
S65-28699 (17 Aug. 1965) --- Astronaut Charles Conrad Jr. (dark shirt), pilot for the Gemini-5 spaceflight, discusses x-rays with members of the medical team at Cape Kennedy. Left to right are Dr. Eugene Tubbs; astronaut Conrad; Dr. Charles A. Berry, chief, Center Medical Programs, Manned Spacecraft Center; and Dr. Robert Moser (seated), Medical Monitor with the U.S. Army.
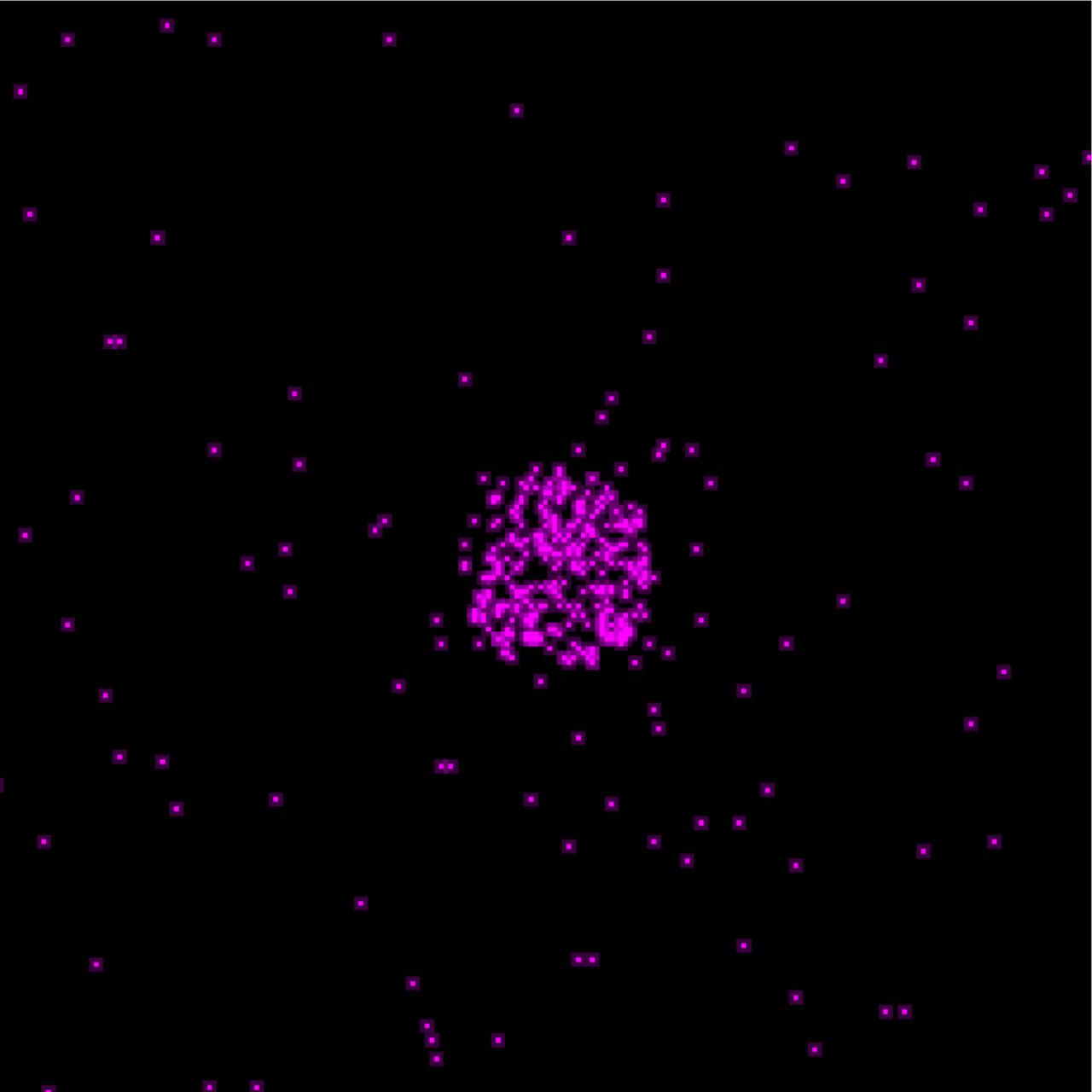
Giving scientists their first look, Chandra observed x-rays produced by fluorescent radiation from oxygen atoms of the Sun in the sparse upper atmosphere of Mars, about 120 kilometers (75 miles) above its surface. The x-ray power detected from the Martian atmosphere is very small, amounting to only 4 megawatts, comparable to the x-ray power of about ten thousand medical x-ray machines. At the time of the Chandra observation, a huge dust storm developed on Mars that covered about one hemisphere, later to cover the entire planet. This hemisphere rotated out of view over the 9-hour observation, but no change was observed in the x-ray intensity indicating that the dust storm did not affect the upper atmosphere. Scientists also observed a halo of x-rays extending out to 7,000 kilometers above the surface of Mars believed to be produced by collisions of ions racing away from the Sun (the solar wind).
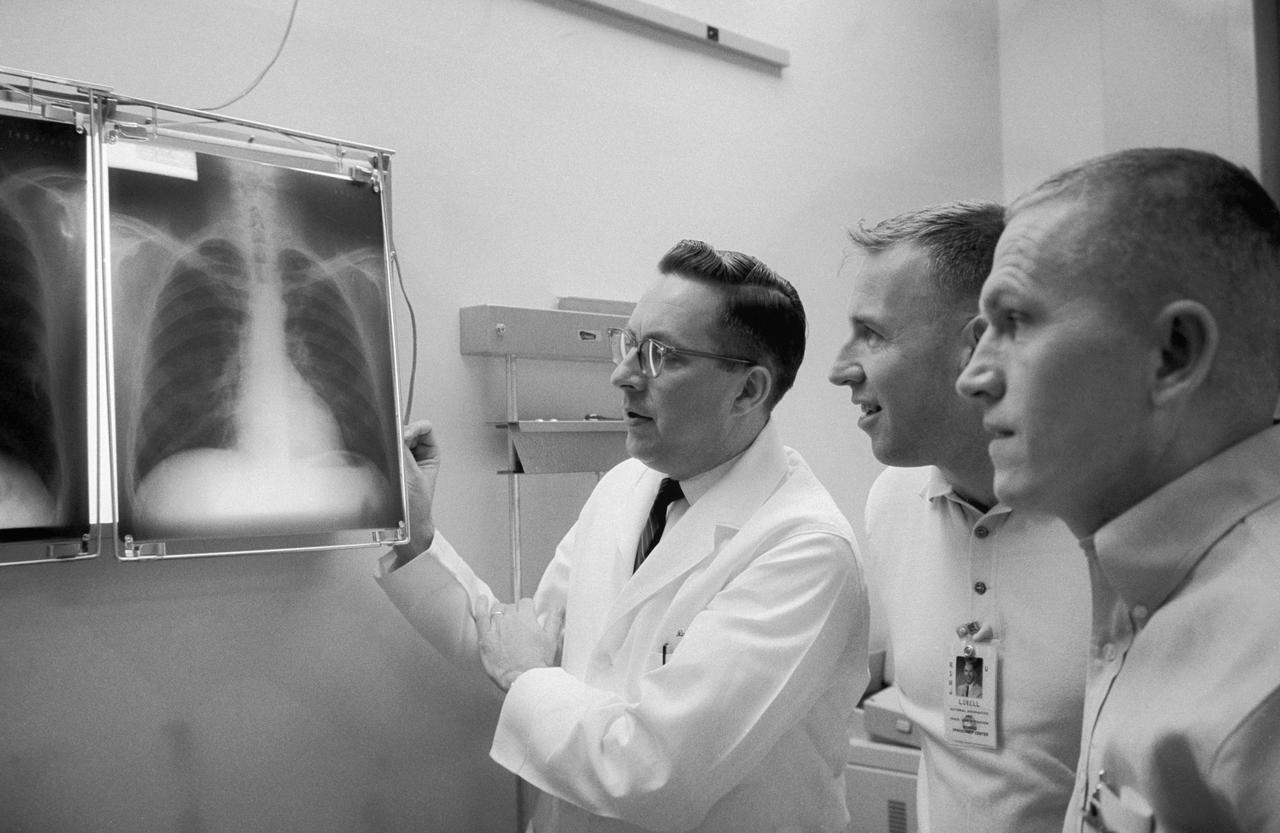
S65-56315 (2 Dec. 1965) --- Dr. Charles A. Berry (left), chief of the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) Medical Programs, and astronauts James A. Lovell Jr. (center), Gemini-7 pilot, and Frank Borman, Gemini-7 command pilot, examine a series of chest x-rays taken during the preflight physical. Photo credit: NASA

