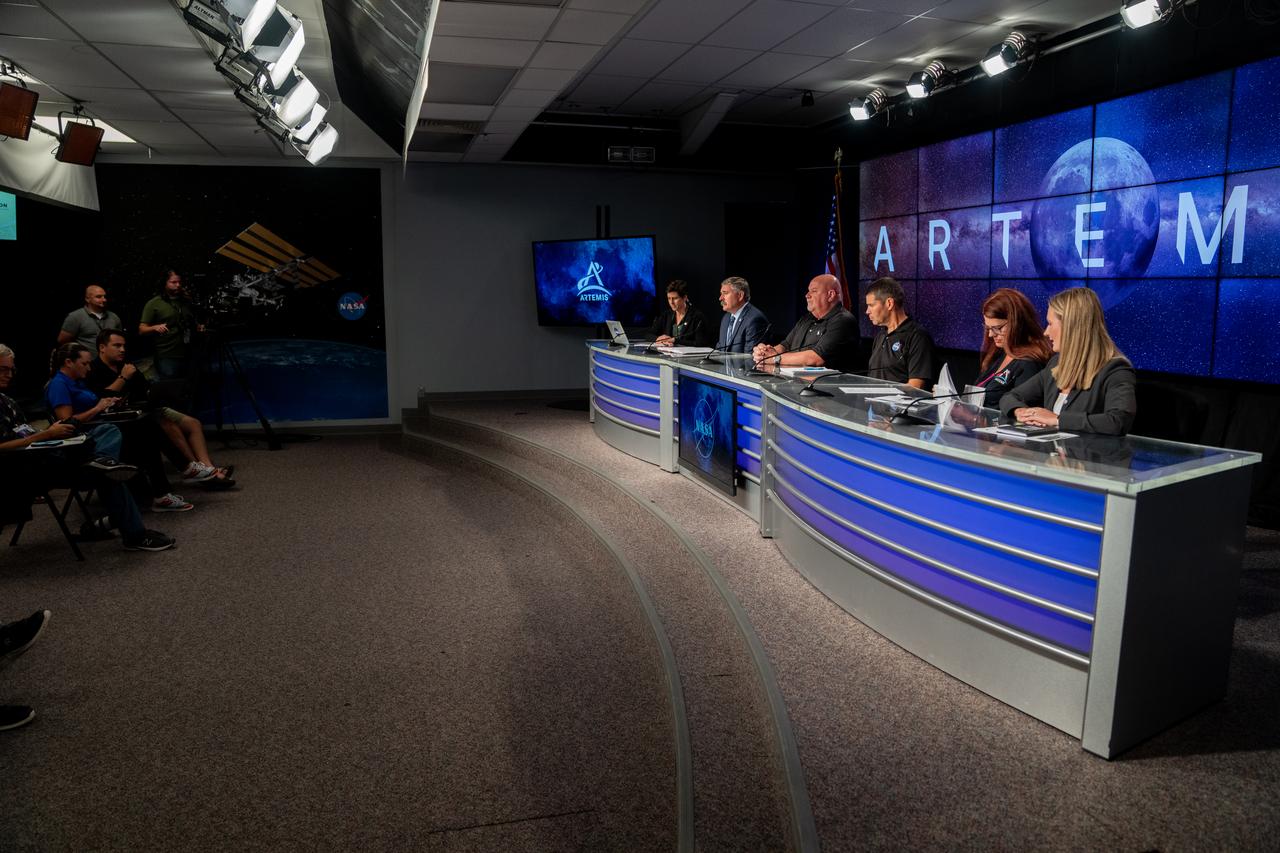

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager; John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

John Honeycutt, Space Launch System program manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters, participates in an Artemis I mission status press briefing at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.

From left, Megan Cruz, NASA Communications; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters; and Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Kennedy Space Center, participate in an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

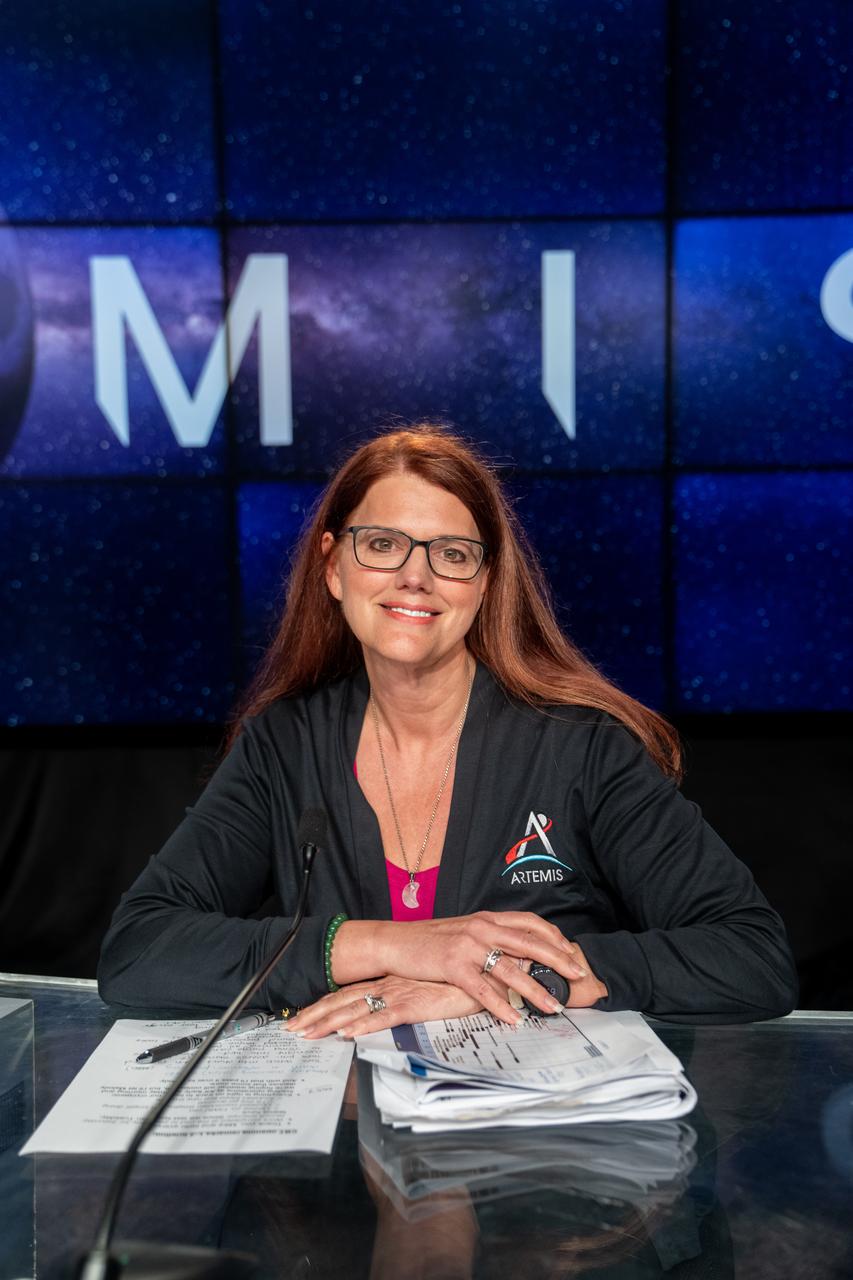
Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

From left, Megan Cruz, NASA Communications; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, NASA Headquarters; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Kennedy Space Center; Melissa Jones, recovery director, Exploration Ground Systems Program, Kennedy; Jacob Bleacher, chief exploration scientist, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters; and Melody Lovin, weather officer, Space Launch Delta 45, participate in an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
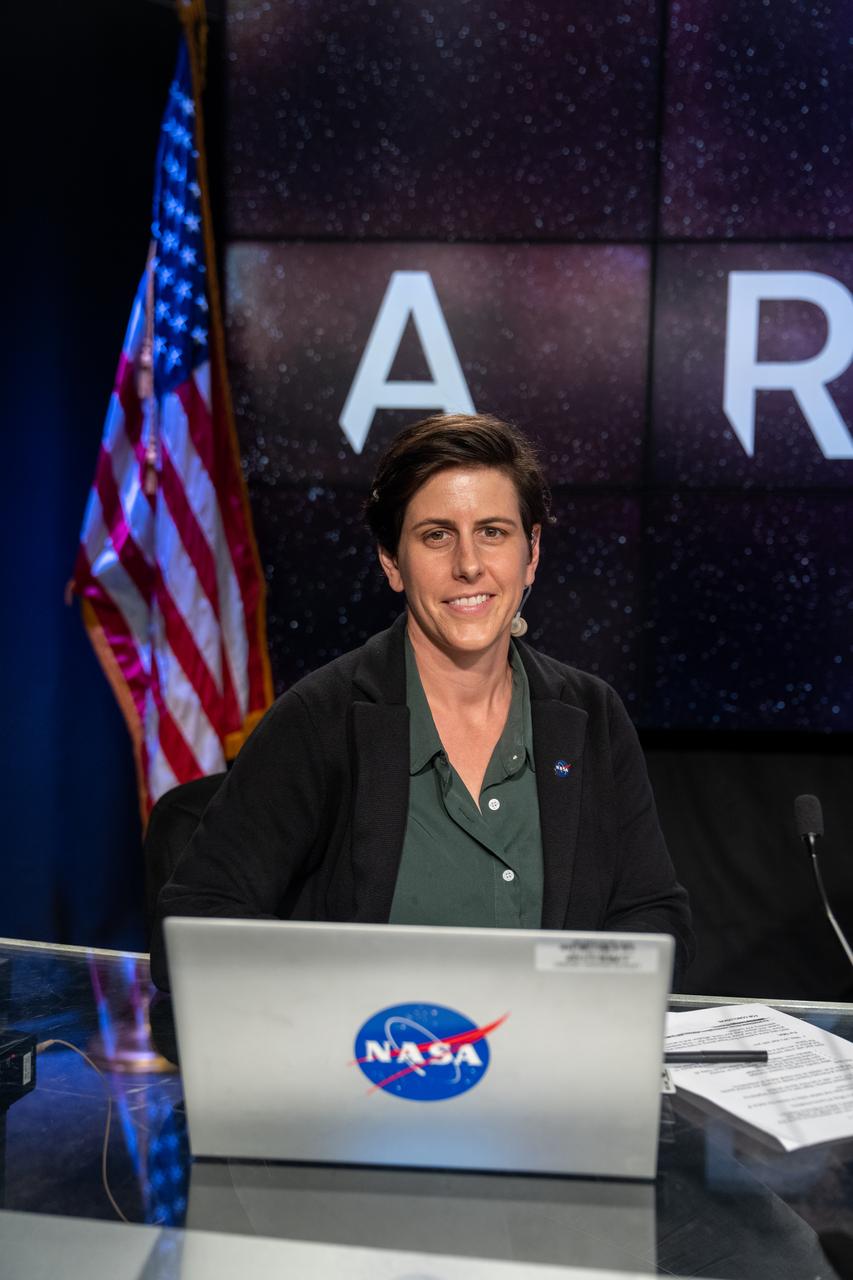

Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis I launch director, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
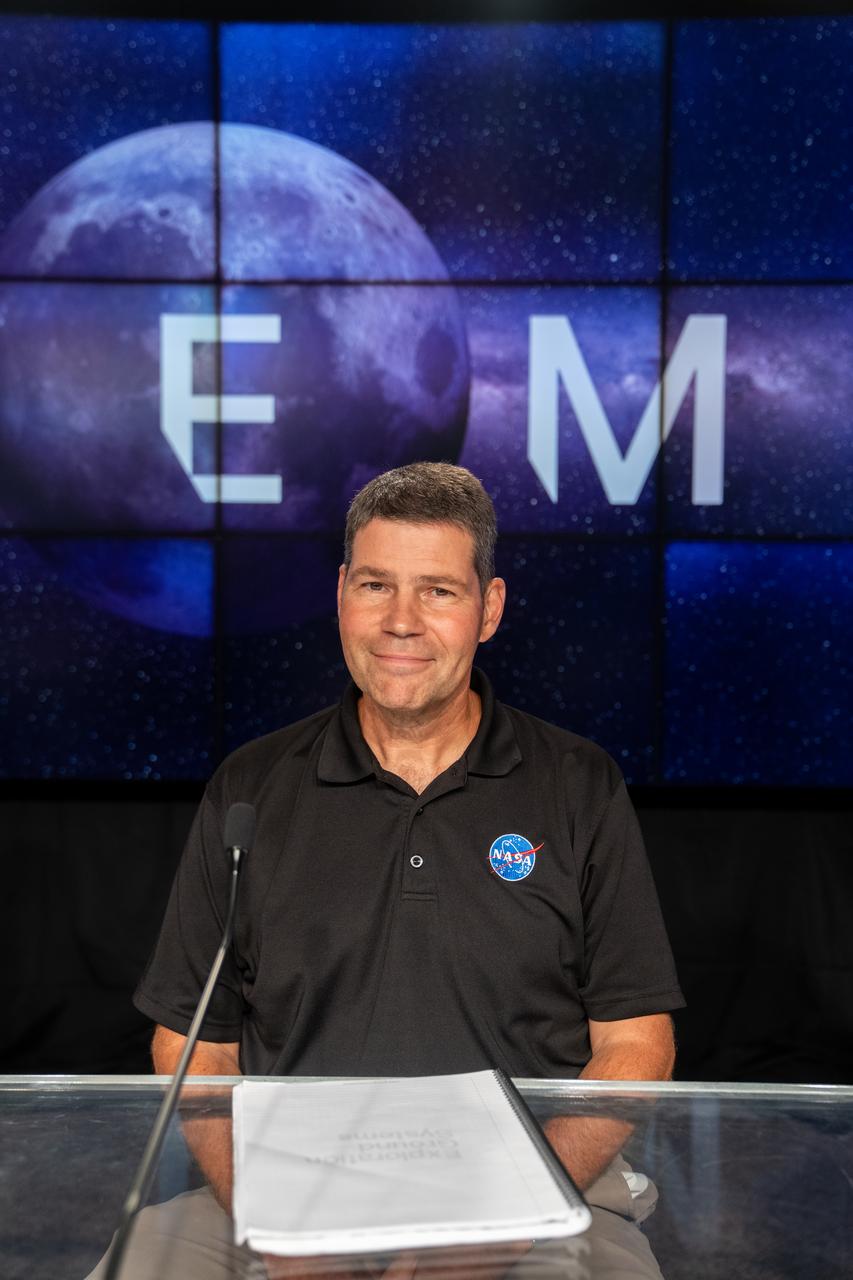

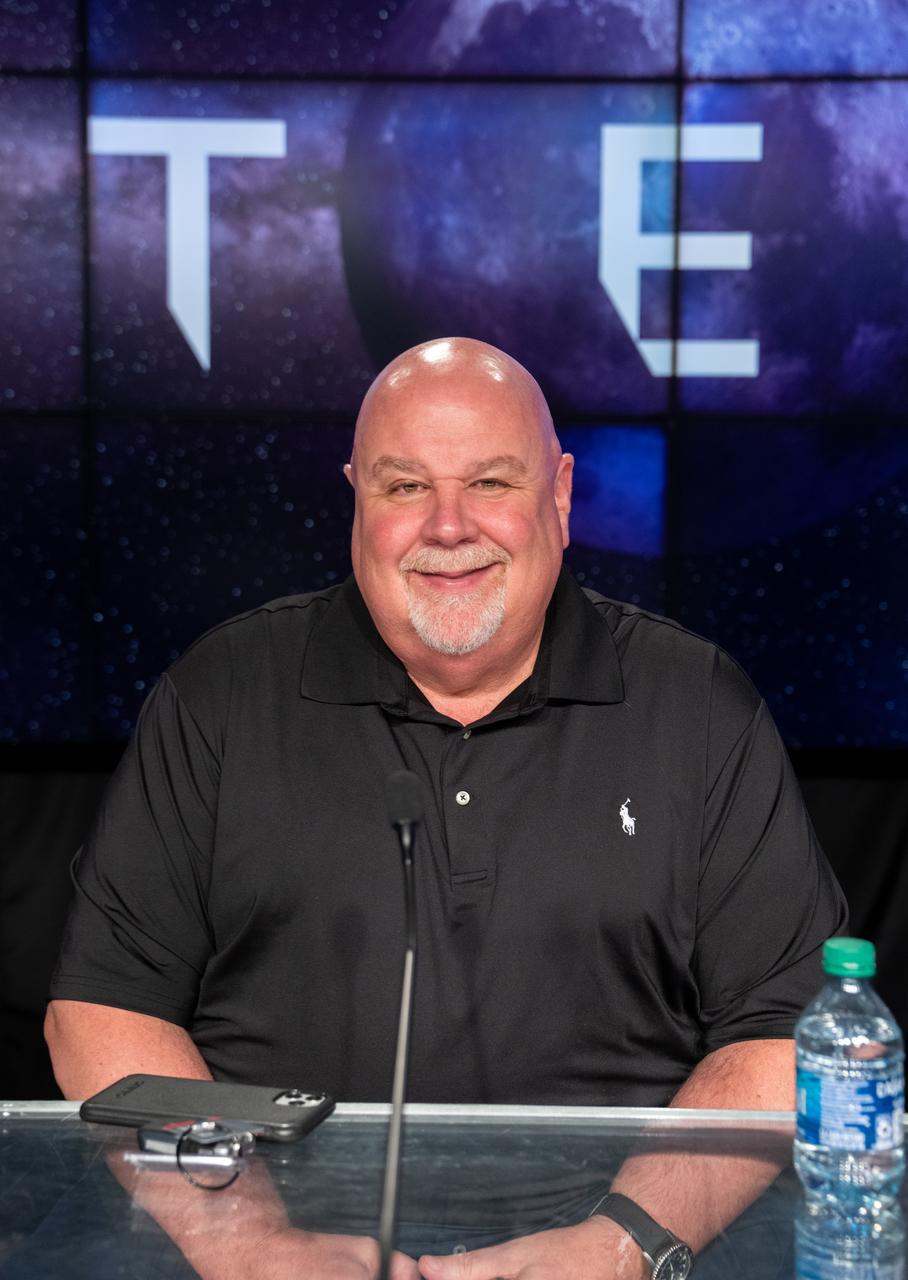
John Blevins, Space Launch System chief engineer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
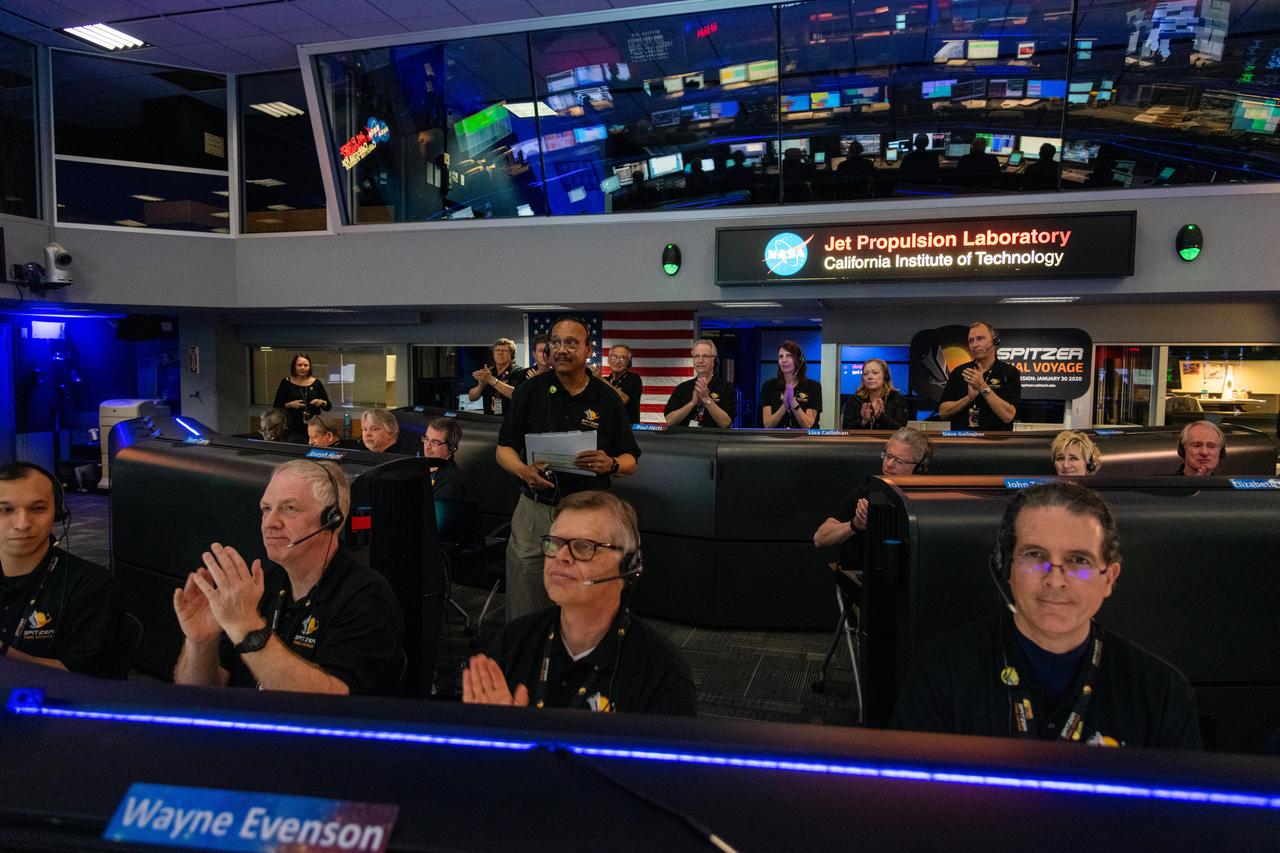

Spitzer Project Manager Joseph Hunt stands in Mission Control at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, on Jan. 30, 2020, declaring the spacecraft decommissioned and the Spitzer mission concluded. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23648
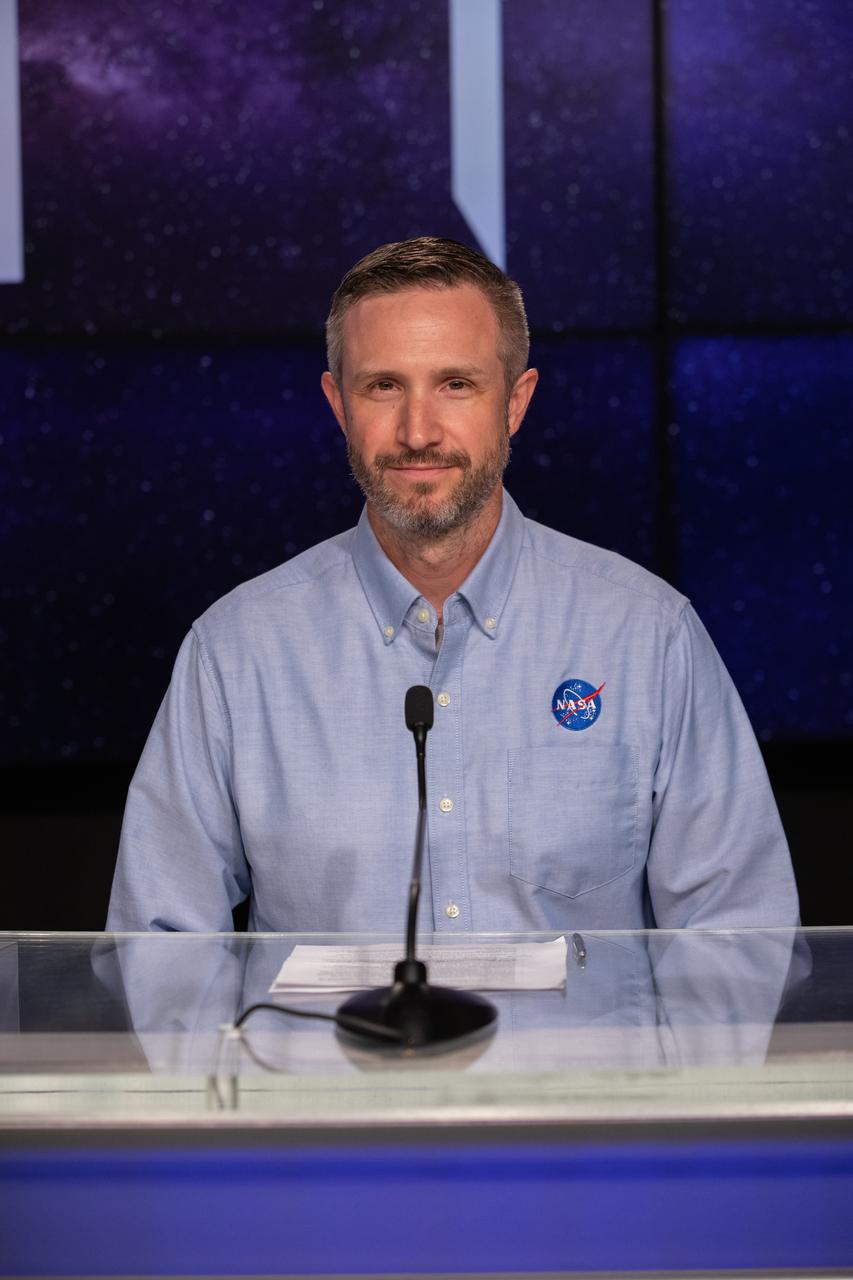

Jacob Bleacher, chief exploration scientist, Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, participates in an Artemis I mission status press briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
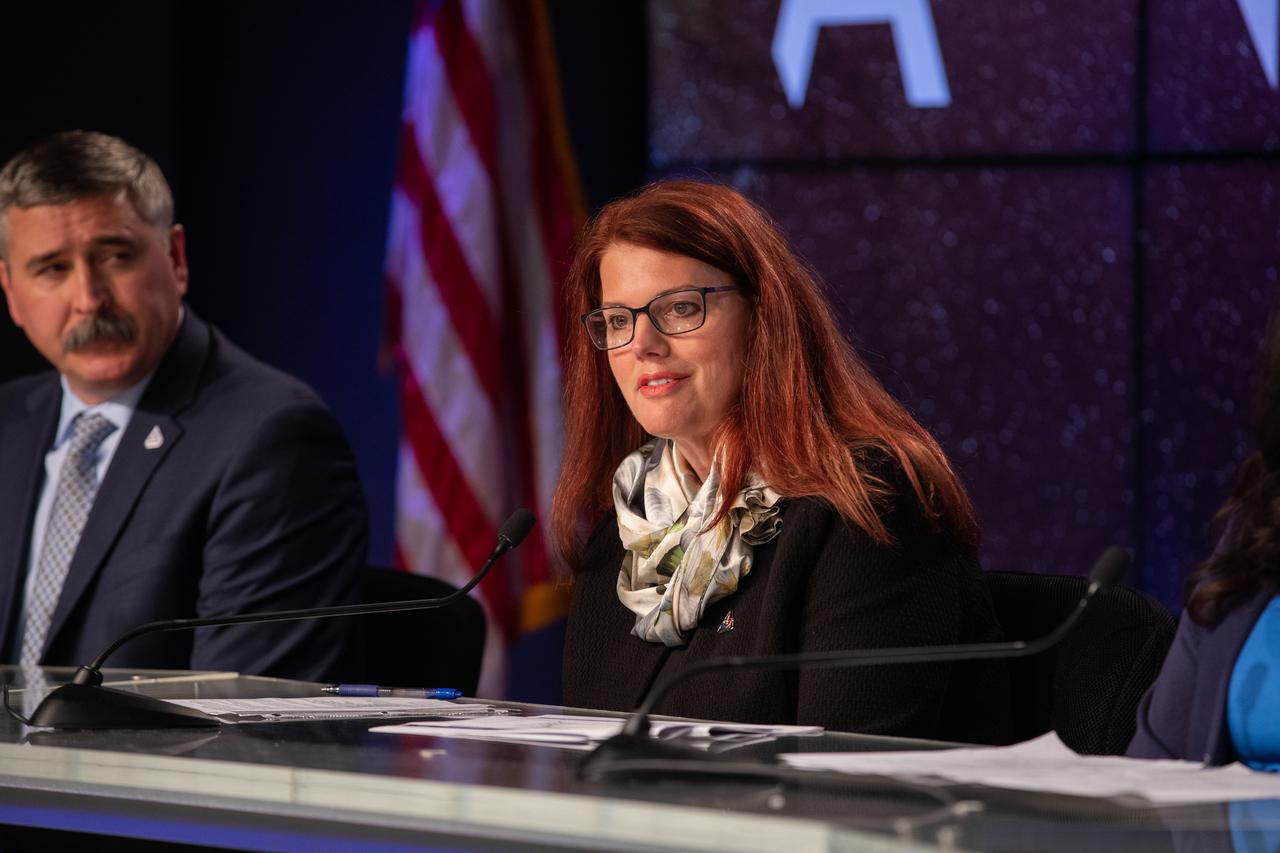

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Kennedy Space Center, listens to a question during an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
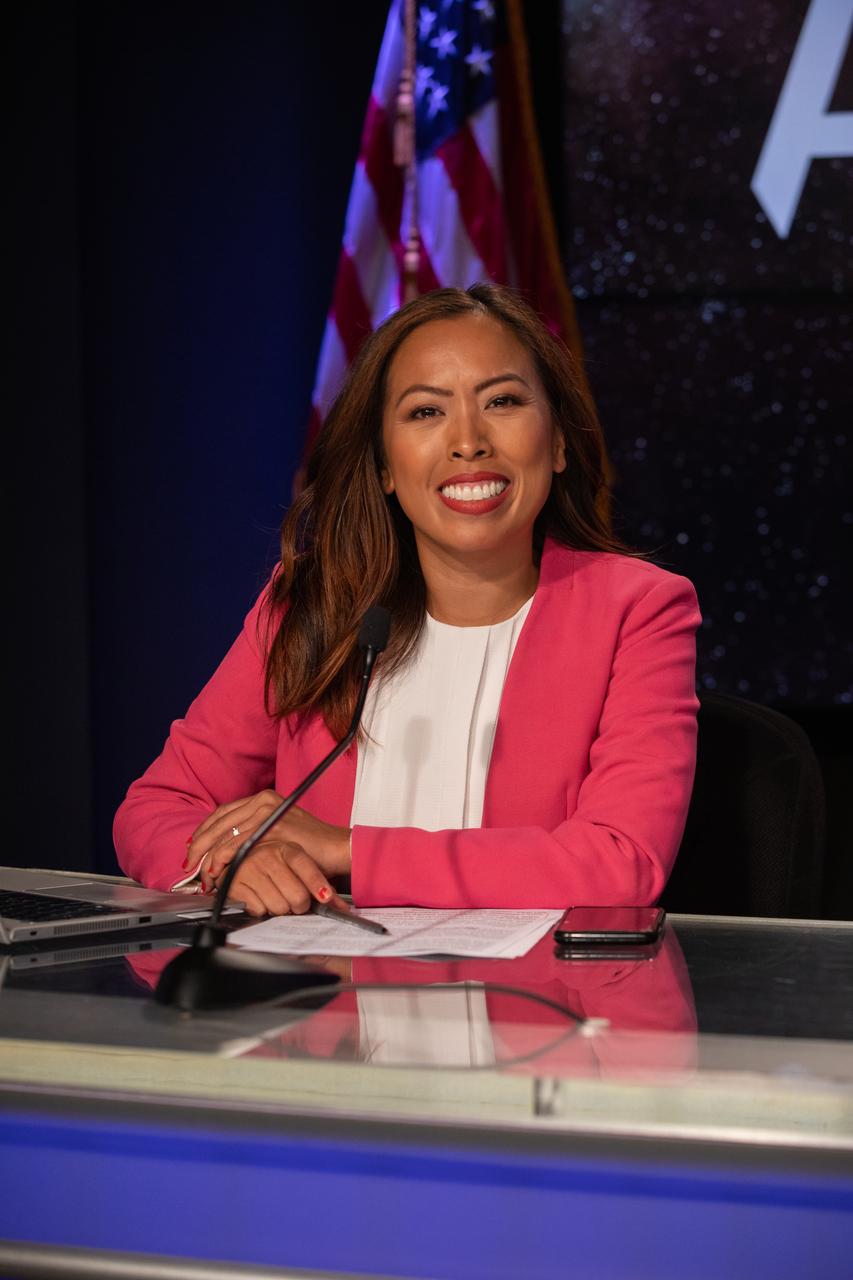

Megan Cruz, NASA Communications, leads an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
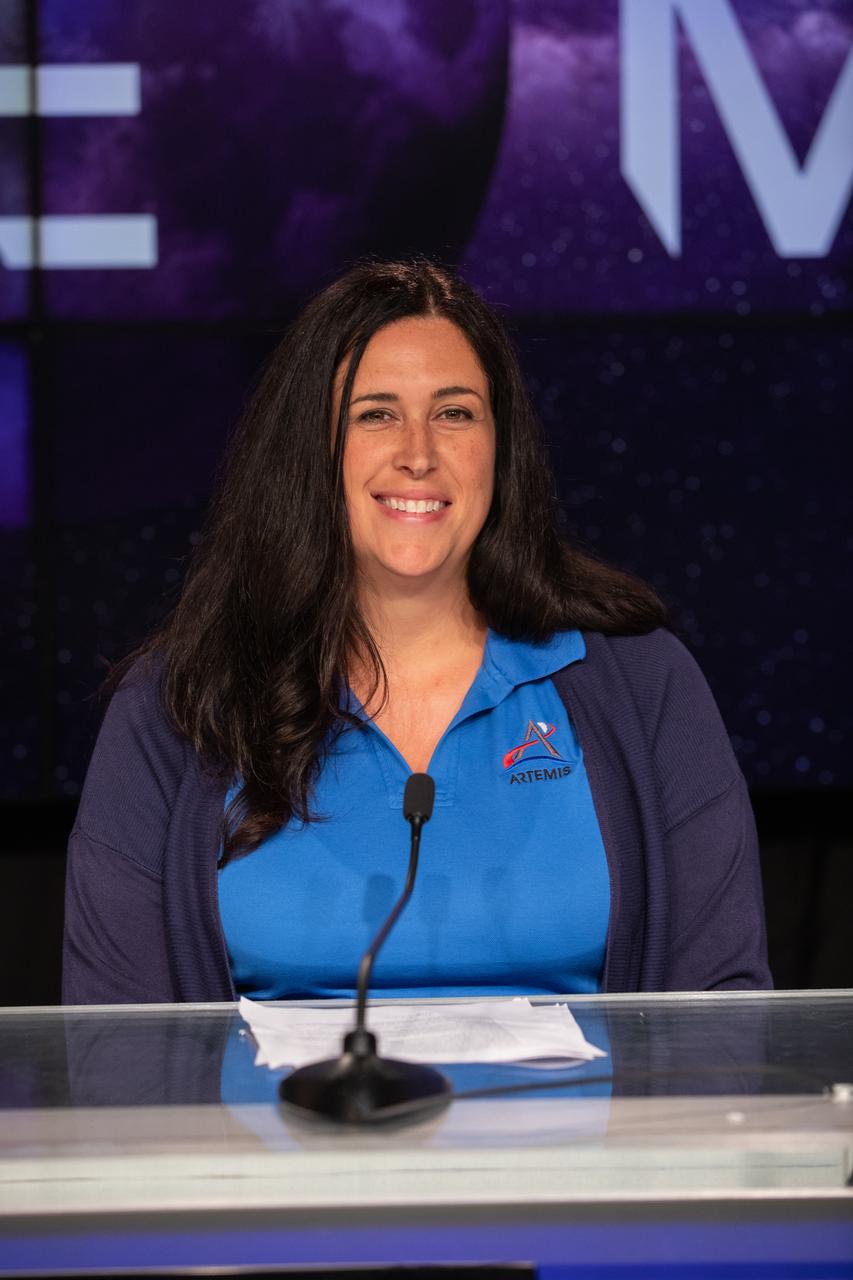

Melissa Jones, recovery director, NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems Program, is introduced during an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
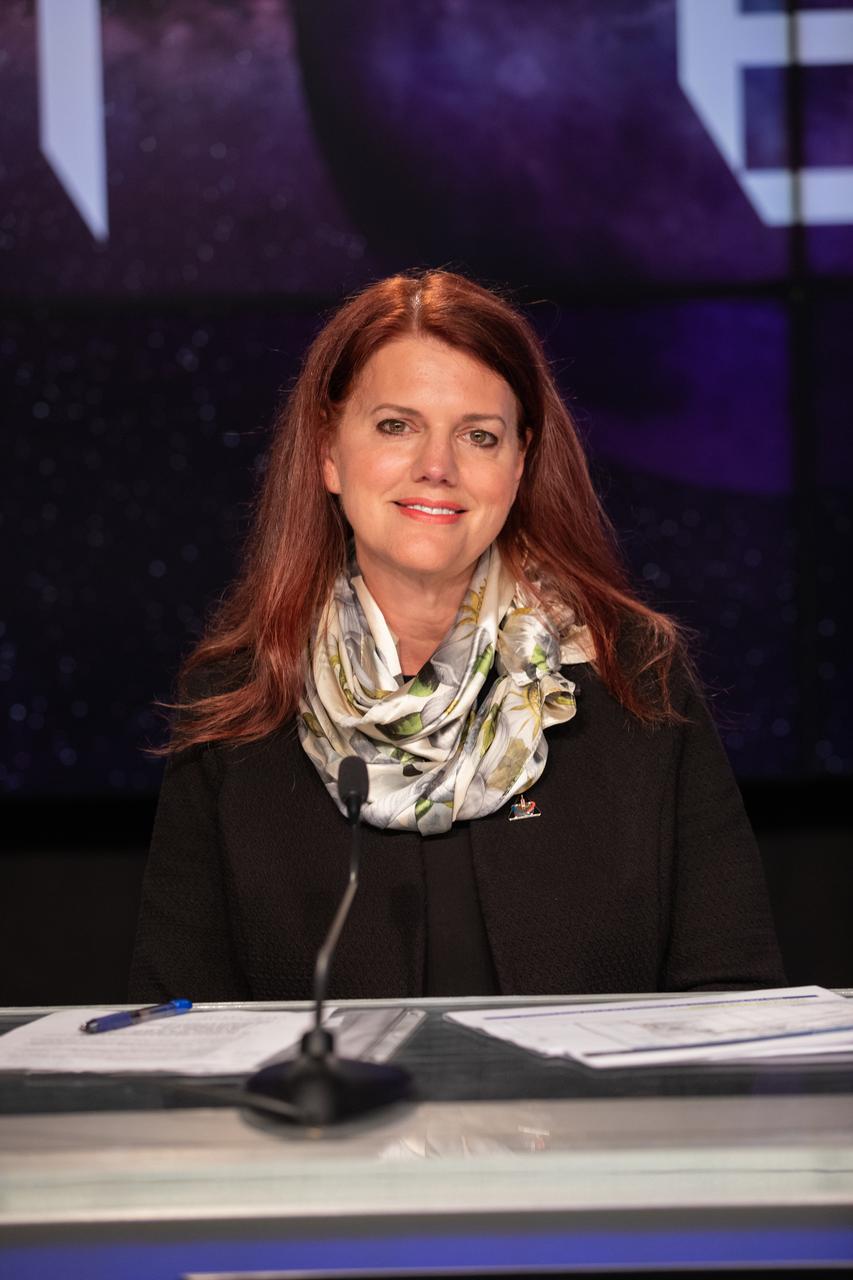

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director, Kennedy Space Center, is introduced during an Artemis I mission status press briefing at Kennedy on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
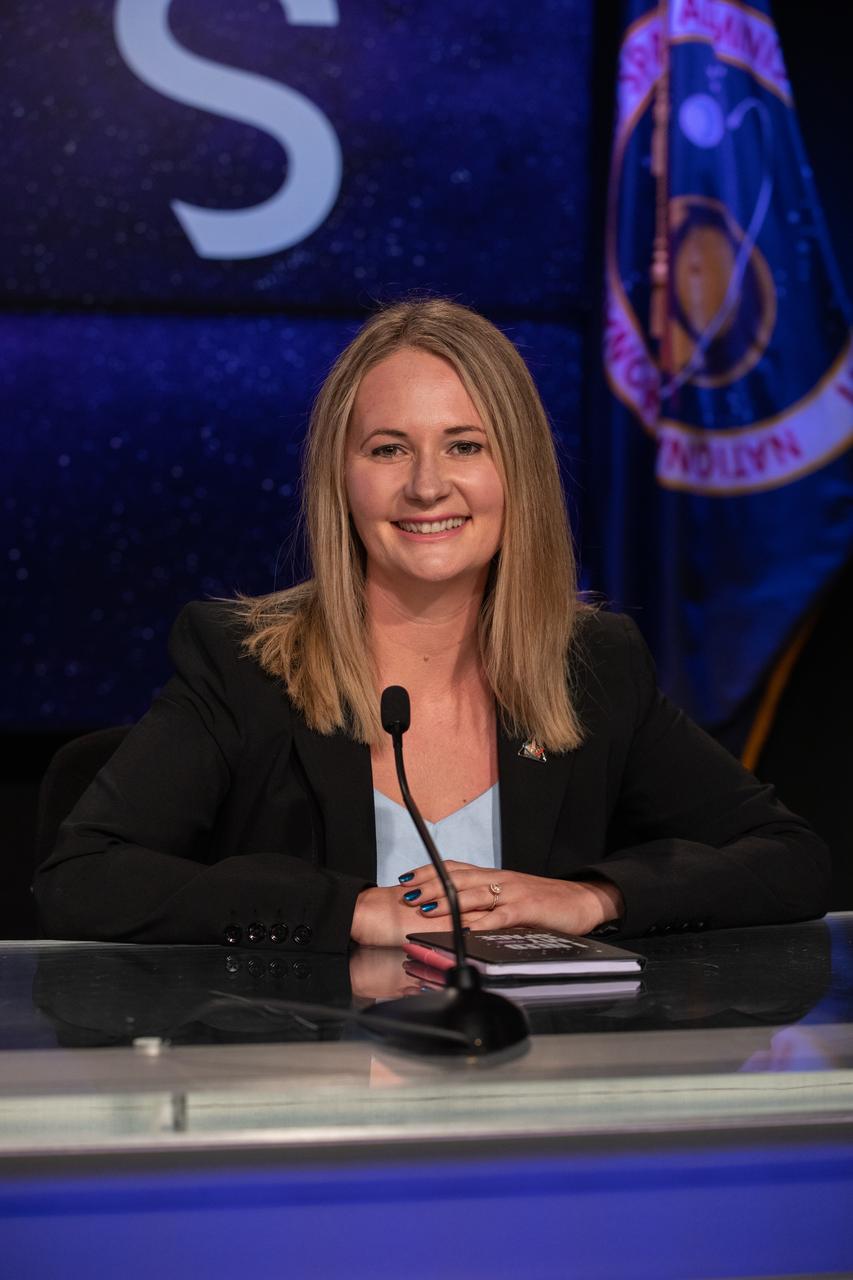

Melody Lovin, weather officer, Space Launch Delta 45, is introduced during an Artemis I mission status press briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.

Members of the media attend an Artemis I mission status press briefing at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 27, 2022. NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft are targeted to lift off from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B no earlier than Aug. 29, 2022, at 8:33 a.m. EDT.
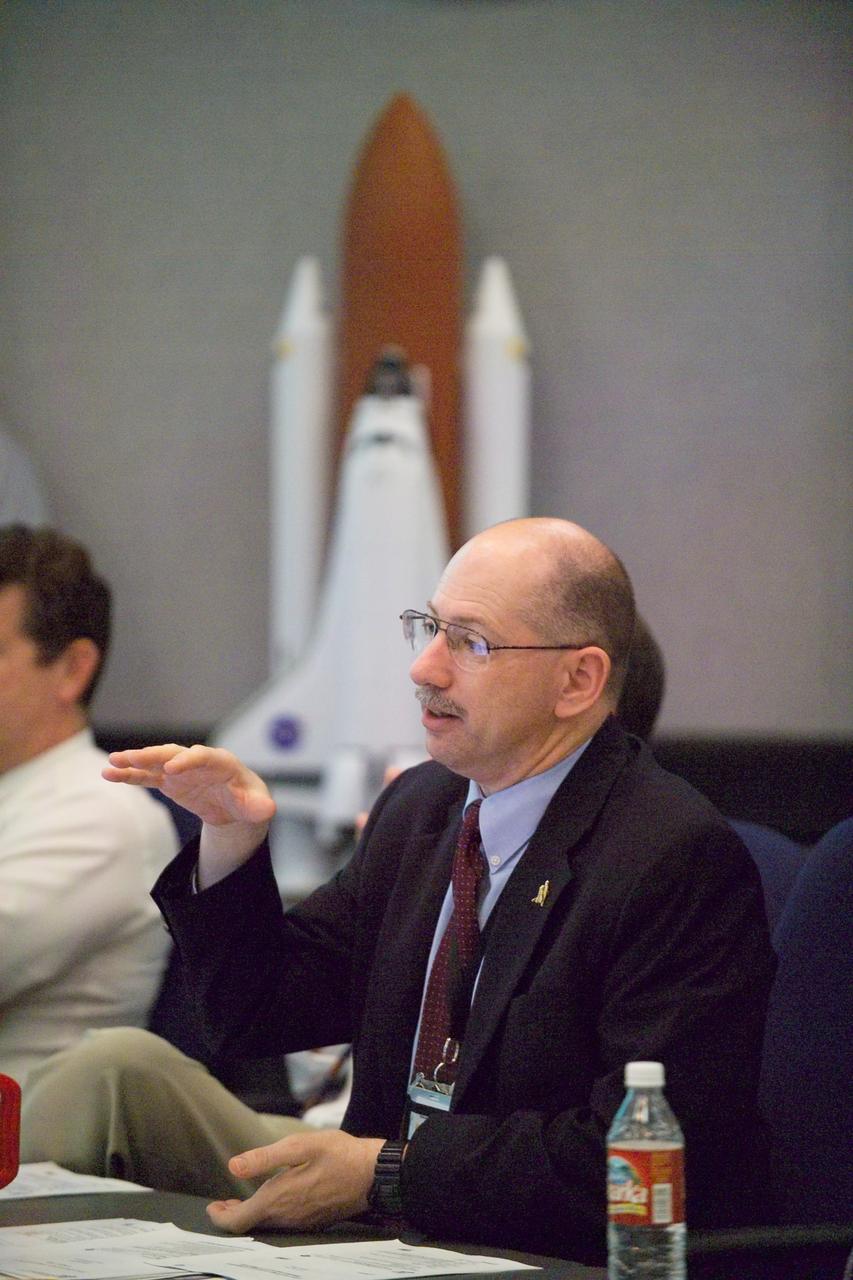

JSC2005-E-32012 (4 August 2005) --- John Muratore, Manager of Space Shuttle Systems Engineering & Integration Office, discusses a key STS-114 issue during the Mission Management Team (MMT) session of the afternoon of August 4. The MMT meets daily in Houston's Mission Control Center.
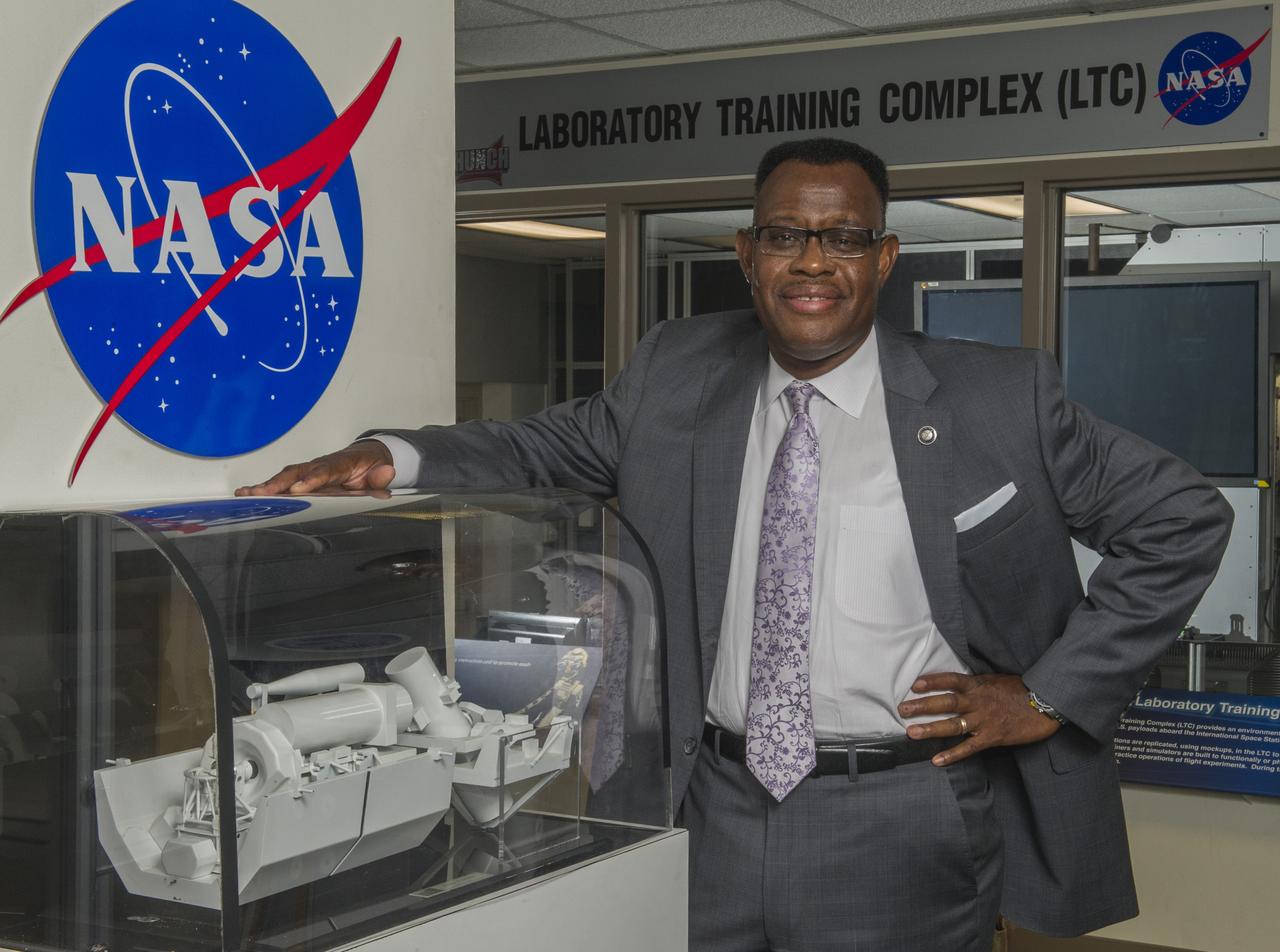

LEWIS WOOTEN MANAGES THE MISSION OPERATIONS LABORATORY. MORE THAN 1600 INVESTIGATIONS AND STUDENT EXPERIMENTS FOR OVER 80 COUNTRIES HAVE BEEN COMPLETED WITH THE HELP OF WOOTEN'S TEAM AT NASA'S MARSHALL SPACE FLIGHT CENTER IN HUNTSVILLE, ALABAMA.
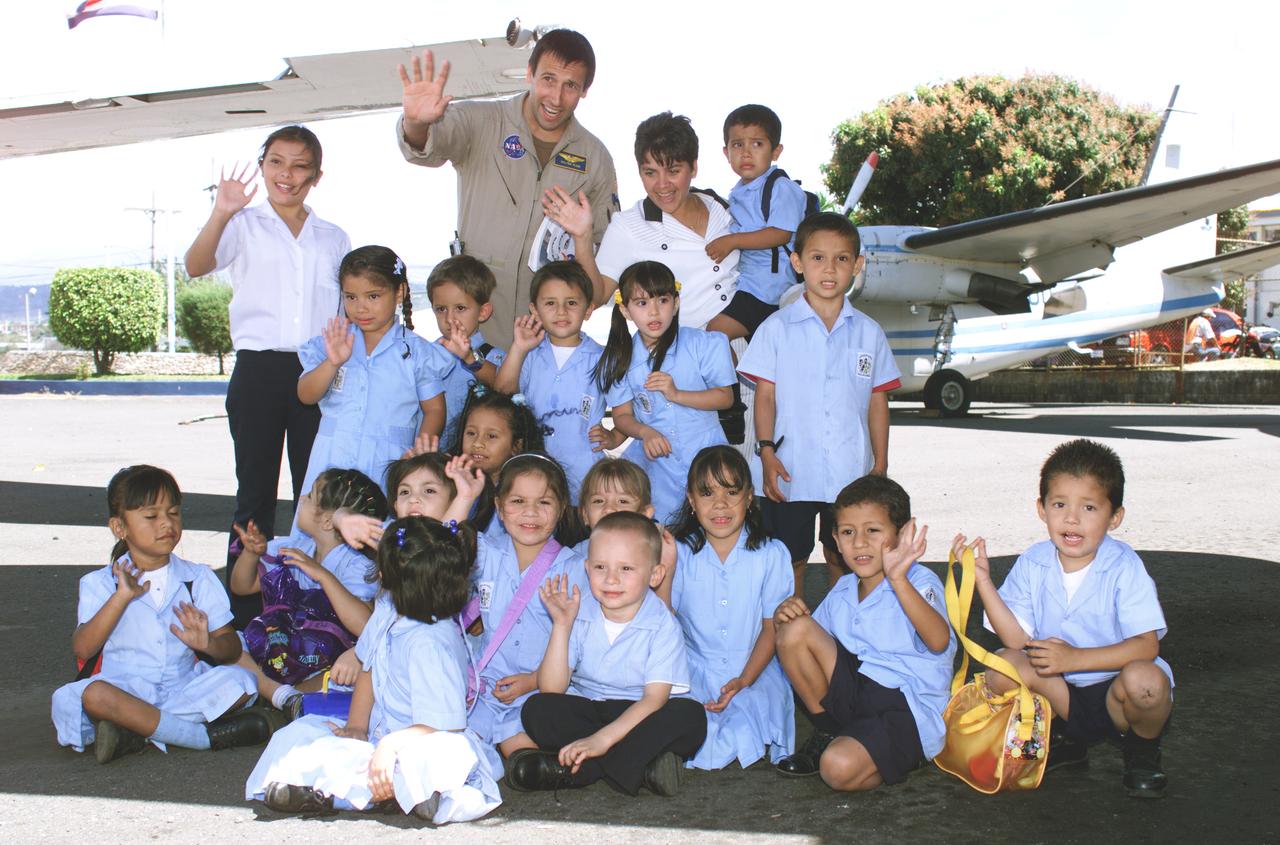

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with school children that visited the airport during AirSAR 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
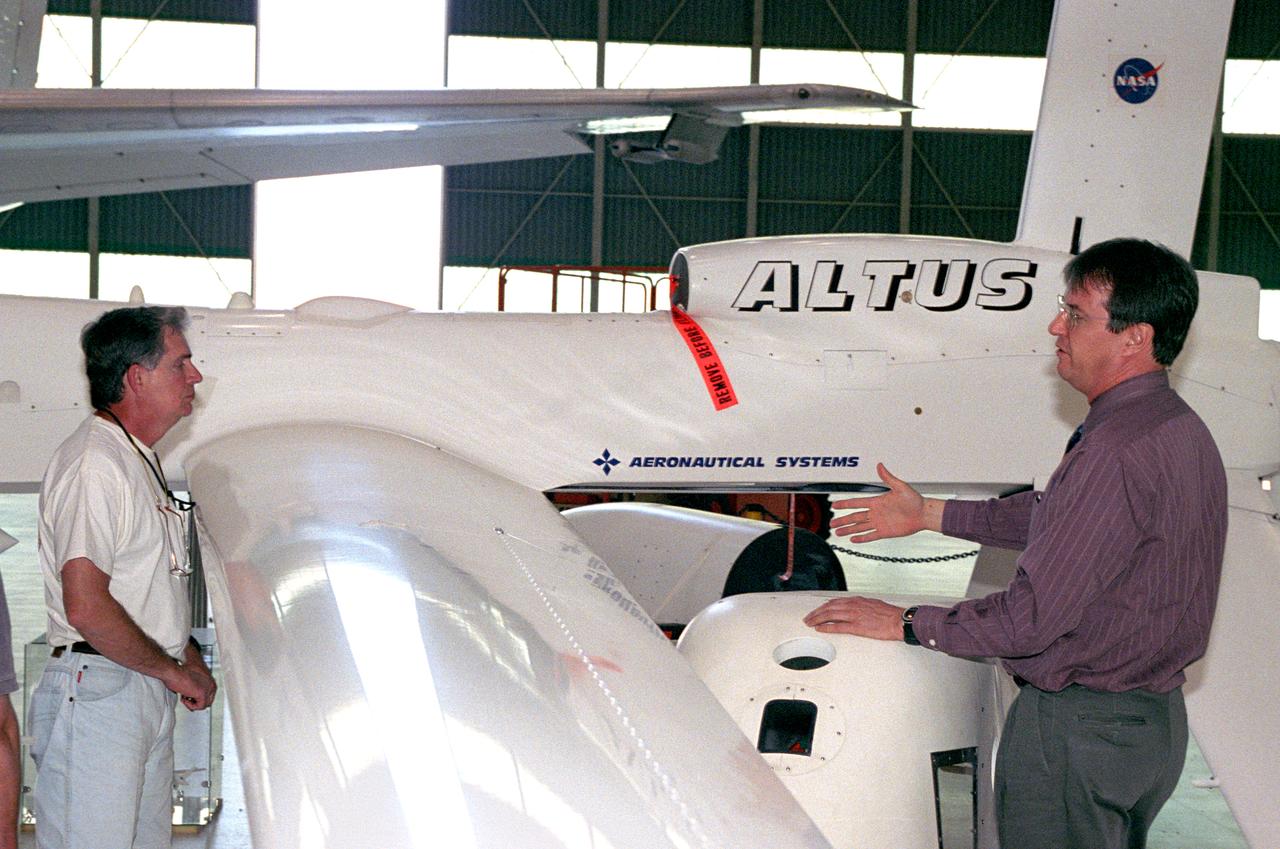

David Bushman, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) mission manager in NASA Dryden's Airborne Science Program, explains the capabilities of the Altus UAV to Charles Hudgins of NASA Langley's Chemistry and Dynamics Branch.
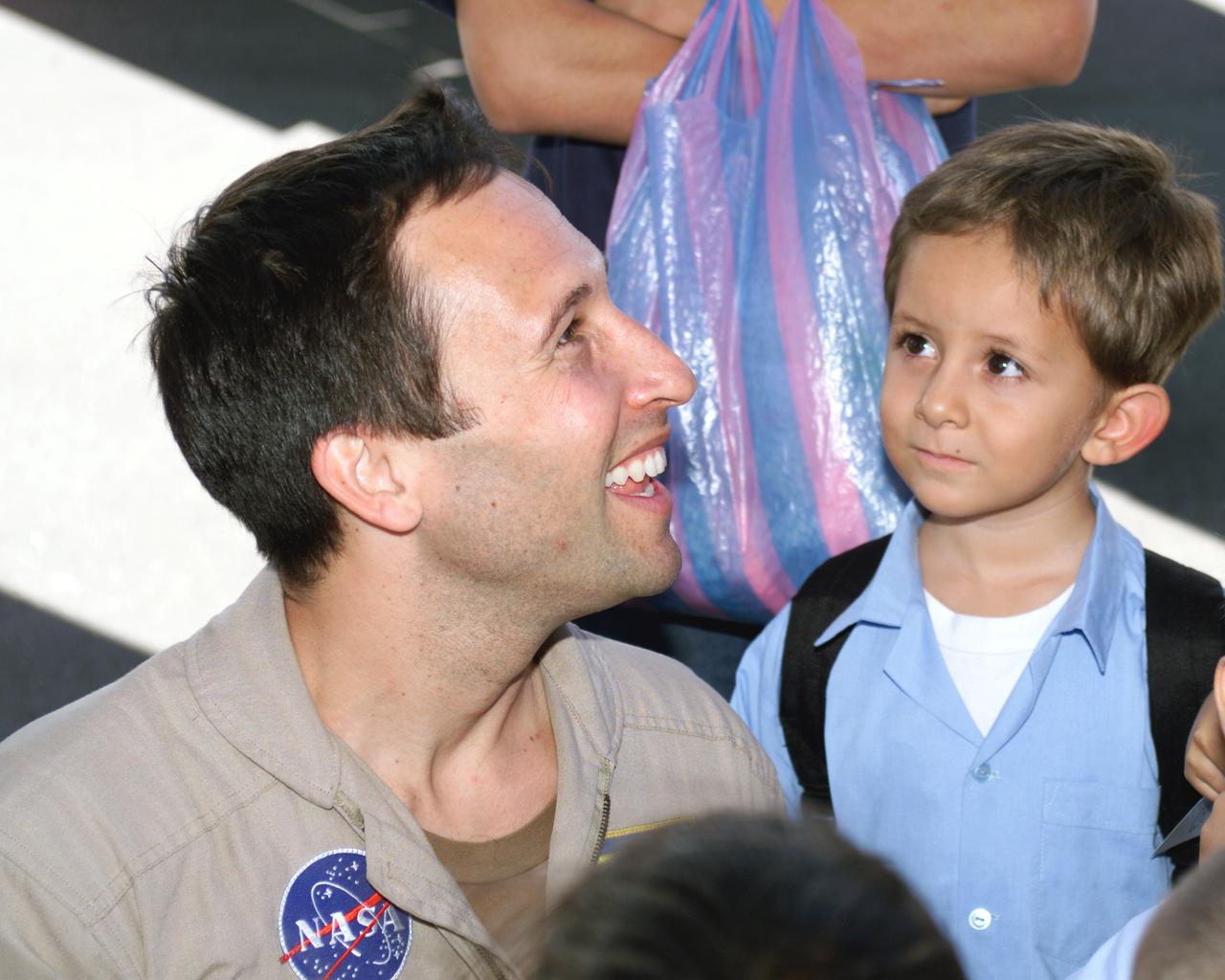

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
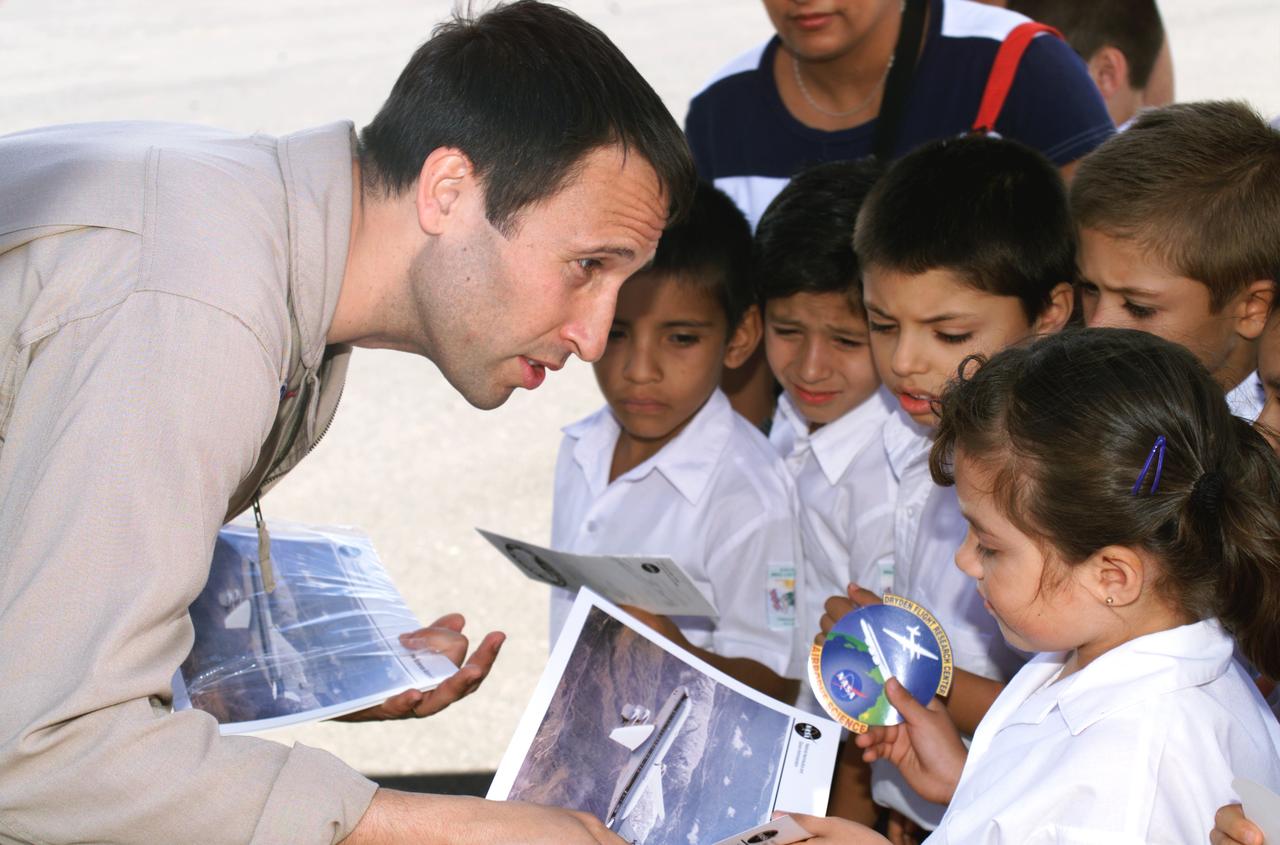

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
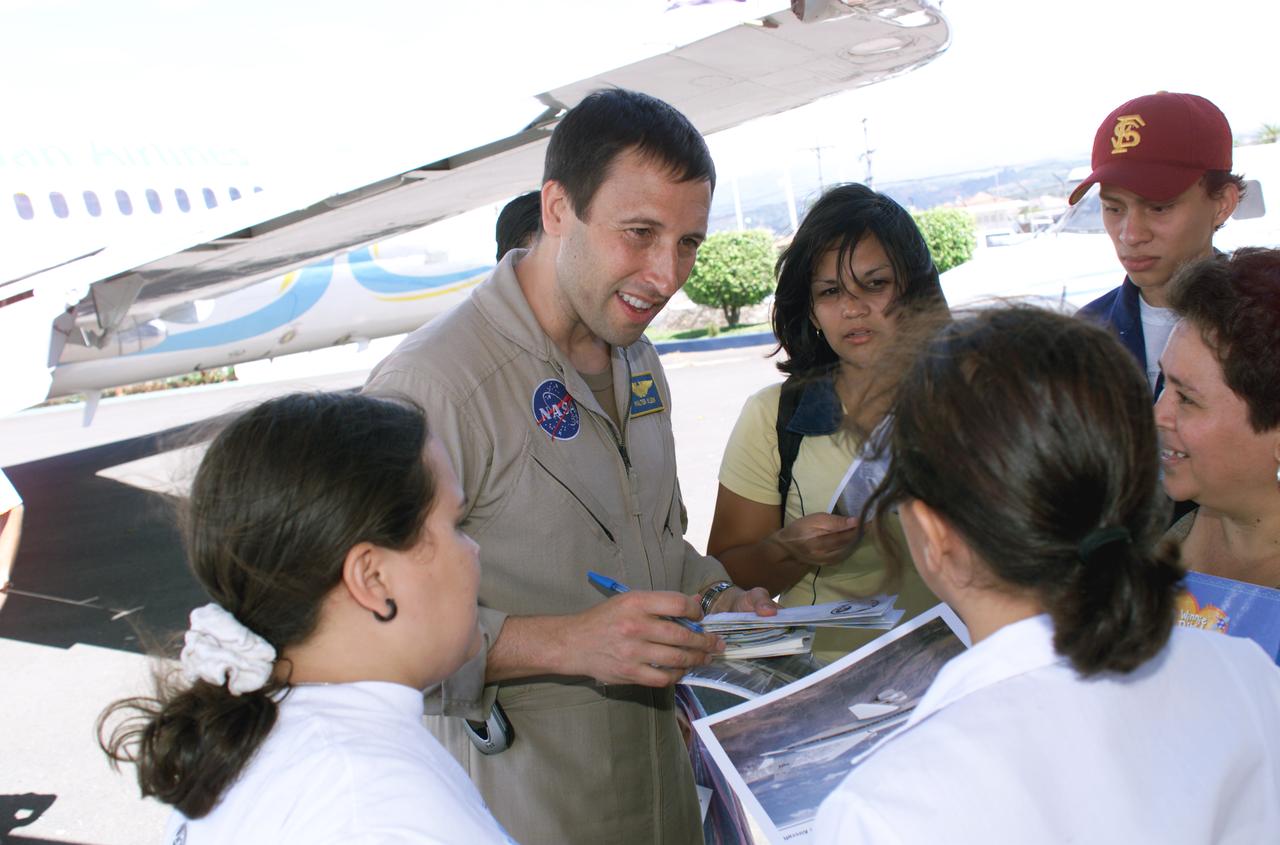

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
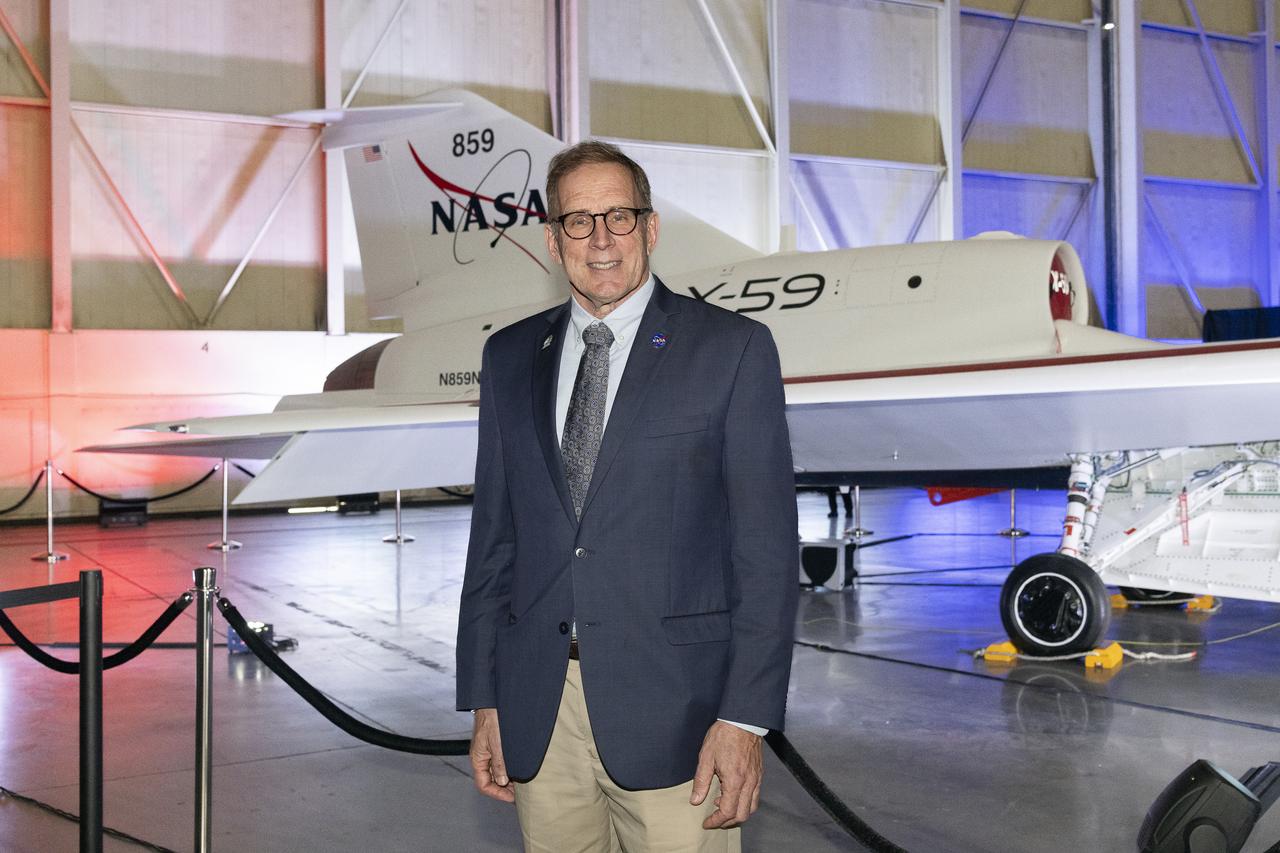

NASA’s mission integration manager for the Quesst mission, Peter Coen, poses in front of the agency’s X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft at a January 12, 2024 event at Lockheed Martin Skunk Works in Palmdale, California. The X-59 is the centerpiece of NASA’s Quesst mission, which seeks to solve one of the major barriers to supersonic flight over land, currently banned in the United States, by making sonic booms quieter.
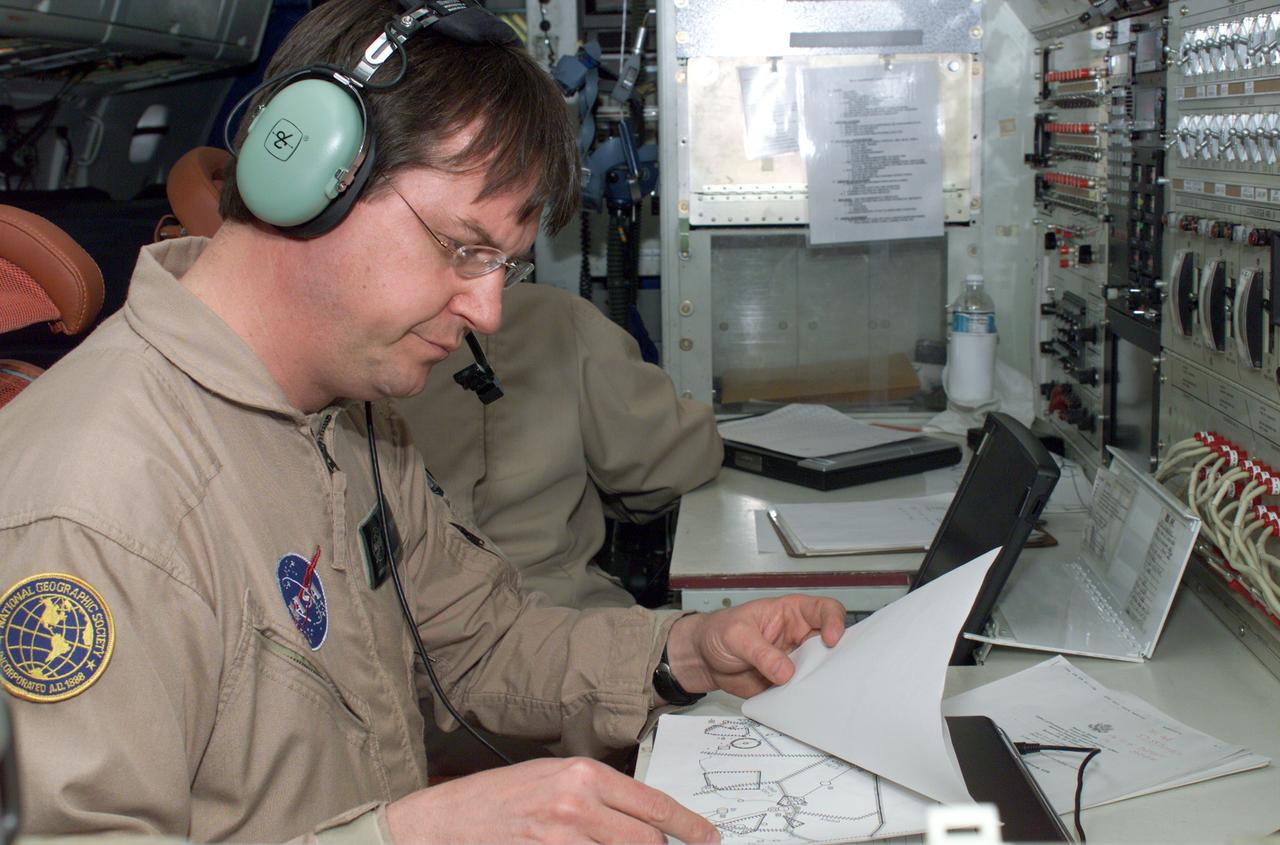

David Bushman at the Mission Manager's console onboard NASA's DC-8 during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
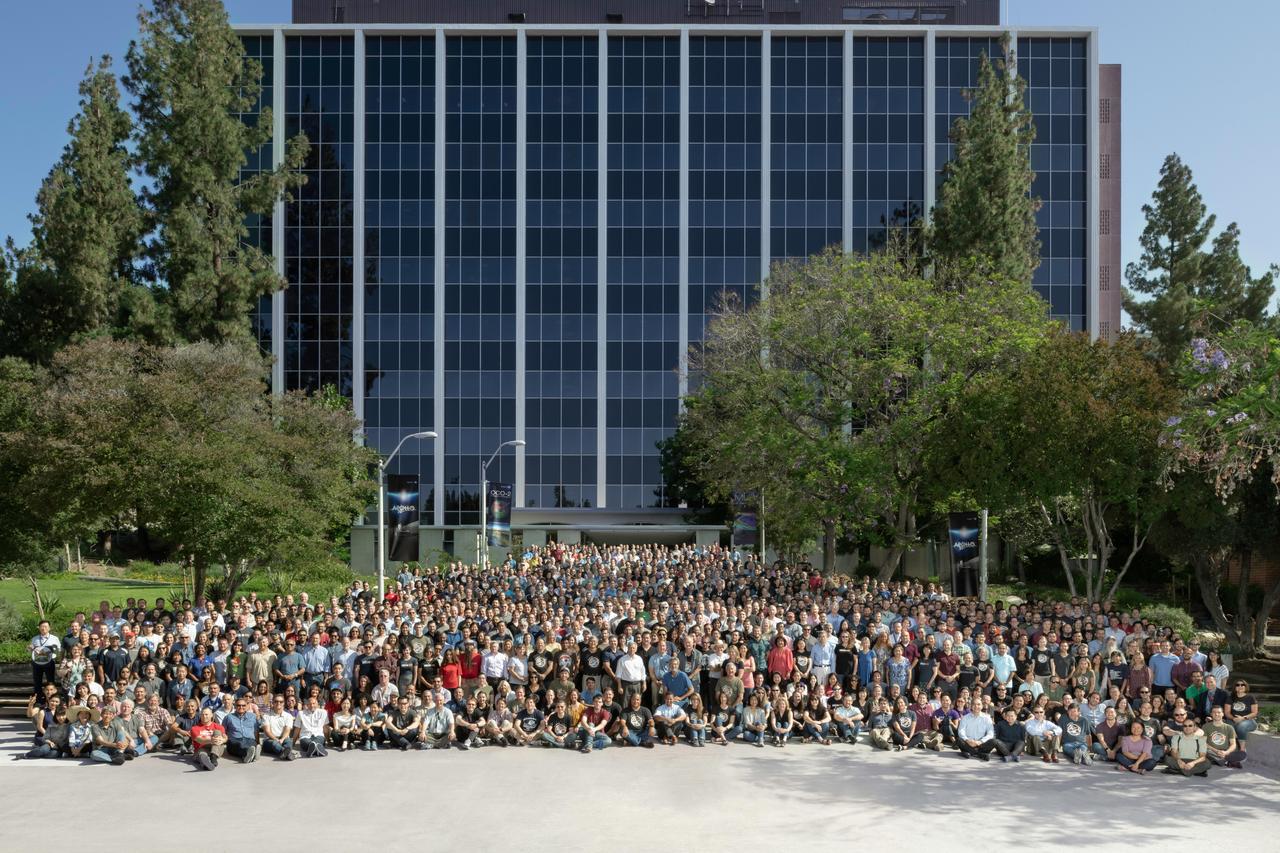

Members of the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission pose at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission, on July 17, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23923
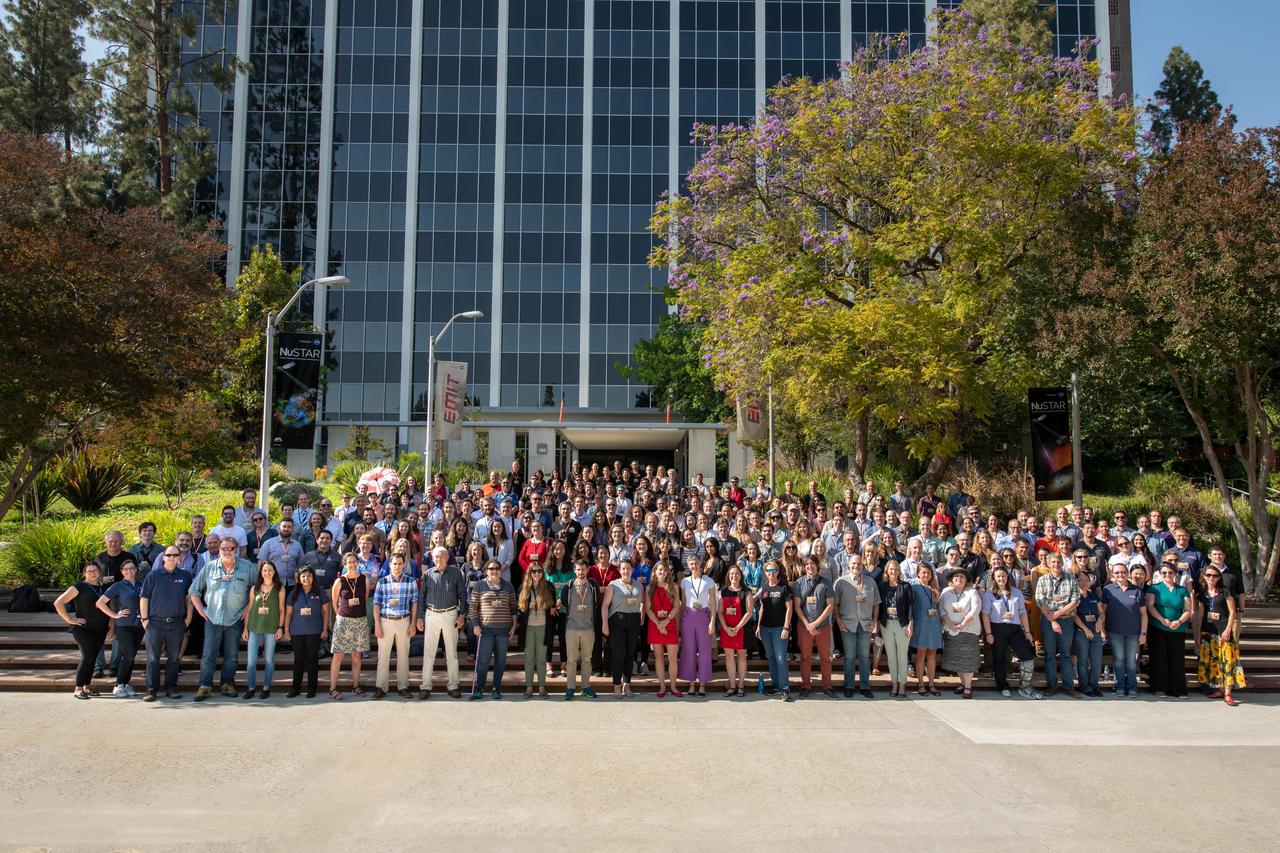

Members of the Perseverance rover Science Team pose on June 7, 2022, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25328
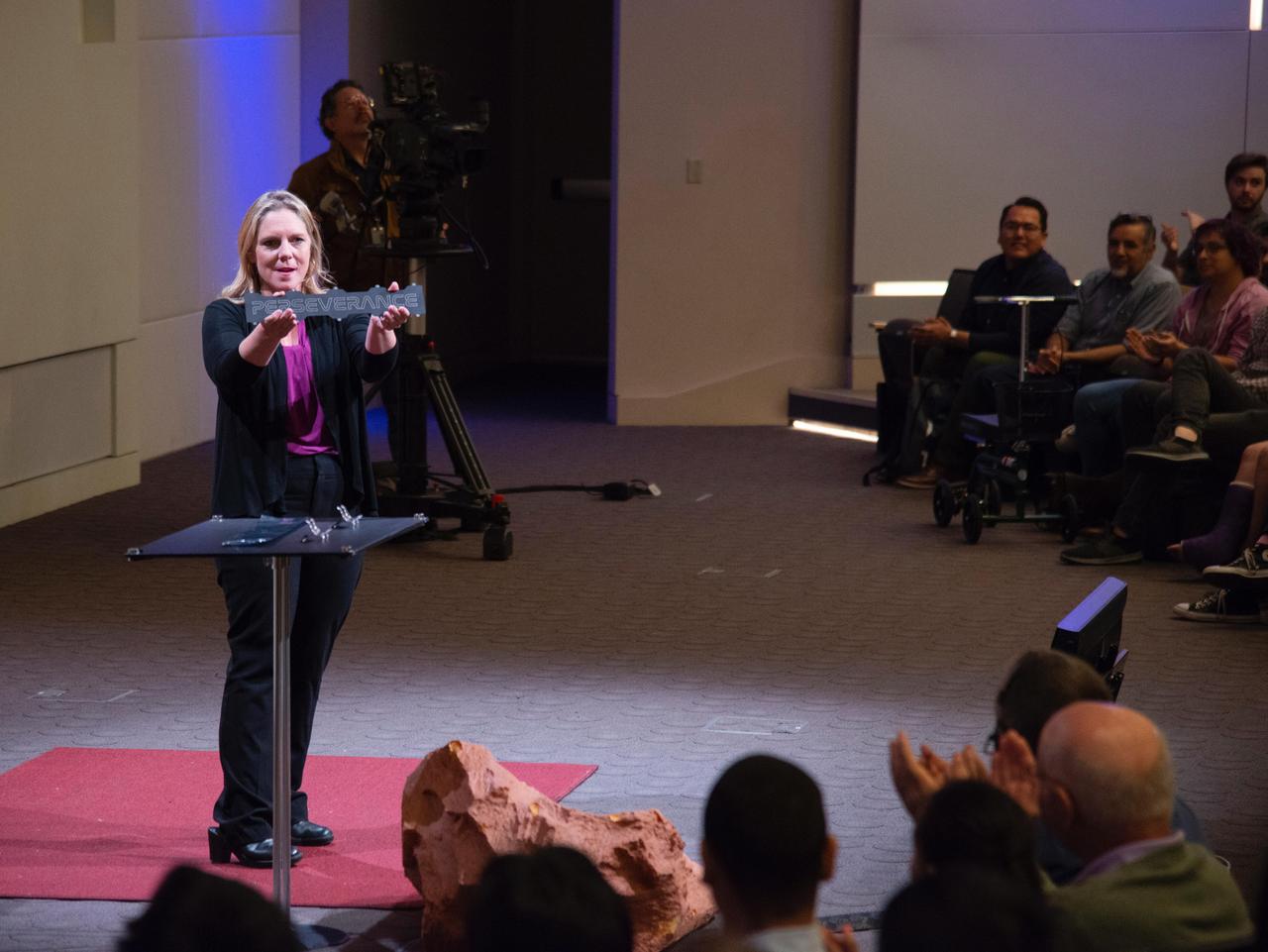

Team members of NASA's next Mars mission applaud as mission manager Jennifer Trosper unveils a nameplate with "Perseverance" laser-etched into its surface. The image was taken at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on March 5, 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23763
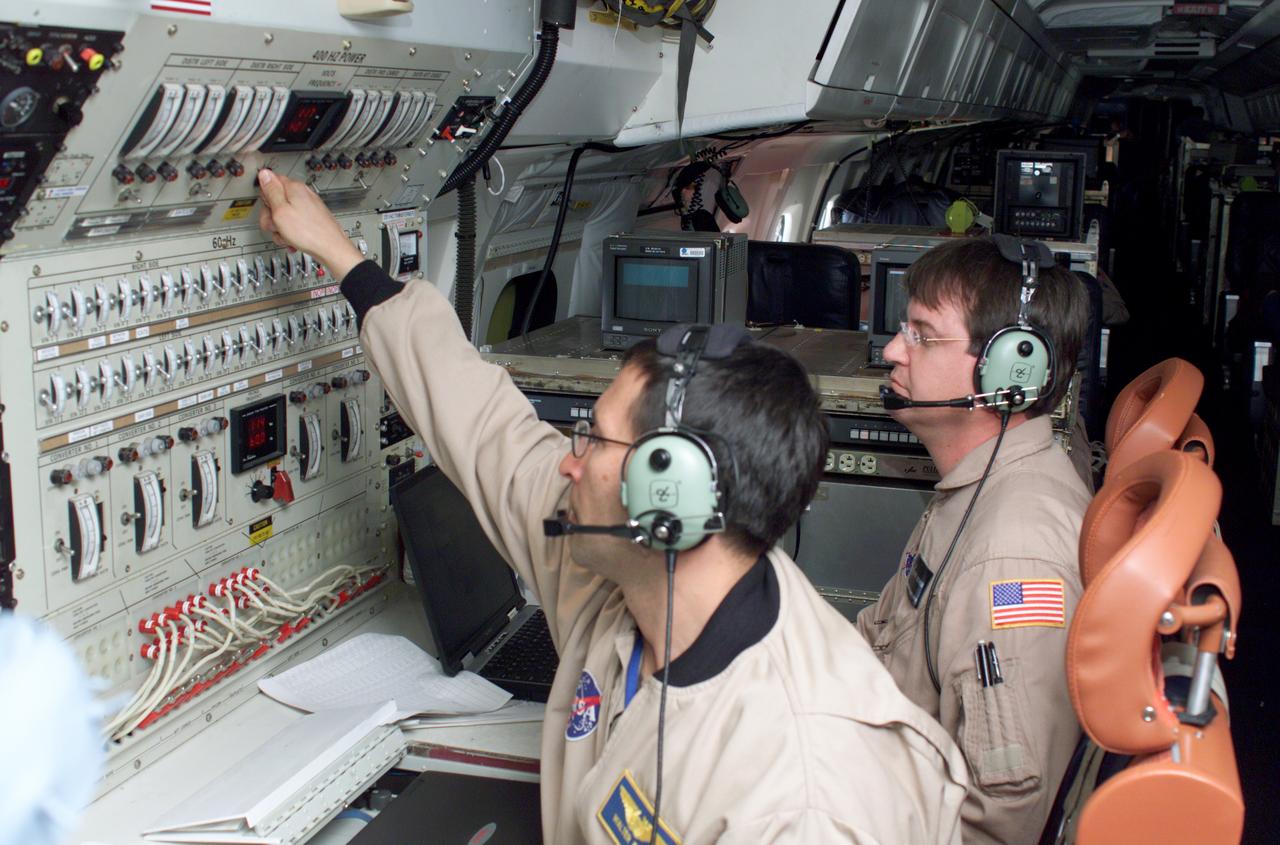

Airborne Science personnel Walter Klein and David Bushman at the Mission Manager's console onboard NASA's DC-8 during the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
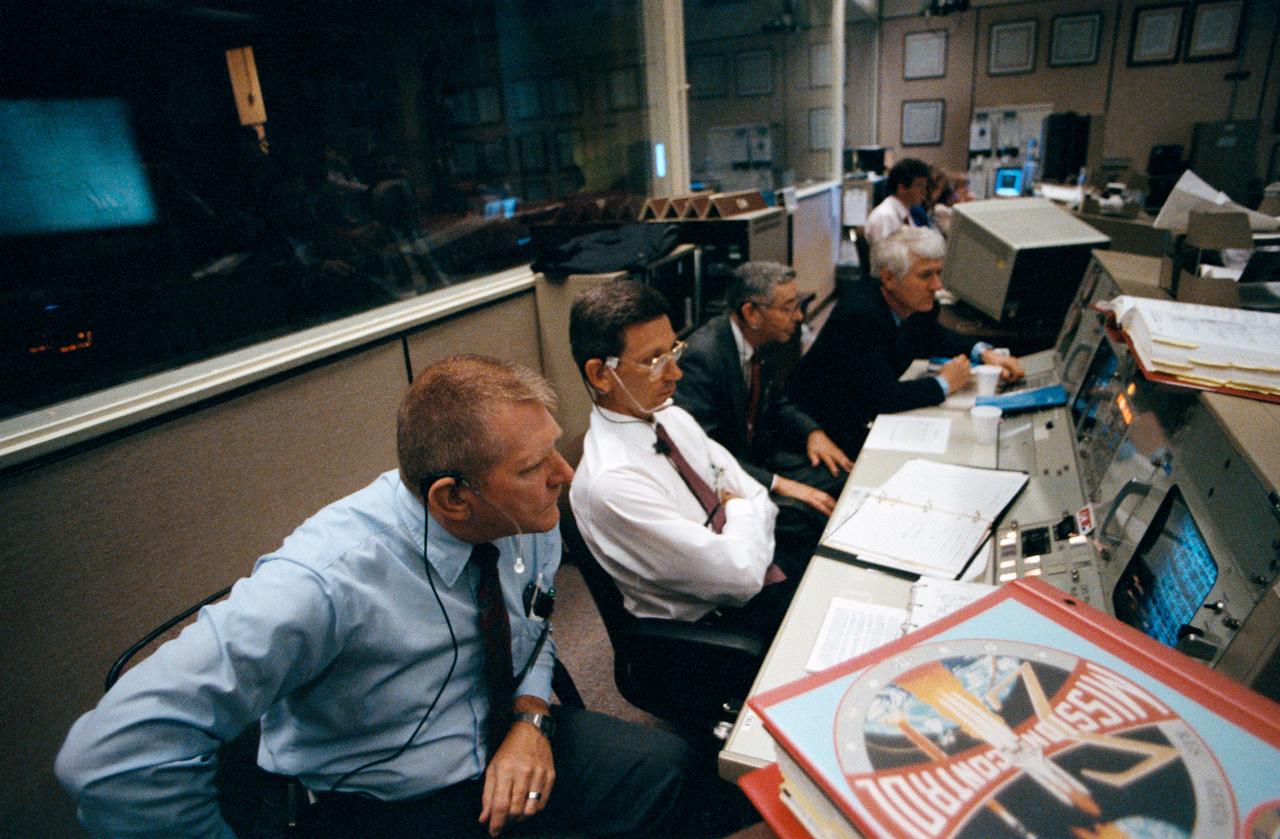

STS030-S-004 (8 May 1989) --- JSC Officials monitor early moments of NASA's STS-30 Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, flight in the Flight Control Room (FCR) of JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) Bldg 30. At the Mission Operations Directorate (MOD) console, MOD Director Eugene F. Kranz (foreground), studiously reviews data on a nearby monitor. Others in the photo are (left to right) Flight Directors Office Deputy Chief Lawrence S. Bourgeois, JSC Director Aaron Cohen, and Flight Crew Operations Deputy Director Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr. Kranz'z replete loose-leaf notebook, bearing the insignia of the flight control team members (MOD insignia), is in the foreground.
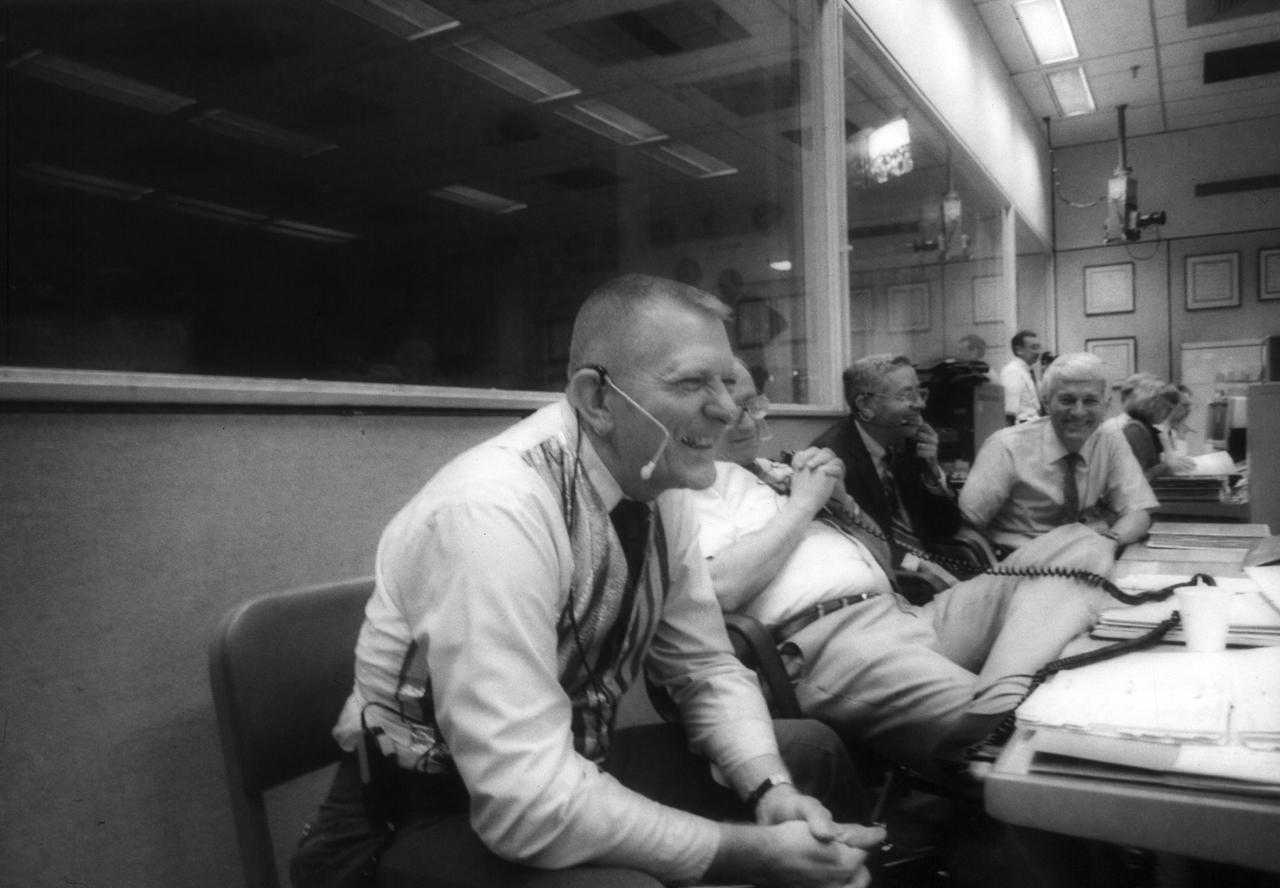

JSC officials, laughing, listen to crewmembers' commentary onboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, during STS-26. In the Flight Control Room (FCR) of JSC's Mission Control Center (MCC) Bldg 30 and seated at the Mission Operations Directorate (MOD) console, MOD Director Eugene F. Kranz (foreground), wearing red, white and blue vest, smiles along with JSC Director Aaron Cohen and Flight Crew Operations Deputy Director Henry W. Hartsfield, Jr. (far right).
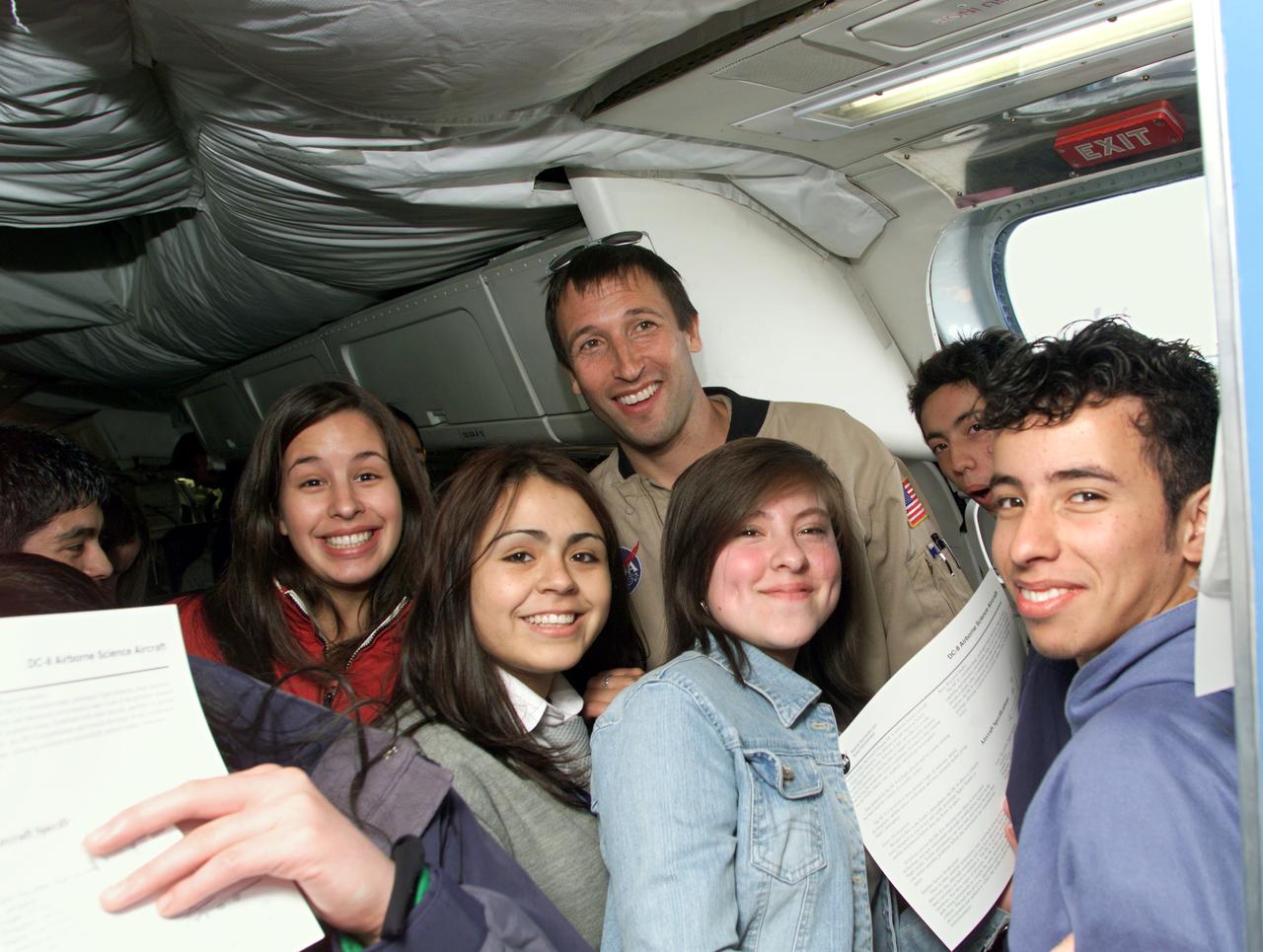

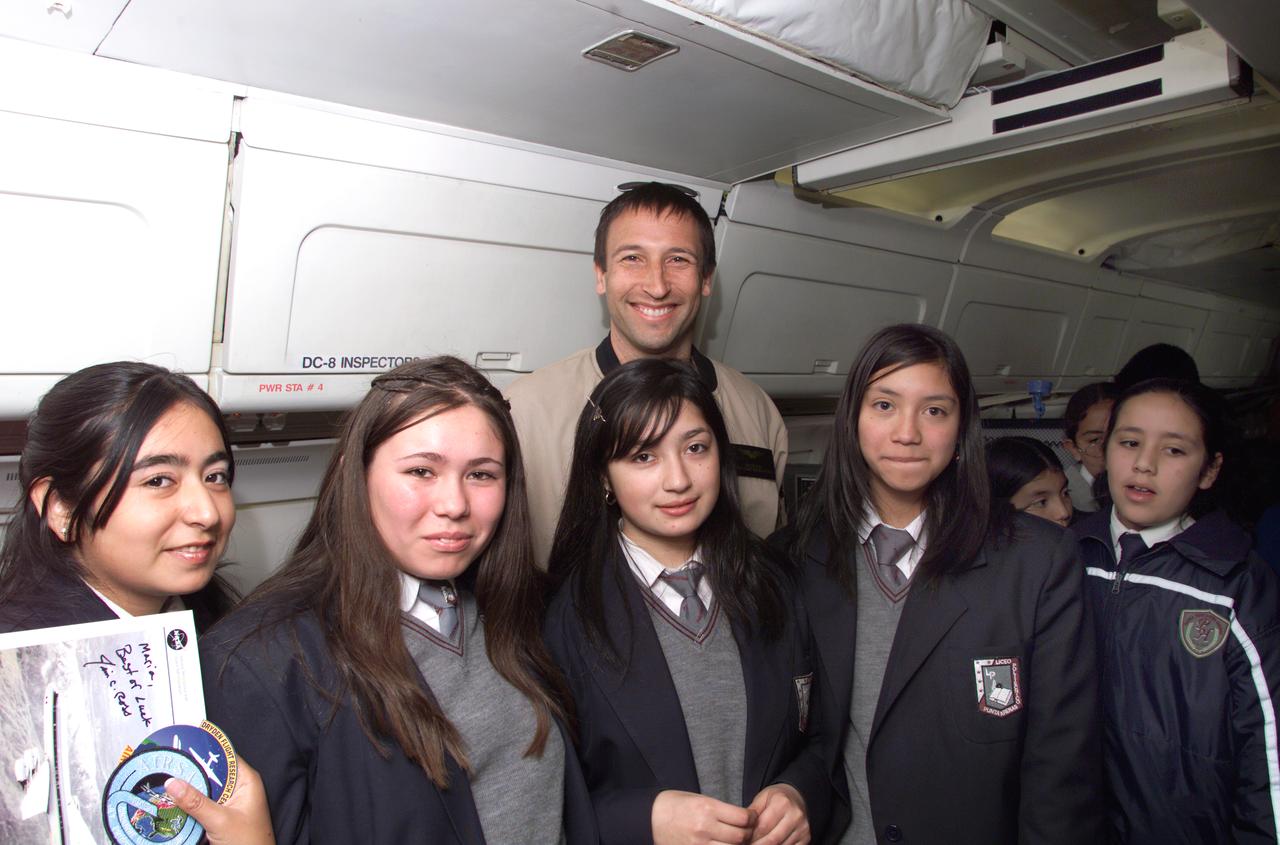
NASA DC-8 Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with a group of Chilean Students onboard the aircraft at Carlos Ibanez del Campo International Airport in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR will collect imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is decreasing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In a brief ceremony in the Space Station Processing Facility, Chuck Hardison (left), Boeing senior truss manager, turns over the “key” for the starboard truss segment S3/S4 to Scott Gahring, ISS Vehicle Office manager (acting), Johnson Space Center. The trusses are scheduled to be delivered to the International Space Station on mission STS-117.
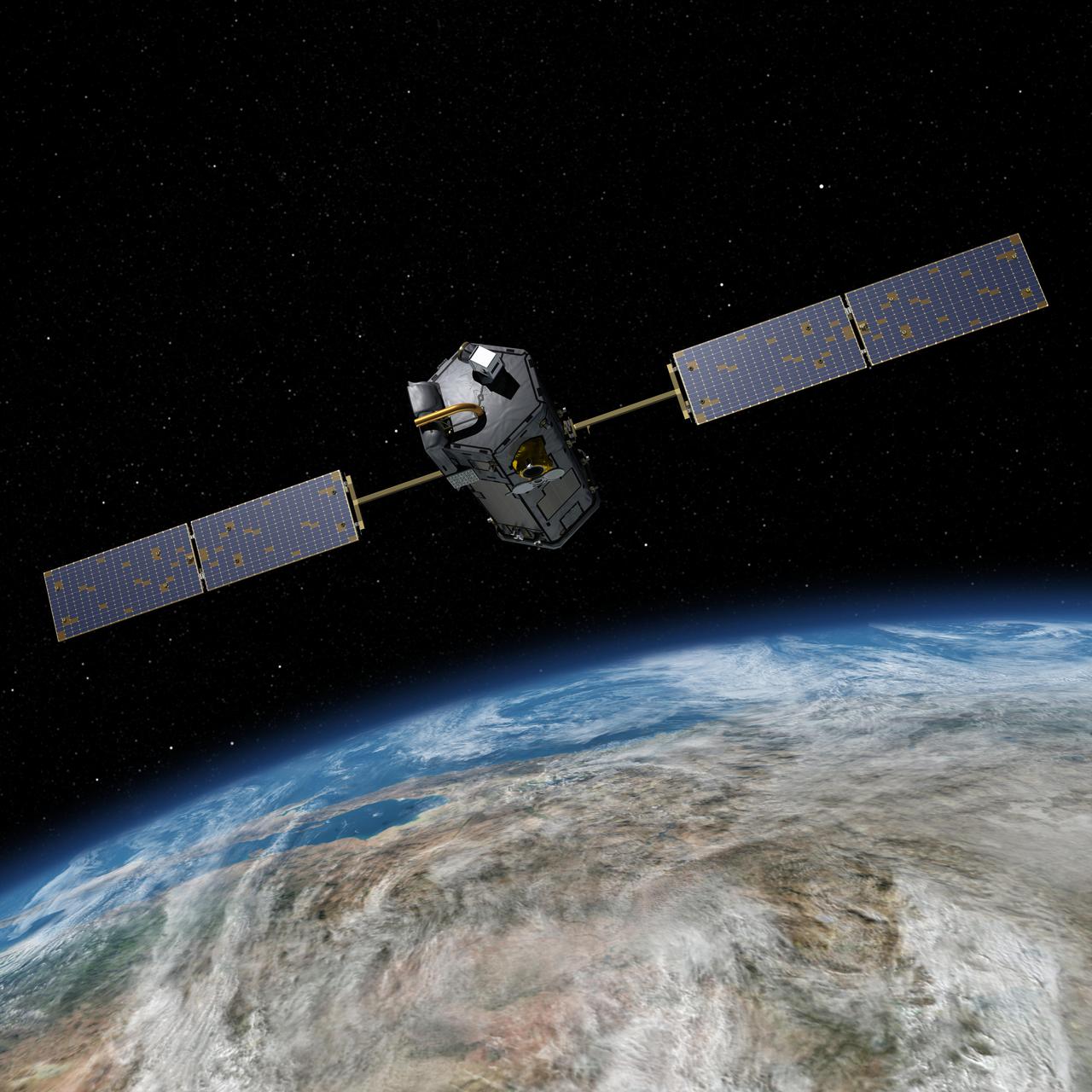

This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
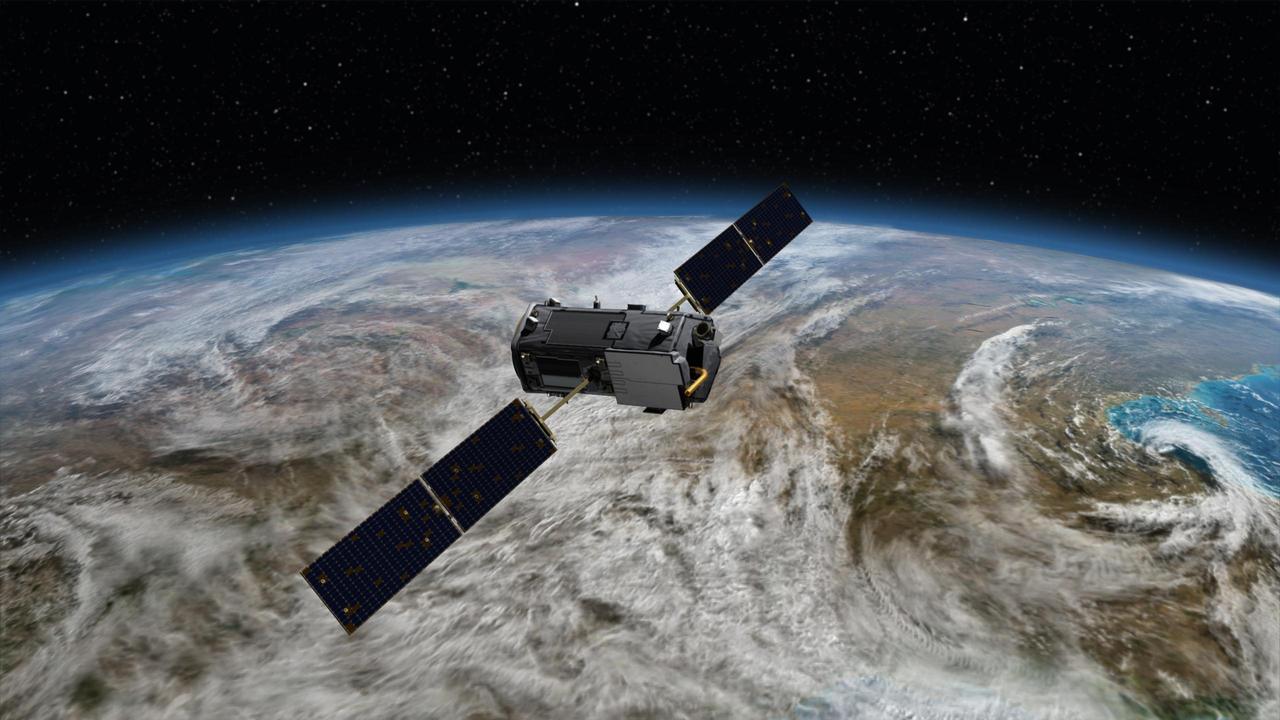

Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.

Charlie Lundquist, NASA Orion deputy program manager, right, presents an American flag flown aboard the Orion capsule during the Exploration Flight Test-1 mission to Armstrong Deputy Director Patrick Stoliker.
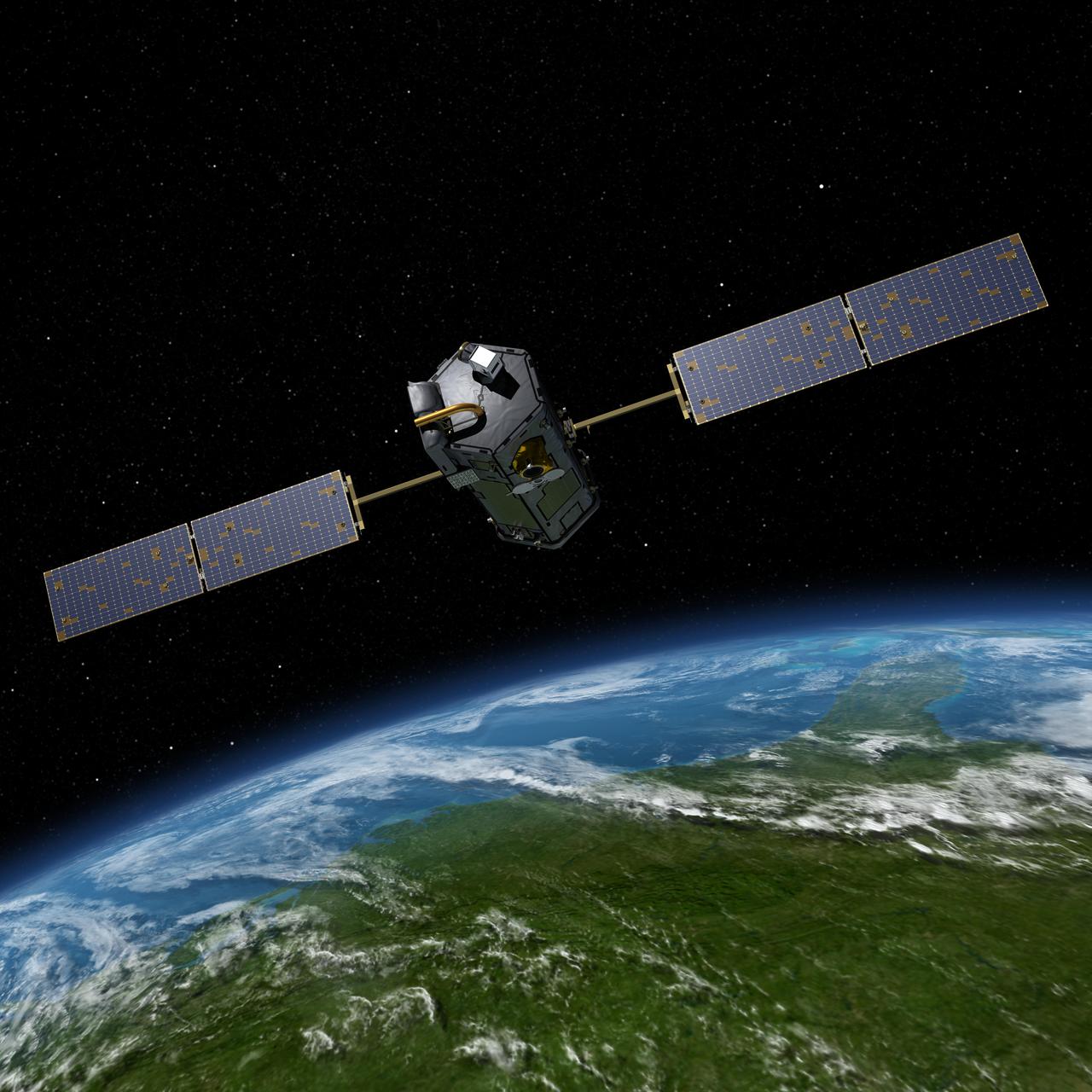

Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.
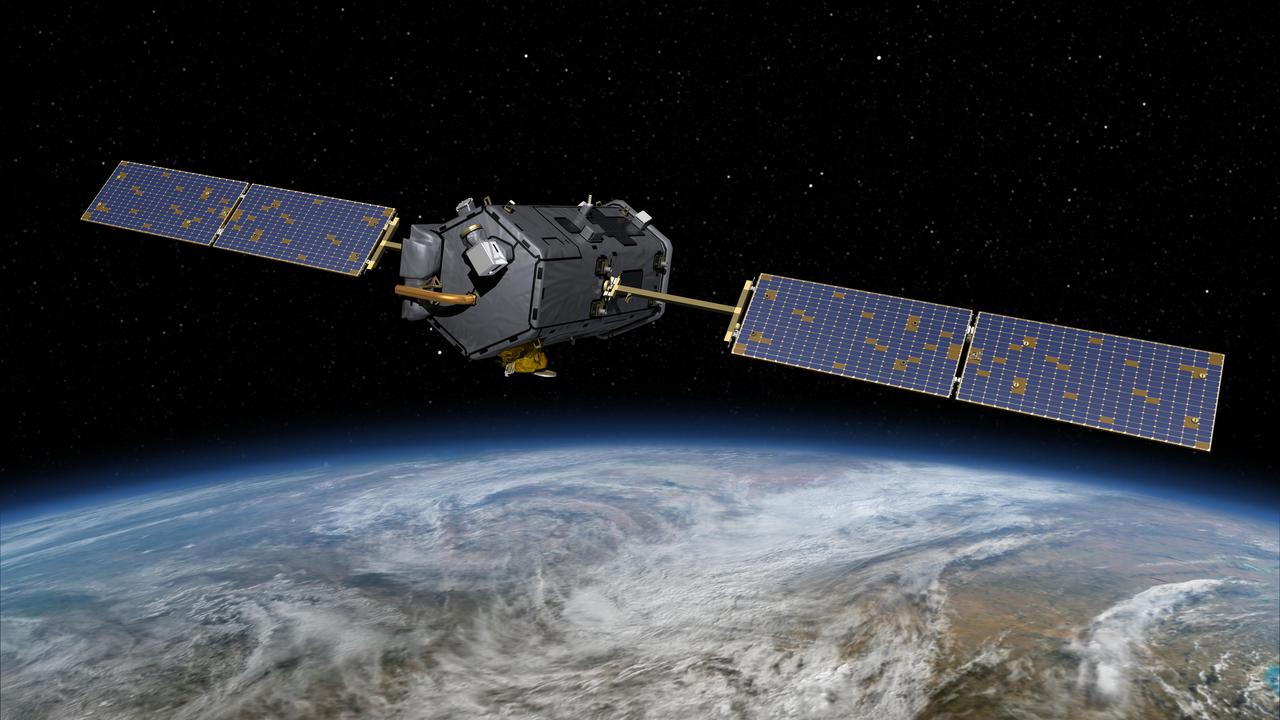

This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
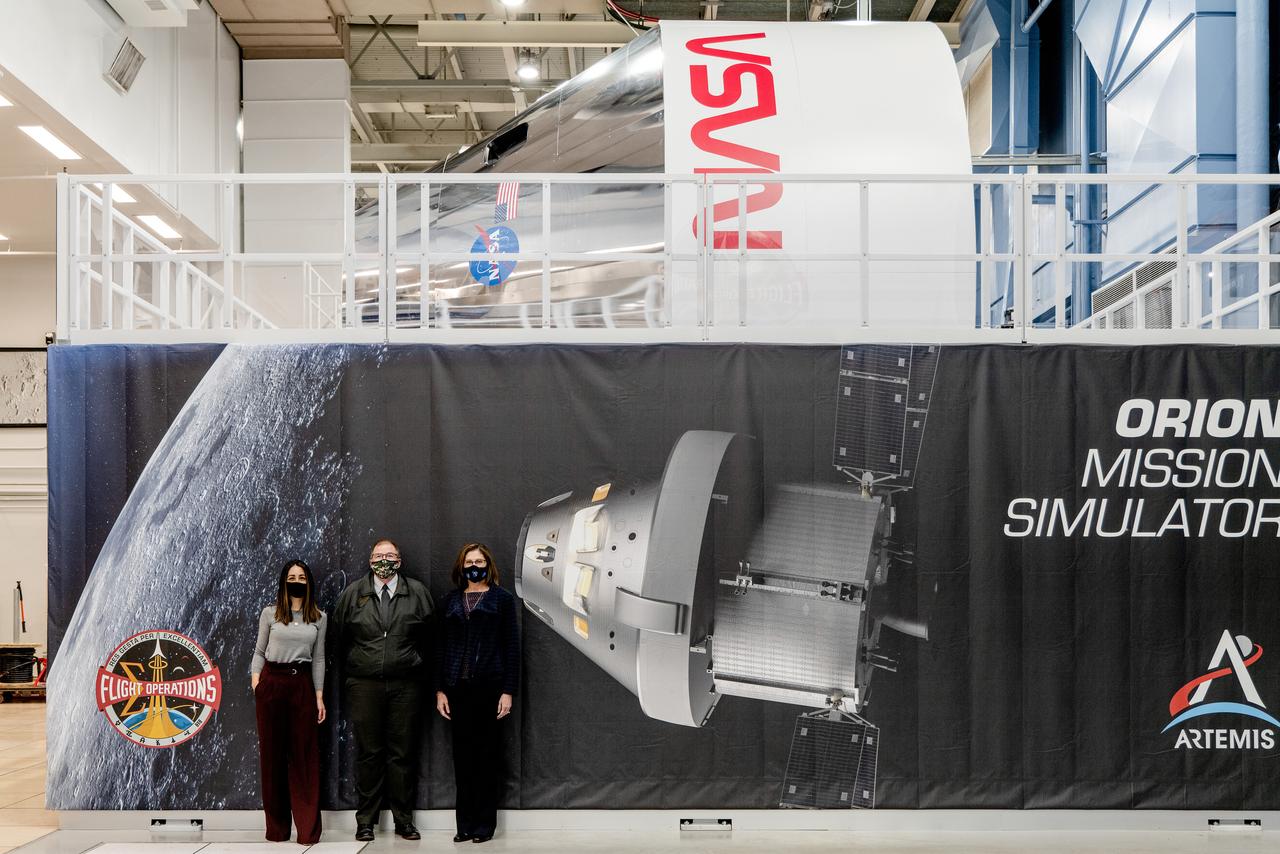

Examination of Orion spacecraft simulator that recently arrived at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston on Dec. 8, 2020. The simulator provides the ability for astronauts, engineers, and flight controllers to train and practice for scenarios during Artemis missions to the Moon. The interior of the simulator is being outfitted with Orion’s display and control system and crew seats to mimic what astronaut will experience during liftoff to the lunar vicinity and on their way back home to Earth.
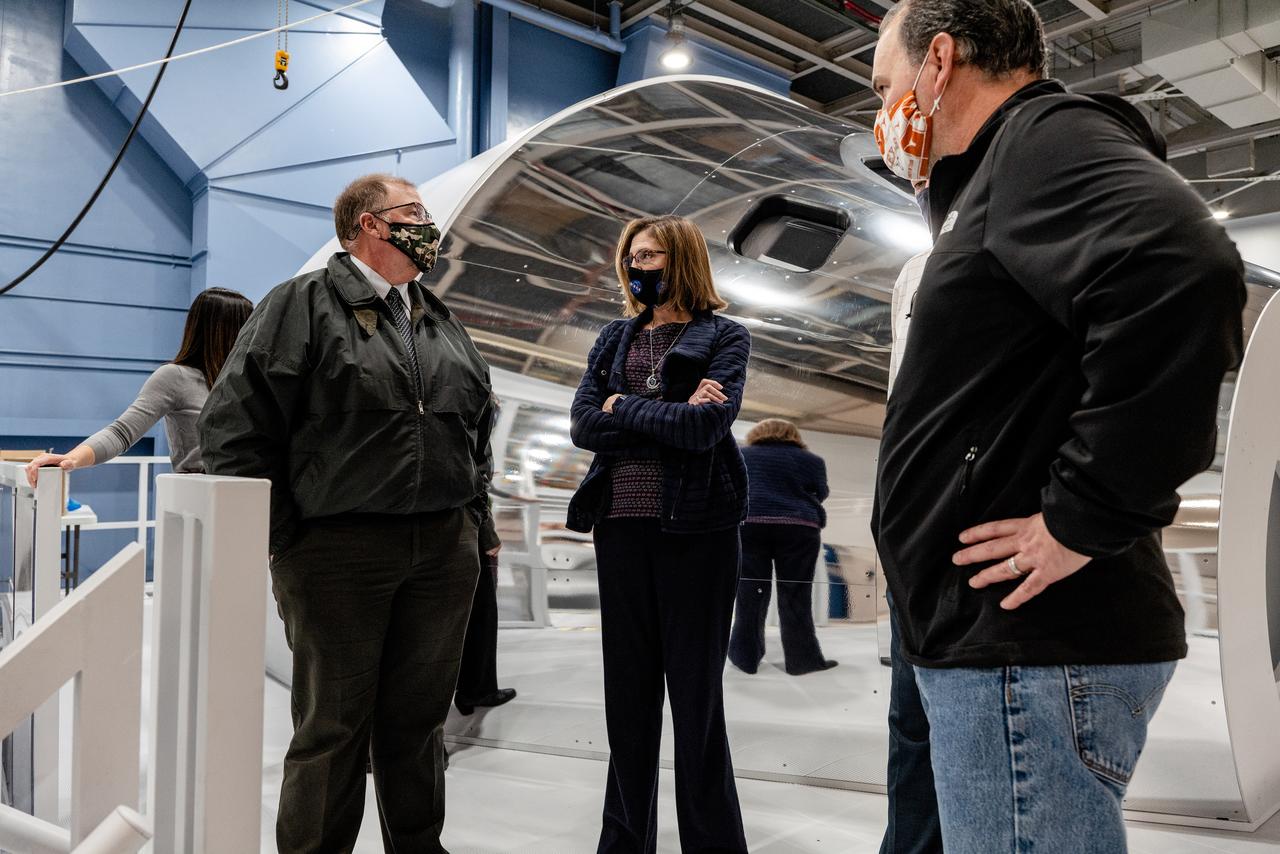

Examination of Orion spacecraft simulator that recently arrived at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston on Dec. 8, 2020. The simulator provides the ability for astronauts, engineers, and flight controllers to train and practice for scenarios during Artemis missions to the Moon. The interior of the simulator is being outfitted with Orion’s display and control system and crew seats to mimic what astronaut will experience during liftoff to the lunar vicinity and on their way back home to Earth.
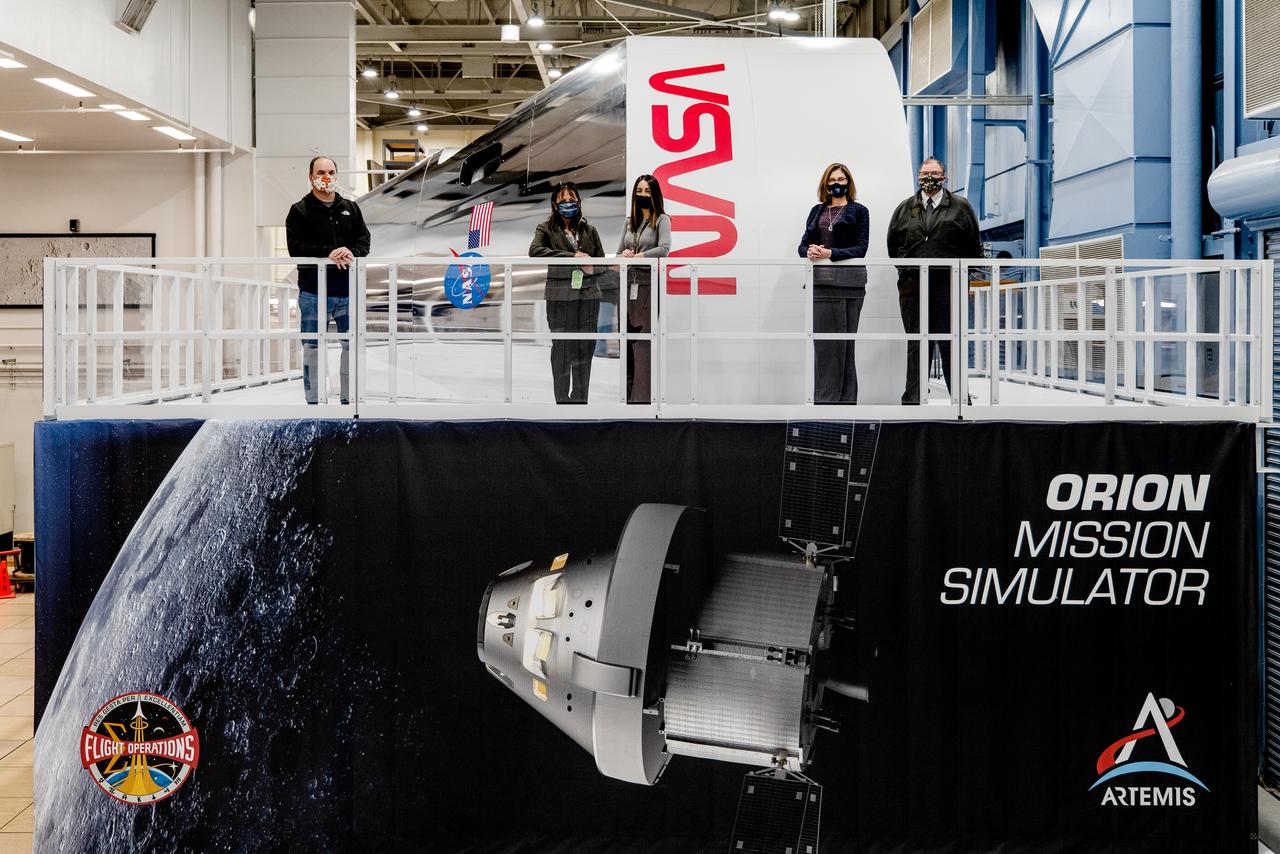

Examination of Orion spacecraft simulator that recently arrived at the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston on Dec. 8, 2020. The simulator provides the ability for astronauts, engineers, and flight controllers to train and practice for scenarios during Artemis missions to the Moon. The interior of the simulator is being outfitted with Orion’s display and control system and crew seats to mimic what astronaut will experience during liftoff to the lunar vicinity and on their way back home to Earth.

Monica Manning, assistant administrator of NASA’s Office of Procurement, addresses a crowd of nearly 900 industry leaders from 33 states at the 29th Marshall Small Business Alliance meeting Feb. 20 at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center. Manning introduced a new model for managing mission support for the agency, with the intent to align and simplify processes.
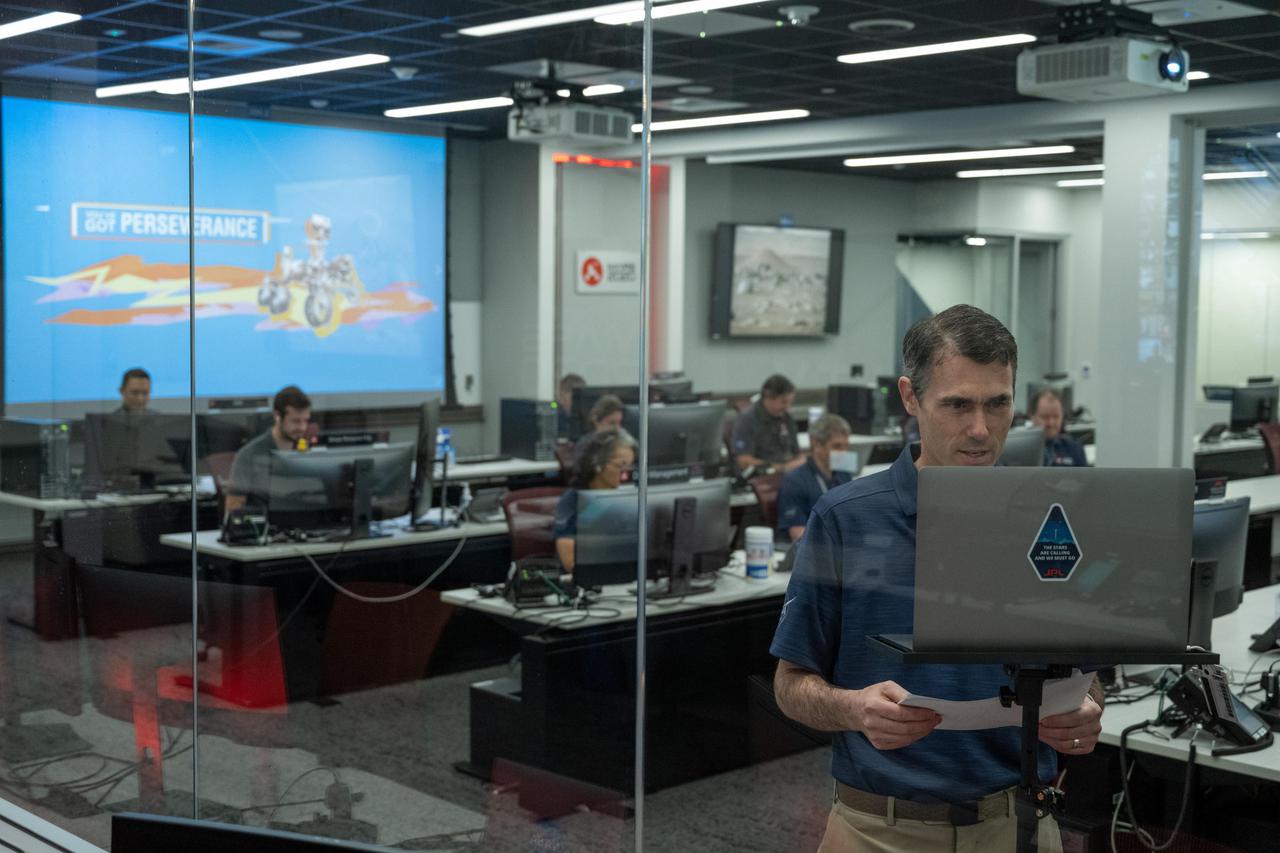

On April 5, 2022, inside the Mars Perseverance rover control room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, the rover team's deputy mission manager, Robert Hogg, and other team members interacted virtually with students who have overcome academic obstacles. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25274

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with school children that visited the DC-8 during AirSAR 2004 in Punta Arenas, Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
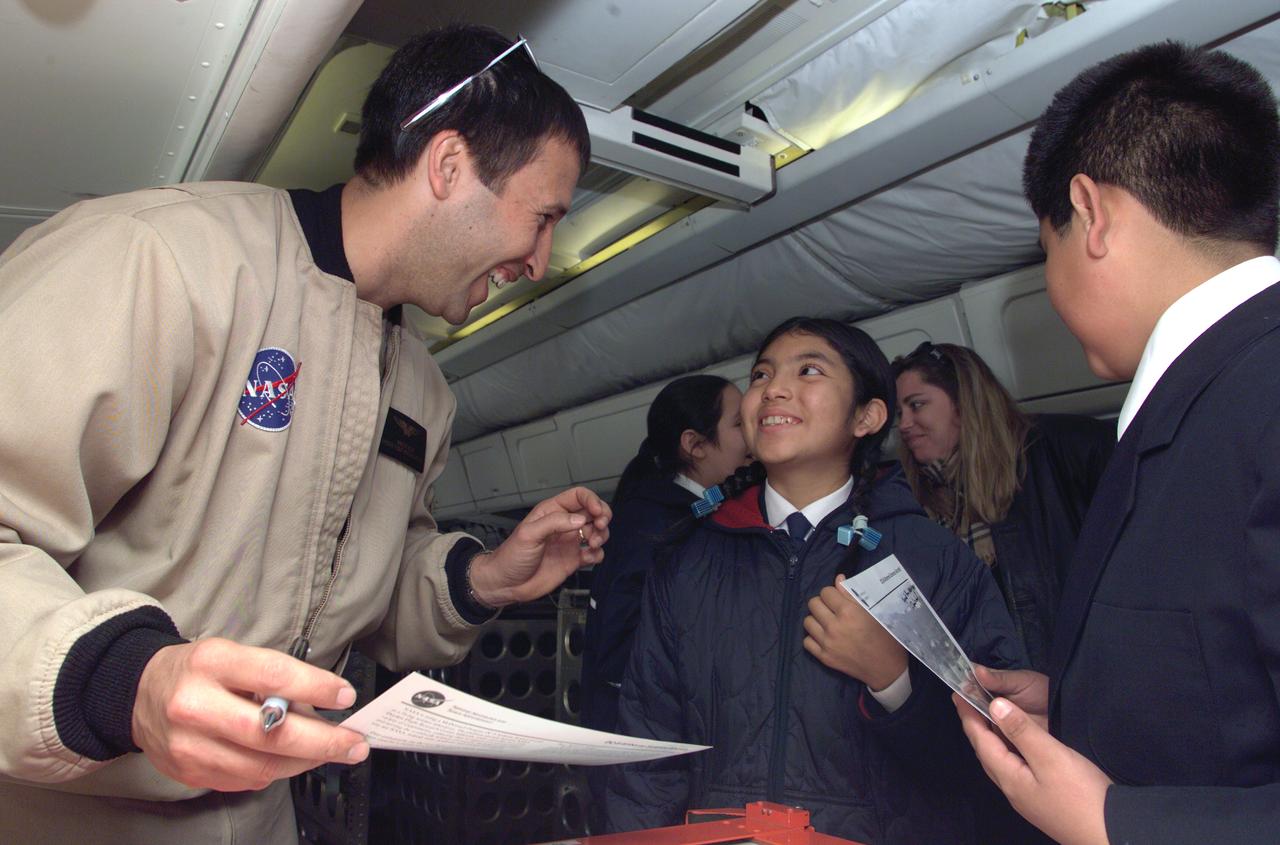

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein talks with school children from Punta Arenas, Chile, during a tour of the DC-8 aircraft while it was in the country supporting the AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central and South America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. In South America and Antarctica, AirSAR collected imagery and data to help determine the contribution of Southern Hemisphere glaciers to sea level rise due to climate change. In Patagonia, researchers found this contribution had more than doubled from 1995 to 2000, compared to the previous 25 years. AirSAR data will make it possible to determine whether that trend is continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
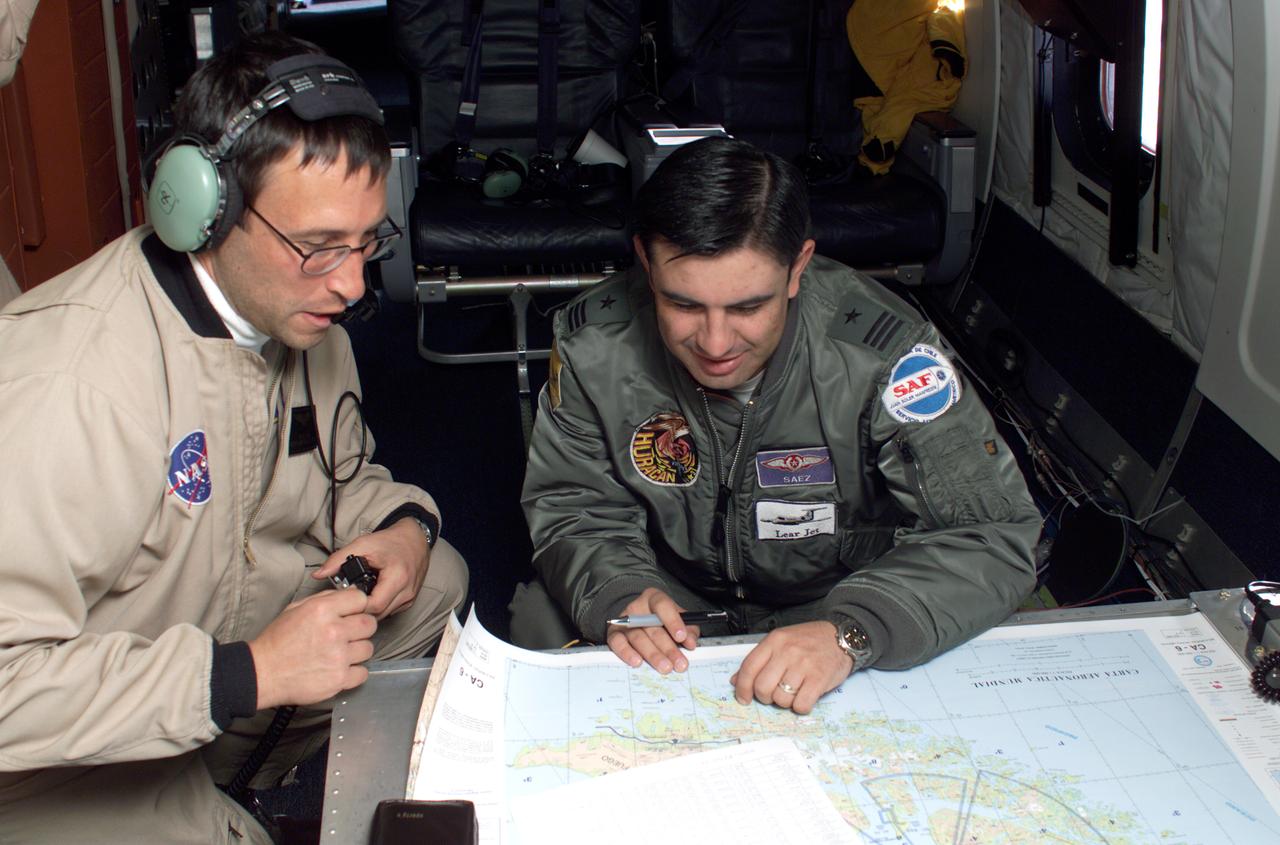

NASA DC-8 Mission Manager Walter Klein and Chilean Air Force Advisor Captain Saez review maps of the Antarctic Peninsula during an AirSAR 2004 mission. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. These photos are from the DC-8 aircraft while flying an AirSAR mission over Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is more similar to Alaska and Patagonia than to the rest of the Antarctic continent. It is drained by fast glaciers, receives abundant precipitation, and melts significantly in the summer months. In recent decades, the Peninsula has experienced significant atmospheric warming (about 2 degrees C since 1950), which has triggered a vast and spectacular retreat of its floating ice shelves, glacier reduction, a decrease in permanent snow cover and a lengthening of the melt season. As a result, the contribution to sea level from this region could be rapid and substantial. With an area of 120,000 km, or ten times the Patagonia ice fields, the Peninsula could contribute as much as 0.4mm/yr sea level rise, which would be the largest single contribution to sea level from anywhere in the world. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
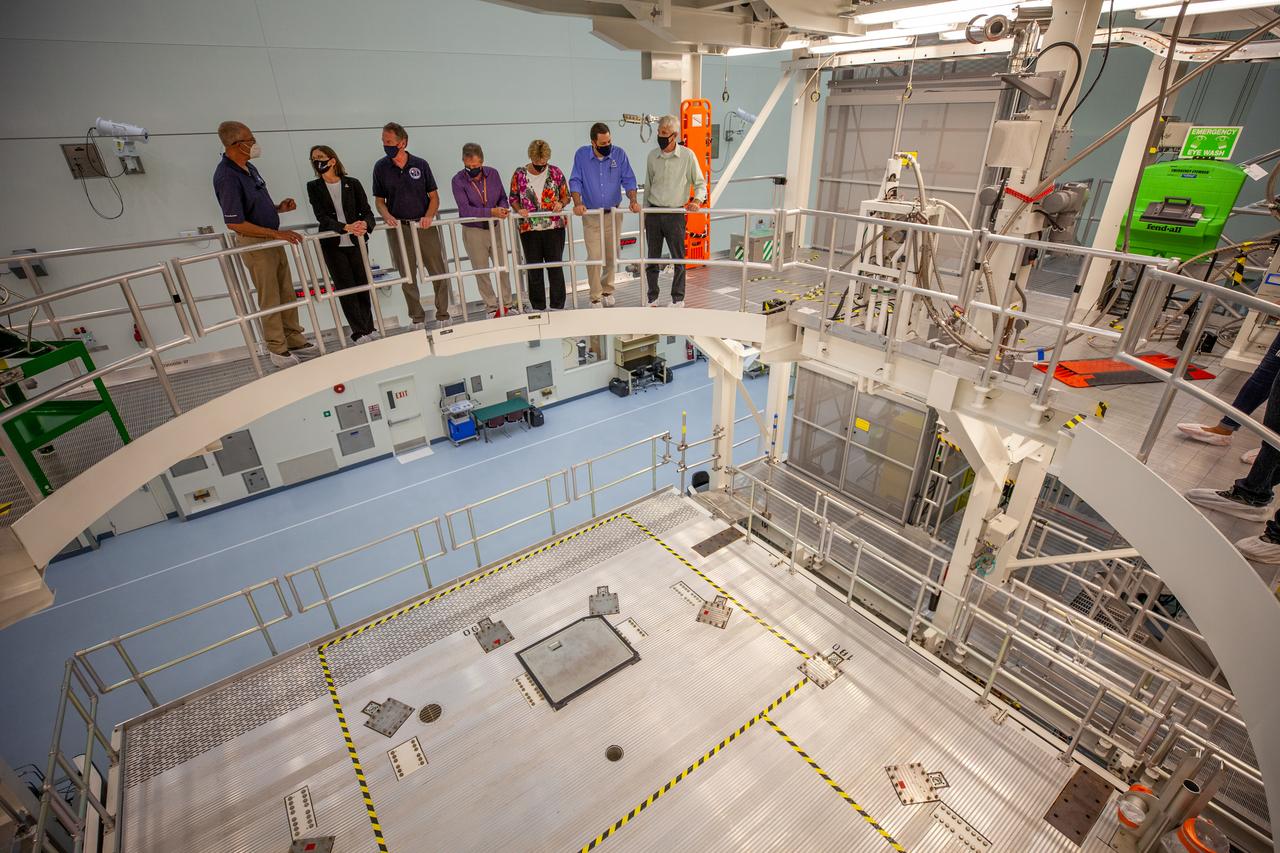

Catherine Koerner, second from left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and TOSC, tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team; Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Nicolas Kindred, TOSC flow manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; and Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
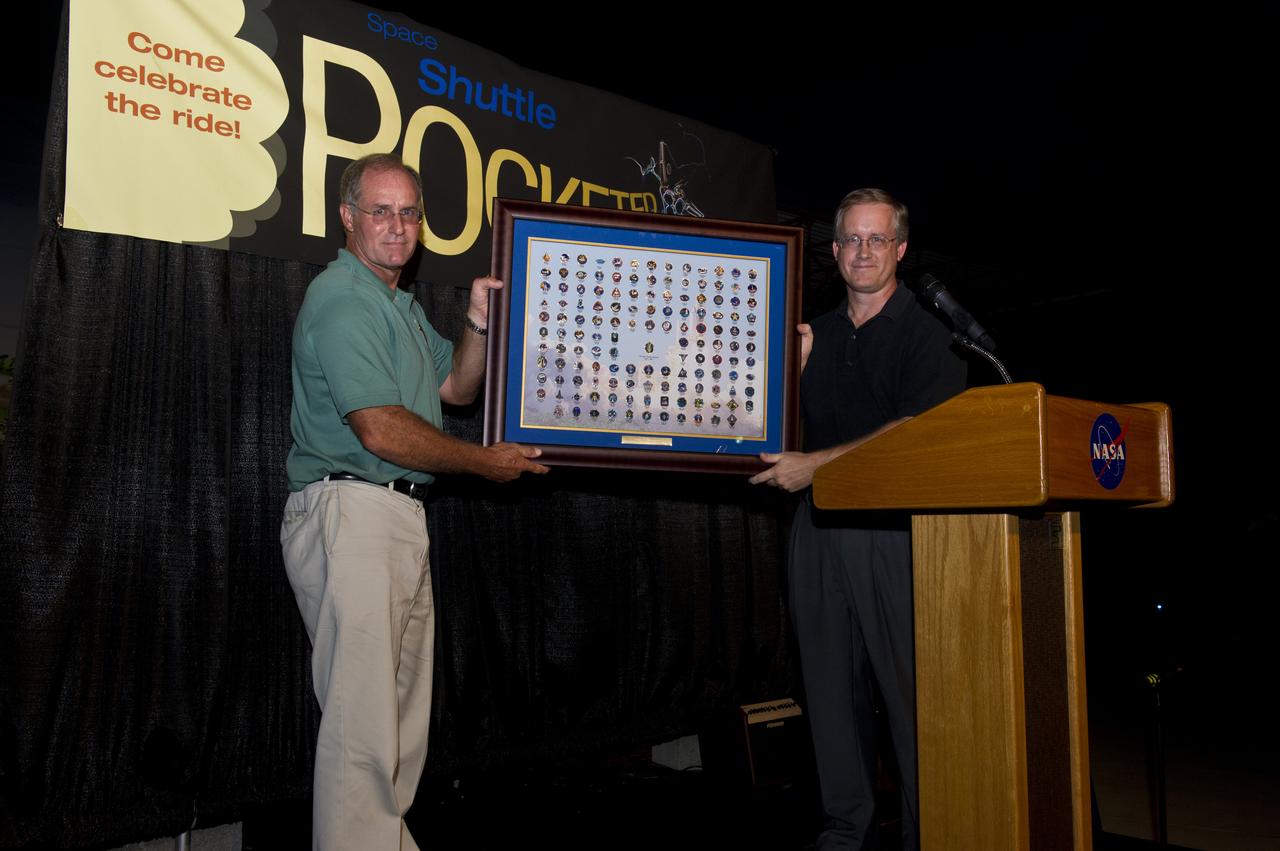

MARSHALL SHUTTLE PROPULSION OFFICE MANAGER STEVE CASH PRESENTS A MISSION PIN PLAQUE TO JOHN SHANNON, MANAGER OF THE SPACE SHUTTLE PROGRAM.
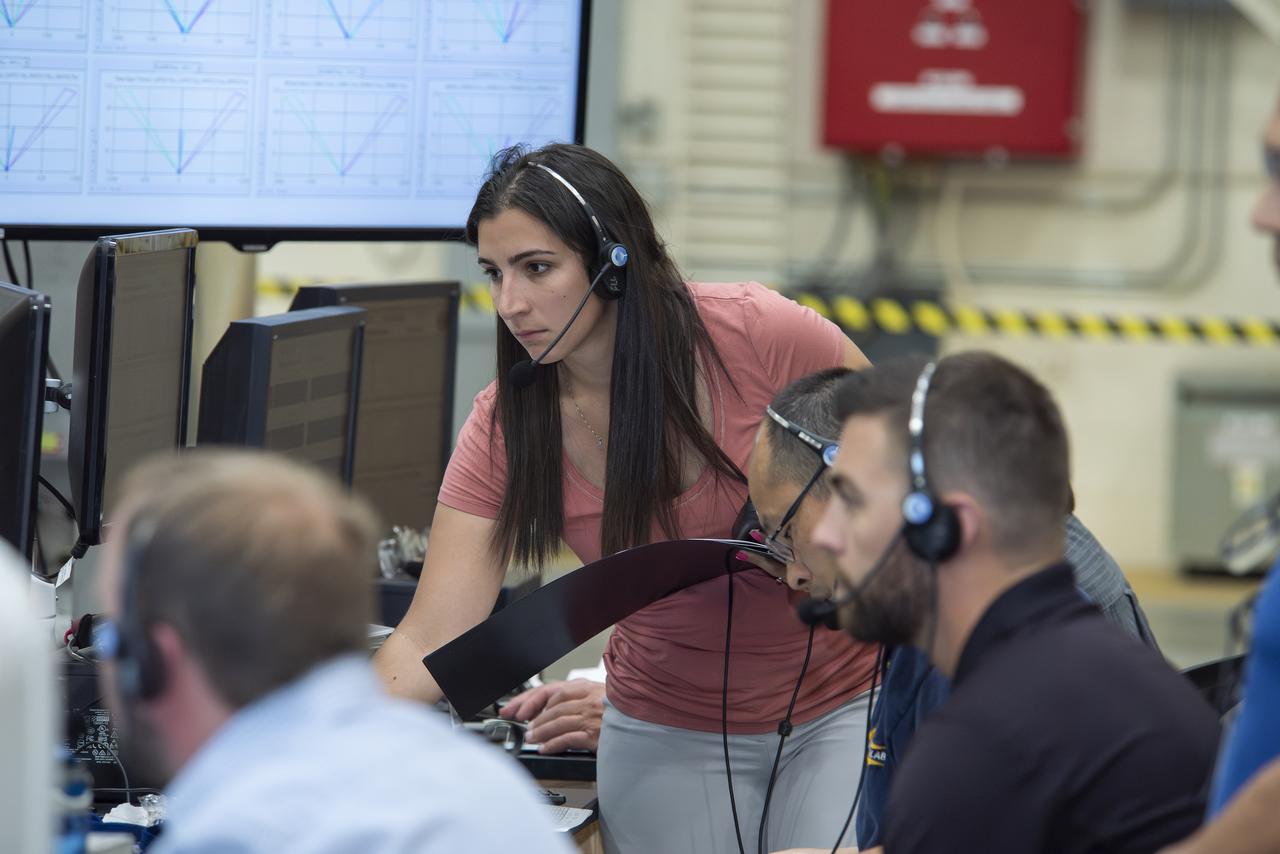

Kirsten Boogaard, Deputy Project Manager for the DC-8 aircraft, leads and manages project planning, integration and resources for airborne science missions since 2020
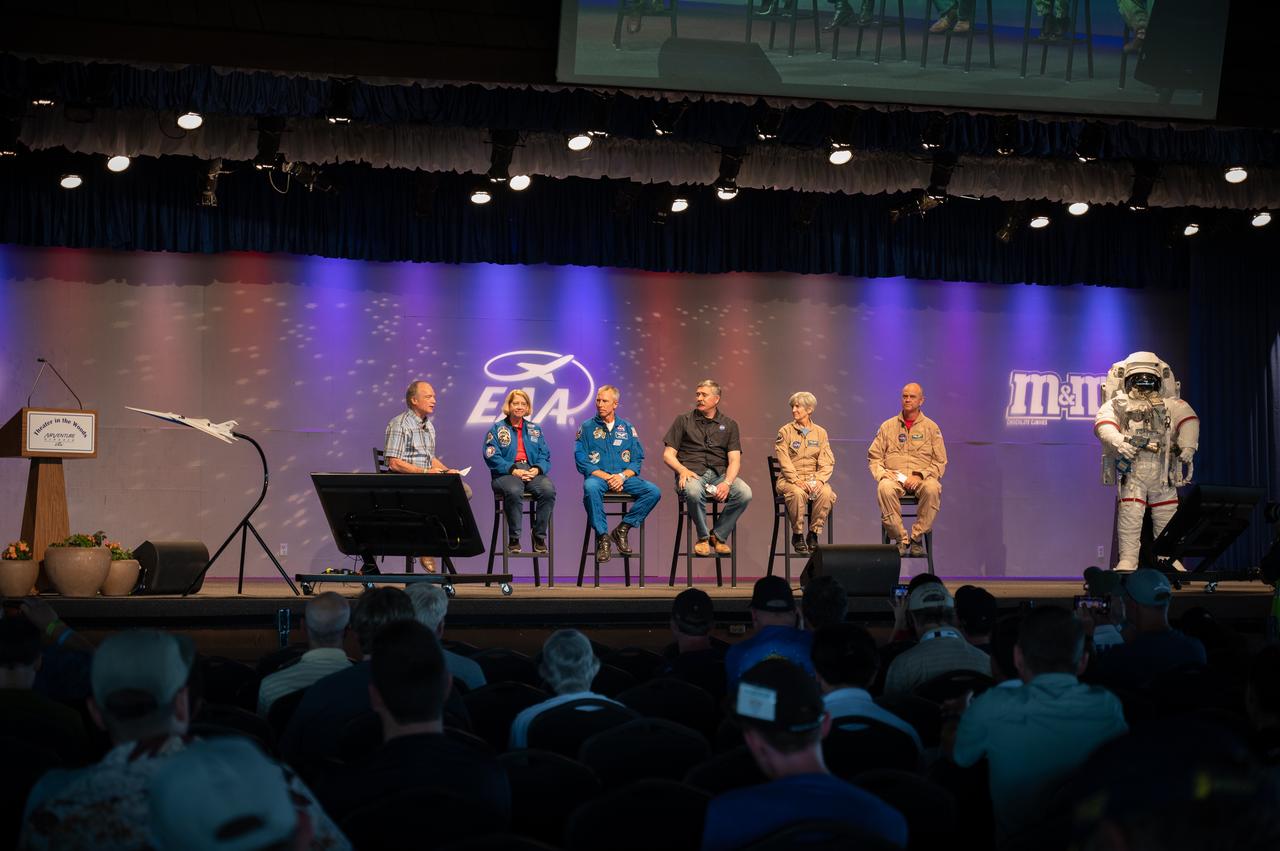

NASA panelists appear at special panel titled “The Next Bold Step: The Future of Space Flight and Aerospace,” on July 29, 2022, at EAA Airventure. Panelists include Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Astronaut Drew Feustel, Artemis Mission Manager Michael Sarafin, Research Pilot Liz Ruth and Test Pilot Nils Larson.
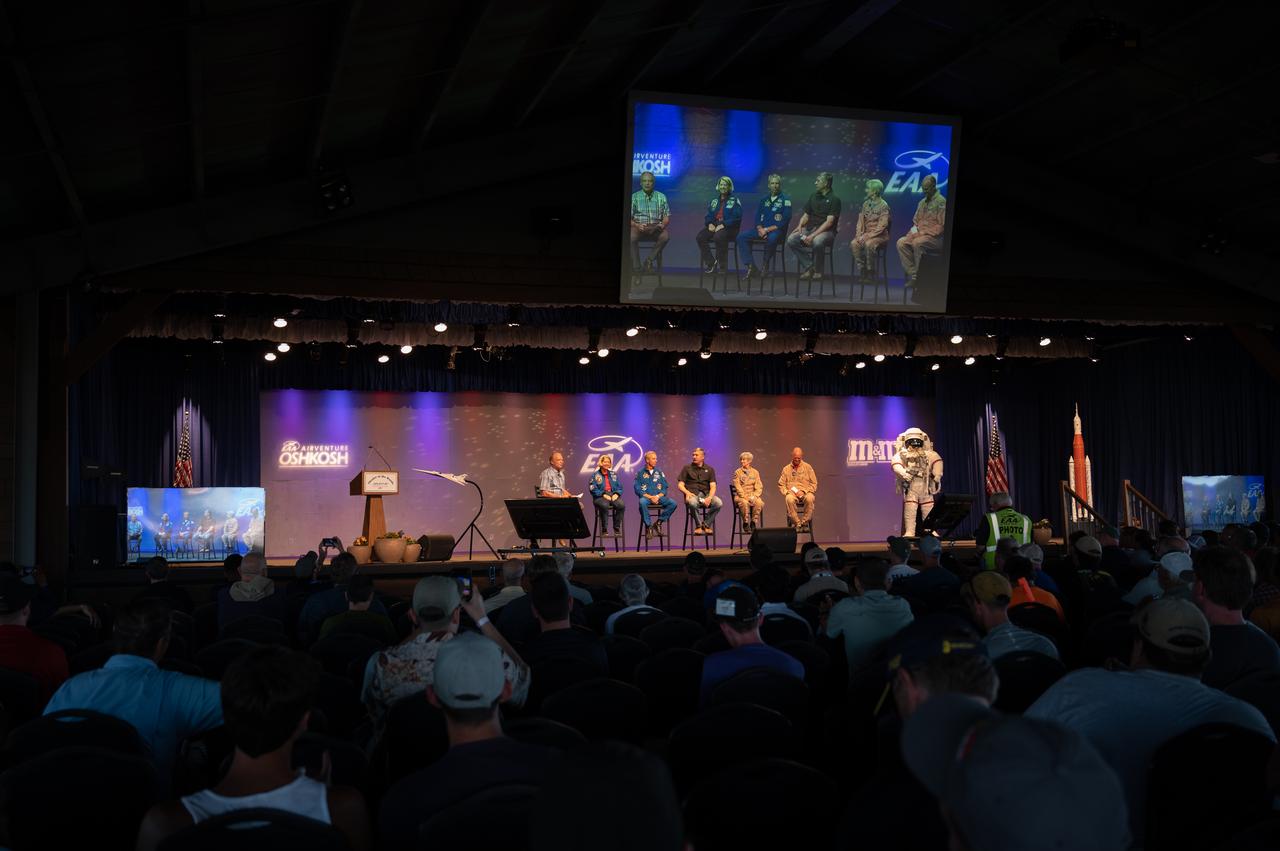

NASA panelists appear at special panel titled “The Next Bold Step: The Future of Space Flight and Aerospace,” on July 29, 2022, at EAA Airventure. Panelists include Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, Astronaut Drew Feustel, Artemis Mission Manager Michael Sarafin, Research Pilot Liz Ruth and Test Pilot Nils Larson.
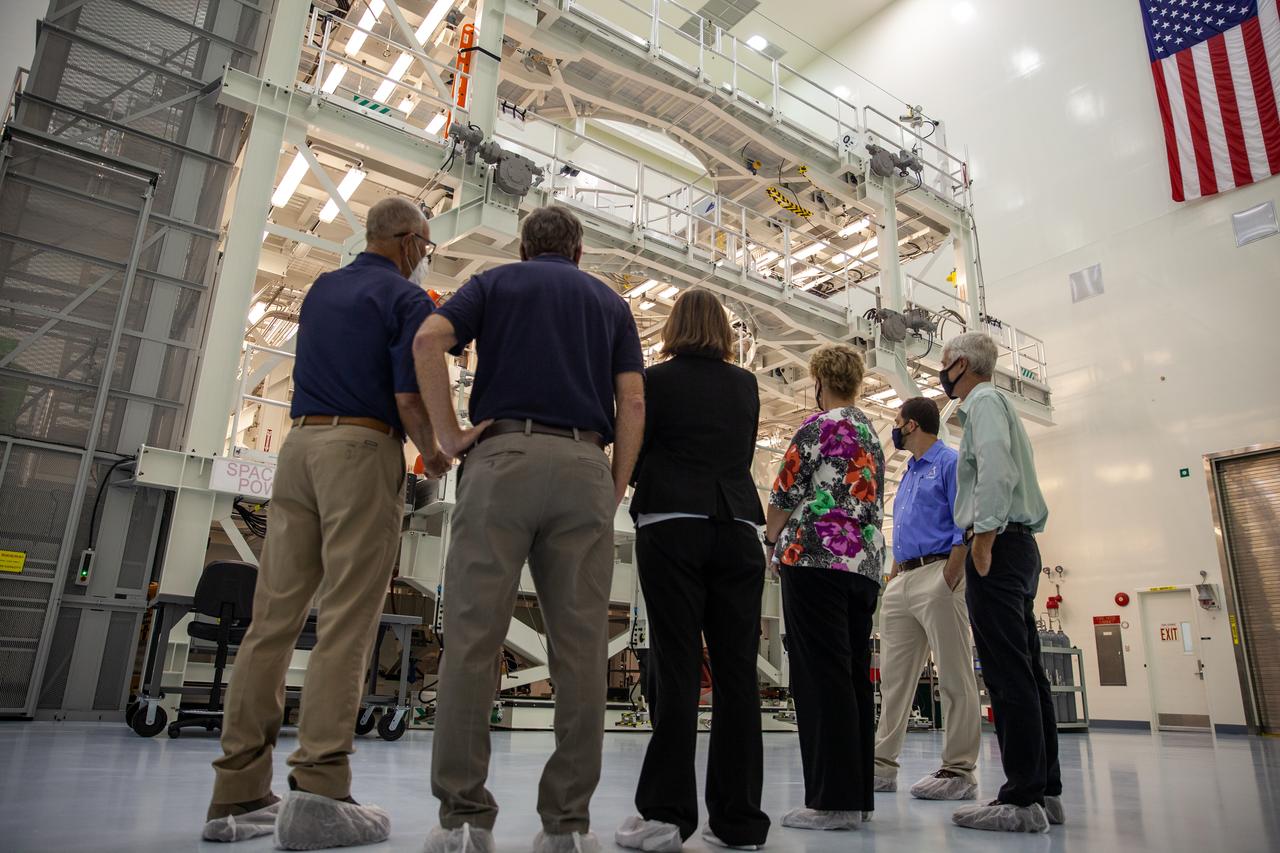

Catherine Koerner, third from left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), visits the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team; Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; and Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

Catherine Koerner, in front, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and TOSC, tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Nicolas Kindred, (partically hidden), TOSC flow manager; Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; Mike Bolger, (partially hidden), EGS manager; and Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
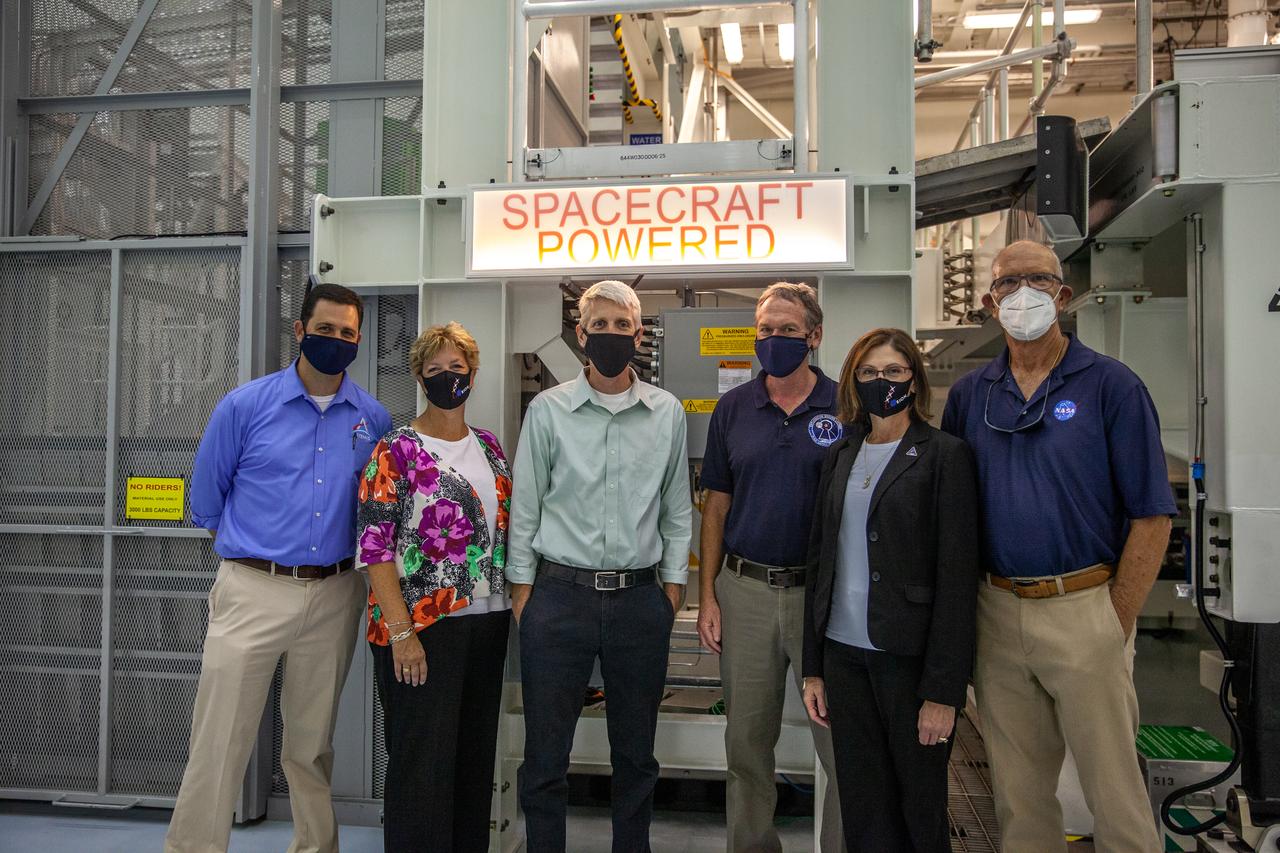

Catherine Koerner, second from right, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; and Mike Bolger, EGS manager. At far right is Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
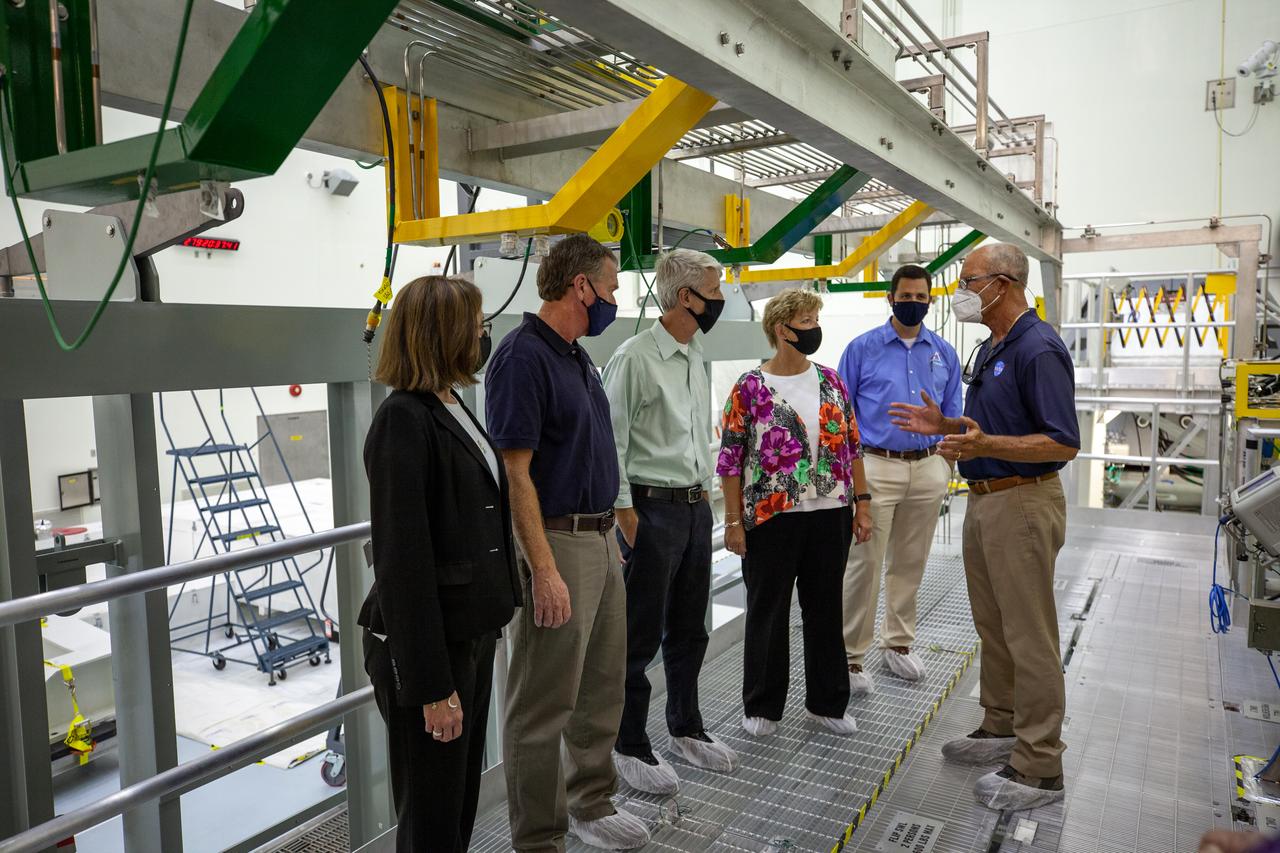

Catherine Koerner, far left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems (EGS), tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Mike Bolger, EGS manager; Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; and Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager. Speaking to the group is Skip Williams, operations manager for the MPPF spacecraft offline element integration team. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
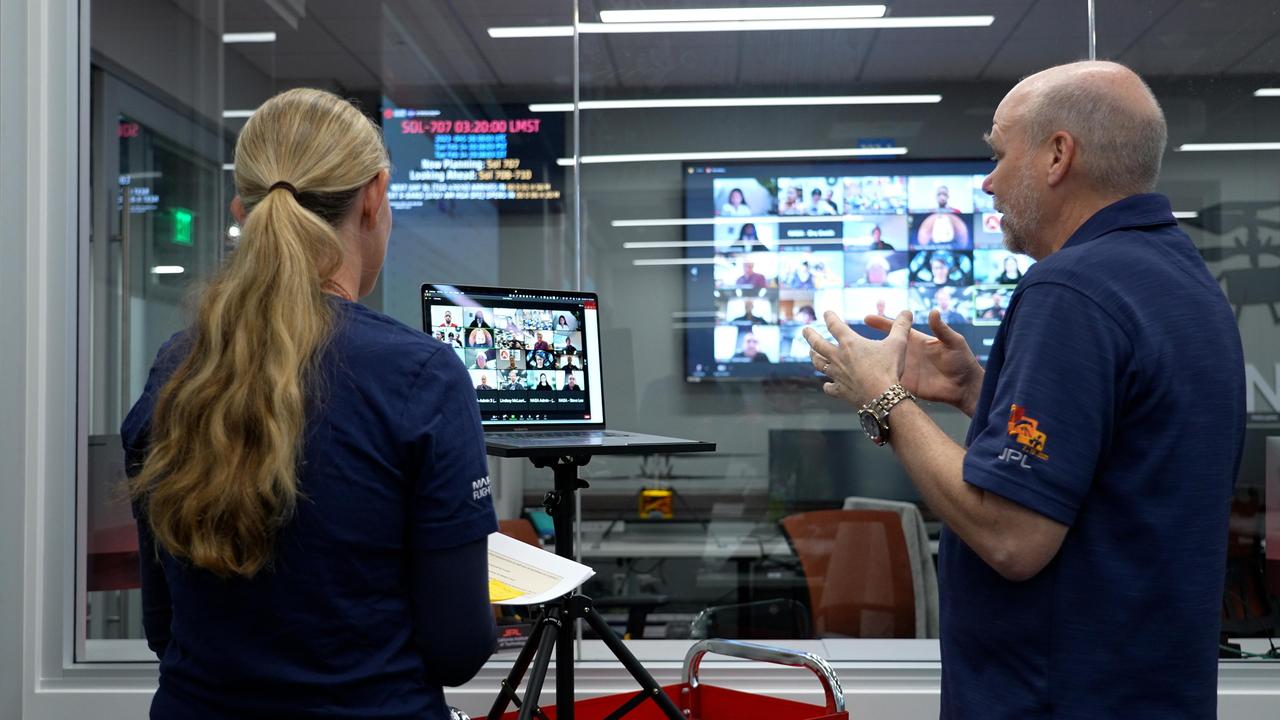

Perseverance Mars Rover Deputy Project Manager Rich Welch and Mission Lead Beth Dewell, spoke with middle- and high-school students during a live webinar from the rover's mission control at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, on Feb. 14, 2023. The event honored students in the "You've Got Perseverance," campaign, which recognizes those who have overcome academic obstacles, with a personalized message to each student. To nominate a student for the next round, go to https://mars.nasa.gov/mars2020/participate/got-perseverance/nominate/. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25796

LADEE them member Butler Hine, Mission Manager
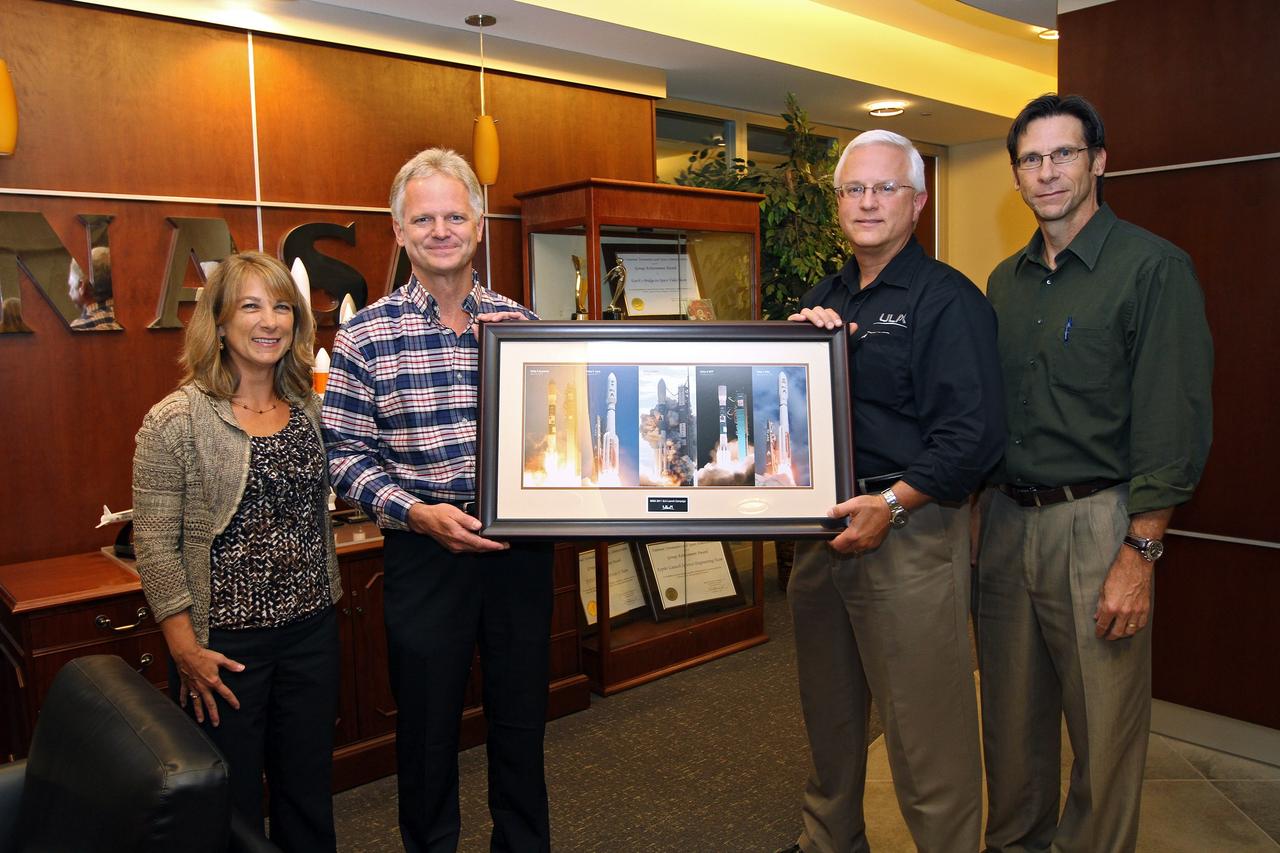

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Launch Services Program, or LSP, Program Manager Amanda Mitskevich, at far left, was presented with a framed commemorative collage of five United Launch Alliance, or ULA, mission photos in 2011 from Jim Sponnick, second from left, vice president of Mission Operations at ULA. Also at the presentation, were ULA Program Manager for NASA Missions Vern Thorp and LSP Deputy Program Manager Chuck Dovale. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
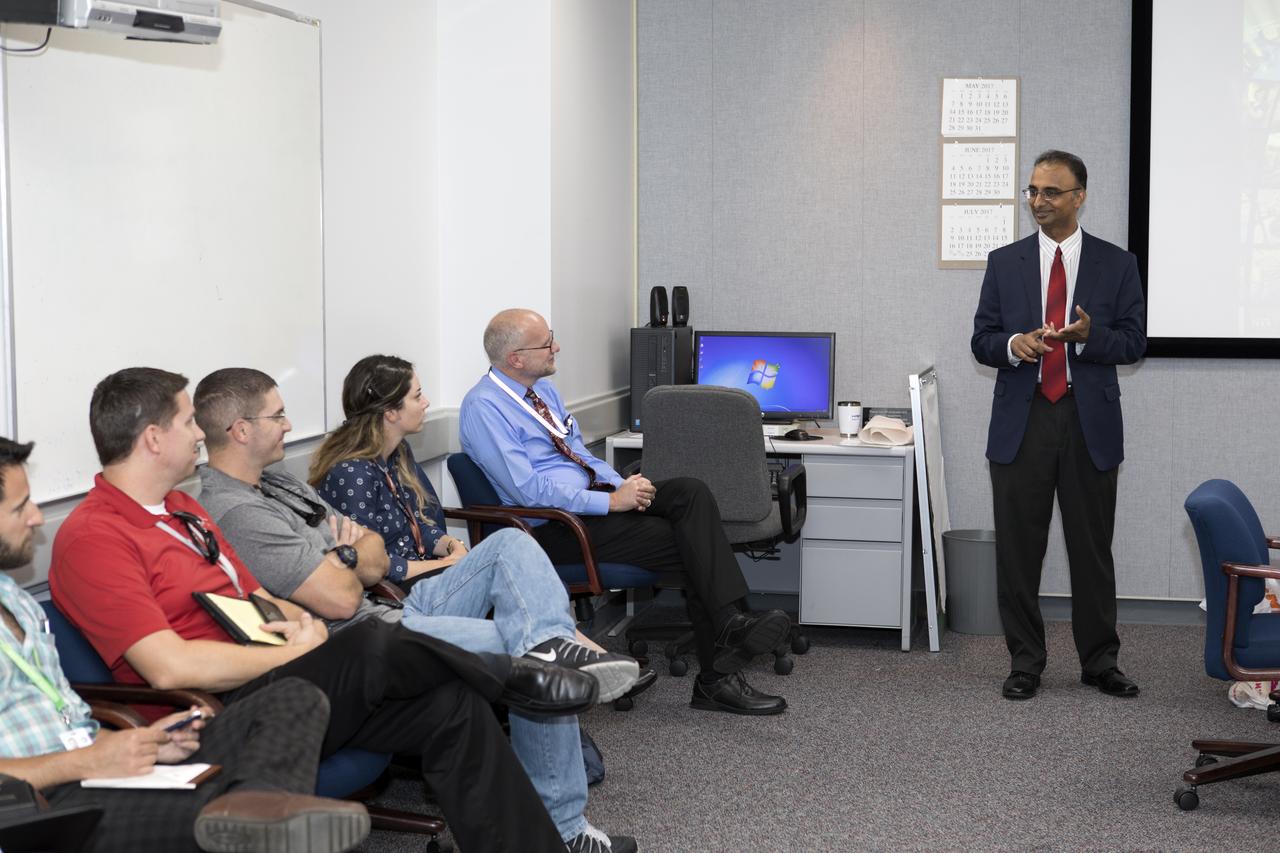

Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator for Management in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate, speaks to Exploration Research and Technology managers in the Space Station Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
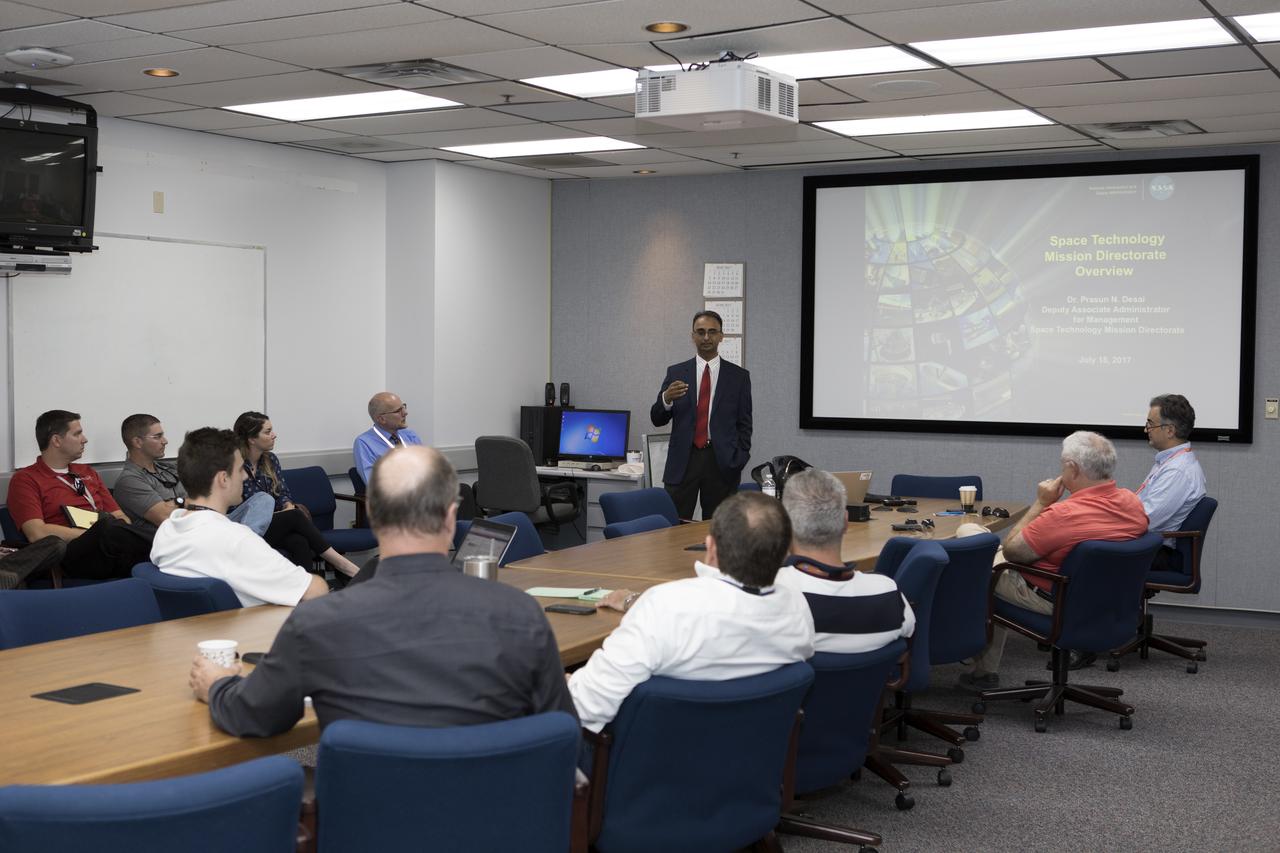

Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator for Management in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate, speaks to Exploration Research and Technology managers in the Space Station Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
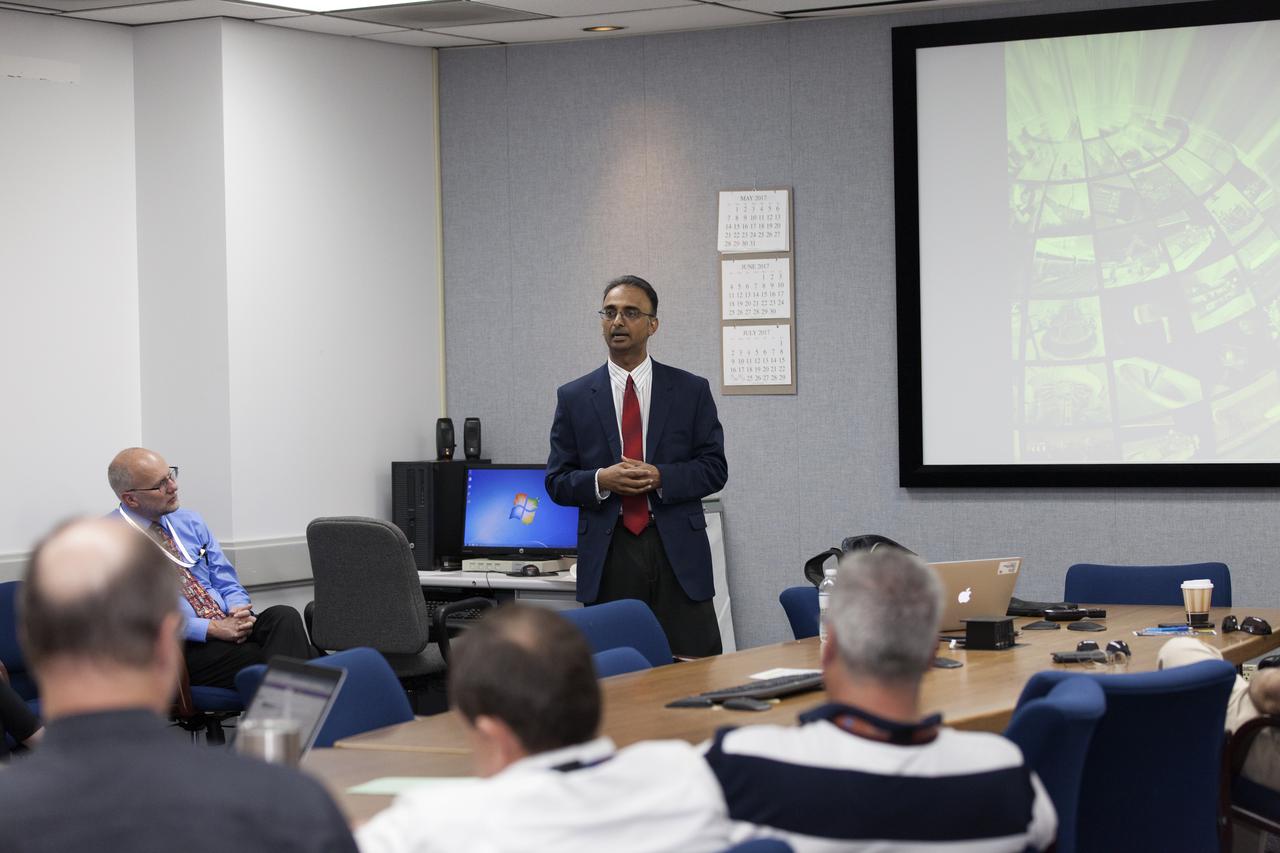

Prasun Desai, deputy associate administrator for Management in NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate, speaks to Exploration Research and Technology managers in the Space Station Processing Facility at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

Catherine Koerner, second from right, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion, Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) and TOSC, tours the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 5, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Scott Wilson, Orion Production Operations manager; Mike Bolger, EGS manager; and Nicolas Kindred, TOSC flow manager. At right is Jeremy Parsons, EGS deputy manager. Koerner viewed spacecraft hardware and processing facilities for the Artemis I and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
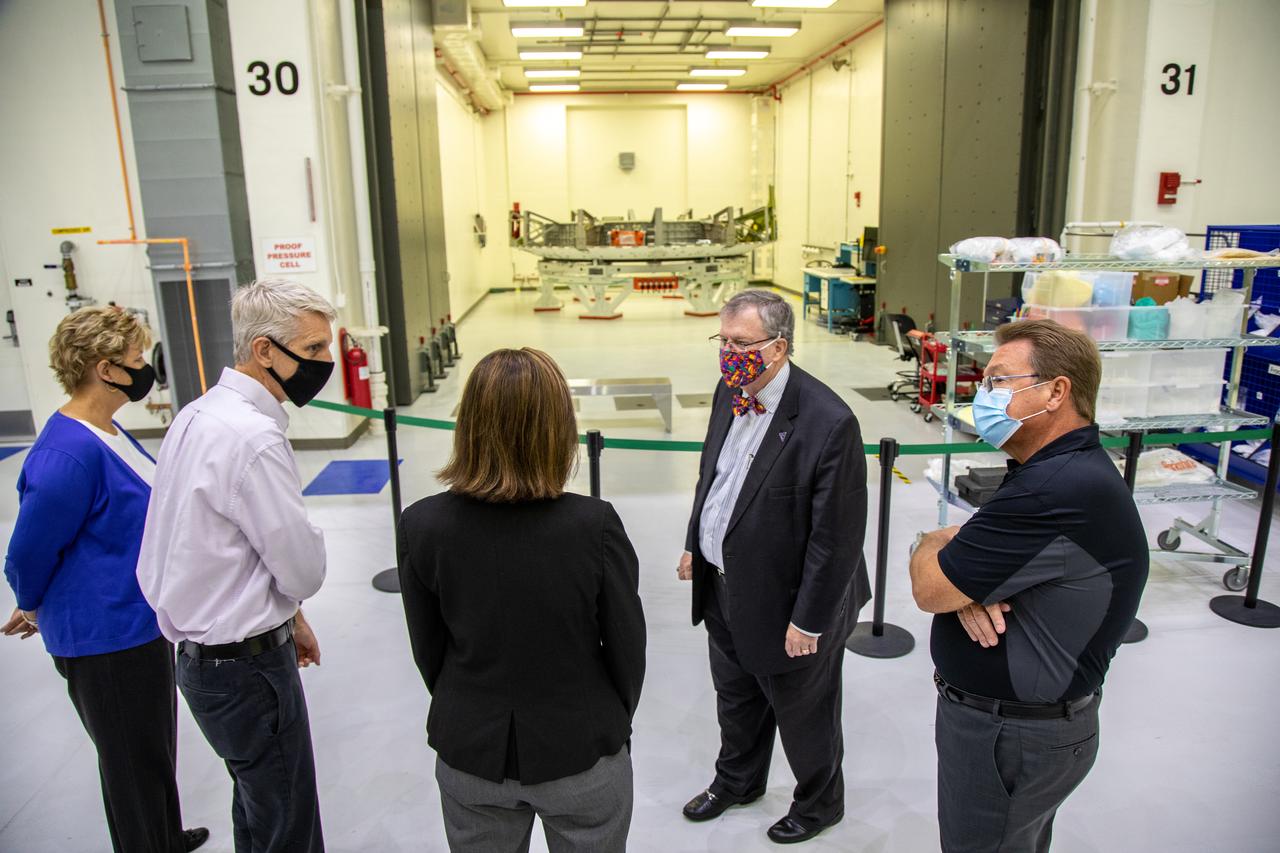

Catherine Koerner, in the center, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tours the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her, from left are Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager, Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager; and Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Assembly, Test and Launch Operations director with Lockheed Martin. Koerner viewed the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions. They are shown with the crew module adapter for the Orion Artemis II mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
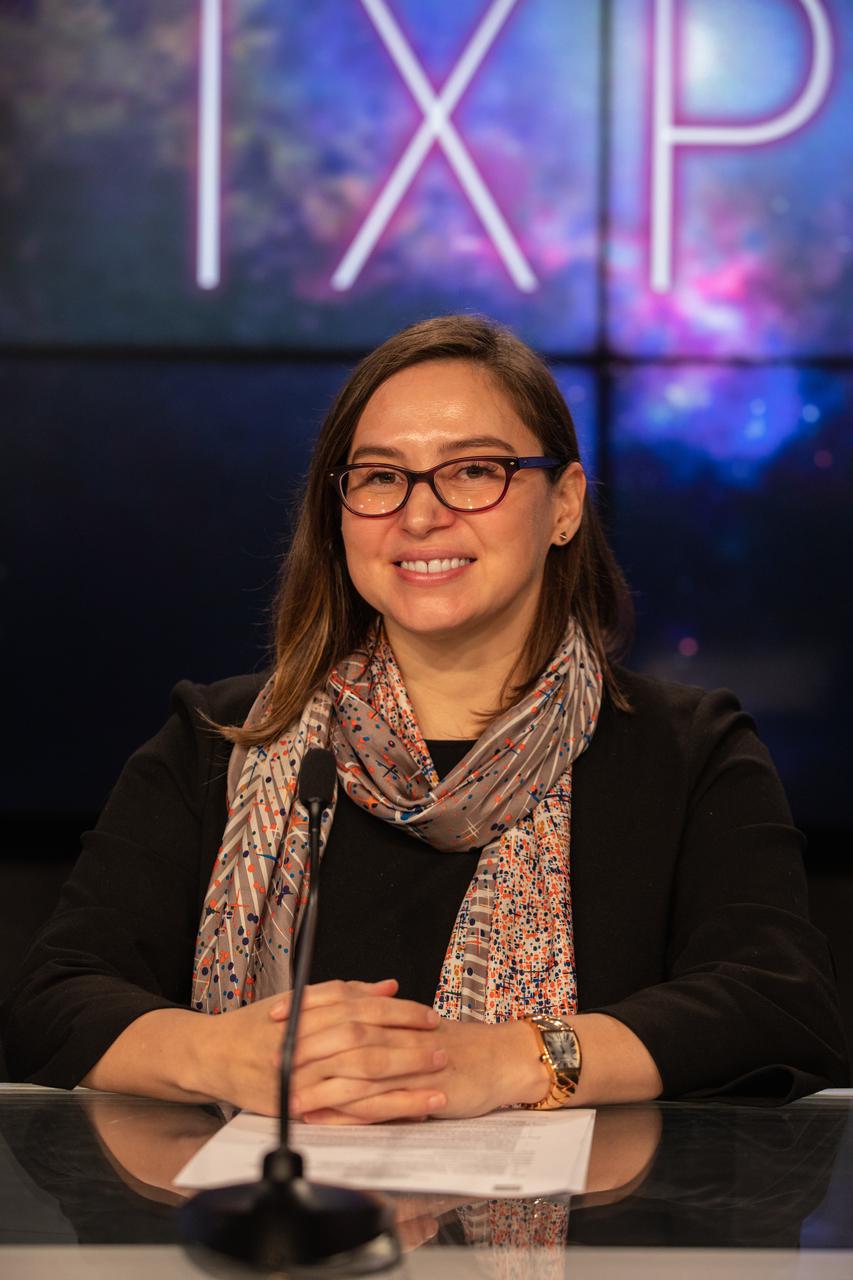

Makenzie Lystrup, vice president and general manager, civil space, Ball Aerospace, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.

From left, Richard Jones, CCP (Commercial Crew Program) deputy program manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Steve Stich, program manager for CCP; Dana Hutcherson, CCP deputy program manager at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida; and Diana Oglesby, director, Strategic Integration and Management Division, Space Operations Mission Directorate, pose with the agency’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission flag near the countdown clock at the NASA News Center at the Kennedy on Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024. Oglesby previously served as manager of CCP’s Program Control and Integration Office at Kennedy. The Crew-9 mission will send NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket.
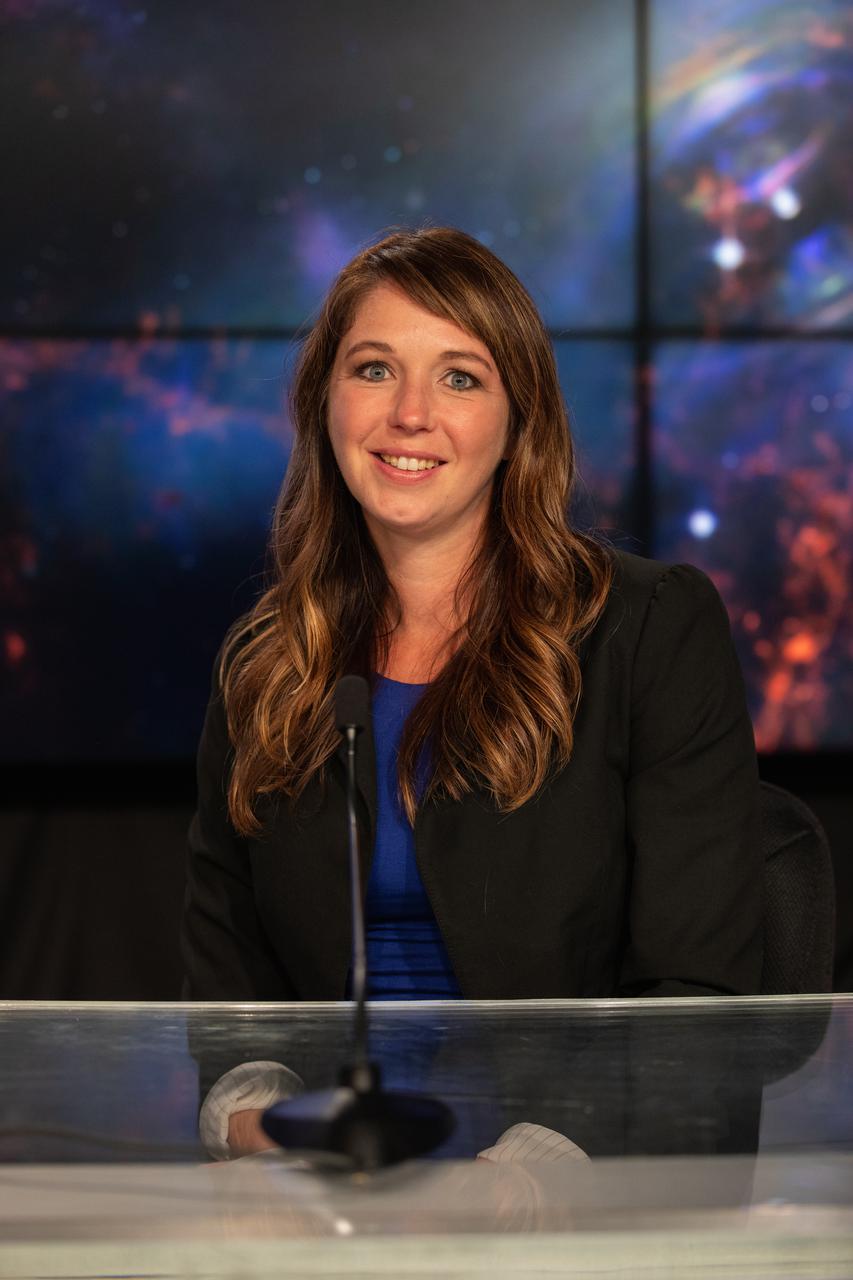

MacKenzie Ferrie, IXPE program manager, Ball Aerospace, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
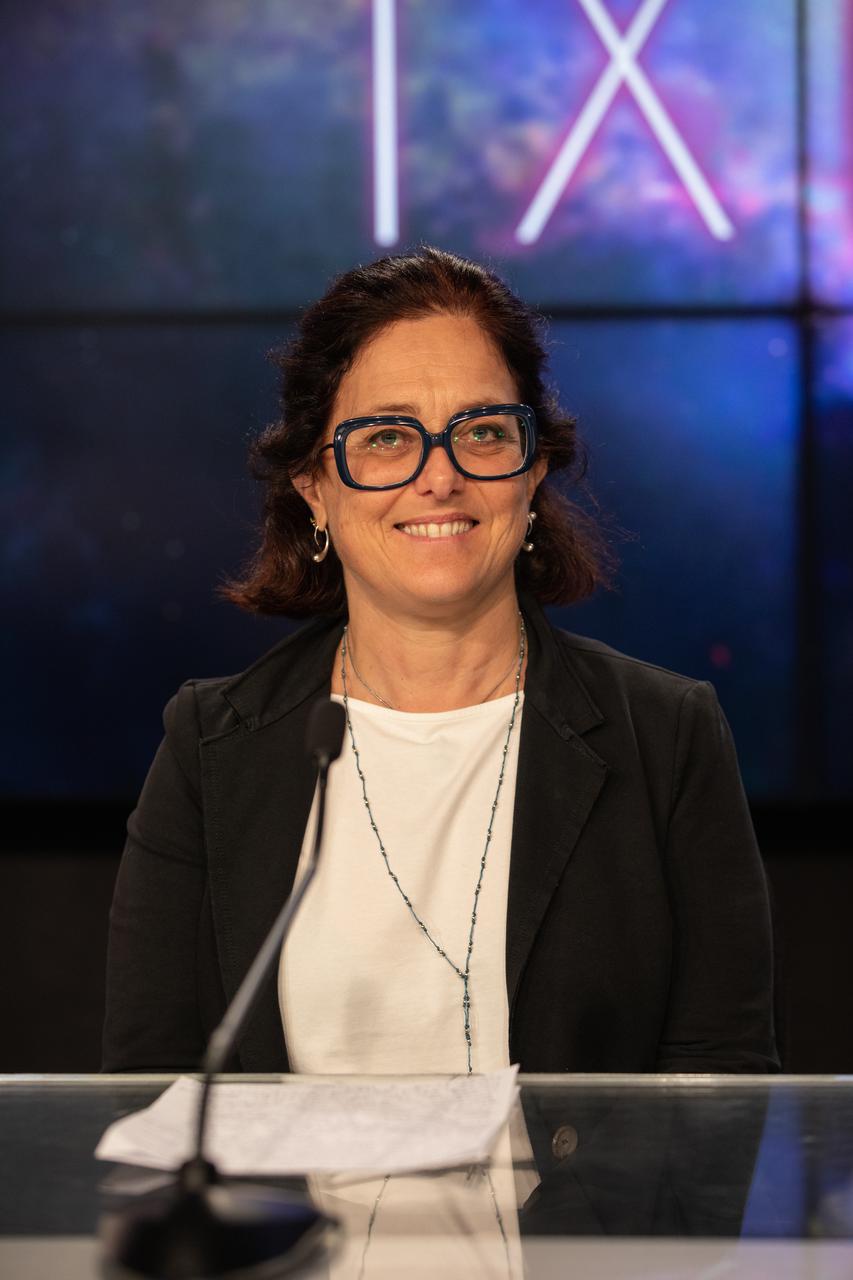

Elisabetta Cavazzuti, ASI IXPE program manager, Italian Space Agency, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
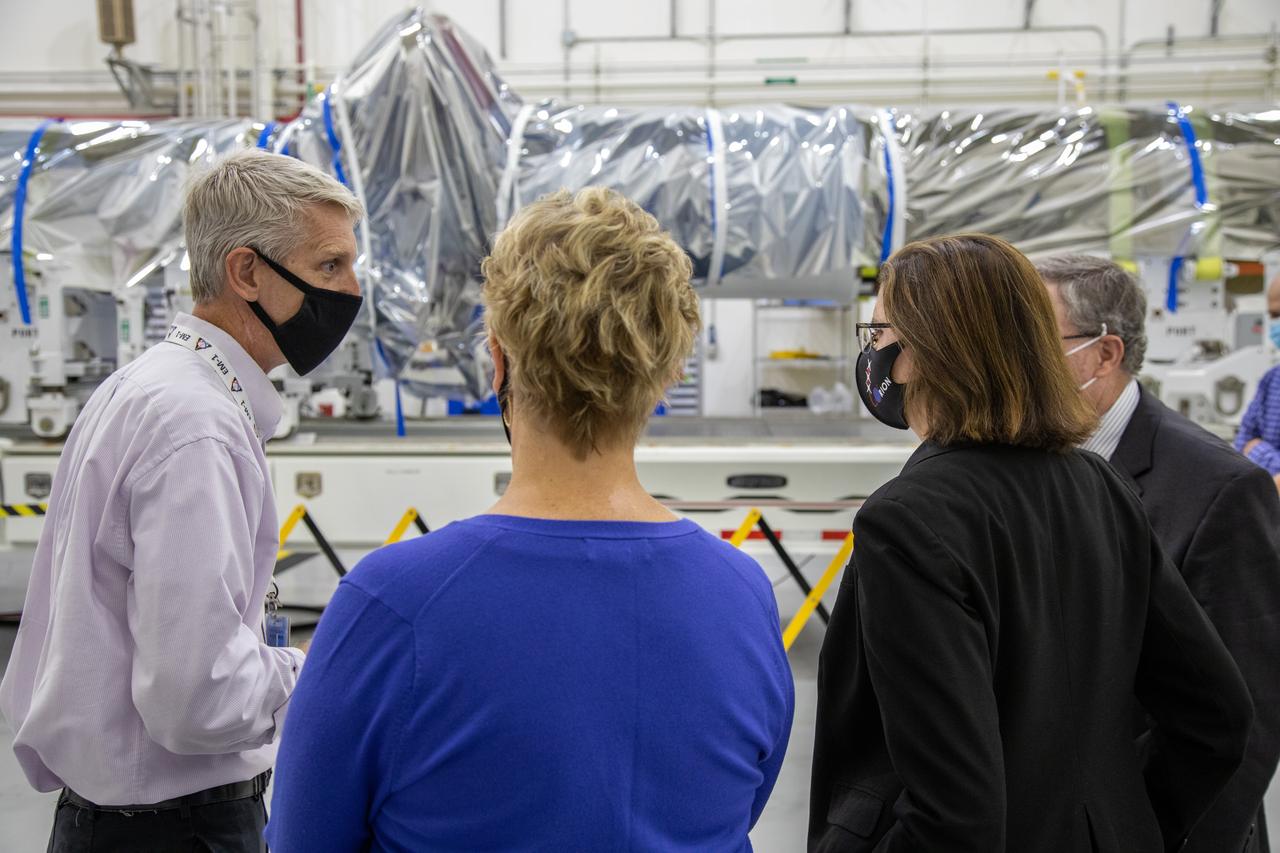

Catherine Koerner, second from right, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tour the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her from left, are Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager; Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager; and Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager. They are viewing the launch abort system for the Artemis II mission. Koerner also viewed the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
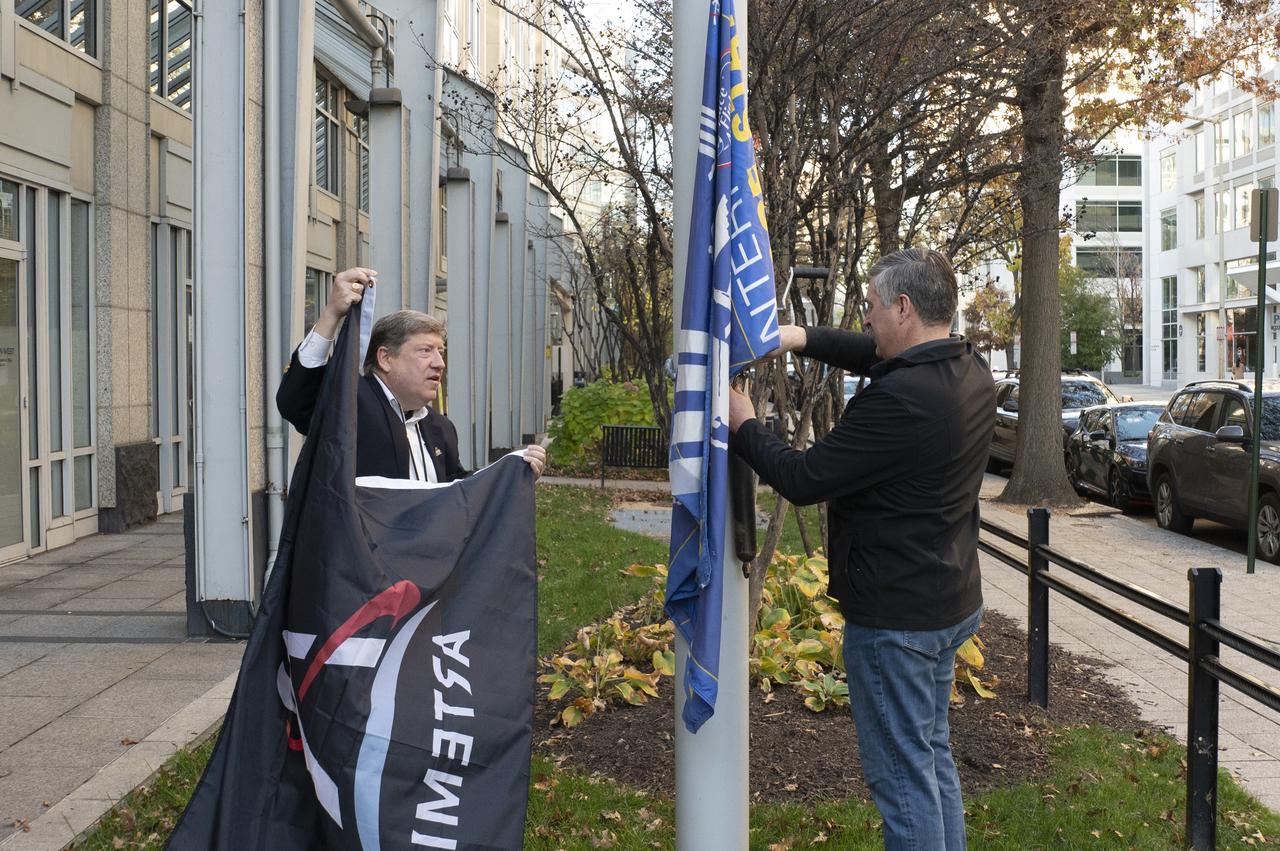

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
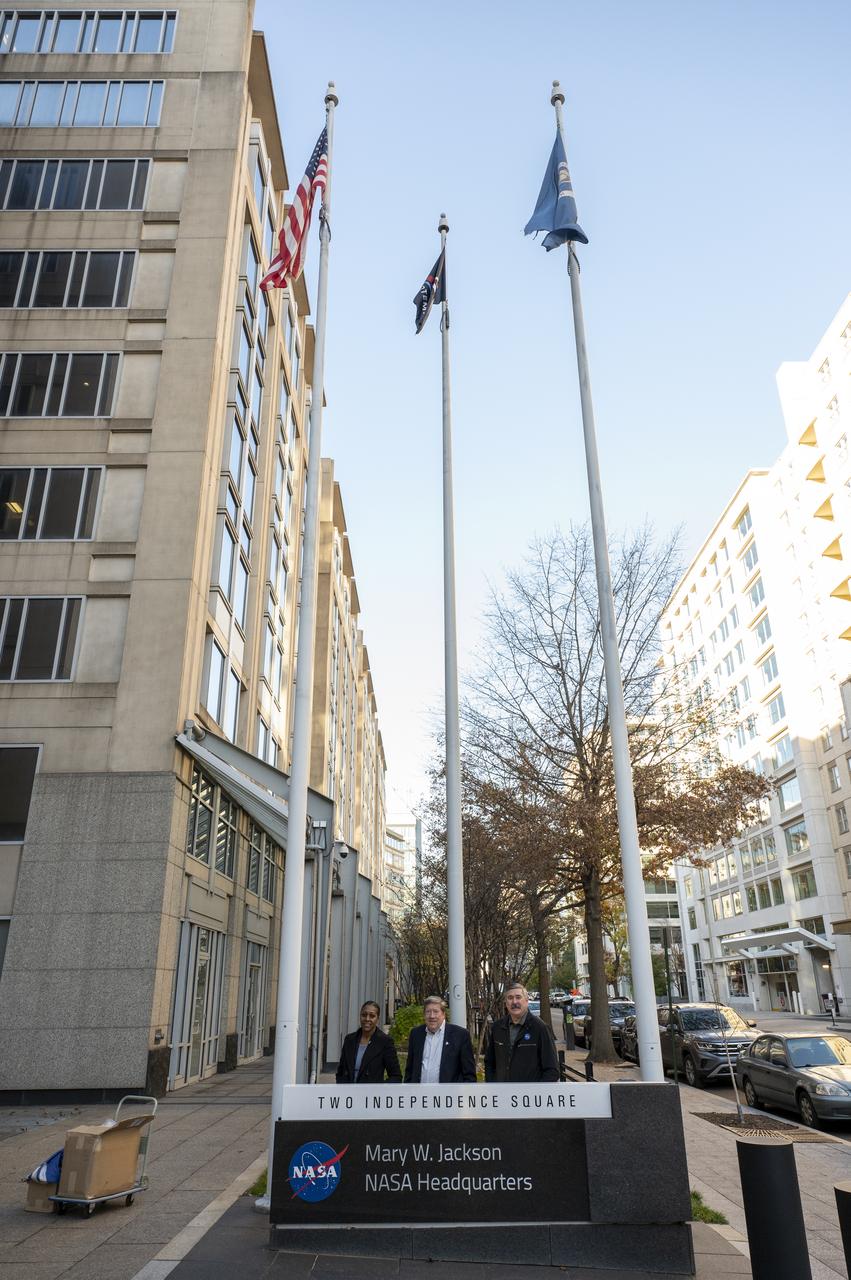

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
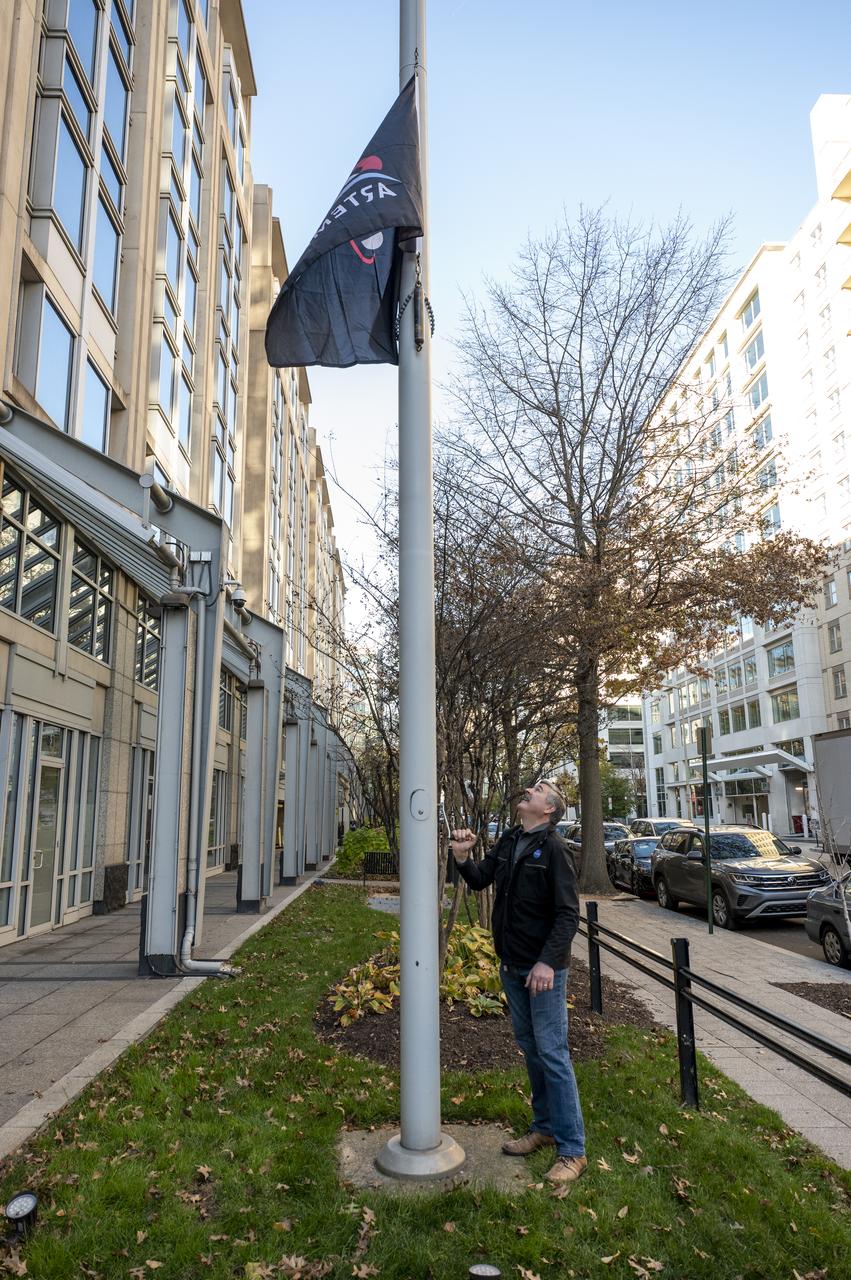

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
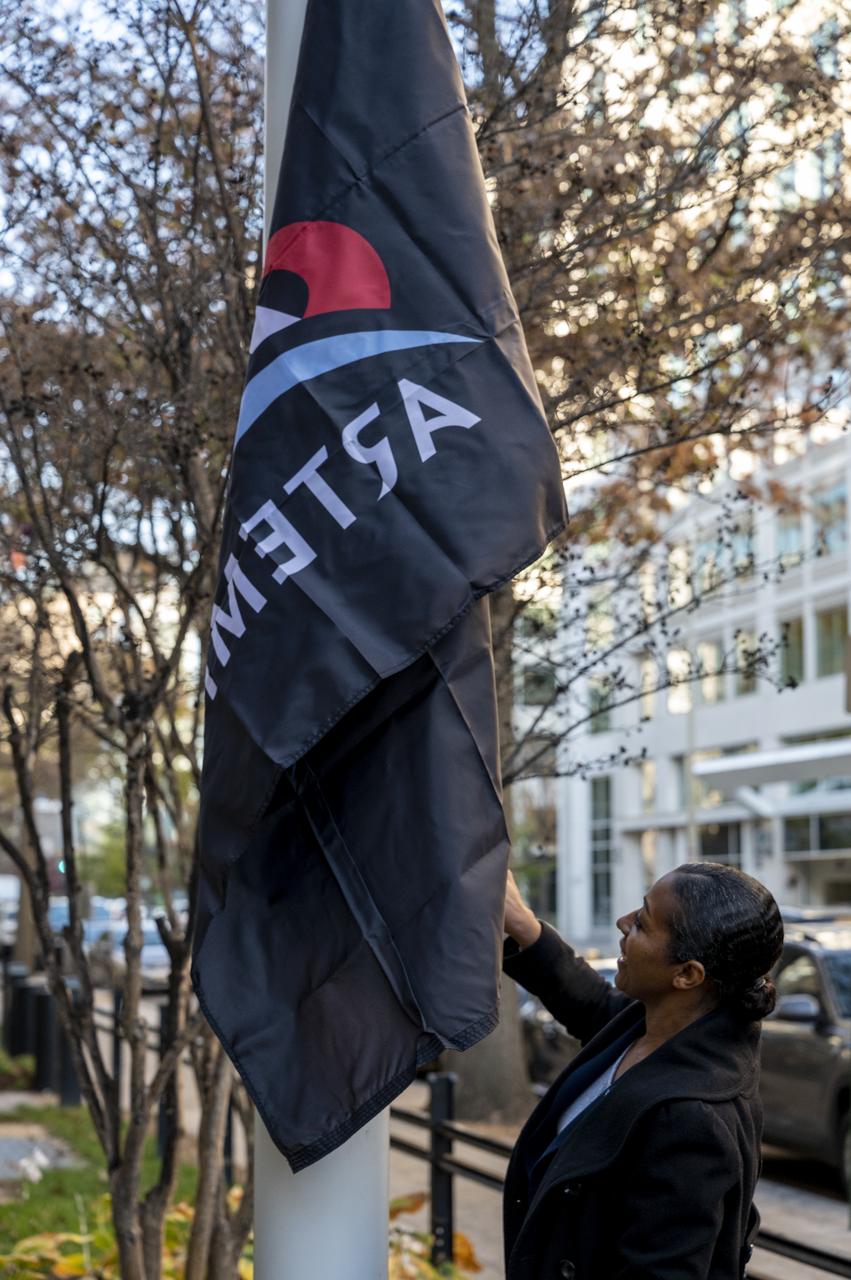

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
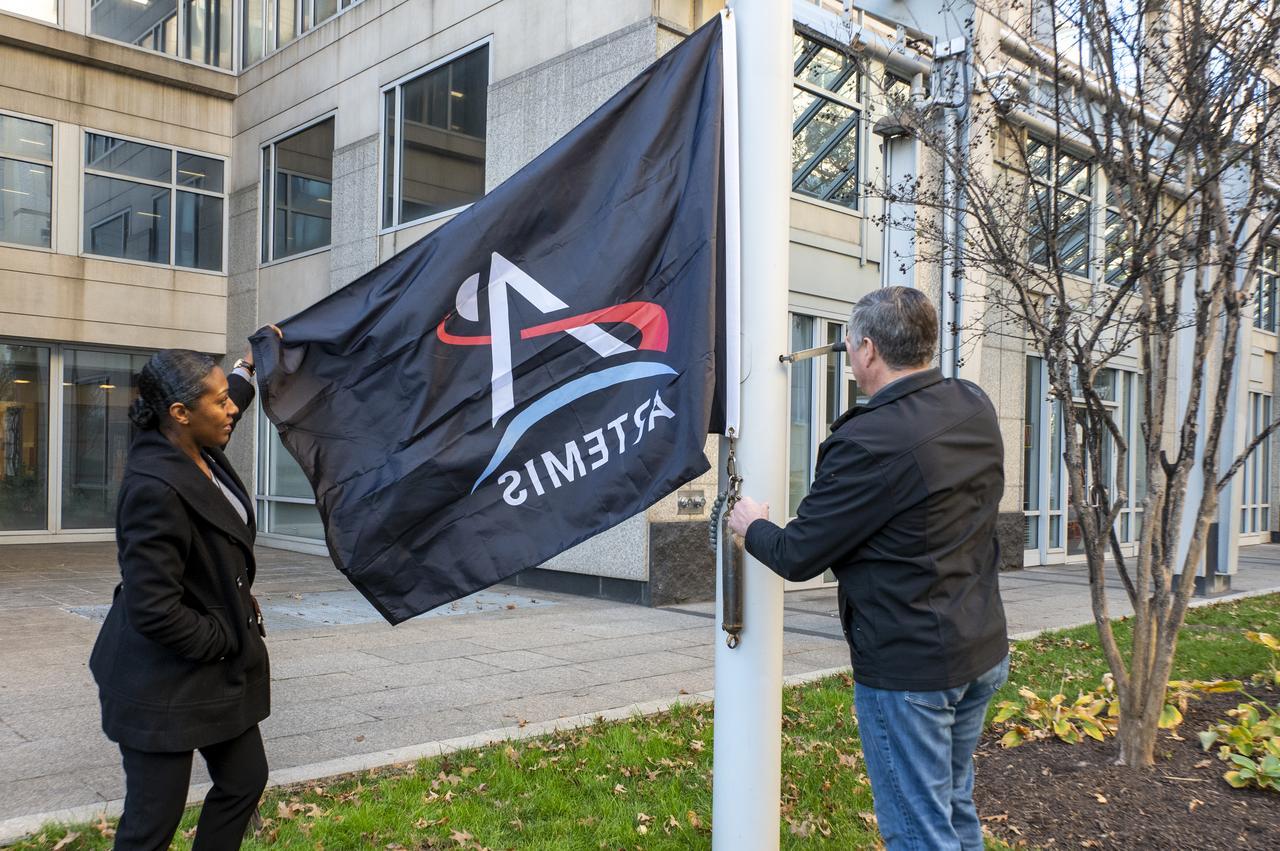

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

Artemis Mission Development Manager Mike Sarafin, Artemis Mission Integration Manager Sheela Logan, and Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for Exploration Systems Development Tom Whitmeyer raise Artemis flags Wednesday, Nov. 23, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
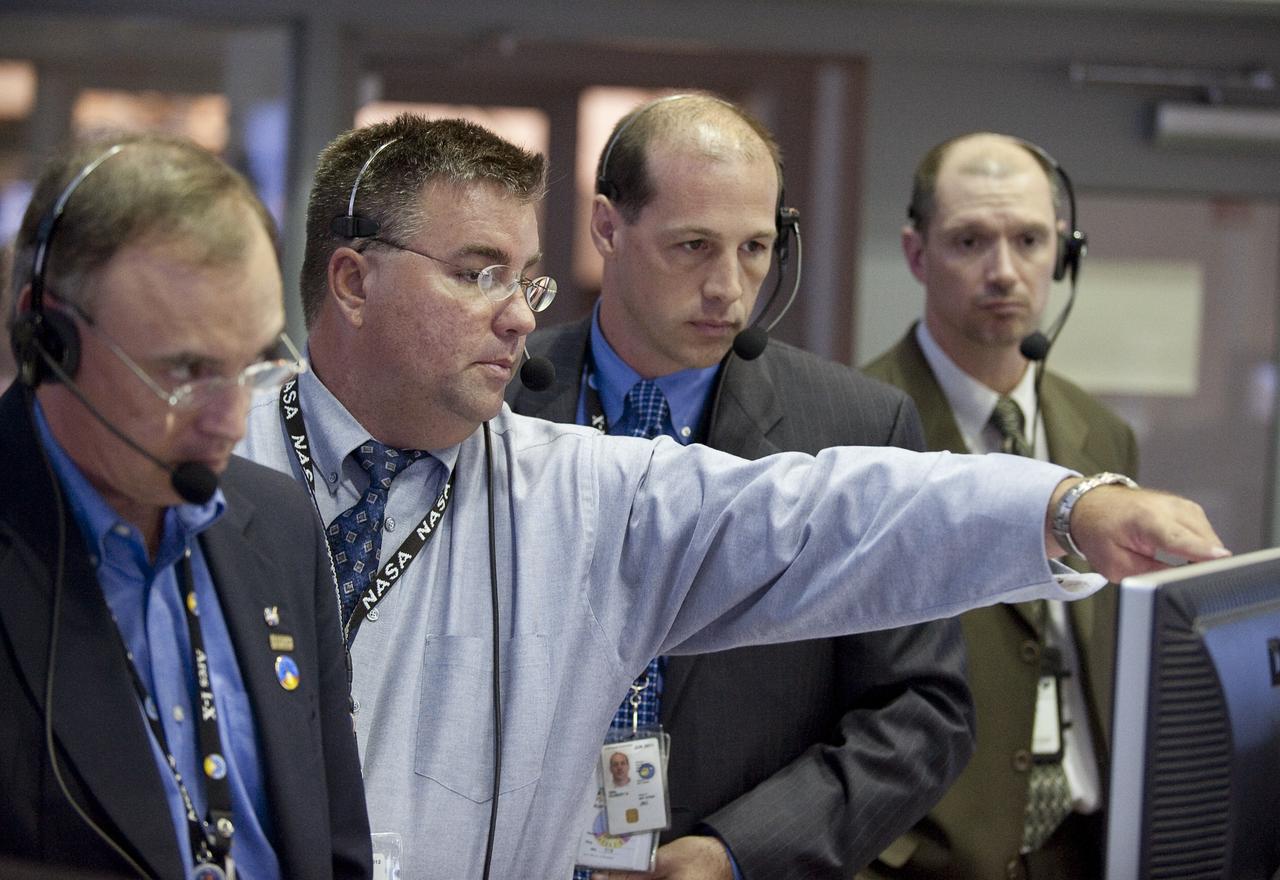

Mission managers, from left, NASA Constellation Program manager Jeff Hanley, Ares I-X Launch Director Ed Mango, Ares I-X mission manager Bob Ess, Ground Operations Manager Philip "Pepper" Phillips, review the latest data in Firing Room One of the Launch Control Center (LCC) at the Kennedy Space Center during the launch countdown of the Ares I-X rocket in Cape Canaveral, Fla., Tuesday, Oct. 27, 2009. The flight test of Ares I-X will provide NASA with an early opportunity to test and prove flight characteristics, hardware, facilities and ground operations associated with the Ares I. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
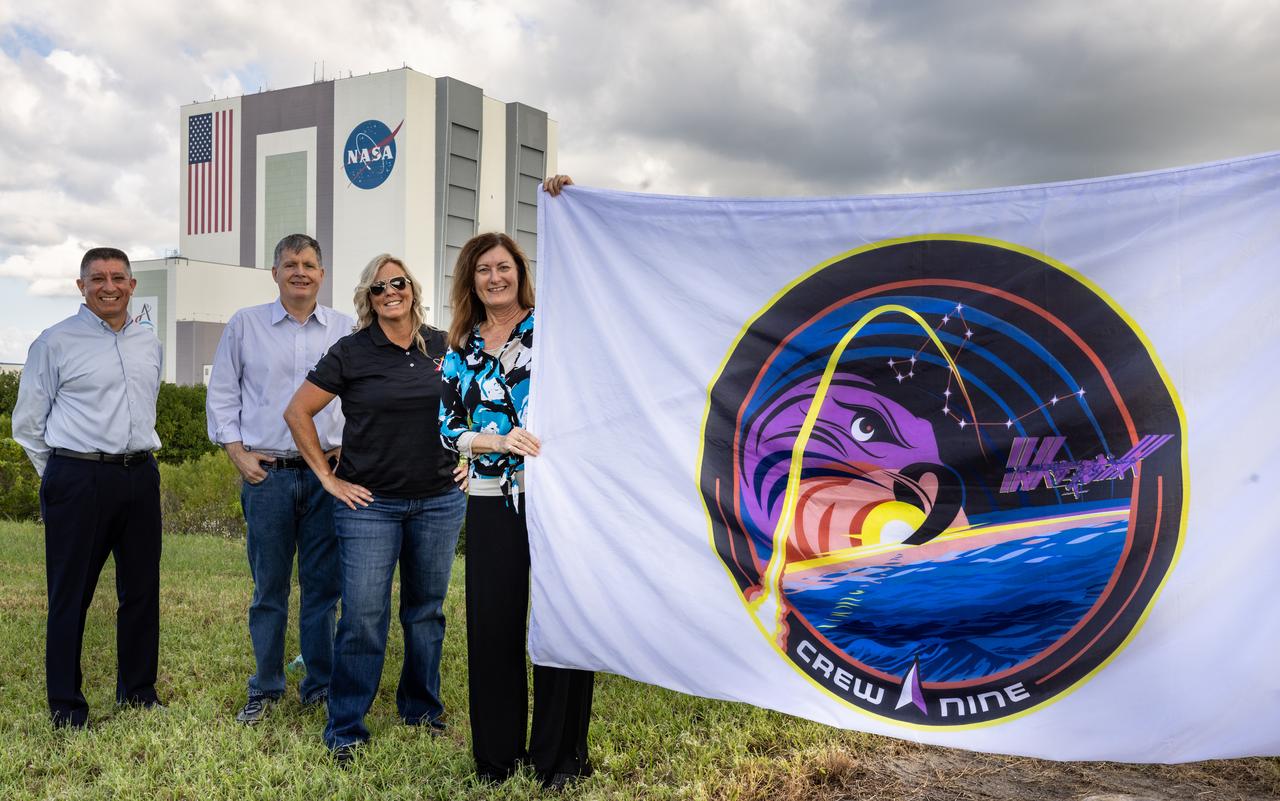

From left, Richard Jones, CCP (Commercial Crew Program) deputy program manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Steve Stich, program manager for CCP; Dana Hutcherson, CCP deputy program manager at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida; and Deb Cole, CCP technical manager, pose with the agency’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission flag near the countdown clock at the NASA News Center at Kennedy on Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024. The Crew-9 mission will send NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket.

LADEE them member Steve Spremo, Deputy Mission Manager
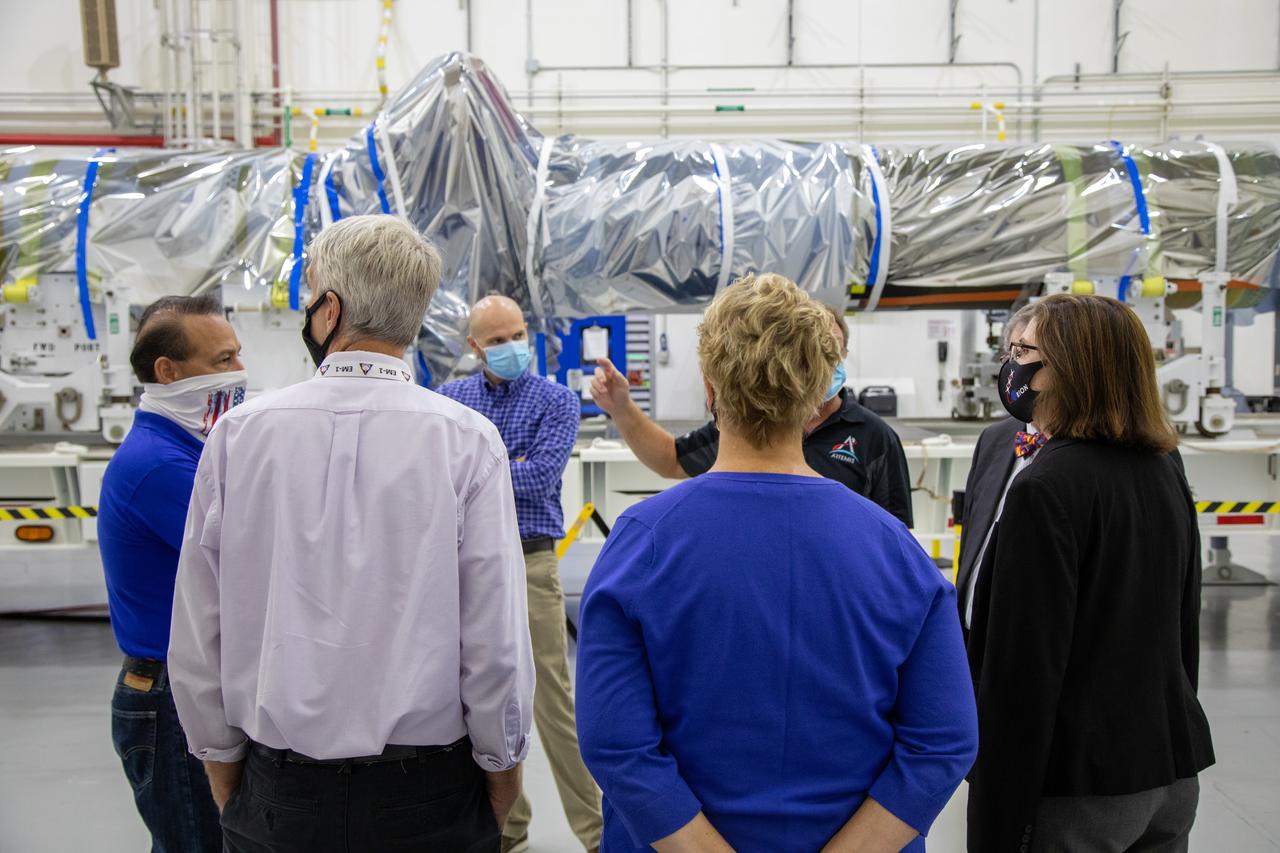

Catherine Koerner, far right, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tour the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her from left, are Carlos Garcia, NASA Kennedy Launch Abort System Assembly, Integration and Test lead and Resident office manager; Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager; Jim Skaggs, Kennedy Operations senior manager with Lockheed Martin; Jules Schneider, Kennedy Assembly, Test and Launch Operations director with Lockheed Martin; Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager; and Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager. They are viewing the launch abort system for the Artemis II mission. Koerner also viewed the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
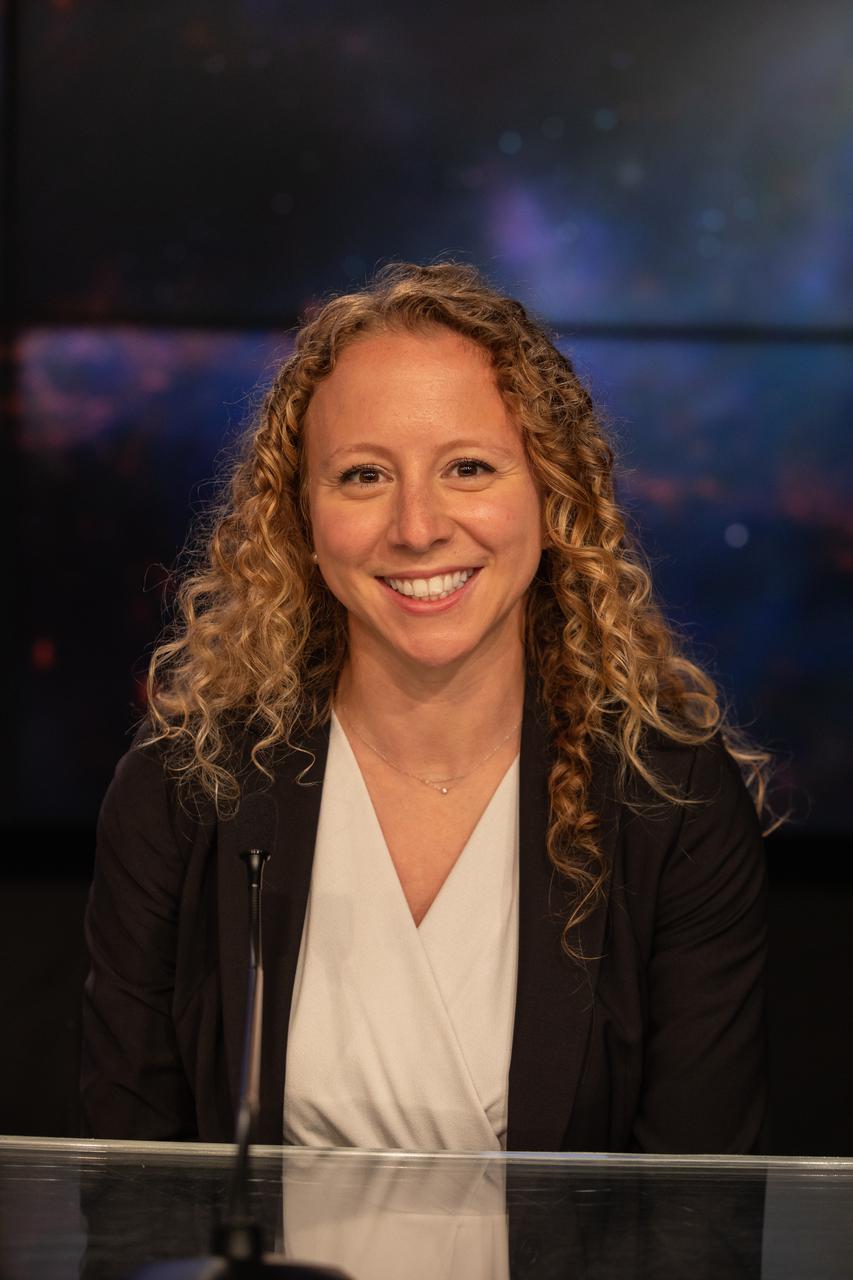

Julianna Scheiman, director, civil satellite missions, SpaceX, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
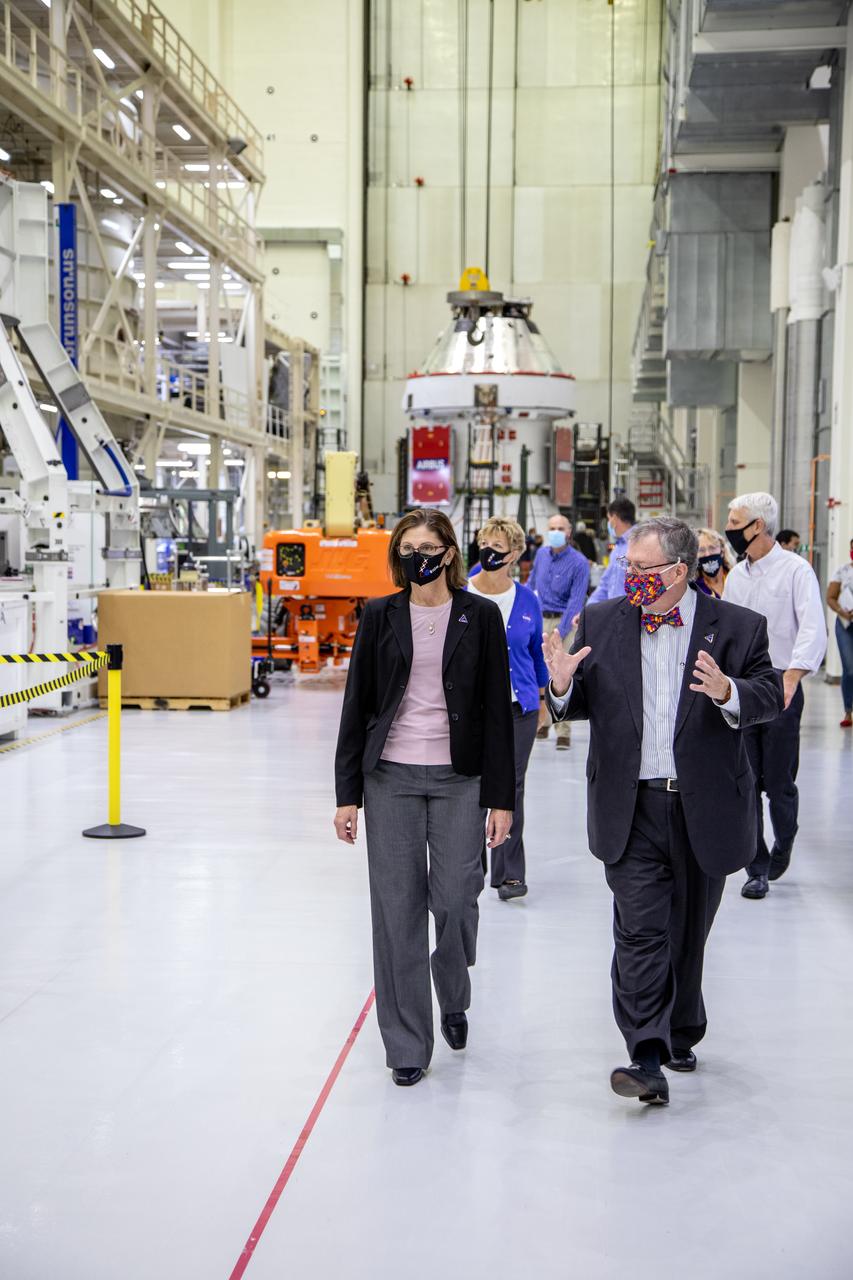

Catherine Koerner, in front at left, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tour the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her, in front at right is Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager. In view behind Koerner is Annette Hasbrook, Orion Program assistant manager. In view behind Hawes is Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager. Koerner viewed Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I, shown in the background, and II missions. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
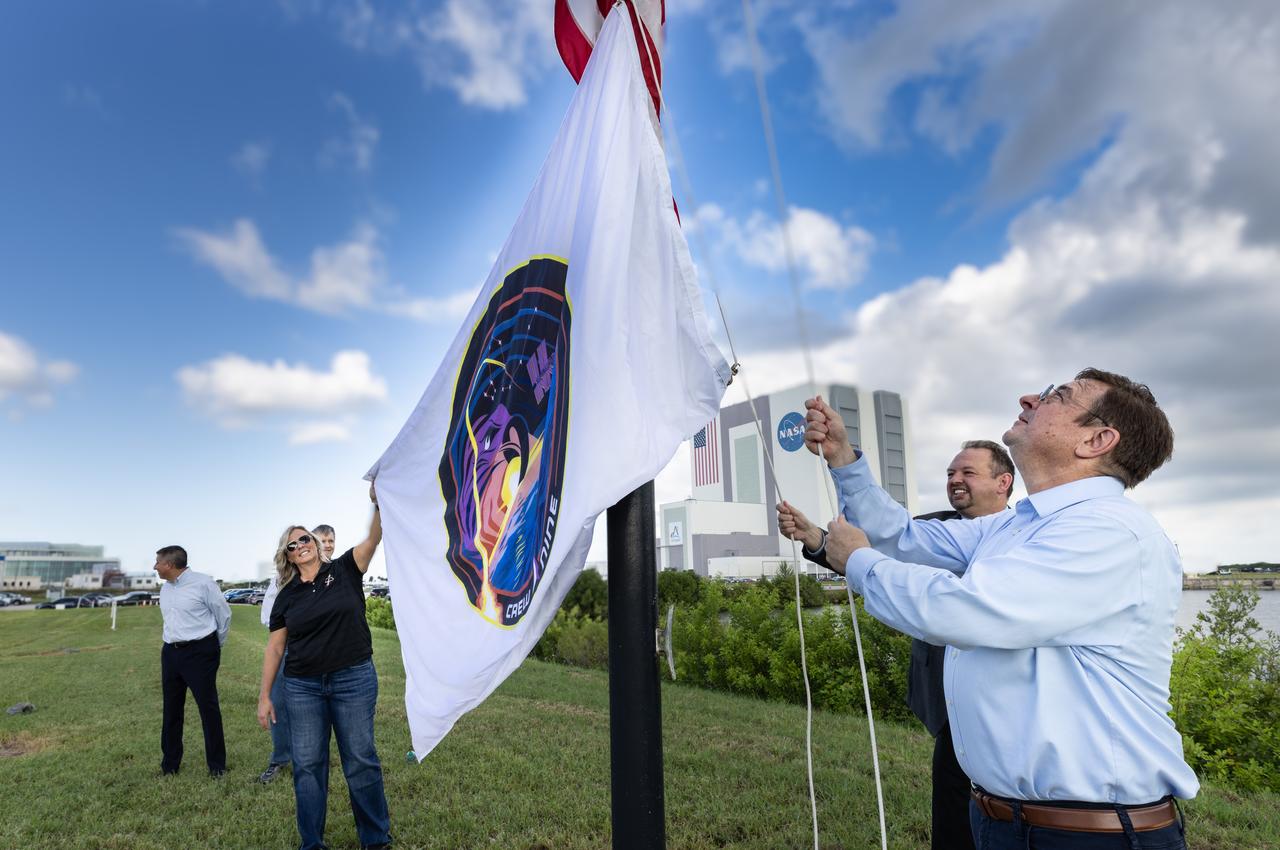

David Forrest (right), deputy manager of the SE&I (Systems Engineering and Integration) Office in NASA’s Commercial Low Earth Orbit Development Program, with help of NASA’s CCP (Commercial Crew Program) Deputy Program Manager Dana Hutcherson and NASA Public Affairs Officer Steven Siceloff, raises the agency’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission flag near the countdown clock at the NASA News Center at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024. Forrest previously served as deputy manager for CCP’s SE&I Office at Kennedy. In the background is CCP’s Deputy Program Manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston Richard Jones (far left) and CCP program manager Steve Stich. The Crew-9 mission will send NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket.
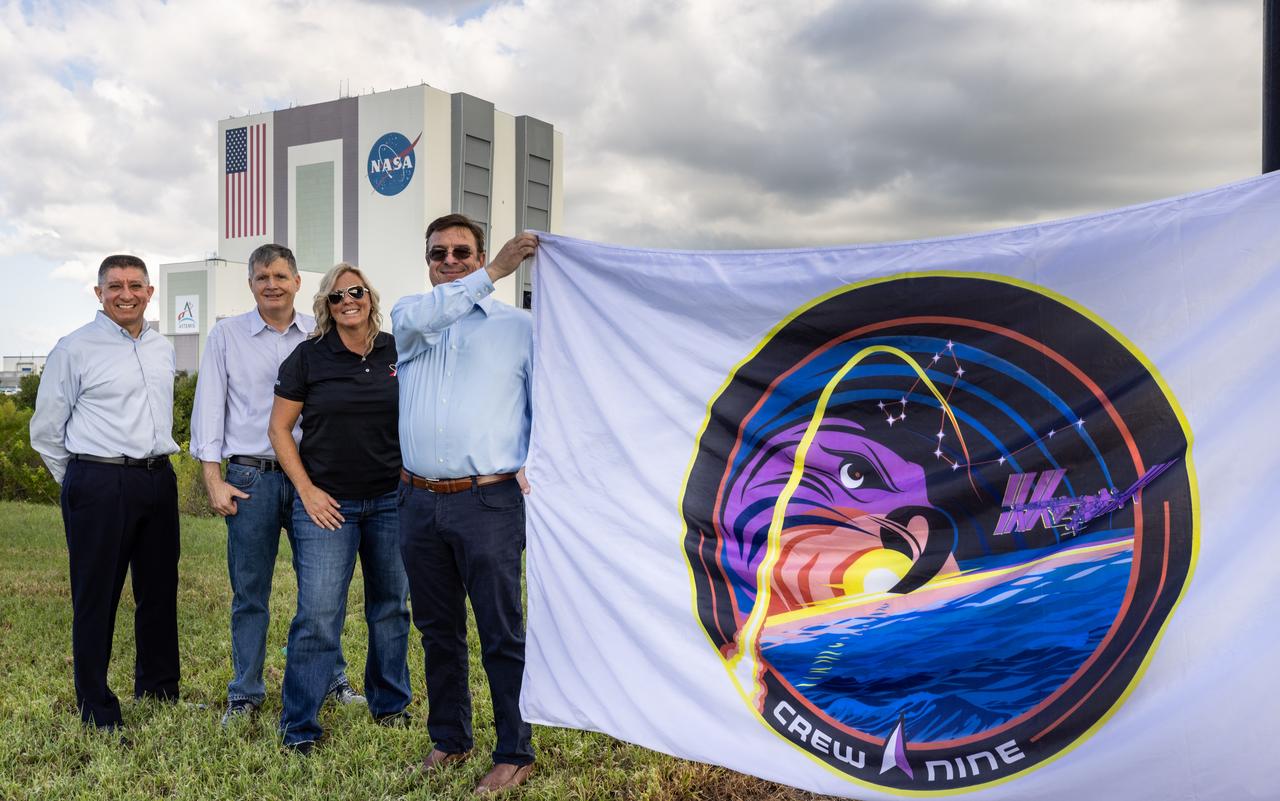

From left, Richard Jones, CCP (Commercial Crew Program) deputy program manager at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston; Steve Stich, program manager for CCP; Dana Hutcherson, CCP deputy program manager at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida; and David Forrest, deputy manager, SE&I (Systems Engineering and Integration) Office, NASA’s Commercial Low Earth Orbit Development Program, pose with the agency’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission flag near the countdown clock at the NASA News Center at Kennedy on Tuesday, Sept. 24, 2024. Forrest previously served as deputy manager for CCP’s SE&I Office at Kennedy. The Crew-9 mission will send NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket.

NASA's NISAR Project Manager Phil Barela (with hands raised) speaks with Indian Space Research Organisation Chairman S. Somanath about the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Feb. 3, 2023. Somanath was among a group of visitors to the facility that included officials from NASA, ISRO, and the Indian Embassy. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25598
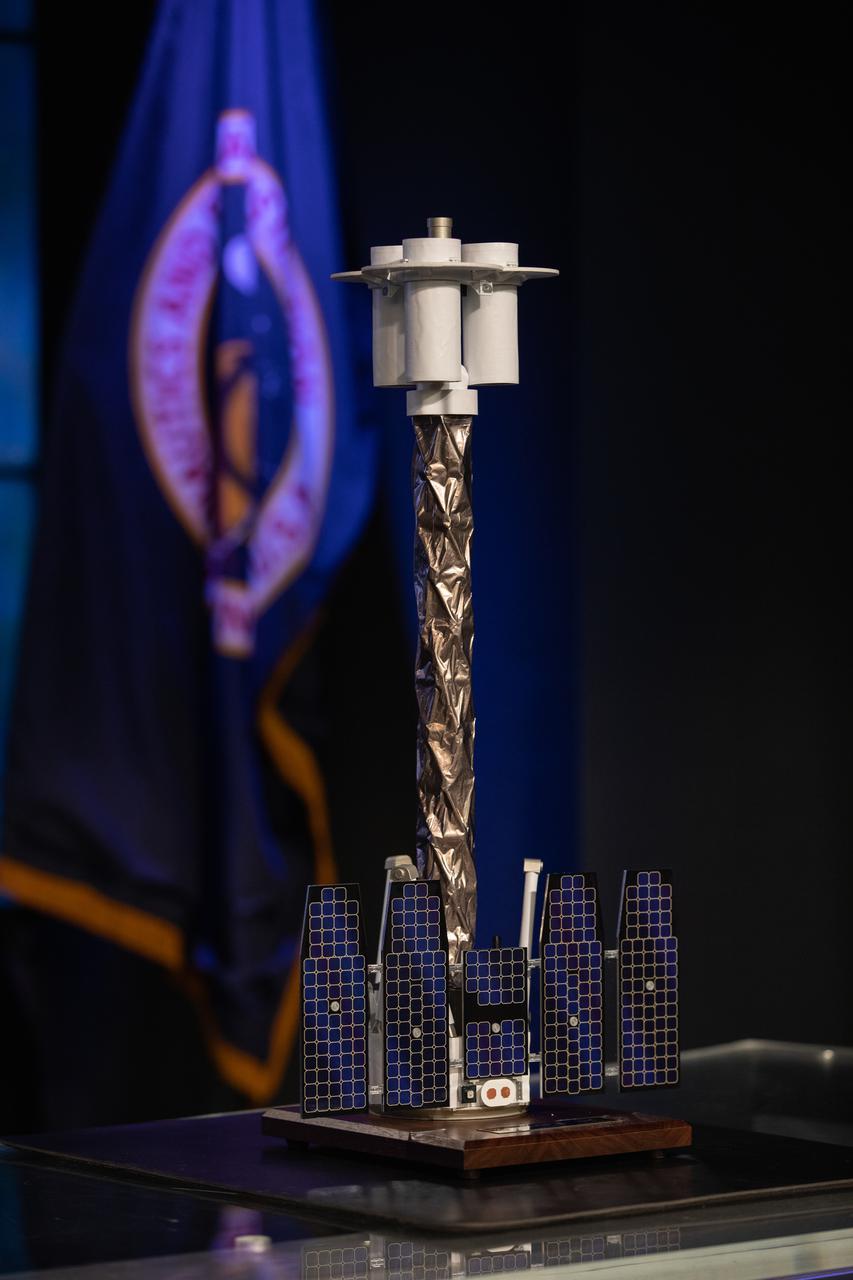

A scale model of NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft is on display during a payload briefing for IXPE on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
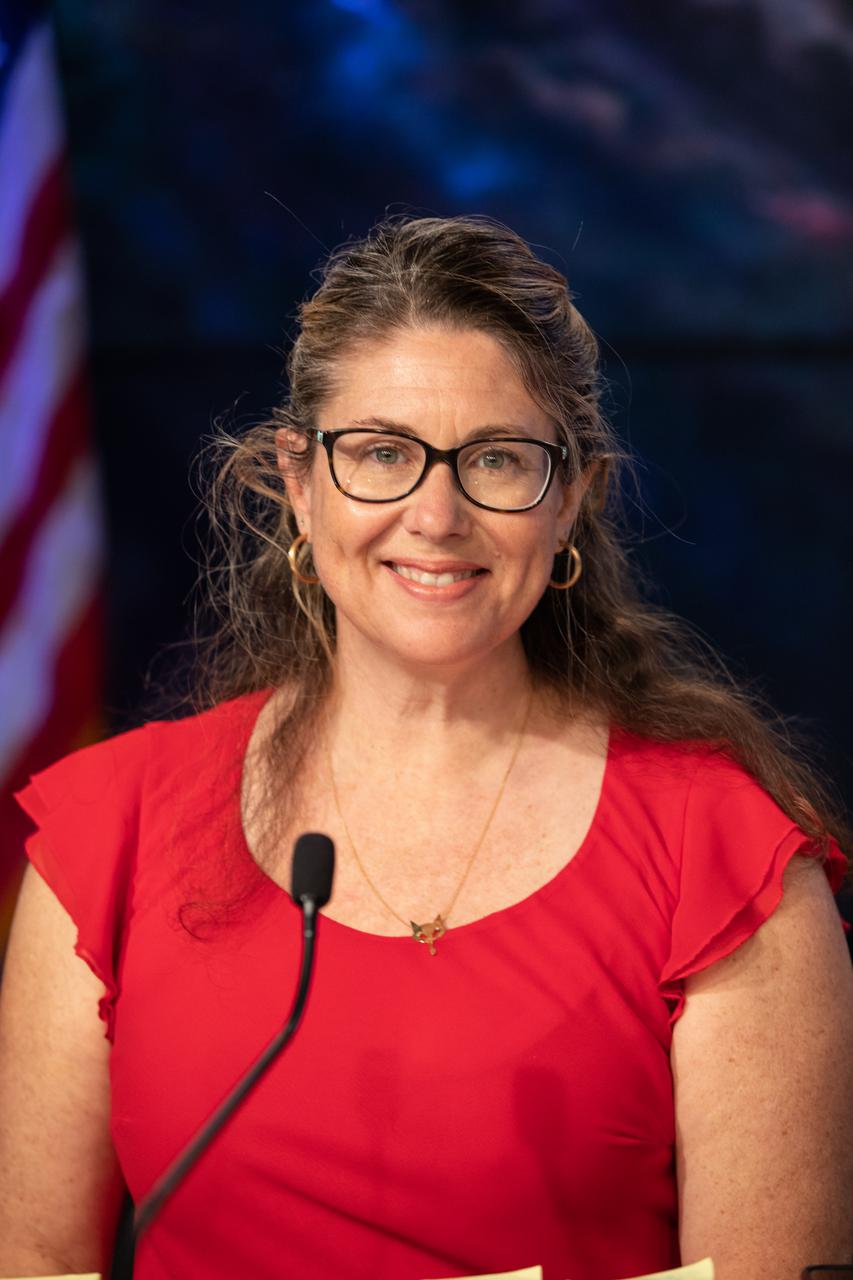

Karen Fox, NASA Communications, moderates a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
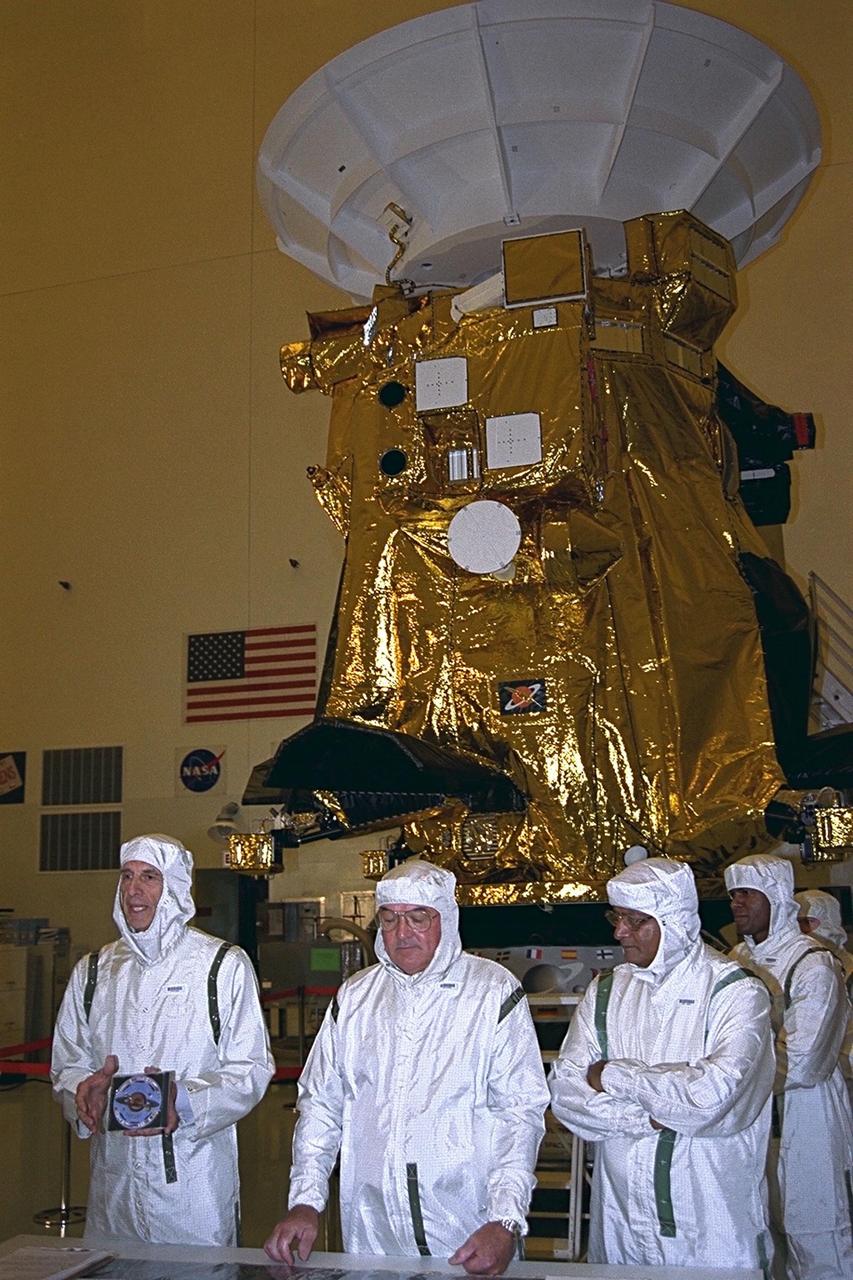

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF), Charley Kohlhase, Cassini's science and mission design manager, who oversaw the development of the Digital Video Disk (DVD), discusses it with members of the press. To Kohlhase's left are Richard J. Spehalski, Cassini project manager, and Hamid Hassan, the European Space Agancy Huygens manager. Kohlhase holds the high-tech data disk that will be installed on the Cassini spacecraft. More than 616,400 signatures from 81 countries around the world are on the disk. The Cassini spacecraft is being prepared for launch on Oct. 6, 1997. It will be launched on an Air Force Titan IV/Centaur launch vehicle on an international scientific mission to the planet Saturn. It is destined to arrive at Saturn in July 2004. The Cassini mission is managed for NASA's Office of Space Science, Washington, D.C., by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif
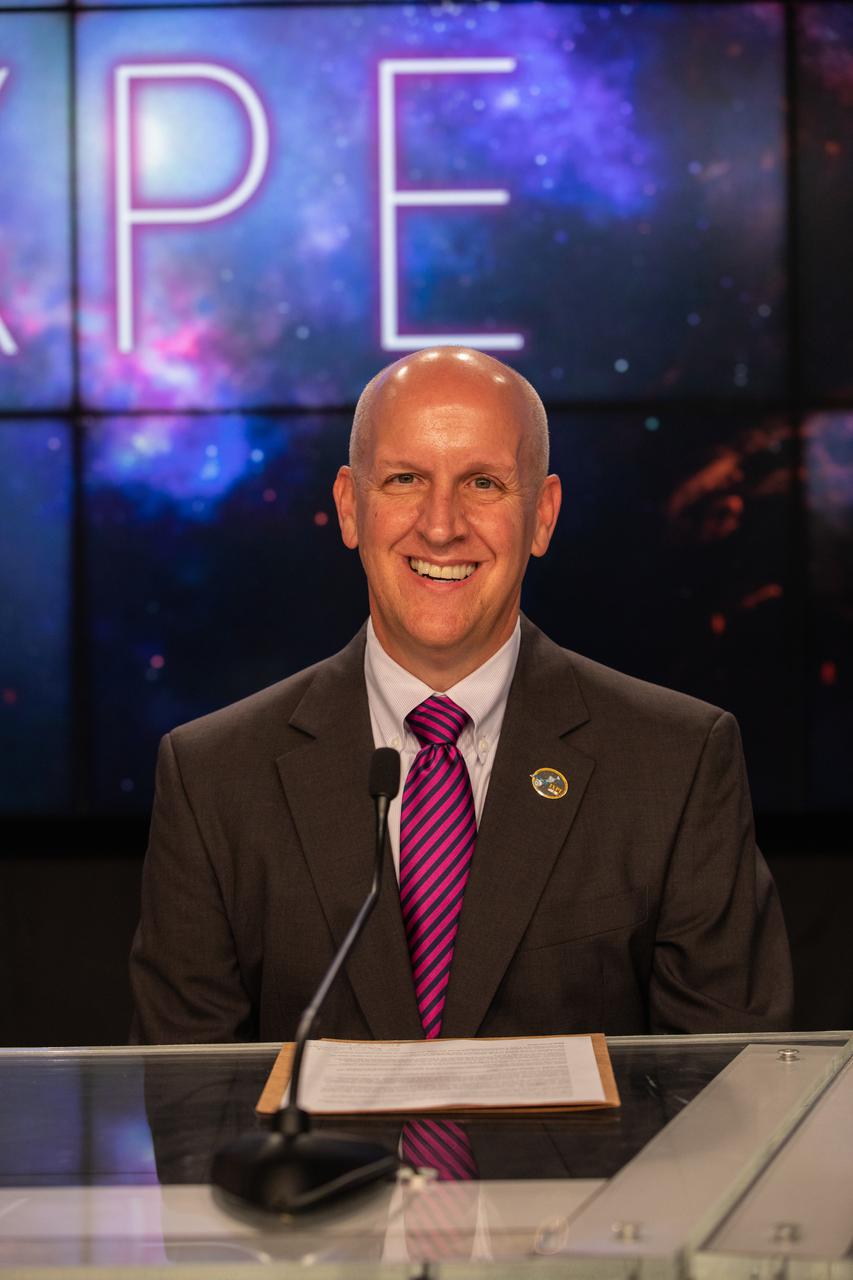

Tim Dunn, launch director, NASA’s Launch Services Program, based at Kennedy Space Center, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
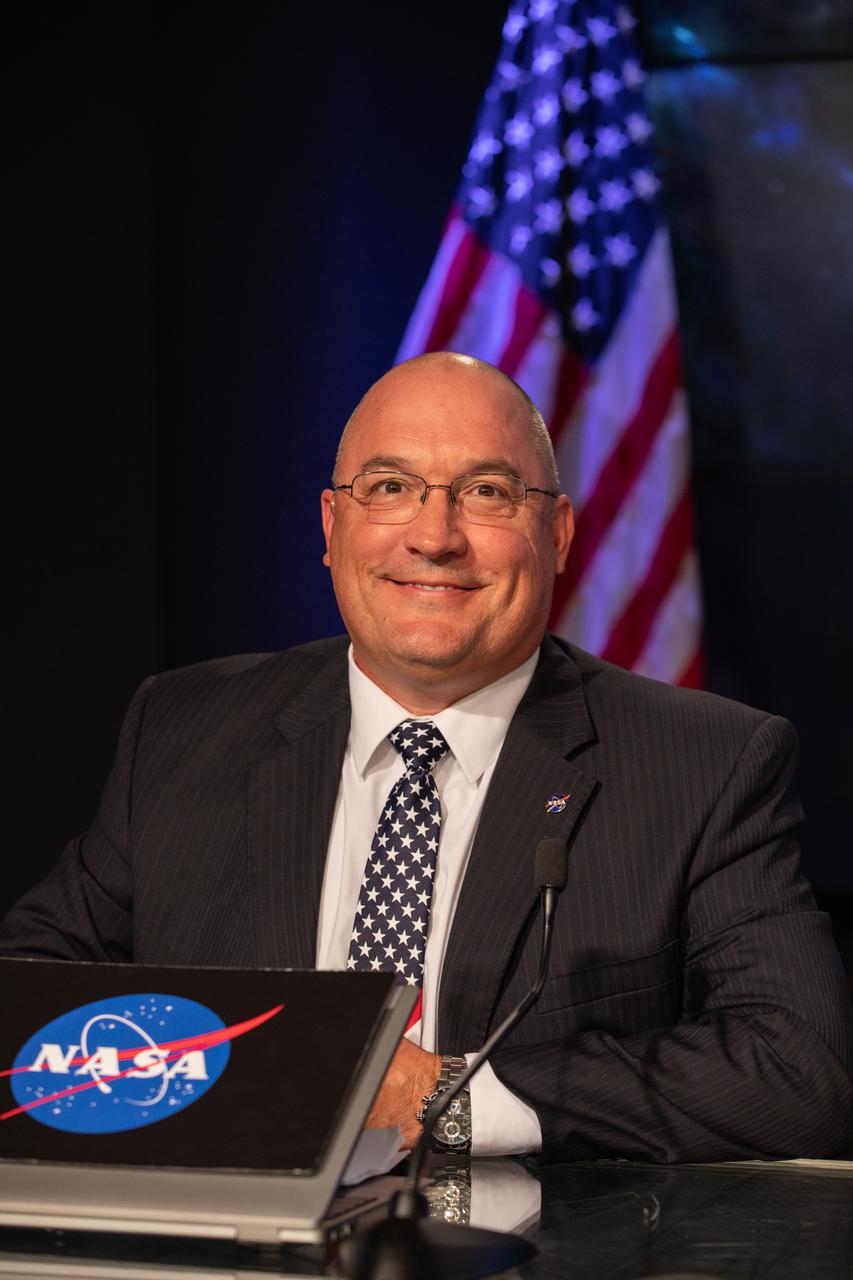

Greg Harland, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
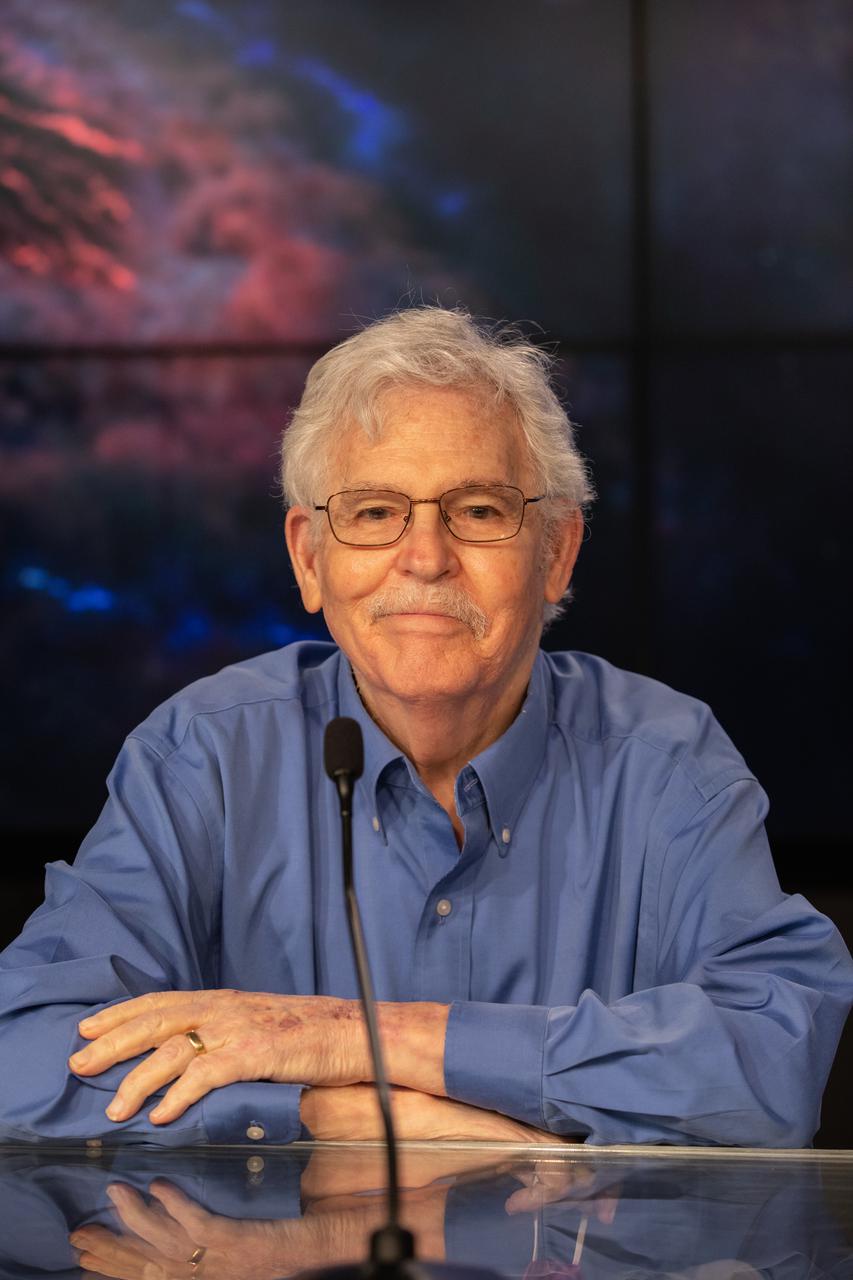

Martin Weisskopf, IXPE principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
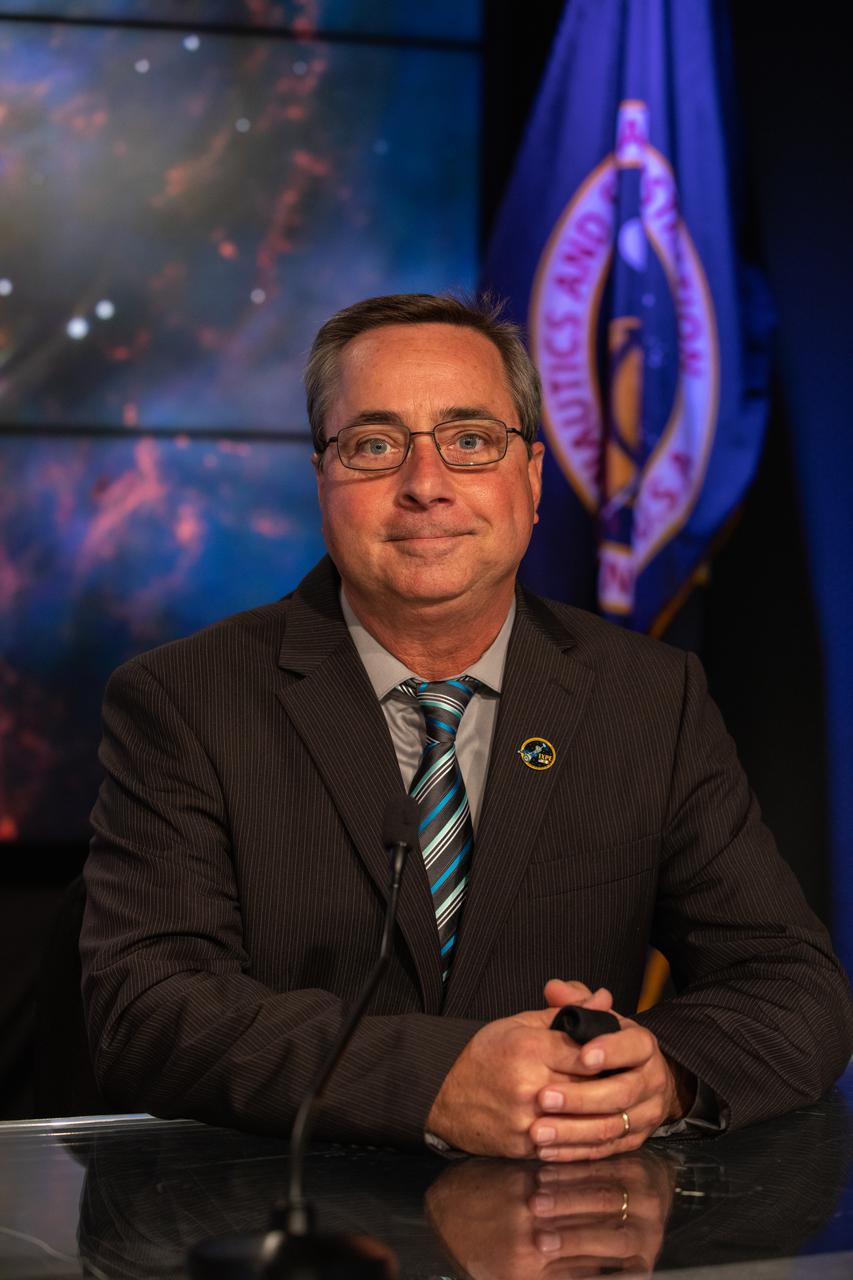

Mike McAleenan, 45th Weather Squadron, Space Launch Delta 45, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
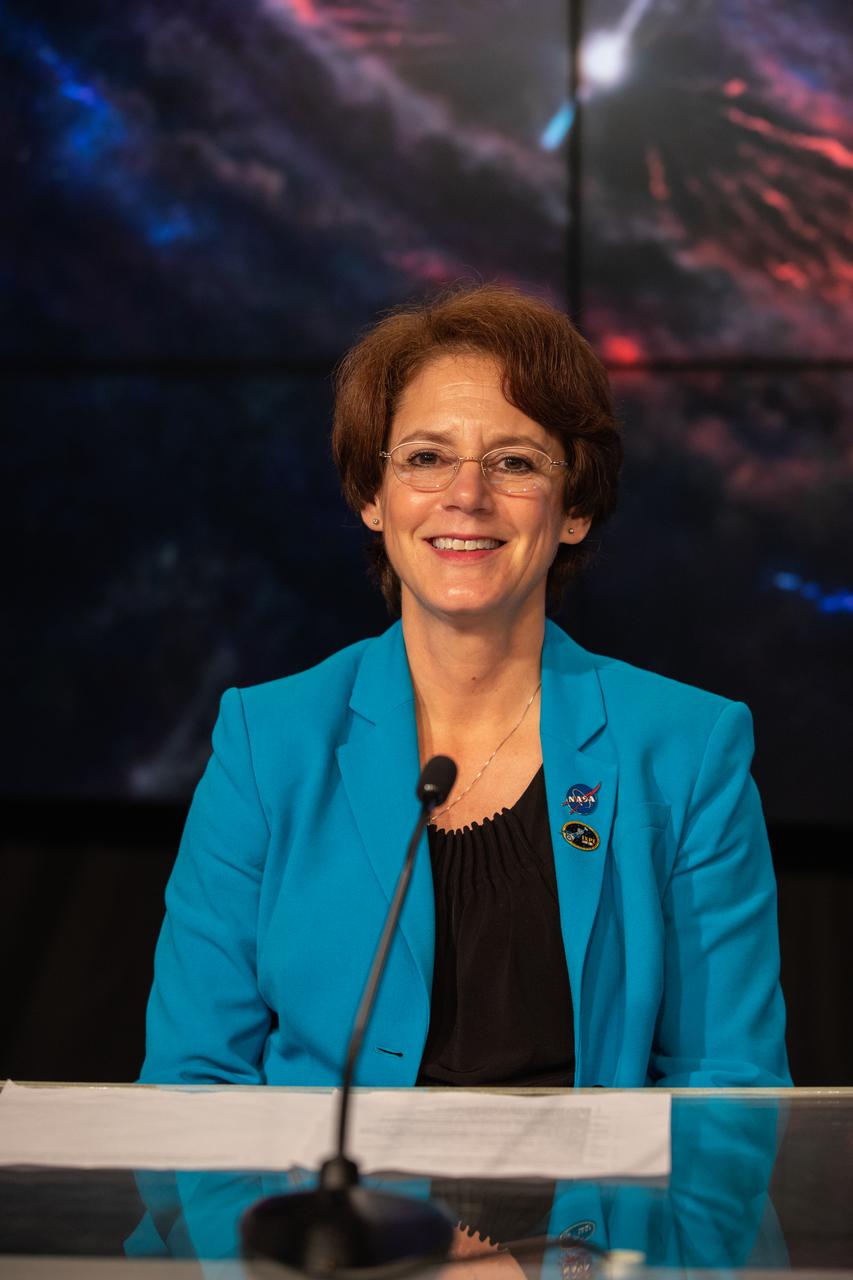

Sandra Connelly, deputy associate administrator for science, NASA Headquarters, participates in a prelaunch news conference for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec. 7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
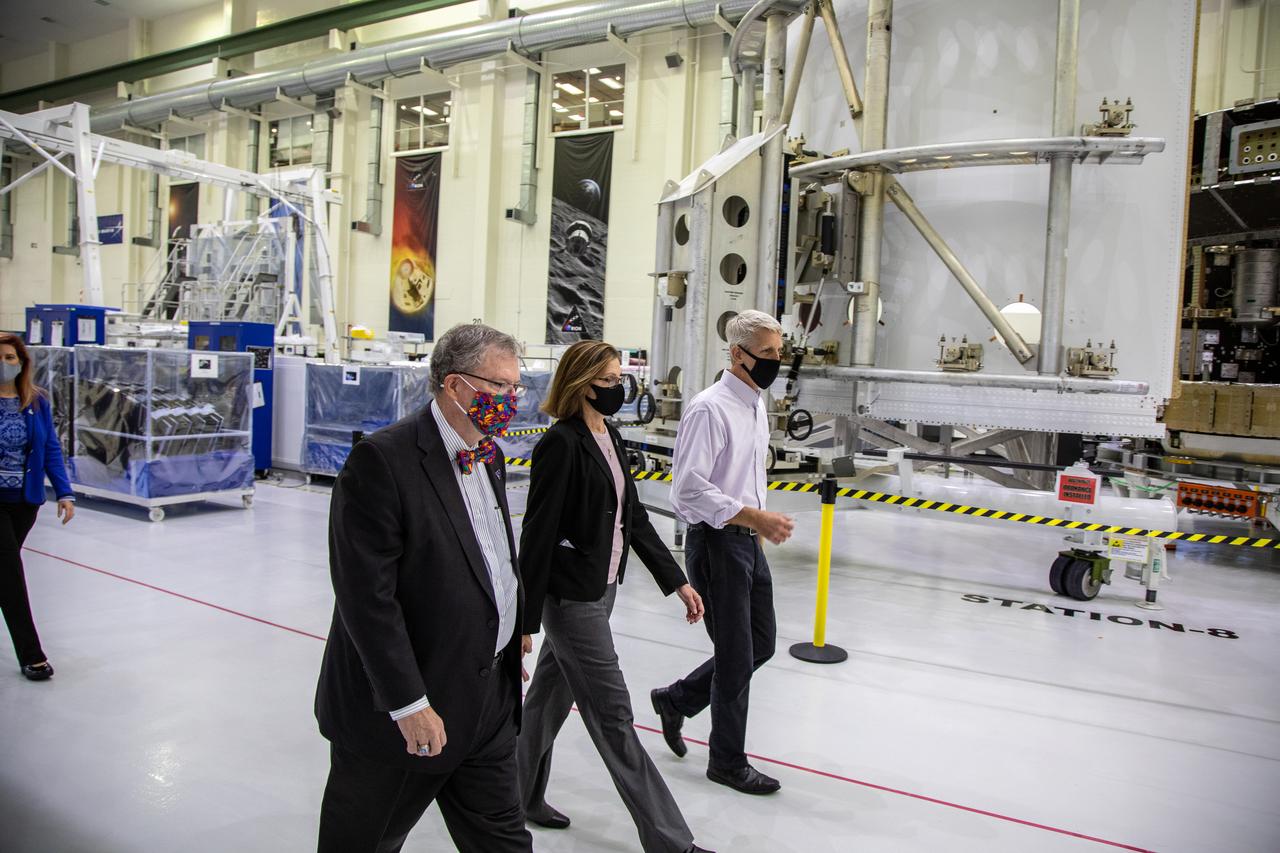
Catherine Koerner, in the center, NASA Orion Program manager, along with senior managers from Orion and Lockheed Martin, tours the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 6, 2020. Accompanying her, at left is Mike Hawes, Lockheed Martin vice president and Orion Program manager; and at right is Scott Wilson, NASA Kennedy Orion Production Operations manager. Koerner viewed the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis I and II missions. They are shown with one of the space adapter jettison fairing panels that will be installed on Orion for the Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
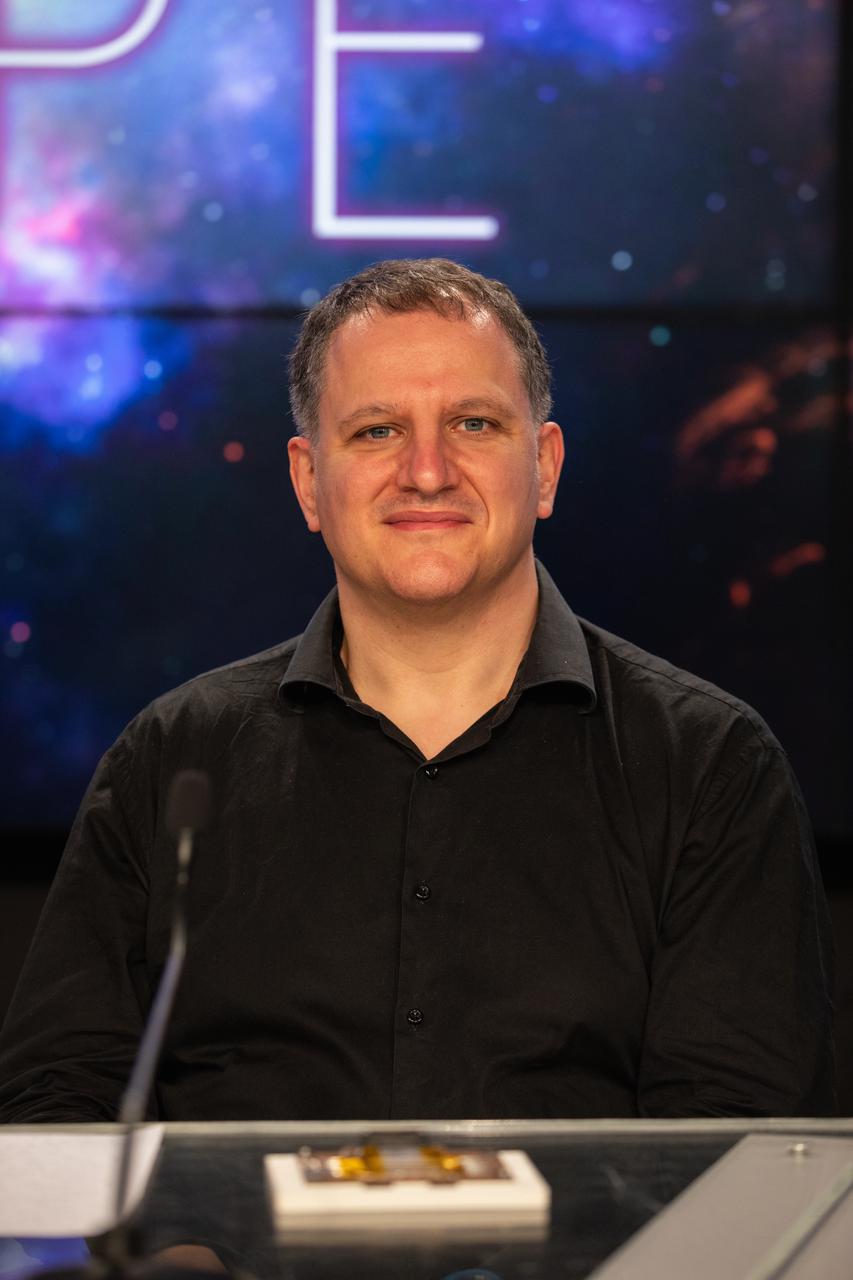

Luca Baldini, Italian co-principal investigator, National Institute for Nuclear Physics, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
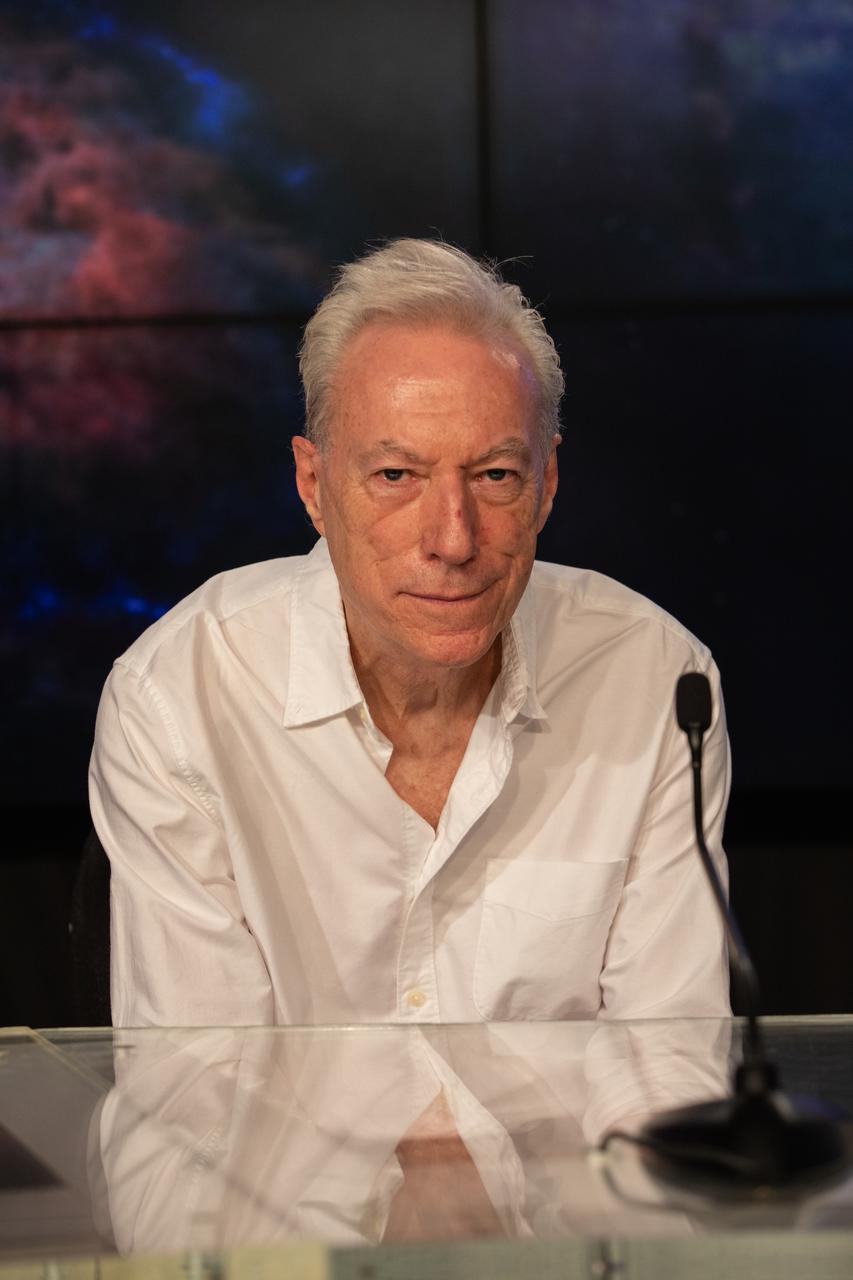

Brian Ramsey, deputy principal investigator, NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, participates in a payload briefing for NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) spacecraft on Dec.7, 2021 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. IXPE is scheduled to launch no earlier than 1 a.m. EST Thursday, Dec. 9, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A. NASA’s Launch Services Program is managing this launch. NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the IXPE mission. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations with support from the University of Colorado at Boulder. NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, manages the Explorers Program for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. The U.S. Space Force’s Space Launch Delta 45 provides range support for this launch. SpaceX is providing the launch vehicle for this mission.
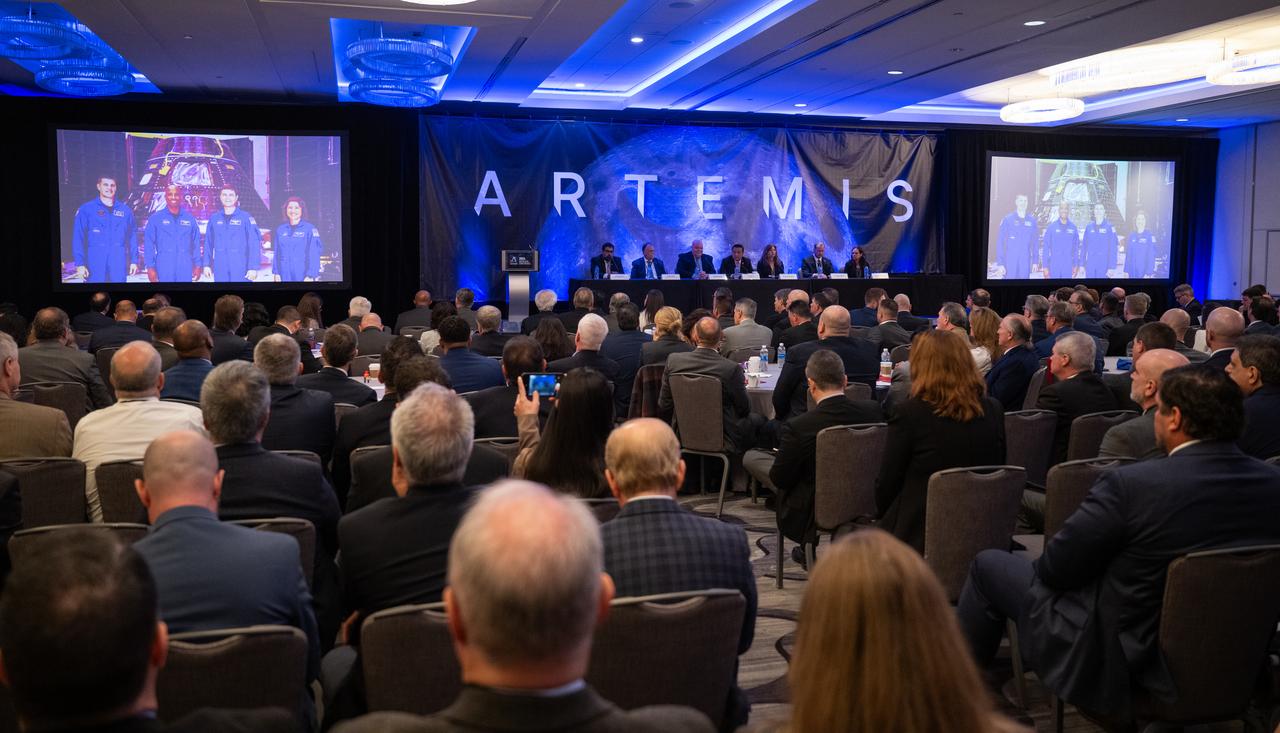

Howard Hu, manager of the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center, center, speaks during an Artemis Program progress update panel at the 2024 Artemis Suppliers Conference, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Washington. Also participating in the panel was, from left, Amit Kshatriya, deputy associate administrator for the Moon to Mars Program in NASA’s Explorations Systems Development Mission Directorate; Shawn Quinn, manager of Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center; John Honeycutt, manager of the Space Launch System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Jon B. Olansen, manager of the Gateway Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; and Lara Kearney, manager of Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
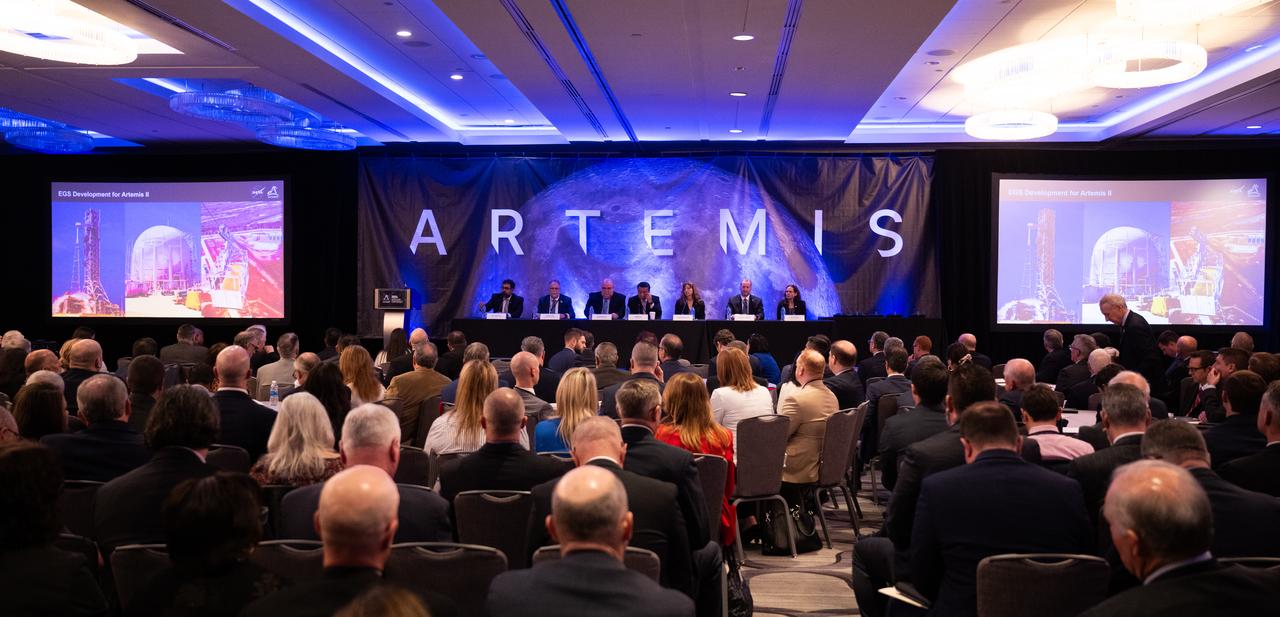

Shawn Quinn, manager of Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center, second from left, speaks during an Artemis Program progress update panel at the 2024 Artemis Suppliers Conference, Tuesday, Feb. 27, 2024, at the Grand Hyatt Hotel in Washington. Also participating in the panel was, from left, Amit Kshatriya, deputy associate administrator for the Moon to Mars Program in NASA’s Explorations Systems Development Mission Directorate; John Honeycutt, manager of the Space Launch System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Howard Hu, manager of the Orion Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of the Human Landing System Program at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center; Jon B. Olansen, manager of the Gateway Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center; and Lara Kearney, manager of Extravehicular Activity and Human Surface Mobility Program at NASA’s Johnson Space Center. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)