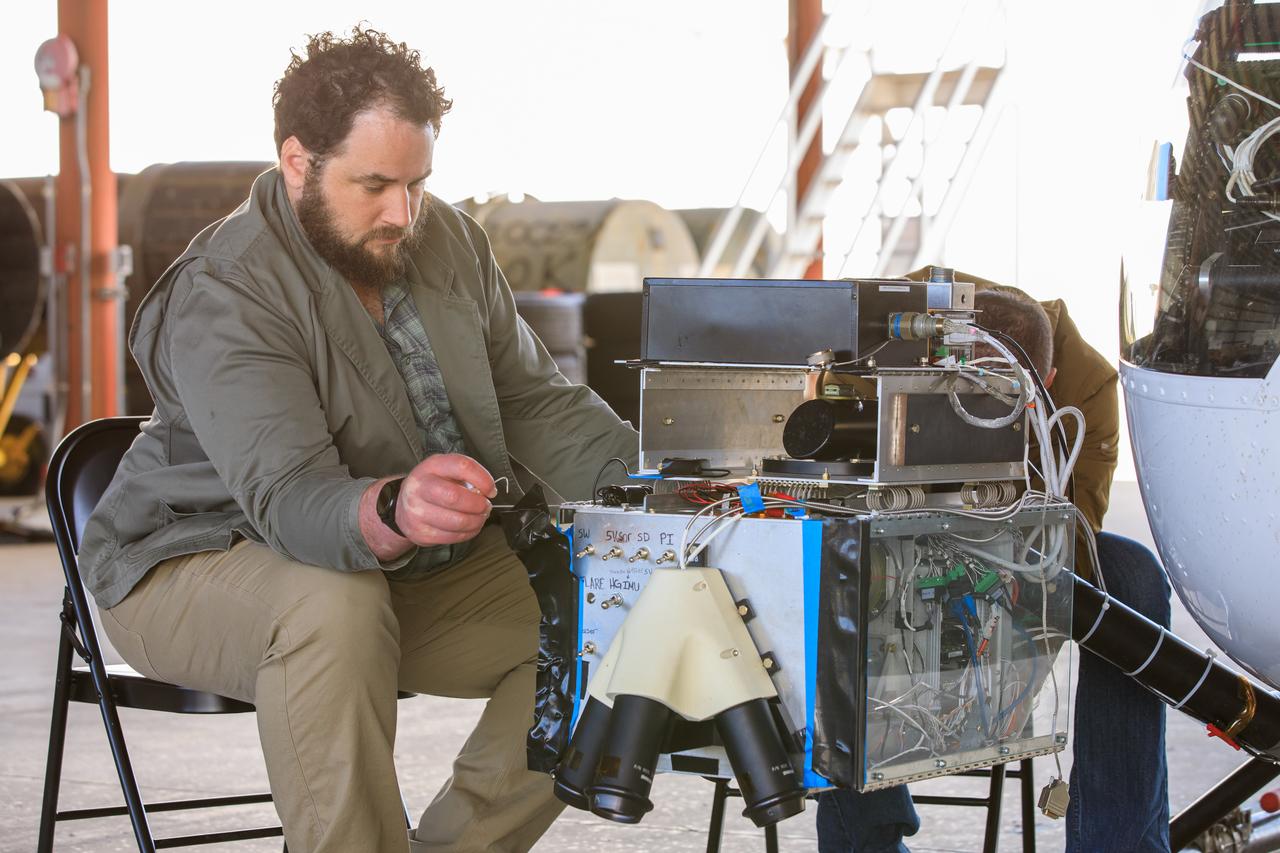

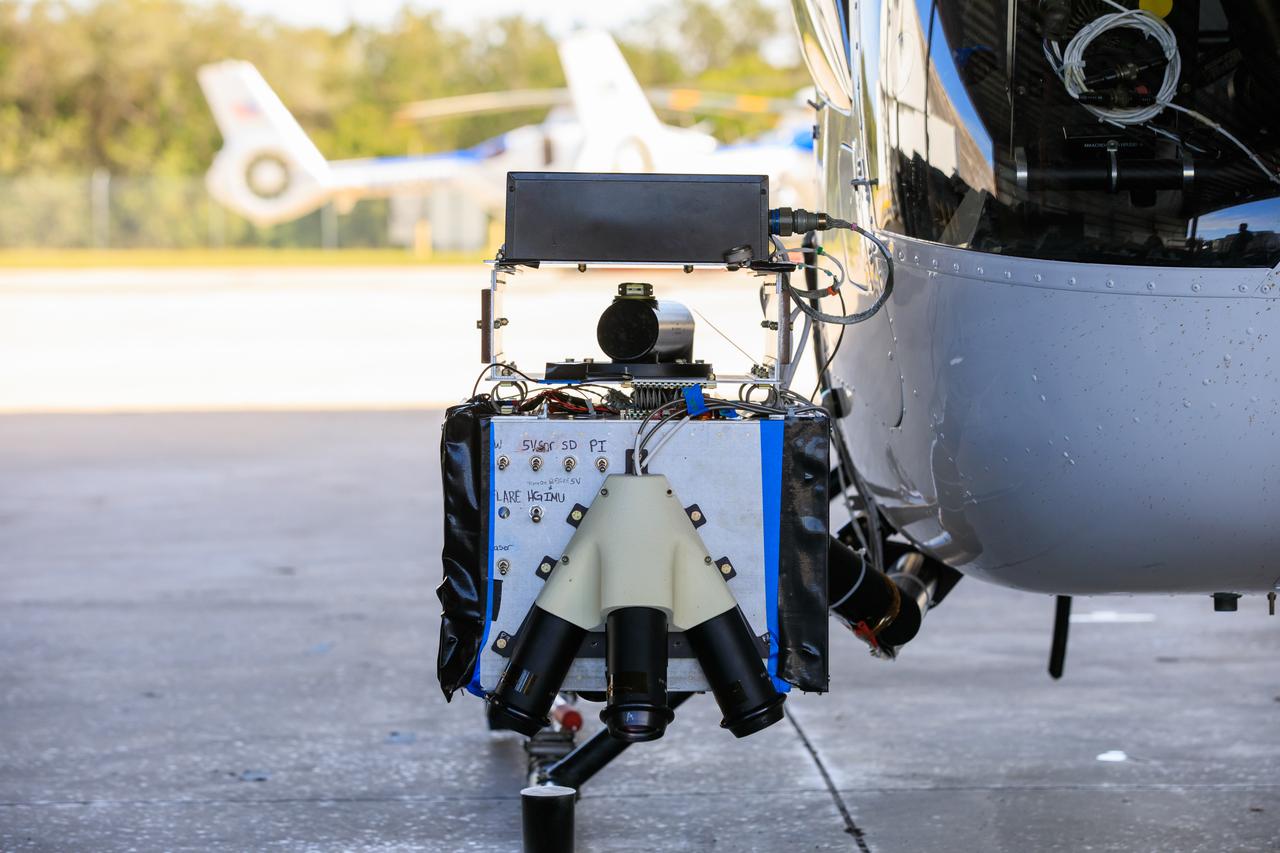
Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
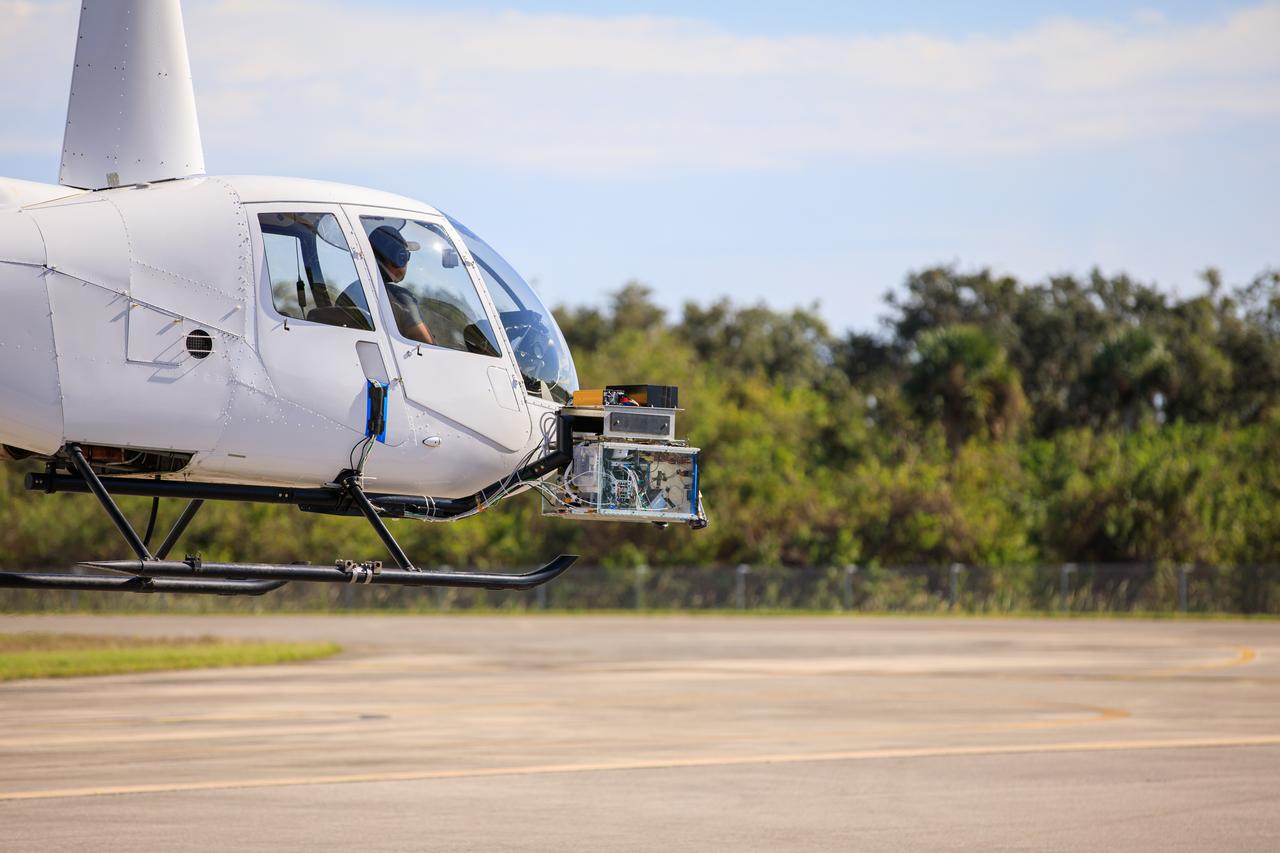

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
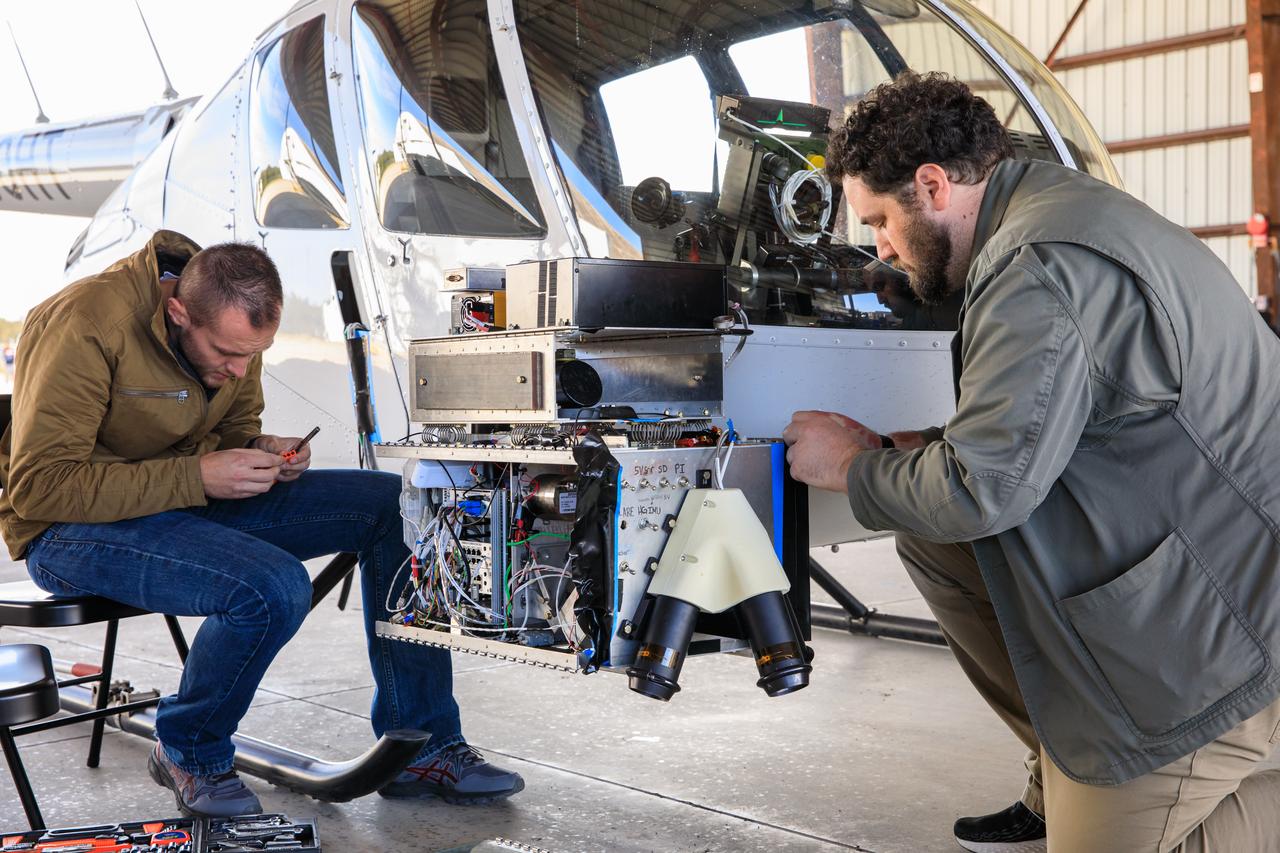

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
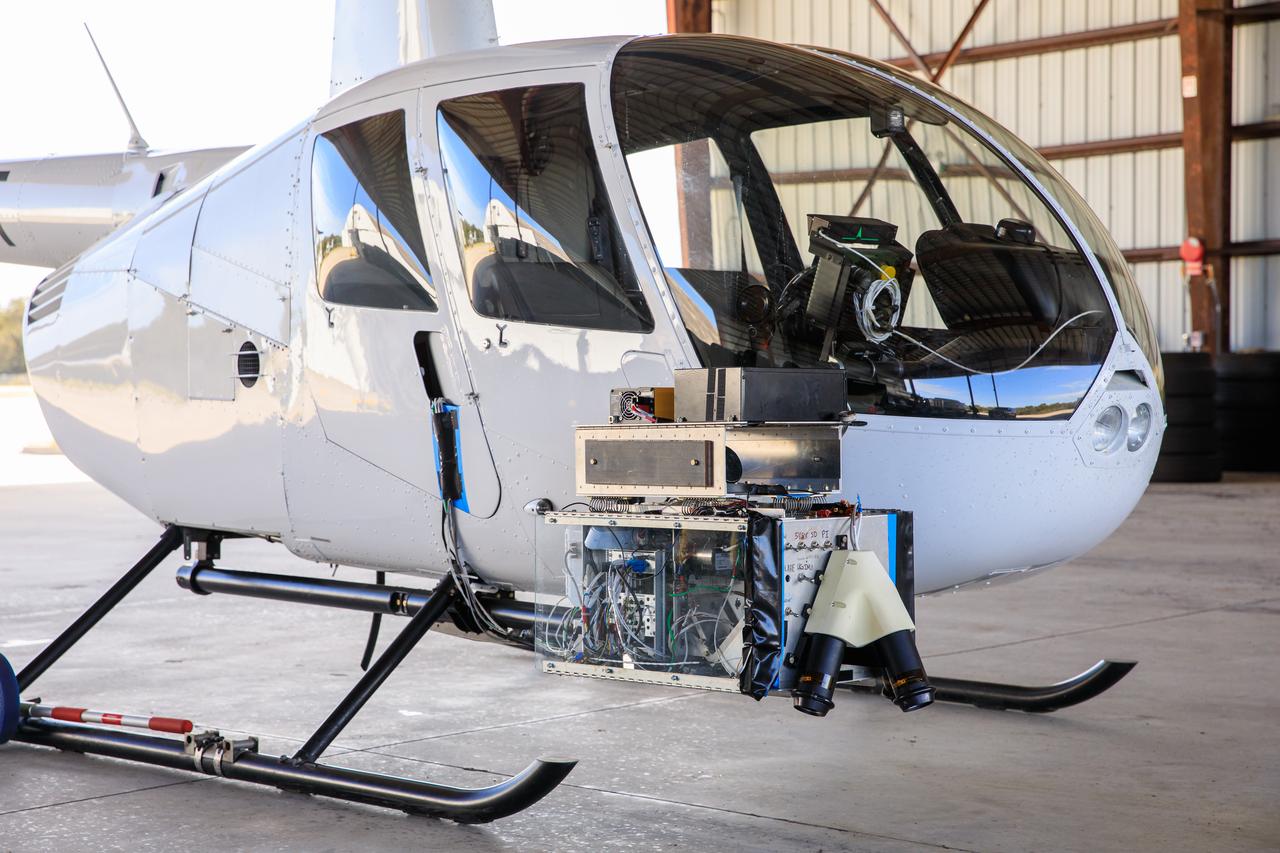

Seen here is Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

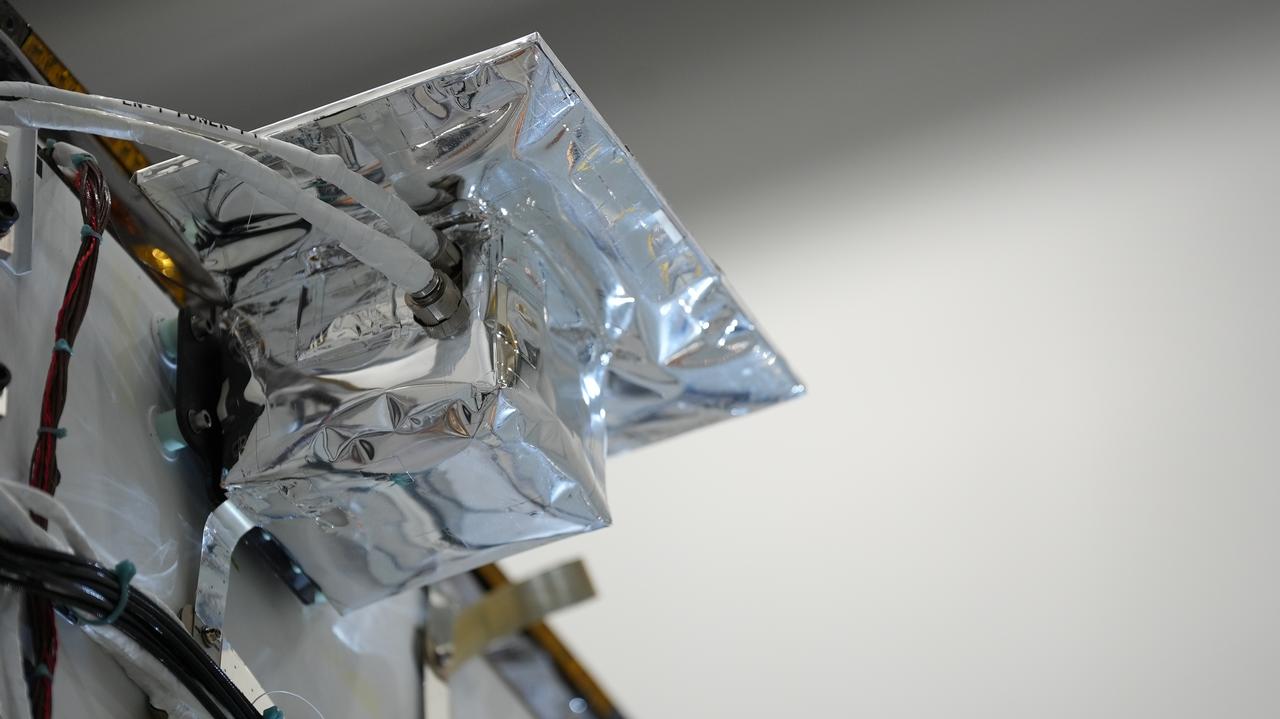
Seen here is a close-up view of Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

IM-1, the first NASA Commercial Launch Program Services launch for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander, will carry multiple payloads to the Moon, including Lunar Node-1, demonstrating autonomous navigation via radio beacon to support precise geolocation and navigation among lunar orbiters, landers, and surface personnel. NASA’s CLPS initiative oversees industry development of small robotic landers and rovers to support NASA’s Artemis campaign.

Lunar Node-1, an autonomous navigation payload that will change how human explorers safely traverse the Moon’s surface and live and work in lunar orbit, awaits liftoff as part of Intuitive Machines’ IM-1 mission, its first under NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative. LN-1 was developed, built, and tested at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander lifts off from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 1:05 a.m. EST on Thursday, Feb. 15, 2024. As part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative and Artemis campaign, Intuitive Machines’ first lunar mission will carry NASA science and commercial payloads to the Moon to study plume-surface interactions, space weather/lunar surface interactions, radio astronomy, precision landing technologies, and a communication and navigation node for future autonomous navigation technologies.
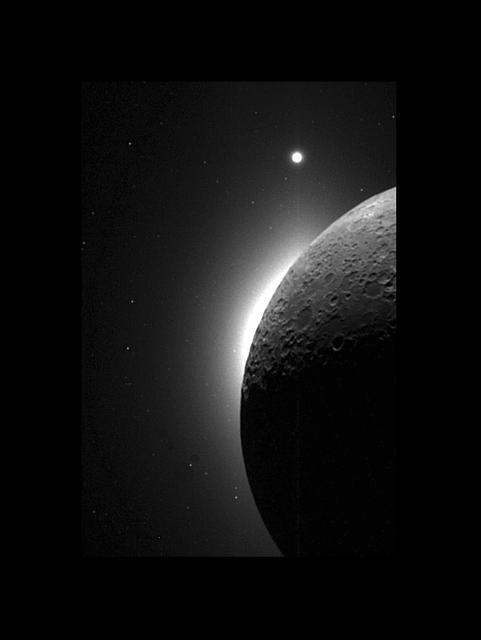

In 1994, during its flight, NASA's Clementine spacecraft returned images of the Moon. In addition to the geologic mapping cameras, the Clementine spacecraft also carried two Star Tracker cameras for navigation. These lightweight (0.3 kg) cameras kept the spacecraft on track by constantly observing the positions of stars, reminiscent of the age-old seafaring tradition of sextant/star navigation. These navigation cameras were also to take some spectacular wide angle images of the Moon. In this picture the Moon is seen illuminated solely by light reflected from the Earth--Earthshine! The bright glow on the lunar horizon is caused by light from the solar corona; the sun is just behind the lunar limb. Caught in this image is the planet Venus at the top of the frame. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00434
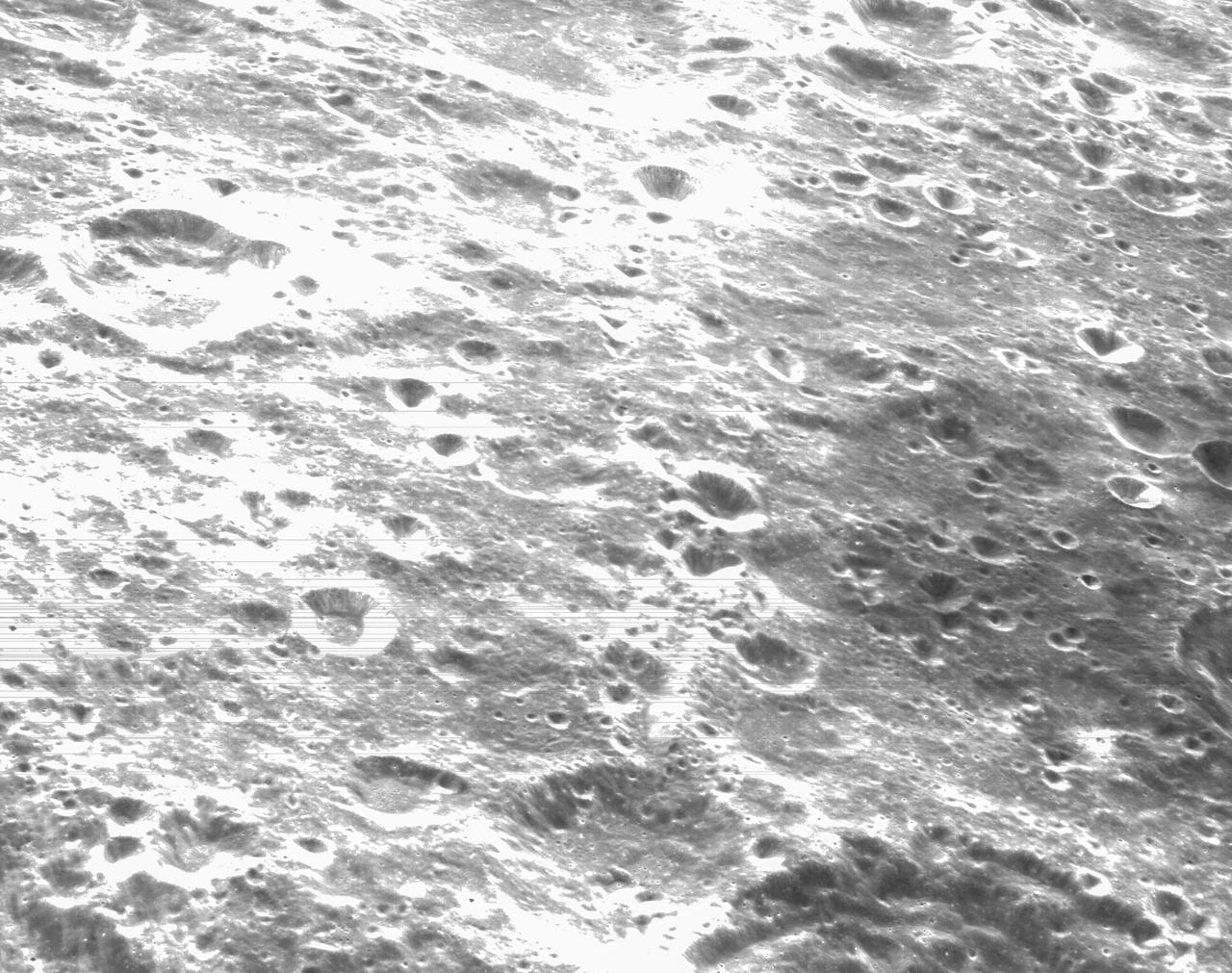

art001e000274 Nov. 21, 2022 -- On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion's optical navigation camera was commanded to take this black-and-white photo of the lunar surface. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
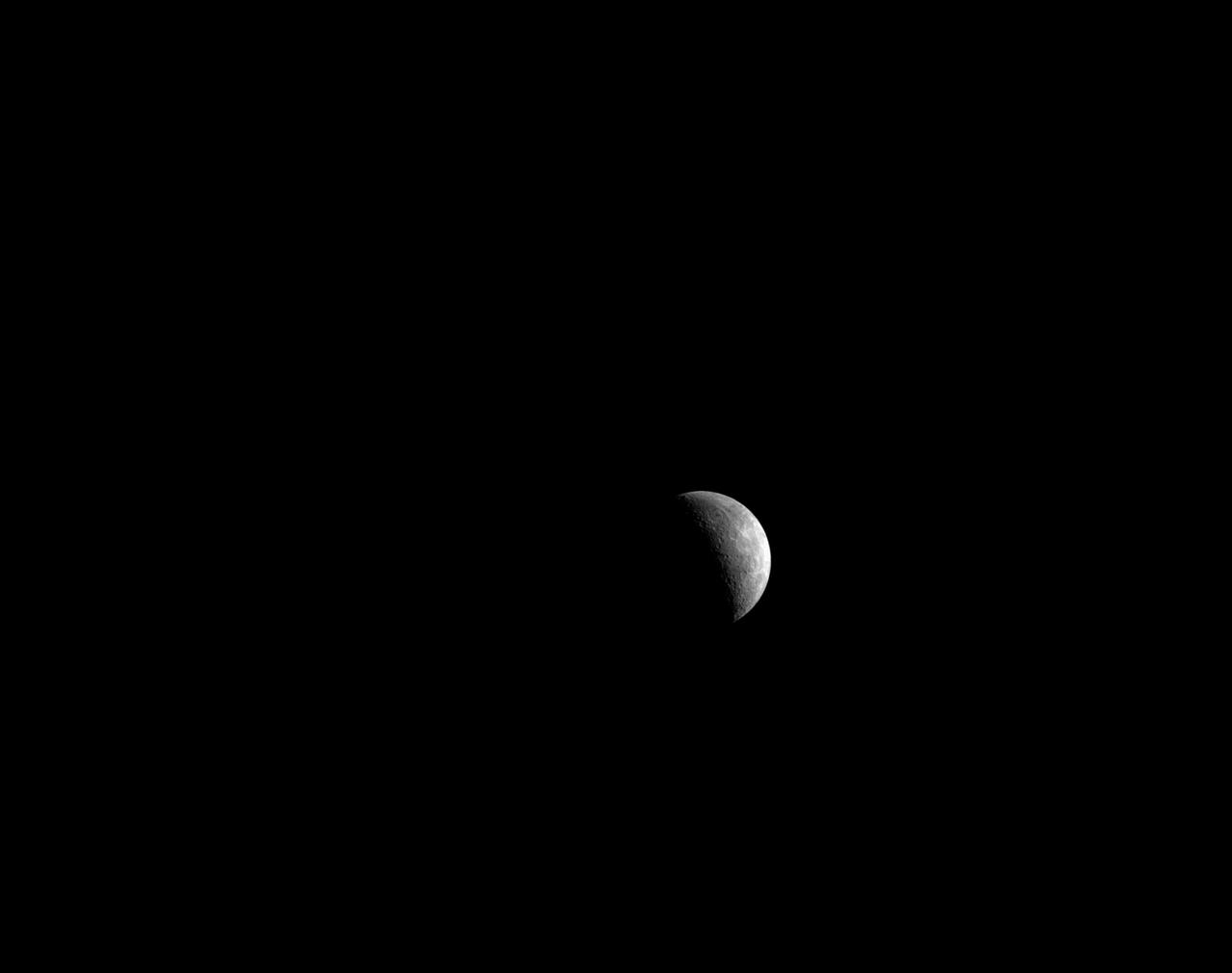

OpNav Moon images: art001e000579 (Nov. 26, 2022) On flight day 11, Orion’s optical navigation camera was used to capture this lunar image as the spacecraft is in distant retrograde orbit around the Moon. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
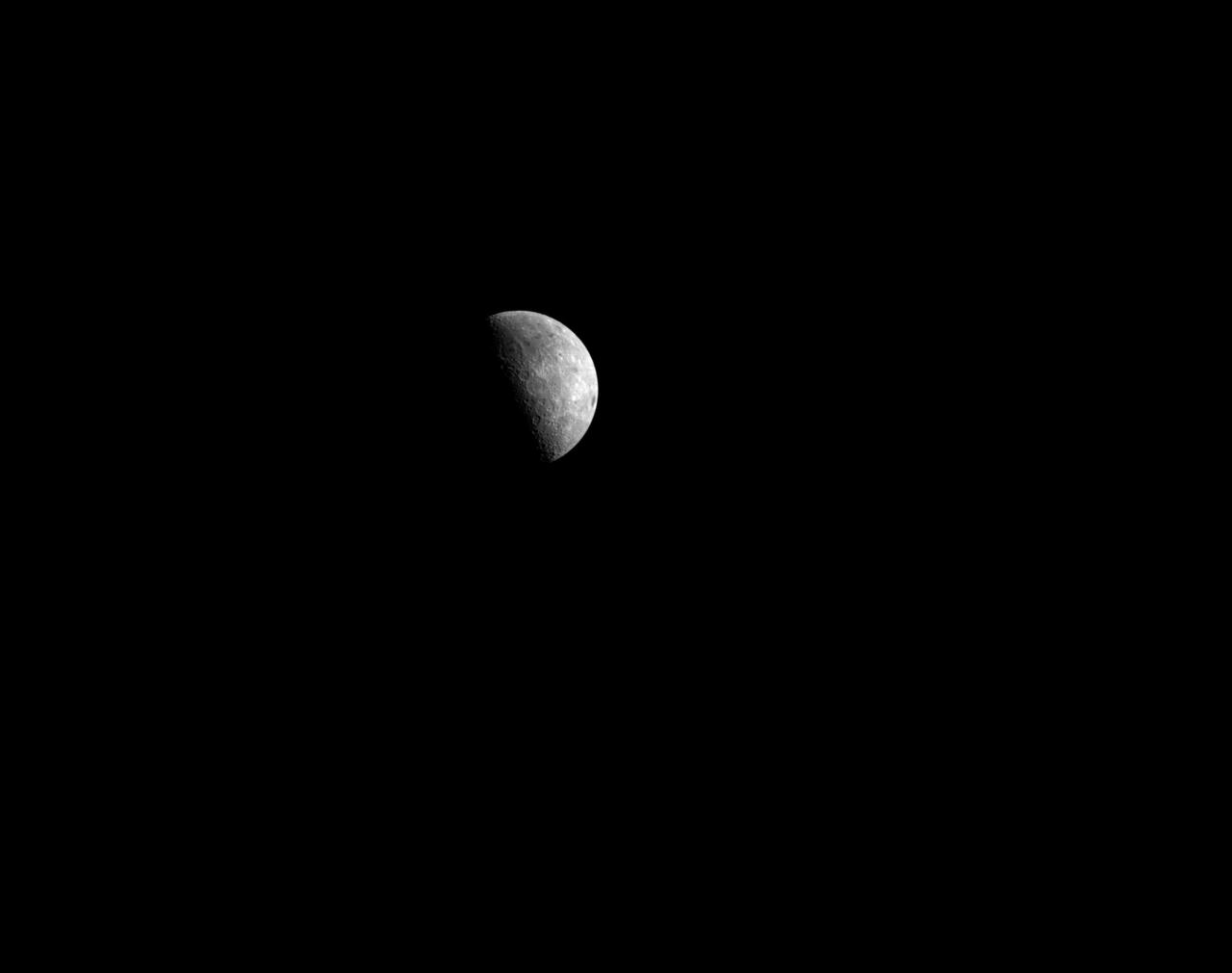

art001e001464 (Nov. 27, 2022) On flight day 12, Orion’s optical navigation camera was used to capture this lunar image as the spacecraft was in distant retrograde orbit around the Moon. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
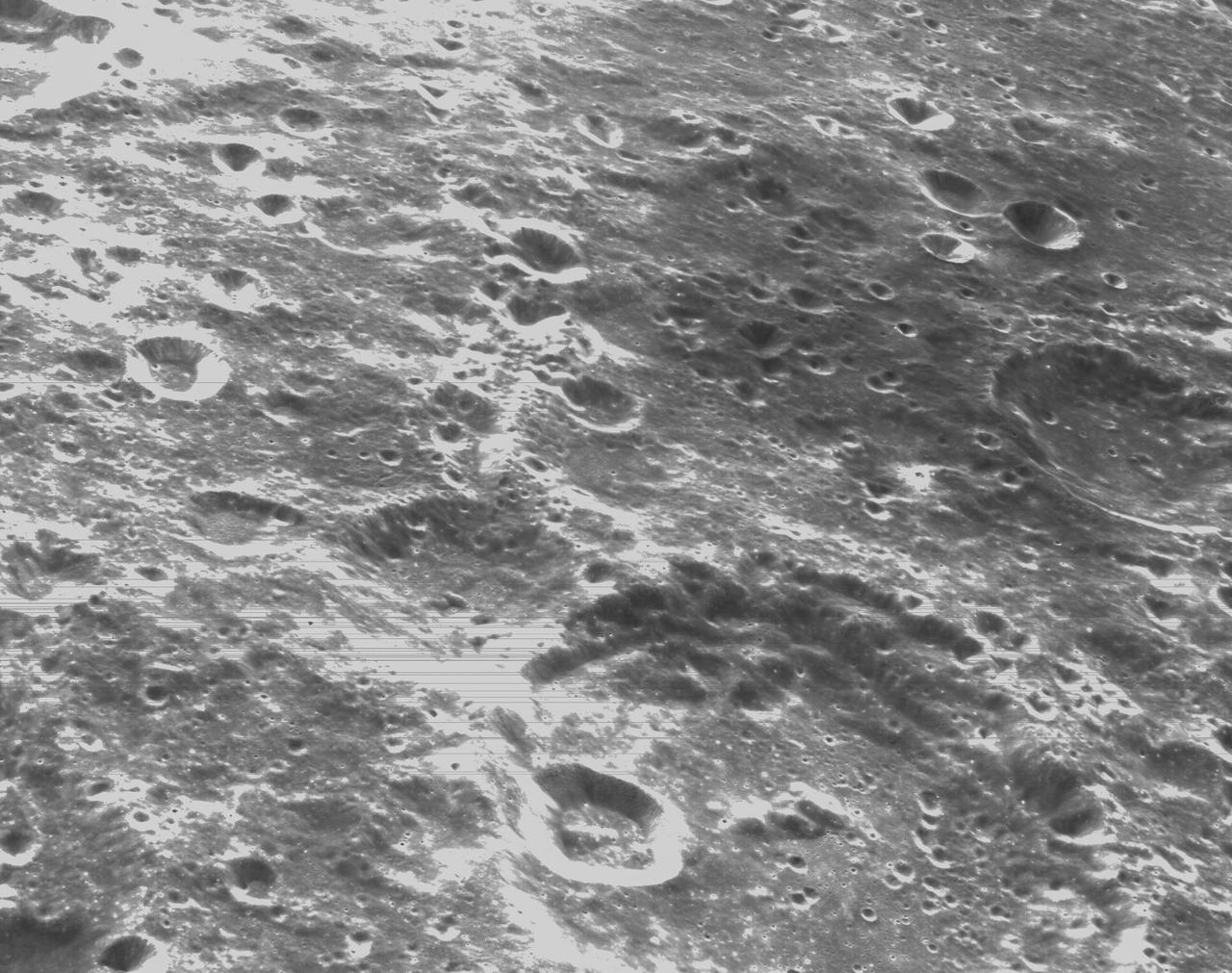

art001e000333 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
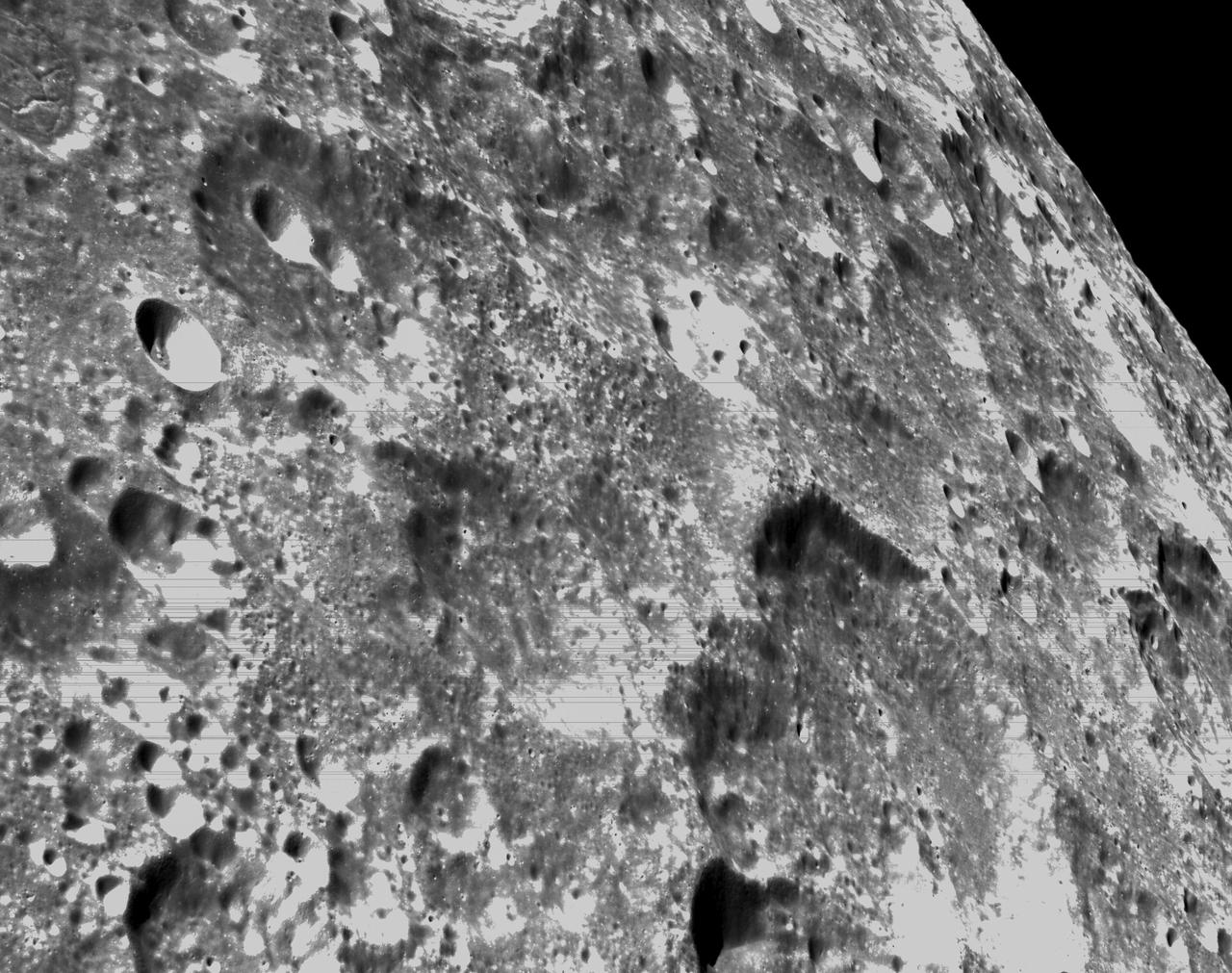
art001e000344 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
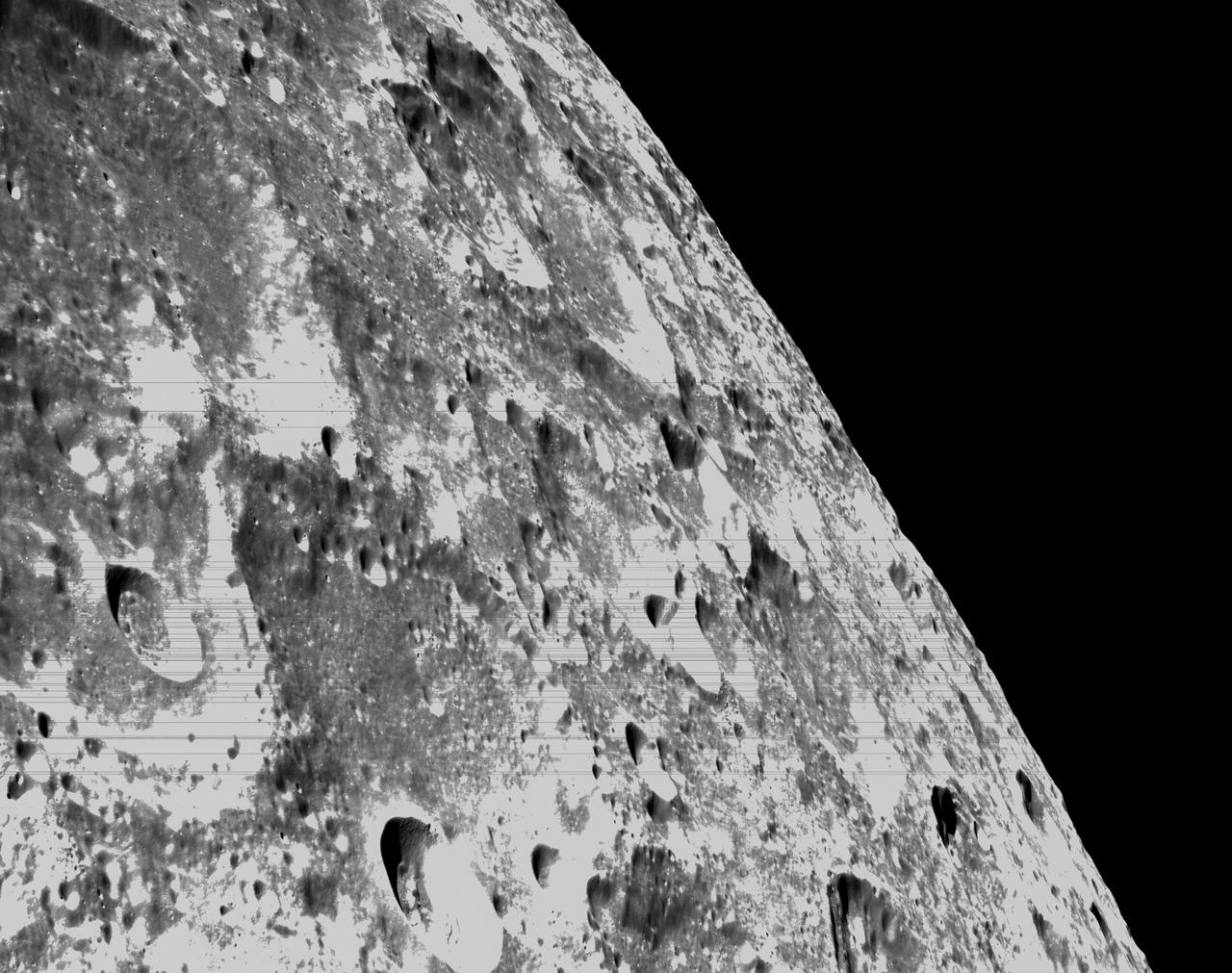

art001e000346 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
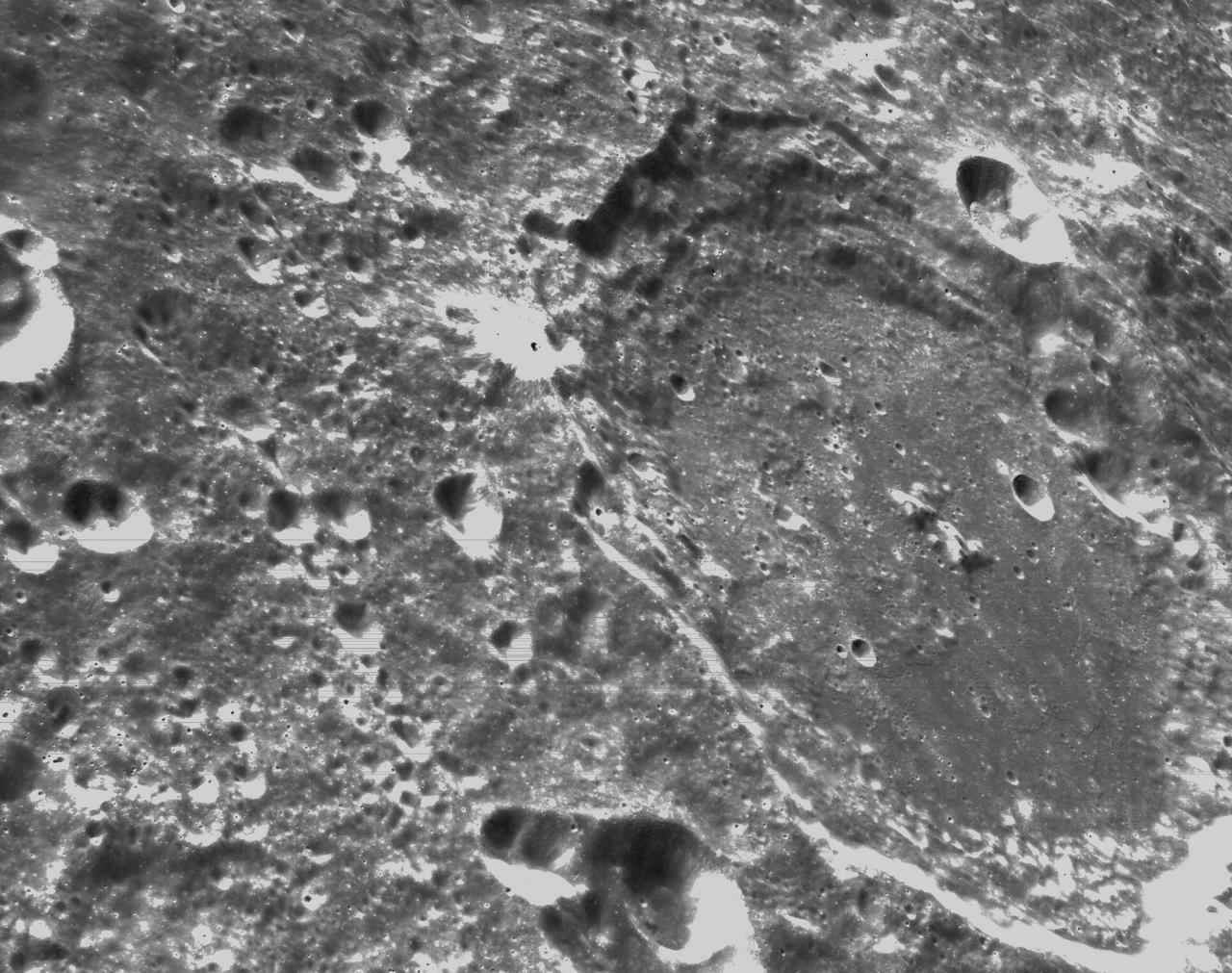

art001e000340 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
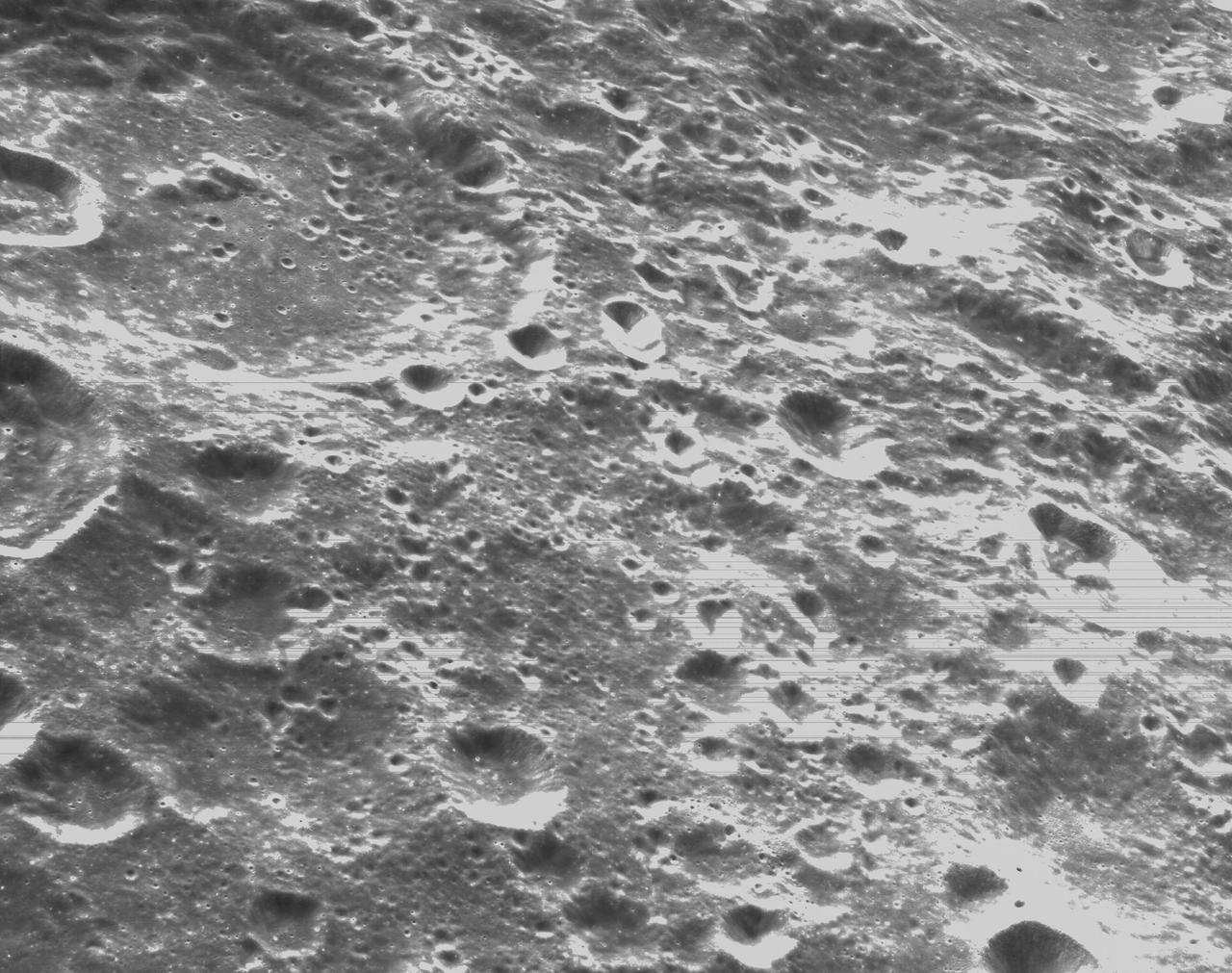

art001e000335 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
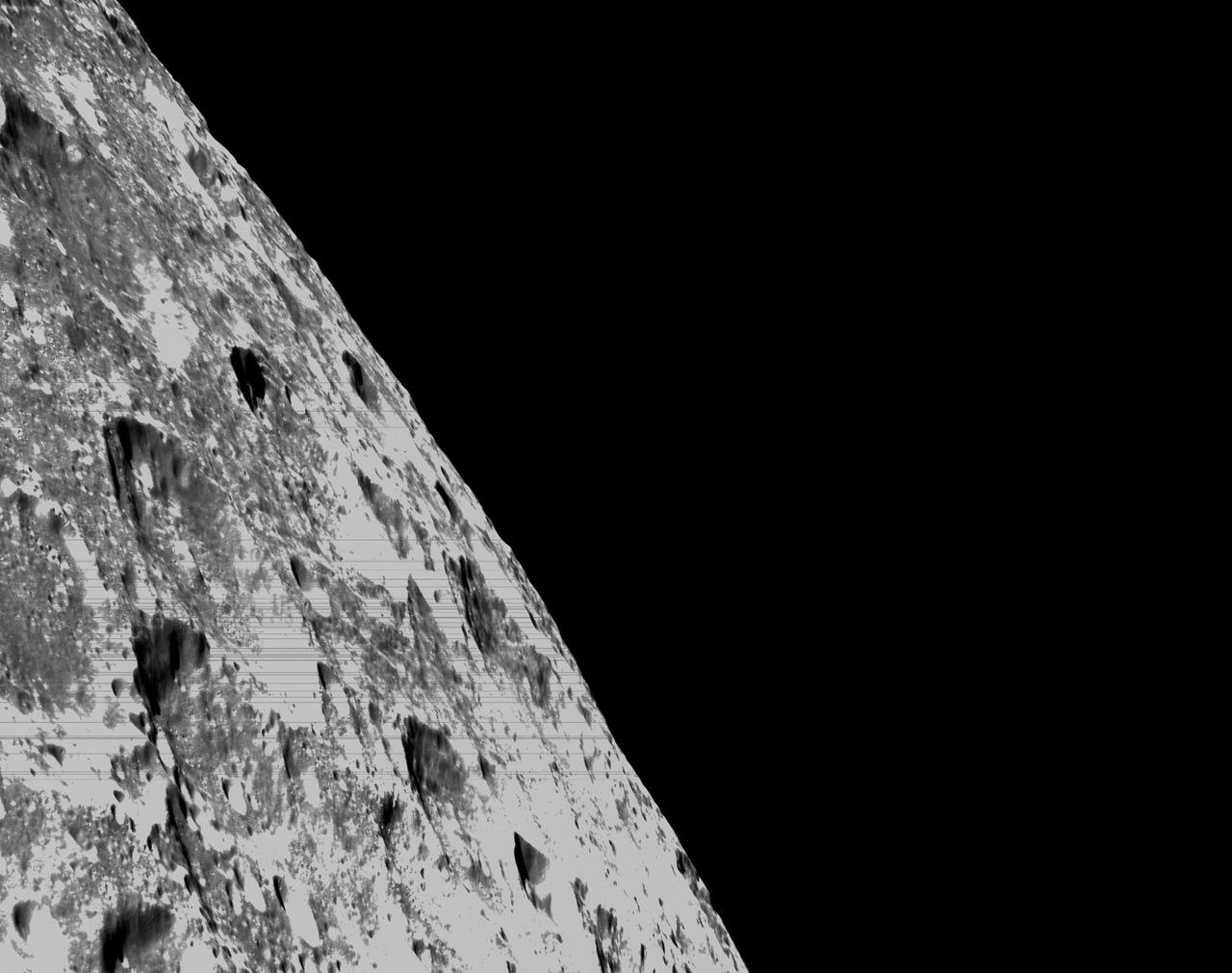

art001e000348 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
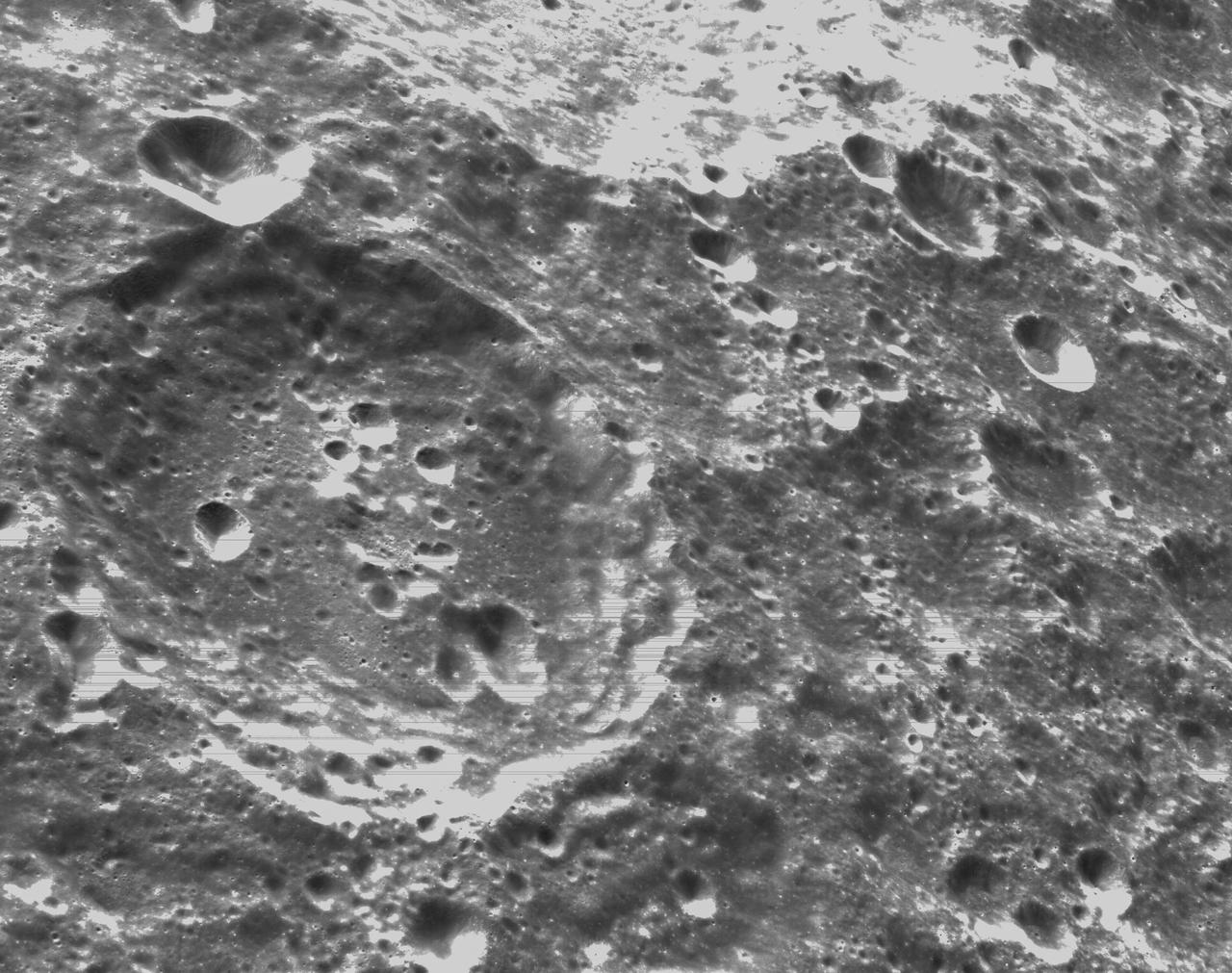

art001e000338 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.

art001e000345 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
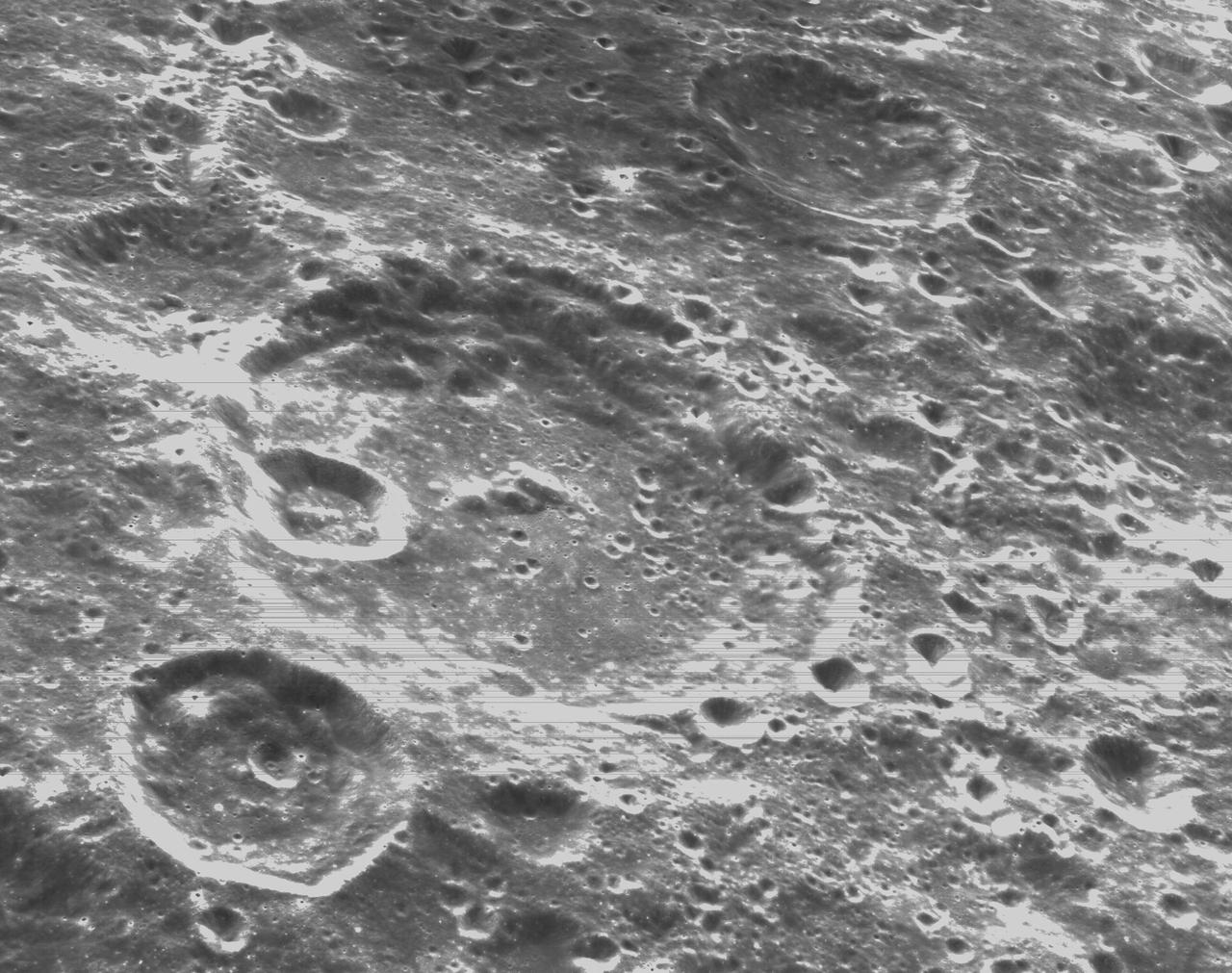
art001e000334 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
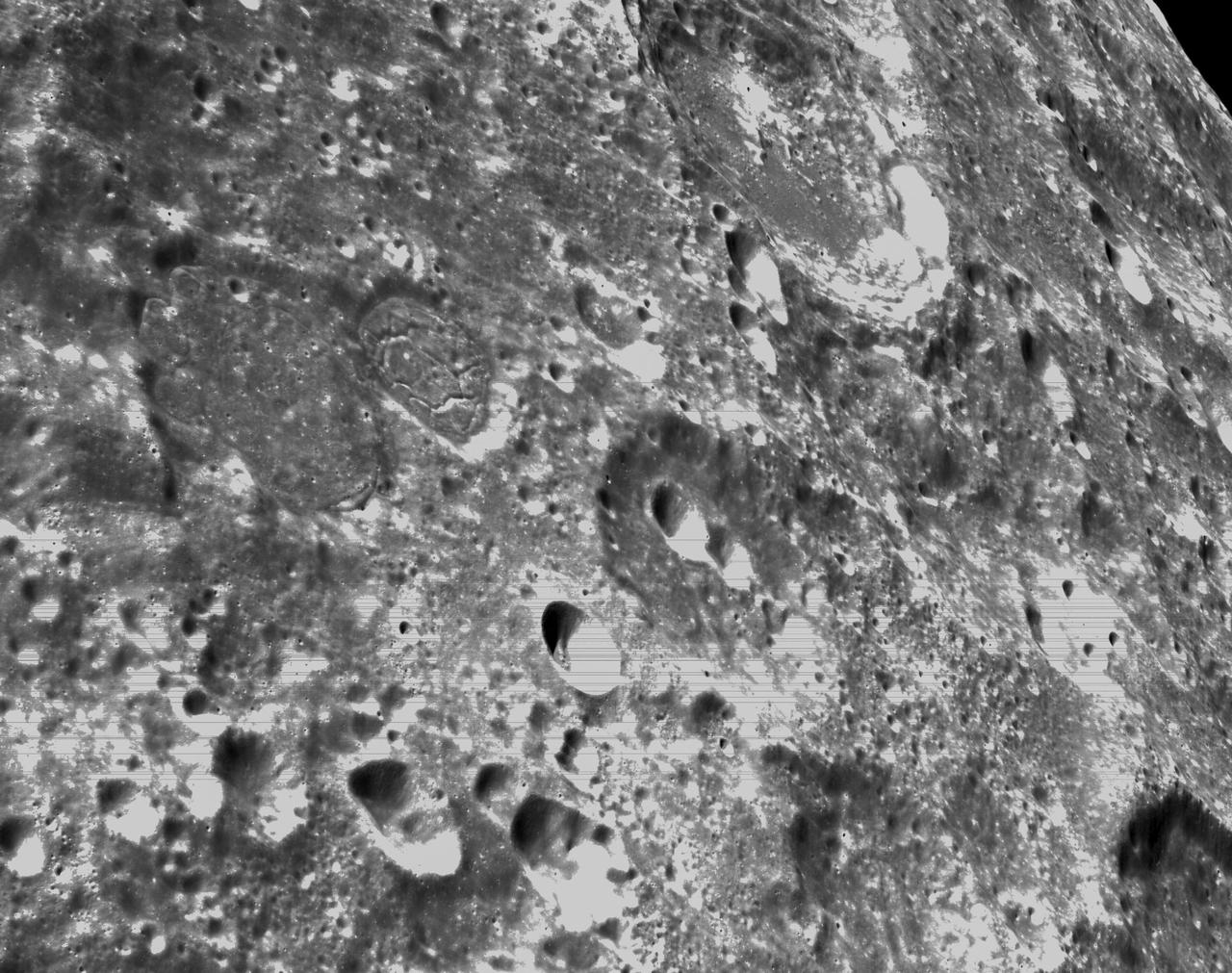

art001e000343 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
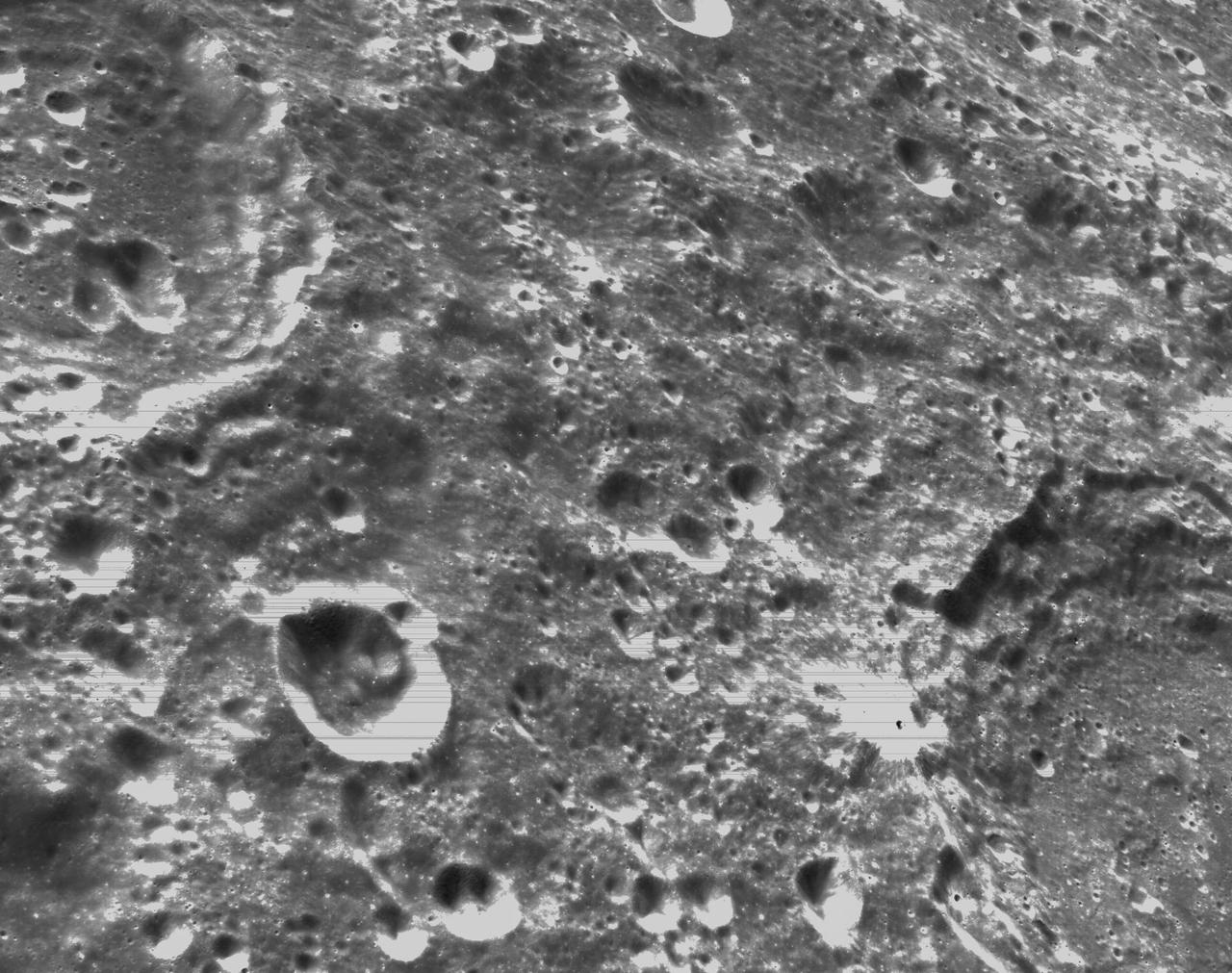
art001e000339 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
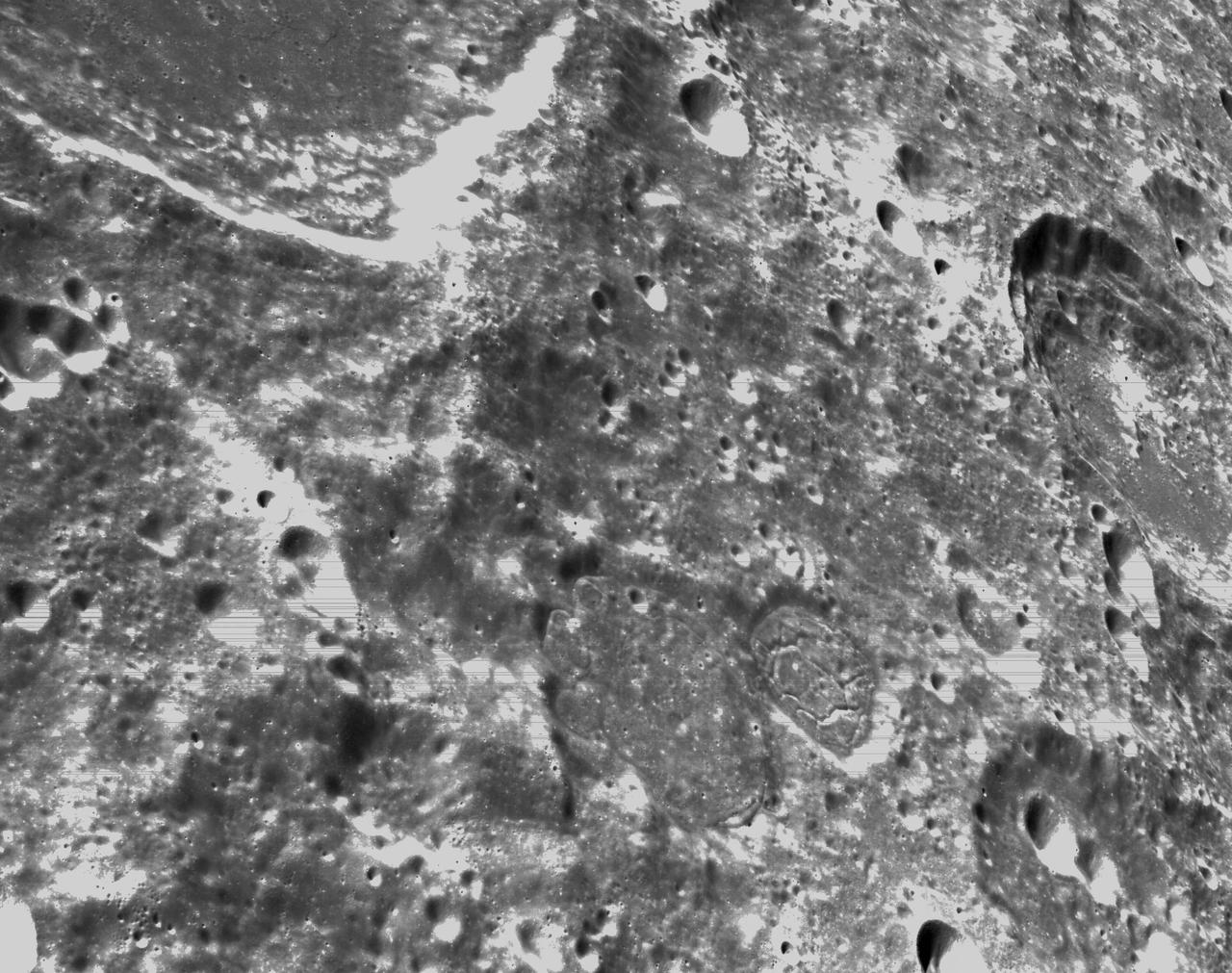

art001e000342 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
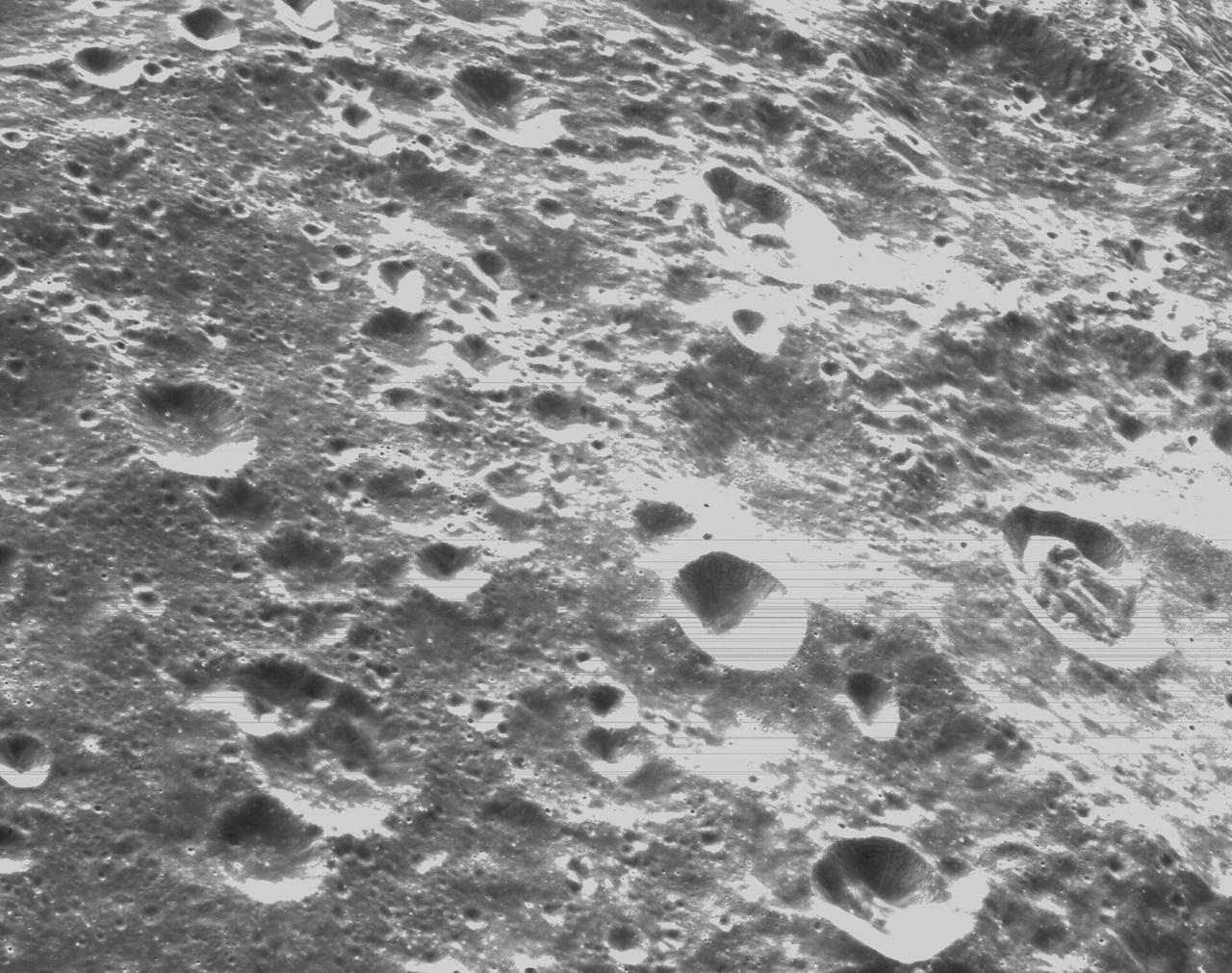

art001e000336 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
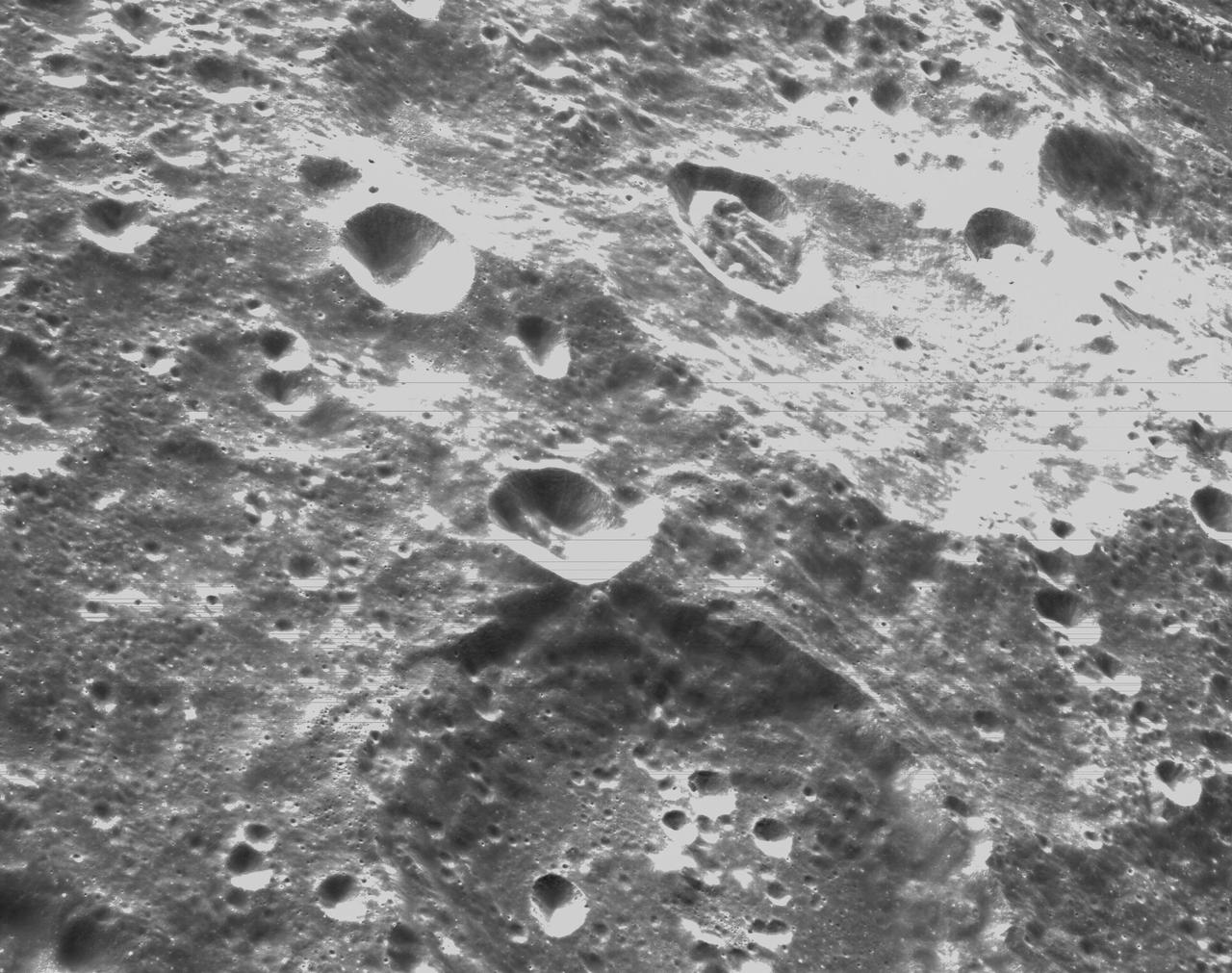

art001e000337 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
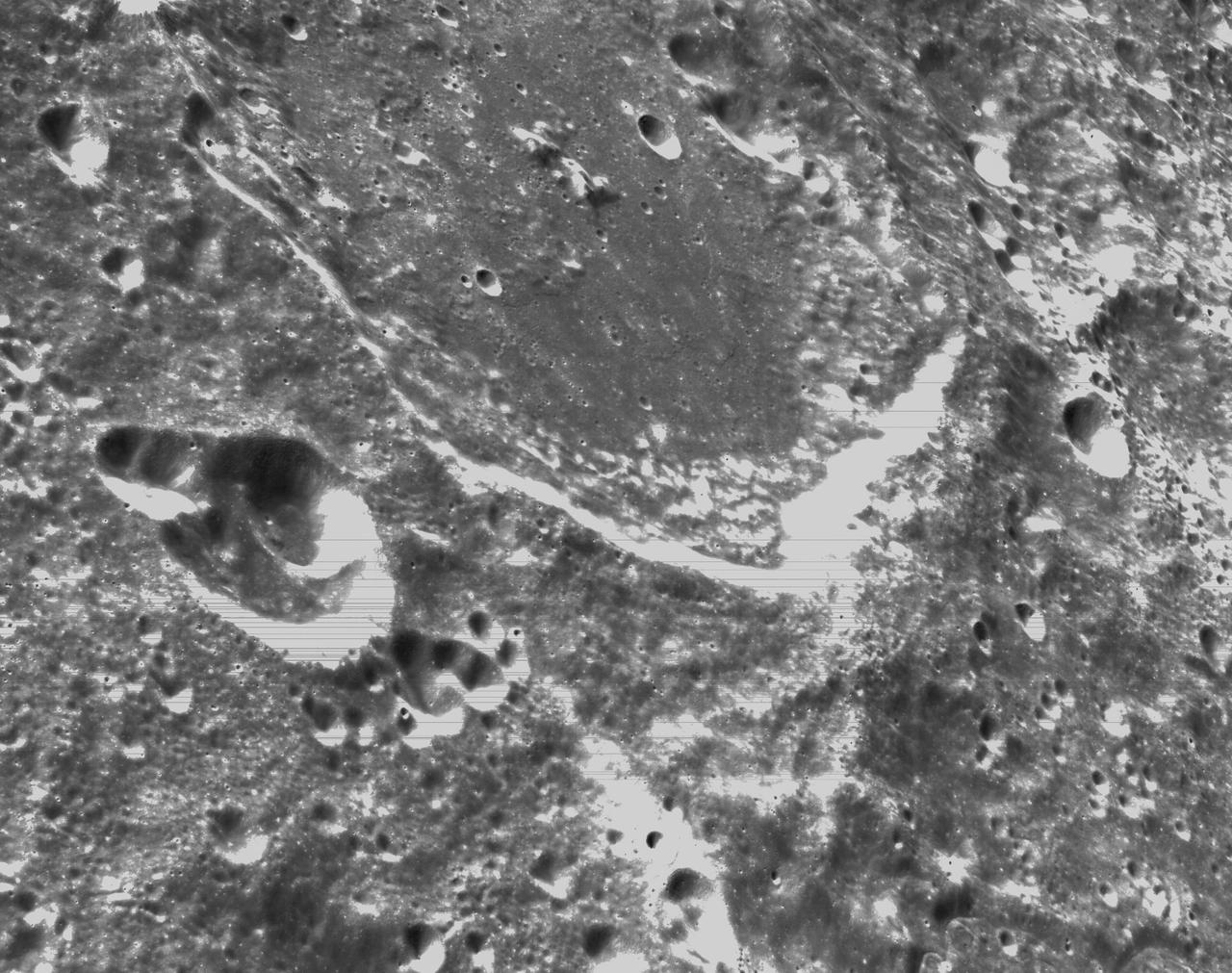
art001e000341 (Nov. 21, 2022) – On the sixth day of the Artemis I mission, Orion’s optical navigation camera captured black-and-white images of craters on the Moon below. Orion uses the optical navigation camera to capture imagery of the Earth and the Moon at different phases and distances, providing an enhanced body of data to certify its effectiveness under different lighting conditions as a way to help orient the spacecraft on future missions with crew.
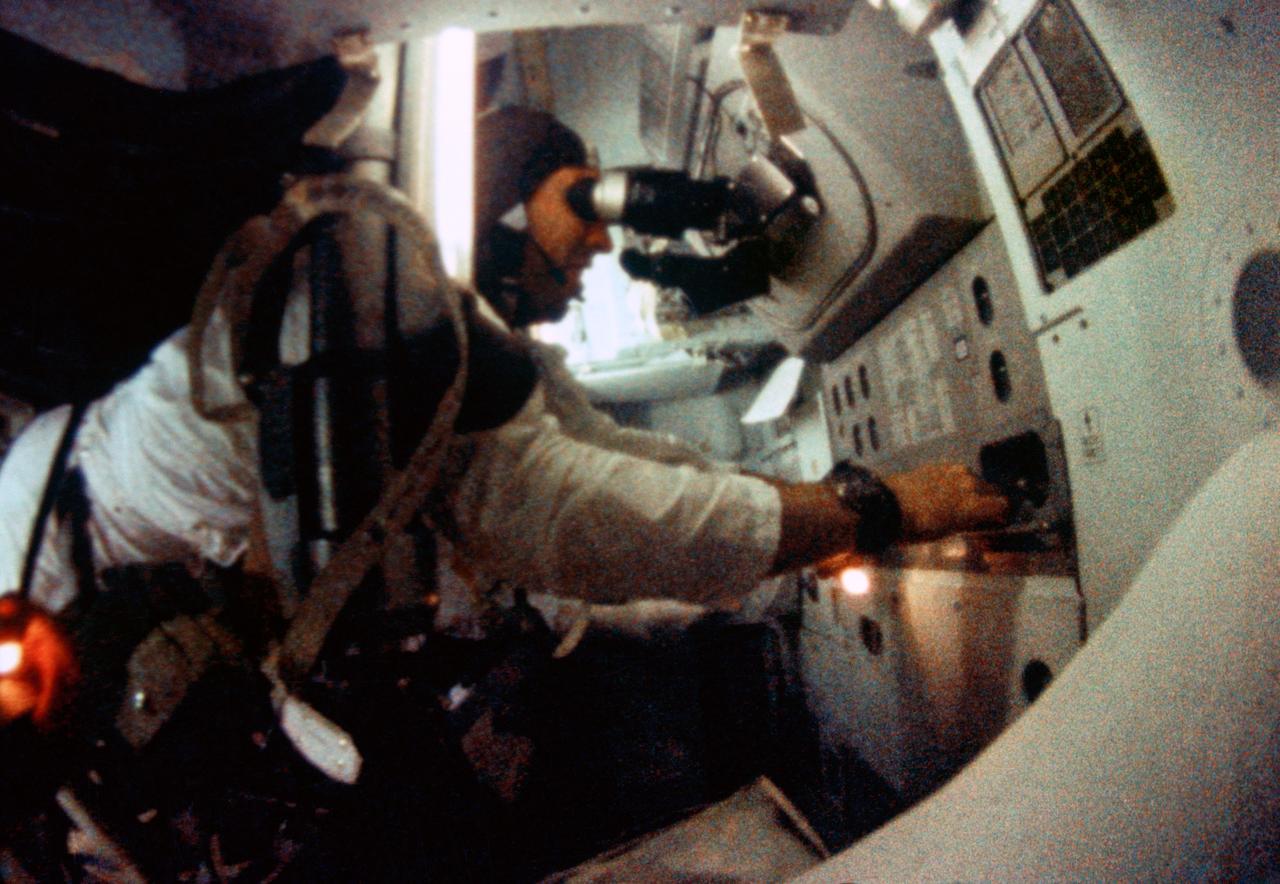

S69-35099 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 8 command module pilot, is seen at the Apollo 8 Spacecraft Command Module's Guidance and Navigation station during the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. This picture was taken from 16mm motion picture film.
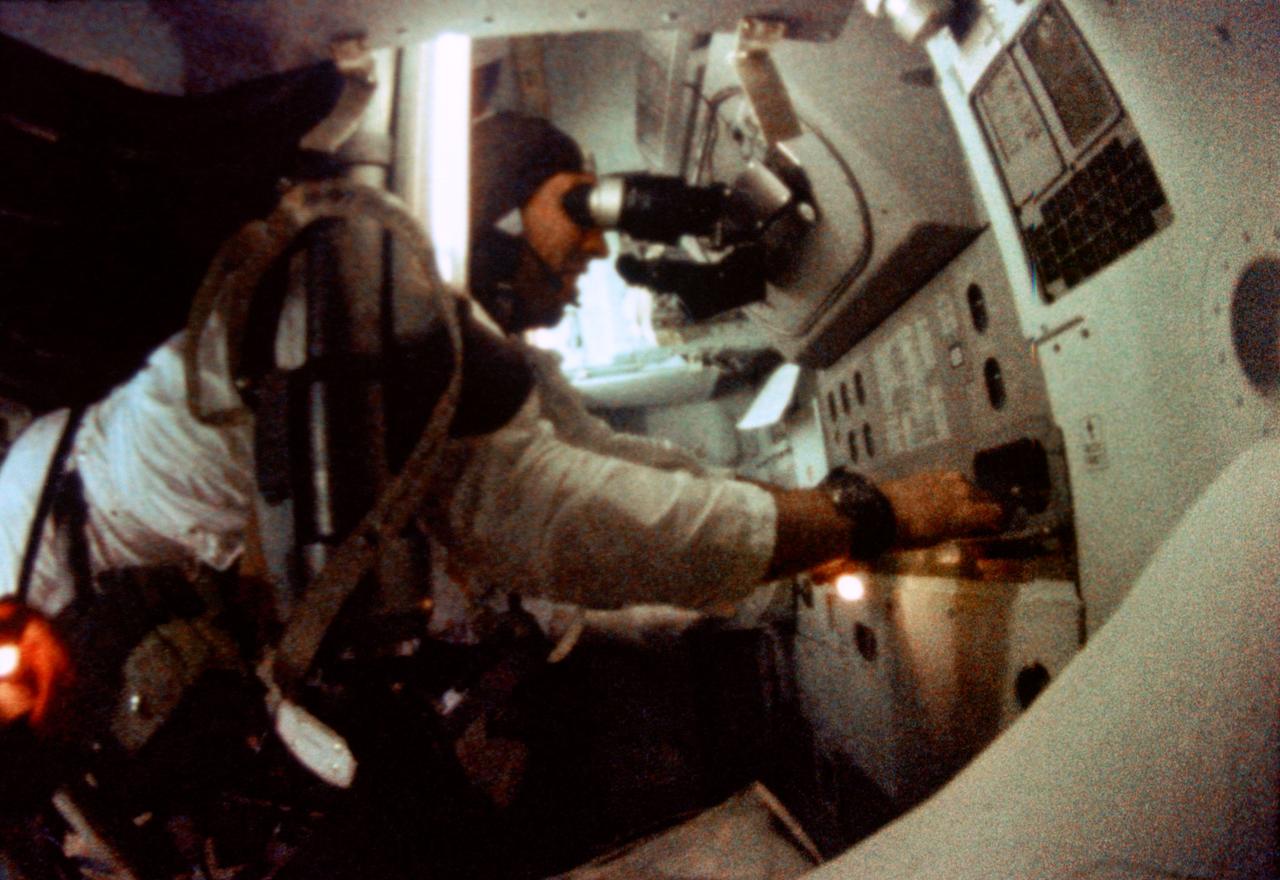

S69-35097 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 8 command module pilot, is seen at the Apollo 8 Spacecraft Command Module's Guidance and Navigation station during the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. This picture was taken from 16mm motion picture film.
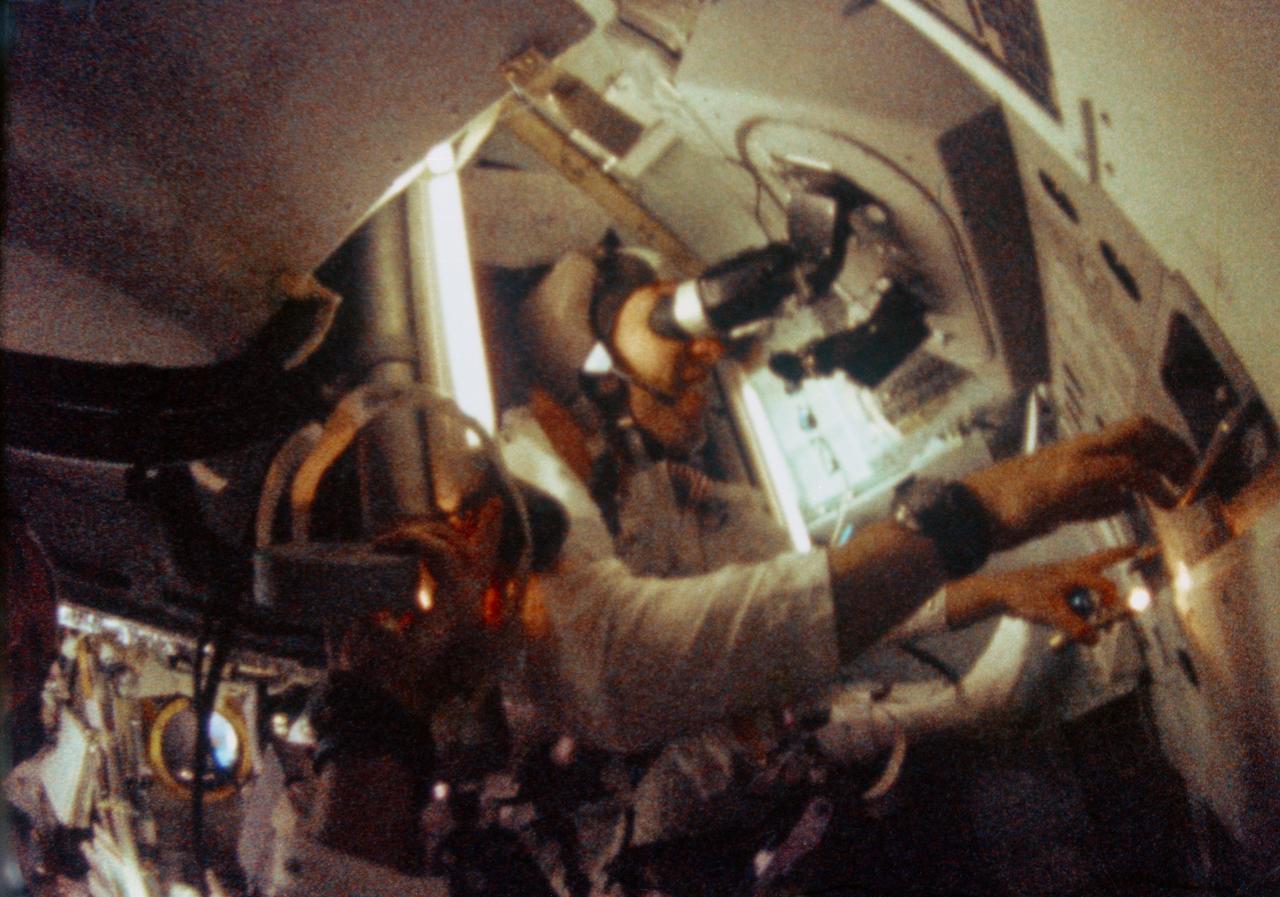

S69-35098 (21-27 Dec. 1968) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 8 command module pilot, is seen at the Apollo 8 Spacecraft Command Module's Guidance and Navigation station during the Apollo 8 lunar orbit mission. This picture was taken from 16mm motion picture film.
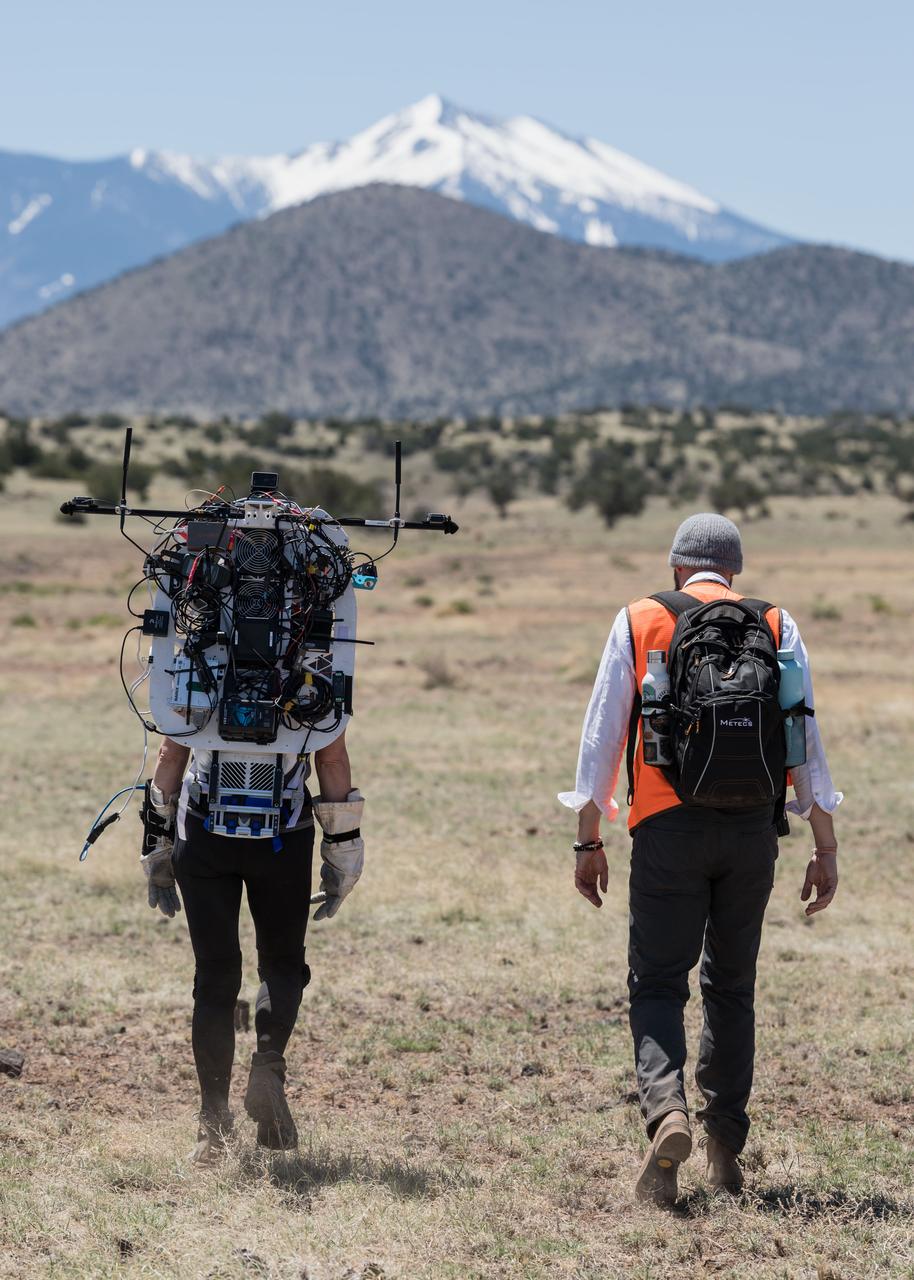

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
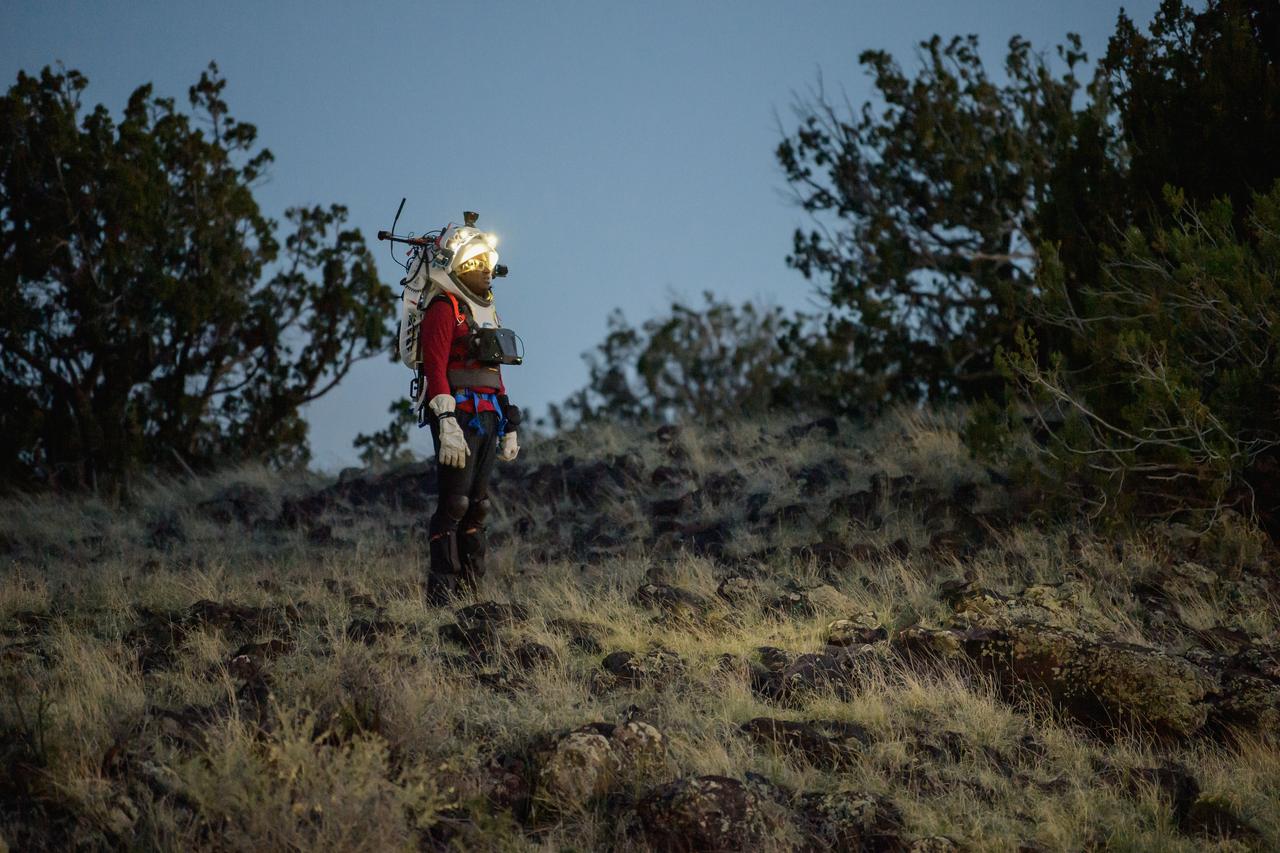

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas views the lunar-like landscape at dusk while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
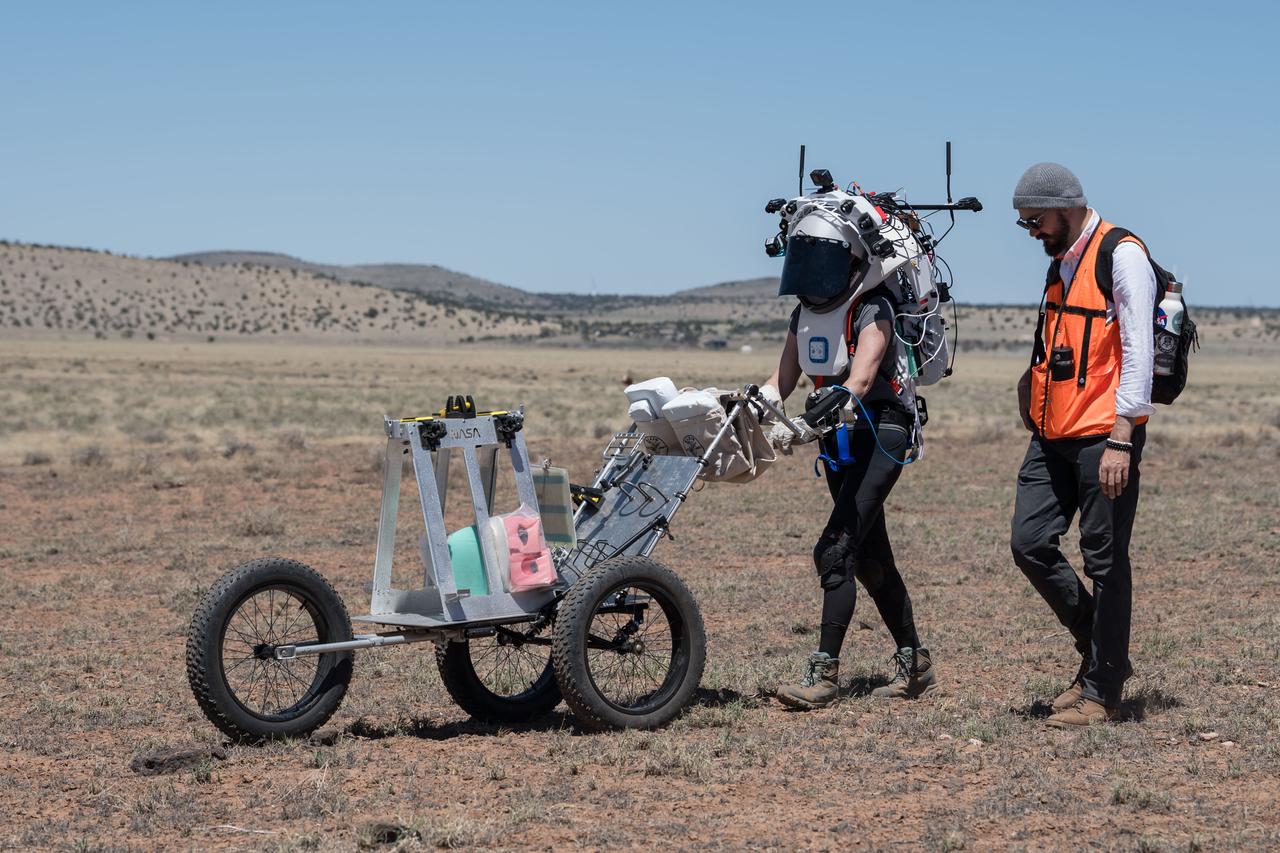

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins pushes a cart through the lunar-like landscape while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
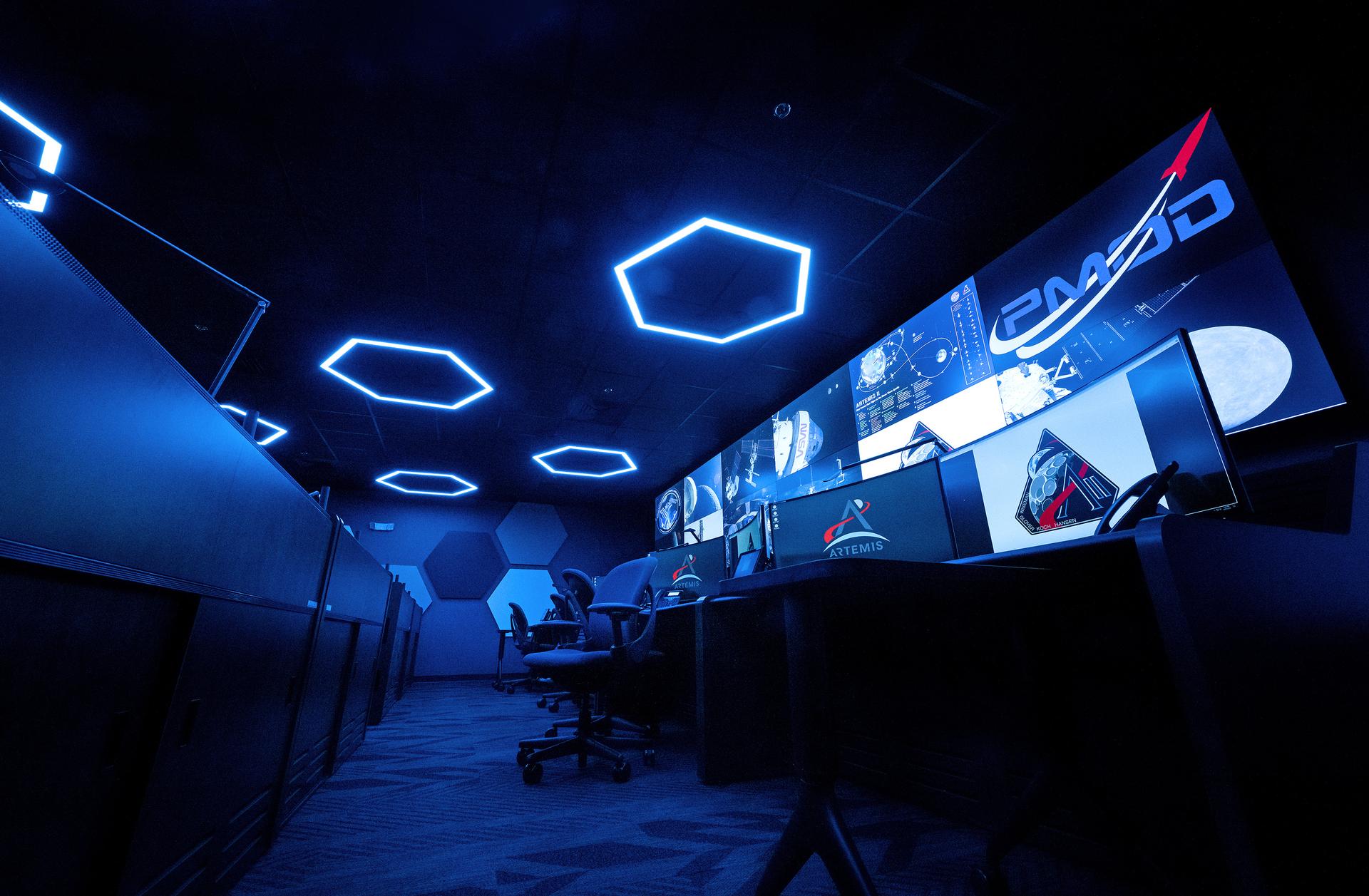

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
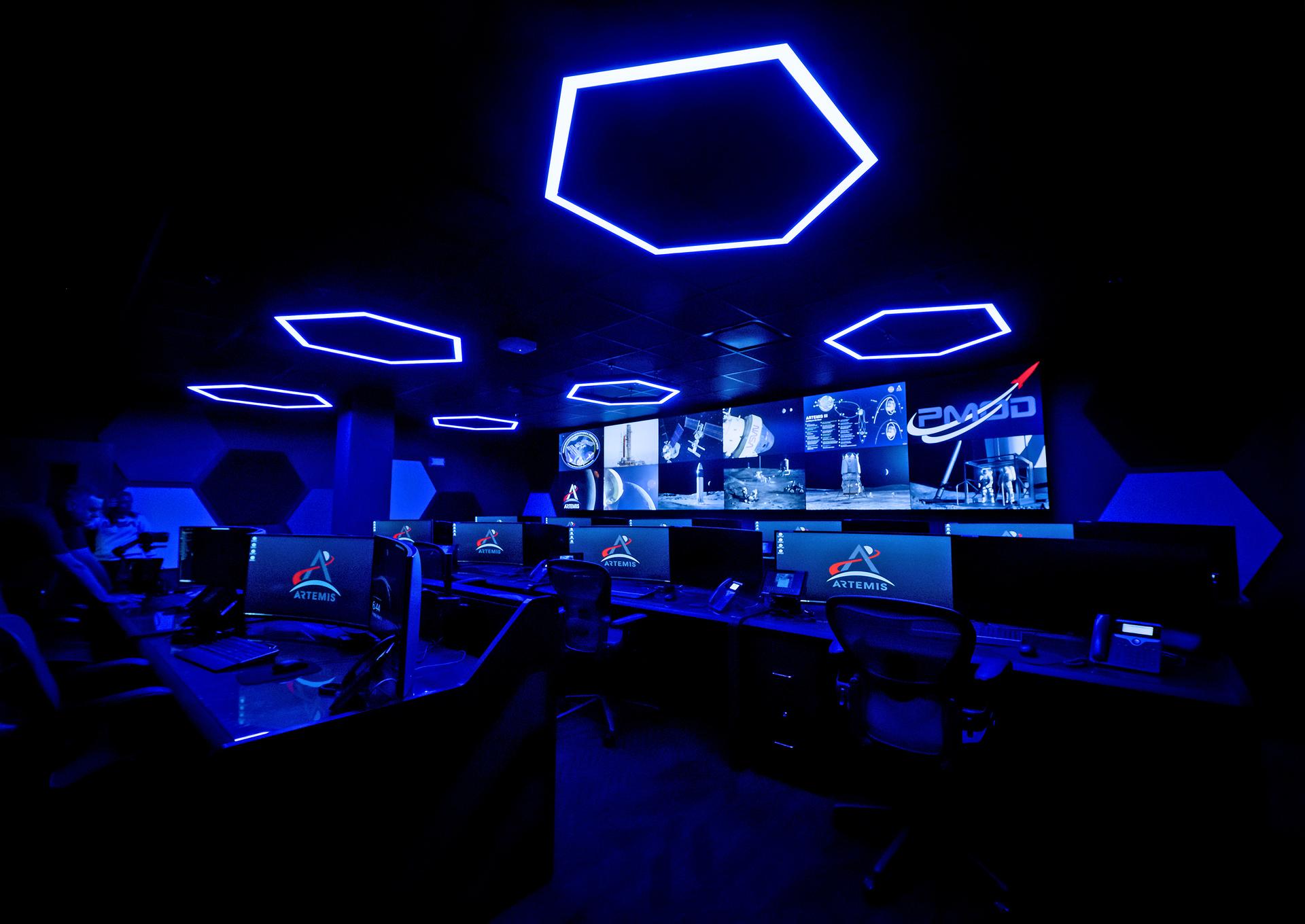

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
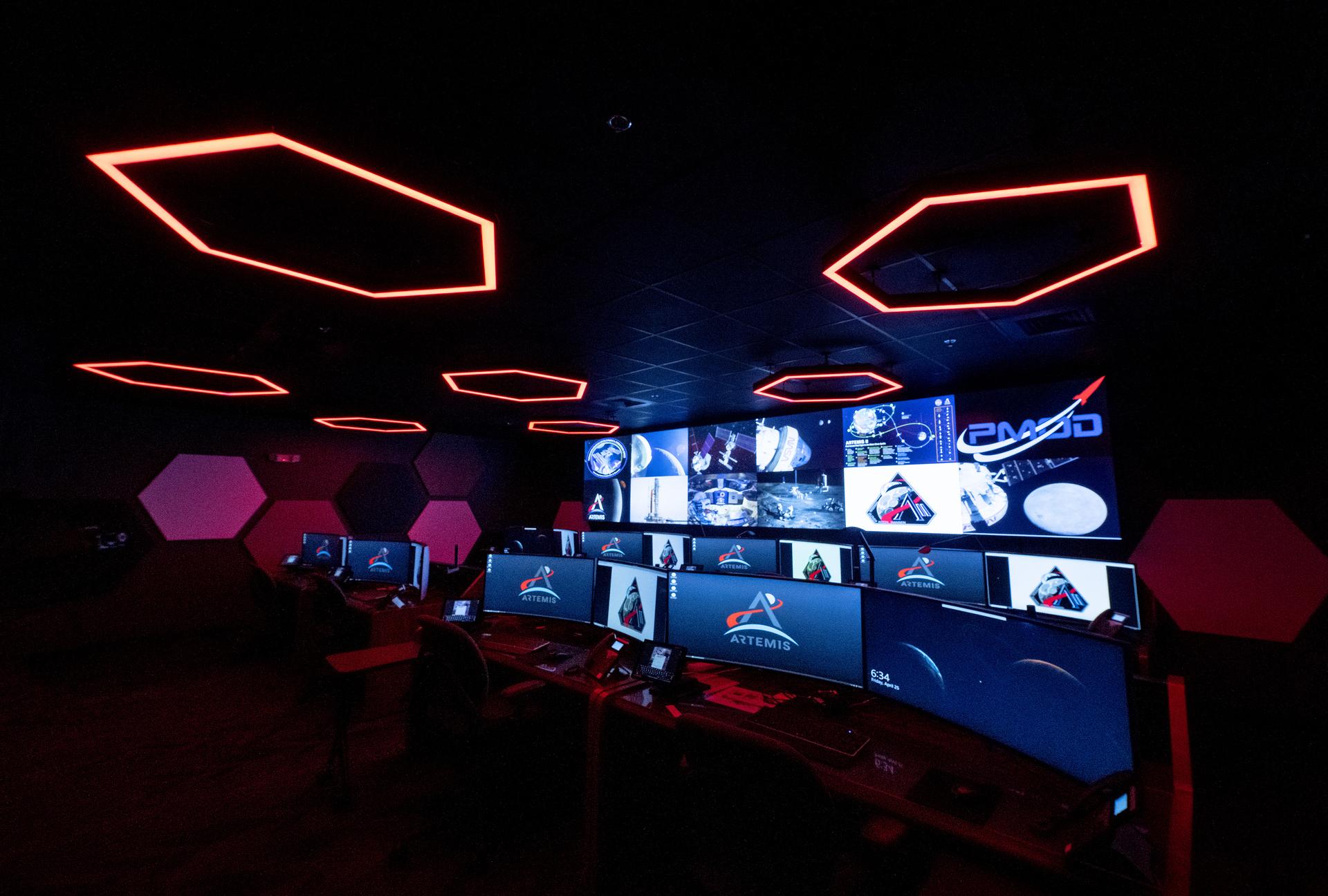

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
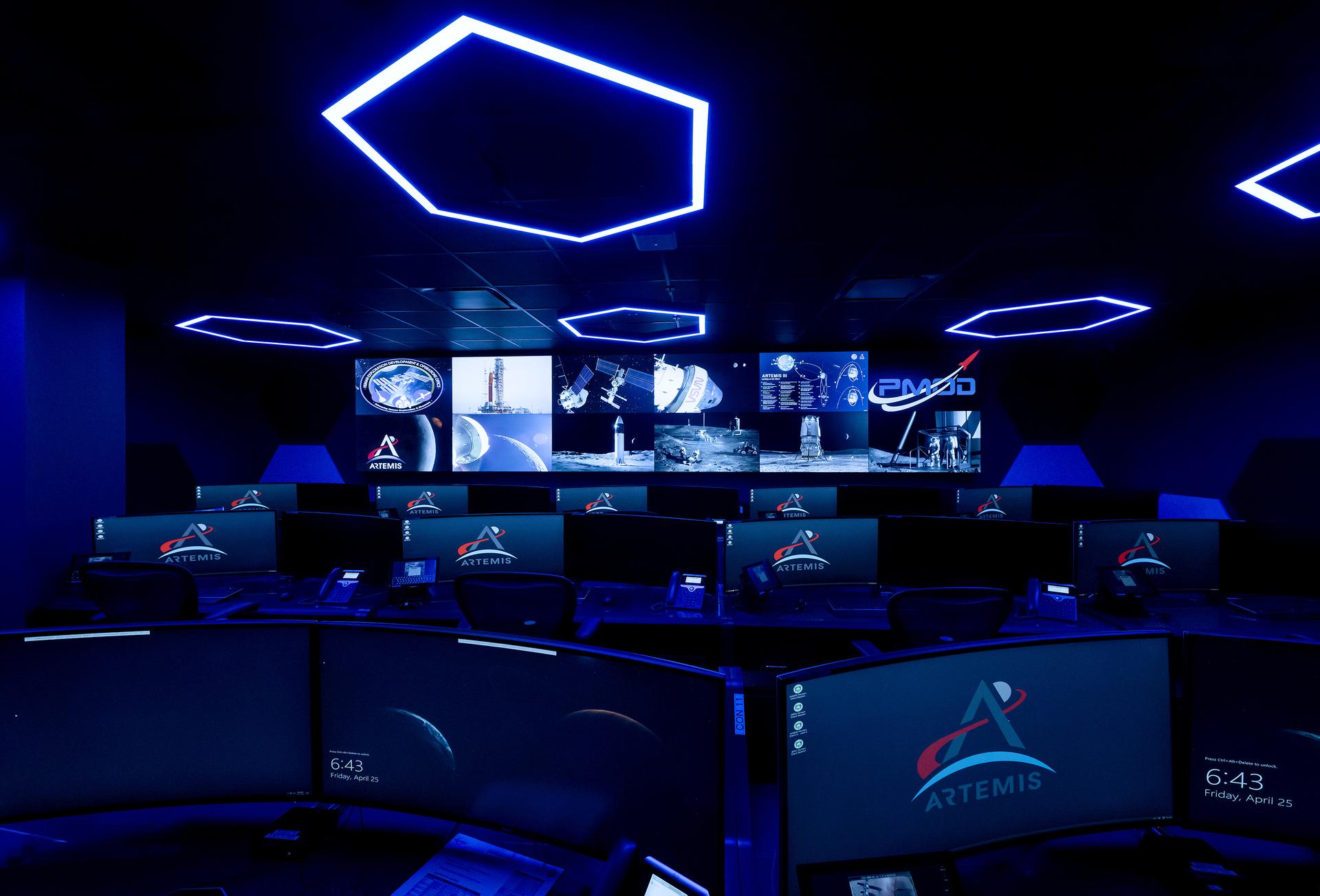

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
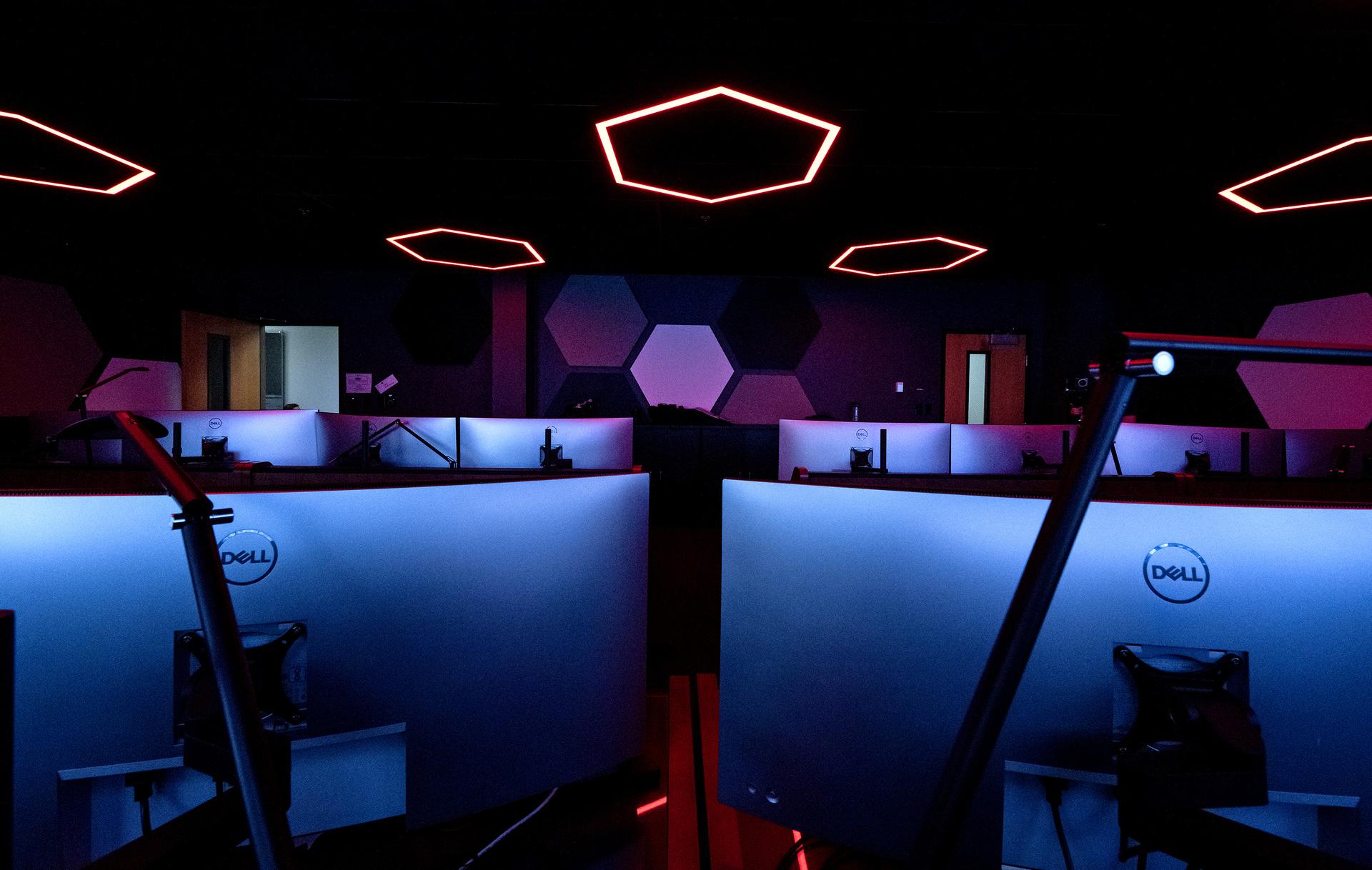

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
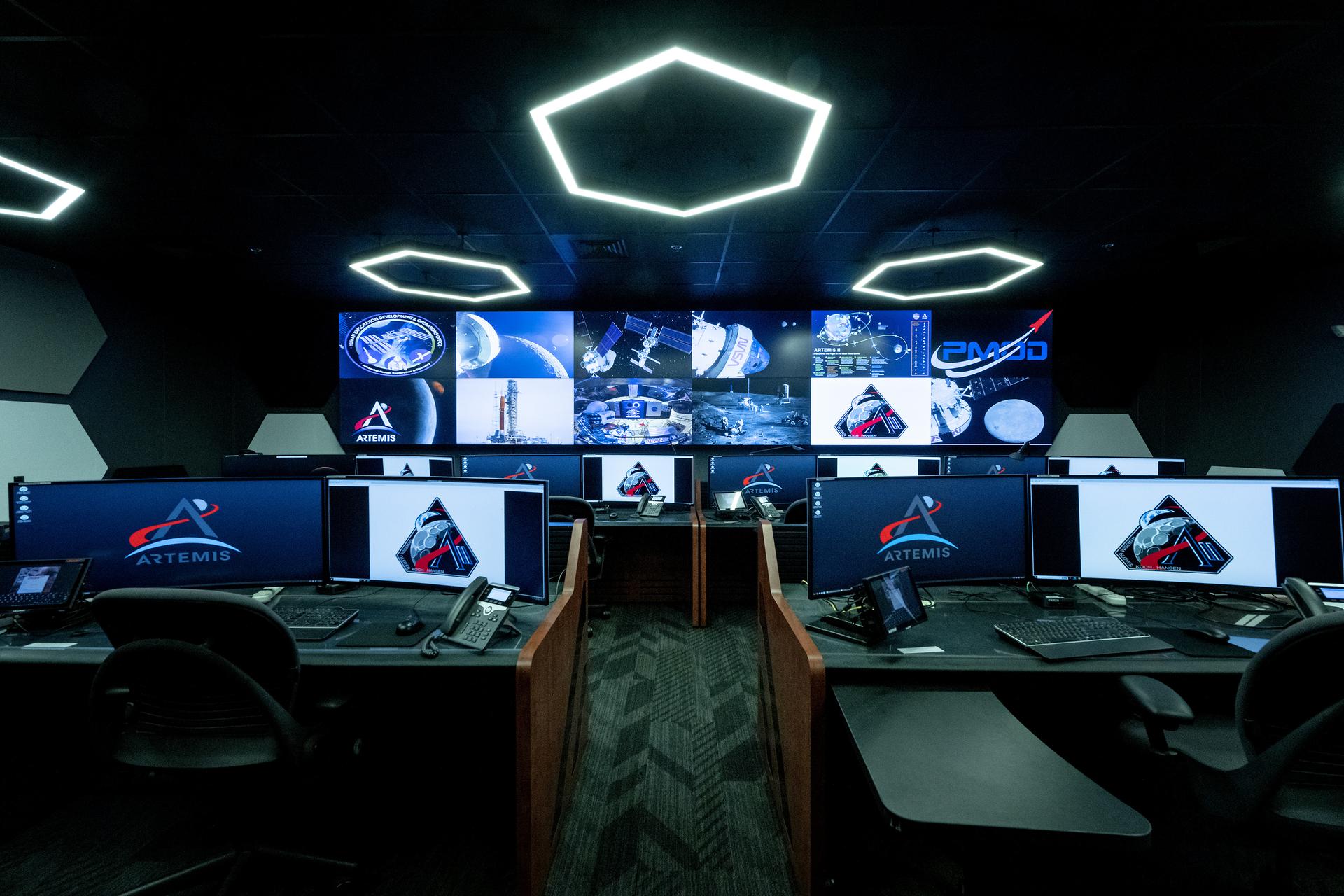

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
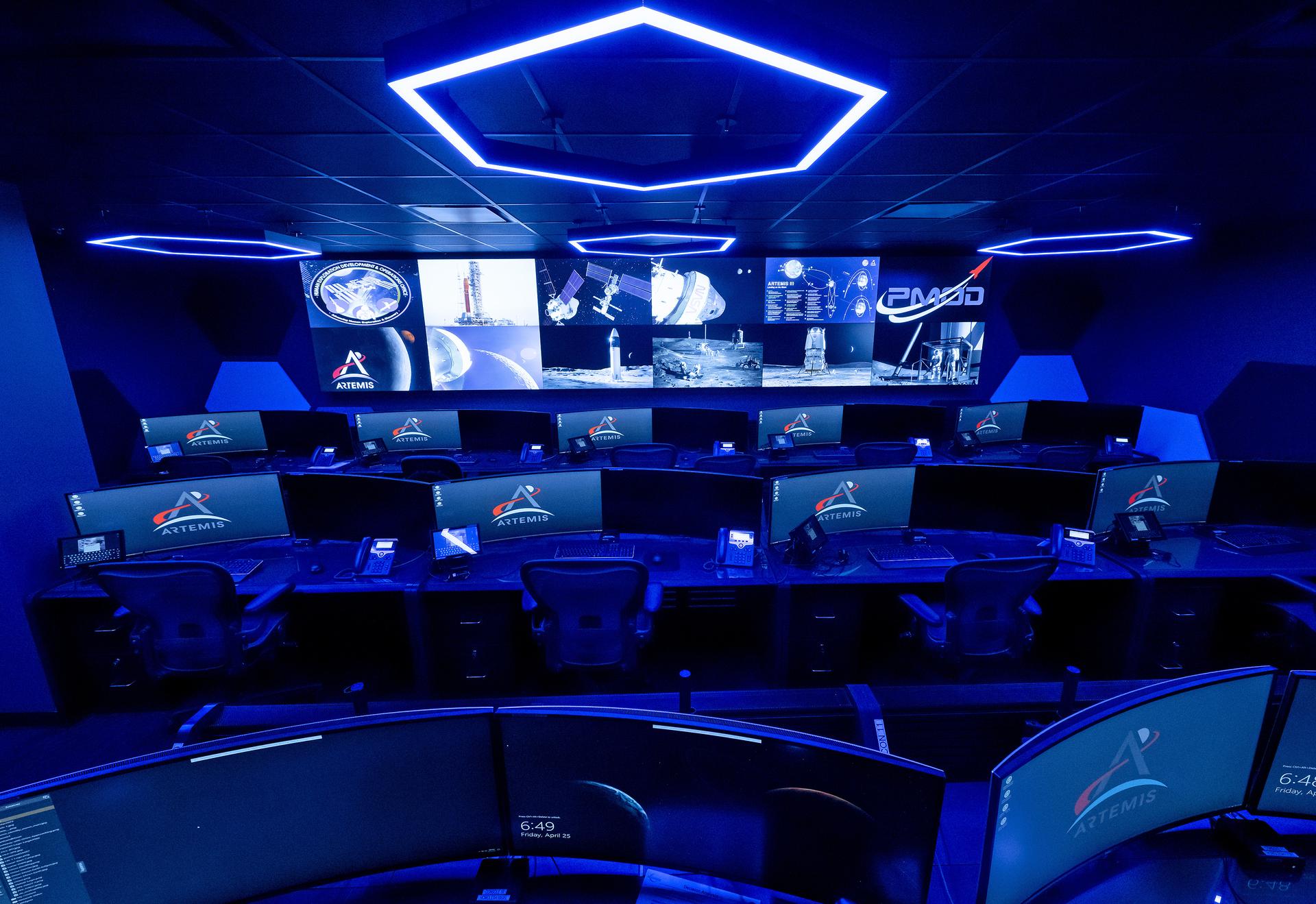

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
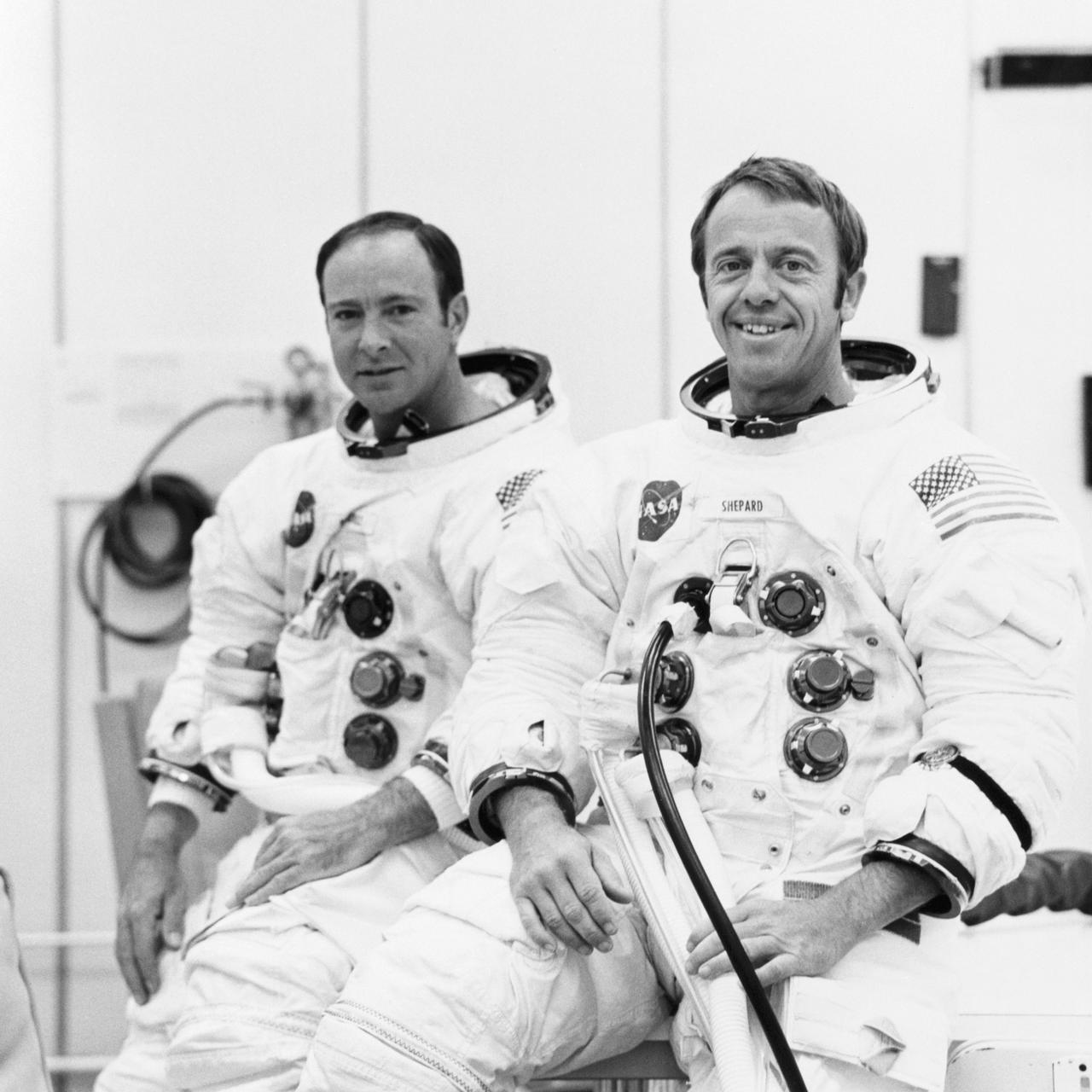

S70-19764 (18 Sept. 1970) --- Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (right), commander, and Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, are suited up for a manned altitude run in the Apollo 14 Lunar Module. The manned run in a vacuum chamber of the Manned Spacecraft Operations Building was conducted to validate the LM's communications and guidance and navigation systems. Apollo 14 is scheduled for launch from Cape Kennedy on Jan. 31, 1971, on a lunar exploration mission which is to carry Shepard and Mitchell down to the moon's rugged Fra Maura highlands region. Astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, will remain with the Apollo 14 Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit while the other two astronauts explore the moon.
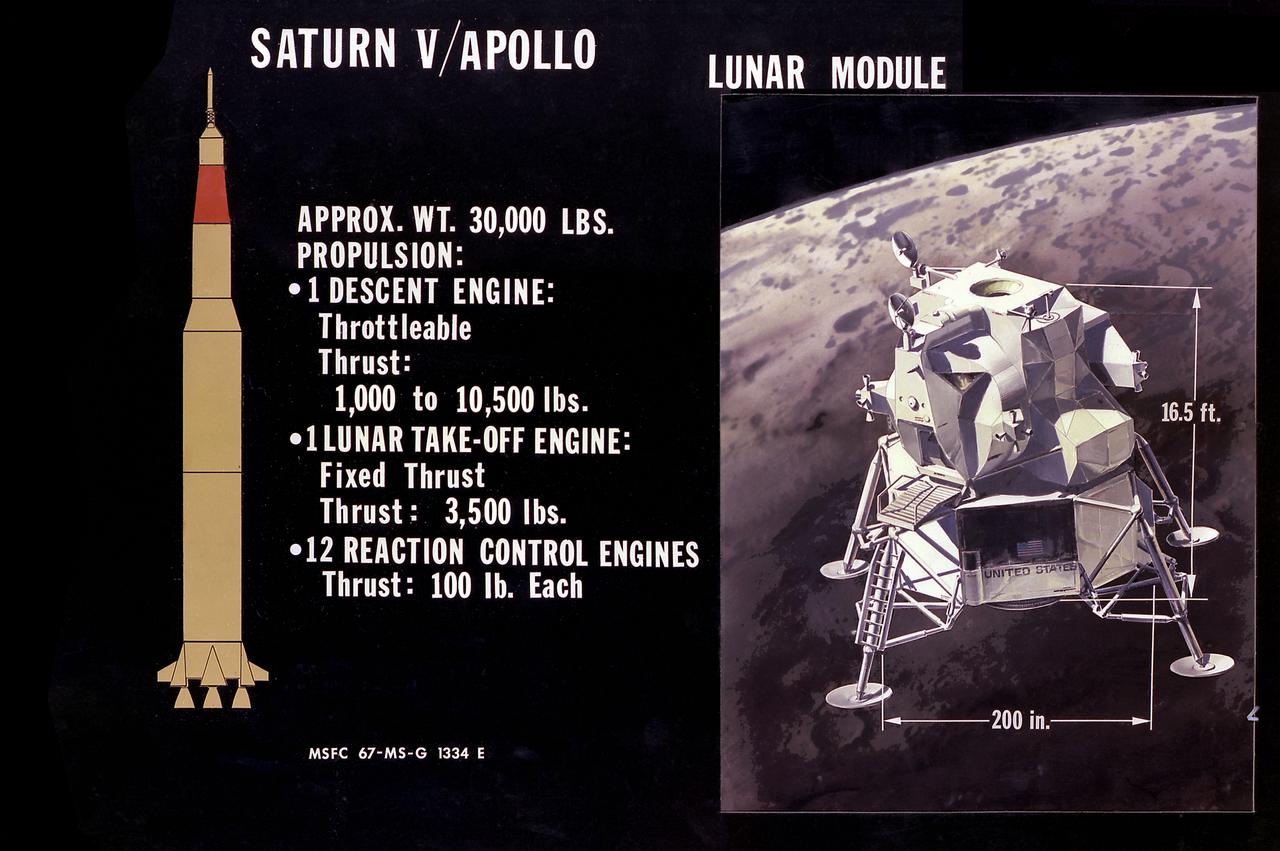
This illustration is the Lunar Module (LM) configuration. The LM was a two part spacecraft. Its lower or descent stage had the landing gear, engines, and fuel needed for the landing. When the LM blasted off the Moon, the descent stage served as the launching pad for its companion ascent stage, which was also home for the two astronauts on the surface of the Moon. The LM was full of gear with which to communicate, navigate, and rendezvous. It also had its own propulsion system, and an engine to lift it off the Moon and send it on a course toward the orbiting Command Module.
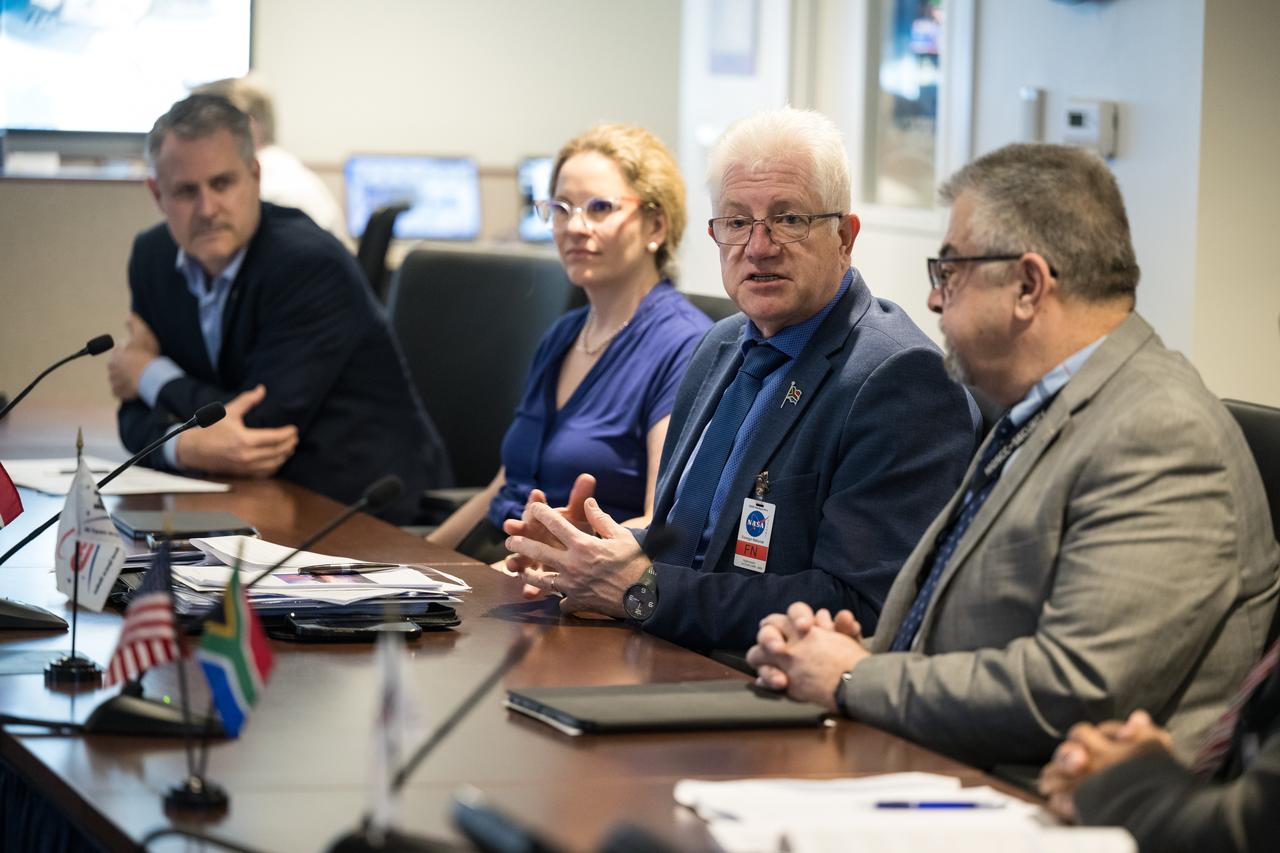

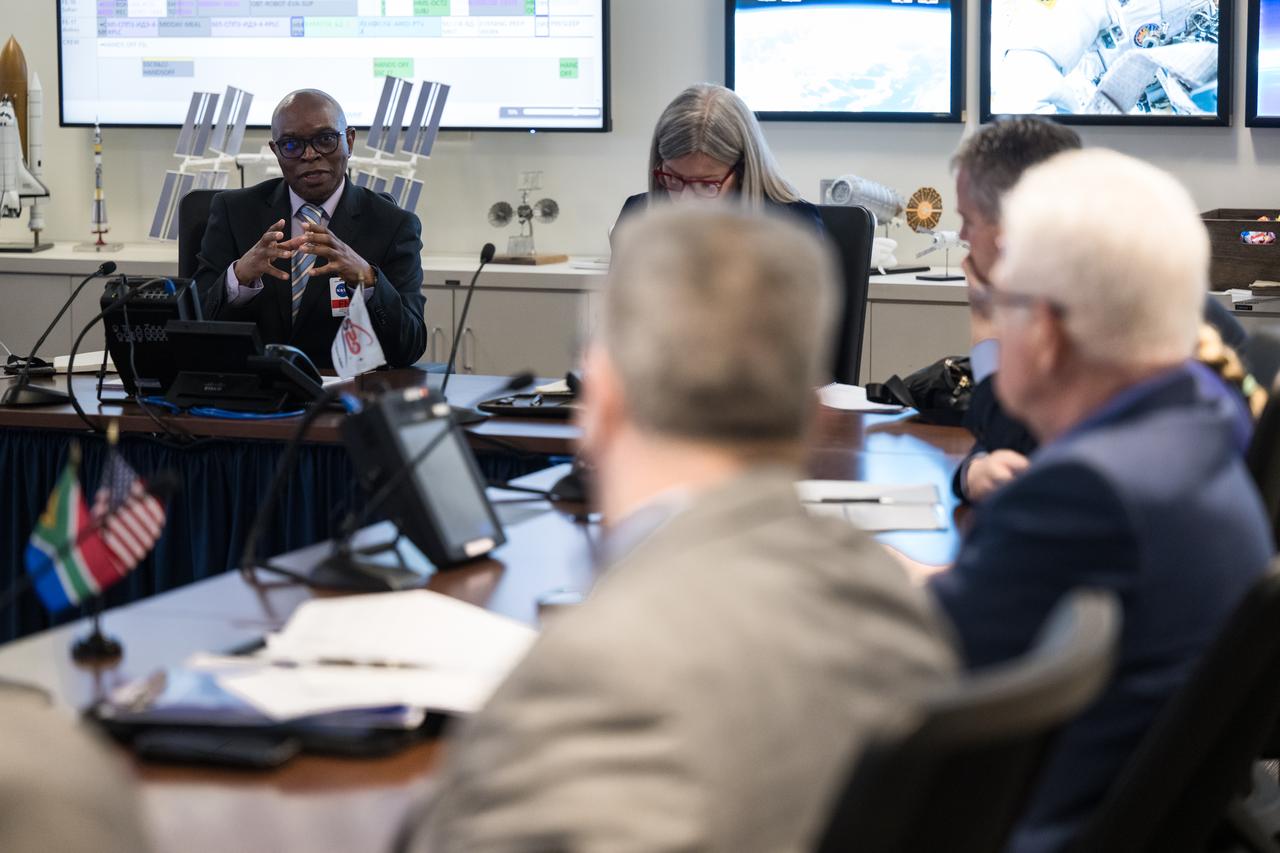
Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, provides remarks during a meeting with NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, right, other NASA representatives, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, provides remarks during a meeting with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, NASA representatives, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
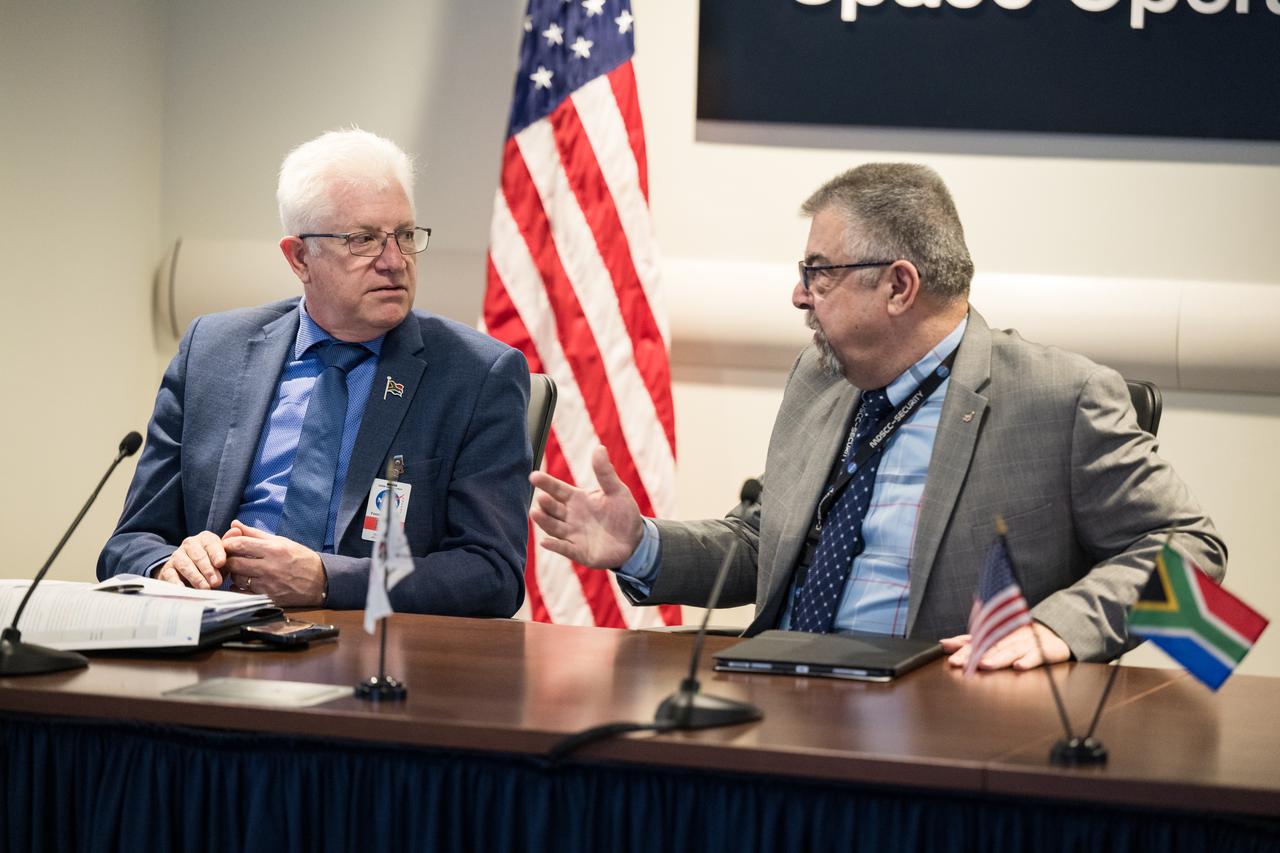

NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, right, speaks with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, during a meeting with NASA representatives and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
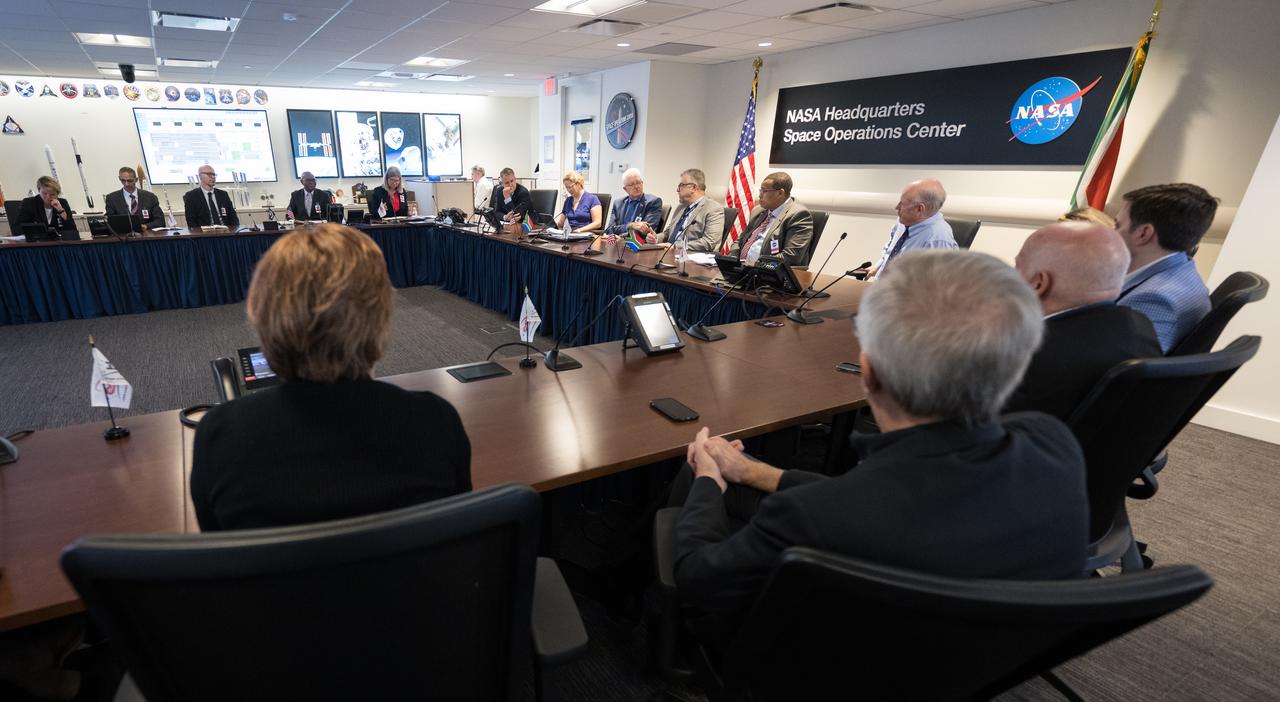

NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, and NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, meet with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
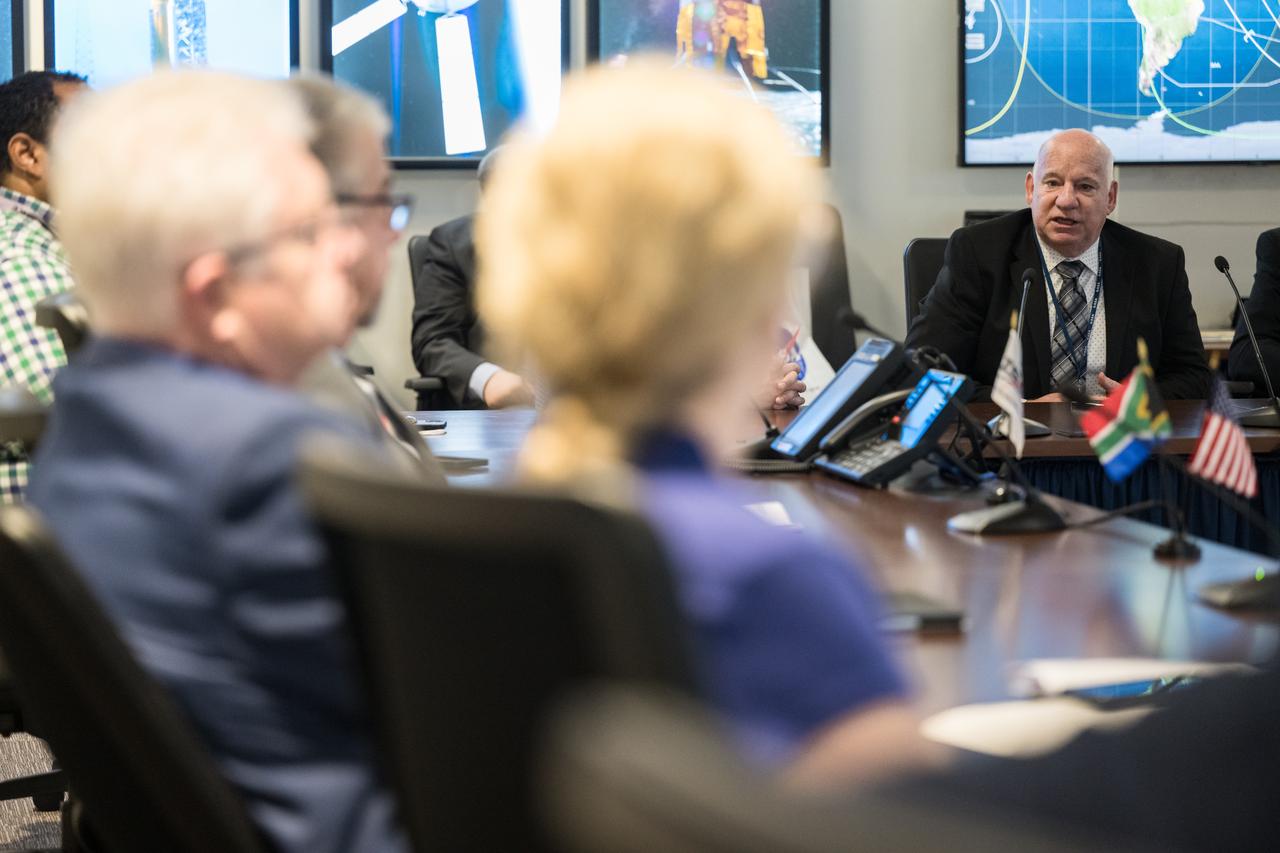

NASA SCaN Development Manager, Bill Marinelli provides remarks during a meeting with NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
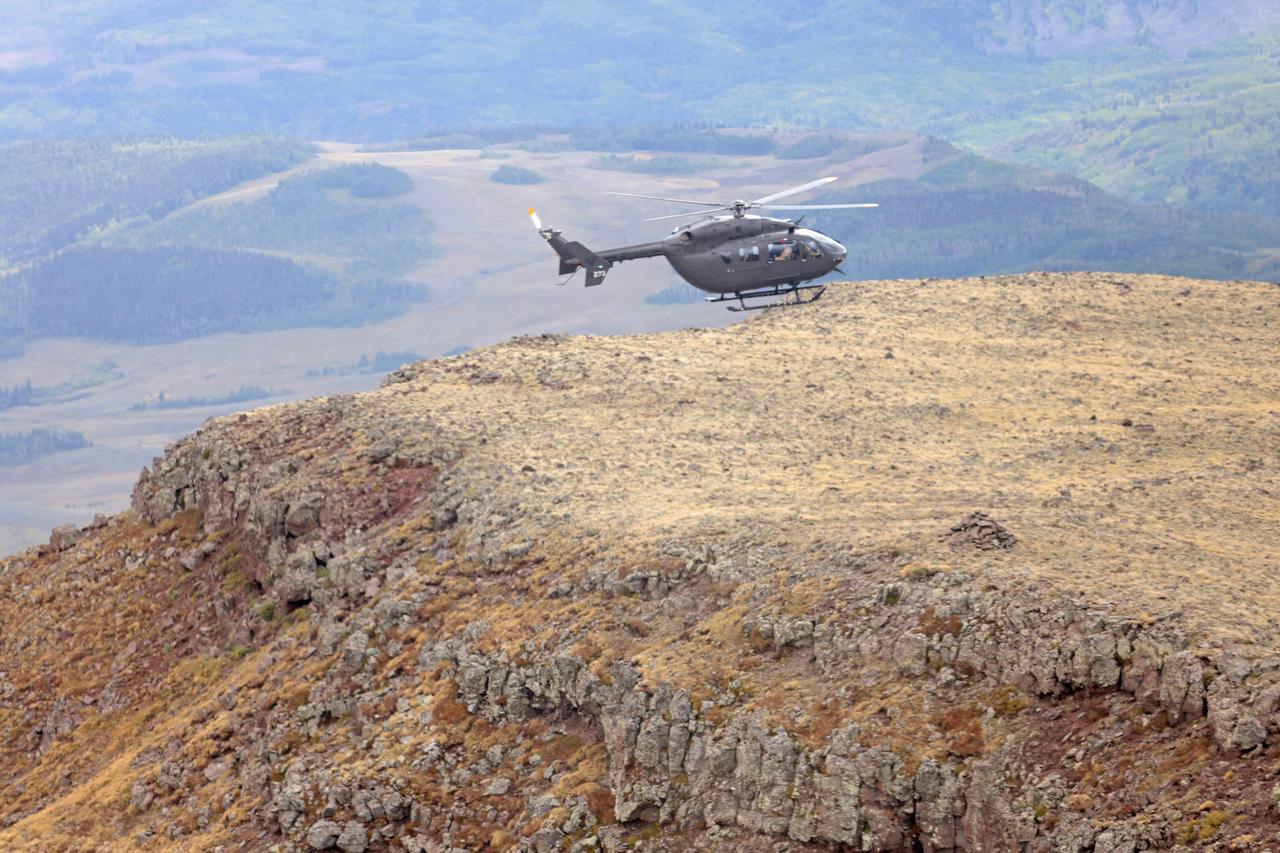

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
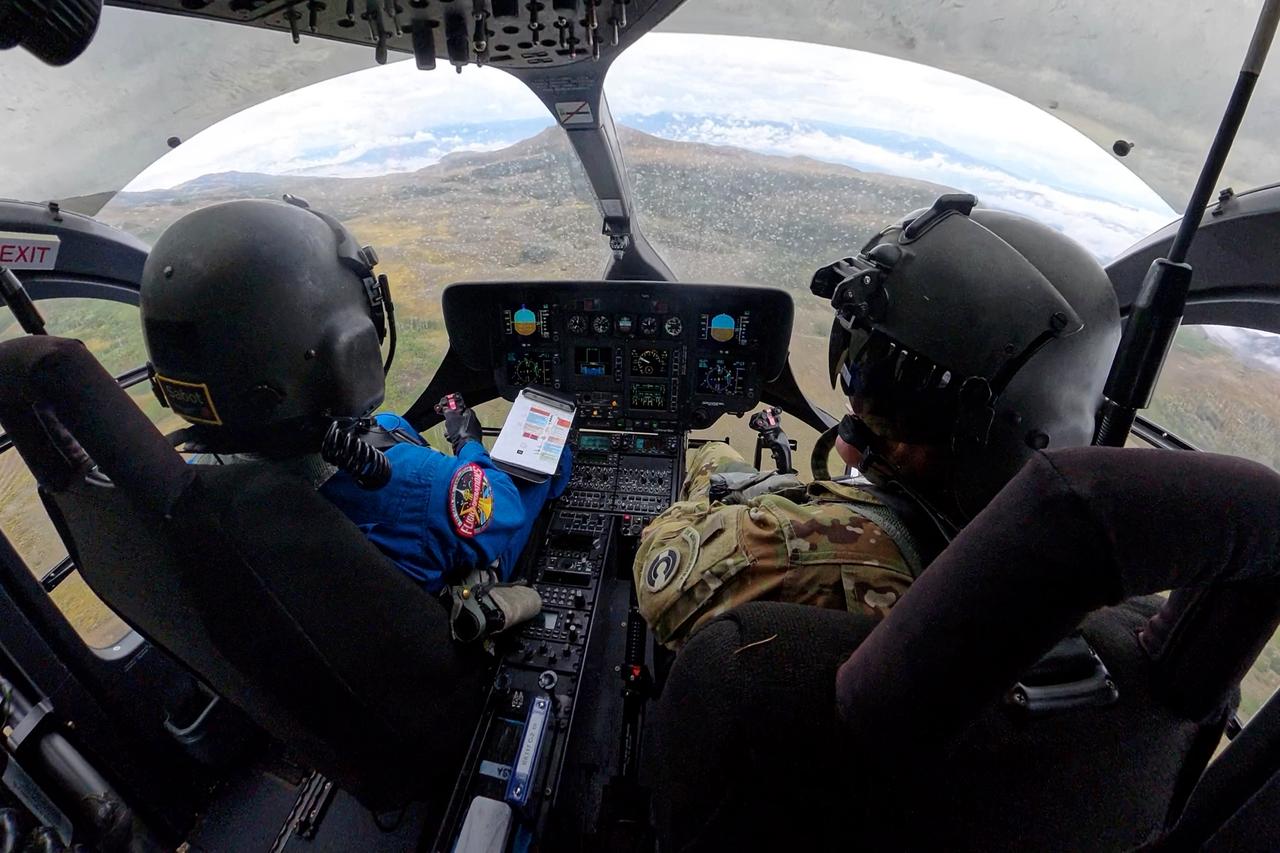

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
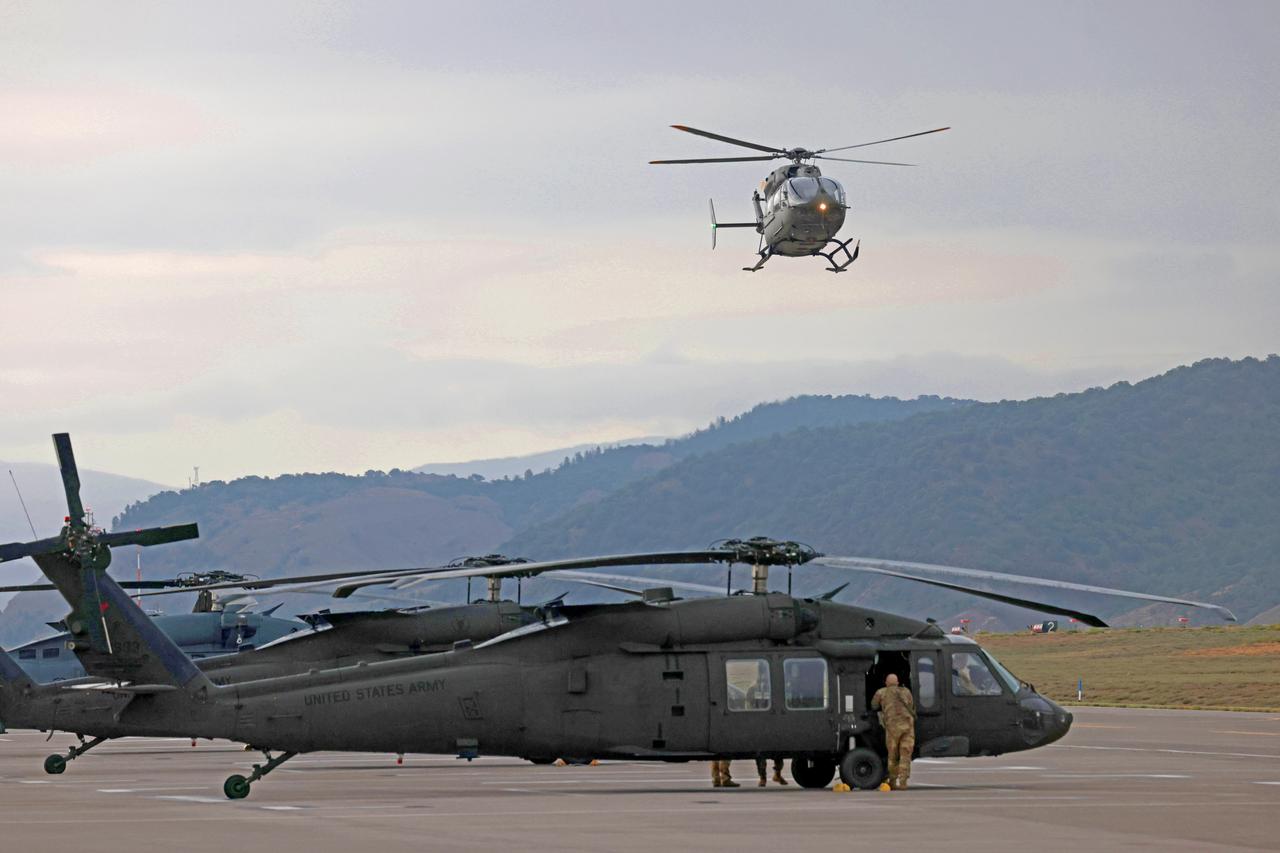

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
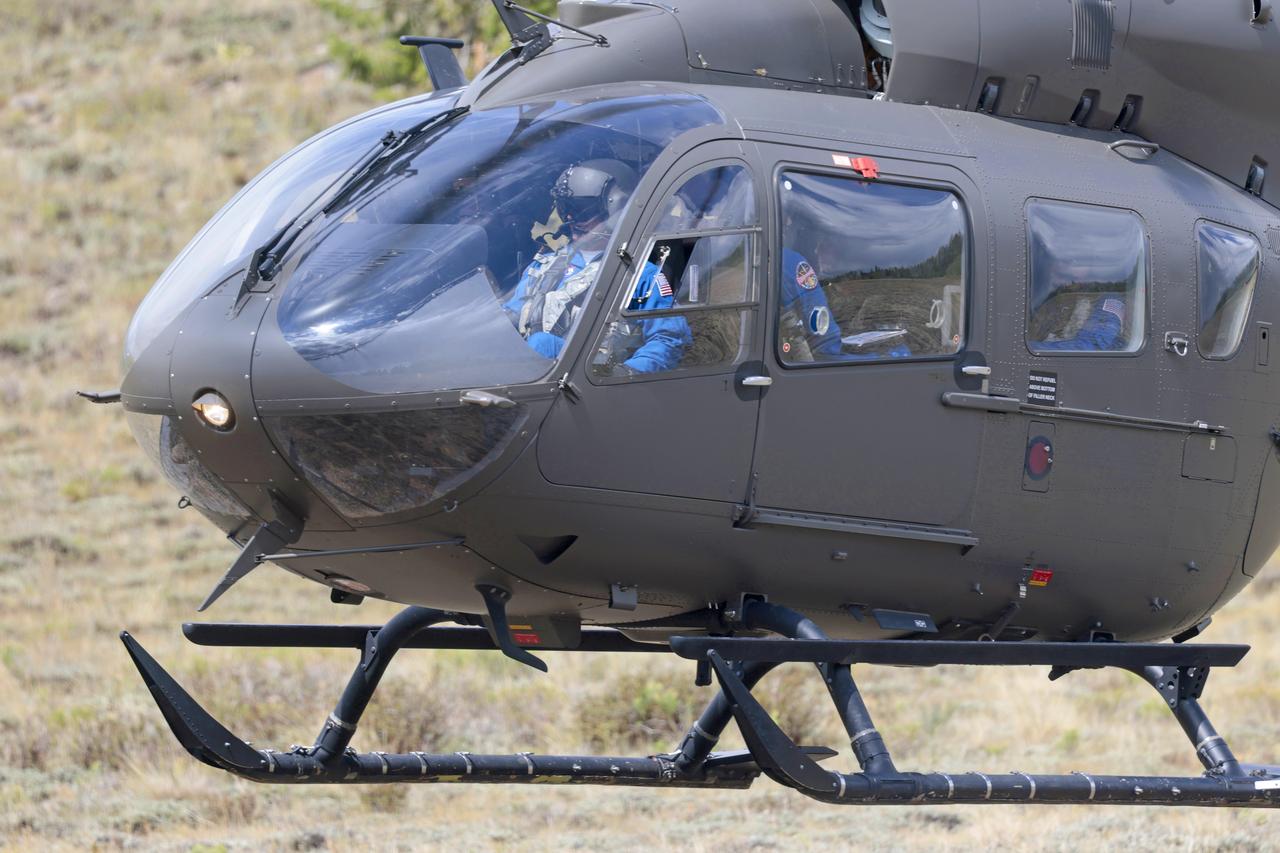

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
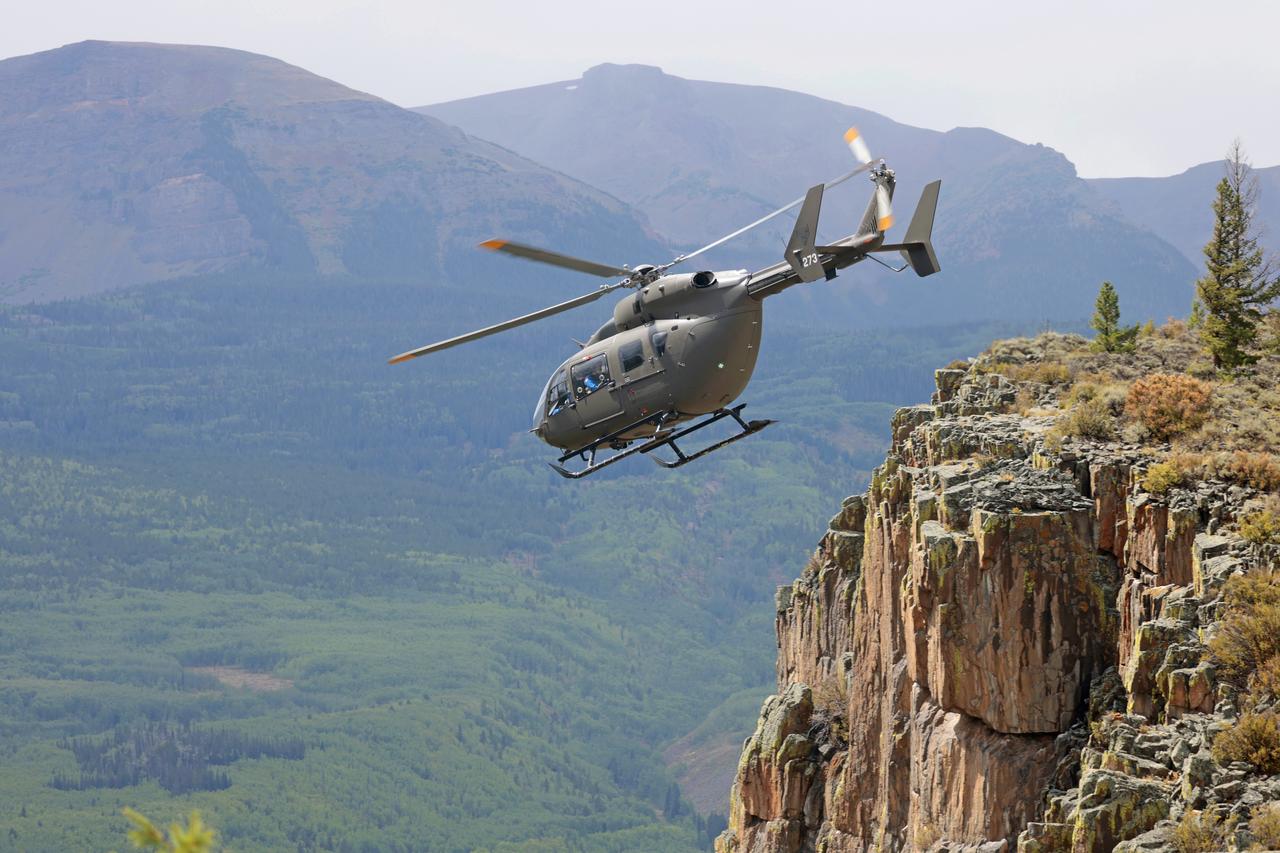

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
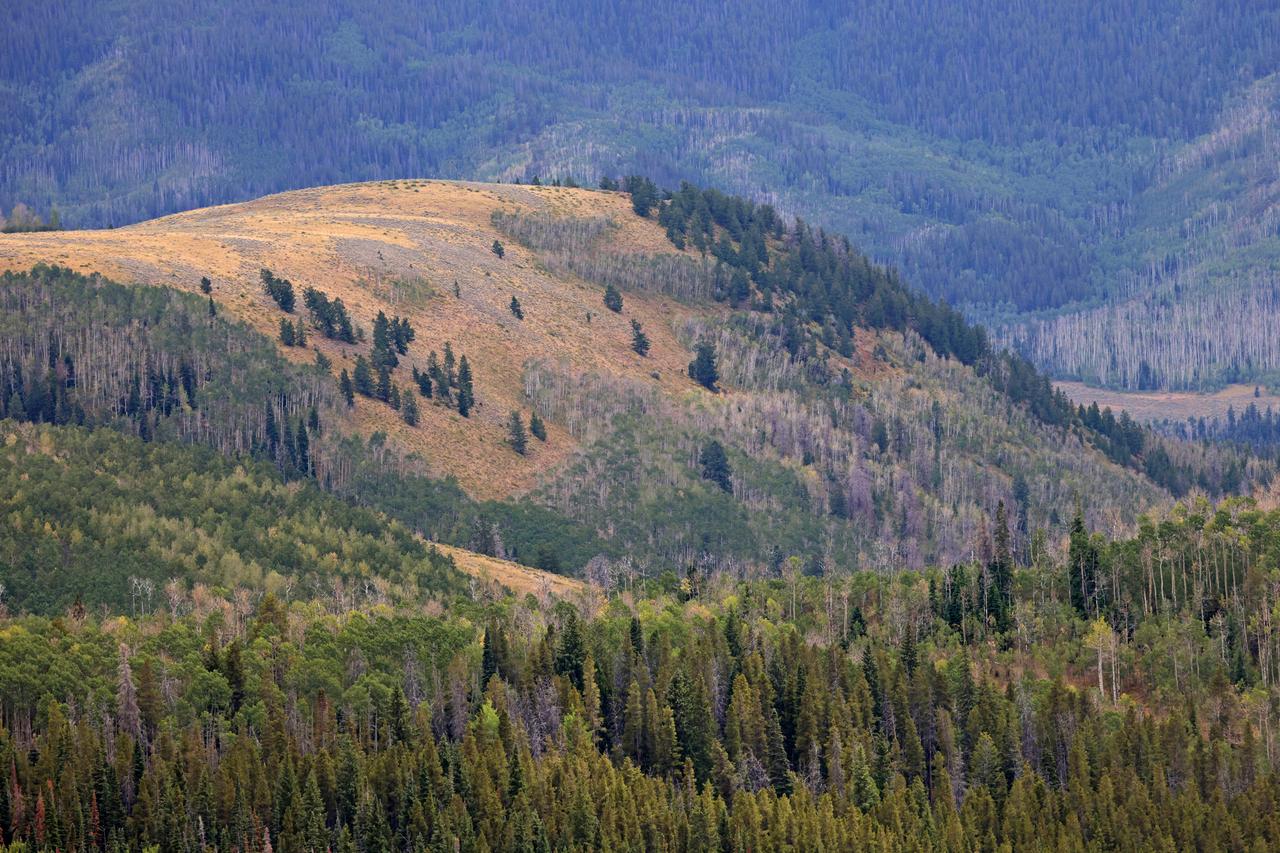

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
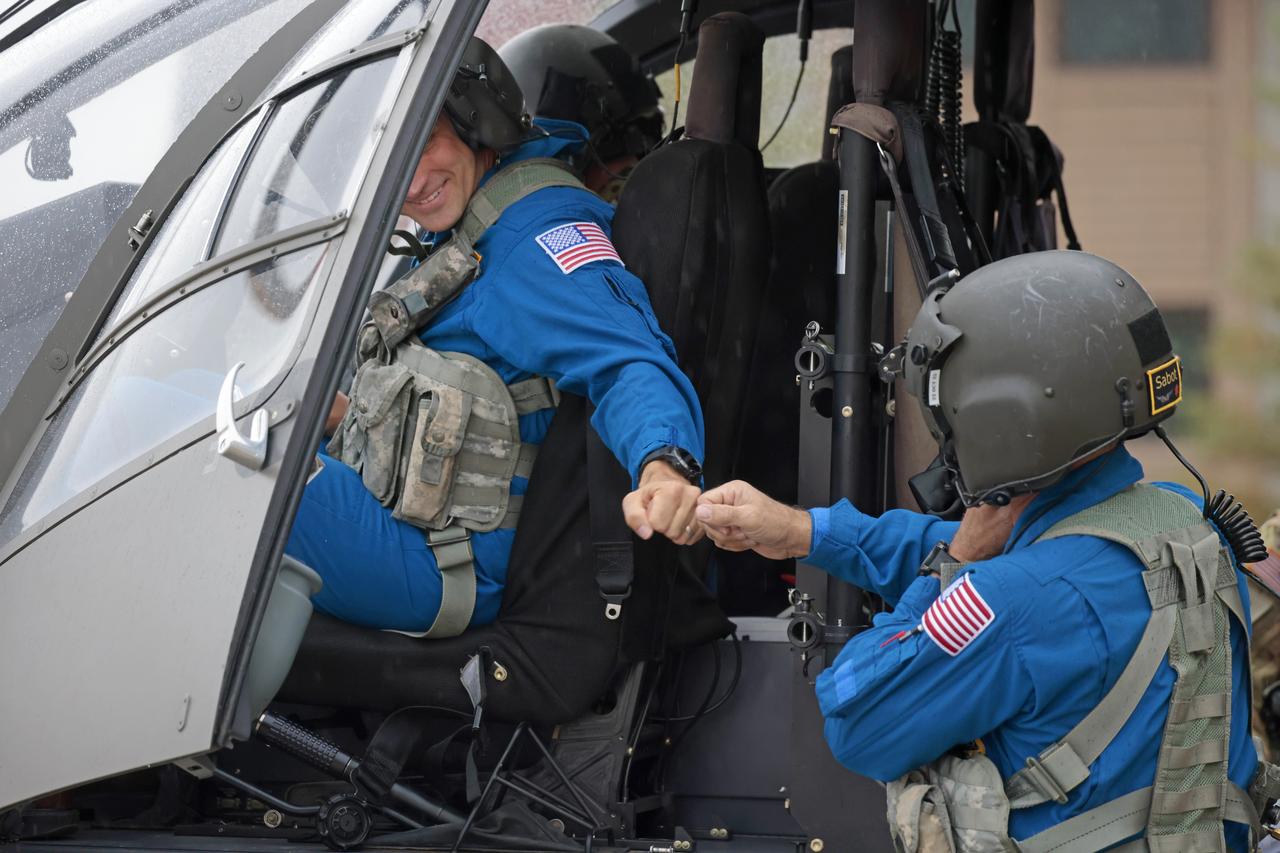

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
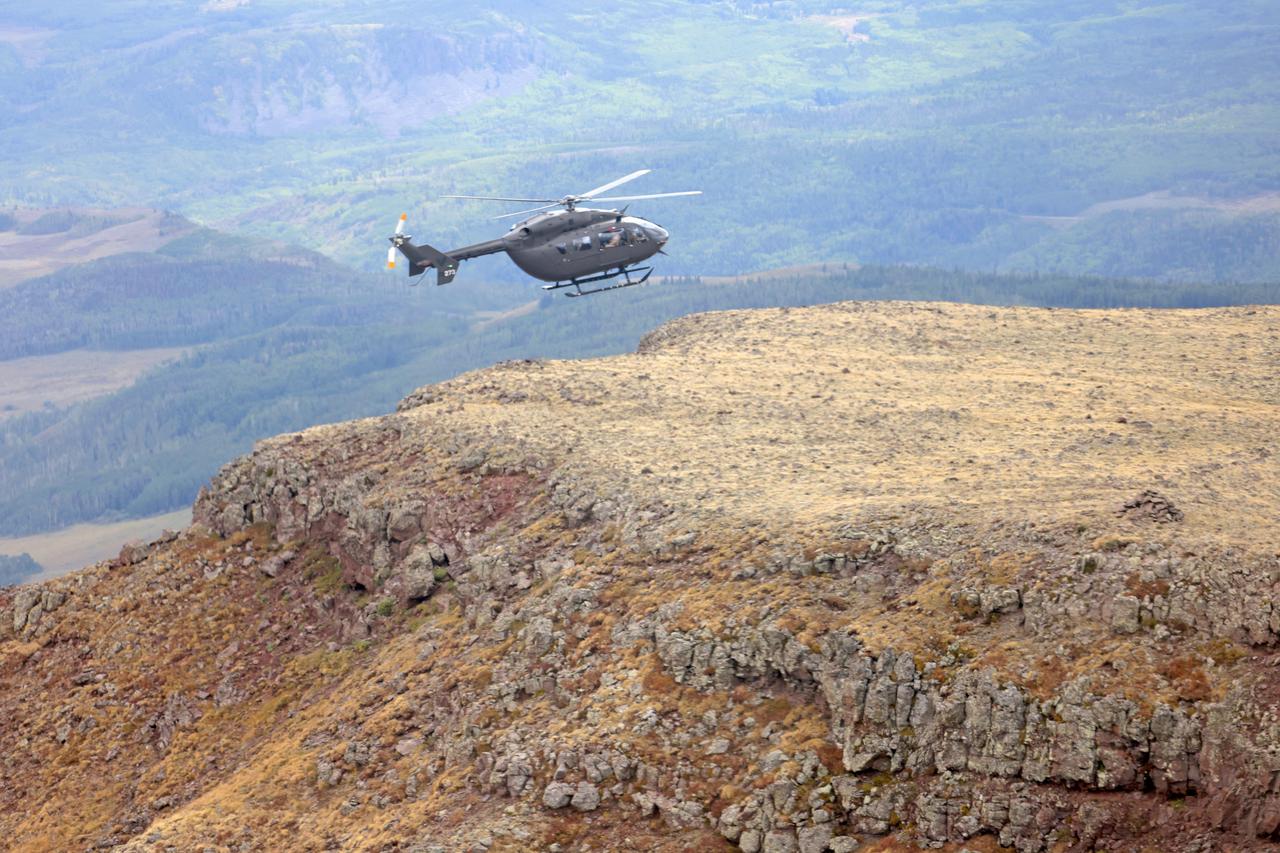

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
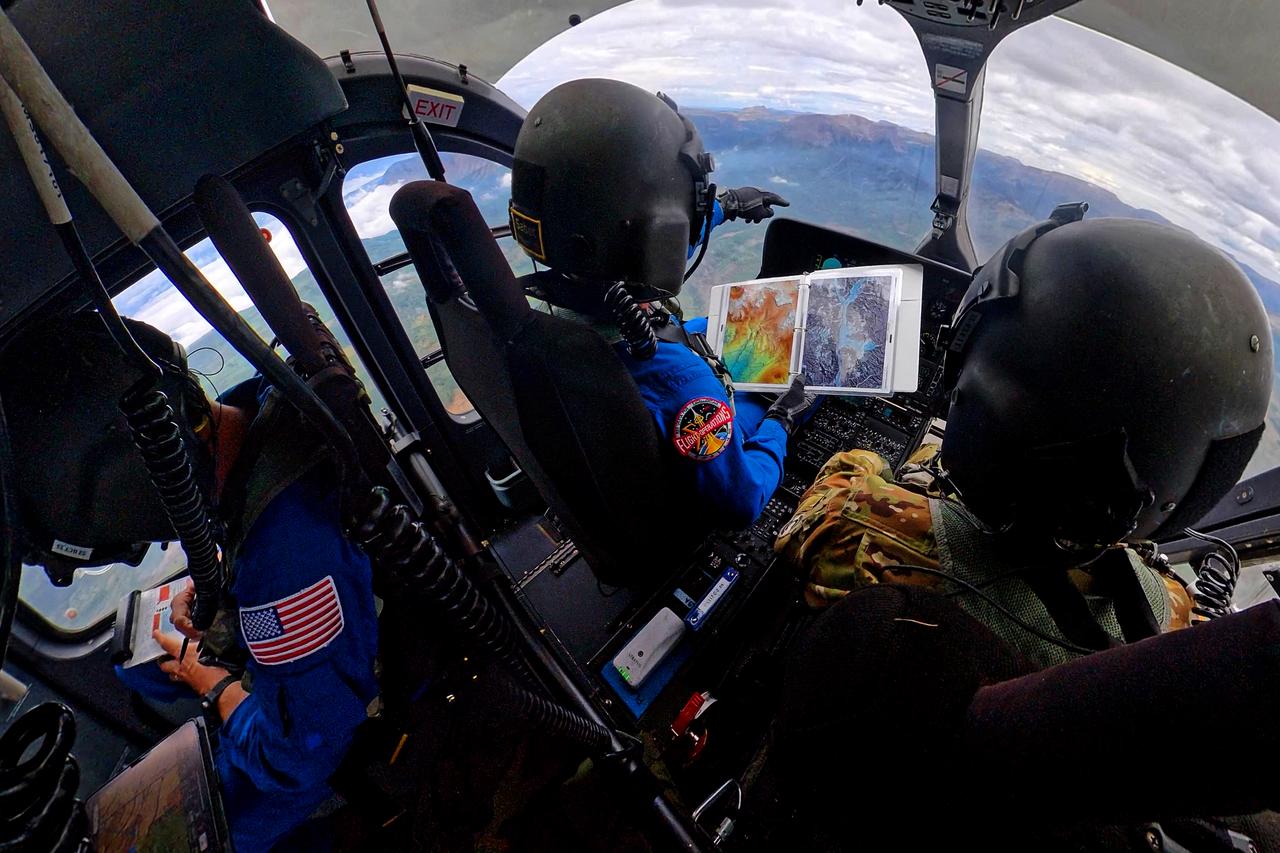

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
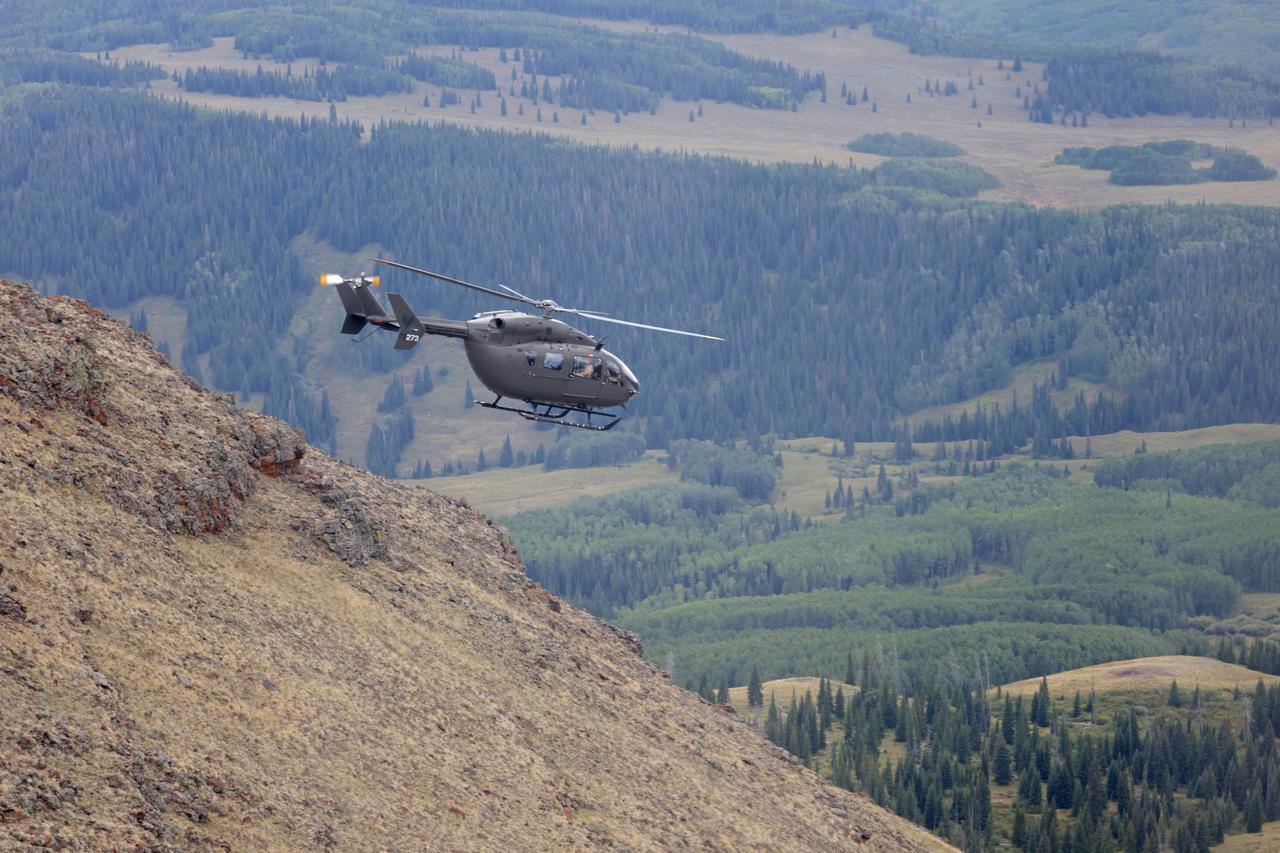

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
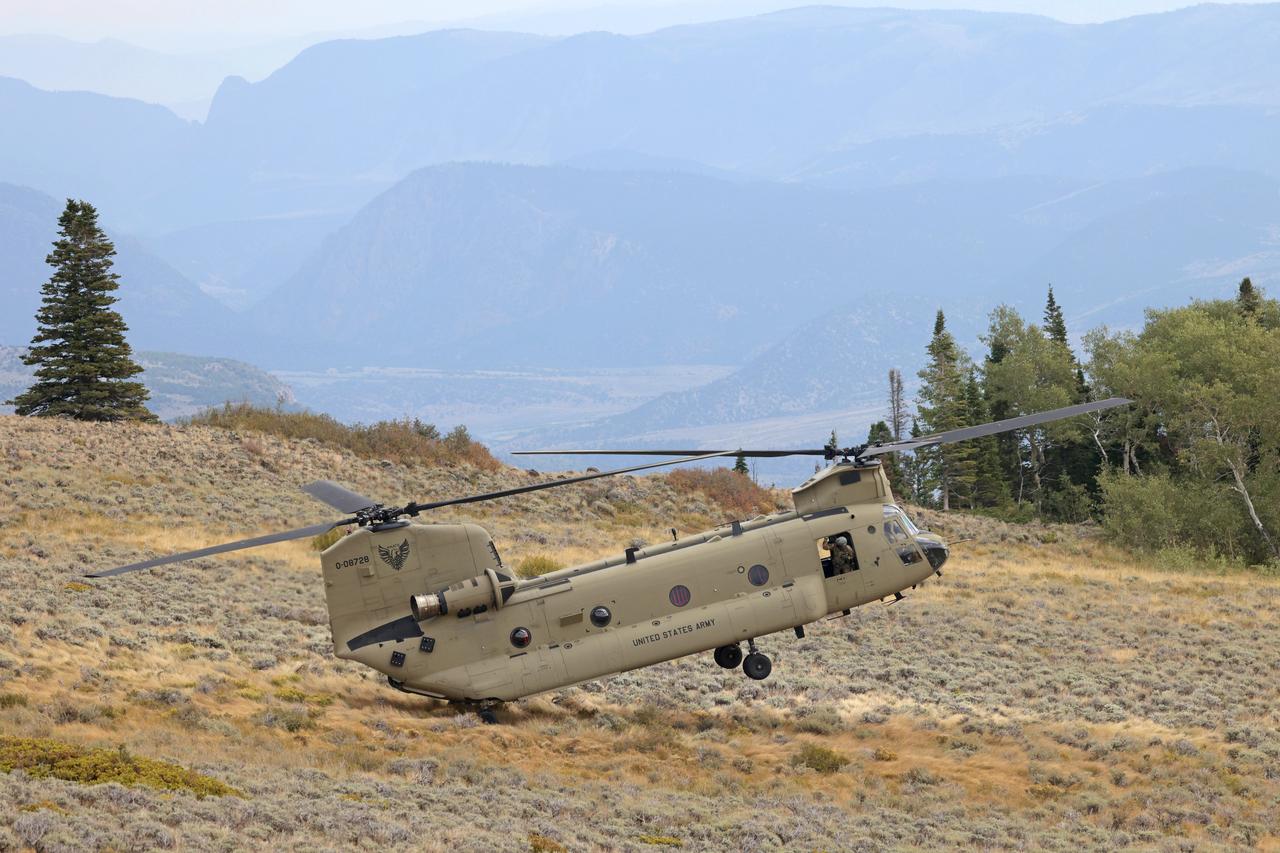

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
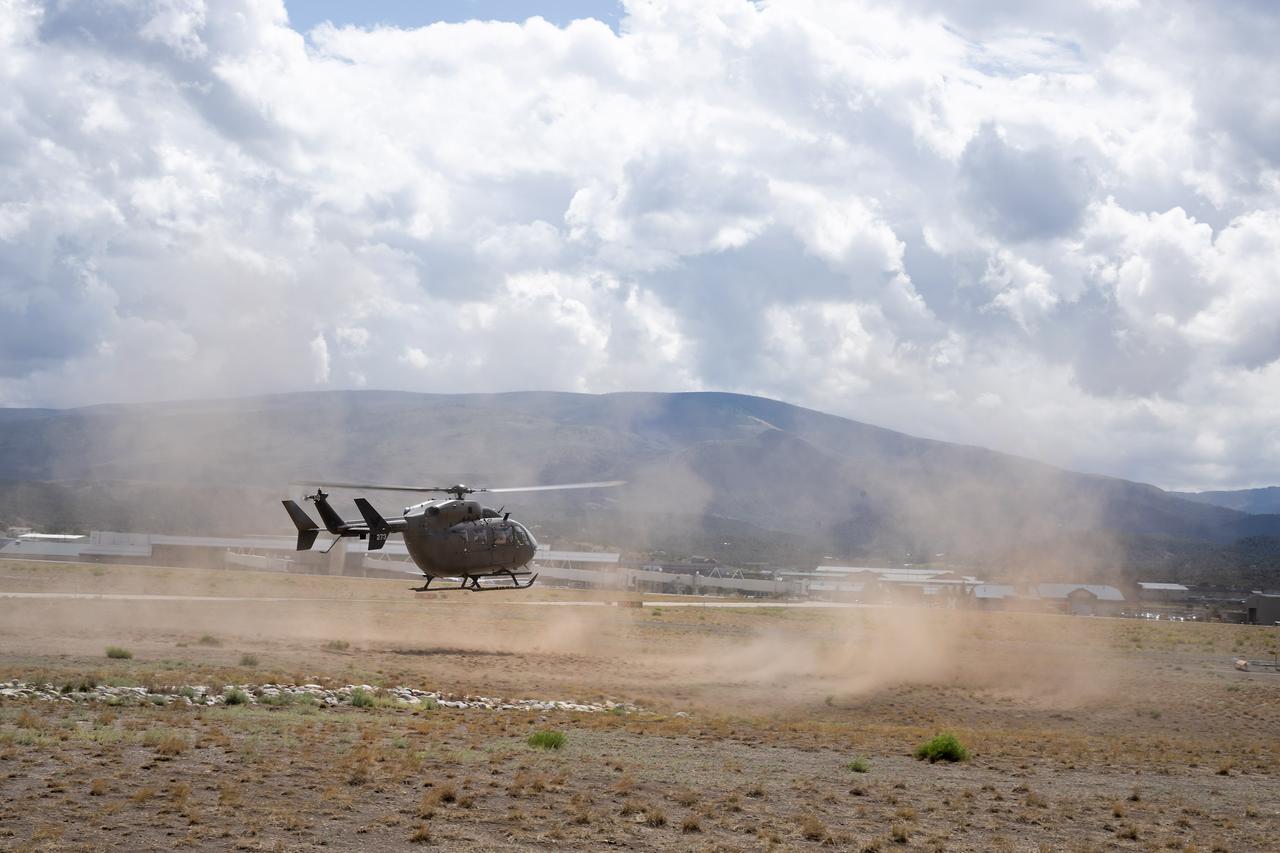

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544

This illustration shows NASA's Lunar Flashlight carrying out a trajectory correction maneuver with the Moon and Earth in the background. Powered by the small satellite's four thrusters, the maneuver is needed to reach lunar orbit. Lunar Flashlight launched Nov. 30, 2022, and will take about four months to reach its science orbit to seek out surface water ice in the darkest craters of the Moon's South Pole. A technology demonstration, the small satellite, or SmallSat, will use a reflectometer equipped with four lasers that emit near-infrared light in wavelengths readily absorbed by surface water ice. To achieve the mission's goals with the satellite's limited amount of propellent, Lunar Flashlight will employ an energy-efficient near-rectilinear halo orbit, taking it within 9 miles (15 kilometers) of the lunar South Pole and 43,000 miles (70,000 kilometers) away at its farthest point. Only one other spacecraft has employed this type of orbit: NASA's Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment (CAPSTONE) mission, which launched in June 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25258
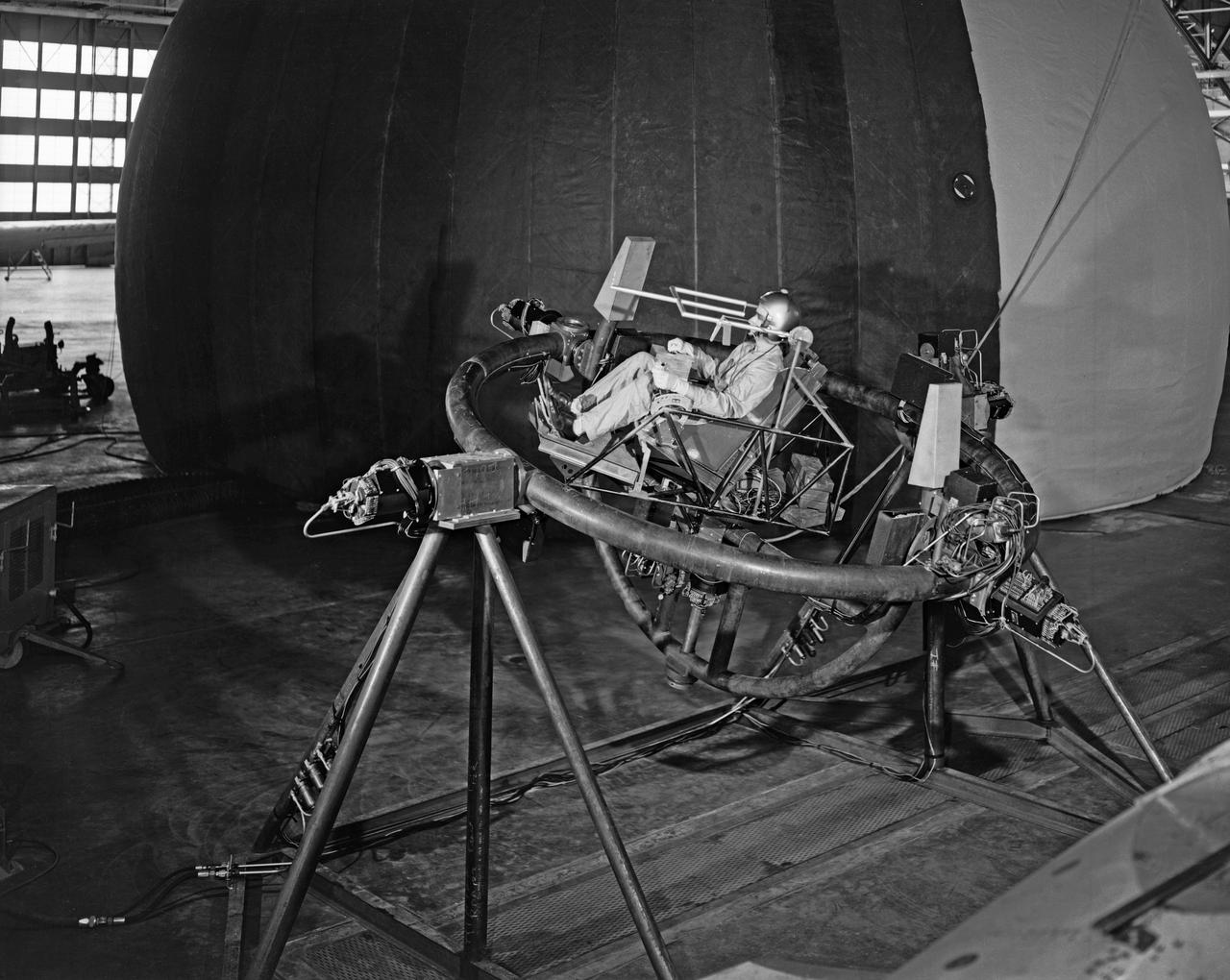
Lunar Take Off Simulator: This simulator is used by scientists at the Langley Research Center ... to help determine human ability to control a lunar launch vehicle in vertical alignment during takeoff from the moon for rendezvous with a lunar satellite vehicle on the return trip to earth. The three-axis chair, a concept which allows the pilot to sit upright during launch, gives the navigator angular motion (pitch, role, and yaw) cues as he operates the vehicle through a sidearm control system. The sight apparatus in front of the pilot's face enables him to align the vehicle on a course toward a chosen star, which will be followed as a guidance reference during the lunar launch. The pilot's right hand controls angular motions, while his left hand manipulates the thrust lever. The simulator is designed for operation inside an artificial planetarium, where a star field will be projected against the ceiling during "flights". The tests are part of an extensive NASA program at Langley in the study of problems relating to a manned lunar mission. (From a NASA Langley, photo release caption.)
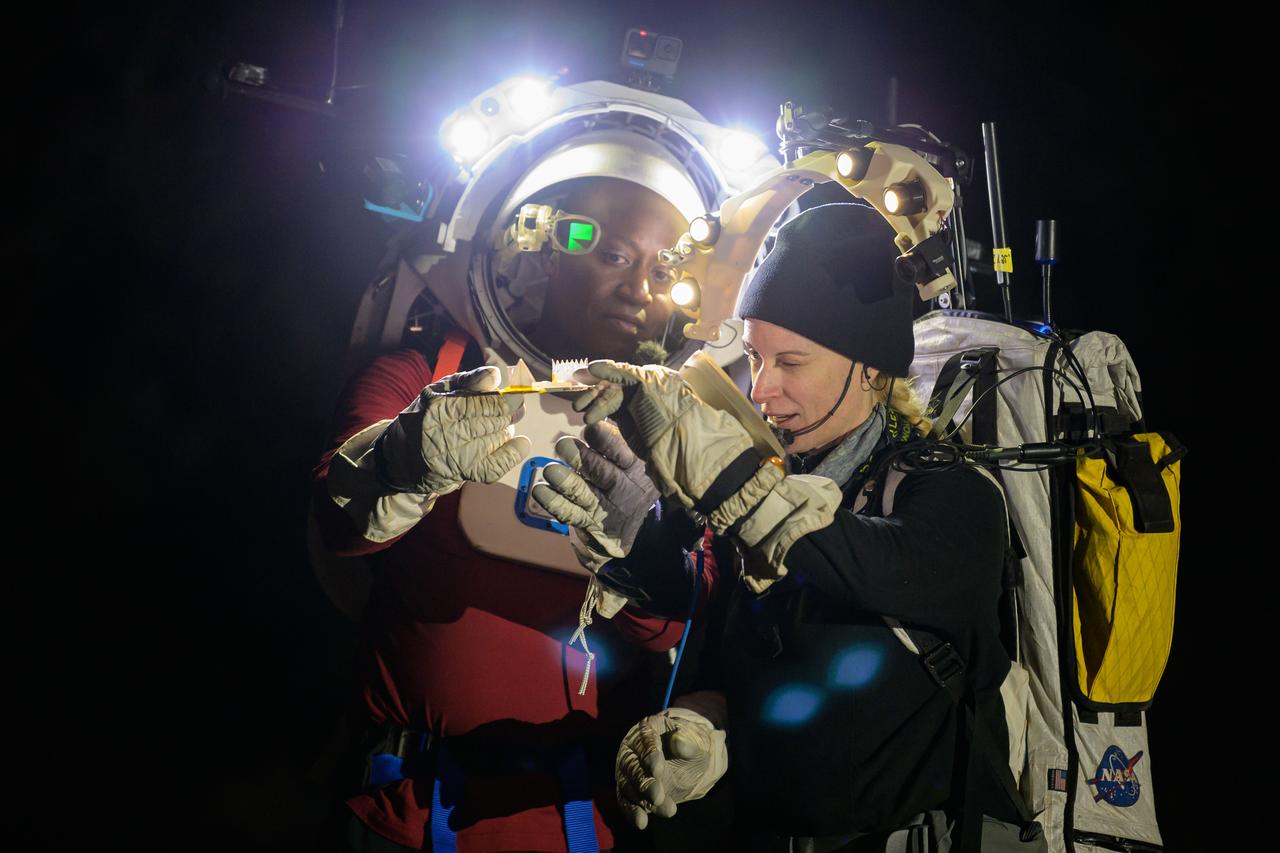

NASA astronauts Andre Douglas and Kate Rubins during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. Douglas is wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
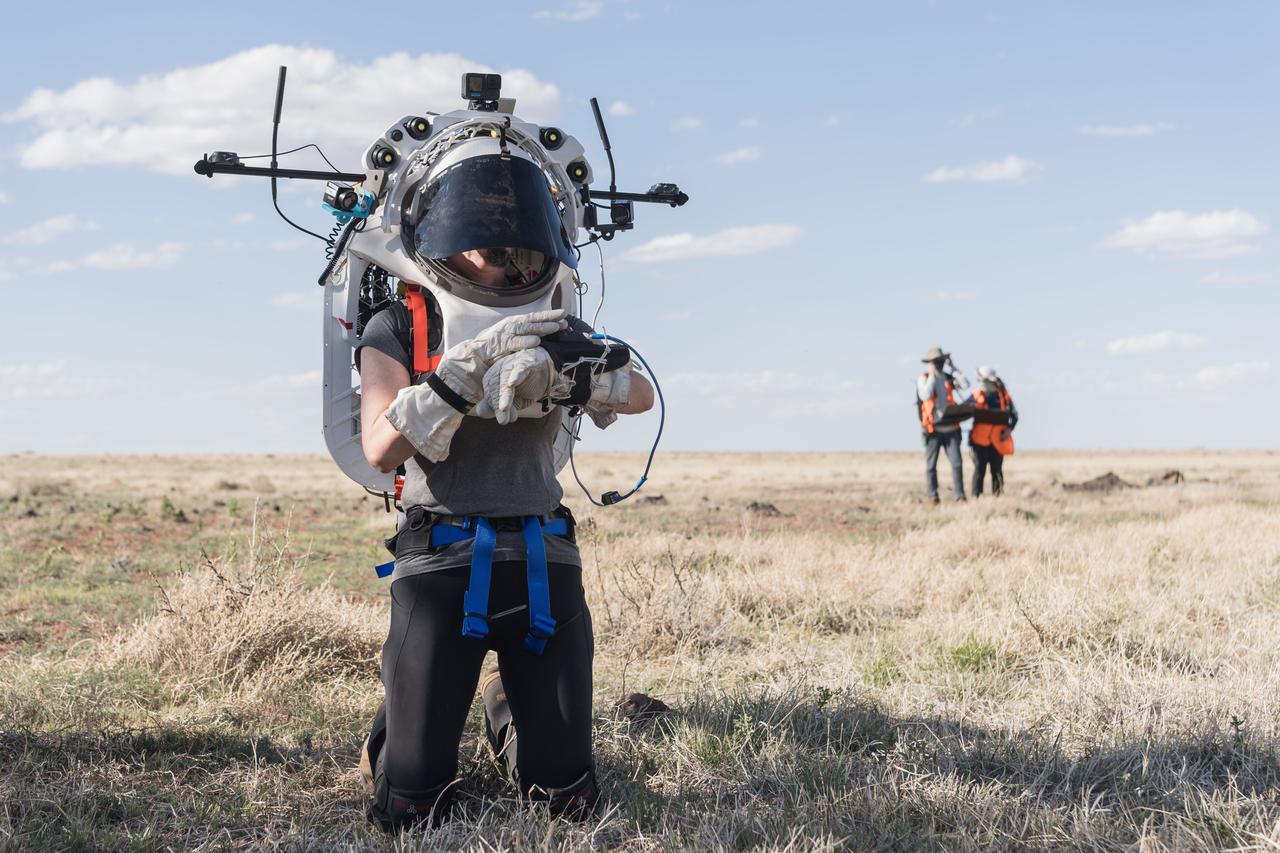

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses the hand controller on her wrist to display information while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
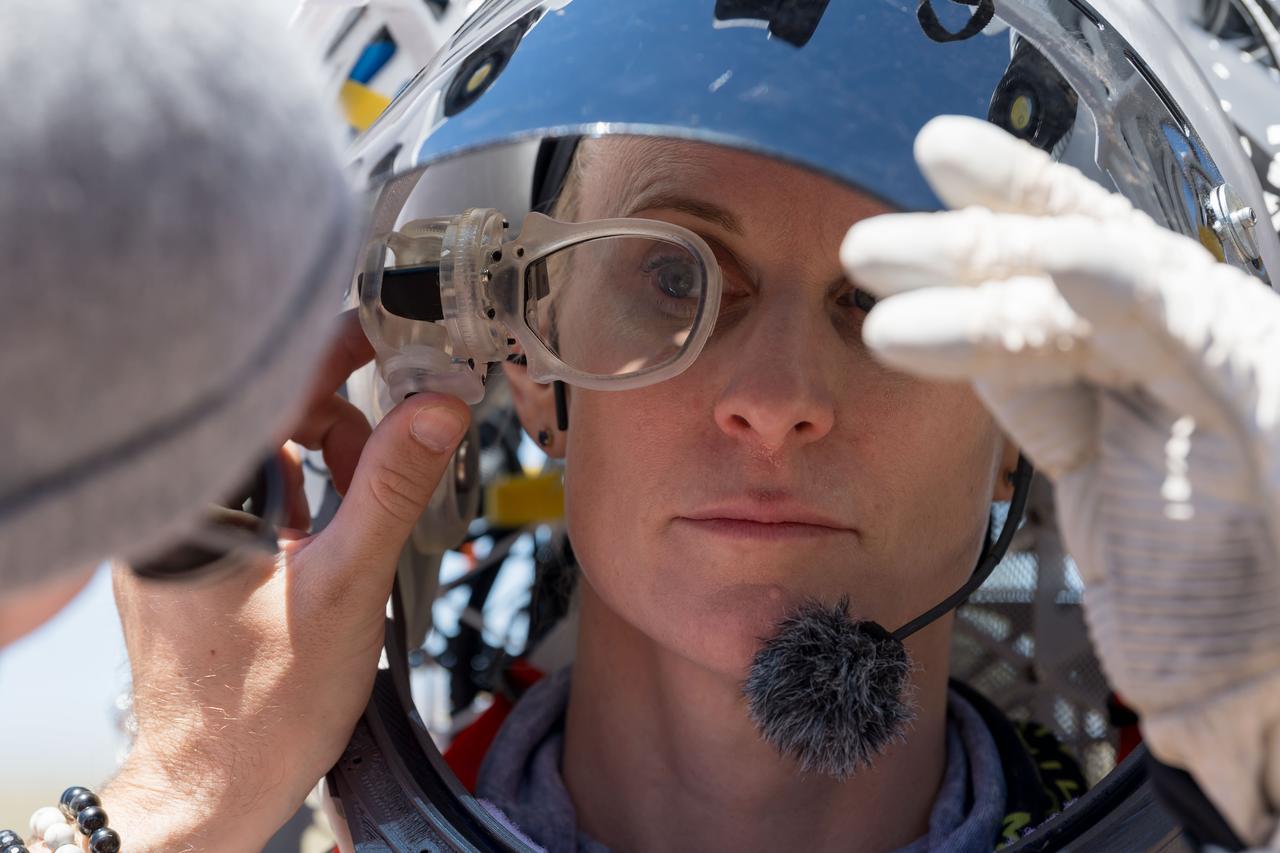

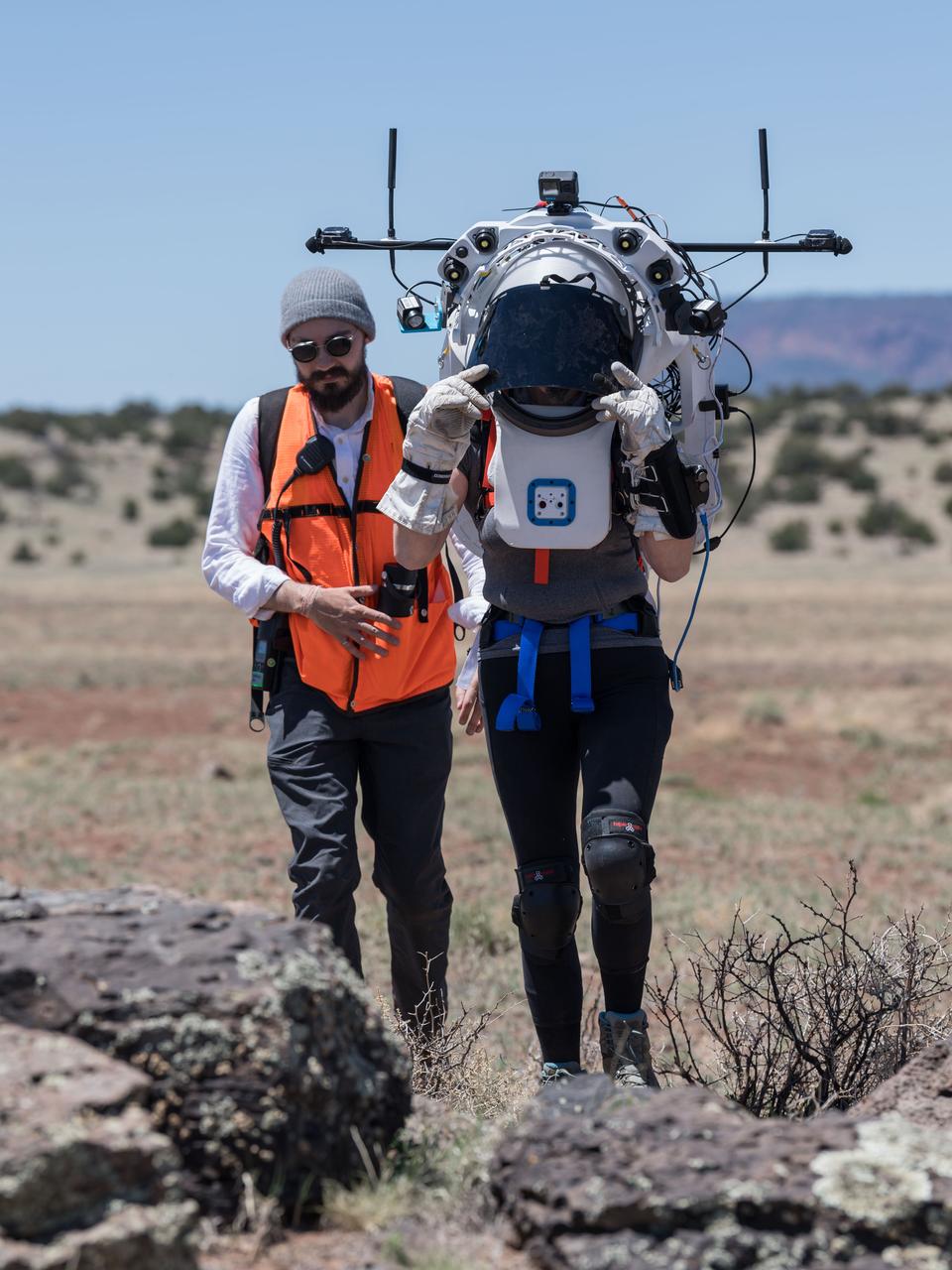
An engineer helps NASA astronaut Kate Rubins adjust the lens on the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display she’s wearing during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
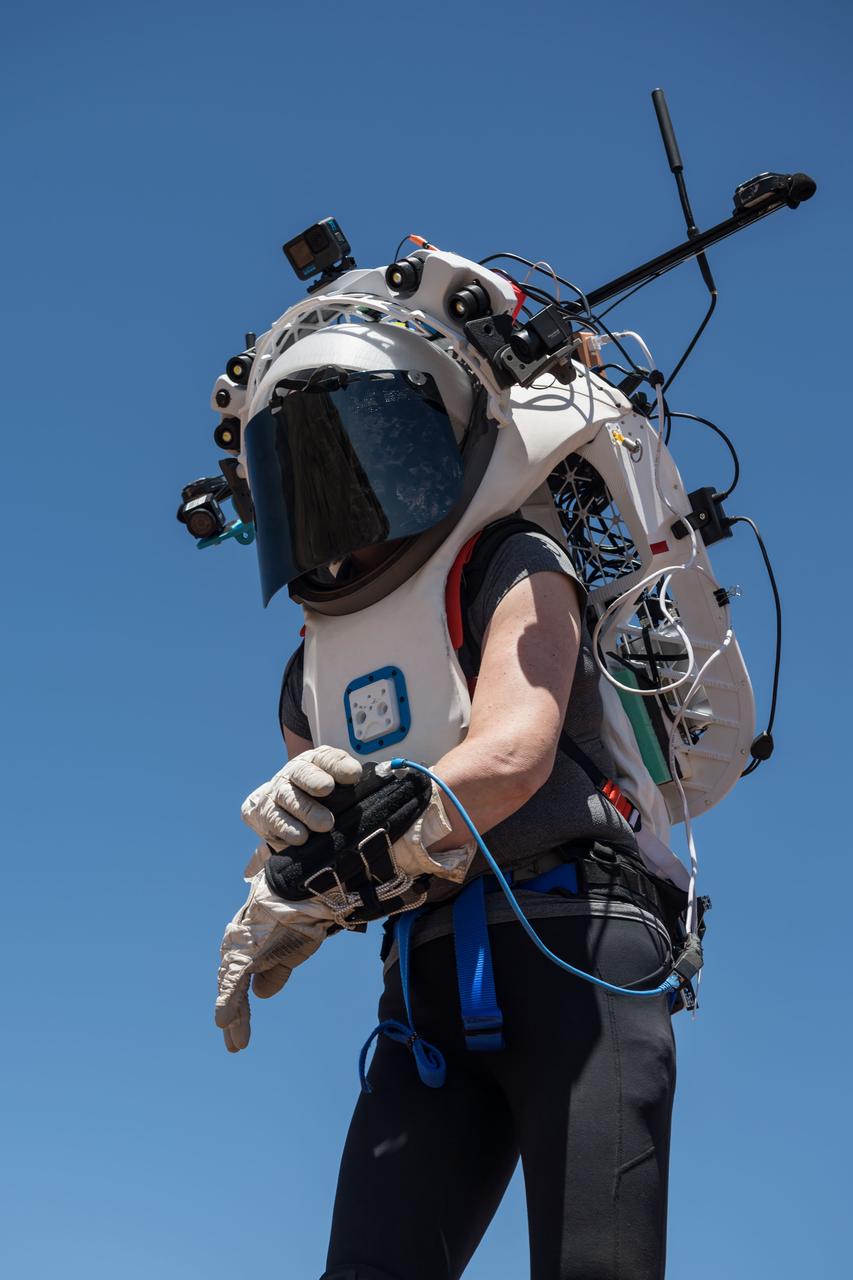

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses the hand controller on her wrist to display information while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

Engineers help NASA astronaut Andre Douglas adjust the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display he’s wearing during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins opens the sun visor on the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display she’s wearing during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
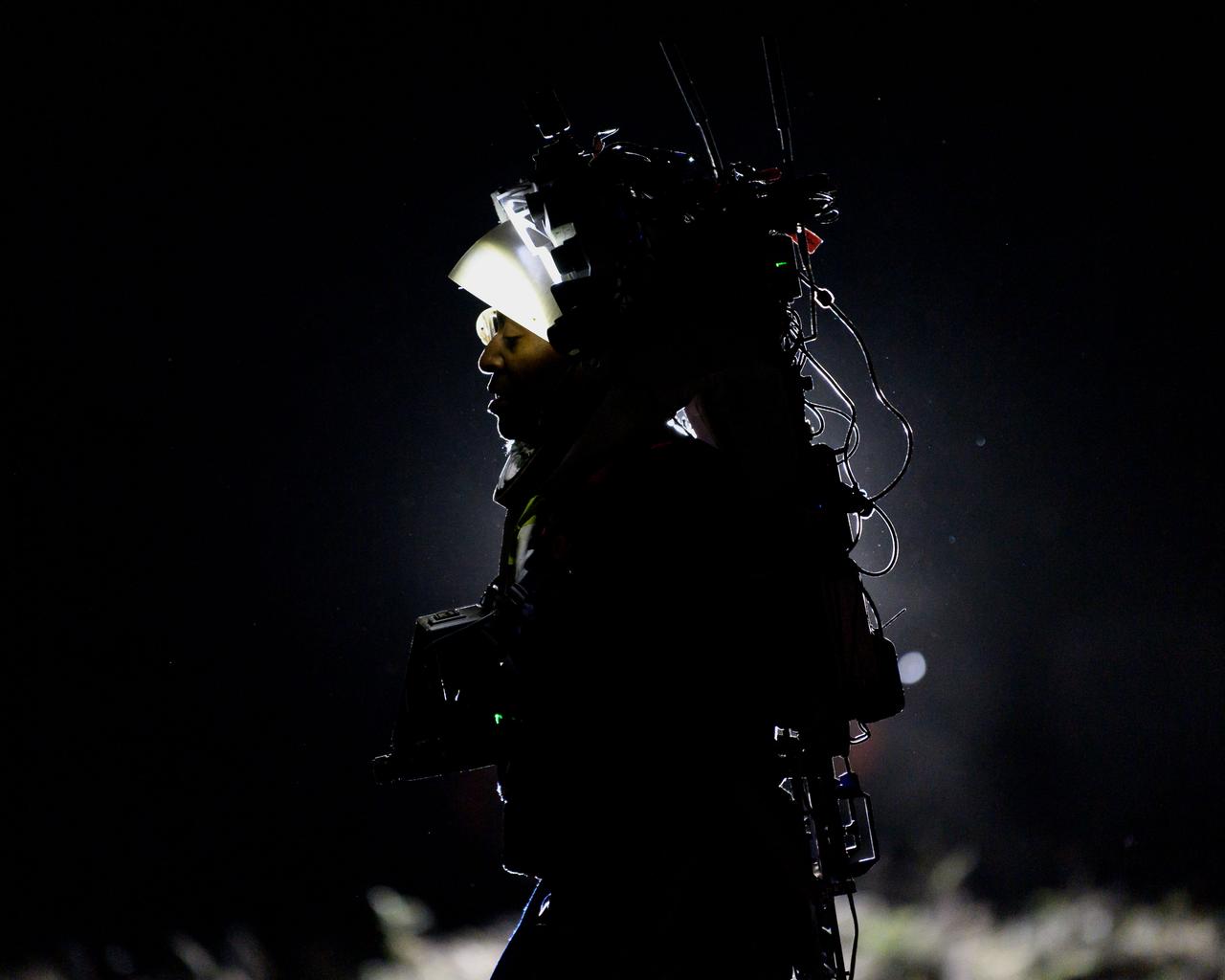

NASA astronaut Andre Douglas wears the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during a nighttime advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
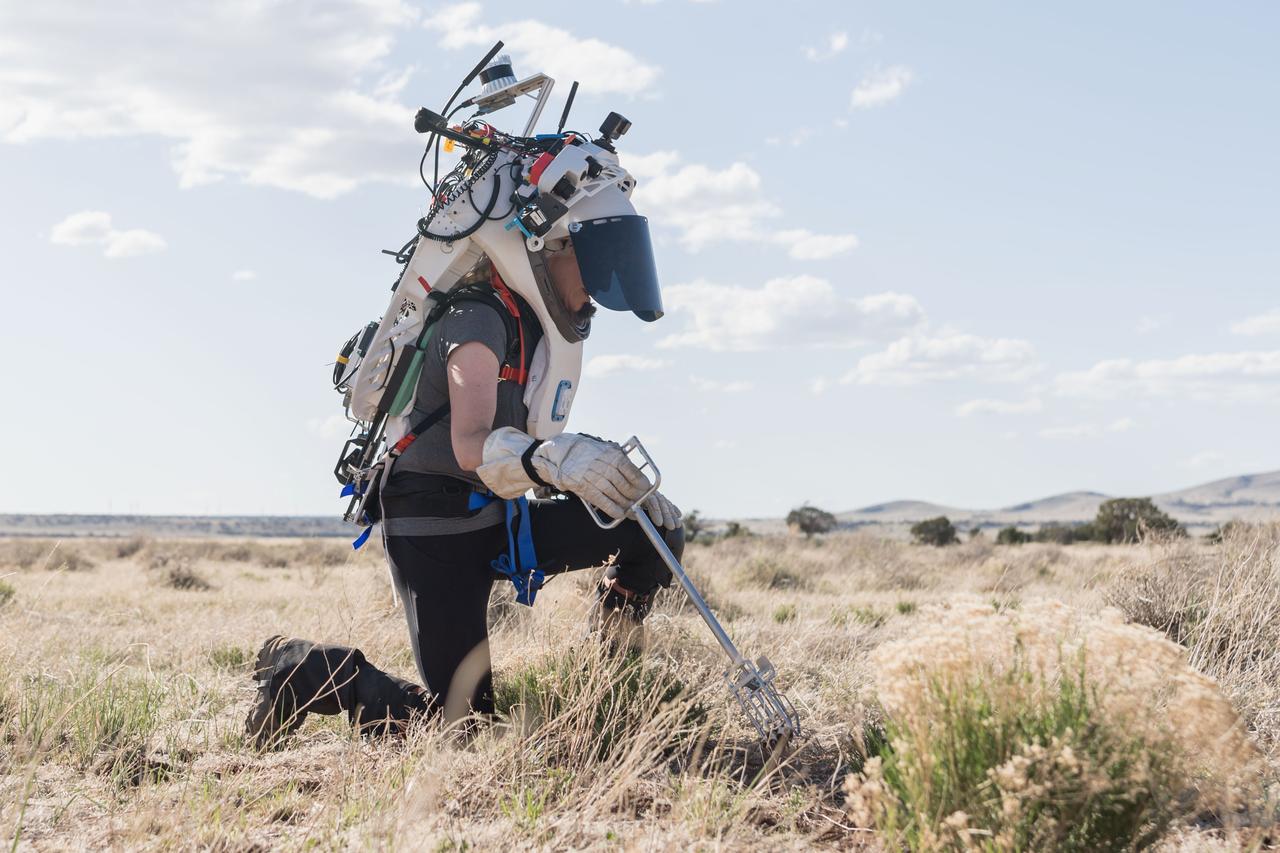

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses tongs to collect geologic samples while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
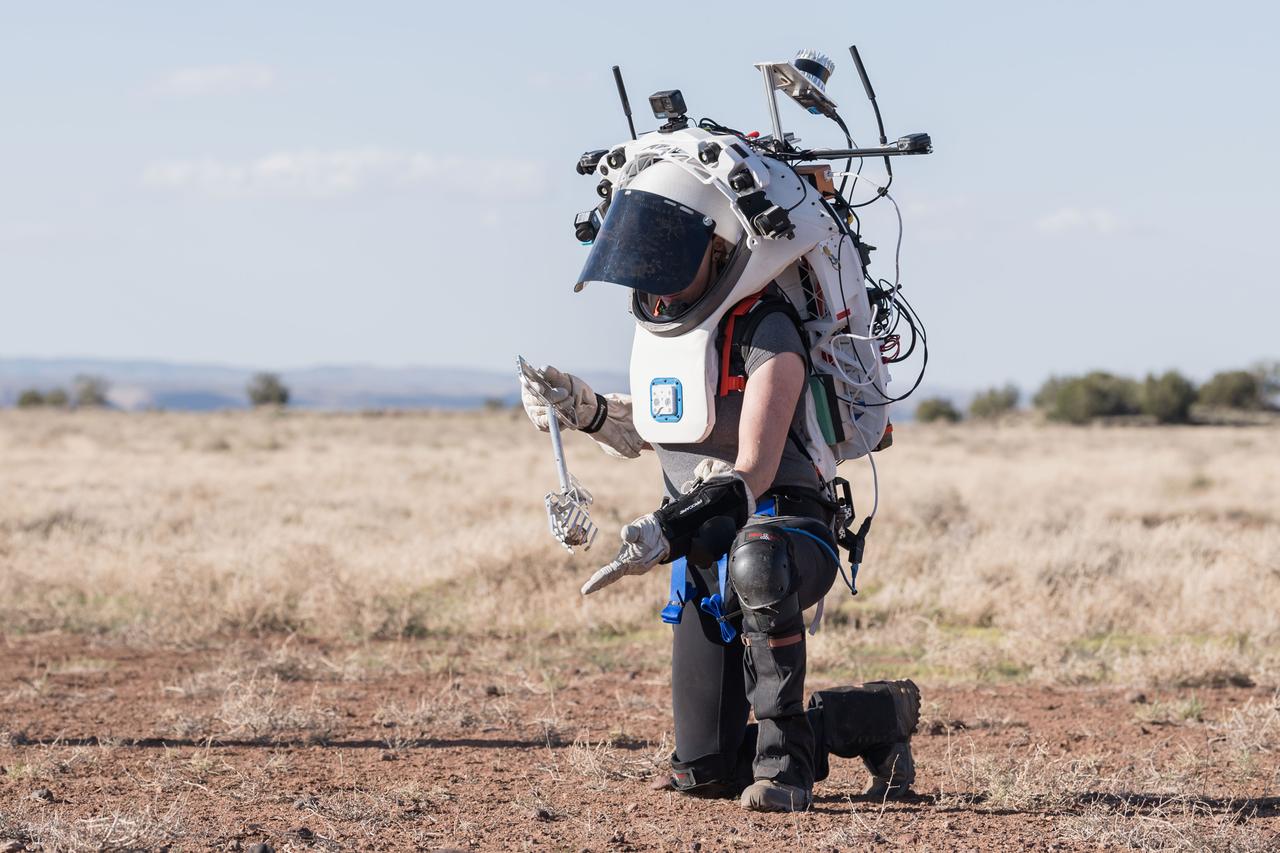

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins uses tongs to pick up a geologic sample while wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 21, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
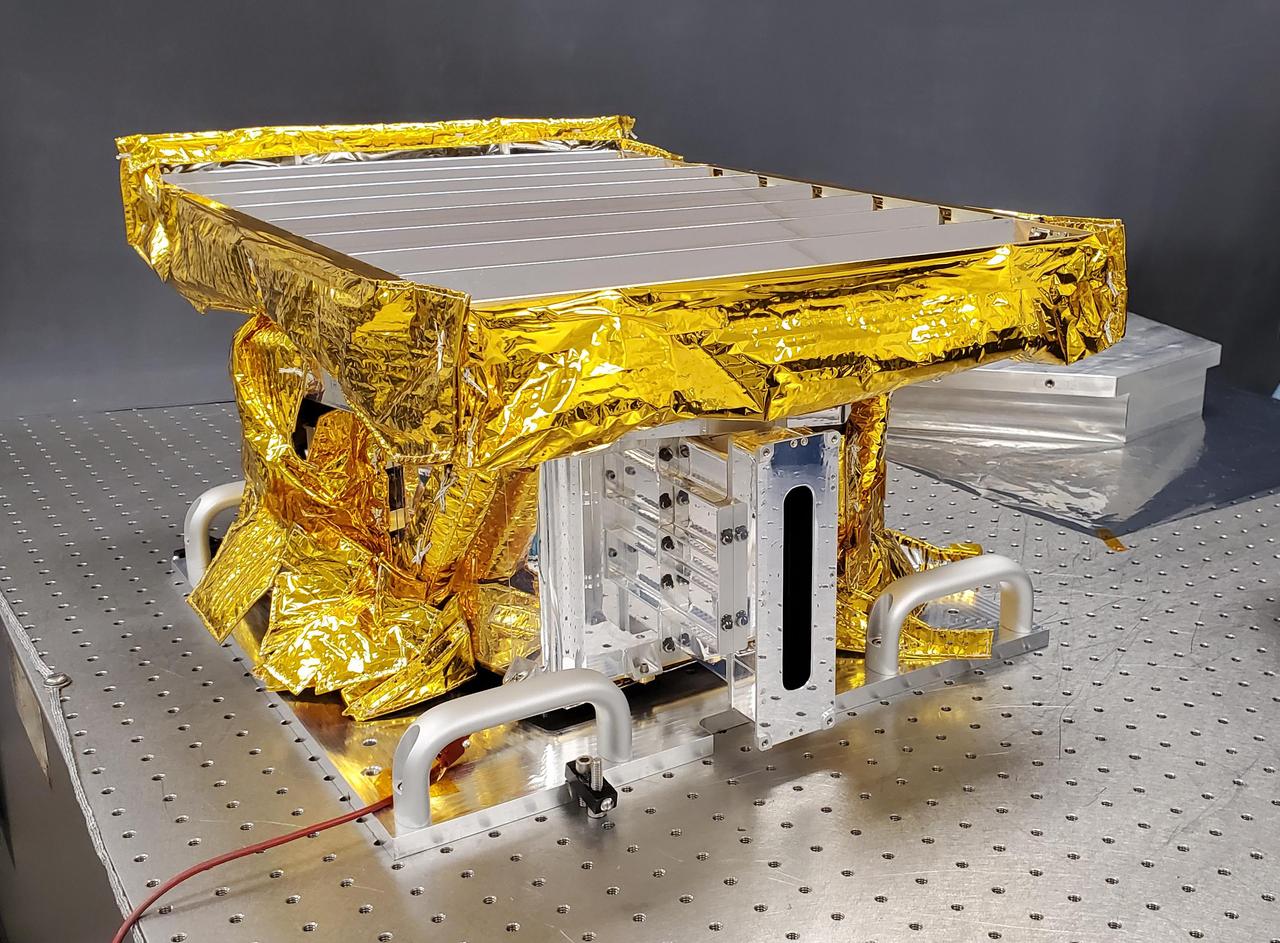

The High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) sits in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California in early December 2022. The JPL-built instrument was later shipped to Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, to be integrated with NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that will detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. A second instrument, the Lunar Thermal Mapper infrared multispectral imager, is being developed by the University of Oxford in the U.K. and is scheduled for delivery and integration in early 2023. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25256
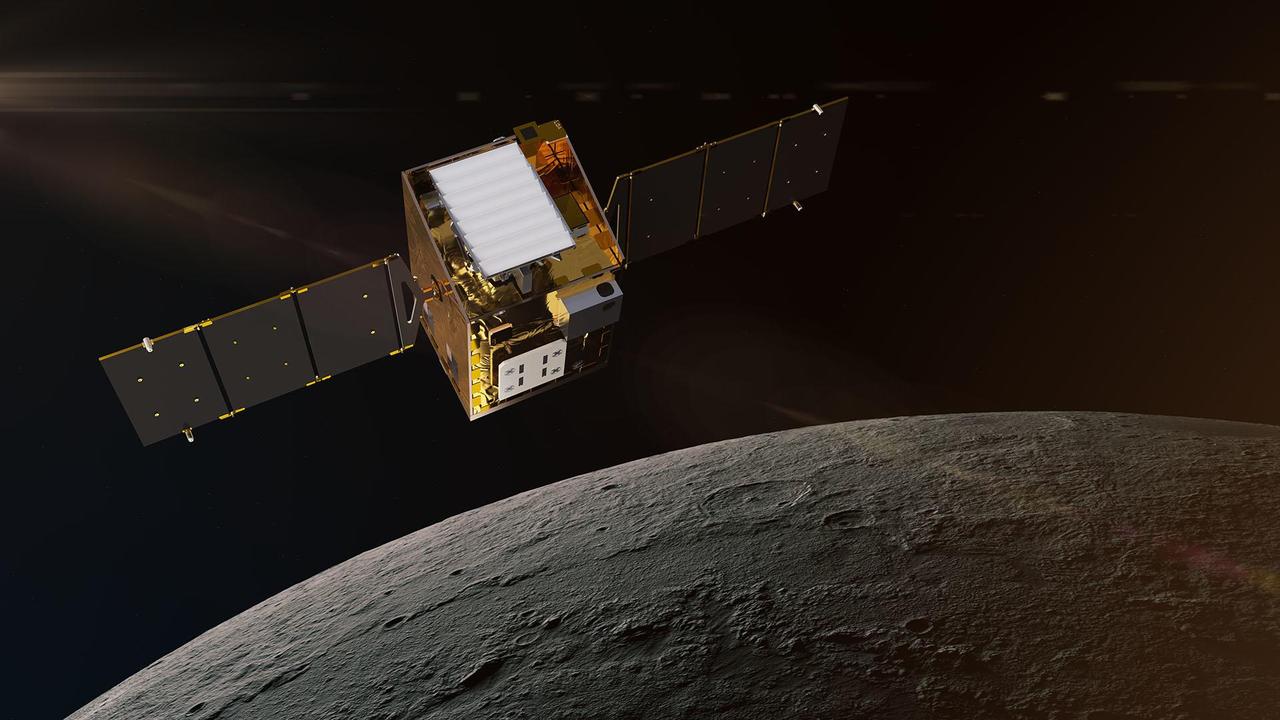

This artist's concept depicts NASA's Lunar Trailblazer in lunar orbit about 60 miles (100 kilometers) from the surface of the Moon. The spacecraft weighs only 440 pounds (200 kilograms) and measures 11.5 feet (3.5 meters) wide when its solar panels are fully deployed. Lunar Trailblazer is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and its science investigation and mission operations are led by Caltech with the mission operations center at IPAC. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM3 instrument, as well as mission design and navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft, integrates the flight system, and supports operations under contract with Caltech. Lunar Trailblazer is part of NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program, which is managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26453
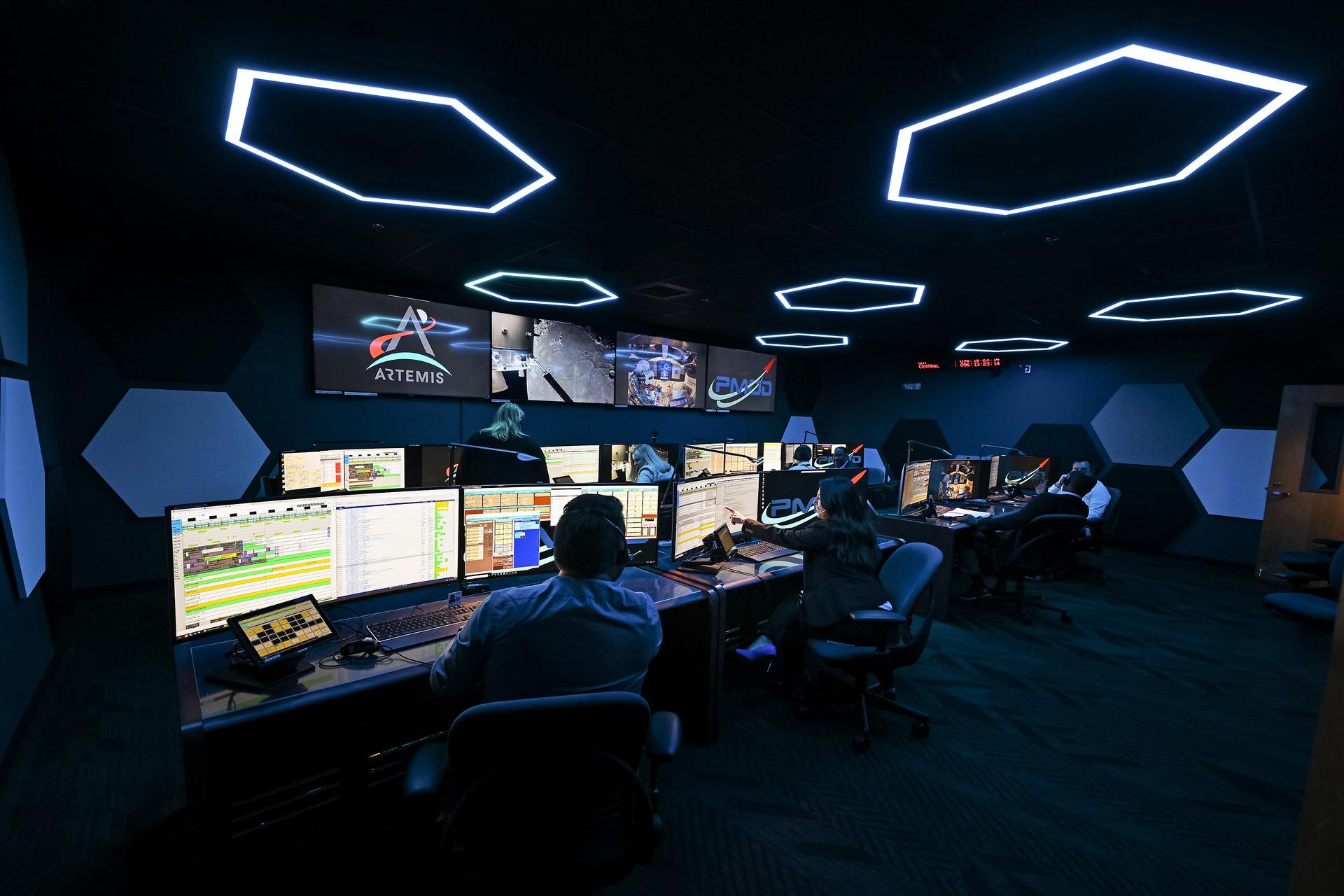

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
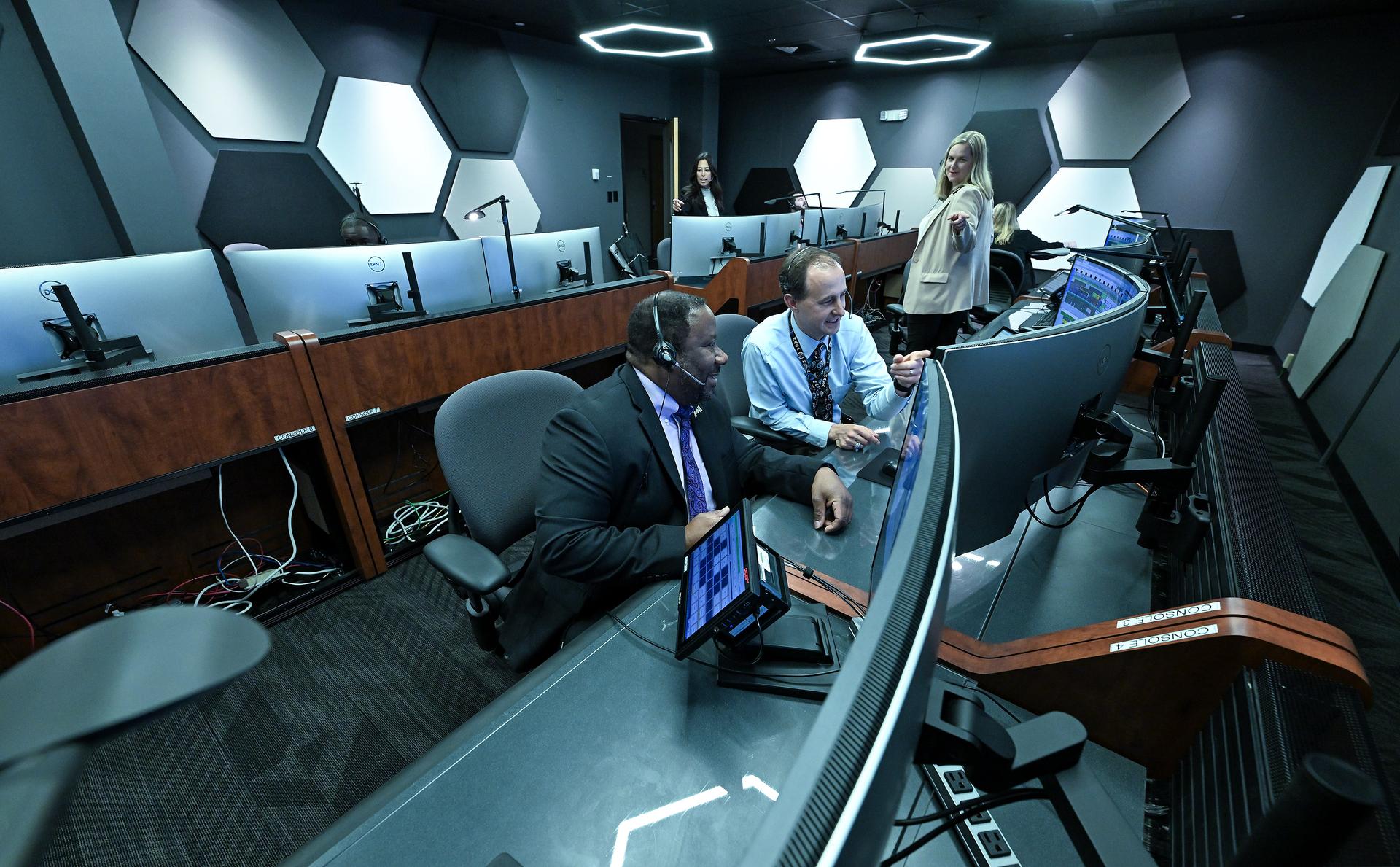

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
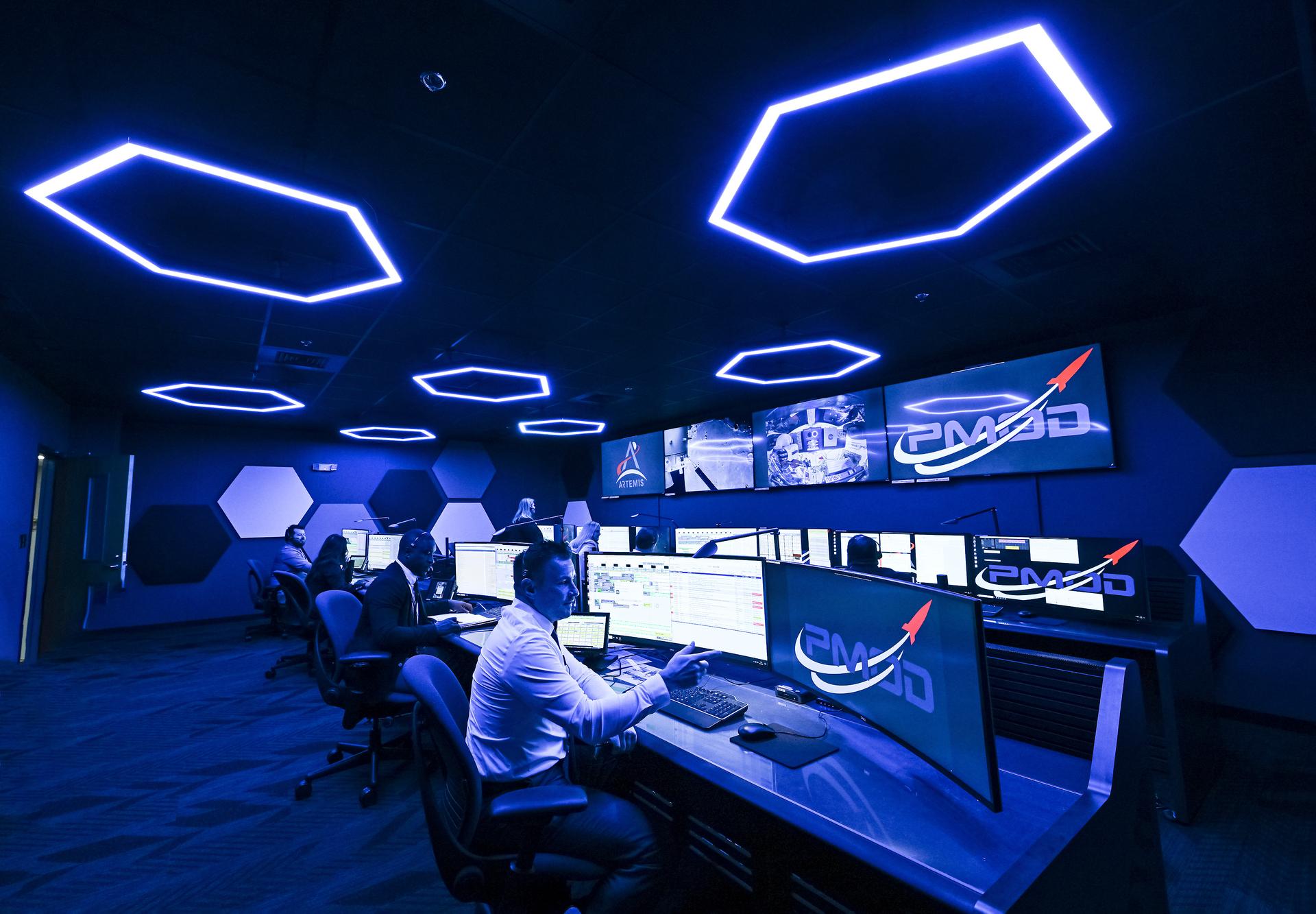

These photos offer a look inside the twin control rooms at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, where engineers will monitor Artemis science and future landing operations for Artemis. The LUCA (Lunar Utilization Control Area) and LESA (Lander Engineering Support Area) rooms are part of the Huntsville Operations Support Center at NASA Marshall. The LUCA is specially designed to support a wide variety of science operations on and around the Moon – and beyond. Engineers in the LUCA monitored operations for the Lunar Node-1 experiment, an autonomous navigation payload that was part of the first NASA Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launch on Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander in 2024. NASA Marshall flight controllers will use the LUCA again for Artemis II to monitor science operations. Beginning with Artemis III, members of the NASA Human Landing System Mission Insight Support Team – a group of engineers, safety leads, flight operations experts, and technical authorities – will work in the LESA. There, they will monitor lander systems in real-time and be involved in key decision-making processes throughout the mission. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
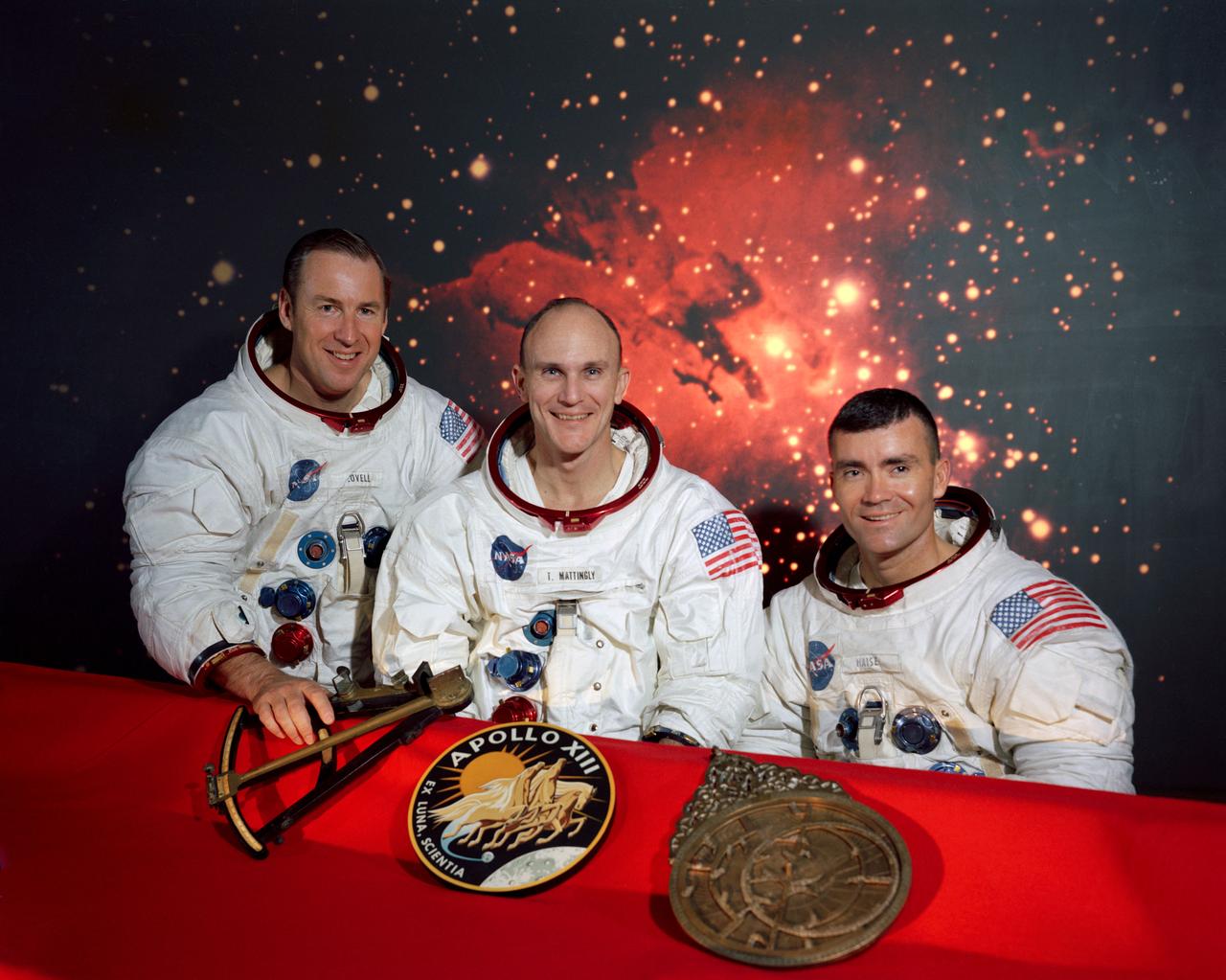

S69-62224 (December 1969) --- The members of the prime crew of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission (left to right) are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. They are seated in front of a scene of the Lagoon Nebula, with the mission insignia and two items of early navigation in the foreground. Represented in the Apollo 13 emblem (center) is Apollo, the sun god of Greek mythology, symbolizing that the Apollo flights have extended the light of knowledge to all mankind. The Latin phrase Ex Luna, Scientia means "From the Moon, Knowledge." The Hindu astrolabe in Sanskrit (on right) was used to predict the position of celestial bodies before the invention of the octant (on left) was used in 1790 to determine the altitude of celestial bodies from aboard ship.

From left to right, the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, and Director-General of the Western Cape Government, Dr. Harry Malila, are seen during a meeting with NASA representatives and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, right, provides remarks during a meeting with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, left, and Director-General of the Western Cape Government, Dr. Harry Malila, second from left, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
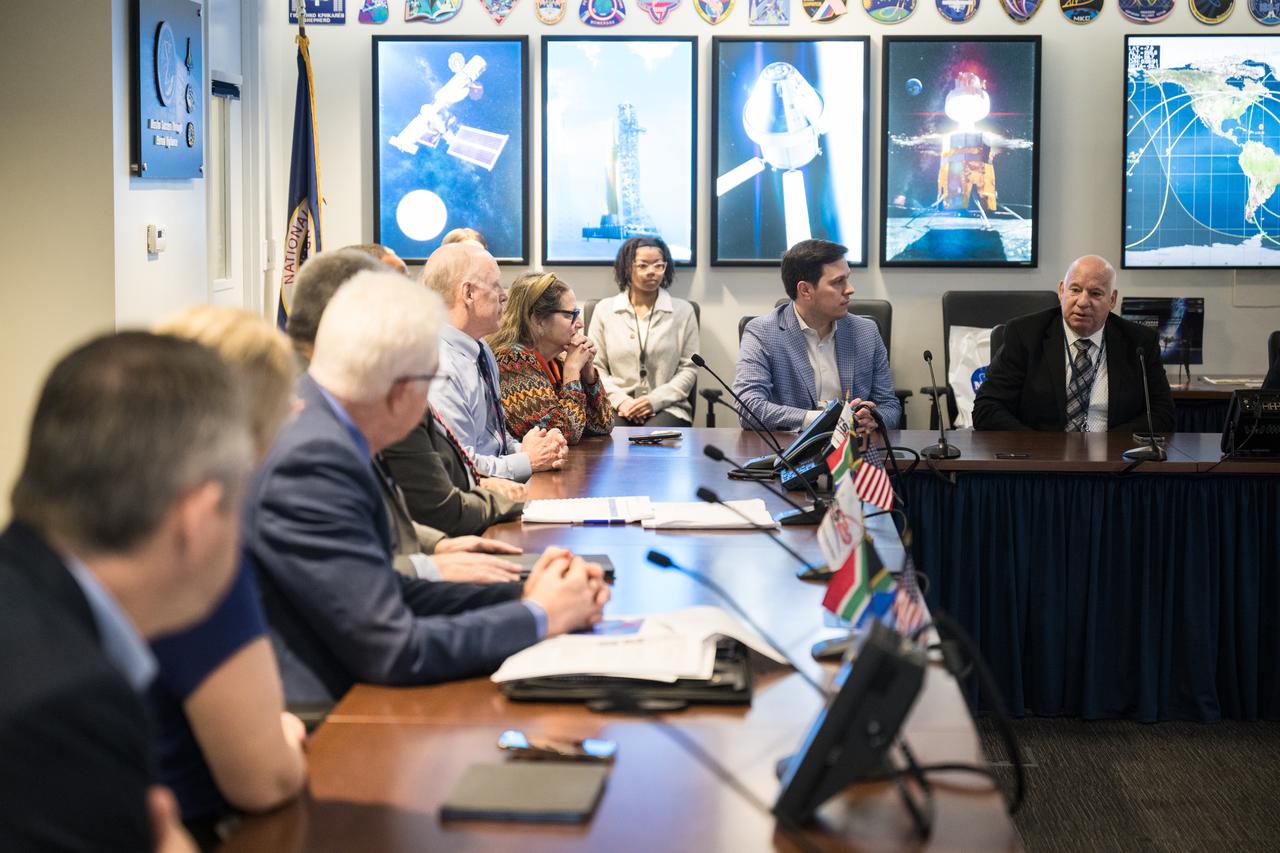

NASA SCaN Development Manager, Bill Marinelli provides remarks during a meeting with the Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
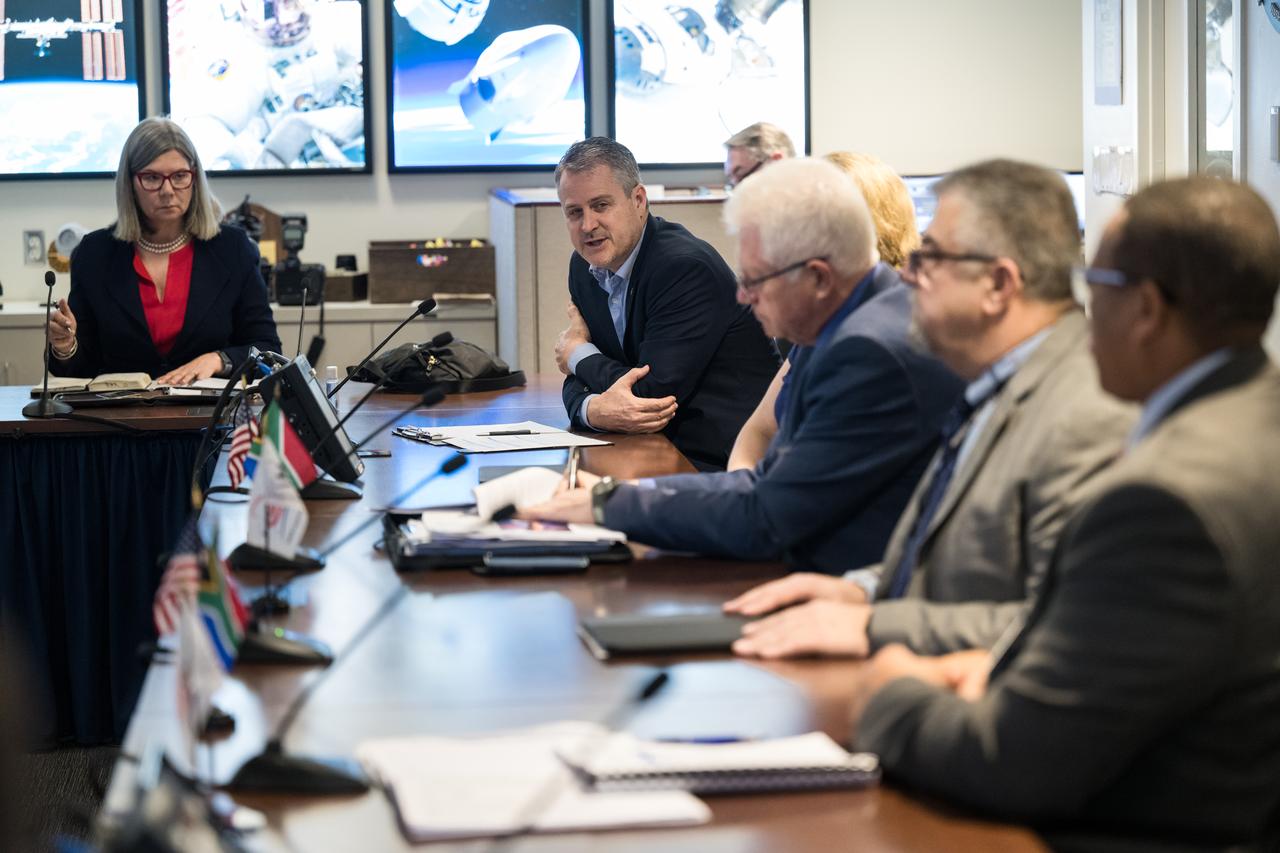

NASA International Program Specialist, Office of International and Interagency Relations, Greg Mann, provide remarks during a meeting with NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, he Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
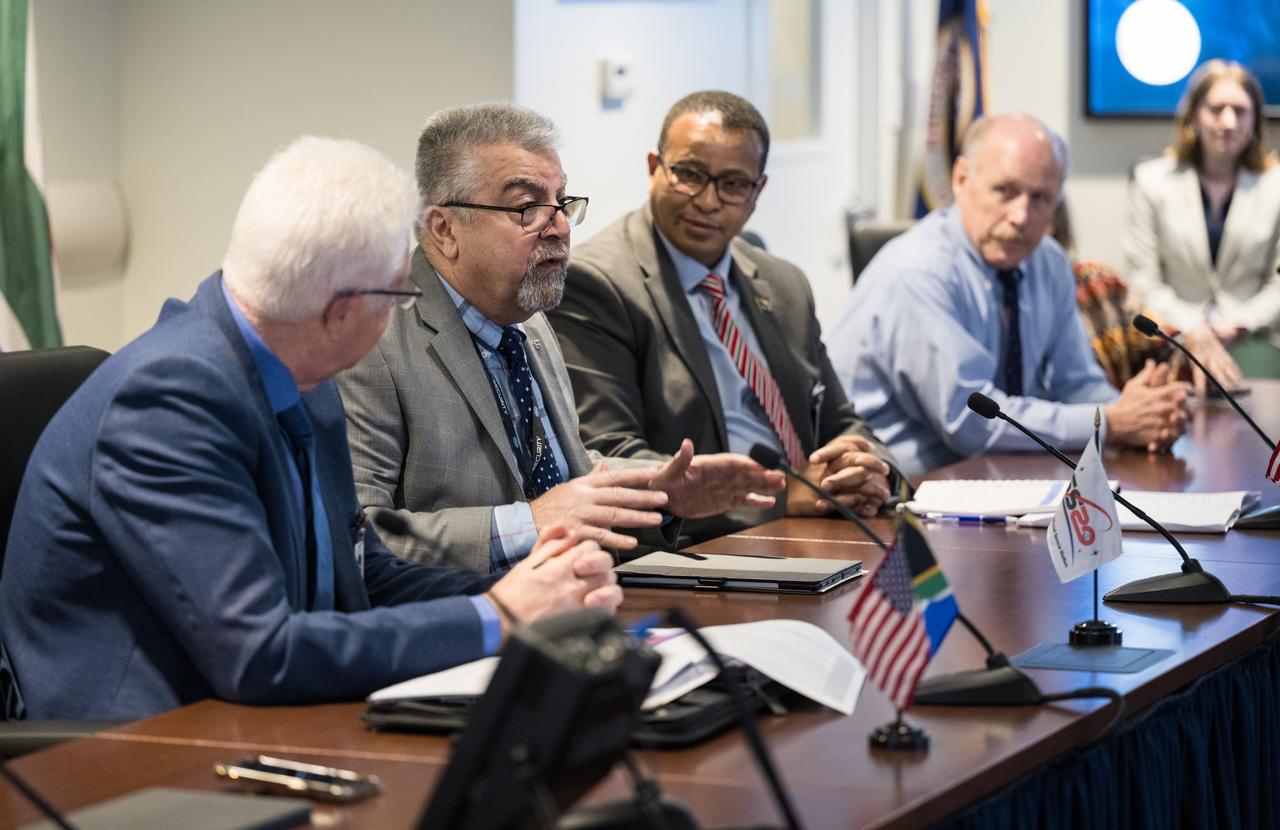

NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, second from left, provides remarks during a meeting with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, left, Director-General of the Western Cape Government, Dr. Harry Malila, third from left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, right, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Side-by-side images depict NASA's Curiosity rover (left) and a moon buggy driven during the Apollo 16 mission. Moon buggies were used during the Apollo missions to carry astronauts, lunar samples and equipment. During the Apollo 17 mission, that equipment included the Traverse Gravimeter Experiment (TGE), a special instrument for measuring gravity. Curiosity wasn't sent to Mars with gravimeters, but it does have accelerometers that are used to navigate the rover. A paper in Science published on Jan. 31, 2019, details how these sensors were repurposed to measure the gravitational pull of Mount Sharp, the mountain Curiosity has been climbing since 2014. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23041
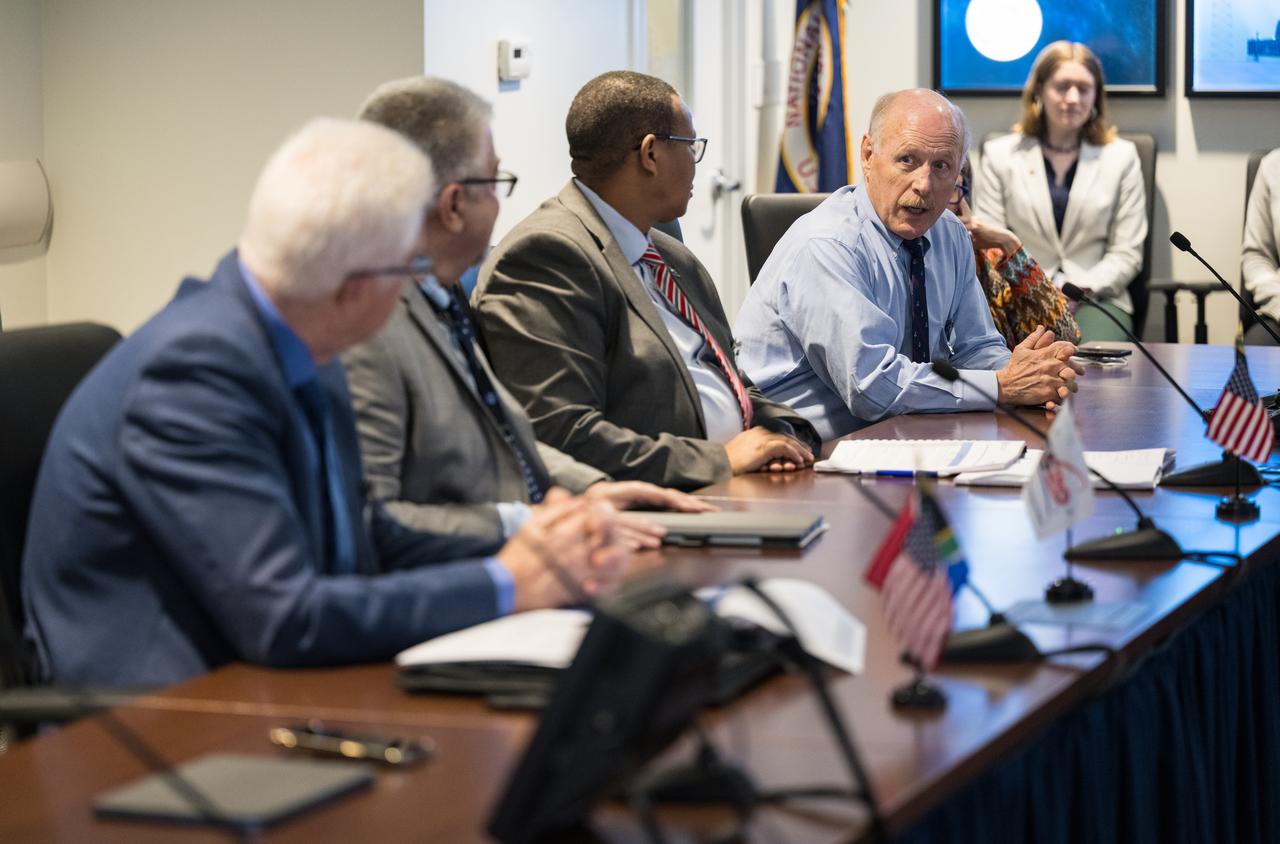

NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, right, provides remarks during a meeting with from left to right, the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, and Director-General of the Western Cape Government, Dr. Harry Malila, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
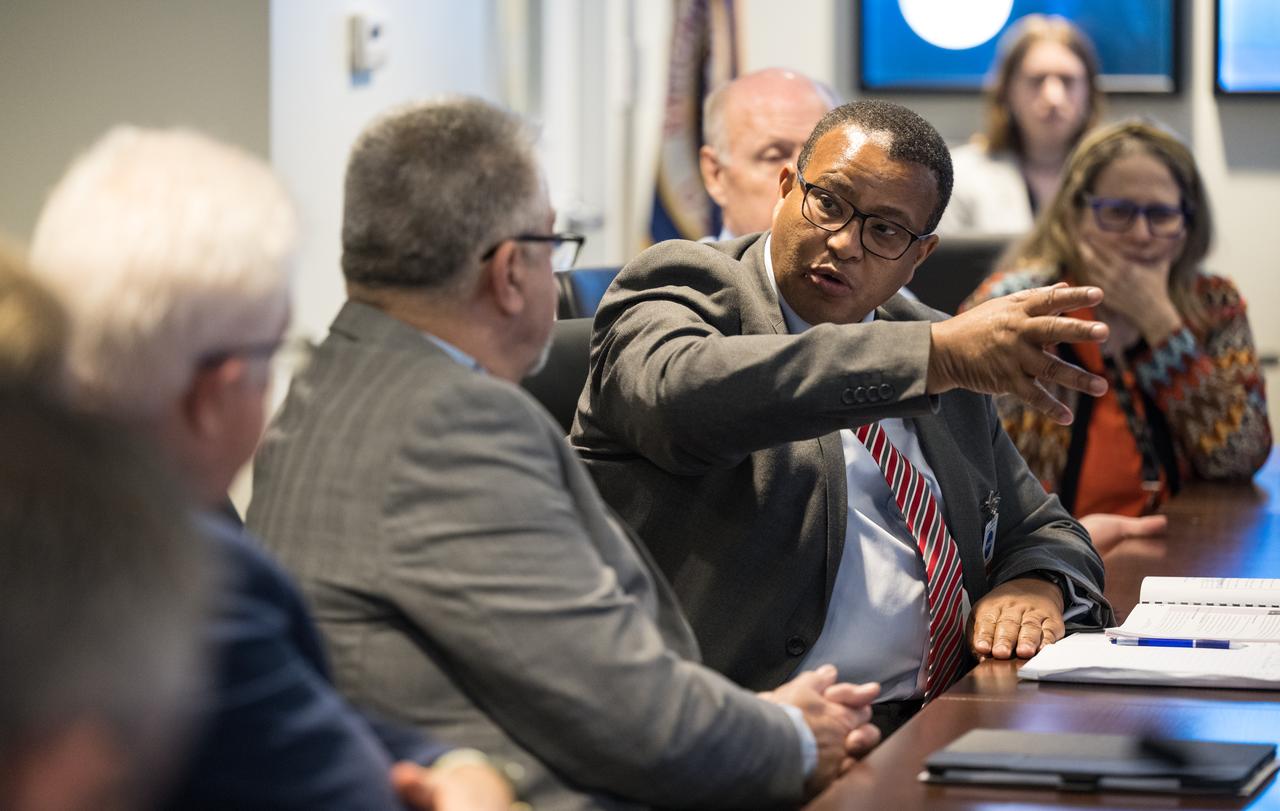

Director-General of the Western Cape Government, Dr. Harry Malila, third from left, provides remarks during a meeting with the Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, left, NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, second from left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Space Operations Mission Directorate, Ken Bowersox, second from right, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Head of Department, Western Cape Government Economic Development and Tourism, Velile Dube, provides remarks during a meeting with NASA Deputy Associate Administrator for Space Communications and Navigation, Badri Younes, Premier of the Western Cape Government, Alan Winde, other NASA representatives, and a delegation from South Africa, to discuss the path forward for development of an antenna for the Lunar Exploration Ground Sites (LEGS) mission in Matjiesfontein, South Africa, and other opportunities, Tuesday, June 13, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
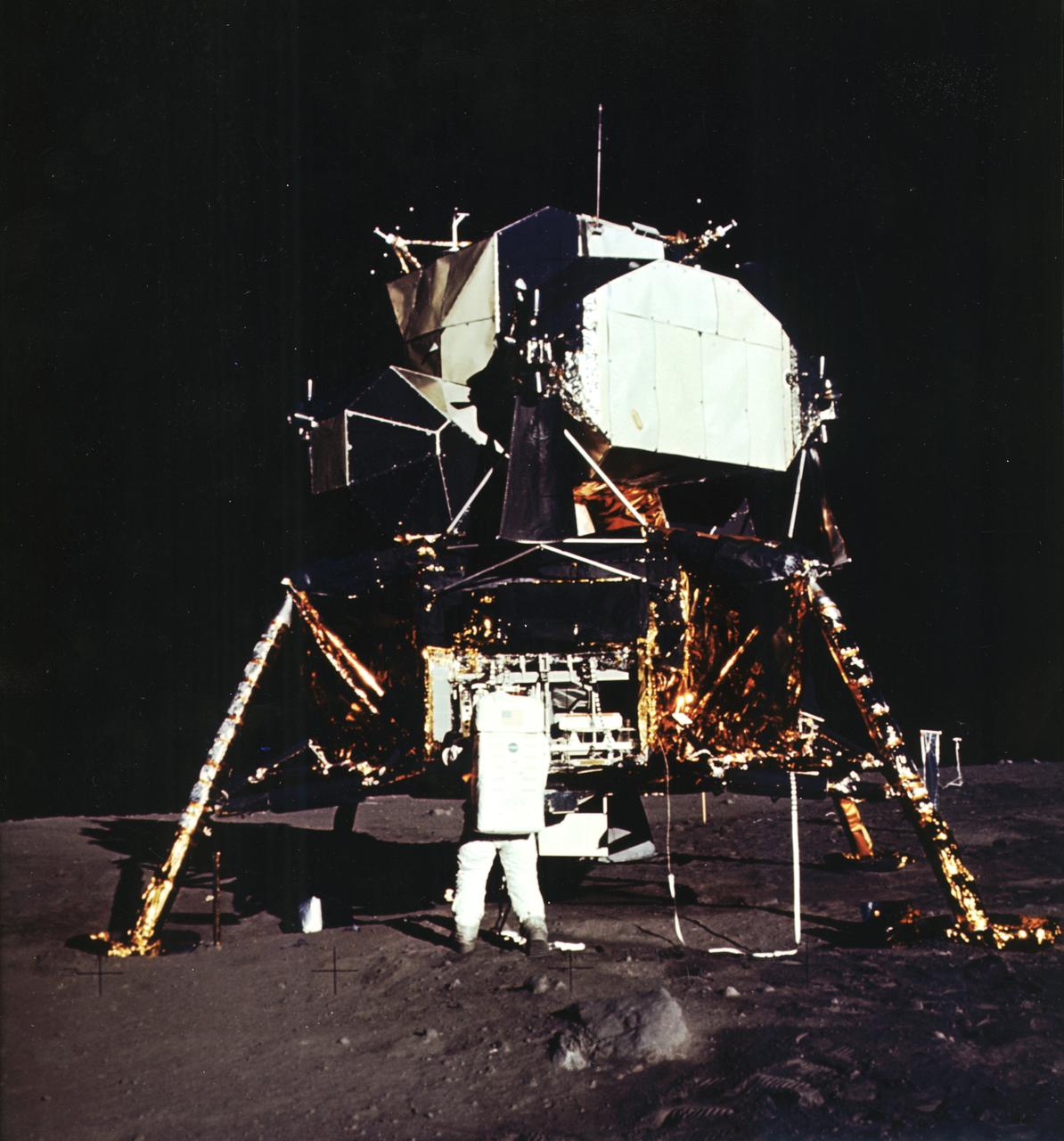
The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. The LM was a two part spacecraft. Its lower or descent stage had the landing gear, engines, and fuel needed for the landing. When the LM blasted off the Moon, the descent stage served as the launching pad for its companion ascent stage, which was also home for the two astronauts on the surface of the Moon. The LM was full of gear with which to communicate, navigate, and rendezvous. It also had its own propulsion system, and an engine to lift it off the Moon and send it on a course toward the orbiting CM. Aldrin is pictured here next to the LM on the lunar surface.
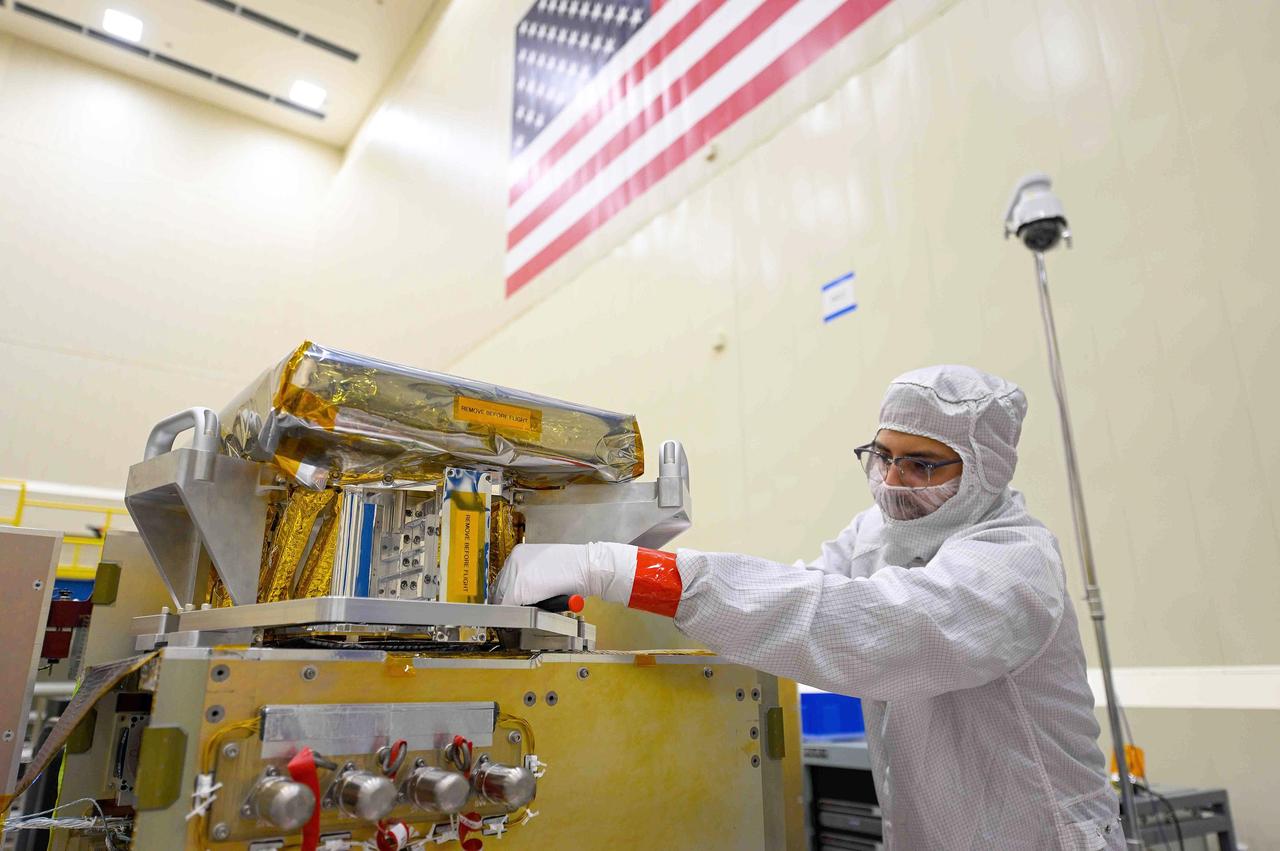

An engineer works on the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM³) for NASA's Lunar Trailblazer spacecraft in a clean room at Lockheed Martin Space in Littleton, Colorado, shortly after the instrument delivered in December 2022. HVM³ is an imaging spectrometer that was developed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. It was shipped from JPL to Lockheed Martin Space, where it was integrated with the spacecraft. HVM³ is one of two instruments that will be used by the mission to detect and map water on the Moon's surface to determine its abundance, location, form, and how it changes over time. Lunar Trailblazer was selected under NASA's Small Innovative Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program in 2019. The Lunar Trailblazer mission is managed by JPL and its science investigation is led by Caltech in Pasadena, California. Managed for NASA by Caltech, JPL also provides system engineering, mission assurance, the HVM³ instrument, as well as navigation. Lockheed Martin Space provides the spacecraft and integrates the flight system, under contract with Caltech. SIMPLEx mission investigations are managed by the Planetary Missions Program Office at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as part of the Discovery Program at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The program conducts space science investigations in the Planetary Science Division of NASA's Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25255
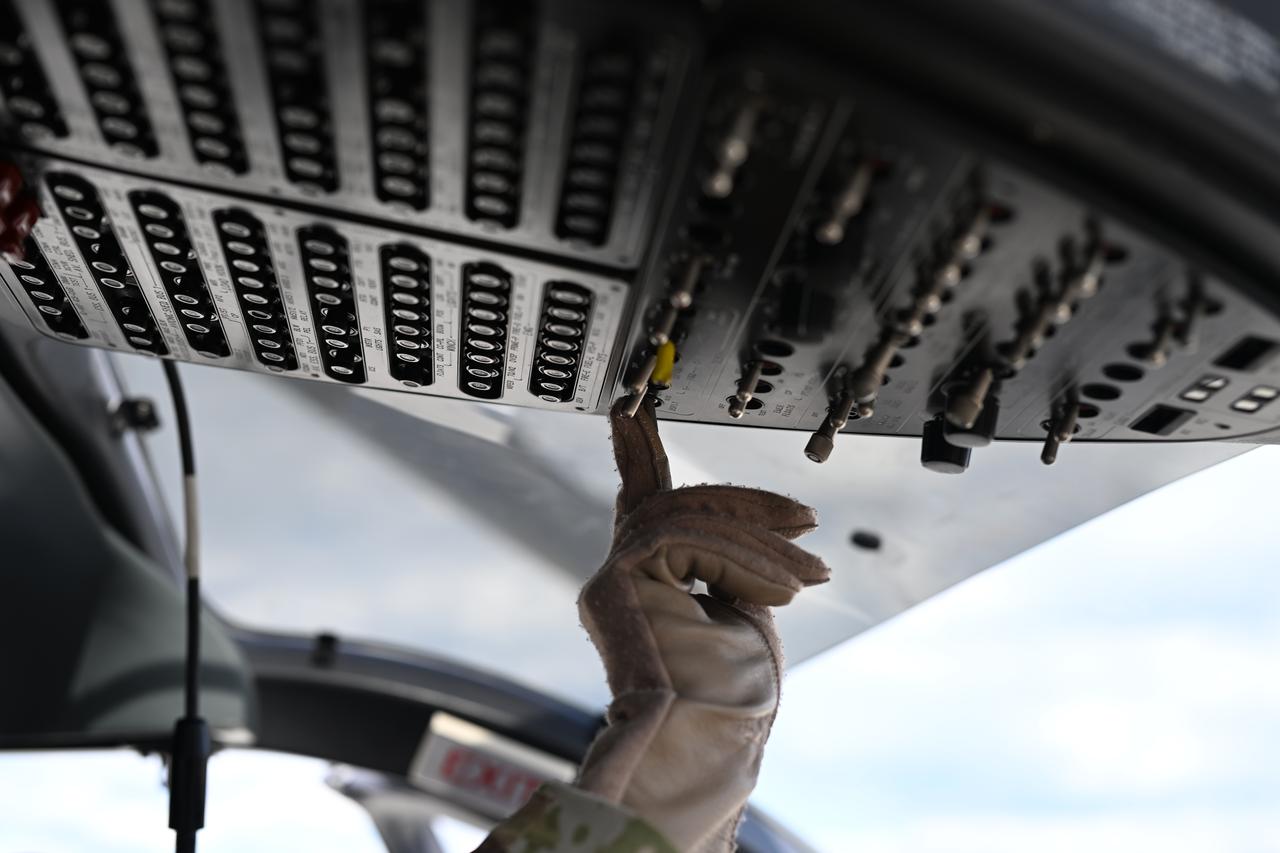

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
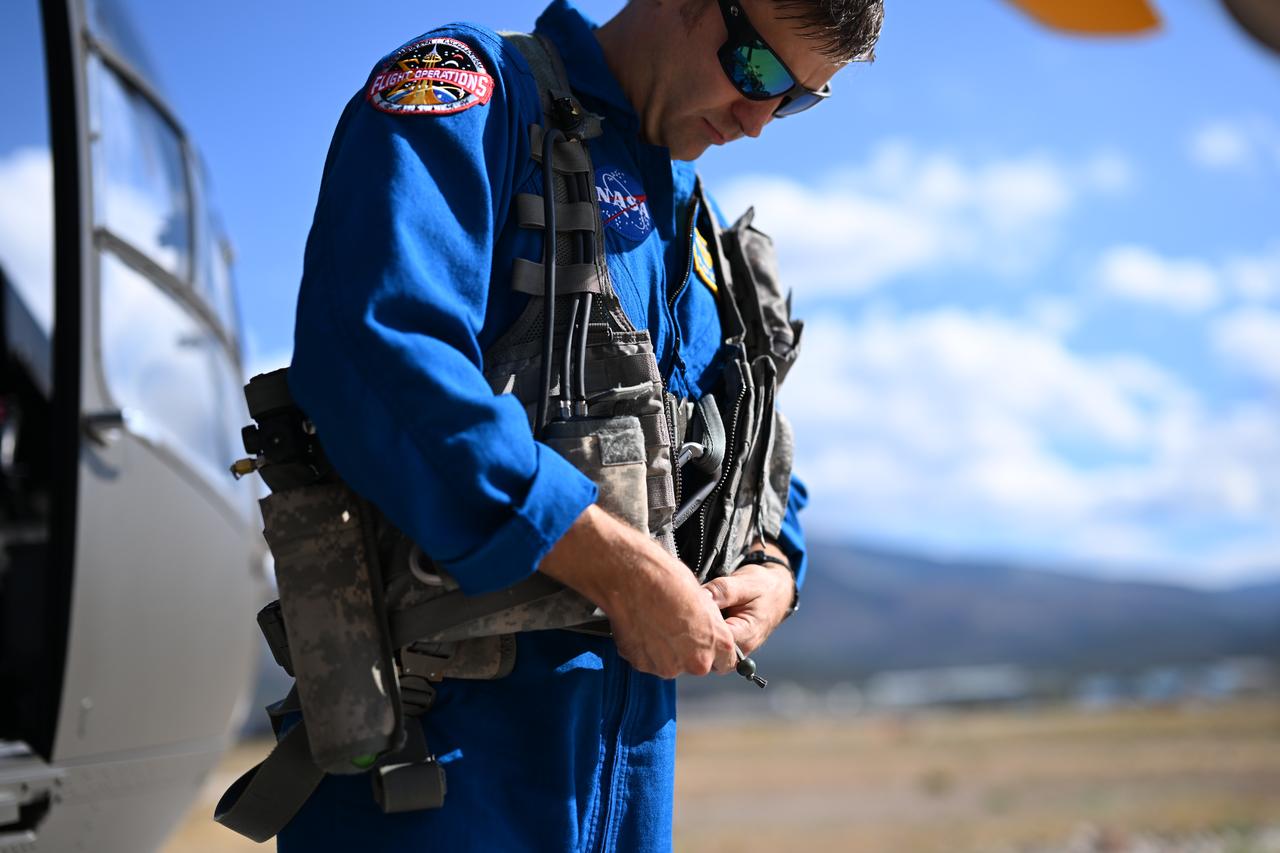

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
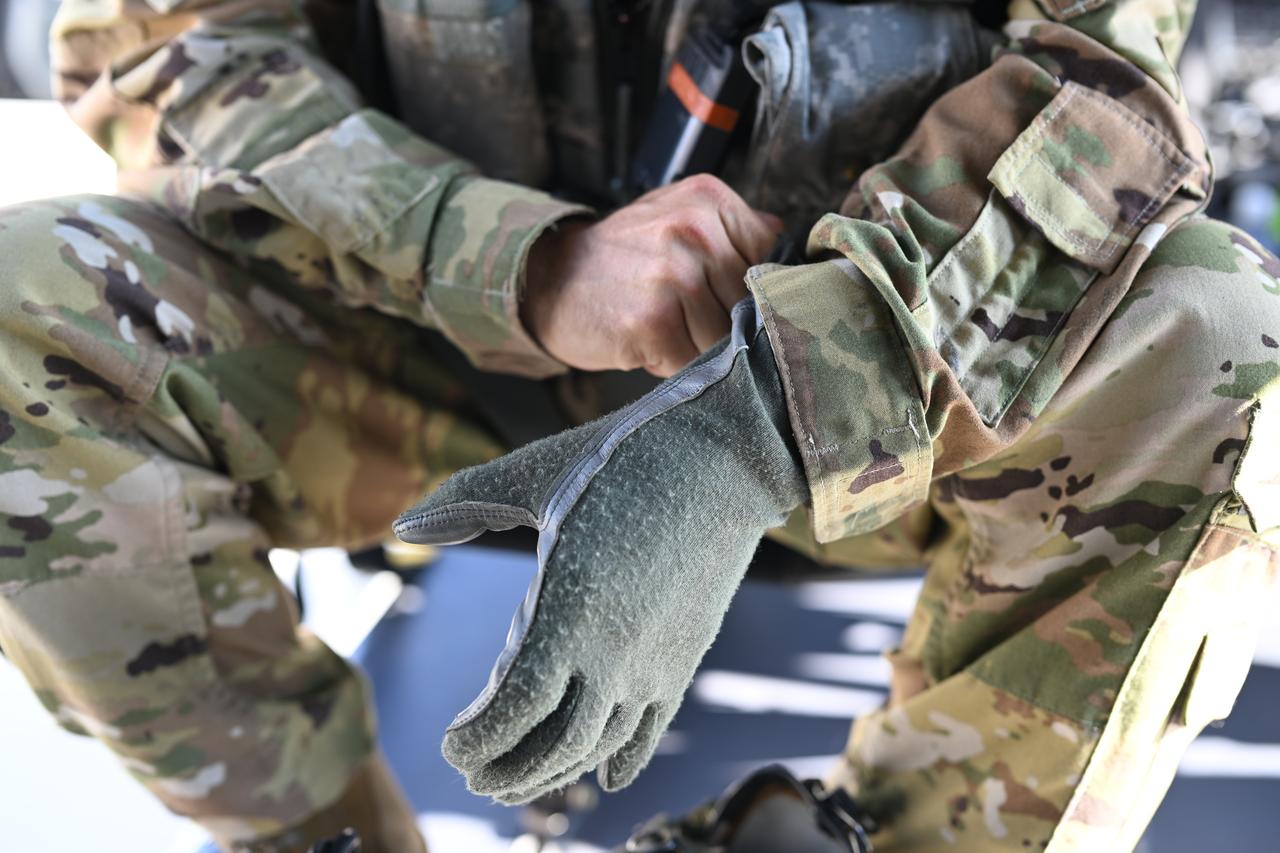

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
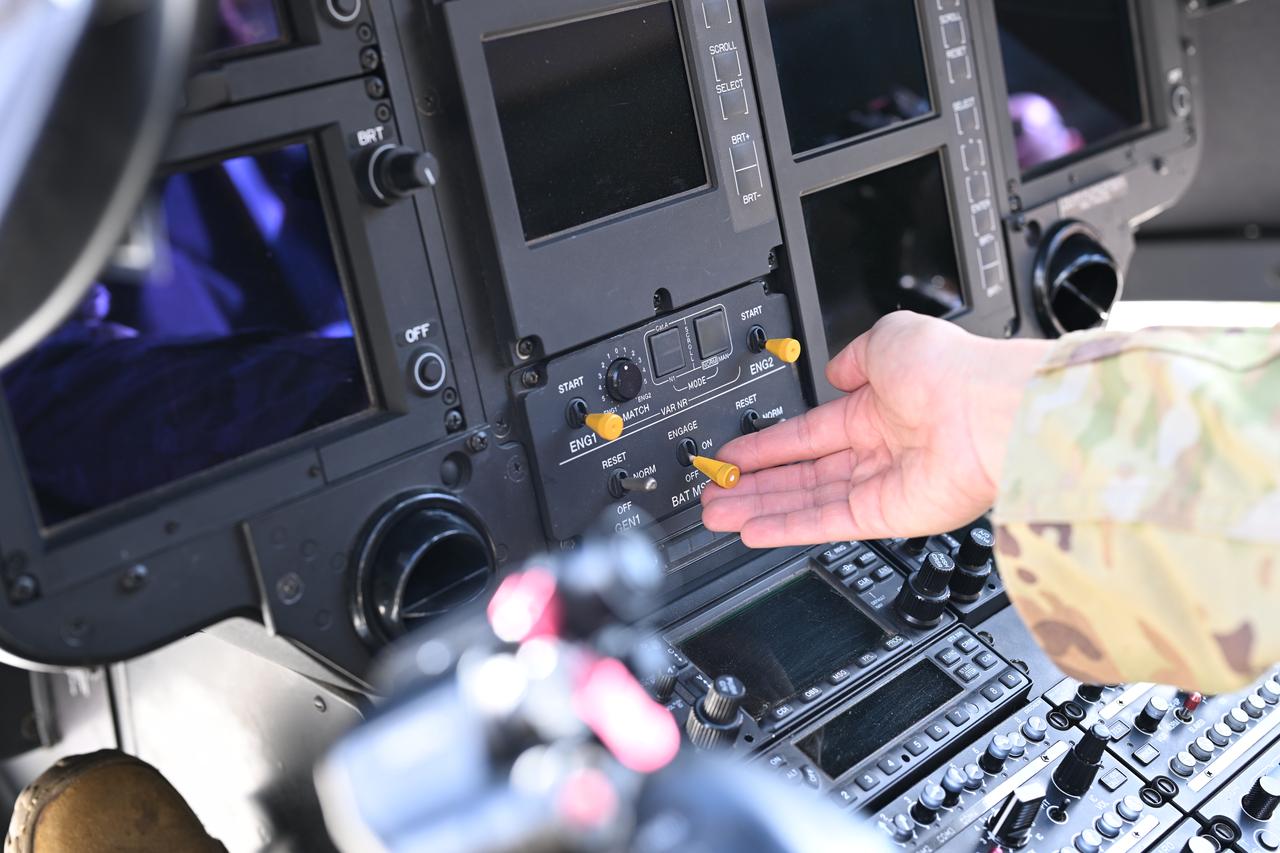

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544
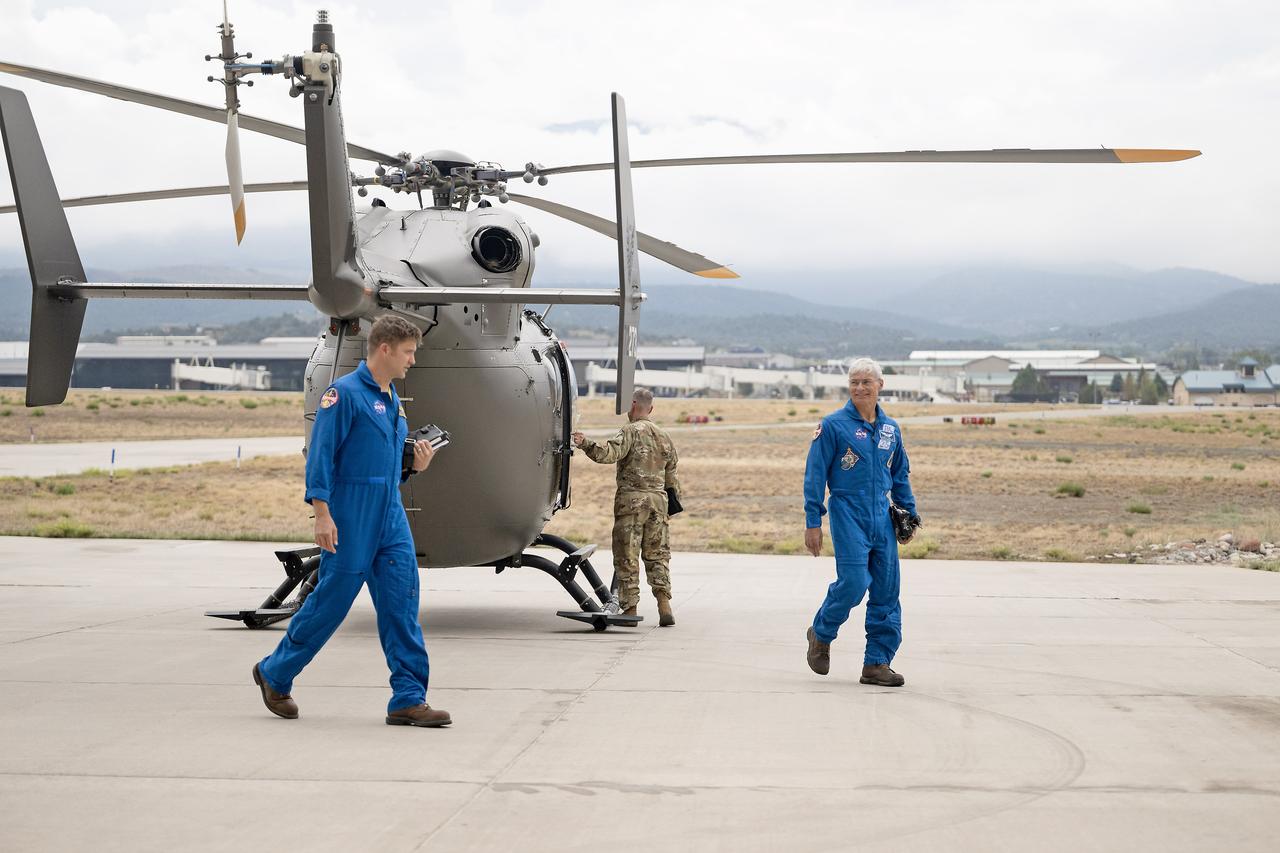

These photos and videos show how NASA certified a new lander flight training course using helicopters in the mountains of northern Colorado. NASA is partnering with the Colorado Army National Guard at its High-Altitude Army National Guard Aviation Training Site near Gypsum, Colorado, to develop the foundational flight training course that will help astronauts practice flight and landing procedures for the Moon. The certification marks an important milestone in crew training for Artemis missions to the Moon, when astronauts will use a commercial human landing system to land on the lunar surface. During the two-week certification run in late August 2025, NASA astronauts Matthew Dominick and Mark Vande Hei participated in flight and landing training to help certify the course. The pair, along with trained instructor pilots with the Army National Guard, took turns flying a helicopter and navigating to landing zones. Artemis flight crew trainers, mission control leads, and lunar lander operational experts from NASA Johnson joined them on each helicopter flight to assess the instruction, training environment, and technical applications for crewed lunar missions. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544