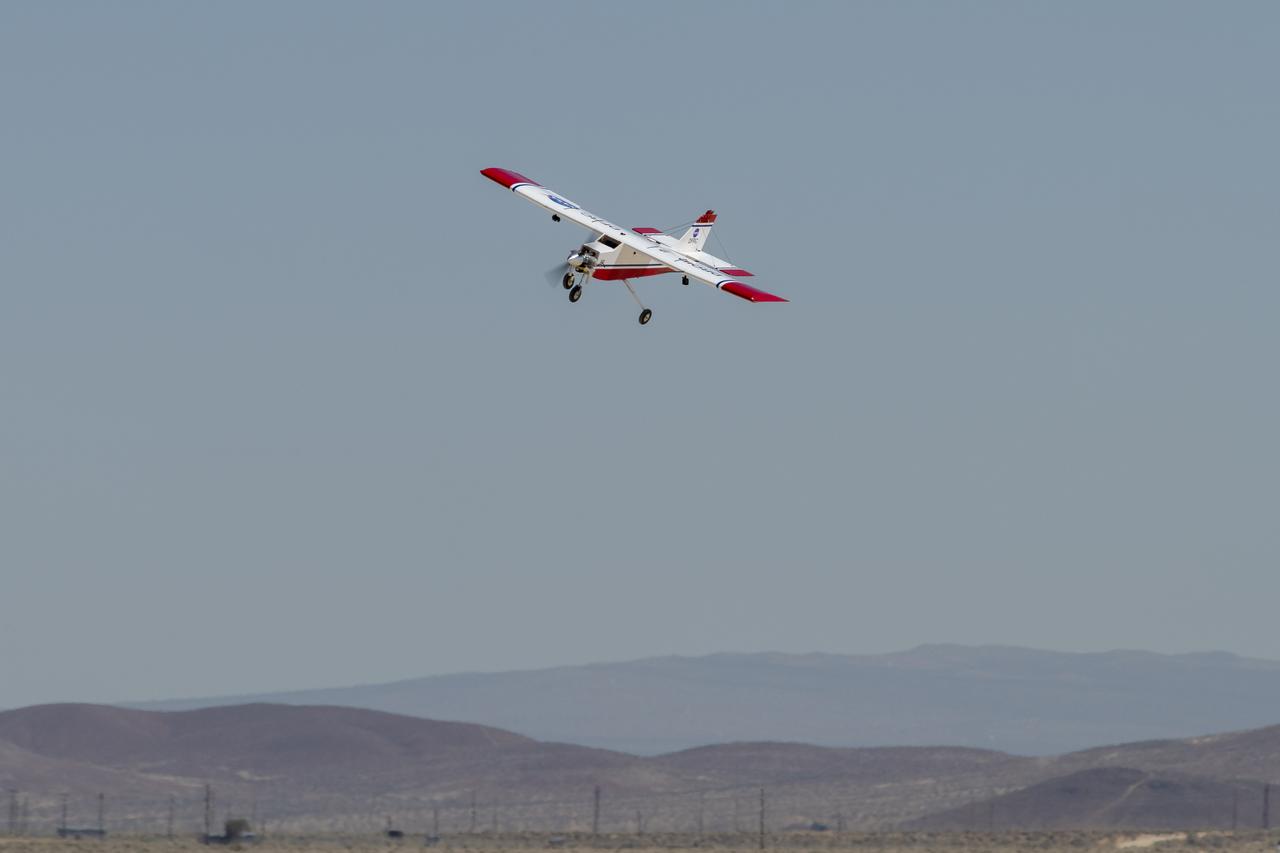

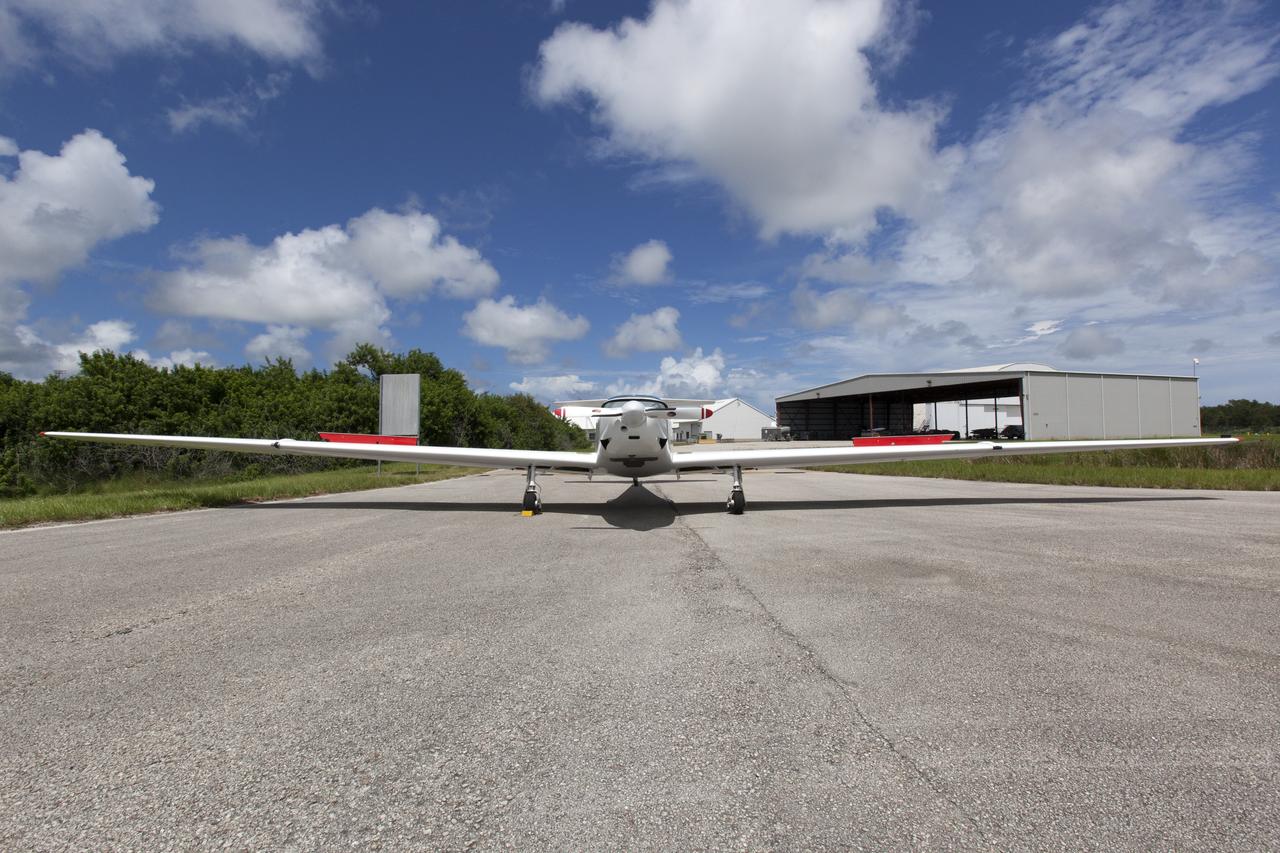
The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
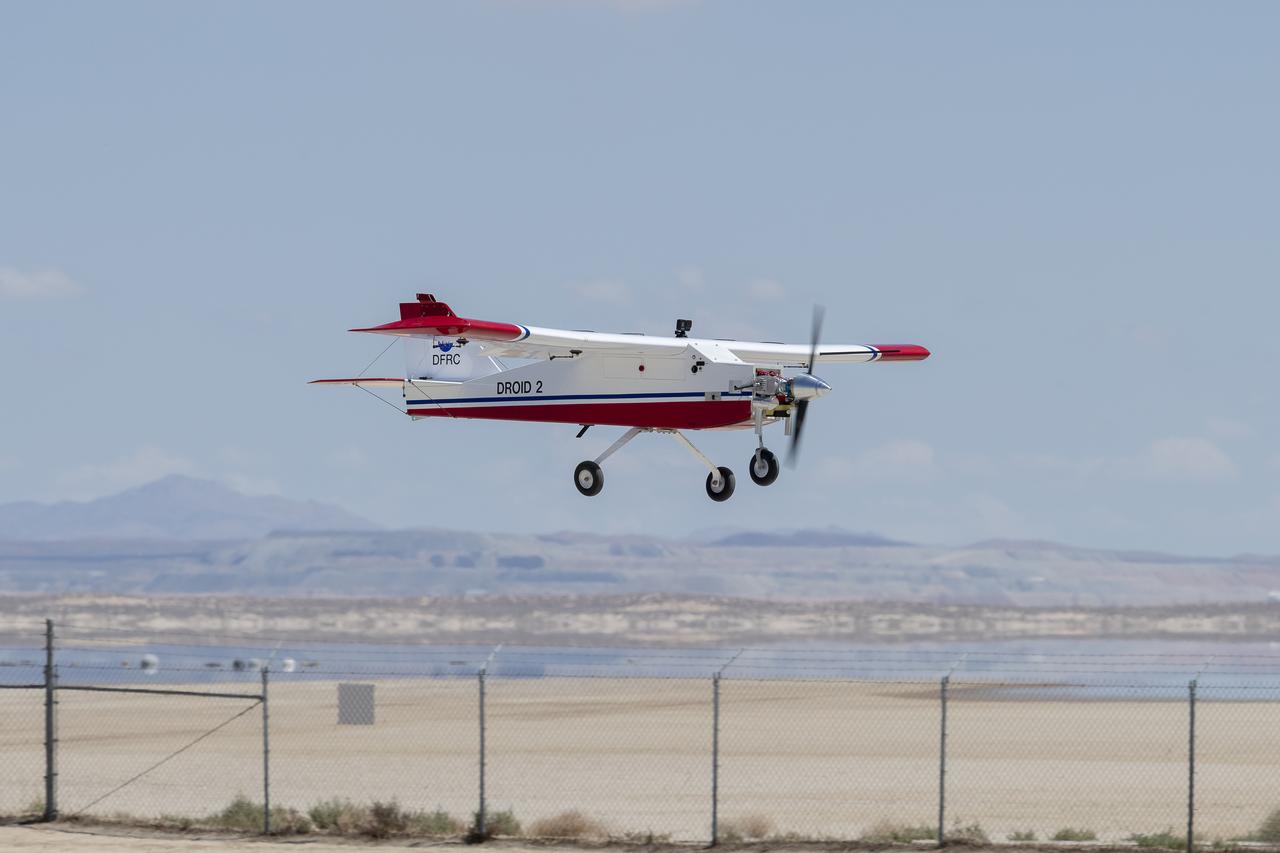

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) prepares to land at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
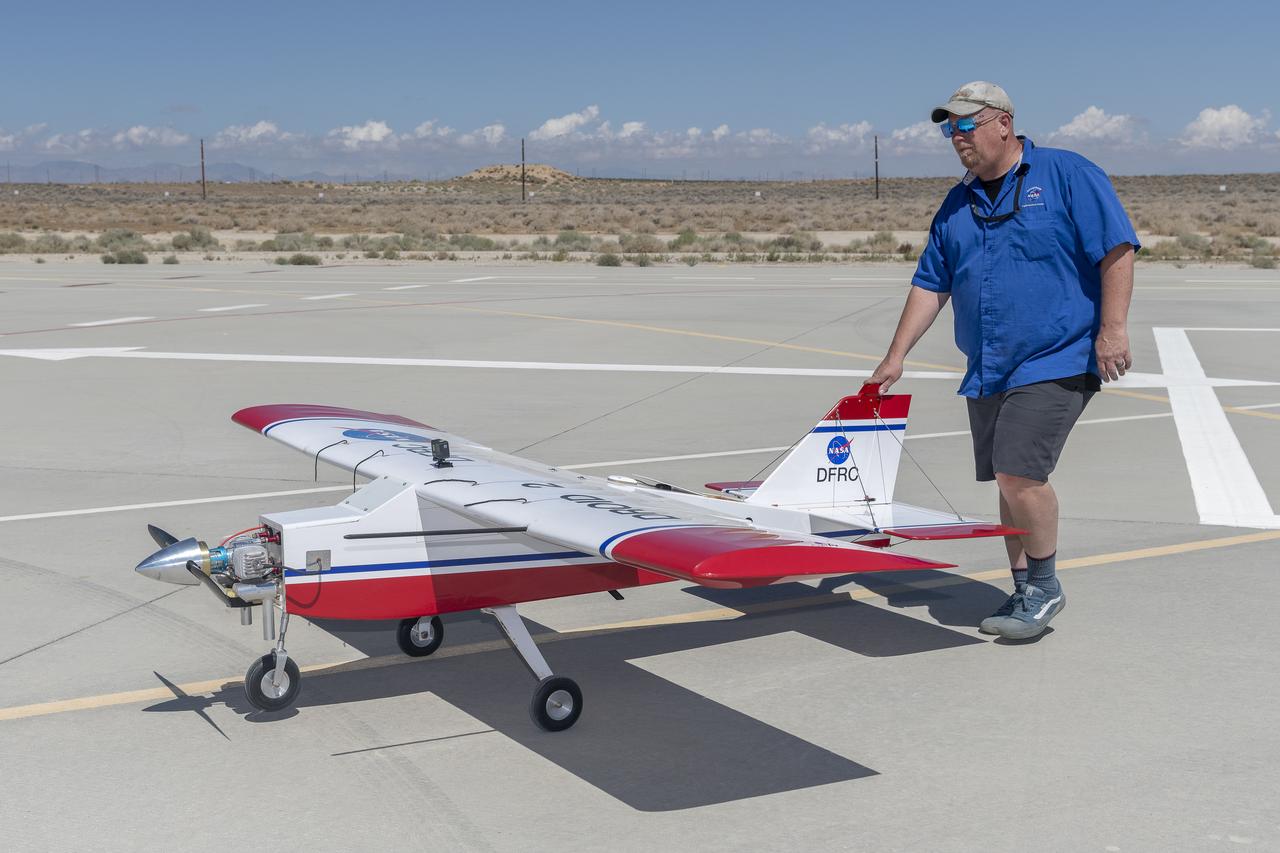

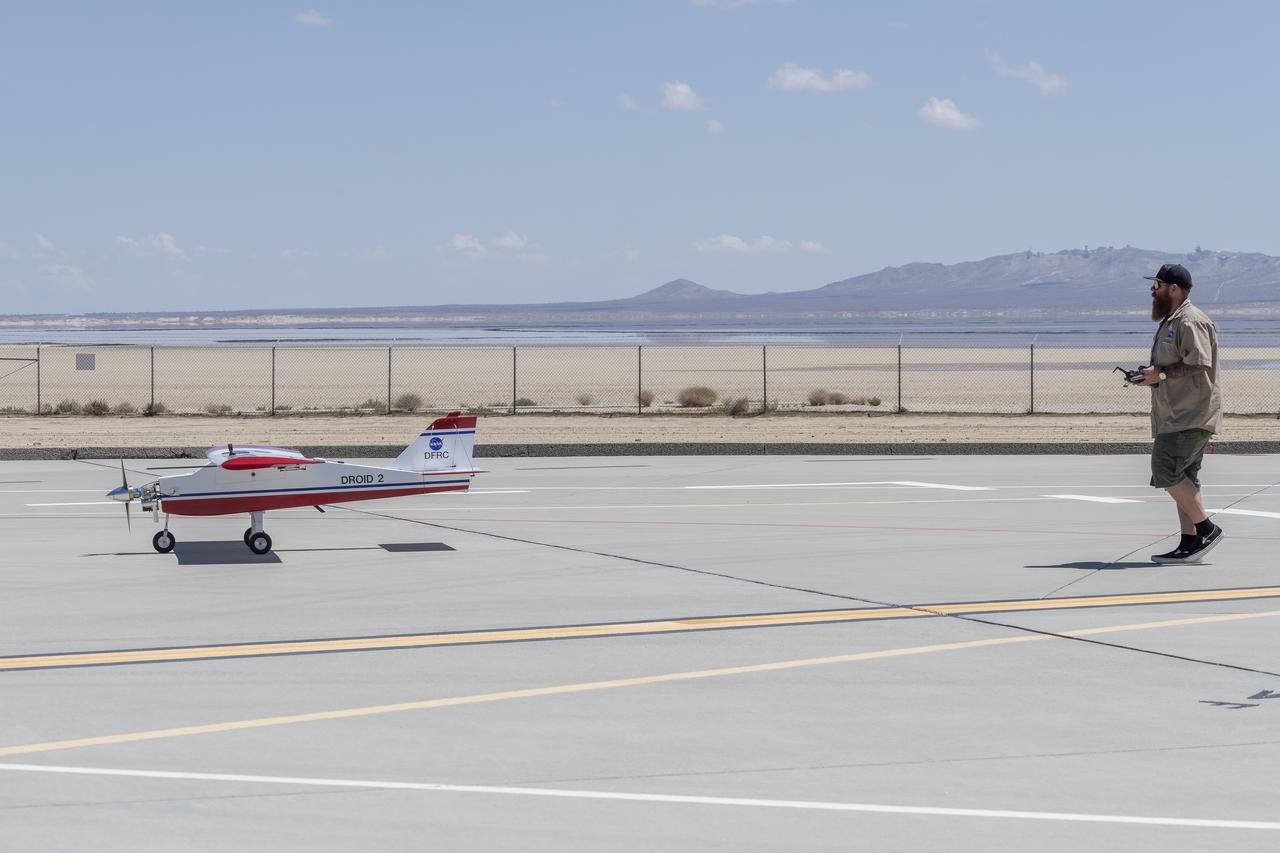
Robert "Red" Jensen positions the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone) aircraft before a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
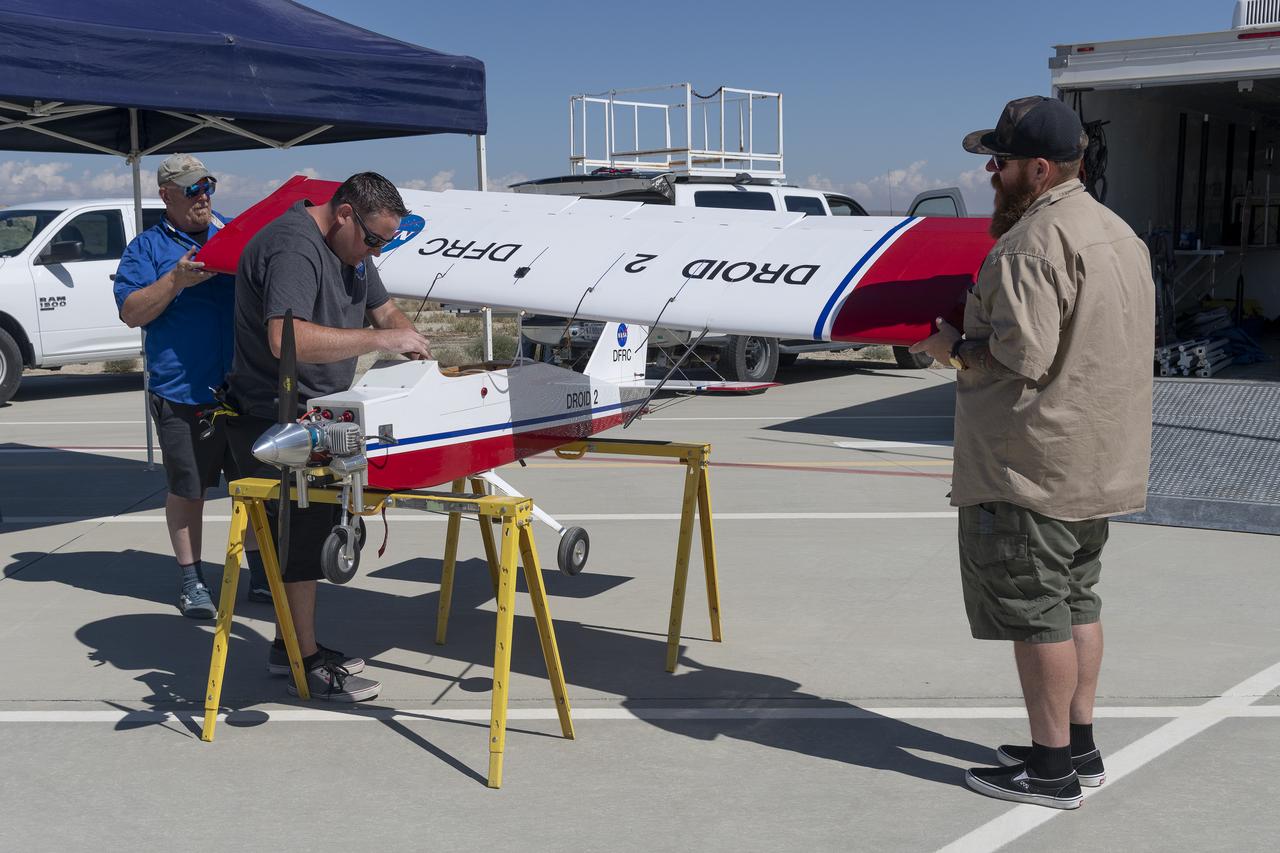

Robert "Red" Jensen, Justin Link, and Justin Hall prepare the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign flights. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
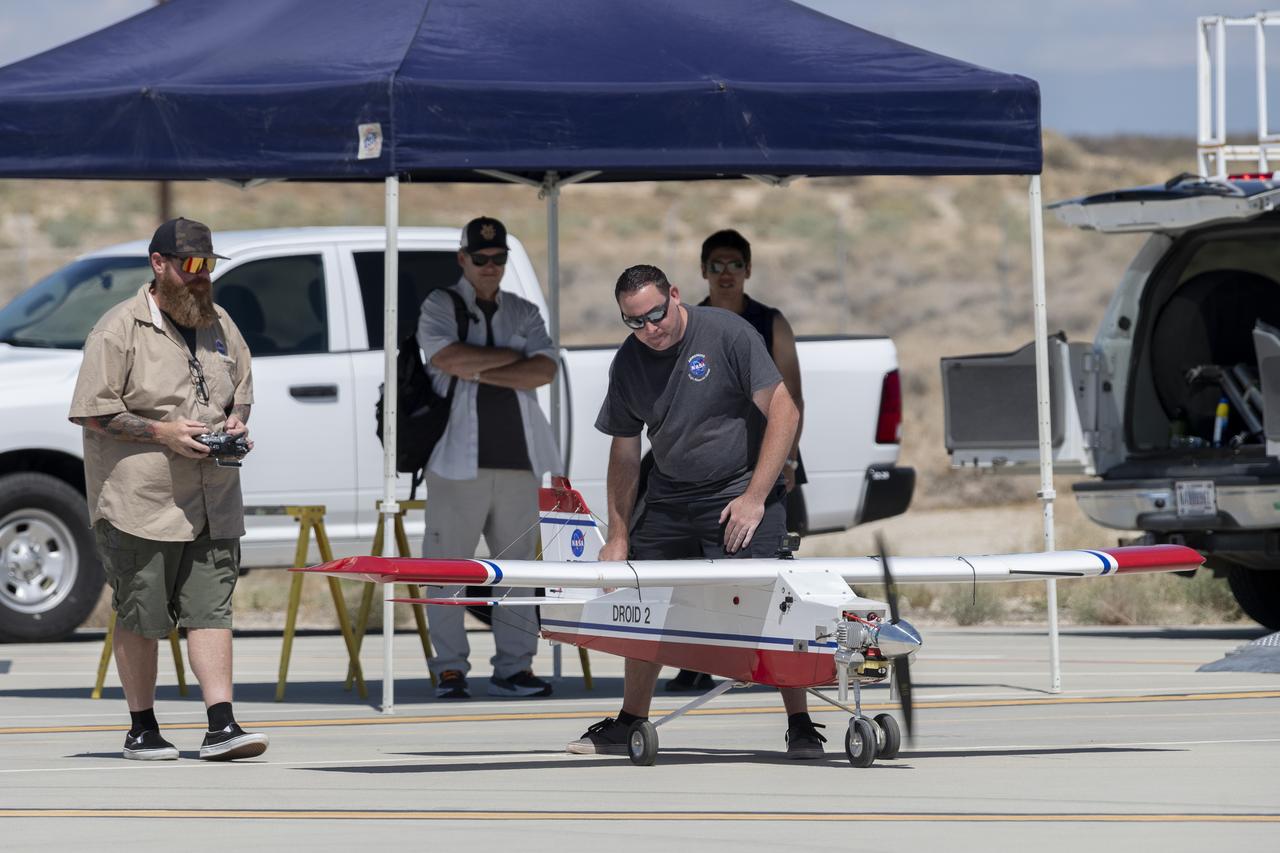

Justin Hall, left, prepares to pilot the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft, as John Melton watches and Justin Link makes a final adjustment. The flight was part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
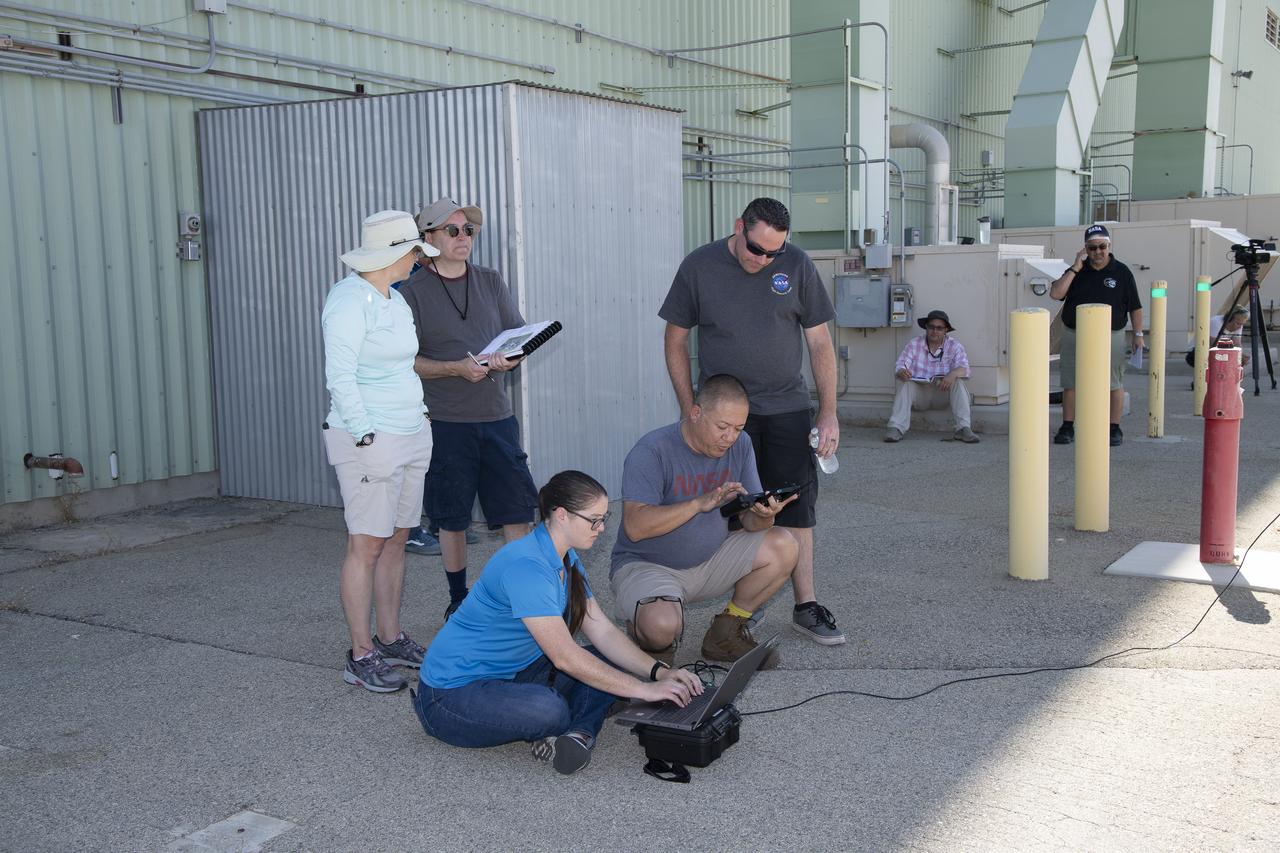

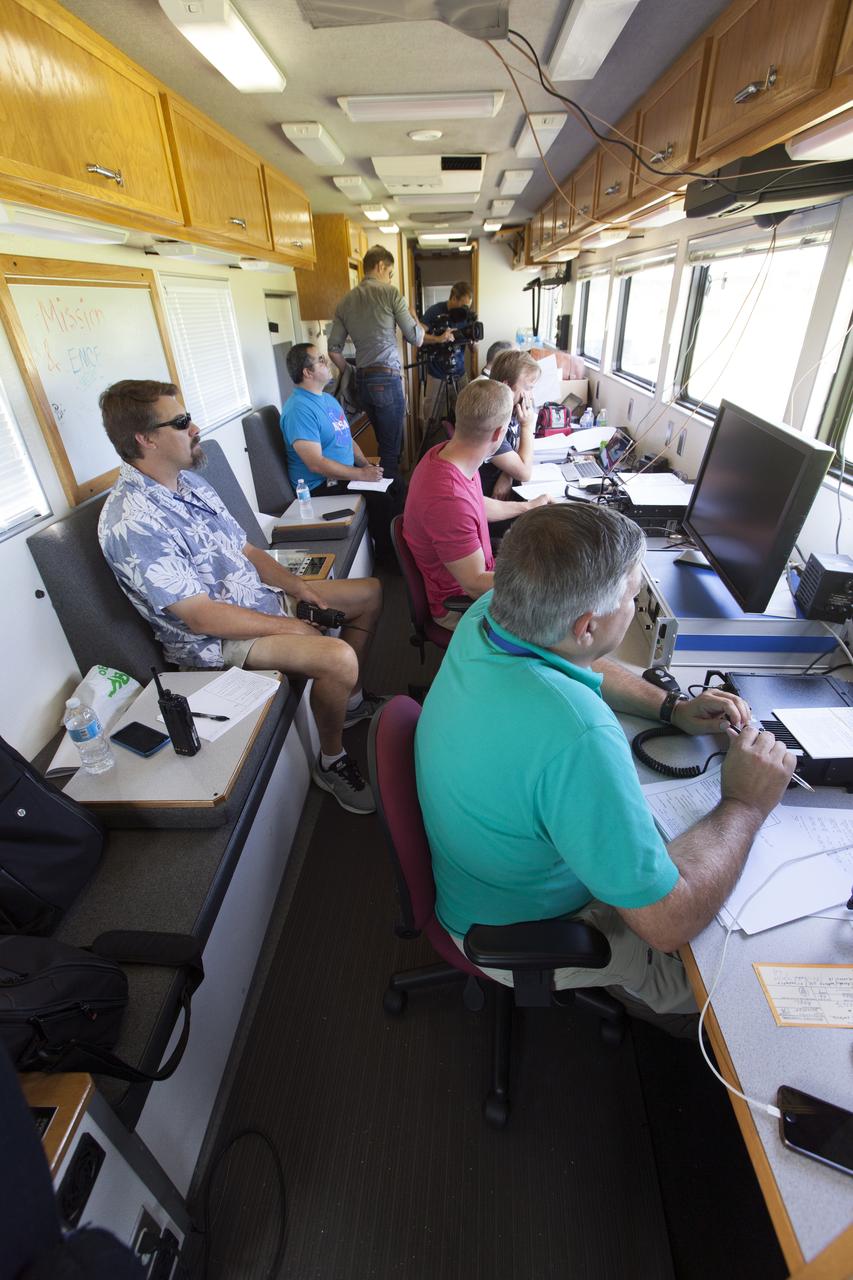
Tyler Willhite, sitting, and Derek Abramson and Justin Link, prepare for an Alta-X aircraft flight. Behind them are Jennifer Fowler, from left and Grady Kock. The Alta-X flight was part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
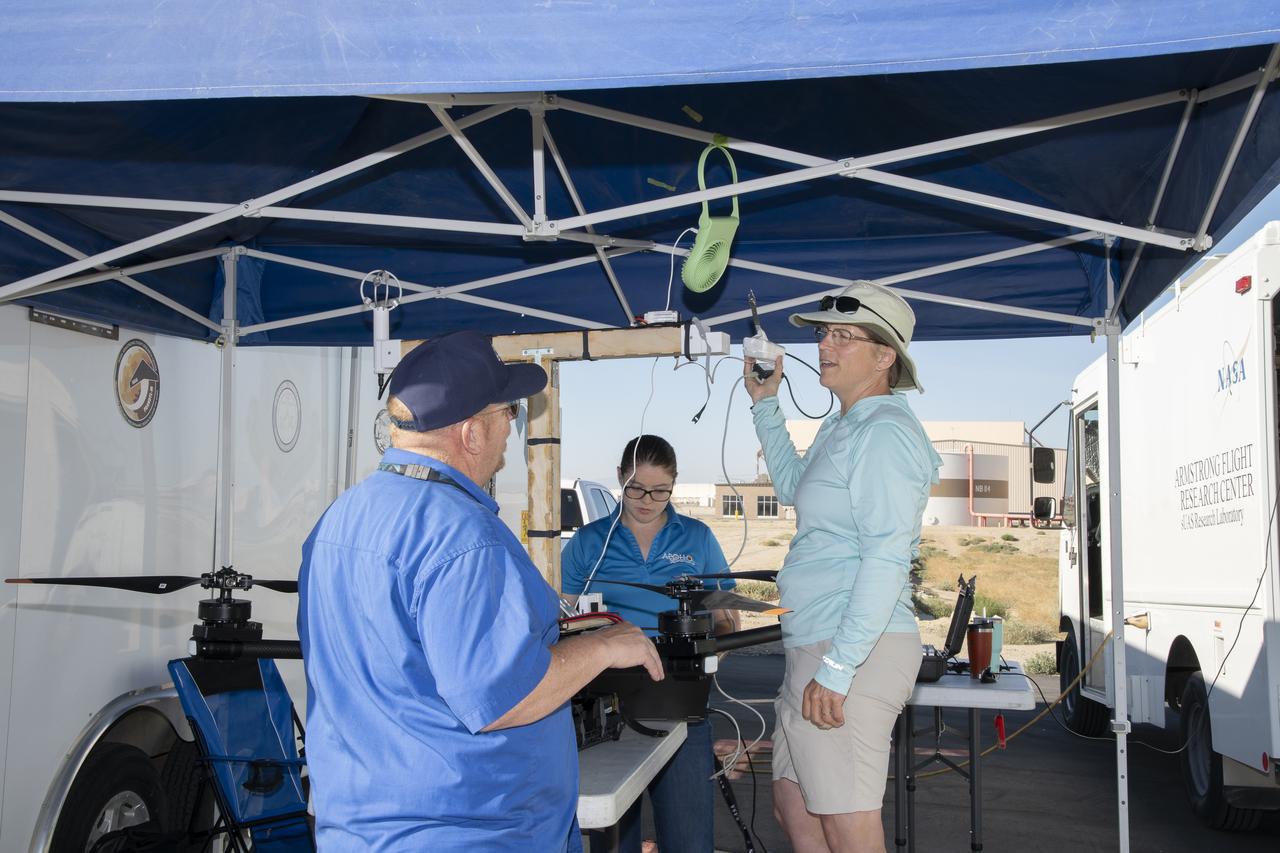

Jennifer Fowler talks to Red Jensen prior to a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. Tyler Willhite completes some equipment checks for the research in the background. The weather study was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
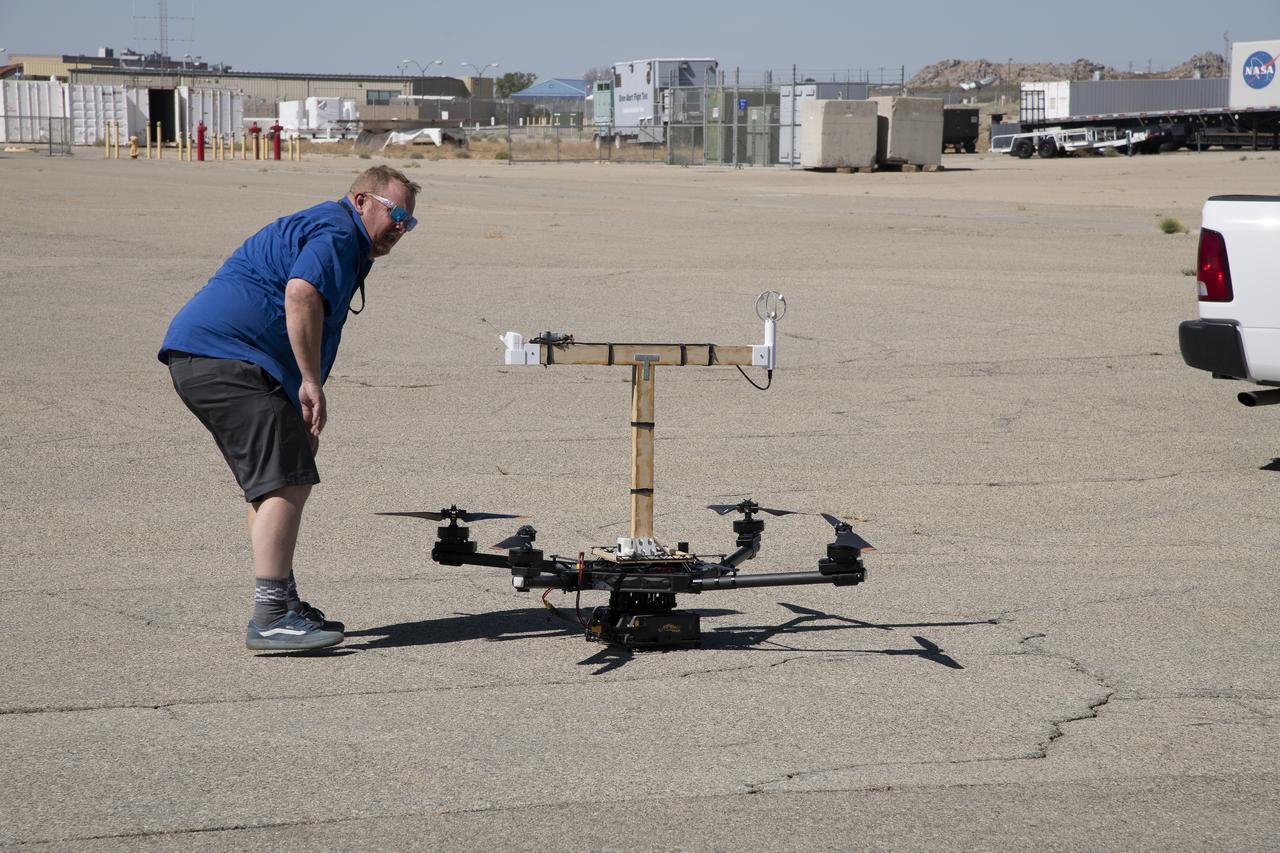

Red Jensen looks over the Alta-X aircraft before a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
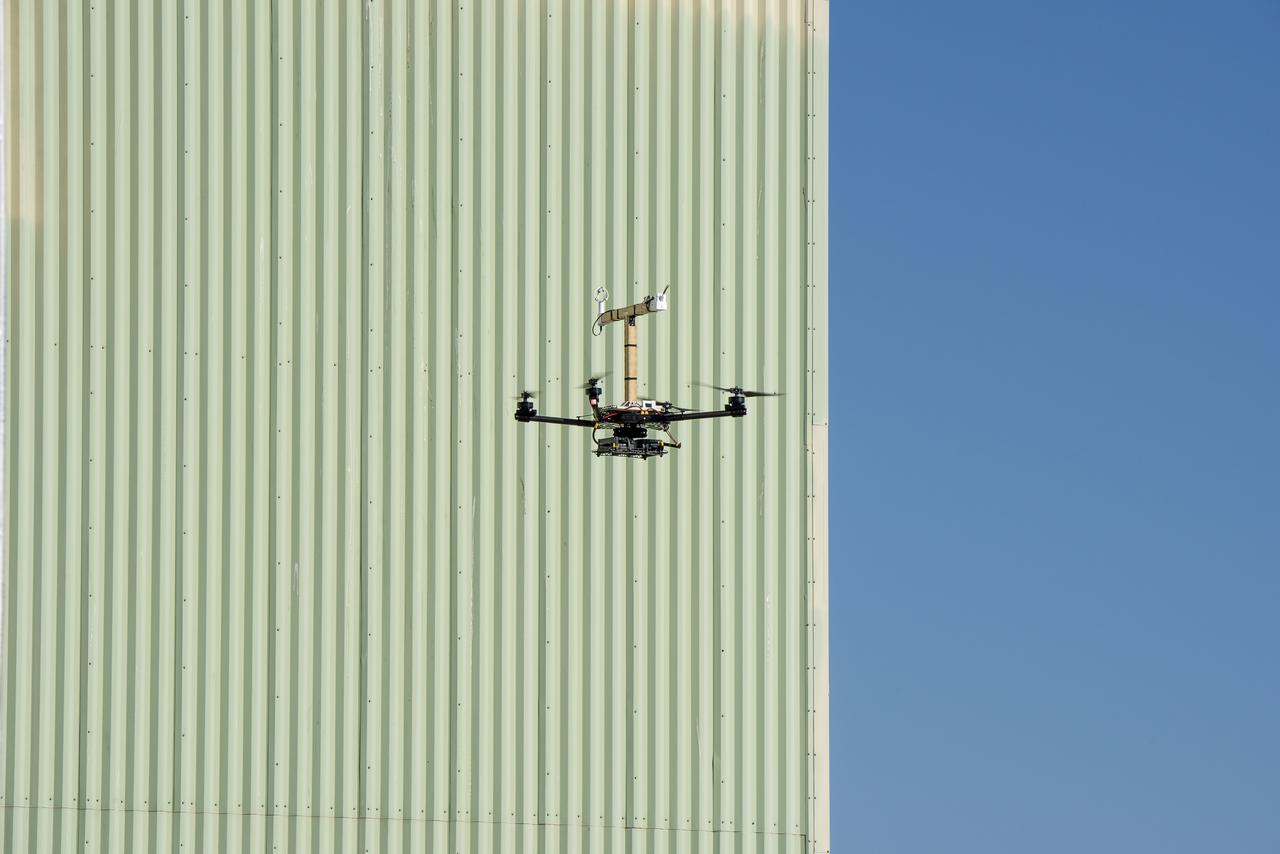

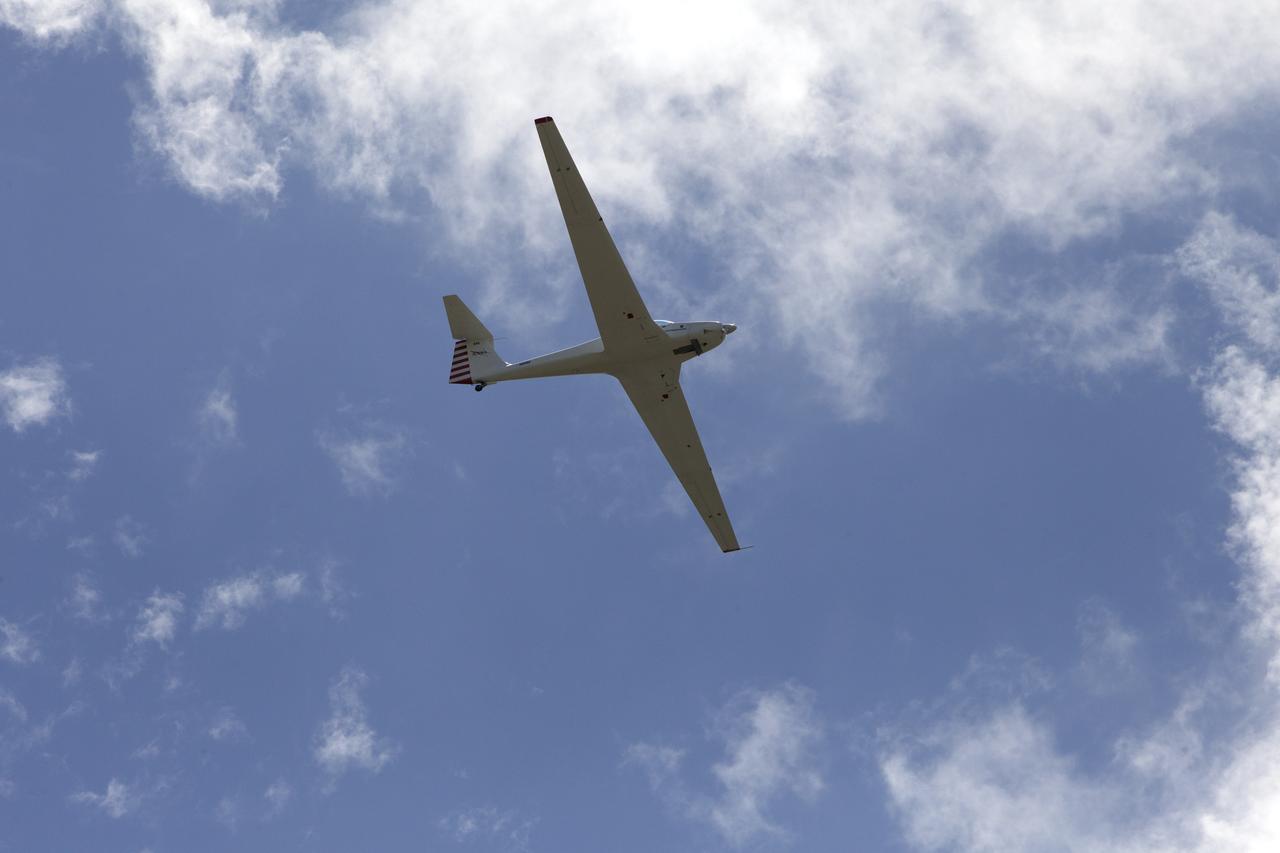
The Alta-X aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong Flight to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
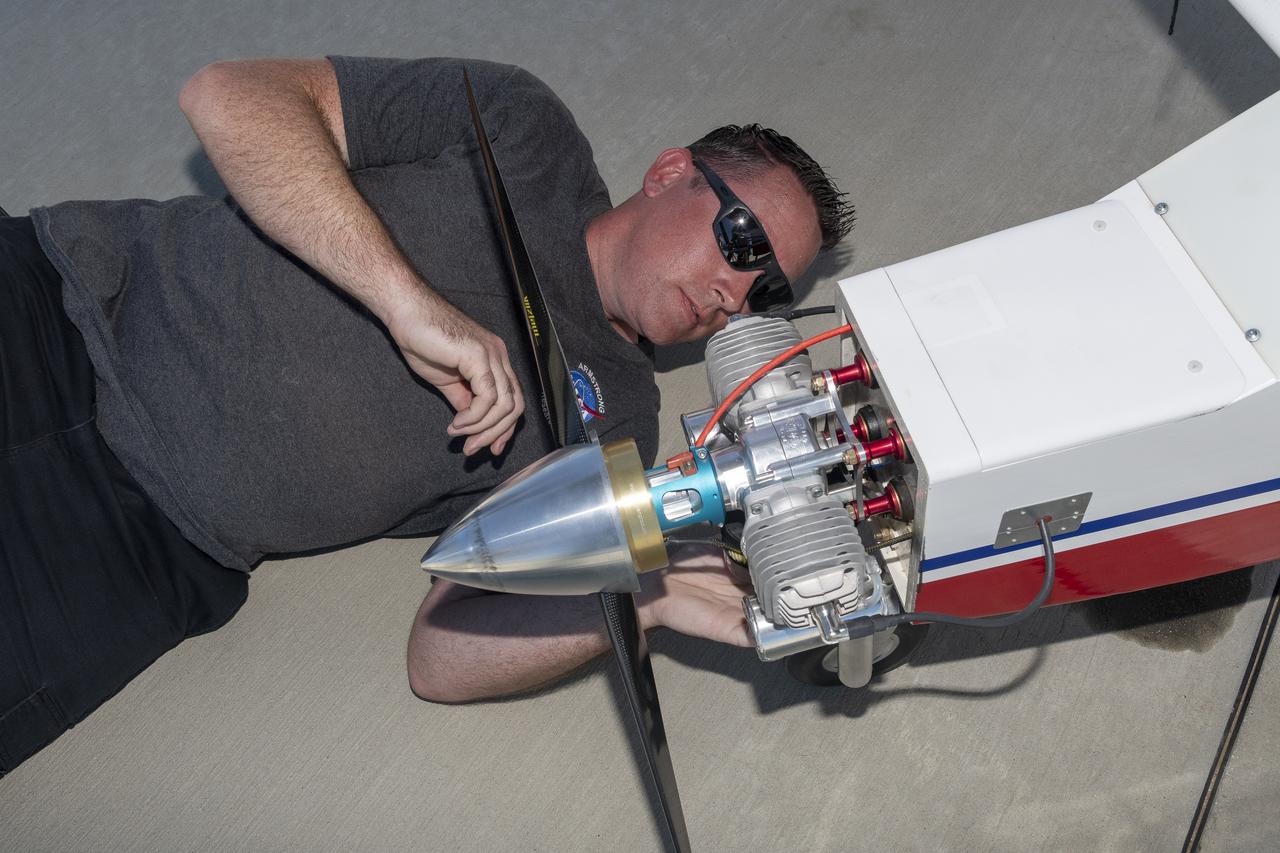

Justin Link prepares the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft before a flight for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
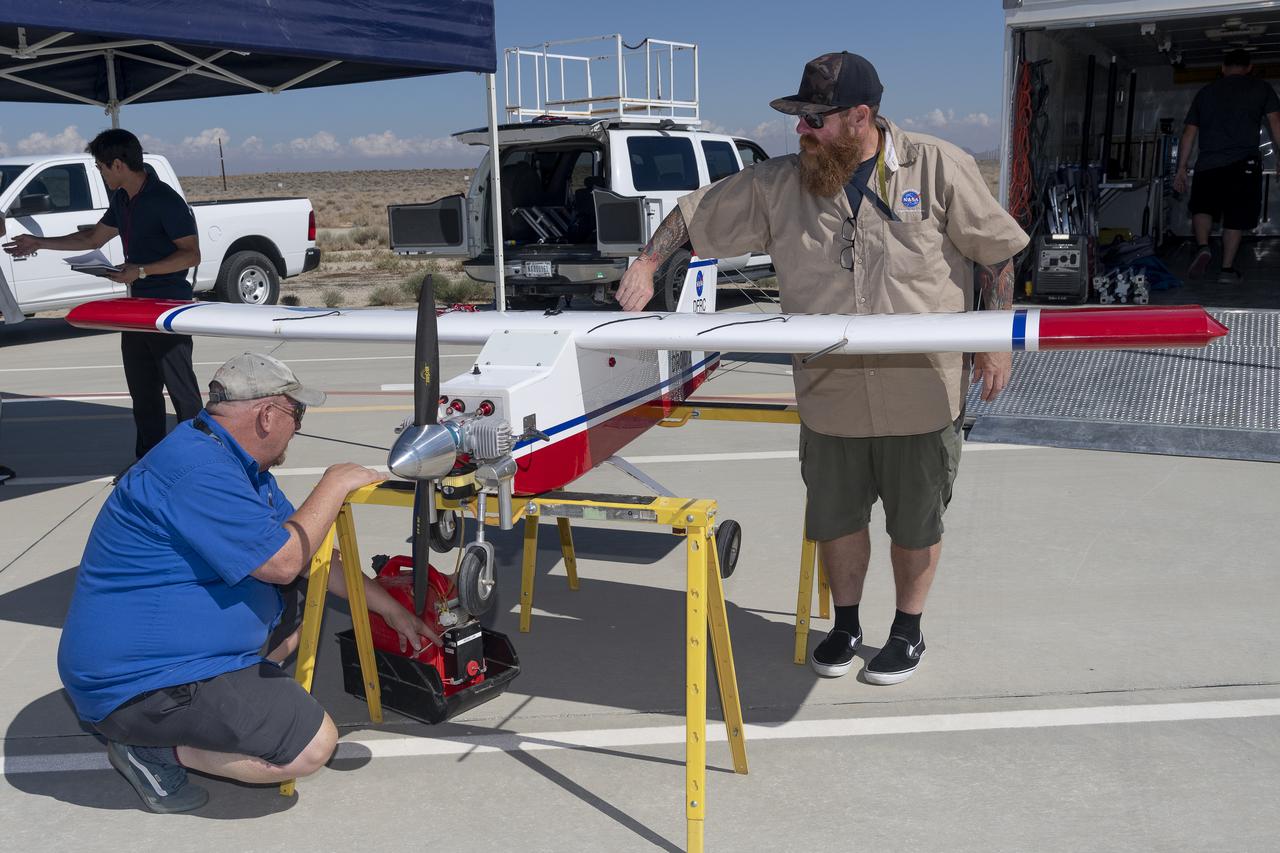

Robert "Red" Jensen and Justin Hall prepare the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign flights. The weather study was at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

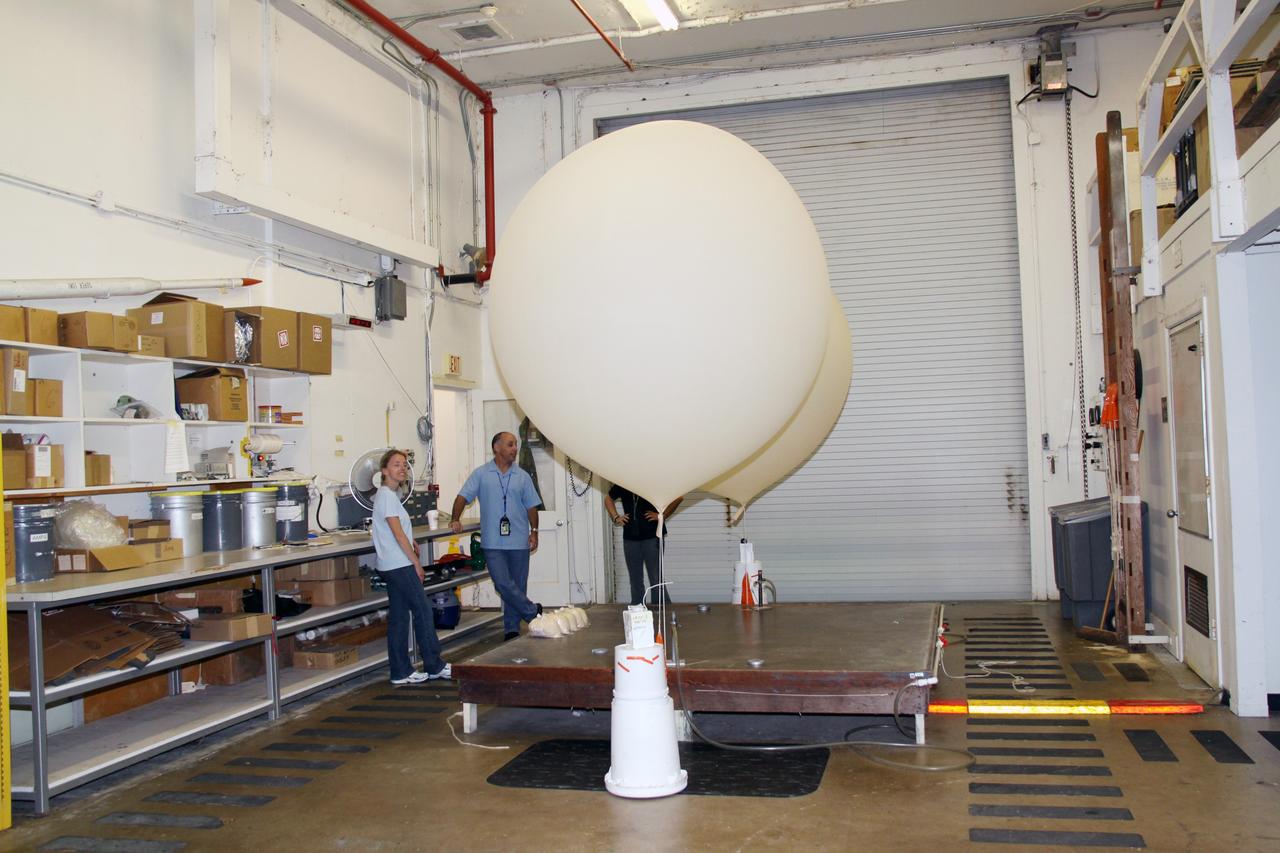
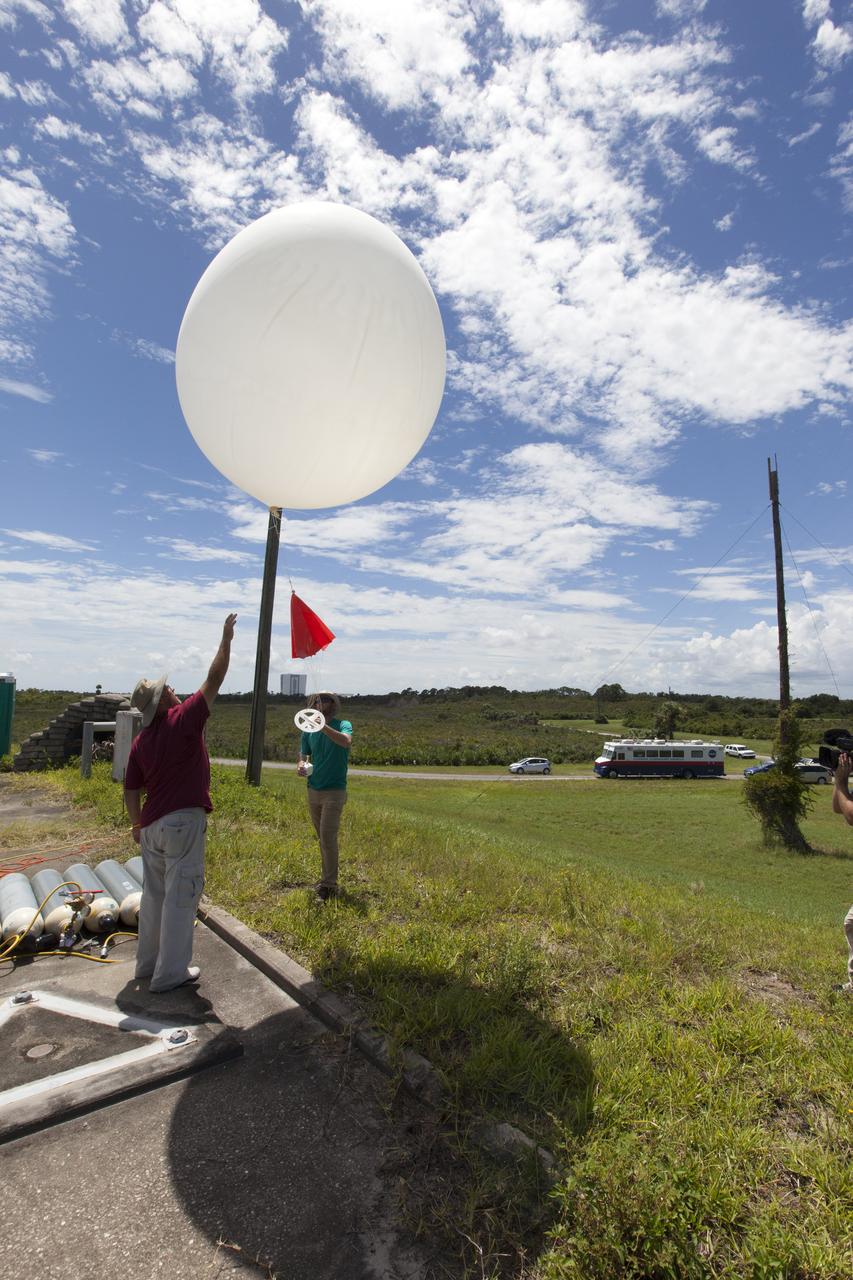
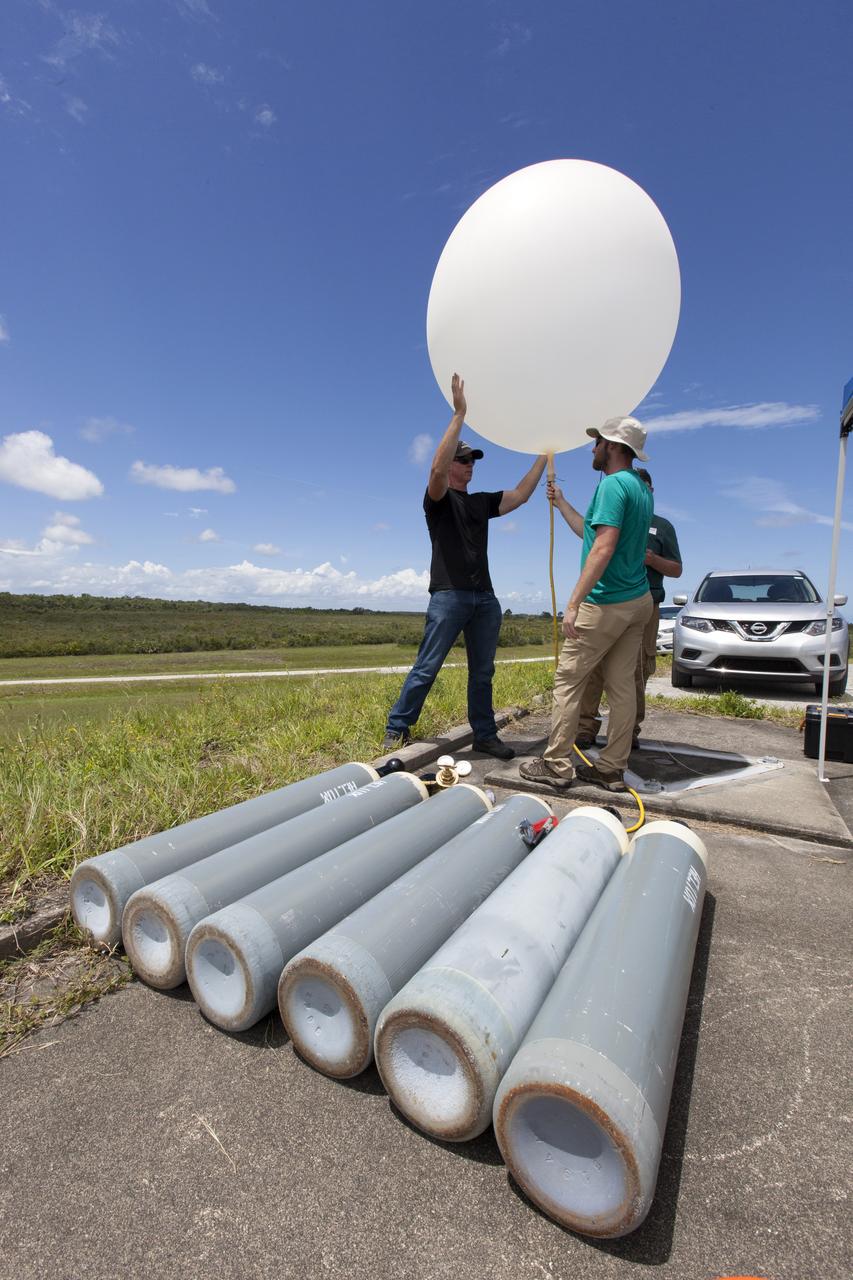
Rocky Garcia and Wesley James prepare a weather balloon to collect wind data for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
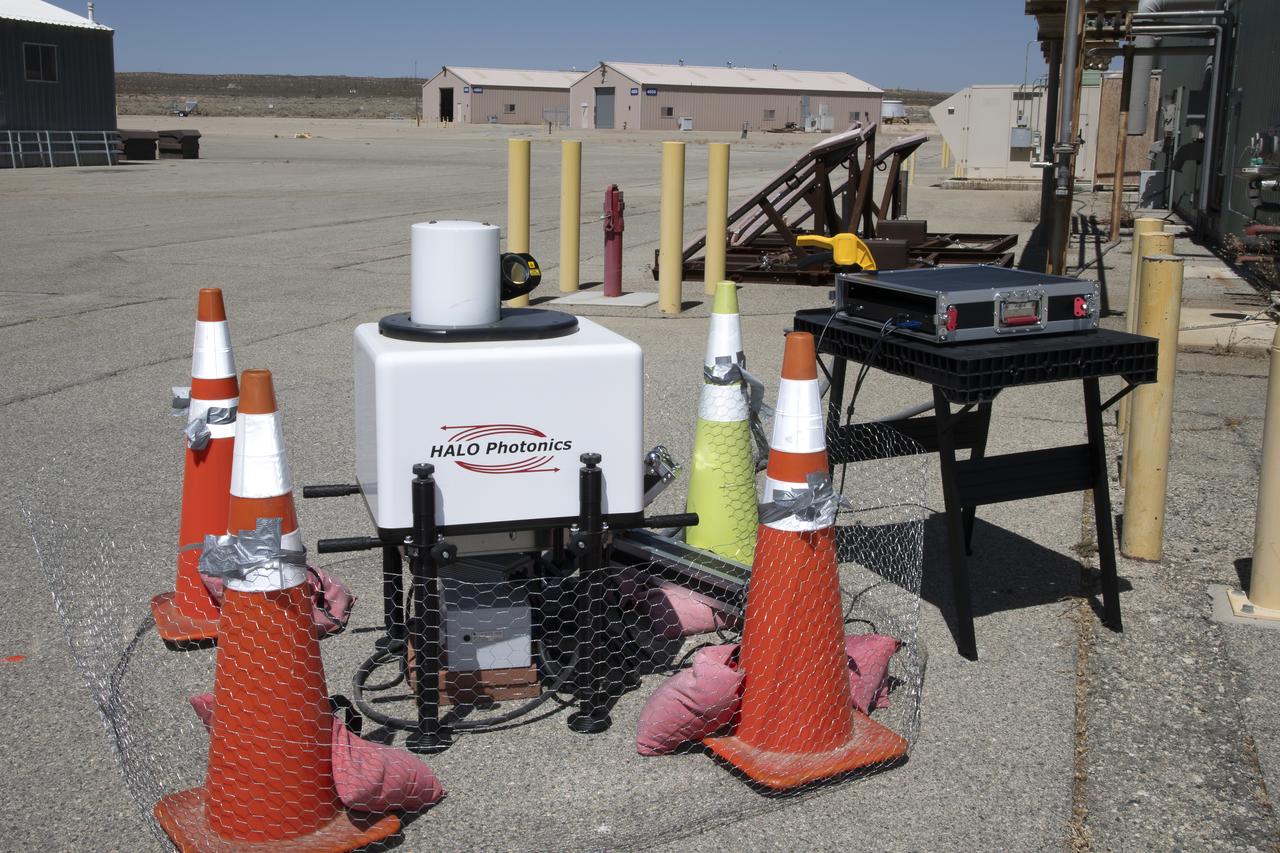

This is one of two lidar units positioned on either end of Building 4833 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, that formed the cutting-edge ‘virtual tower concept.’ The units use lasers to measure airflow from the ground level to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports, and to potentially improve weather prediction. It was part of the multi-faceted Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign.

The Alta-X aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.

Justin Hall lands the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
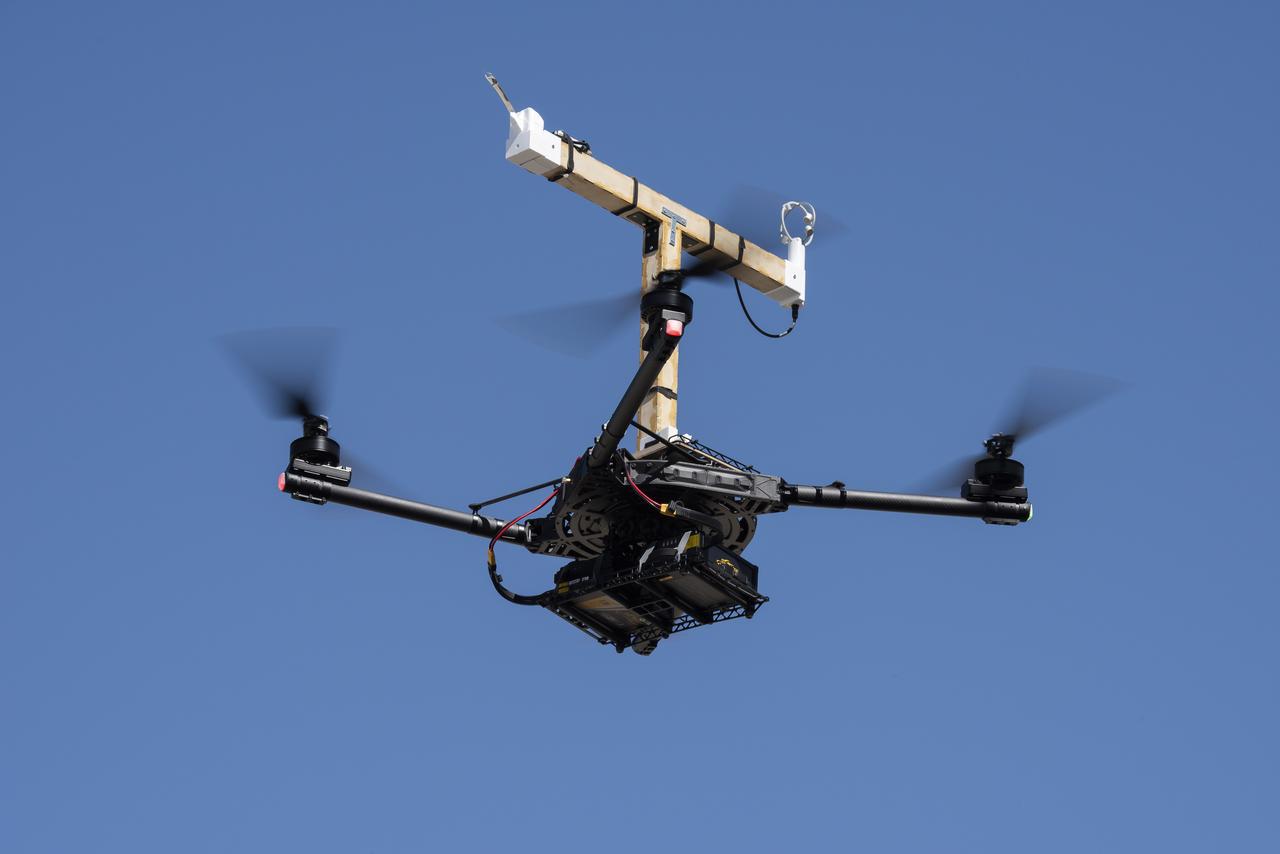

The Alta-X aircraft flies at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
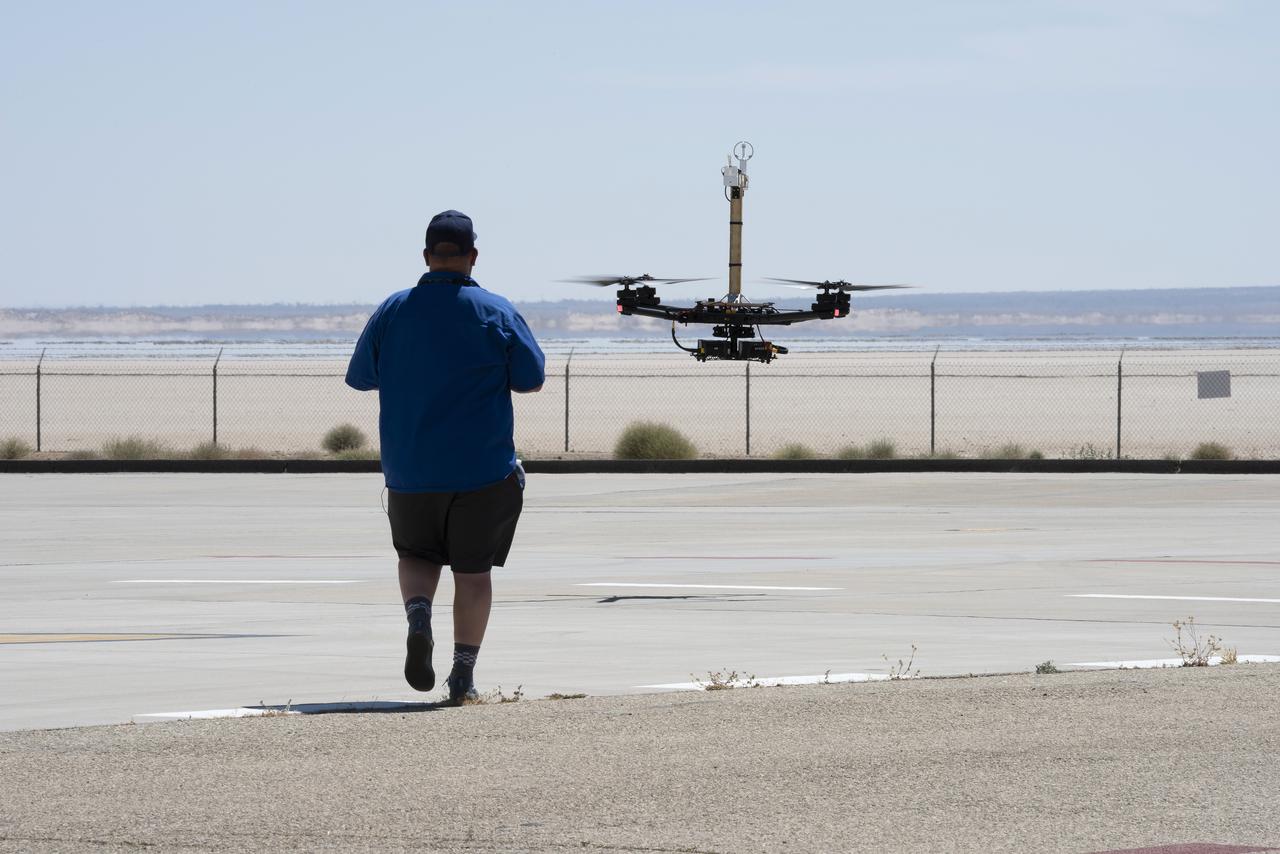

Red Jensen lands the Alta-X aircraft at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
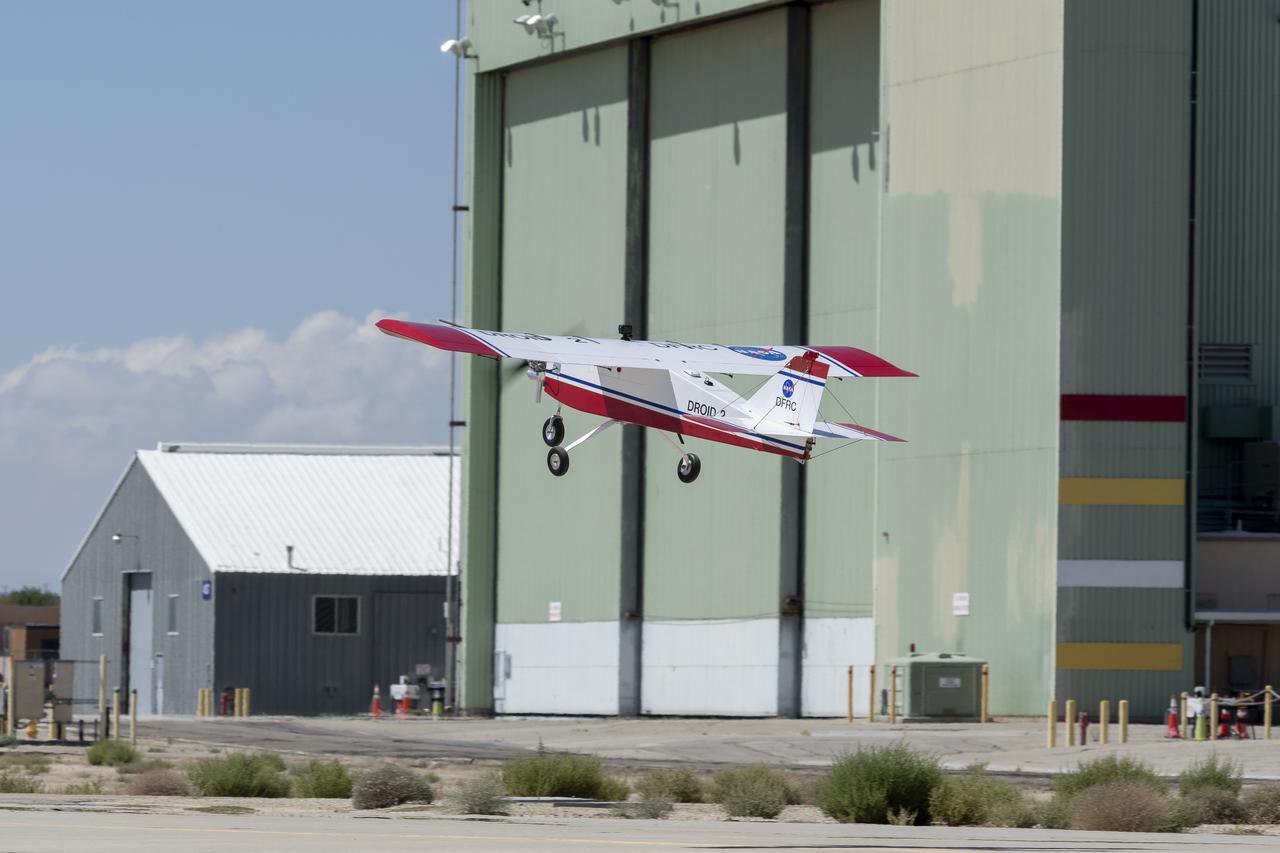

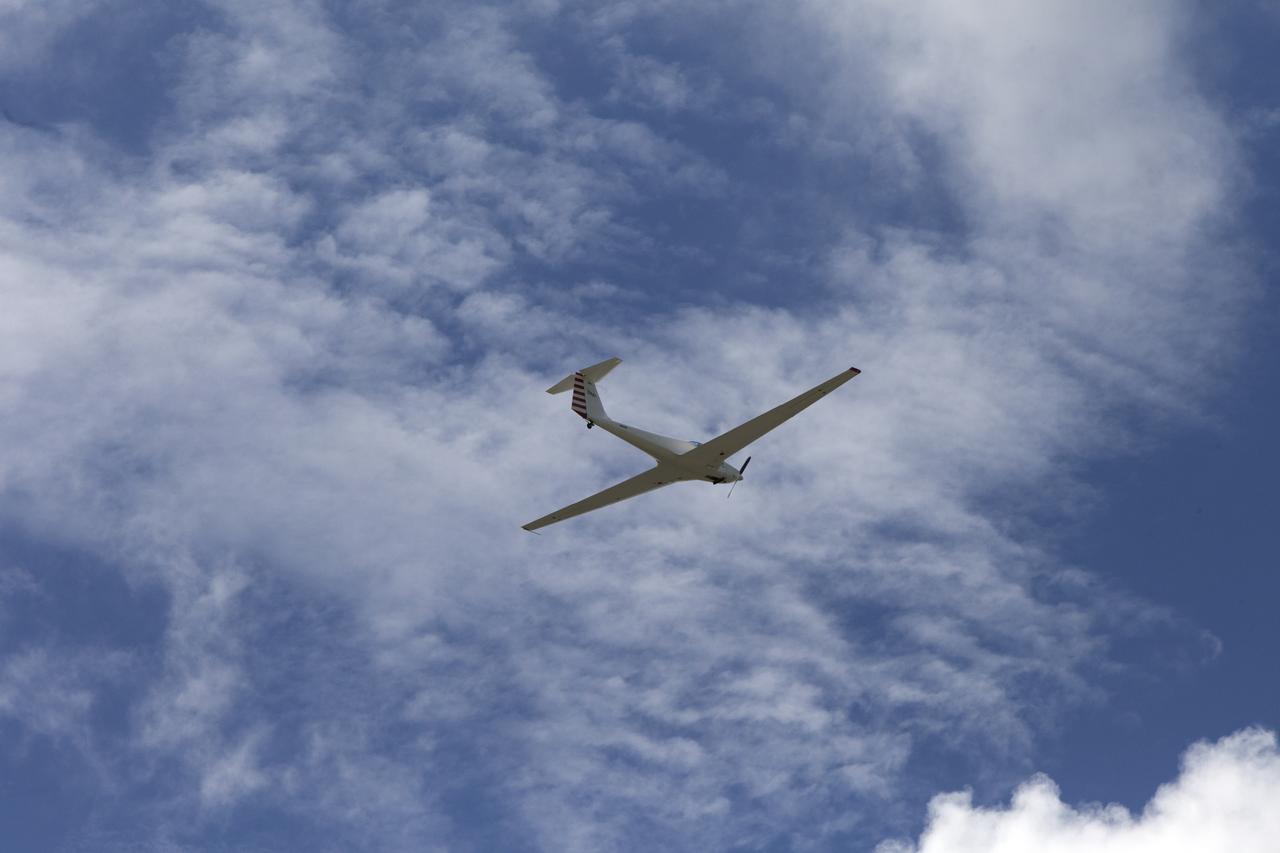
The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft flies by the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
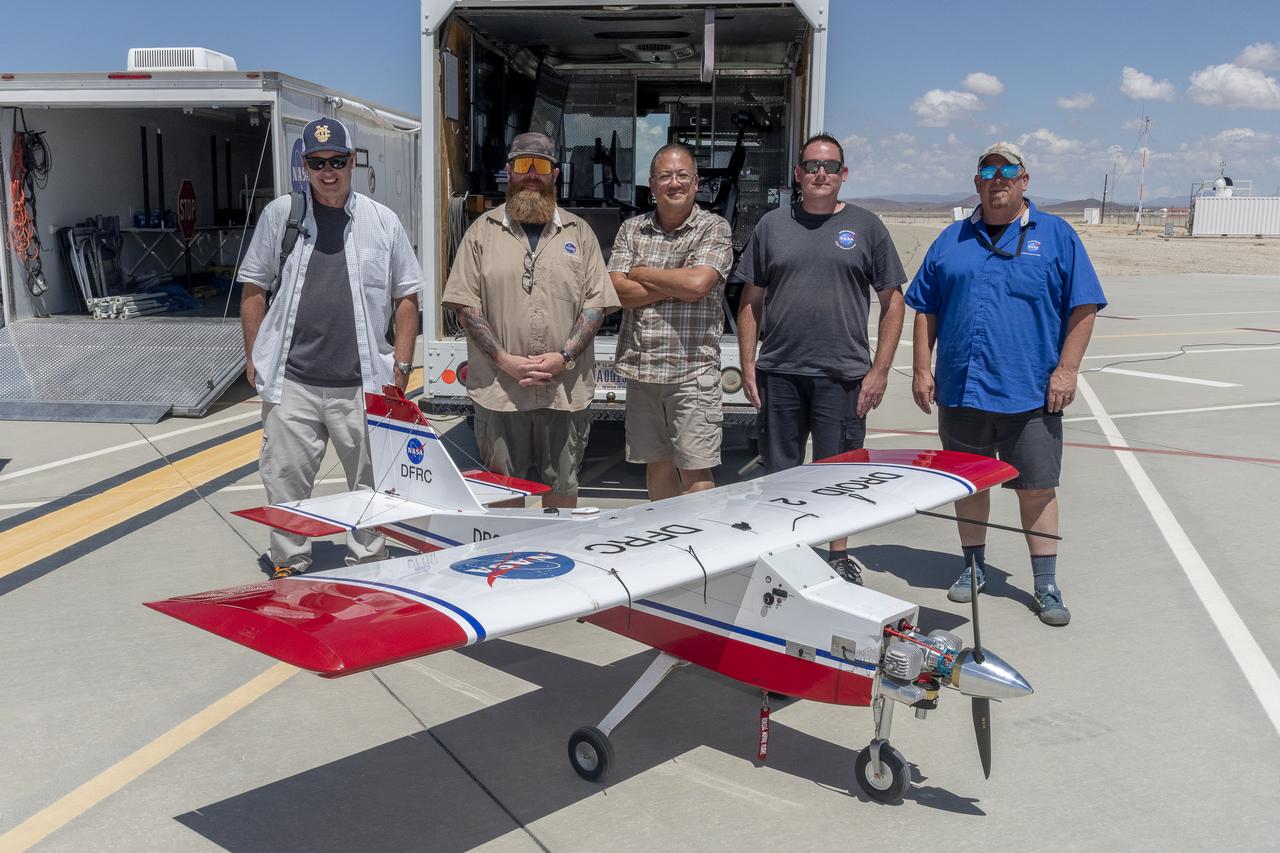

John Melton, Justin Hall, Derek Abramson, Justin Link, and Robert "Red" Jensen were key on mission day for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft supported the campaign at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
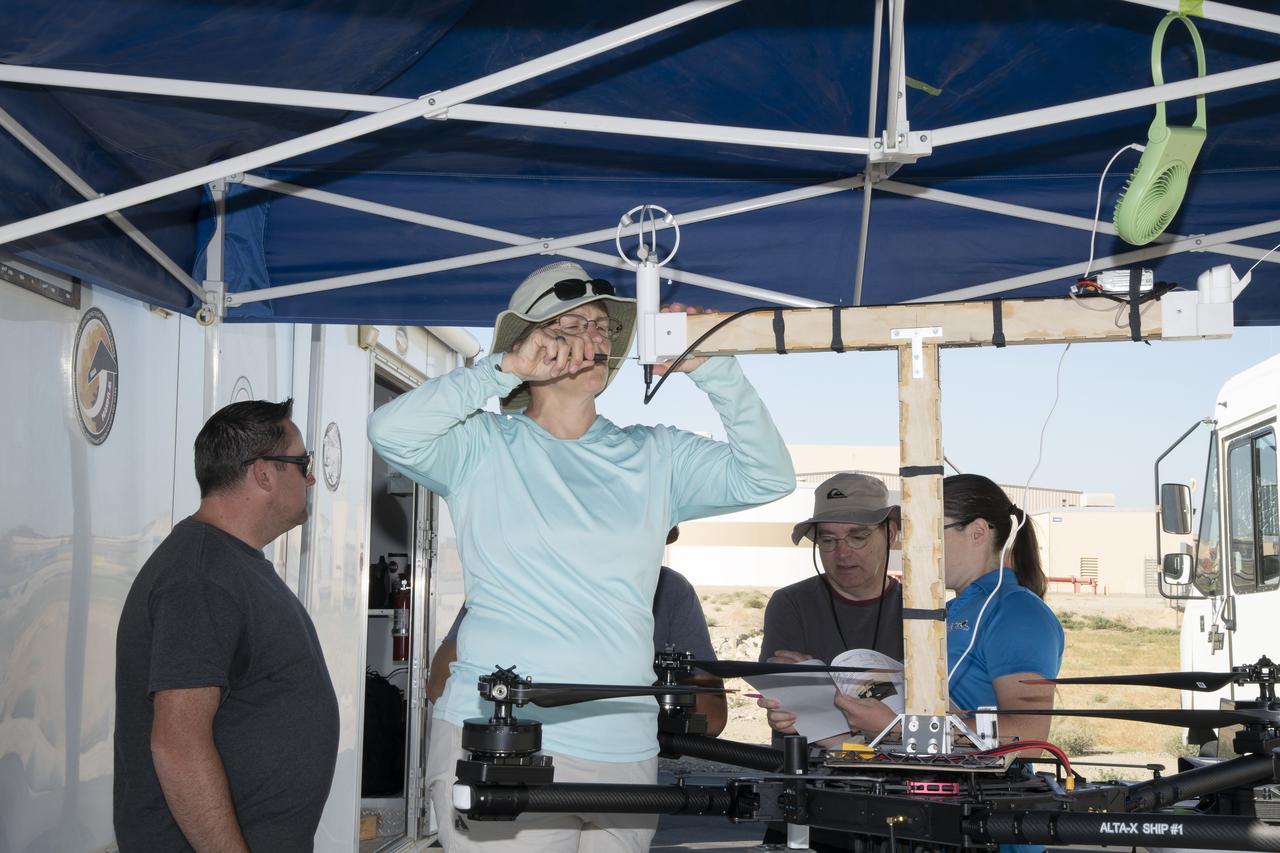

Jennifer Fowler works on securing sensors onto the test fixture on the Alta-X aircraft. Justin Link, Grady Koch, and Tyler Willhite are in the background. The Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies by a 140-foot instrumented tower and the former space shuttle hangar at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
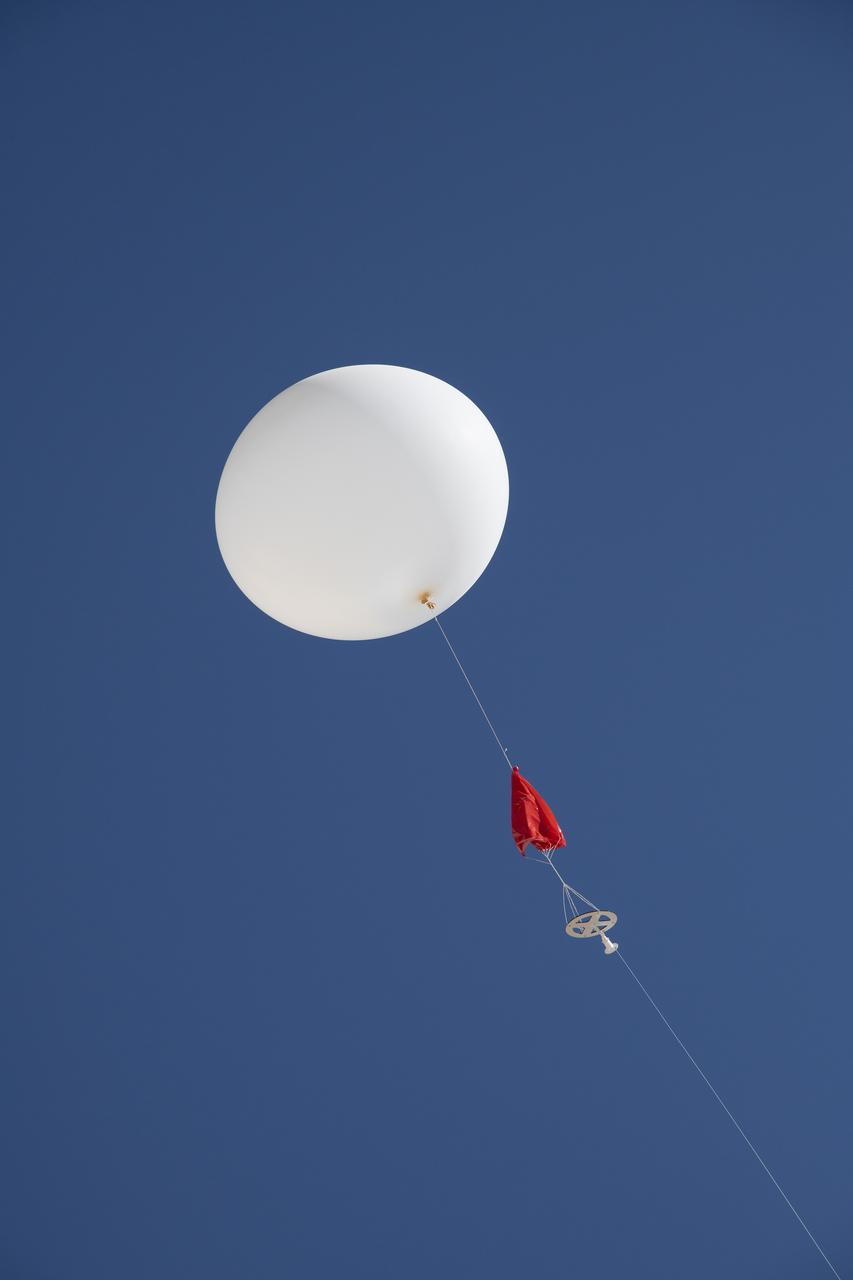

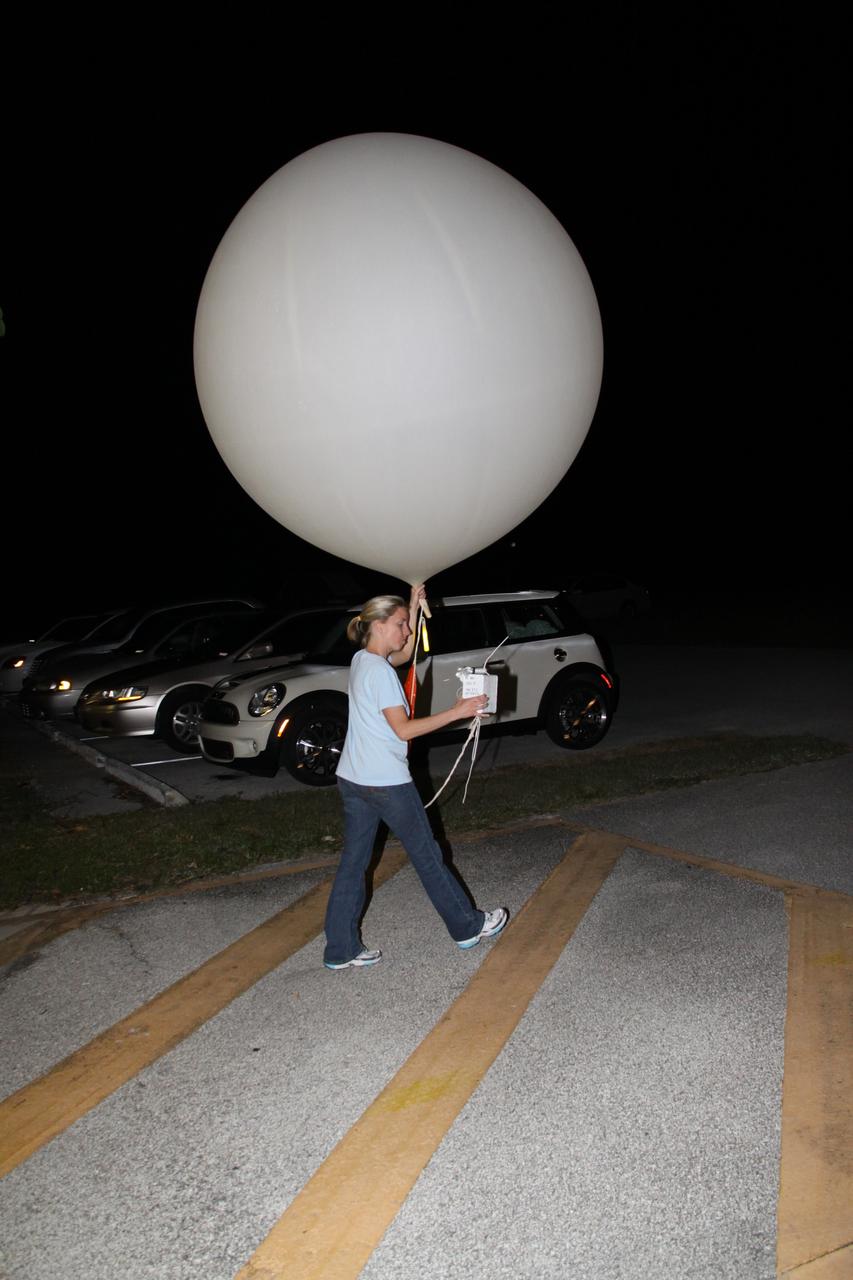
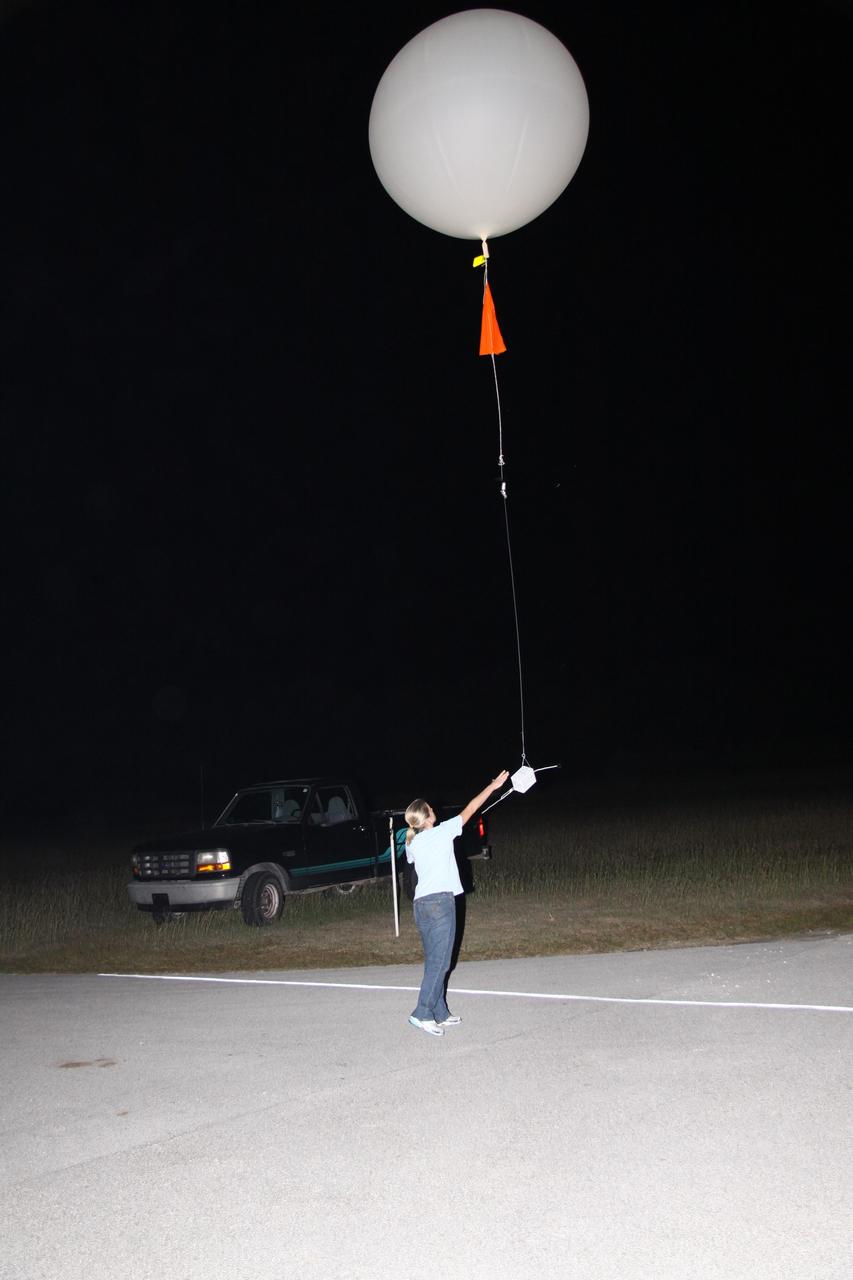
A weather balloon is launched to collect wind data for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
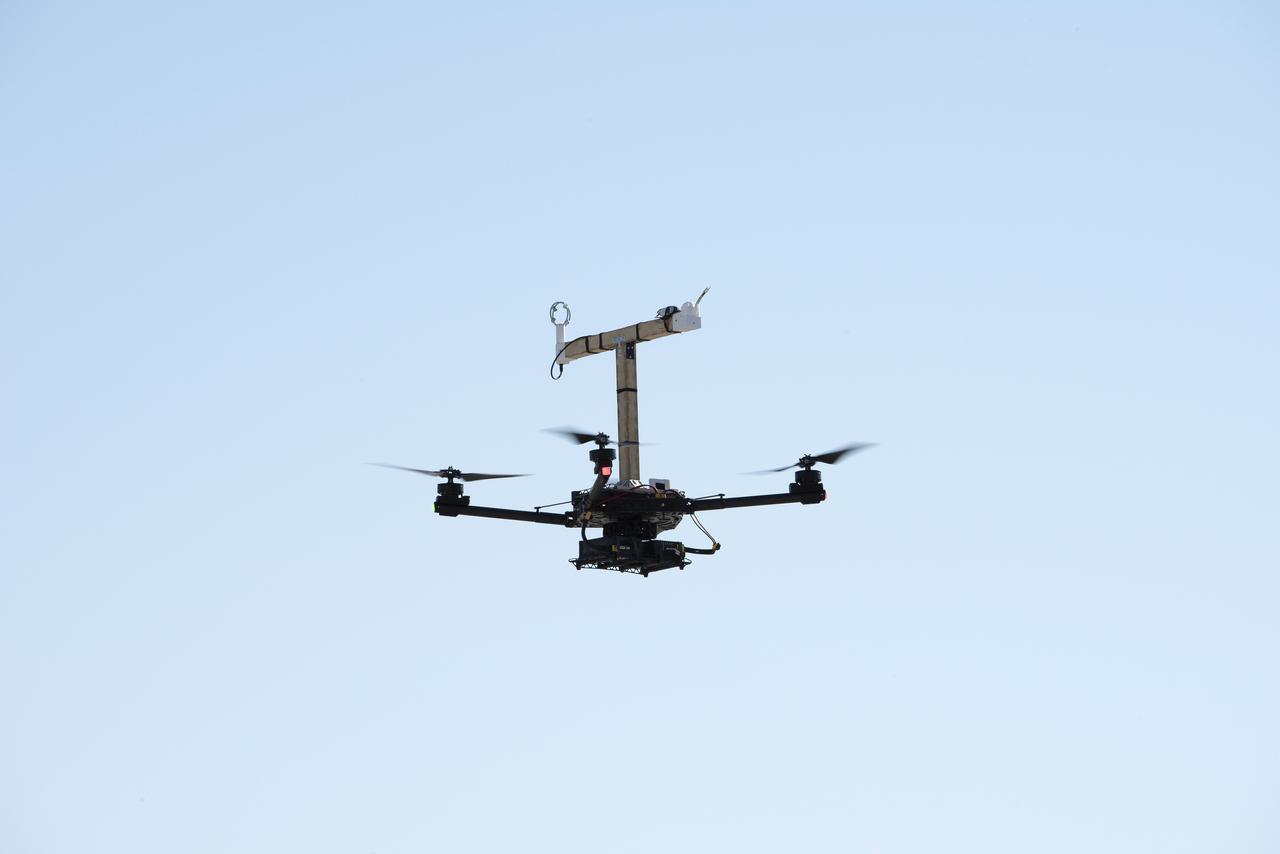

The Alta-X aircraft flies at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.

Justin Link, left, Red Jensen and Derek Abramson prepare for an Alta-X aircraft flight as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. In the background are Grady Koch and Jennifer Fowler. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
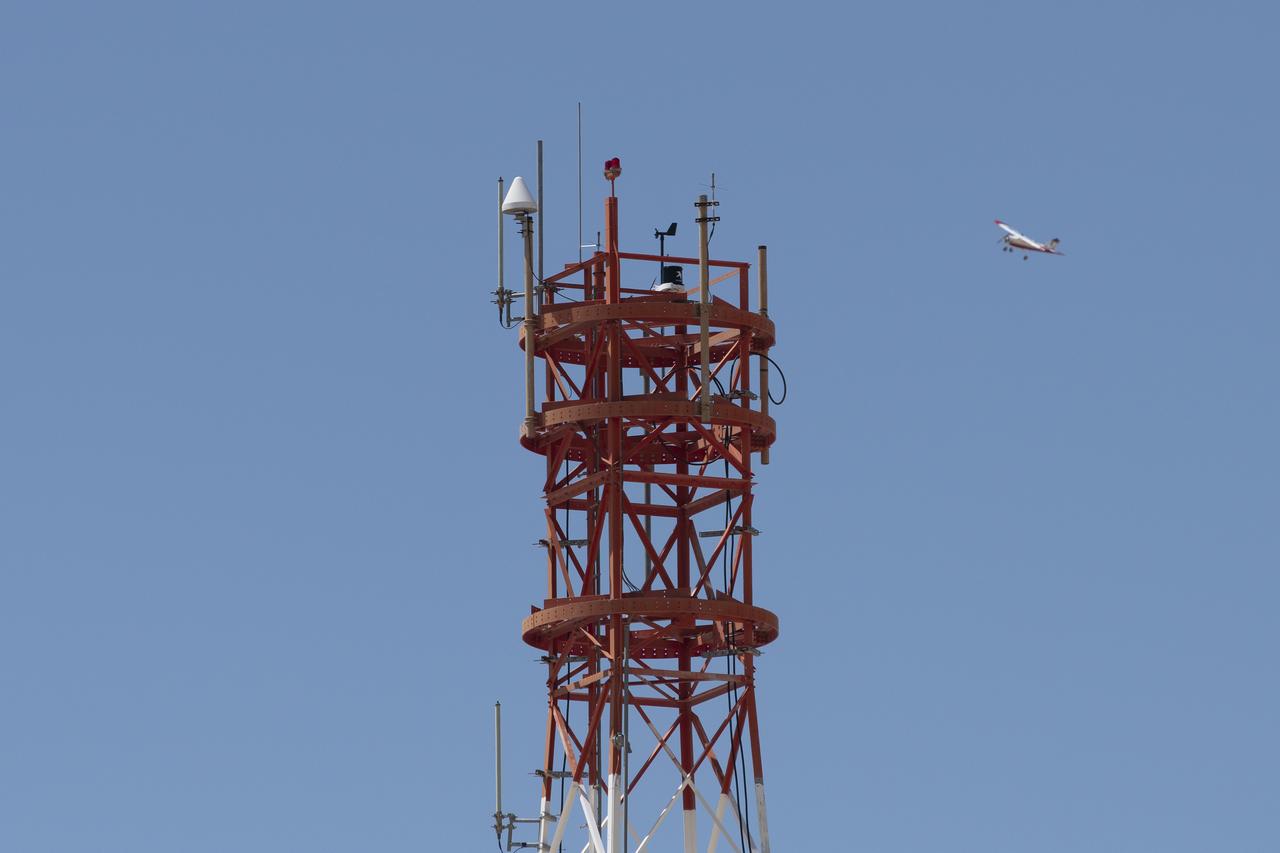

The DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) flies by a 140-foot instrumented tower at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

Robert "Red" Jensen lands the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.
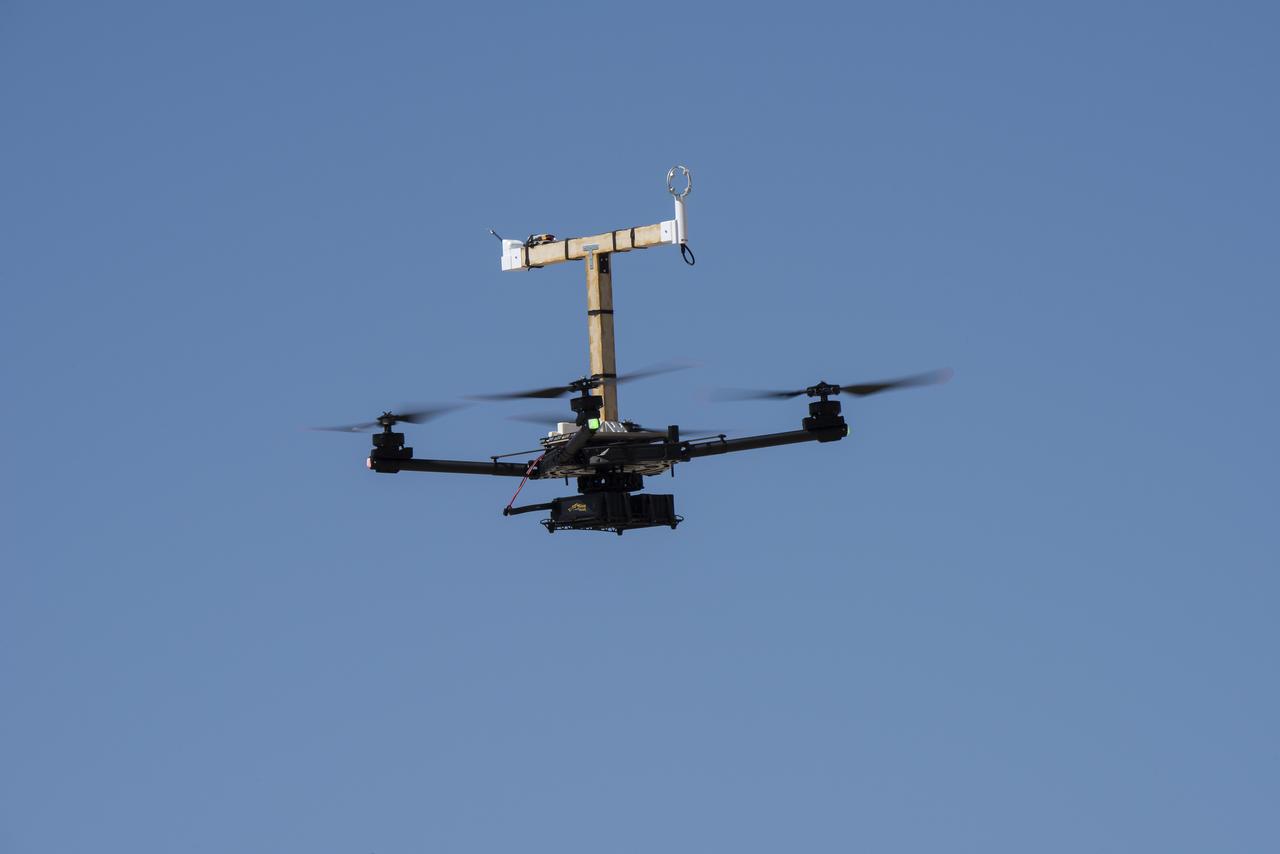

The Alta-X aircraft flies at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
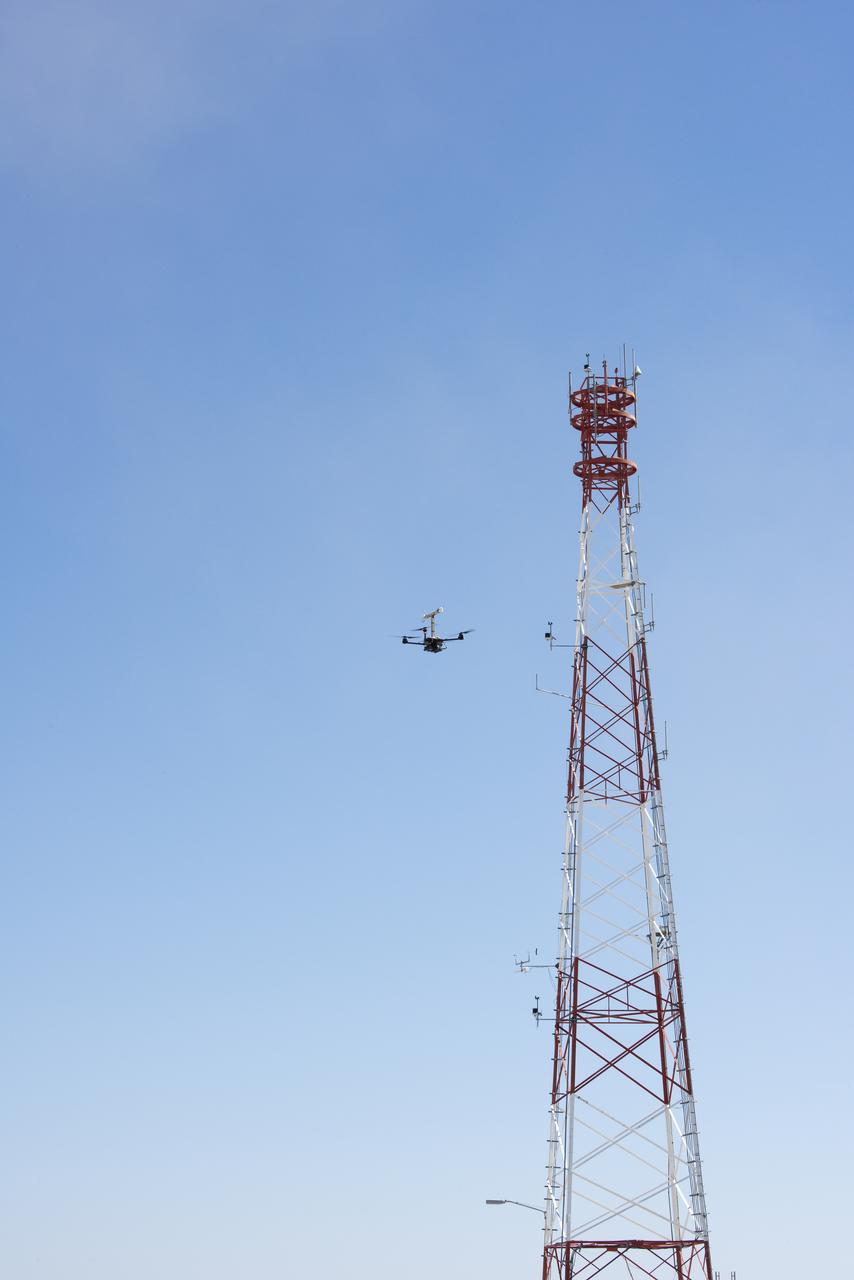

The Alta-X aircraft flies by a 140-foot instrumented tower at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The campaign was at NASA Armstrong to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
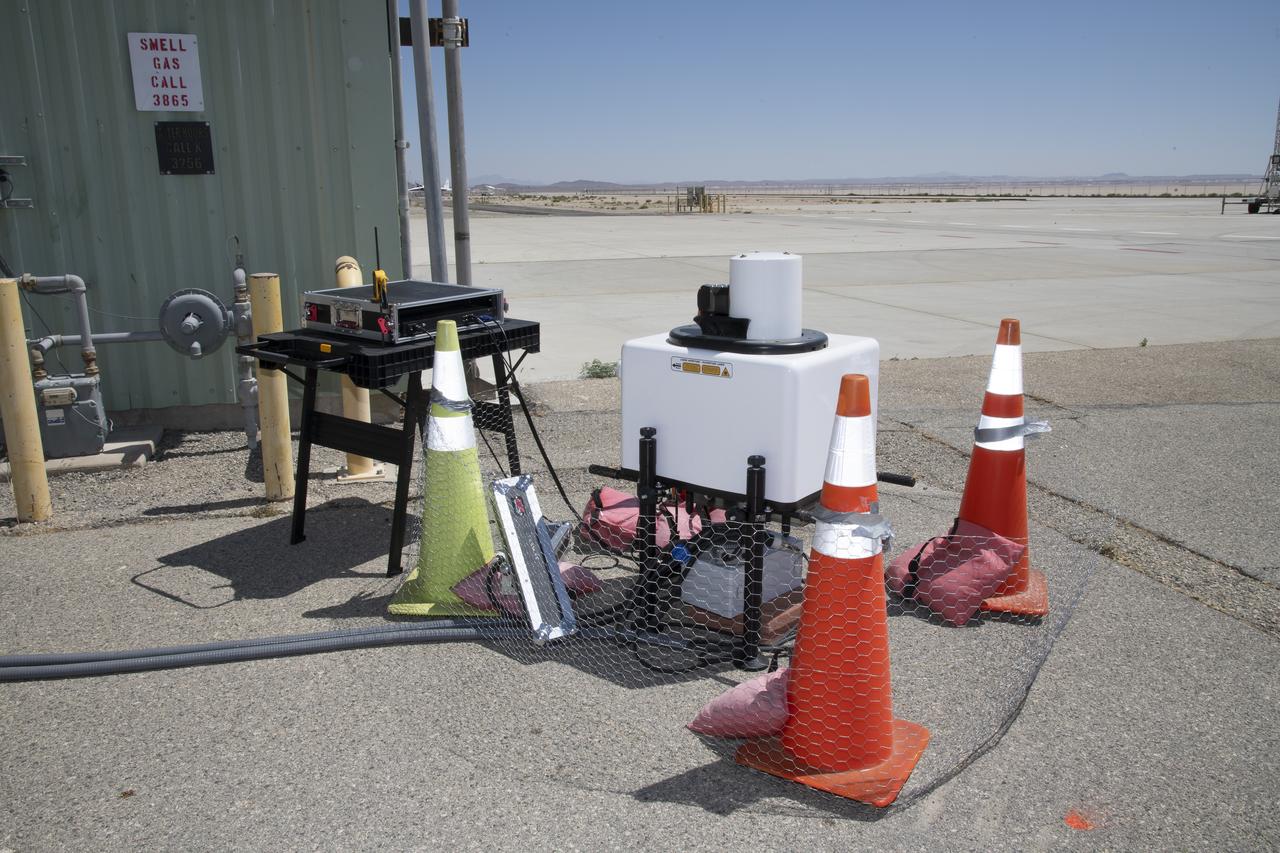

This is one of two lidar units positioned on either end of Building 4833 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, that formed the cutting-edge ‘virtual tower concept.’ The units use lasers to measure airflow from the ground level to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports, and to potentially improve weather prediction. It was part of the multi-faceted Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign.
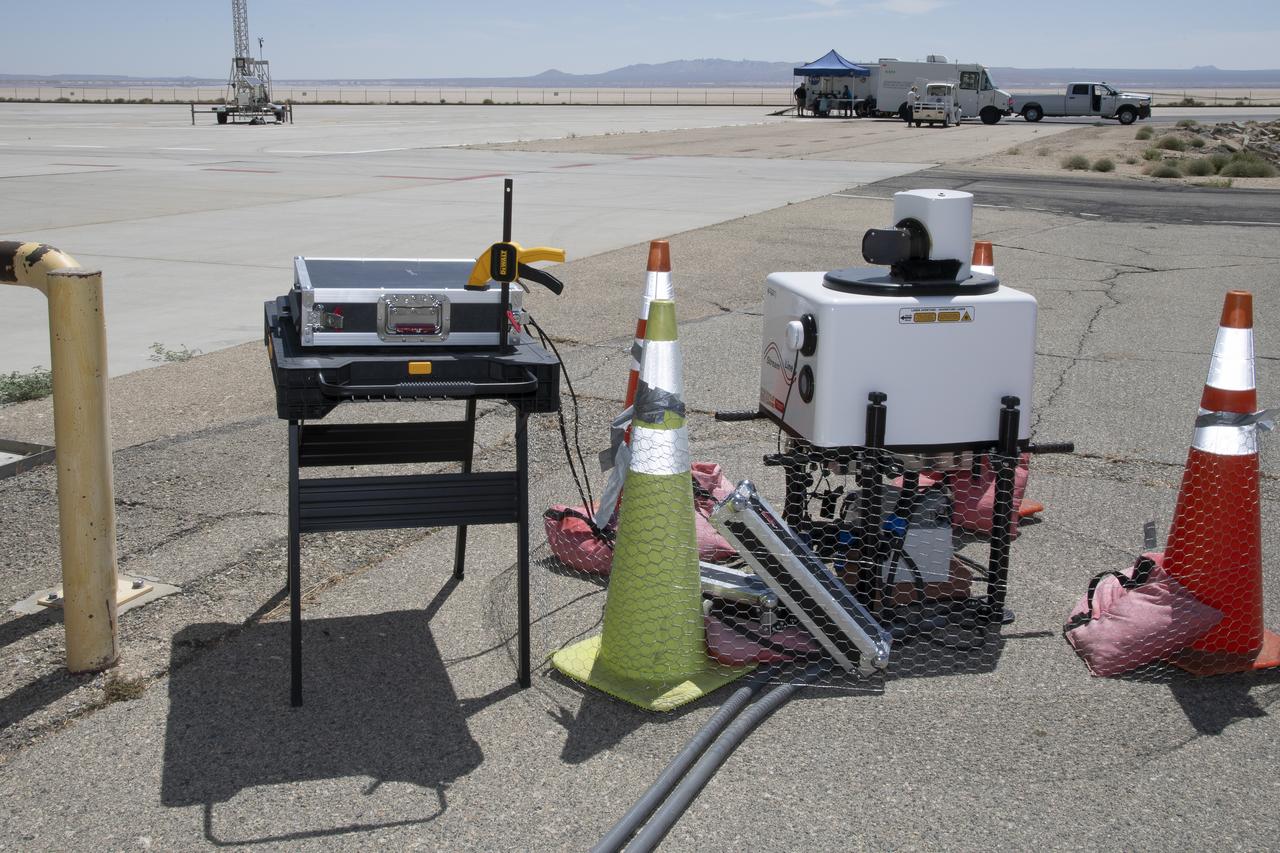

This is one of two lidar units positioned on either end of Building 4833 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, that formed the cutting-edge ‘virtual tower concept.’ The units use lasers to measure airflow from the ground level to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports, and to potentially improve weather prediction. It was part of the multi-faceted Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign.
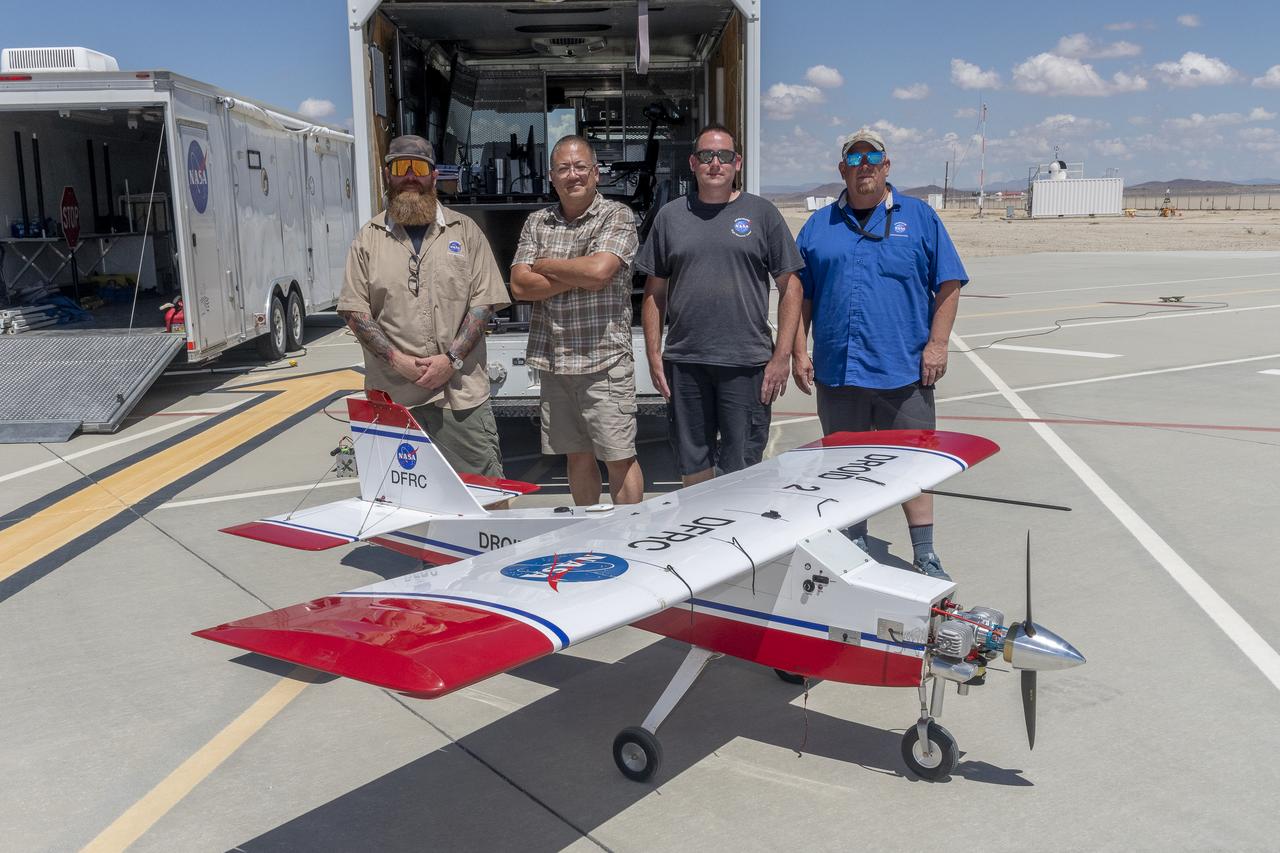

Justin Hall, Derek Abramson, Justin Link, and Robert "Red" Jensen were key to a successful mission for the DROID 2 (Dryden Remotely Operated Integrated Drone 2) aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The aircraft flew as part of the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation, and Technology campaign. The focus was to study wind to provide data for safe takeoff and landing of future air taxis.

This is one of two lidar units positioned on either end of Building 4833 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, that formed the cutting-edge ‘virtual tower concept.’ The units use lasers to measure airflow from the ground level to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports, and to potentially improve weather prediction. It was part of the multi-faceted Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign.
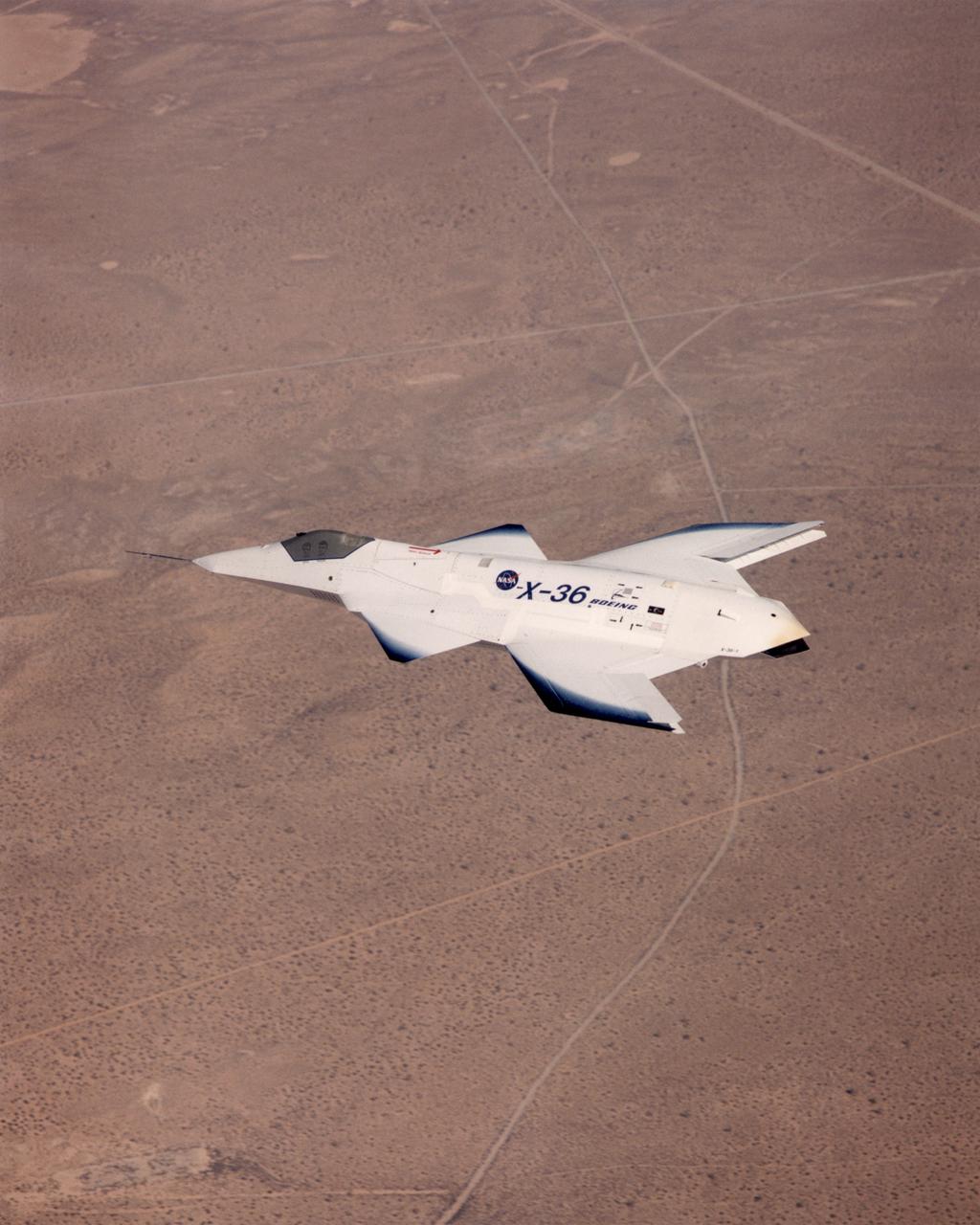

The tailless X-36 technology demonstrator research aircraft cruises over the California desert at low altitude during a 1997 research flight.
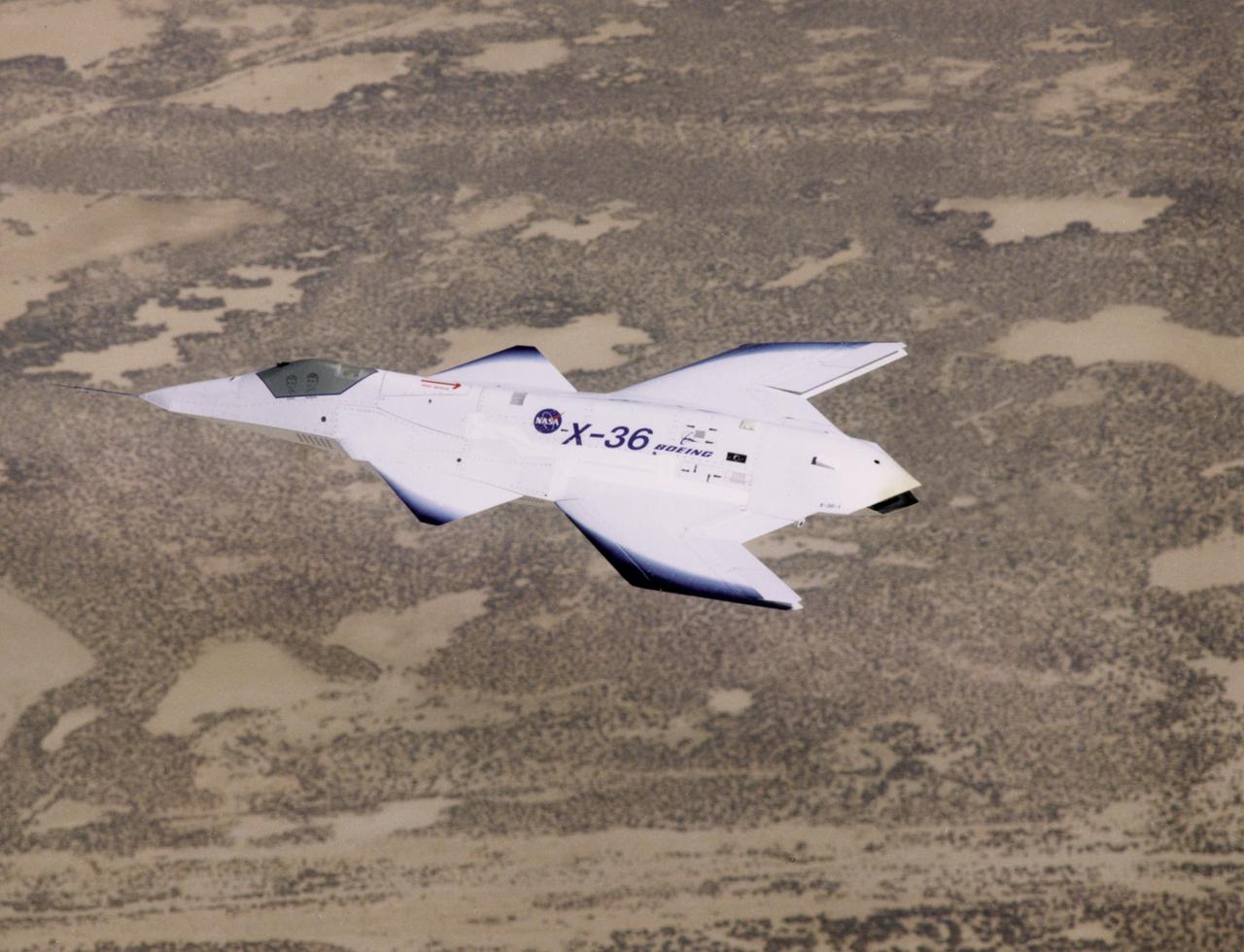

The unusual lines of the X-36 technology demonstrator contrast sharply with the desert floor as the remotely piloted aircraft scoots across the California desert at low altitude during a research flight on October 30, 1997.
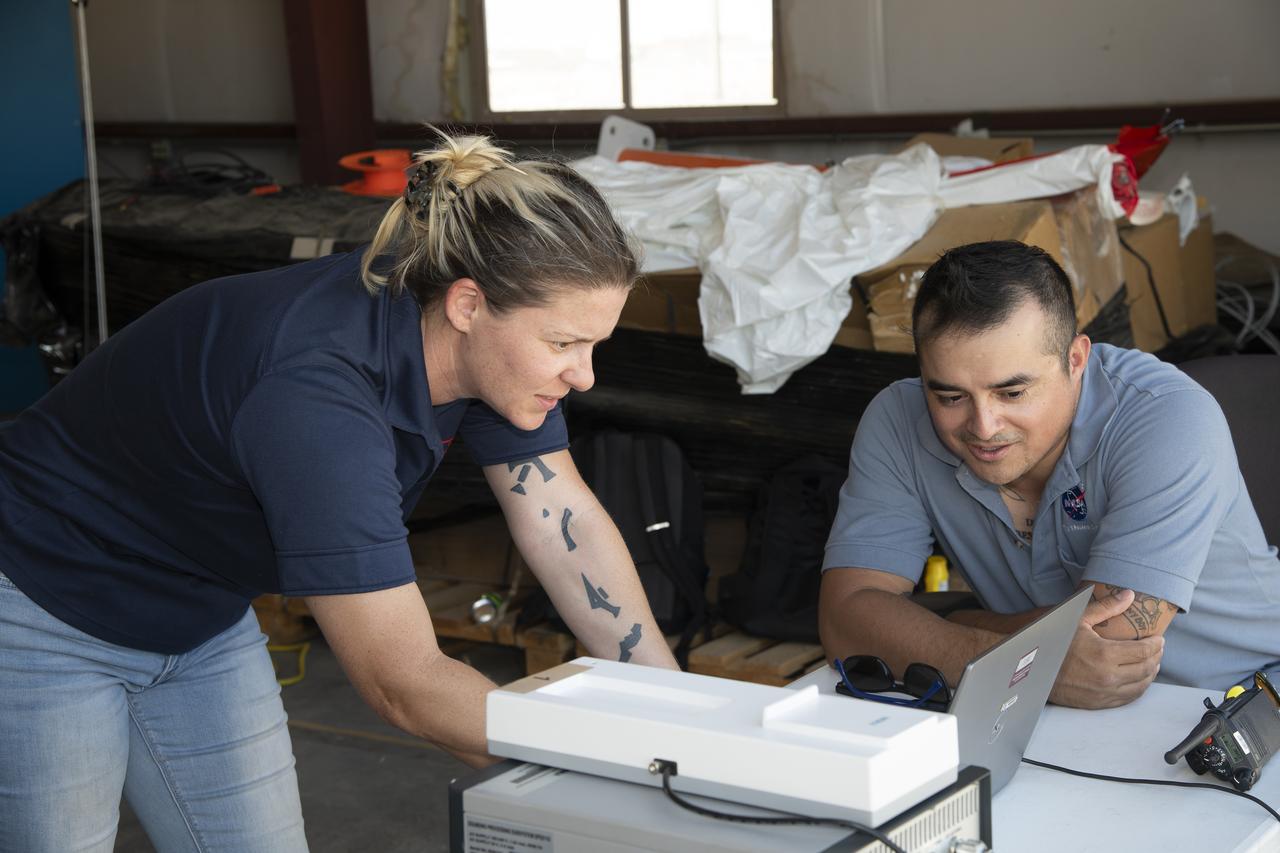

Tegan French and Rocky Garcia are at a weather balloon system’s ground station monitoring temperature, humidity, pressure, and winds transmitted from an instrument package on the balloon as it ascends. The balloon is part of the different methods to collect wind and weather data for the Advanced Exploration of Reliable Operation at Low Altitudes: Meteorology, Simulation and Technology campaign. The weather study was at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The focus was to study wind from the ground to 2,000 feet to provide data to assist future drones to safely land on rooftop hubs called vertiports and to potentially improve weather prediction.
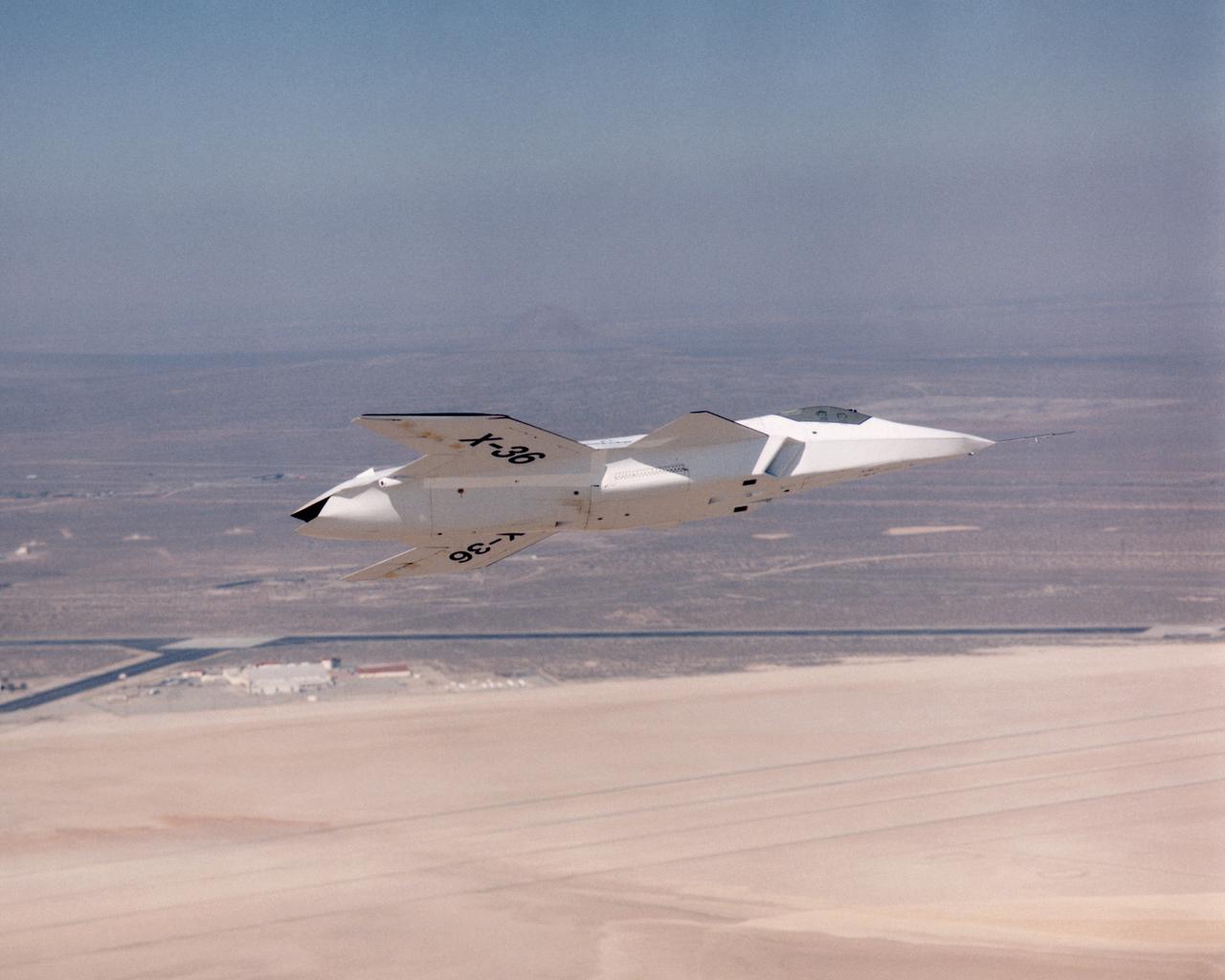

The lack of a vertical tail on the X-36 technology demonstrator is evident as the remotely piloted aircraft flies a low-altitude research flight above Rogers Dry Lake at Edwards Air Force Base in the California desert on October 30, 1997.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Life Sciences Laboratory near NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Mars Simulation Chamber is being prepared for the Microorganisms in the Stratosphere, or MIST, mission support. The chamber allows MIST scientists and engineers to simulate the stratosphere prior to high altitude flight experiments. The MIST mission will fly a small biological payload in low altitudes aboard a blimp in July to measure microbial survival and cellular responses to exposure in the upper atmosphere. Later in the year, the MIST mission will deploy samples at even high altitudes in the stratosphere using scientific balloons. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the weather station on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a meteorological data specialist prepares to release a low resolution flight element rawinsonde to support the countdown for the flight test of NASA's Ares I-X rocket. A GPS-tracked weather balloon, a rawinsonde has a tethered instrument package which radios its altitude to the ground along with atmospheric data such as temperature, dewpoint and humidity, and wind speed and direction. Rawinsondes can reach altitudes up to 110,000 feet. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the weather station on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, meteorological data specialists prepare two low resolution flight element rawinsonde to support the countdown for the flight test of NASA's Ares I-X rocket. A GPS-tracked weather balloon, a rawinsonde has a tethered instrument package which radios its altitude to the ground along with atmospheric data such as temperature, dewpoint and humidity, and wind speed and direction. Rawinsondes can reach altitudes up to 110,000 feet. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the weather station on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a meteorological data specialist prepares a low resolution flight element rawinsonde to support the countdown for the flight test of NASA's Ares I-X rocket. A GPS-tracked weather balloon, a rawinsonde has a tethered instrument package which radios its altitude to the ground along with atmospheric data such as temperature, dewpoint and humidity, and wind speed and direction. Rawinsondes can reach altitudes up to 110,000 feet. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - At the weather station on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, a meteorological data specialist releases a low resolution flight element rawinsonde to support the countdown for the flight test of NASA's Ares I-X rocket. A GPS-tracked weather balloon, a rawinsonde has a tethered instrument package which radios its altitude to the ground along with atmospheric data such as temperature, dewpoint and humidity, and wind speed and direction. Rawinsondes can reach altitudes up to 110,000 feet. For information on the Ares I-X vehicle and flight test, visit http://www.nasa.gov/aresIX. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
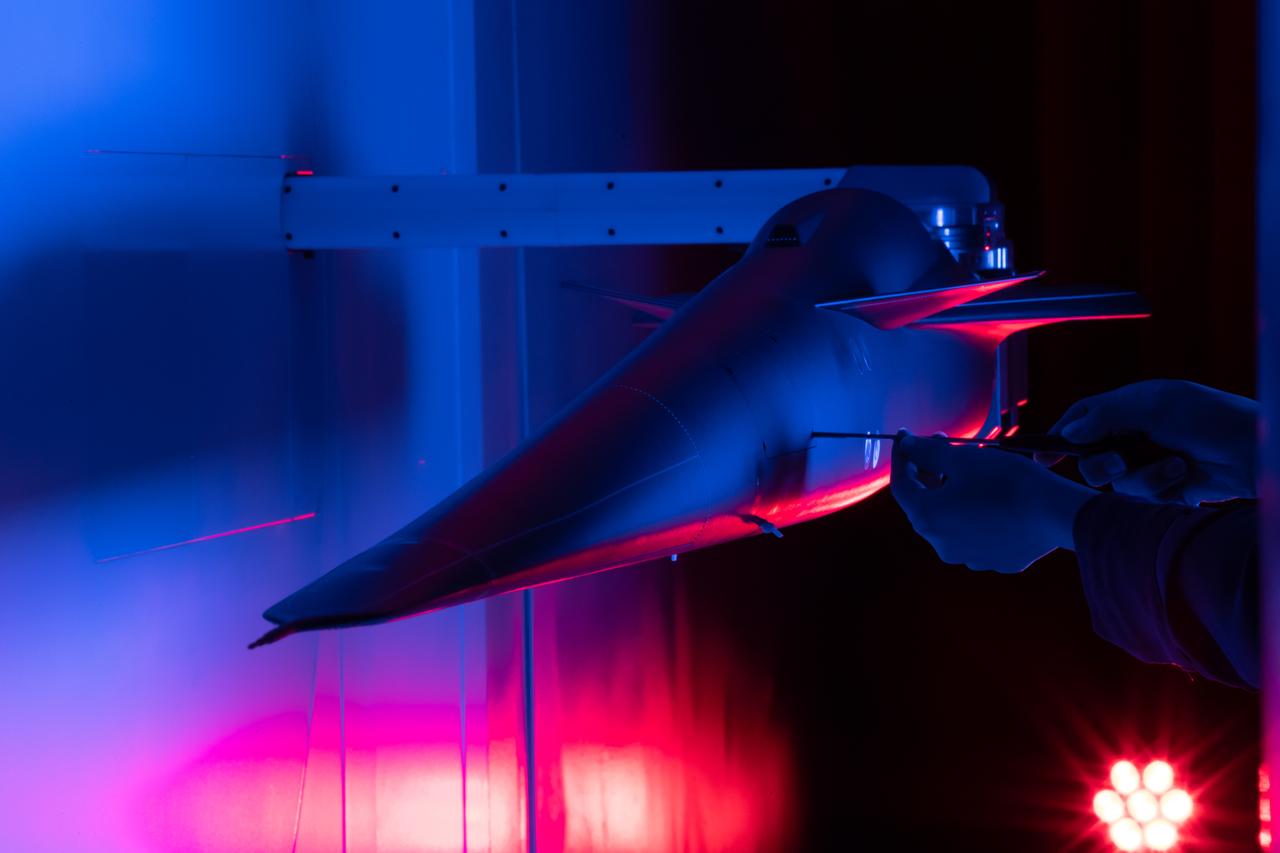

Event: Forebody and Nose - Windtunnel Testing A technician works on the X-59 model during testing in the low-speed wind tunnel at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. These tests gave the team measurements of wind flow angle around the aircraft’s nose and confirmed computer predictions made using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software tools. The data will be fed into the aircraft flight control system to tell the pilot the aircraft’s altitude, speed, and angle. This is part of NASA’s Quesst mission which plans to help enable supersonic air travel over land.
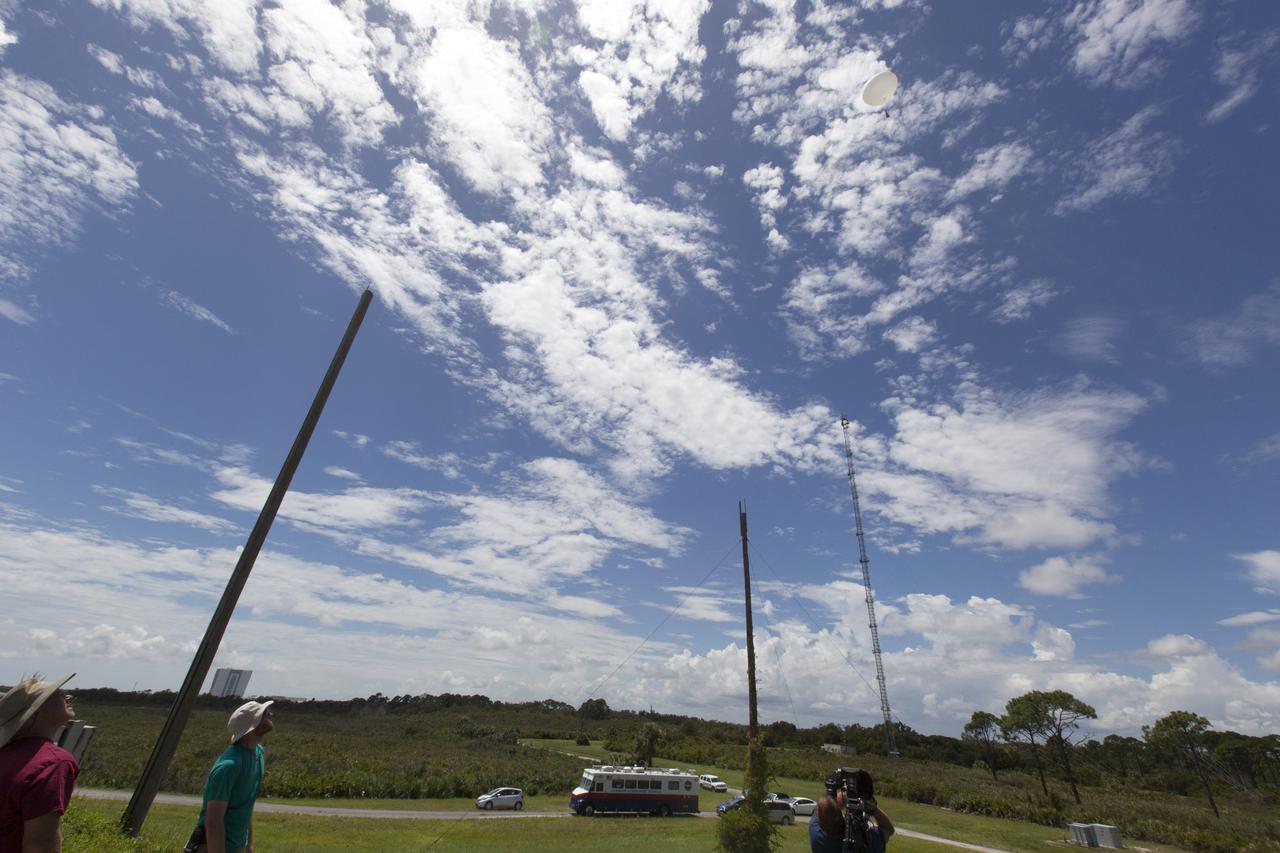

A weather balloon is released at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
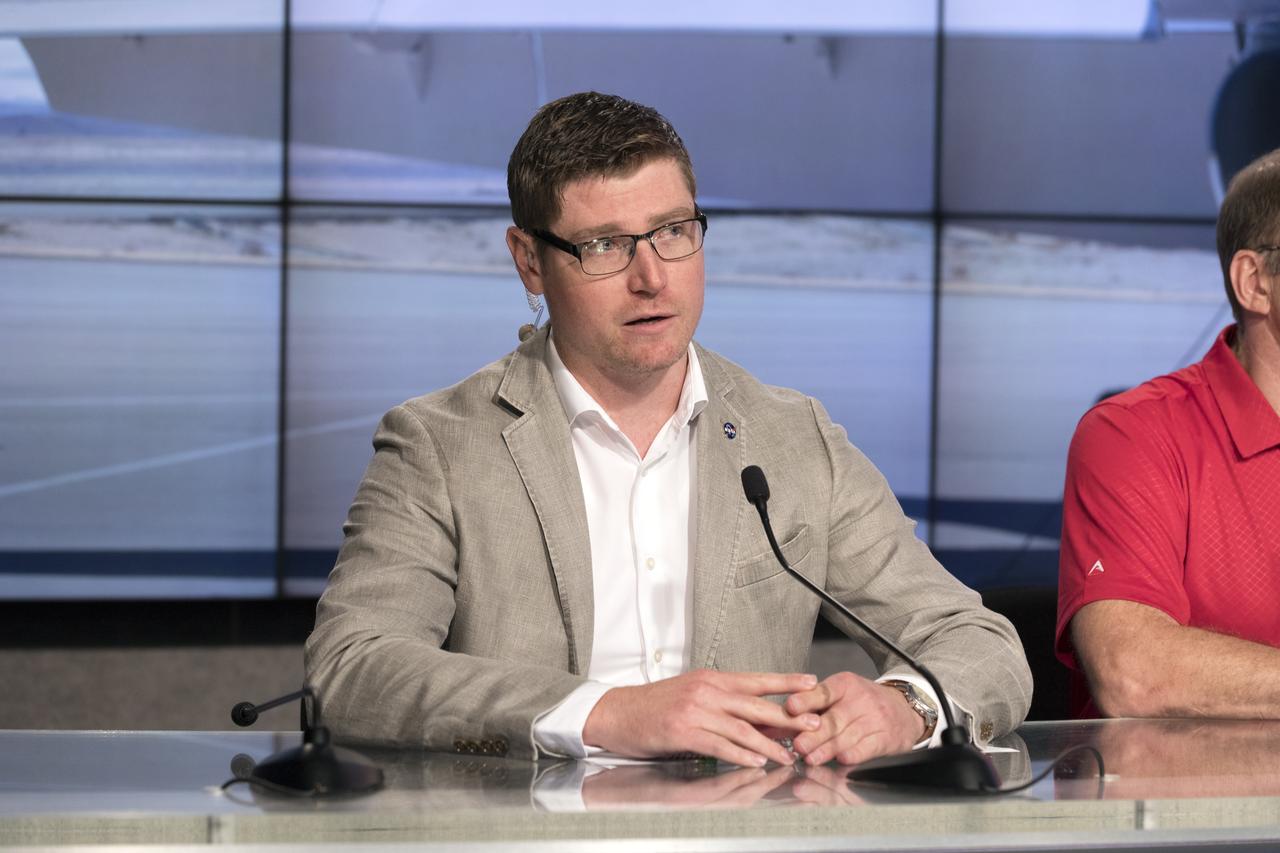

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Matthew Kamlet of NASA Communications at the Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, speaks to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
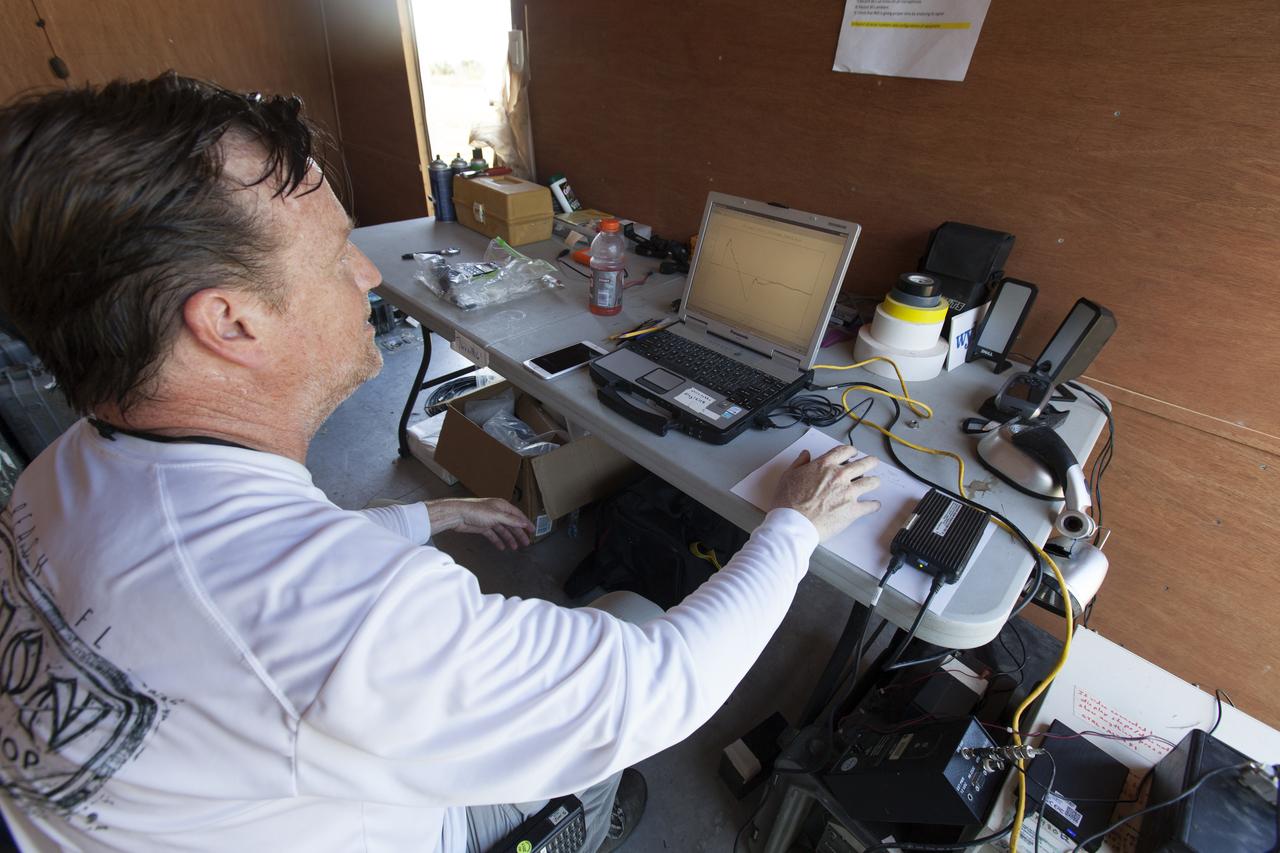

An engineer in a control trailer at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida monitors data before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
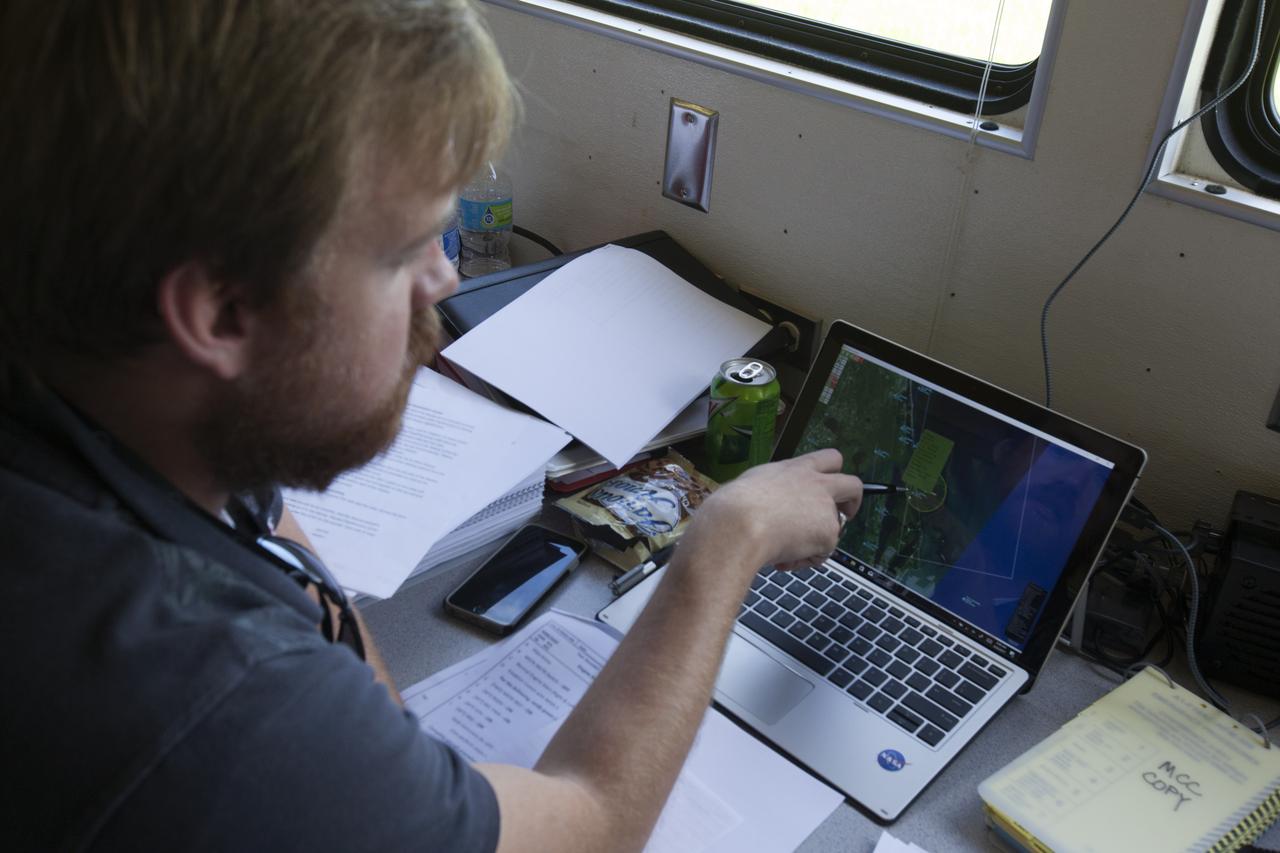

An engineer in a control trailer at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida monitors data before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

Engineers staff a control trailer at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A weather balloon is released at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A weather balloon is about to be released at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Larry Cliatt, SonicBAT Fluid Mechanics at Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, speaks to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
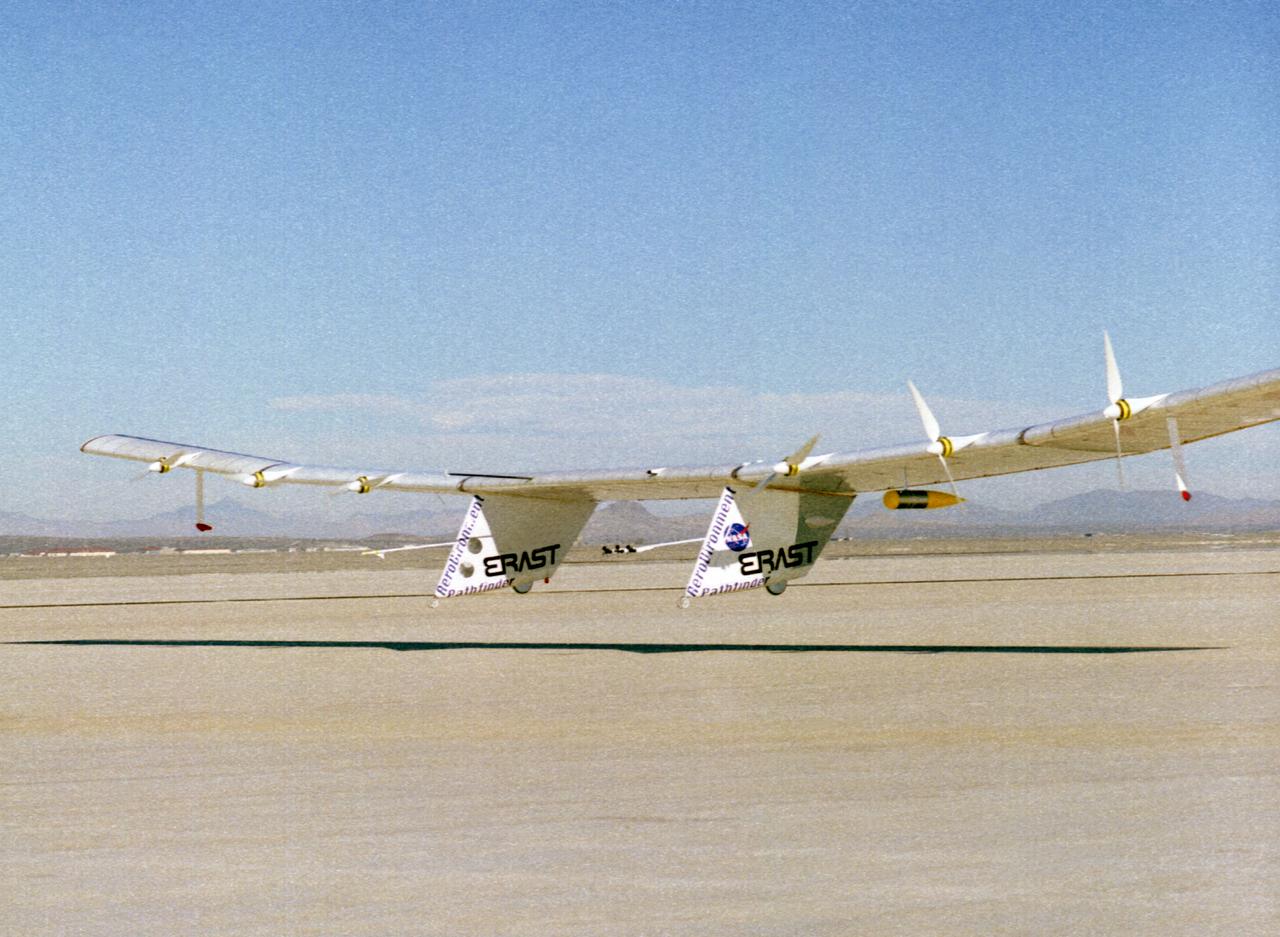

The Pathfinder solar-powered research aircraft settles in for landing on the bed of Rogers Dry Lake at the Dryden Flight Research Center, Edwards, California, after a successful test flight Nov. 19, 1996. The ultra-light craft flew a racetrack pattern at low altitudes over the flight test area for two hours while project engineers checked out various systems and sensors on the uninhabited aircraft. The Pathfinder was controlled by two pilots, one in a mobile control unit which followed the craft, the other in a stationary control station. Pathfinder, developed by AeroVironment, Inc., is one of several designs being evaluated under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program.

A weather balloon is about to be released at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida before flights of agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
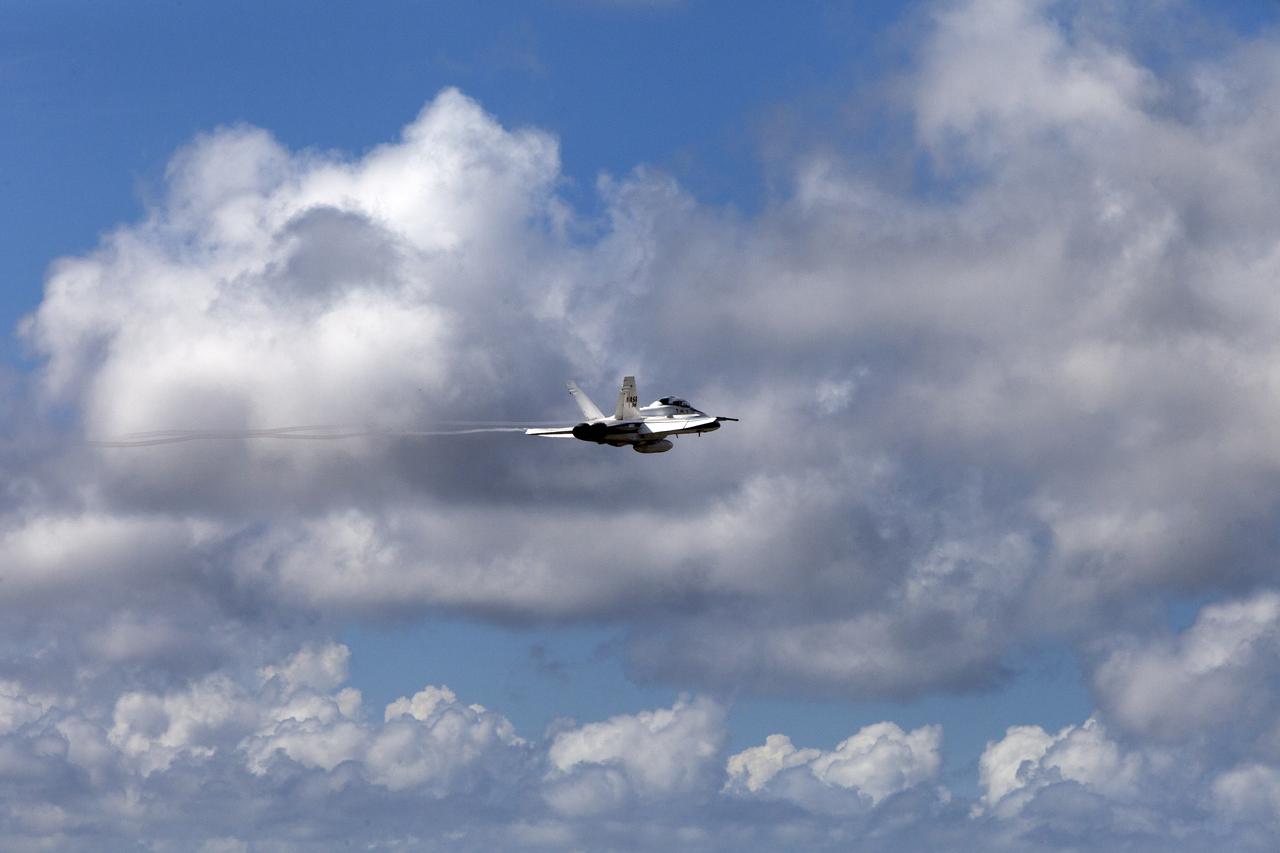

A NASA F-18 jet has taken off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
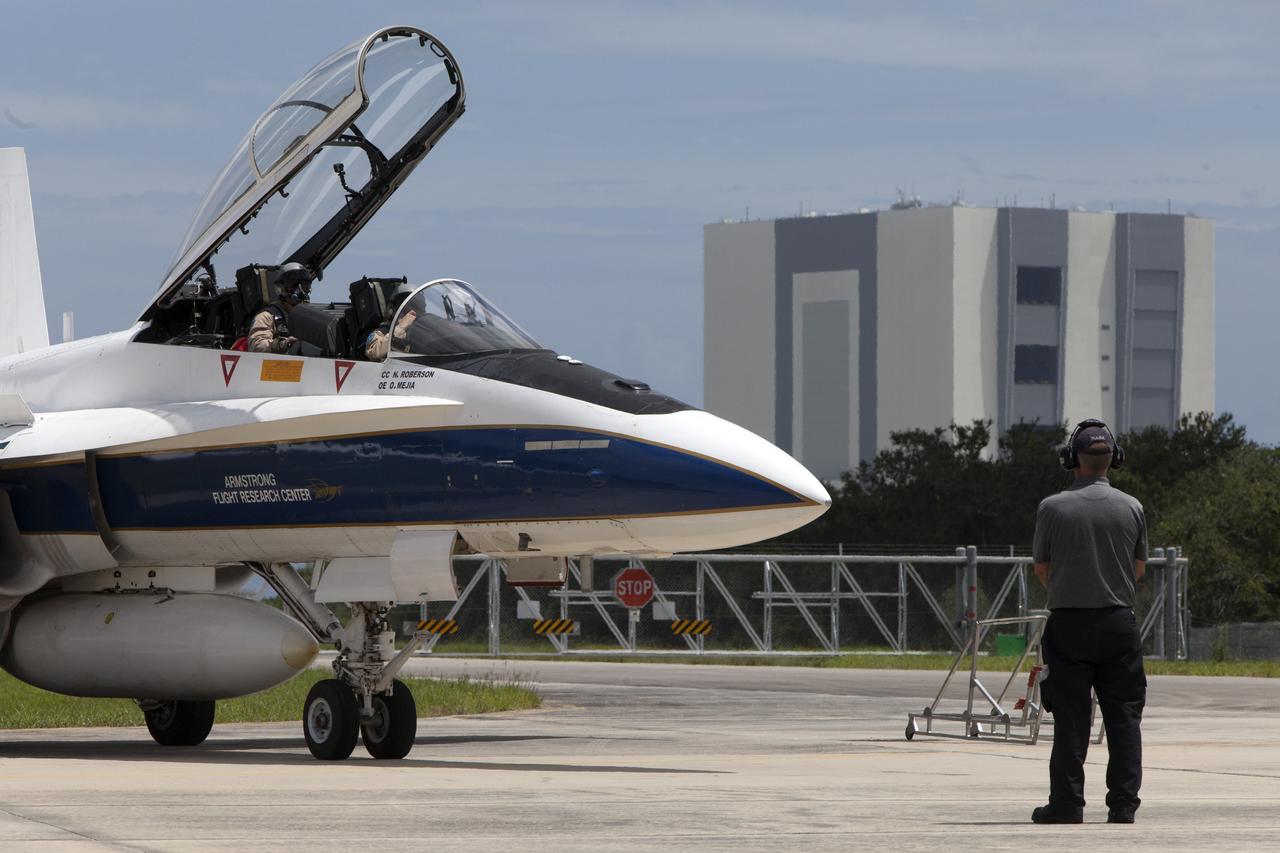

A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
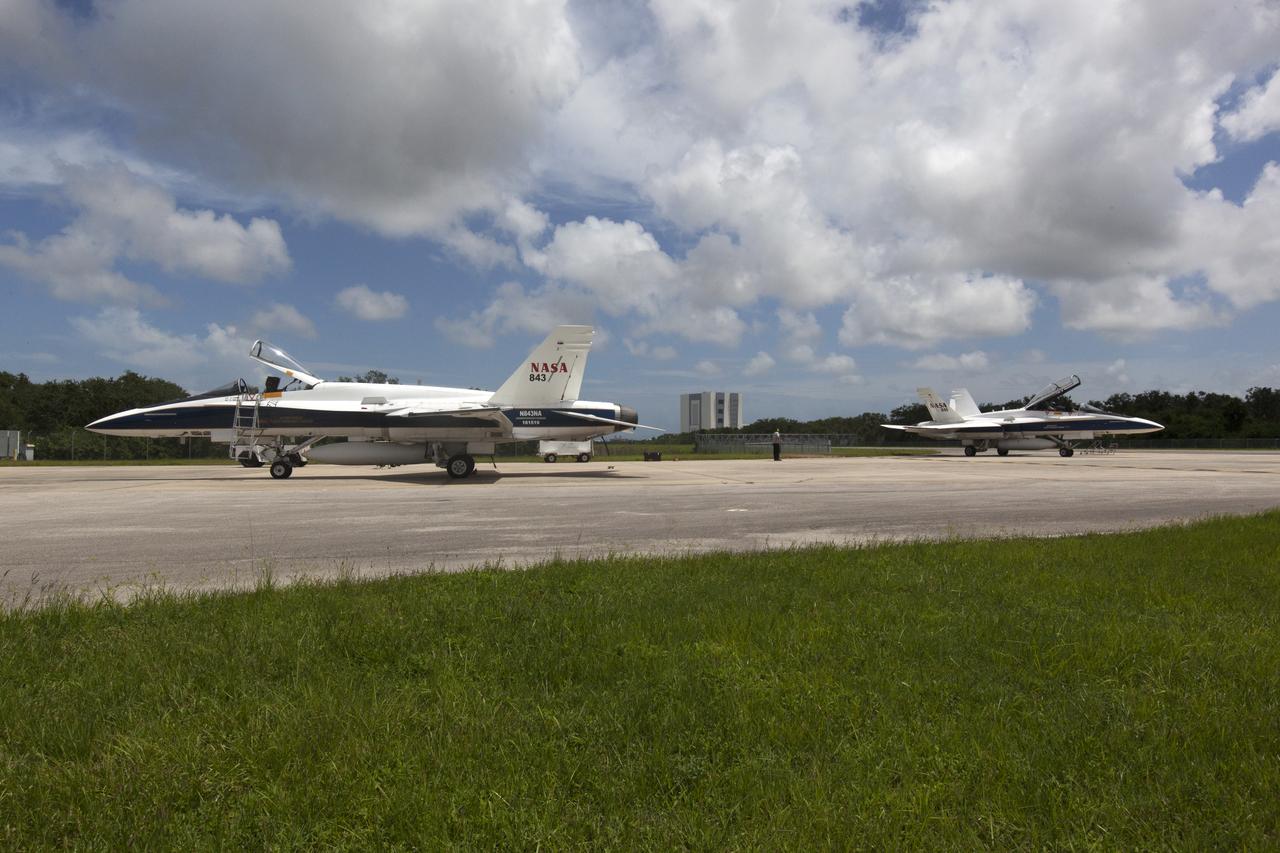

NASA F-18 jets prepare for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
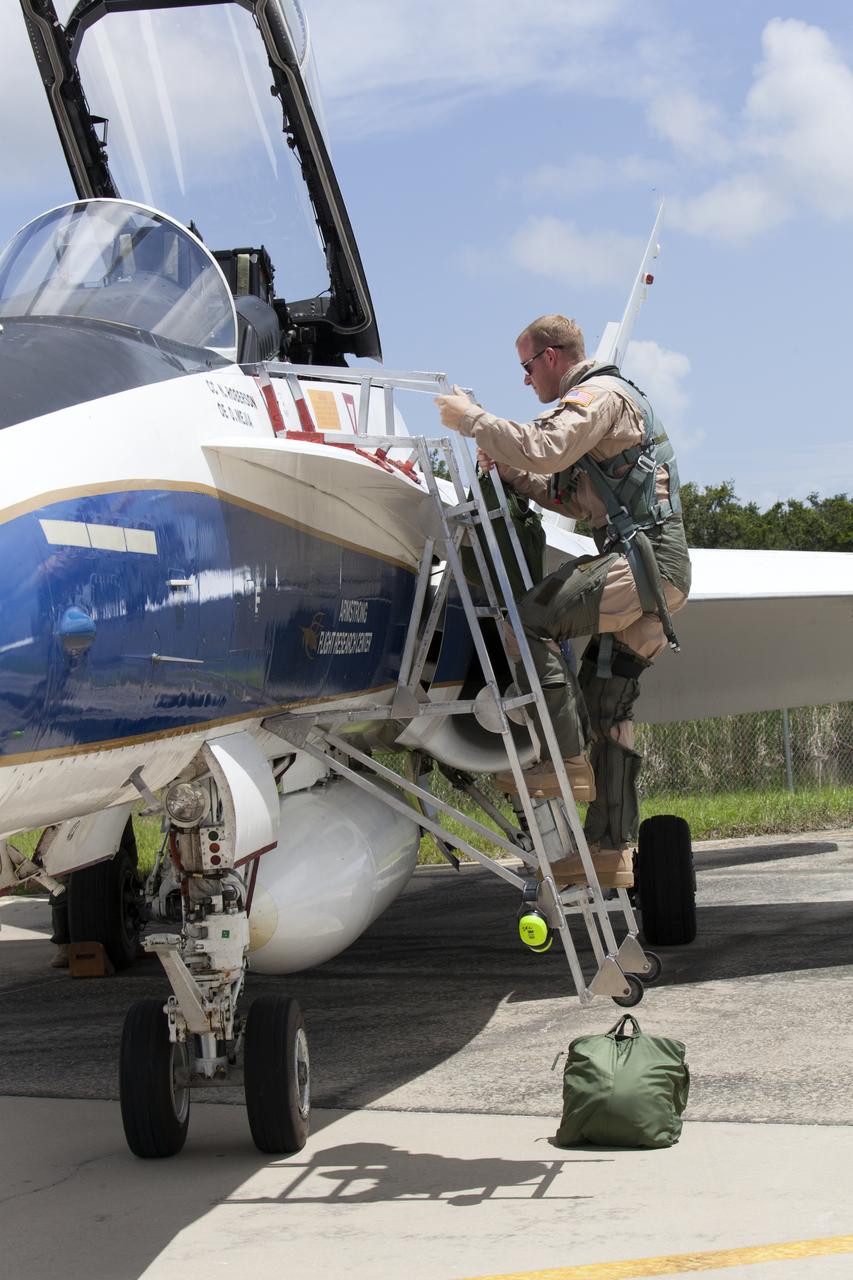

A NASA pilot boards an F-18 jet prior to take off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A NASA F-18 jet has taken off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Peter Coen, SonicBAT Mission Analysis at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Virginia, speaks to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
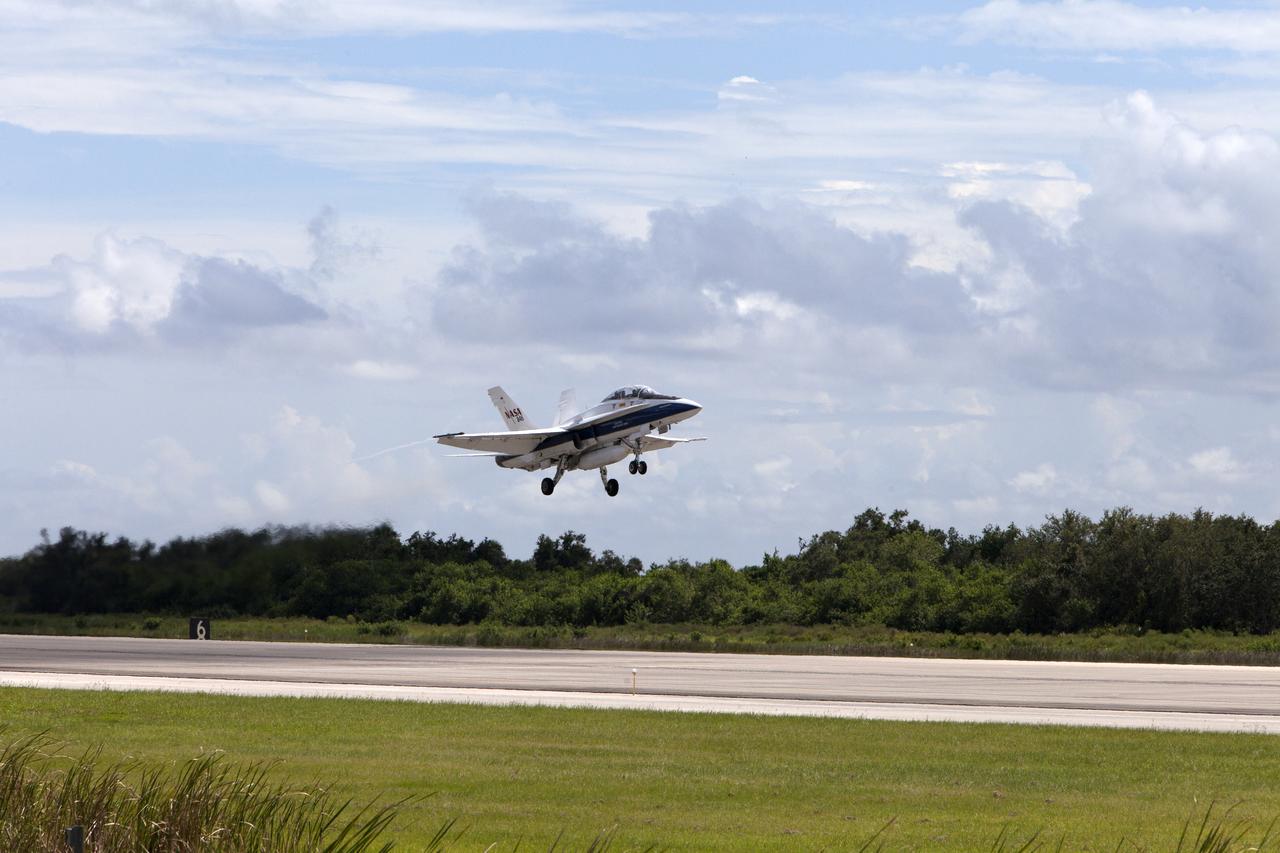

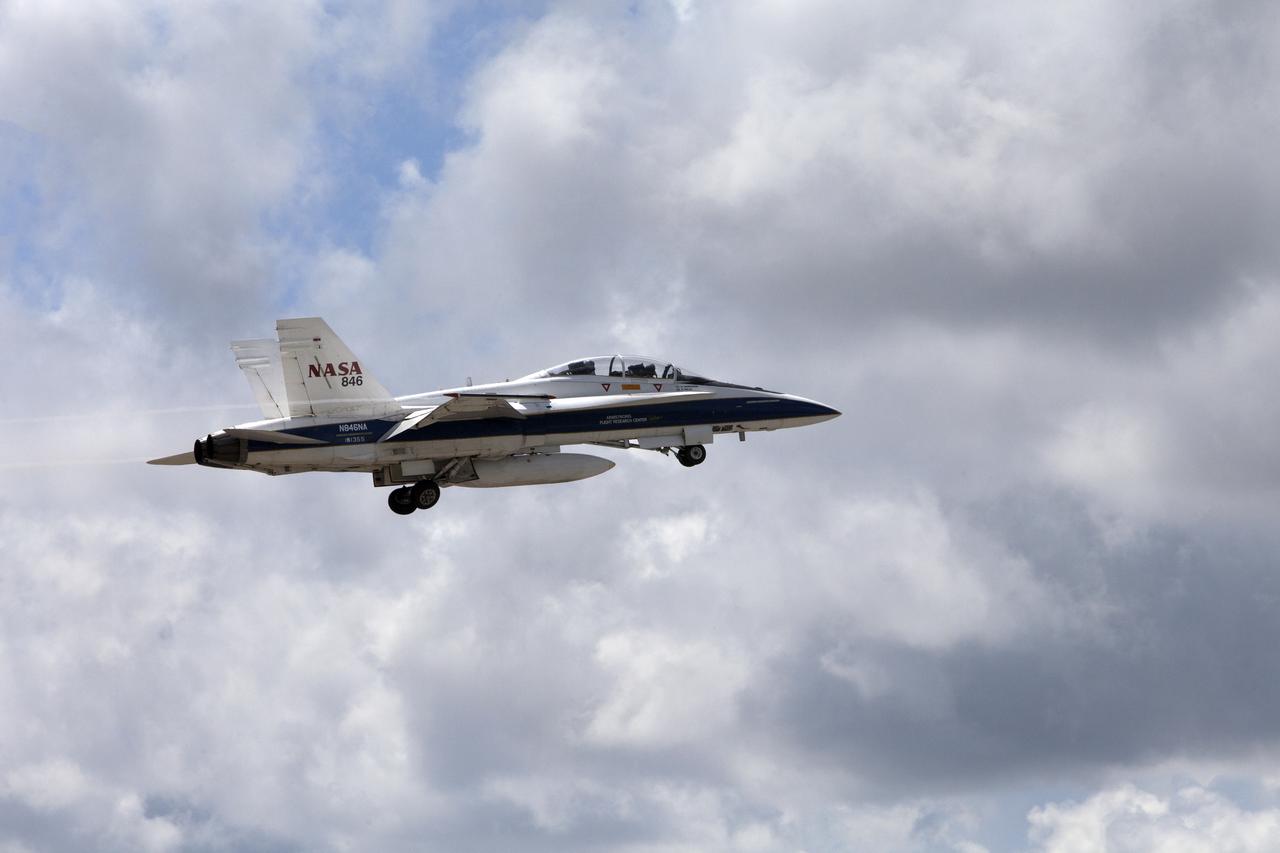
A NASA F-18 jet takes off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
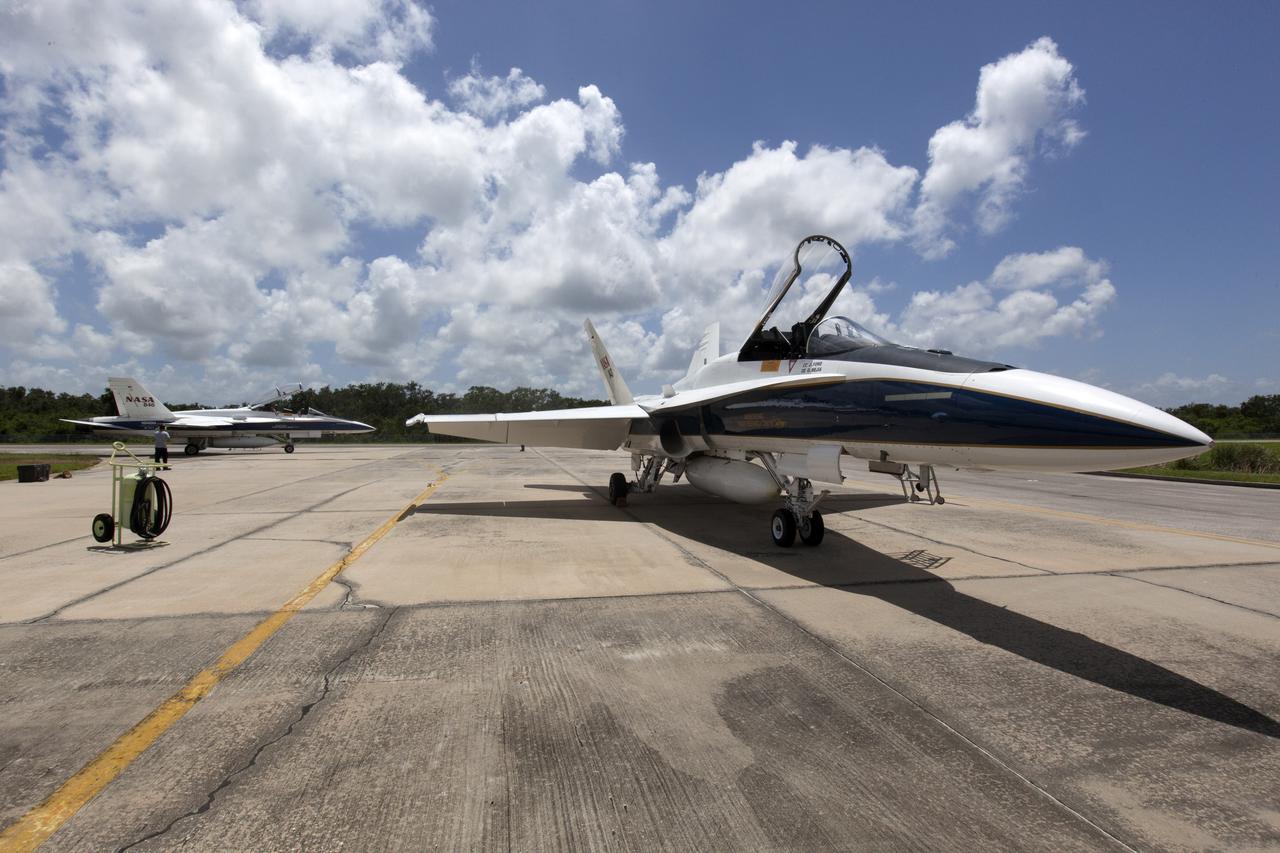

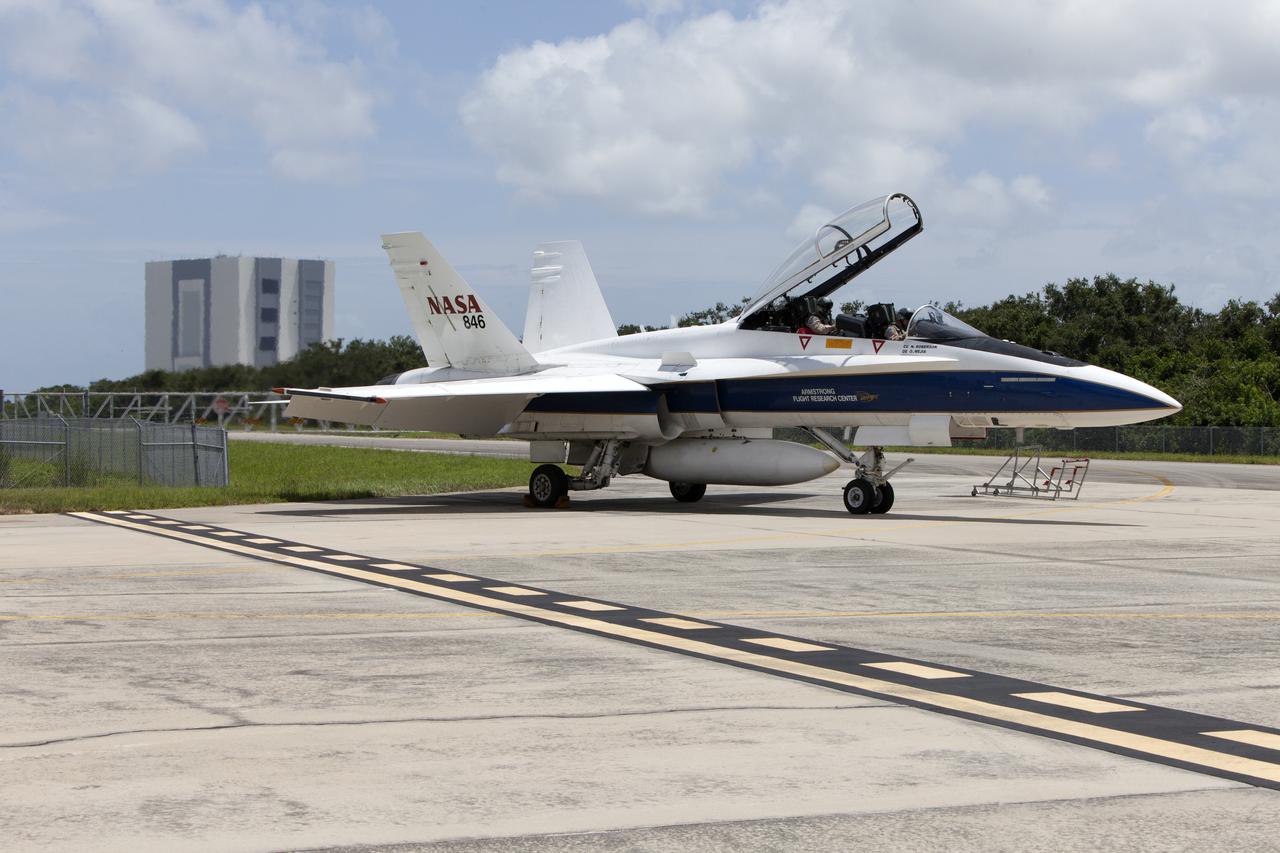
A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
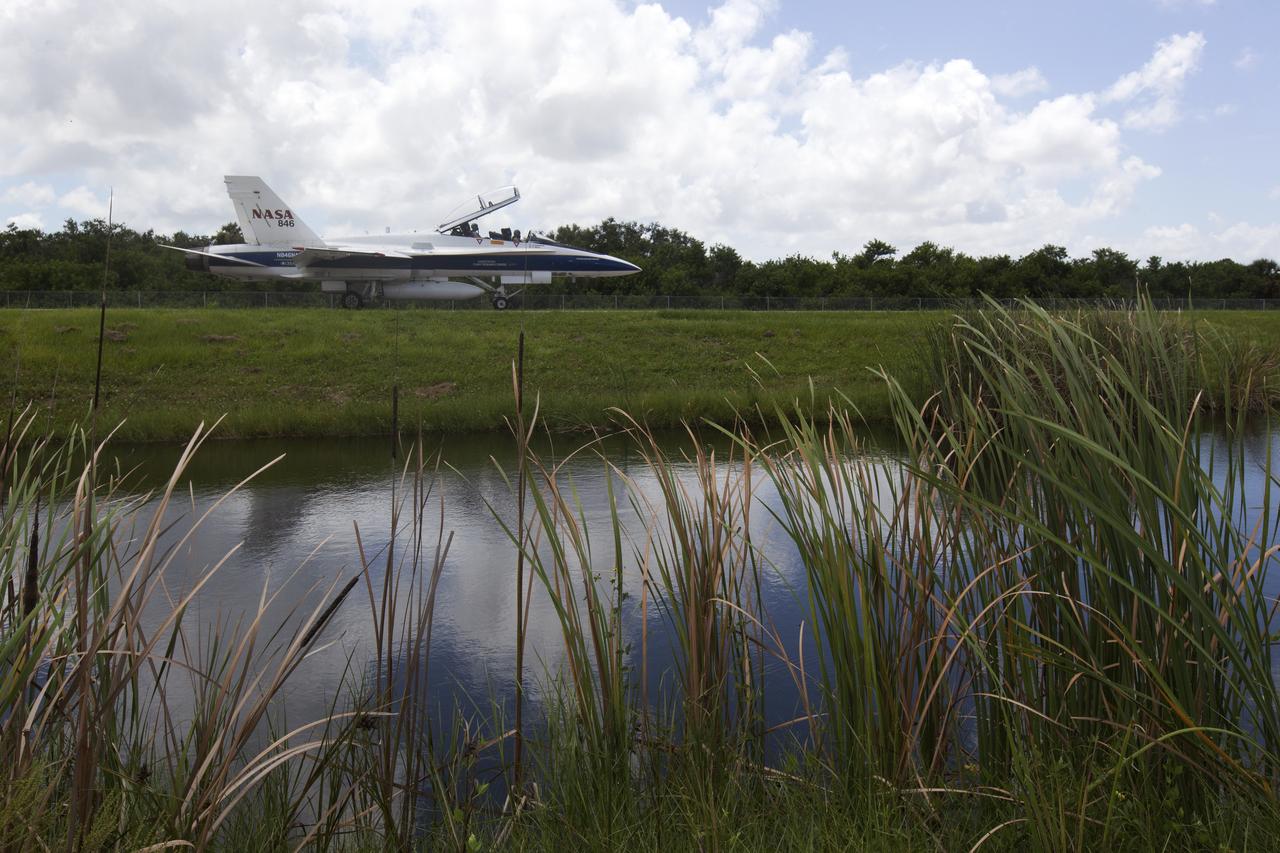

A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Laura Henning, public information officer for the Canaveral National Seashore, speaks to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
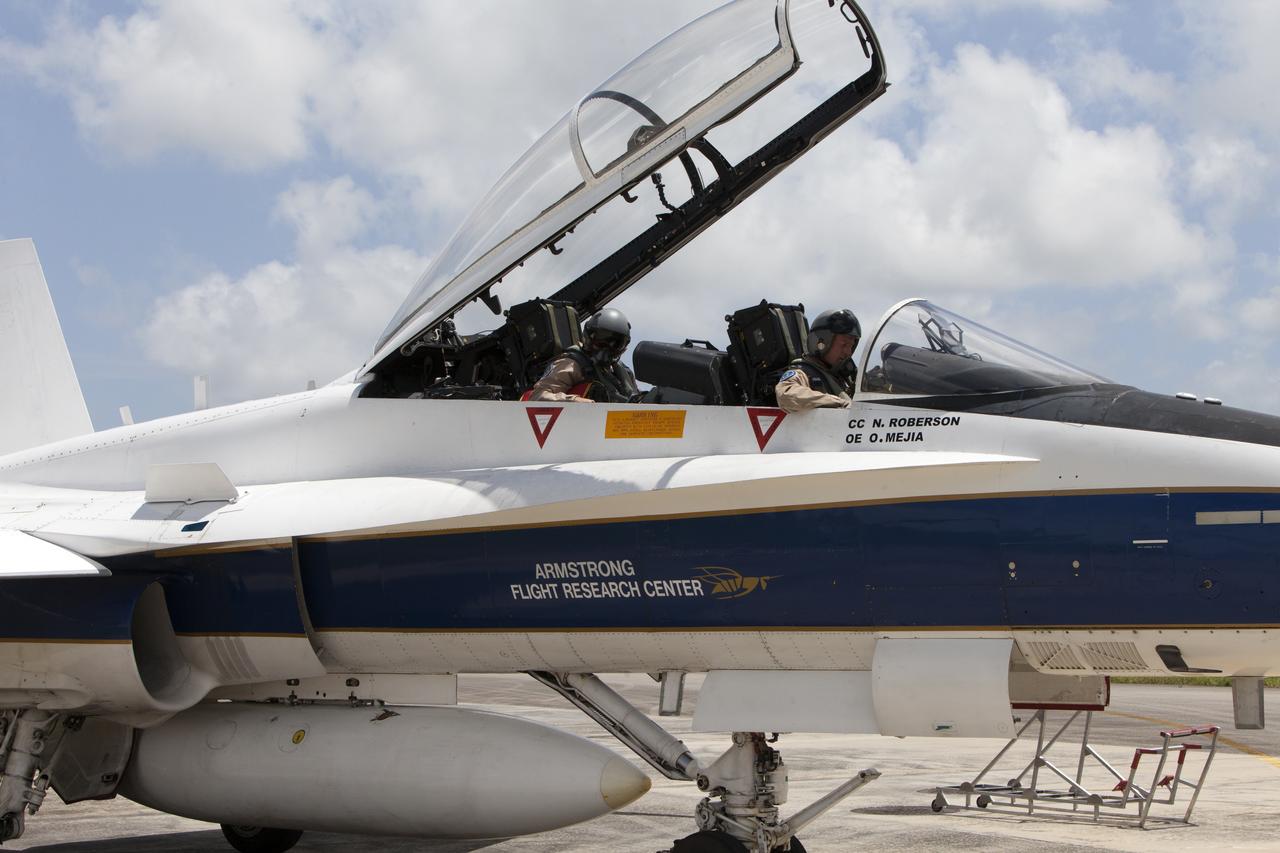

A NASA F-18 jet is prepared for takeoff from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
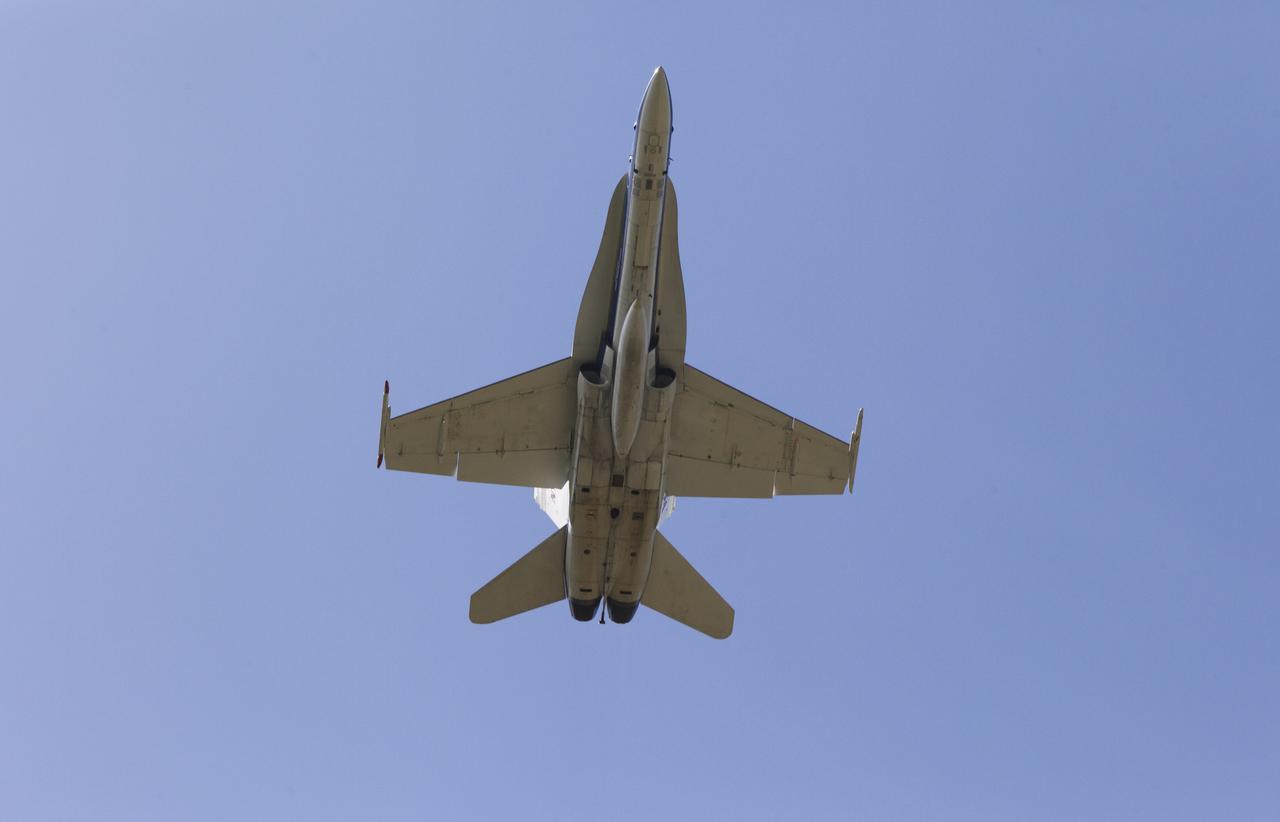

A NASA F-18 jet takes off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
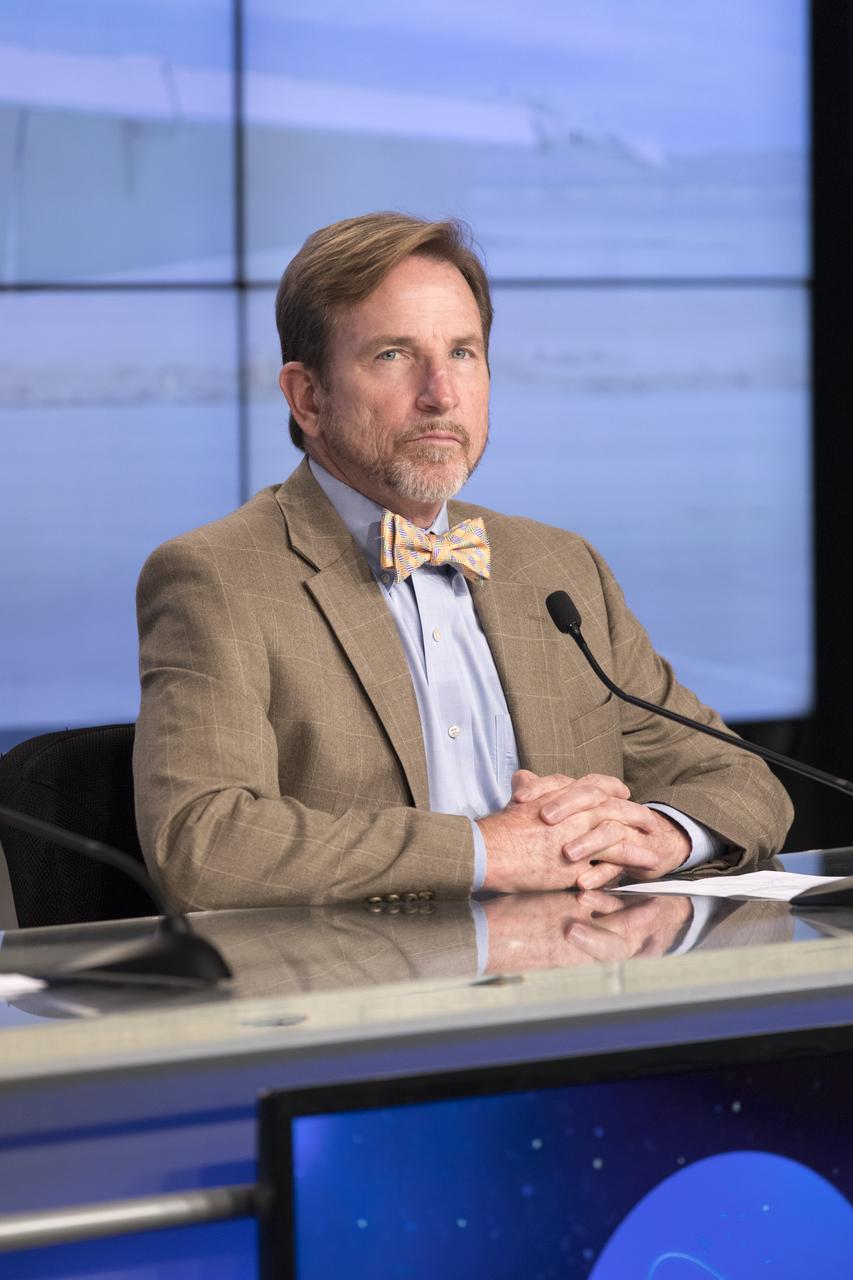

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Dale Ketcham chief of Strategic Alliances for Space Florida, speaks to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
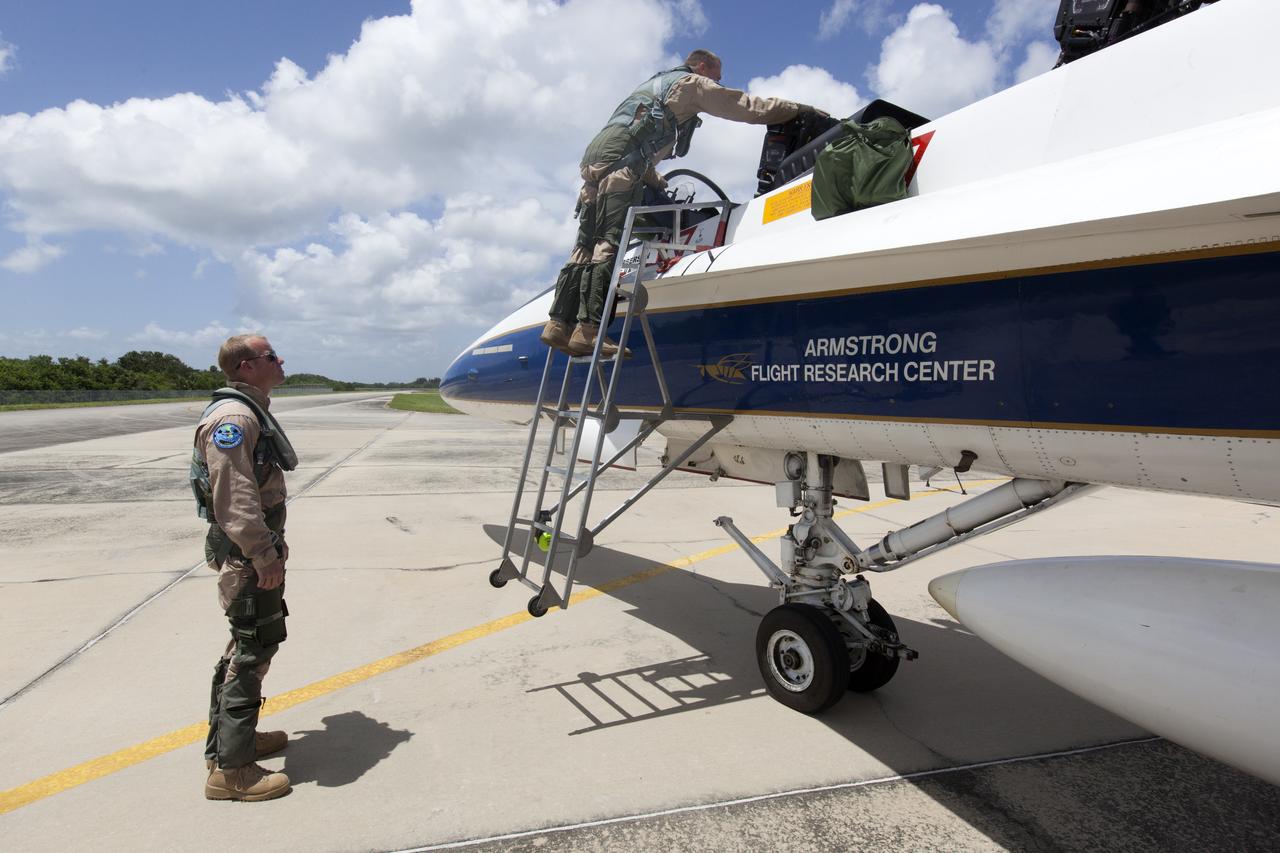

NASA pilots board an F-18 jet prior to take off from the agency's Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 to measure the effects of sonic booms. It is part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
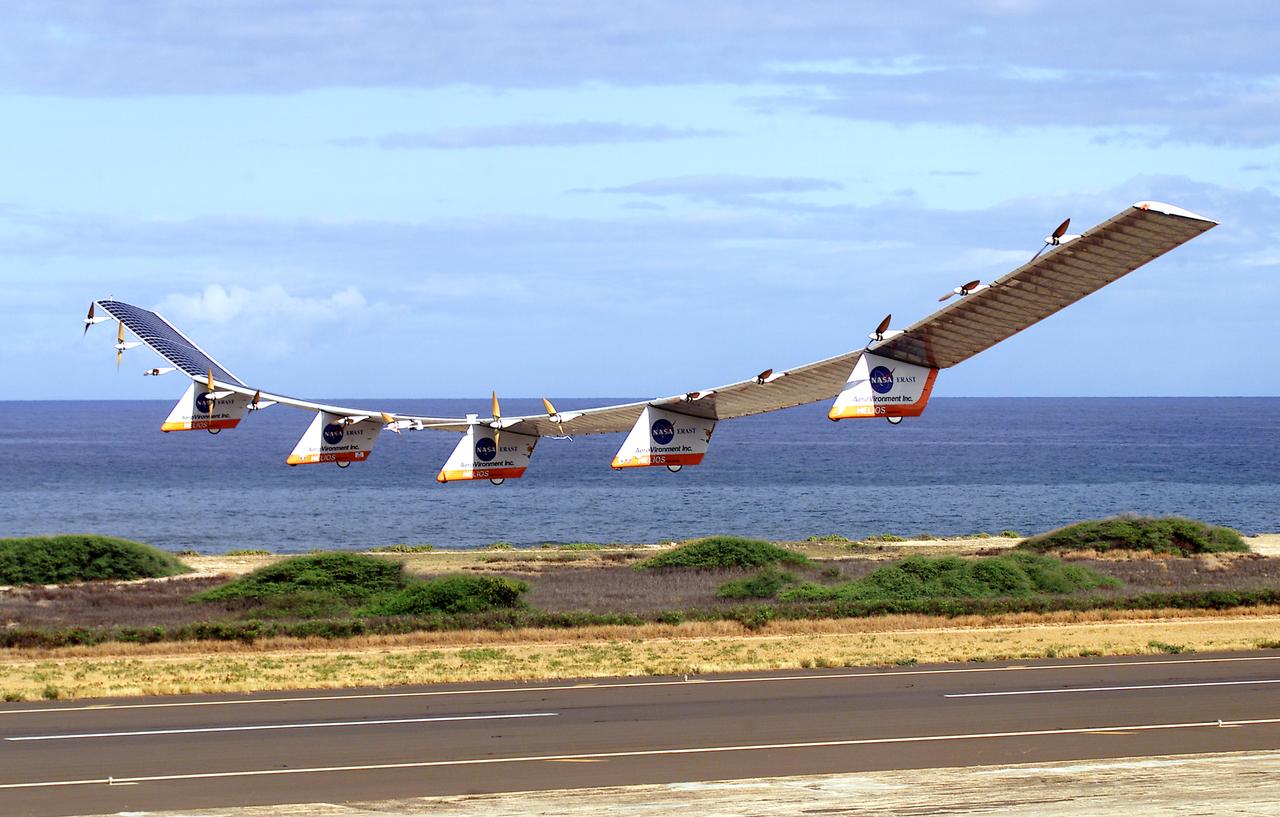

NASA's Helios Prototype aircraft taking off from the Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii, for the record flight. As a follow-on to the Centurion (and earlier Pathfinder and Pathfinder-Plus) aircraft, the solar-powered Helios Prototype is the latest and largest example of a slow-flying ultralight flying wing designed for long-duration, high-altitude Earth science or telecommunications relay missions in the stratosphere. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, California, under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the unique craft is intended to demonstrate two key missions: the ability to reach and sustain horizontal flight at 100,000 feet altitude on a single-day flight in 2001, and to maintain flight above 50,000 feet altitude for at least four days in 2003, with the aid of a regenerative fuel cell-based energy storage system now in development. Both of these missions will be powered by electricity derived from non-polluting solar energy. The Helios Prototype is an enlarged version of the Centurion flying wing, which flew a series of test flights at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late 1998. The craft has a wingspan of 247 feet, 41 feet greater than the Centurion, 2 1/2 times that of its solar-powered Pathfinder flying wing, and longer than the wingspans of either the Boeing 747 jetliner or Lockheed C-5 transport aircraft. The remotely piloted, electrically powered Helios Prototype went aloft on its maiden low-altitude checkout flight Sept. 8, 1999, over Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the Southern California desert. The initial flight series was flown on battery power as a risk-reduction measure. In all, six flights were flown in the Helios Protoype's initial development series. In upgrading the Centurion to the Helios Prototype configuration, AeroVironment added a sixth wing section and a fifth landing gear pod, among other improvements. The additional wingsp
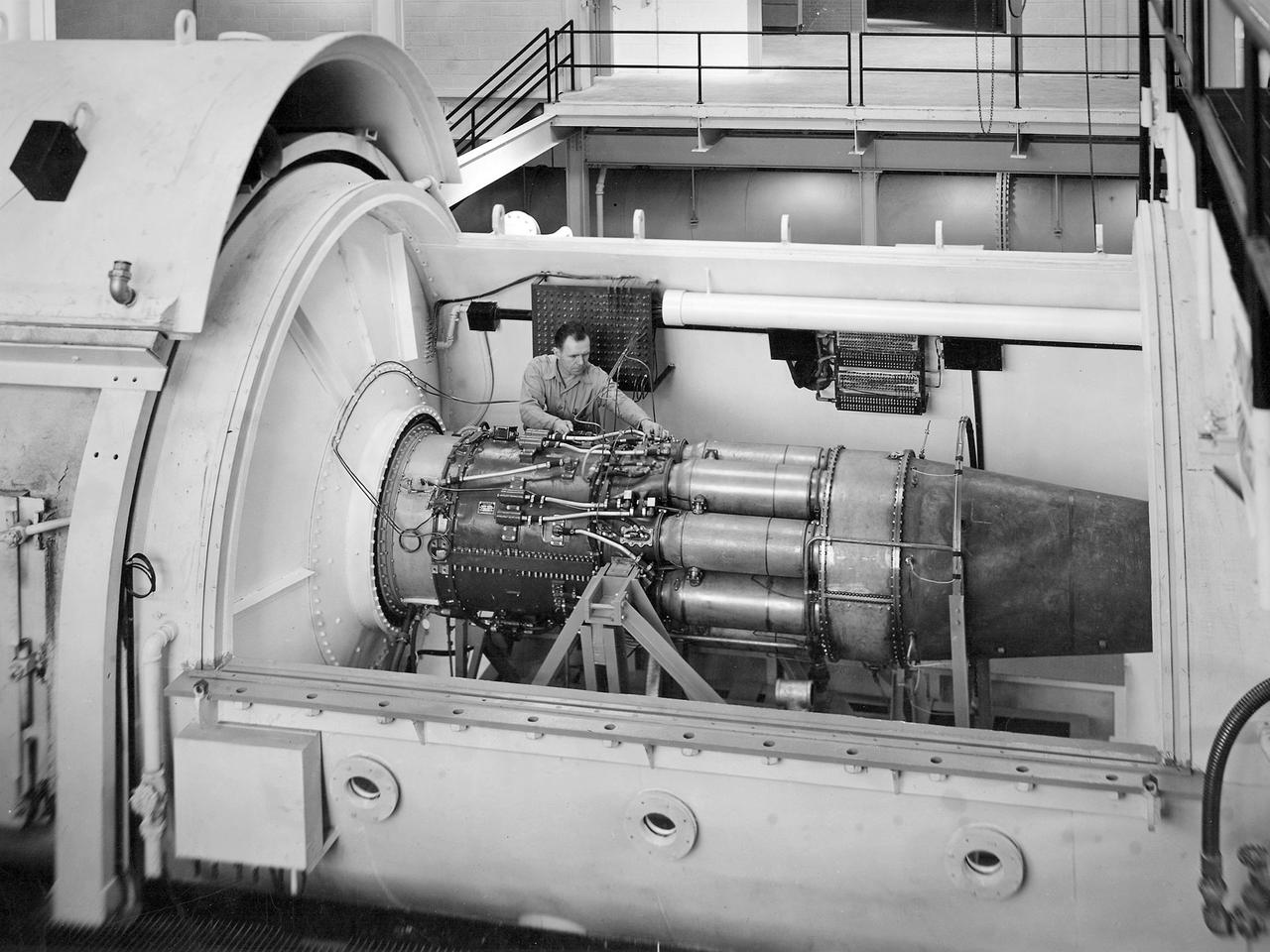
One of the two altitude simulating-test chambers in Engine Research Building at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The two chambers were collectively referred to as the Four Burner Area. NACA Lewis’ Altitude Wind Tunnel was the nation’s first major facility used for testing full-scale engines in conditions that realistically simulated actual flight. The wind tunnel was such a success in the mid-1940s that there was a backlog of engines waiting to be tested. The Four Burner chambers were quickly built in 1946 and 1947 to ease the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s congested schedule. The Four Burner Area was located in the southwest wing of the massive Engine Research Building, across the road from the Altitude Wind Tunnel. The two chambers were 10 feet in diameter and 60 feet long. The refrigeration equipment produced the temperatures and the exhauster equipment created the low pressures present at altitudes up to 60,000 feet. In 1947 the Rolls Royce Nene was the first engine tested in the new facility. The mechanic in this photograph is installing a General Electric J-35 engine. Over the next ten years, a variety of studies were conducted using the General Electric J-47 and Wright Aeronautical J-65 turbojets. The two test cells were occasionally used for rocket engines between 1957 and 1959, but other facilities were better suited to the rocket engine testing. The Four Burner Area was shutdown in 1959. After years of inactivity, the facility was removed from the Engine Research Building in late 1973 in order to create the High Temperature and Pressure Combustor Test Facility.
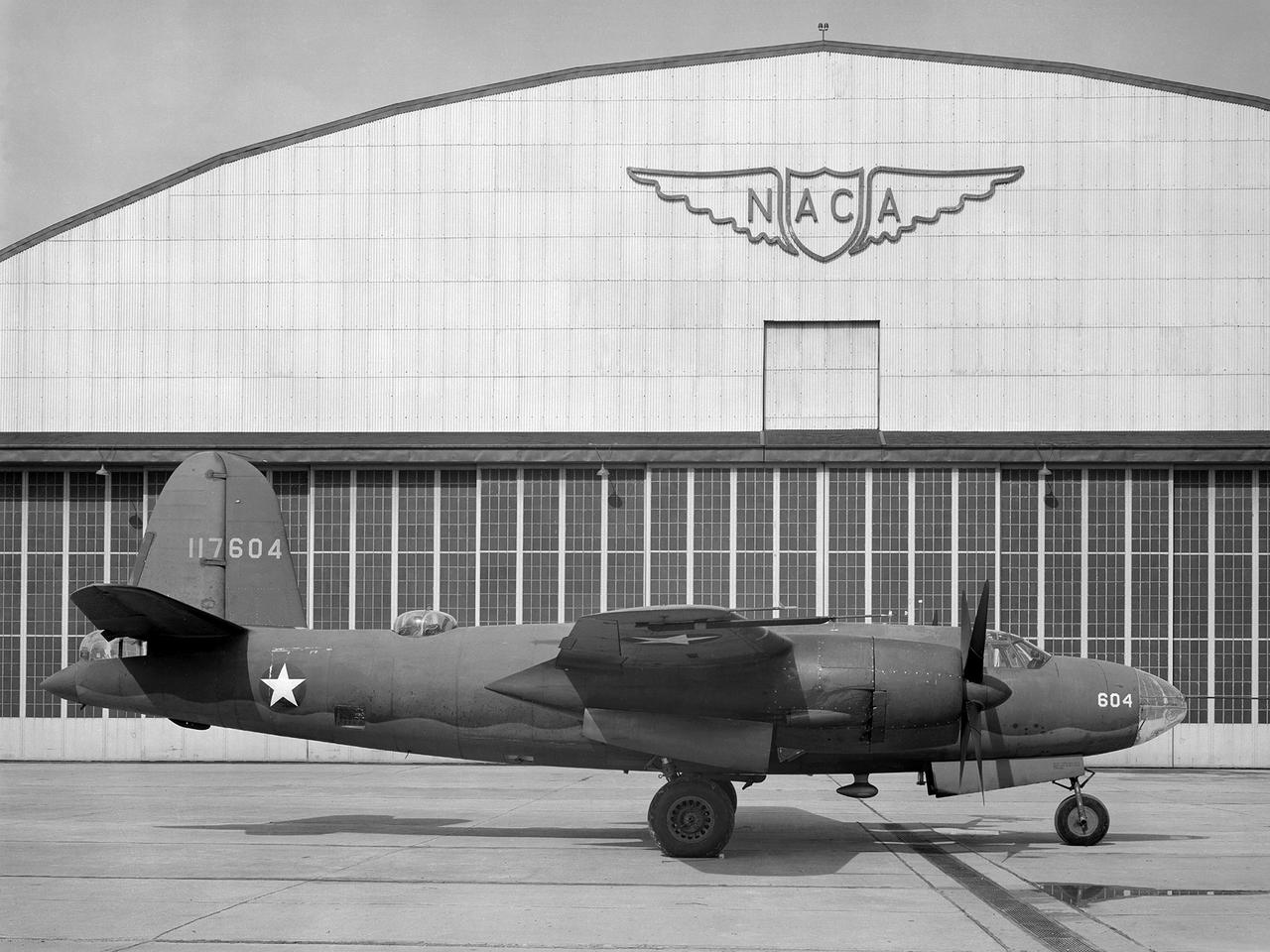

The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s first aircraft, a Martin B–26B Marauder, parked in front of the Flight Research Building in September 1943. The military loaned the B–26B to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to augment the lab’s studies of the Wright Aeronautical R–2800 engines. The military wanted to improve the engine cooling in order to increase the bomber’s performance. On March 17, 1943, the B–26B performed the very first research flight at the NACA’s new engine laboratory. The B–26B received its “Widowmaker” nickname during the rushed effort to transition the new aircraft from design to production and into the sky. During World War II, however, the B–26B proved itself to be a capable war machine. The U.S. lost fewer Marauders than any other type of bomber employed in the war. The B–26B was originally utilized at low altitudes in the Pacific but had its most success at high altitudes over Europe. The B–26B’s flight tests in Cleveland during 1943 mapped the R-2800 engine’s behavior at different altitudes and speeds. The researchers were then able to correlate engine performance in ground facilities to expected performance at different altitudes. They found that air speed, cowl flap position, angle of attack, propeller thrust, and propeller speed influenced inlet pressure recovery and exhaust distribution. The flight testing proceeded quickly, and the B–26B was transferred elsewhere in October 1943.
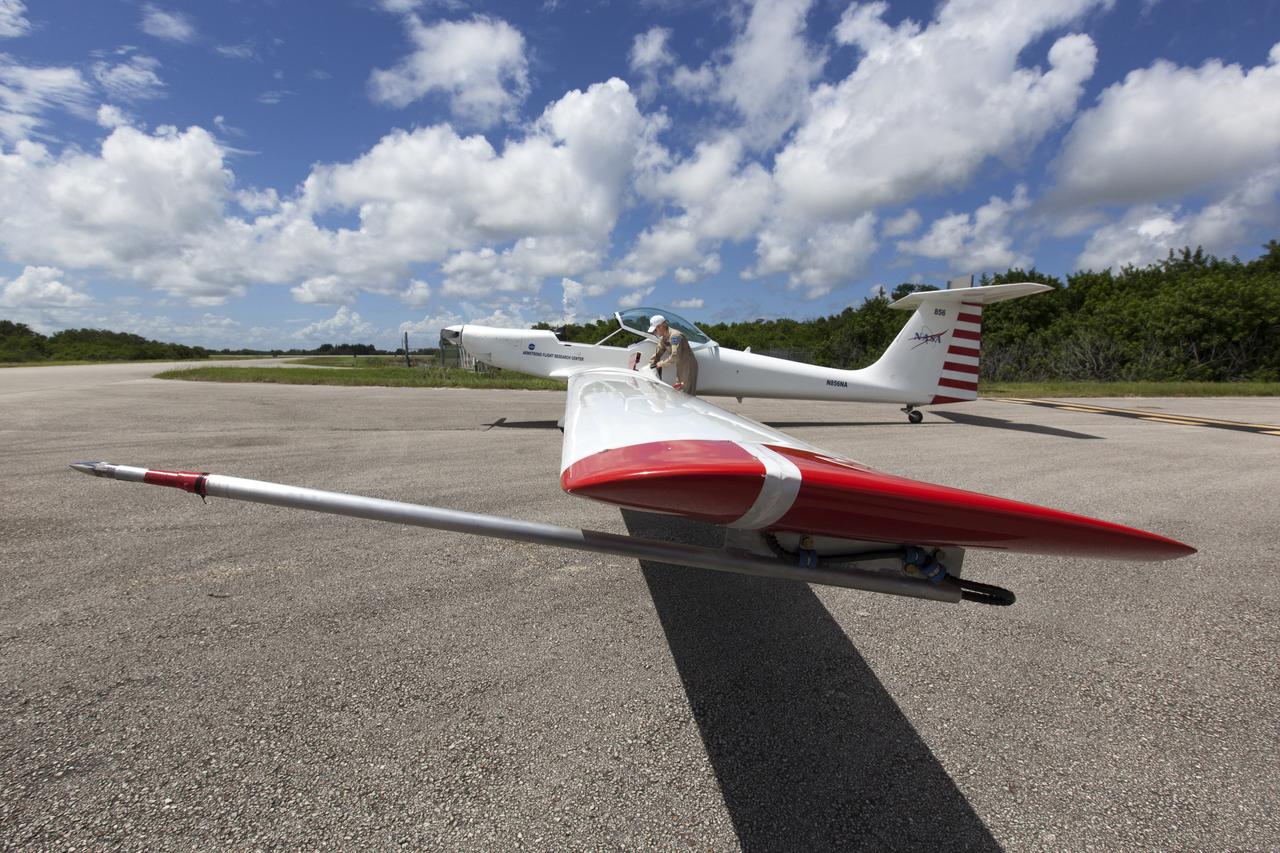

A motorized glider prepares to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
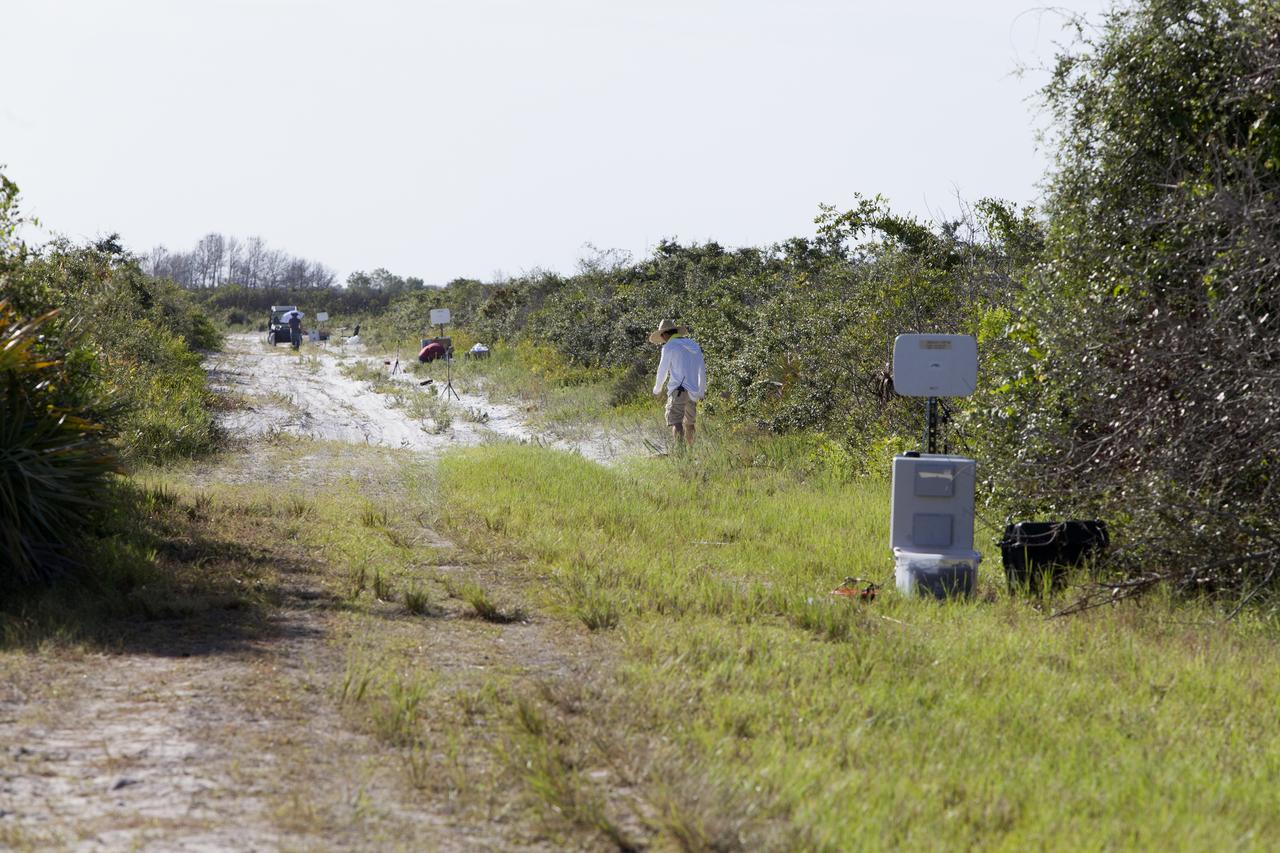

Microphone arrays are strategically positioned along the ground at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to collect sound signatures from sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets flying faster than the speed of sound. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A motorized glider has taken off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
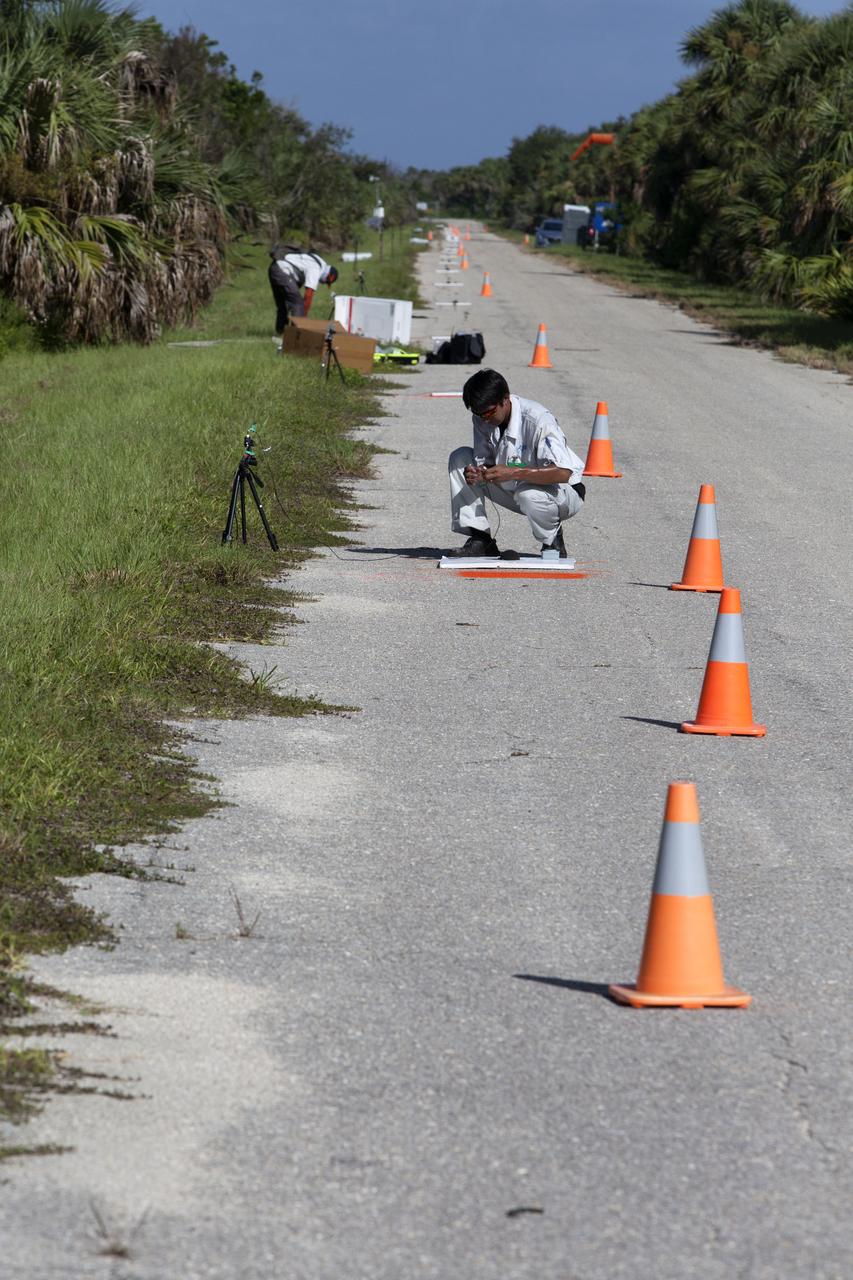

Microphone arrays are strategically positioned along the ground at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to collect sound signatures from sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets flying faster than the speed of sound. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A motorized glider prepares to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

An engineer checks readings from microphone arrays that were strategically positioned along the ground at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to collect sound signatures from sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets flying faster than the speed of sound. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A motorized glider has taken off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
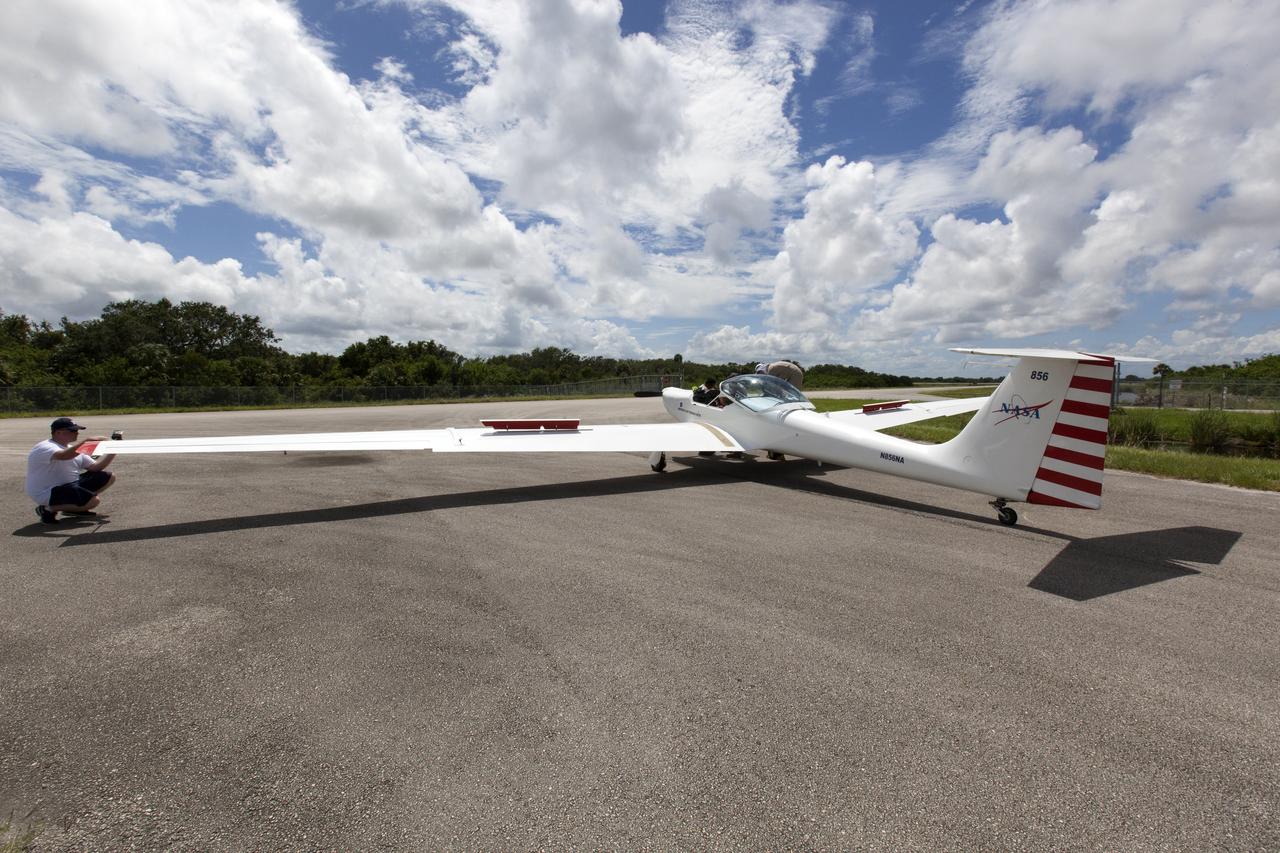

A motorized glider prepares to take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
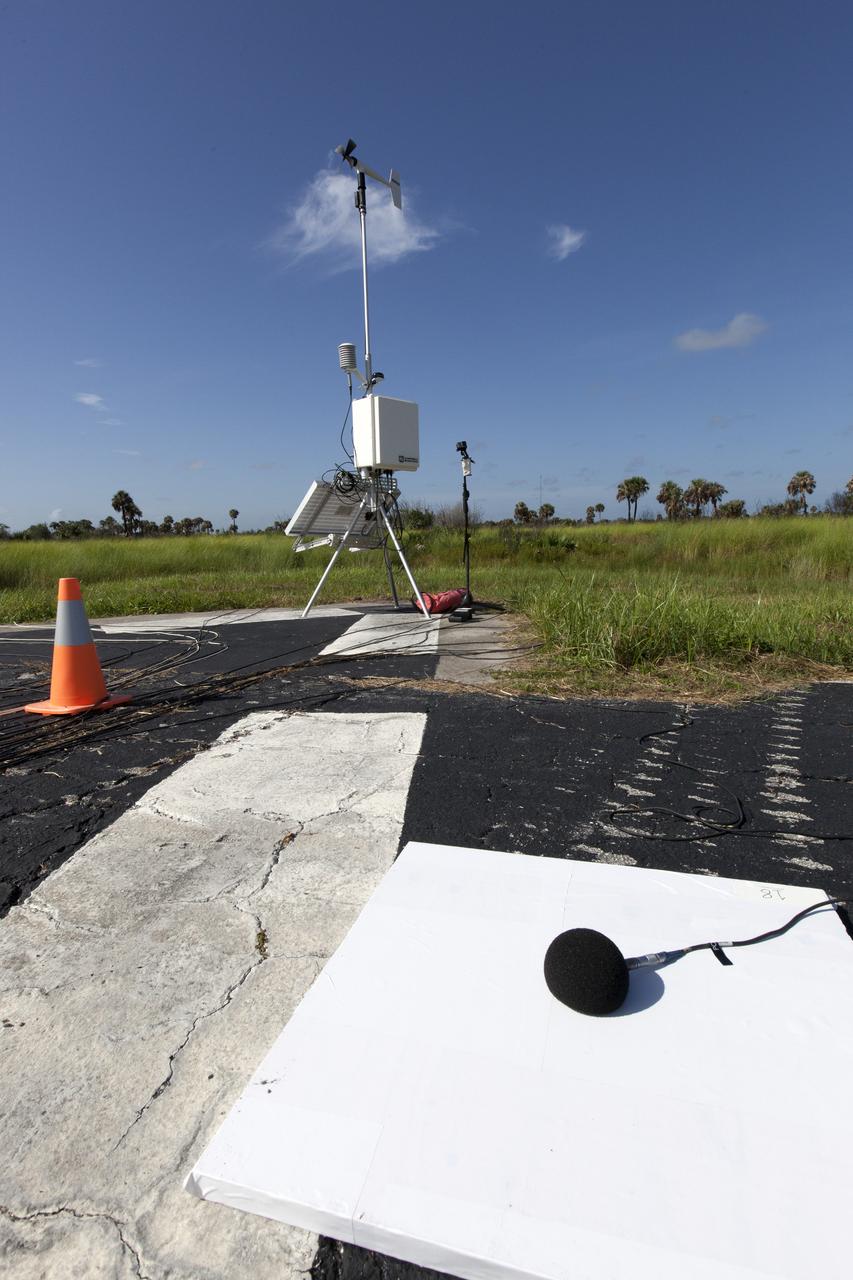

Microphone arrays and other instrumentation are strategically positioned along the ground at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. They have been set up to collect sound signatures from sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets flying faster than the speed of sound. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.
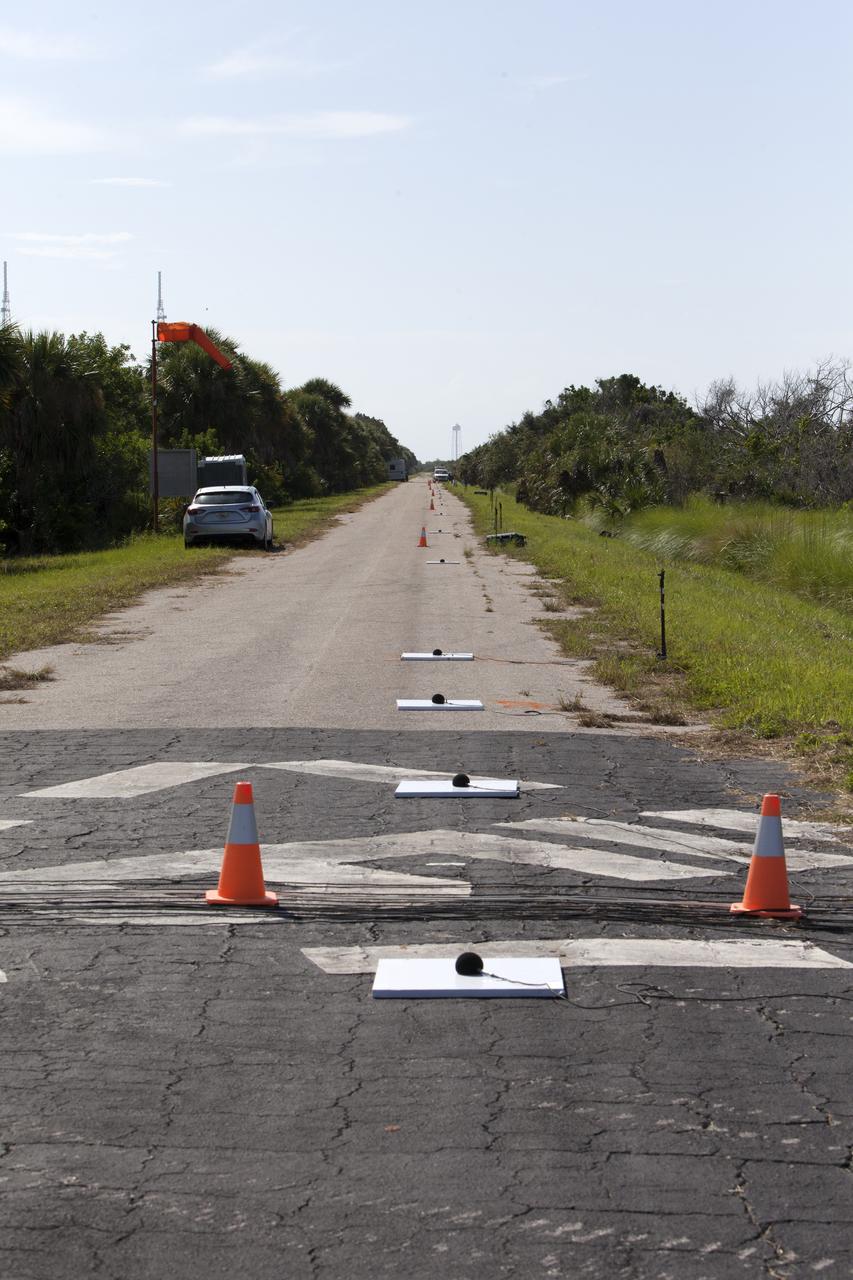

Microphone arrays and other instrumentation are strategically positioned along the ground at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. They have been set up to collect sound signatures from sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets flying faster than the speed of sound. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

A motorized glider has taken off from the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Flying with its engine off, the glider will be positioned above the 14,000-foot level to measure sonic booms created by agency F-18 jets to measure the effects of sonic booms. Several flights a day have been taking place the week of Aug. 21, 2017 as part of NASA's Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence, or SonicBAT II Program. NASA at Kennedy is partnering with the agency's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California, Langley Research Center in Virginia, and Space Florida for a program in which F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence caused by sonic booms.

STS059-227-050 (9-20 April 1994) --- A low altitude, and unusually clear air, provided perhaps the most detailed view of Los Angeles, California ever obtained during a shuttle flight. Orient with the bulk of the ocean to the lower left. Then Long Beach is in the lower right, just east of the Palos Verdes Hills that extend into the Pacific Ocean. Marina del Rey is cut into the straight segment of beach, with Los Angeles International Airport (LAX) clearly visible to the southeast. Downtown Los Angeles is the light-toned sprawl in the upper right, with the rectangular grid pattern of Pasadena extending out of the picture. The Santa Monica Mountains to the upper left extend east-west, separating the San Fernando Valley (epicenter of the 1993 earthquake) from the Los Angeles Basin proper. It is impossible to determine by photo interpretation whether or not the de-vegetated scars along the southern edge of the mountains represent man-made features (real-estate development) or wildfires.

STS068-244-022 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- (San Francisco, San Pablo Bay Area) Photographed through the Space Shuttle Endeavour's flight deck windows, the heavily populated bay area is featured in this 70mm frame. The relatively low altitude of Endeavour's orbit (115 nautical miles) and the use of a 250mm lens on the Hasselblad camera allowed for capturing detail in features such as the Berkeley Marina (frame center). The region's topography is well depicted with the lowland areas heavily populated and the hills much more sparsely covered. The Oakland Hills in the right lower center appear to be re-vegetated after a devastating fire. The Golden Gate Recreation Area in the upper left also shows heavy vegetation. The three bridges across the main part of the bay and their connecting roads are prominent. Cultural features such as Golden Gate Park and the Presidio contrast with the gray of the city.
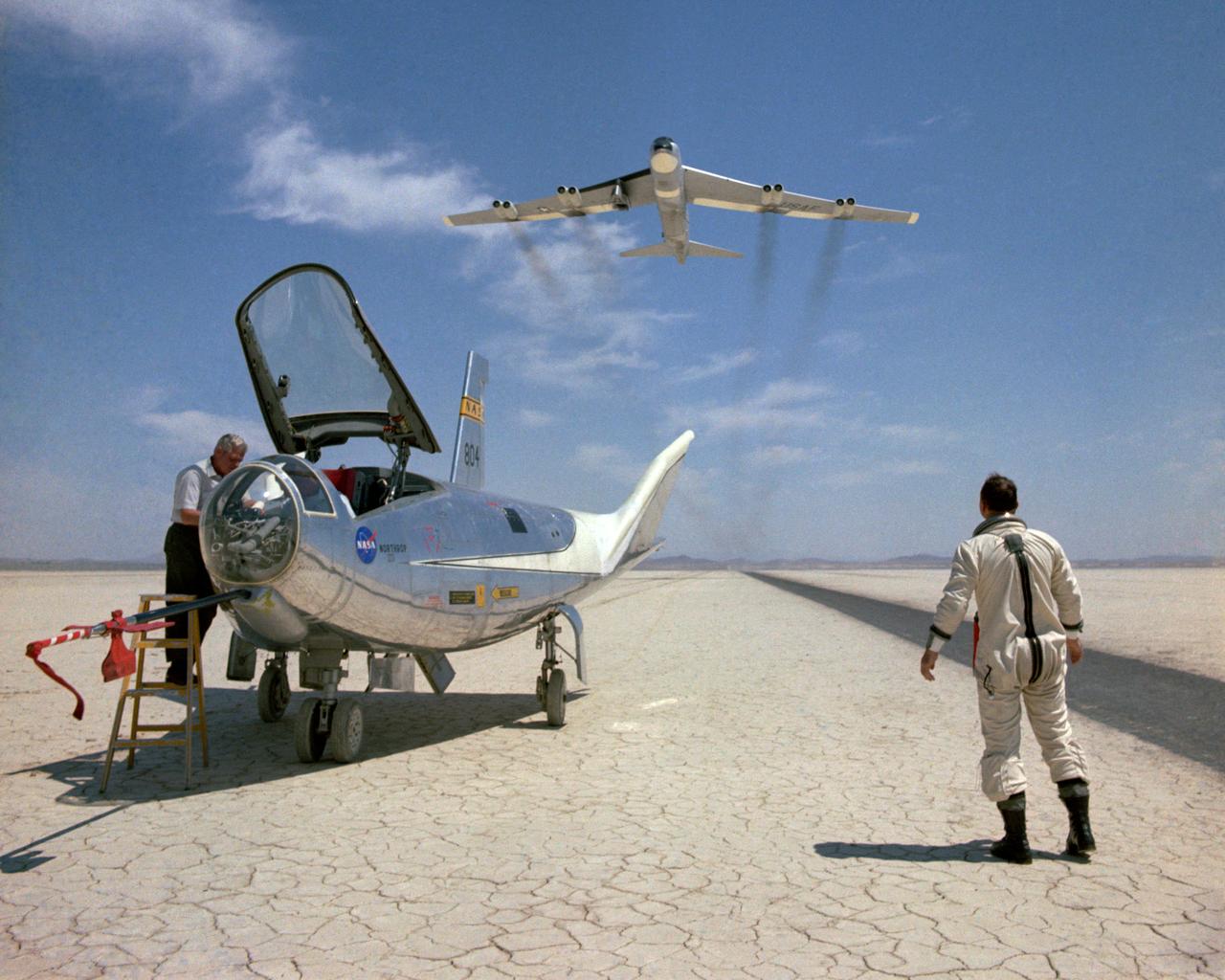

The HL-10 was one of five heavyweight lifting-body designs flown at NASA's Flight Research Center (FRC--later Dryden Flight Research Center), Edwards, California, from July 1966 to November 1975 to study and validate the concept of safely maneuvering and landing a low lift-over-drag vehicle designed for reentry from space. Northrop Corporation built the HL-10 and M2-F2, the first two of the fleet of "heavy" lifting bodies flown by the NASA Flight Research Center. The contract for construction of the HL-10 and the M2-F2 was $1.8 million. "HL" stands for horizontal landing, and "10" refers to the tenth design studied by engineers at NASA's Langley Research Center, Hampton, Va. After delivery to NASA in January 1966, the HL-10 made its first flight on Dec. 22, 1966, with research pilot Bruce Peterson in the cockpit. Although an XLR-11 rocket engine was installed in the vehicle, the first 11 drop flights from the B-52 launch aircraft were powerless glide flights to assess handling qualities, stability, and control. In the end, the HL-10 was judged to be the best handling of the three original heavy-weight lifting bodies (M2-F2/F3, HL-10, X-24A). The HL-10 was flown 37 times during the lifting body research program and logged the highest altitude and fastest speed in the Lifting Body program. On Feb. 18, 1970, Air Force test pilot Peter Hoag piloted the HL-10 to Mach 1.86 (1,228 mph). Nine days later, NASA pilot Bill Dana flew the vehicle to 90,030 feet, which became the highest altitude reached in the program. Some new and different lessons were learned through the successful flight testing of the HL-10. These lessons, when combined with information from it's sister ship, the M2-F2/F3, provided an excellent starting point for designers of future entry vehicles, including the Space Shuttle.
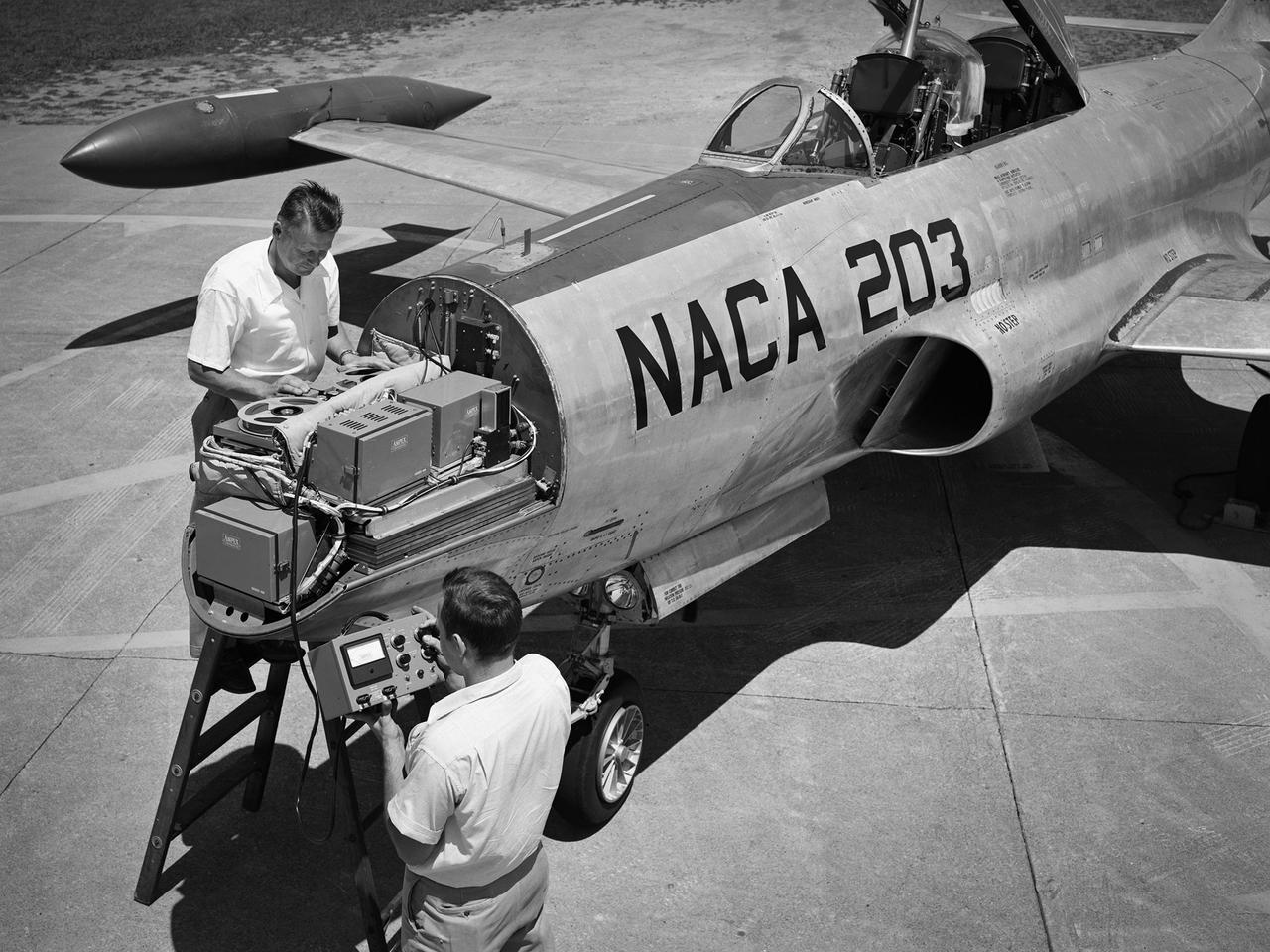

A Lockheed F-94B Starfire being equipped with an audio recording machine and sensors at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The NACA was investigating the acoustic effects caused by the engine’s nozzle and the air flowing along the fuselage. Airline manufacturers would soon be introducing jet engines on their passenger aircraft, and there was concern regarding the noise levels for both the passengers and public on the ground. NACA Lewis conducted a variety of noise reduction studies in its wind tunnels, laboratories, and on a F2H-2B Banshee aircraft. The F2H-2B Banshee’s initial test flights in 1955 and 1956 measured the noise emanating directly from airflow over the aircraft’s surfaces, particularly the wings. This problem was particularly pronounced at high subsonic speeds. The researchers found the majority of the noise occurred in the low and middle octaves. These investigations were enhanced with a series of flights using the F-94B Starfire. The missions measured wall-pressure, turbulence fluctuations, and mean velocity profiles. Mach 0.3 to 0.8 flights were flown at altitudes of 10,000, 20,000, and 30,000 feet with microphones mounted near the forward fuselage and on a wing. The results substantiated the wind tunnel findings. This photograph shows the tape recorder being installed in the F-94B’s nose.

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, NASA and other government leaders speak to members of the media at a news conference to discuss upcoming flight tests to study the effects of sonic booms. Participants from left are: Matthew Kamlet of NASA Communications at the Armstrong Flight Research Center in California; Peter Coen, SonicBAT Mission Analysis at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Virginia; Larry Cliatt, SonicBAT Fluid Mechanics at Armstrong; Dale Ketcham chief of Strategic Alliances for Space Florida; and Laura Henning, public information officer for the Canaveral National Seashore. Kennedy is partnering with Armstrong, Langley and Space Florida for a program called SonicBAT for Sonic Booms in Atmospheric Turbulence. Starting in August, NASA F-18 jets will take off from the Shuttle Landing Facility and fly at supersonic speeds while agency researchers on the ground measure the effects of low-altitude turbulence on sonic booms. The study could lead to technology mitigating the annoying sonic booms making possible supersonic flights over populated areas.
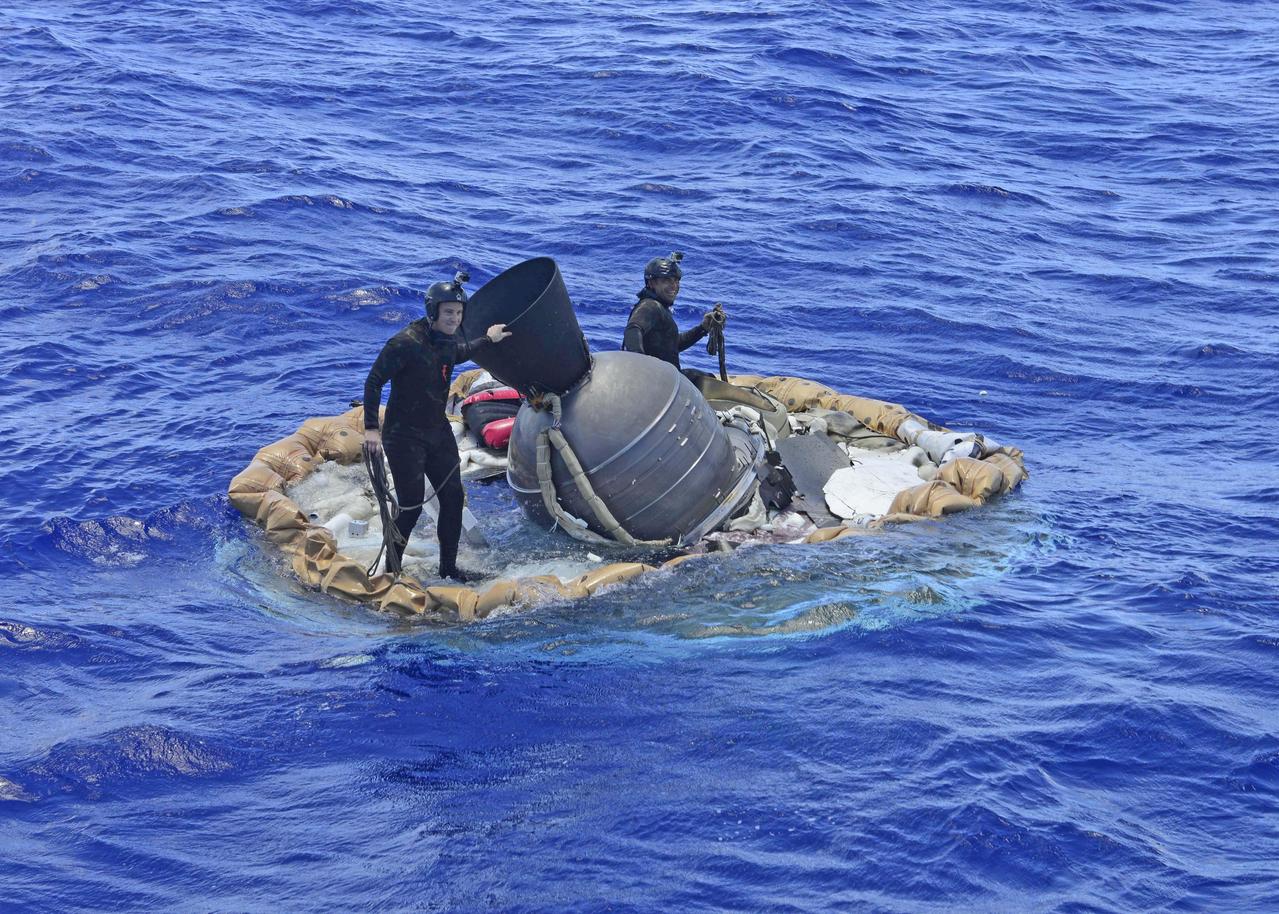

Two members of the U.S. Navy's Mobile Diving Salvage Unit (MDSU) 1 Explosive Ordnance Detachment work on recovering the test vehicle for NASA's Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD) project. The saucer-shaped LDSD craft splashed down at 11:49 a.m. HST (2:49 PDT/5:49 p.m. EDT) Monday, June 8, 2015, in the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of the Kauai, Hawaii, after a four-hour experimental flight test that investigated new technologies for landing future robotic and human Mars missions. During the flight test, a Supersonic Inflatable Aerodynamic Decelerator (SIAD) and a supersonic parachute were deployed. The SIAD operated as expected, dramatically slowing the test vehicle's velocity. When the parachute was deployed into the supersonic slipstream, it appeared to blossom to full inflation prior to the emergence of a tear which then propagated and destroyed the parachute's canopy. As a result, the saucer's splashdown in the Pacific Ocean was hard, resulting in fracturing parts of the structure. Memory cards containing comprehensive test data -- including high-speed, high-resolution imagery recorded during the flight -- were successfully recovered. Also recovered were the test vehicle and its components, the supersonic parachute, the ballute used to deploy the parachute, and a large weather balloon that initially carried the saucer to an altitude of 120,000 feet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19684
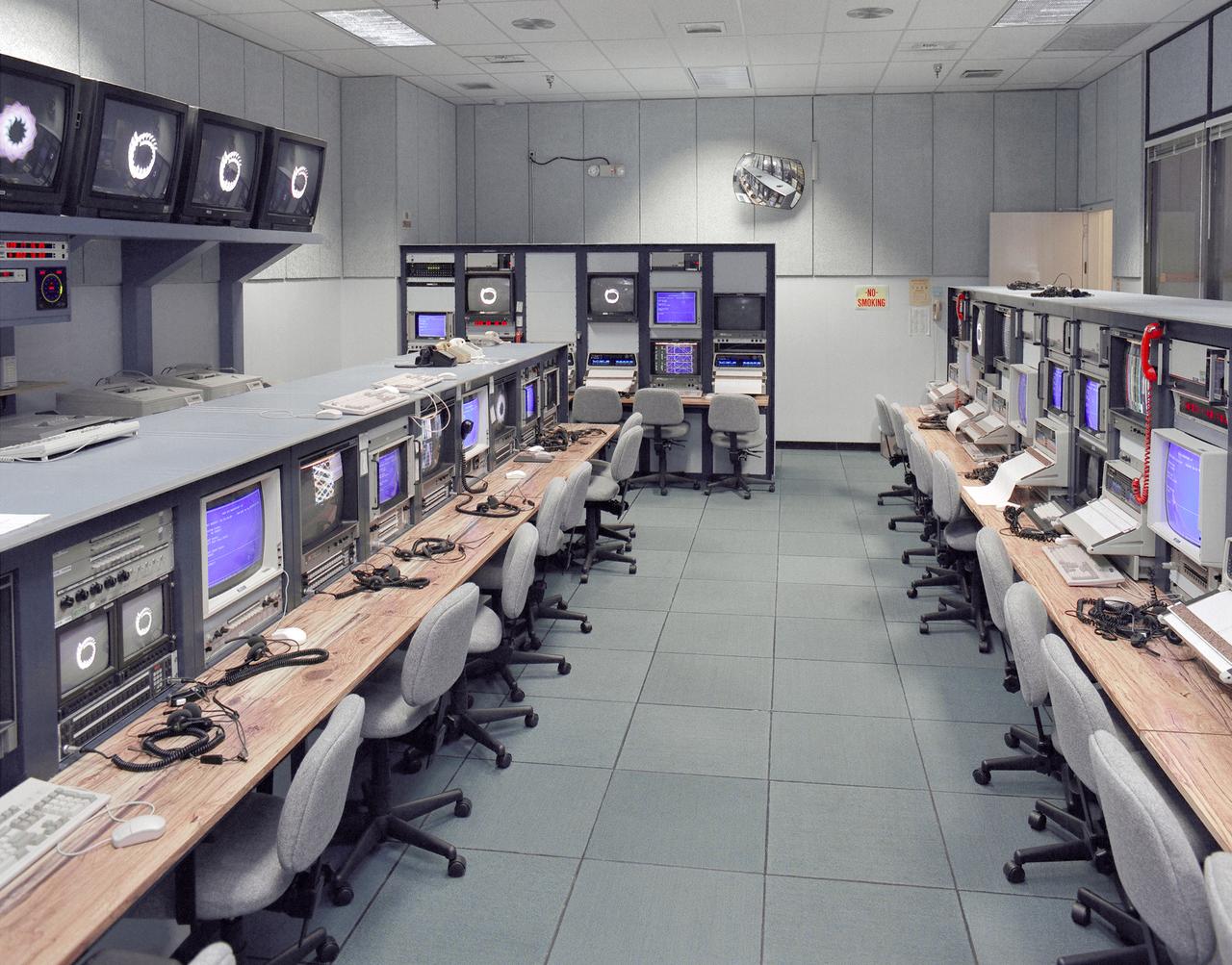

Mission control Blue Room, seen here, in building 4800 at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center, is part of the Western Aeronautical Test Range (WATR). All aspects of a research mission are monitored from one of two of these control rooms at Dryden. The WATR consists of a highly automated complex of computer controlled tracking, telemetry, and communications systems and control room complexes that are capable of supporting any type of mission ranging from system and component testing, to sub-scale and full-scale flight tests of new aircraft and reentry systems. Designated areas are assigned for spin/dive tests, corridors are provided for low, medium, and high-altitude supersonic flight, and special STOL/VSTOL facilities are available at Ames Moffett and Crows Landing. Special use airspace, available at Edwards, covers approximately twelve thousand square miles of mostly desert area. The southern boundary lies to the south of Rogers Dry Lake, the western boundary lies midway between Mojave and Bakersfield, the northern boundary passes just south of Bishop, and the eastern boundary follows about 25 miles west of the Nevada border except in the northern areas where it crosses into Nevada.
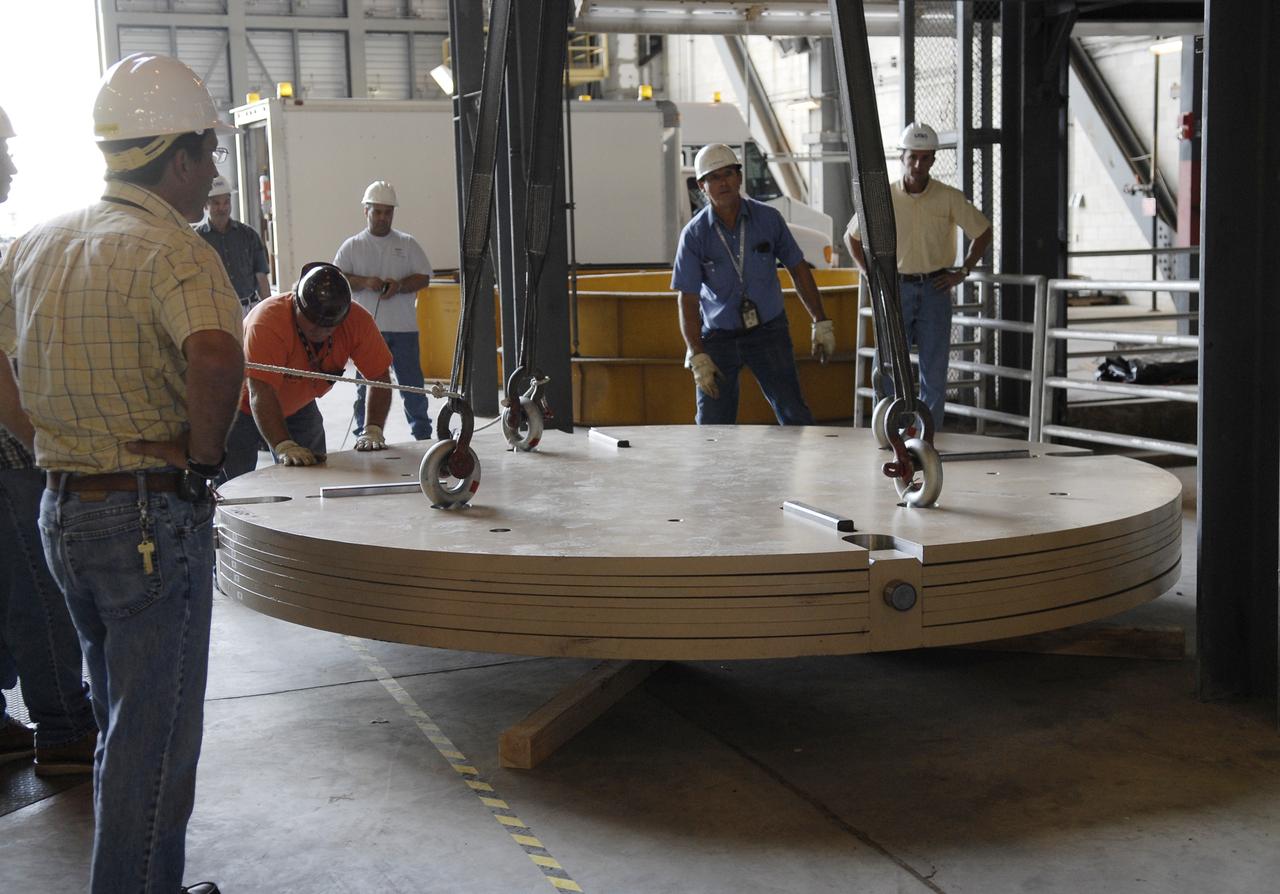

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers lower an Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assembly onto the floor of high bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
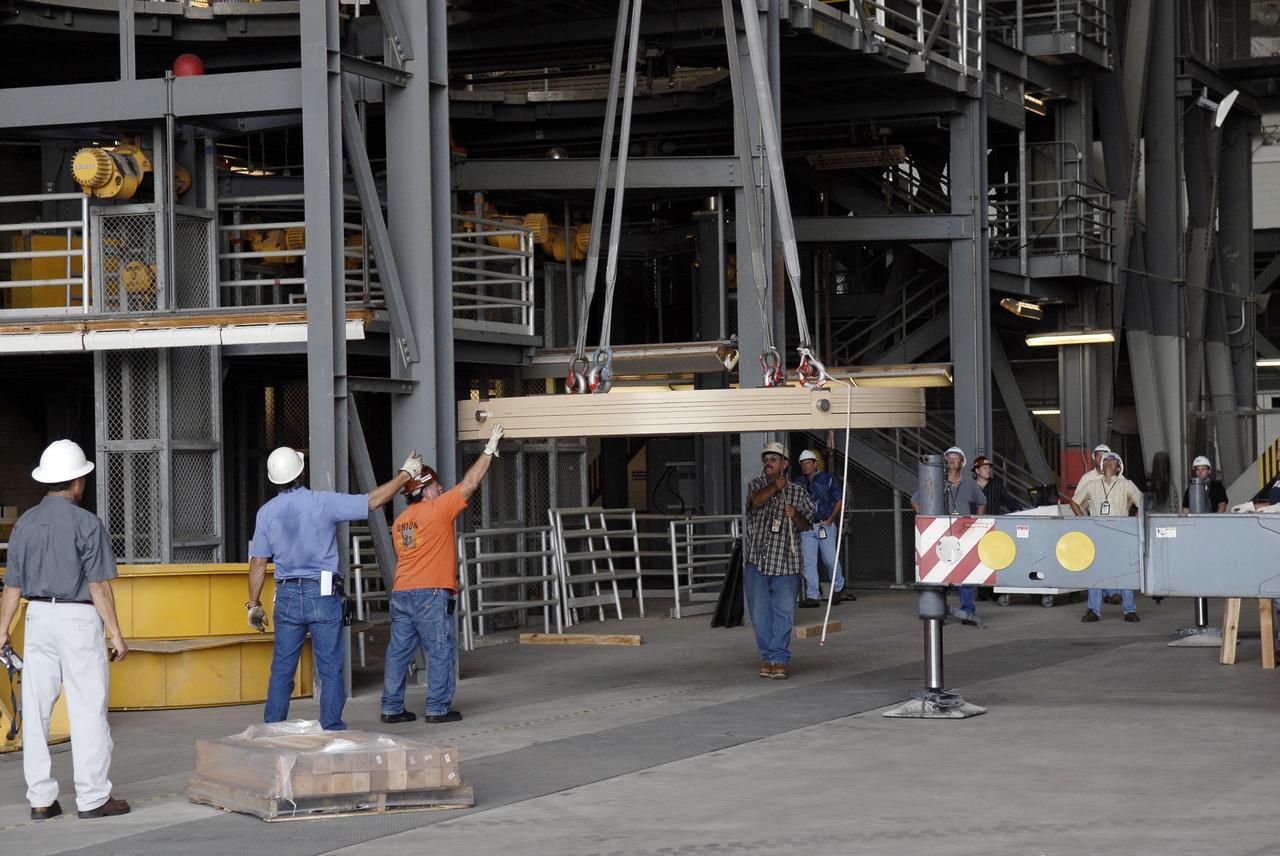

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers lift the Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies off a truck in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
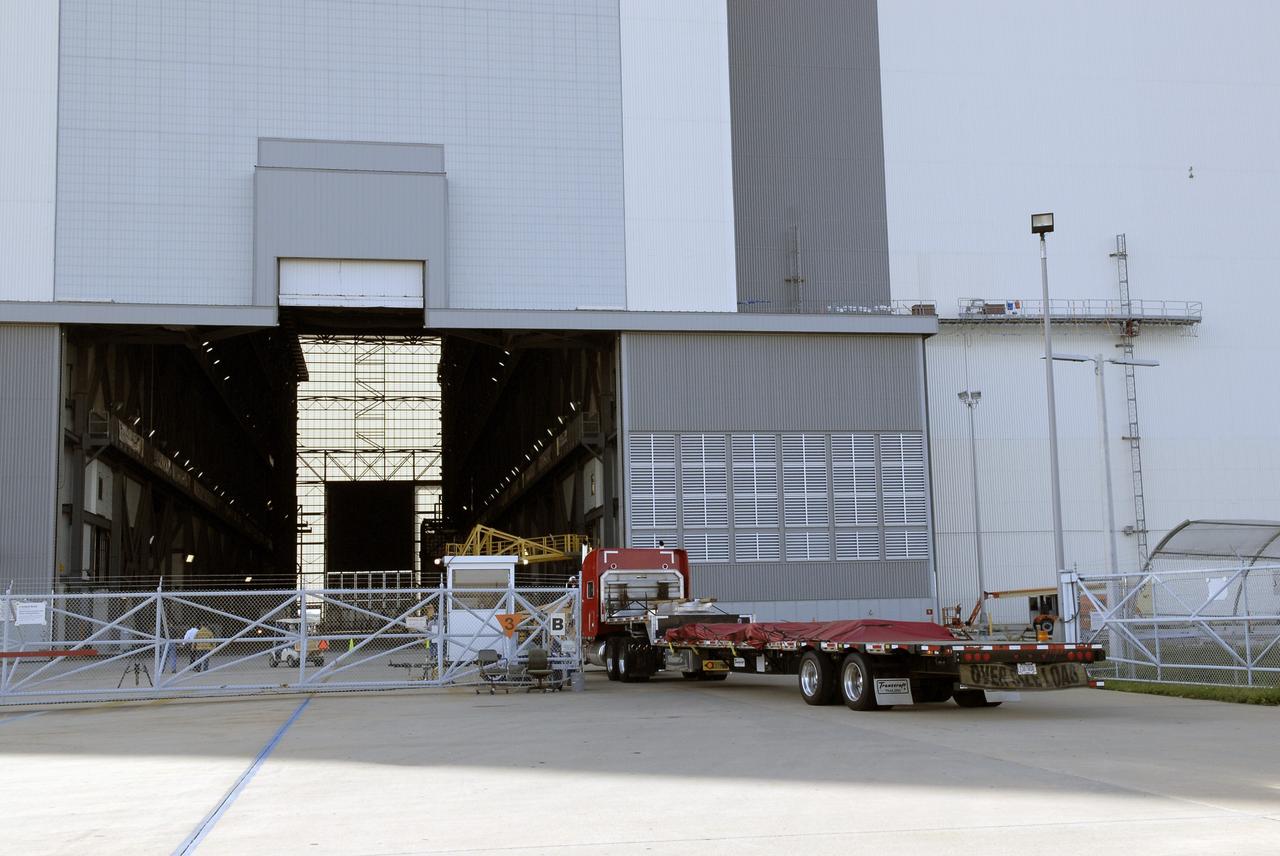

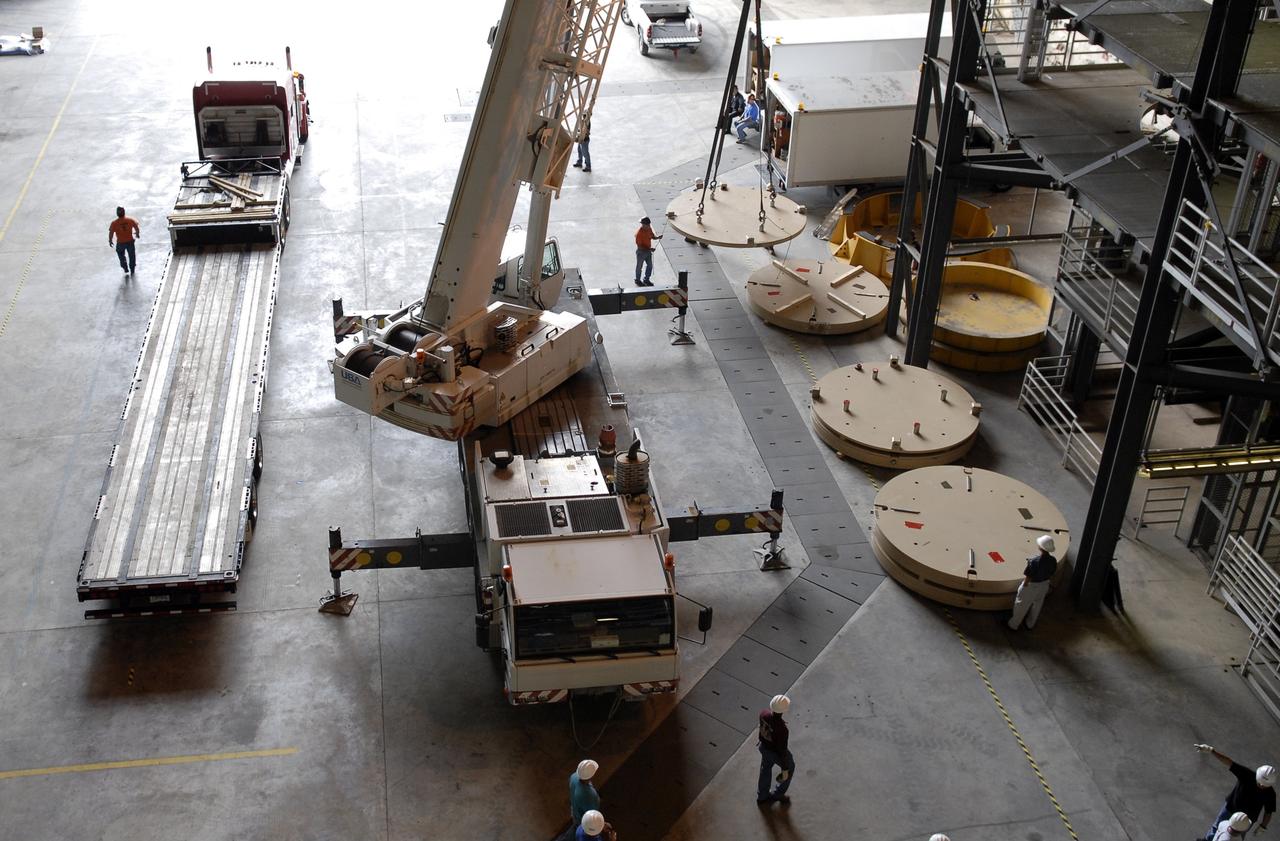
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - One of five trucks transporting the Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies arrives at the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
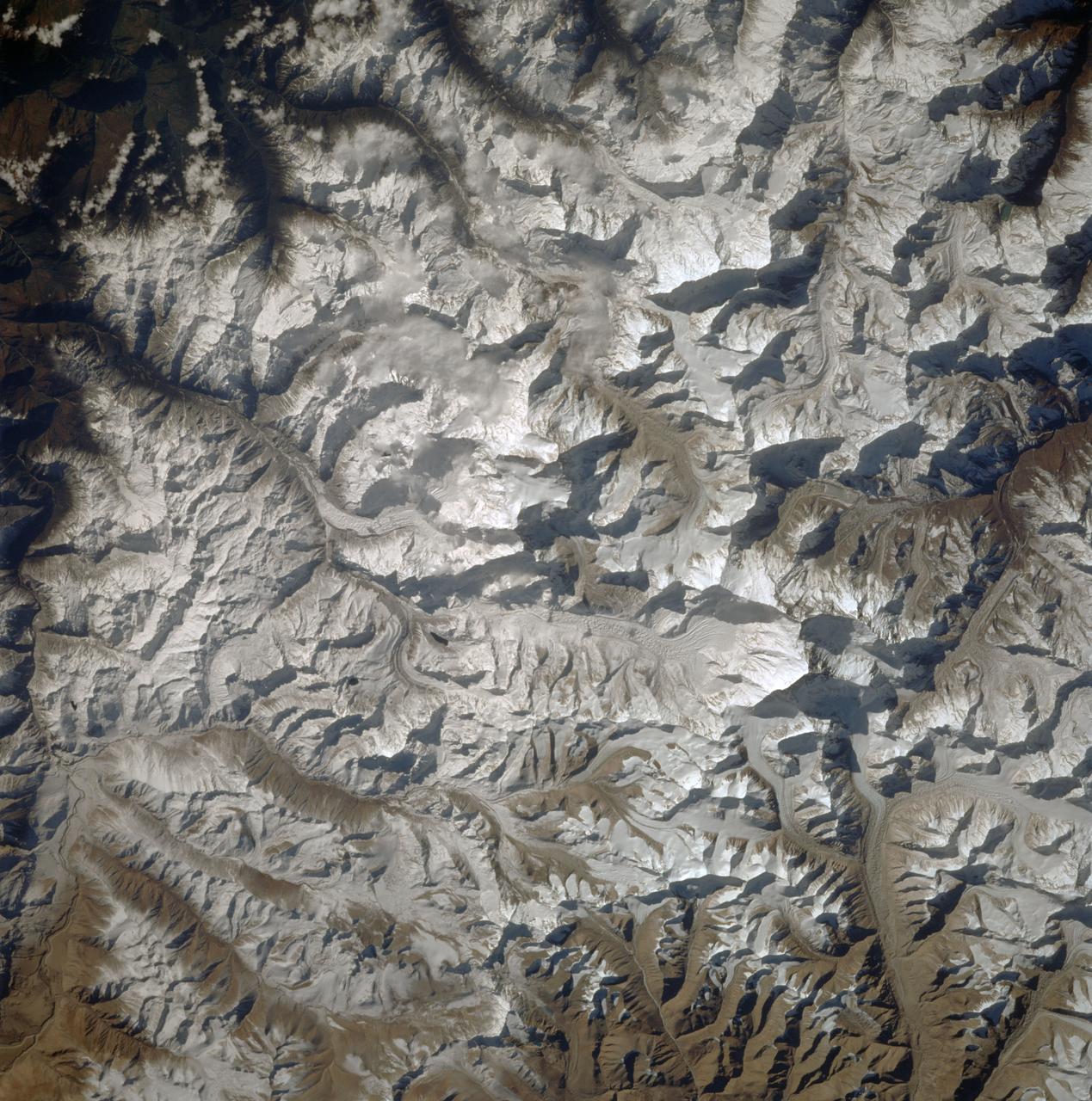

STS087-716-080 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- Featured in this view is Mount Everest. It is called “Sagarmatha” in Nepal and “Qomolangma Feng” Qomolangma in China (both names meaning “Goddess Mother of the World”), but is known to the western world as Mount Everest. At an altitude of 29,028 feet (8,848 meters) the summit of tallest mountain on Earth (above sea level) reaches two-thirds of the way through the atmosphere. Situated on the border between Nepal and China (27°59’N, 86°56’E), Mount Everest with its low oxygen levels, powerful winds, and extremely cold temperatures has captured the imagination of adventuresome men and women. Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay were the first persons to surmount Mount Everest in 1953. While climbing Everest can be challenging, it can also be tragic. On May 10, 1996, after reaching the summit and descending to camp, several climbers were trapped by a severe and sudden storm. A total of eight people died, making this day the deadliest single tragedy in the history of Mount Everest. This picture is one of the 70mm Earth observations visuals used by the crew at its post flight presentation events.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies have arrived at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and are positioned along the floor of high bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers position Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies along the floor of high bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies are positioned along the floor of high bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
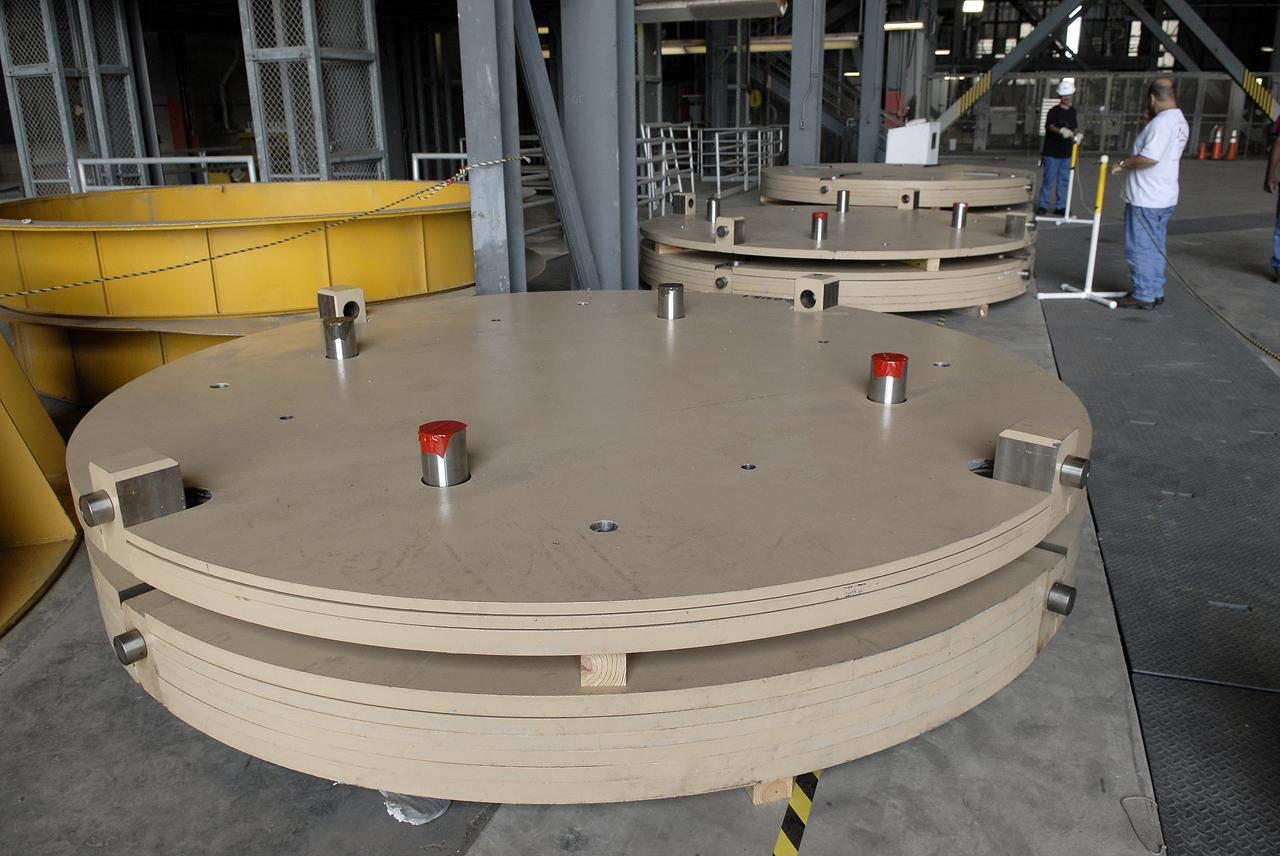

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies have arrived at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center and are positioned along the floor of high bay 4 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
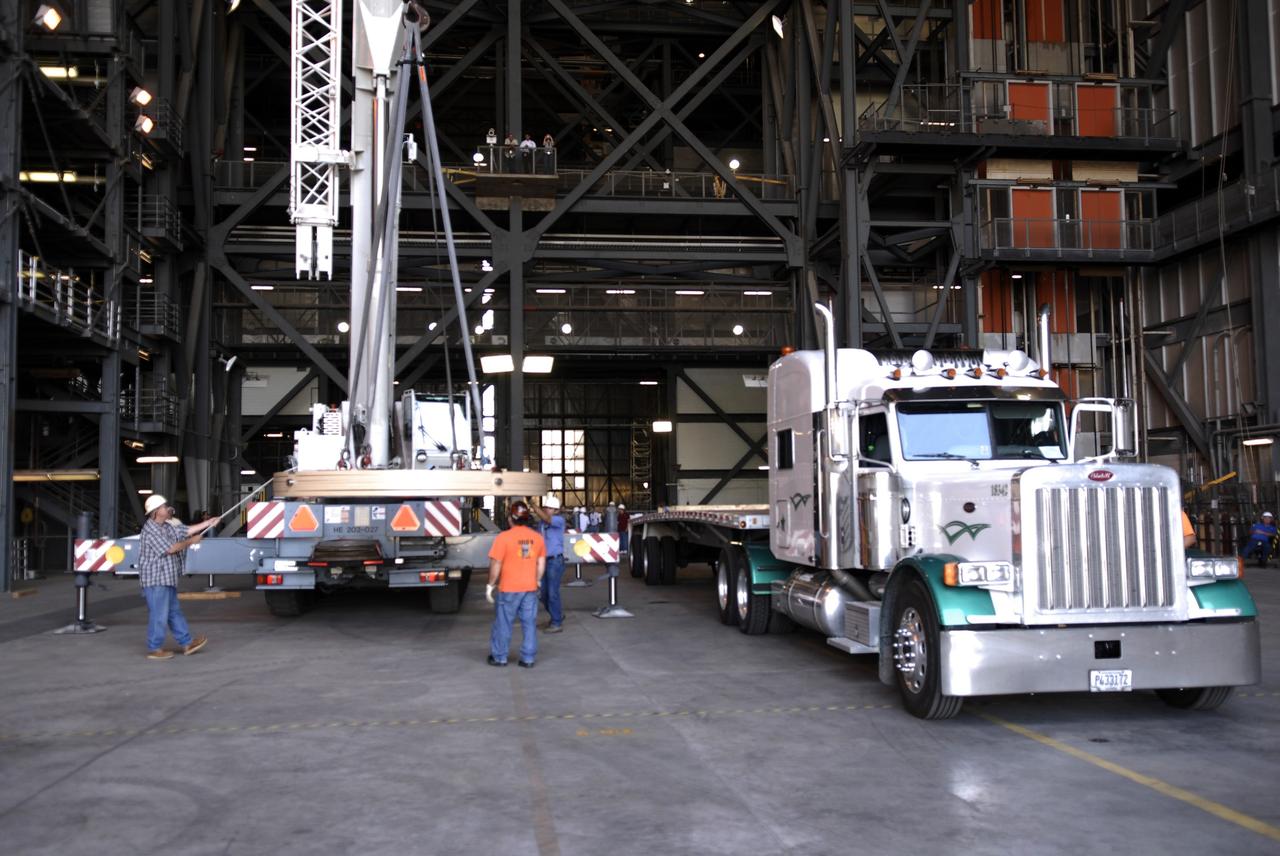

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Ares IX upper stage segments’ ballast assemblies are offloaded from one of five trucks which delivered them to the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, part of the preparations for the test of the Ares IX rocket. These ballast assemblies will be installed in the upper stage 1 and 7 segments and will mimic the mass of the fuel. Their total weight is approximately 160,000 pounds. The test launch of the Ares IX in 2009 will be the first designed to determine the flight-worthiness of the Ares I rocket. Ares I is an in-line, two-stage rocket that will transport the Orion crew exploration vehicle to low-Earth orbit. The Ares I first stage will be a five-segment solid rocket booster based on the four-segment design used for the space shuttle. Ares I’s fifth booster segment allows the launch vehicle to lift more weight and reach a higher altitude before the first stage separates from the upper stage, which ignites in midflight to propel the Orion spacecraft to Earth orbit. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
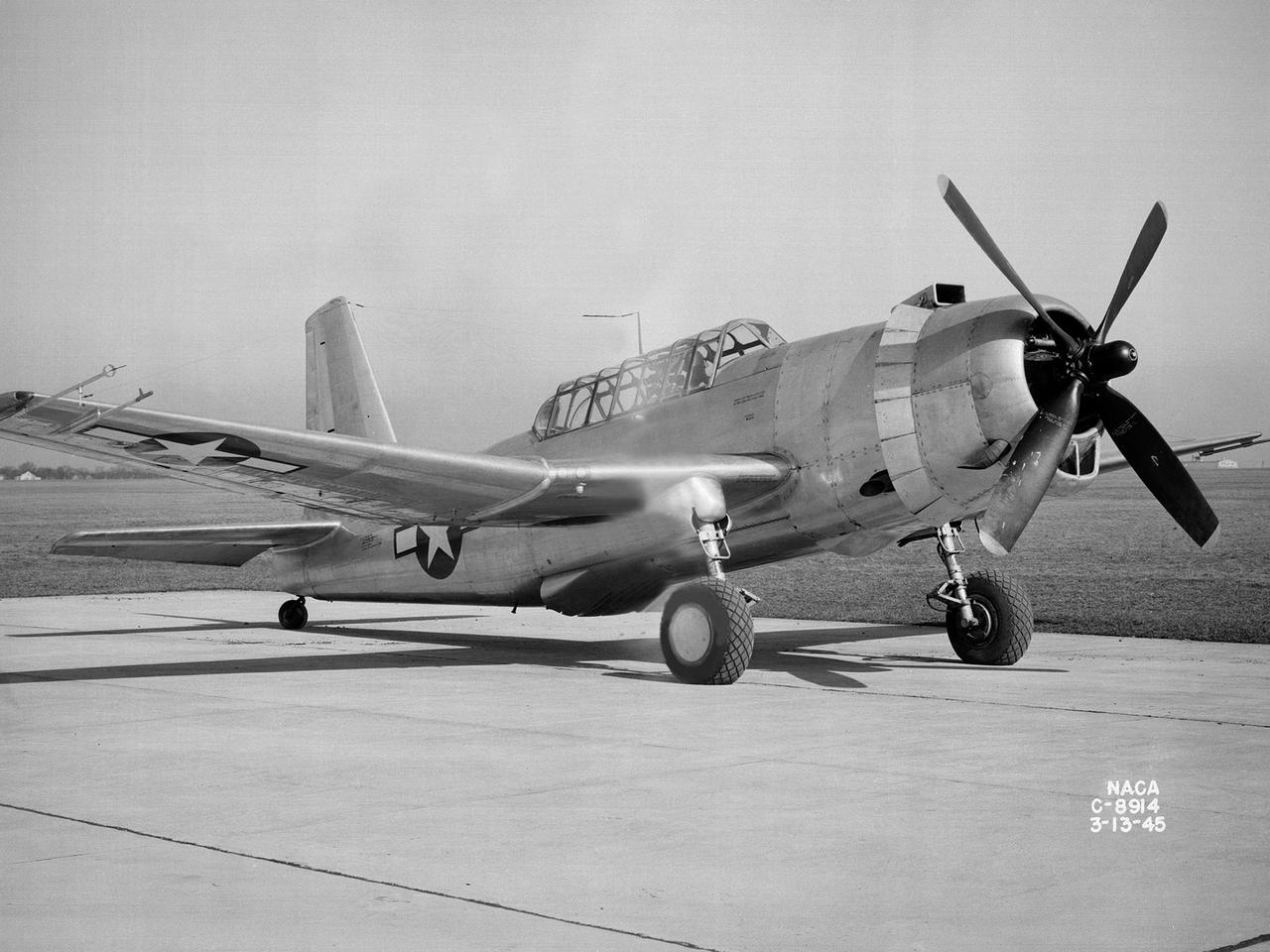

A Bell P-39 Airacobra in the NACA Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s Icing Research Tunnel for a propeller deicing study. The tunnel, which began operation in June 1944, was built to study the formation of ice on aircraft surfaces and methods of preventing or eradicating that ice. Ice buildup adds extra weight to aircraft, effects aerodynamics, and sometimes blocks airflow through engines. NACA design engineers added the Icing Research Tunnel to the new AERL’s original layout to take advantage of the massive refrigeration system being constructed for the Altitude Wind Tunnel. The Icing Research Tunnel is a closed-loop atmospheric wind tunnel with a 6- by 9-foot test section. The tunnel can produce speeds up to 300 miles per hour and temperatures from about 30 to -45⁰ F. During World War II AERL researchers analyzed different ice protection systems for propeller, engine inlets, antennae, and wings in the icing tunnel. The P-39 was a vital low-altitude pursuit aircraft of the US during the war. NACA investigators investigated several methods of preventing ice buildup on the P-39’s propeller, including the use of internal and external electrical heaters, alcohol, and hot gases. They found that continual heating of the blades expended more energy than the aircraft could supply, so studies focused on intermittent heating. The results of the wind tunnel investigations were then compared to actual flight tests on aircraft.