

A look at the X-59’s engine nozzle, where the thrust -the force that moves the aircraft- will exit. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
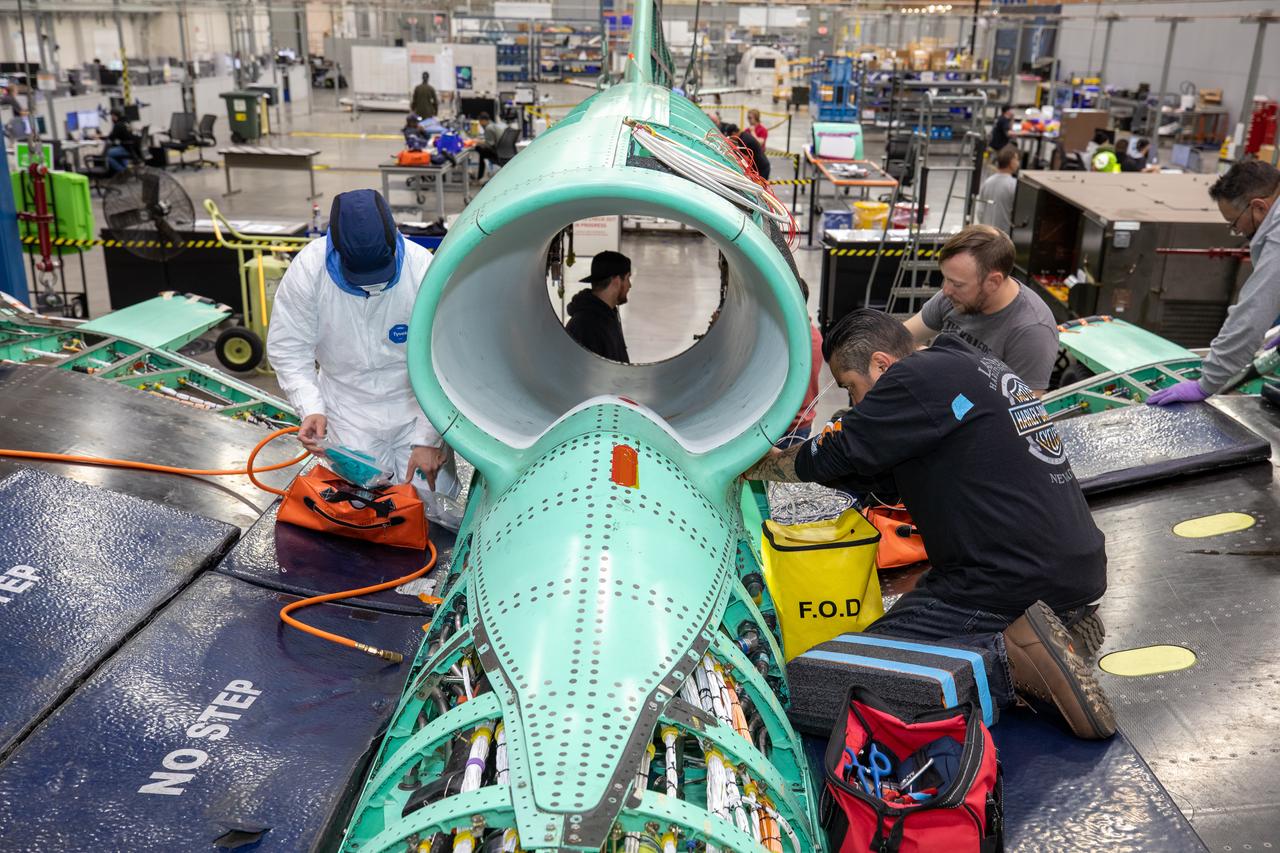

The X-59 team working on the aircraft’s wiring around the engine inlet prior to the engine being installed. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates (L to R) Raja Chari, Bob Hines, Joshua Kutryk, Jasmin Moghbeli, Jonny Kim, and Jessica Watkins toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the left, NASA’s, X-59 pilot, briefs them on use of F-15 for studying sonic booms during the development of the low-boom X-59 aircraft that is planned to fly supersonically over land. Low-level supersonic flight is not allowed at this time because of the loud noise levels generated when flying beyond the speed of sound.

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
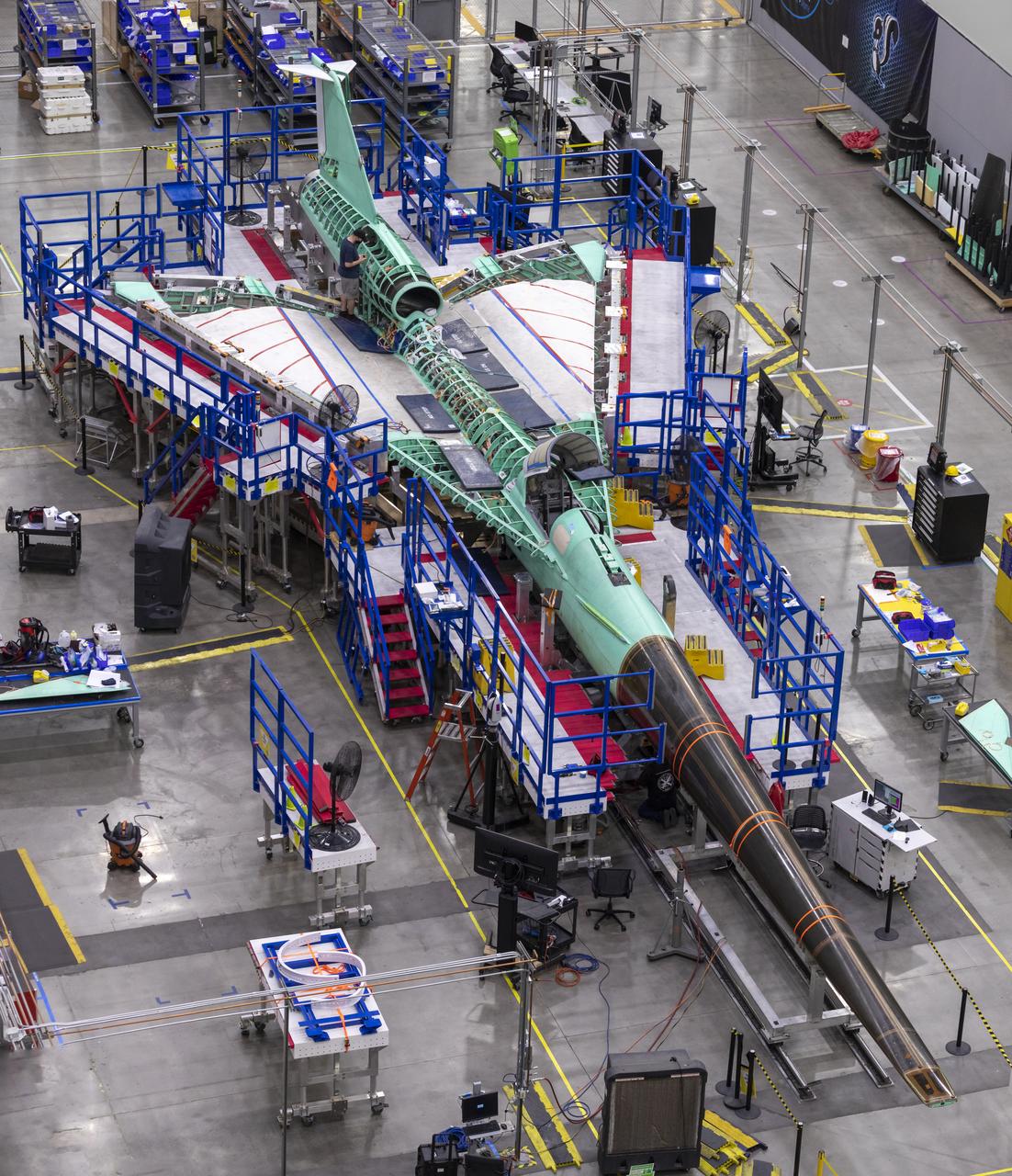

A overhead view of the X-59 with its nose on. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The plane is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
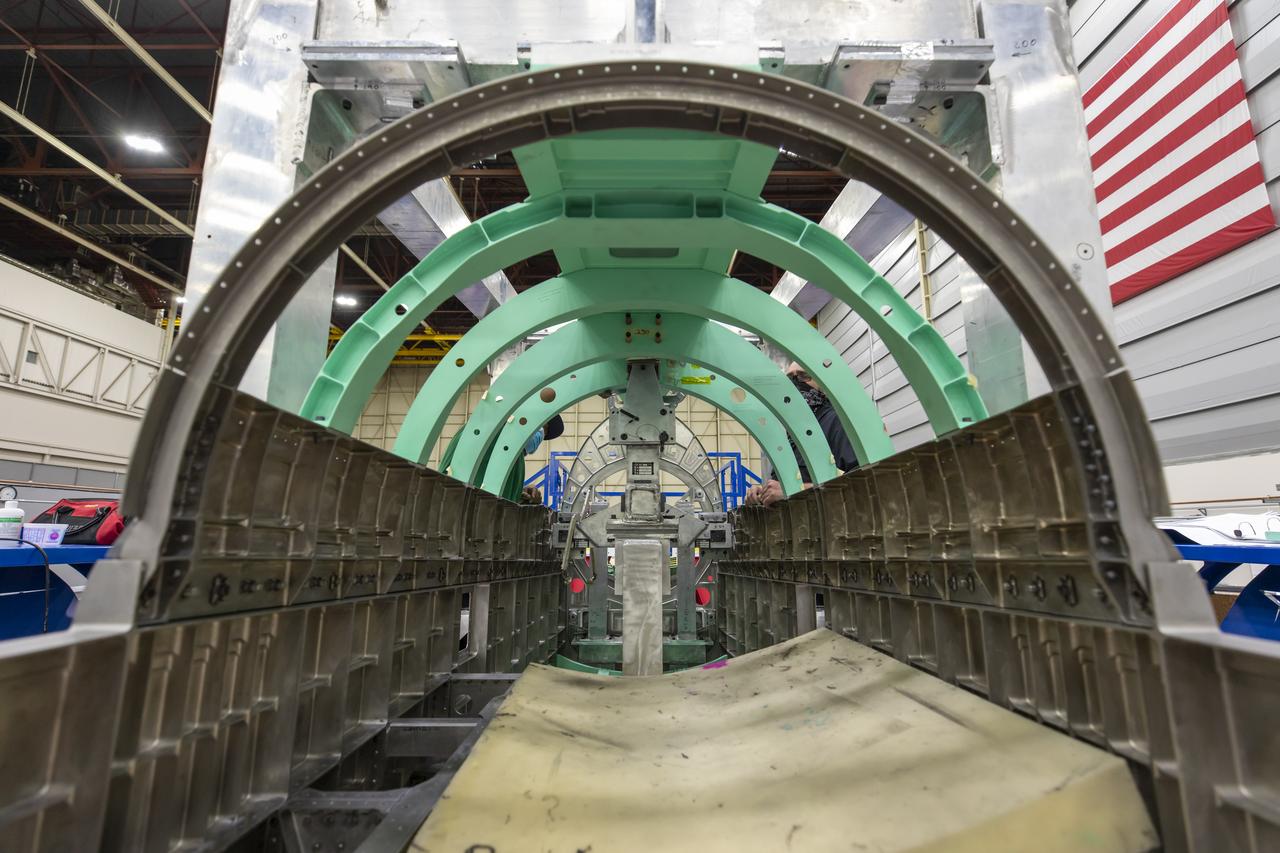

Event: SEG 510 Upper Empennage An inside peek at the X-59 gives us a view from the aft end looking at the engine bay. Later in the assembly process, the engine will be placed inside this section. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
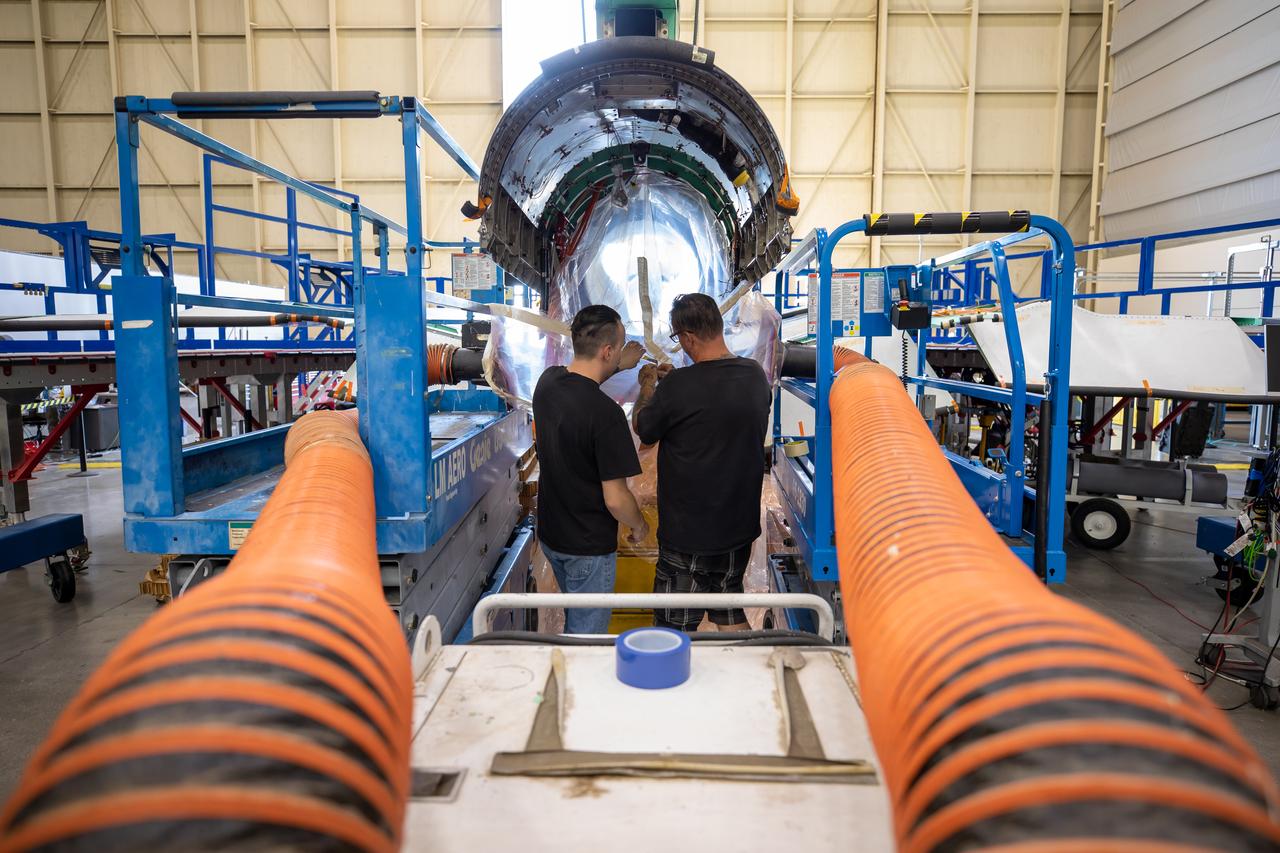

This image shows the extensive ventilation system that has been placed adjacent to the X-59 during the recent painting of the aircraft’s engine inlet. Once the aircraft build and ground testing are complete, the X-59 airplane will begin flight testing, working towards demonstrating the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
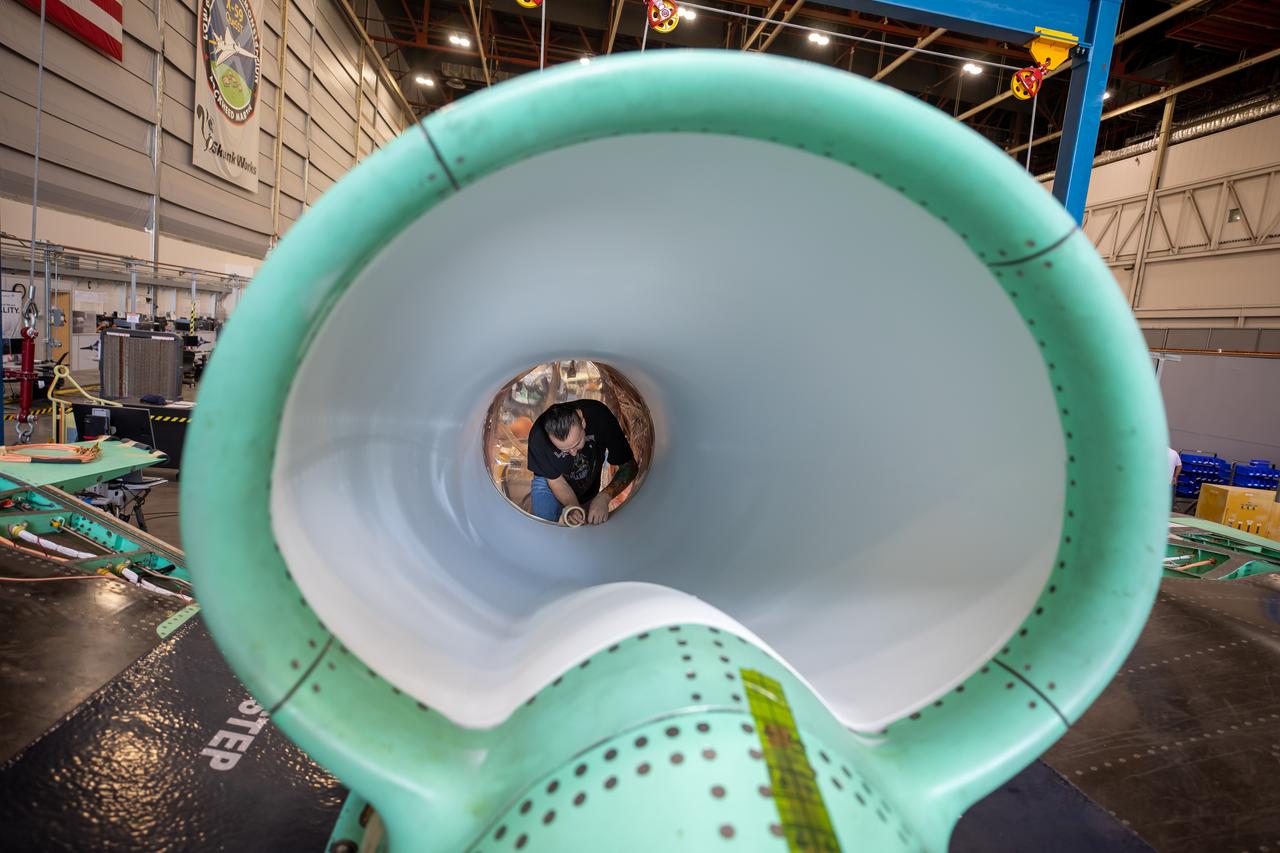

This is an up-close view of the X-59’s engine inlet – fresh after being painted. The 13-foot F414-GE-100 engine will be placed inside the inlet bringing the X-59 aircraft one step closer to completion. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will begin flight operations, working toward demonstration of the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump, helping to enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.

Event: SEG 230 Nose - Craned Onto Tooling A close-up of the X-59’s duckbill nose, which is a crucial part of its supersonic design shaping. The team prepares the nose for a fit check. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
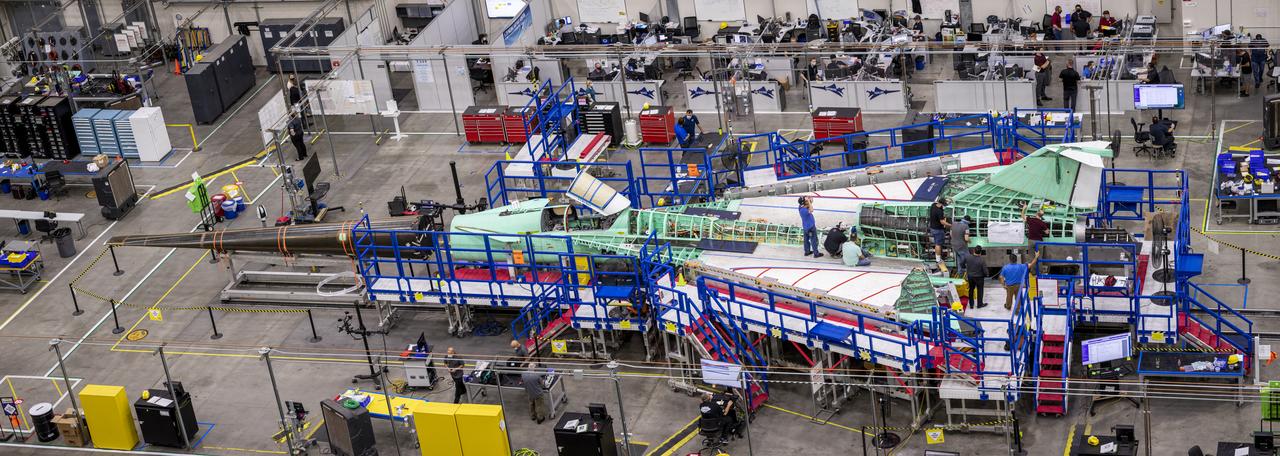

A panoramic side view of the left top of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
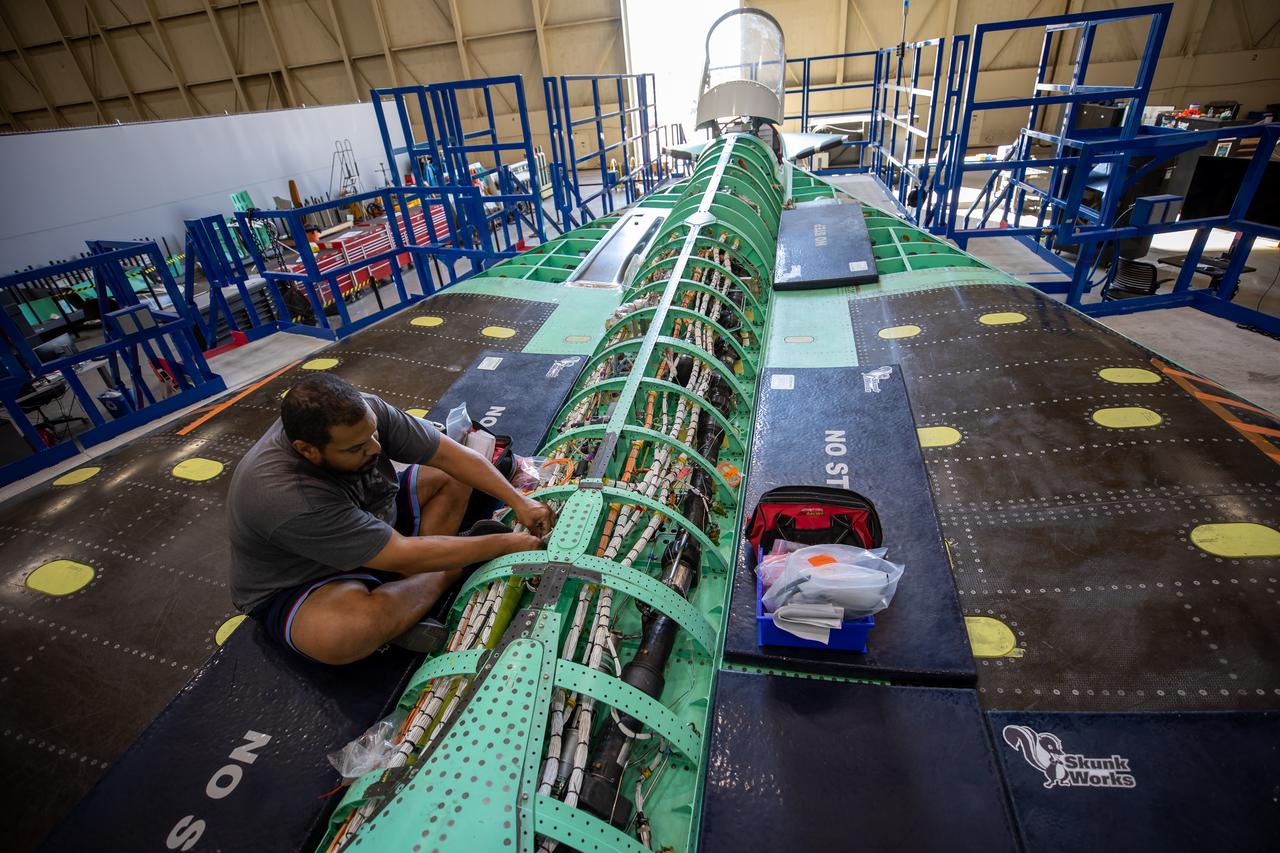

