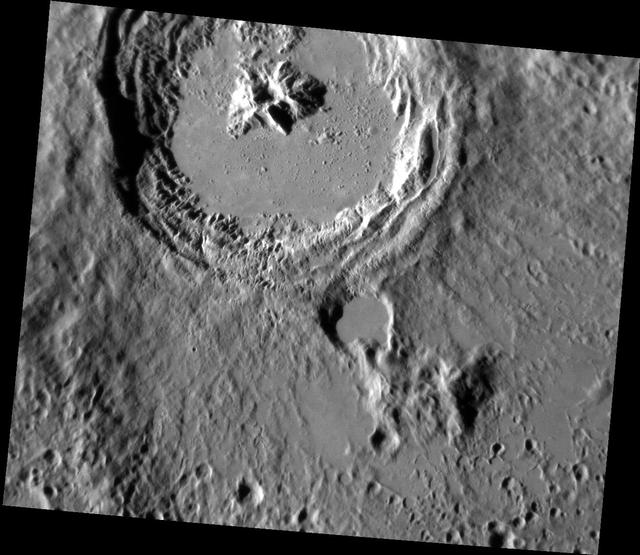

The Kuiper Melt

I Melt With You
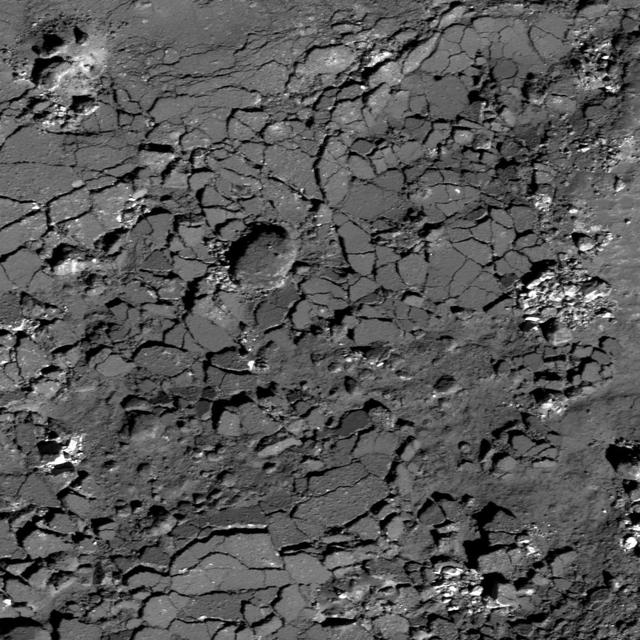

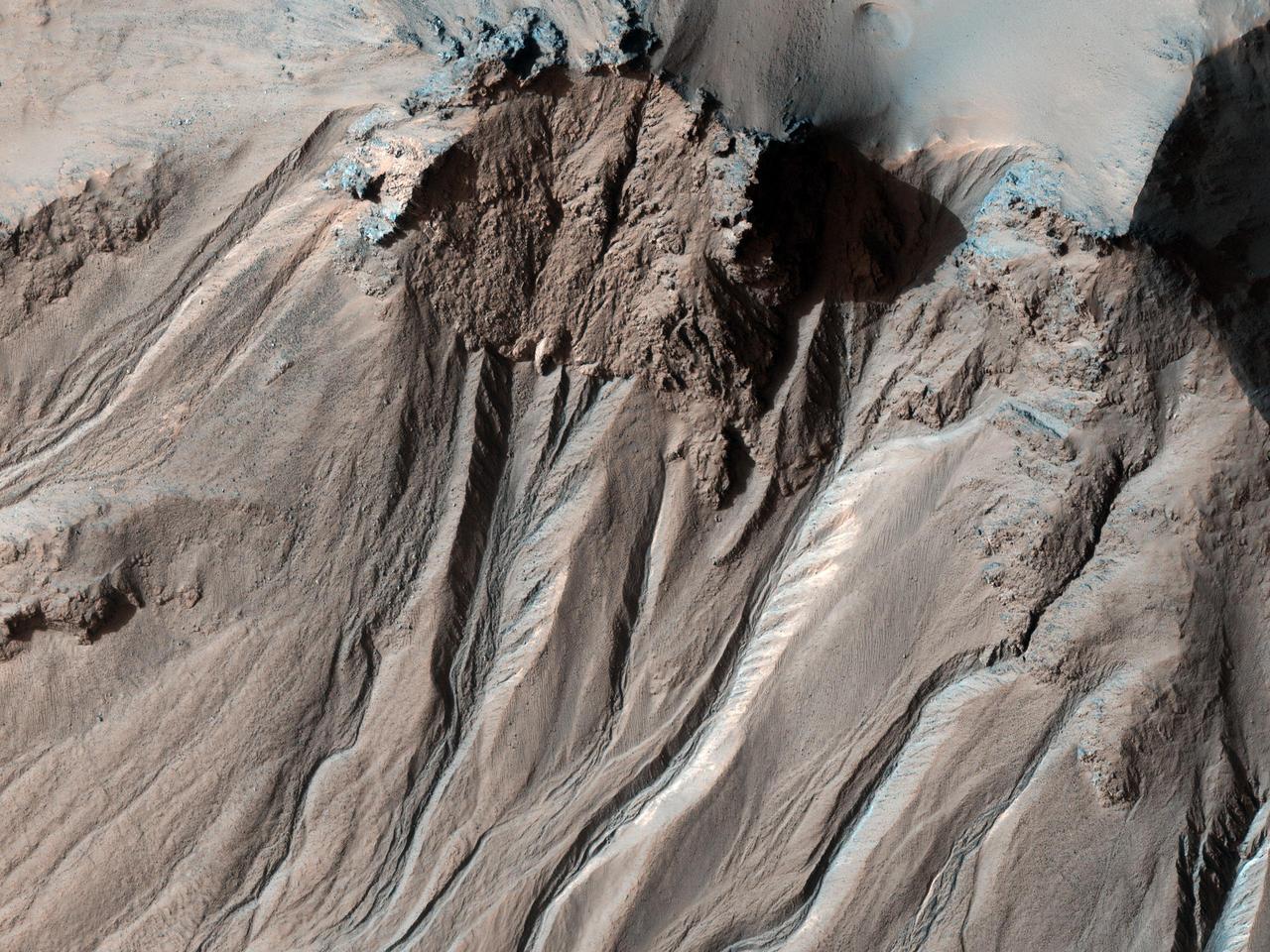
Fragmented Impact Melt

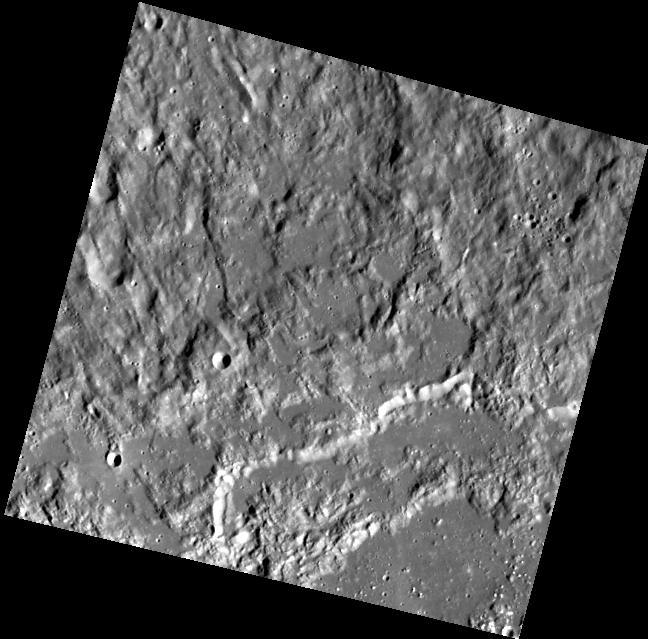
Impact Melt at Necho Crater

Mounds in a Melt Pond
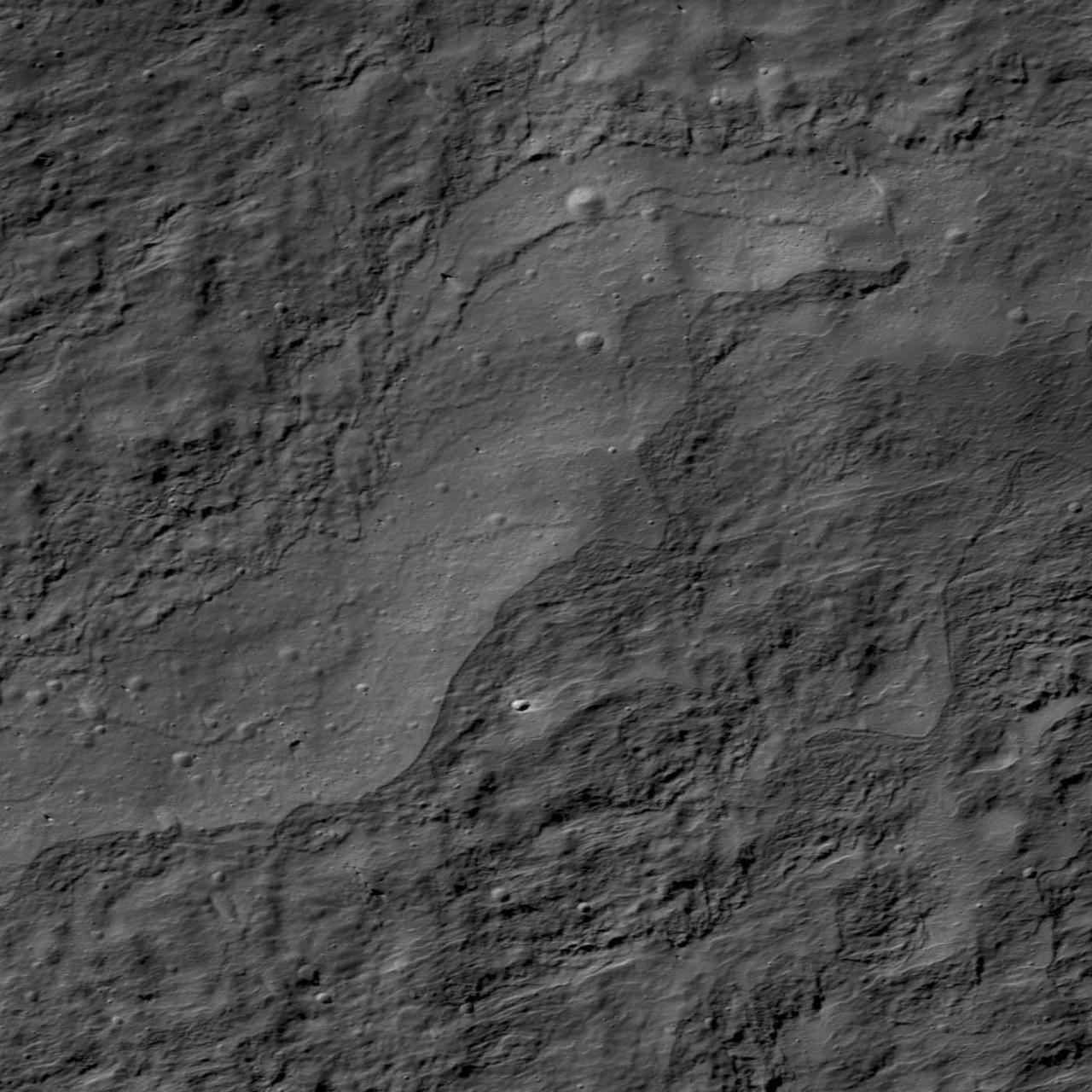

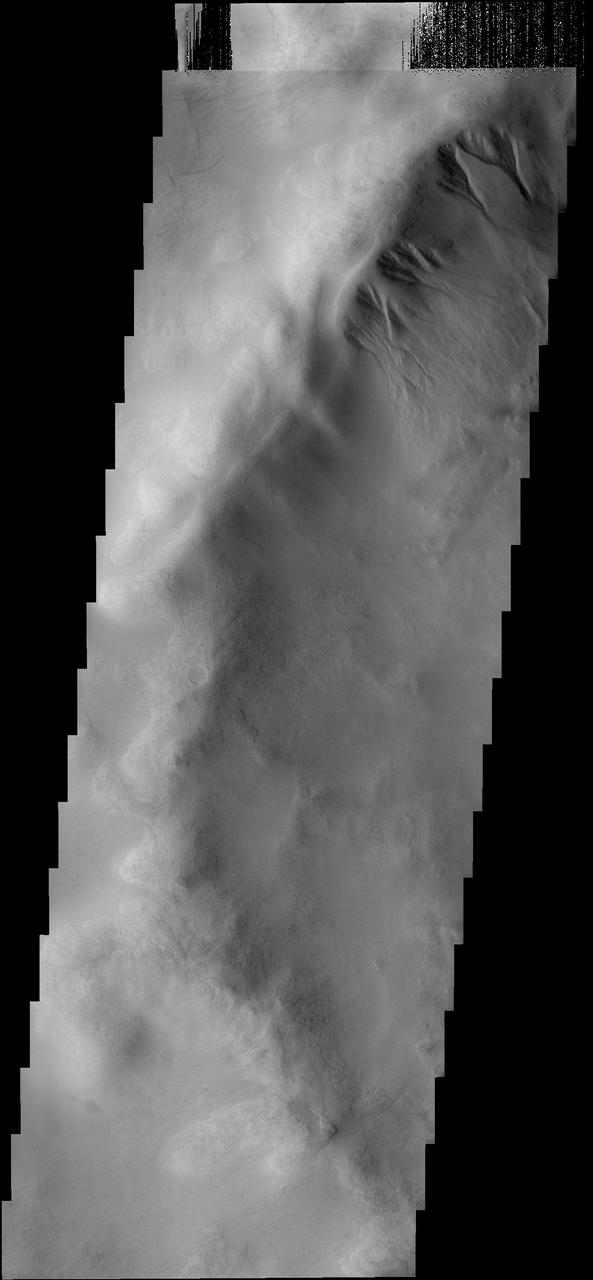
Impact Melt on Klute W Wall
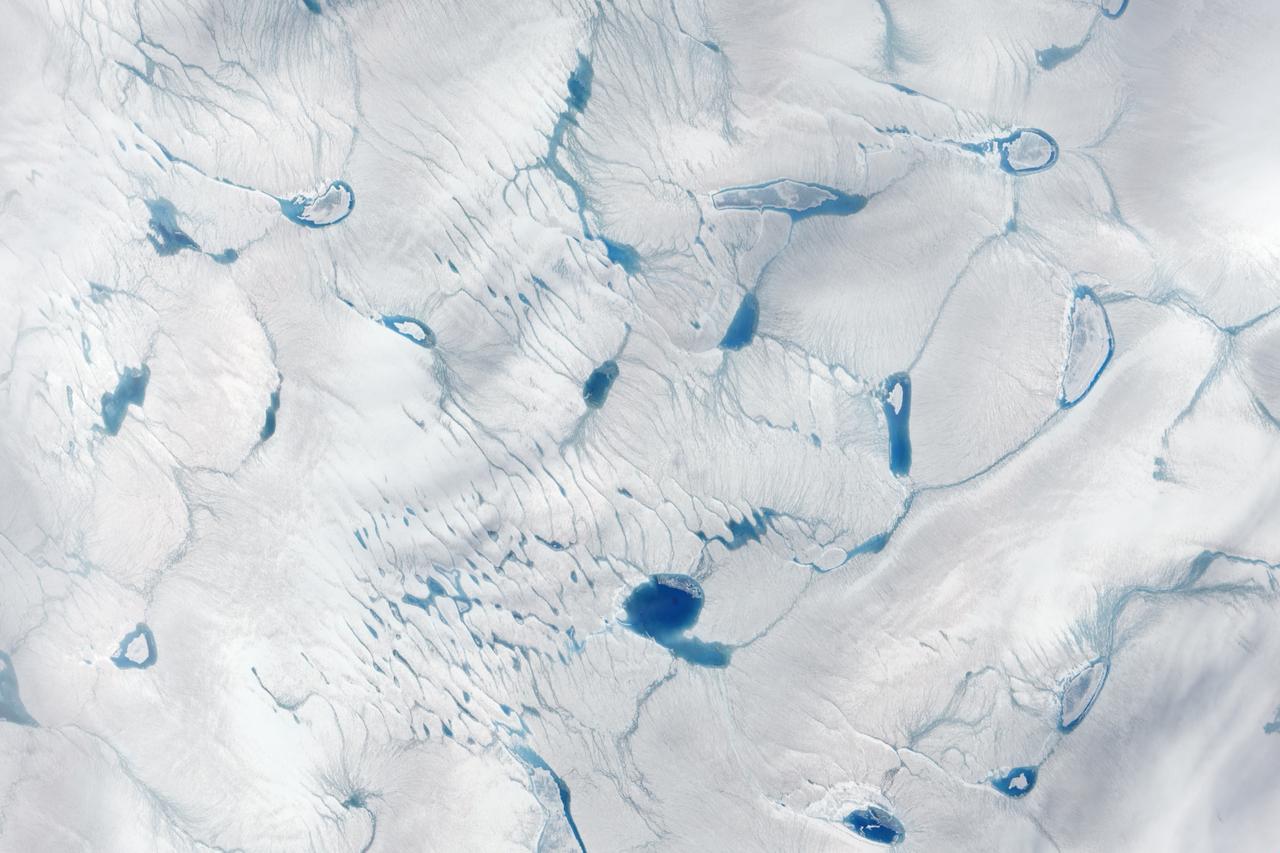
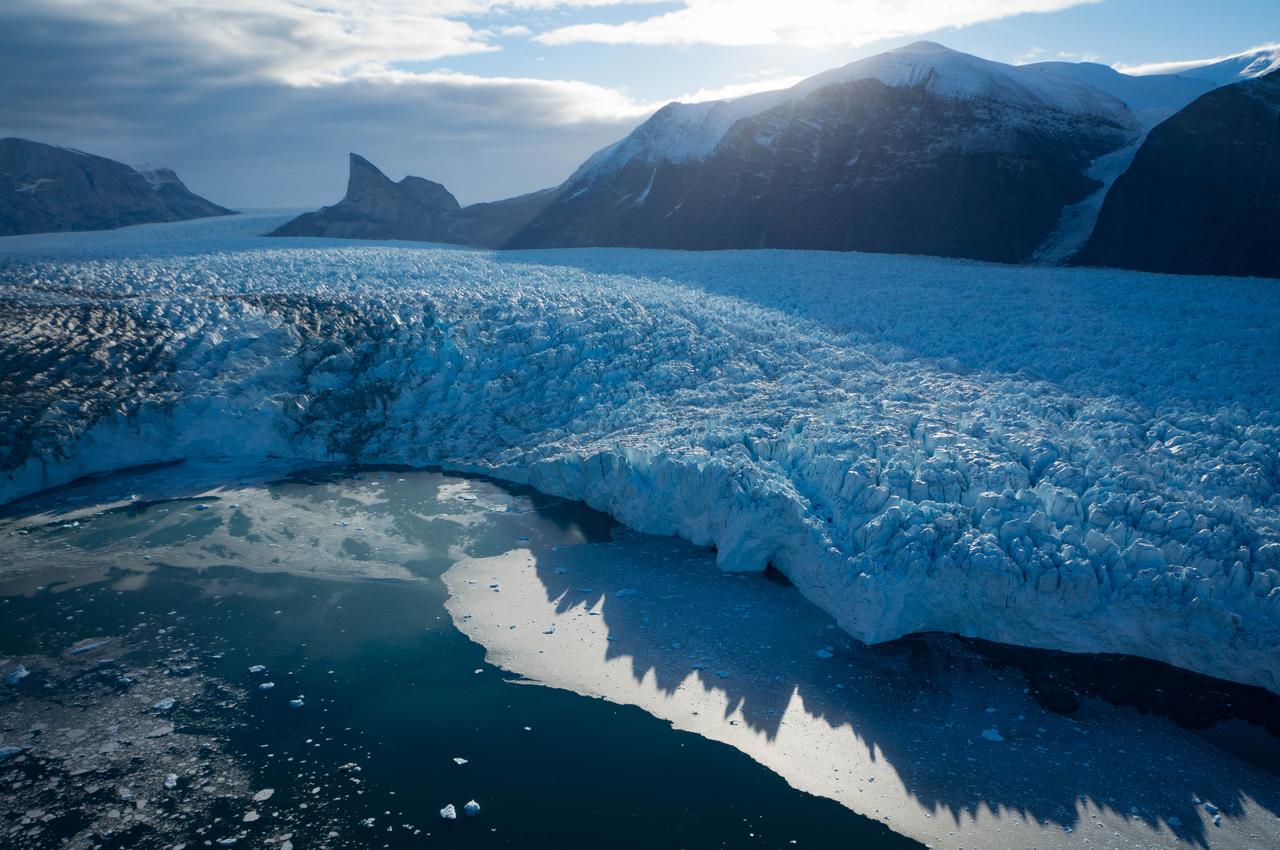
On June 15, 2016, the Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 satellite acquired a natural-color image of an area just inland from the coast of southwestern Greenland (120 kilometers southeast of Ilulisat and 500 kilometers north-northeast of Nuuk). According to Marco Tedesco, a professor at Columbia University’s Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, melting in this area began relatively early in April but was not sustained. It started up again in May and grew into the watery June scene pictured above. Surface melt can directly contribute to sea level rise via runoff. It can also force its way through crevasses to the base of a glacier, temporarily speeding up ice flow and indirectly contributing to sea level rise. Also, ponding of meltwater can “darken” the ice sheet’s surface and lead to further melting. Read more: <a href="https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=88288" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=88288</a> Credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Sea level rise is a natural consequence of the warming of our planet. We know this from basic physics. When water heats up, it expands. So when the ocean warms, sea level rises. When ice is exposed to heat, it melts. And when ice on land melts and water runs into the ocean, sea level rises. For thousands of years, sea level has remained relatively stable and human communities have settled along the planet’s coastlines. But now Earth’s seas are rising. Globally, sea level has risen about eight inches since the beginning of the 20th century and more than two inches in the last 20 years alone. All signs suggest that this rise is accelerating. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1heZn29" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1heZn29</a> Caption: An iceberg floats in Disko Bay, near Ilulissat, Greenland, on July 24, 2015. The massive Greenland ice sheet is shedding about 300 gigatons of ice a year into the ocean, making it the single largest source of sea level rise from melting ice. Credits: NASA/Saskia Madlener <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
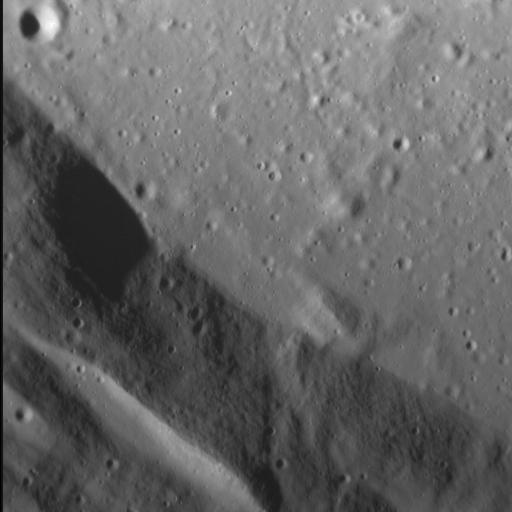

Impact crater floors are commonly flat and relatively smooth, the result of the cooling and solidification of impact melt generated by the impact event itself. Often, the pool of impact melt cracks as it cools, a process well illustrated by the striking Abedin crater. Although not visible in the frame above, this crater also hosts cooling cracks on its floor. It also boasts numerous terraces along its inner wall, which likely formed after the impact melt solidified. Note how the fine-grained texture of the inner walls contrasts with the crater's floor. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19231
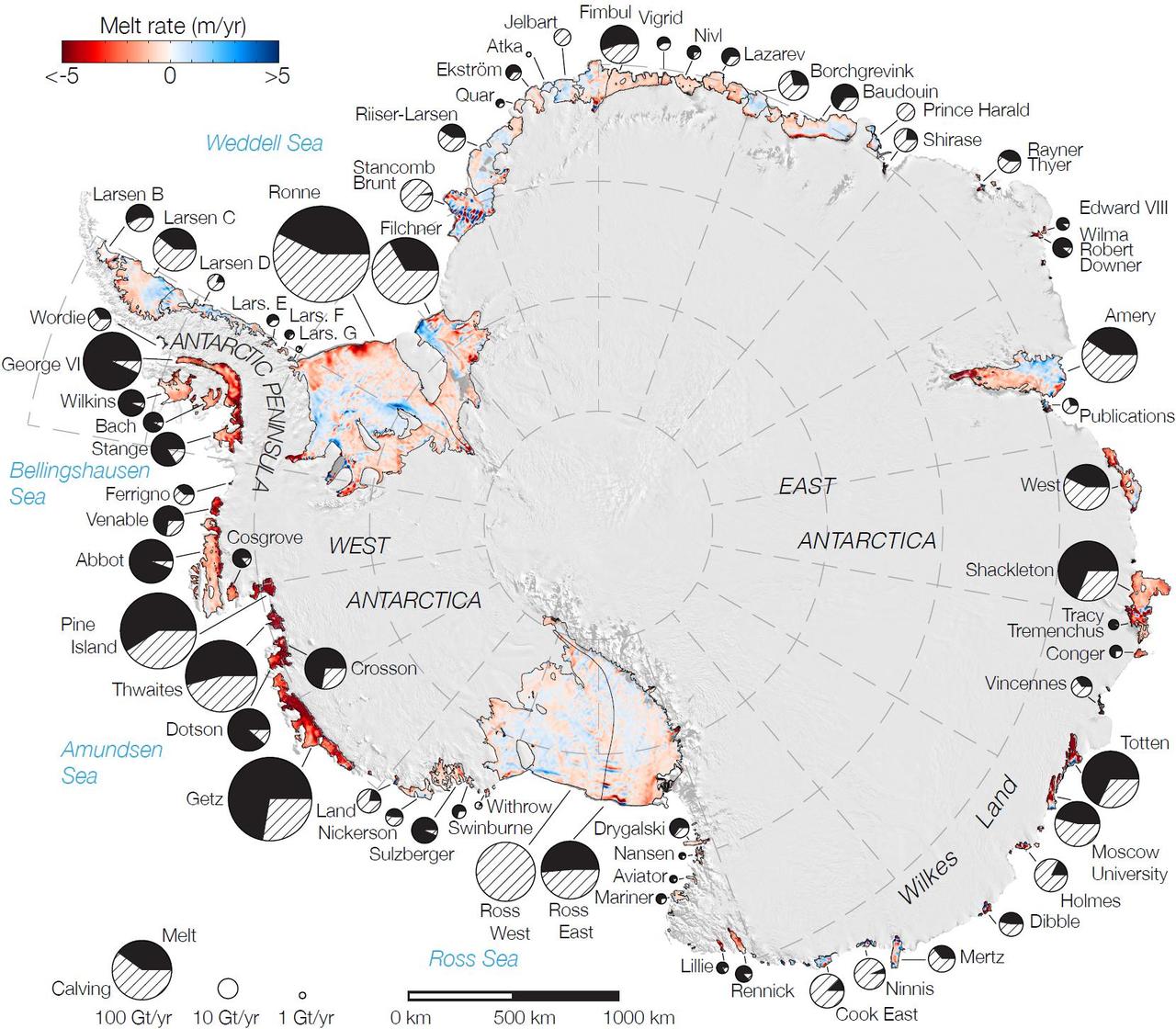
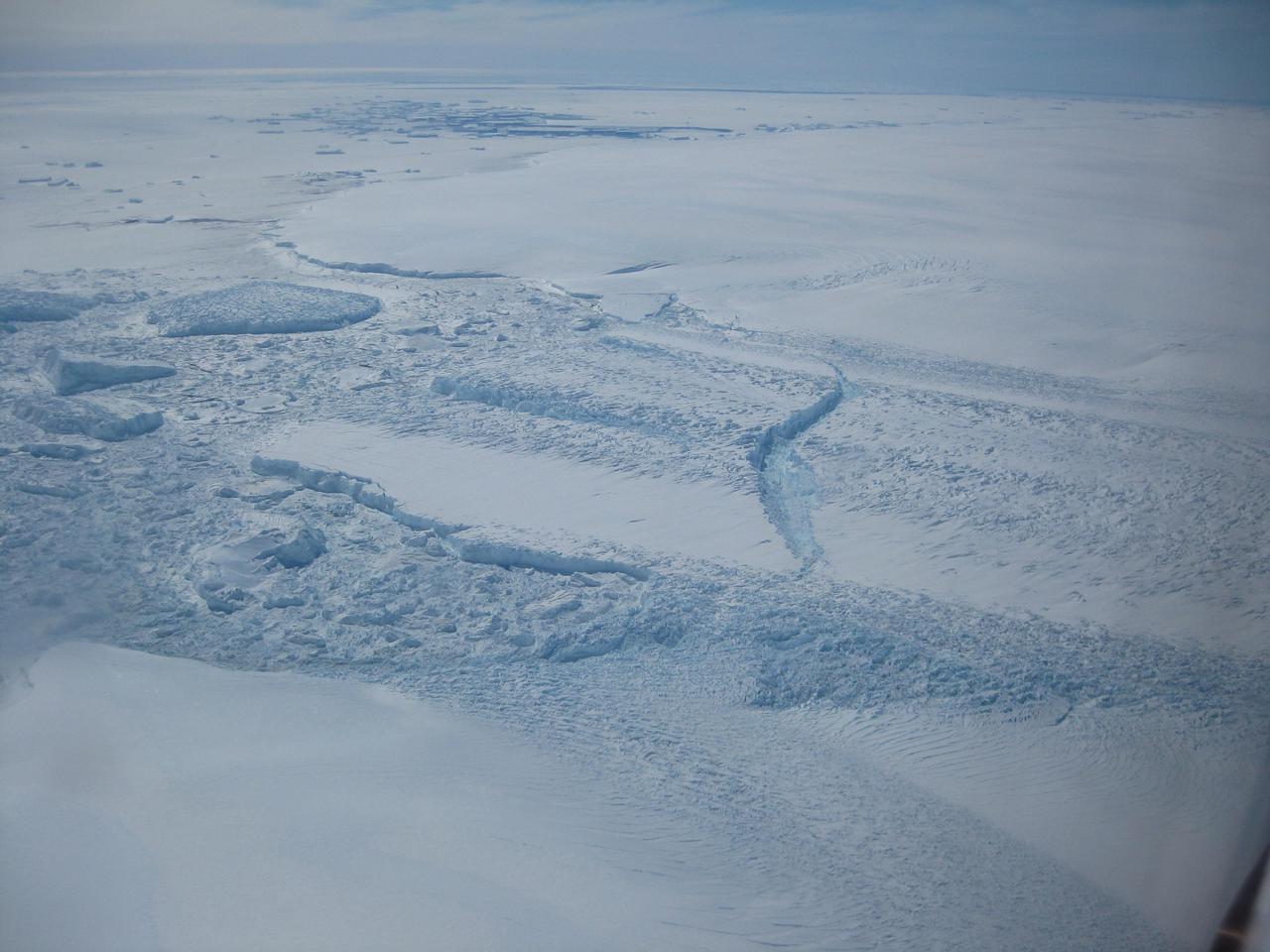
Rates of basal melt of Antarctic ice shelves melting of the shelves from underneath overlaid on a 2009 mosaic of Antarctica created from data from NASA Terra and Aqua spacecraft.
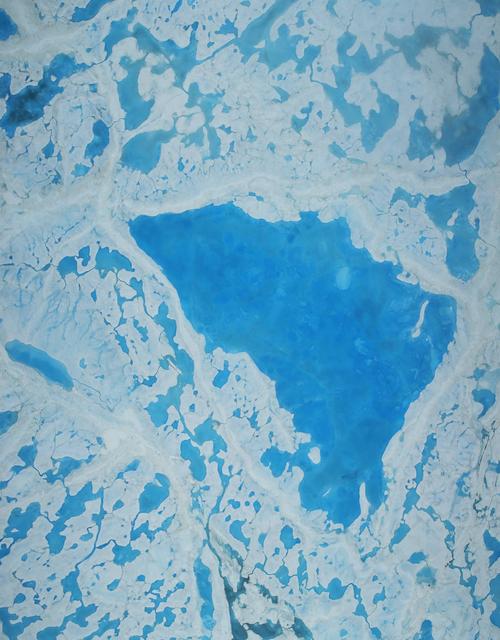

This summer, with sea ice across the Arctic Ocean shrinking to below-average levels, a NASA airborne survey of polar ice just completed its first flights. Its target: aquamarine pools of melt water on the ice surface that may be accelerating the overall sea ice retreat. NASA’s Operation IceBridge completed the first research flight of its new 2016 Arctic summer campaign on July 13. The science flights, which continue through July 25, are collecting data on sea ice in a year following a record-warm winter in the Arctic. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/29T6mxc" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/29T6mxc</a> Caption: A large pool of melt water over sea ice, as seen from an Operation IceBridge flight over the Beaufort Sea on July 14, 2016. During this summer campaign, IceBridge will map the extent, frequency and depth of melt ponds like these to help scientists forecast the Arctic sea ice yearly minimum extent in September. Credit: NASA/Operation IceBridge
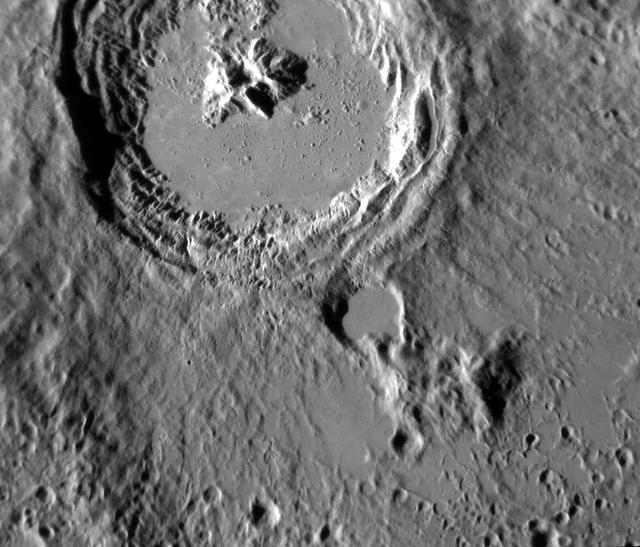

Date acquired: April 05, 2013 This striking image of Kuiper shows the crater in a new perspective. This image highlights the crater's smooth impact melt and central peaks. Kuiper, first seen by Mariner 10, is an easily identifiable feature on Mercury's surface due to its bright rays, similar to Hokusai. This image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation. Targeted observations are images of a small area on Mercury's surface at resolutions much higher than the 200-meter/pixel morphology base map. It is not possible to cover all of Mercury's surface at this high resolution, but typically several areas of high scientific interest are imaged in this mode each week. The MESSENGER spacecraft is the first ever to orbit the planet Mercury, and the spacecraft's seven scientific instruments and radio science investigation are unraveling the history and evolution of the Solar System's innermost planet. During the first two years of orbital operations, MESSENGER acquired over 150,000 images and extensive other data sets. MESSENGER is capable of continuing orbital operations until early 2015. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
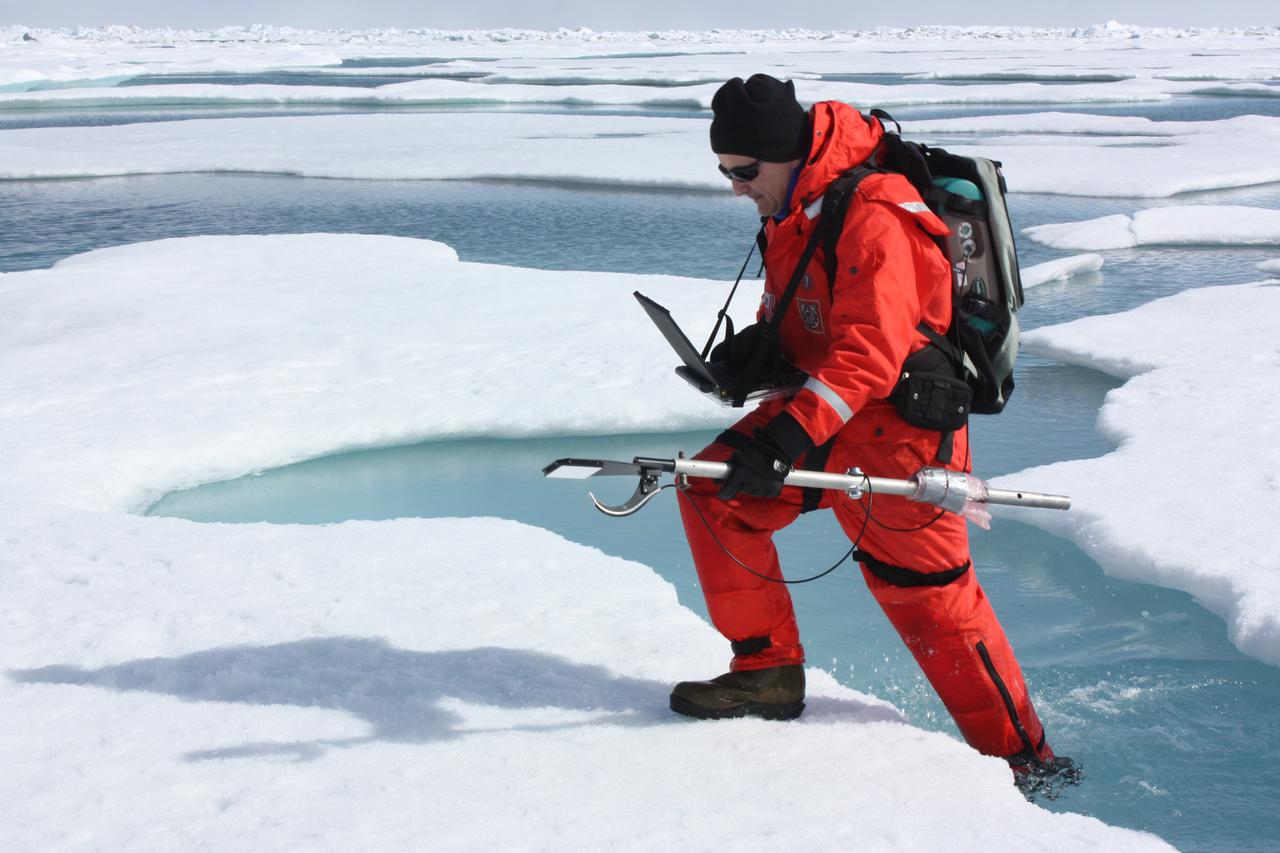

On July 10, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, maneuvered through melt ponds collecting optical data along the way to get a sense of the amount of sunlight reflected from sea ice and melt ponds in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
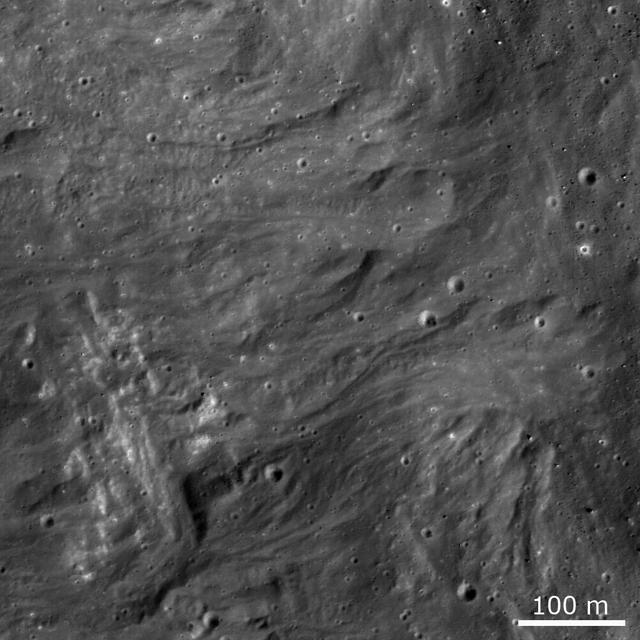

Frozen impact melt flows on the ejecta blanket of the young impact crater Giordano Bruno in this image from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
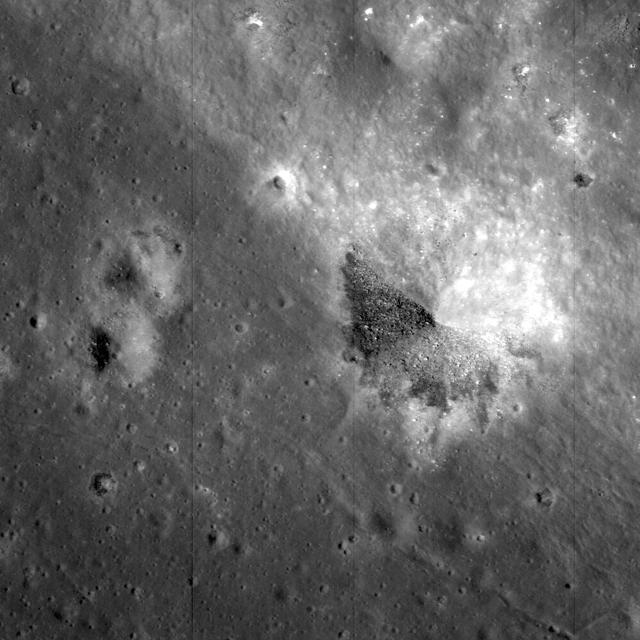

NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter looks near the northeast edge of the unusually large melt pond adjacent to the lunar far side crater King.
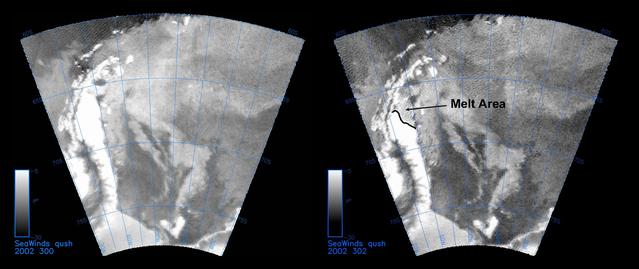
The SeaWinds instrument on NASA Quick Scatterometer QuikScat spacecraft captured these near-real-time backscatter images of melting on the Larsen C ice shelf in Antarctica Weddell Sea between October 27 left and October 29 right.
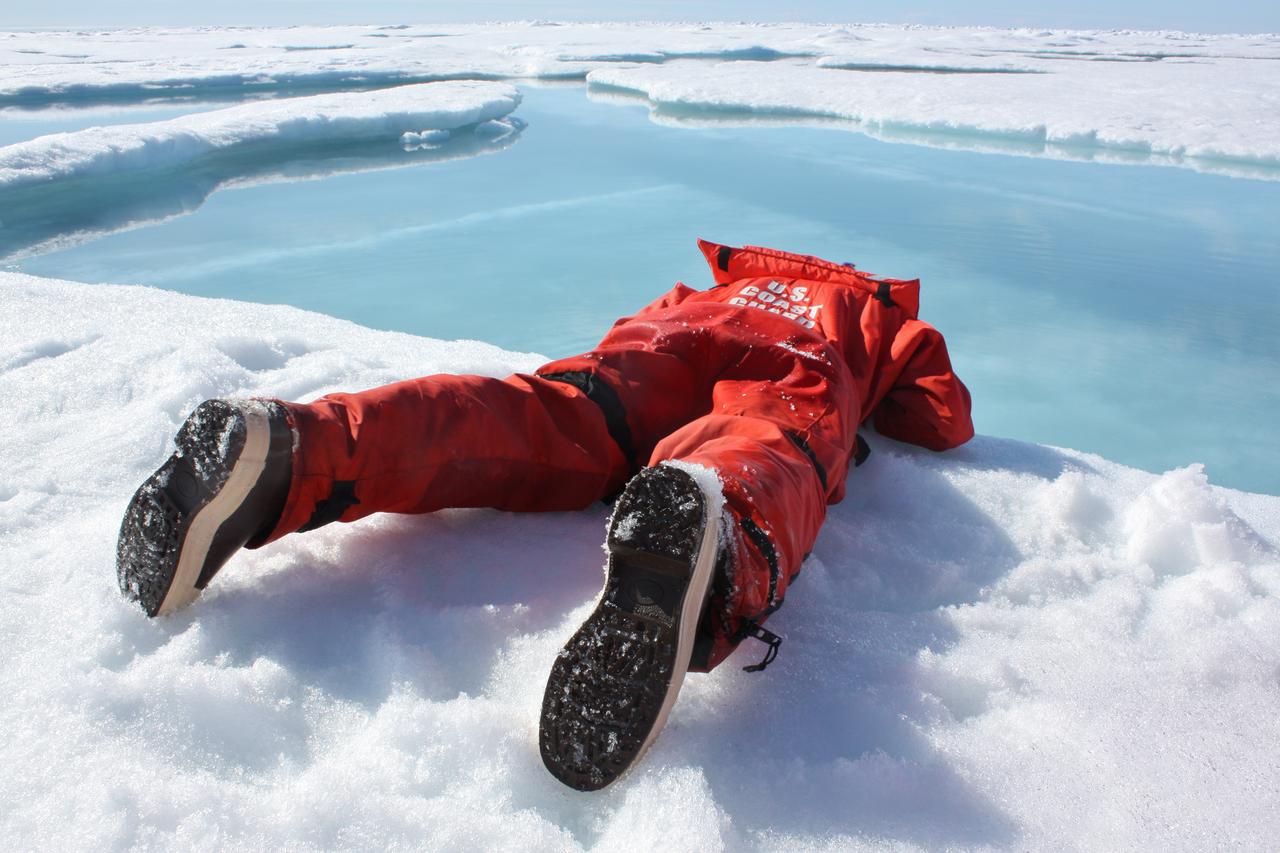

On July 19, 2011, Zachary Brown of Stanford University sipped freshwater from a melt pond on sea ice in the Arctic ocean. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
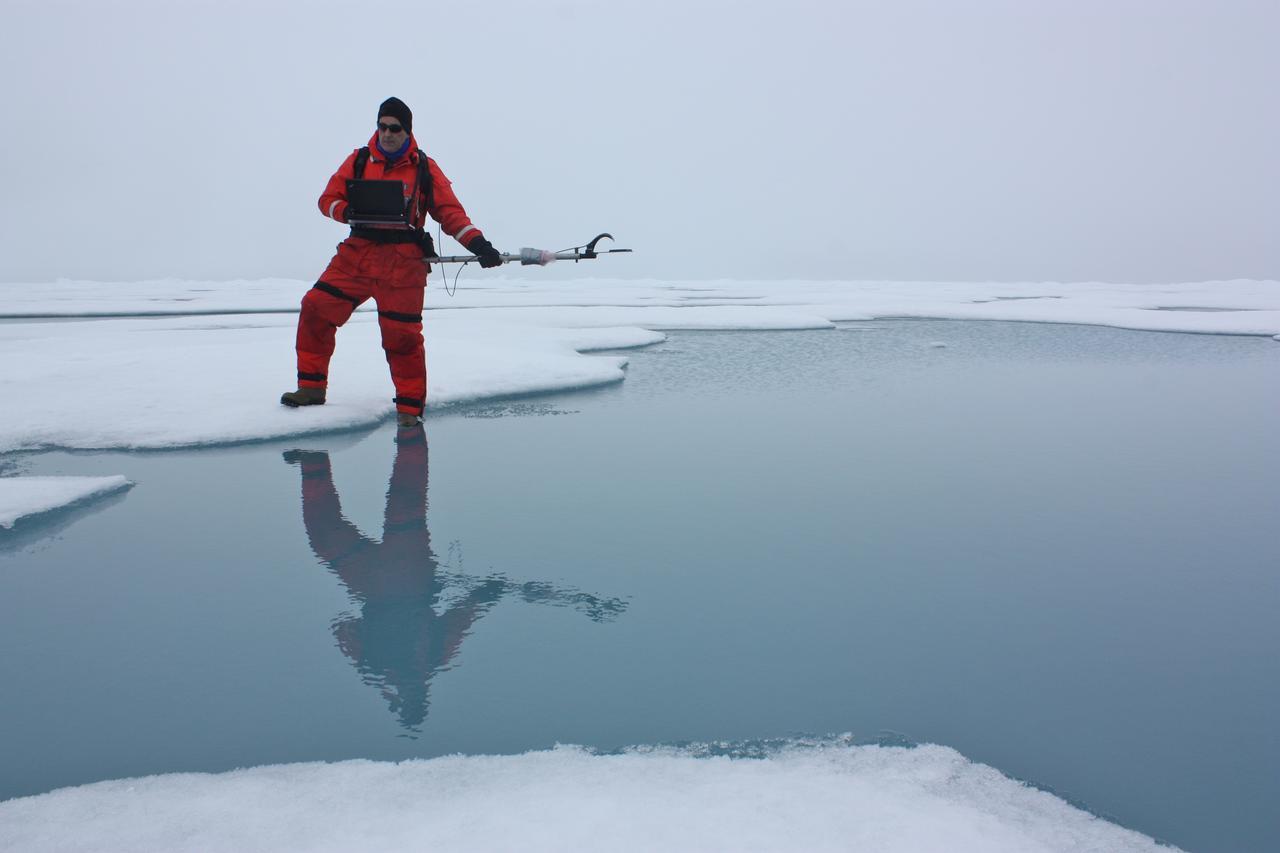

On July 6, 2011, Don Perovich, of Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, used a spectroradiometer to measure the amount of sunlight reflected from the surface of ice and melt ponds in the Chukchi Sea. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
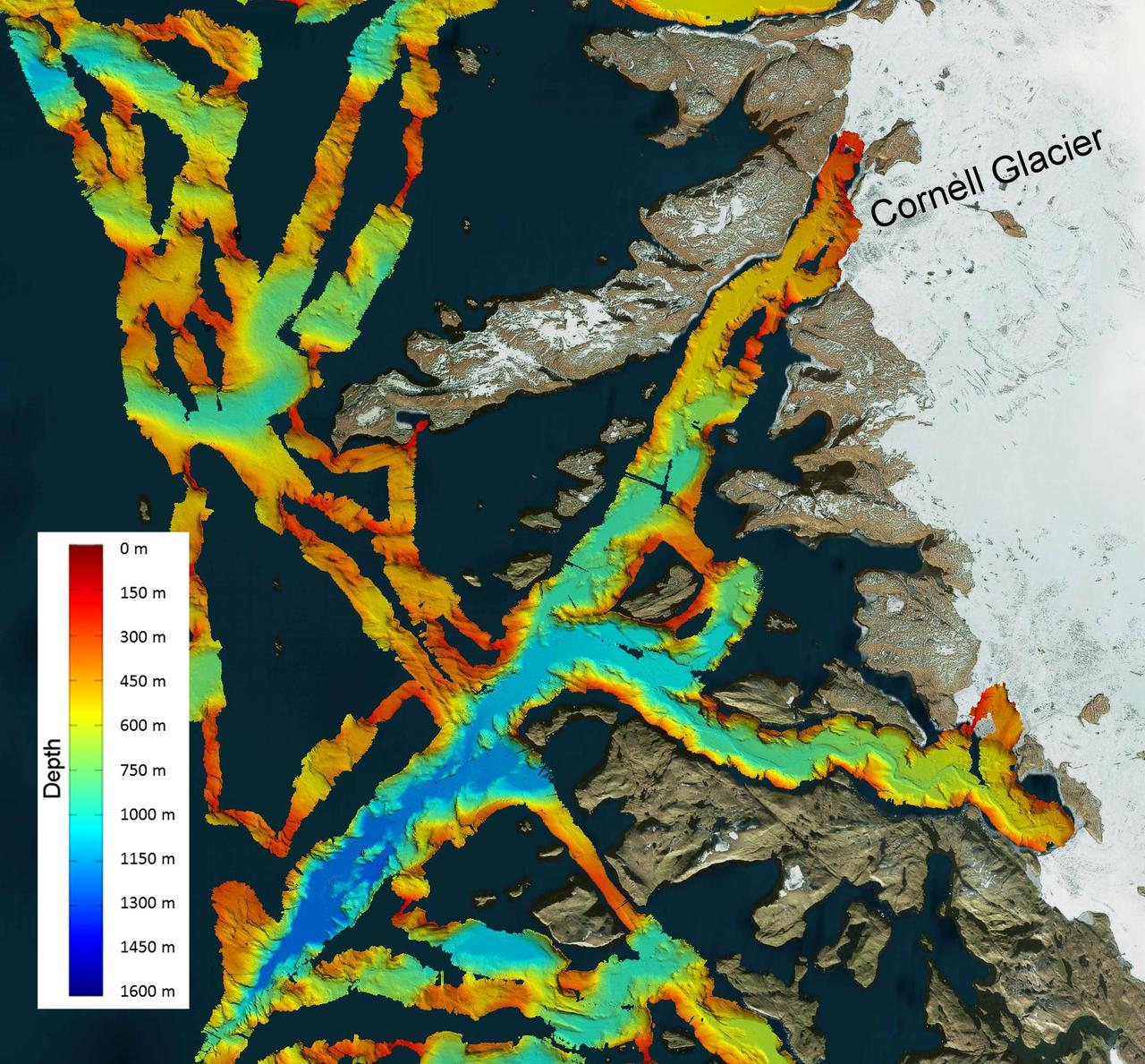

This image shows a region of the sea floor off the coast of northwest Greenland mapped as part of NASA Oceans Melting Greenland OMG mission. The data shown here will be used to understand the pathways by which warm water can reach glacier edges.
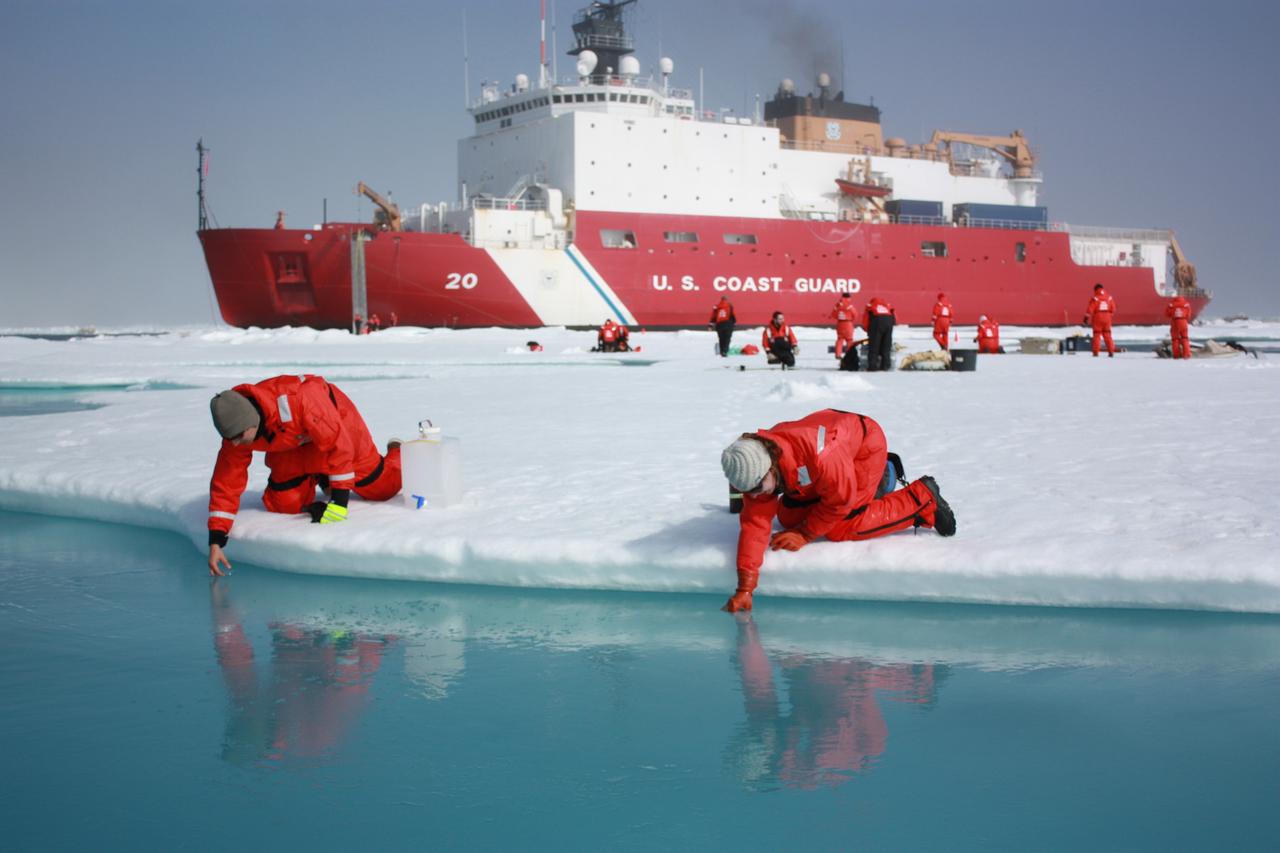

On July 10, 2011, Jens Ehn of Scripps Institution of Oceanography (left), and Christie Wood of Clark University (right), scooped water from melt ponds on sea ice in the Chukchi Sea. The water was later analyzed from the Healy's onboard science lab. The ICESCAPE mission, or "Impacts of Climate on Ecosystems and Chemistry of the Arctic Pacific Environment," is a NASA shipborne investigation to study how changing conditions in the Arctic affect the ocean's chemistry and ecosystems. The bulk of the research took place in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas in summer 2010 and 2011. Credit: NASA/Kathryn Hansen <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
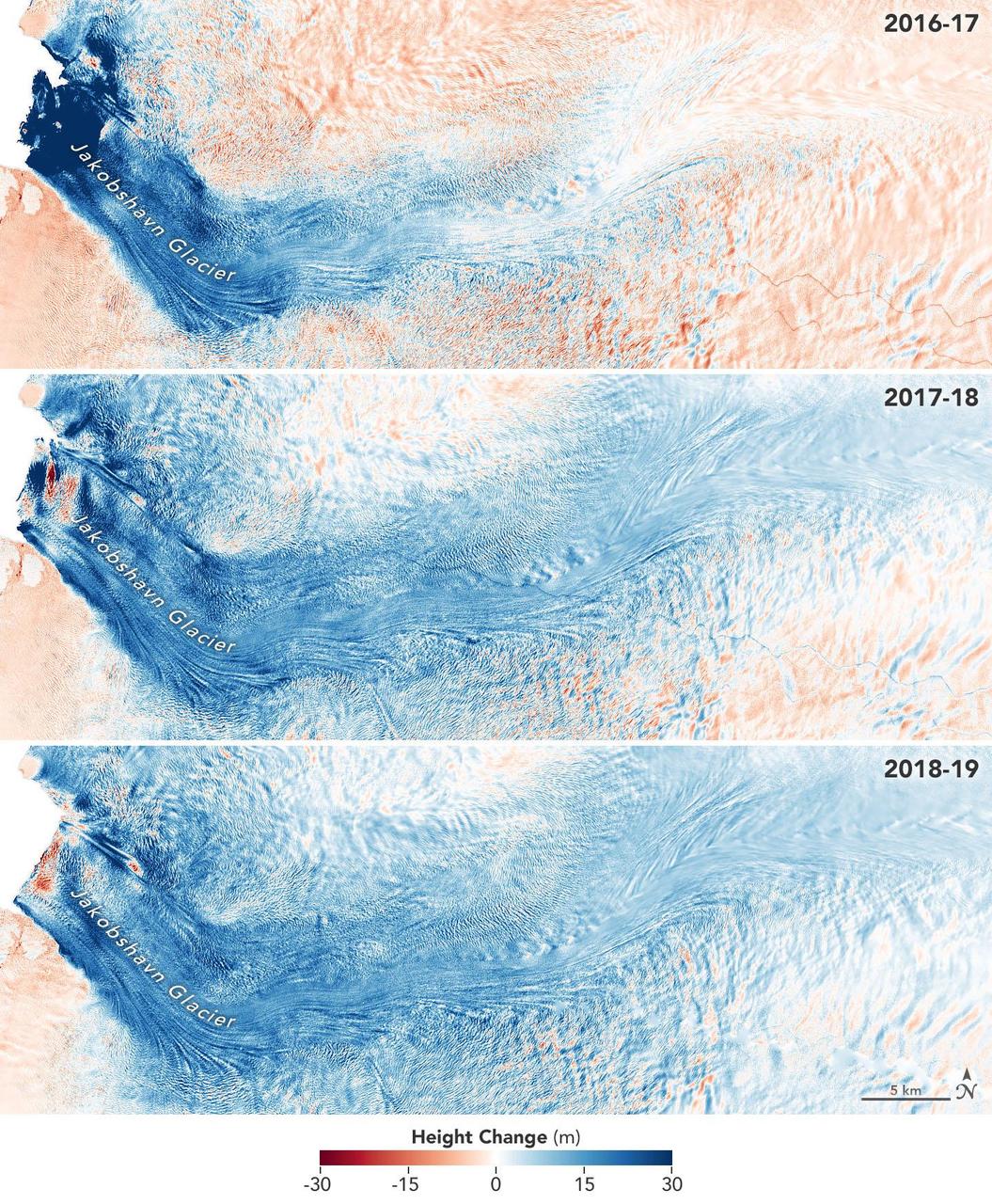
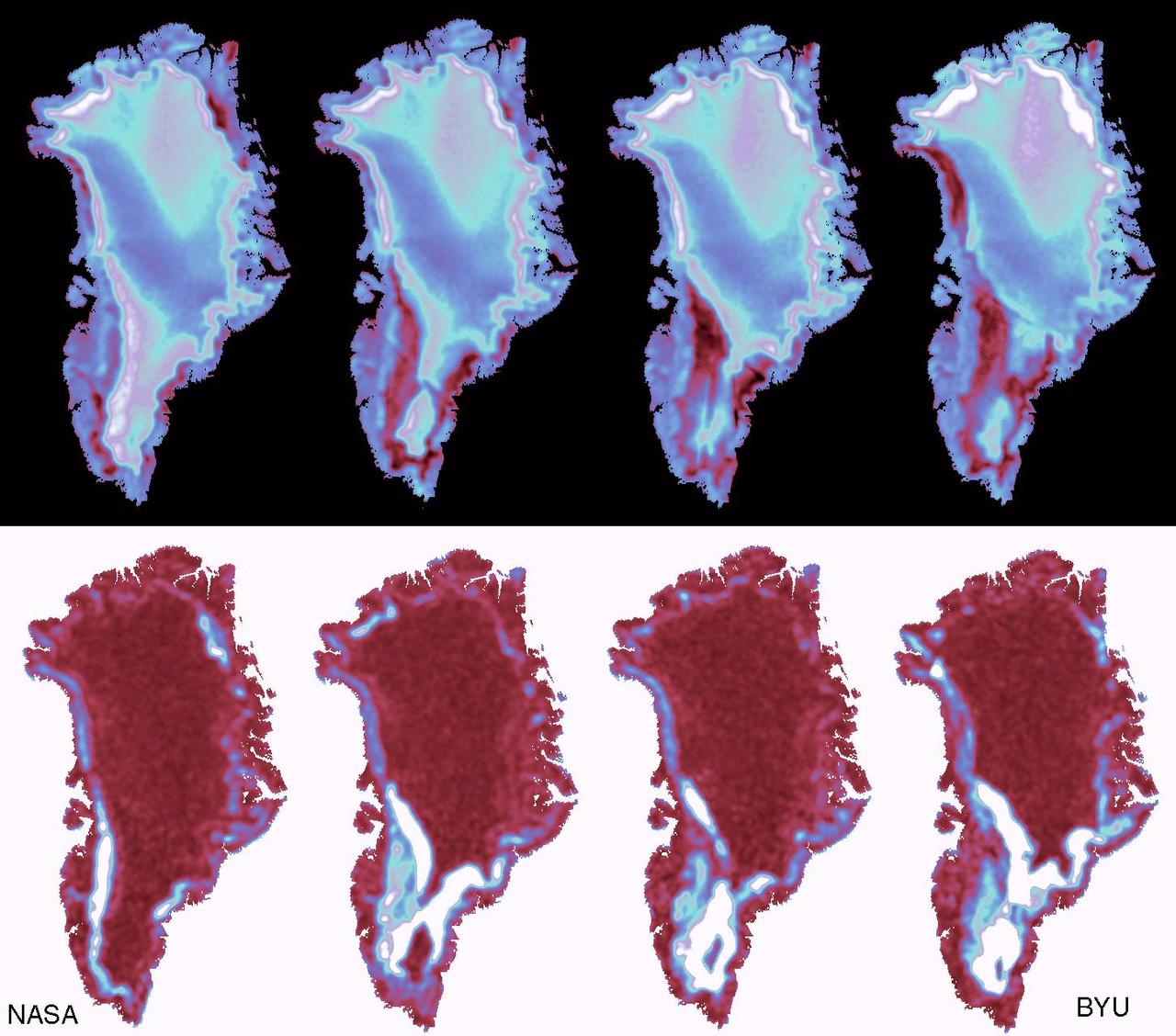
These images show the mass Greenland's Jakobshavn Glacier has gained from 2016-17, 2017-18 and 2018-19. Areas with the most growth — about 33 yards (30 meters) — are shown in dark blue. Red areas represent thinning. The images were produced using GLISTIN-A radar data as part of NASA's Ocean's Melting Greenland (OMG) mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23147
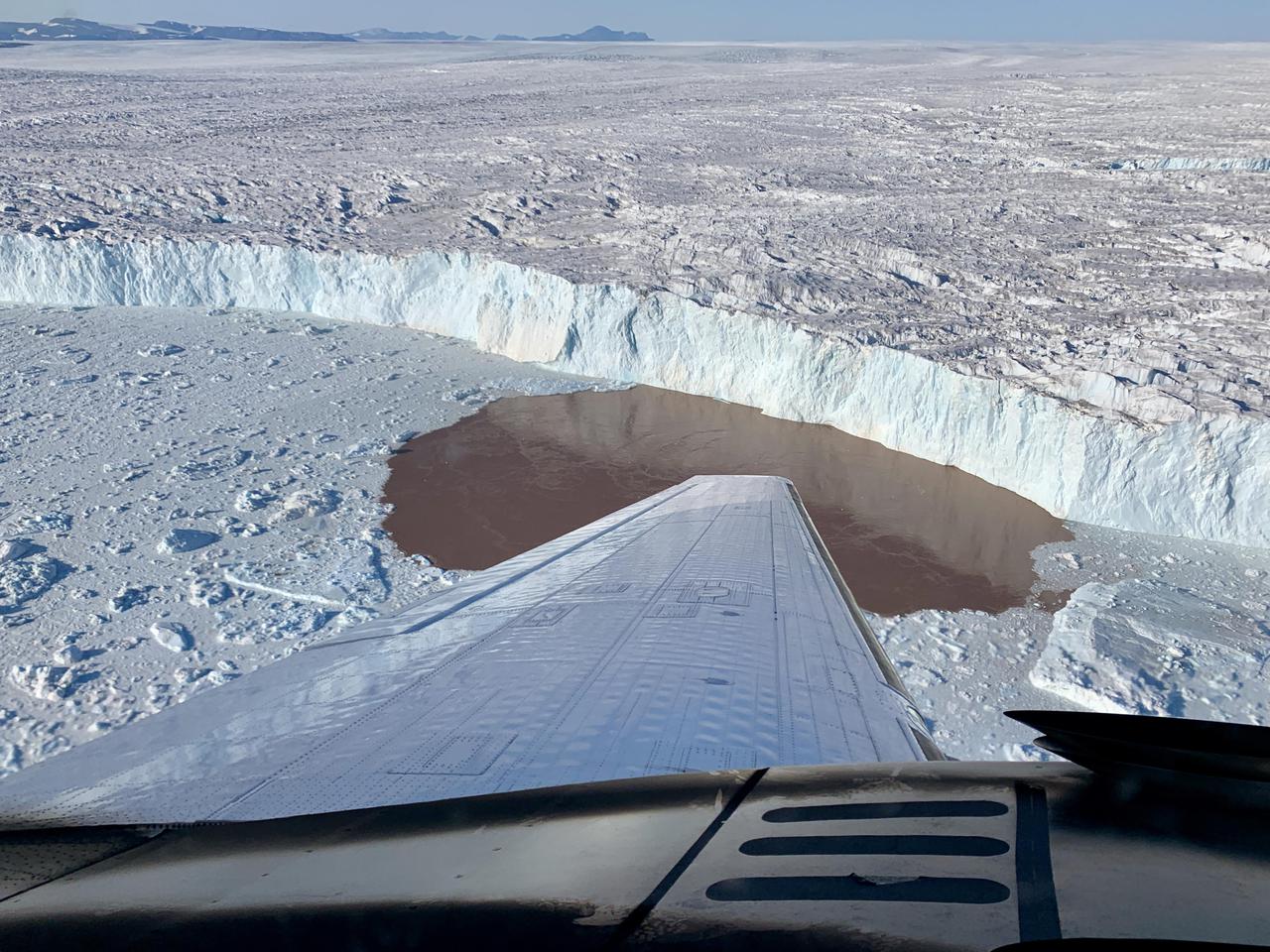

In this aerial view, a glacier along Greenland's craggy coastline is actively undergoing undercutting, a process in which meltwater flowing out from the bottom of the glacier enters the fjord. The brown water in front of the glacier is caused by sediment being dredged up from the base of the glacier by meltwater plumes reaching the surface of the fjord. Because the meltwater contains no salt, it is lighter and rises through the saltier ocean water, dragging the warm ocean water into contact with the ice at the glacier's base. The result is increased melting at the bottom of the glacier, which creates and overhanging layer of ice that breaks off (or calves) as icebergs. As the climate warms, the ocean water temperature and the amount of meltwater both increase, combining to hasten this undercutting process and speed up the ice loss from Greenland's Ice Sheet. The image was taken on Aug. 25, 2019 by a probe-dropping airplane as part of the Oceans Melting Greenland (OMG) mission. OMG has been studying glaciers that plunge into Greenland's steep-sided inlets, or fjords, for the past five years, gathering precise measurements of fjord depth and water salinity from probes dropped by plane, supplemented by measurements made by boat. The aim is to better understand how the warming ocean water around Greenland is hastening ice melt and calving of these marine-terminating glaciers. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24162
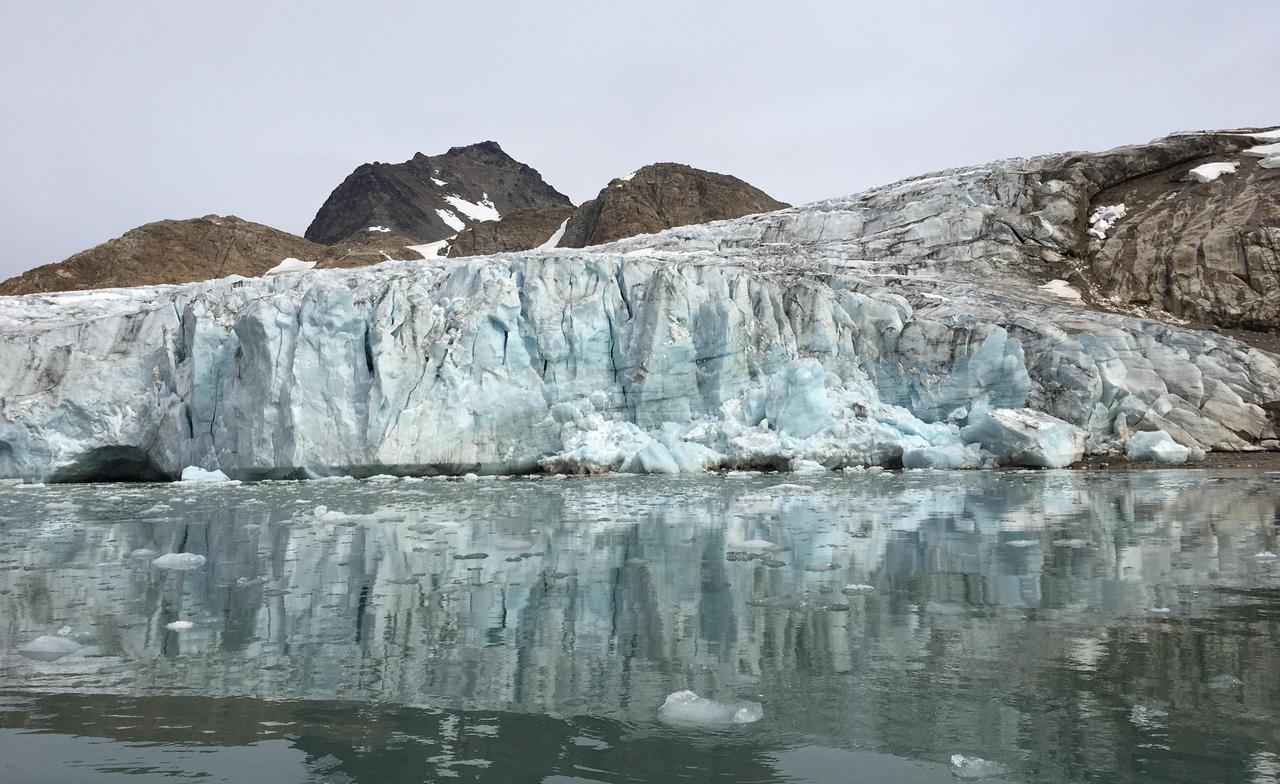

NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland airborne mission found that most of Greenland's glaciers that empty into the ocean are at greater risk of rapid ice loss than previously understood. OMG's six-year field campaign studied the ocean's role in glacial ice loss by gathering precise measurements of ocean depth, temperature, and salinity in front of more than 220 glaciers. The mission's goal was to clarify our understanding of sea level rise over the next 50 years. This photo of Apusiaajik Glacier was taken near Kulusuk, Greenland, on Aug. 26, 2018, during OMG's field operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24983

NASA's IceBridge, an airborne survey of polar ice, flew over the Helheim/Kangerdlugssuaq region of Greenland on Sept. 11, 2016. This photograph from the flight captures Greenland's Steenstrup Glacier, with the midmorning sun glinting off of the Denmark Strait in the background. IceBridge completed the final flight of the summer campaign to observe the impact of the summer melt season on the ice sheet on Sept. 16. The IceBridge flights, which began on Aug. 27, are mostly repeats of lines that the team flew in early May, so that scientists can observe changes in ice elevation between the spring and late summer. For this short, end-of-summer campaign, the IceBridge scientists flew aboard an HU-25A Guardian aircraft from NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. Credit: NASA/John Sonntag <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
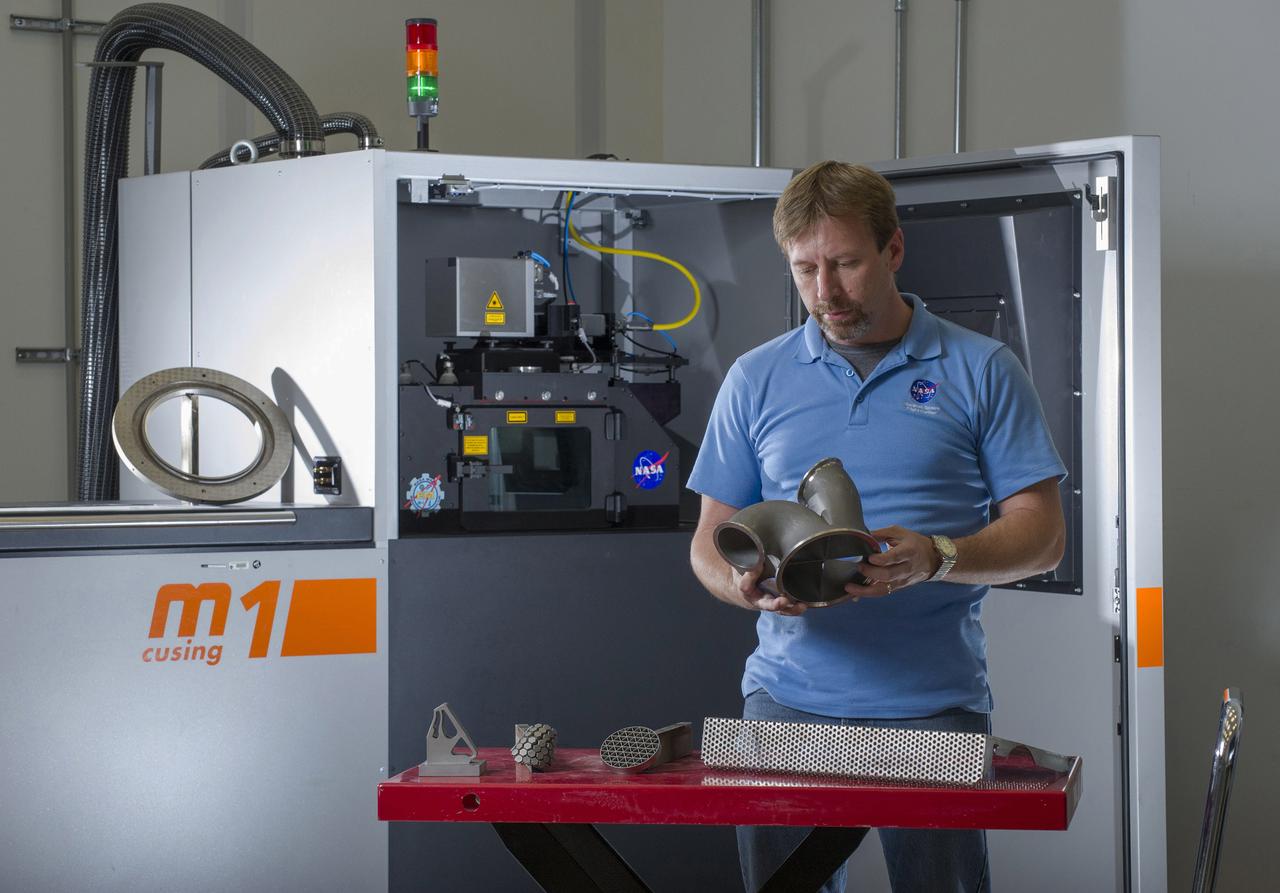

KEN COOPER, TEAM LEAD OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH NICKEL ALLOY 718 PARTS FABRICATED USING THE M1 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M1 MACHINE IS DEDICATED TO BUILDING QUALIFICATION SAMPLES AND HARDWARE DEMONSTRATORS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE PROJECT.
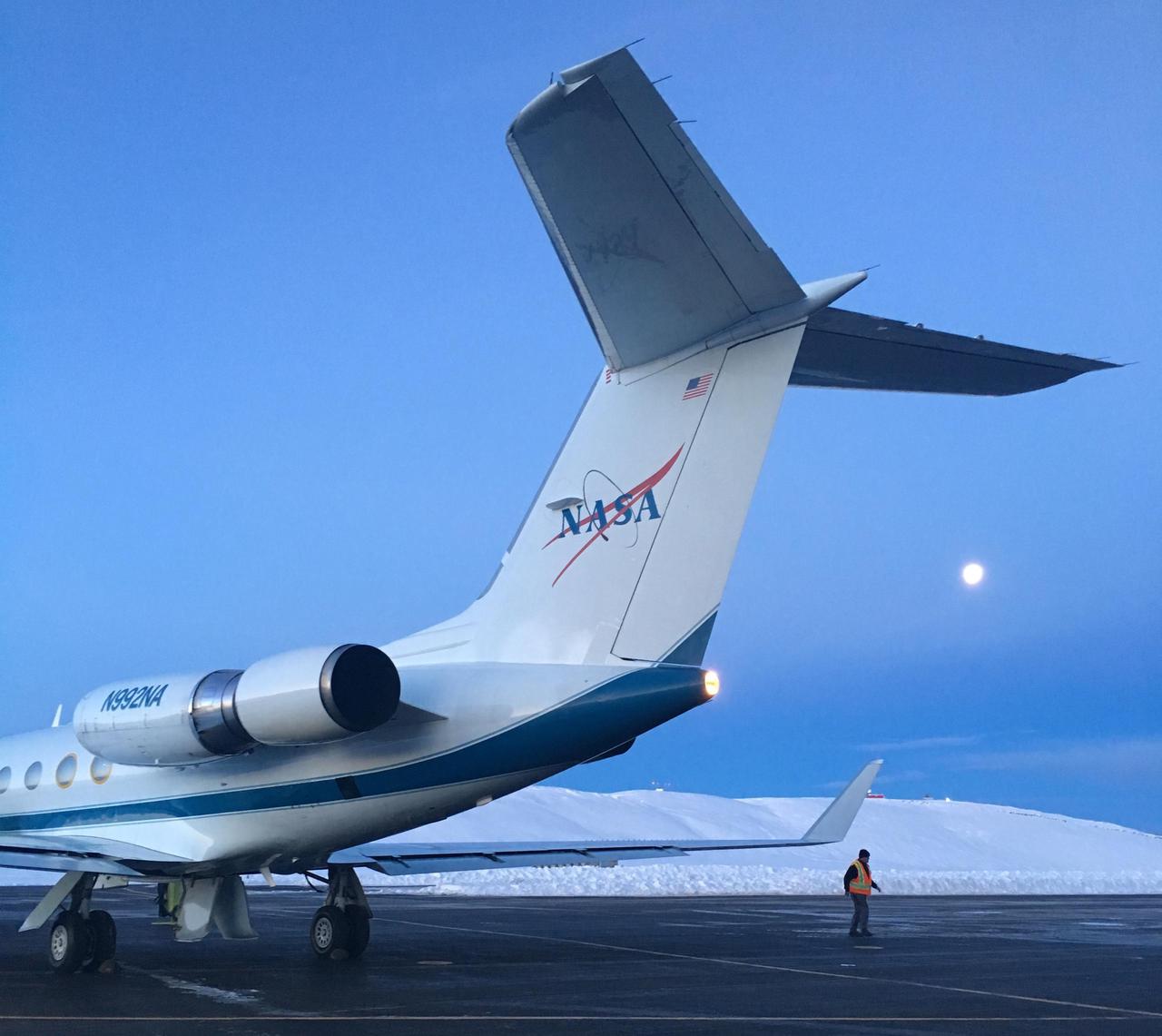

NASA's Gulfstream III was one of several research aircraft that NASA's Oceans Melting Greenland mission used during its six-year field campaign to record the temperature, salinity, and depth of the ocean around the entire island. OMG used airports in Greenland, Iceland, and Norway as bases for research flights. This image was taken at Thule Air Base, Greenland, on Sept. 18, 2016. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24984
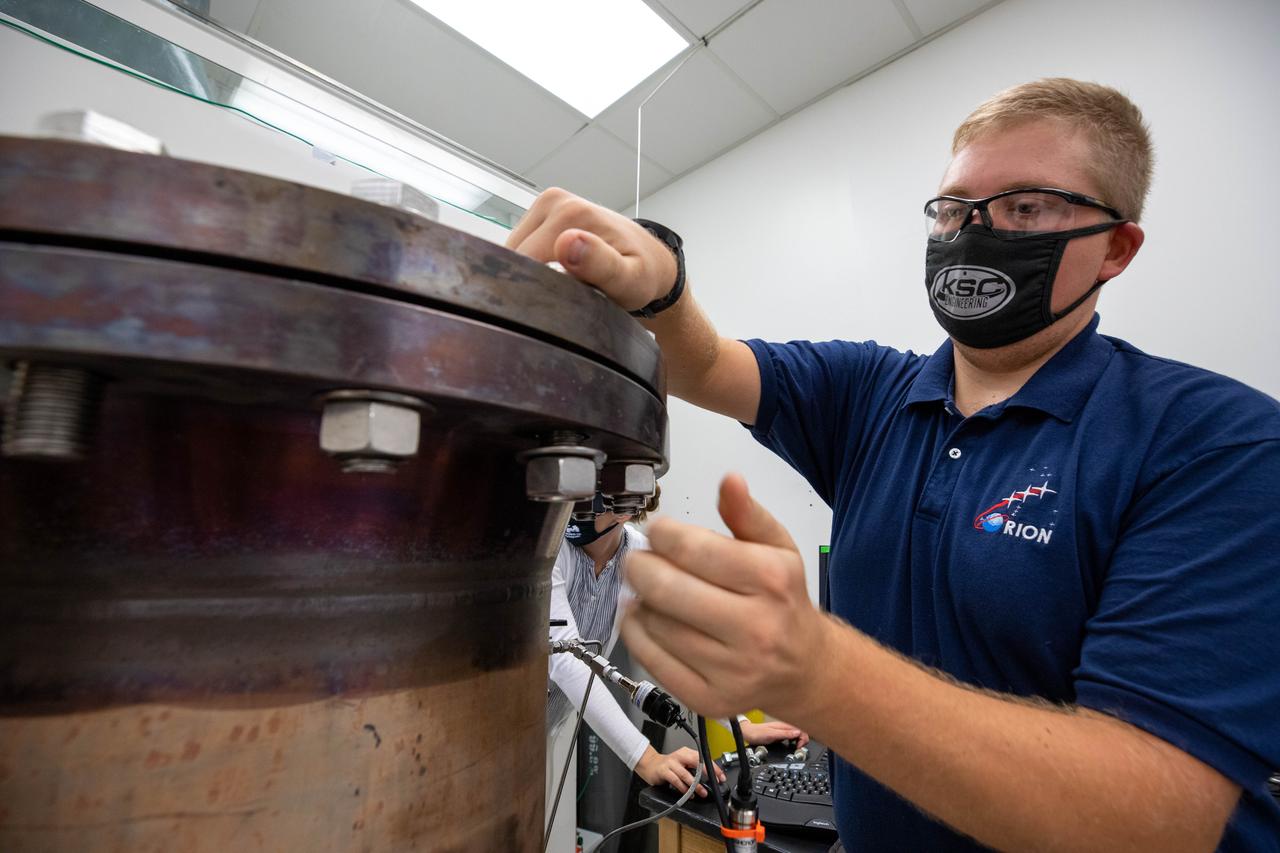

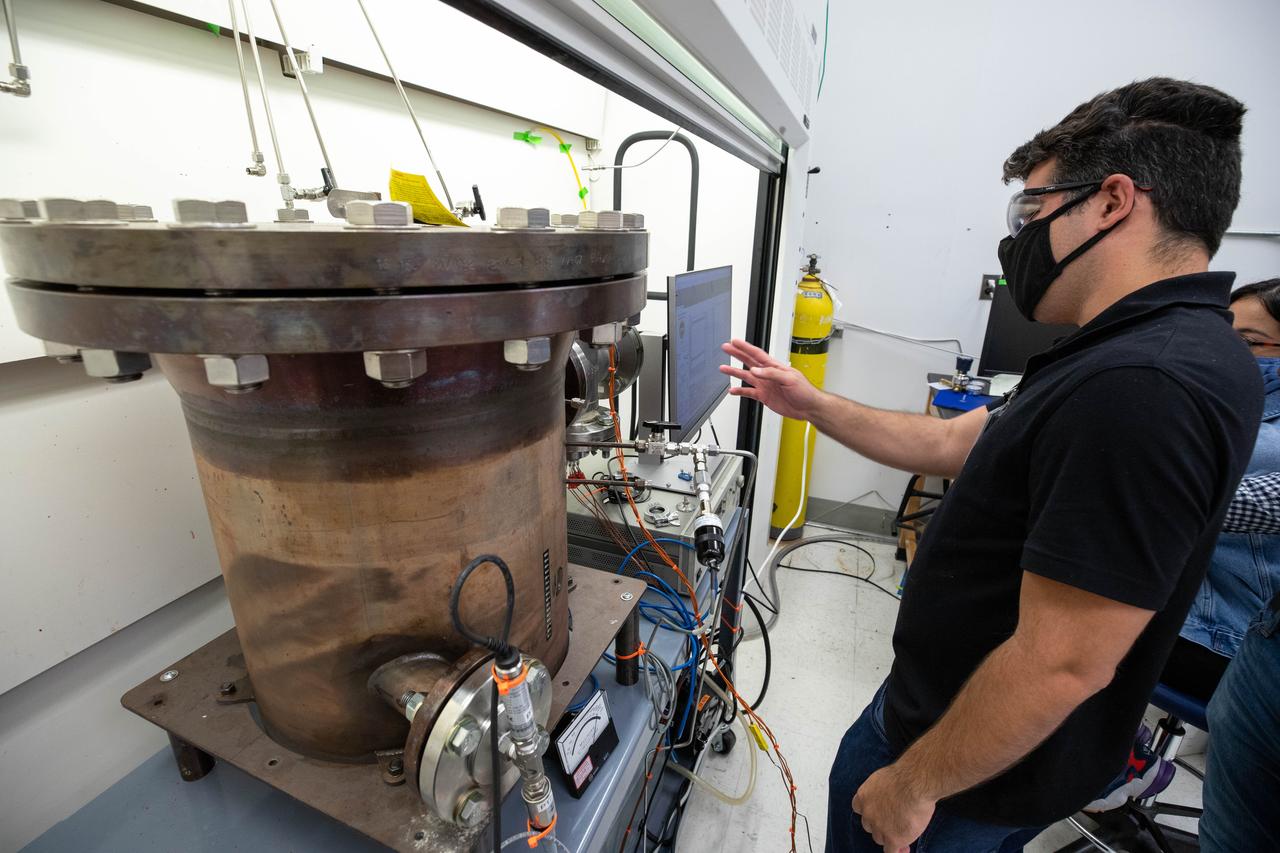
Evan Bell, a mechanical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
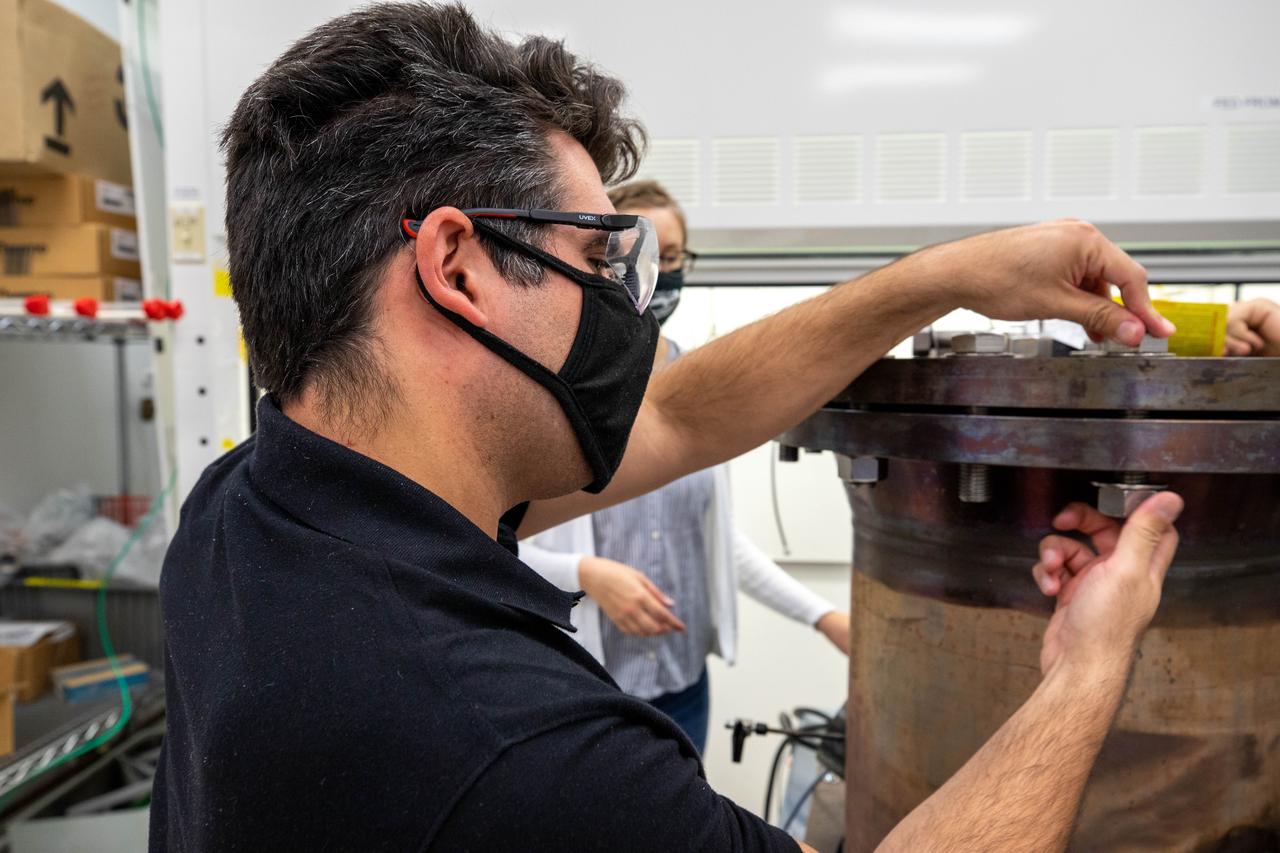

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.

Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and Evan Bell, GaLORE mechanical engineer, inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – stimulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
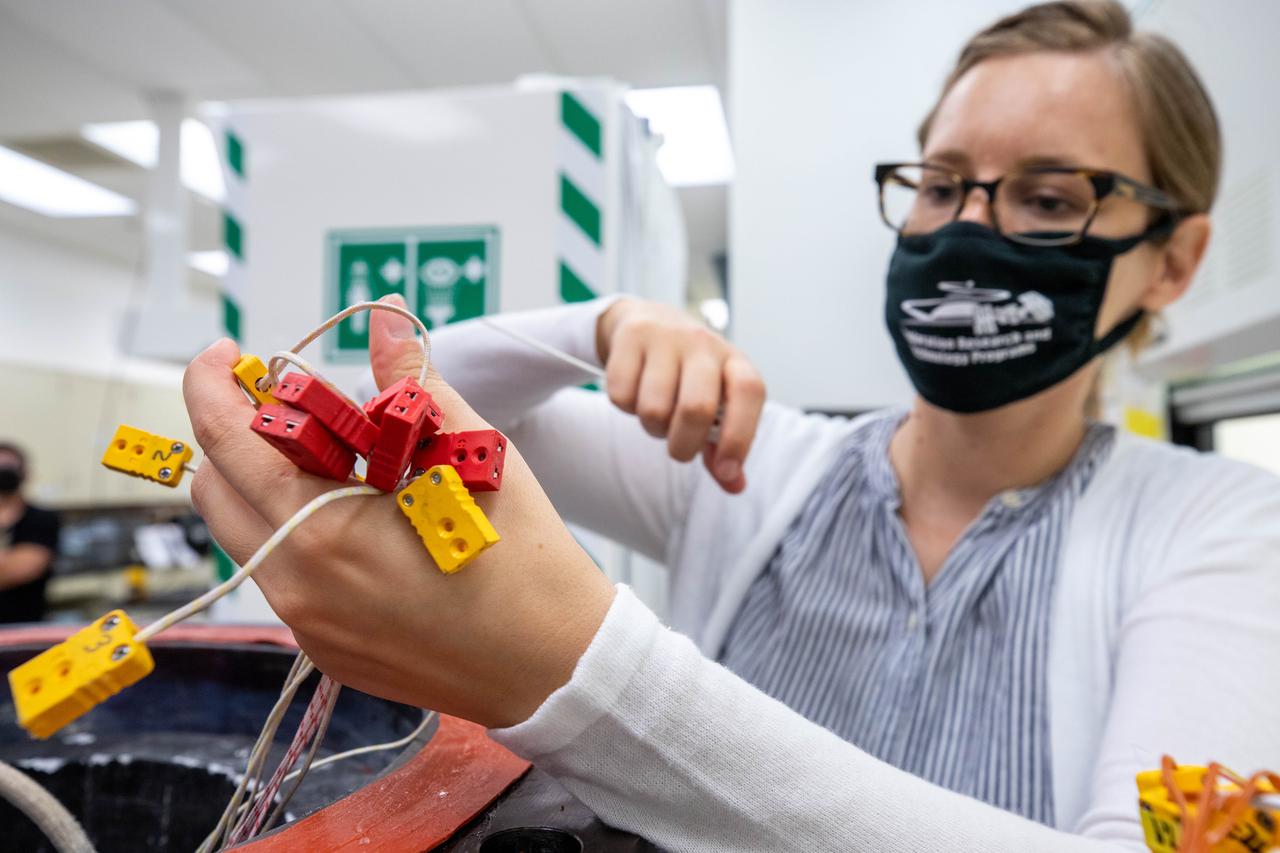

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects some of the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
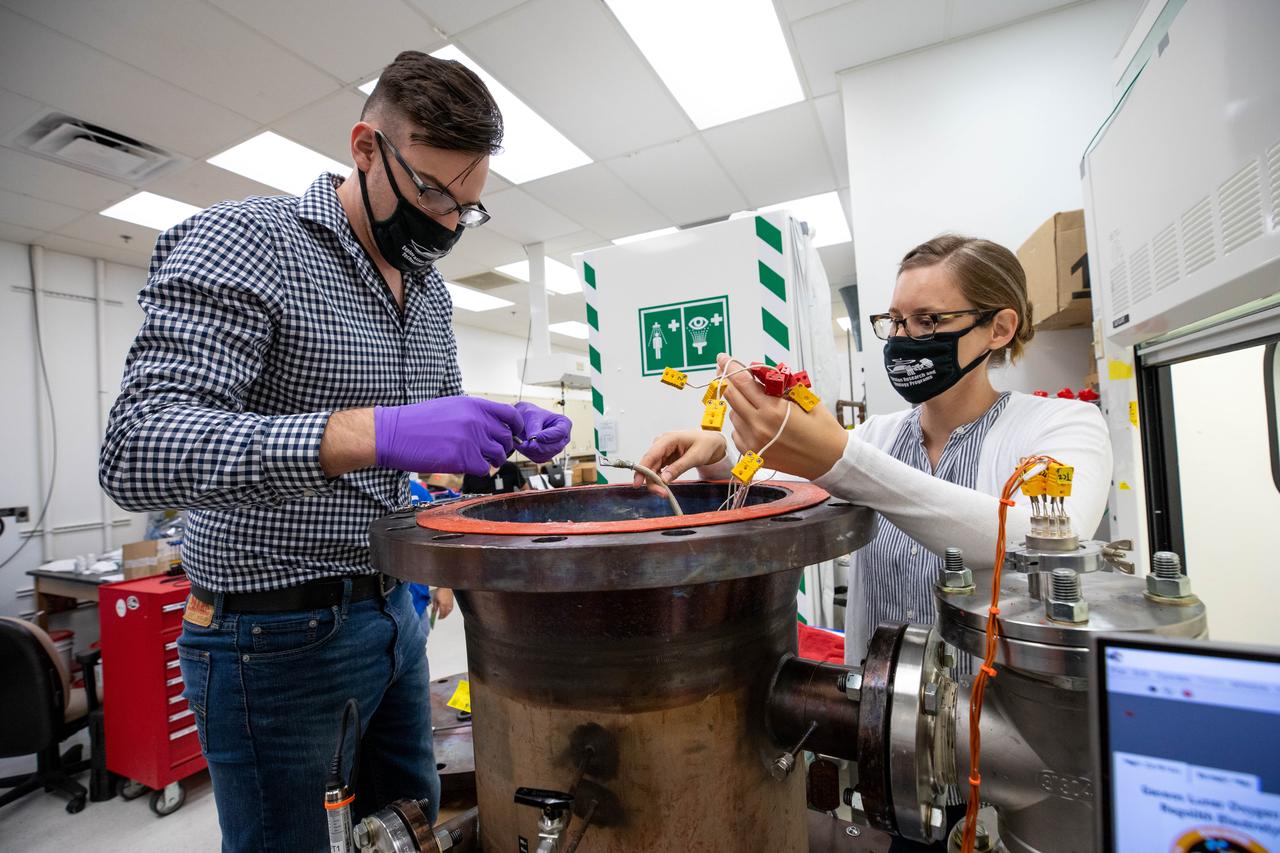

Kevin Grossman, left, principal investigator of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project, and Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the GaLORE team, check some of the project’s hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
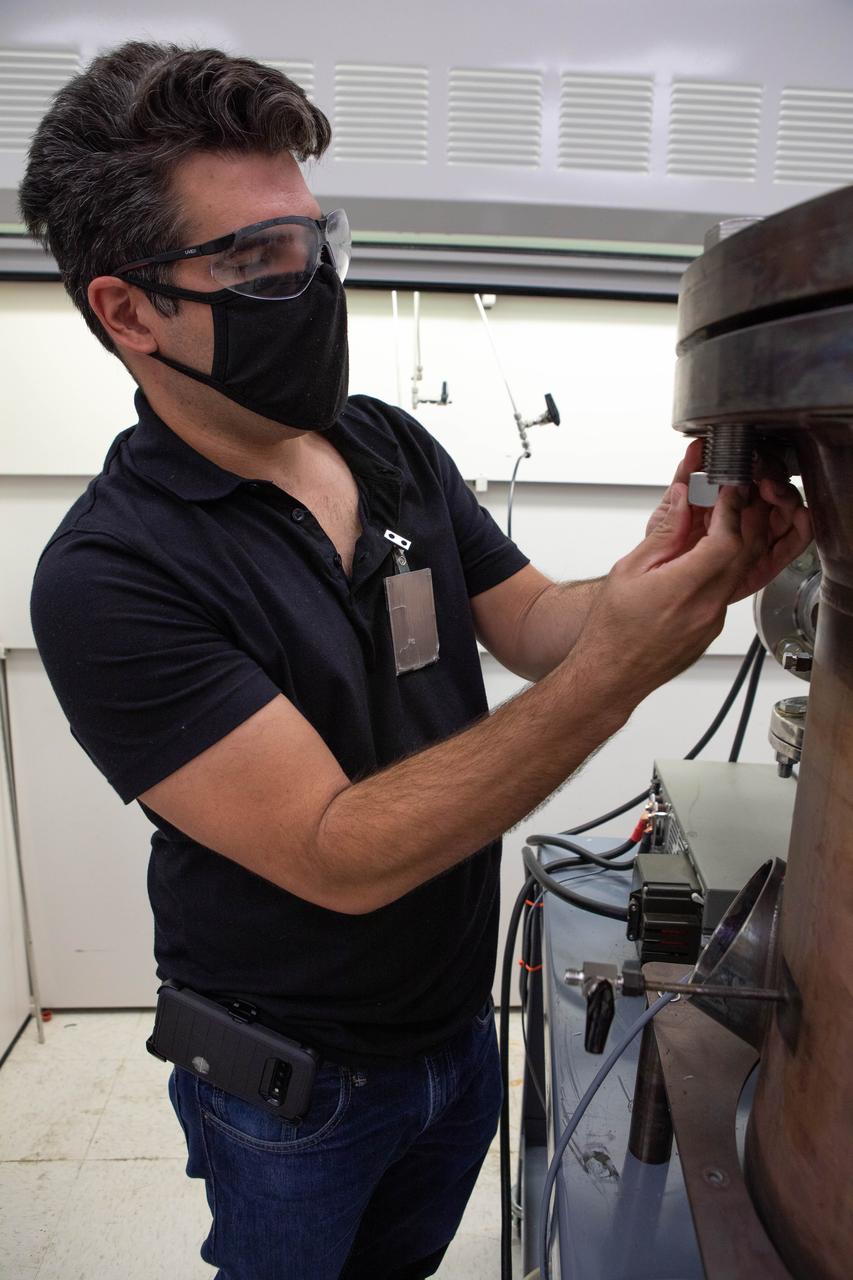

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
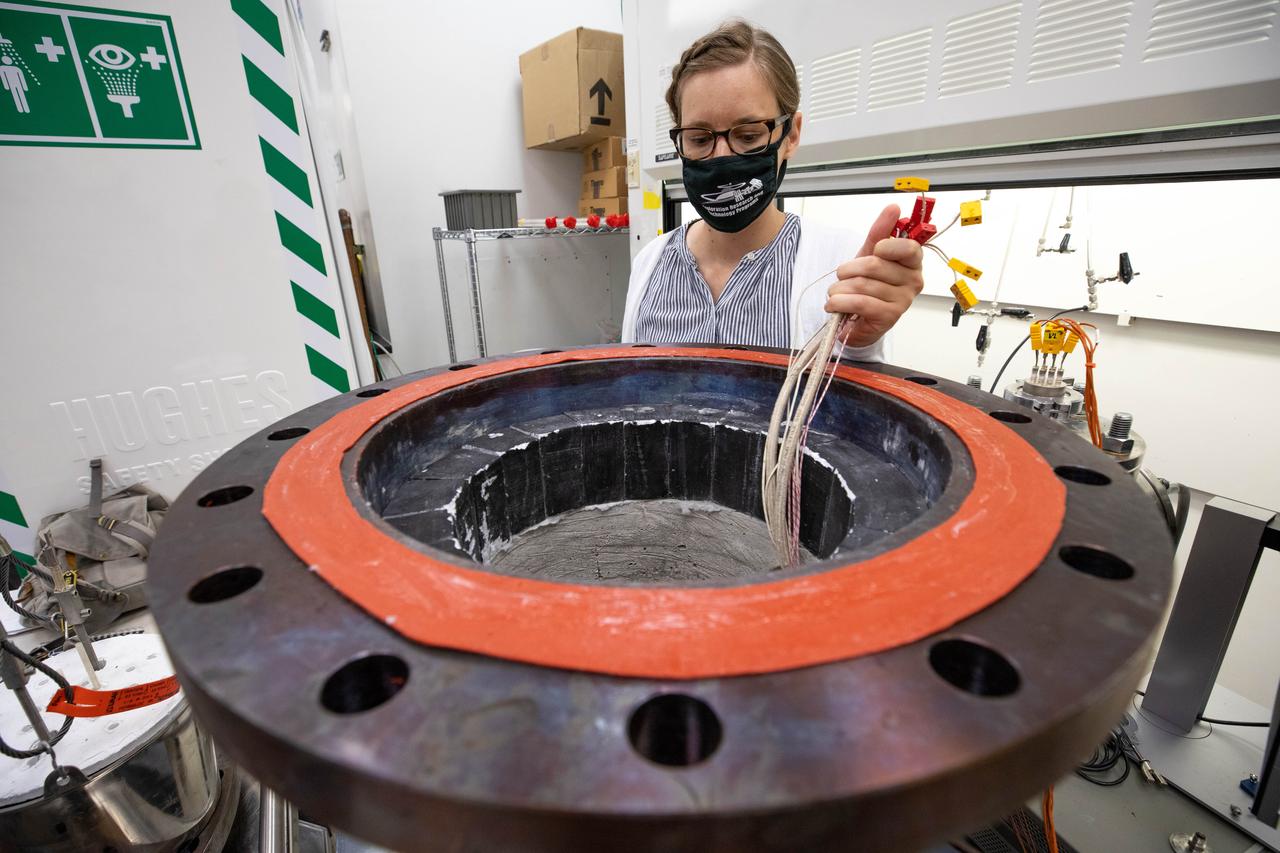

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects hardware before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
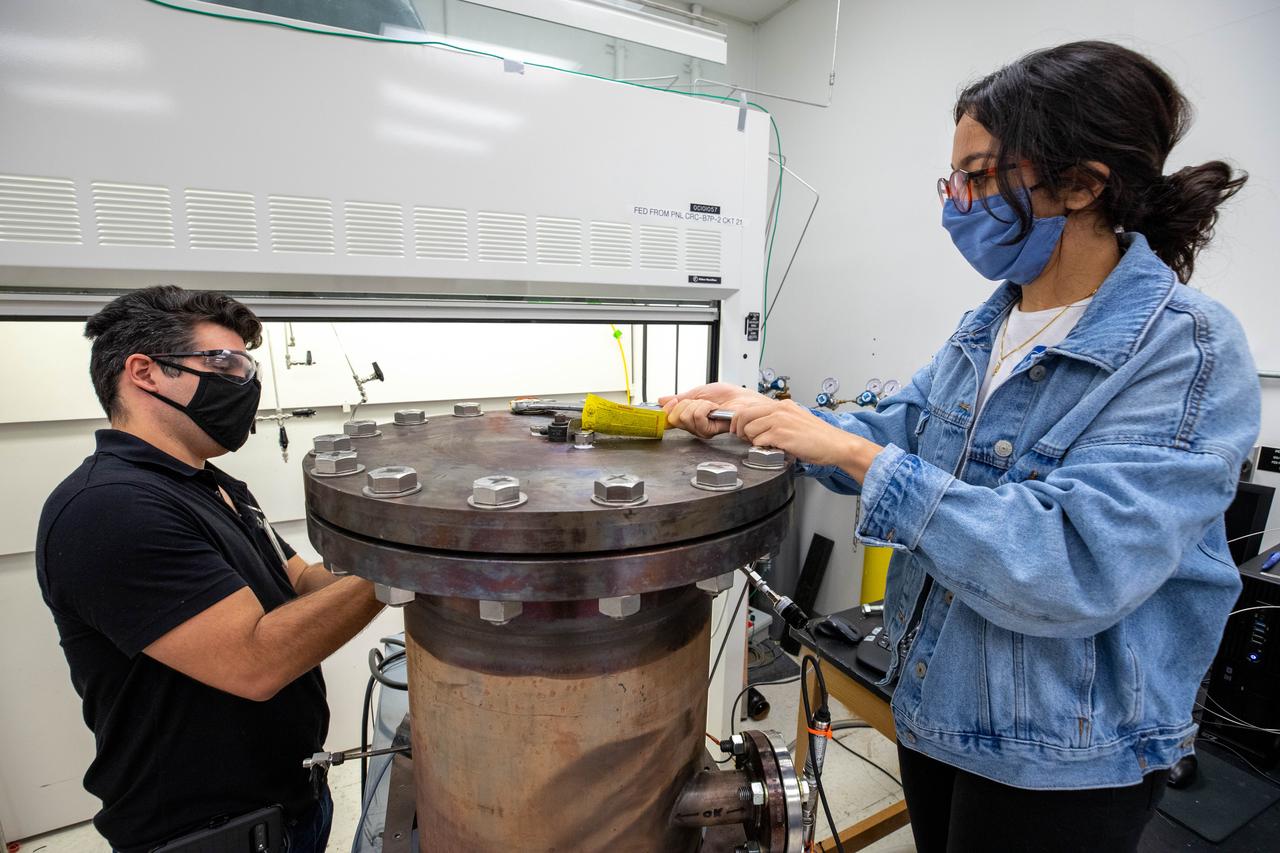

Members of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team inspect hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.

Jaime Toro, a mechanical engineer supporting the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, checks the hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
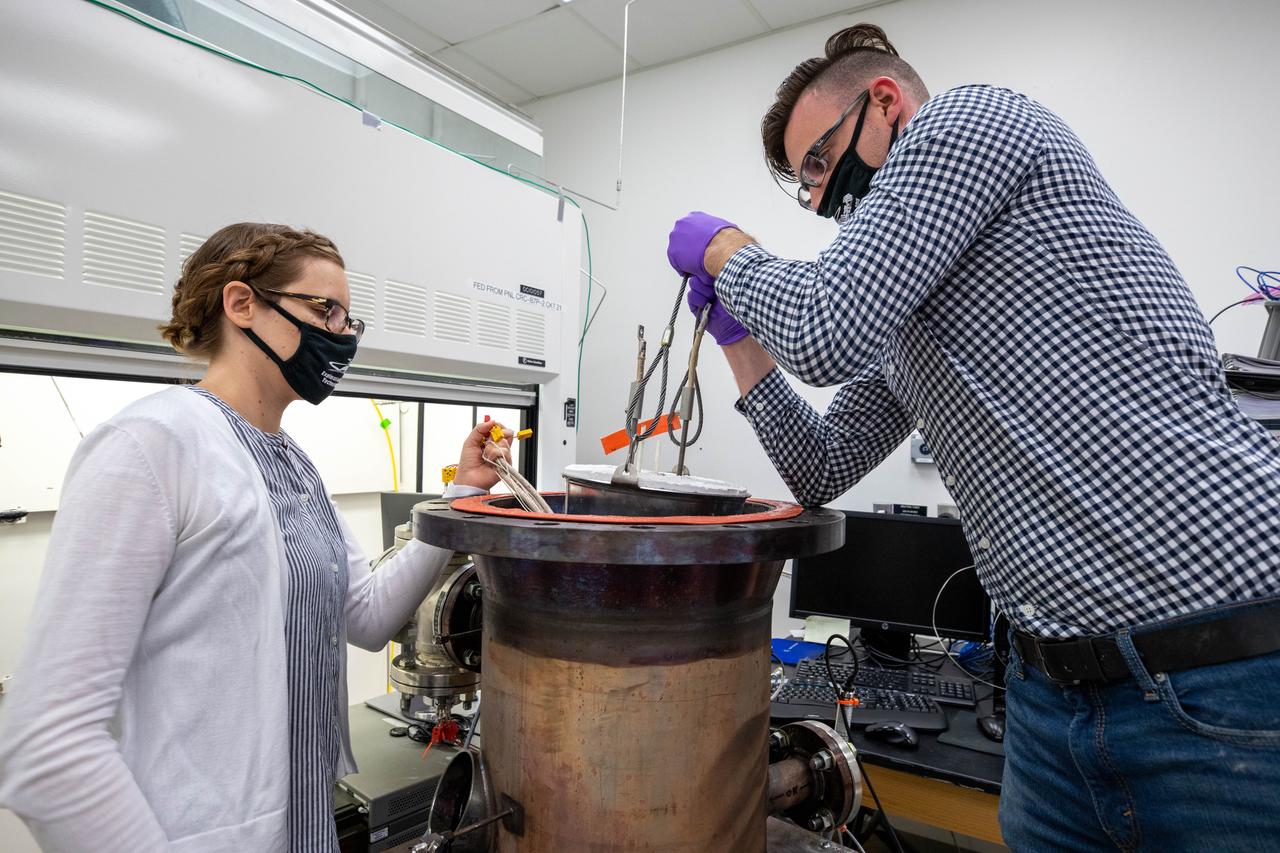

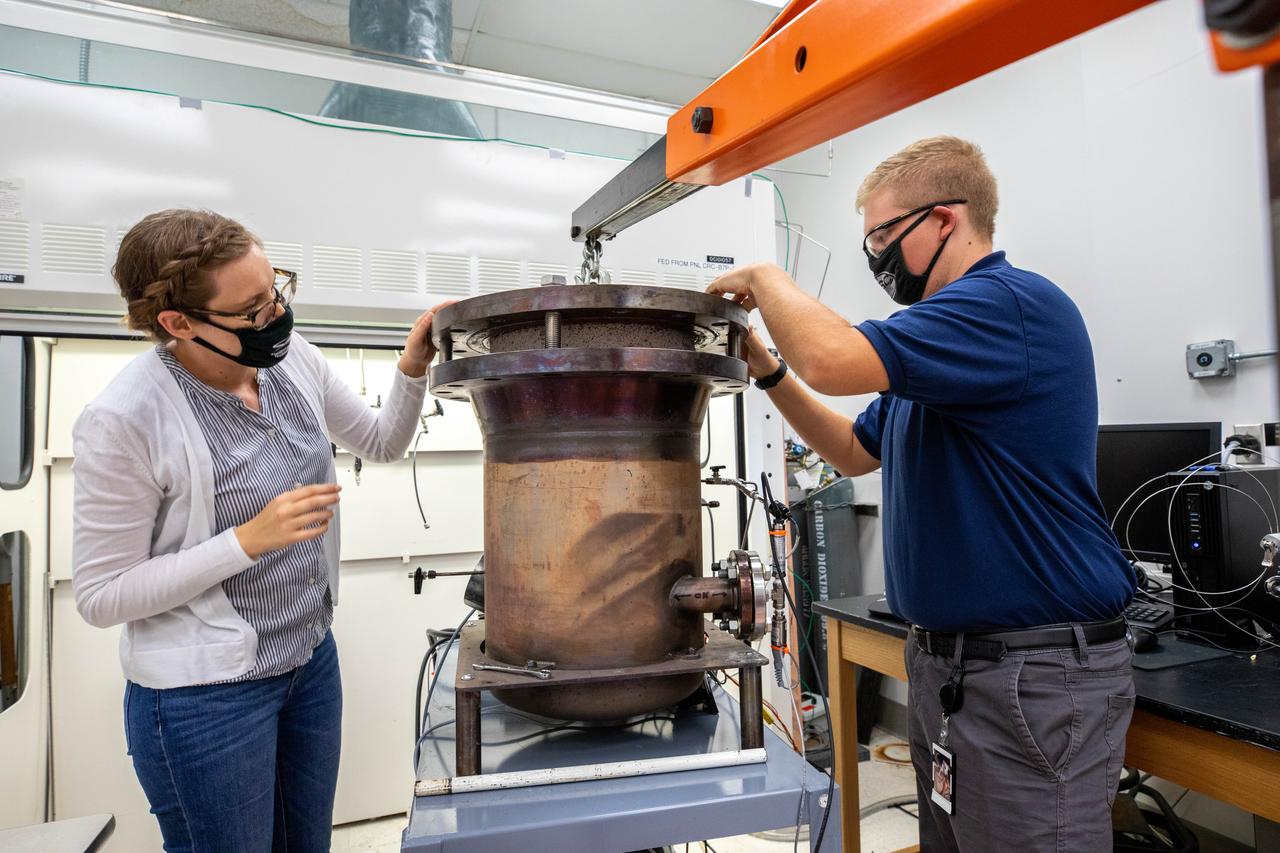
Elspeth Petersen, left, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team, and Kevin Grossman, GaLORE principal investigator, inspect a reactor before a test to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
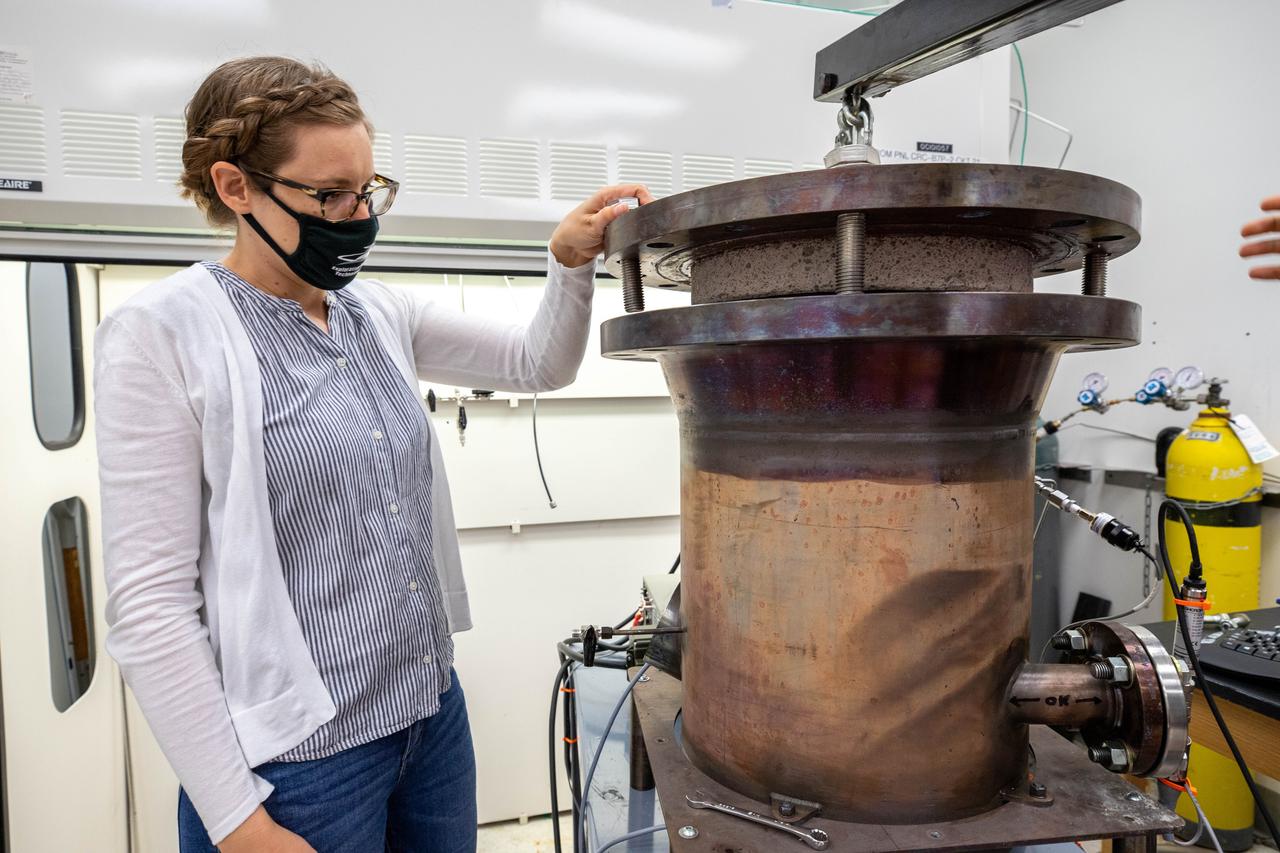

Elspeth Petersen, a chemical engineer and member of the Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project team at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, inspects the GaLORE hardware that will be used to melt lunar regolith – dirt and dust on the Moon made from crushed rock – simulants during a test inside a laboratory at Kennedy’s Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Oct. 29, 2020. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate, and the team was tasked with developing a device that could melt lunar regolith and turn it into oxygen. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars.
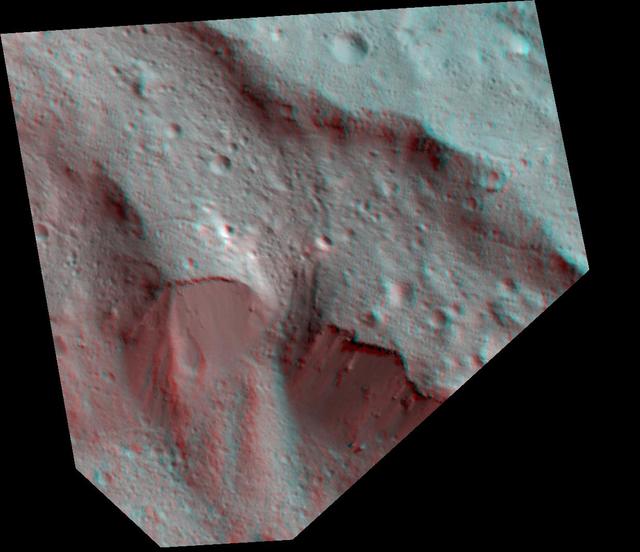

The Dawn spacecraft captured these stereo images of Occator crater on the dwarf planet Ceres in 2018. Framing camera images were used to construct this anaglyph view (which requires red-blue stereo glasses for viewing) of part of the northeastern rim of the crater. This area is approximately 4 miles (7 kilometers) wide and features a thin mantling layer of impact melt draped over faulted terrace blocks. Impact melt flowed through a gap in the blocks in the center of the frame. The spatial resolution of the stereo images is about 11 feet (3.5 meters) per pixel. Occator Crater, named after the Roman god of the agricultural practice of harrowing, is about 57 miles (92 kilometers) in diameter. The conclusion of Dawn's mission operations was Oct. 31, 2018, when the spacecraft depleted its hydrazine used for attitude control. This image was produced by Dr. Paul Schenk at the Lunar and Planetary Institute in Houston. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24064
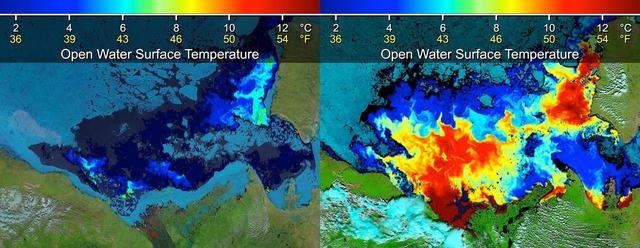
Beaufort Sea surface temperatures where Canada Mackenzie River discharges into the Arctic Ocean, measured by NASA MODIS instrument; warm river waters had broken through a shoreline sea ice barrier to enhance sea ice melt.
This frame from a NASA MODIS animation depicts warming sea surface temperatures in the Arctic Beaufort Sea after warm waters from Canada Mackenzie River broke through a shoreline sea ice barrier in summer 2012, enhancing the melting of sea ice.

A new NASA-funded study has identified which glaciers in West Greenland are most susceptible to thinning in the coming decades by analyzing how they’re shaped. The research could help predict how much the Greenland Ice Sheet will contribute to future sea level rise in the next century, a number that currently ranges from inches to feet. “There are glaciers that popped up in our study that flew under the radar until now,” said lead author Denis Felikson, a graduate research assistant at The University of Texas Institute for Geophysics (UTIG) and a Ph.D. student in The University of Texas Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics. Felikson’s study was published in Nature Geoscience on April 17. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2pJJwNA" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2pJJwNA</a> Caption: Terminus of Kangerlugssuup Sermerssua glacier in west Greenland Photo credit: Denis Felikson, Univ. of Texas <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
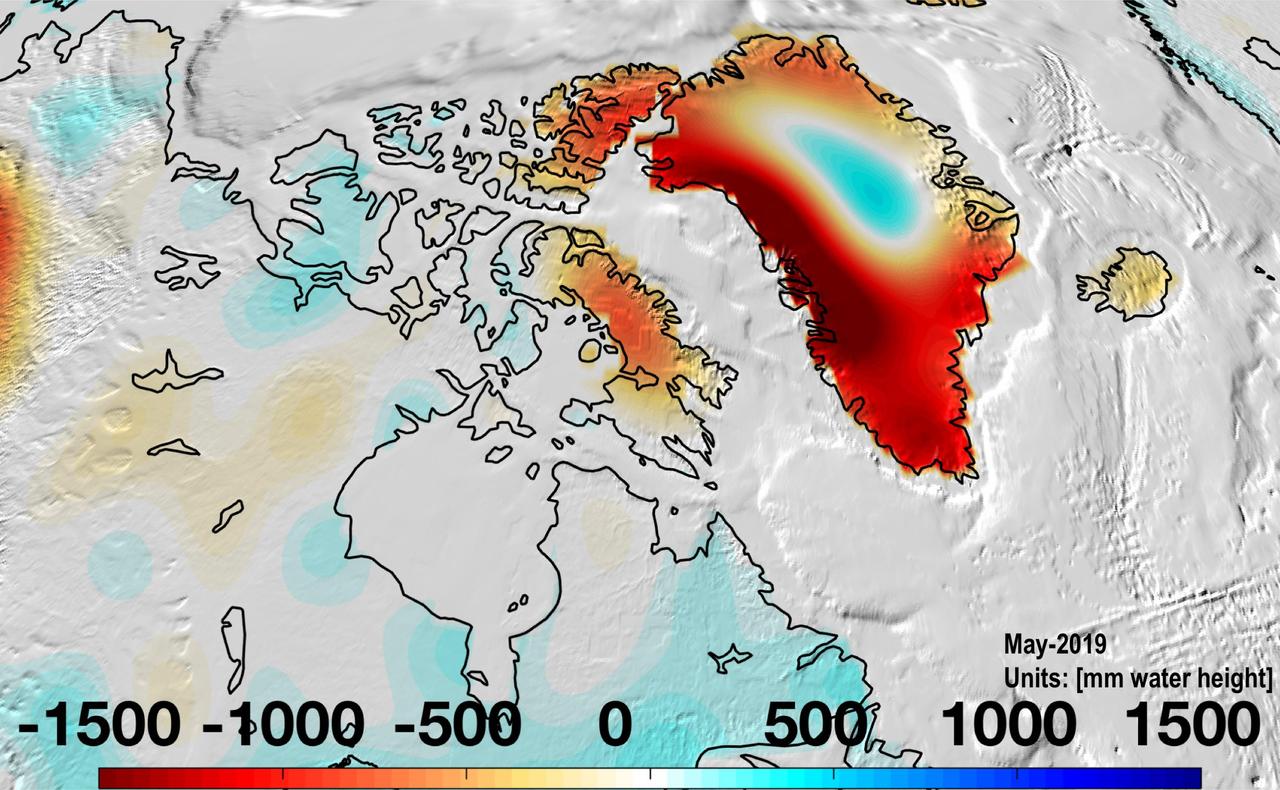
Almost all of Greenland continued to lose mass in May 2019 as the ice sheet continues to melt. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23340
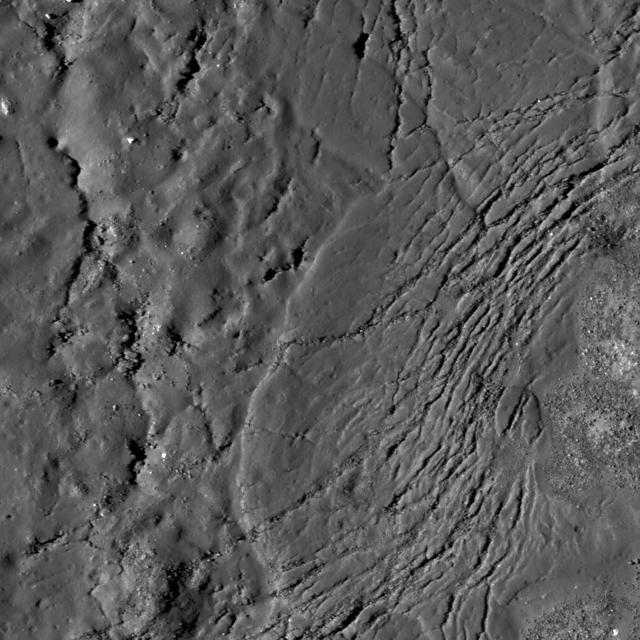

Cracks form in the impact melt sheet on the floor of Necho Crater in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.

This doublet crater looks like a melting snowman tipped on his side.Warmth is in the air, as the southern hemisphere of Mars enters spring
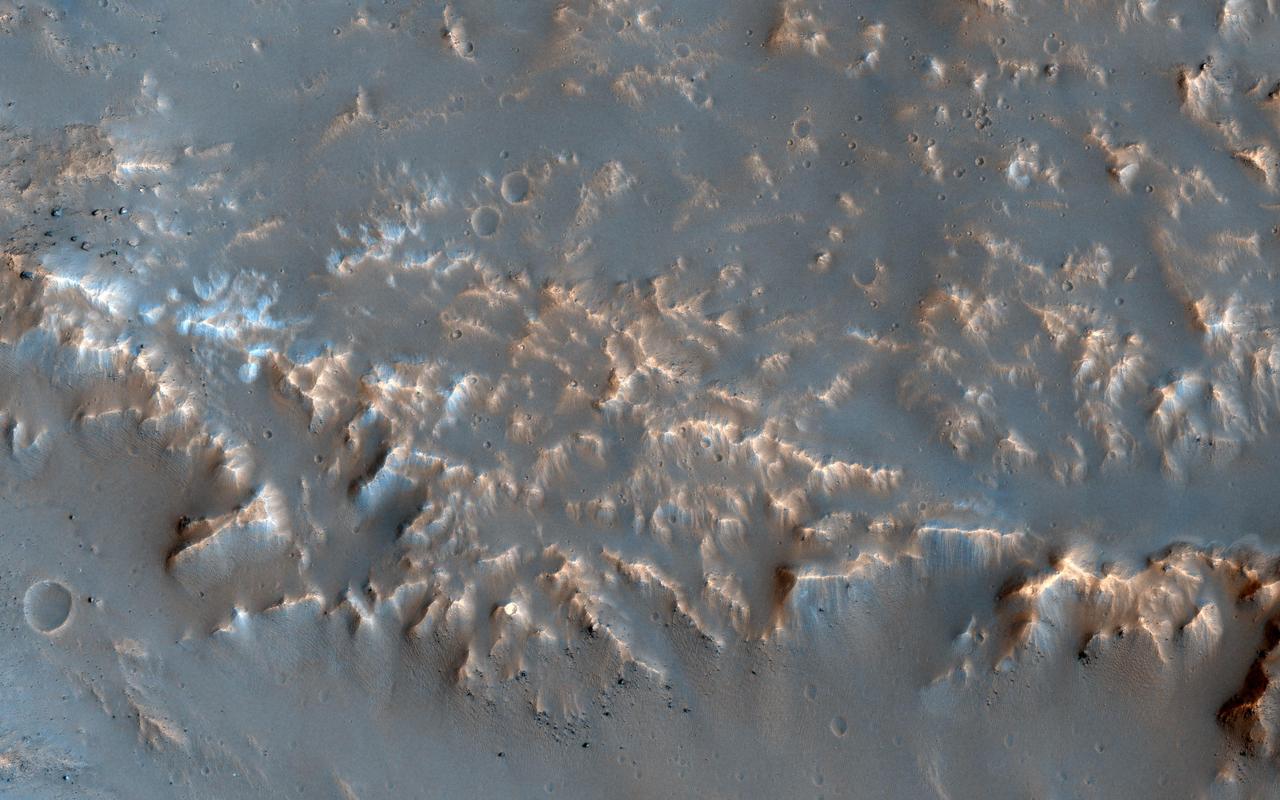

This image of a well-preserved unnamed elliptical crater in Terra Sabaea, is illustrative of the complexity of ejecta deposits forming as a by-product of the impact process that shapes much of the surface of Mars. Here we see a portion of the western ejecta deposits emanating from a 10-kilometer impact crater that occurs within the wall of a larger, 60-kilometer-wide crater. In the central part is a lobe-shaped portion of the ejecta blanket from the smaller crater. The crater is elliptical not because of an angled (oblique) impact, but because it occurred on the steep slopes of the wall of a larger crater. This caused it to be truncated along the slope and elongated perpendicular to the slope. As a result, any impact melt from the smaller crater would have preferentially deposited down slope and towards the floor of the larger crater (towards the west). Within this deposit, we can see fine-scale morphological features in the form of a dense network of small ridges and pits. These crater-related pitted materials are consistent with volatile-rich impact melt-bearing deposits seen in some of the best-preserved craters on Mars (e.g., Zumba, Zunil, etc.). These deposits formed immediately after the impact event, and their discernible presence relate to the preservation state of the crater. This image is an attempt to visualize the complex formation and emplacement history of these enigmatic deposits formed by this elliptical crater and to understand its degradation history. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA13078
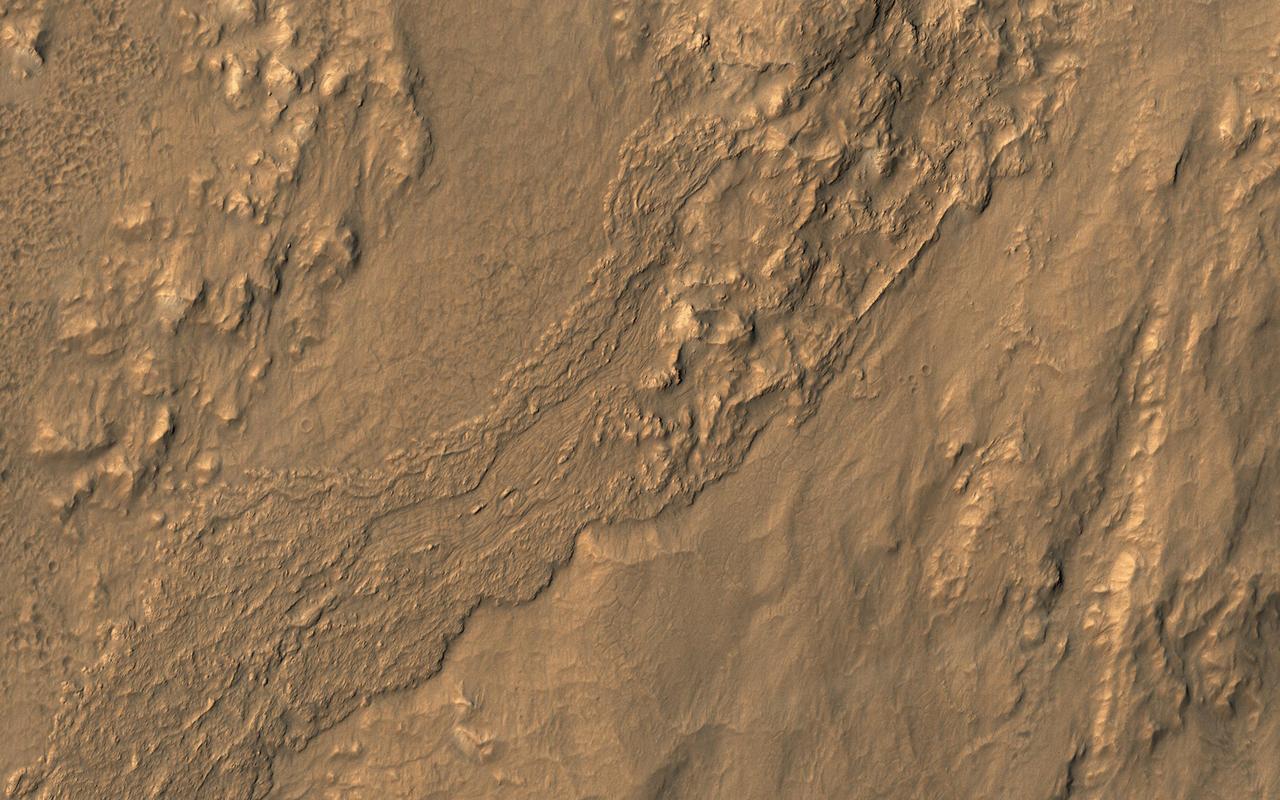

This oblique view from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a small part of the near-rim ejecta from Tooting Crater. The flow extending from upper left to lower right looks much like a typical lava flow, but doesn't emanate from a volcanic vent. Instead, this must be either melted rock from the impact event, or a wet debris flow from melting of ice. The surface is dusty so color variations are minor. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21648
The frequent coverage provided by NASA SeaWinds instrument on the QuikScat satellite in 1999 provided unprecedented capability to monitor daily and seasonal changes in the key melt zones of Greenland.

This layered region is between Aonia Planum and the south pole. The edges of the top layer have a moothed appearance that may be due to ice melting.
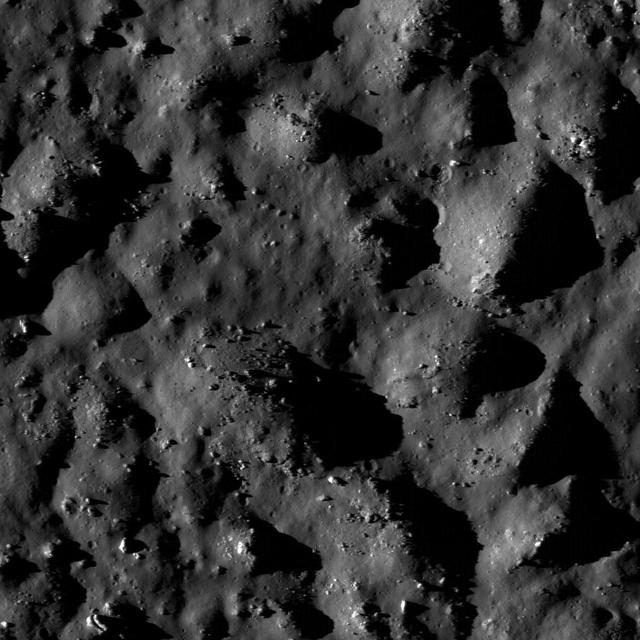

NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows boulders and impact melt line the floor of the 85-km crater Tycho, a potential site for future human exploration.
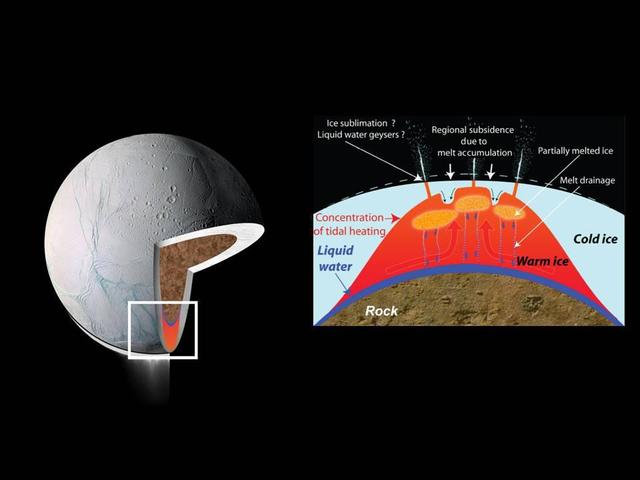
These drawings depict explanations for the source of intense heat that has been measured coming from Enceladus south polar region. These models predict that water could exist in a deep layer as an ocean or sea and also near the surface.

Elorza Crater is a complex crater located north of Coprates Chasma. This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter centers on the southwestern portion of the central uplift, characterized by numerous bedrock exposures and coherent impact melt flows.
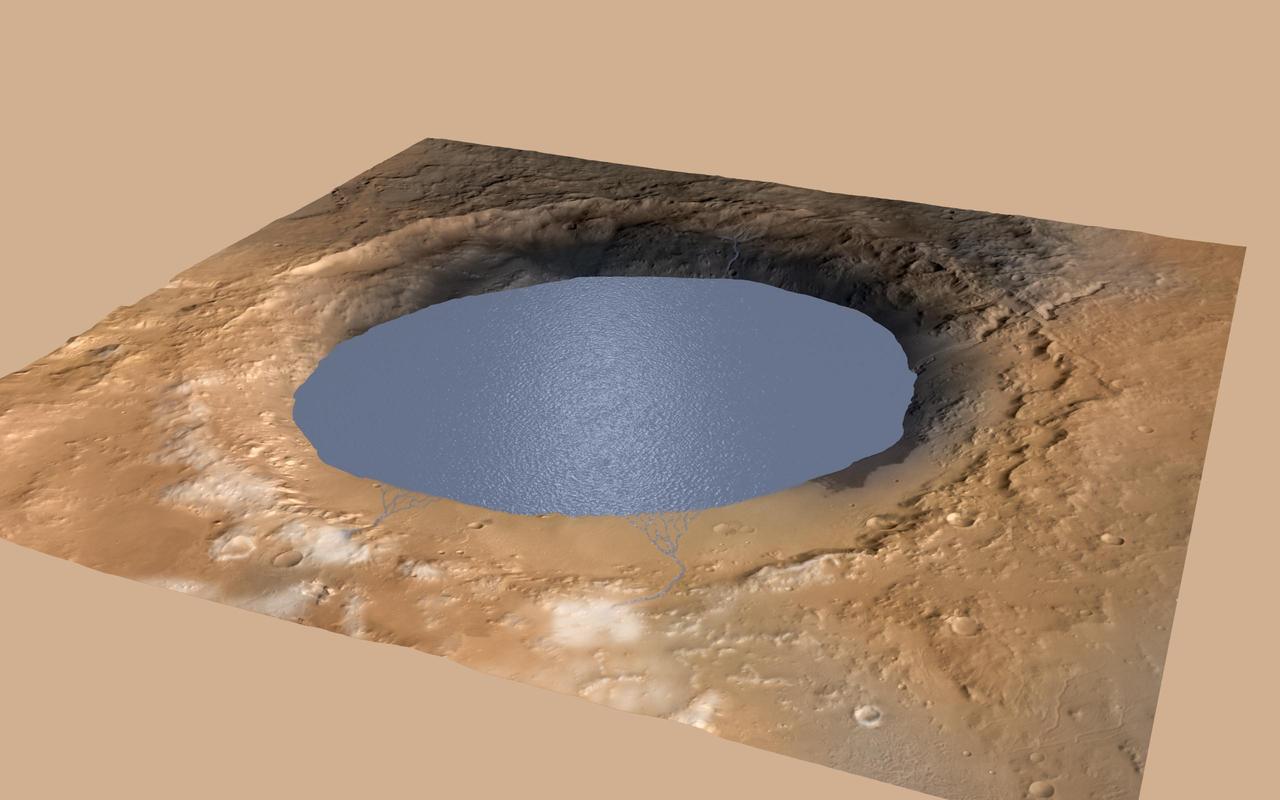

This simulation depicts a lake partially filling Mars Gale Crater, receiving runoff from snow melting on the crater rim, showing evidence that NASA Curiosity rover has found ancient streams, deltas and lakes.
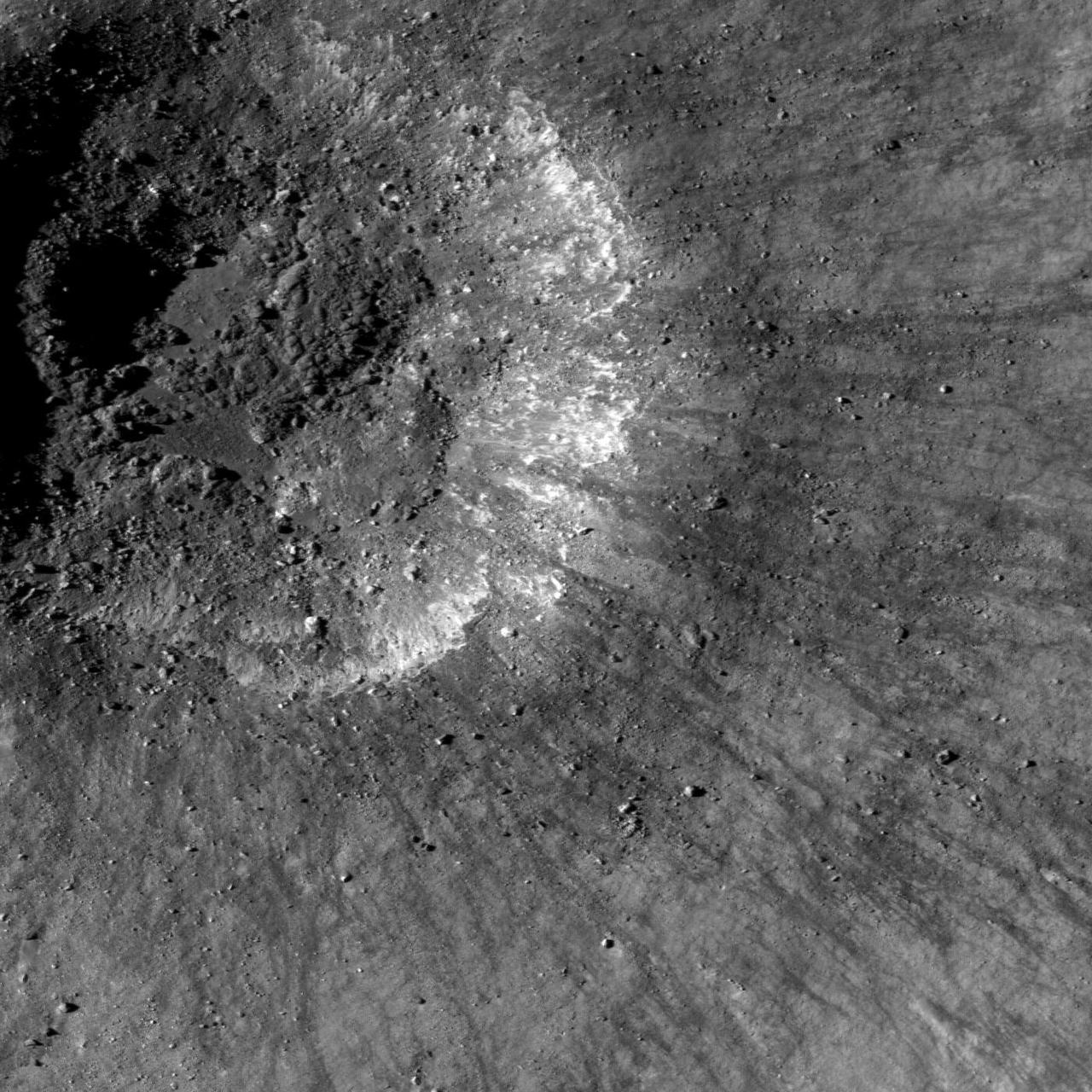

This is a view from NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter of a very young impact crater in Balmer basin. The dark streamers are impact melt splashes thrown out during the crater formation.
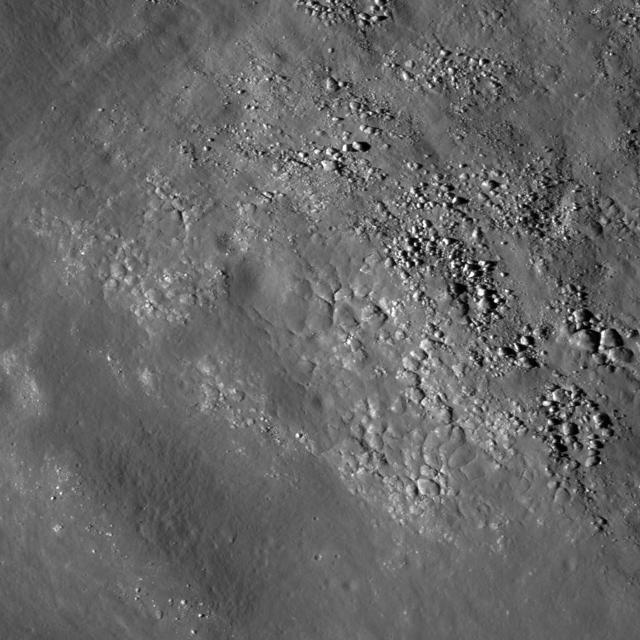

Diverse textures on the floor of Saha E which could be the result of impact melt coating boulders and other deposits on the floor of the crater on the lunar farside in this image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
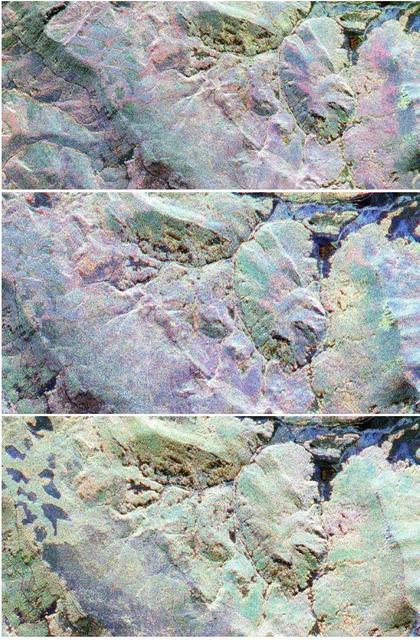
This sequence of three images in northern Colorado, taken by NASA Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar AIRSAR in 2002, shows Fraser, Colorado, before snowfall, the morning after snow, and after the snow melted.
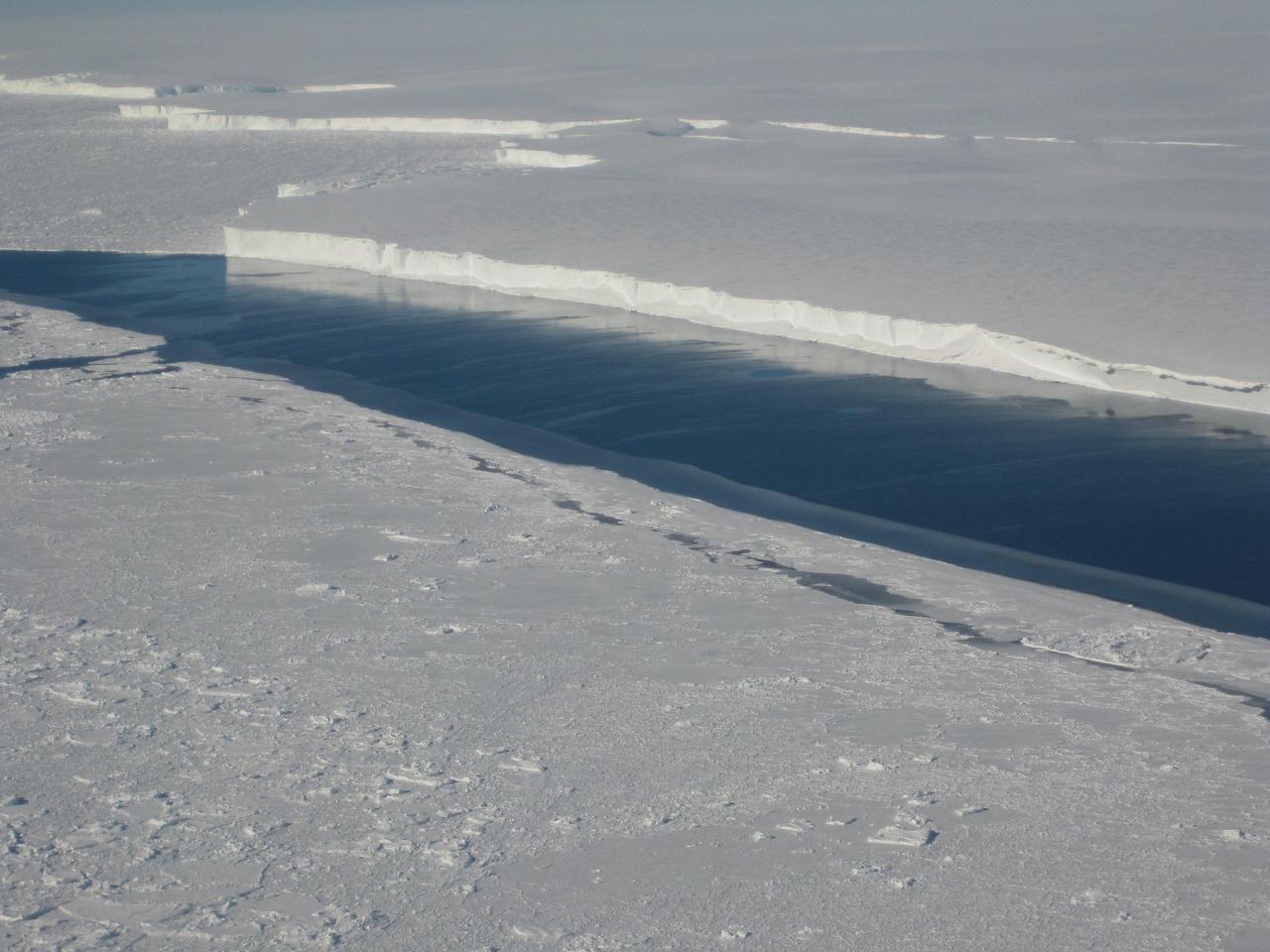

This photo, taken onboard the Chilean Navy P3 aircraft, shows the ice front of Venable Ice Shelf, West Antarctica, in October 2008. It is an example of a small-size ice shelf that is a large melt water producer.
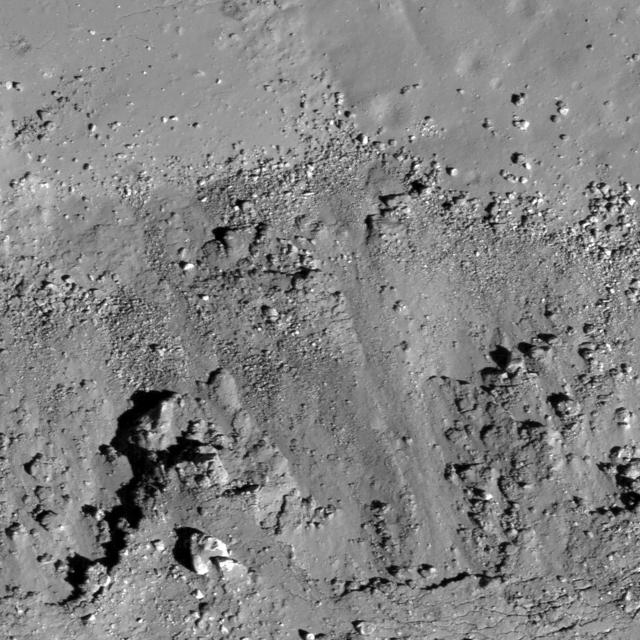

A subset of NAC Image M112162602L showing landslides bottom covering impact melt on the floor top of a fresh Copernican-age crater at the edge of Oceanus Procellarum and west of Balboa crater taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter.
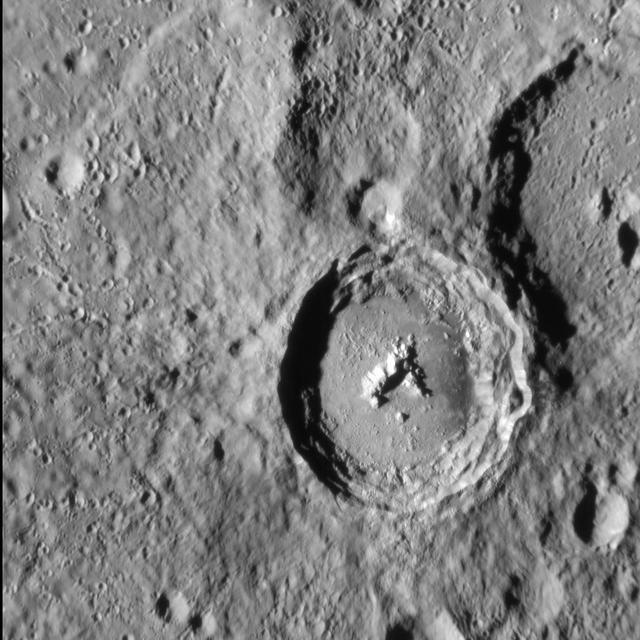
Situated high in Mercury southern hemisphere, NASA MESSENGER sees Han Kan, a 50-km-diameter impact crater with a well preserved central peak and a smooth floor that is likely solidified impact melt.
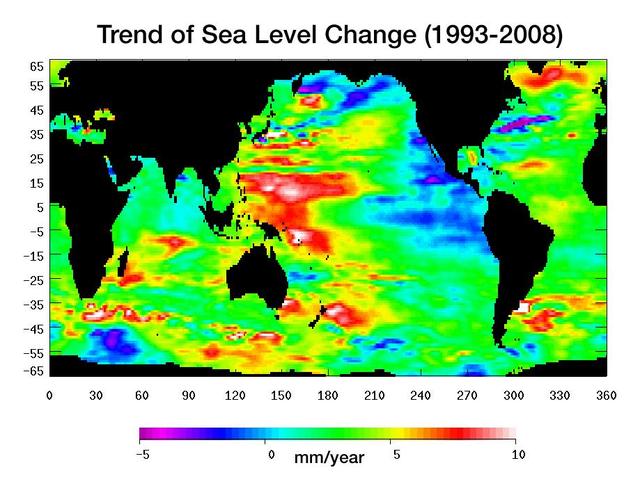
Warming water and melting land ice have raised global mean sea level 4.5 centimeters 1.7 inches from 1993 to 2008. But the rise is by no means uniform.
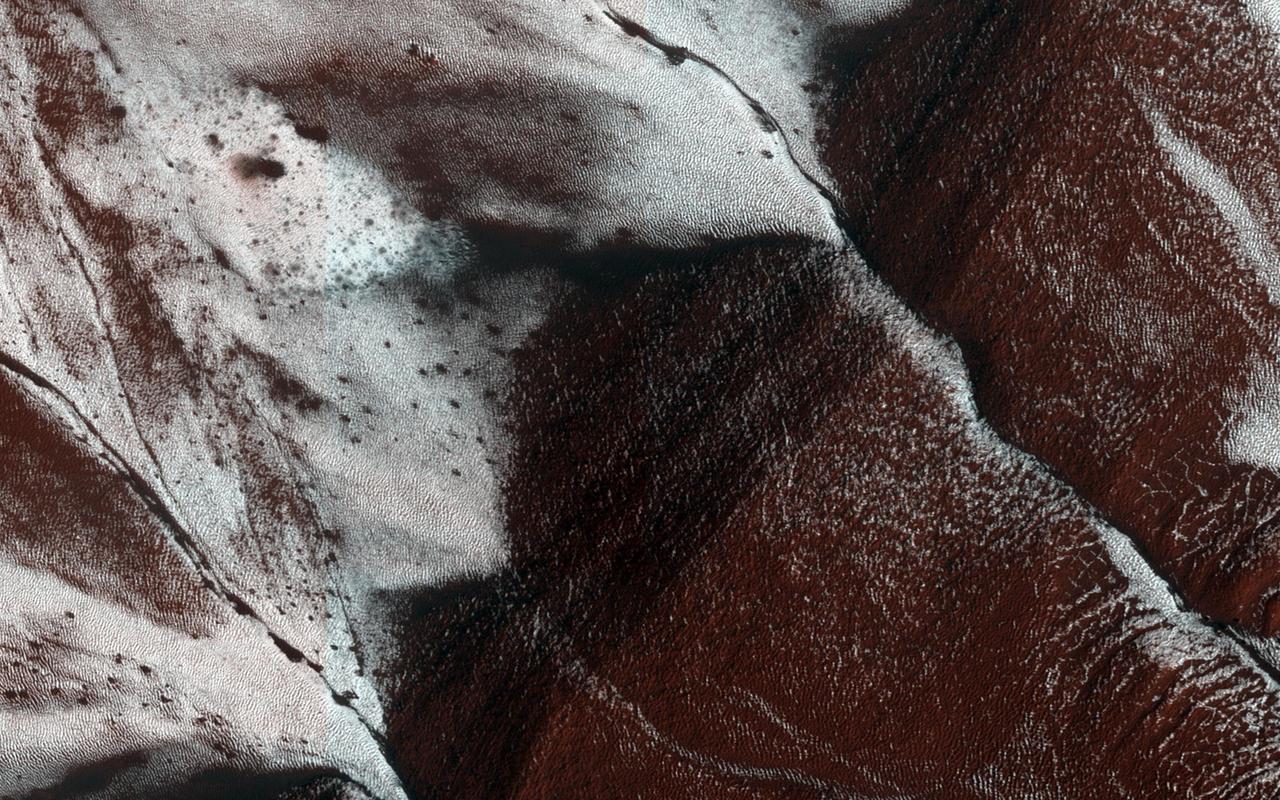

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows frosted gullies on a south-facing slope within a crater. At this time of year only south-facing slopes retain the frost, while the north-facing slopes have melted.

This mosaic of oblique images from NASA MESSENGER spacecraft highlights the spectacular interior of Abedin crater. The crater floor is covered with once-molten rock melted by the impact event that formed Abedin. Cracks that formed as this melt cooled are visible. Particularly intriguing is the shallow depression that lies amidst the central peaks of the crater and may be volcanic in origin. Color imaging shows that this depression is surrounded by reddish material, as seen at other sites of explosive volcanism across Mercury. Instrument: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Center Latitude: 61.7° Center Longitude: 349.3° E Scale: Abedin crater is 116 km (72 miles) in diameter http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19423
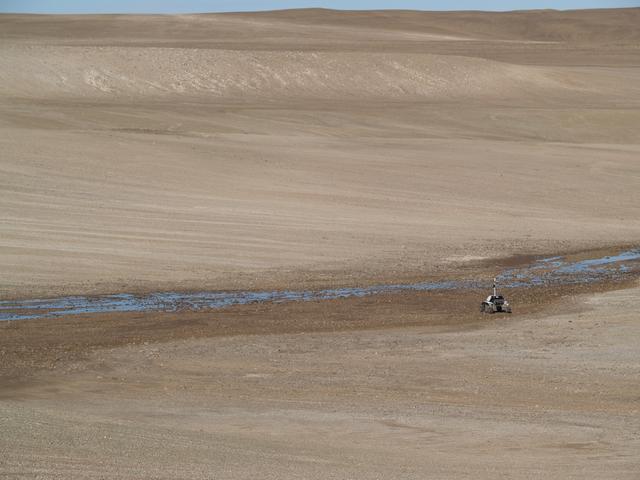

K-10 Black crossing snow melt on Devon Island, Canada. photo credit NASA/Lorenzo Fluckiger.

QUINCY BEAN OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH TITANIUM ALLOY TURBOPUMP COMPONENT FABRICATED WITH MSFC’S ELECTRON BEAM MELTING SYSTEM (BACKGROUND).

The gullies at the top of the image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft occur on the rim of an unnamed crater on the larger rim of the Argyre Basin. It has been postulated that this type of gully may form due to the melting of a snow/ice cover

This photo, aken onboard a National Science Foundation/NASA chartered Twin Otter aircraft, shows the ice front of Dibble Ice Shelf, East Antarctica, a significant melt water producer from the Wilkes Land region, East Antarctica.

This image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the southern latitude Hale Crater, a rather large, pristine elliptical crater possessing sharp features, impact melt bodies ponded throughout the structure and few overprinting impact craters.

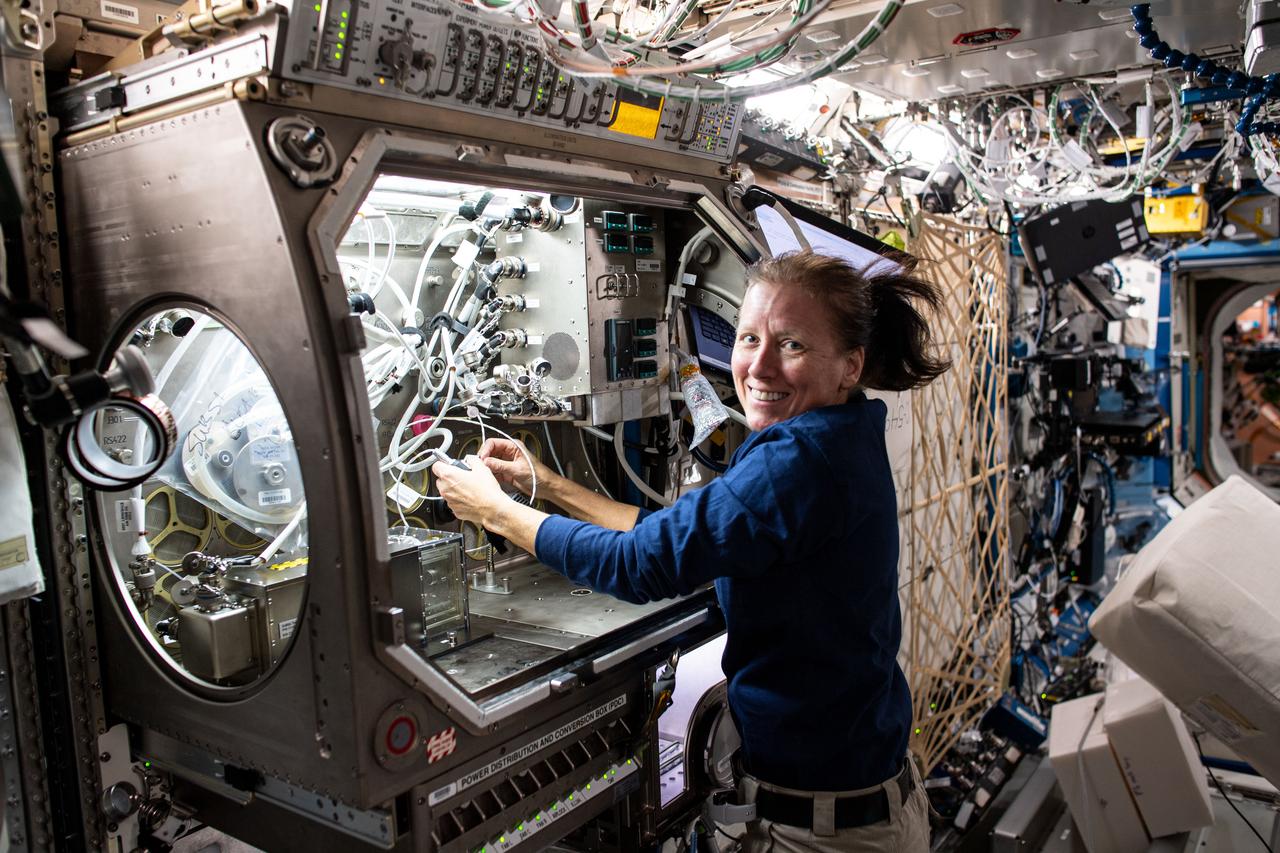
iss065e084906 (June 1, 2021) --- Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Thomas Pesquet of ESA (European Space Agency) swaps samples inside the Microgravity Sciences Glovebox for an experiment called Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA. The physics investigation explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
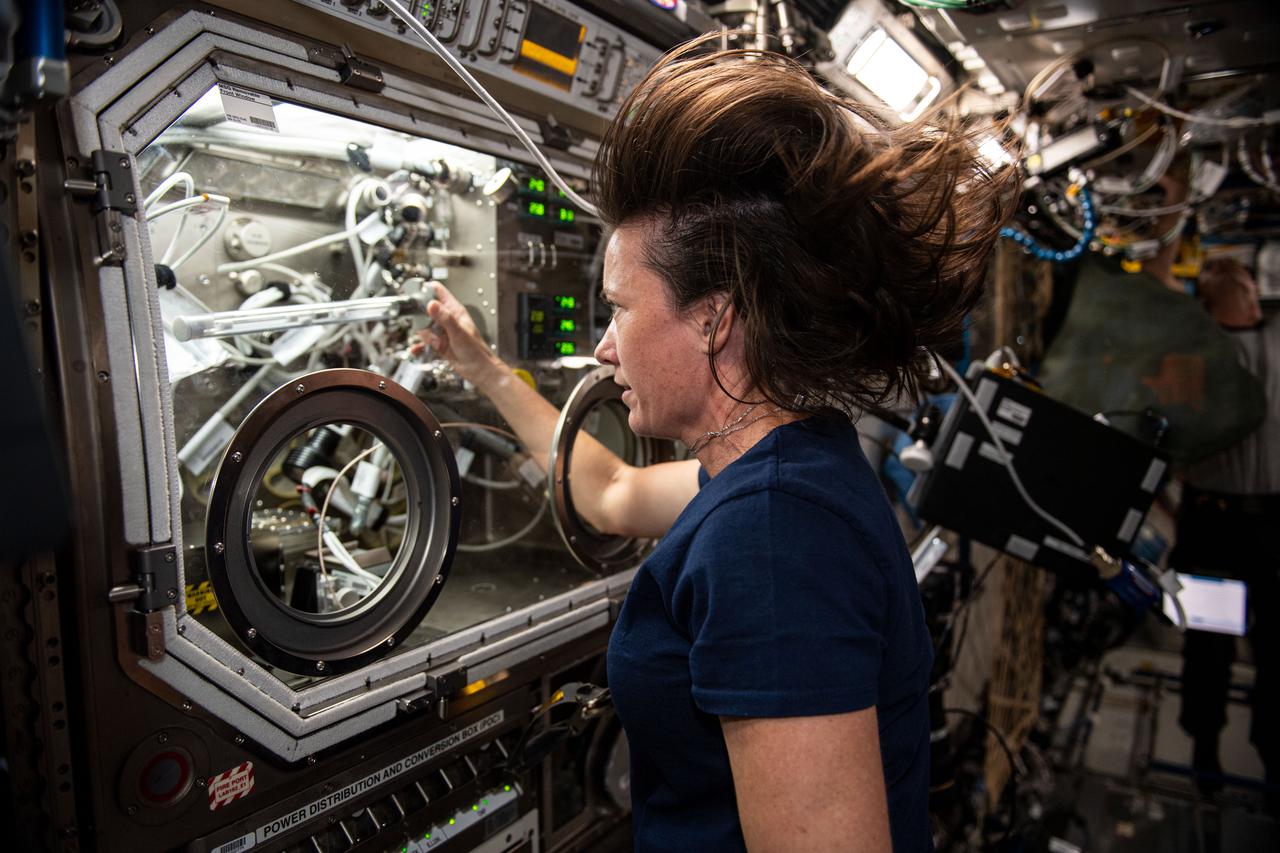

iss065e061407 (May 24, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur works in the Microgravity Science Glovebox swapping samples for an experiment called Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA. The physics investigation explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
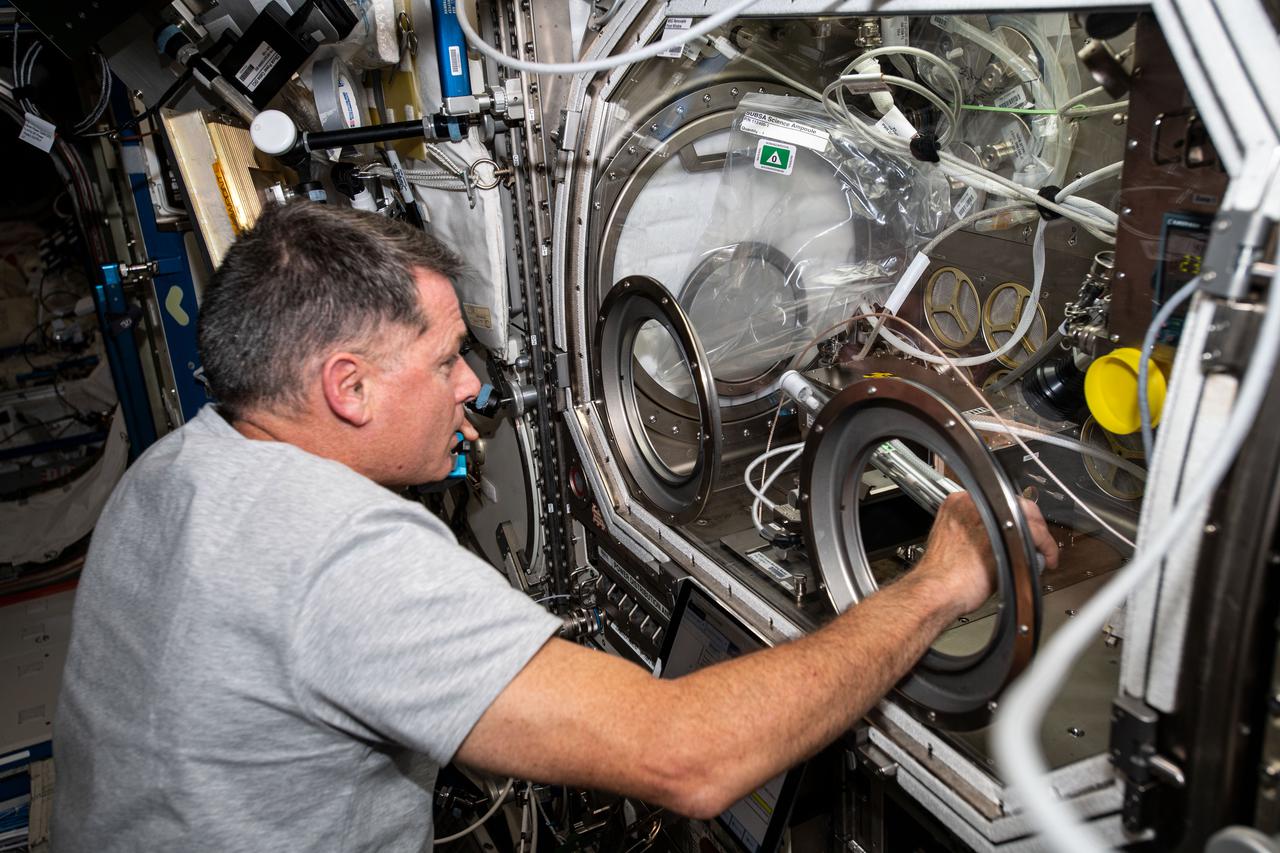

iss065e050120 (May 21, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough swaps samples inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for an experiment called Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA. The physics investigation explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.

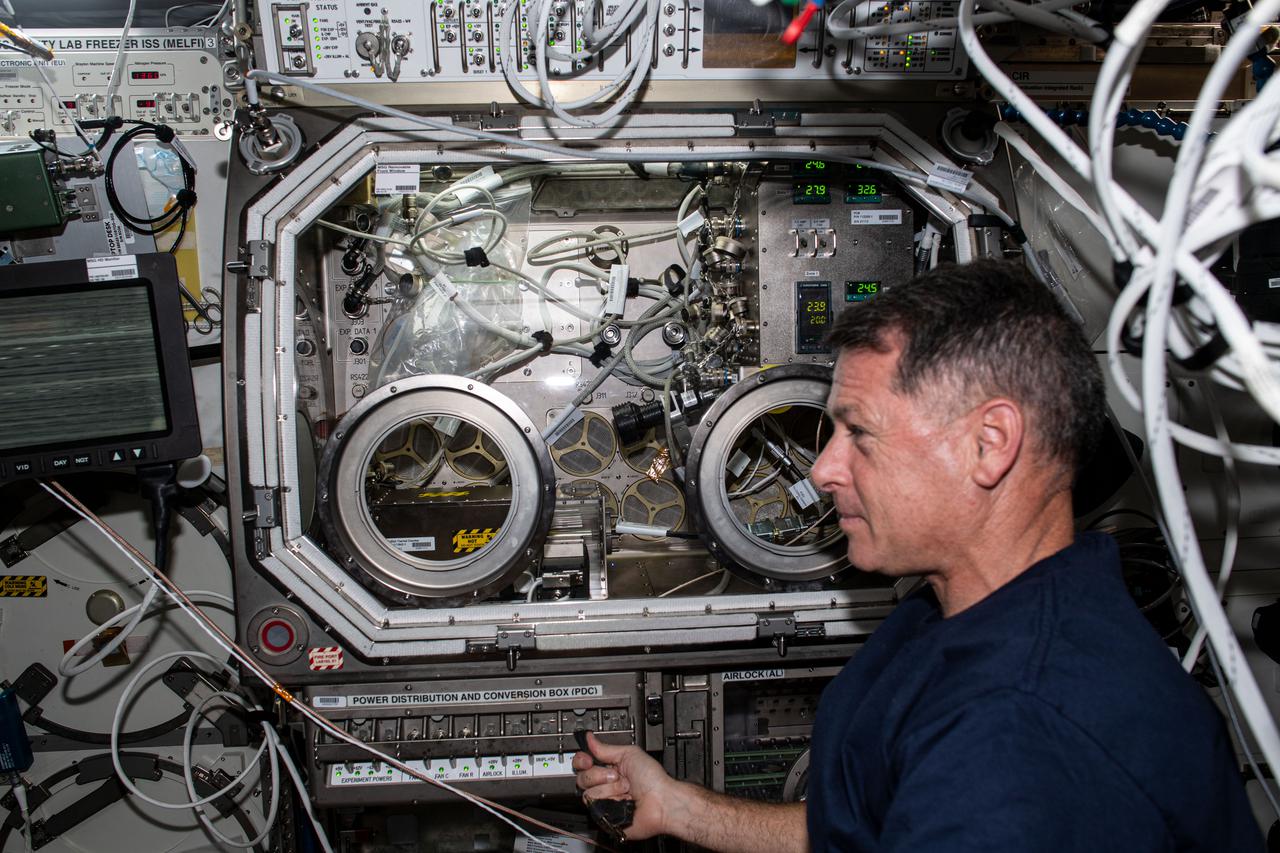
iss064e016385 (Dec. 29, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Shannon Walker sets up hardware inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox for the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) experiment. SUBSA crystallizes melts in microgravity to learn more about the process of semiconductor crystal growth to benefit Earth and space industries. Results may lead to reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.

iss065e020580 (May 5, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Shane Kimbrough is pictured in front of the Microgravity Science Glovebox setting up hardware for a physics investigation. The experiment known as Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules, or SUBSA, explores experimental methods of crystallizing melts in microgravity and is expected to result in reduced fluid motion in the melt, leading to better distribution of subcomponents and the potential for improved technology used in producing semiconductor crystals.
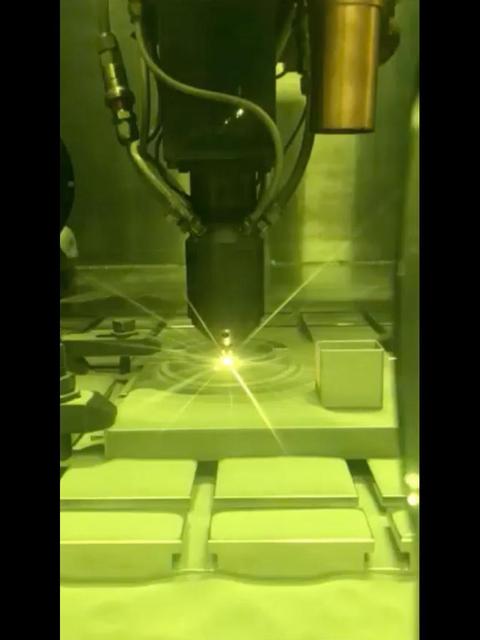

This video clip shows a 3D printing technique where a printer head scans over each layer of a part, blowing metal powder that is melted by a laser. It's one of several ways parts are 3D printed at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, but was not used to create the parts aboard the Perseverance rover. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23972
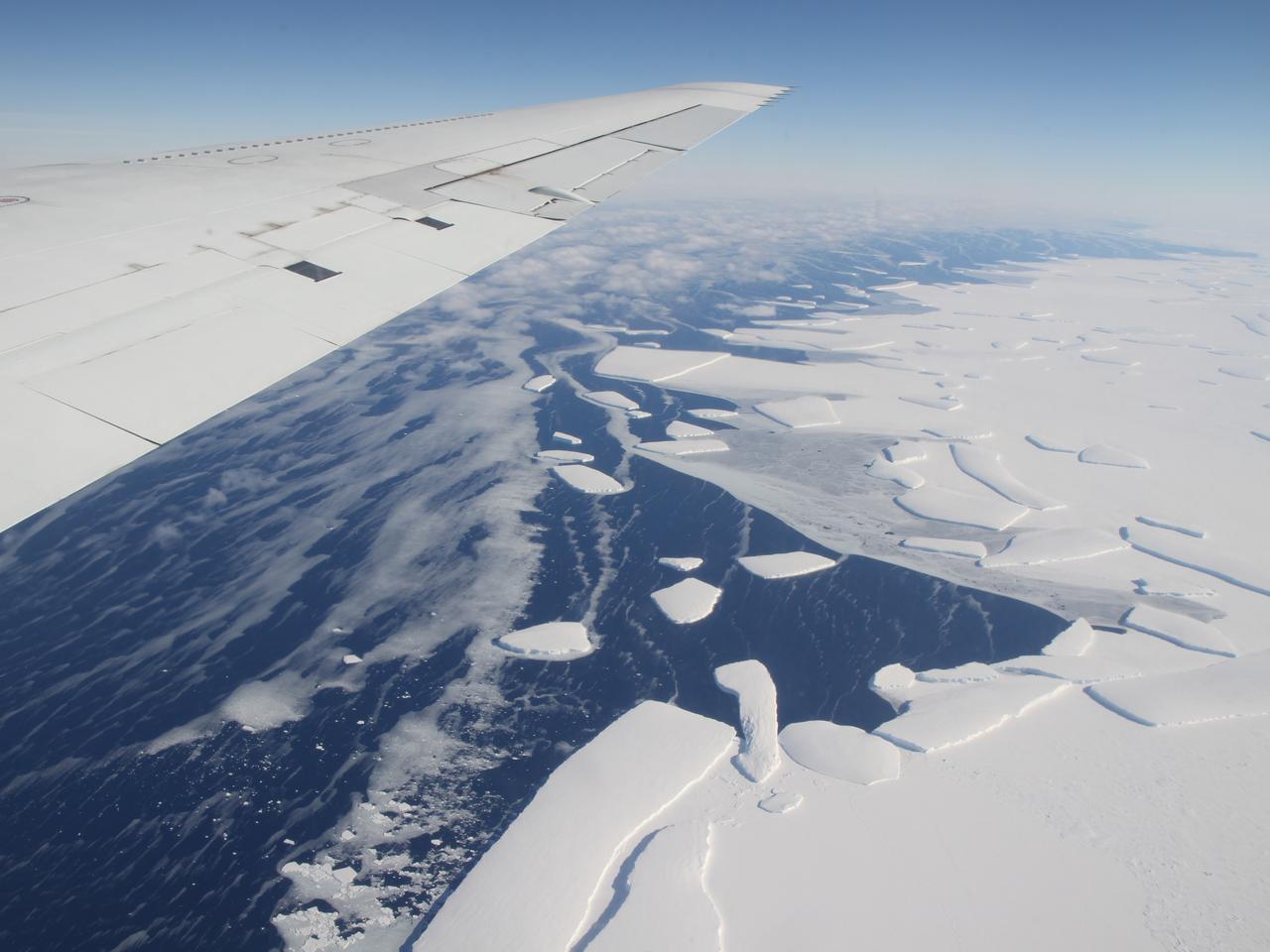

Calving front of an ice shelf in West Antarctica. The traditional view on ice shelves, the floating extensions of seaward glaciers, has been that they mostly lose ice by shedding icebergs. A new study by NASA and university researchers has found that warm ocean waters melting the ice sheets from underneath account for 55 percent of all ice shelf mass loss in Antarctica. This image was taken during the 2012 Antarctic campaign of NASA's Operation IceBridge, a mission that provided data for the new ice shelf study. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/earth20130613.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/earth/features/earth20130613.html</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jefferson Beck <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
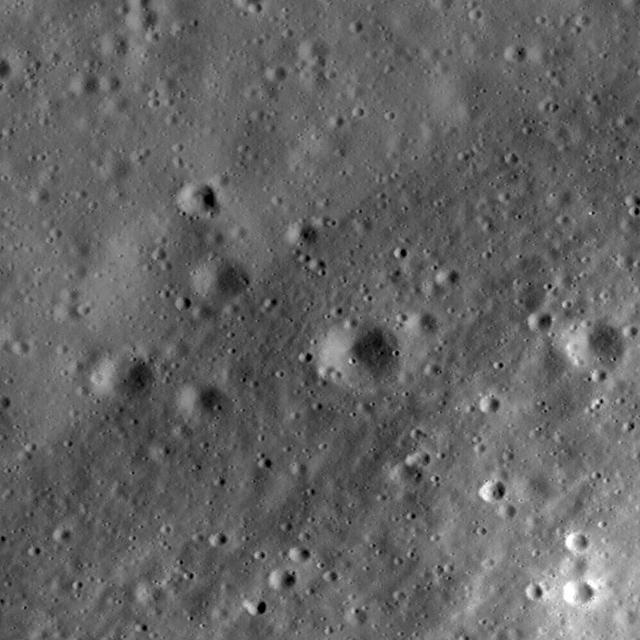

This image taken NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is a high-resolution view of part of the floor of Riccioli Crater. The view is centered on the boundary between a spur of the crater central peak materials and volcanic lava flow deposits.
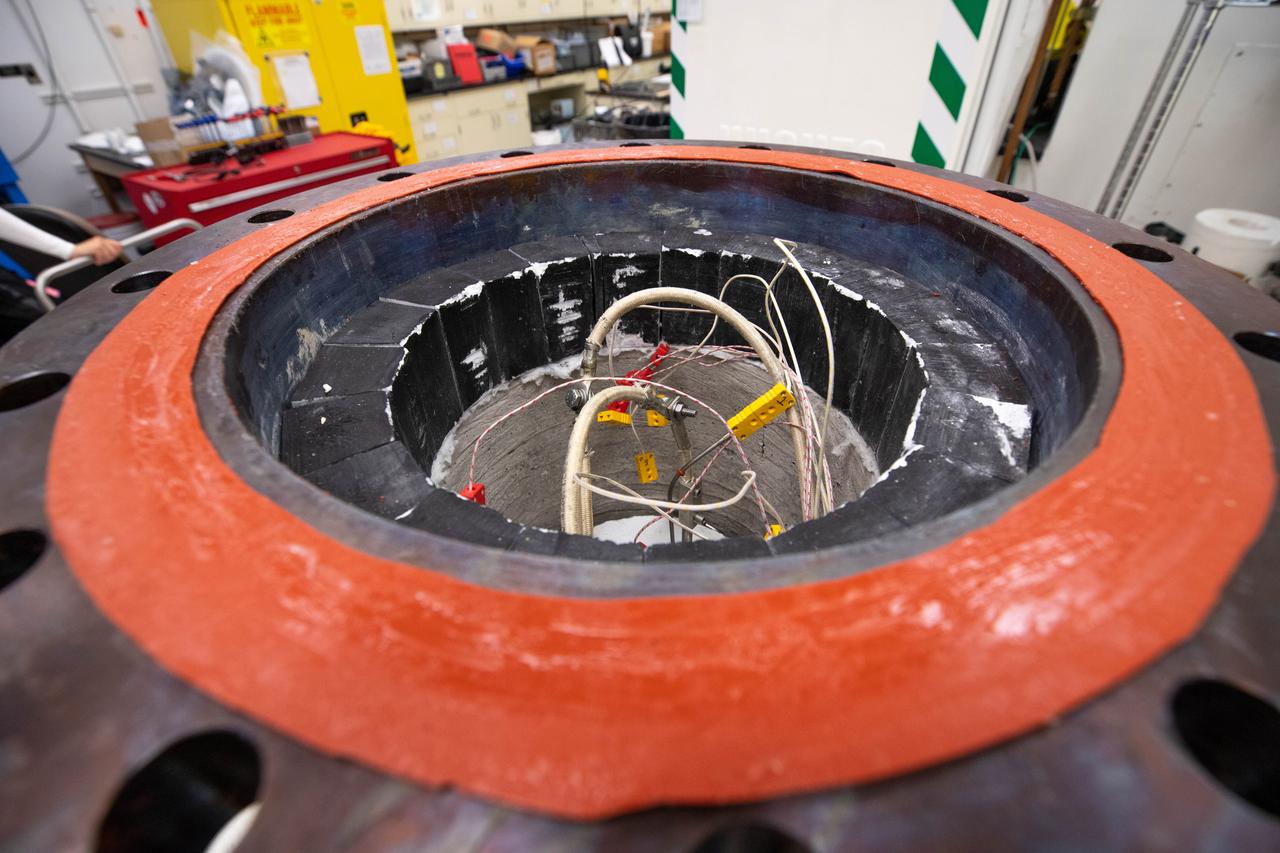

A team investigating molten regolith electrolysis prepares to test a reactor inside a laboratory in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 29, 2020. The Gaseous Lunar Oxygen from Regolith Electrolysis (GaLORE) project seeks to develop technology to extract oxygen and metals from the crushed rock, or regolith, that covers the Moon’s surface. As NASA prepares to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024 as part of the Artemis program, technology such as this can assist with sustainable human lunar exploration and long-duration missions to Mars. GaLORE was selected as an Early Career Initiative project by the agency’s Space Technology Mission directorate.
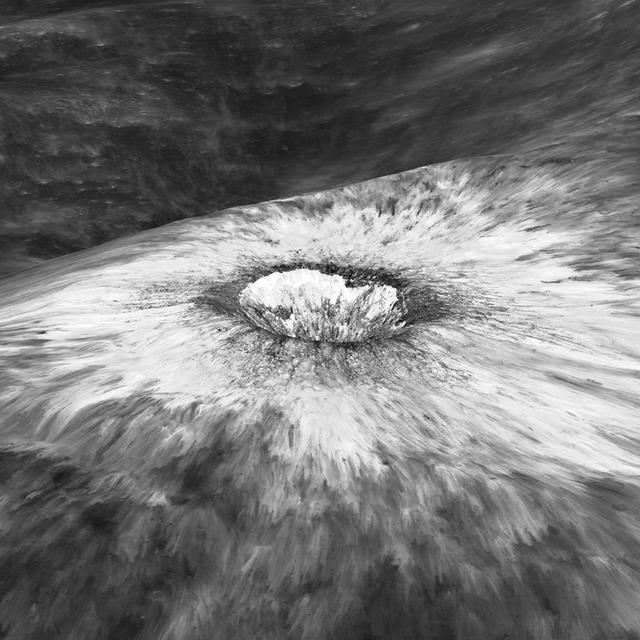

Looking east to west across the rim and down into Chaplygin crater reveals this beautiful example of a fresh young crater and its perfectly preserved ejecta blanket. The delicate patterns of flow across, over, and down local topography clearly show that ejecta traveled as a ground hugging flow for great distances, rather than simply being tossed out on a ballistic trajectory. Very near the rim lies a dark, lacy, discontinuous crust of now frozen impact melt. Clearly this dark material is on top of the bright material so it was the very last material ejected from the crater. The melt was formed as the tremendous energy of impact was converted to heat and the lunar crust was melted at the impact point. As the crater rebounded and material sloughed down the walls of the deforming crater the melt was splashed out over the rim and froze. Its low reflectance is mostly due to a high percentage of glass because the melt cooled so quickly that minerals did not have time to crystallize. The fact that the delicate splash patterns are so well preserved testifies to the very young age of this crater. But how young? For comparison "Chappy" (informal name) is 200 m larger than Meteor crater (1200 m diameter) in Arizona, which is about 50,000 years old. Craters of this size form every 100,000 years or so on the Moon and the Earth. Since there are very few superposed craters on Chappy, and its ejecta is so perfectly preserved it may be much younger than Meteor crater. However, we can't know the true true absolute age of "Chappy" until we can obtain a sample of its impact melt for radiometric age dating. Investigate all of Chappy's ejecta, at full resolution: <a href="http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/901" rel="nofollow">lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/901</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University/LRO/LROC
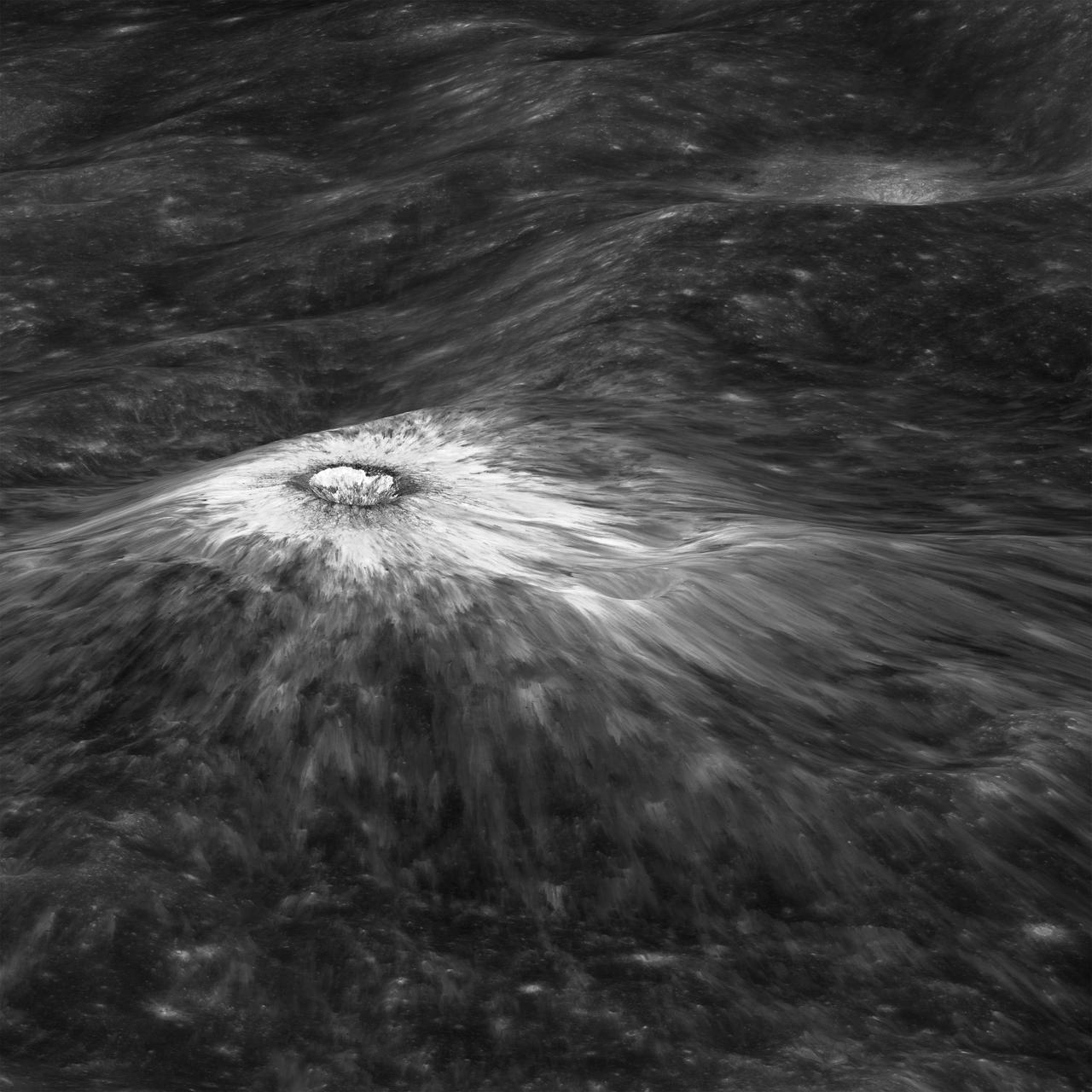

Looking east to west across the rim and down into Chaplygin crater reveals this beautiful example of a fresh young crater and its perfectly preserved ejecta blanket. The delicate patterns of flow across, over, and down local topography clearly show that ejecta traveled as a ground hugging flow for great distances, rather than simply being tossed out on a ballistic trajectory. Very near the rim lies a dark, lacy, discontinuous crust of now frozen impact melt. Clearly this dark material is on top of the bright material so it was the very last material ejected from the crater. The melt was formed as the tremendous energy of impact was converted to heat and the lunar crust was melted at the impact point. As the crater rebounded and material sloughed down the walls of the deforming crater the melt was splashed out over the rim and froze. Its low reflectance is mostly due to a high percentage of glass because the melt cooled so quickly that minerals did not have time to crystallize. The fact that the delicate splash patterns are so well preserved testifies to the very young age of this crater. But how young? For comparison "Chappy" (informal name) is 200 m larger than Meteor crater (1200 m diameter) in Arizona, which is about 50,000 years old. Craters of this size form every 100,000 years or so on the Moon and the Earth. Since there are very few superposed craters on Chappy, and its ejecta is so perfectly preserved it may be much younger than Meteor crater. However, we can't know the true true absolute age of "Chappy" until we can obtain a sample of its impact melt for radiometric age dating. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University/LRO/LROC
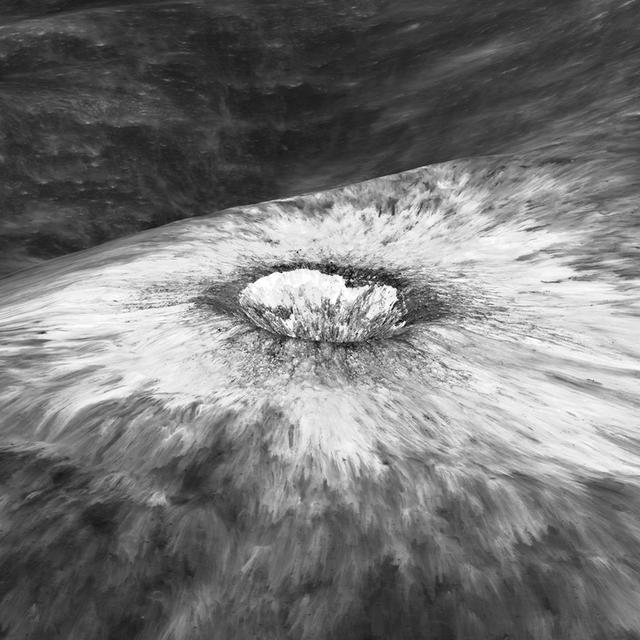

Looking east to west across the rim and down into Chaplygin crater reveals this beautiful example of a fresh young crater and its perfectly preserved ejecta blanket. The delicate patterns of flow across, over, and down local topography clearly show that ejecta traveled as a ground hugging flow for great distances, rather than simply being tossed out on a ballistic trajectory. Very near the rim lies a dark, lacy, discontinuous crust of now frozen impact melt. Clearly this dark material is on top of the bright material so it was the very last material ejected from the crater. The melt was formed as the tremendous energy of impact was converted to heat and the lunar crust was melted at the impact point. As the crater rebounded and material sloughed down the walls of the deforming crater the melt was splashed out over the rim and froze. Its low reflectance is mostly due to a high percentage of glass because the melt cooled so quickly that minerals did not have time to crystallize. The fact that the delicate splash patterns are so well preserved testifies to the very young age of this crater. But how young? For comparison "Chappy" (informal name) is 200 m larger than Meteor crater (1200 m diameter) in Arizona, which is about 50,000 years old. Craters of this size form every 100,000 years or so on the Moon and the Earth. Since there are very few superposed craters on Chappy, and its ejecta is so perfectly preserved it may be much younger than Meteor crater. However, we can't know the true true absolute age of "Chappy" until we can obtain a sample of its impact melt for radiometric age dating. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University/LRO/LROC
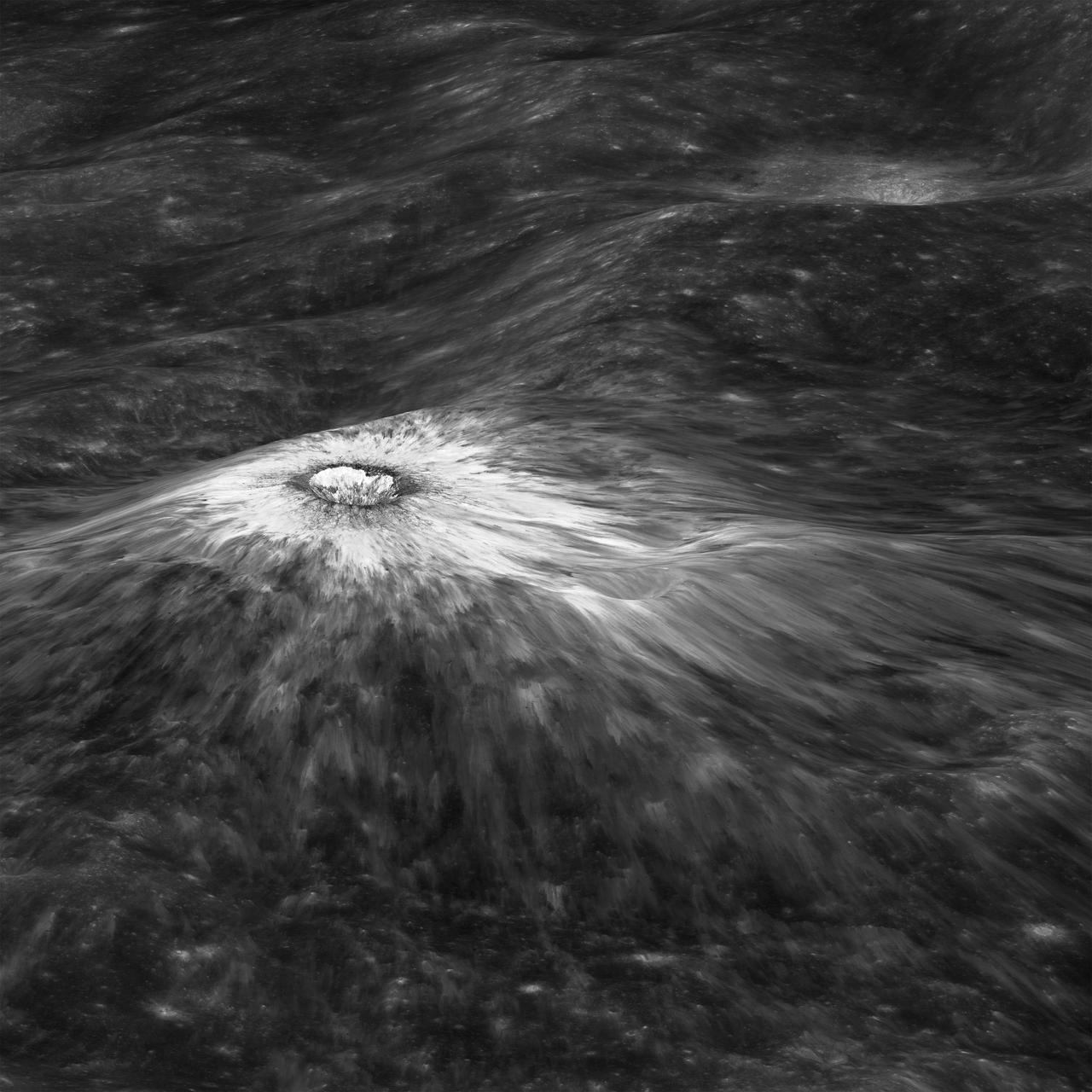

Looking east to west across the rim and down into Chaplygin crater reveals this beautiful example of a fresh young crater and its perfectly preserved ejecta blanket. The delicate patterns of flow across, over, and down local topography clearly show that ejecta traveled as a ground hugging flow for great distances, rather than simply being tossed out on a ballistic trajectory. Very near the rim lies a dark, lacy, discontinuous crust of now frozen impact melt. Clearly this dark material is on top of the bright material so it was the very last material ejected from the crater. The melt was formed as the tremendous energy of impact was converted to heat and the lunar crust was melted at the impact point. As the crater rebounded and material sloughed down the walls of the deforming crater the melt was splashed out over the rim and froze. Its low reflectance is mostly due to a high percentage of glass because the melt cooled so quickly that minerals did not have time to crystallize. The fact that the delicate splash patterns are so well preserved testifies to the very young age of this crater. But how young? For comparison "Chappy" (informal name) is 200 m larger than Meteor crater (1200 m diameter) in Arizona, which is about 50,000 years old. Craters of this size form every 100,000 years or so on the Moon and the Earth. Since there are very few superposed craters on Chappy, and its ejecta is so perfectly preserved it may be much younger than Meteor crater. However, we can't know the true true absolute age of "Chappy" until we can obtain a sample of its impact melt for radiometric age dating. Investigate all of Chappy's ejecta, at full resolution: <a href="http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/901" rel="nofollow">lroc.sese.asu.edu/posts/901</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University/LRO/LROC
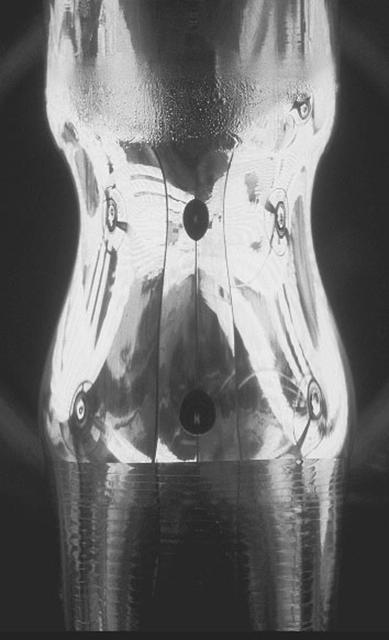
Crystal Growth in magnetic fields, a float-zone sample, the surface tension of the melt keeps the sample suspended between the sample rods in the furnace forming an actual liquid bridge. Principal Investigator: Dr. Frank Szofran
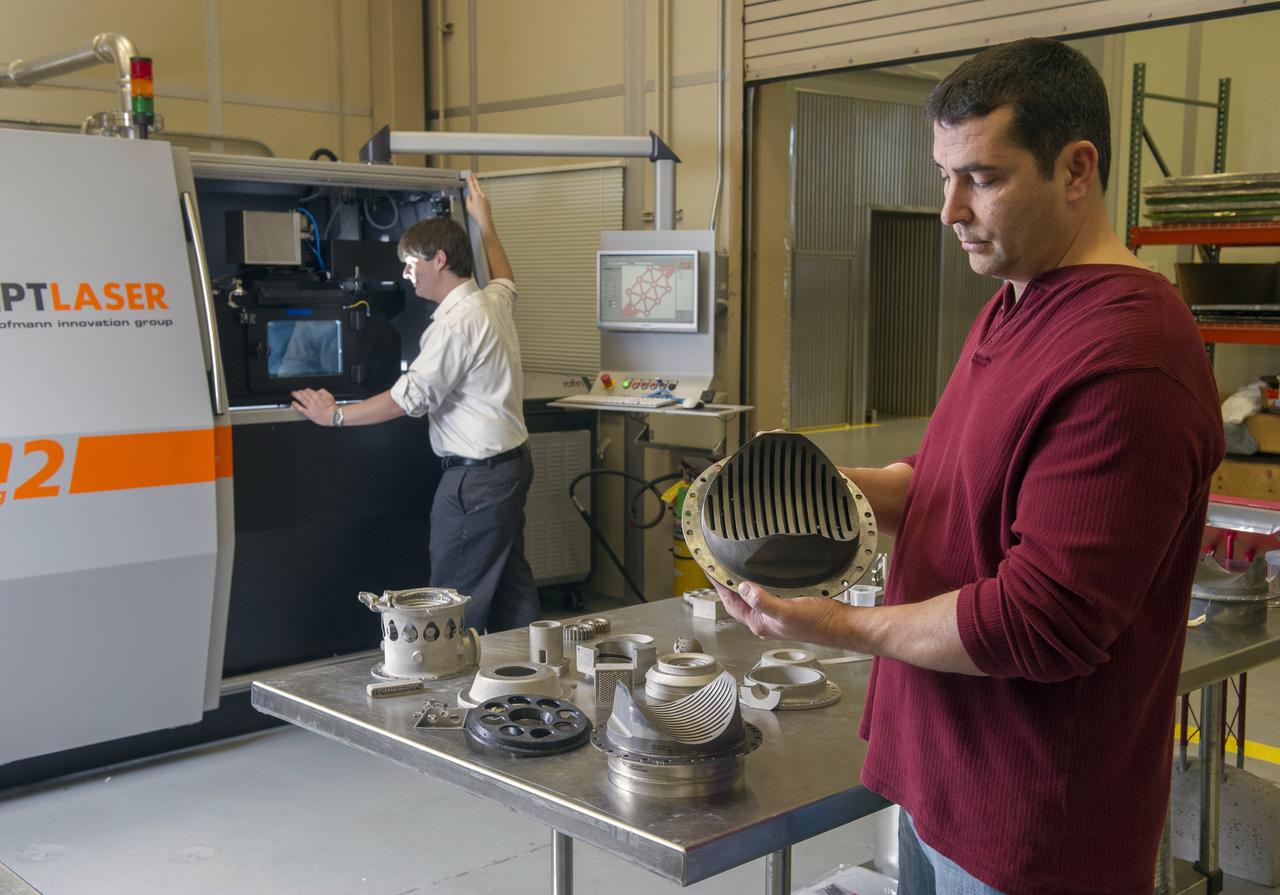

ZACK JONES AND JIM LYDON OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.
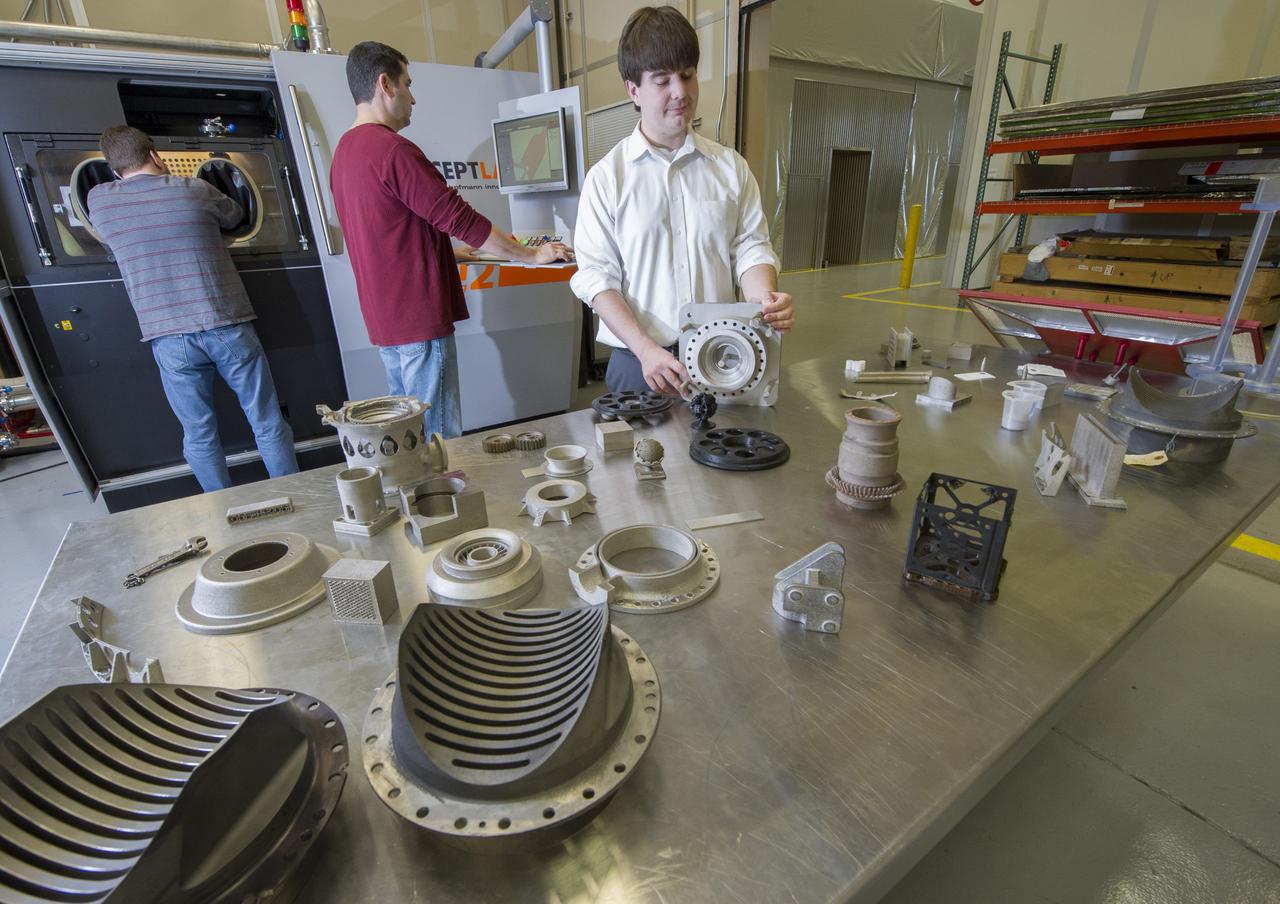

QUINCY BEAN, JIM LYDON, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S M2 SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. THE M2 IS CURRENTLY DEDICATED TO ADVANCED COPPER MATERIAL DEVELOPMENT FOR THE LOW COST UPPER STAGE PROGRAM.

NASA Airborne Snow Observatory is two instruments combined that provides information on every patch of snow, including how deep it is and how fast it melting. This is a frame from an animation.
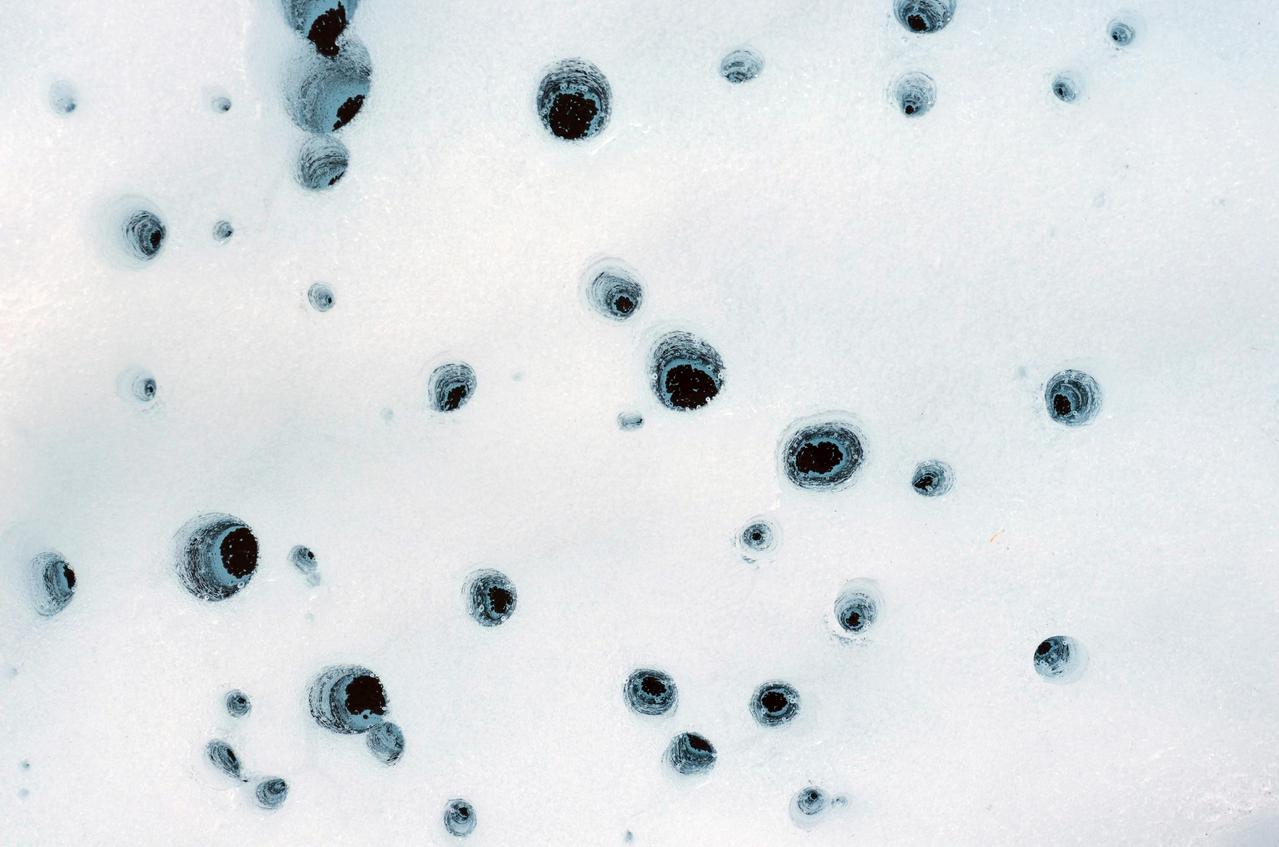
These holes, captured on Alaska's Matanuska Glacier in July 2012, are formed by cryoconite – dust particles that melt into the ice over time, eventually forming small pockets of water below the glacier's surface. Scientists believe similar pockets of water – called cryoconite holes on Earth – could form within dusty water ice on Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26409
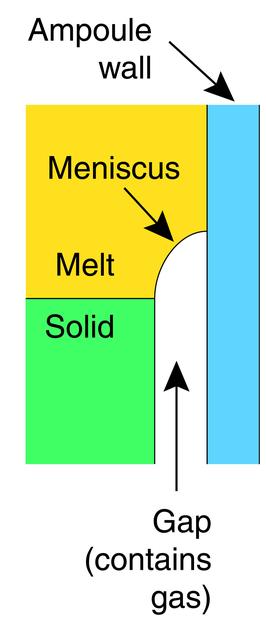
While the microgravity environment of orbit eliminates a number of effects that impede the formation of materials on Earth, the change can also cause new, unwanted effects. A mysterious phenomenon, known as detached solidification, apparently stems from a small hydrostatic force that turns out to be pervasive. The contact of the solid with the ampoule transfers stress to the growing crystal and causing unwanted dislocations and twins. William Wilcox and Liya Regel of Clarkson University theorize that the melt is in contact with the ampoule wall, while the solid is not, and the melt and solid are cornected by a meniscus. Their work is sponsored by NASA's Office of Biological and Physical Researcxh, and builds on earlier work by Dr. David Larson of the State University of New York at Stony Brook.
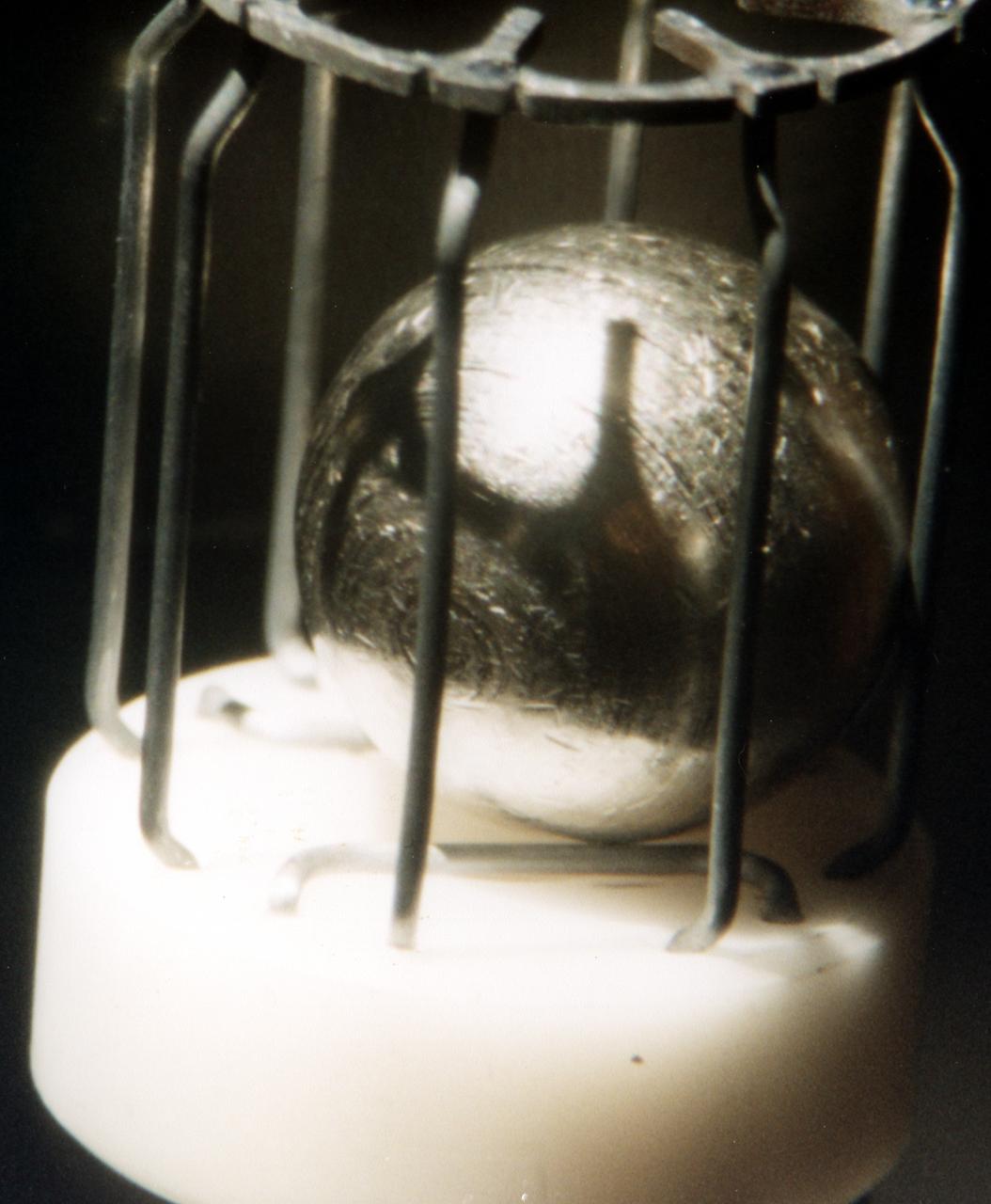

Typical metal sample that was processed by TEMPUS (Tiegelfreies Elektromagnetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit), an electromagnetic levitation facility developed by German researchers and flown on the IML-2 and MSL-1 and 1R Spacelab missions. Electromagnetic levitation is used commonly in ground-based experiments to melt and then cool metallic melts below their freezing points without solidification occurring. Sample size is limited in ground-based experiments. Research with TEMPUS aboard Spacelab allowed scientists to study the viscosity, surface tension, and other properties of several metals and alloys while undercooled (i.e., cooled below their normal solidification points). The sample is about 1 cm (2/5 inch) in diameter.
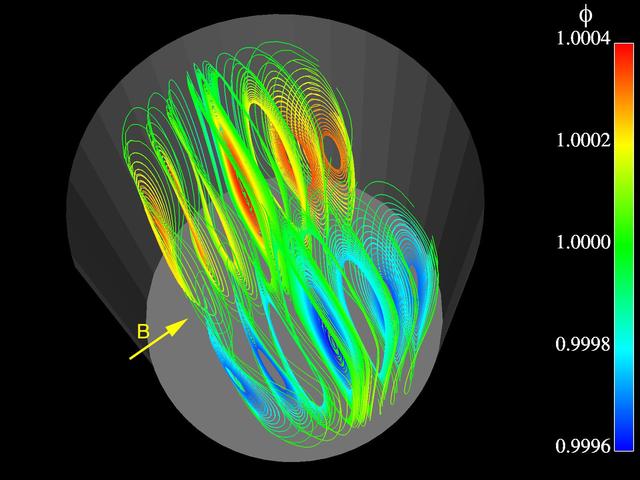
Advanced finite element models are used to study three-dimensional, time-dependent flow and segregation in crystal growth systems. In this image of a prototypical model for melt and crystal growth, pathlines at one instant in time are shown for the flow of heated liquid silicon in a cylindrical container. The container is subjected to g-jitter disturbances along the vertical axis. A transverse magnetic field is applied to control them. Such computations are extremely powerful for understanding melt growth in microgravity where g-jitter drives buoyant flows. The simulation is part of the Theoretical Analysis of 3D, Transient Convection and Segregation in Microgravity Bridgman Crystal Growth investigation by Dr. Jeffrey J. Derby of the University of Mirnesota, Minneapolis.
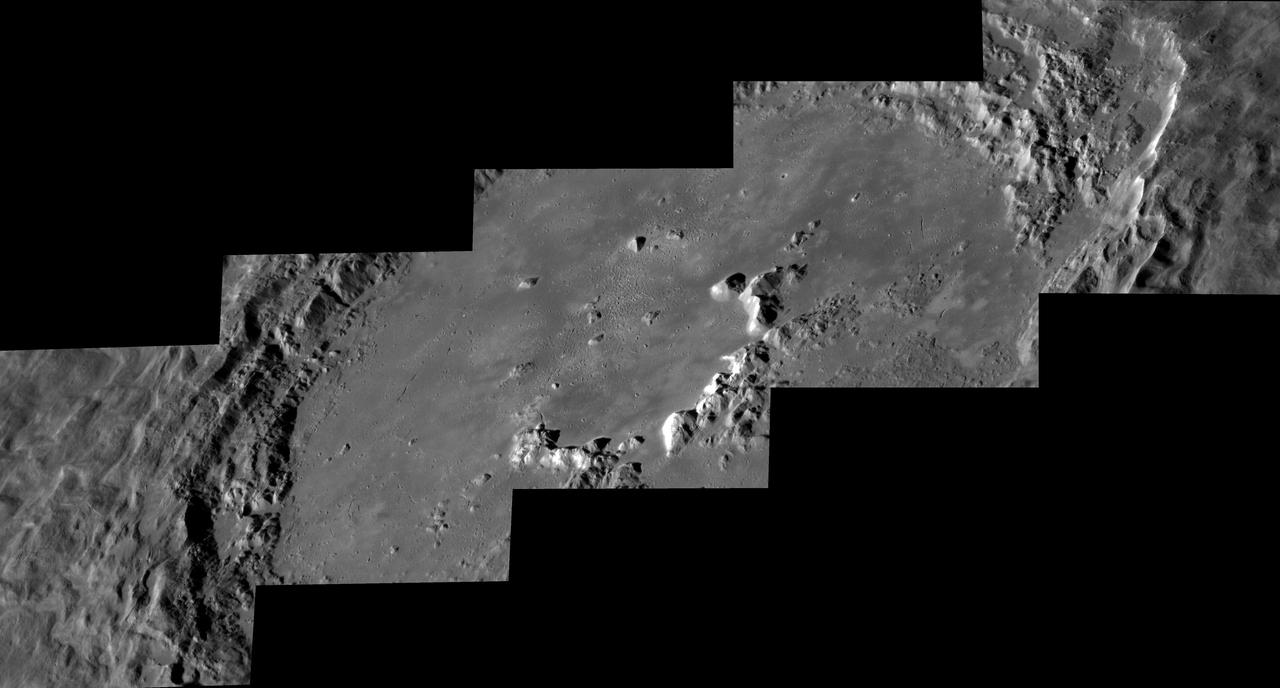

Hokusai crater's rays extend across much of the planet, but its interior is spectacular in its own right. This series of oblique images from NASA's MESSENGER spacecraft shows the central peaks, beautiful terraces, and frozen sea of impact melt on the crater floor. Instrument: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) Center Latitude: 57.8° Center Longitude: 16.8° E Scale: Hokusai crater is 114 km (71 miles) in diameter http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19406

Expedition Five flight engineer Peggy Whitson is shown installing the Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules (SUBSA) experiment in the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) in the Destiny laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). SUBSA examines the solidification of semiconductor crystals from a melted material. Semiconductor crystals are used for many products that touch our everyday lives. They are found in computer chips, integrated circuits, and a multitude of other electronic devices, such as sensors for medical imaging equipment and detectors of nuclear radiation. Materials scientists want to make better semiconductor crystals to be able to further reduce the size of high-tech devices. In the microgravity environment, convection and sedimentation are reduced, so fluids do not remove and deform. Thus, space laboratories provide an ideal environment of studying solidification from the melt. This investigation is expected to determine the mechanism causing fluid motion during production of semiconductors in space. It will provide insight into the role of the melt motion in production of semiconductor crystals, advancing our knowledge of the crystal growth process. This could lead to a reduction of defects in semiconductor crystals produced in space and on Earth.

Scientists are exploring how aerogel, a translucent, Styrofoam-like material, could be used as a building material on Mars. Aerogel retains heat; structures built with it could raise temperatures enough to melt water ice on the Martian surface. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23343
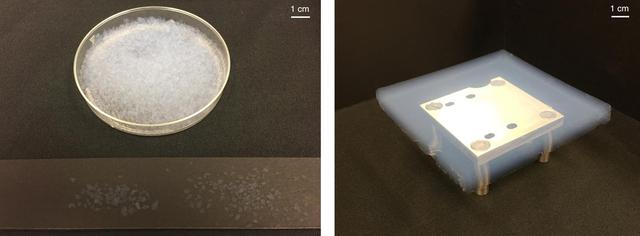
Scientists tested these samples of aerogel to see how they could be used as building materials on Mars. In an experiment, both the crushed and solid samples of aerogel were able to raise temperatures to melt water ice — ideal for a Martian greenhouse in which crops could grow. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23342
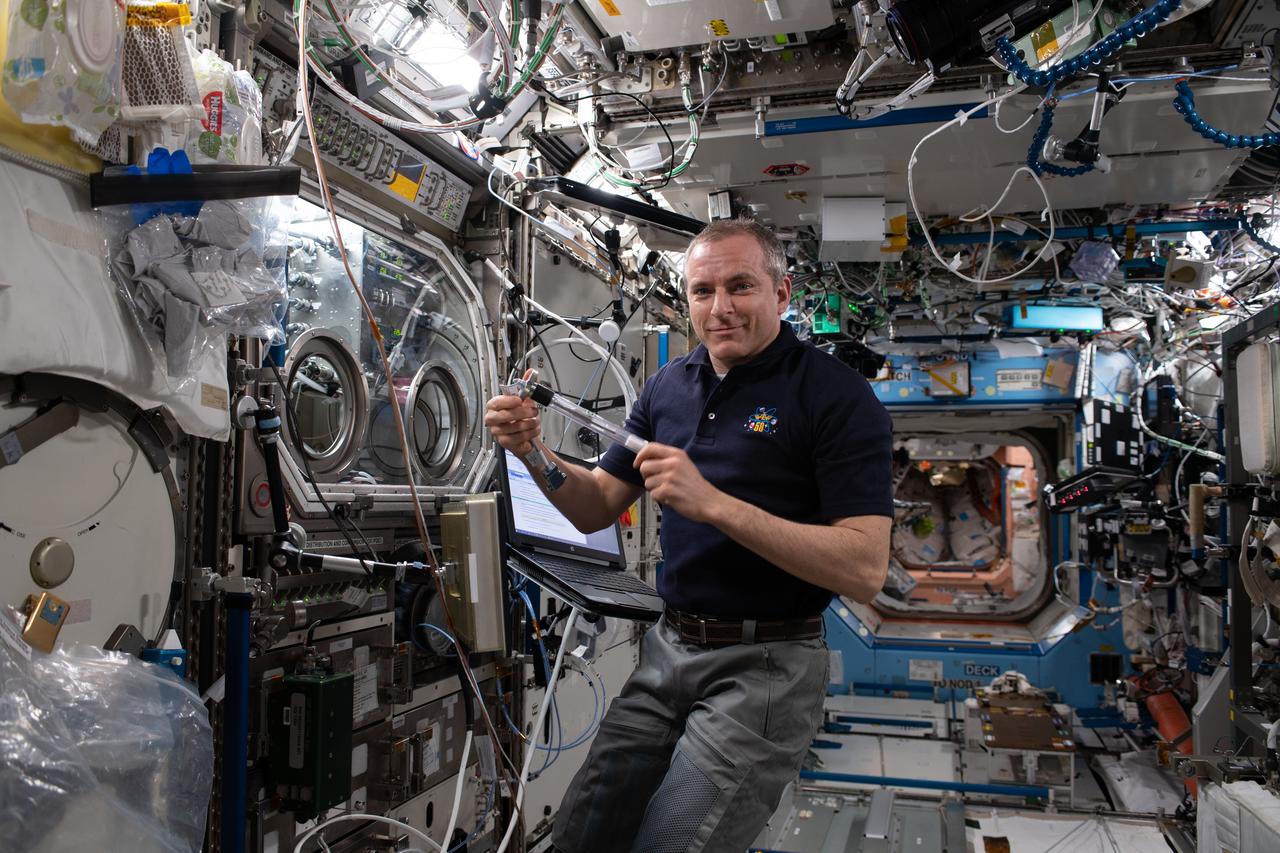

iss059e027344 (April 19, 2019) --- Astronaut David Saint-Jacques of the Canadian Space Agency studies how crystals melt and solidify using the Microgravity Science Glovebox inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module. The Solidification Using a Baffle in Sealed Ampoules study explores how to produce high-quality semi-conductor crystals in microgravity.

iss059e034612 (April 23, 2019) --- Severe flooding is seen near Basrah, Iraq, as unusually heavy and persistent rain doused several Middle Eastern countries in late March and early April 2019. At the same time, mountains were beginning to lose their snow cover to melting.
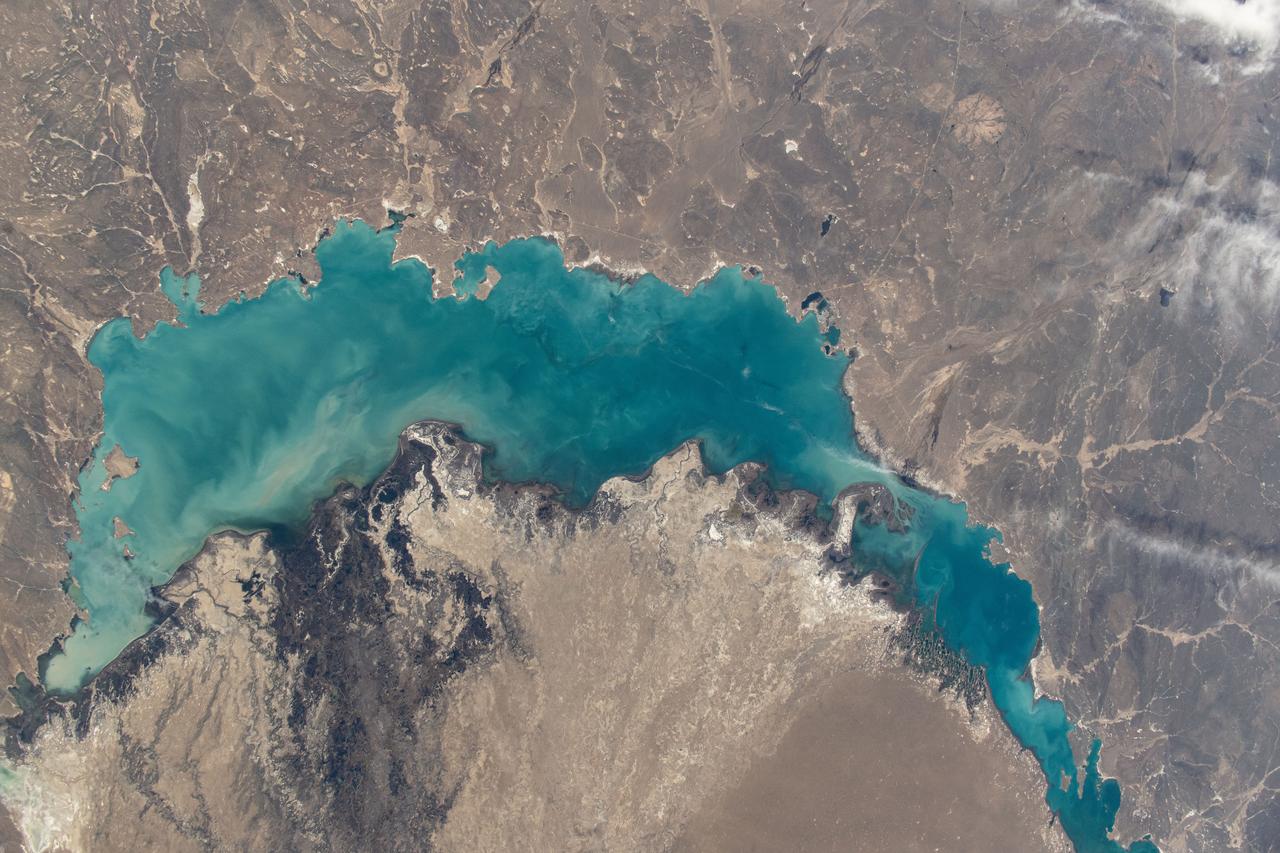

iss071e012112 (April 19, 2024) -- In southeastern Kazakhstan lies Lake Balkhash, one of the largest in Asia. Its turquoise color comes from winter ice melting. As the International Space Station soared nearly 260 miles above, NASA astronaut Mike Barratt captured this photo.
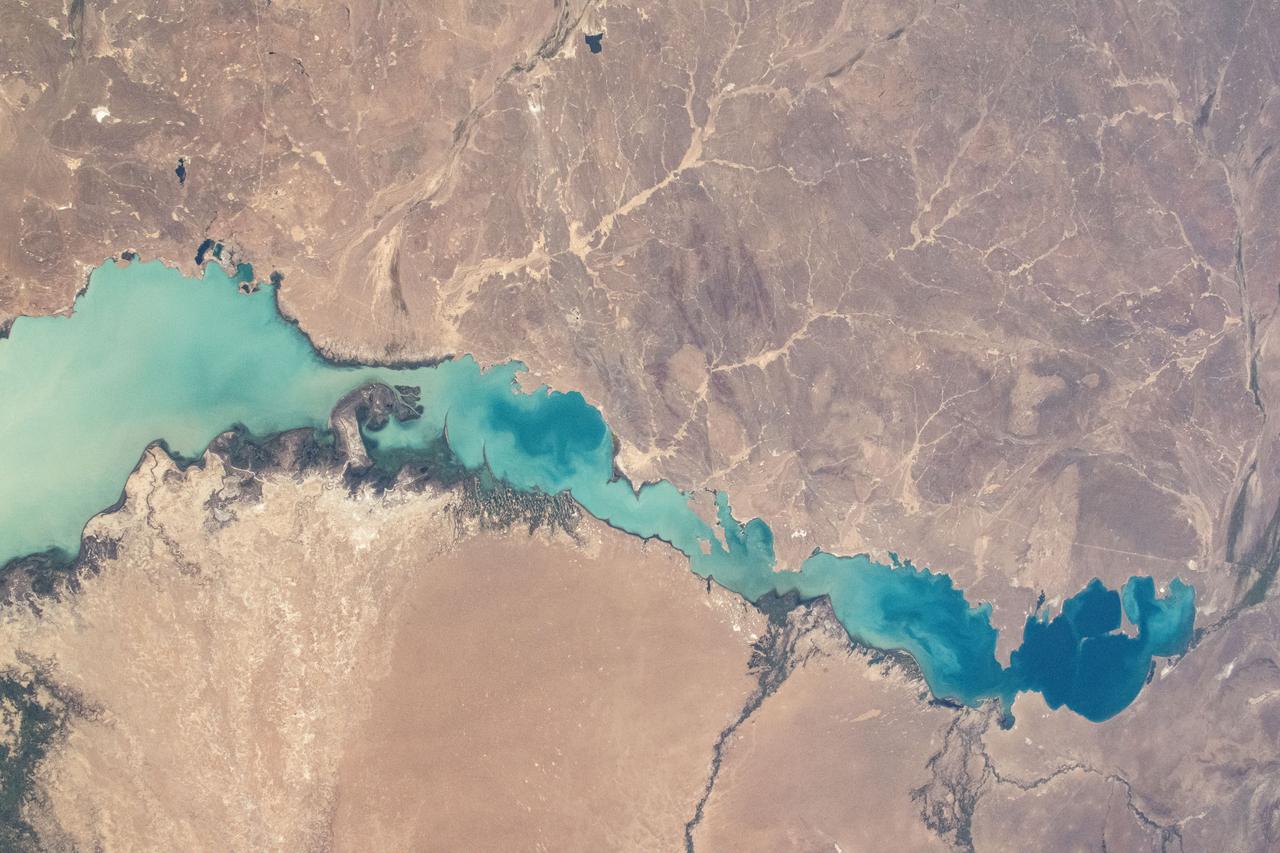

iss071e413751 (Aug. 1, 2024) -- Lake Balkhash is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 259 miles above Kazakhstan. Its turquoise water, stark against the surrounding terrain, comes from nearby winter ice melting.
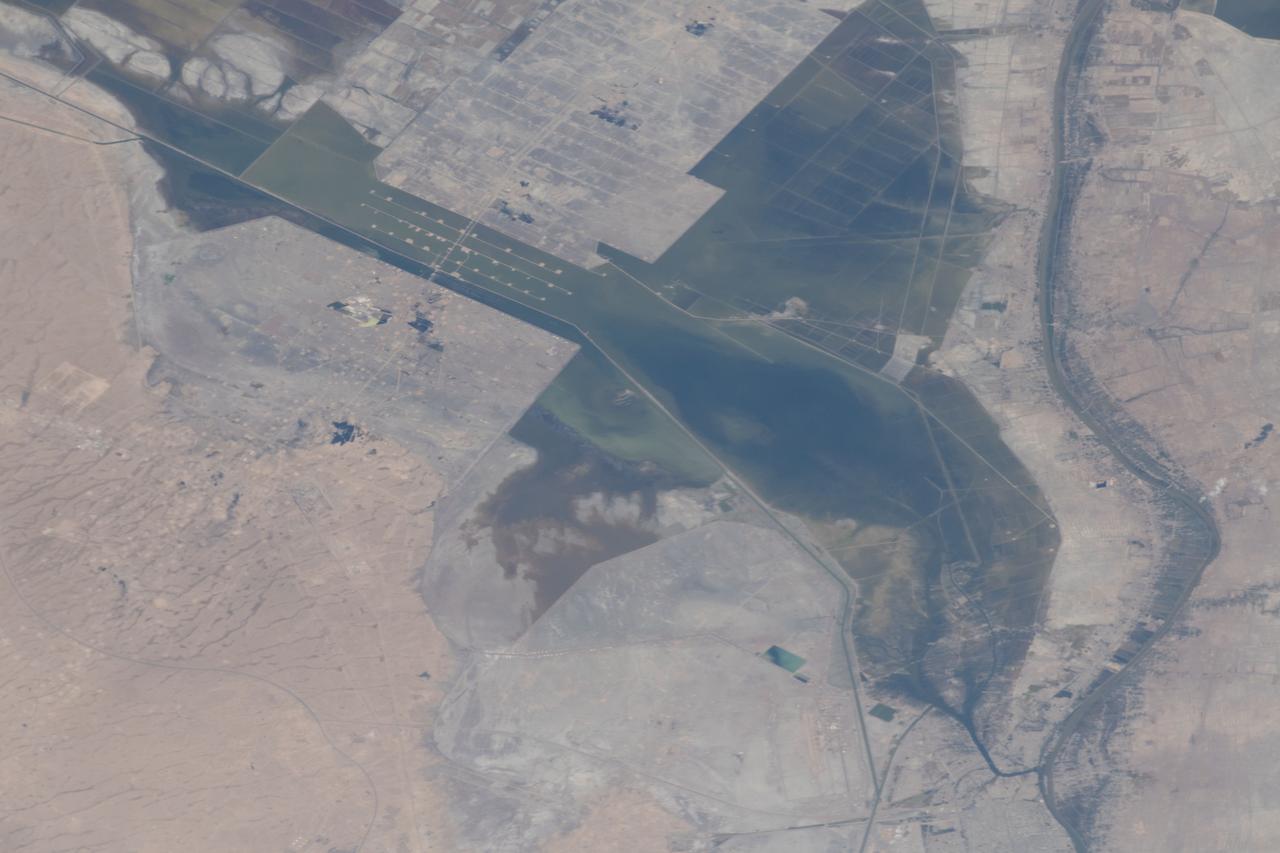

iss059e034570 (April 23, 2019) --- Severe flooding is seen near Basrah, Iraq, as unusually heavy and persistent rain doused several Middle Eastern countries in late March and early April 2019. At the same time, mountains were beginning to lose their snow cover to melting.
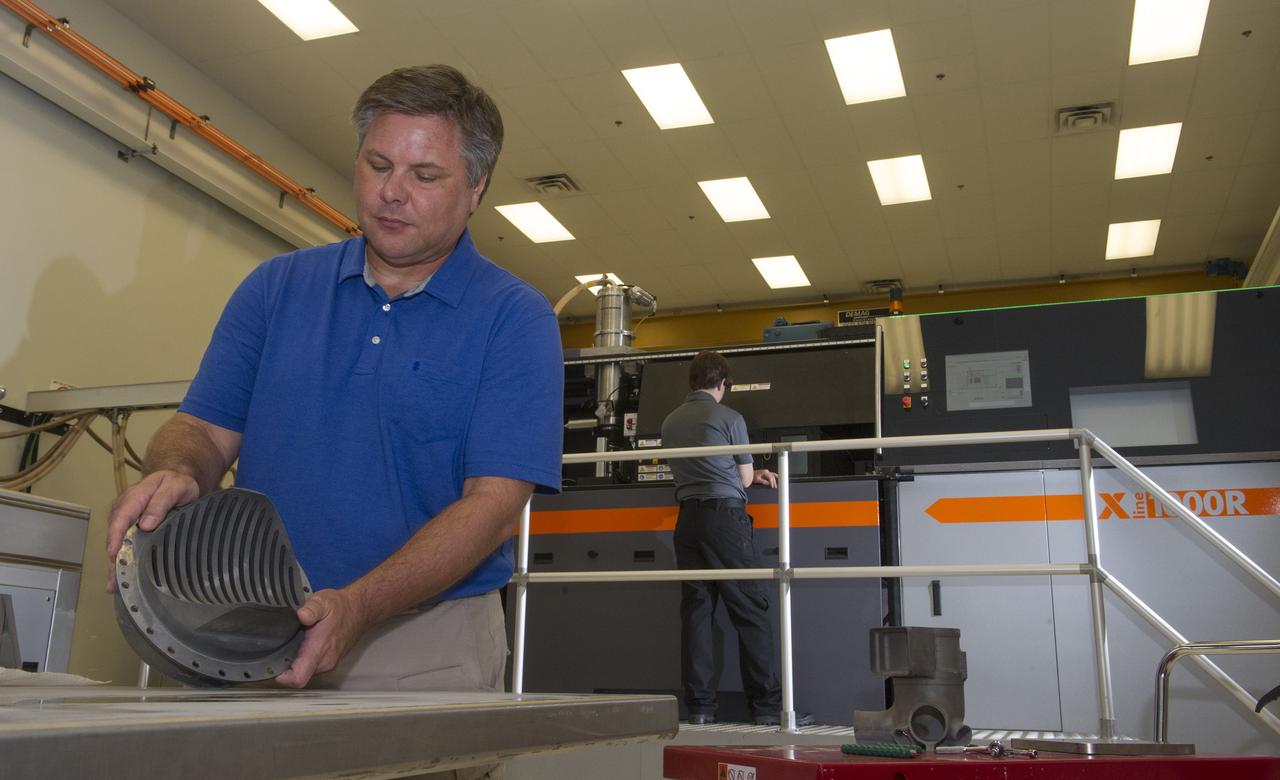

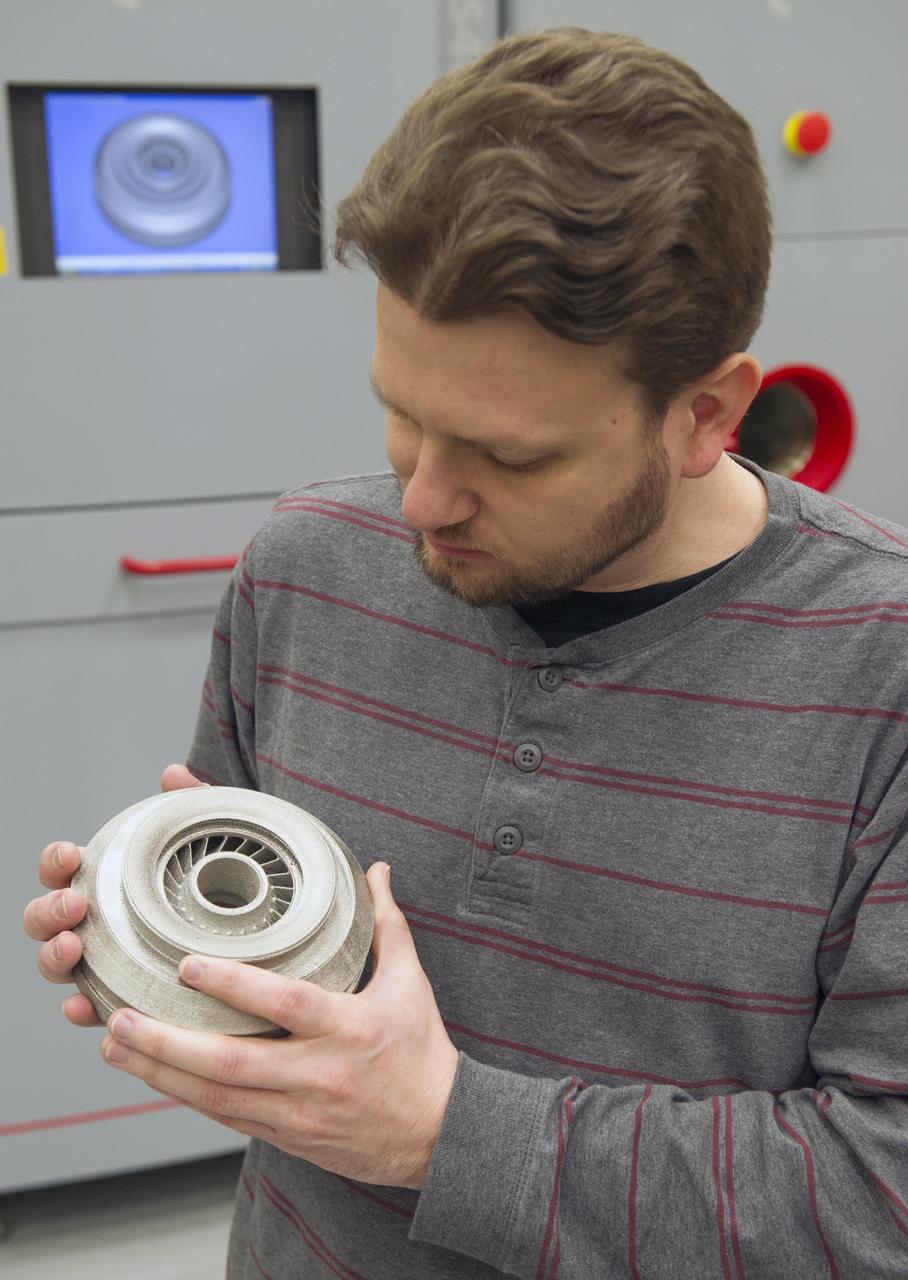
ANDY HARDIN, A PROPULSION ENGINEER AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA, SHOWS A 3-D PRINTED ROCKET PART MADE WITH A SELECTIVE LASER MELTING MACHINE. PARTS FOR THE SPACE LAUNCH SYSTEM'S RS-25 ROCKET ENGINE ARE BEING MADE WITH THE MACHINE IN THE BACKGROUND
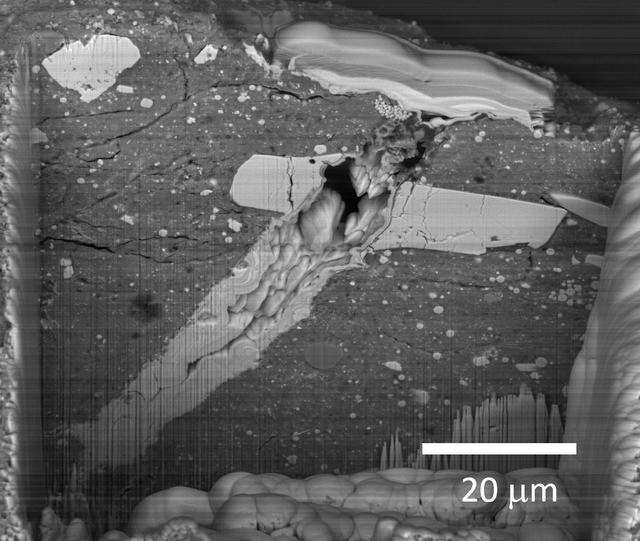
A scanning electron microscope image of a micrometeorite impact crater in a particle of asteroid Bennu material. Scientists found microscopic craters and tiny splashes of once-molten rock – known as impact melts – on the surfaces of samples, signs that the asteroid was bombarded by micrometeorites.
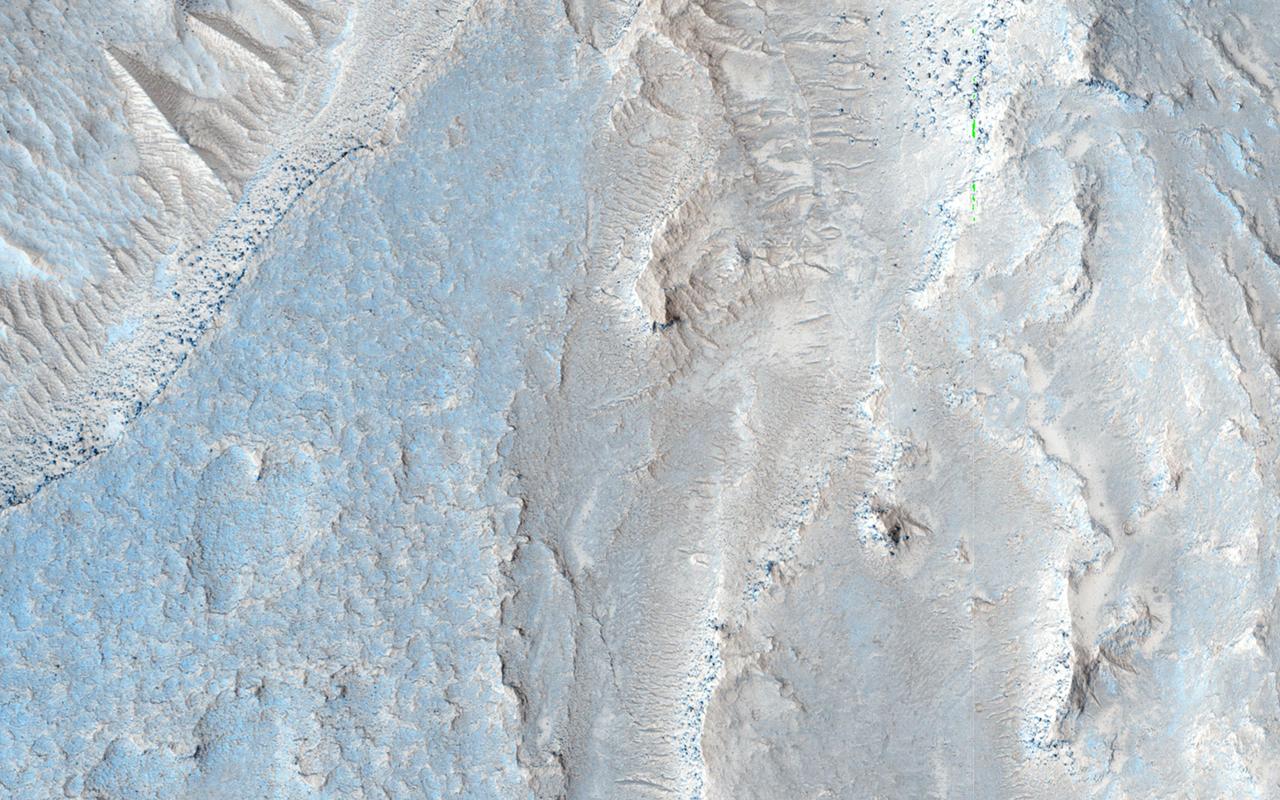

The image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is approximately 6 by 6 kilometers and is located east of Noctis Labyrinthus, in a portion the large canyon system Valles Marineris.
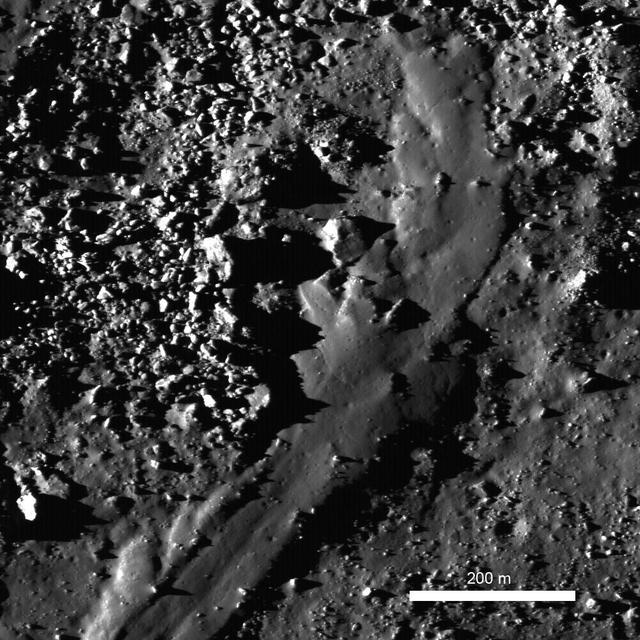

This image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows the spectacularly preserved viscous flow on the NE rim of Byrgius A crater.