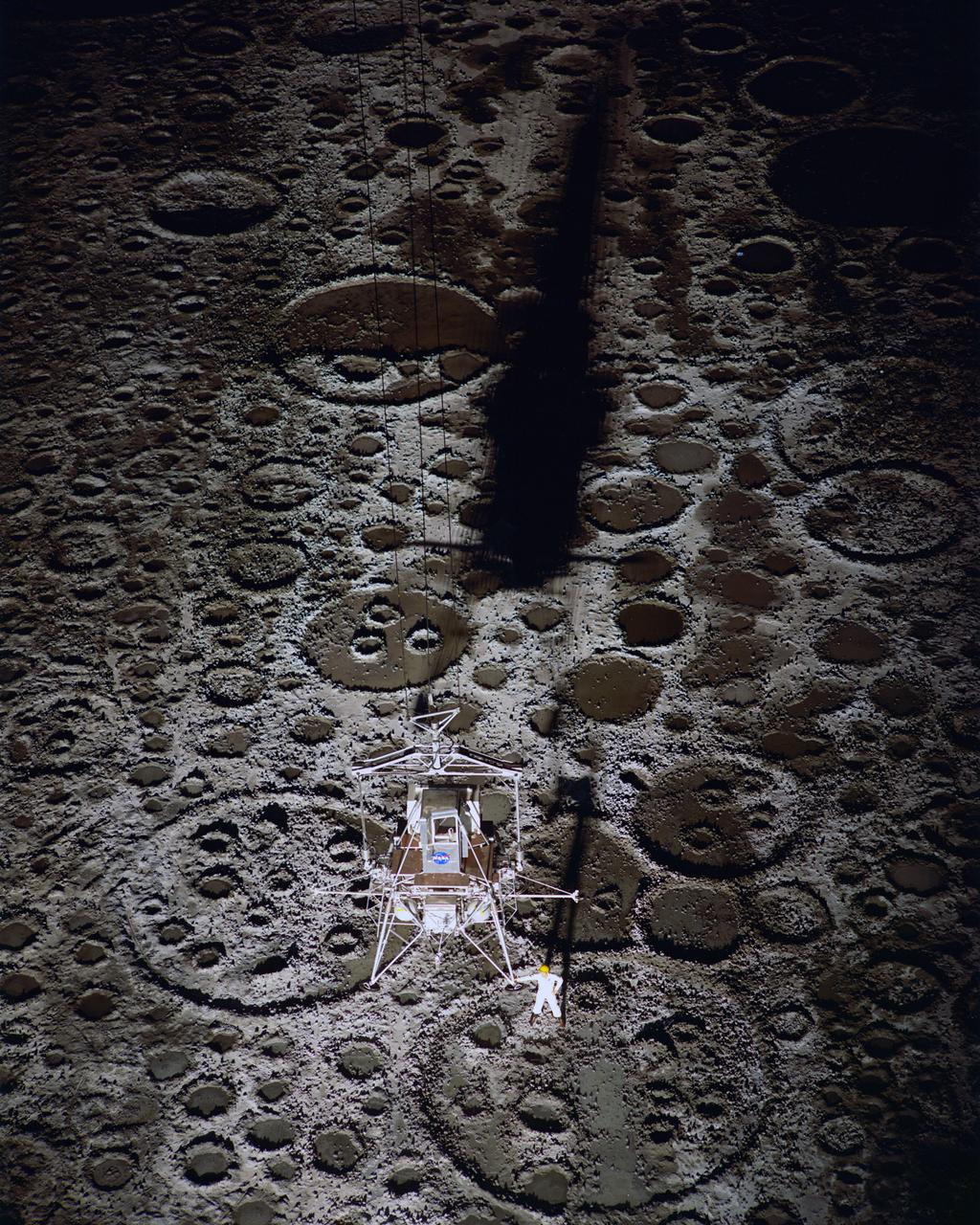

Lunar Landing Module photographed at night at the Lunar Landing Research Facility. Gantry facility 1297.
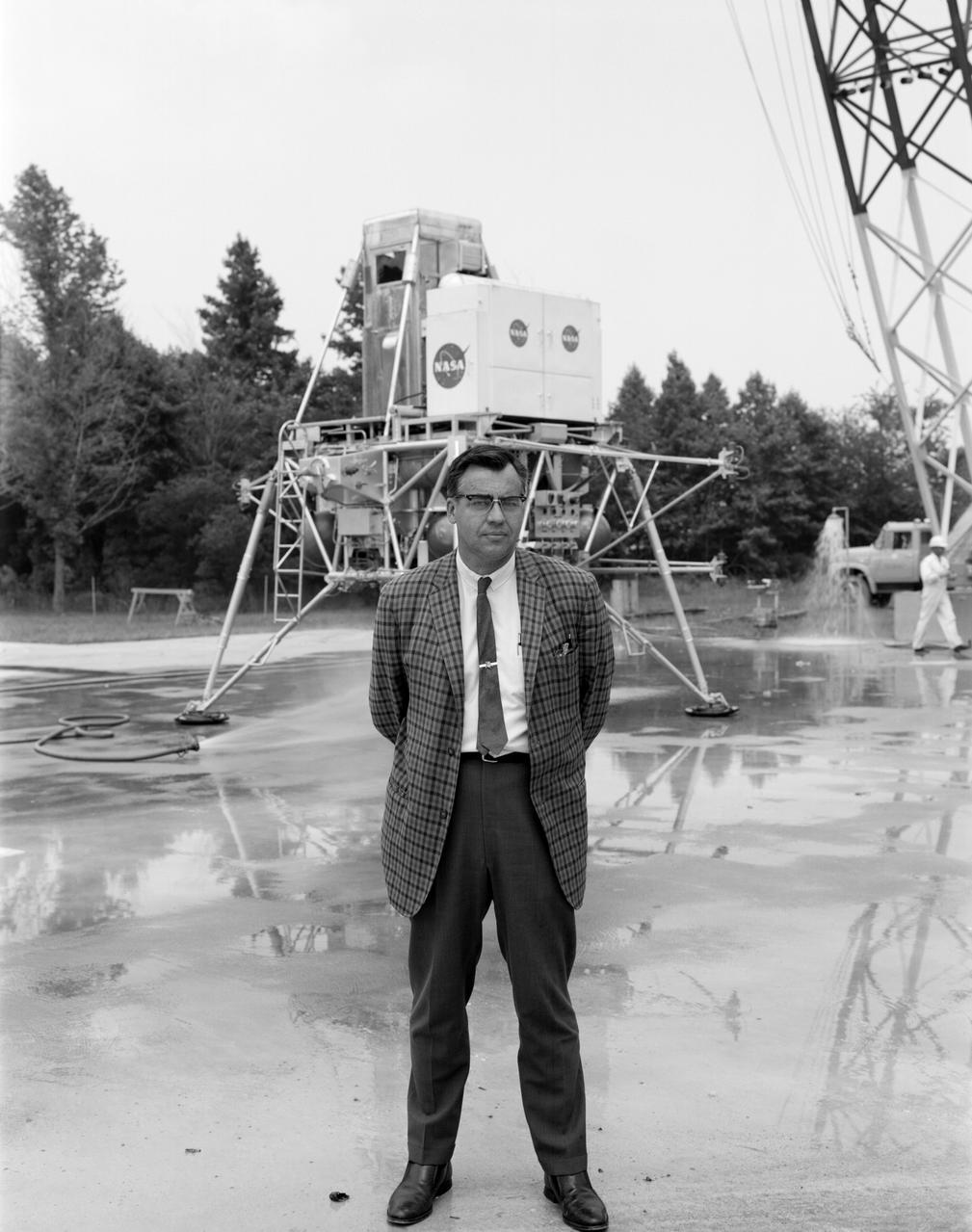

Donald Hewes at Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF). Donald Hewes, head of the Spacecraft Research Branch, managed the facility. Piles of cinders simulated the lunar craters and terrain features. Published in the book " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers. pg. 97
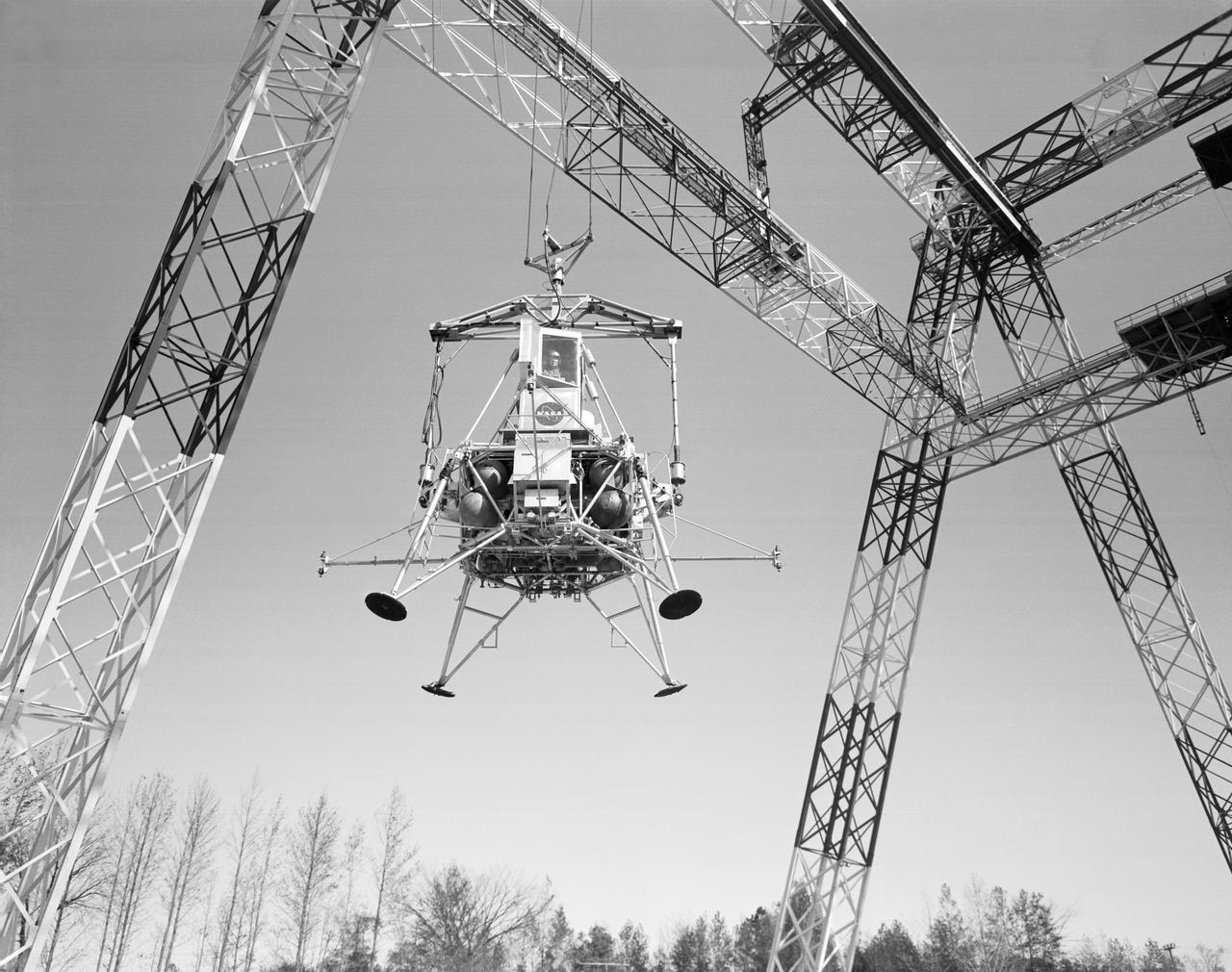

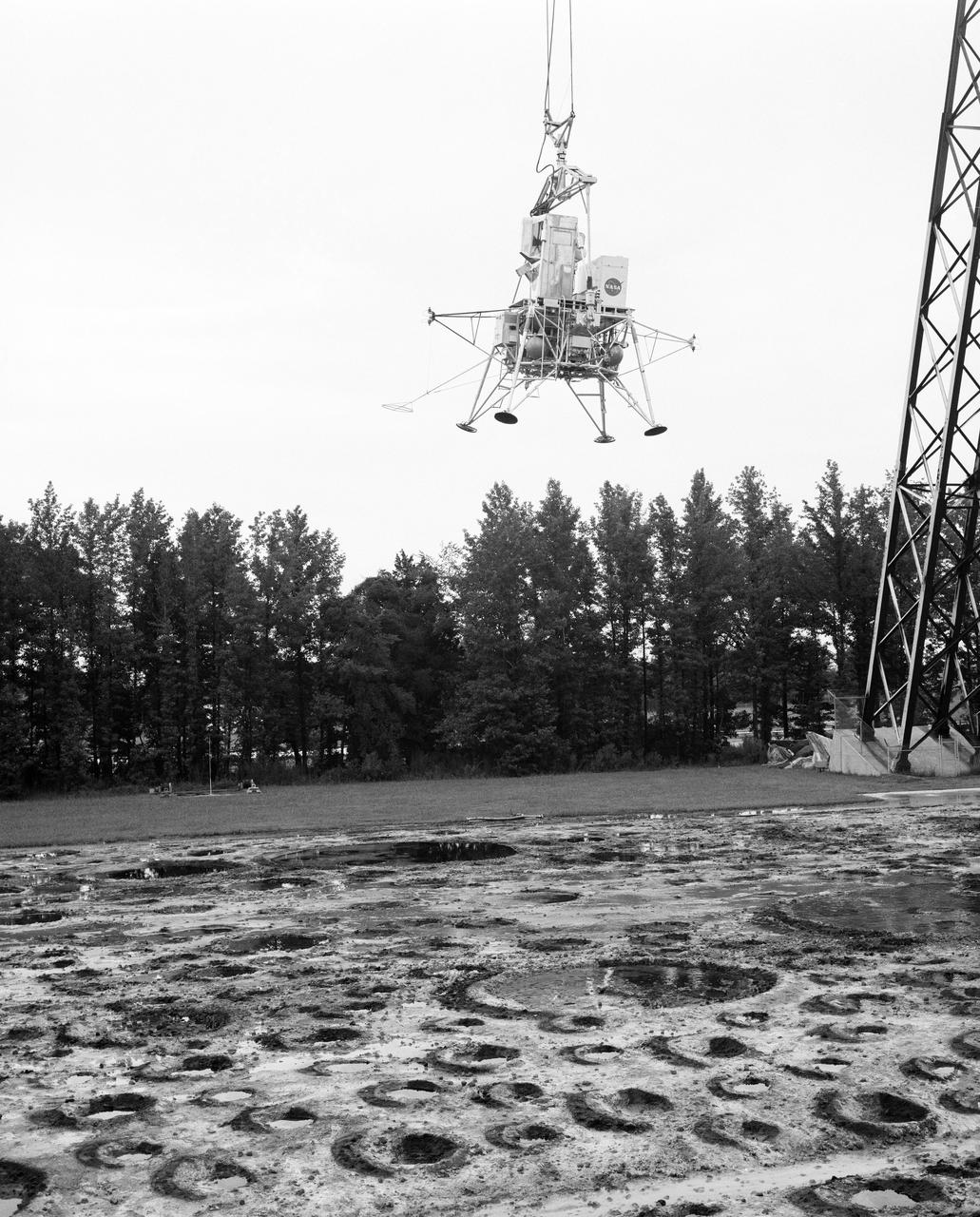
Lunar landing test of LEM at LLRF Lunar Landing Research Facility: A NASA Langley research pilot flies a lunar lander in a test conducted in the Lunar Landing Research Facility.
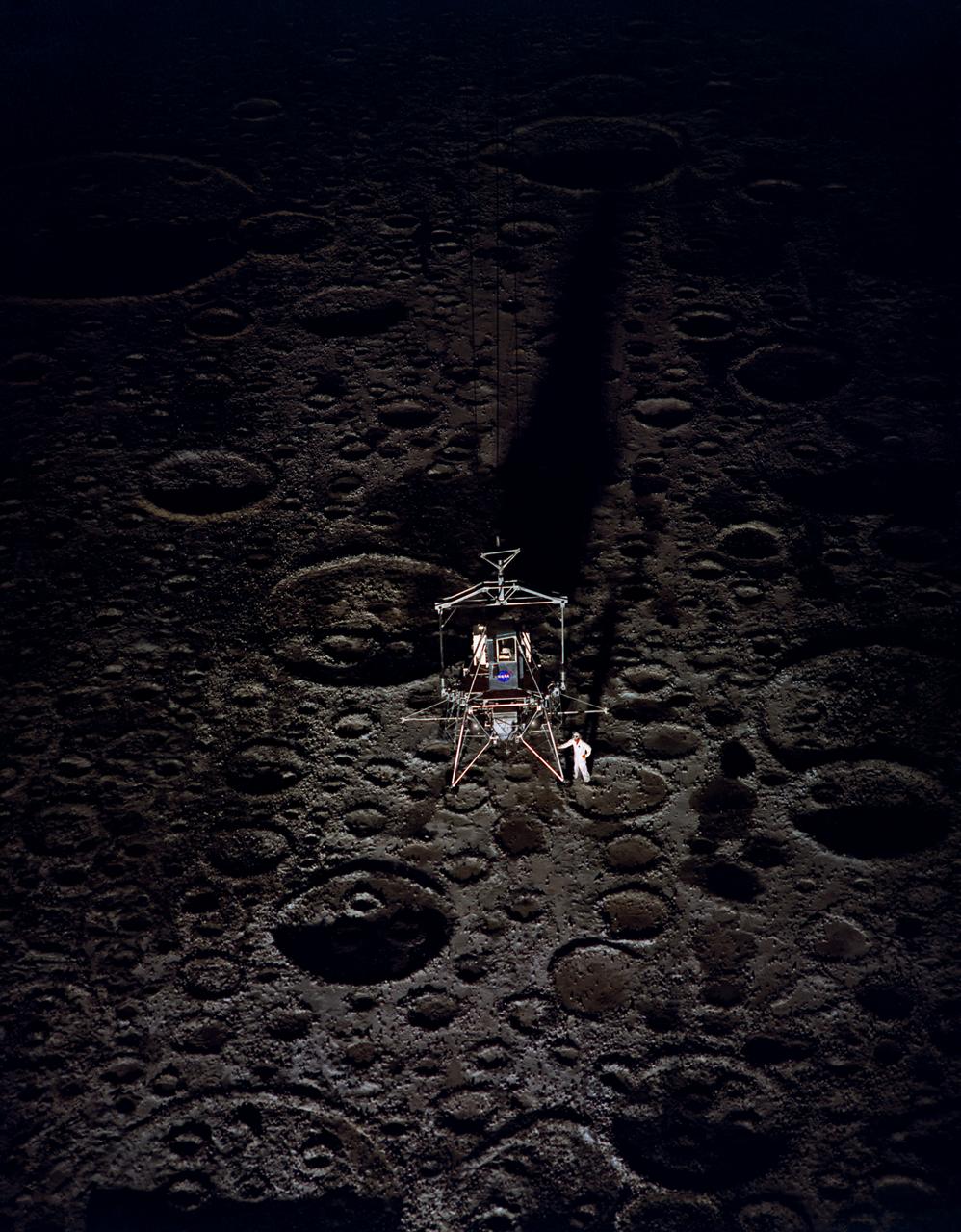

Lunar Landing Module photographed at night at the Lunar Landing Research Facility. Gantry facility 1297. Upright cockpit design lander over moonscape pavement at LLRF. 69-4872 was published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary Publication of NASA, P.88, by James Schultz.
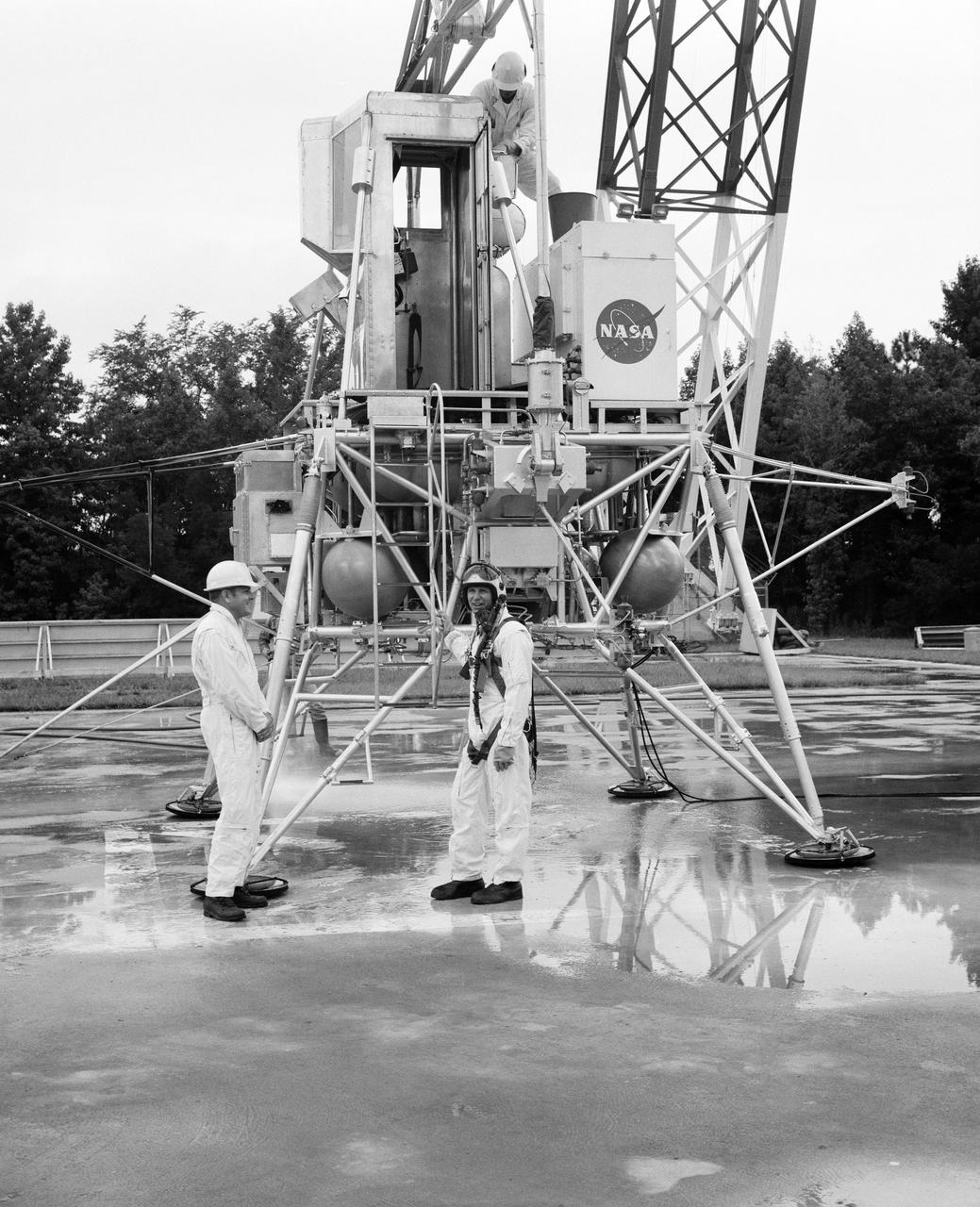

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
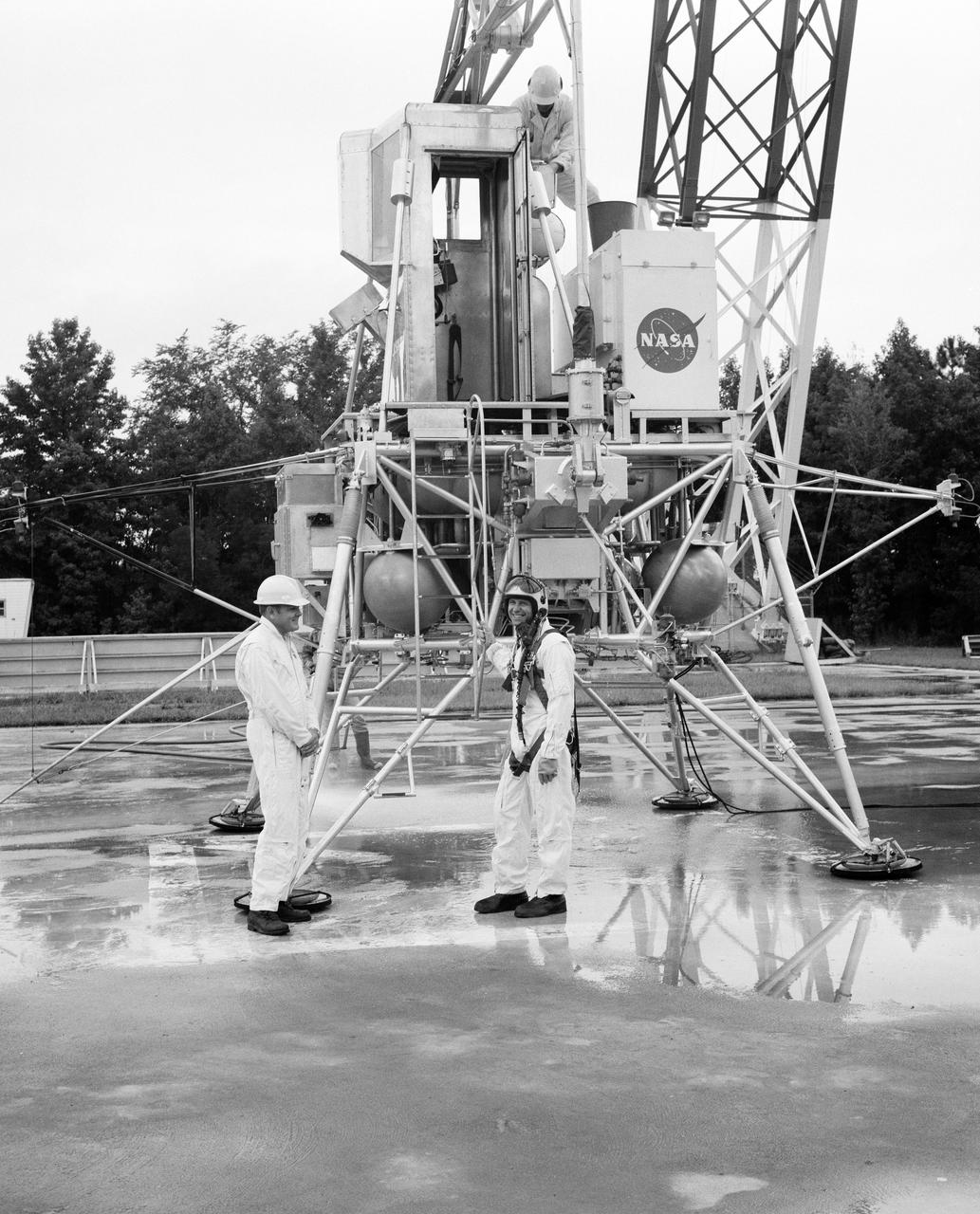

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
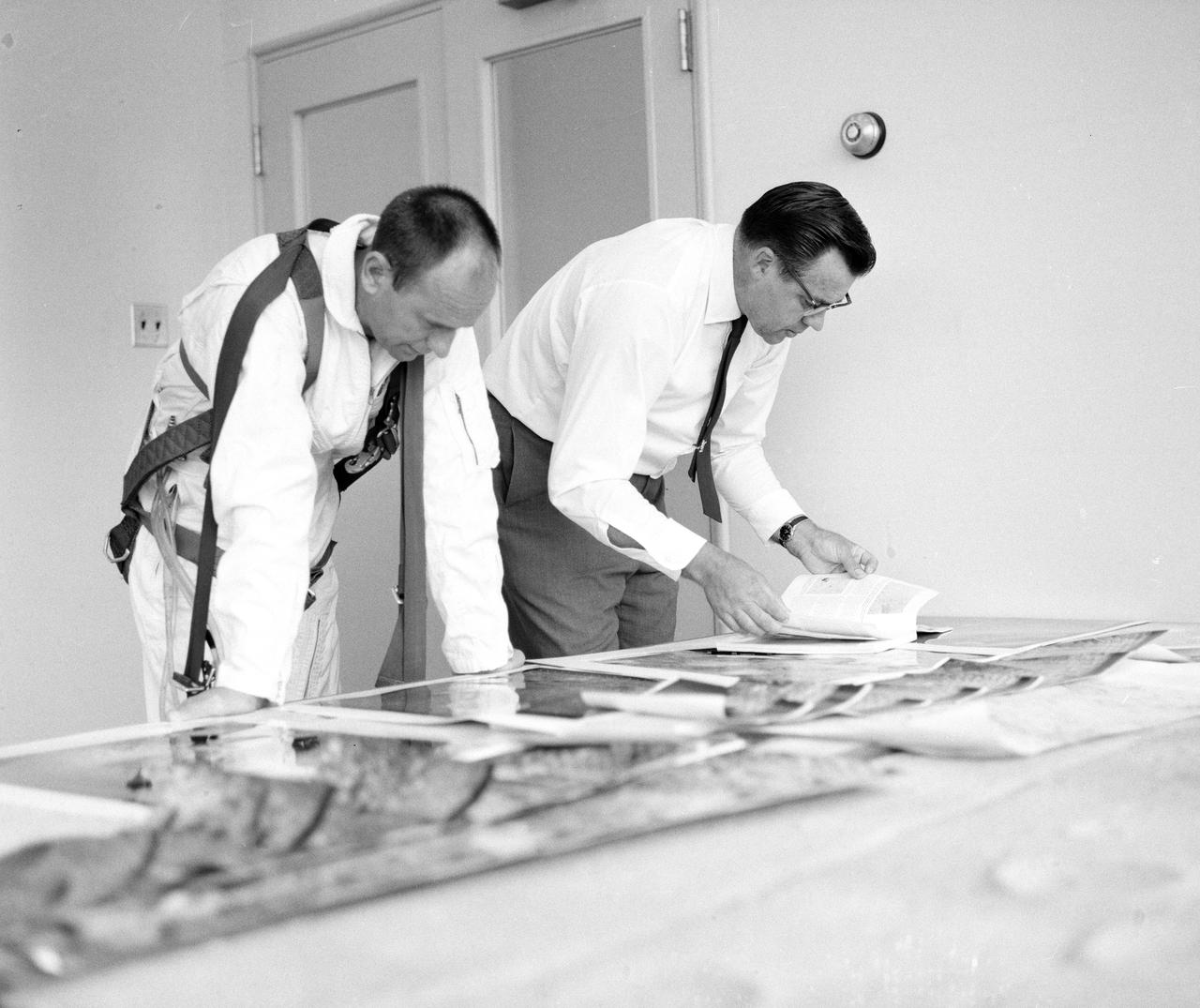

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
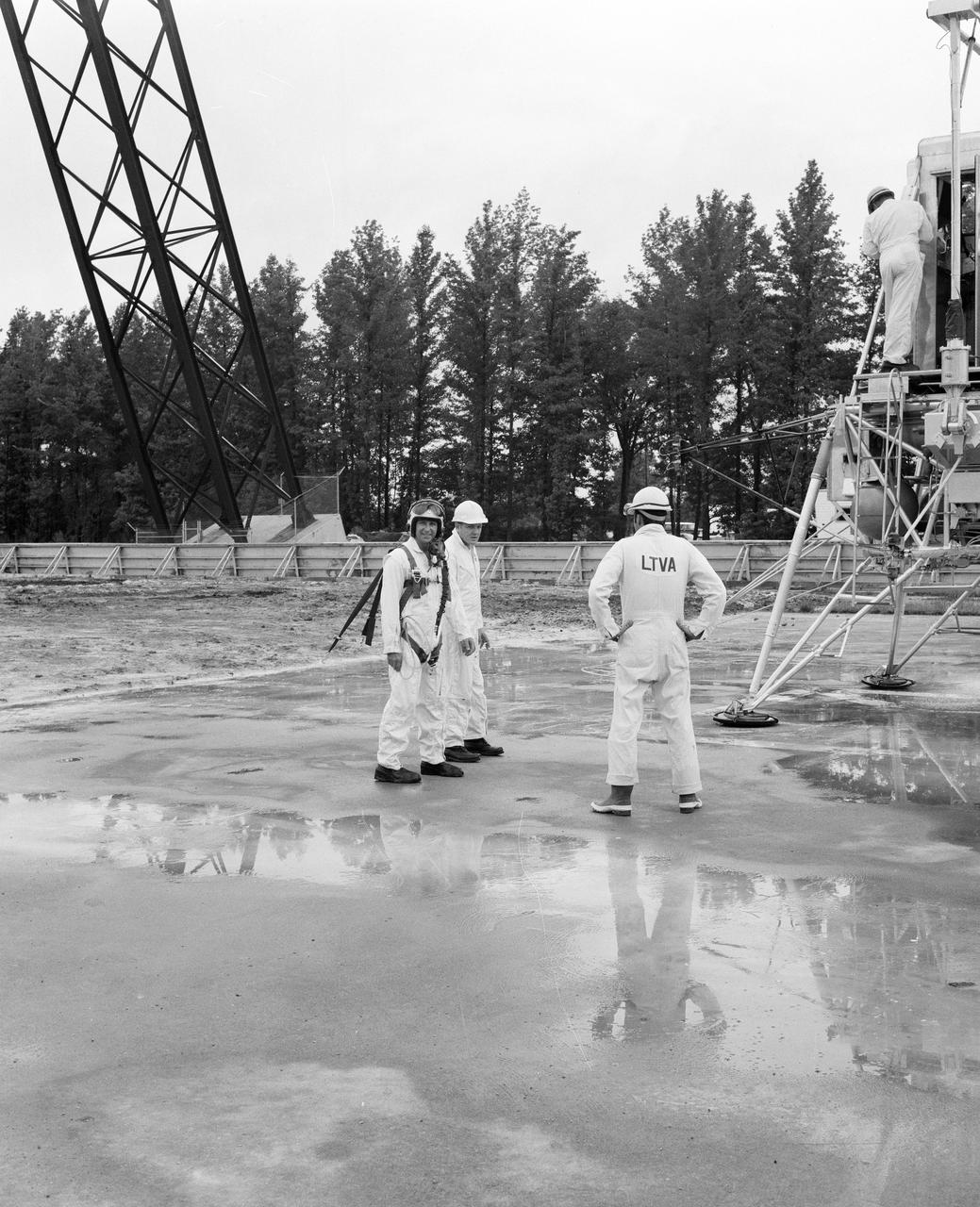

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
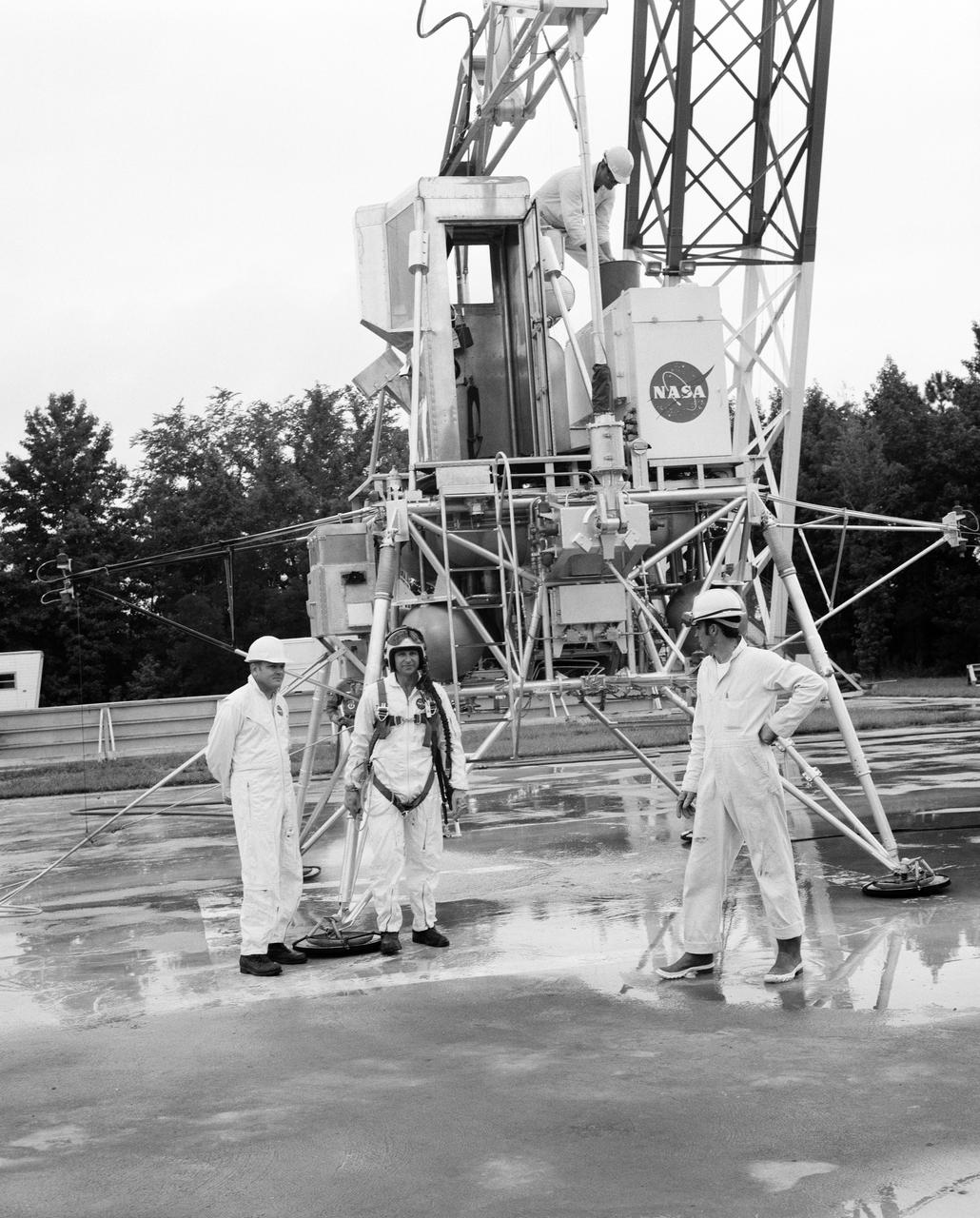

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
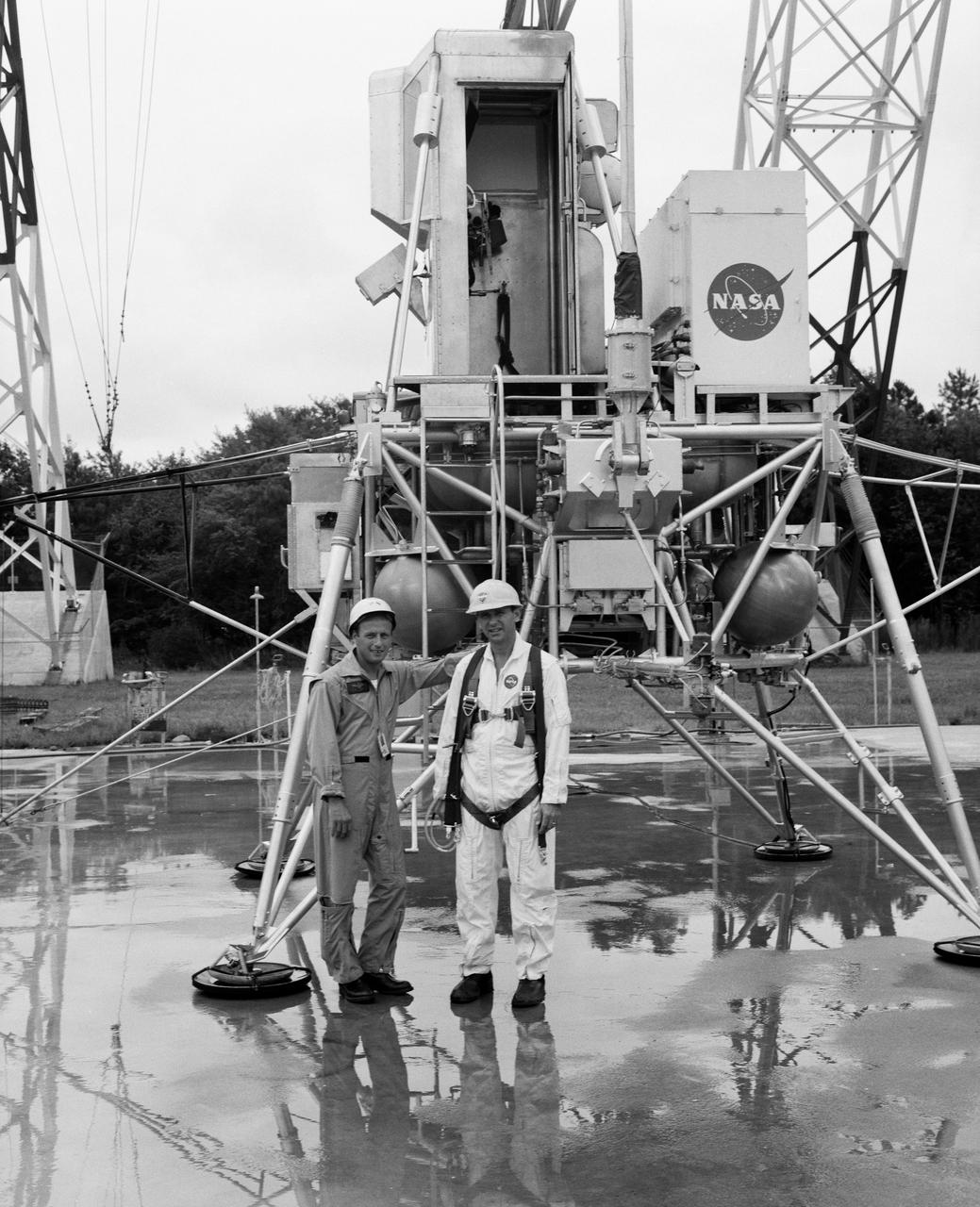

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
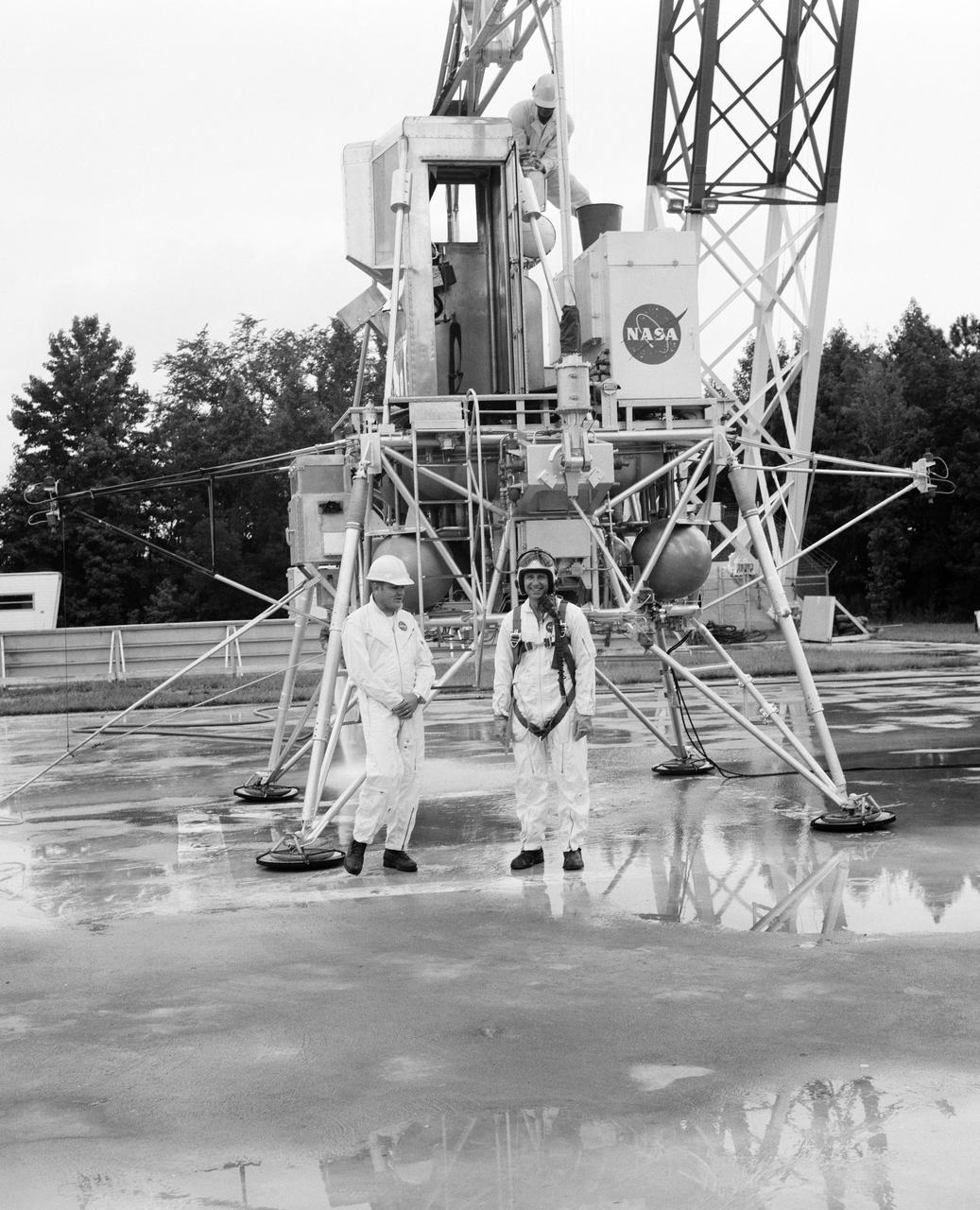

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
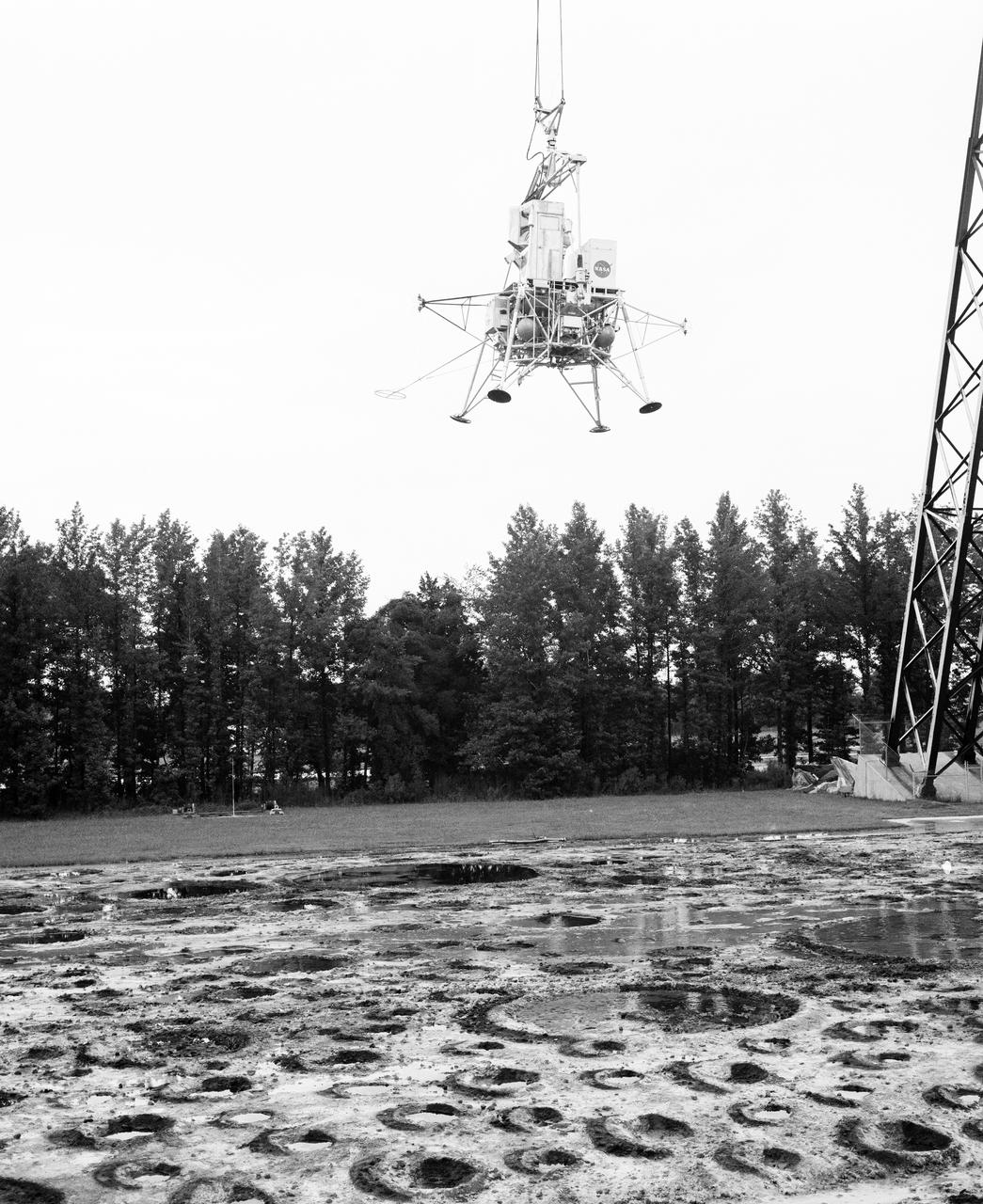

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
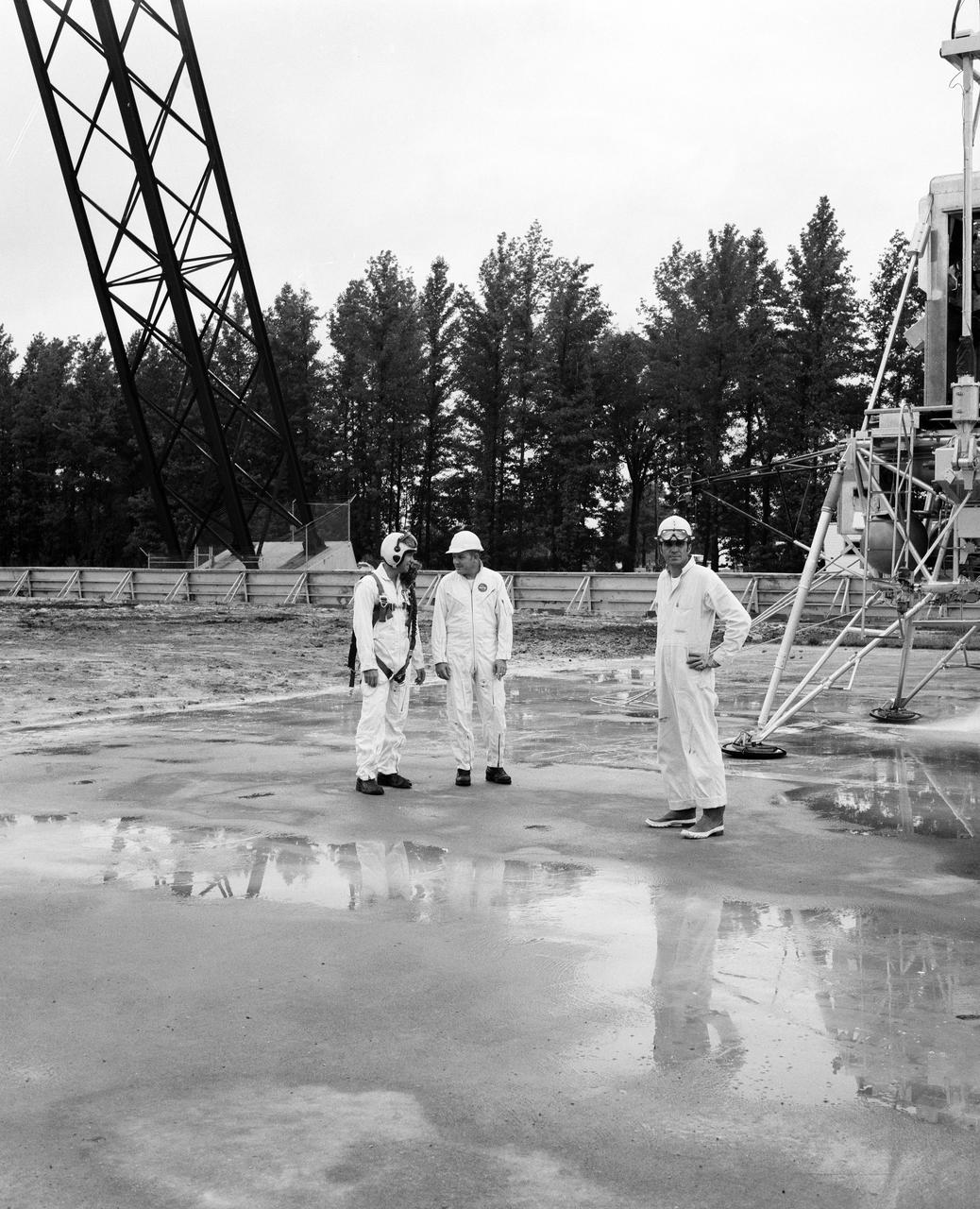

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
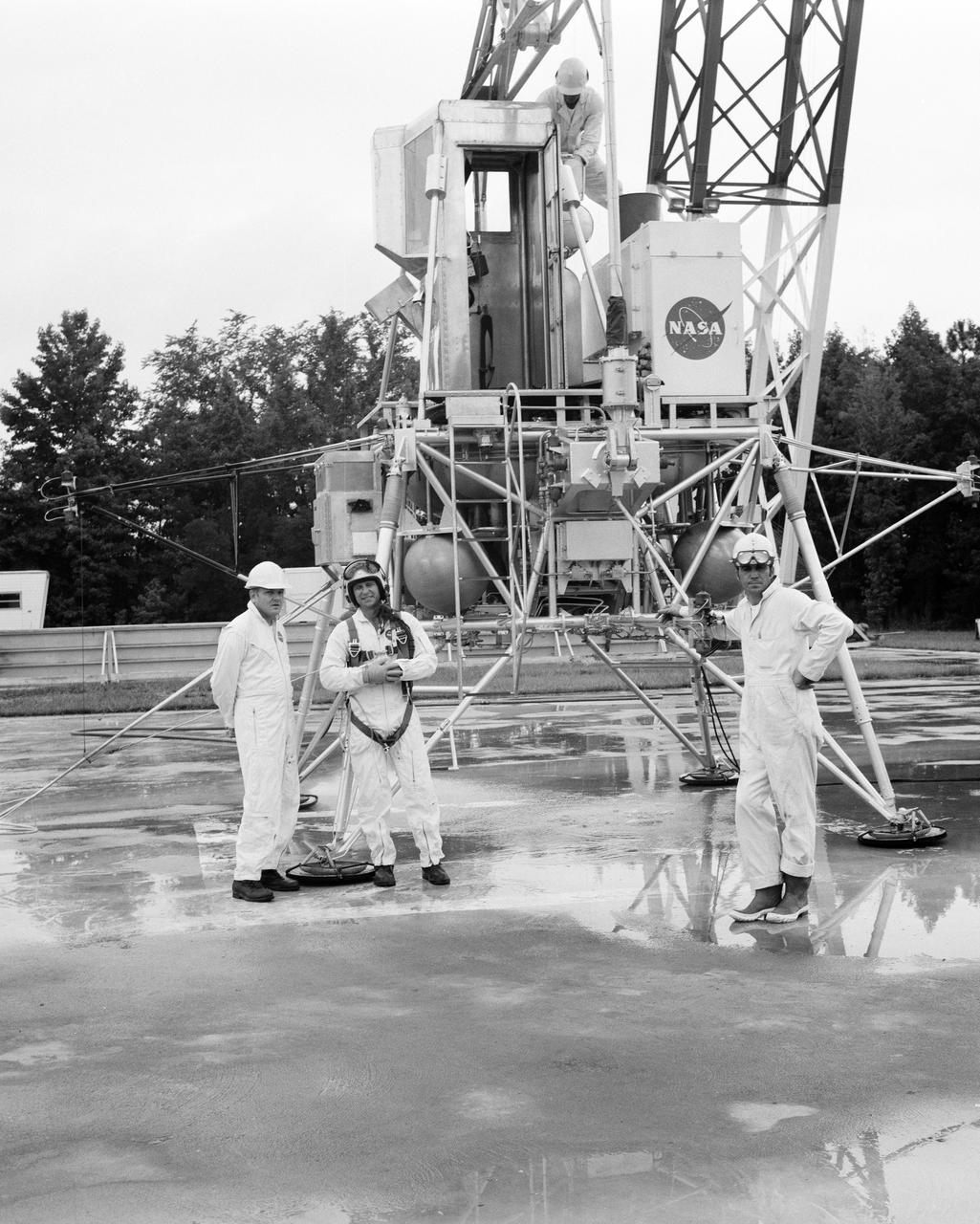

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
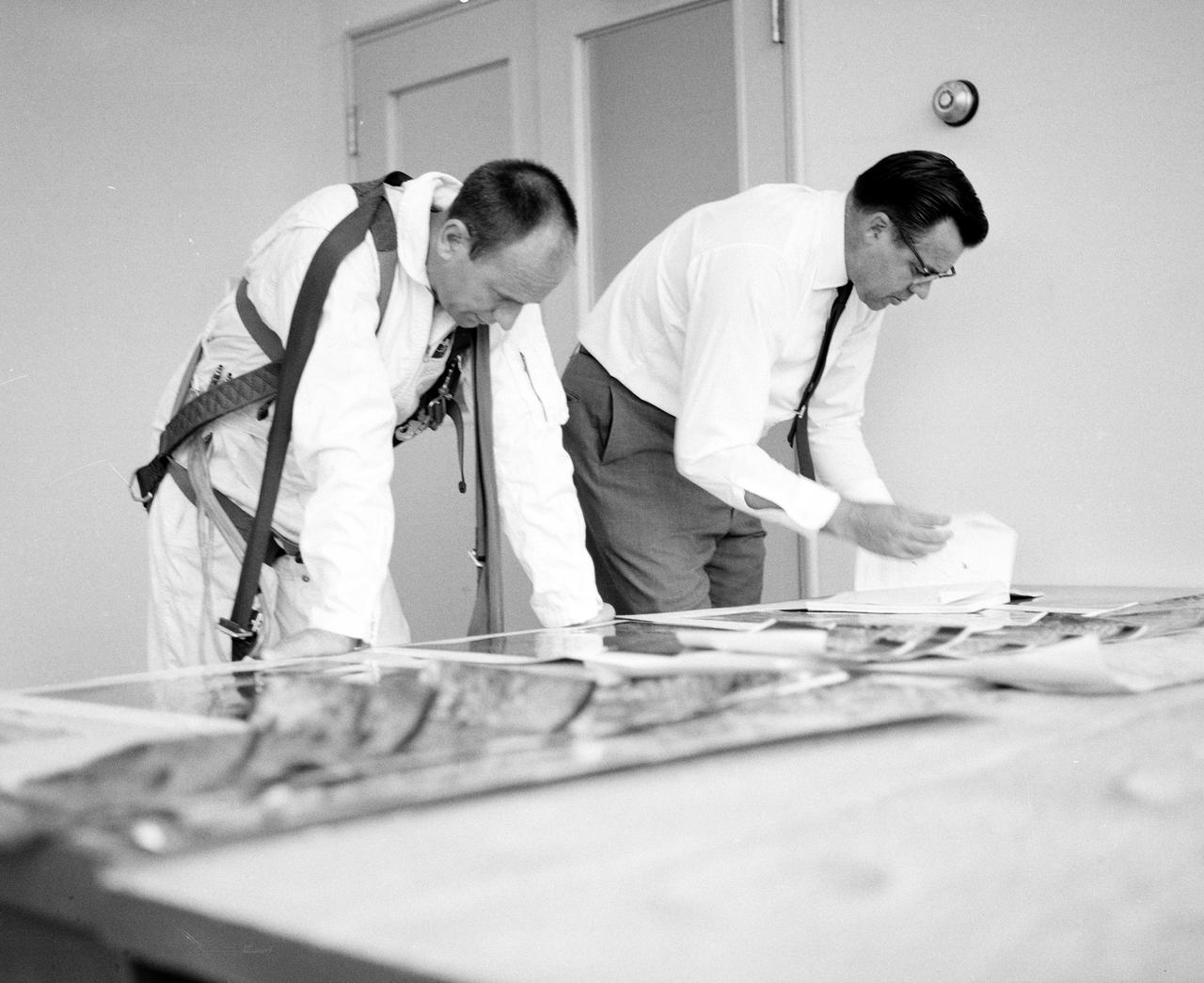

Astronauts Conrad and Bean at Lunar Landing Research Facility. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions. In September of 1962, Mr. Conrad was selected as an astronaut by NASA. His first flight was Gemini V, which established the space endurance record and placed the United States in the lead for man-hours in space. As commander of Gemini XI, Mr. Conrad helped to set a world's altitude record. He then served as commander of Apollo XII, the second lunar landing. On Mr. Conrad's final mission, he served as commander of Skylab II, the first United States Space Station. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former for more information.
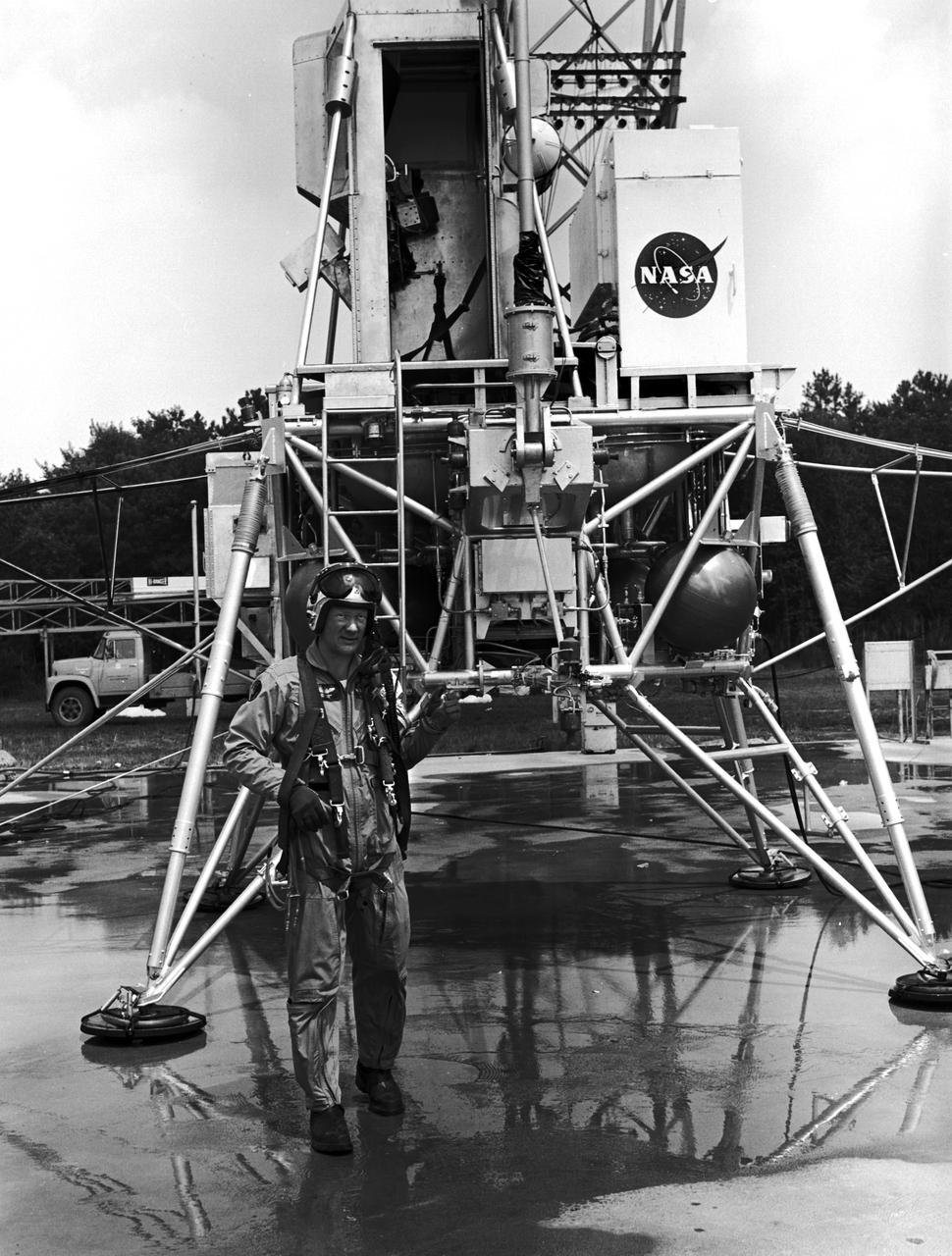

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
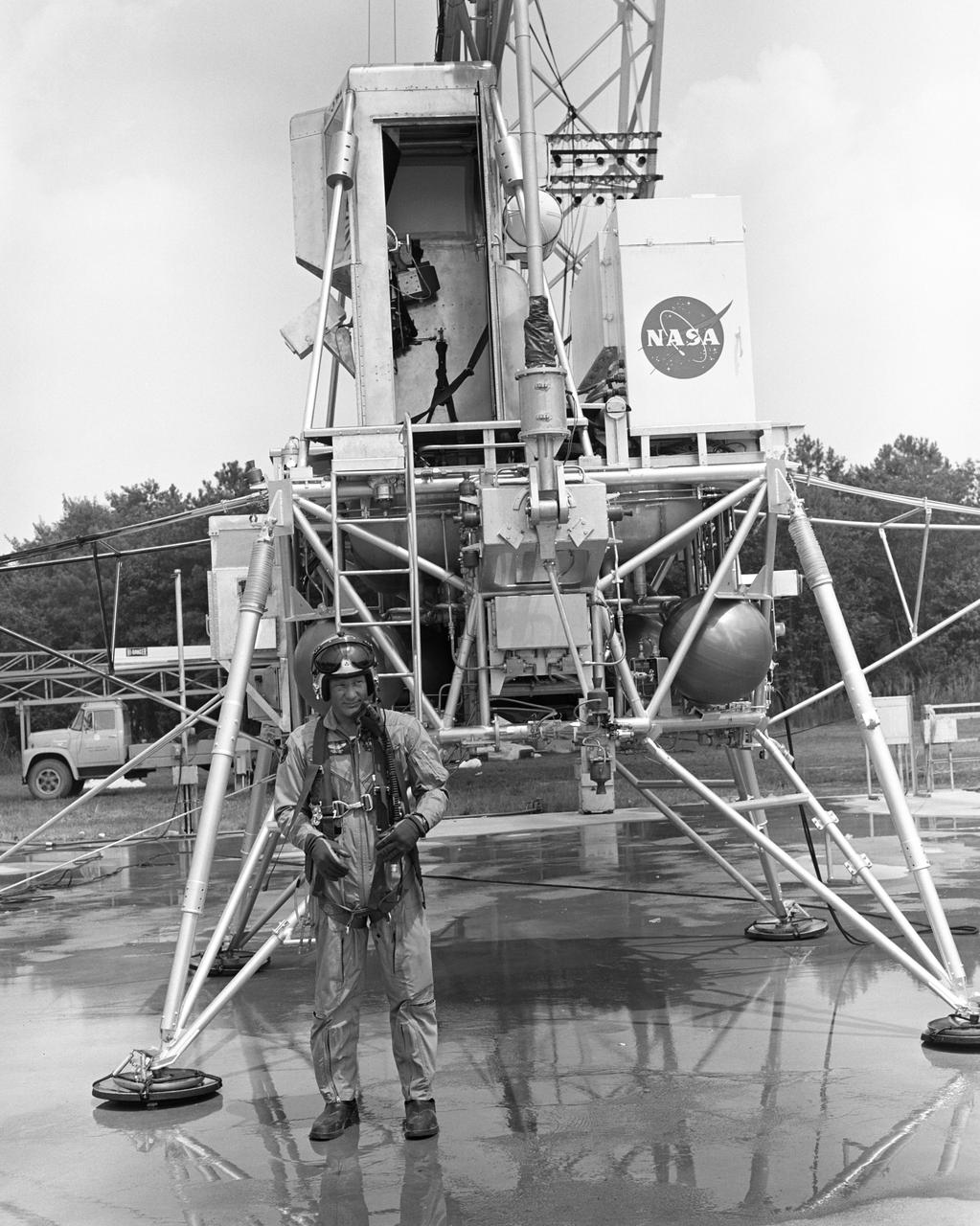

Astronaut Edwin Buzz Aldrin Lunar Module Pilot at the (LLRF) Lunar Landing Research Facility. Aldrin was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. On November 11, 1966, he and command pilot James Lovell were launched into space in the Gemini 12 spacecraft on a 4-day flight, which brought the Gemini program to a successful close. Aldrin established a new record for extravehicular activity (EVA), spending 5-1/2 hours outside the spacecraft. He served as lunar module pilot for Apollo 11, July 16-24, 1969, the first manned lunar landing mission. Aldrin followed Neil Armstrong onto the lunar surface on July 20, 1969, completing a 2-hour and 15 minute lunar EVA. In July 1971, Aldrin resigned from NASA. Aldrin has logged 289 hours and 53 minutes in space, of which, 7 hours and 52 minutes were spent in EVA. https://www.nasa.gov/astronauts/biographies/former
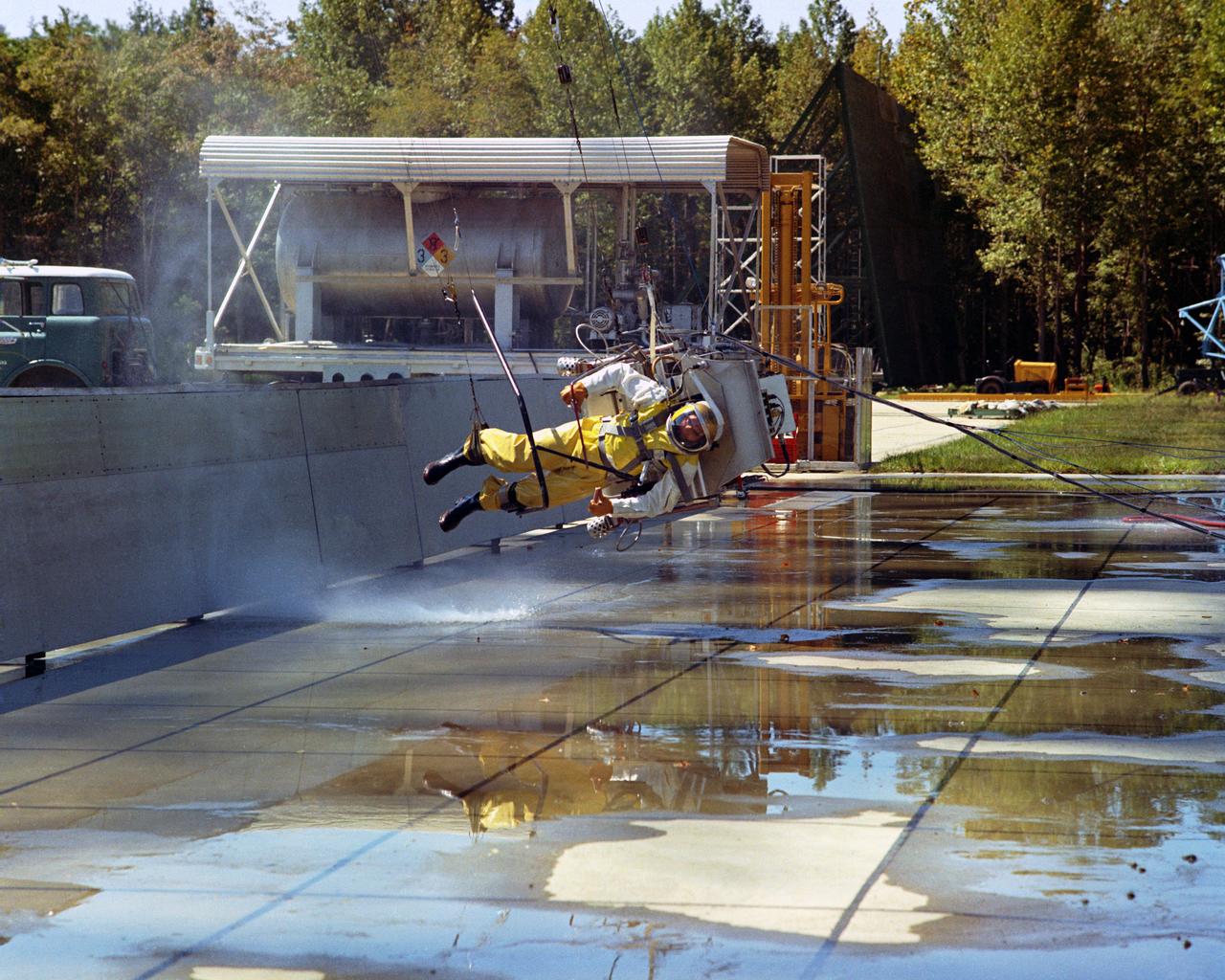

Icarus Lunar Walker,Lunar Landing Research Facility. Langley study of the backpack propulsion unit, by Bell Aerosystems. Icarus full scale test at Lunar Landing Research Facility - low gravity simulator. A NASA Langley researcher moon walks under the Lunar Landing Research Facility's gantry. More information on this can be read in the Document. "STUDIES OF PILOTING PROBLEMS OF ONE-MAN FLYING UNITS OPERATED IN SIMULATED LUNAR GRAVITY" BY Donald E. Hewes
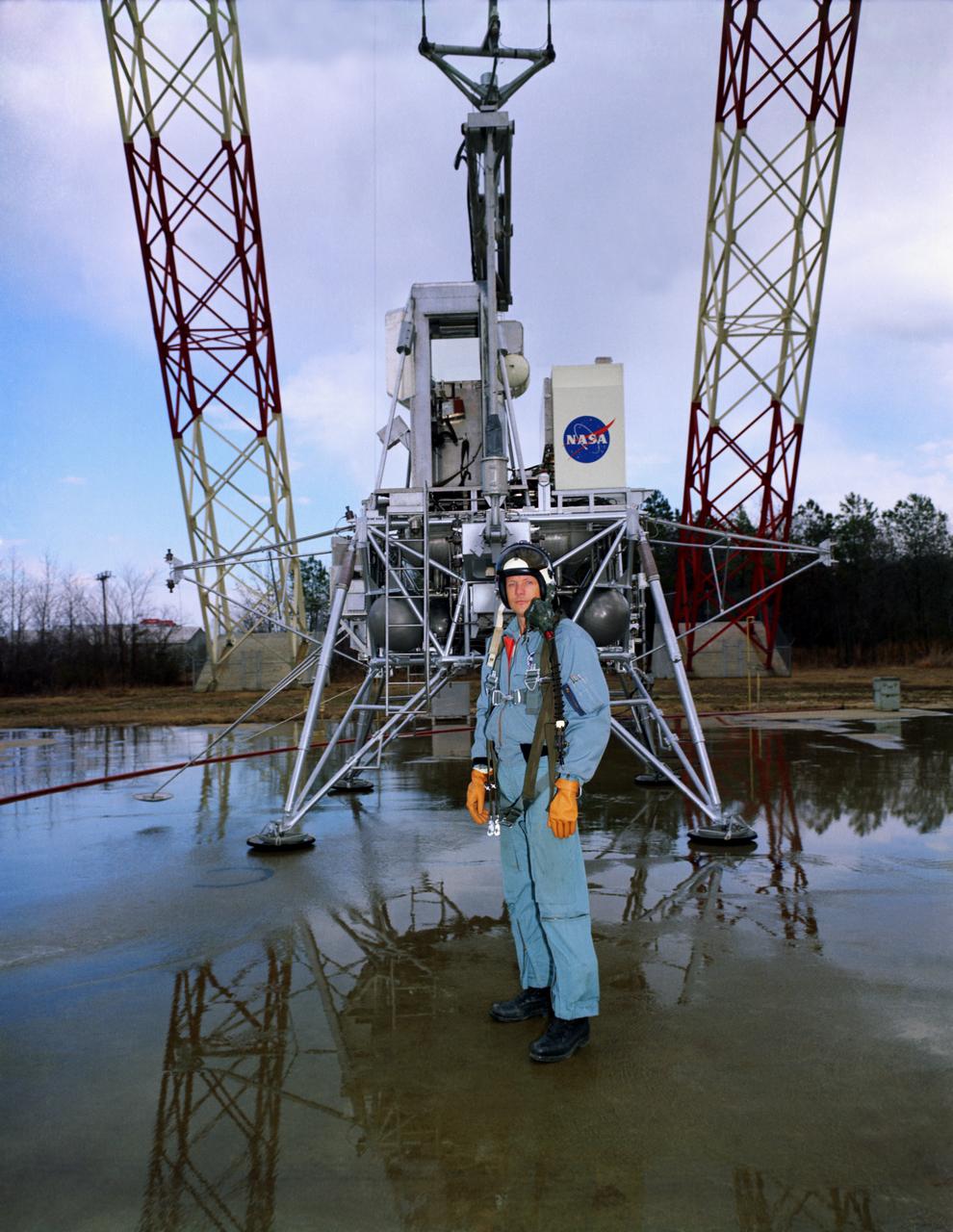

Neil Armstrong with the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM). Caption: "Not long after this photo was taken in front of the Lunar Landing Research Facility, astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first human to step upon the surface of the Moon." Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, by James Schultz, page 91. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 95

Lunar Landing Research Facility. Gantry facility 1297
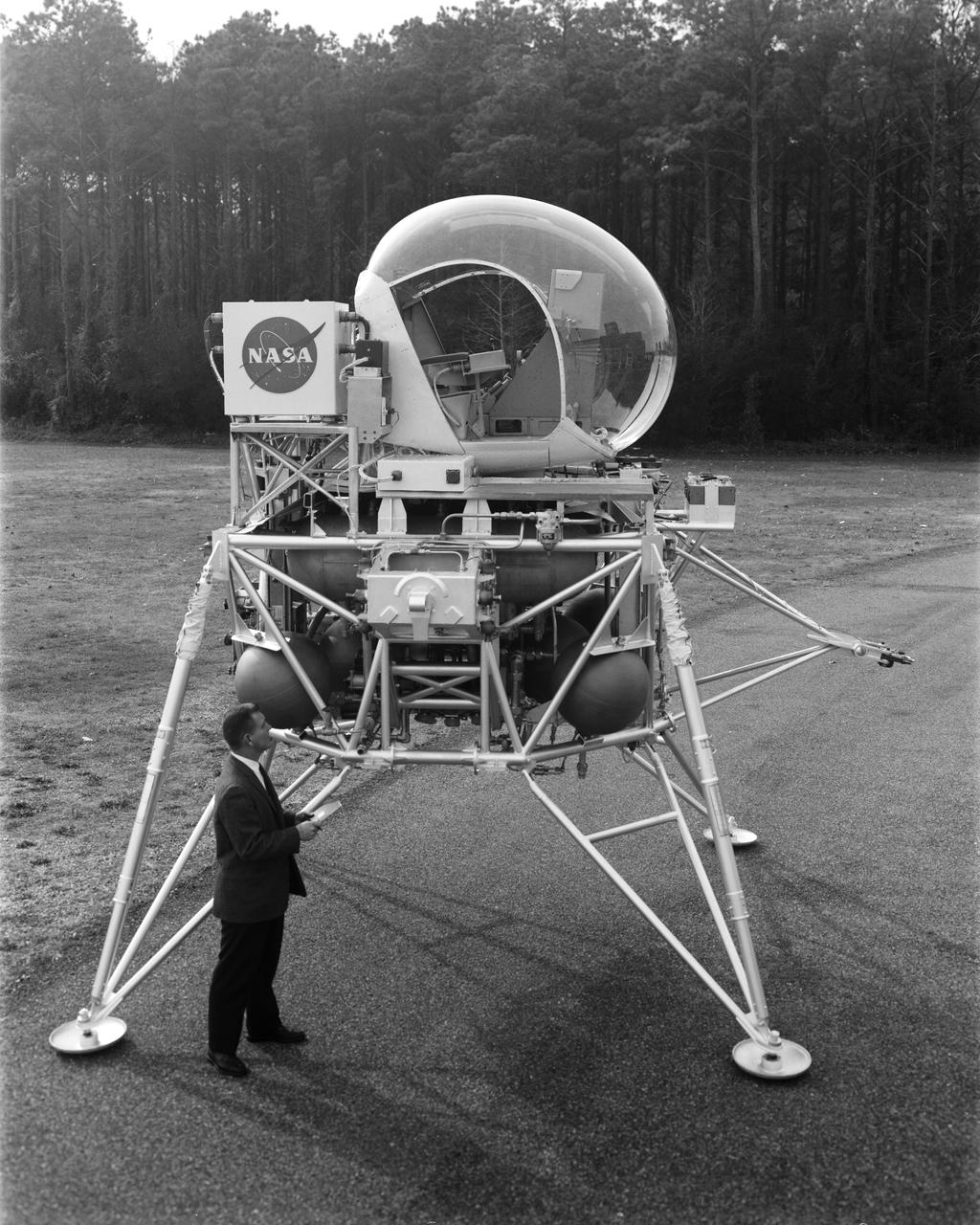

Vehicle for Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia.
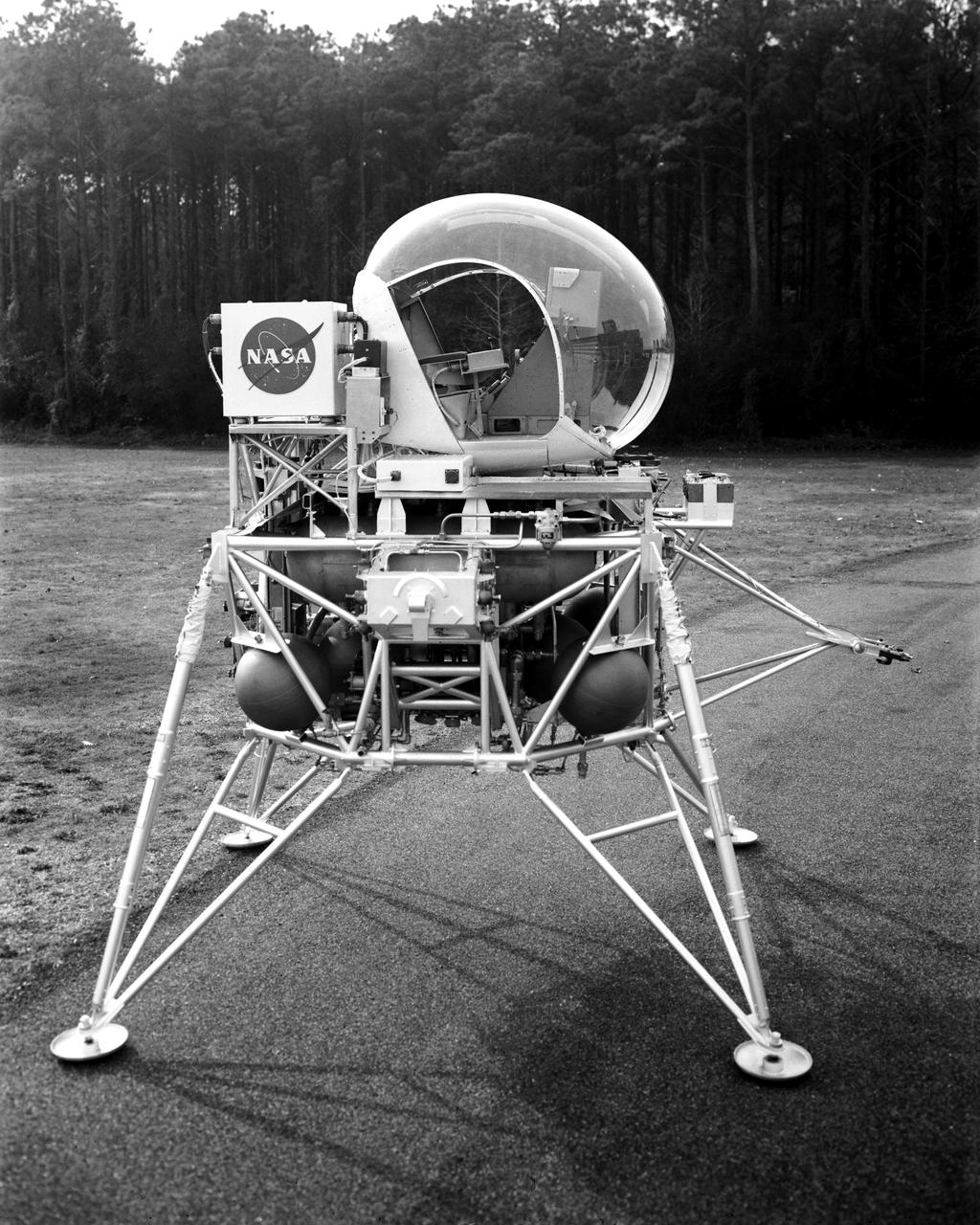

Vehicle for Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia.
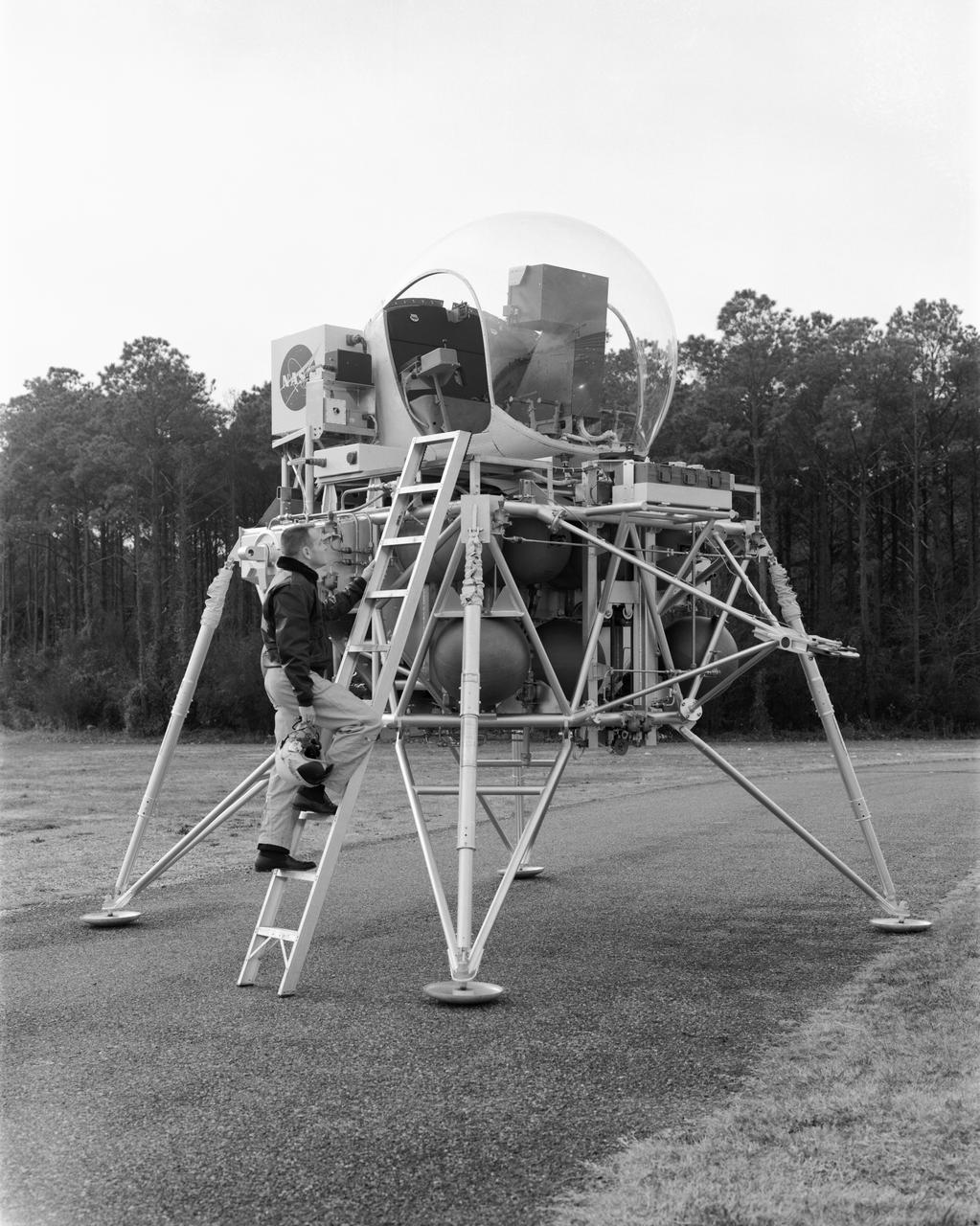

Vehicle for Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia.

Vehicle for Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia.

Lunar landing test of LEM at Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF).
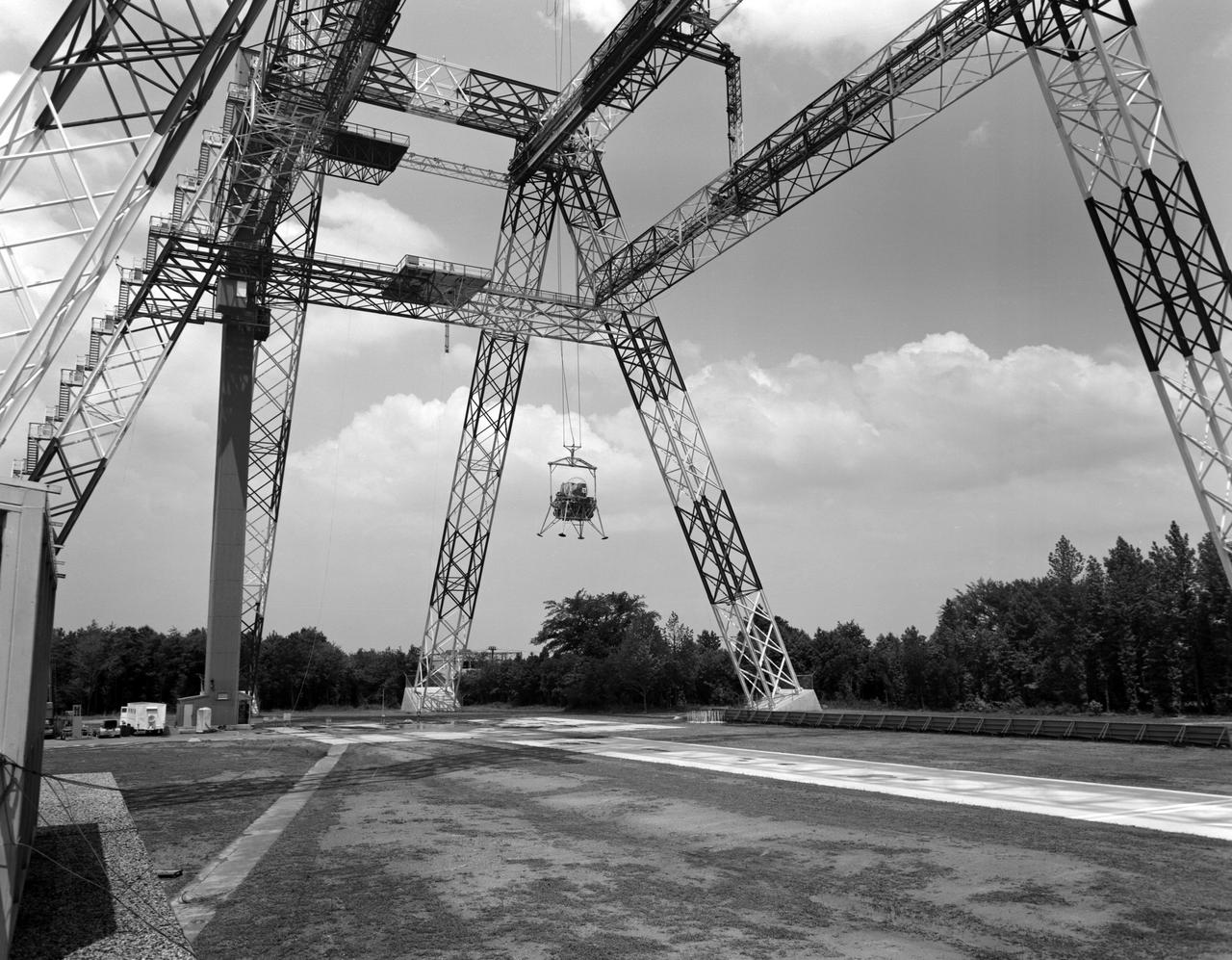

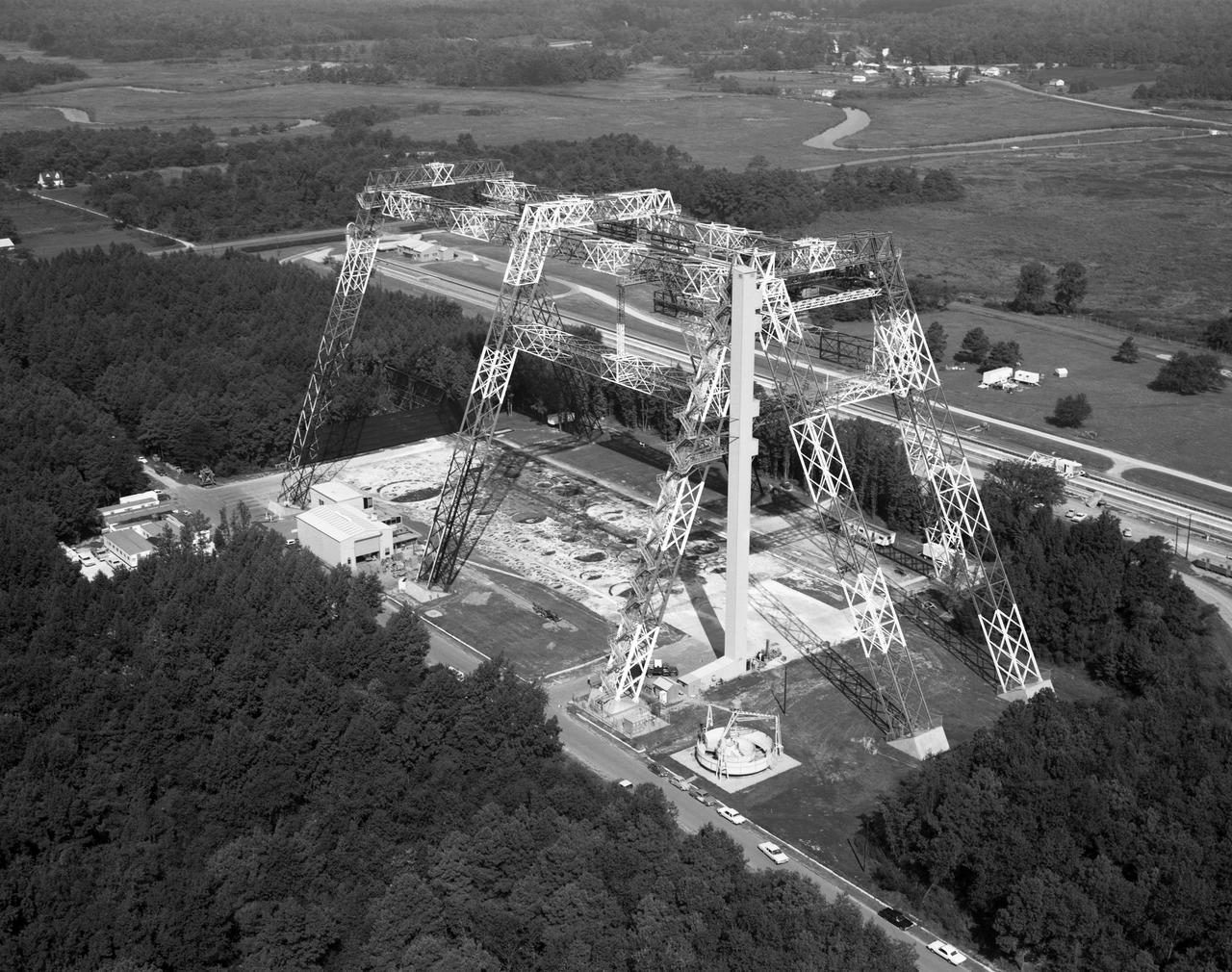
The Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center has been put into operation. The facility, 250 feet high and 400 feet long, provides a controlled laboratory in which NASA scientists will work with research pilots to explore and develop techniques for landing a rocket-powered vehicle on the Moon, where the gravity is only one sixth as strong as on Earth. The Lunar Landing Research Facility, a controlled laboratory for exploring and developing techniques for landing a rocket-powered vehicle on the Moon, has been put into operation at the Langley Research Center. The $3.5 million facility includes a rocket-powered piloted flight test vehicle which is operated· while partially supported from a 250-foot high, 400-foot long gantry structure to simulate the one-sixth earth gravity of the Moon in research to obtain data on the problems of lunar landing. Excerpt from Langley Researcher July 2, 1965
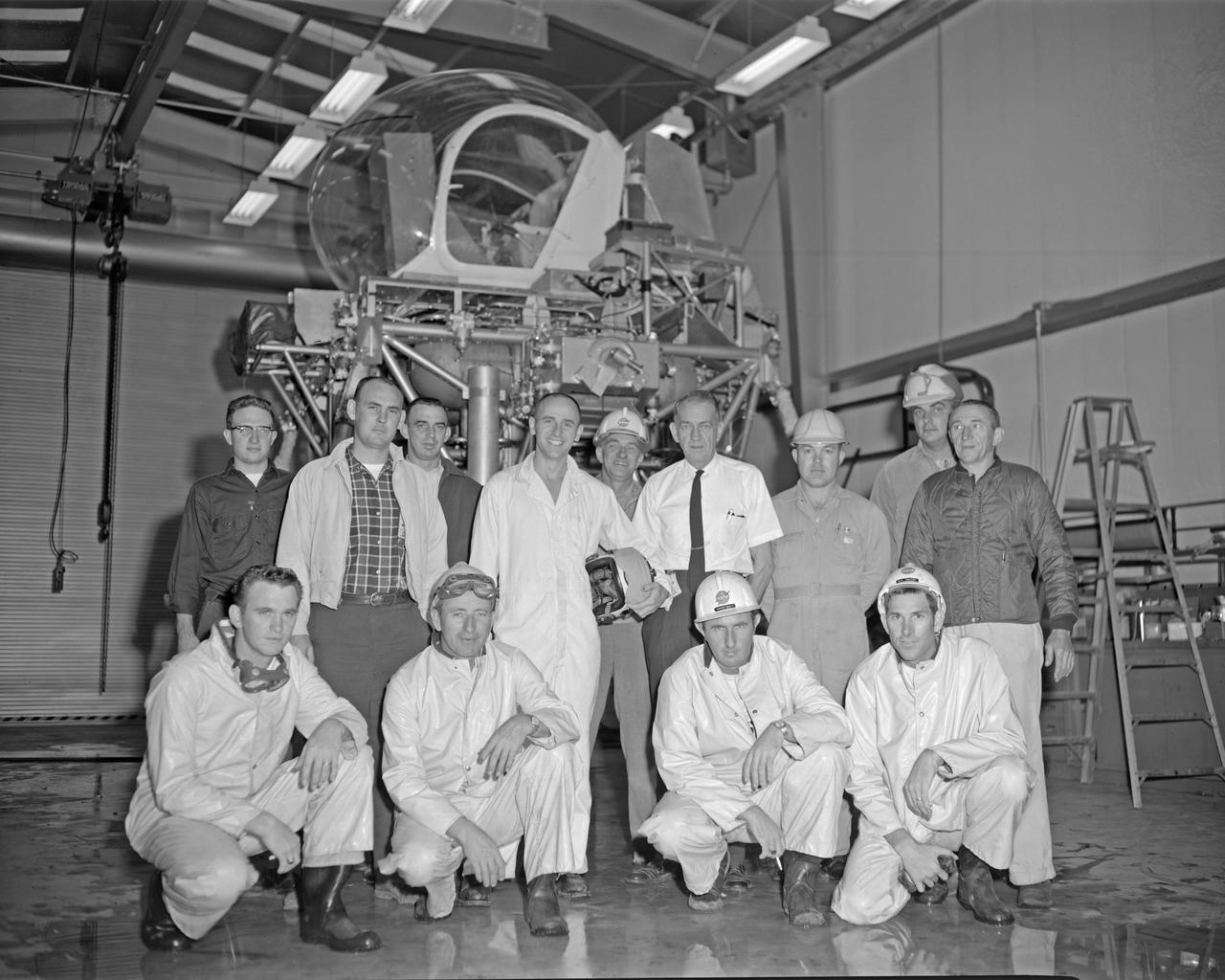

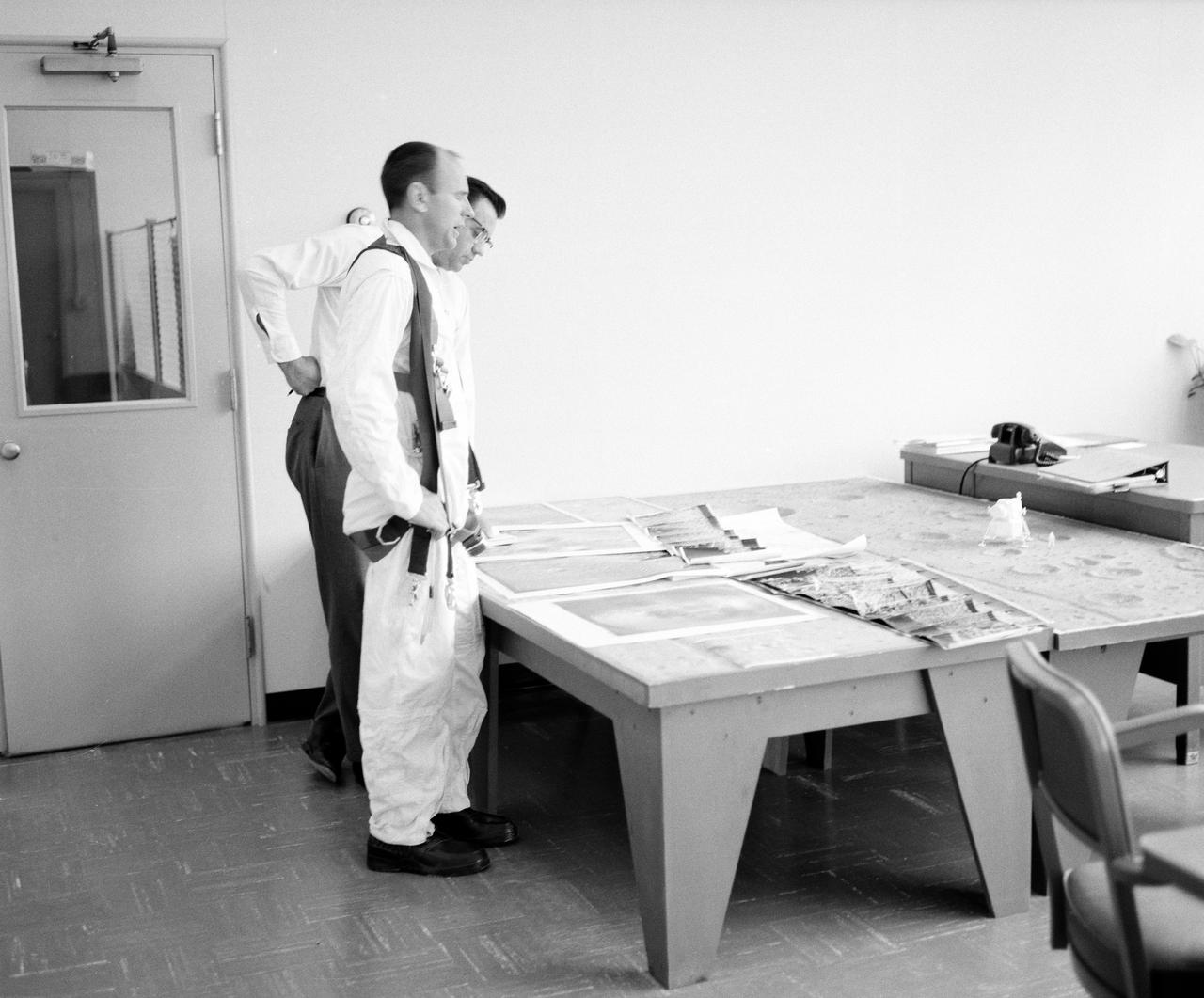
Astronaut Allen Bean with Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) crew. Alan Bean was one of the third group of astronauts named by NASA in October 1963. He served as backup astronaut for the Gemini 10 and Apollo 9 missions.
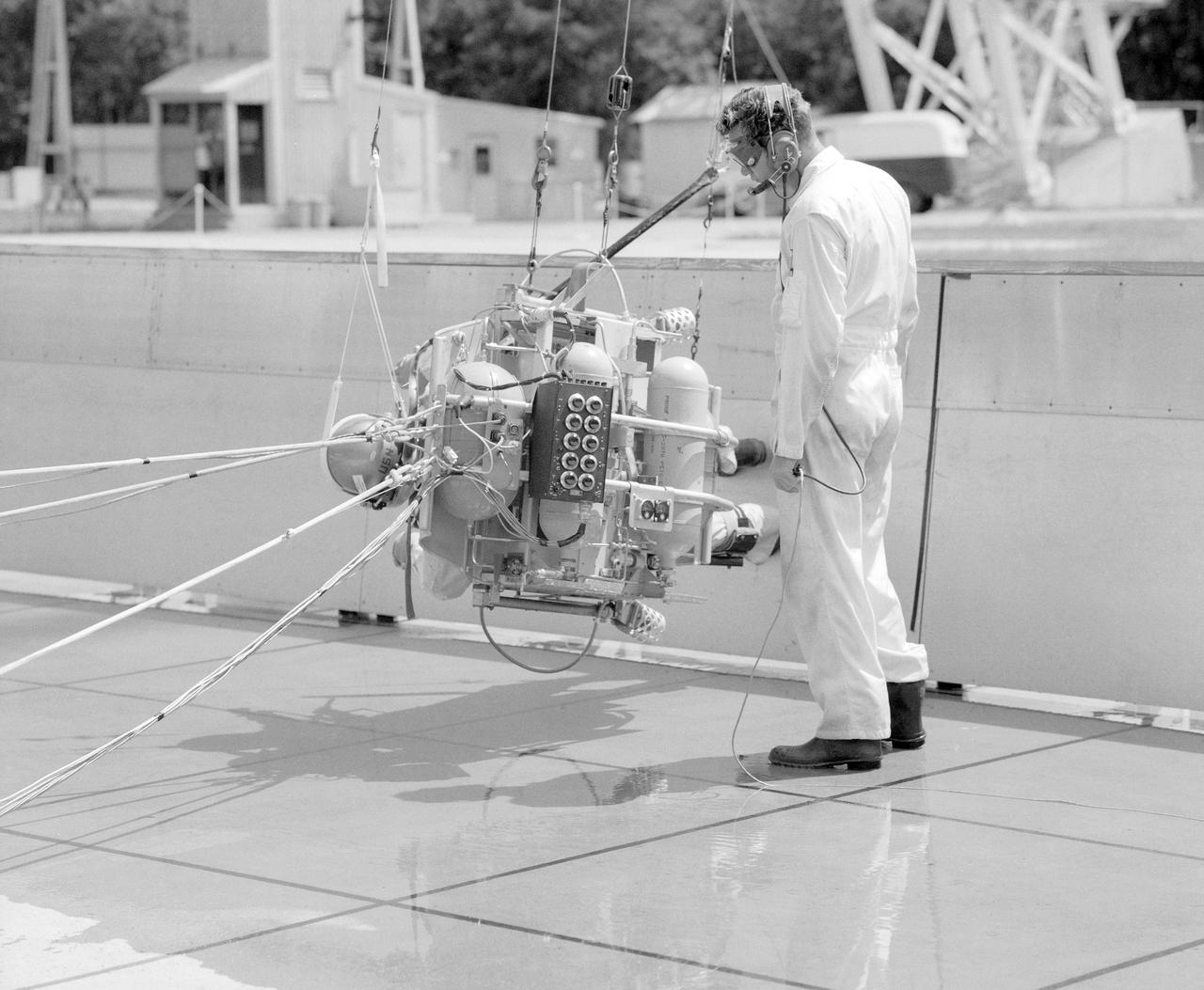

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility or Gantry.
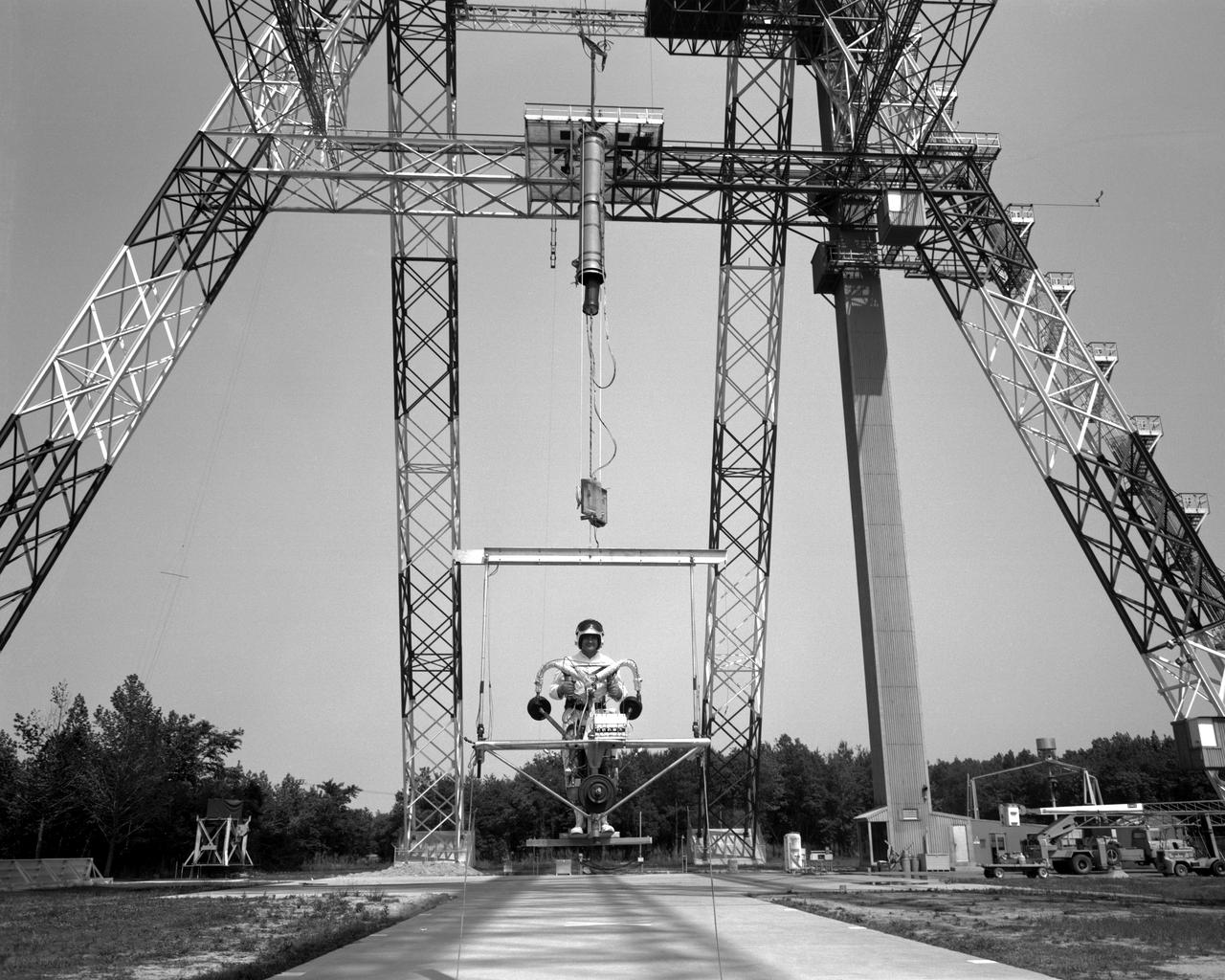

POGO is a device that uses cables connected to the ceiling to suspend an astronaut. POGO supports five-sixths of a person's weight; it mimics the one-sixth gravity of the moon. An astronaut walking around on POGO has the sensation of walking on the moon. POGO has been around since the Apollo days - in fact, the device gets its name from the way Apollo astronauts tended to bounce when suspended from it. The real name for POGO is the Partial Gravity Simulator.
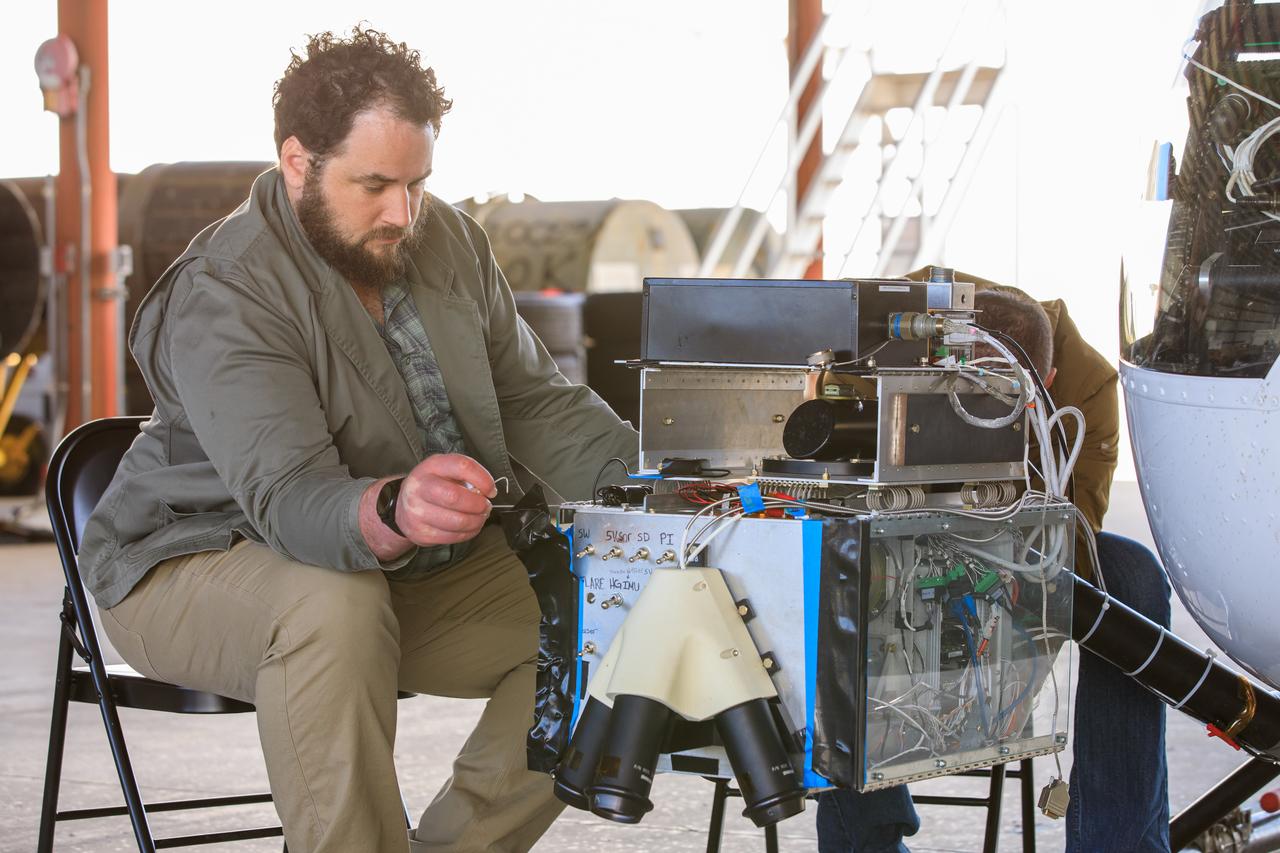

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
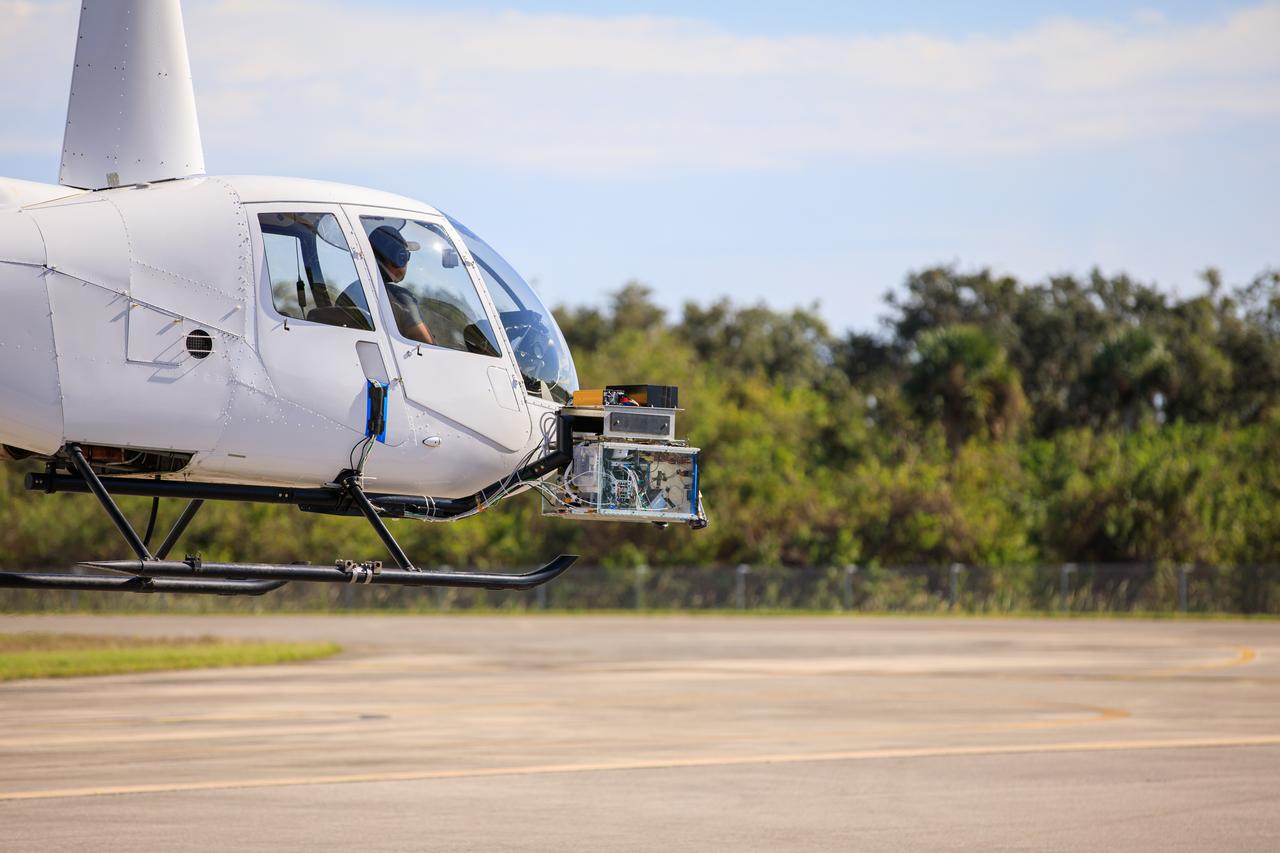

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
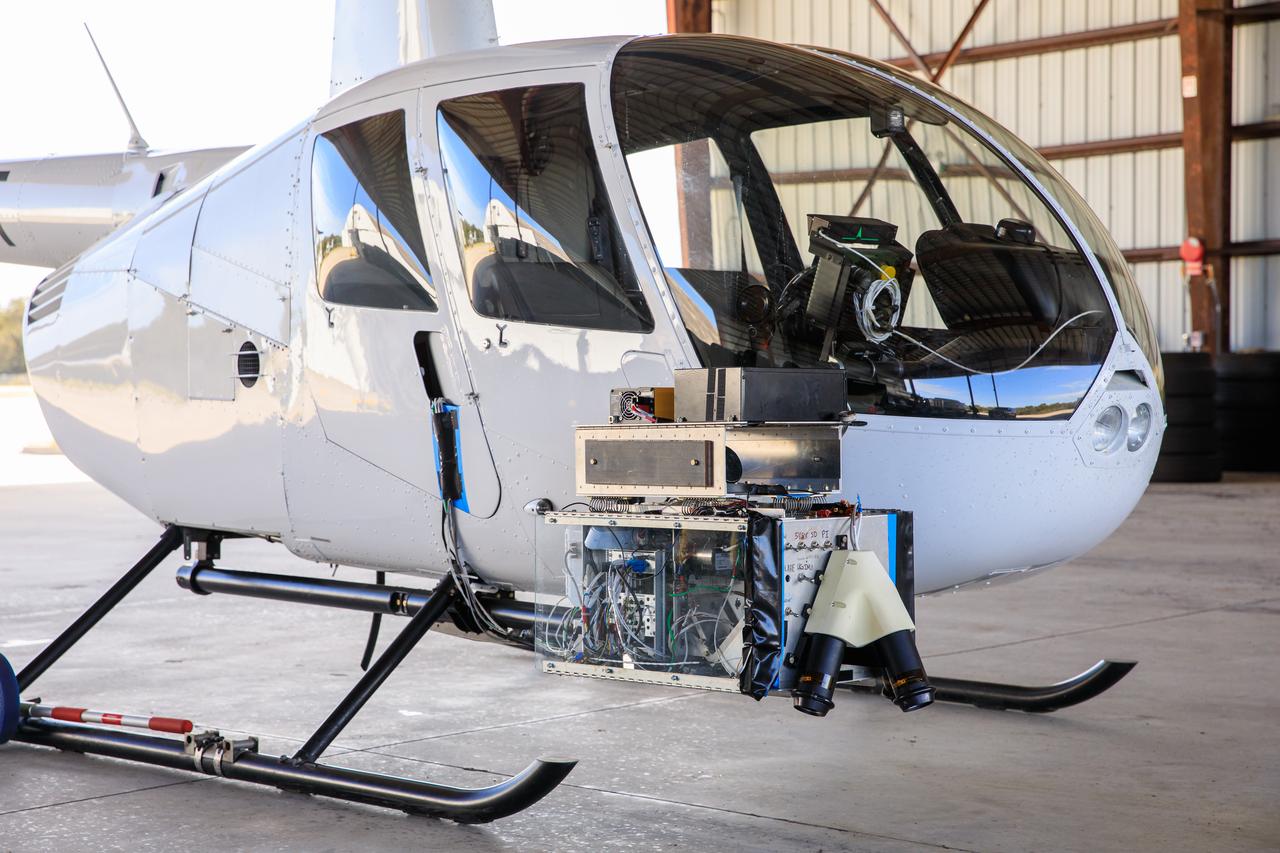

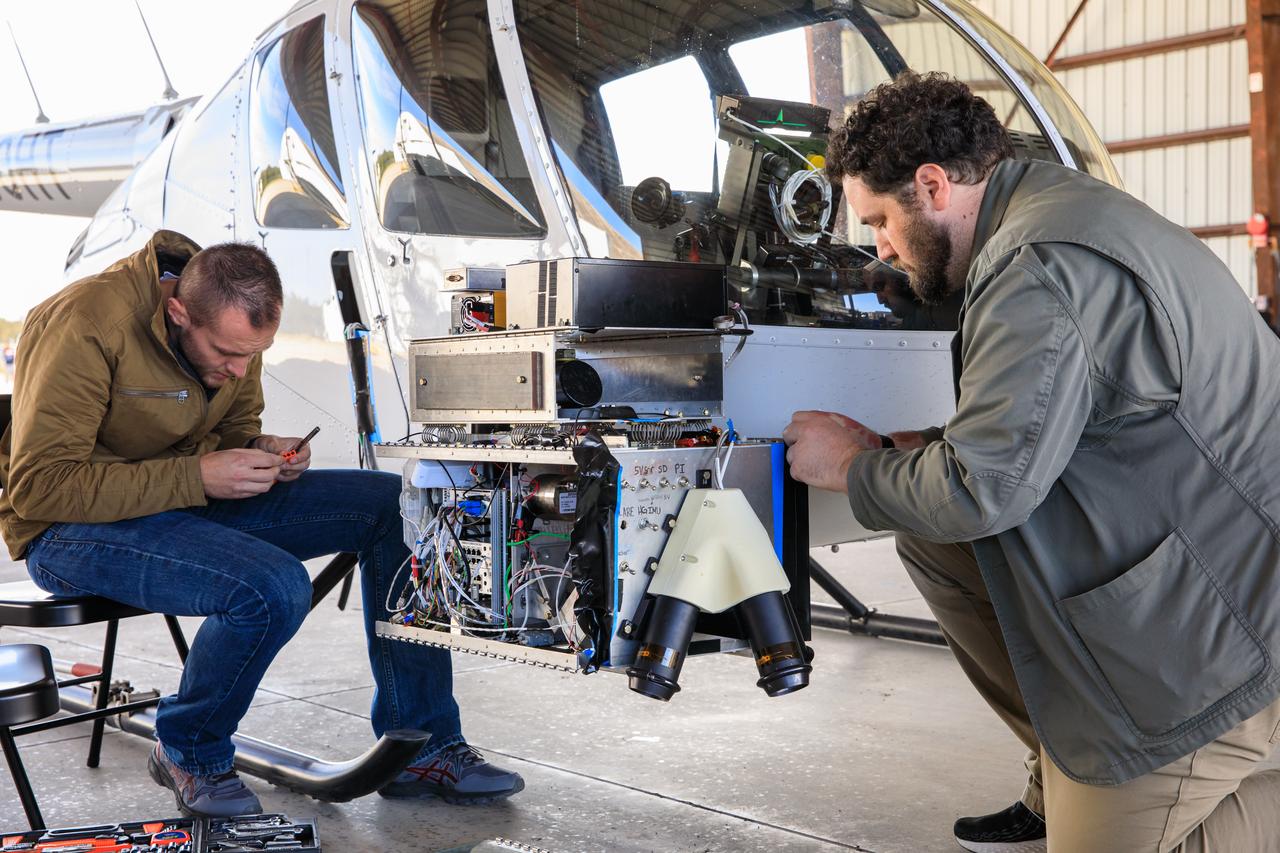
Seen here is Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
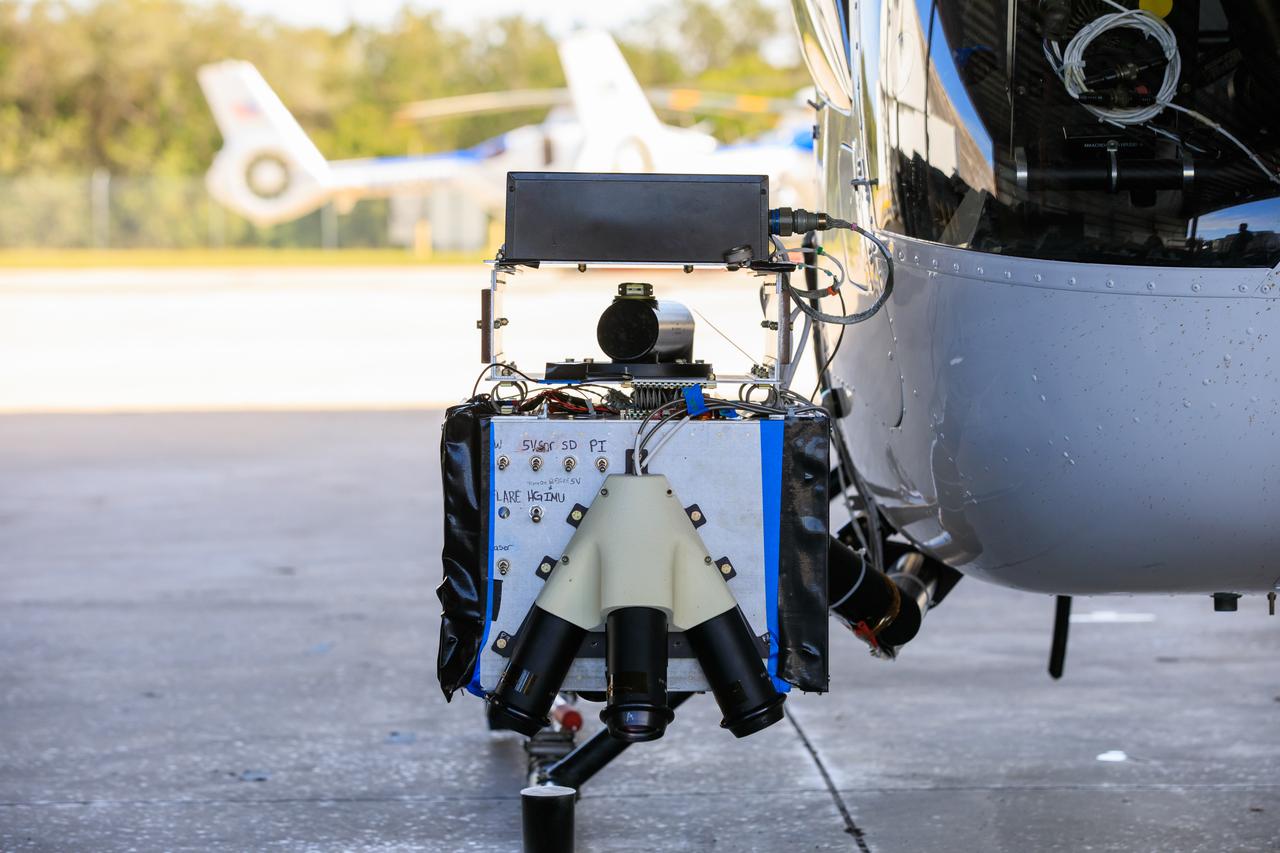

Seen here is a close-up view of Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
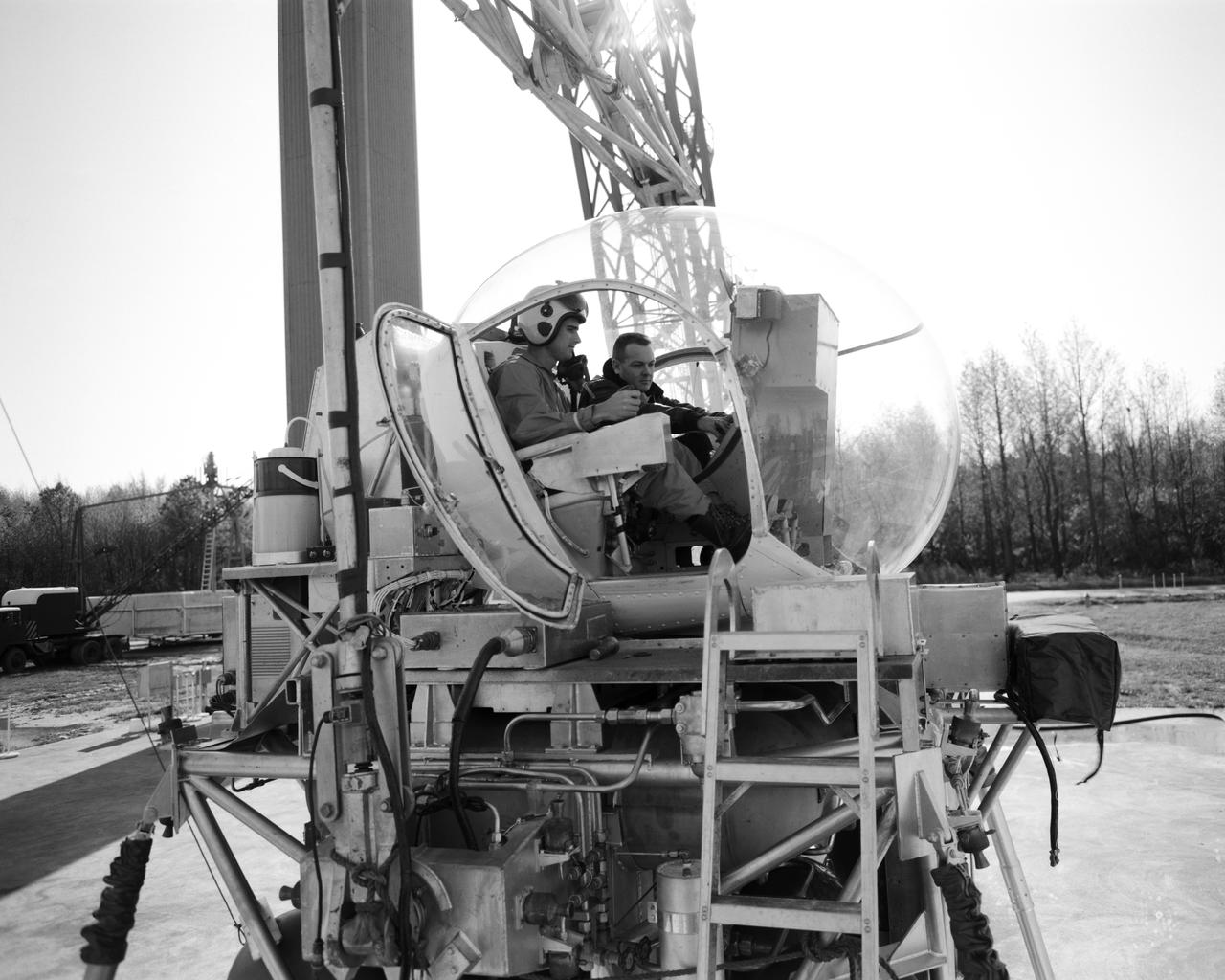

Lunar Landing Simulator: Astronaut Roger B. Chaffee (left) receives instruction from Maxwell W. Goode, a scientist at NASA s Langley Research Center. Goode is explaining the operation of the Lunar Landing Simulator at the Lunar Landing Research Facility. Chaffee was one of the third group of astronauts selected by NASA in October 1963. In addition to participating in the overall training program, he was also tasked with working on flight control communications systems, instrumentation systems, and attitude and translation control systems in the Apollo Branch of the Astronaut office. On March 21, 1966, he was selected as one of the pilots for the AS-204 mission, the first 3-man Apollo flight. Lieutenant Commander Chaffee died on January 27, 1967, in the Apollo spacecraft flash fire during a launch pad test at Kennedy Space Center, Florida.
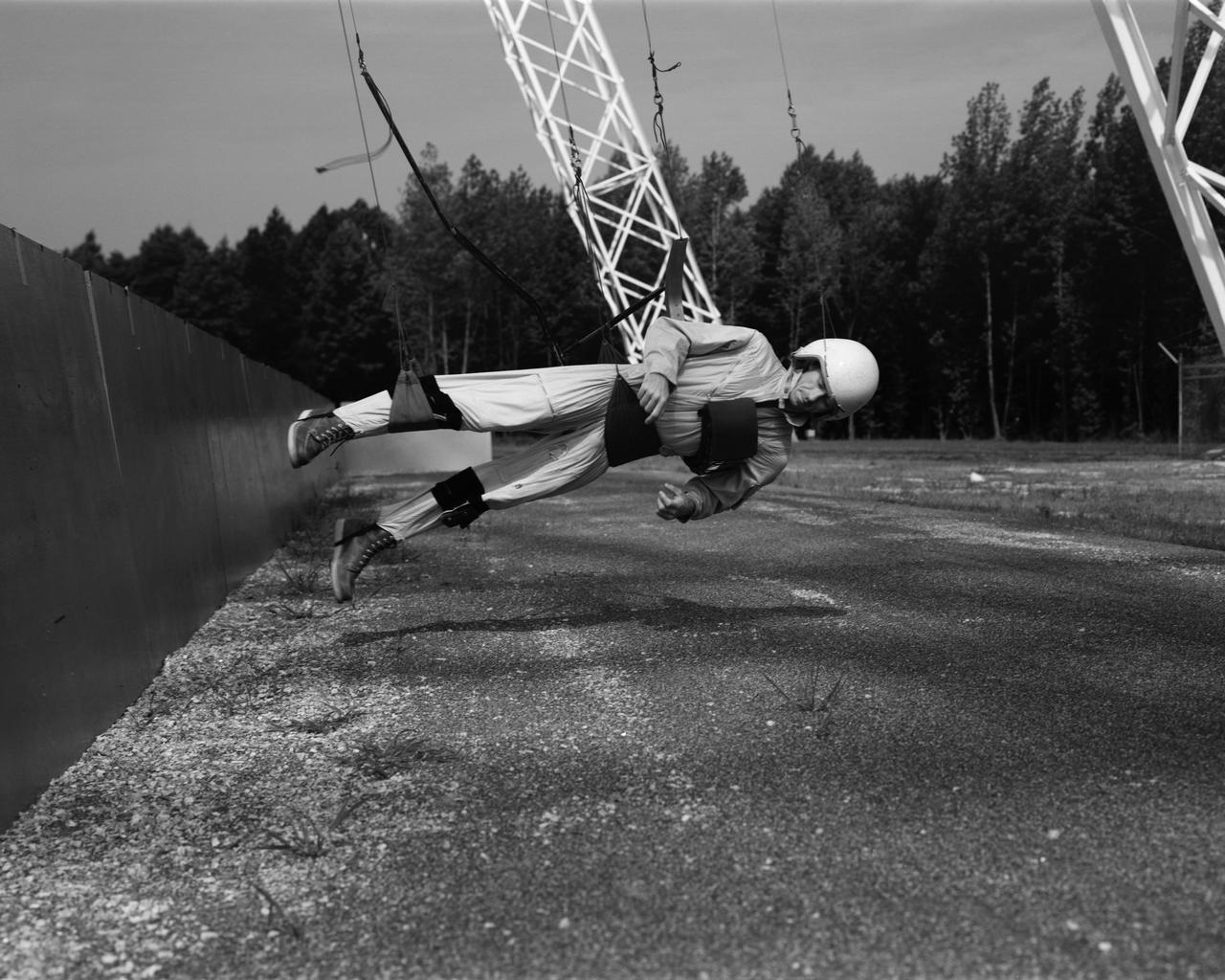

Astronaut Walt Cunningham on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
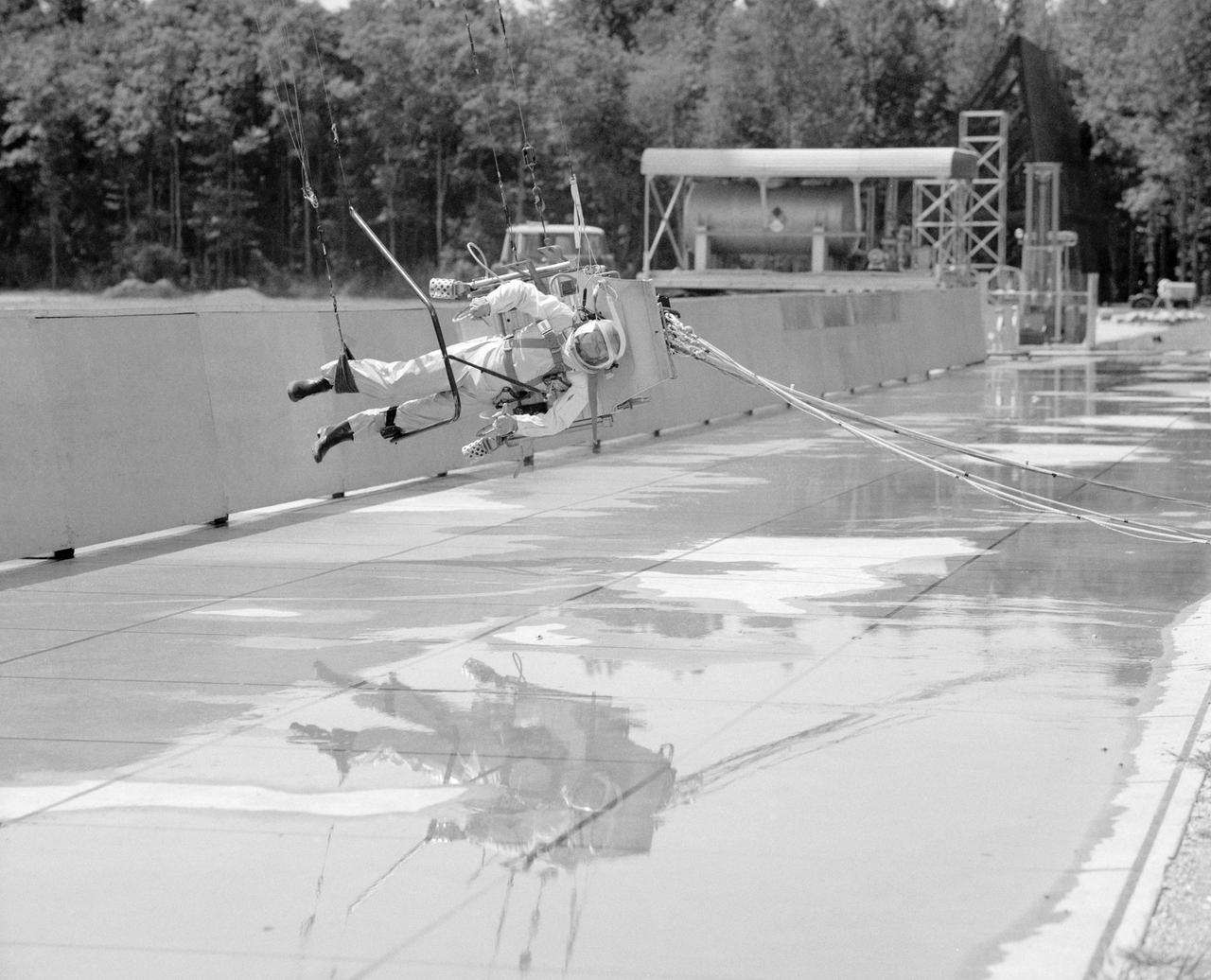

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility gantry.
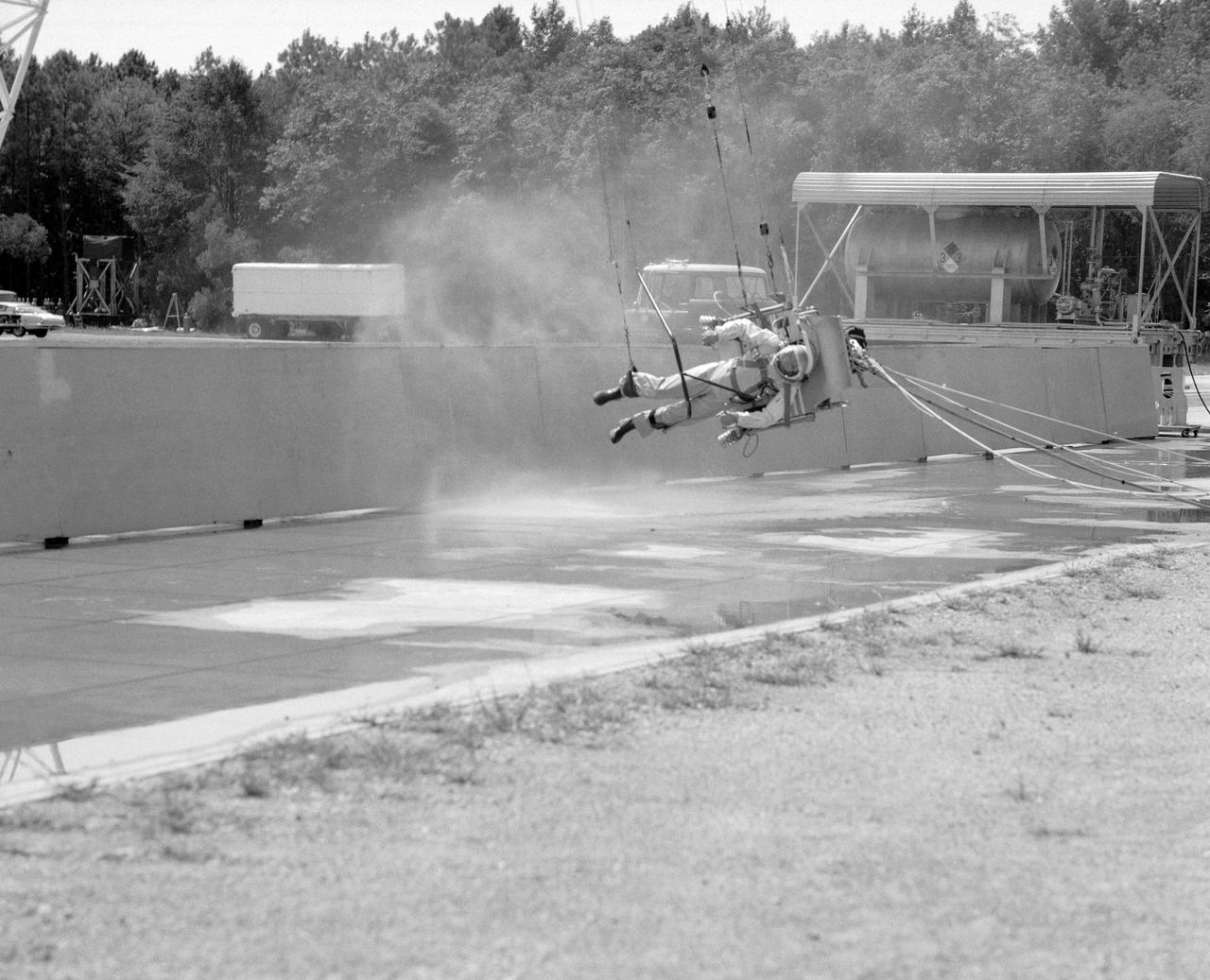

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility gantry.
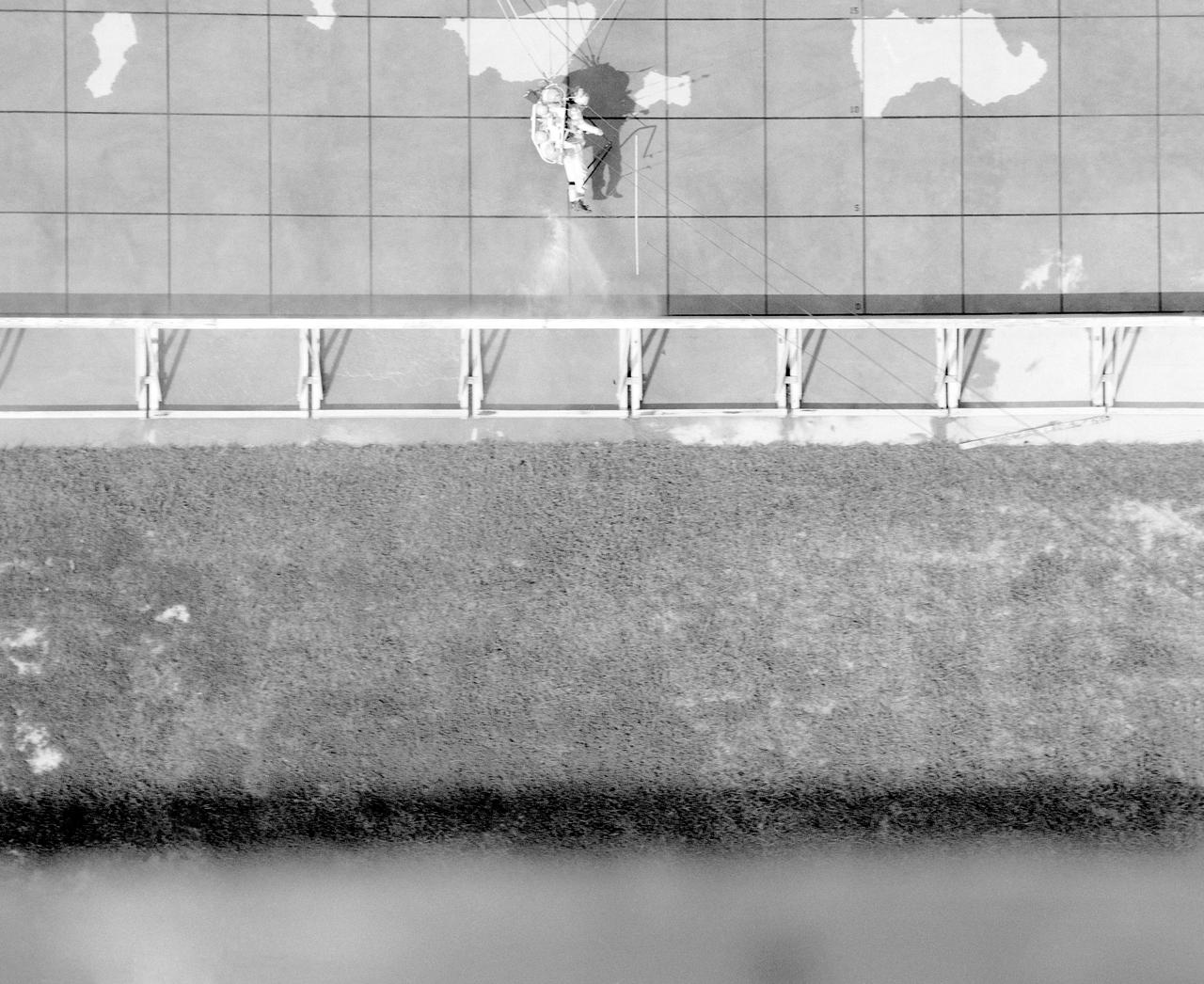

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility gantry.
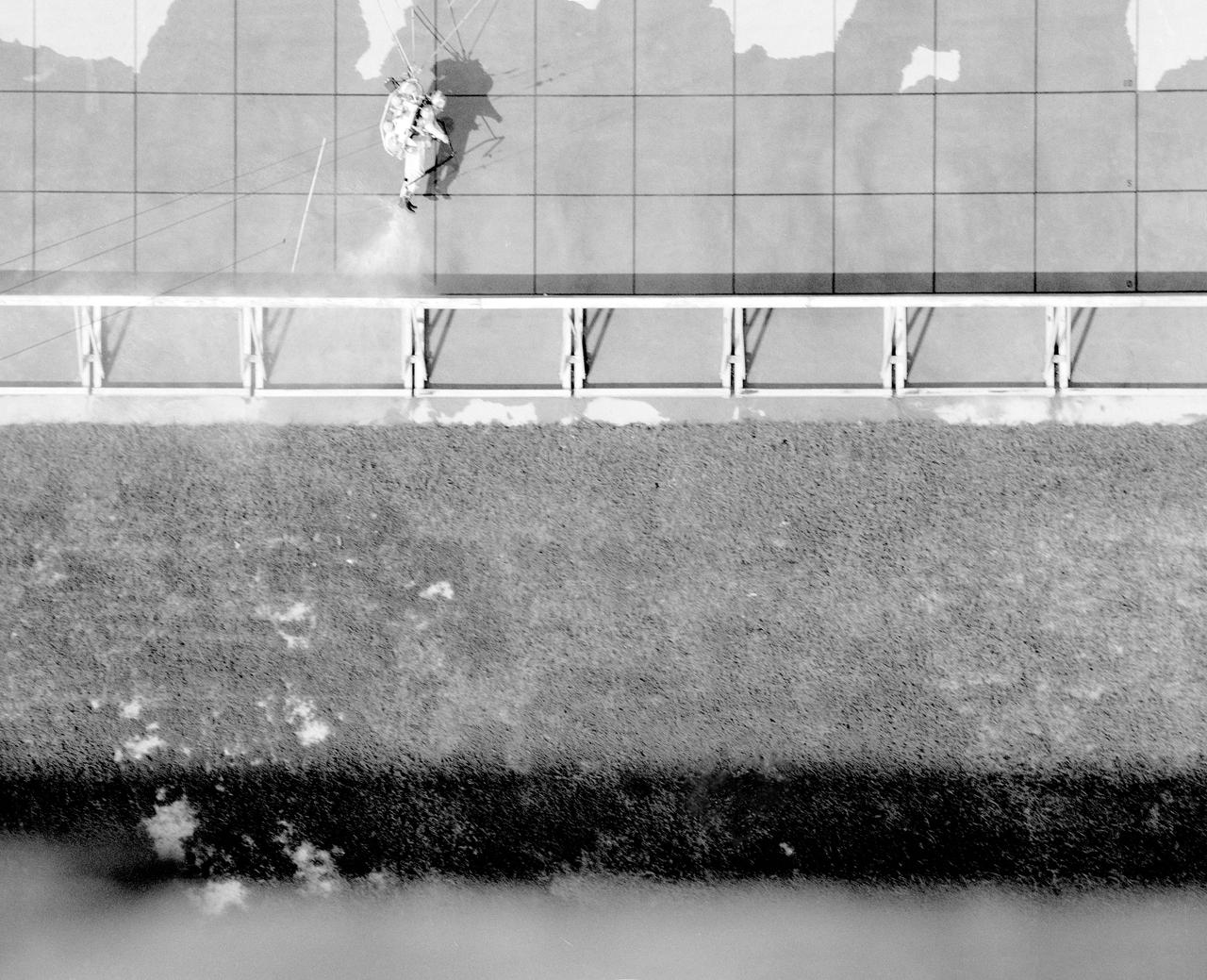

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility gantry.
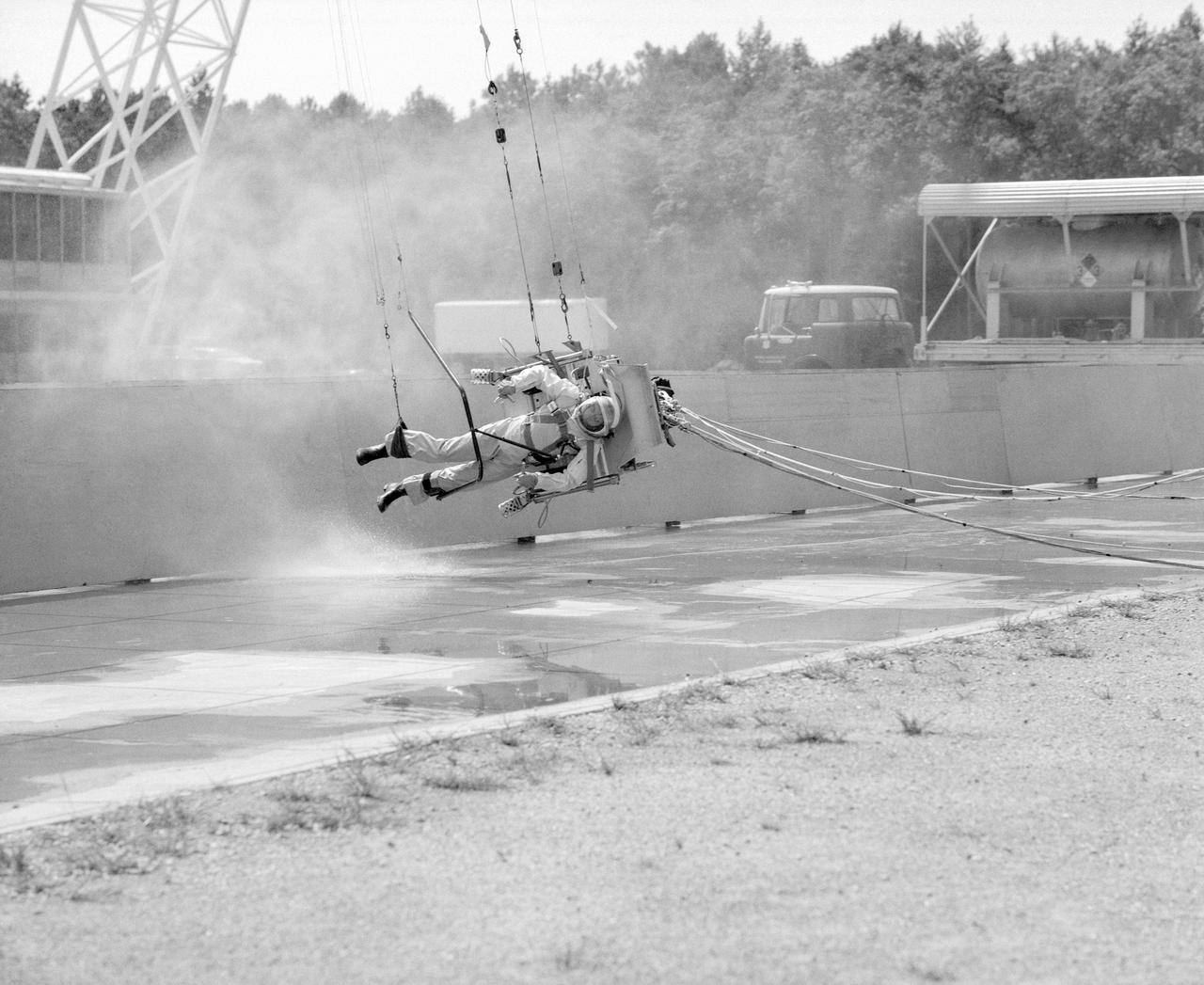

ICARUS - Lunar Walker with Pilot Dick Yenni. Yenni in ICARUS rig for jet propelled lunar mobility, at Lunar Landing Research Facility gantry.
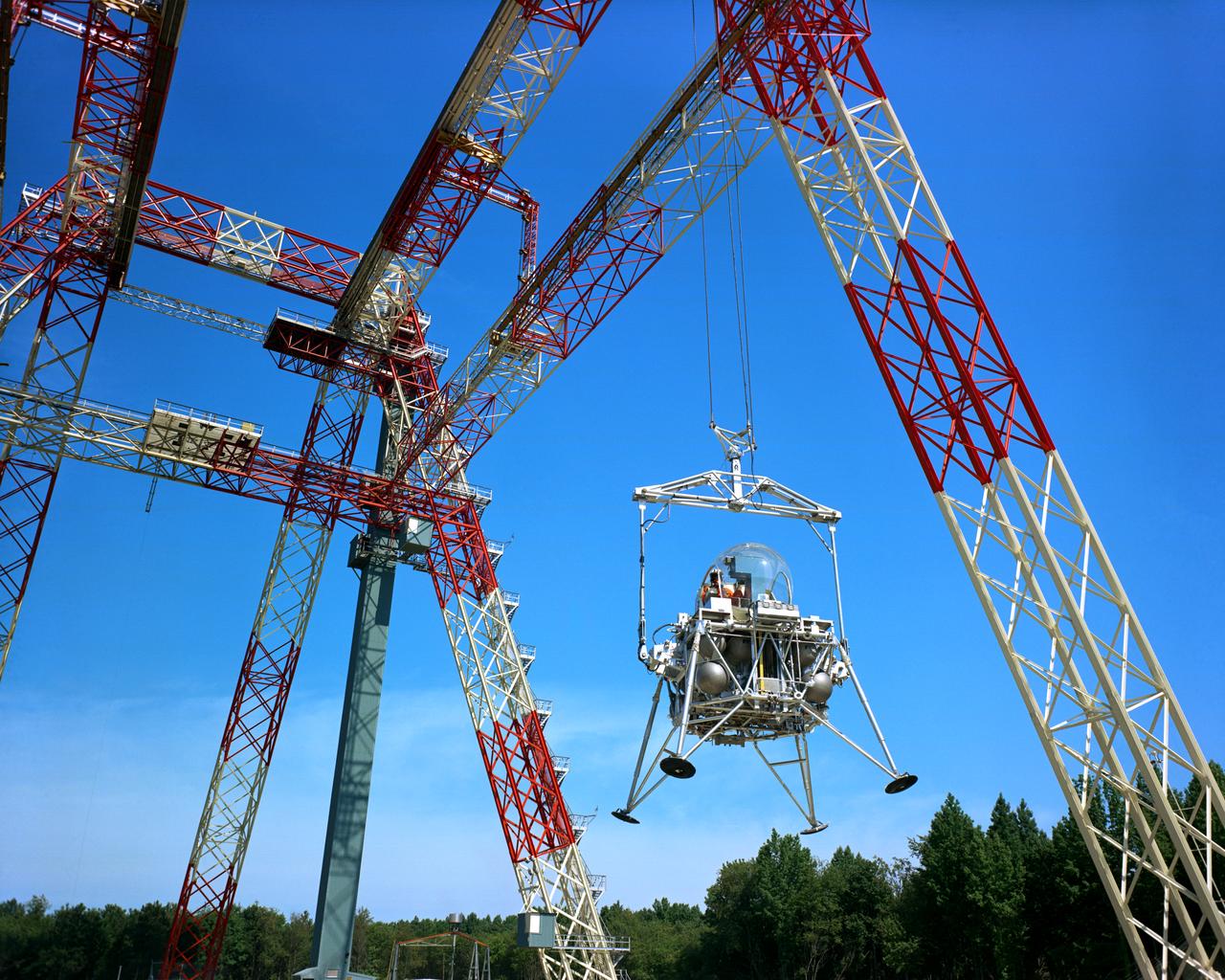

The Lunar Landing Research Facility at Langley Research Center has been put into operation. The facility, 250 feet high and 400 feet long, provides a controlled laboratory in which NASA scientists will work with research pilots to explore and develop techniques for landing a rocket-powered vehicle on the Moon, where the gravity is only one sixth as strong as on Earth. The Lunar Landing Research Facility, a controlled laboratory for exploring and developing techniques for landing a rocket-powered vehicle on the Moon, has been put into operation at the Langley Research Center. The $3.5 million facility includes a rocket-powered piloted flight test vehicle which is operated· while partially supported from a 250-foot high, 400-foot long gantry structure to simulate the one-sixth earth gravity of the Moon in research to obtain data on the problems of lunar landing. Excerpt from Langley Researcher July 2, 1965
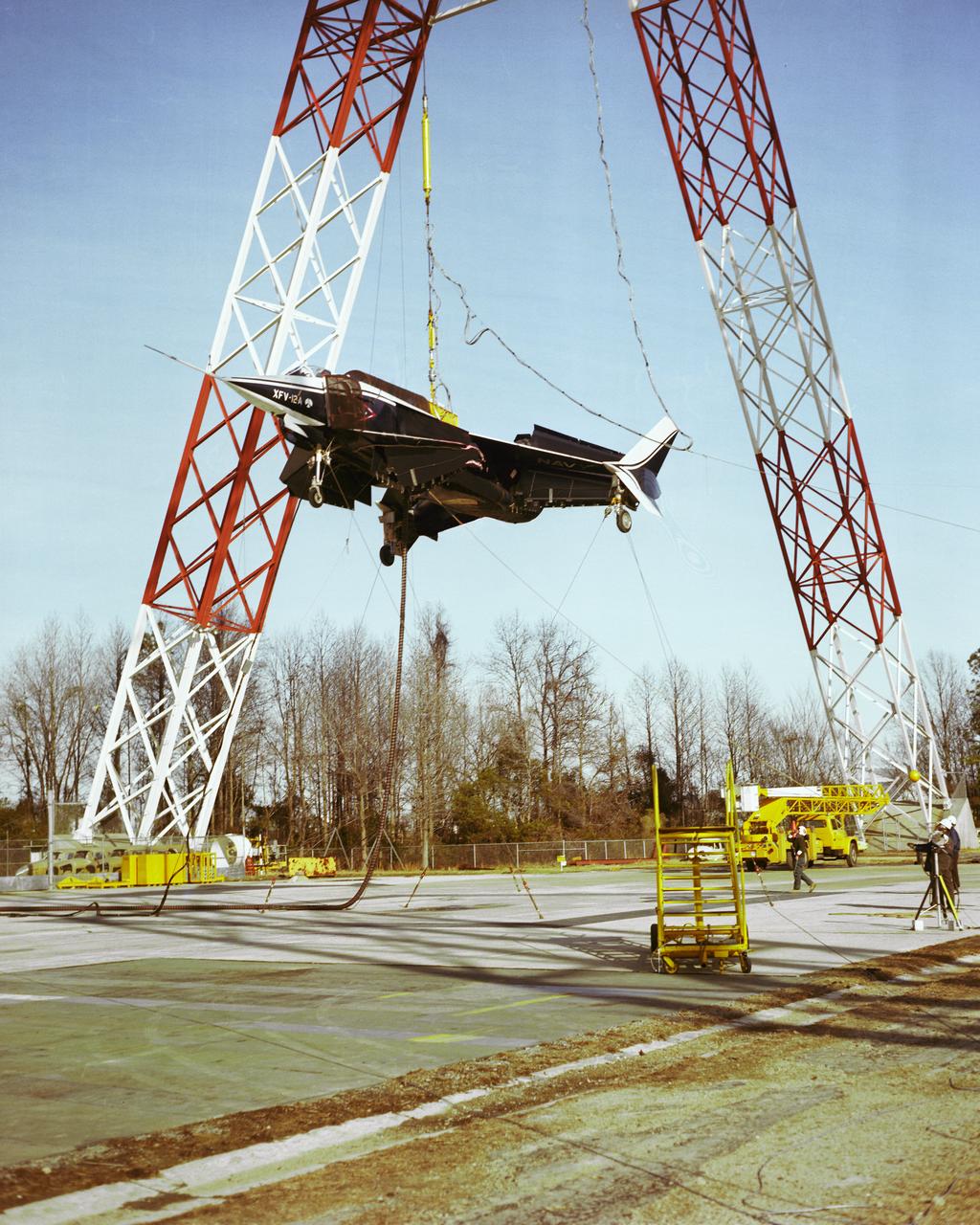

Photographed on: 01/12/78. -- Various views of a model aircraft at the Lunar Landing Facility.
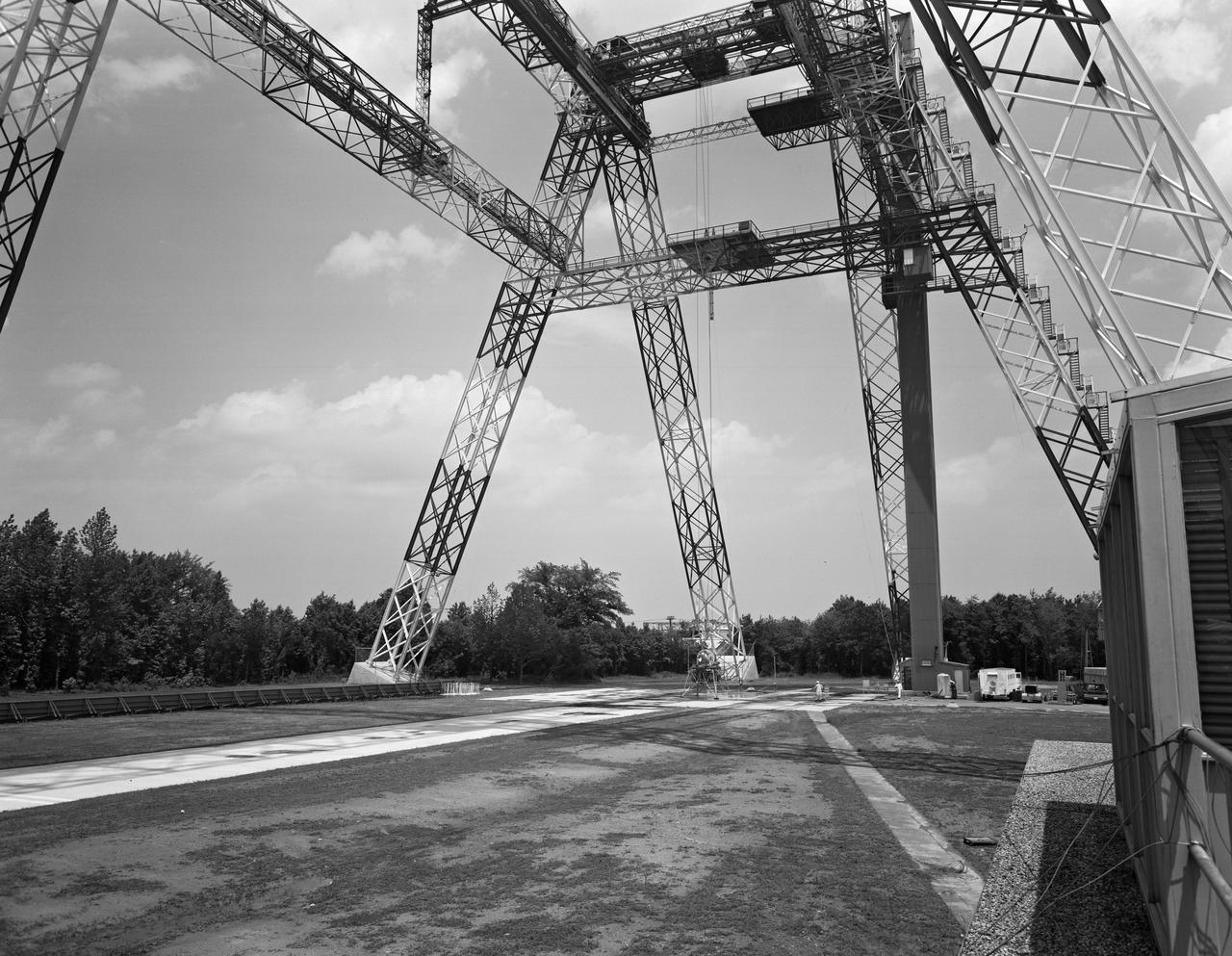

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
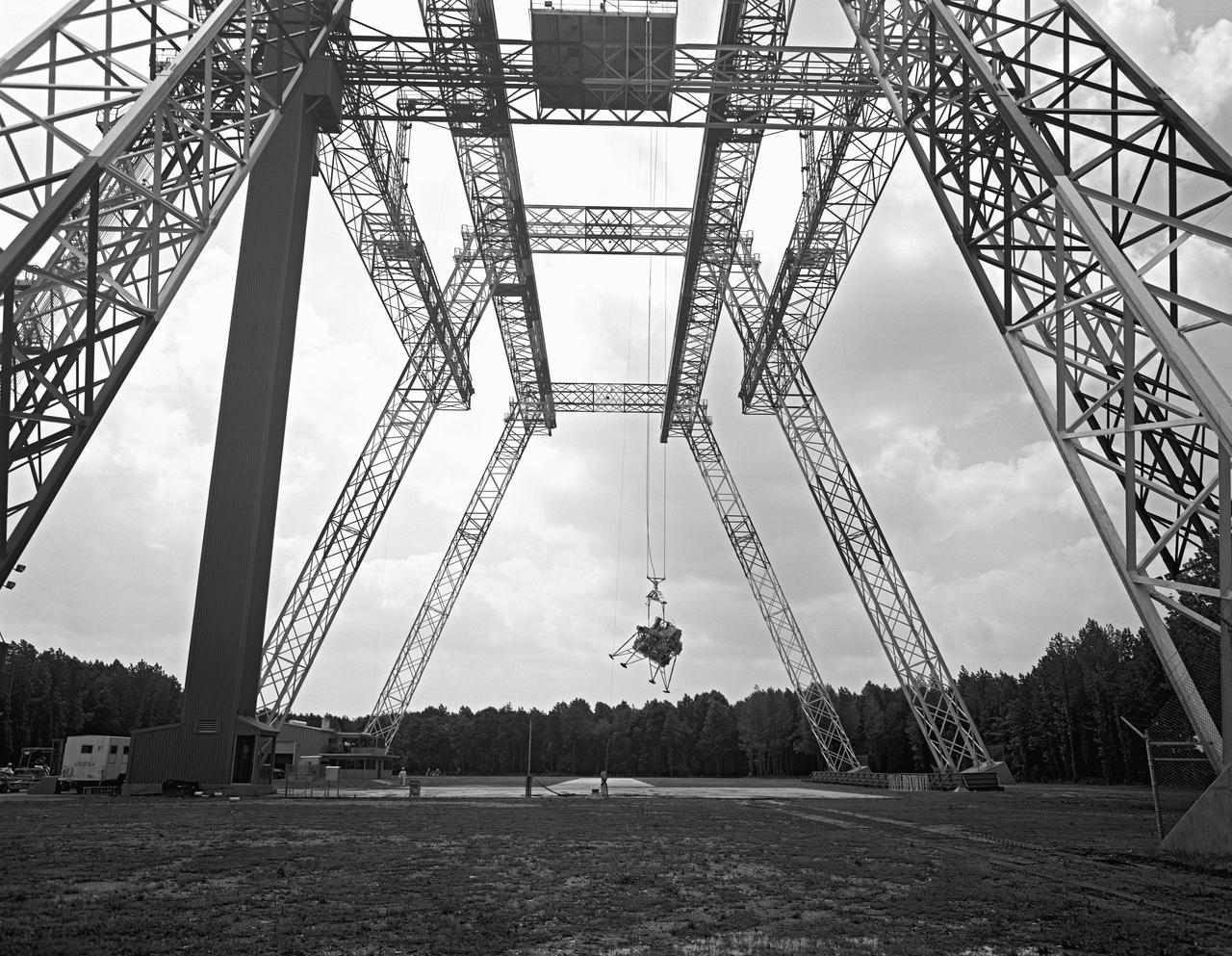

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
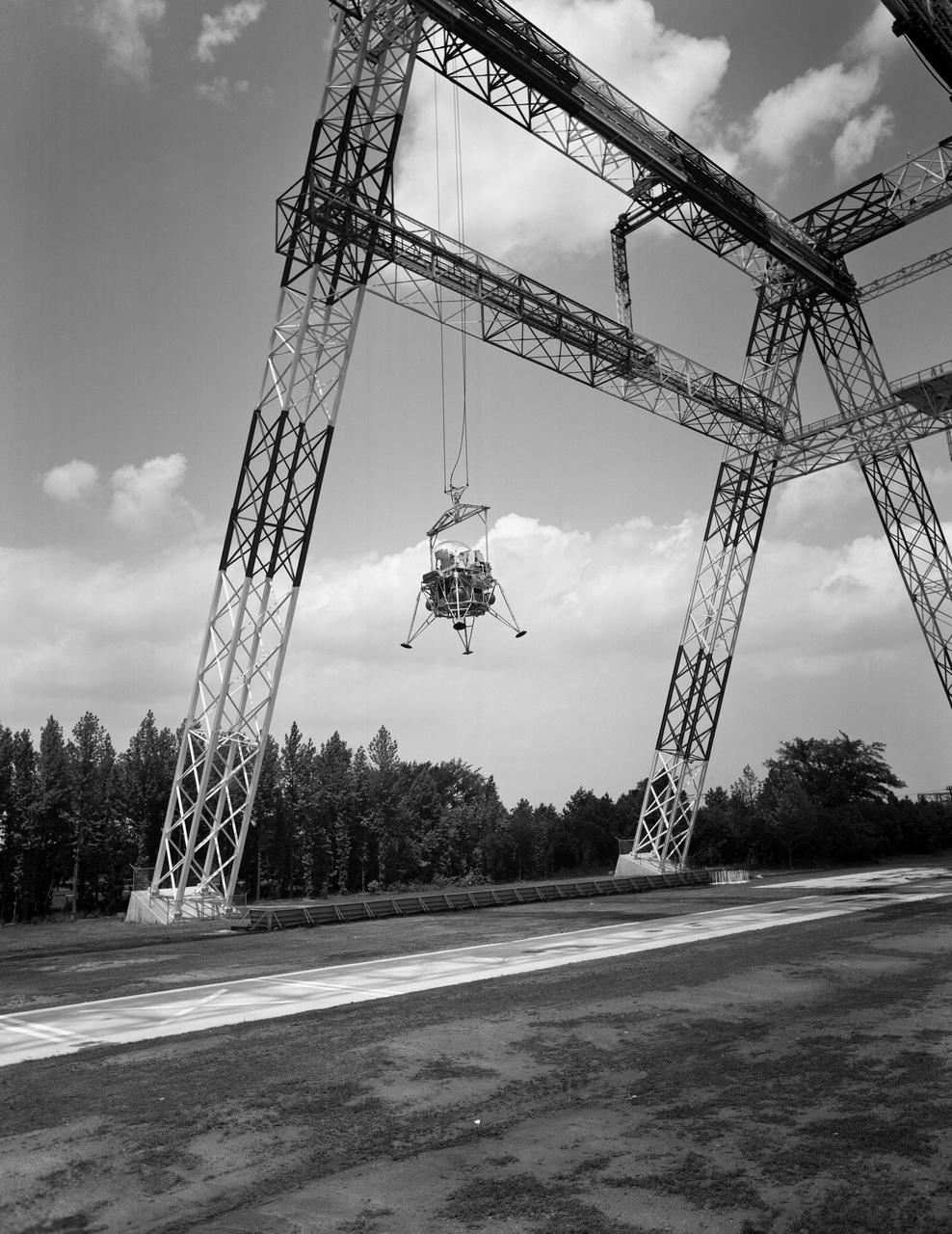

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
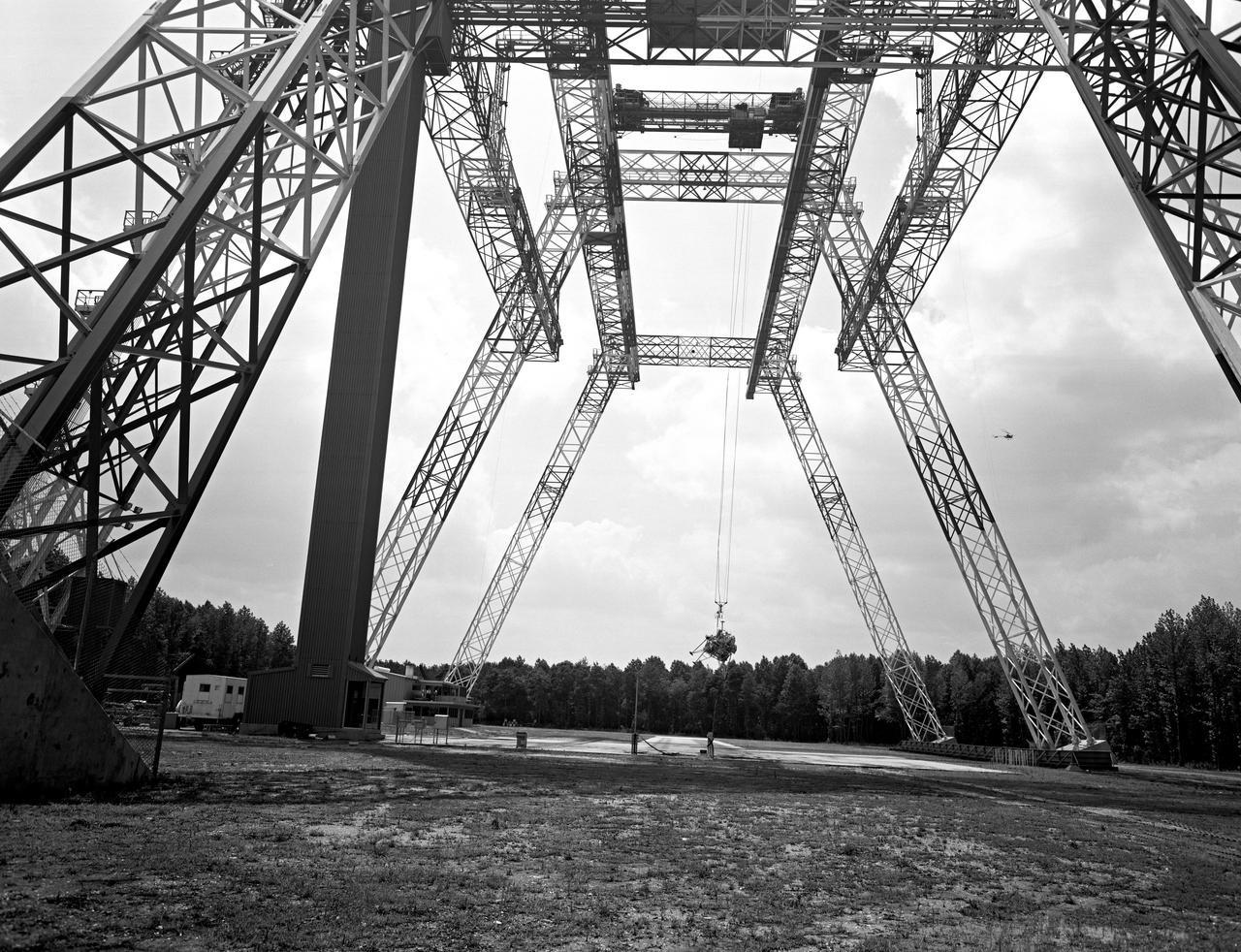

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
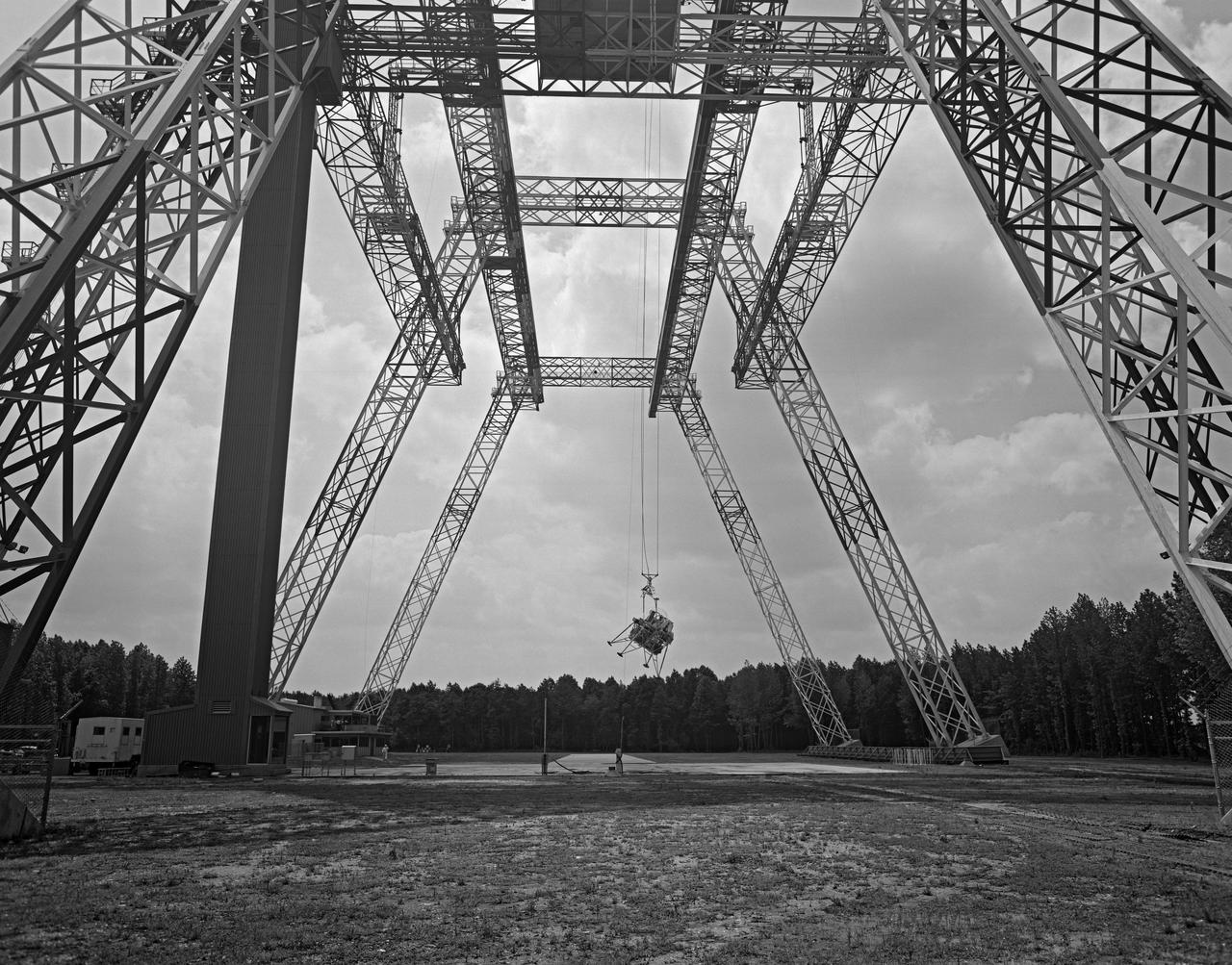

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
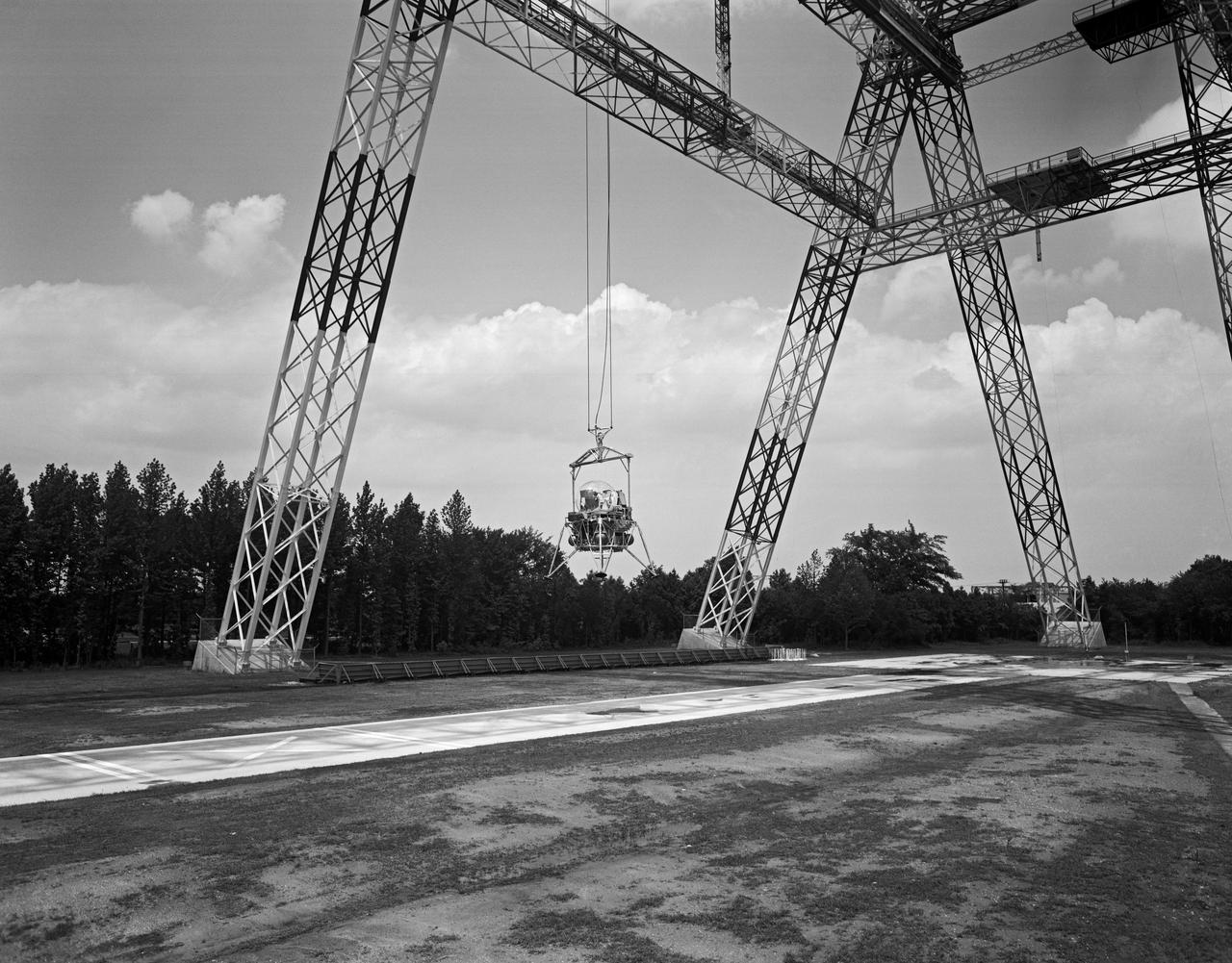

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
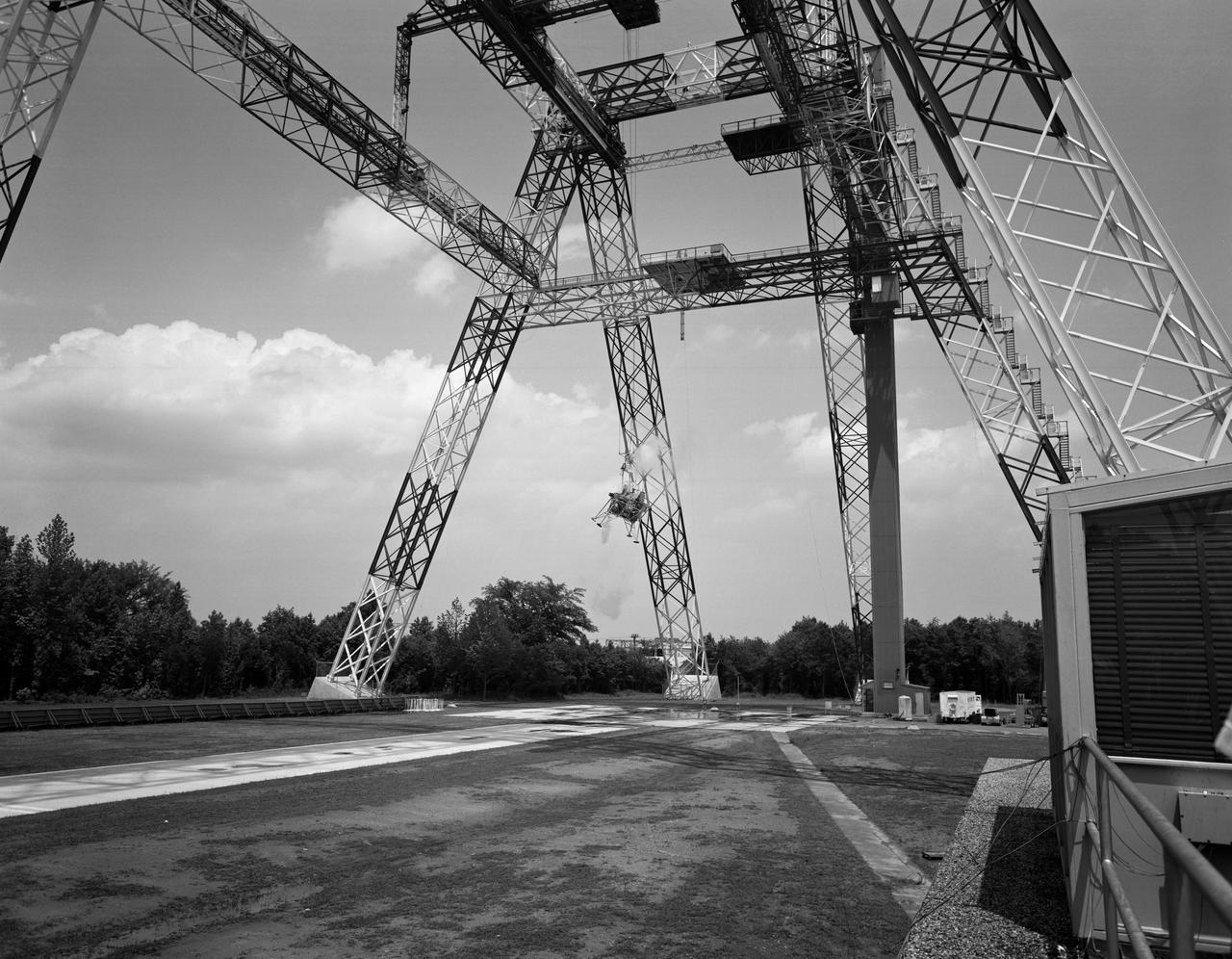

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
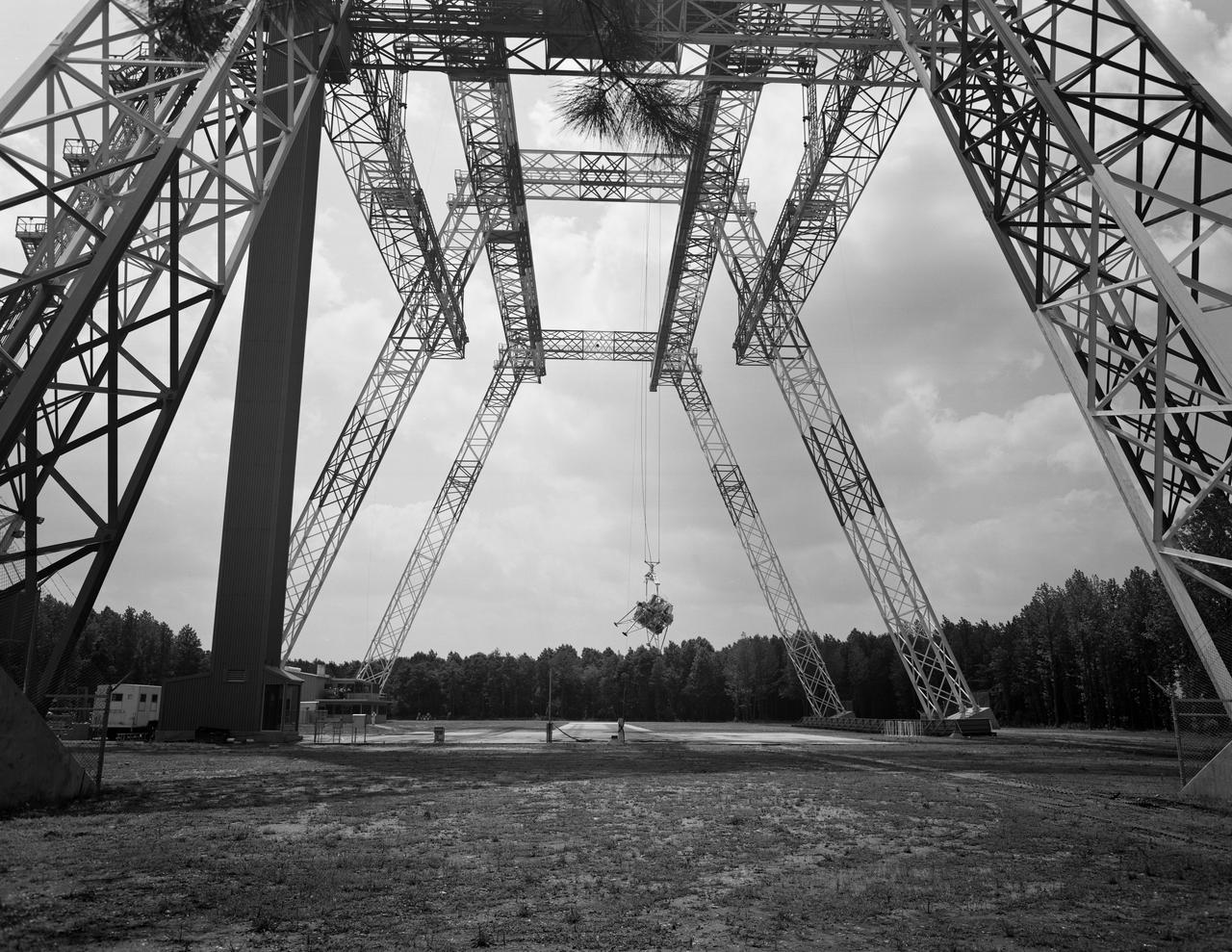

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
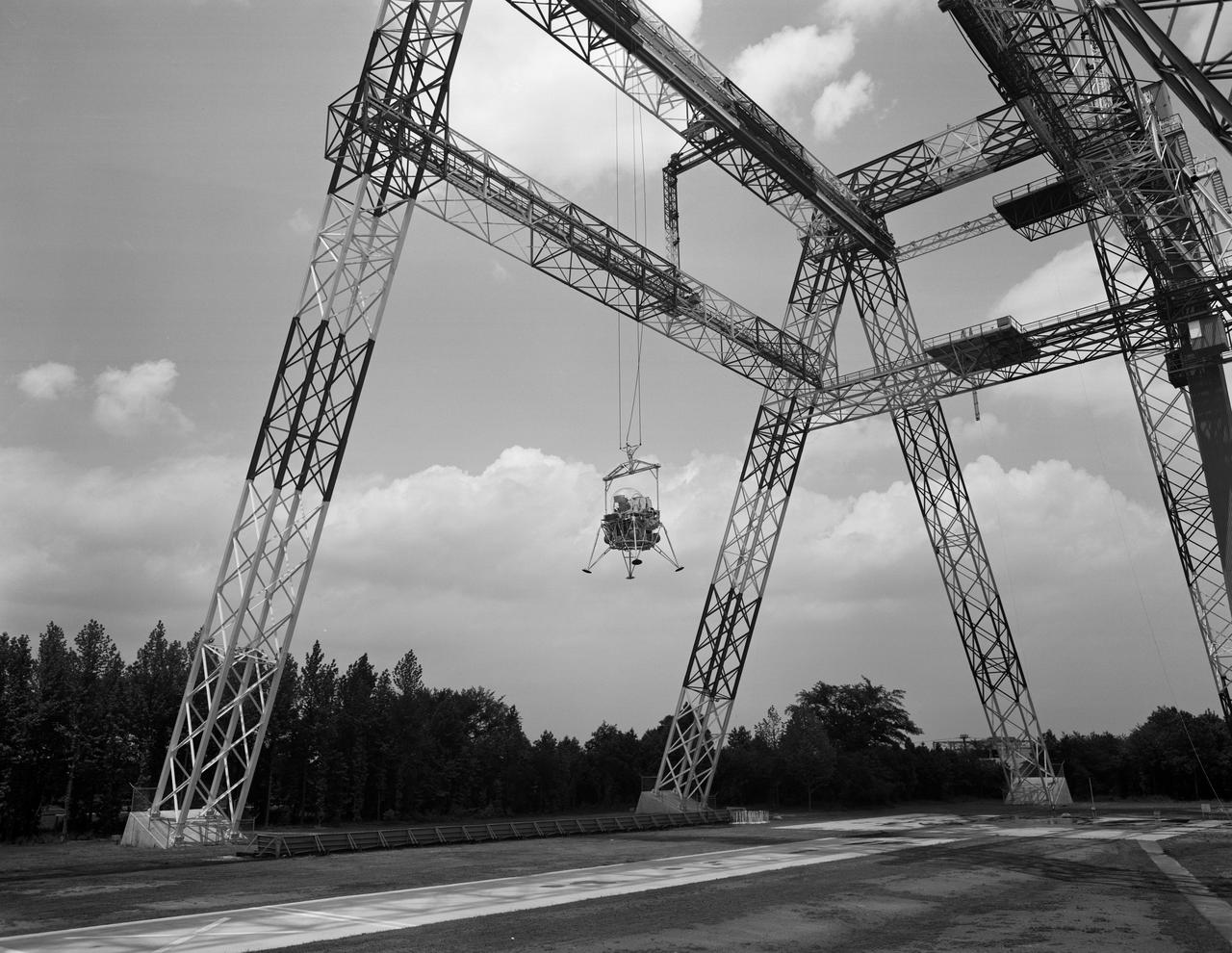

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
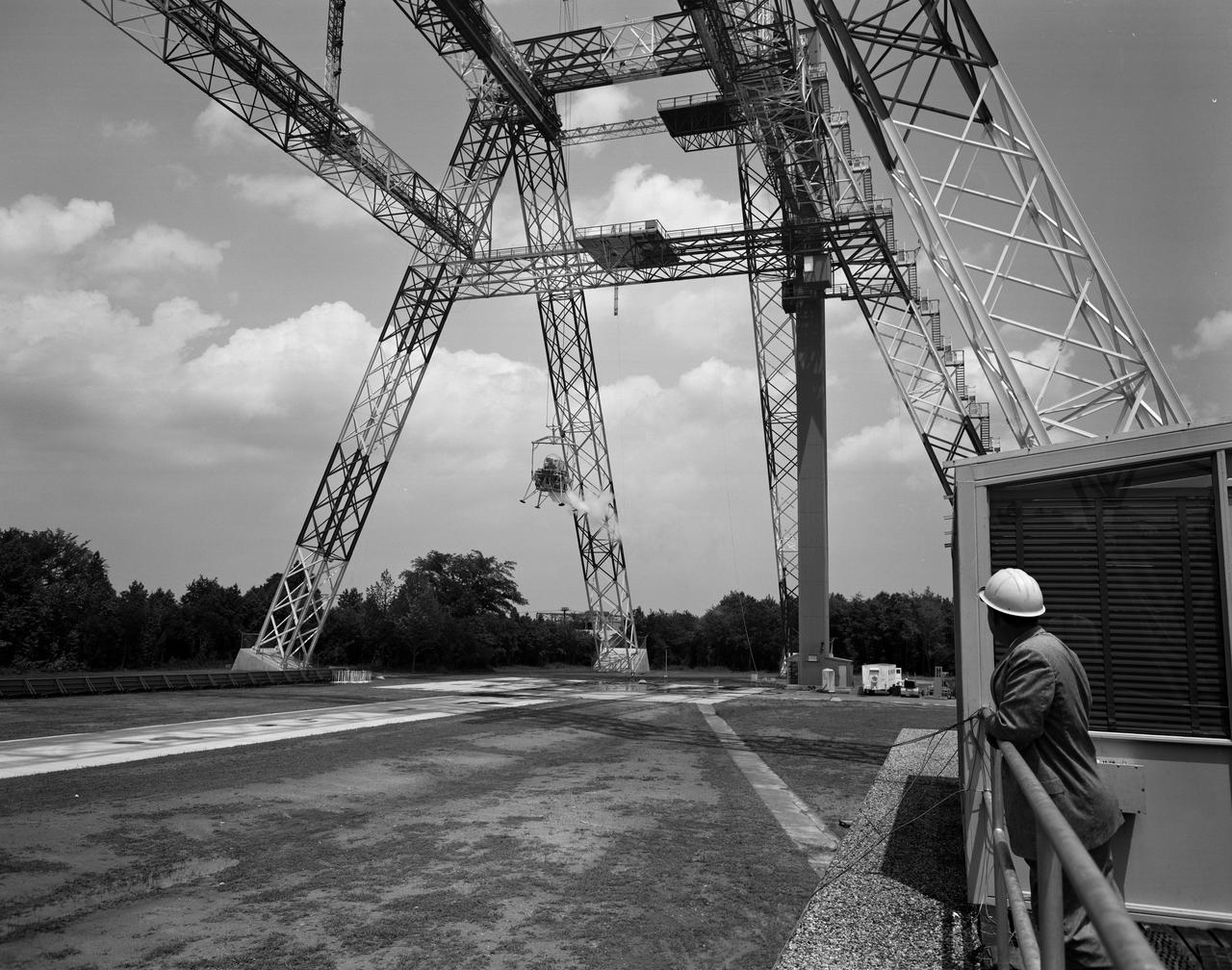

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
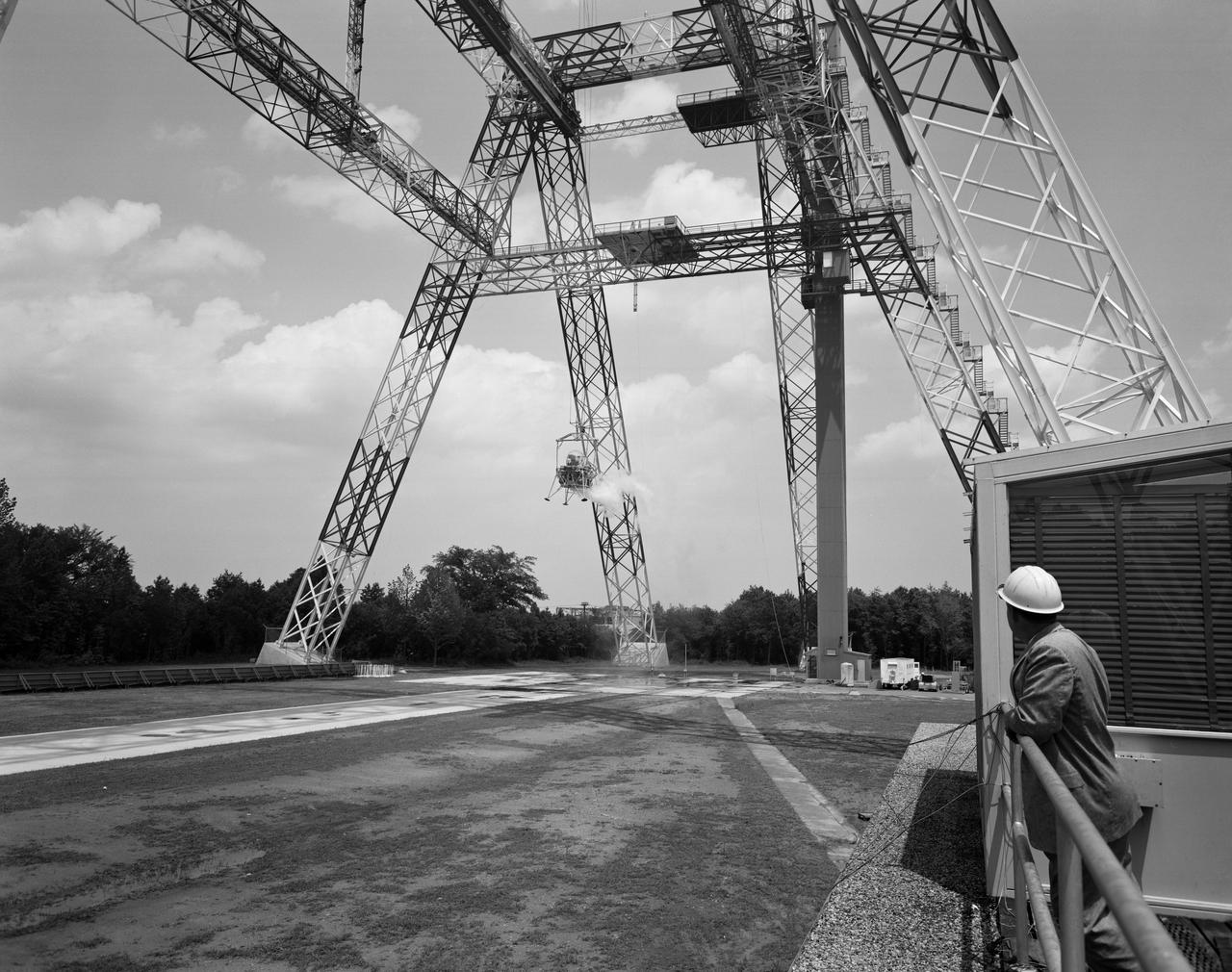

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
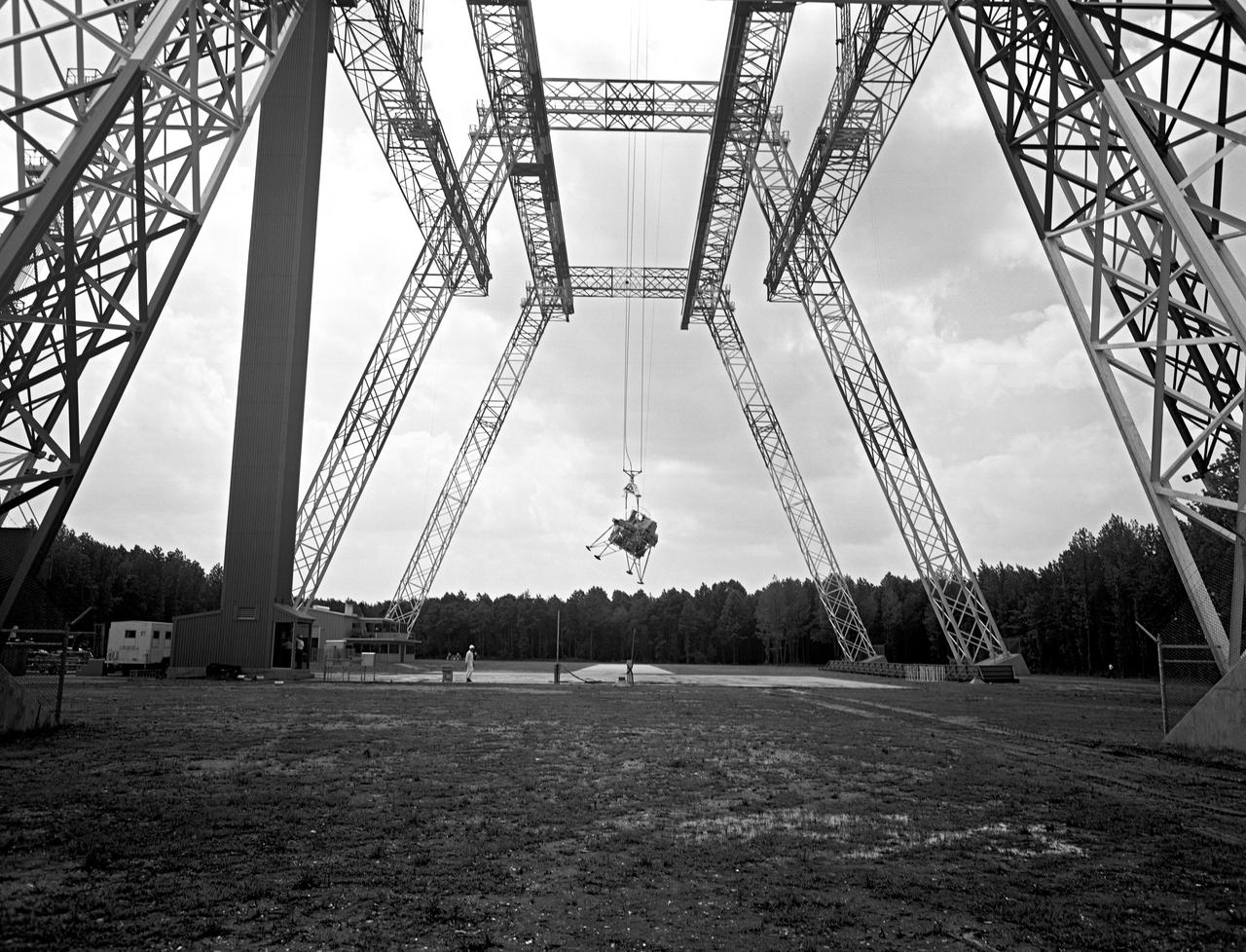

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
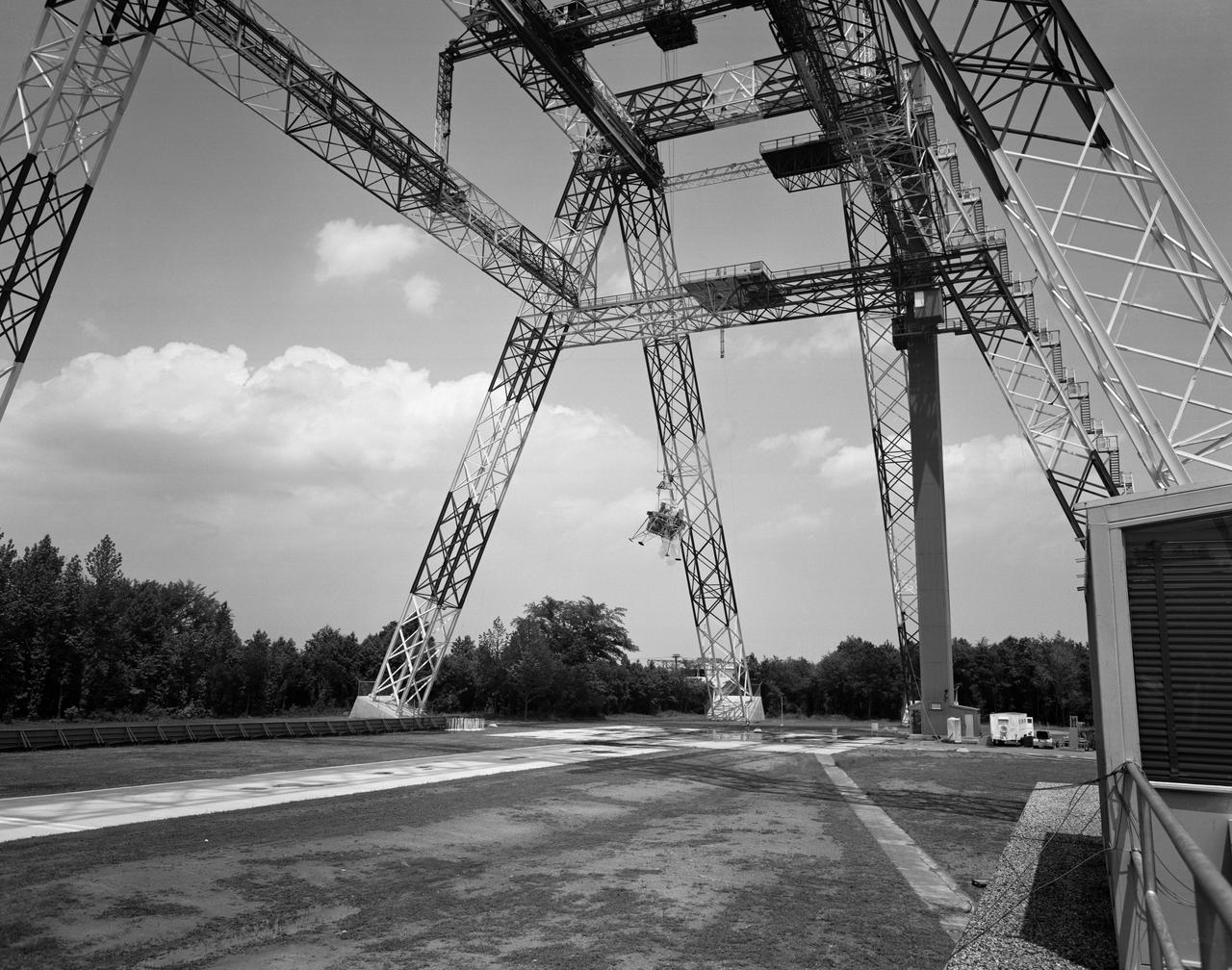

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
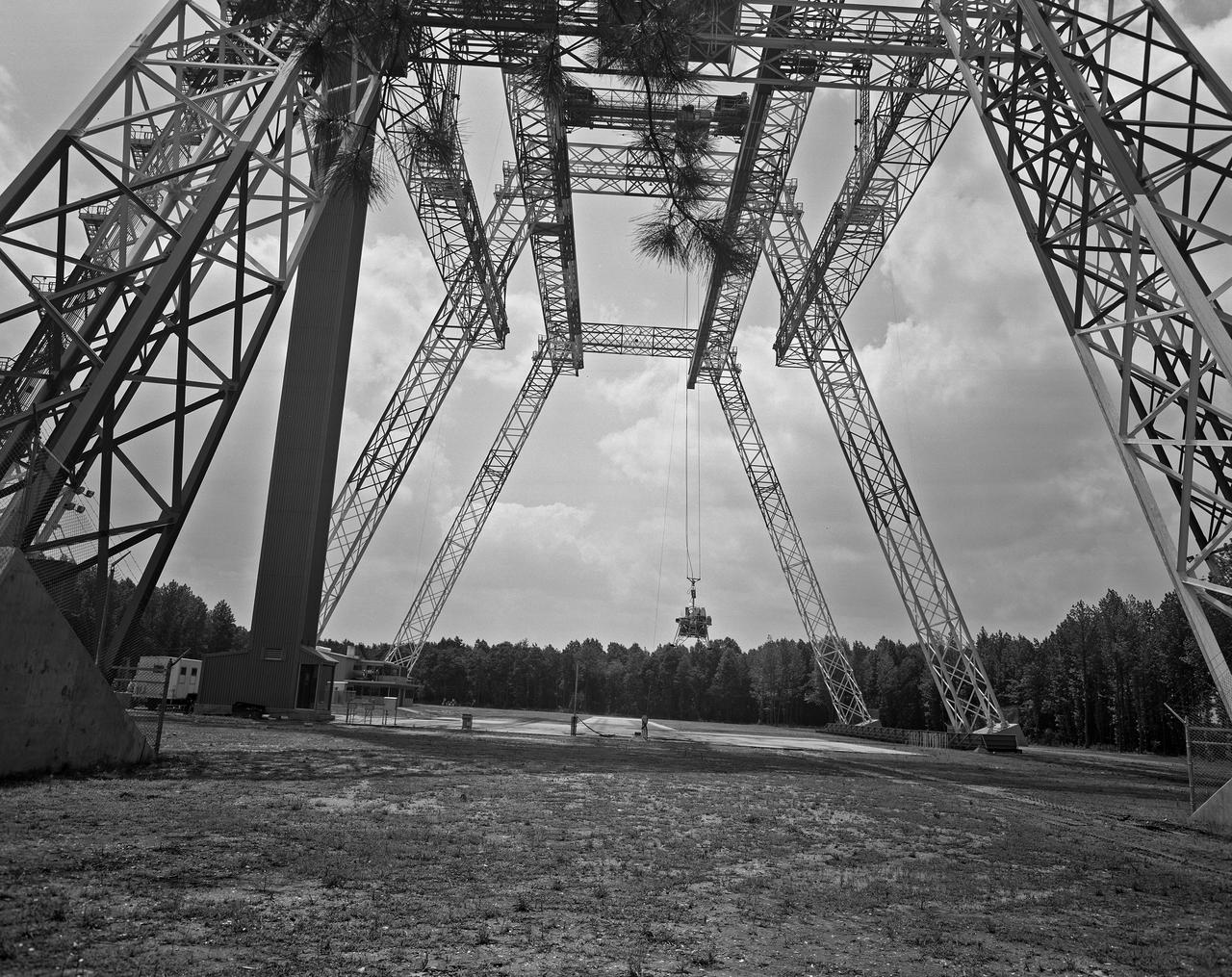

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
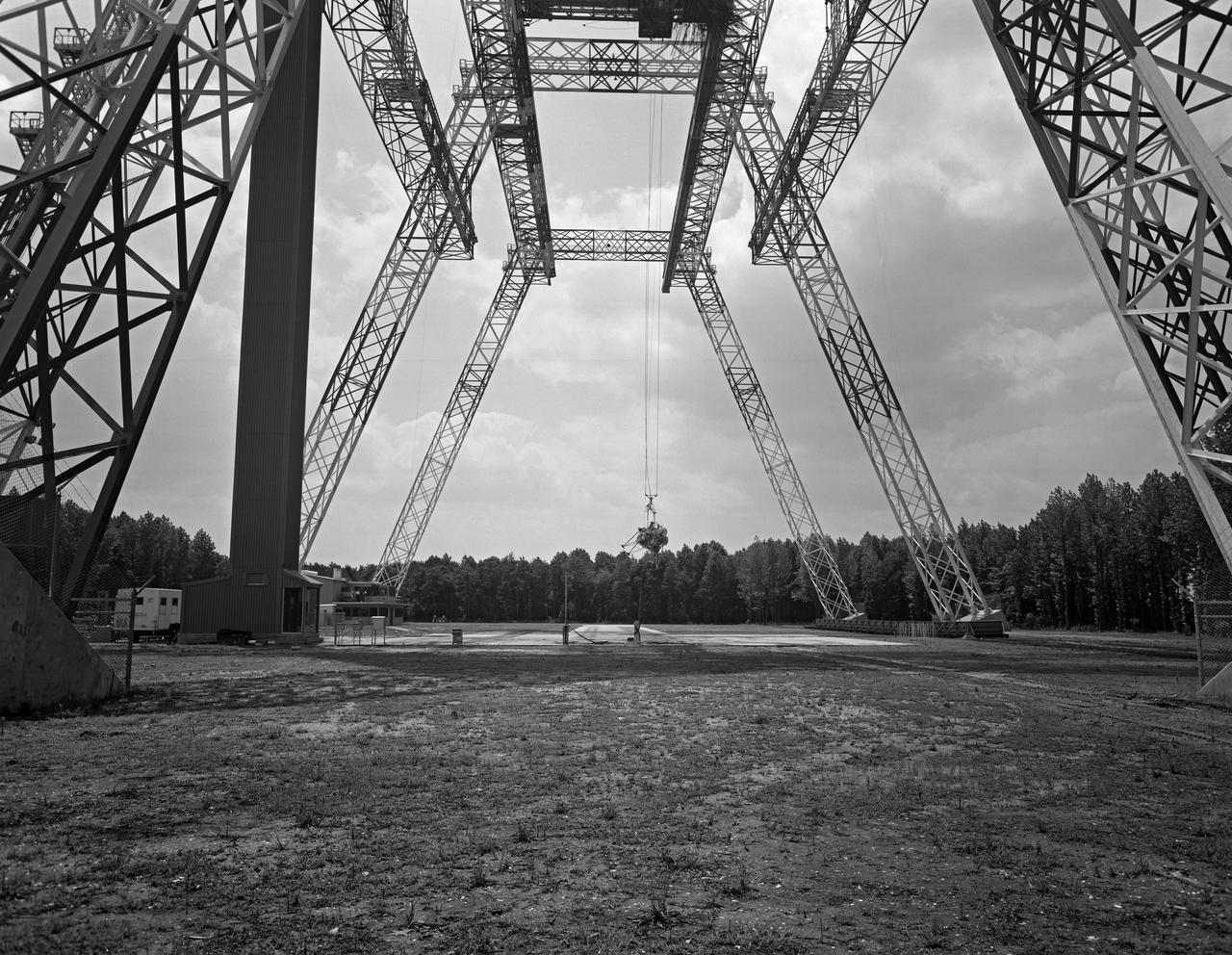

Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. Lunar Landing Testing at NASA Langley. A simulated environment that contributed in a significant way to the success of Apollo project was the Lunar Landing Research Facility, an imposing 250 foot high, 400 foot long gantry structure that became operational in 1965. Published in the book "Space Flight Revolution" NASA SP-4308 pg. 376
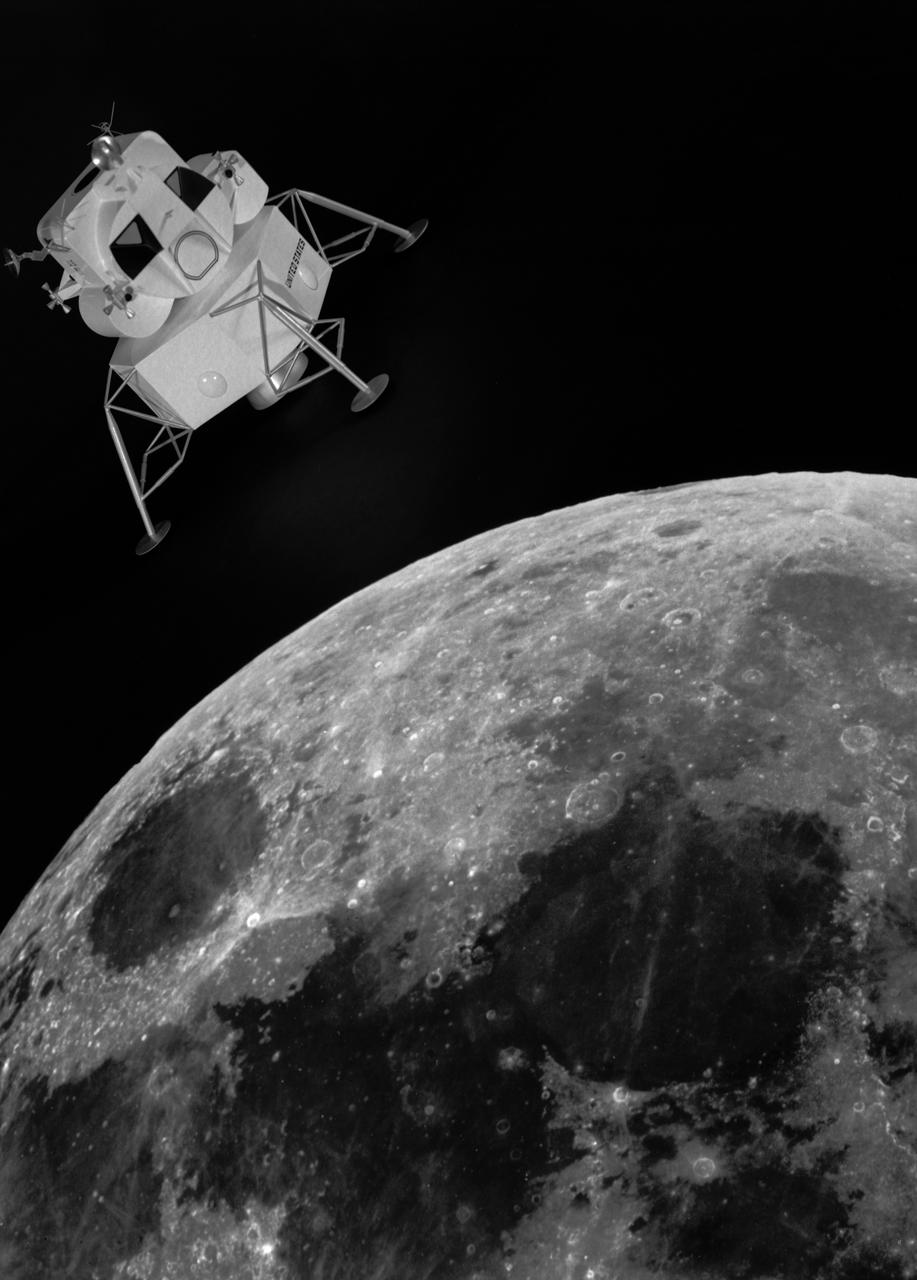

Artist rendering of the lunar excursion module approaching the moon. The lunar module design underwent gradual evolution from the first configuration proposed by Grumman in 1962. This model is a 1964 rendering. Langley had the task of building a simulator for the astronauts to practice lunar landings. The configuration of the initial vehicle used with the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) was changed in 1967 to more accurately reflect the standing position of the astronauts, cockpit arrangement, instrumentation, controls and field of view.

This montage depicts the flight crew patches for the manned Apollo 7 thru Apollo 17 missions. The Apollo 7 through 10 missions were basically manned test flights that paved the way for lunar landing missions. Primary objectives met included the demonstration of the Command Service Module (CSM) crew performance; crew/space vehicle/mission support facilities performance and testing during a manned CSM mission; CSM rendezvous capability; translunar injection demonstration; the first manned Apollo docking, the first Apollo Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA), performance of the first manned flight of the lunar module (LM); the CSM-LM docking in translunar trajectory, LM undocking in lunar orbit, LM staging in lunar orbit, and manned LM-CSM docking in lunar orbit. Apollo 11 through 17 were lunar landing missions with the exception of Apollo 13 which was forced to circle the moon without landing due to an onboard explosion. The craft was,however, able to return to Earth safely. Apollo 11 was the first manned lunar landing mission and performed the first lunar surface EVA. Landing site was the Sea of Tranquility. A message for mankind was delivered, the U.S. flag was planted, experiments were set up and 47 pounds of lunar surface material was collected for analysis back on Earth. Apollo 12, the 2nd manned lunar landing mission landed in the Ocean of Storms and retrieved parts of the unmanned Surveyor 3, which had landed on the Moon in April 1967. The Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) was deployed, and 75 pounds of lunar material was gathered. Apollo 14, the 3rd lunar landing mission landed in Fra Mauro. ALSEP and other instruments were deployed, and 94 pounds of lunar materials were gathered, using a hand cart for first time to transport rocks. Apollo 15, the 4th lunar landing mission landed in the Hadley-Apennine region. With the first use of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), the crew was bale to gather 169 pounds of lunar material. Apollo 16, the 5th lunar landing mission, landed in the Descartes Highlands for the first study of highlands area. Selected surface experiments were deployed, the ultraviolet camera/spectrograph was used for first time on the Moon, and the LRV was used for second time for a collection of 213 pounds of lunar material. The Apollo program came to a close with Apollo 17, the 6th and final manned lunar landing mission that landed in the Taurus-Littrow highlands and valley area. This mission hosted the first scientist-astronaut, Schmitt, to land on the Moon. The 6th automated research station was set up, and 243 ponds of lunar material was gathered using the LRV.
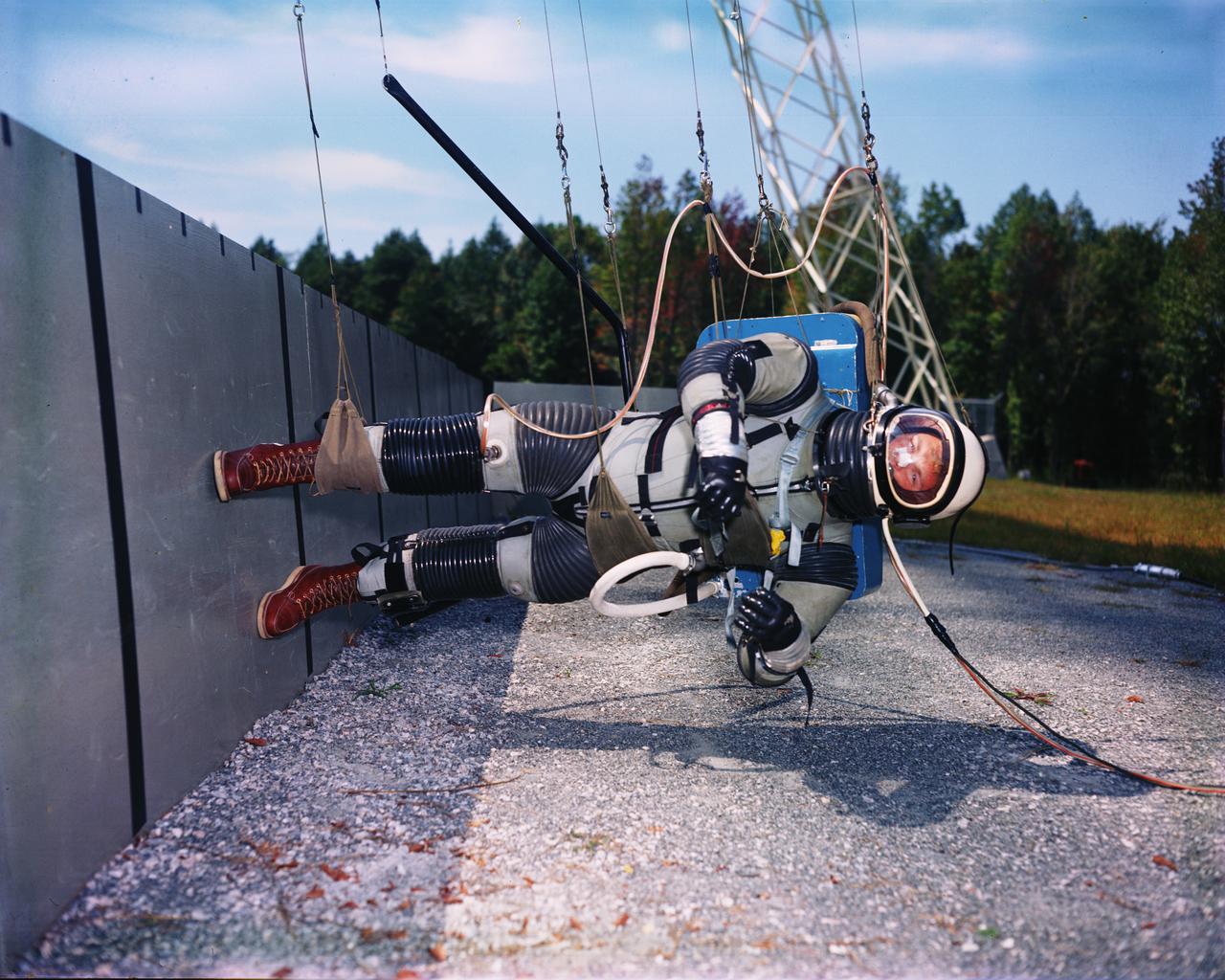
Lunar Landing Walking Simulator: Researchers at Langley study the ability of astronauts to walk, run and perform other tasks required during lunar exploration. The Reduced Gravity Simulator gave researchers the opportunity to look at the effects of one-sixth normal gravity on self-locomotion. Several Apollo astronauts practiced lunar waling at the facility.
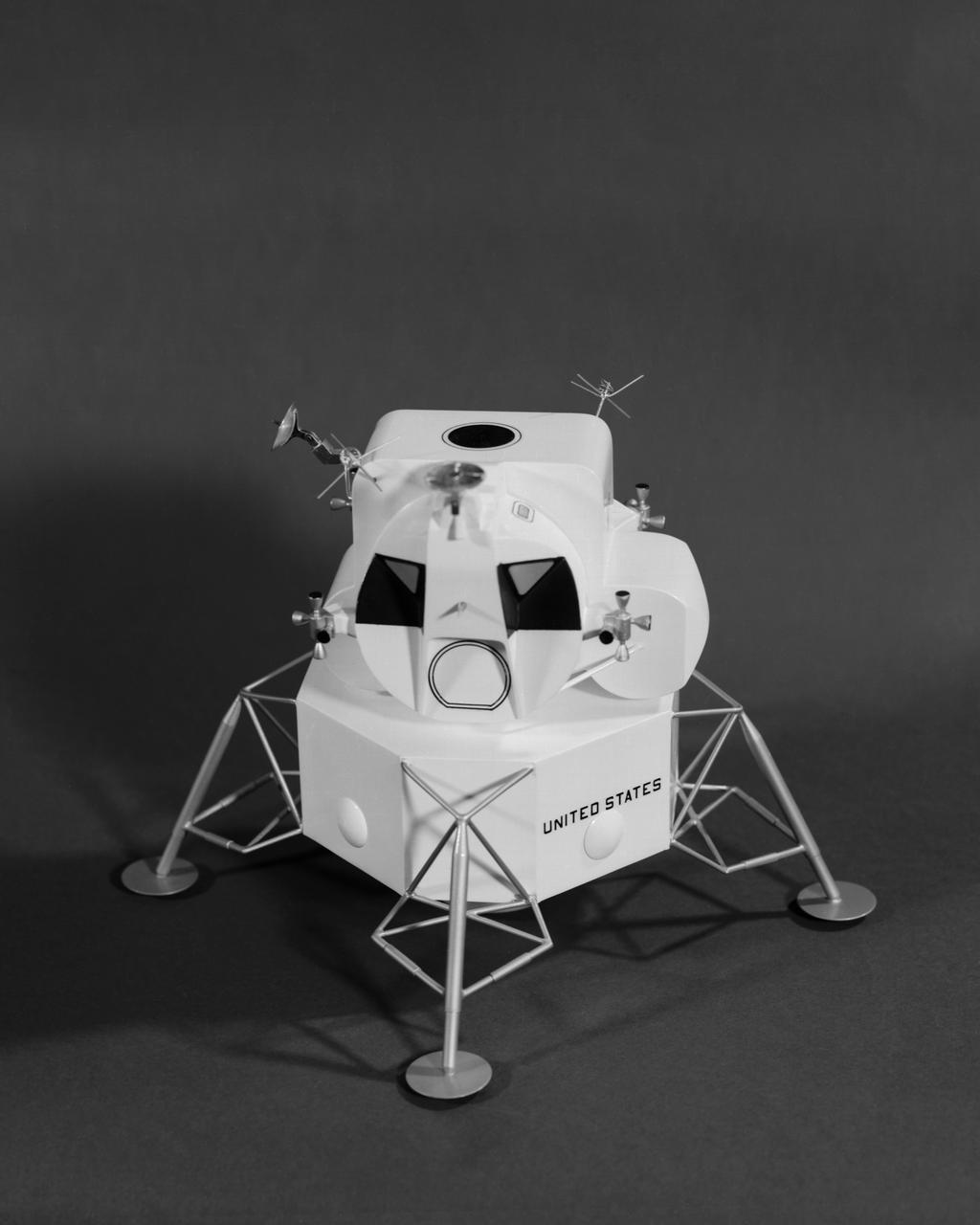

The lunar module design underwent gradual evolution from the first configuration proposed by Grumman in 1962. This model is the 1964 version. Langley had the task of building a simulator for the astronauts to practice lunar landings. The configuration of the initial vehicle used with the Lunar Landing Research Facility (LLRF) was changed in 1967 to more accurately reflect the standing position of the astronauts, cockpit arrangement, instrumentation, controls and field of view.
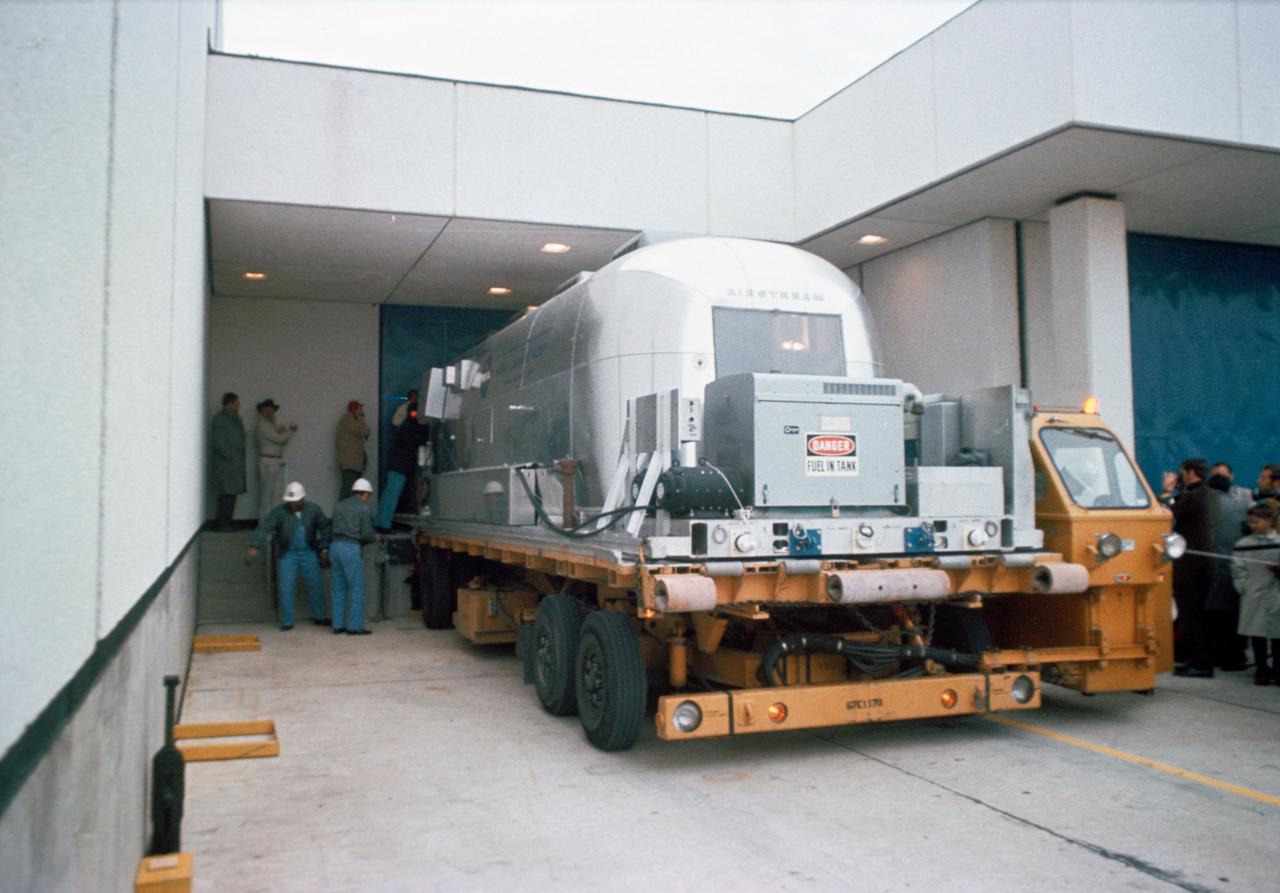

A Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), with the crew of the Apollo XII Lunar Landing Mission aboard, is shown on arriving at JSC, Saturday morning, 11/29/1969.
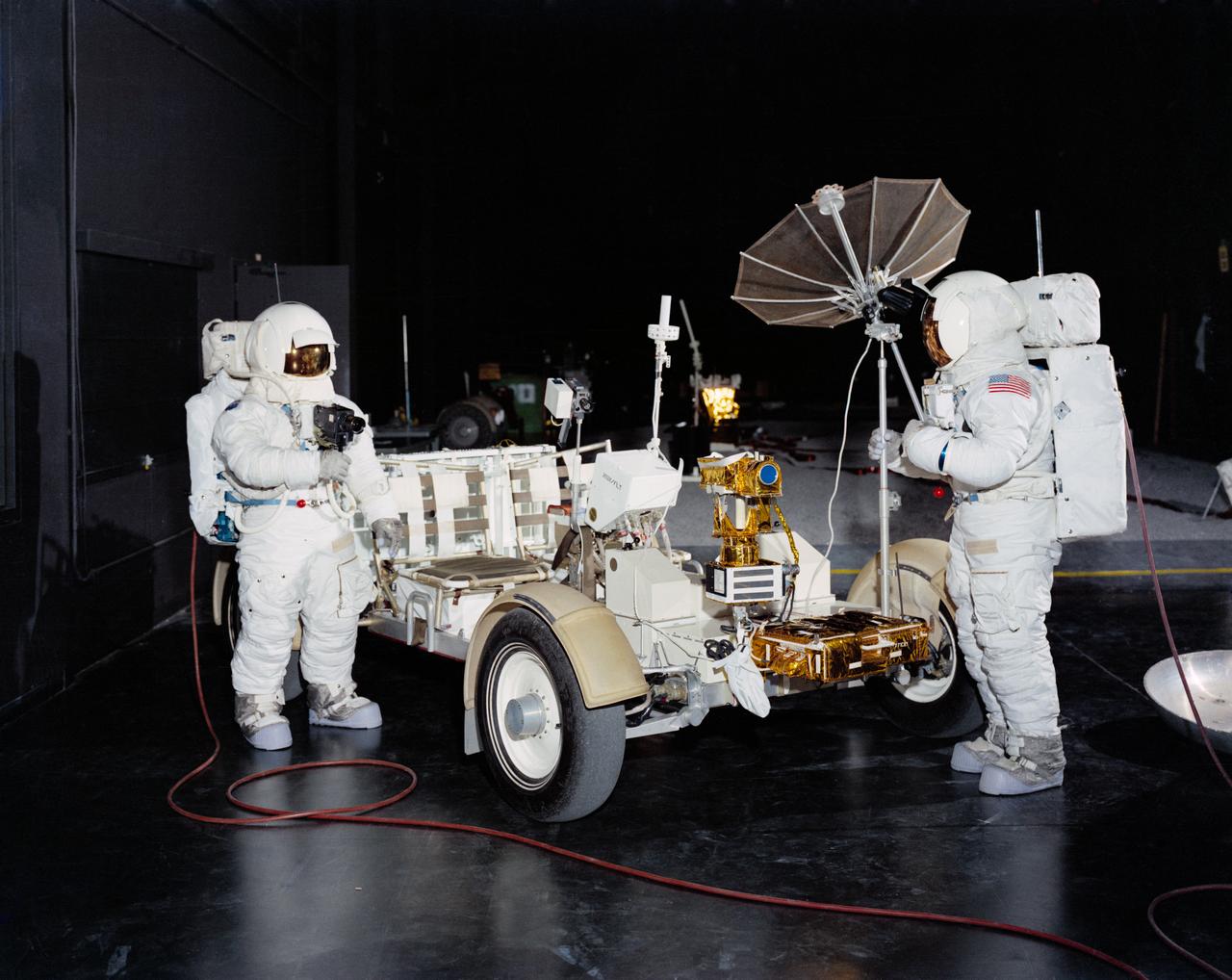

S71-16722 (January 1971) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission are shown with the Lunar Roving Vehicle "one G" trainer in Building 5, Mission Simulation and Training Facility, Manned Spacecraft Center. Astronaut David R. Scott (on right) is the Apollo 15 commander; and astronaut James B. Irwin is the lunar module pilot. A Lunar Roving Vehicle similar to this trainer will be used by Scott and Irwin during their Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity.
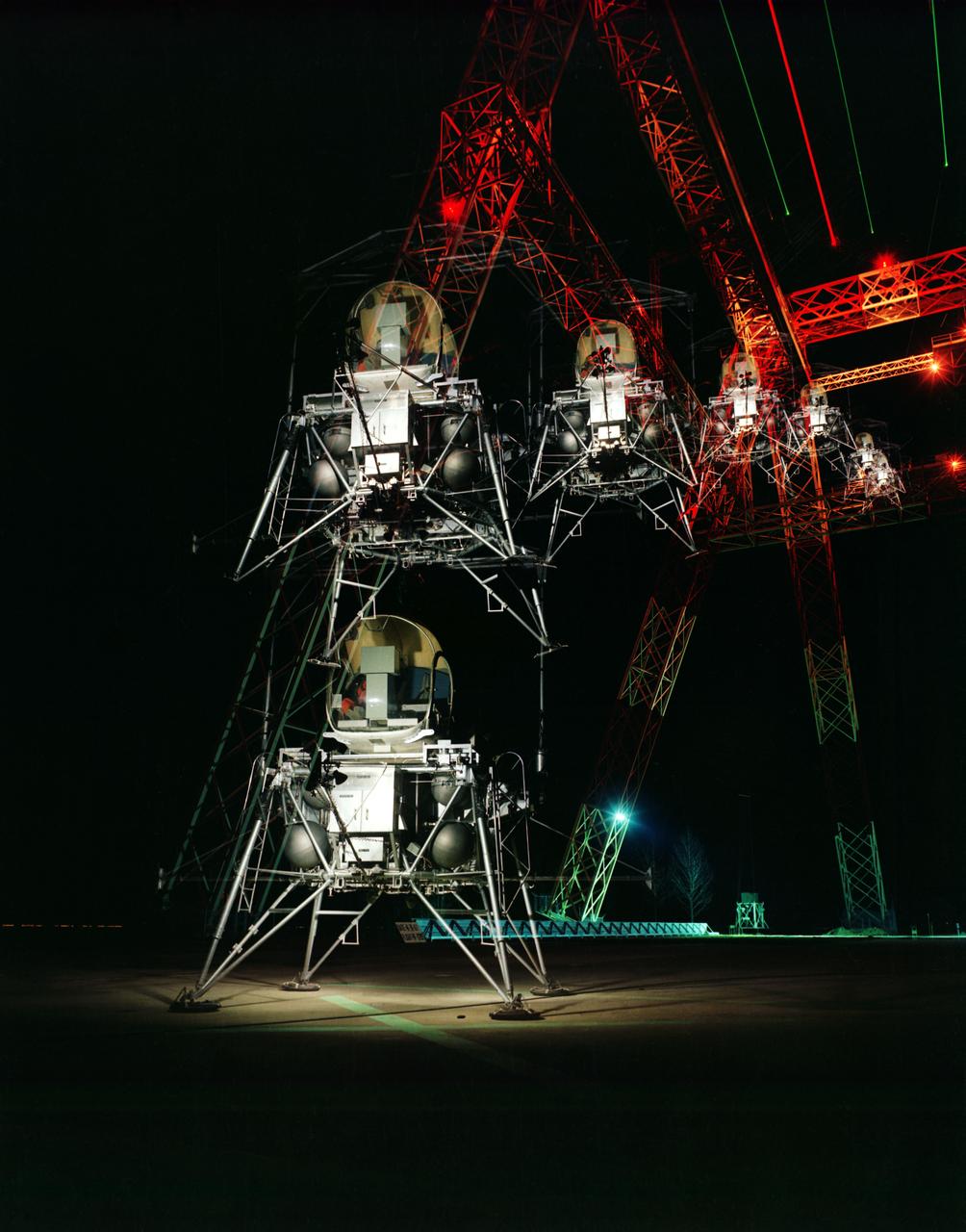

During a nighttime training session, a multiple exposure captures the movement of the Lunar Excursion Module Simulator (LEMS). The LEMS was a manned vehicle used to familiarize the Apollo astronauts with the handling characteristics of lunar-landing type vehicle. The Apollo Program is best known for the astronaut Neal Armstrong s first step on the Moon July 20, 1969. In its earliest test period, the LEMS featured a helicopter crew cabin atop the lunar landing module. Later, the helicopter crew cabin was replaced with a stand-up rectangular cabin which was more efficient for controlling maneuvers and for better viewing by the pilot. The vehicle was designed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA. This multiple exposure shows a simulated Moon landing of the (LEMS) trainer at Langley s Lunar Landing Research Facility. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 70), by James Shultz. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 93.
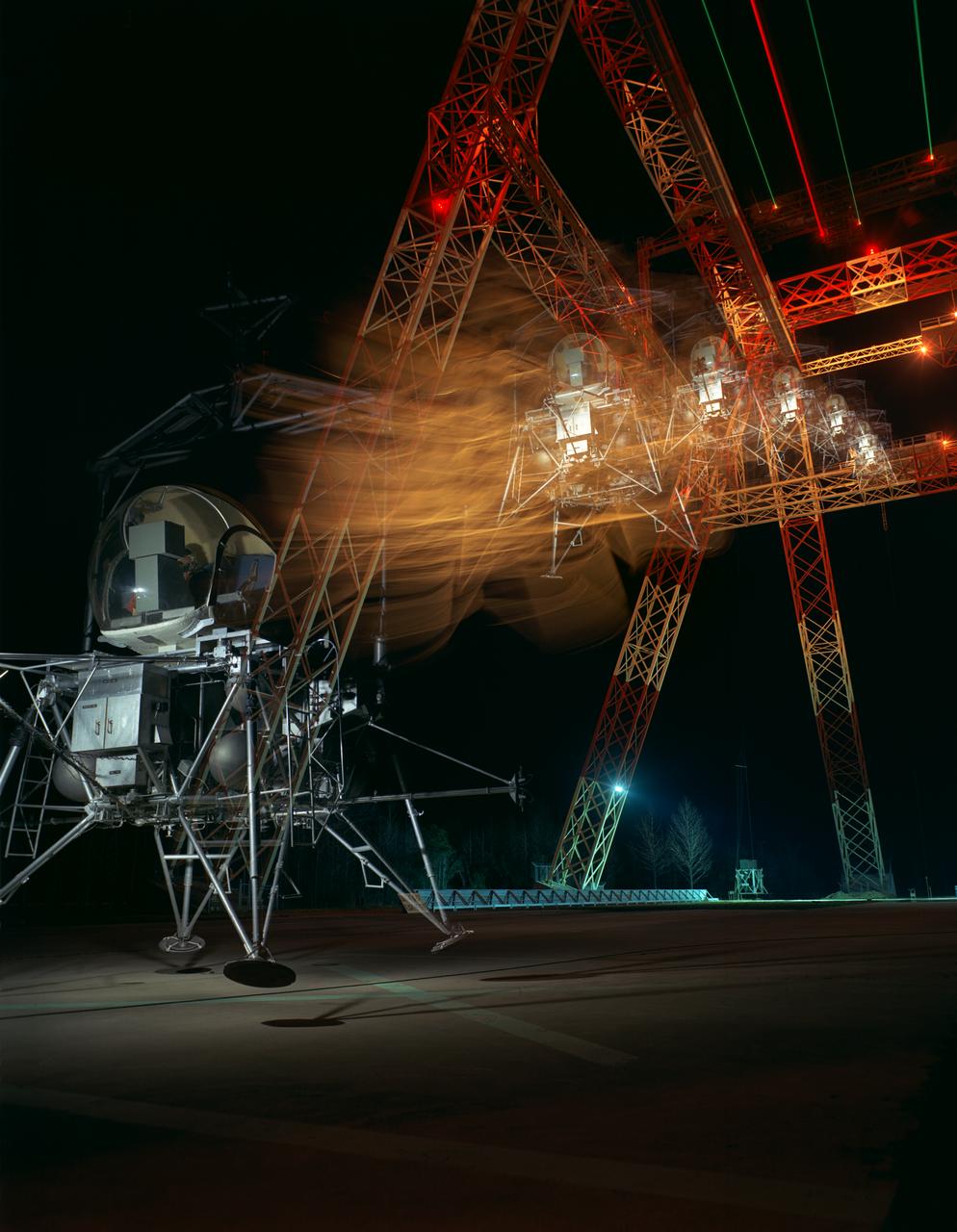

During a nighttime training session, a multiple exposure captures the movement of the Lunar Excursion Module Simulator (LEMS). The LEMS was a manned vehicle used to familiarize the Apollo astronauts with the handling characteristics of lunar-landing type vehicle. The Apollo Program is best known for the astronaut Neal Armstrong s first step on the Moon July 20, 1969. In its earliest test period, the LEMS featured a helicopter crew cabin atop the lunar landing module. Later, the helicopter crew cabin was replaced with a stand-up rectangular cabin which was more efficient for controlling maneuvers and for better viewing by the pilot. The vehicle was designed at Langley Research Center in Hampton, VA. This multiple exposure shows a simulated Moon landing of the (LEMS) trainer at Langley s Lunar Landing Research Facility. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 70), by James Shultz. Also published in " A Century at Langley" by Joseph Chambers, pg. 93.
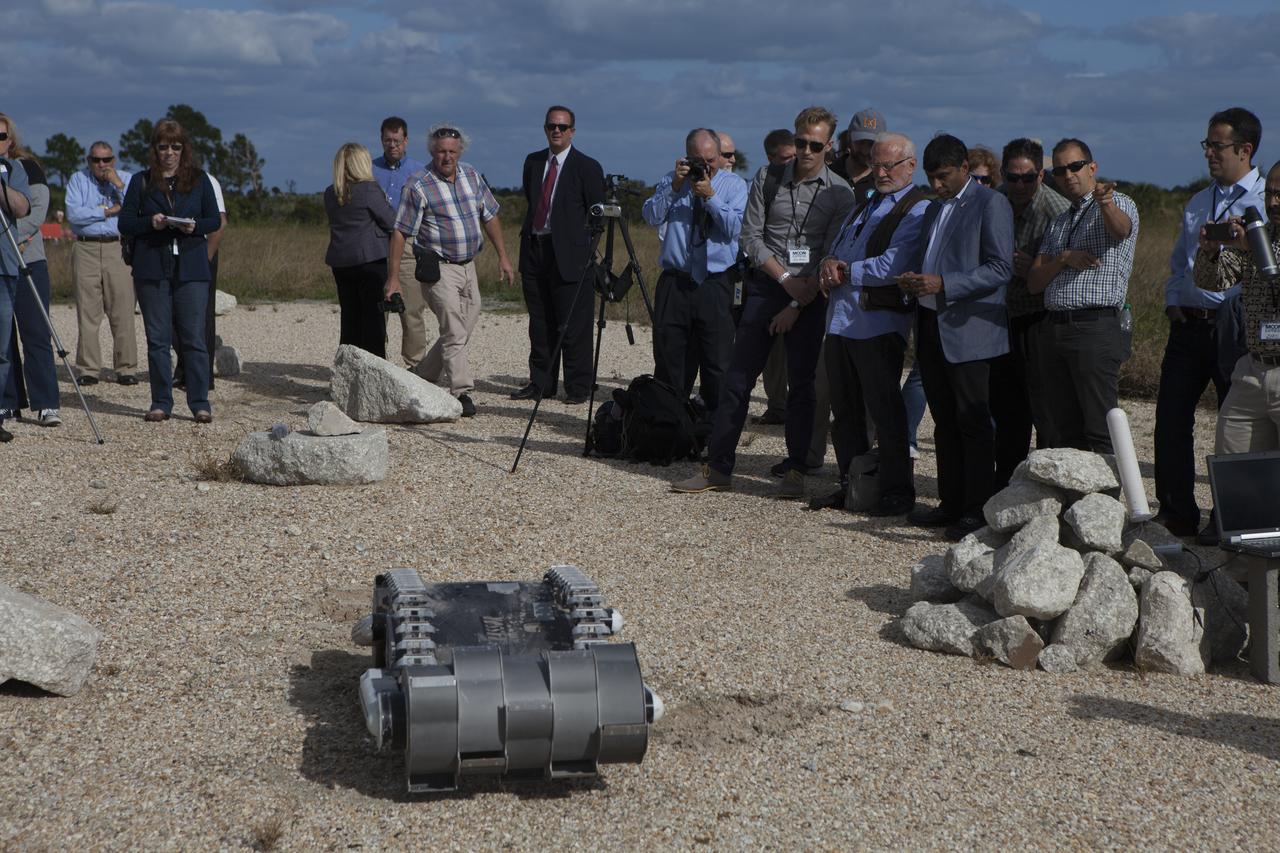

Members of the media watch a demonstration of the Regolith Advanced Surface System Operations Robot, or RASSOR, during a media event at the automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Tom Engler, center, in the suit, deputy director of Kennedy's Center Planning and Development, announced Moon Express Inc., of Moffett Field, California is selected to utilize Kennedy facilities for NASA's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST.
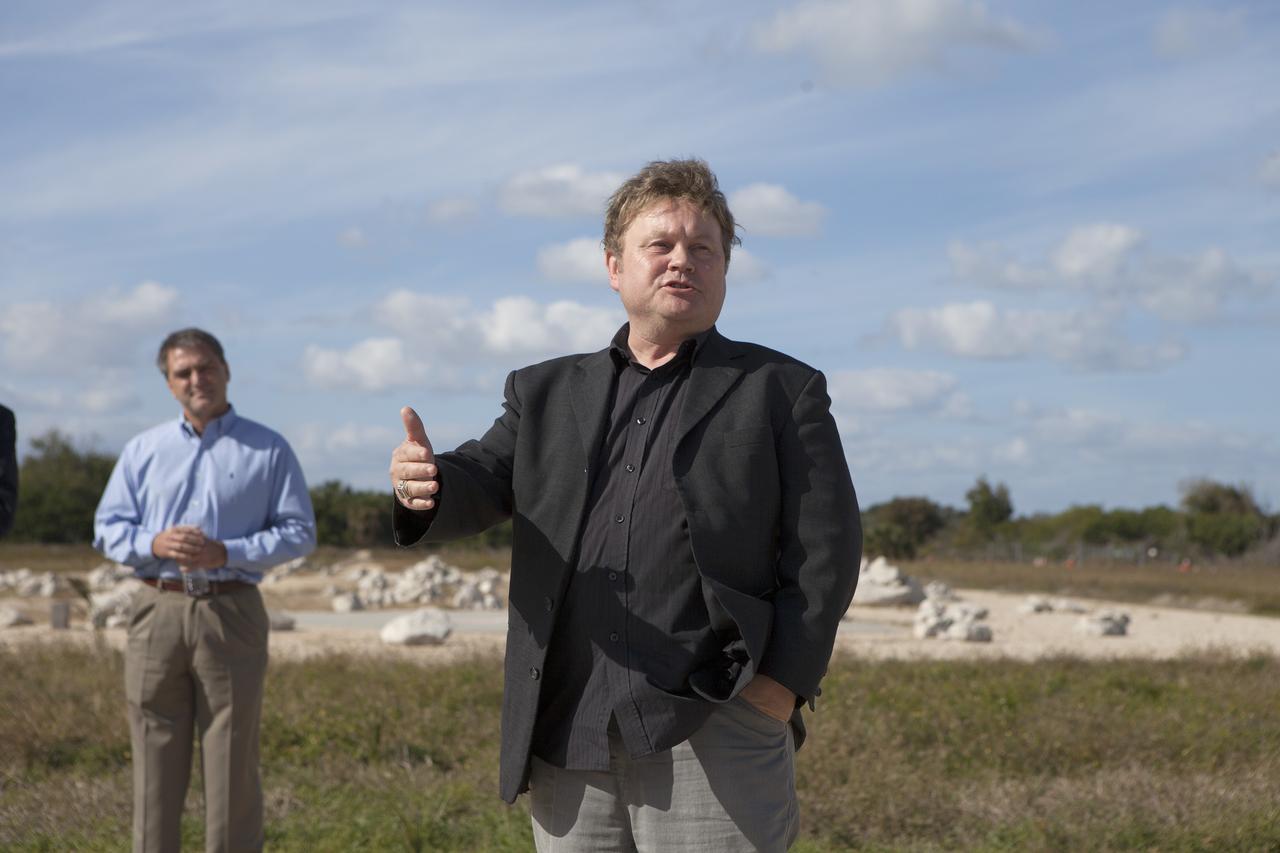

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Bob Richards, co-founder and chief executive officer of Moon Express Inc., of Moffett Field, California, speaks to the media during an event to announce the company's selection to use Kennedy Space Center's facilities as part of NASA's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
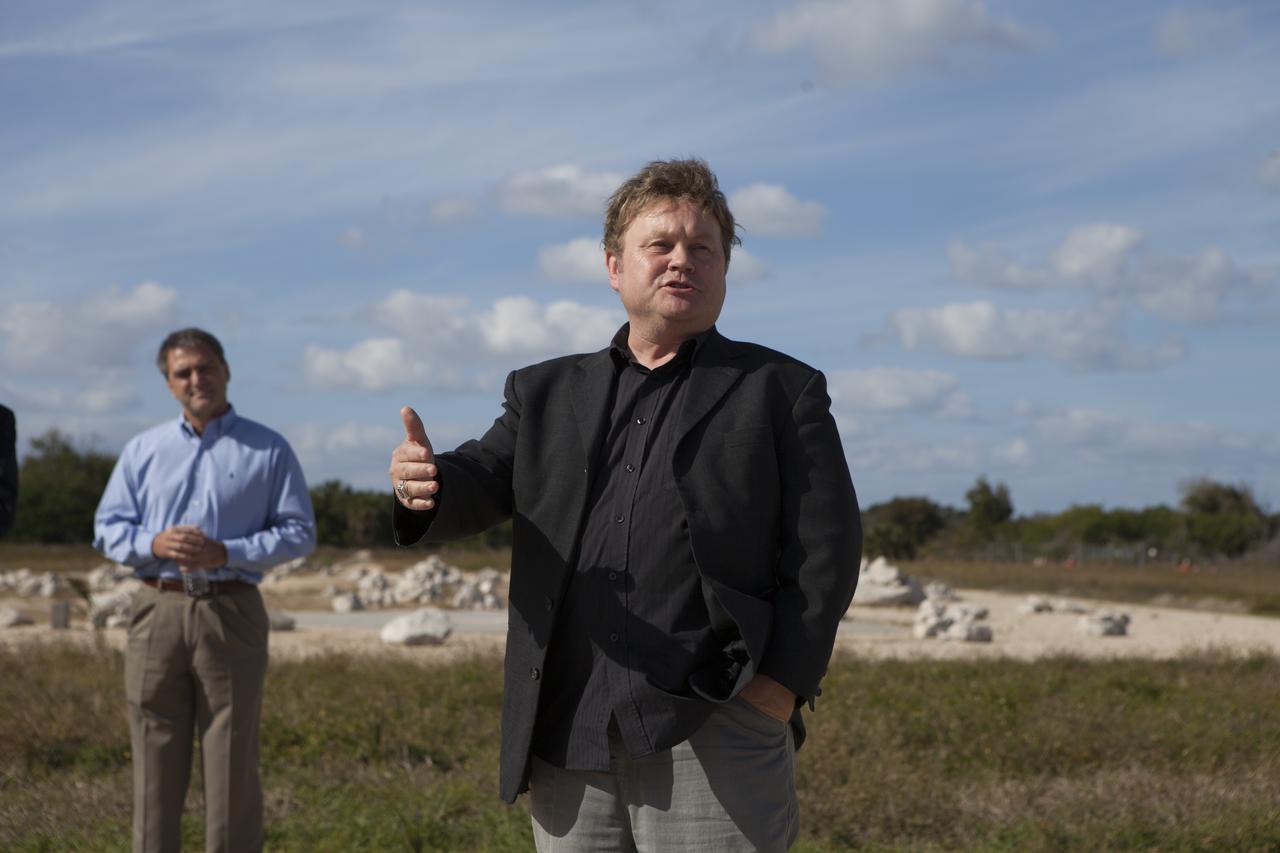

Bob Richards, co-founder and chief executive officer of Moon Express Inc., of Moffett Field, California, speaks to the media during an event to announce the company's selection to use Kennedy Space Center's facilities as part of NASA's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST.
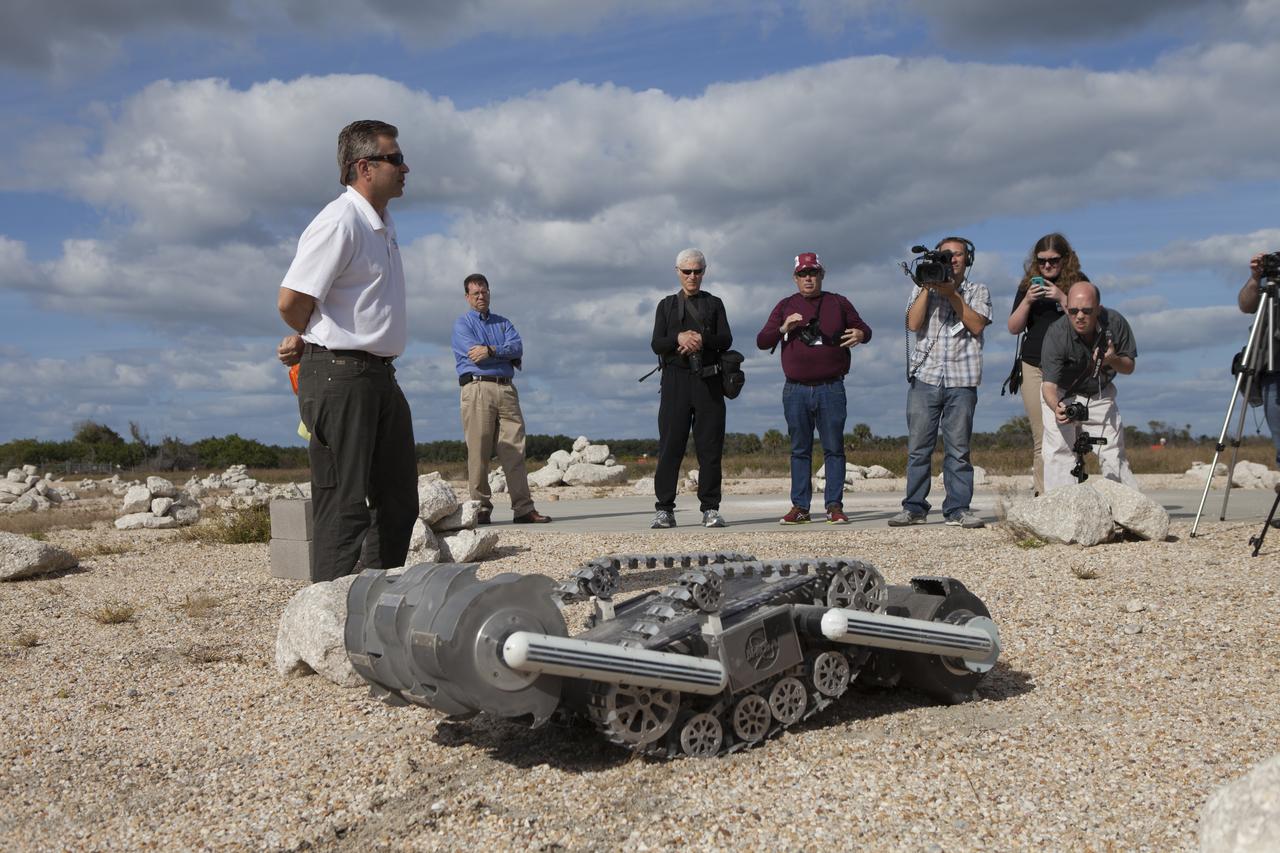

Rob Mueller, NASA senior technologist in the Surface Systems Office in Kennedy Space Center's Engineering and Technology Directorate, demonstrates the Regolith Advanced Surface System Operations Robot, or RASSOR, during a media event at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. The event was held to announce Moon Express Inc., of Moffett Field, California is selected to utilize Kennedy facilities for NASA's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST.
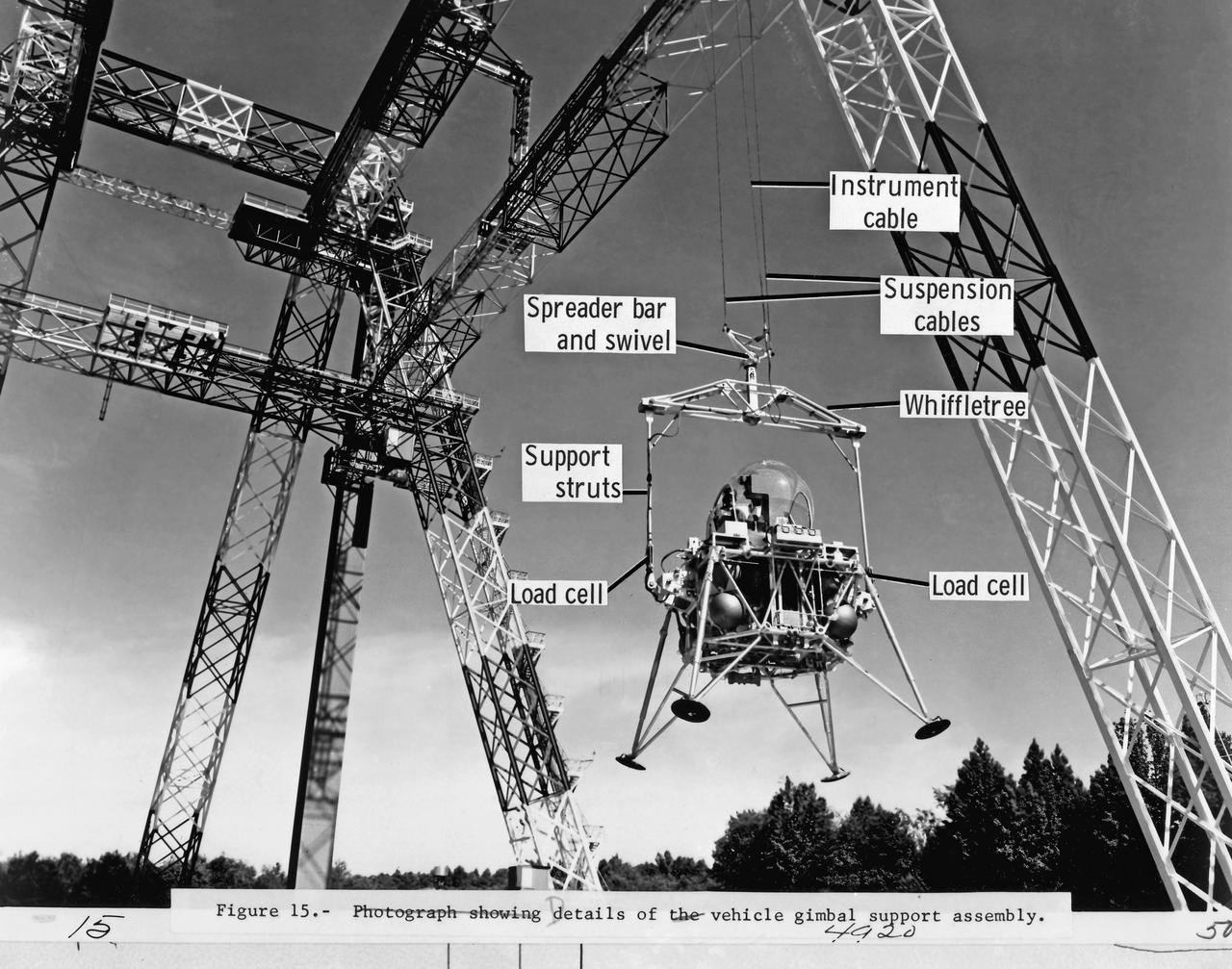
NASA TN D-3828 Figure 15. OPERATIONAL FEATURES OF THE LANGLEY LUNAR LANDING RESEARCH FACILITY by Thomas C. O'Bryan and Donald E. Hewes Details of vehicle gamble support assembly.

Principal investigator, Dr. Janine Captain, attaches a mass spectrometer sensor to electronics inside a vacuum chamber in the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 12, 2018. The Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument is a commercial off-the-shelf mass instrument modified to work in space, and can identify molecules at lunar landing sites. These MSolo instruments are part of NASA’s efforts to return to the Moon with the Commercial Lunar Payload Services Landers Program.

The smiling Apollo 12 astronauts peer out of the window of the mobile quarantine facility aboard the recovery ship, USS Hornet. Pictured (Left to right) are Spacecraft Commander, Charles Conrad; Command Module (CM) Pilot, Richard Gordon; and Lunar Module (LM) Pilot, Alan L. Bean. The crew were housed in the quarantine facility immediately after the Pacific recovery operation took place. The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. Apollo 12 returned safely to Earth on November 24, 1969.
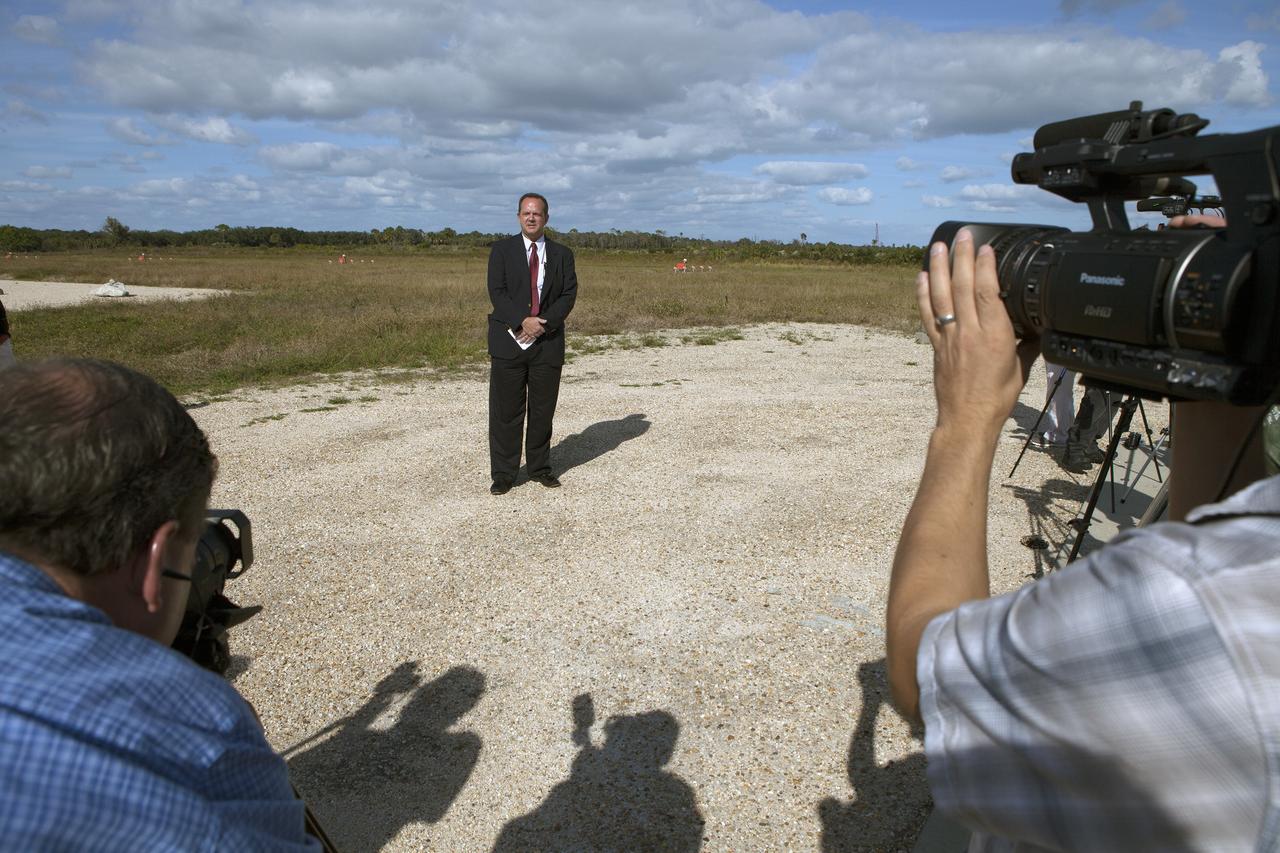

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Tom Engler, deputy director of Center Planning and Development at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the media during an event to announce the agency's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative and introduced one of the partners, Moon Express Inc. of Moffett Field, California. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
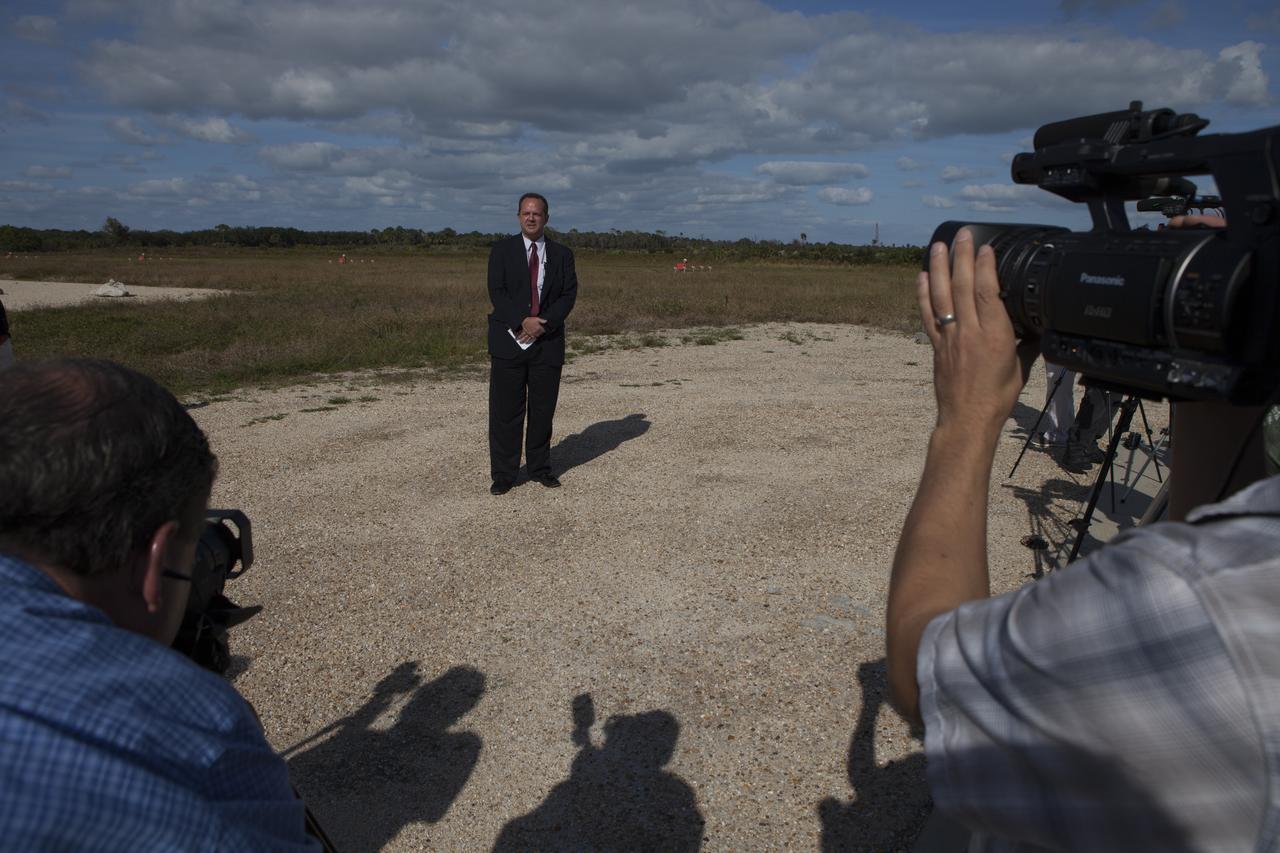

Tom Engler, deputy director of Center Planning and Development at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, speaks to members of the media during an event to announce the agency's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative and introduced one of the partners, Moon Express Inc. of Moffett Field, California. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST.
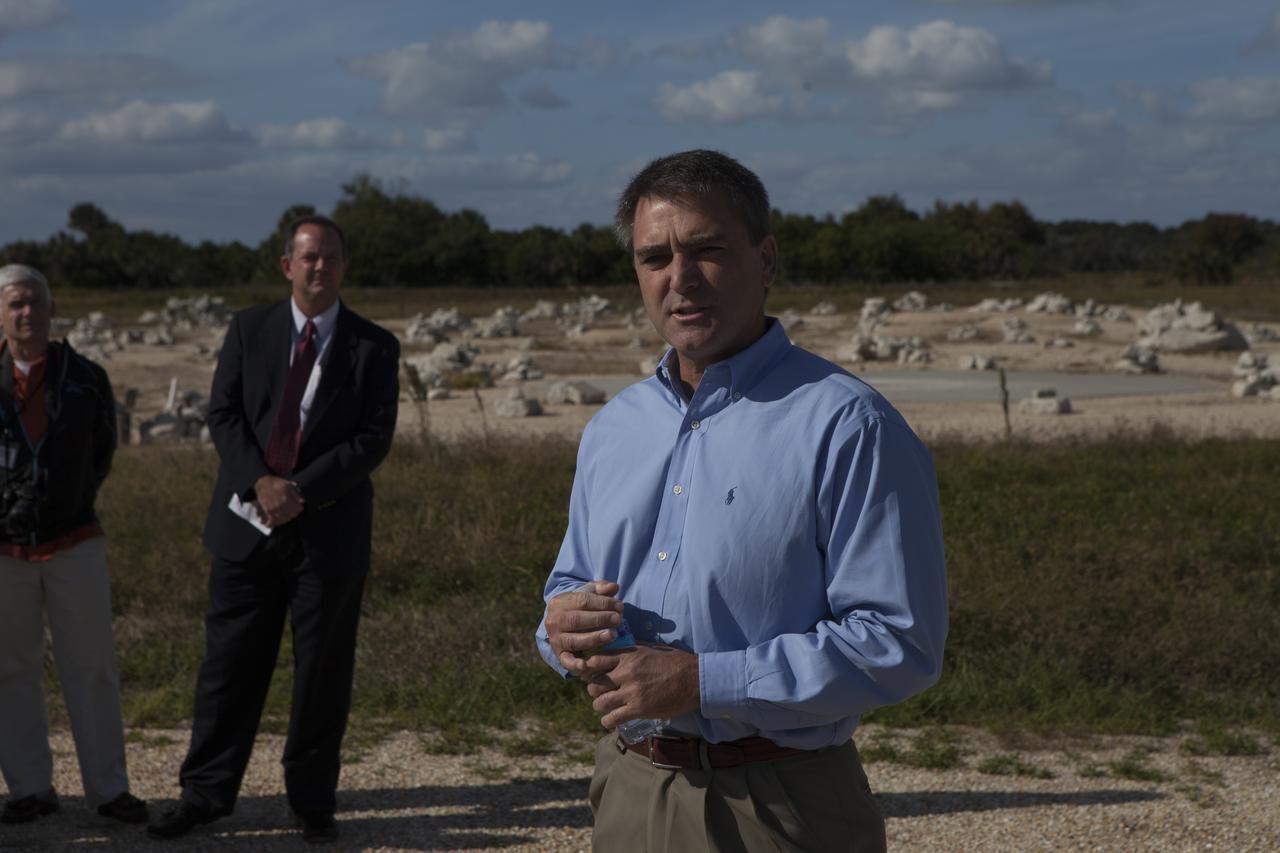

Greg C. Shavers, Lander Technology director at Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, speaks to members of the media during an event to announce the agency's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative and introduced one of the partners, Moon Express Inc. of Moffett Field, California. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST.
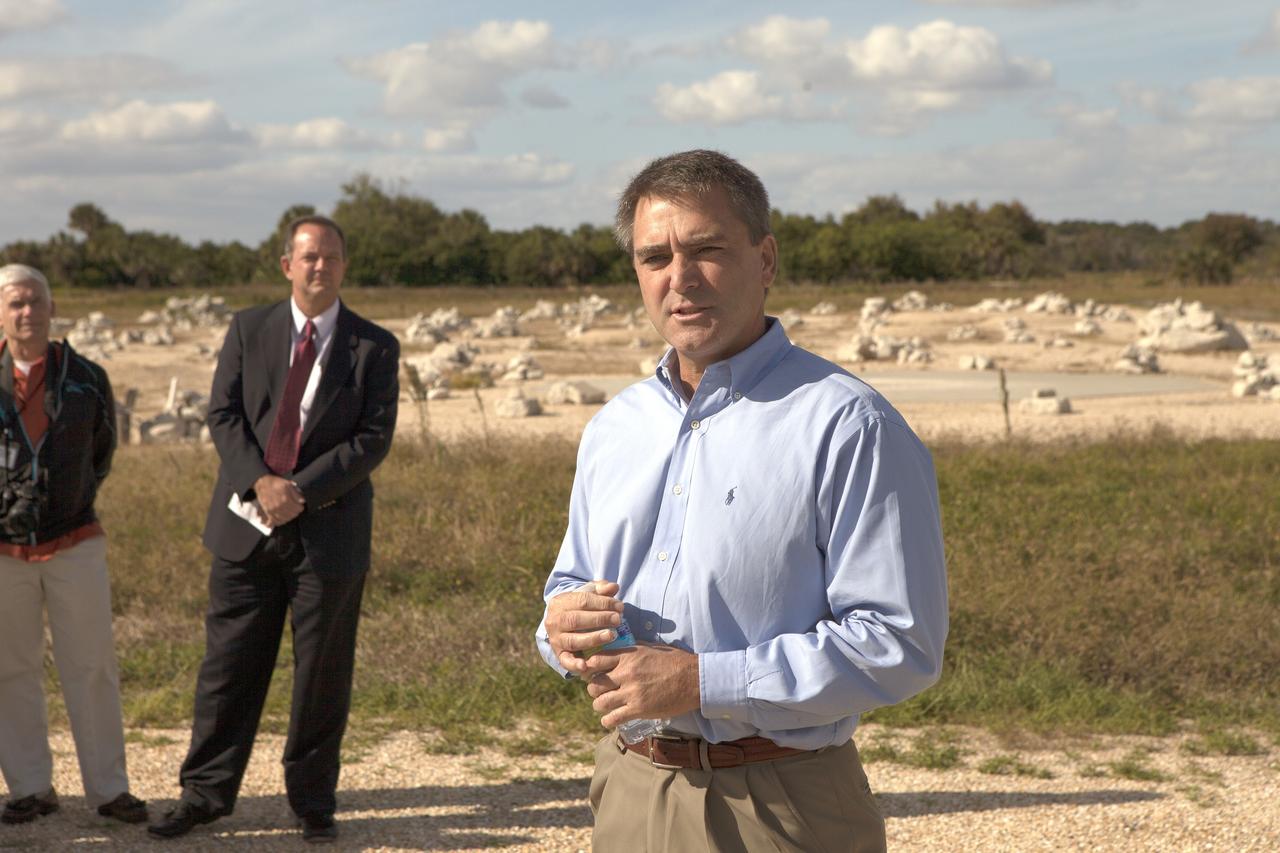

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Greg C. Shavers, Lander Technology director at Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, speaks to members of the media during an event to announce the agency's Lunar Cargo Transportation and Landing by Soft Touchdown, or Lunar CATALYST, initiative and introduced one of the partners, Moon Express Inc. of Moffett Field, California. The event took place at Kennedy's automated landing and hazard avoidance technology, or ALHAT, hazard field at the north end of the Shuttle Landing Facility. Moon Express is developing a lander with capabilities that will enable delivery of payloads to the surface of the moon, as well as new science and exploration missions of interest to NASA and scientific and academic communities. Moon Express will base its activities at Kennedy and utilize the Morpheus ALHAT field and a hangar nearby for CATALYST testing. The Advanced Exploration Systems Division of NASA's Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate manages Lunar CATALYST. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
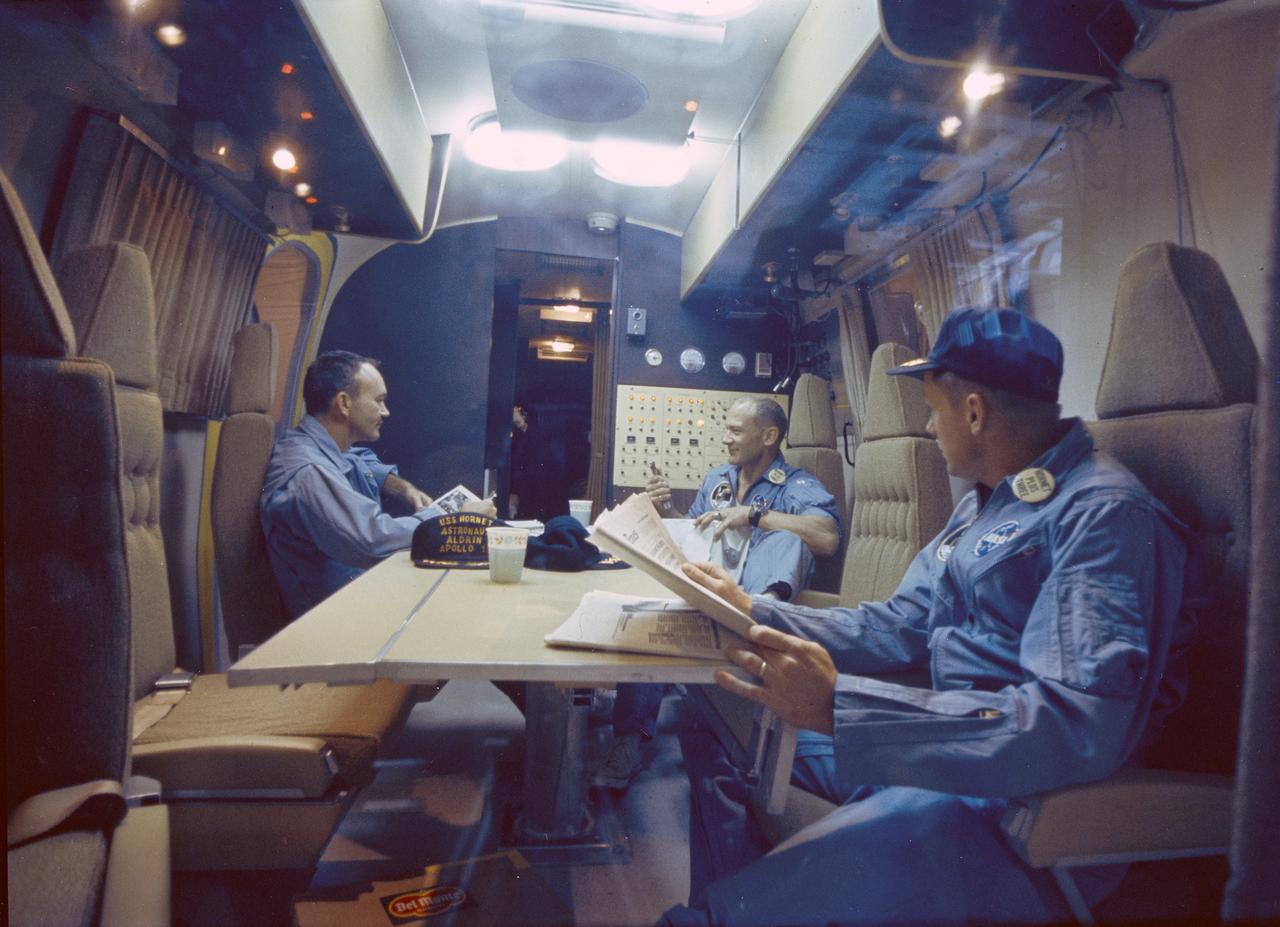

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module pilot. The Command Module (CM), piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the Lunar Module (LM), named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. The surface exploration was concluded in 2½ hours, in which the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. Upon splash down in the Pacific Ocean, Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was taken to safety aboard the USS Hornet, where they were quartered in a mobile quarantine facility. Shown here is the Apollo 11 crew inside the quarantine facility. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
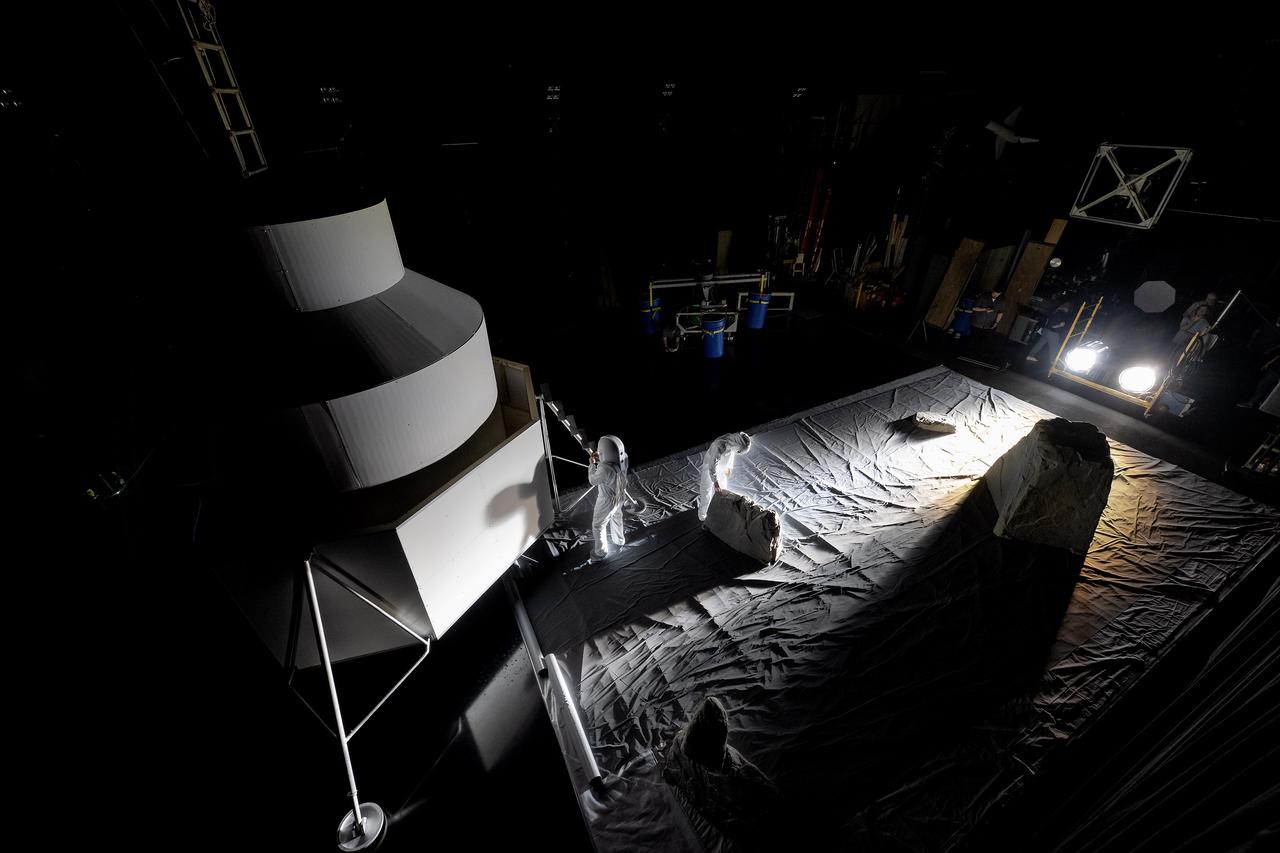

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
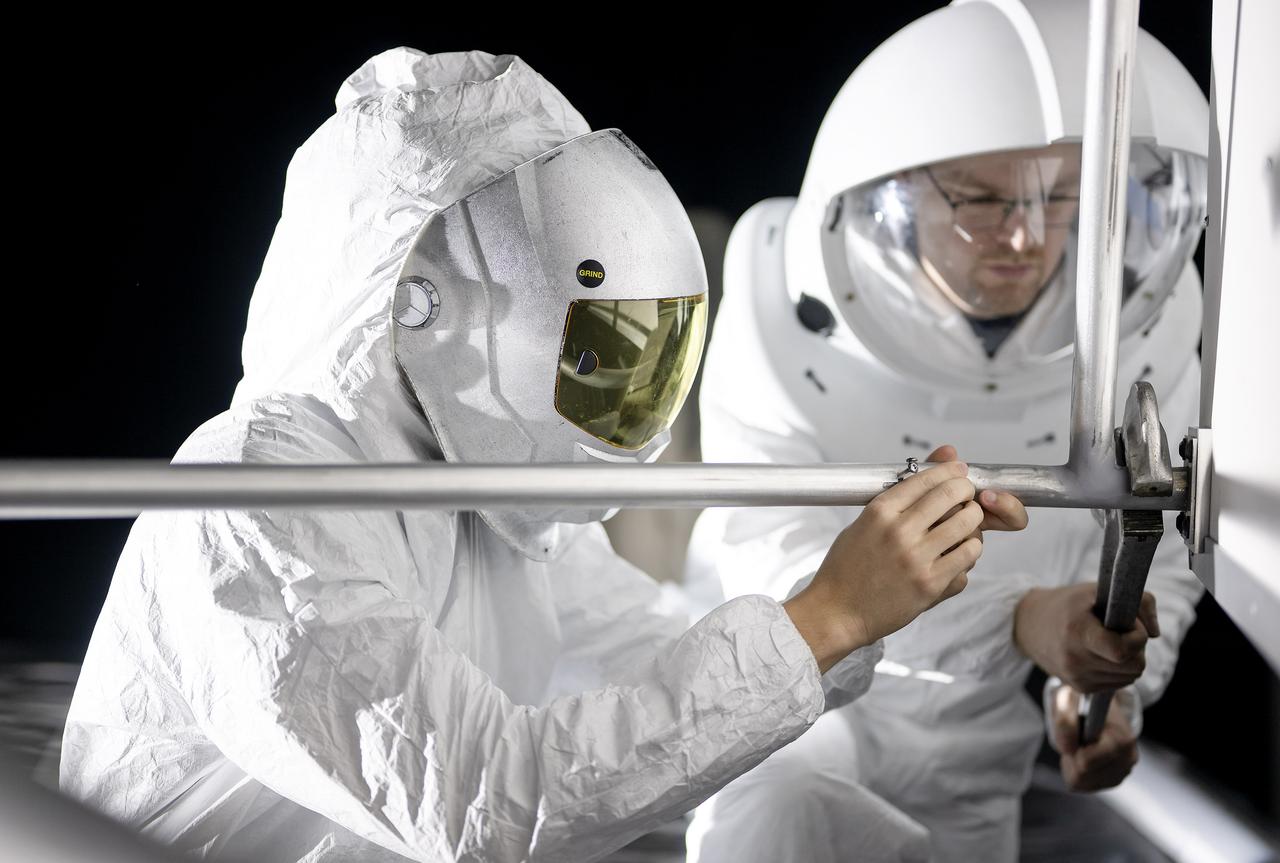

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
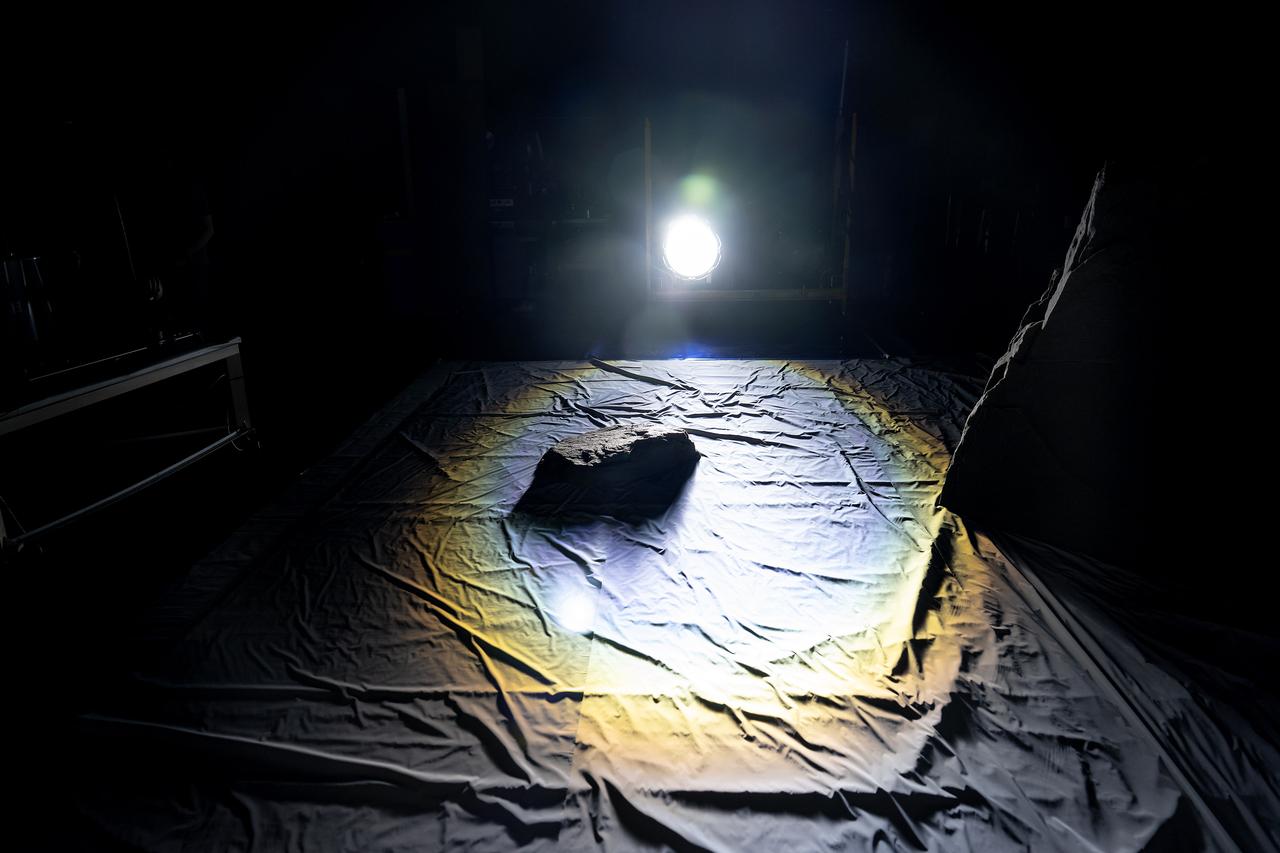

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
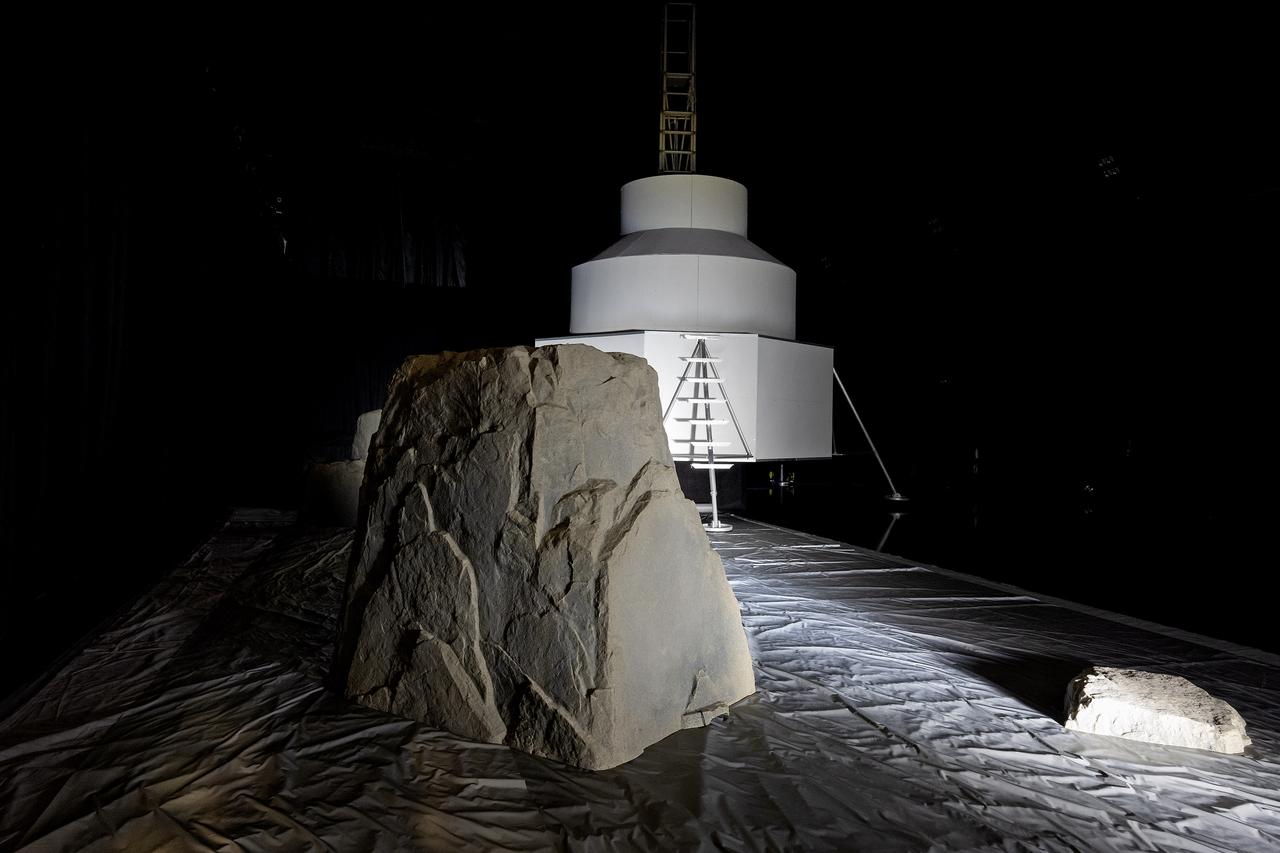

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
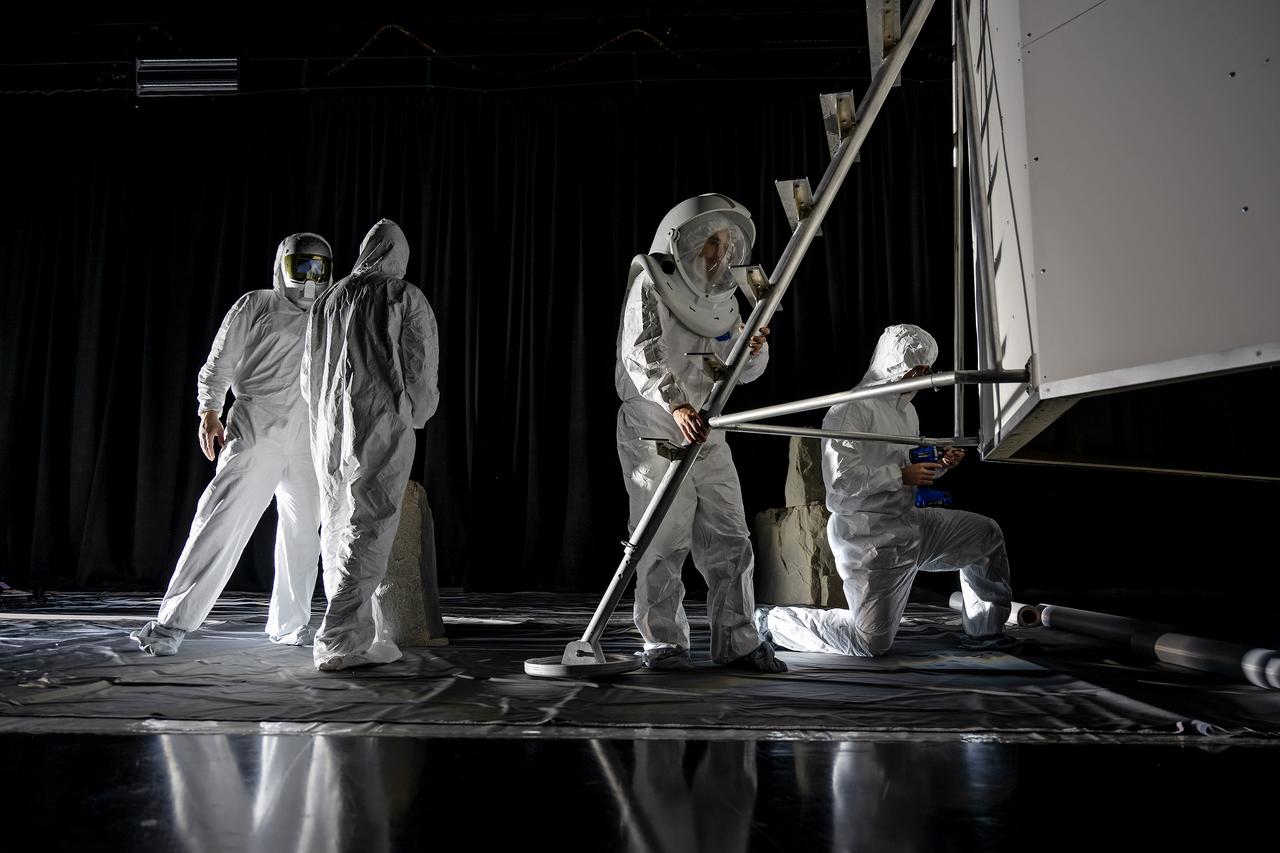

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
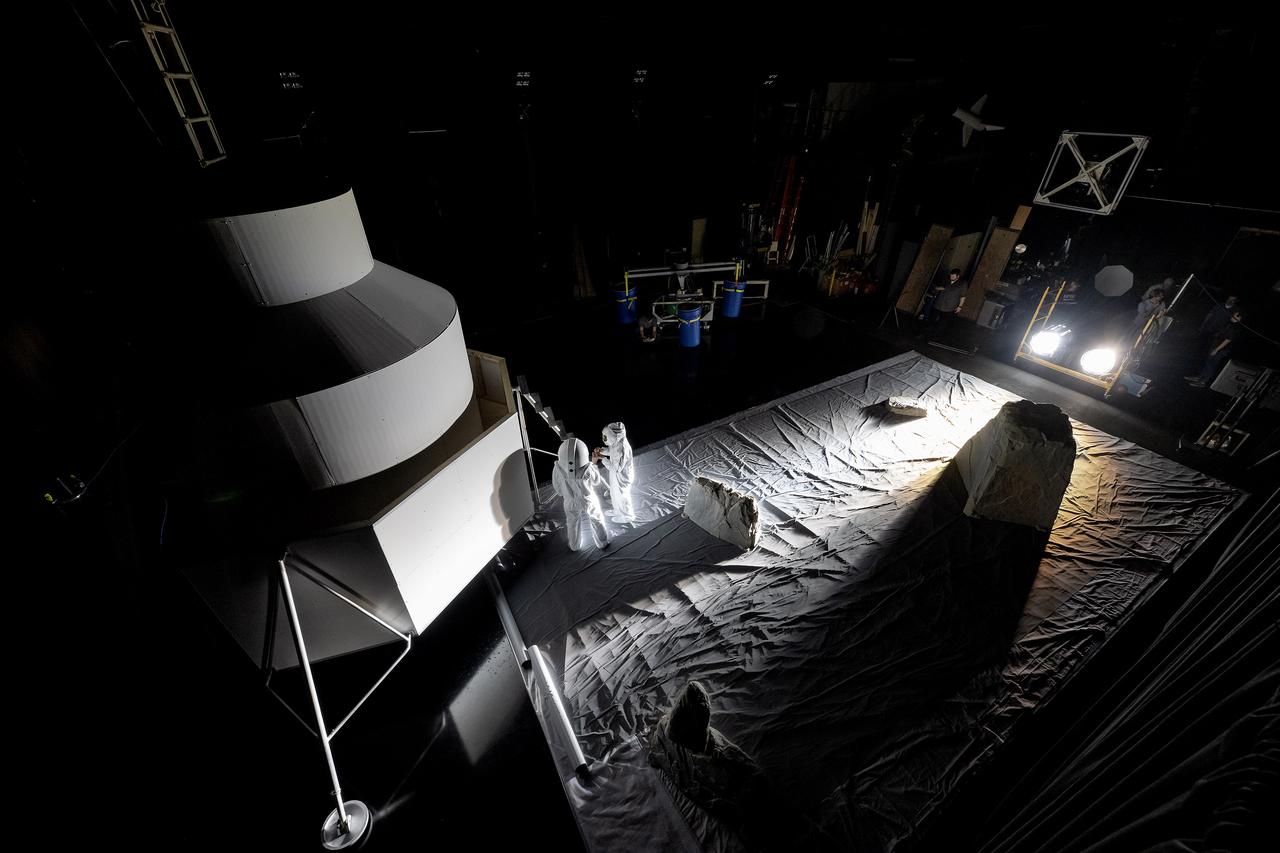

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are using the Flat Floor Facility (Building 4619) to understand the lunar lighting environment in preparation for the Artemis III crewed lunar landing mission, slated for 2027. The Flat Floor Facility is an air-bearing floor, providing full-scale simulation capabilities for lunar surface systems by simulating zero gravity in two dimensions. Wearing low-fidelity materials, test engineers can understand how the extreme lighting of the Moon’s South Pole could affect surface operations during Artemis III. High-intensity lights are positioned at a low angle to replicate the strong shadows that are cast across the lunar South Pole by the Sun. Data and analysis from testing at NASA Marshall are improving models Artemis astronauts will use in preparation for lander and surface operations on the Moon during Artemis III. Testing in the facility is also helping cross-agency teams evaluate various tools astronauts may use. NASA Marshall manages the Human Landing System (HLS) Program. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
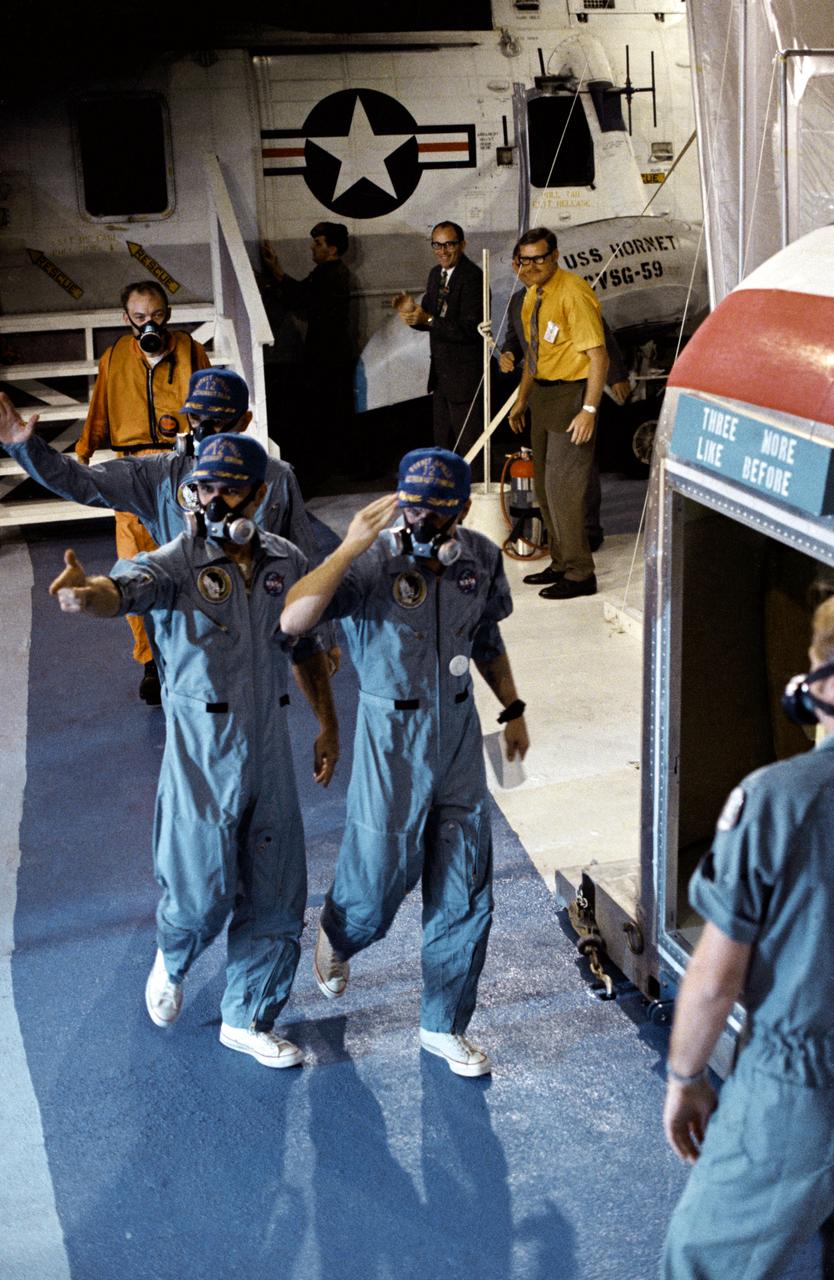

S69-22849 (24 Nov. 1969) --- USS Hornet crewmen are greeted by the crew of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission as the three astronauts are transferred from a U.S. Navy helicopter to a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) aboard the prime recovery vessel. Charles Conrad Jr., right, commander; Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, left front; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, splashed down safely at 2:58 p.m., Nov. 24, 1969.
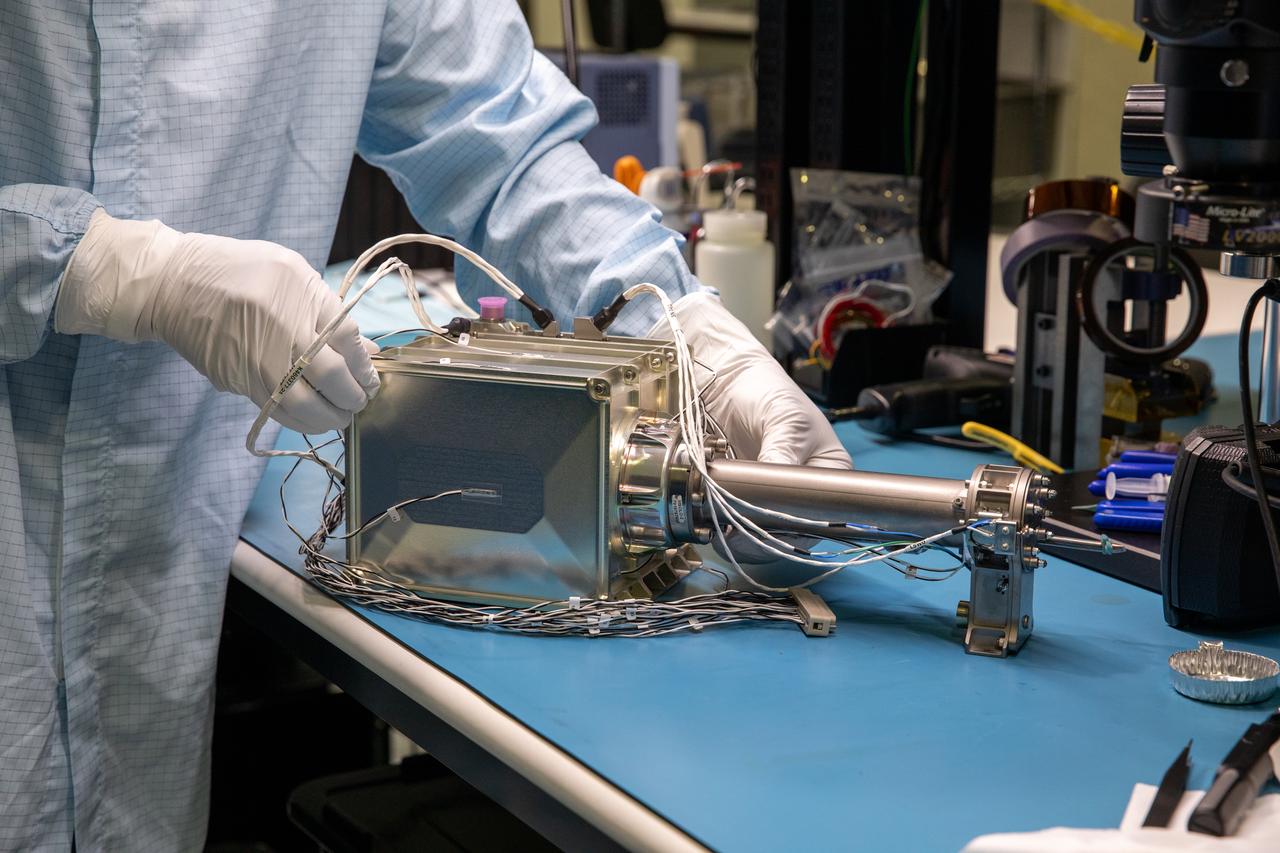

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
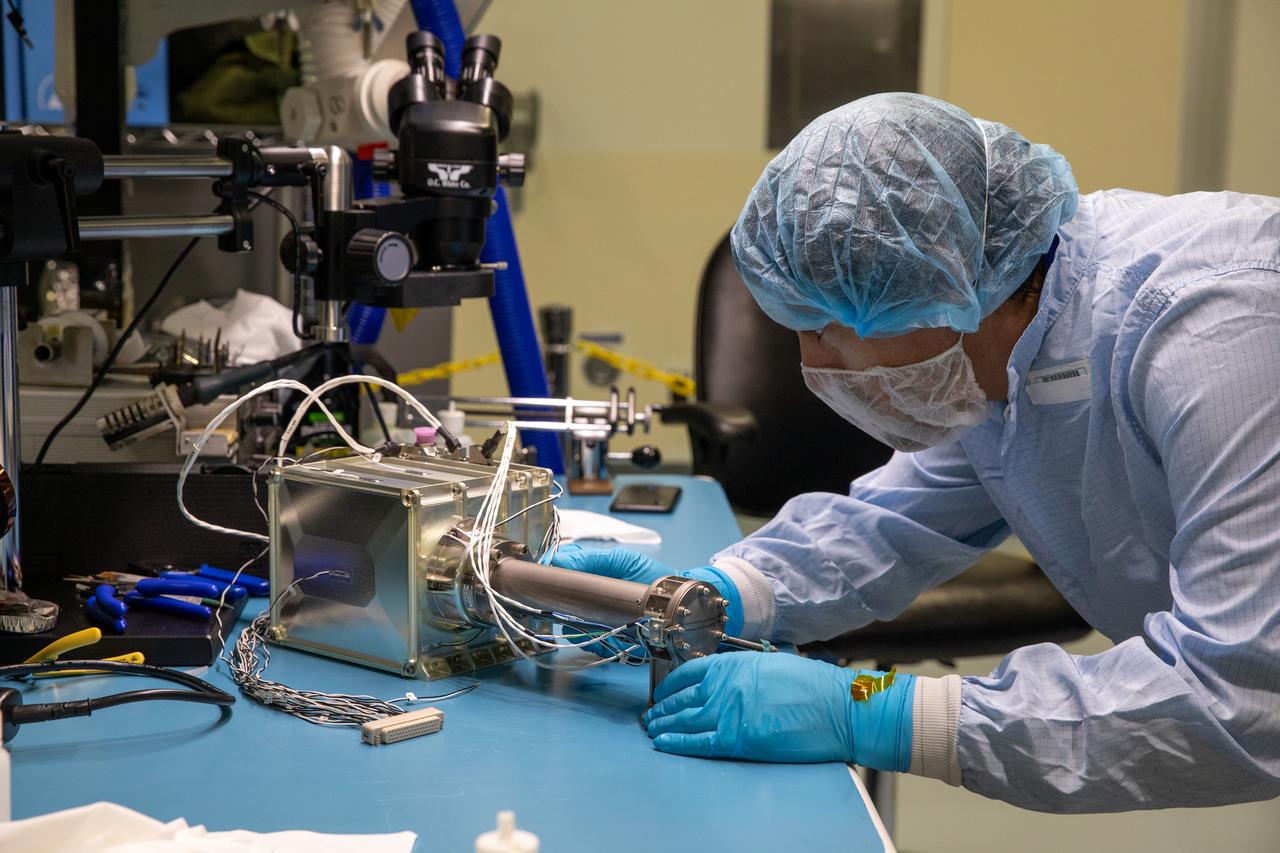

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
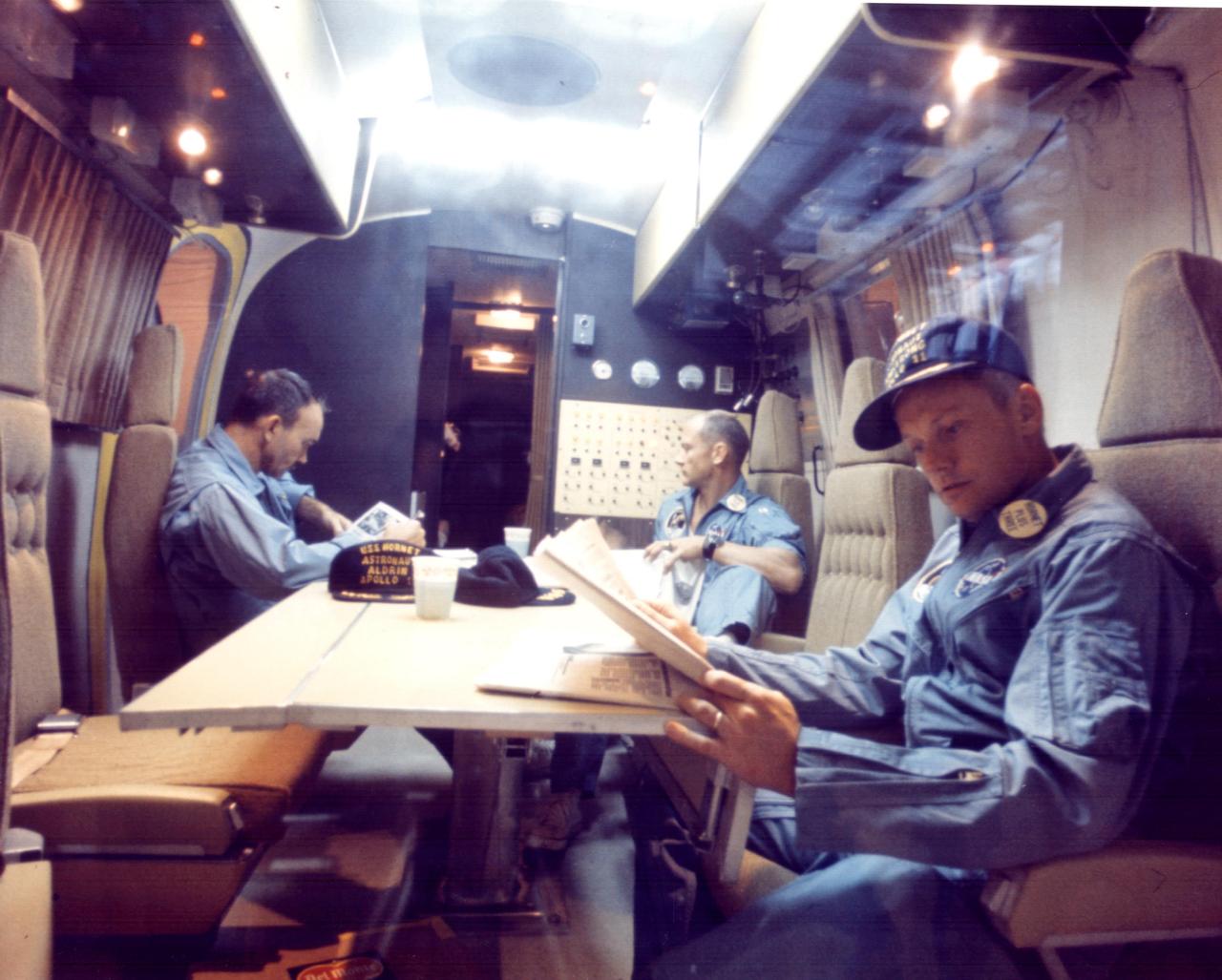

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Within the Mobile Quarantine Facility, Apollo 11 astronauts (left to right) Michael Collins, Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. and Neil A. Armstrong relax following their successful lunar landing mission. They spent two-and-one-half days in the quarantine trailer enroute from the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship, to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston. The Hornet docked at Pearl Harbor where the trailer was transferred to a jet aircraft for the flight to Houston.
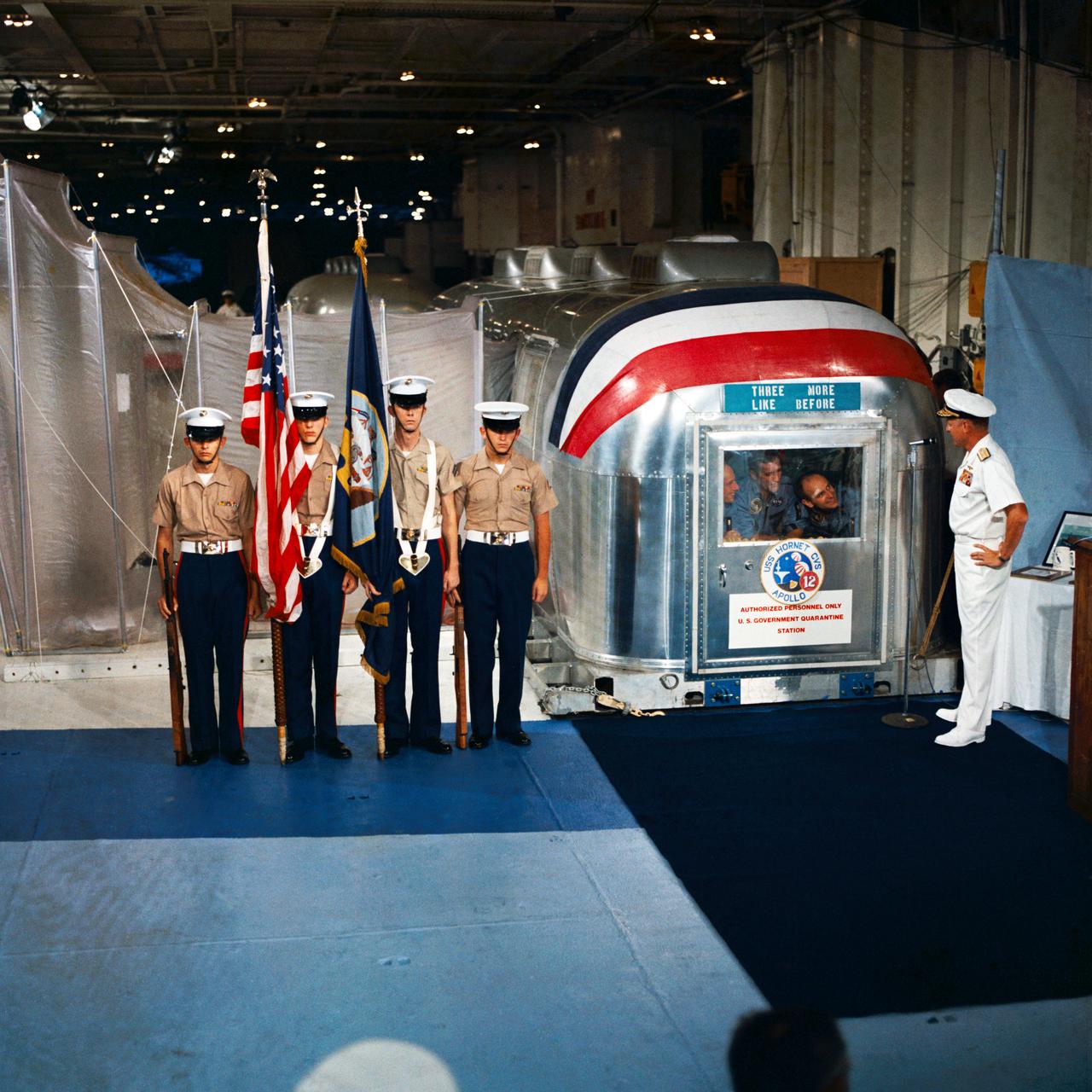

S69-22876 (24 Nov. 1969) --- Rear Admiral Donald C. David, Commander, Manned Spacecraft Recovery Force, Pacific, welcomes the crew of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission aboard the USS Hornet, prime recovery vessel for the mission. A color guard was also on hand for the welcoming ceremonies. Inside the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) are (left to right) astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot.

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
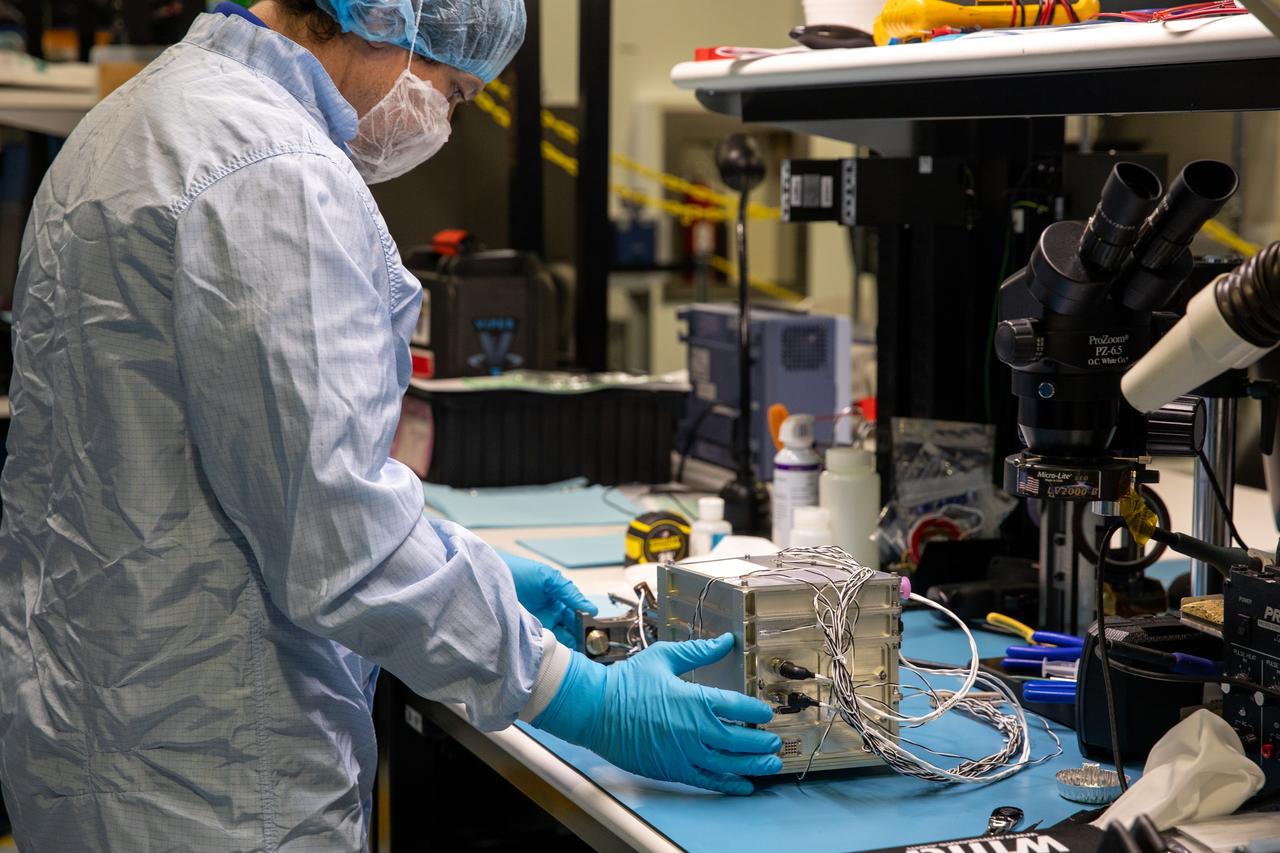

A team of engineers and technicians finished the final assembly step for the MSOLO-2 (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight instrument by installing the Calibration Gas System inside of the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on June 21, 2023. MSOLO is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface.
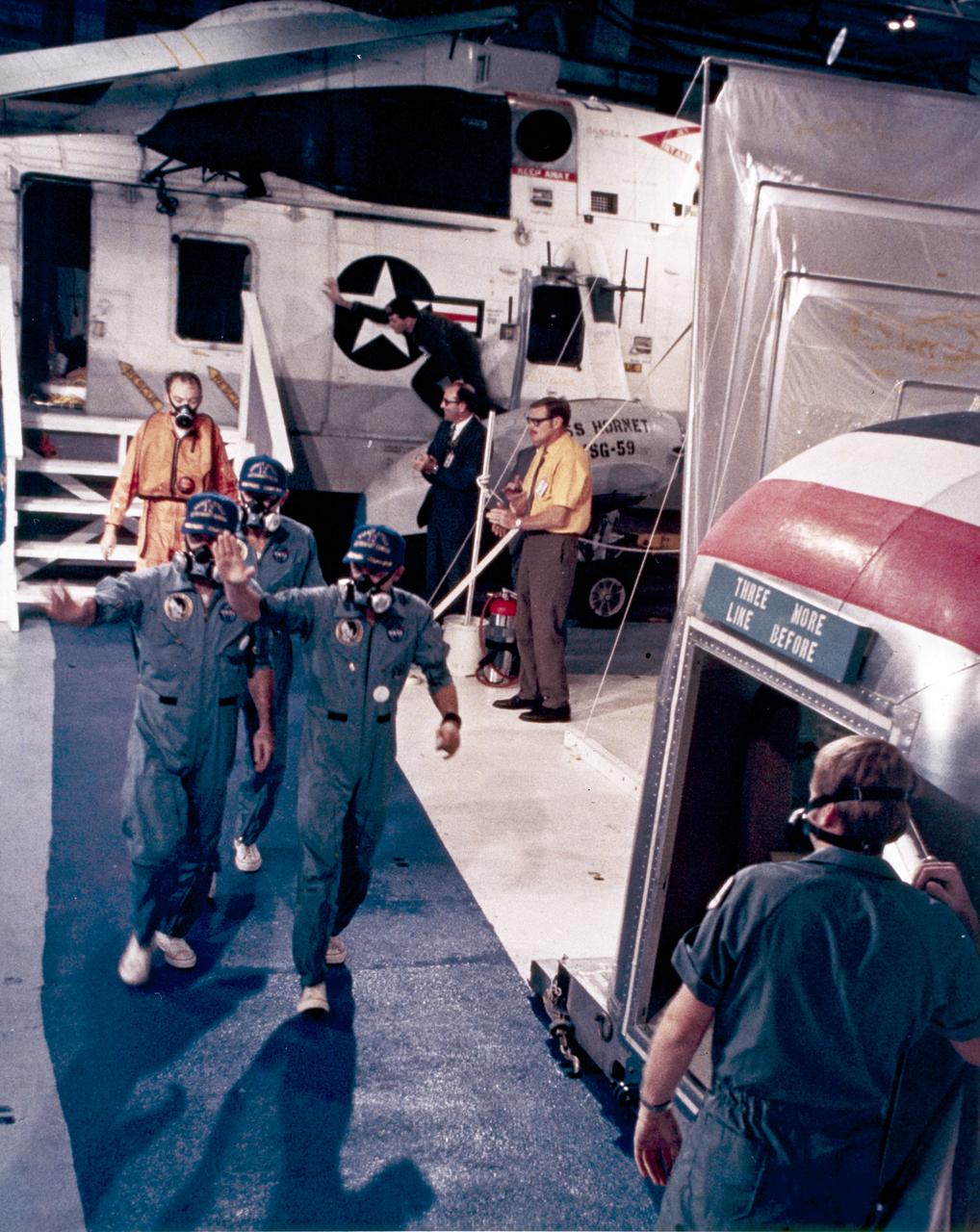

Aboard the recovery ship, USS Hornet, Apollo 12 astronauts wave to the crowd as they enter the mobile quarantine facility. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean after the splashdown of the Command Module capsule. Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 12 crew. The second manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 12 launched from launch pad 39-A at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on November 14, 1969 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. The Saturn V was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard Apollo 12 was a crew of three astronauts: Alan L. Bean, pilot of the Lunar Module (LM), Intrepid; Richard Gordon, pilot of the Command Module (CM), Yankee Clipper; and Spacecraft Commander Charles Conrad. The LM, Intrepid, landed astronauts Conrad and Bean on the lunar surface in what’s known as the Ocean of Storms while astronaut Richard Gordon piloted the CM, Yankee Clipper, in a parking orbit around the Moon. Lunar soil activities included the deployment of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), finding the unmanned Surveyor 3 that landed on the Moon on April 19, 1967, and collecting 75 pounds (34 kilograms) of rock samples. Apollo 12 safely returned to Earth on November 24, 1969.
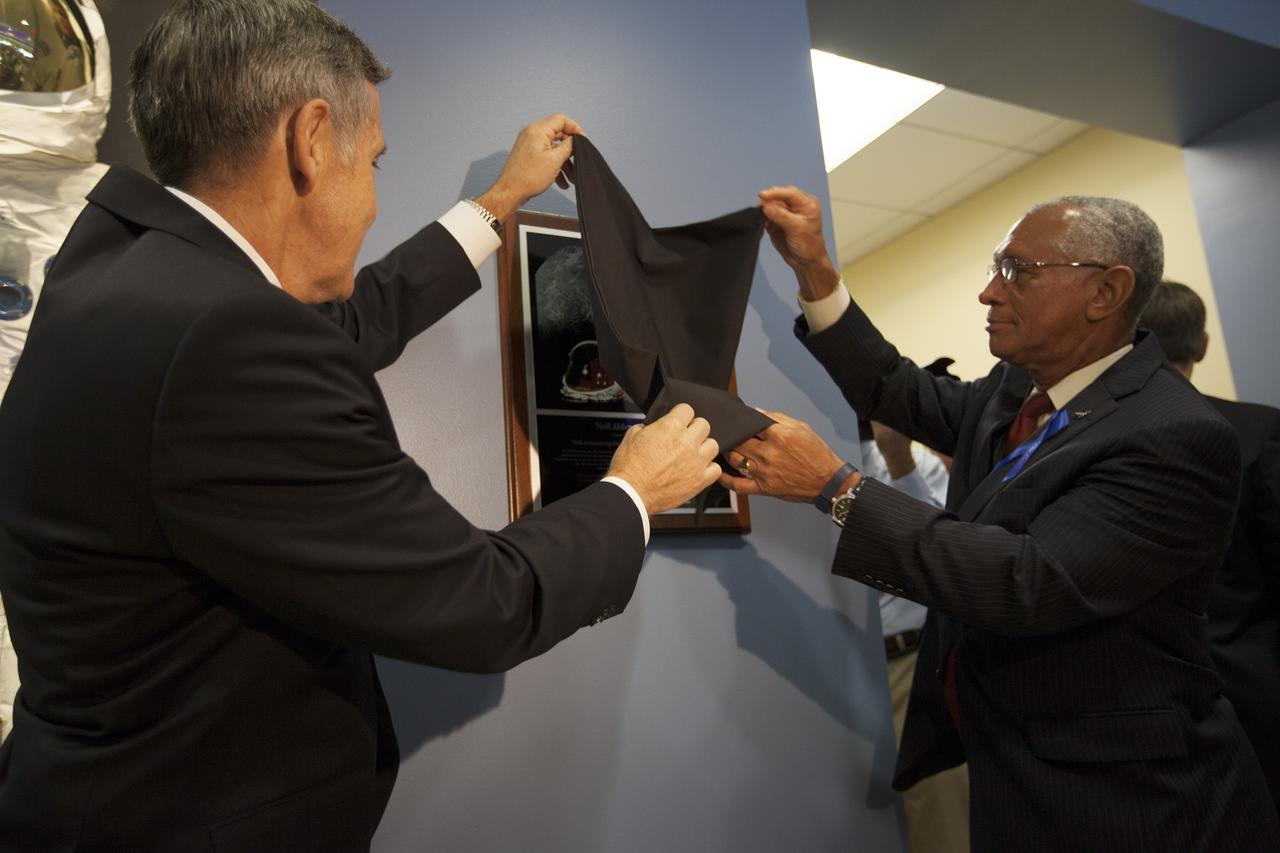

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Robert Cabana, left, and NASA Administrator Charles Bolden unveil a plaque on display in the lobby of the newly named Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The facility has been renamed for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft and is the same spaceport facility where the Apollo 11 command/service module and lunar module were prepped for the first lunar landing mission in 1969. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The unveiling was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module, Eagle, on July 20, 1969, as the command module, Columbia, orbited overhead. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission/ Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
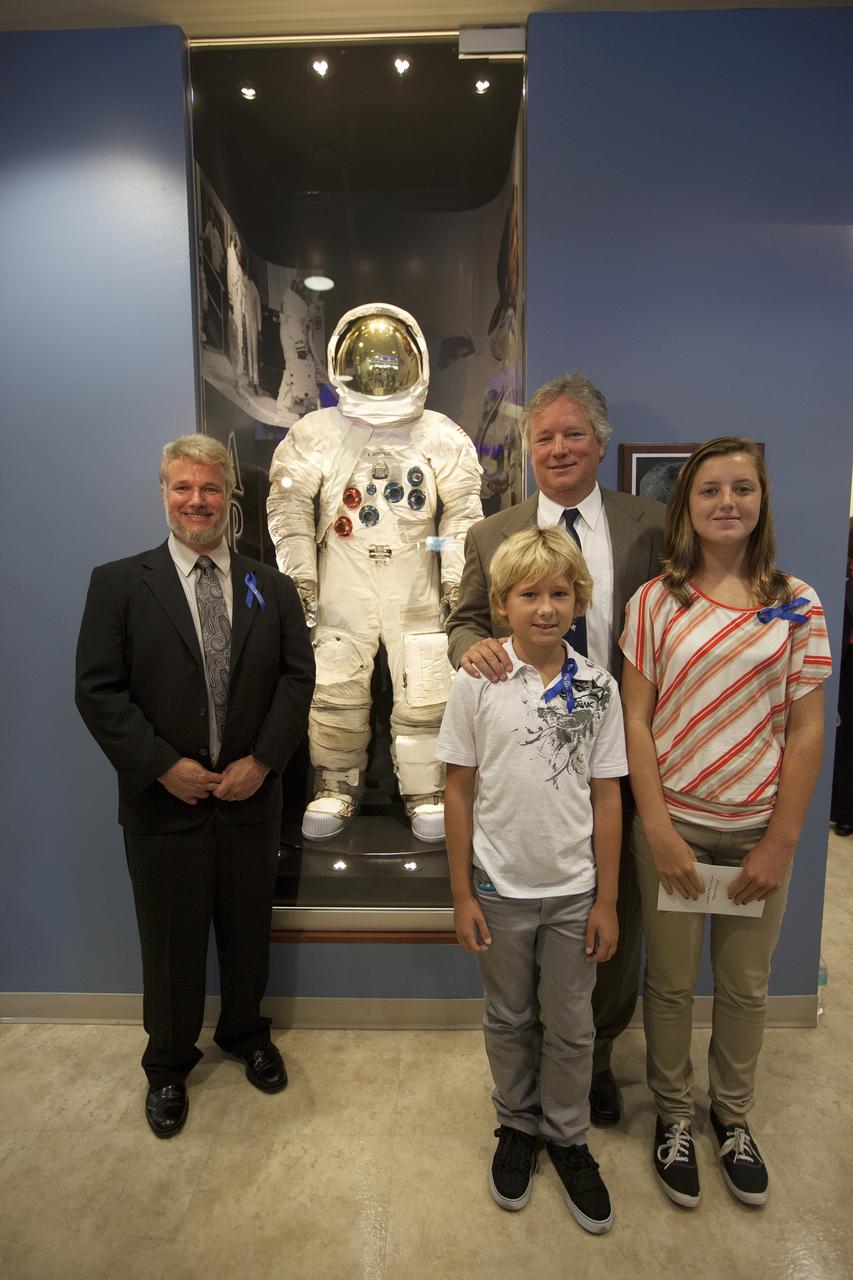

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Armstrong family pose for a portrait with an Apollo-era spacesuit following its unveiling in the lobby of the newly named Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The facility has been renamed for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. From left are Armstrong's son Mark, his grandson Bryce, his son Rick and his granddaughter Lily. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft and is the same spaceport facility where the Apollo 11 command/service module and lunar module were prepped for the first lunar landing mission in 1969. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The unveiling was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module, Eagle, on July 20, 1969, as the command module, Columbia, orbited overhead. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission/ Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
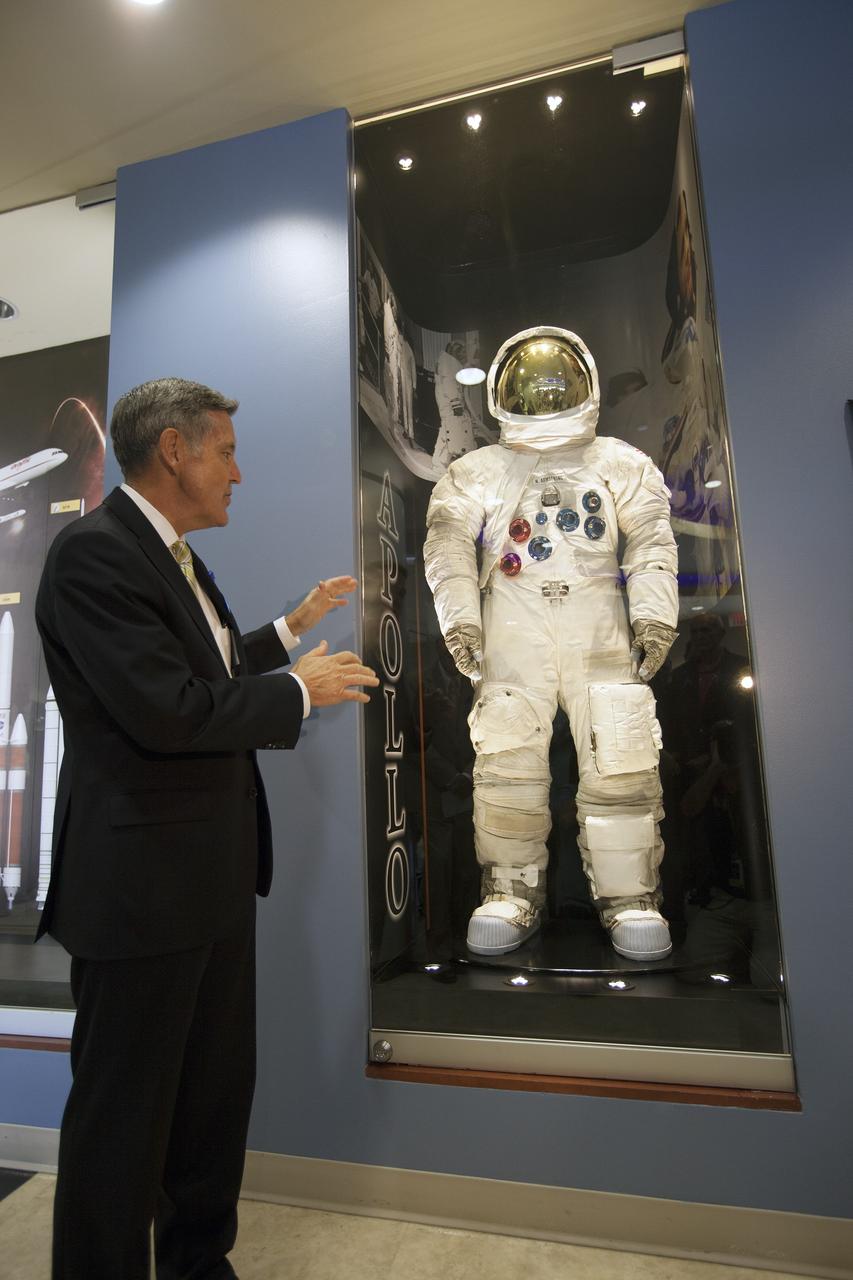

KSC-2014-3220 – CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Center Director Robert Cabana unveils an Apollo-era spacesuit on display in the lobby of the newly named Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The facility has been renamed for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft and is the same spaceport facility where the Apollo 11 command/service module and lunar module were prepped for the first lunar landing mission in 1969. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The unveiling was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module, Eagle, on July 20, 1969, as the command module, Columbia, orbited overhead. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission/ Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
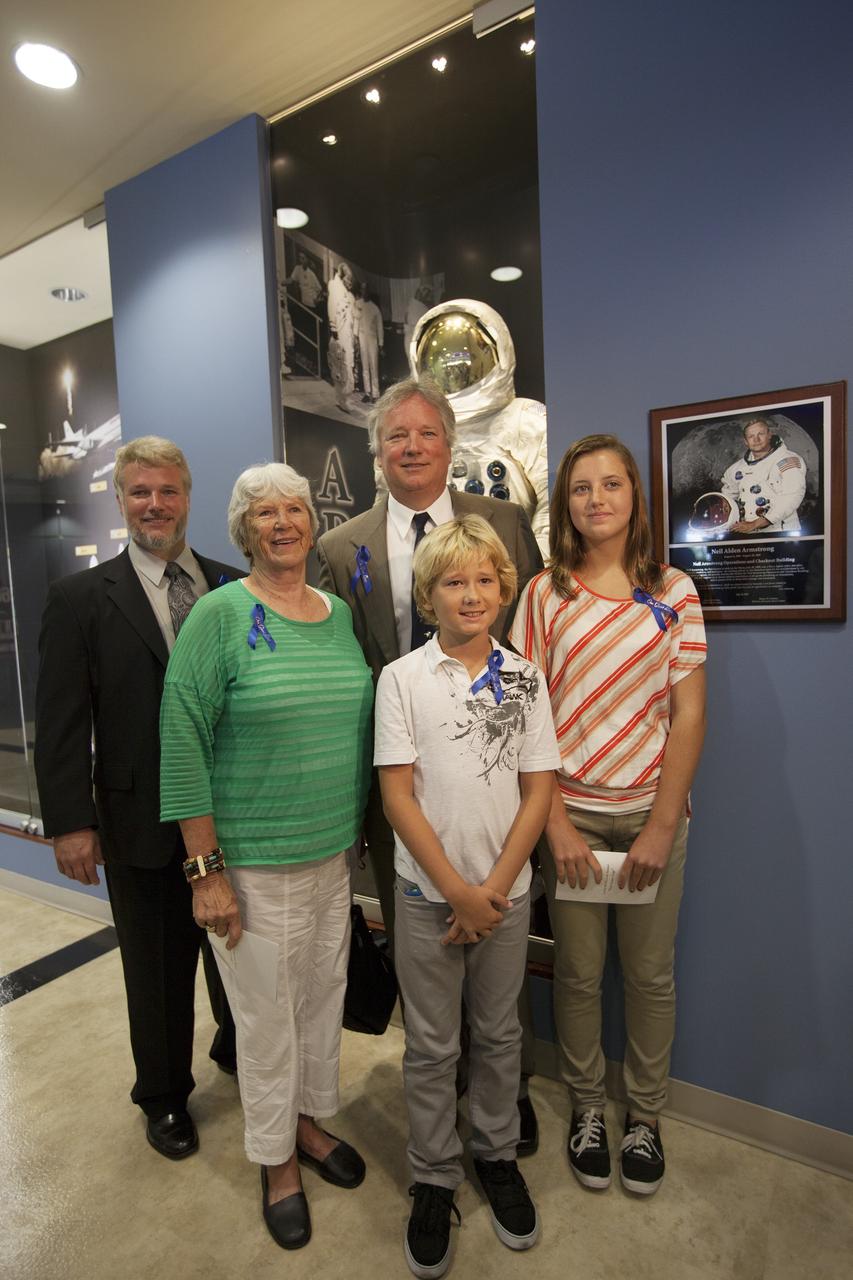

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Armstrong family pose beside a plaque following its unveiling in the lobby of the newly named Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The facility has been renamed for Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong, the first person to set foot on the moon. From left are Armstrong's son Mark, his former wife Janet, his son Rick, his grandson Bryce, and his granddaughter Lily. The building's high bay is being used to support the agency's new Orion spacecraft and is the same spaceport facility where the Apollo 11 command/service module and lunar module were prepped for the first lunar landing mission in 1969. Orion is designed to take humans farther than they’ve ever gone before, serving as the exploration vehicle that will carry astronauts to deep space and sustain the crew during travel to destinations such as an asteroid or Mars. The unveiling was part of NASA's 45th anniversary celebration of the Apollo 11 moon landing. As the world watched, Apollo 11 astronauts landed in the moon's Sea of Tranquility aboard the lunar module, Eagle, on July 20, 1969, as the command module, Columbia, orbited overhead. For more: http://www.nasa.gov/press/2014/july/nasa-honors-historic-first-moon-landing-eyes-first-mars-mission/ Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett