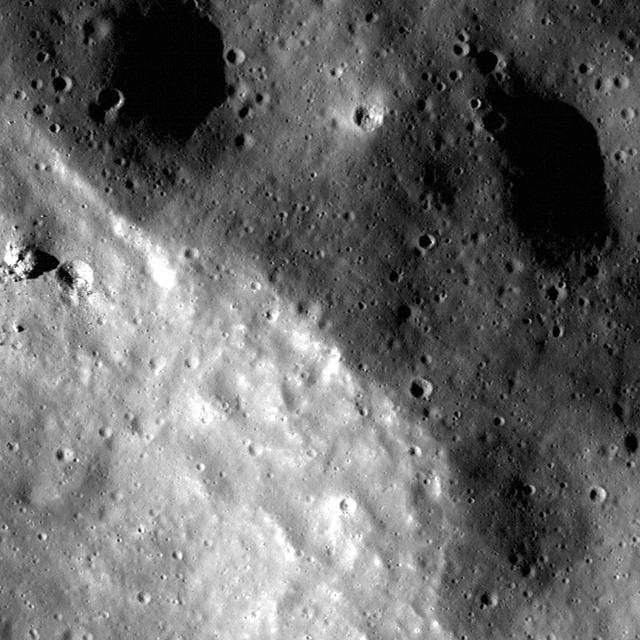

Eratosthenes Crater and the Lunar Timescale
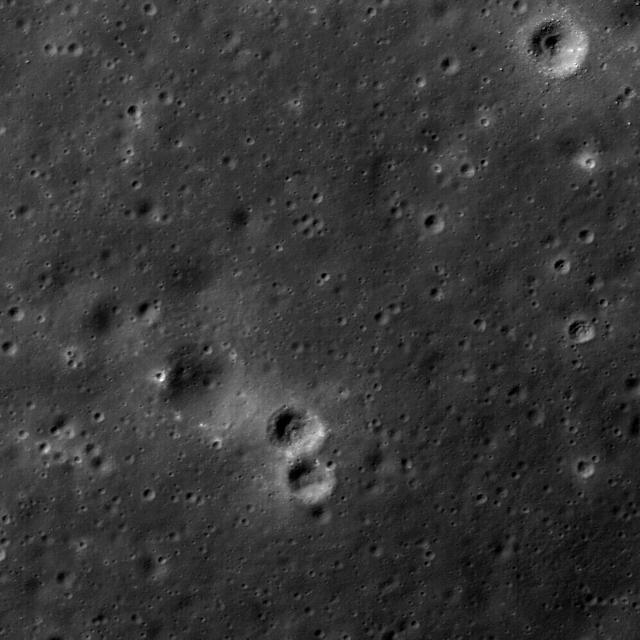

Lunar Swirls at the Mare Ingenii
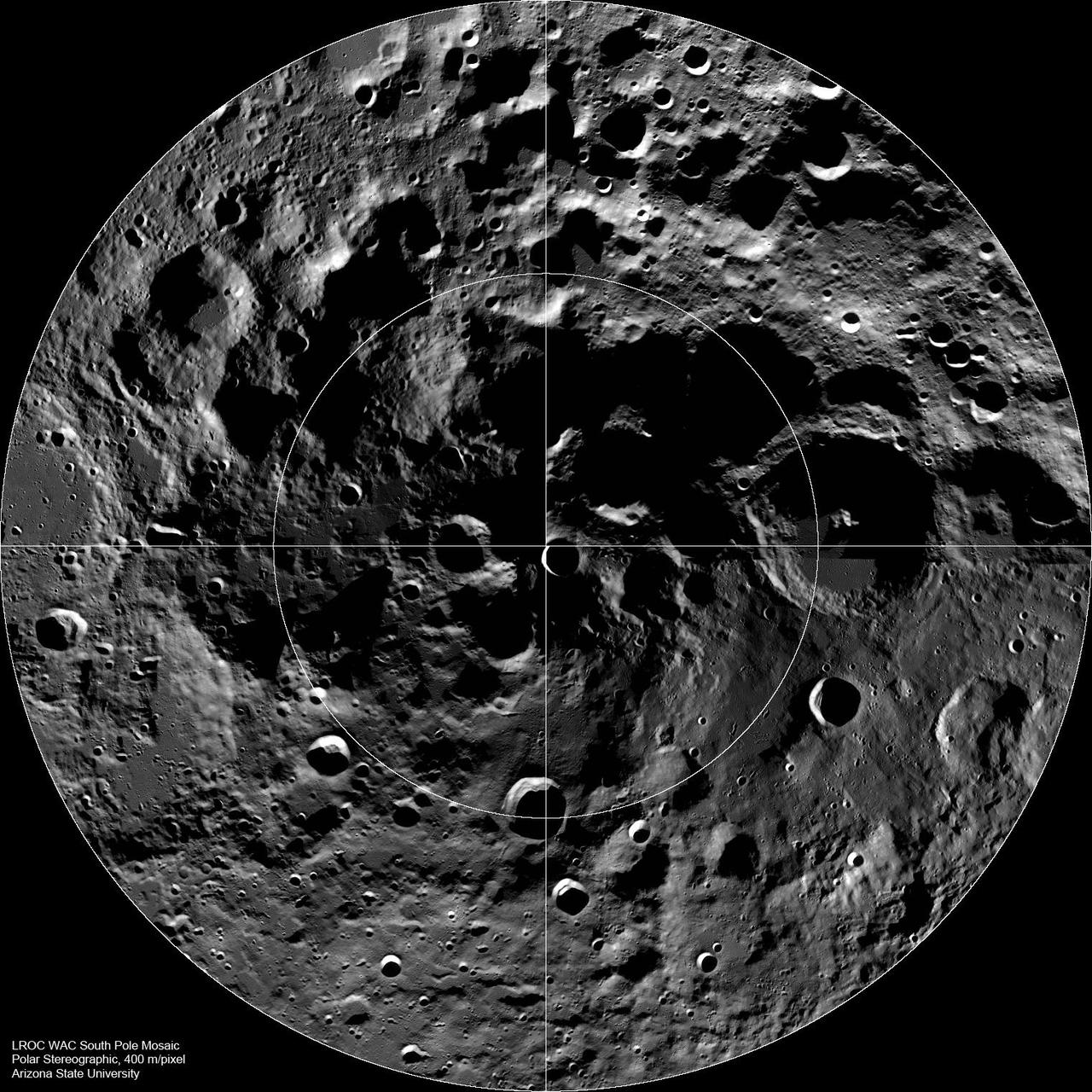
The Lunar South Pole
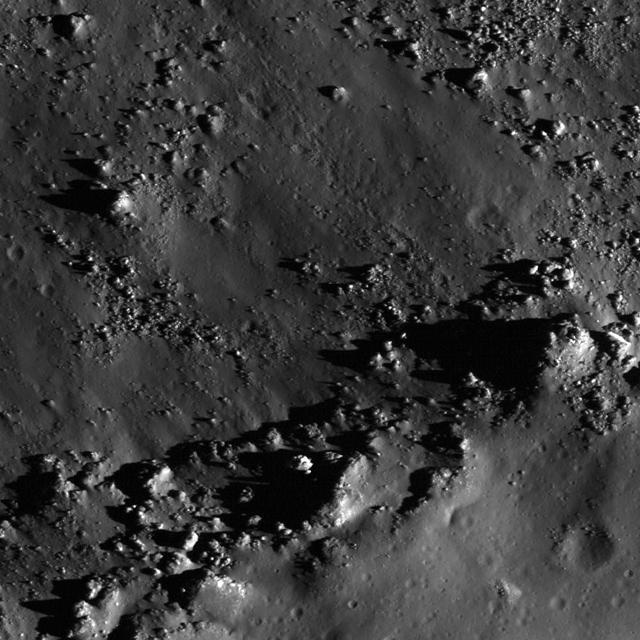

Copernicus Crater and The Lunar Timescale
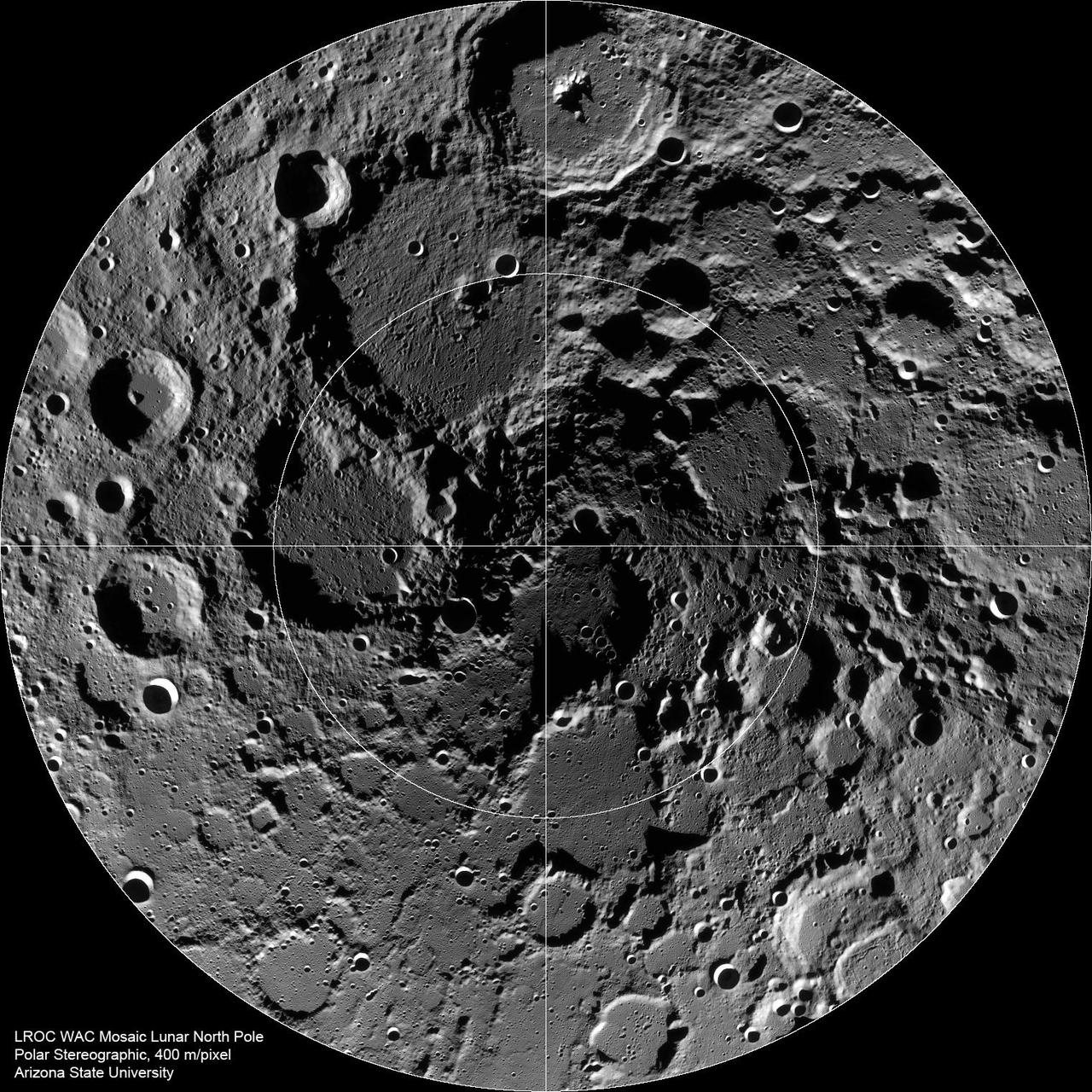

The Lunar North Pole
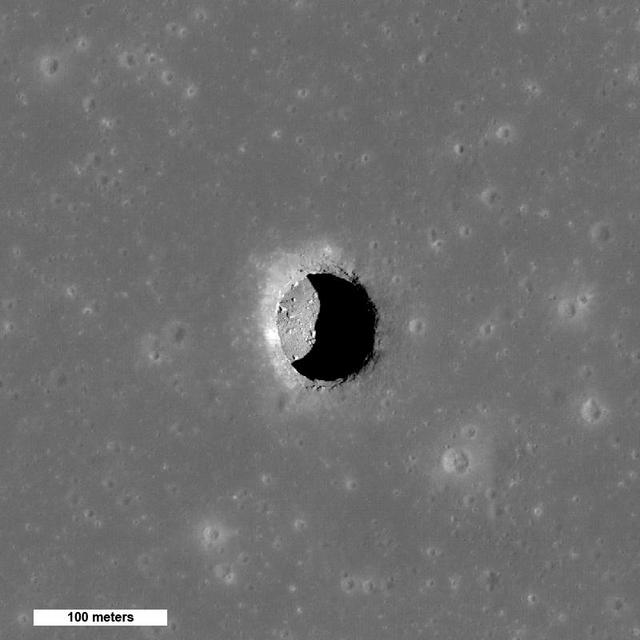

New Views of Lunar Pits
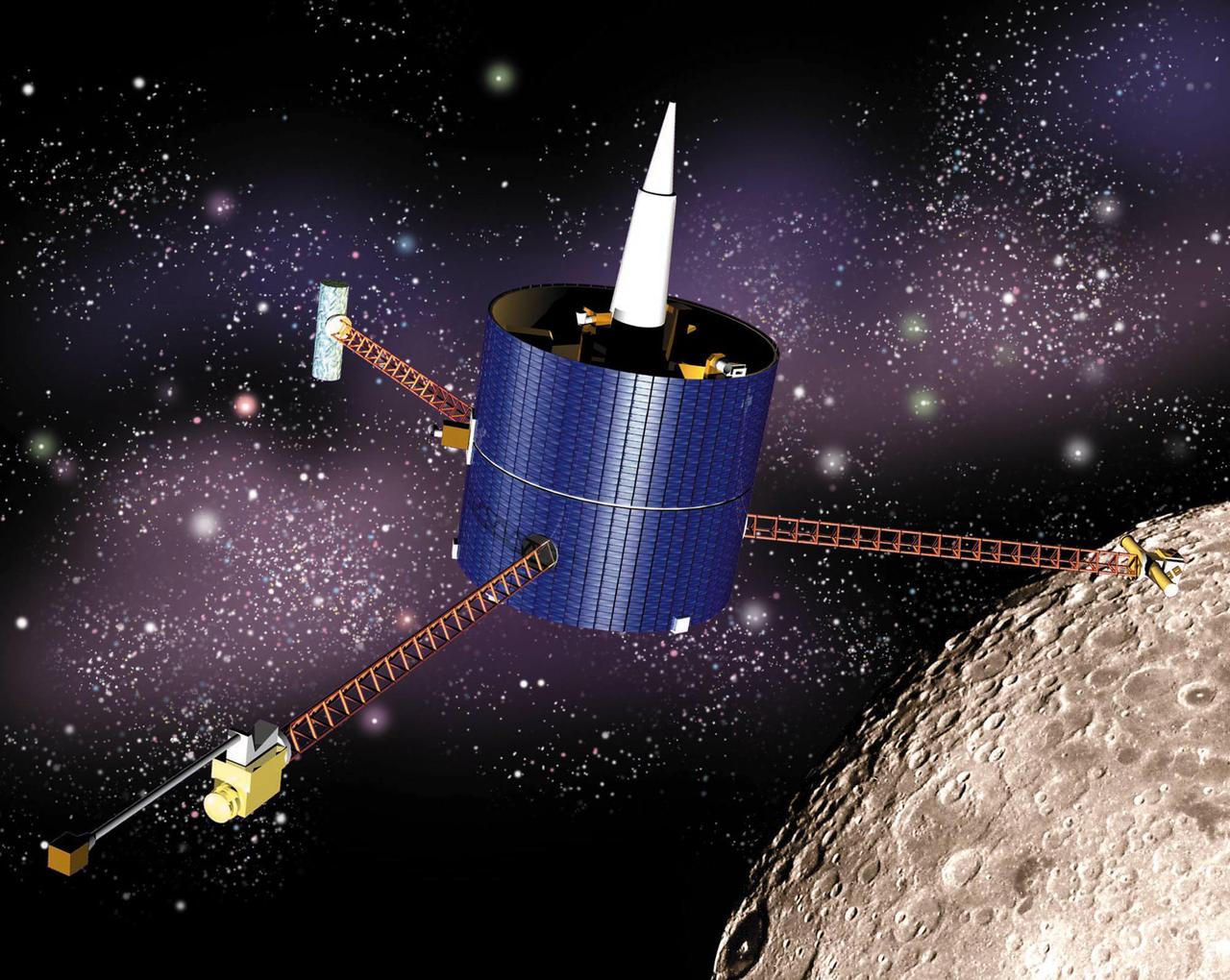

This artist concept of the Lunar Prospector shows the spacecraft in lunar orbit. Instrument masts are fully deployed. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18162
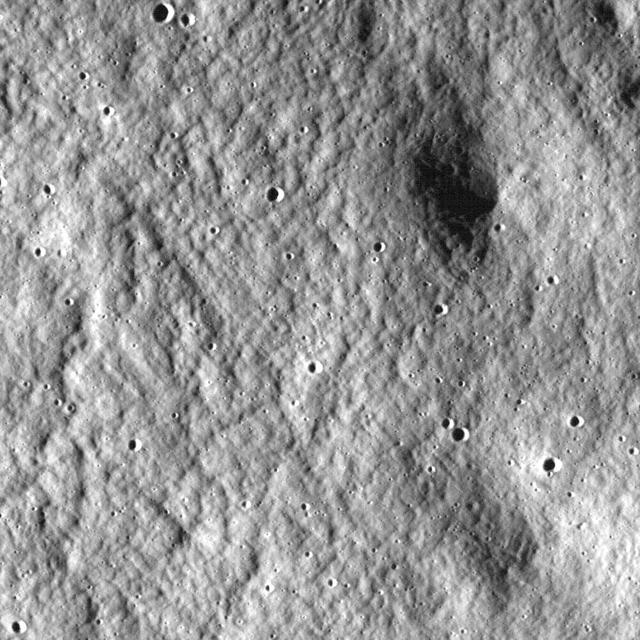

Close-up view of the lunar highlands, northeast of Clavius crater, taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
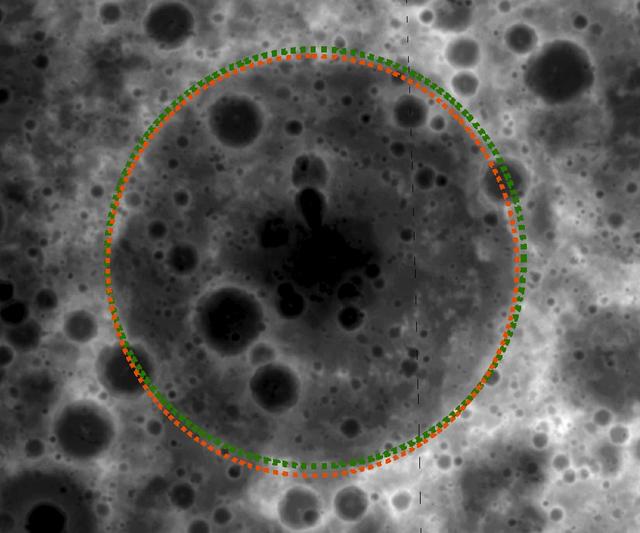
Hunting for Ancient Lunar Impact Basins
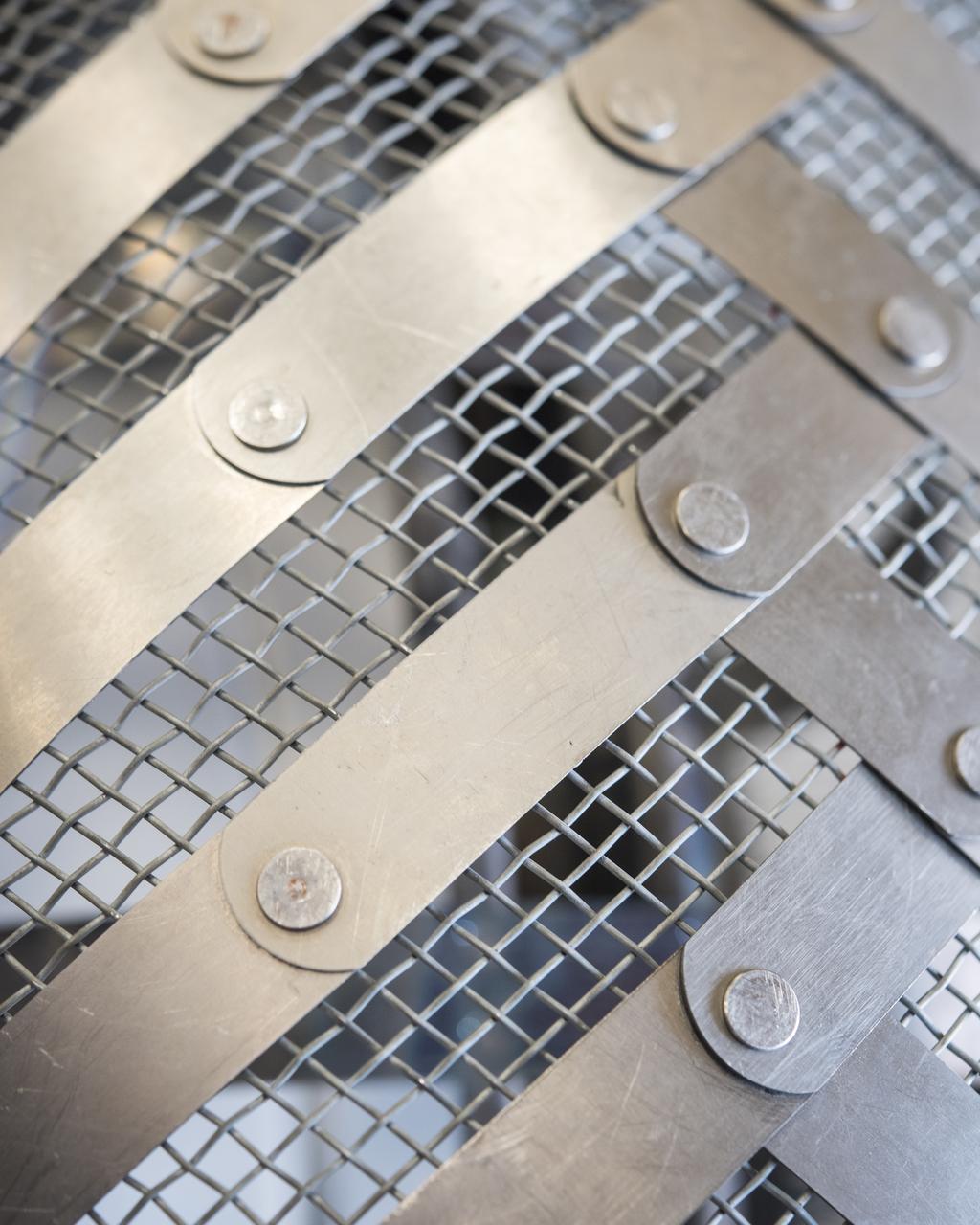

This is a close-up of an exact replica of the Apollo-era Lunar Roving Vehicle Wheel, of which twelve originals still rest on the surface of the Moon. The tire was designed to flex under load, without air, and was formed from a mesh of plated piano wire. Metal straps were hand riveted onto the mesh to reduce sinking into loose lunar soils. These replica wheels were tested in NASA Glenn's SLOPE Lab to establish a baseline for future improvements.
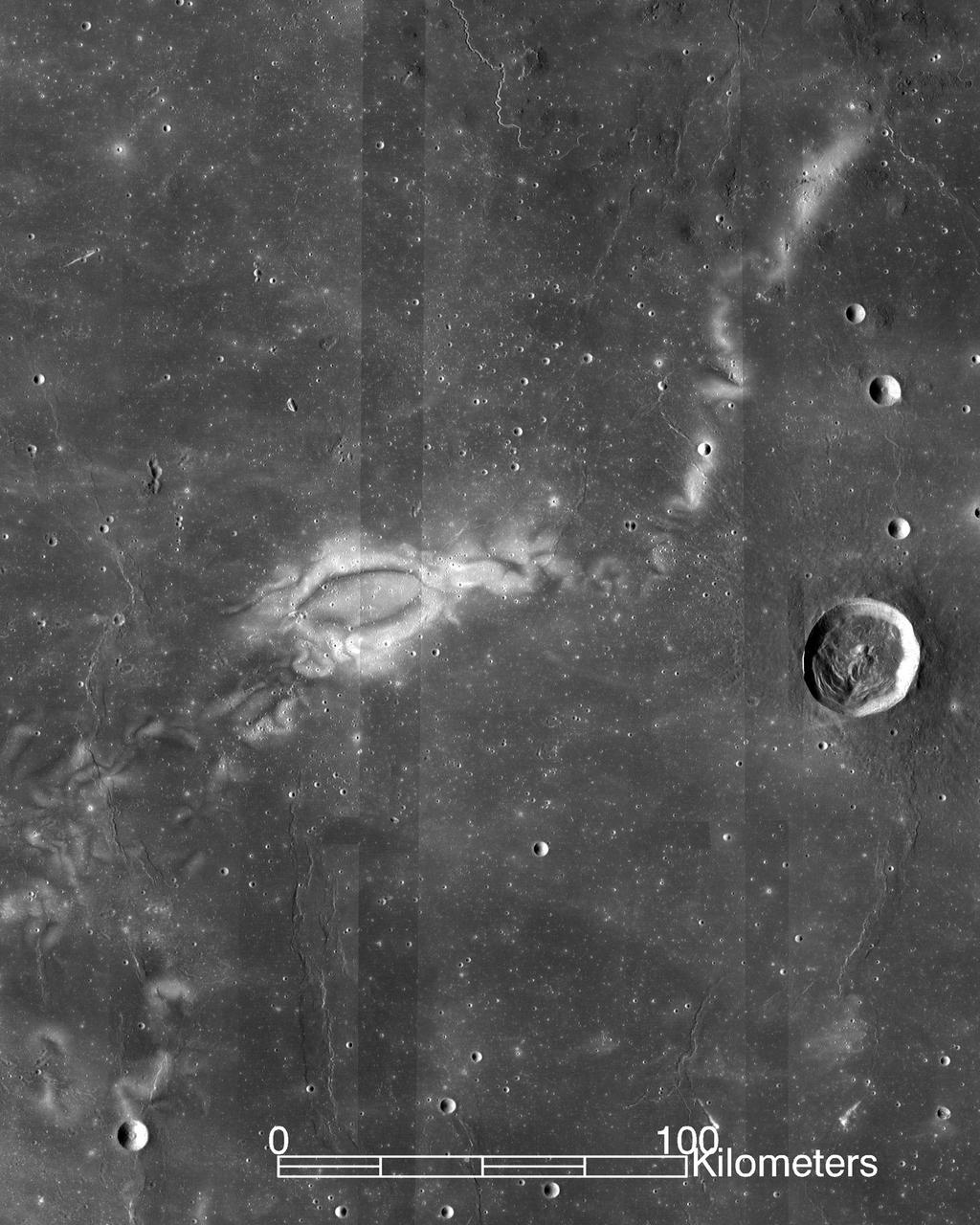
Research using data from NASA's ARTEMIS mission suggests that lunar swirls, like the Reiner Gamma lunar swirl imaged here by NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, could be the result of solar wind interactions with the Moon's isolated pockets of magnetic field. Credits: NASA LRO WAC science team

The Diviner instrument following integration to NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. Diviner is one of seven instruments aboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
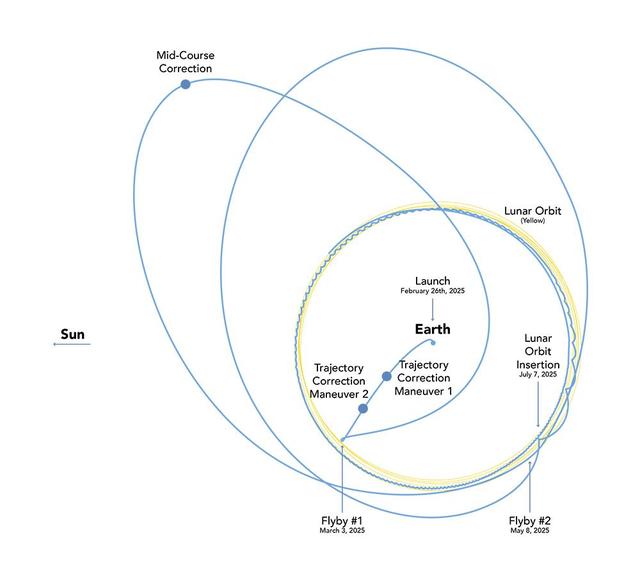
Lunar Trailblazer's voyage to the Moon will take between four and seven months, depending on the day it launches. This orbital diagram shows the low-energy transfer trajectory of the NASA mission should it launch on Feb. 26, the earliest date in a four-day launch period. If it launches that date, the spacecraft is expected to arrive in lunar orbit about four months later. Shown in this diagram are key dates of trajectory correction maneuvers, when the spacecraft will use its thrusters to shape its orbit, and lunar flybys. Lunar Trailblazer was a selection of NASA's SIMPLEx (Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration), which provides opportunities for low-cost science spacecraft to ride-share with selected primary missions. To maintain the lower overall cost, SIMPLEx missions have a higher risk posture and lighter requirements for oversight and management. This higher risk acceptance allows NASA to test pioneering technologies, and the definition of success for these missions includes the lessons learned from more experimental endeavors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26459
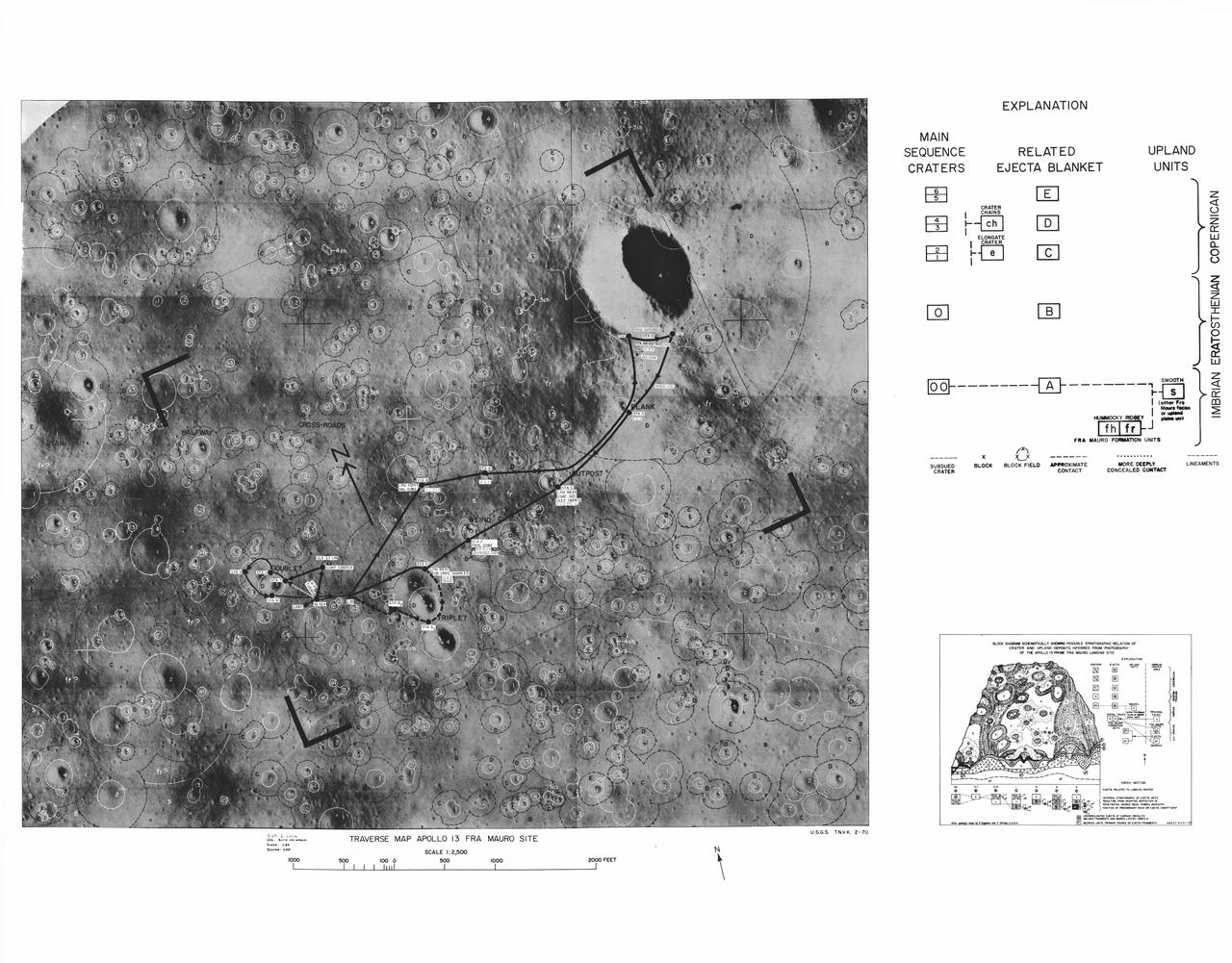
This lunar map shows the traverse plans for the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. Areas marked include Lunar module landing site, areas for the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiment Package (ALSEP) and areas for gathering of core samples.
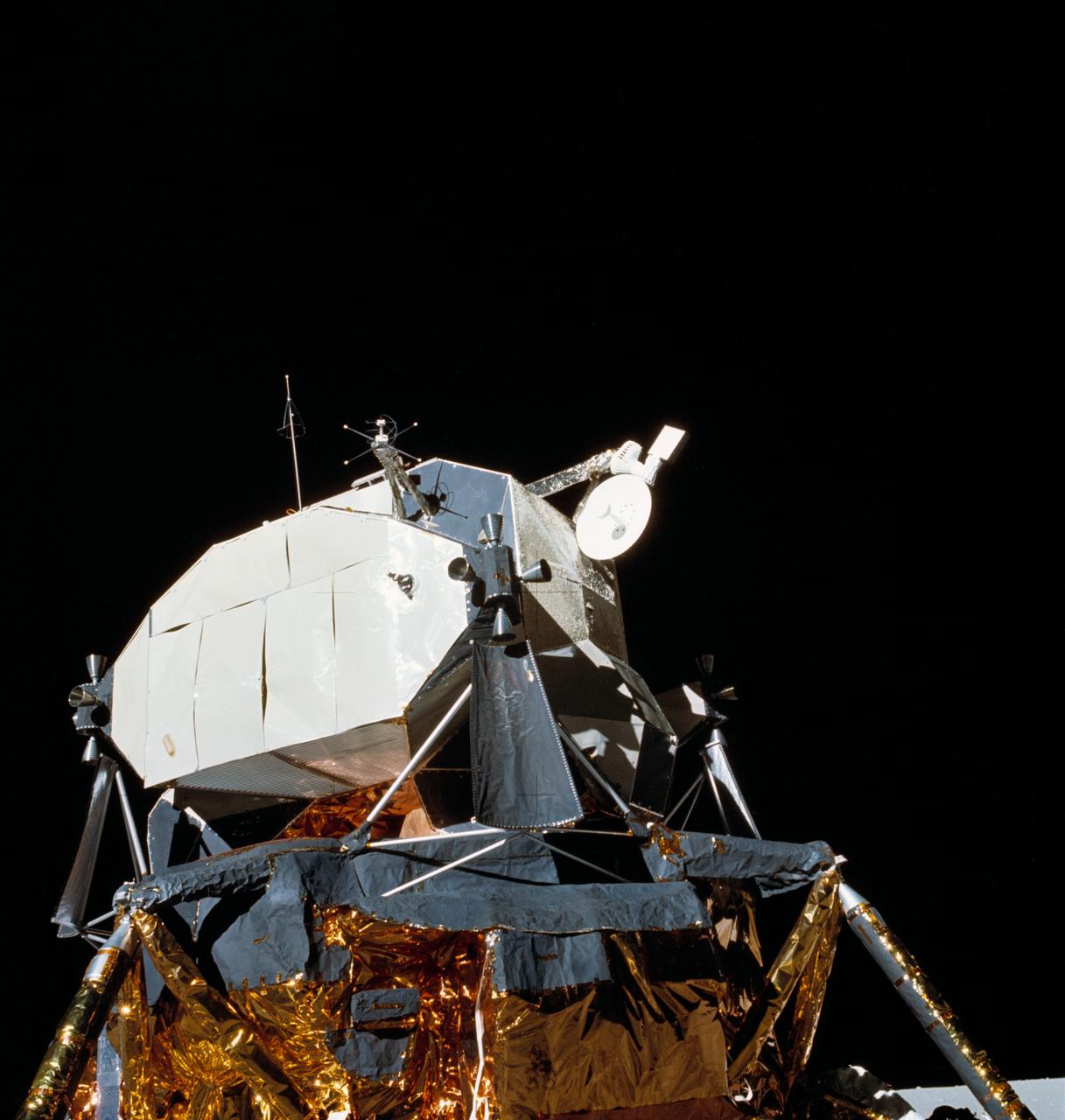

AS16-113-18334 (21 April 1972) --- View of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" parked on the lunar surface. During their post mission press conference, the Apollo 16 crewmembers called attention to the steerable S-band antenna, which was "frozen" in a yaw axis during much of the flight. This view of the LM was photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., the lunar module pilot, during the mission's first extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Duke had earlier descended in the LM to explore the Descartes region of the moon, while astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
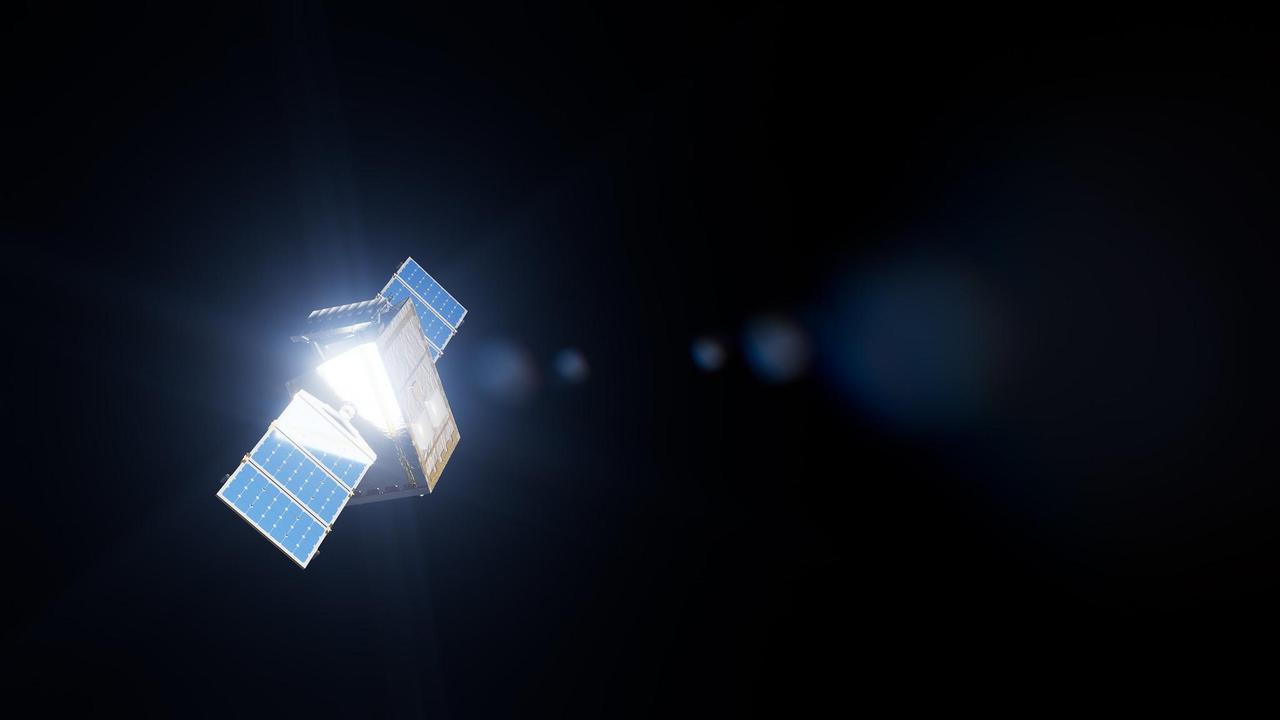
Sunlight gleams off NASA's Lunar Trailblazer in this artist's concept depicting the small satellite in lunar orbit. The spacecraft weighs only 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide when its solar panels are fully deployed. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26429
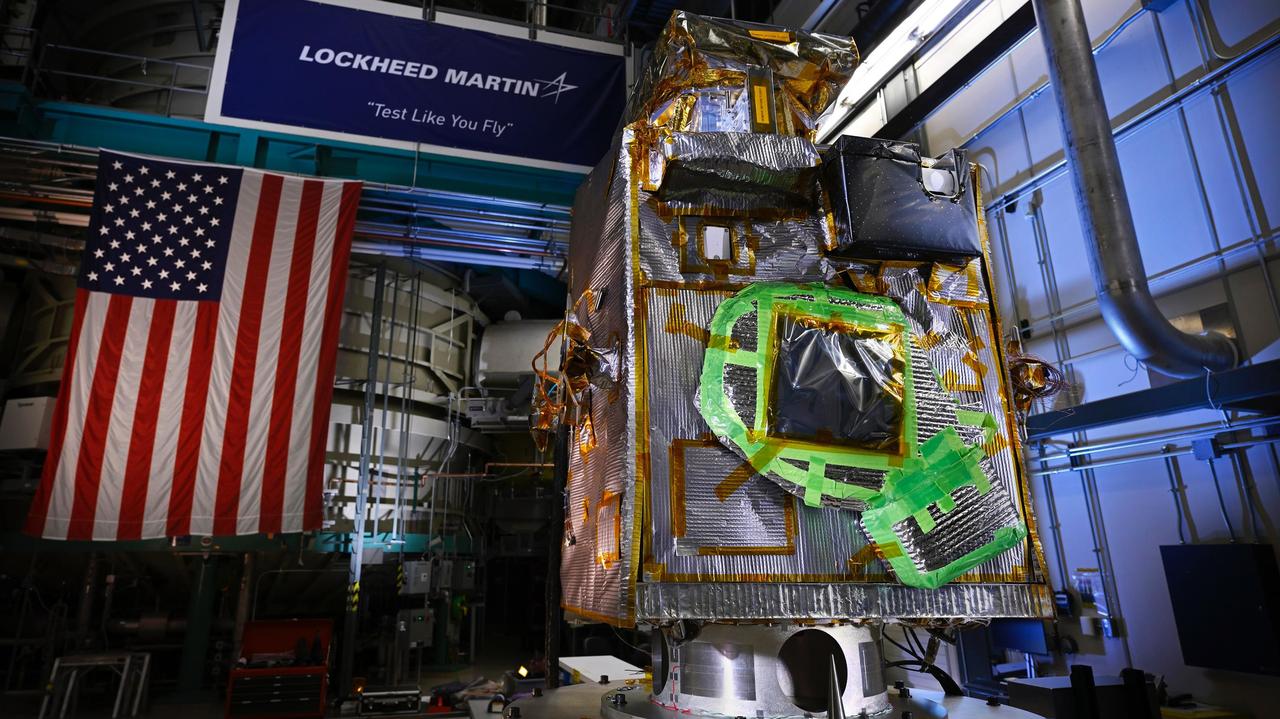

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer sits in a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, shortly after being integrated with its second and final science instrument in June 2023. Called the Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM), the instrument is visible as a black rectangular box in the upper right of the spacecraft's body. Green tape on the spacecraft will be removed before launch. Built by the University of Oxford in England and contributed by the UK Space Agency, LTM joins the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) that was integrated with the spacecraft late last year. Together, the instruments will enable scientists to determine the abundance, location, and form of the Moon's water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25837
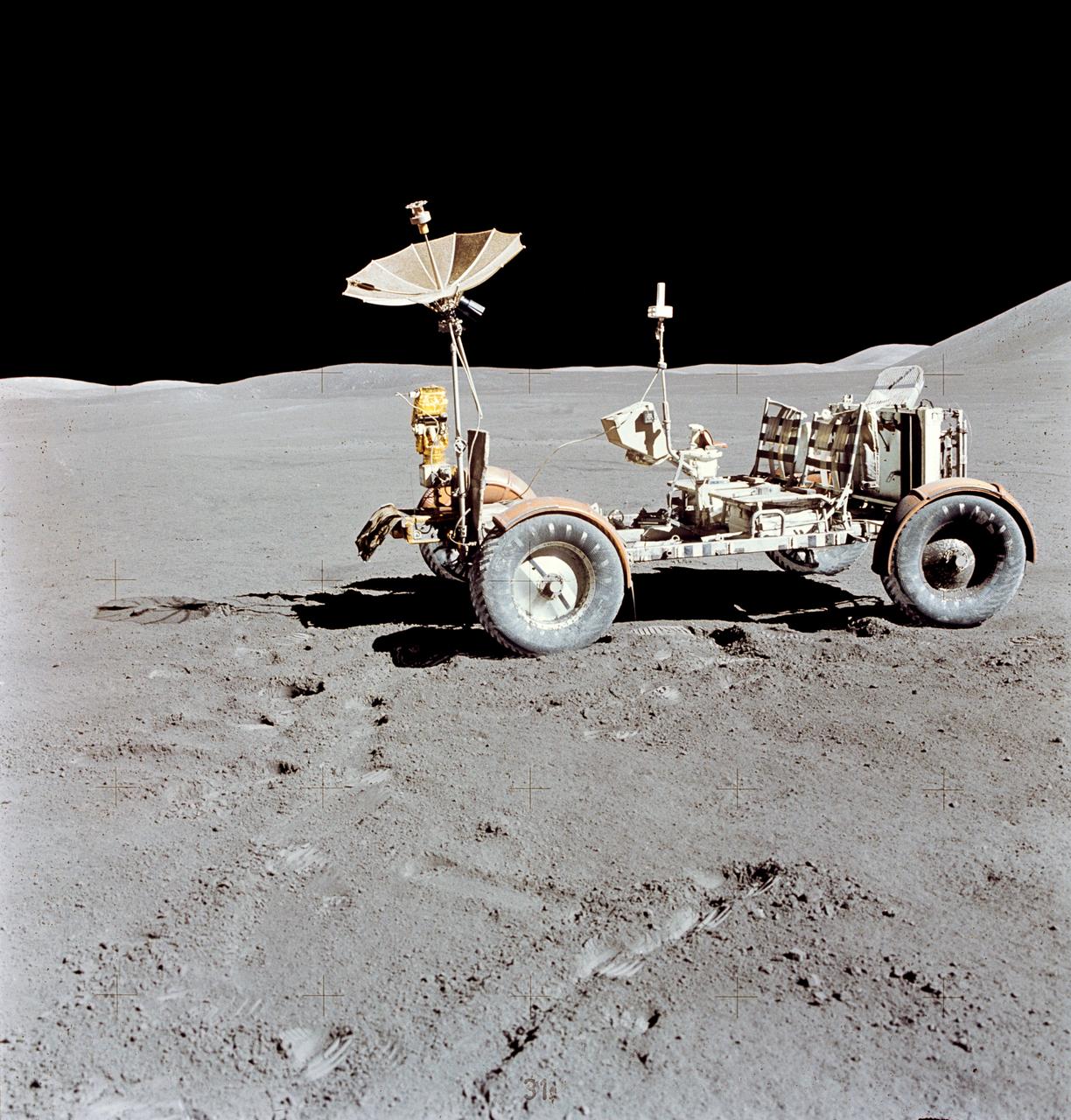

AS15-88-11901 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is photographed alone against the desolate lunar background during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. This view is looking north. The west edge of Mount Hadley is at the upper right edge of the picture. Mount Hadley rises approximately 4,500 meters (about 4,765 feet) above the plain. The most distant lunar feature visible is approximately 25 kilometers (about 15.5 statute miles) away. While astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
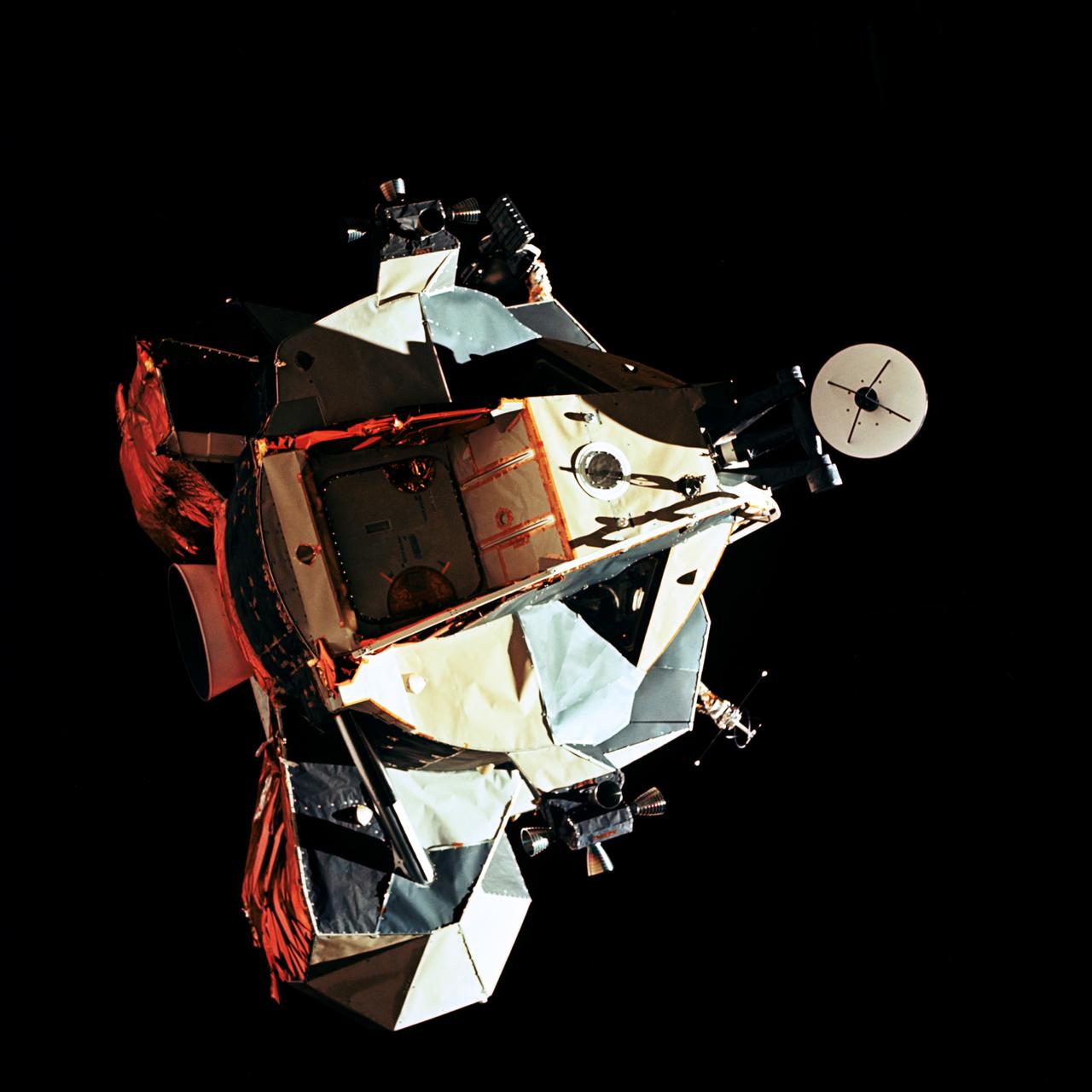

AS17-149-22857 (14 Dec. 1972) --- This 70mm view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" in lunar orbit before rendezvous with the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM). While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Challenger to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the CSM "America" in lunar orbit.
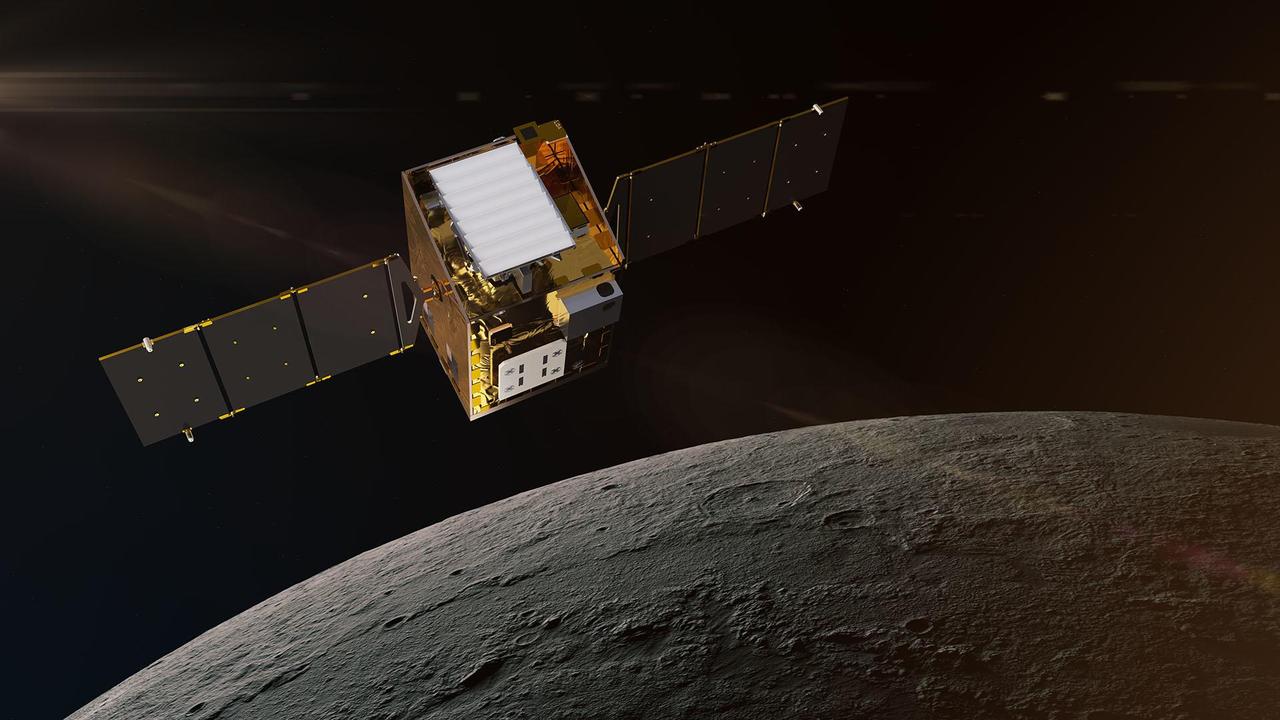

This artist's concept depicts NASA's Lunar Trailblazer in lunar orbit about 60 miles (100 kilometers) from the surface of the Moon. The spacecraft weighs only 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide when its solar panels are fully deployed. Lunar Trailblazer is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and its science investigation and mission operations are led by Caltech with the mission operations center at IPAC. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM3 instrument, as well as mission design and navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft, integrates the flight system, and supports operations under contract with Caltech. Lunar Trailblazer is part of NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program, which is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26453
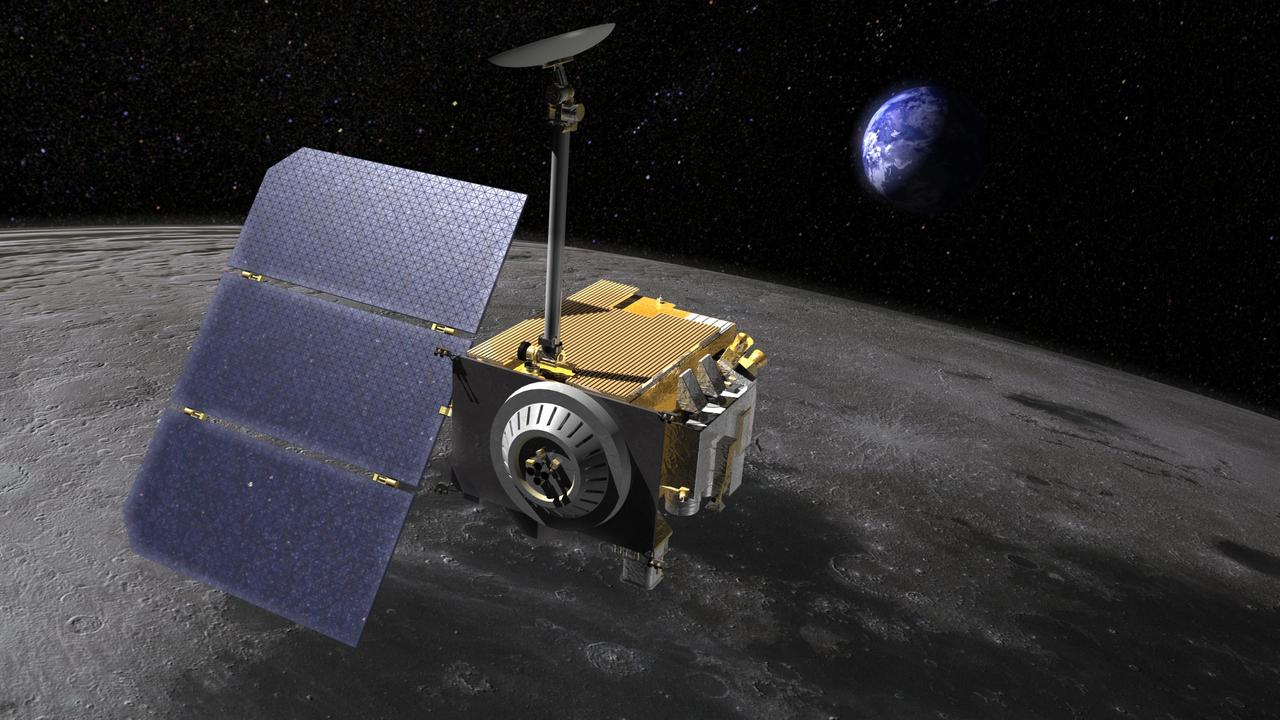

Artist rendering of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter LRO, above the moon. LRO carries seven instruments that make comprehensive remote sensing observations of the moon and measurements of the lunar radiation environment. The LRO mission is managed by NASA Goddard for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18163
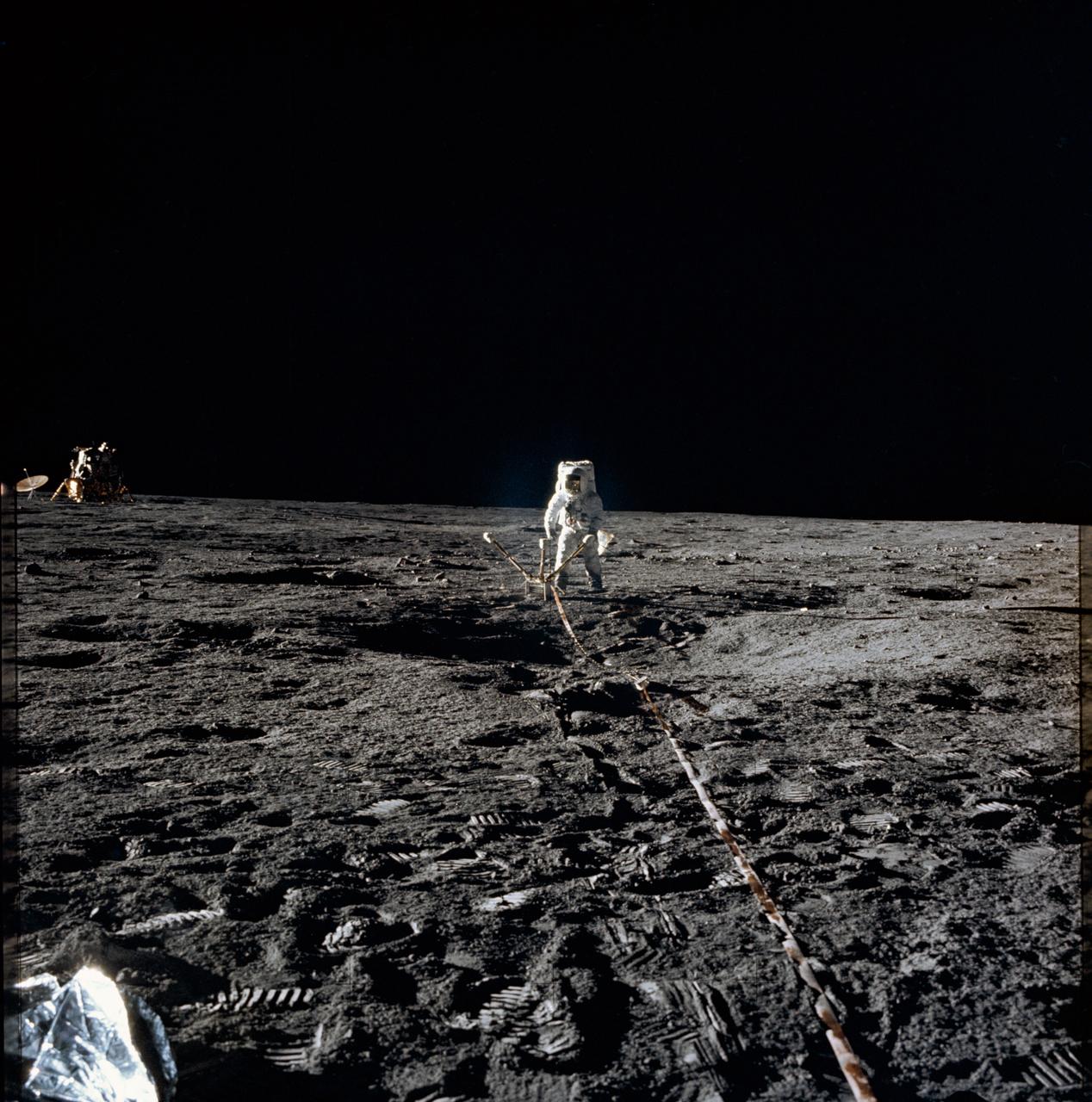

Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, deploys the Lunar Surface Magnetometer (LSM) during the first Apollo 12 extravehicular activity on the Moon. The LSM is a component of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). The Lunar Module can be seen in the left background.

AS16-107-17436 (21 April 1972) --- An excellent view of the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" and Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), as photographed by astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. Astronaut John W. Young, commander, can be seen directly behind the LRV. The lunar surface feature in the left background is Stone Mountain. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
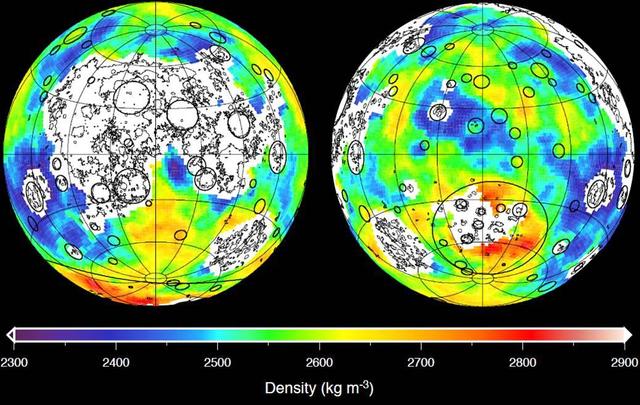
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
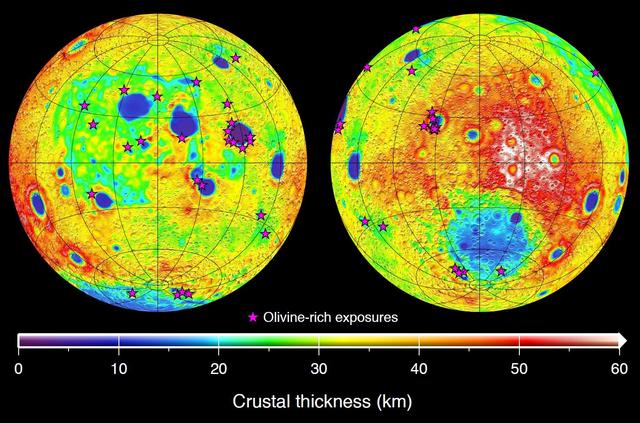
This graphic depicting the bulk density of the lunar highlands on the near and far sides of the moon was generated using gravity data from NASA GRAIL mission and topography data from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
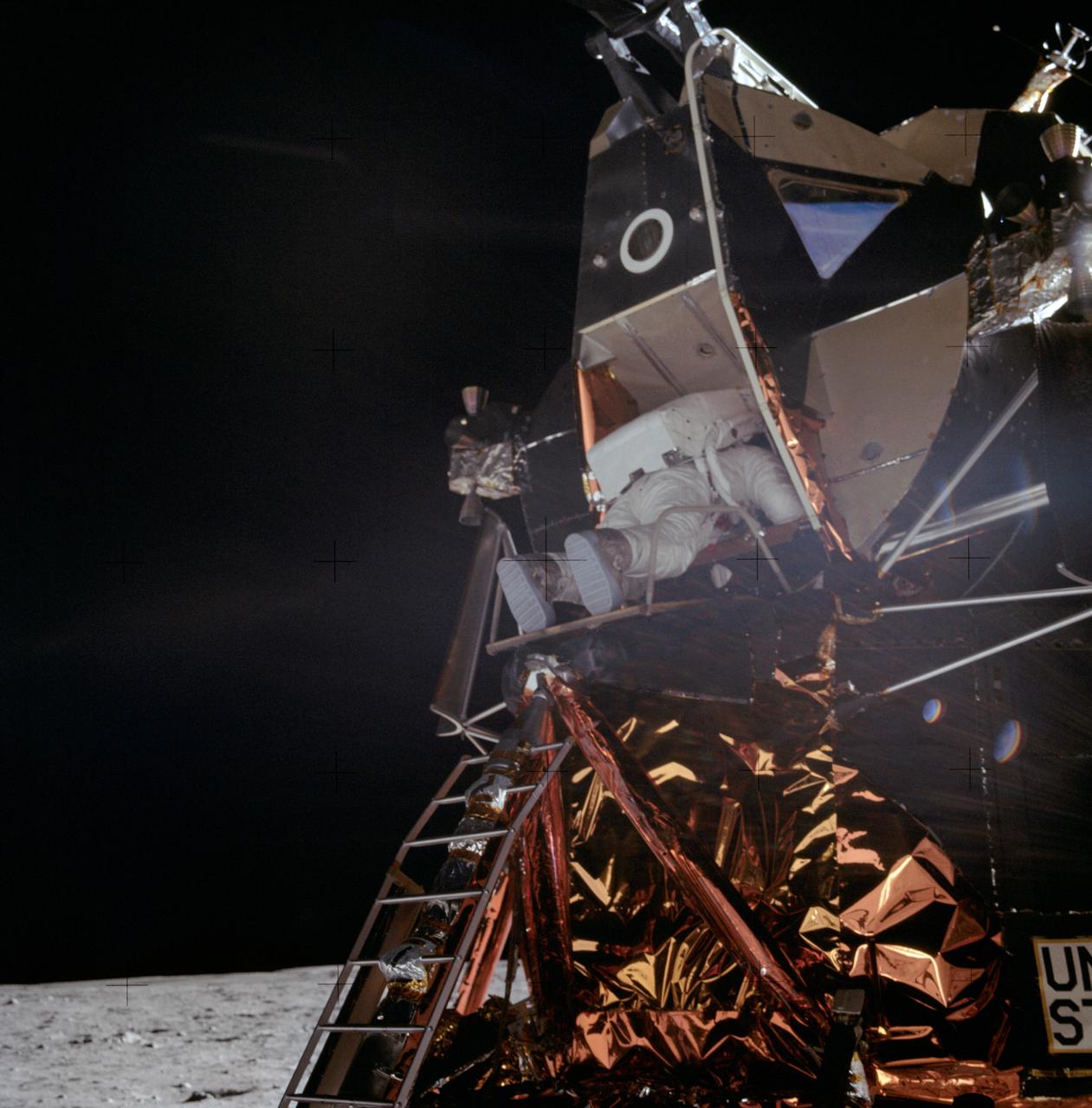

AS11-40-5863 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed egressing the Lunar Module (LM) during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
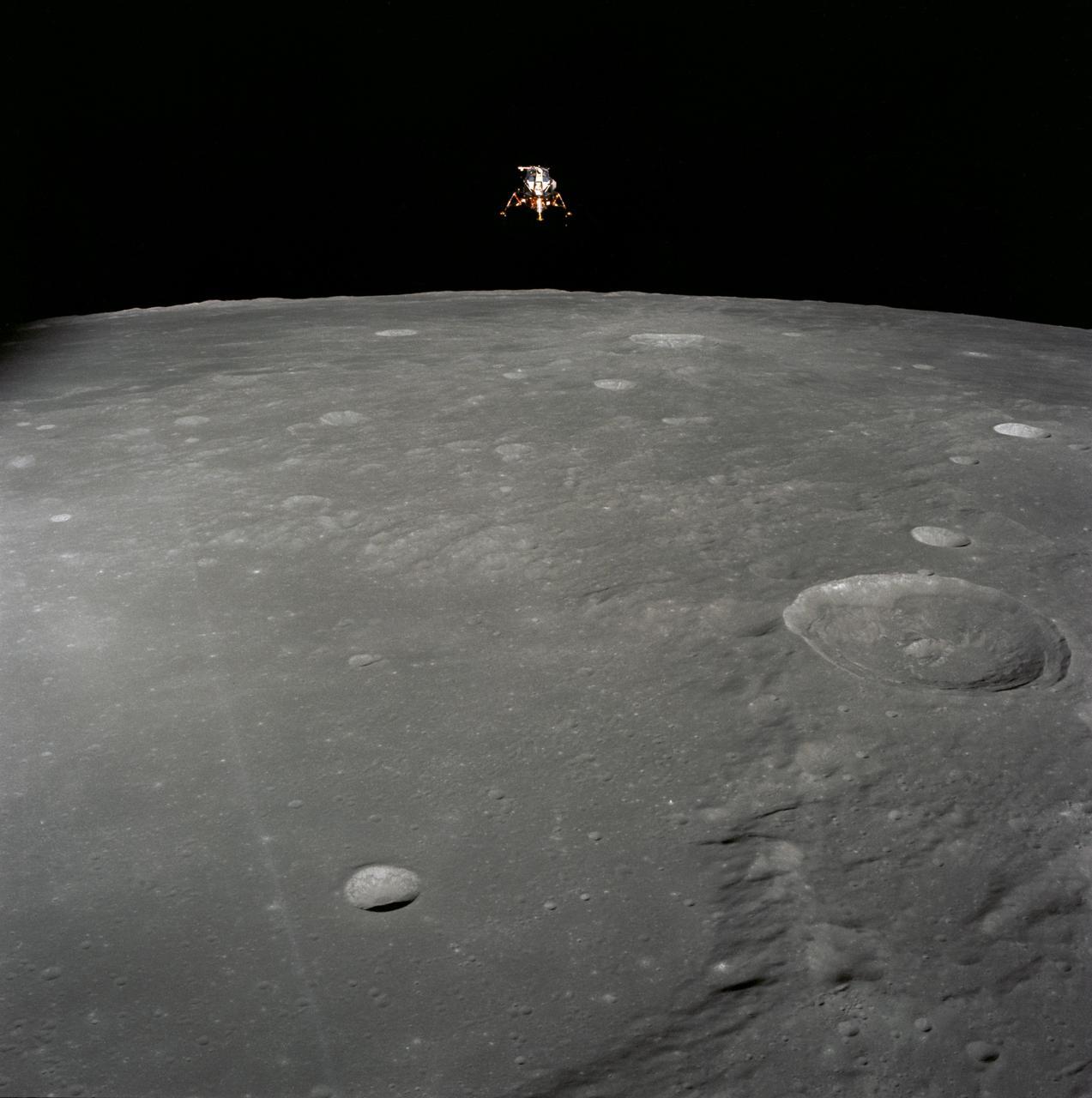

AS12-51-7507 (19 Nov. 1969) --- The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM), in a lunar landing configuration, is photographed in lunar orbit from the Command and Service Modules (CSM). The coordinates of the center of the lunar surface shown in picture are 4.5 degrees west longitude and 7 degrees south latitude. The largest crater in the foreground is Ptolemaeus; and the second largest is Herschel. Aboard the LM were astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. Astronaut Richard R. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the surface of the moon. Photo credit: NASA

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight carrying out a trajectory correction maneuver with the Moon and Earth in the background. Powered by the small satellite's four thrusters, the maneuver is needed to reach lunar orbit. Lunar Flashlight launched Nov. 30, 2022, and will take about four months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, the small satellite, or SmallSat, will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. To achieve the mission's goals with the satellite's limited amount of propellent, Lunar Flashlight will employ an energy-efficient near-rectilinear halo orbit, taking it within 9 miles (15 kilometers) of the lunar South Pole and 43,000 miles (70,000 kilometers) away at its farthest point. Only one other spacecraft has employed this type of orbit: NASA's Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) mission, which launched in June 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25258

NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter captured this image of the ejecta blanket and rim of Timocharis crater in southeastern Mare Imbrium.
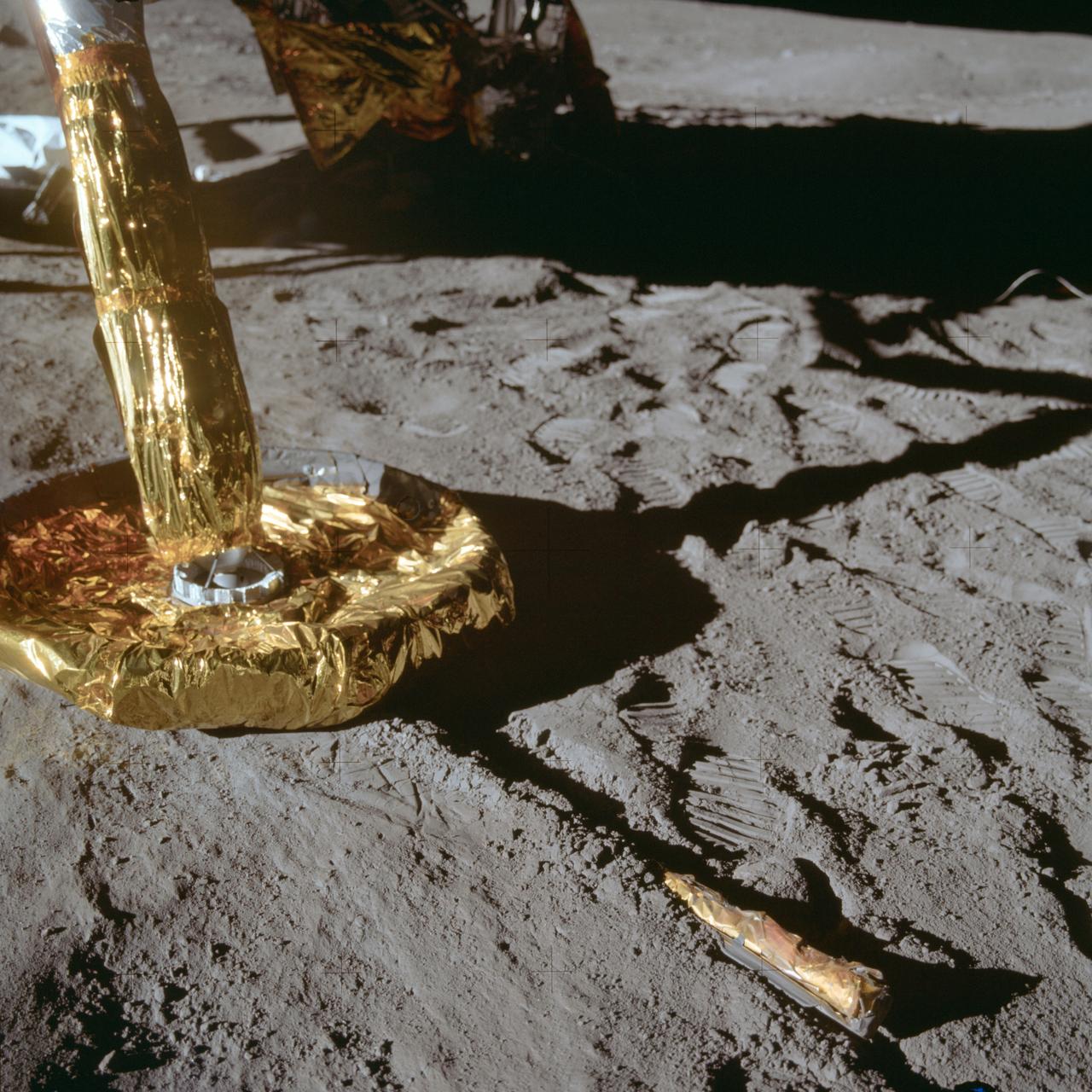

A close-up view of a footpad of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module as it rested on the surface of the Moon. The stick-like protruding object is a lunar surface sensing probe. This photograph was take with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the extravehicular activity of Astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin on July 20, 1969.
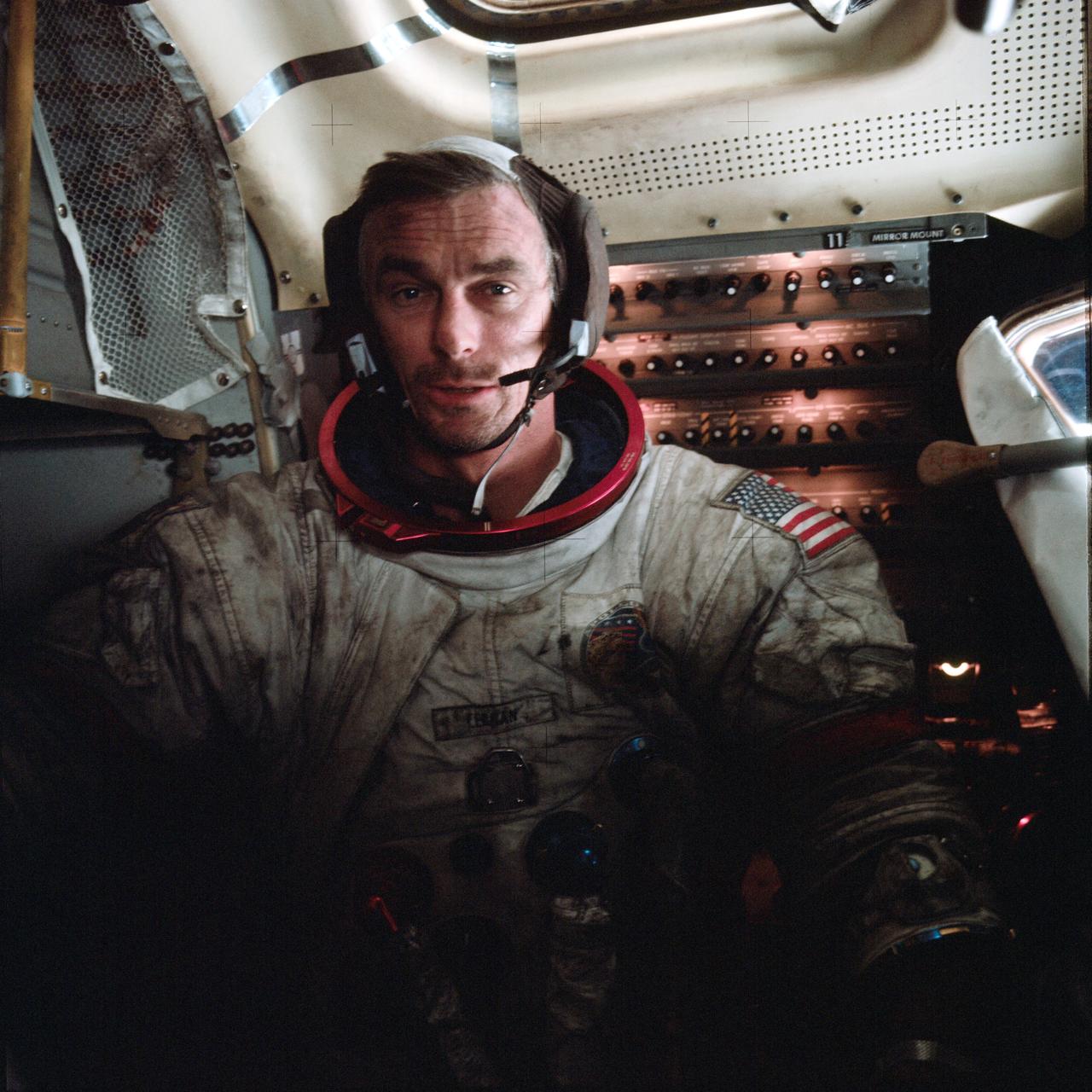

AS17-145-22224 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, is photographed inside the lunar module on the lunar surface following the second extravehicular activity (EVA) of his mission. Note lunar dust on his suit. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, using a 70mm handheld Hasselblad camera and S0-368 film.
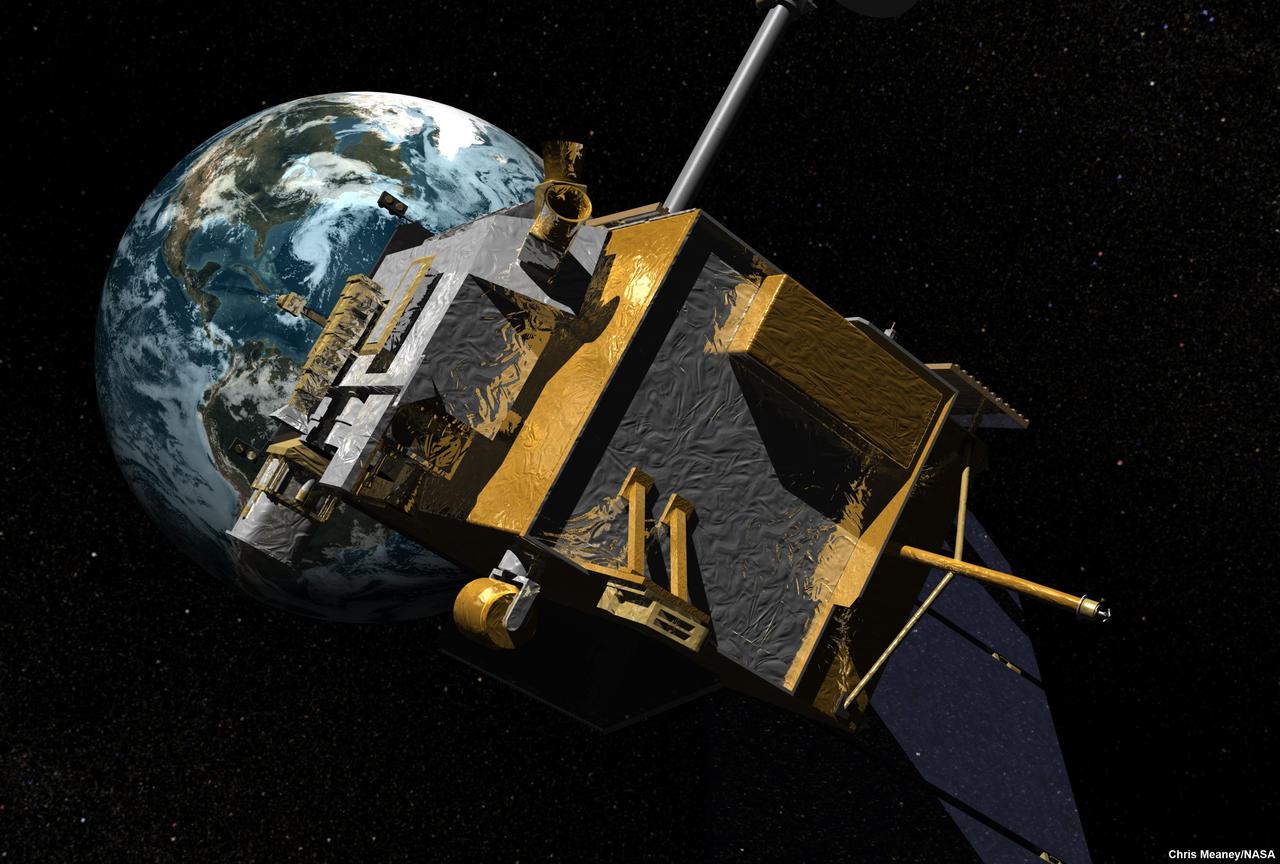

NASA is scheduled to launch the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, an unmanned mission to comprehensively map the entire moon, on June 18, 2009.
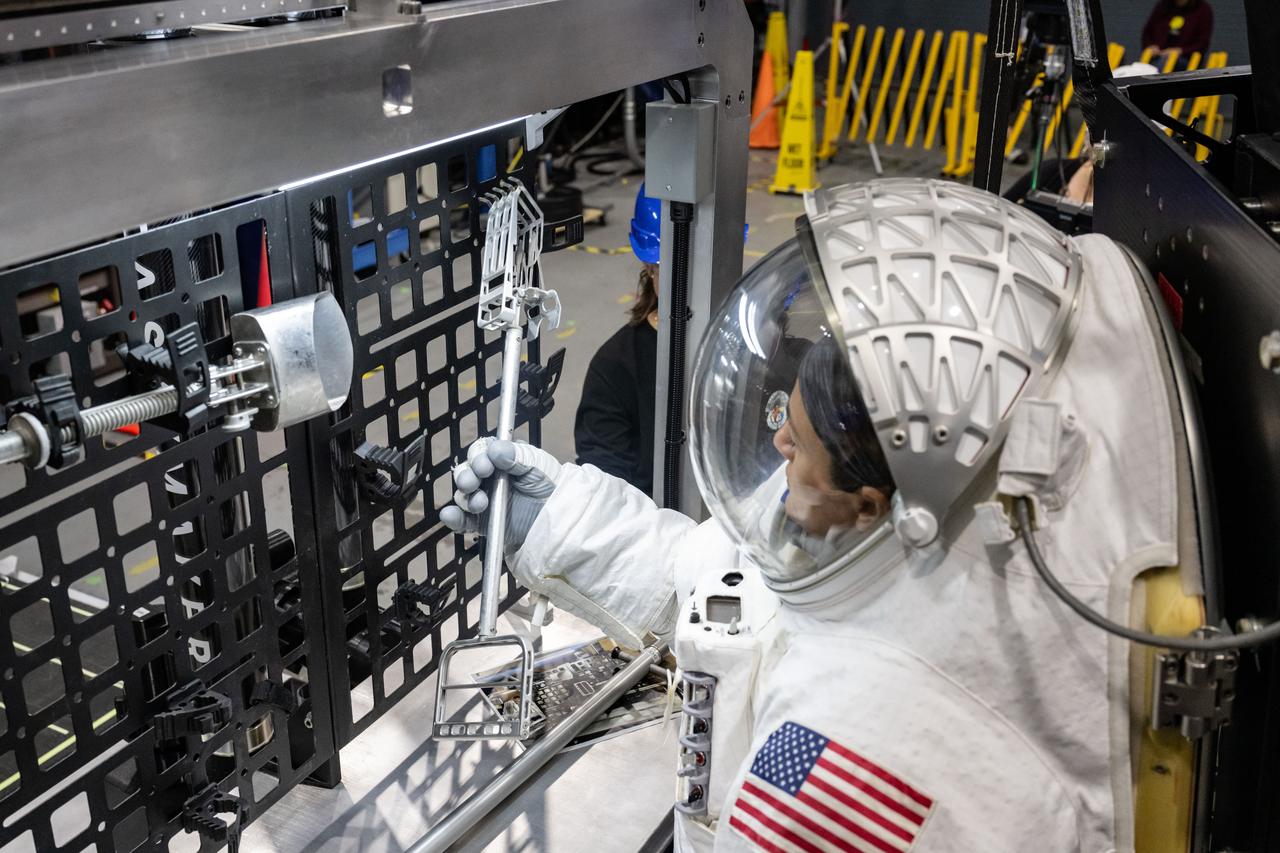

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir grabs a lunar geology tool from a tool rack on Lunar Outpost’s Eagle lunar terrain vehicle during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/James Blair
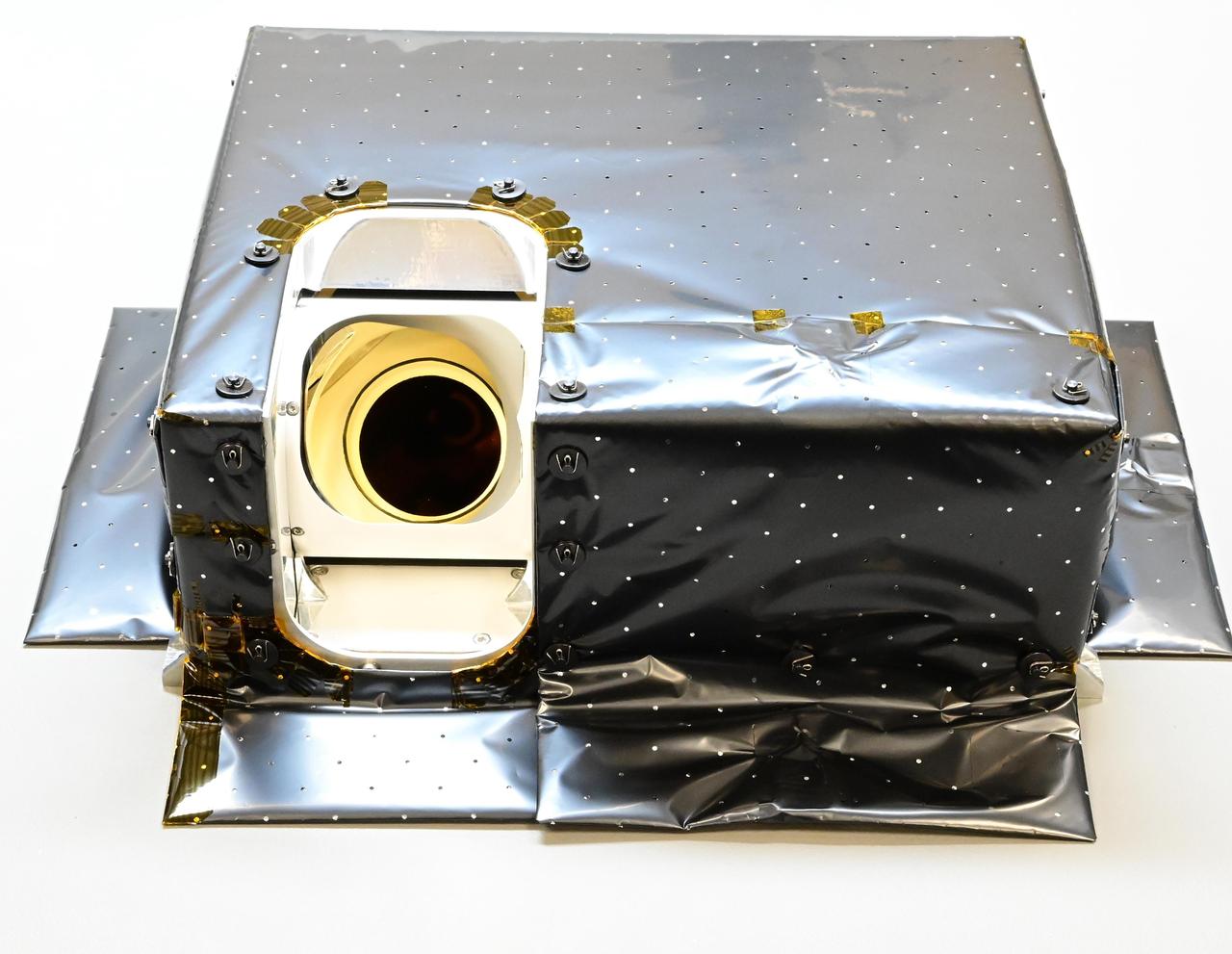

Seen here before being shipped from the U.K. to the U.S., the Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM) is one of two instruments that will be carried by NASA's Lunar Trailblazer. Launching in 2023, the small spacecraft – measuring only about 11 feet (3.5 meters) wide with its solar panels fully deployed – will also carry the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³). The two instruments will work together to help detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how and why it varies by location and time. In February 2023, LTM completed qualification for flight and calibration at the University of Oxford in England. The instrument will provide maps of lunar surface temperature from about minus 261 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 163 degrees Celsius) to 261 F (127 C) using four broad-band infrared channels covering wavelengths from 6.25 to 100 micrometers. The instrument also has 11 narrower infrared channels that are sensitive enough to detect and map small variations in the composition of silicate minerals that make up the rocks and soils of the Moon's surface. The instrument is shown here wrapped with a multilayer insulation blanket to assist with thermal control. Not covered by insulation is LTM's single "eye" – a scan mirror that can pivot down to look at the Moon's surface or outward into space for calibration purposes. The scan mirror collects a line of pixels at a time to form an image via the motion of the spacecraft. During vacuum testing the instrument viewed external targets that varied in temperature between minus 261 F (minus 163 C) and 243 F (117 C) so that it could be calibrated. The alignment, spectral, and radiometric (temperature) accuracy of LTM was checked both before and after the instrument was tested via vibration and cycling through thermal environments identical to what it will experience during launch and operation in lunar orbit. With these tests complete, the instrument was packed and shipped for integration with the Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft at Lockheed Martin Space in Colorado. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25831
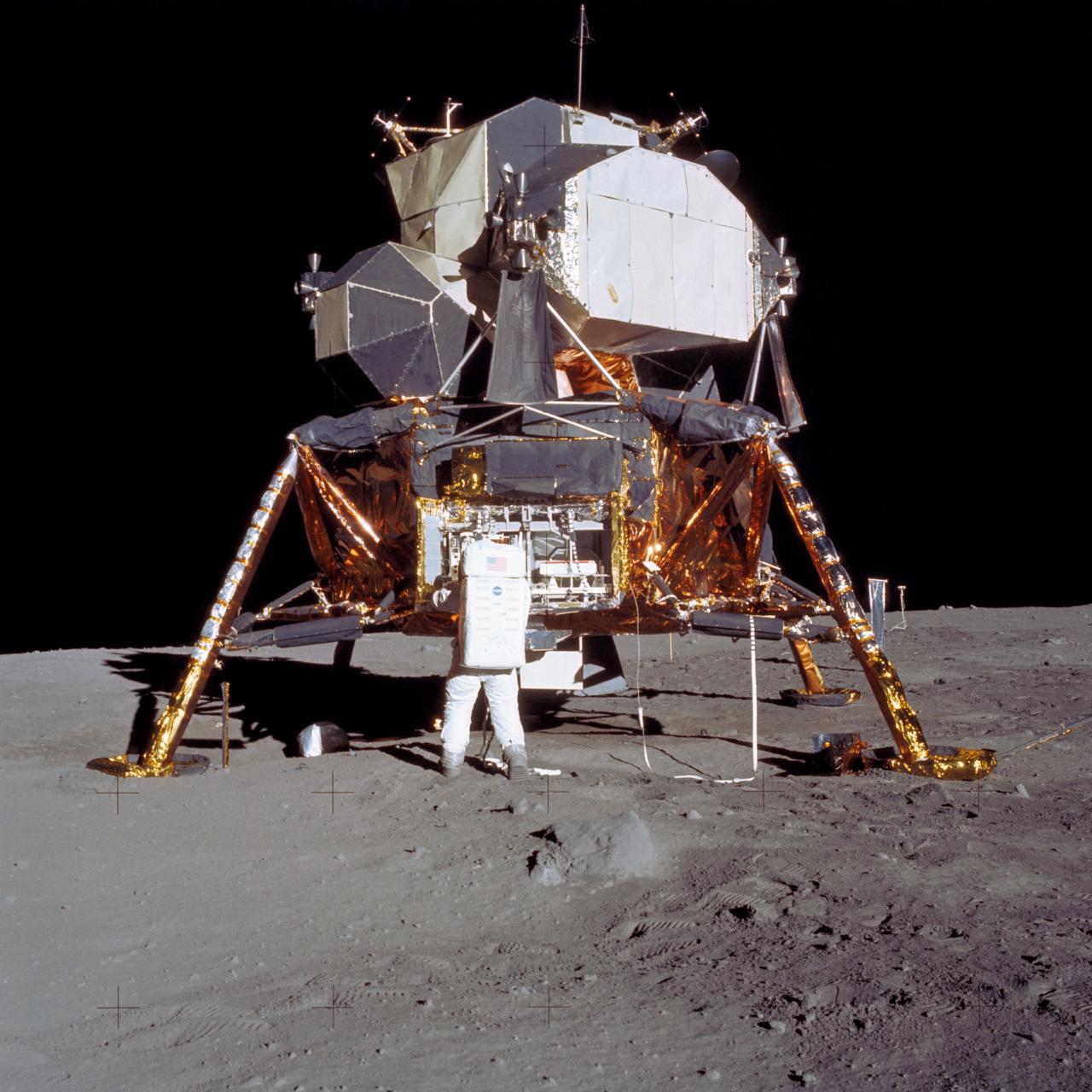

AS11-40-5927 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, prepares to deploy the Early Apollo Scientific Experiments Package (EASEP) during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this picture with a 70mm lunar surface camera. During flight the EASEP is stowed in the Lunar Module's (LM) scientific equipment bay at the left year quadrant of the descent stage looking forward. Aldrin is removing the EASEP from its stowed position. Photo credit: NASA
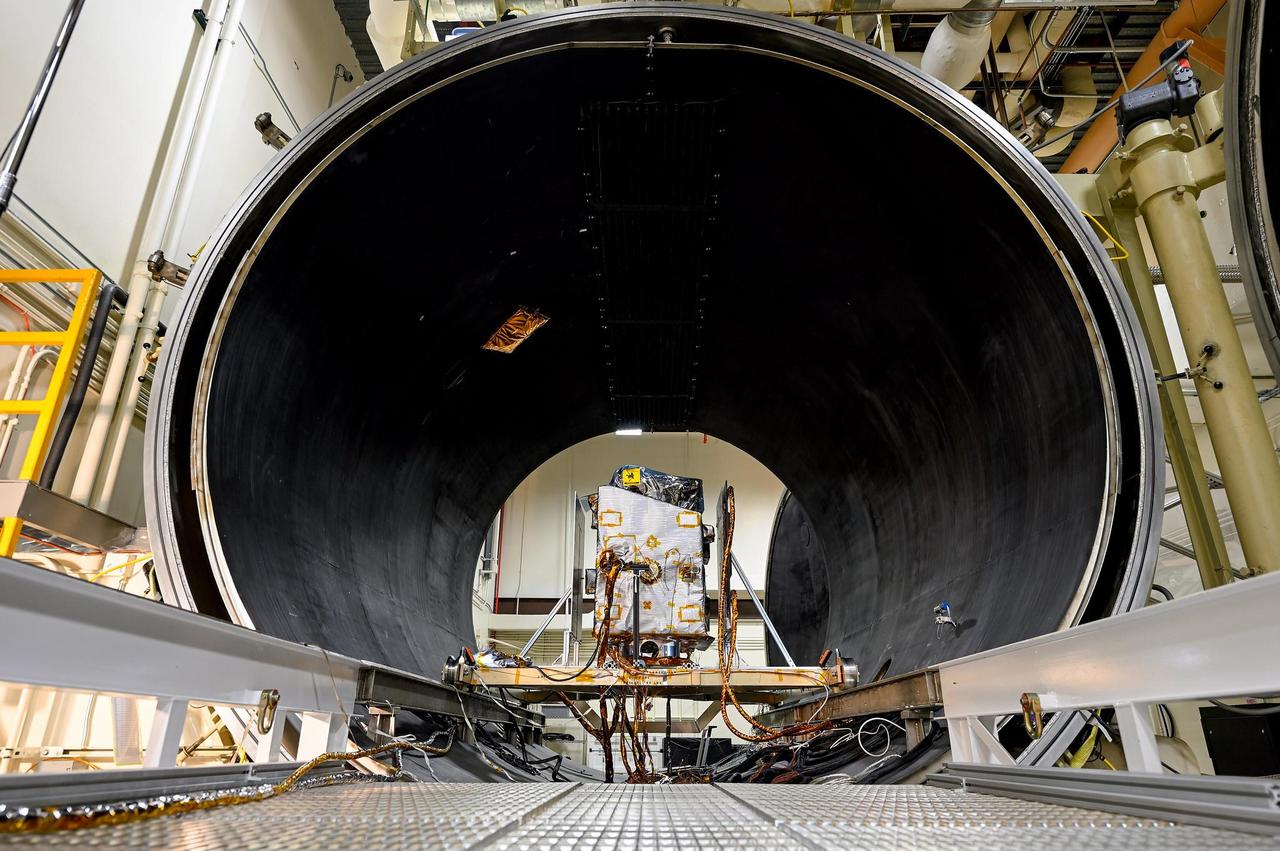

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer undergoes thermal vacuum chamber (TVAC) testing at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, in June 2023. The extremely low pressures and temperatures during these tests simulate the conditions that the spacecraft will experience during in space. Lunar Trailblazer, which has a mass of about 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures only 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide with its solar panels deployed, has now completed TVAC testing and is nearing completion before its planned launch in early 2024. The spacecraft's two science instruments will map the form, abundance, and locations of water in on the lunar surface while also revealing the thermal properties and surface composition of those regions. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25836
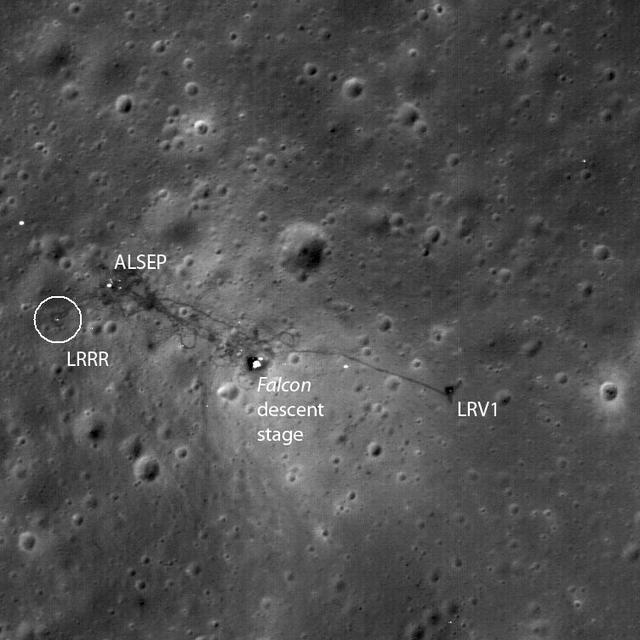

The Apollo 15 Lunar Laser Ranging Retroreflector - A Fundamental Point on the Moon
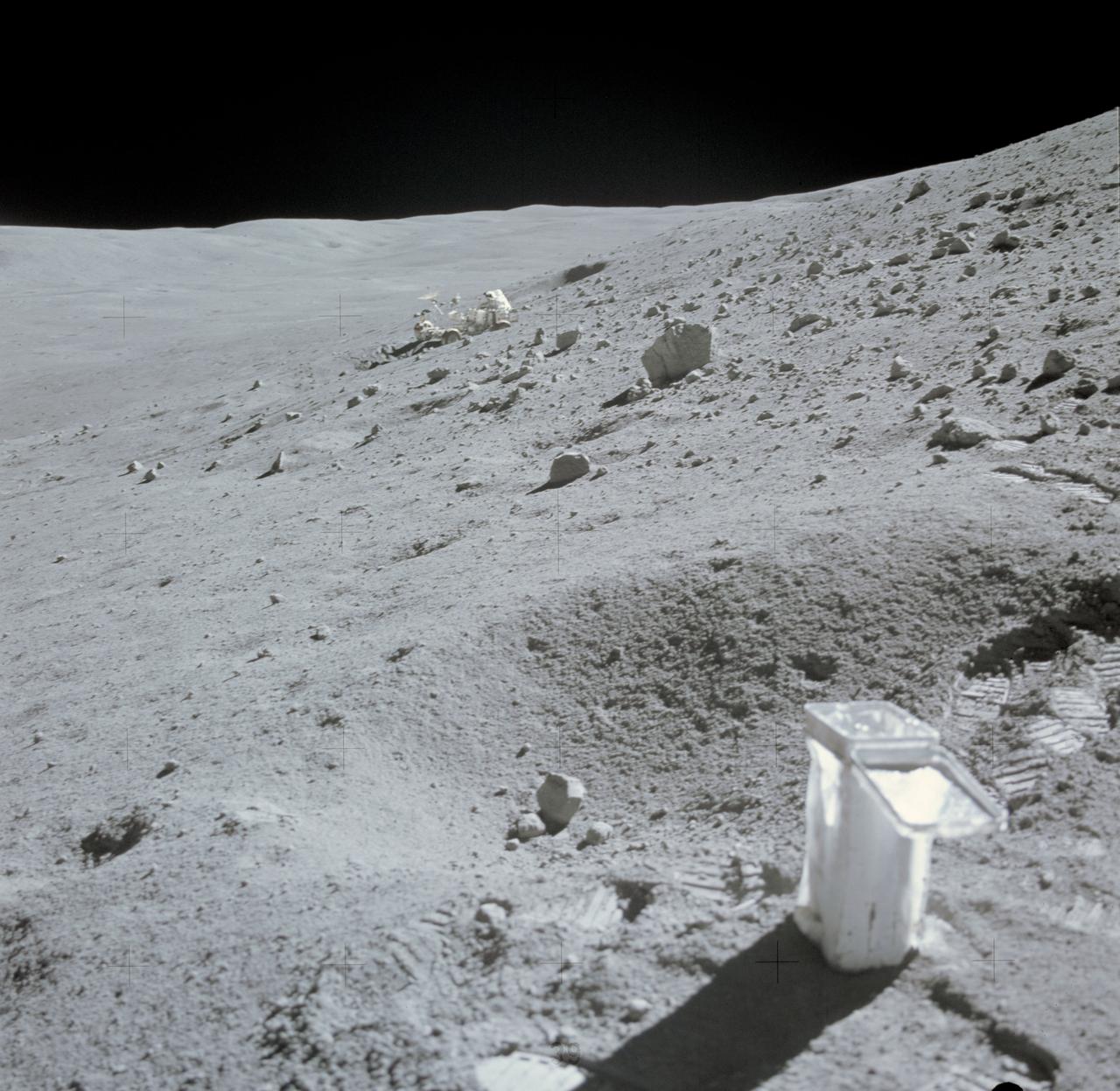

AS16-107-17473 (22 April 1972) --- The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) appears to be parked in a deep lunar depression, on the slope of Stone Mountain. This photograph of the lunar scene at Station No. 4 was taken during the second Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Descartes landing site. A sample collection bag is in the right foreground. Note field of small boulders at upper right. While astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
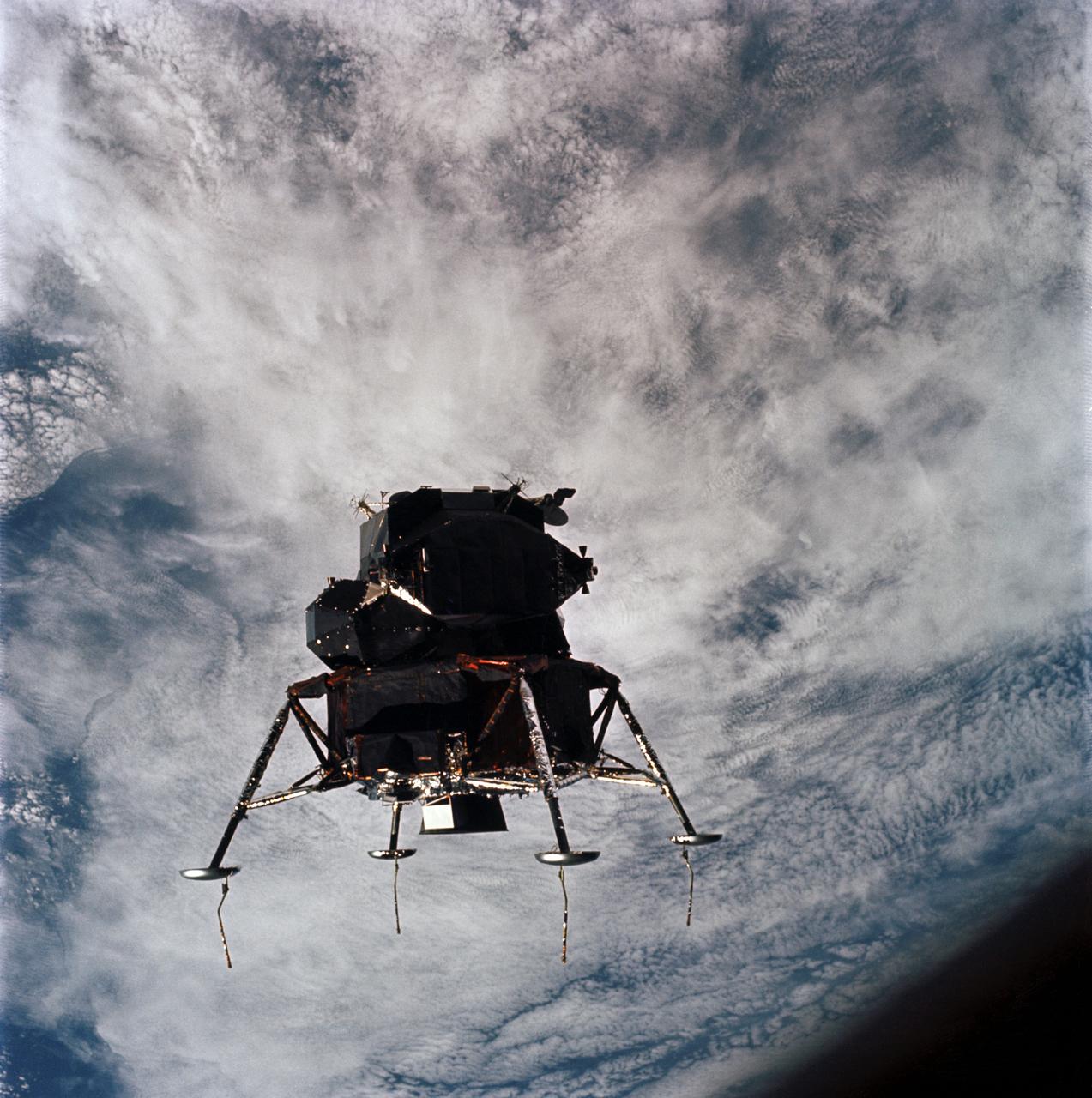

AS09-21-3199 (7 March 1969) --- Excellent view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module, "Spider," in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from the landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module, "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
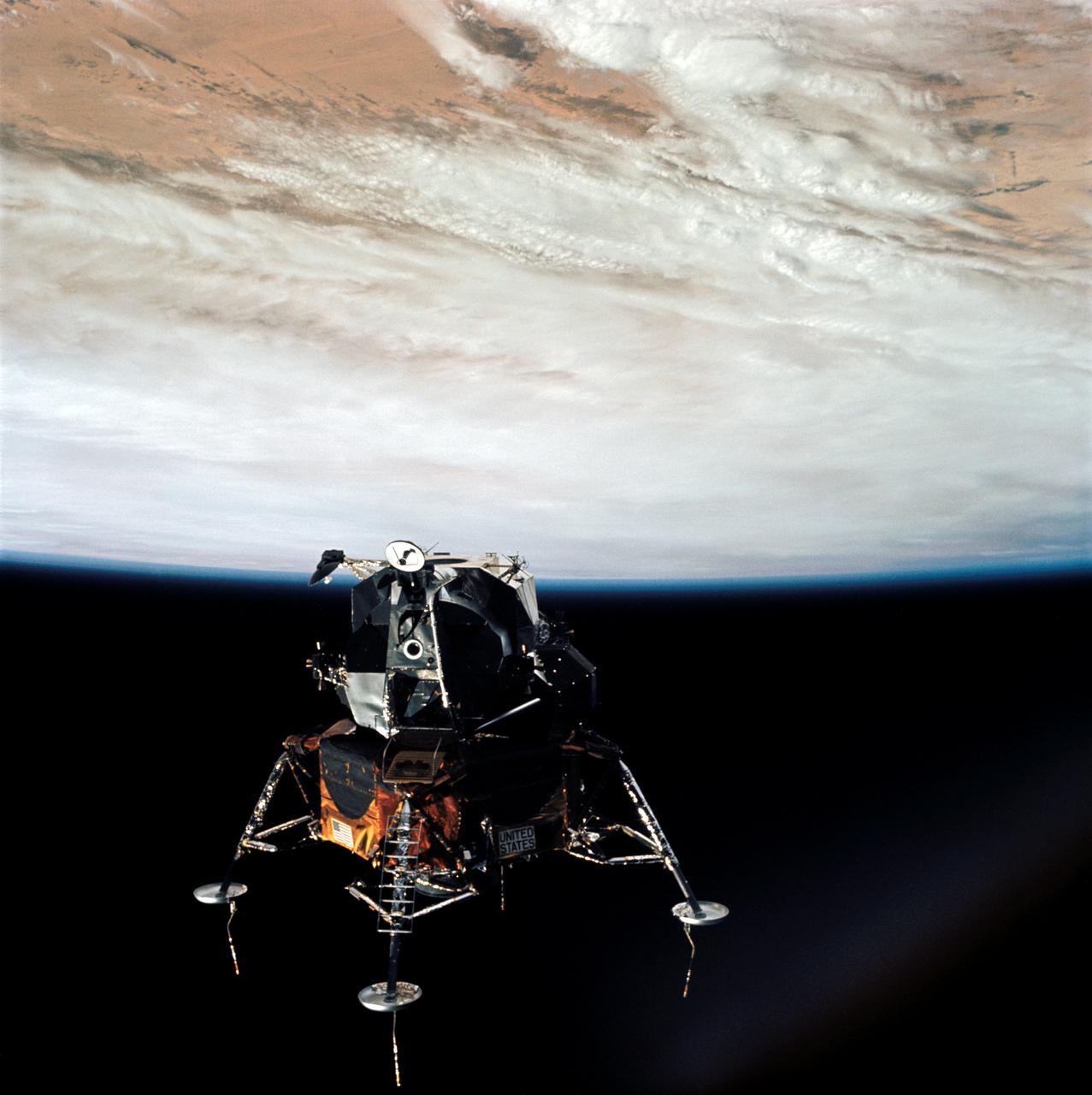

AS09-21-3212 (7 March 1969) --- A view of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider", in a lunar landing configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Lunar surface probes (sensors) extend out from landing gear foot pads. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop", while the other two astronauts checked out the Lunar Module.
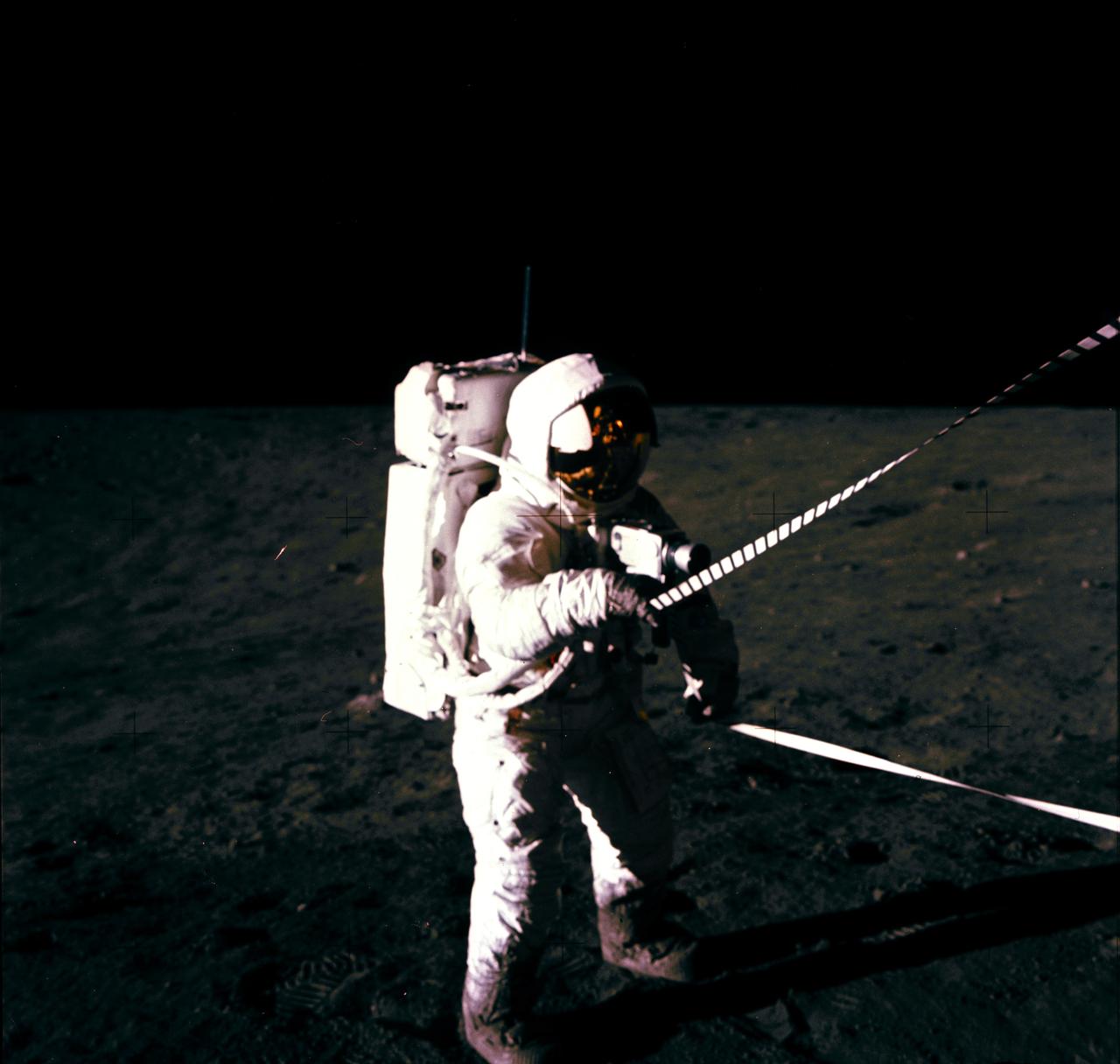

Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, uses the lunar equipment conveyer (LEC) at the Lunar Module during the Apollo 12 extravehicular activity on the lunar surface. This photograph was taken by Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot.
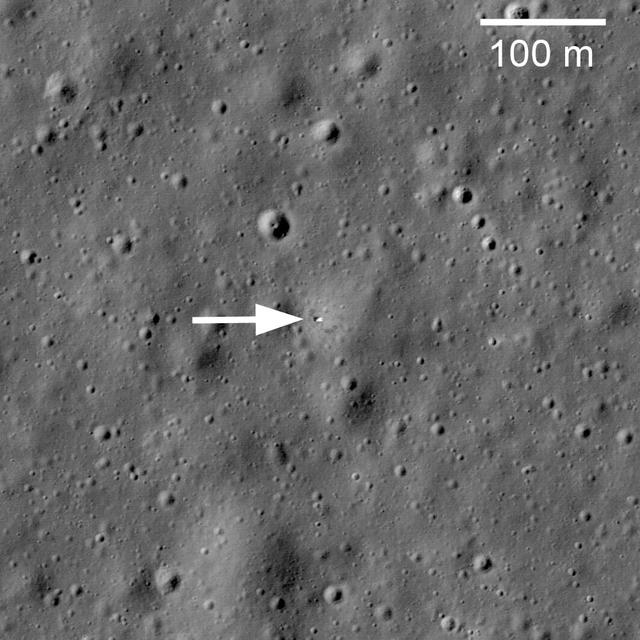
This image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows Soviet robotic lander Luna 17 still sitting on Mare Imbrium where it delivered the Lunokhod 1 Rover in November 1970.

AS11-40-5902 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. The astronauts' bootprints are clearly visible in the foreground. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
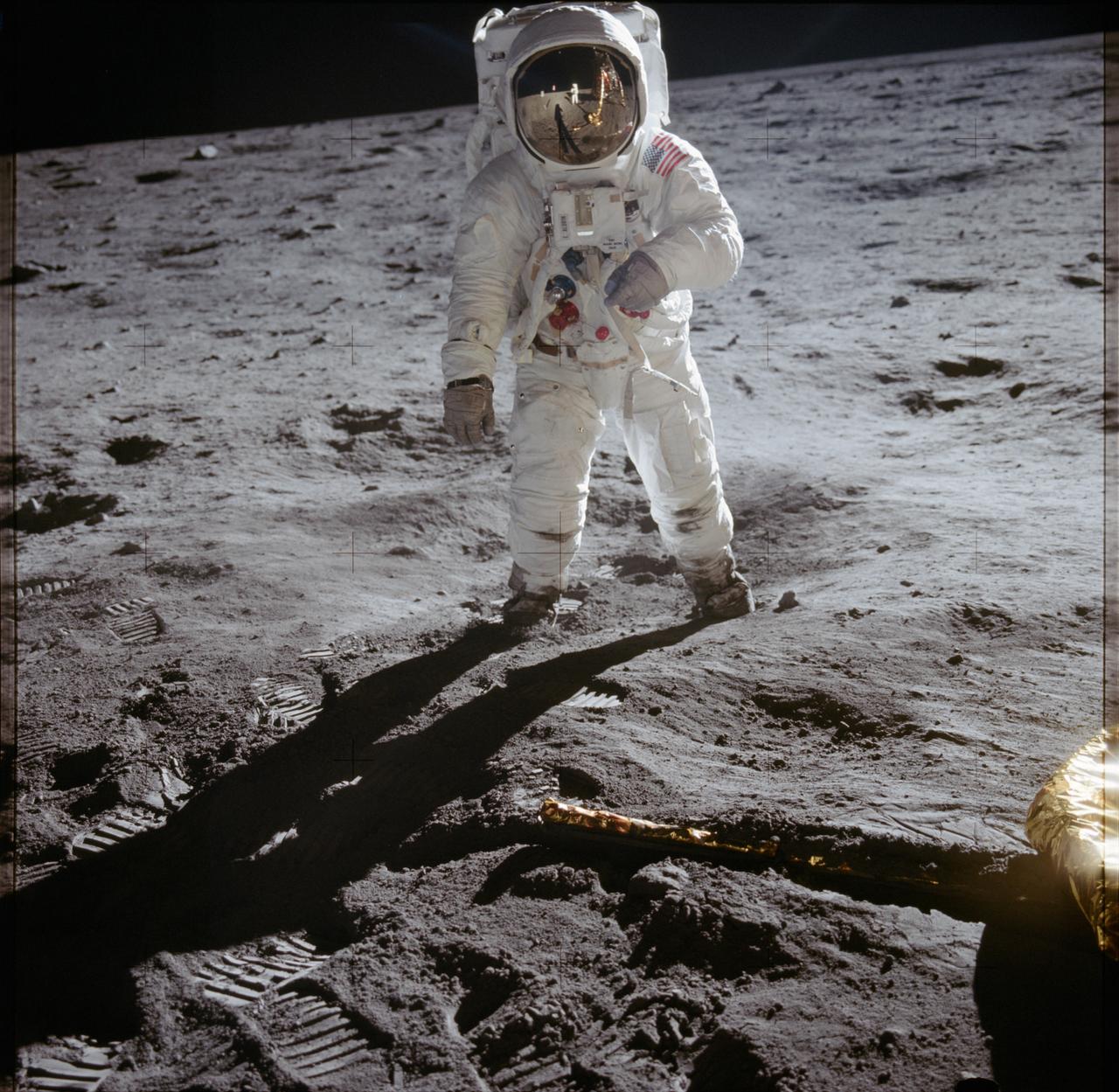

AS11-40-5903 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
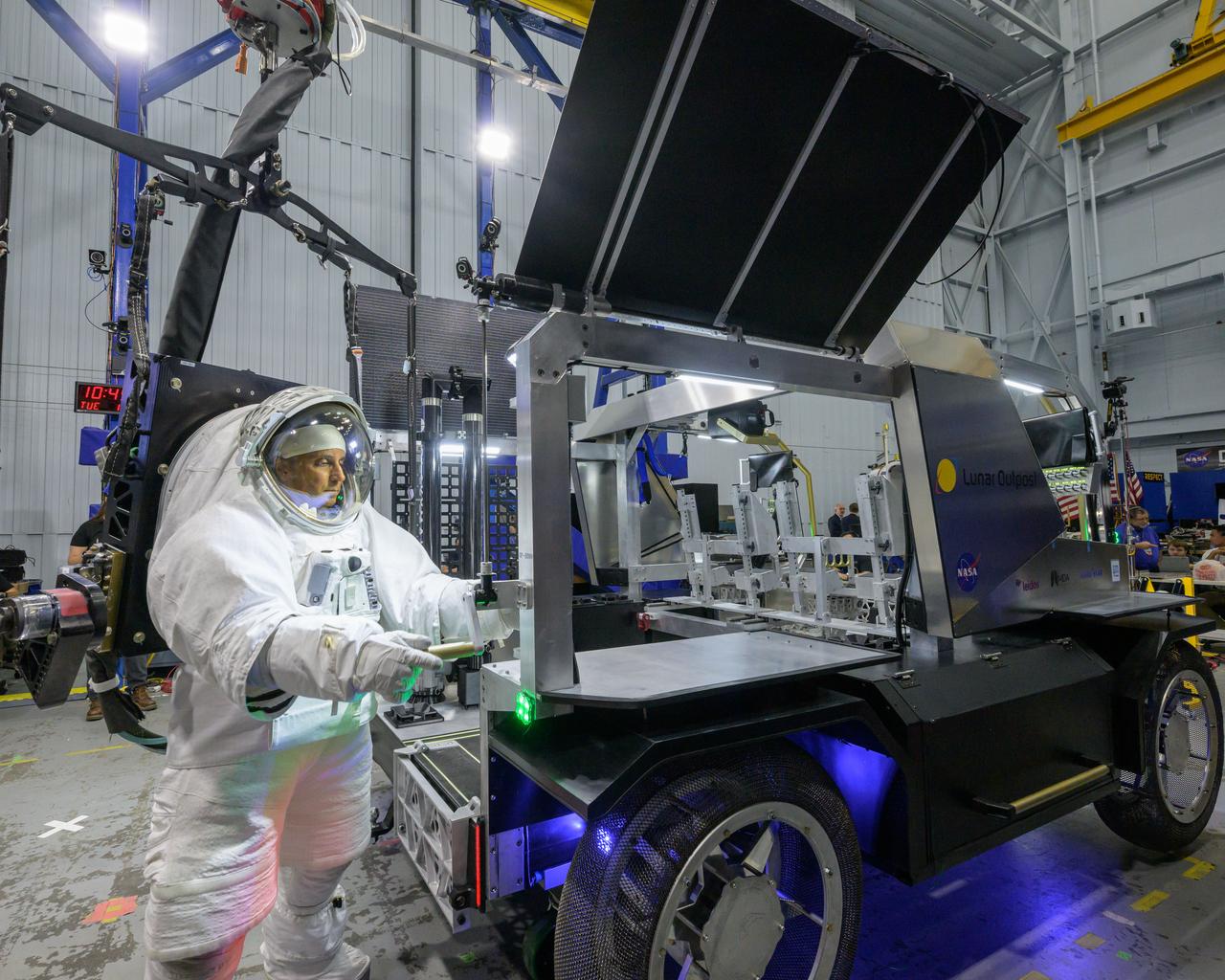

NASA astronaut Joe Acaba raises the solar array panel on Lunar Outpost’s Eagle lunar terrain vehicle during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins picks up a lunar geology tool from a stowage drawer on Astrolab’s FLEX lunar terrain vehicle during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz

AS11-40-5878 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
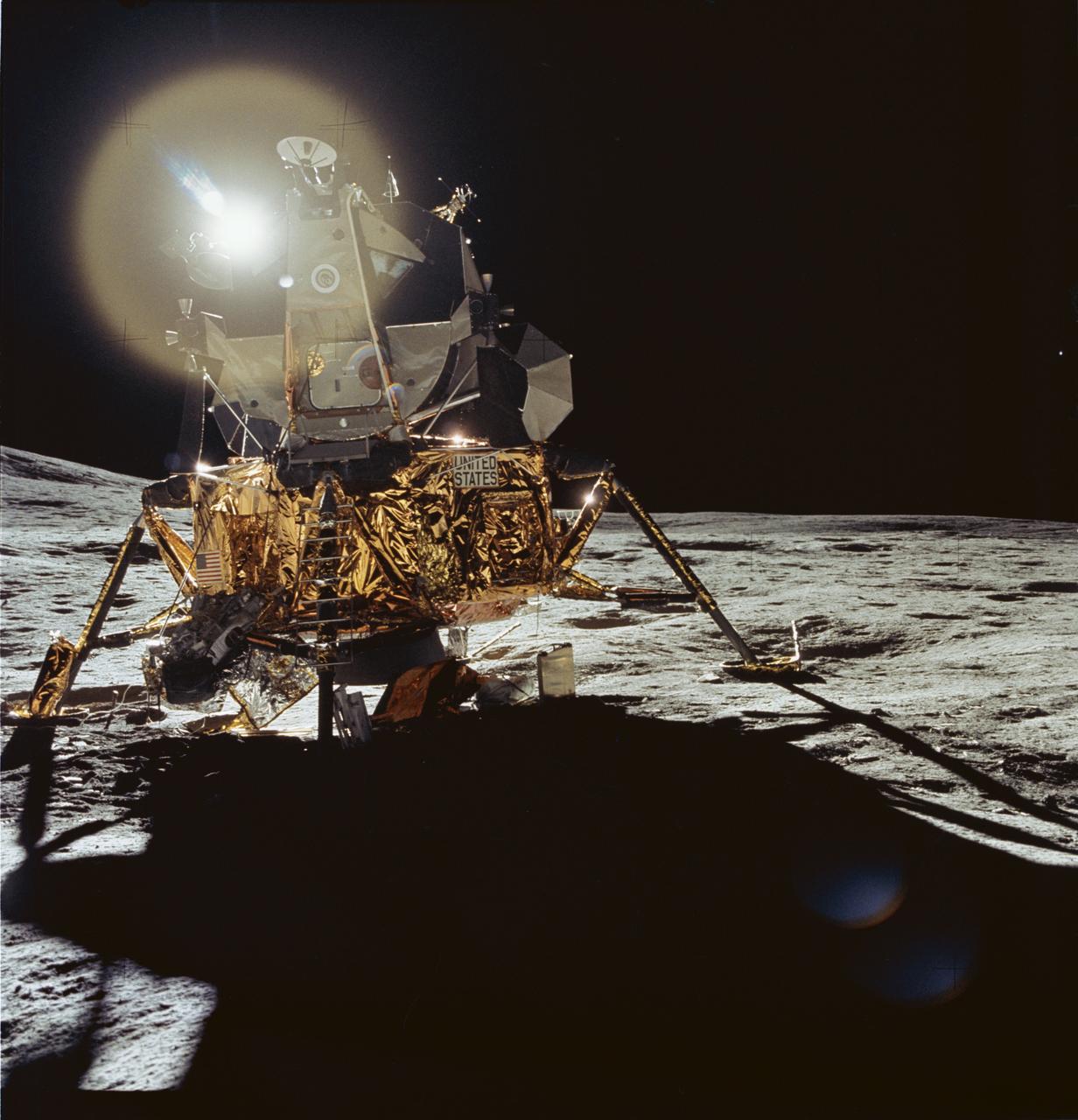

AS14-66-9306 (5 Feb. 1971) --- A front view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM), which reflects a circular flare caused by the brilliant sun, as seen by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission during their first extravehicular activity (EVA). The unusual ball of light was said by the astronauts to have a jewel-like appearance. At the extreme left the lower slope of Cone Crater can be seen. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander; and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot; descended in the LM, while astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot; remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
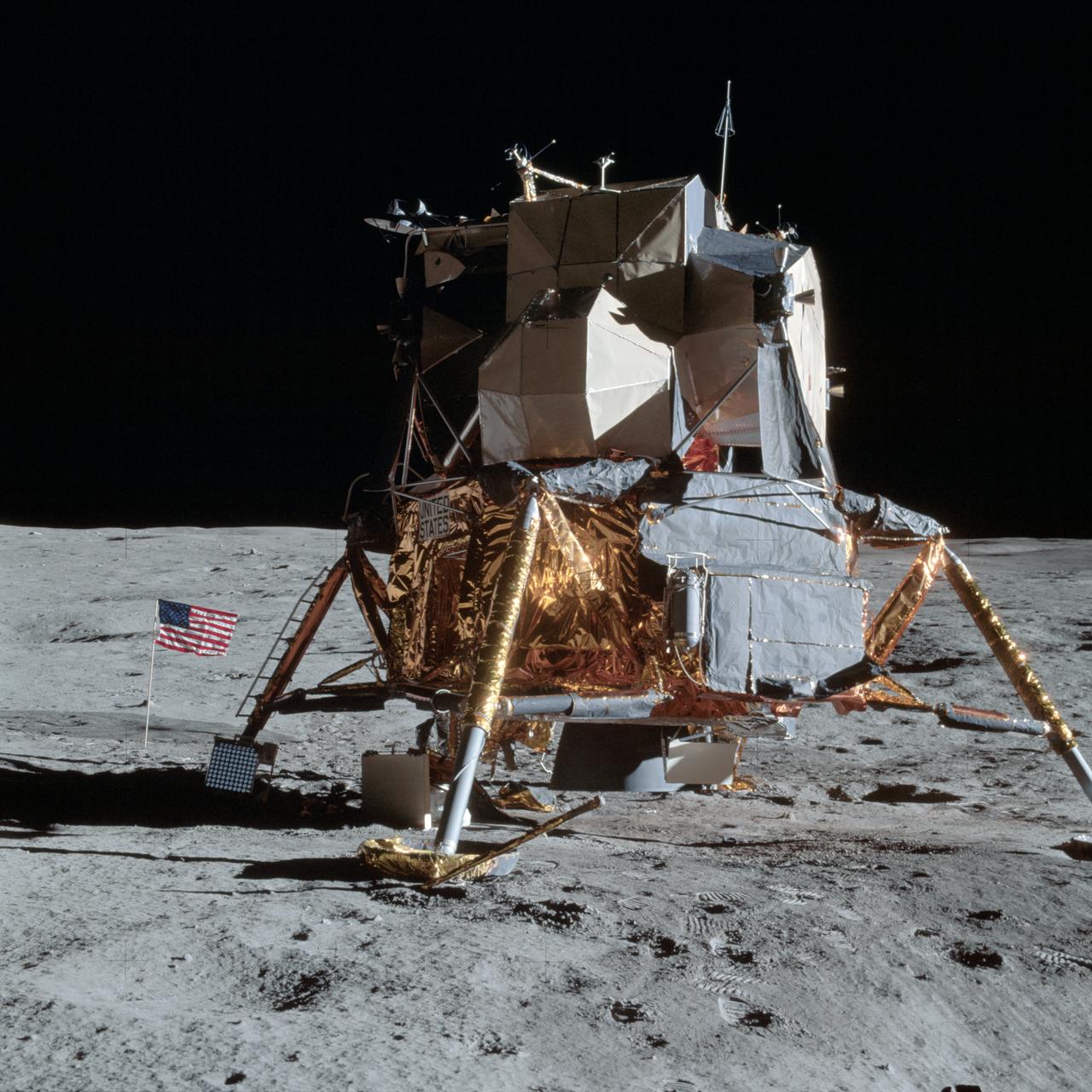
AS14-66-9277 (5 Feb. 1971) --- An excellent view of the Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) on the moon, as photographed during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface. The astronauts have already deployed the U.S. flag. Note the laser ranging retro reflector (LR-3) at the foot of the LM ladder. The LR-3 was deployed later. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

Peering into the Moon's permanently shadowed regions, Lunar Trailblazer will detect signatures of water ice in reflected light, and it will pinpoint the locations of micro-cold traps less than a football field in size. The small satellite will collect measurements at multiple times of day over sunlit regions, helping scientists understand if the water signature on the illuminated surface changes as the lunar surface temperature changes by hundreds of degrees over the course of a lunar day. The goal is to produce high-resolution maps to locate water ice in support of NASA's Artemis Program, which aims to establish a sustainable human presence on the Moon and prepare for future missions to Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24161
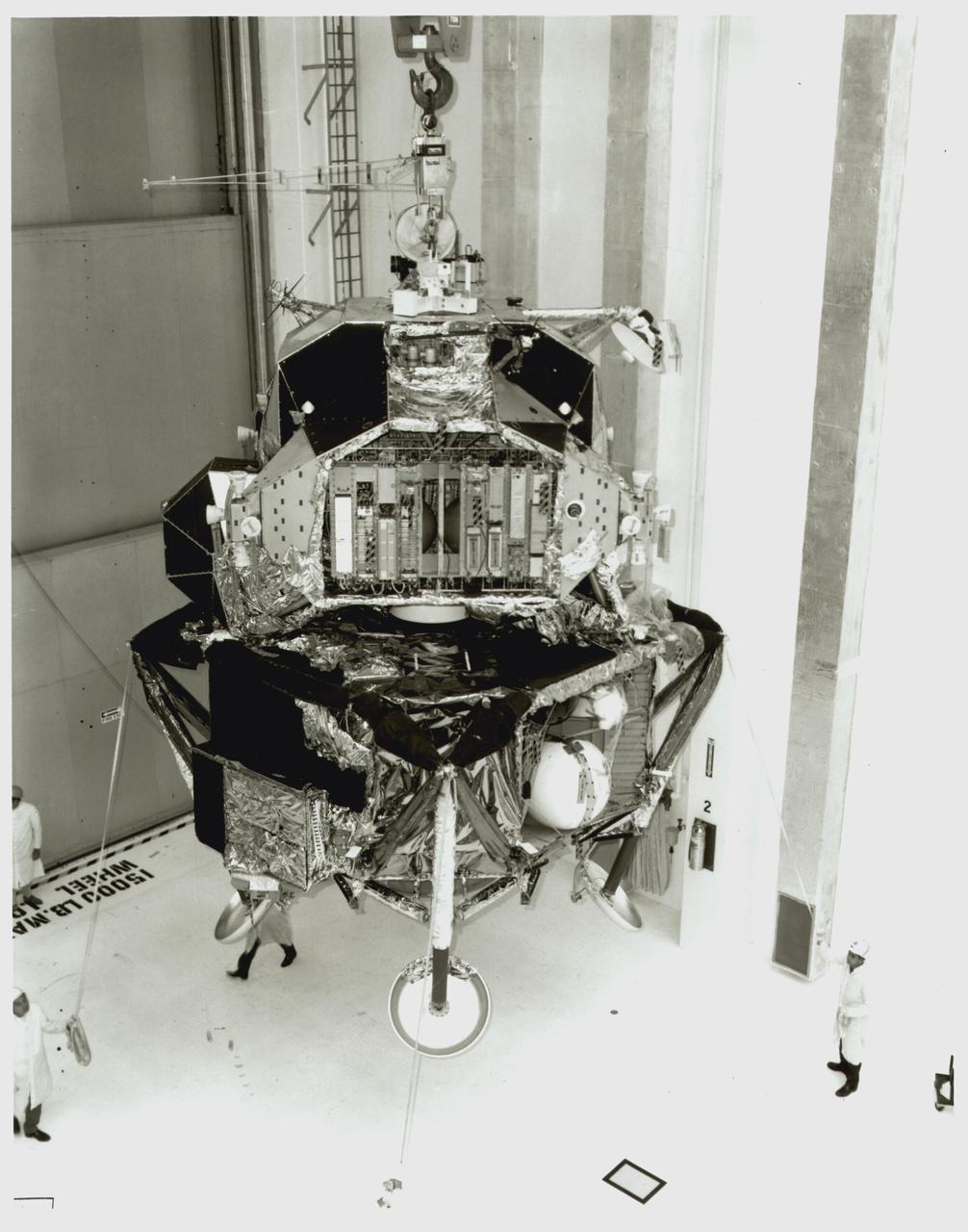
The Lunar Module for Apollo 11 moves from the landing gear fixture and mate to the spacecraft-lunar module adapter.
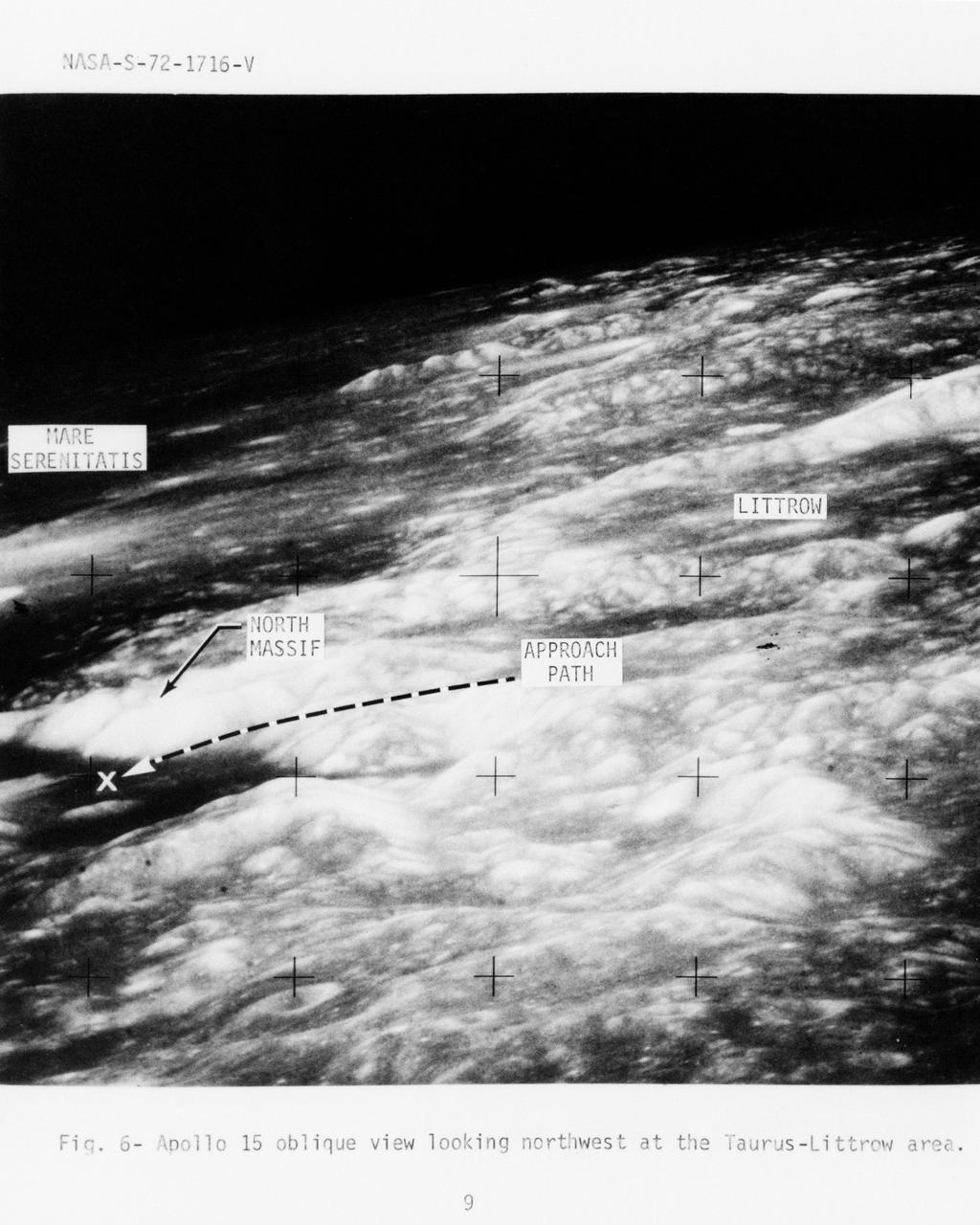
S72-01716 (July 1972) --- An oblique view of the Taurus-Littrow area on the lunar nearside, as photographed from the Apollo 15 spacecraft in lunar orbit. This is an enlarged view. The "X" marks the landing site of the scheduled Apollo 17 lunar landing mission. The overlay points out several features in the photograph. The coordinates of the Apollo 17 touchdown point are 30 degrees 44 minutes 58 seconds east longitude and 20 degrees 9 minutes 50 seconds north latitude.
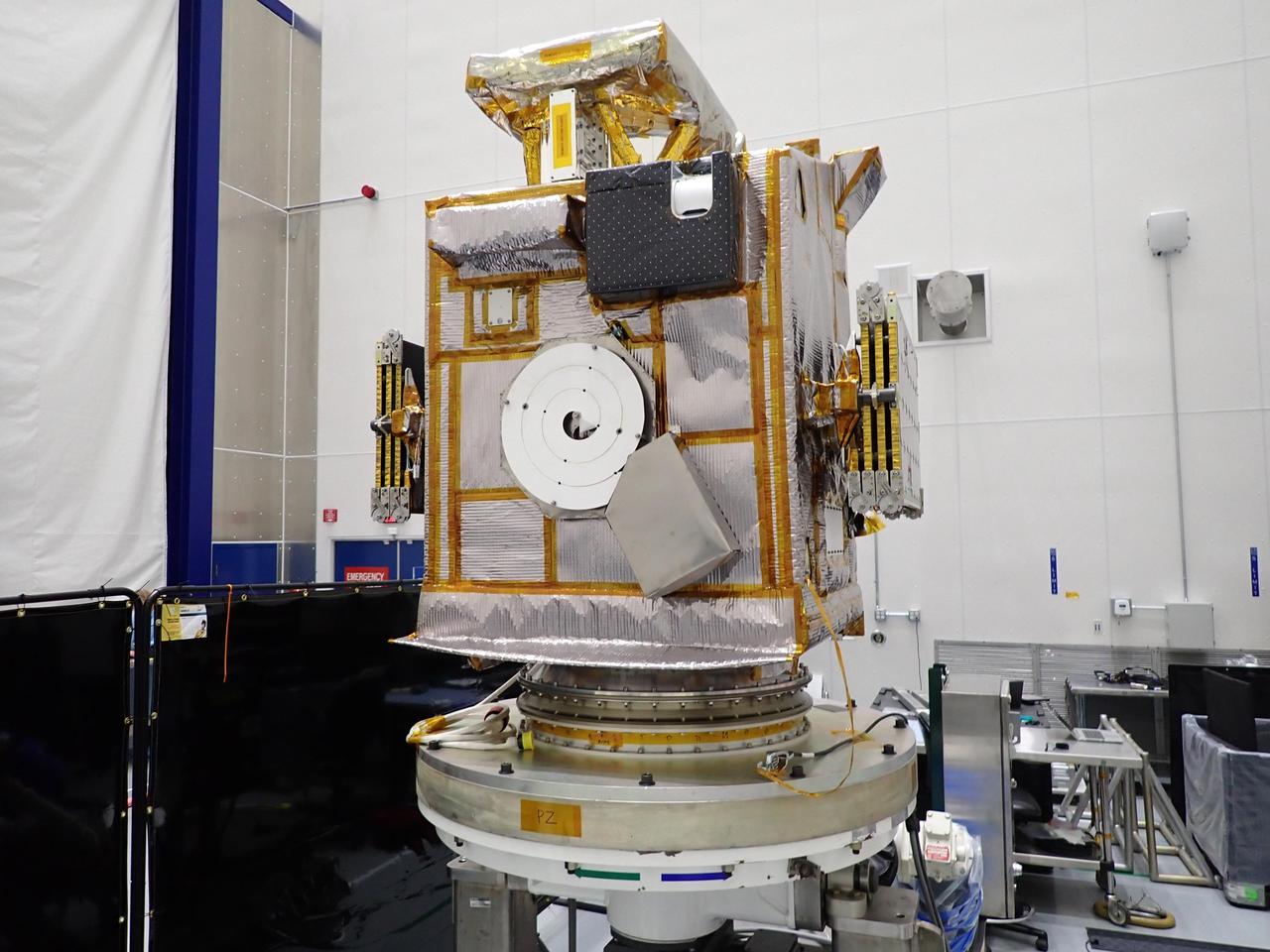

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer sits on its rotation fixture after being fueled and prior to being installed to the EELV Secondary Payload Adapter (ESPA) ring at SpaceX's payload processing facility in NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in early February 2025. The ESPA ring is an adaptor used for launching secondary payloads on launch vehicles. Figure A shows the spacecraft mounted horizontally, in its launch configuration, to the ESPA ring. The mission's two science instruments are visible. The High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) is the angular structure atop the spacecraft; the Lunar Thermal Mapper (LTM) is the black square on the upper right of the front facing panel. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26460
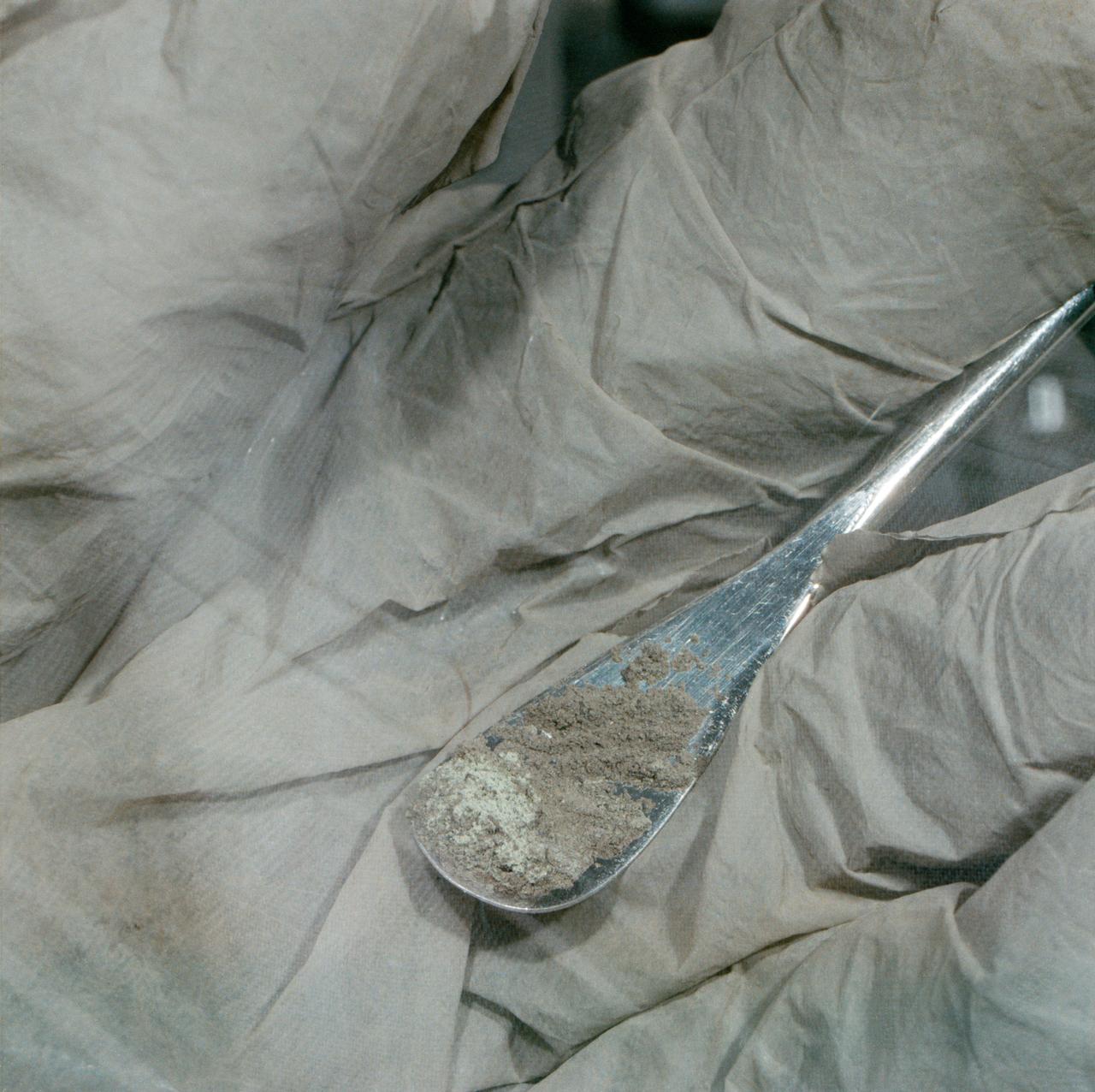

S71-43050 (August 1971) --- A close-up view of Apollo 15 lunar sample No. 15305 in the Non-sterile Nitrogen Processing Line (NNPL) in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL) at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). This sample, pictured on a small spatula in a lab technician's glove, is green and is one of six recently taken from container No. 173, made up of comprehensive fines from the Apennine Front, Site No. 7. Astronauts David R. Scott, commander; and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, took the sample during their second extravehicular activity (EVA), at a ground elapsed time (GET) of 146:05 to 146:06.
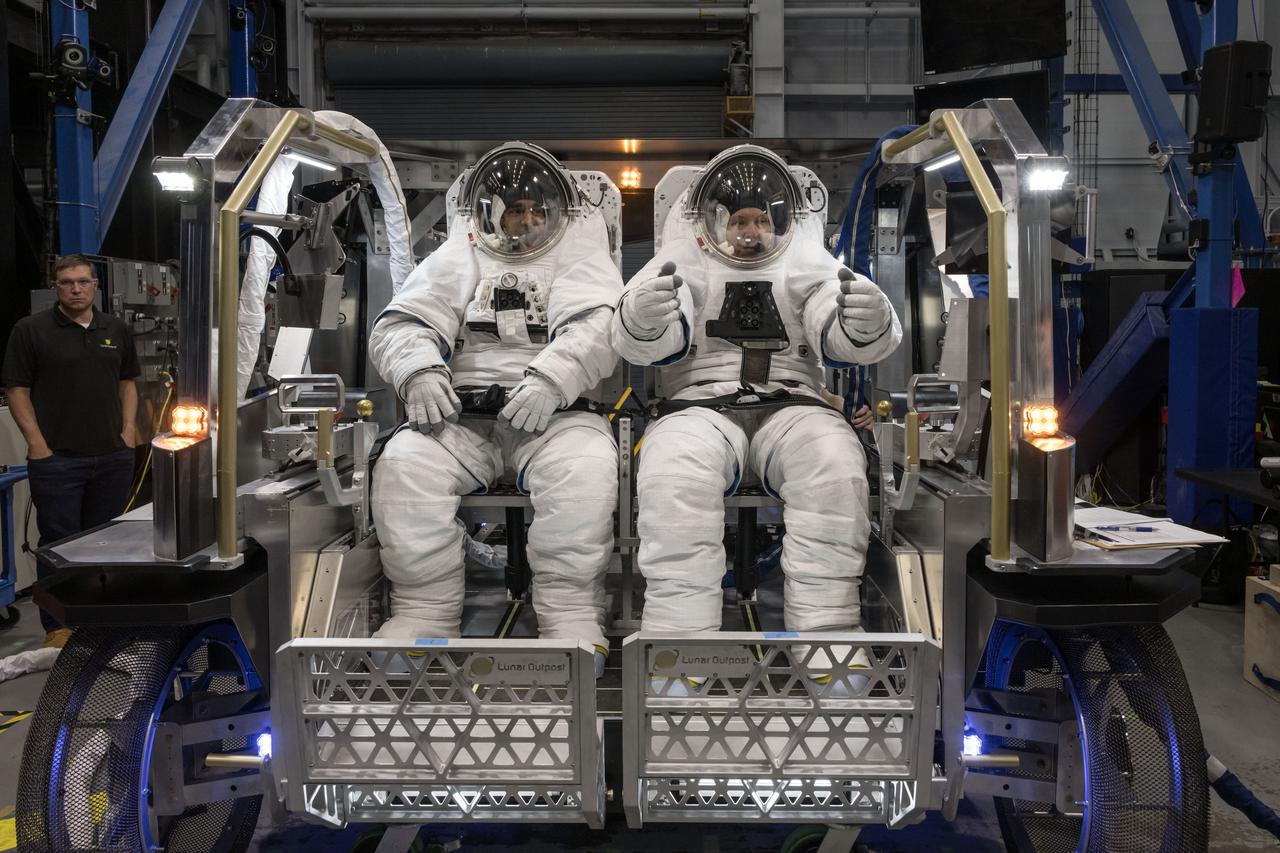

NASA astronauts Raja Chari (left) and Randy Bresnik (right) sit inside Lunar Outpost’s Eagle lunar terrain vehicle evaluating the seat configuration during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/David DeHoyos
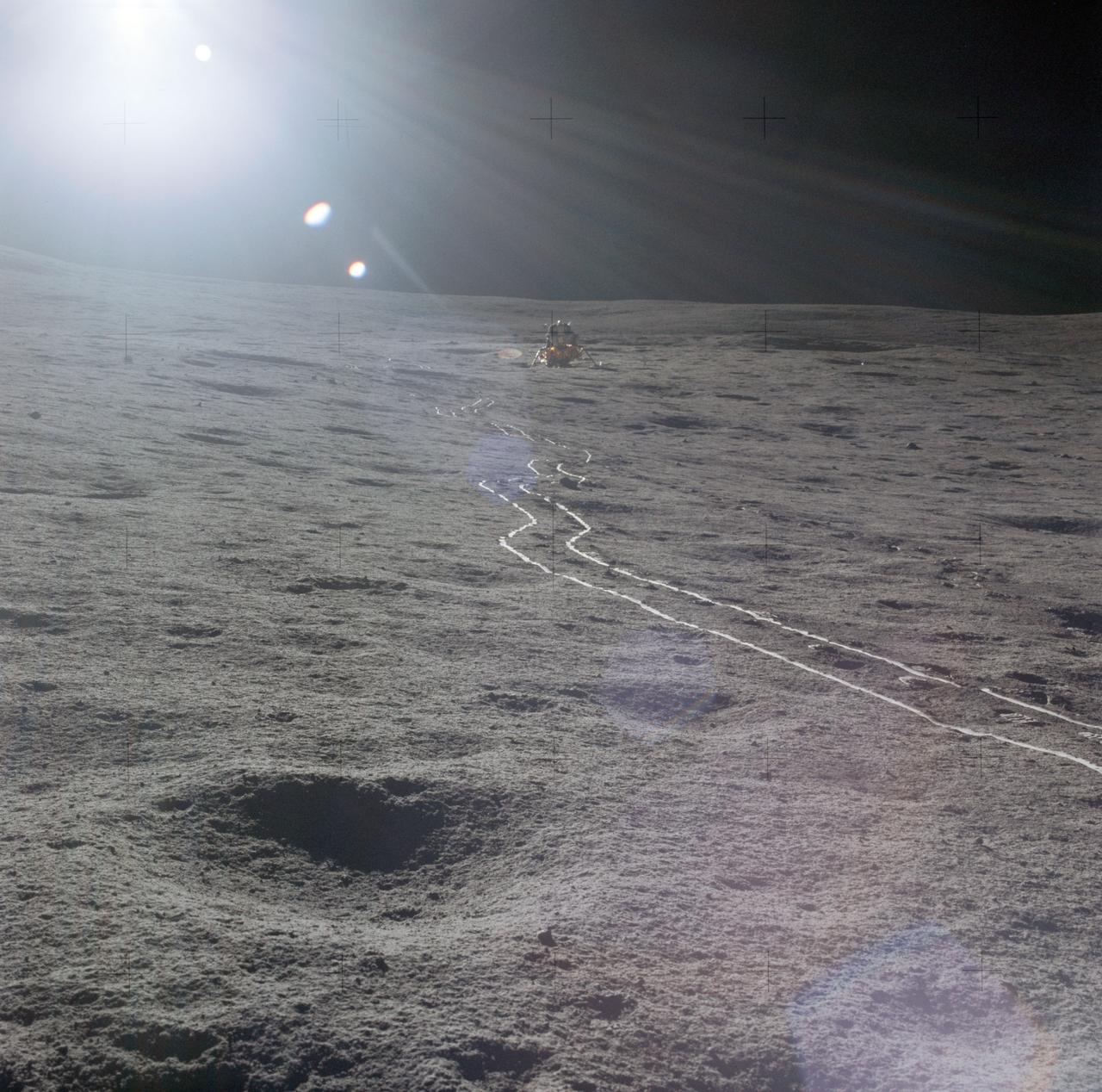

AS14-67-9367 (5 Feb. 1971) --- The Apollo 14 Lunar Module (LM) as seen by the two moon-exploring crewmen of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, photographed against a brilliant sun glare during the first extravehicular activity (EVA). A bright trail left in the lunar soil by the two-wheeled modularized equipment transporter (MET) leads from the LM. While astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, were exploring the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, was maneuvering the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

Lunar Commericial Payload Services Announcement was made at Godddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate congratulated three companies for providing first lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond
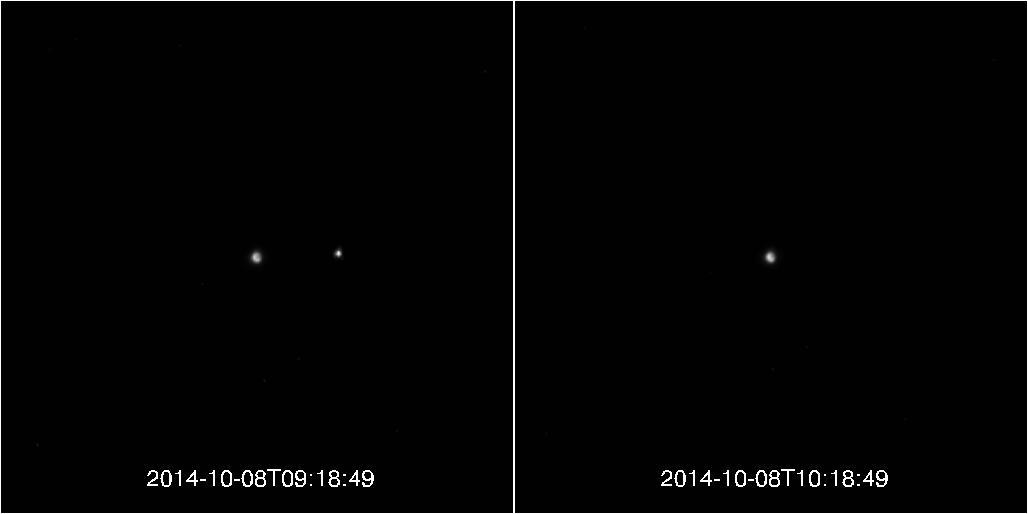

Lunar Eclipse, as Viewed by MESSENGER!
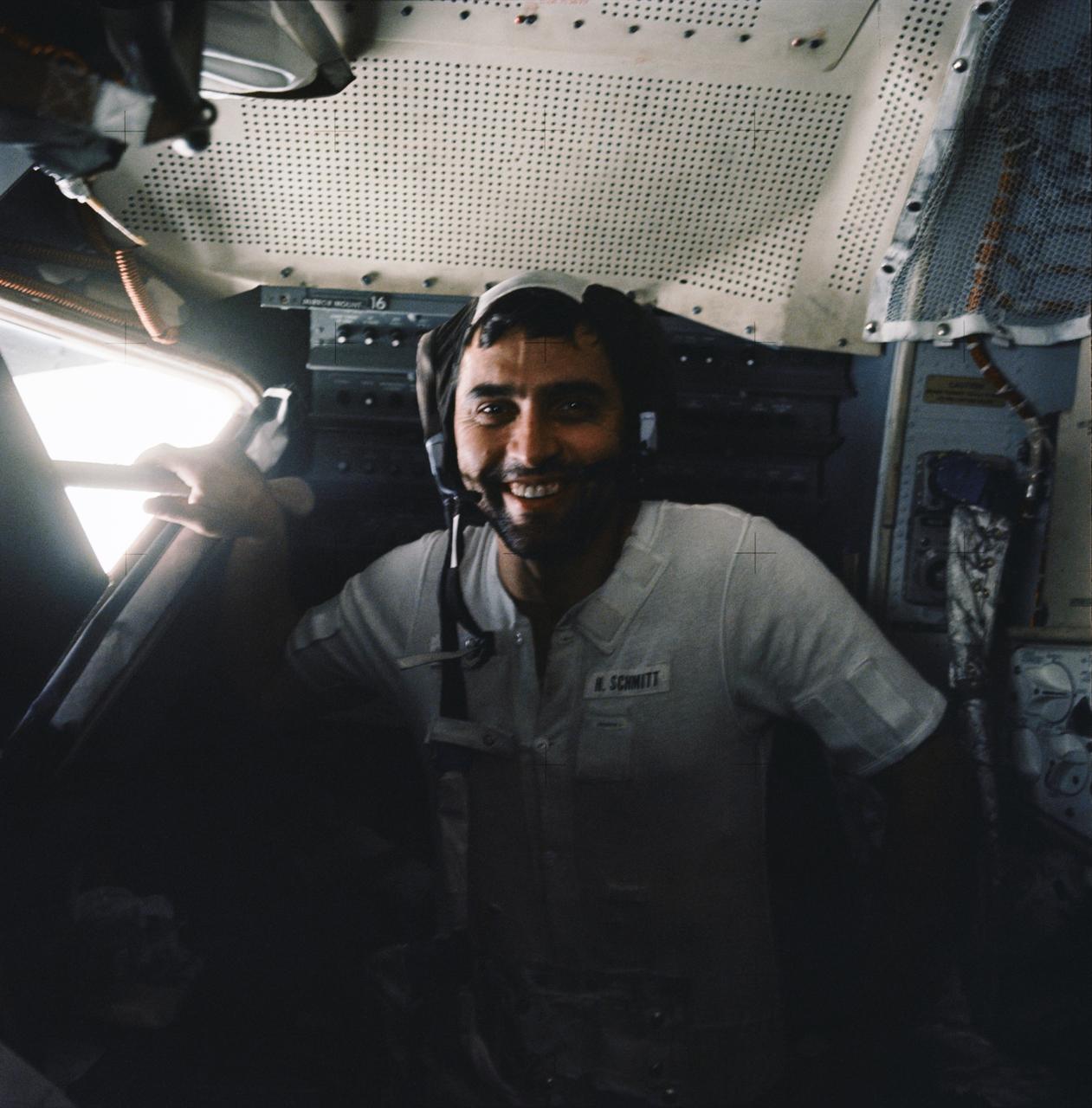

AS17-134-20530 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, displays several days of growth on his beard aboard the Lunar Module (LM) prior to its liftoff from the moon's surface. The photograph was taken by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander. The two later re-joined astronaut Ronald E. Evans, who was orbiting the moon in the Apollo 17 Command and Service Modules (CSM).
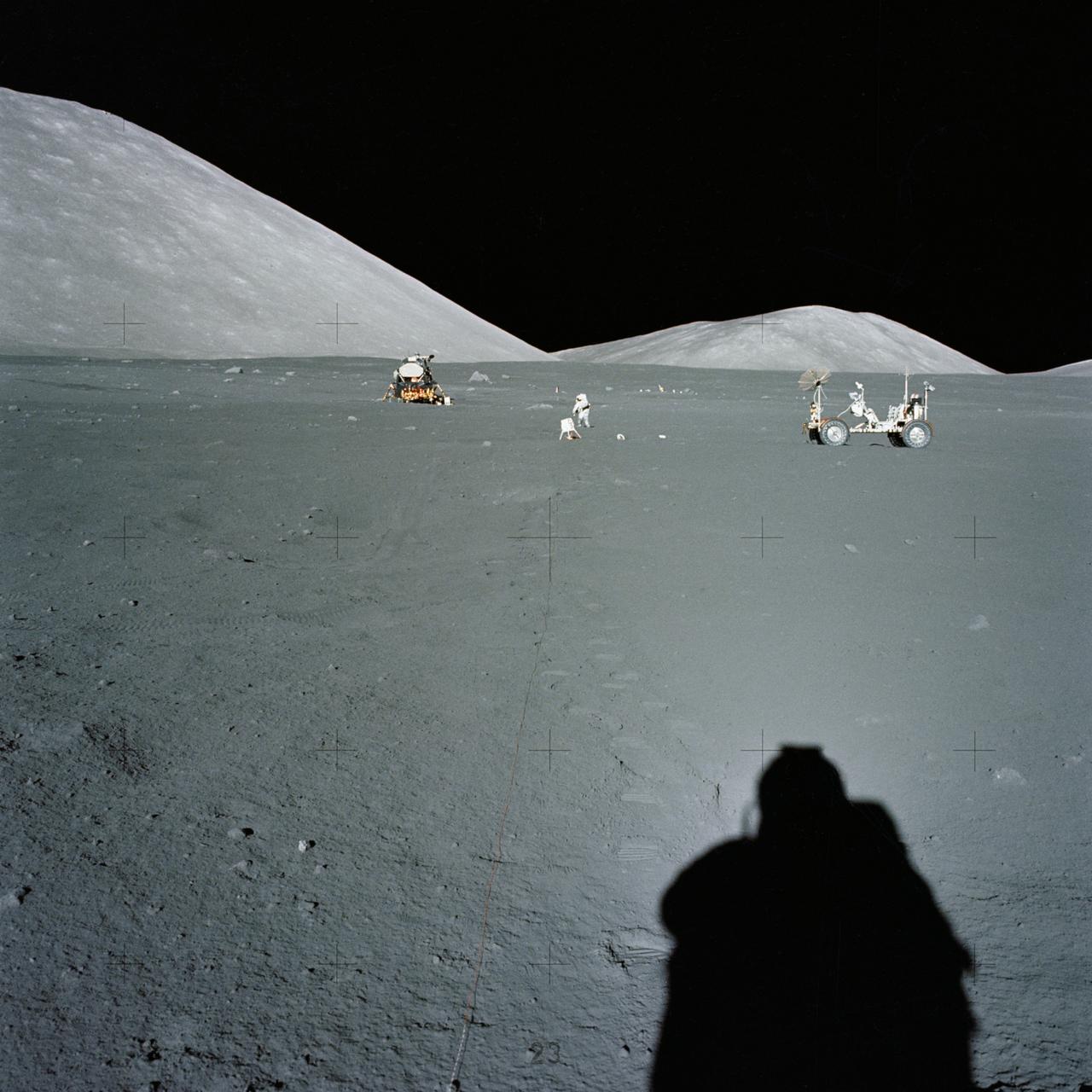

AS17-134-20435 (10 Dec. 1972) --- Wide-angle view of the Apollo 17 Taurus-Littrow lunar landing site. To the left in the background is the Lunar Module. To the right in the background is the Lunar Roving vehicle. An Apollo 17 crewmember is photographed between the two points. The shadow of the astronaut taking the photograph can be seen in the right foreground.
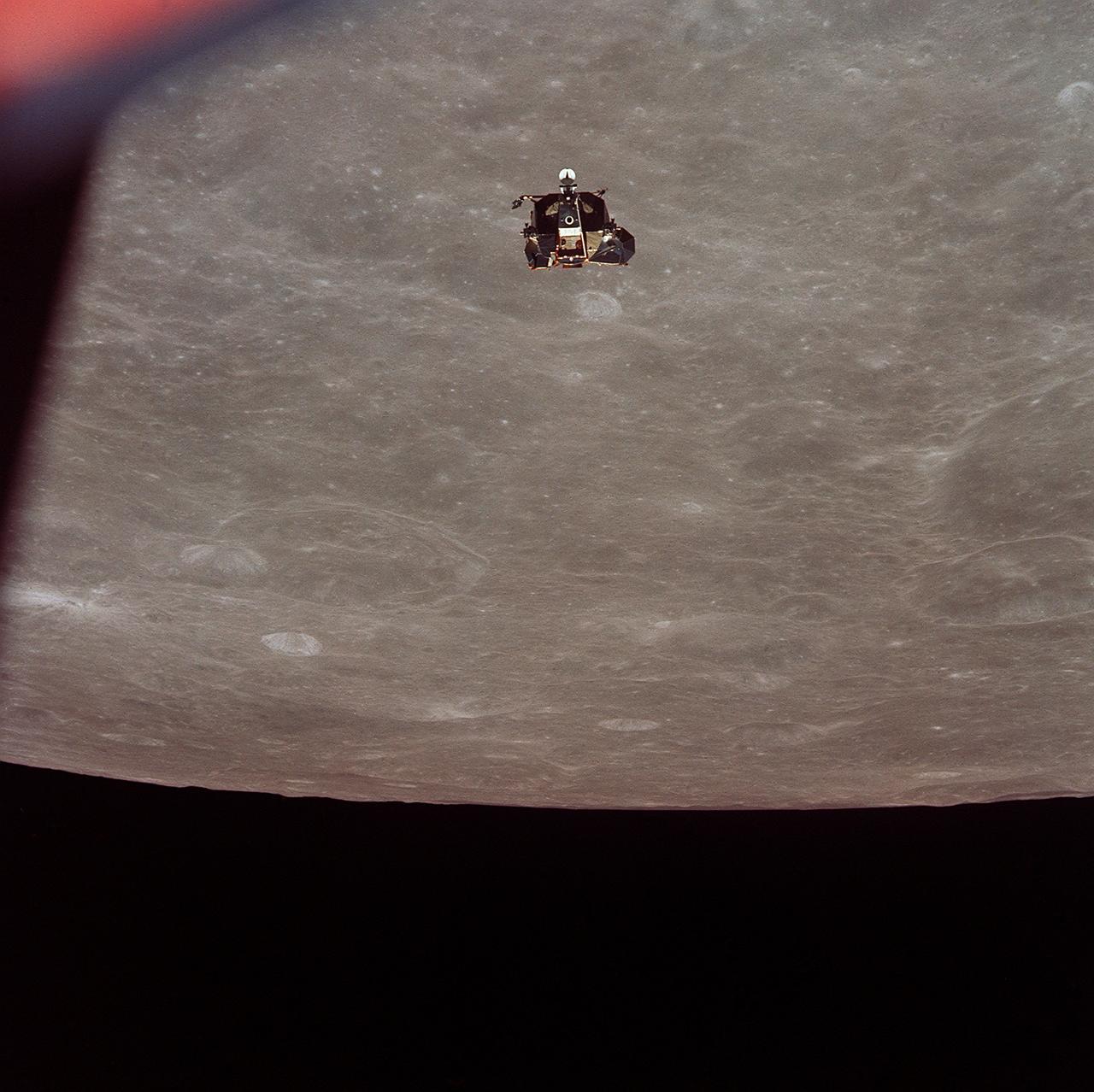

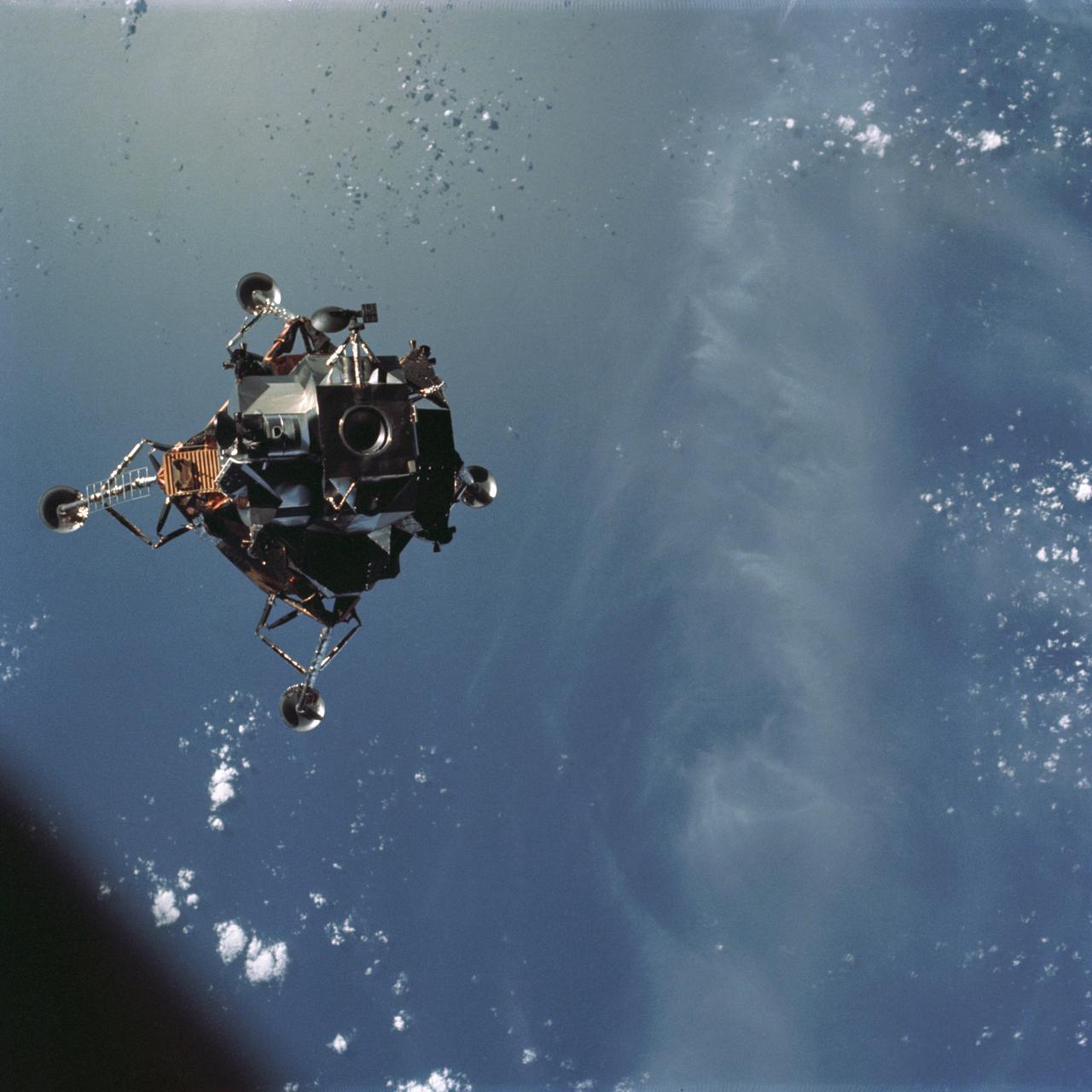
AS11-44-6626 (21 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage, with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. aboard, is photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit. Astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit while Armstrong and Aldrin explored the moon. The LM is approaching from below. The coordinates of the center of the lunar terrain seen below is located at 102 degrees east longitude and 1 degree north latitude.
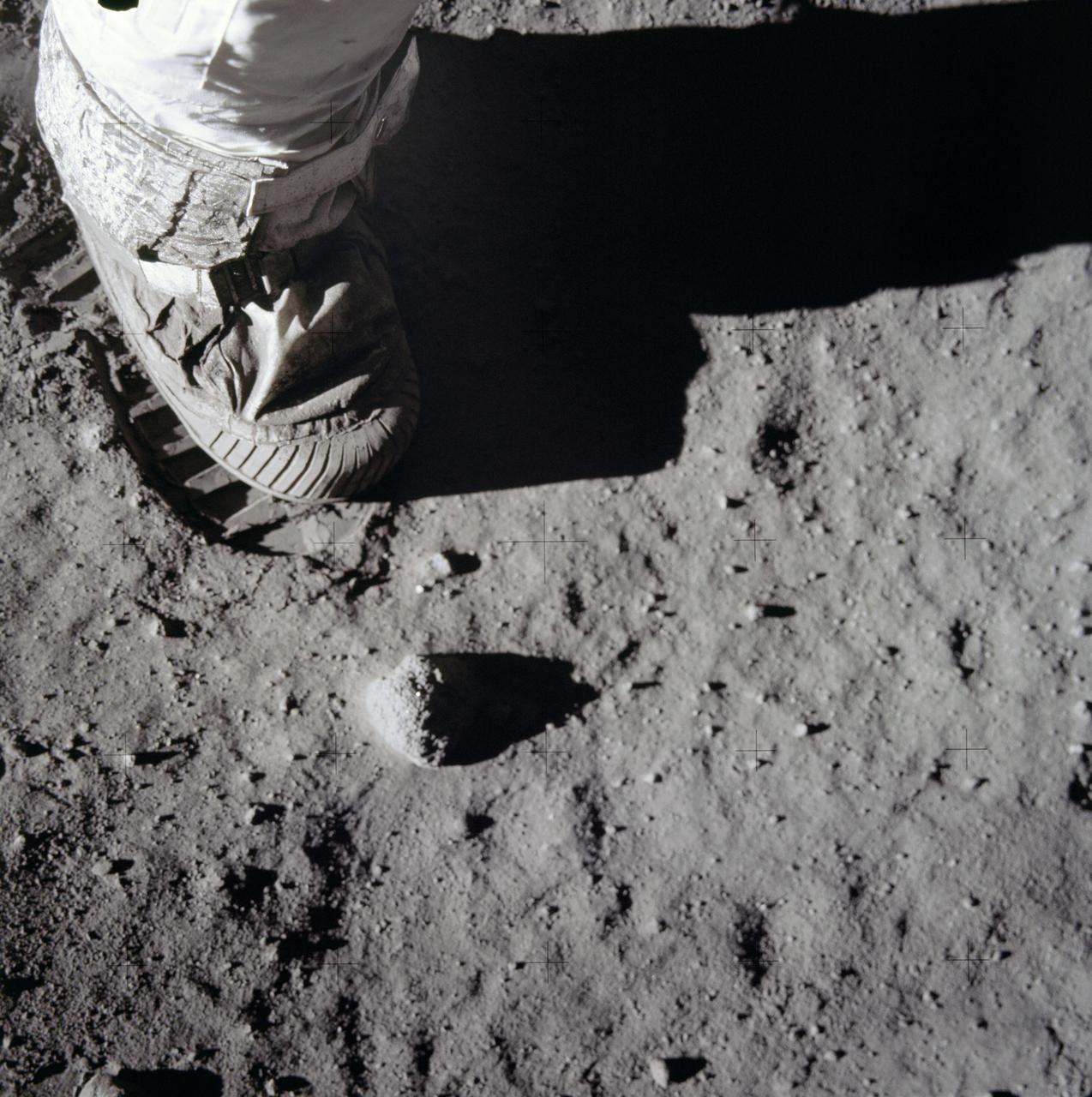

AS11-40-5880 (20 July 1969) --- A close-up view of an astronaut's boot and bootprint in the lunar soil, photographed with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander, and Edwin A. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM)" Columbia" in lunar orbit.
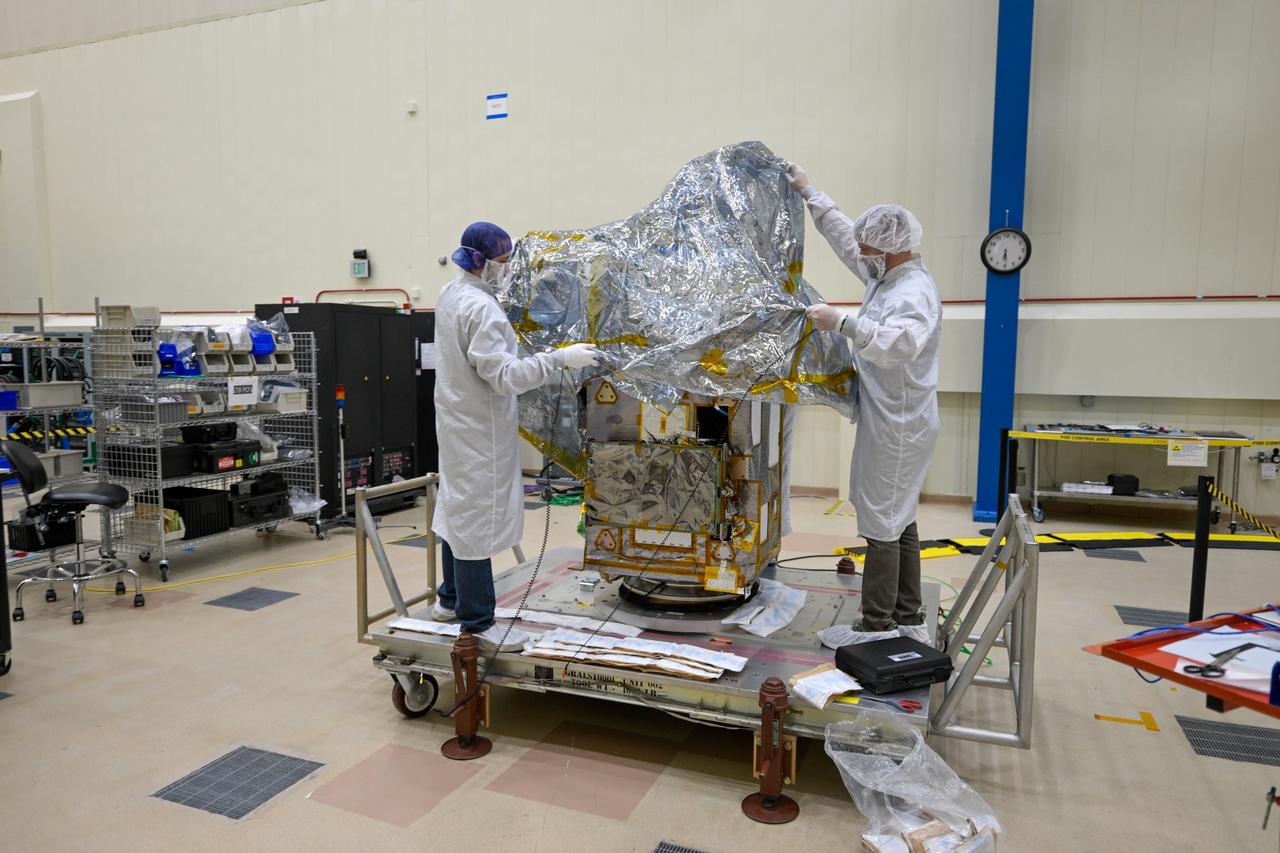

NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft gets covered in anti-static wrap before being shipped from Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, to Florida, where it arrived on Jan. 29, 2025. The spacecraft was built and tested at Lockheed and will launch no earlier than Feb. 26 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency's Kennedy Space Center. Lunar Trailblazer was a selection of NASA's SIMPLEx (Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration), which provides opportunities for low-cost science spacecraft to ride-share with selected primary missions. To maintain the lower overall cost, SIMPLEx missions have a higher risk posture and lighter requirements for oversight and management. This higher risk acceptance allows NASA to test pioneering technologies, and the definition of success for these missions includes the lessons learned from more experimental endeavors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26458

AS16-113-18339 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut John W. Young, commander of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, leaps from the lunar surface as he salutes the United States flag at the Descartes landing site during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, took this picture. The Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" is on the left. The Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) is parked beside the LM. The object behind Young (in the shade of the LM) is the Far Ultraviolet Camera/Spectrograph (FUC/S). Stone Mountain dominates the background in this lunar scene. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
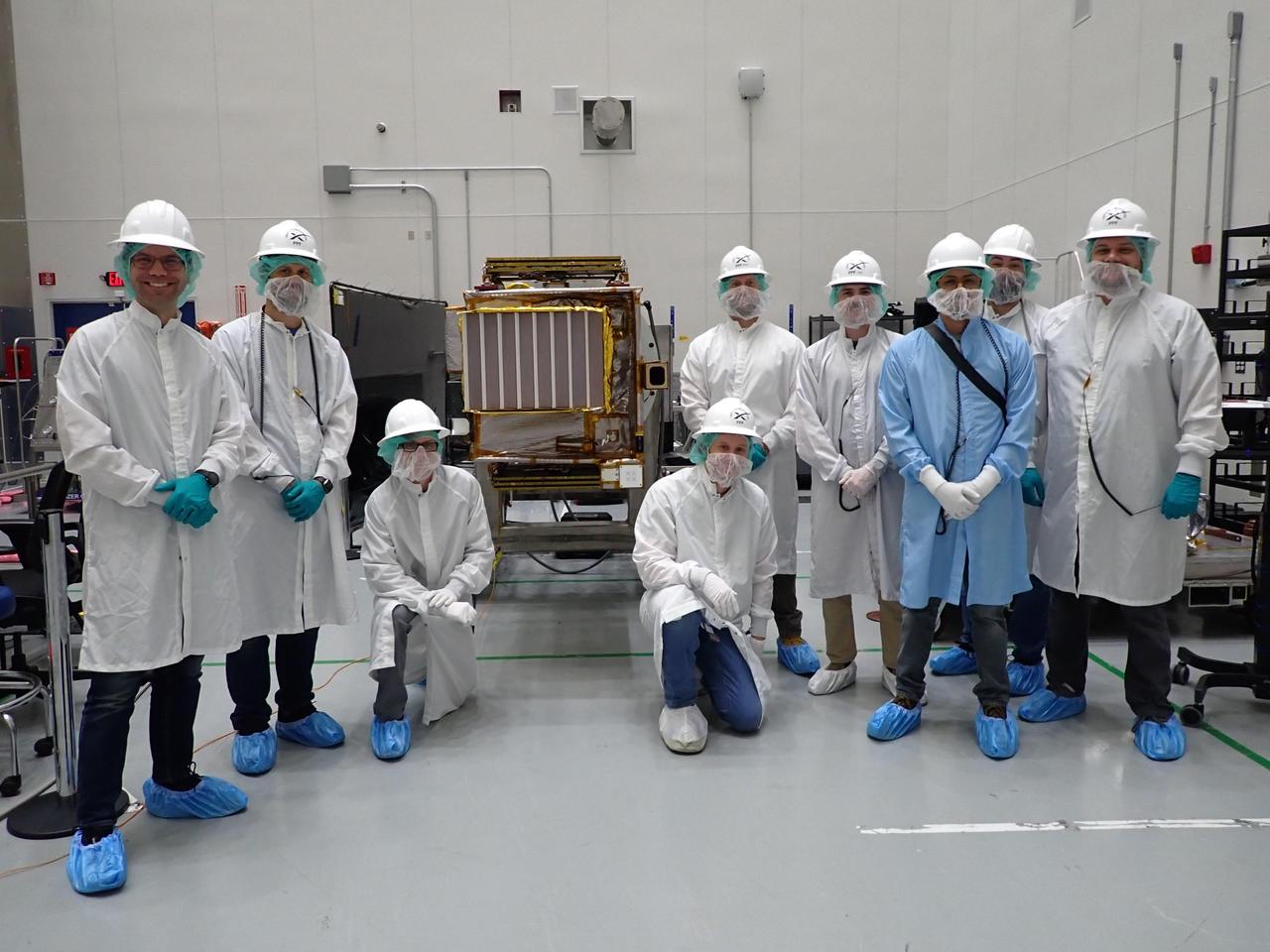

Members of NASA's Lunar Trailblazer team pose with the spacecraft at SpaceX's payload processing facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in early February 2025. The grated radiator of the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) instrument is facing the camera. Pictured, from left: Andrew Klesh, Jeff Pyle, Ryan Kressler, Willie Parker, Jon Newman, Alex Sugarman, David Rodriquez, Chris Calamateos-Brown, and David Hobbs. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26581
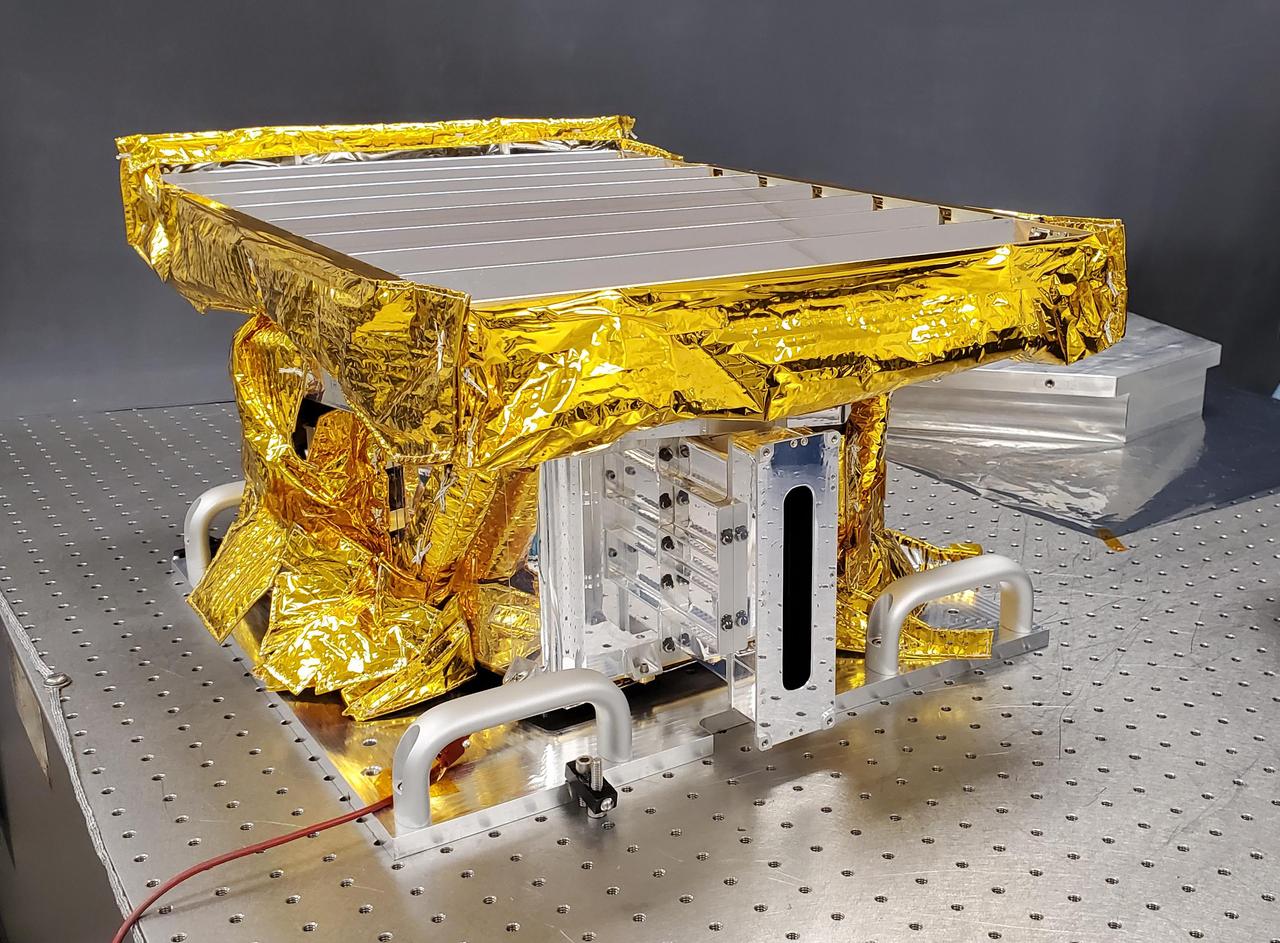

The High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) sits in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in early December 2022. The JPL-built instrument was later shipped to Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, to be integrated with NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that will detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. A second instrument, the Lunar Thermal Mapper infrared multispectral imager, is being developed by the University of Oxford in the U.K. and is scheduled for delivery and integration in early 2023. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25256
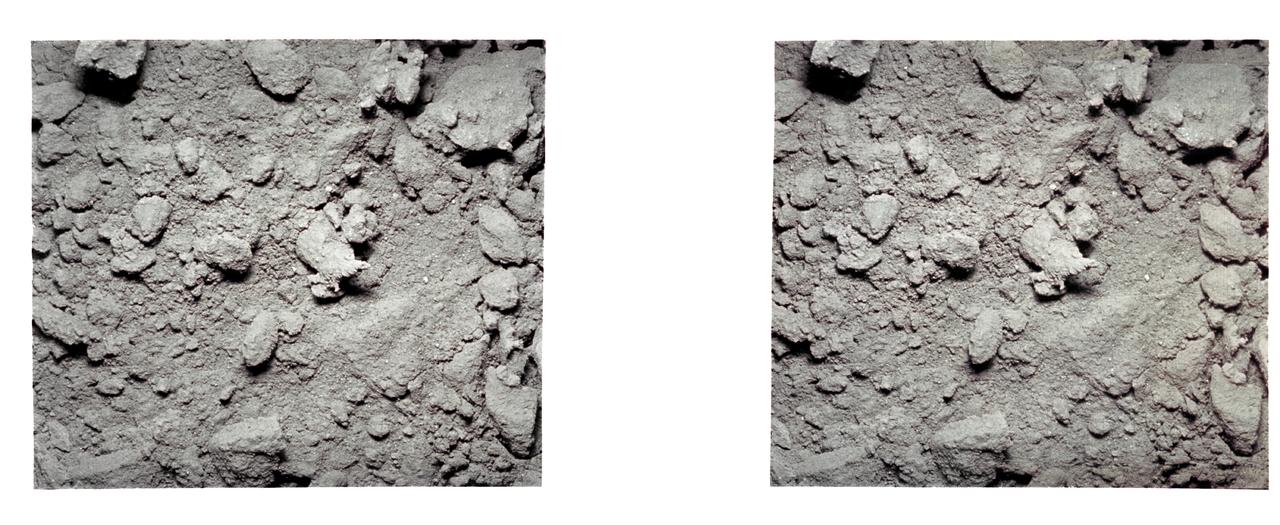

AS12-57-8455 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
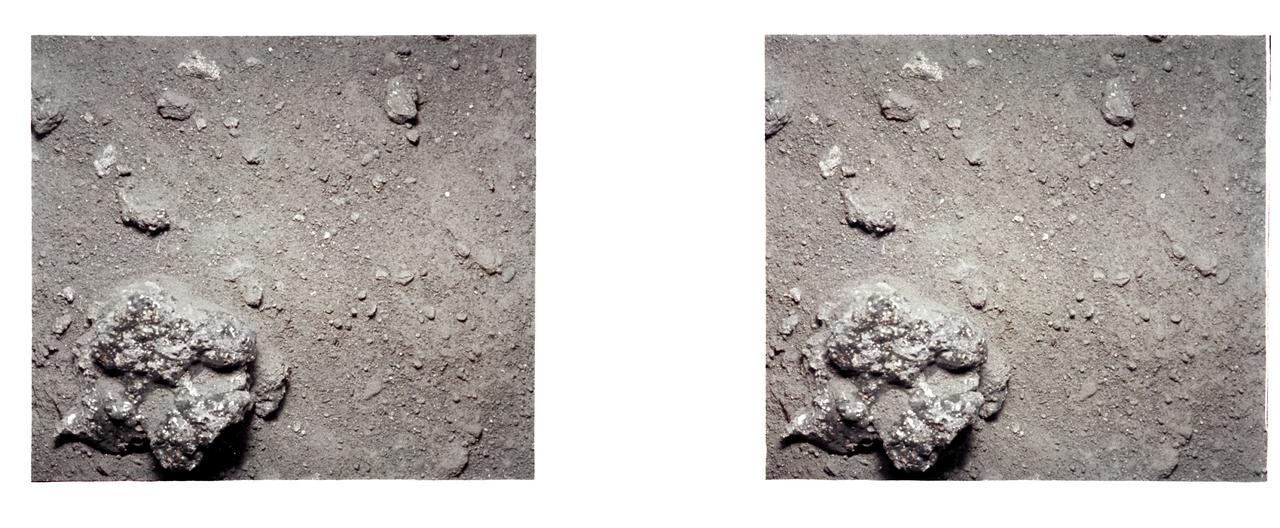

AS12-57-8452 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
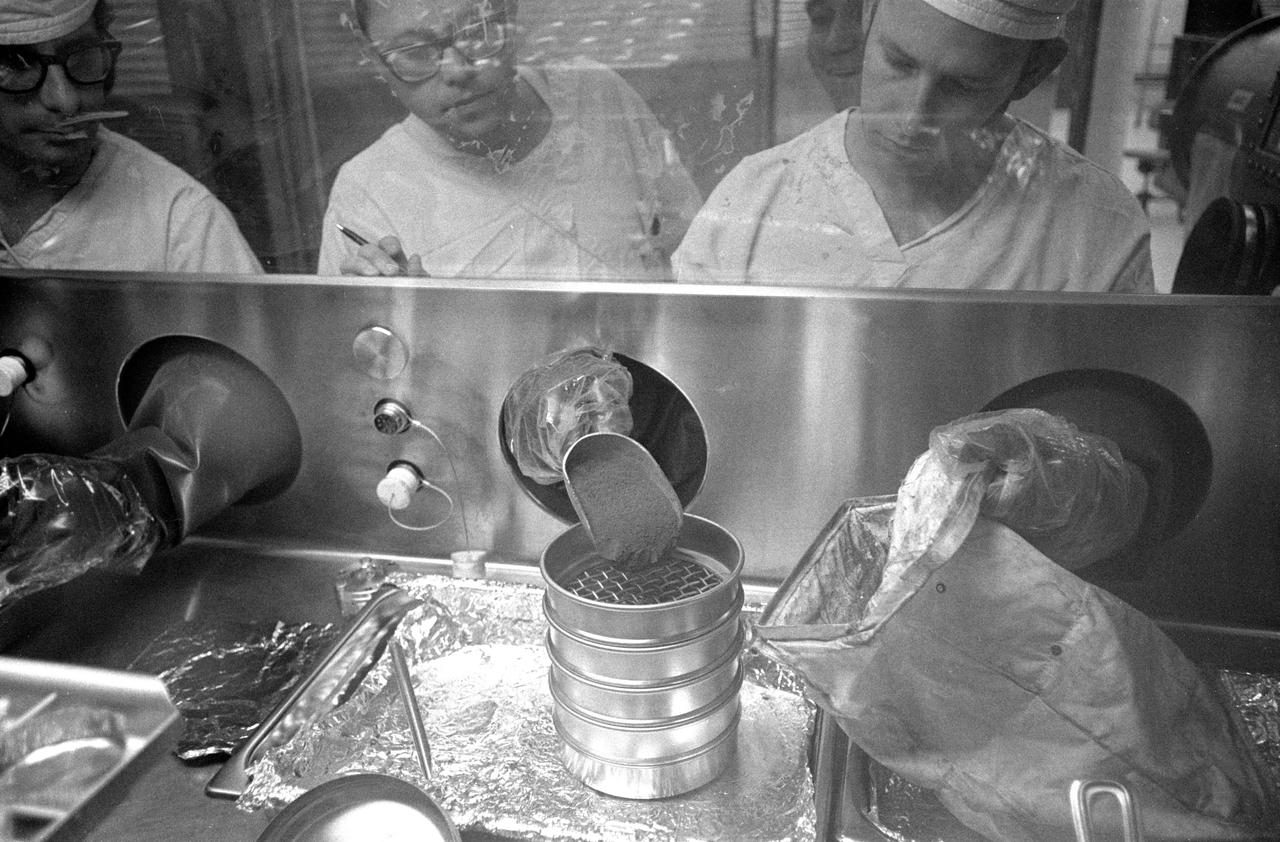

S71-19489 (18 Feb. 1971) --- Glove handlers work with freshly opened Apollo 14 lunar sample material in modularized cabinets in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center. The glove operator on the right starts to pour fine lunar material which he has just taken from a tote bag. The powdery sample was among the last to be revealed of the 90-odd pounds of material brought back to Earth by the Apollo 14 crew members.

Loading the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter into the thermal vacuum chamber at Goddard Space Flight Center. Diviner is one of seven instruments aboard NASA LRO Mission.

AS09-21-3181 (7 March 1969) --- A View of the Apollo 9 Lunar Module (LM), "Spider," in a lunar lading configuration, as photographed from the Command and Service Modules (CSM) on the fifth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The landing gear on the "Spider" has been deployed. Inside the "Spider" were astronauts James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander; and Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the Command Module (CM), "Gumdrop," while the other two astronauts checked out the LM.

IM-1, the first NASA Commercial Launch Program Services launch for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander, will carry multiple payloads to the Moon, including Lunar Node-1, demonstrating autonomous navigation via radio beacon to support precise geolocation and navigation among lunar orbiters, landers, and surface personnel. NASA’s CLPS initiative oversees industry development of small robotic landers and rovers to support NASA’s Artemis campaign.
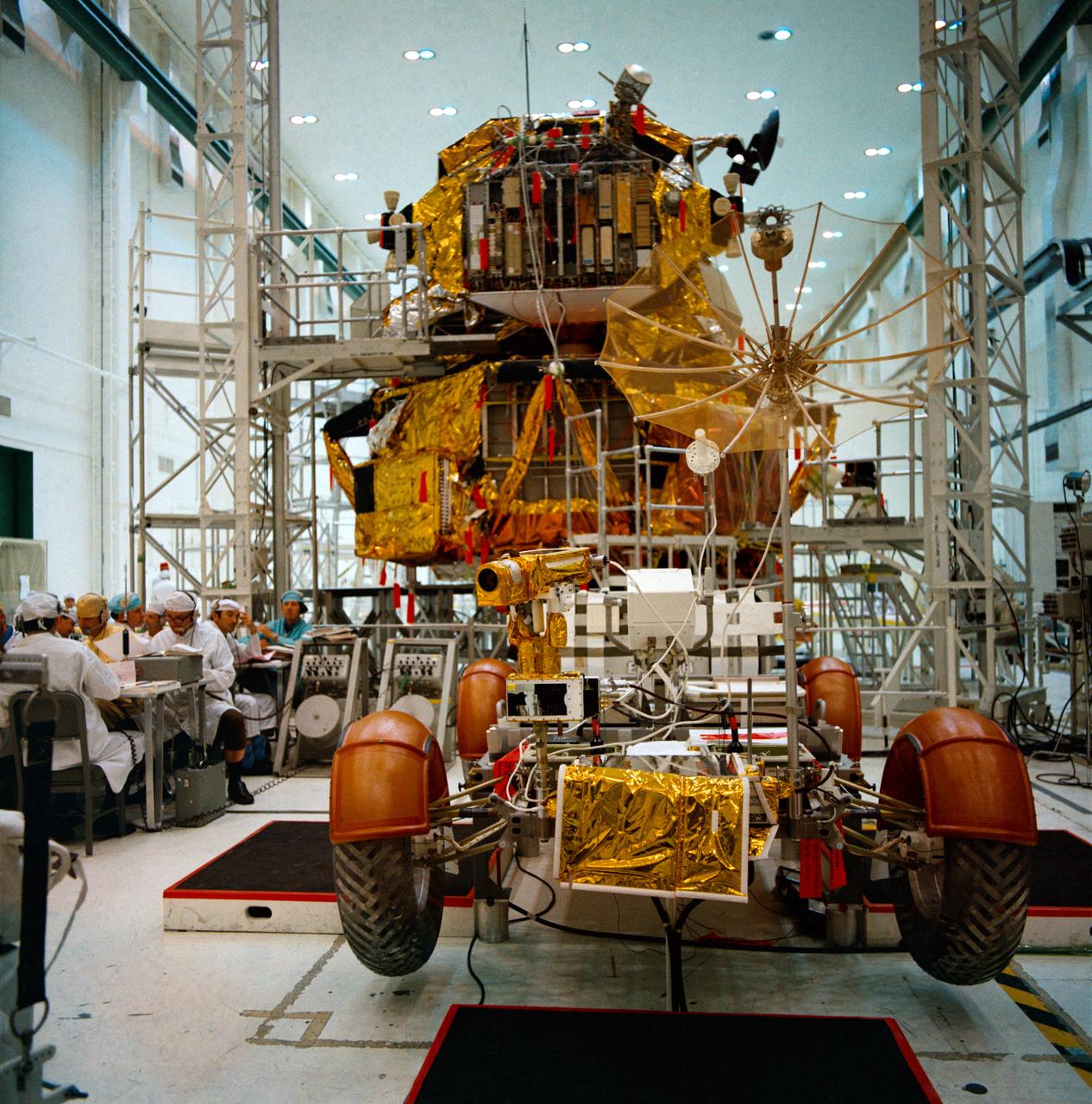

S71-30542 (21 April 1971) --- An overall view of the Apollo 15 Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and the Lunar Module (LM) during simulations at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, will man the LRV on the lunar surface during their August 1971 traverses. Rover 1 will permit the astronauts to cover a larger area of the moon for exploration and sample collecting than on previous missions.
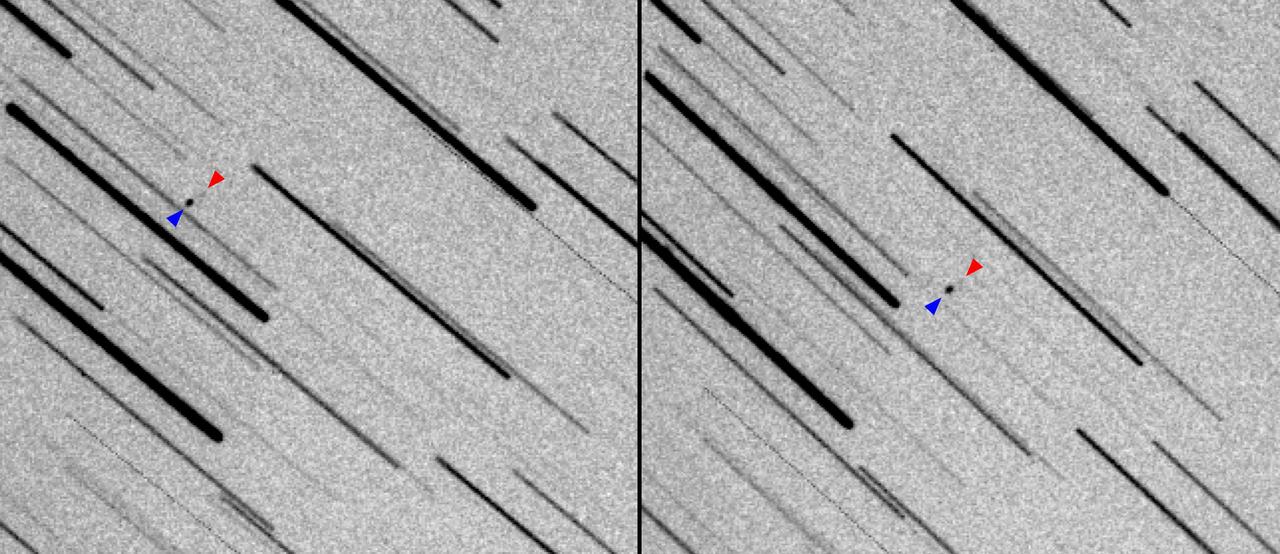
These images show two observations of NASA's Lunar Flashlight and the private ispace HAKUTO-R Mission 1 as the two spacecraft, seen as a pair of dots, journey to the Moon. In Figure A, the images have been joined sequentially to create an animated GIF. The larger HAKUTO-R lunar lander appears as a large black dot, whereas the smaller Lunar Flashlight, which is about the size of a briefcase, appears as a fuzzy grouping of gray pixels. Stars appear as long trails. Both missions launched on Dec. 11, 2022, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, with Lunar Flashlight and HAKUTO-R spacecraft subsequently deploying from it. Astronomer Vishnu Reddy and graduate student Adam Battle, both from University of Arizona's Lunar and Planetary Laboratory and Space4 Center, used a remote 0.5-meter (1.6-foot) telescope in Australia to track the small spacecraft. They used data from the Horizons System at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to find their position in the sky. These images were acquired about 39 hours after launch, when the two spacecraft were 145,000 miles (235,000 kilometers) from Earth. Black and white in the images have been inverted so that the brighter the object, the darker it is. To detect the faint reflected light from both spacecraft, they stacked 80 images, each from a 10-second exposure (for a total exposure time of 800 seconds), based on the rate of motion and direction of the spacecraft. This method resulted in stars appearing as long trails and the two spacecraft appearing as dots. Lunar Flashlight is a small satellite mission planning to use lasers to seek out surface water ice inside permanently shadowed craters at the Moon's South Pole. The small satellite is expected to reach its science orbit around the Moon in April 2023. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25257
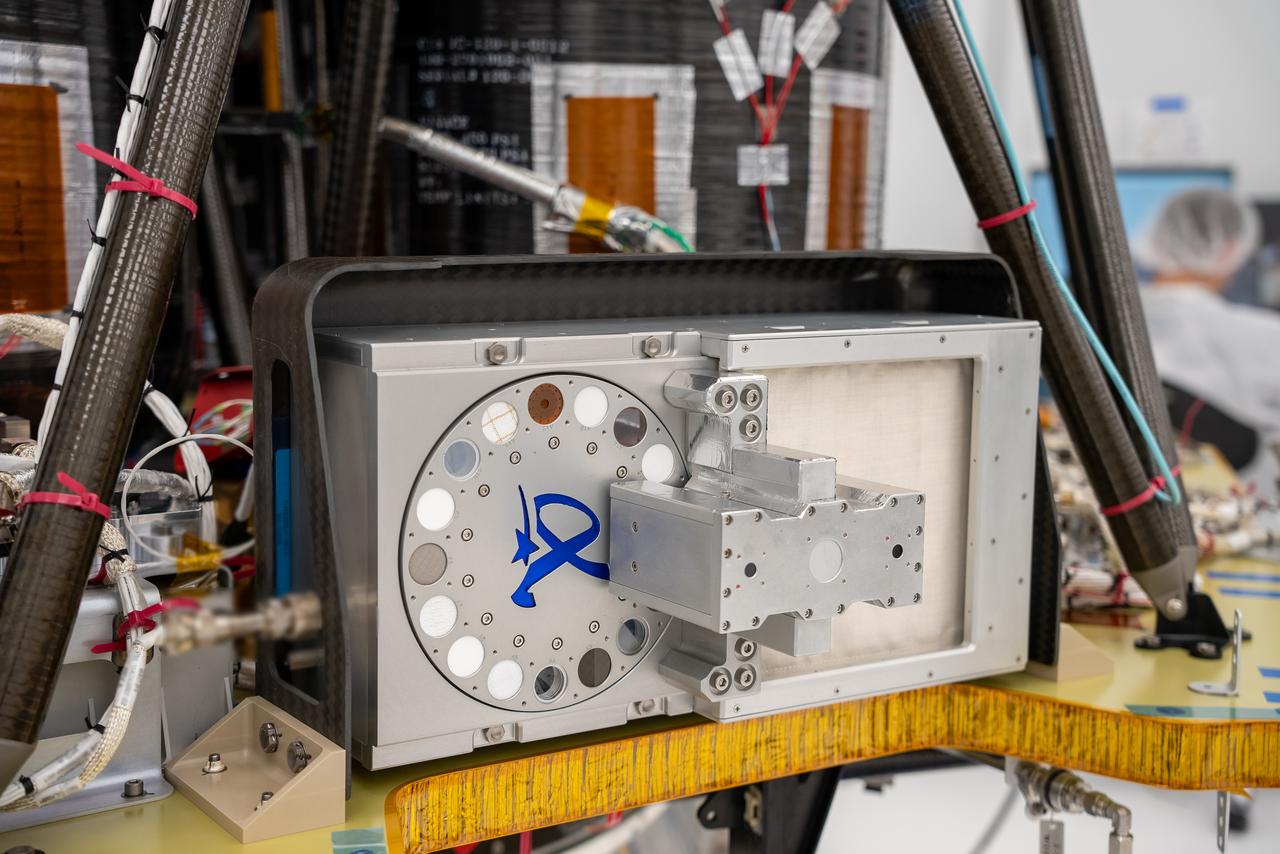
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
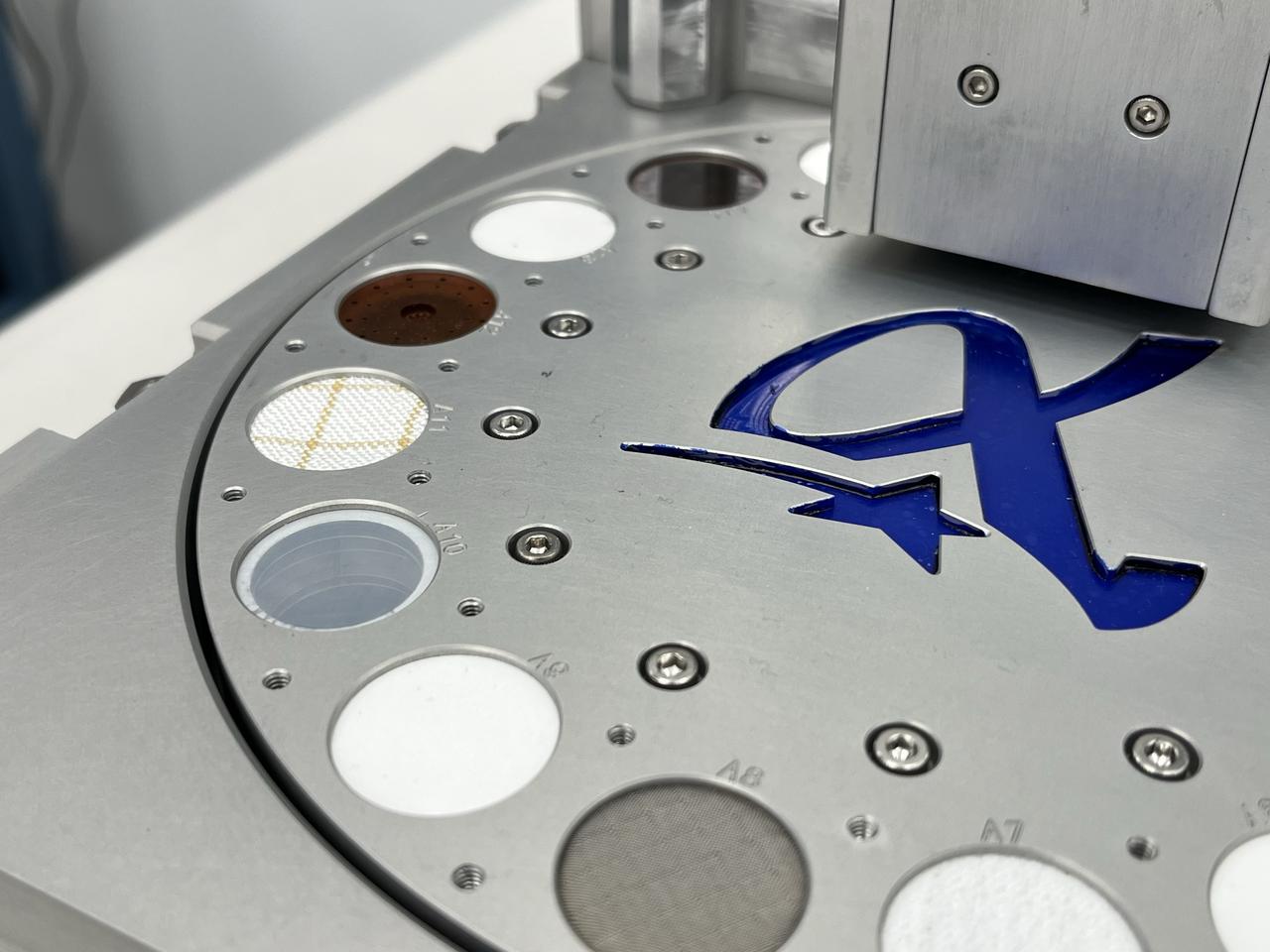
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
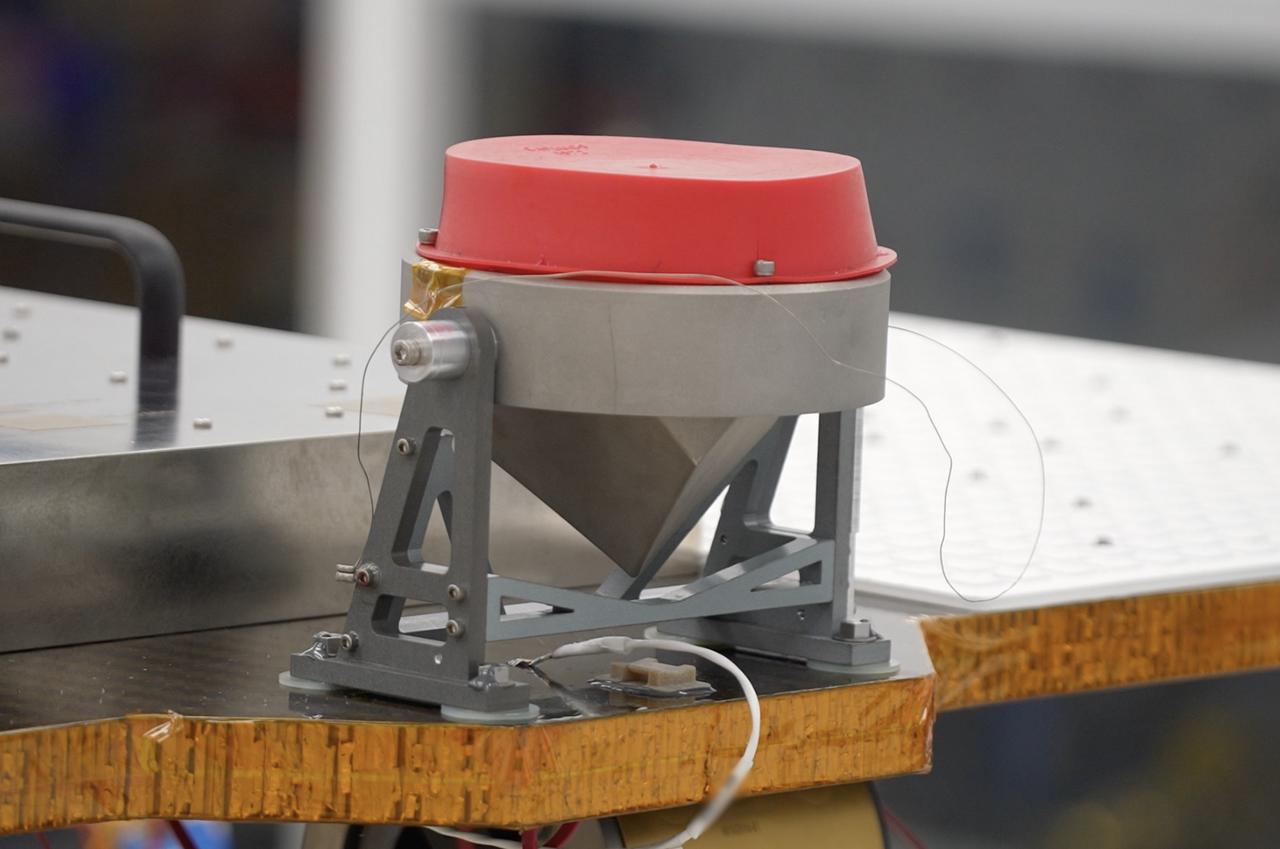

A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is expected to significantly expand our knowledge of the Moon. Next Generation Lunar Retroreflector, or NGLR-1, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by the University of Maryland in College Park, NGLR-1 is designed to reflect very short laser pulses from Earth-based lunar laser ranging observatories using a retroreflector, or a mirror designed to reflect the incoming light back in the same incoming direction. Investigations and demonstrations, such as NGLR-1, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
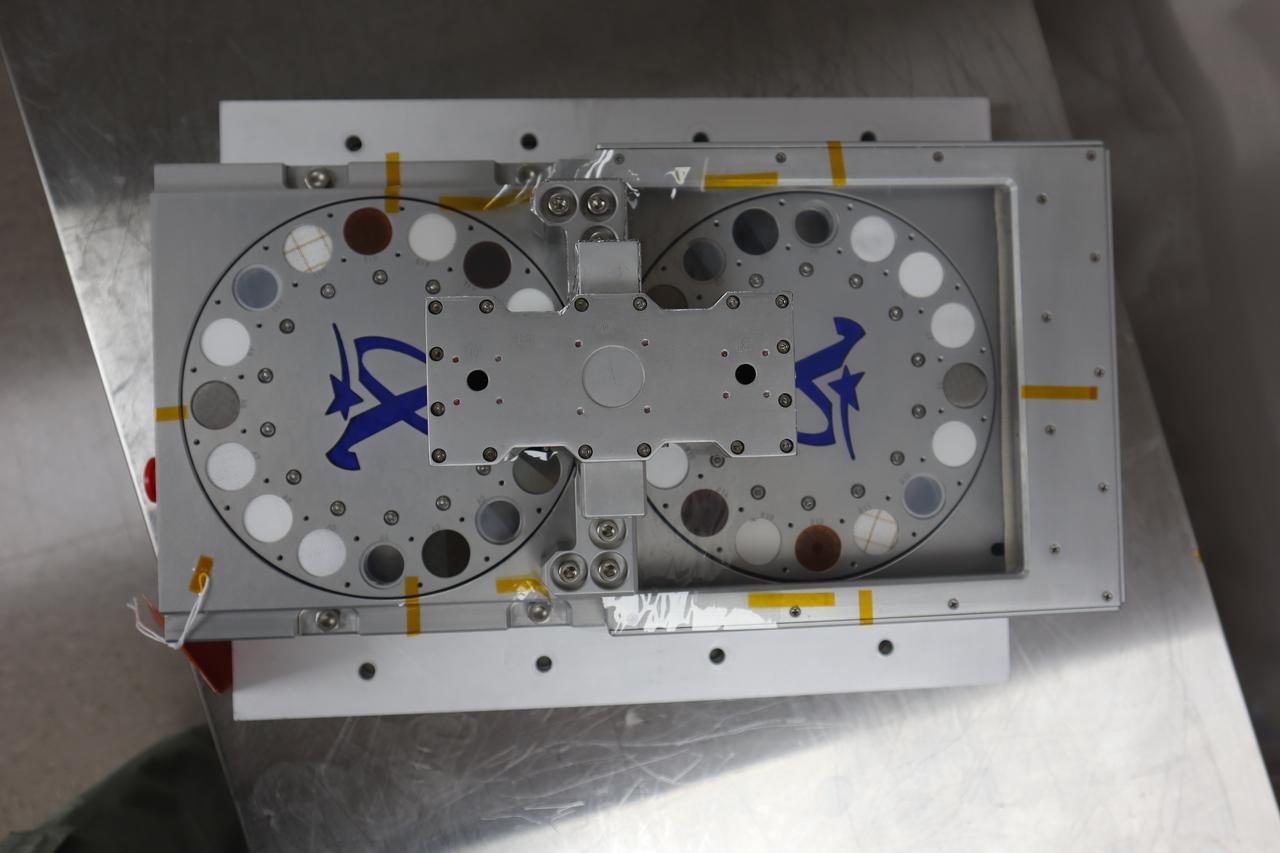
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

AS16-114-18423 (21 April 1972) --- Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, is photographed collecting lunar samples at Station No. 1, during the first Apollo 16 extravehicular activity (EVA), at the Descartes landing site. This picture, looking eastward, was taken by astronaut John W. Young, commander. Duke is standing at the rim of Plum Crater. The parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) can be seen in the left background. While astronauts Young and Duke descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands region of the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
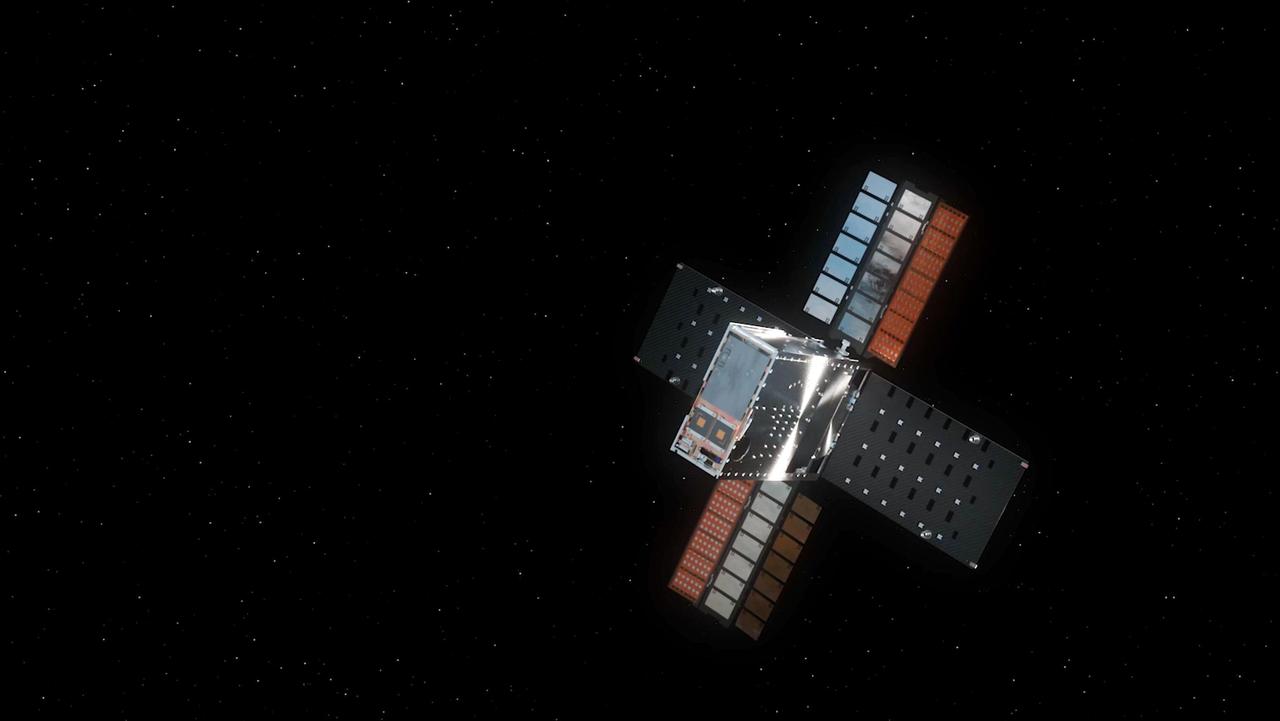

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight, with its four solar arrays deployed, shortly after launch. The small satellite, or SmallSat, launched Nov. 30, 2022, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket as a rideshare with ispace's HAKUTO-R Mission 1. It will take about three months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, Lunar Flashlight will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. This is the first time that multiple colored lasers will be used to seek out ice inside these dark regions on the Moon, which haven't seen sunlight in billions of years. Should the lasers hit bare rock or regolith (broken rock and dust), the light will reflect back to the spacecraft. But if the target absorbs the light, that would indicate the presence of water ice. The greater the absorption, the more ice there may be. The science data collected by the mission will be compared with observations made by other lunar missions to help reveal the distribution of surface water ice on the Moon for potential use by future astronauts. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25626
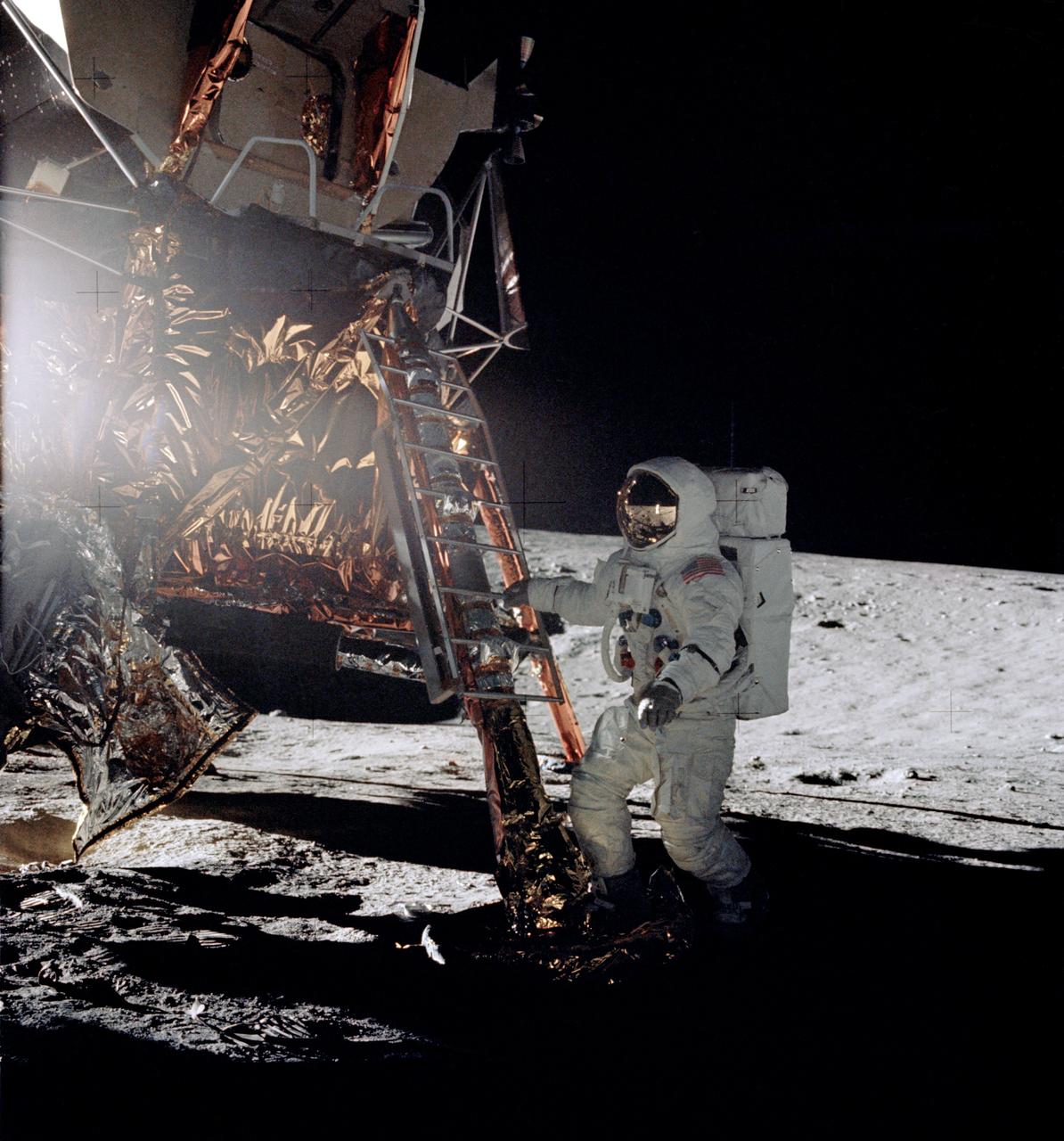

AS12-46-6729 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, steps from the ladder of the Lunar Module to join astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, in extravehicular activity on Nov. 19, 1969. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
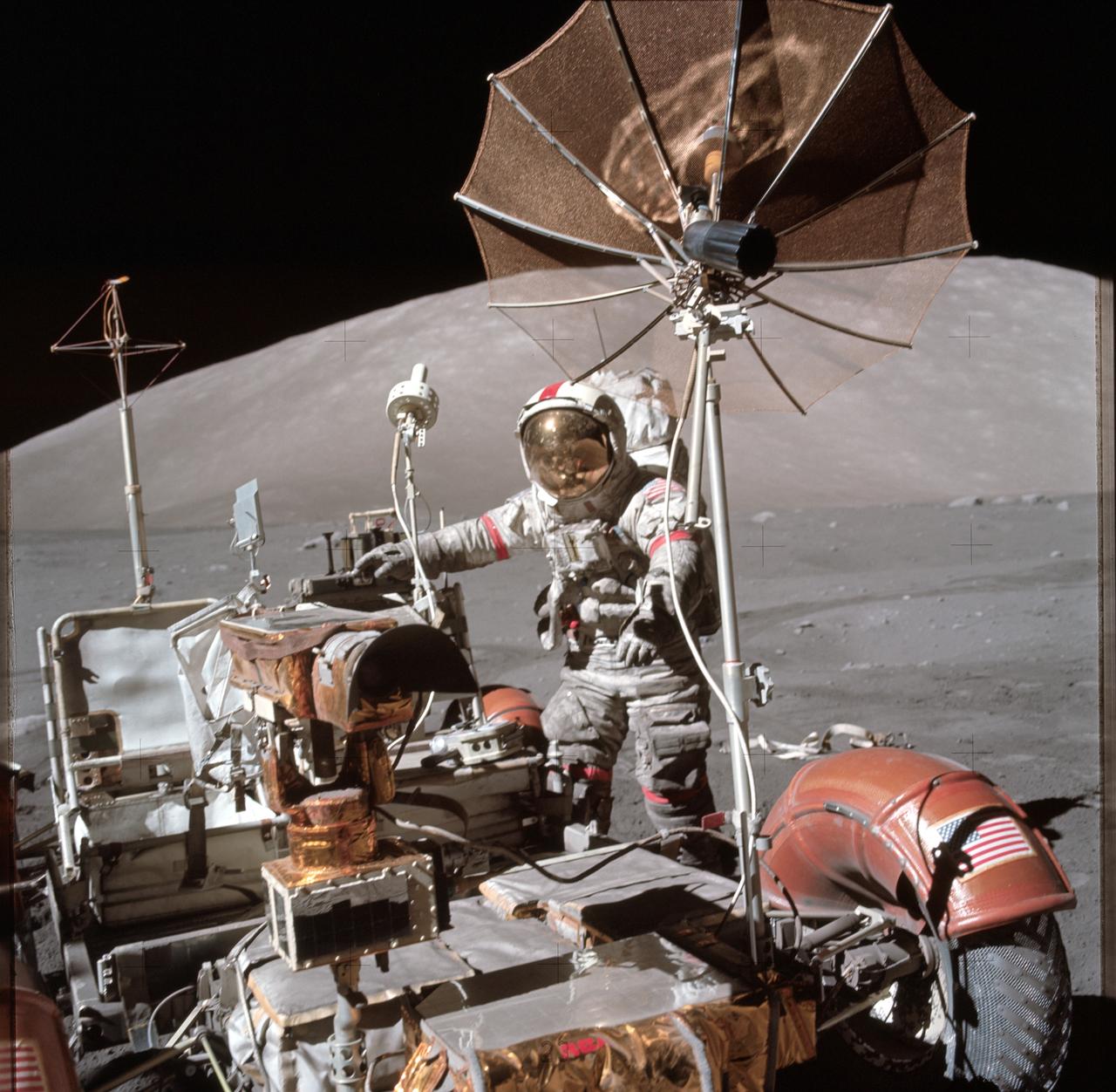

AS17-134-20476 (13 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 17 commander, approaches the parked Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) on the lunar surface during the flight's third period of extravehicular activity (EVA). South Massif can be seen in the background. The photograph was taken with a hand-held Hasselblad camera by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While the two explored the surface of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
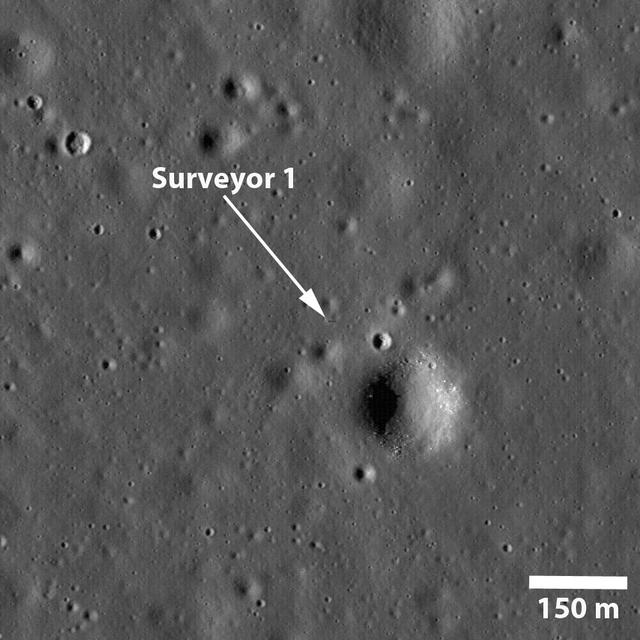

NASA Surveyor 1 spacecraft sitting silently on Oceanus Procellarum, the first US spacecraft to land on another planet on June 2, 1966 in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
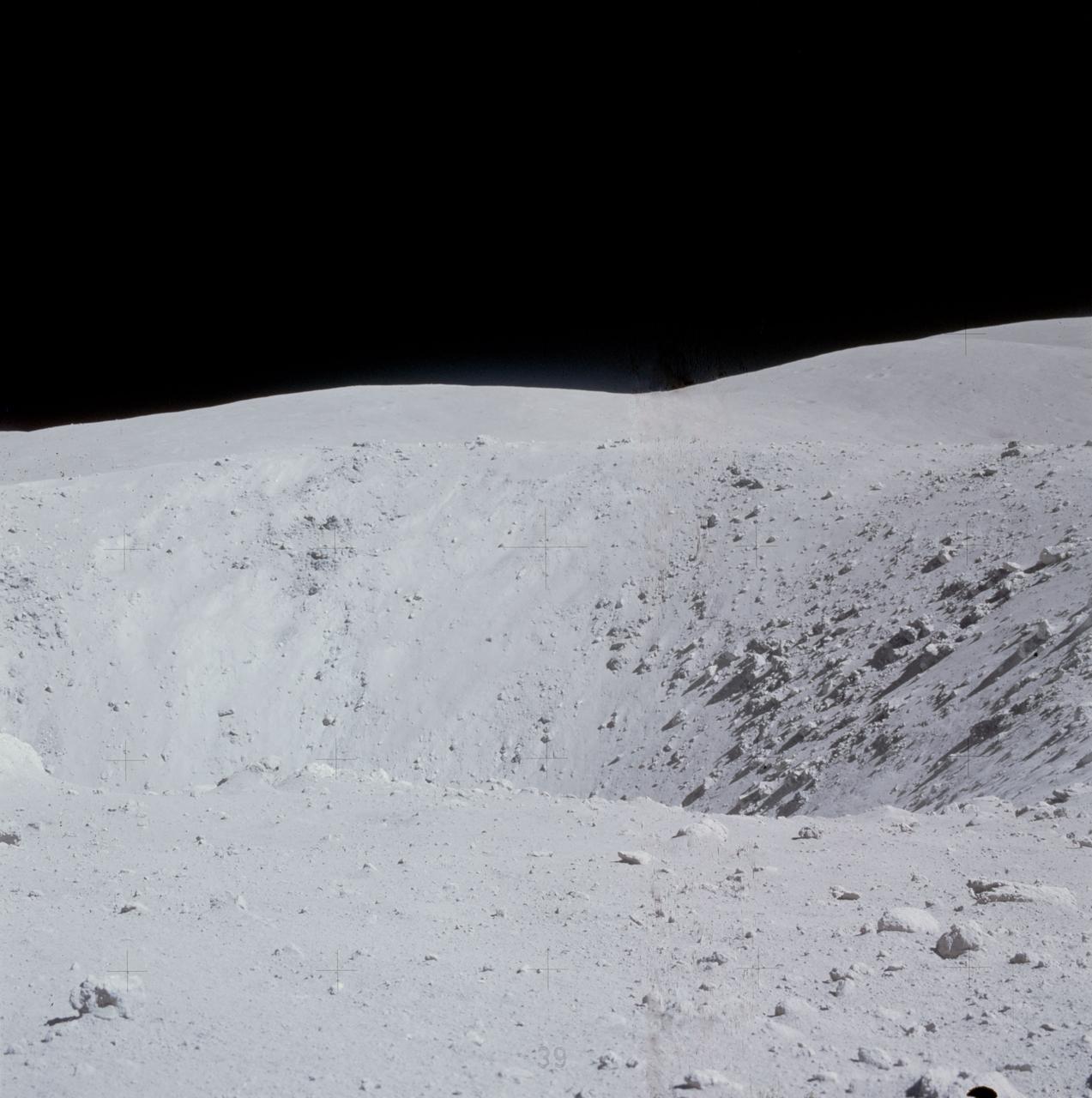

AS16-116-18599 (21 April 1972) --- A close-up view of Buster Crater, which was visited by the two moon-exploring crew men of the Apollo 16 lunar landing mission, during the first extravehicular activity (EVA), April 21, 1972. Astronaut Charles M. Duke Jr. said the crater appeared to be larger than 50 meters, and he called it a very spectacular crater. This was the second stop for astronauts John W. Young and Duke on the mission's first EVA. Young exposed this view with his 70mm Hasselblad camera. While astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.

NASA astronaut Jessica Watkins stores science payloads on Astrolab’s FLEX lunar terrain vehicle during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/Robert Markowitz
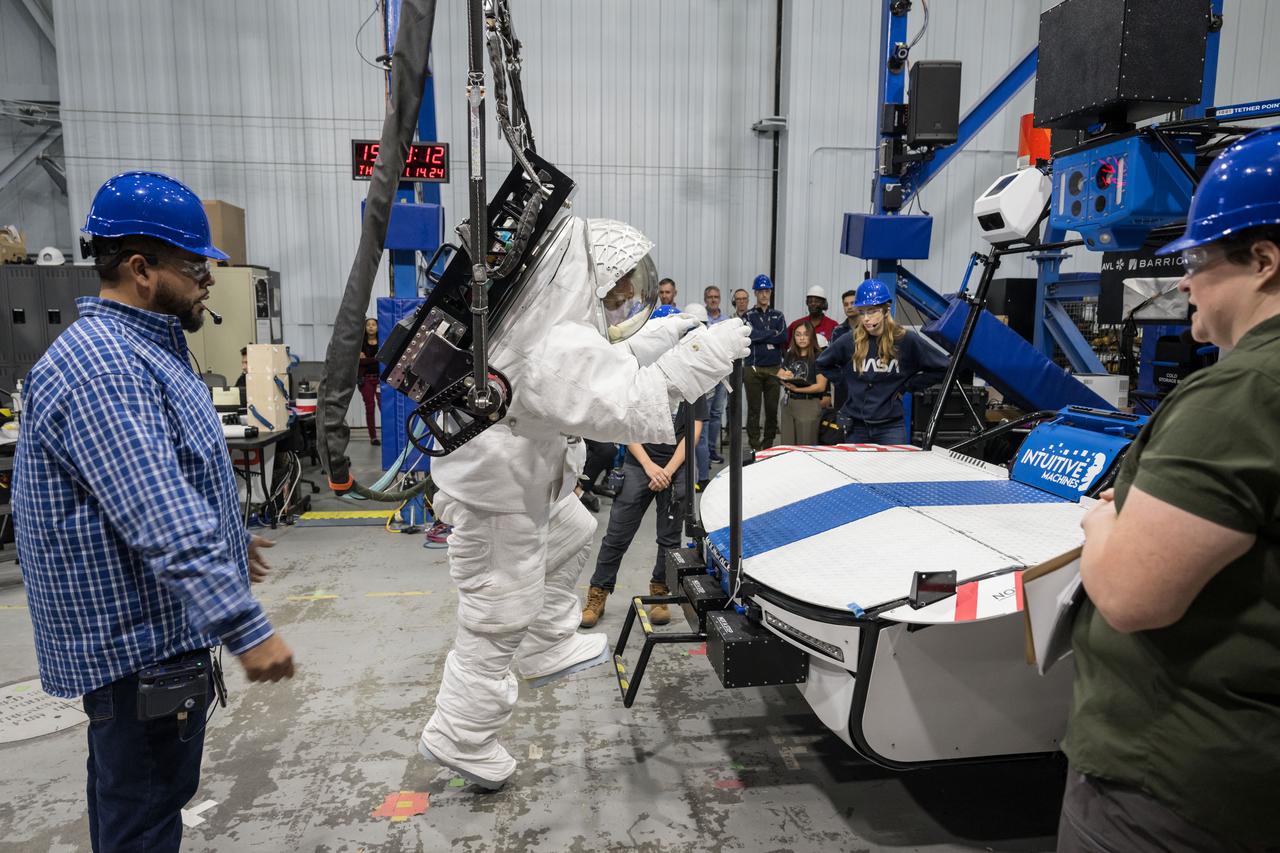

NASA astronaut Joe Acaba prepares to climb on top of Intuitive Machines’ Moon RACER lunar terrain vehicle to get to a science payload during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
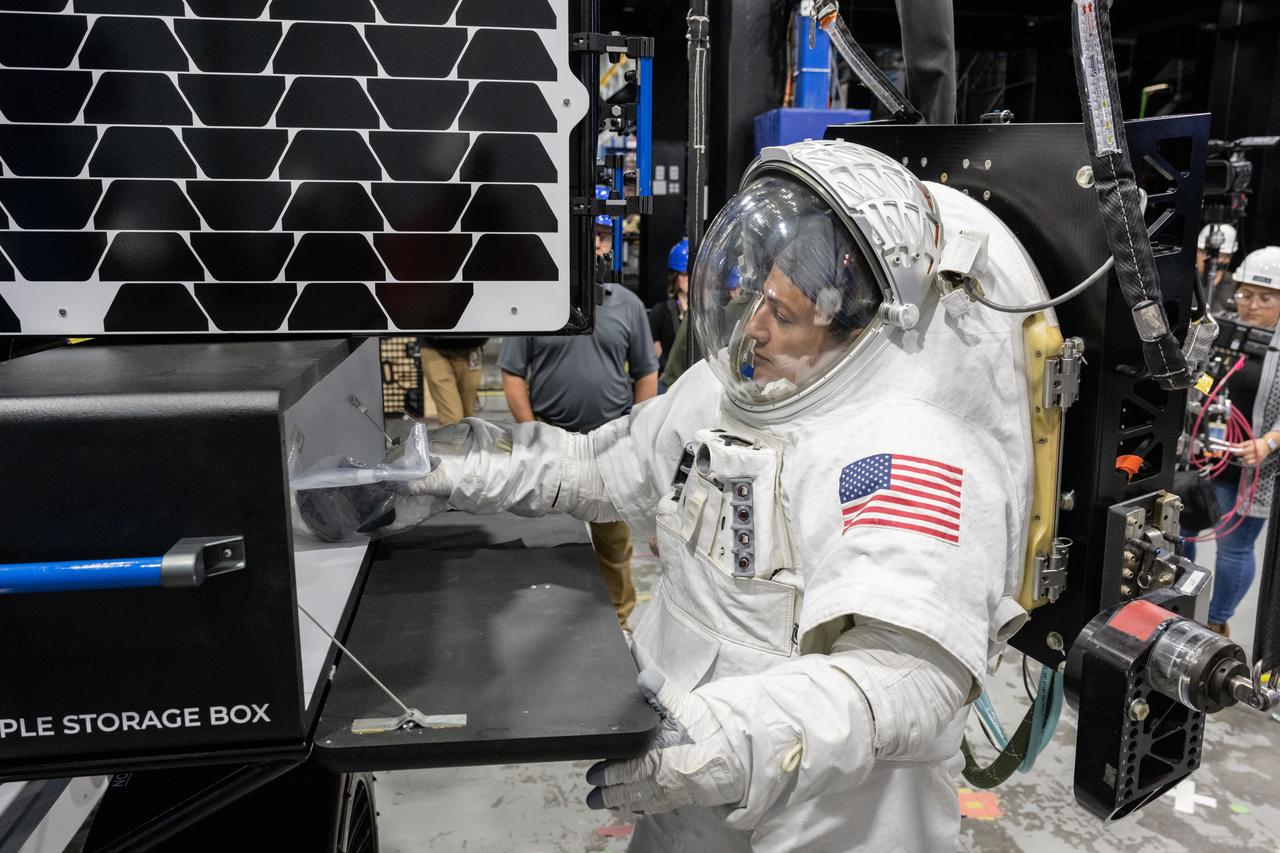

NASA astronaut Jessica Meir puts a science sample inside of a storage box on Intuitive Machines’ Moon RACER lunar terrain vehicle during testing at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Image Credit: NASA/James Blair
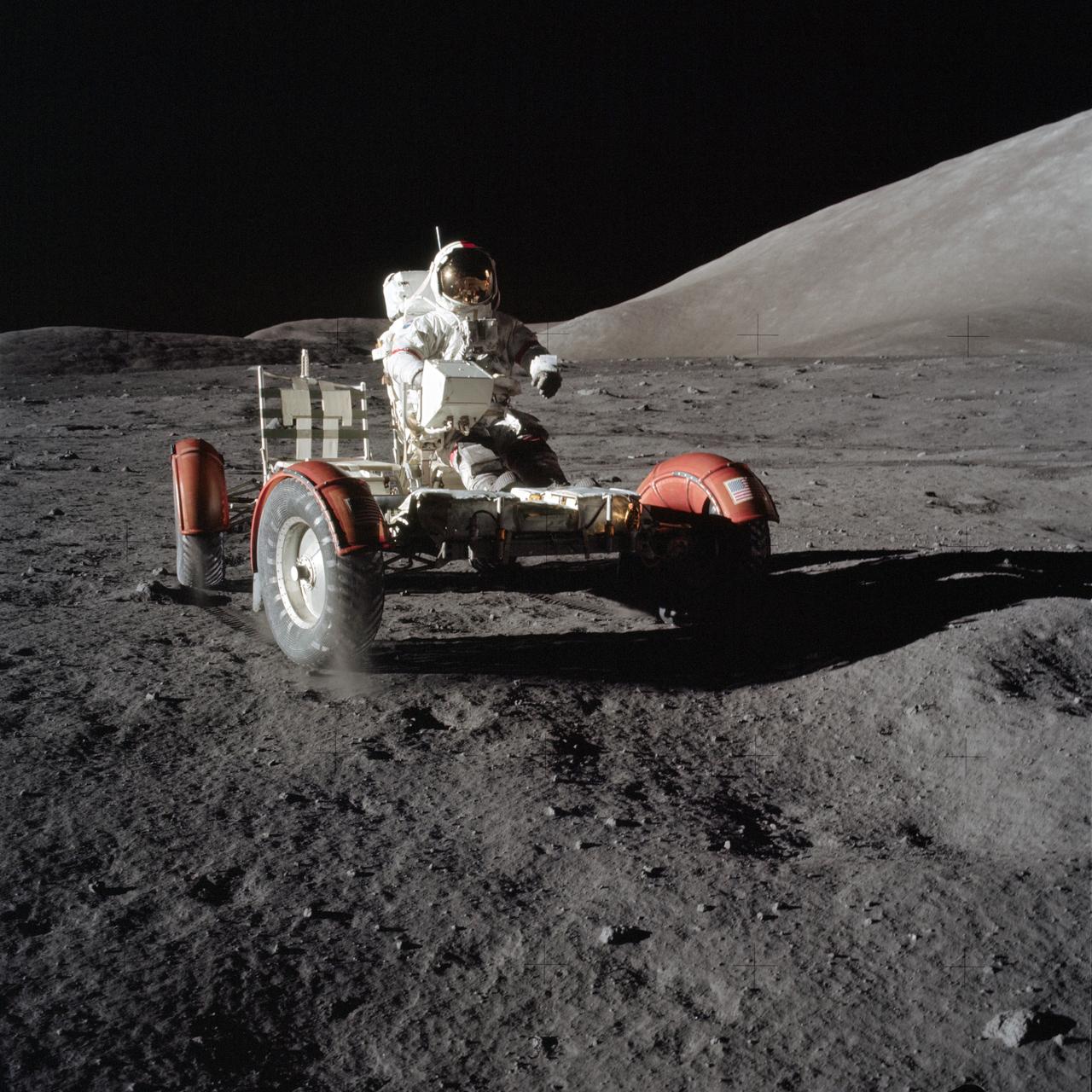

AS17-147-22526 (11 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander, makes a short checkout of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the early part of the first Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. This view of the "stripped down" LRV is prior to loading up. Equipment later loaded onto the LRV included the ground-controlled television assembly, the lunar communications relay unit, hi-gain antenna, low-gain antenna, aft tool pallet, lunar tools and scientific gear. This photograph was taken by scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. The mountain in the right background is the east end of South Massif. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
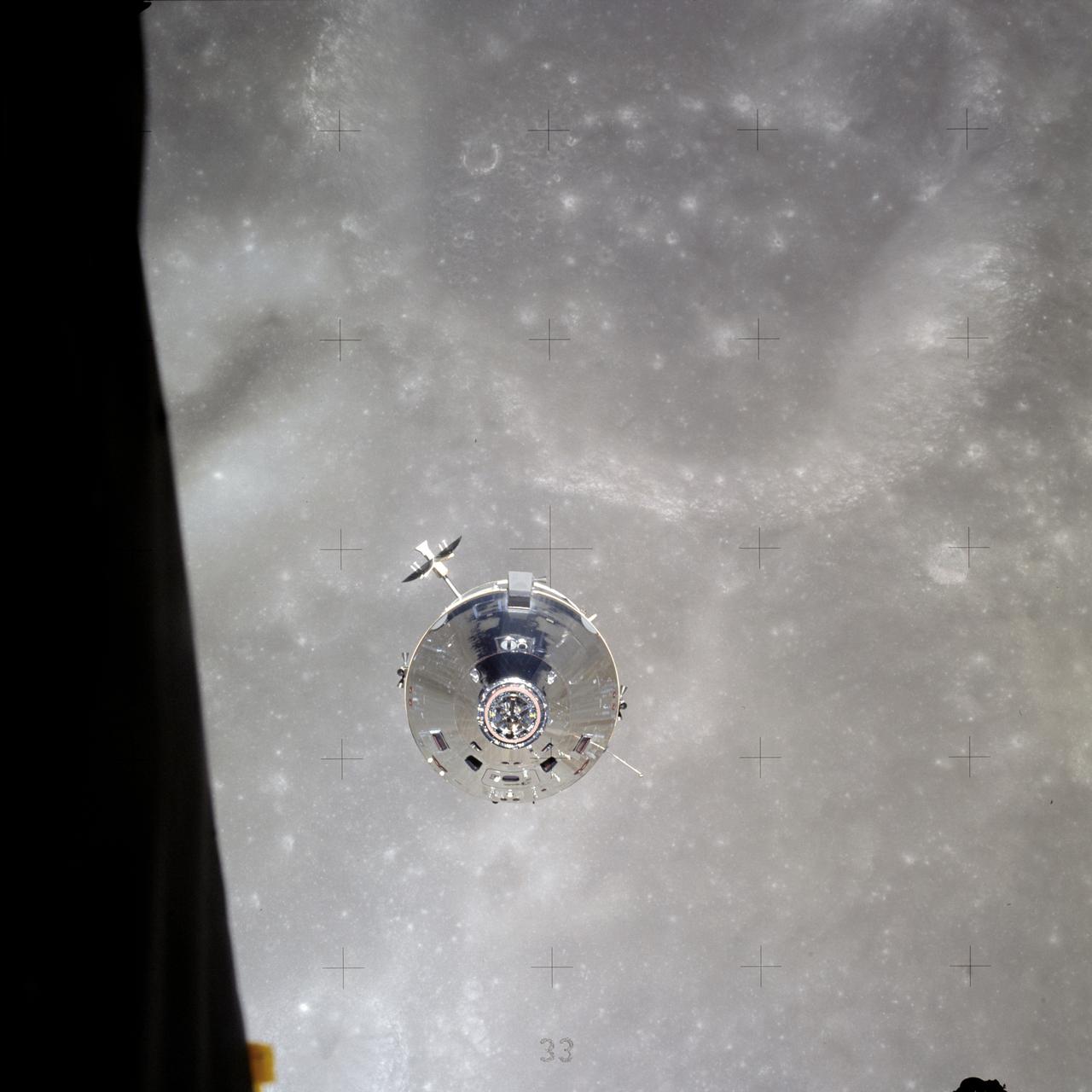

AS16-113-18282 (23 April 1972) --- The Apollo Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" approaches the Lunar Module (LM) "Orion", from which this photograph was made. The two spacecraft are about to make their final rendezvous of the mission, on April 23, 1972. Astronauts John W. Young, commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard the LM, were returning to the CSM, in lunar orbit, after three successful days on the lunar surface. Astronaut Thomas K. (Ken) Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the CSM in lunar orbit, while Young and Duke descended in the LM to explore the Descartes region of the moon.
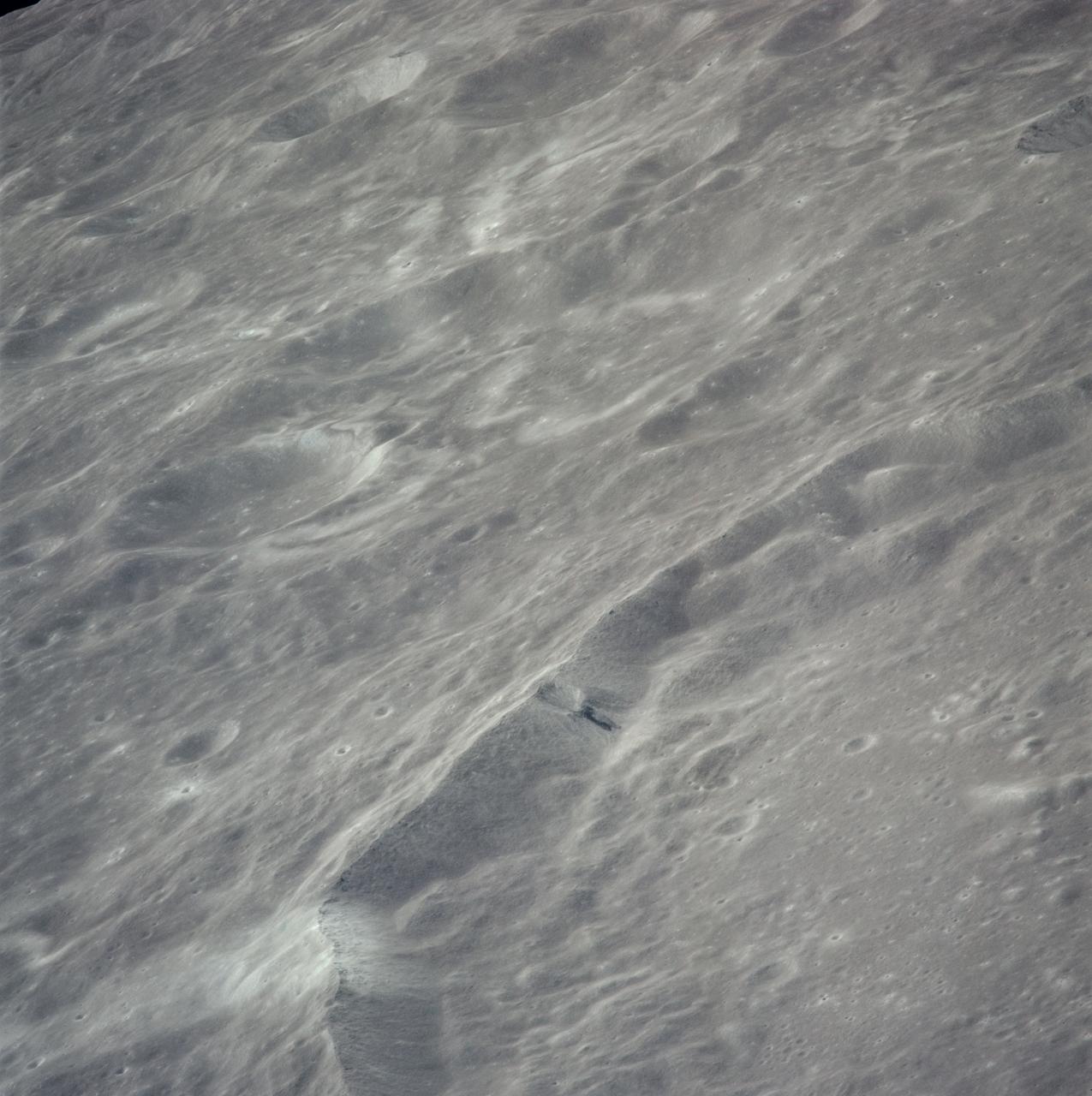

AS16-121-19407 (April 1972) --- An oblique view of a rim of Guyot Crater on the lunar farside, as photographed from the Apollo 16 spacecraft in lunar orbit. The coordinates of the center of Guyot Crater are 116.5 degrees east longitude and 10.5 degrees north latitude. Note the black coloration which appears to be lava flow down the side of the crater rim. While astronauts John W. Young, commander; and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands site on the moon, astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
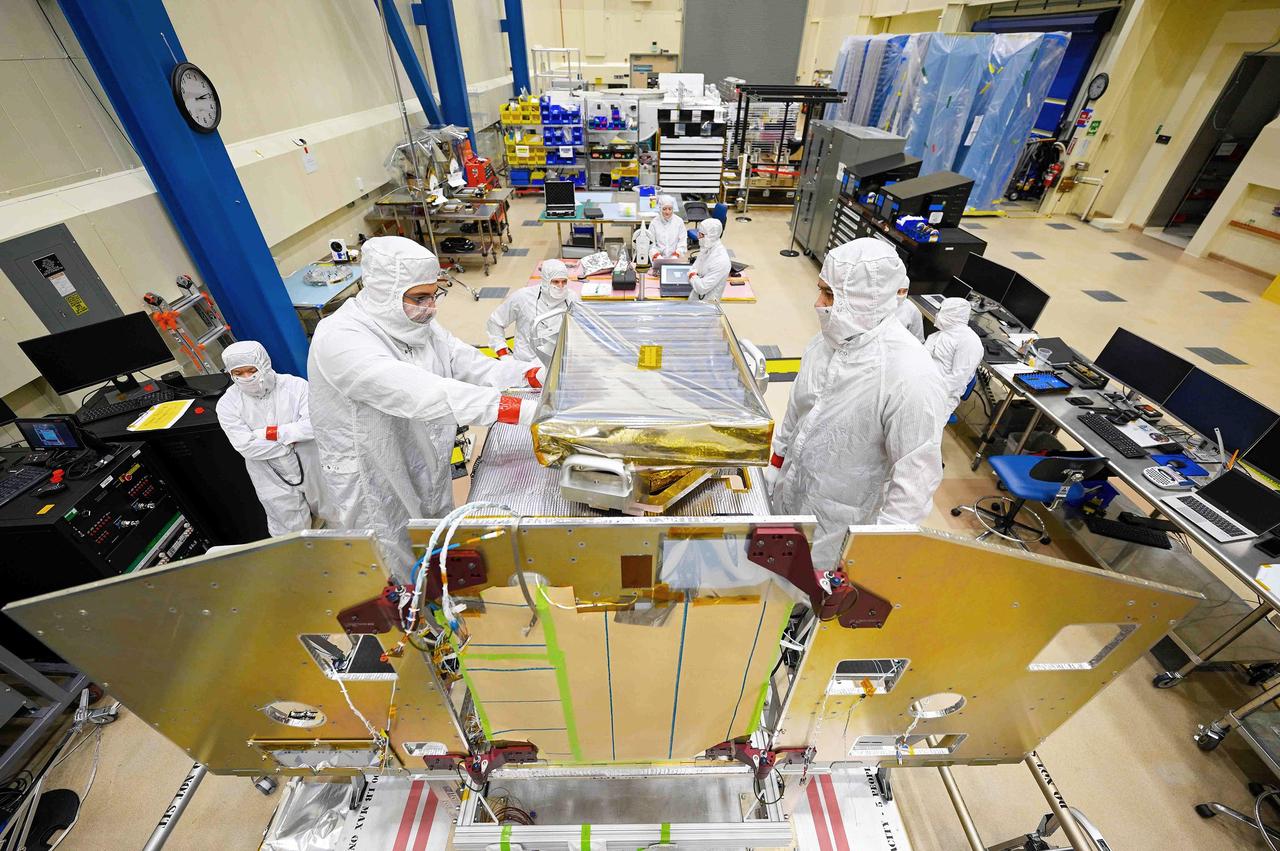

Engineers work on the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) for NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft in a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, shortly after the instrument was delivered there in December 2022. The large silver grate wrapped in transparent plastic in the center of the image is the radiator that will maintain the instrument's temperature when in space. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that was developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. It was shipped from JPL to Lockheed Martin Space, where it was integrated with the spacecraft. HVM³ is one of two instruments that will be used by the mission to detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25254
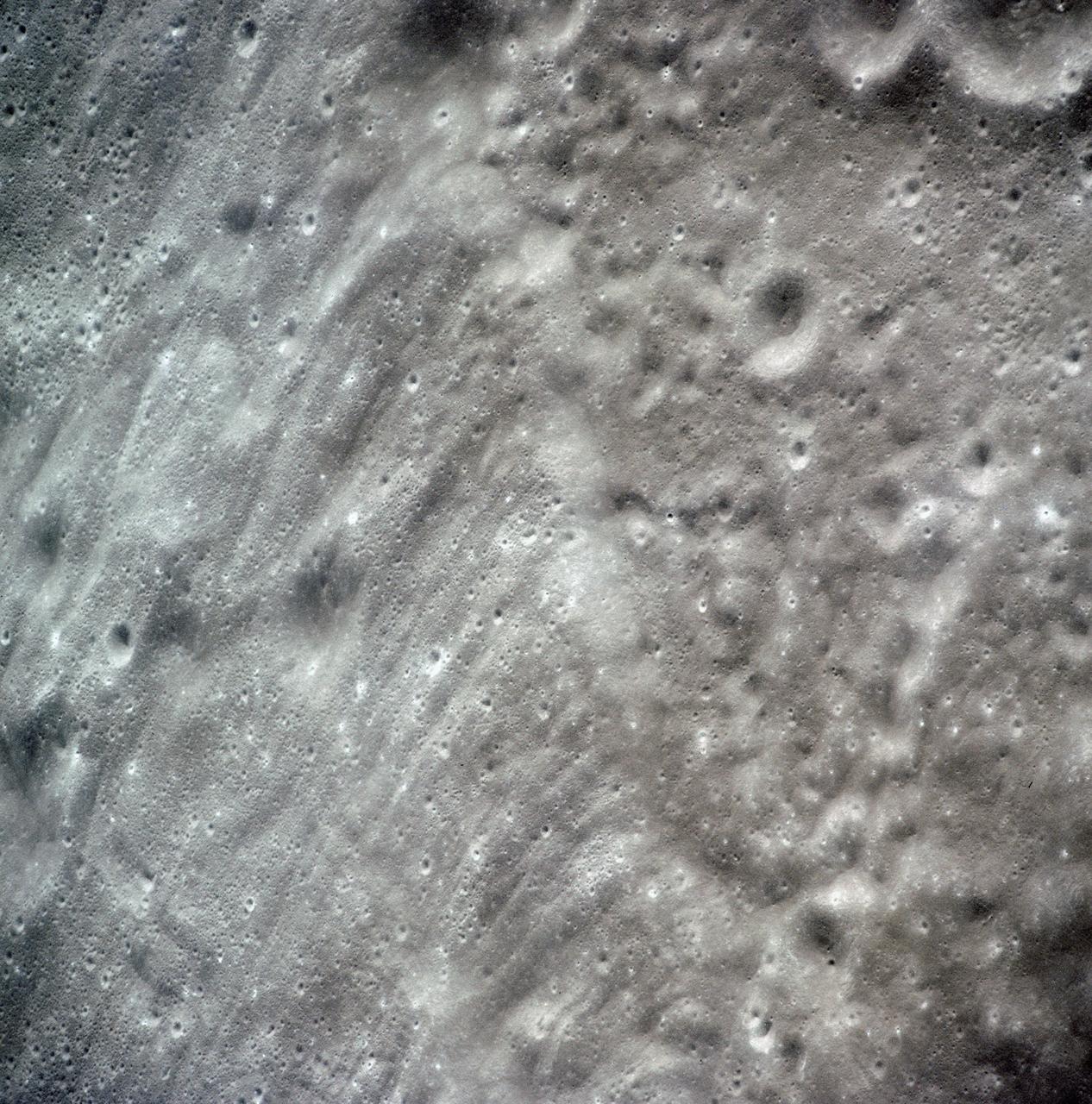

AS15-97-13168 (31 July-2 Aug. 1971) --- A view of the flow structure on the rim and edge of the crater Tsiolkovsky in the highlands of the lunar farside, as photographed from lunar orbit by astronaut Alfred M. Worden in the Apollo 15 Command and Service Module (CSM). Note the scarp at the edge of the flow and elongated grooves on the flow surface. While astronauts David R. Scott and James B. Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Falcon" to explore the moon's Hadley-Apennine landing site, Worden remained with the CSM in lunar orbit.
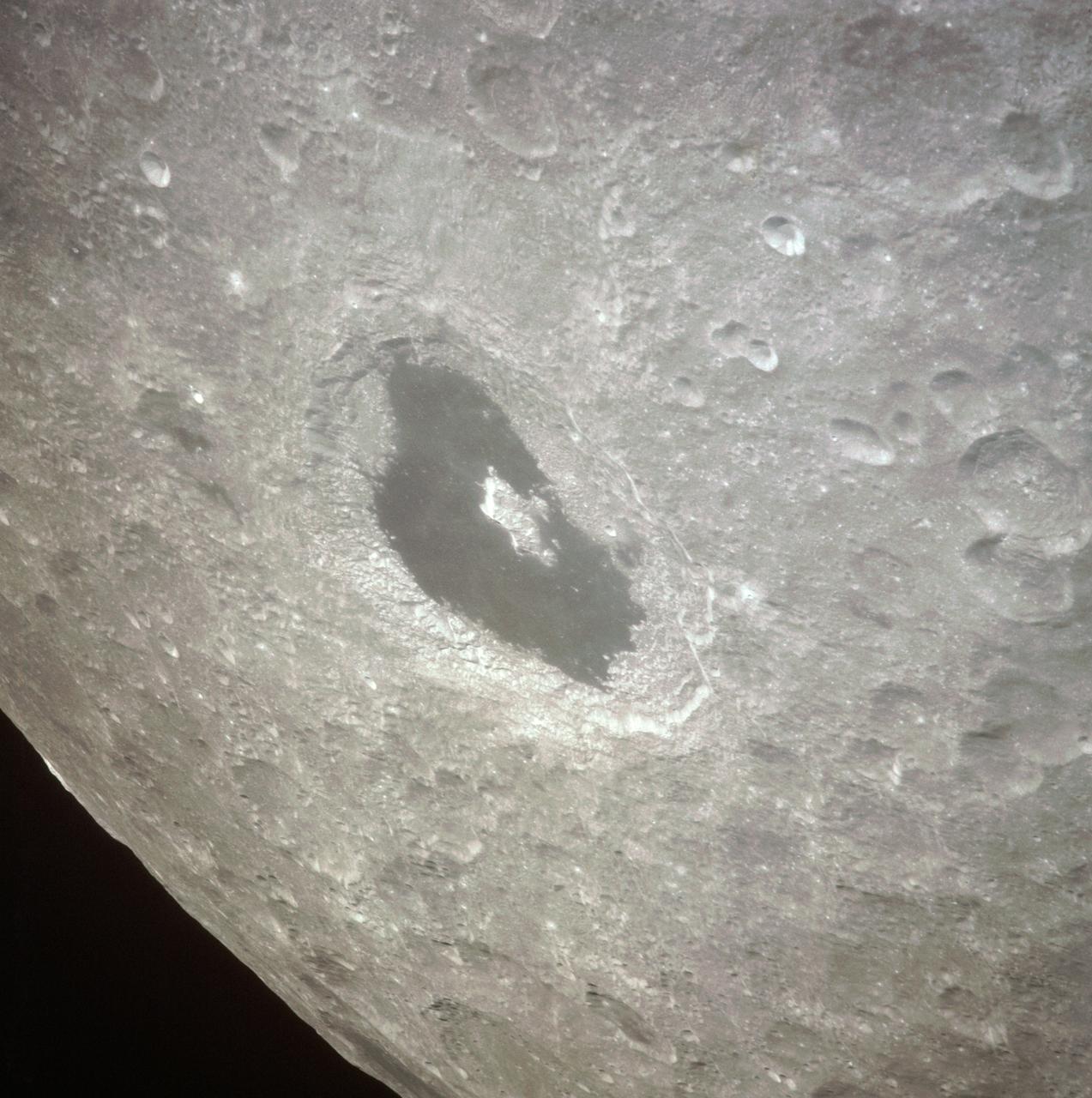

AS13-60-8659 (14 April 1970) --- Excellent view of the lunar farside showing the crater Tsiolkovsky, as photographed by the crew of the Apollo 13 mission during their lunar pass. The view is looking southeast toward the lunar horizon. The approximate coordinates of Tsiolkovsky are 128.5 degrees east longitude and 20.5 degrees south latitude. The Apollo 13 crew members were forced to cancel their scheduled lunar landing because of an apparent explosion of oxygen tank number two in the Service Module (SM).
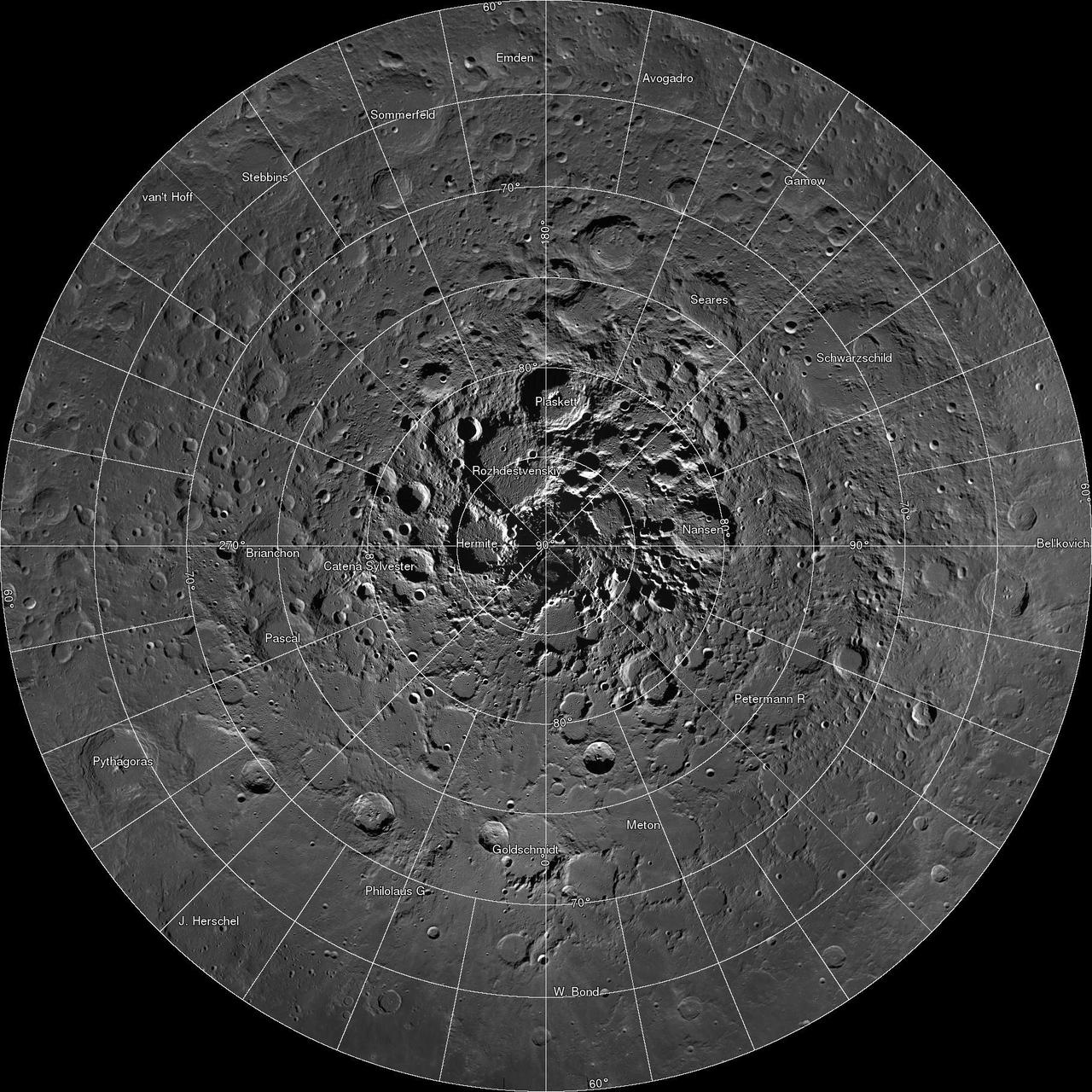

Scientists, using cameras aboard NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter LRO, have created the largest high resolution mosaic of our moon north polar region.
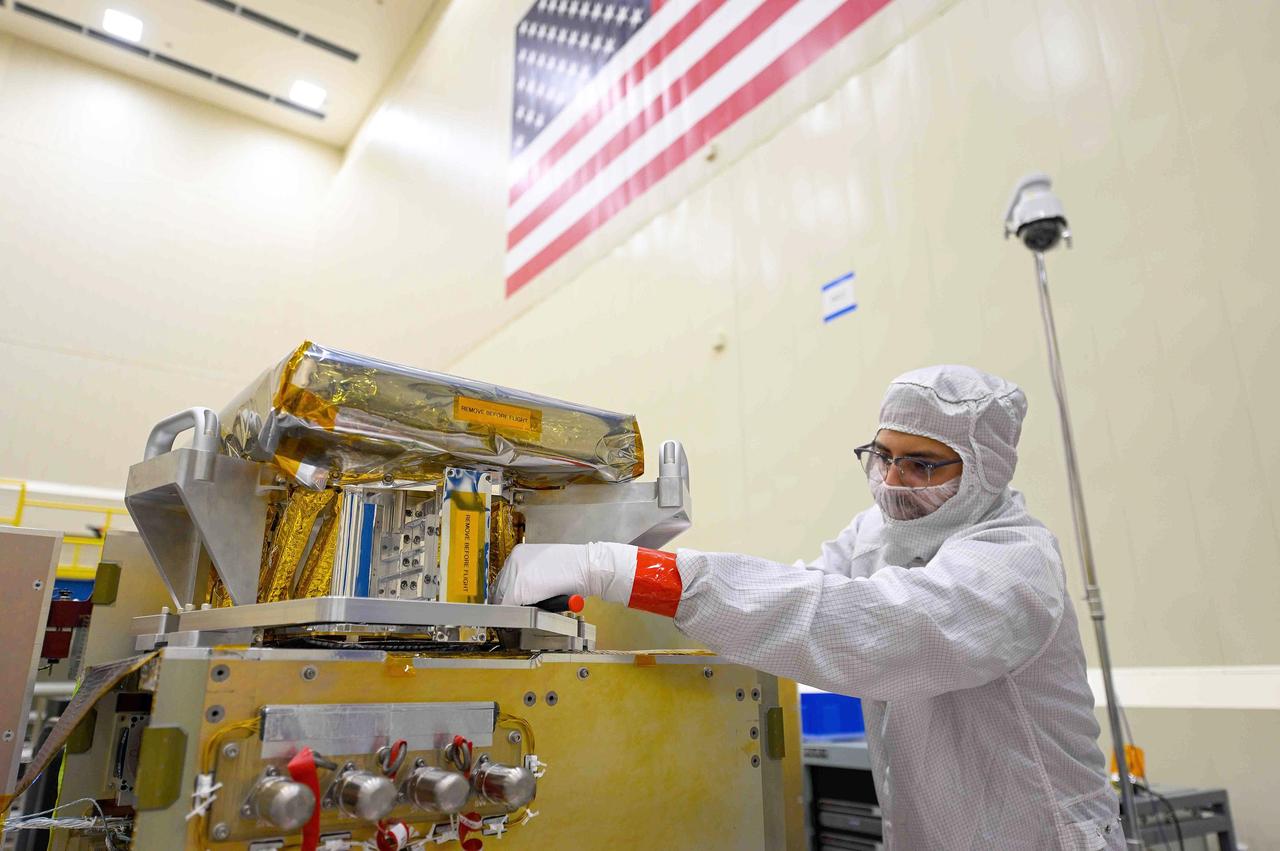

An engineer works on the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) for NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft in a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, shortly after the instrument delivered in December 2022. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that was developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. It was shipped from JPL to Lockheed Martin Space, where it was integrated with the spacecraft. HVM³ is one of two instruments that will be used by the mission to detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25255
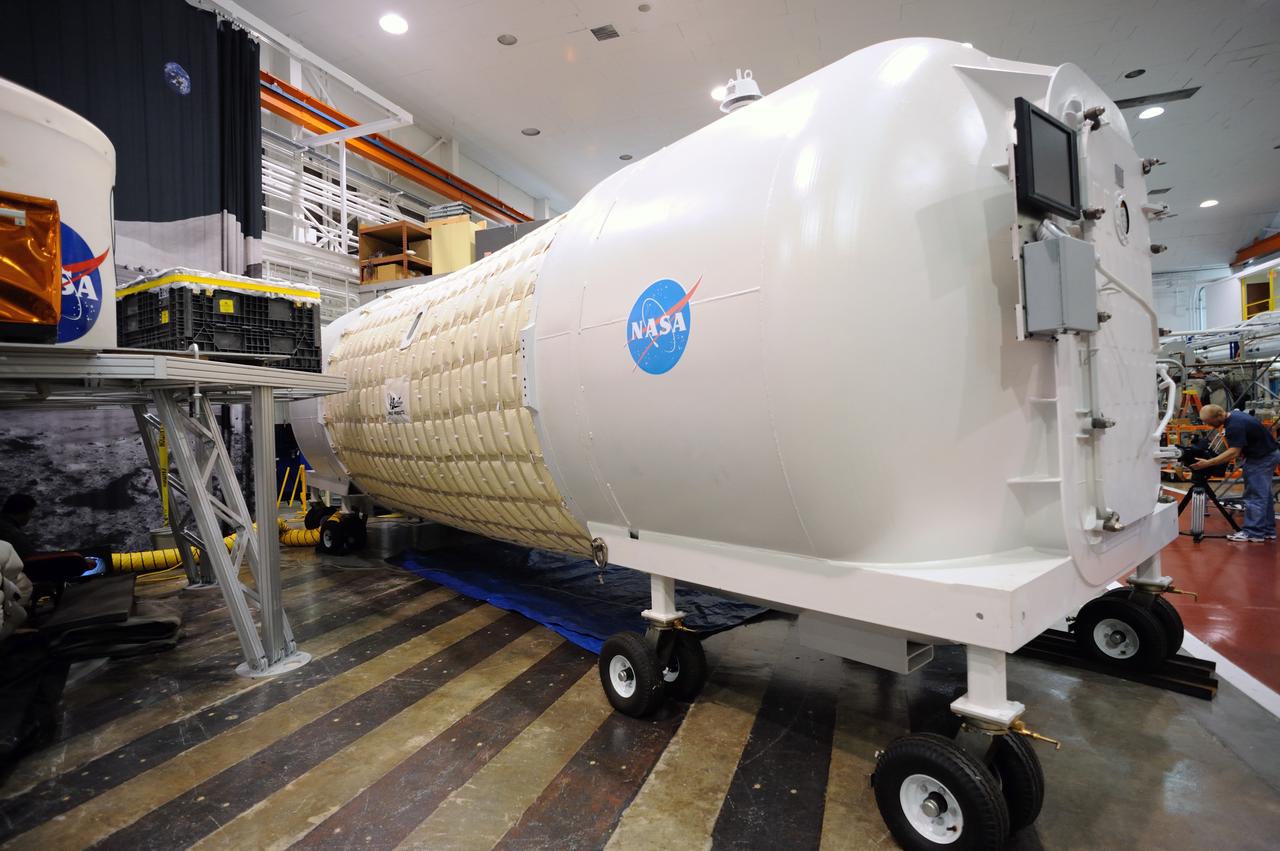

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
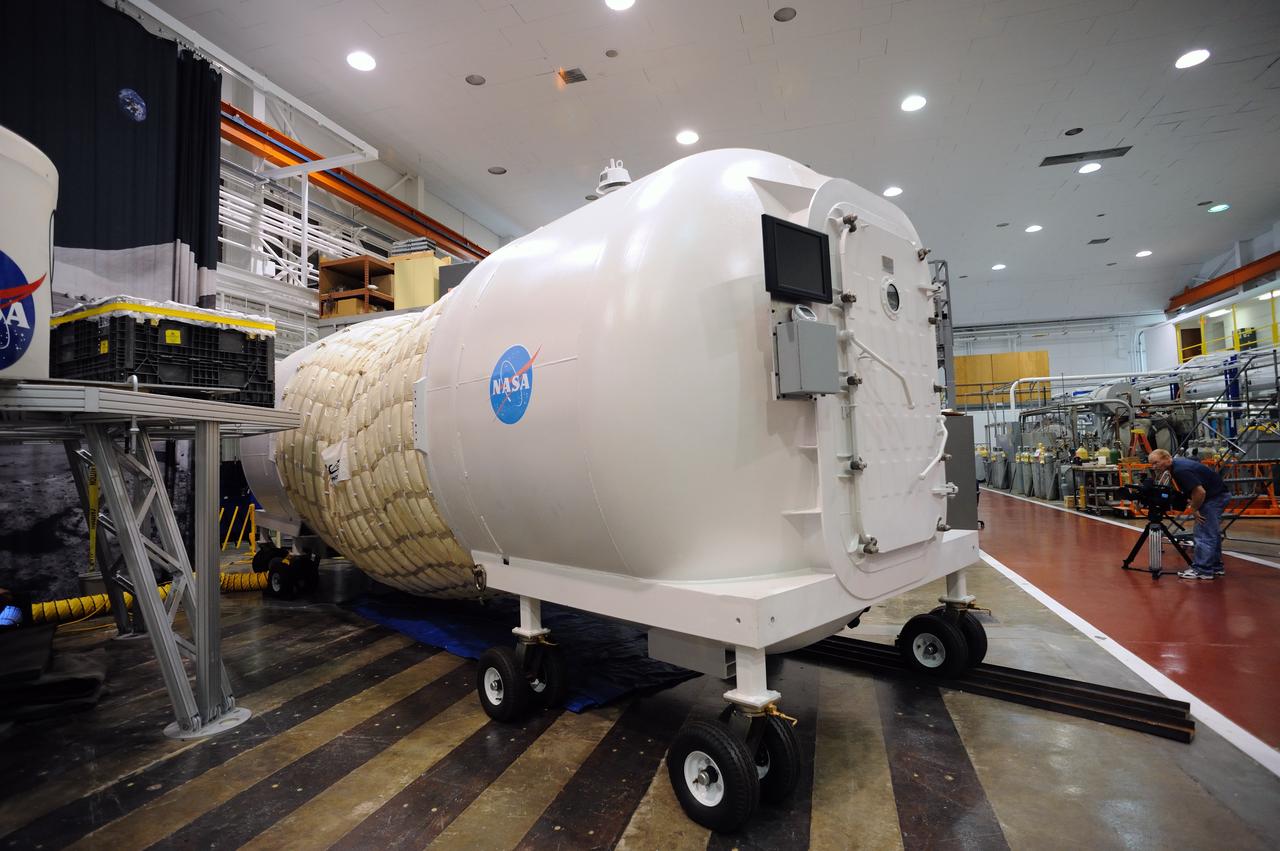

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
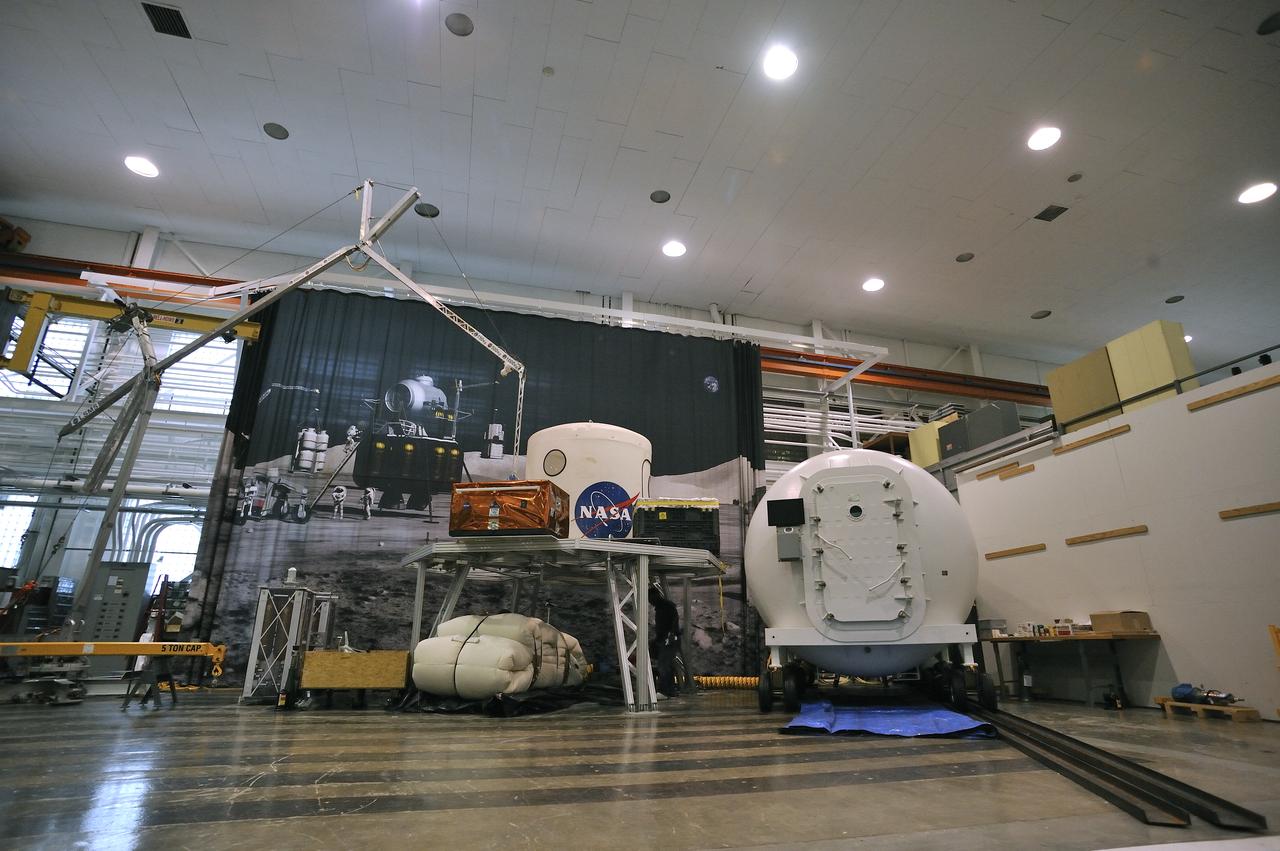

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
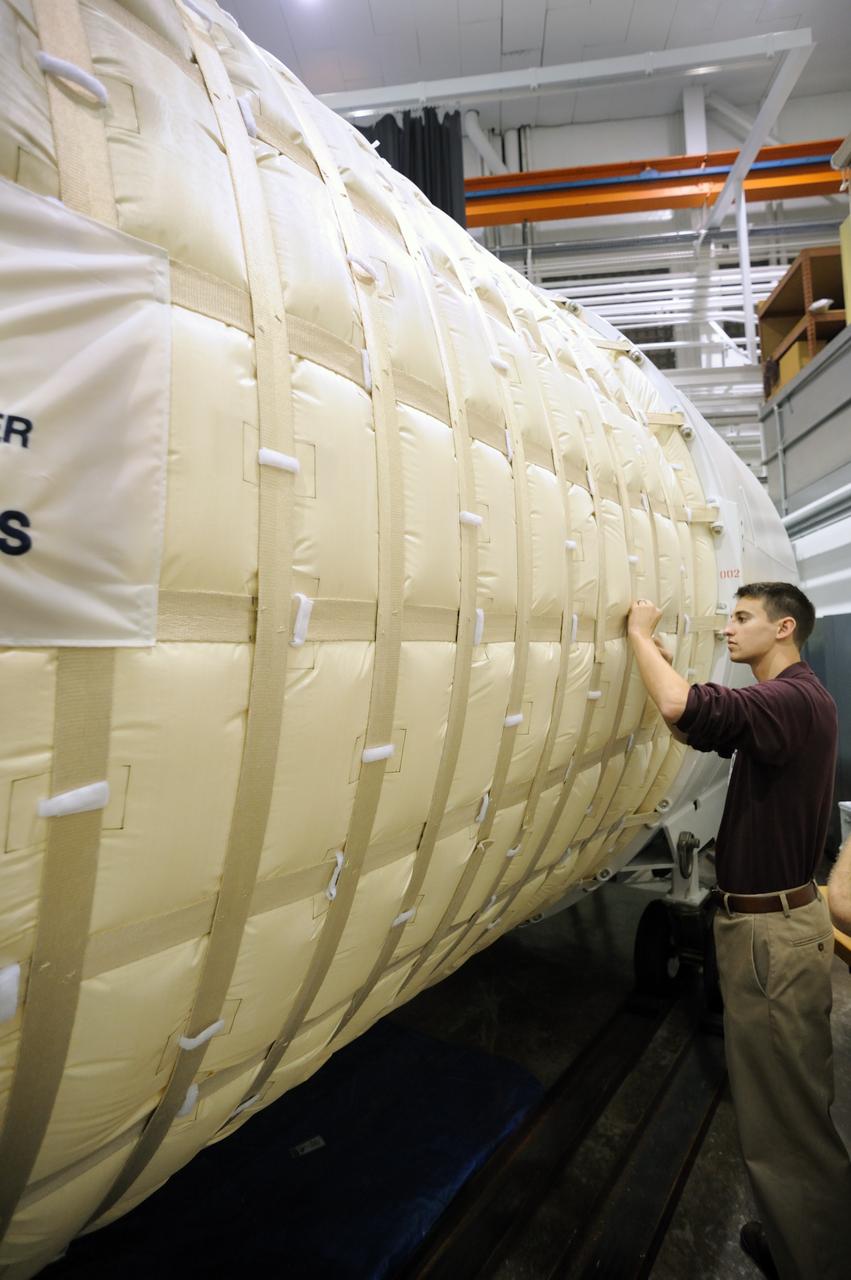

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.
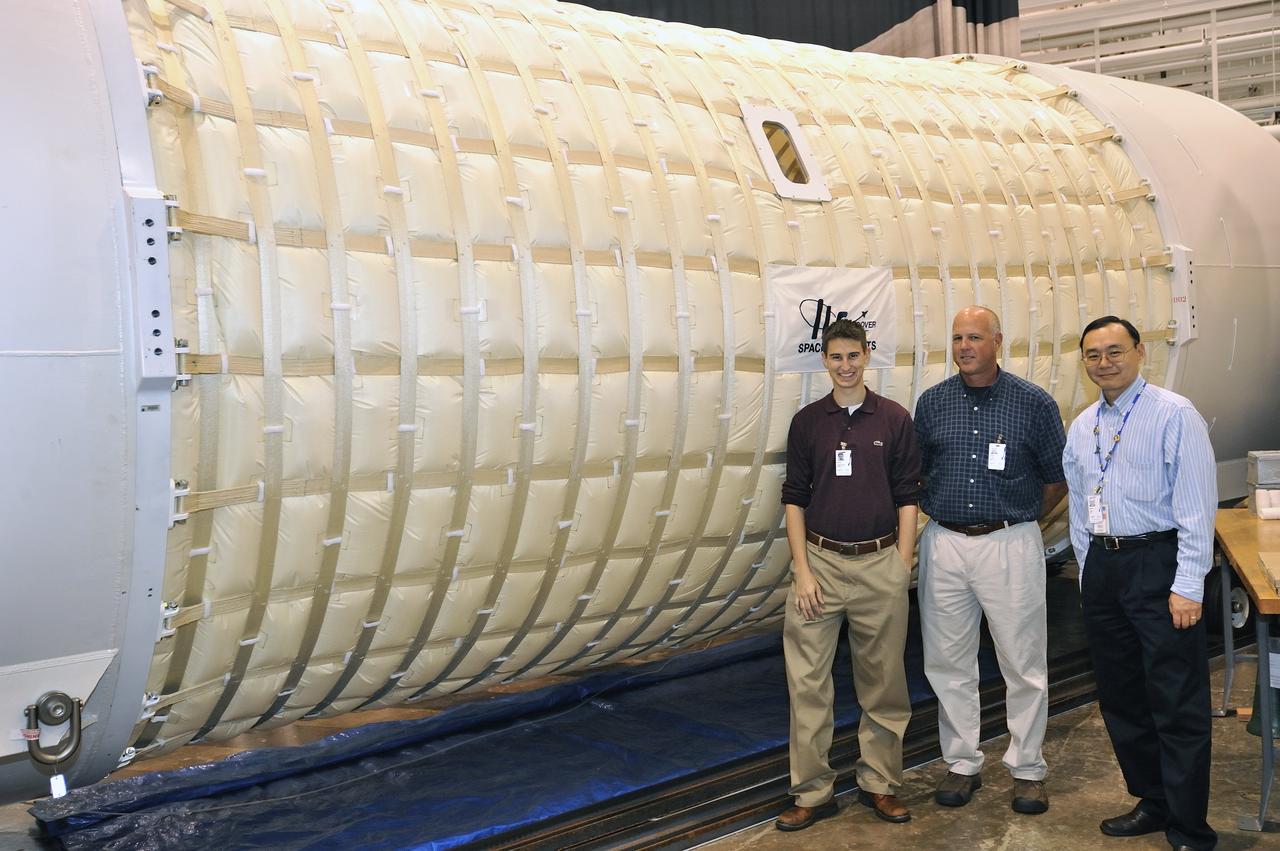

Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab).ILC Dover, under contract by NASA Langley Research Center, and in cooperation with NASA Johnson Space Center has designed and manufactured an expandable lunar habitat. This cylindrical habitat, or Expandable Lunar Habitat (X-Hab) is a hybrid system with two hard end caps and a deployable softgoods section in the center.