A Lockheed Martin technician works to complete wiring on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
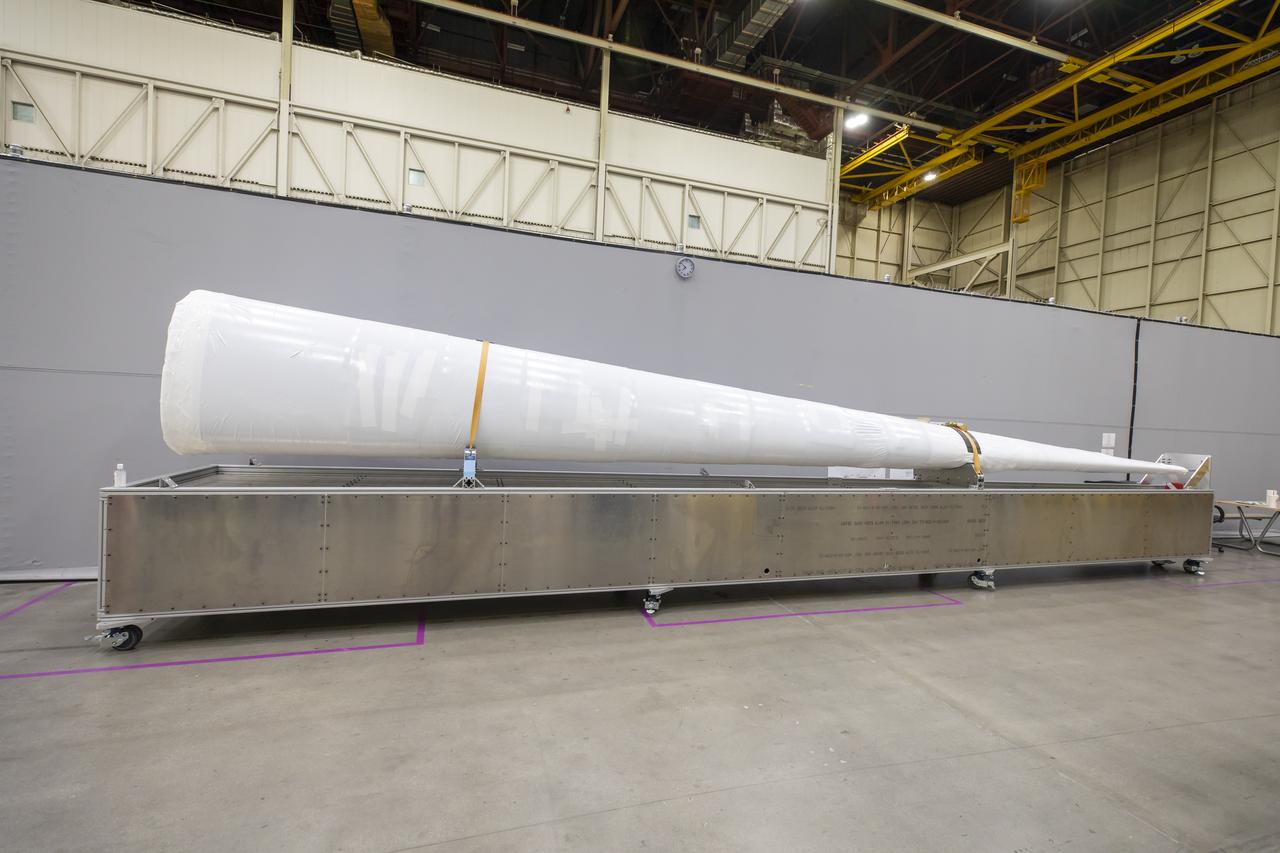

Event: SEG 230 Nose The X-59’s nose is wrapped up safely and rests on a dolly before the team temporarily attaches it to the aircraft for fit checks at Lockheed Martin in Palmdale, California. The full length of the X-plane’s nose is 38-feet – making up one third of the plane’s full length. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, once in the air will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
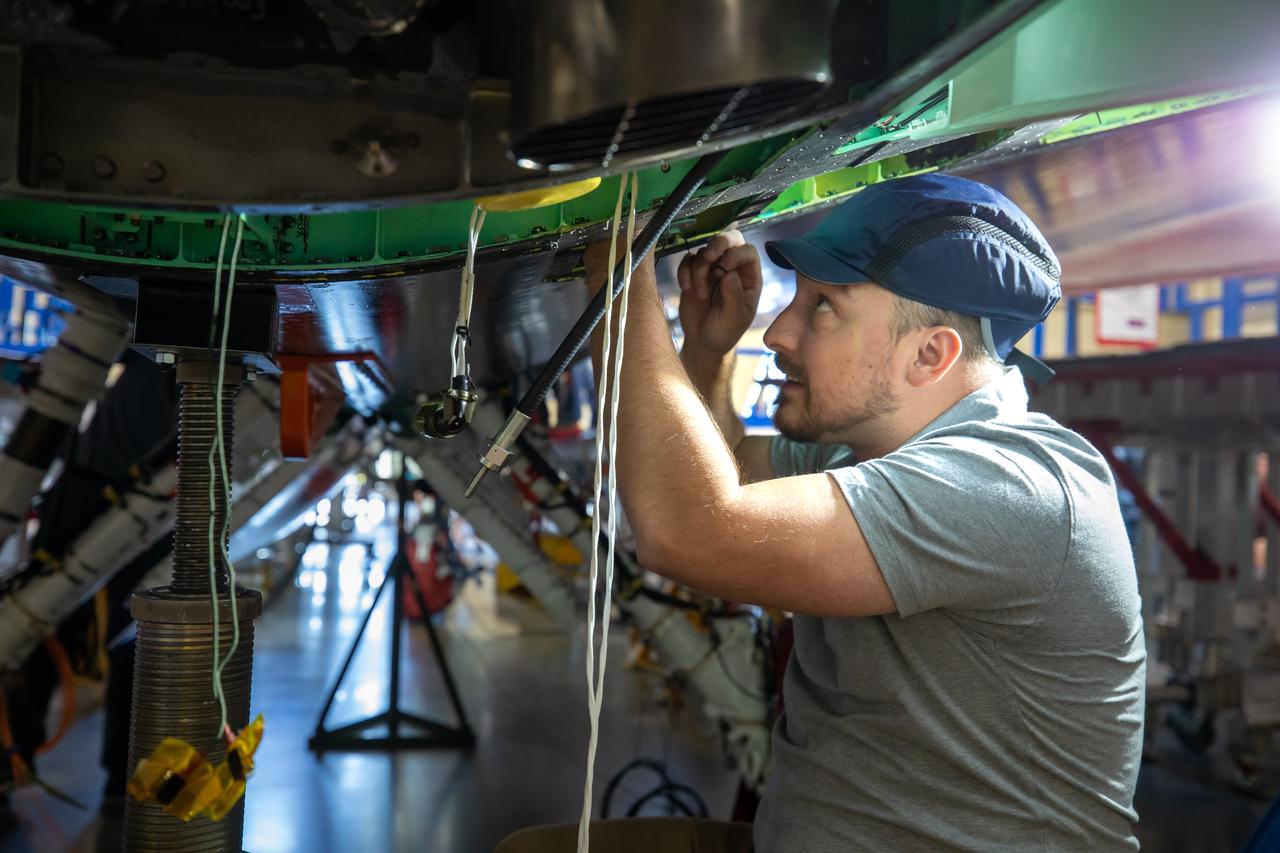

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician works to complete wiring on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
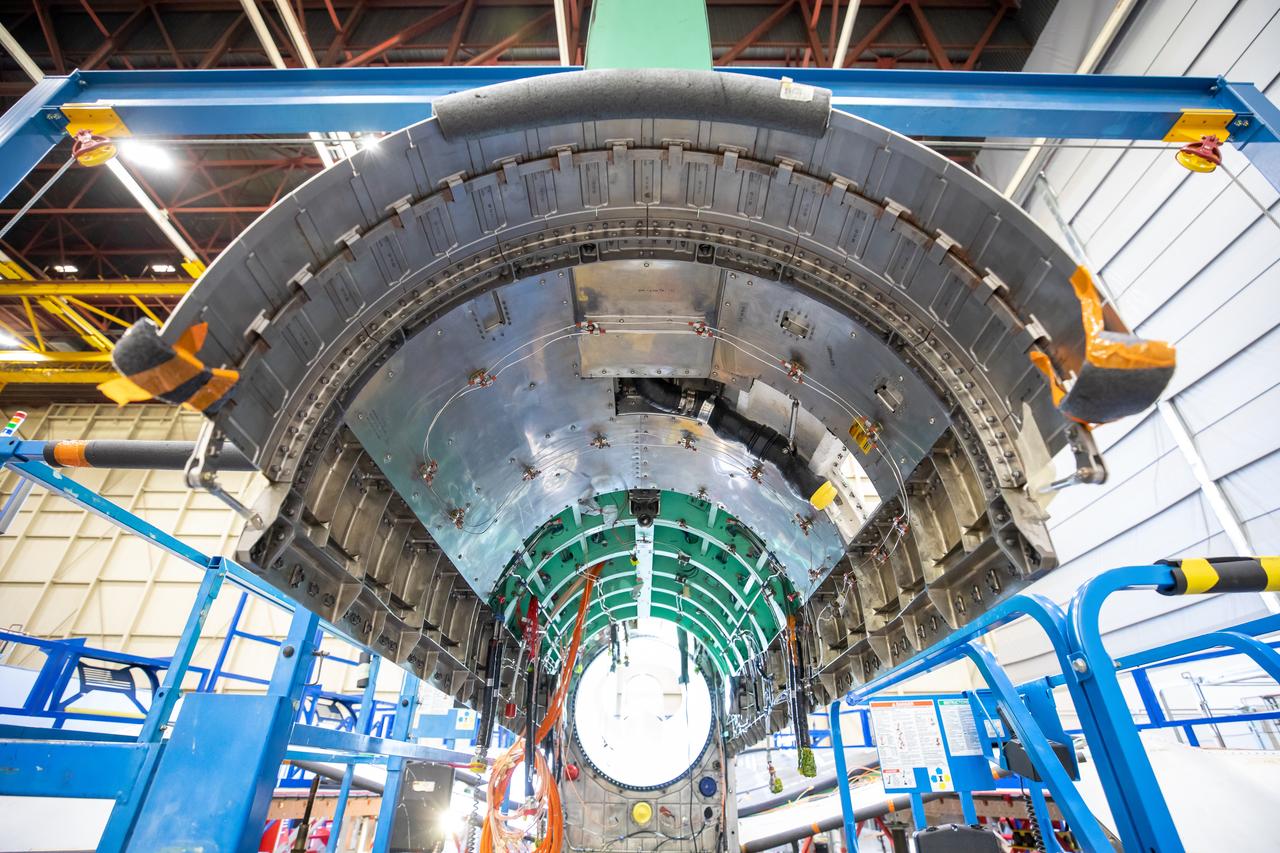

The upper empennage, or tail section of the plane, and engine bay is surrounded by a blue gantry that is used to assist with ground installation and removal of the X-59’s lower empennage and engine. Once fully assembled, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
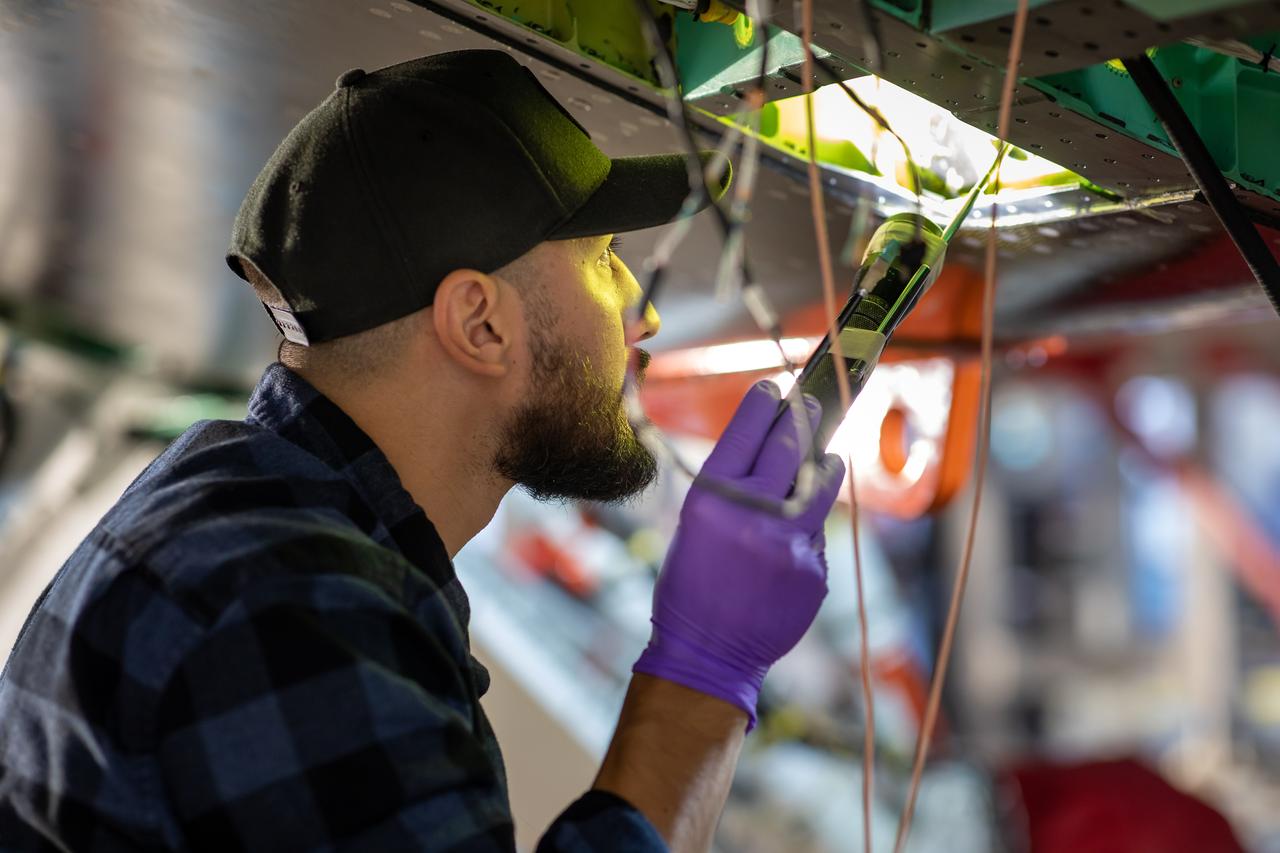

A Lockheed Martin Skunk Works technician inspects some of the wiring and sensors on the X-59 aircraft in preparation for the first power-on system checkouts. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.

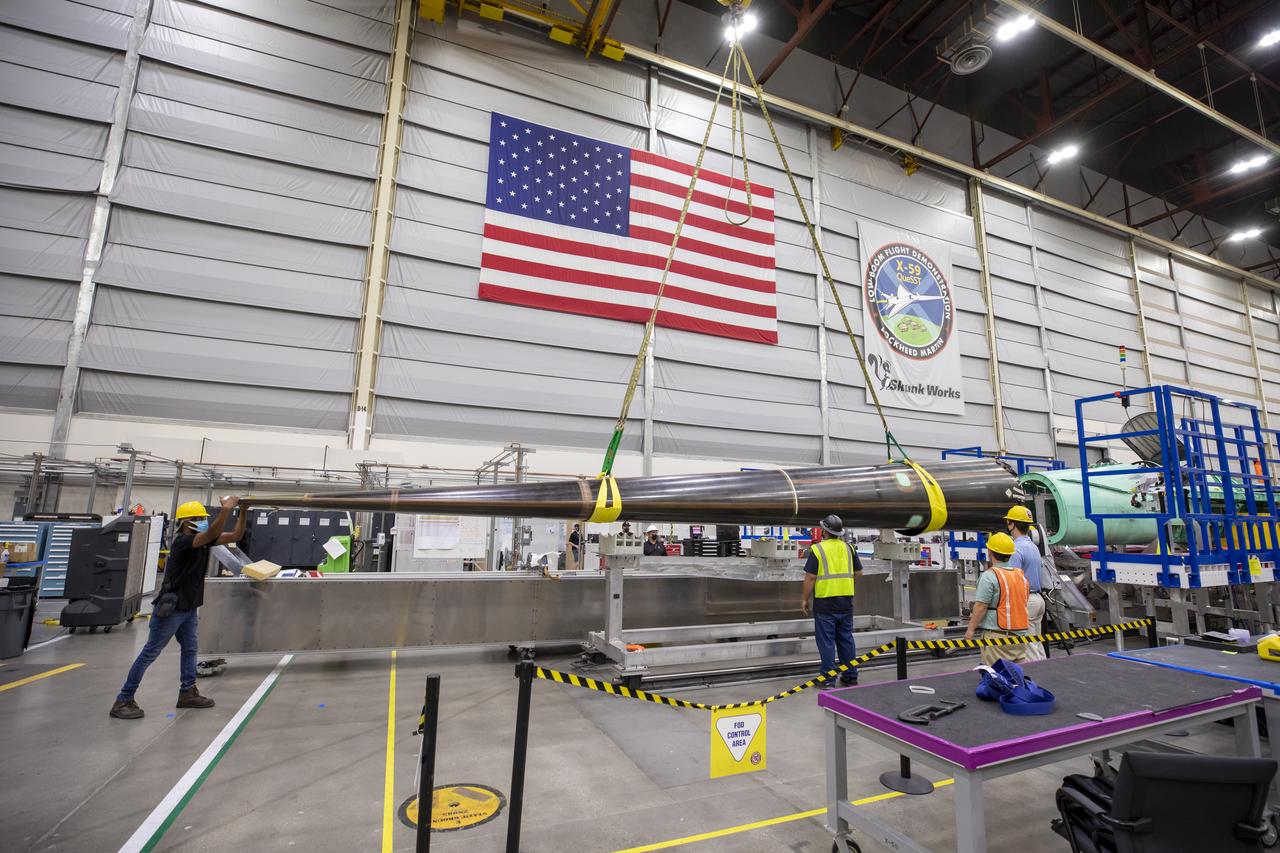
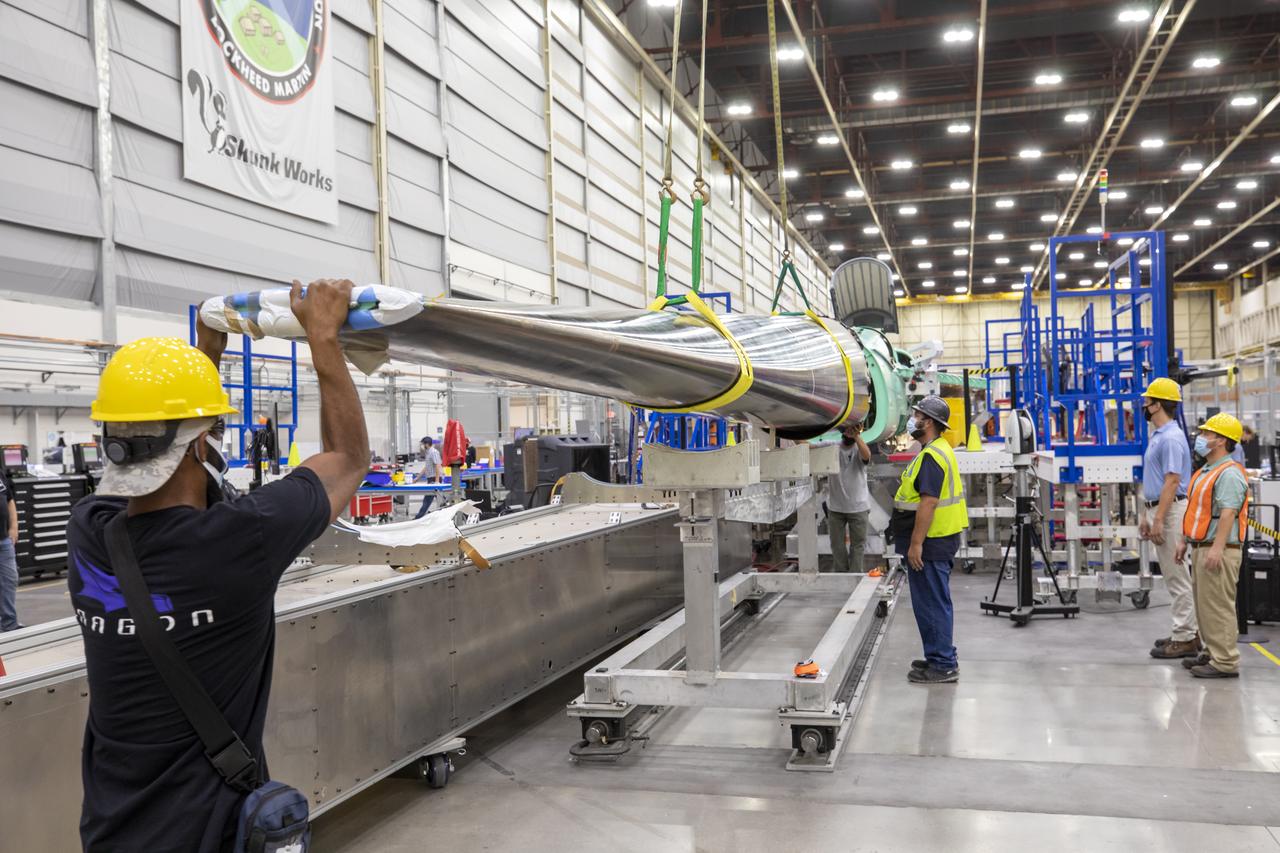
Here is an image of the X-59’s 13-foot General Electric F414 engine as the team prepares for a fit check. Making sure components, like the aircraft’s hydraulic lines, which help control functions like brakes or landing gear, and wiring of the engine, fit properly is essential to the aircraft’s safety. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
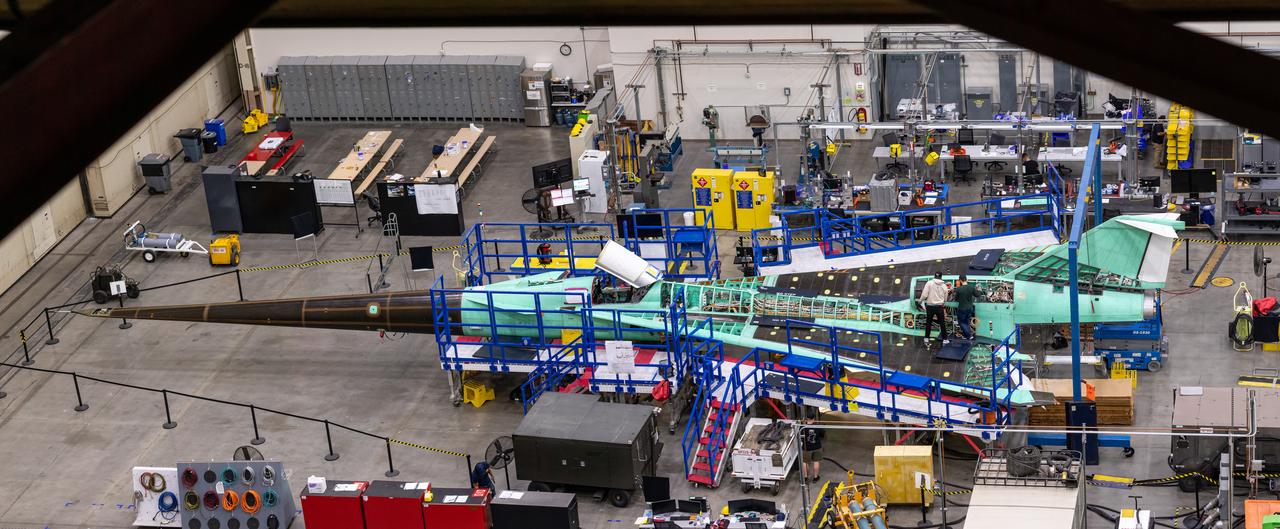

This is an overhead view of the X-59 aircraft at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The nose was installed, and the plane awaits engine installation. Technicians continue to wire the aircraft as the team preforms several system checkouts to ensure the safety of the aircraft. The X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
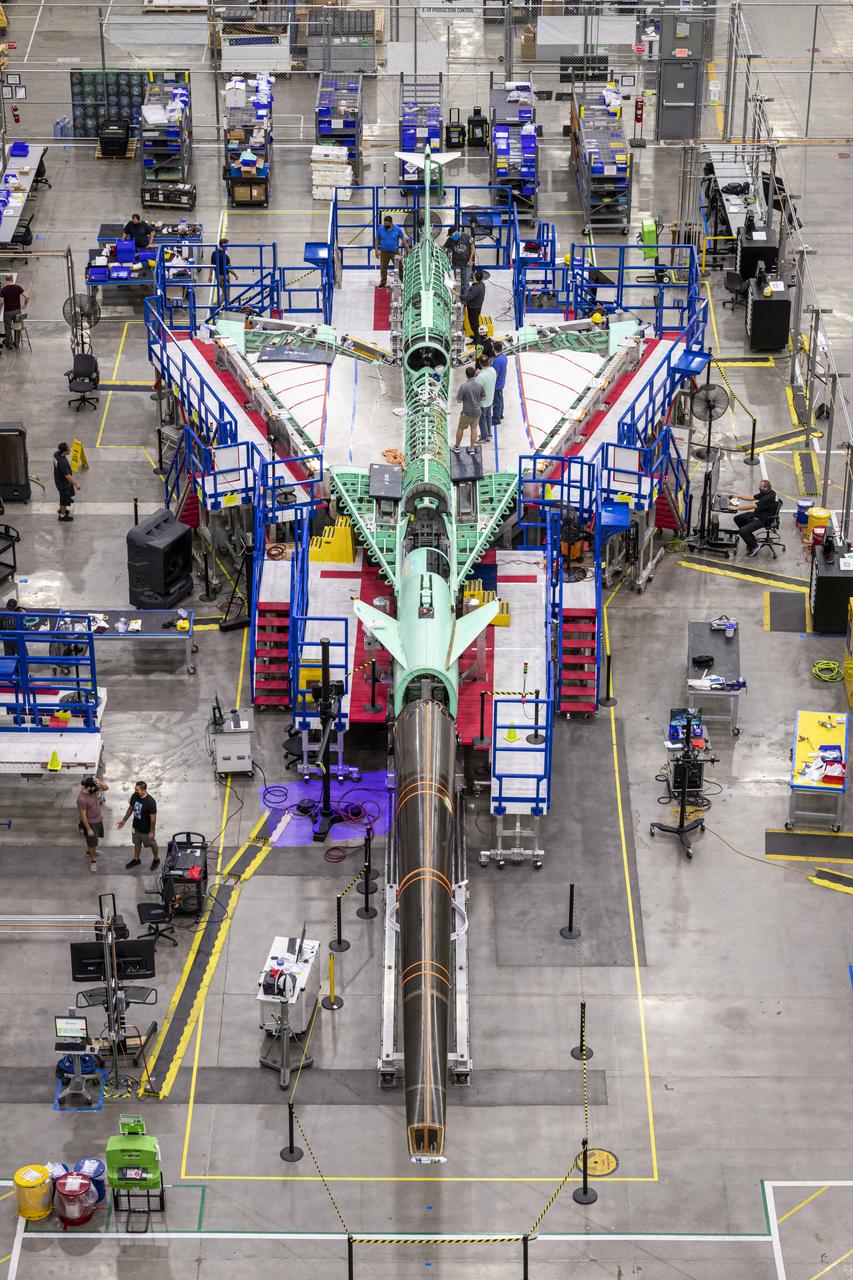

An overhead view of the X-59 supersonic plane with the tail on and the nose in the process of installation. The X-59’s nose is 38-feet long – approximately one third of the length of the entire aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump.
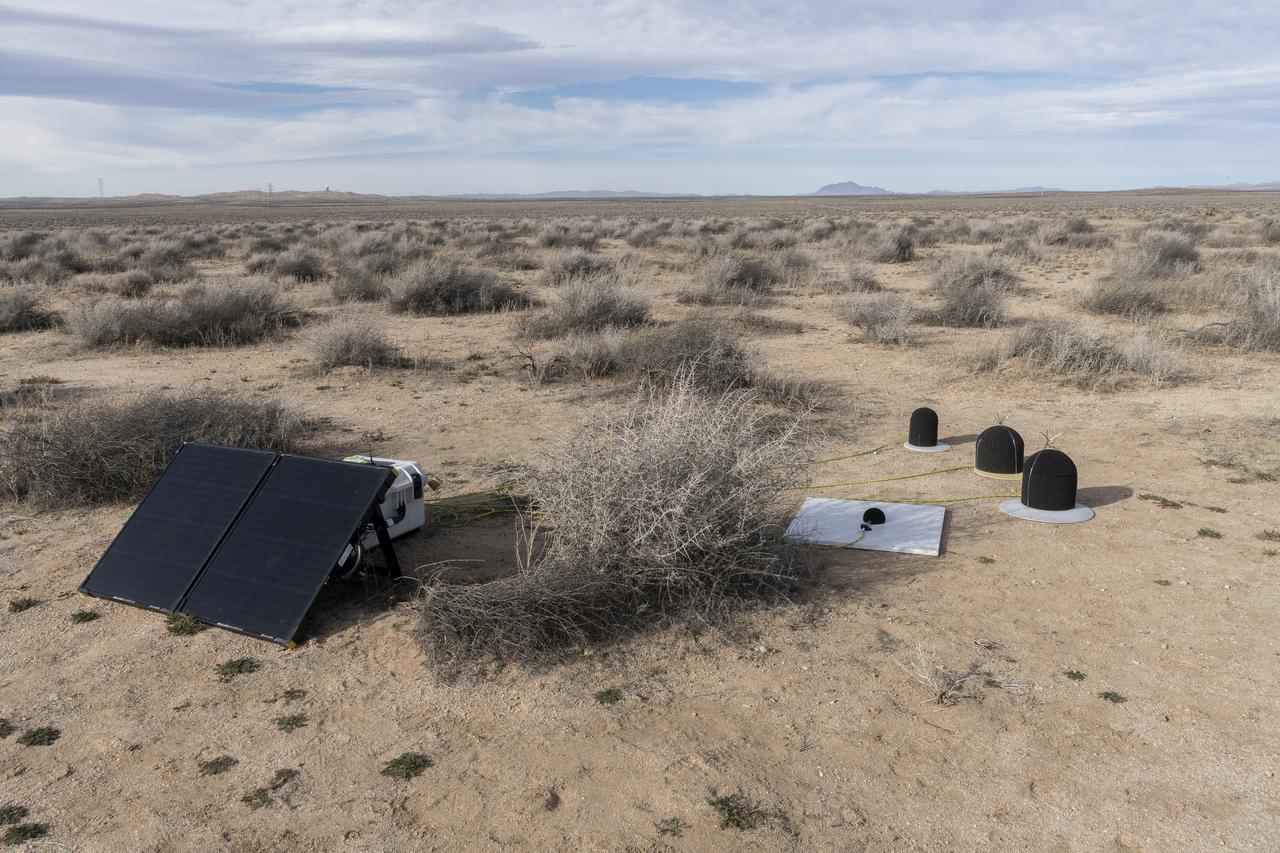

The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. Shown is one of 10 ground recording stations set up along a 30-mile stretch of desert to record sonic booms during the third phase of the of CarpetDIEM, Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems.
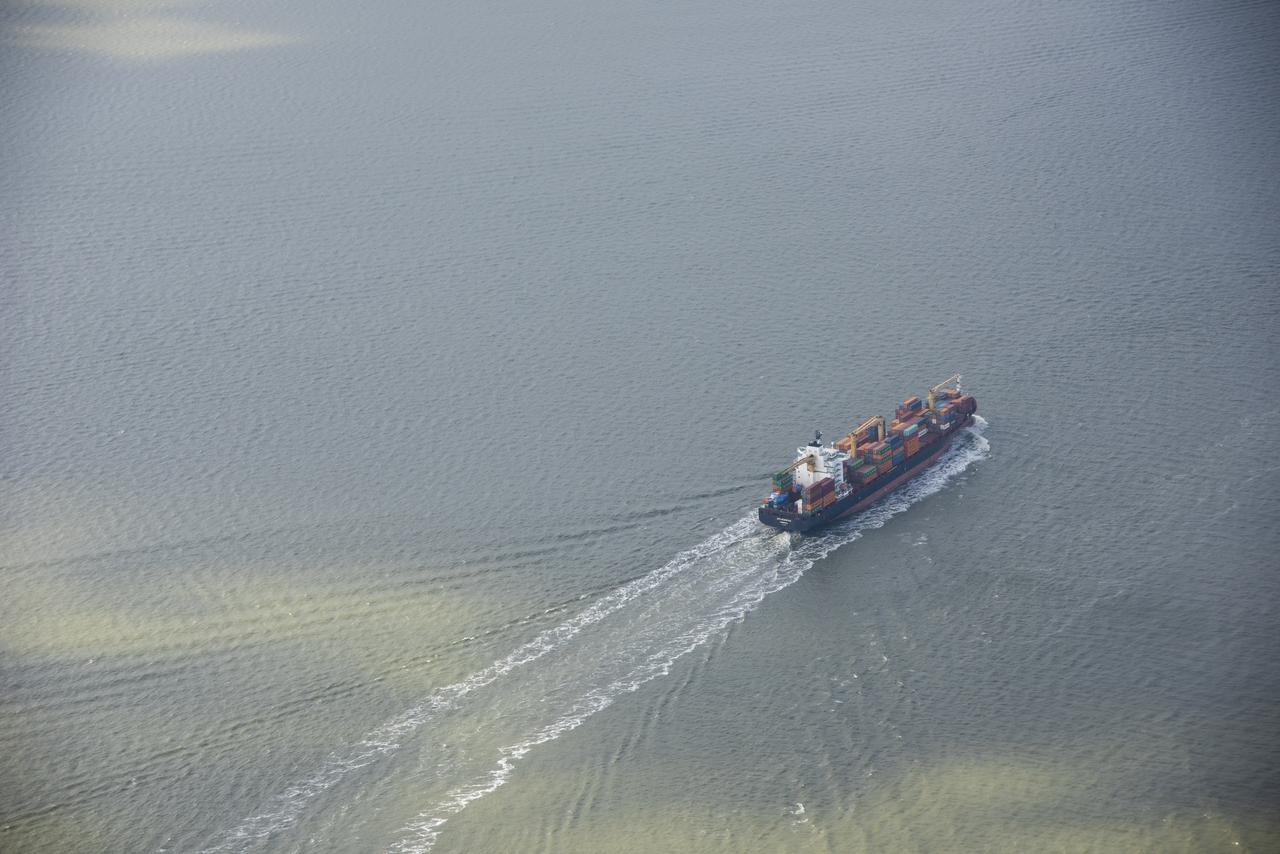

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
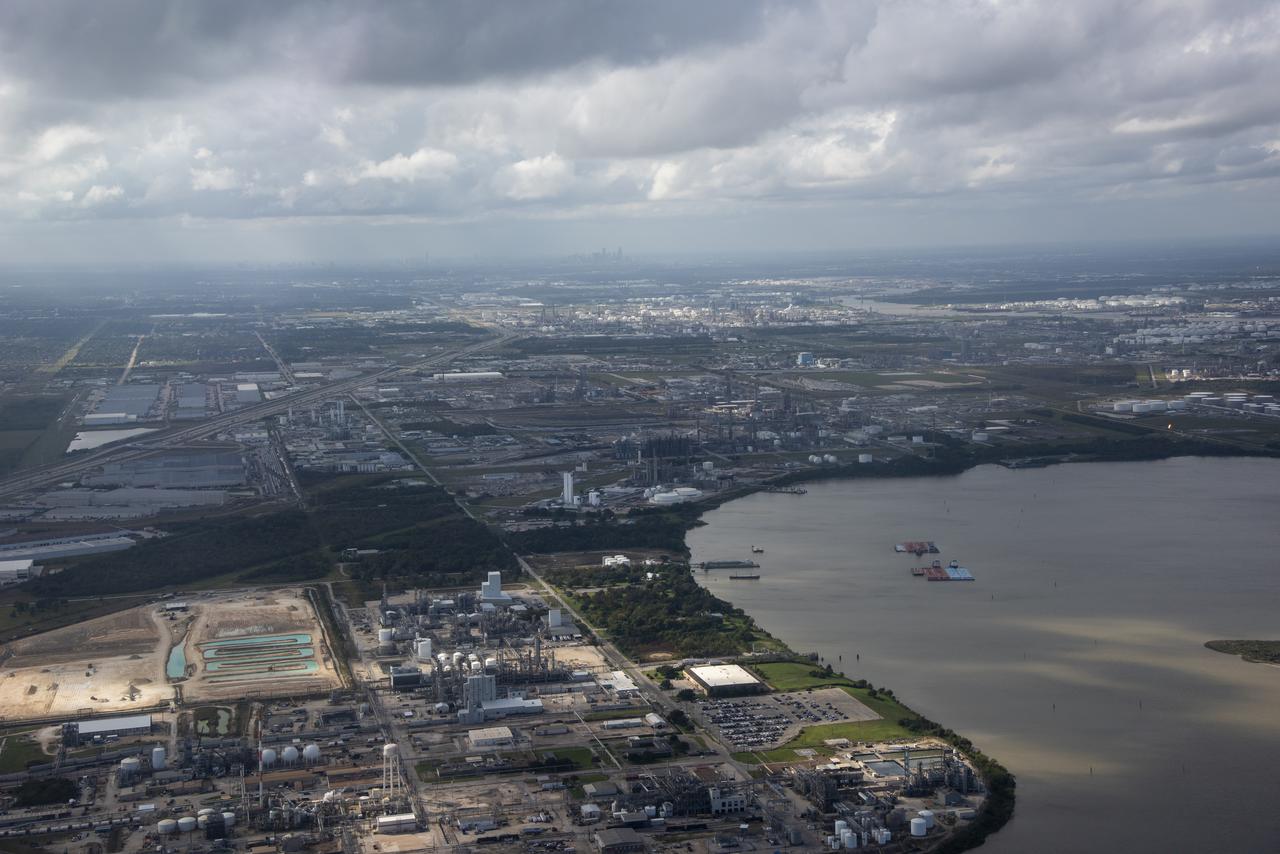

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
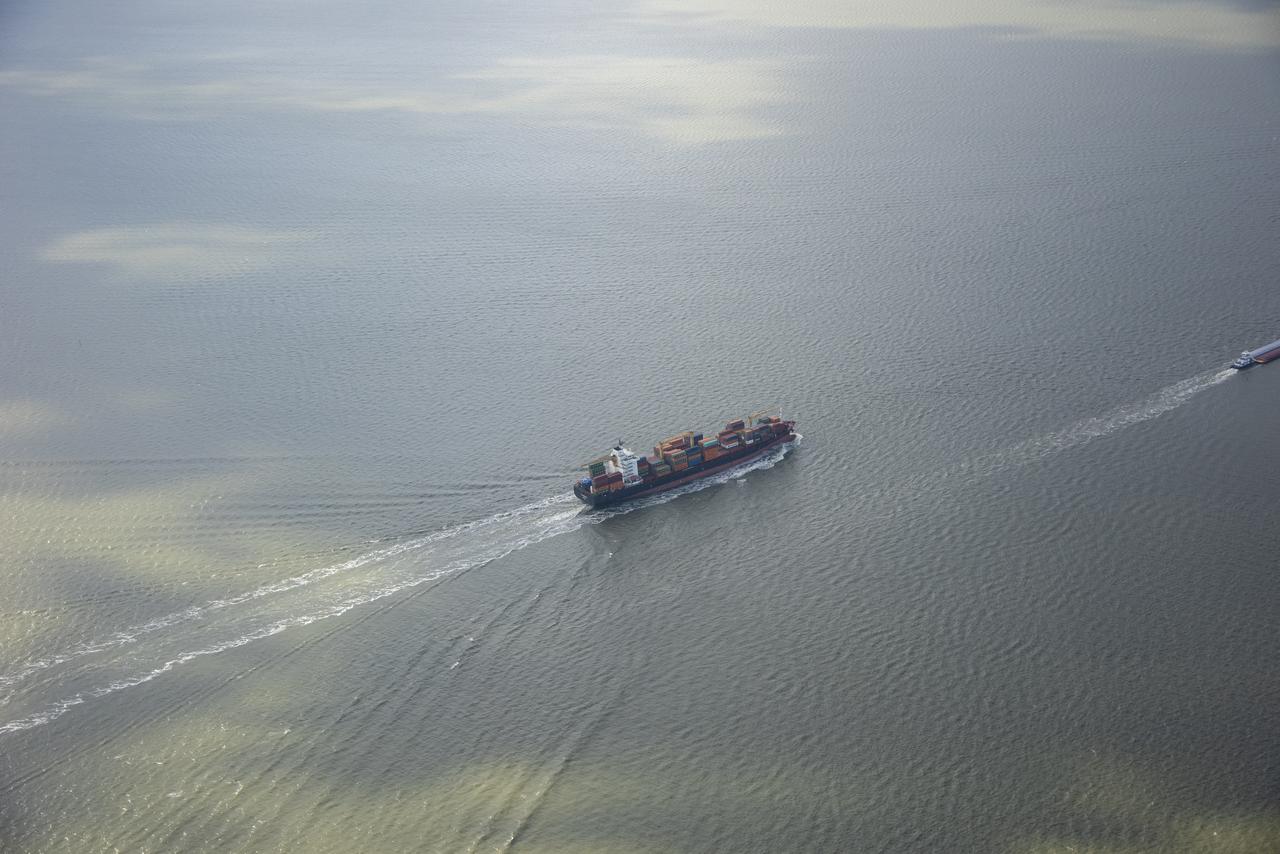

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
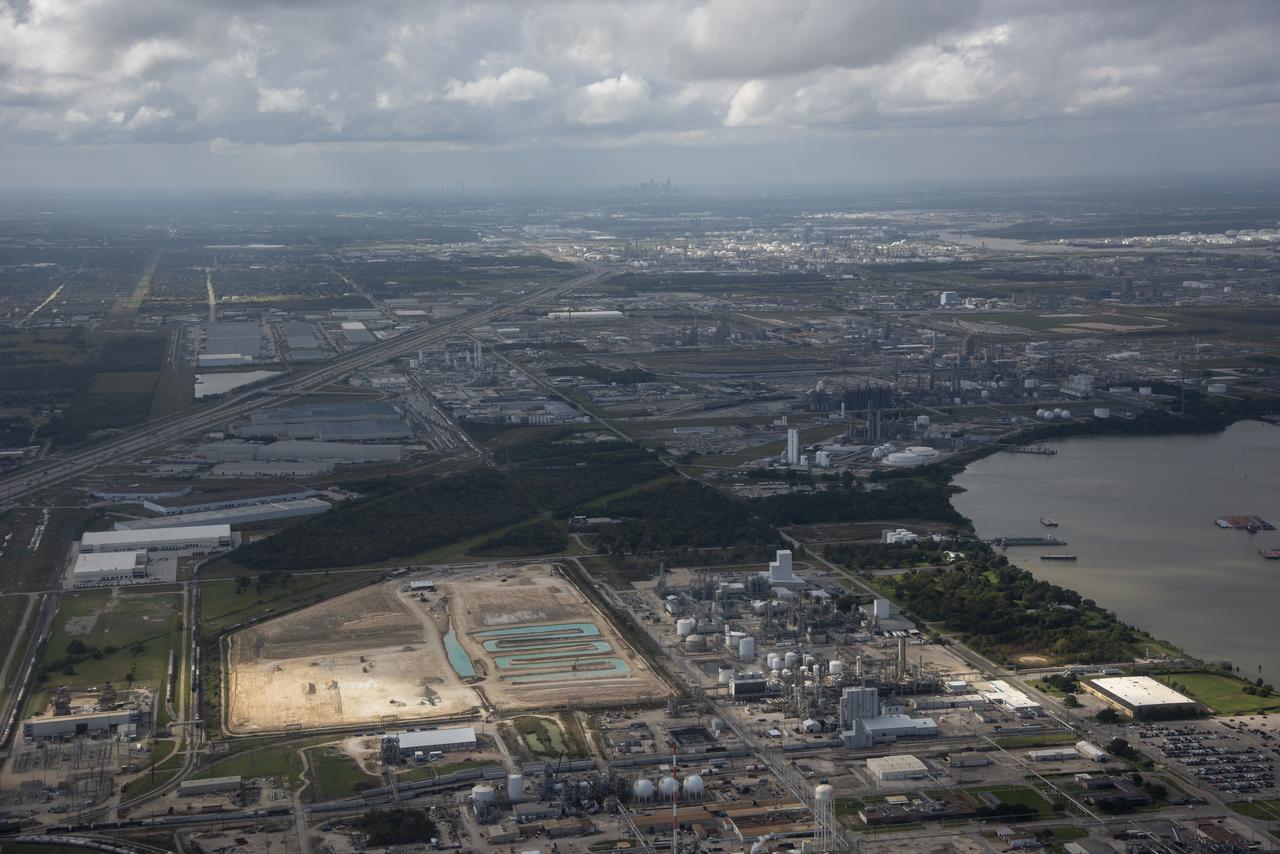

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
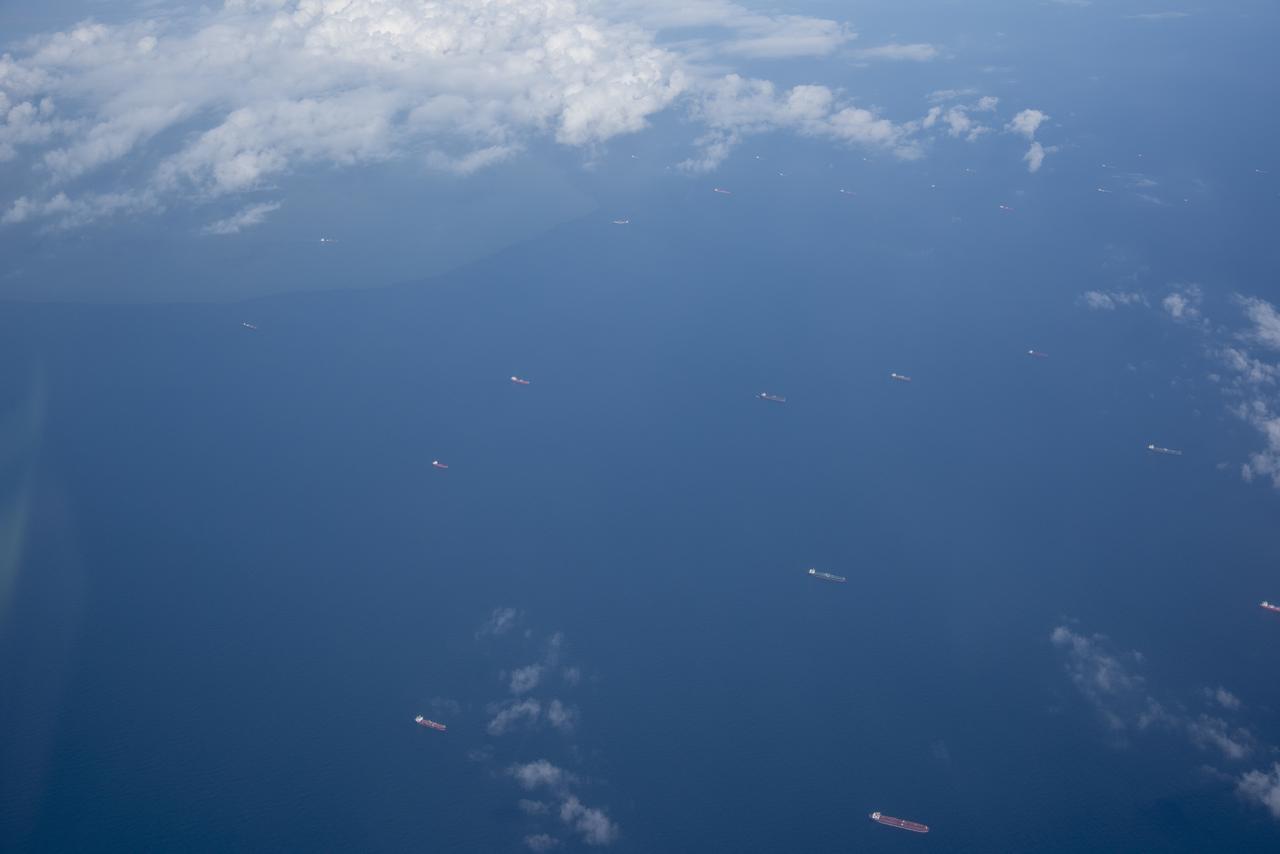

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
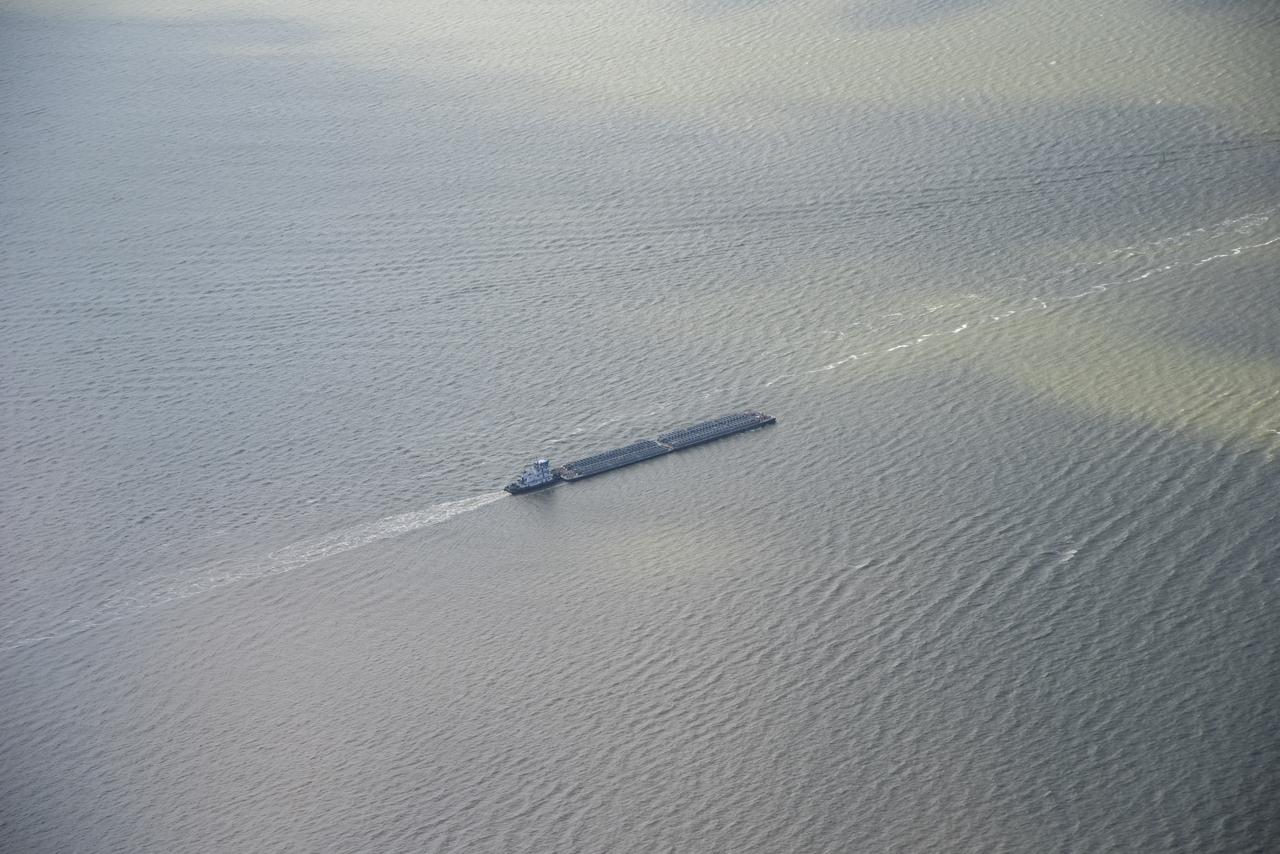

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
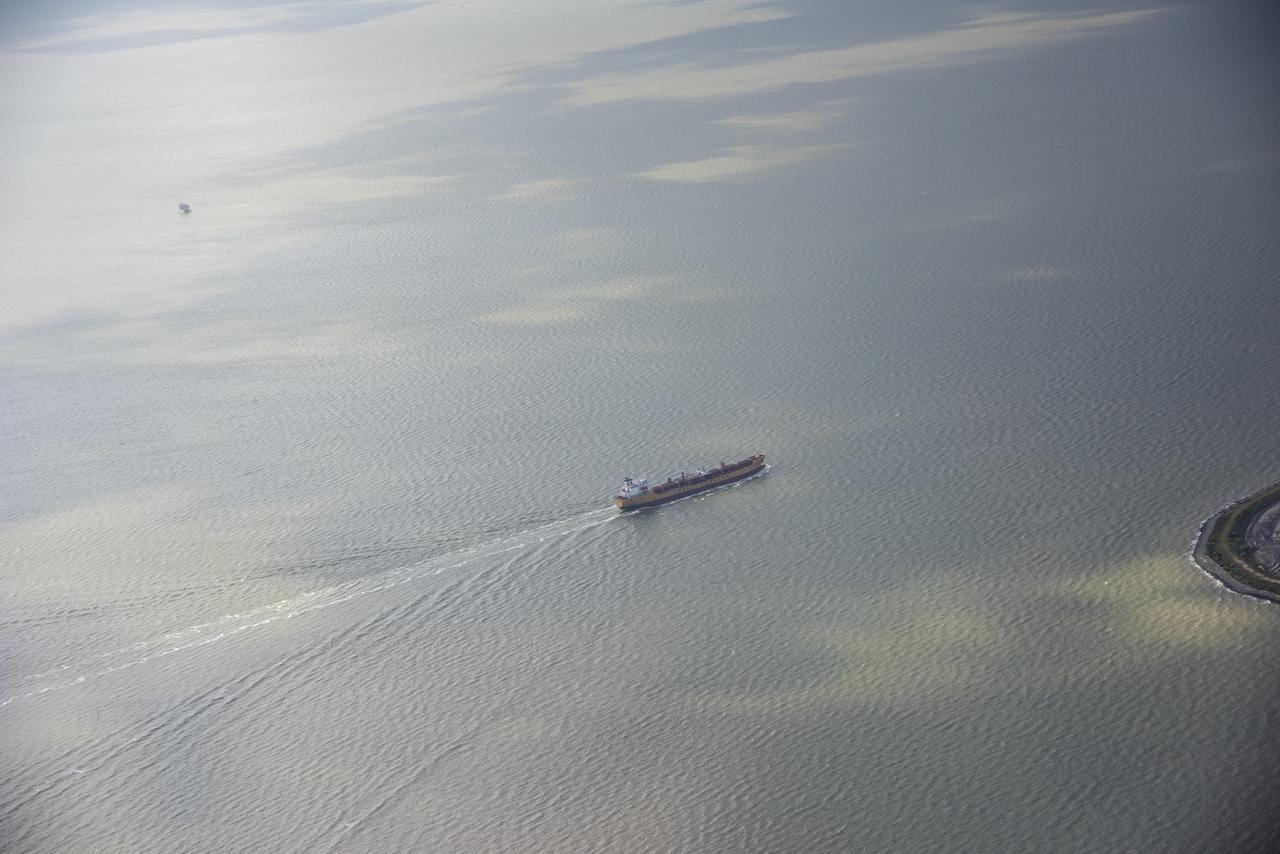

While the quiet supersonic dive maneuver produces a quieter version of the sonic boom in a necessary area, it produces a loud sonic boom out over the ocean. Doing so over the busiest waterway in the country makes it necessary to provide high levels of situational awareness to vessels below, through communications between NASA public affairs officers and the U.S. Coast Guard command center.
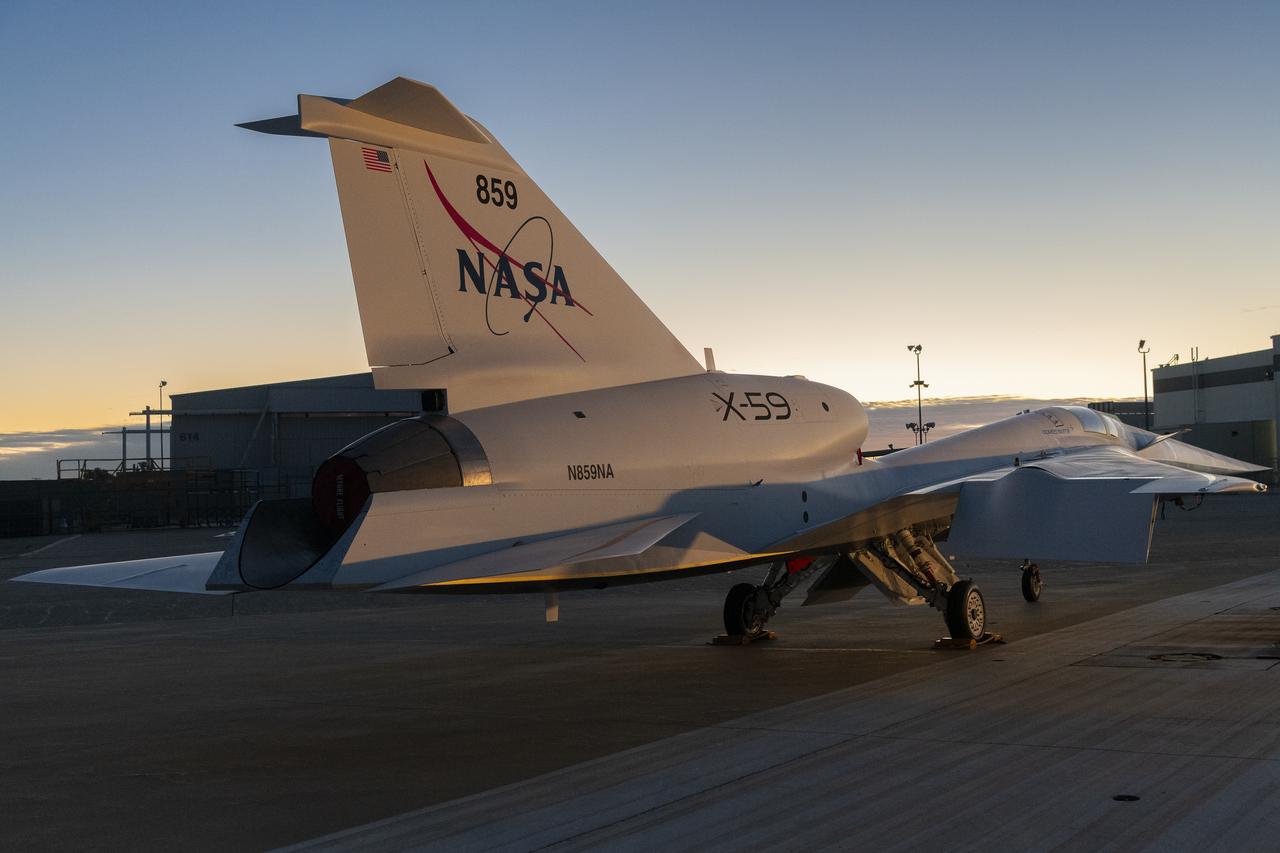

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
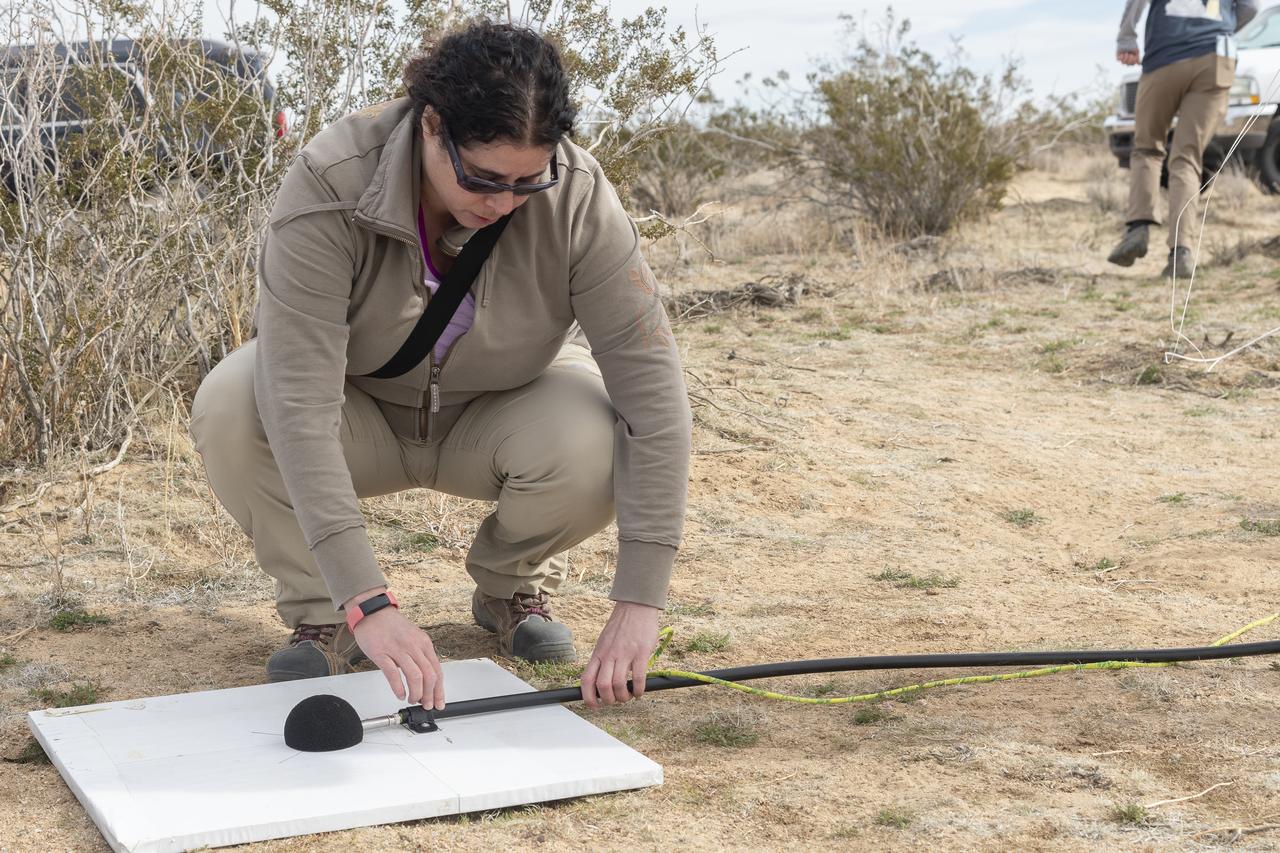

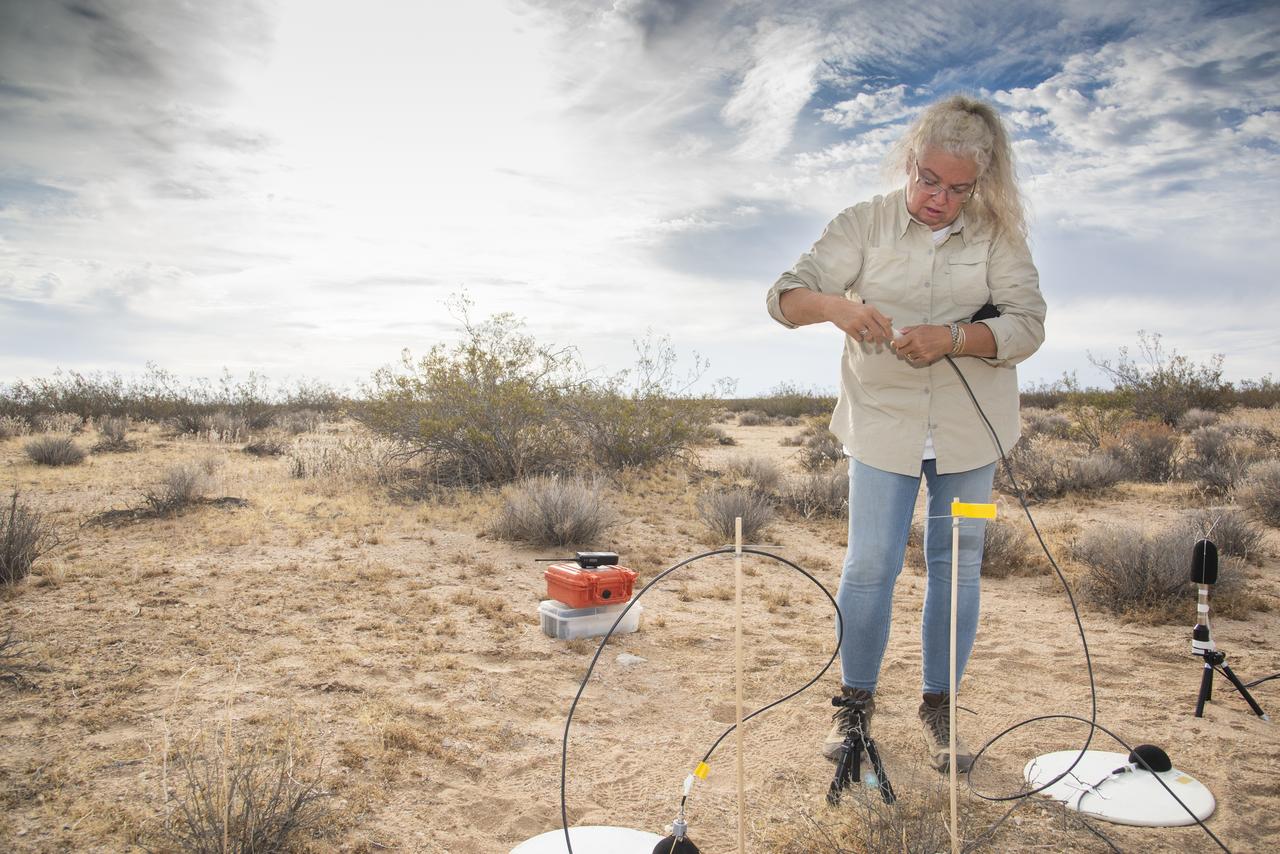
Dr. Alexandra Loubeau, one of the technical co-leads for sonic boom community testing for the Quesst mission, sets out a microphone in the California desert. . The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
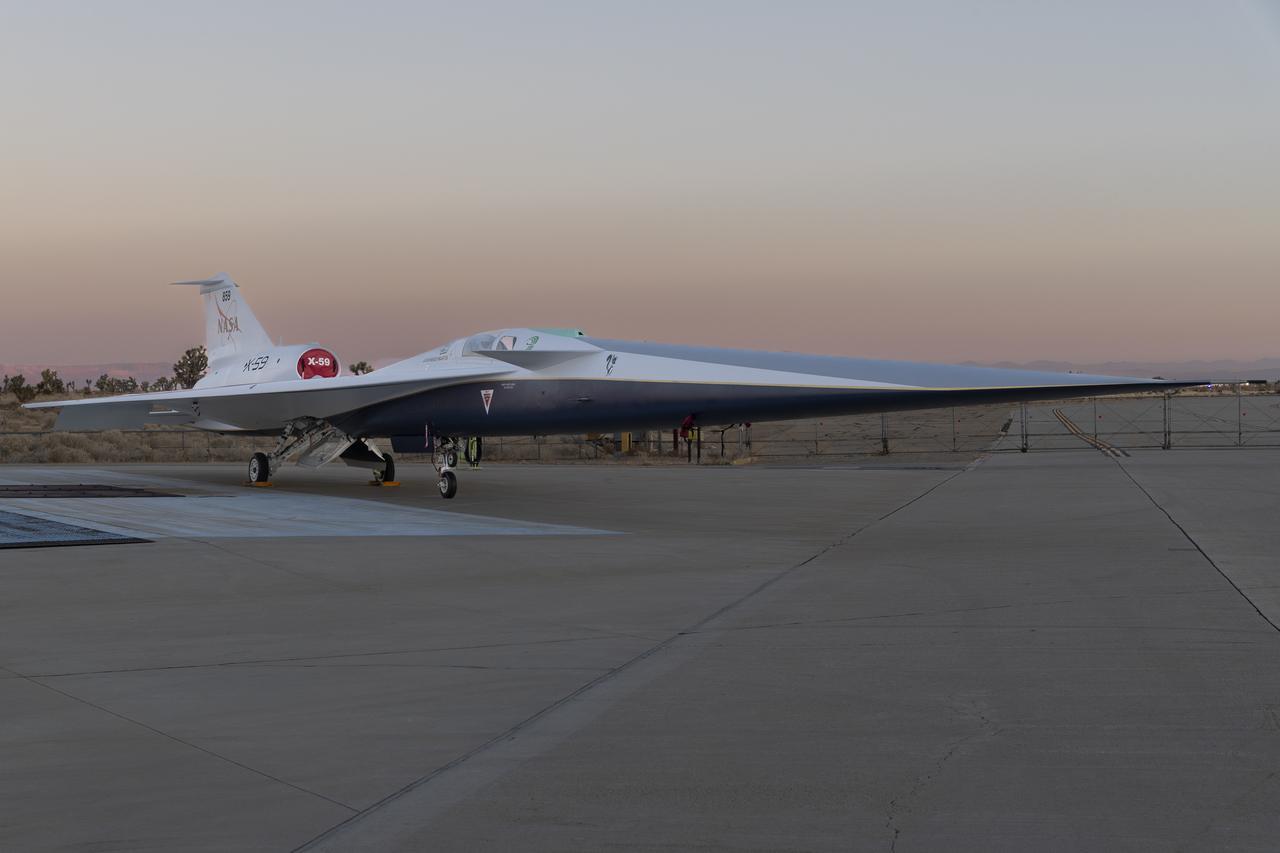

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
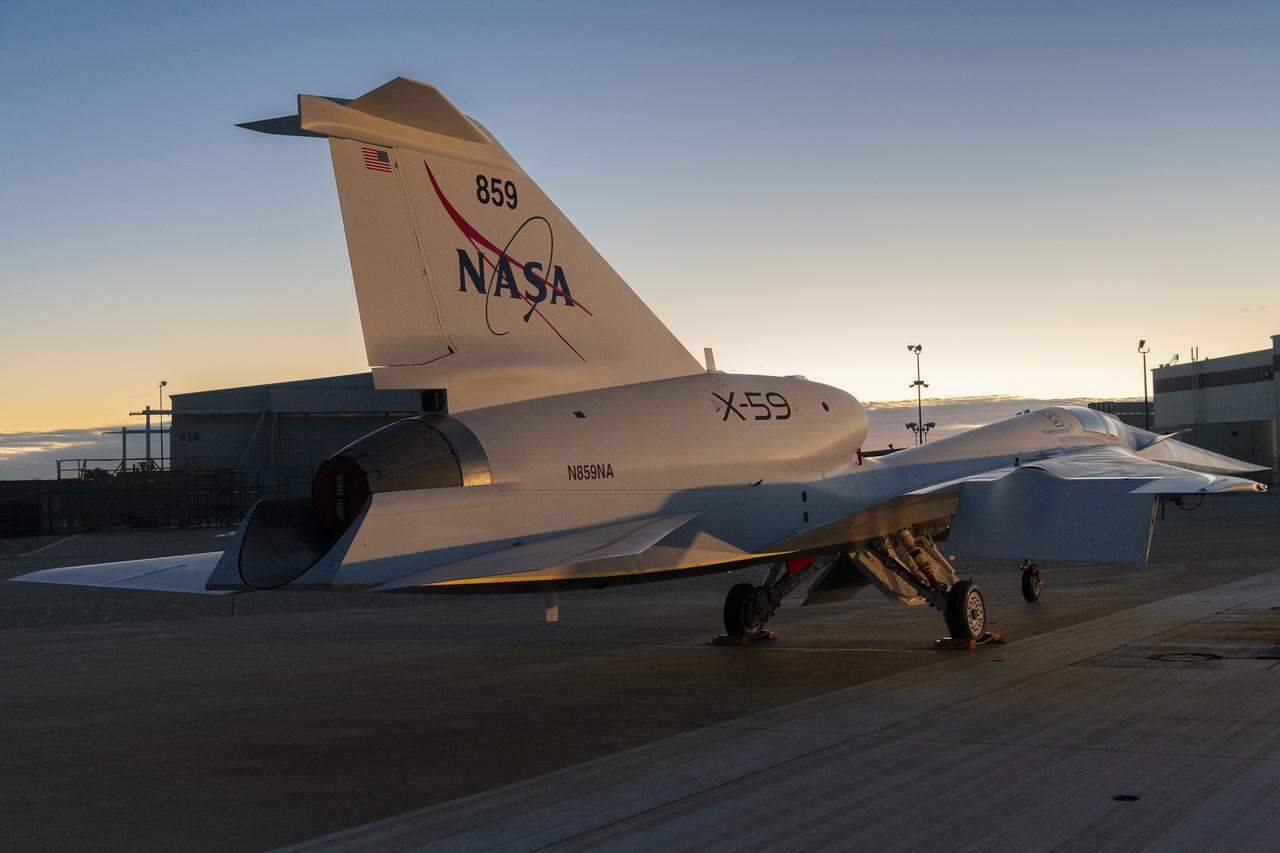

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
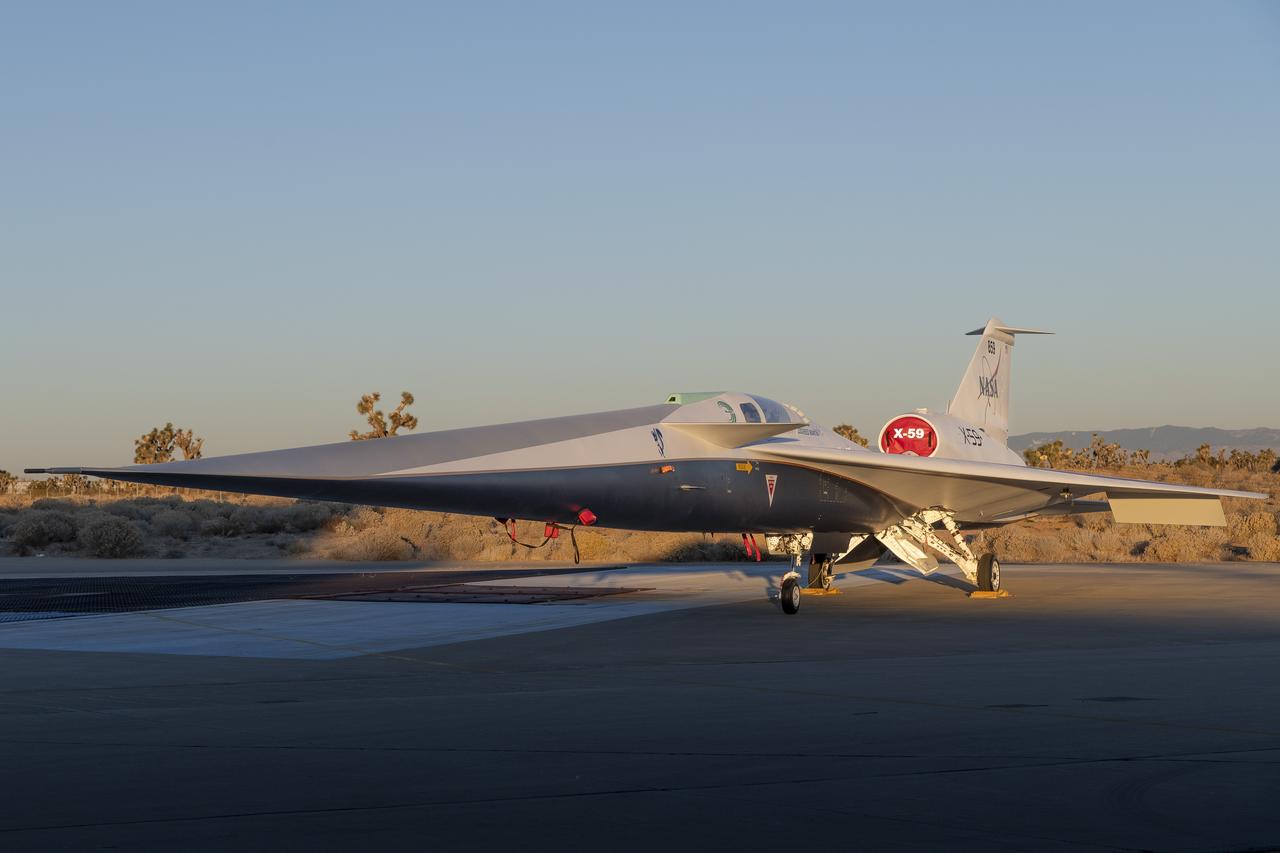

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
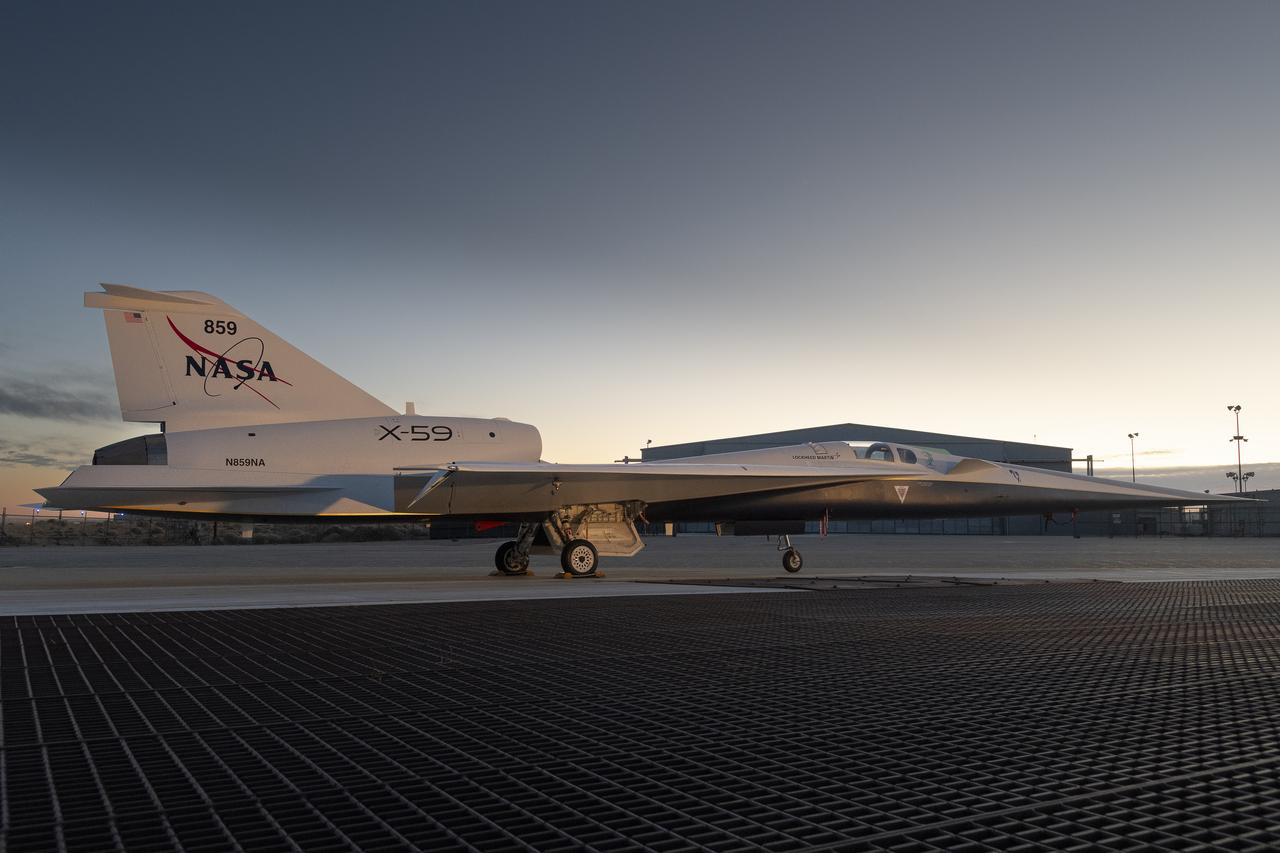

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
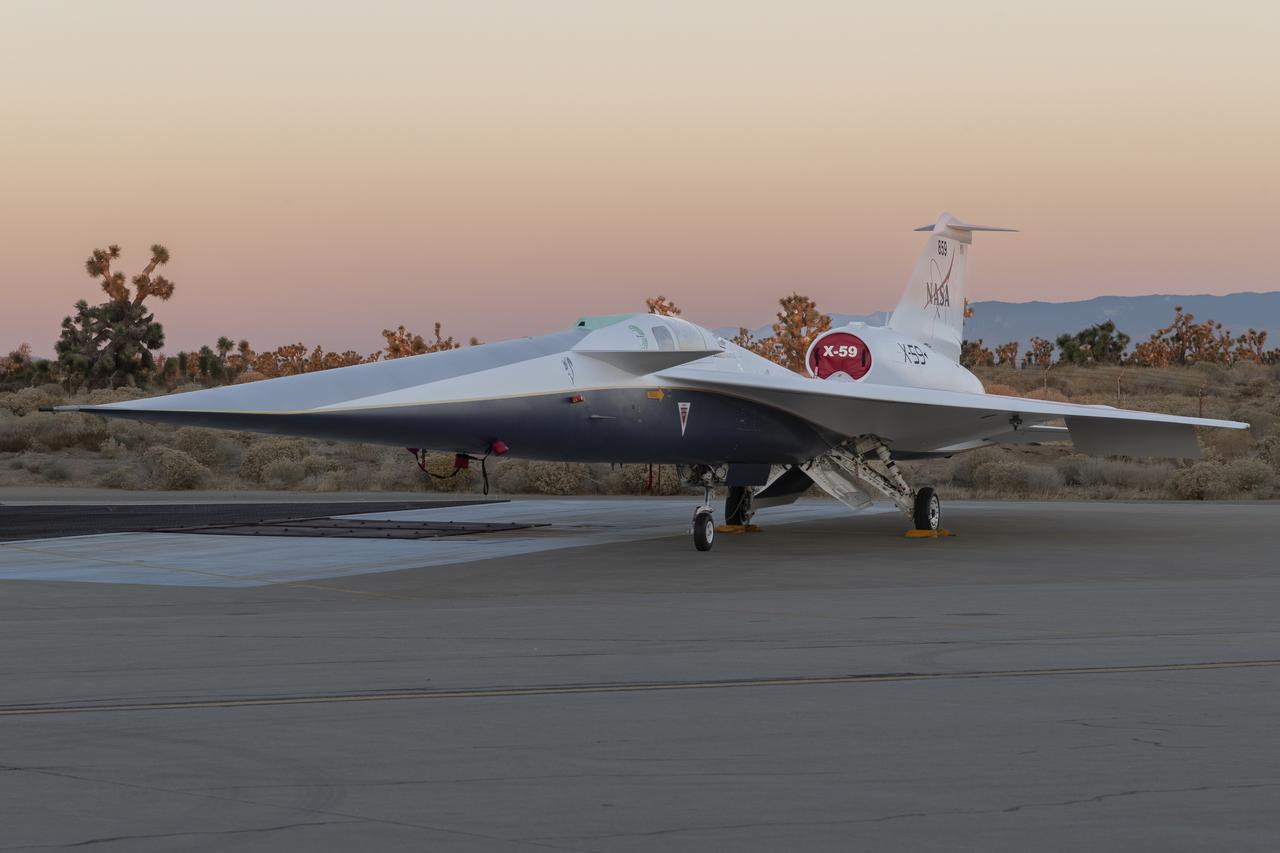

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California during sunrise, shortly after completion of painting. With its unique design, including a 38-foot-long nose, the X-59 was built to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, while reducing the typically loud sonic boom produced by aircraft at such speeds to a quieter sonic “thump”. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.

The X-59 simulator at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, will help pilots prepare for Quesst missions. Quesst is NASA's mission to demonstrate how the X-59 can fly supersonic without generating loud sonic booms and then survey what people hear when it flies overhead.
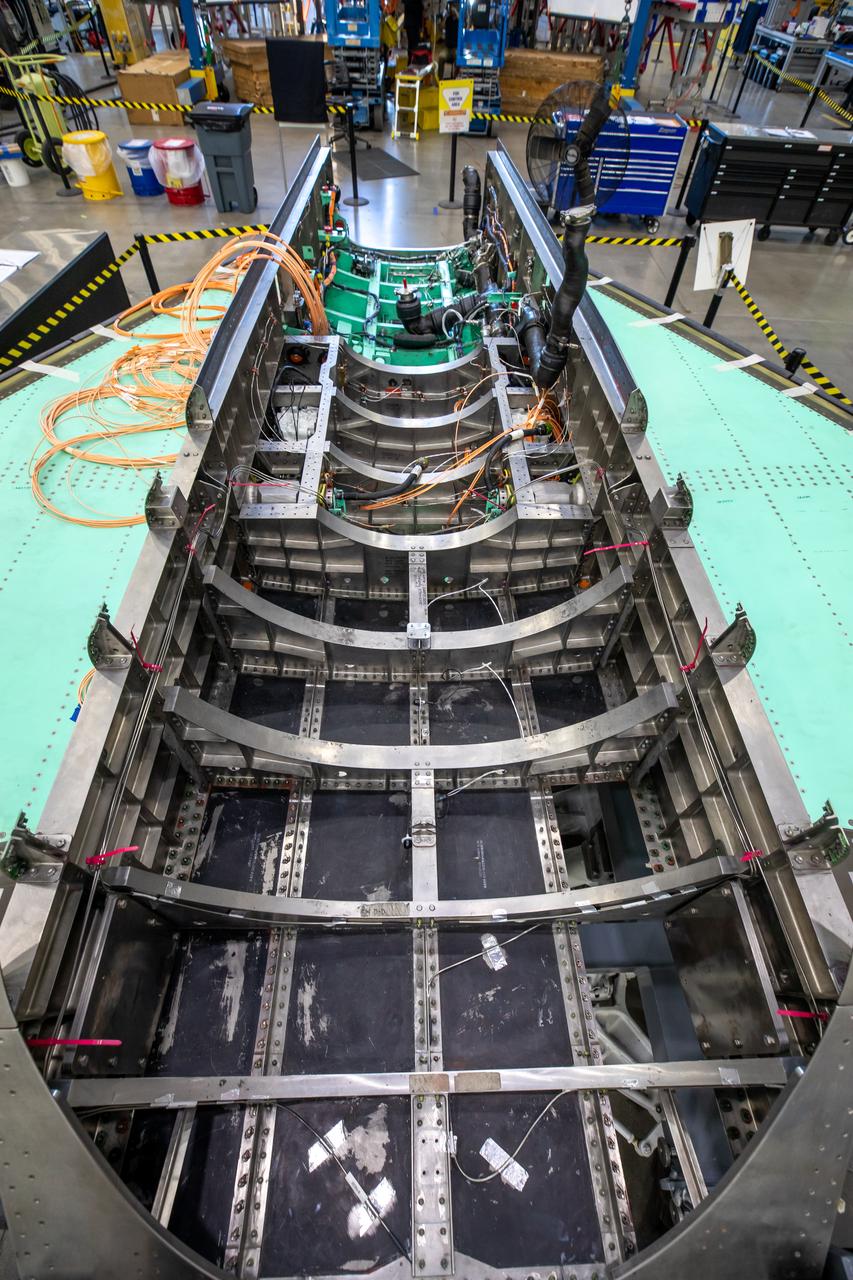
This image shows the X-59 aircraft’s lower empennage structure, or tail section of the plane, that was installed. The stabilators, the outer surfaces also seen in the photo, attach to the lower empennage and are used to help regulate the aircraft pitch which controls the up and down movement of the motion of the plane. The 13-foot engine will pack 22,000 pounds of propulsion and energy and power the X-plane to its planned cruising speed of Mach 1.4. Once complete, the X-59 aircraft will demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump and help enable commercial supersonic air travel over land. This aircraft is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission.
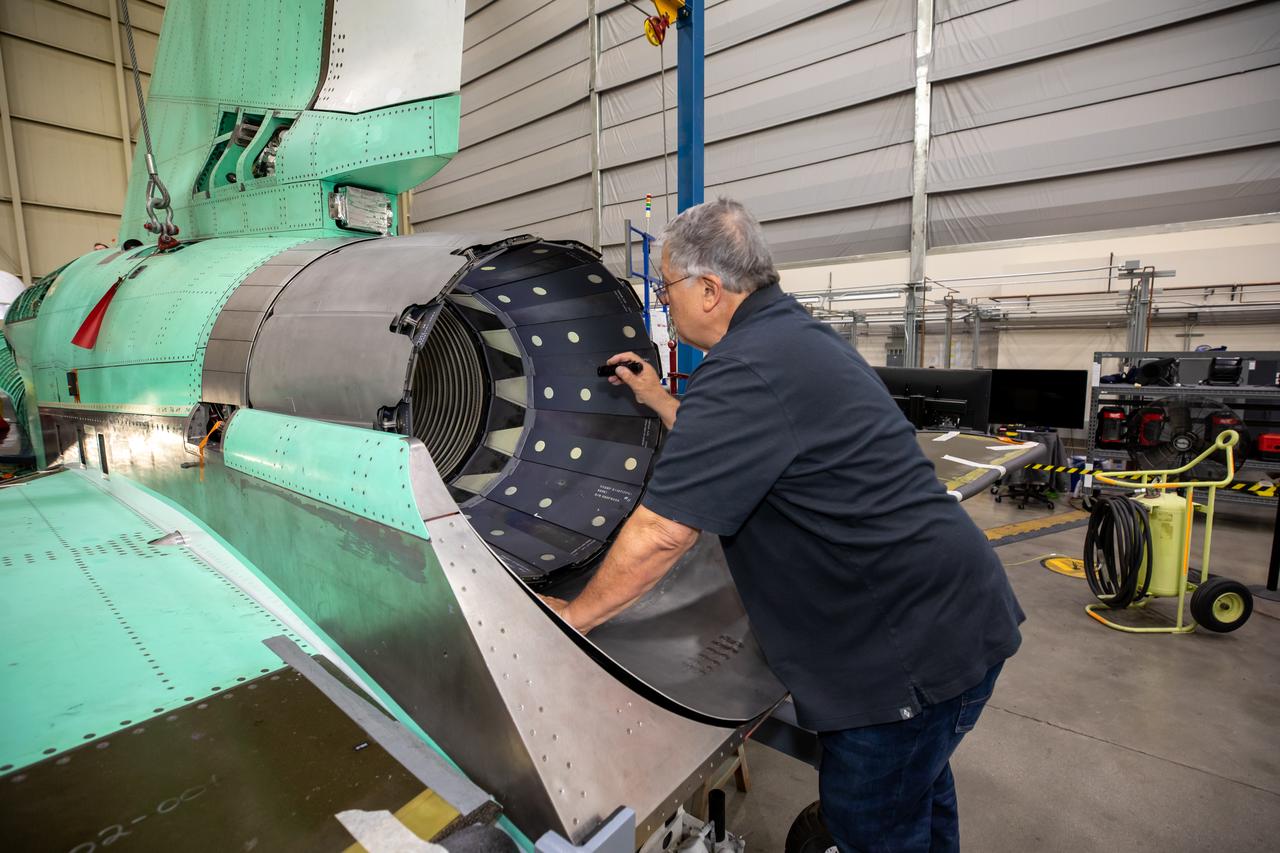

A quality inspector inspects the GE F-414 engine nozzle after installation at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
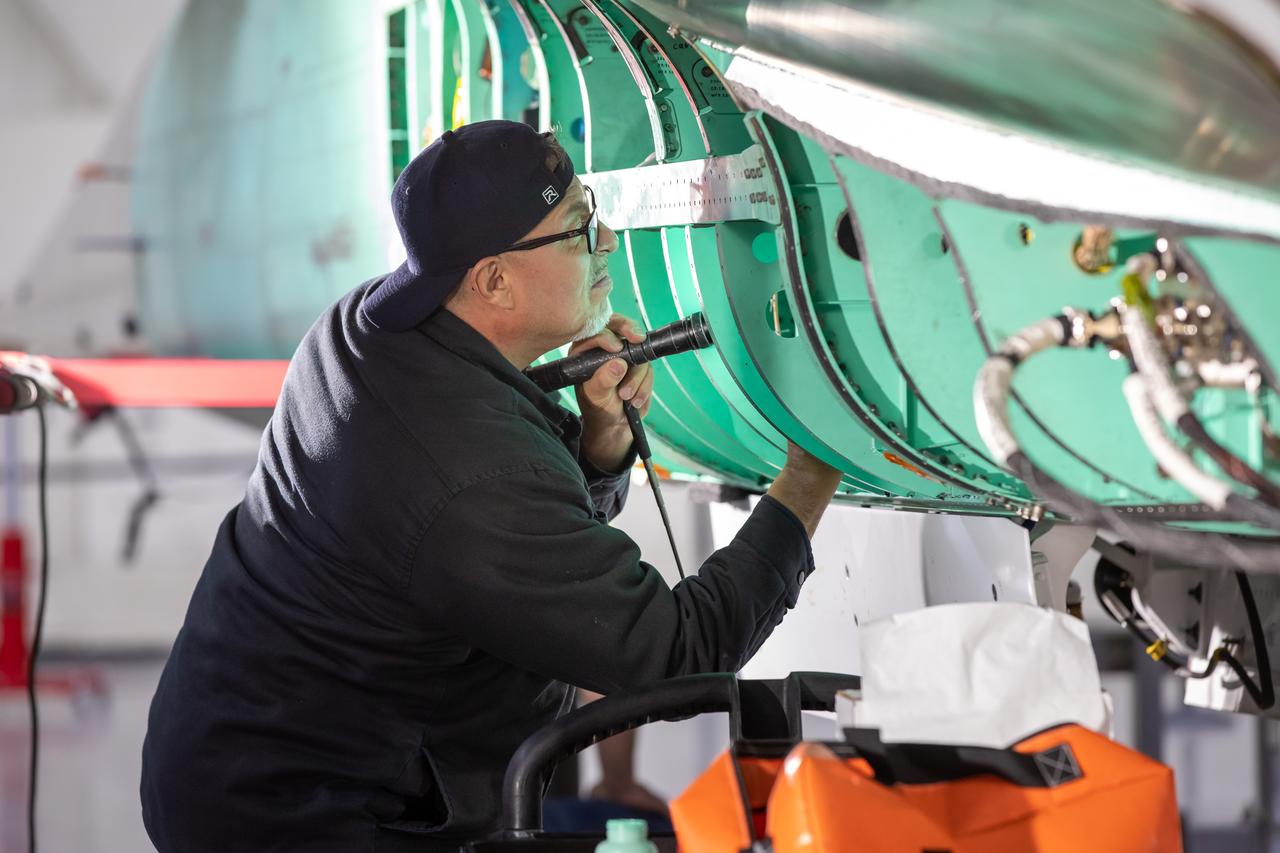

A quality inspector checks NASA’s X-59 aircraft during the construction phase. The X-59 was built in Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land.
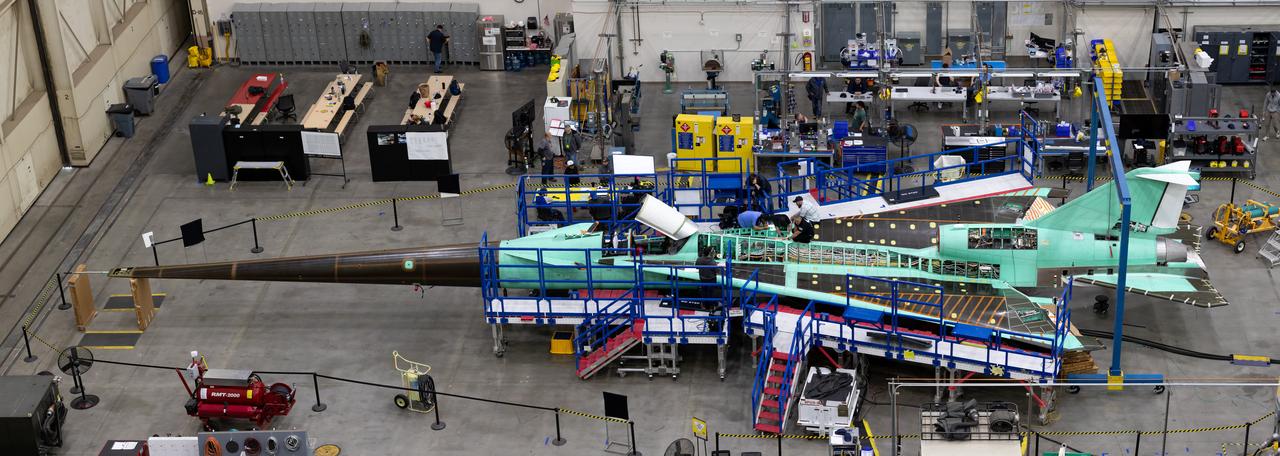

An overhead view of the X-59 during assembly in spring 2023. Assembly took place at Lockheed Martin’s Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. Once complete, the X-59 is designed to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom. The Quesst mission could help change the rules for commercial supersonic air travel over land.
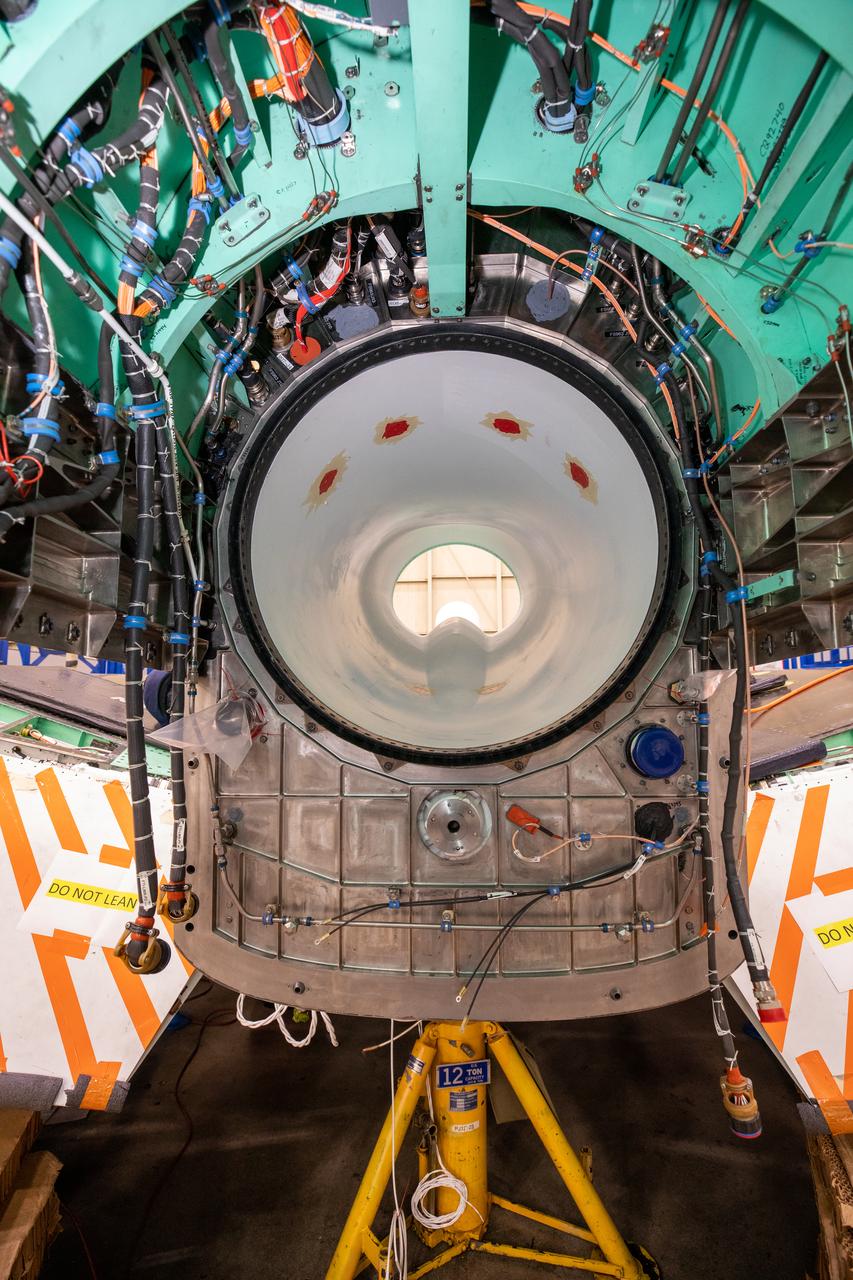

This image shows the X-59’s engine inlet from the aft view, which is the rear of the airplane, looking forward. Once the aircraft and ground testing are complete, the X-59 will undergo flight testing, which will demonstrate the plane’s ability to fly supersonic - faster than the speed of sound - while reducing the loud sonic boom. This could enable commercial supersonic air travel over land again.
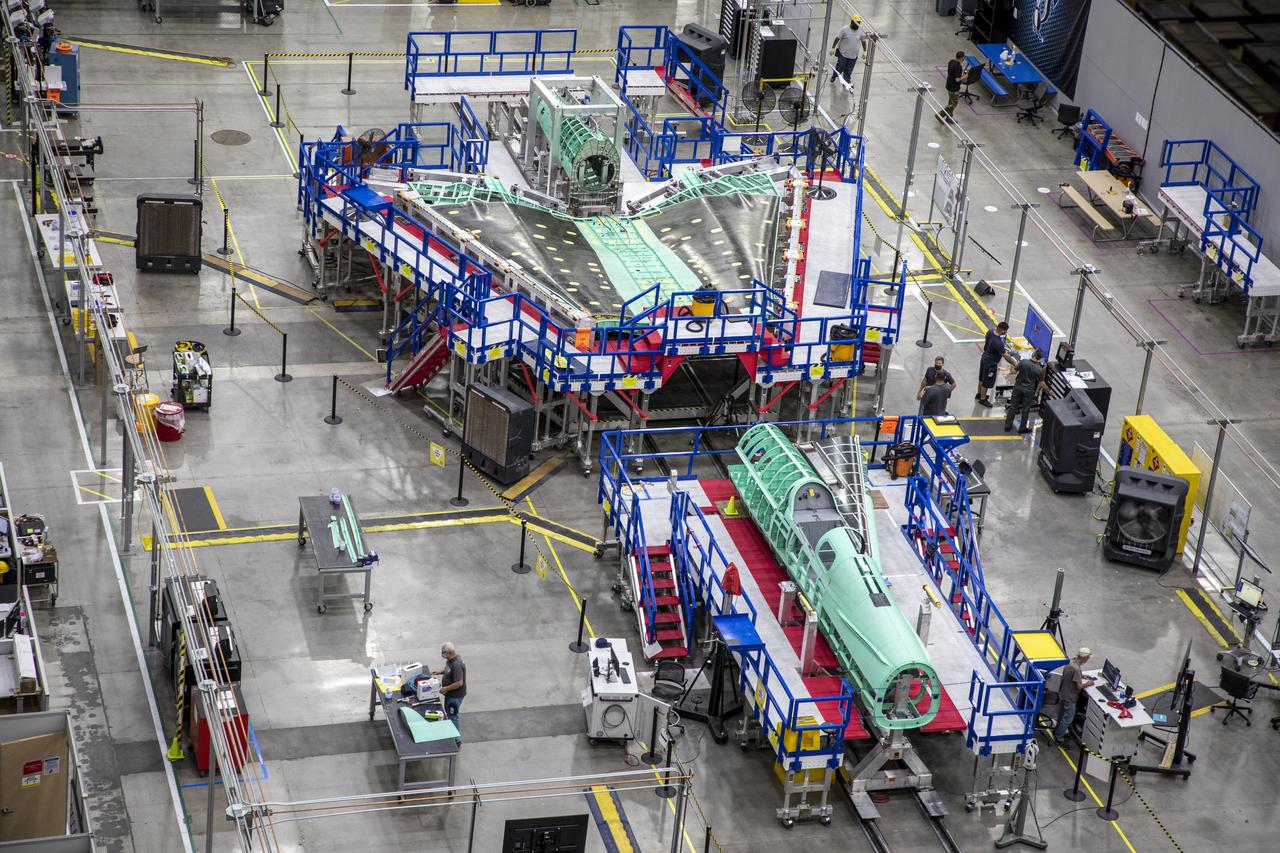

This overhead shot of the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft shows the assembly progress of the vehicle during Spring 2021. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599

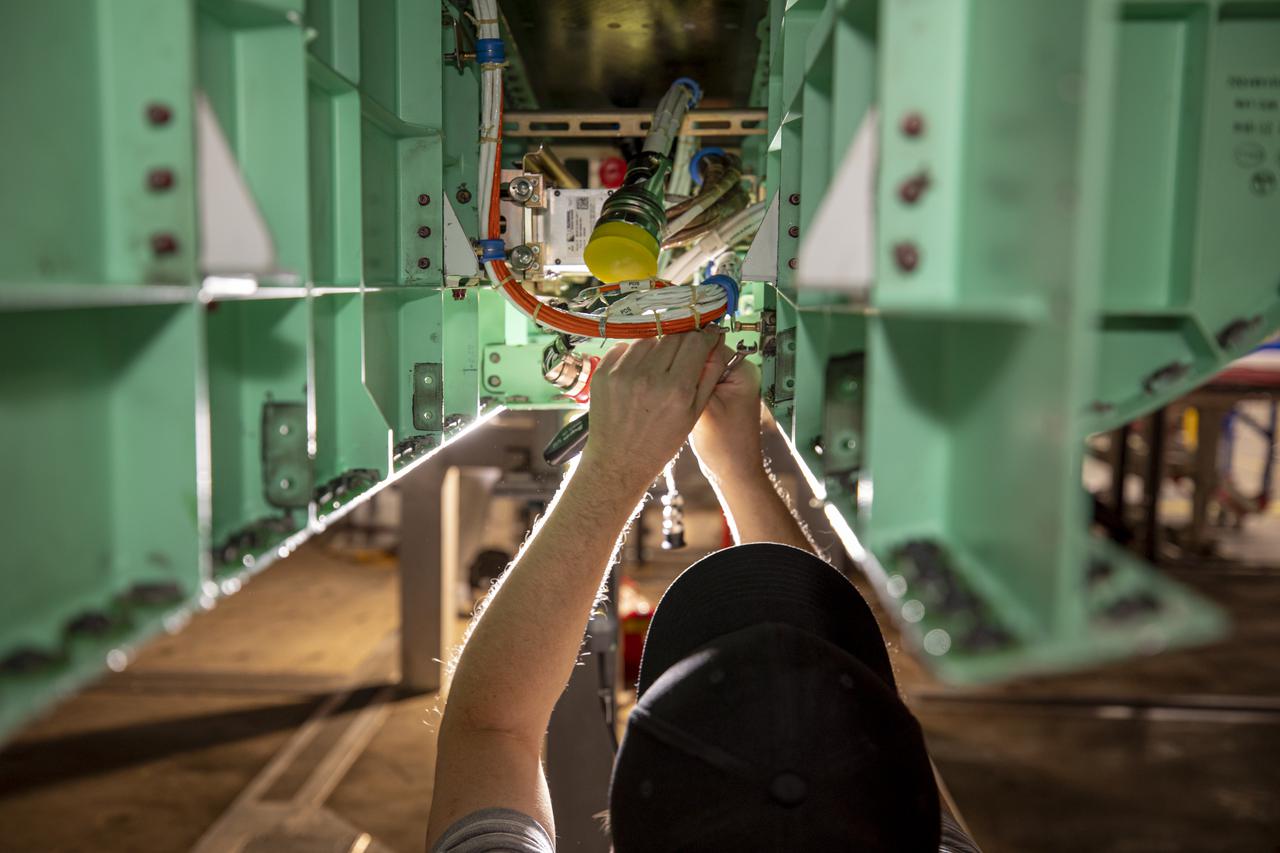
Technicians preform some installation work in the mid-bay on the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 450 Mid Bay - Encoders Date: 4/28/2021

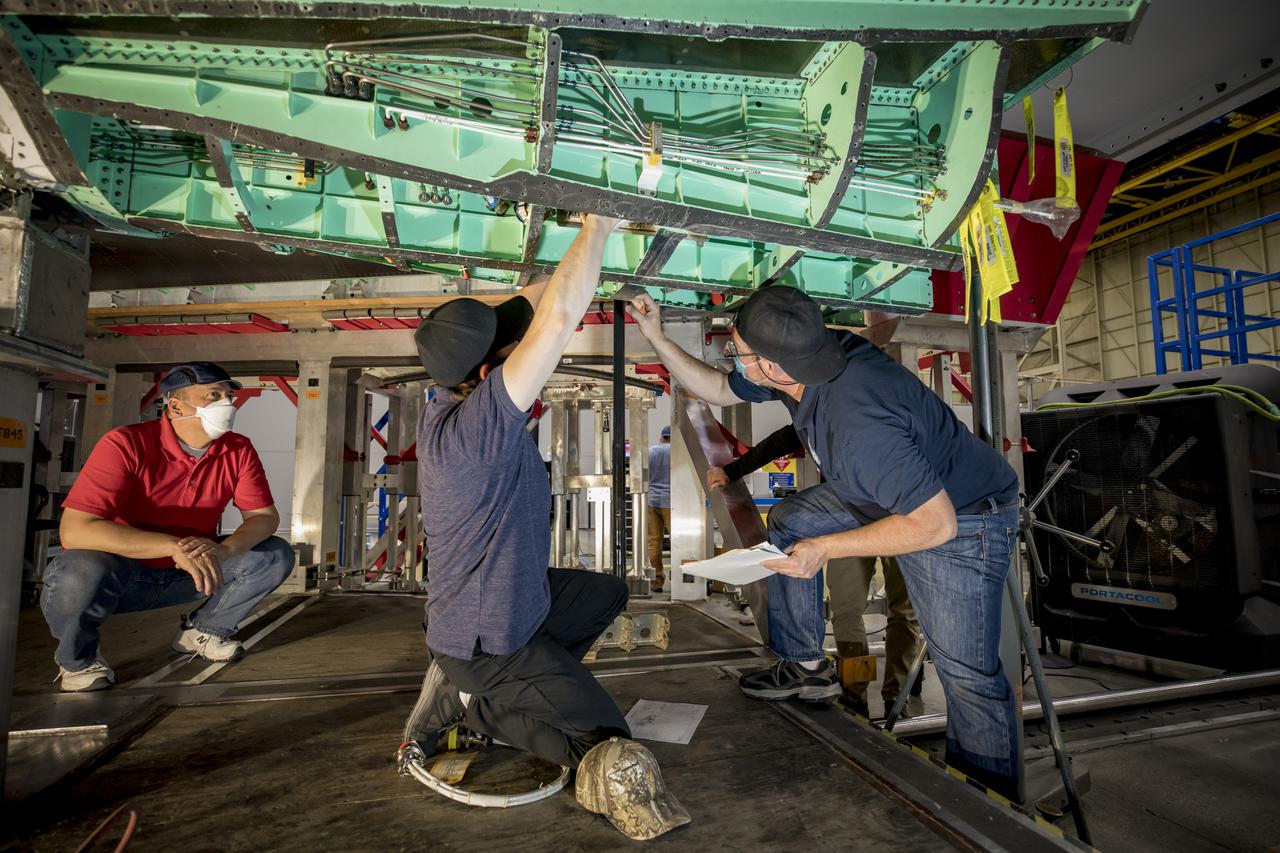
A technician is shown working on the underside of the X-59. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 450 Mid Bay - PDS Fit Check Date: 5/03/2021
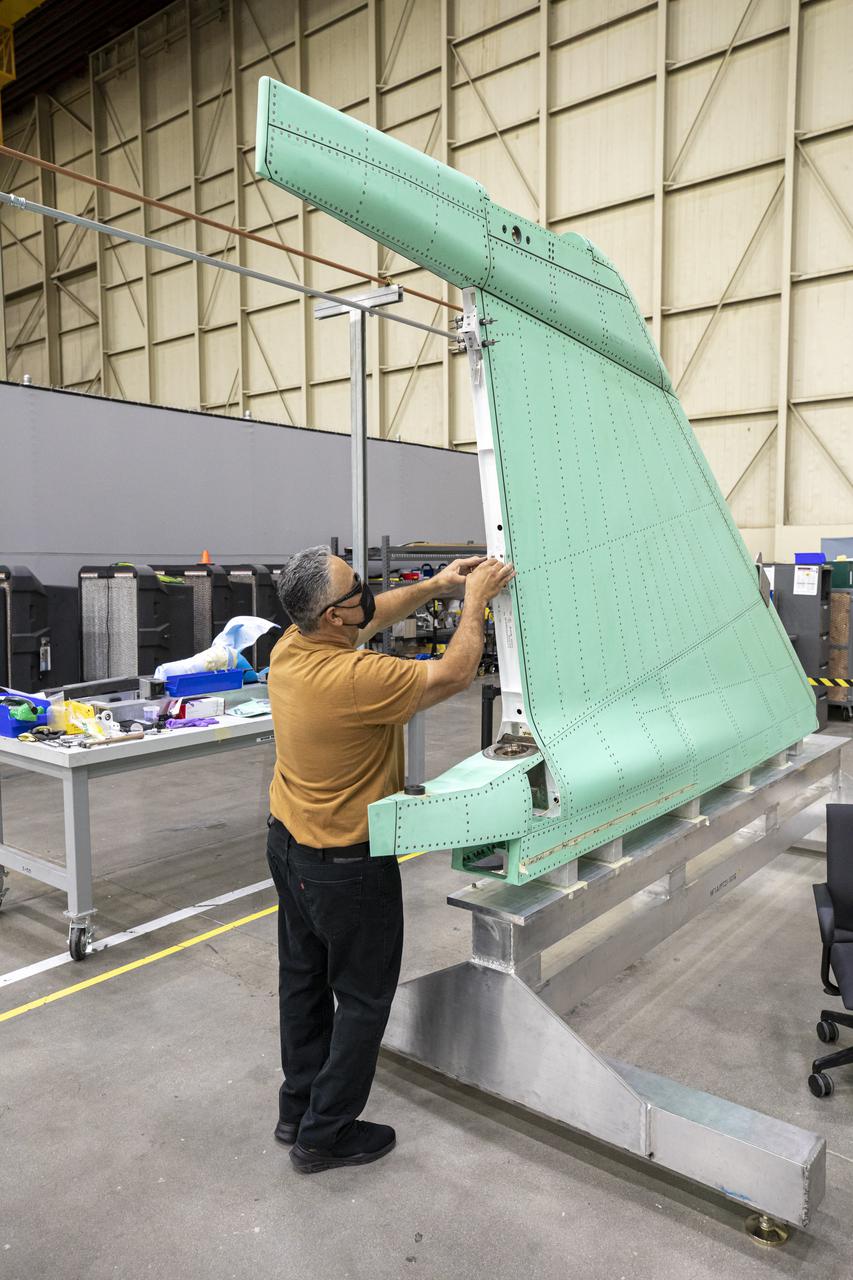

A technician is shown working on the X-59 vertical tail prior to installation at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The aircraft will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail, Landing Gear Bay Doors Date: 4/28/2021

Juliet Page, a physical scientist with the Volpe National Transportation Systems Center, calibrates a microphone station during the CarpetDIEM flight series. The array featured high-fidelity microphones arranged in several configurations, giving researchers the ability to obtain accurate sound data and assess the loudness of the sonic booms, just as they will measure the quiet sonic thumps from the X-59.
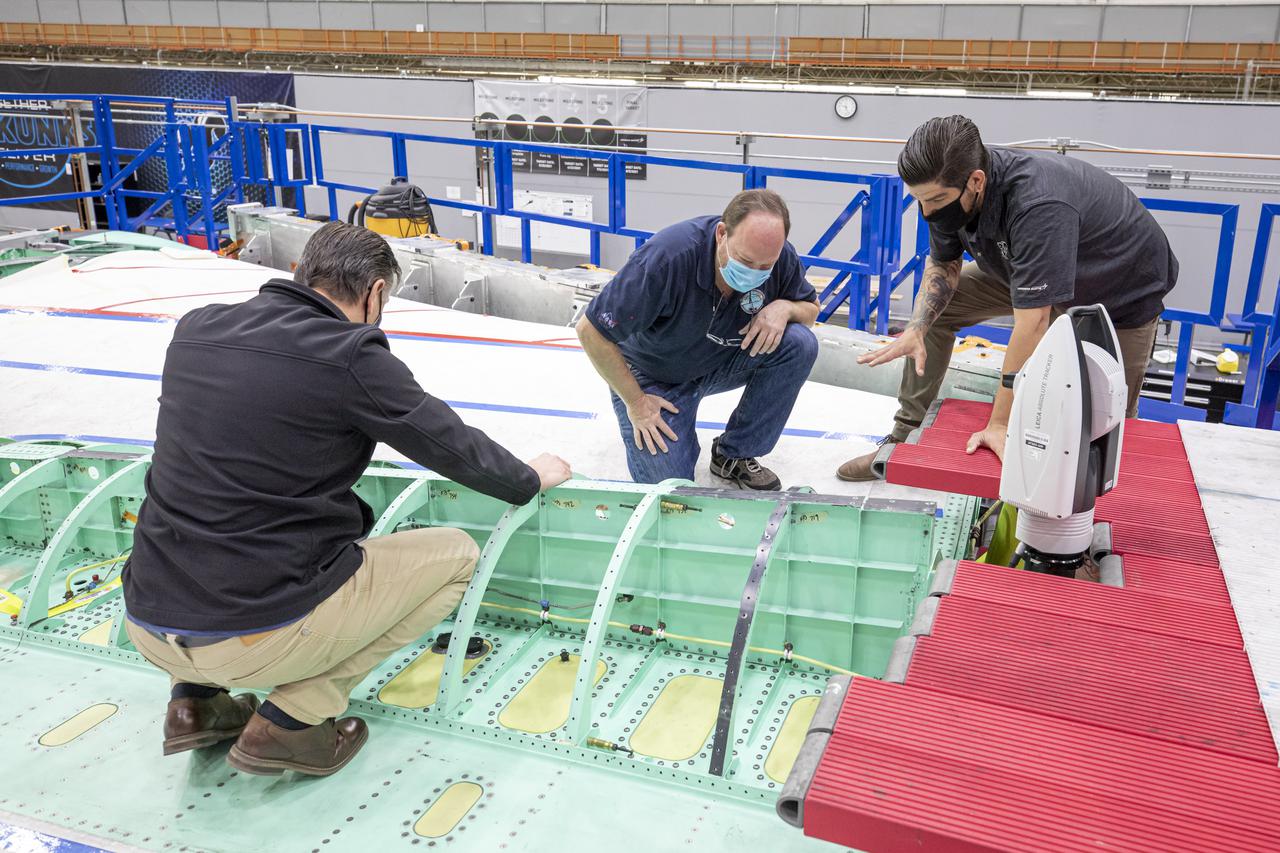

Technicians work with a laser measuring system on the X-59 spine. The X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology, or QueSST, aircraft is under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, and will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 400 Main Wing Assembly, SEG 430 Spine, SEG 500 Empennage Date: 4/28/2021
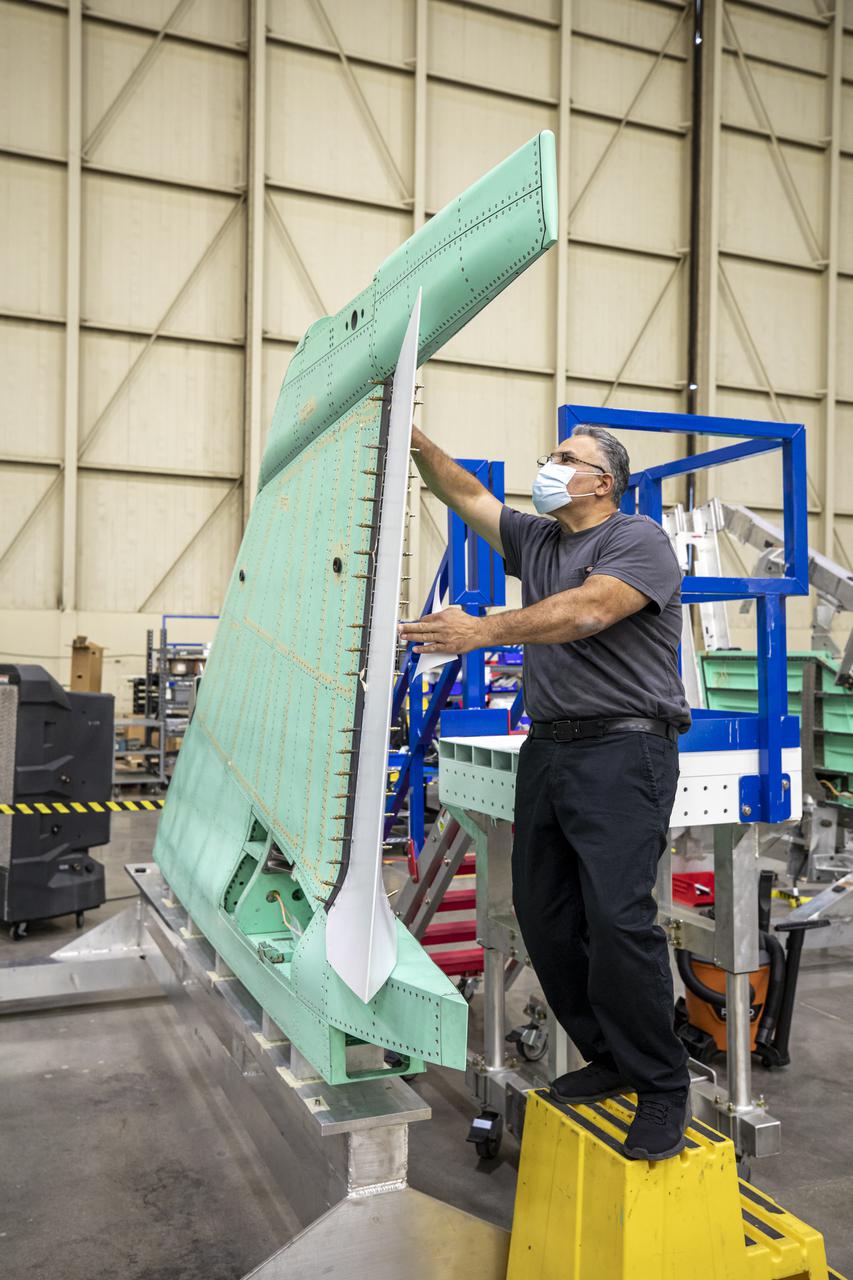

A technician is shown working on the X-59 vertical tail prior to installation. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 530 Vertical Tail - Rudder Installed Date: 5/12/2021

NASA’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft successfully completed electromagnetic interference (EMI) testing at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. During EMI tests, the team examined each of the X-59’s internal electronic systems, ensuring they worked with one another without interference. The X-59 is designed to fly faster than the speed of sound while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quieter sonic thump.
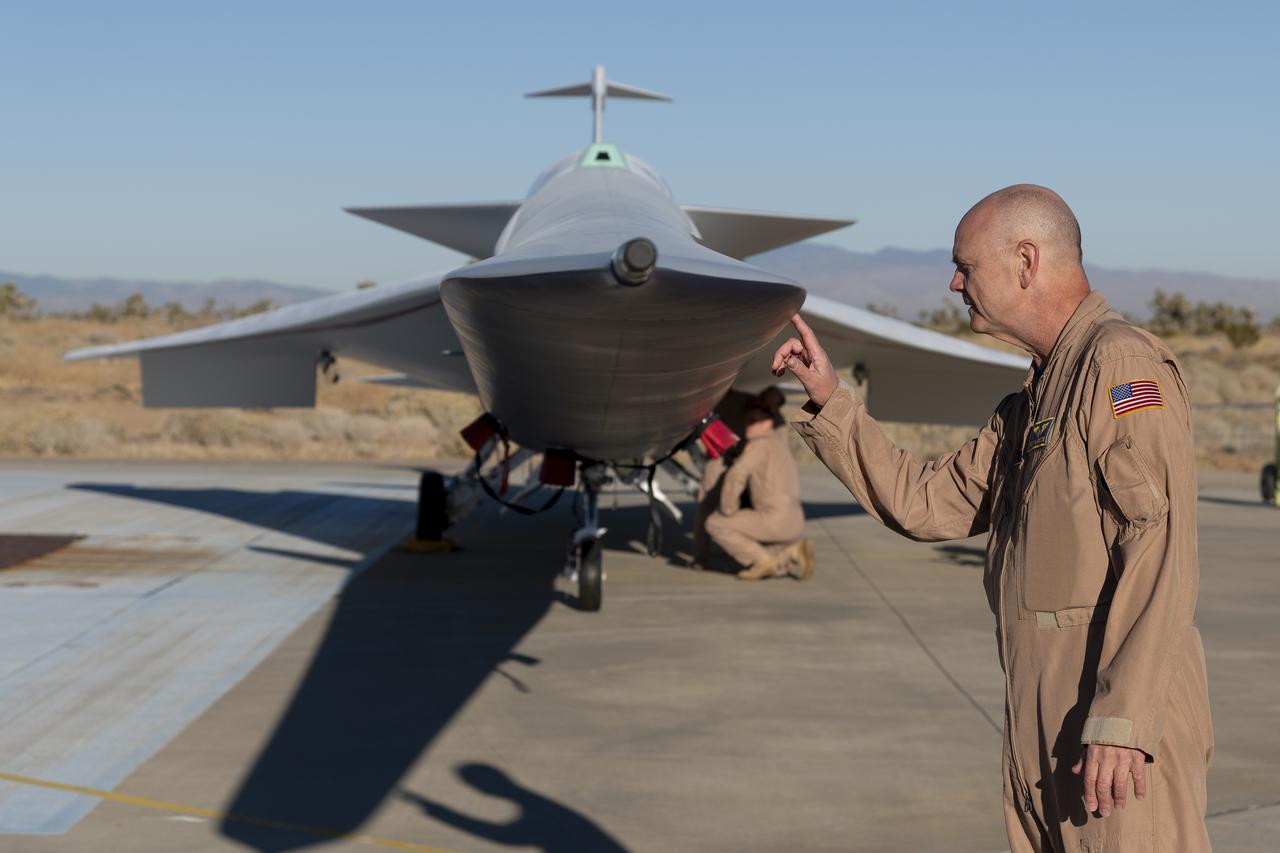

NASA test pilot Nils Larson gets an initial look at the painted X-59 as it sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. Larson, one of three test pilots training to fly the X-59 inspects the side of the 38-foot-long nose; a primary design feature to the X-59’s purpose of demonstrating the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than sound, without creating a loud sonic boom. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
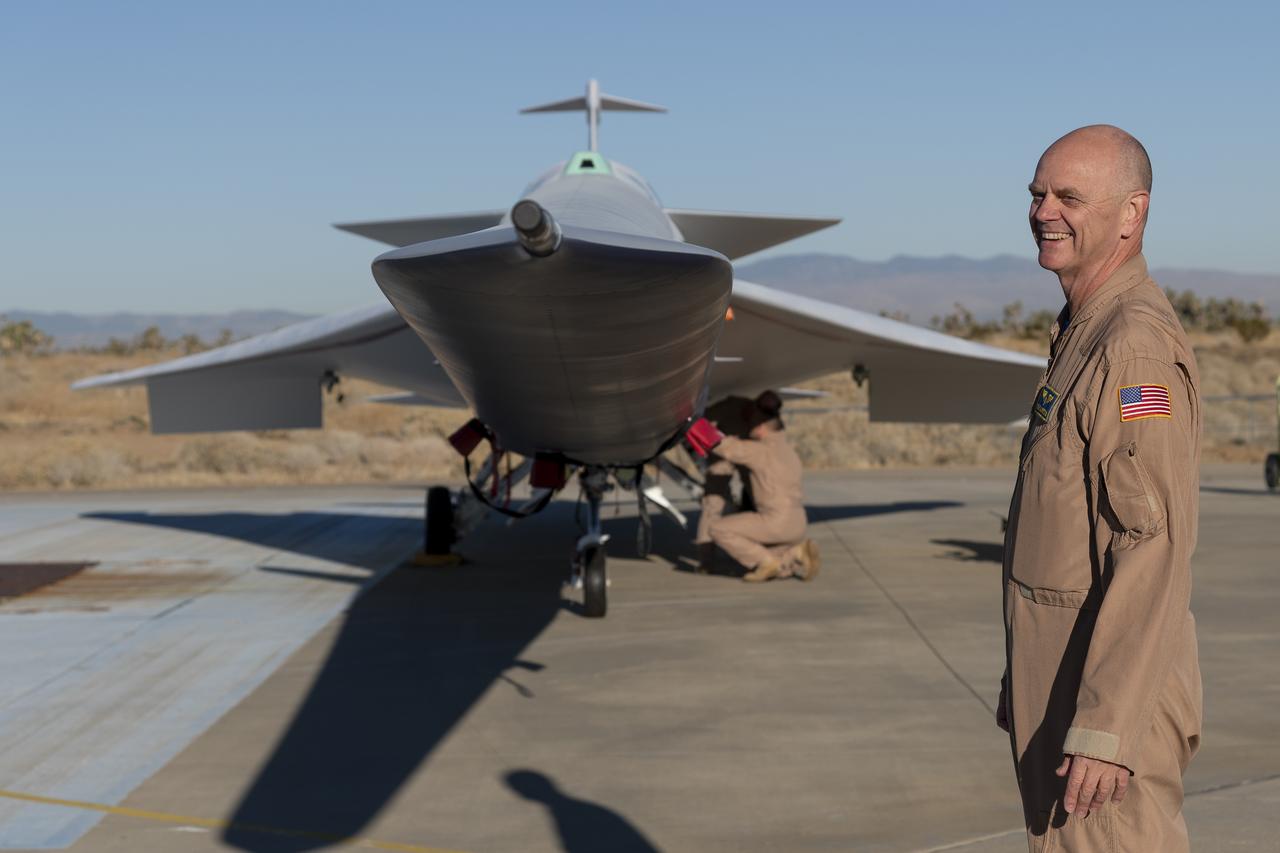

NASA test pilot Nils Larson gets an initial look at the painted X-59 as it sits on the ramp at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. Larson, one of three test pilots training to fly the X-59 inspects the side of the 38-foot-long nose; a primary design feature to the X-59’s purpose of demonstrating the ability to fly supersonic, or faster than sound, without creating a loud sonic boom. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
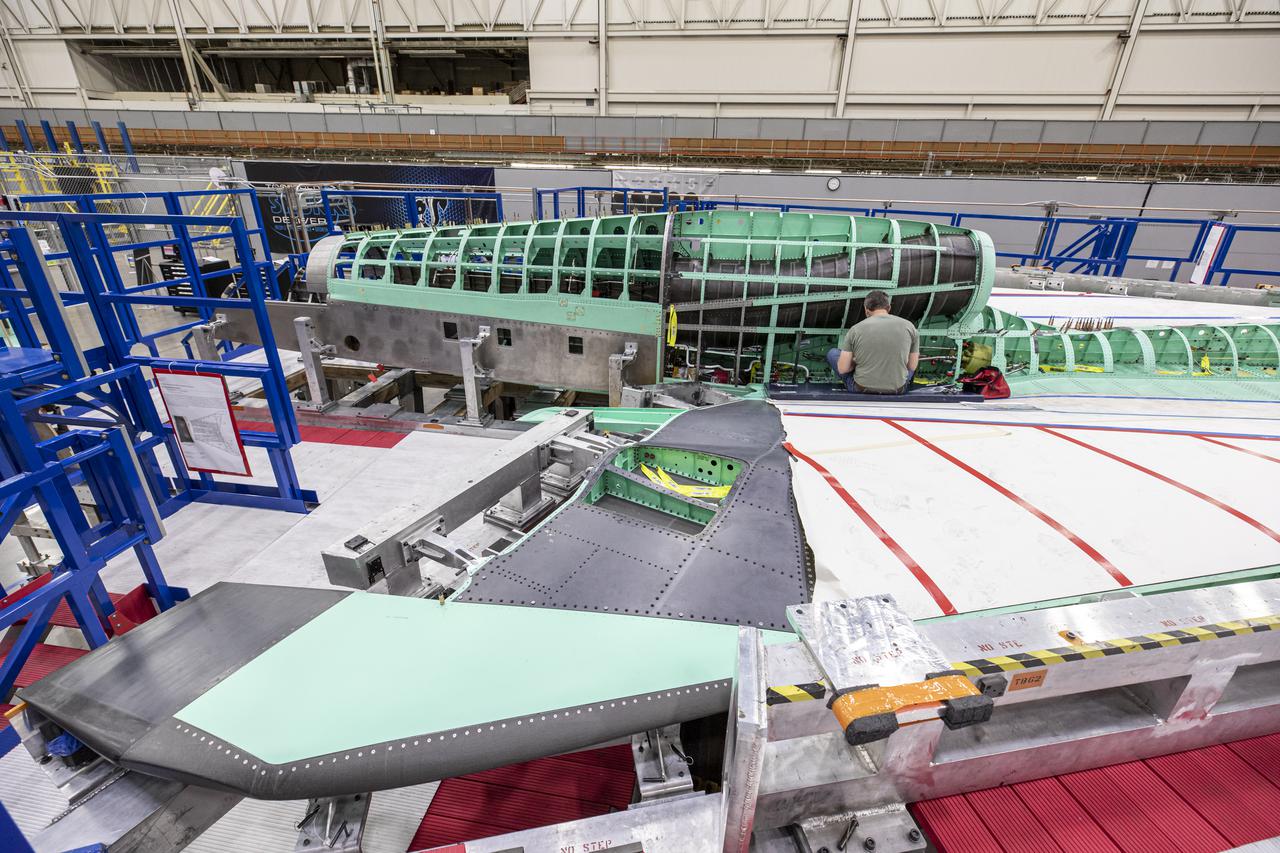

Here is a wide shot of the wing, engine and engine inlet area of NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology or QueSST aircraft. The aircraft, under construction at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California, will fly to demonstrate the ability to fly supersonic while reducing the loud sonic boom to a quiet sonic thump. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: SEG 400 Main Wing Assembly, SEG 430 Spine, SEG 500 Empennage Date: 4/28/2021
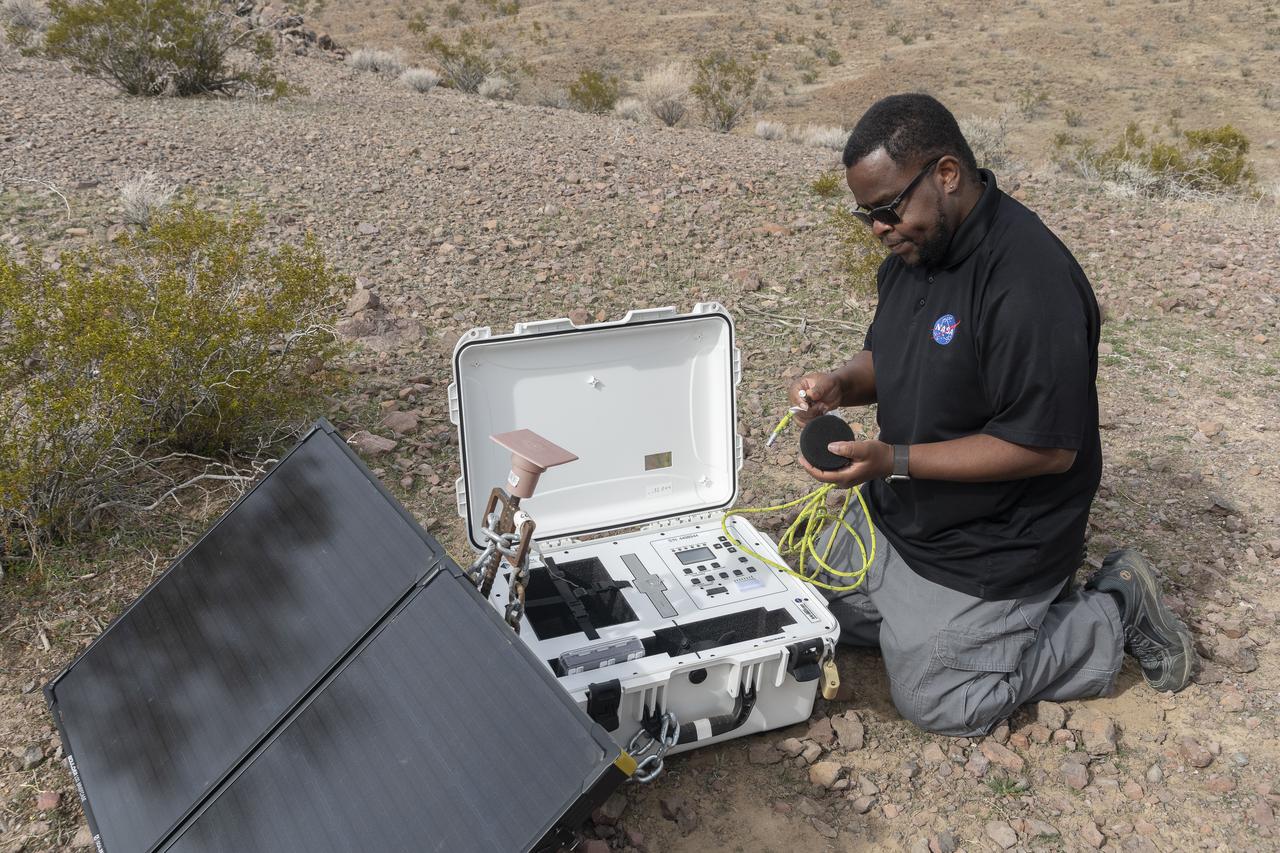

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager and technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
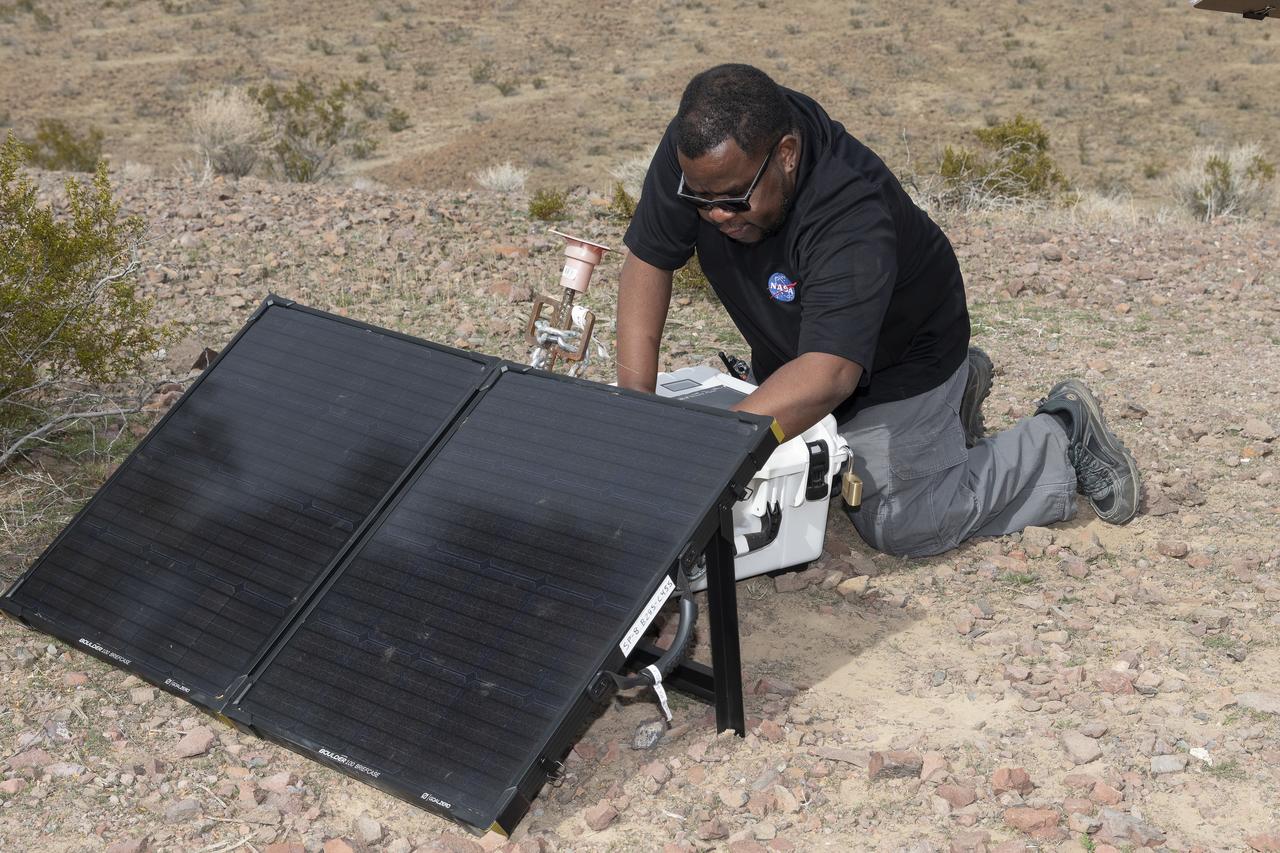

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager abd technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
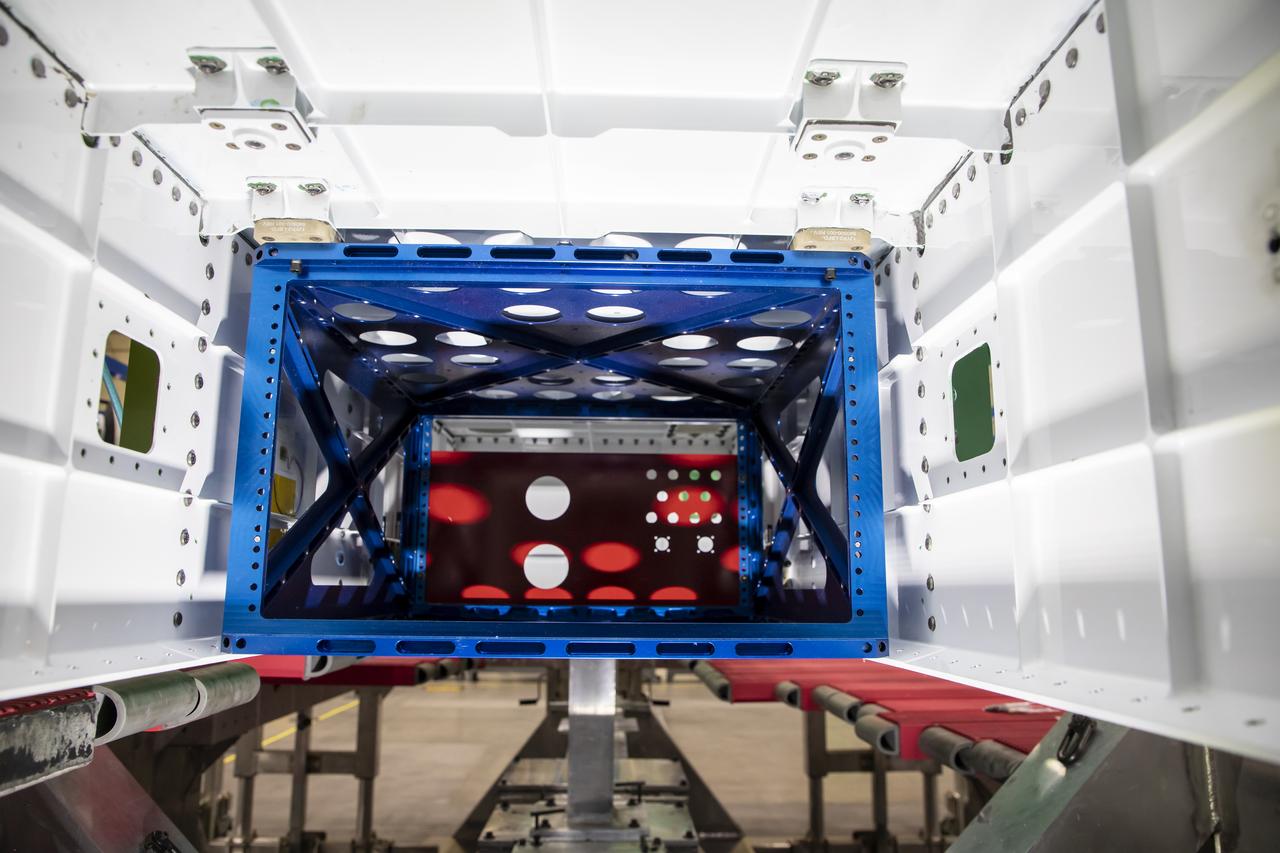
Following the successful installation of mounting brackets, technicians successfully installed the pallet for the eXternal Visibility System, or XVS, onto the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane, also known as X-59 QueSST. The pallet installation marks an assembly milestone as the first NASA flight systems hardware to be installed onto the vehicle. X-59 will fly to demonstrate the ability to produce quiet thumps at supersonic speeds, instead of the typical, loud sonic booms associated with supersonic flight.
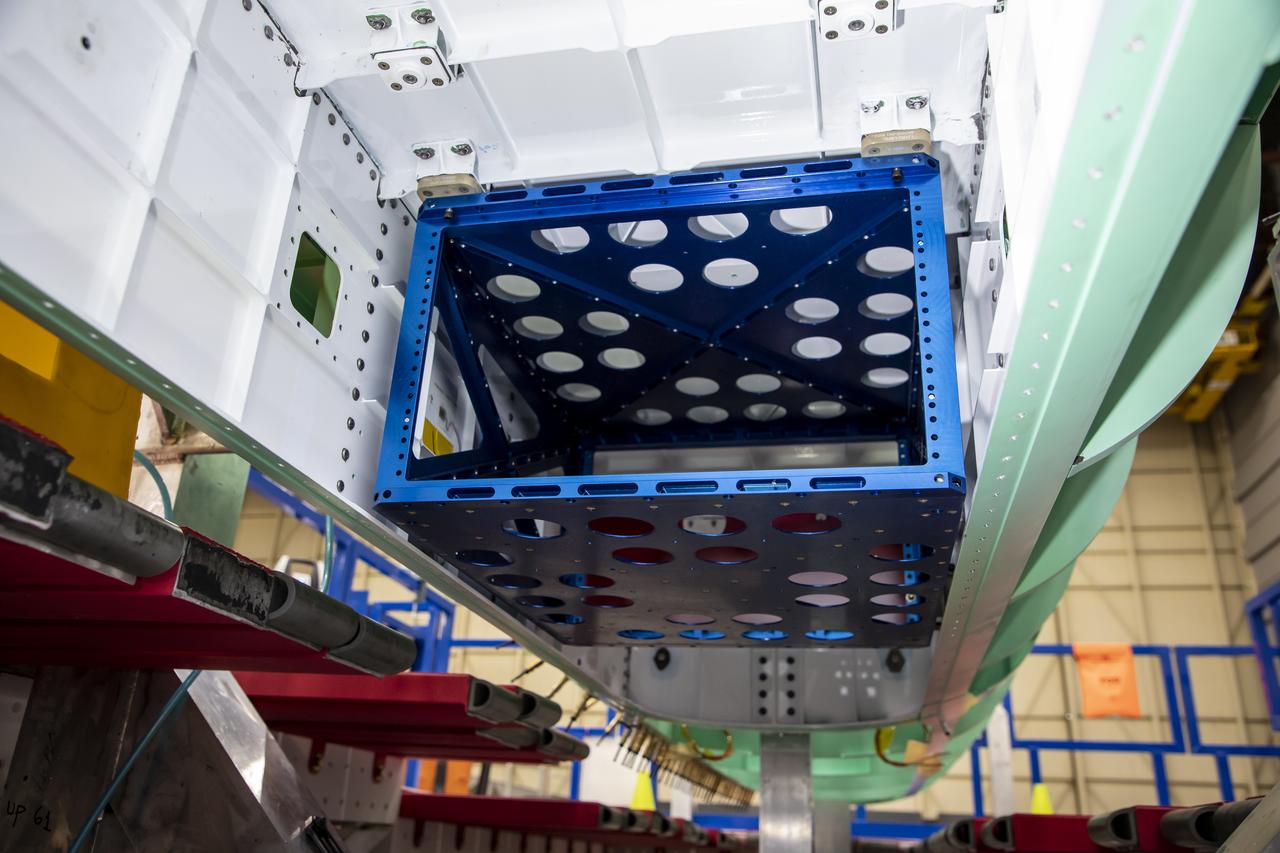

Following the successful installation of mounting brackets, technicians successfully installed the pallet for the eXternal Visibility System, or XVS, onto the X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane, also known as X-59 QueSST. The pallet installation marks an assembly milestone as the first NASA flight systems hardware to be installed onto the vehicle. X-59 will fly to demonstrate the ability to produce quiet thumps at supersonic speeds, instead of the typical, loud sonic booms associated with supersonic flight.
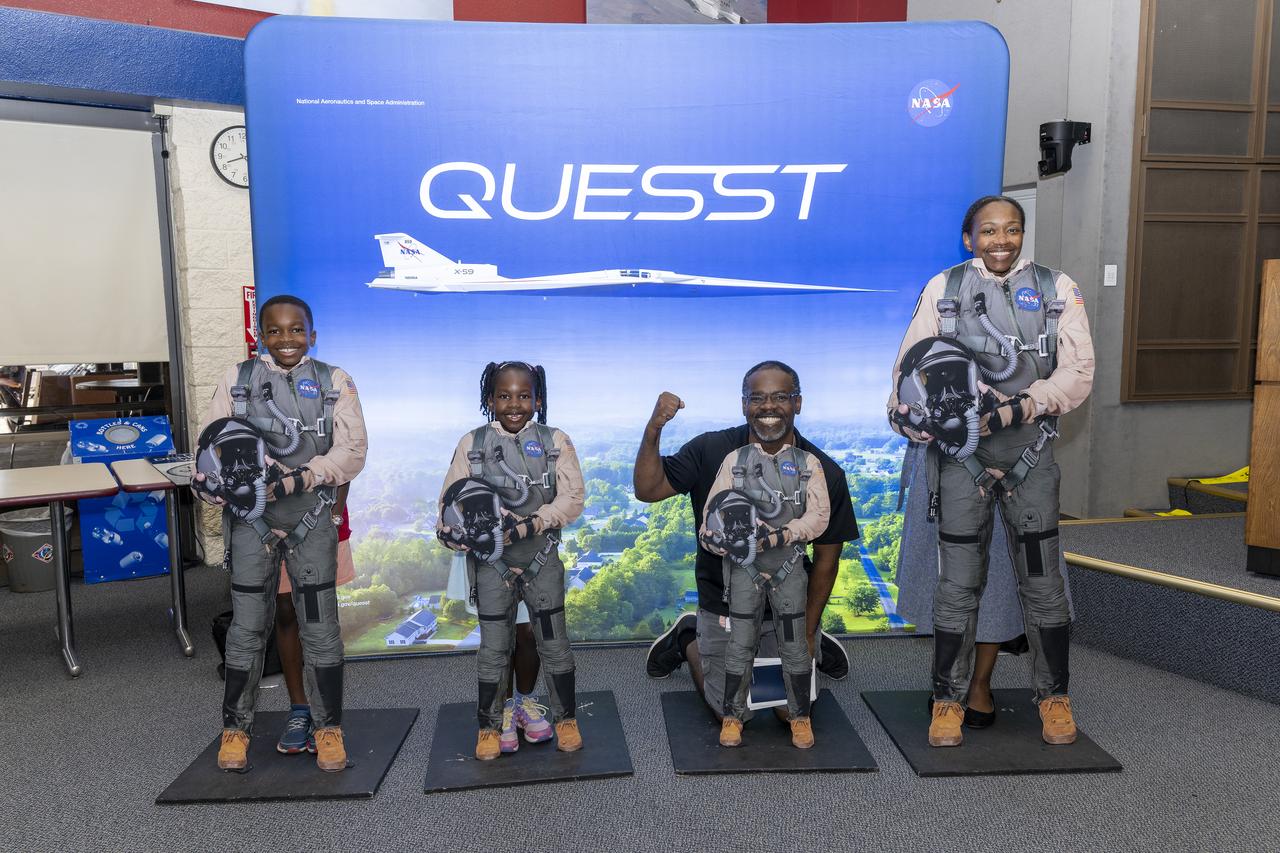

During Bring Kids to Work Day at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on June 17, 2025, participants pose with flight suit cutouts in front of NASA’s Quesst display. NASA's Quesst mission, which features the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic experimental aircraft, will demonstrate technology to fly supersonic, or faster than the speed of sound, without generating loud sonic booms.
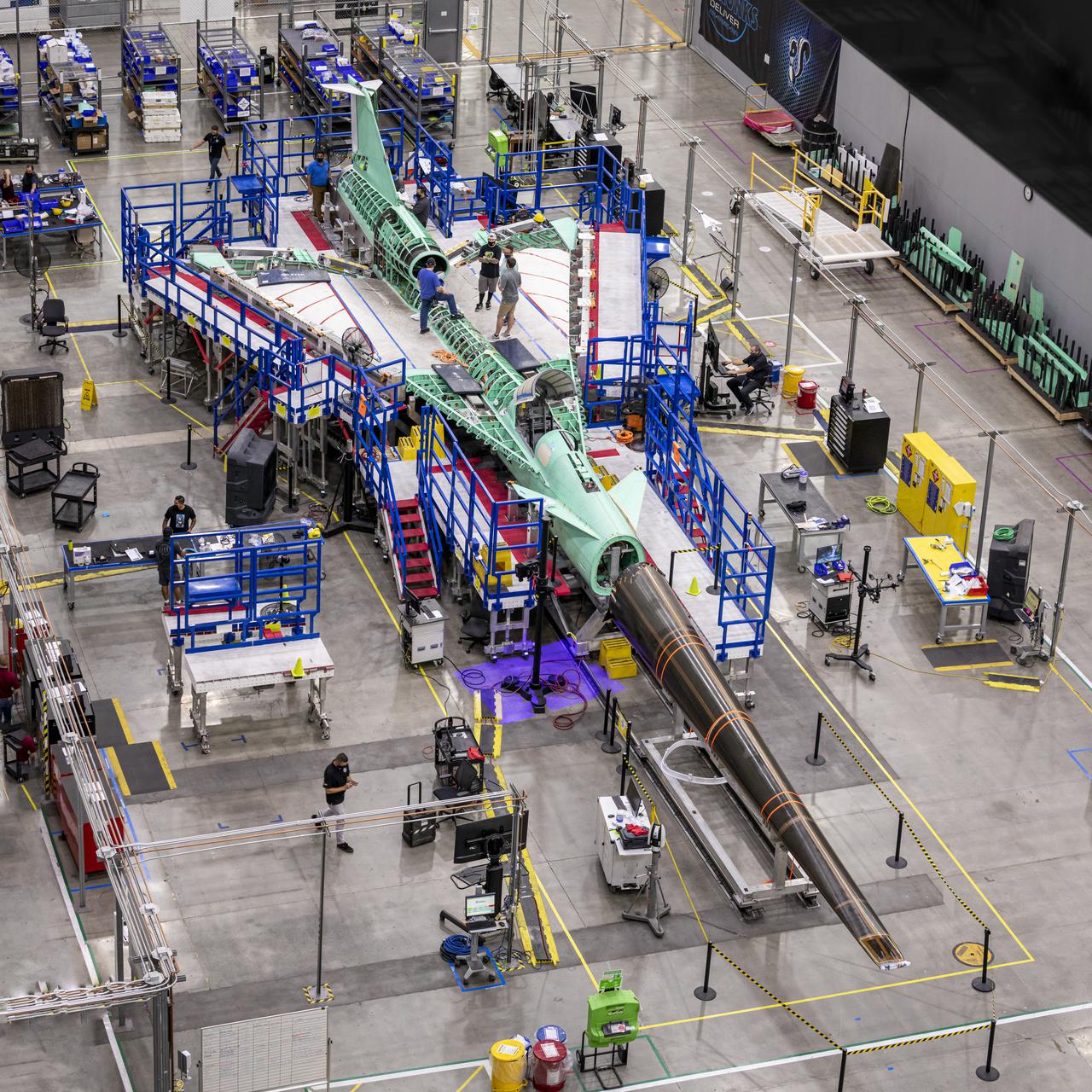

The X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology (QueSST) aircraft is taking shape at the Lockheed Martin Skunk Works facility in Palmdale, California. The team positioned the X-59 QueSST's nose at the front of the aircraft. As one of the more recognizable features of the X-59, the nose makes up almost a third of the aircraft length and will be essential in shaping shock waves during supersonic flight, resulting in quiet sonic thumps instead of loud sonic booms. The nose was attached and then removed from the front of the aircraft in preparation for its shipment to Fort Worth, Texas where it will undergo additional testing. The X-59 will fly at supersonic speeds above communities as part of the Low-Boom Flight Demonstration mission, during which NASA will gather community feedback to the sound of quiet supersonic flight. These findings will be shared with regulators to inform decisions on current restrictions of supersonic flight over land. Lockheed Martin Photography By Garry Tice 1011 Lockheed Way, Palmdale, Ca. 93599 Event: Manufacturing Area From Above Date: 8/18/2021 Additional Info:
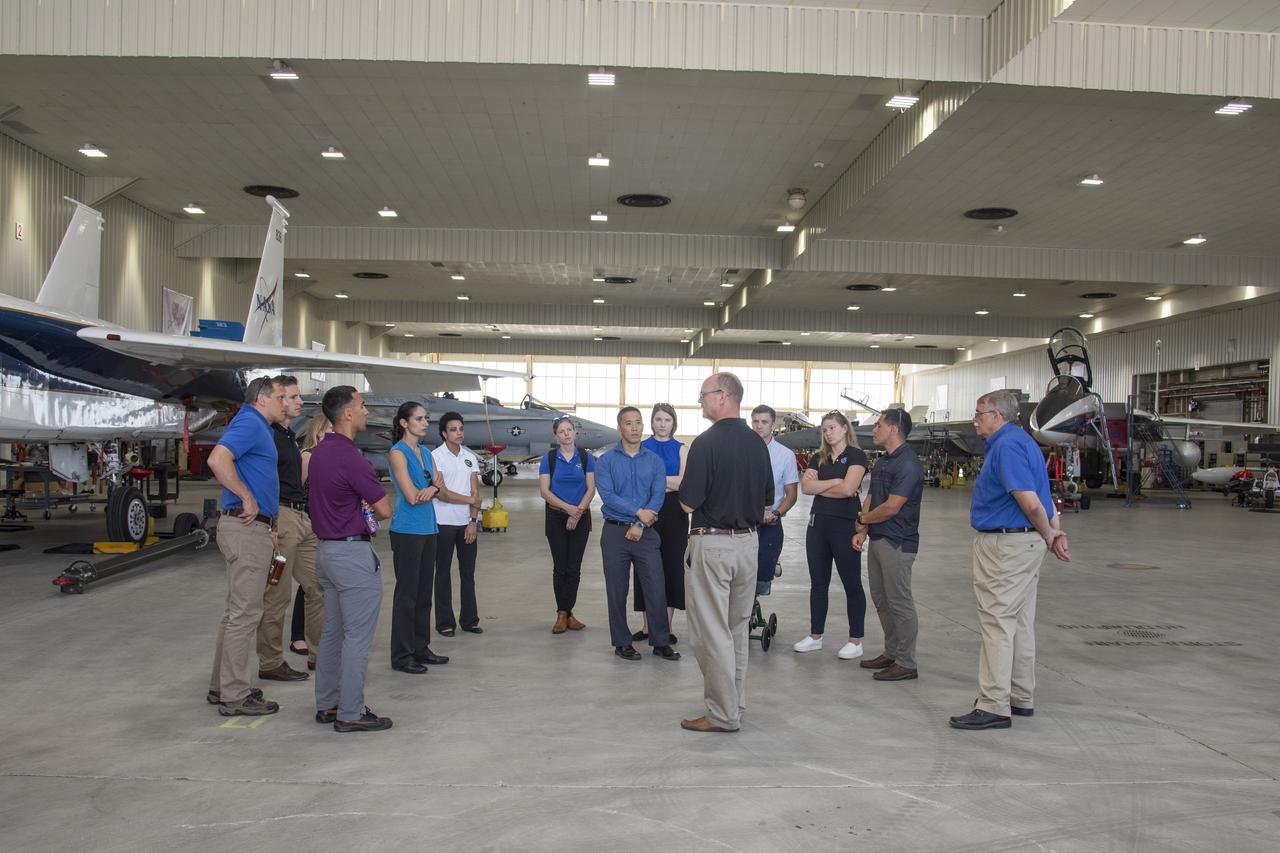

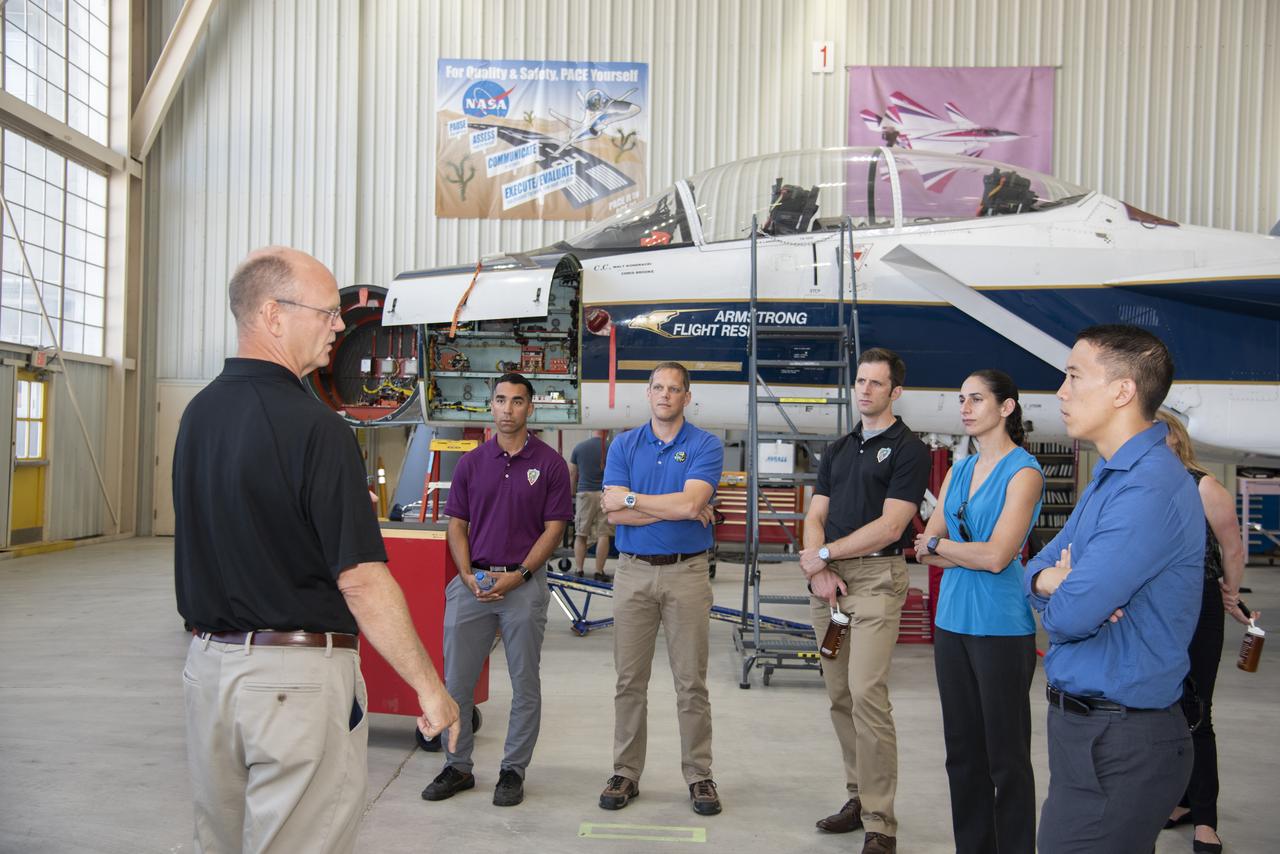
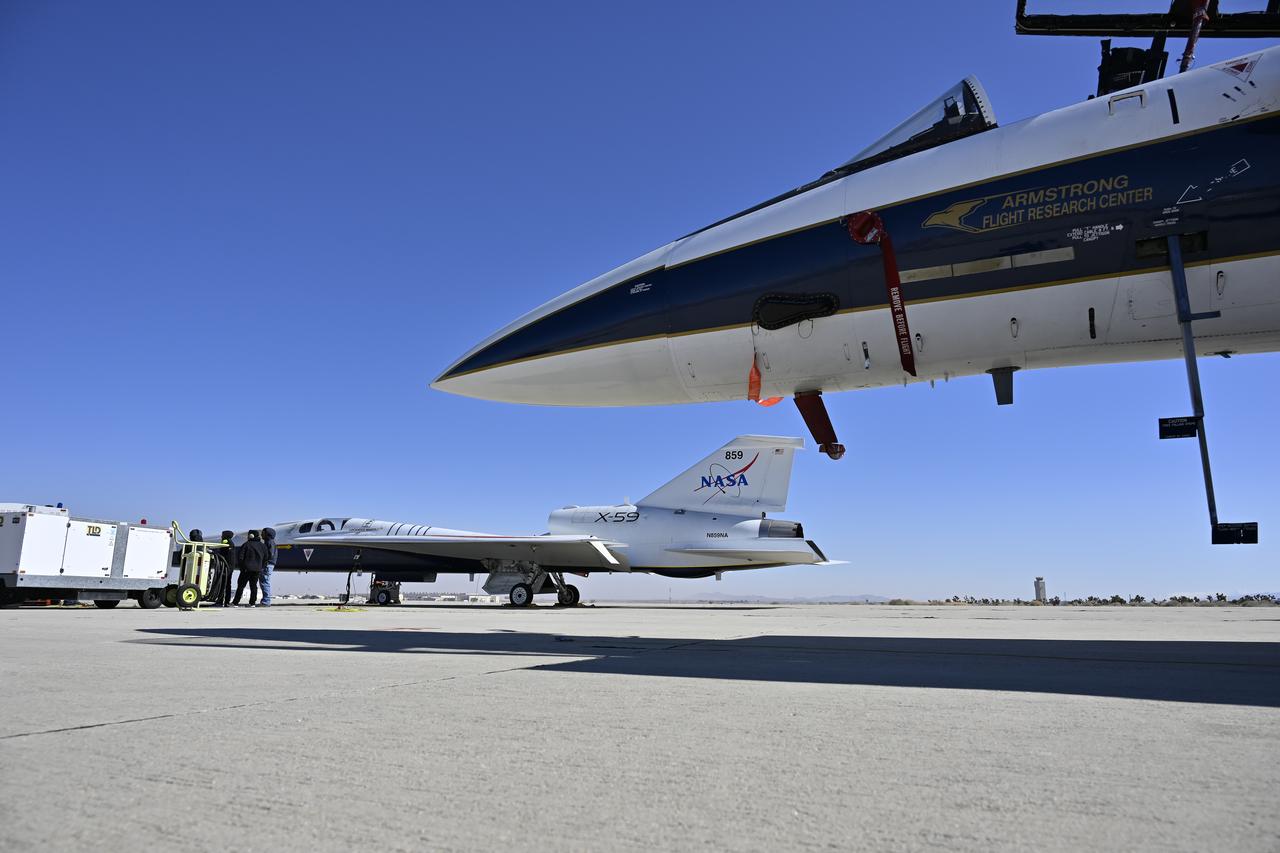
NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
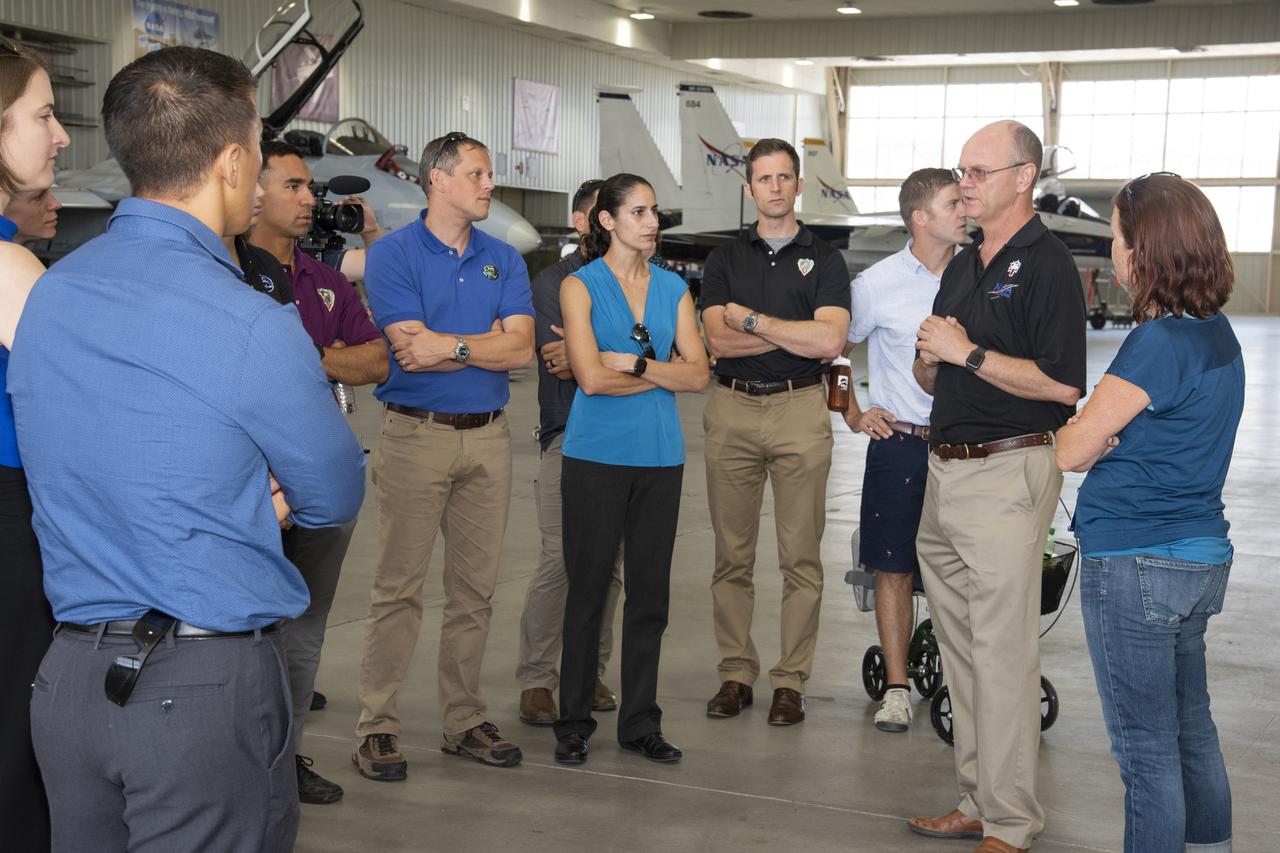

NASA’s 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA’s, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong’s fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.
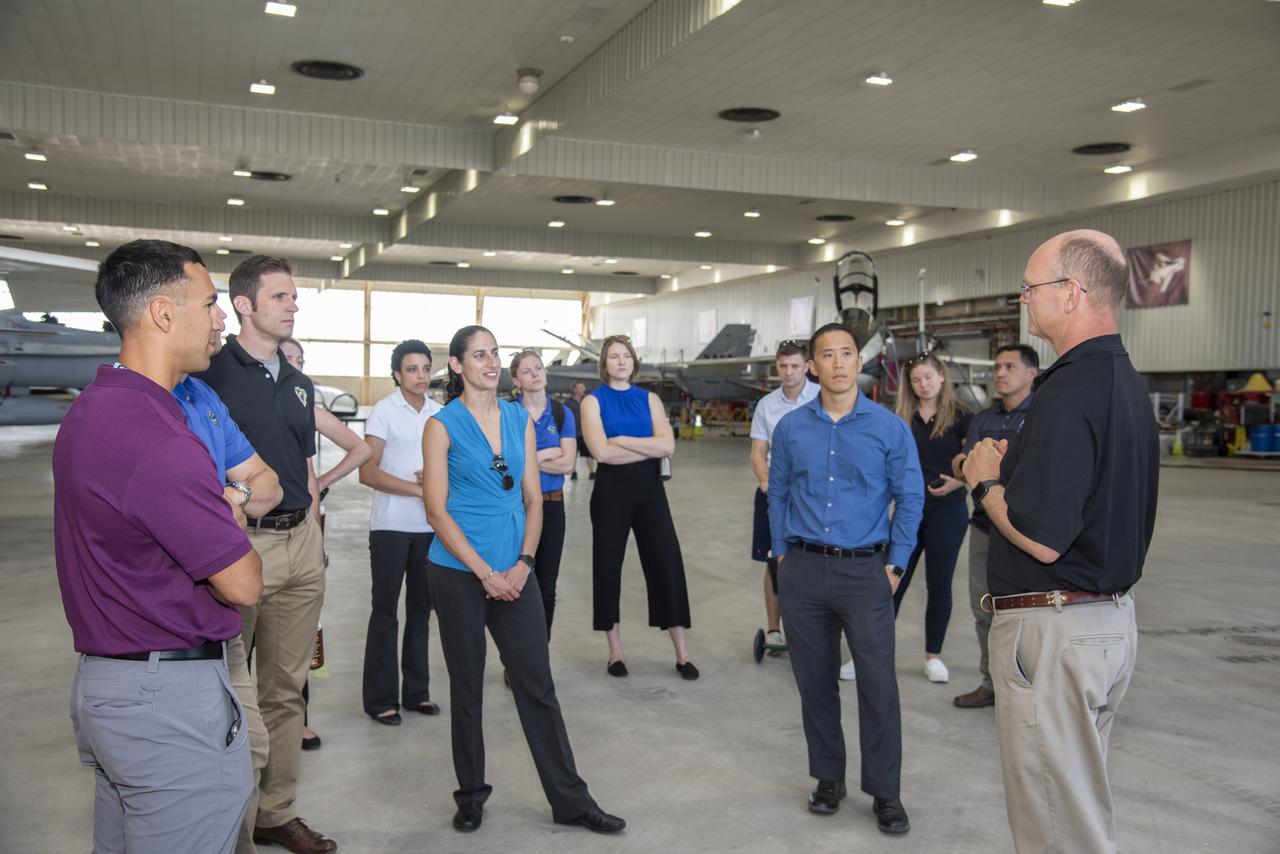

NASA's 2017 astronaut candidates toured aircraft hangar at Armstrong Flight Research Center, in Southern California. On the right, NASA's, X-59 pilot Nils Larsen, briefs the astronauts as they look at Armstrong's fleet of supersonic research support aircraft, including the F-15, which will fly in tandem with the X-59 QueSST during early flight test stages, and the F-18, which is conducting supersonic research in support of the overall mission.