
Entering Saturn Magnetosphere with a Boom

Jupiter Magnetosphere Made Visible

MMS Spacecraft Animation The Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth's magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration, and turbulence. These processes occur in all astrophysical plasma systems but can be studied in situ only in our solar system and most efficiently only in Earth's magnetosphere, where they control the dynamics of the geospace environment and play an important role in the processes known as "space weather." Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Goddard The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

MMS Spacecraft Animation The Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth's magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration, and turbulence. These processes occur in all astrophysical plasma systems but can be studied in situ only in our solar system and most efficiently only in Earth's magnetosphere, where they control the dynamics of the geospace environment and play an important role in the processes known as "space weather." Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Chris Gunn The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
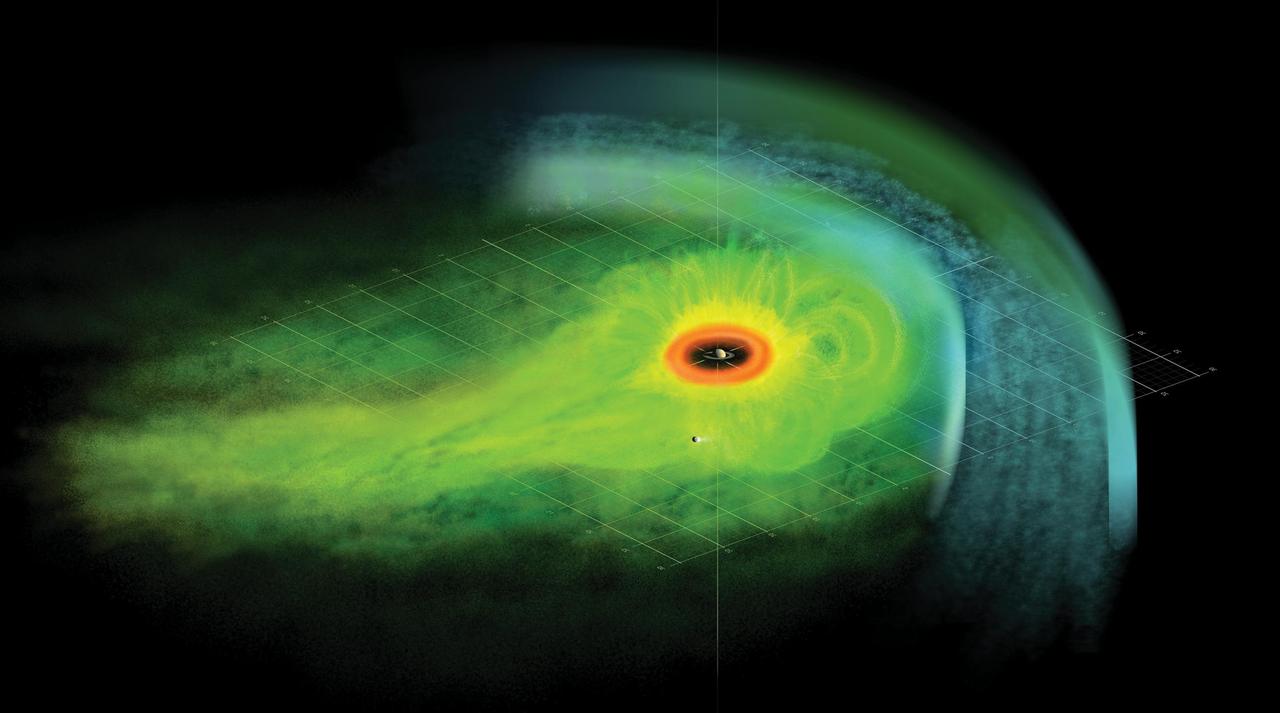
Artist Concept of Particle Population in Saturn Magnetosphere
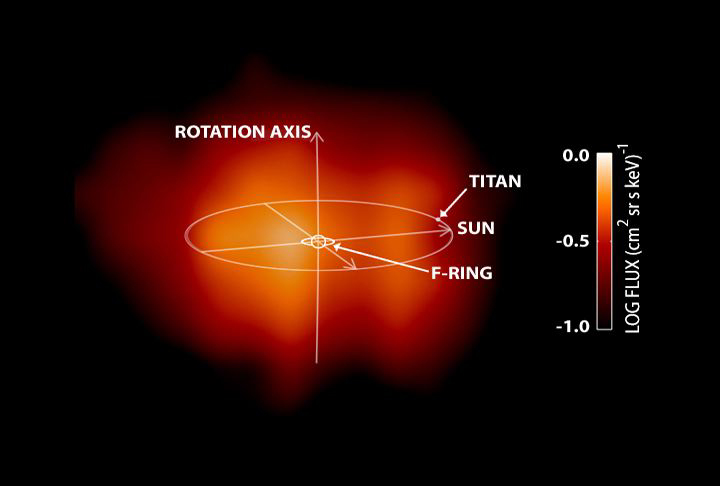
Saturn's magnetosphere is seen for the first time in this image taken by the Cassini spacecraft on June 21, 2004. A magnetosphere is a magnetic envelope of charged particles that surrounds some planets, including Earth. It is invisible to the human eye, but Cassini's Magnetospheric Imaging Instrument was able to detect the hydrogen atoms (represented in red) that escape it. The emission from these hydrogen atoms comes primarily from regions far from Saturn, well outside the planet's rings, and perhaps beyond the orbit of the largest moon Titan. The image represents the first direct look at the shape of Saturn's magnetosphere. Previously, NASA's Voyager mission had inferred what Saturn's magnetosphere would look like in the same way that a blind person might feel the shape of an elephant. With Cassini, the "elephant" has been revealed in a picture. This picture was taken by the ion and neutral camera, one of three sensors that comprise the magnetosphereic imaging instrument, from a distance of about 3.7 million miles (about 6 million kilometers) from Saturn. The magnetospheric imaging instrument will continue to study Saturn's magnetosphere throughout the mission's four-year lifetime. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06345
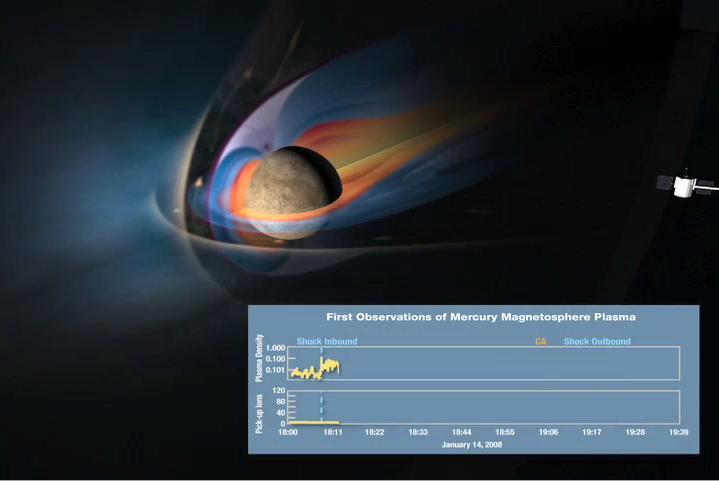
This frame from an animation shows a conceptual sketch of Mercury magnetosphere at the time of NASA MESSENGER spacecraft flyby.
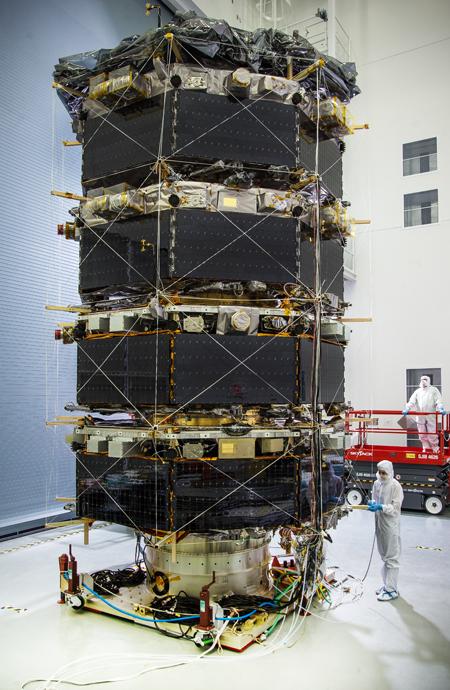

MMS Stacked – View of the fully stacked MMS prior to being bagged for vibration tests. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Chris Gunn The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

MMS Four Separate – View of all four spacecraft in the MMS Cleanroom getting prepared for stacking operations. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Chris Gunn The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
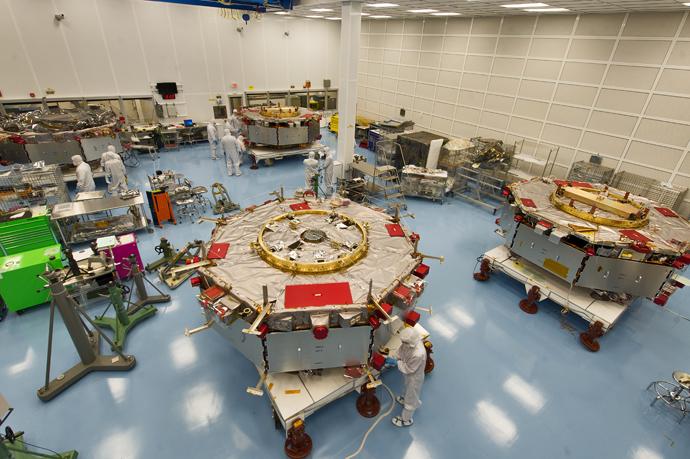

MMS Four Separate – View of all four spacecraft in the MMS Cleanroom getting prepared for stacking operations. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Chris Gunn The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
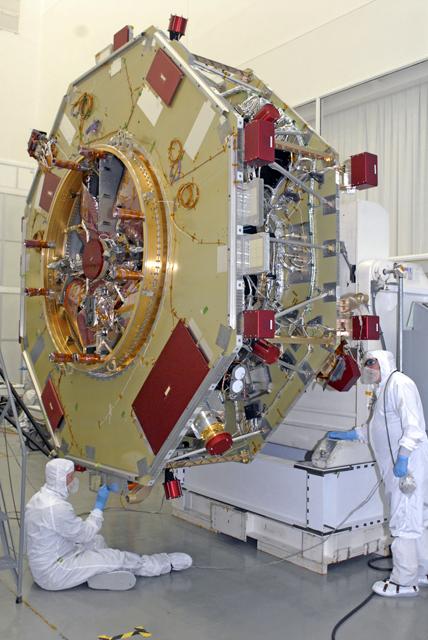

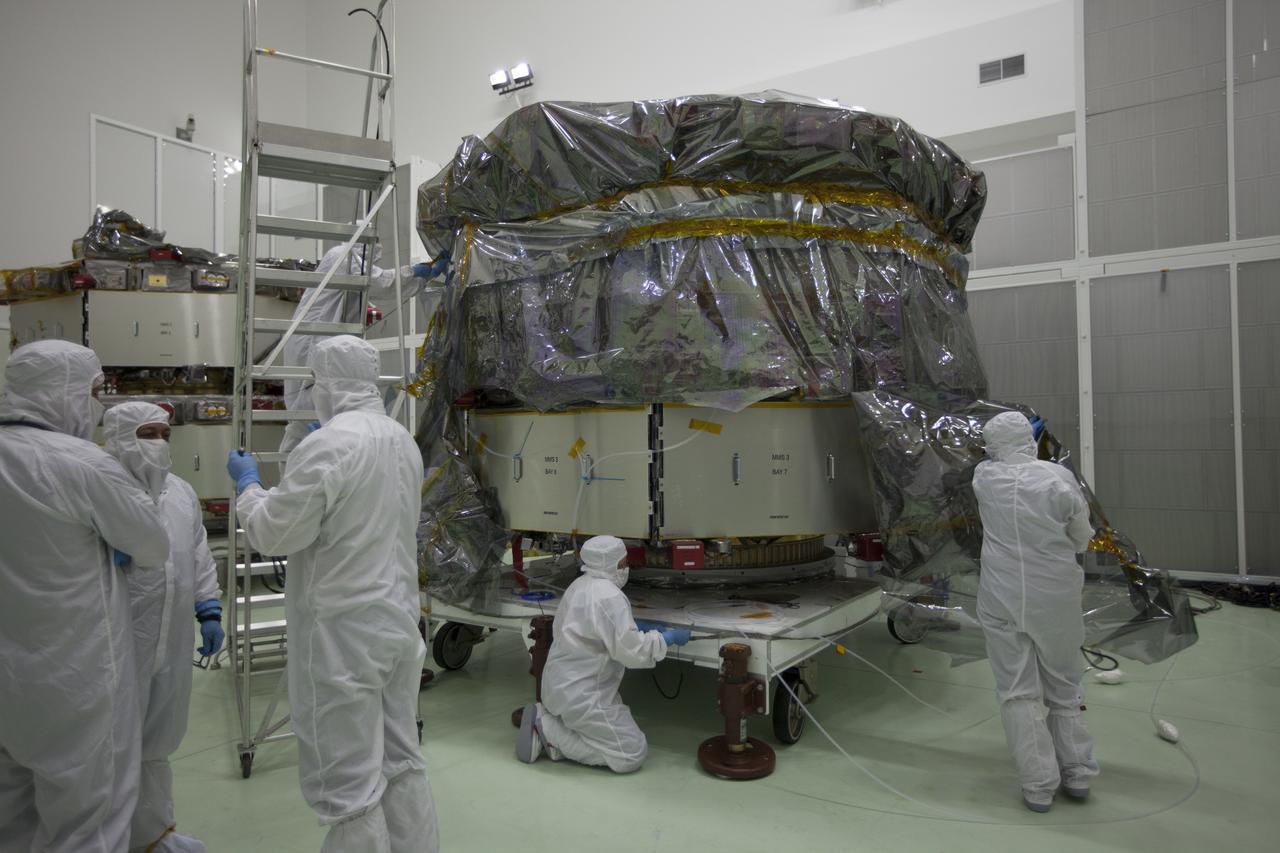
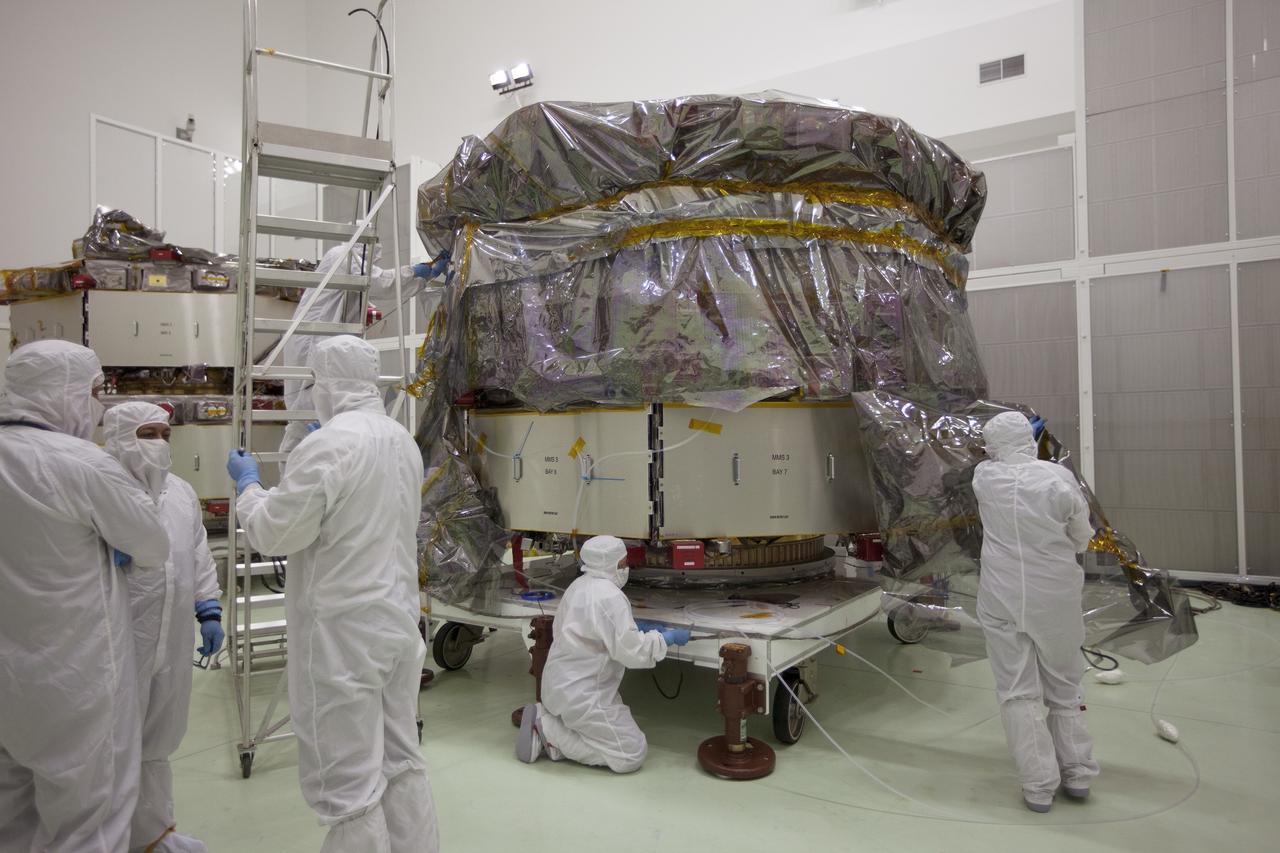
Observatory #1 is shown here on the Ransome table, tilted in a vertical position to provide better access for the engineers and technicians. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Goddard The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
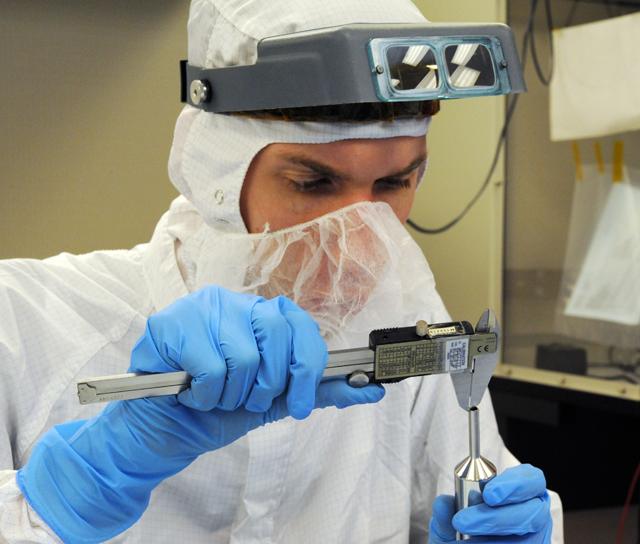

Propulsion engineer measures the flight filters during the receiving inspection. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Goddard The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
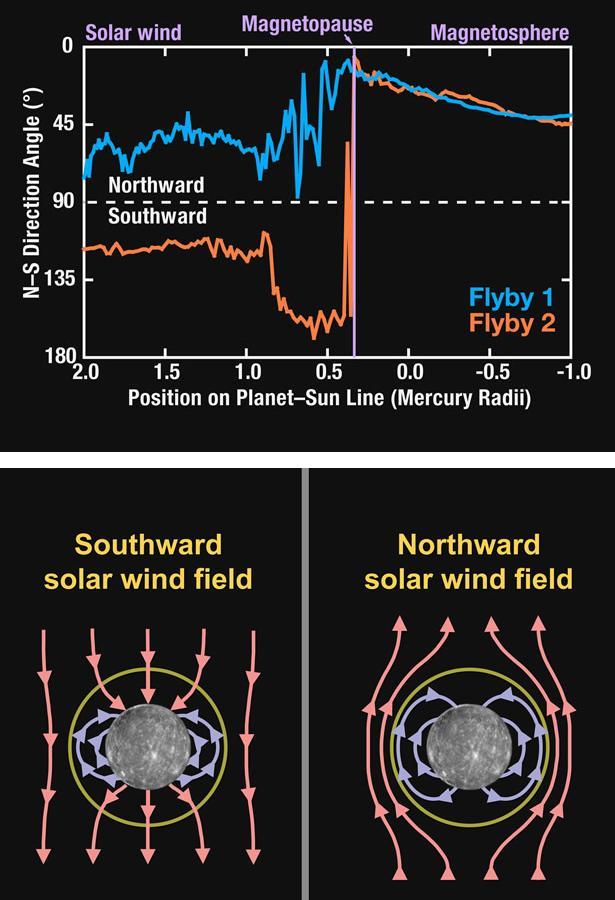
MESSENGER Explores Interactions between Mercury Magnetosphere and the Solar Wind
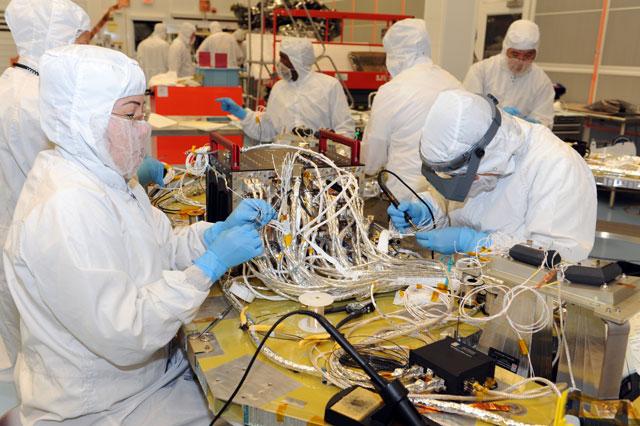

Electrical technicians work diligently to build the connector harnessing for the Command and Data Handling (C&DH) unit, (black box with two red handles) that is installed on spacecraft Deck for MMS #4. Learn more about MMS at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mms" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mms</a> Credit NASA/Goddard The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, will study how the sun and the Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, an explosive process that can accelerate particles through space to nearly the speed of light. This process is called magnetic reconnection and can occur throughout all space. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
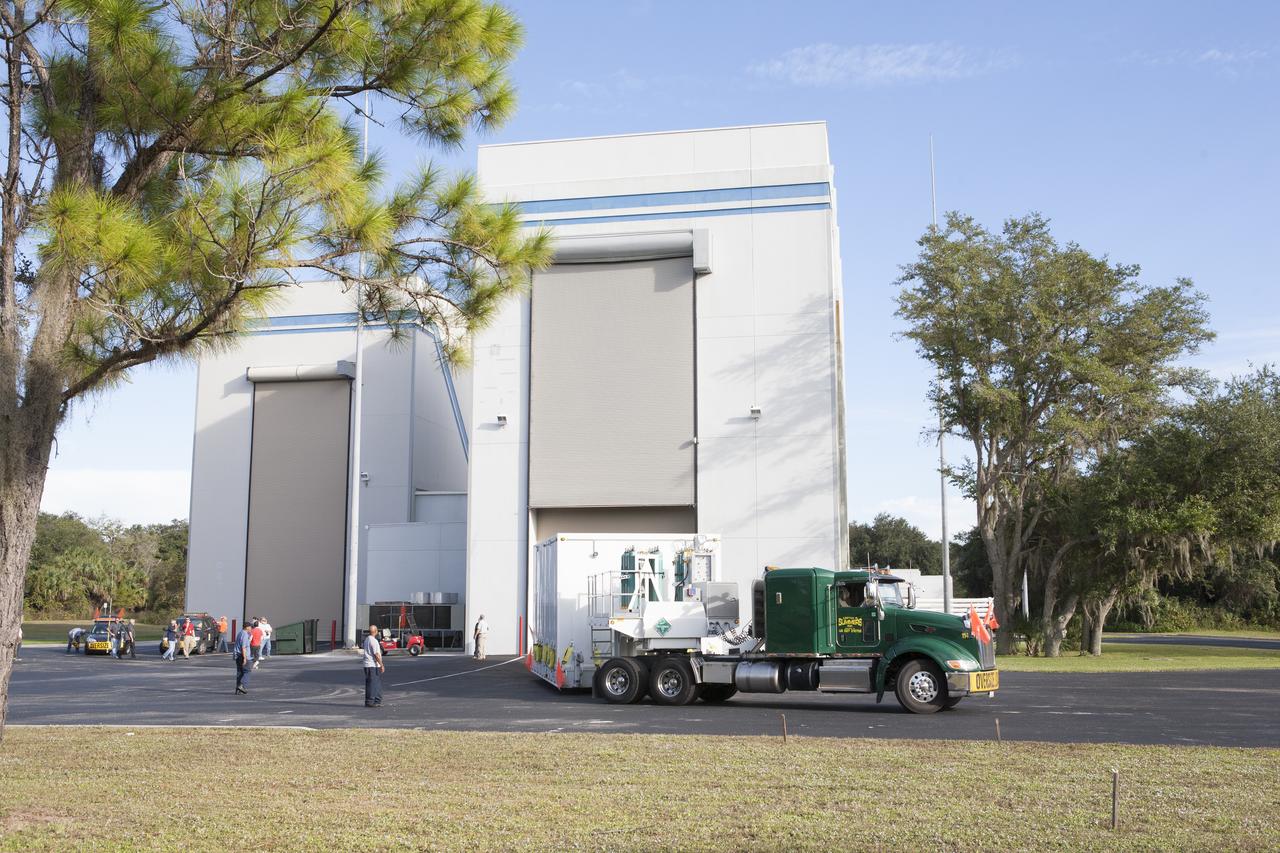

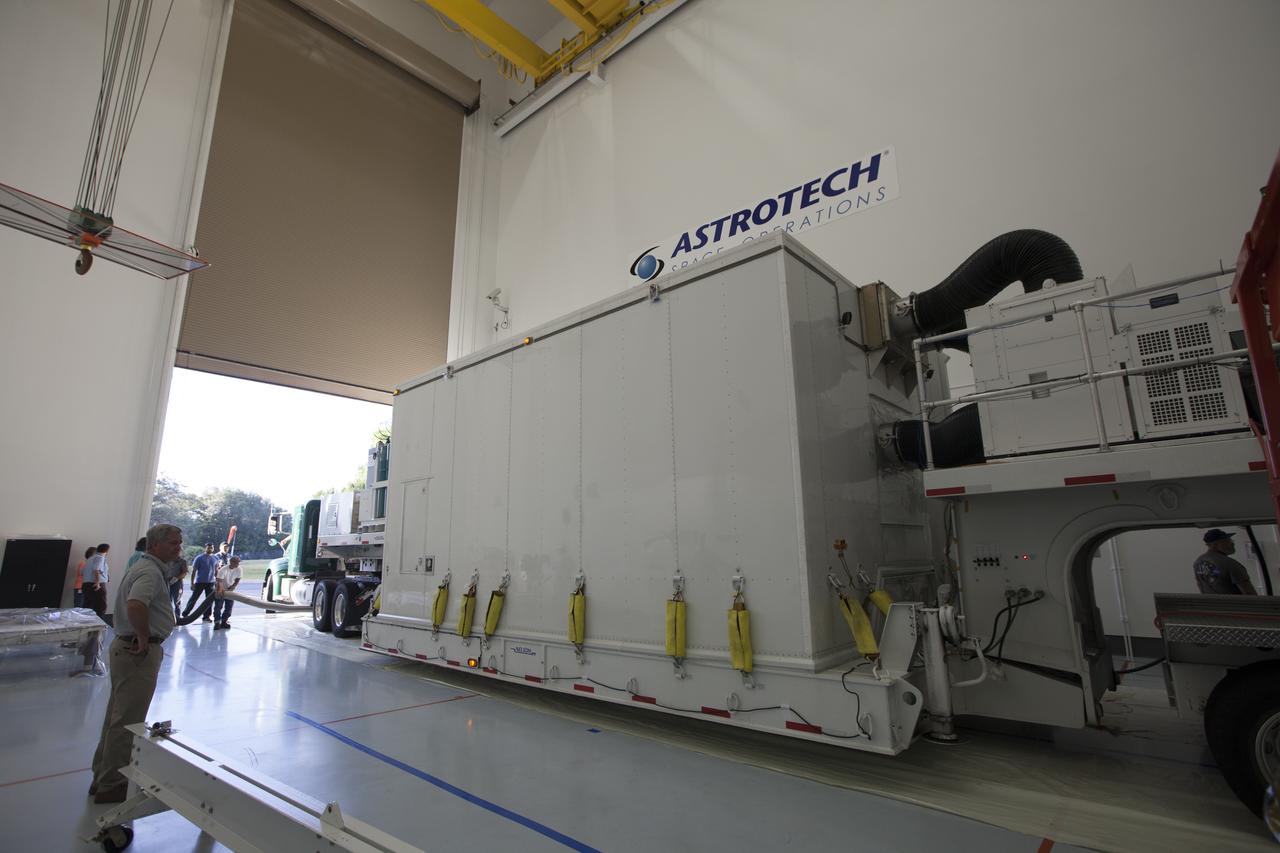
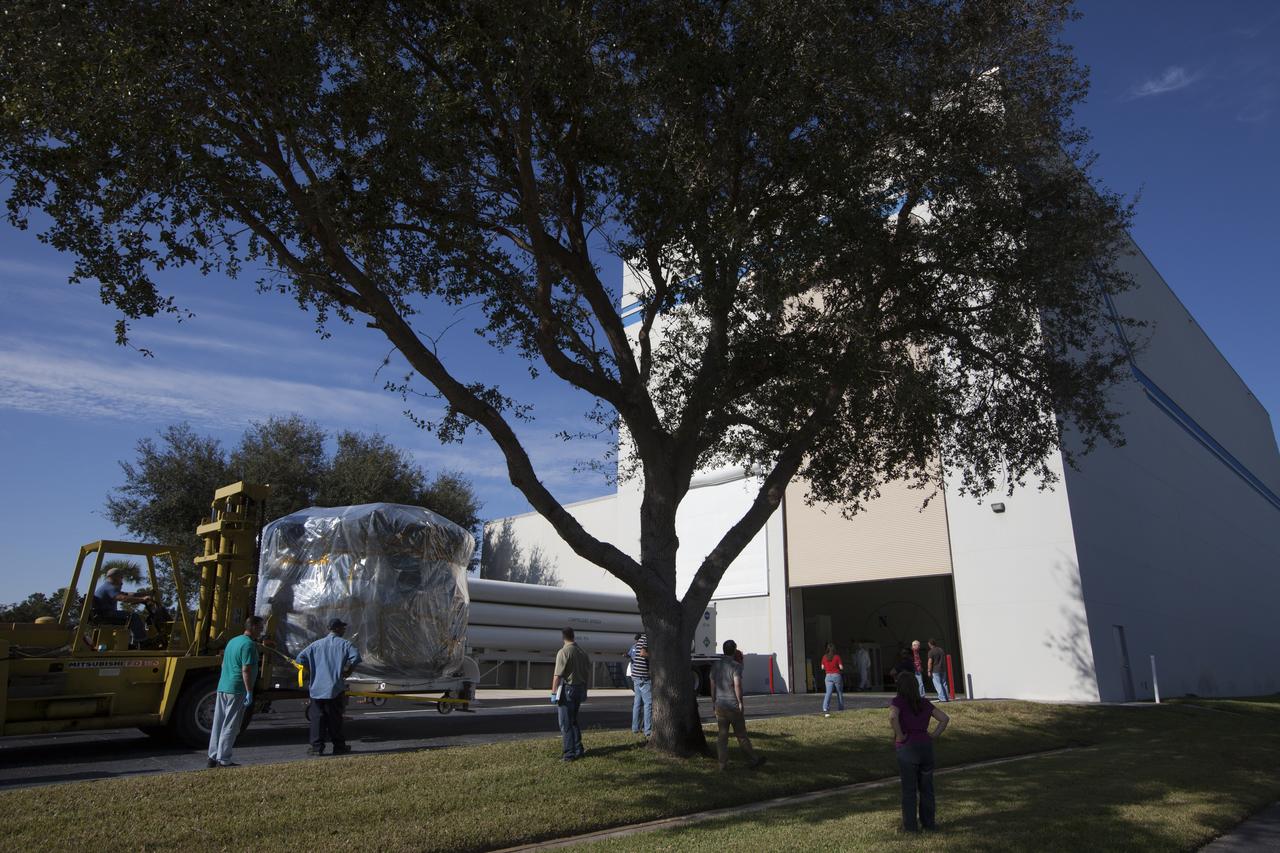
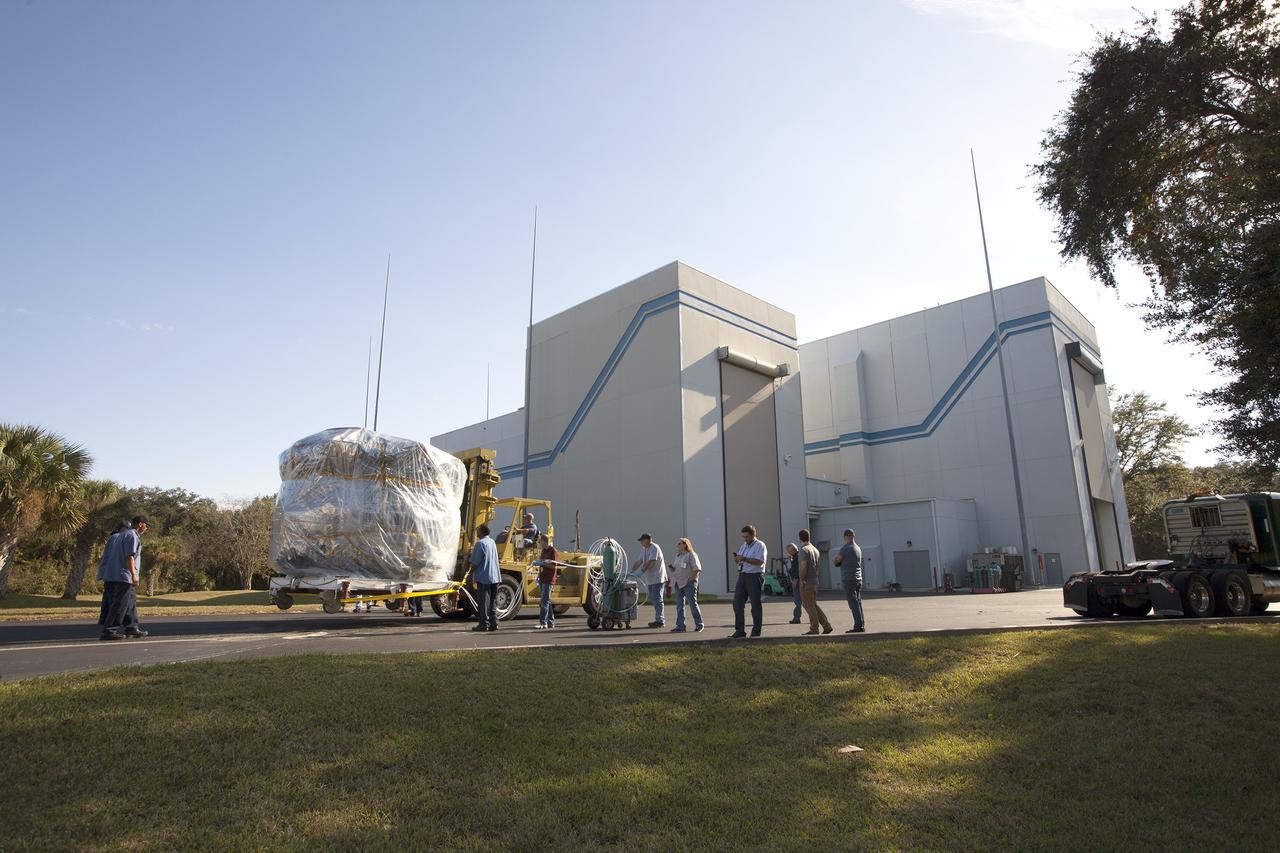
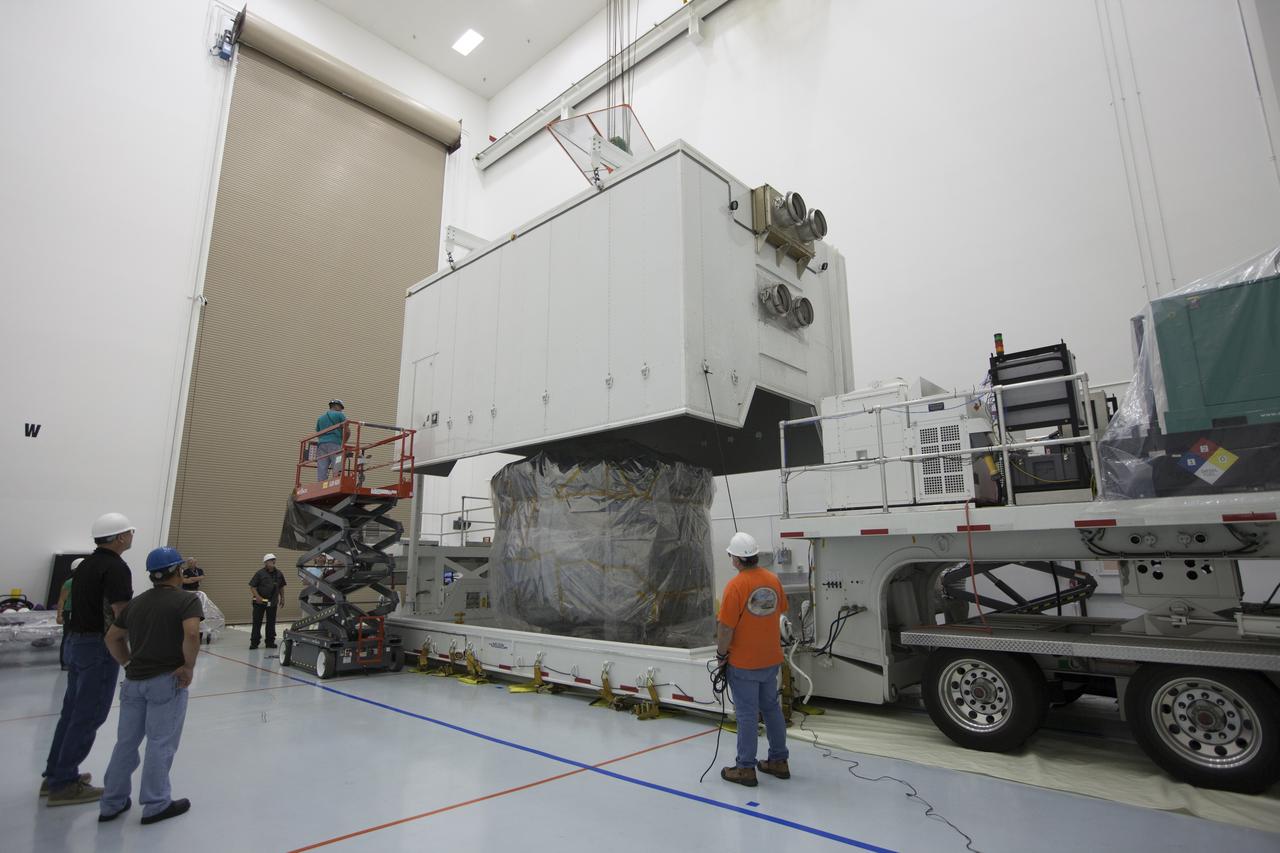
Two Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
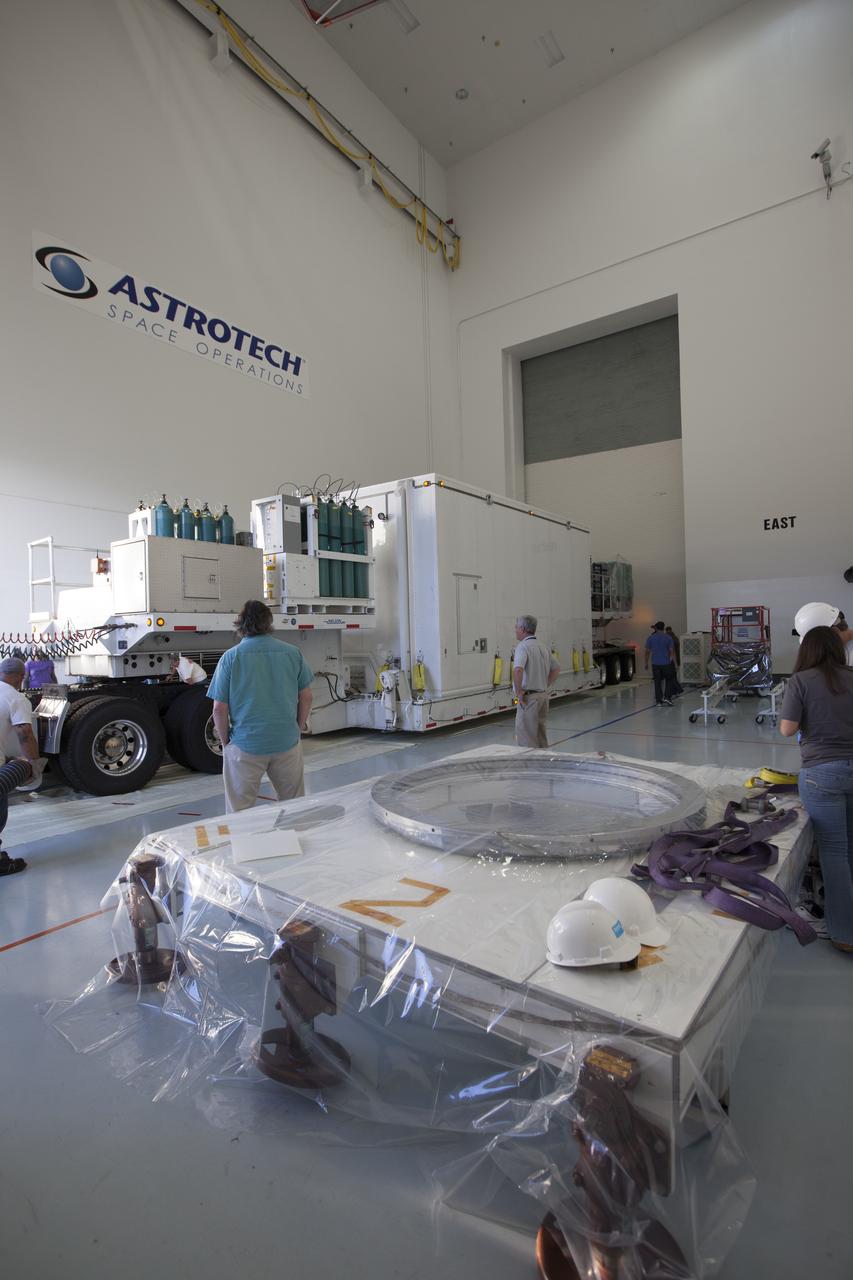

Operations are underway to remove two of the the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft from their protective shipping container in the airlock of Building 2 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
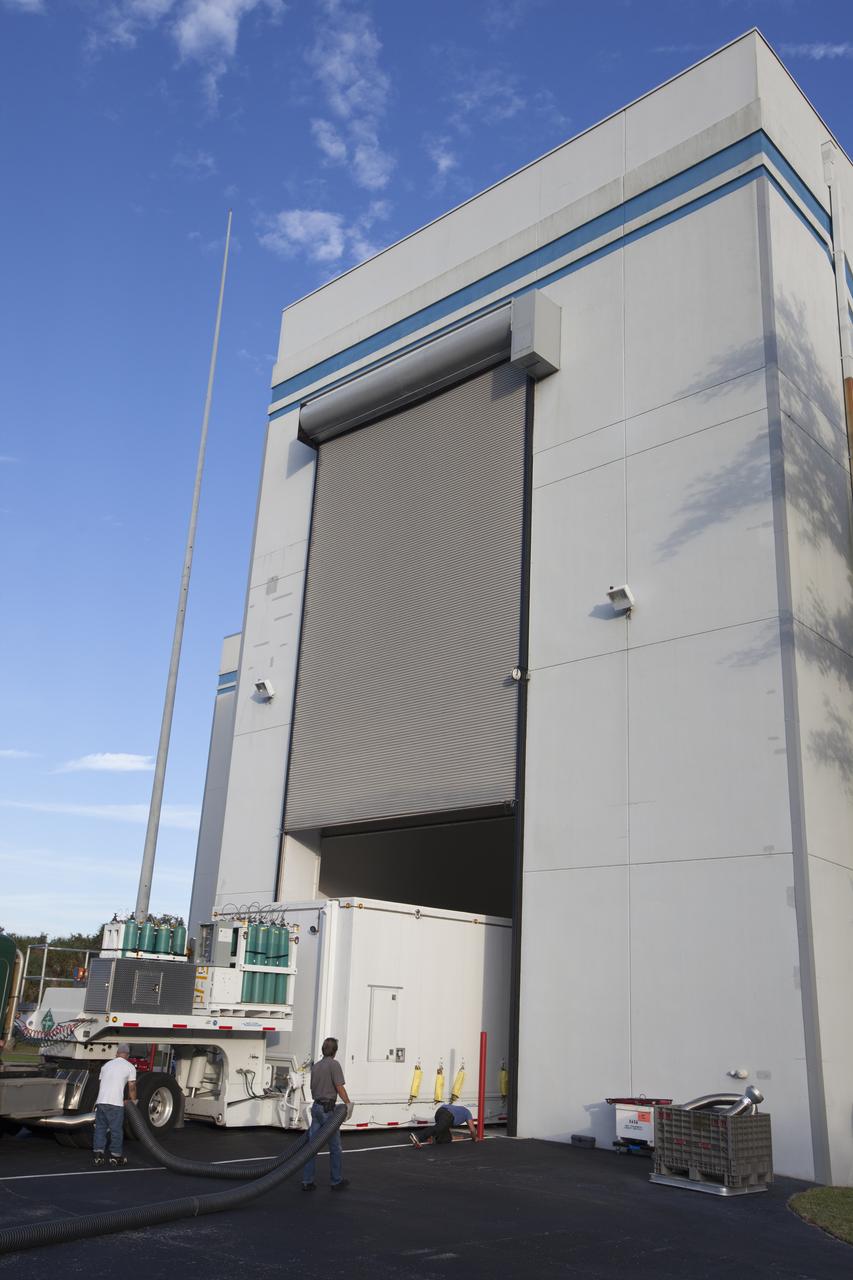

The airlock door opens at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center, for ingress of the protective shipping container enclosing the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

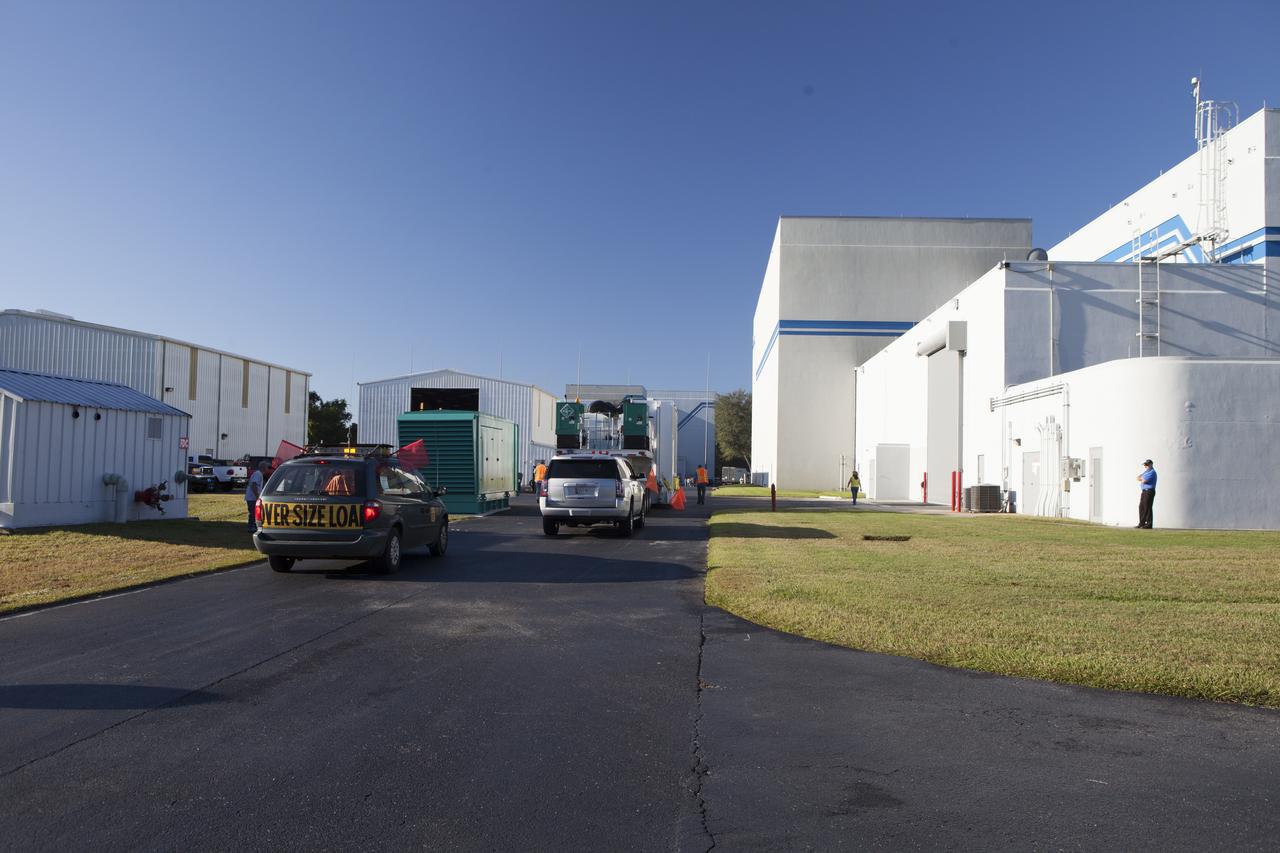
Two Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are positioned into the airlock of Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

The airlock door opens at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center, for ingress of the protective shipping container enclosing the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

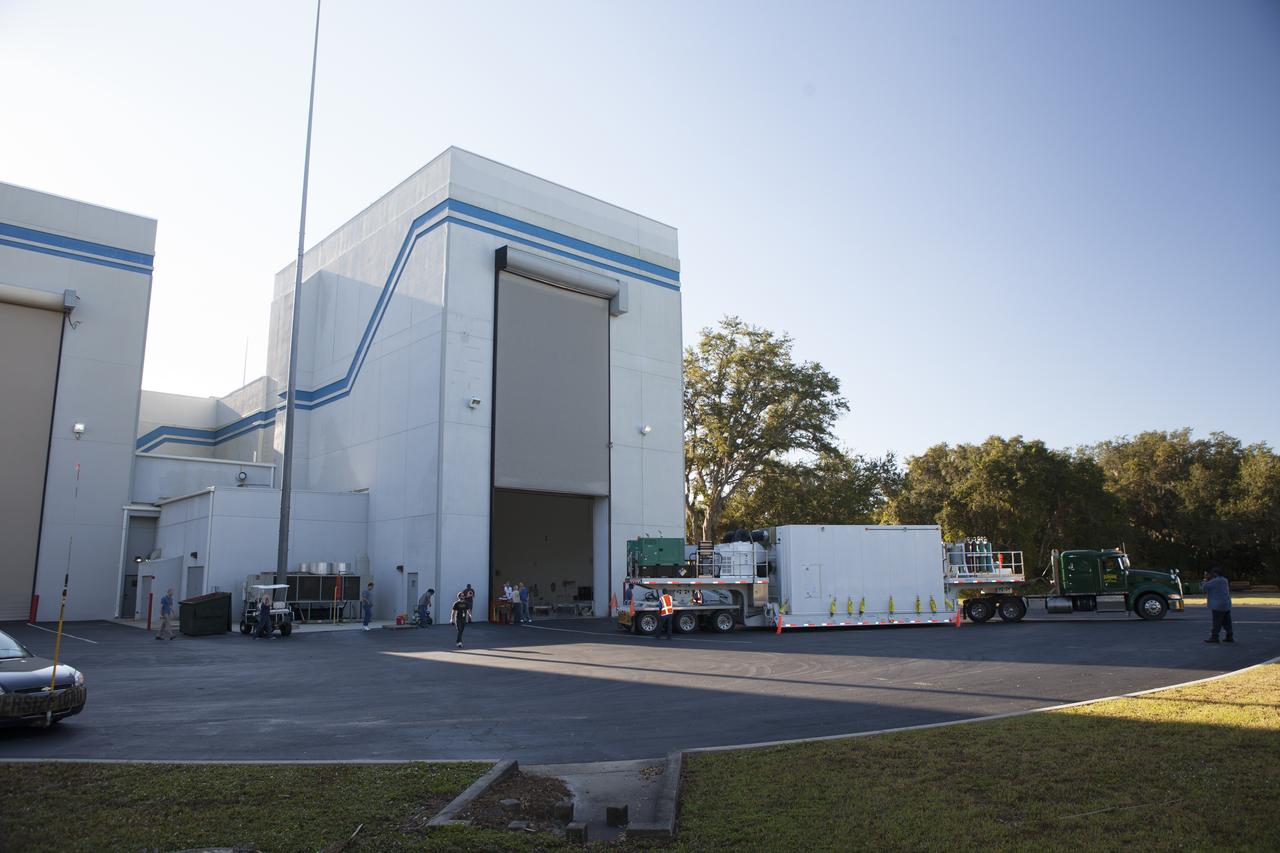
The Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, arrive at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

The Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
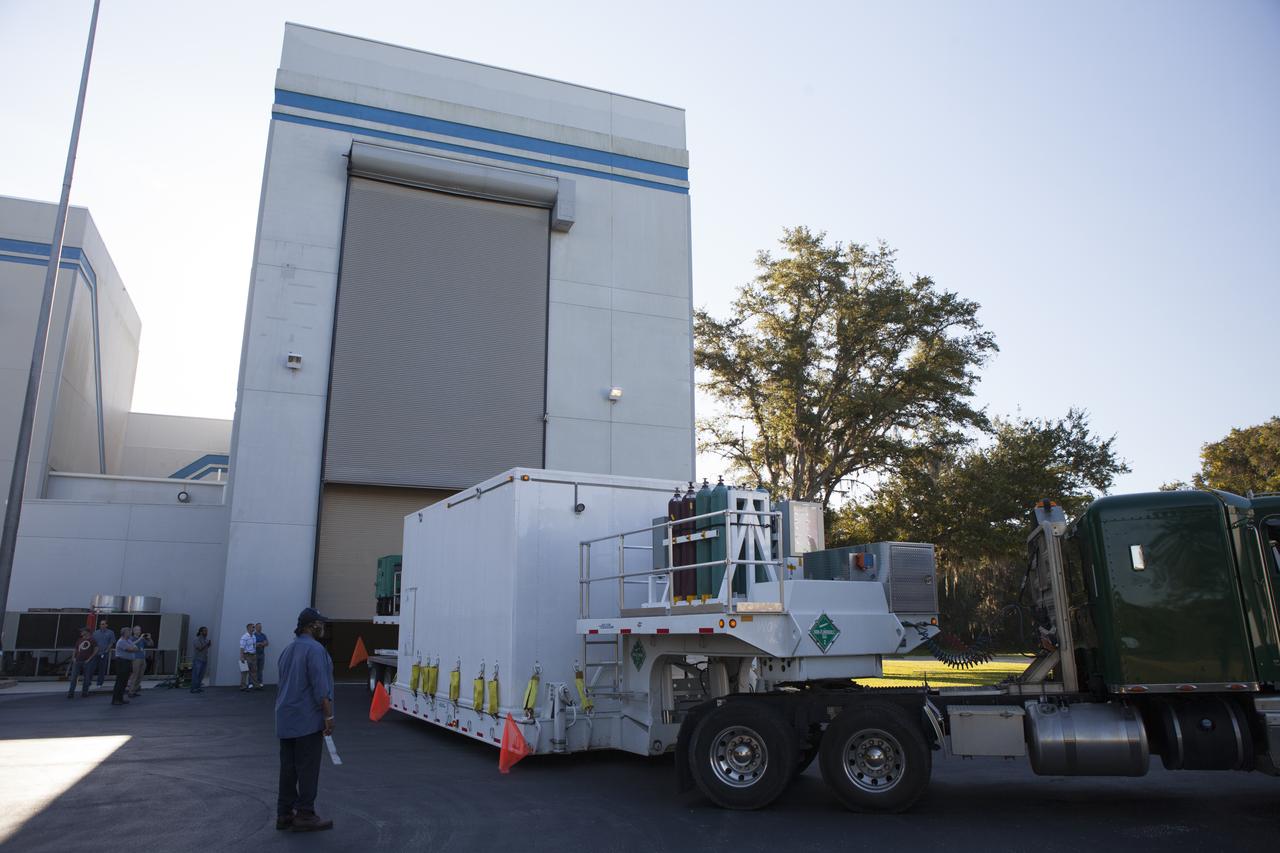

Operations are underway to move the protective shipping container enclosing the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft into the airlock of Building 2 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. MMS is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
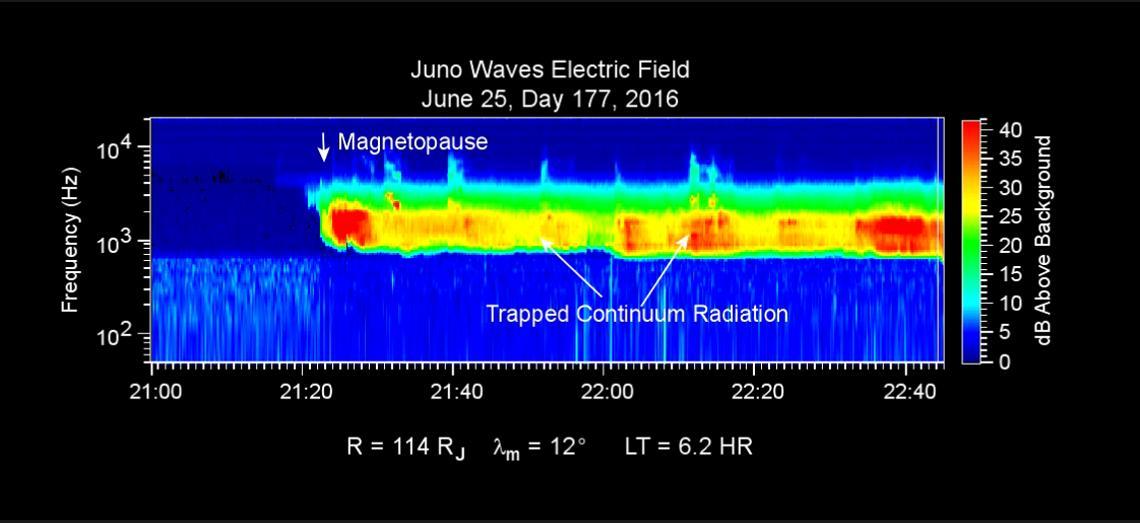
This chart presents data that the Waves investigation on NASA's Juno spacecraft recorded as the spacecraft crossed the bow shock just outside of Jupiter's magnetosphere on June 24, 2016, while approaching Jupiter. Audio accompanies the animation, with volume and pitch correlated to the amplitude and frequency of the recorded waves. The graph is a frequency-time spectrogram with color coding to indicate wave amplitudes as a function of wave frequency (vertical axis, in hertz) and time (horizontal axis, with a total elapsed time of two hours). During the hour before Juno reached the bow shock, the Waves instrument was detecting mainly plasma oscillations just below 10,000 hertz (10 kilohertz). The frequency of these oscillations is related to the local density of electrons; the data yield an estimate of approximately one electron per cubic centimeter (about 16 per cubic inch) in this region just outside Jupiter's bow shock. The broadband burst of noise marked "Bow Shock" is the region of turbulence where the supersonic solar wind is heated and slowed by encountering the Jovian magnetosphere. The shock is analogous to a sonic boom generated in Earth's atmosphere by a supersonic aircraft. The region after the shock is called the magnetosheath. The vertical bar to the right of the chart indicates the color coding of wave amplitude, in decibels (dB) above the background level detected by the Waves instrument. Each step of 10 decibels marks a tenfold increase in wave power. When Juno collected these data, the distance from the spacecraft to Jupiter was about 5.56 million miles (8.95 million kilometers), indicated on the chart as 128 times the radius of Jupiter. Jupiter's magnetic field is tilted about 10 degrees from the planet's axis of rotation. The note of 22 degrees on the chart indicates that at the time these data were recorded, the spacecraft was 22 degrees north of the magnetic-field equator. The "LT" notation is local time on Jupiter at the longitude of the planet directly below the spacecraft, with a value of 6.2 indicating approximately dawn. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20753
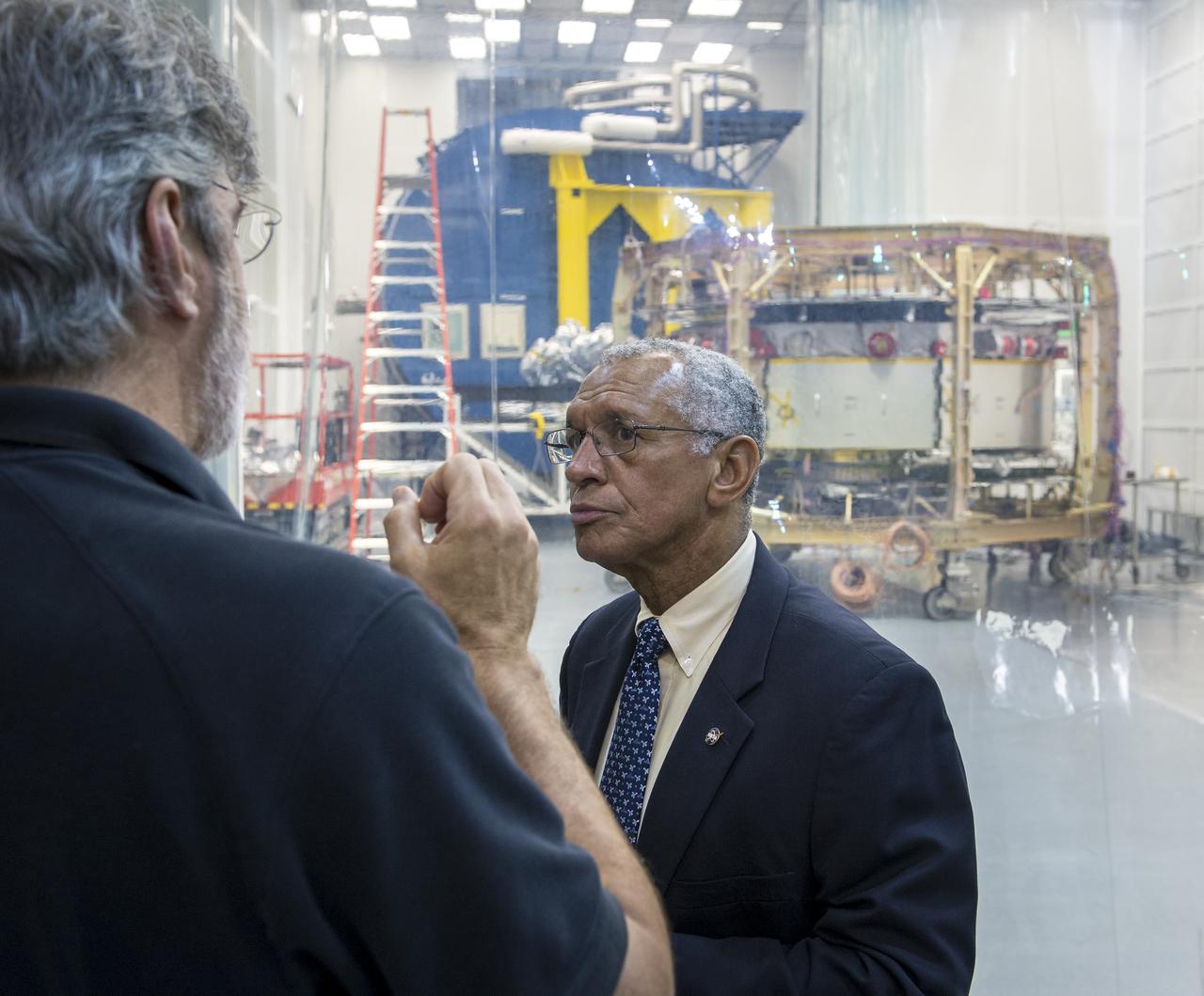

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden listens to Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) Mission Project Manager Craig Tooley talk about the MMS mission outside of a Naval Research Laboratory cleanroom where one of four Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft is currently undergoing testing, Monday, August 4, 2014, in Washington. The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission will study the mystery of how magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect, explosively releasing energy via a process known as magnetic reconnection. The four identical spacecraft are scheduled to launch in 2015 from Cape Canaveral and will orbit around Earth in varying formations through the dynamic magnetic system surrounding our planet to provide the first three-dimensional views of the magnetic reconnection process. The goal of the STP Program is to understand the fundamental physical processes of the space environment from the sun to Earth, other planets, and the extremes of the solar system boundary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
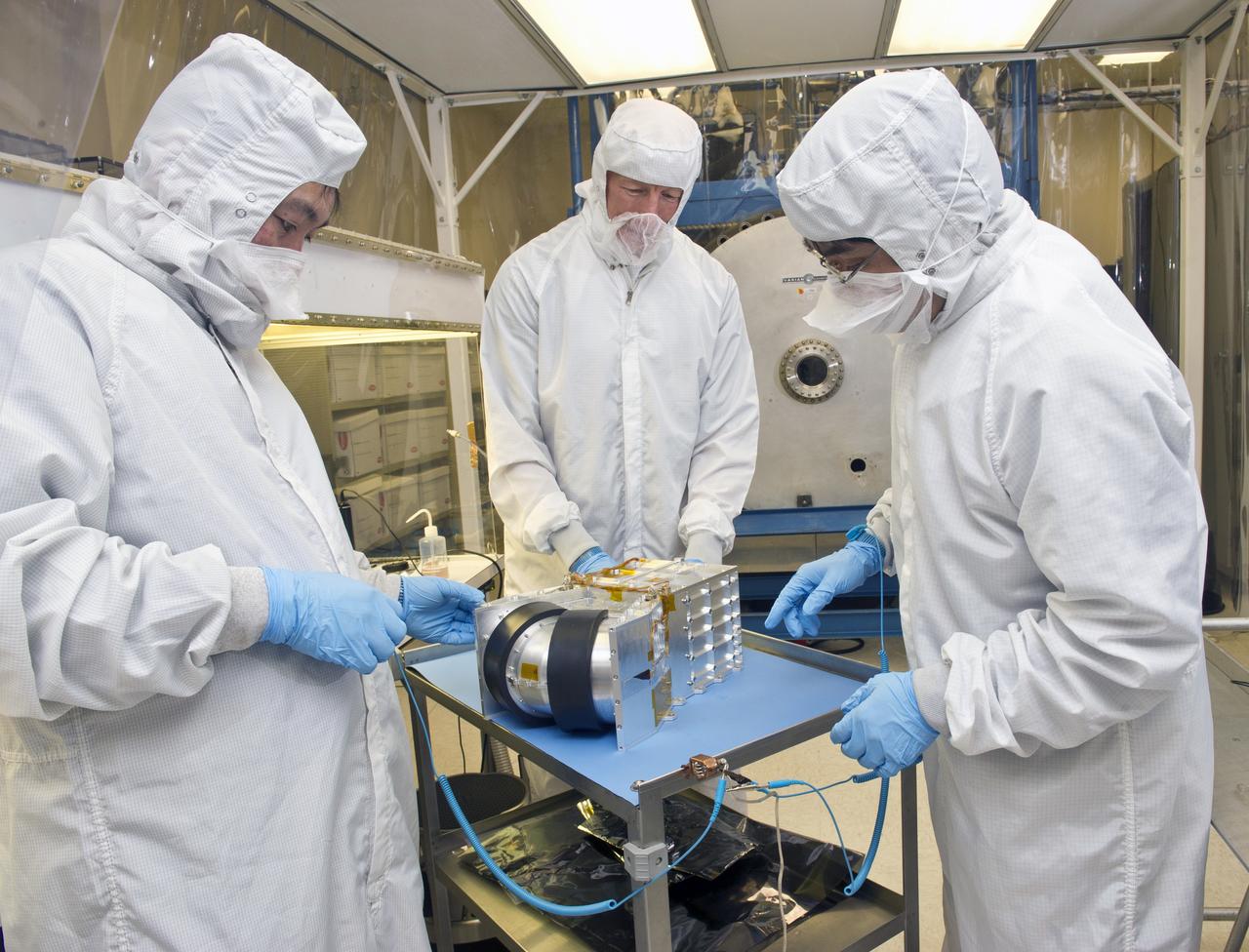

(L TO R) TAKZNOBU OMOTO (JAXA), MARK SLOAN (MSFC), AND TOSHIHIRO KOBZYASHI (JAXA) IN CLEAN TENT TESTING MMS, (MAGNETOSPHERIC MULTISCALE MISSION)
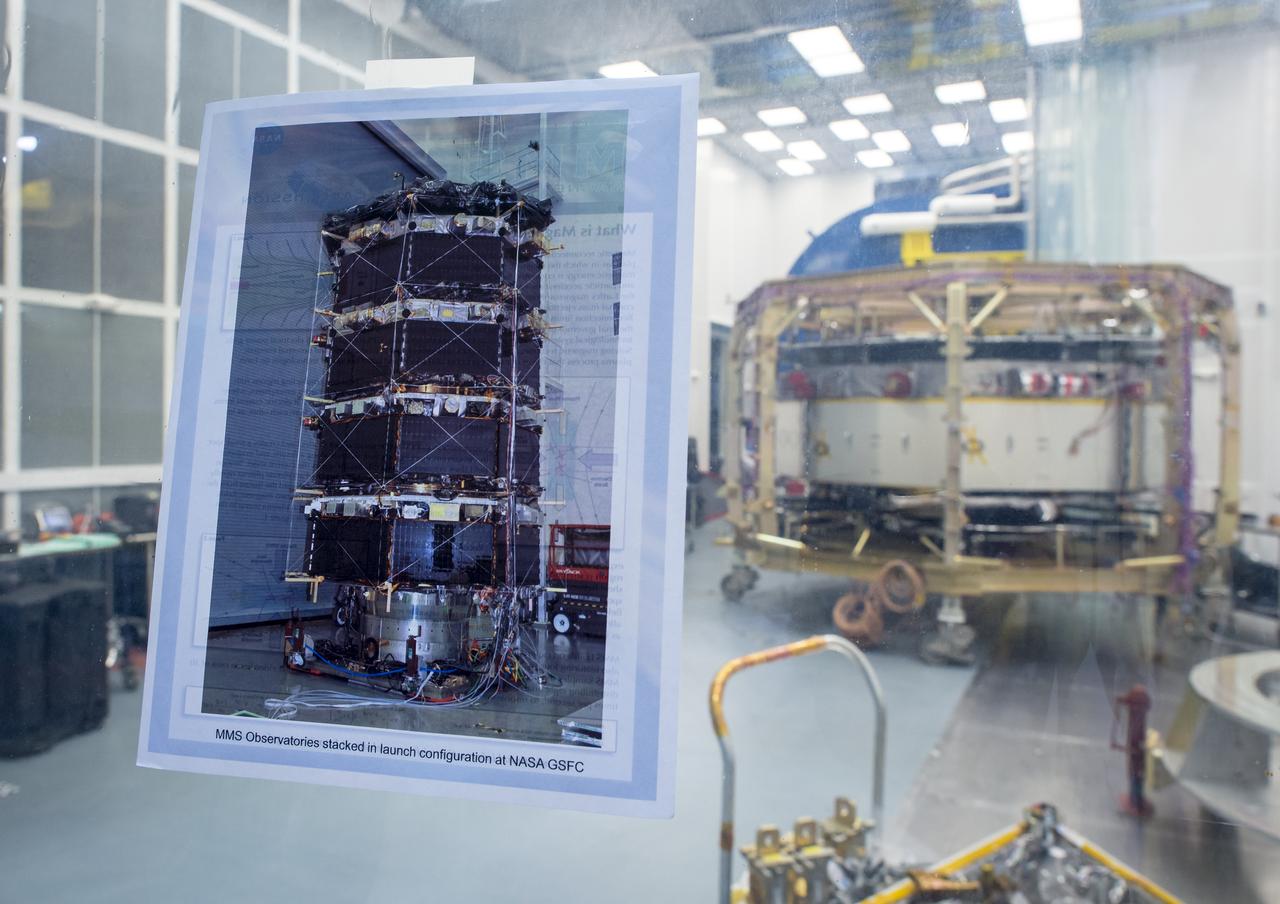
A photograph showing what all four Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft look like when stacked is seen taped to the window of a Naval Research Laboratory cleanroom where one of the four spacecraft is undergoing testing, Monday, August 4, 2014, in Washington. The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission will study the mystery of how magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect, explosively releasing energy via a process known as magnetic reconnection. The four identical spacecraft are scheduled to launch in 2015 from Cape Canaveral and will orbit around Earth in varying formations through the dynamic magnetic system surrounding our planet to provide the first three-dimensional views of the magnetic reconnection process. The goal of the STP Program is to understand the fundamental physical processes of the space environment from the sun to Earth, other planets, and the extremes of the solar system boundary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
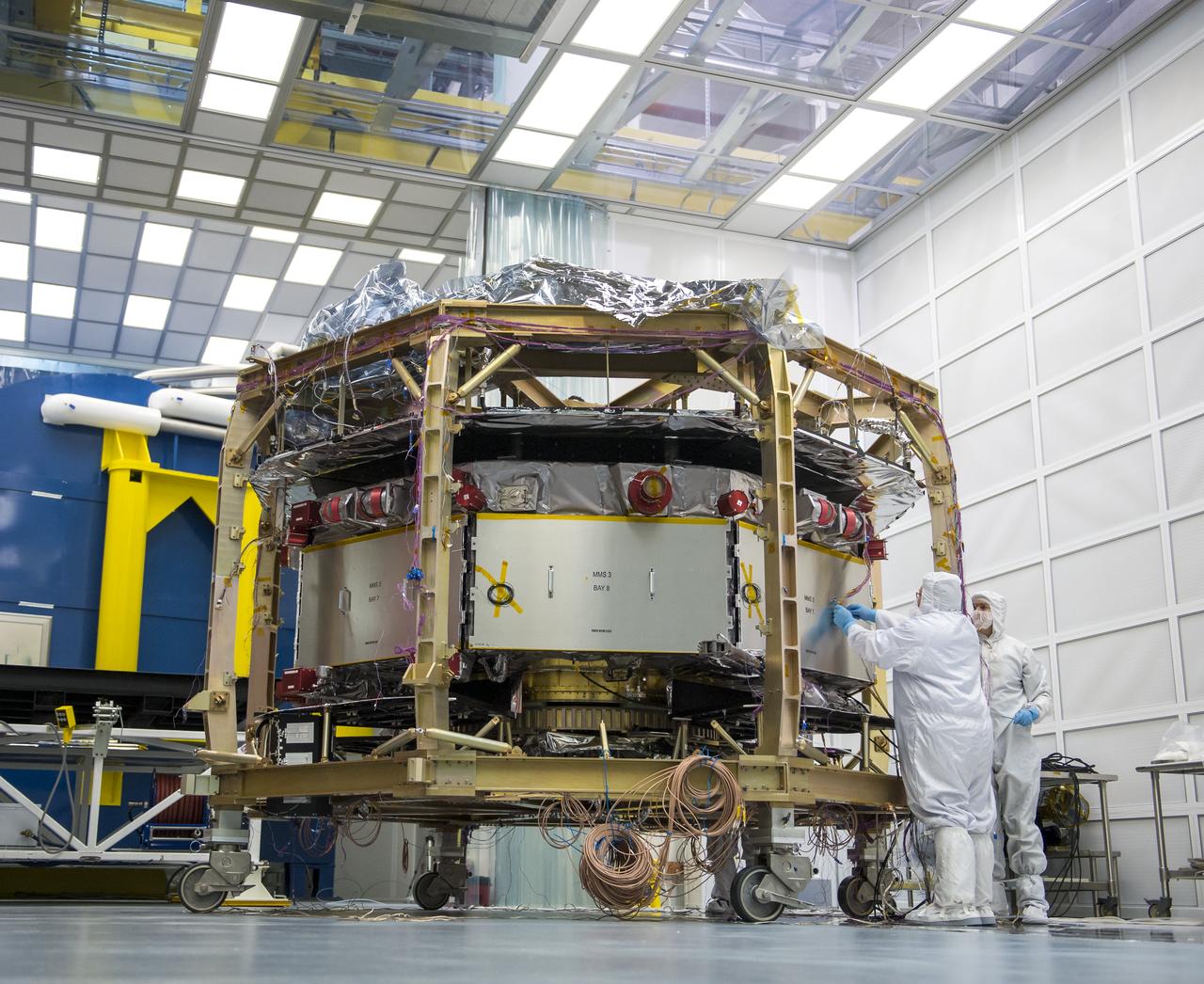

Engineers work on one of four Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft in a cleanroom at the Naval Research Lab, Monday, August 4, 2014, in Washington. The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission will study the mystery of how magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect, explosively releasing energy via a process known as magnetic reconnection. The four identical spacecraft are scheduled to launch in 2015 from Cape Canaveral and will orbit around Earth in varying formations through the dynamic magnetic system surrounding our planet to provide the first three-dimensional views of the magnetic reconnection process. The goal of the STP Program is to understand the fundamental physical processes of the space environment from the sun to Earth, other planets, and the extremes of the solar system boundary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

One of four Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft, in the background, is seen in a cleanroom at the Naval Research Lab’s, Naval Center for Space Technology, Monday, August 4, 2014, in Washington. The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission will study the mystery of how magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect, explosively releasing energy via a process known as magnetic reconnection. The four identical spacecraft are scheduled to launch in 2015 from Cape Canaveral and will orbit around Earth in varying formations through the dynamic magnetic system surrounding our planet to provide the first three-dimensional views of the magnetic reconnection process. The goal of the STP Program is to understand the fundamental physical processes of the space environment from the sun to Earth, other planets, and the extremes of the solar system boundary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
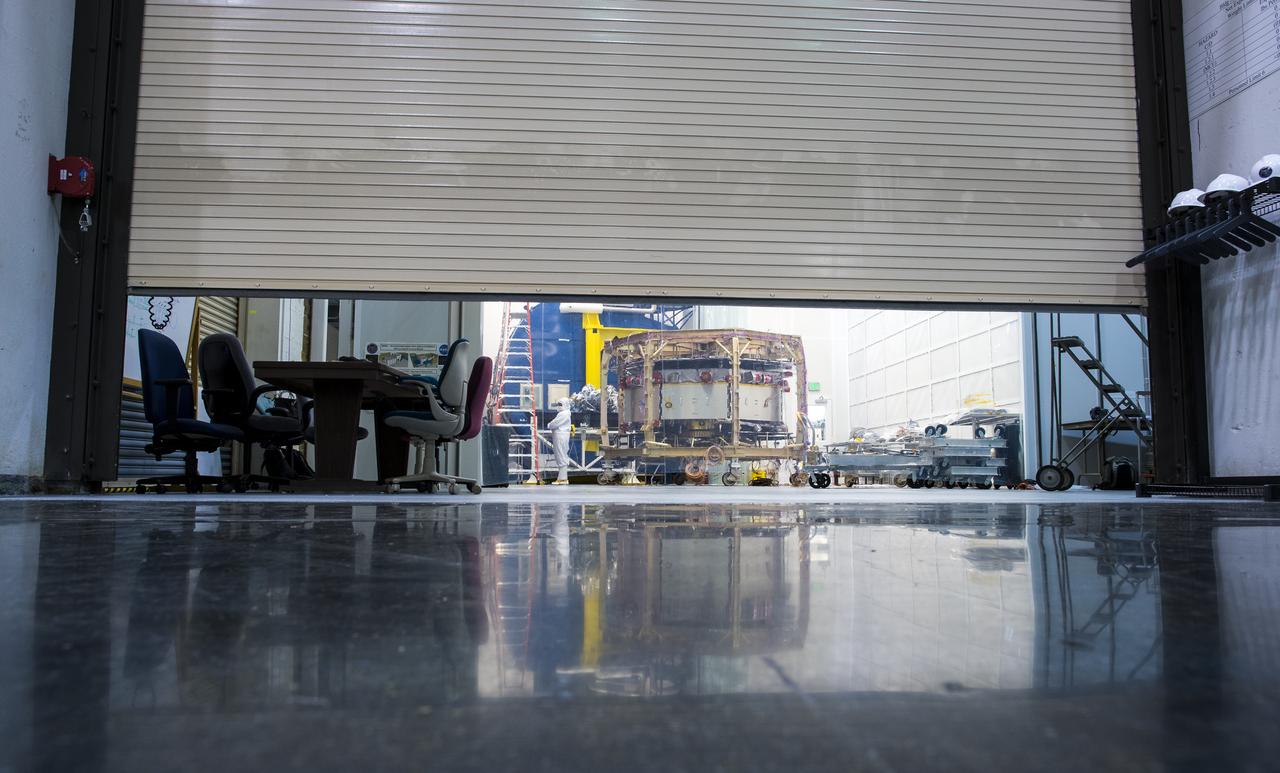

One of four Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) spacecraft, in the background, is seen in a cleanroom at the Naval Research Lab’s, Naval Center for Space Technology, Monday, August 4, 2014, in Washington. The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, mission will study the mystery of how magnetic fields around Earth connect and disconnect, explosively releasing energy via a process known as magnetic reconnection. The four identical spacecraft are scheduled to launch in 2015 from Cape Canaveral and will orbit around Earth in varying formations through the dynamic magnetic system surrounding our planet to provide the first three-dimensional views of the magnetic reconnection process. The goal of the STP Program is to understand the fundamental physical processes of the space environment from the sun to Earth, other planets, and the extremes of the solar system boundary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
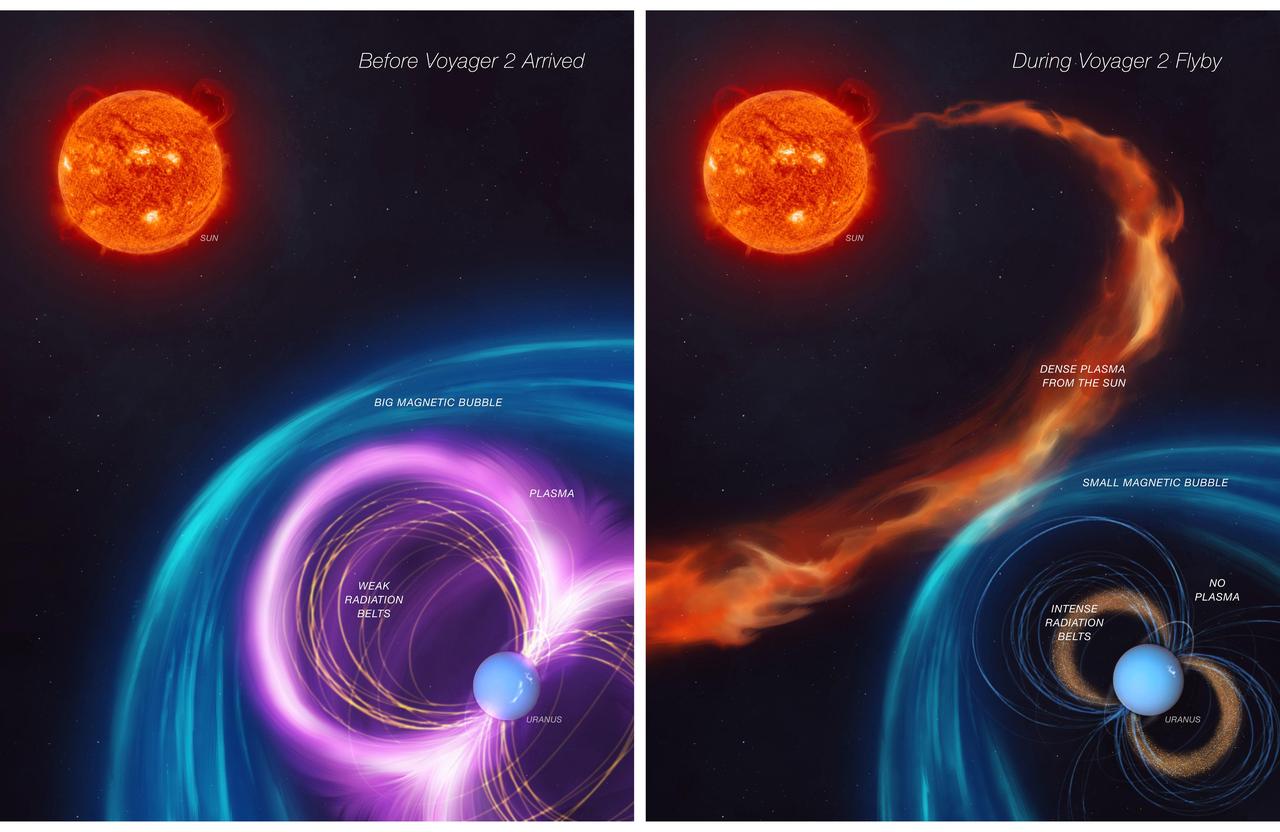

When NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by Uranus in 1986, it provided scientists' first – and, so far, only – close glimpse of this outer planet. Scientists were confronted by a mystery: The energized particles around the planet defied their understanding of how magnetic fields work to trap particle radiation. The first panel of this artist's concept depicts how Uranus's magnetosphere (its protective bubble) was behaving before Voyager 2's flyby. The second panel shows that an unusual kind of solar weather was happening at the same time as the spacecraft's flyby, giving scientists a skewed view of Uranus's magnetosphere. The work, led by a scientist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and described in a paper published in Nature Astronomy in November 2024, contributes to scientists' understanding of this enigmatic planet. It also opens the door to the possibility that Uranus' five major moons may be active. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26069
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) and university scientists from the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama, are watching the Sun in an effort to better predict space weather - blasts of particles and magnetic fields from the Sun that impact the magnetosphere, the magnetic bubble around the Earth. Filled by charged particles trapped in the Earth's magnetic field, the spherical comet-shaped magnetosphere extends out 40,000 miles from Earth's surface in the sunward direction and more in other directions. This image illustrates the Sun-Earth cornection. When massive solar explosions, known as coronal mass ejections, blast through the Sun's outer atmosphere and plow toward Earth at speeds of thousands of miles per second, the resulting effects can be harmful to communication satellites and astronauts outside the Earth's magnetosphere. Like severe weather on Earth, severe space weather can be costly. On the ground, magnetic storms wrought by these solar particles can knock out electric power. By using the Solar Vector Magnetograph, a solar observation facility at MSFC, scientists are learning what signs to look for as indicators of potential severe space weather.
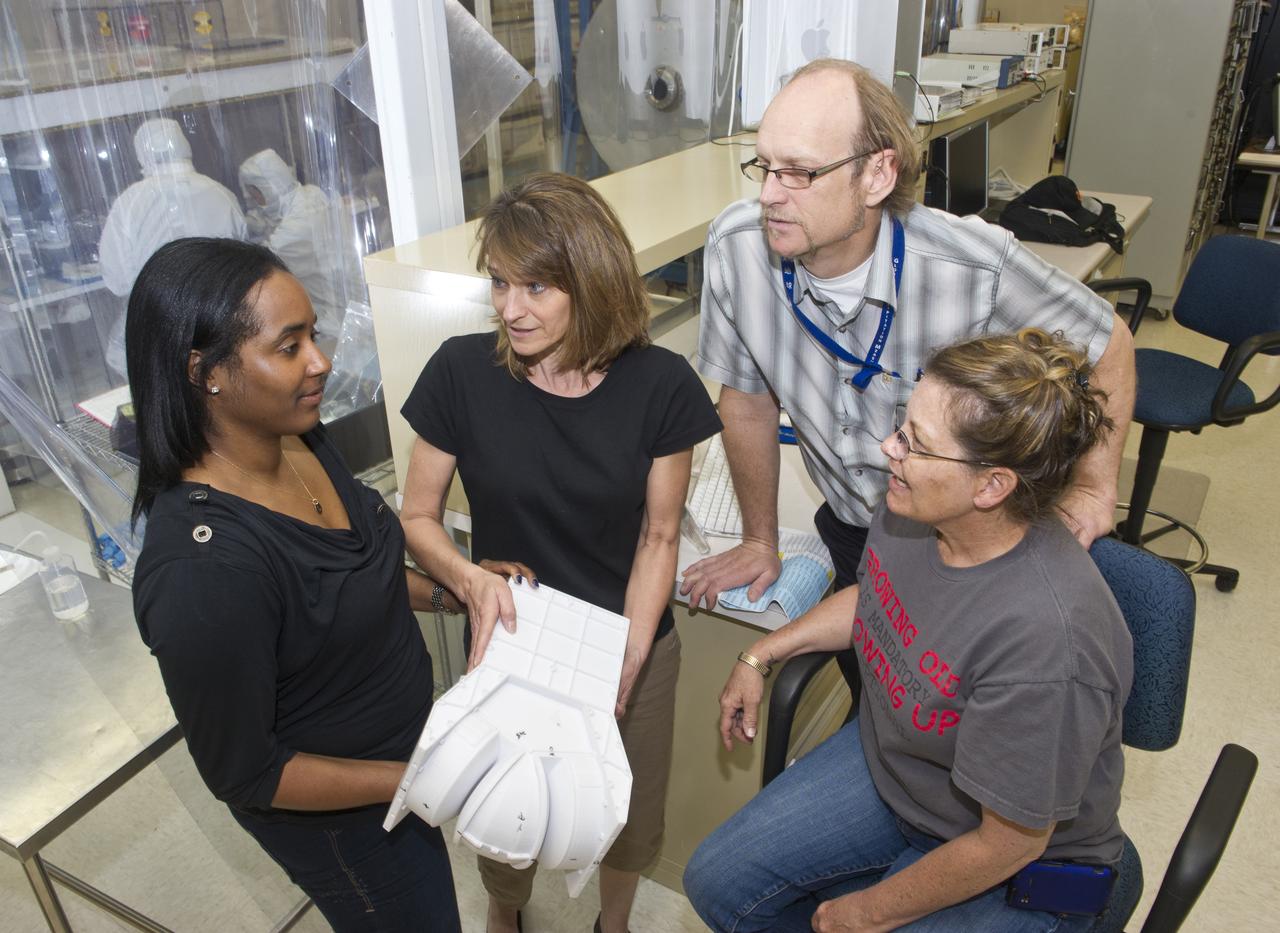

(L TO R) CHANEL DUNCAN (GSFC), VICTORIA COFFEY (MSFC), JIM LOBELL (GSFC) AND TRACI ROSNACK (GSFC) EXAMINE MMS, (MAGNETOSPHERIC MULTISCALE MISSION) MODEL PRIOR TO TESTING.
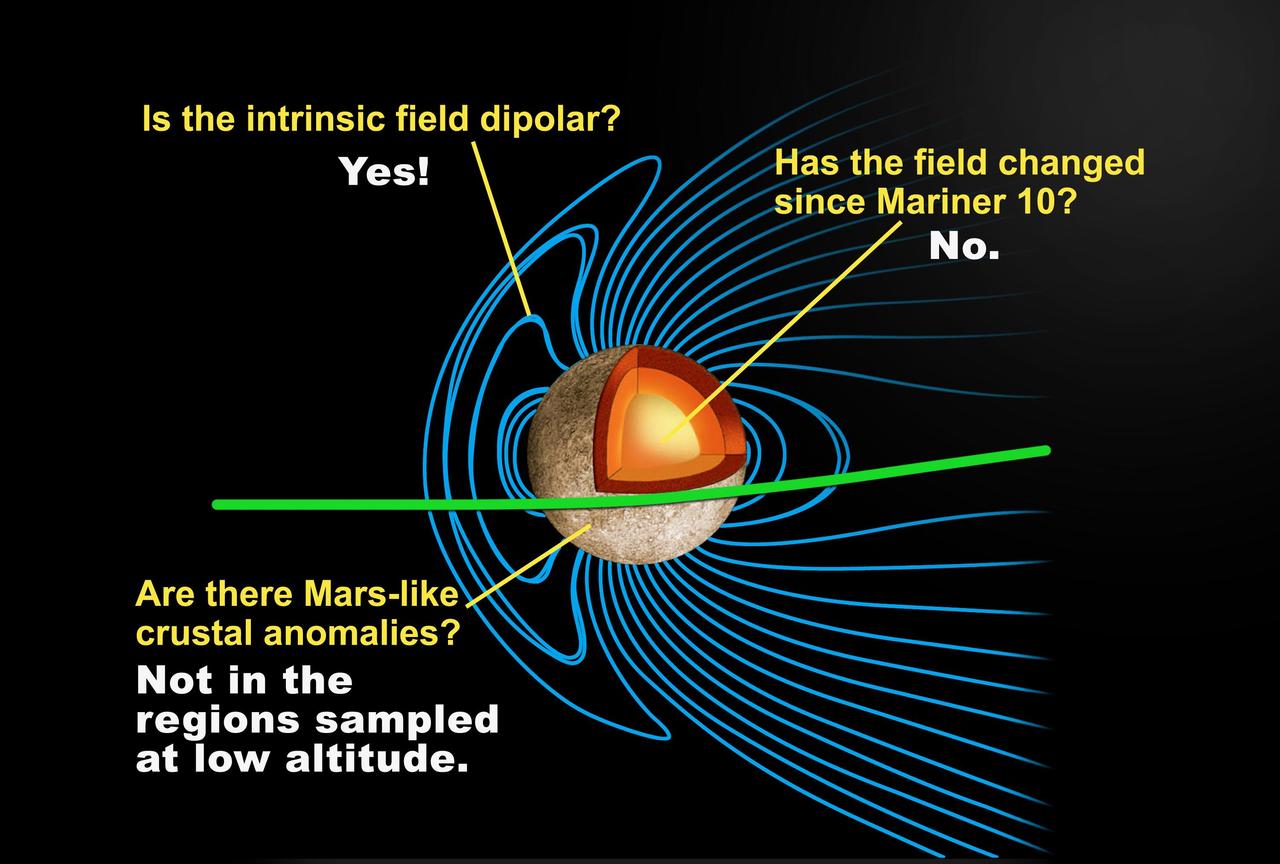
This depiction of a simulated Mercury magnetosphere shows representations of the distortions of the planetary magnetic field lines blue by the solar wind.

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
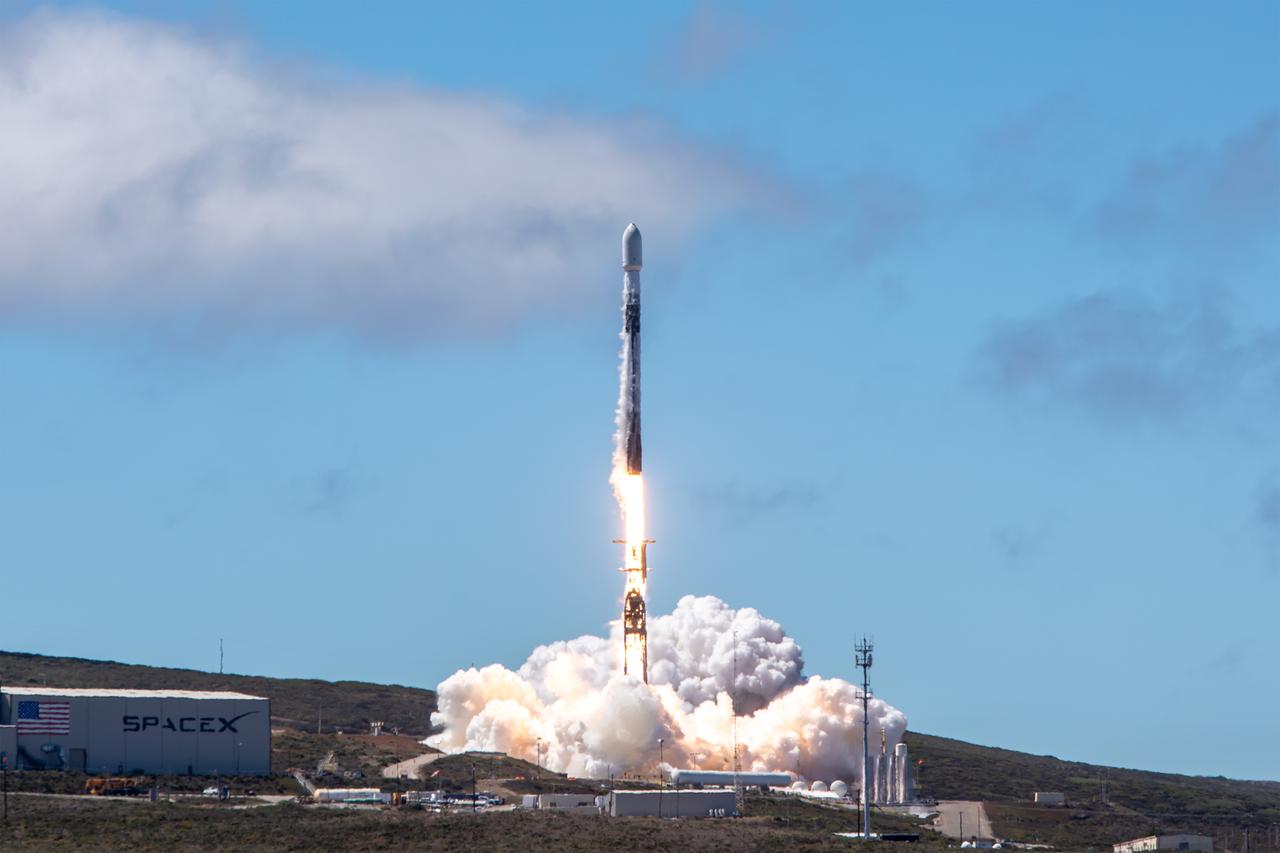

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
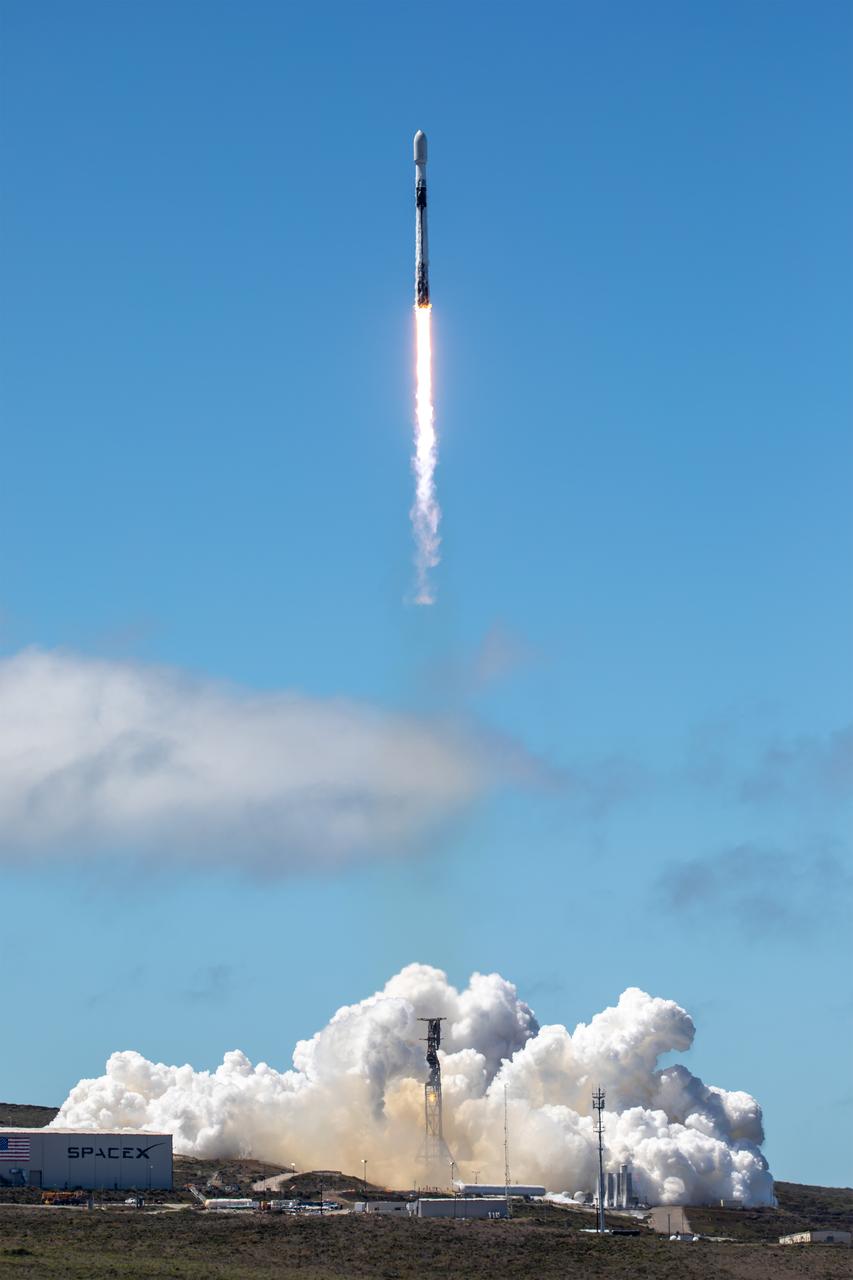

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
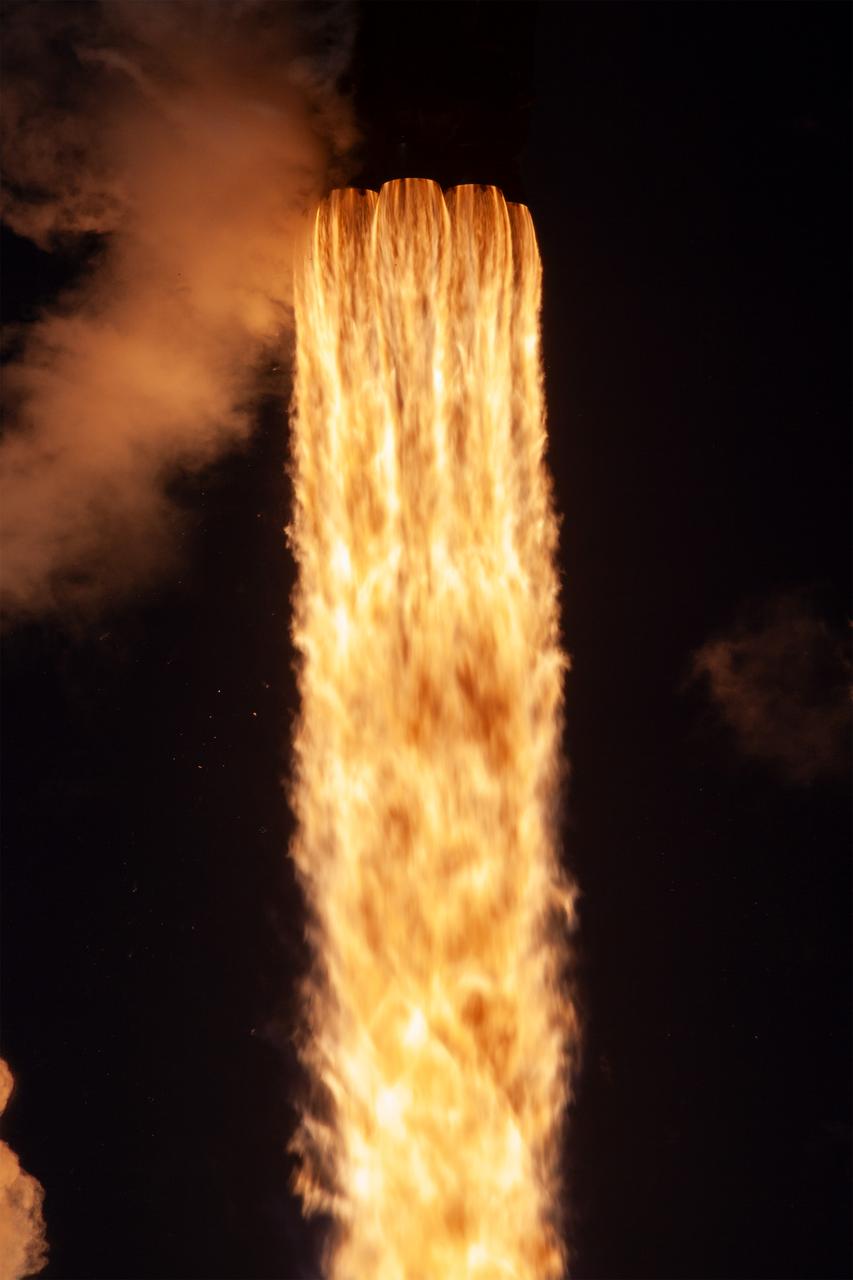

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
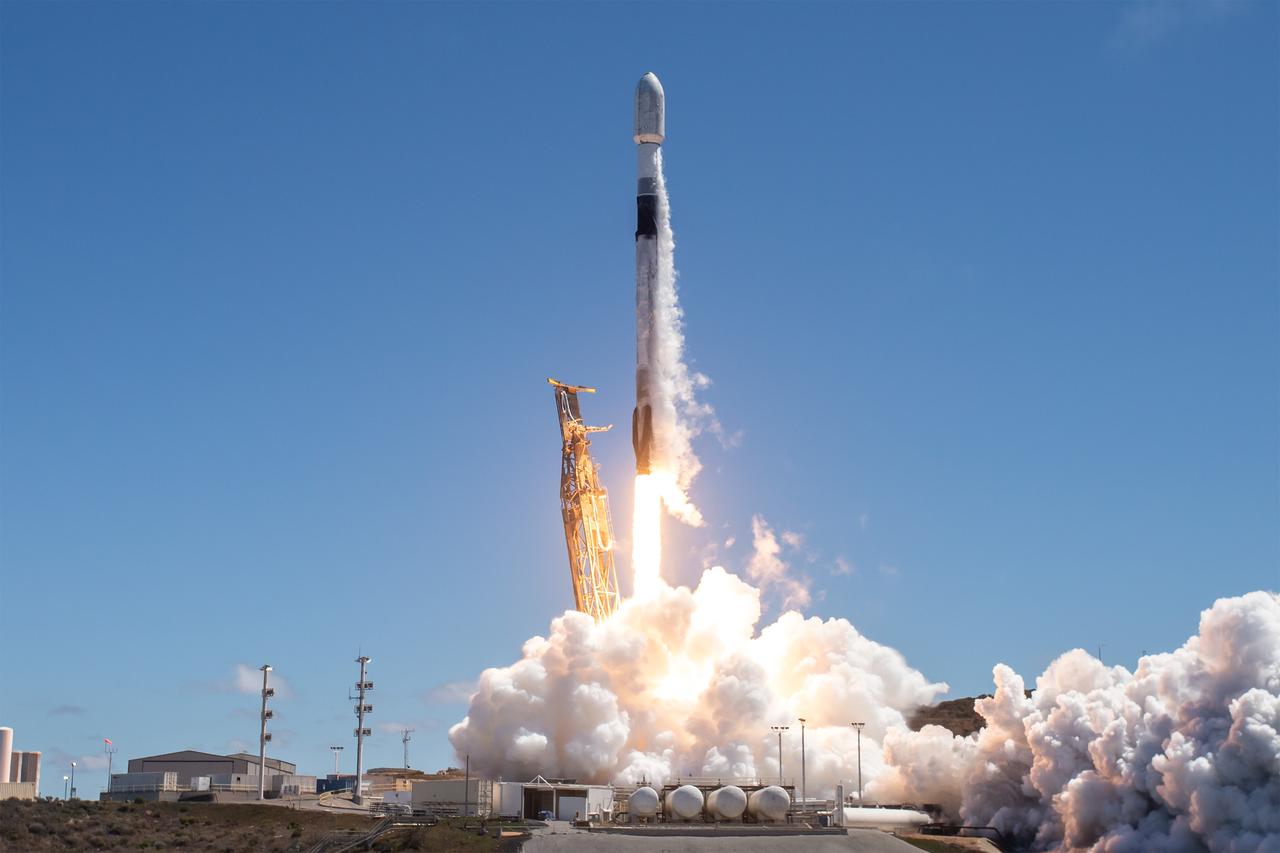

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
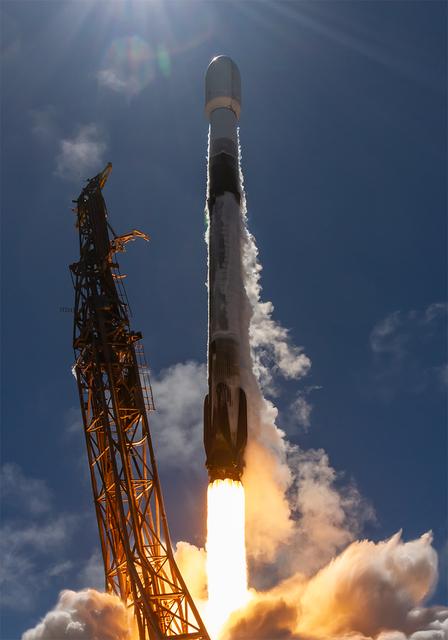

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.

NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission launches at 11:13 a.m. PDT (2:13 p.m. EDT) on Wednesday, July 23, 2025, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.

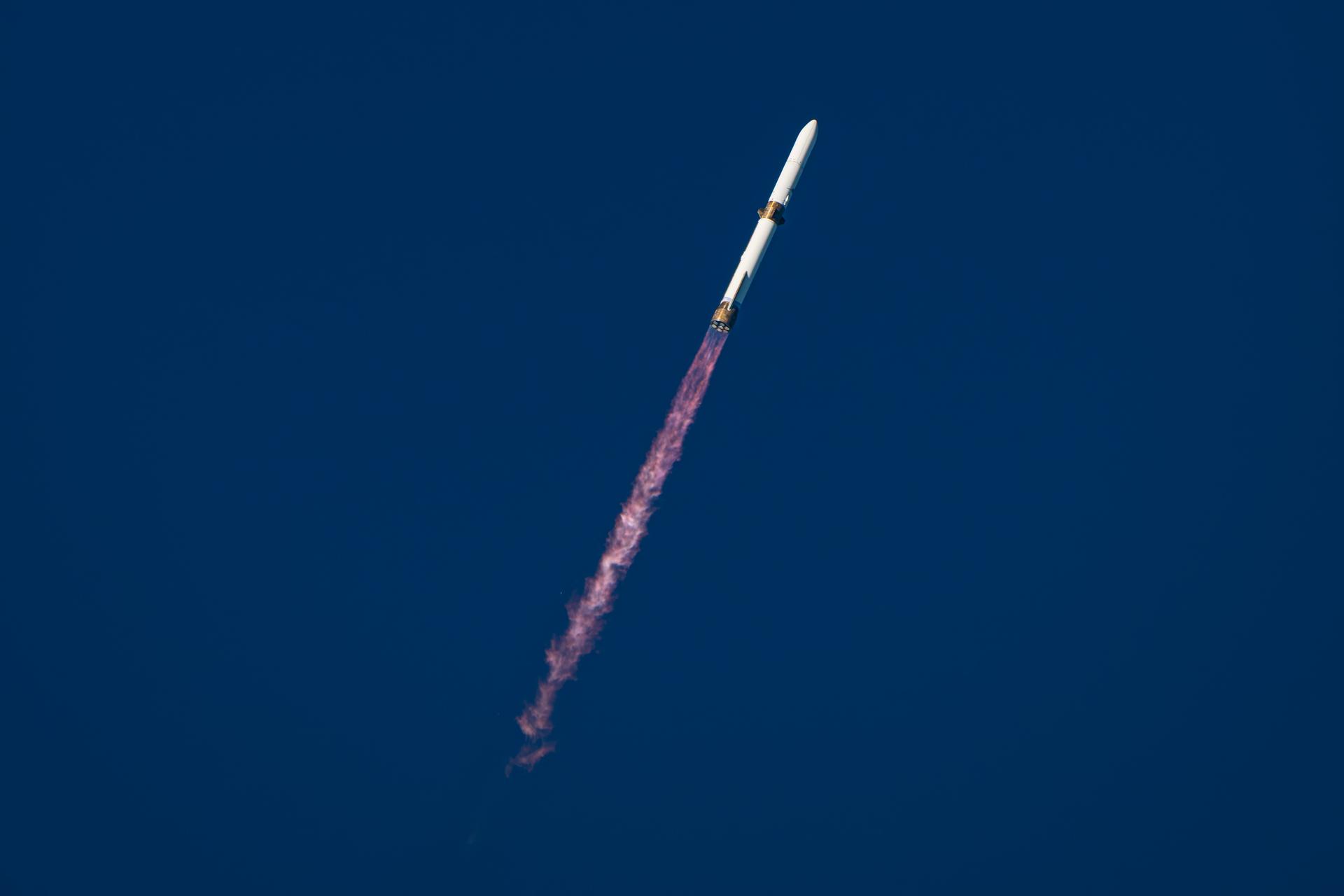
A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission stands vertical Tuesday, July 22, 2025, at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
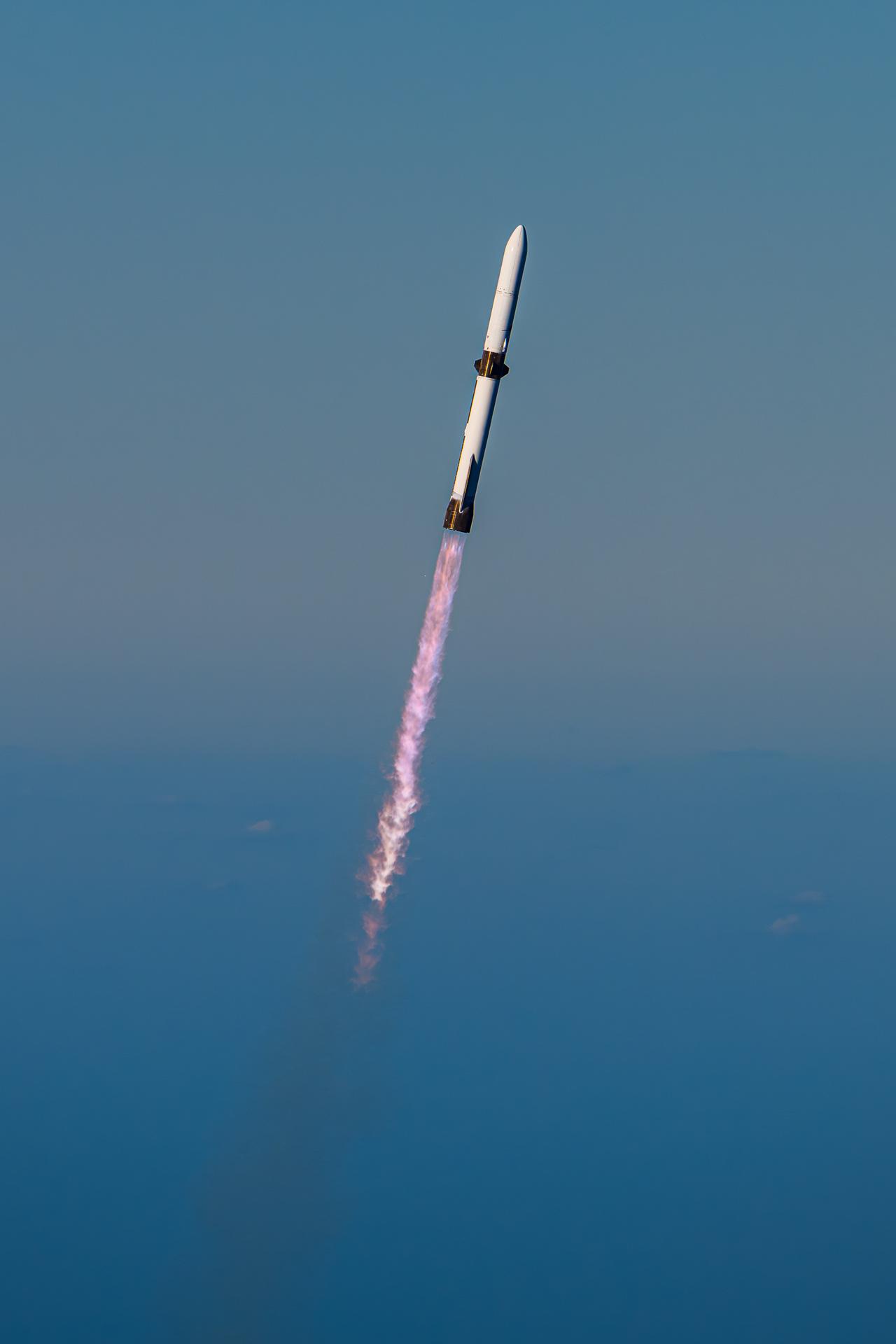

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
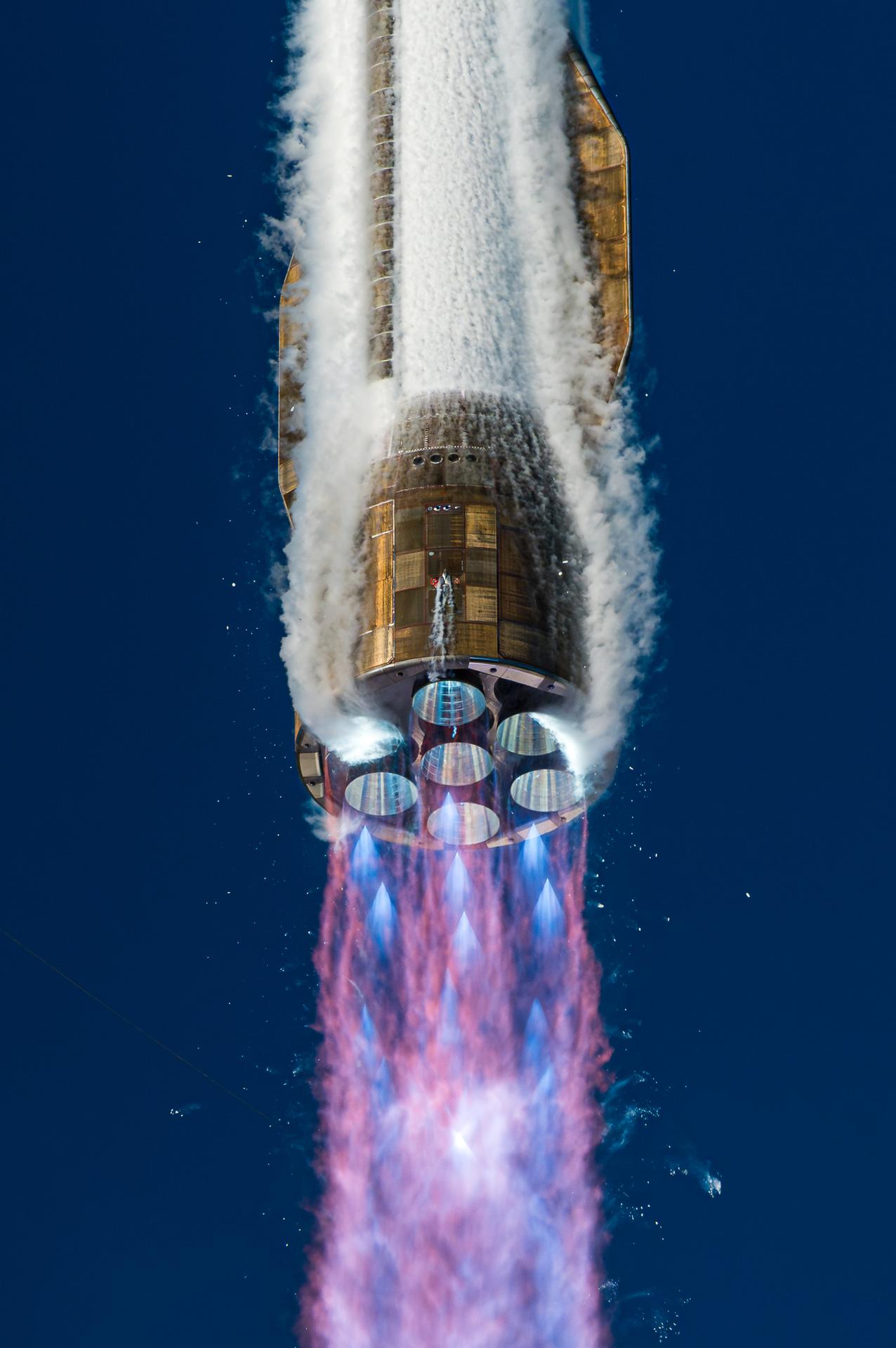

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
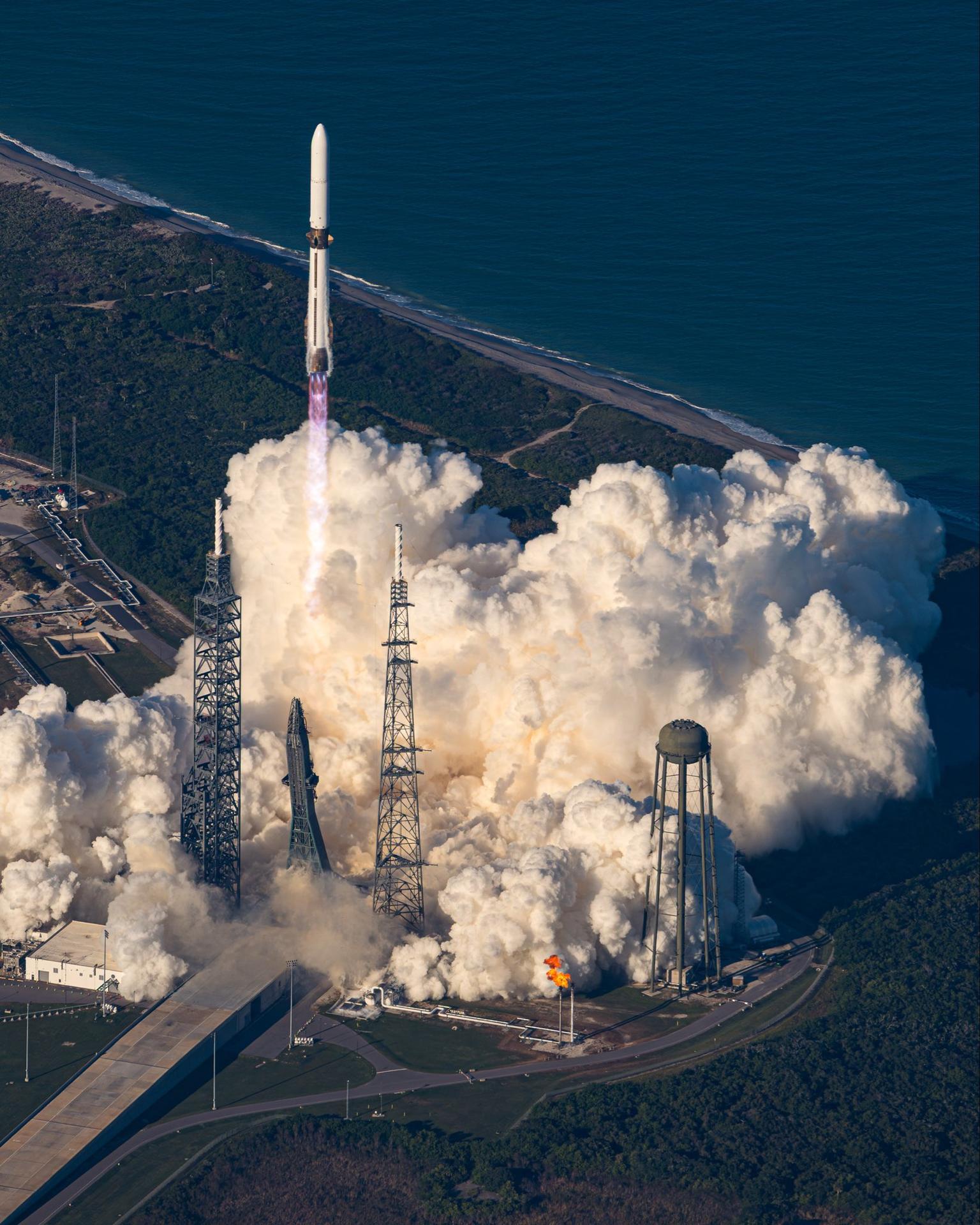

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
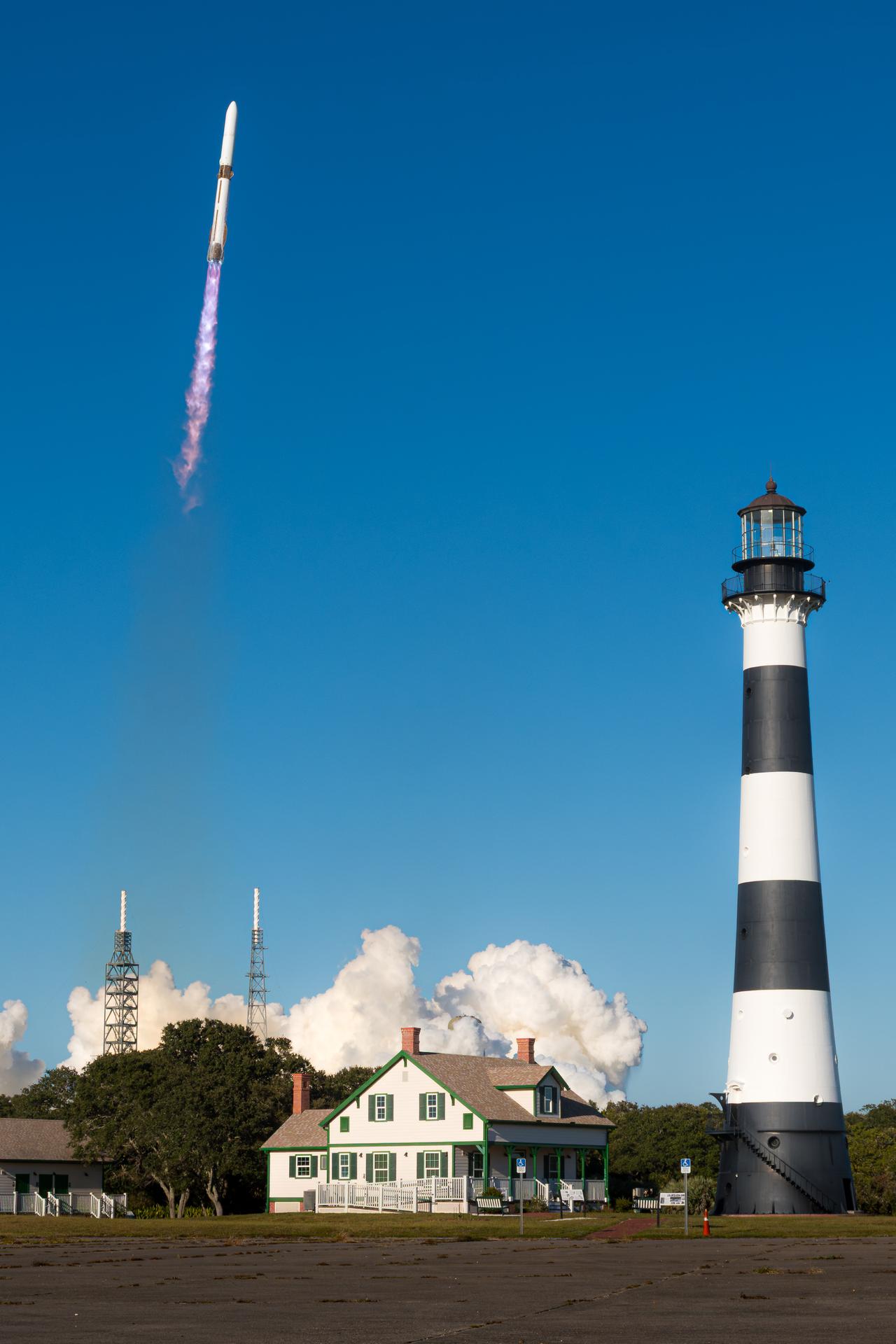

Near Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
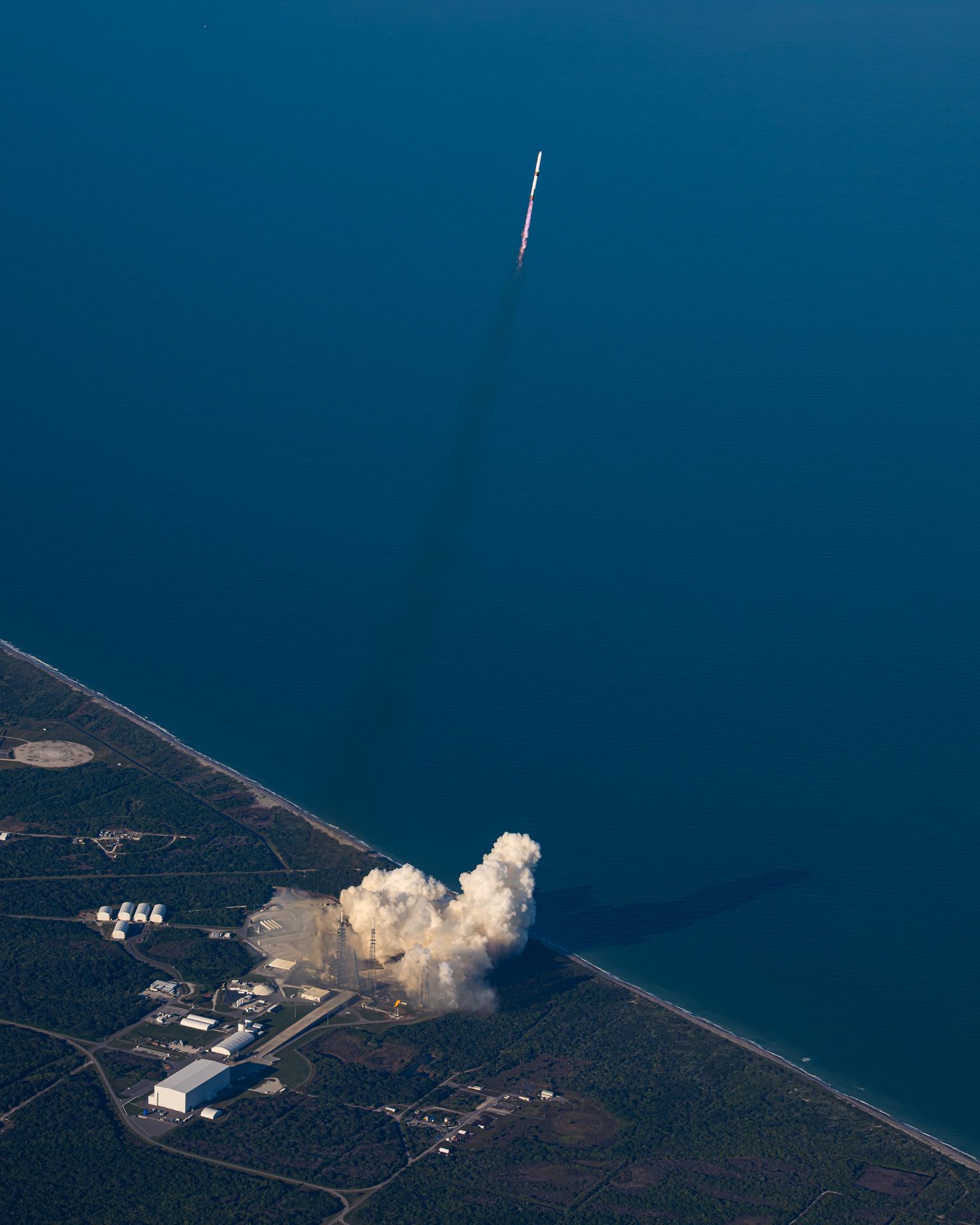

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
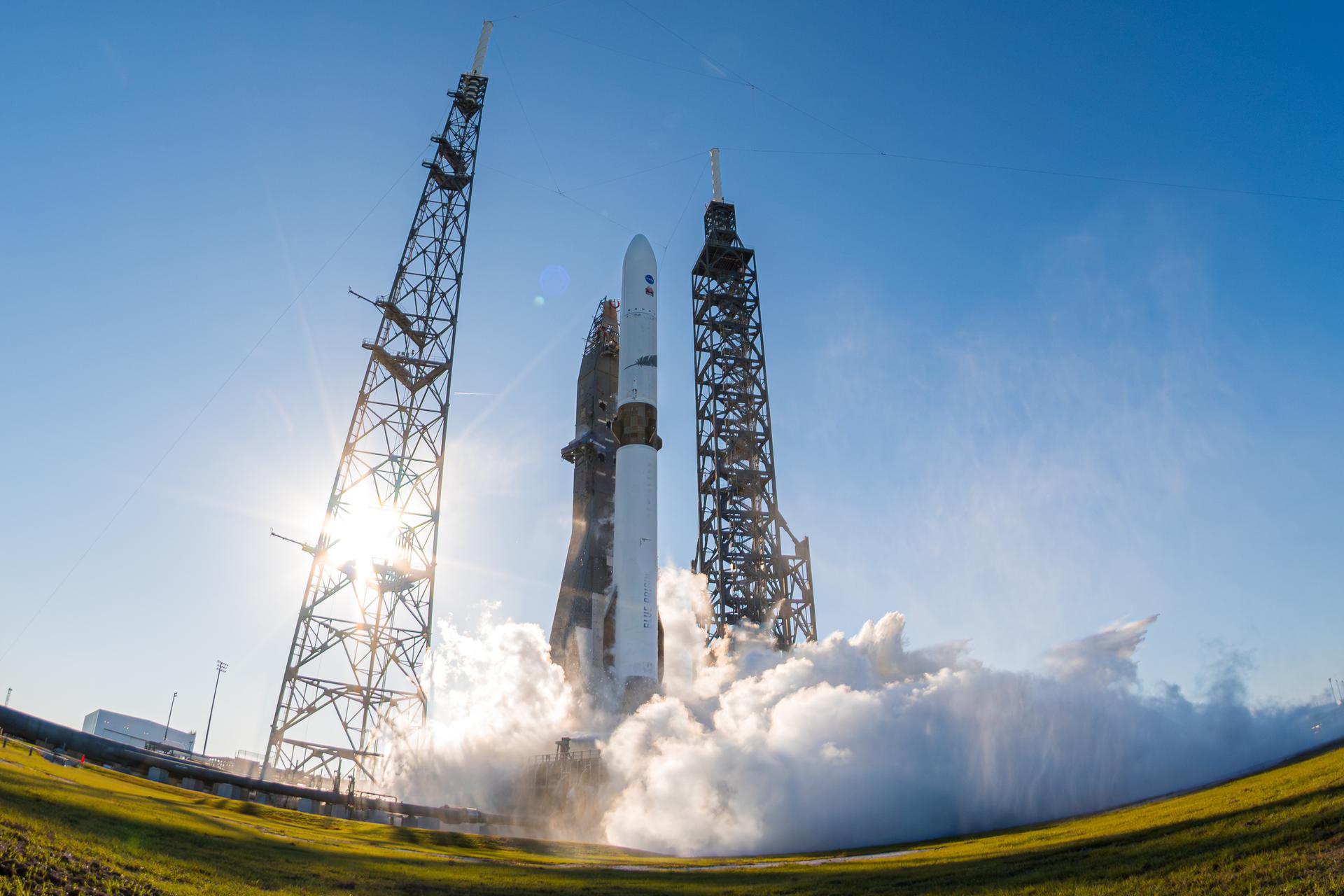

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn first stage rocket successfully lands for the first time on a drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean following the launching of NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
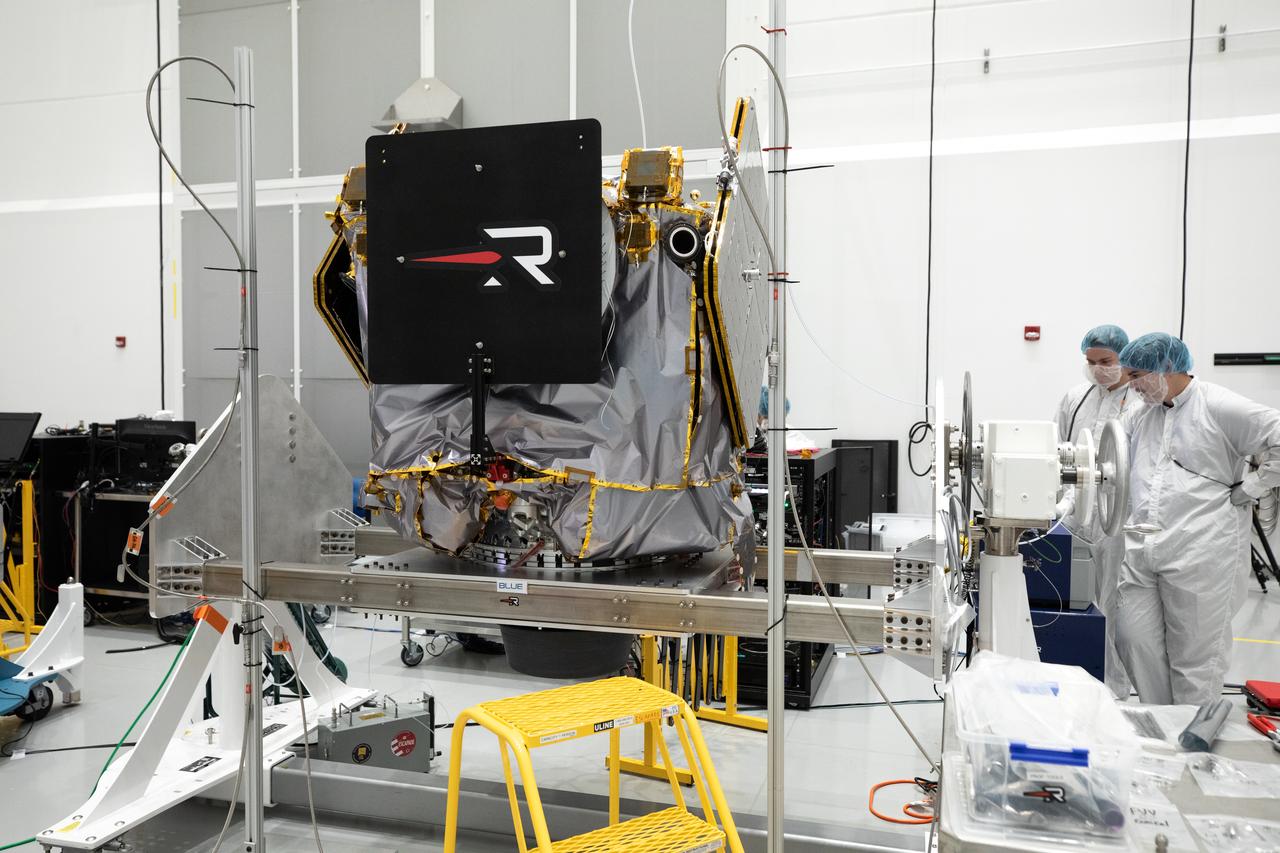

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
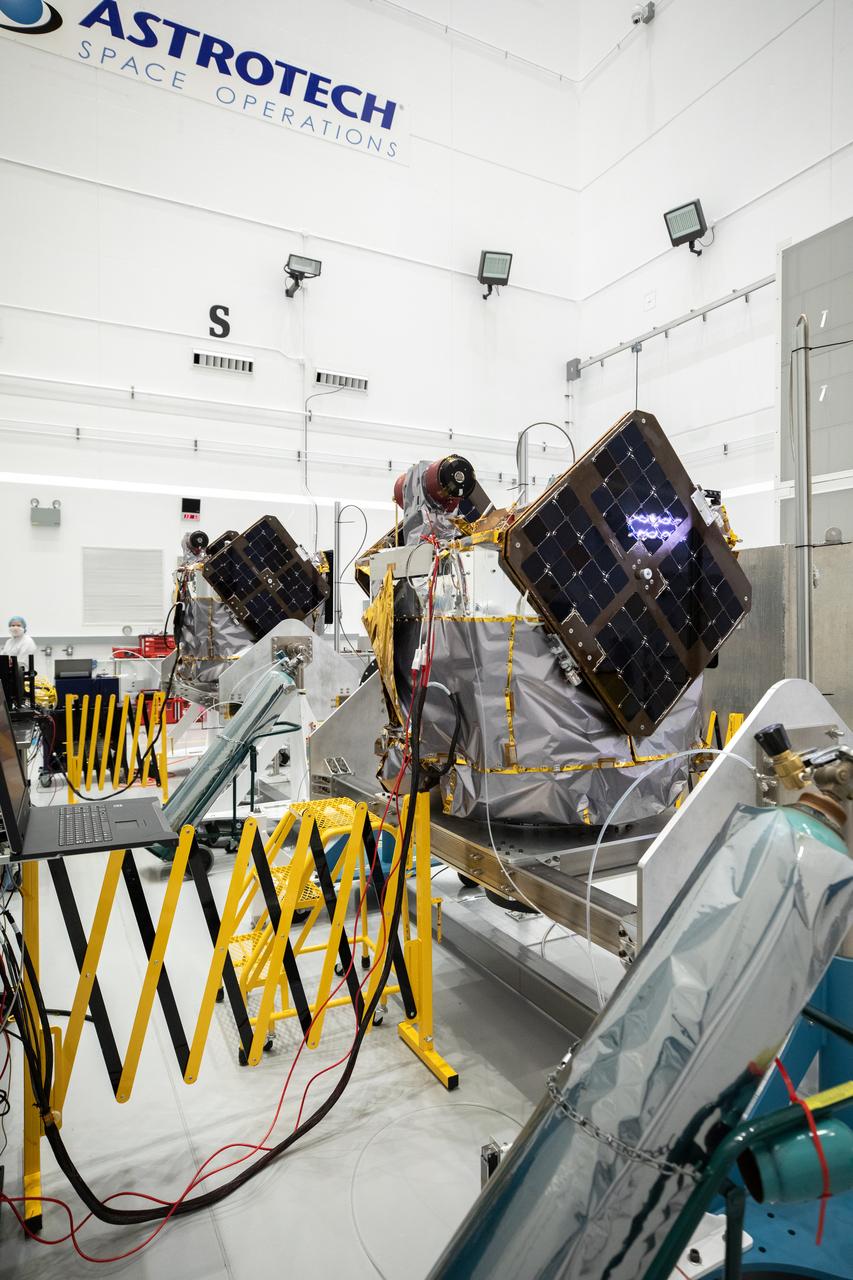

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
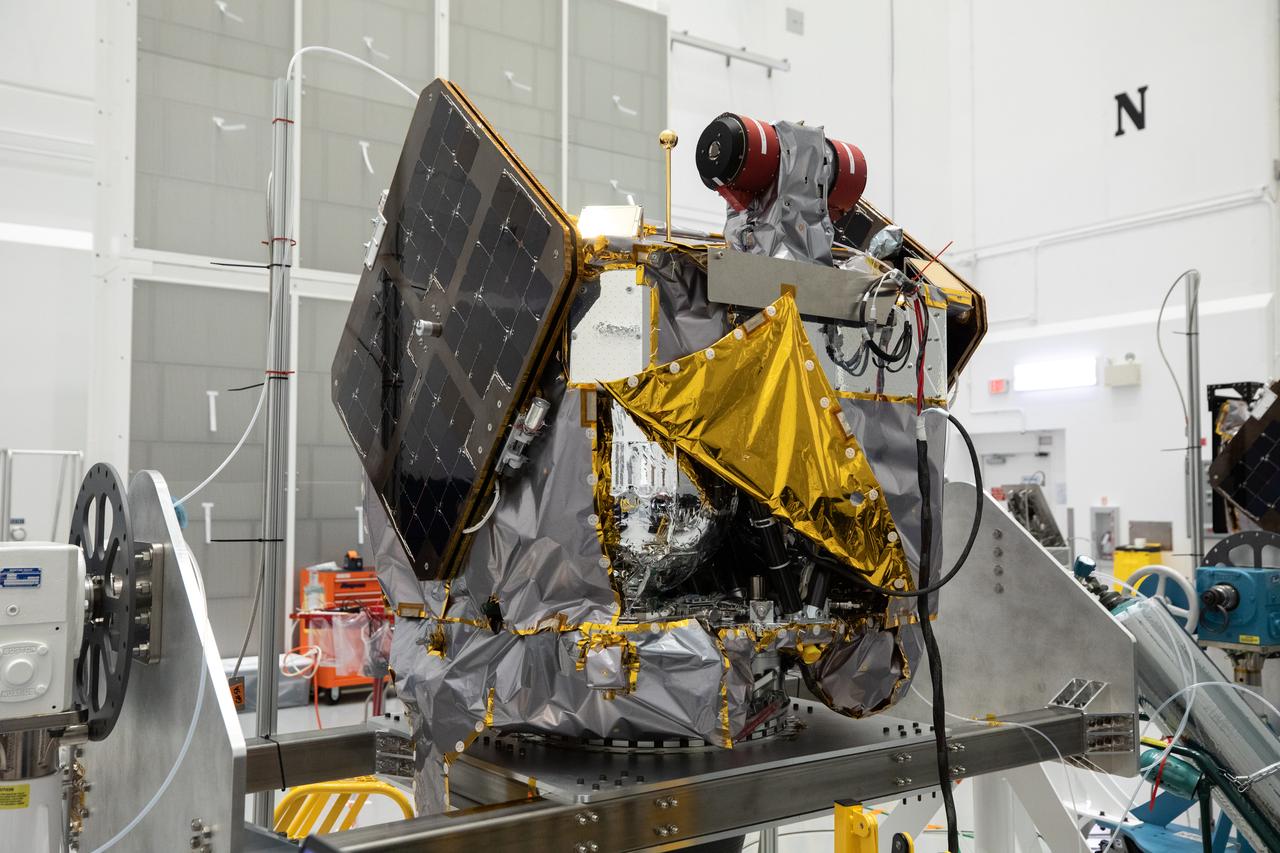

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
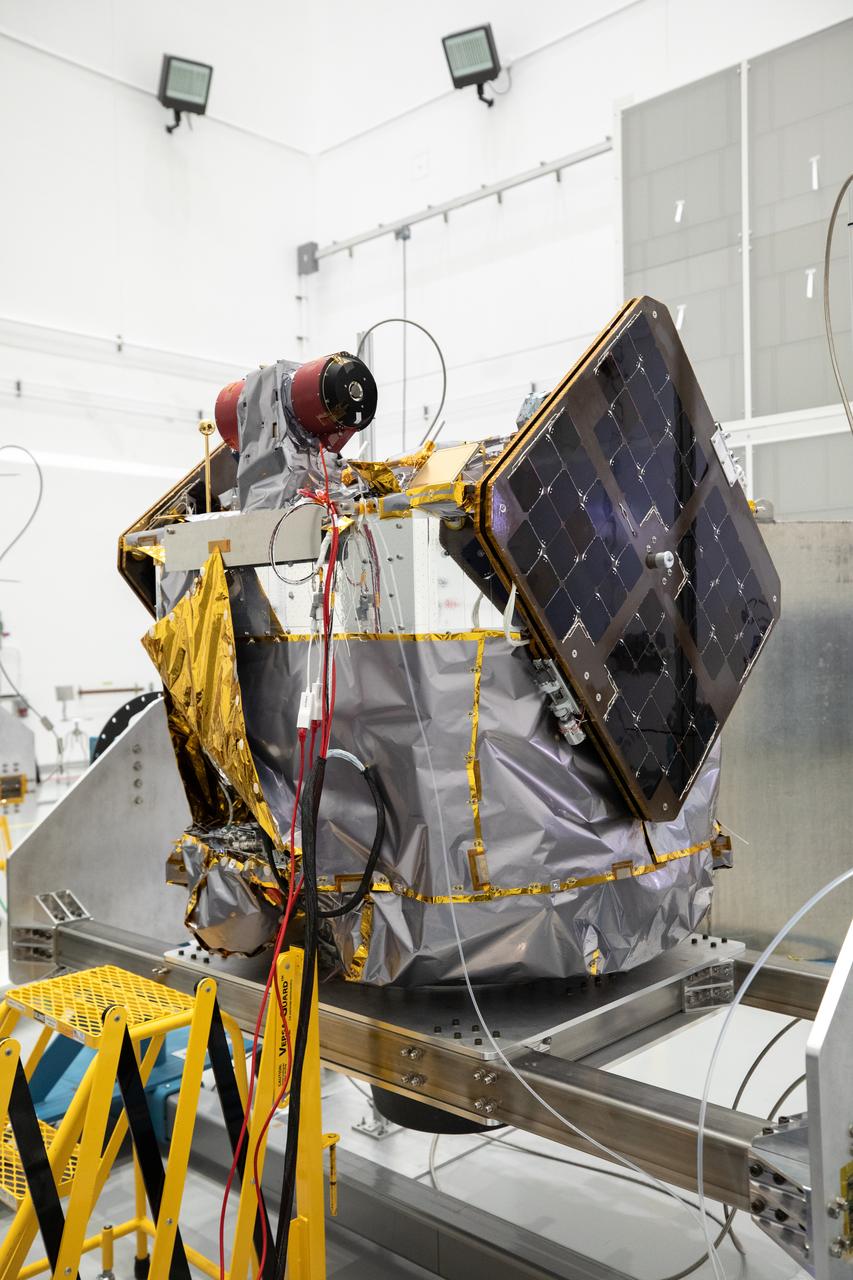

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
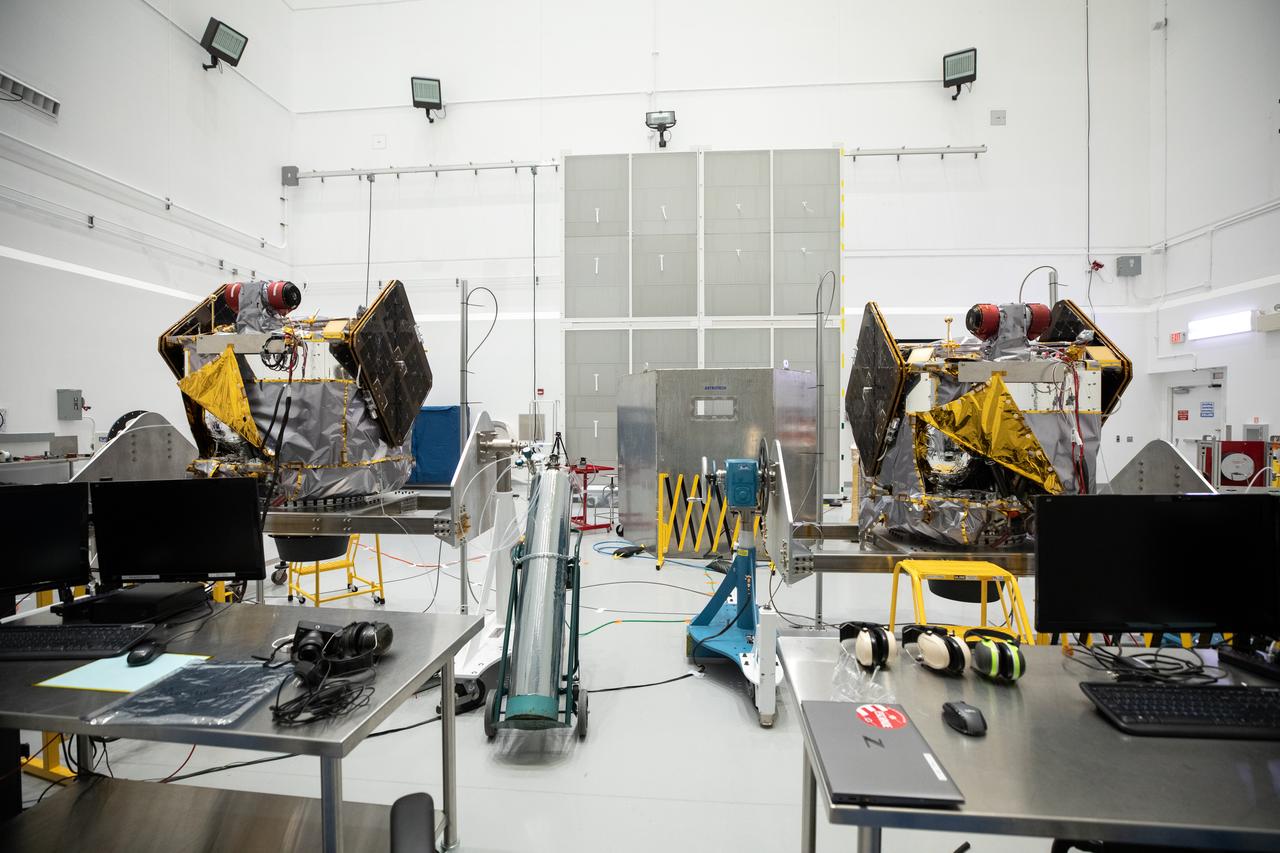

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
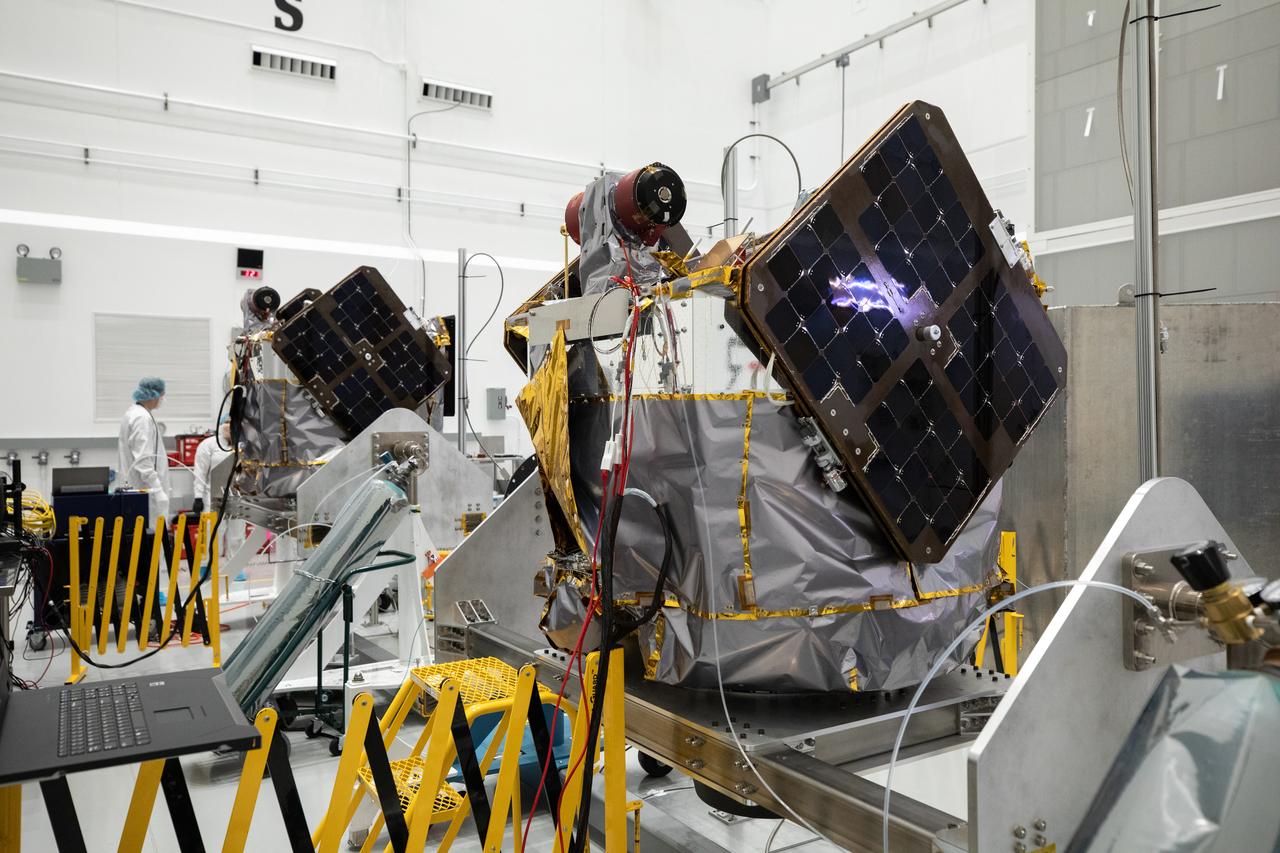

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
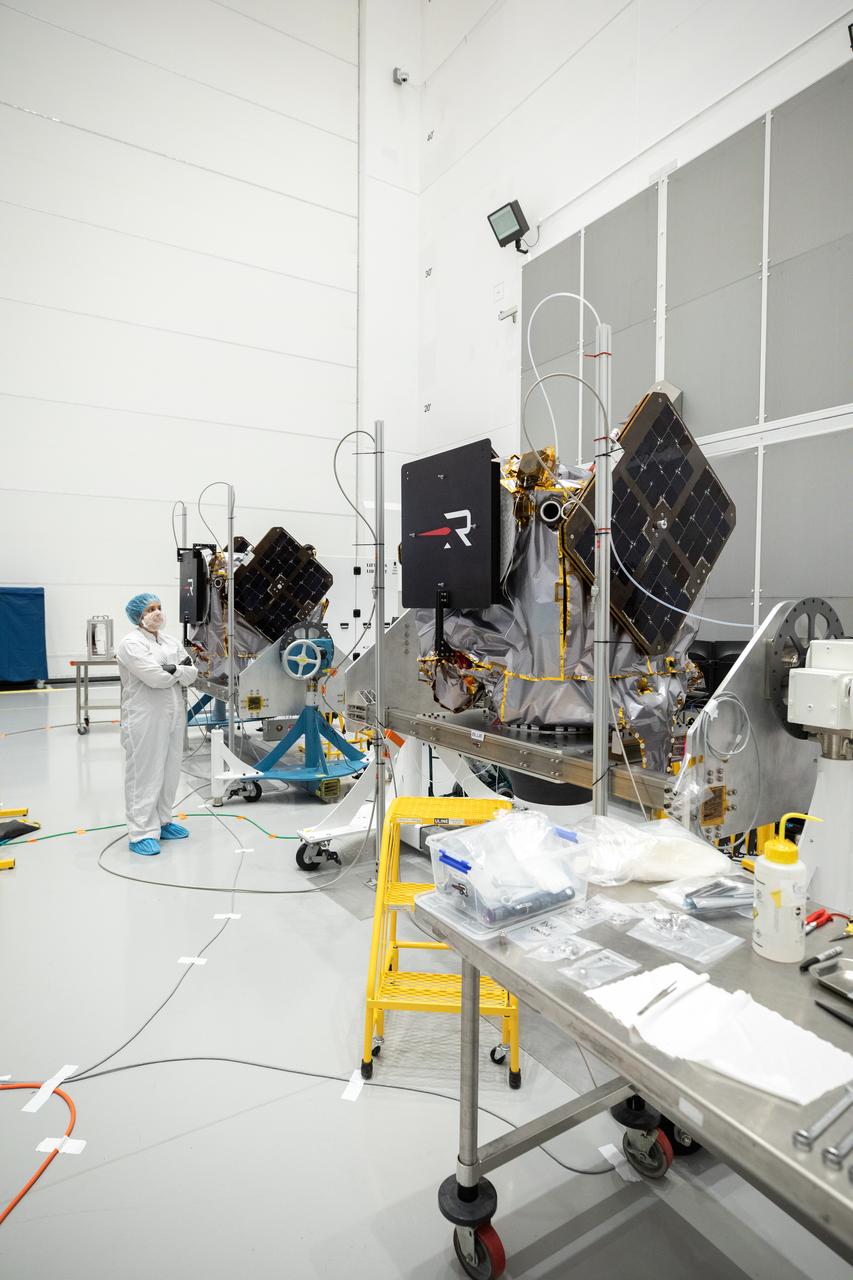

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
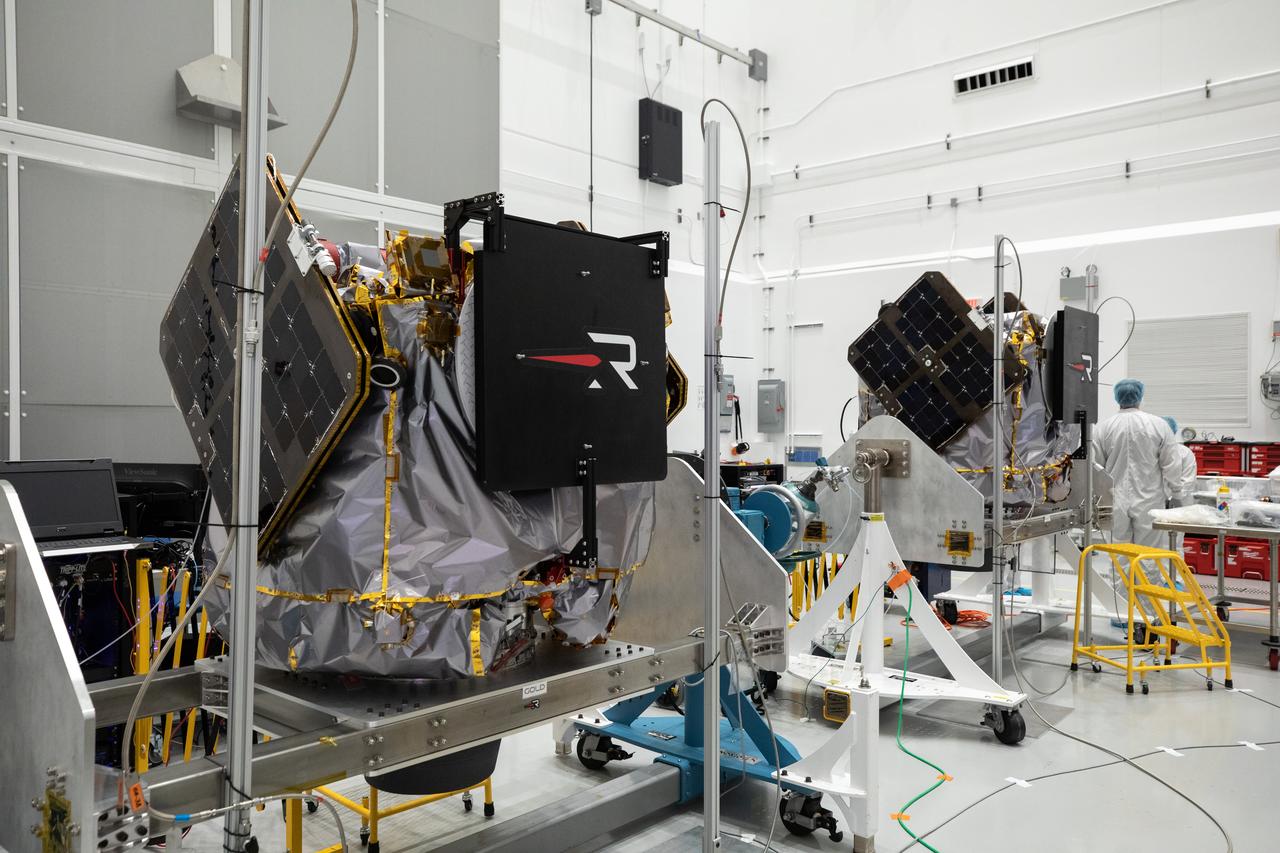

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.

NASA’s ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) identical dual spacecraft are inspected and processed on dollies in a high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations Facility near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Thursday, Aug. 22, 2024. As the first multi-spacecraft orbital science mission to Mars, ESCAPADE’s twin orbiters will take simultaneous observations from different locations around the planet and reveal the real-time response to space weather and how the Martian magnetosphere changes over time.
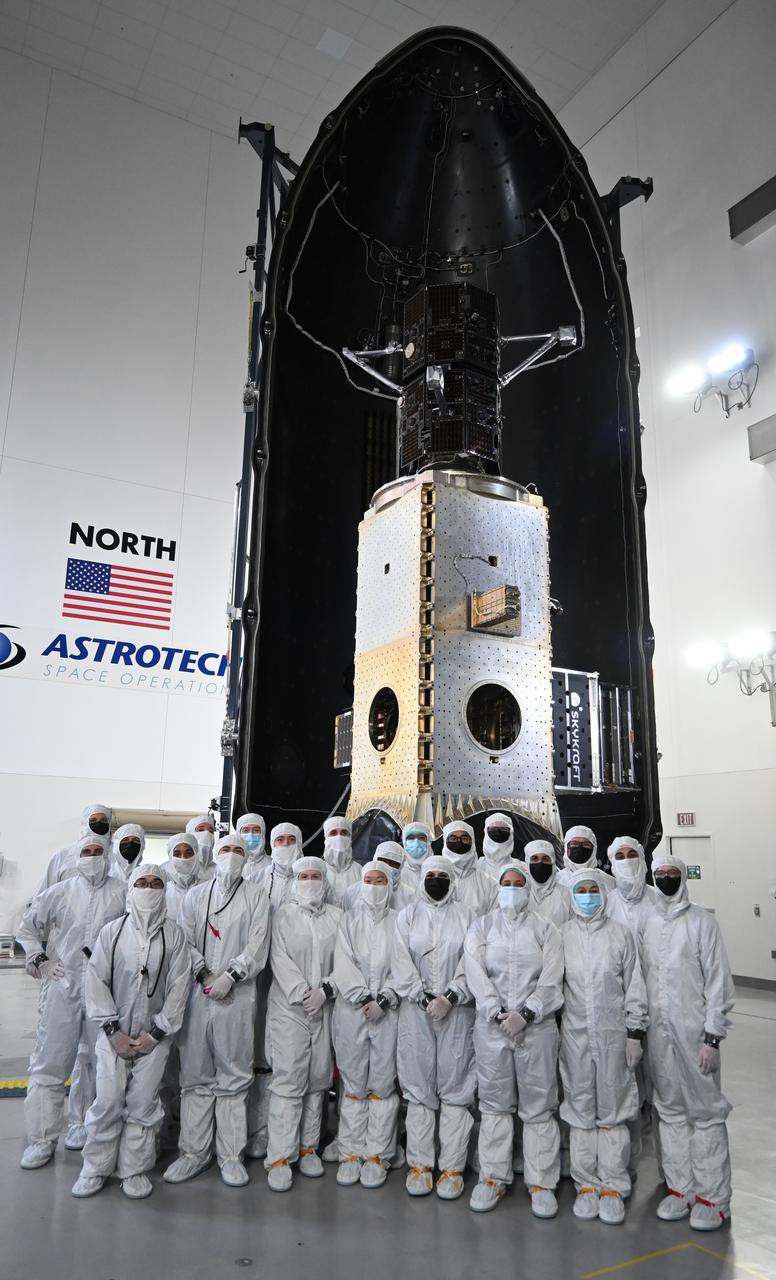

Technicians encapsulate the black twin satellites of NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission within a payload fairing atop a shiny metallic stack of several other rideshare payloads at the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California. The TRACERS mission is a pair of twin satellites that will study how Earth’s magnetic shield — the magnetosphere — protects our planet from the supersonic stream of material from the Sun called solar wind.

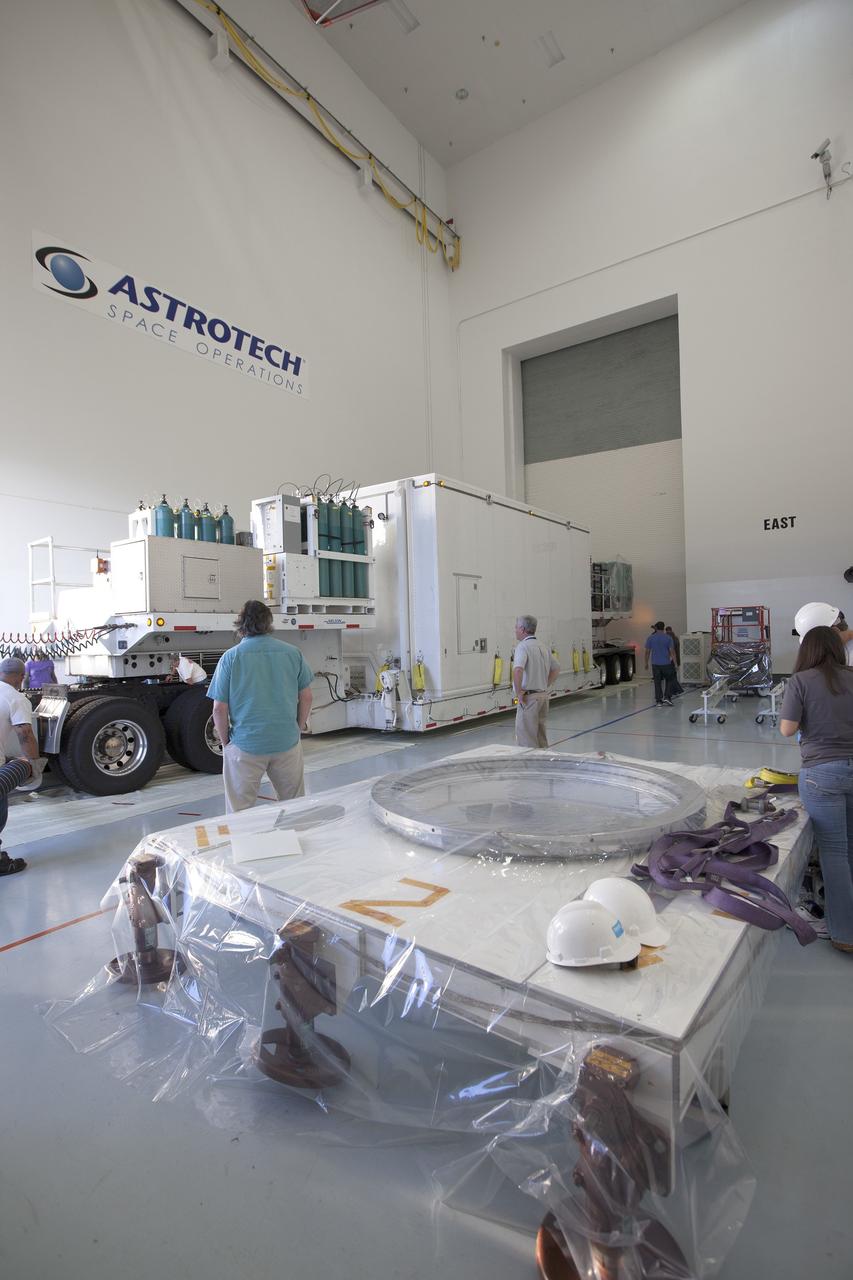
Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are transported to the airlock of Building 1 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
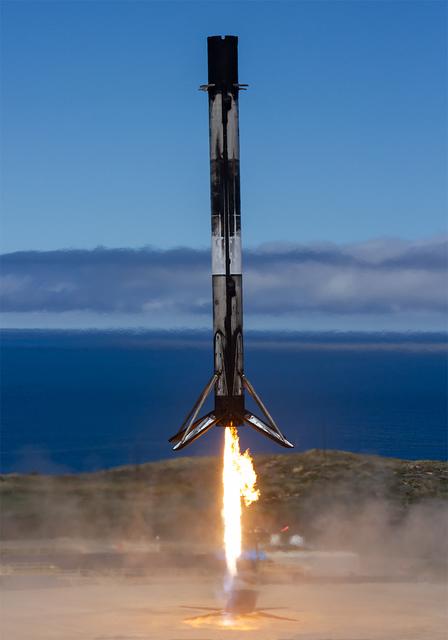

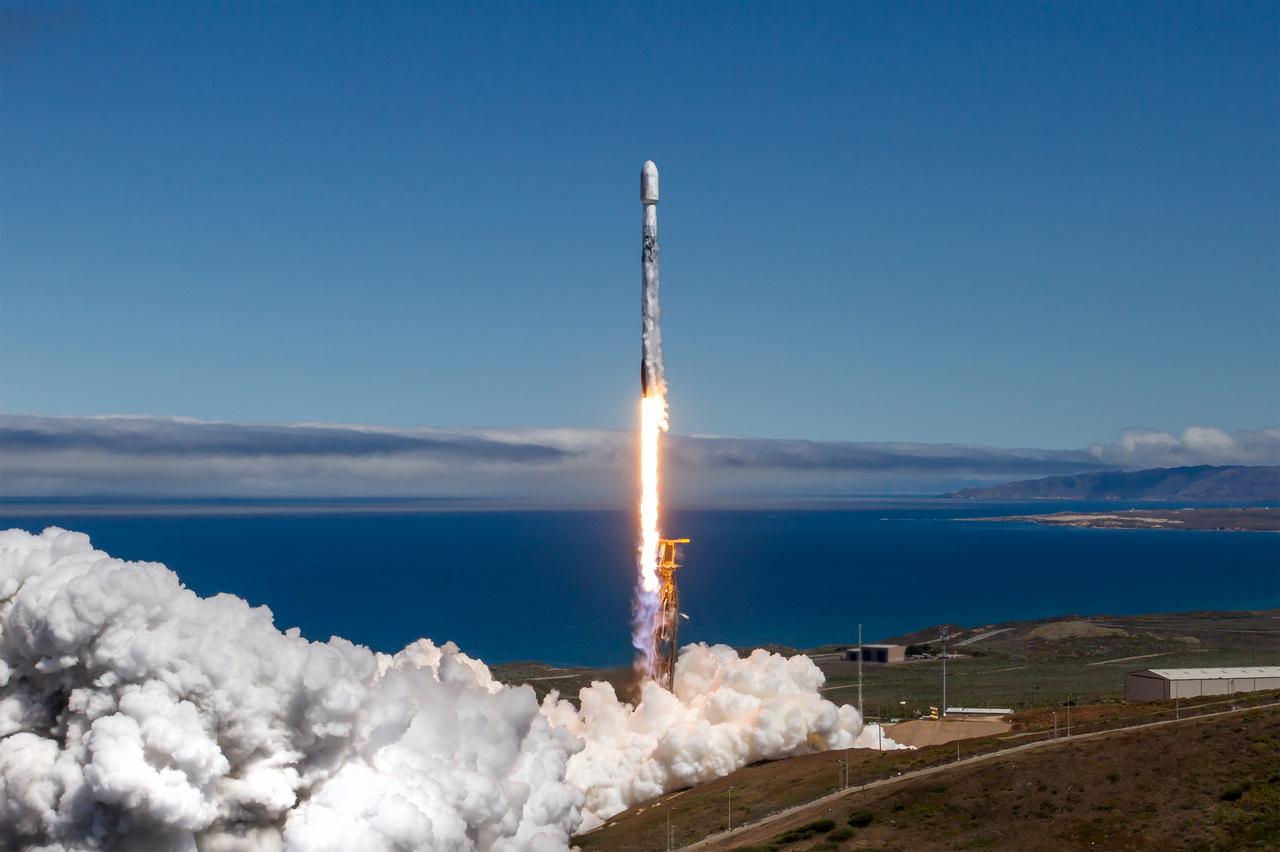
A SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage booster lands on Landing Zone 4 following liftoff of NASA’s TRACERS (Tandem Reconnection and Cusp Electrodynamics Reconnaissance Satellites) mission at Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Wednesday, July 23, 2025. This was the 16th flight for the first stage booster, which has previously launched these NASA missions - PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem, NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7, and Commercial Resupply Services-29. The TRACERS mission will study magnetic reconnection around Earth — a process in which electrically charged plasmas exchange energy in the atmosphere — to understand how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with the magnetosphere, Earth’s protective magnetic shield.
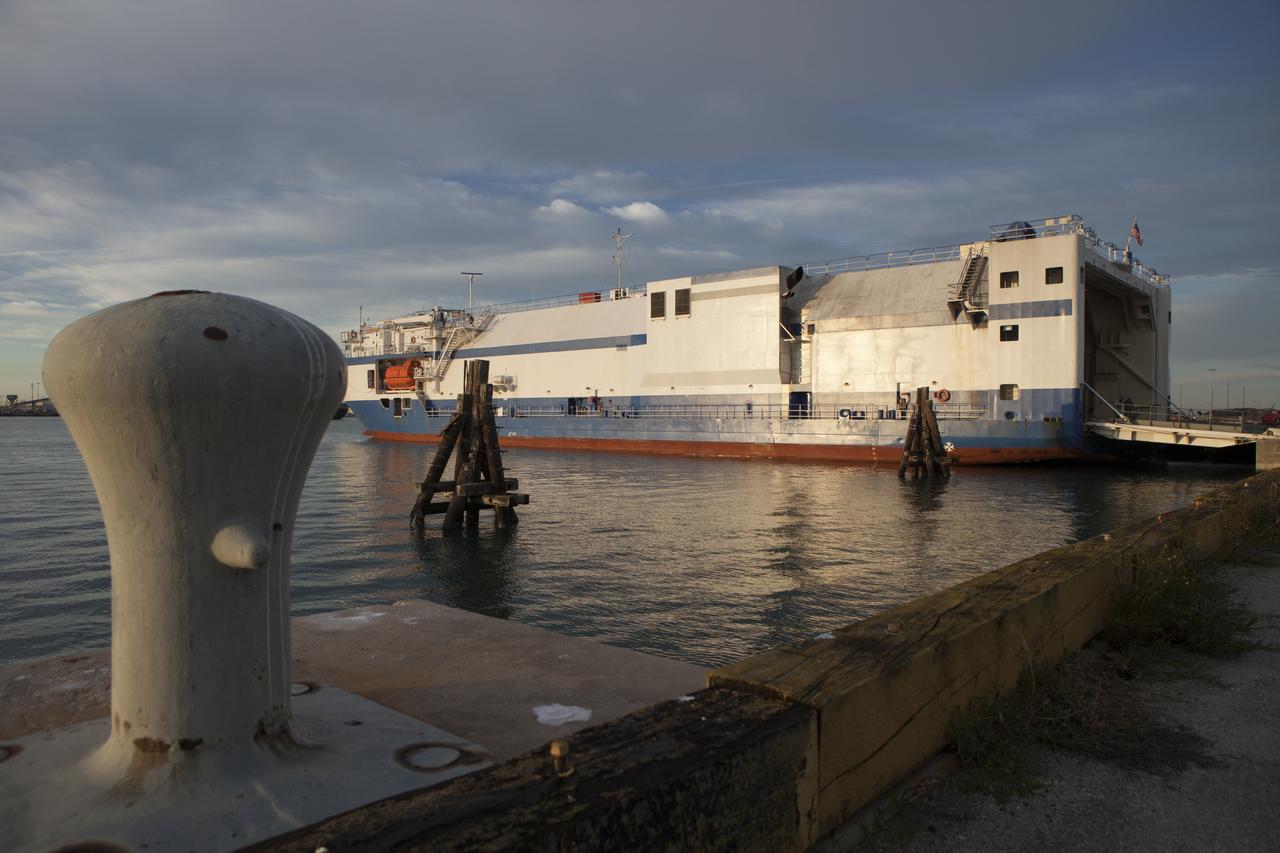

The United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner arrives at Port Canaveral to deliver the Atlas V rocket that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
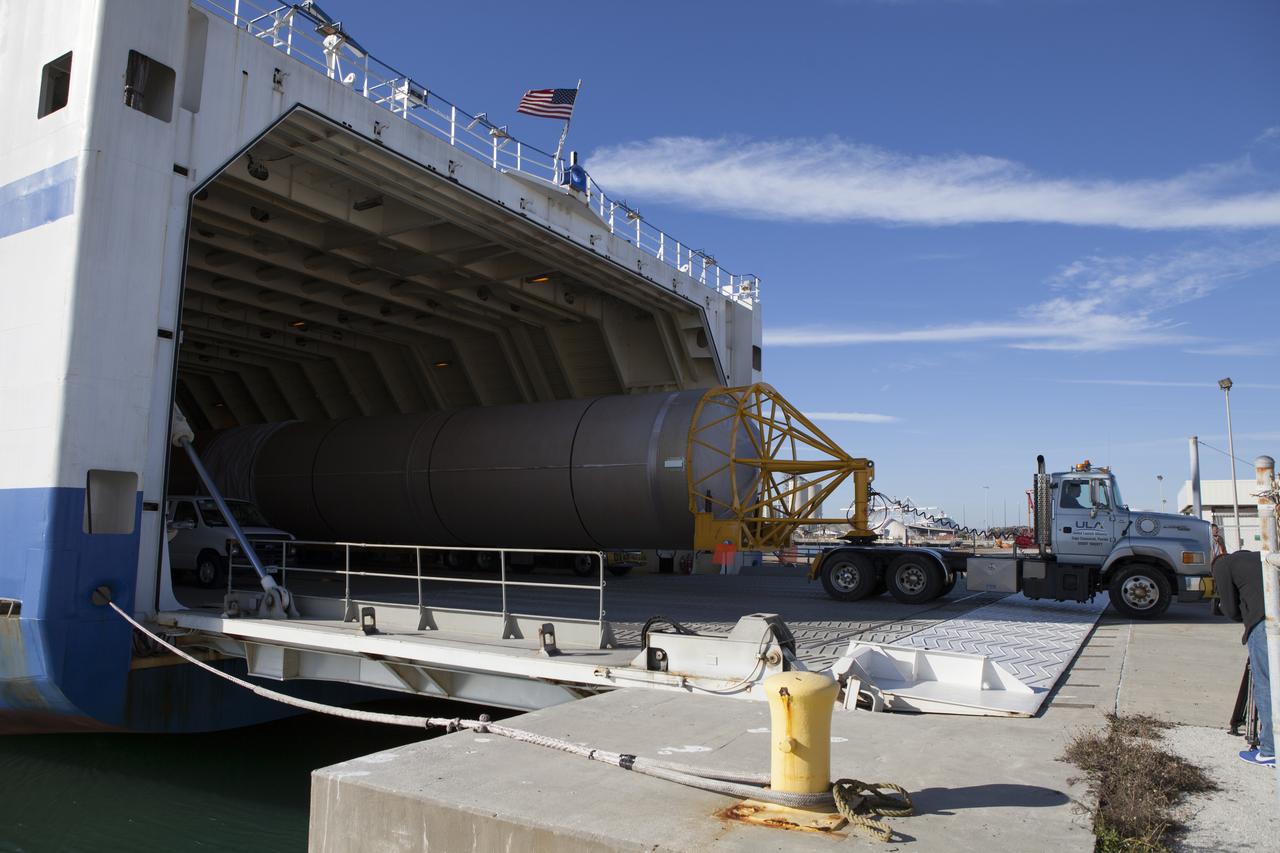

A truck begins to transport the Atlas V booster stage from the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
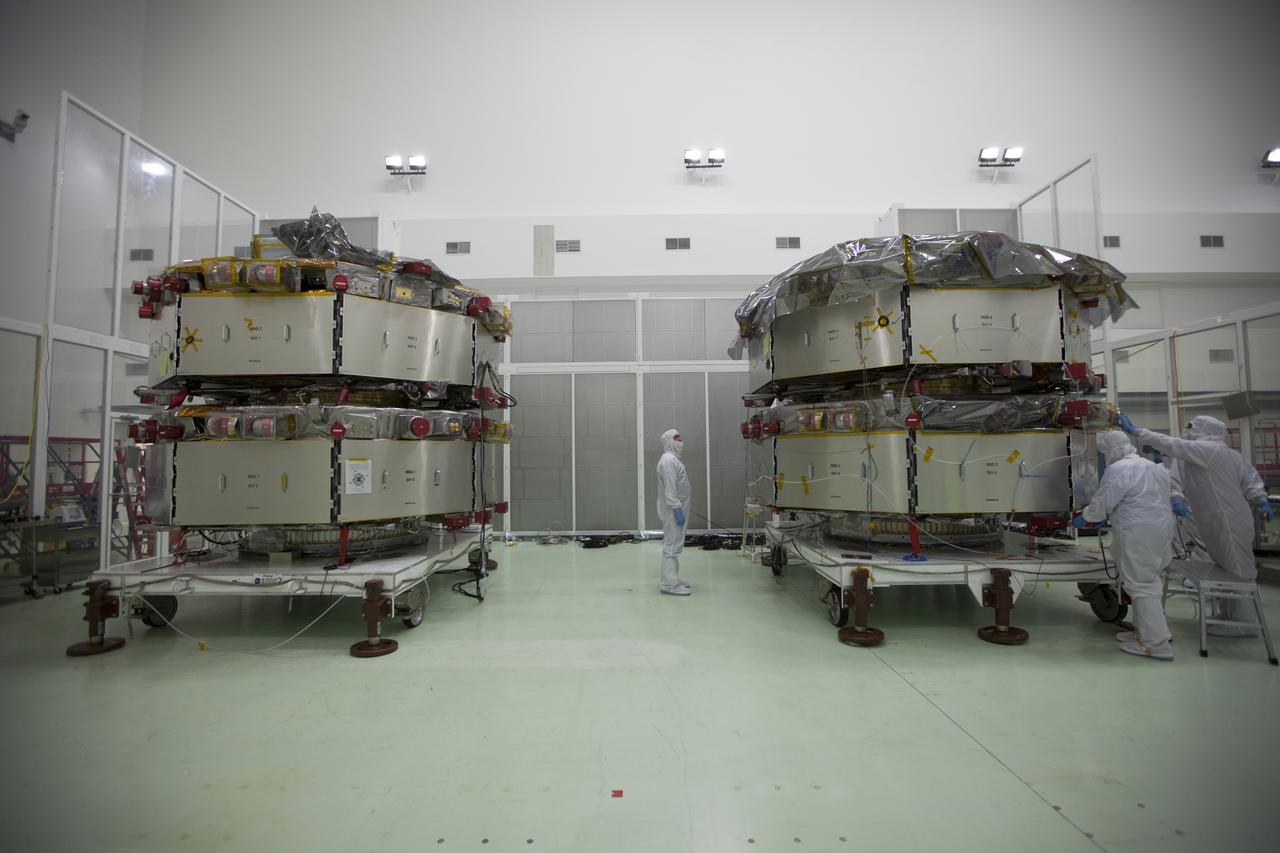

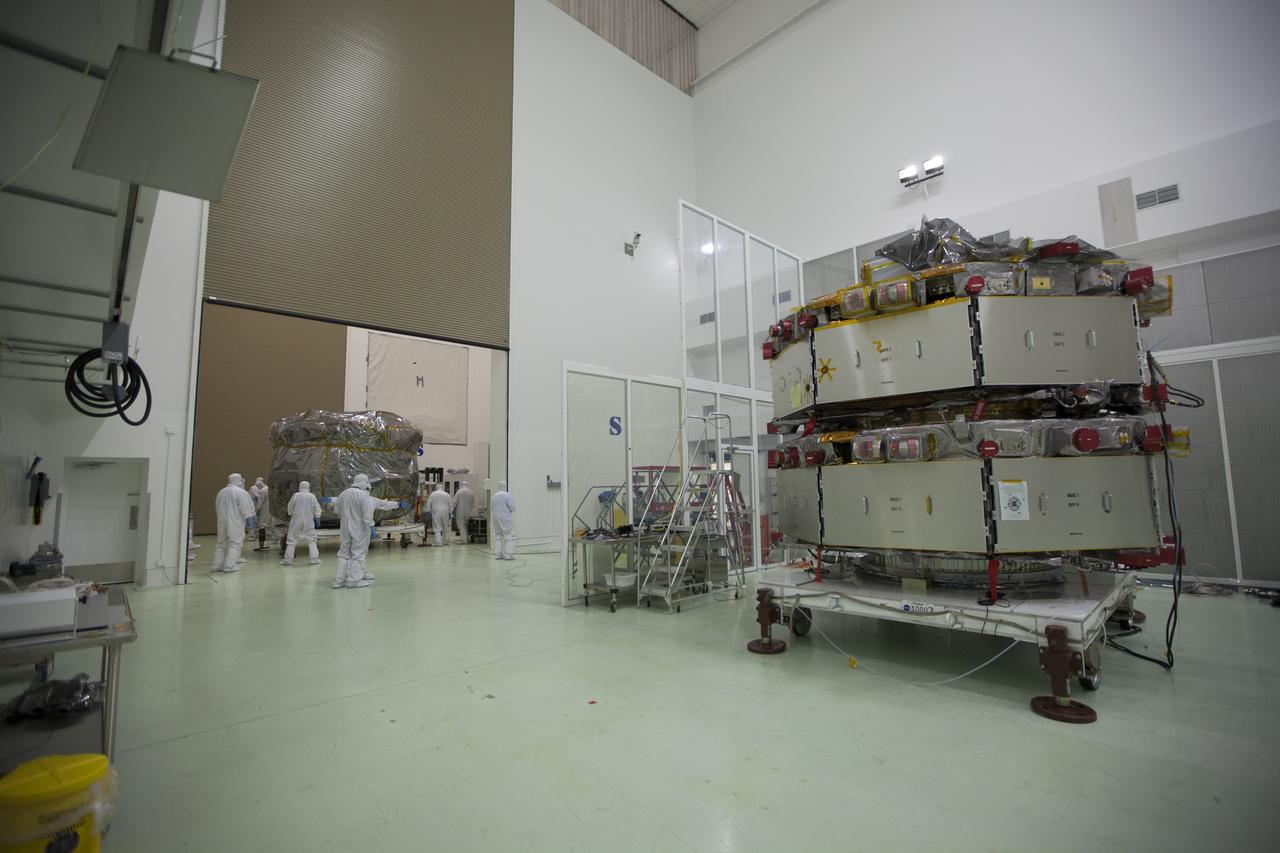
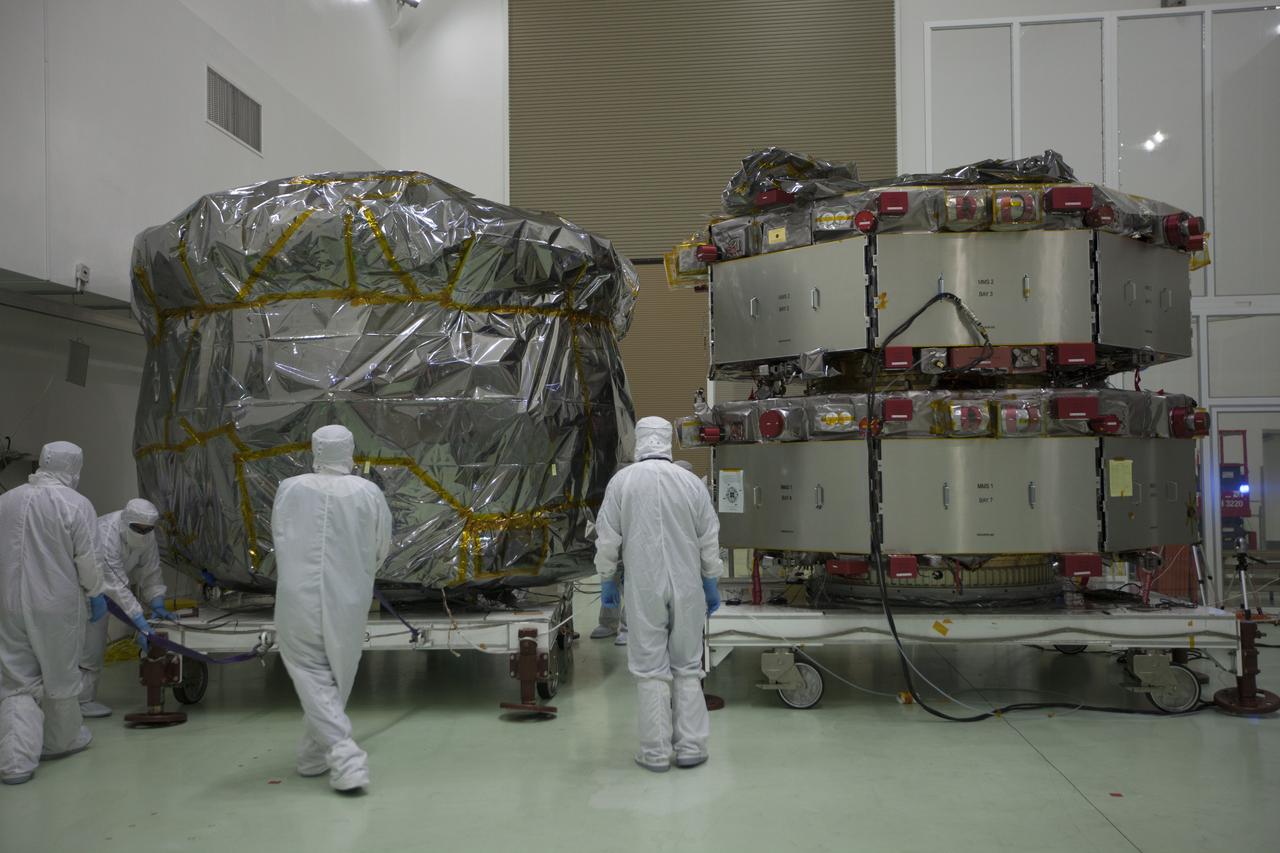
All four of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft have arrived in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack arrive in the Building 1 airlock of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack, in the high bay uat right, arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale , or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are lowered onto a payload dolly in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
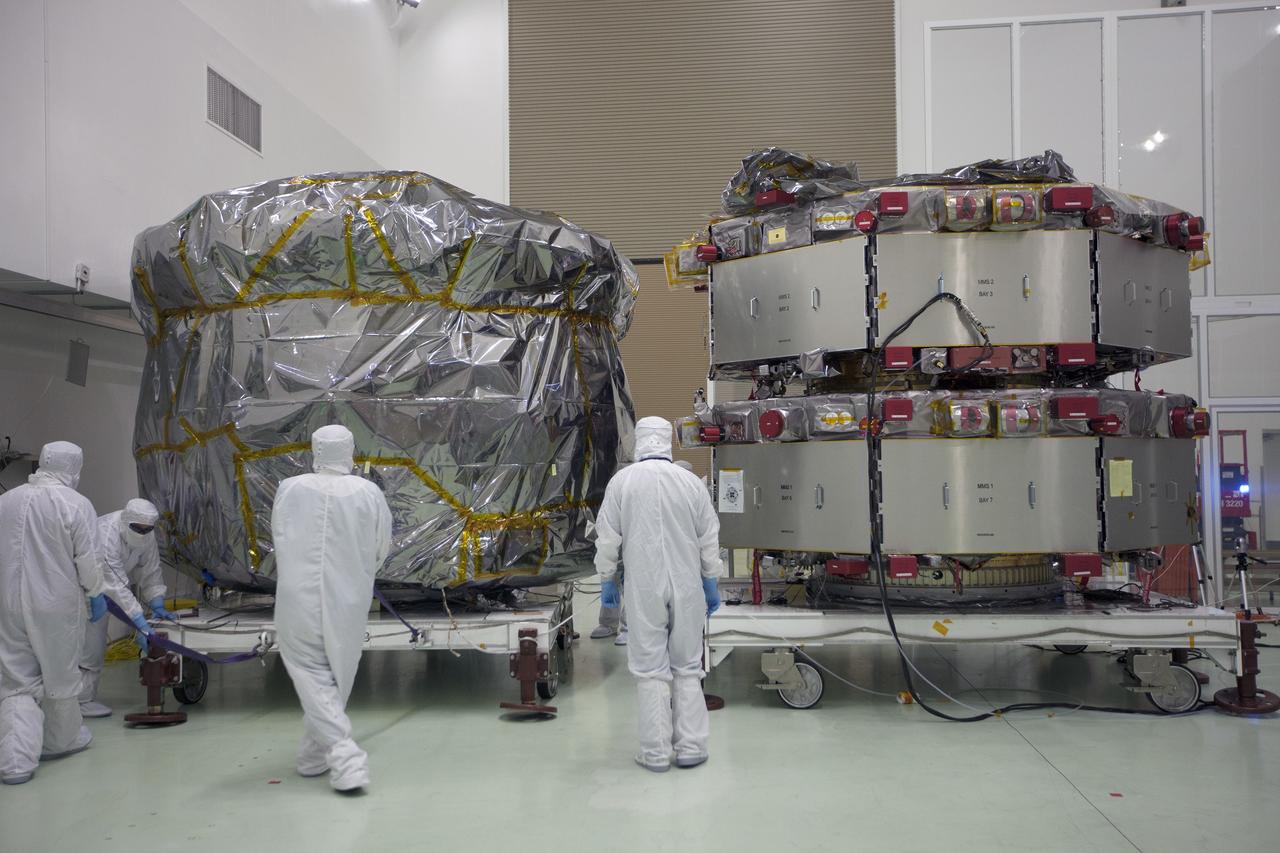

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack, at left, arrive in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack, at right, arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are towed between Buildings 1 and 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

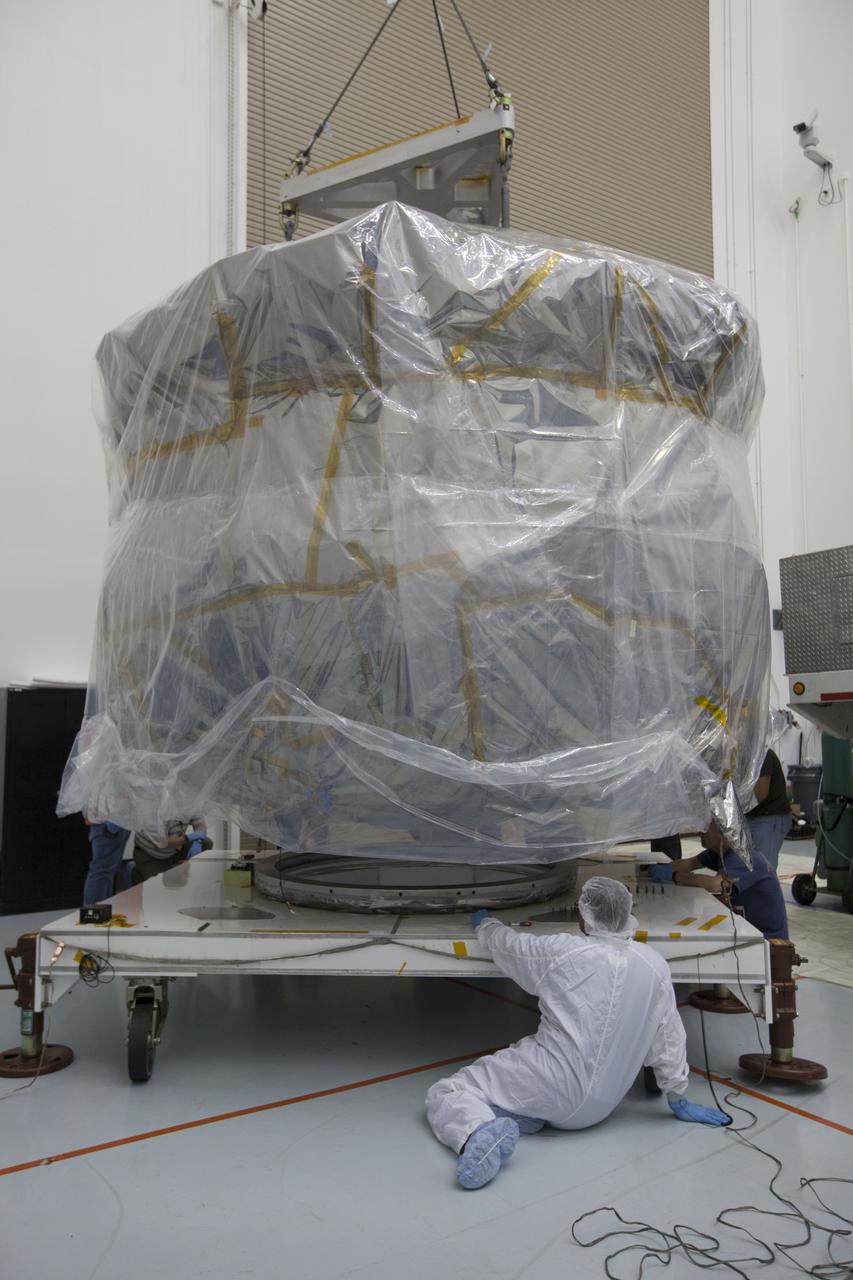
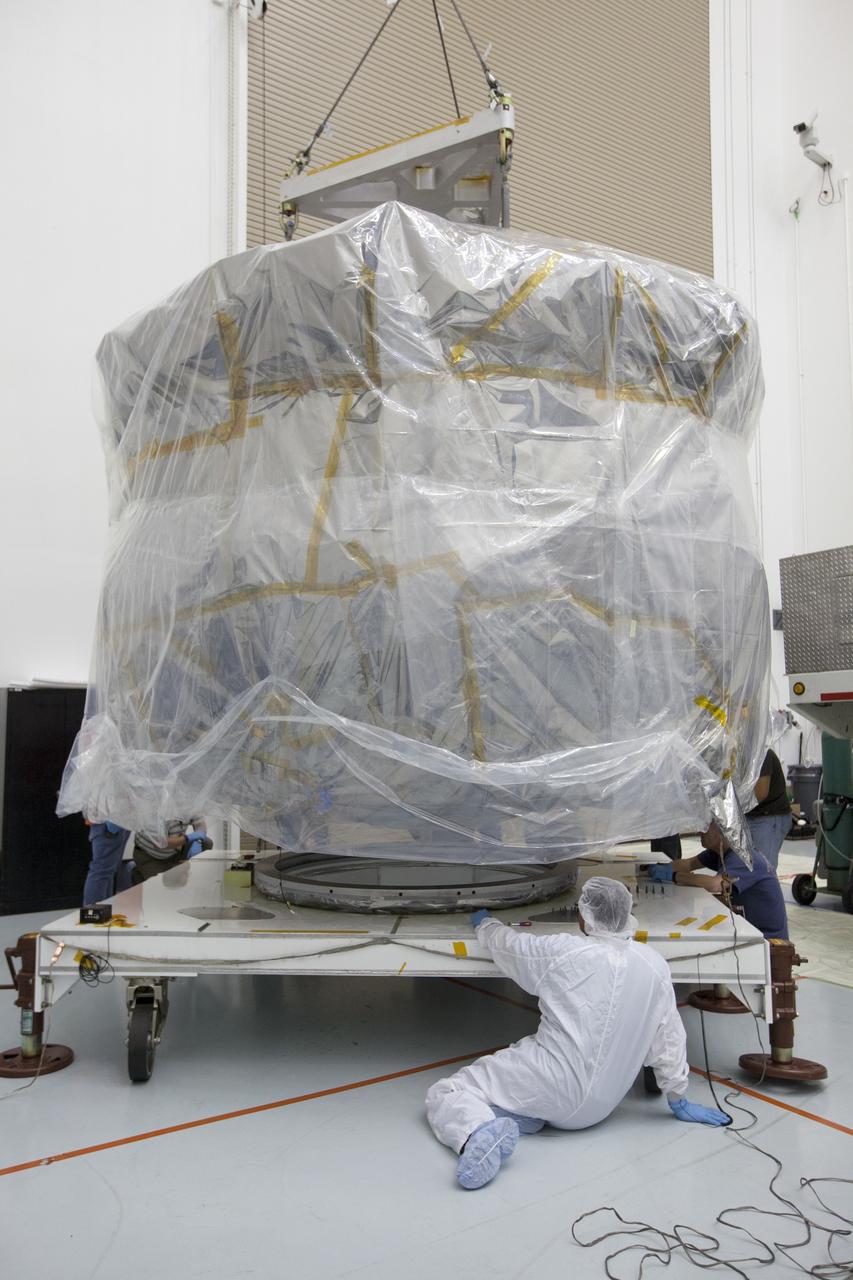
The protective shipping container is removed from around the upper stack of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
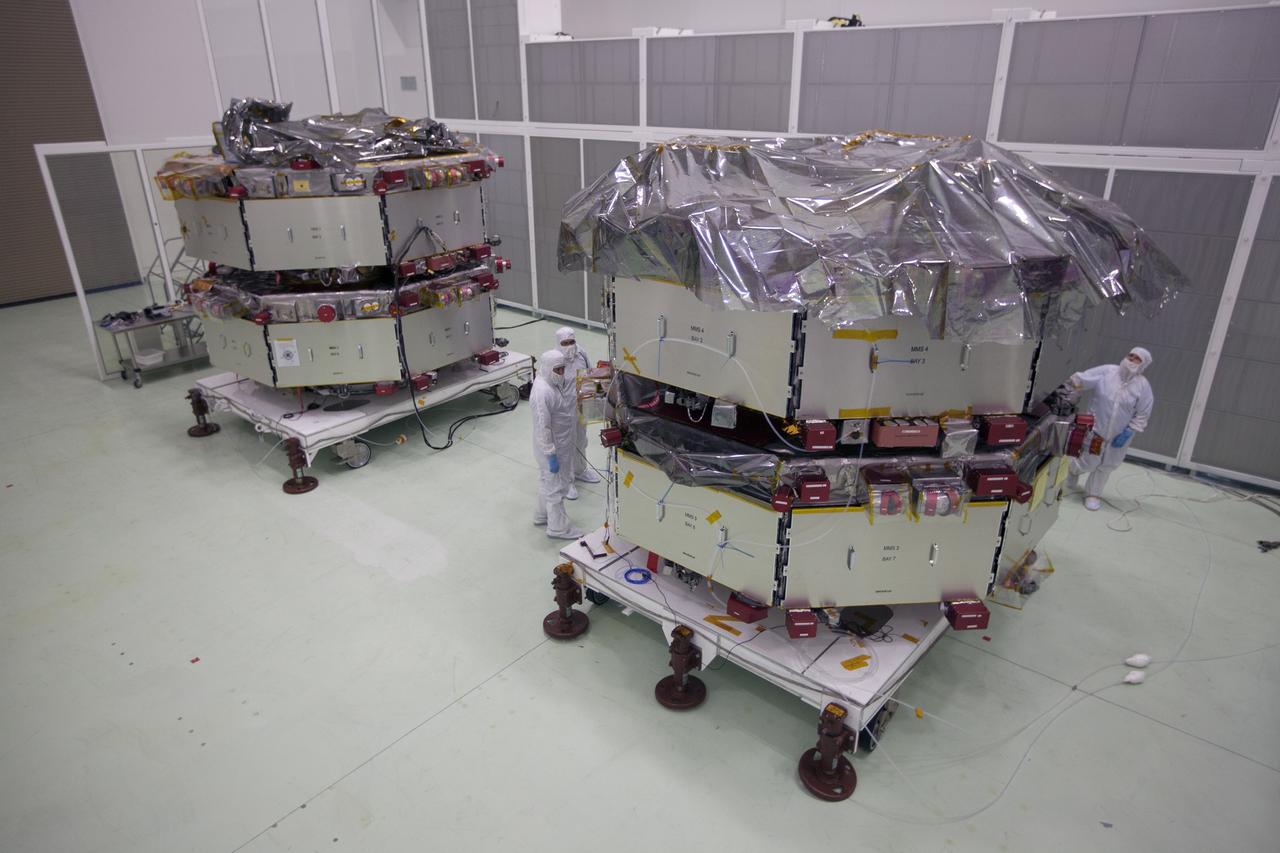

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft will undergo final processing for launch now that all four are in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

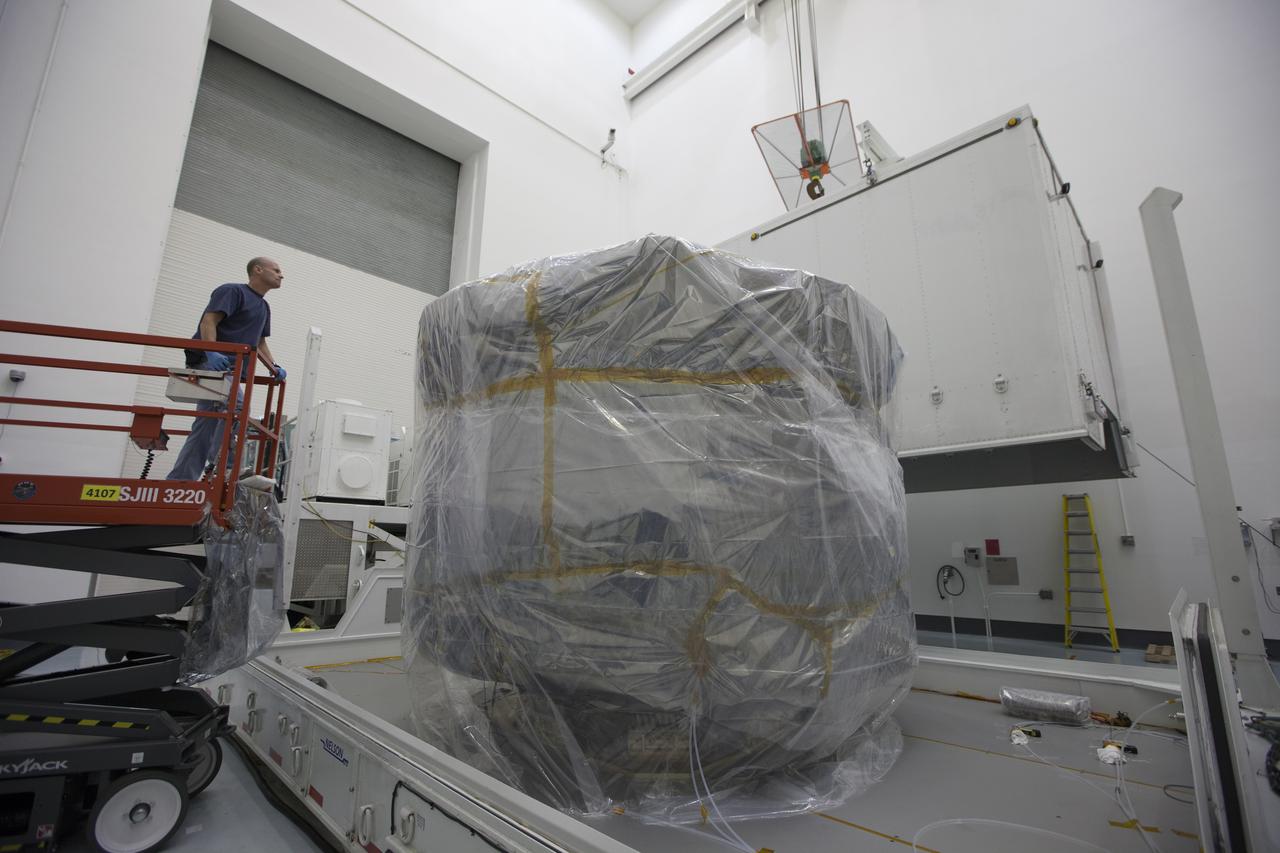
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Operations are underway to remove two of the the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft from their protective shipping container in the airlock of Building 2 at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale , or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are lowered onto a payload dolly in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft, comprising the mission's upper stack, come into view as the shipping container is removed in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

The protective covering is removed from the two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The protective covering is removed from the two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack, at left, arrive in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack, at right, arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – All four of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft have arrived in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
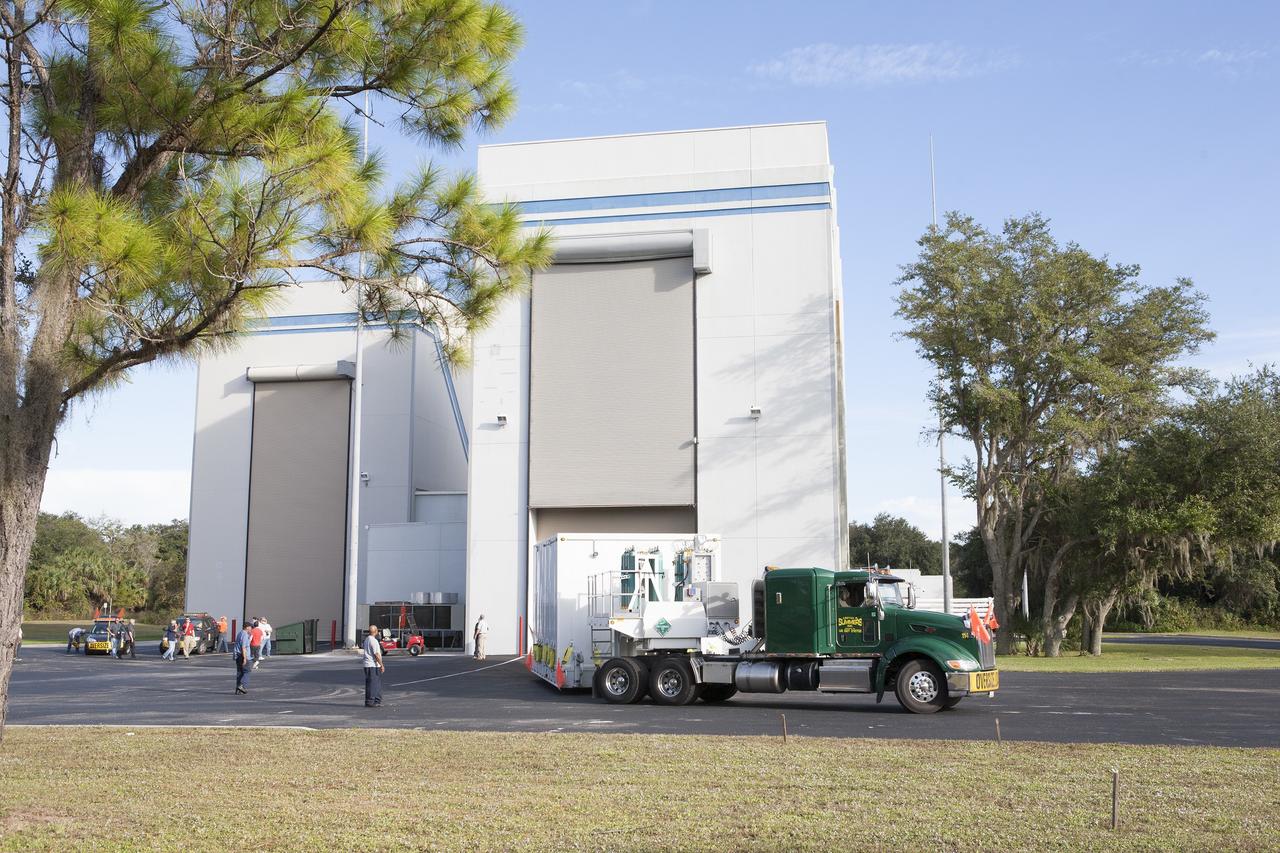

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are delivered by truck to the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
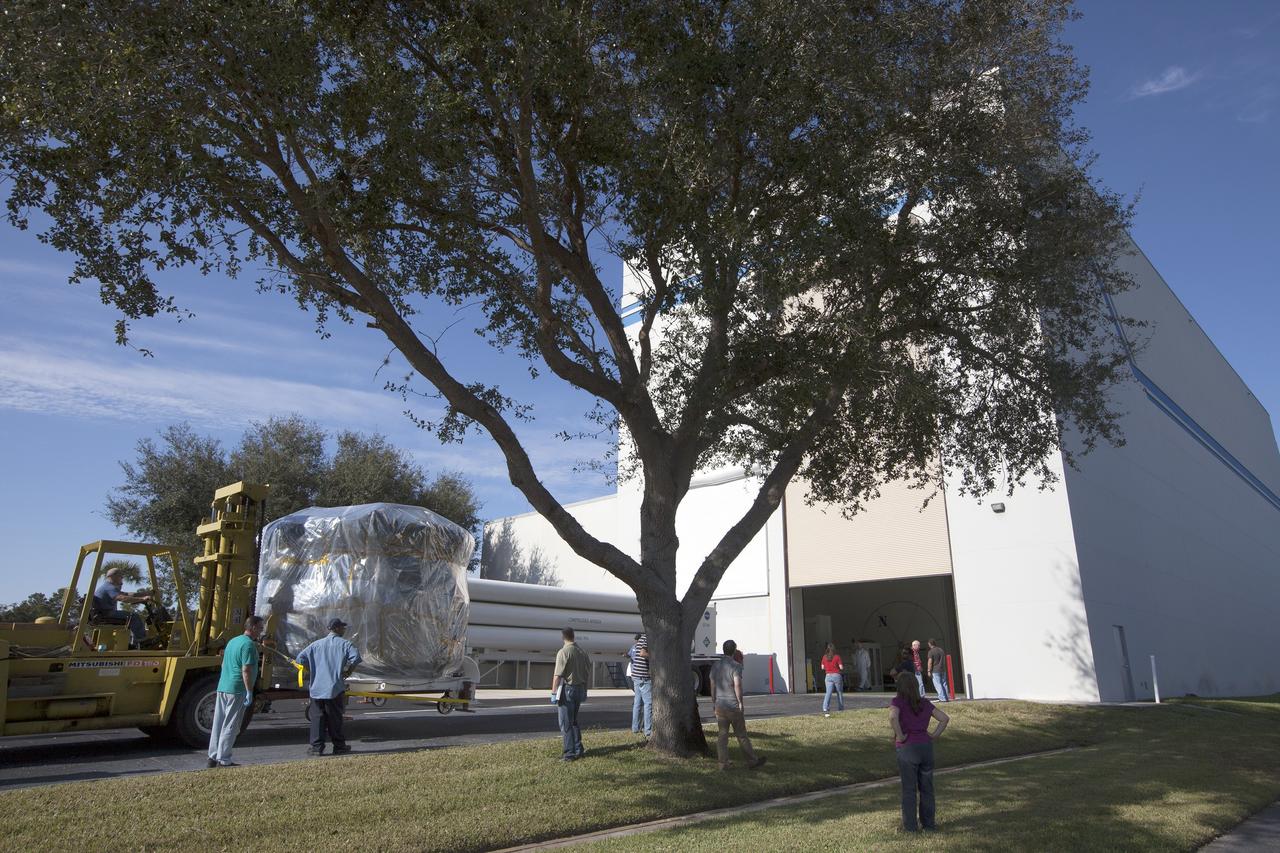

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are transported to the airlock of Building 1 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
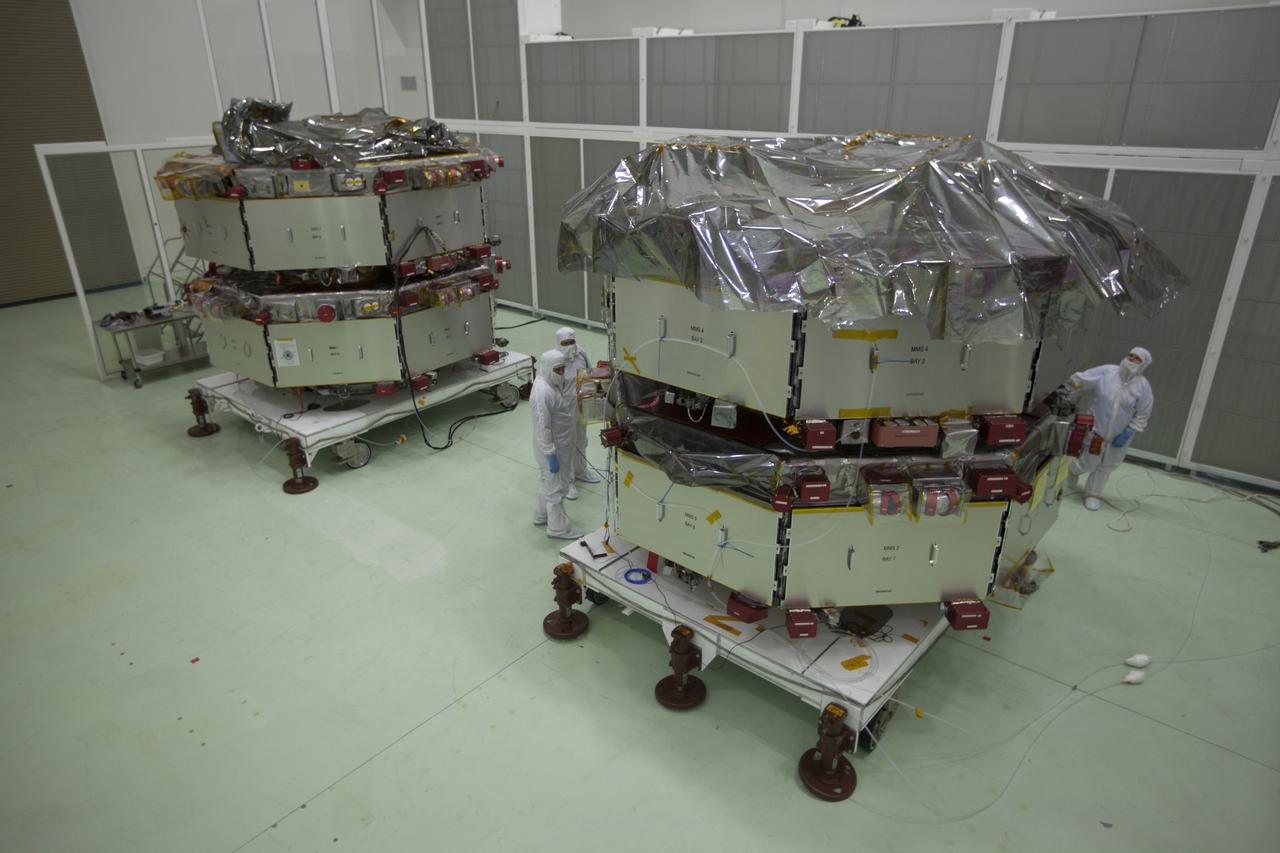

The Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft will undergo final processing for launch now that all four are in the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the upper deck arrived Nov. 12; the two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
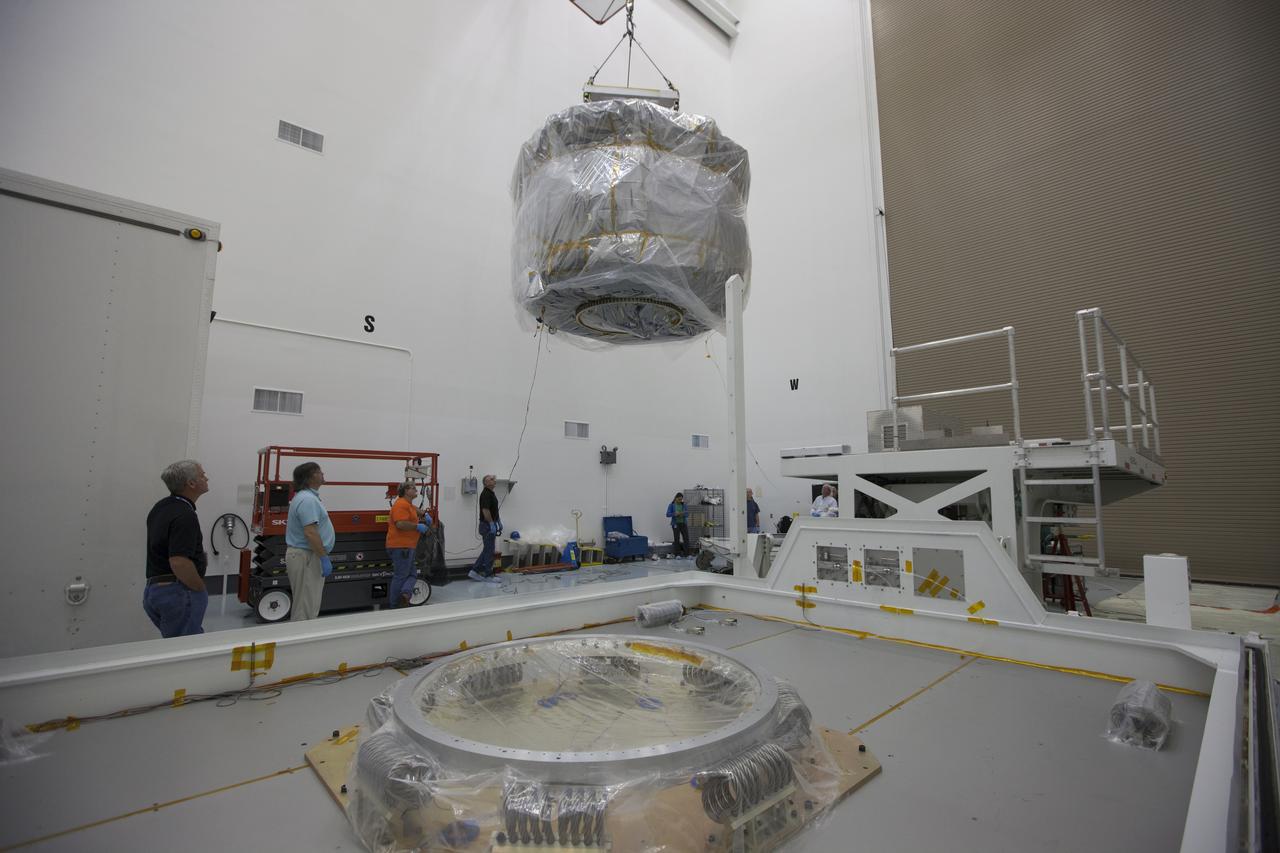

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are lifted from the transporter in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
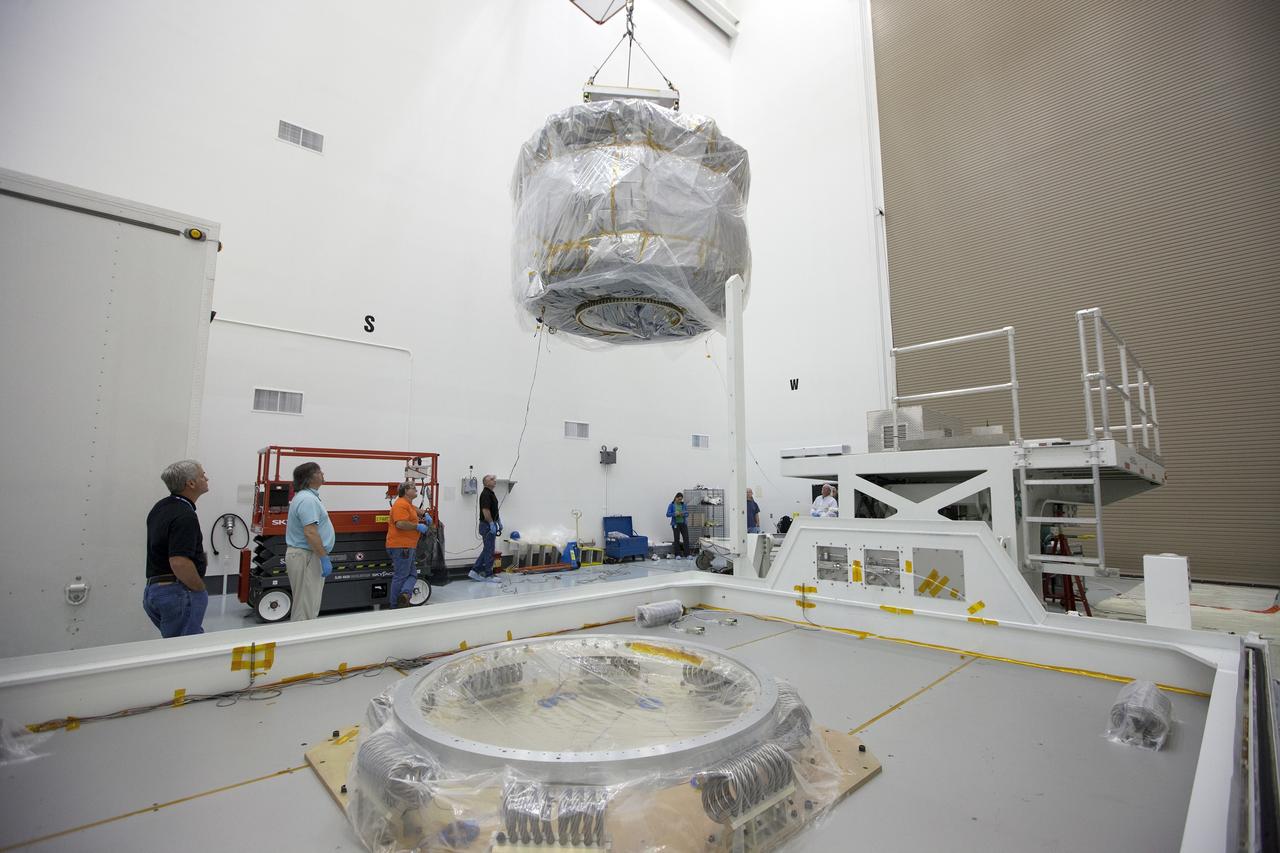

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are lifted from the transporter in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
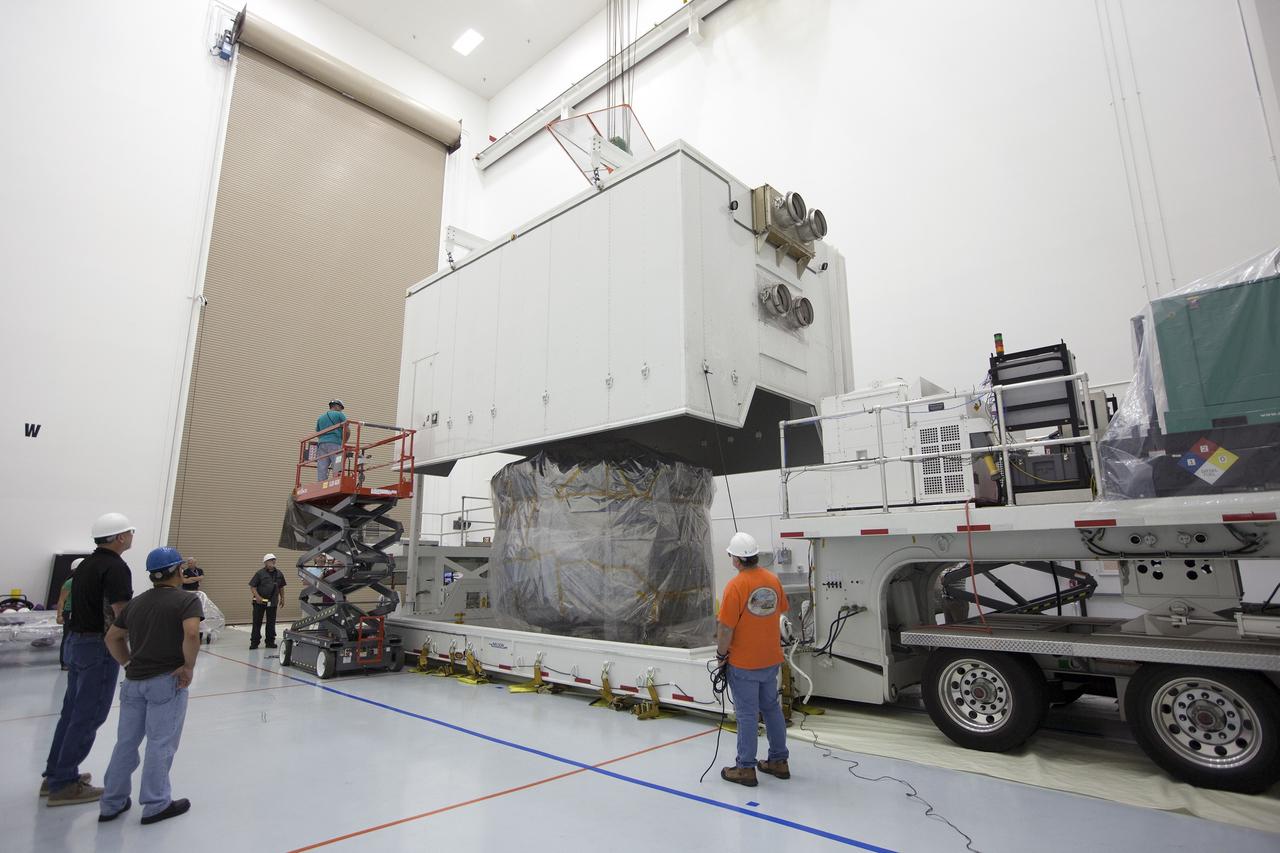

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft, comprising the mission's upper stack, come into view as the shipping container is removed in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
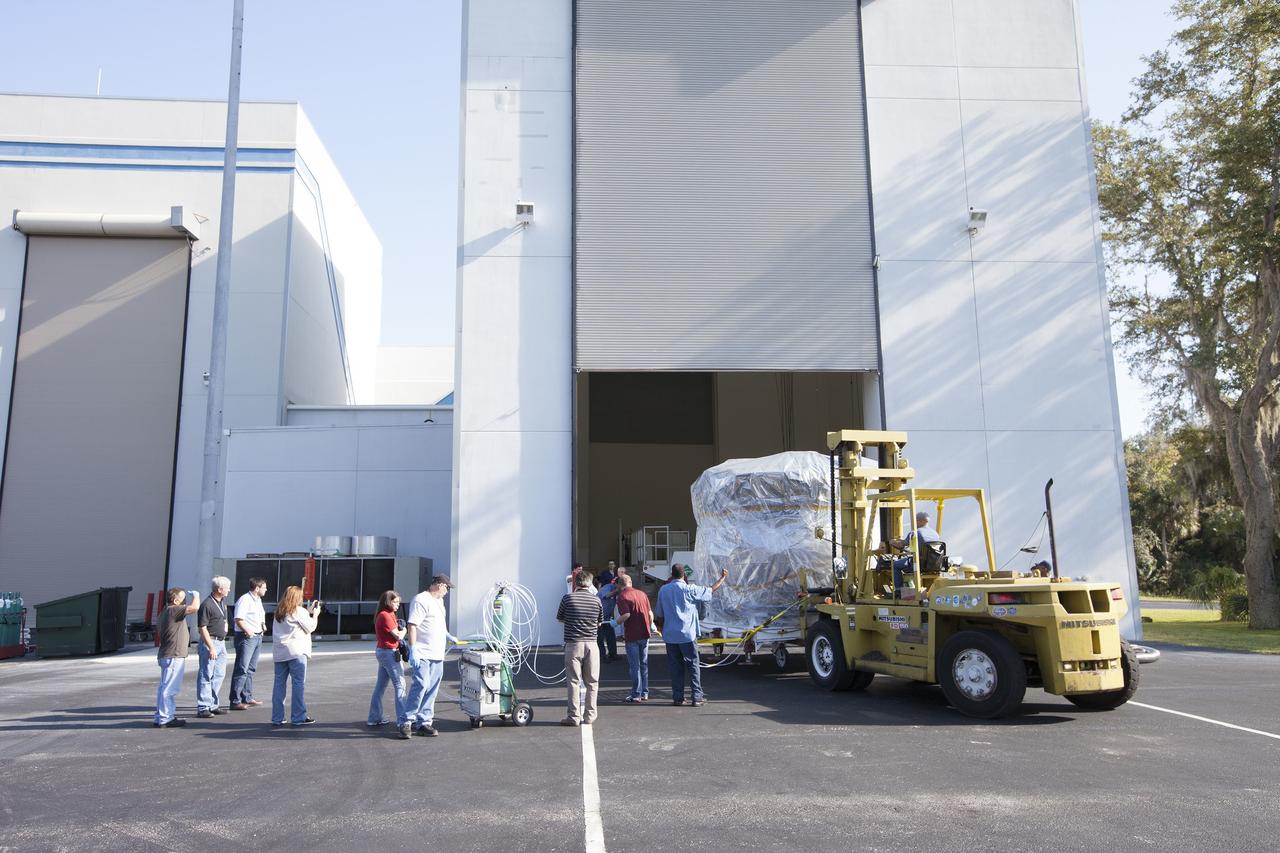

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are towed from Building 2 to the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
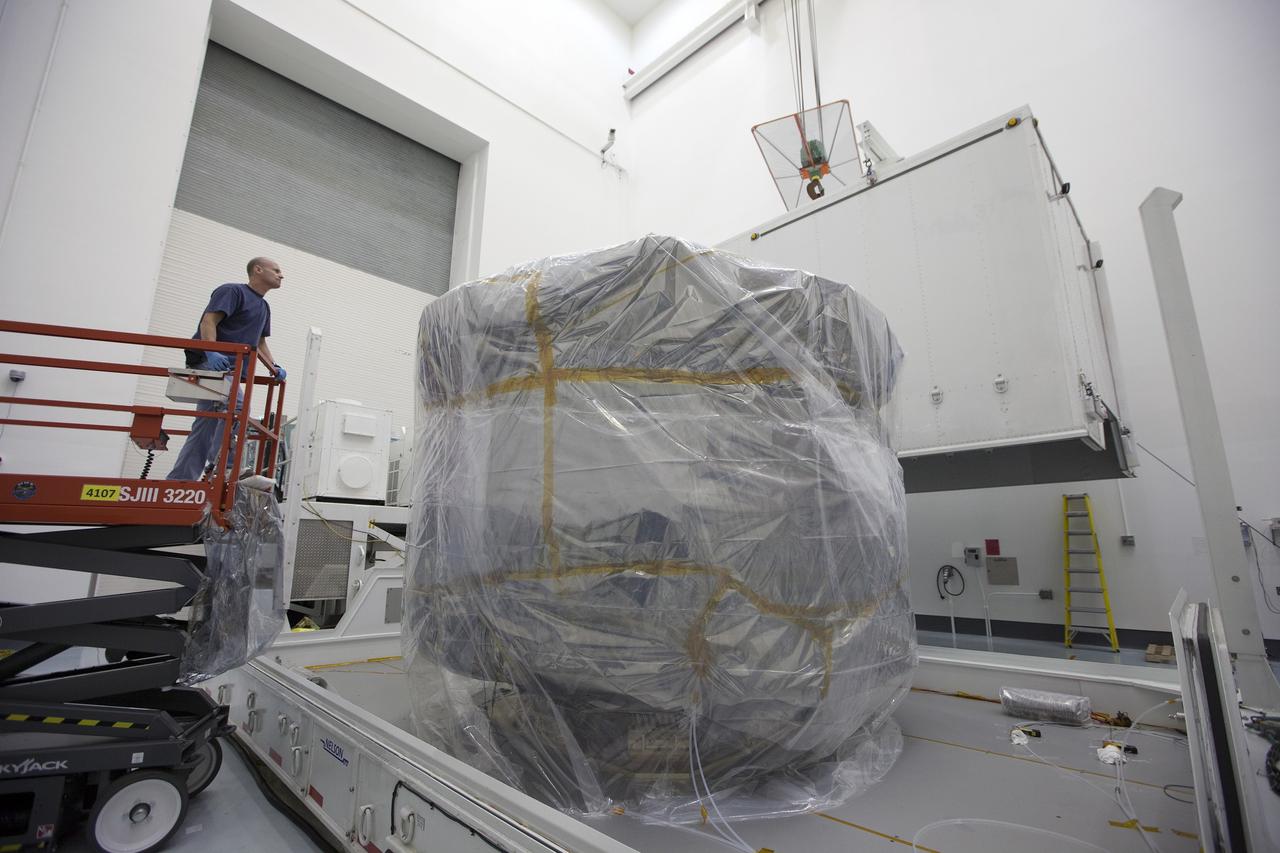

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The protective shipping container is removed from around the upper stack of the Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft in Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
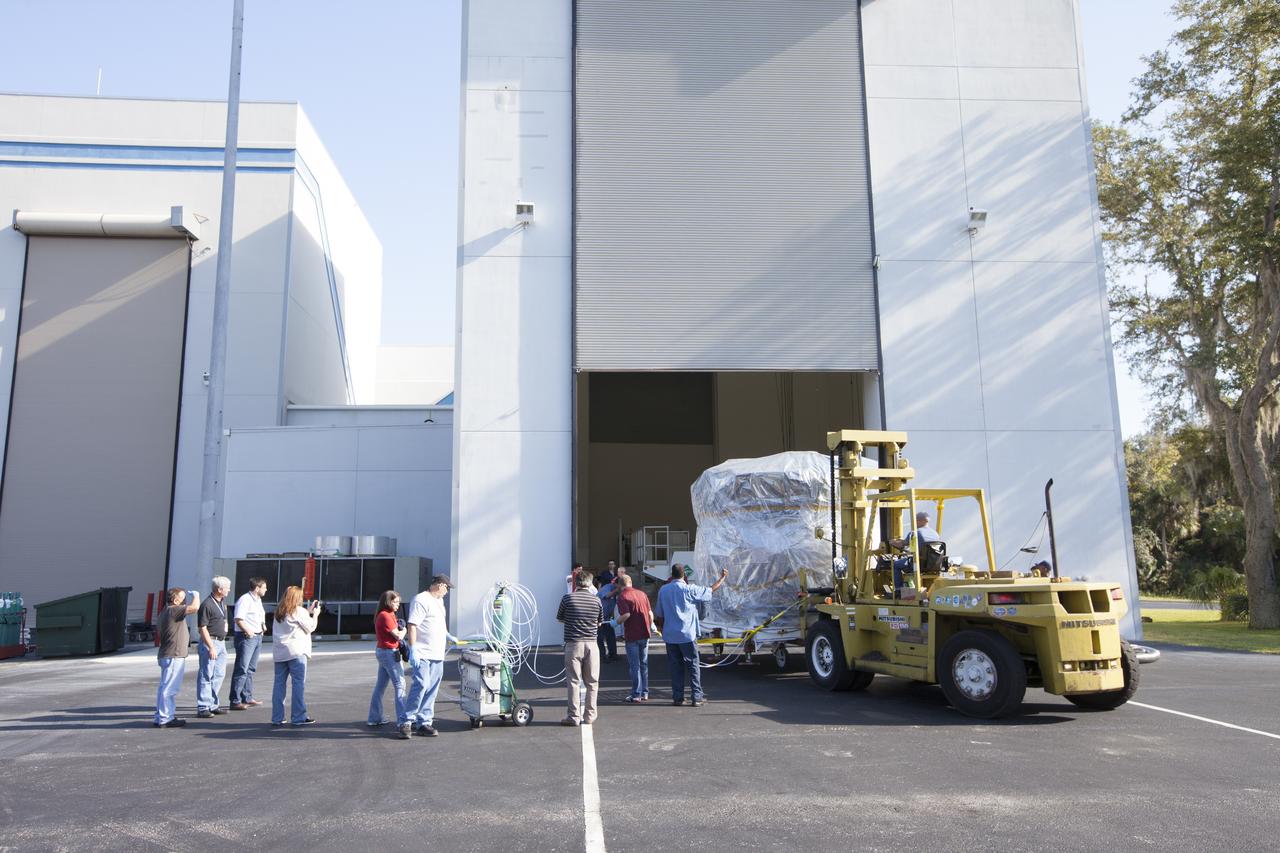

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are towed from Building 2 to the Building 1 high bay of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.
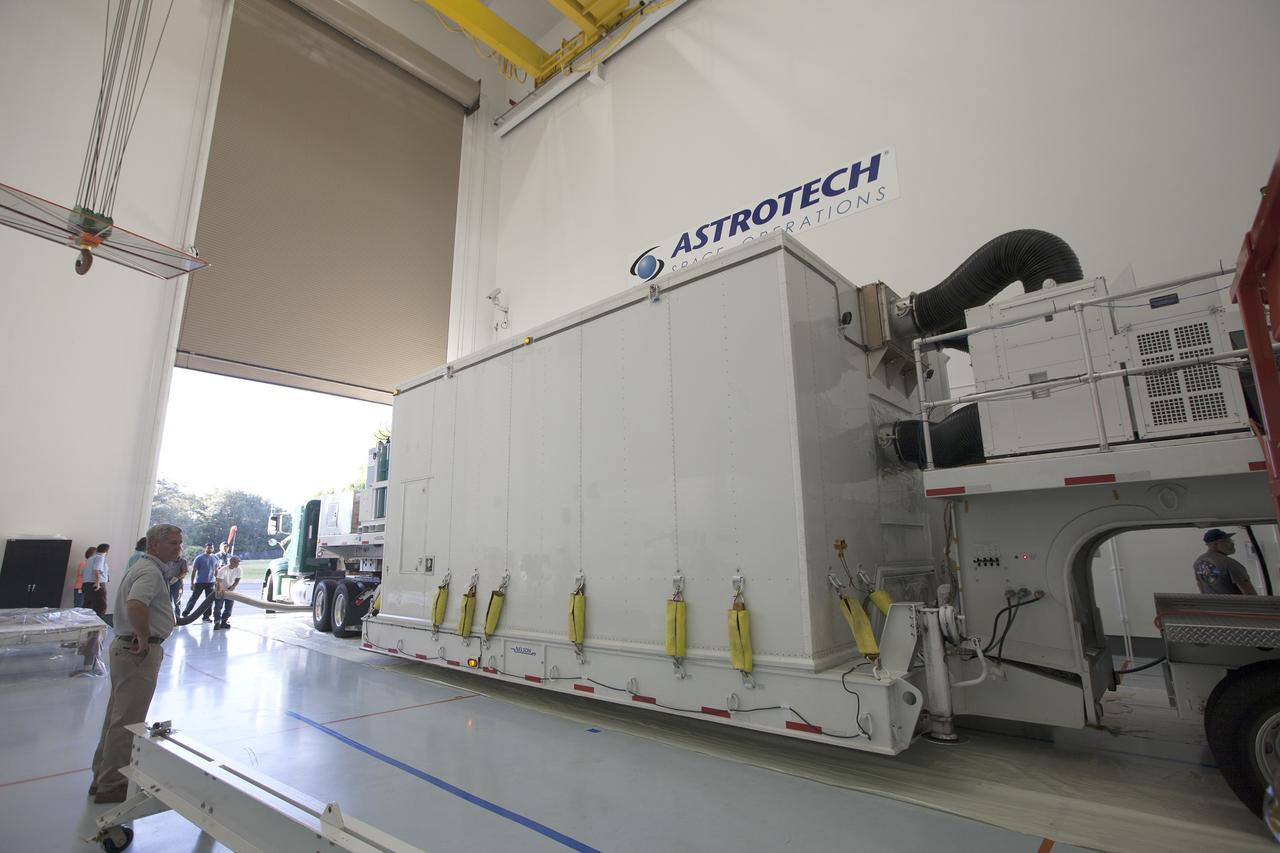

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft, enclosed in a protective shipping container, are positioned into the airlock of Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
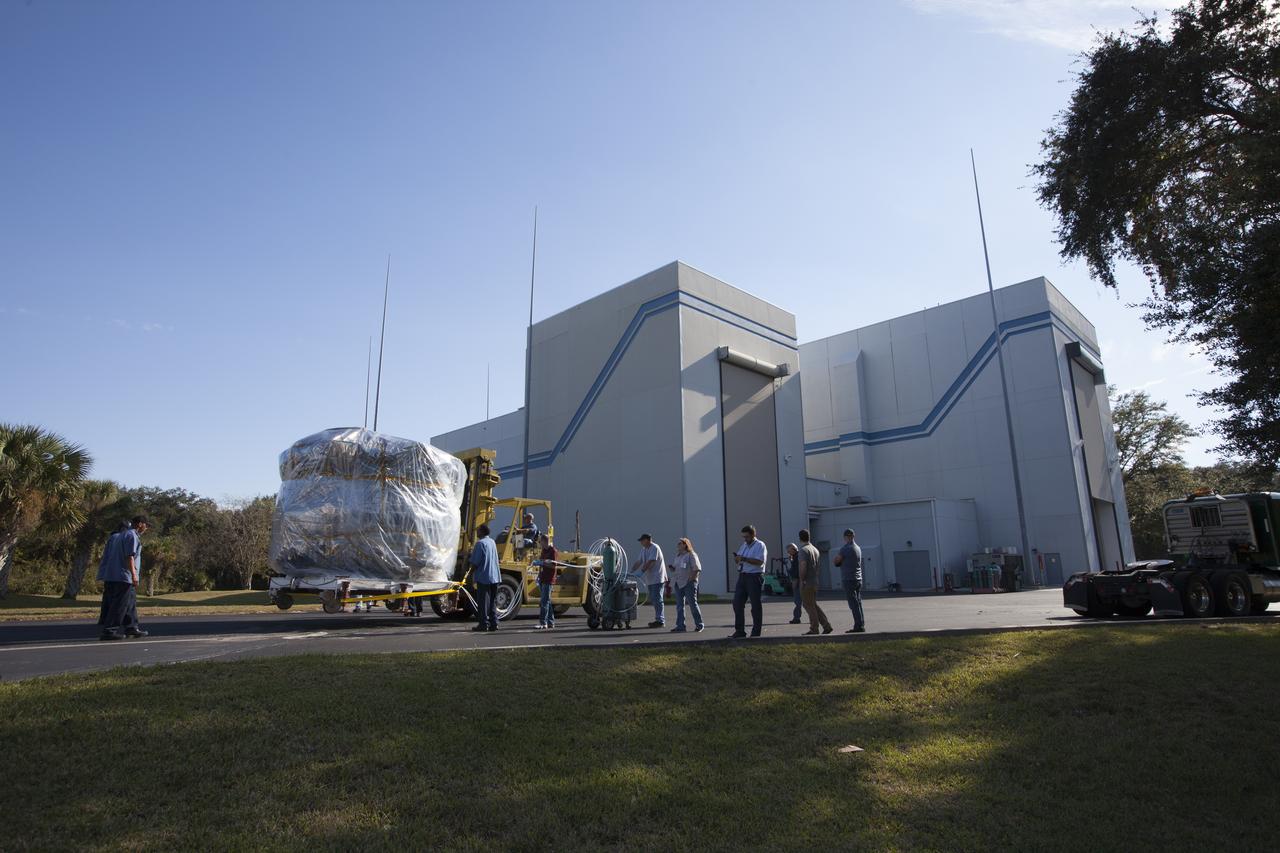

Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack are towed between Buildings 1 and 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The airlock door opens at Building 2 of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center, for ingress of the protective shipping container enclosing the Magnetospheric Multiscale spacecraft. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission, or MMS, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. These two spacecraft comprise the mission's upper stack. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
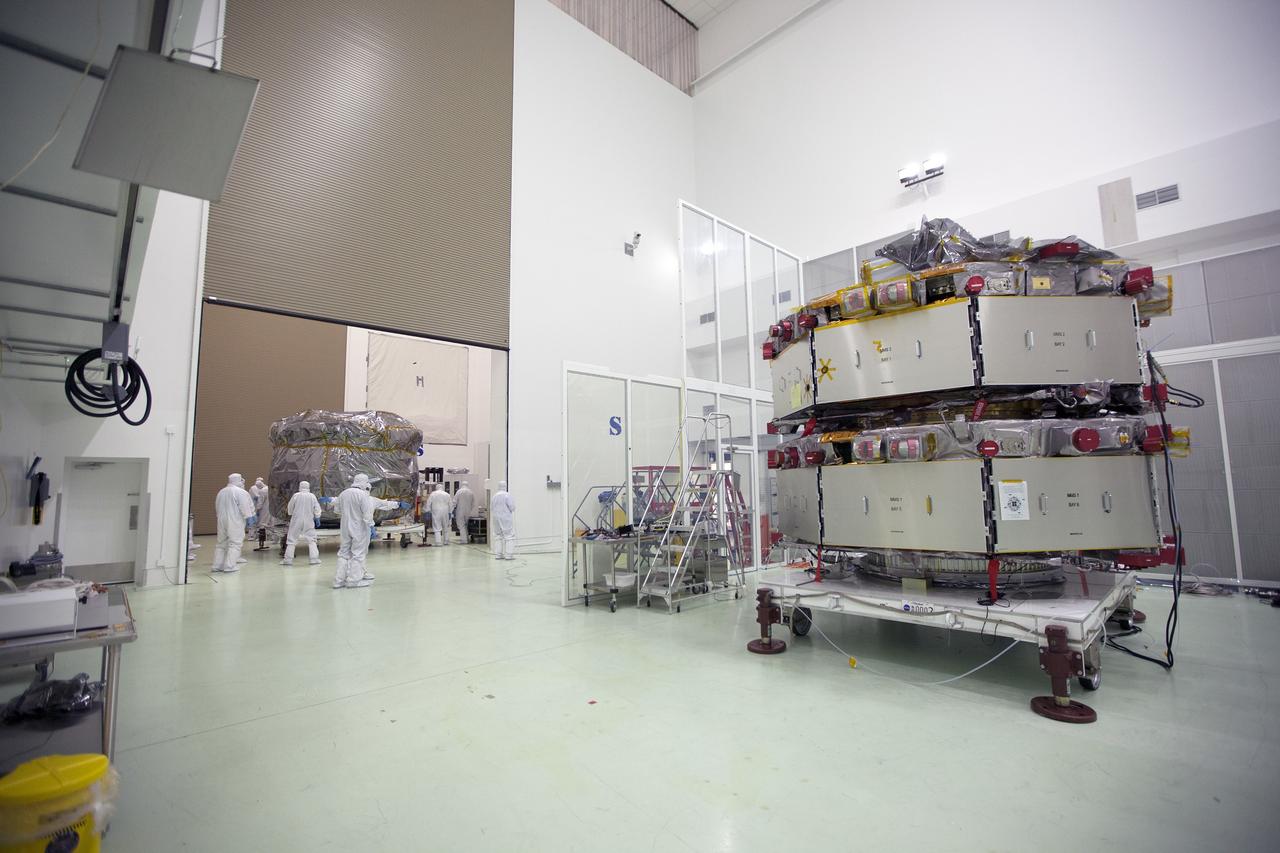

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Two Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft comprising the mission’s upper stack arrive in the Building 1 airlock of the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near Kennedy Space Center. The two MMS spacecraft comprising the lower stack, in the high bay uat right, arrived at Astrotech on Oct. 29. The Magnetospheric Multiscale mission is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission comprising four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015. To learn more about MMS, visit http://mms.gsfc.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
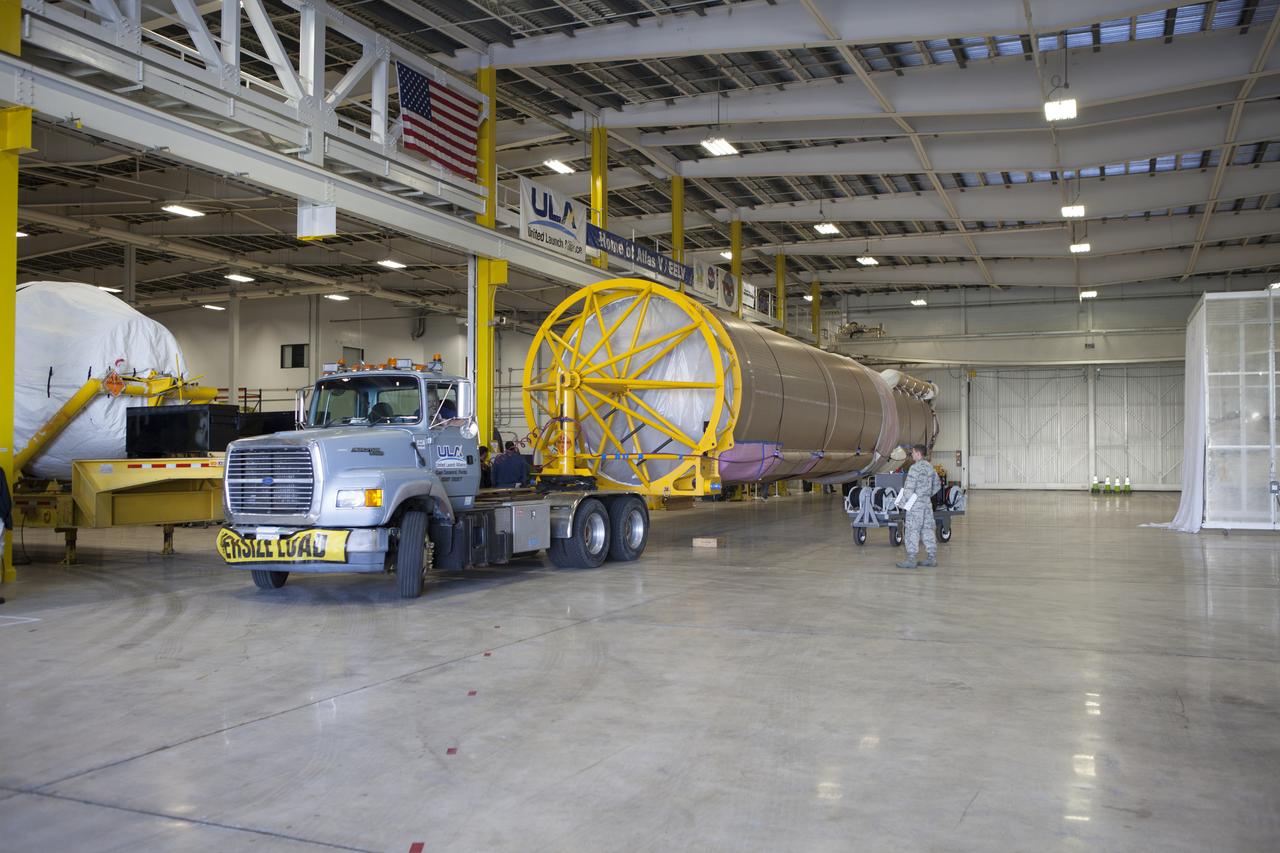

A truck positions an Atlas V booster stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
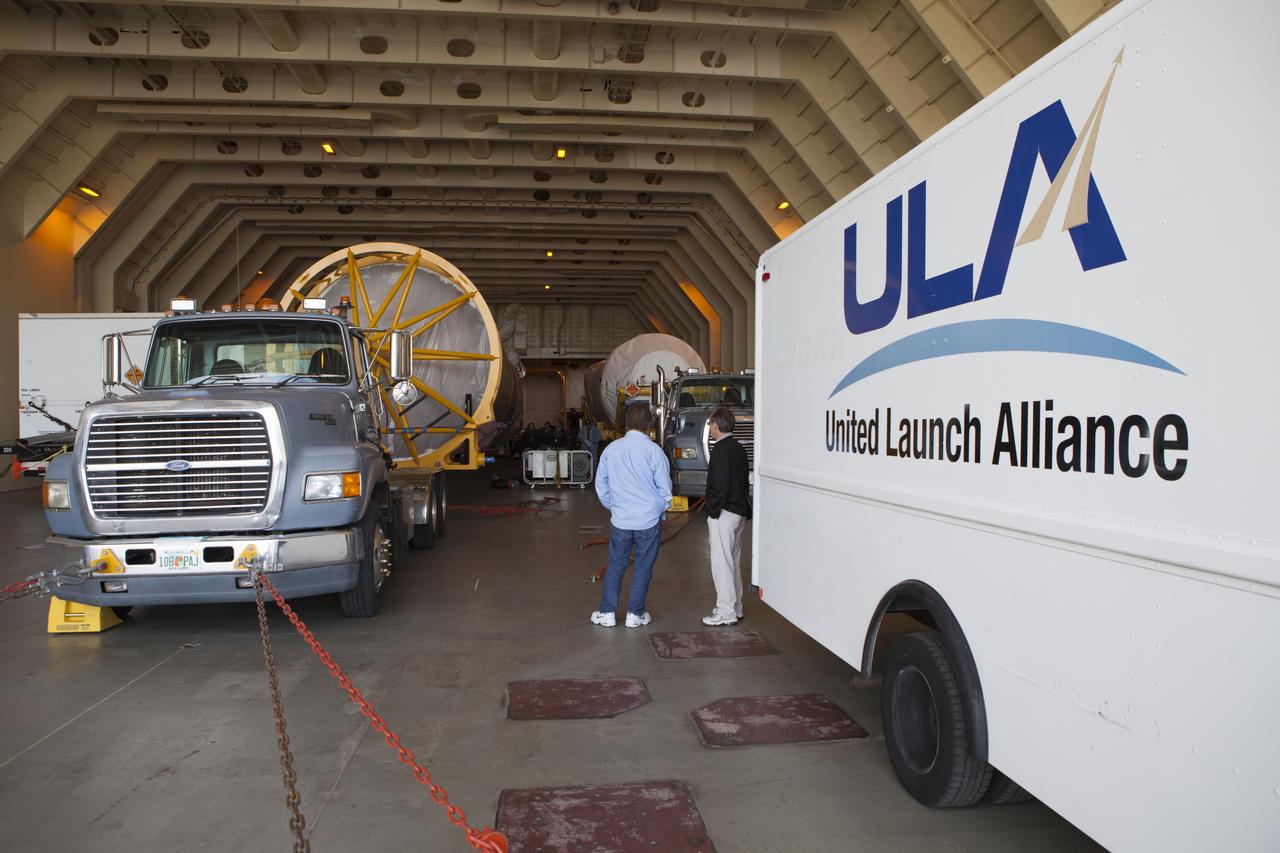

Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
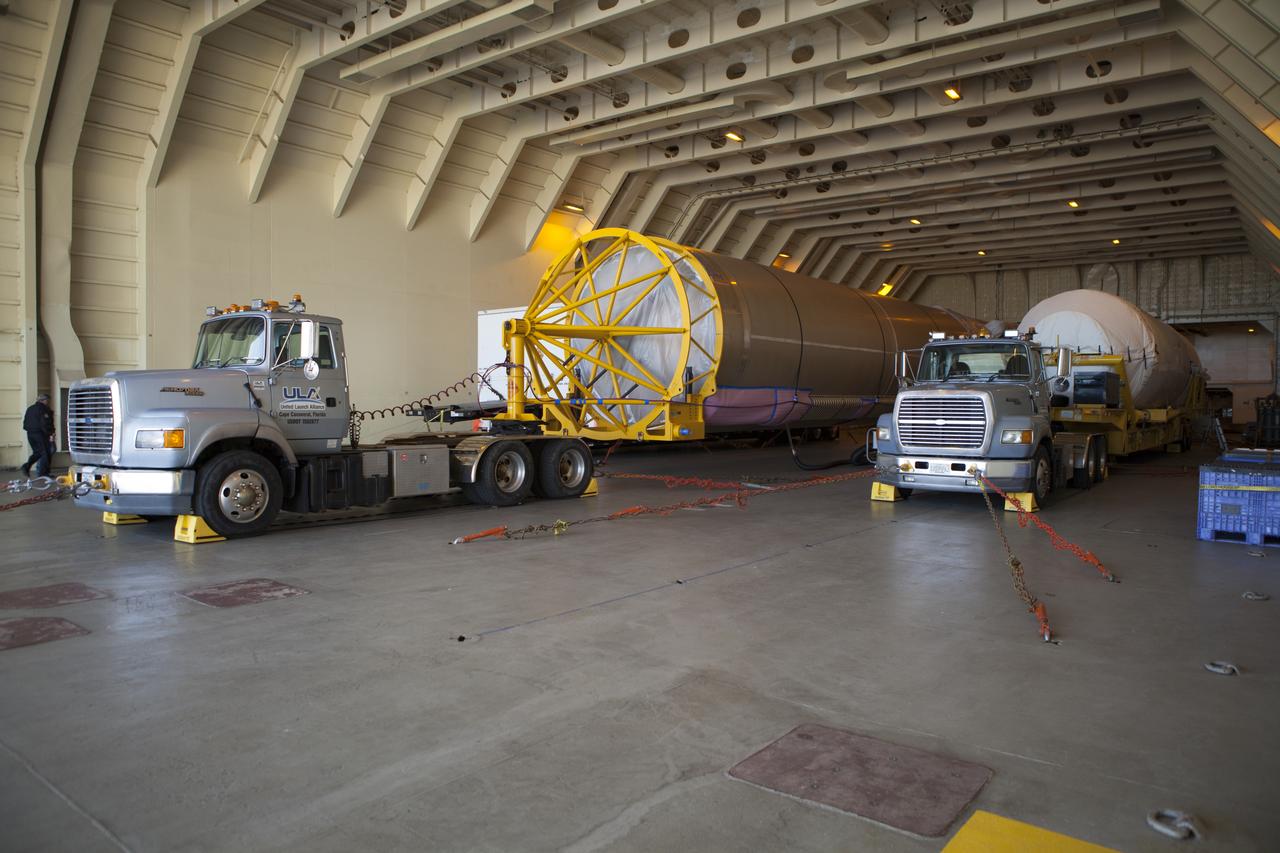

Trucks inside the United Launch Alliance Delta Mariner prepare to transport the Atlas V rocket and Centaur upper stage that will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.
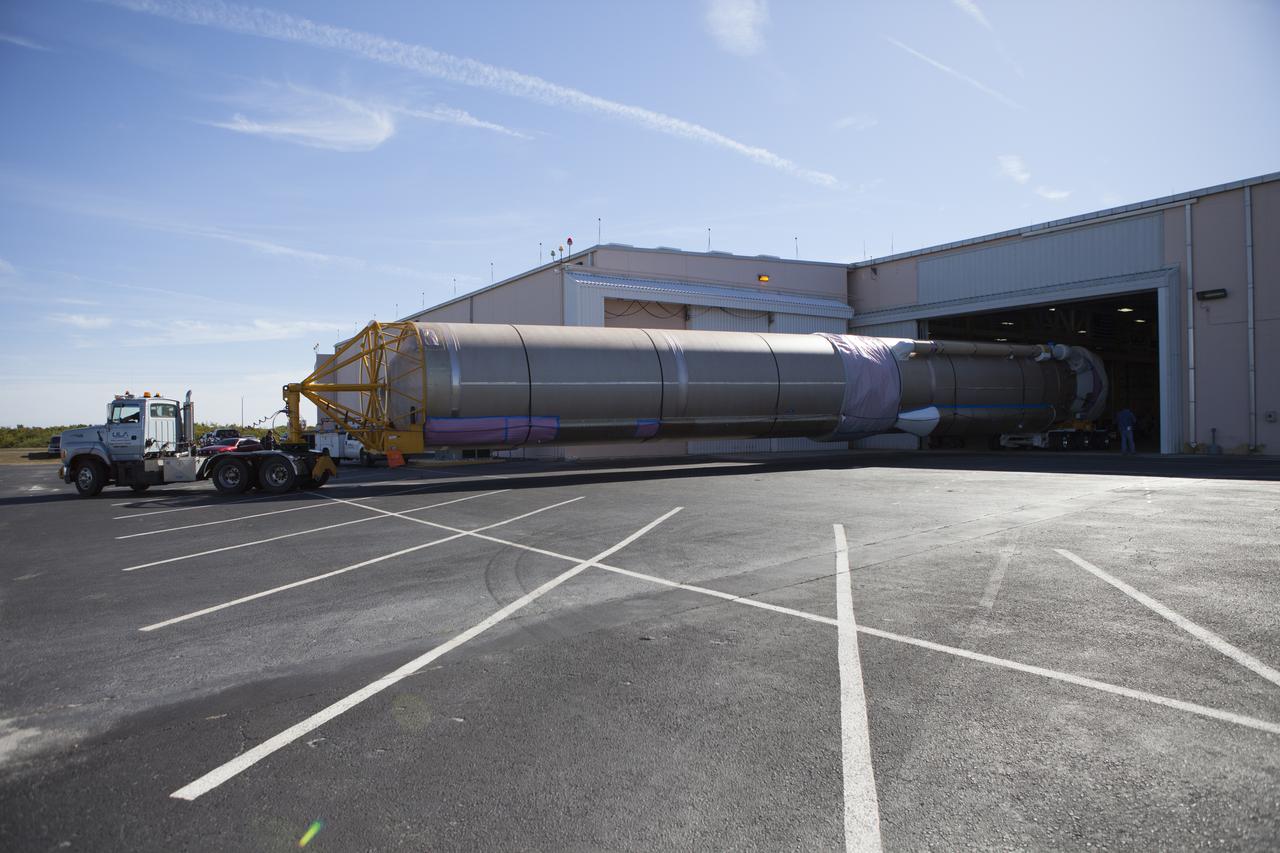

A truck positions an Atlas V booster stage inside the hangar at the Atlas V Spaceflight Operations Center at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The rocket will be used to launch NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale mission.

A plaque affixed to the side of a Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatory dedicates the mission to Richard “Richy” D’Antonio, now deceased, in grateful appreciation for his dedicated service to NASA’s MMS mission. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

A plaque affixed to the side of a Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatory dedicates the mission to Dr. John William Klein, now deceased, who served the MMS team as the standing review board chairman. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.

A plaque affixed to the side of a Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, observatory dedicates the mission to George S. Moore, now deceased, an engineer who was a beloved colleague and friend to the MMS team. MMS, led by a team from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, is a Solar Terrestrial Probes mission consisting of four identically instrumented spacecraft that will use Earth’s magnetosphere as a laboratory to study the microphysics of three fundamental plasma processes: magnetic reconnection, energetic particle acceleration and turbulence. Launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station is targeted for March 12, 2015.