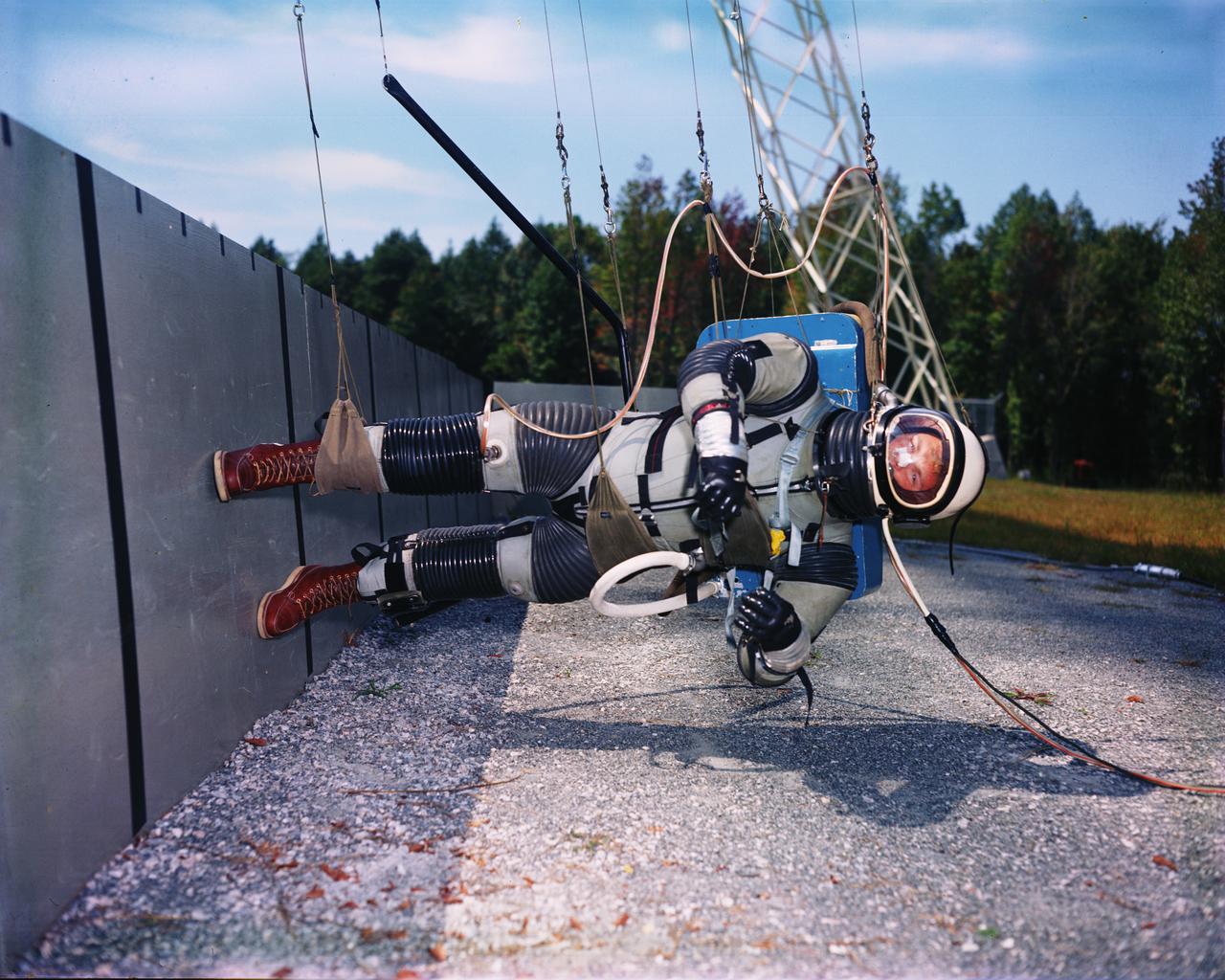
Lunar Landing Walking Simulator: Researchers at Langley study the ability of astronauts to walk, run and perform other tasks required during lunar exploration. The Reduced Gravity Simulator gave researchers the opportunity to look at the effects of one-sixth normal gravity on self-locomotion. Several Apollo astronauts practiced lunar waling at the facility.

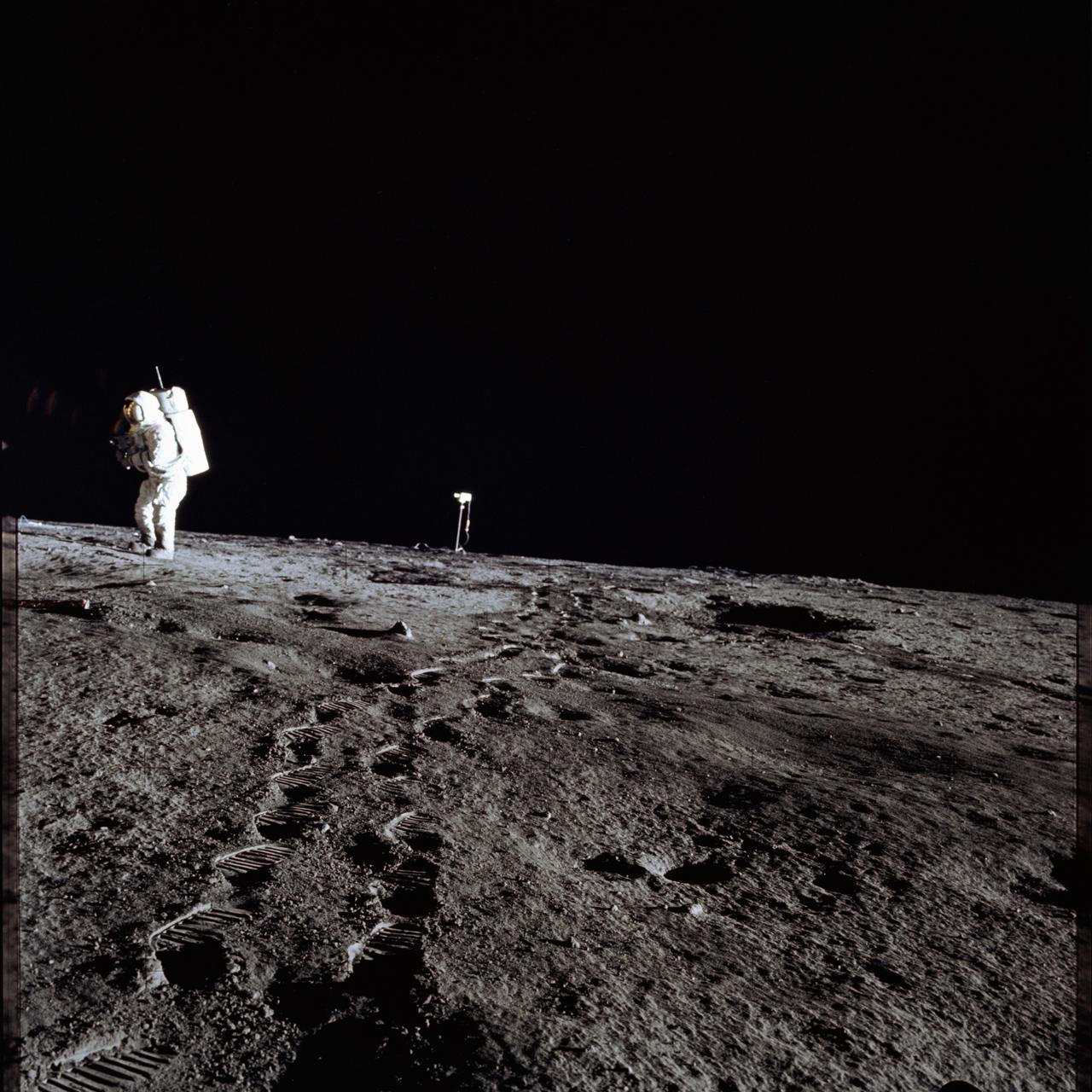
AS11-40-5902 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, Apollo 11 commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. The astronauts' bootprints are clearly visible in the foreground. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.
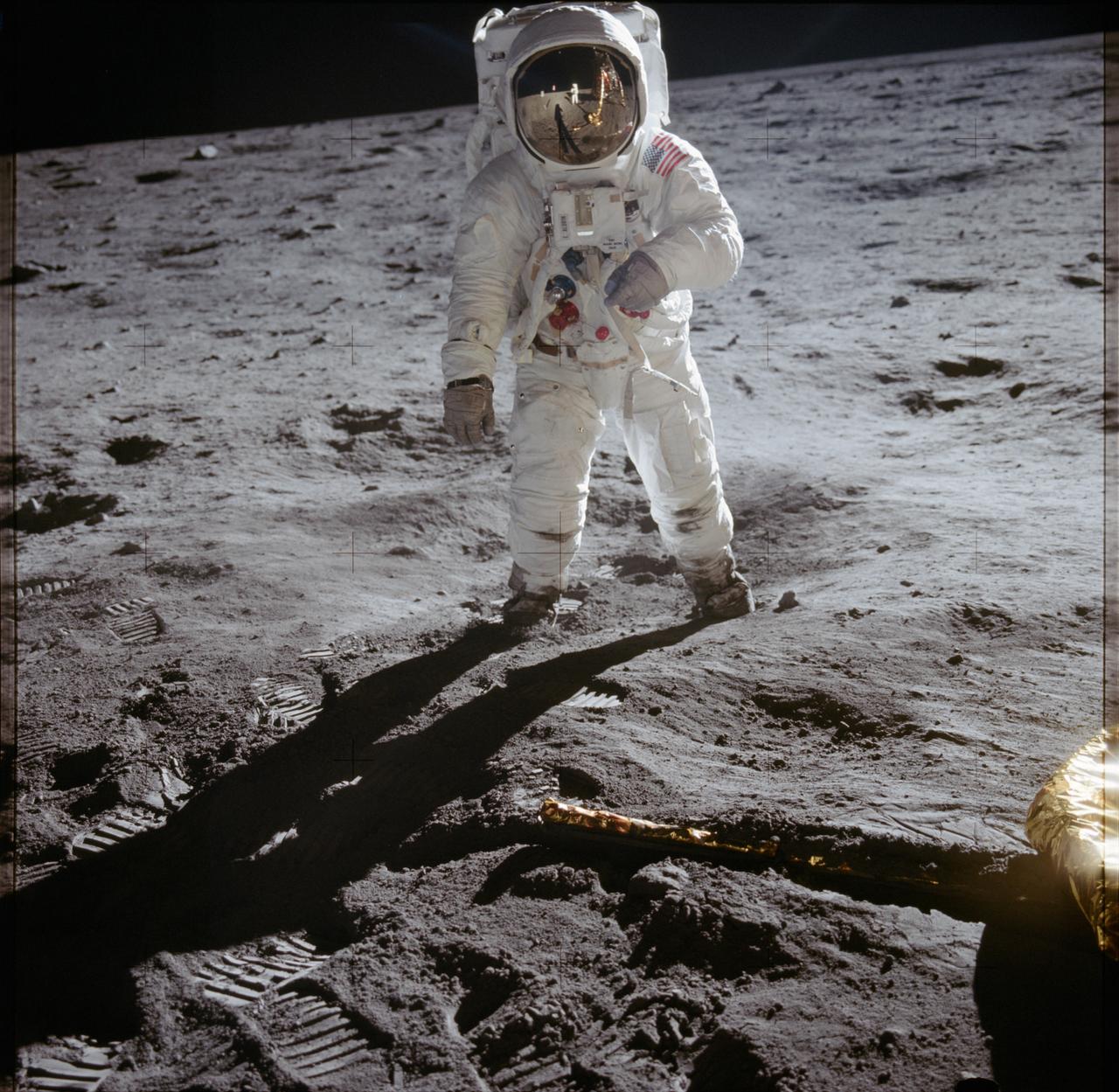

AS11-40-5903 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, walks on the surface of the moon near the leg of the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). Astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, took this photograph with a 70mm lunar surface camera. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil wrote in his paper Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject' s weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed. -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377 A.W. Vigil, Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research, Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology, Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.

AS11-40-5868 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, descends the steps of the Lunar Module (LM) ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. He had just egressed the LM. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

Astronaut Walt Cunningham on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
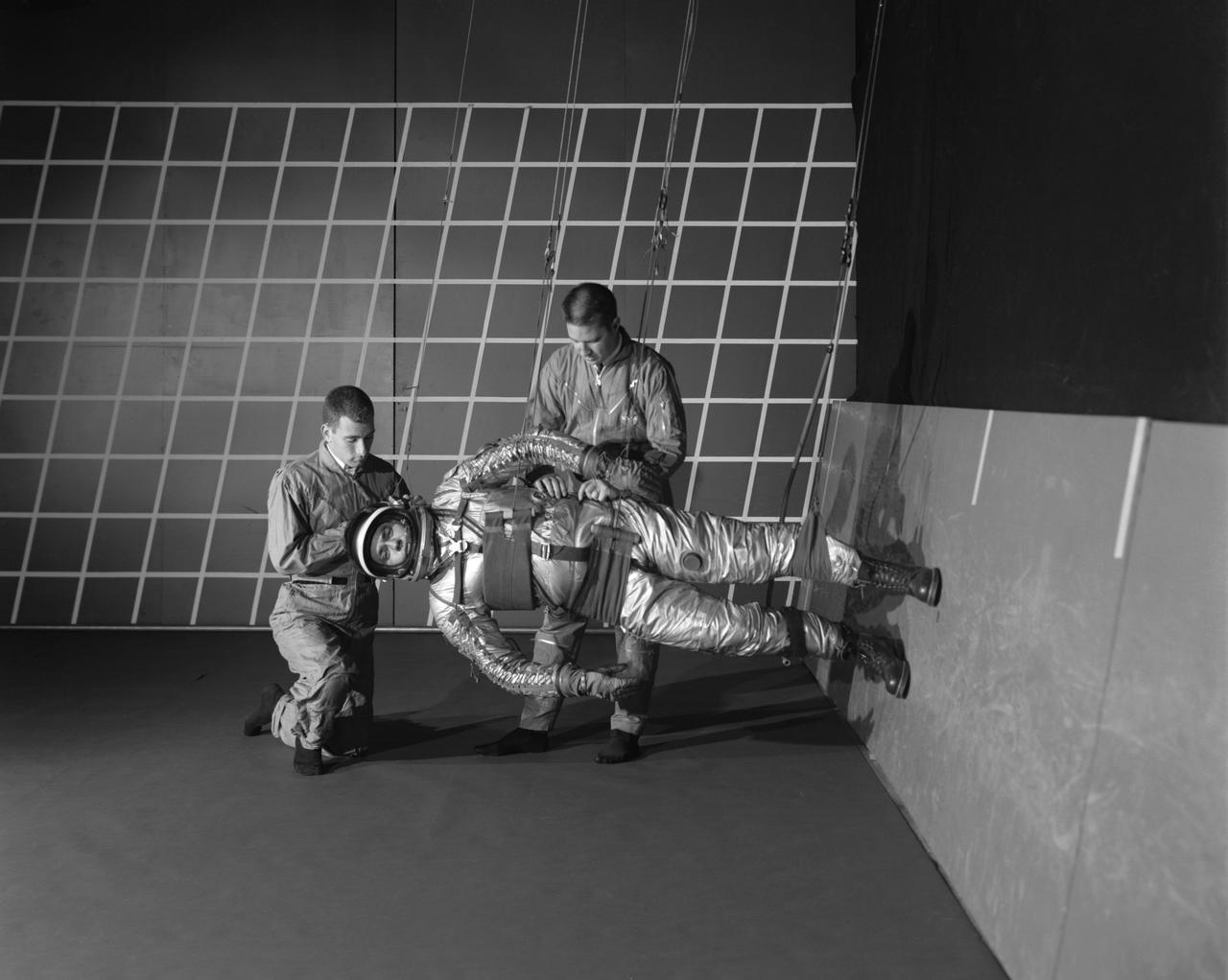

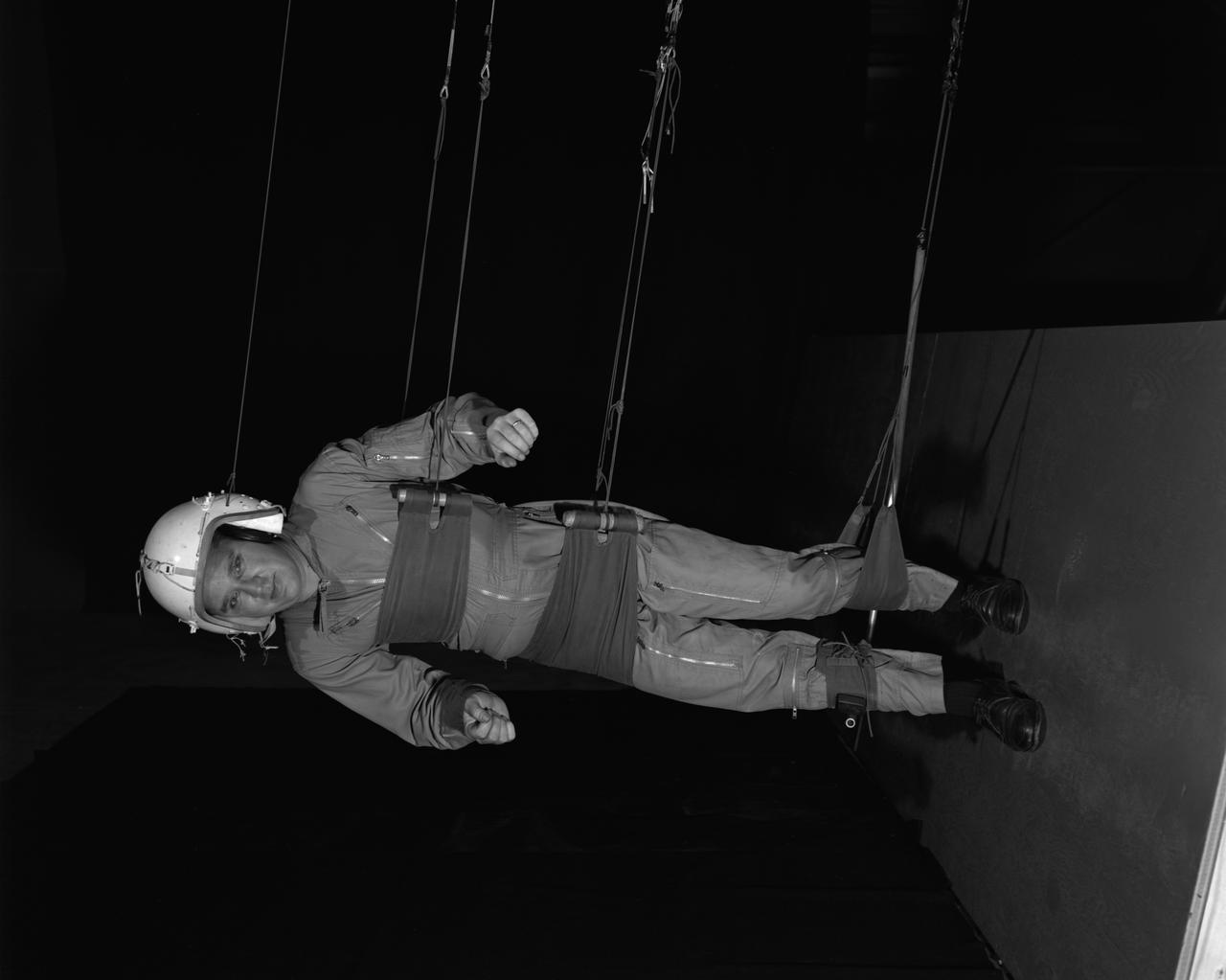
A test subject being suited up for studies on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. Francis B. Smith wrote in his paper "Simulators For Manned Space Research," "I would like to conclude this talk with a discussion of a device for simulating lunar gravity which is very effective and yet which is so simple that its cost is in the order of a few thousand dollars at most, rather than hundreds of thousands. With a little ingenuity, one could almost build this type simulator in his backyard for children to play on. The principle is ...if a test subject is suspended in a sling so that his body axis makes an angle of 9 1/2 degrees with the horizontal and if he then "stands" on a platform perpendicular to his body axis, the component of the earth's gravity forcing him toward the platform is one times the sine of 9 1/2 degrees or approximately 1/6 of the earth's normal gravity field. That is, a 180 pound astronaut "standing" on the platform would exert a force of only 30 pounds - the same as if he were standing upright on the lunar surface." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators For Manned Space Research," Paper for 1966 IEEE International Convention, New York, NY, March 21-25, 1966
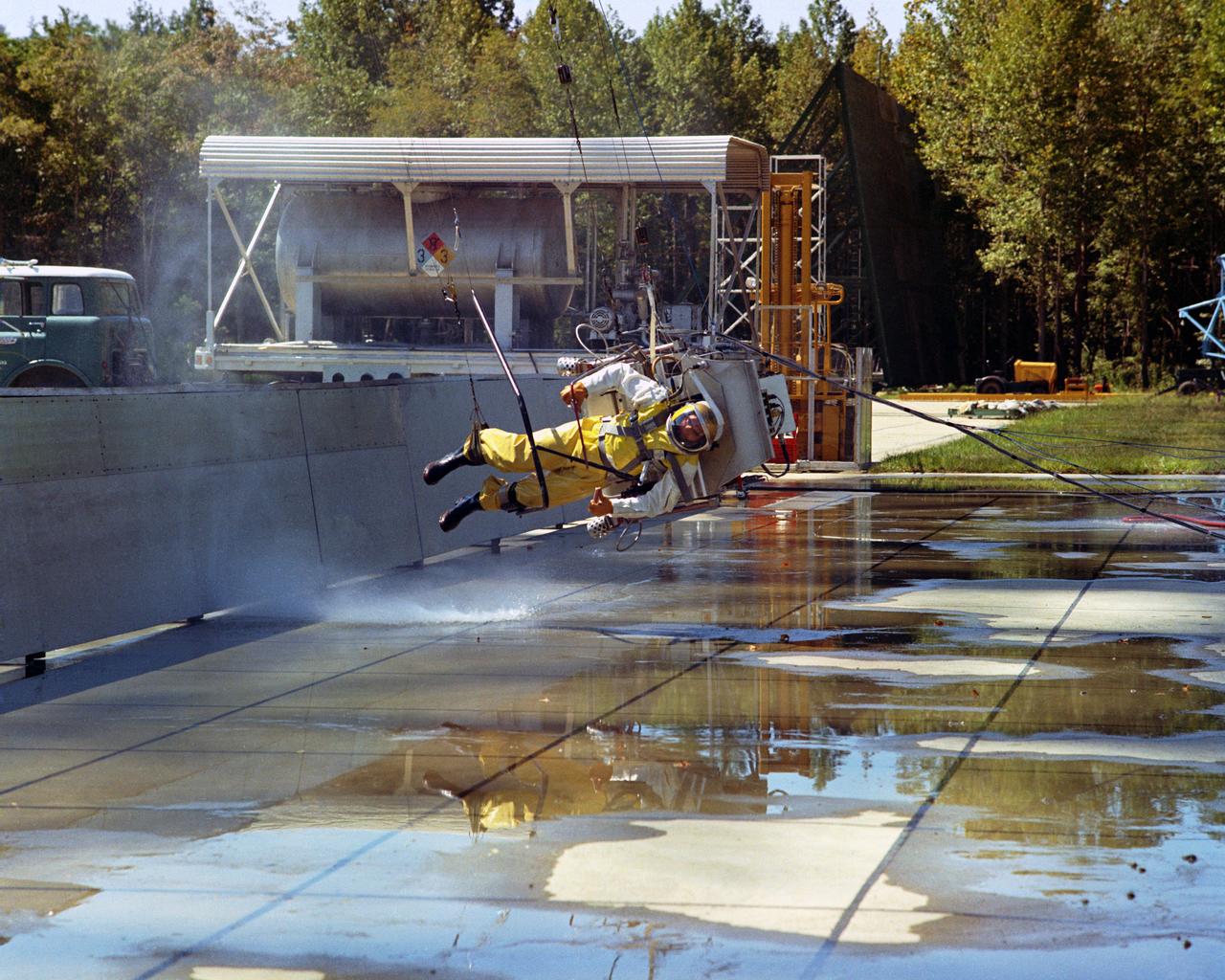

Icarus Lunar Walker,Lunar Landing Research Facility. Langley study of the backpack propulsion unit, by Bell Aerosystems. Icarus full scale test at Lunar Landing Research Facility - low gravity simulator. A NASA Langley researcher moon walks under the Lunar Landing Research Facility's gantry. More information on this can be read in the Document. "STUDIES OF PILOTING PROBLEMS OF ONE-MAN FLYING UNITS OPERATED IN SIMULATED LUNAR GRAVITY" BY Donald E. Hewes
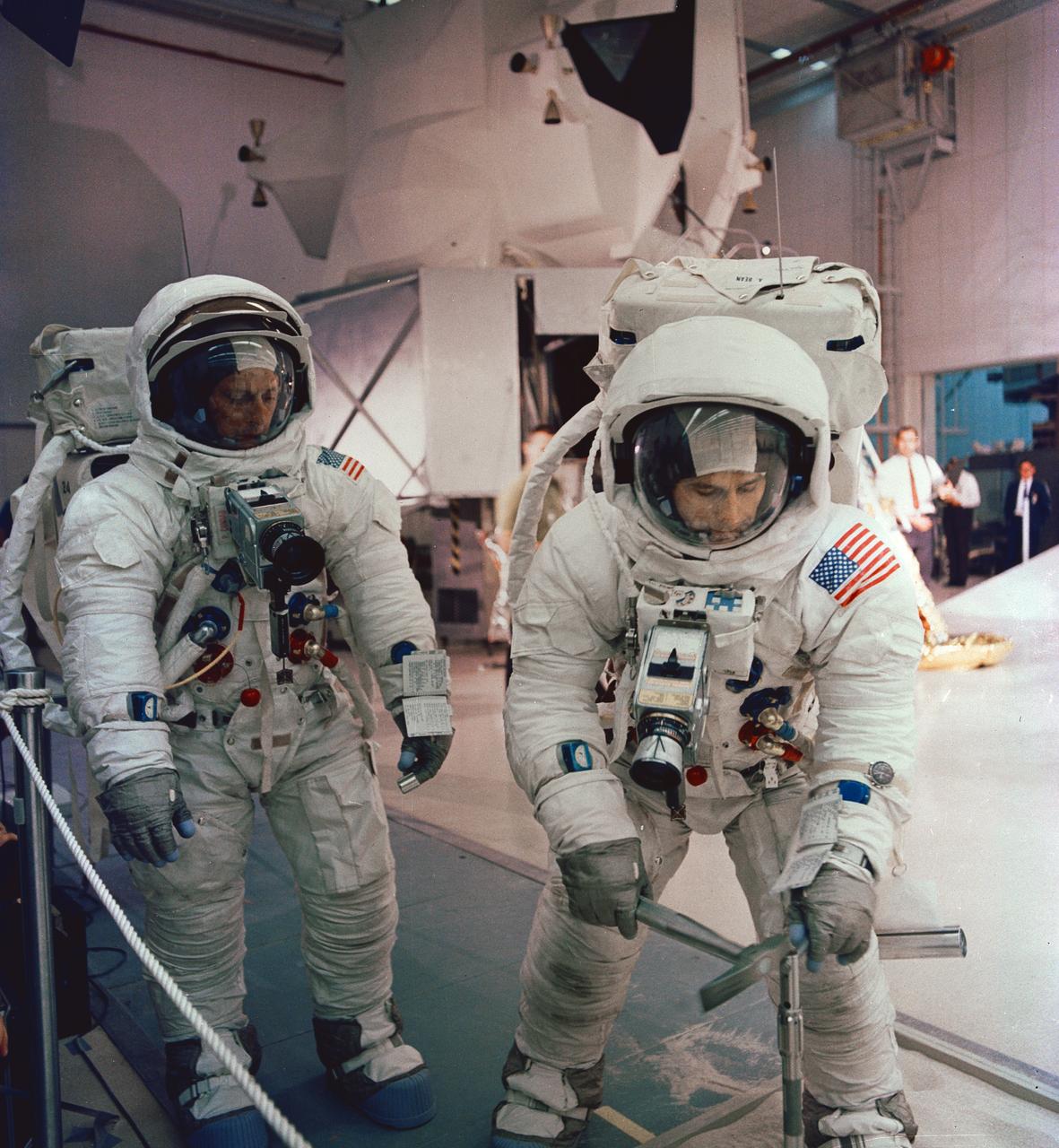

S69-55362 (6 Oct. 1969) --- The two assigned moon-walking crew members for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission participate in lunar surface extravehicular activity simulations in the Kennedy Space Center's Flight Crew Training Building. Here, astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, simulates driving core tube into lunar surface to obtain a sample. Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, looks on. A Lunar Module mock-up is in the center background. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. walks on the surface of the Moon near a leg of the Lunar Module during the Apollo 11 EVA. Armstrong also took this picture with the 70-mm lunar surface camera. Note footprints in the foreground.

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - A view of the Earth appears over the lunar horizon as the Apollo 11 Command Module comes into view of the Moon before astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin Jr. leave in the Lunar Module, Eagle, to become the first men to walk on the Moon's surface.
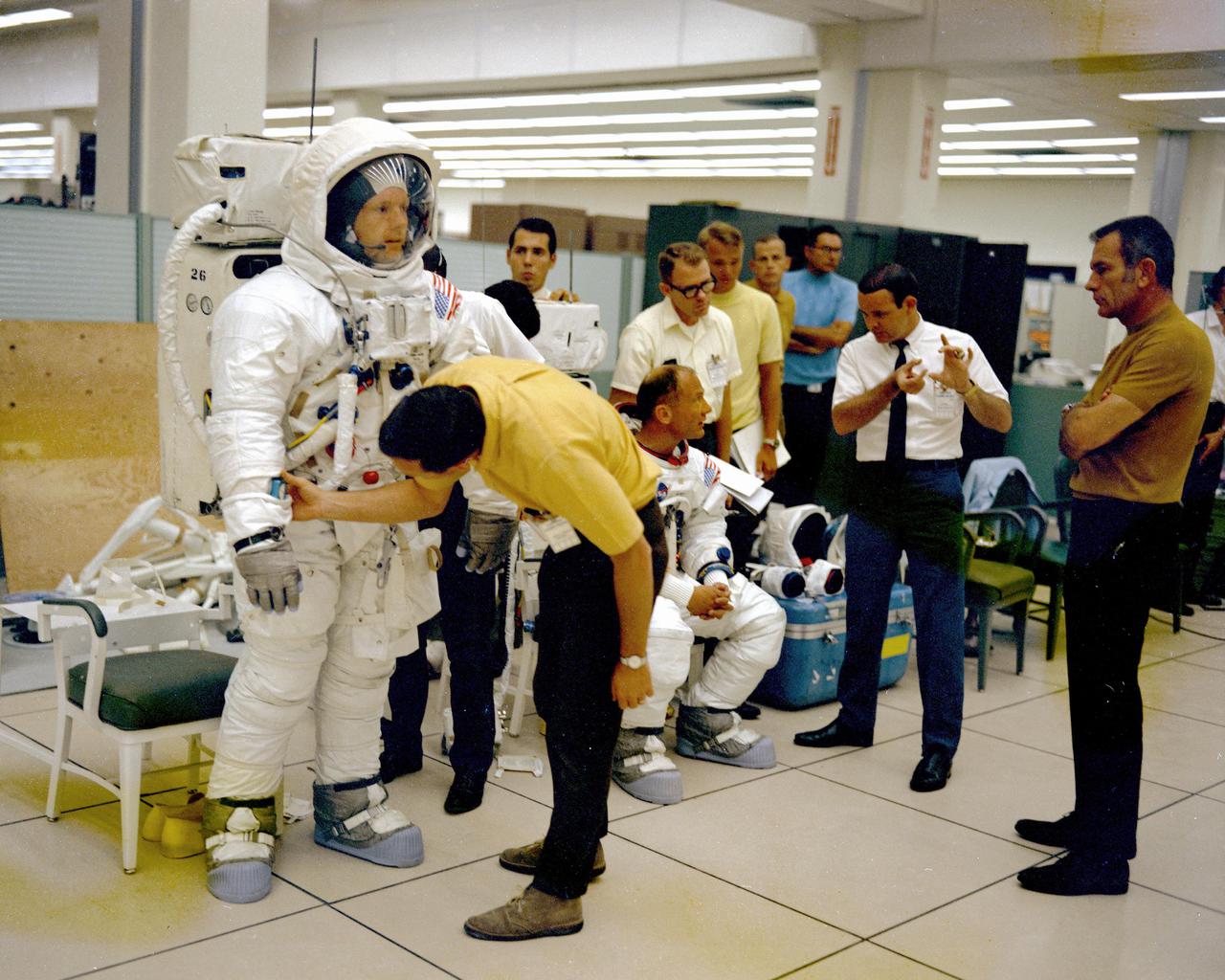

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Apollo 11 flight crew are given instructions by technicians and management while undergoing the Extravehicular Activity (EVA) training and the Lunar Module walk-through in preparation for the first manned landing on the Moon.
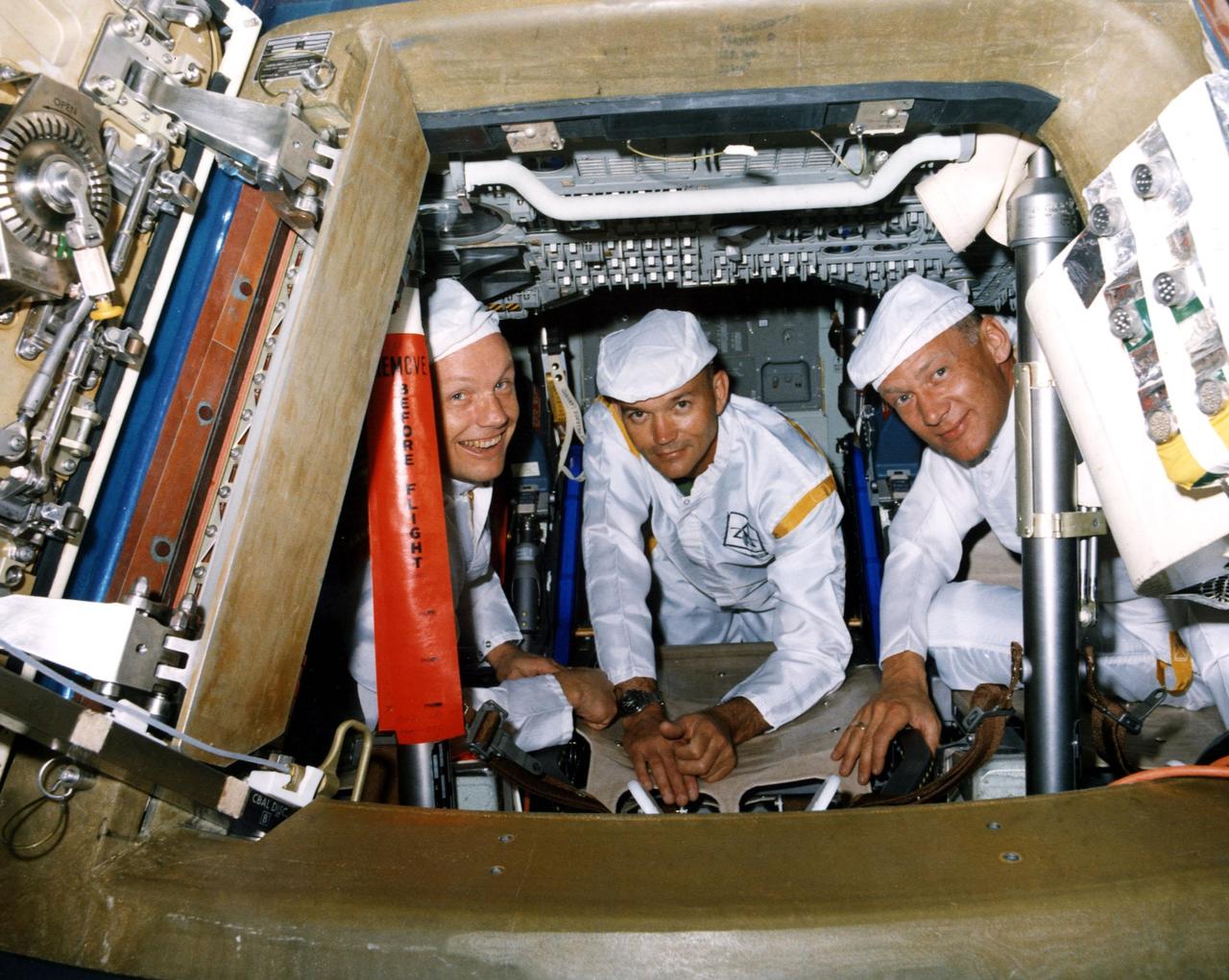

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Apollo 11 prime crew poses for a photograph during a walk-through egress test. The hands-on test is in preparation for the first manned lunar landing mission scheduled for liftoff in July

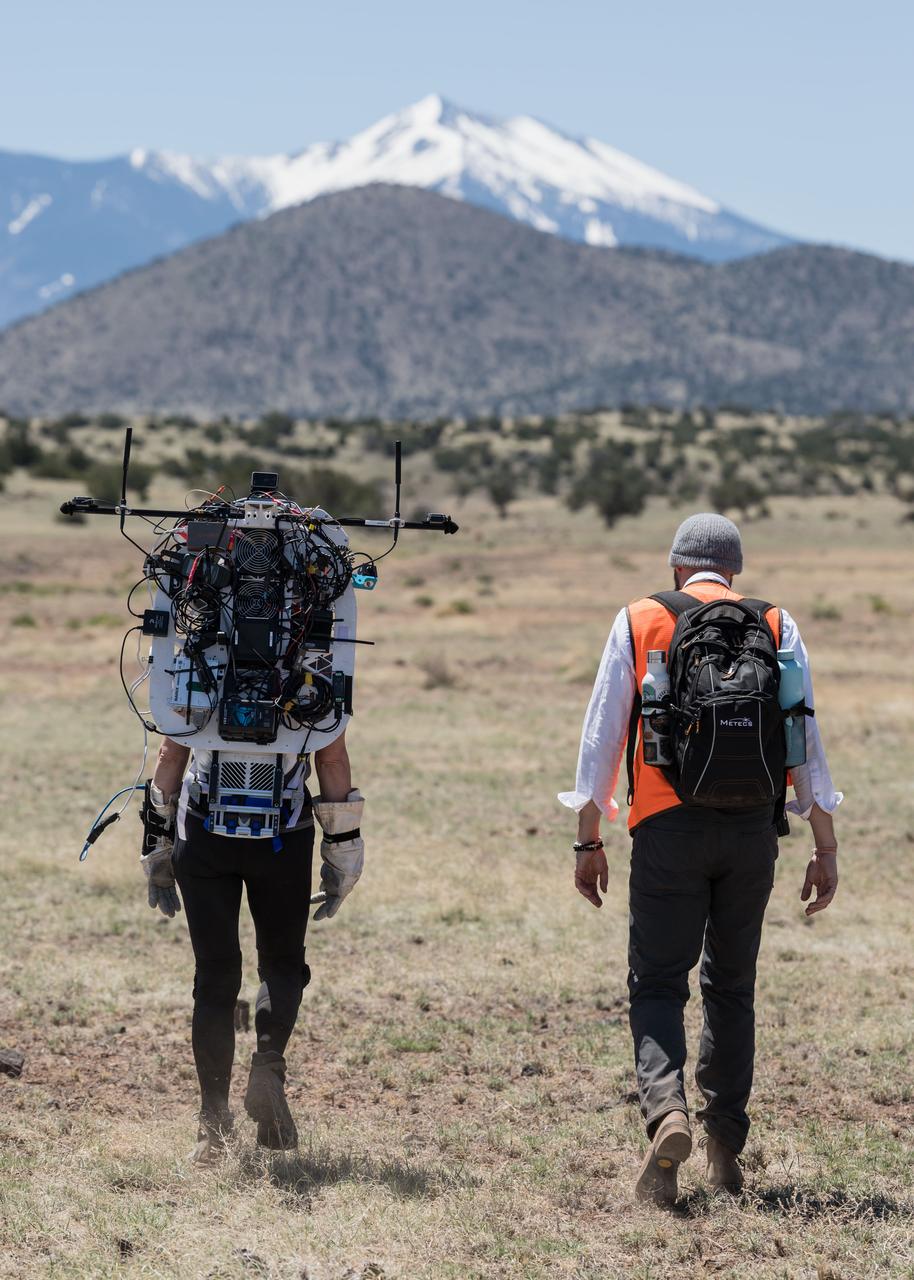
NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks in the lunar-like landscape during a nighttime simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 16, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
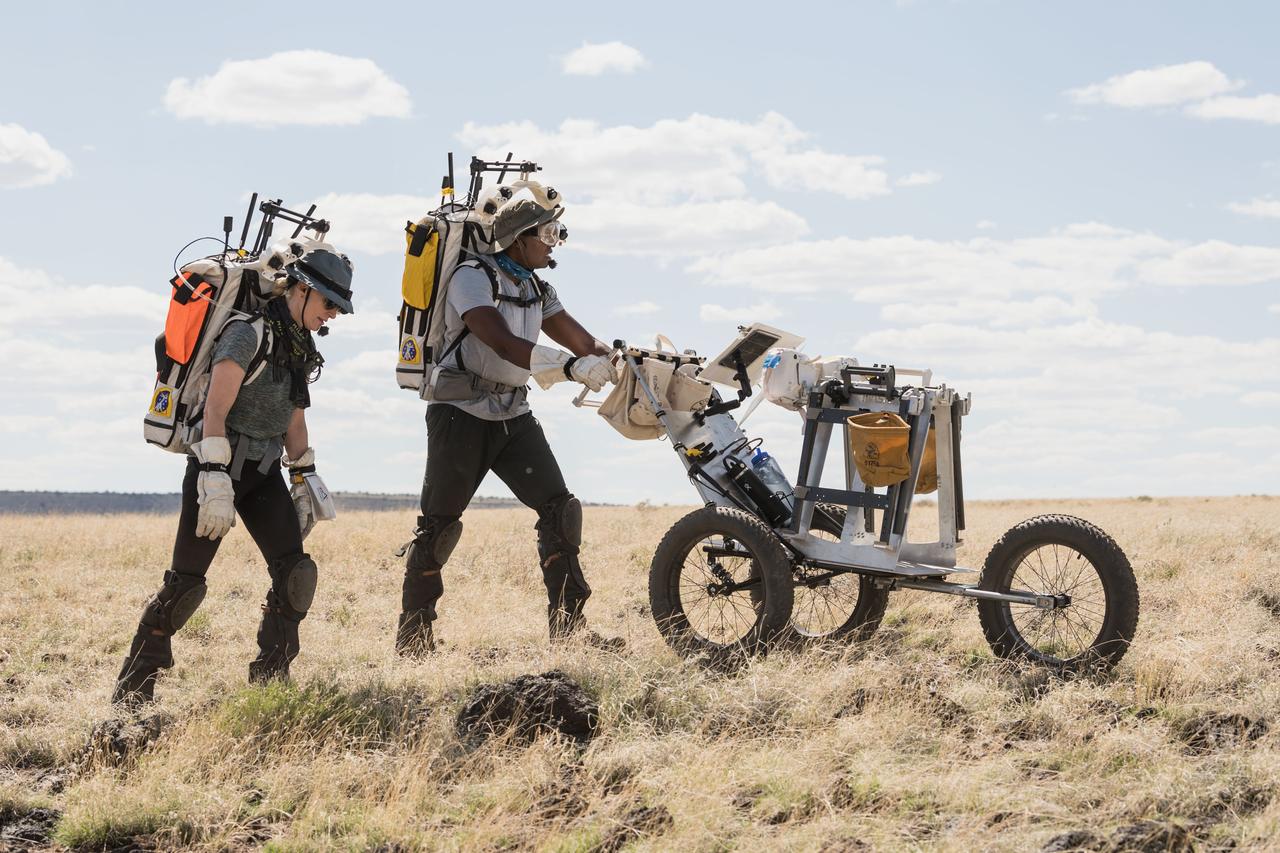

NASA astronauts Kate Rubins and Andre Douglas walk through the lunar-like landscape during a simulated moonwalk in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 17, 2024. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
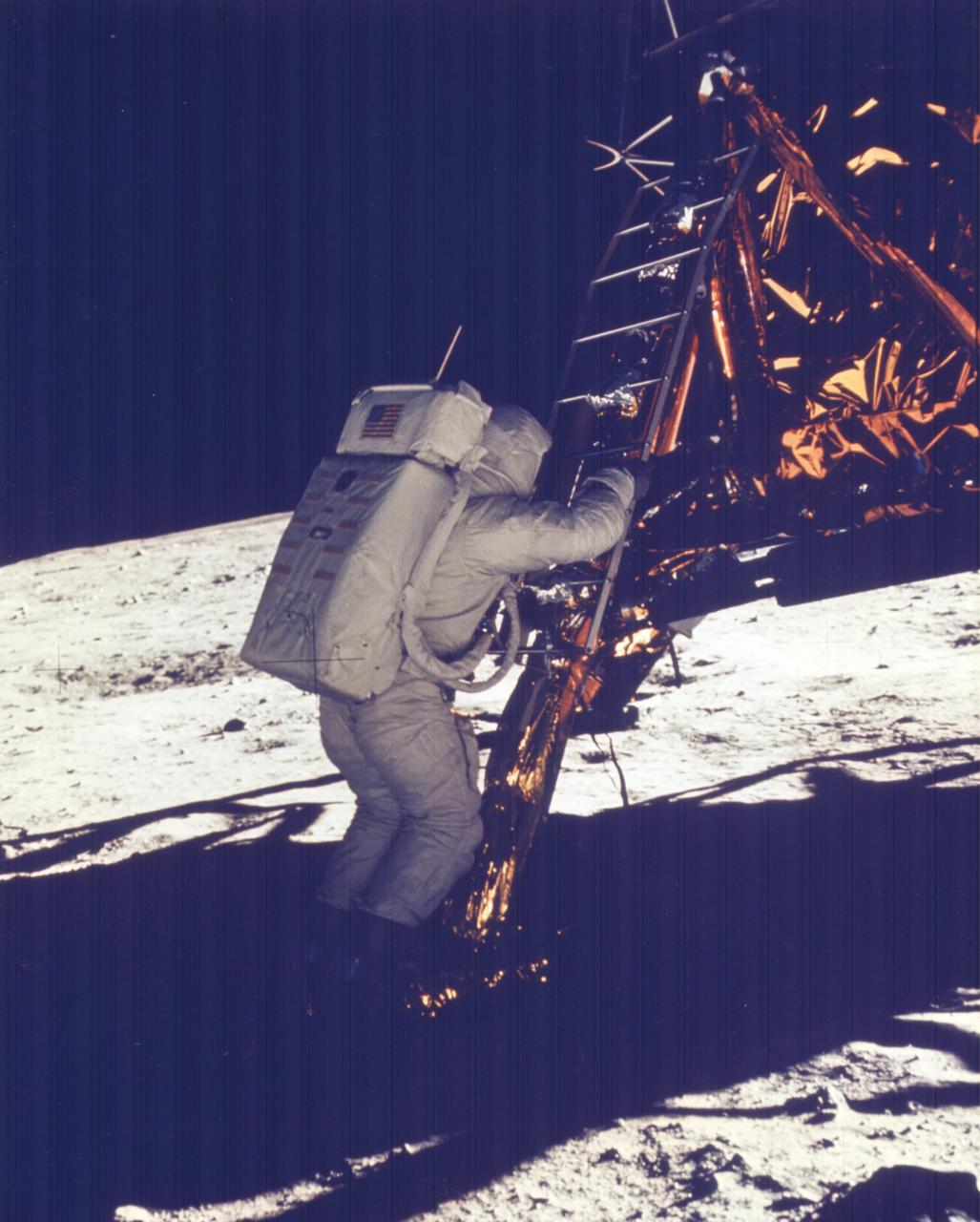

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - Apollo 11 Onboard Film -- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot, descends the steps of the Lunar module ladder as he prepares to walk on the Moon. He had just egressed the LM. This picture was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70-mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity.
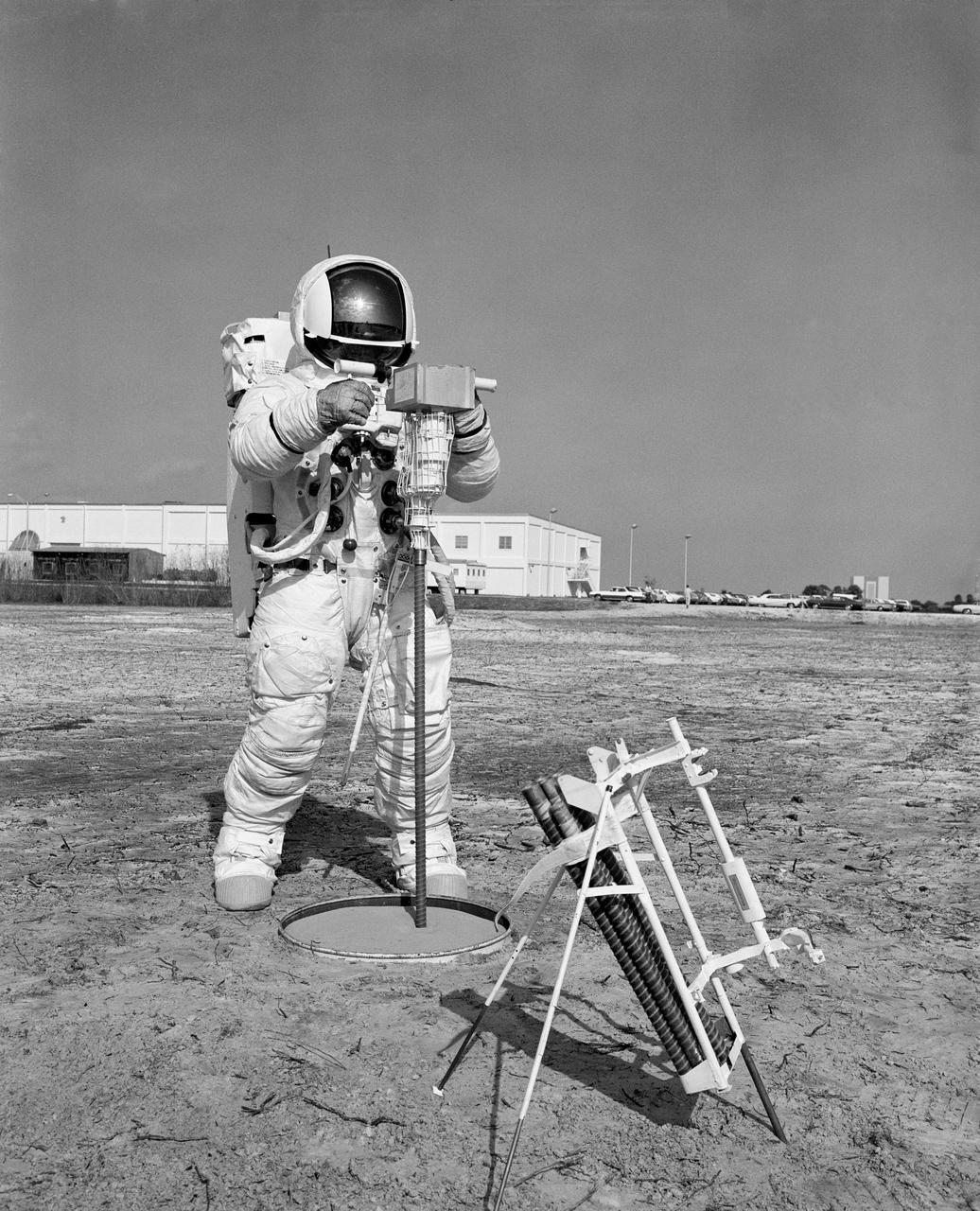

S70-29673 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Haise uses an Apollo Lunar Surface Drill to dig a three-meter heat flow probe hole. The heat flow experiment on Apollo 13 will have an electronic instrument which will measure the outward flux of heat from the moon?s interior.
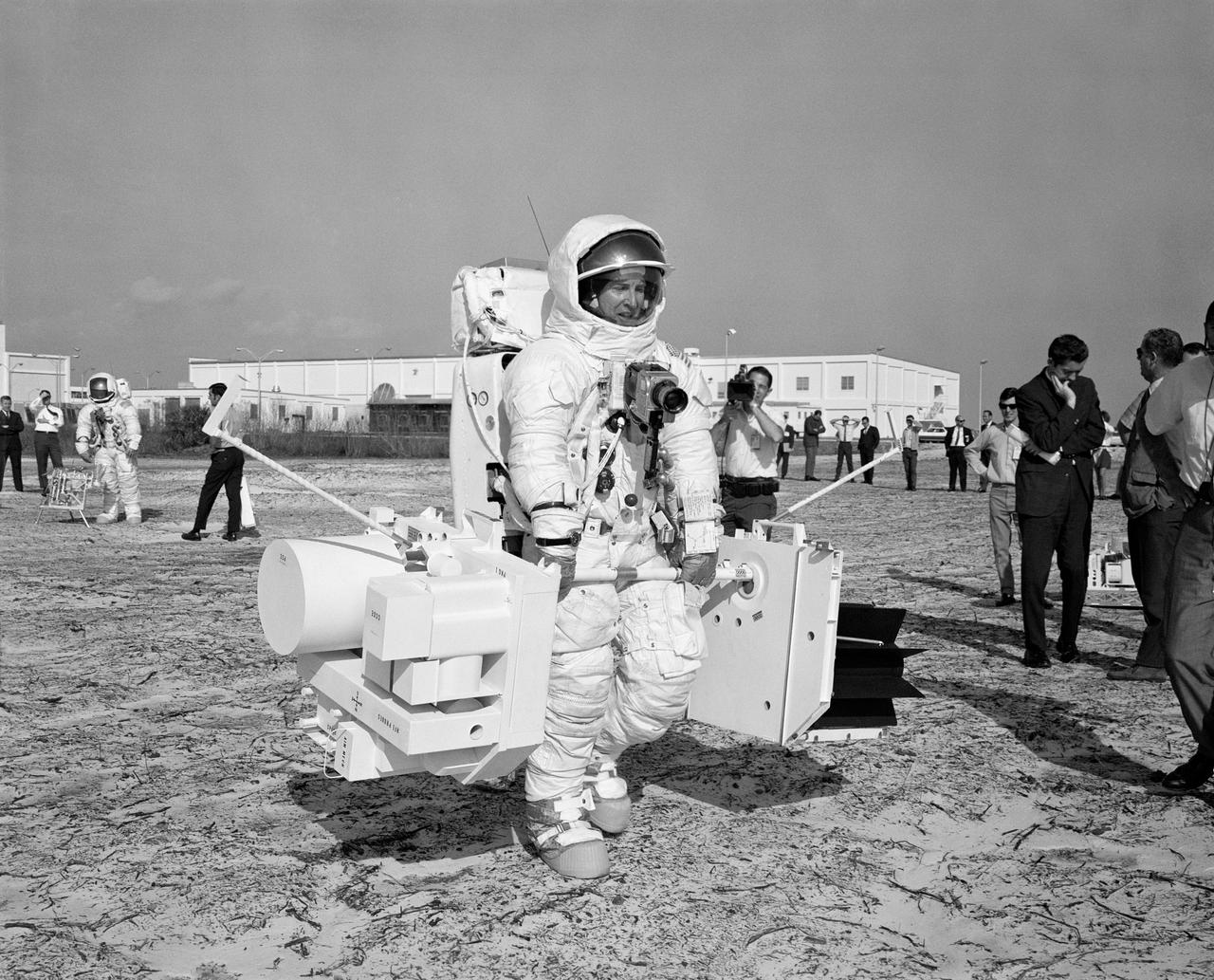

S70-29672 (28 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission, participates in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline at the Kennedy Space Center. Here, Lovell, using mock-ups, traverses with the two subpackages of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP). Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, is standing in the left background.

AS12-46-6780 (19 Nov. 1969) --- Astronaut Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot for the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, walks from the color lunar surface television camera (center) toward the Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM - out of frame). The photograph was taken by astronaut Charles Conrad Jr., commander, during the first extravehicular activity (EVA) of the mission. While astronauts Conrad and Bean descended in the LM "Intrepid" to explore the Ocean of Storms region of the moon, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Yankee Clipper" in lunar orbit.

AS15-85-11363 (31 July 1971) --- A 70mm handheld Hasselblad was aimed through the viewing port of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module (LM) to record this image of the lunar surface in the vicinity of the Hadley-Apennine landing site. Later, astronauts David R. Scott, commander, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, made the mission's first moon walk. The pair had descended from lunar orbit in the LM to explore the moon while astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS17-140-21388 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, mission commander, walks toward the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site of NASA's sixth and final Apollo lunar landing mission. The photograph was taken by astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. While astronauts Cernan and Schmitt descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.

AS11-40-5866 (20 July 1969) --- Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, egresses the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" and begins to descend the steps of the LM ladder as he prepares to walk on the moon. This photograph was taken by astronaut Neil A. Armstrong, commander, with a 70mm lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA
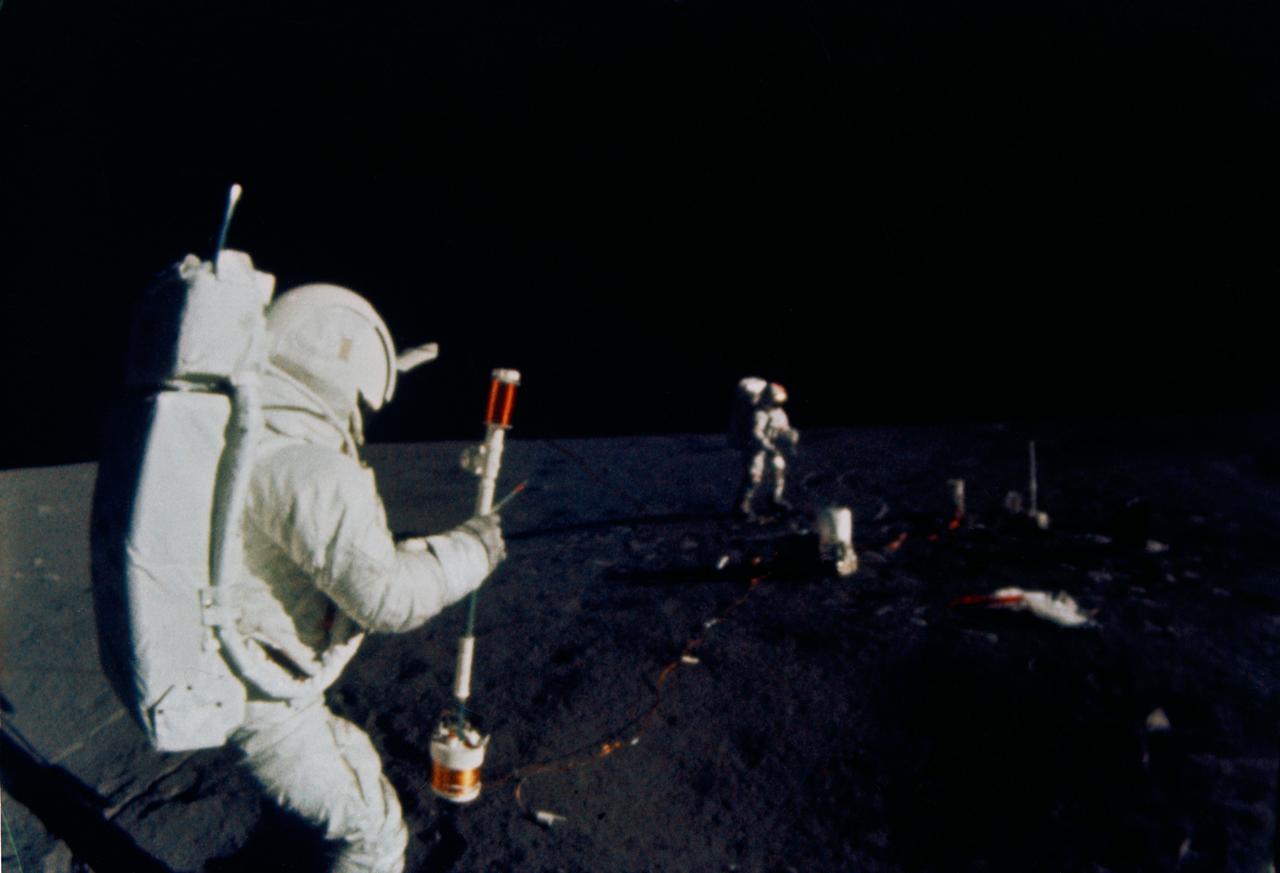

S71-19509 (5 Feb. 1971) --- Astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, lunar module pilot, operates the Active Seismic Experiment's (ASE) thumper during the first Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA) on the moon. Astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., commander, walks near deployed components of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP) in the background. This photograph was taken by an automatic 16mm camera mounted on the Apollo lunar hand tool carrier aboard the Modularized Equipment Transporter (MET). While astronauts Shepard and Mitchell descended in the LM to explore the moon, astronaut Stuart A. Roosa, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.
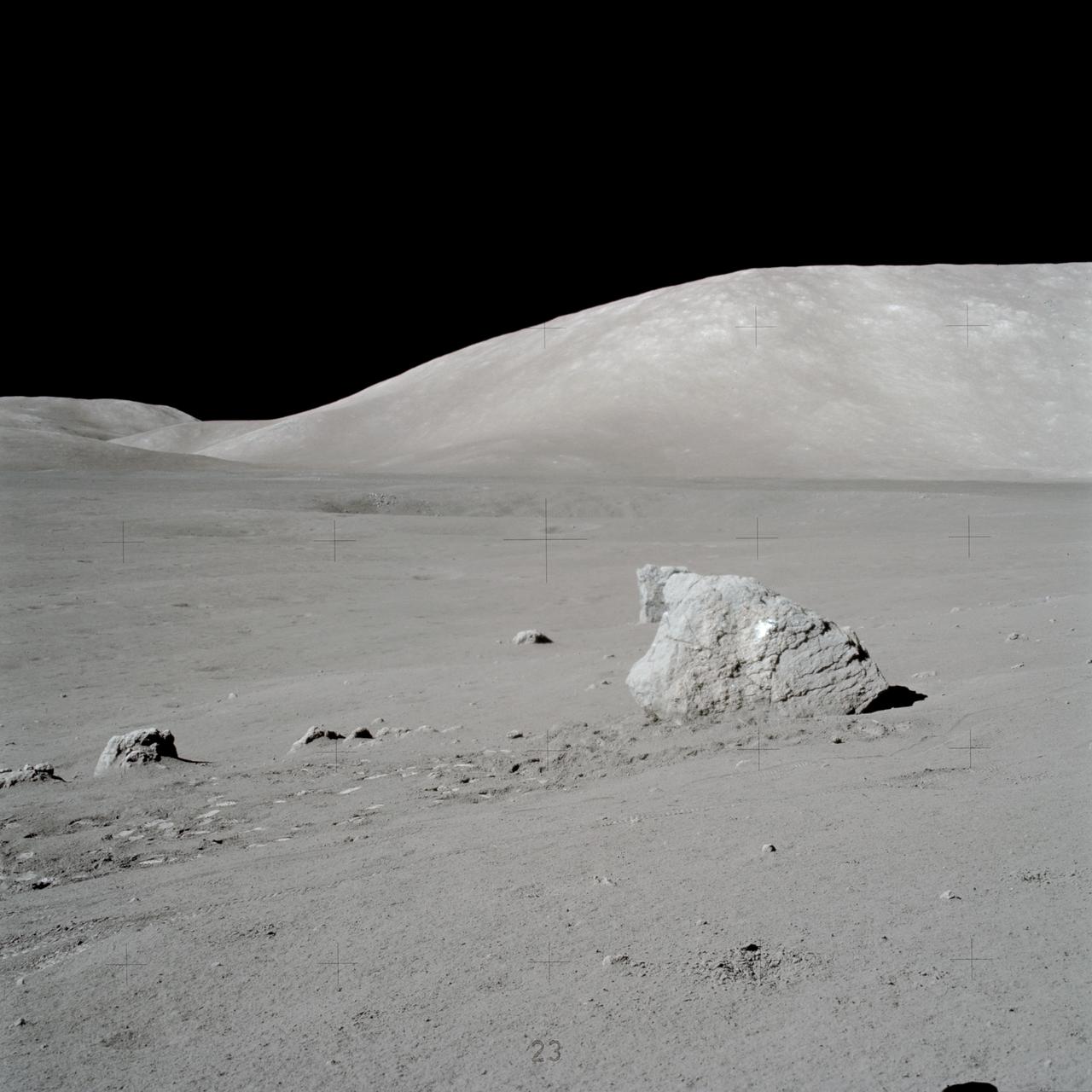

AS17-146-22351 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- This view, photographed by astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, shows a large boulder which was discovered by astronauts Cernan and Harrison H. Schmitt during one of their space walks. The astronauts later pointed out light clasts on the boulder. South Massif is in the background. Tracks left by the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) can be seen near foreground. While astronauts Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
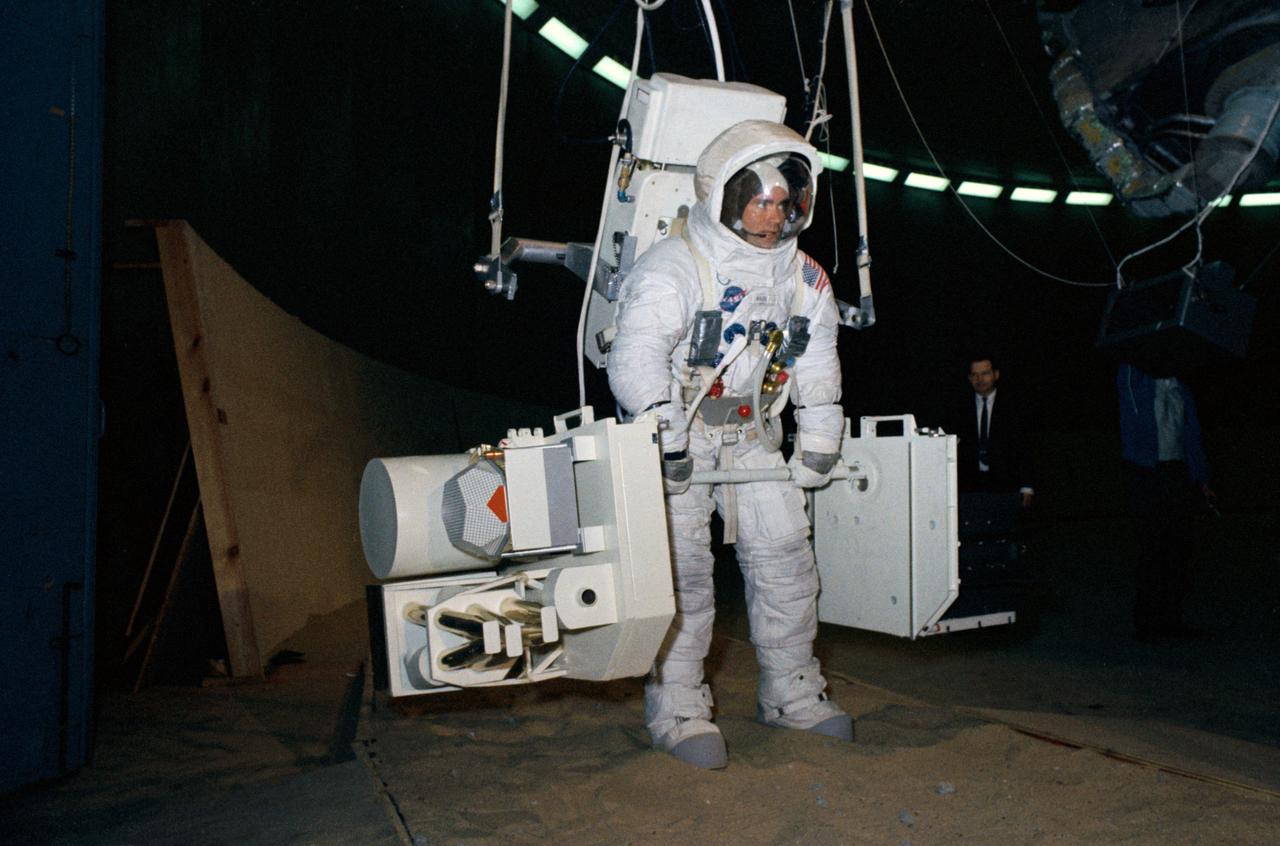

S70-24009 (19 Jan. 1970) --- Astronaut Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, trains for his scheduled April lunar space walk at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Haise carries a training version of the Apollo Lunar Surface Experiments Package (ALSEP), while connected to a "Six Degrees of Freedom" simulator. Out of frame is astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander, who will share the lunar extravehicular activity (EVA) with Haise. EDITOR'S NOTE: In April 1970 the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) experienced an explosion en route to the moon. The three-man crew was forced to circumnavigate the moon and return to Earth.

S72-55168 (12 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (on left) and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt walk through a field of small boulders during the second Apollo 17 extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site, as seen in this black and white reproduction taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Cernan is the Apollo 17 commander; and Schmitt is the lunar module pilot. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit. (Their backs are toward the camera)

S72-55298 (13 Dec. 1972) --- The two moon-exploring Apollo 17 crewmen are seen walking beside a large boulder during the third extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Taurus-Littrow landing site. They are scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt (in front), lunar module pilot; and astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, commander. This black and white reproduction was taken from a color television transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle. Astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.
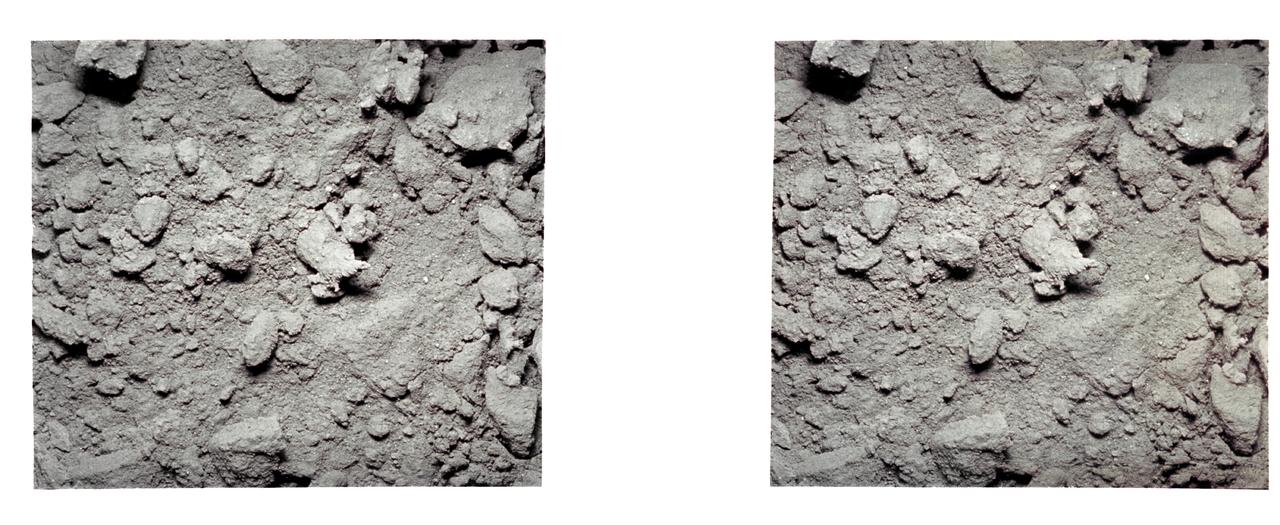

AS12-57-8455 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
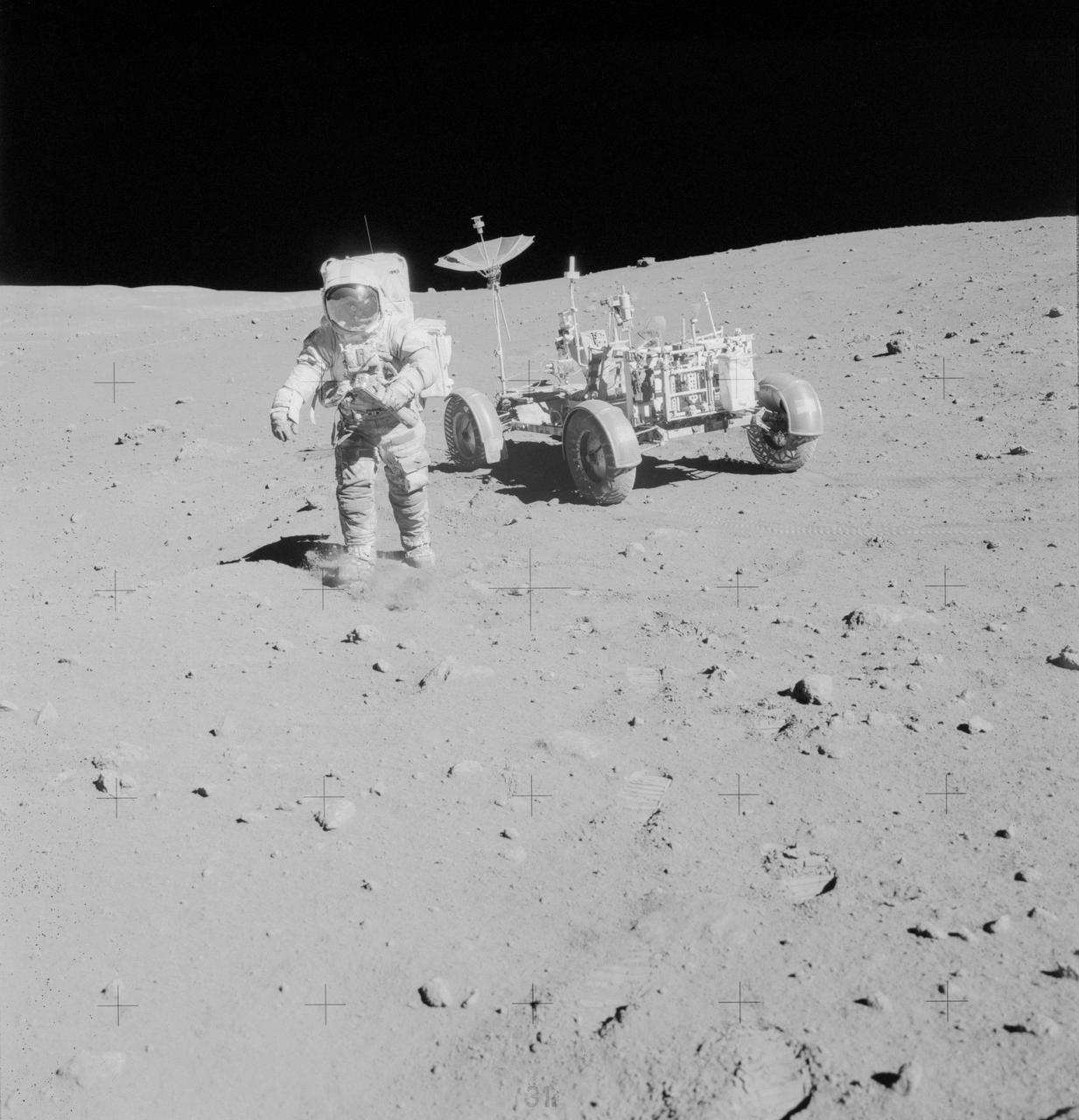

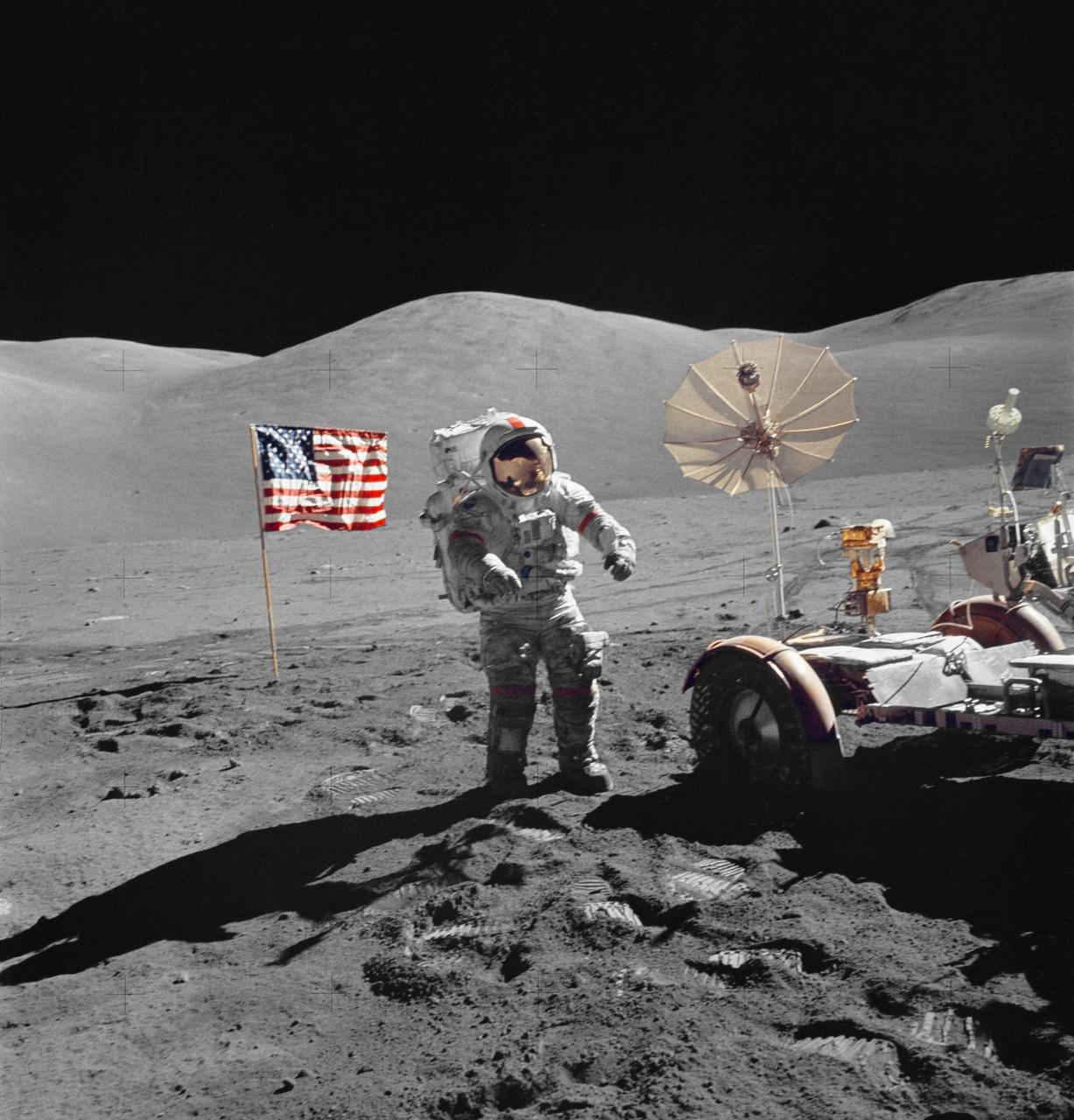
AS15-82-11168 (2 Aug. 1971) --- Astronaut James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, walks away from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) during the third Apollo 15 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) at the Hadley-Apennine landing site. The LRV is parked a short distance from the rim of Hadley Rille. The far wall of the rille is in the distance at extreme upper left. Irwin is holding the 500mm Hasselblad camera in his left hand. This photograph was taken by astronaut David R. Scott, commander. While astronauts Scott and Irwin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) to explore the moon, astronaut Alfred M. Worden, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit.

AS12-57-8452 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface. The exposure was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera during extravehicular activity of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander, and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot, descended in the Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the moon while astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit in the capacity of command module pilot.
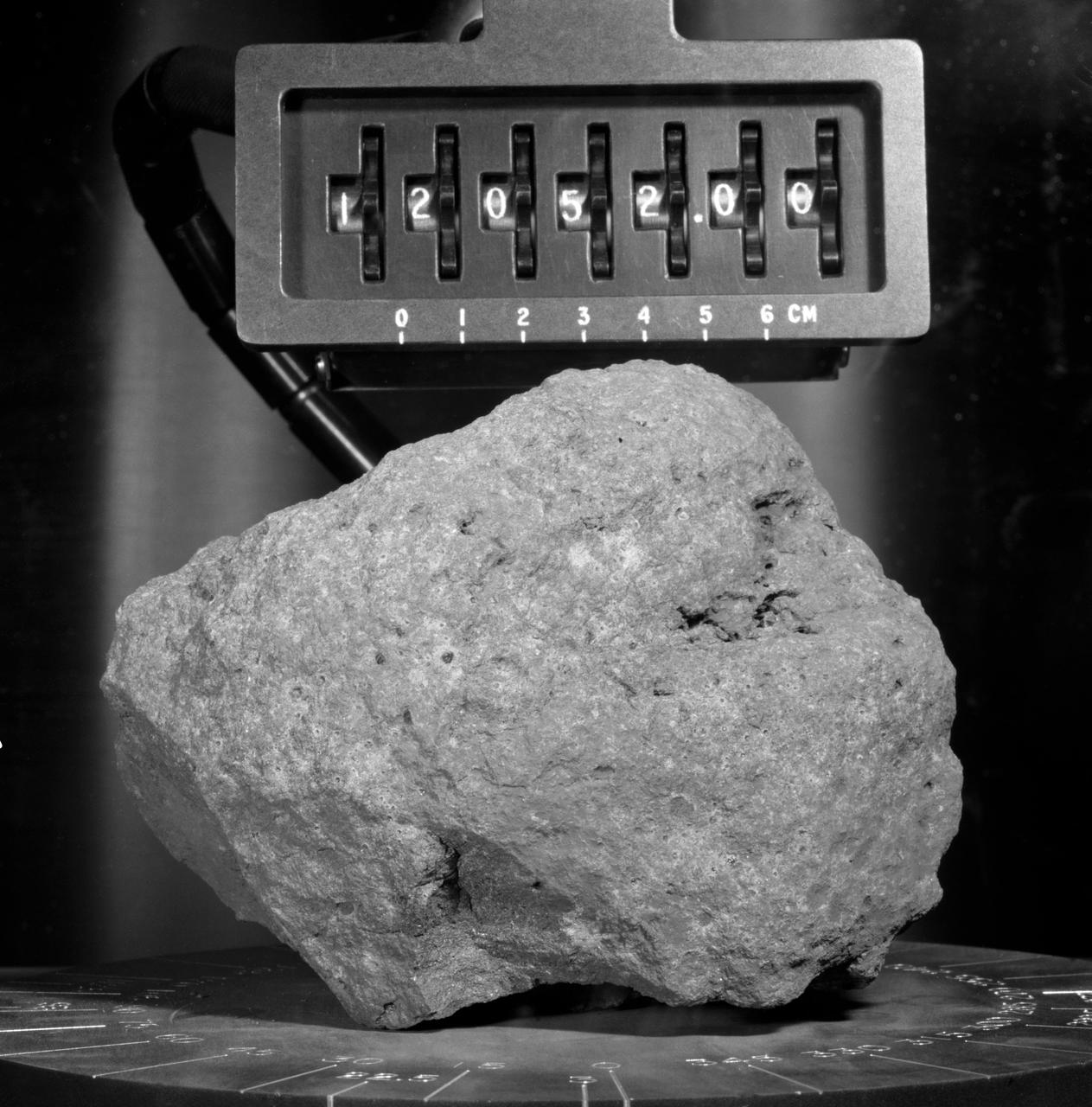

S69-60909 (November 1969) --- A close-up view of lunar sample 12,052 under observation in the Manned Spacecraft Center's Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., and Alan L. Bean collected several rocks and samples of finer lunar matter during their Apollo 12 lunar landing mission extravehicular activity (EVA). This particular sample was picked up during the second space walk (EVA) on Nov. 20, 1969. It is a typically fine-grained crystalline rock with a concentration of holes on the left part of the exposed side. These holes are called vesicles and have been identified as gas bubbles formed during the crystallization of the rock. Several glass-lined pits can be seen on the surface of the rock.
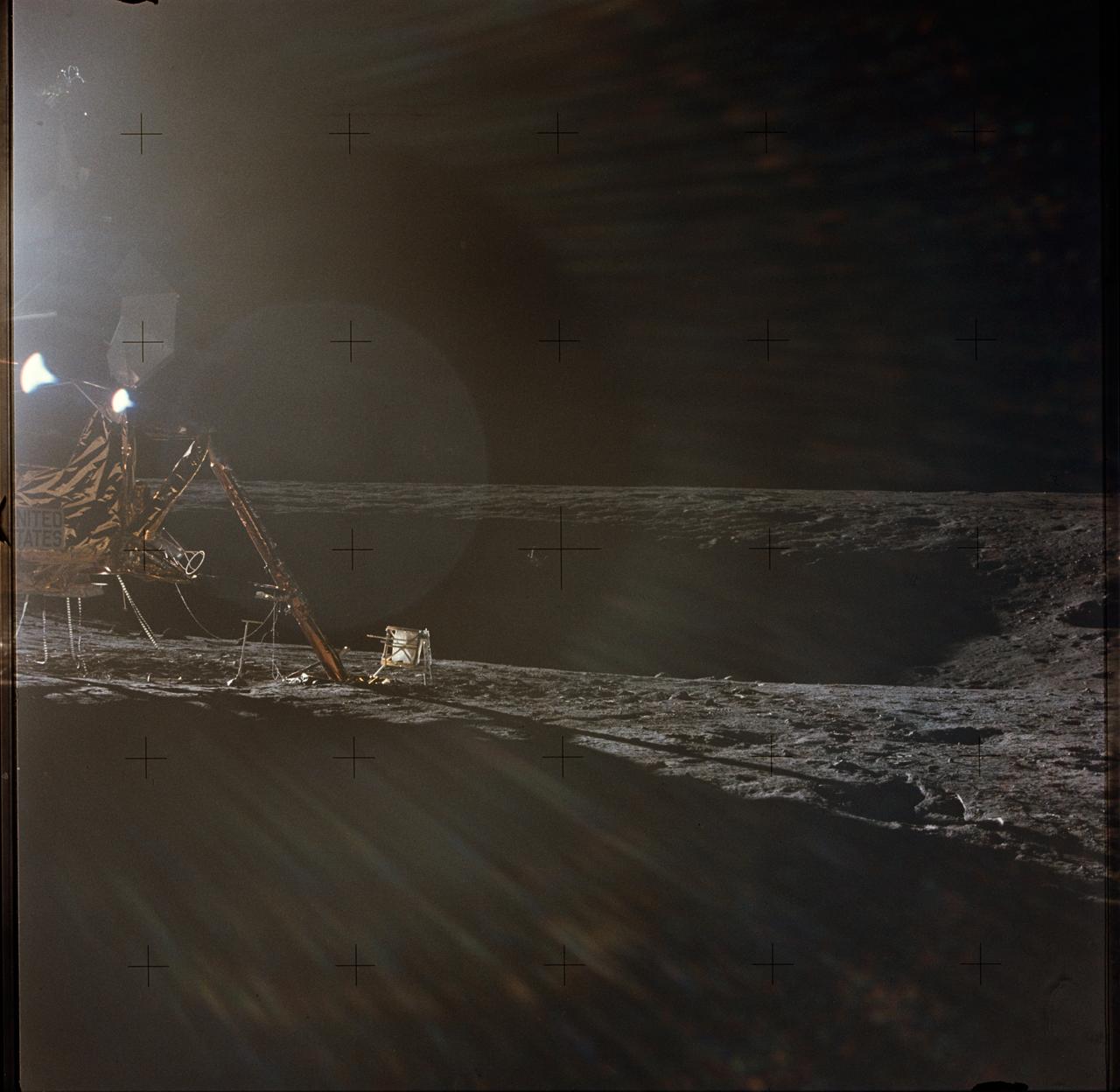

AS12-47-6949 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- A photograph of the Apollo 12 lunar landing site taken during the extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., commander; and Alan L. Bean, lunar module pilot. The Apollo 12 Lunar Module (LM) is on the left. Barely visible in the center of the picture, in the shadows on the farside of the crater, is the Surveyor 3 spacecraft. The two spacecraft are about 600 feet apart. Conrad and Bean walked over to Surveyor 3 during their second EVA. The television camera and several other pieces were taken from Surveyor 3 and brought back to Earth for scientific examination. Astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr., command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) in lunar orbit, while astronauts Conrad and Bean descended in the LM to explore the moon. The considerable glare in the picture is caused by the position of the sun. The Apollo tool carrier is the object next to the LM footpad.
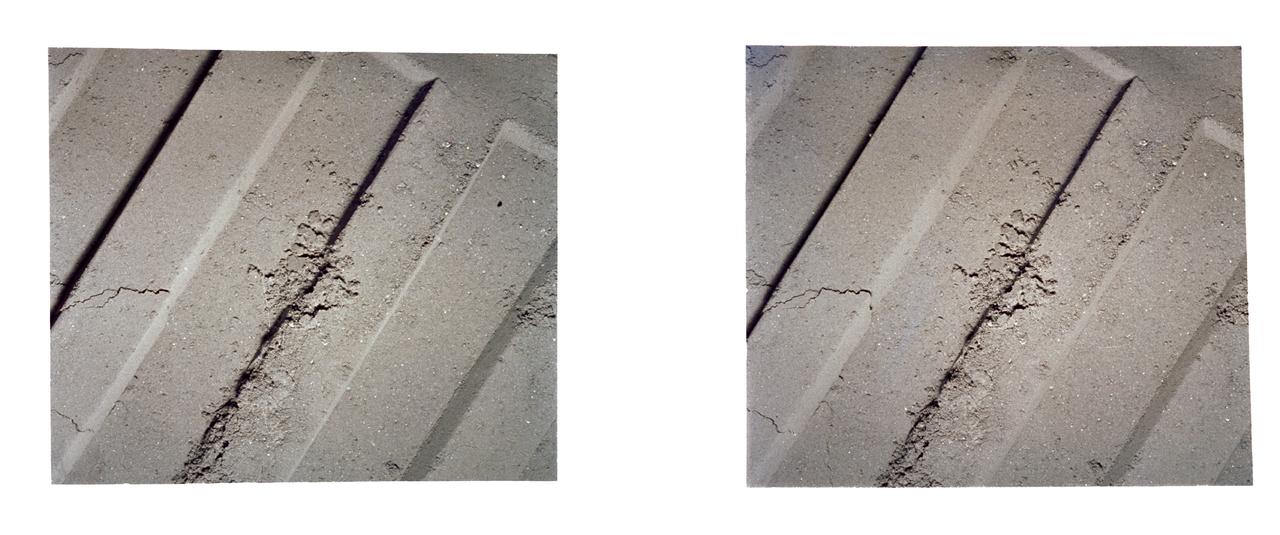

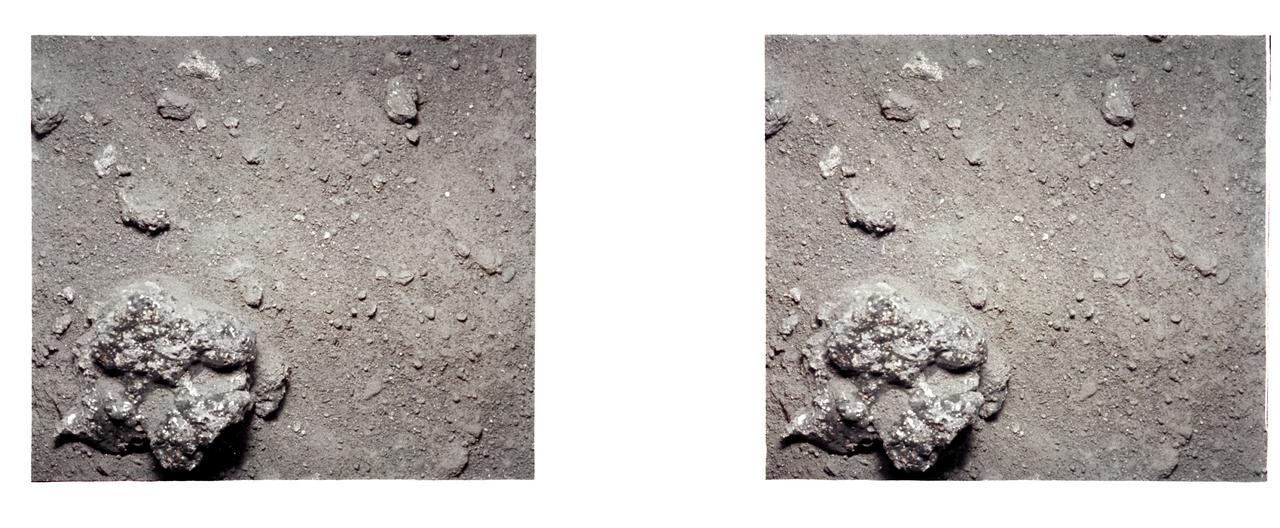
AS12-57-8448 (19-20 Nov. 1969) --- An Apollo 12 stereo view showing a three-inch square of the lunar surface upon which an astronaut had stepped. Taken during extravehicular activity of astronauts Charles Conrad Jr. and Alan L. Bean, the exposure of the boot imprint was made with an Apollo 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. The three-inch square is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. While astronauts Conrad and Bean descended in their Apollo 12 Lunar Module to explore the lunar surface, astronaut Richard F. Gordon Jr. remained with the Command and Service Modules in lunar orbit.

This is a photo of the Apollo 15 Lunar Module, Falcon, on the lunar surface. Apollo 15 launched from Kennedy Space Center (KSC) on July 26, 1971 via a Saturn V launch vehicle. Aboard was a crew of three astronauts including David R. Scott, Mission Commander; James B. Irwin, Lunar Module Pilot; and Alfred M. Worden, Command Module Pilot. The first mission designed to explore the Moon over longer periods, greater ranges and with more instruments for the collection of scientific data than on previous missions, the mission included the introduction of a $40,000,000 lunar roving vehicle (LRV) that reached a top speed of 16 kph (10 mph) across the Moon's surface. The successful Apollo 15 lunar landing mission was the first in a series of three advanced missions planned for the Apollo program. The primary scientific objectives were to observe the lunar surface, survey and sample material and surface features in a preselected area of the Hadley-Apennine region, setup and activation of surface experiments and conduct in-flight experiments and photographic tasks from lunar orbit. Apollo 15 televised the first lunar liftoff and recorded a walk in deep space by Alfred Worden. Both the Saturn V rocket and the LRV were developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
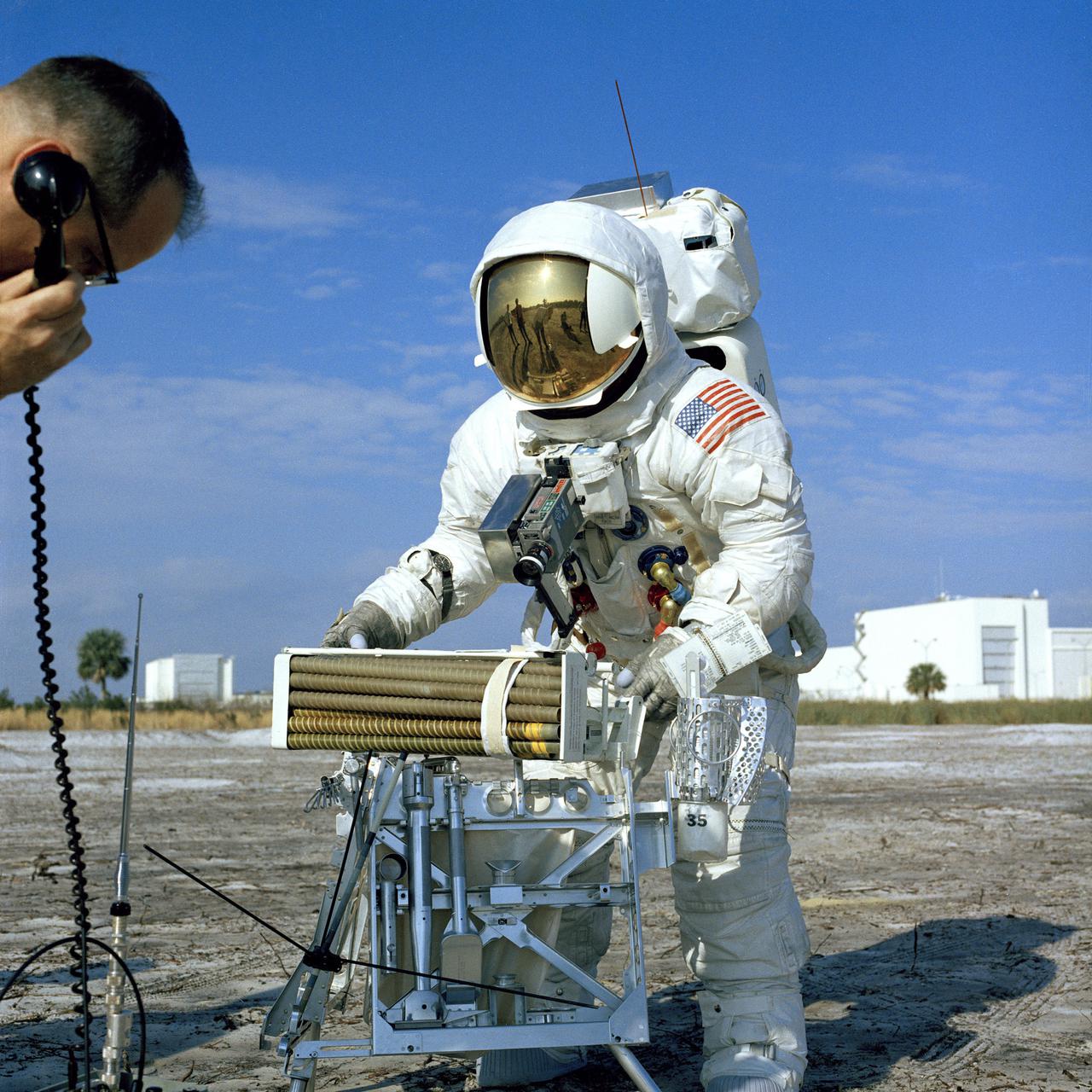

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Fred W. Haise Jr., Apollo 13 lunar module pilot, participated in a walk-through of the extravehicular activity timeline near the Flight Crew Training Building here today. In the foreground is the lunar surface tool carrier topped by auger-like pipes to be used with a motorized device to obtain soil sample cores in the moon's rugged Fra Mauro region. Apollo 13 is scheduled for launch from Complex 39A no earlier than April 11. The other crew members are James A. Lovell Jr., commander, and Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot. Photo credit: NASA

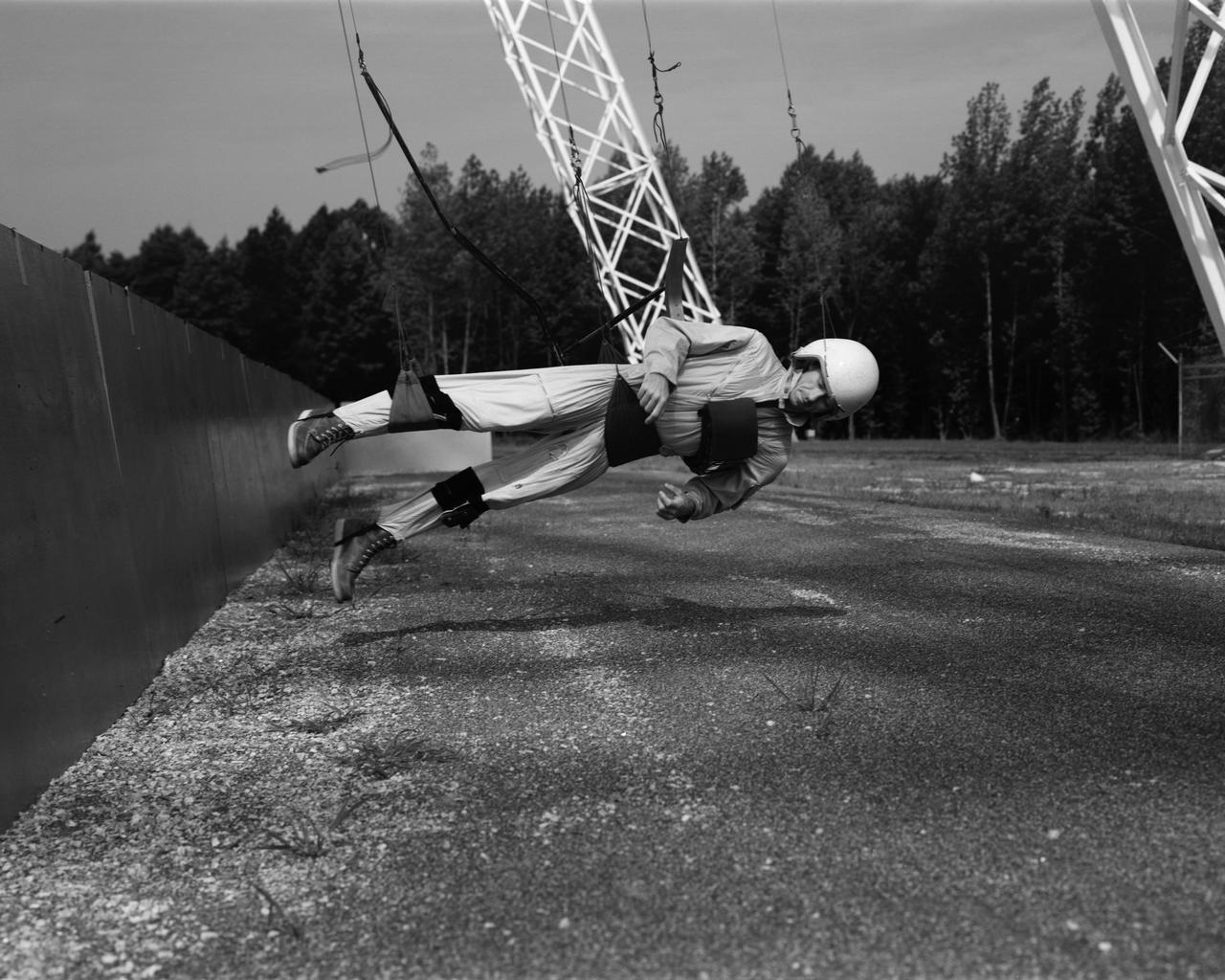
Astronaut Roger Chaffee on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil, described the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
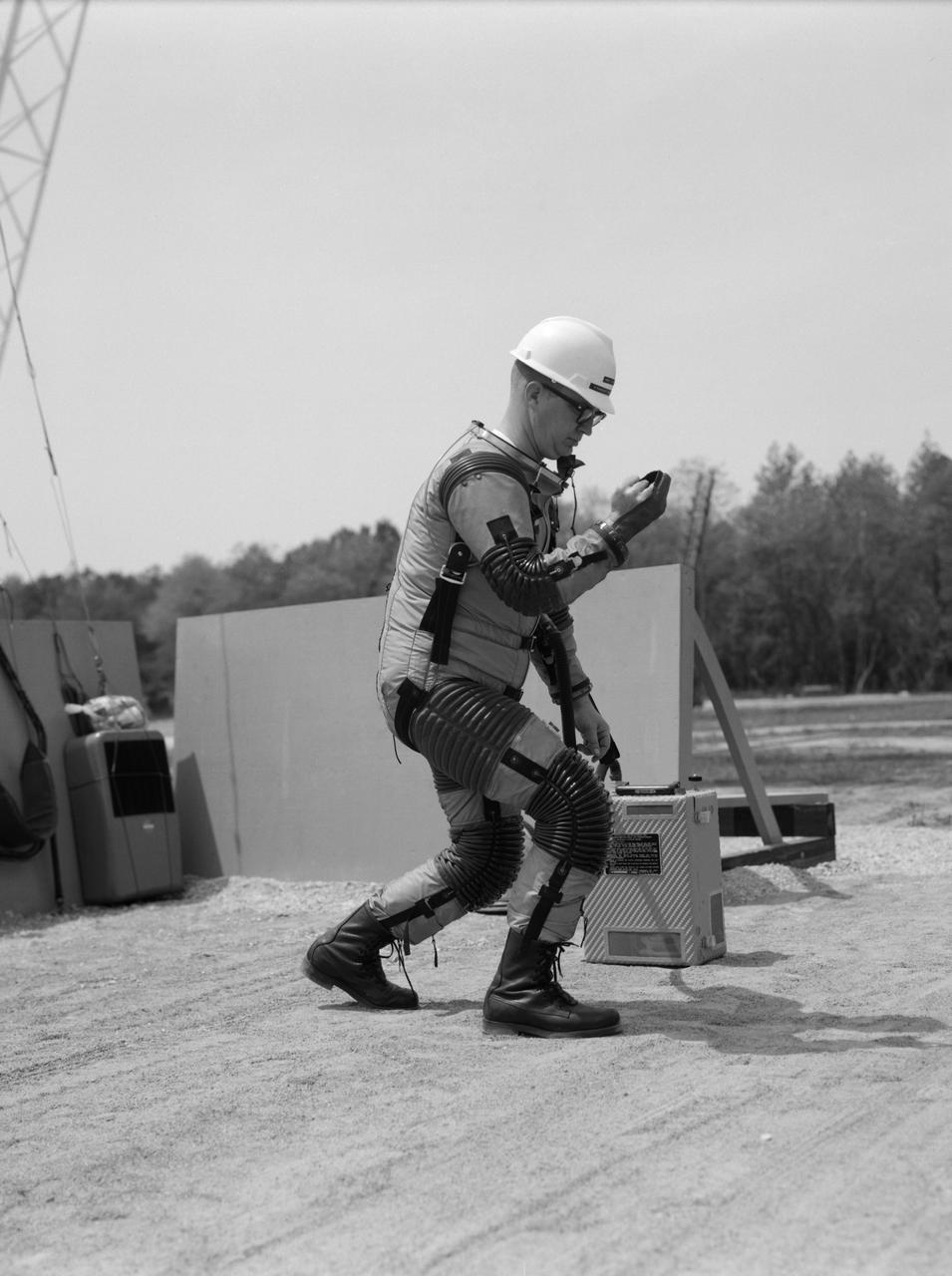

Special "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
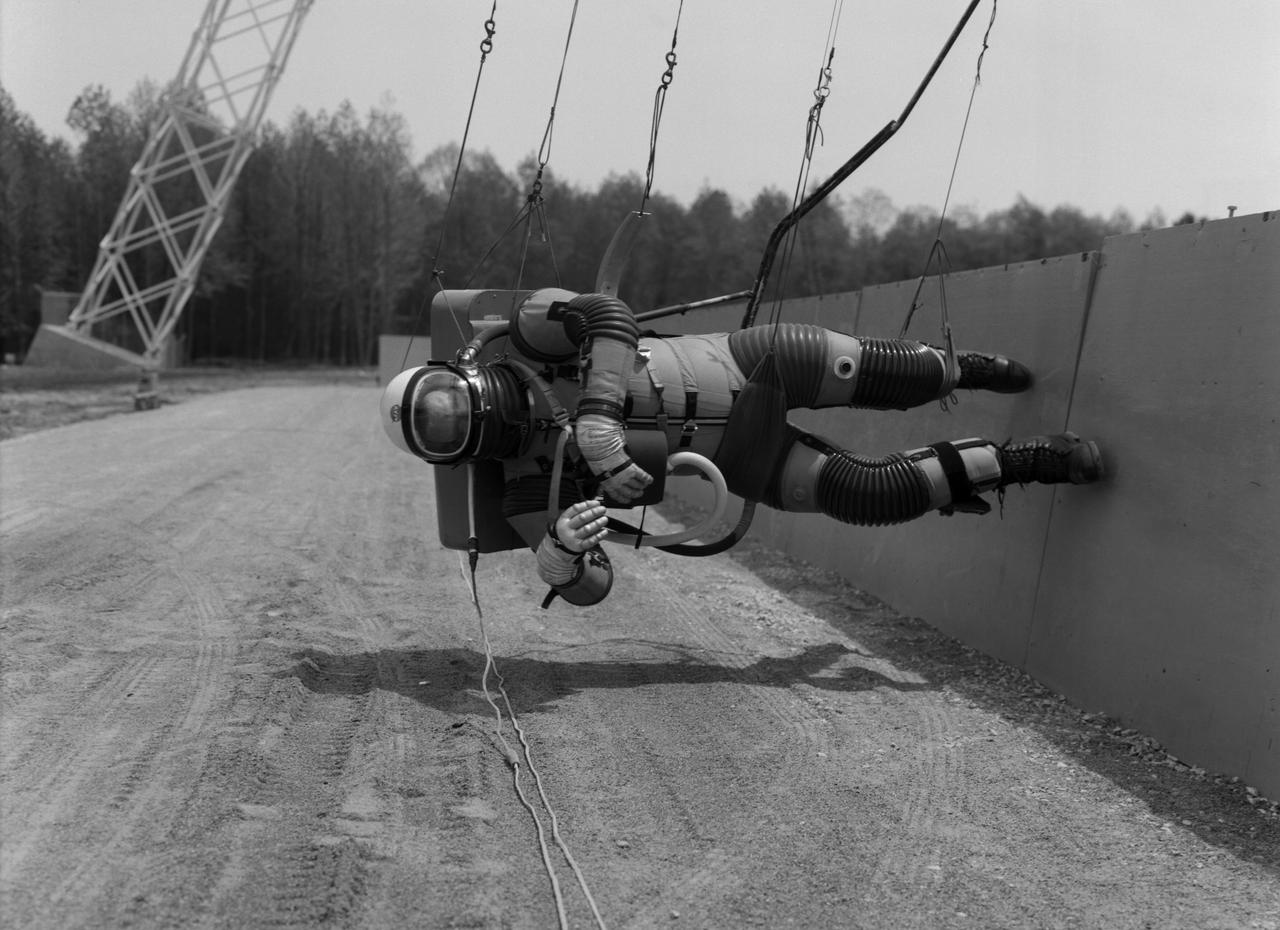

Test subject wearing the pressurized "space" suit for the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator in his paper "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
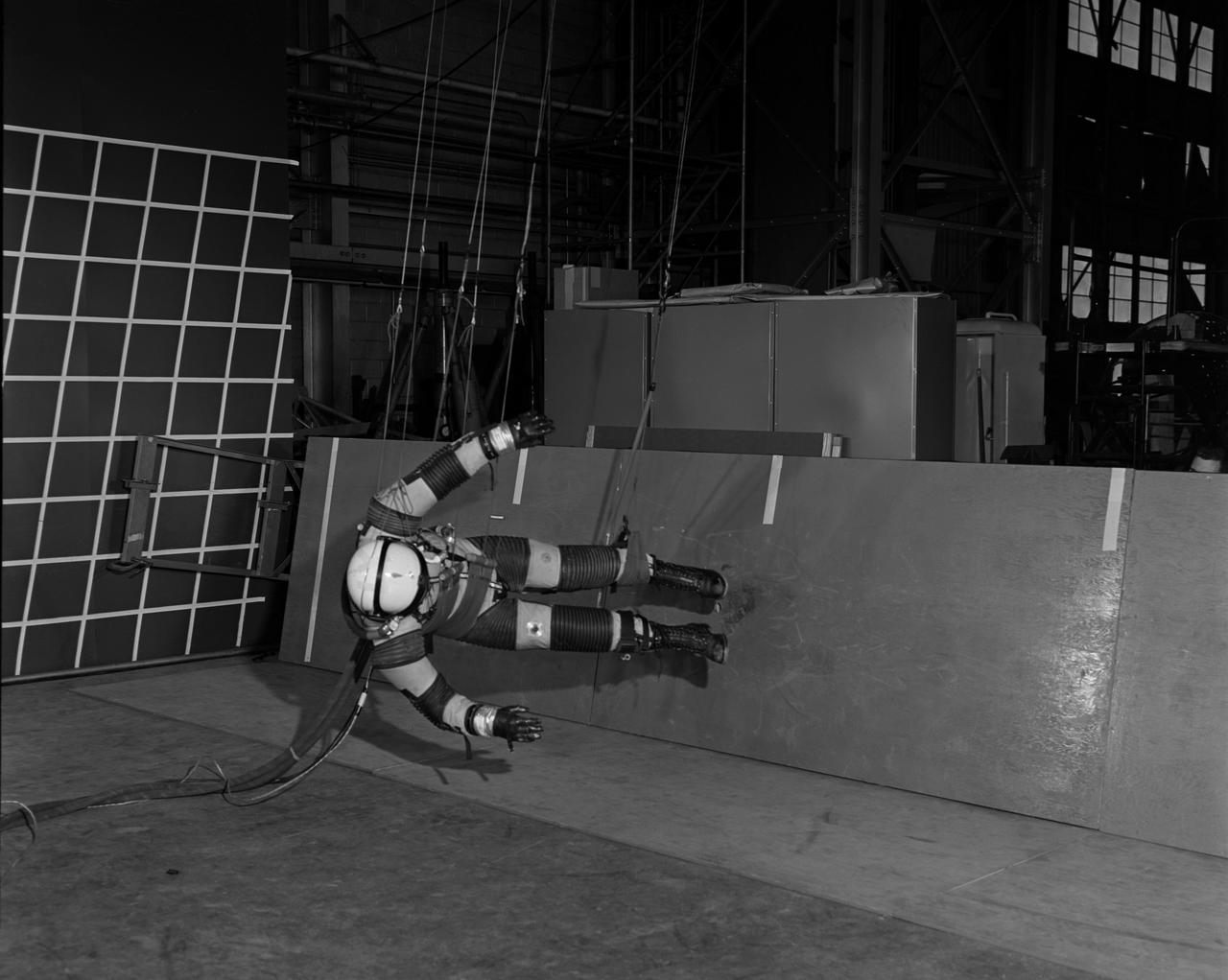

A "suited" test subject on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator located in the hangar at Langley Research Center. The initial version of this simulator was located inside the hangar. Later a larger version would be located at the Lunar Landing Facility. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. Francis B. Smith wrote in "Simulators For Manned Space Research:" "The cables which support the astronaut are supported by an overhead trolley about 150 feet above the center line of the walkway and the support is arranged so that the subject is free to walk, run, jump, and perform other self-locomotive tasks in a more-or-less normal manner, even though he is constrained to move in one place." "The studies thus far show that an astronaut should have no particular difficulty in walking in a pressurized space suit on a hard lunar surface. Rather, the pace was faster and the suit was found to be more comfortable and less fatiguing under lunar "g" than under earth "g." When the test subject wished to travel hurriedly any appreciable distance, a long loping gait at about 10 feet per second was found to be most comfortable." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995), p. 377; Francis B. Smith, "Simulators For Manned Space Research," Paper for 1966 IEEE International Convention, New York, NY, March 21-25, 1966.
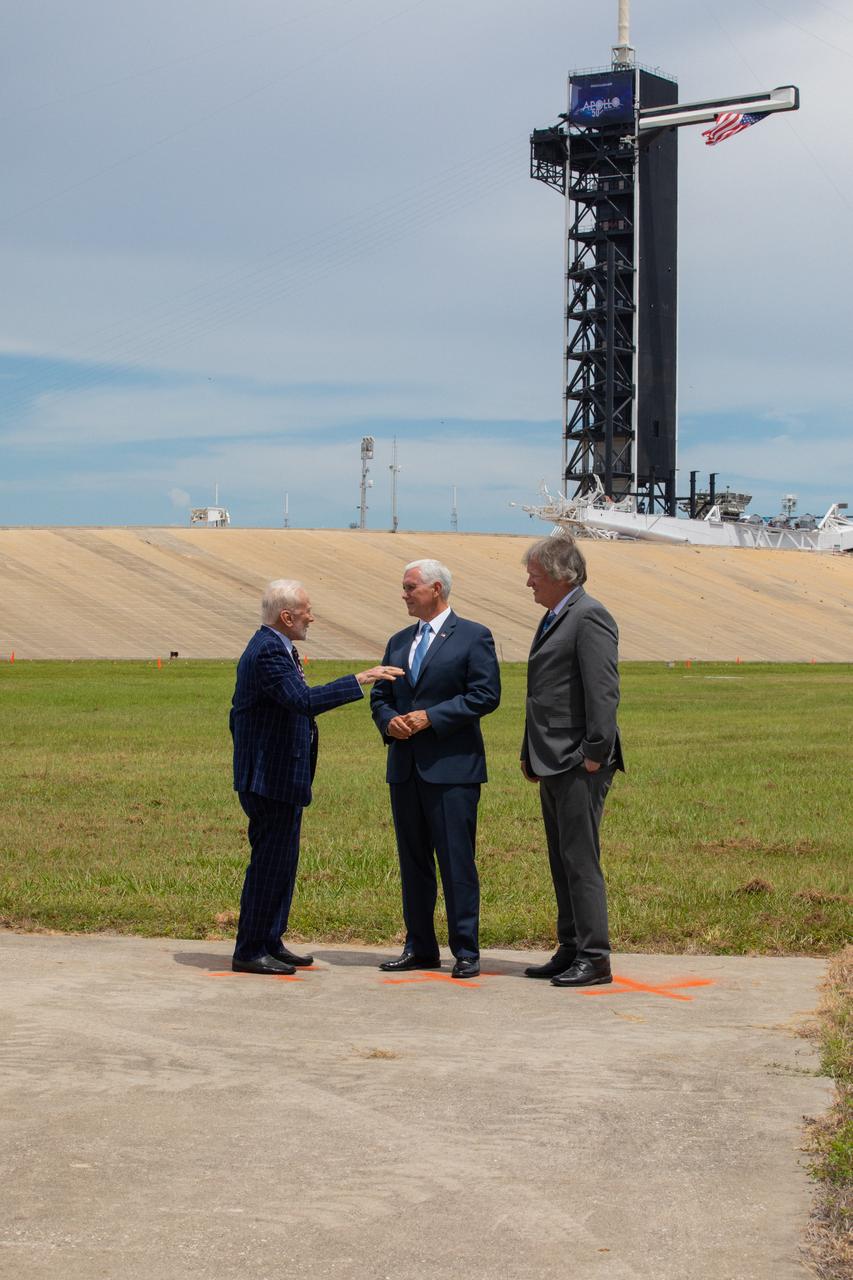

Vice President Mike Pence, center, celebrates the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing during a visit to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on July 20, 2019. Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins launched from Pad 39A aboard a Saturn V rocket on July 16, 1969. Four days later, Armstrong and Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module Eagle on the Moon, becoming the first two humans to walk on the lunar surface. Pence recognized the extraordinary achievements of the Apollo 11 team, while looking forward to NASA’s plans to return to the Moon and on to Mars. At left is Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Buzz Aldrin. At right is Rick Armstrong, Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong's son.
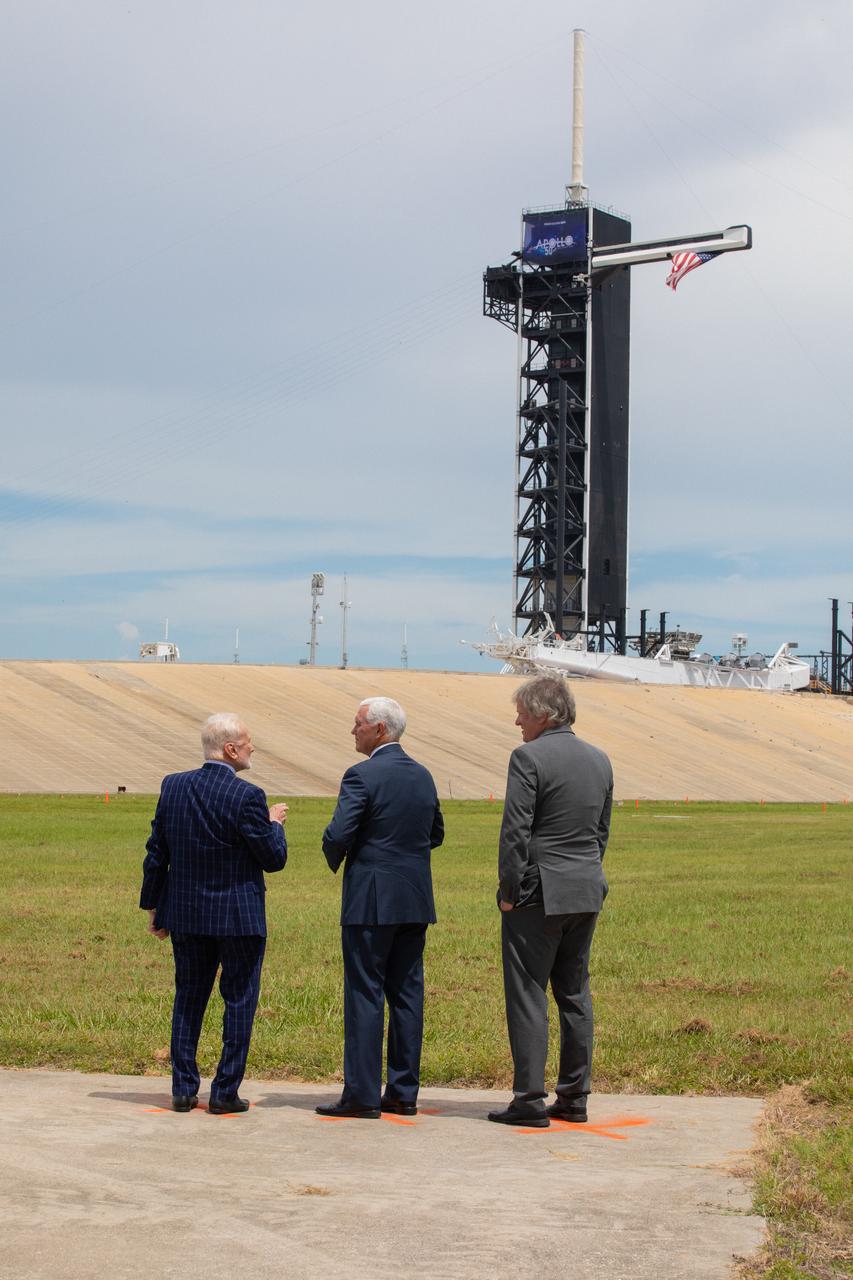

Vice President Mike Pence, center, celebrates the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing during a visit to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on July 20, 2019. Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins launched from Pad 39A aboard a Saturn V rocket on July 16, 1969. Four days later, Armstrong and Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module Eagle on the Moon, becoming the first two humans to walk on the lunar surface. Pence recognized the extraordinary achievements of the Apollo 11 team, while looking forward to NASA’s plans to return to the Moon and on to Mars. At left is Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Buzz Aldrin. At right is Rick Armstrong, son of Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong.

S69-40753 (24 July 1969) --- The Apollo 11 crewmen, wearing biological isolation garments, arrive aboard the USS Hornet during recovery operations in the central Pacific. They are walking toward the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF), in which they will be confined until they arrive at the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC), Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). Apollo 11, with astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot, onboard, splashed down at 11:49 a.m. (CDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii and only 12 nautical miles from the USS Hornet to conclude their historic lunar landing mission.
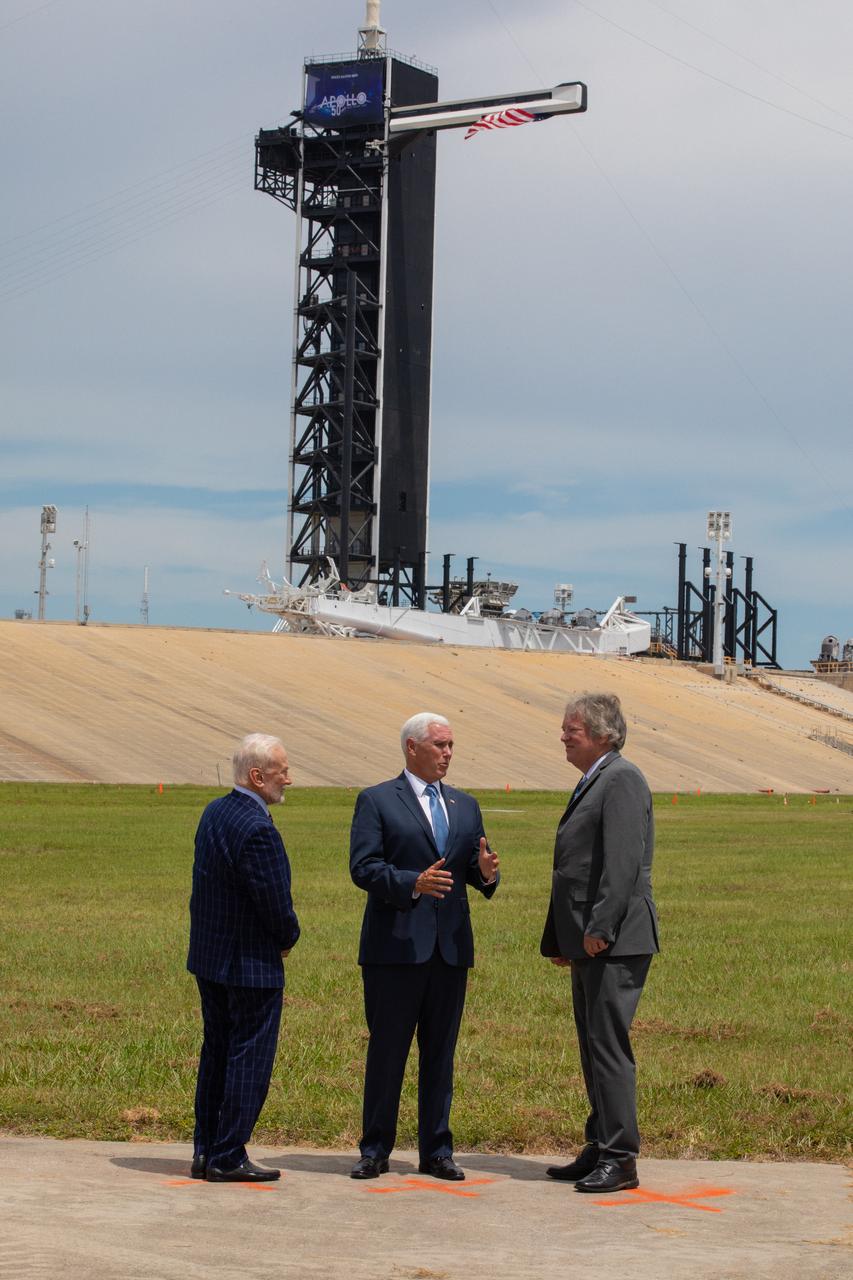

Vice President Mike Pence, center, celebrates the 50th anniversary of the Apollo 11 Moon landing during a visit to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39A on July 20, 2019. Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins launched from Pad 39A aboard a Saturn V rocket on July 16, 1969. Four days later, Armstrong and Aldrin landed the Apollo Lunar Module Eagle on the Moon, becoming the first two humans to walk on the lunar surface. Pence recognized the extraordinary achievements of the Apollo 11 team, while looking forward to NASA’s plans to return to the Moon and on to Mars. At left is Apollo 11 Lunar Module Pilot Buzz Aldrin. At right is Rick Armstrong, Apollo 11 Commander Neil Armstrong's son.

S72-35971 (21 April 1972) --- A 360-degree field of view of the Apollo 16 Descartes landing site area composed of individual scenes taken from color transmission made by the color RCA TV camera mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV). This panorama was made while the LRV was parked at the rim of North Ray Crater (Stations 11 & 12) during the third Apollo 16 lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) by astronauts John W. Young and Charles M. Duke Jr. The overlay identifies the directions and the key lunar terrain features. The camera panned across the rear portion of the LRV in its 360-degree sweep. Note Young and Duke walking along the edge of the crater in one of the scenes. The TV camera was remotely controlled from a console in the Mission Control Center (MCC). Astronauts Young, commander; and Duke, lunar module pilot; descended in the Apollo 16 Lunar Module (LM) "Orion" to explore the Descartes highlands landing site on the moon. Astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Casper" in lunar orbit.
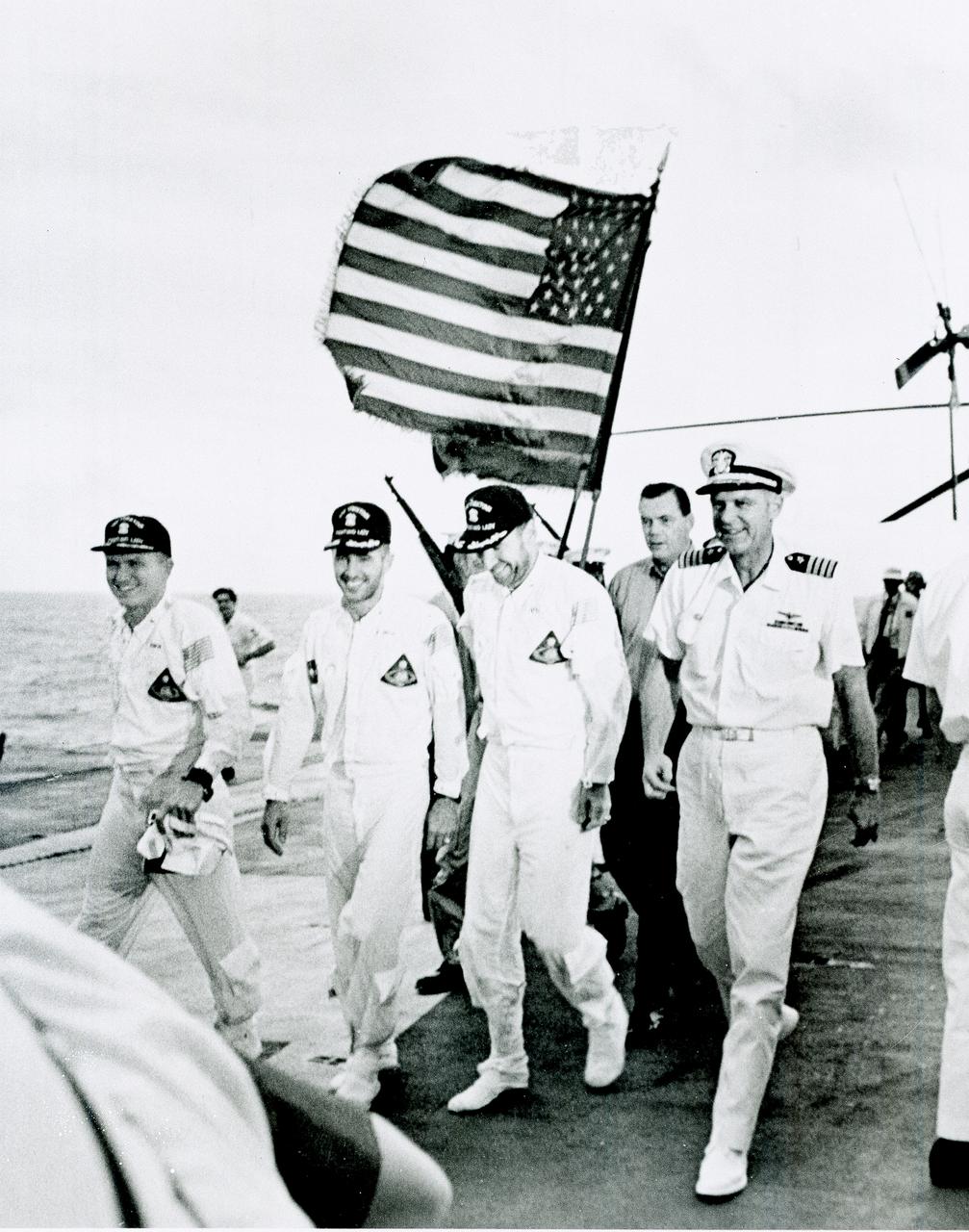

Apollo 8 astronauts and commanding officer of the recovery ship U.S.S. Yorktown walk the red carpet of the flight deck after splashdown recovery in the Pacific Ocean. Apollo 8 served as the first manned lunar orbit mission and the first manned flight of the Saturn V space vehicle, developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Liftoff occurred on December 21, 1968, carrying astronauts Frank Borman, commander; William Anders, Lunar Module (LM) Pilot; and James Lovell, Command Module (CM) pilot. The three safely returned to Earth on December 27, 1968. The mission achieved operational experience and tested the Apollo command module systems, including communications, tracking, and life-support, in cis-lunar space and lunar orbit, and allowed evaluation of crew performance on a lunar orbiting mission. The crew photographed the lunar surface, both far side and near side, obtaining information on topography and landmarks as well as other scientific information necessary for future Apollo landings. All systems operated within allowable parameters and all objectives of the mission were achieved.
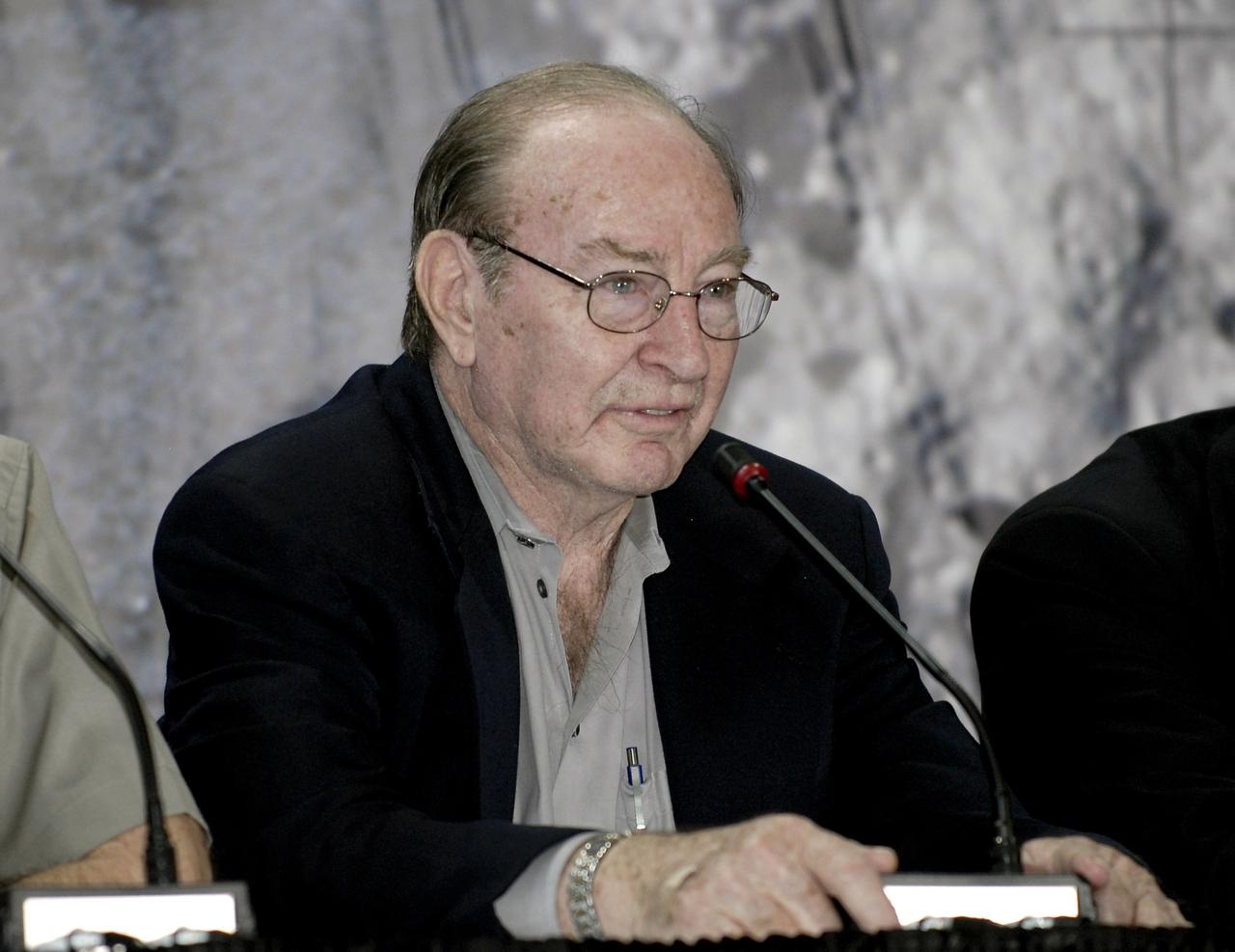

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Edgar Mitchell shares his experiences with an eager crowd gathered for NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. Mitchell walked on the moon on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971 and was backup lunar module pilot for Apollo 16. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
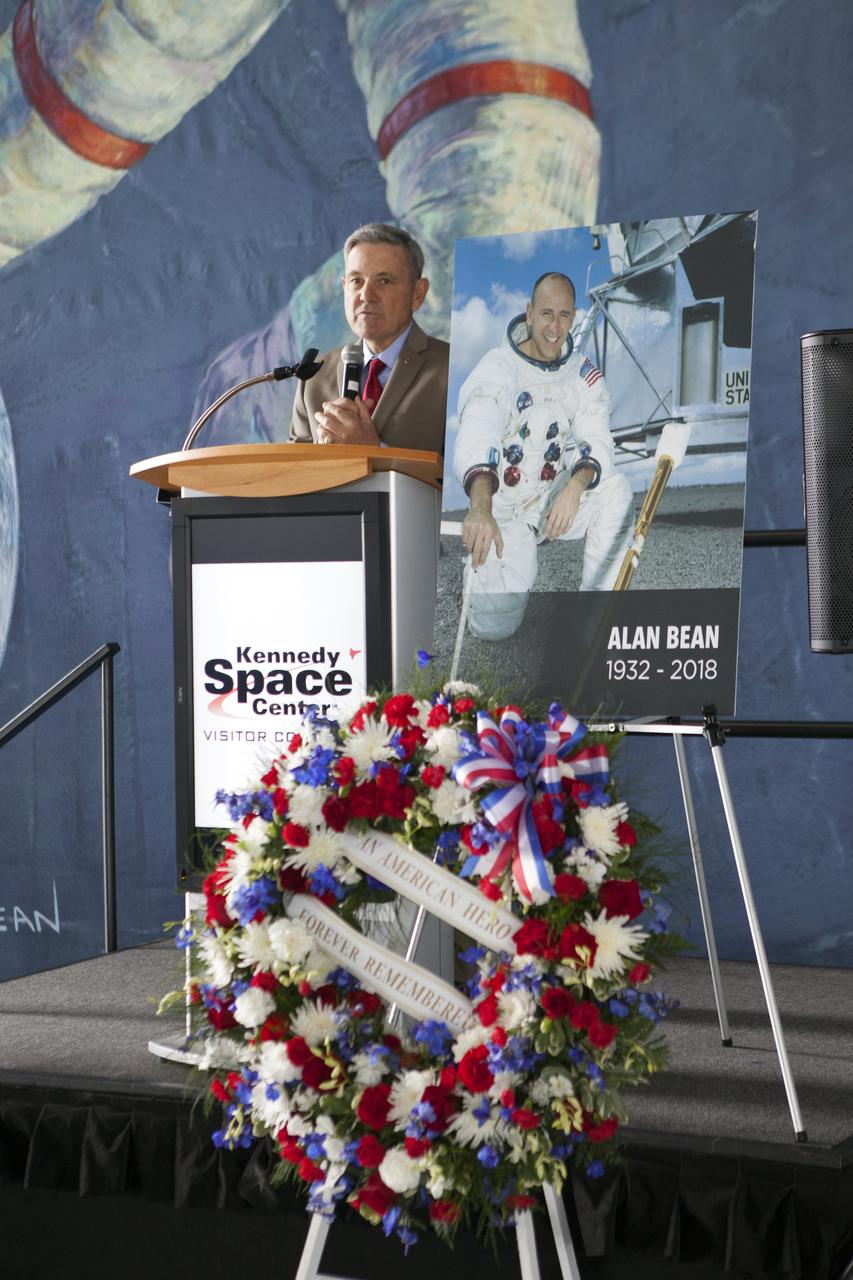

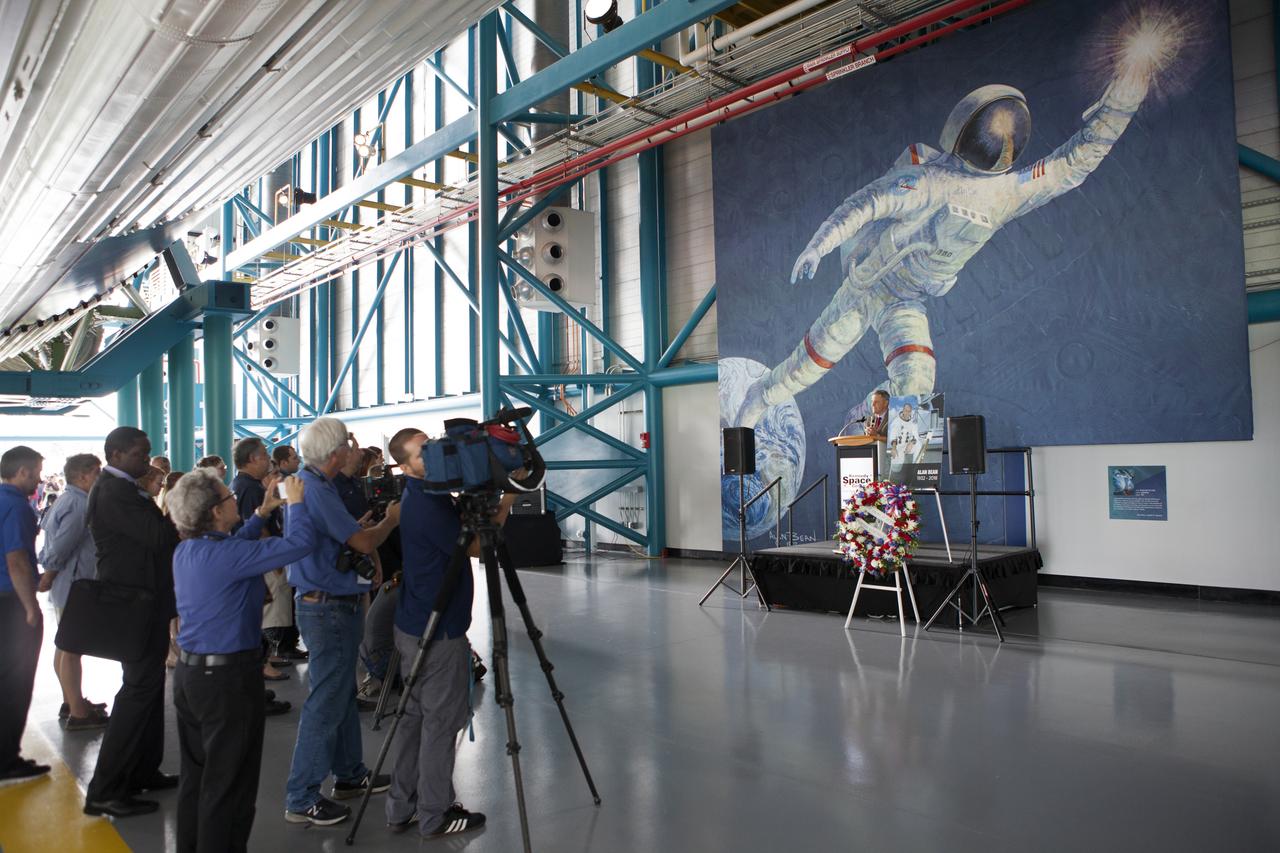
Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to guests in the Apollo-Saturn V Center at the spaceport's visitor complex on Wednesday, May 30, 2018. The ceremony is honoring the memory of former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. As lunar module pilot on Apollo 12, Bean was the fourth person to walk on the Moon in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.
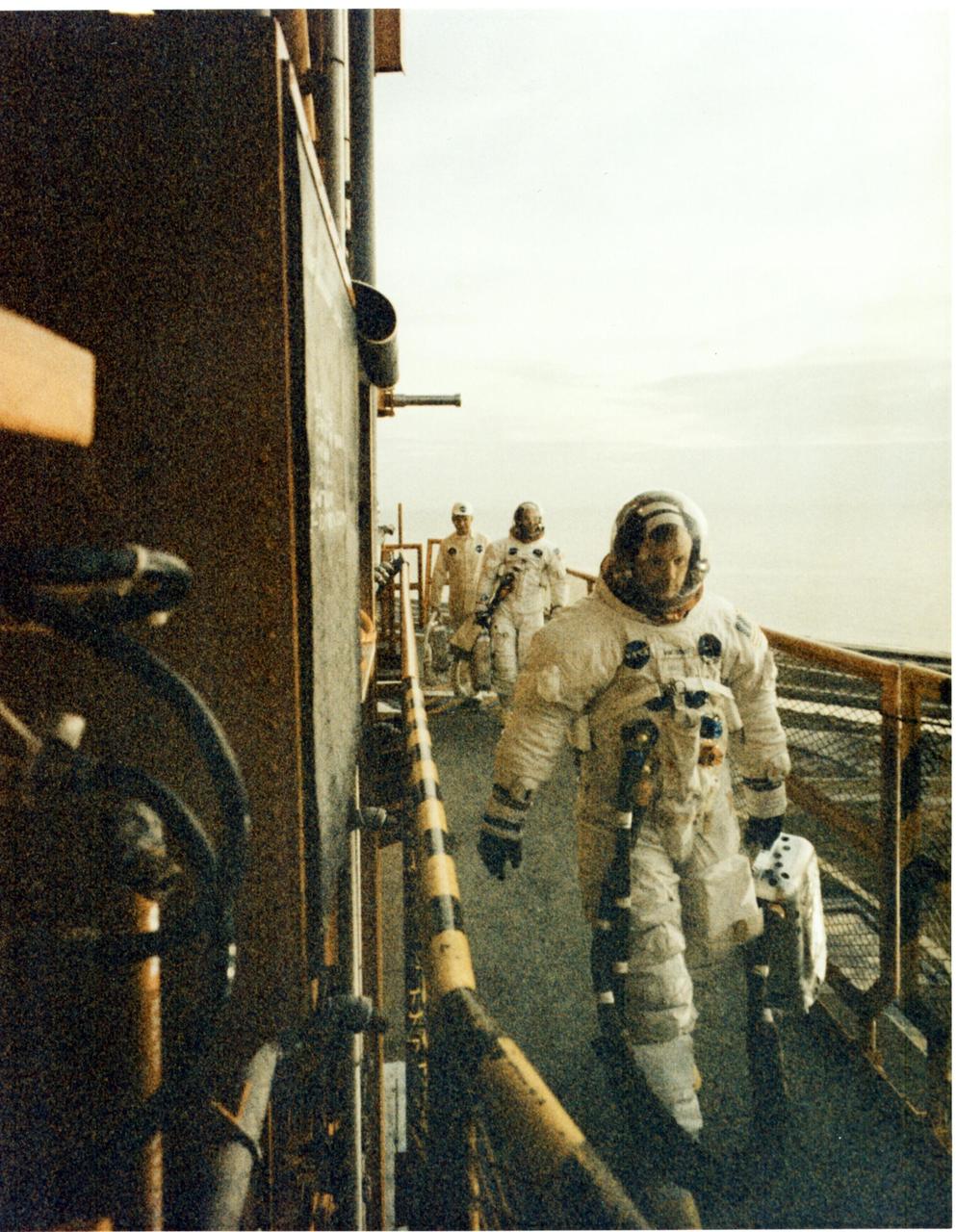

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong (front) and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. walk across the mobile launcher to enter their Apollo 11 spacecraft. Along with them is Joe Schmidt, a suit technician from Johnson Space Center. Not shown is the third member of the crew, astronaut Michael Collins. Liftoff of Apollo 11 is scheduled at 9:32 a.m. EDT from Pad 39A, which will begin man's first lunar landing mission.
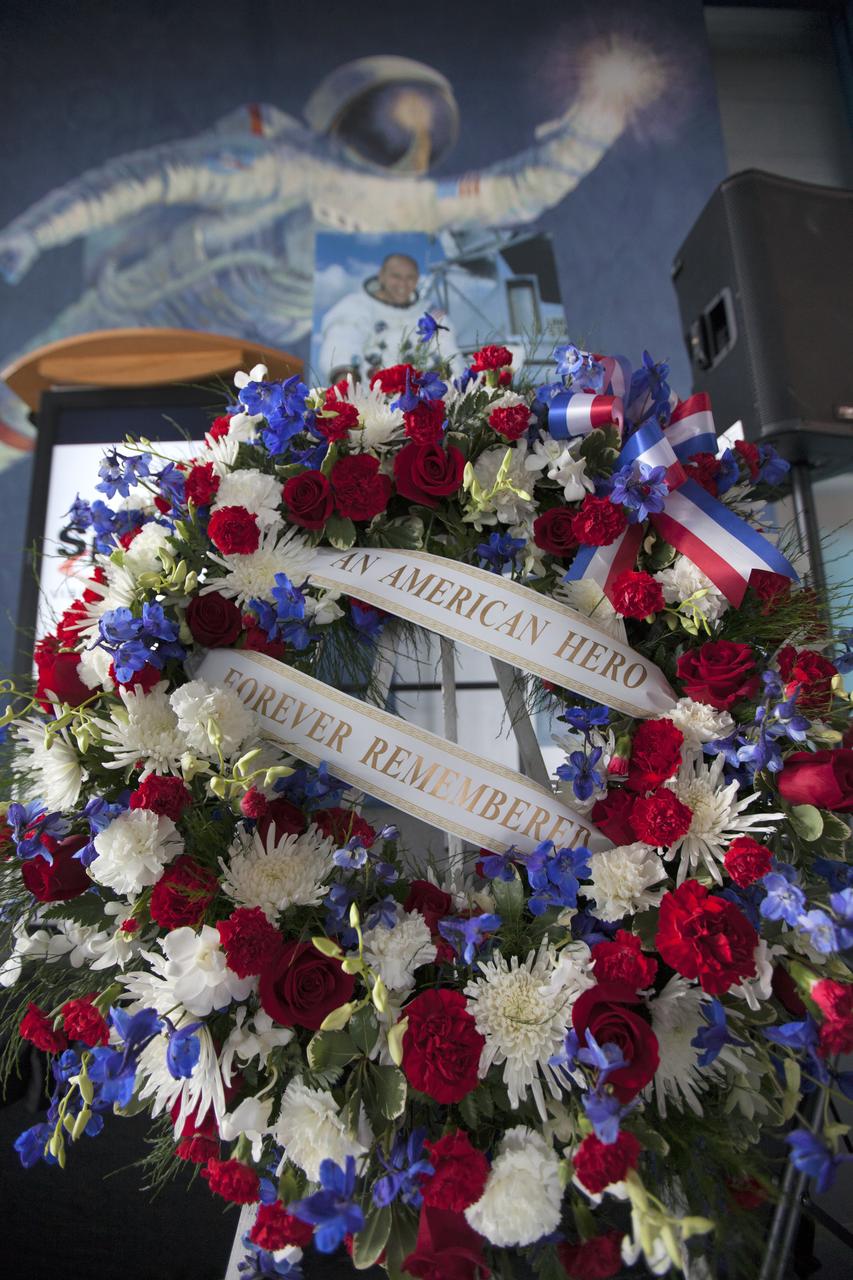

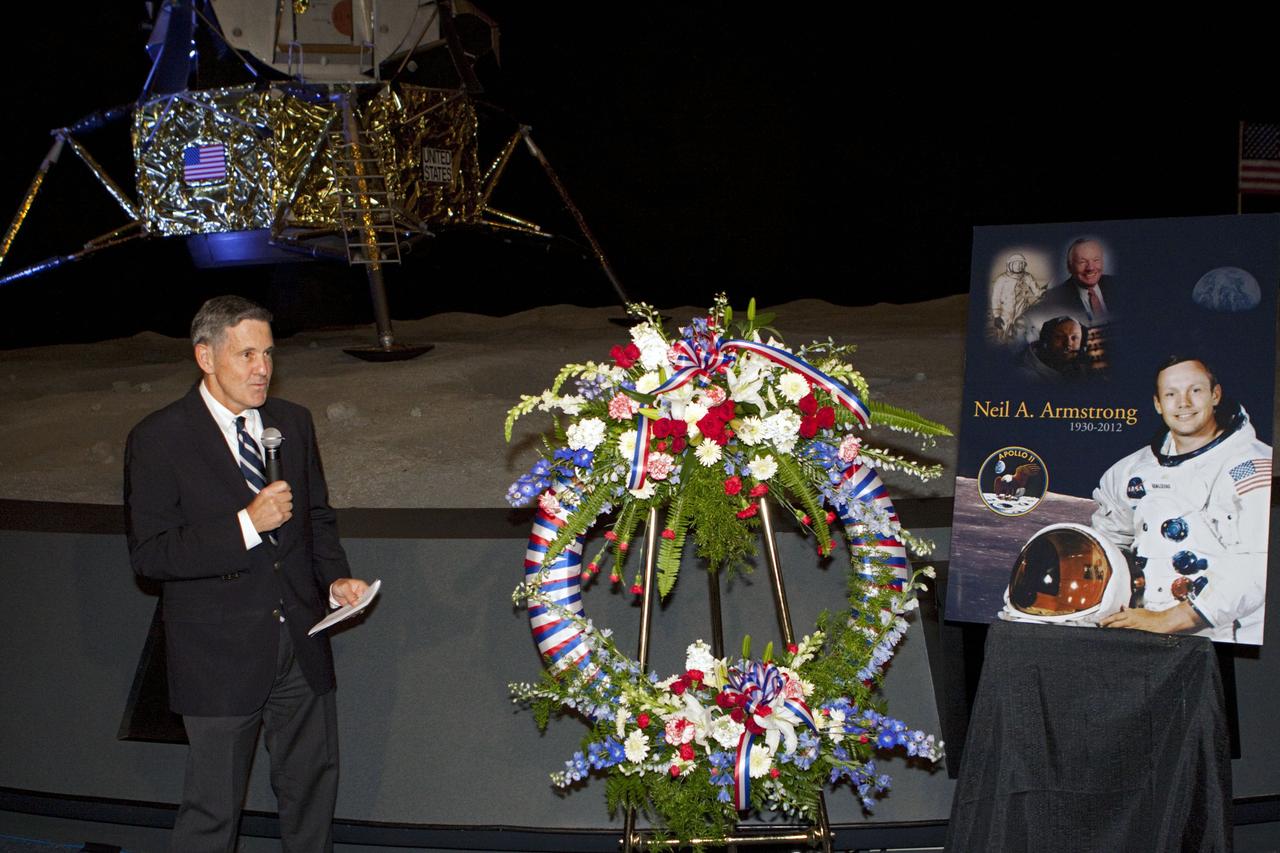
A memorial wreath placed in the Apollo-Saturn V Center of the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on Wednesday, May 30, 2018, honors former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. He was the fourth person to walk on the Moon as lunar module pilot on Apollo 12 in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Inside NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Apollo/Saturn V Center, CBS correspondent Ed Bradley (center) points to the lunar module behind him overhead during the taping of his interview with former astronaut Neil Armstrong (left). During the interview, Armstrong talked about his historic milestone - walking on the moon - and the public’s response and affect on his career afterward. The show aired Nov. 6.
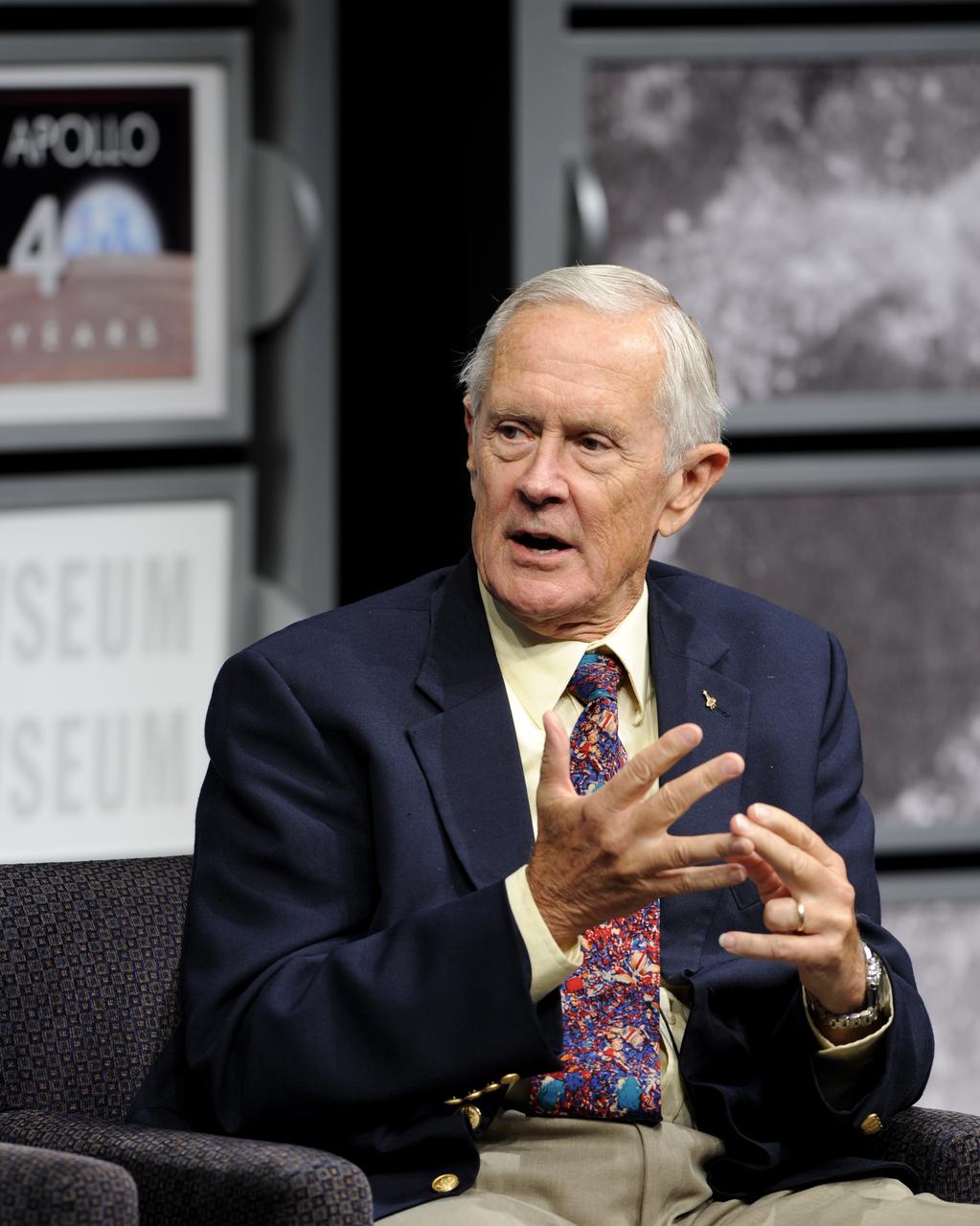

Apollo 16 astronaut Charlie Duke, the 10th person to walk on the moon who spent 71 hours on the lunar surface, talks during a panel discussion, Monday, July 20, 2009, hosted by Nick Clooney at the Newseum in Washington as part of the commemoration of the 40th Anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
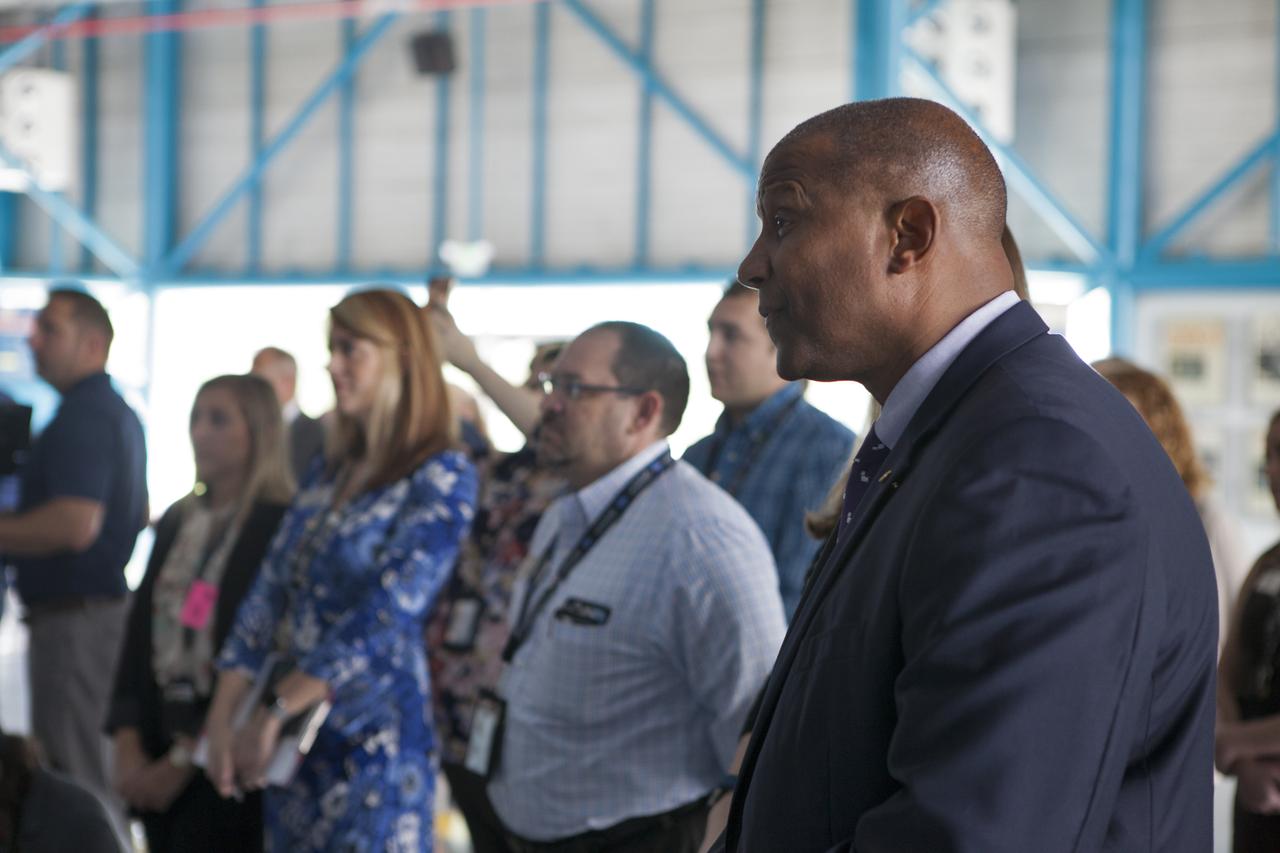

Associate Kennedy Space Center Director Kelvin Manning joins guests in a ceremony on Wednesday, May 30, 2018, honoring former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. As lunar module pilot on Apollo 12, Bean was the fourth person to walk on the Moon in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.
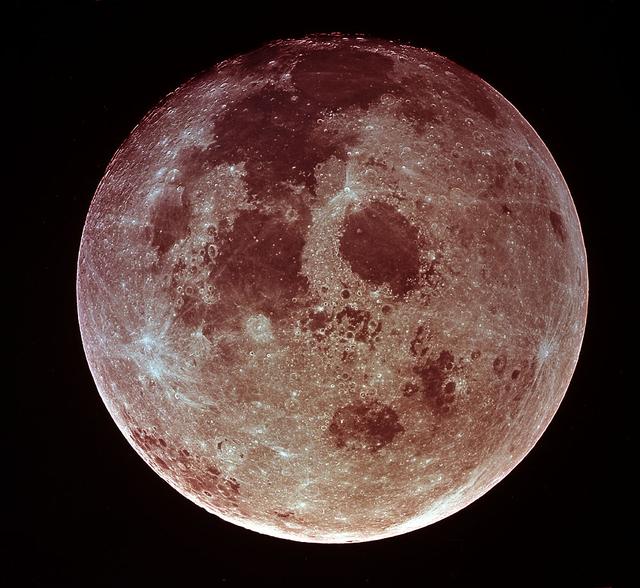
On July 21, 1969, only days after walking on the Moon's surface, Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin leave lunar orbit and begin the journey back to the space ship Columbia and its return to Earth. As they leave the Moon's orbit, a look back gives them a new perspective of where they were and where man's future lies. This was their final sight of the moon before they began docking procedures with Columbia.
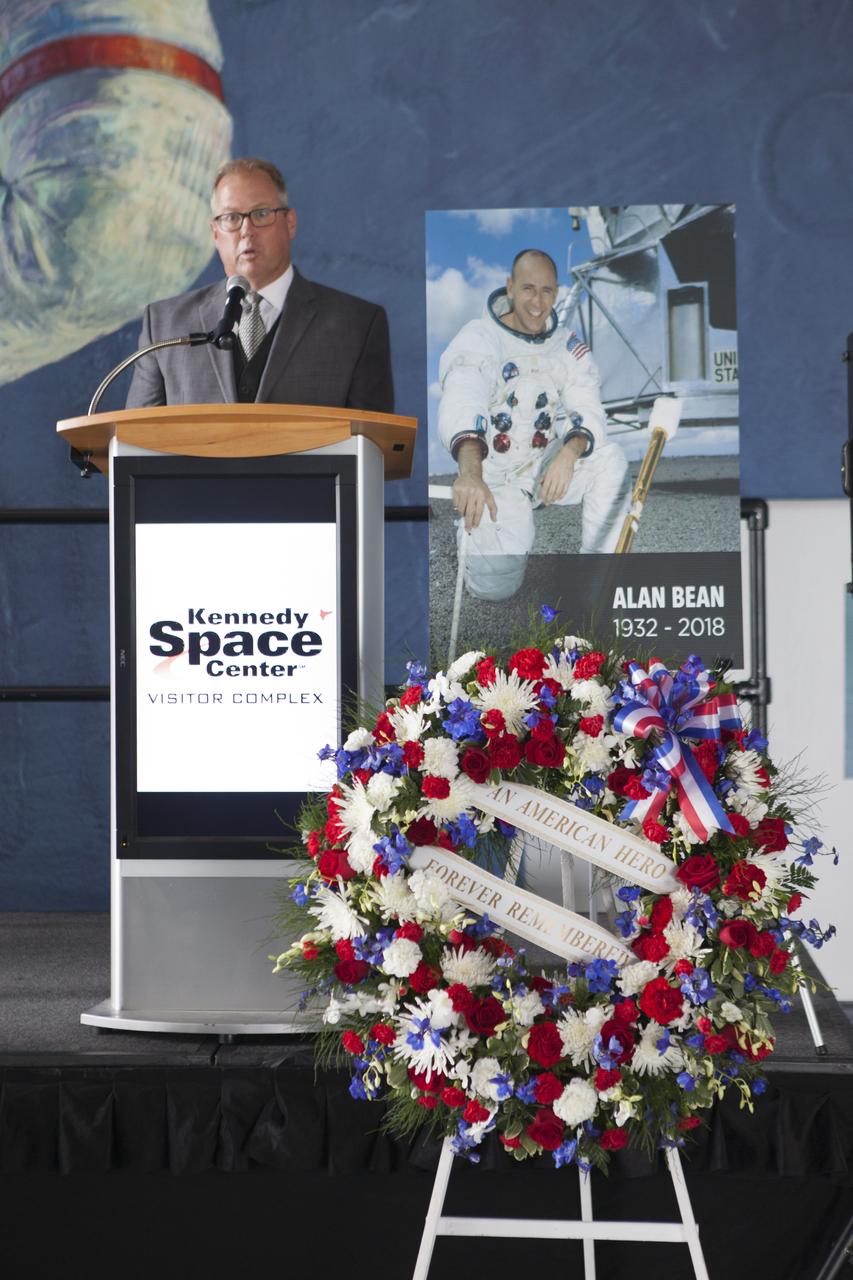

Therrin Protze, COO at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, speaks in the Apollo-Saturn V Center during a ceremony on Wednesday, May 30, 2018, honoring former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. As lunar module pilot on Apollo 12, Bean was the fourth person to walk on the Moon in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.

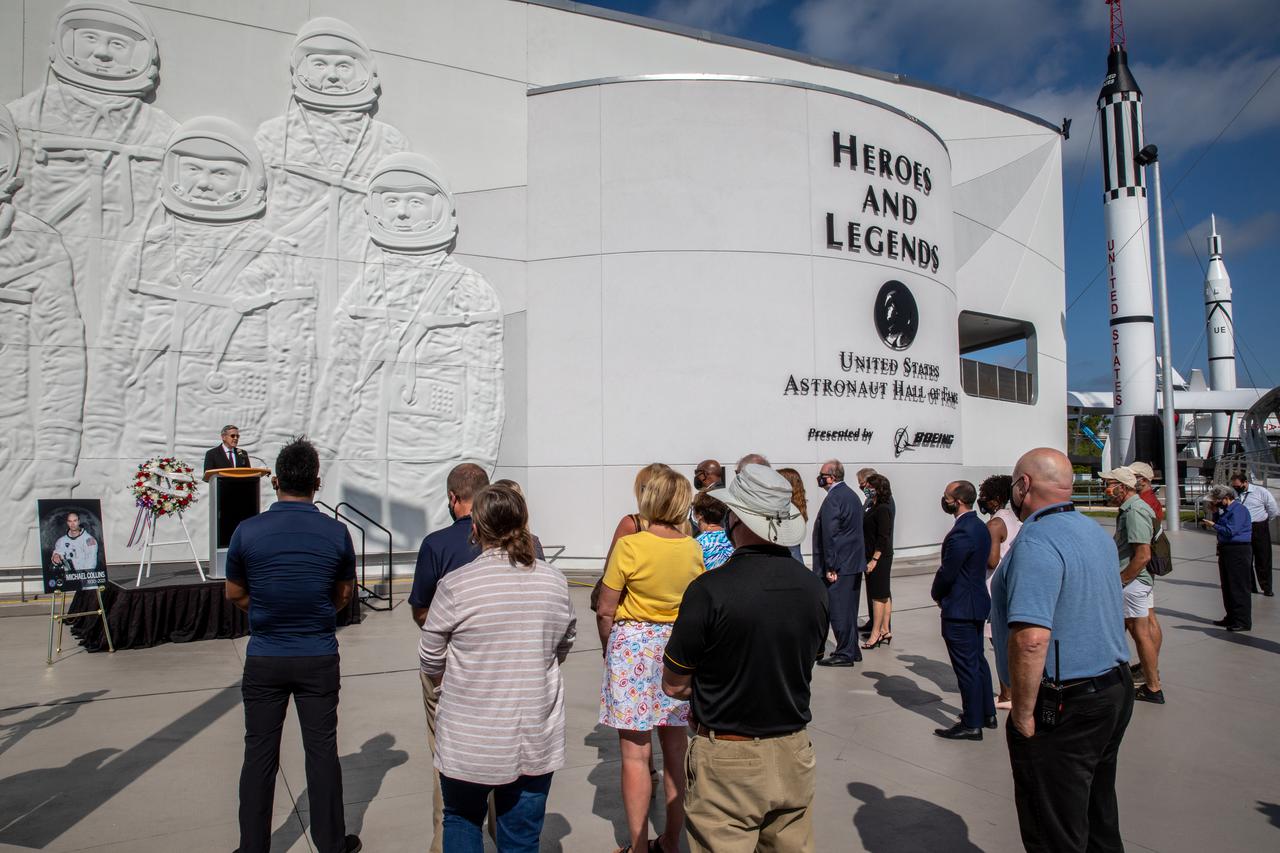
The Astronaut Hall of Fame display for astronaut Michael Collins is shown following a wreath-laying ceremony honoring his memory on April 30, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Edgar Mitchell is introduced during NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration of the July 1969 launch and landing on the moon. He was joined by seven others involved in the program. Mitchell walked on the moon on the Apollo 14 mission in 1971 and was backup lunar module pilot for Apollo 16. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Apollo/Saturn V Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Apollo astronaut Buzz Aldren is introduced during NASA's 40th Anniversary of Apollo Celebration. He was joined by seven others involved in the program. Aldrin walked on the moon during the first lunar landing, Apollo 11, on July 20, 1969. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
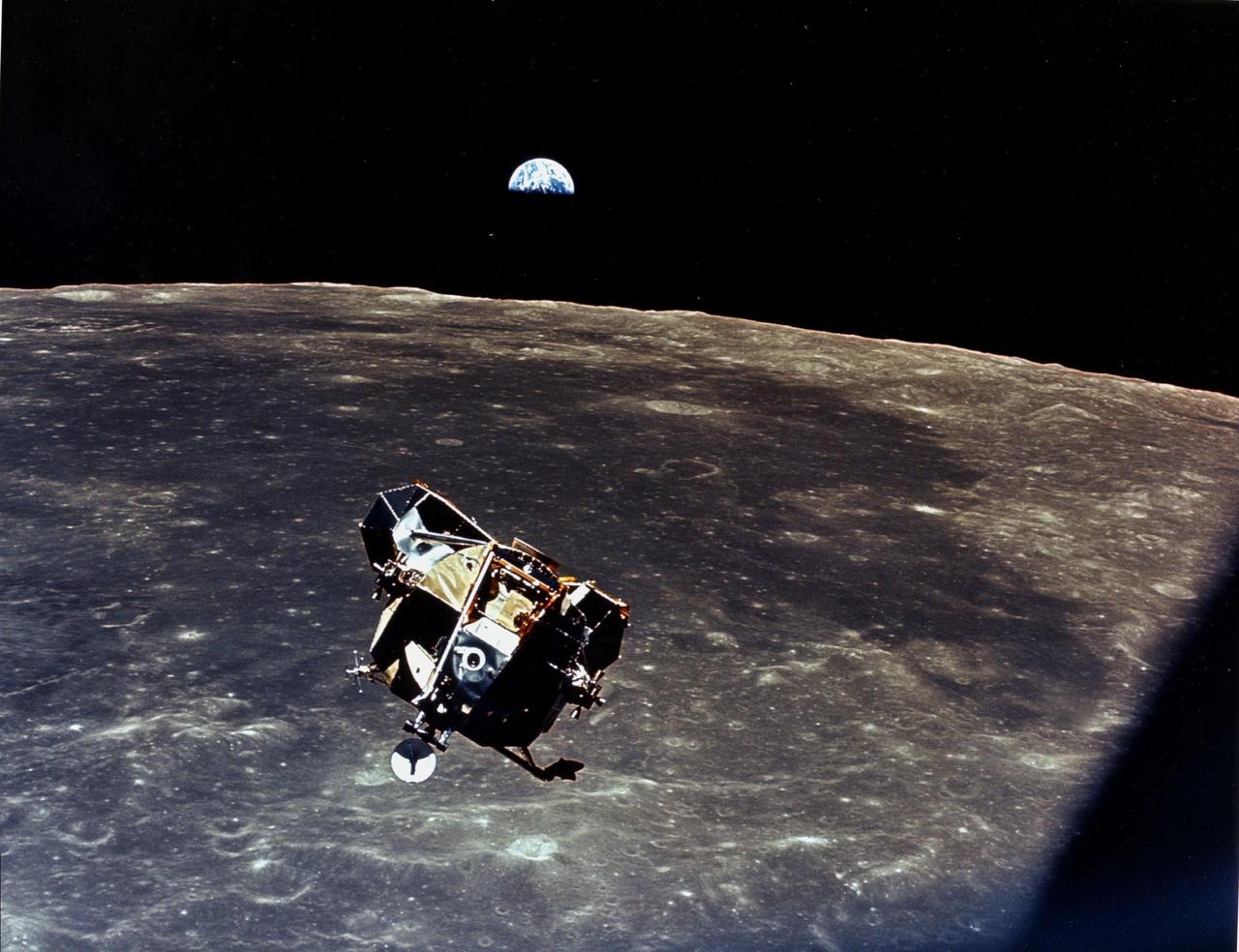

JOHNSON SPACE CENTER, HOUSTON, TEXAS - With a half-Earth in the background, the Lunar Module ascent stage with Moon-walking astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin Jr. approaches for a rendezvous with the Apollo Command Module manned by Michael Collins. The Apollo 11 liftoff from the Moon came early, ending a 22-hour stay on the Moon by Armstrong and Aldrin.
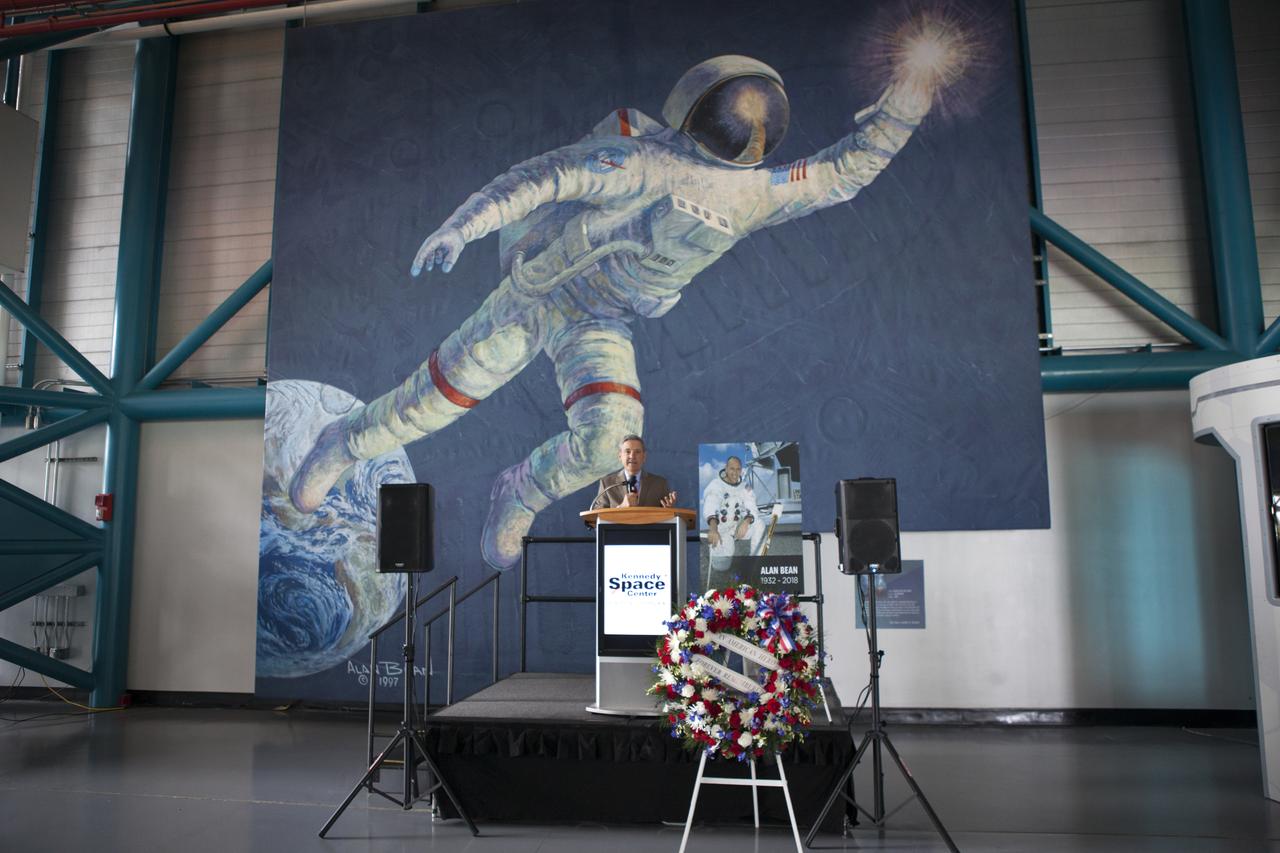

A memorial wreath placed in the Apollo-Saturn V Center of the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on Wednesday, May 30, 2018, honors former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. He was the fourth person to walk on the Moon as lunar module pilot on Apollo 12 in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. In the background is a large mural of a painting by Bean who became an accomplished artist after leaving NASA. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.
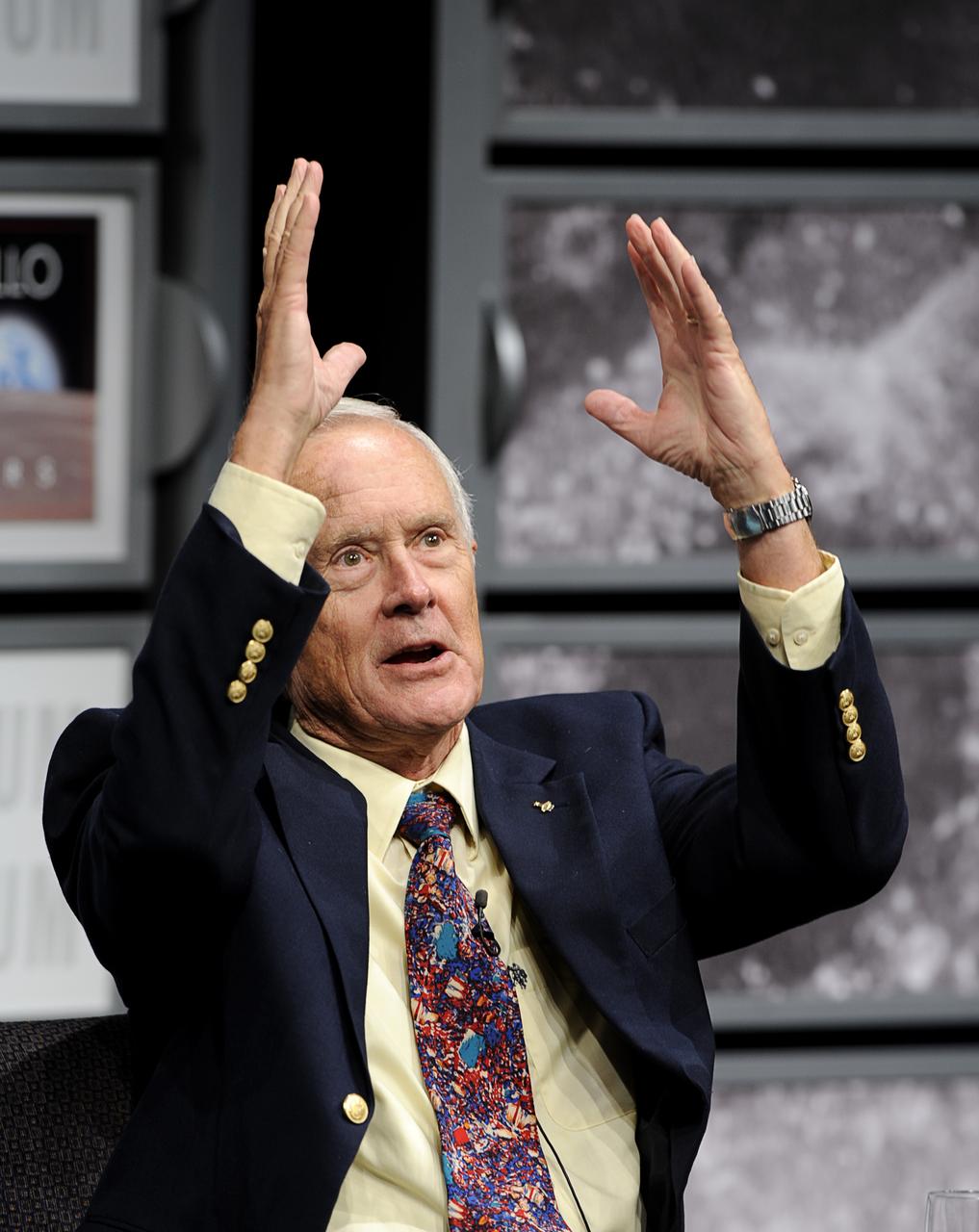

Apollo 16 astronaut Charlie Duke, the 10th person to walk on the moon who spent 71 hours on the lunar surface, talks during a panel discussion, Monday, July 20, 2009, hosted by Nick Clooney at the Newseum in Washington as part of the commemoration of the 40th Anniversary of the Apollo 11 moon landing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

jsc2012e052599 - Panorama view of Apollo 16 lunar surface photos as lunar module pilot Charles M. Duke Jr. is photographed by commander John W. Young collecting lunar samples at Station No. 1 during the first moonwalk of the mission at the Descartes landing site. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 16 images starting with frame AS16-114-18416 thru end frame AS16-114-18431. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun. With significant overlap and time delay between frames, it is possible to create two different versions of this panorama with astronaut Charles Duke (Apollo 16) in the center (jsc2012e052598) and both in the center and walking away to the right (jsc2012e052599).

jsc2012e052598 - Panorama view of Apollo 16 lunar surface photos as lunar module pilot Charles M. Duke Jr. is photographed by commander John W. Young collecting lunar samples at Station No. 1 during the first moonwalk of the mission at the Descartes landing site. The panoramas were built by combining Apollo 16 images starting with frame AS16-114-18416 thru end frame AS16-114-18431. The panoramic images received minimal retouching by NASA imagery specialists, including the removal of lens flares that were problematic in stitching together the individual frames and blacking out the sky to the lunar horizon. These adjustments were made based on observations of the Moon walkers who reported that there are no stars visible in the sky due to the bright lunar surface reflection of the Sun. With significant overlap and time delay between frames, it is possible to create two different versions of this panorama with astronaut Charles Duke (Apollo 16) in the center (jsc2012e052598) and both in the center and walking away to the right (jsc2012e052599).
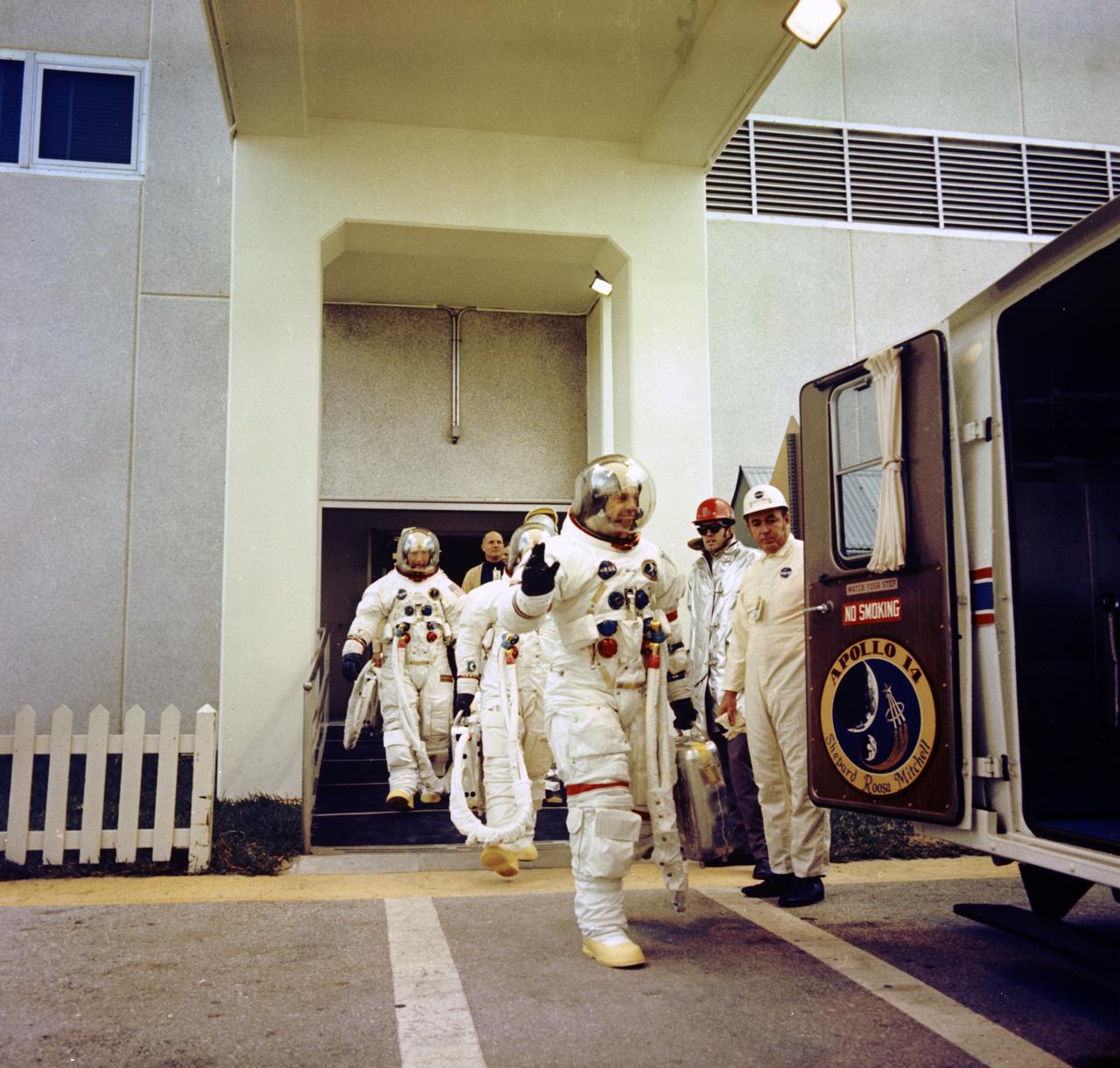

Apollo 14 Mission Commander, Alan B. Shepard, Jr., waves to well-wishers as he and astronauts Stuart A. Roosa, Command Module pilot; and Edgar D. Mitchell, Lunar Module pilot, walk to the transfer van during the countdown demonstration test. The Apollo 14, carrying the crew of three lifted off from launch complex 39A at KSC on January 31, 1971. It was the third manned lunar landing, the first manned landing in exploration of the lunar highlands, and it demonstrated pinpoint landing capability. The major goal of Apollo 14 was the scientific exploration of the Moon in the foothills of the rugged Fra Mauro region. The lunar surface extravehicular activity (EVA) of astronauts Shepard and Mitchell included setting up an automated scientific laboratory called Apollo Lunar Scientific Experiments Package (ALSEP), and collecting a total of about 95 pounds (43 kilograms) of Moon rock and soil for a geological investigation back on the Earth. Apollo 14 safely returned to Earth on February 9, 1971.
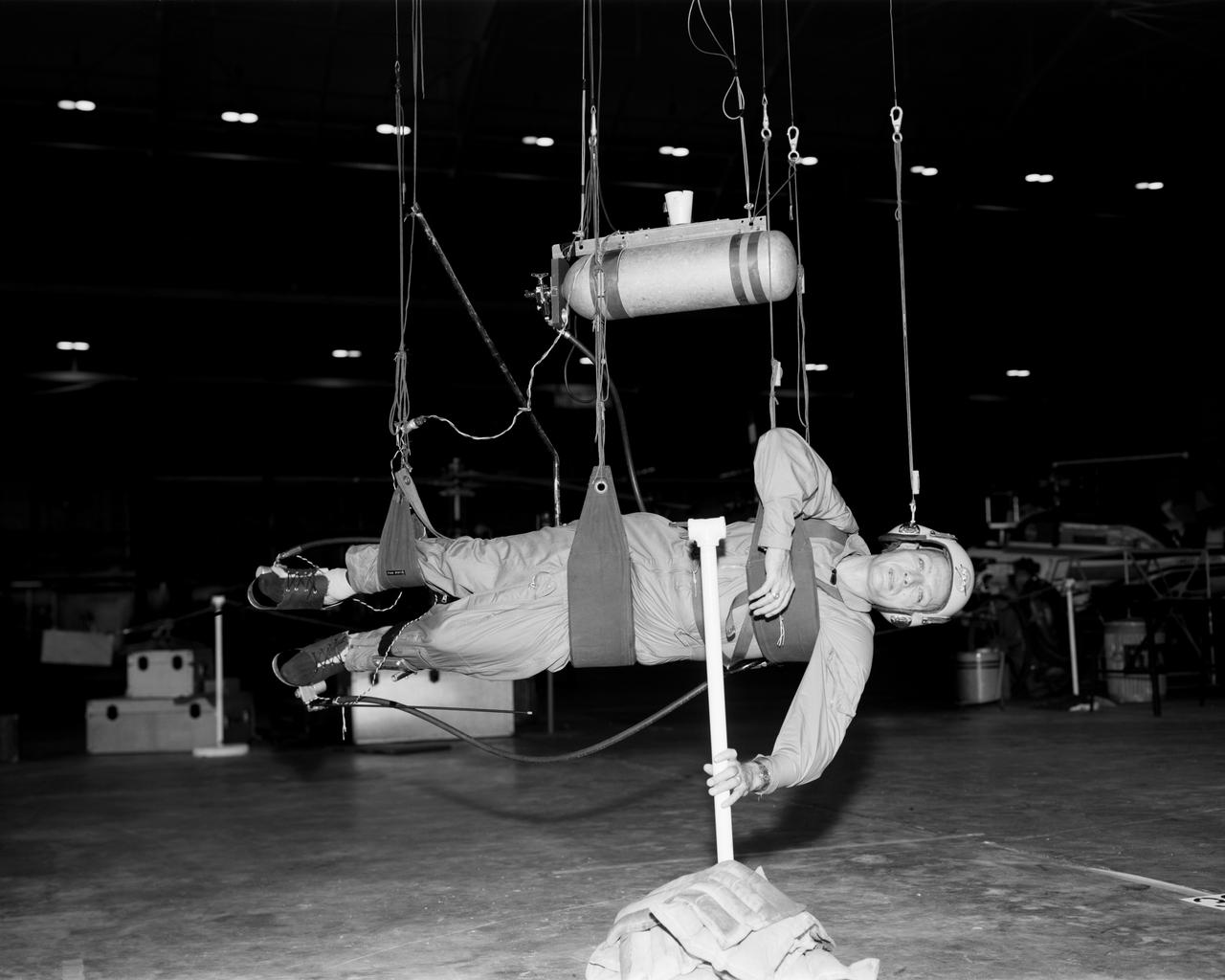

Cable system which supports the test subject on the Reduced Gravity Walking Simulator. The purpose of this simulator was to study the subject while walking, jumping or running. Researchers conducted studies of various factors such as fatigue limit, energy expenditure, and speed of locomotion. A.W. Vigil described the purpose of the simulator as follows: "When the astronauts land on the moon they will be in an unfamiliar environment involving, particularly, a gravitational field only one-sixth as strong as on earth. A novel method of simulating lunar gravity has been developed and is supported by a puppet-type suspension system at the end of a long pendulum. A floor is provided at the proper angle so that one-sixth of the subject's weight is supported by the floor with the remainder being supported by the suspension system. This simulator allows almost complete freedom in vertical translation and pitch and is considered to be a very realistic simulation of the lunar walking problem. For this problem this simulator suffers only slightly from the restrictions in lateral movement it puts on the test subject. This is not considered a strong disadvantage for ordinary walking problems since most of the motions do, in fact, occur in the vertical plane. However, this simulation technique would be severely restrictive if applied to the study of the extra-vehicular locomotion problem, for example, because in this situation complete six degrees of freedom are rather necessary. This technique, in effect, automatically introduces a two-axis attitude stabilization system into the problem. The technique could, however, be used in preliminary studies of extra-vehicular locomotion where, for example, it might be assumed that one axis of the attitude control system on the astronaut maneuvering unit may have failed." -- Published in James R. Hansen, Spaceflight Revolution: NASA Langley Research Center From Sputnik to Apollo, (Washington: NASA, 1995); A.W. Vigil, "Discussion of Existing and Planned Simulators for Space Research," Paper presented at Conference on the Role of Simulation in Space Technology," Blacksburg, VA, August 17-21, 1964.
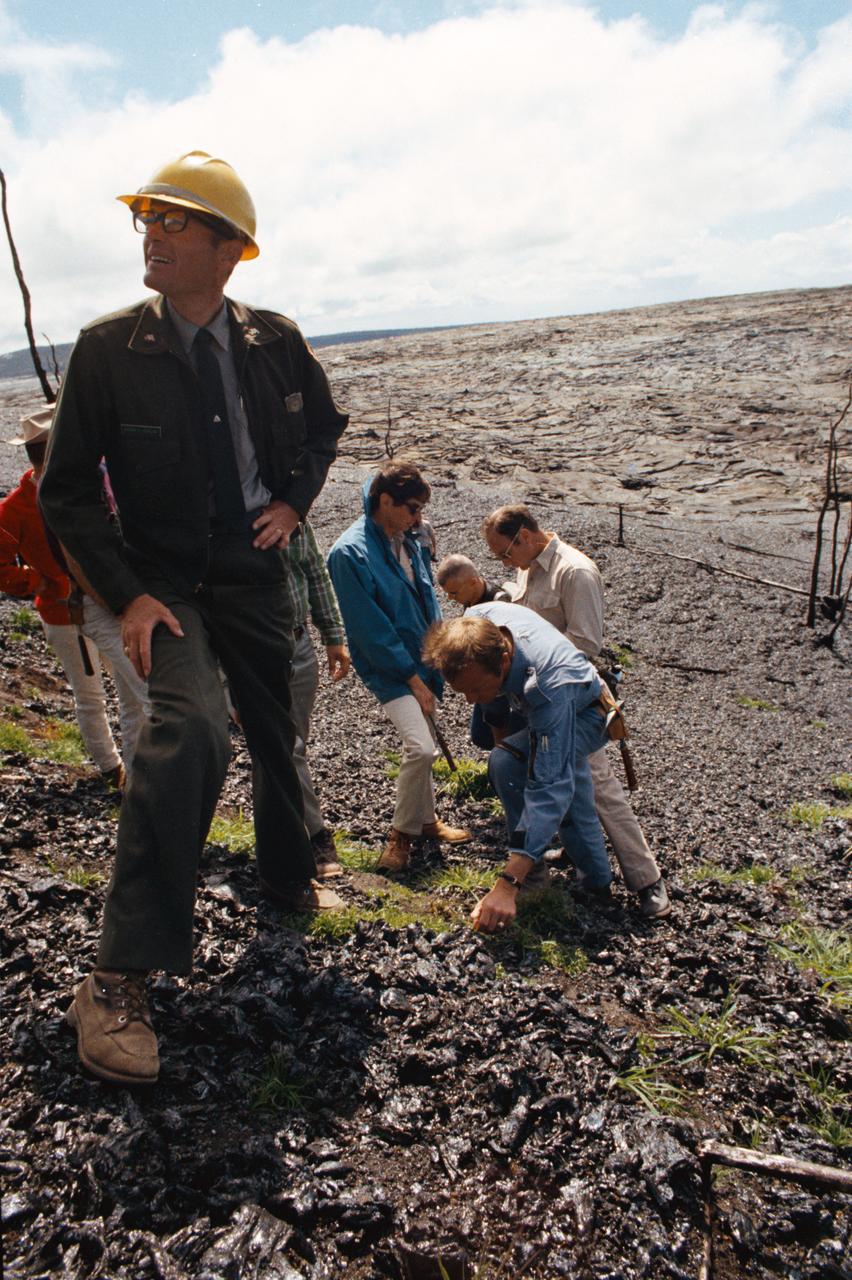

S70-34421 (April 1970) --- Prime crew men and backup crew men, of the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission, look over an area near the site of a volcanic eruption on Dec. 30, 1969. Astronauts Alan B. Shepard Jr. (leaning with left hand on ground) and Edgar D. Mitchell (behind Shepard, wearing dark glasses) are the prime crew men scheduled to walk on the moon. Astronauts Eugene A. Cernan (almost obscured at extreme left) and Joe H. Engle (partially visible, on Cernan's right) are backup crew commander and lunar module pilot, respectively, for the mission. Others in the photograph are Pat Crosland (in hard hat), a geologist and a park ranger in Hawaii Volcanoes State Park; Michael C. McEwen (facing Mitchell) of the Geology Branch, Lunar and Earth Sciences Division, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC); and astronaut Bruce McCandless II, who made the trip to serve as a spacecraft communicator during simulations of extravehicular activity (EVA) on the lunar surface.
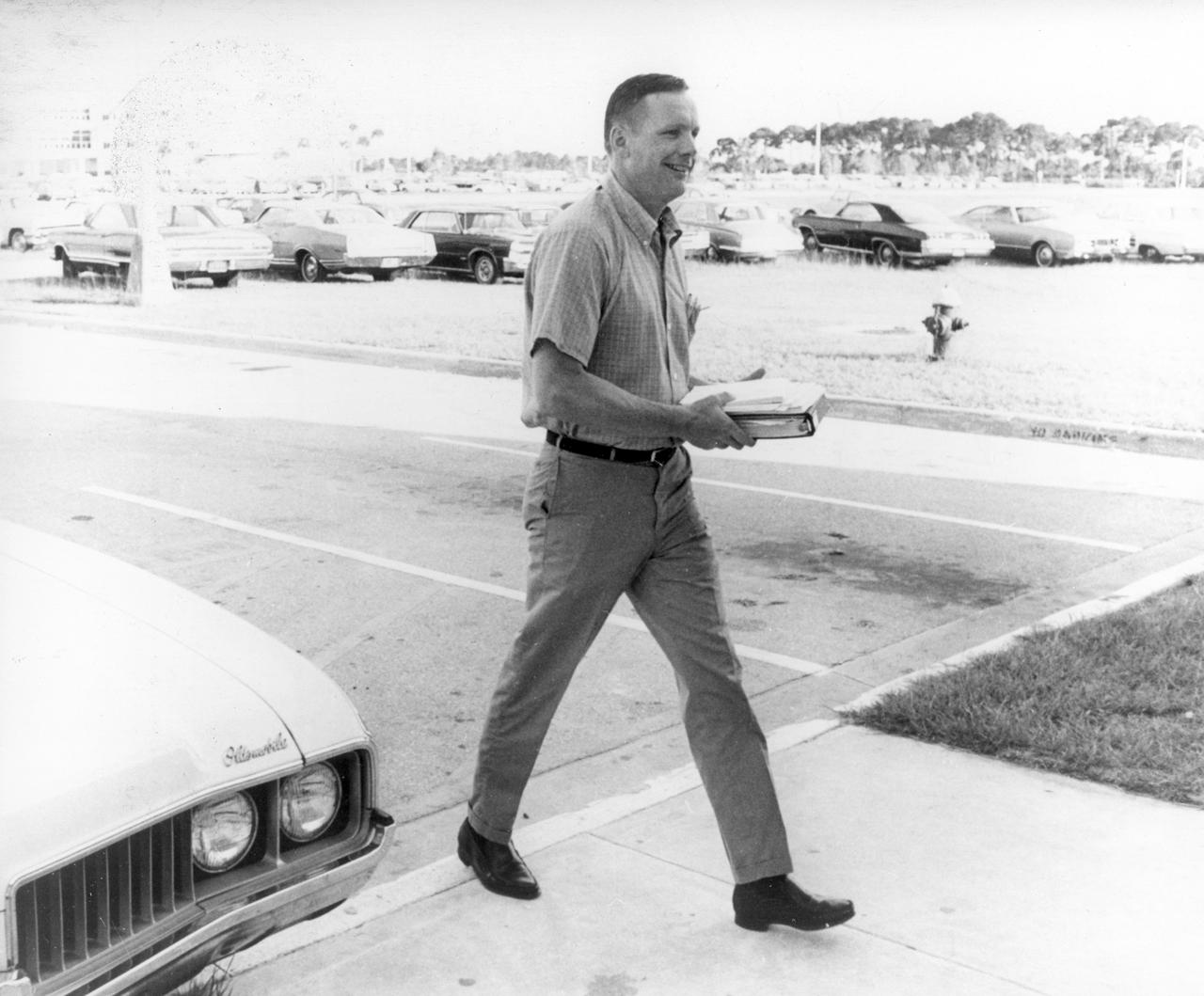

In this photograph, Apollo 11 astronaut Neil Armstrong walks to the flight crew training building at the NASA Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida, one week before the nation’s first lunar landing mission. The Apollo 11 mission launched from KSC via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
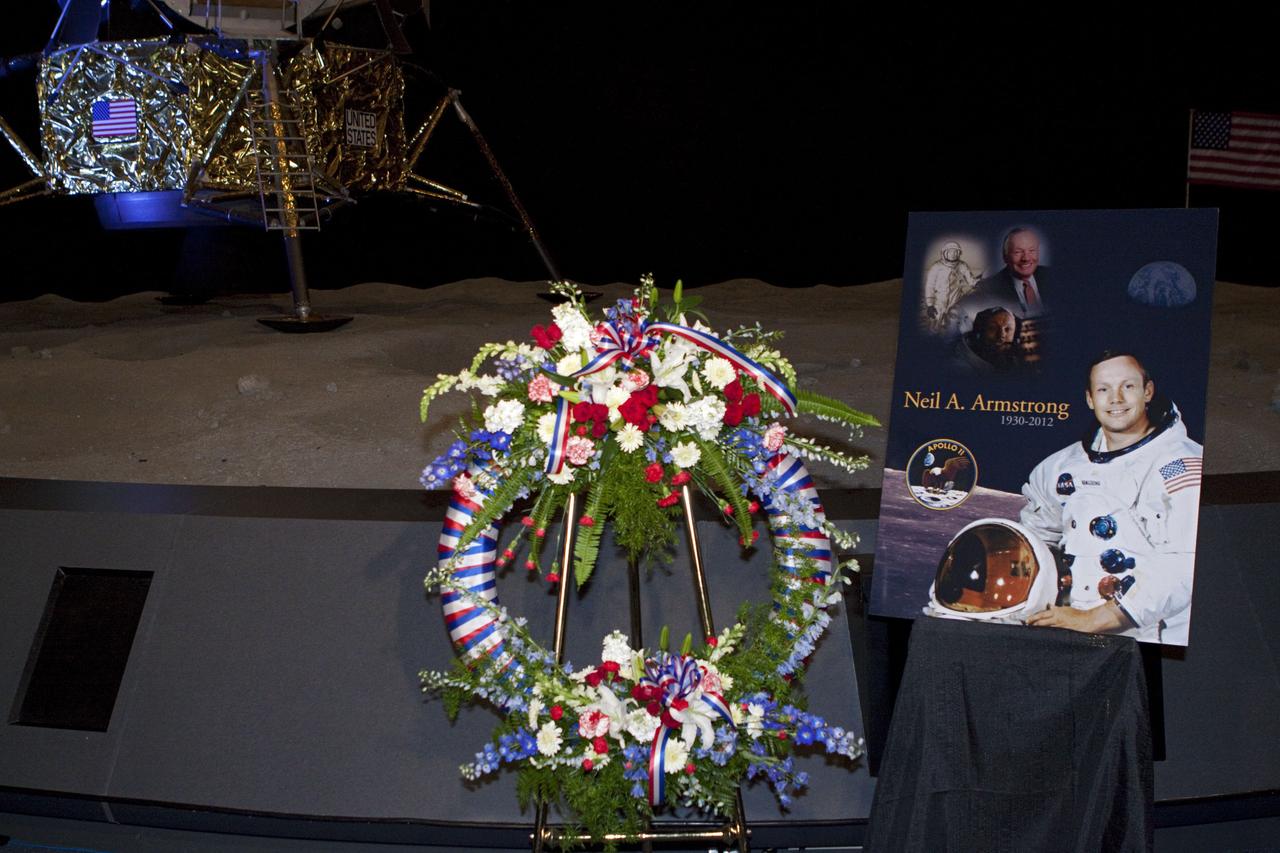

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Kennedy Space Center employees and guests gathered for a brief ceremony on Aug. 31, 2012 honoring Neil Armstrong, who died Aug. 25, 2012 at the age of 82. Armstrong was hailed by Center Director Bob Cabana as one of our heroes and a truly a great American. Cabana placed a wreath near a replica lunar module at the spaceport's Apollo-Saturn V Center. Selected as an astronaut in 1962, Neil Armstrong flew on NASA's Gemini 8 with David Scott in March 1966 and the first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, with Mike Collins and Buzz Aldine in July 1969. On July 20, 1969, he became the first human to walk on the moon. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/news/neil_armstrong.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana spoke to spaceport employees and guests at a brief ceremony on Aug. 31, 2012 honoring Neil Armstrong, who died Aug. 25, 2012 at the age of 82. Armstrong was hailed by Cabana as one of our heroes and a truly a great American. Cabana, also a former astronaut, placed a wreath near a replica lunar module at the spaceport's Apollo-Saturn V Center. Selected as an astronaut in 1962, Neil Armstrong flew on NASA's Gemini 8 with David Scott in March 1966 and the first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, with Mike Collins and Buzz Aldine in July 1969. On July 20, 1969, he became the first human to walk on the moon. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/news/neil_armstrong.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
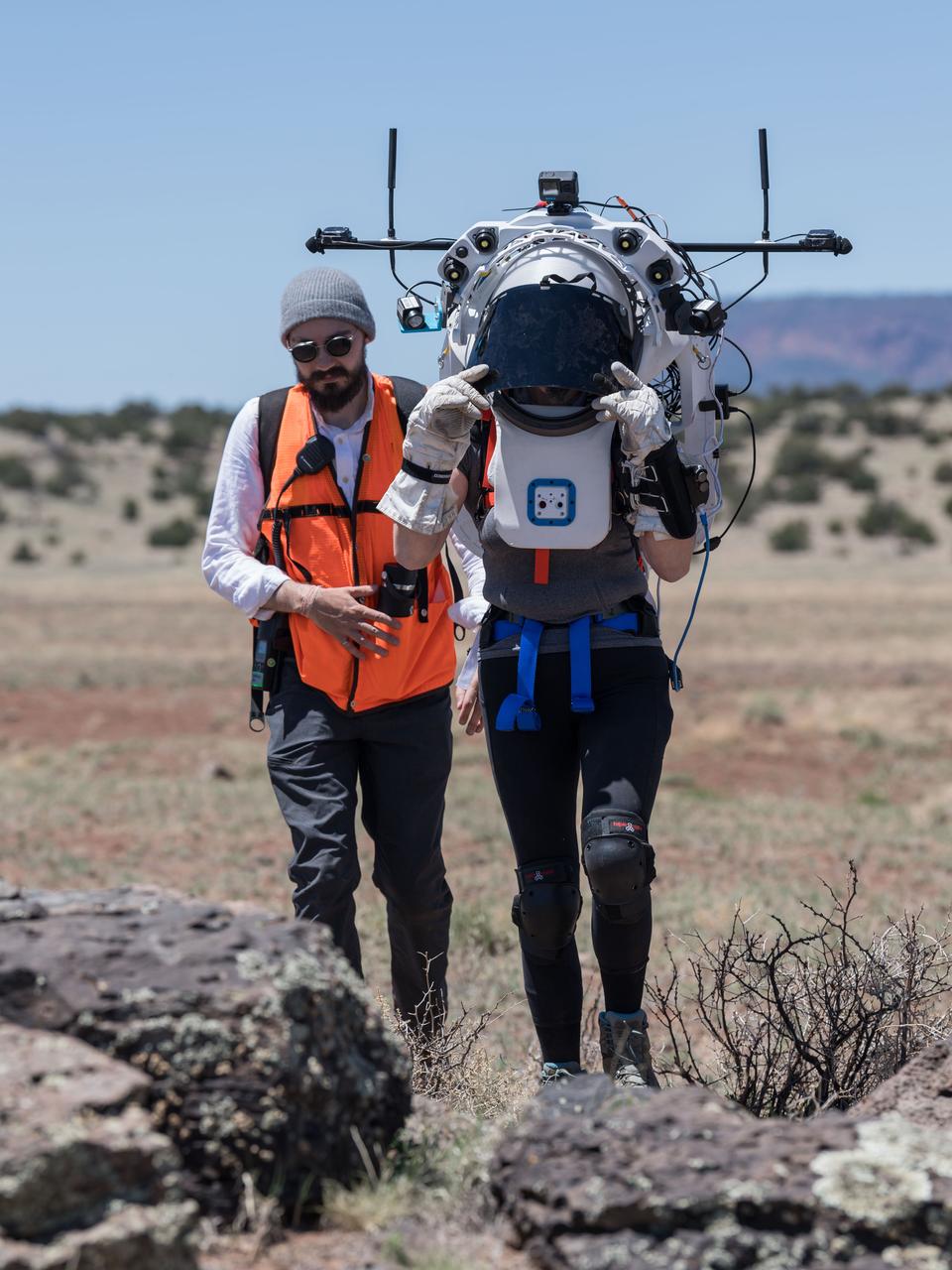

NASA astronaut Kate Rubins walks through the lunar-like landscape wearing the Joint AR (Joint Augmented Reality Visual Informatics System) display during an advanced technology run in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Northern Arizona on May 19, 2024. The suit display features include navigation, photo capture, graphical format of consumables, procedure viewing, mission control updates, and other augmented reality cues and graphics. The team successfully tested navigation displays using data from four different data streams: GPS (Global Positioning System)/IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), camera/IMU, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), and static maps. Technology like this may be used for future Artemis missions to augment mission control communication and help guide crew back to the lunar lander. Credit: NASA/Josh Valcarcel

Members of the news media assemble to cover a ceremony on Wednesday, May 30, 2018, during which a memorial wreath is placed in the Apollo-Saturn V Center of the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex honoring former NASA astronaut Alan Bean. In the background is a large mural of a painting by Alan Bean who became an accomplished artist after leaving NASA. Bean was the fourth person to walk on the Moon as lunar module pilot on Apollo 12 in November 1969. He went on to command the 59-day Skylab 3 mission in 1973. He died in Houston on May 26, 2018, at the age of 86.

A wreath-laying ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins is held outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on April 30, 2021. Kennedy Director Bob Cabana and Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at the visitor complex, provided remarks during the ceremony. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.
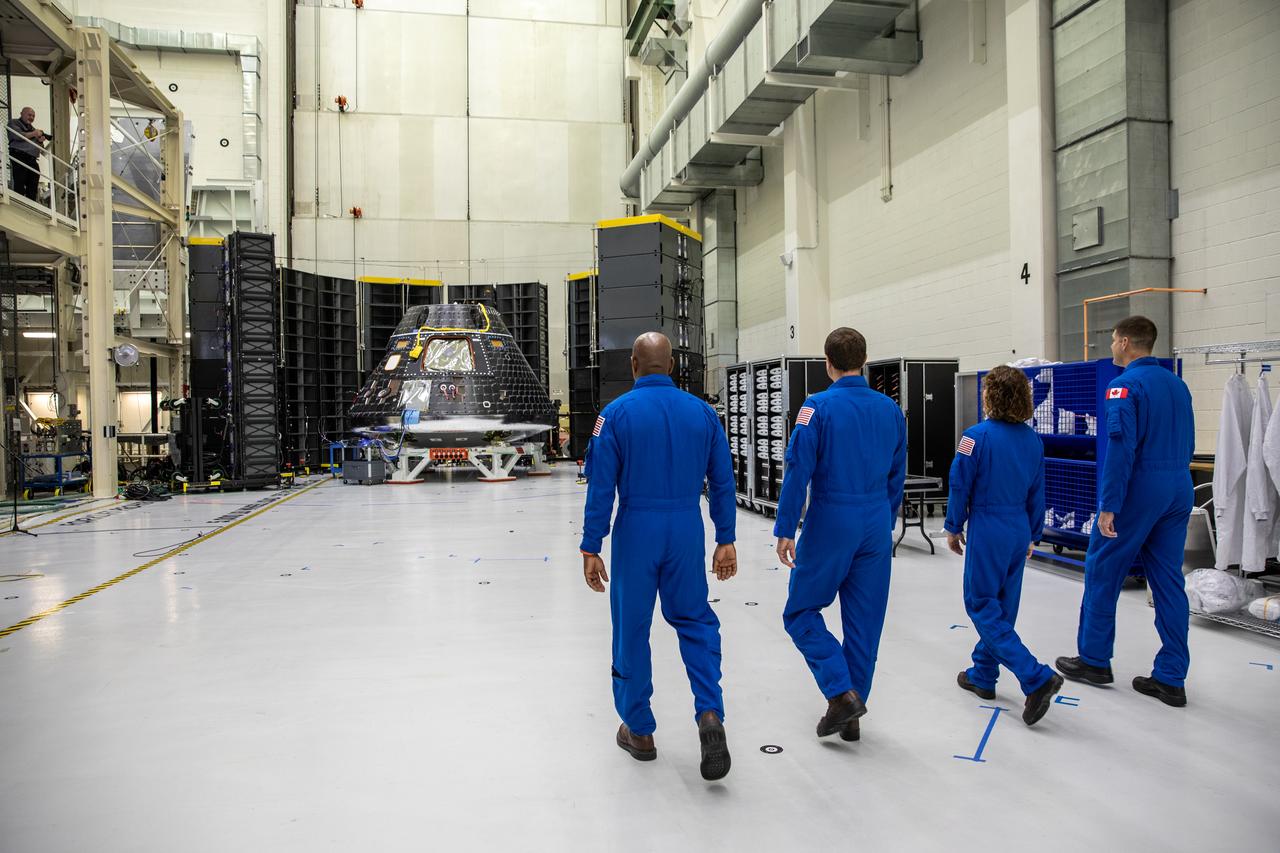

Artemis II crew members, shown inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, walk toward their Orion crew module on Aug. 8, 2023. From left are: Victor Glover, pilot; Reid Wiseman, commander; Christina Hammock Koch, mission specialist; and Jeremy Hansen, mission specialist. The crew module is undergoing acoustic testing ahead of integration with the European Service Module. Artemis II is the first crewed mission on NASA’s path to establishing a long-term lunar presence for science and exploration under Artemis.
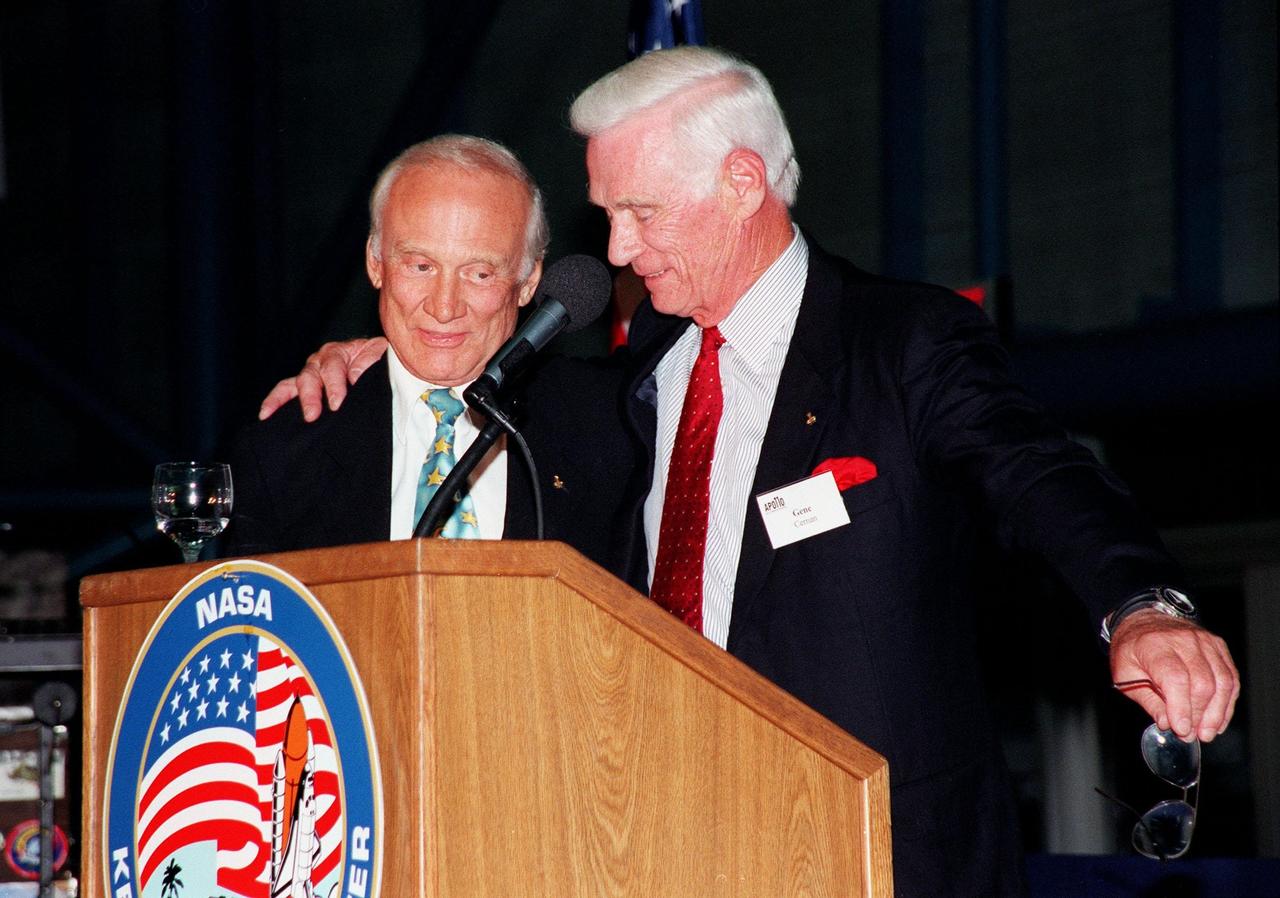

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former Apollo astronauts Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin (left) and Gene Cernan share stories about their missions for an audience attending an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Wally Schirra, Gene Cernan and Walt Cunningham. Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
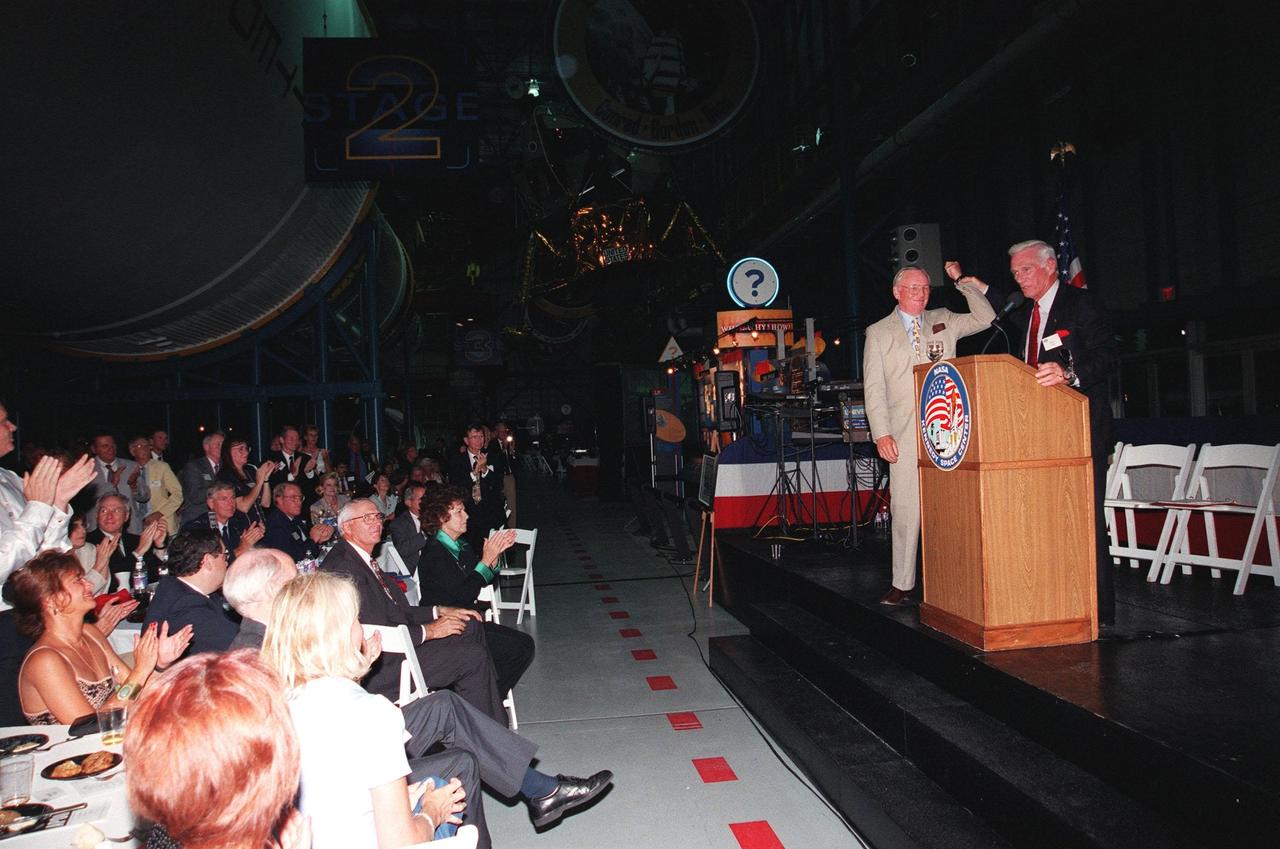

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong (left) and Gene Cernan entertain the audience during an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Wally Schirra, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Walt Cunningham. Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Cernan was the last
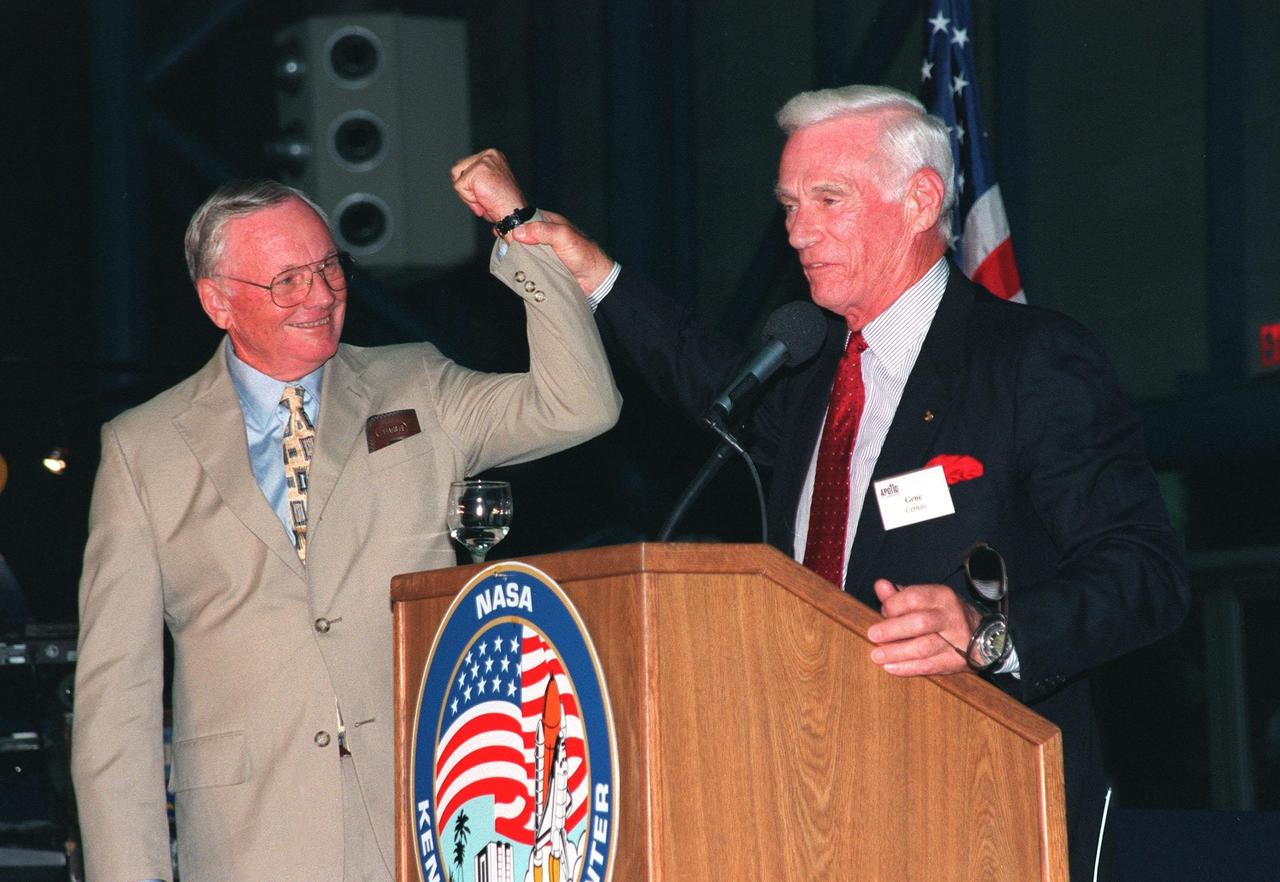

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong (left) and Gene Cernan entertain the audience during an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Wally Schirra, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Walt Cunningham. Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
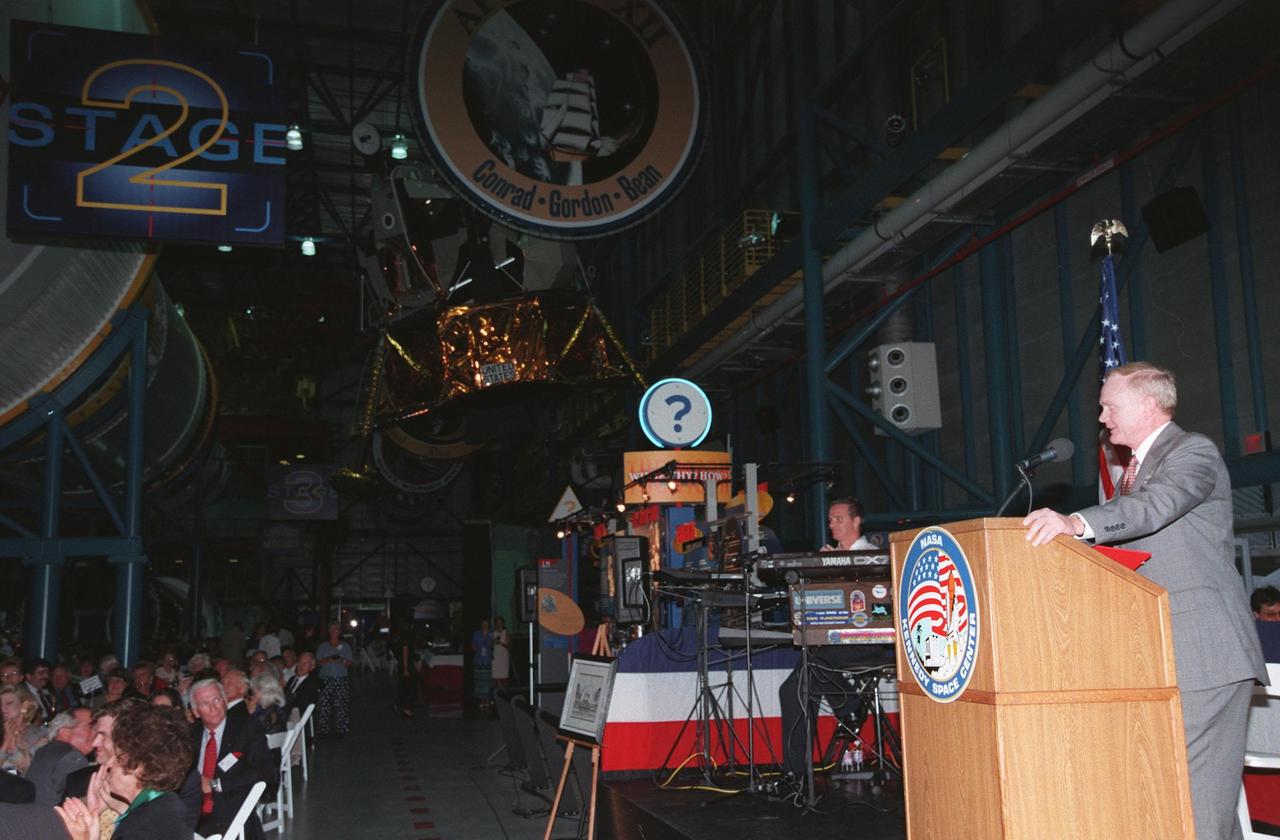

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible, Center Director Roy D. Bridges offers remarks. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Among the guests at the banquet were astronauts Neil Armstrong, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin, Wally Schirra, Gene Cernan and Walt Cunningham. Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
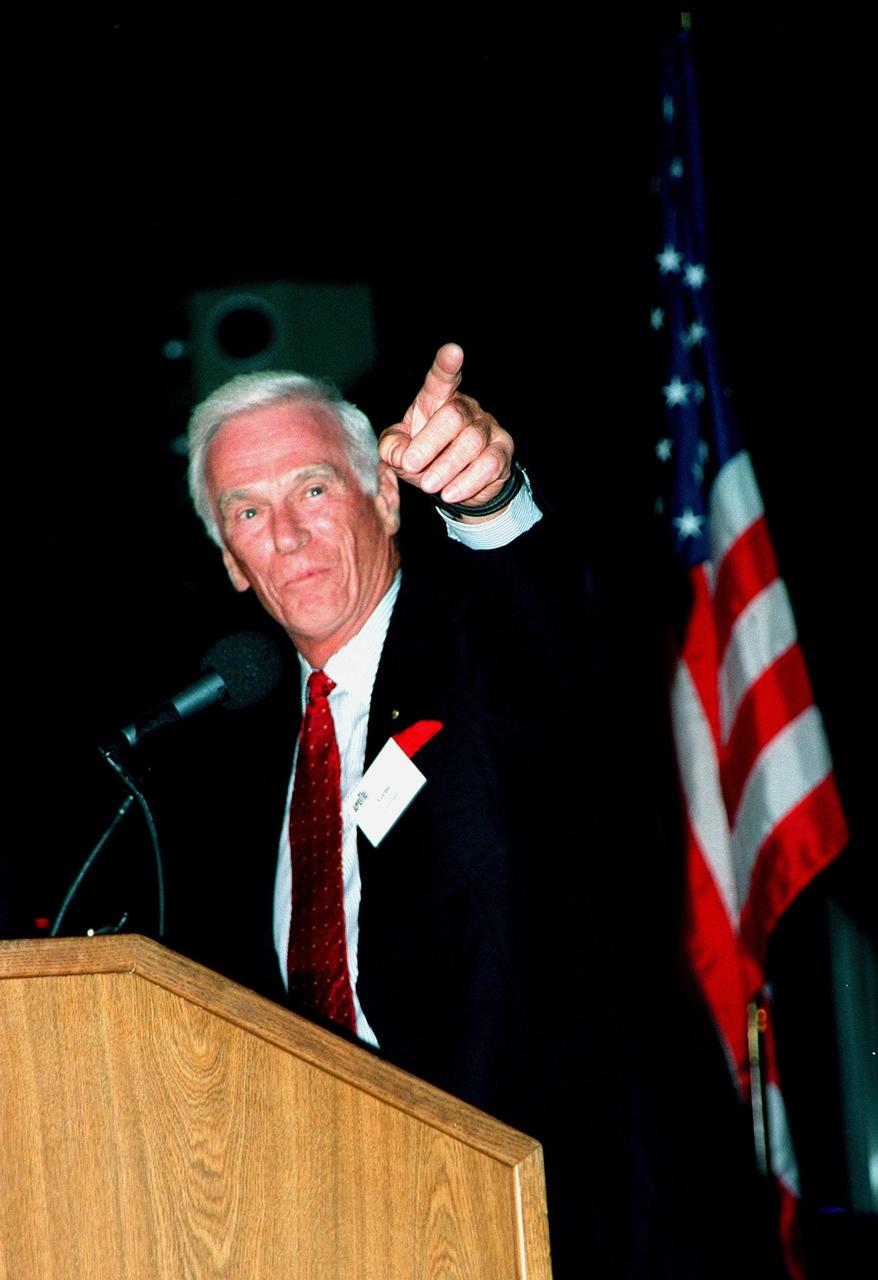

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Former Apollo astronaut Gene Cernan makes a point during a presentation at the Apollo 11 anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Cernan appeared with other former astronauts Neil Armstrong, the first man to walk on the moon; Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin; Walt Cunningham; and others
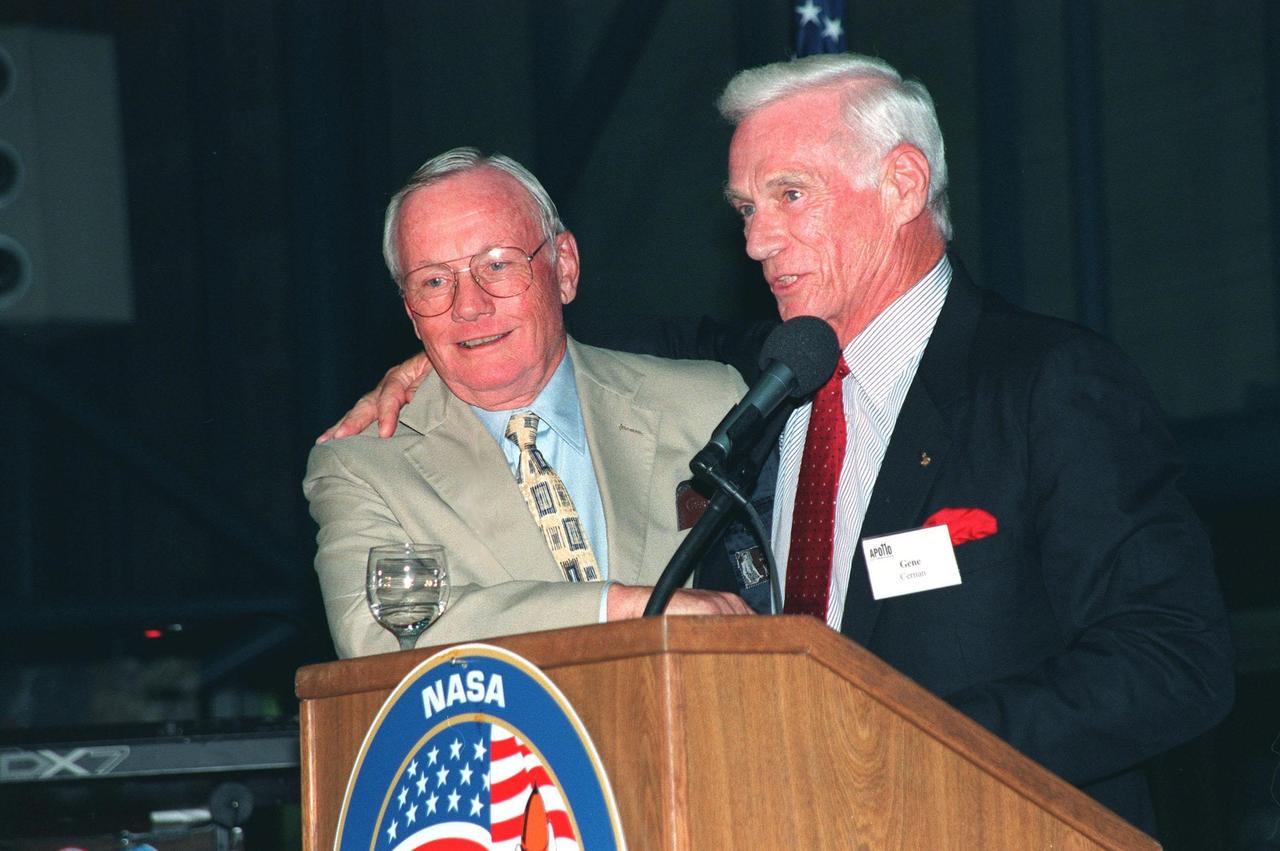

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible, former Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong (left) and Gene Cernan talk about their experiences. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Wally Schirra, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Walt Cunningham. Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
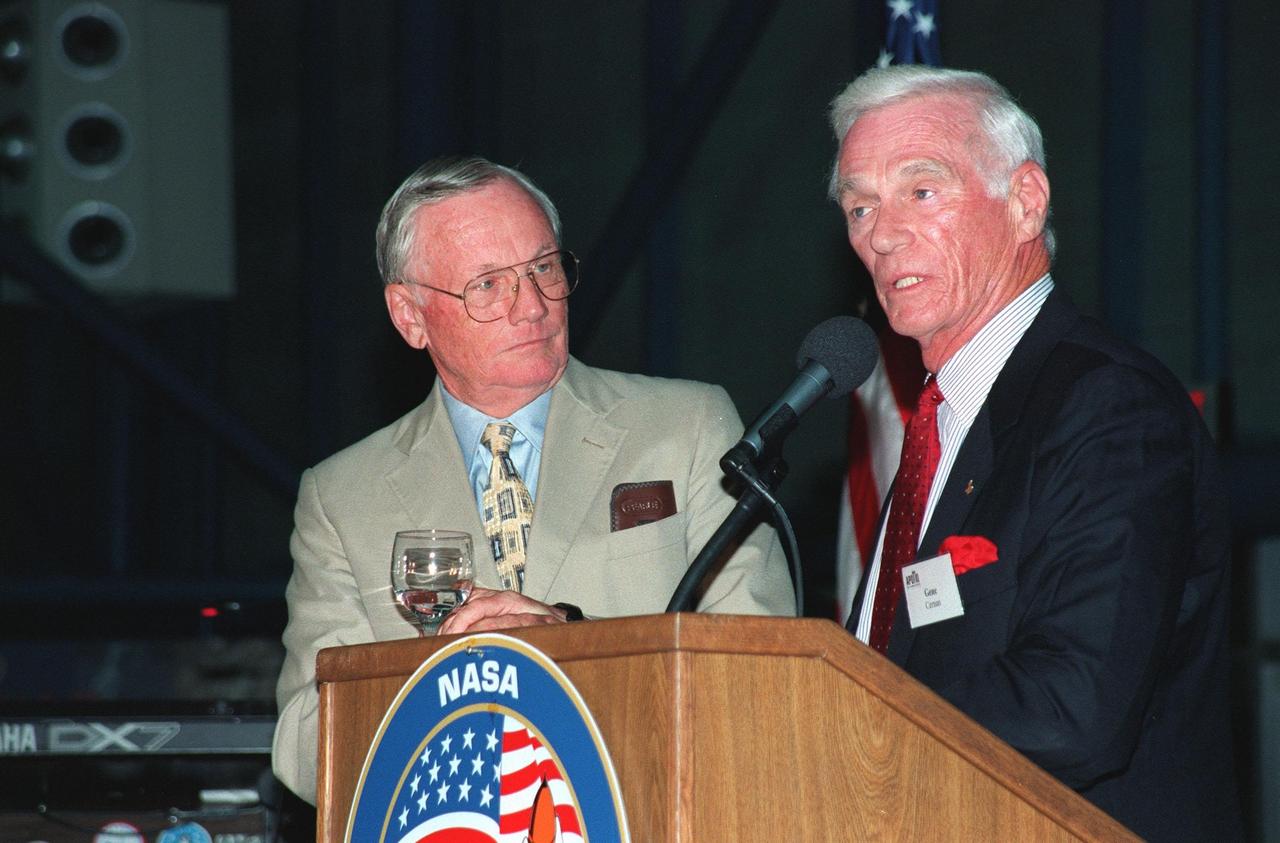

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible, former Apollo astronauts Neil Armstrong (left) and Gene Cernan talk about their experiences. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were astronauts Wally Schirra, Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin and Walt Cunningham. Neil Armstrong was the first man to walk on the moon; Gene Cernan was the last
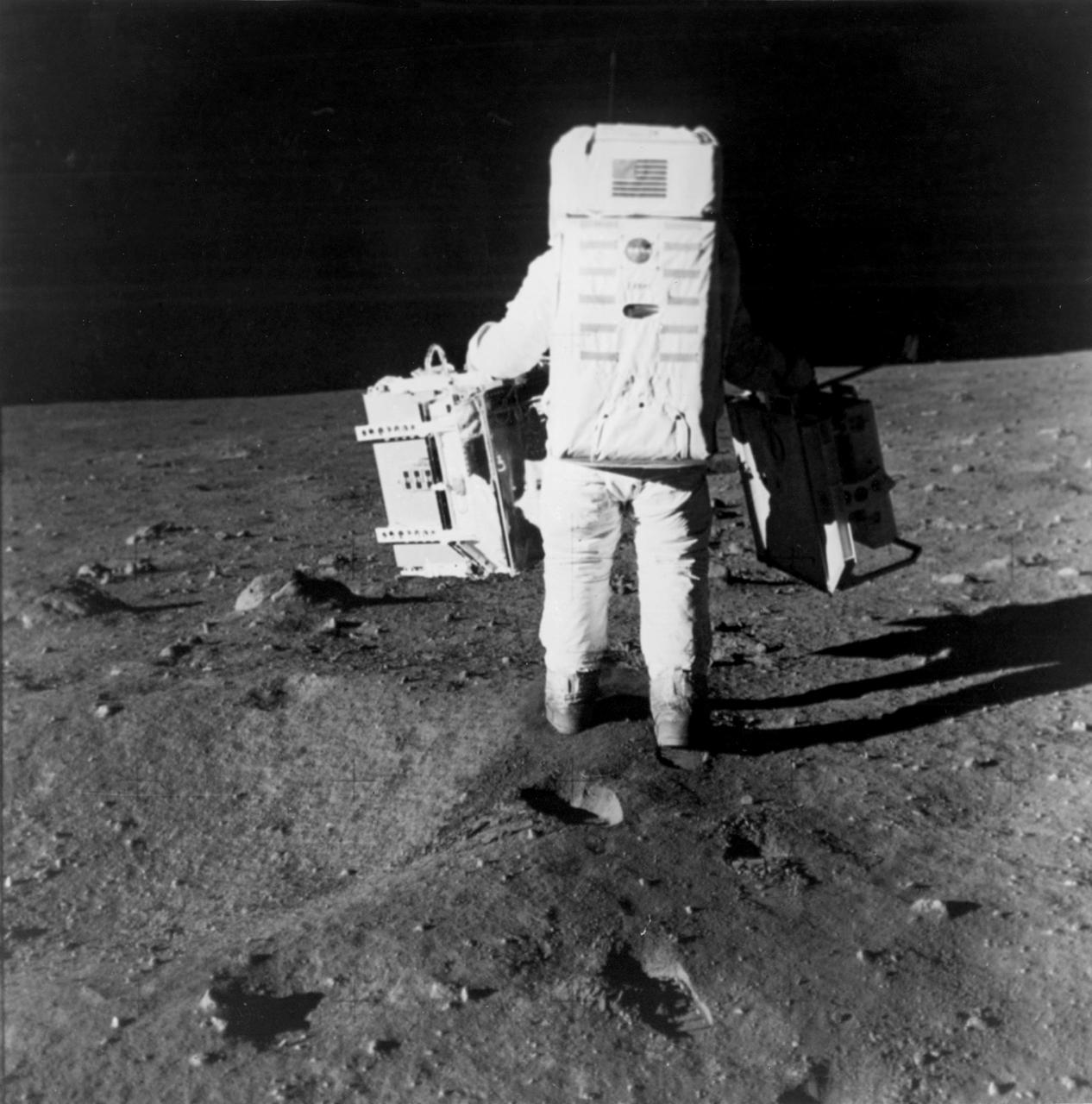

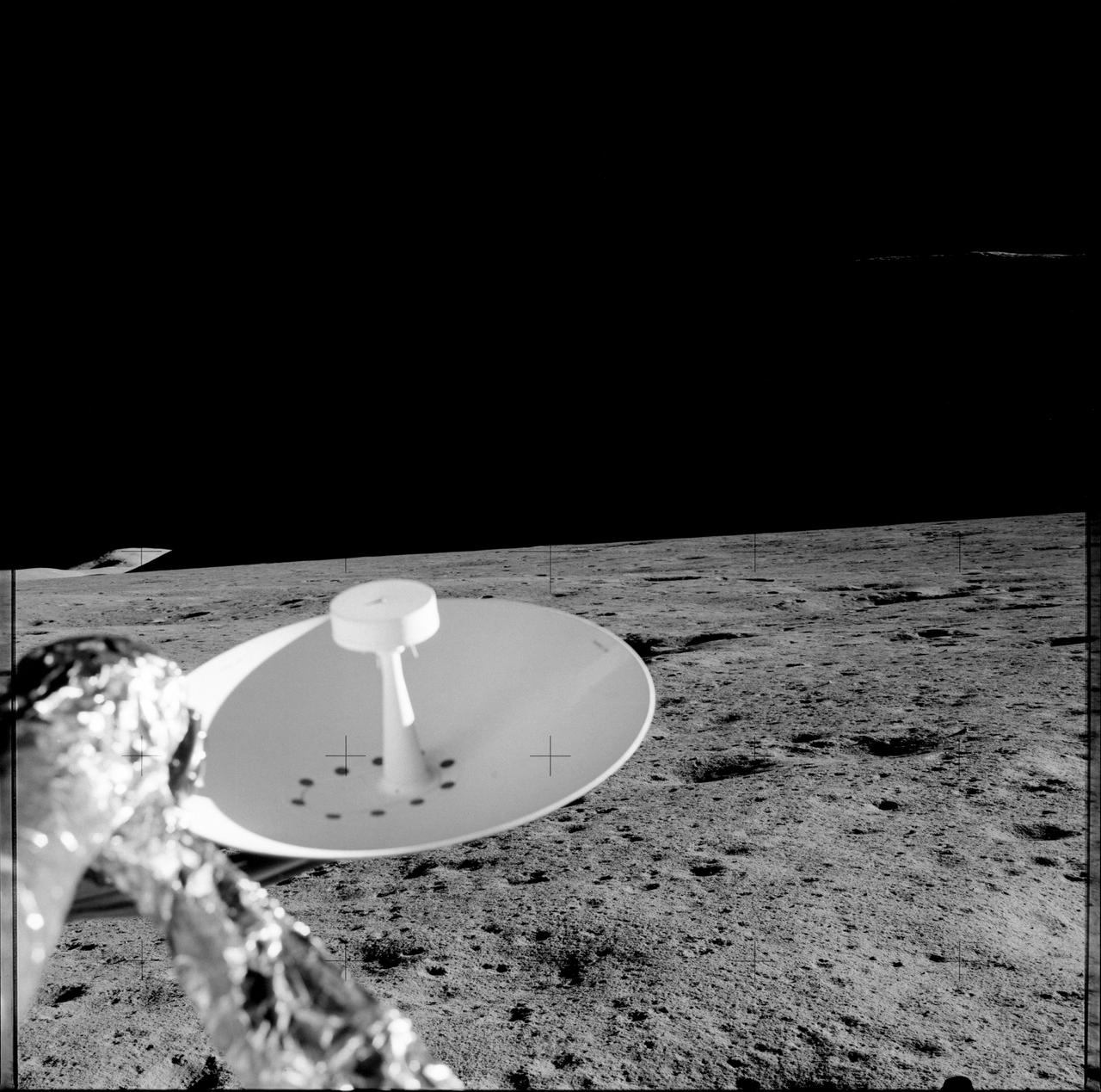
The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin walks past some rocks, easily carrying scientific equipment which would have been too heavy to carry on Earth. The two packages made up the Early Apollo Scientific Experiment Package (EASEP) on Apollo 11. On the left is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP) and on the right is the Laser Ranging Retroreflector (LRR).
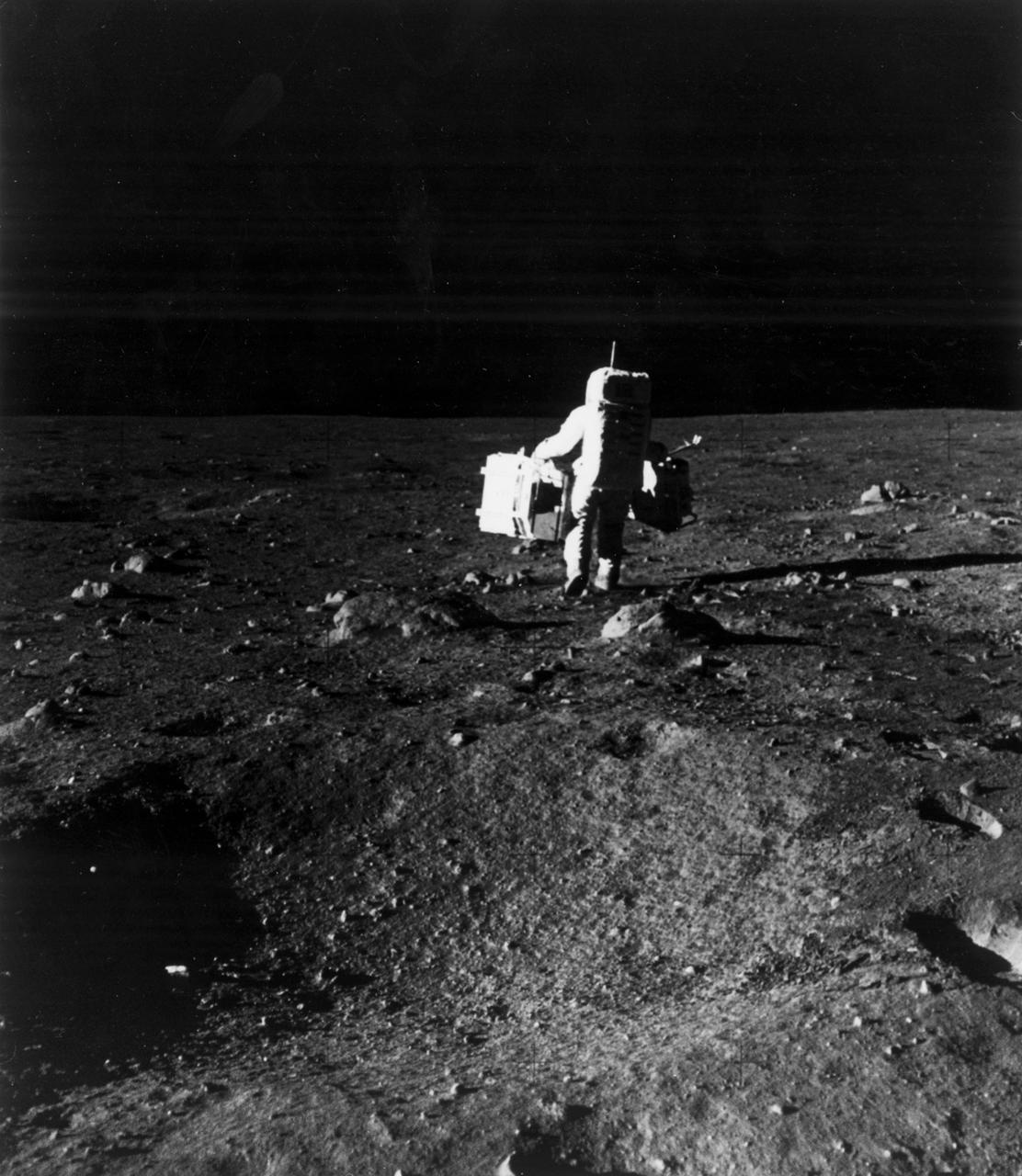

The first manned lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon, while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon in the Sea of Tranquility. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew set up experiments, collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth, planted the U.S. Flag, and left a message for all mankind. In this photograph, Aldrin walks past some rocks, easily carrying scientific equipment experiements, which would have been to heavy too carry on Earth. The two packages made up the Early Apollo Scientific Experiment Package (EASEP) on Apollo 11. On the left is the Passive Seismic Experiment Package (PSEP) and on the right is the Laser Ranging Retroreflector (LRRR).
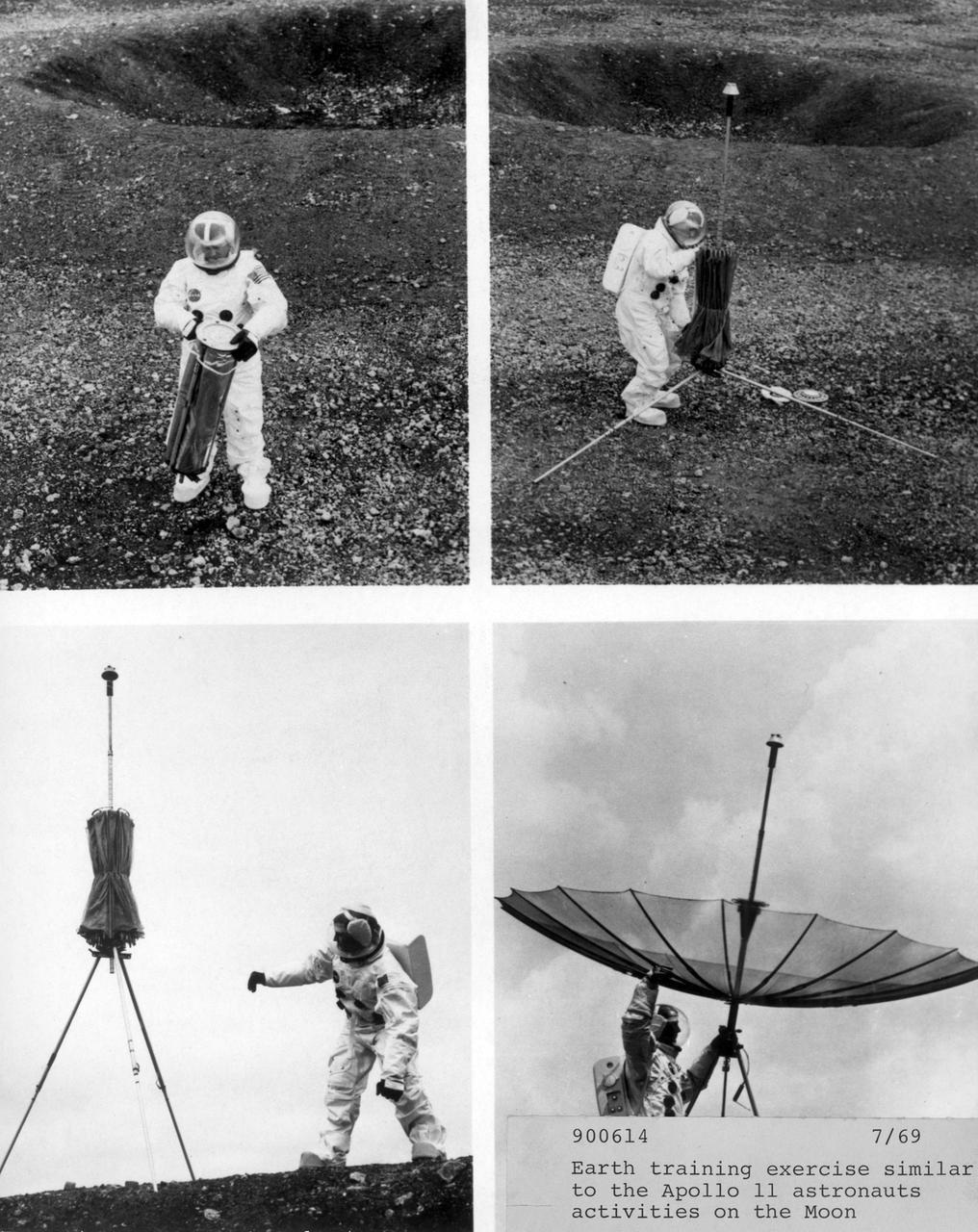

In preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11 crew members underwent training to practice activities they would be performing during the mission. In this photograph, taken at the Manned Spacecraft Center in Houston, Texas, an engineer, Bob Mason, donned in a space suit, goes through some of those training exercises on the mock lunar surface. He performed activites similar to those planned for astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin during their moon walk. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
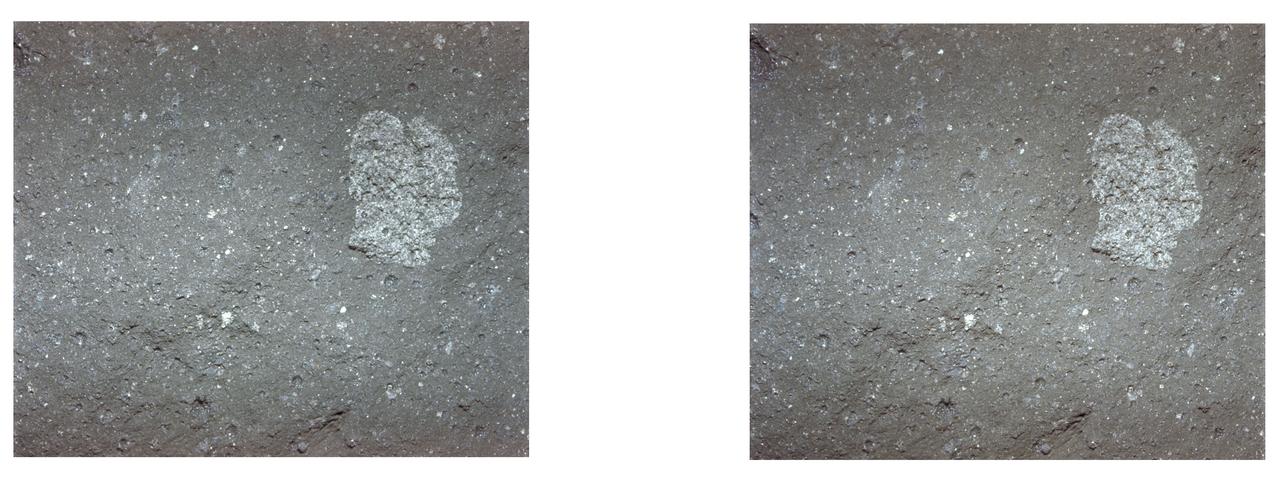
AS11-45-6709 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view of the surface of a lunar rock showing an embedded three-fourths inch fragment of a different color. On the surface several small pits are seen; mostly less than one-eighth inch in size, and with a glazed surface. They have a raised rim, characteristic of pits made by high-velocity micro meteorite impacts. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
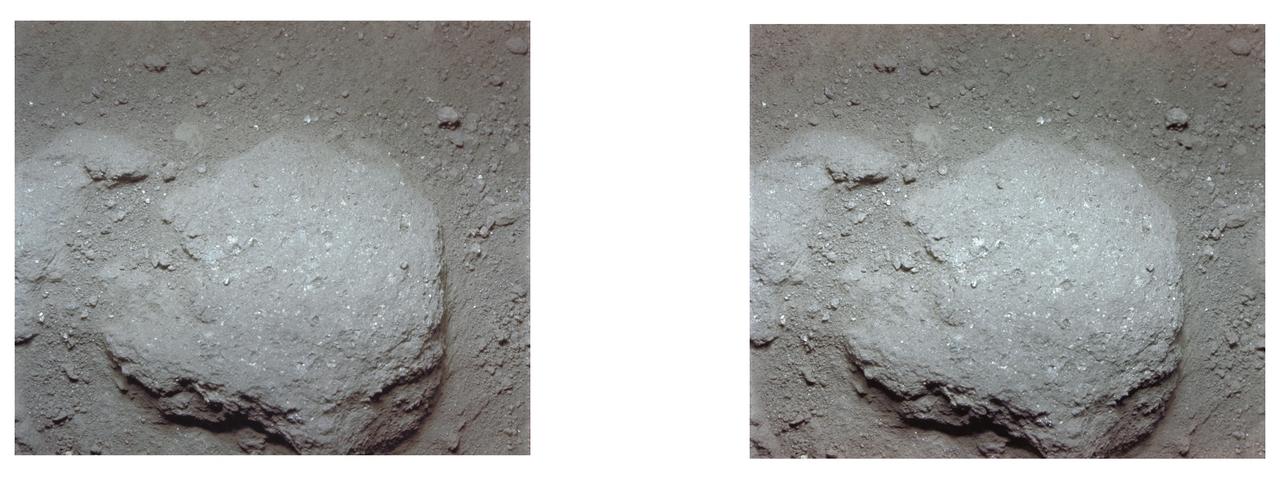

AS11-45-6712 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view of a stone, about two and one-half inches long, embedded in the powdery lunar surface material. The little pieces closely around it suggest that it has suffered some erosion. On the surface several small pits are seen, mostly less than one-eighth inch in size, and with a glazed surface. They have a raised rim, characteristic of pits made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
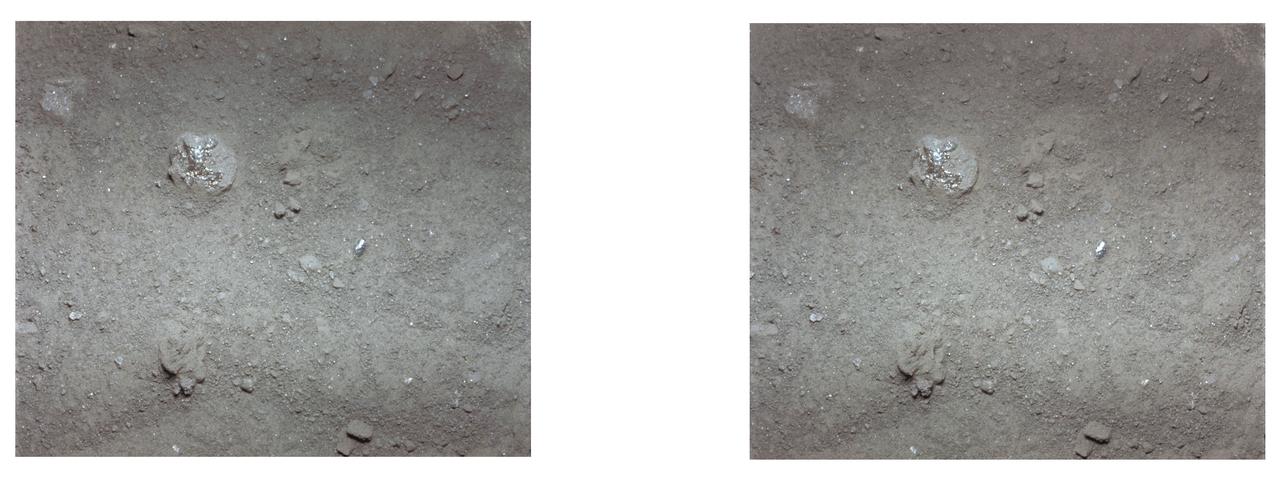
AS11-45-6704 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo stereo view showing a close-up of a small lump of lunar surface powder about a half inch across, with a splash of a glassy material over it. It seems that a drop of molten material fell on it, splashed and froze. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Dr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
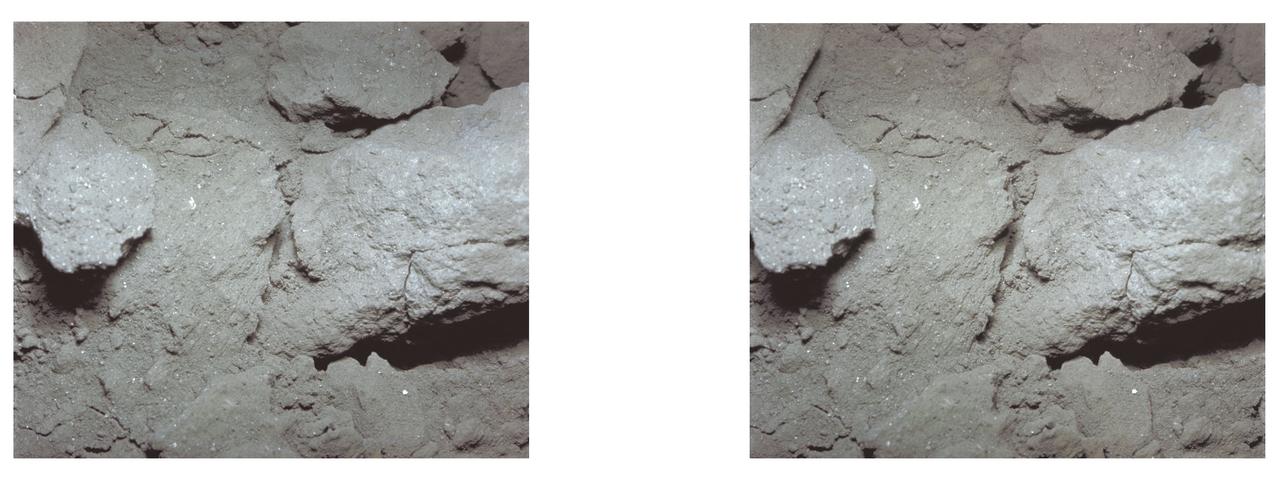

AS11-45-6706 (20 July 1969) --- An Apollo 11 stereo view showing a clump of lunar surface powder, with various small pieces of different color. Many small, shiny spherical particles can be seen. The picture is three inches across. The exposure was made by the Apollo 11 35mm stereo close-up camera. The camera was specially developed to get the highest possible resolution of a small area. A three-inch square area is photographed with a flash illumination and at a fixed distance. The camera is mounted on a walking stick, and the astronauts use it by holding it up against the object to be photographed and pulling the trigger. The pictures are in color and give a stereo view, enabling the fine detail to be seen very clearly. The project is under the direction of Professor T. Gold of Cornell University and Mr. F. Pearce of NASA. The camera was designed and built by Eastman Kodak. Professor E. Purcell of Harvard University and Dr. E. Land of the Polaroid Corporation have contributed to the project. The pictures brought back from the moon by the Apollo 11 crew are of excellent quality and allow fine detail of the undisturbed lunar surface to be seen. Scientists hope to be able to deduce from them some of the processes that have taken place that have shaped and modified the surface.
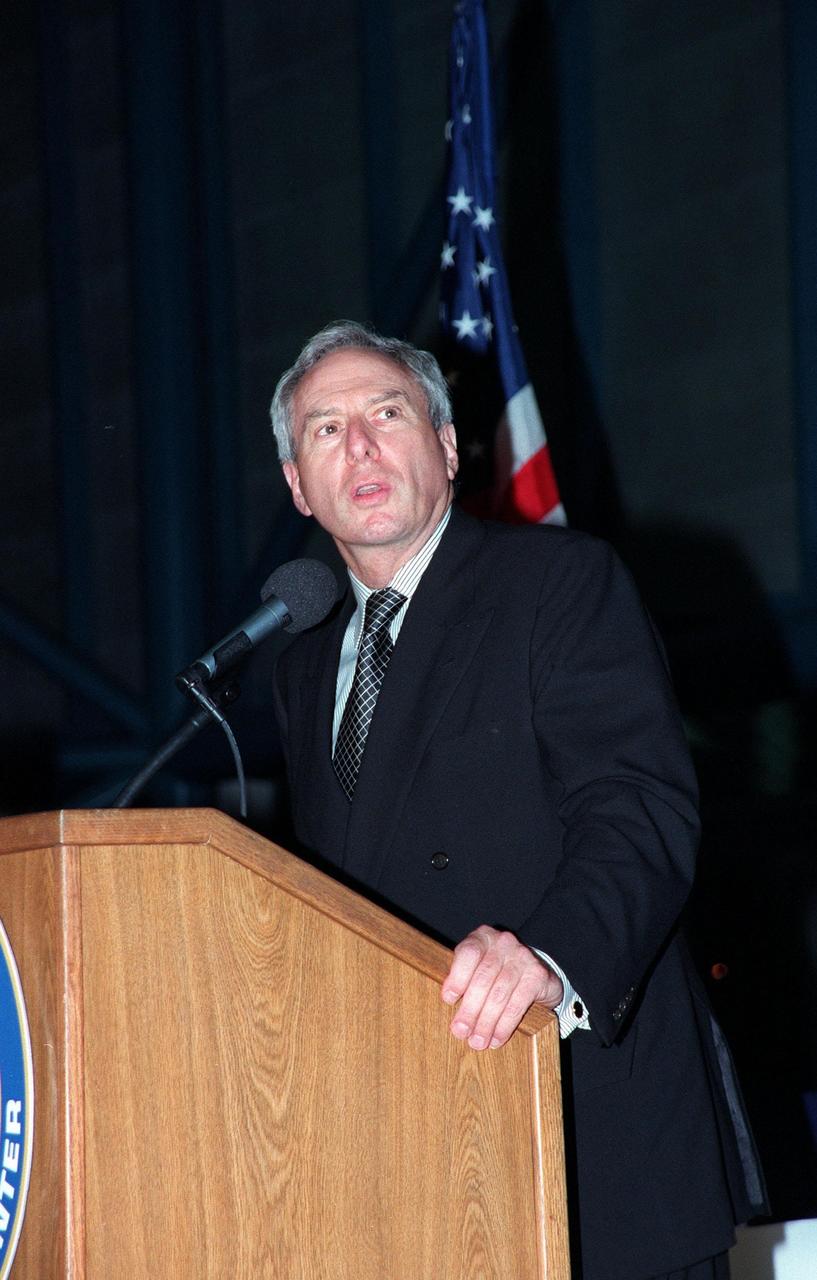

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin addresses the audience at the Apollo 11 anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Among the guests at the banquet were former Apollo astronauts are Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch of the first moon landing; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17 and was the last man to walk on the moon; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7
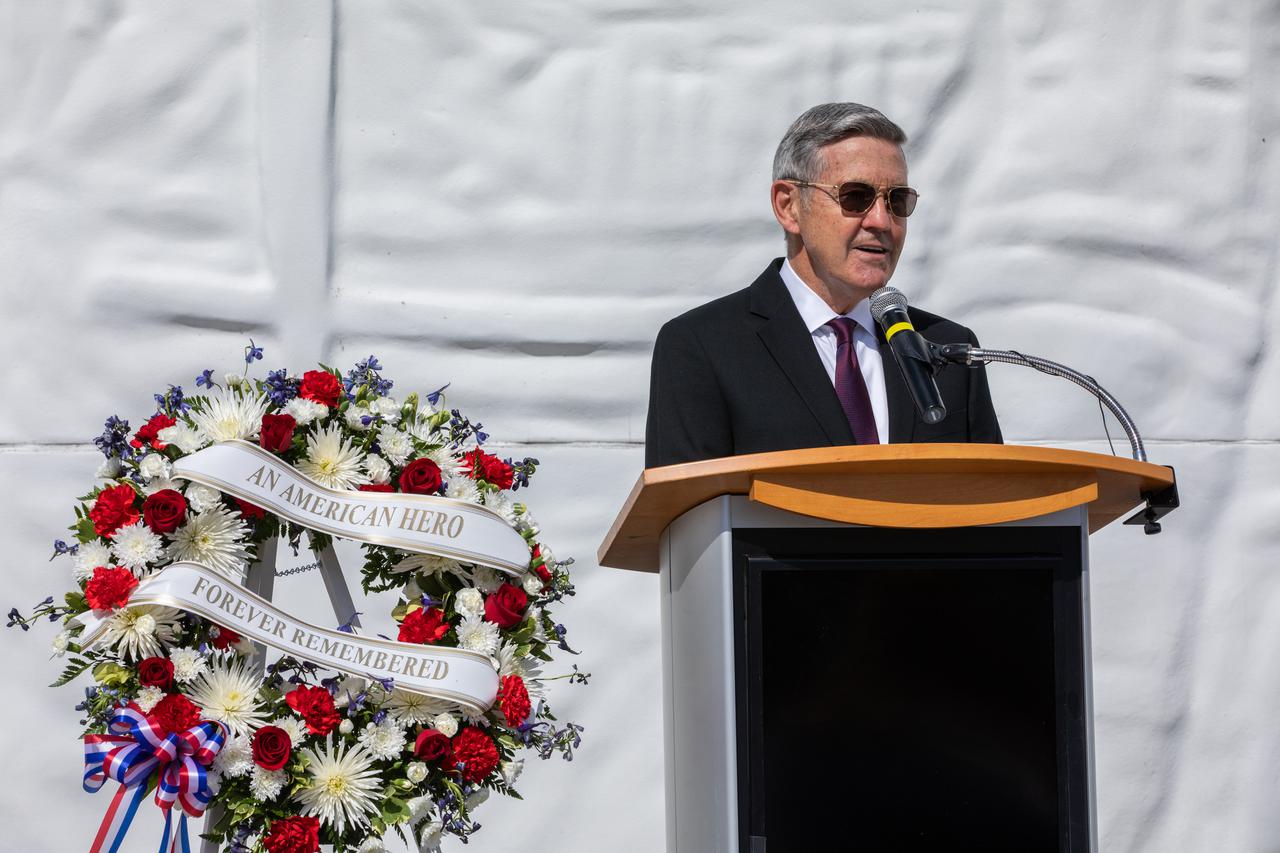

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.
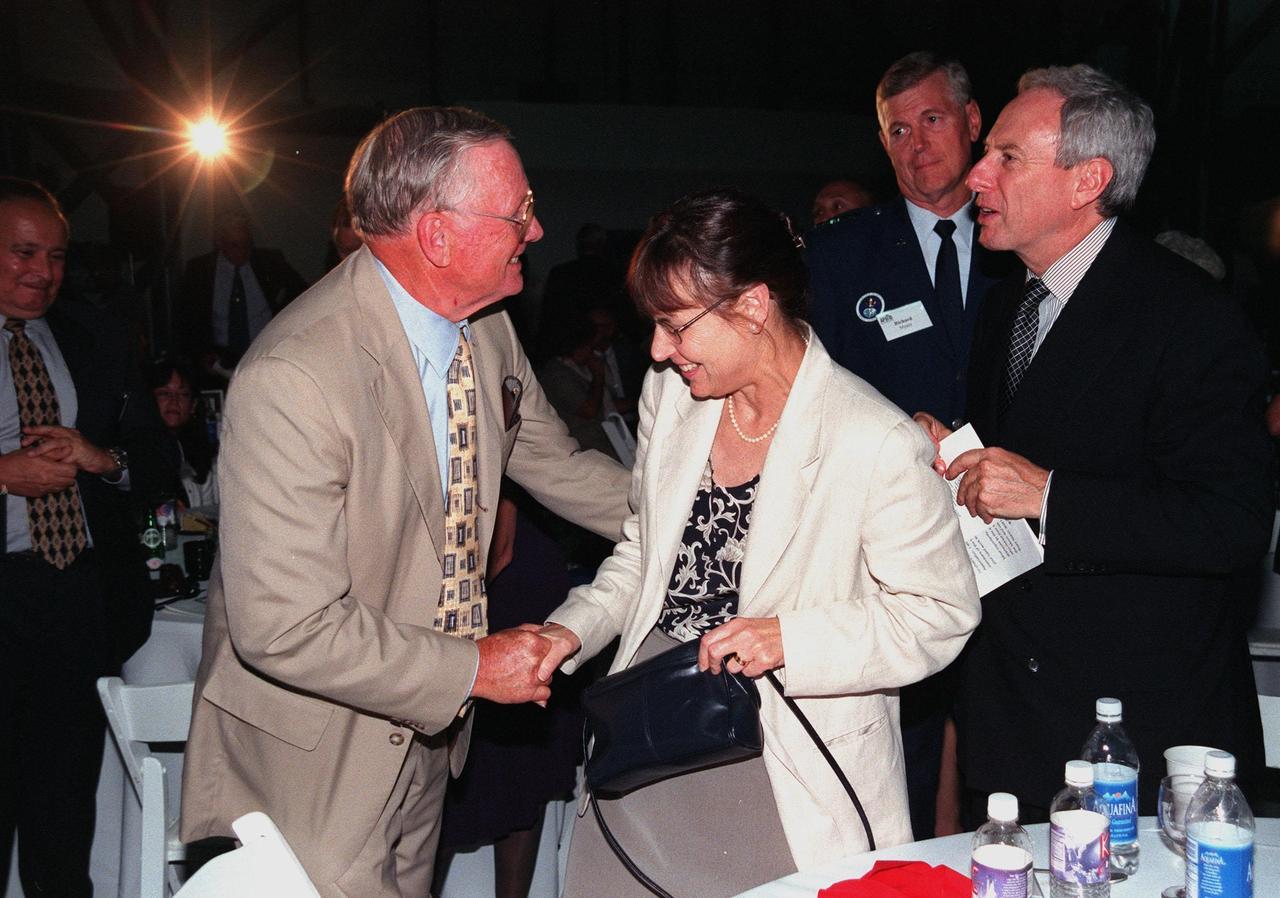

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible, former Apollo astronaut Neil A. Armstrong (left) shakes the hand of Judy Goldin (center), wife of NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin (right). The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Among the guests at the banquet were former Apollo astronauts are Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch of the first moon landing; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17 and was the last man to walk on the moon; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7
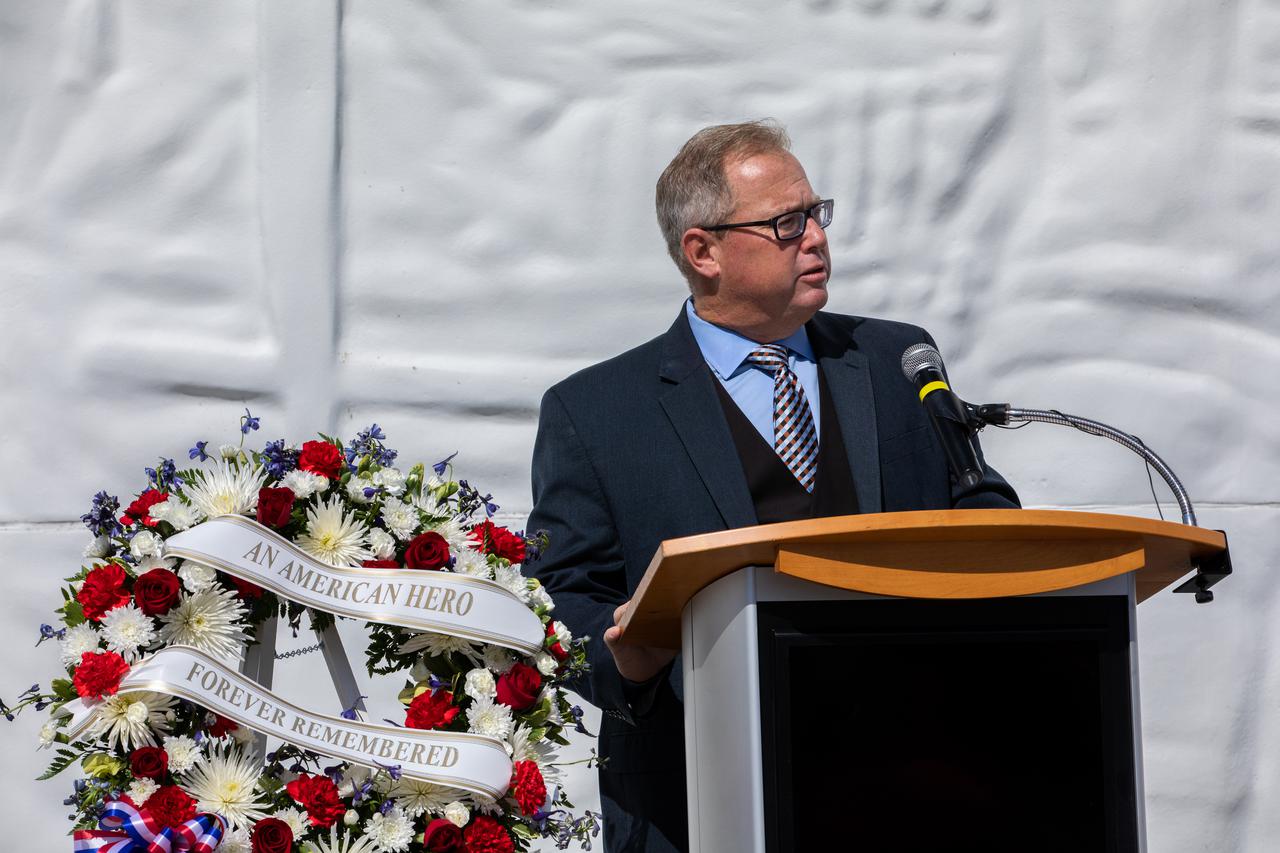

Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex, provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Kennedy Director Bob Cabana also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the Florida spaceport’s visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Kennedy Space Center employees and guests gathered for a brief ceremony on Aug. 31, 2012 honoring Neil Armstrong, who died Aug. 25, 2012 at the age of 82. Armstrong was hailed by Center Director Bob Cabana as one of our heroes and a truly a great American. Cabana placed a wreath in the spaceport's Apollo-Saturn V Center. Selected as an astronaut in 1962, Neil Armstrong flew on NASA's Gemini 8 with David Scott in March 1966 and the first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, with Mike Collins and Buzz Aldine in July 1969. On July 20, 1969, he became the first human to walk on the moon. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/news/neil_armstrong.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
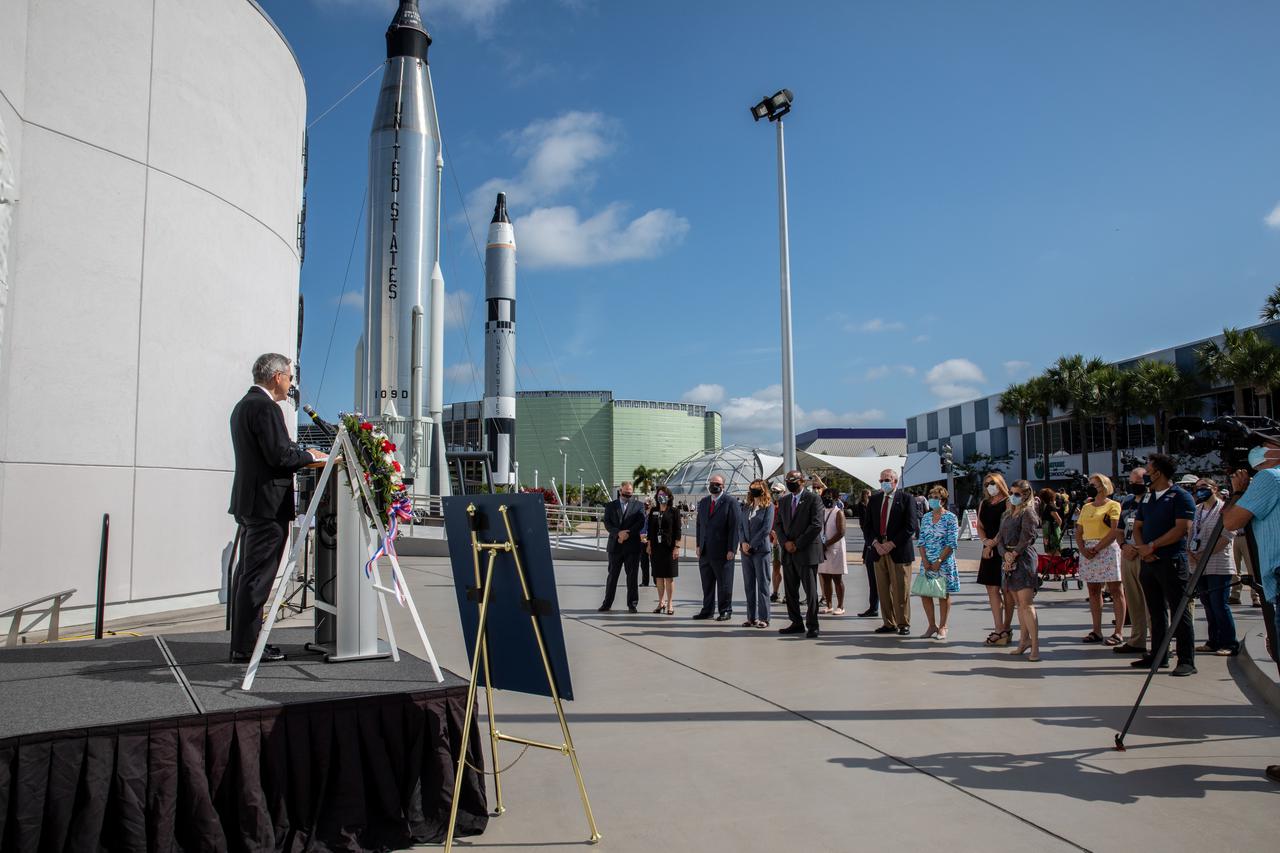

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana provides remarks during a wreath-laying ceremony in Florida, honoring the memory of former Apollo 11 astronaut Michael Collins on April 30, 2021. Therrin Protze, chief operating officer of Delaware North at Kennedy’s visitor complex, also spoke during the ceremony, held just outside of the Heroes and Legends exhibit at the visitor complex. Collins served as pilot on the three-day Gemini X mission in 1966, and he was the command module pilot for the historic Apollo 11 mission in 1969, where he remained in lunar orbit while Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin become the first people to walk on the Moon. Collins passed away on April 28, 2021, at the age of 90.
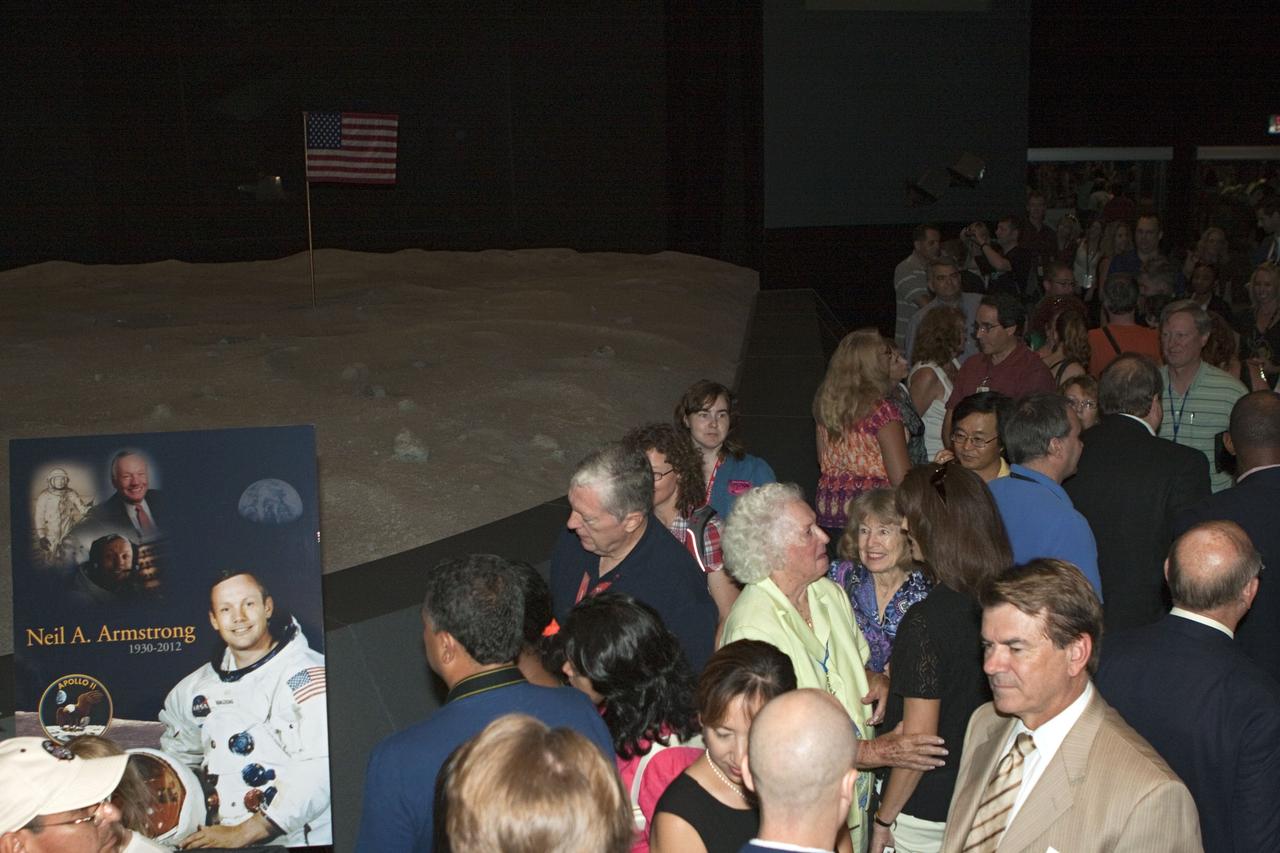

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Kennedy Space Center employees and guests gathered for a brief ceremony on Aug. 31, 2012 honoring Neil Armstrong, who died Aug. 25, 2012 at the age of 82. Armstrong was hailed by Center Director Bob Cabana as one of our heroes and a truly a great American. Cabana placed a wreath in the spaceport's Apollo-Saturn V Center. Selected as an astronaut in 1962, Neil Armstrong flew on NASA's Gemini 8 with David Scott in March 1966 and the first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11, with Mike Collins and Buzz Aldine in July 1969. On July 20, 1969, he became the first human to walk on the moon. For more information, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/kennedy/news/neil_armstrong.html Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
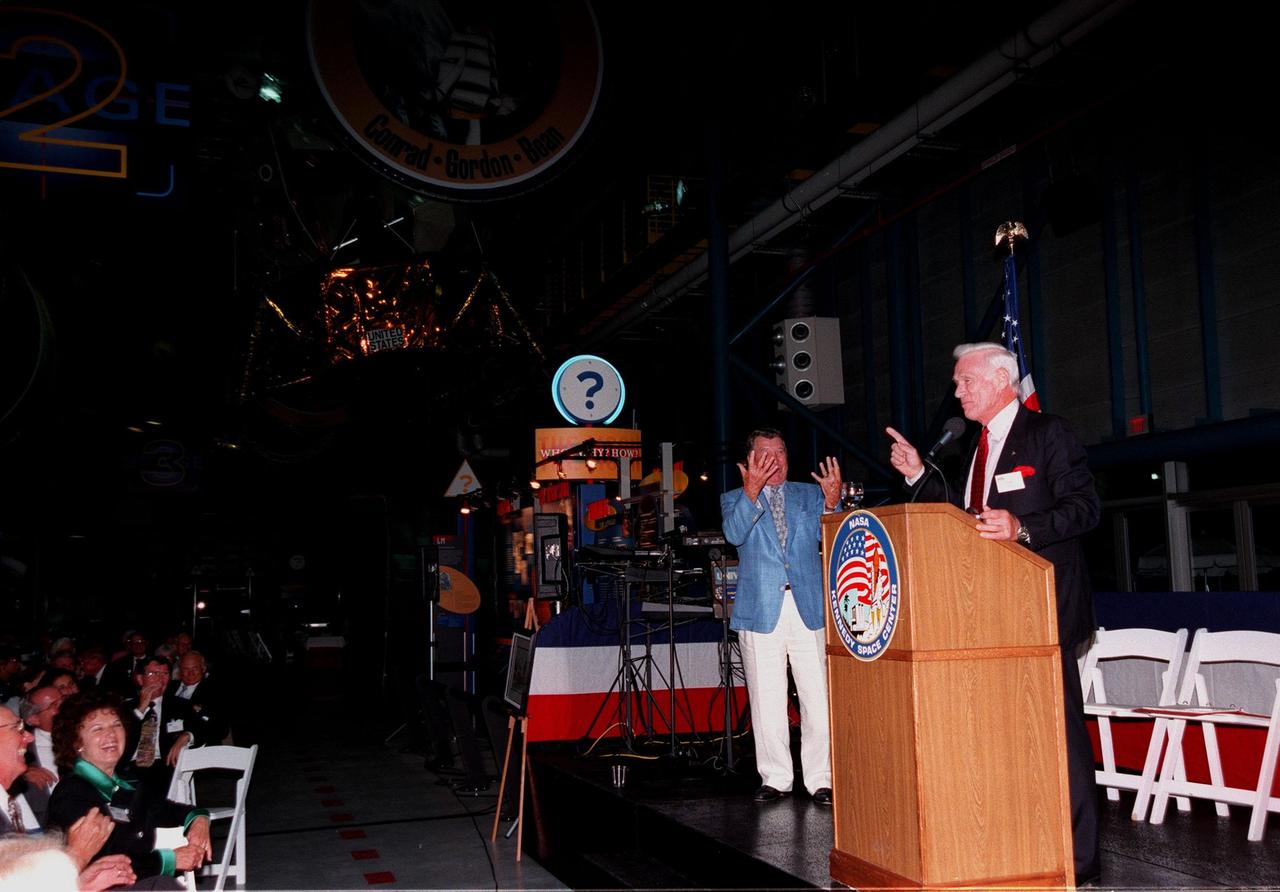

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- During an anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo program team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible, former Apollo astronaut Gene Cernan relates a humorous comment while Wally Schirra (background) gestures behind him. Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17, was the last man to walk on the moon; Schirra flew on Apollo 7. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex. This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Other guests at the banquet were former Apollo astronauts are Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch of the first moon landing, and Walt Cunningham, who also flew on Apollo 7
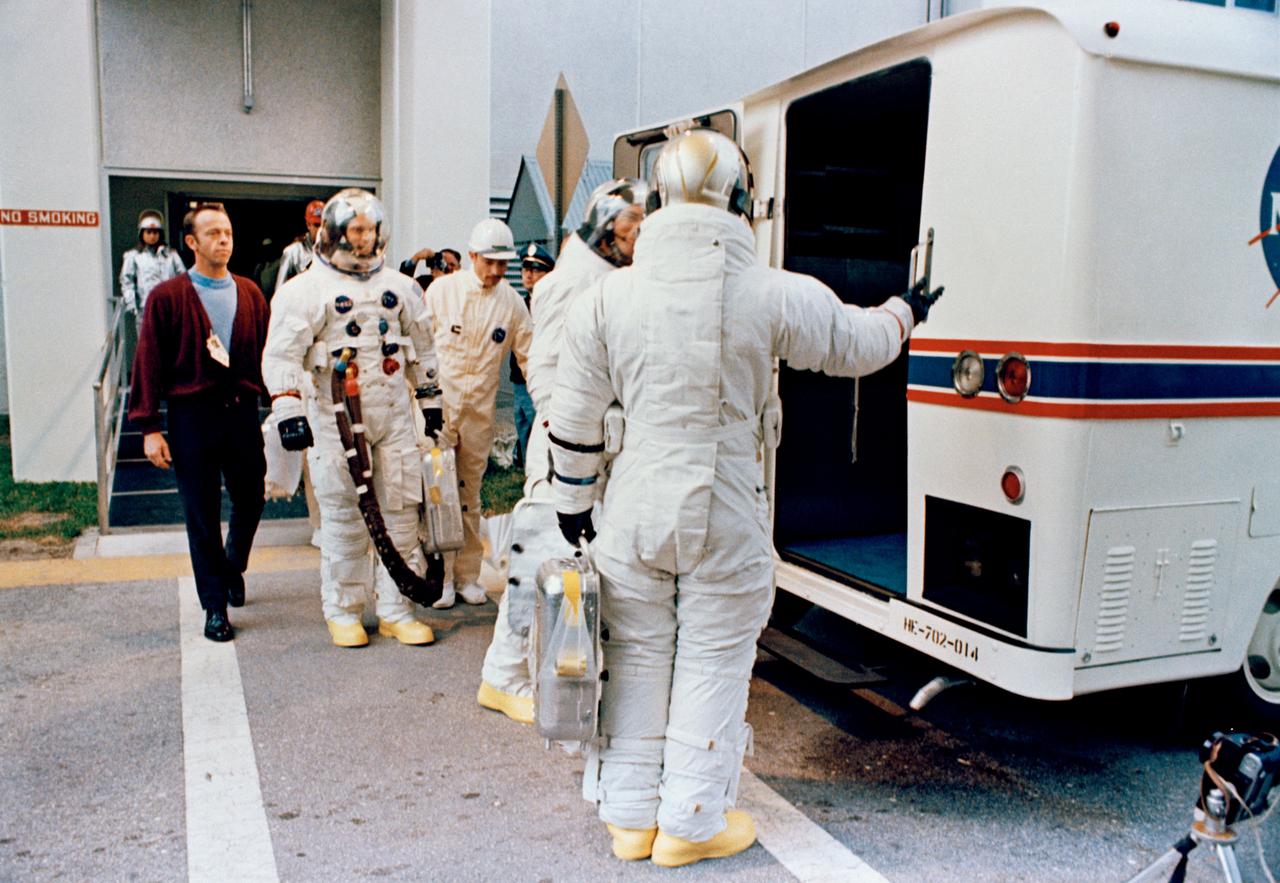

S69-25881 (3 March 1969) --- The Apollo 9 crew leaves the Kennedy Space Center's Manned Spacecraft Operations Building during the Apollo 9 prelaunch countdown. The crewman entered the special transfer van which transported them to their waiting spacecraft at Pad A, Launch Complex 39. Astronaut James A. McDivitt (back to camera) is the commander. McDivitt appears to be inviting astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, to step first into van. In background is astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot. Walking along almost behind Schweickart is astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., chief, Astronaut Office, Manned Spacecraft Center. Apollo 9 was launched at 11 a.m. (EST), March 3, 1969, on a 10-day Earth-orbital mission.
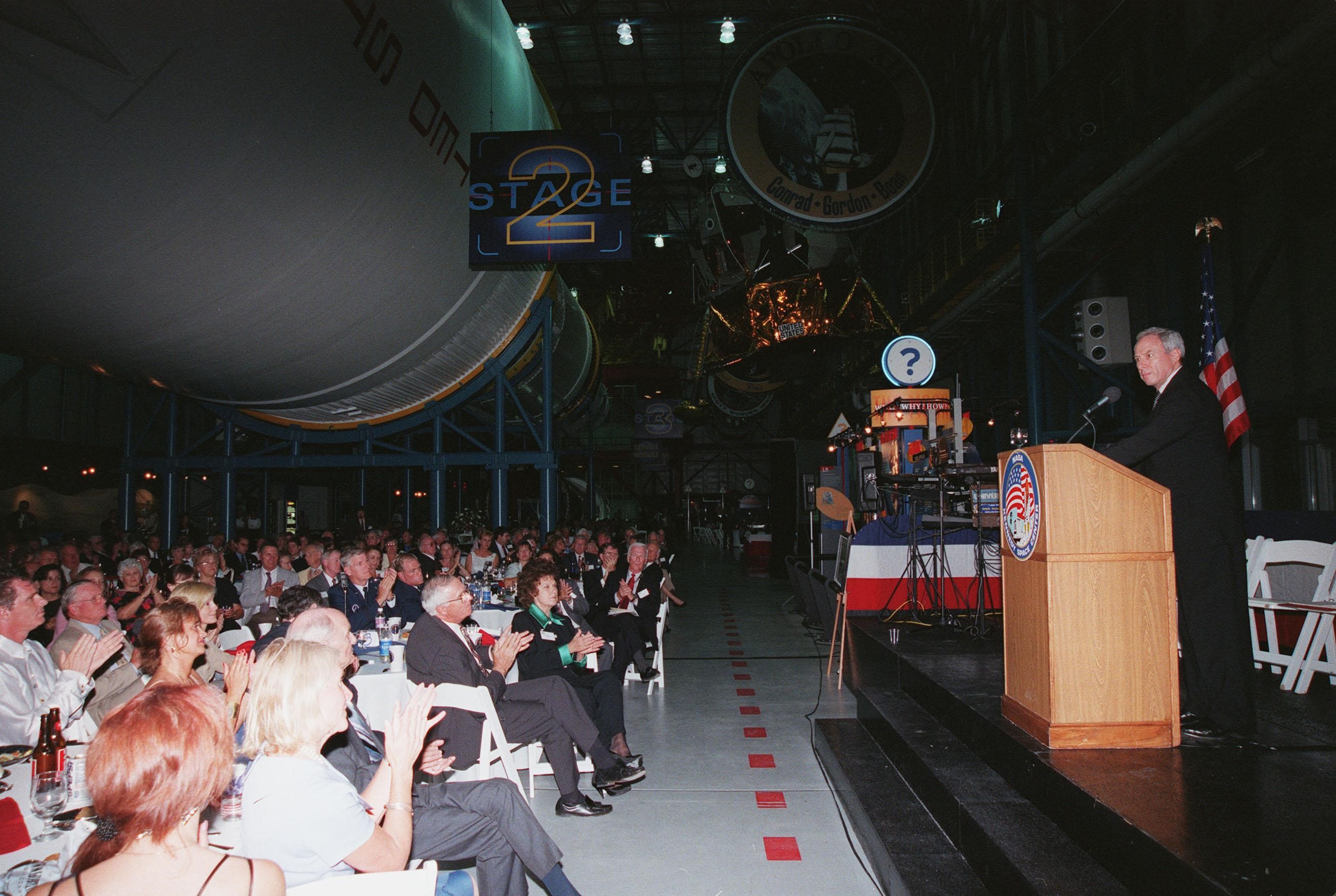

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- NASA Administrator Daniel S. Goldin (right) addresses the audience at the Apollo 11 anniversary banquet honoring the Apollo team, the people who made the entire lunar landing program possible. The banquet was held in the Apollo/Saturn V Center, part of the KSC Visitor Complex, with seating under an unused Saturn V rocket like those that powered the Apollo launches . This is the 30th anniversary of the Apollo 11 launch and moon landing, July 16 and July 20, 1969. Among the guests at the banquet were former Apollo astronauts are Neil A. Armstrong and Edwin "Buzz" Aldrin who flew on Apollo 11, the launch of the first moon landing; Gene Cernan, who flew on Apollo 10 and 17 and was the last man to walk on the moon; and Walt Cunningham, who flew on Apollo 7

In preparation of the nation’s first lunar landing mission, Apollo 11 crew members underwent training to practice activities they would be performing during the mission. In this photograph, astronaut Collins (left) and chief astronaut and director of flight crew operations, Donald K. Slayton, walk away from a T-38 jet plane at Patrick Air Force Base. The two had been flying arcs to give Collins more time under weightless conditions. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. (Buzz) Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished