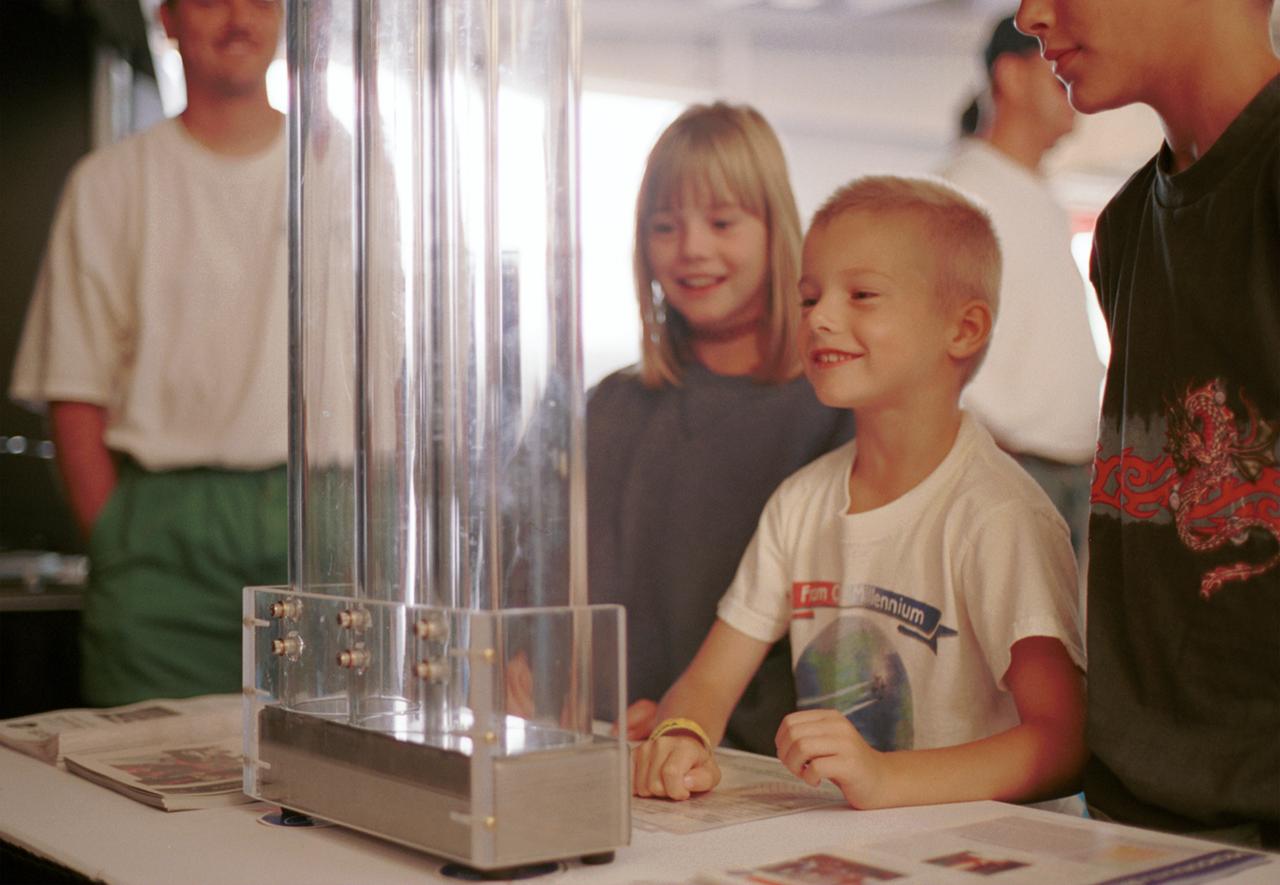

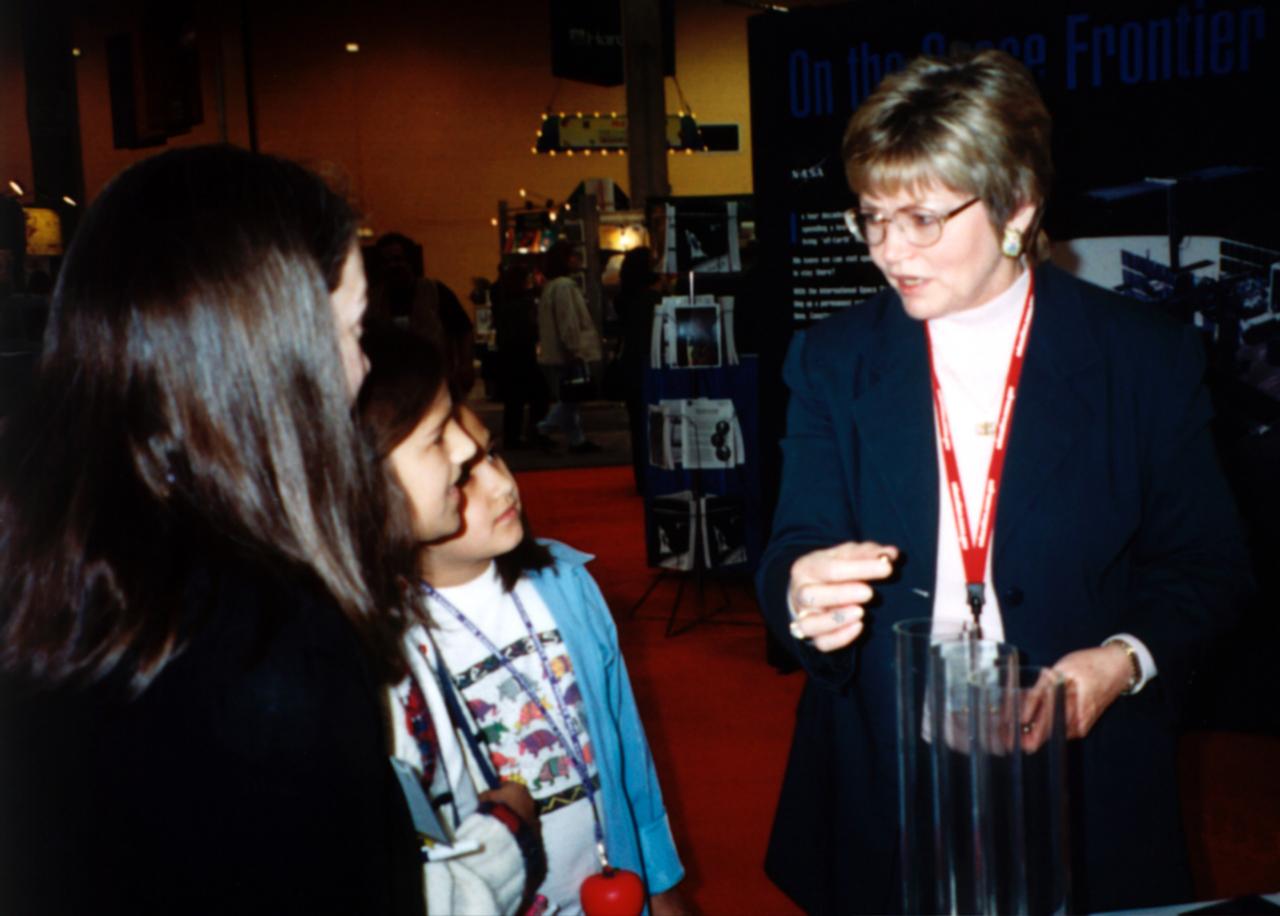
An entranced youngster watches a demonstration of the enhanced resilience of undercooled metal alloys as compared to conventional alloys. Steel bearings are dropped onto plates made of steel, titanium alloy, and zirconium liquid metal alloy, so-called because its molecular structure is amorphous and not crystalline. The bearing on the liquid metal plate bounces for a minute or more longer than on the other plates. Experiments aboard the Space Shuttle helped scientists refine their understanding of the physical properties of certain metal alloys when undercooled (i.e., kept liquid below their normal solidification temperature). This new knowledge then allowed scientists to modify a terrestrial production method so they can now make limited quantities marketed under the Liquid Metal trademark. The exhibit was a part of the NASA outreach activity at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI.

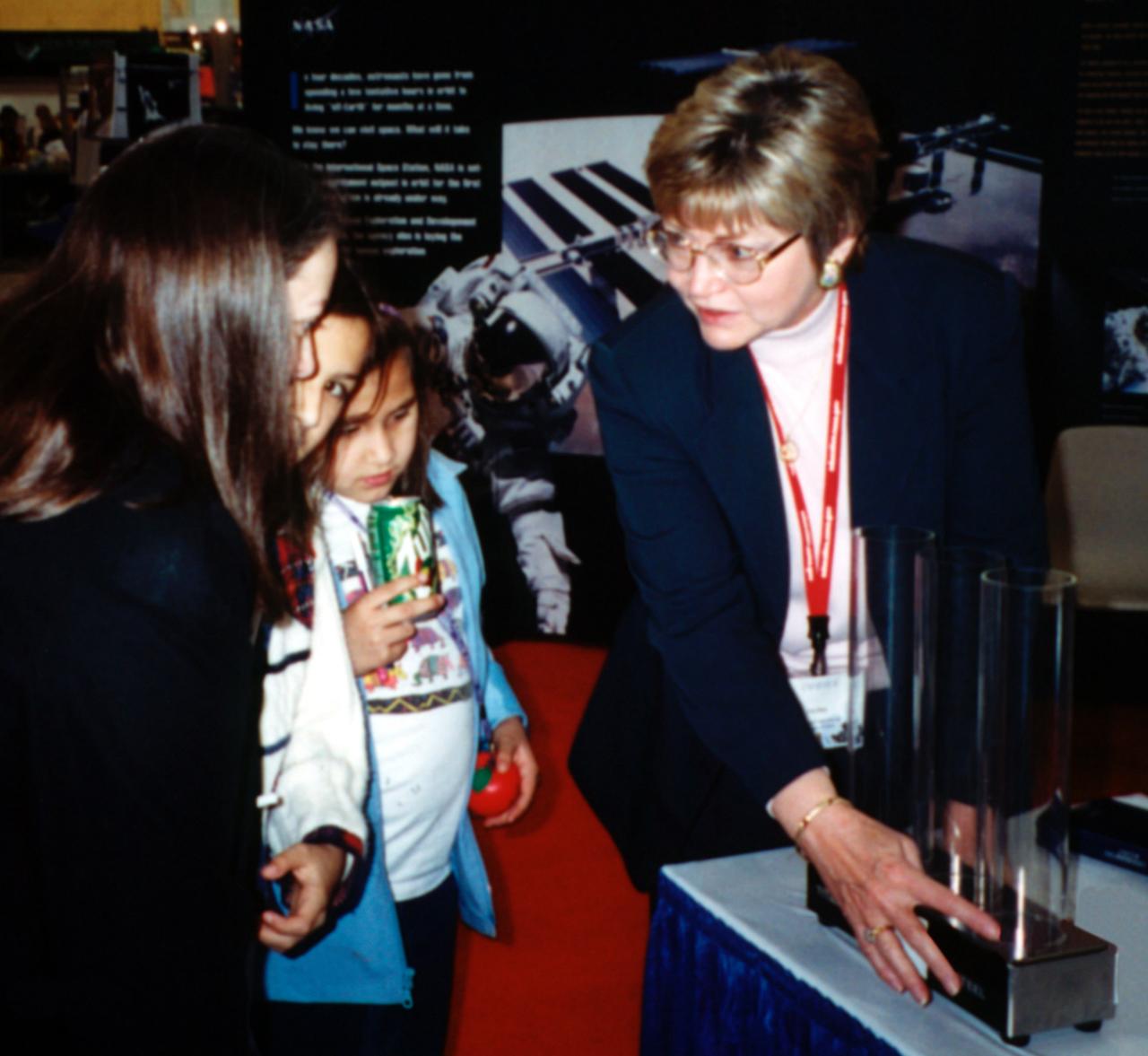
Angie Jackman, a NASA project manager in microgravity research, demonstrates the enhanced resilience of undercooled metal alloys as compared to conventional alloys. Experiments aboard the Space Shuttle helped scientists refine their understanding of the physical properties of certain metal alloys when undercooled (i.e., kept liquid below their normal solidification temperature). This new knowledge then allowed scientists to modify a terrestrial production method so they can now make limited quantities marketed under the Liquid Metal trademark. The exhibit was a part of the NASA outreach activity at AirVenture 2000 sponsored by the Experimental Aircraft Association in Oshkosh, WI.
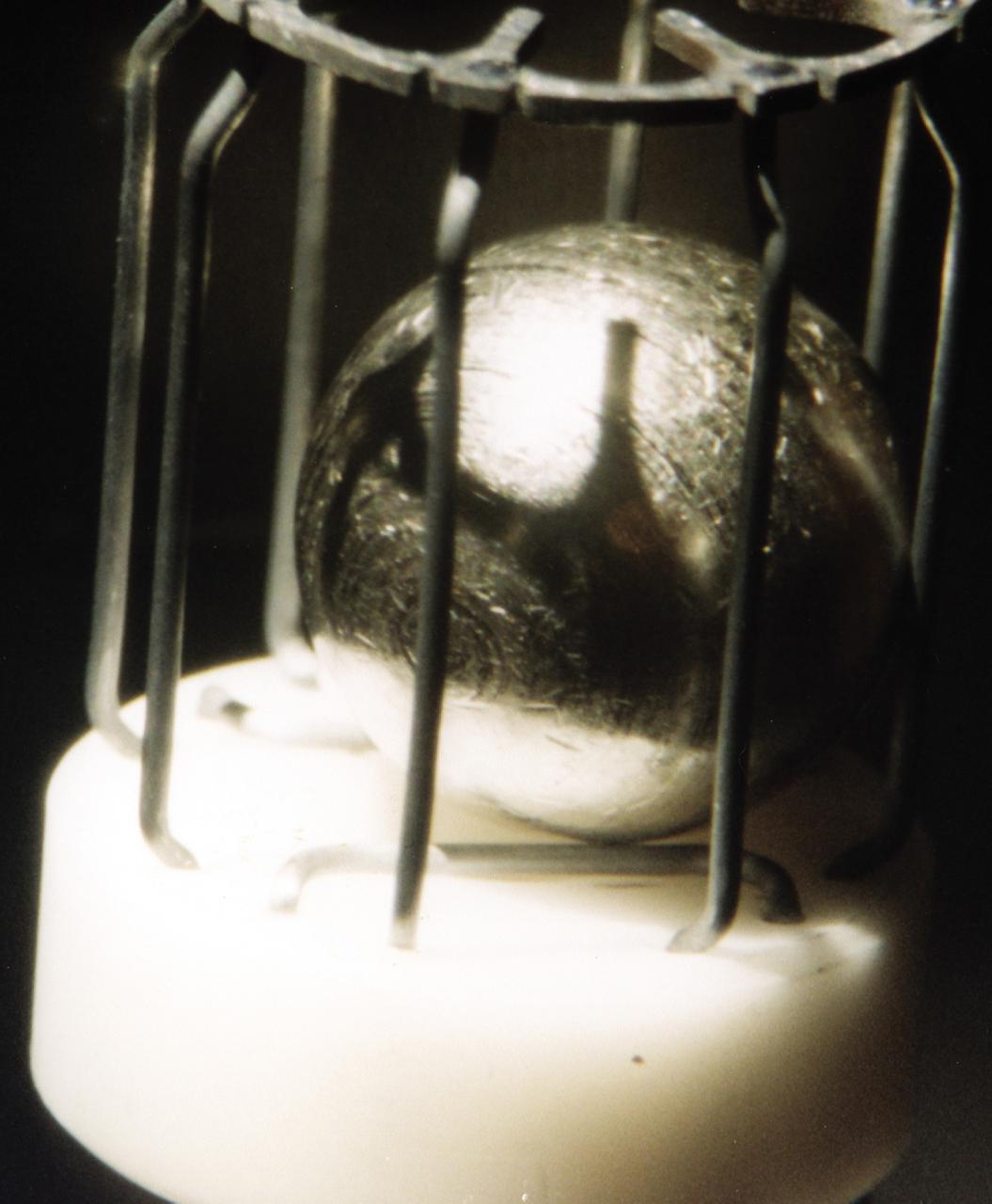
This metal sample, which is approximately 1 cm in diameter, is typical of the metals that were studied using the German designed electromagnetic containerless processing facility. The series of experiments that use this device is known as TEMPUS which is the acronym that stands for the German Tiegelfreies Elektromanetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit. Most of the TEMPUS experiments focused on various aspects of undercooling liquid metal and alloys. Undercooling is the process of melting a material and then cooling it to a temperature that is below its normal freezing or solidification point. The TEMPUS experiments that used the metal cages as shown in the photograph, often studied bulk metallic glass, a solid material with no crystalline structures. We study metals and alloys not only to build things in space, but to improve things that are made on Earth. Metals and alloys are everywhere around us; in our automobiles, in the engines of aircraft, in our power-plants, and elsewhere. Despite their presence in everyday life, there are many scientific aspects of metals that we do not understand.
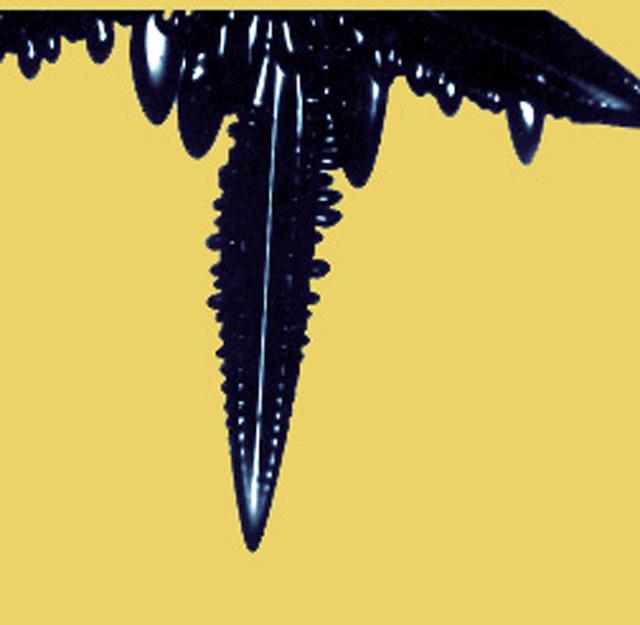

Researchers have found that as melted metals and alloys (combinations of metals) solidify, they can form with different arrangements of atoms, called microstructures. These microstructures depend on the shape of the interface (boundary) between the melted metal and the solid crystal it is forming. There are generally three shapes that the interface can take: planar, or flat; cellular, which looks like the cells of a beehive; and dendritic, which resembles tiny fir trees. Convection at this interface can affect the interface shape and hide the other phenomena (physical events). To reduce the effects of convection, researchers conduct experiments that examine and control conditions at the interface in microgravity. Microgravity also helps in the study of alloys composed of two metals that do not mix. On Earth, the liquid mixtures of these alloys settle into different layers due to gravity. In microgravity, the liquid metals do not settle, and a solid more uniform mixture of both metals can be formed.
Researchers have found that as melted metals and alloys (combinations of metals) solidify, they can form with different arrangements of atoms, called microstructures. These microstructures depend on the shape of the interface (boundary) between the melted metal and the solid crystal it is forming. There are generally three shapes that the interface can take: planar, or flat; cellular, which looks like the cells of a beehive; and dendritic, which resembles tiny fir trees. Convection at this interface can affect the interface shape and hide the other phenomena (physical events). To reduce the effects of convection, researchers conduct experiments that examine and control conditions at the interface in microgravity. Microgravity also helps in the study of alloys composed of two metals that do not mix. On Earth, the liquid mixtures of these alloys settle into different layers due to gravity. In microgravity, the liquid metals do not settle, and a solid more uniform mixture of both metals can be formed.
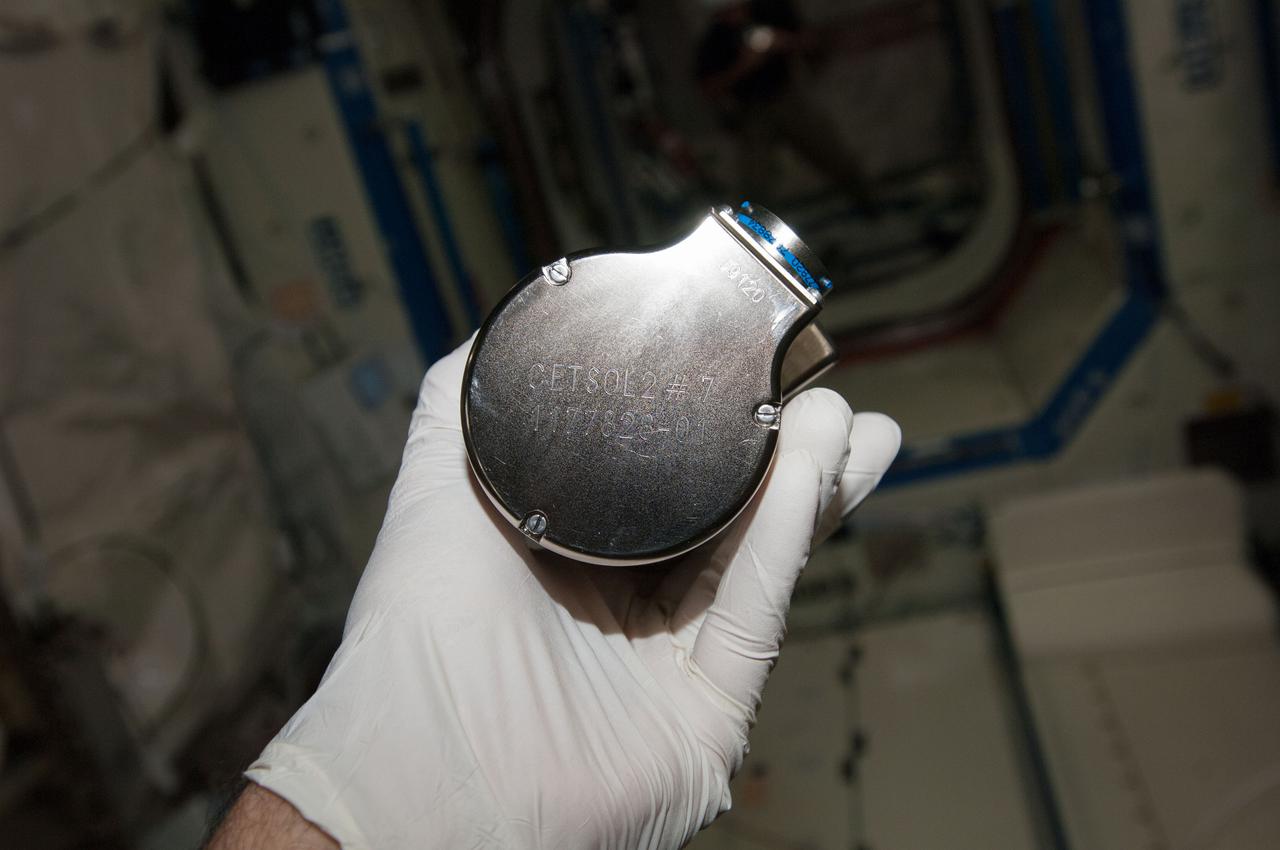

iss038e045758 (2/12/2014) --- A view of Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Solidification Processing-2 (CETSOL-2) test sample 7 which is to be installed into the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF). This investigation aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. The patterns of the crystals resulting from transitions of liquids to solids is important for processes used to produce materials such as solar cells, thermoelectrics, and metal alloys.
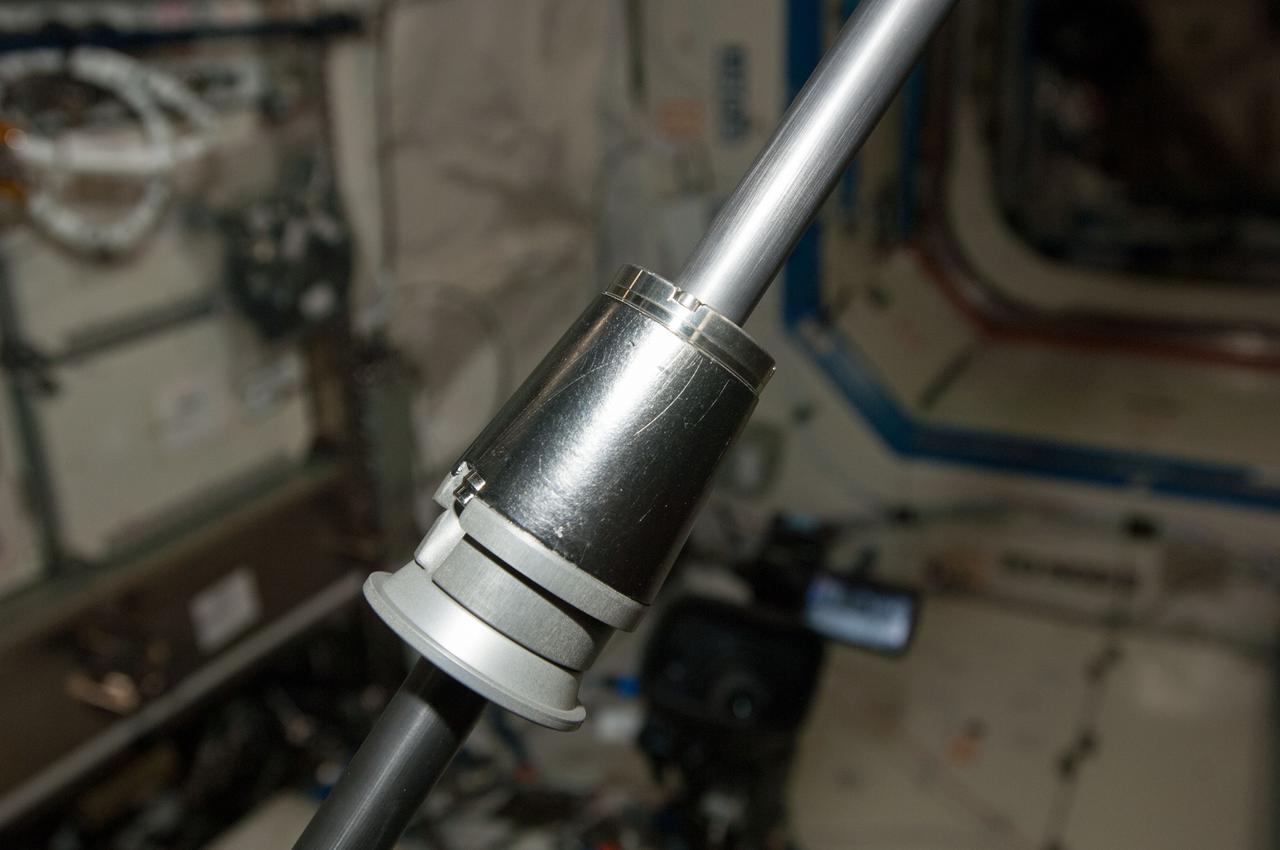

iss038e045760 92/12/2014) --- A view of Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition in Solidification Processing-2 (CETSOL-2) test sample 7 which is to be installed into the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF). This investigation aims to deepen the understanding of the physical principles that govern solidification processes in metal alloys. The patterns of the crystals resulting from transitions of liquids to solids is important for processes used to produce materials such as solar cells, thermoelectrics, and metal alloys.

jsc2020e017722 (3/30/2020) --- A preflight view of an Alumina ampoule containing an Al-10%Cu alloy sample. The thermocouple wires are secured to the outside of the ampoule with refractory bonding material, while the metal clips provide additional support.

Pat Doty (right) of NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) demonstrates the greater bounce to the ounce of metal made from a supercooled bulk metallic glass alloy that NASA is studying in space experiments. The metal plates at the bottom of the plexiglass tubes are made of three different types of metal. Bulk metallic glass is more resilient and, as a result, the dropped ball bearing bounces higher. Experiments in space allow scientists to study fundamental properties that carnot be observed on Earth. This demonstration was at the April 200 conference of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in Chicago. photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

Pat Doty (right) of NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) demonstrates the greater bounce to the ounce of metal made from a supercooled bulk metallic glass alloy that NASA is studying in space experiments. The metal plates at the bottom of the plexiglass tubes are made of three different types of metal. Bulk metallic glass is more resilient and, as a result, the dropped ball bearing bounces higher. Experiments in space allow scientists to study fundamental properties that carnot be observed on Earth. This demonstration was at the April 2000 conference of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics in Chicago. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
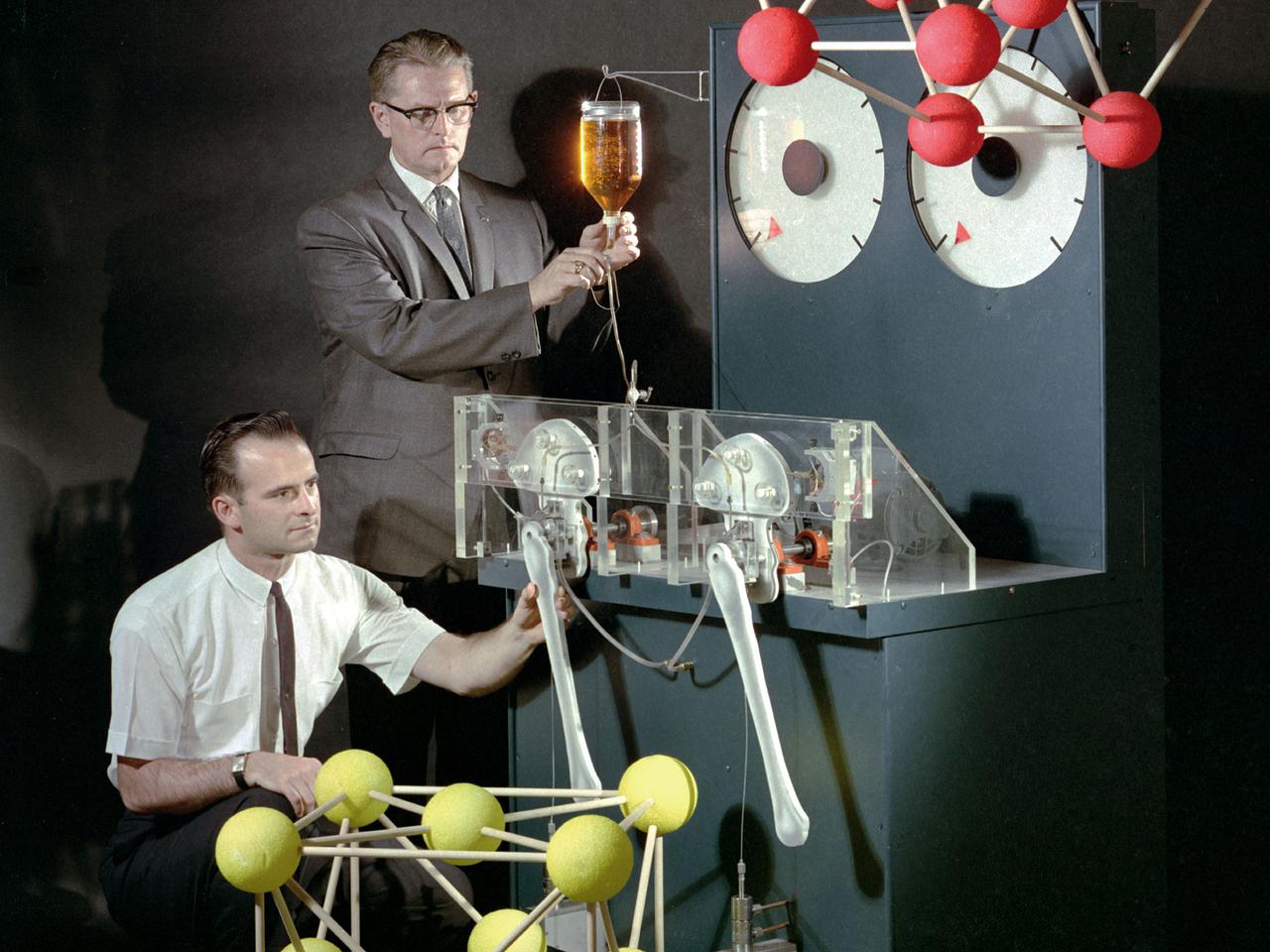

Robert Johnson, top, sets the lubricant flow while Donald Buckley adjusts the bearing specimen on an artificial hip simulator at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The simulator was supplemented by large crystal lattice models to demonstrate the composition of different bearing alloys. This this image by NASA photographer Paul Riedel was used for the cover of the August 15, 1966 edition of McGraw-Hill Product Engineering. Johnson was chief of Lubrication Branch and Buckley head of the Space Environment Lubrication Section in the Fluid System Components Division. In 1962 they began studying the molecular structure of metals. Their friction and wear testing revealed that the optimal structure for metal bearings was a hexagonal crystal structure with proper molecular space. Bearing manufacturers traditionally preferred cubic structures over hexagonal arrangements. Buckley and Johnson found that even though the hexagonal structural was not as inherently strong as its cubic counterpart, it was less likely to cause a catastrophic failure. The Lewis researchers concentrated their efforts on cobalt-molybdenum and titanium alloys for high temperatures applications. The alloys had a number of possible uses, included prosthetics. The alloys were similar in composition to the commercial alloys used for prosthetics, but employed the longer lasting hexagonal structure.
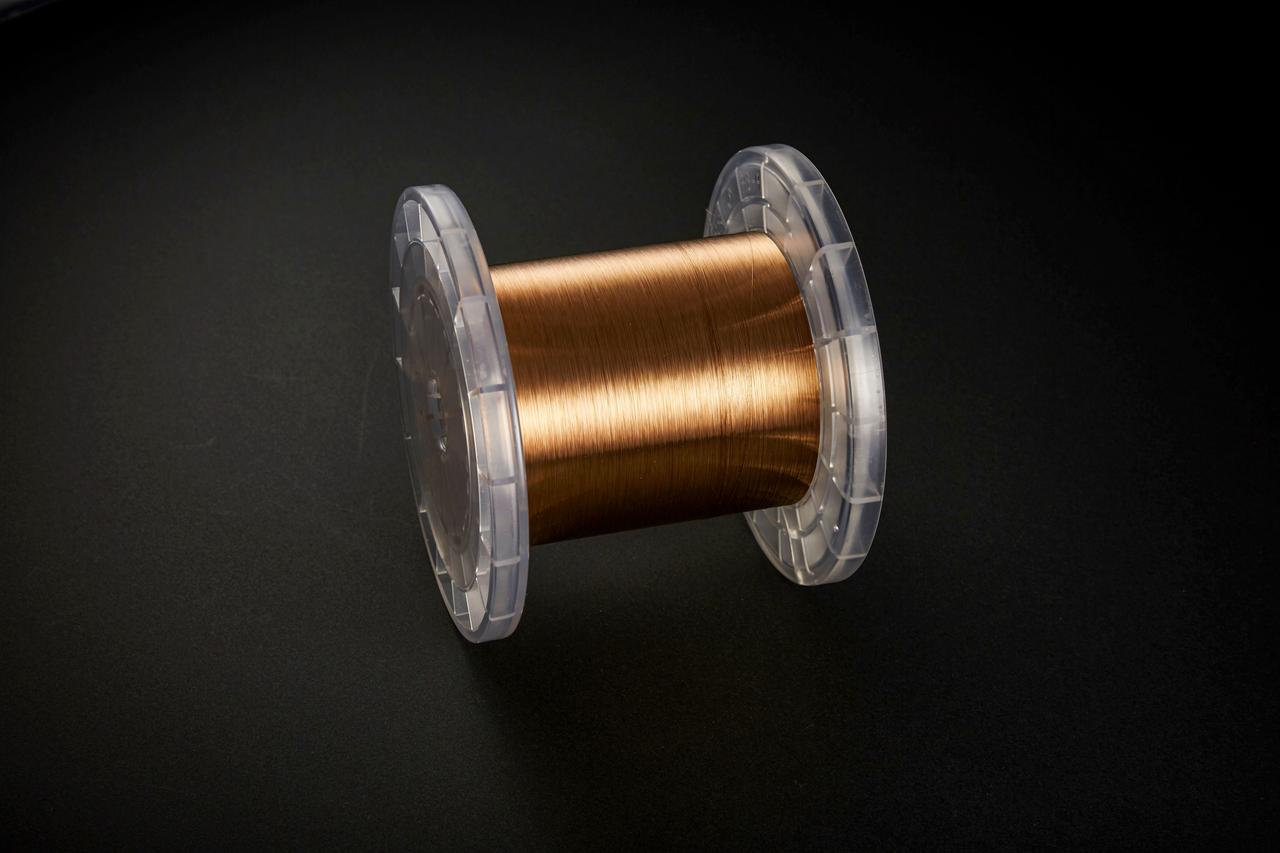

jsc2020e040942 (4/18/2015) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040941 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..

jsc2020e040940 (9/3/2018) --- Copper zirconium alloy wire being produced. The Exposure Experiment of Copper-Zirconium Antenna Metal Mesh to the Space Environment (ExHAM-Antenna Metal Mesh) investigation tests how well an antenna metal mesh, made from copper and zirconium, performs in the space environment in low-Earth orbit (LEO). While in space, the antenna metal mesh is exposed to cosmic rays and atomic oxygen in the LEO space environment - which can degrade antenna performance. Image Credit: NGK Insulators, Ltd., Taiyo Wire Cloth Co., Ltd., Technosolver Corporation, Koyo Materica Corporation, JAXA..
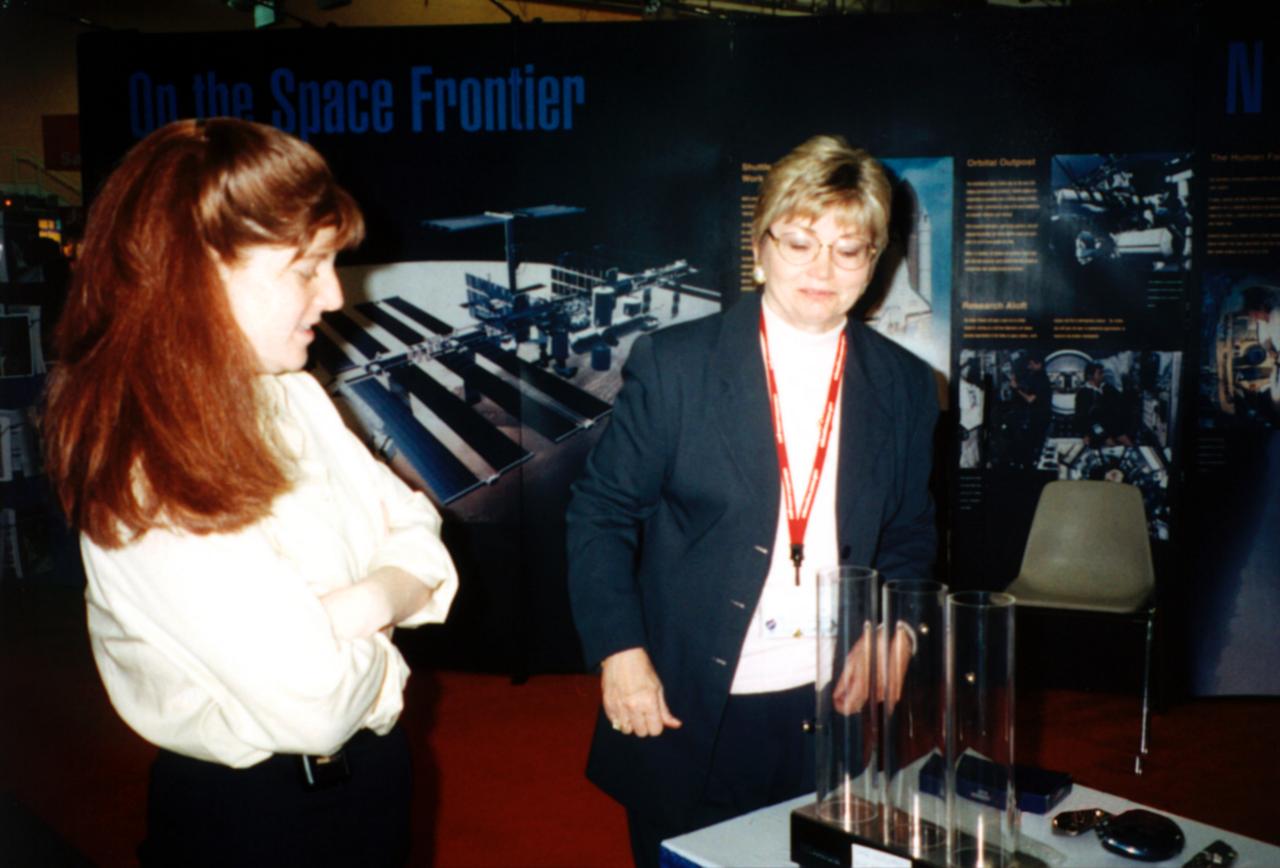

Pat Doty (right) of NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) demonstrates the greater bounce to the ounce of metal made from a supercooled bulk metallic glass alloy that NASA is studying in space expepriments. The metal plates at the bottom of plexiglass tubes are made of three different types of metal. Bulk mettalic glass is more resilient and, as a result, the dropped ball bearing bounces higher. Experiments in space allow scientists to study fundamental properties that carnot be observed on Earth. This demonstration was at the April 2000 conference of the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in Chicago. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)
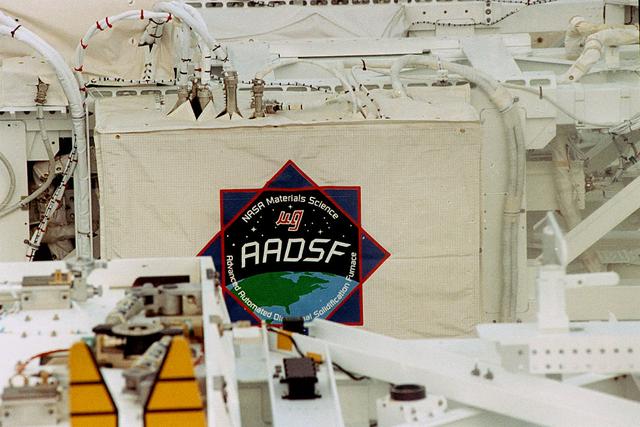

The purpose of the experiments for the Advanced Automated Directional Solidification Furnace (AADSF) is to determine how gravity-driven convection affects the composition and properties of alloys (mixtures of two or more materials, usually metal). During the USMP-4 mission, the AADSF will solidify crystals of lead tin telluride and mercury cadmium telluride, alloys of compound semiconductor materials used to make infrared detectors and lasers, as experiment samples. Although these materials are used for the same type application their properties and compositional uniformity are affected differently during the solidification process.
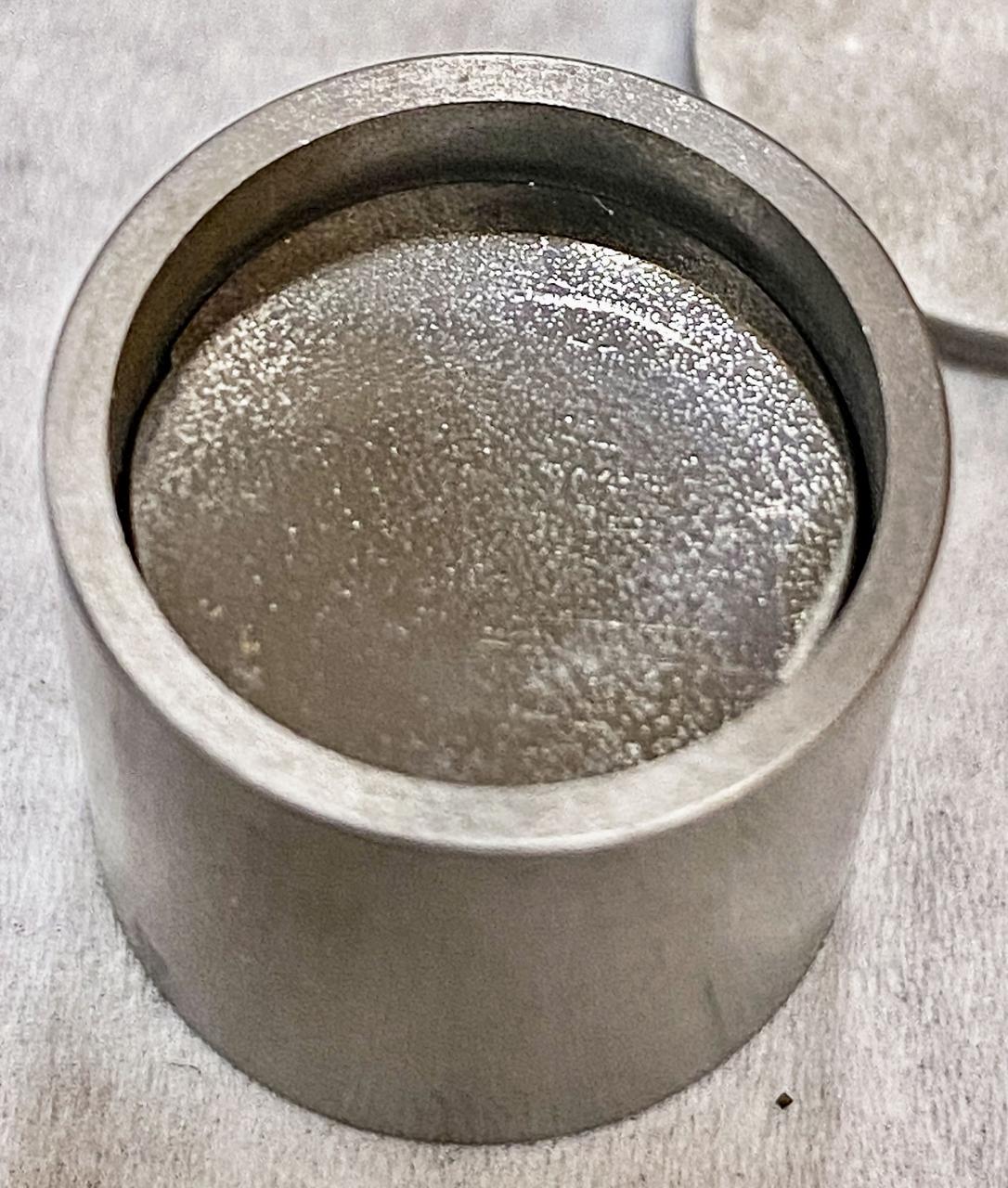

jsc2022e072974 (4/15/2022) --- A preflight sample from the Fabrication of Amorphous Metals in Space (MSL SCA-FAMIS) investigation shows tungsten spheres embedded in a glass-forming alloy loaded into a tungsten crucible. Image courtesy of Douglas Hofmann, NASA JPL/Caltech.
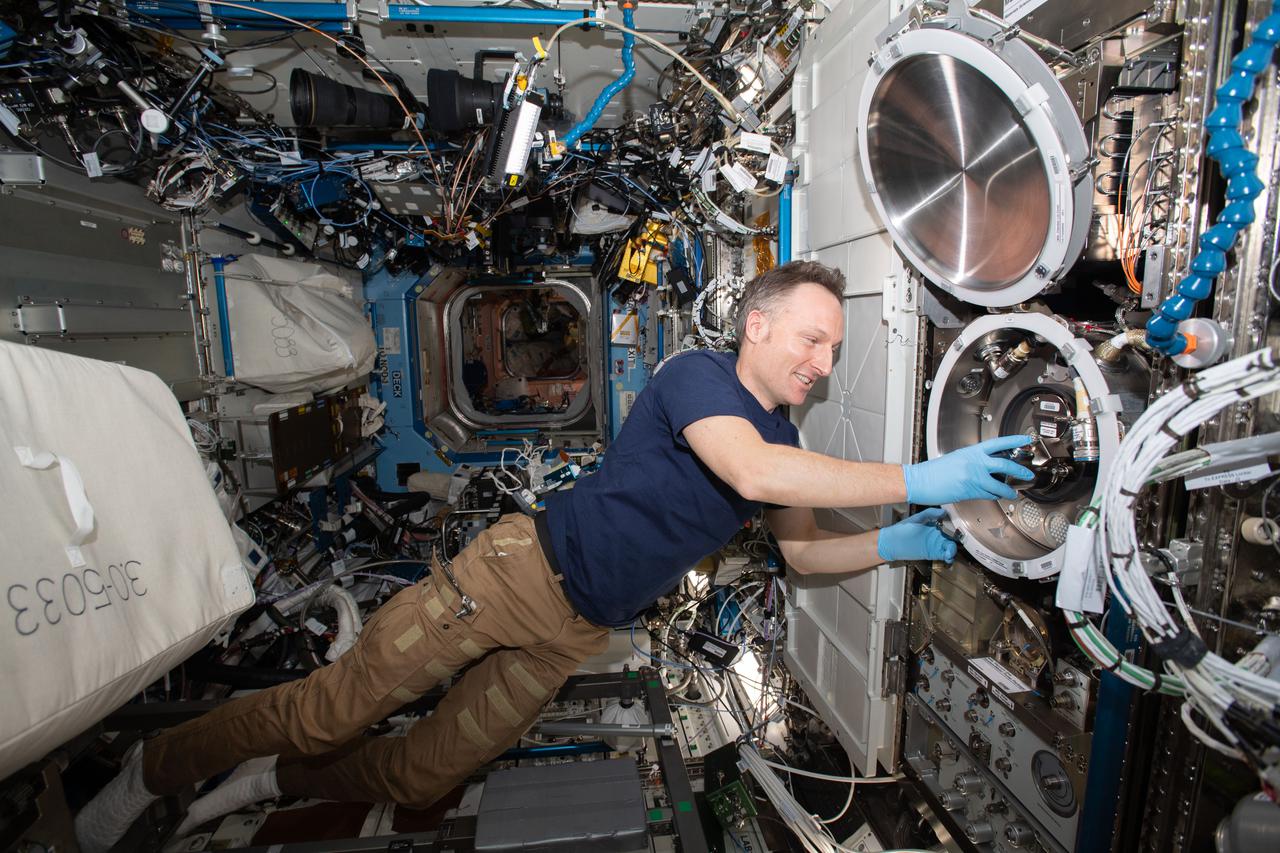

iss066e114140 (Jan. 12, 2022) --- ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Matthias Maurer swaps samples inside the Materials Science Laboratory, a physics research device that observes metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
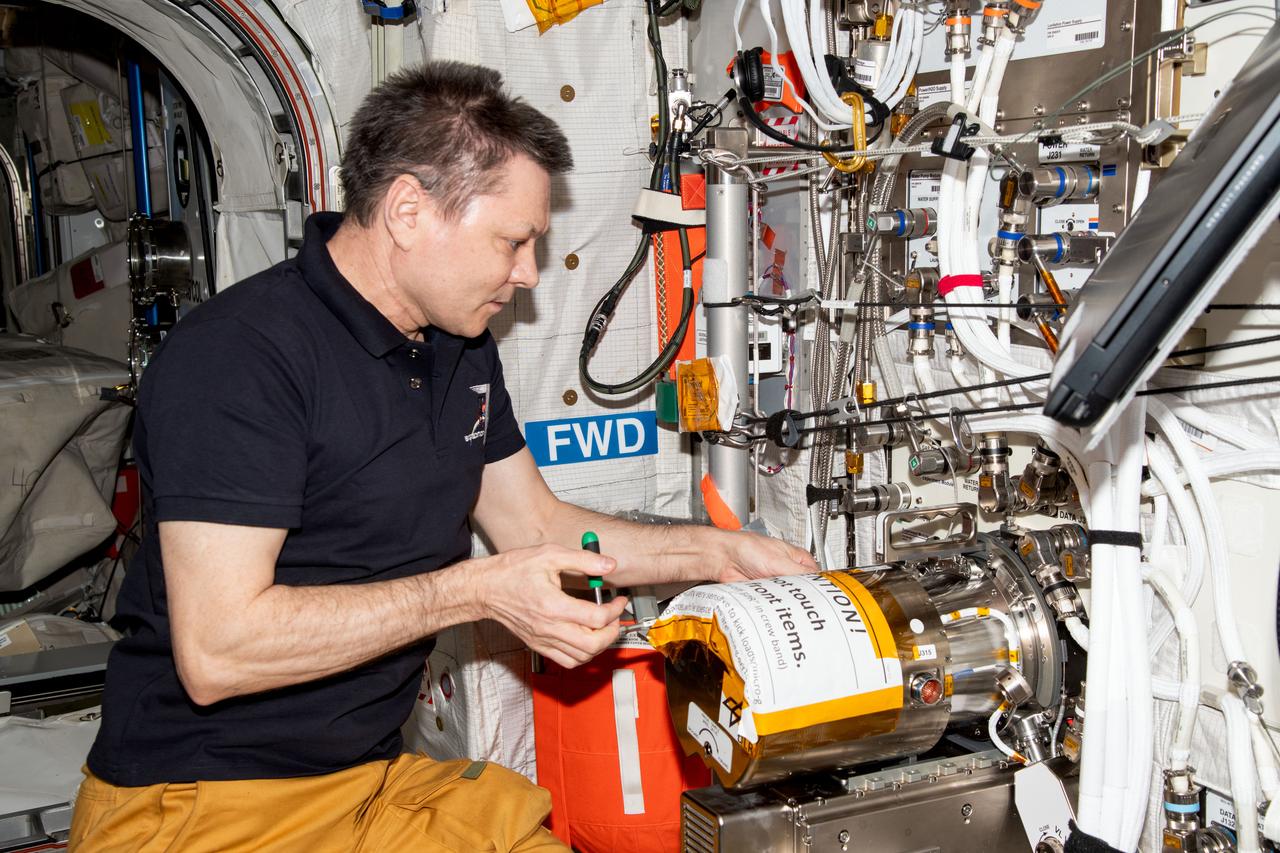

iss071e580240 (AUg. 29, 2024) --- Roscosmos cosmonaut and Expedition 71 Commander Oleg Kononenko swaps sample chambers inside the Electromagnetic Levitator (EML) located aboard the International Space Station's Columbus laboratory module. The EML is a physics research device that measures the thermophysical properties of liquid metallic alloys at high temperatures.
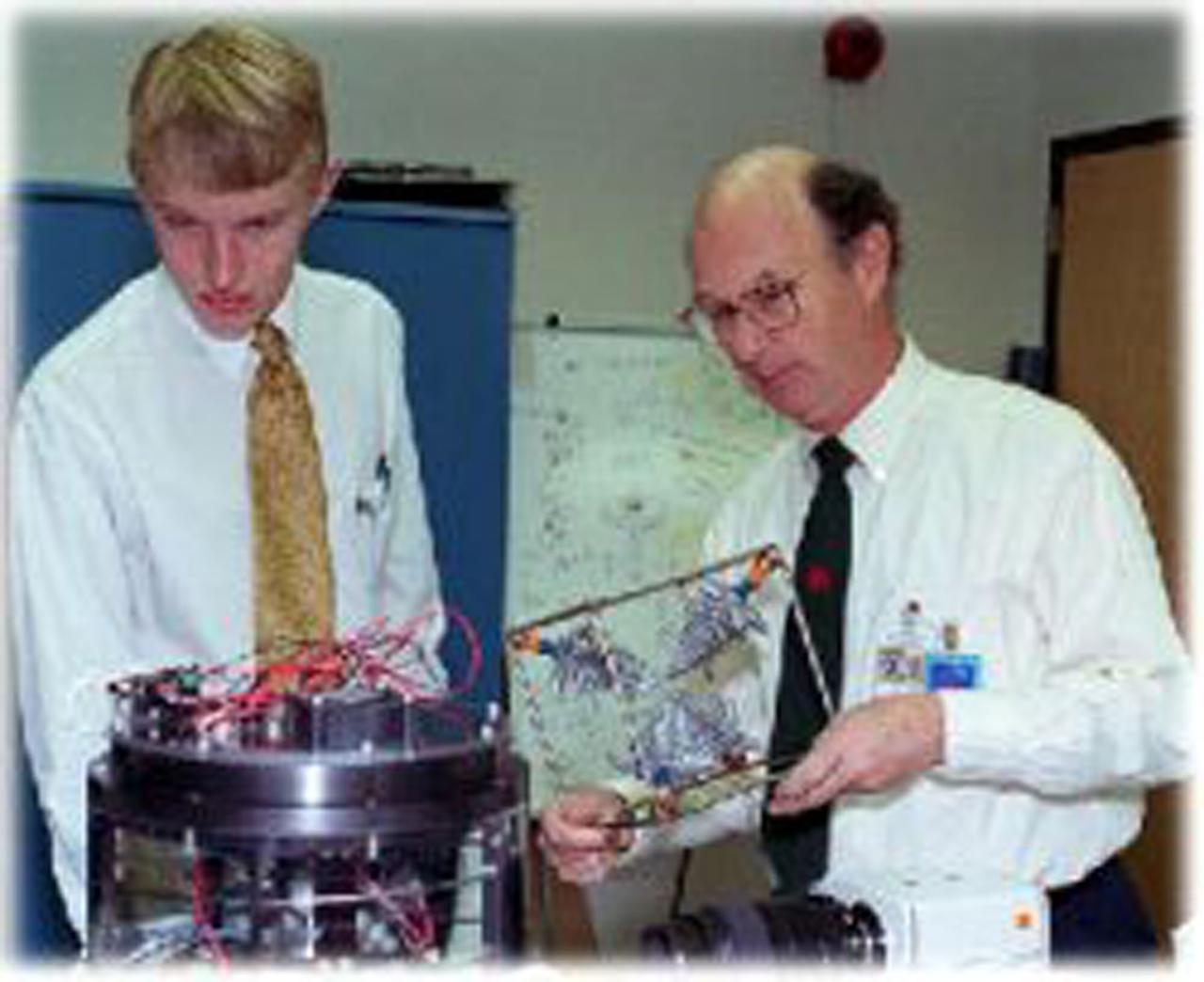

Dr. Donald Gilles, the Discipline Scientist for Materials Science in NASA's Microgravity Materials Science and Applications Department, demonstrates to Carl Dohrman a model of dendrites, the branch-like structures found in many metals and alloys. Dohrman was recently selected by the American Society for Metals International as their 1999 ASM International Foundation National Merit Scholar. The University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign freshman recently toured NASA's materials science facilities at the Marshall Space Flight Center.
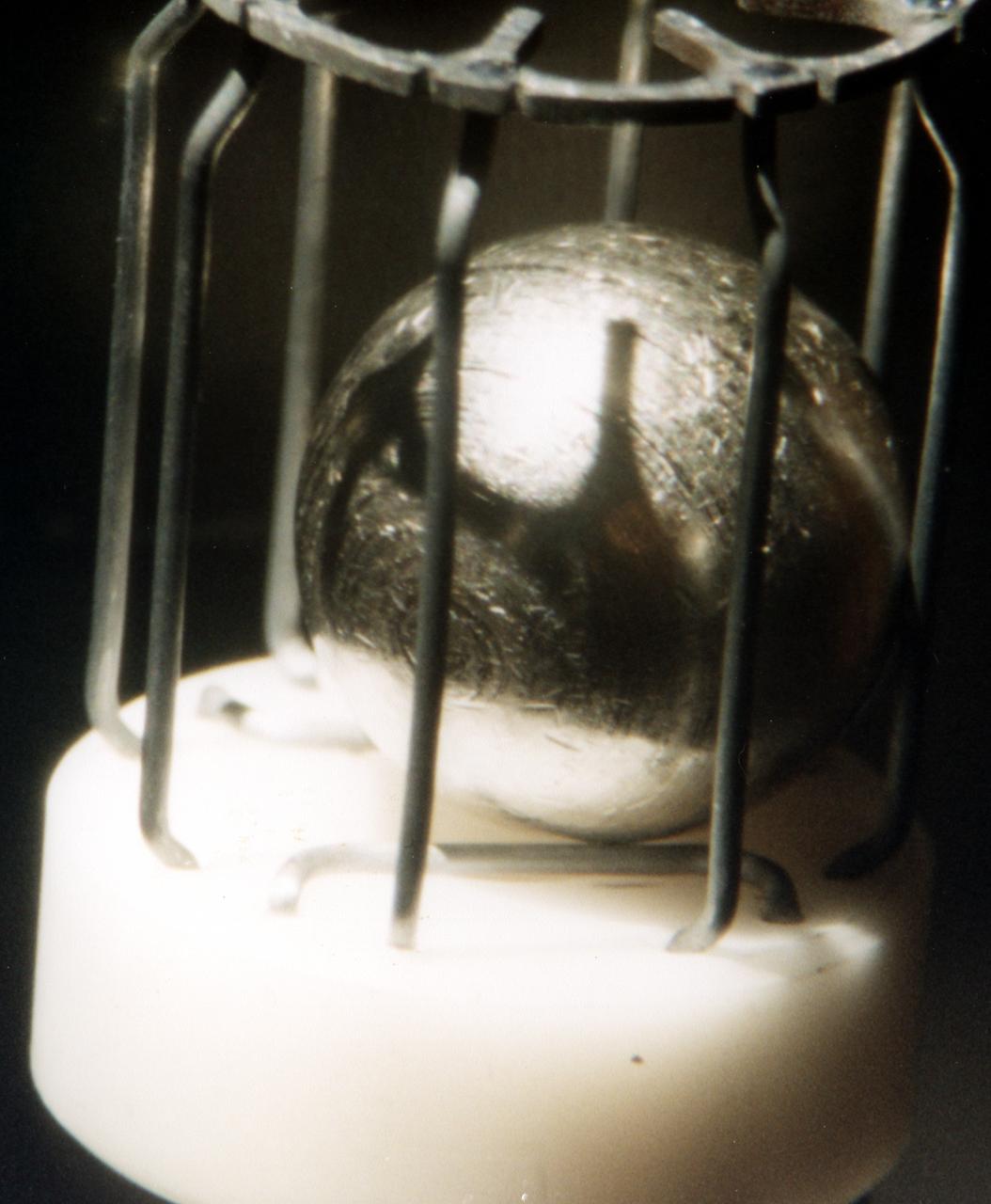

Typical metal sample that was processed by TEMPUS (Tiegelfreies Elektromagnetisches Prozessieren Unter Schwerelosigkeit), an electromagnetic levitation facility developed by German researchers and flown on the IML-2 and MSL-1 and 1R Spacelab missions. Electromagnetic levitation is used commonly in ground-based experiments to melt and then cool metallic melts below their freezing points without solidification occurring. Sample size is limited in ground-based experiments. Research with TEMPUS aboard Spacelab allowed scientists to study the viscosity, surface tension, and other properties of several metals and alloys while undercooled (i.e., cooled below their normal solidification points). The sample is about 1 cm (2/5 inch) in diameter.
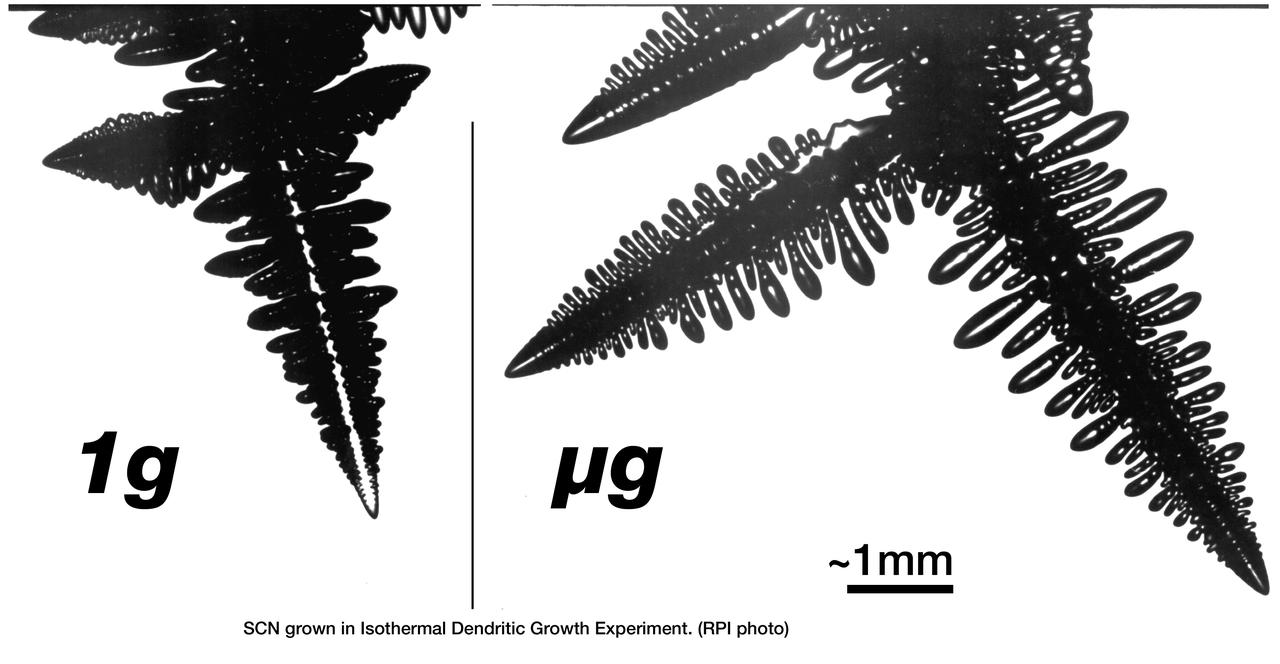
The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. IDGE used transparent organic liquids that form dendrites (treelike structures) similar to the crystals that form inside metal alloys. Comparing Earth-based and space-based dentrite growth velocity, tip size and shape provid a better understanding of the fundamentals of dentritic growth, including gravity's effects. These shadowgraphic images show succinonitrile (SCN) dentrites growing in a melt (liquid). The space-grown crystals also have cleaner, better defined sidebranches. IDGE was developed by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institude (RPI) and NASA/ Glenn Research Center(GRC). Advanced follow-on experiments are being developed for flight on the International Space Station. Photo gredit: NASA/Glenn Research Center
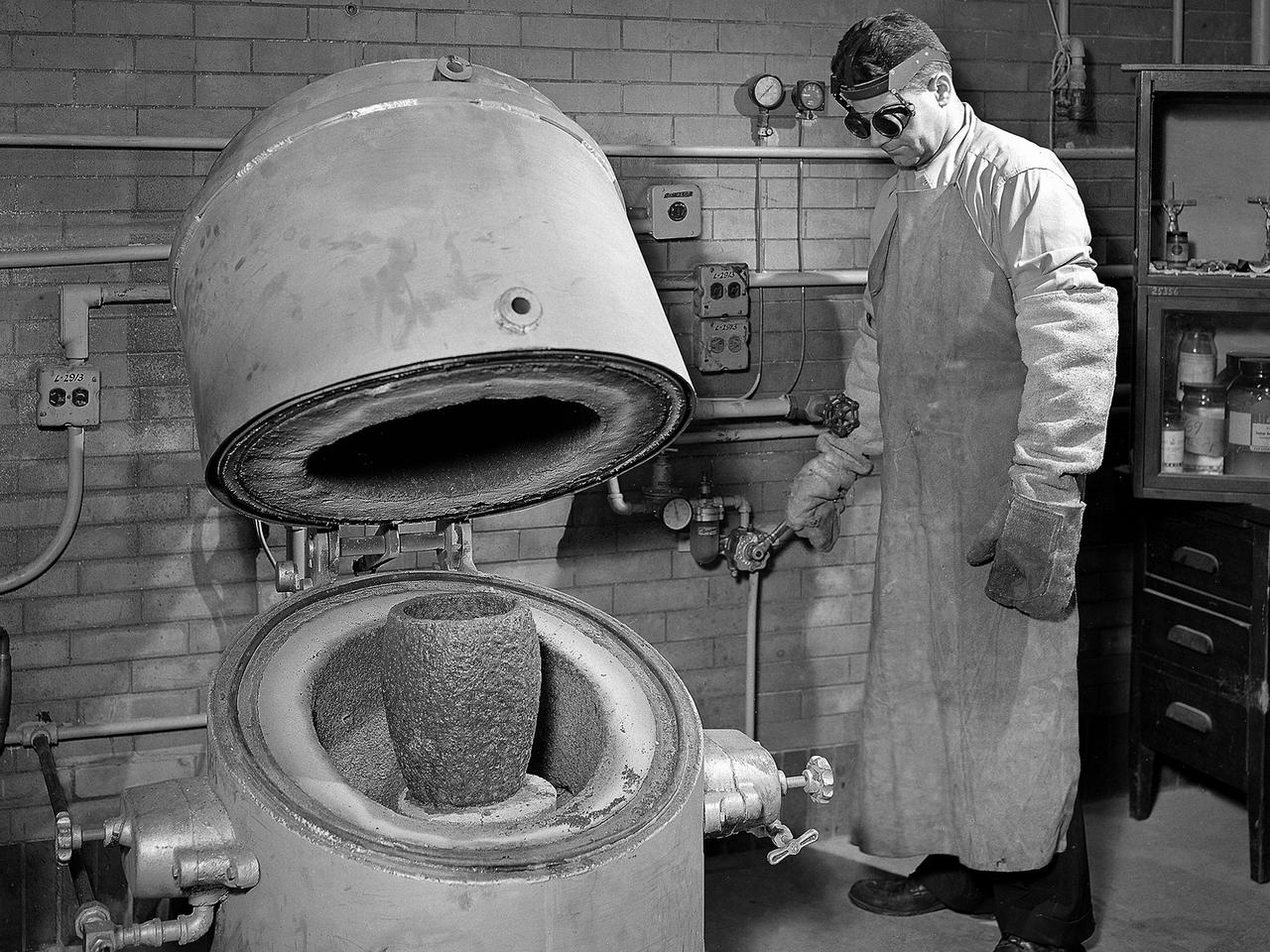

A technician prepares a metal component for a high-temperature bake in the Heat Treatment Shop at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. Fabrication Division under Dan White and John Dalgleish created almost all of the equipment and models used at the laboratory. The Technical Services Building, referred to as the Fab Shop, contained a number of specialized shops in the 1940s and 1950s. These included a Machine Shop, Sheet Metal Shop, Wood and Pattern Shop, Instrument Shop, Thermocouple Shop, Heat Treating Shop, Metallurgical Laboratory, and Fabrication Office. The Metallurgical Laboratory contained a control lab for the Heat Treating Shop and a service lab for the NACA Lewis research divisions. This metallurgical group performed tensile and impact tests on metals to determine their suitability for specific research or equipment. The Heat Treating Shop heated metal parts to optimize their physical properties and contained a Precision Castings Foundry to manufacture equipment made of heat resisting alloys.
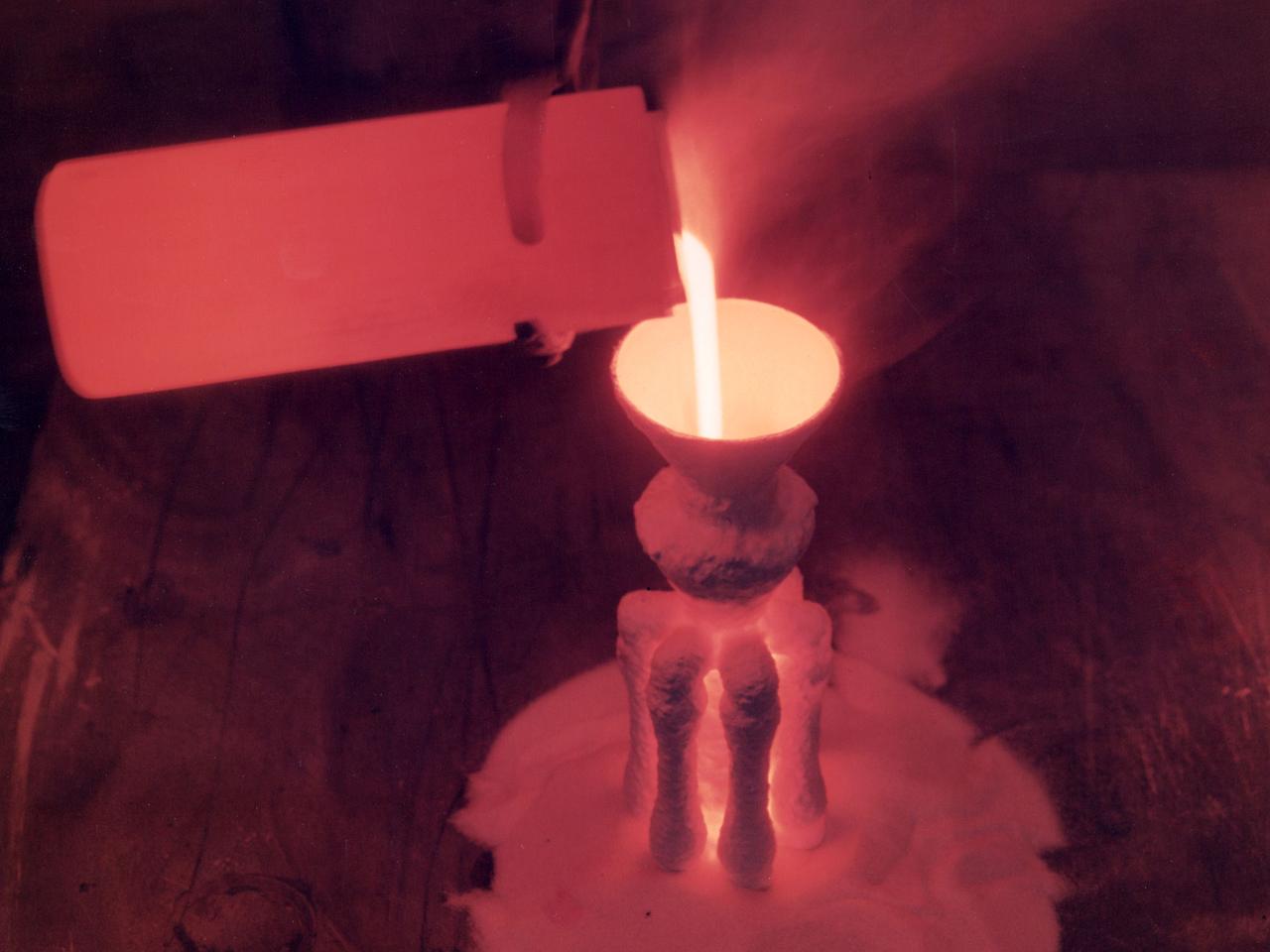

A nickel alloy developed at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center being poured in a shop inside the Technical Services Building. Materials technology is an important element in the successful development of both advanced airbreathing and rocket propulsion systems. An array of dependable materials is needed to build different types of engines for operation in diverse environments. NASA Lewis began investigating the characteristics of different materials shortly after World War II. In 1949 the materials research group was expanded into its own division. The Lewis researchers studied and tested materials in environments that simulated the environment in which they would operate. Lewis created two programs in the early 1960s to create materials for new airbreathing engines. One concentrated on high-temperature alloys and the other on cooling turbine blades. William Klopp, Peter Raffo, Lester Rubenstein, and Walter Witzke developed Tungsten RHC, the highest strength metal at temperatures over 3500⁰ F. The men received an IR-100 Award for their efforts. Similarly a cobalt-tungsten alloy was developed by the Fatigue and Alloys Research Branch. The result was a combination of high temperature strength and magnetic properties that were applicable for generator rotor application. John Freche invented and patented a nickel alloy while searching for high temperature metals for aerospace use. NASA agreed to a three-year deal which granted Union Carbide exclusive use of the new alloy before it became public property.
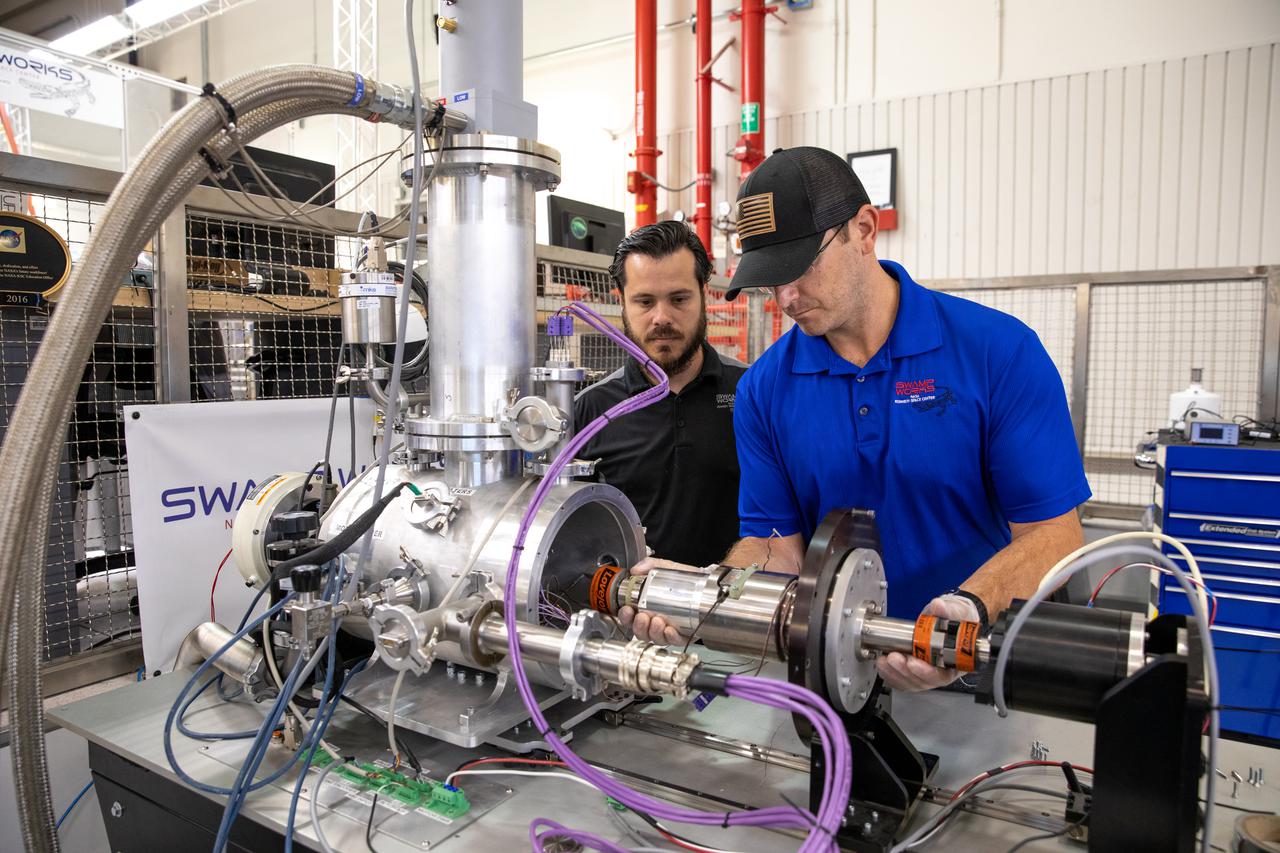

A.J. Nick, left, and Drew Smith, robotics engineers with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, test Bulk Metallic Glass Gears (BMGGs) in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.
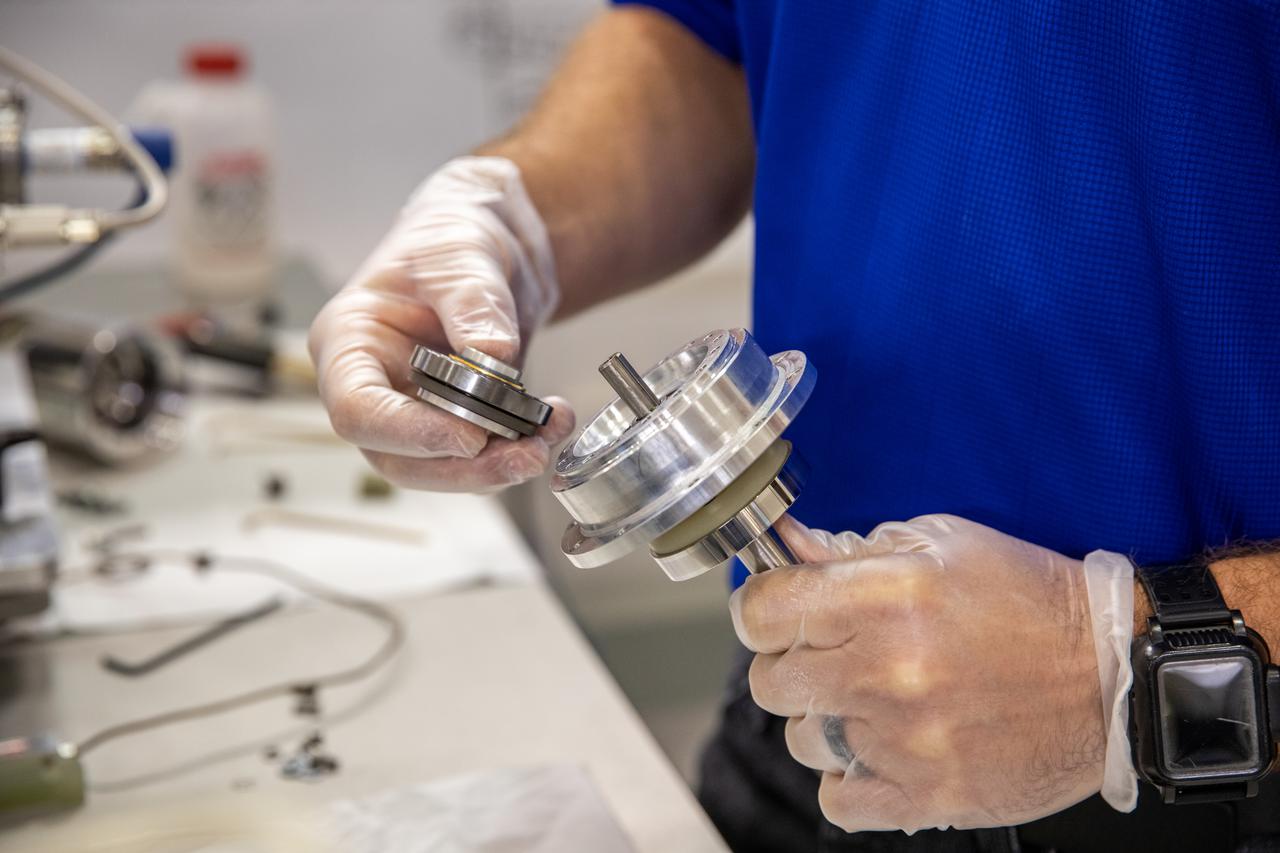

Drew Smith, a robotics engineer and lab manager with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, prepares a Bulk Metallic Glass Gear (BMGG) for ambient temperature tests in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.

Drew Smith, a robotics engineer and lab manager with the Exploration Research and Technology programs at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, prepares a Bulk Metallic Glass Gear (BMGG) for ambient temperature tests in a vacuum inside a cryogenic cooler at Kennedy's Granular Mechanics and Regolith Operations lab on June 17, 2021. Made from a custom bulk metallic glass alloy, BMGGs could be used in heater-free gearboxes at extremely low temperatures in locations such as the Moon, Mars, and Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory is working with commercial partners to create the gears.
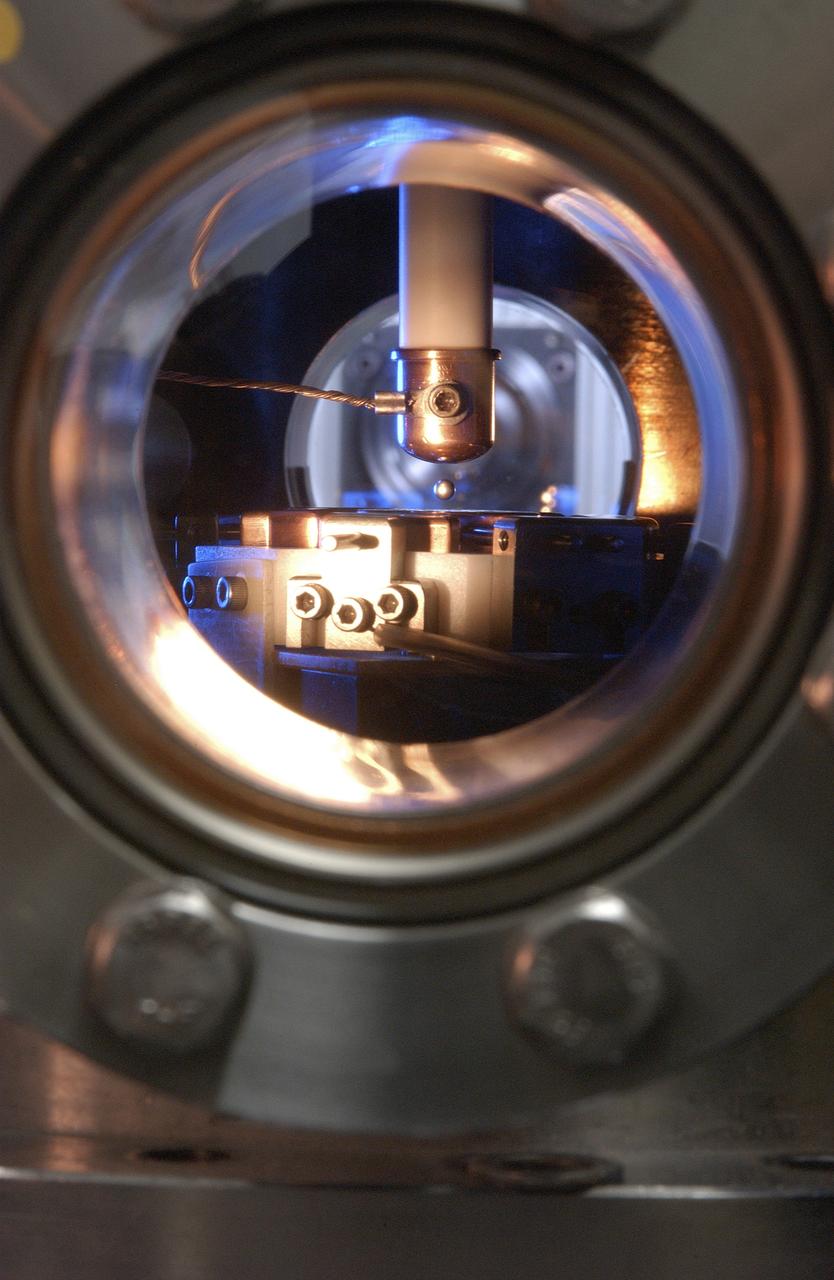
This Photo, which appeared on the July cover of `Physics Today', is of the Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The ESL uses static electricity to suspend an object (about 3-4 mm in diameter) inside a vacuum chamber allowing scientists to record a wide range of physical properties without the sample contracting the container or any instruments, conditions that would alter the readings. Once inside the chamber, a laser heats the sample until it melts. The laser is then turned off and the sample cools, changing from a liquid drop to a solid sphere. In this particular shot, the ESL contains a solid metal sample of titanium-zirconium-nickel alloy. Since 1977, the ESL has been used at MSFC to study the characteristics of new metals, ceramics, and glass compounds. Materials created as a result of these tests include new optical materials, special metallic glasses, and spacecraft components.
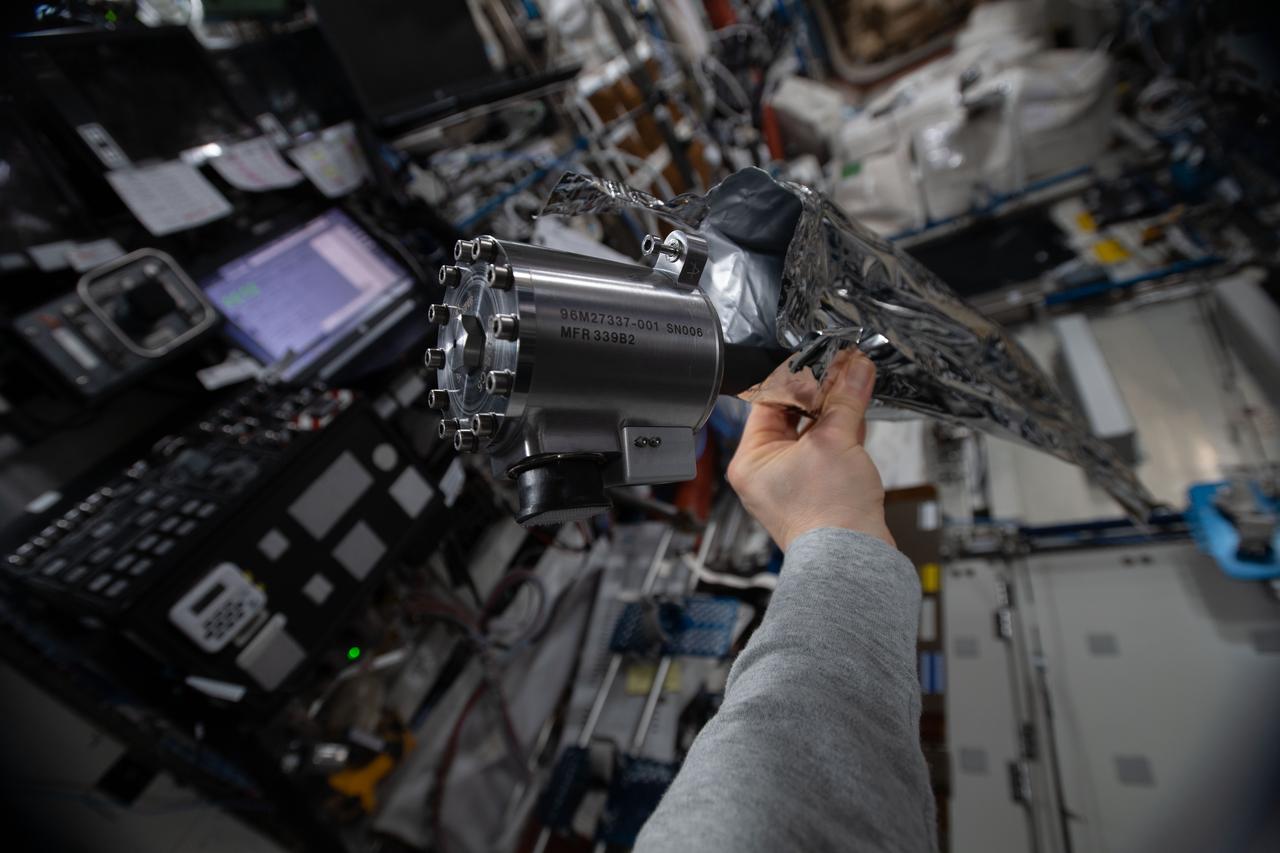

iss061e092274 (12/18/2019) --- A view of the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) Sample Cartridge Assembly (SCA) in the Destiny module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) is used for basic materials research in the microgravity environment of the International Space Station (ISS). The MSL can accommodate and support diverse Experiment Modules. In this way many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, can be studied to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
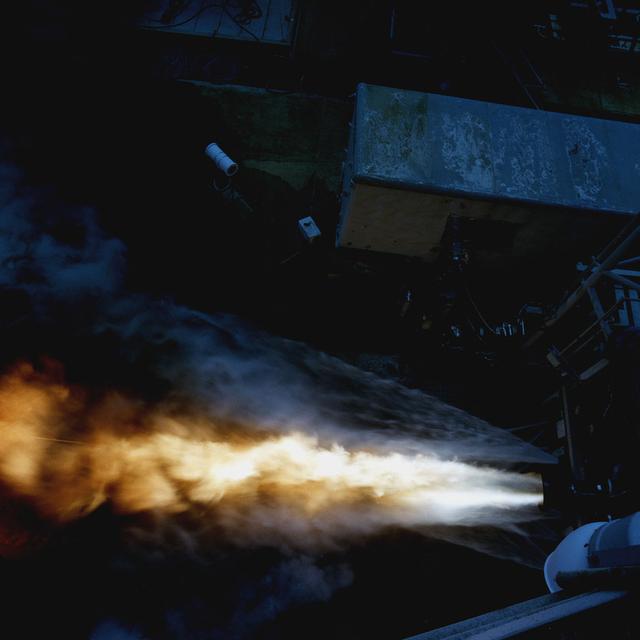

This shot offers a bird's eye-view of a Fastrac II engine duration test at Marshall's Test Stand 116. The Fastrac II engine was designed as a part of the low cost X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The purpose for these tests was to test the different types of metal alloys in the nozzle. Beside the engine were six additional nozzels which spray a continuous stream of water onto the test stand to reduce damage to the test stand and the engines. The X-34 program was cancelled in 2001.
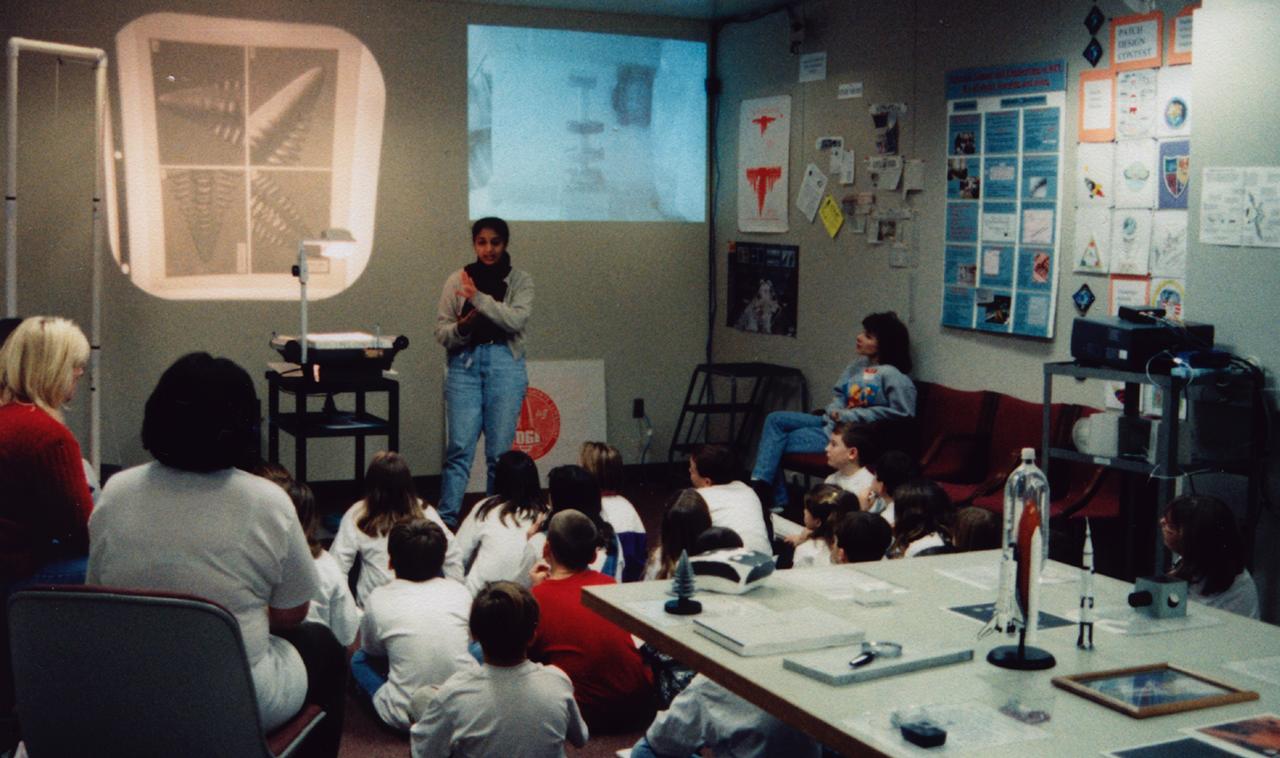

Pratima Rao lectures students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
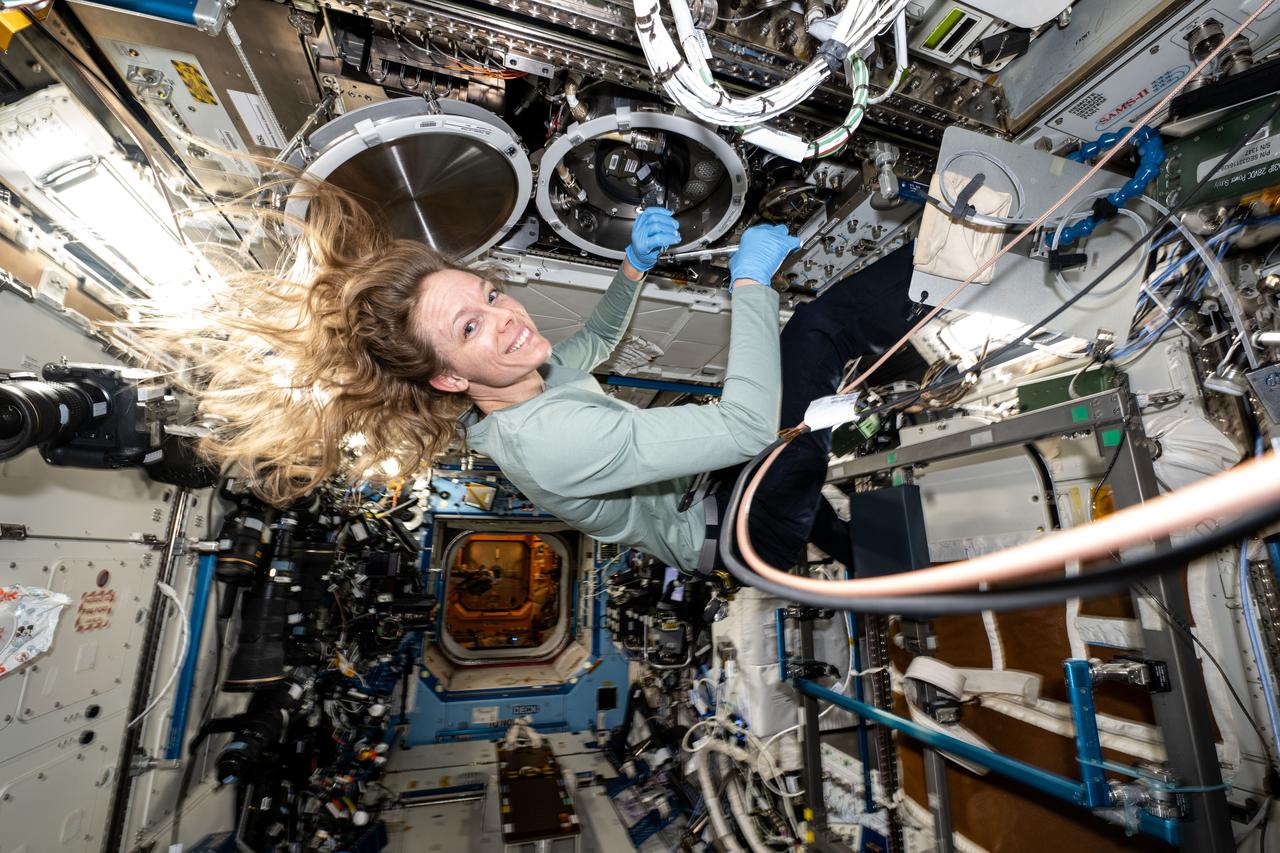

iss073e0071487 (May 15, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Nichole Ayers swaps sample cartridges inside the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) that supports high temperature space physics research using furnaces aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The properties of many types of materials such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, can be studied in the MSL to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
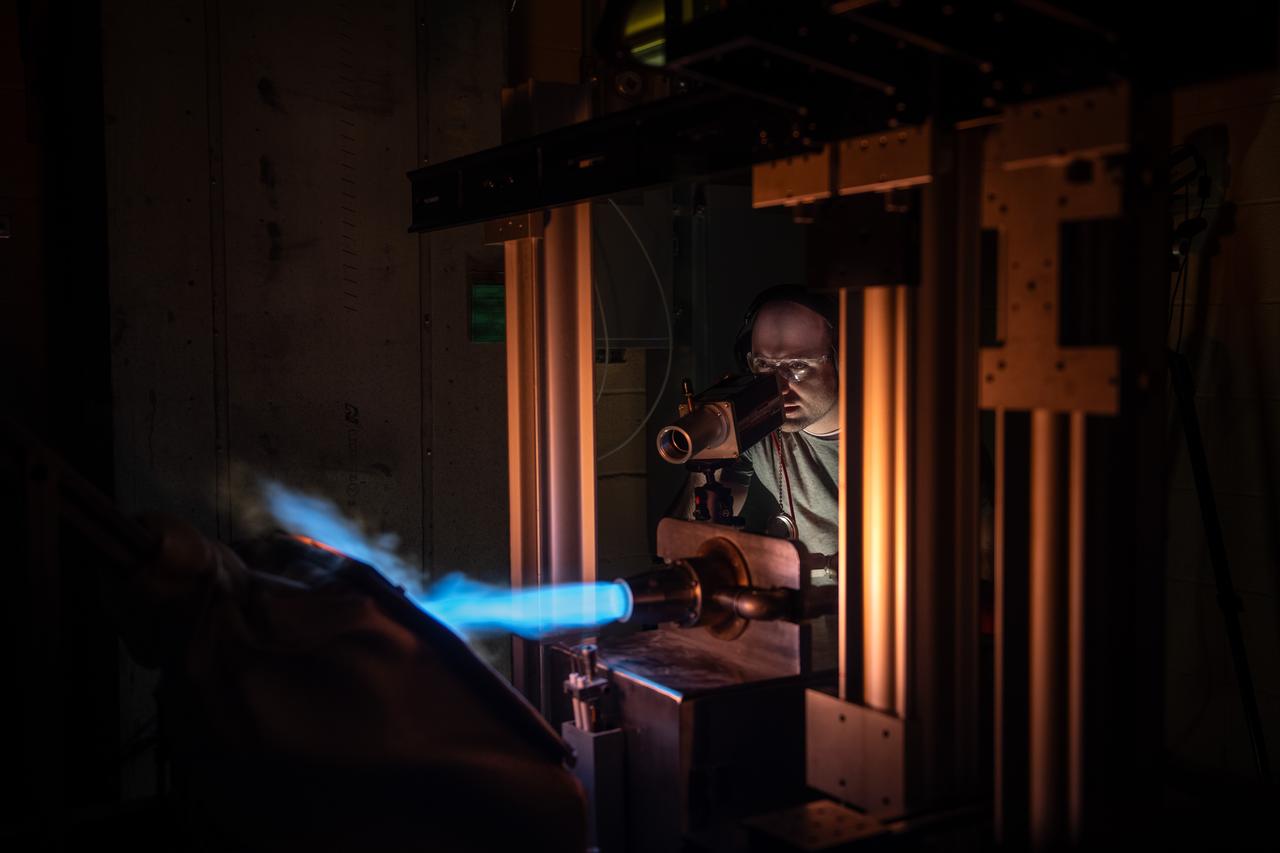

NASA Glenn’s Natural Gas/Oxygen Burner Rig is used to study the high temperature performance of various metal alloys, ceramics, and protective coatings for aero and space propulsion systems. The burner rig provides an easily accessible and economical method to simulate engine operating conditions to understand thermomechanical and thermochemical degradation of materials and structures. In the photo, Materials Research Engineer Michael Presby uses an infrared pyrometer to monitor the surface temperature of the material for a test on February 23, 2024. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
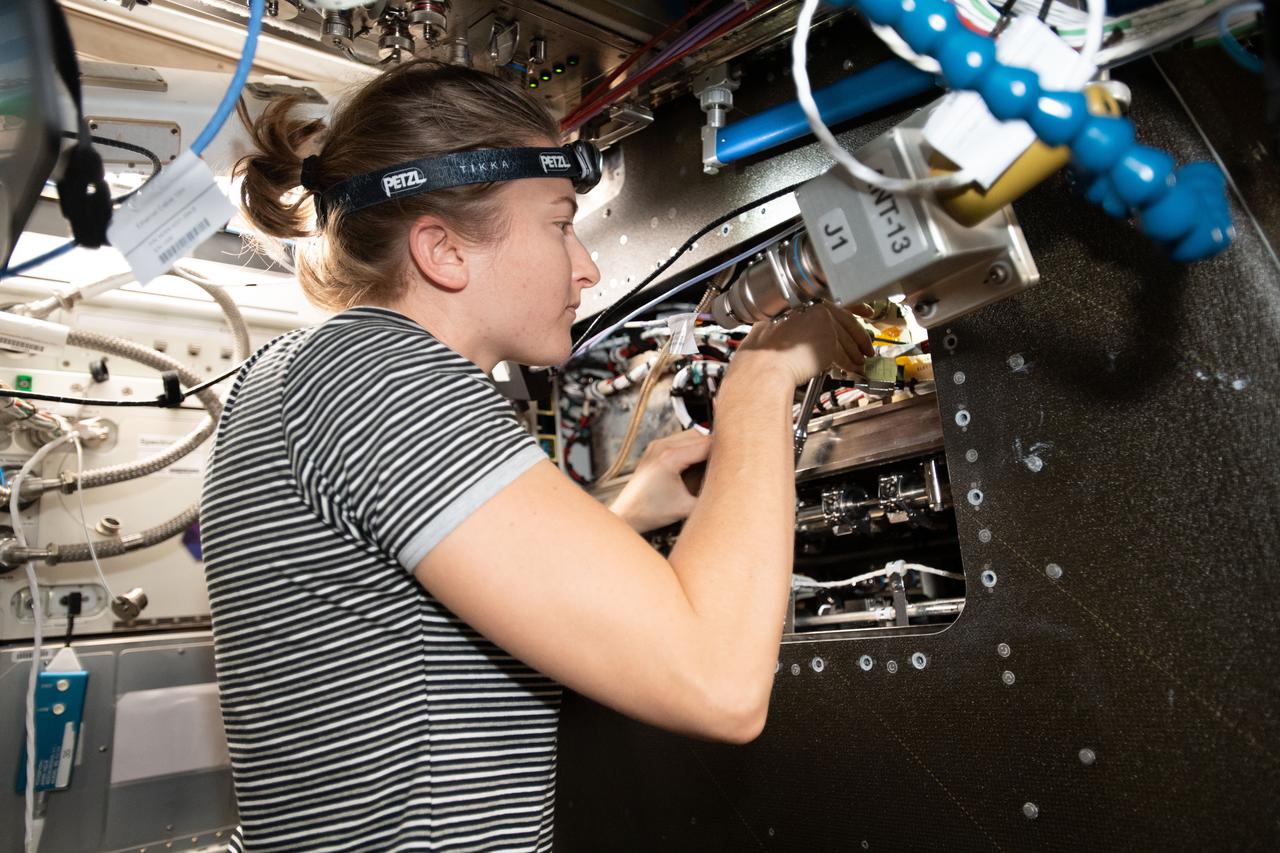

iss066e086417 (Dec. 4, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 66 Flight Engineer Kayla Barron inspects cables inside the Materials Science Research Rack. The space physics research device enables the observation of many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to study and discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
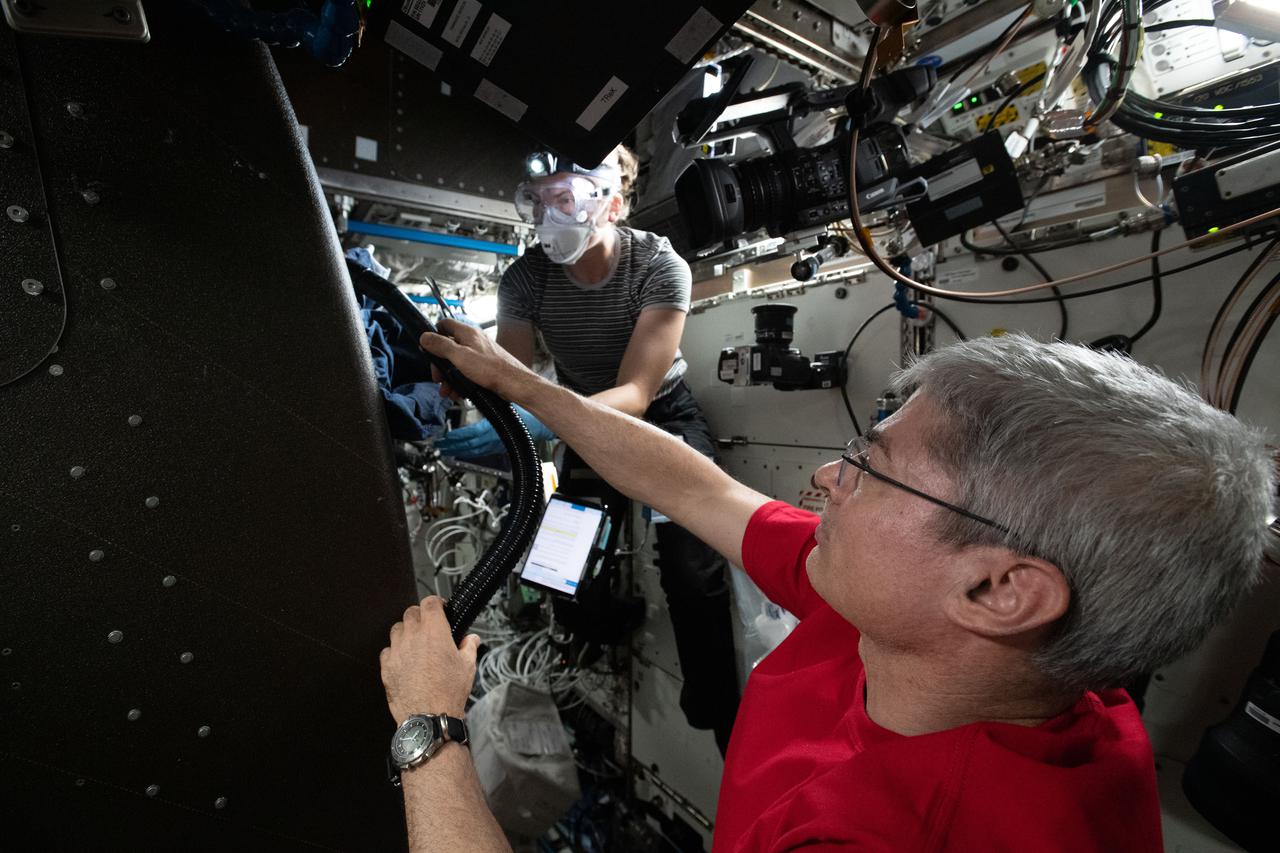

iss066e086431 (Dec. 4, 2021) --- NASA astronauts and Expedition 66 Flight Engineers Mark Vande Hei and Kayla Barron inspect cables inside the Materials Science Research Rack. The space physics device enables the observation of many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to study and discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
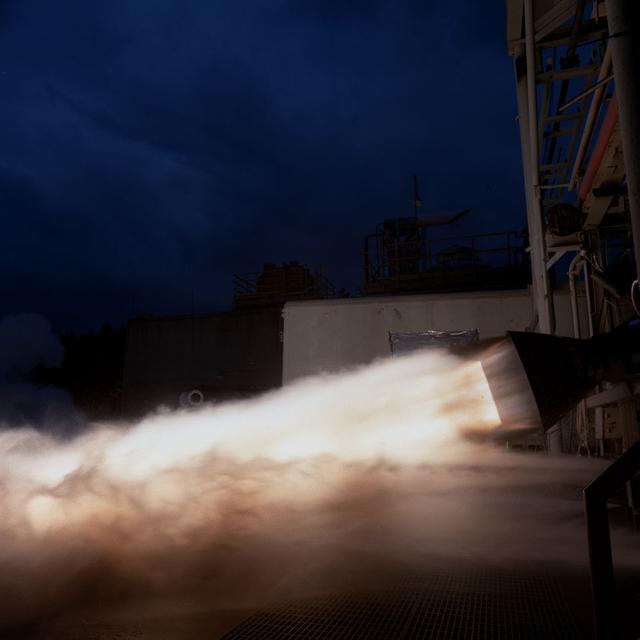

A close-up view of Bantam duration testing of the 40K Fastrac II Engine for X-34 at Marshall Space Flight Center's (MSFC) test stand 116. The Bantam test refers to the super lightweight engines of the Fastrac program. The engines were designed as part of the low cost X-34 Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV). The testing of these engines at MSFC allowed the engineers to determine the capabilities of these engines and the metal alloys that were used in their construction. The Fastrac and X-34 programs were cancelled in 2001.
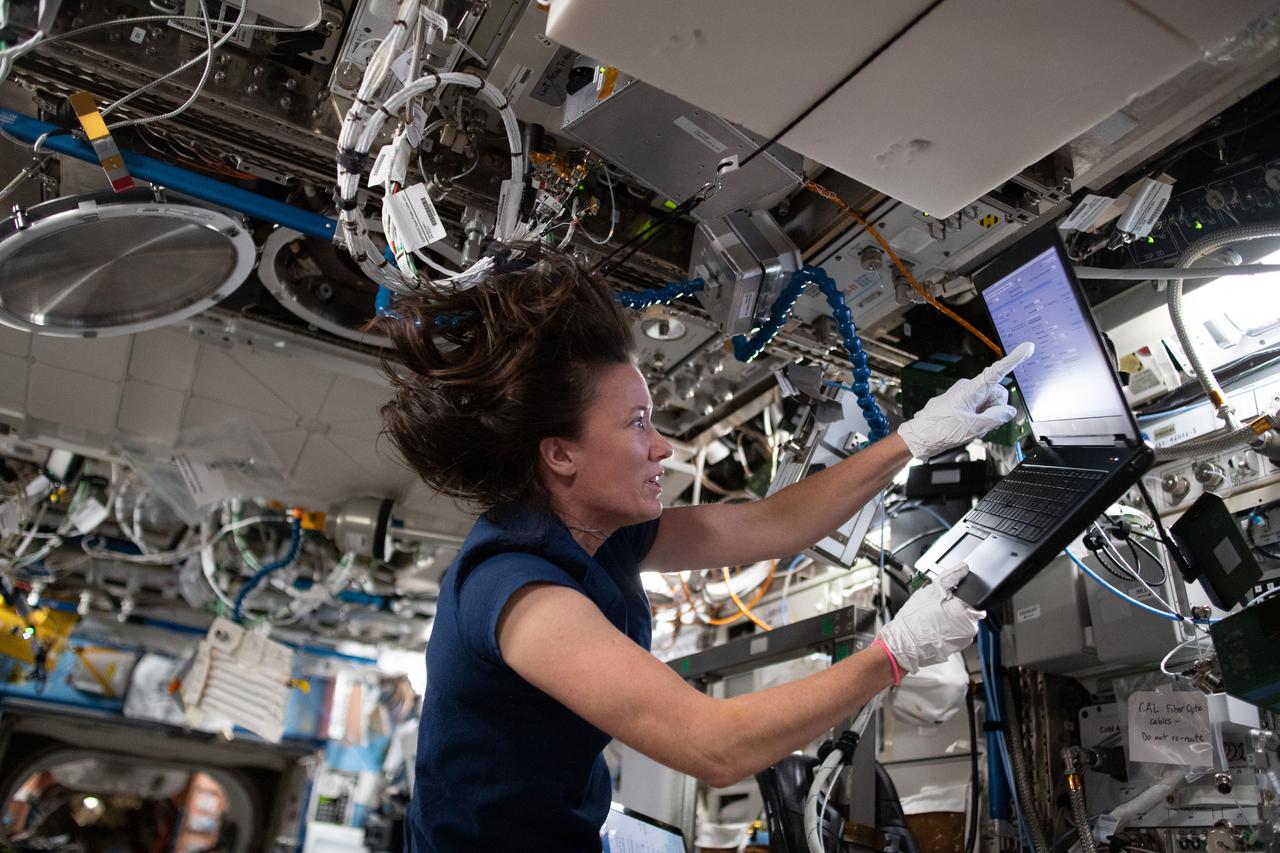

iss065e081296 (May 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur reviews procedures to swap sample cartridges inside the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL). The MSL enables research into microgravity's affects on materials such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses. Observations may reveal new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.

Matthew Koss lectures middle-school students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
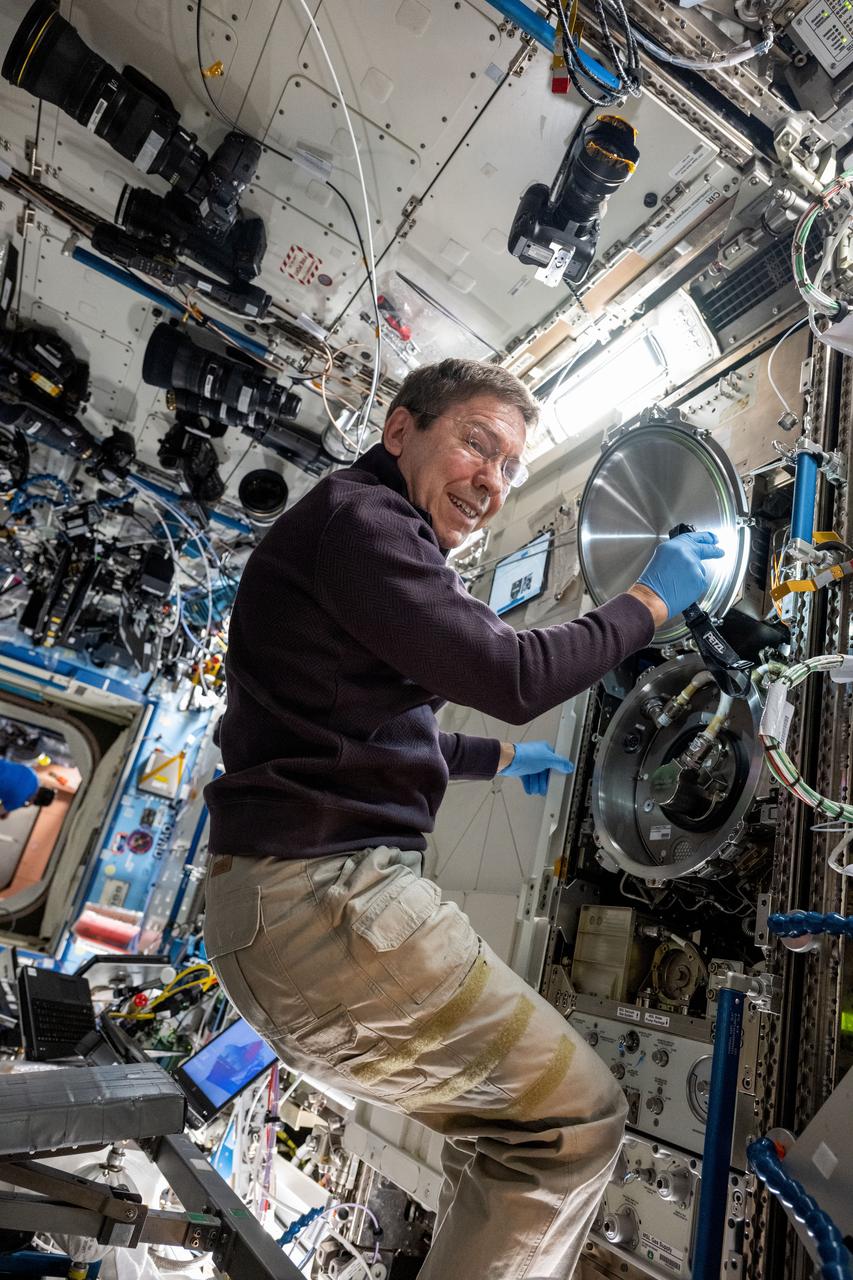

iss071e522745 (Aug. 19, 2024) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 71 Flight Engineer Mike Barratt swaps sample cartridges inside the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL), a research furnace facilitating discoveries of new and improved materials as well as new uses for existing materials such as metals, alloys, polymers, and more. The MSL is located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module.
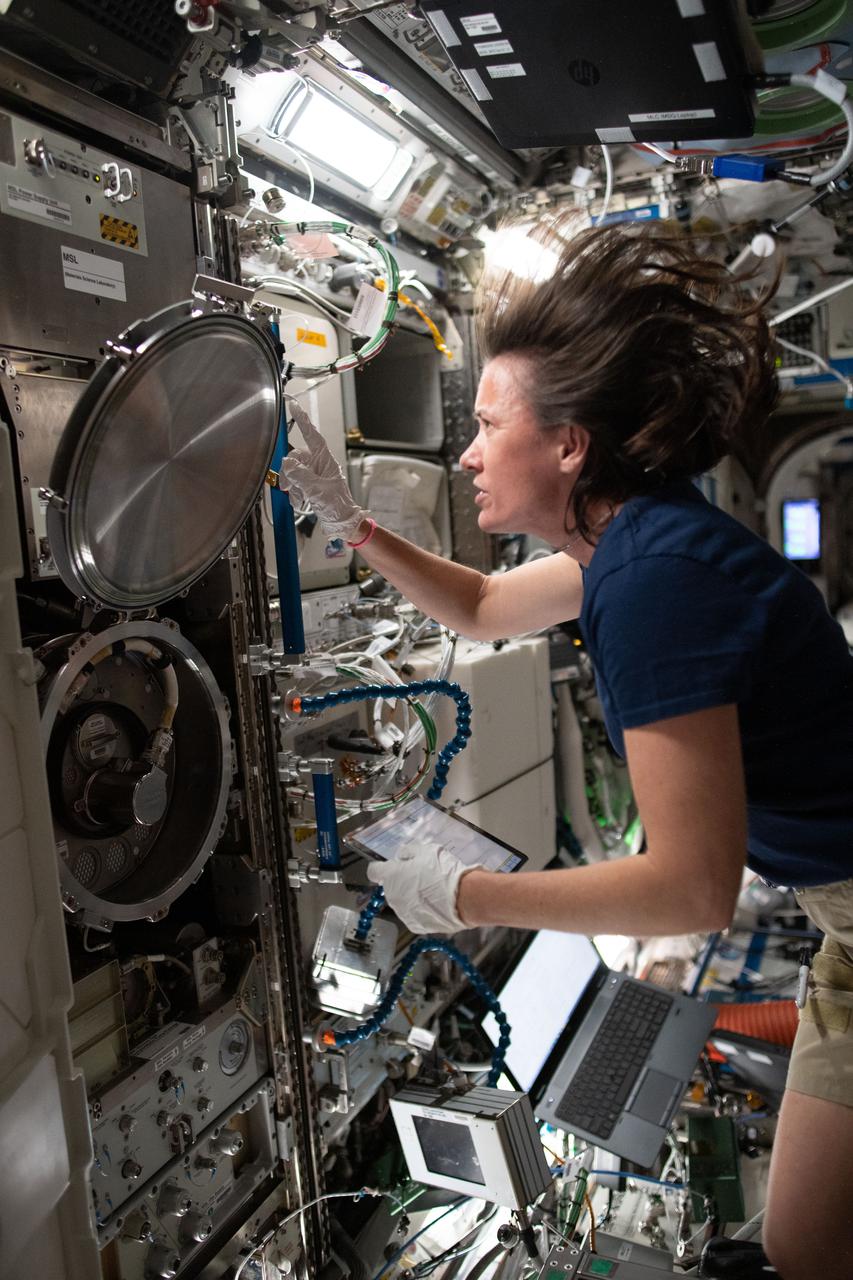

iss065e081297 (May 28, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur swaps sample cartridges inside the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) rack. The MSL enables observations of microgravity's impact on a variety metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
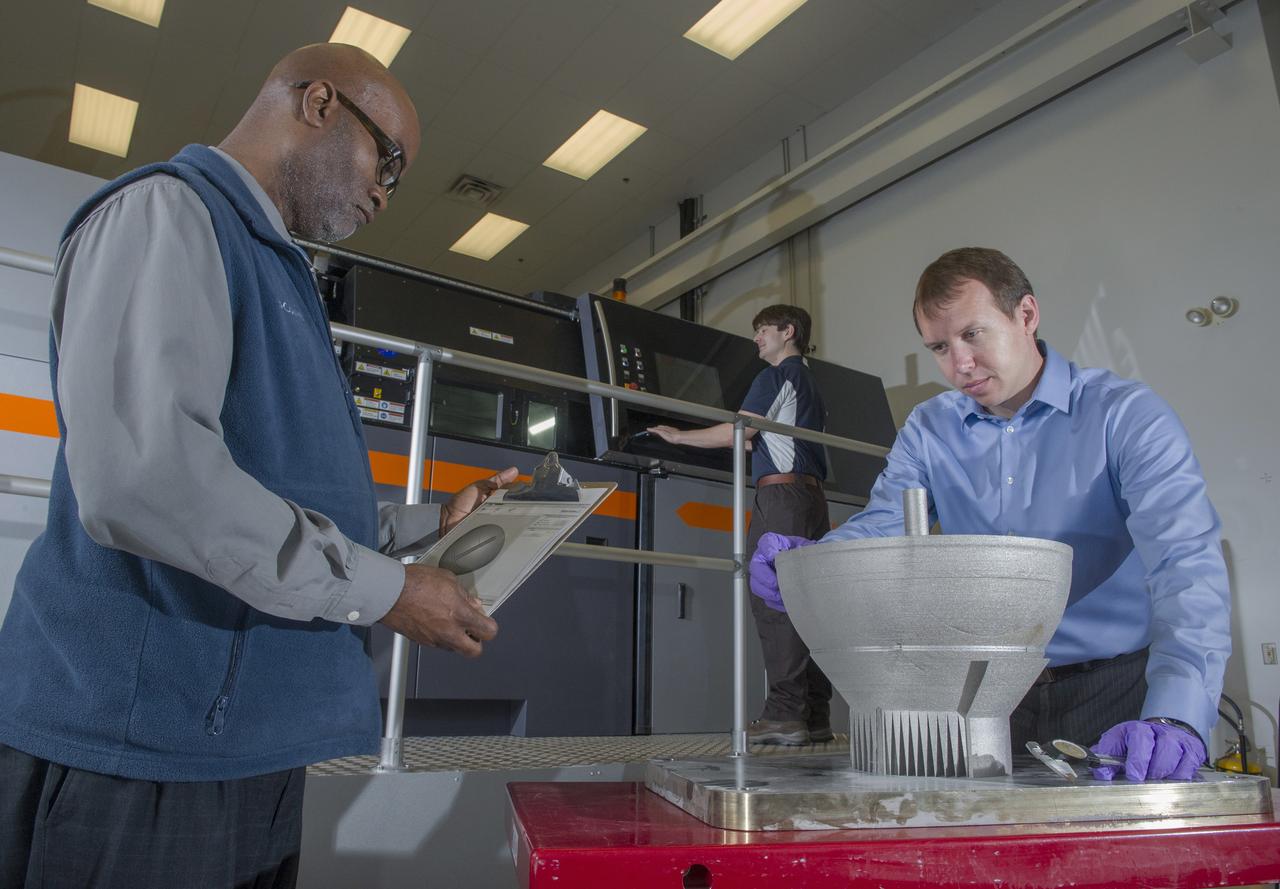

JOHNNIE CLARK, BRIAN WEST, AND ZACK JONES OF MSFC’S ADVANCED MANUFACTURING TEAM, WITH MSFC’S XLINE SELECTIVE LASER MELTING SYSTEM. CURRENTLY ONE OF THE LARGEST METAL 3D PRINTERS, THE XLINE AT MARSHALL IS BEING USED TO DEVELOP AND CERTIFY NICKEL ALLOY 718 MATERIAL PROPERTIES AND LARGE MANUFACTURING TECH DEMOS FOR THE RS25 ENGINE AND THE COMMERCIAL CREWED VEHICLE PROJECTS.
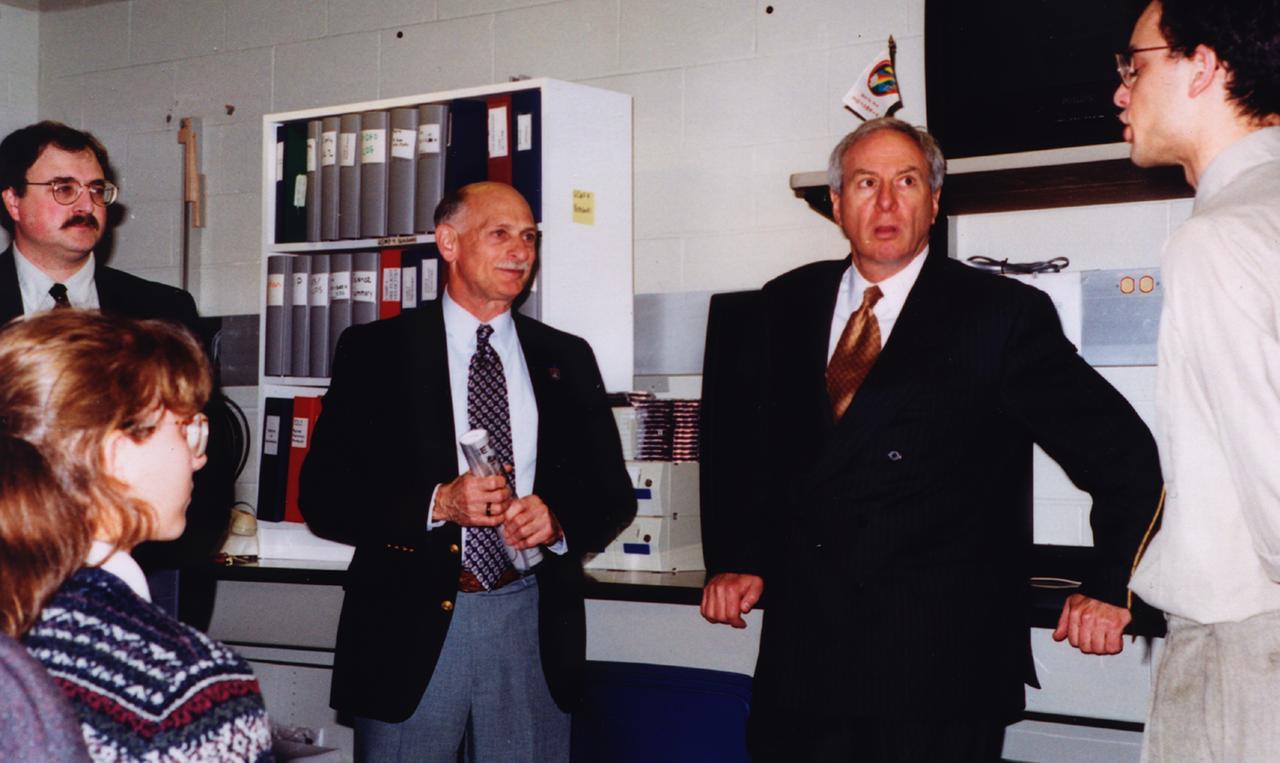

NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin (second from right) visits the control room of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) in Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)in Troy, NY, during RPI's 175th arniversary. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: RPI
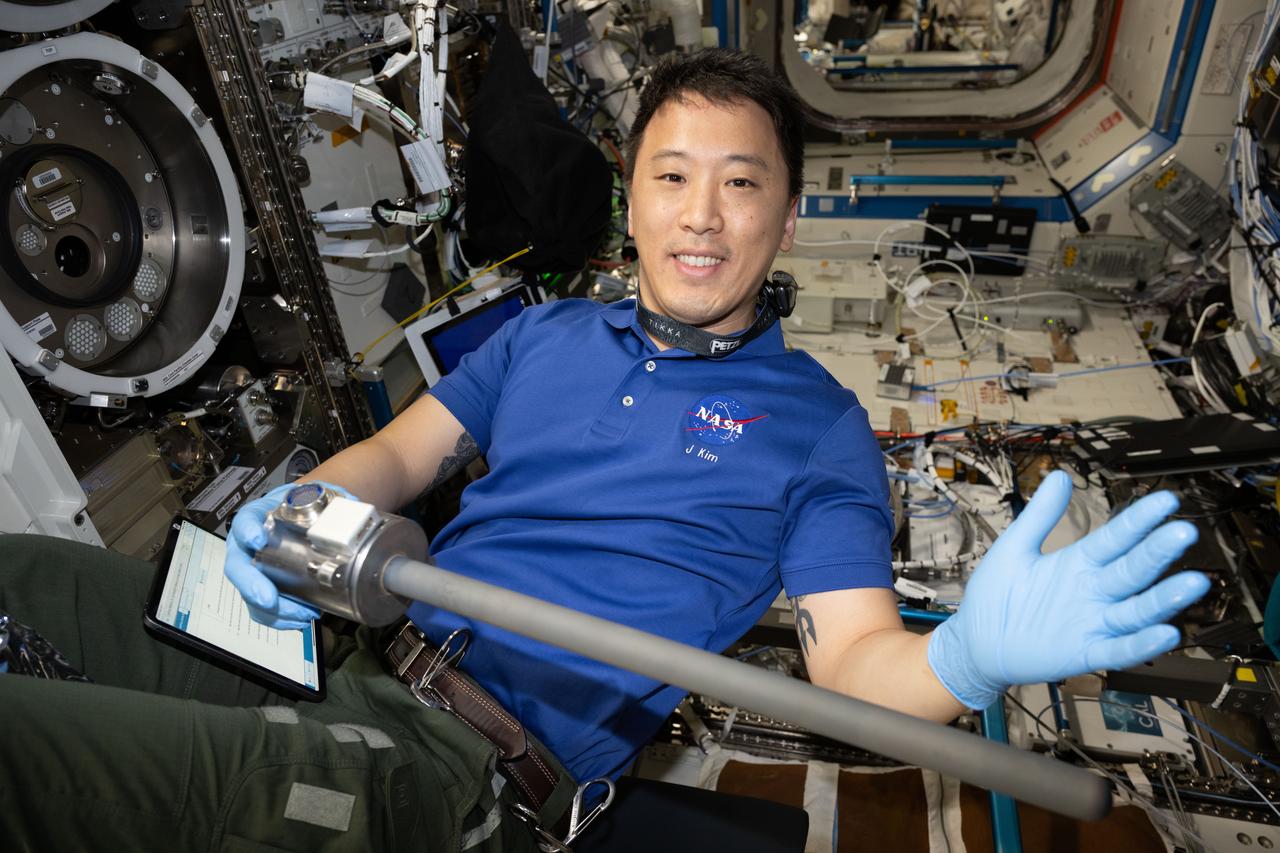
iss073e0222463 (June 16, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim waves for a portrait while removing research hardware from inside the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The MSL uses two different furnaces that operate one at a time to discover new applications for existing materials, such as metals, alloys, polymers, and new or improved materials.
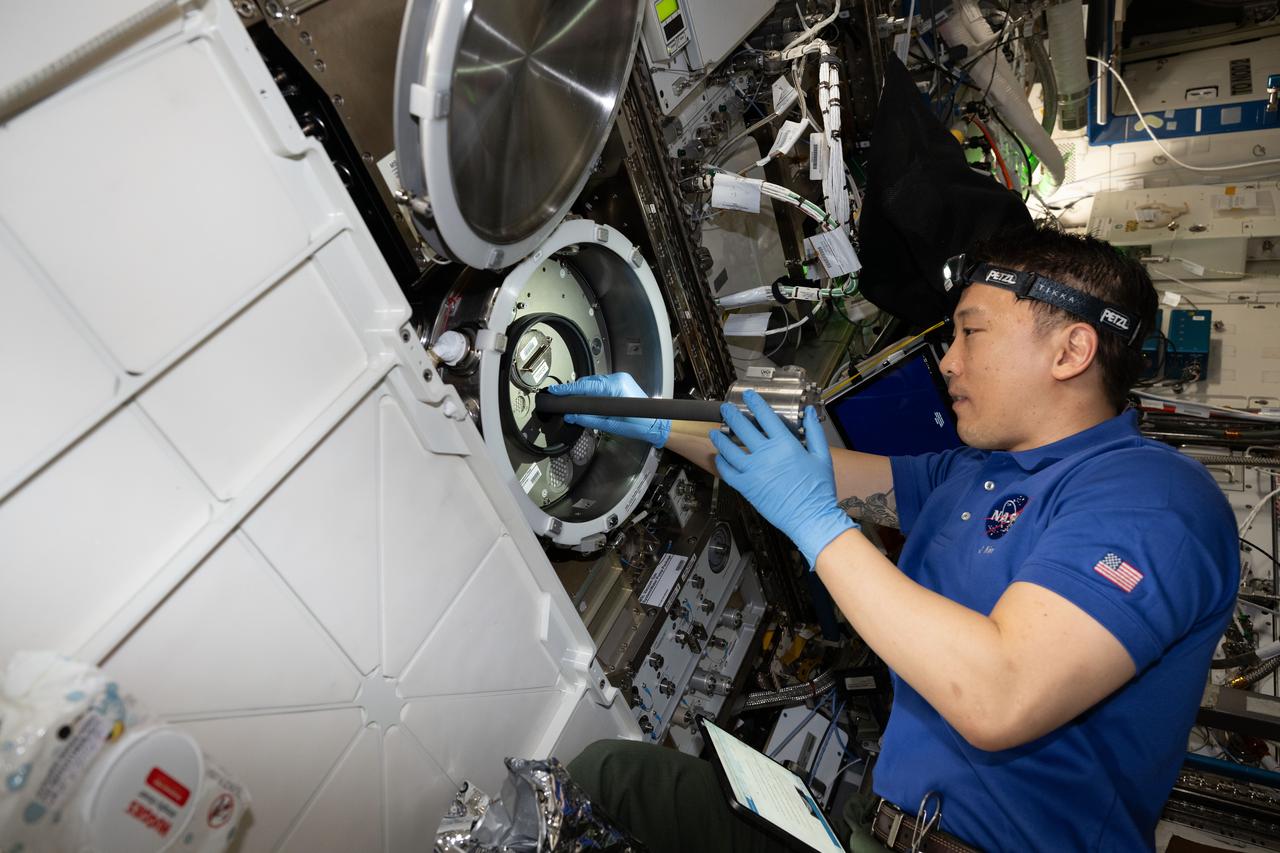

iss073e0222456 (June 27, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim removes research hardware from inside the Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) located inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The MSL uses two different furnaces that operate one at a time to discover new applications for existing materials, such as metals, alloys, polymers, and new or improved materials.
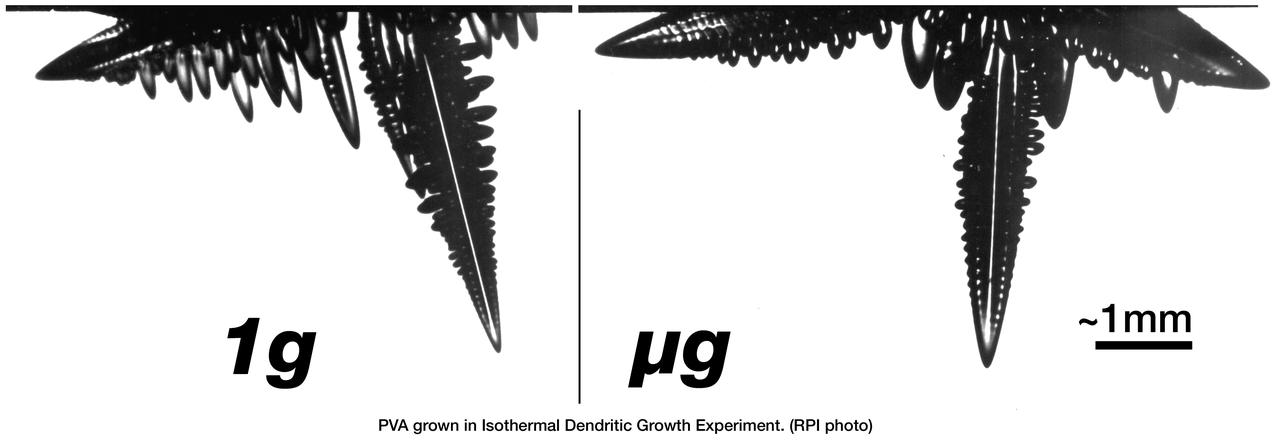

The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. IDGE used transparent organic liquids that form dendrites (treelike structures) similar to those inside metal alloys. Comparing Earth-based and space-based dendrite growth velocity, tip size and shape provides a better understanding of the fundamentals of dentritic growth, including gravity's effects. Shalowgraphic images of pivalic acid (PVA) dendrites forming from the melt show the subtle but distinct effects of gravity-driven heat convection on dentritic growth. In orbit, the dendrite grows as its latent heat is liberated by heat conduction. This yields a blunt dendrite tip. On Earth, heat is carried away by both conduction and gravity-driven convection. This yields a sharper dendrite tip. In addition, under terrestrial conditions, the sidebranches growing in the direction of gravity are augmented as gravity helps carry heat out of the way of the growing sidebranches as opposed to microgravity conditions where no augmentation takes place. IDGE was developed by Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute and NASA/Glenn Research Center. Advanced follow-on experiments are being developed for flight on the International Space Station. Photo Credit: NASA/Glenn Research Center

A mechanic and apprentice work on a wooden impeller in the Fabrication Shop at the NACA Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 260-person Fabrication Division created almost all of the equipment and models used at the laboratory. The Technical Services Building, referred to as the “Fab Shop”, contained a number of specialized shops in the 1940s and 1950s. These included a Machine Shop, Sheet Metal Shop, Wood and Pattern Shop, Instrument Shop, Thermocouple Shop, Heat Treating Shop, Metallurgical Laboratory, and Fabrication Office. The Machine Shop fabricated research equipment not commercially available. During World War II these technicians produced high-speed cameras for combustion research, impellers and other supercharger components, and key equipment for the lab’s first supersonic wind tunnel. The Wood and Pattern Shop created everything from control panels and cabinets to aircraft model molds for sheet metal work. The Sheet Metal Shop had the ability to work with 0.01 to 4-inches thick steel plates. The Instrument Shop specialized in miniature parts and instrumentation, while the Thermocouple Shop standardized the installation of pitot tubes and thermocouples. The Metallurgical Laboratory contained a control lab for the Heat Treating Shop and a service lab for the NACA Lewis research divisions. The Heat Treating Shop heated metal parts to optimize their physical properties and contained a Precision Castings Foundry to manufacture equipment made of heat resisting alloys.

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, is inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to begin testing on the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.
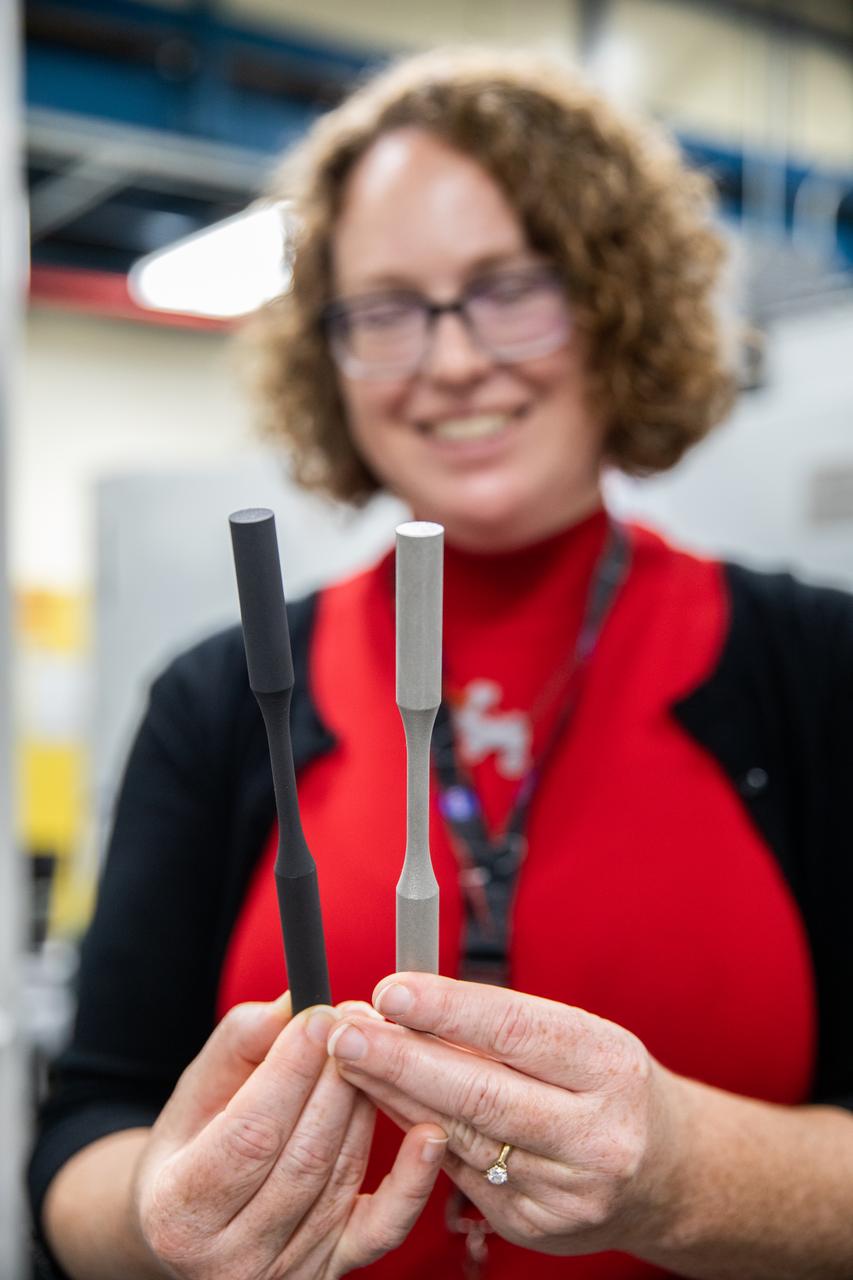

Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, displays two fatigue samples that will be tested in the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiments inside the Prototype Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied to spacecraft and launch vehicles.

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, handles a sample that is being prepared for fatigue and corrosion testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.

Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a ten percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
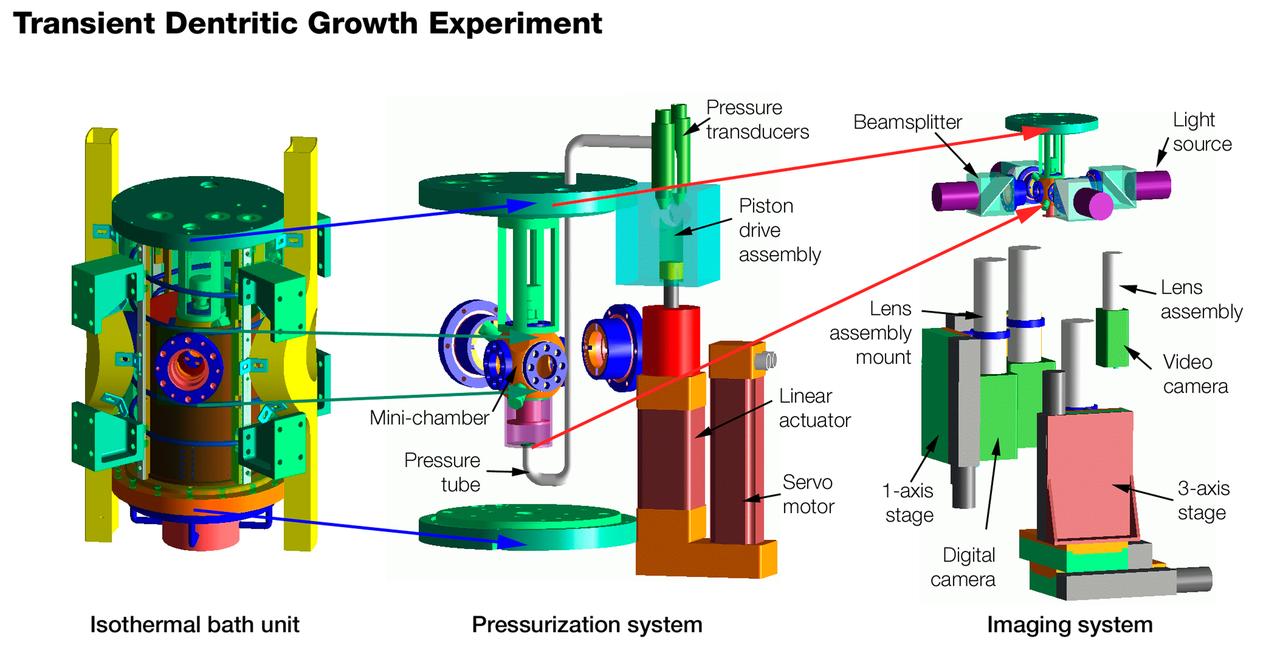
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior or widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of the TDSE. A similar view is availble without labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) specimens for testing inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
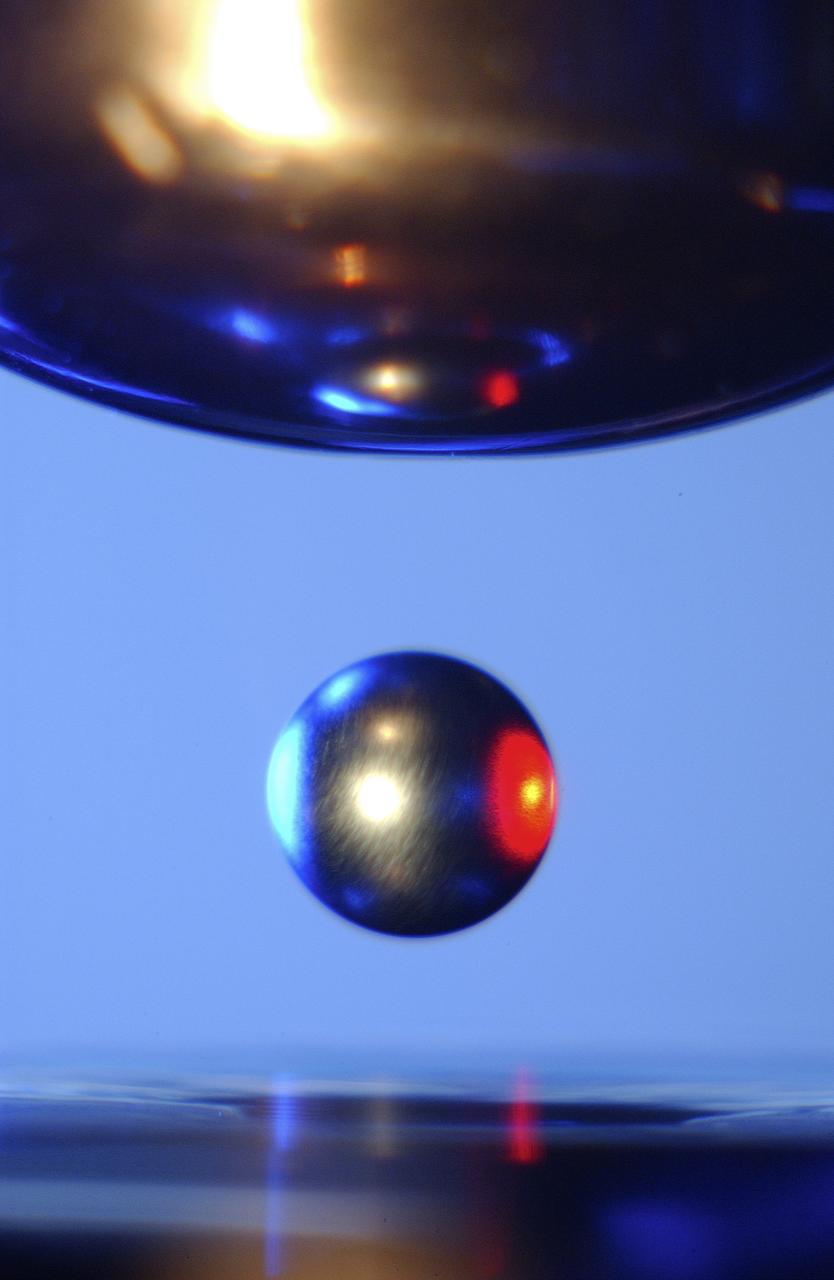
This is a close-up of a sample of titanium-zirconium-nickel alloy inside the Electrostatic Levitator (ESL) vacuum chamber at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The ESL uses static electricity to suspend an object (about 3-4 mm in diameter) inside a vacuum chamber allowing scientists to record a wide range of physical properties without the sample contracting the container or any instruments, conditions that would alter the readings. Once inside the chamber, a laser heats the sample until it melts. The laser is then turned off and the sample cools, changing from a liquid drop to a solid sphere. Since 1977, the ESL has been used at MSFC to study the characteristics of new metals, ceramics, and glass compounds. Materials created as a result of these tests include new optical materials, special metallic glasses, and spacecraft components.
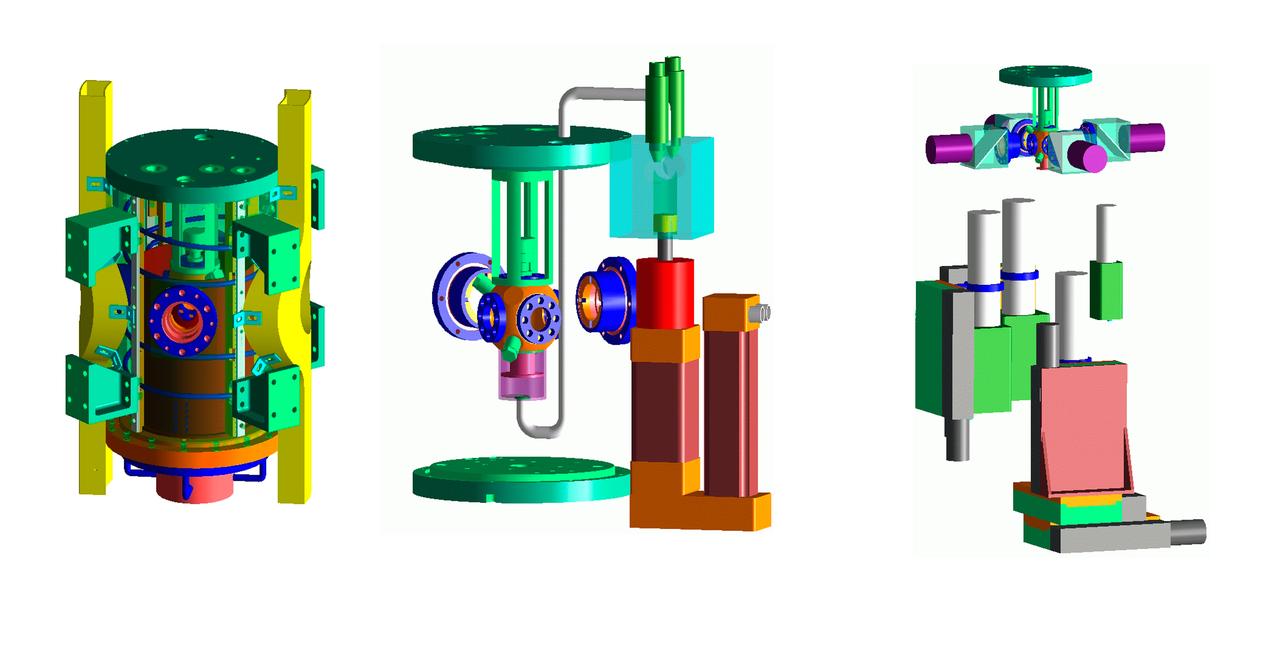
The Transient Dendritic Solidification Expepriment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dendrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle missions of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Expepriment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dendrites. Shown here is an exploded view of major elements of TDSE. A similar view is available with labels. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Photo credit: NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC)

Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician with NASA, prepares a sample for testing for the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) project inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
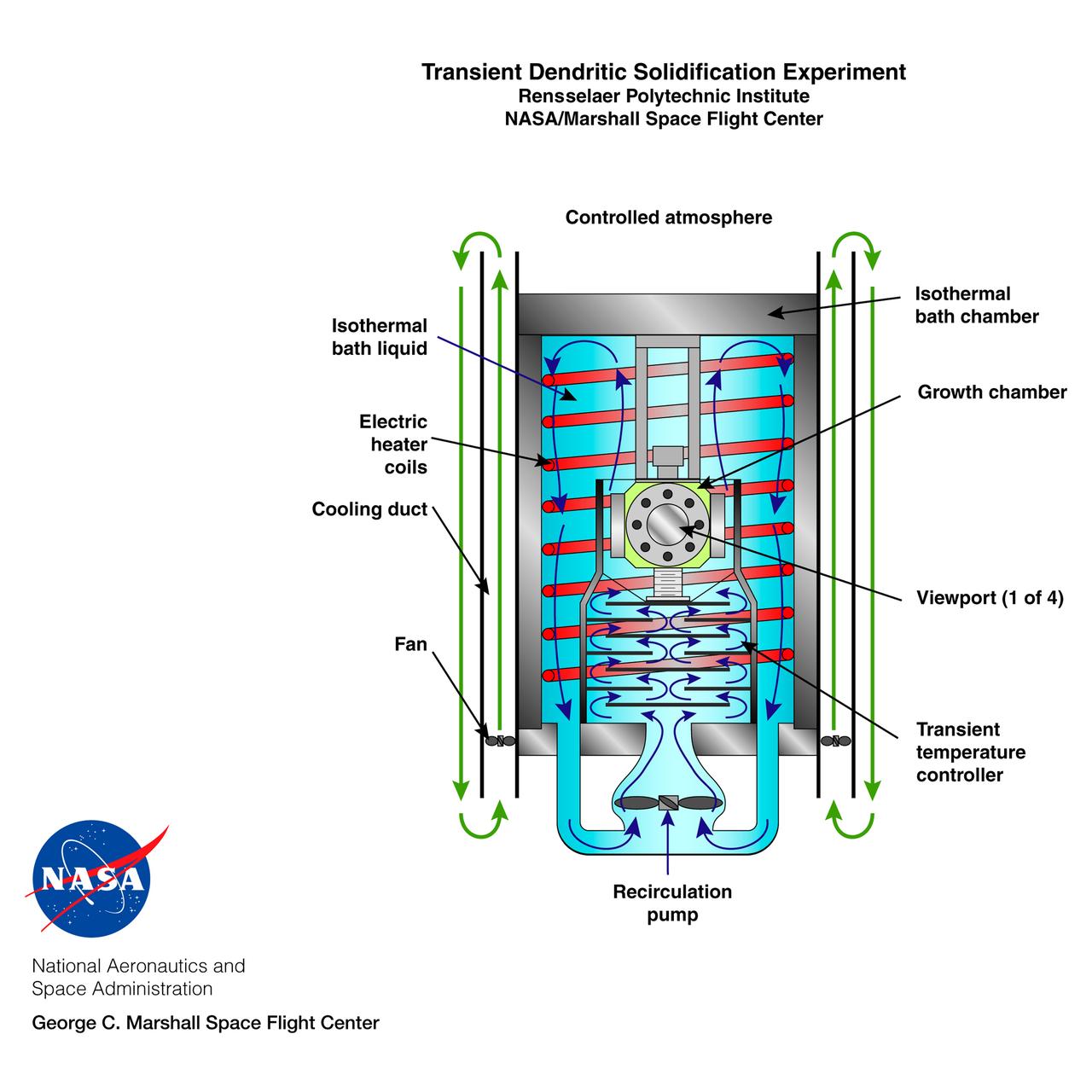
The Transient Dentritic Solidification Experiment (TDSE) is being developed as a candidate for flight aboard the International Space Station. TDSE will study the growth of dentrites (treelike crystalline structures) in a transparent material (succinonitrile or SCN) that mimics the behavior of widely used iron-based metals. Basic work by three Space Shuttle flights (STS-62, STS-75, and STS-87) of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. The TDSE is similar to IDGE, but will maintain a constant temperature while varying pressure on the dentrites. Shown here is a cutaway of the isothermal bath containing its growth cell at the heart of the TDSE. The principal investigator is Matthew Koss of College of the Holy Cross in Worcester, MA. Note: an Acrobat PDF version is available from http://microgravity.nasa.gov/gallery

From left, Dr. Jennifer Williams, a NASA research chemical engineer, and Gerard Moscoso, a mechanical engineer technician, inspect specimens prepared forthe Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied used on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
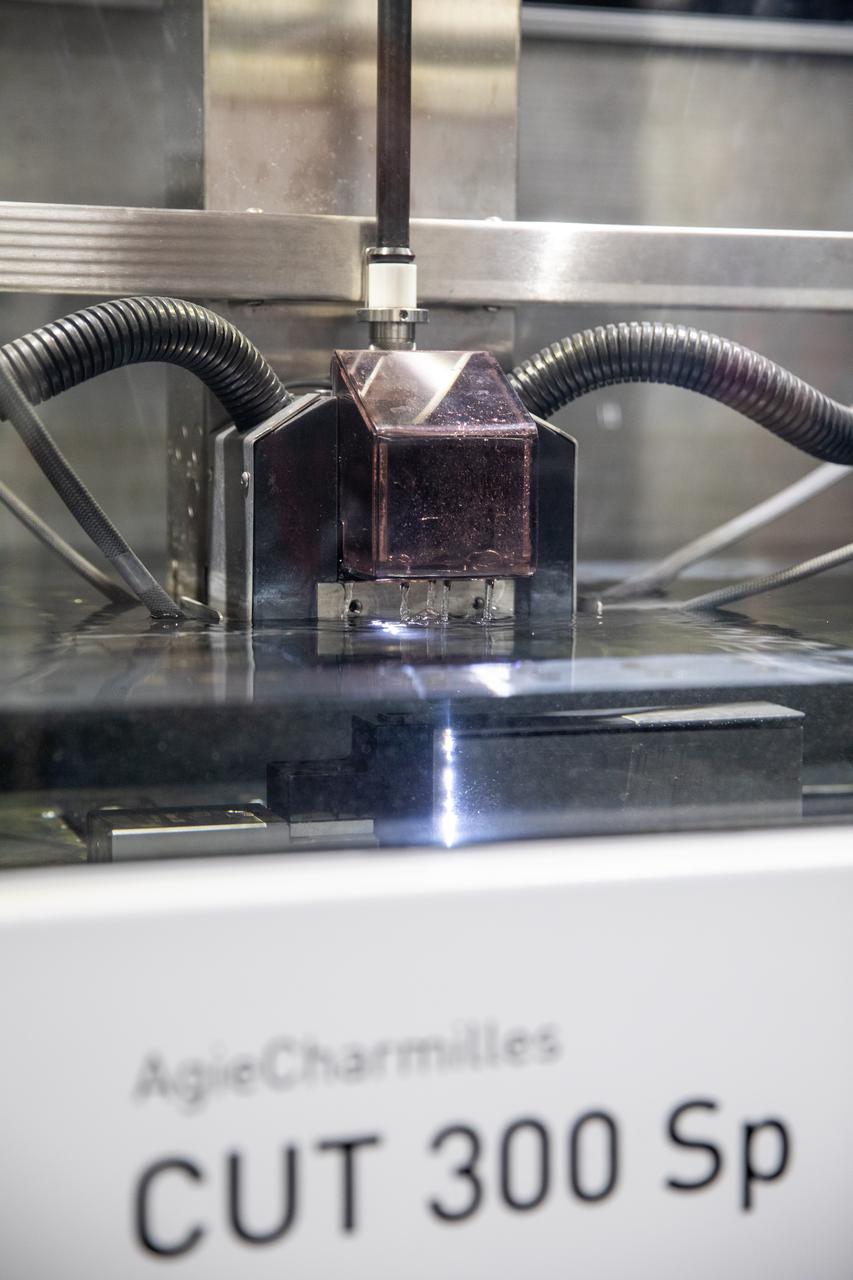
Testing of the Plasma Rapid Oxidation Technique for Extending Component Tenability (PROTECT) experiment is underway inside the Prototype Development Laboratory at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 2, 2022. Plasma electrolytic oxidation is a surface coating technology that produces oxide layers on the surface of light metals and their alloys to improve their performance characteristics. These coatings are tailored to provide a combination of characteristics such as corrosion protection, wear resistance, thermal management, extreme hardness, and fatigue performance. PROTECT is expected to demonstrate a 10 percent improved fatigue performance and a 70 percent improvement in corrosion characteristics on the interior of treated 3-D printed metallic parts when compared to non-treated parts. PROTECT could be applied on spacecraft and launch vehicles.
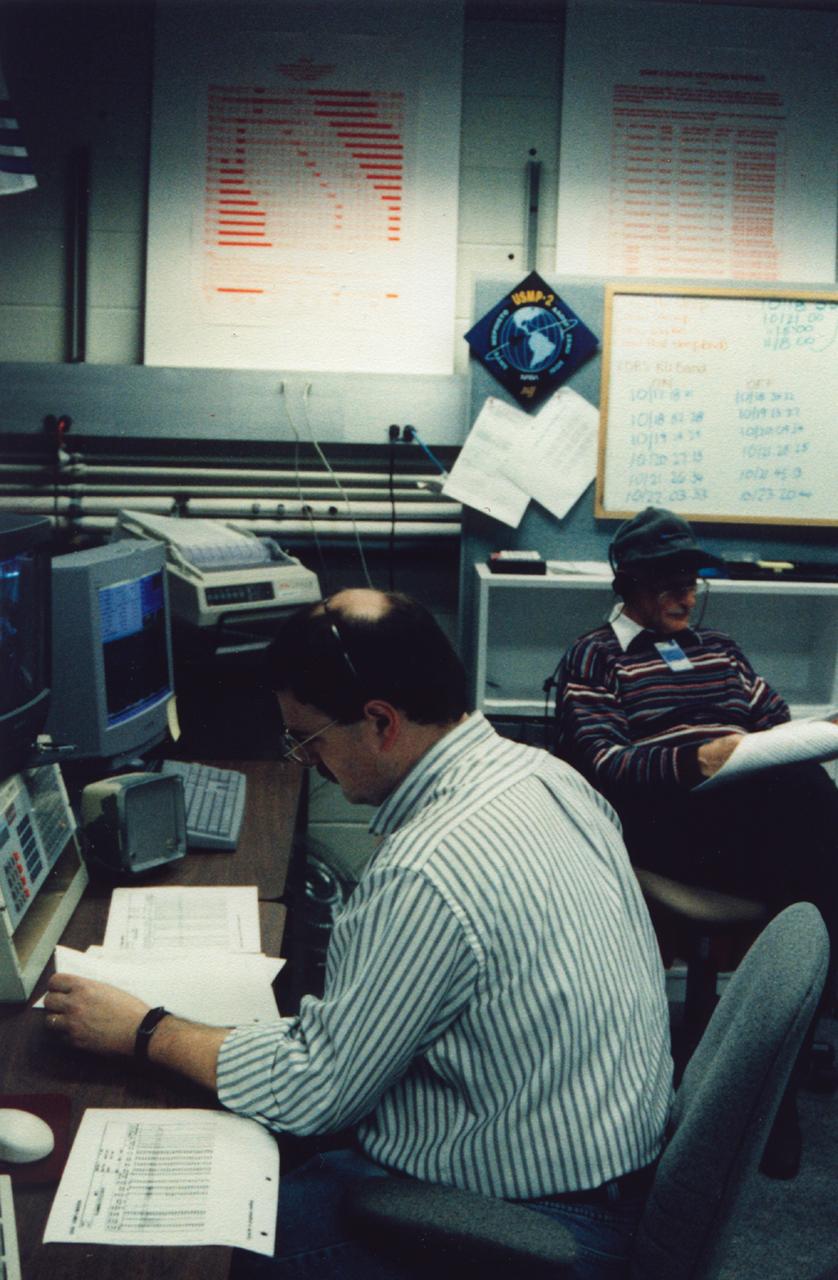

Matthew Koss (forground) and Martin Glicksman (rear), principal investigator and lead scientist (respectively), review plans for the next step in the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997). Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) like this one, at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, will become more common during operations with the International Space Station. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relavent metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
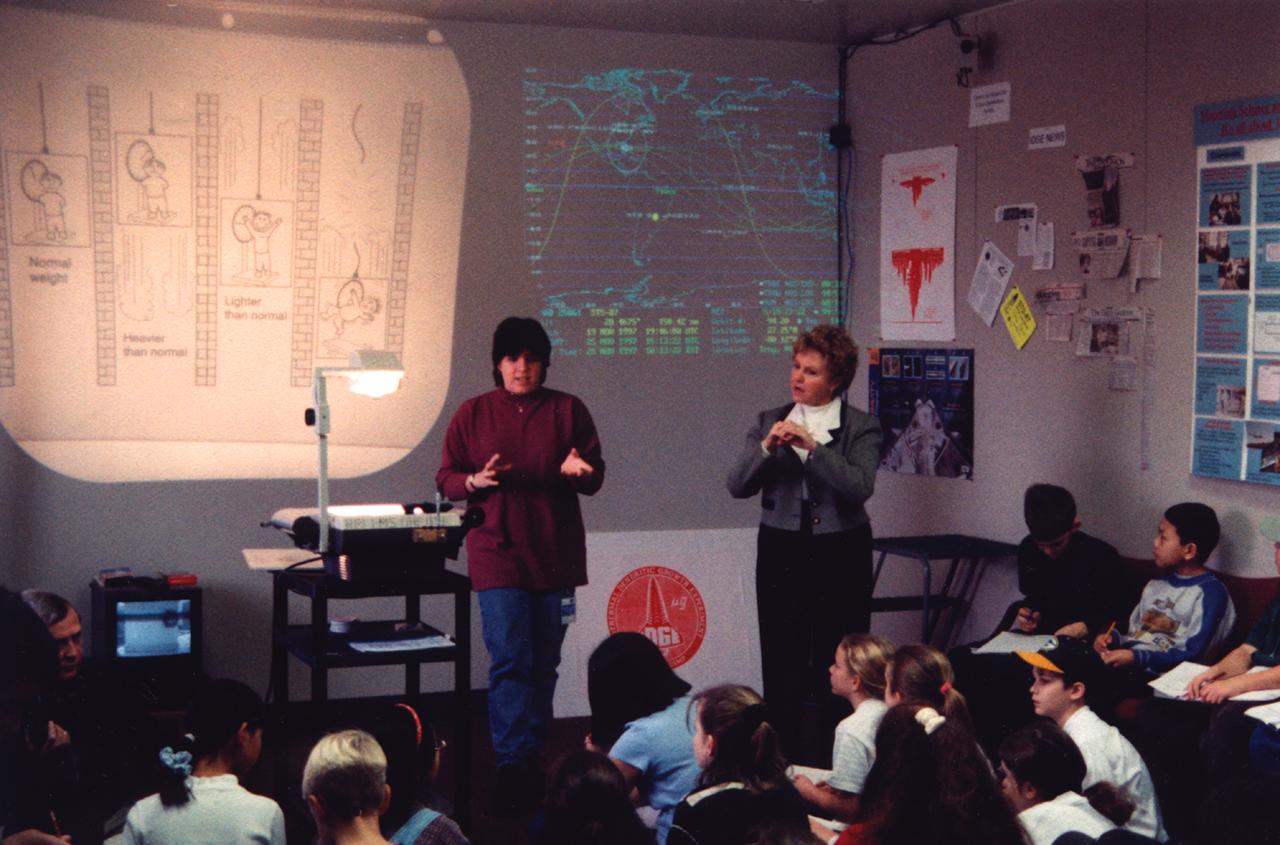

Paula Crawford (assisted by an American Sign Language interpreter) lectures students about materials science research in space during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997) in the visitor's center set up by the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) team at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle mission, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operation. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
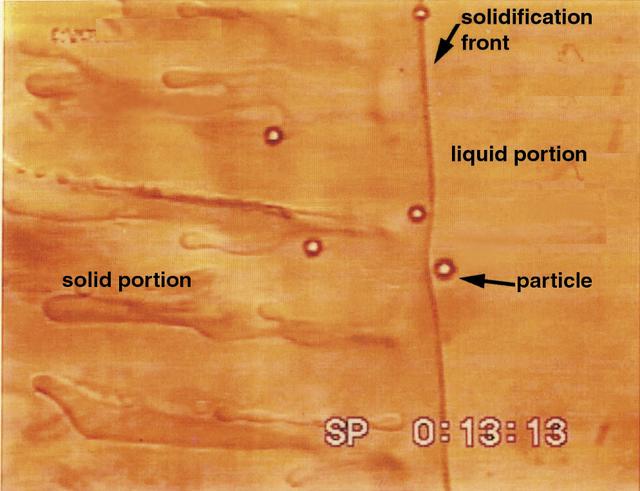
As a liquefied metal solidifies, particles dispersed in the liquid are either pushed ahead of or engulfed by the moving solidification front. Similar effects can be seen when the ground freezes and pushes large particles out of the soil. The Particle Engulfment and Pushing (PEP) experiment, conducted aboard the fourth U.S. Microgravity Payload (USMP-4) mission in 1997, used a glass and plastic beads suspended in a transparent liquid. The liquid was then frozen, trapping or pushing the particles as the solidifying front moved. This simulated the formation of advanced alloys and composite materials. Such studies help scientists to understand how to improve the processes for making advanced materials on Earth. The principal investigator is Dr. Doru Stefanescu of the University of Alabama. This image is from a video downlink.
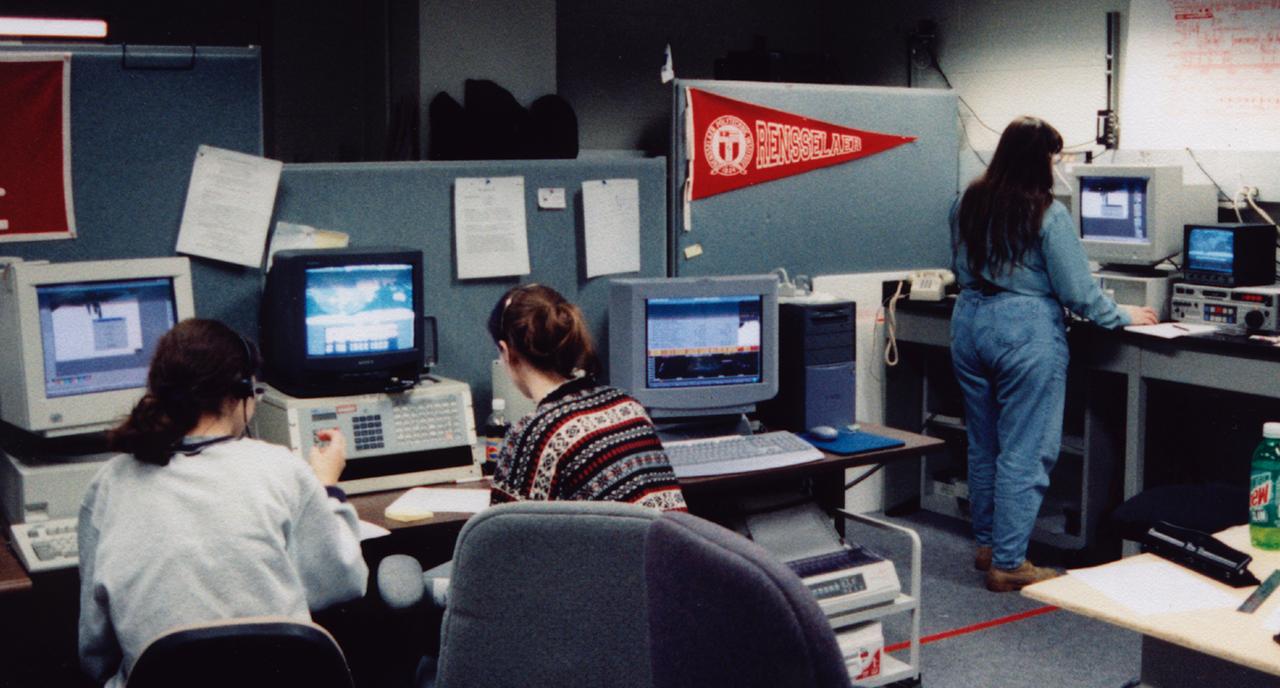

Students at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, monitor the progress of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87, Nov. 19 - Dec. 5, 1997). Remote Operation Control Center (ROCC) like this one will become more common during operations with International Space Station. IDGE, flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Renssenlaer Polythnic Institute (RPI)
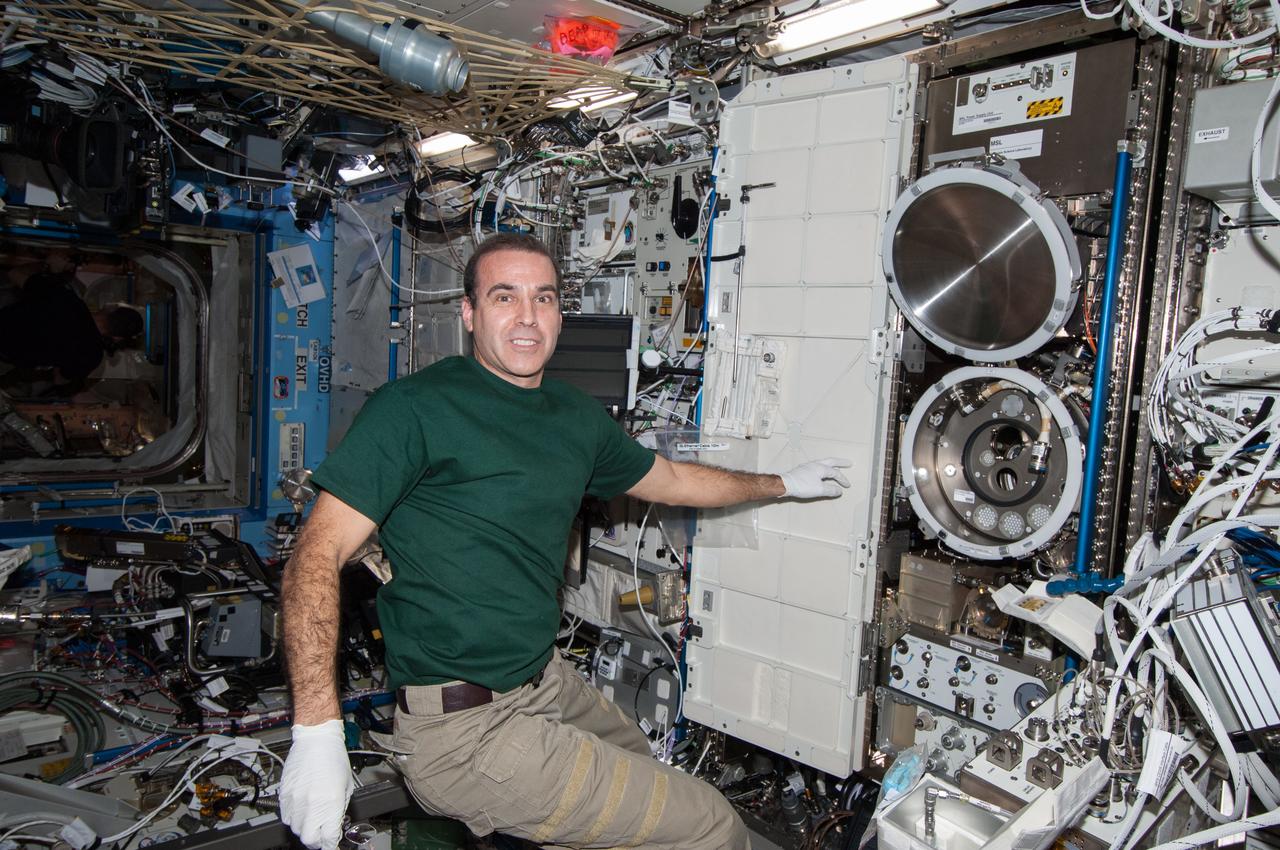

ss038e008298 (11/26/2013) --- A view of NASA astronaut Rick Mastracchio, during the Material Science Laboratory (MSL) Solidification and Quench Furnace (SQF) Sample Cartridge Exchange aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Materials Science Laboratory (MSL) is used for basic materials research in the microgravity environment of the ISS. The MSL can accommodate and support diverse Experiment Modules. In this way many material types, such as metals, alloys, polymers, semiconductors, ceramics, crystals, and glasses, can be studied to discover new applications for existing materials and new or improved materials.
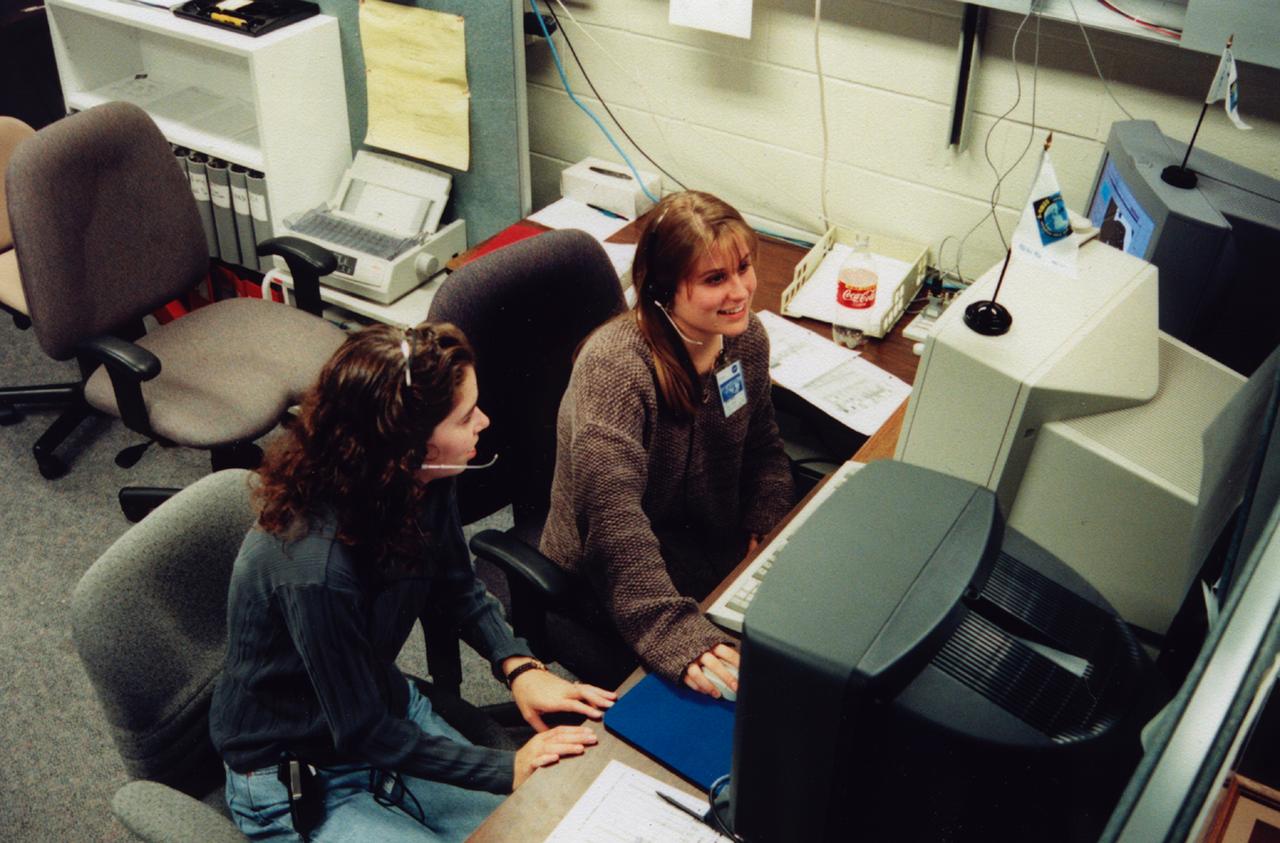

Undergraduate students Kristina Wines and Dena Renzo at Rensselaer Poloytech Institute (RPI) in Troy, NY, monitor the progress of the Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE) during the U.S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) mission (STS-87), Nov. 19 - Dec.5, 1997). Remote Operations Control Center (ROCC) like this one will become more common during operations with the International Space Station. The Isothermal Dendritic Growth Experiment (IDGE), flown on three Space Shuttle missions, is yielding new insights into virtually all industrially relevant metal and alloy forming operations. Photo credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI)
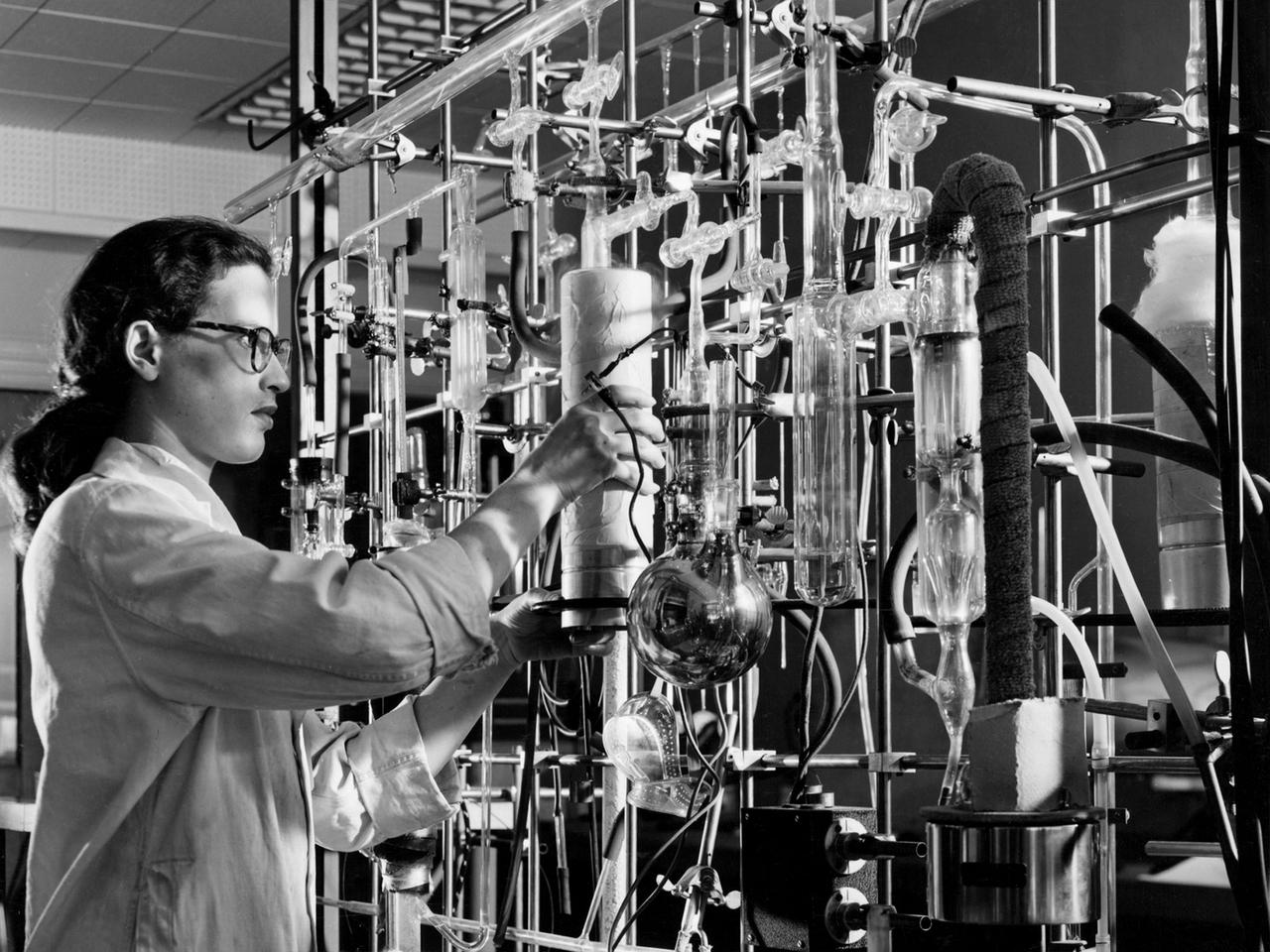

A materials researcher at the NACA’s Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory examines a surface crack detection apparatus in the Materials and Stresses Building during December 1952. Materials research was an important aspect of propulsion technology. Advanced engine systems relied upon alloys, and later composites, that were strong, lightweight, and impervious to high temperatures. Jet engines which became increasingly popular in the late 1940s, produced much higher temperatures than piston engines. These higher temperatures stressed engine components, particularly turbines. Although Lewis materials research began during World War II, the Materials and Thermodynamics Division was not created until 1949. Its primary laboratories were located in the Materials and Stresses Building. The group sought to create new, improved materials and to improve engine design through increased understanding of materials. The Lewis materials researchers of the 1950s made contributions to nickel-aluminum alloys, cermet blades, metal matrix composites, oxide dispersion strengthened superalloys, and universal slopes.

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
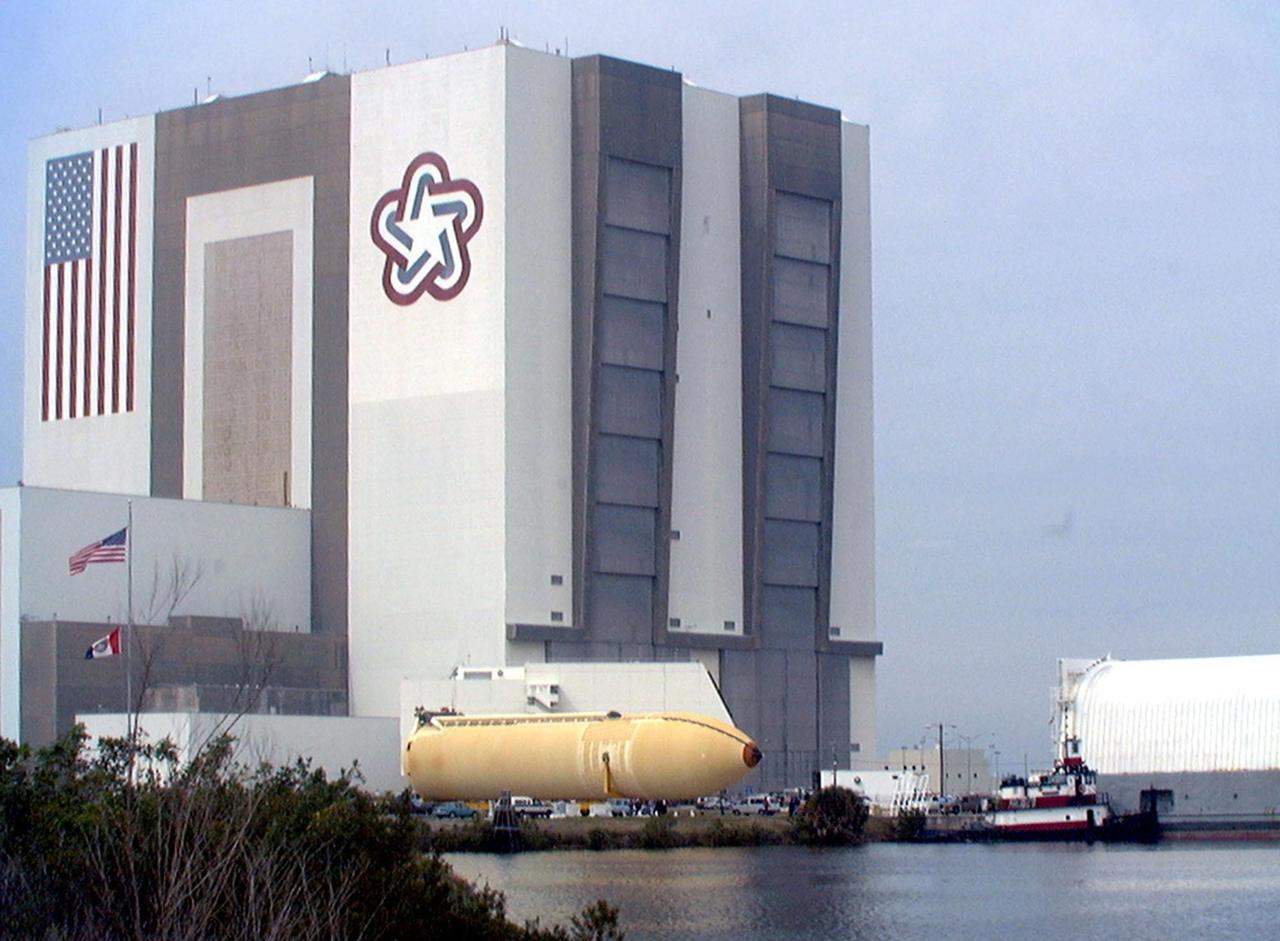

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
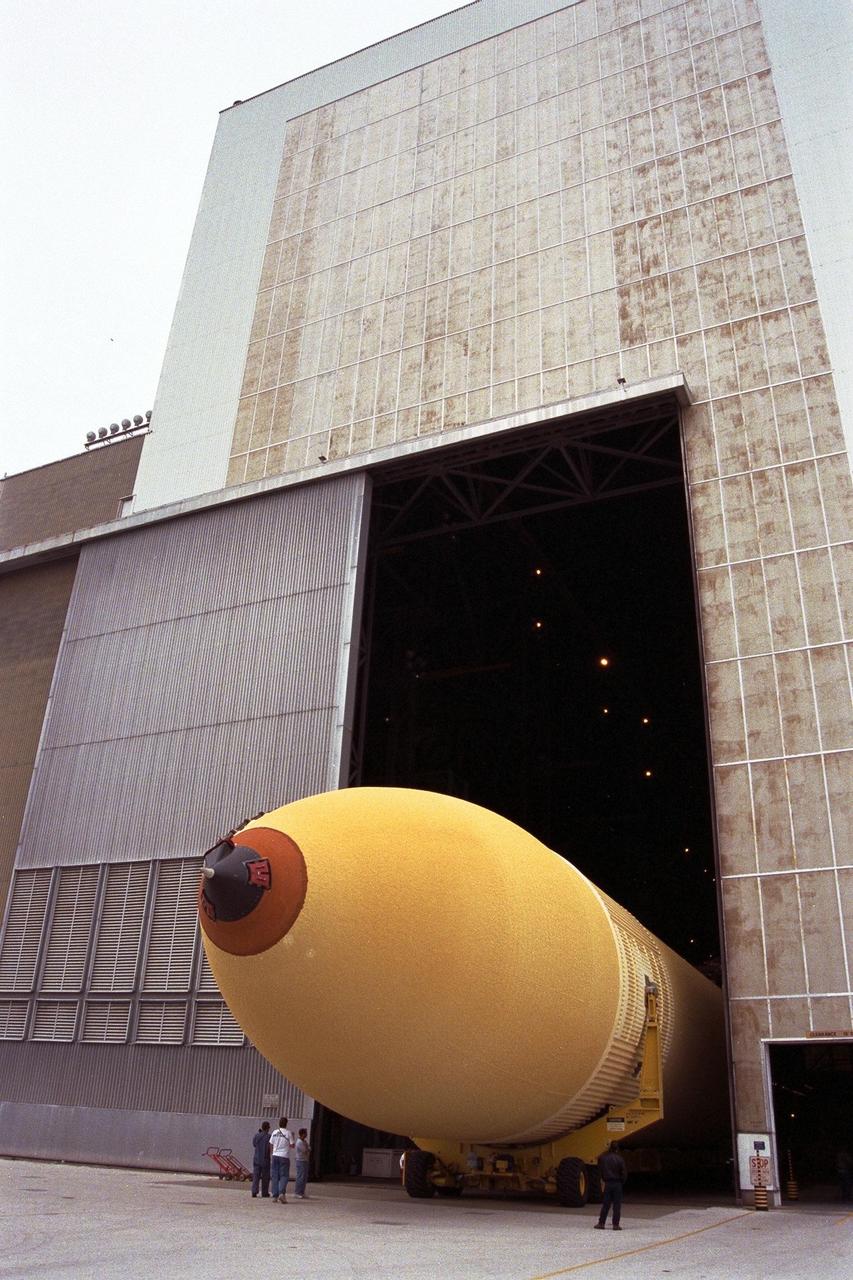

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way into Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
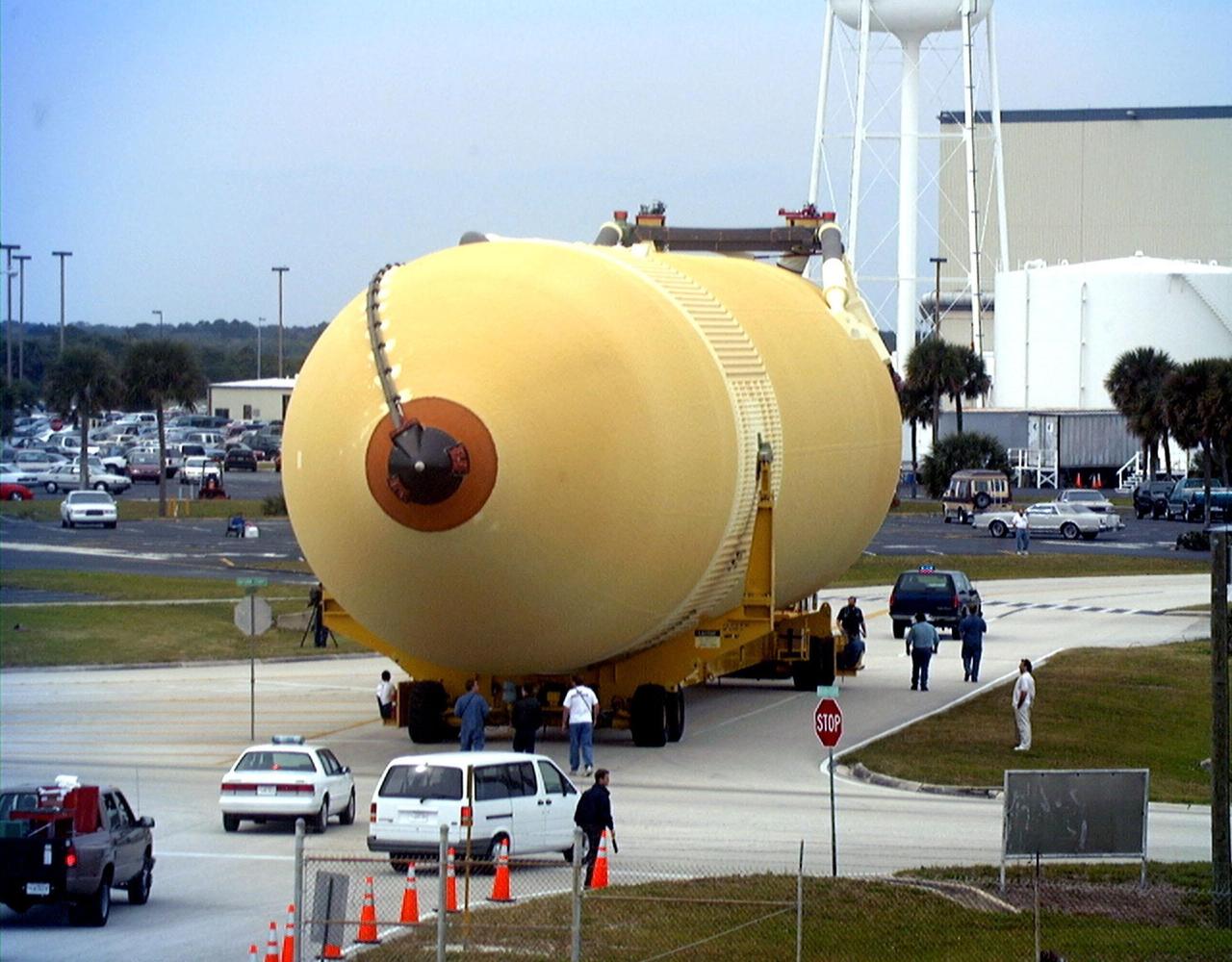

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well

This is a macro photograph of an etched surface of the Mundrabilla meteorite, a small piece of the approximately 3.9 billion-year-old meteorite that was first discovered in Western Australia in 1911. Two more giant chunks, together weighing about 17 tons, were found in 1966. Researchers can learn much from this natural crystal growth experiment since it has spent several hundred million years cooling, and would be impossible to emulate in a lab. This single slice, taken from a 6 ton piece recovered in 1966, measures only 2 square inches. The macro photograph shows a metallic iron-nickel alloy phase of kamcite (38% Ni) and taenite (6% Ni) at bottom right, bottom left, and top left. The darker material is an iron sulfide (FeS or troilite) with a parallel precipitates of duabreelite (iron chromium sulfide (FeCr2S4).
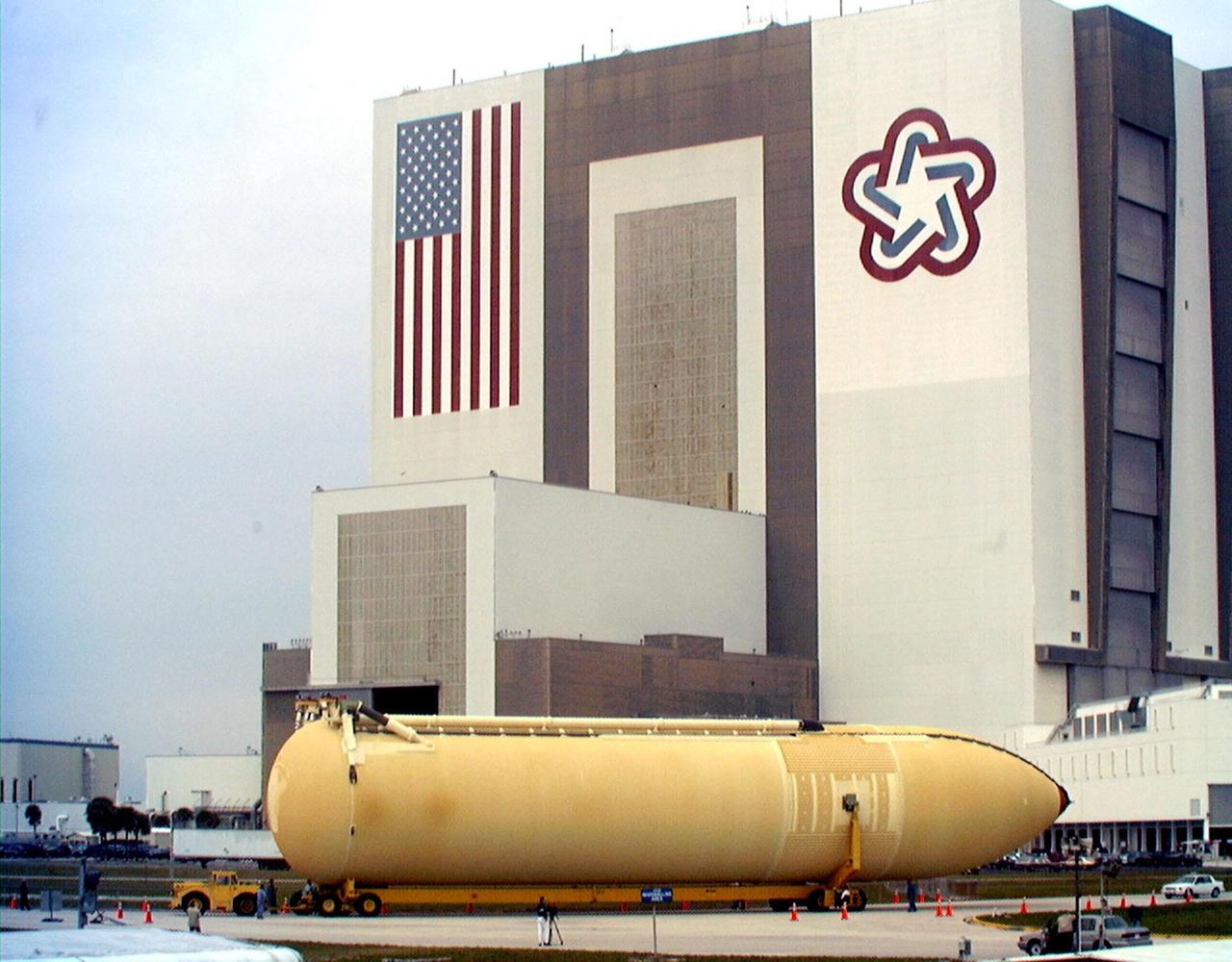

The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
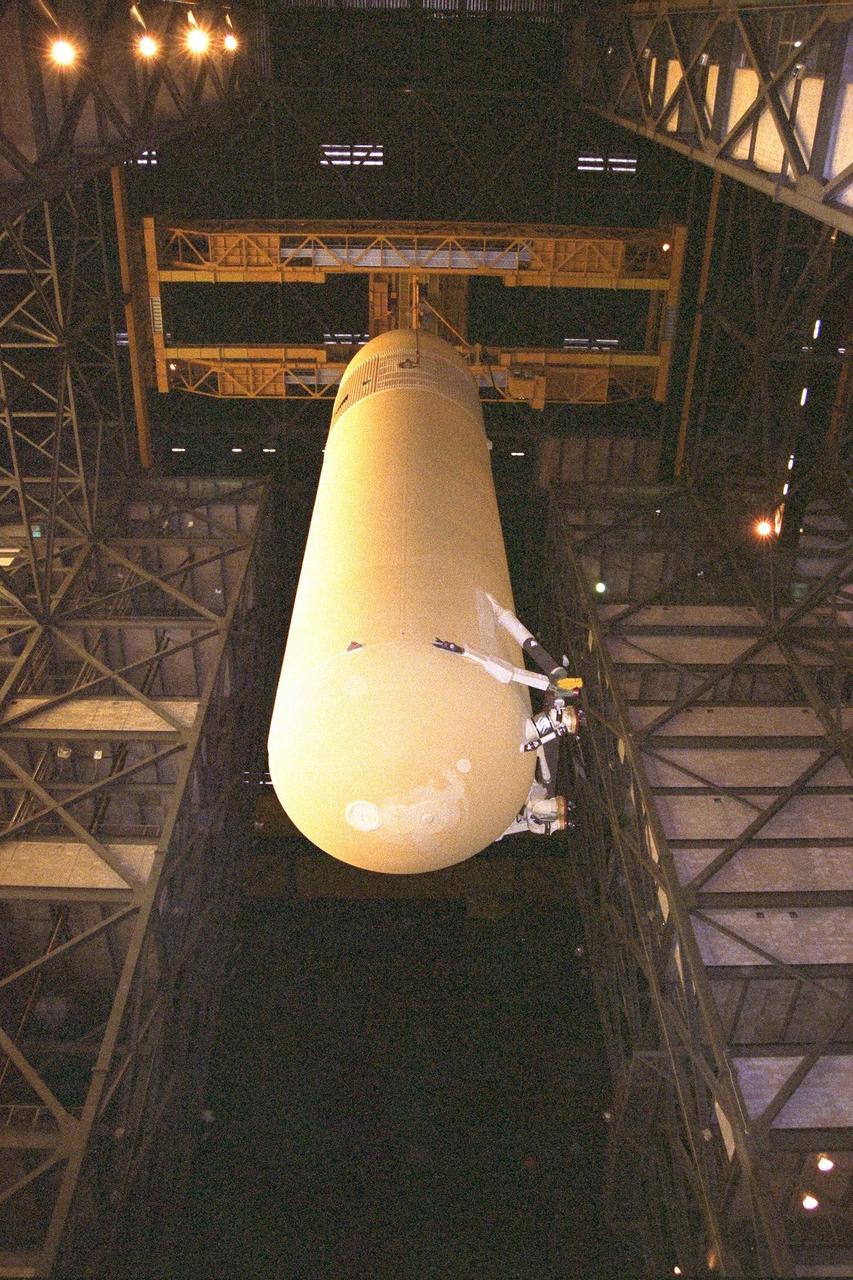

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
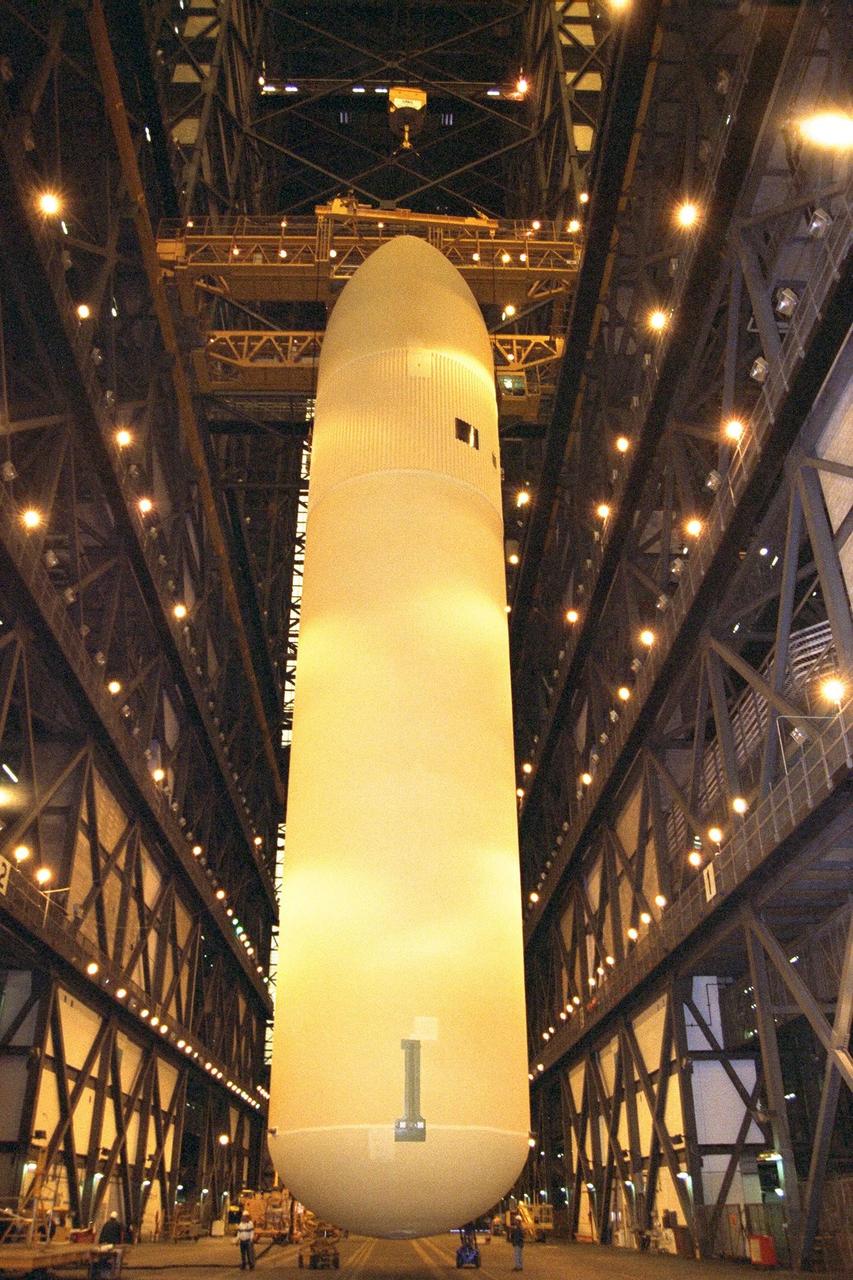

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
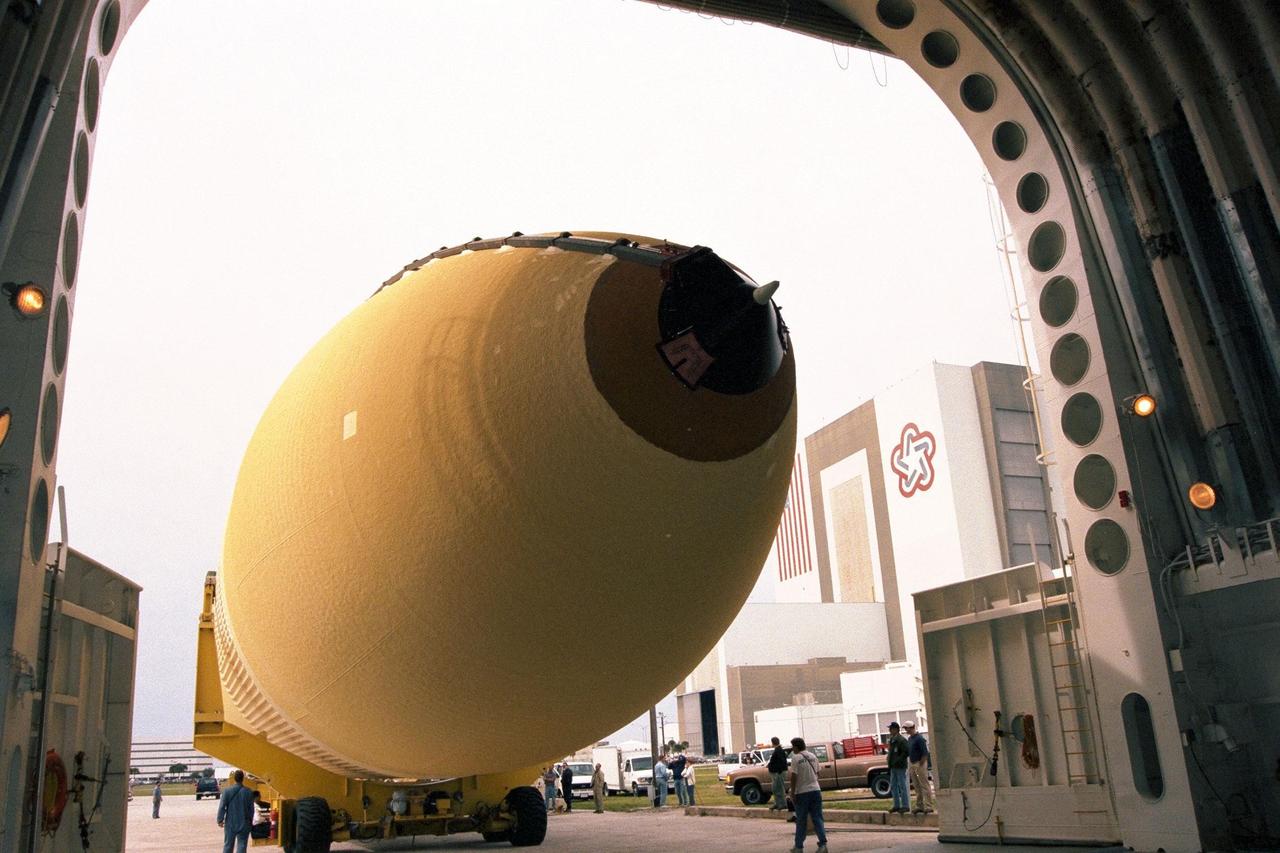

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. It was moved by barge to KSC on Feb. 6. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
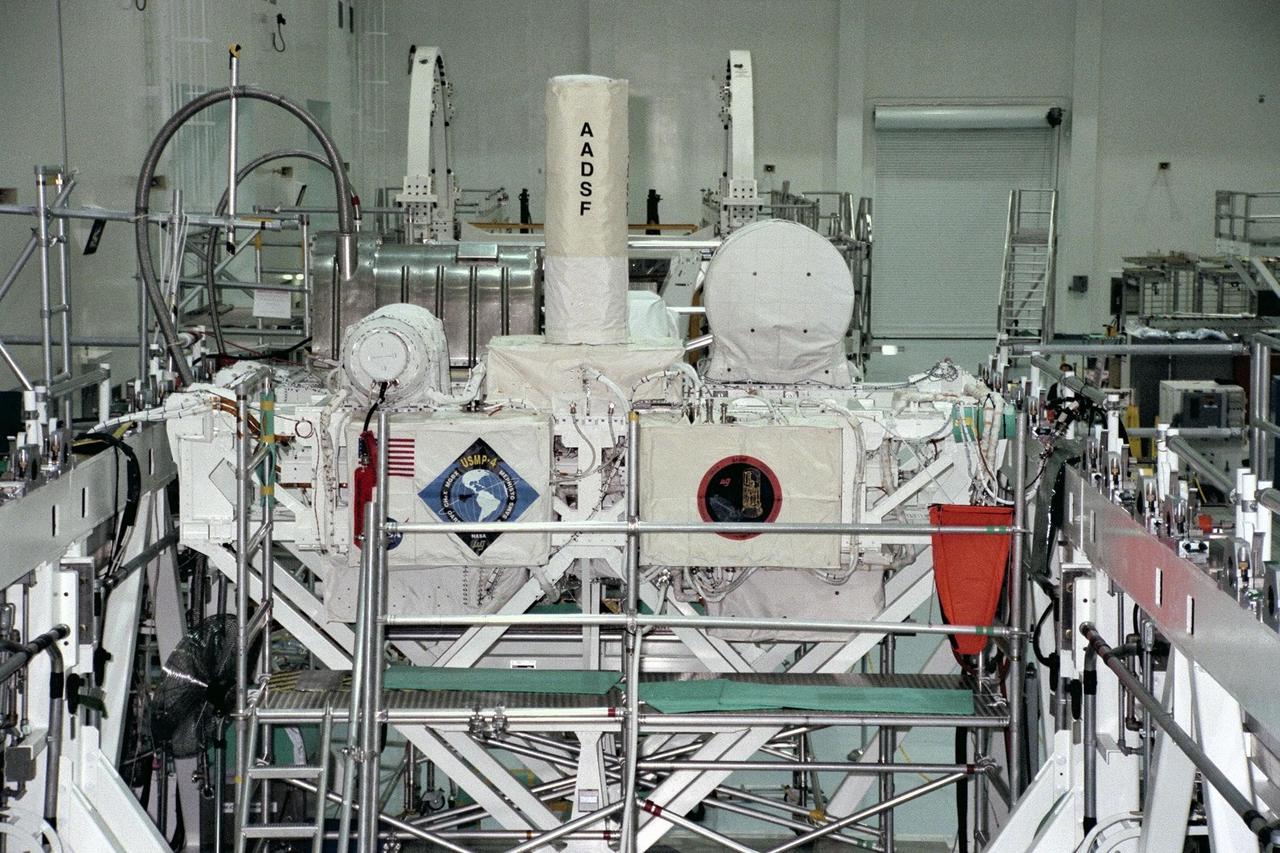
United States Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) experiments are prepared to be flown on Space Shuttle mission STS-87 in the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center (KSC). Seen in the foreground at right is the USMP-4 logo with the acronyms of its experiments. Above the American flag at left is the MEPHISTO experiment, a cooperative American and French investigation of the fundamentals of crystal growth. Scientists will study changes in solidification rates, temperature, and interface shape of an alloy to understand how these changes affect composition and properties of the metal produced. Under the multi-layer insulation with the American flag and mission logo is the Space Acceleration Measurement System, or SAMS, which measures the microgravity conditions in which the experiments are conducted. All USMP-4 experiments are scheduled for launch aboard STS-87 on Nov. 19 from KSC
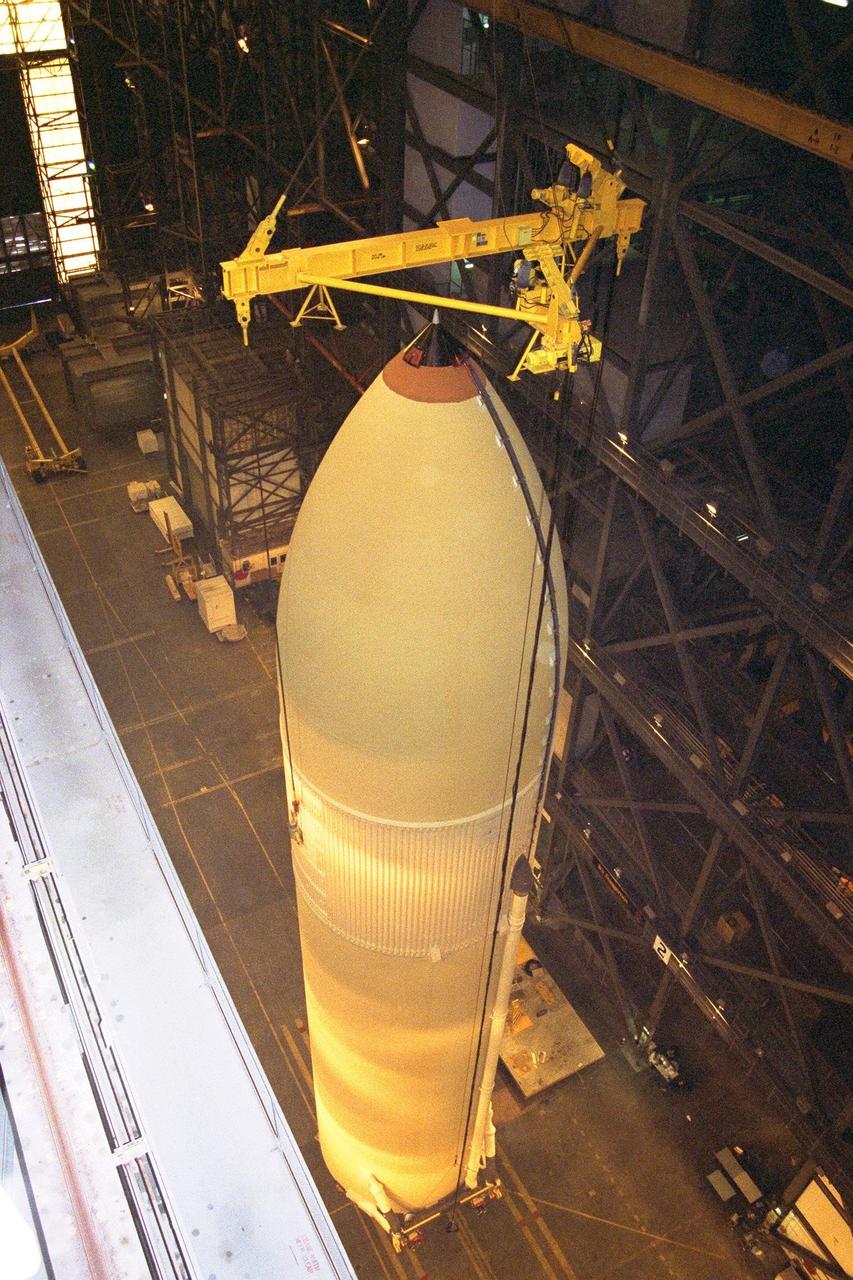

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is lifted in KSC's Vehicle Assembly Building for STS-91 pre-flight processing. STS-91 is targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
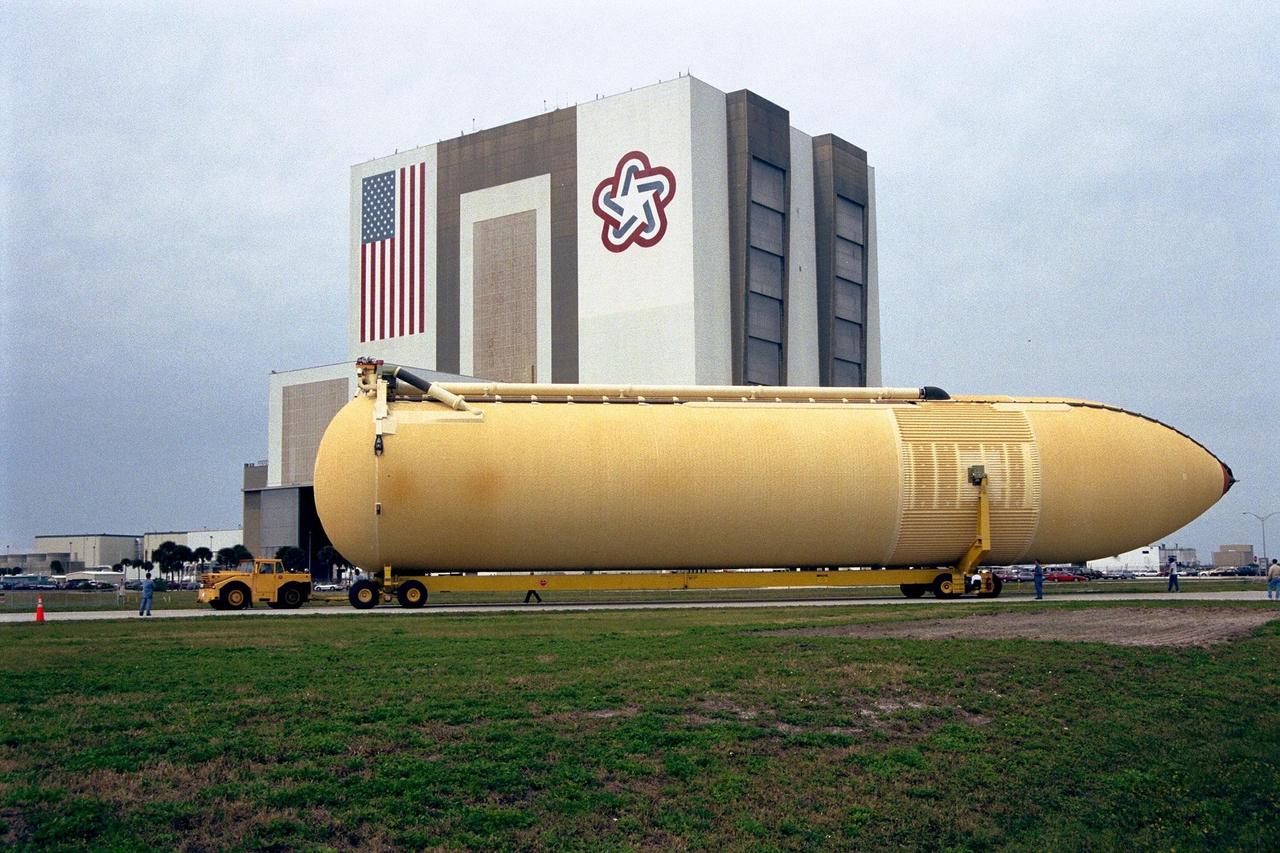

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
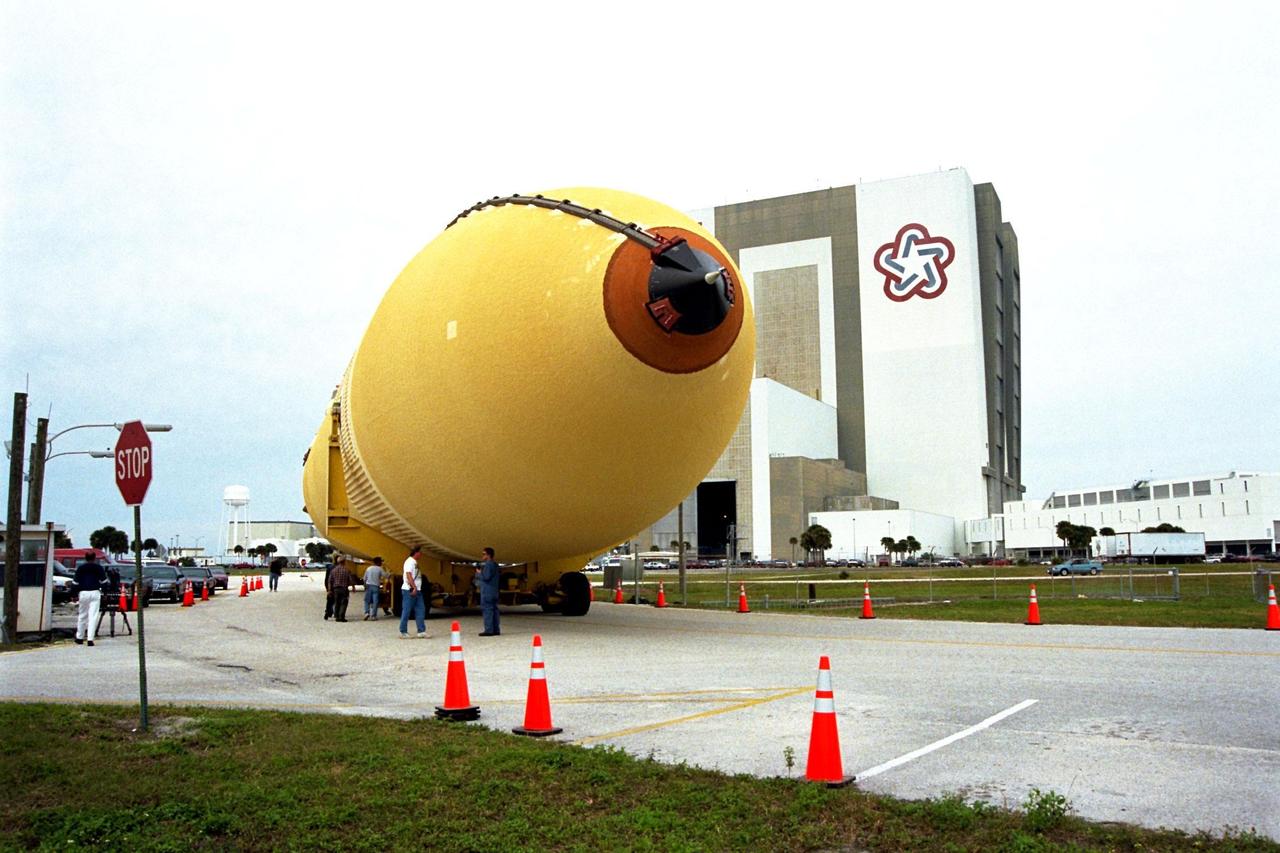

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank is on its way to Kennedy Space Center's Vehicle Assembly Building for processing. The tank, which is scheduled for flight on STS-91 in late May, arrived Feb. 3 in Port Canaveral, where it remained until Feb. 6 due to high winds. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well
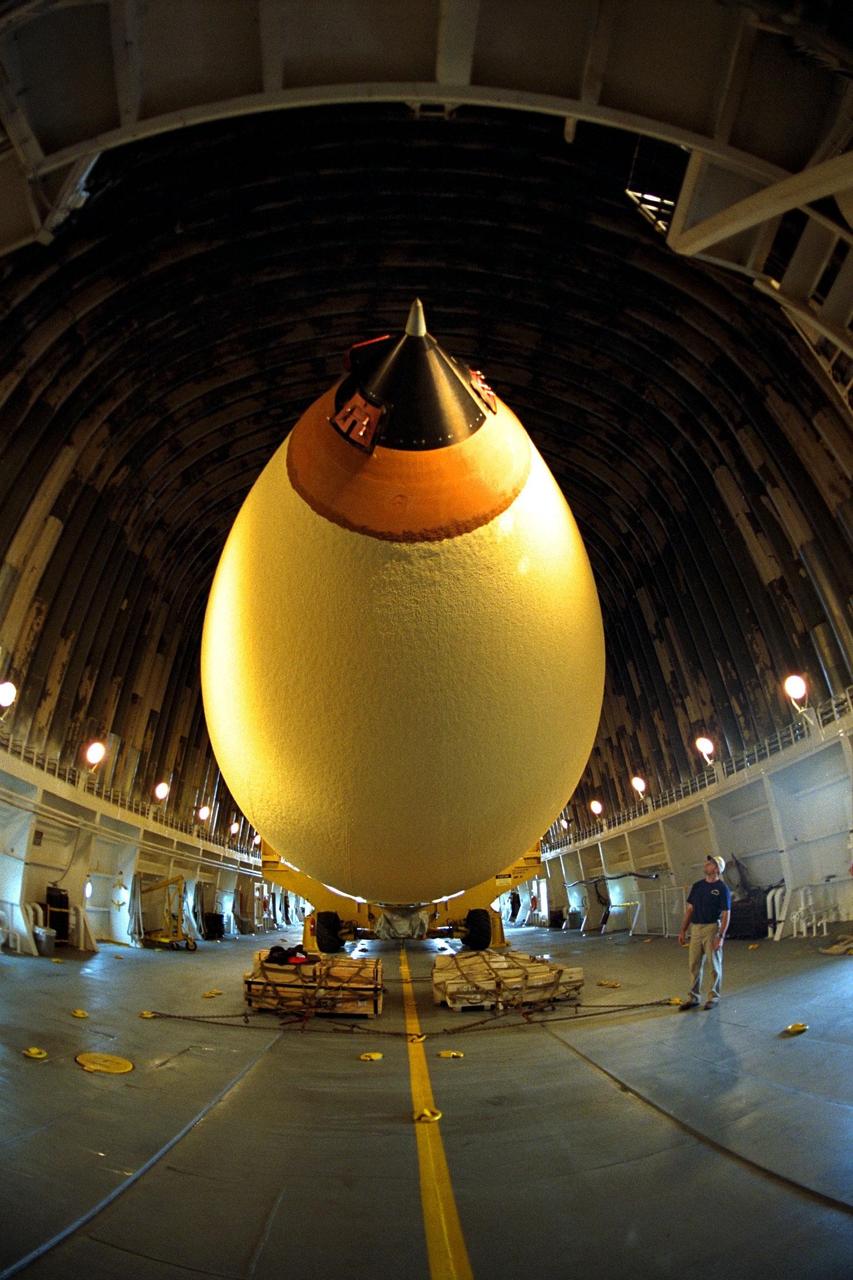

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Bren Wade, chief mate of the "Liberty Star," looks up at the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank as it is moved on a barge to Port Canaveral, Fla. The tank is scheduled to undergo processing at Kennedy Space Center for flight on STS-91, targeted for launch in late May. The improved tank is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. From the outside, the new orange-colored tank appears identical to tanks currently used on Shuttle flights. Major changes, however, include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability as well. This photograph was taken with a wide-angle lens
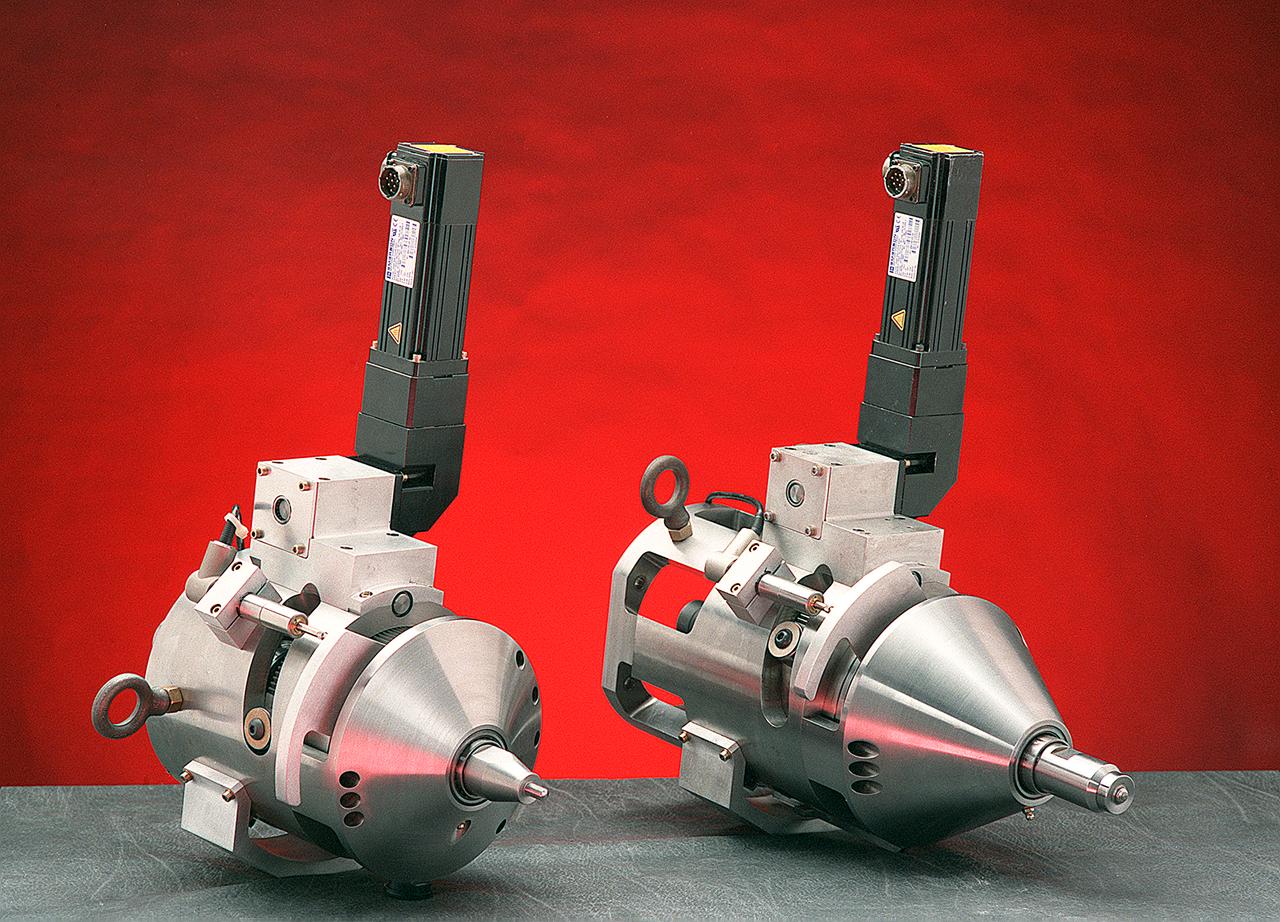

Two companies have successfully commercialized a specialized welding tool developed at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Friction stir welding uses the high rotational speed of a tool and the resulting frictional heat created from contact to crush, "stir" together, and forge a bond between two metal alloys. It has had a major drawback, reliance on a single-piece pin tool. The pin is slowly plunged into the joint between two materials to be welded and rotated as high speed. At the end of the weld, the single-piece pin tool is retracted and leaves a "keyhole," something which is unacceptable when welding cylindrical objects such as drums, pipes and storage tanks. Another drawback is the requirement for different-length pin tools when welding materials of varying thickness. An engineer at the MSFC helped design an automatic retractable pin tool that uses a computer-controlled motor to automatically retract the pin into the shoulder of the tool at the end of the weld, preventing keyholes. This design allows the pin angle and length to be adjusted for changes in material thickness and results in a smooth hole closure at the end of the weld. Benefits of friction stir welding, using the MSFC retractable pin tool technology, include the following: The ability to weld a wide range of alloys, including previously unweldable and composite materials; provision of twice the fatigue resistance of fusion welds and no keyholes; minimization of material distortion; no creation of hazards such as welding fumes, radiation, high voltage, liquid metals, or arcing; automatic retraction of the pin at the end of the weld; and maintaining full penetration of the pin.
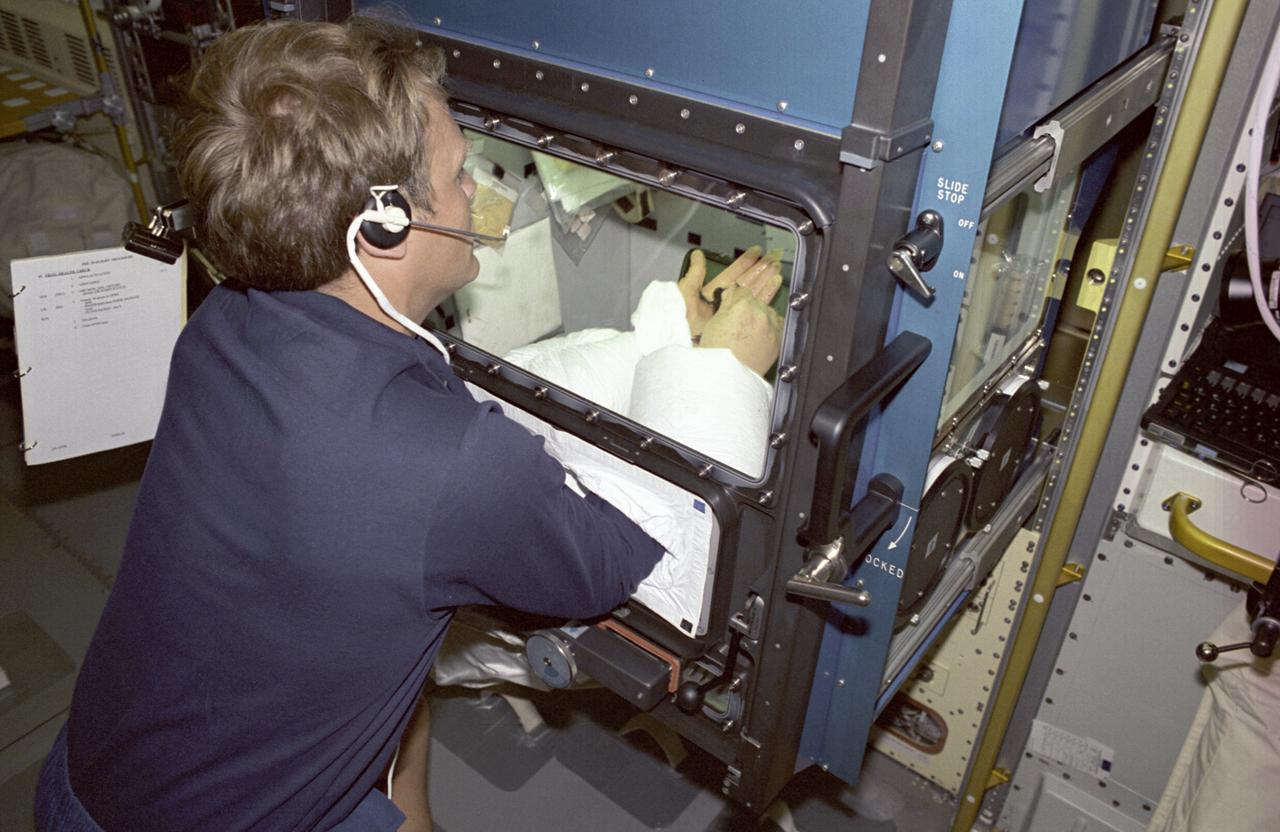

The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows astronaut Mark Lee working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
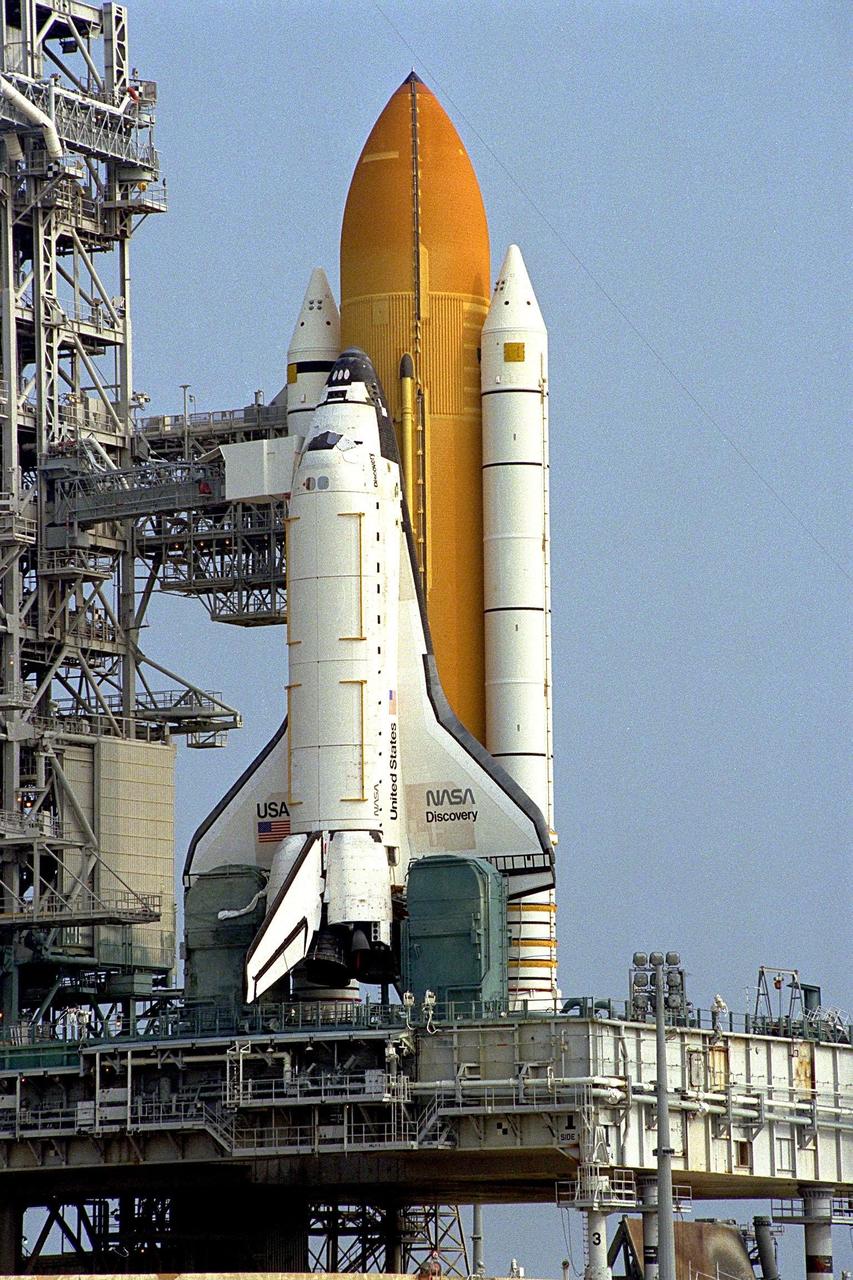

Preliminary reports indicate the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank (SLWT) is in excellent condition following the completion of a tanking test yesterday during a simulated launch countdown at Launch Pad 39A. The pad's Rotating Service Structure will be closed around Discovery later today as preparations for the STS-91 launch on June 2 continue. The primary objectives of the test were to evaluate the strut loads between the tank and the solid rocket boosters and to verify the integrity of the new components of the tank. The SLWT is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability, as well. The STS-91 mission will also feature the ninth Shuttle docking with the Russian Space Station Mir, the first Mir docking for Discovery, and the conclusion of Phase I of the joint U.S.-Russian International Space Station Program

Japanese astronaut, Mamoru Mohri, talks to Japanese students from the aft flight deck of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour during the Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission. The SL-J mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.

STS052-S-001 (July 1992) --- The insignia, designed by the STS-52 crew members, features a large gold star to symbolize the crew's mission on the frontiers of space. A gold star is often used to symbolize the frontier period of the American West. The red star in the shape of the Greek letter lambda represents both the laser measurements to be taken from the Laser Geodynamic Satellite (LAGEOS II) and the Lambda Point Experiment, which is part of the United States Microgravity Payload (USMP-1). The LAGEOS II is a joint Italian\United States satellite project intended to further our understanding of global plate tectonics. The USMP-1 is a microgravity facility which has French and United States experiments designed to test the theory of cooperative phase transitions and to study the solid\liquid interface of a metallic alloy in the low gravity environment. The Remote Manipulator System (RMS) and maple leaf are emblematic of the Canadian payload specialist who will conduct a series of Canadian flight experiments (CANEX-2), including the Space Vision System test. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

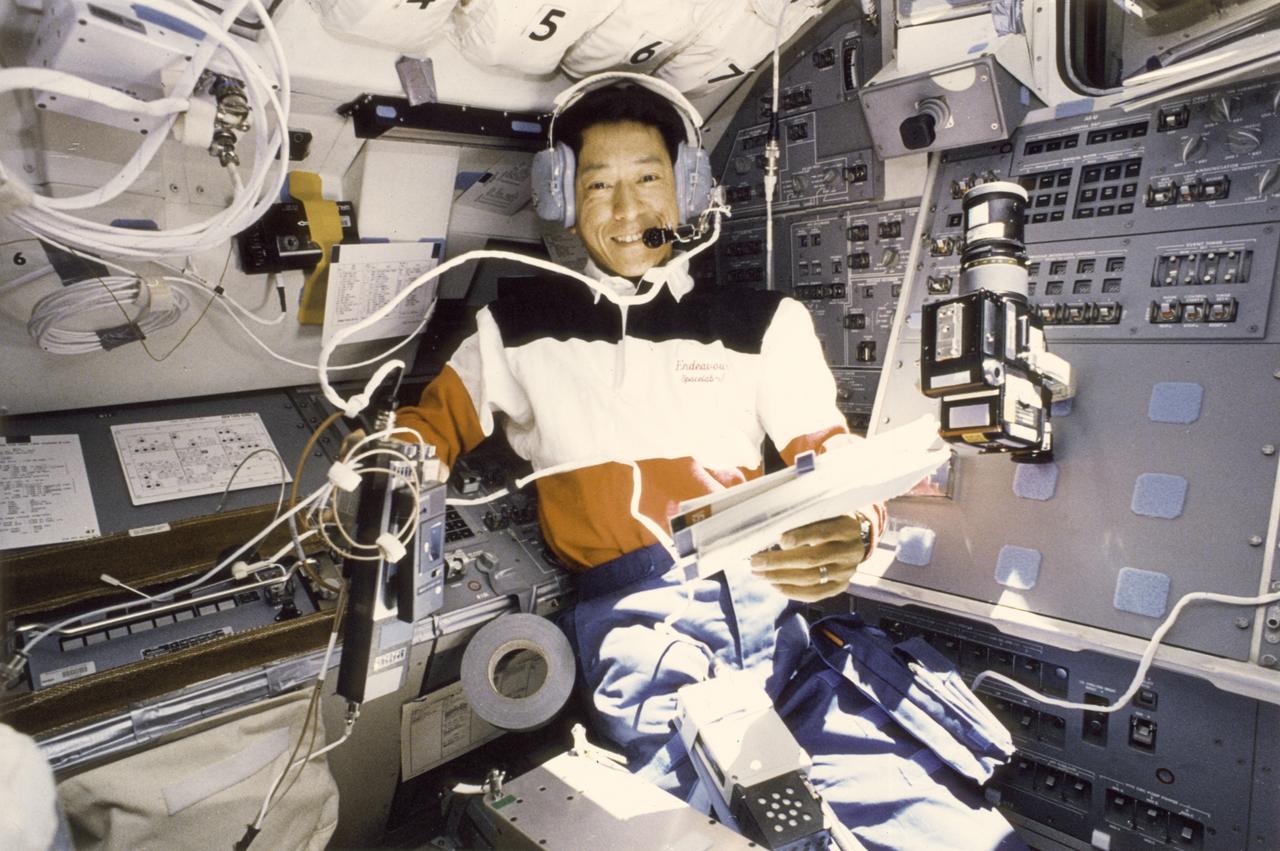
The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. From the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC), NASDA President, Mr. Yamano, speaks to Payload Specialist Mamoru Mohri, a Japanese crew member aboard the STS-47 Spacelab J mission.
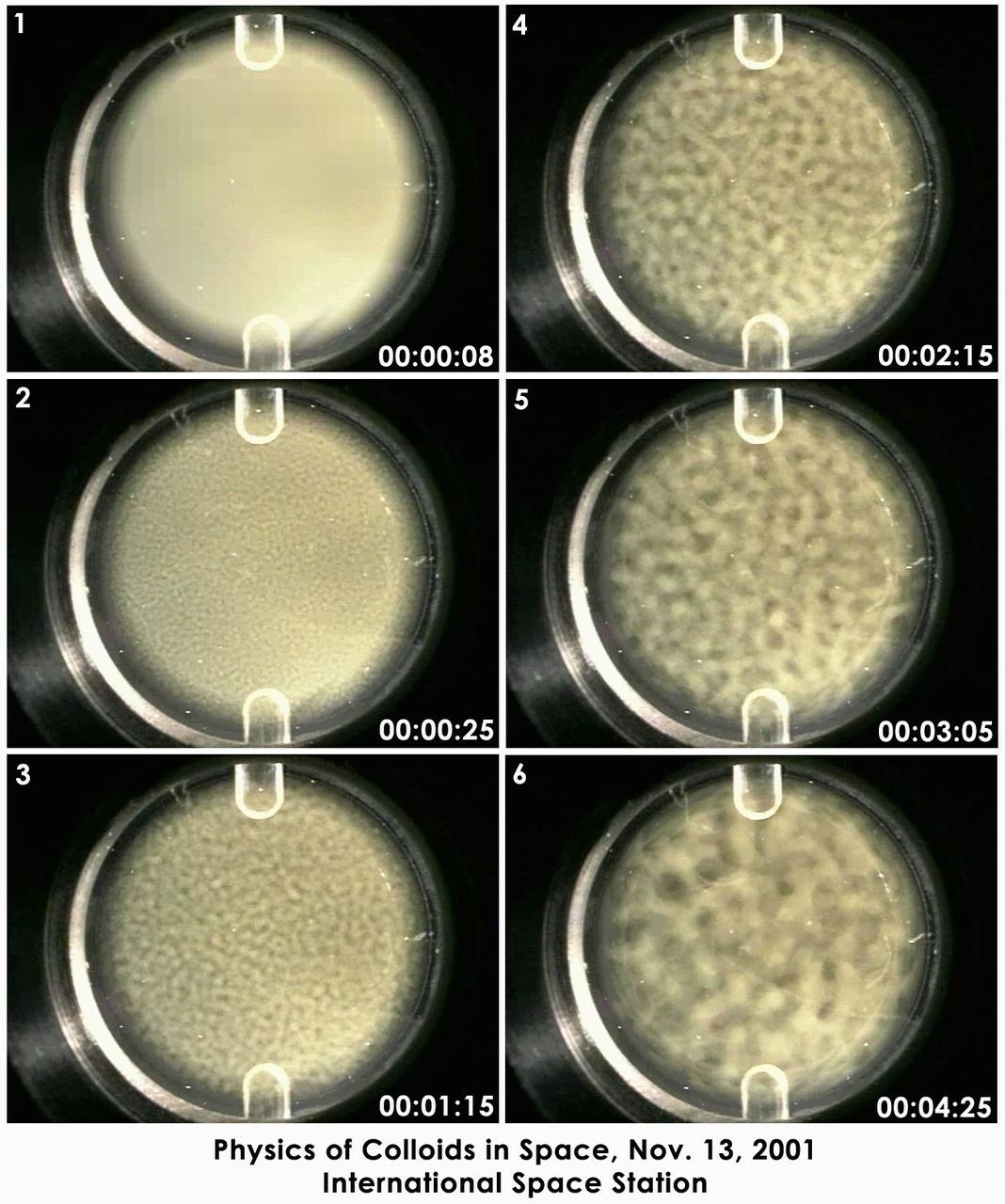
Still photographs taken over 16 hours on Nov. 13, 2001, on the International Space Station have been condensed into a few seconds to show the de-mixing -- or phase separation -- process studied by the Experiment on Physics of Colloids in Space. Commanded from the ground, dozens of similar tests have been conducted since the experiment arrived on ISS in 2000. The sample is a mix of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA or acrylic) colloids, polystyrene polymers and solvents. The circular area is 2 cm (0.8 in.) in diameter. The phase separation process occurs spontaneously after the sample is mechanically mixed. The evolving lighter regions are rich in colloid and have the structure of a liquid. The dark regions are poor in colloids and have the structure of a gas. This behavior carnot be observed on Earth because gravity causes the particles to fall out of solution faster than the phase separation can occur. While similar to a gas-liquid phase transition, the growth rate observed in this test is different from any atomic gas-liquid or liquid-liquid phase transition ever measured experimentally. Ultimately, the sample separates into colloid-poor and colloid-rich areas, just as oil and vinegar separate. The fundamental science of de-mixing in this colloid-polymer sample is the same found in the annealing of metal alloys and plastic polymer blends. Improving the understanding of this process may lead to improving processing of these materials on Earth.

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Featured together in joint ground activities during the SL-J mission are NASA/NASDA personnel at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
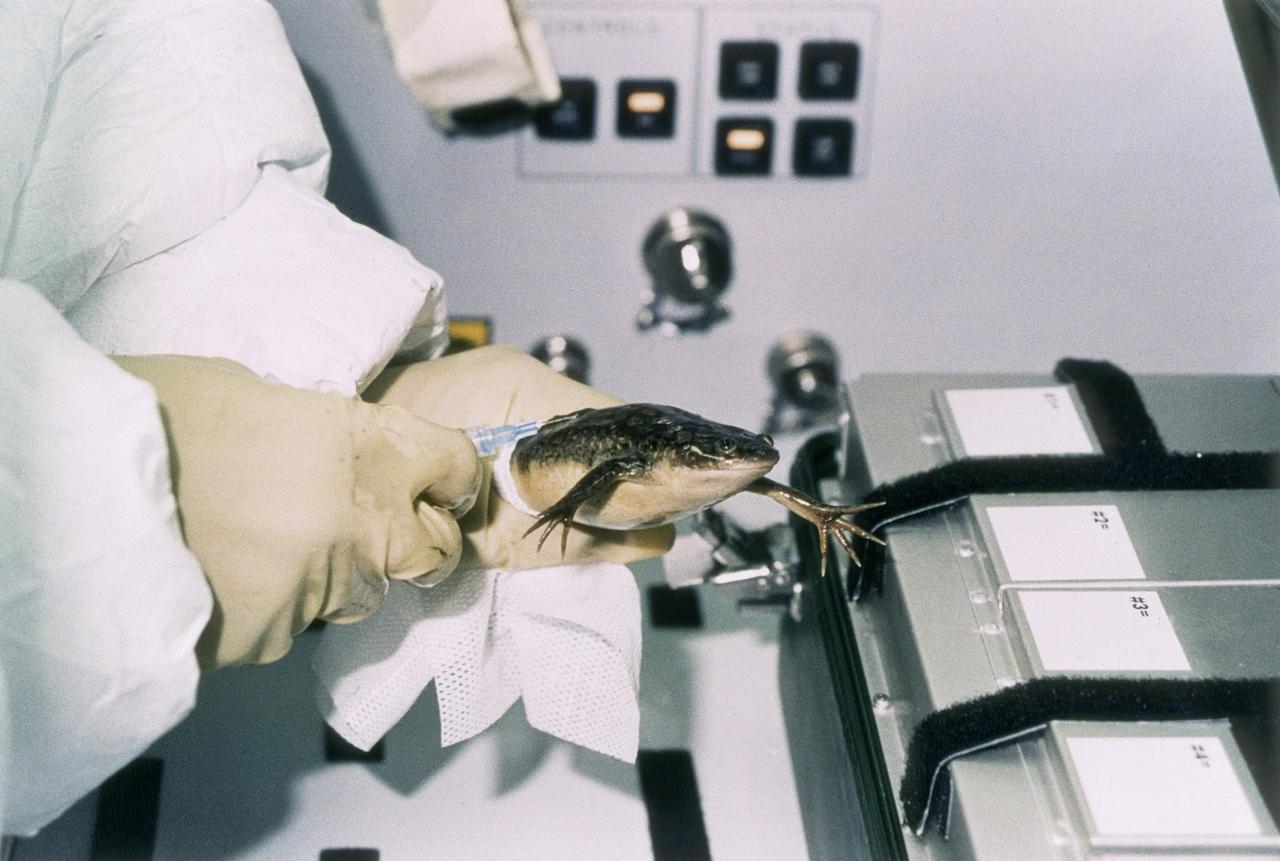
The Spacelab-J (SL-J) mission was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Before long-term space ventures are attempted, numerous questions must be answered: how will gravity play in the early development of an organism, and how will new generations of a species be conceived and develop normally in microgravity. The Effects of Weightlessness on the Development of Amphibian Eggs Fertilized in Space experiment aboard SL-J examined aspects of these questions. To investigate the effect of microgravity on amphibian development, female frogs carried aboard SL-J were induced to ovulate and shed eggs. These eggs were then fertilized in the microgravity environment. Half were incubated in microgravity, while the other half were incubated in a centrifuge that spins to simulate normal gravity. This photograph shows an astronaut working with one of the adult female frogs inside the incubator. The mission also examined the swimming behavior of tadpoles grown in the absence of gravity. The Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Pictured in the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) of Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are NASDA alternate payload specialists Dr. Doi and Dr. Mukai.
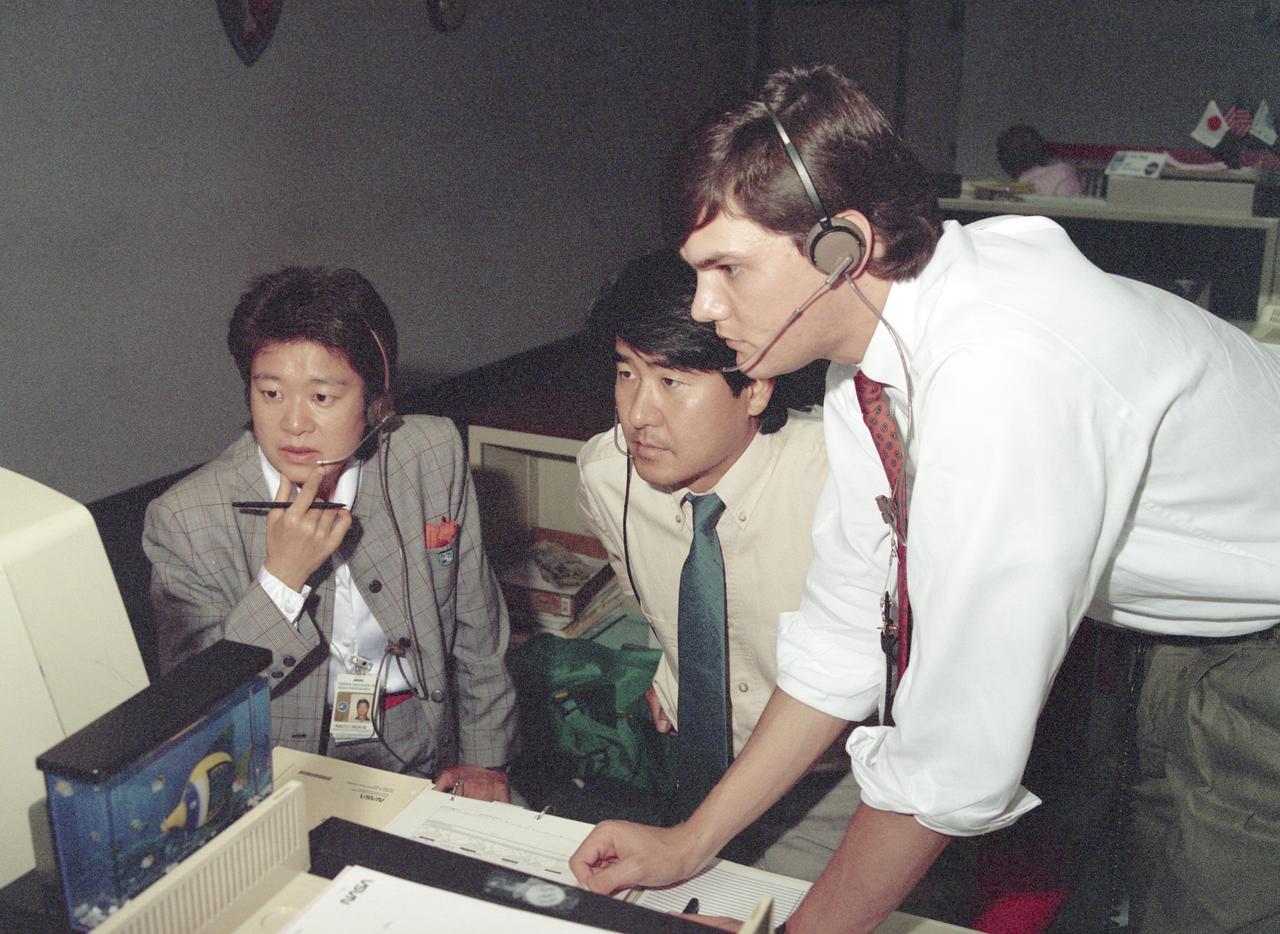

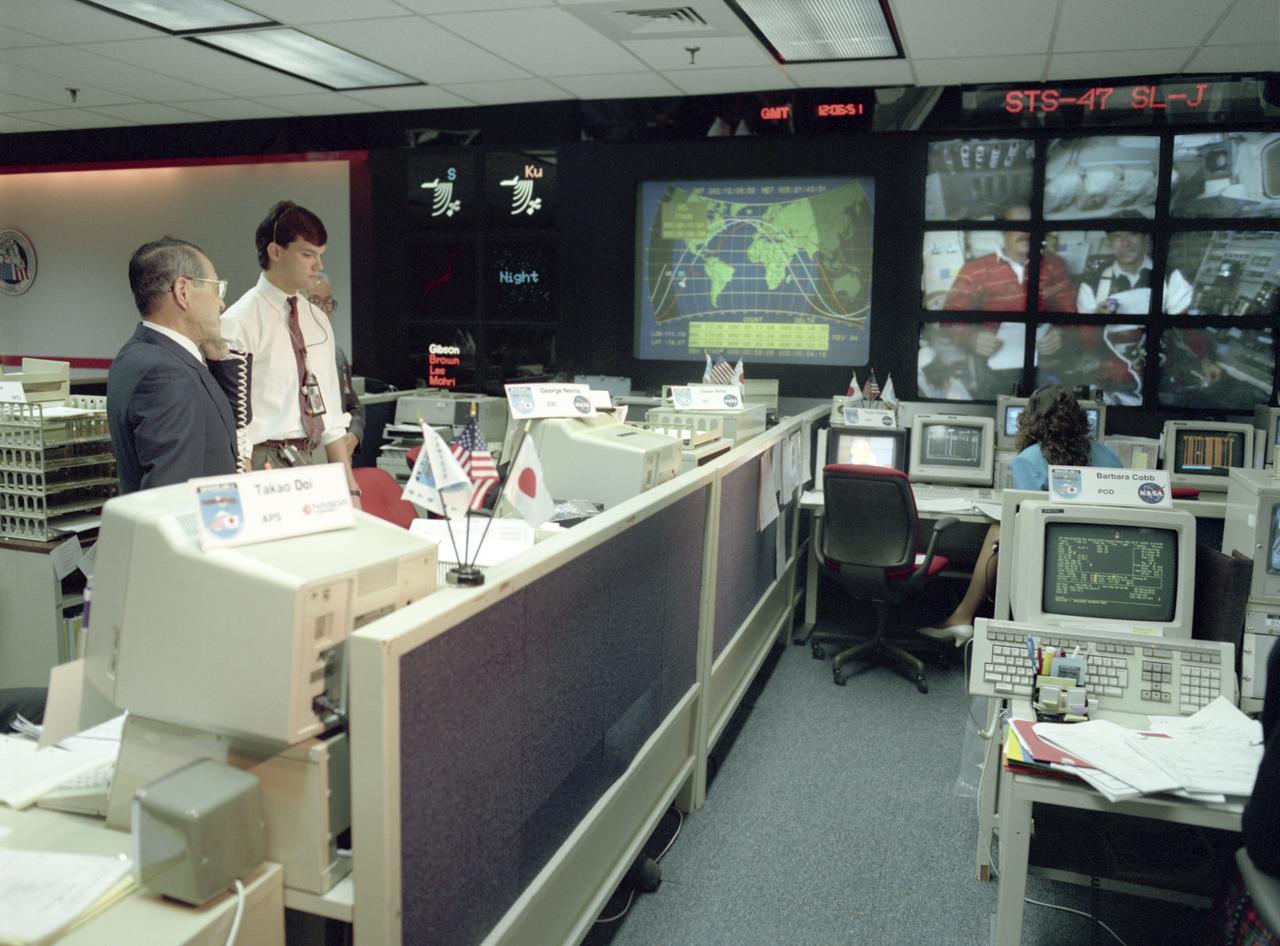
The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Pictured along with George Norris in the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) are NASDA alternate payload specialists Dr. Doi and Dr. Mukai.
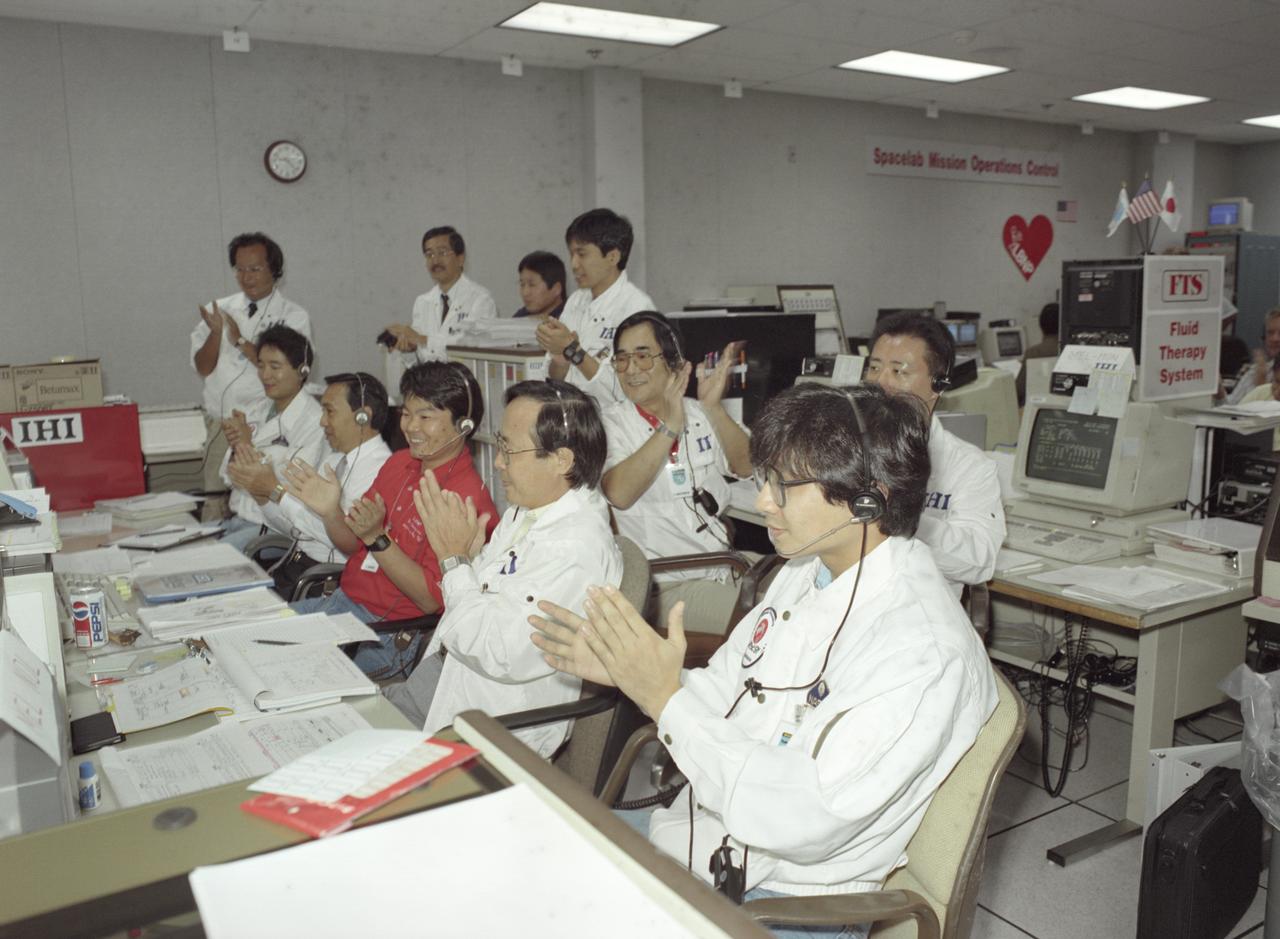

The science laboratory, Spacelab-J (SL-J), flown aboard the STS-47 flight was a joint venture between NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a manned Spacelab module. The mission conducted 24 materials science and 20 life science experiments, of which 35 were sponsored by NASDA, 7 by NASA, and two collaborative efforts. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, and frogs and frog eggs. Featured together in the Science Operation Area (SOA) are payload specialists’ first Materials Processing Test during NASA/NASDA joint ground activities at the Huntsville Operations Support Center (HOSC) Spacelab Payload Operations Control Center (SL POCC) at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC).
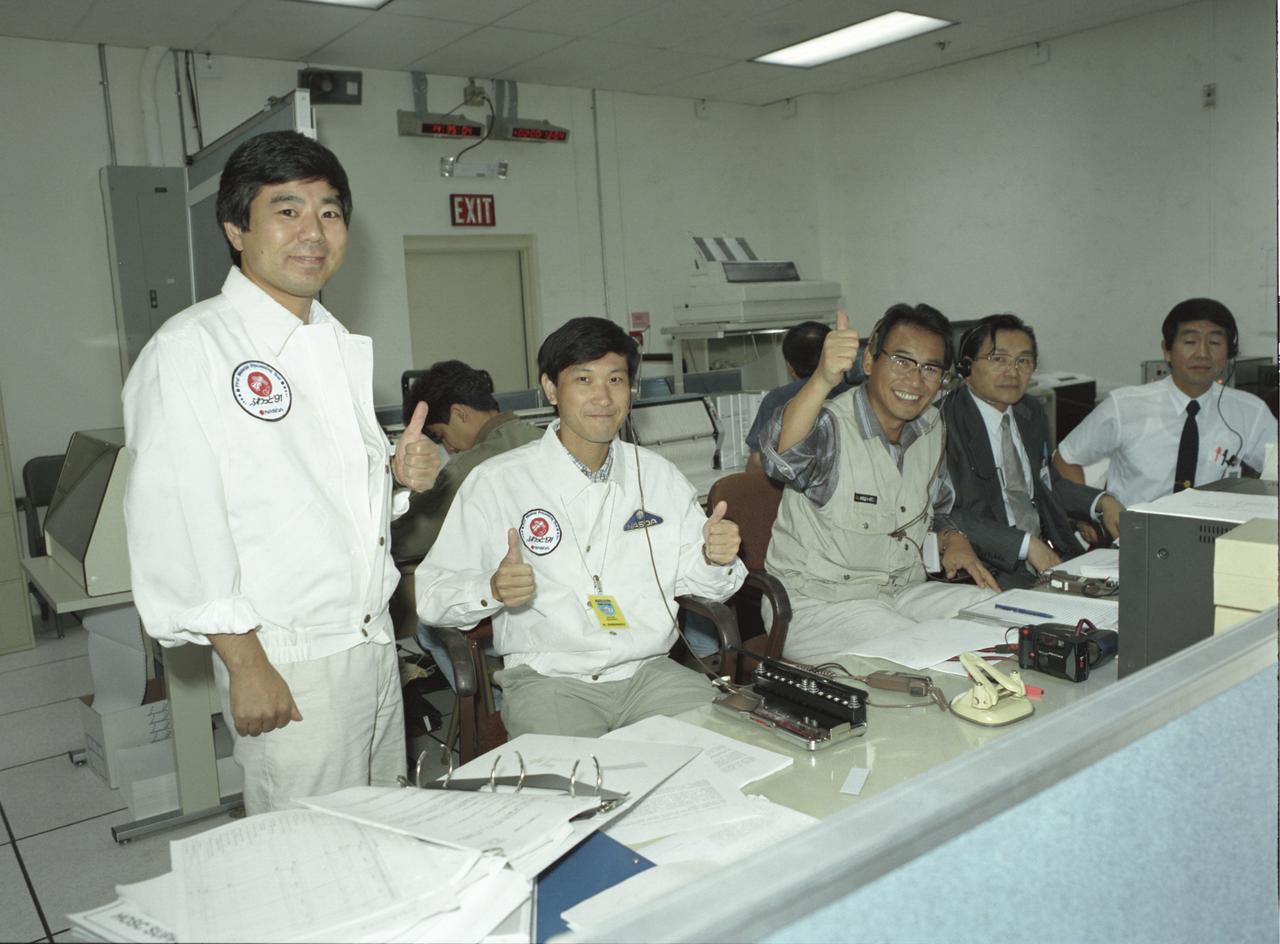

The group of Japanese researchers of the Spacelab-J (SL-J) were thumbs-up in the Payload Operations Control Center (POCC) at the Marshall Space Flight Center after the successful launch of Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour that carried their experiments. The SL-J was a joint mission of NASA and the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA) utilizing a marned Spacelab module. The mission conducted microgravity investigations in materials and life sciences. Materials science investigations covered such fields as biotechnology, electronic materials, fluid dynamics and transport phenomena, glasses and ceramics, metals and alloys, and acceleration measurements. Life sciences included experiments on human health, cell separation and biology, developmental biology, animal and human physiology and behavior, space radiation, and biological rhythms. Test subjects included the crew, Japanese koi fish (carp), cultured animal and plant cells, chicken embryos, fruit flies, fungi and plant seeds, frogs, and frog eggs. The POCC was the air/ground communications channel between the astronauts and ground control teams during the Spacelab missions. The Spacelab science operations were a cooperative effort between the science astronaut crew in orbit and their colleagues in the POCC. Spacelab-J was launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavour on September 12, 1992.
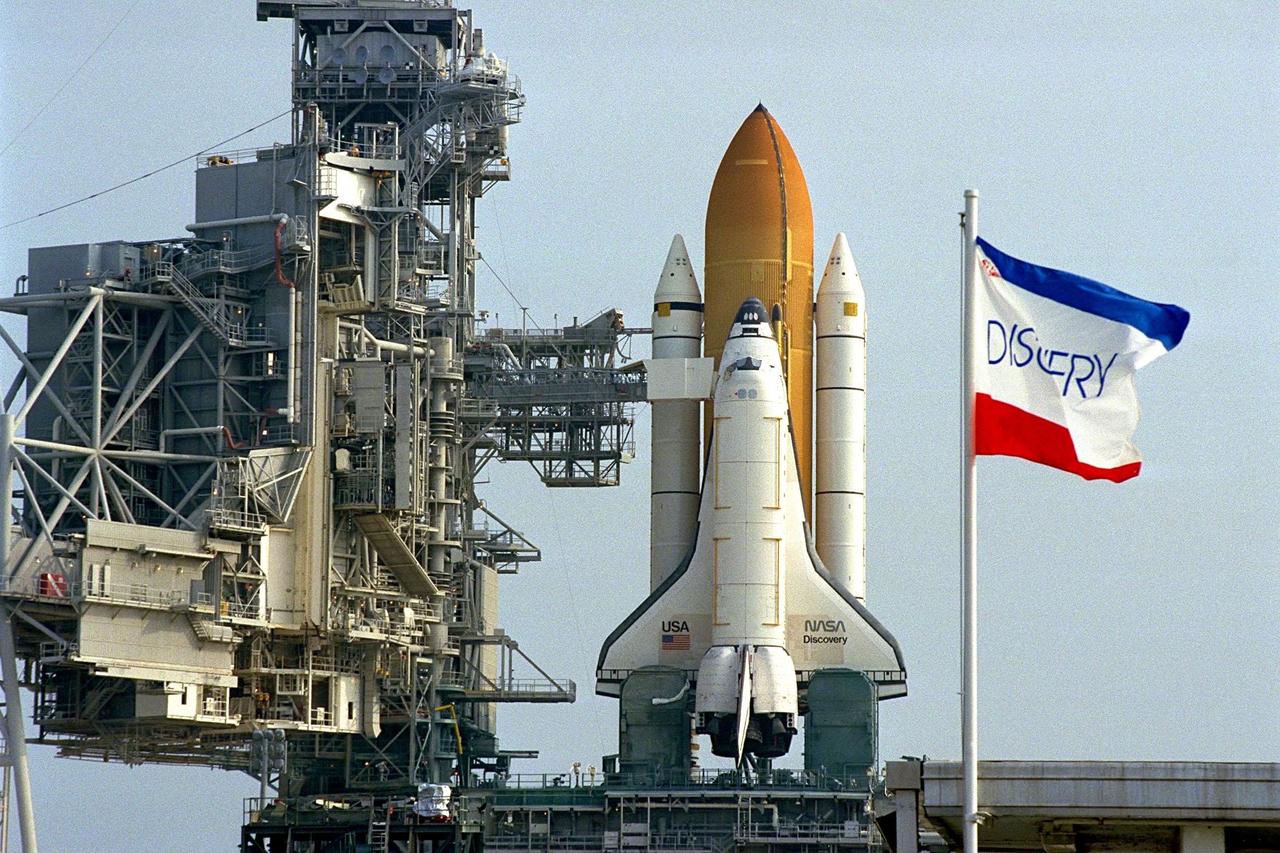
Preliminary reports indicate the Space Shuttle's first super lightweight external tank (SLWT) is in excellent condition following the completion of a tanking test yesterday during a simulated launch countdown at Launch Pad 39A. The pad's Rotating Service Structure will be closed around Discovery later today as preparations for the STS-91 launch on June 2 continue. The primary objectives of the test were to evaluate the strut loads between the tank and the solid rocket boosters and to verify the integrity of the new components of the tank. The SLWT is 7,500 pounds lighter than its predecessors and was developed to increase the Shuttle payload capacity on International Space Station assembly flights. Major changes to the lighter tank include the use of new materials and a revised internal design. The new liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen tanks are constructed of aluminum lithium a lighter, stronger material than the metal alloy currently used. The redesigned walls of the liquid hydrogen tank were machined to provide additional strength and stability, as well. The STS-91 mission will also feature the ninth Shuttle docking with the Russian Space Station Mir, the first Mir docking for Discovery, and the conclusion of Phase I of the joint U.S.-Russian International Space Station Program

In early 2022, the Cold Operable Lunar Deployable Arm (COLDArm) project – led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California – successfully integrated special gears into pieces of a robotic arm that is planned to perform a robot-controlled lunar surface experiment with imagery in the coming years. These bulk metallic glass (BMG) gears, integrated into COLDArm's joints and actuators, were developed through the Game Changing Development bulk metallic glass gears project to operate at extreme temperatures below minus 280 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius). The gear alloys have a disordered atomic-scale structure, making them both strong and elastic enough to withstand these exceptionally low temperatures. Typical gearboxes require heating to operate at such cryogenic temperatures. The BMG gear motors have been tested and successfully operated at roughly minus 279 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 173 degrees Celsius) without heating assistance. This gear motor is one of the key technologies to enable the robotic arm to operate in extremely cold environments, such as during lunar night. Each of the four joints containing BMG gears will be tested once the arm is fully assembled, which is scheduled for spring of 2022. Robotic joint testing will include dynamometer testing to measure torque/rotational speed, as well as cryogenic thermal vacuum testing to understand how the equipment would perform in an environment similar to space. Once proven, the BMG gears and COLDArm capabilities will enable future missions to work in extreme environments on the Moon, Mars, and ocean worlds. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24567