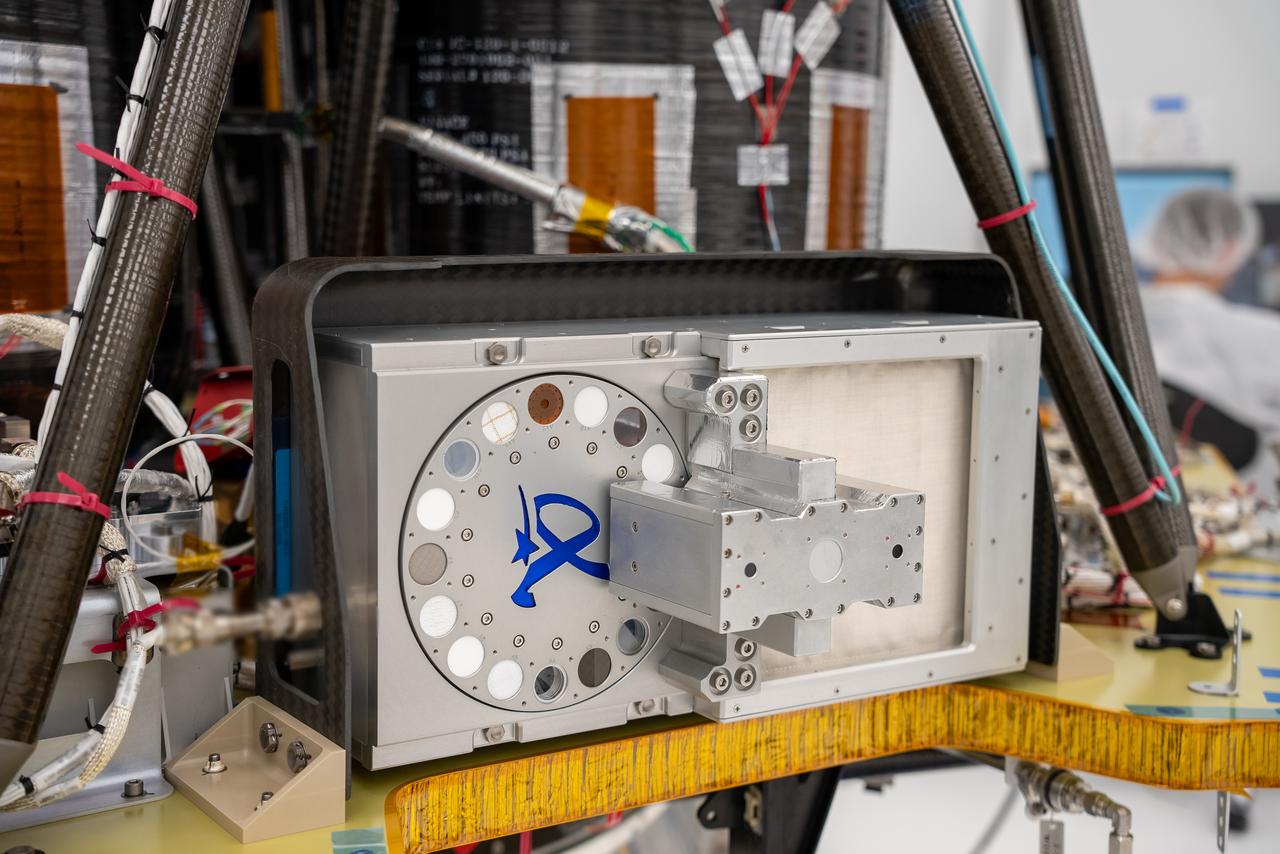
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
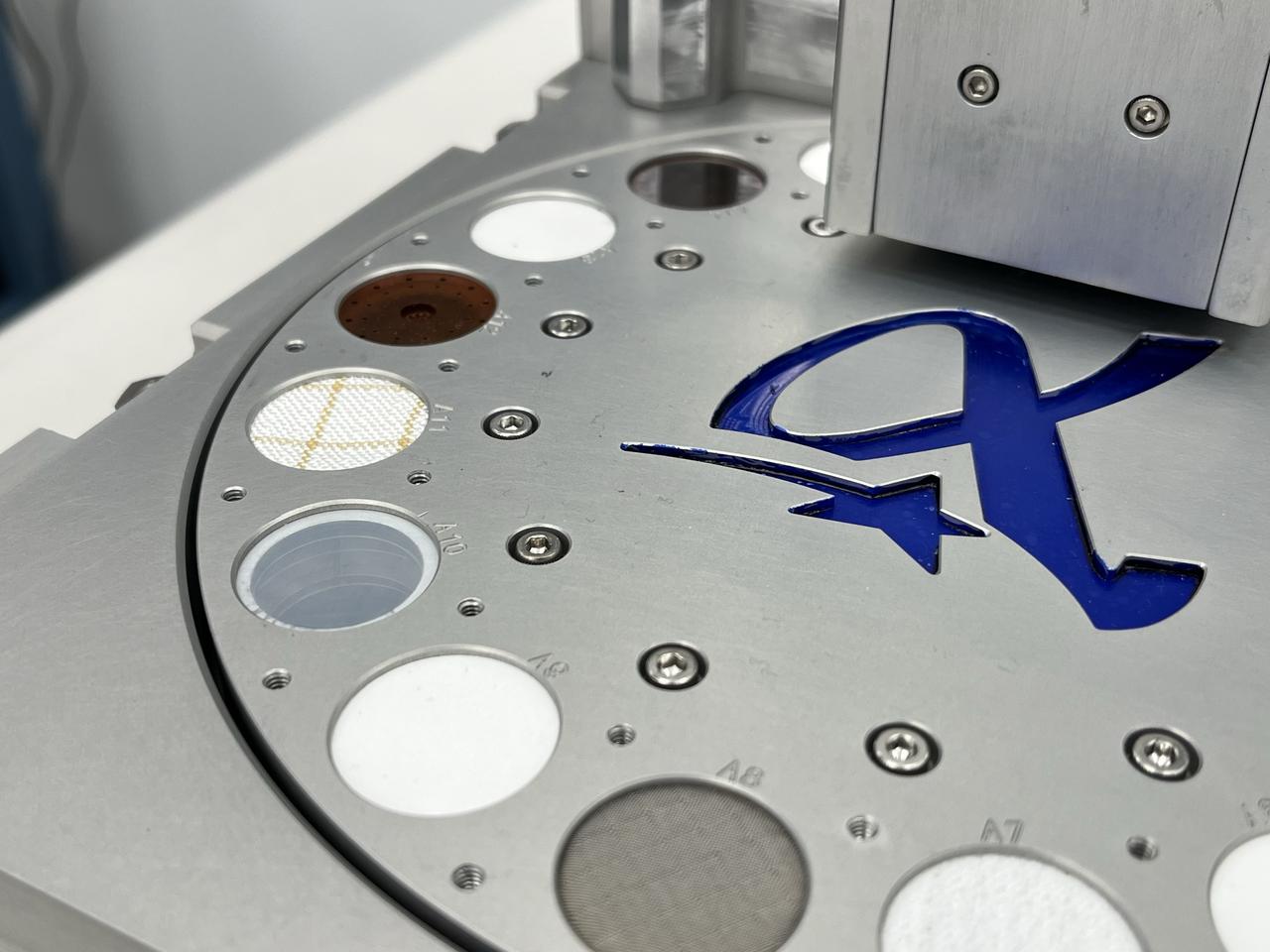
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
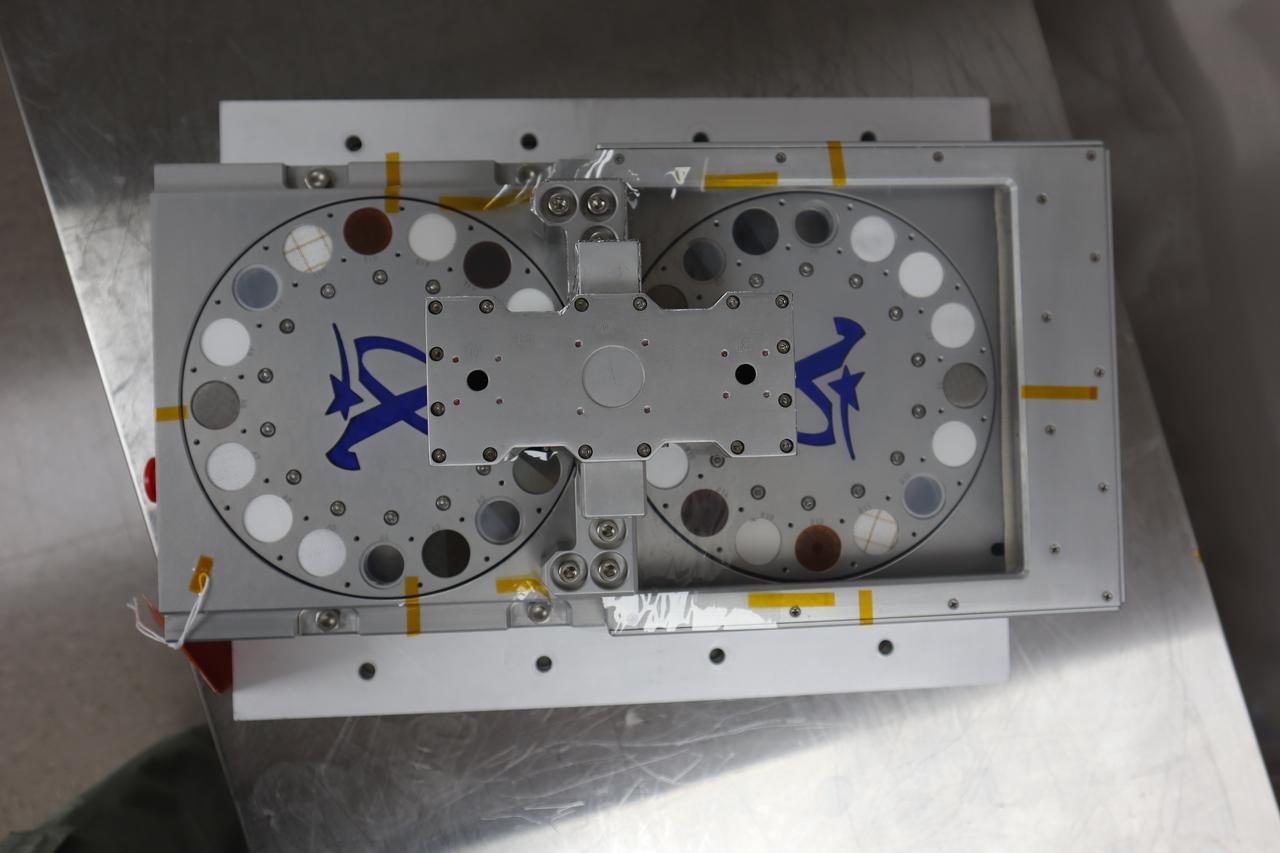
A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is planning to study how different materials react to the lunar environment. Regolith Adherence Characterization, or RAC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Aegis Aerospace, RAC’s wheels feature a series of different sample materials, helping researchers to better understand how lunar dust repels or attaches to each. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RAC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine talks with Barbara Cohen, associate project scientist for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland during a event where it was announced that nine U.S. companies are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
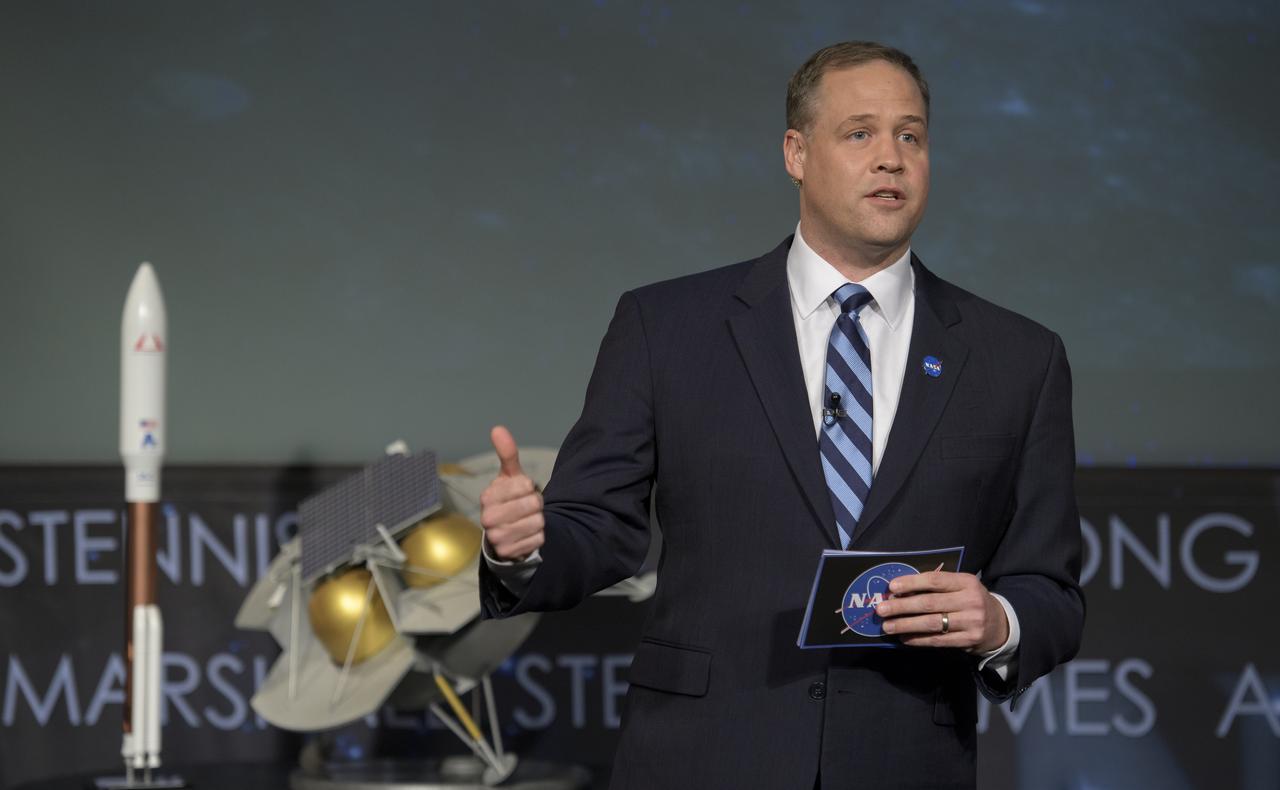

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine announces the nine U.S. companies that are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, answer questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
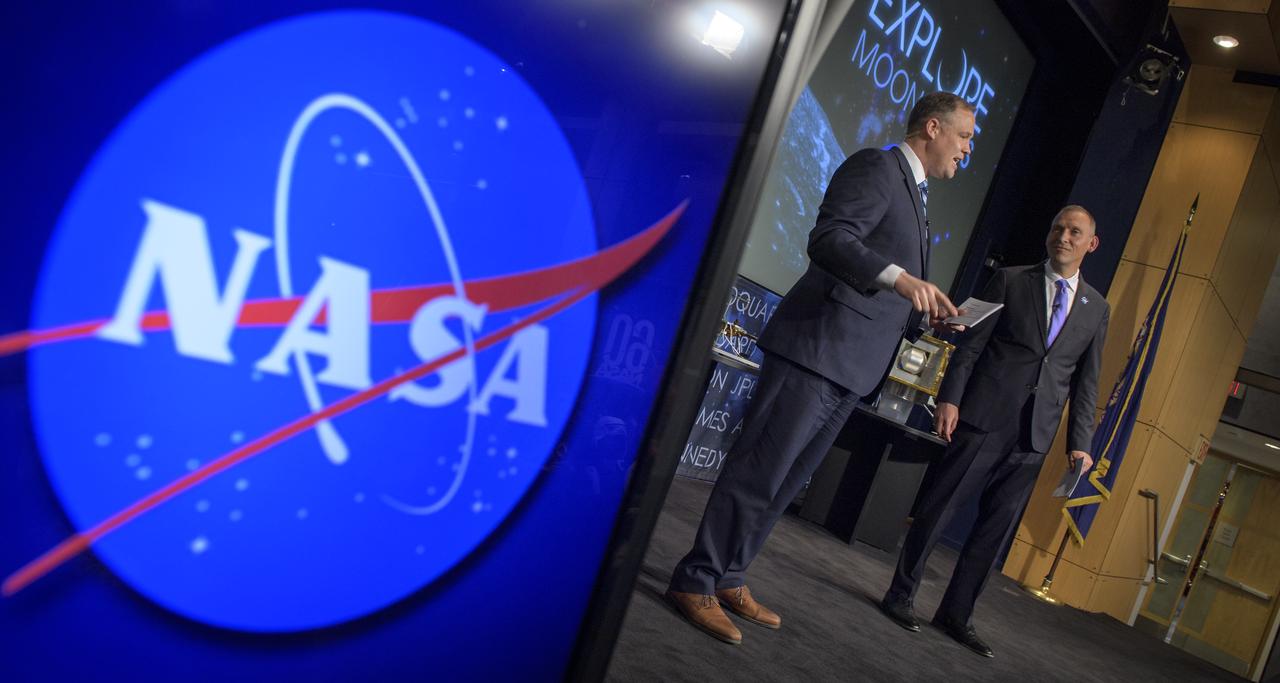

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, answer questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine talks via satellite with Andrea Mosie, Apollo sample laboratory manager, and NASA astronaut Stan Love from NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston during a event where it was announced that nine U.S. companies are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, answer questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Thalia Patrinos, and Jason Townsend from NASA's Social Media Teamm monitor questions coming in from social media during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
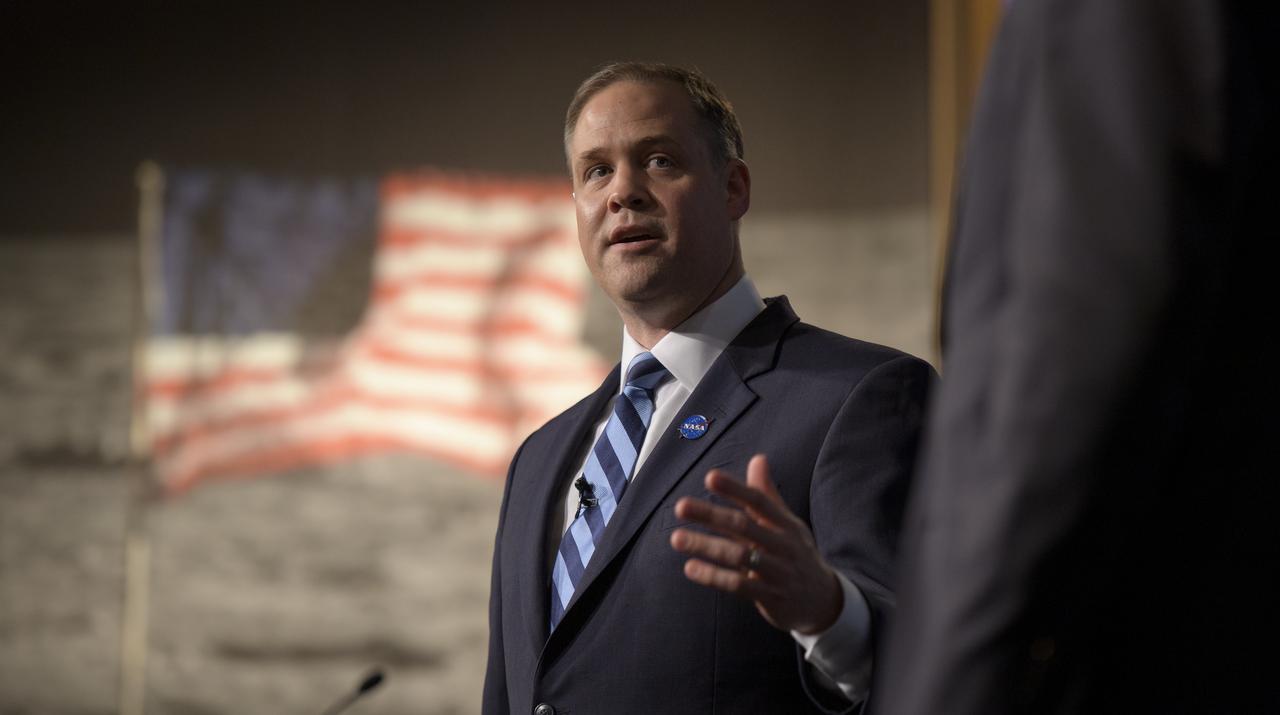

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine answers questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
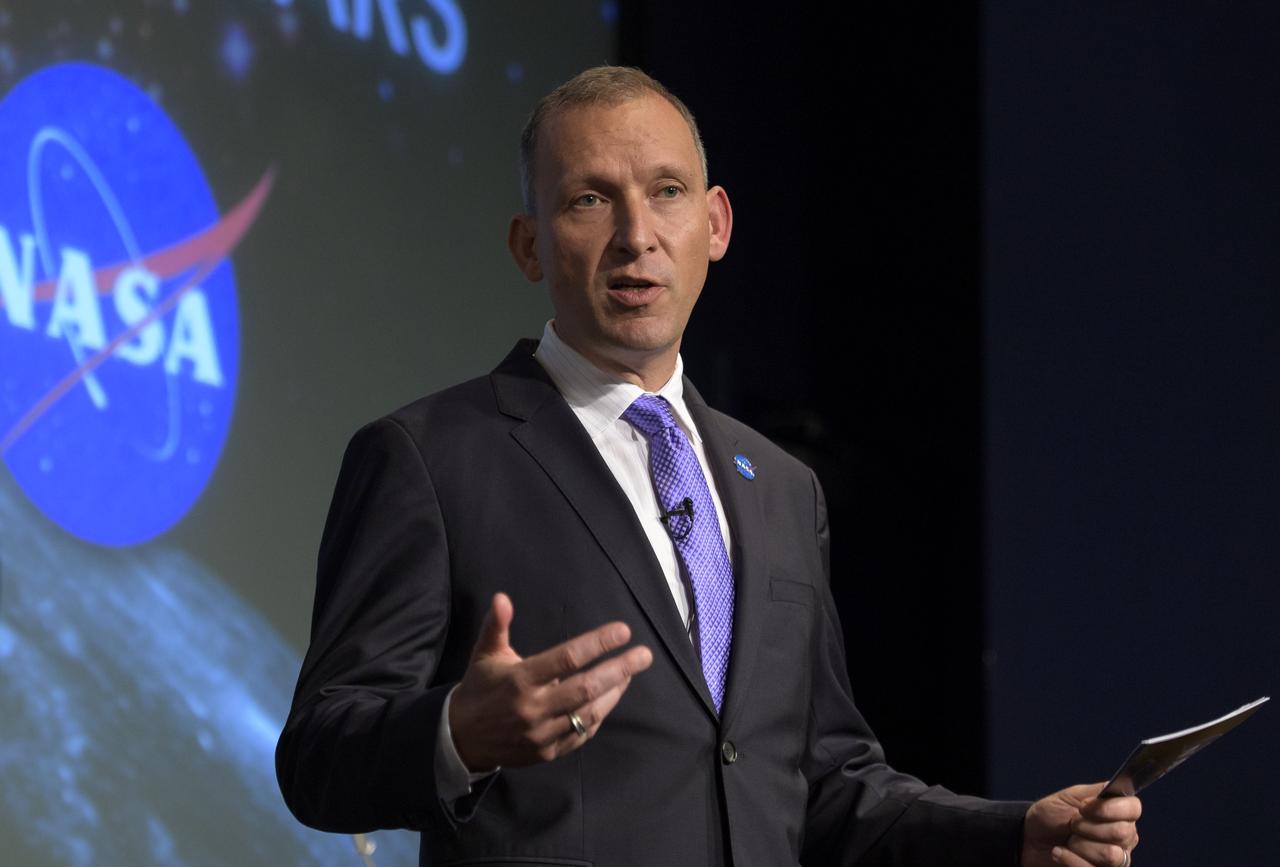

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, answers questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine talks via satellite with NASA astronaut Stan Love from NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston during an event where it was announced that nine U.S. companies are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine answers questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, answers questions during an event where nine U.S. companies where named as eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
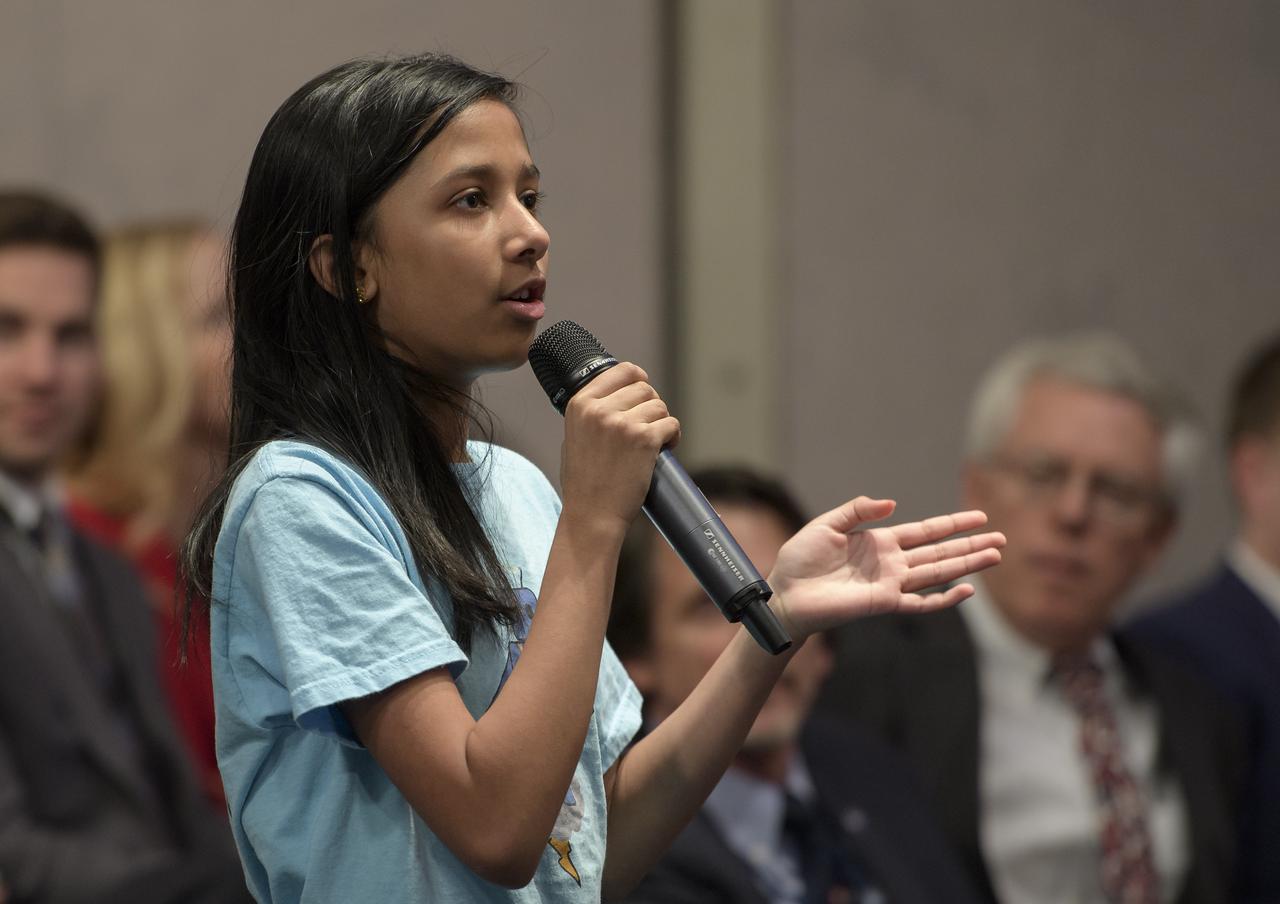

A Cascades Thunderbots "Robotics for Youth" team member from Sterling, Virginia asks a question during an Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) announcement, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Nine companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
A Nova Labs Robotics "BrainStorm Troopers" team member from Reston, Virginia asks a question during an Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) announcement, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Nine companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
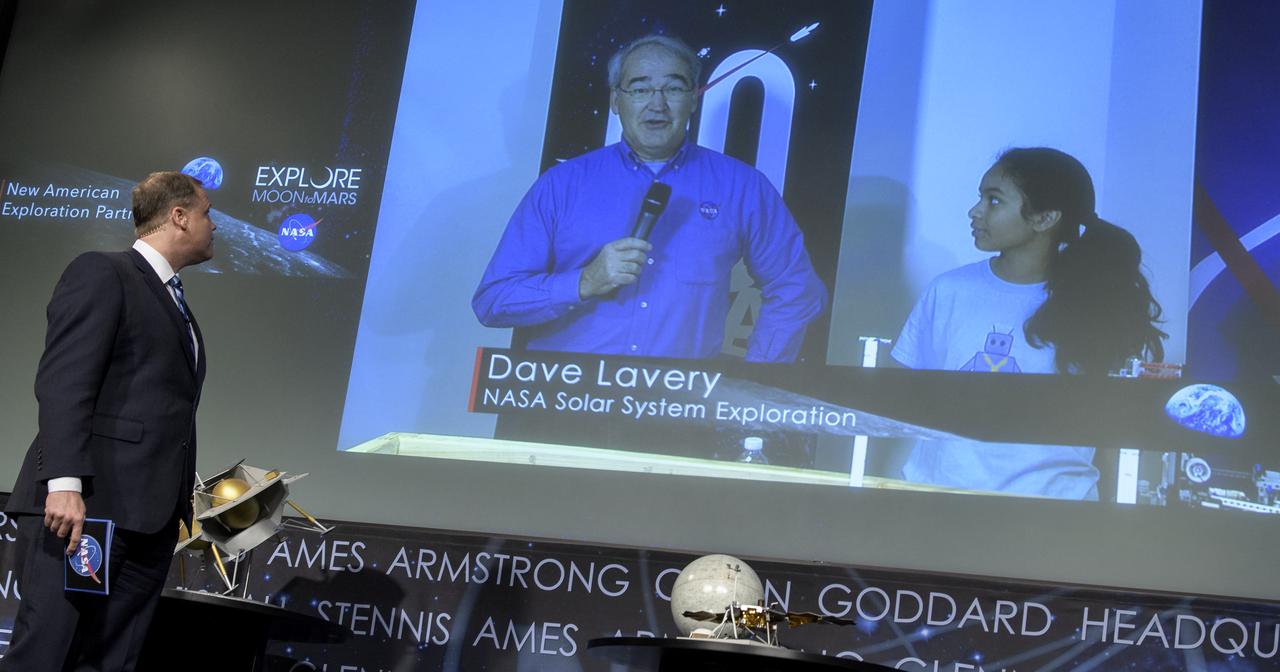
NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine talks with Dave Lavery, Program Executive for Solar System Exploration, and Dishaa Bhat, 14, from Mary Henderson Middle School in Falls Church, Virginia, during a event where it was announced that nine U.S. companies are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The companies will be able to bid on delivering science and technology payloads for NASA, including payload integration and operations, launching from Earth and landing on the surface of the Moon. NASA expects to be one of many customers that will use these commercial landing services. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
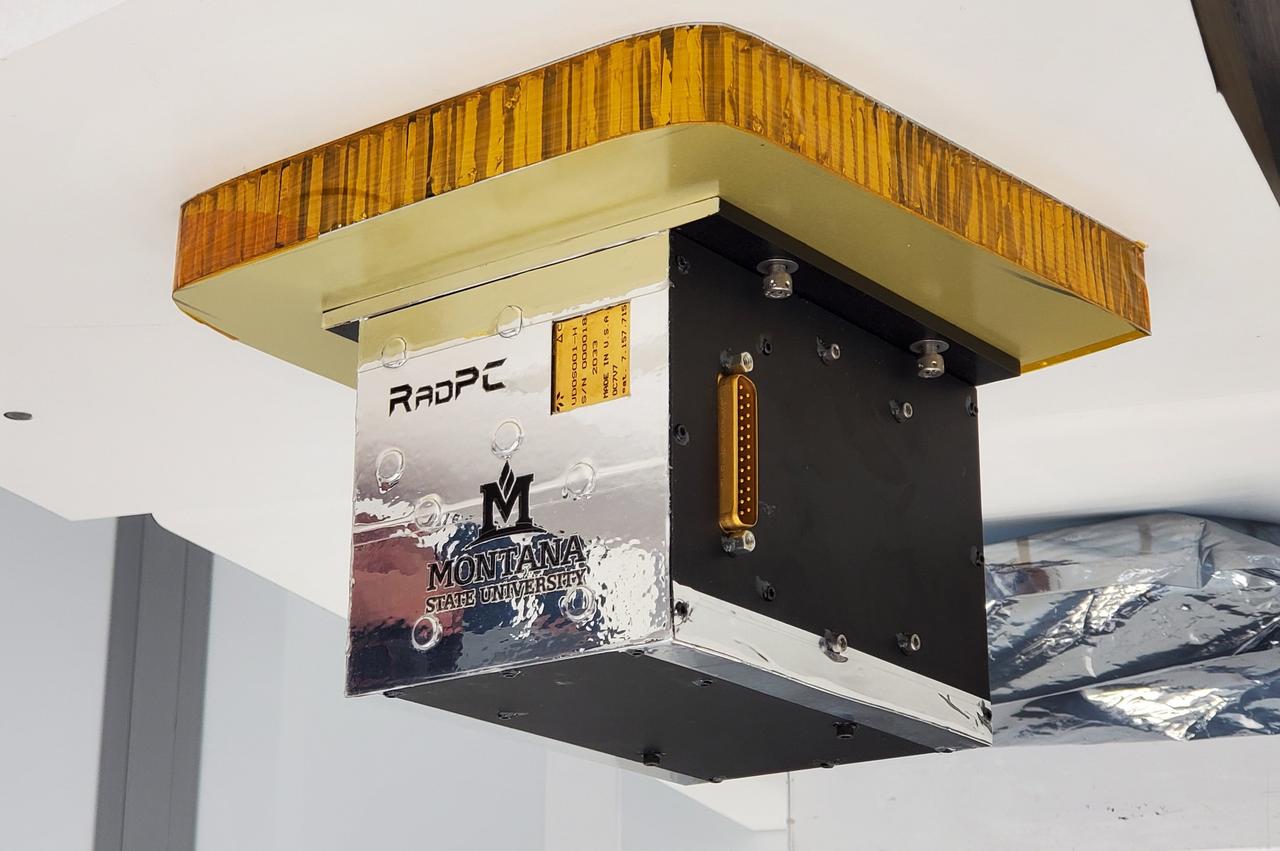

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help mitigate radiation effects on computers in space. Radiation Tolerant Computer, or RadPC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Montana State University in Bozeman, RadPC is designed designed to demonstrate computer recovery from faults caused by single-event effects of ionizing radiation. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RadPC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
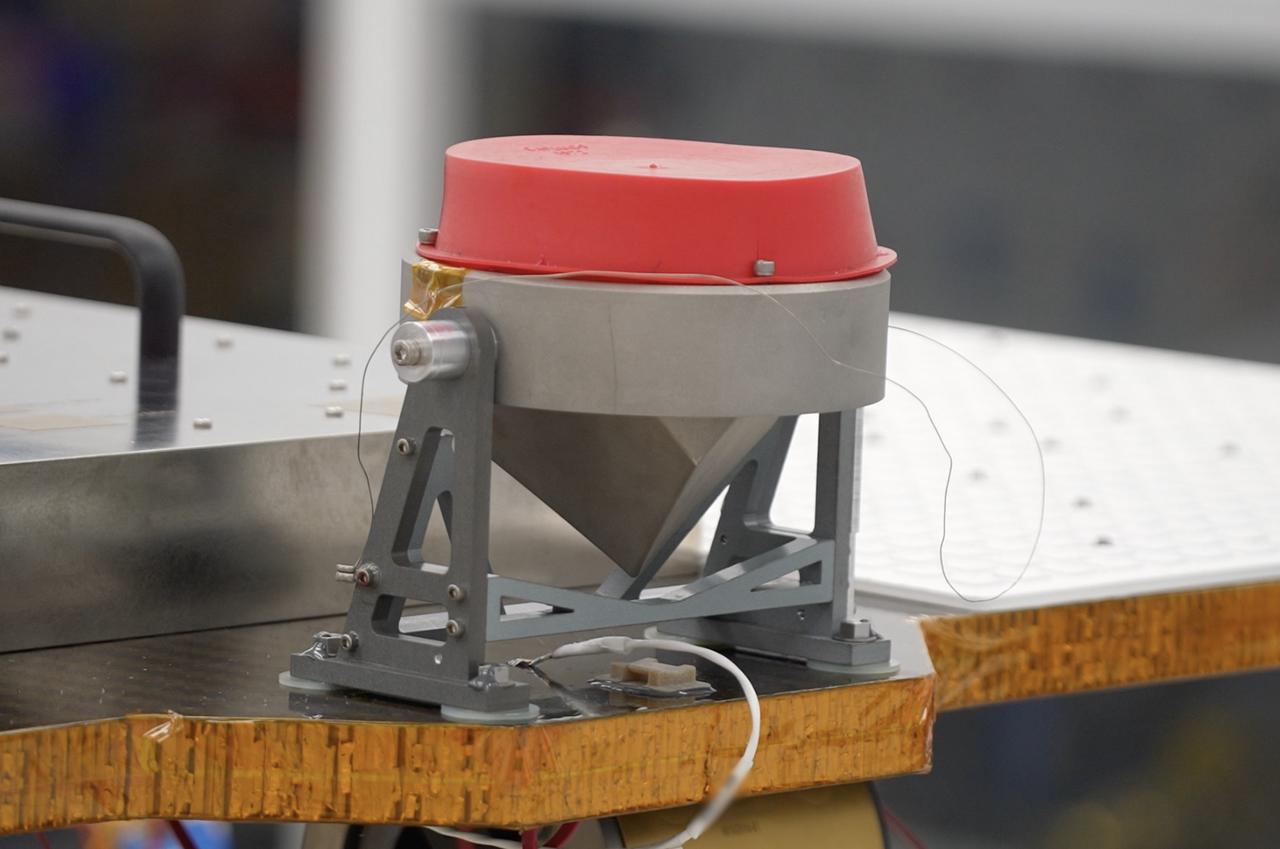

A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative is expected to significantly expand our knowledge of the Moon. Next Generation Lunar Retroreflector, or NGLR-1, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by the University of Maryland in College Park, NGLR-1 is designed to reflect very short laser pulses from Earth-based lunar laser ranging observatories using a retroreflector, or a mirror designed to reflect the incoming light back in the same incoming direction. Investigations and demonstrations, such as NGLR-1, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
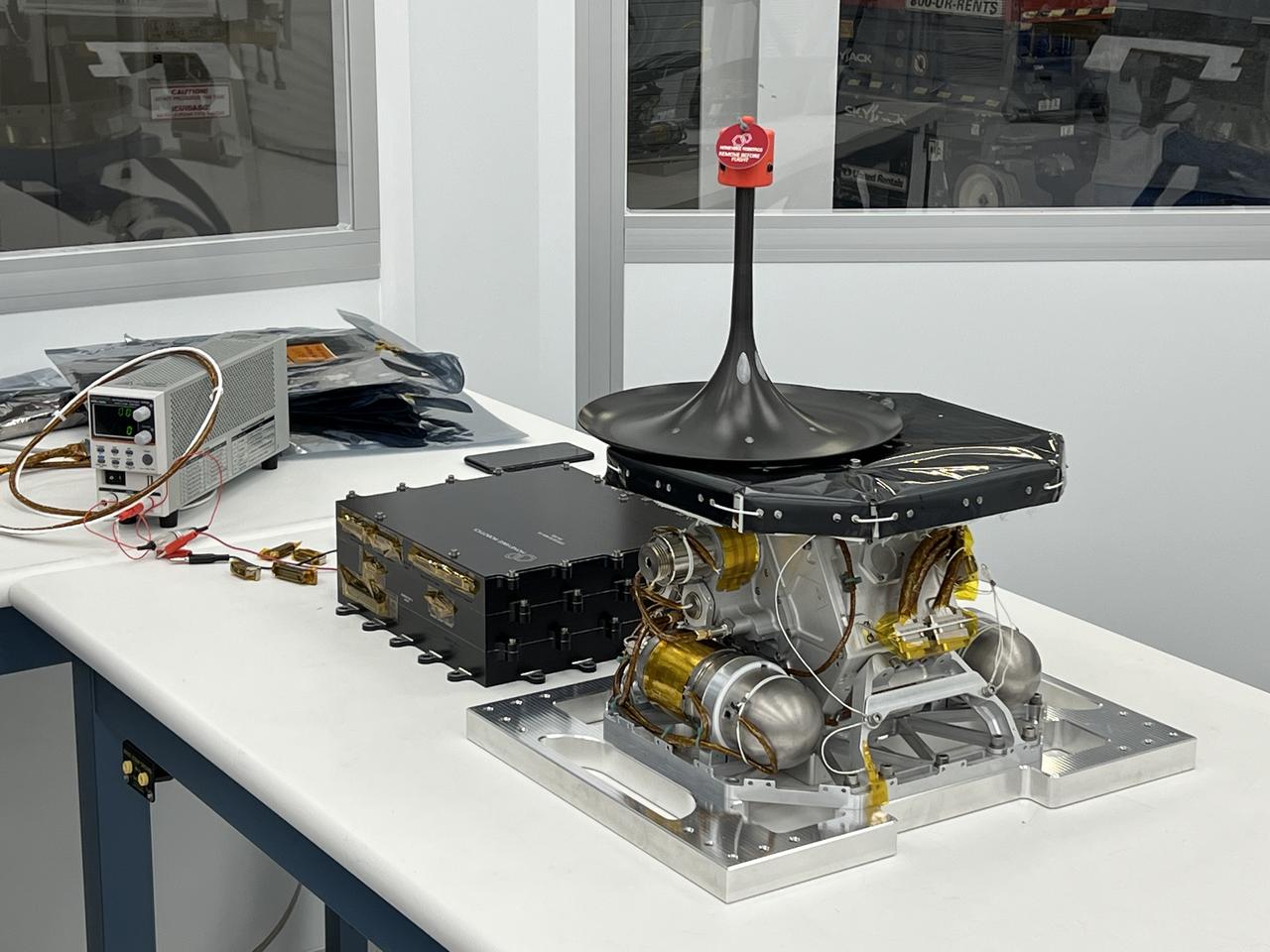

A science instrument flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help improve our understanding of the Moon. The Lunar Instrumentation for Subsurface Thermal Exploration with Rapidity, or LISTER, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed jointly by Texas Tech University and Honeybee Robotics, LISTER’s planned mission is to measure the flow of heat from the Moon’s interior using a specialized drill. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LISTER, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development and operations for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, left, and NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen, right, pose for a photograph with the representatives of the nine U.S. companies that are eligible to bid on NASA delivery services to the lunar surface through Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) contracts, Thursday, Nov. 29, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. The representatives of the companies are: Steve Altemus, President and CEO of Intuitive Machines; 2nd from left, Sean Mahoney, CEO, Masten Space Systems Inc; Eric Salwan, Director of Commercial Business Development, Firefly Aerospace; Jennifer Jensen, Vice President, National Security & Space, Draper; Joe Landon, VP of Advanced Programs, Commercial Civil Space, Lockheed Martin Space; Steve Bailey, Deep Space Systems Inc; Daven Maharaj, Chief Operating Officer, Moon Express Inc; John Thornton, CEO, Astrobotic Technology Inc; and Jeff Patton, Chief Engineering Advisor, Orbit Beyond Inc, 2nd from right. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
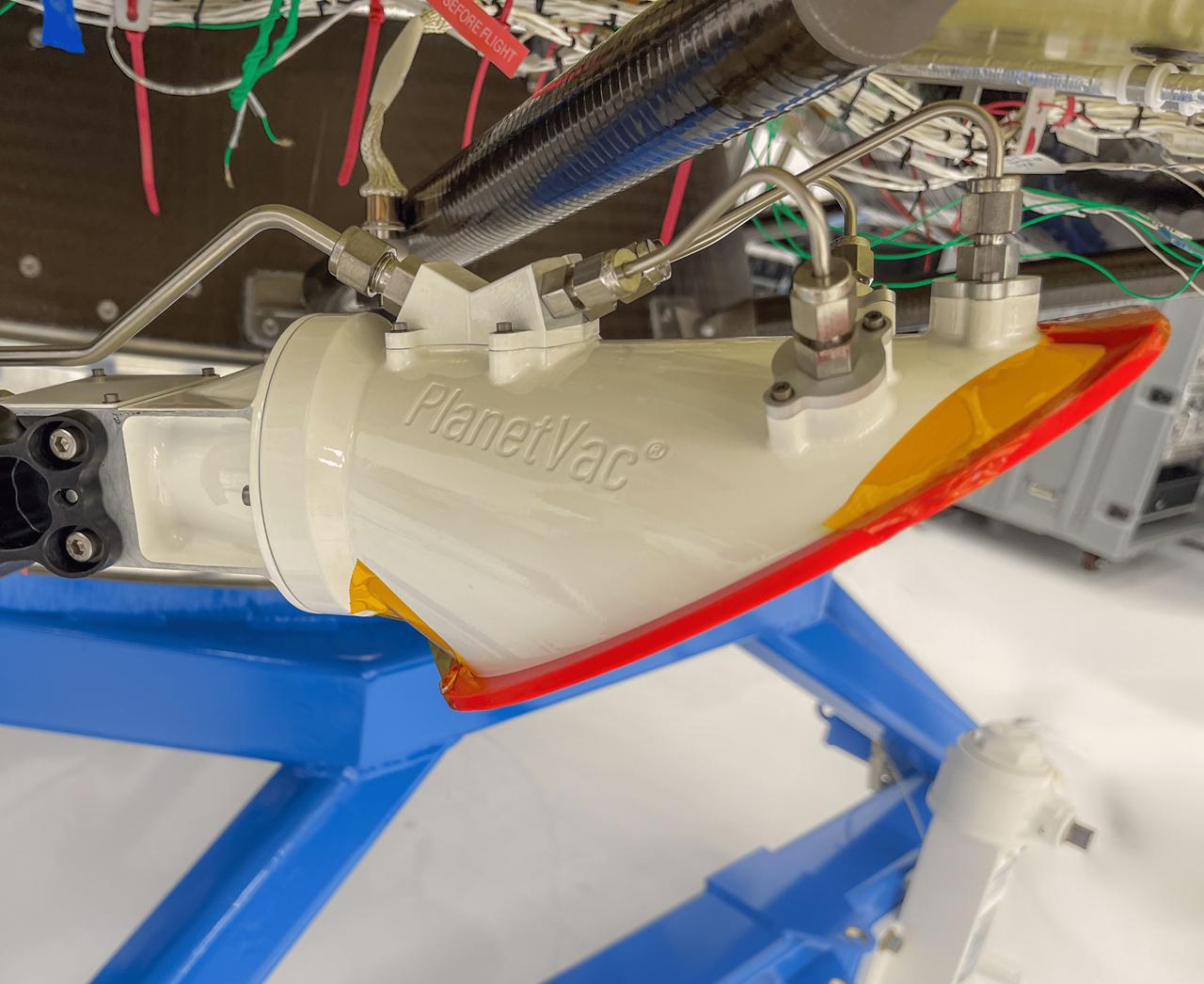

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
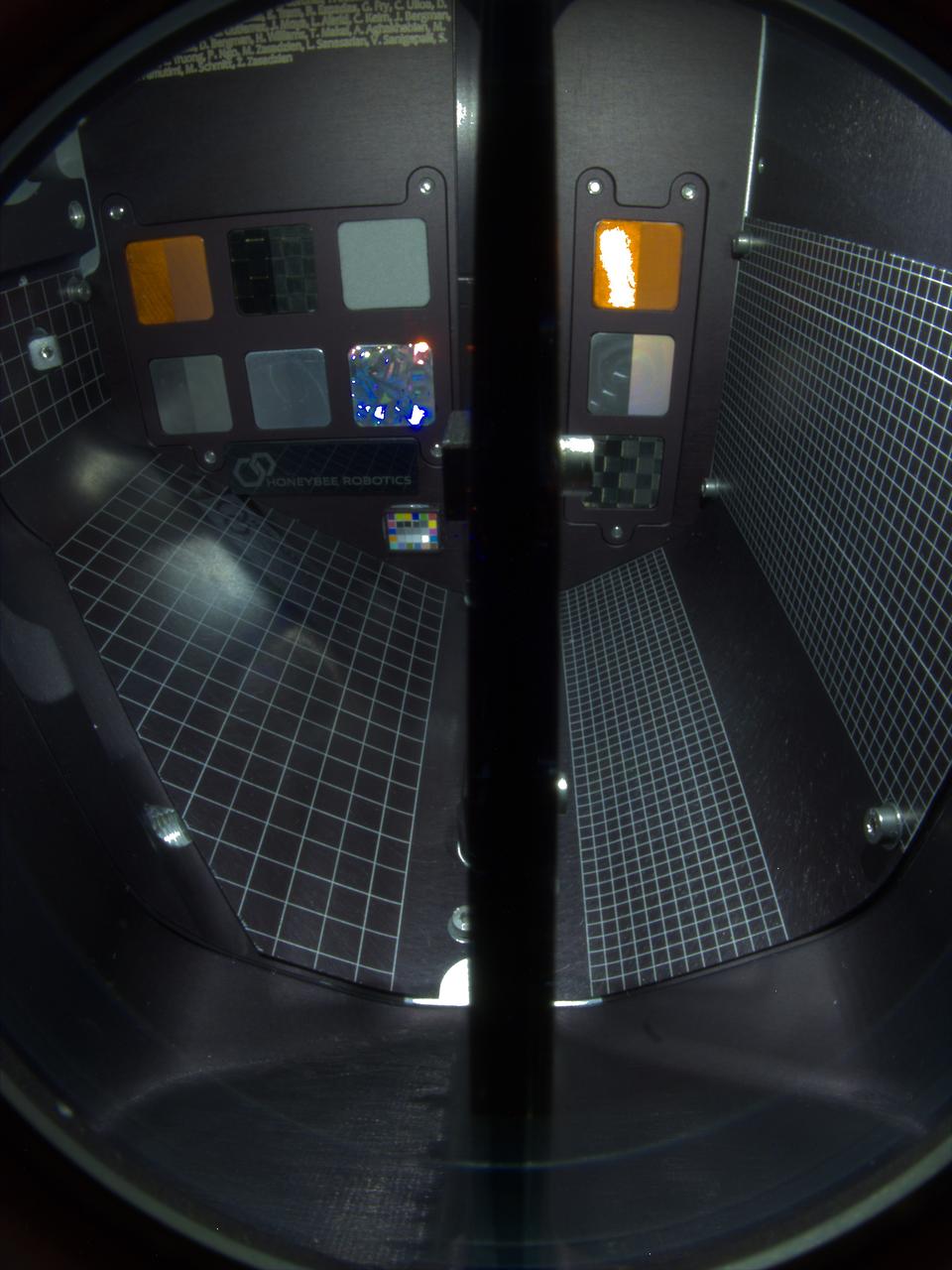

A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could change how research teams collect and study soil and rock samples on other planetary bodies. Lunar PlanetVac, or LPV, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Honeybee Robotics, a Blue Origin company of Altadena, California, LPV is designed to, essentially, operate as a vacuum cleaner with a pneumatic, compressed gas-powered sample acquisition and delivery system to efficiently collect and transfer lunar soil from the surface to other science instruments or sample return containers. Investigations and demonstrations, such as LPV, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.

Lunar Commericial Payload Services Announcement was made at Godddard May 31, 2019. Tom Zurbuchen, AA Science Mission Directorate congratulated three companies for providing first lunar landers for Artemis: Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines and OrbitBeyond

Goddard Space Flight Center employees are seen looking at the lunar landers from above, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
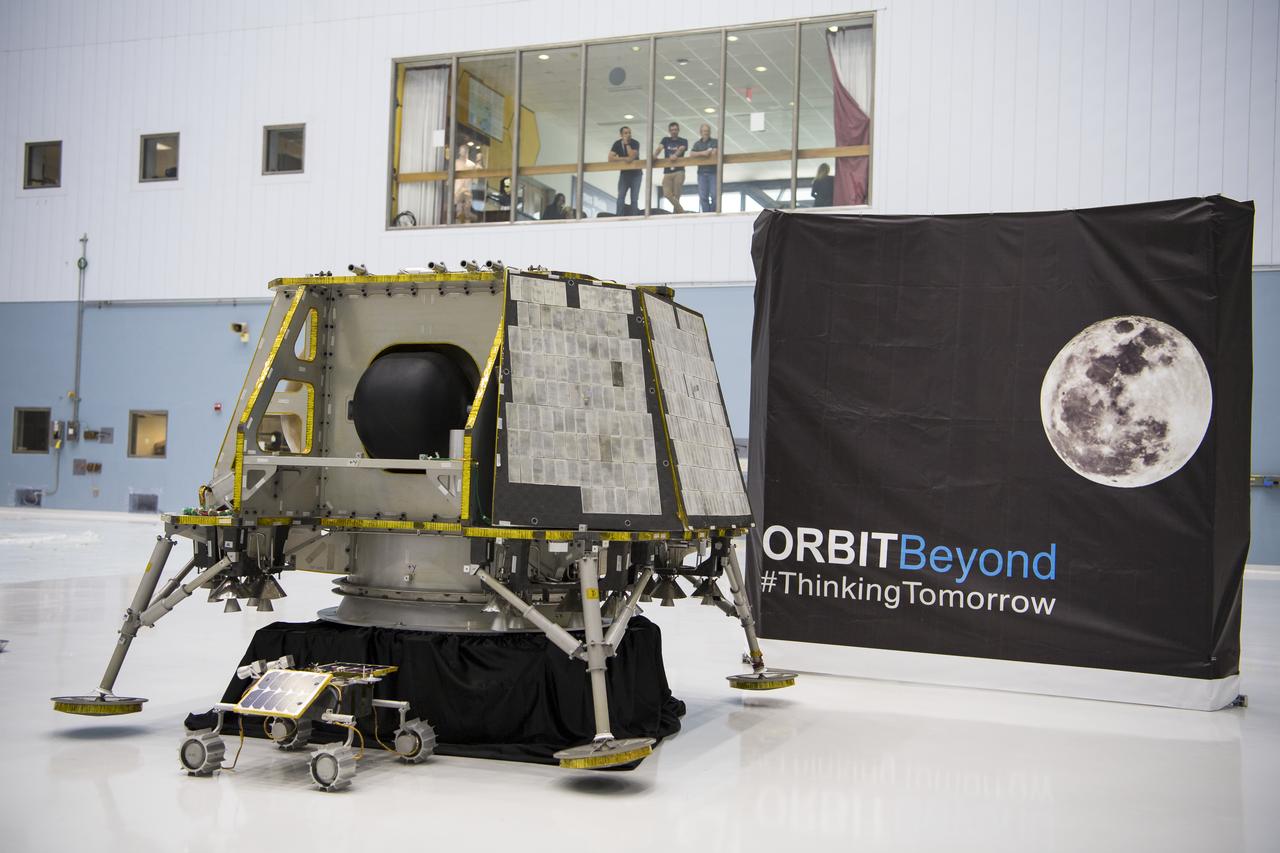

The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
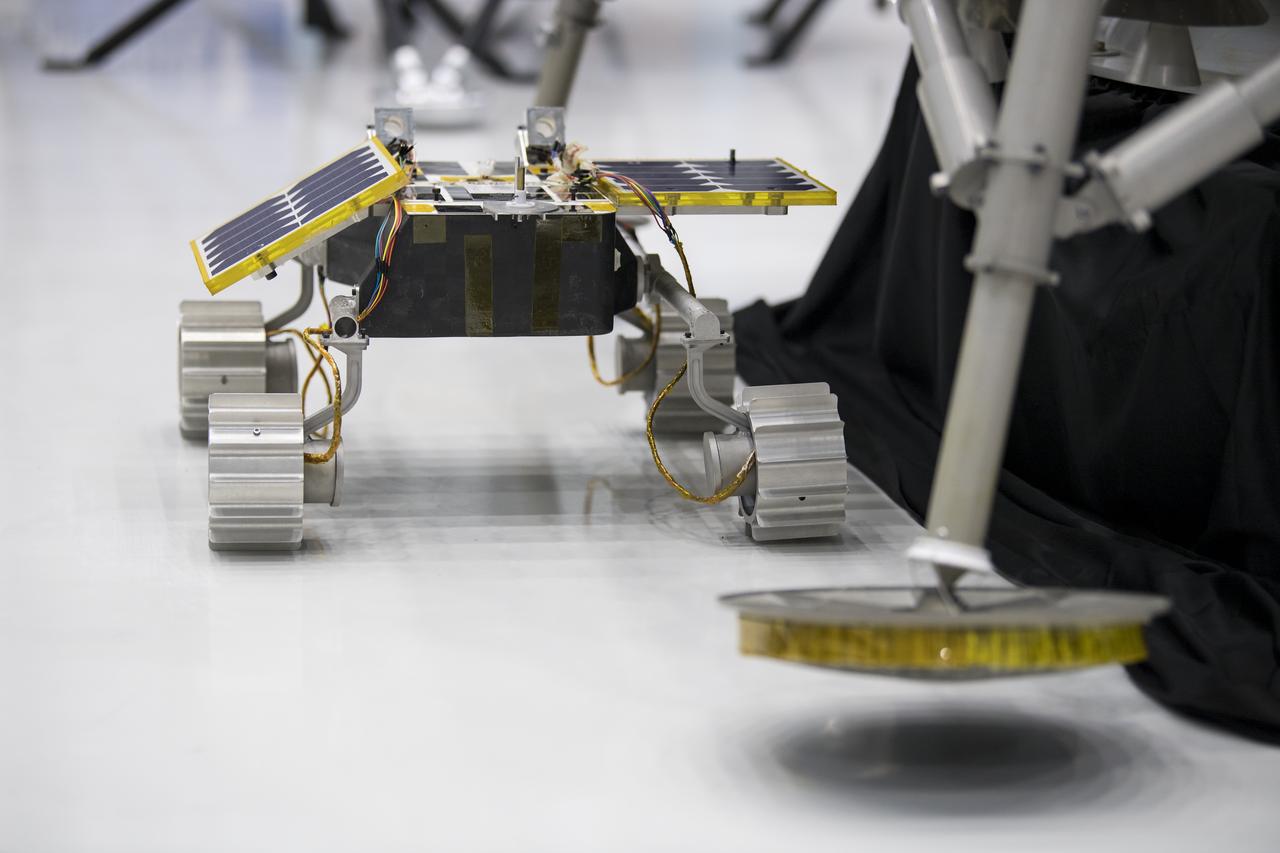

The OrbitBeyond lunar rover is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
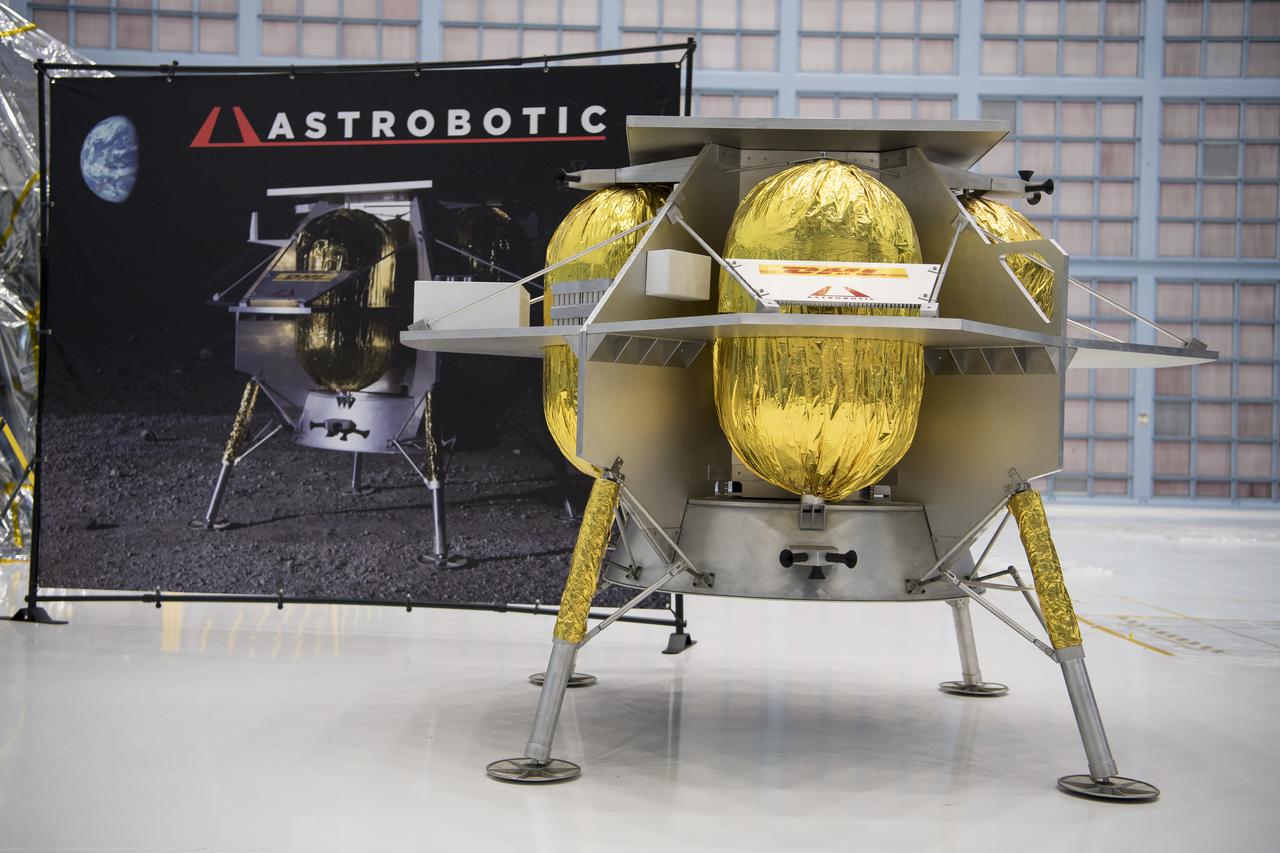

The Astrobotic lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
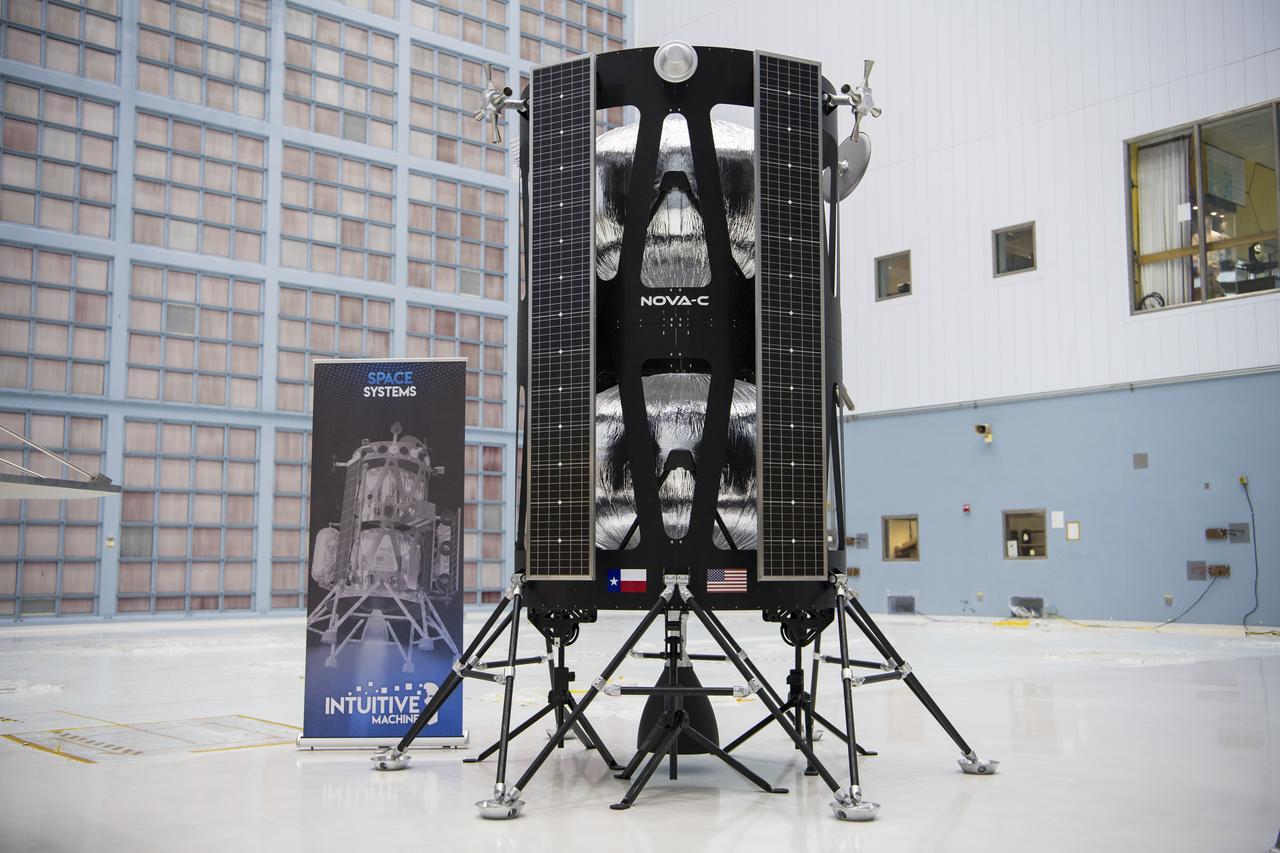

The Intuitive Machines lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
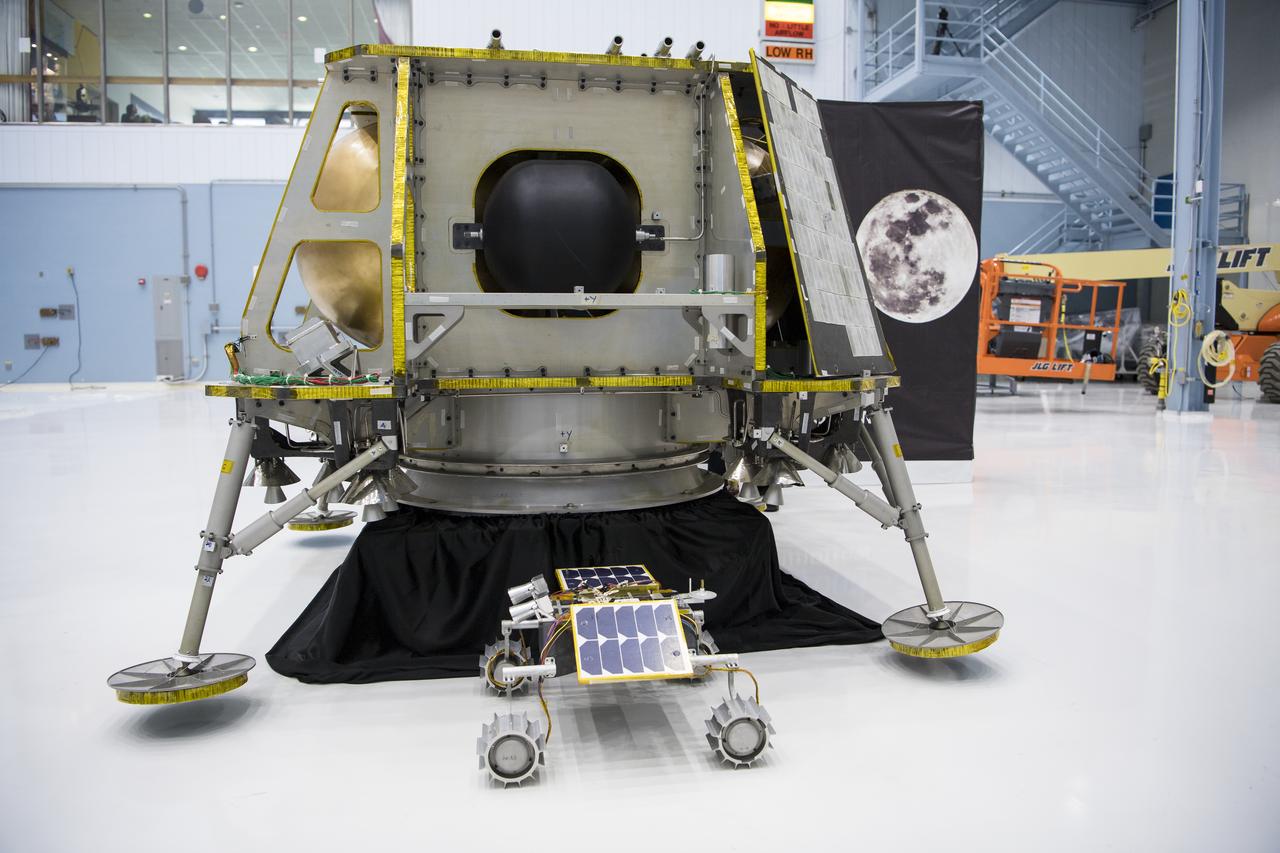

The OrbitBeyond lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
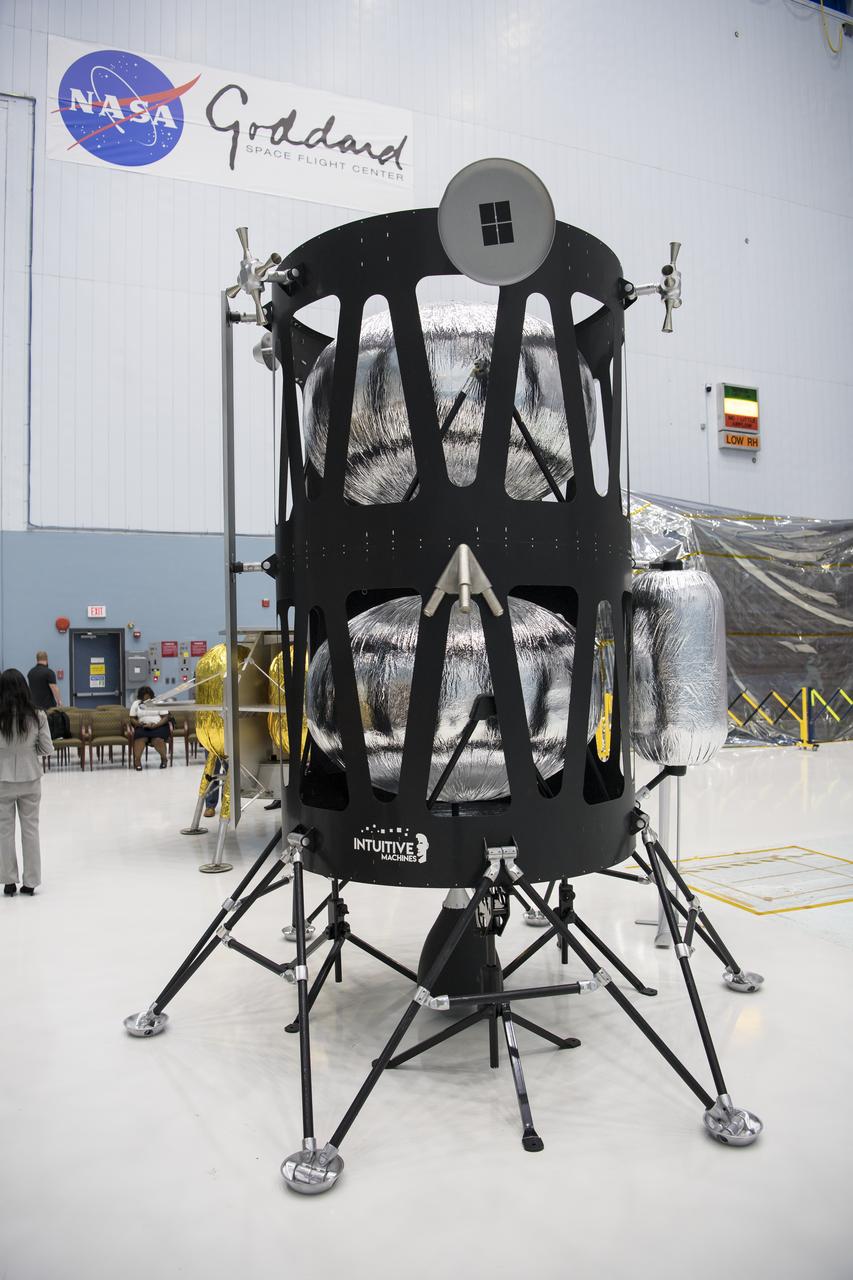

The Intuitive Machines lunar lander is seen, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

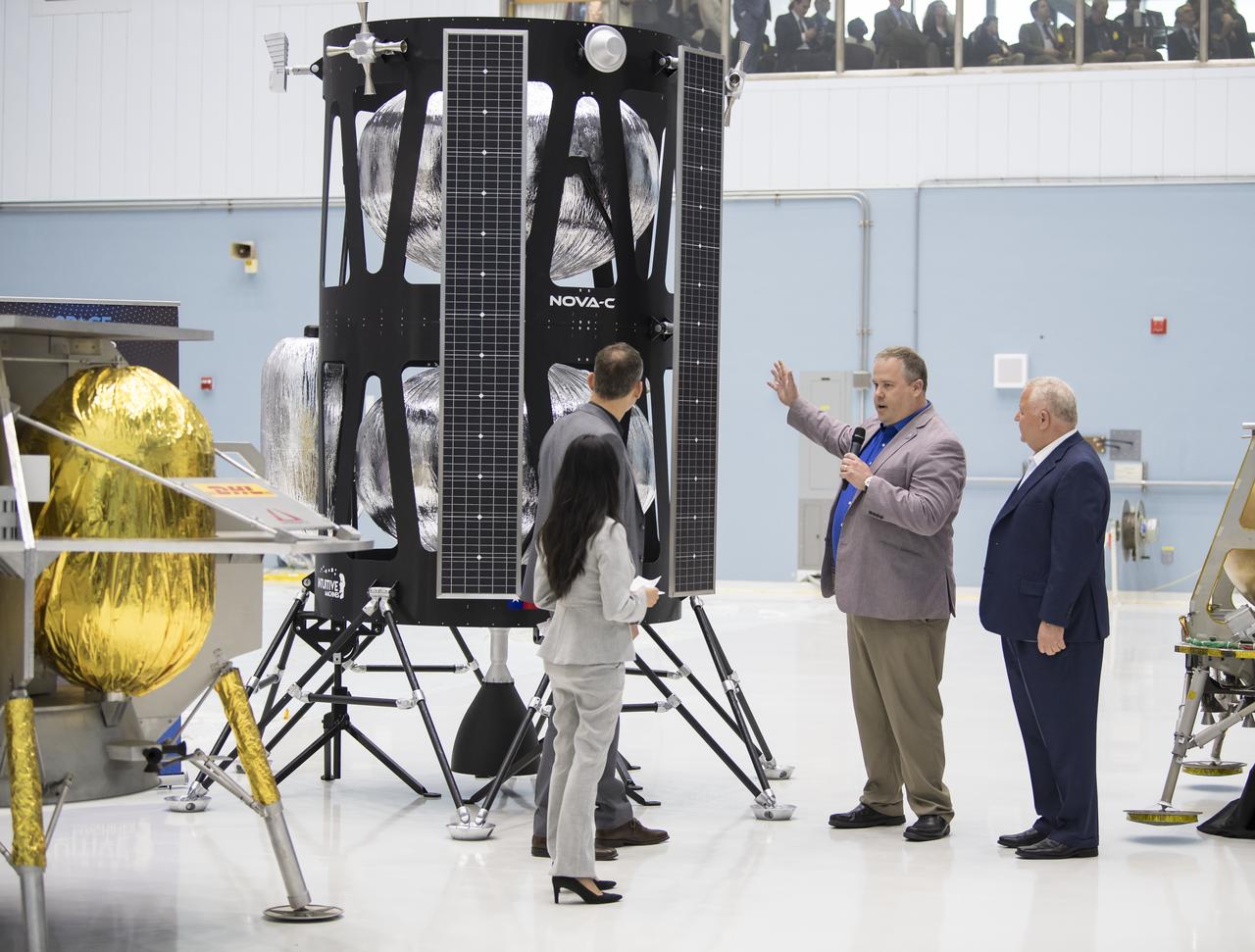
Vice President of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, speaks about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Press Officer Felicia Chou, introduces a pre-recorded video announcement by NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine about the companies selected to provide the first commercial lunar landers, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Intuitive Machines, Astrobotic, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, left, and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, speak about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
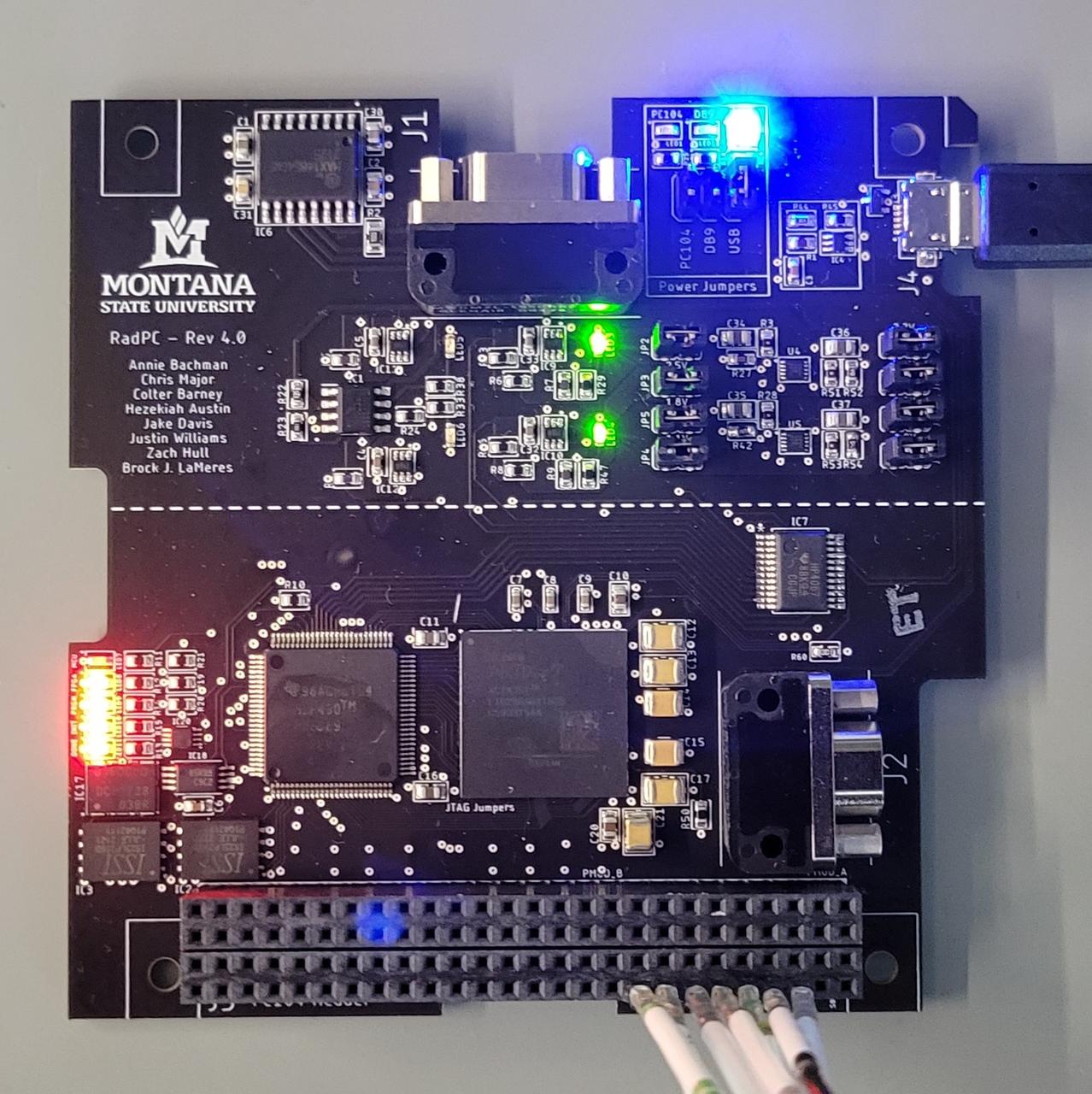
A technology demonstration flying aboard the next delivery for NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative could help mitigate radiation effects on computers in space. Radiation Tolerant Computer, or RadPC, is one of 10 payloads set to be carried to the Moon by the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander in 2025. Developed by Montana State University in Bozeman, RadPC is designed designed to demonstrate computer recovery from faults caused by single-event effects of ionizing radiation. Investigations and demonstrations, such as RadPC, launched on CLPS flights will help NASA study Earth’s nearest neighbor under Artemis and pave the way for future crewed missions on the Moon. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the development for seven of the 10 CLPS payloads that will be carried on Firefly’s Blue Ghost lunar lander.
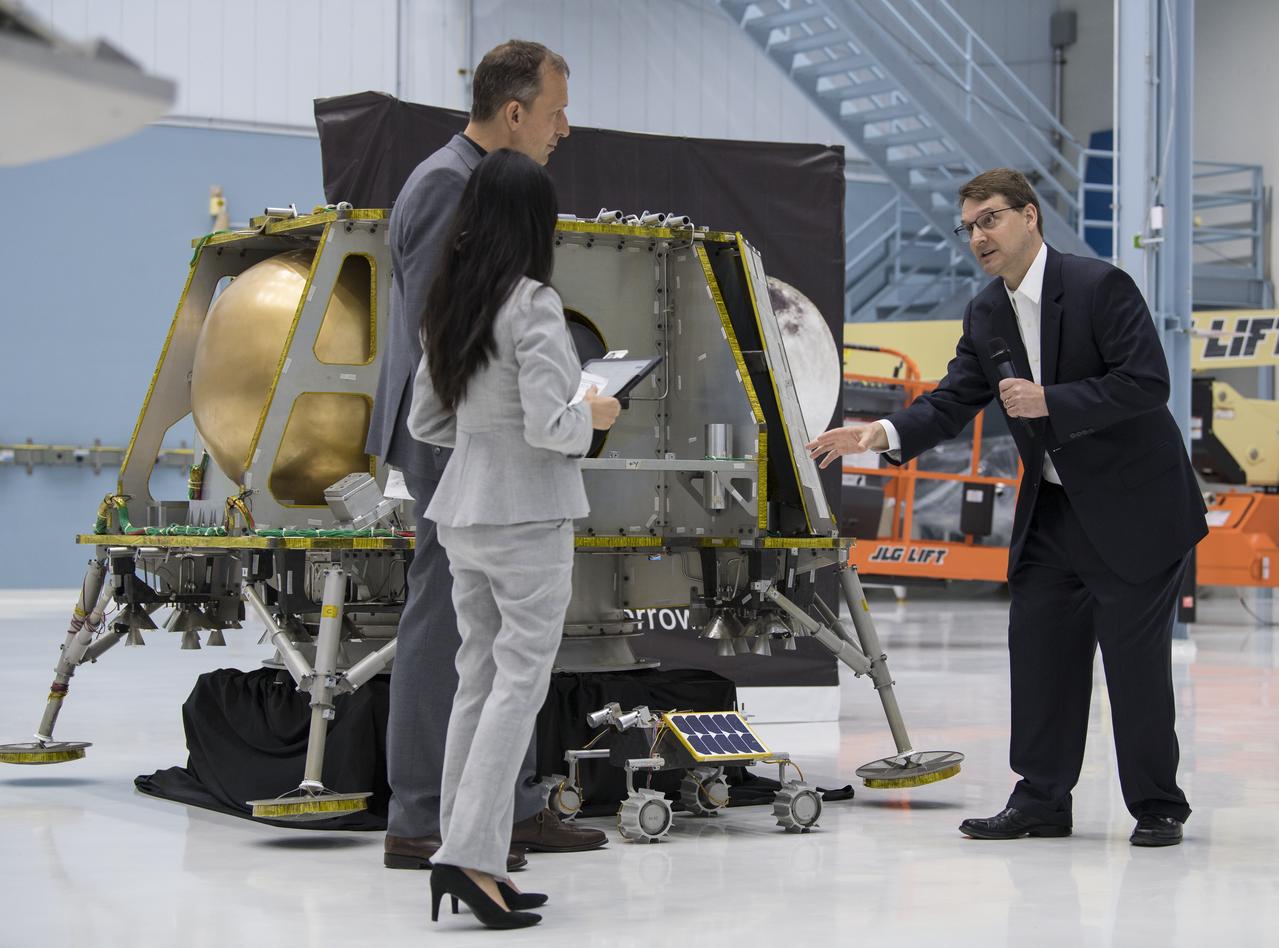

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second left, listens as Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, speaks about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
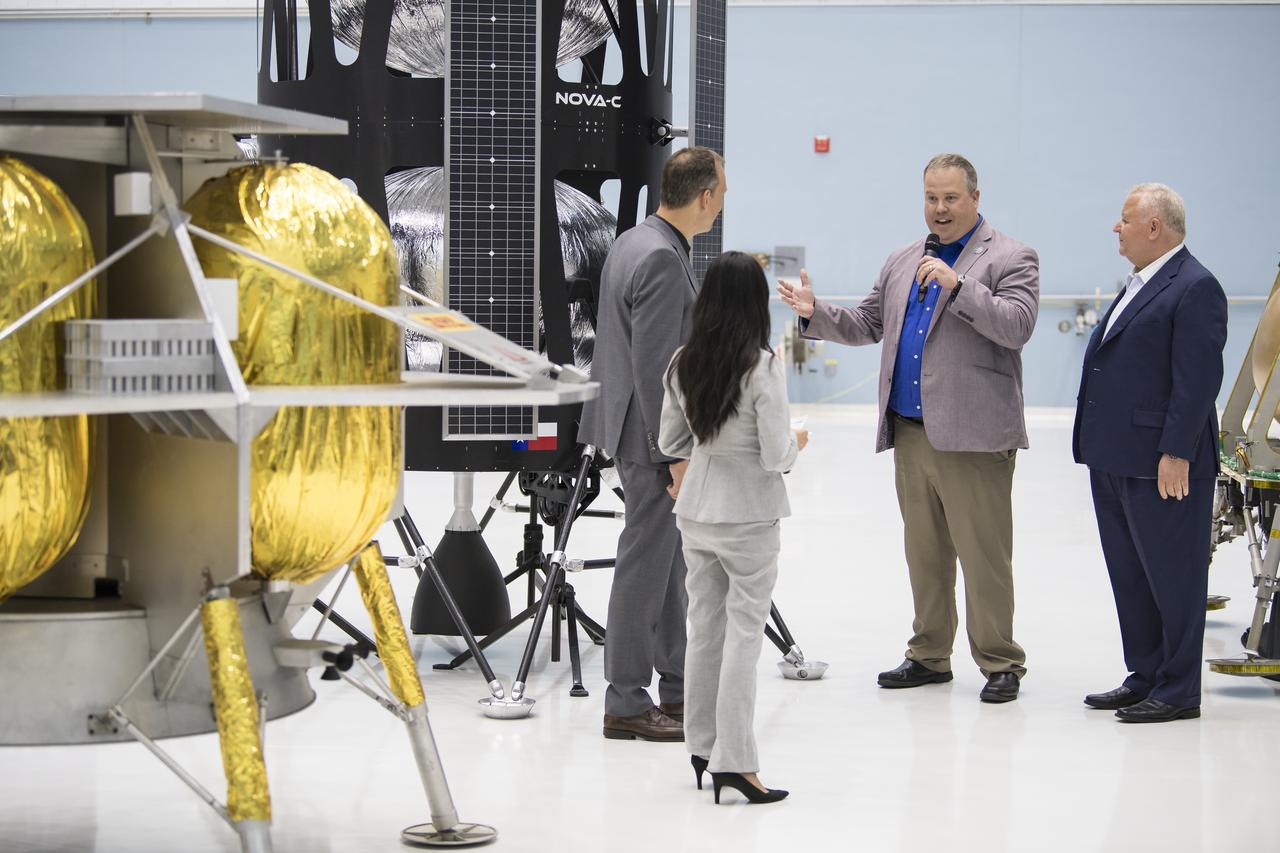

VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, speaks with NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
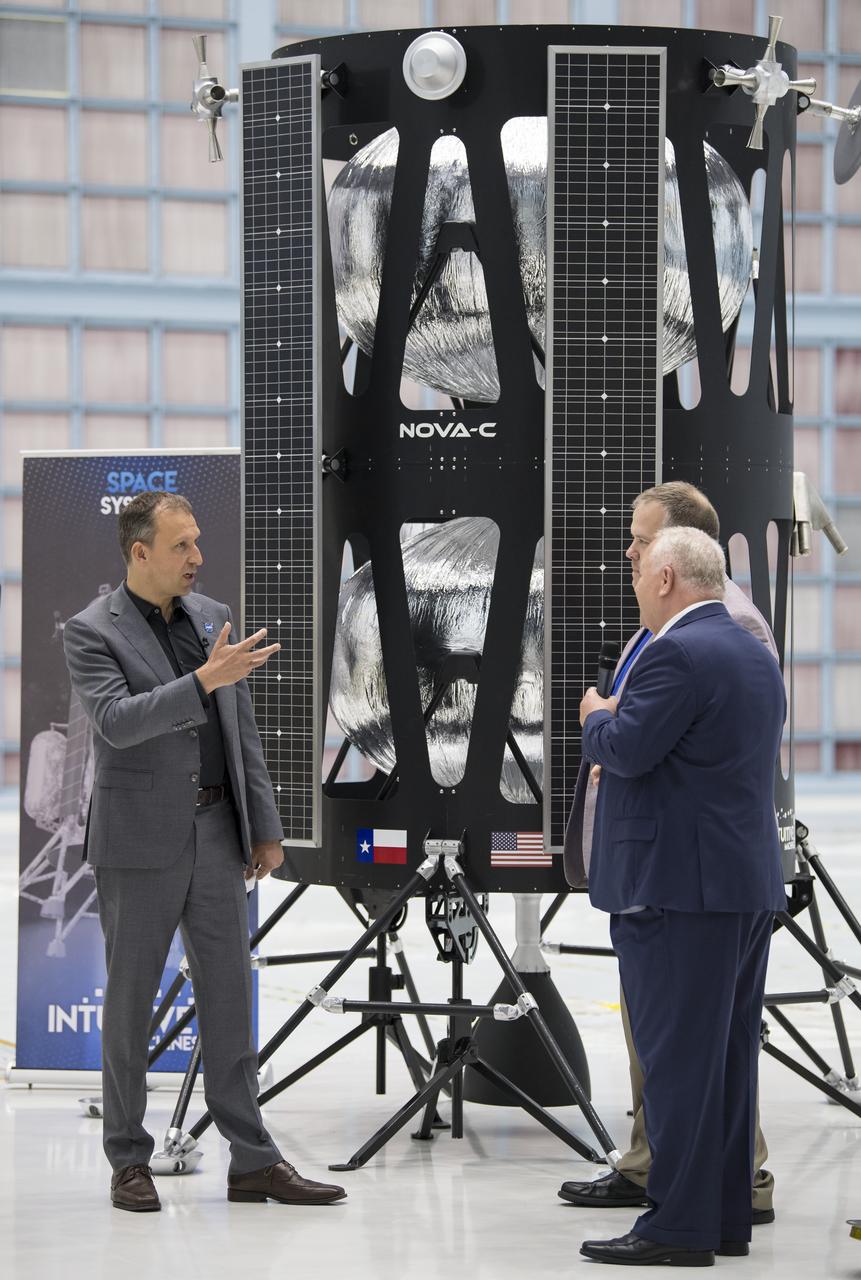

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, left, speaks to, Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian, right, and VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, second from left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
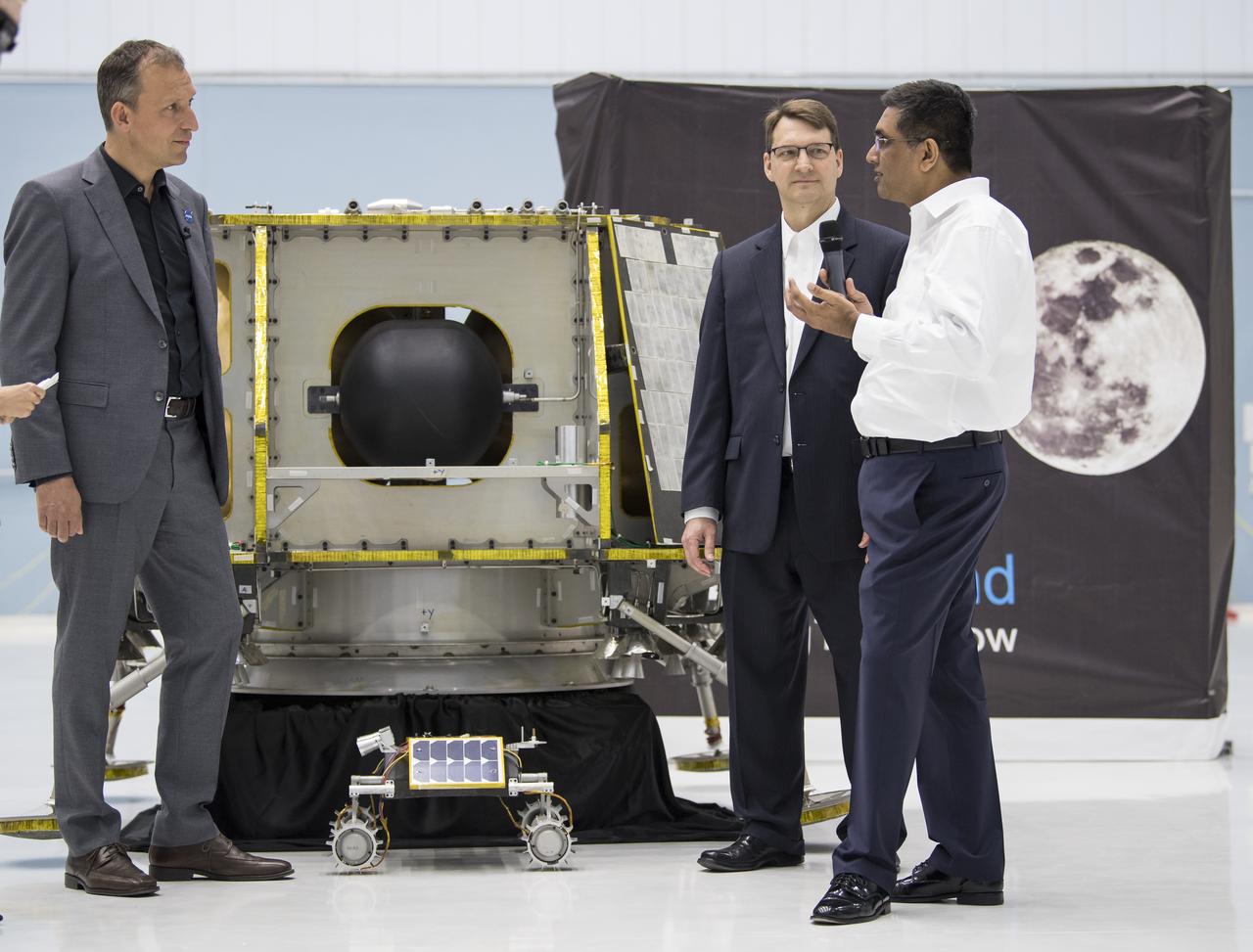

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, left, speaks to, President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, right, and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain, second from right, speaks with NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
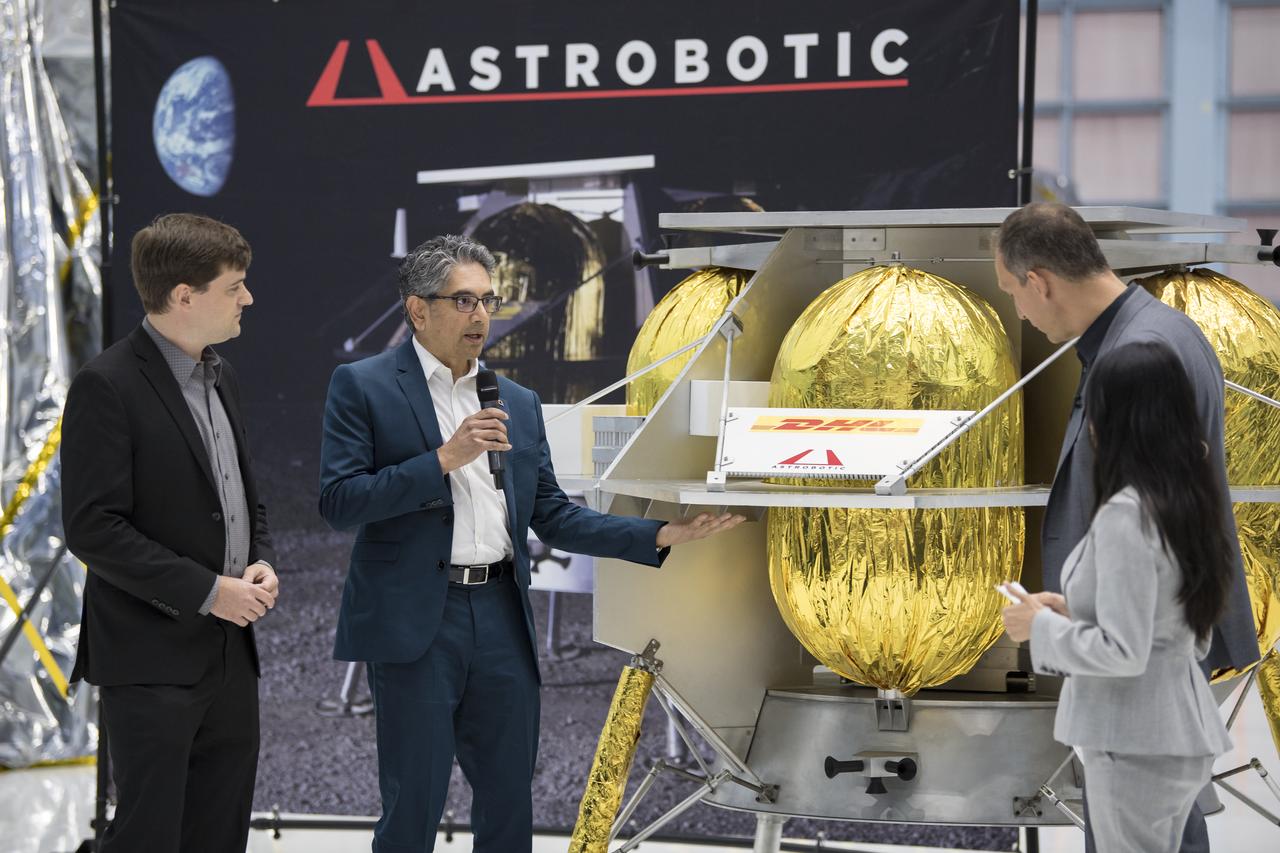

NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen, second from right, speaks to Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, left, and Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran, second from left, about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.

Ahead of launch as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, Astrobotic’s Peregrine lunar lander is preparing to be encapsulated in the payload fairing, or nose cone, of United Launch Alliance’s Vulcan rocket on Nov. 21, 2023, at Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Launch of Astrobotic’s Peregrine Mission One will carry NASA and commercial payloads to the Moon in early 2024 to study the lunar exosphere, thermal properties, and hydrogen abundance of the lunar regolith, magnetic fields, and the radiation environment of the lunar surface.
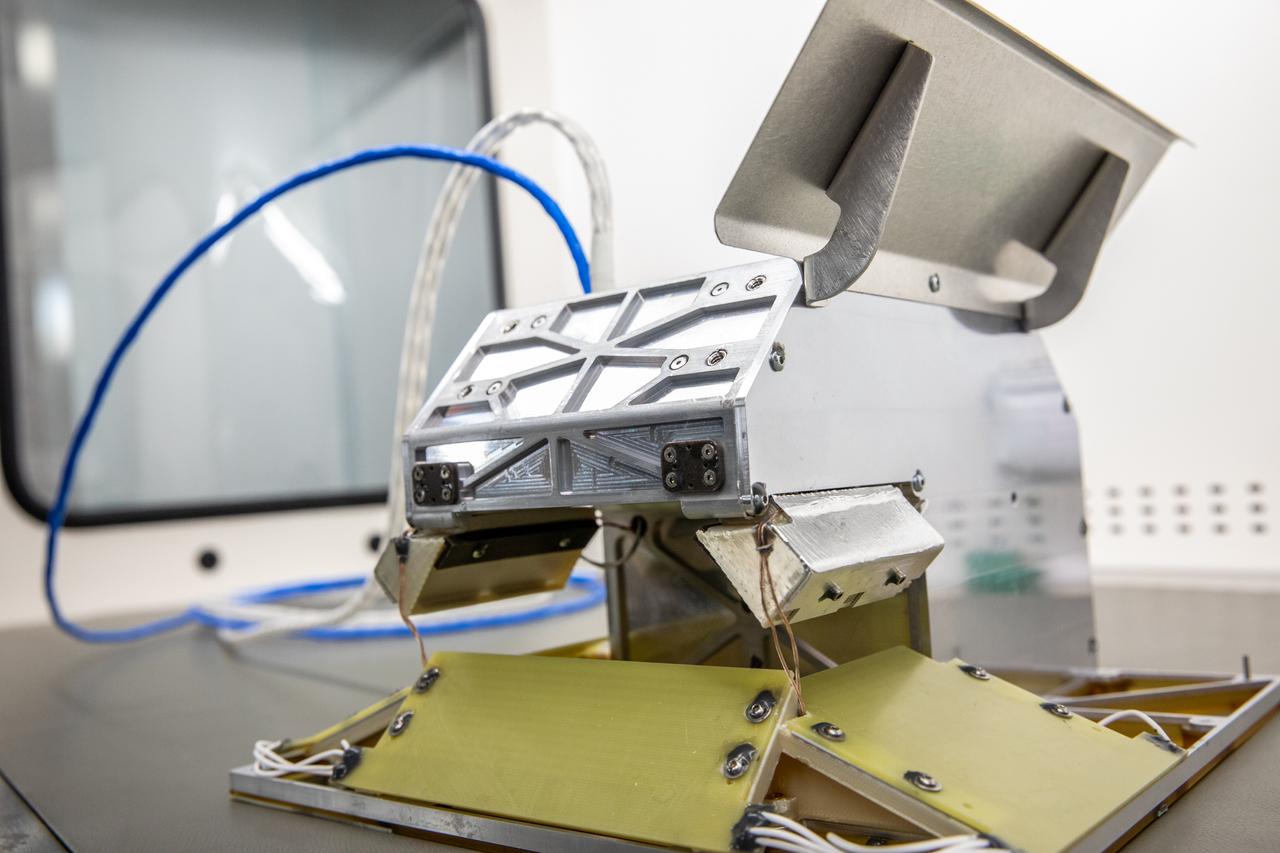
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
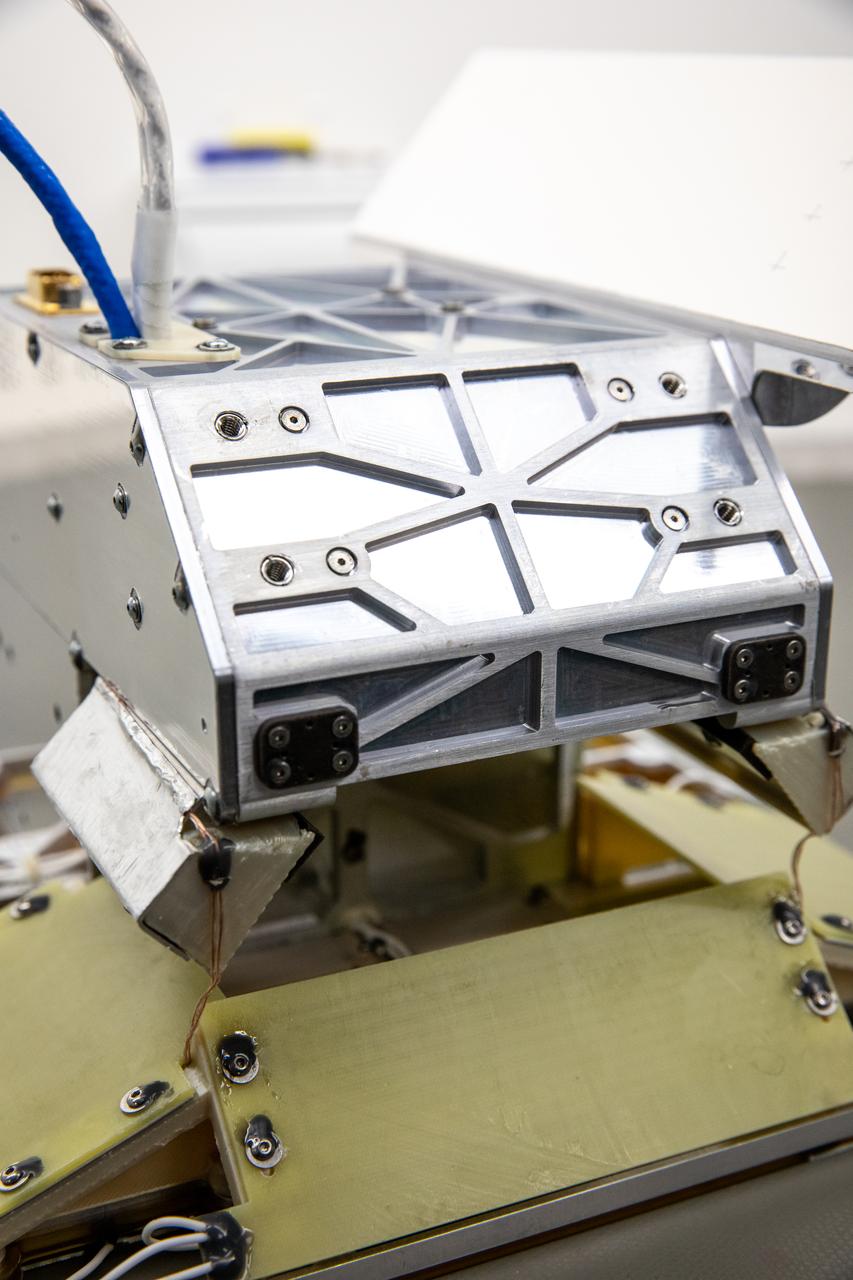
Inside of the Electrostatics and Surface Physics Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an electrodynamic dust shield (EDS) is in view on Jan. 18, 2023. The dust shield is one of the payloads that will fly aboard Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative. During the mission, EDS will generate a non-uniform electric field using varying high voltage on multiple electrodes. This traveling field, in turn, carries away the particles and has potential applications in thermal radiators, spacesuit fabrics, visors, camera lenses, solar panels, and many other technologies. The CLPS initiative is a key part of NASA’s Artemis lunar exploration efforts. The science and technology payloads sent to the Moon’s surface as part of the initiative will help lay the foundation for human missions and a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
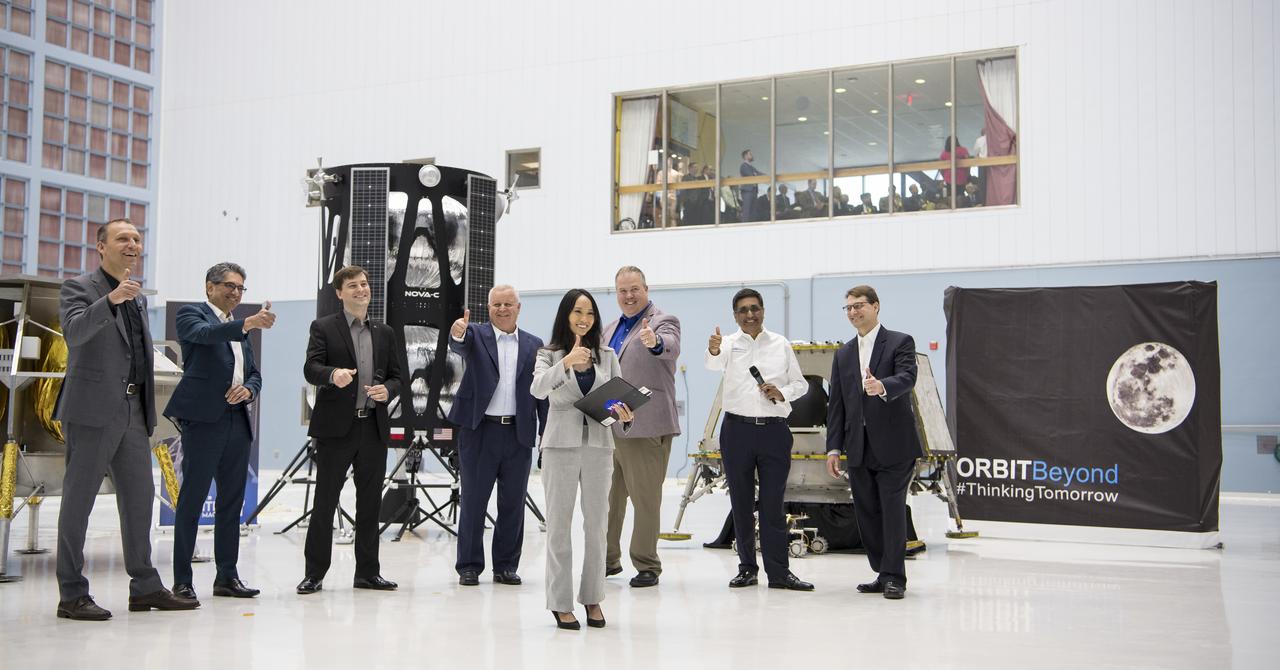

From left to right, NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse; and NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou, front center, put their thumbs up at the conclusion of an event announcing the companies that will provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
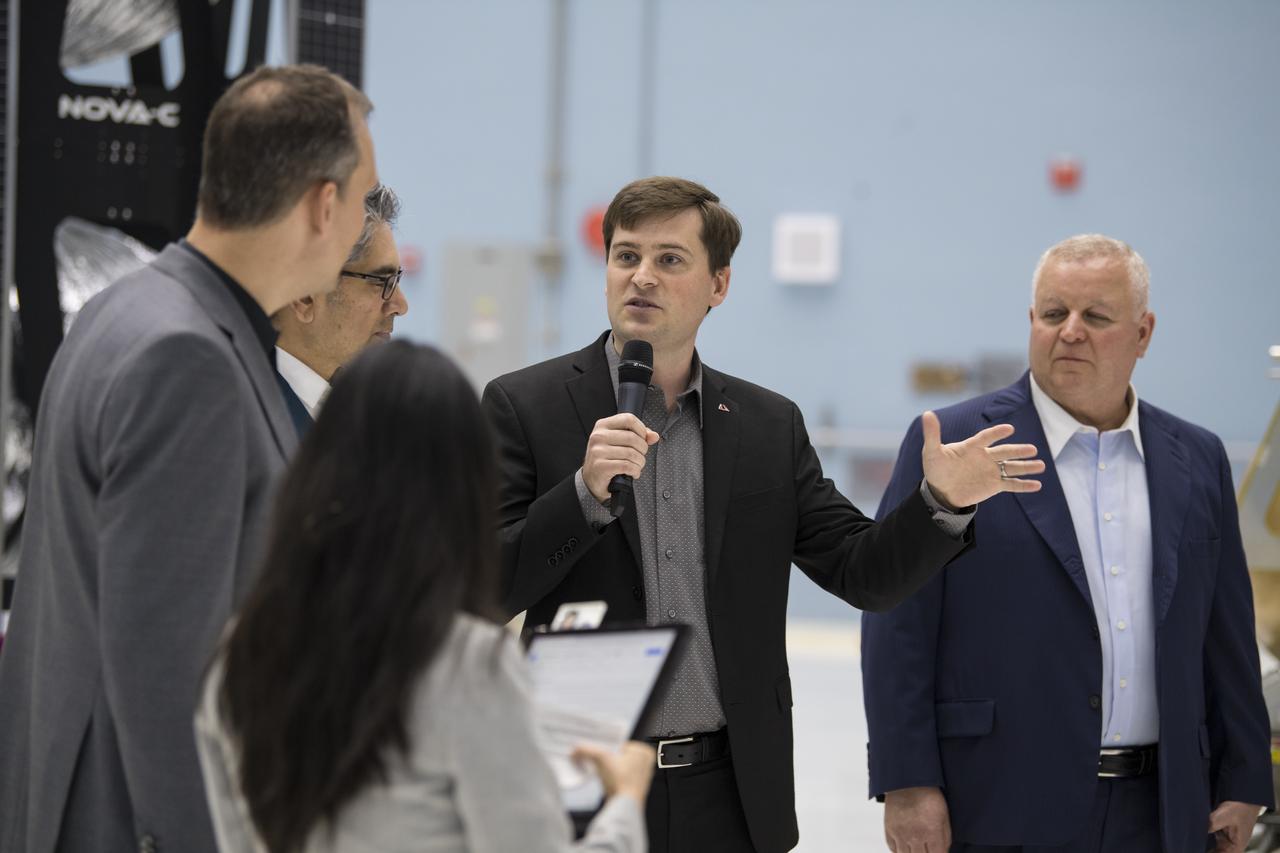

Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, second from right, speaks about their lunar lander, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Orbit Beyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
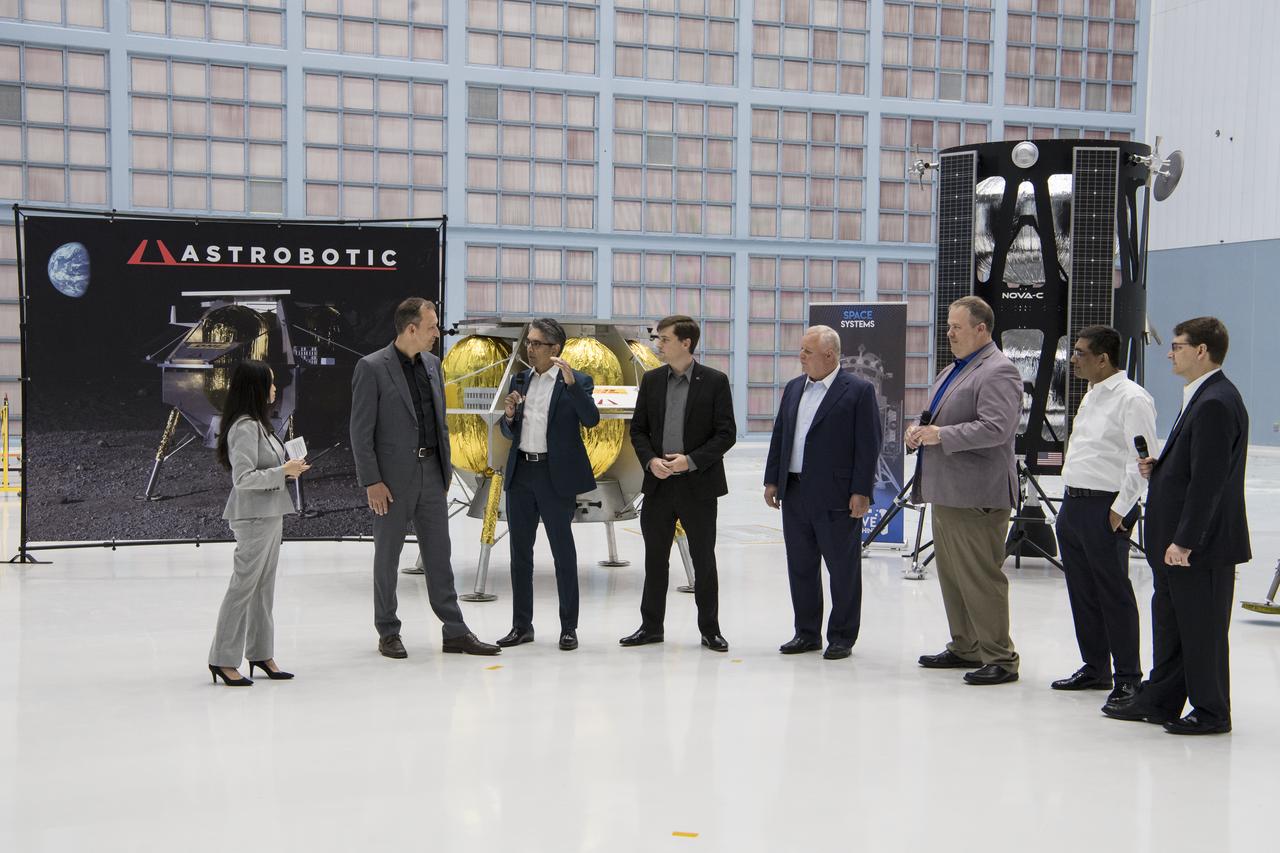

Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran , third from left, speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
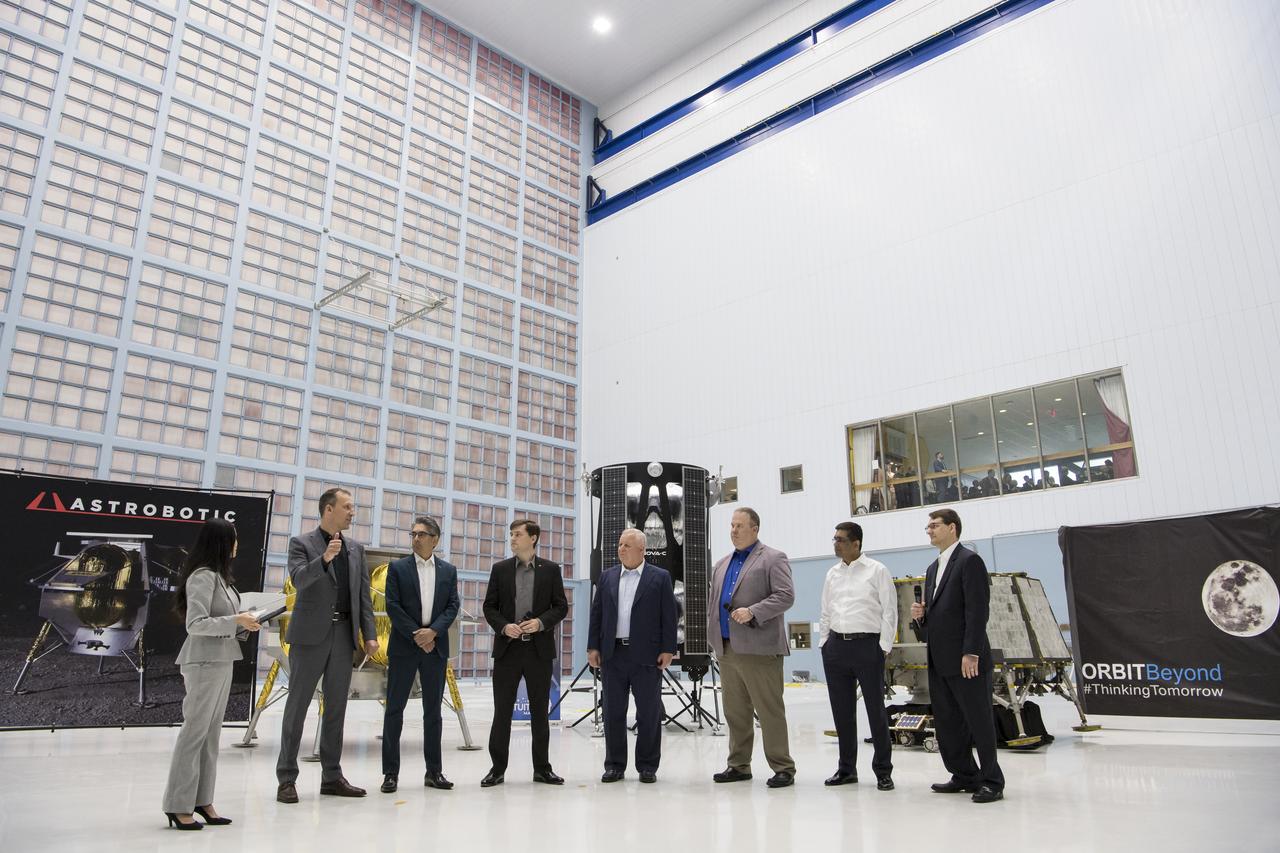

From left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse talk about their lunar landers, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
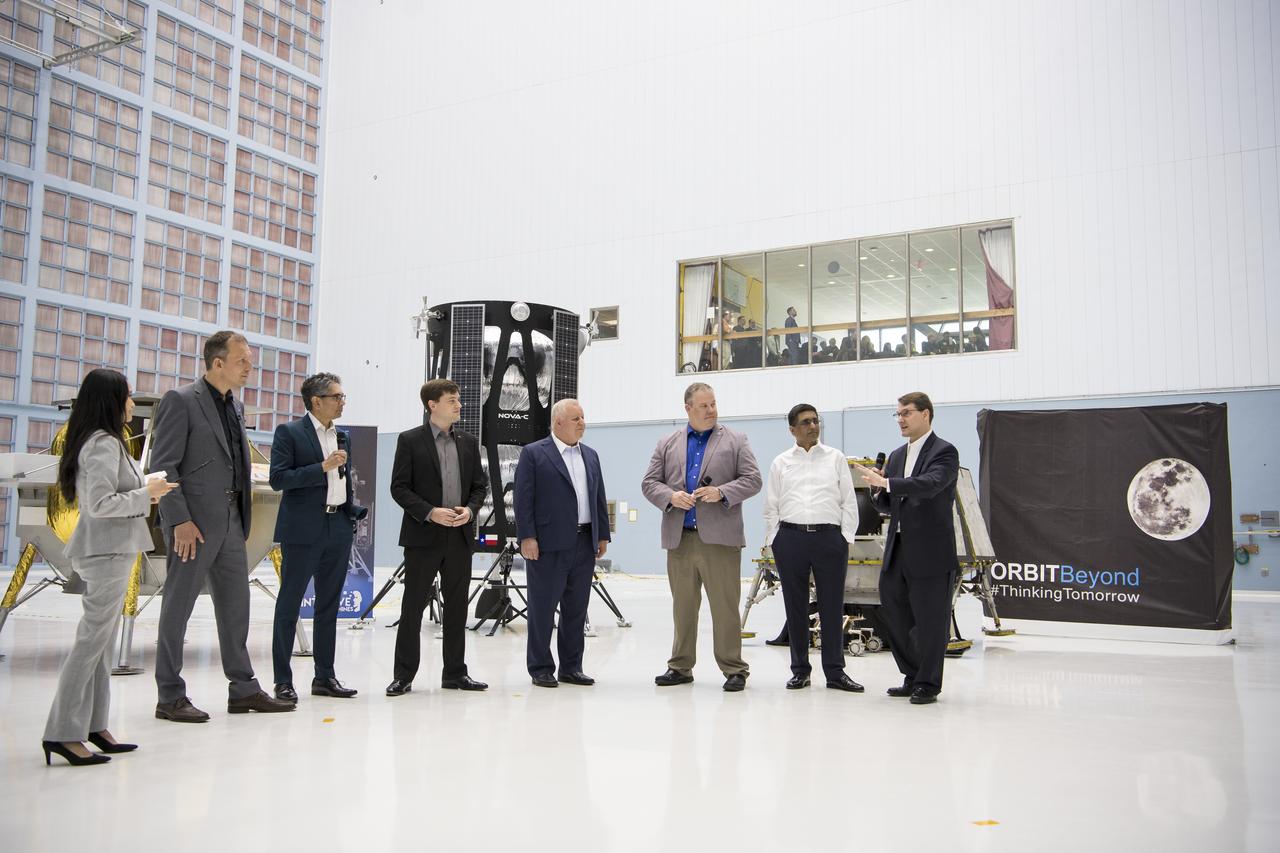

Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Astrobotic CEO, John Thornton, fourth from left, speaks about their lunar lander with, from left to right, NASA Press Officer, Felicia Chou; NASA Associate Administrator, Science Mission Directorate, Thomas Zurbuchen; Astrobotic Mission Director, Sharad Bhaskaran; Chairman of the Board of Intuitive Machines, Kam Ghaffarian; VP of Research and Development of Intuitive Machines, Tim Crain; President and CEO of OrbitBeyond, Siba Padhi; and Chief Science Officer, OrbitBeyond, Jon Morse, Friday, May 31, 2019, at Goddard Space Flight Center in Md. Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and OrbitBeyond have been selected to provide the first lunar landers for the Artemis program's lunar surface exploration. Photo credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
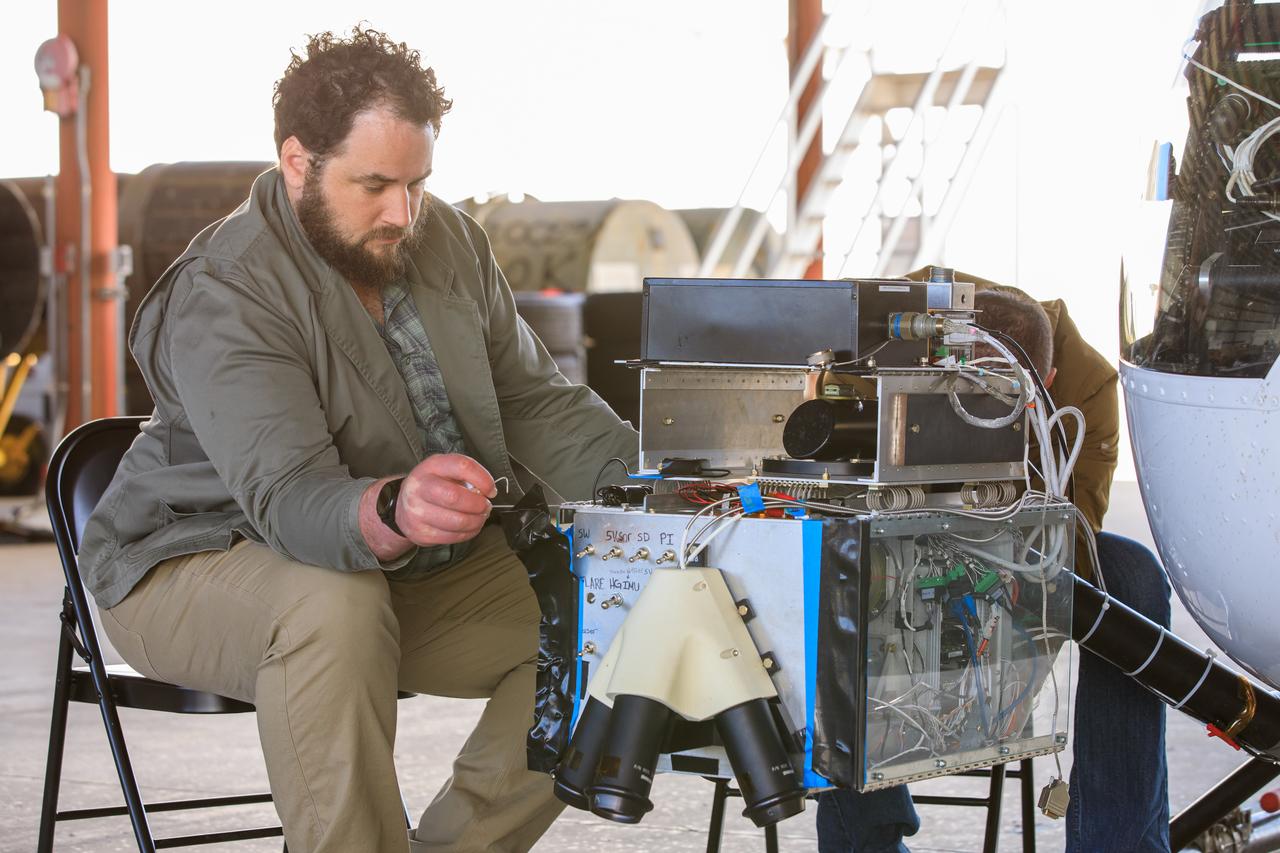

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
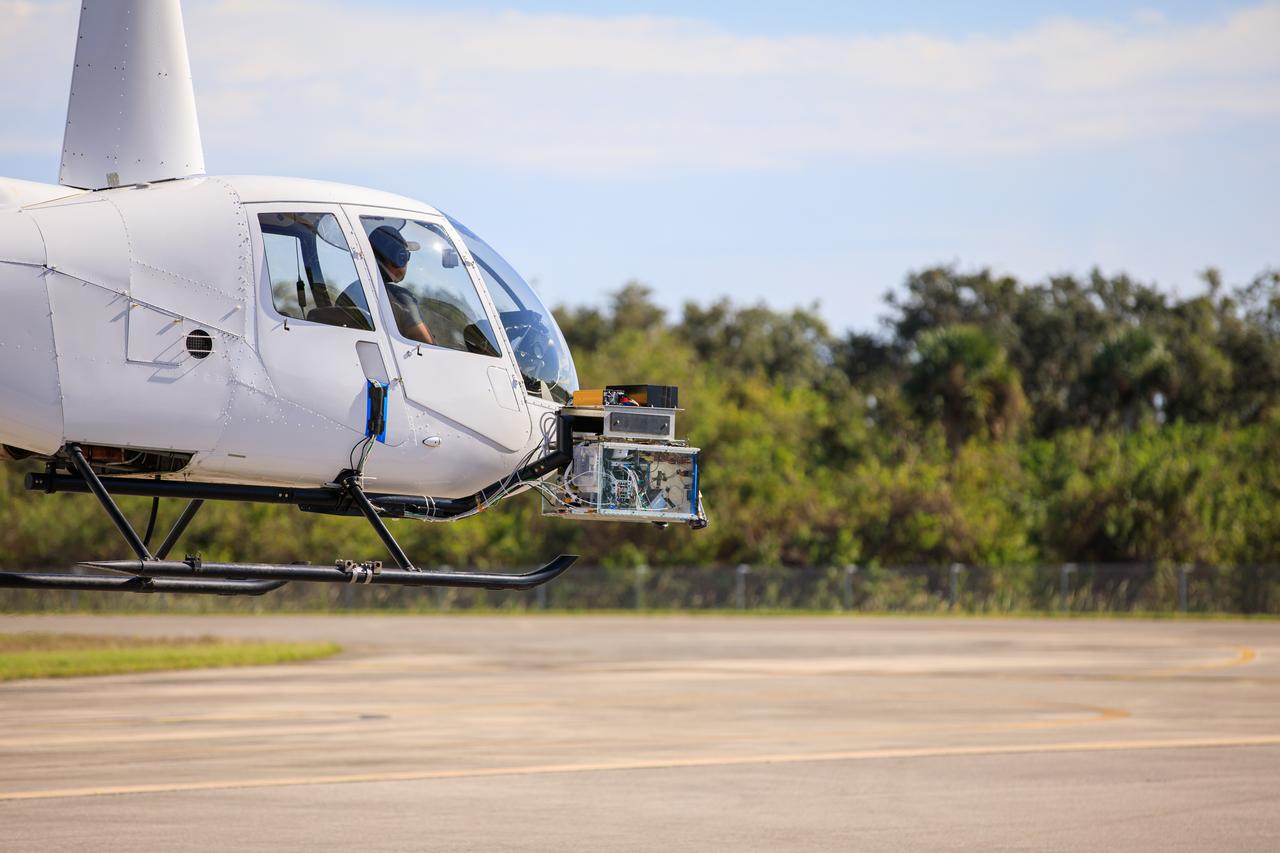

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.

Testing of navigation pod sensors for Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lunar lander is underway at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
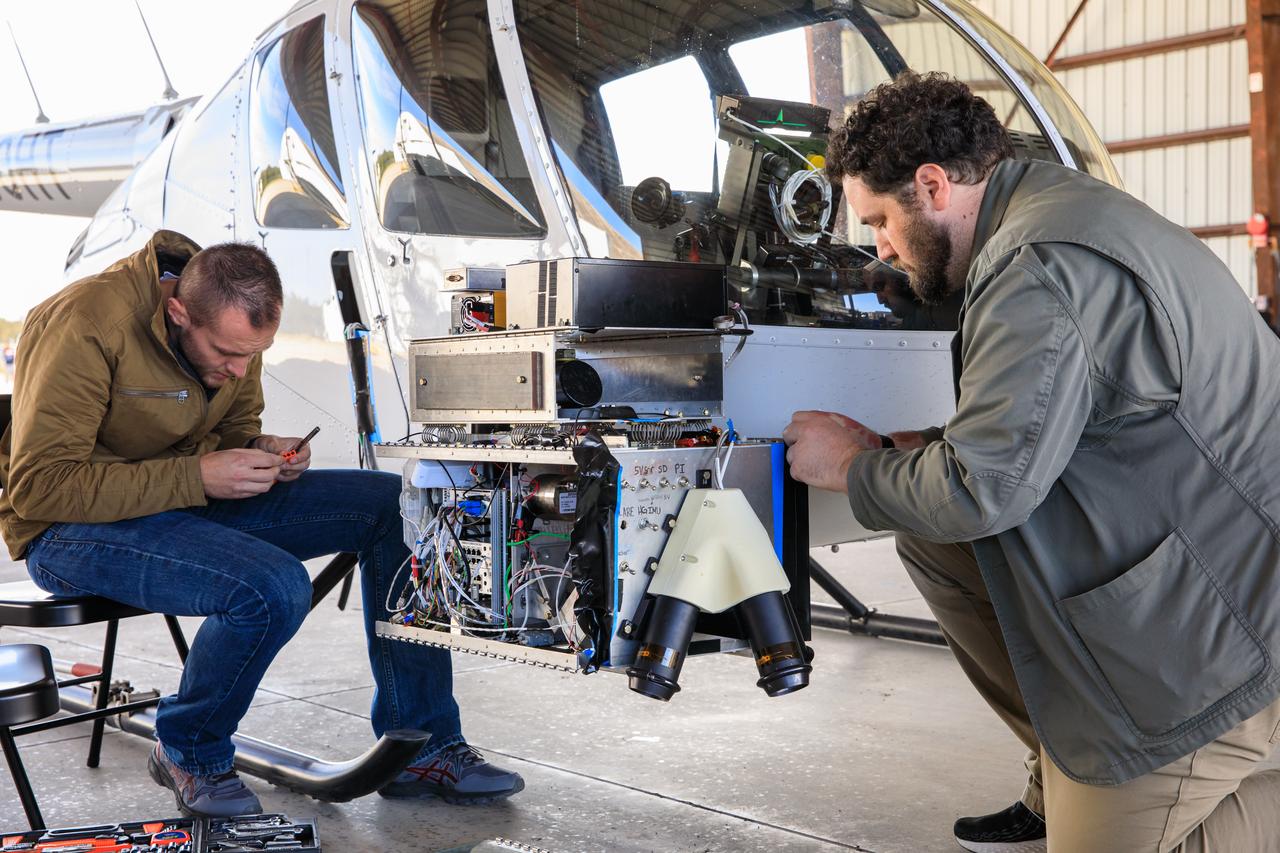

Two Intuitive Machines employees ready navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander in preparation for testing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
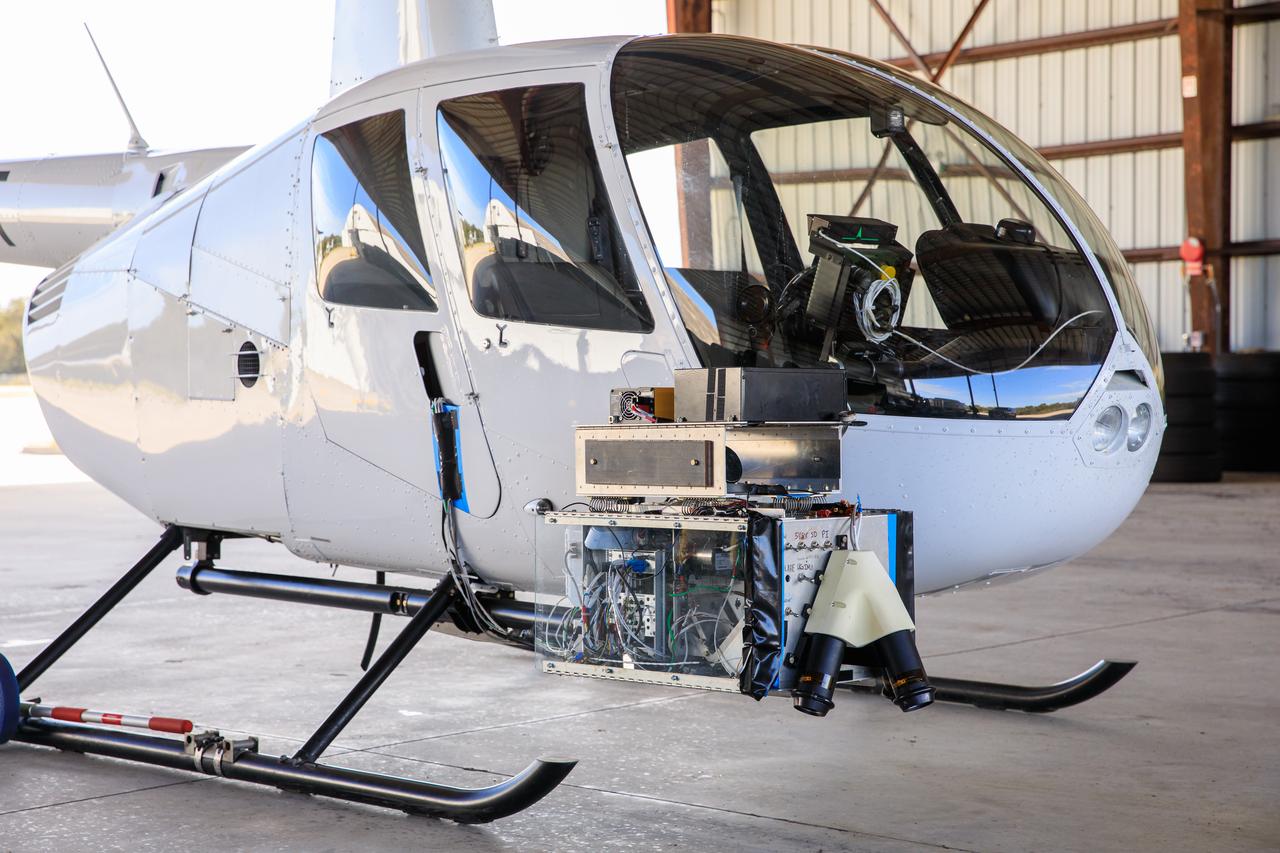

Seen here is Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
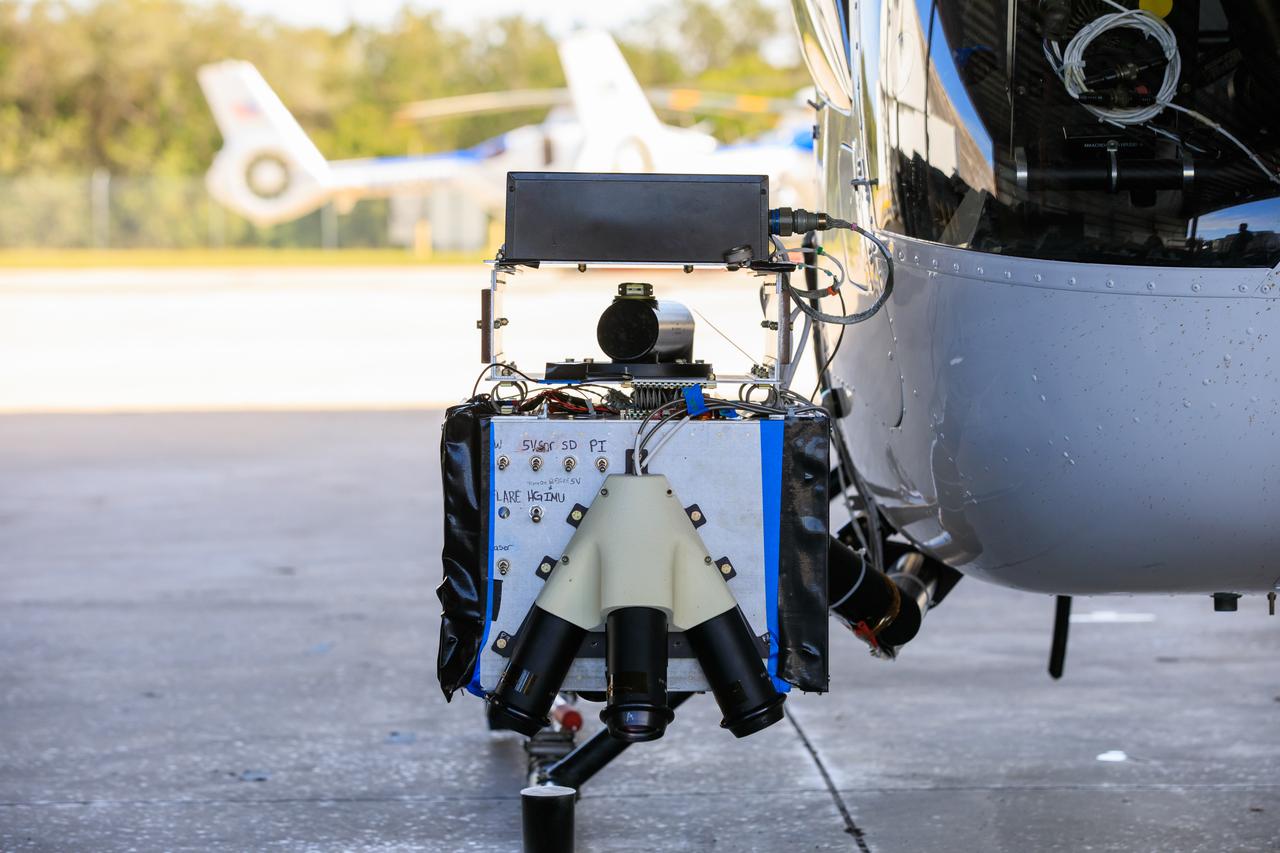

Seen here is a close-up view of Intuitive Machines’ navigation pod sensors for the company’s Nova-C lunar lander ahead of testing done at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 18, 2022. The test involved flying the sensors over a simulated lunar surface at the Launch and Landing Facility on a private helicopter. Intuitive Machines is scheduled to launch two missions to the Moon in 2023 – one of which will carry NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) instrument that will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. Through NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative, the agency selected Intuitive Machines to deliver science and technology demonstration payloads to the Moon, contributing to NASA’s goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the lunar surface.
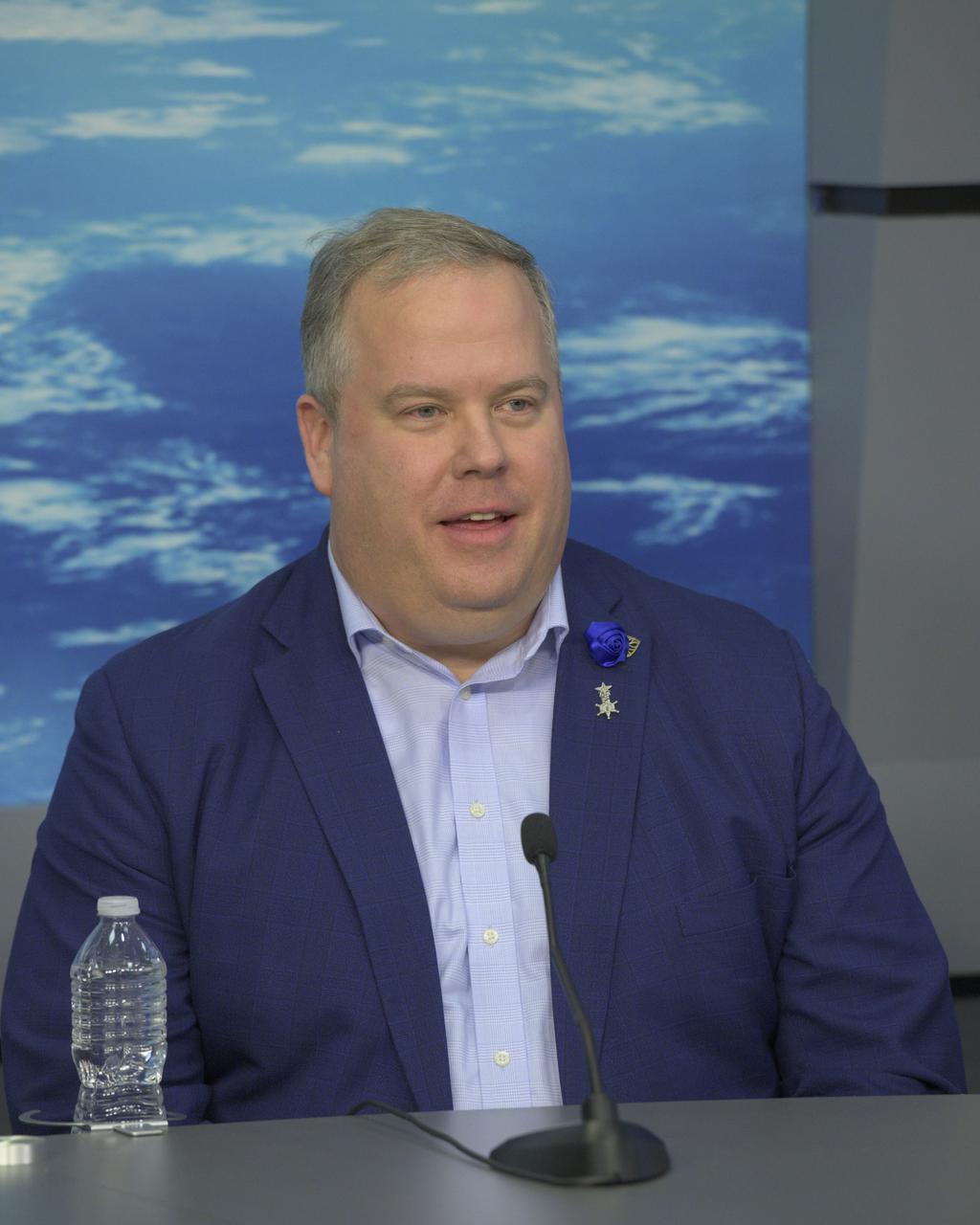

Tim Crain, chief technology officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston to discuss the company’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
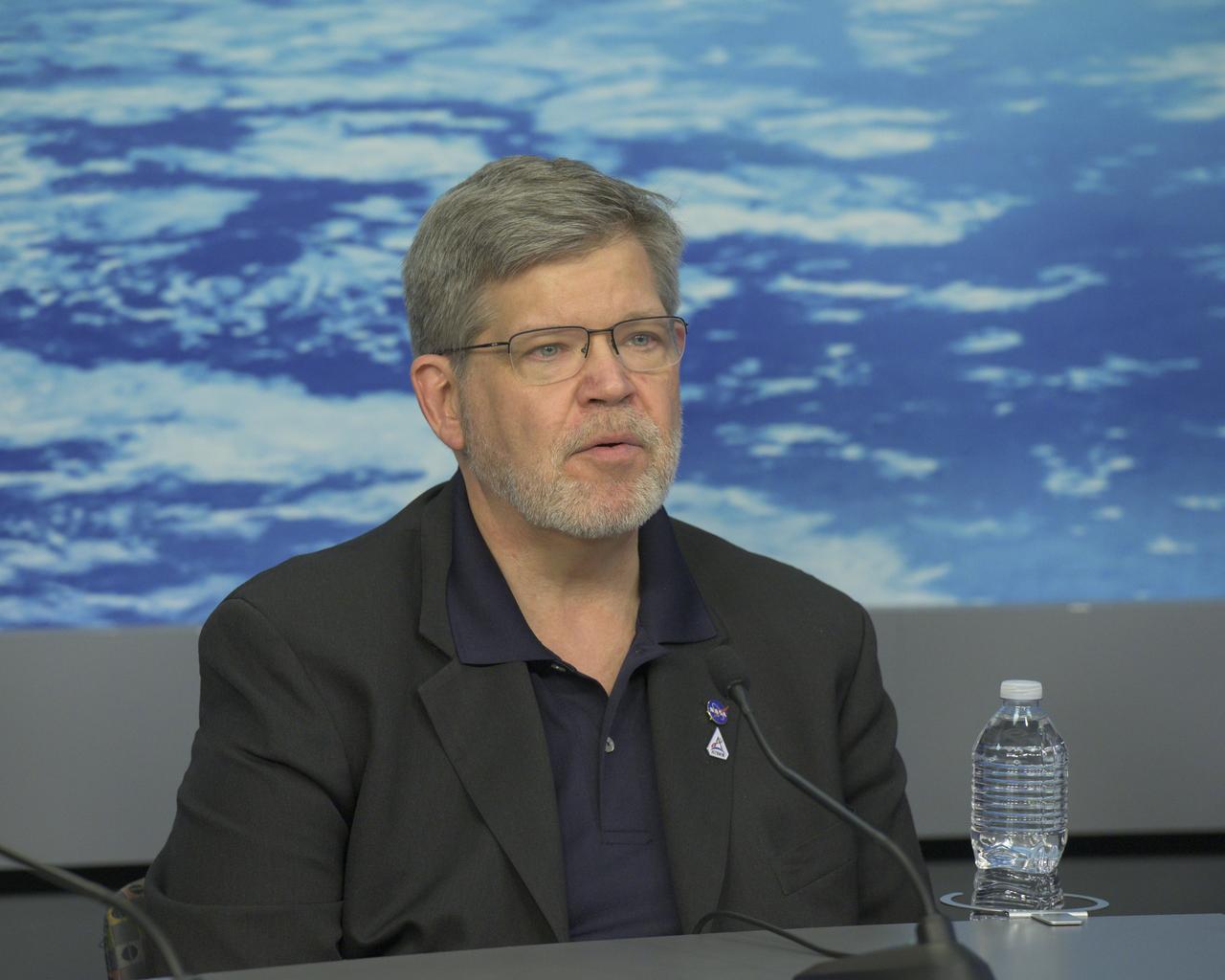

Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for Exploration, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Kearns was on hand to discuss the NASA science and technology aboard Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
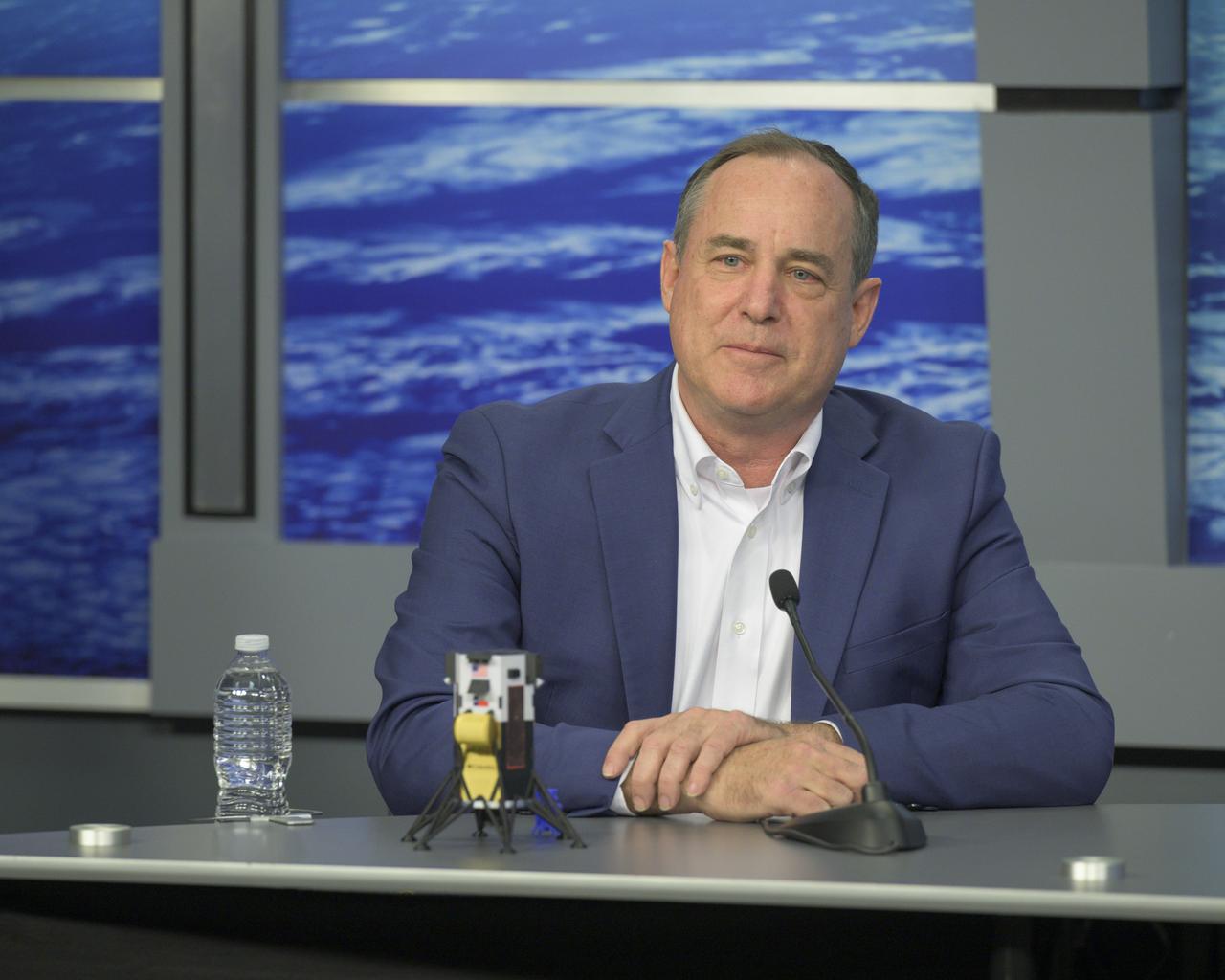

Steve Altemus, chief executive officer and co-founder, Intuitive Machines, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston to discuss the company’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.

Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator, Space Technology Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, participates in a news conference Feb. 23, 2024, at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Desai was on hand to discuss the NASA science and technology aboard the Intuitive Machine’s Nova-C lander, called Odysseus, and its successful soft landing on the Moon Feb. 22, 2024. The mission is the first landing under NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, and the first American lunar landing in more than 50 years.
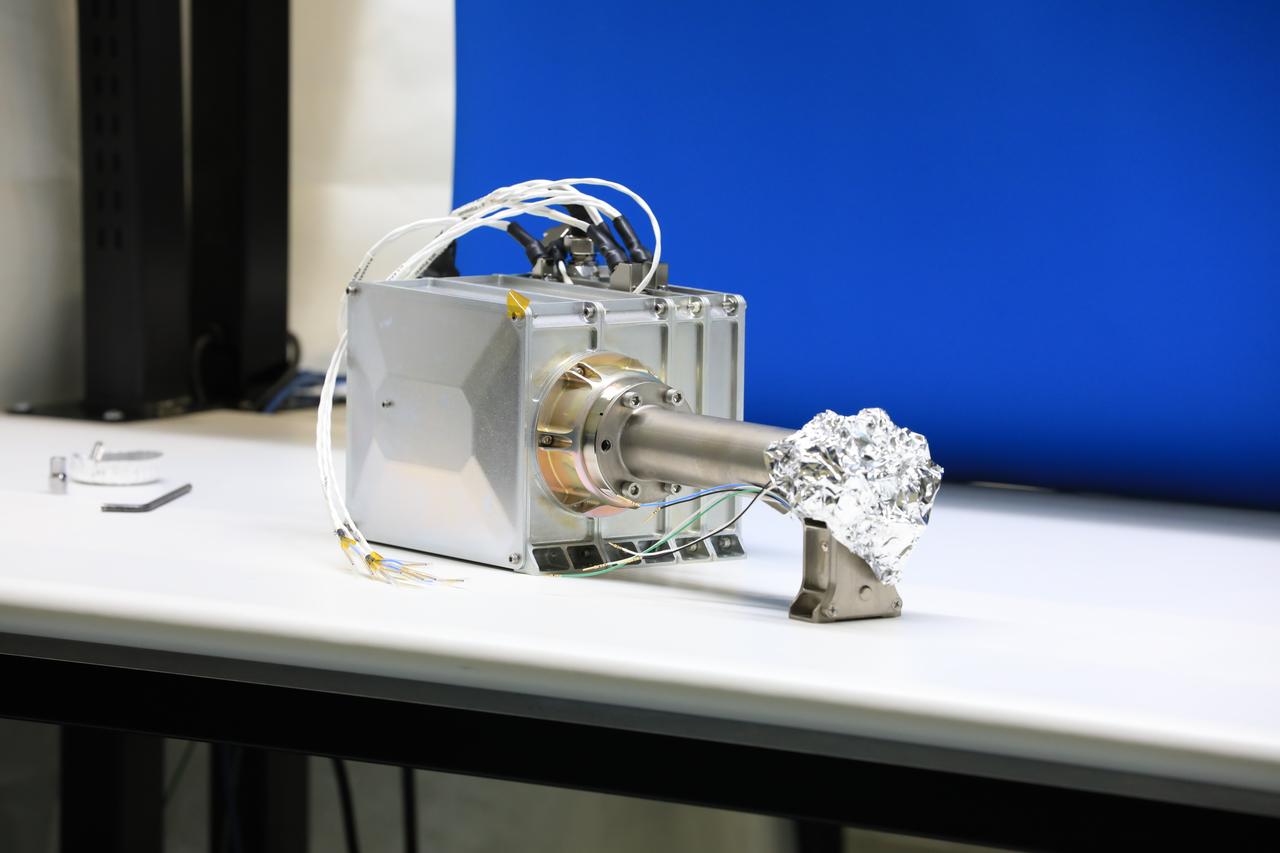
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
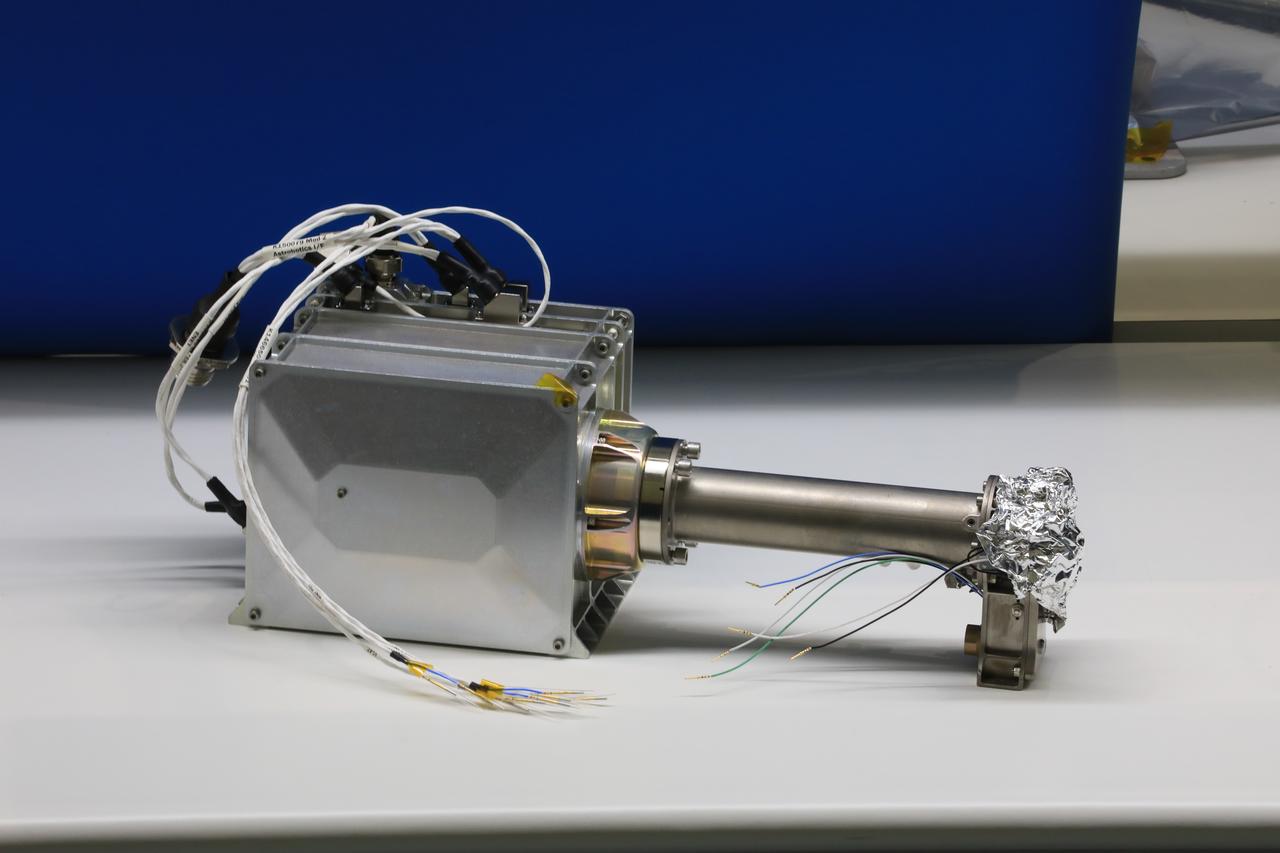
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida are preparing the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) for launch inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo hardware is a payload for a robotic mission to the Moon as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
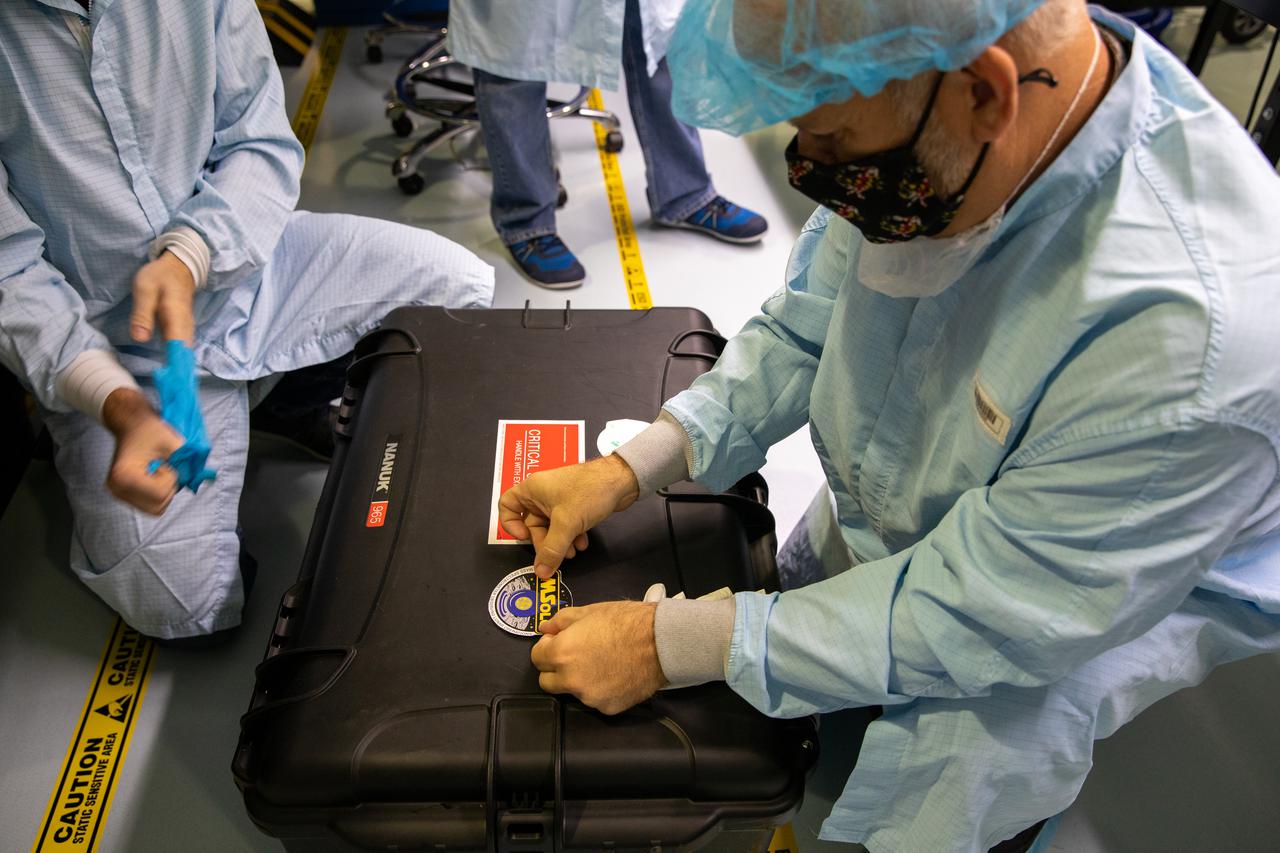

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
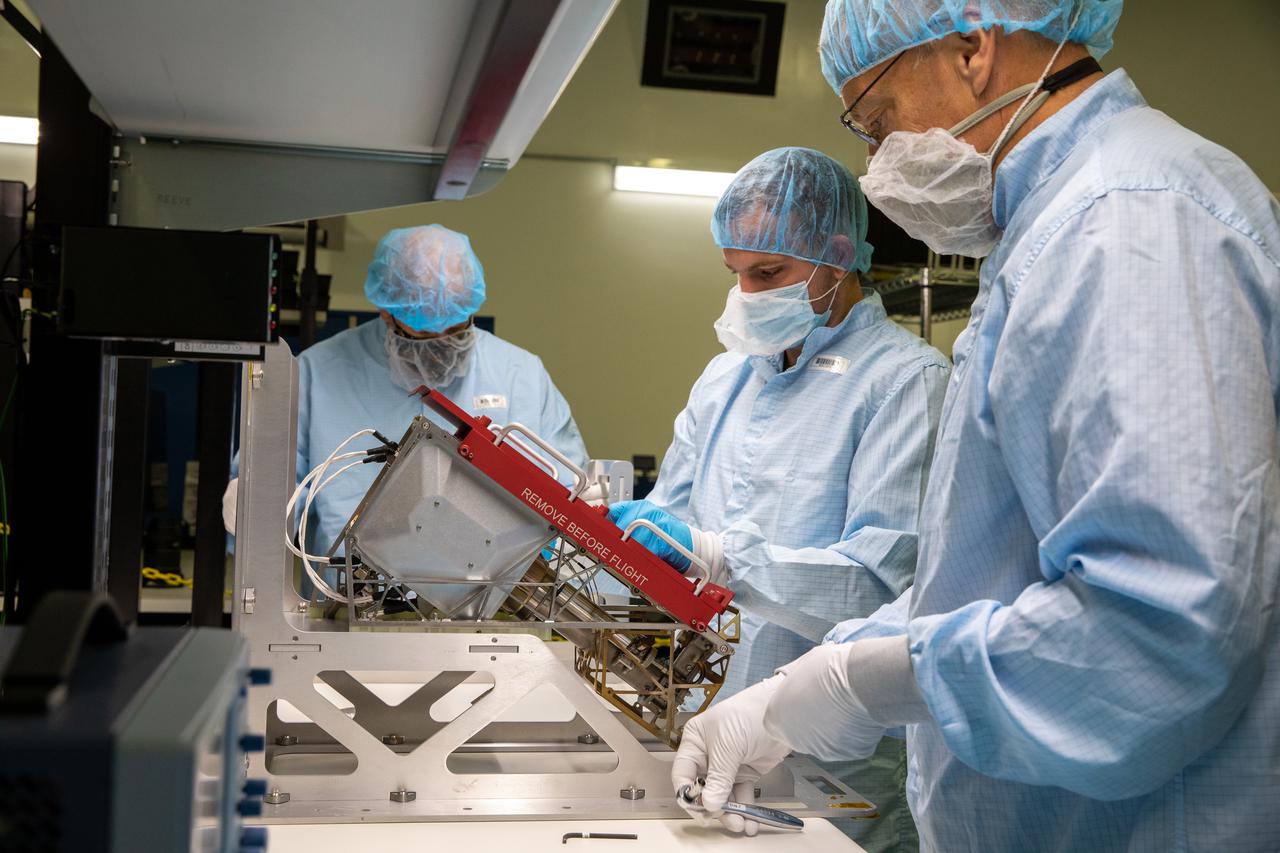

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
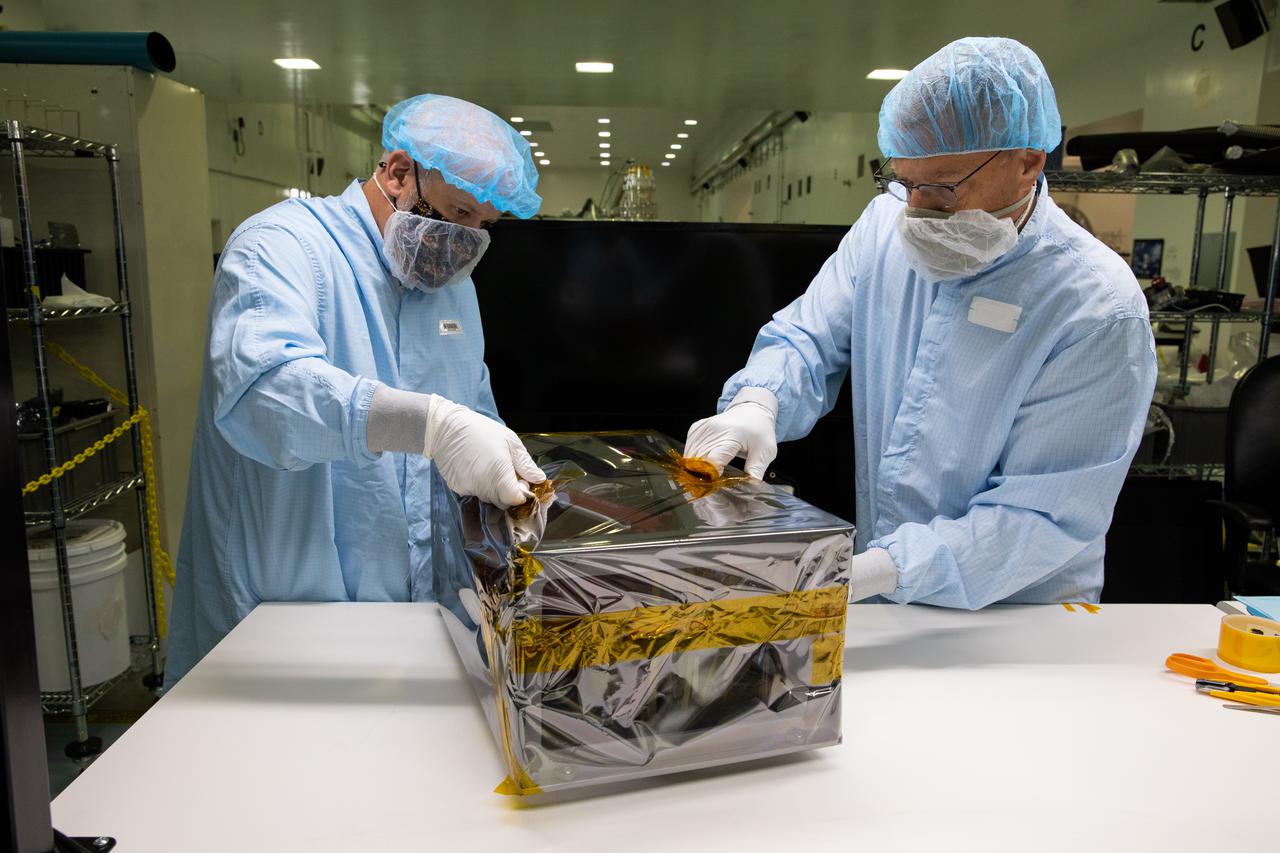

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
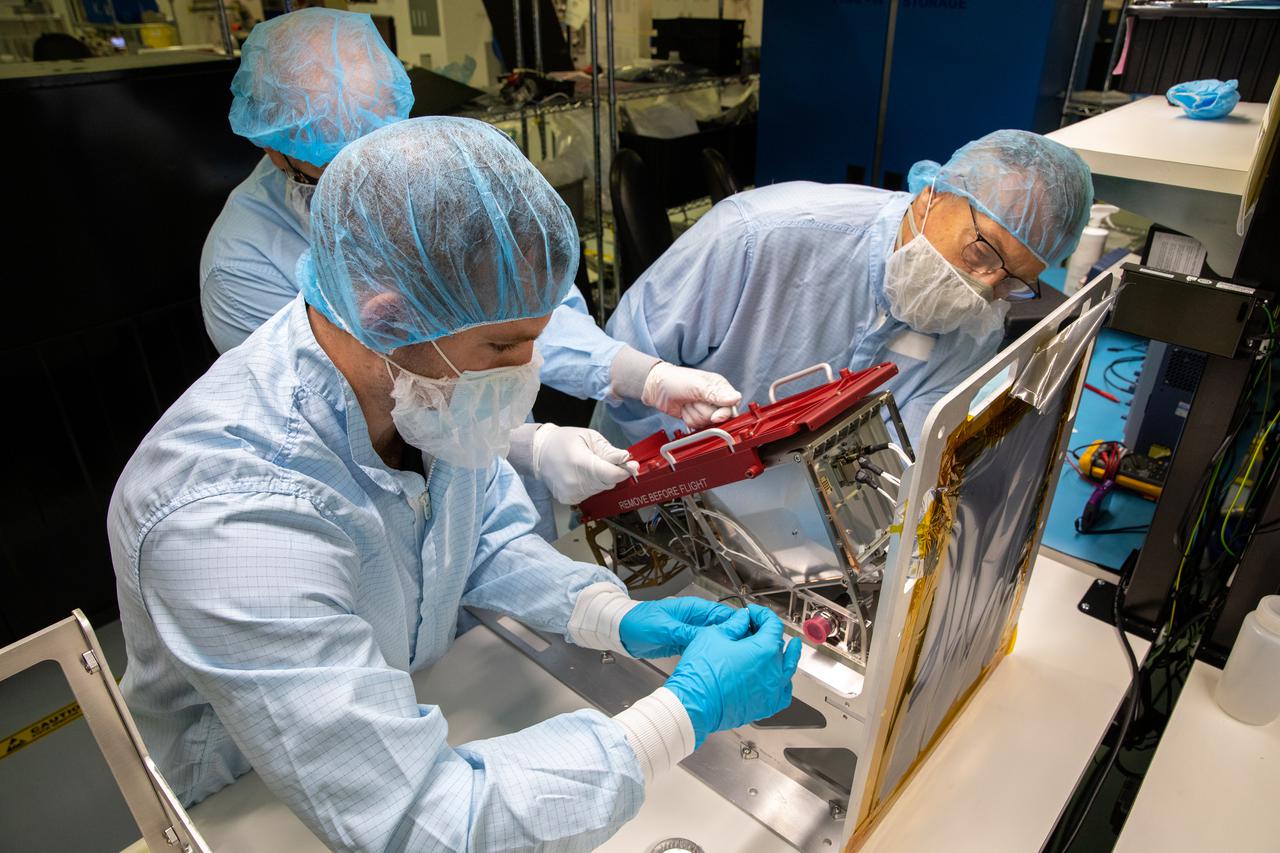

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) team prepare MSolo flight hardware for shipment in preparation for launch in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2022 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
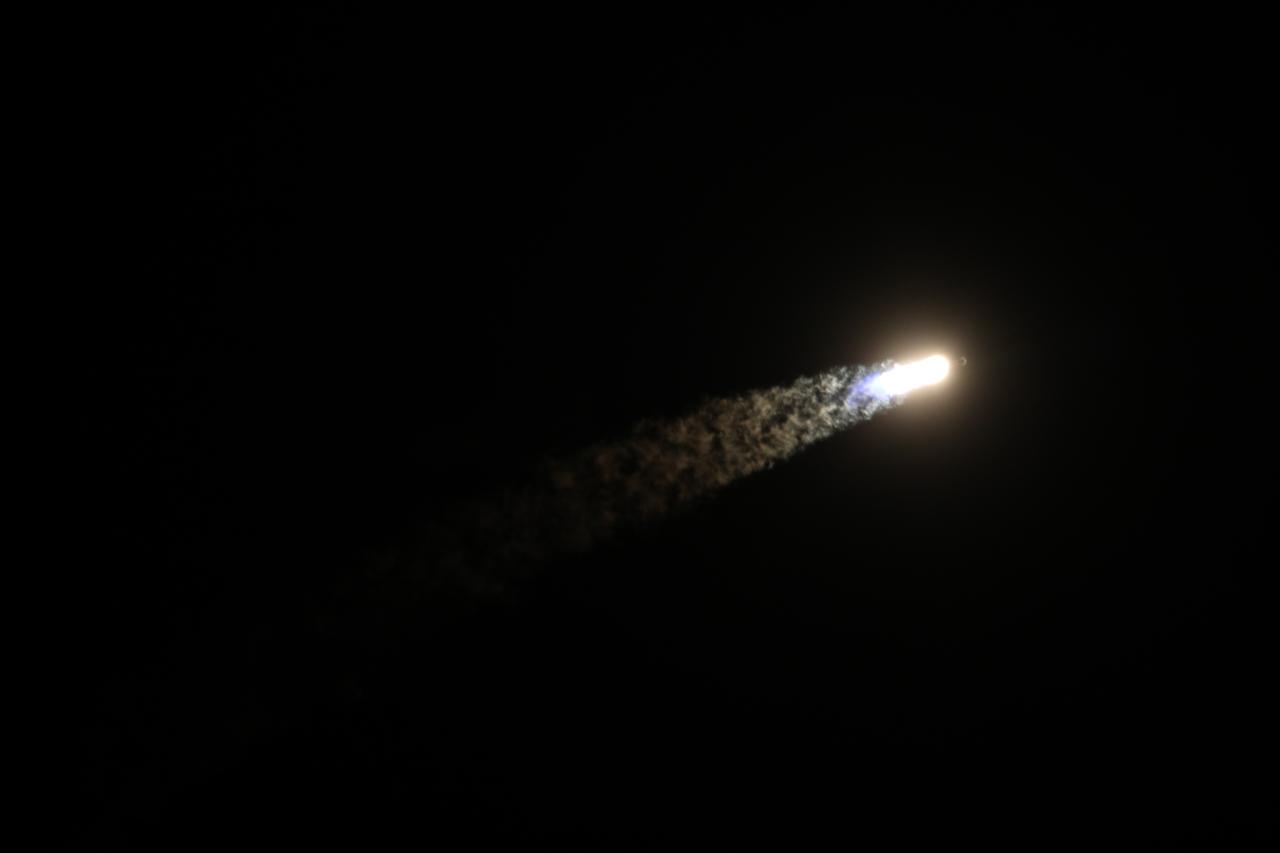

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One is on its way to the Moon as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander launched from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 carrying 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One is on its way to the Moon as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander launched from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 carrying 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.
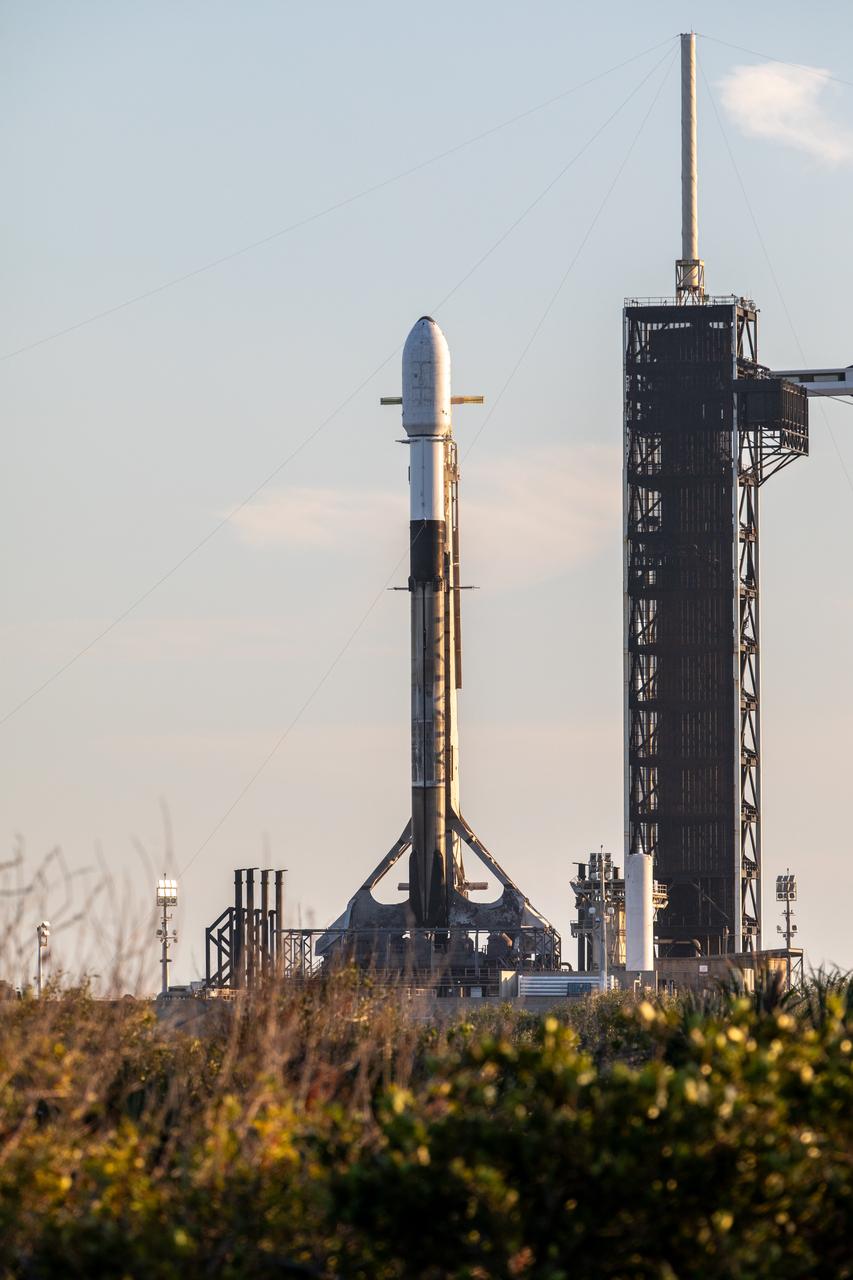

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
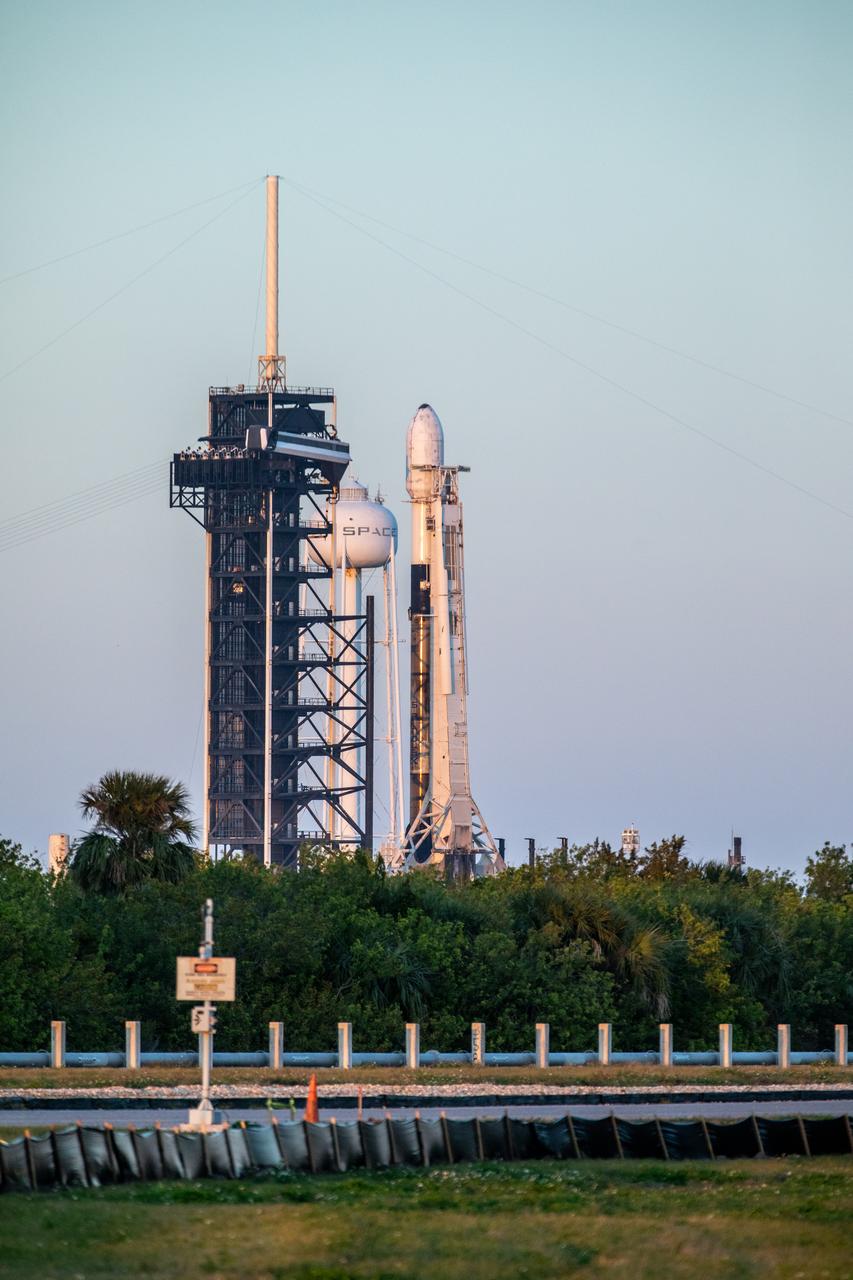

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
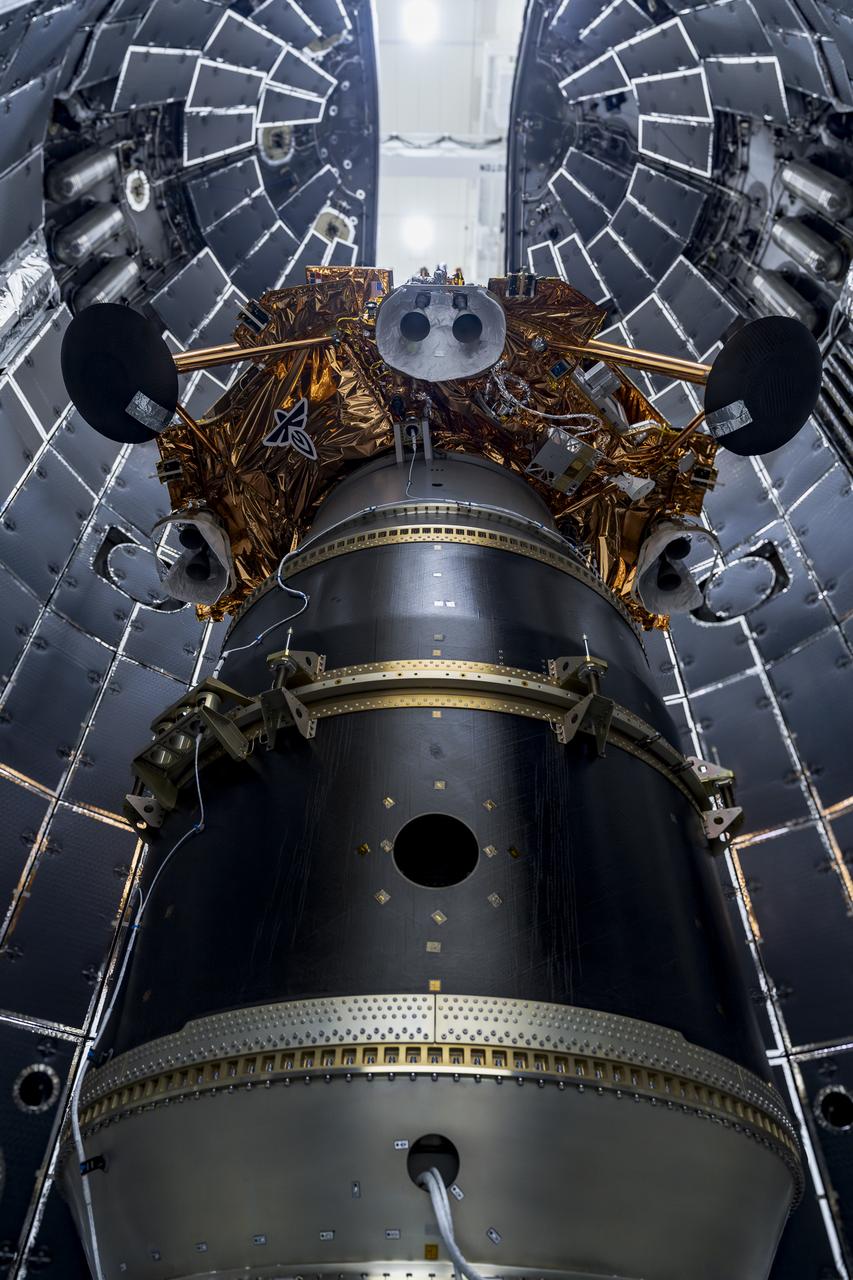

Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is encapsulated inside SpaceX’s rocket fairing ahead of its targeted liftoff for 1:11 a.m. EST Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Firefly’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 will be the company’s first flight to the Moon as part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services or CLPS initiative and Artemis campaign.
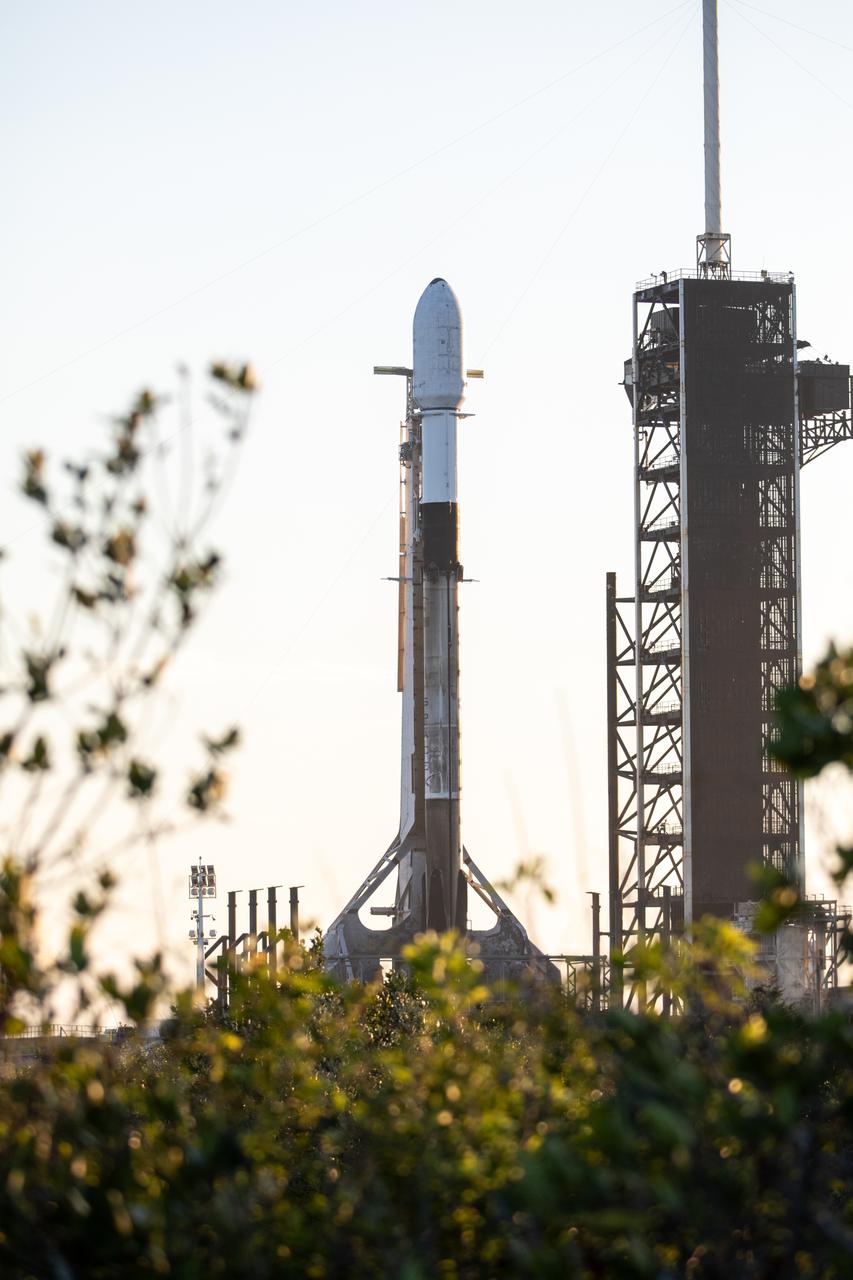

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
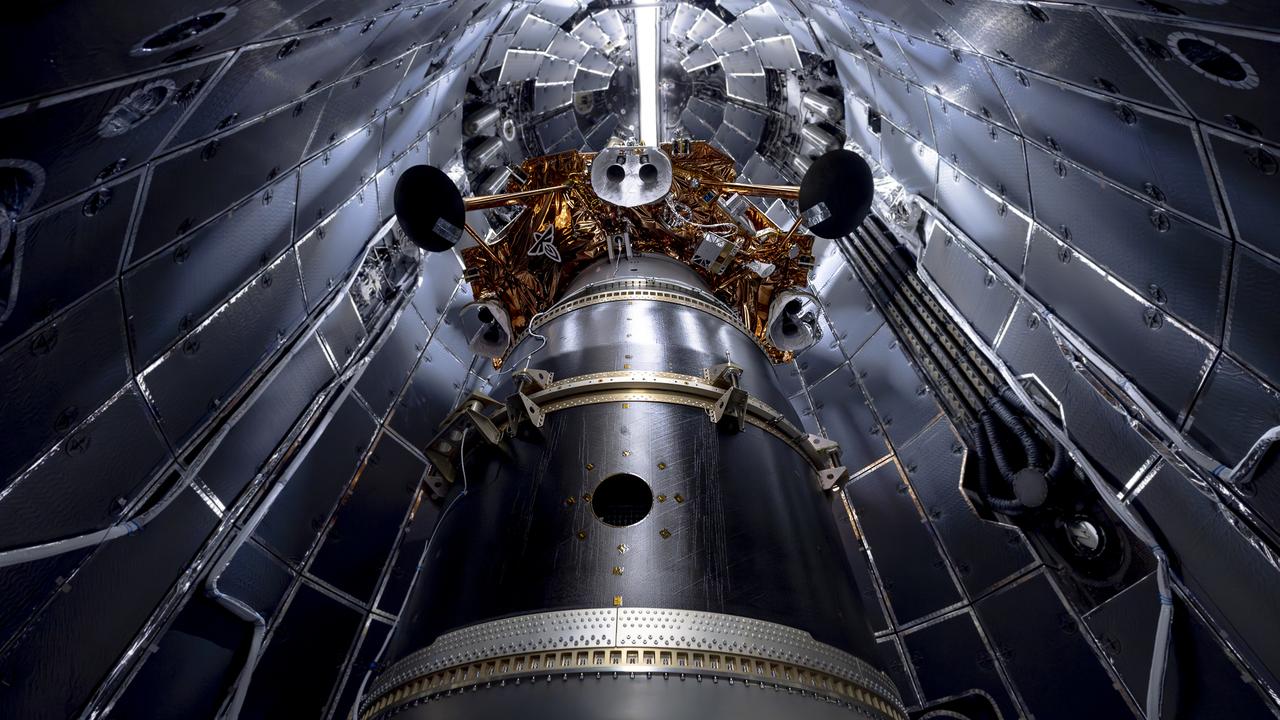
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is encapsulated inside SpaceX’s rocket fairing ahead of its targeted liftoff for 1:11 a.m. EST Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Firefly’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 will be the company’s first flight to the Moon as part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services or CLPS initiative and Artemis campaign.
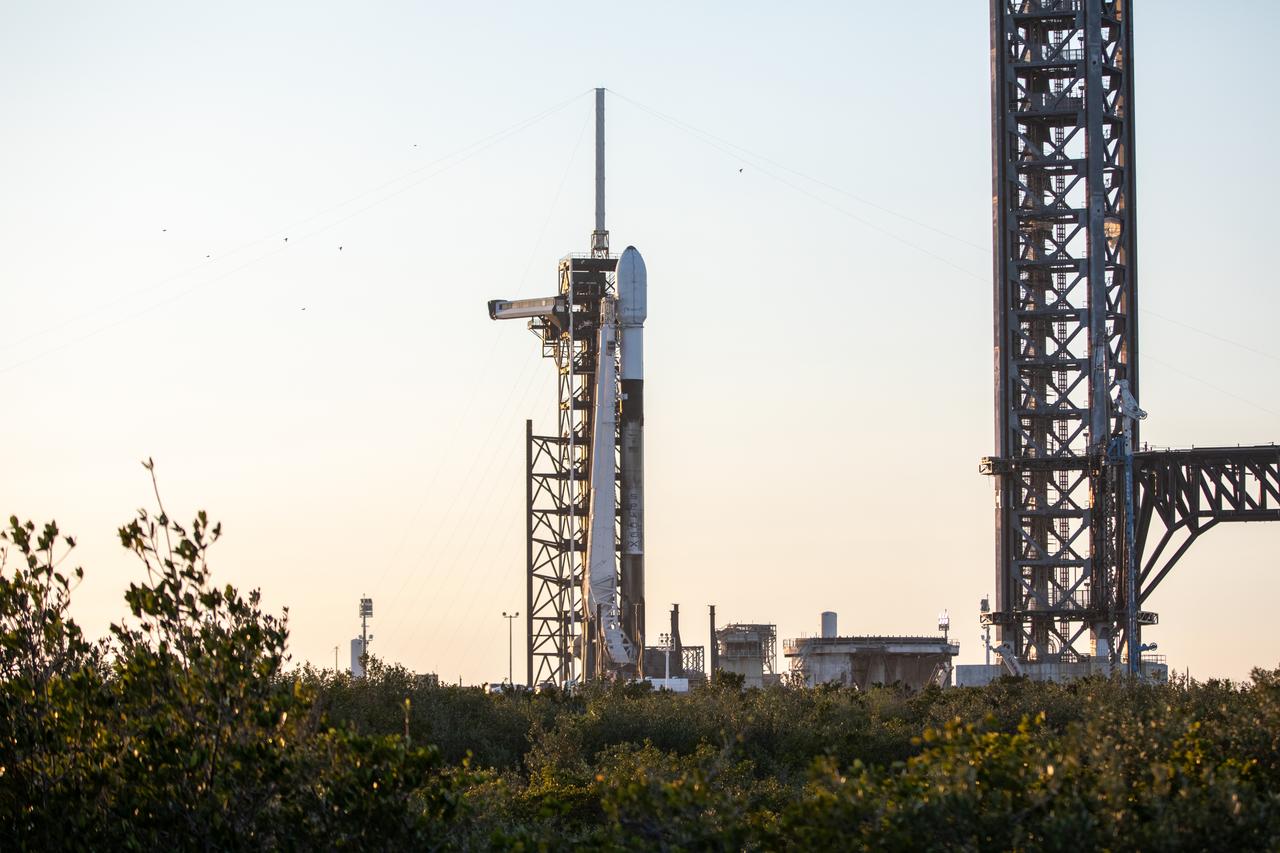

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One is on its way to the Moon as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander launched from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 carrying 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.

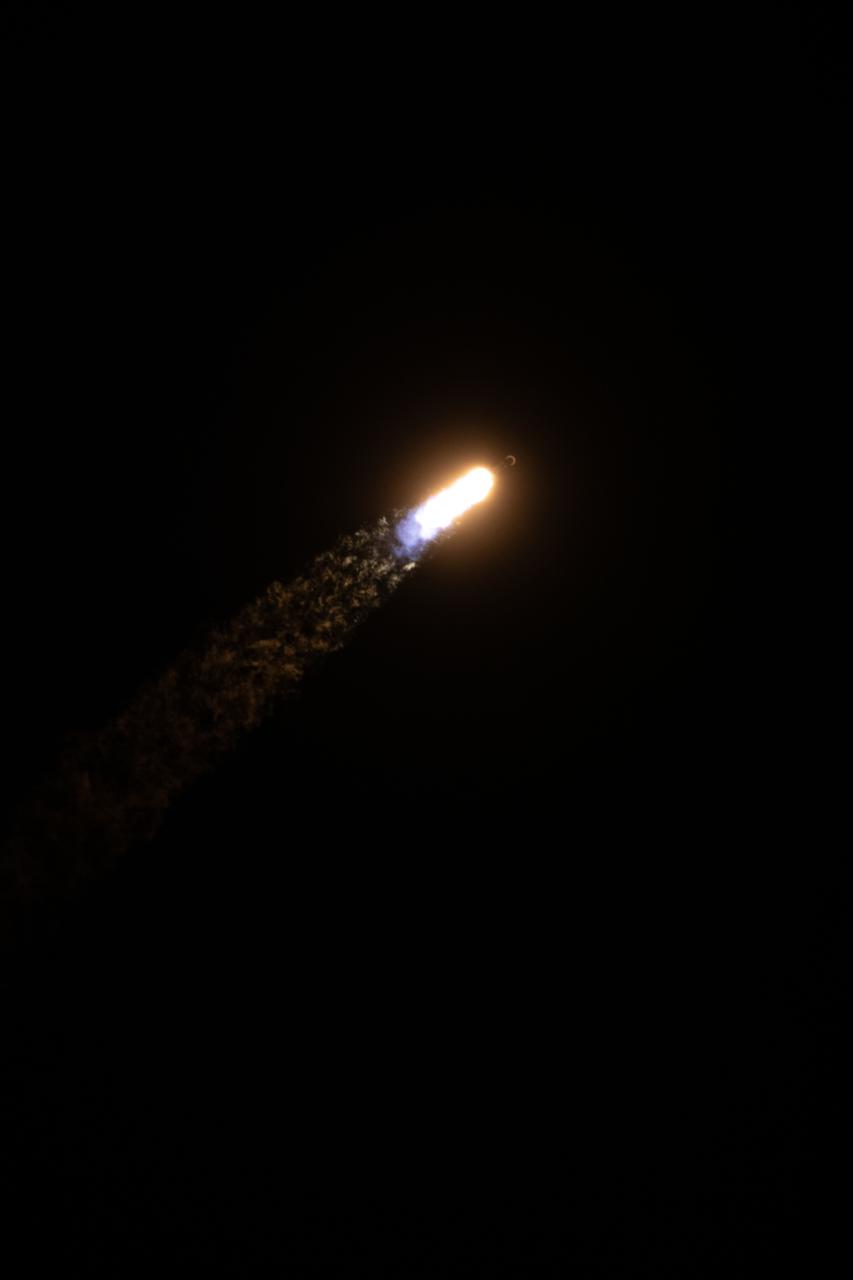
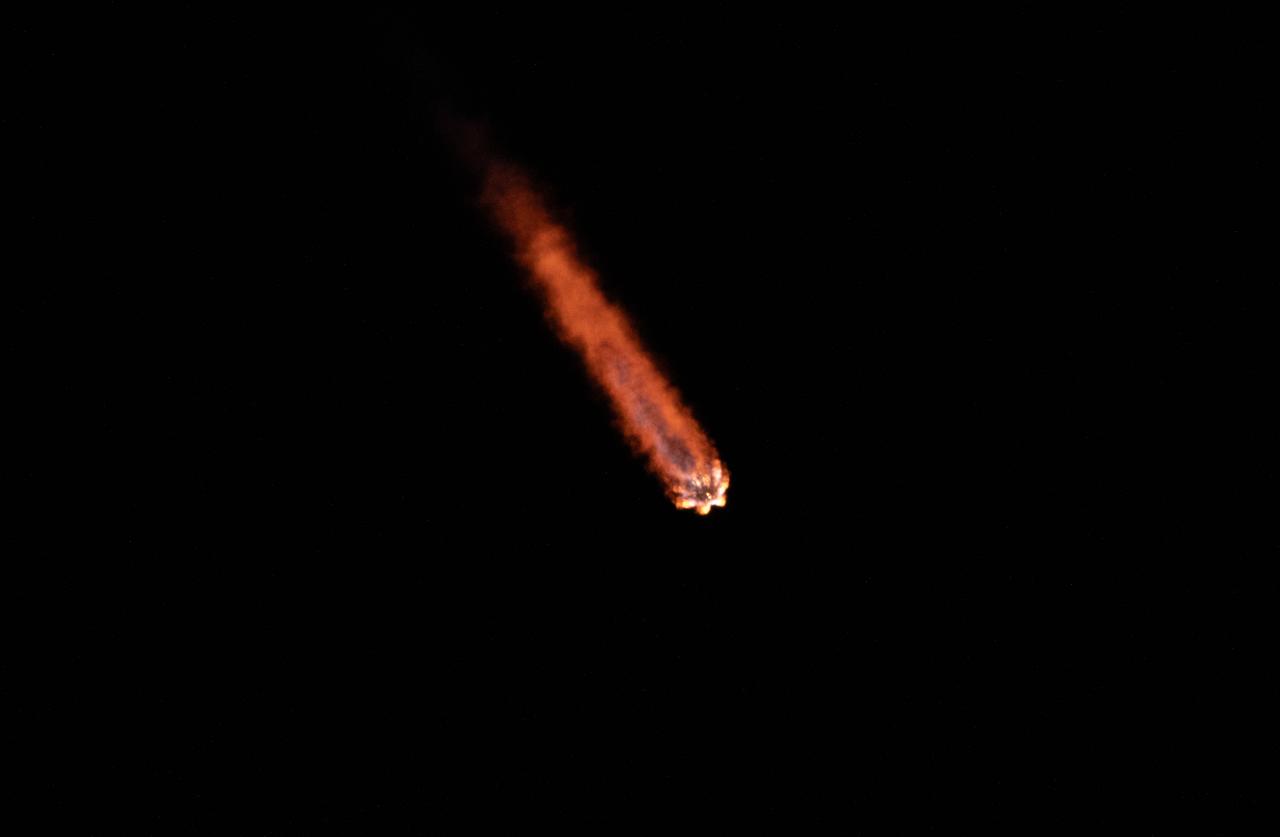
Creating a golden streak in the night sky, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.
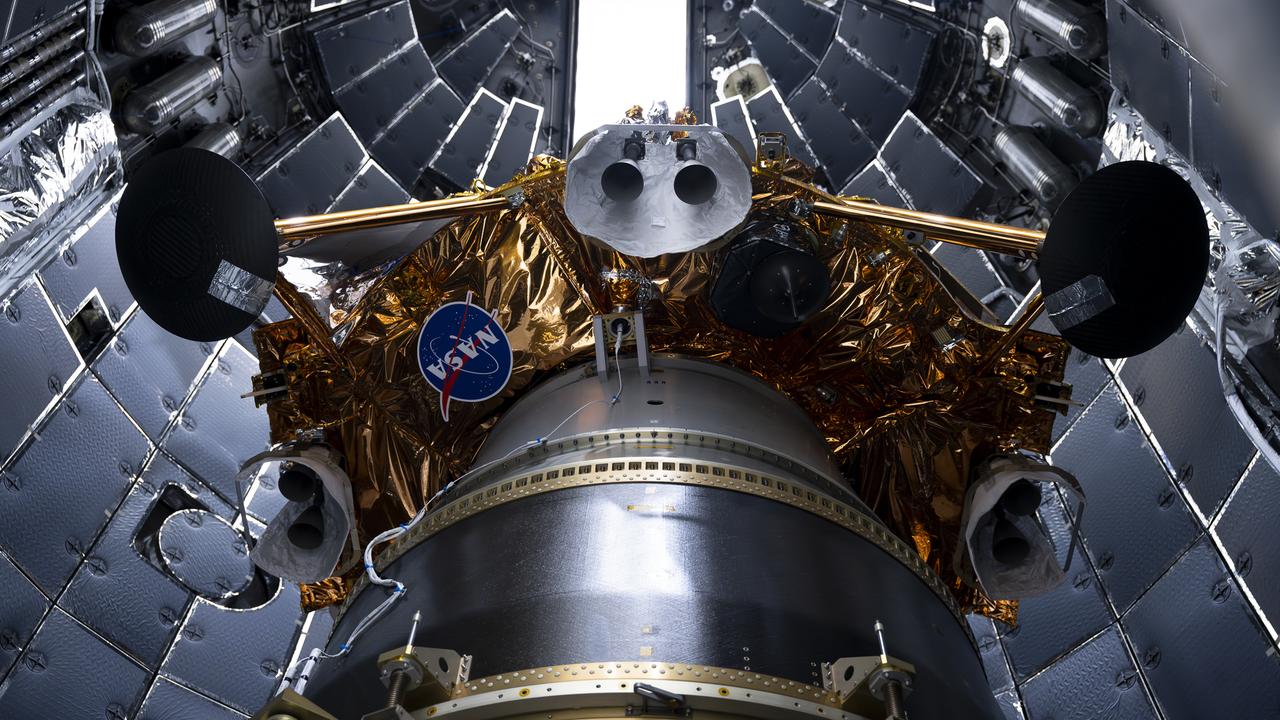
Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is encapsulated inside SpaceX’s rocket fairing ahead of its targeted liftoff for 1:11 a.m. EST Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Firefly’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 will be the company’s first flight to the Moon as part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services or CLPS initiative and Artemis campaign.
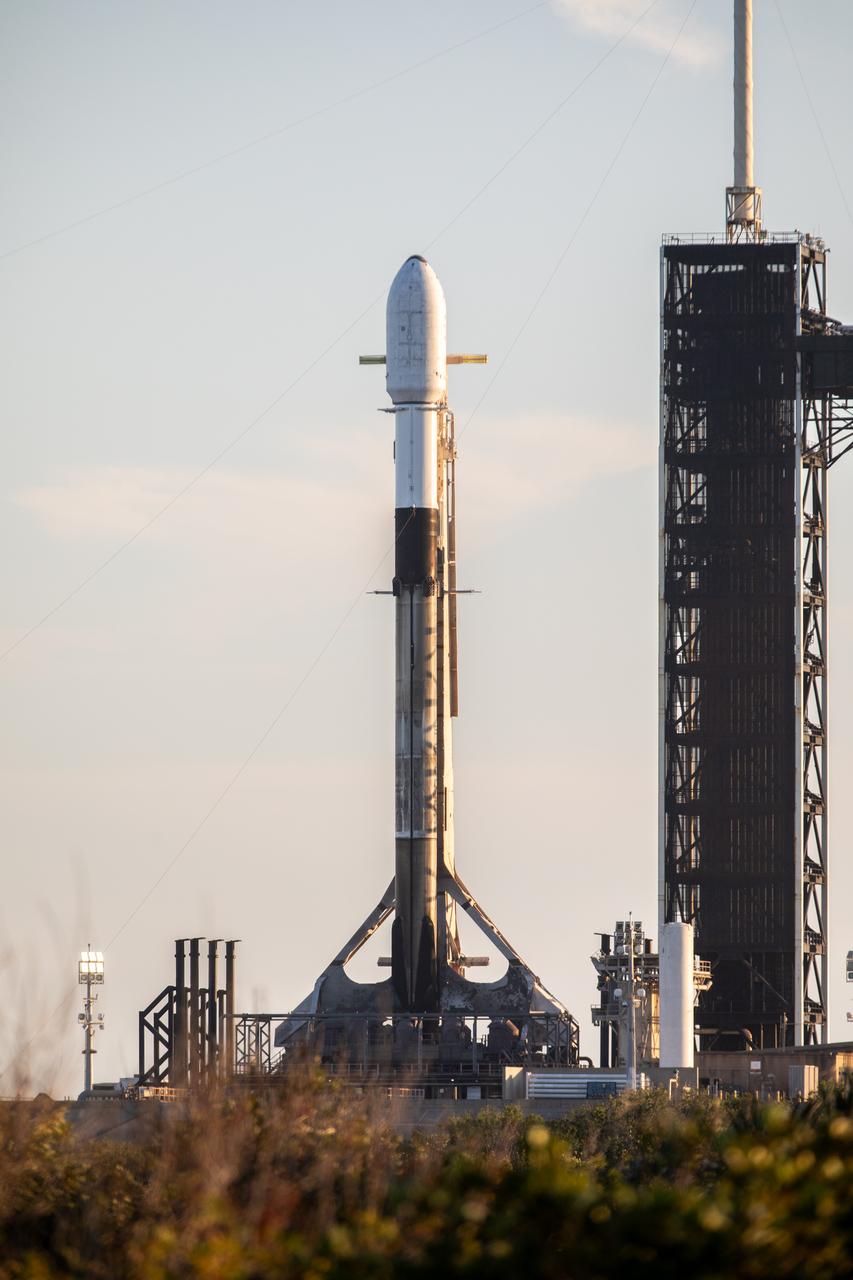

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
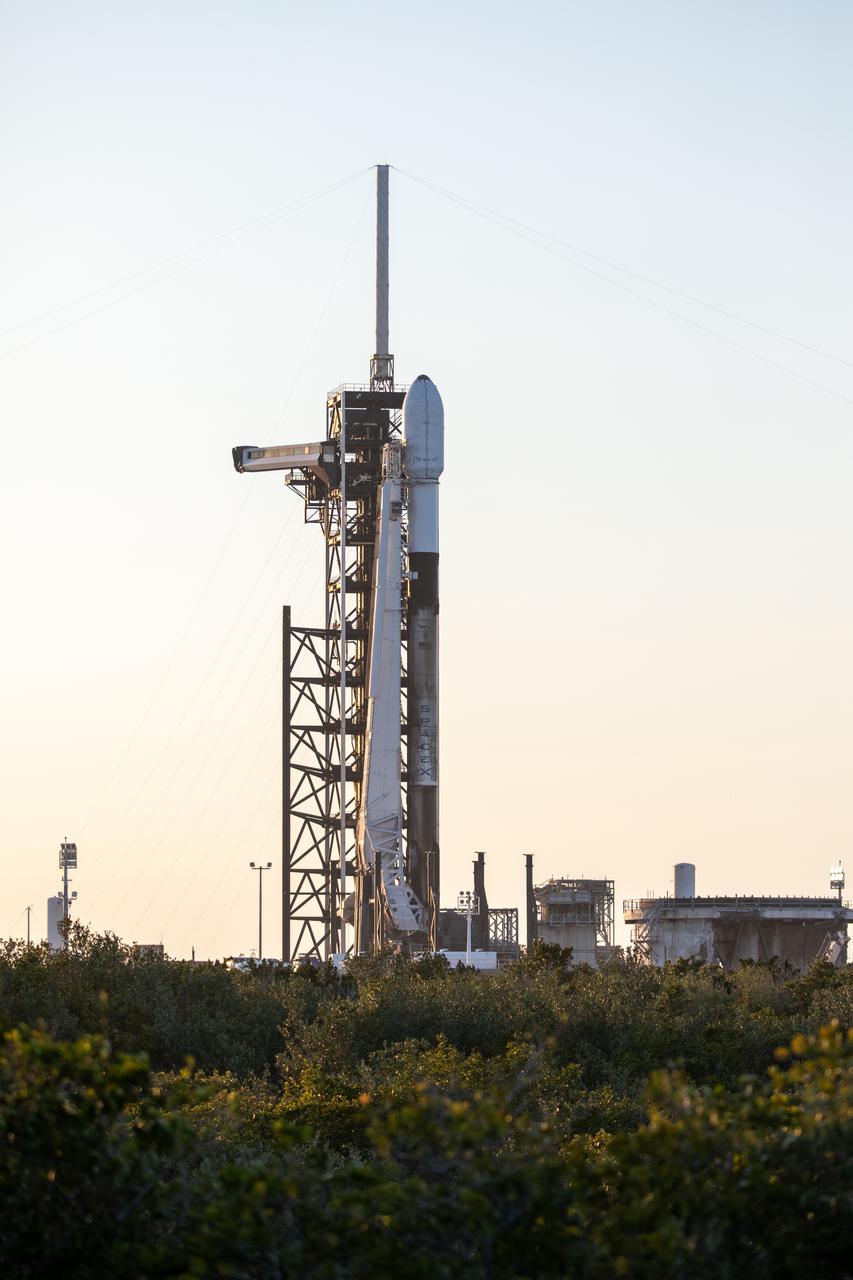

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
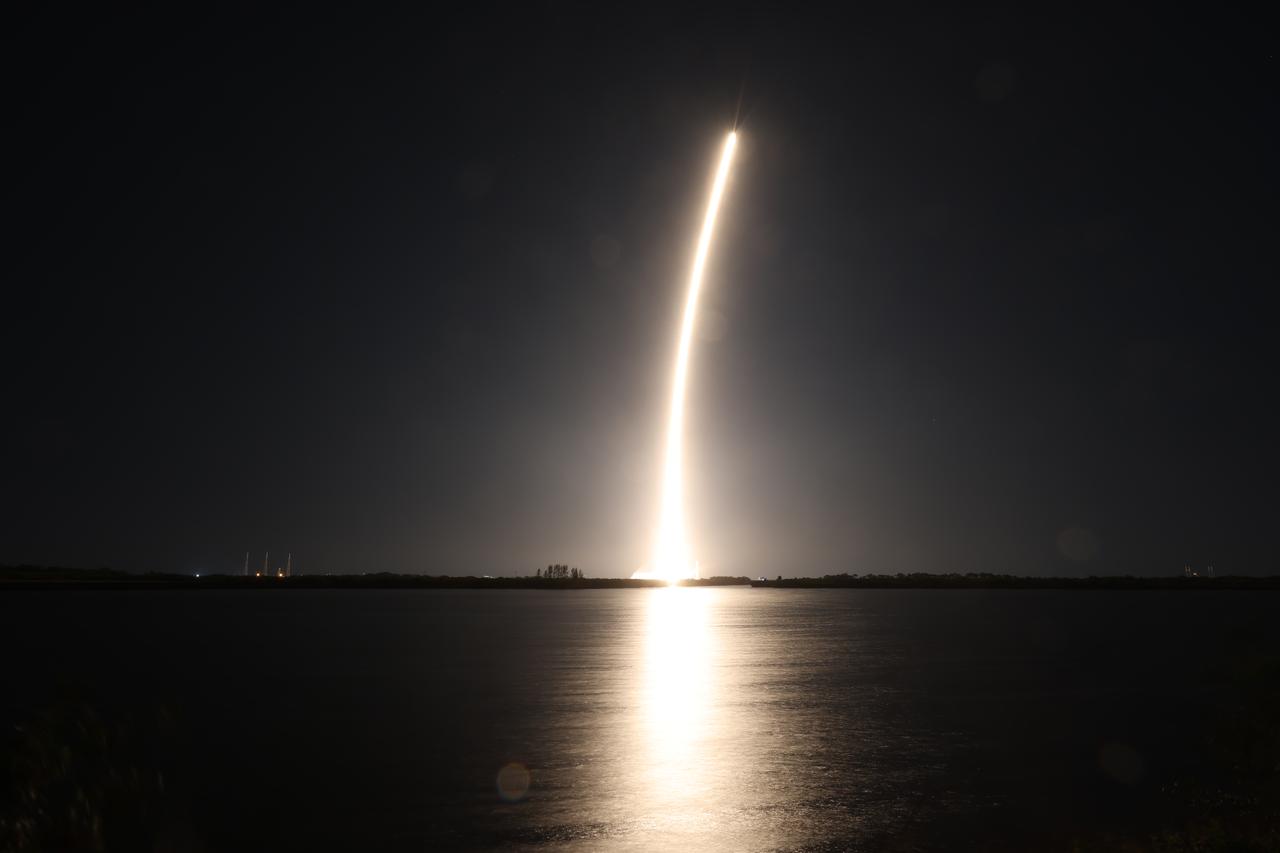

Creating a golden streak in the night sky, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.
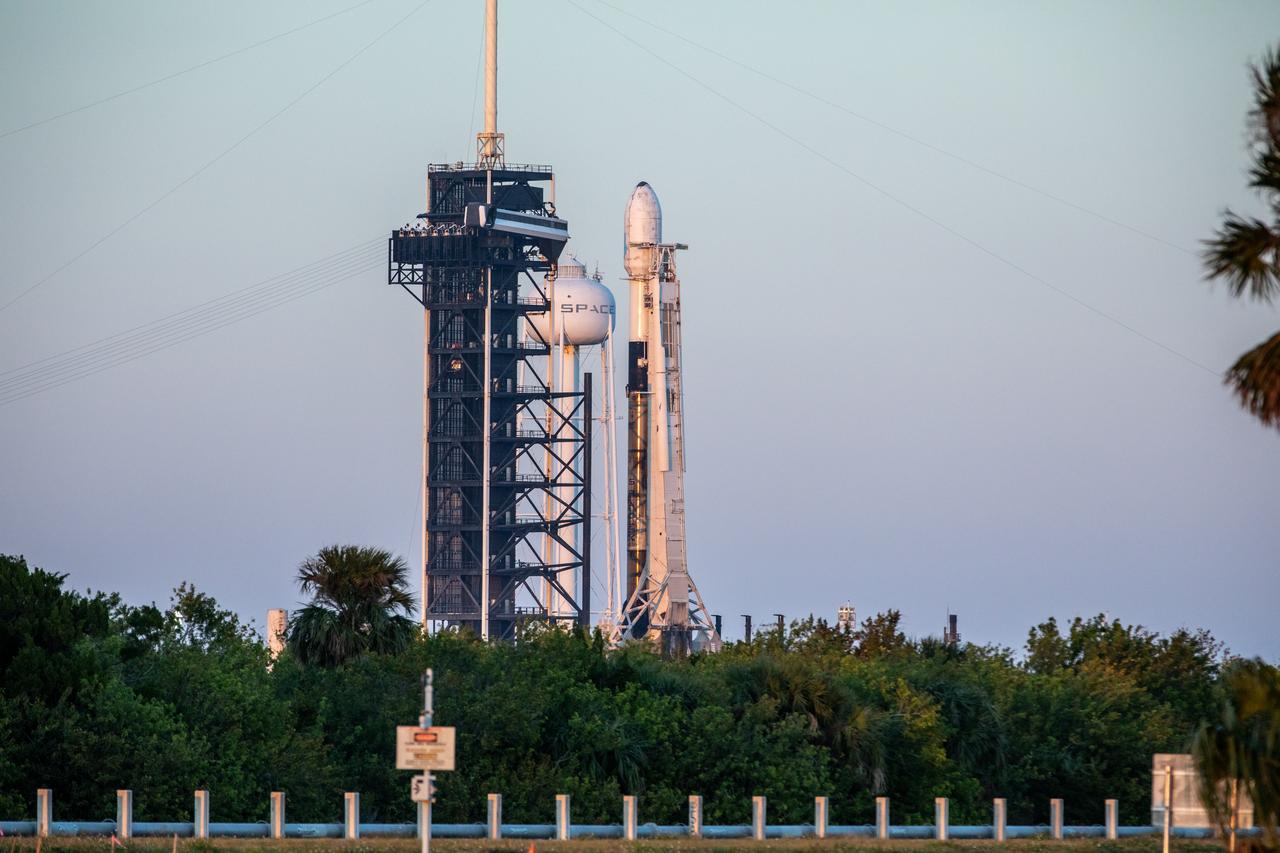

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander prepares for a launch to the Moon on Tuesday, Jan. 14, 2025 from Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions. Liftoff is targeted for 1:11 a.m. EST.
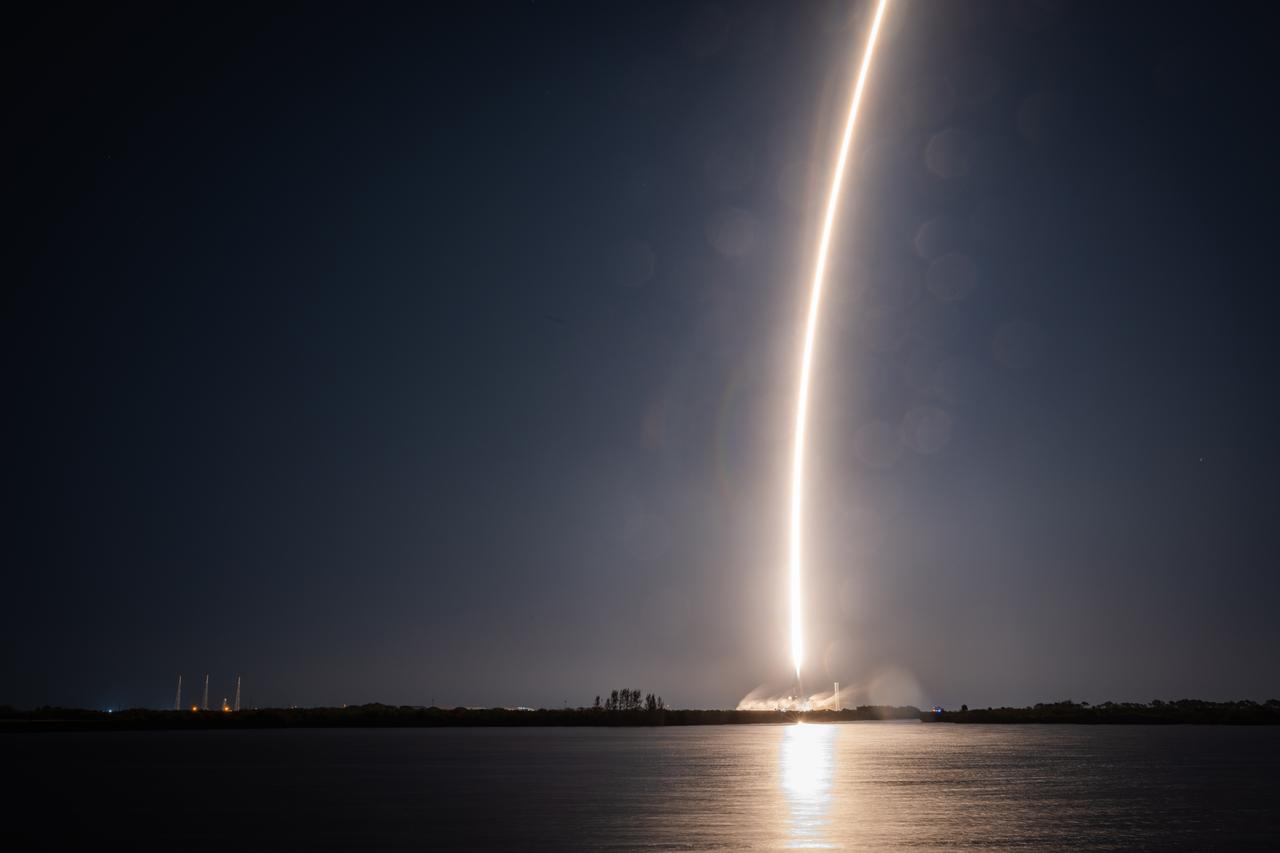

Creating a golden streak in the night sky, a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission One lander soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025 as part of NASA’s CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative. The Blue Ghost lander will carry 10 NASA science and technology instruments to the lunar surface to further understand the Moon and help prepare for future human missions.
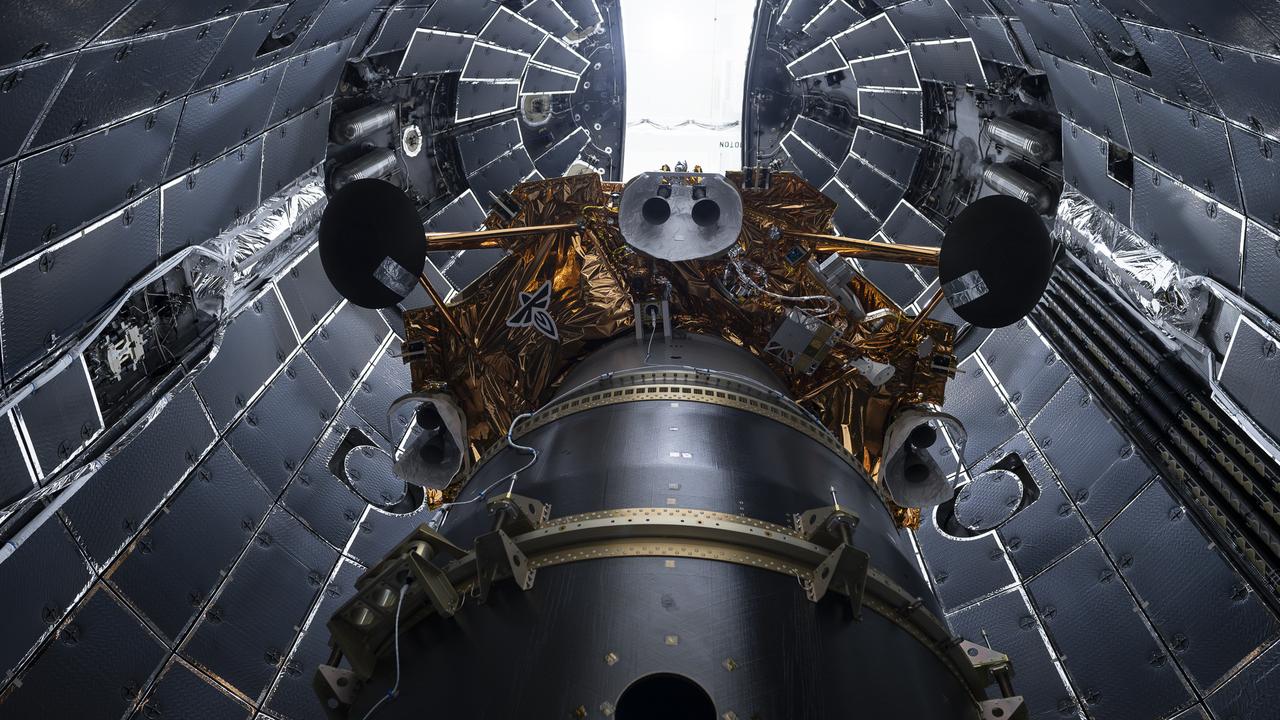

Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost lunar lander is encapsulated inside SpaceX’s rocket fairing ahead of its targeted liftoff for 1:11 a.m. EST Wednesday, Jan. 15, 2025, from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Firefly’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 will be the company’s first flight to the Moon as part of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services or CLPS initiative and Artemis campaign.
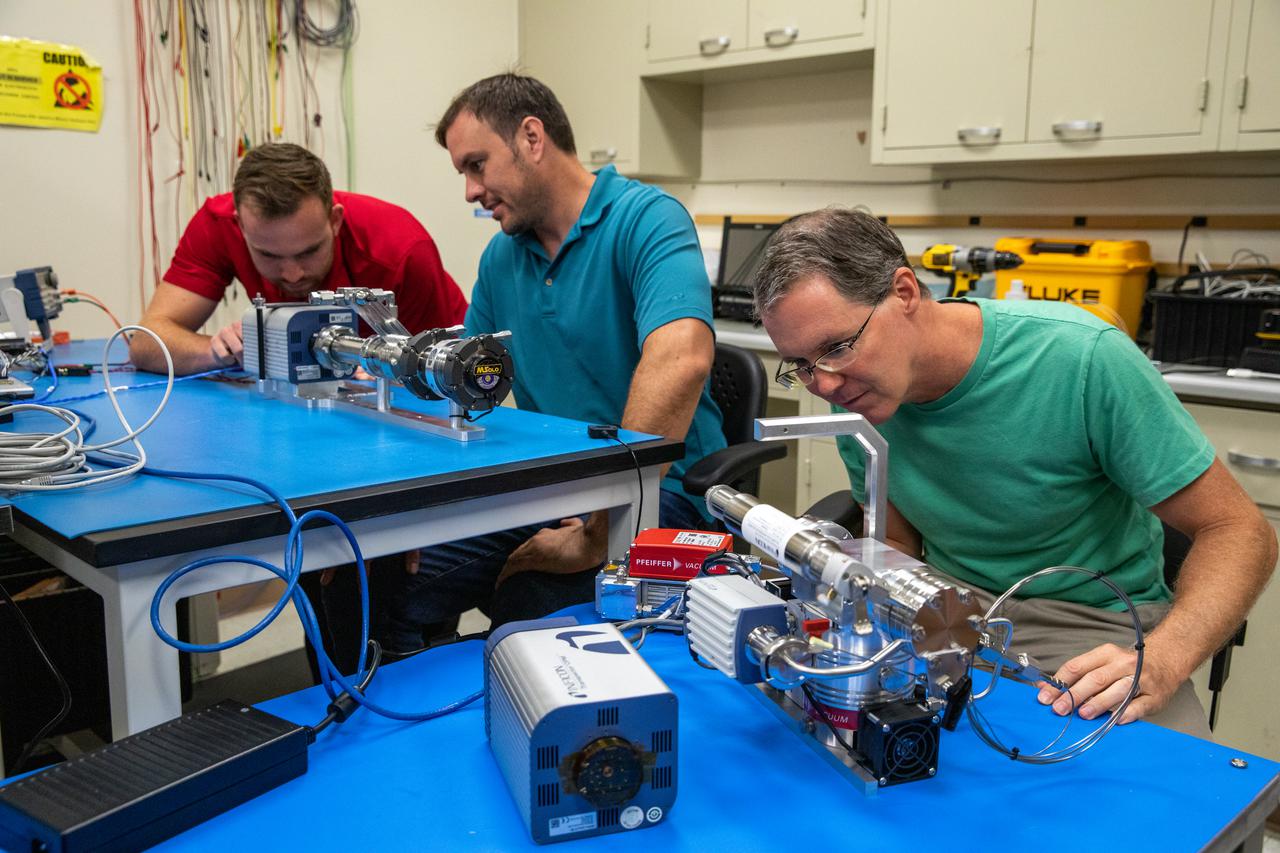
From left to right, Kennedy Space Center employees Stefan Tomovic, Beau Peacock, and Chris Bond work with MSolo (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) test hardware at the Florida spaceport on July 13, 2021. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified by the team at Kennedy to work in the harsh, rigorous conditions of the Moon. MSolo is heading to the Moon on four of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative or CLPS missions, including the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) and NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER. Kennedy is working in partnership with INFICON, of Syracuse, New York, to develop the mass spectrometer.
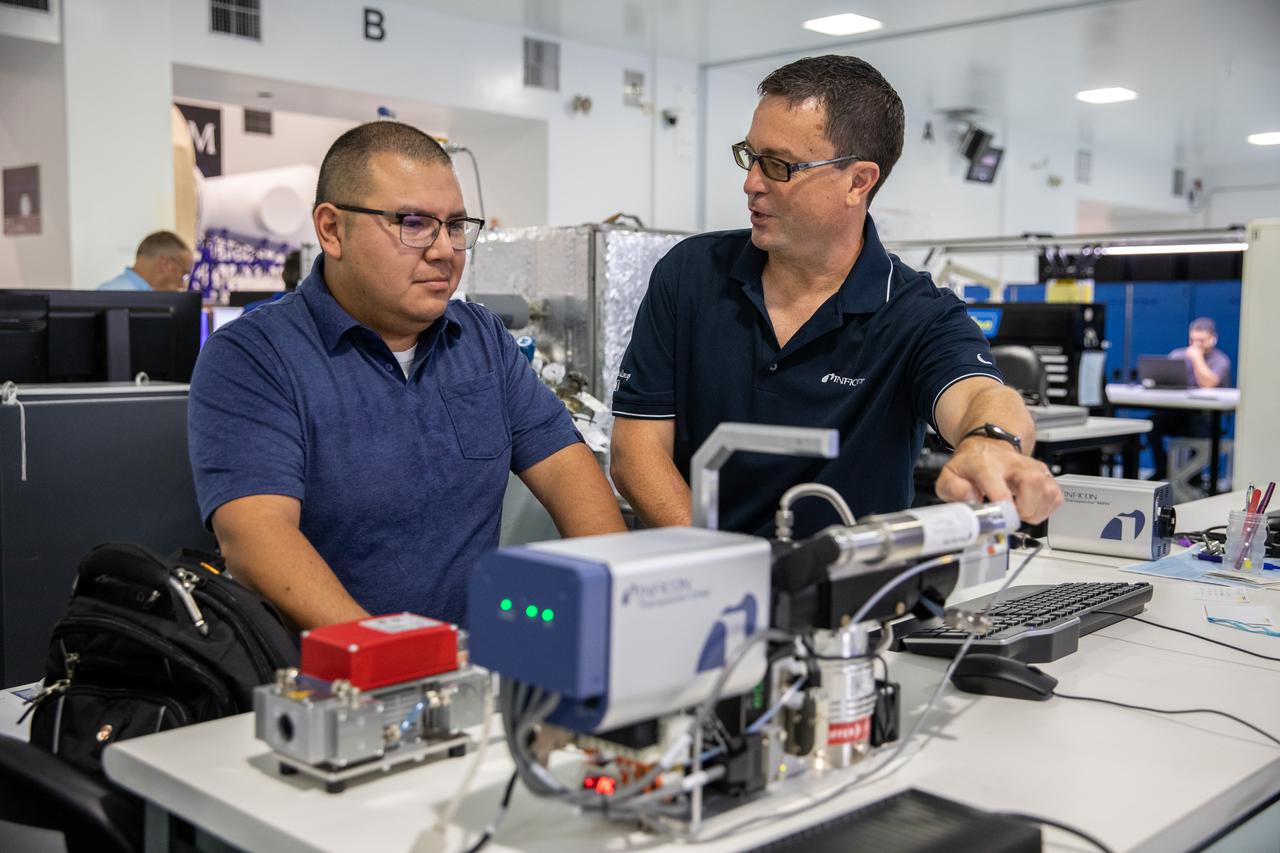

Kennedy Space Center employee Roberto Aguilar Ayala, left, and Ken Wright of INFICON work with MSolo (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) test hardware at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 2021. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified by the team at Kennedy to work in the harsh, rigorous conditions of the Moon. MSolo is heading to the Moon on four of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative or CLPS missions, including the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) and NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER. Kennedy is working in partnership with INFICON, of Syracuse, New York, to develop the mass spectrometer.
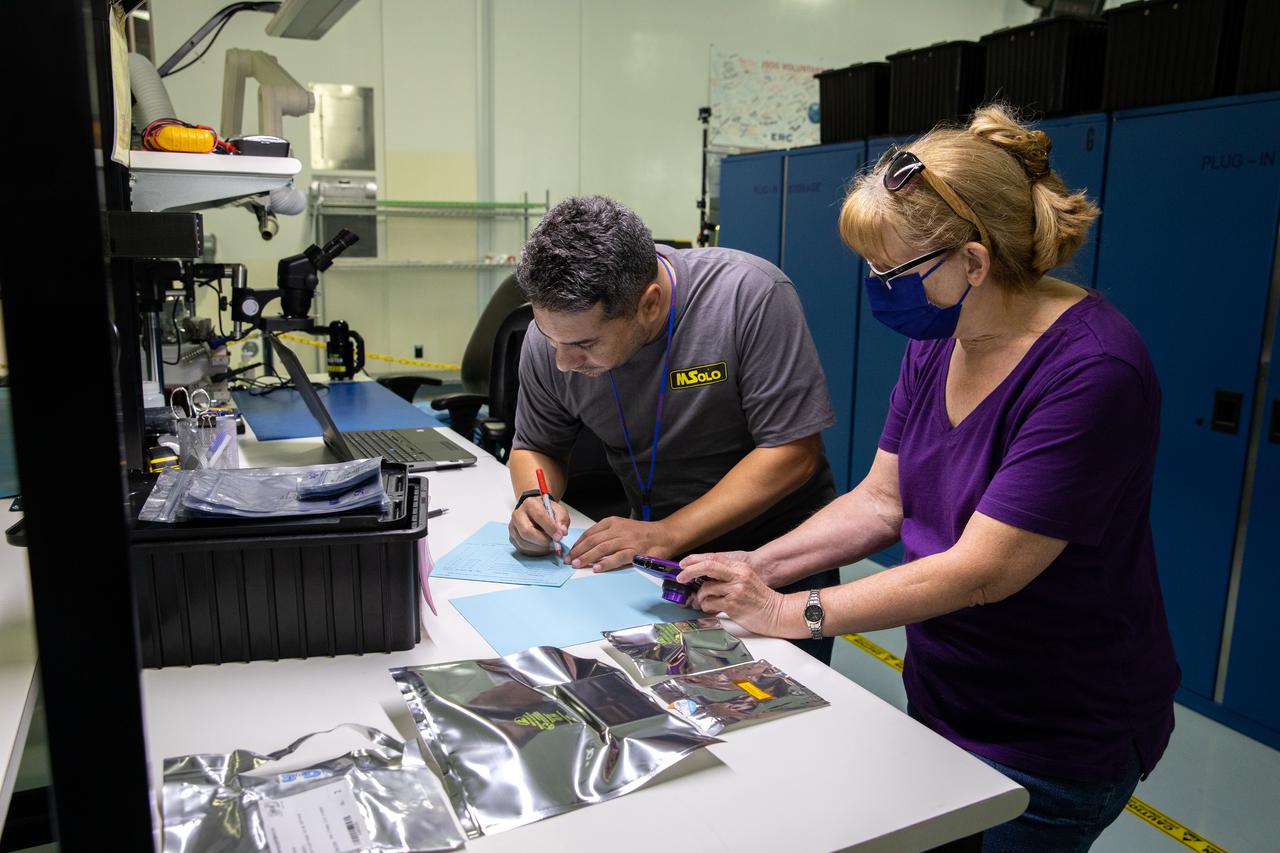

Kennedy Space Center employees Alex Decamargo, left, and JoAnn Robinson work with MSolo (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) flight hardware at the Florida spaceport on July 13, 2021. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified by the team at Kennedy to work in the harsh, rigorous conditions of the Moon. MSolo is heading to the Moon on four of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative or CLPS missions, including the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) and NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER. Kennedy is working in partnership with INFICON, of Syracuse, New York, to develop the mass spectrometer.

Kennedy Space Center employee Chris Johnson, left, and Jamie Winfield of INFICON work with MSolo (Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations) test hardware at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 13, 2021. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified by the team at Kennedy to work in the harsh, rigorous conditions of the Moon. MSolo is heading to the Moon on four of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services initiative or CLPS missions, including the Polar Resources Ice Mining Experiment-1 (PRIME-1) and NASA’s Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, or VIPER. Kennedy is working in partnership with INFICON, of Syracuse, New York, to develop the mass spectrometer.
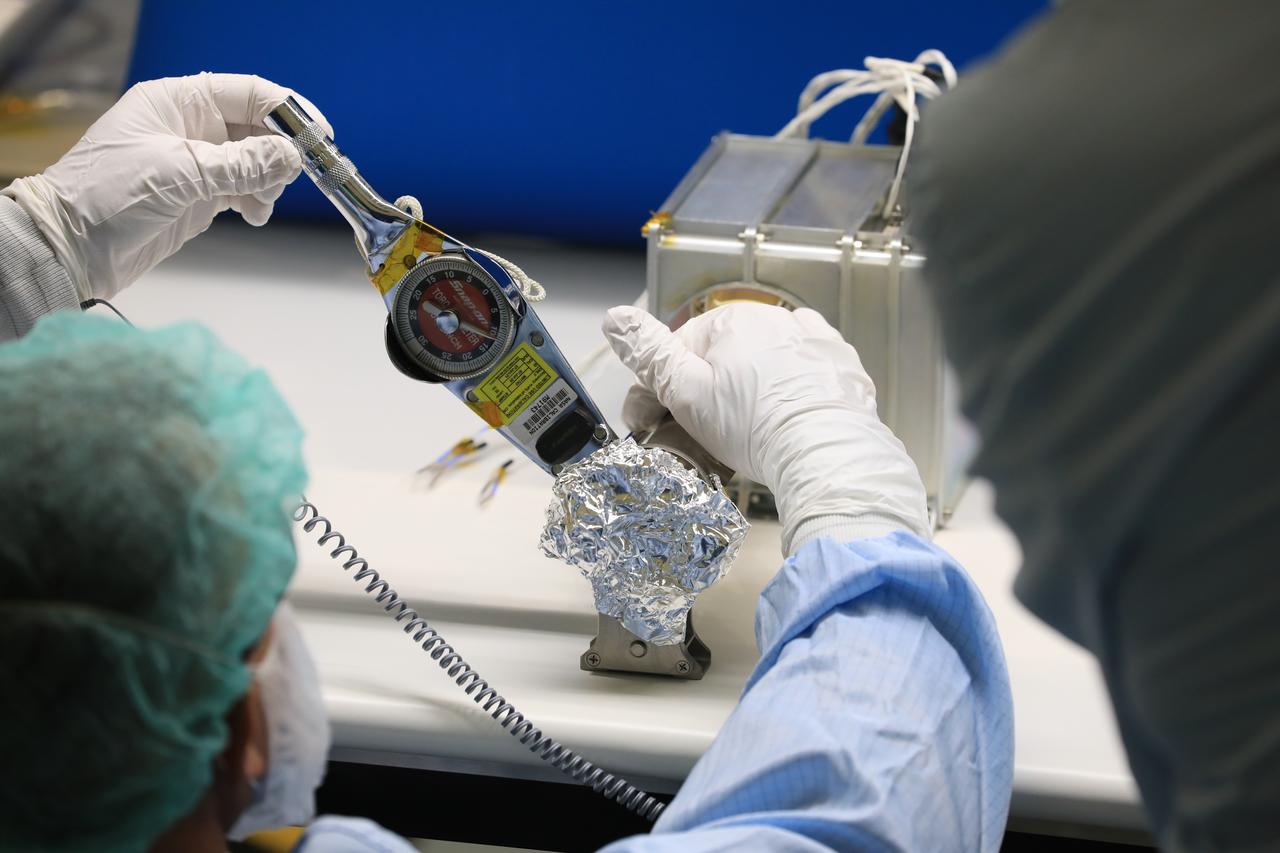

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
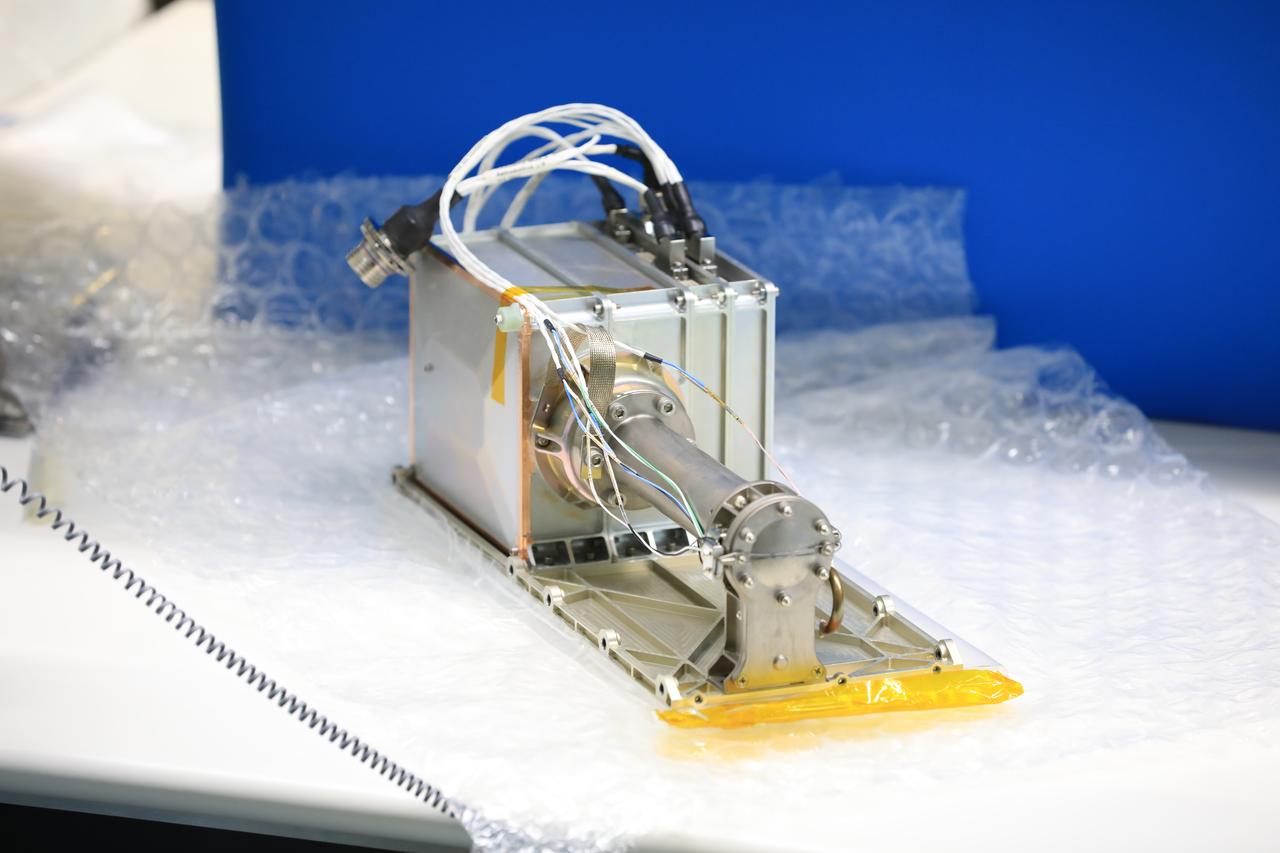

The Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida following installation of its radiator on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
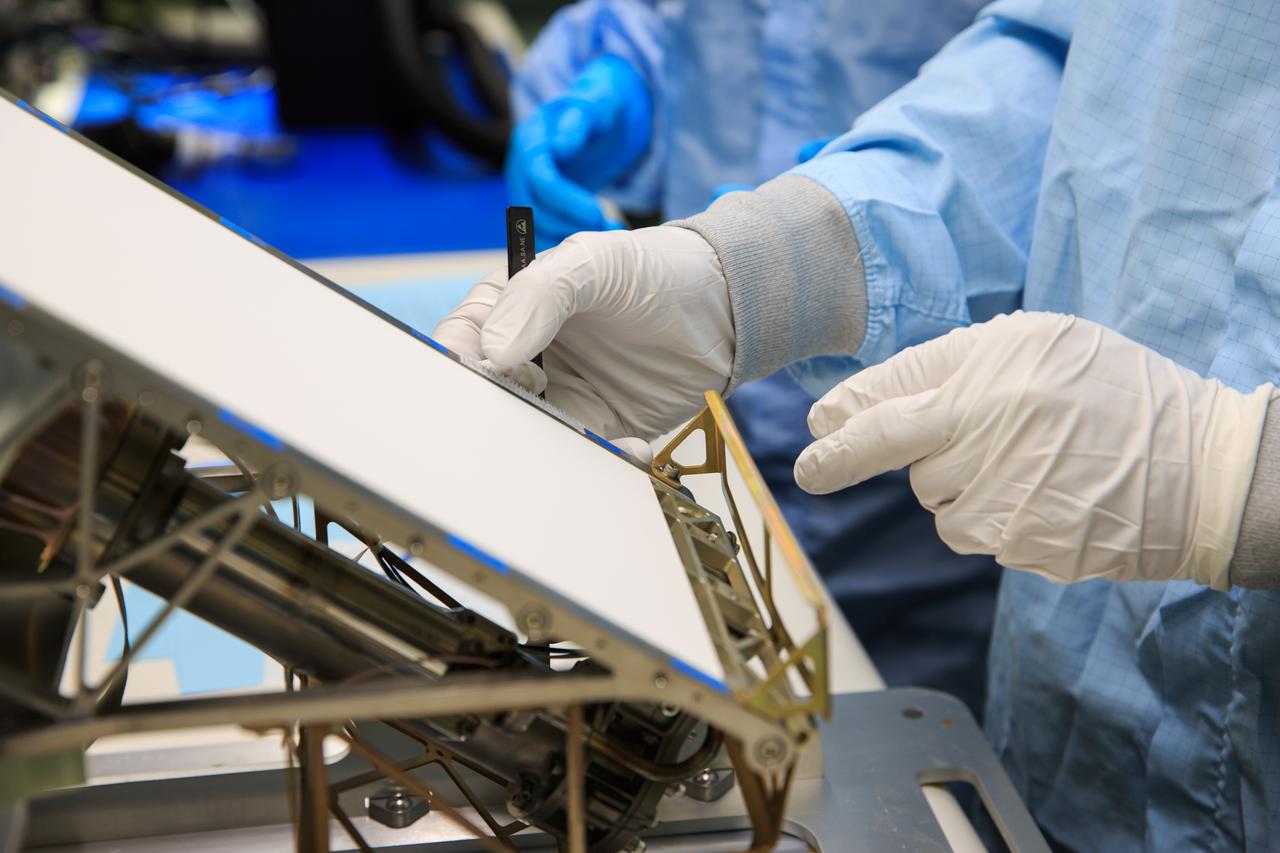

Team members working inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Sept. 23, 2021, meticulously assemble ground support equipment that will protect shipment of the Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) flight hardware for preparations before it launches in 2022. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. MSolo, scheduled to first launch in 2022, is part of four of the agency’s Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries will include science experiments, testing of technologies and demonstrations of capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
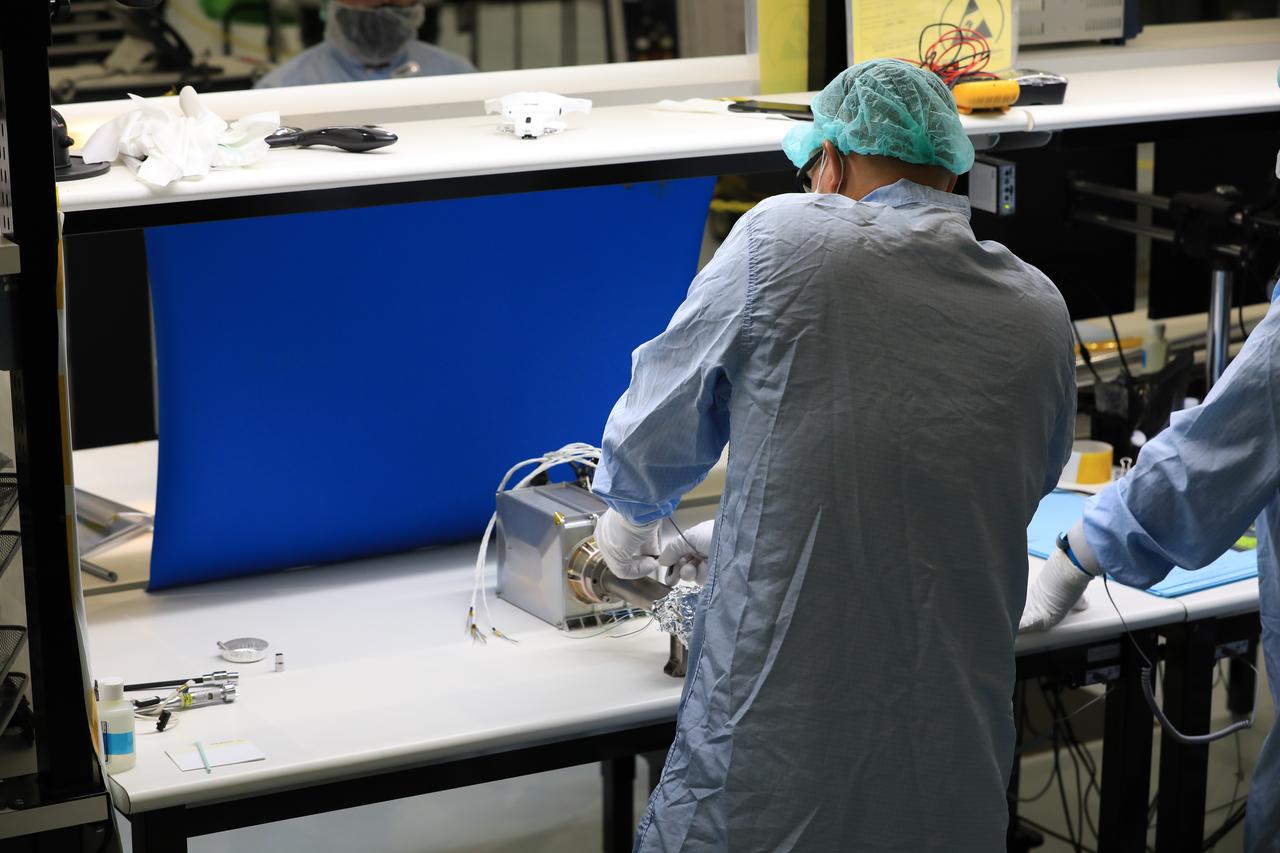

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida work with instruments for Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) inside the Space Station Processing on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This work is preparing MSolo hardware for a robotic mission as part of the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) launching to exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon in 2021. A future mission will send a mobile robot named the Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover (VIPER) to the Moon to prospect for water. VIPER will have several instruments that will allow it to detect and sample water including MSolo, the Neutron Spectrometer System, the Near Infrared Volatiles Spectrometer System and The Regolith and Ice Drill for Exploring New Terrain (TRIDENT).
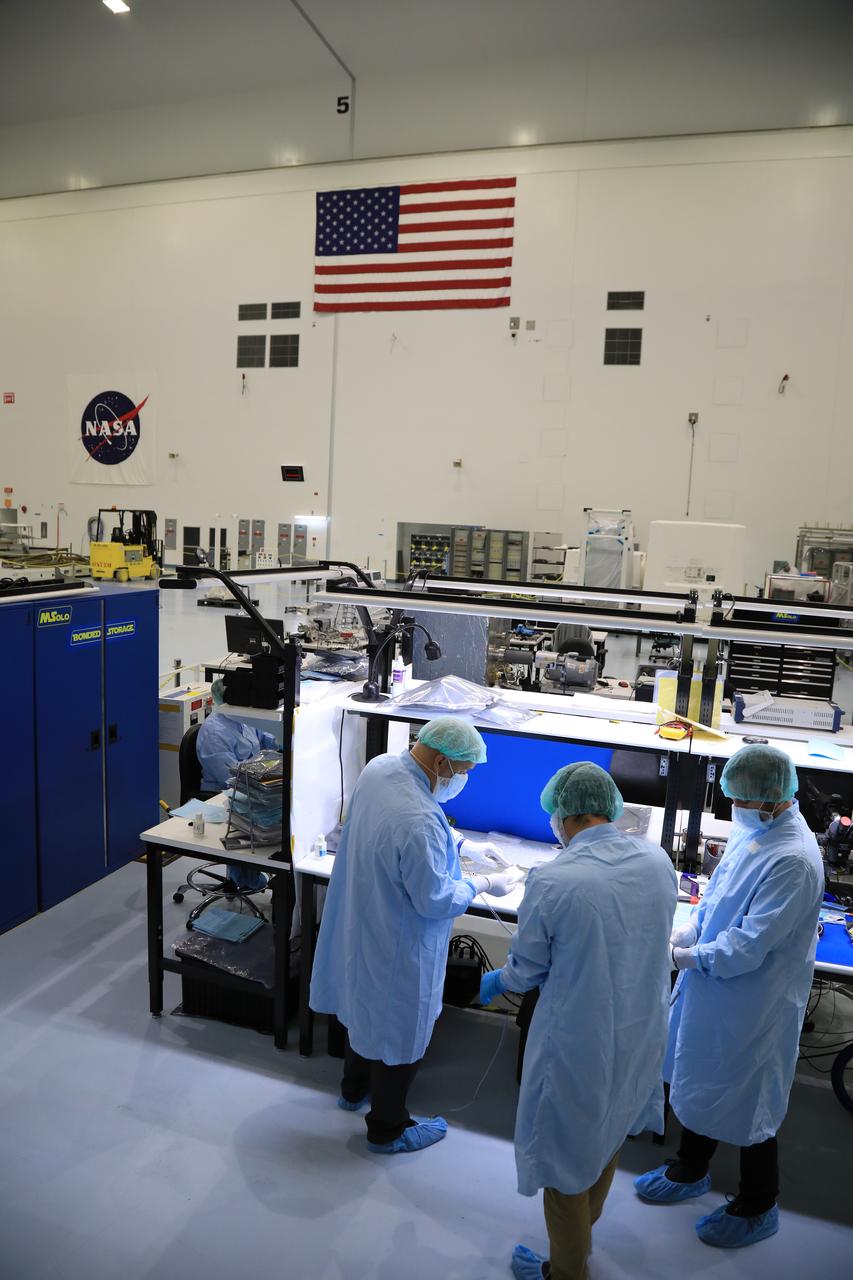

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
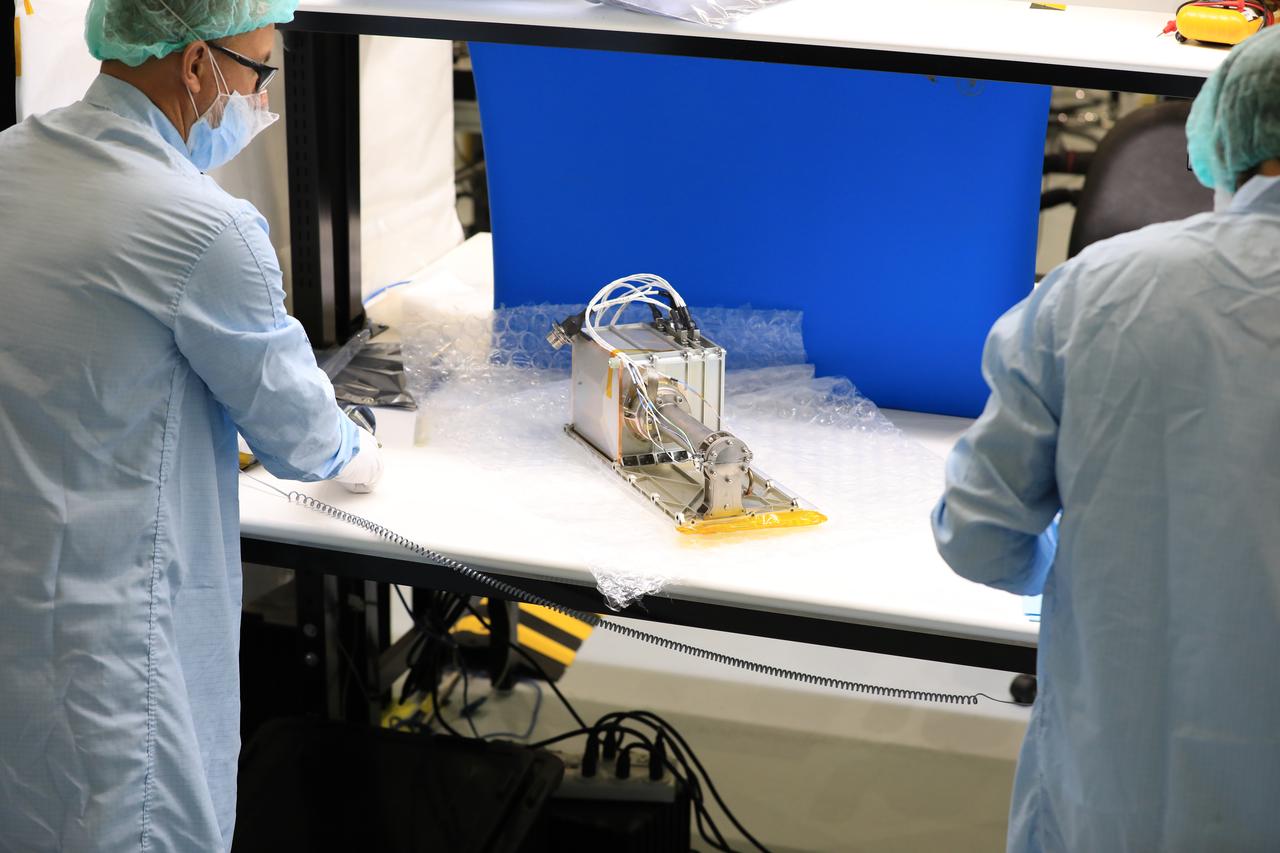
Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.
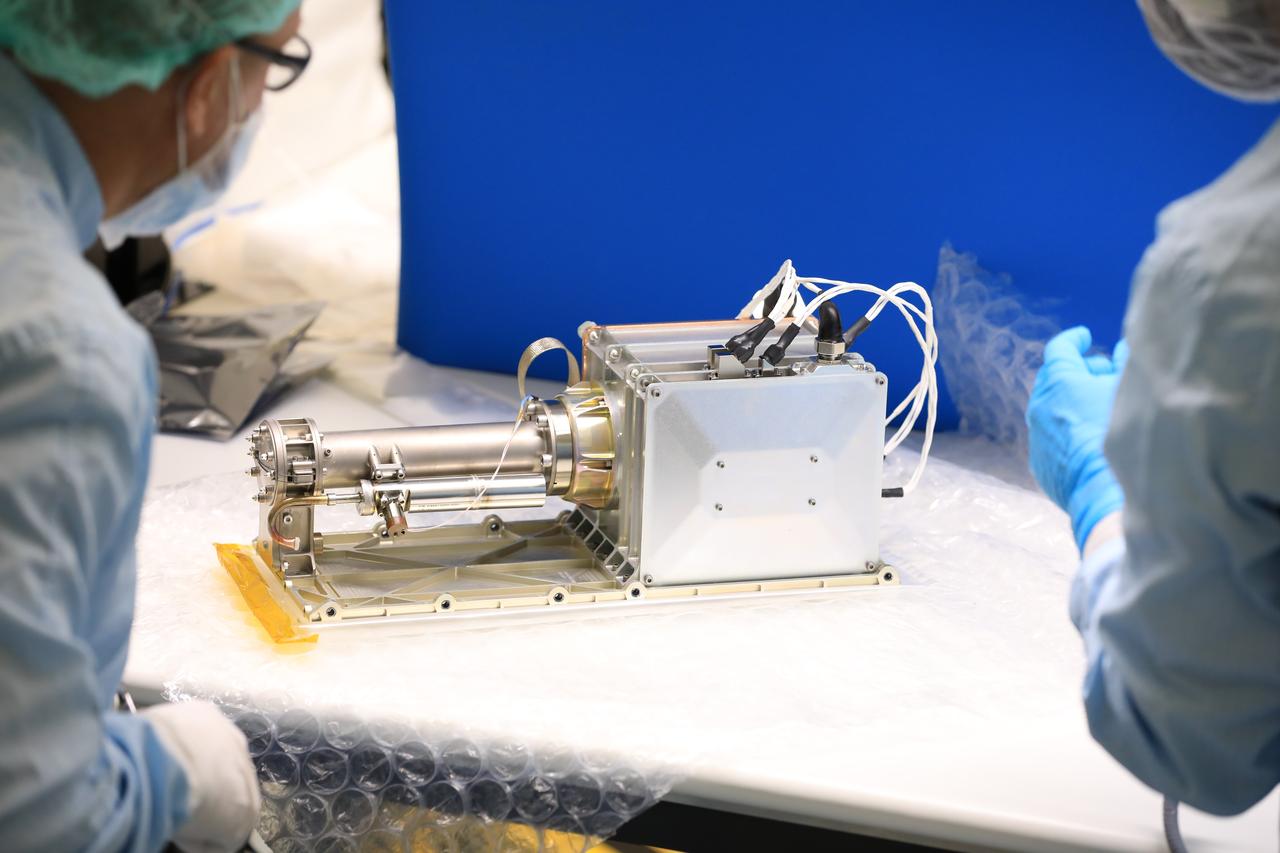

Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida install the radiator for the Mass Spectrometer Observing Lunar Operations (MSolo) instrument inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Sept. 25, 2020. MSolo will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. The radiator will help keep the instrument’s temperature stable in the extreme heat and cold it will encounter. MSolo instruments are scheduled to launch on multiple robotic missions as part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), with the first of these missions exploring Lacus Mortis, a large crater on the near side of the Moon, beginning in 2021. MSolo also will be one of three instruments on the agency’s water-hunting Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover, VIPER, scheduled to launch to the Moon’s South Pole in late 2023.