The high-tech art of digital signal processing (DSP) was pioneered at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in the mid-1960s for use in the Apollo Lunar Landing Program. Designed to computer enhance pictures of the Moon, this technology became the basis for the Landsat Earth resources satellites and subsequently has been incorporated into a broad range of Earthbound medical and diagnostic tools. DSP is employed in advanced body imaging techniques including Computer-Aided Tomography, also known as CT and CATScan, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). CT images are collected by irradiating a thin slice of the body with a fan-shaped x-ray beam from a number of directions around the body's perimeter. A tomographic (slice-like) picture is reconstructed from these multiple views by a computer. MRI employs a magnetic field and radio waves, rather than x-rays, to create images. In this photograph, a patient undergoes an open MRI.

The high-tech art of digital signal processing (DSP) was pioneered at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in the mid-1960s for use in the Apollo Lunar Landing Program. Designed to computer enhance pictures of the Moon, this technology became the basis for the Landsat Earth resources satellites and subsequently has been incorporated into a broad range of Earthbound medical and diagnostic tools. DSP is employed in advanced body imaging techniques including Computer-Aided Tomography, also known as CT and CATScan, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). CT images are collected by irradiating a thin slice of the body with a fan-shaped x-ray beam from a number of directions around the body's perimeter. A tomographic (slice-like) picture is reconstructed from these multiple views by a computer. MRI employs a magnetic field and radio waves, rather than x-rays, to create images.

The high-tech art of digital signal processing (DSP) was pioneered at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in the mid-1960s for use in the Apollo Lunar Landing Program. Designed to computer enhance pictures of the Moon, this technology became the basis for the Landsat Earth resources satellites and subsequently has been incorporated into a broad range of Earthbound medical and diagnostic tools. DSP is employed in advanced body imaging techniques including Computer-Aided Tomography, also known as CT and CATScan, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). CT images are collected by irradiating a thin slice of the body with a fan-shaped x-ray beam from a number of directions around the body's perimeter. A tomographic (slice-like) picture is reconstructed from these multiple views by a computer. MRI employs a magnetic field and radio waves, rather than x-rays, to create images.

The high-tech art of digital signal processing (DSP) was pioneered at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in the mid-1960s for use in the Apollo Lunar Landing Program. Designed to computer enhance pictures of the Moon, this technology became the basis for the Landsat Earth resources satellites and subsequently has been incorporated into a broad range of Earthbound medical and diagnostic tools. DSP is employed in advanced body imaging techniques including Computer-Aided Tomography, also known as CT and CATScan, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). CT images are collected by irradiating a thin slice of the body with a fan-shaped x-ray beam from a number of directions around the body's perimeter. A tomographic (slice-like) picture is reconstructed from these multiple views by a computer. MRI employs a magnetic field and radio waves, rather than x-rays, to create images.
jsc2022e062020 (6/30/2022) --- Space Health will create a digital twin of the astronaut from the data collected by the Bio-Monitor and demonstrate how this could be used for autonomous health monitoring on future space missions. (Image courtesy of CSA)

STS054-S-001 (July 1992) --- Designed by the crew members, the STS-54 crew patch depicts our national symbol, the American bald eagle, soaring above the Earth; and represents the United States Space Shuttle as a national asset in service to America and the world. The eagle is clutching an eight pointed star in its talons and is placing this larger star among a constellation of four others representing the placement of the fifth Tracking and Data Relay Satellite (TDRS) into orbit among the four already in service. The blackness of space with stars conspicuously absent represents the mission?s other primary objective in carrying the Diffuse X-ray Spectrometer into orbit to conduct astronomical observations of x-ray sources within the galaxy and throughout the universe. The depiction of our planet showing the crew?s home continent of North America is an expression of their and NASA?s intention that the medical and scientific experiments conducted onboard are for the benefit of all mankind. The clouds and blue of the Earth represent the crew?s part in NASA?s Mission to Planet Earth in conducting Earth observation photography. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA