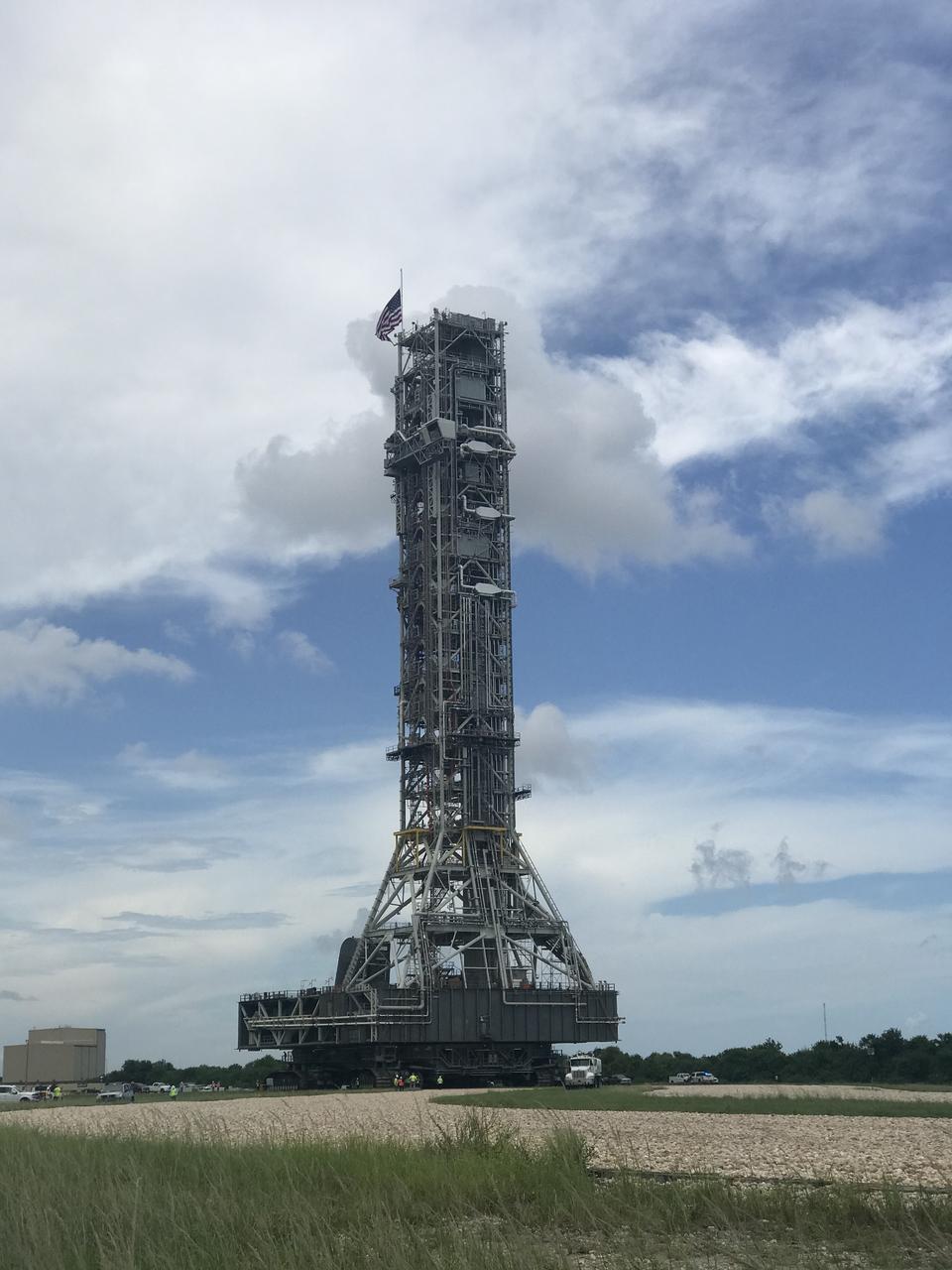

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 begins its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
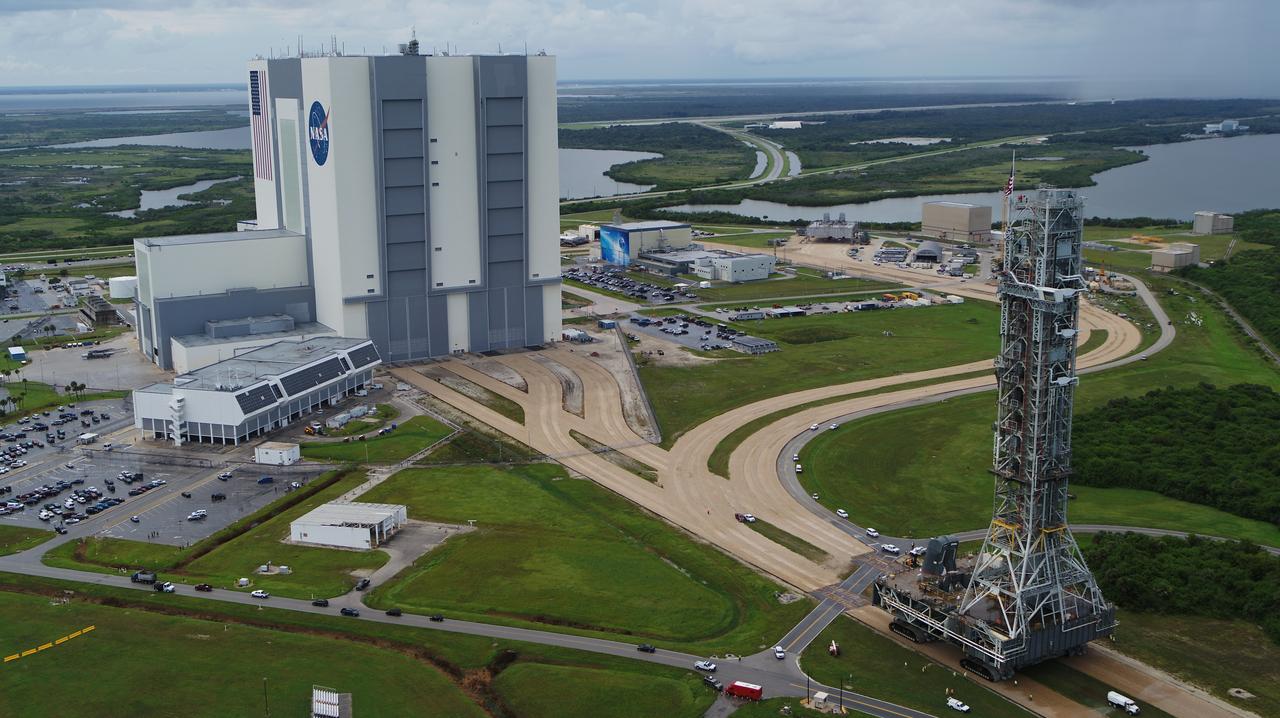

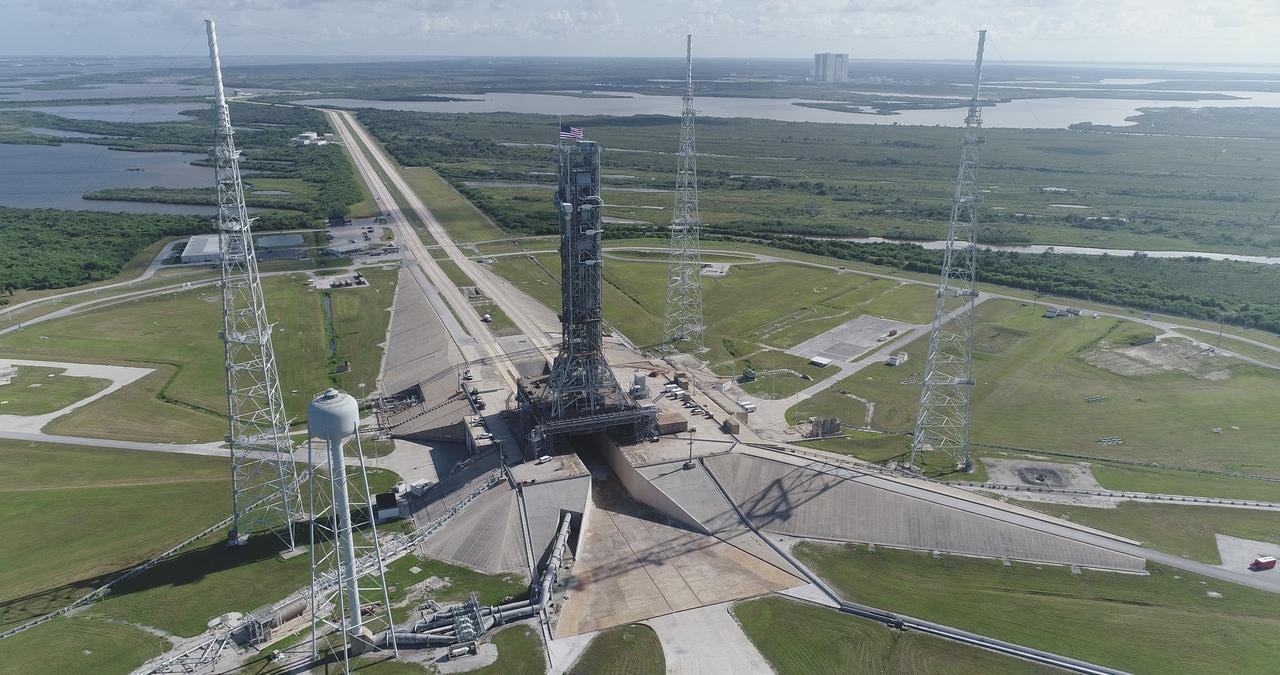
An aerial view of NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 as it begins its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
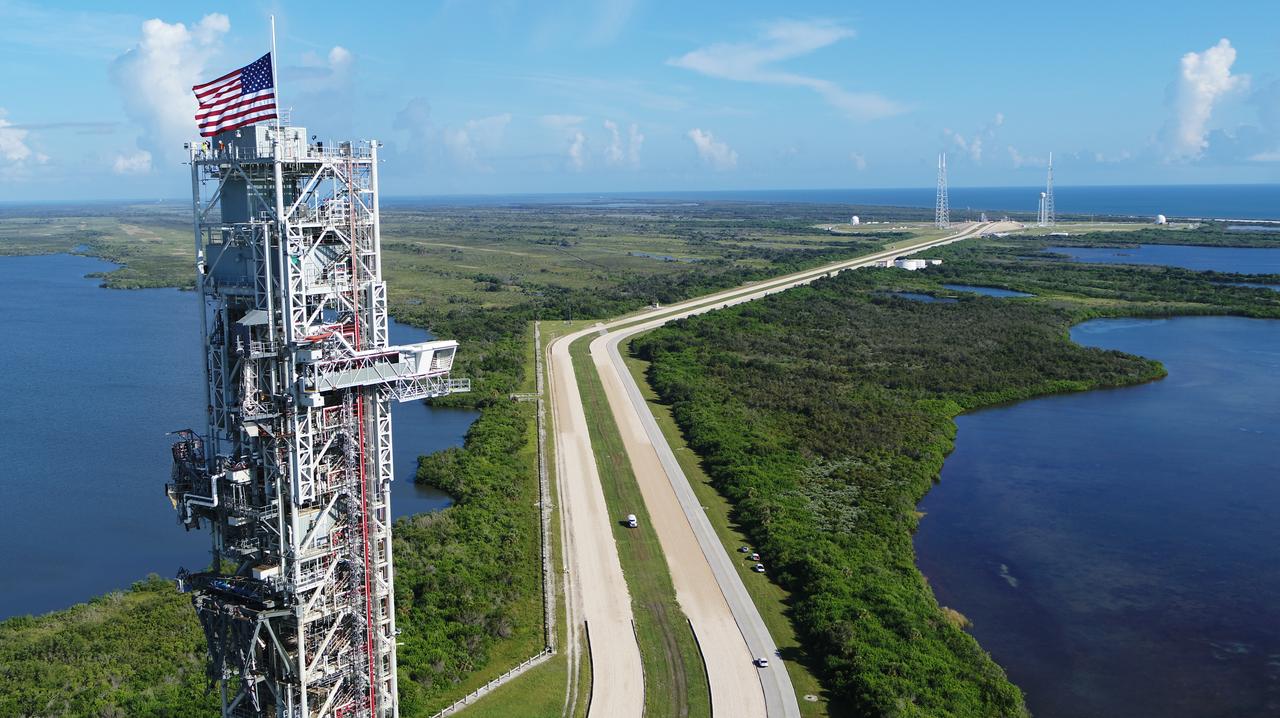

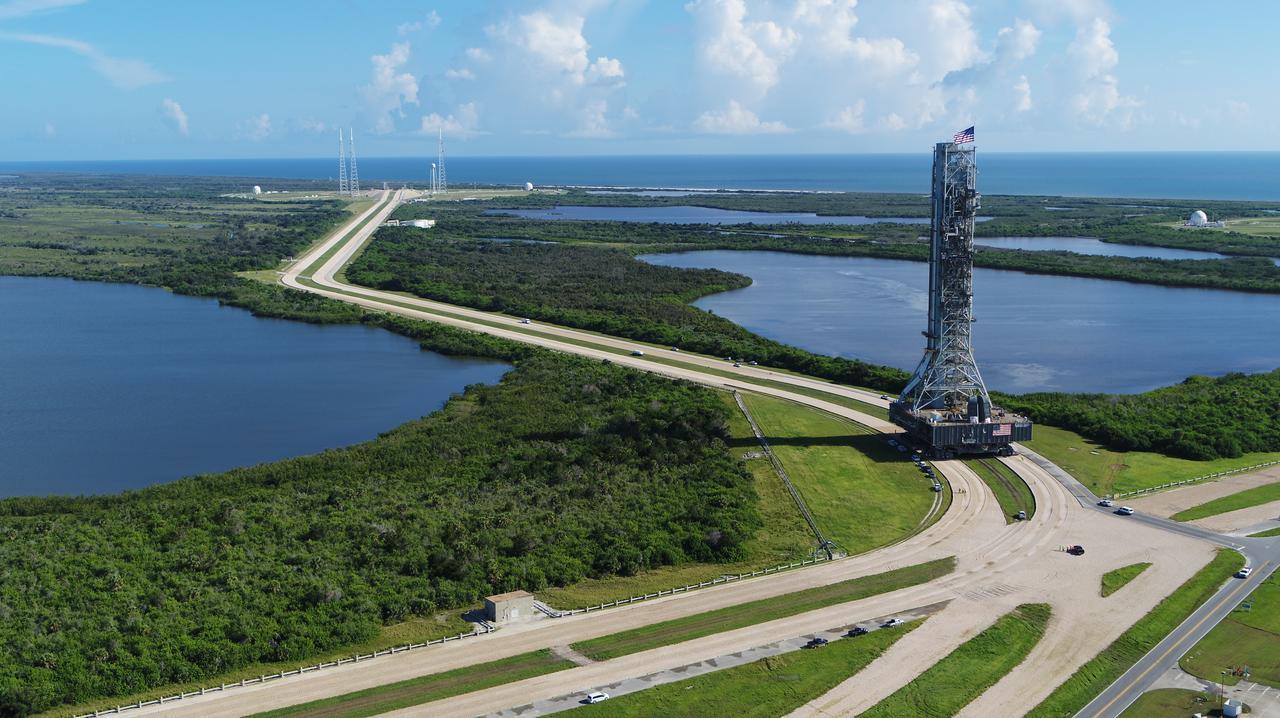
An aerial view of NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 as it moves along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view on top of the ML is the American flag. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
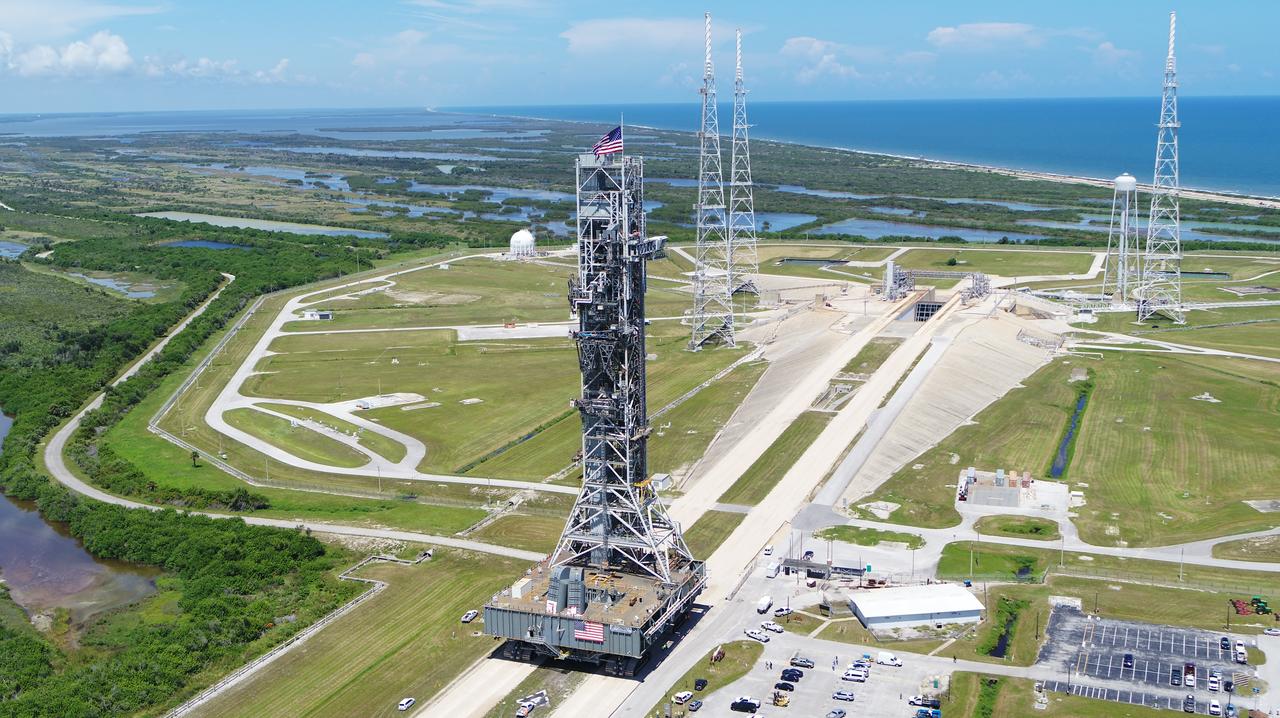

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 arrives at Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

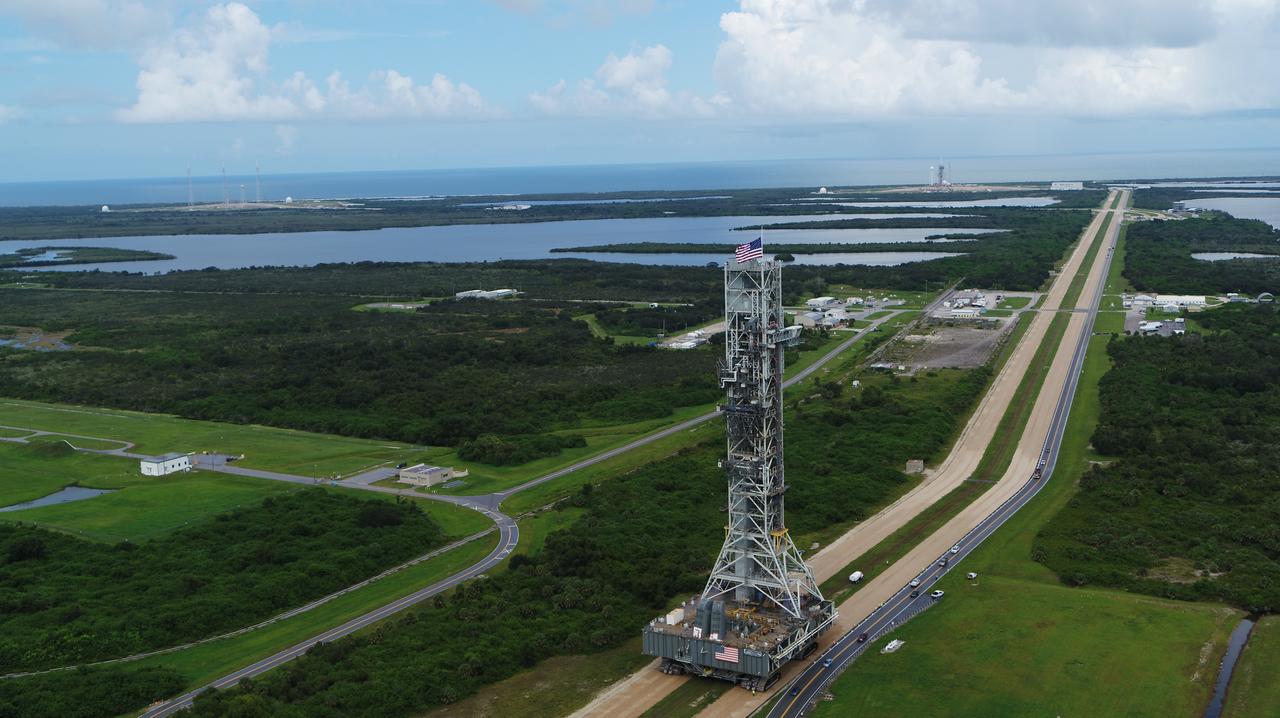
An aerial view of NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 as it moves along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

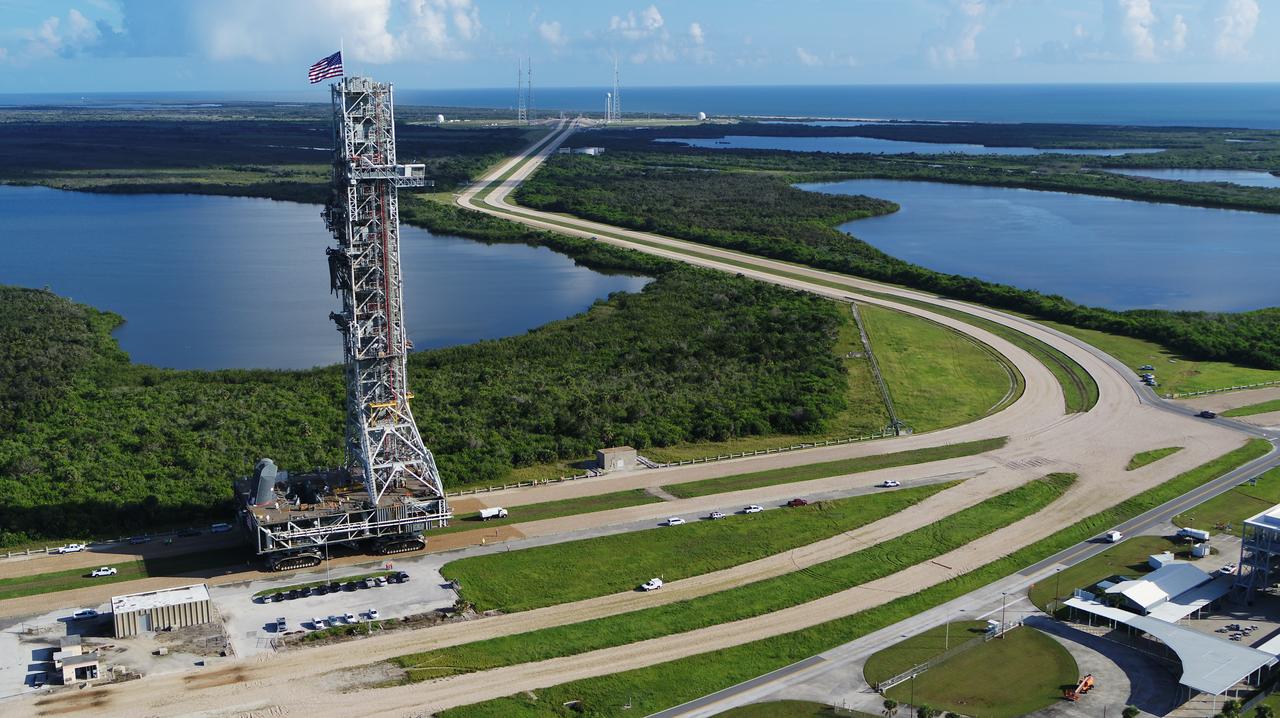
An aerial view of NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 as it moves along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
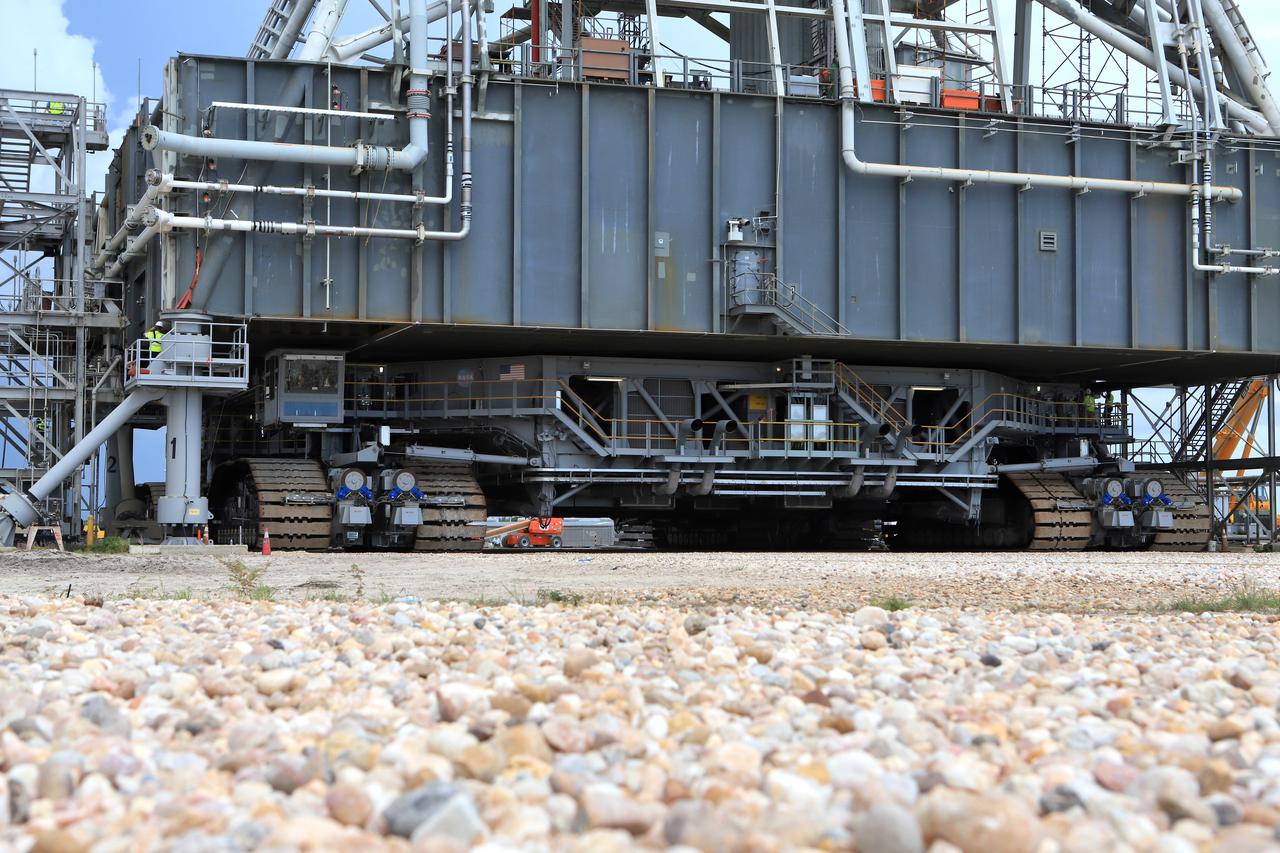

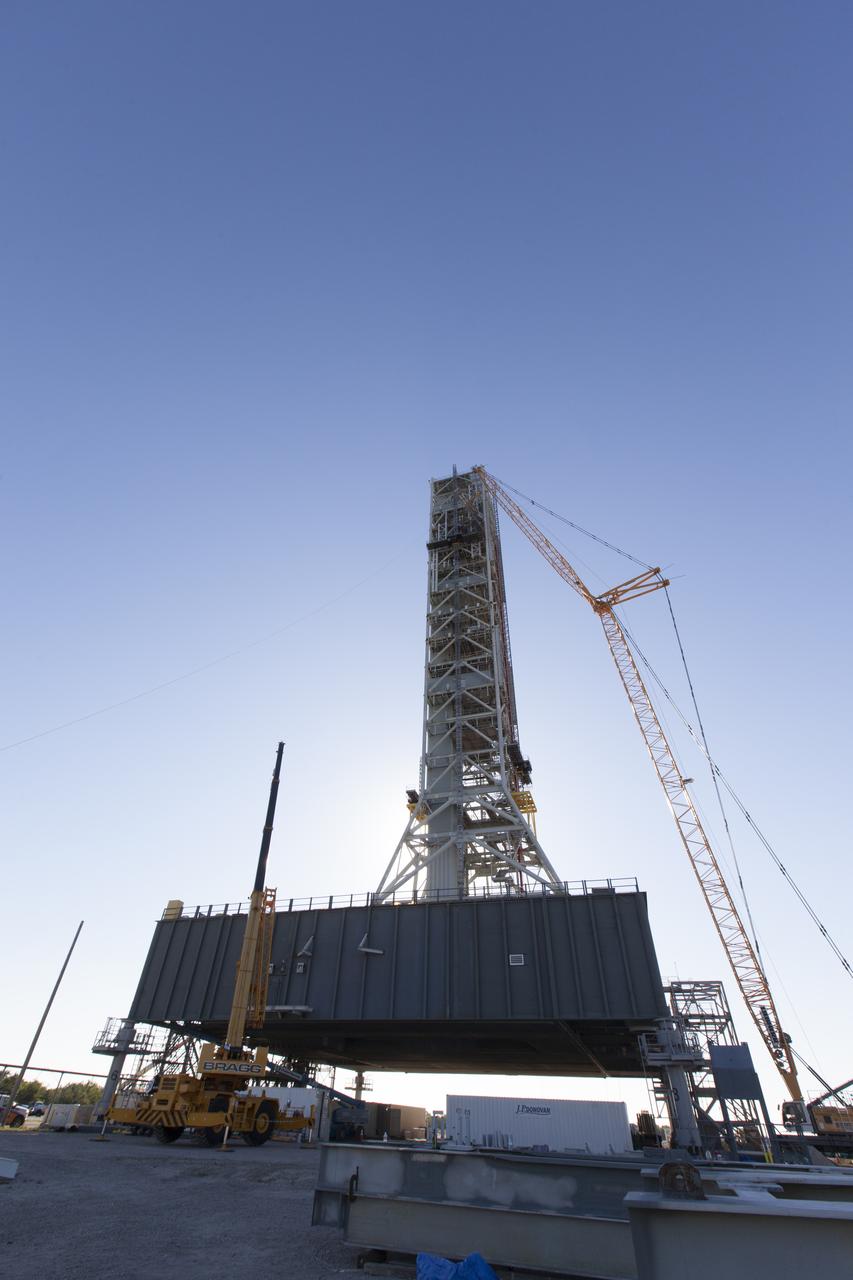
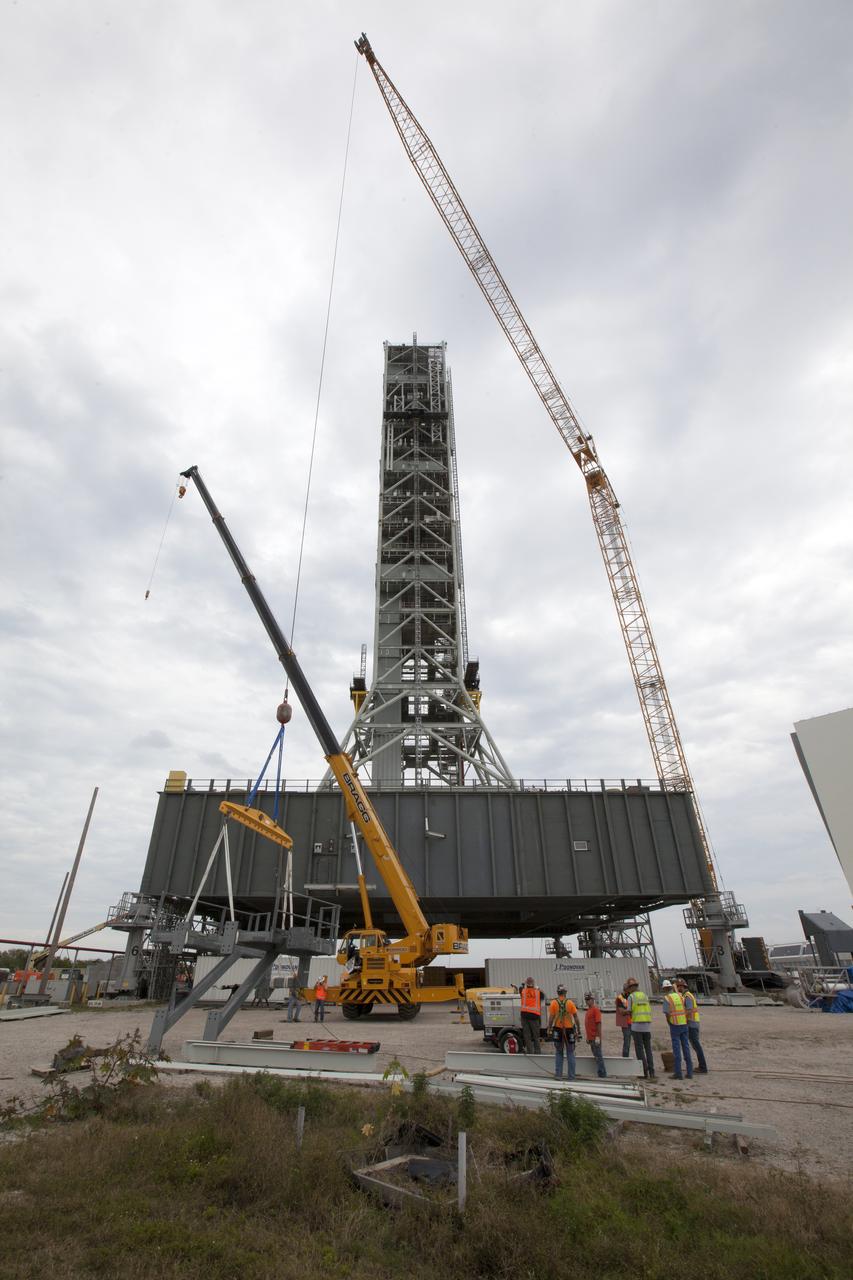
A close-up view of NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop as it slowly moves along the crawlerway on its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
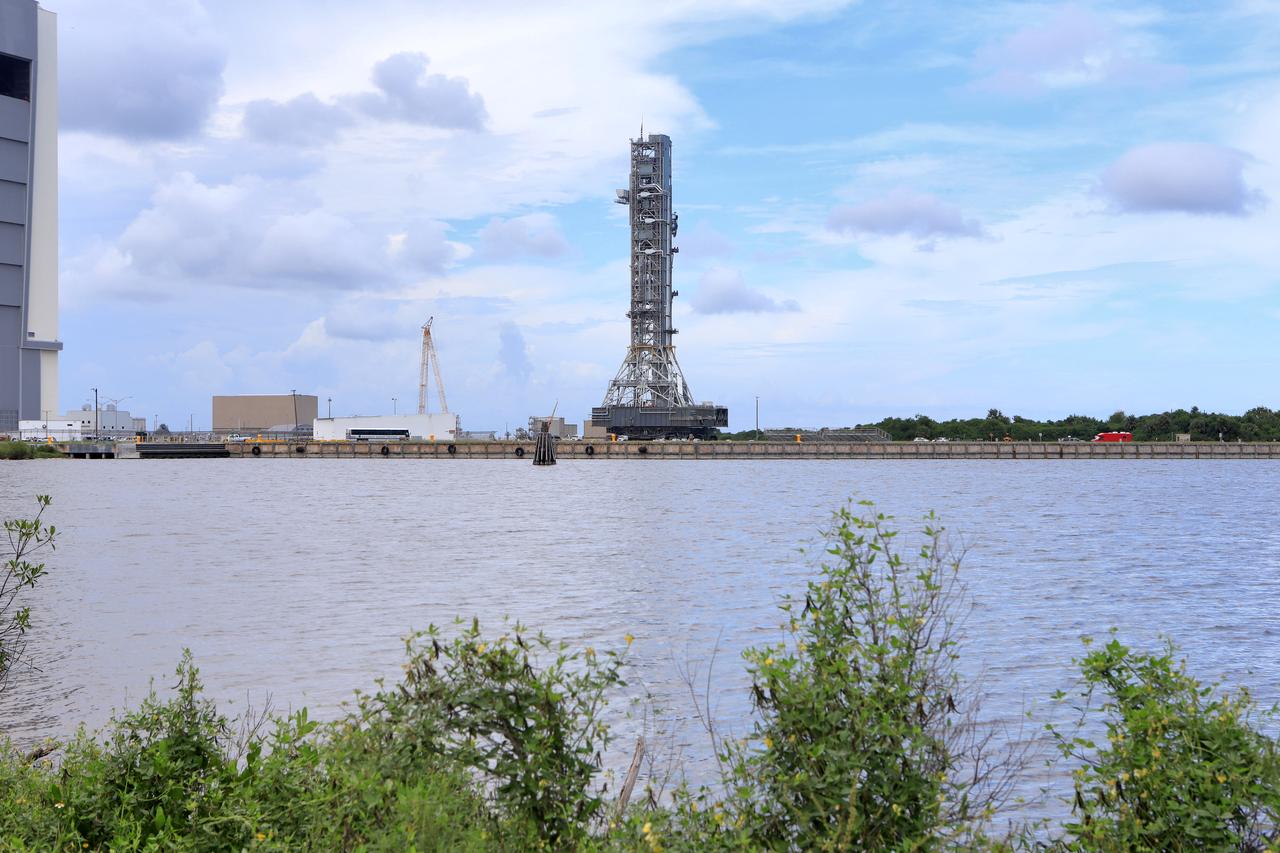

NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop begins its trek along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

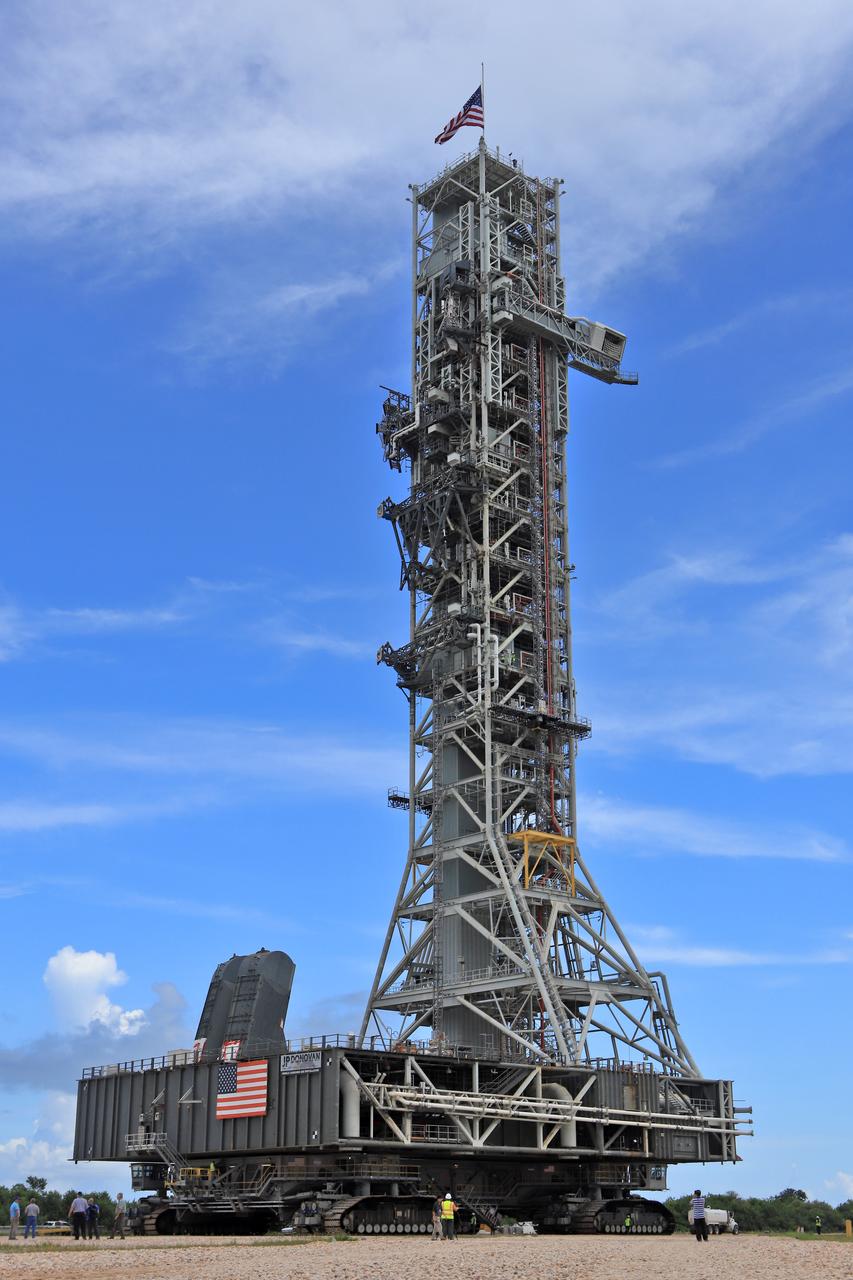
NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
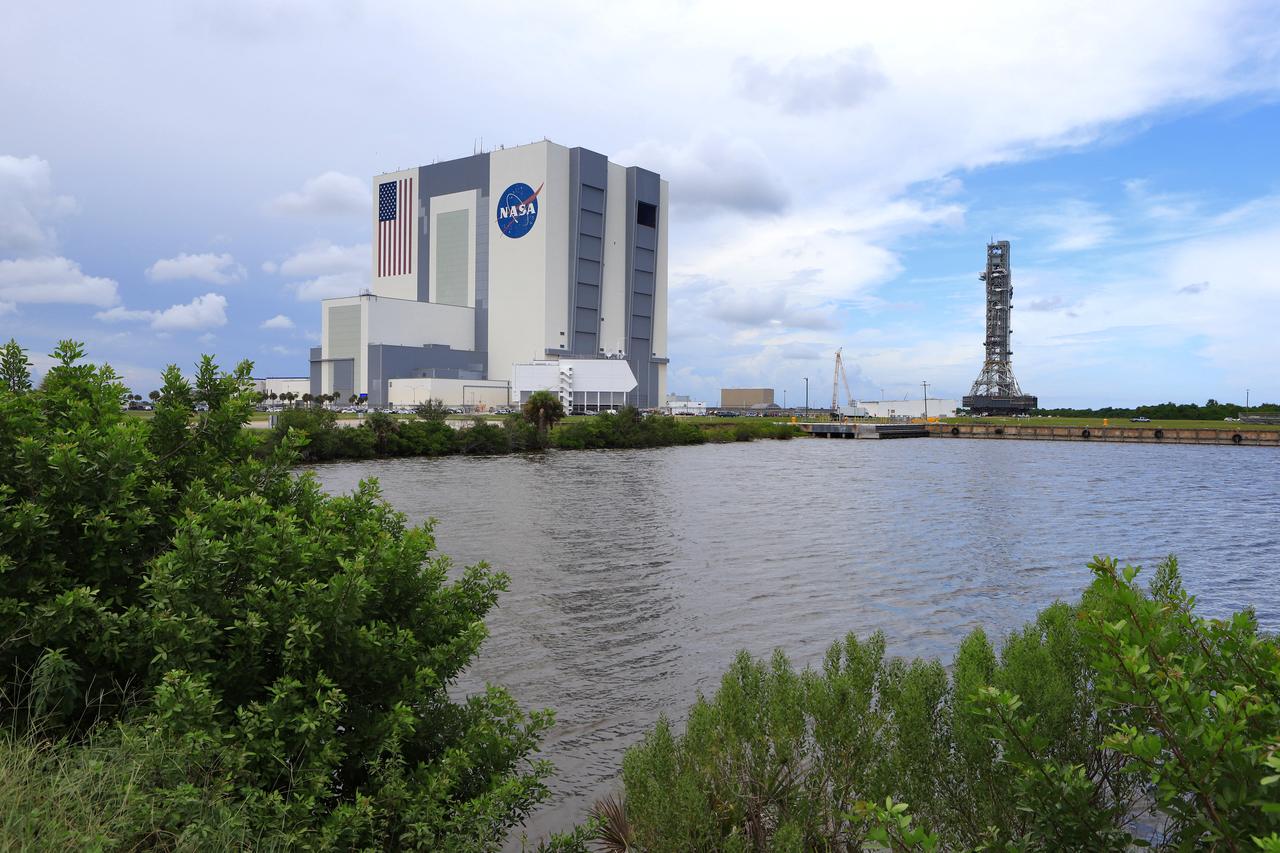

NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop begins its trek along the crawlerway to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left is the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop slowly moves along the crawlerway on its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
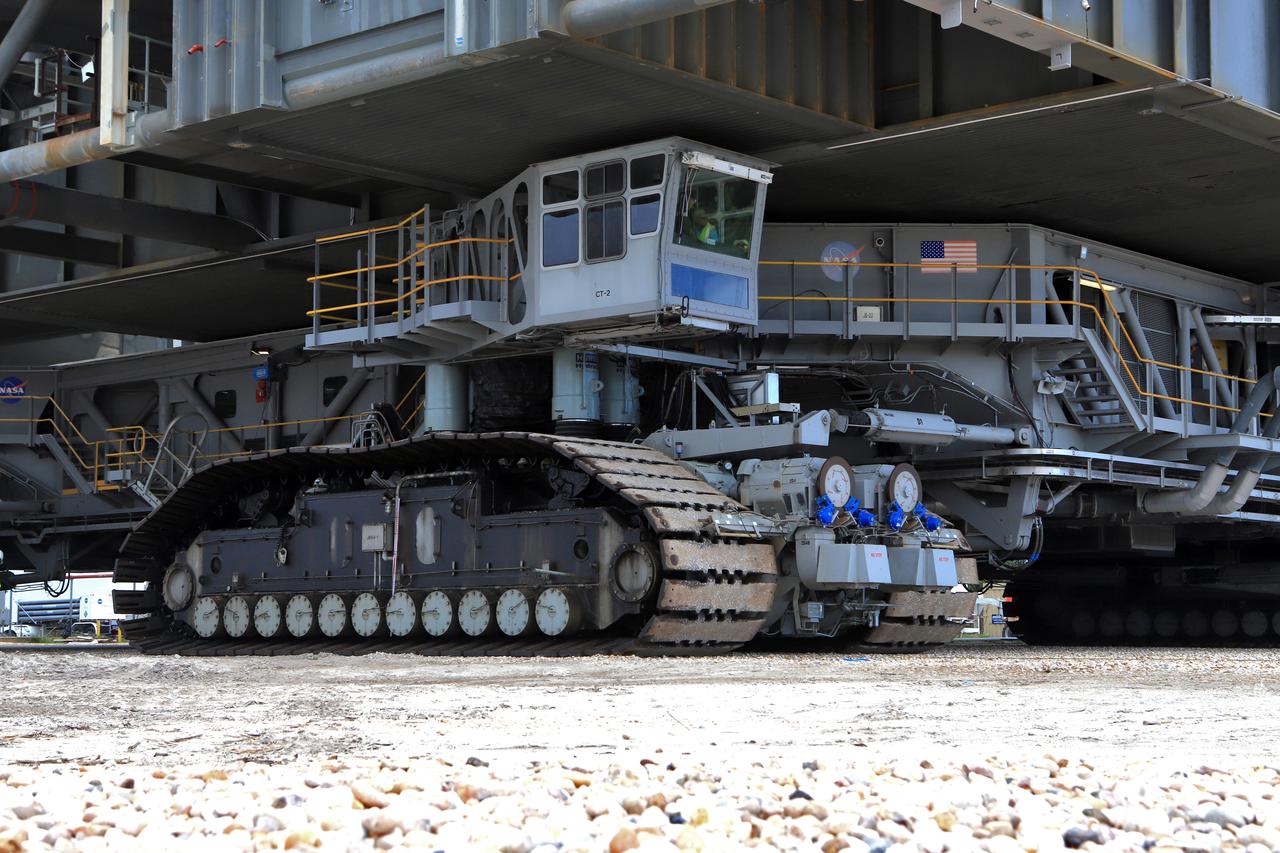

A close-up view of NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop as it slowly moves along the crawlerway on its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) moves along the crawlerway on its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

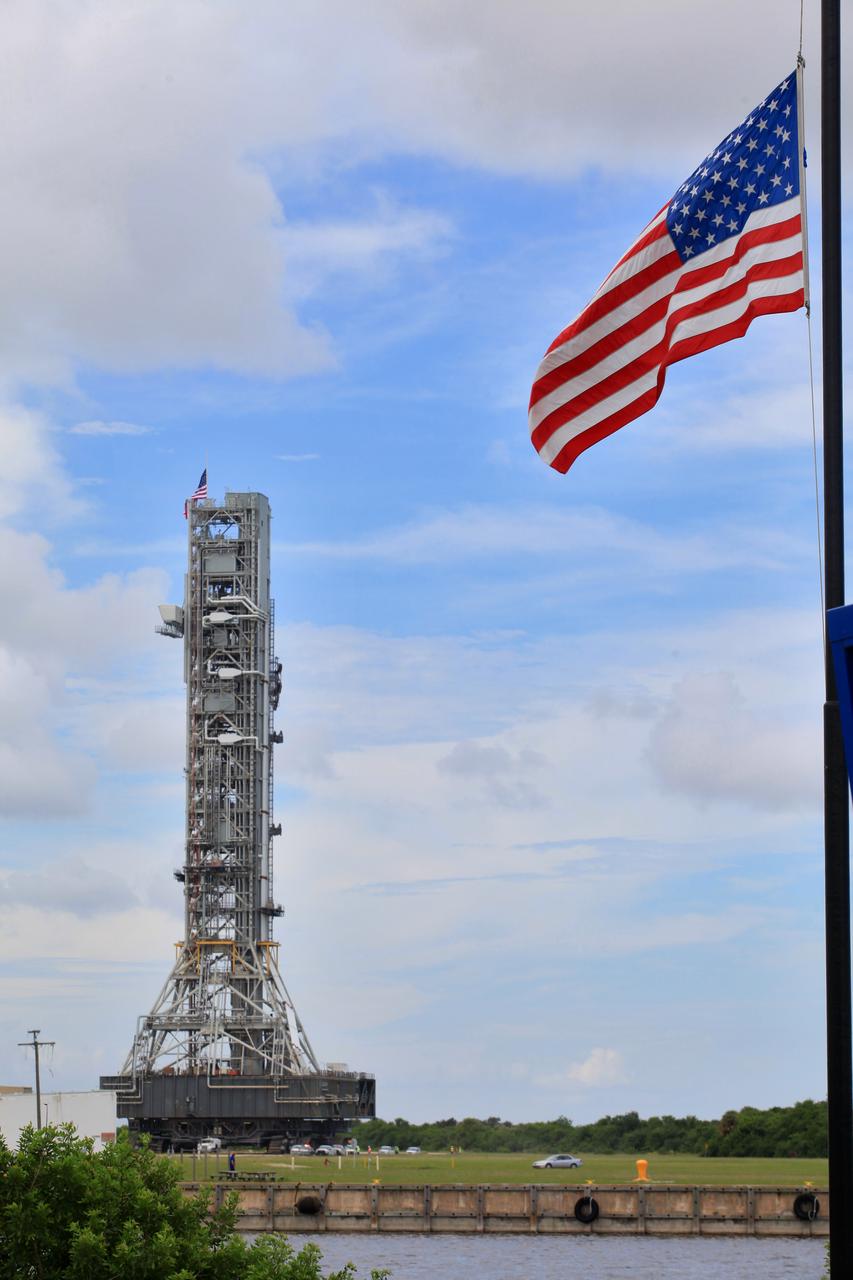
An aerial view of NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 as it moves along the crawlerway, making the turn to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view on top of the ML is the American flag. The ML will undergo a fit check on the surface of the pad, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
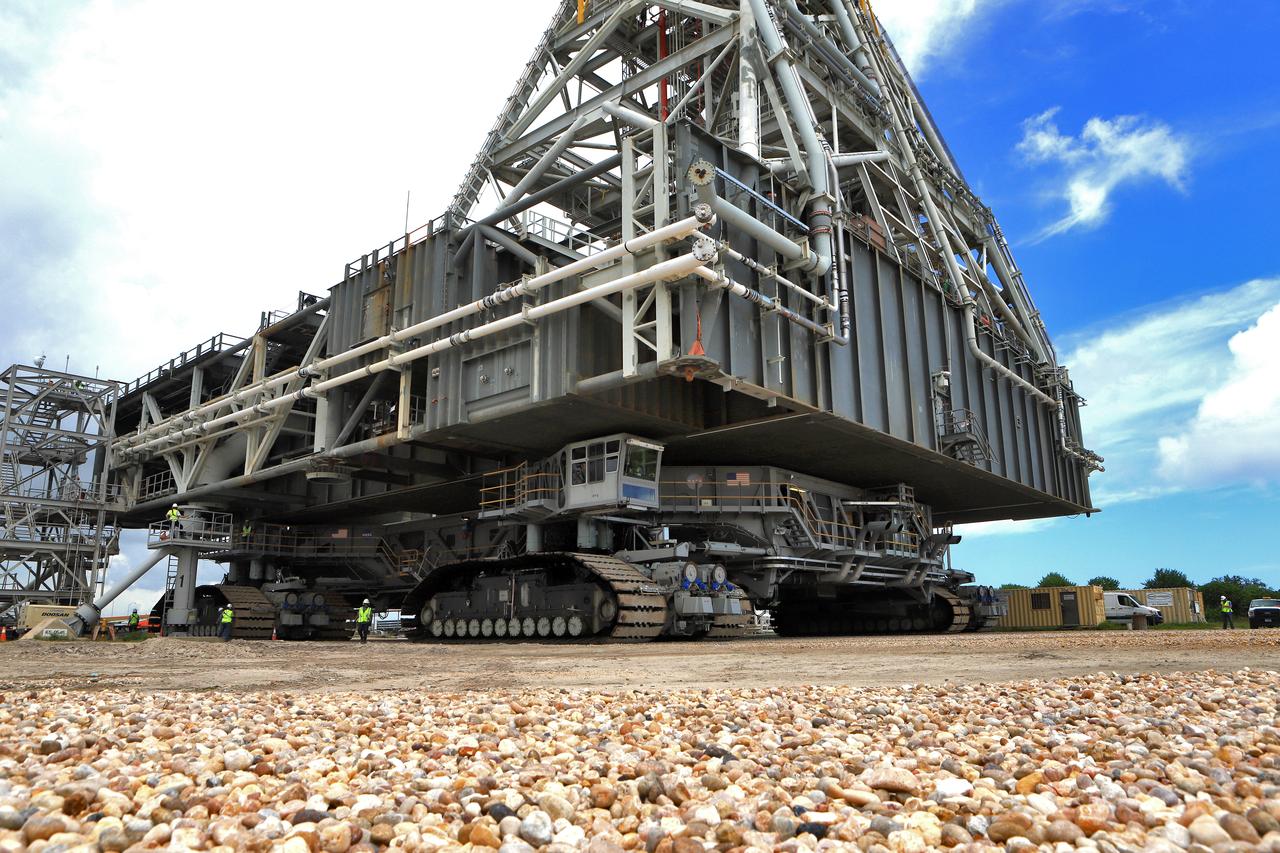

A close-up view of NASA's crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) with the mobile launcher (ML) atop as it slowly moves along the crawlerway on its trek to Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 30, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. CT-2 will move the ML up to the surface of the pad where it will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
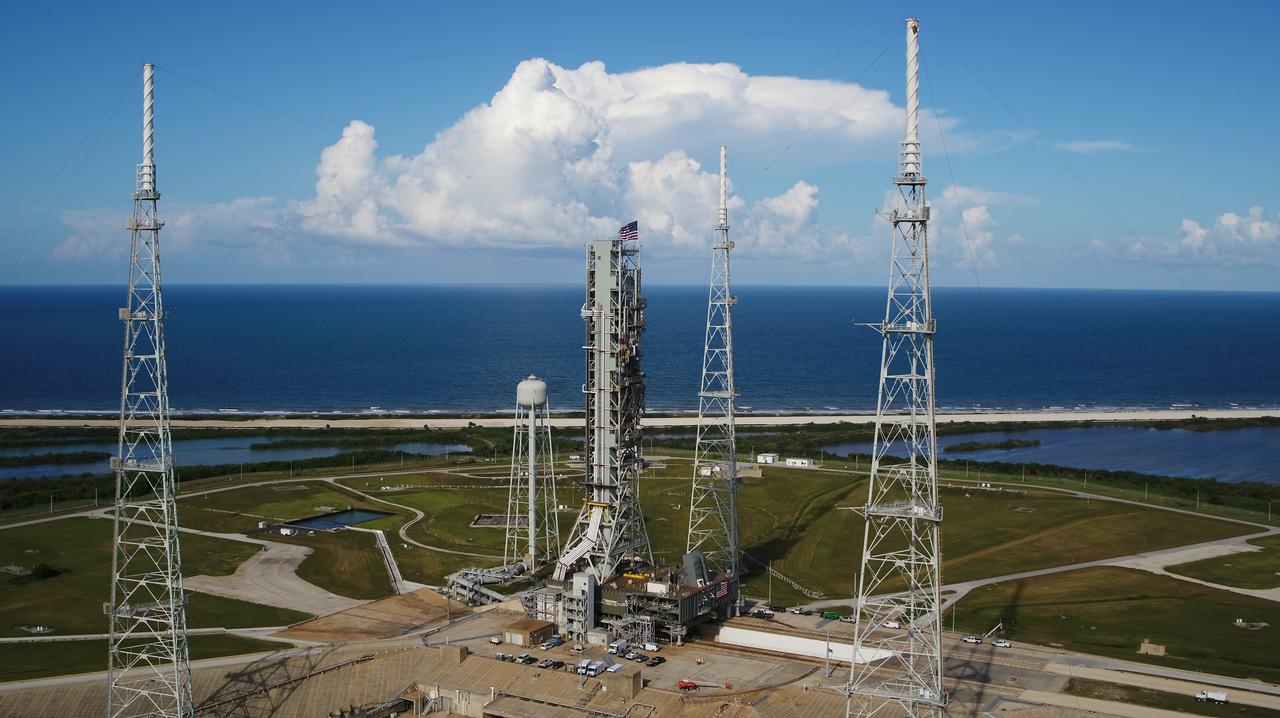

NASA's mobile launcher (ML) atop crawler-transporter 2 is at the top of Launch Pad 39B on Aug. 31, 2018, at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML will undergo a fit check, followed by several days of systems testing. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars. Photo credit: NASA/Jamie Peer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b>
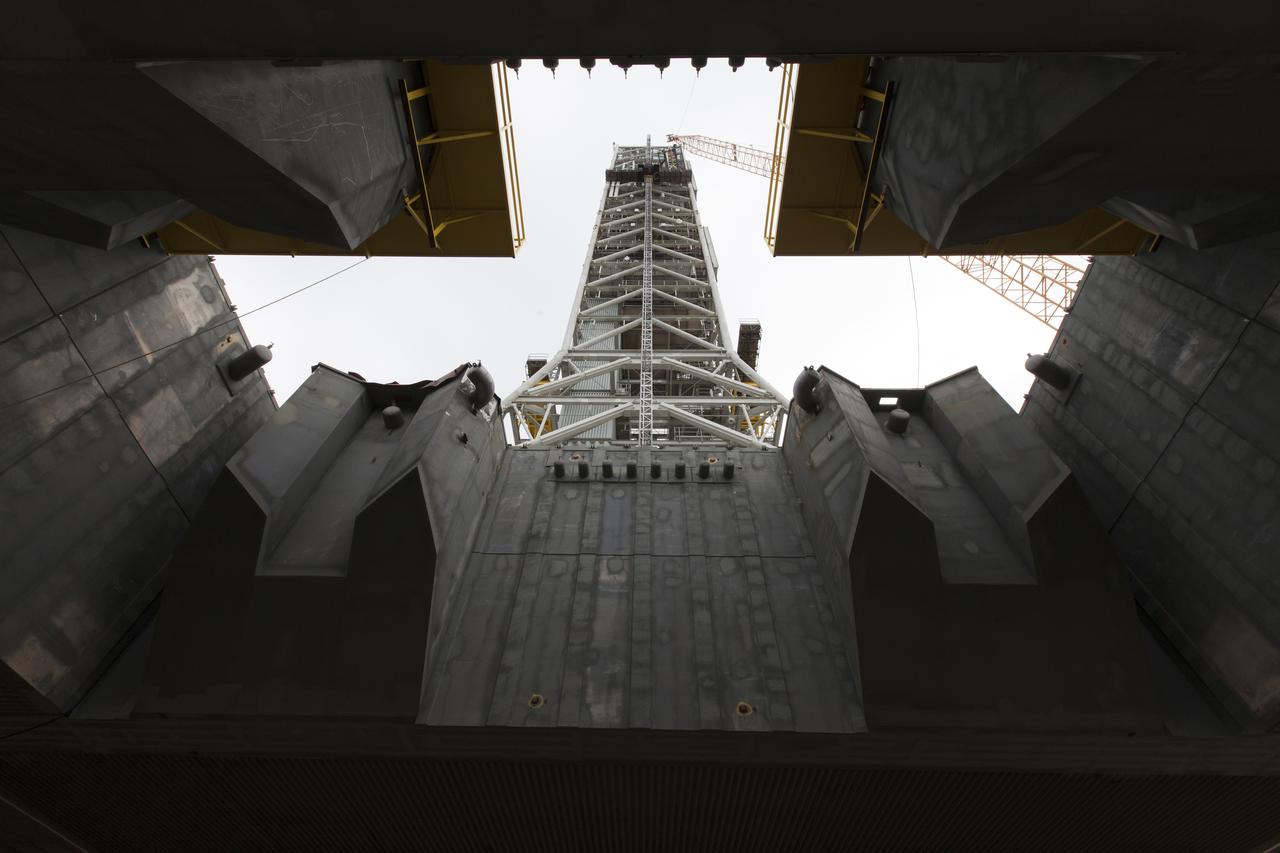

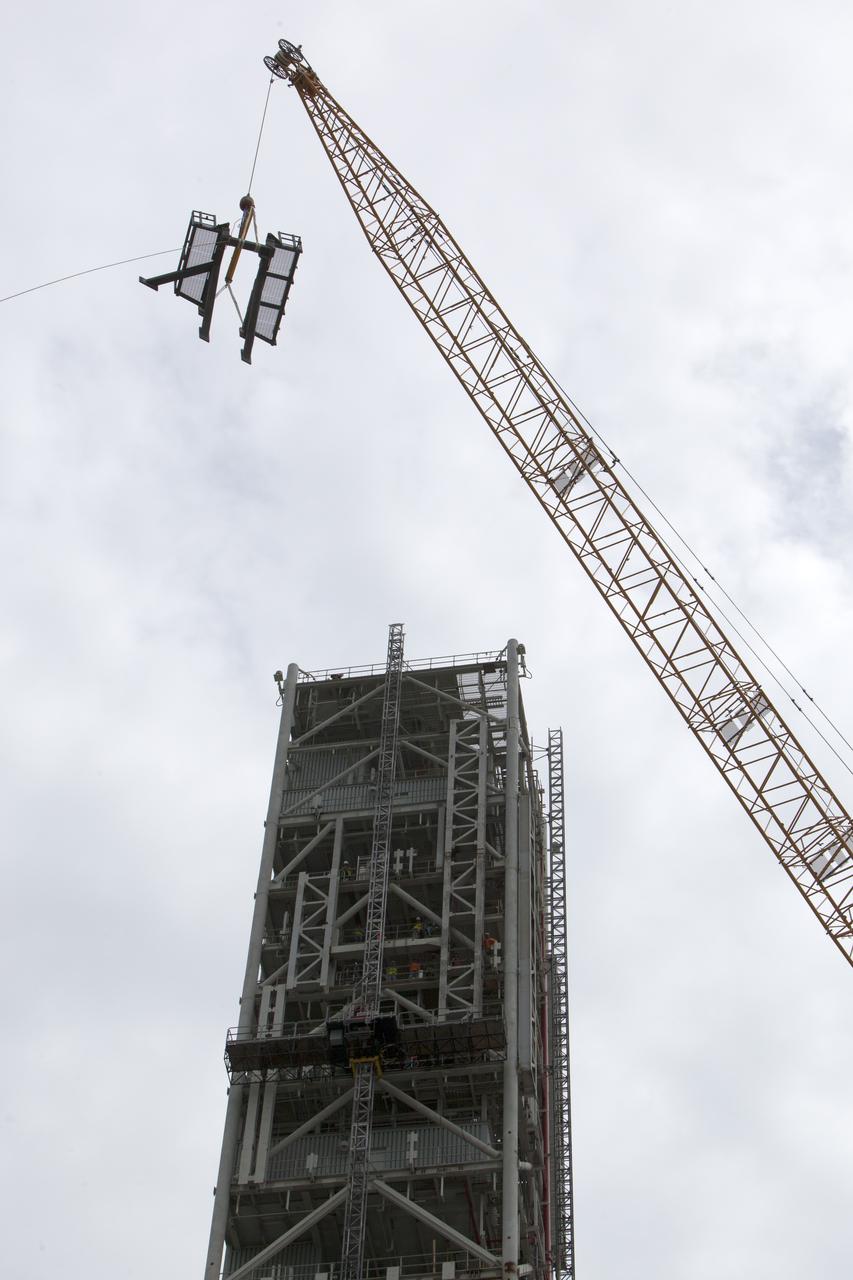
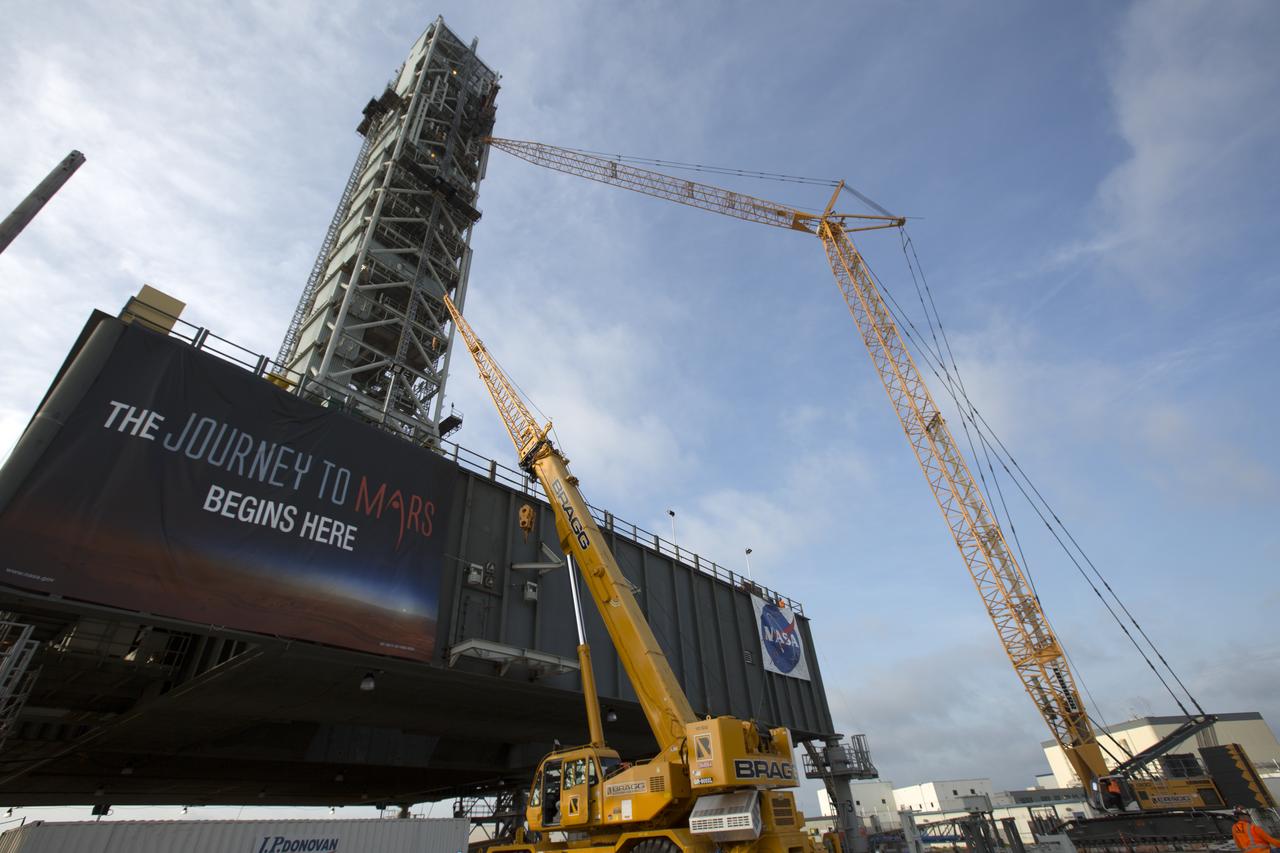
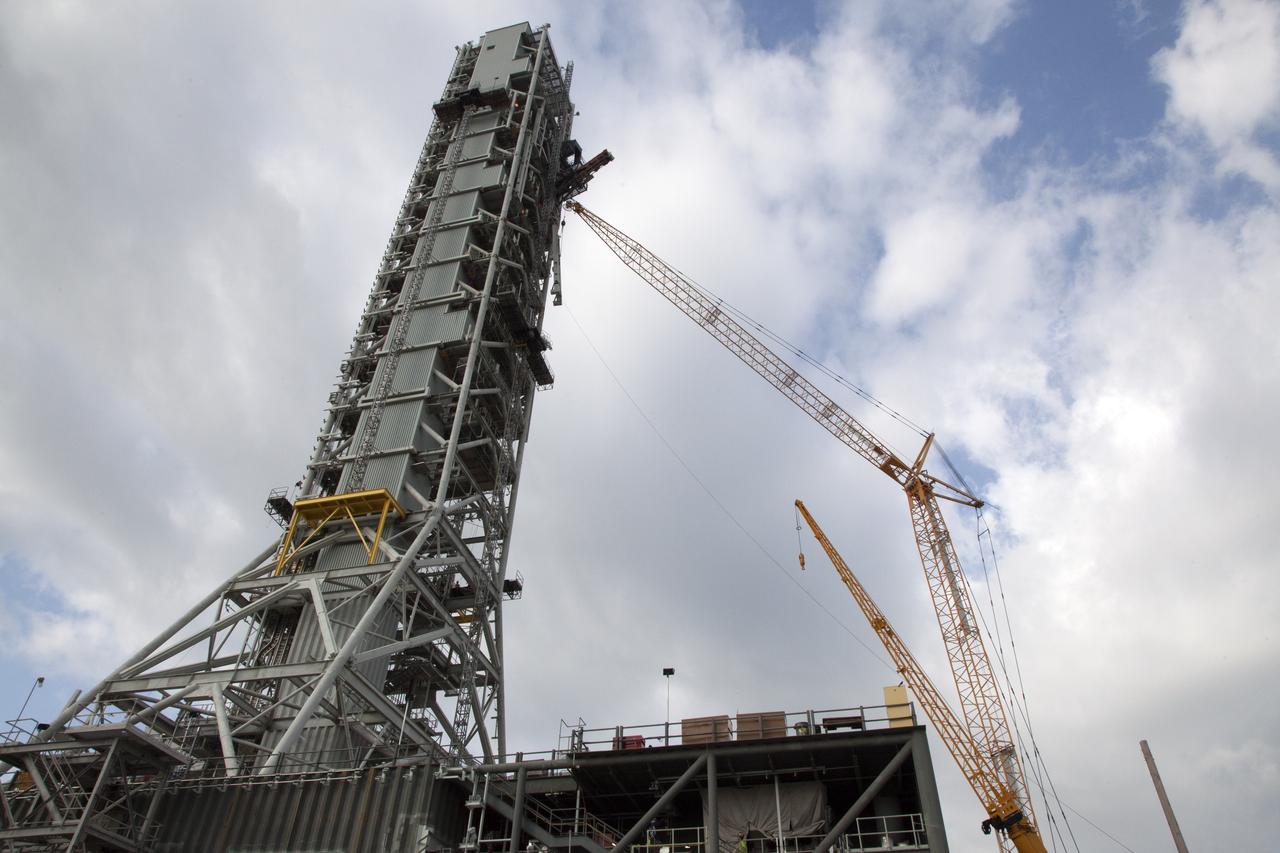
A view from below the mobile launcher shows a crane positioning the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
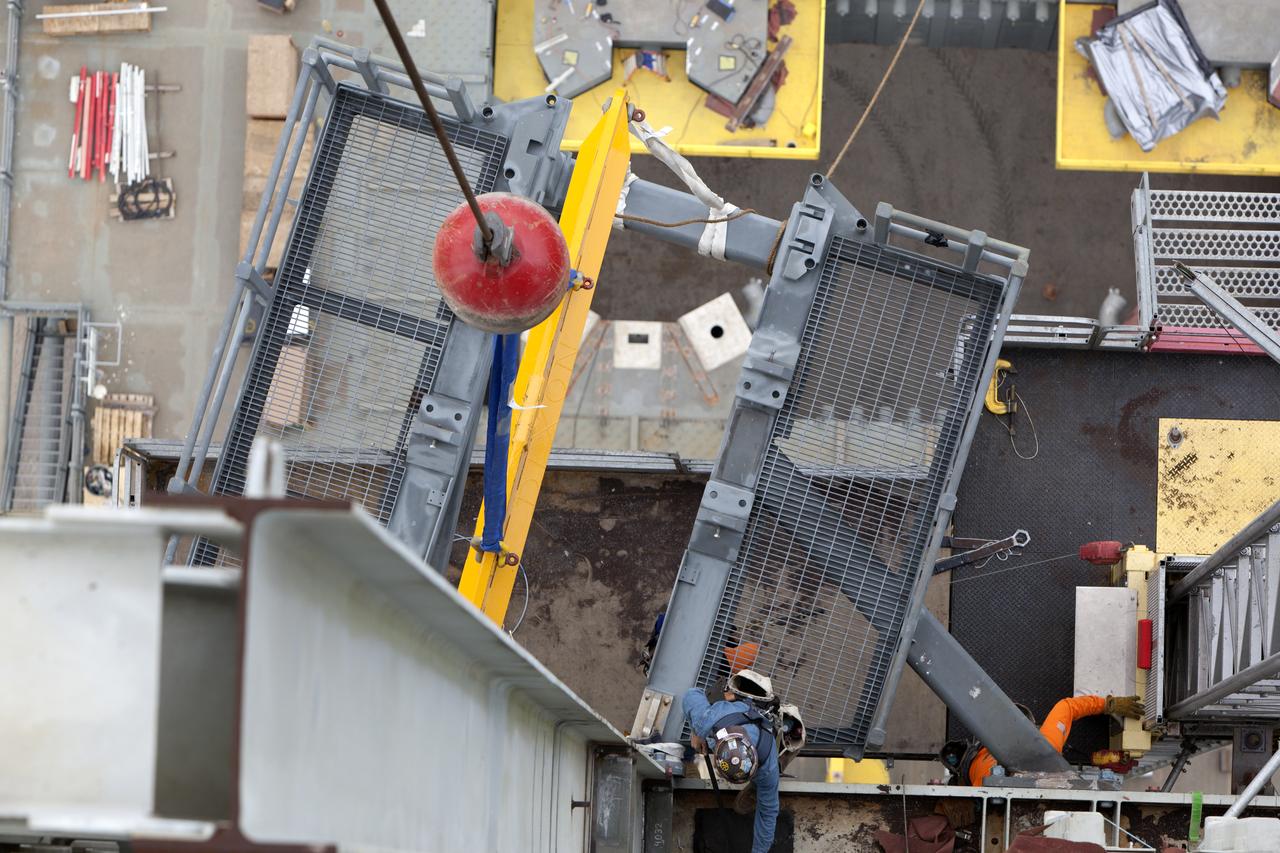

In this view looking down from high up on the mobile launcher, a crane positions the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
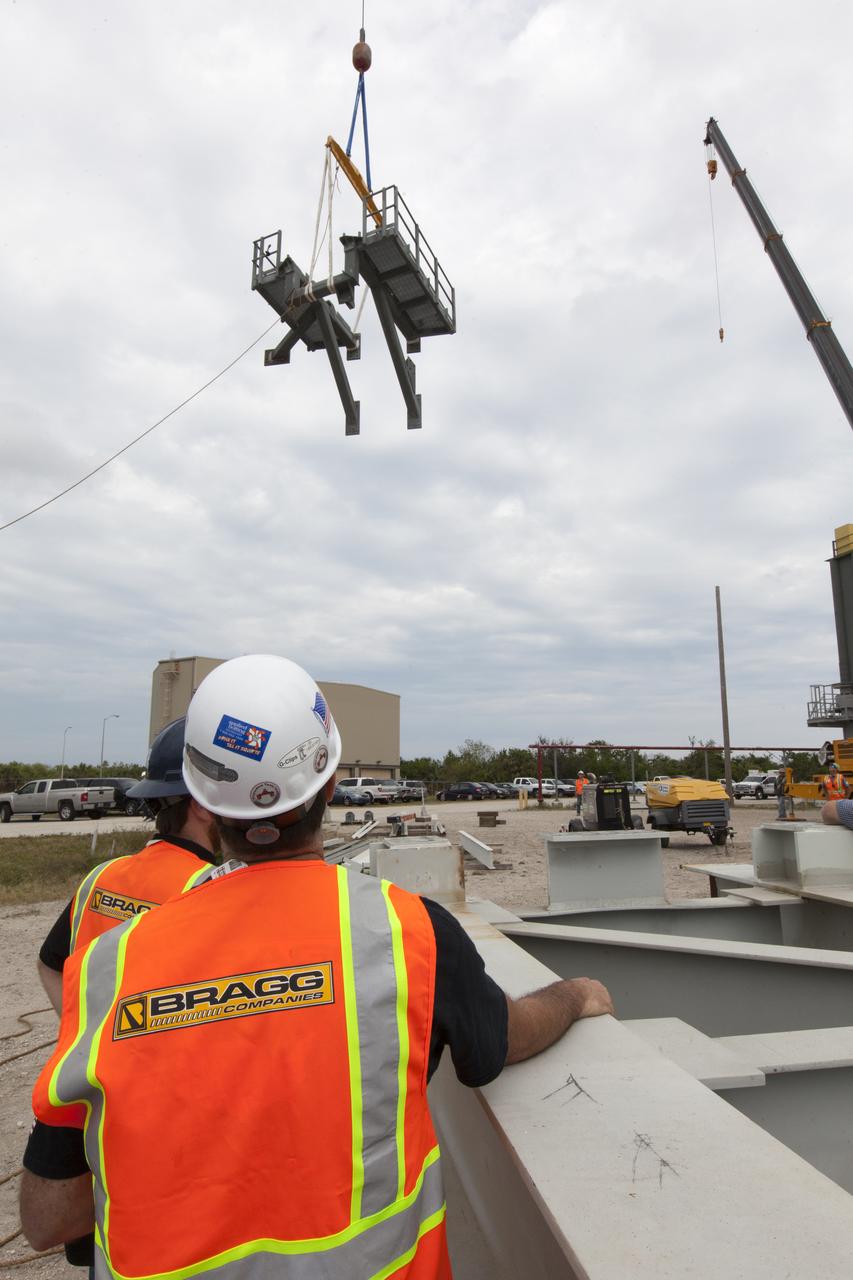

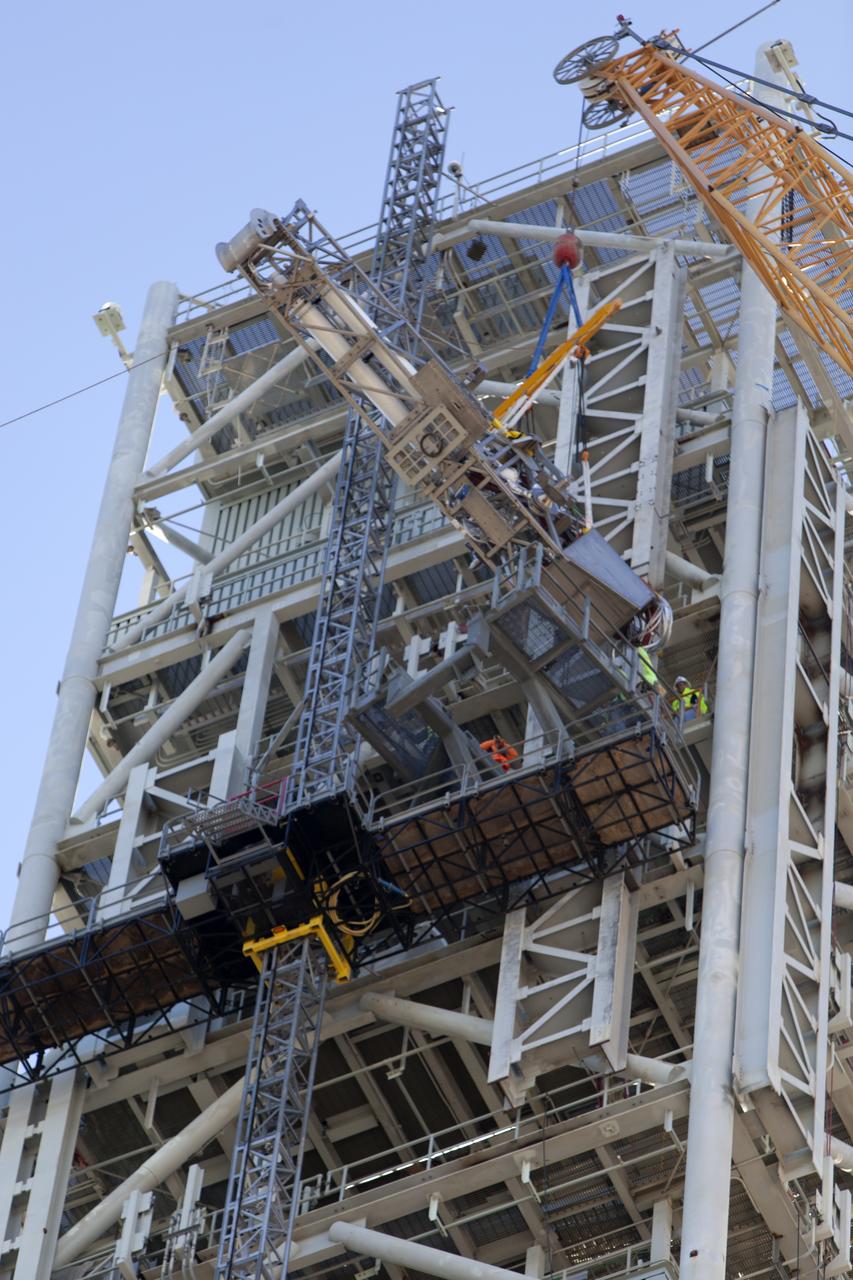
Crane specialists monitor the progress as the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) is lifted up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
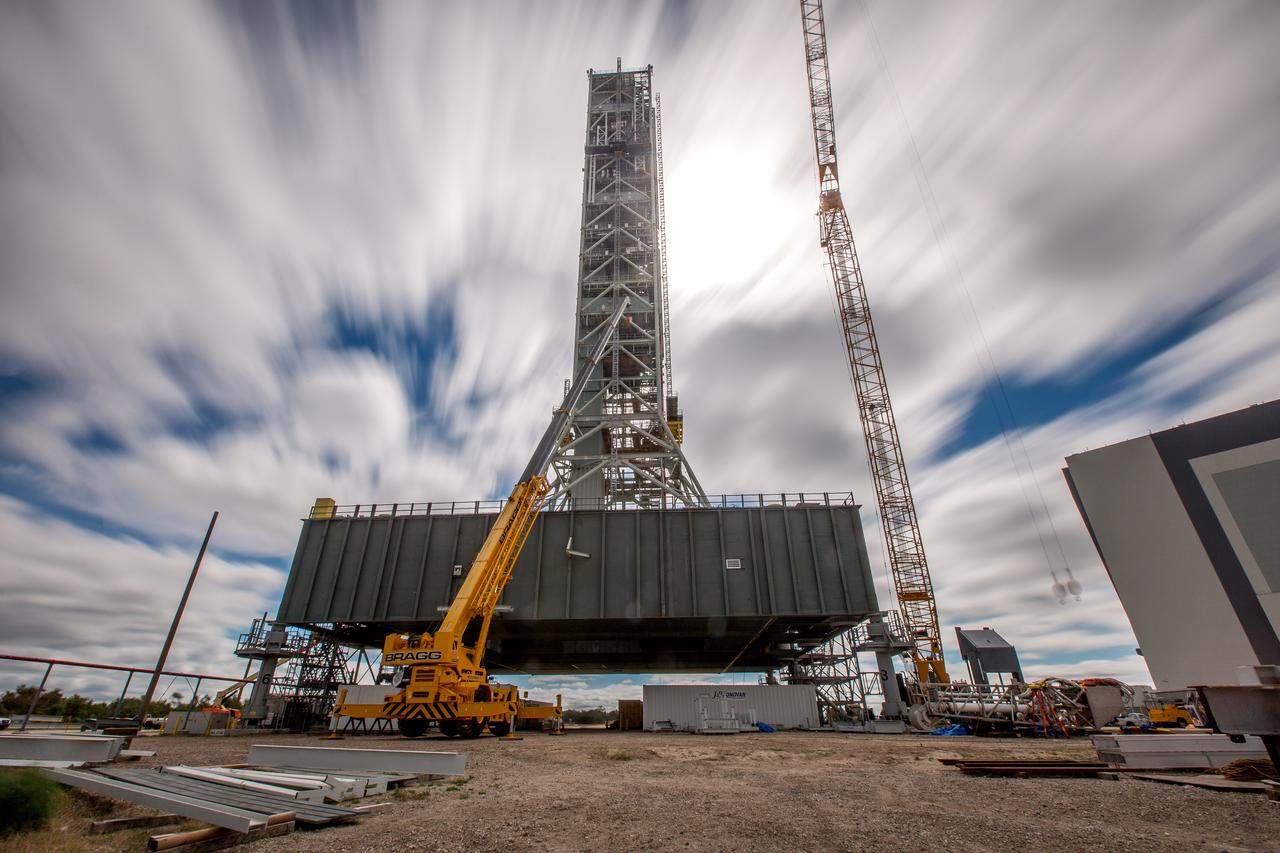

A long-exposure view of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cranes and rigging are being used to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower. The tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
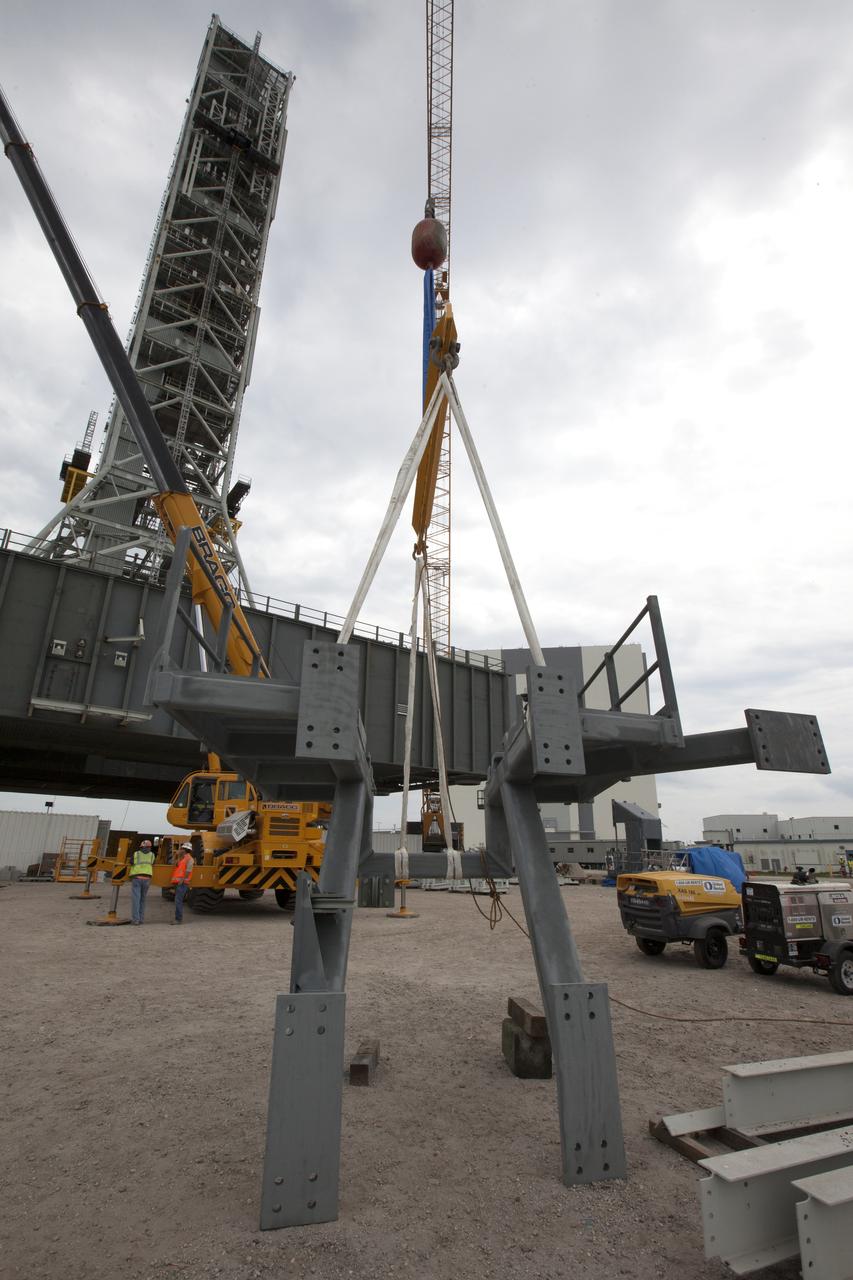

Preparations are underway to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A crane and rigging are used to position the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation high up on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
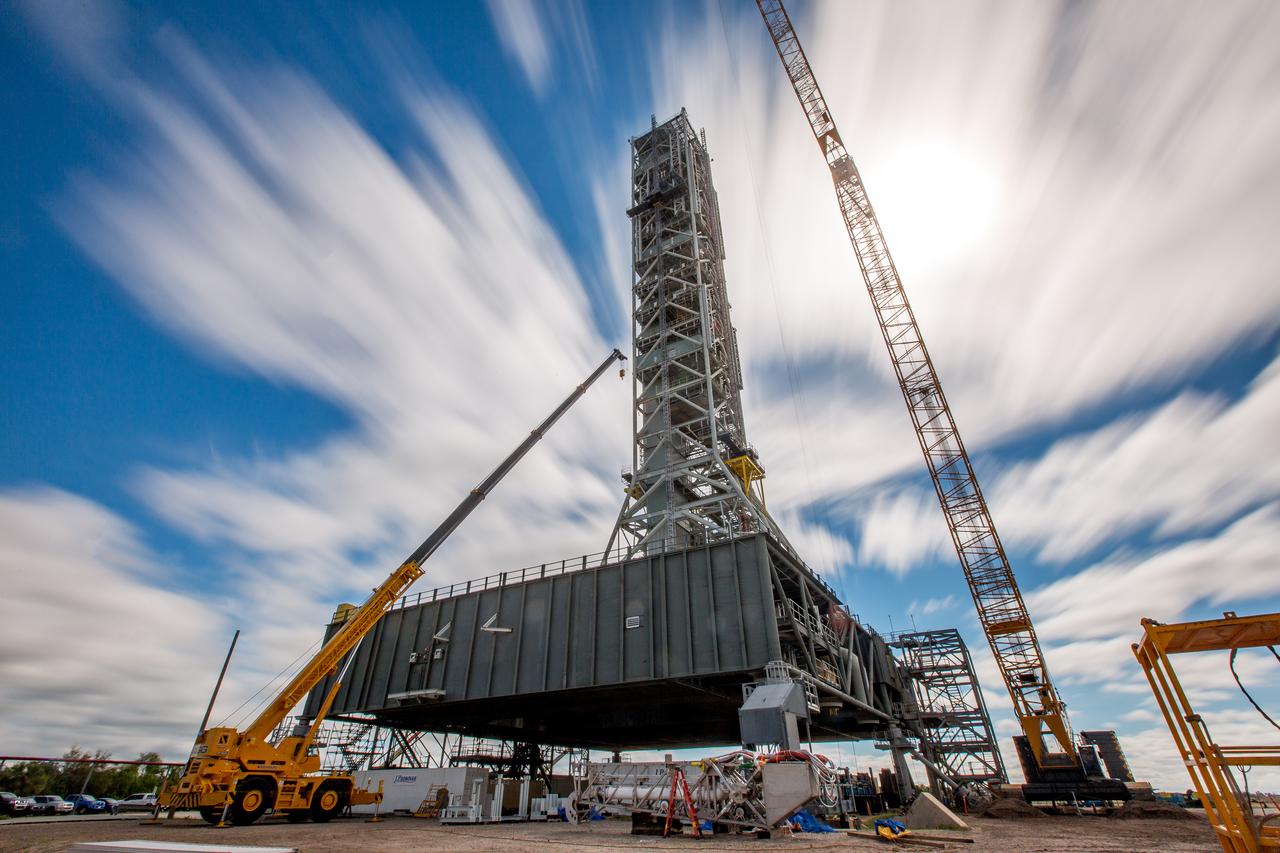

A long-exposure view of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cranes and rigging are being used to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower. The tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Preparations are underway to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
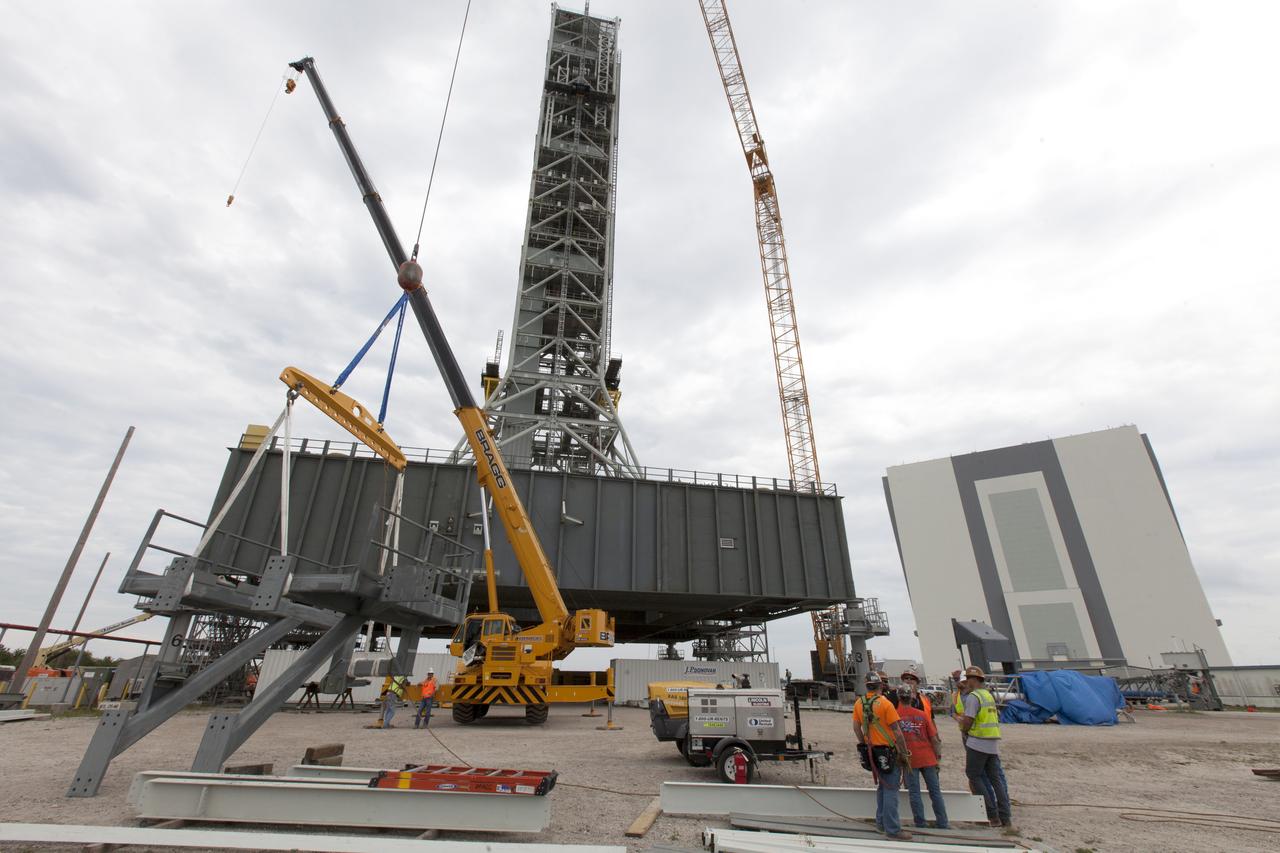

Preparations are underway to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

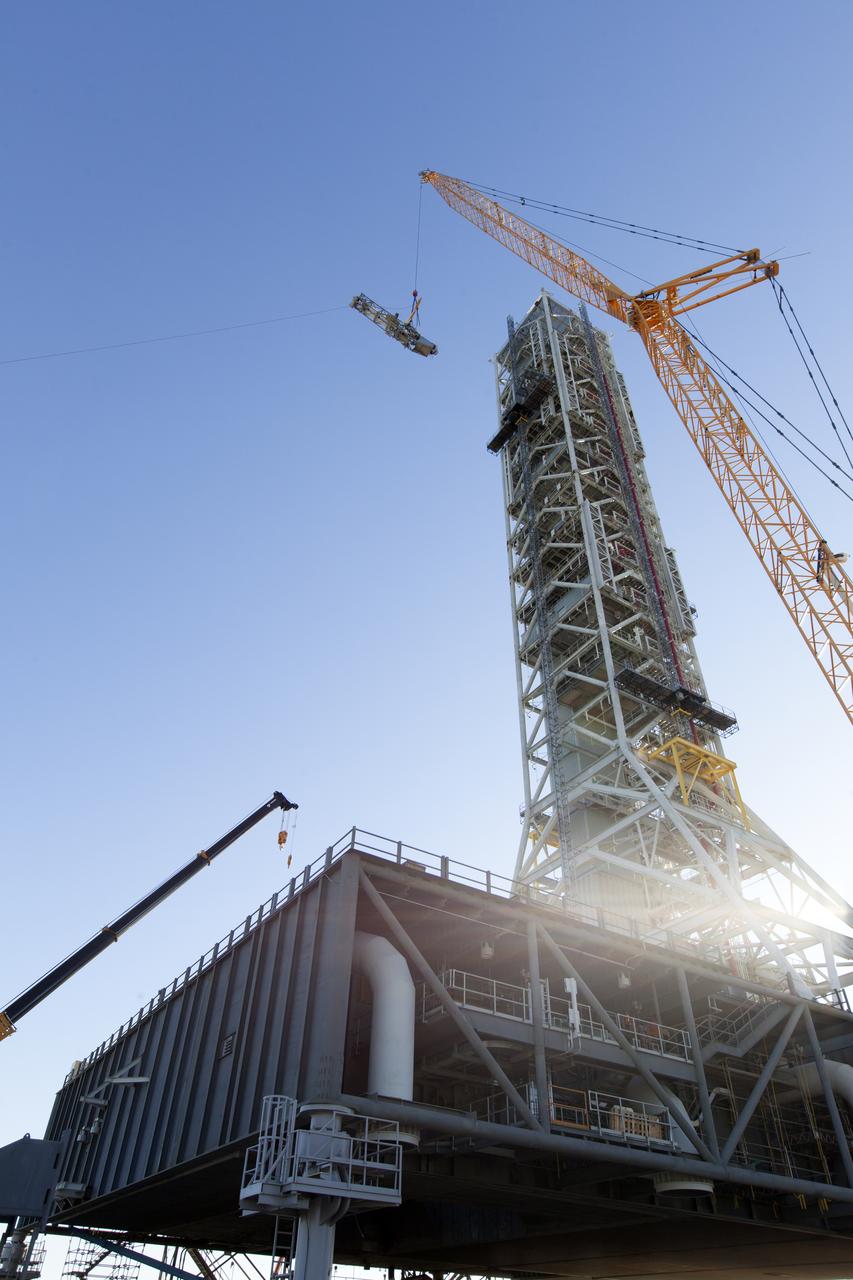
A crane and rigging are used to position the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation high up on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

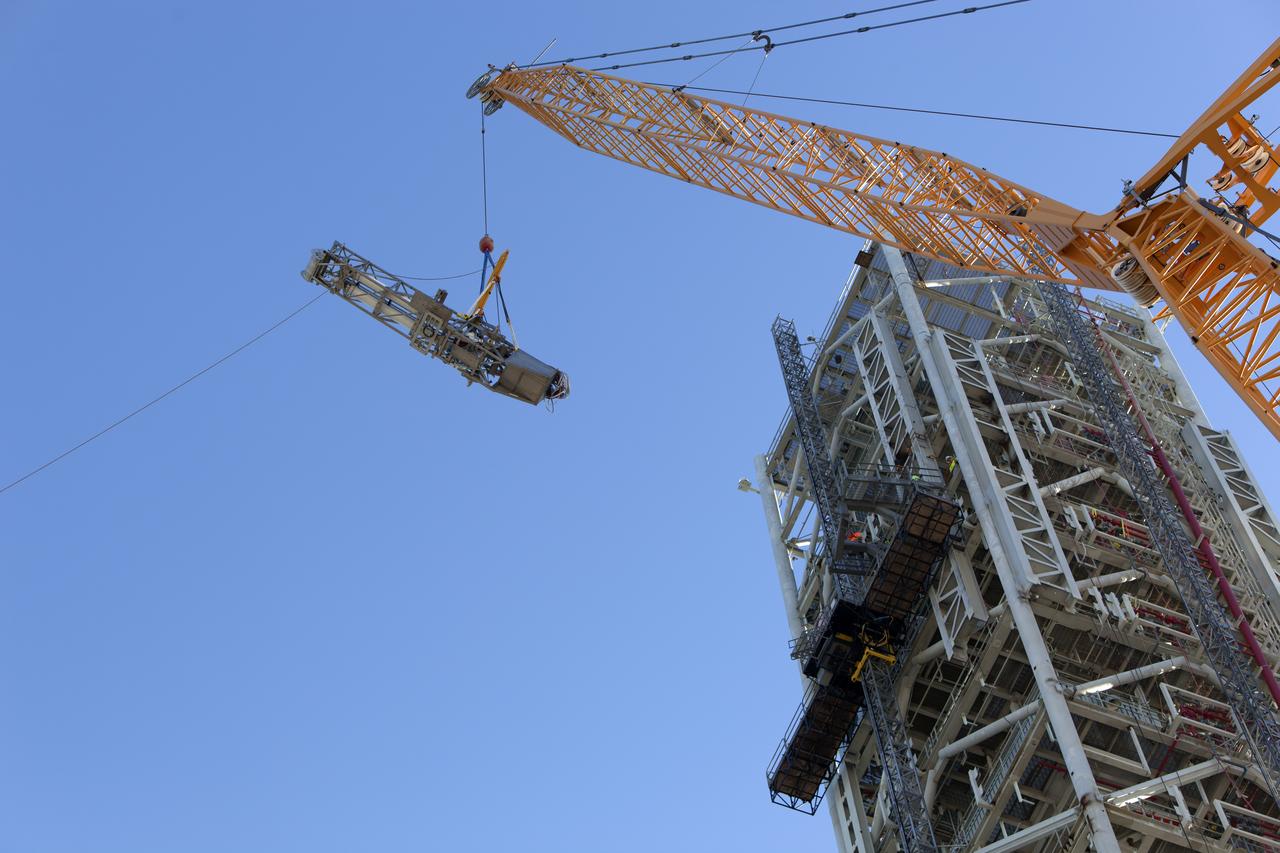
A crane lifts the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A crane and rigging are used to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
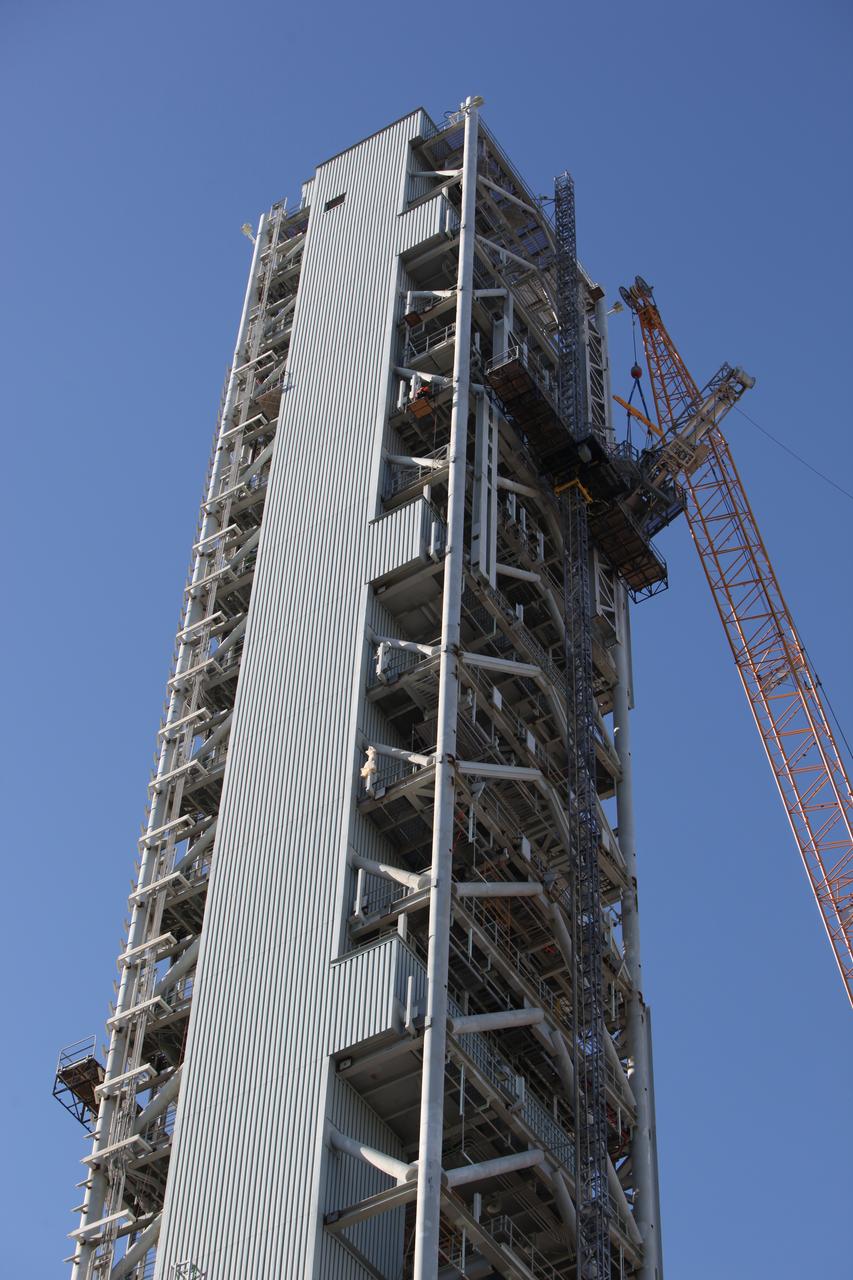

A crane and rigging are used to position the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation high up on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
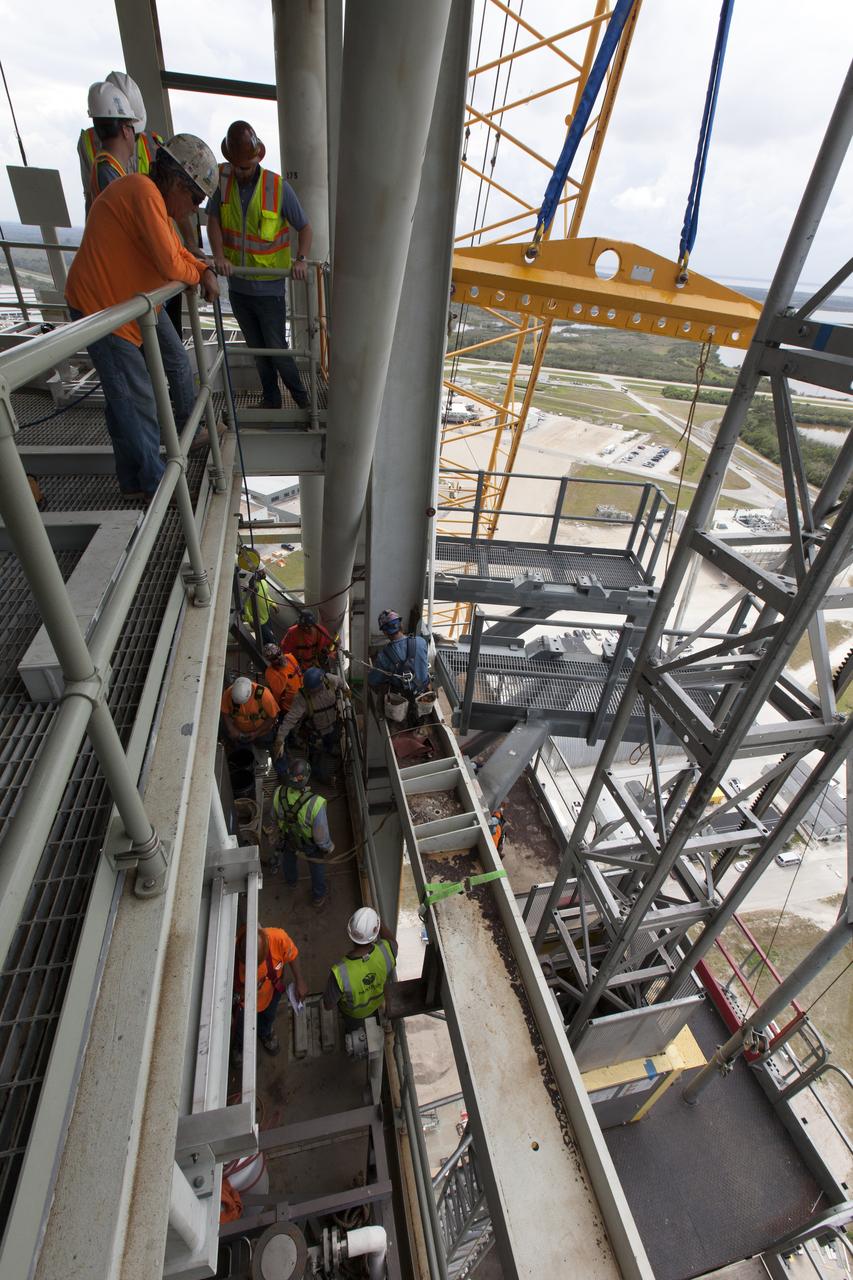

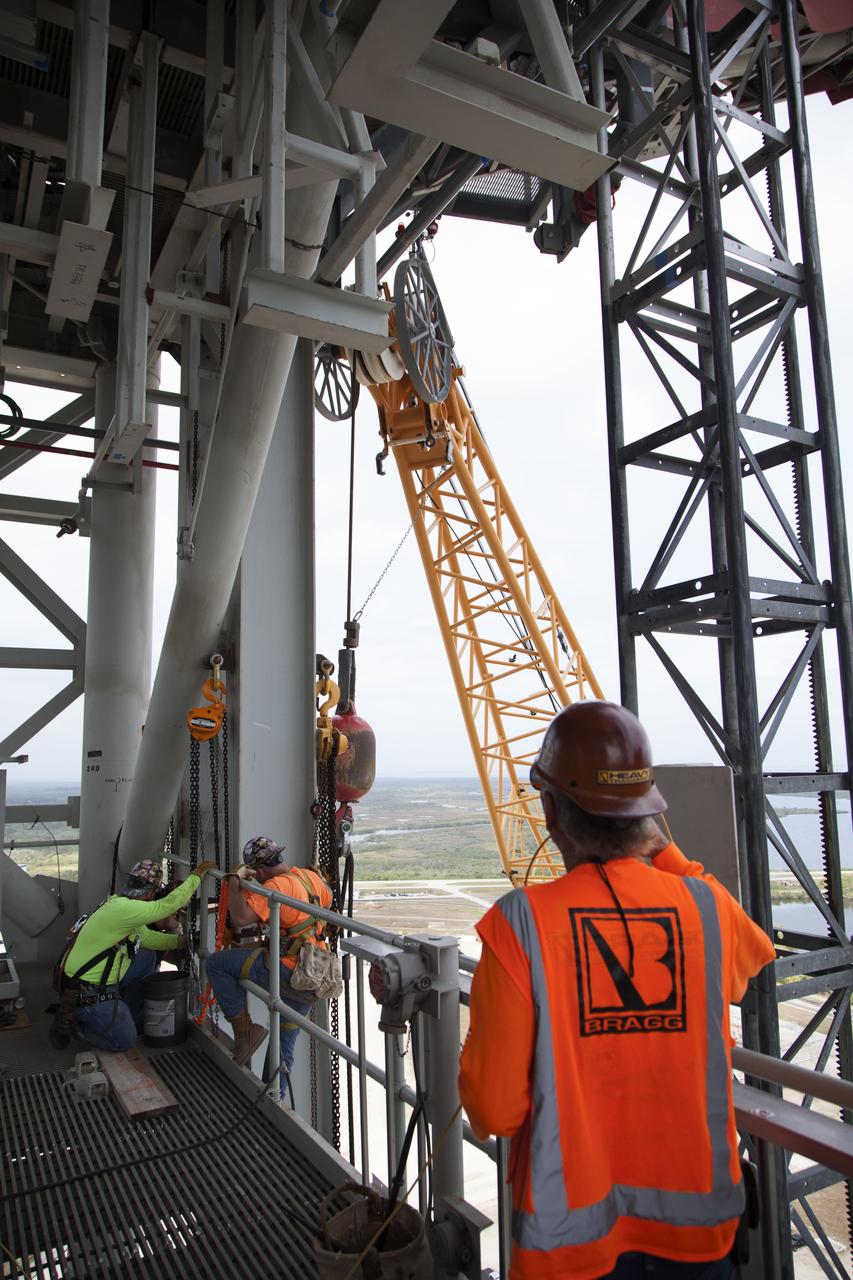
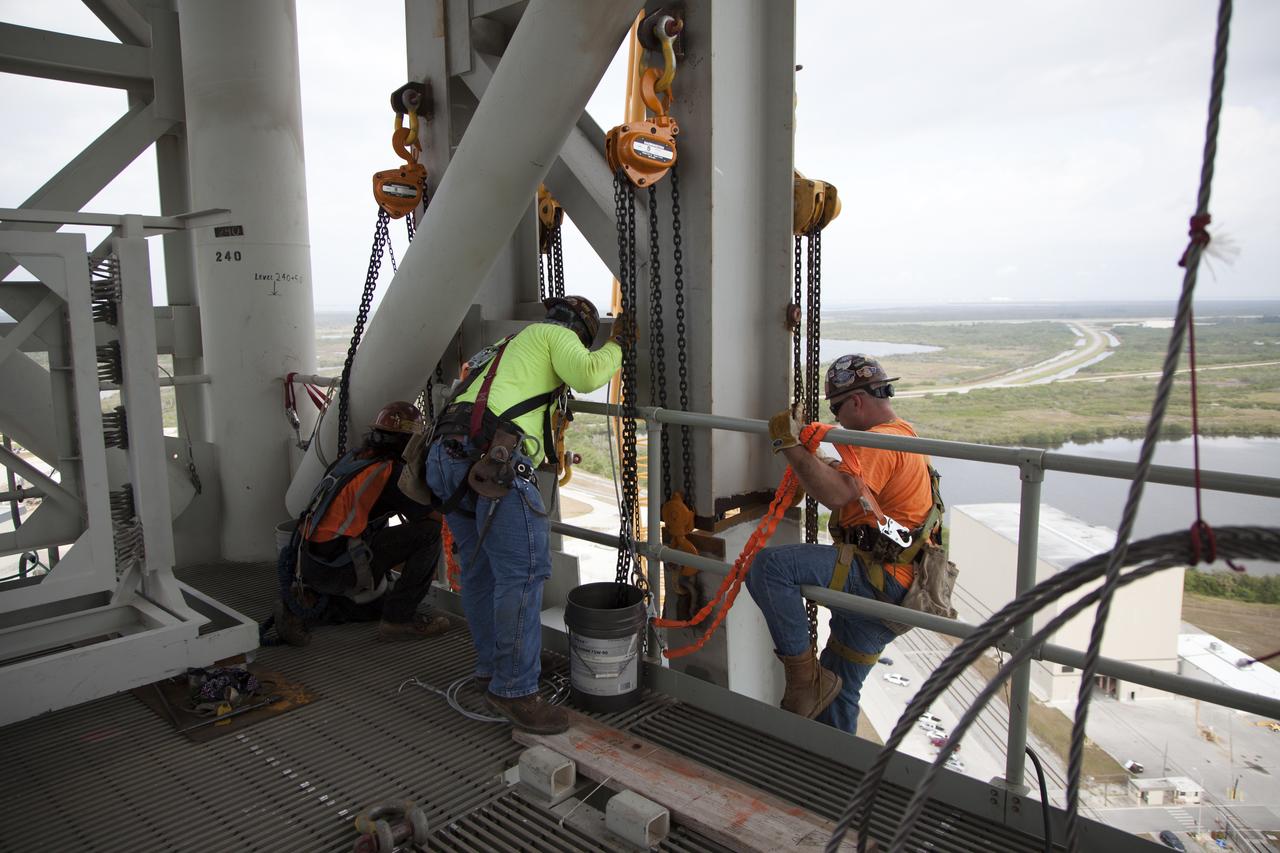
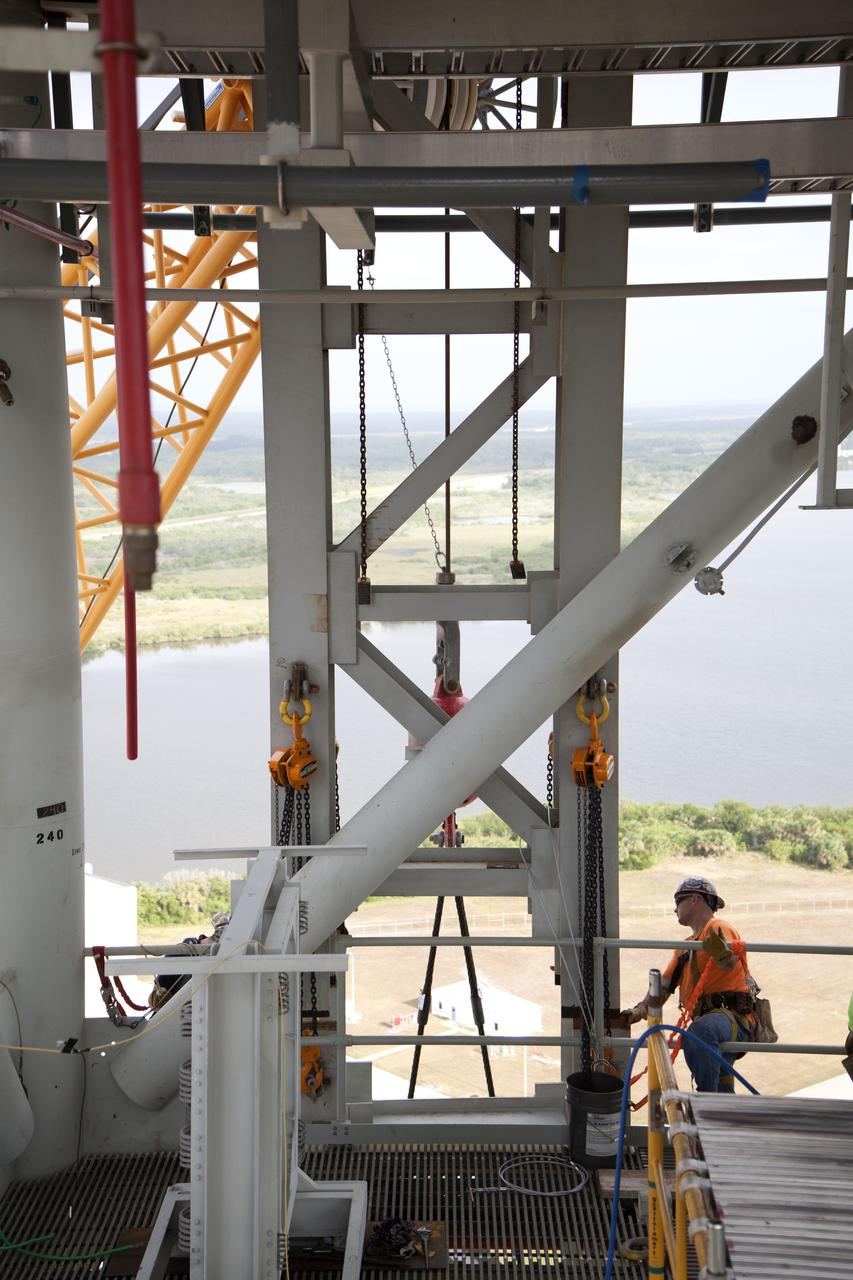
Construction workers and crane specialists high up on the mobile launcher tower monitor the progress as a crane positions the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
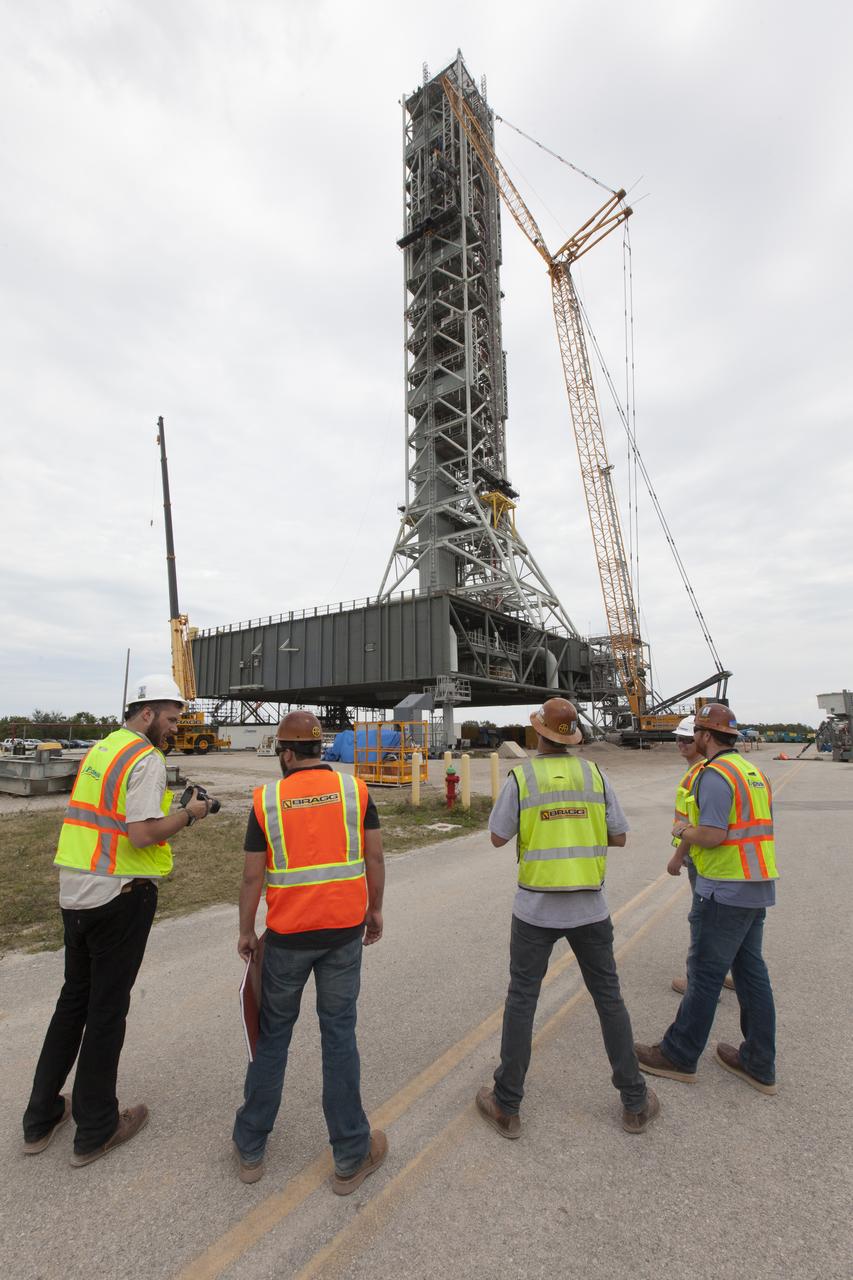

Crane specialists monitor the progress as the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) is lifted high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
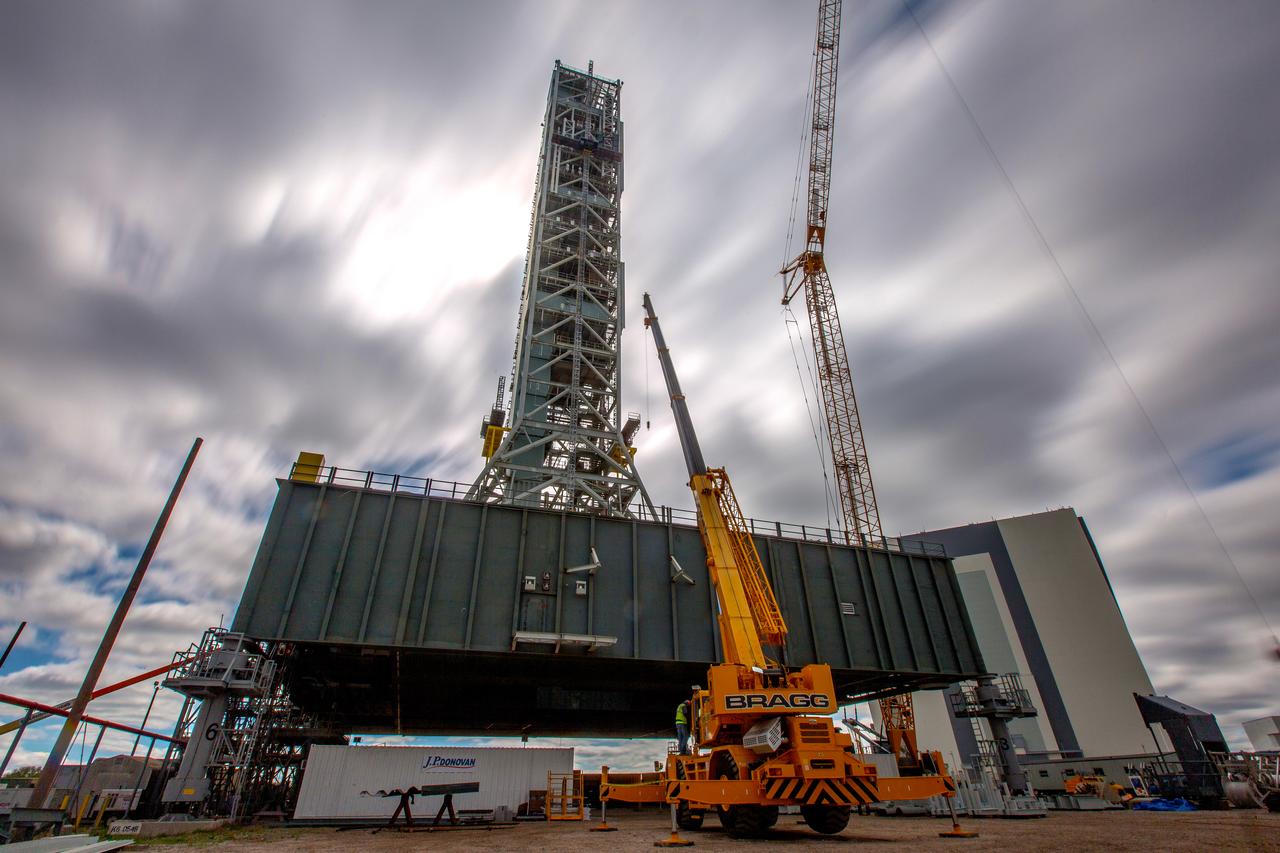

A long-exposure view of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Cranes and rigging are being used to lift the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower. The tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A crane and rigging are used to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A crane and rigging are used to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
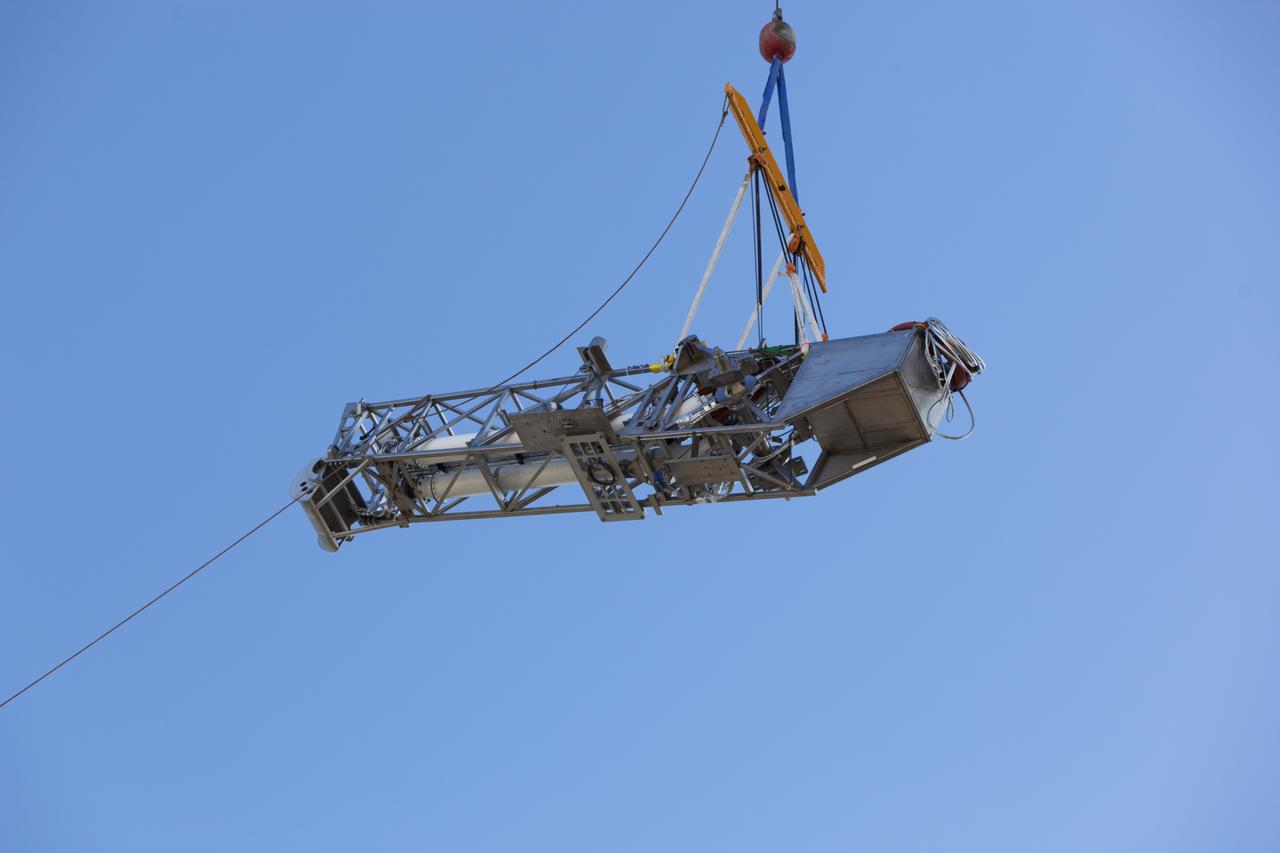

Seeming to hang in midair, the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) is lifted high up by crane for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
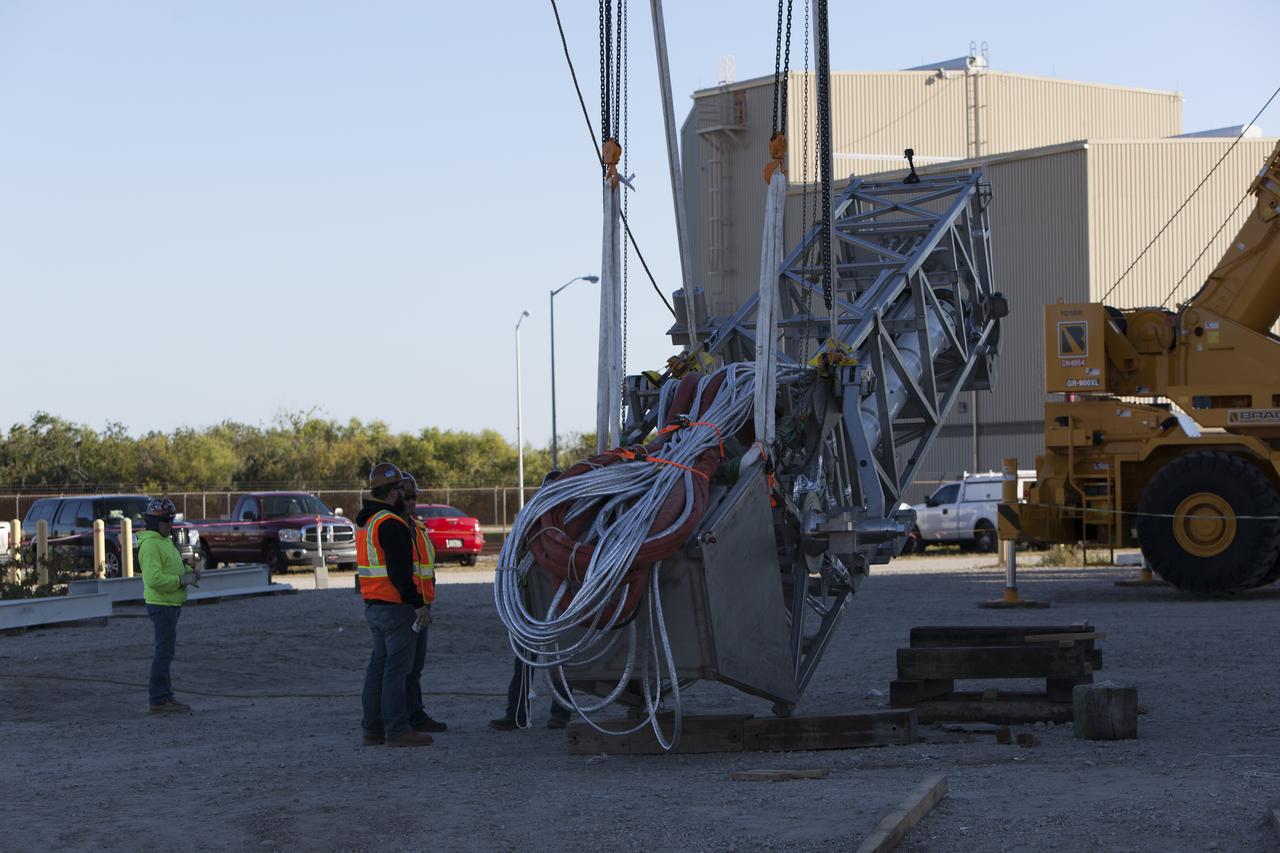

Preparations are underway to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

A crane lifts the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) high up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
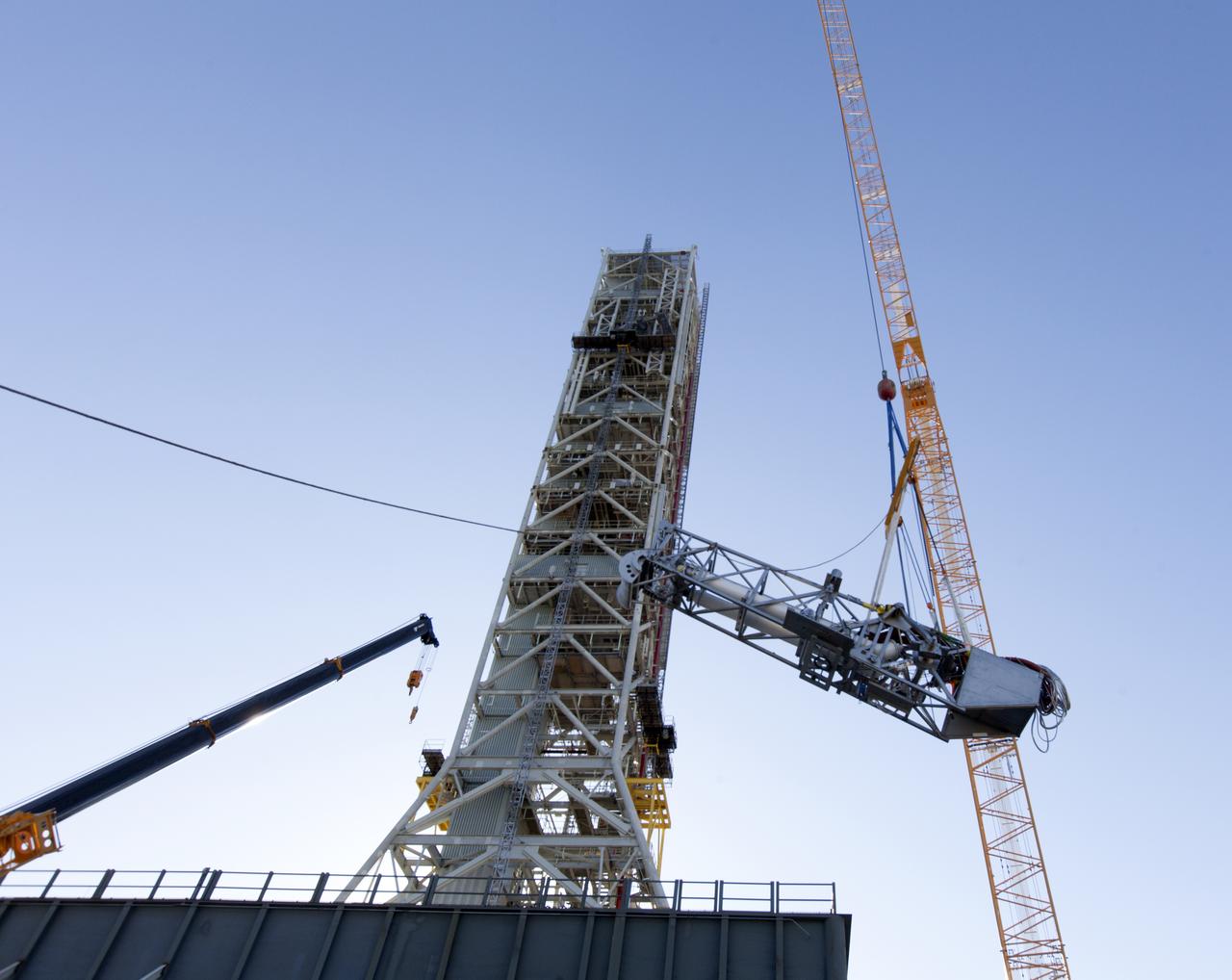

A crane and rigging are used to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
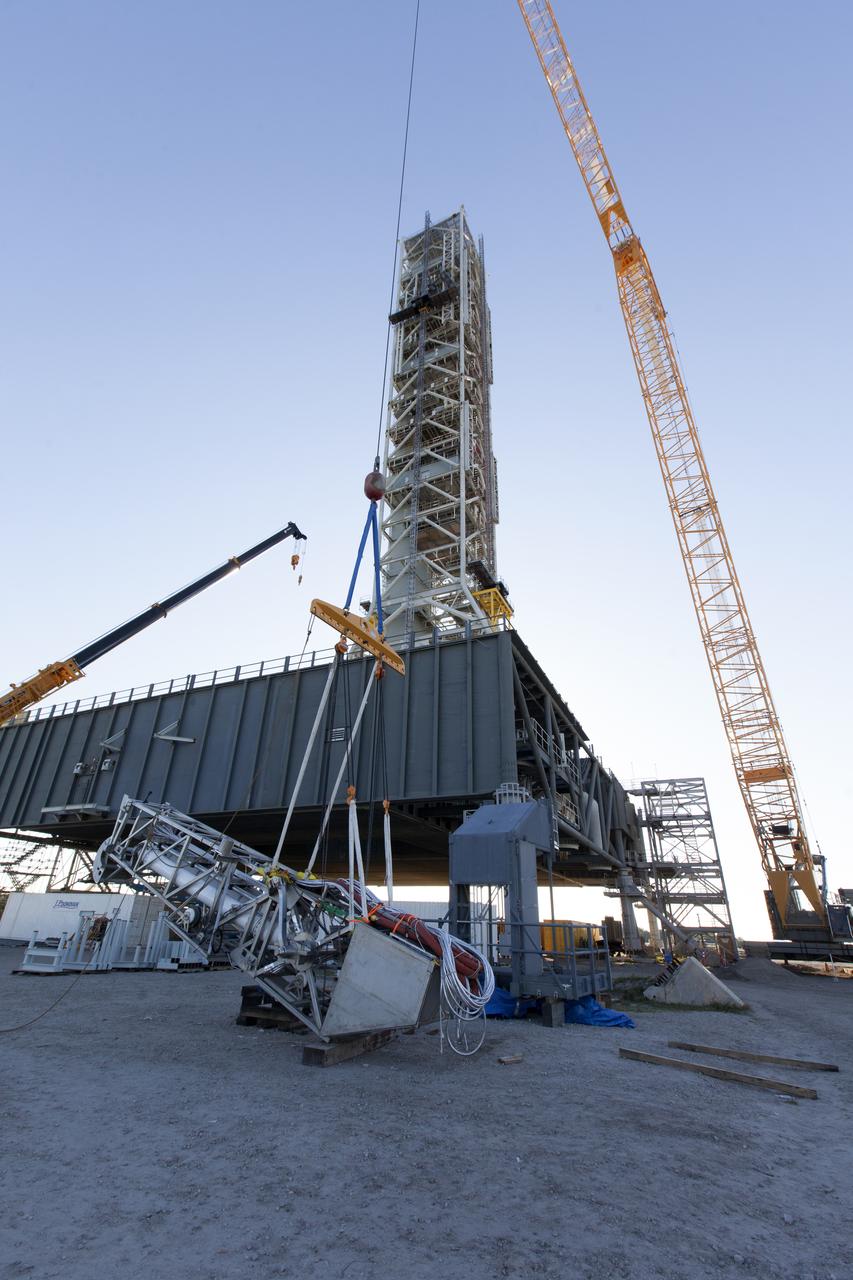

Preparations are underway to lift the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
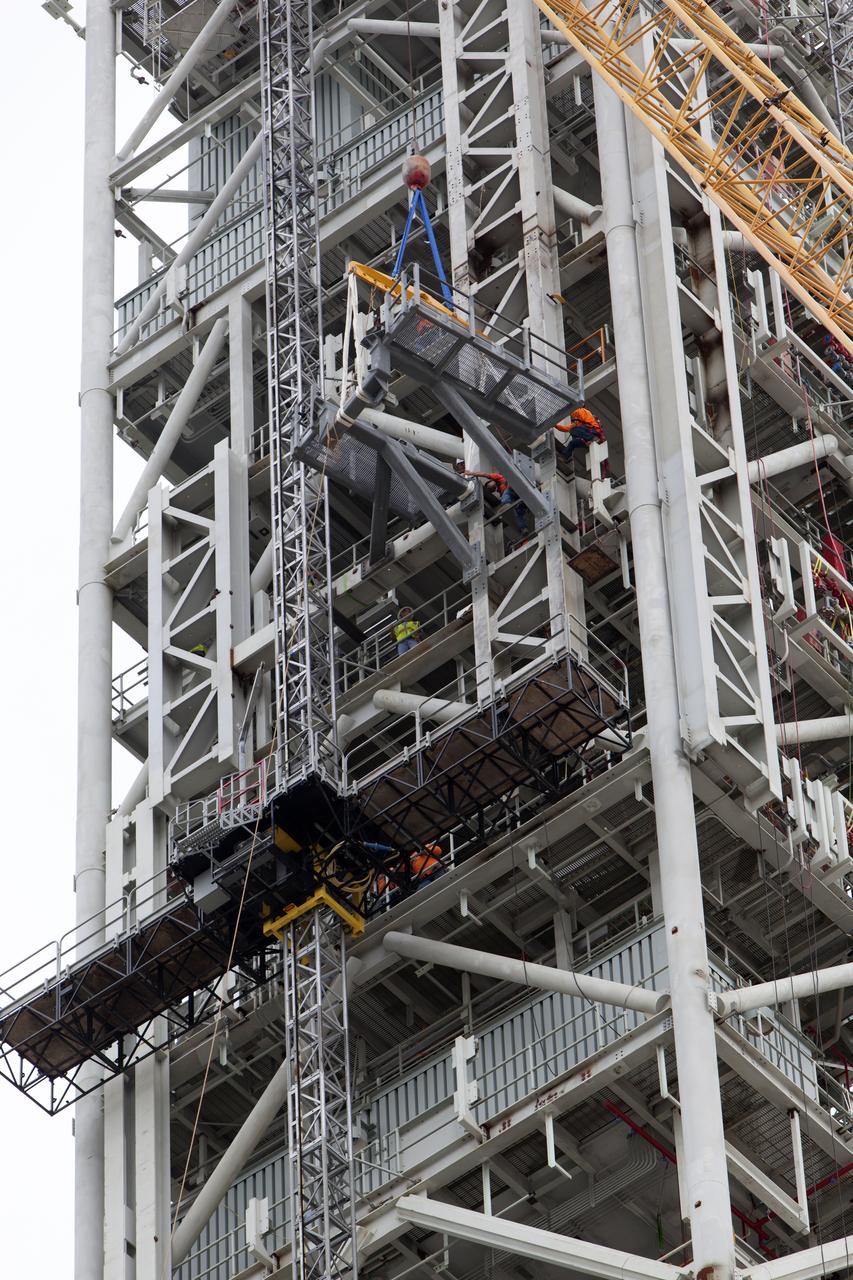

A crane positions the bracket for the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
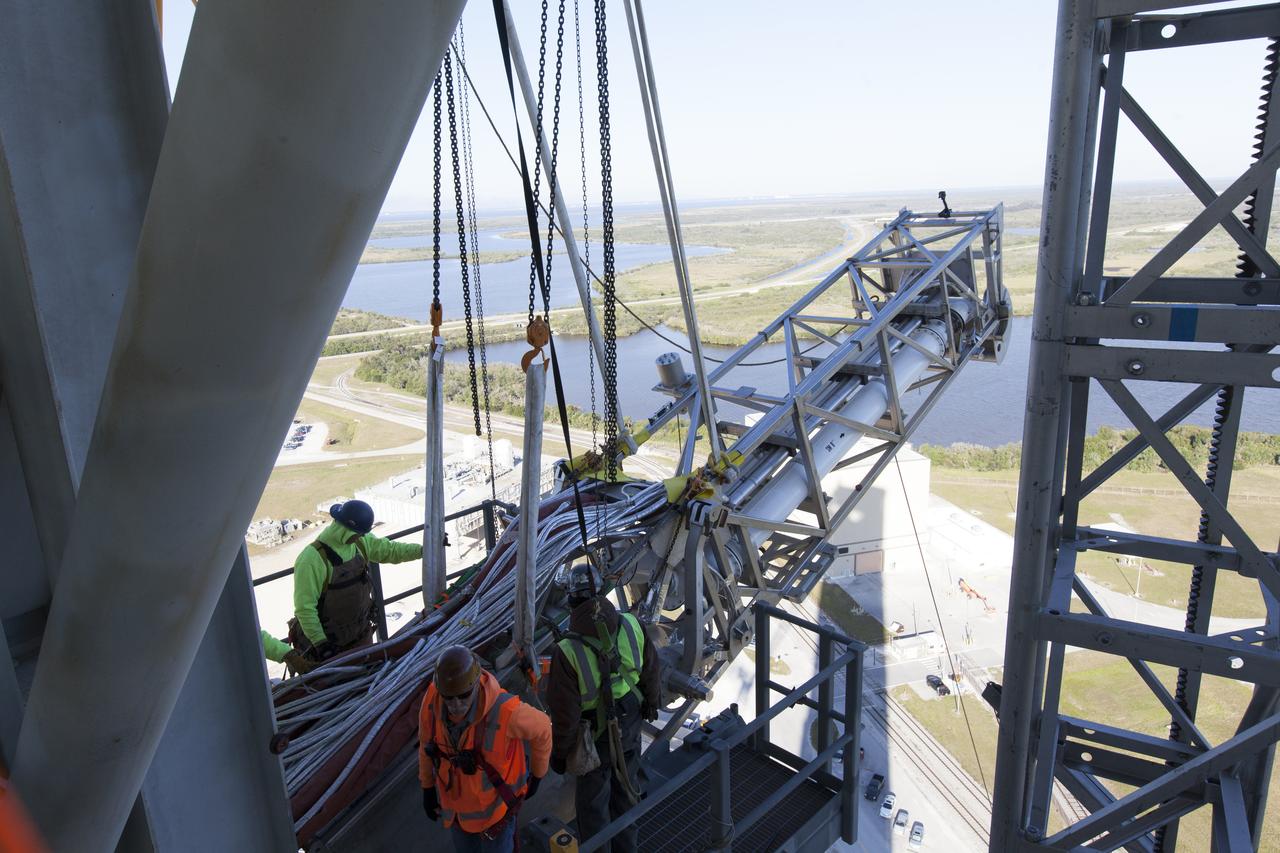

Construction workers assist as a crane and rigging are used to position the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) for installation high up on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Teams with Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.
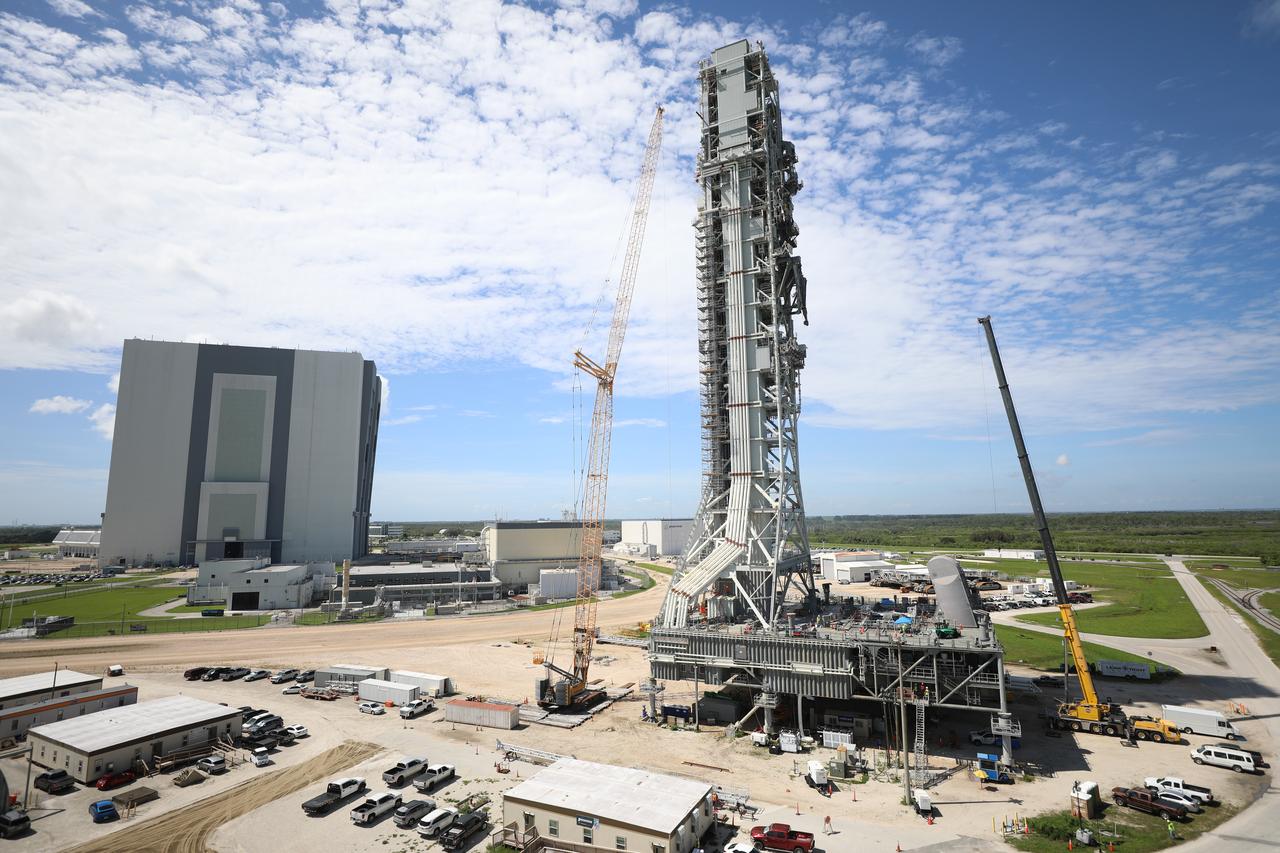

With the iconic Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida nearby, teams with Exploration Ground Systems make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.
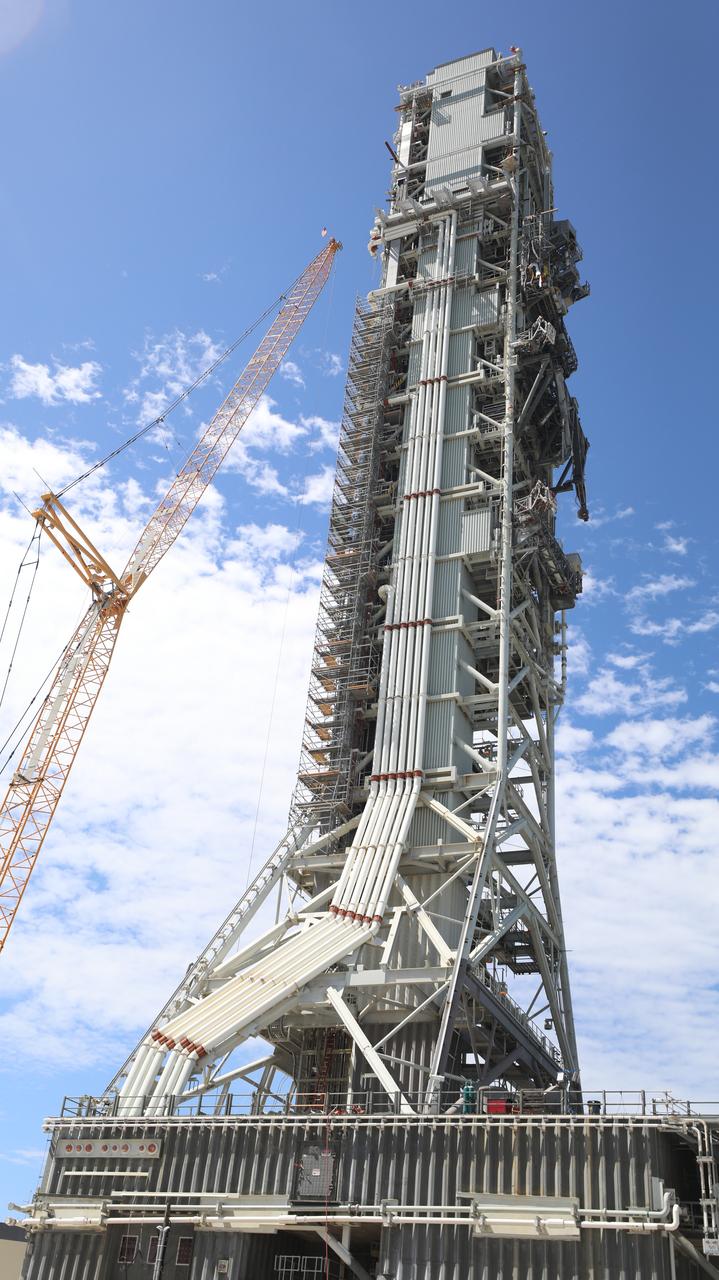

Teams with Exploration Ground Systems at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida make upgrades and repairs on mobile launcher 1 at its park site location on July 20, 2023, ahead of the first critical ground testing for Artemis II. Under Artemis, the mobile launcher will transport NASA’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft to Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B for liftoff. Artemis II will be the first Artemis mission flying crew aboard Orion.

A brilliant sunrise serves as the backdrop in this panoramic view of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the mobile launcher and ground systems necessary to process and launch the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

A colorful sunrise serves as the backdrop in this view of the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion spacecraft. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the mobile launcher and ground systems necessary to process and launch the SLS and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
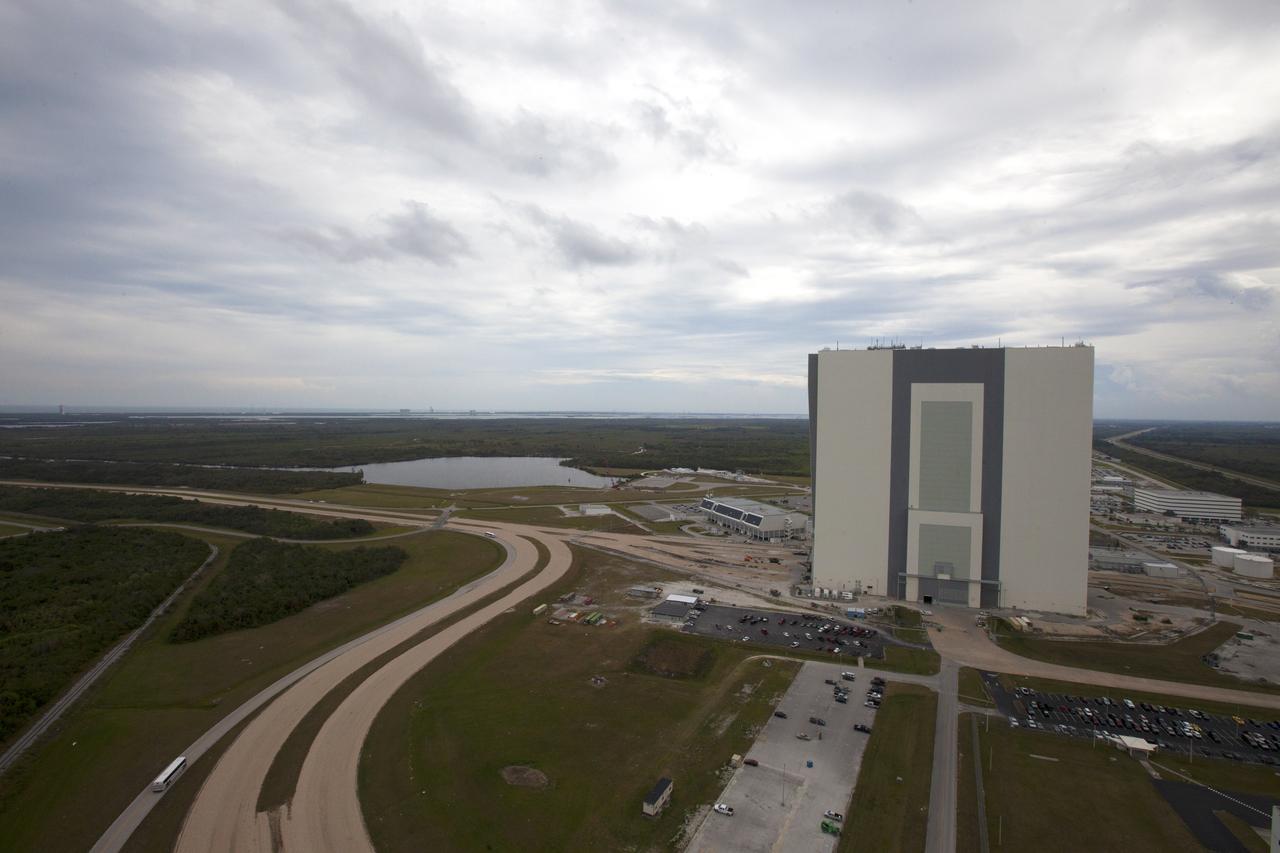

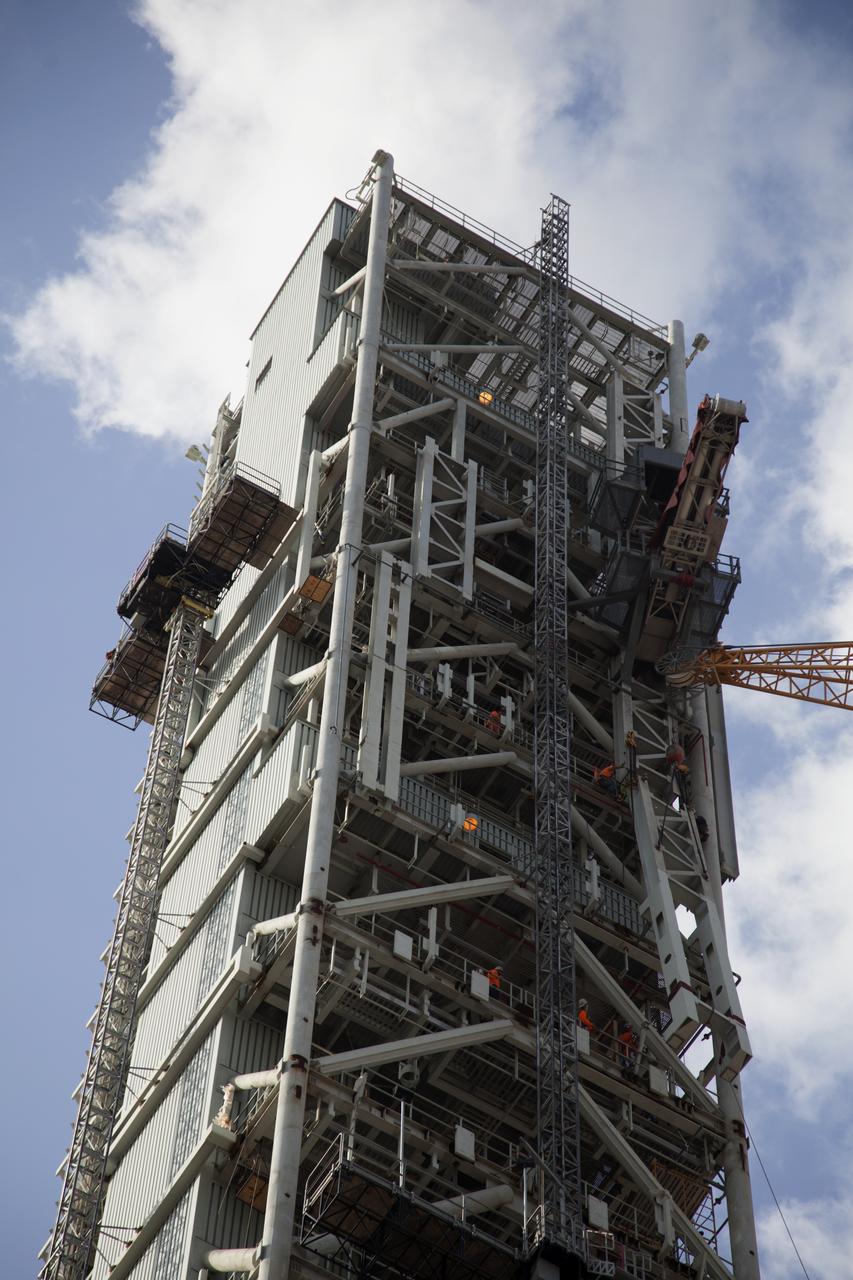
A view of the north side of the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) from the top of the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the VAB, 10 levels of platforms, 20 platform halves altogether, have been installed in High Bay 3. The platforms will surround NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and the Orion spacecraft and allow access during processing for missions, including the first uncrewed flight test of Orion atop the SLS rocket in 2018. Crawler-transporter 2 will carry the rocket and spacecraft atop the mobile launcher to Launch Pad 39B for Exploration Mission 1. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, with support from the center's Engineering Directorate, is overseeing upgrades and modifications to the VAB and the mobile launcher.
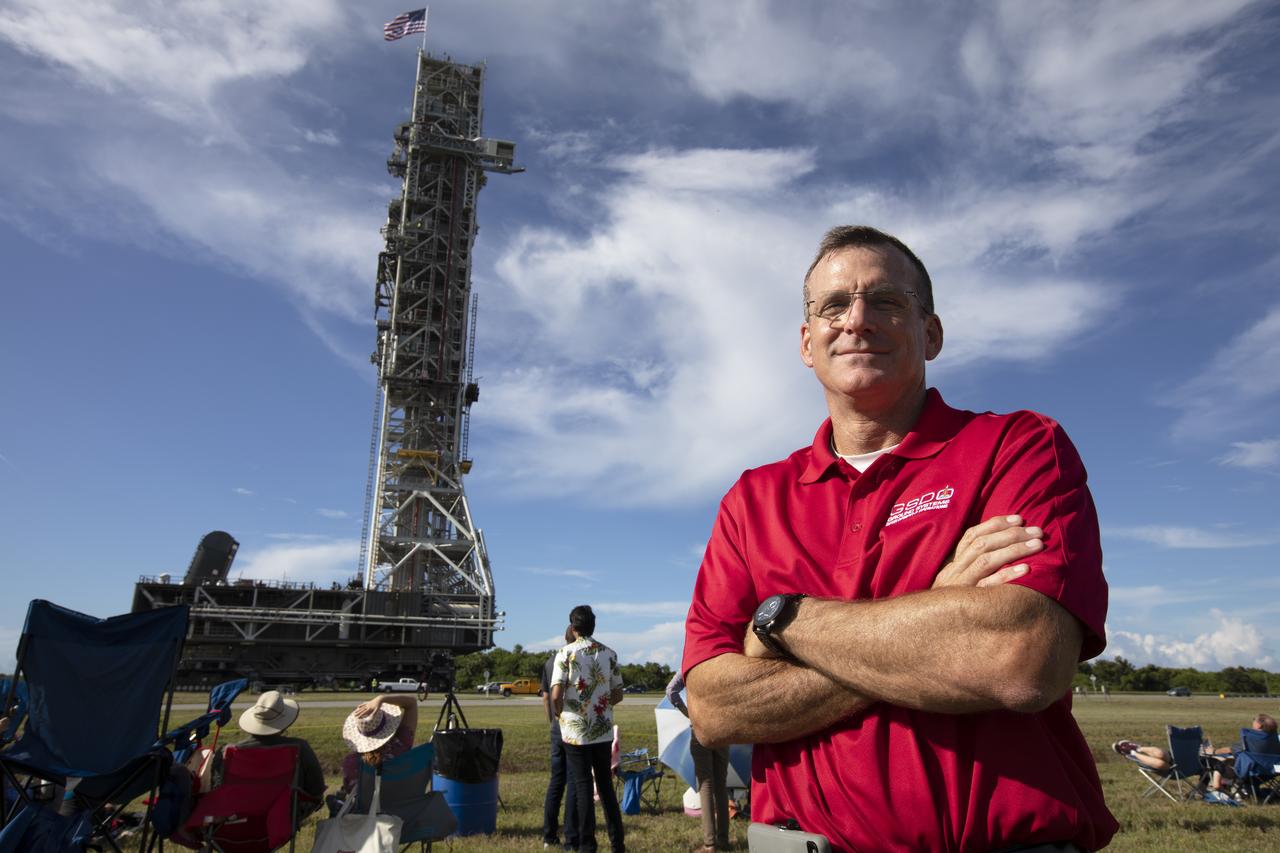

Cliff Lanham, NASA project manager for the mobile launcher, takes a break to attend the employee event for the mobile launcher move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, began its trek from Launch Pad 39B along the crawlerway after undergoing a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
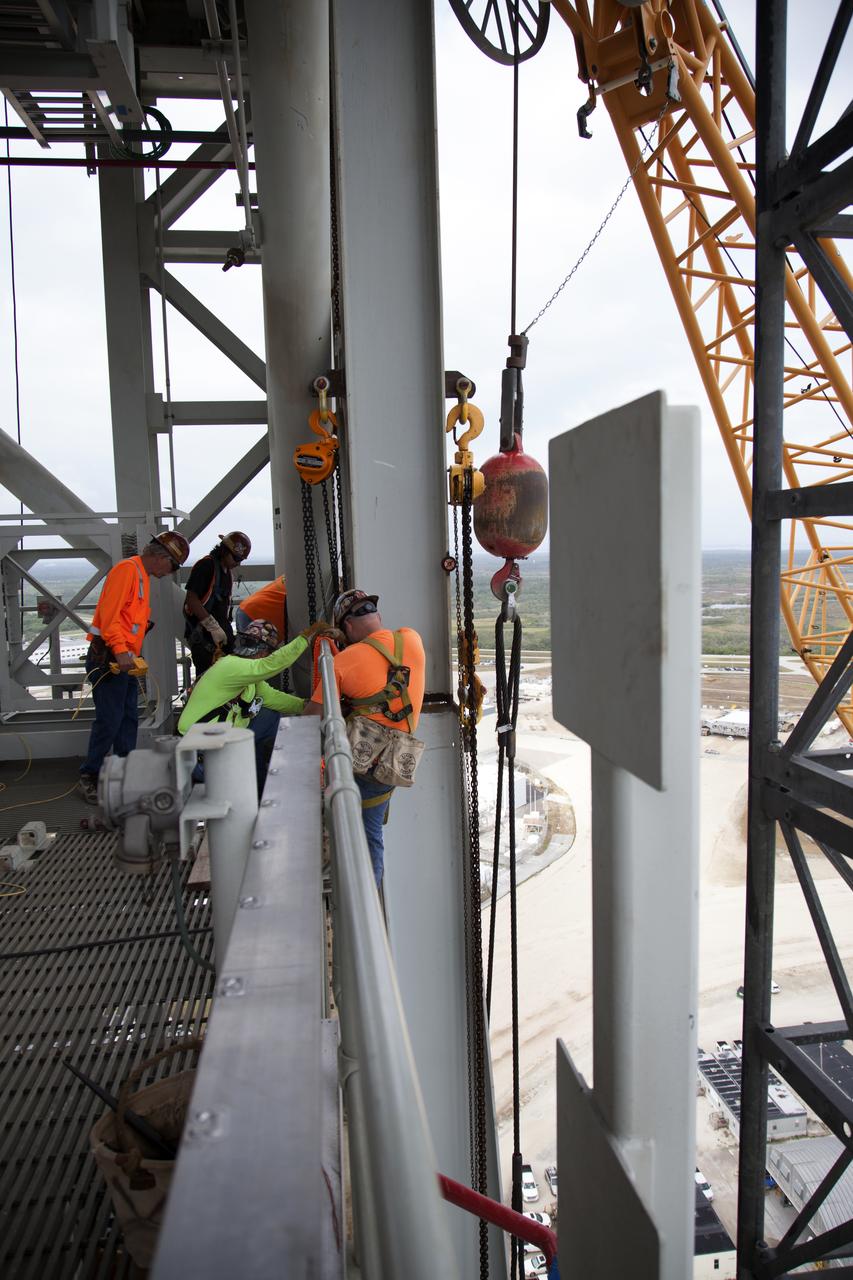

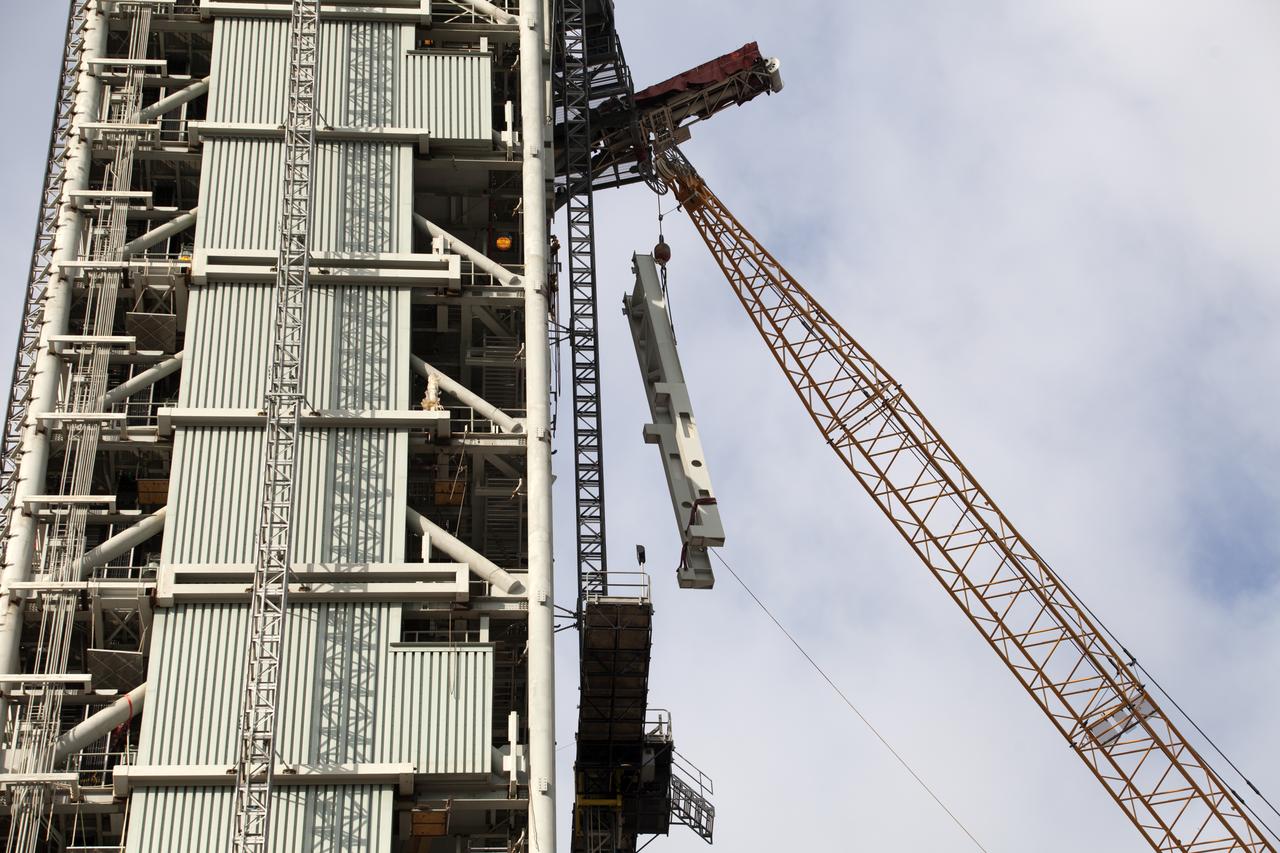
Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
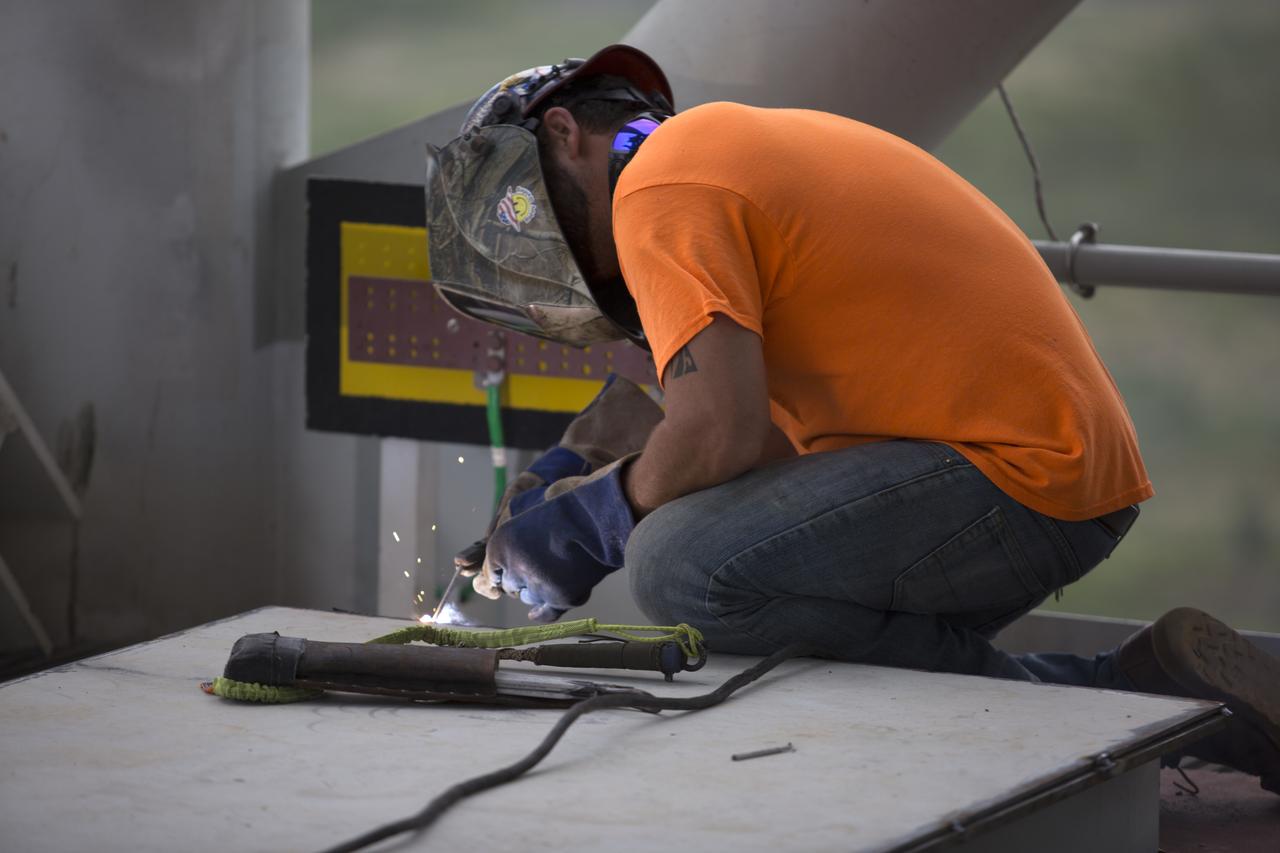

A construction worker welds a metal part during installation of the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
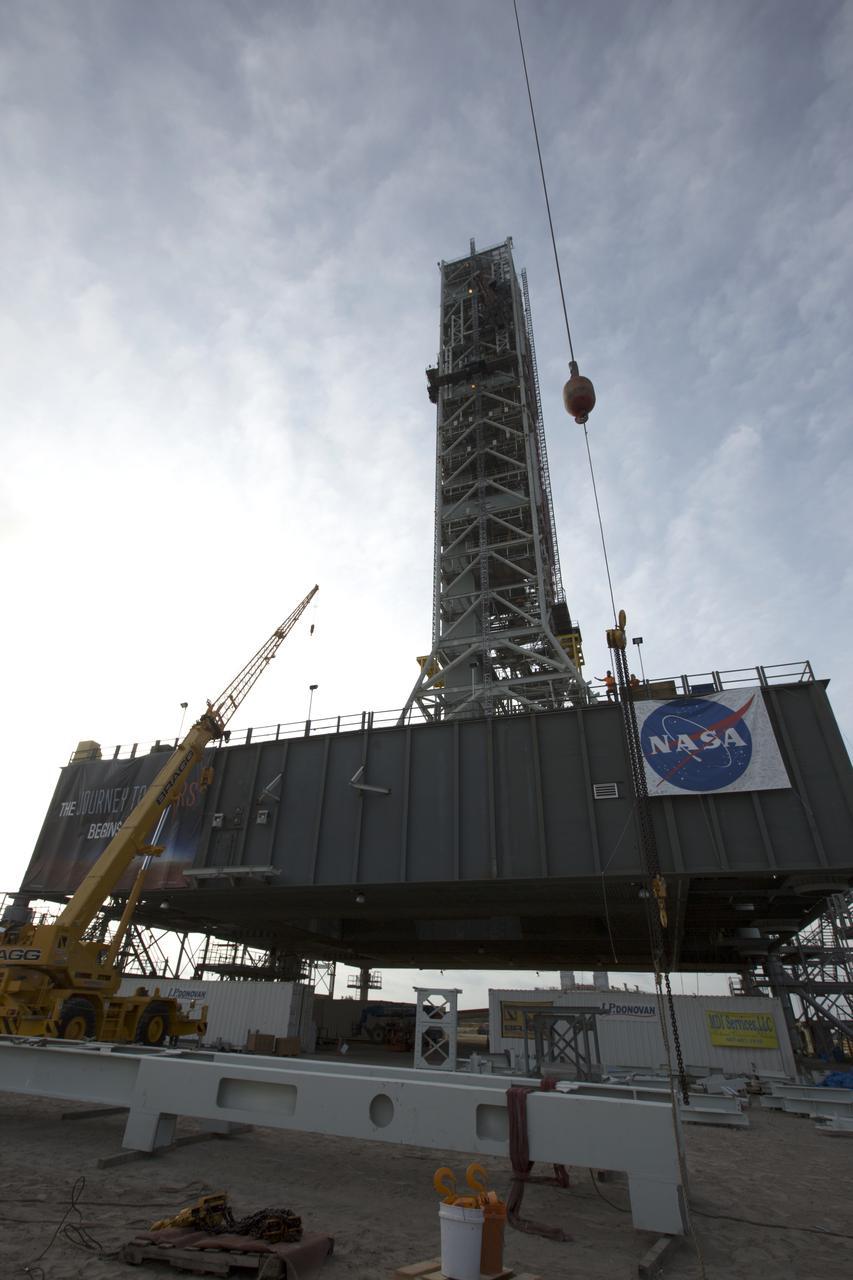

A crane has been attached to the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) to lift it up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
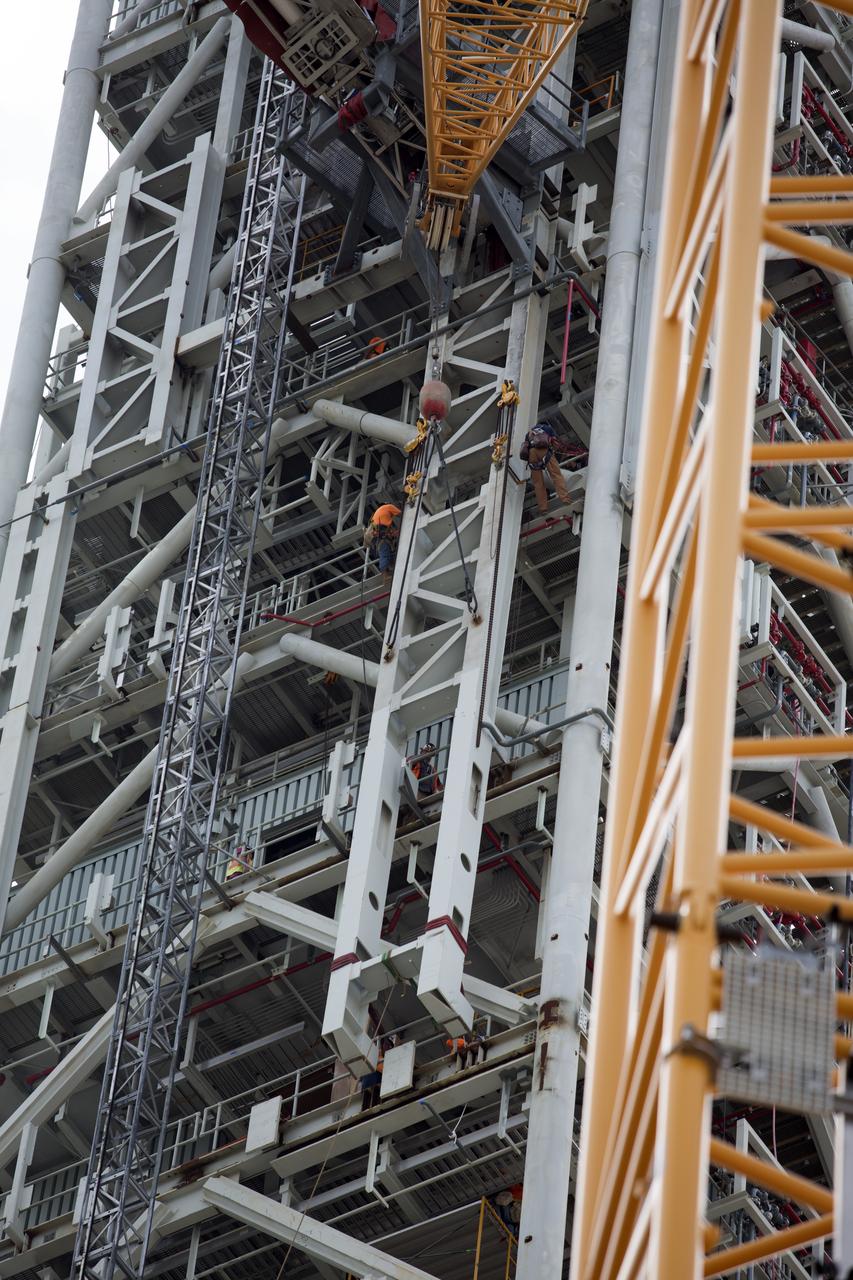

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
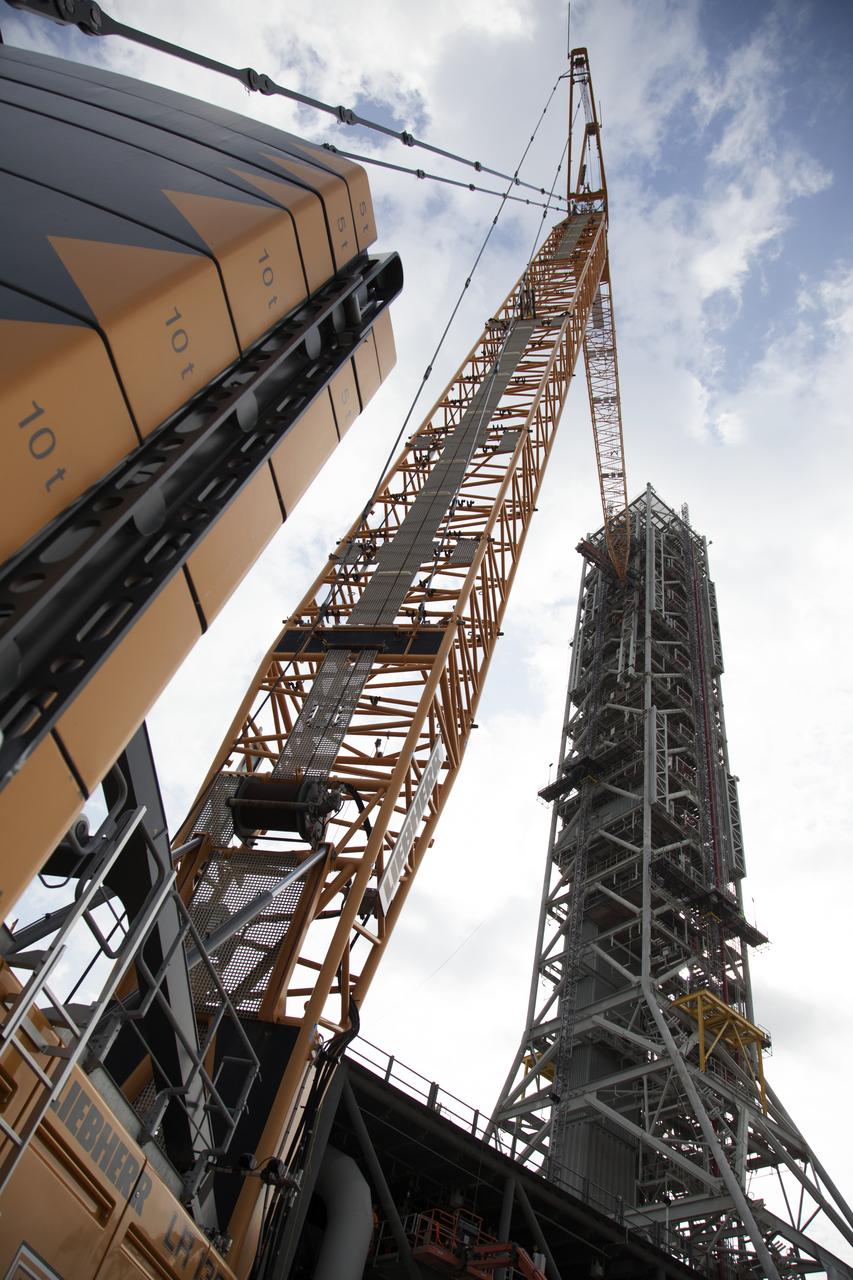

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) into position for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Cranes and rigging are being used to lift up the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.

Construction workers assist as a crane lifts the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical up for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
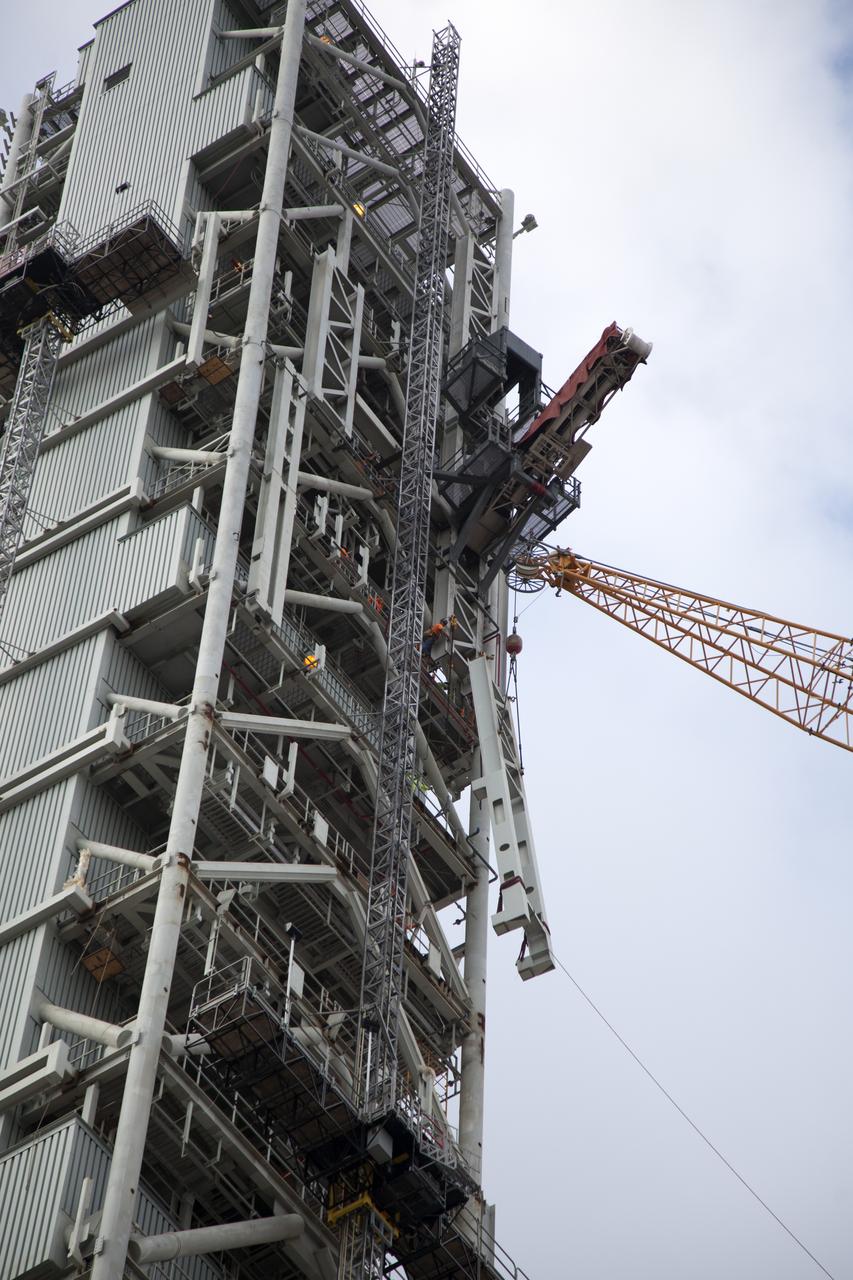

Seeming to hang in midair, the Core Stage Forward Skirt Umbilical (CSFSU) is lifted high up by crane for installation on the mobile launcher tower at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The CSFSU will be located at about the 180-foot level on the tower, above the liquid oxygen tank. The CSFSU is an umbilical that will swing into position to provide connections to the core stage forward skirt of the SLS rocket, and then swing away before launch. Its main purpose is to provide conditioned air/GN2 to the SLS core stage forward skirt cavity. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
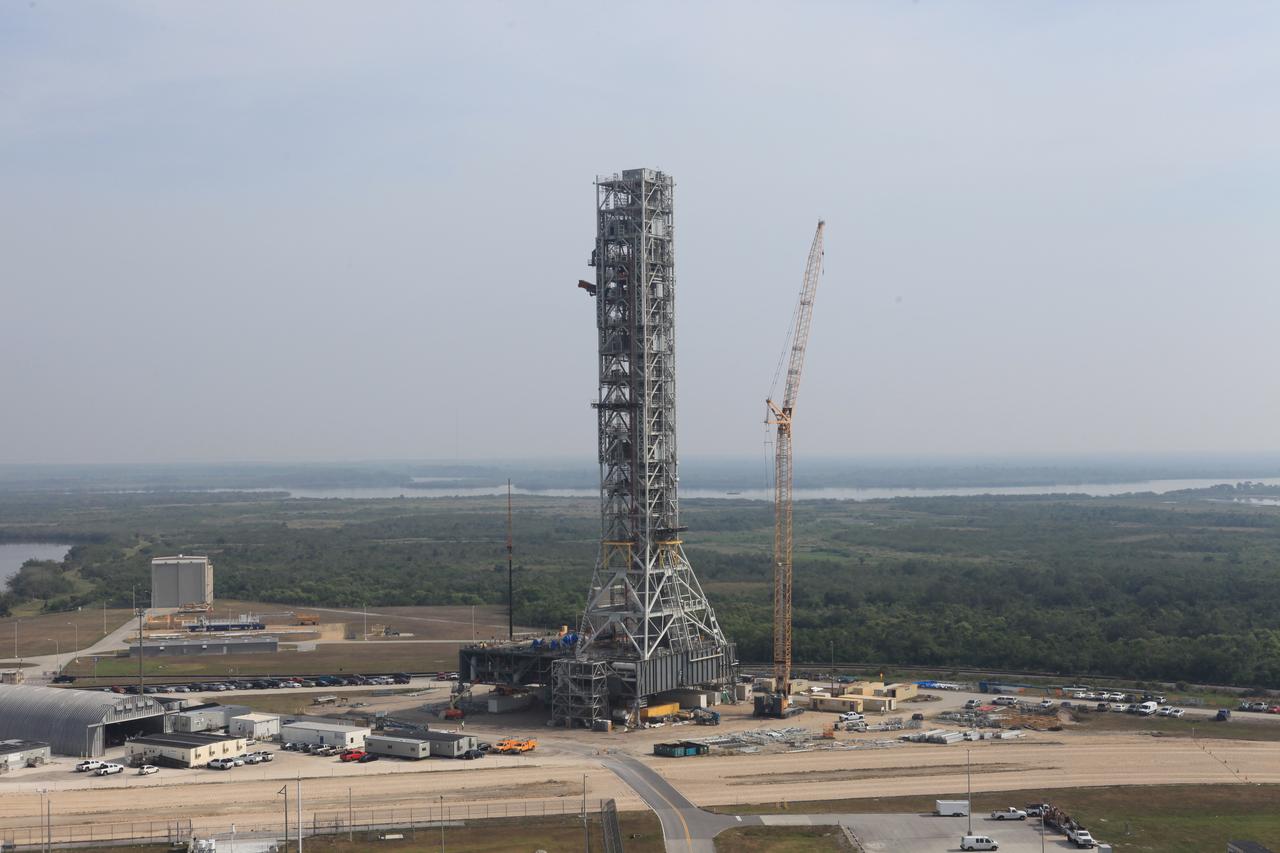

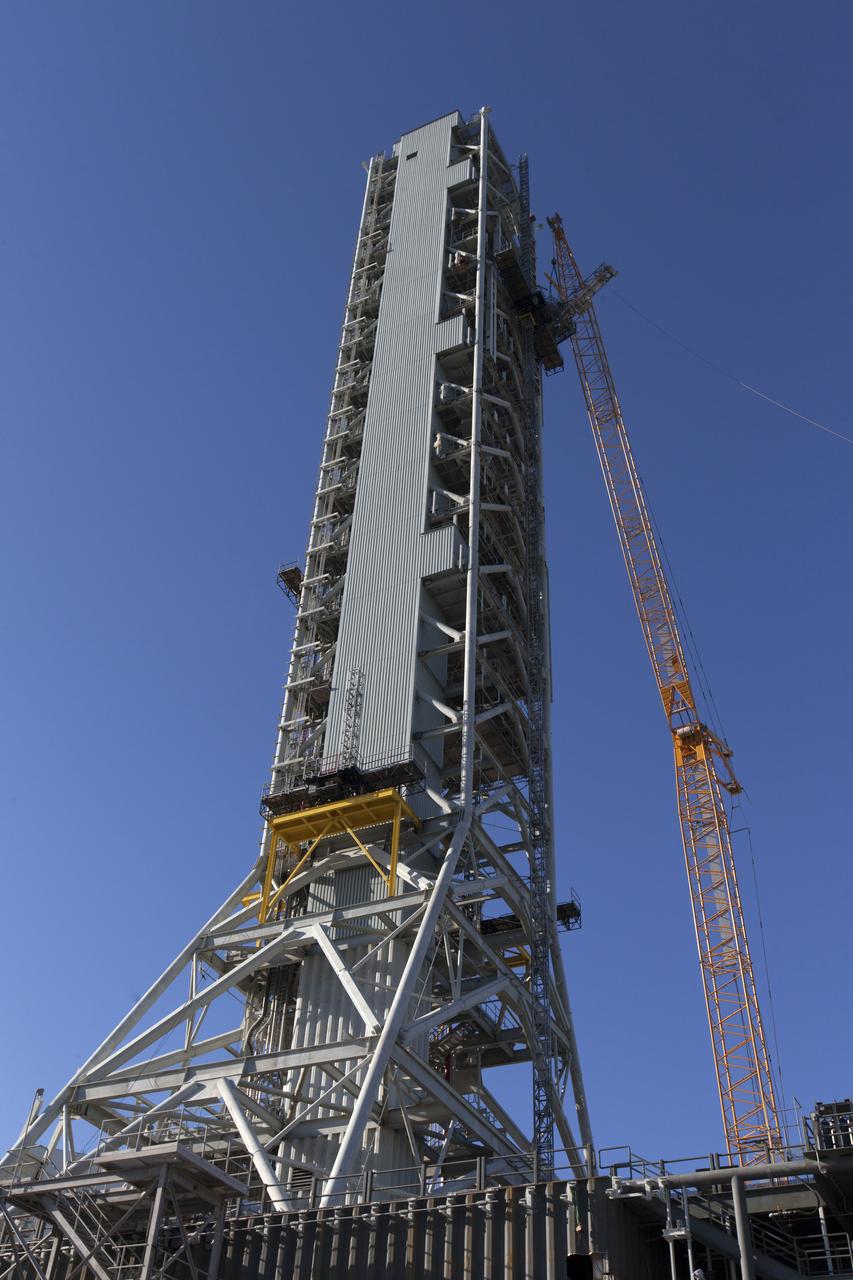
A view of the mobile launcher (ML) taken from the "eyebrow" of the nearby Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ML tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The Orion Service Module Umbilical and Core State Forward Skirt Umbilical were recently installed on the ML. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
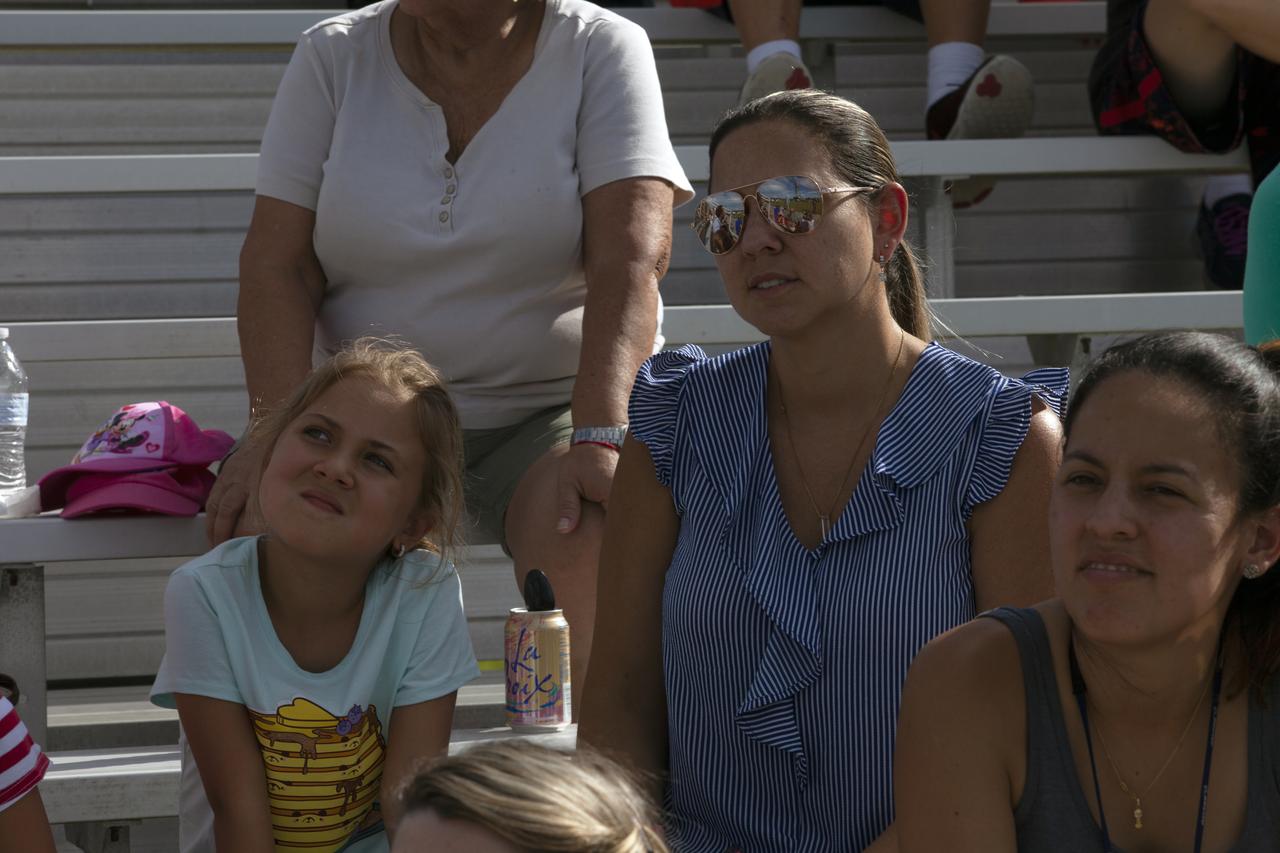
During an employee event, workers and guests watch from bleachers as NASA's mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, moves slowly along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher underwent a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
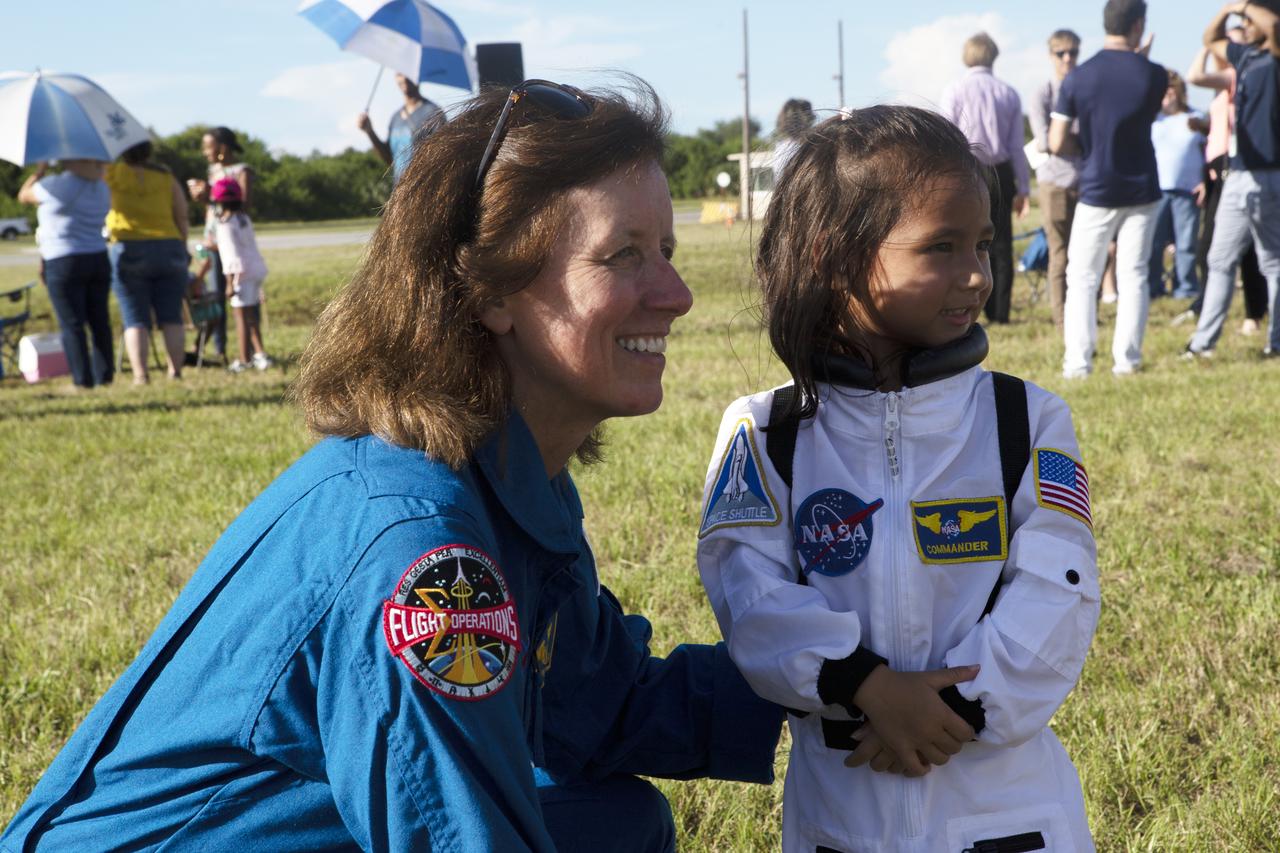

NASA astronaut Shannon Walker visits with a future astronaut during an employee event for workers and their guests for the mobile launcher move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, began its trek from Launch Pad 39B along the crawlerway after undergoing a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
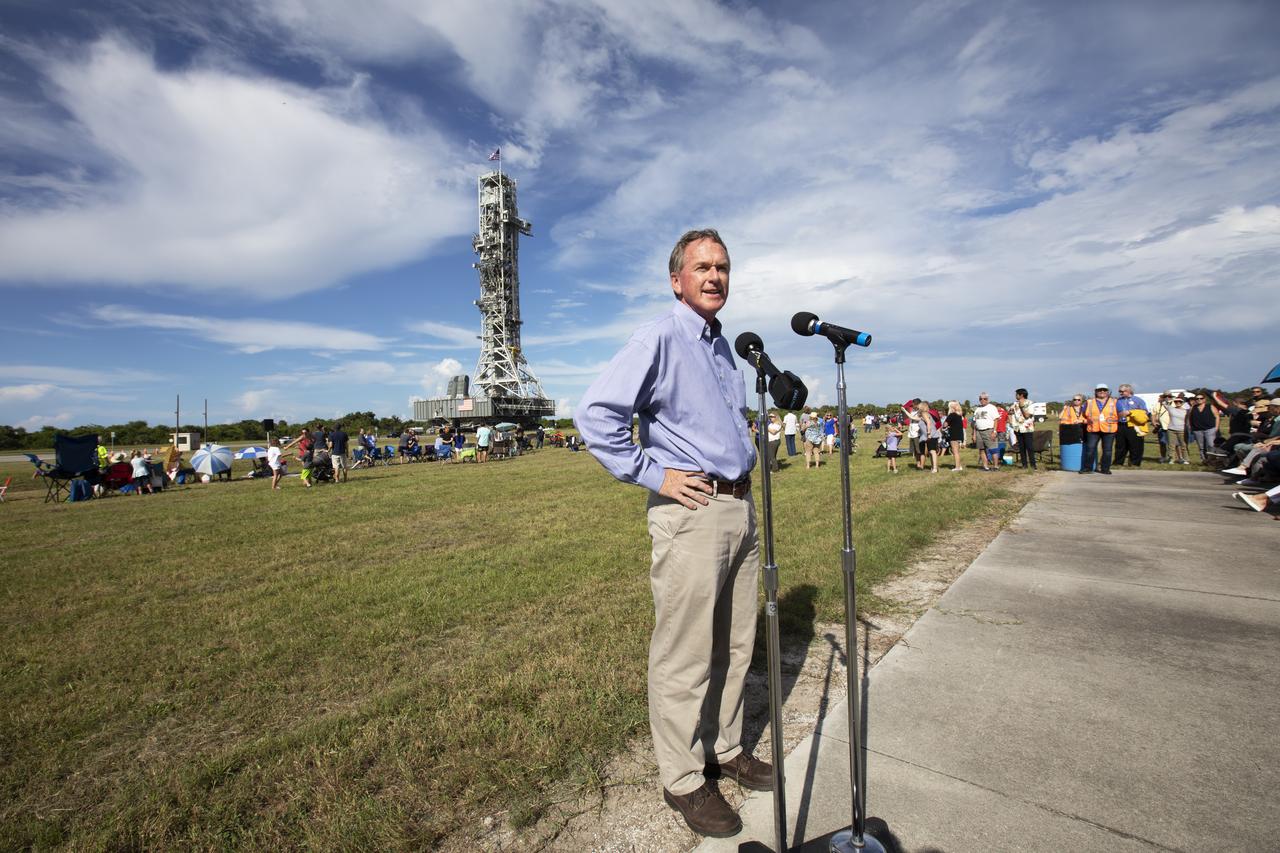

Mike Bolger, program manager of Exploration Ground Systems, speaks to workers and guests during an employee event for the mobile launcher move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, began its trek from Launch Pad 39B along the crawlerway after undergoing a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
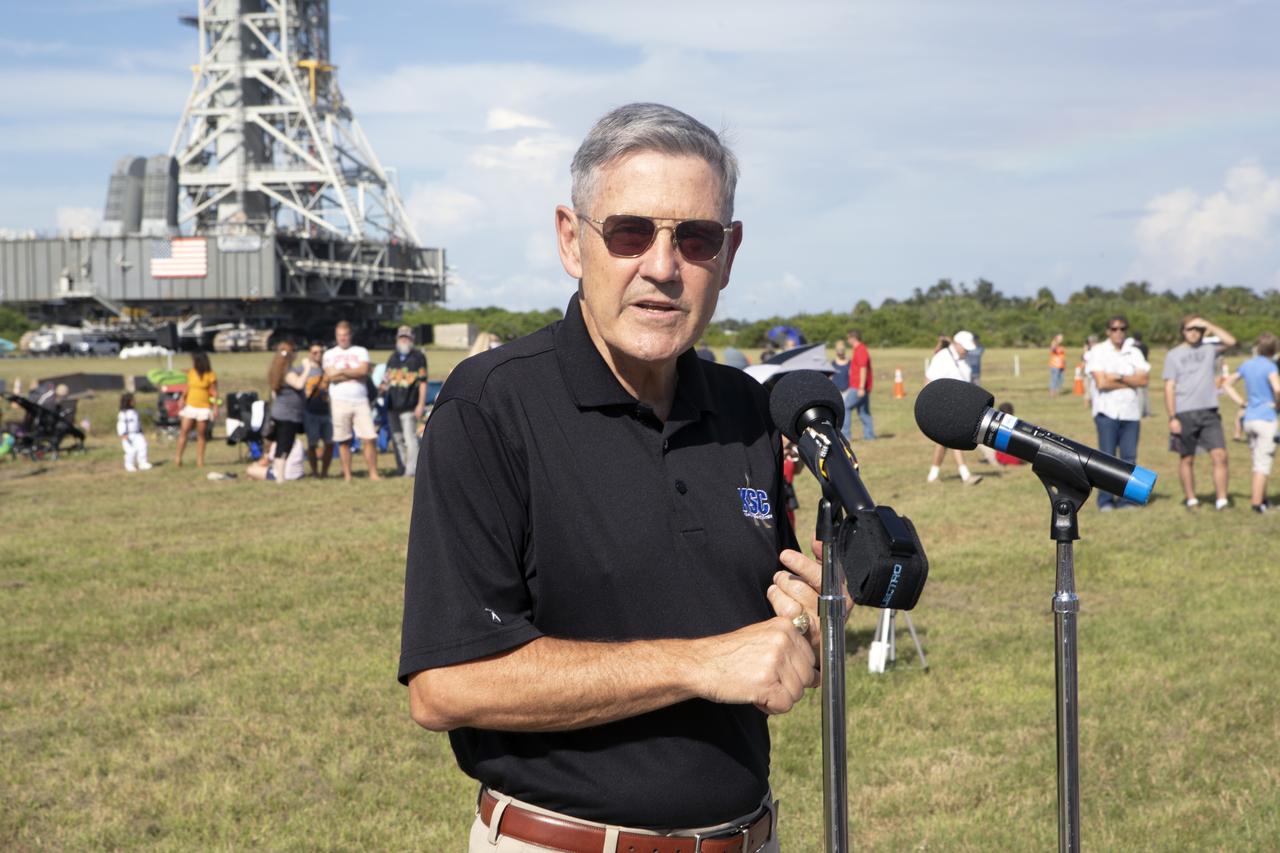

Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana speaks to workers and guests during an employee event for the mobile launcher move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, began its trek from Launch Pad 39B along the crawlerway after undergoing a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
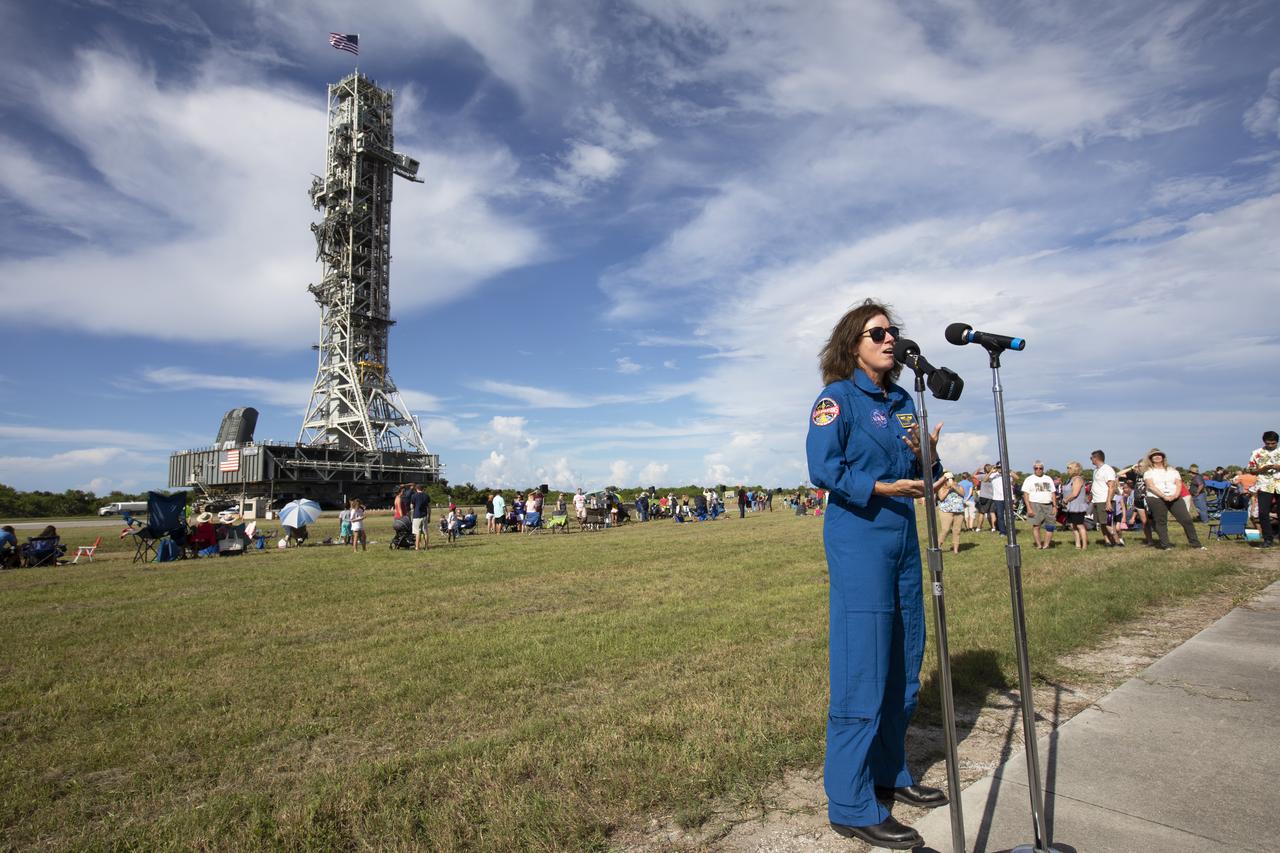

NASA astronaut Shannon Walker speaks to workers and guests during an employee event for the mobile launcher move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, began its trek from Launch Pad 39B along the crawlerway after undergoing a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

During an employee event, workers and guests watch as NASA's mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, moves slowly along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher underwent a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.
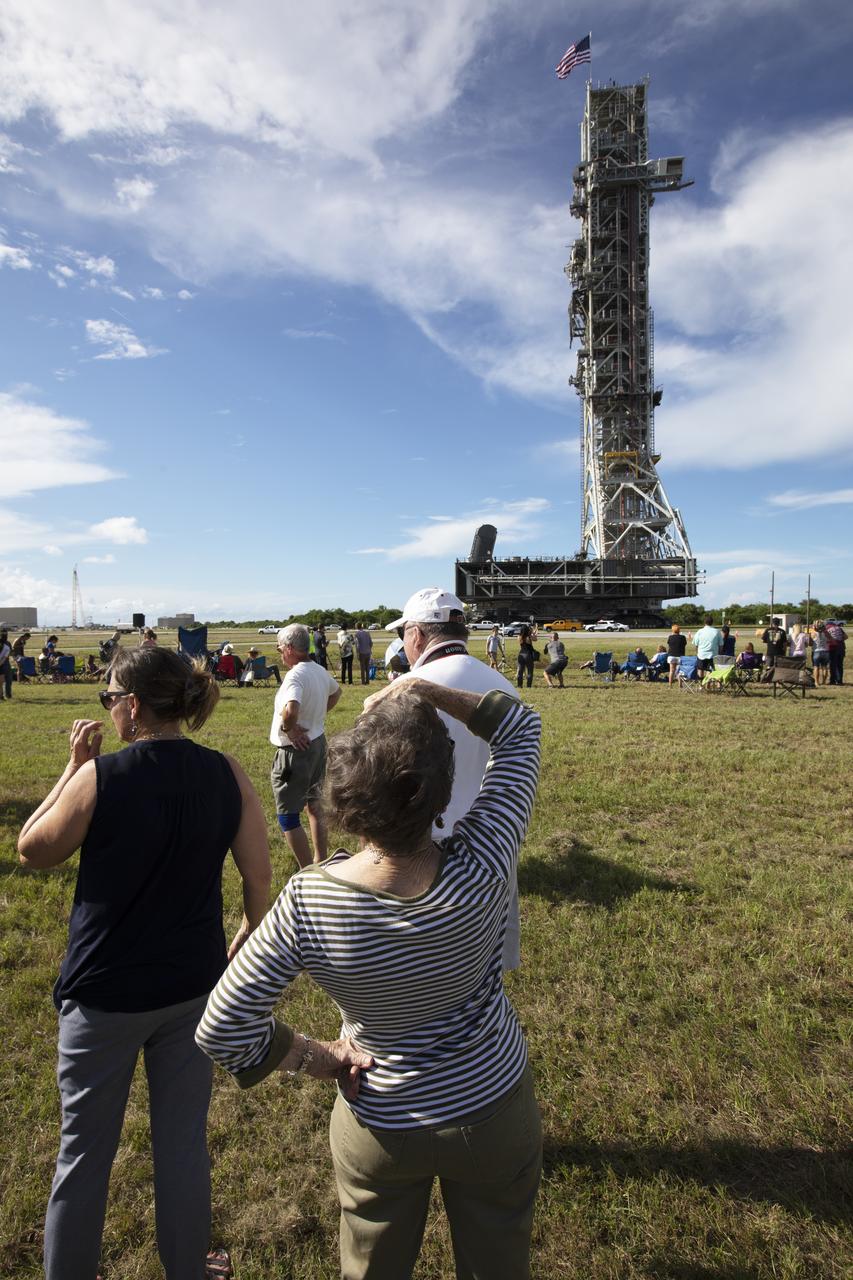

During an employee event, workers and guests watch as NASA's mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, moves slowly along the crawlerway toward the Vehicle Assembly Building on Sept. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mobile launcher underwent a fit check and several days of systems testing with the pad. This is the first time that the modified mobile launcher made the trip to the pad. The 380-foot-tall mobile launcher is equipped with the crew access arm and several umbilicals that will provide power, environmental control, pneumatics, communication and electrical connections to the agency's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. The mobile launcher will spend seven months in the VAB undergoing testing. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to launch SLS and Orion on Exploration Mission-1, missions to the Moon and on to Mars.

A sliver of the Moon is visible just before sunrise at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is one of the steel structures of the mobile launcher (ML). Several launch umbilicals have been installed on the ML tower. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML to prepare for the first integrated test flight of the Orion spacecraft on the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1.
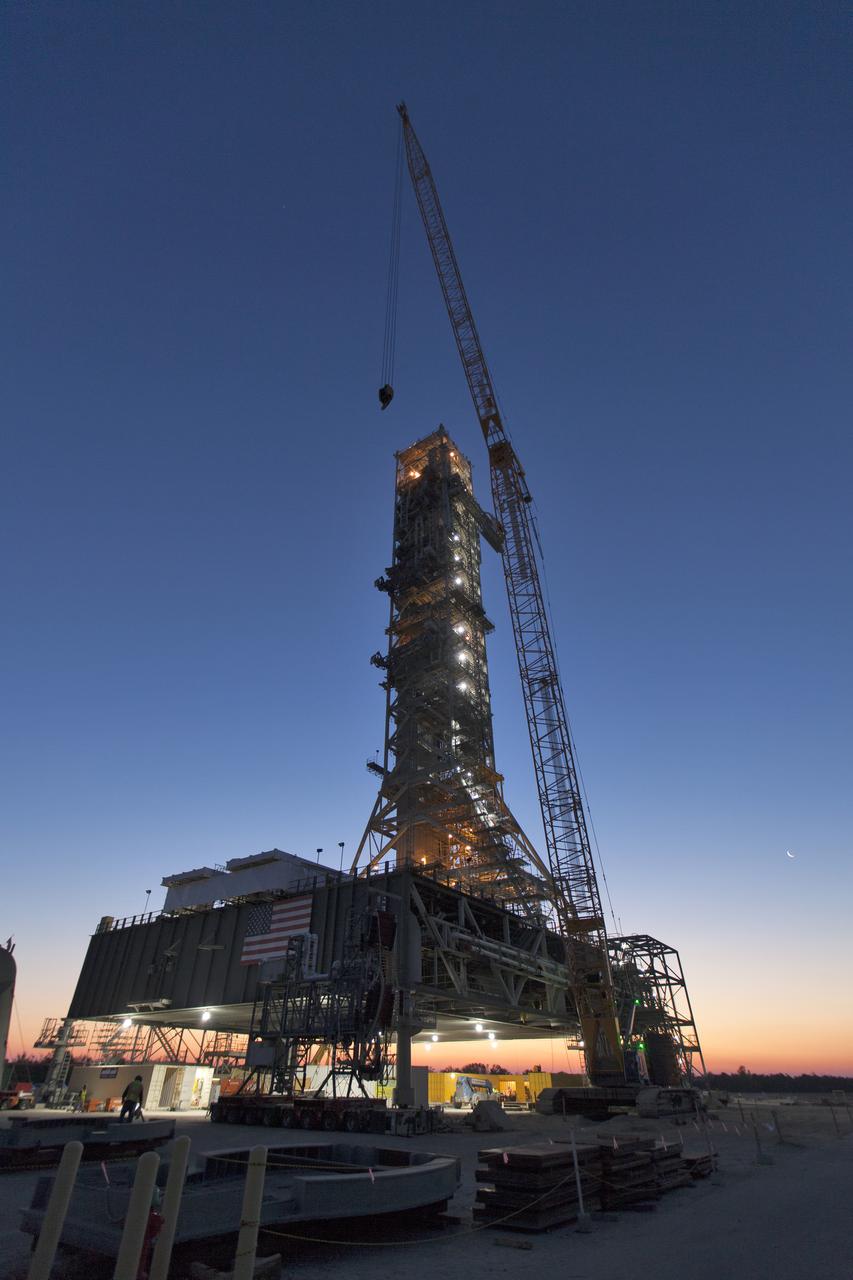

A colorful sunrise serves as the backdrop for the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several launch umbilicals have been installed on the ML tower. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML to prepare for the first integrated test flight of the Orion spacecraft on the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1.
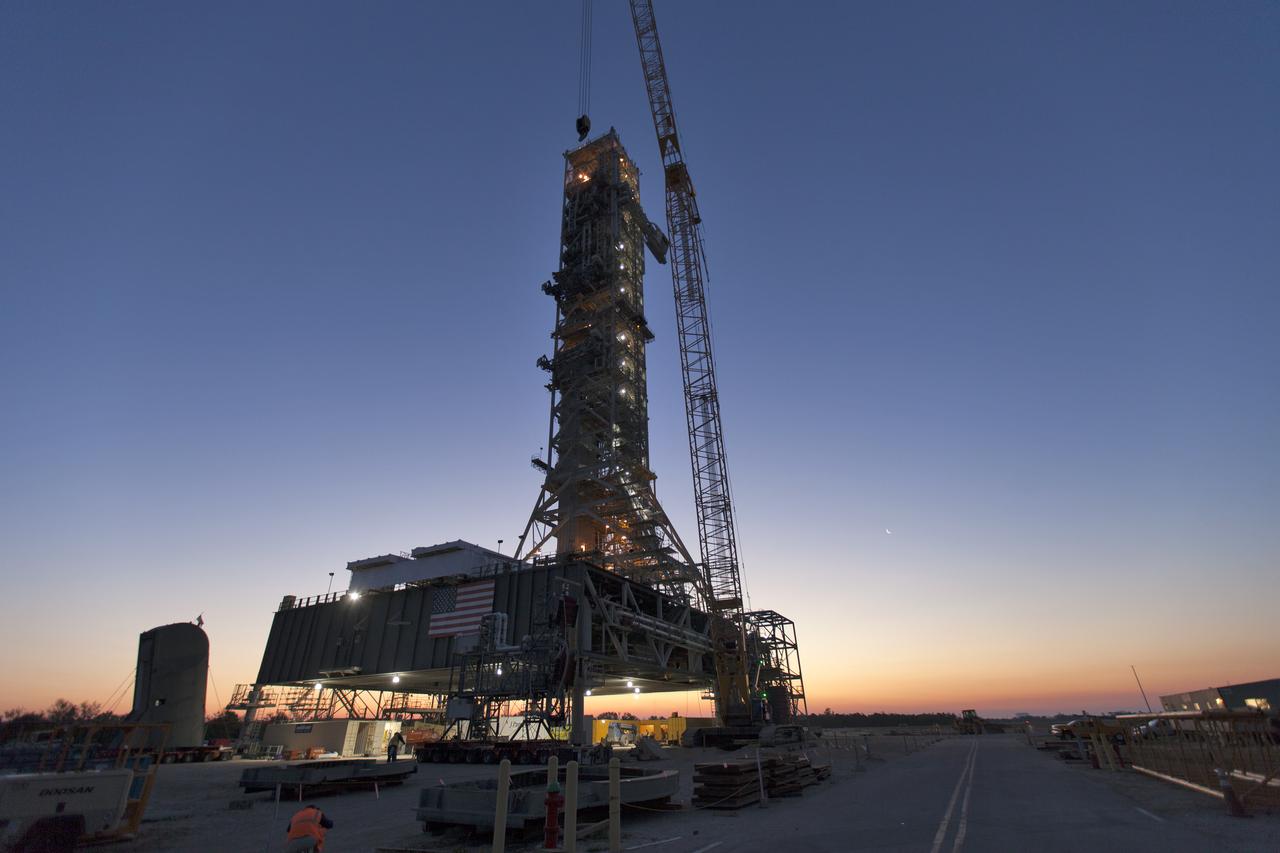

A colorful sunrise serves as the backdrop for the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Several launch umbilicals have been installed on the ML tower. Exploration Ground Systems is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML to prepare for the first integrated test flight of the Orion spacecraft on the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Exploration Mission-1.
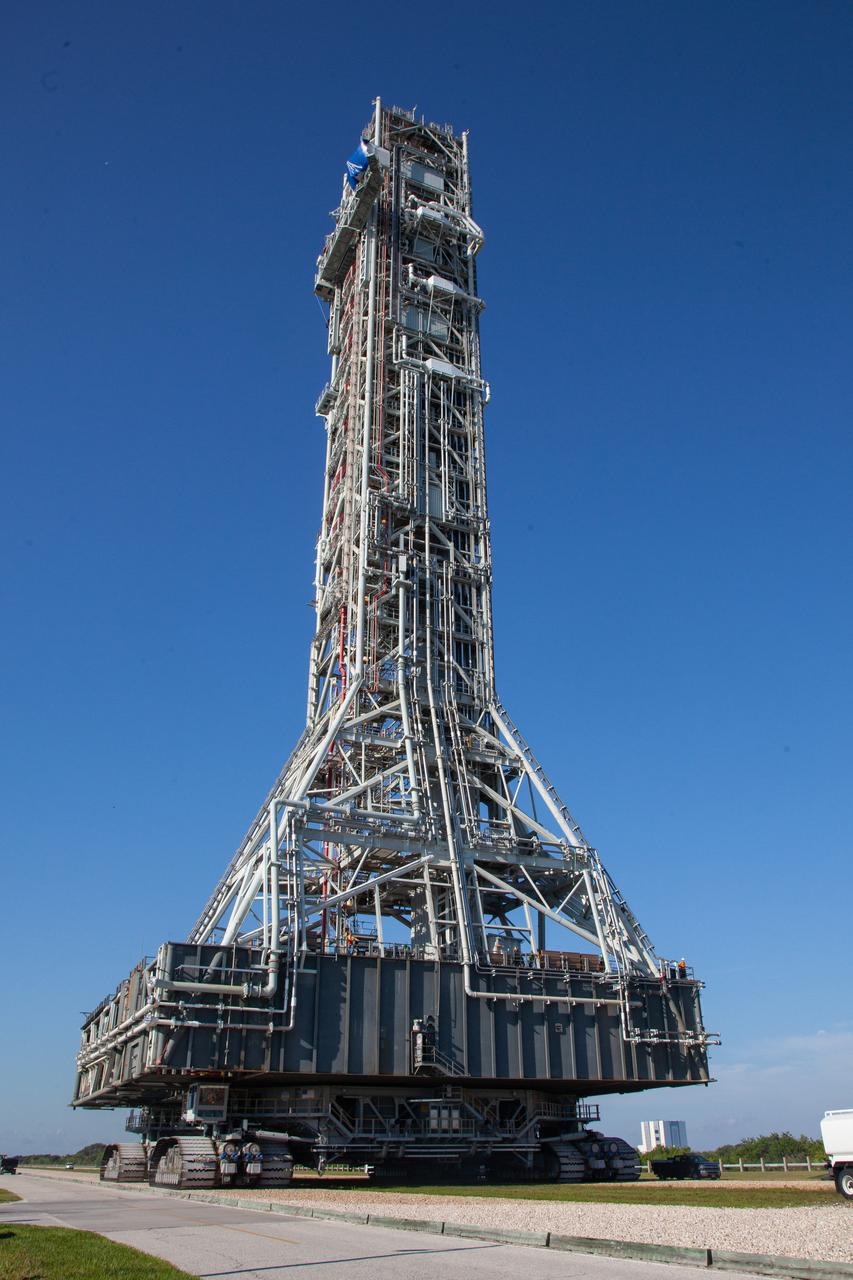

On June 27, 2019, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) on June 27, 2019, for its final solo trek to Launch Complex 39B in Florida. The mobile launcher departed from the VAB at midnight for the 10-hour journey to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
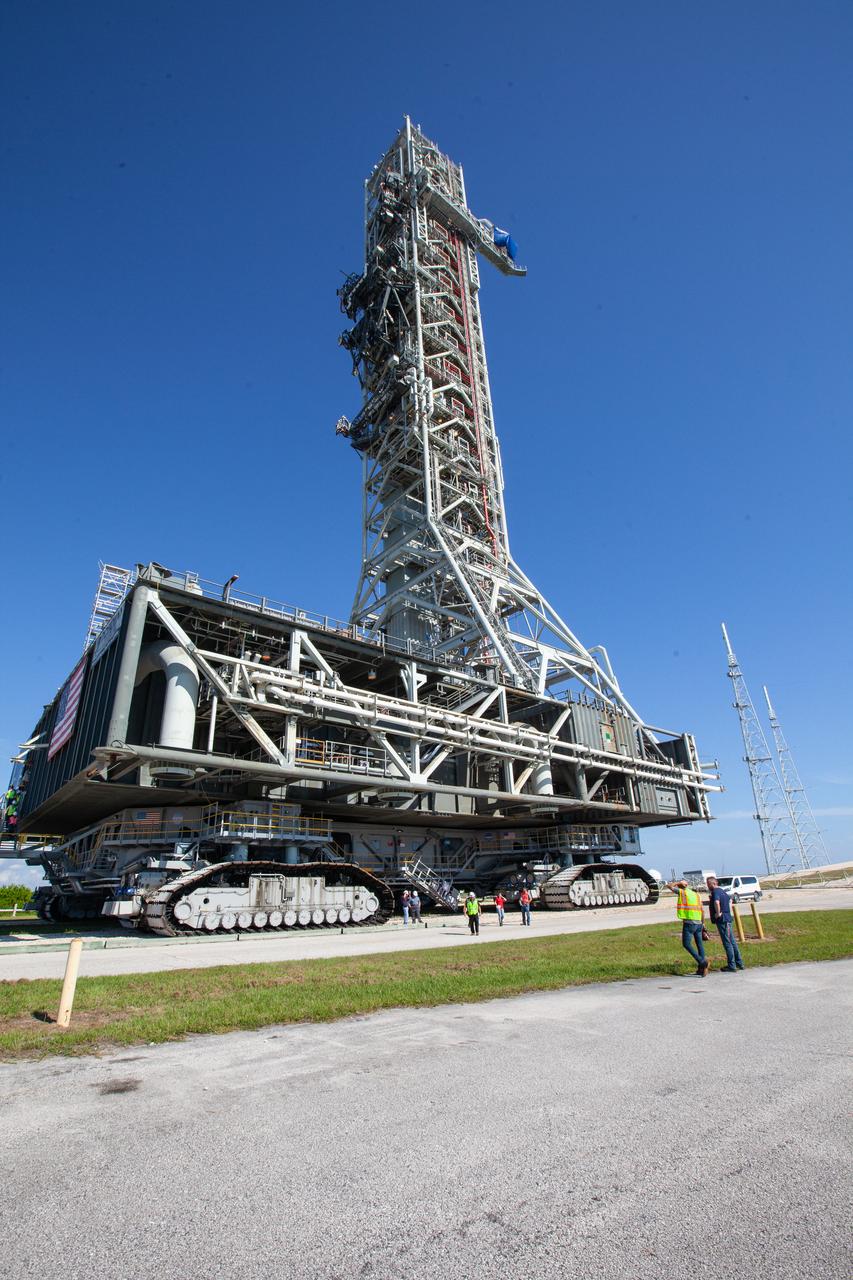

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher is seen atop crawler-transporter 2 at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for its last solo trek to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
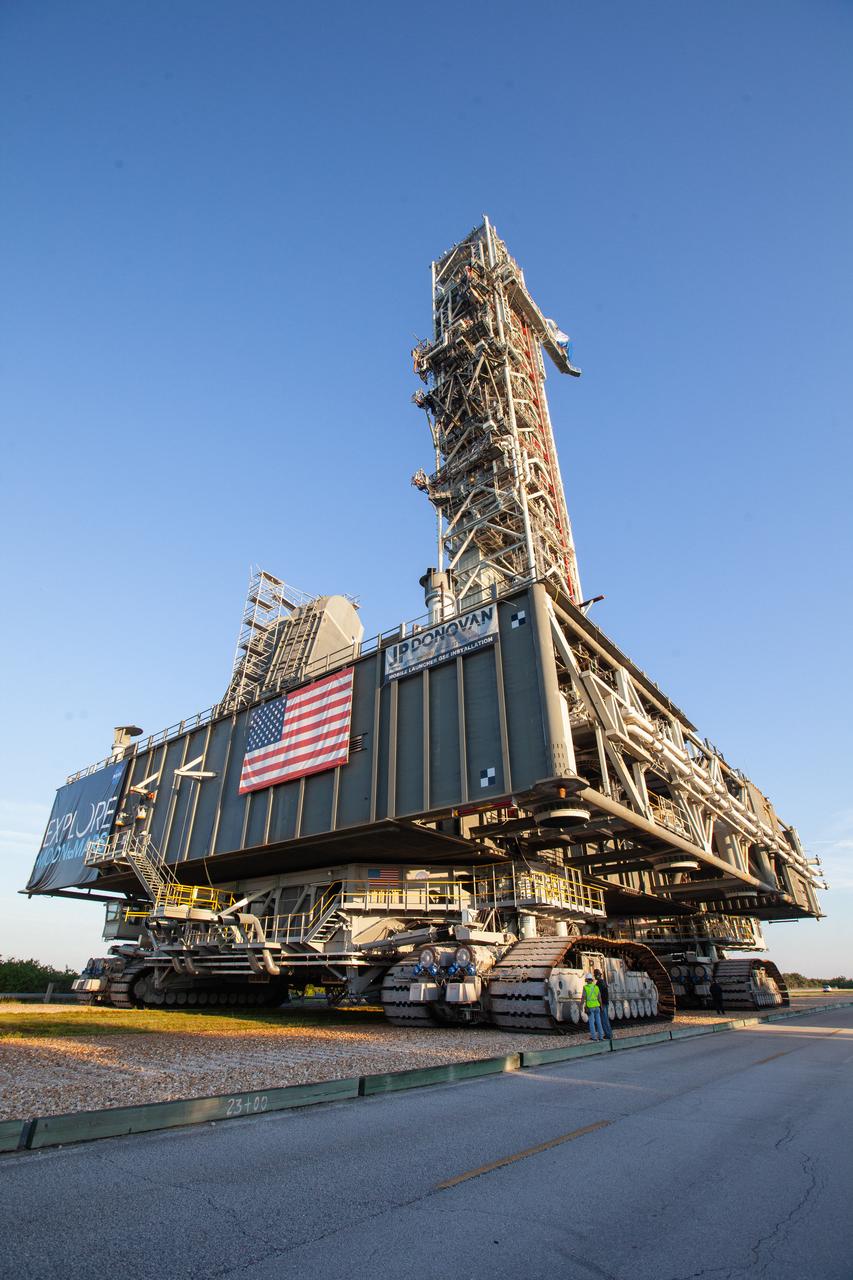

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher makes its last solo trek along the crawlerway atop crawler-transporter 2 to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad and will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
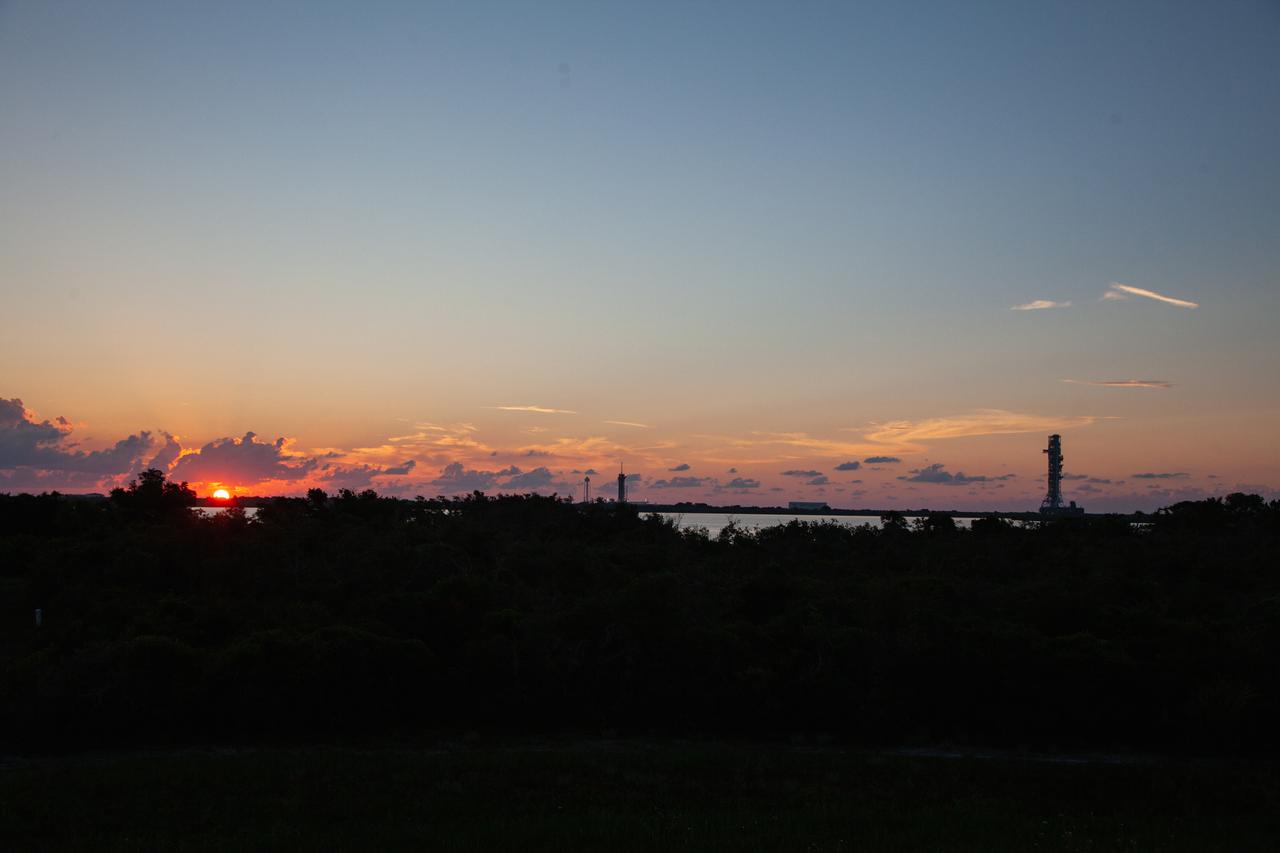

With a sunrise serving as the backdrop, Exploration Ground Systems' mobile launcher makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. It will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
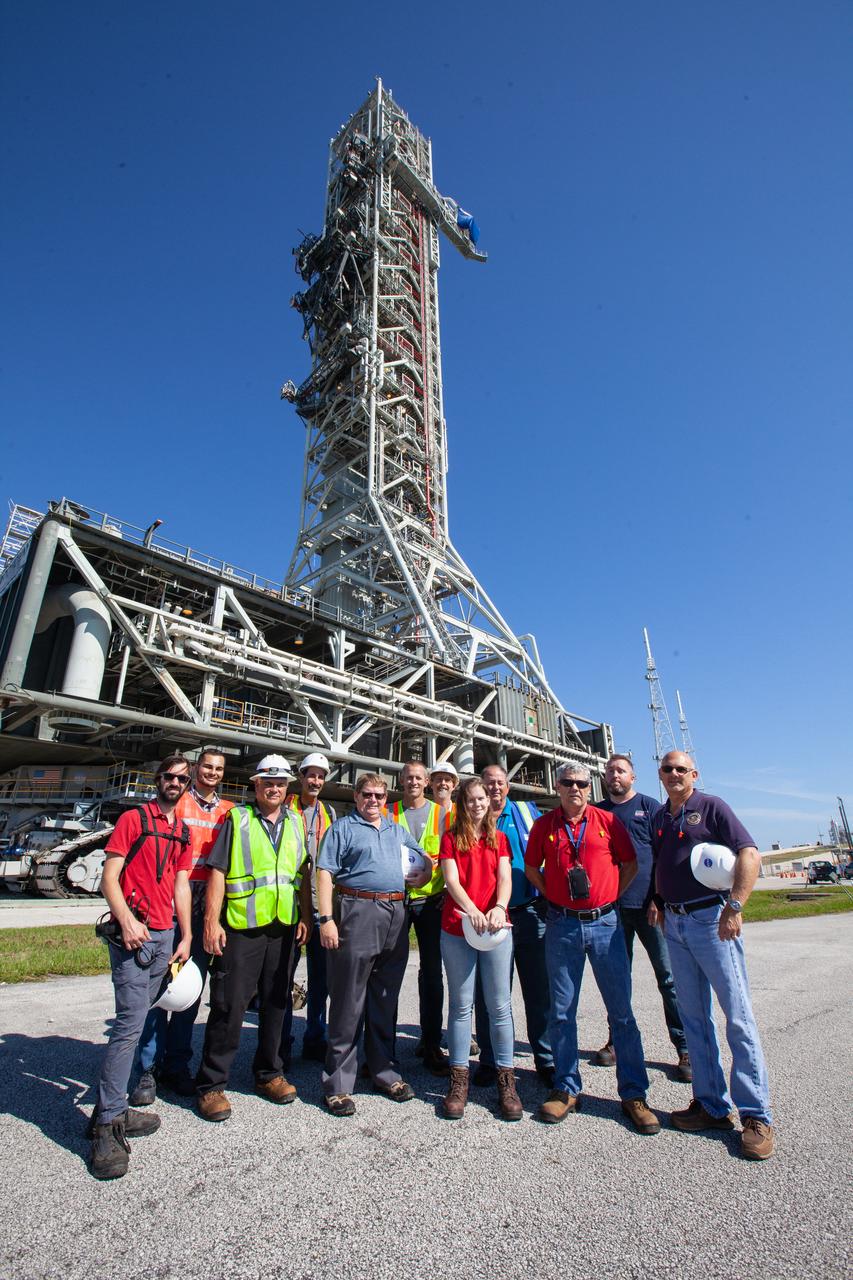

NASA’s Kennedy Space Center crawler team is photographed in front of the agency’s mobile launcher at Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. After departing from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27, the mobile launcher made its final solo trek to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
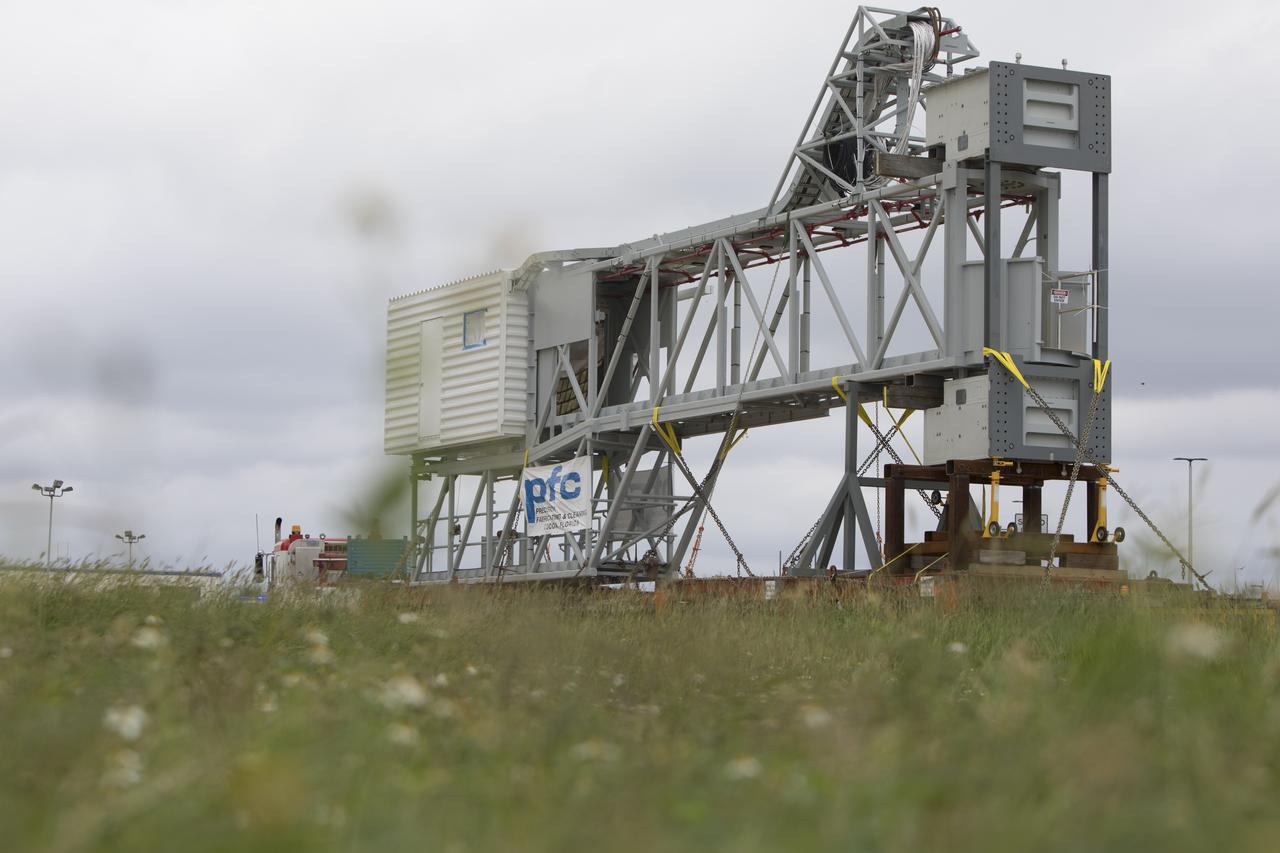

A heavy-load transport truck carrying the Orion crew access arm makes its way toward the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew access arm will be installed at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML tower to prepare for Exploration Mission-1.
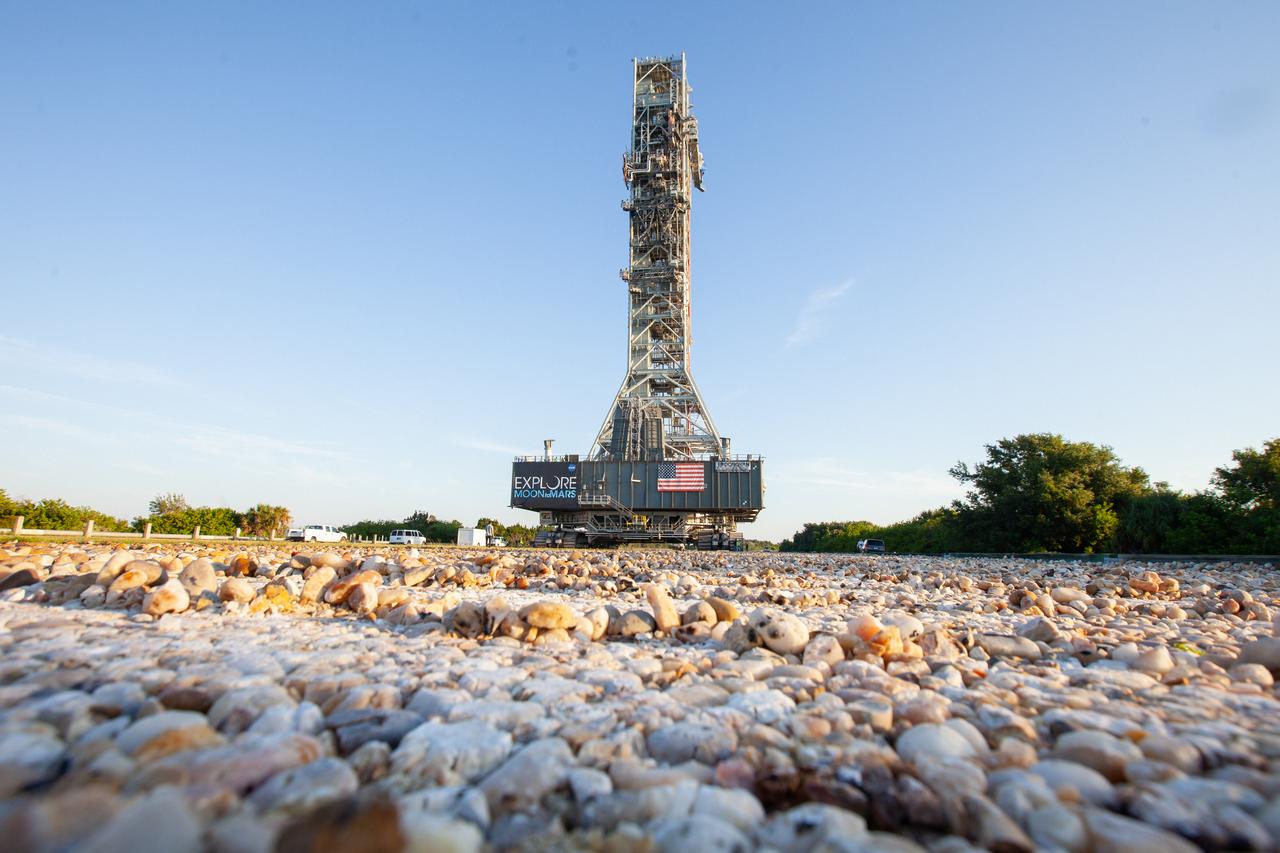

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher makes its last solo trek along the crawlerway atop crawler-transporter 2 to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad and will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
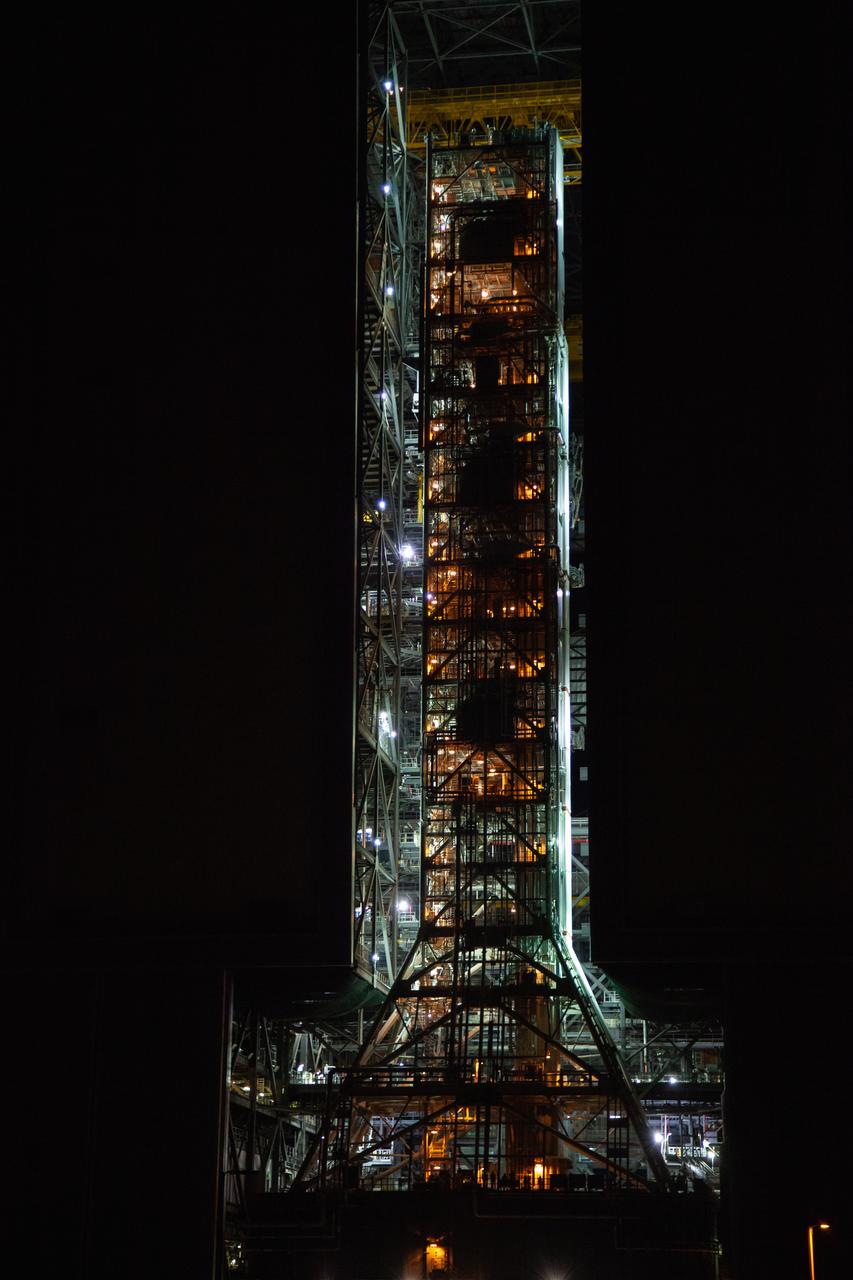

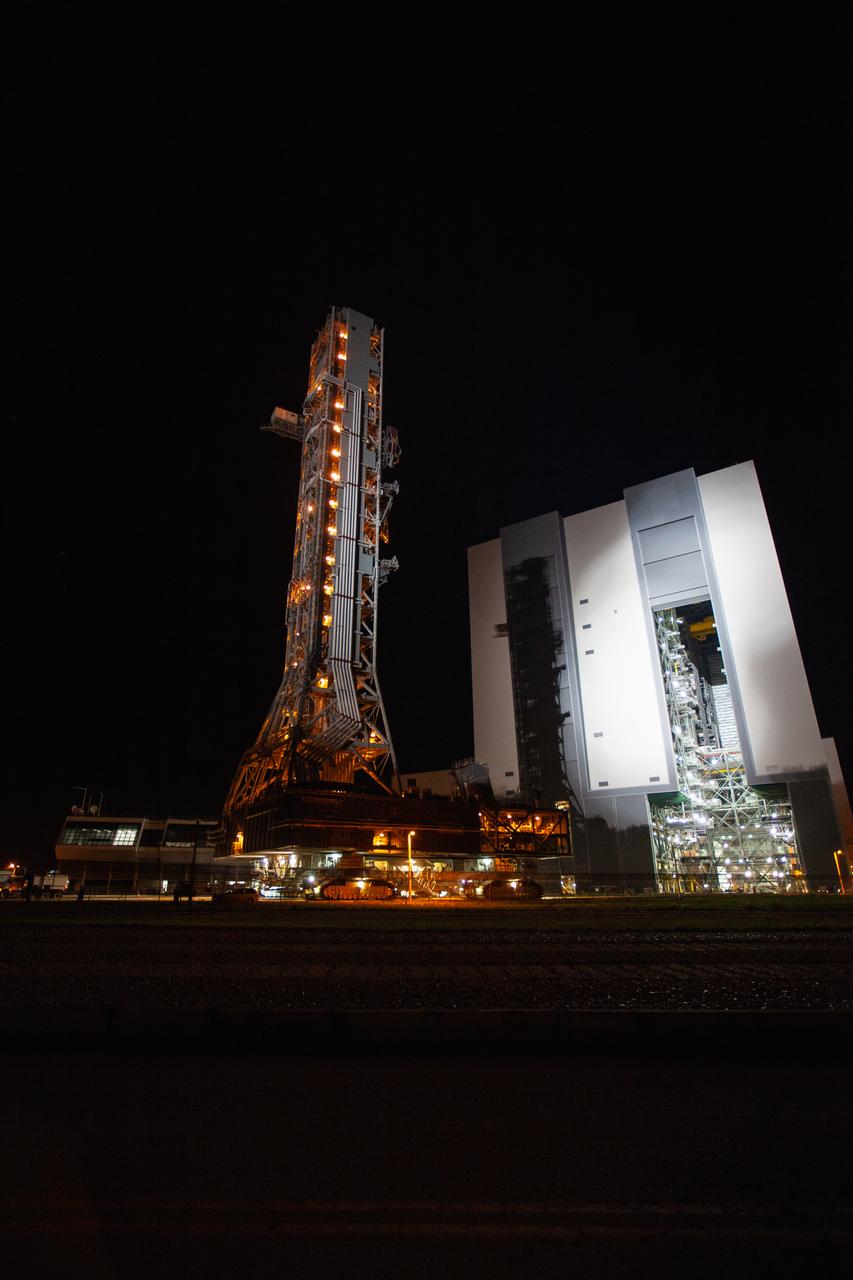
Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher is illuminated in the night as it makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
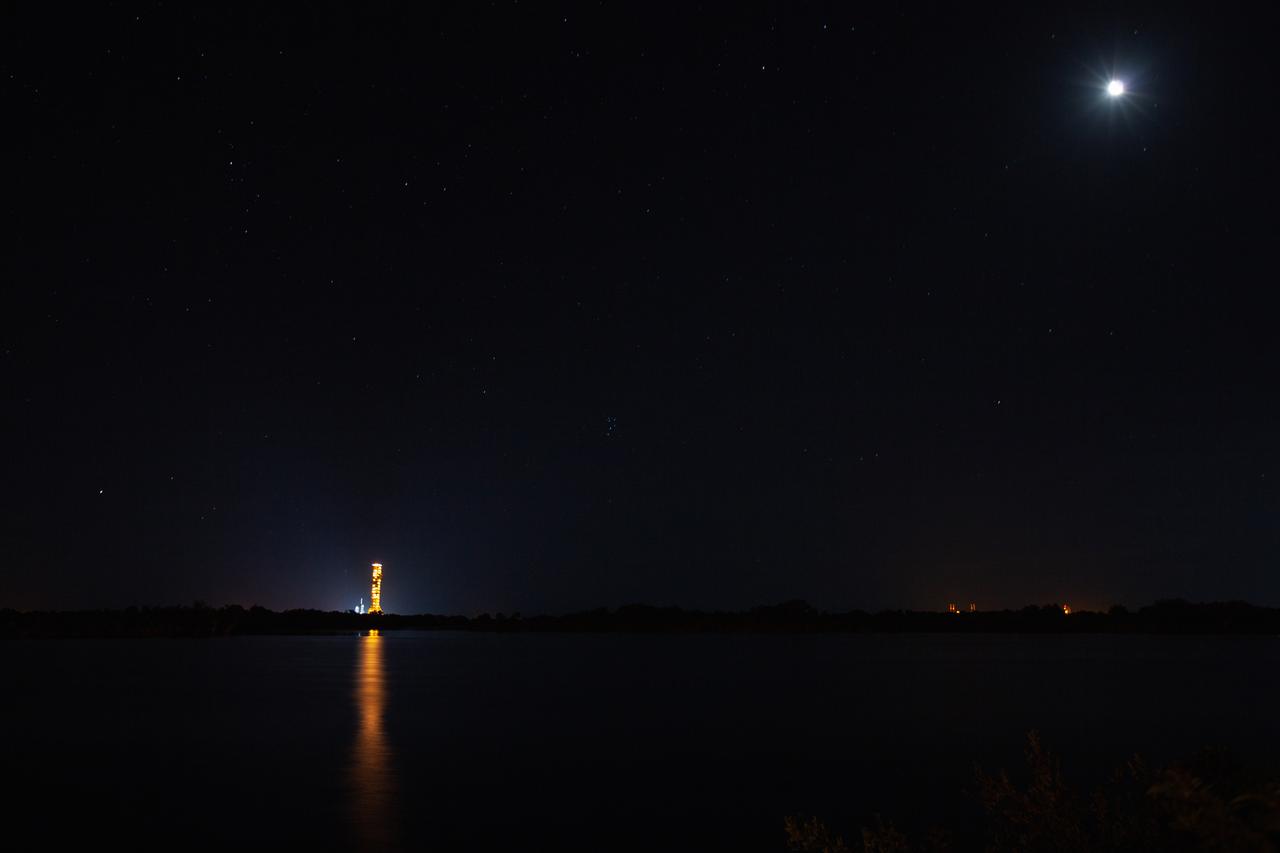

With the nighttime sky serving as the backdrop, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad and will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
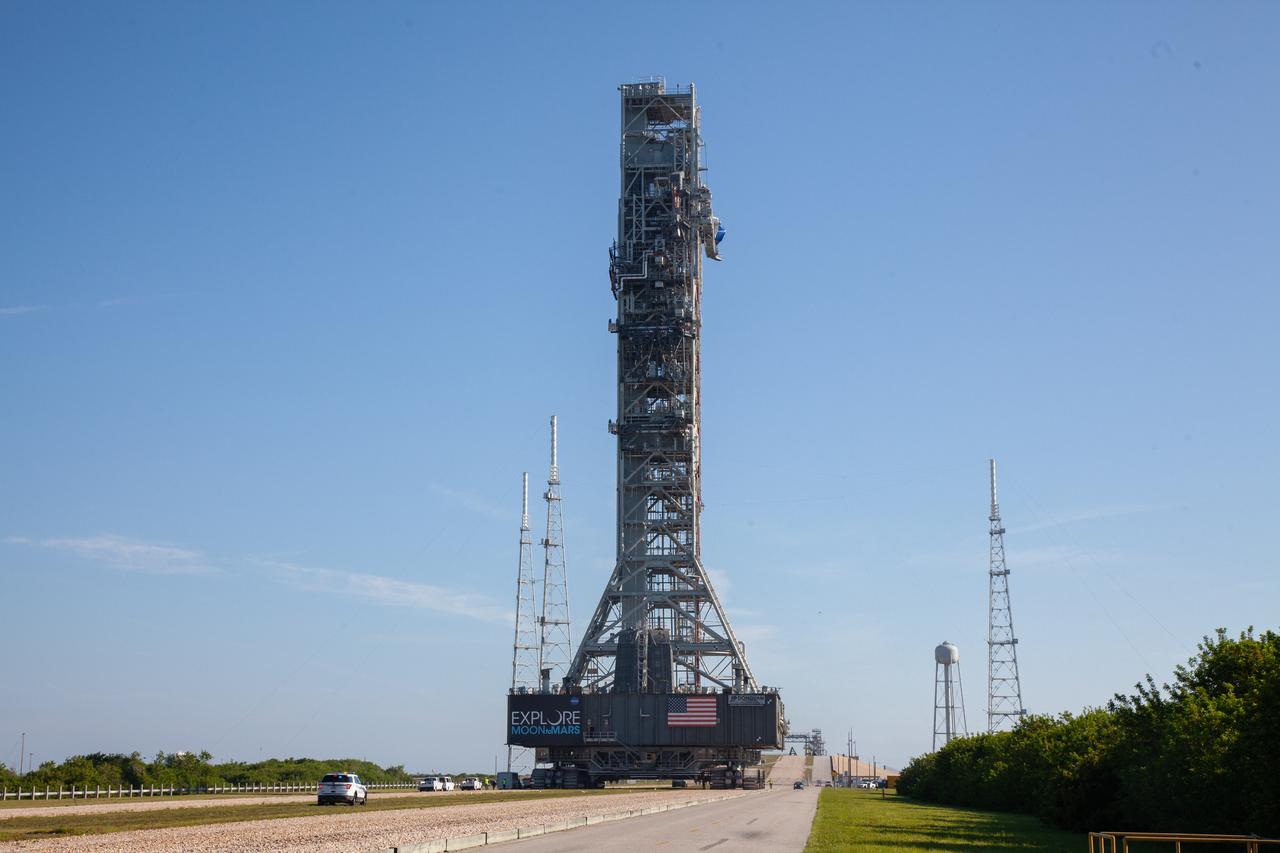

On June 27, 2019, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher, atop crawler-transporter 2, approaches Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
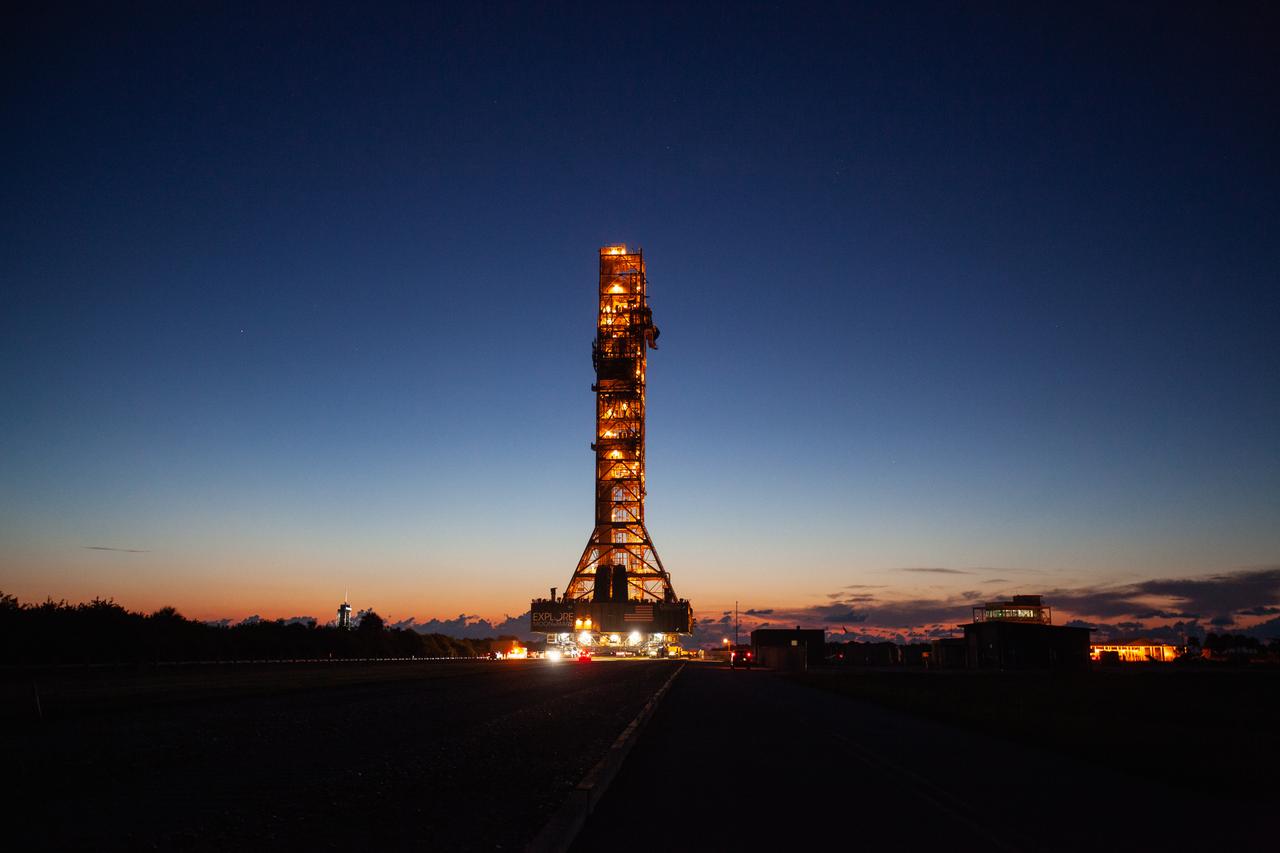

With a sunrise serving as the backdrop, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. It will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
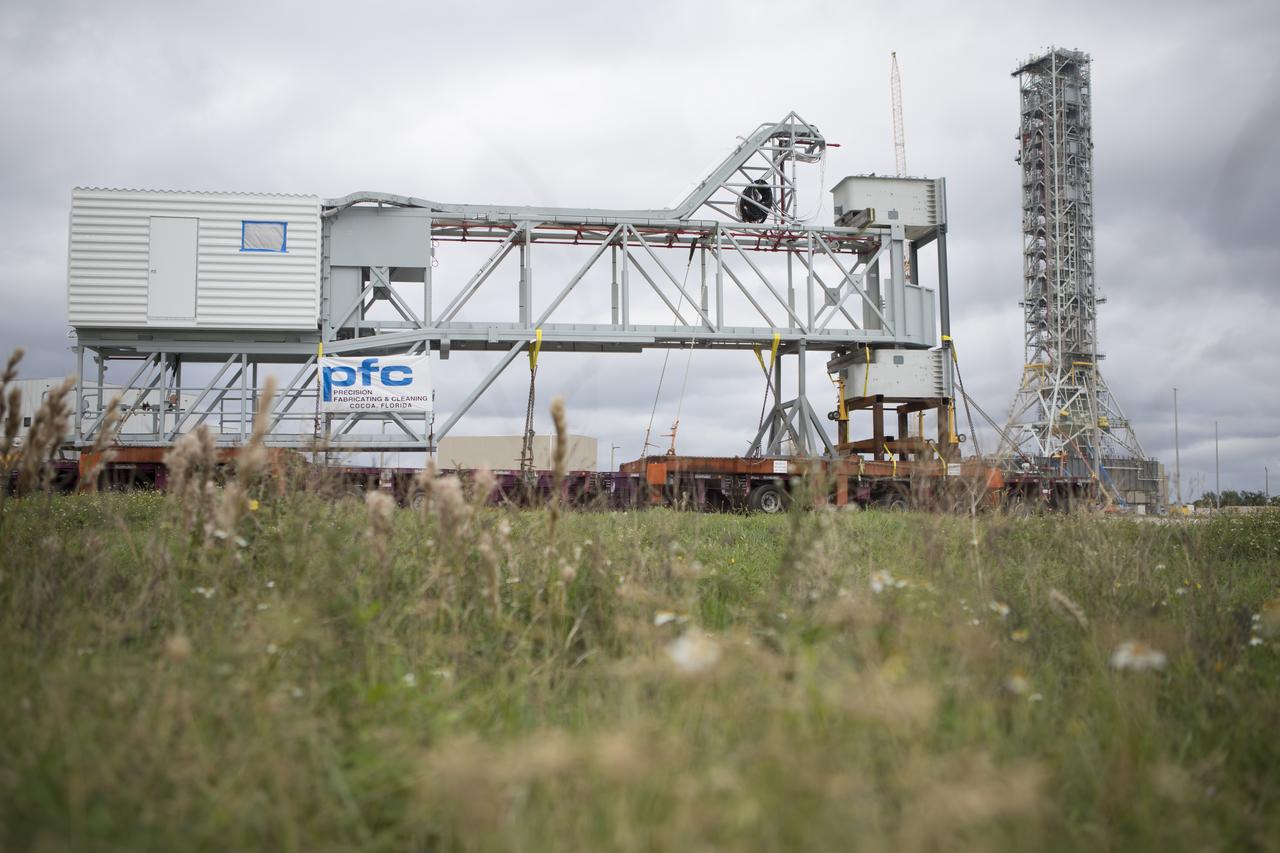

A heavy-load transport truck carrying the Orion crew access arm nears the mobile launcher (ML) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The crew access arm will be installed at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML tower to prepare for Exploration Mission-1.
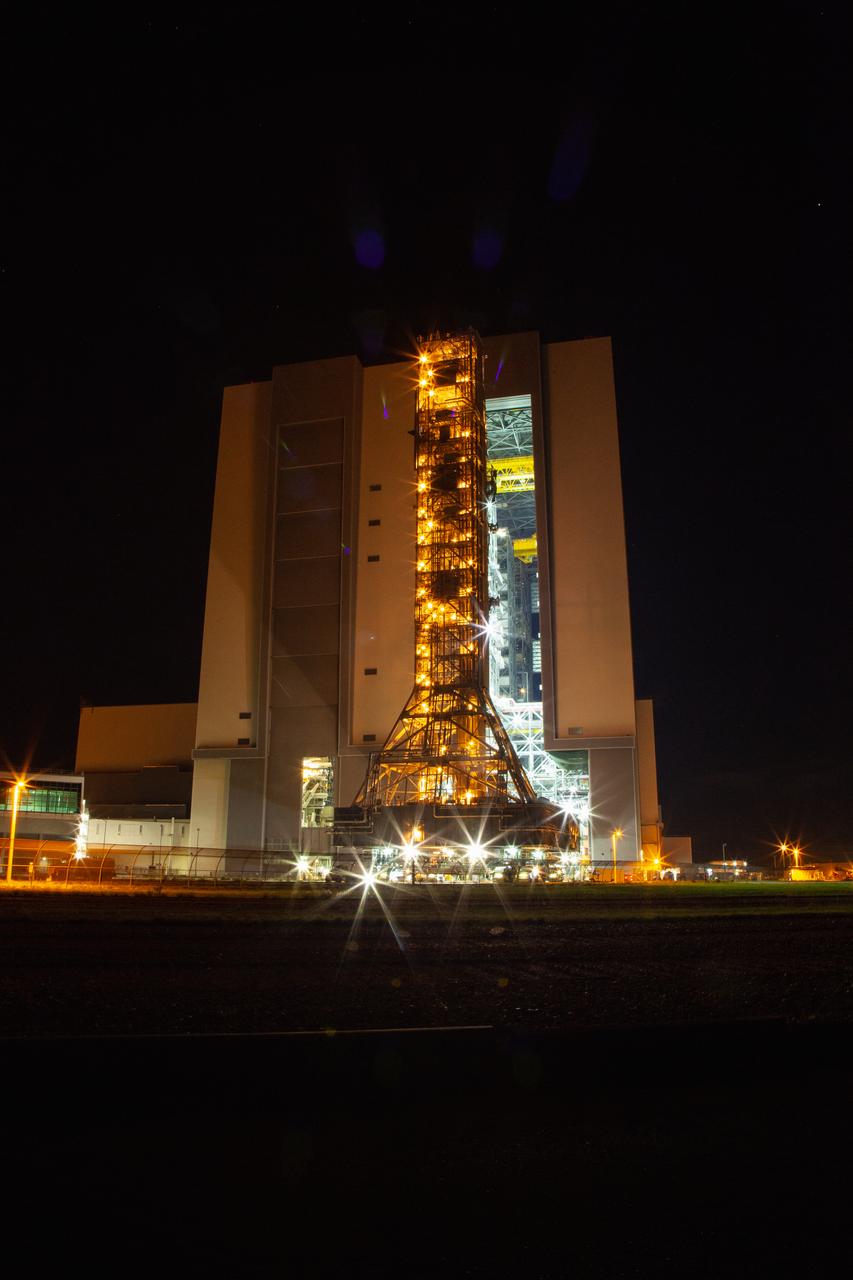

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher departs from Kennedy Space Center’s Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27, 2019, for its final solo trek to Launch Complex 39B in Florida. After the 10-hour journey to the pad, the mobile launcher will remain there for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
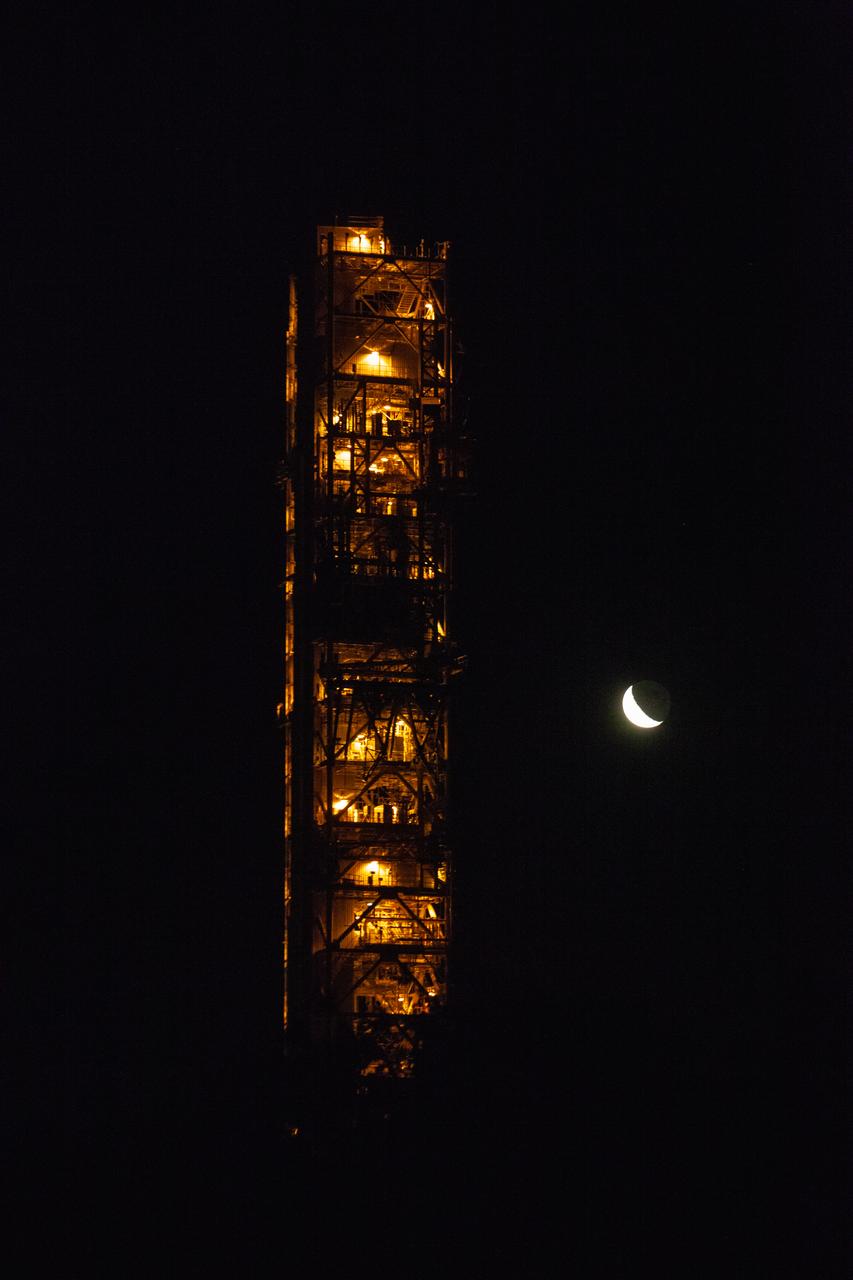

With the Moon and nighttime sky serving as the backdrop, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher is illuminated in the night as it makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
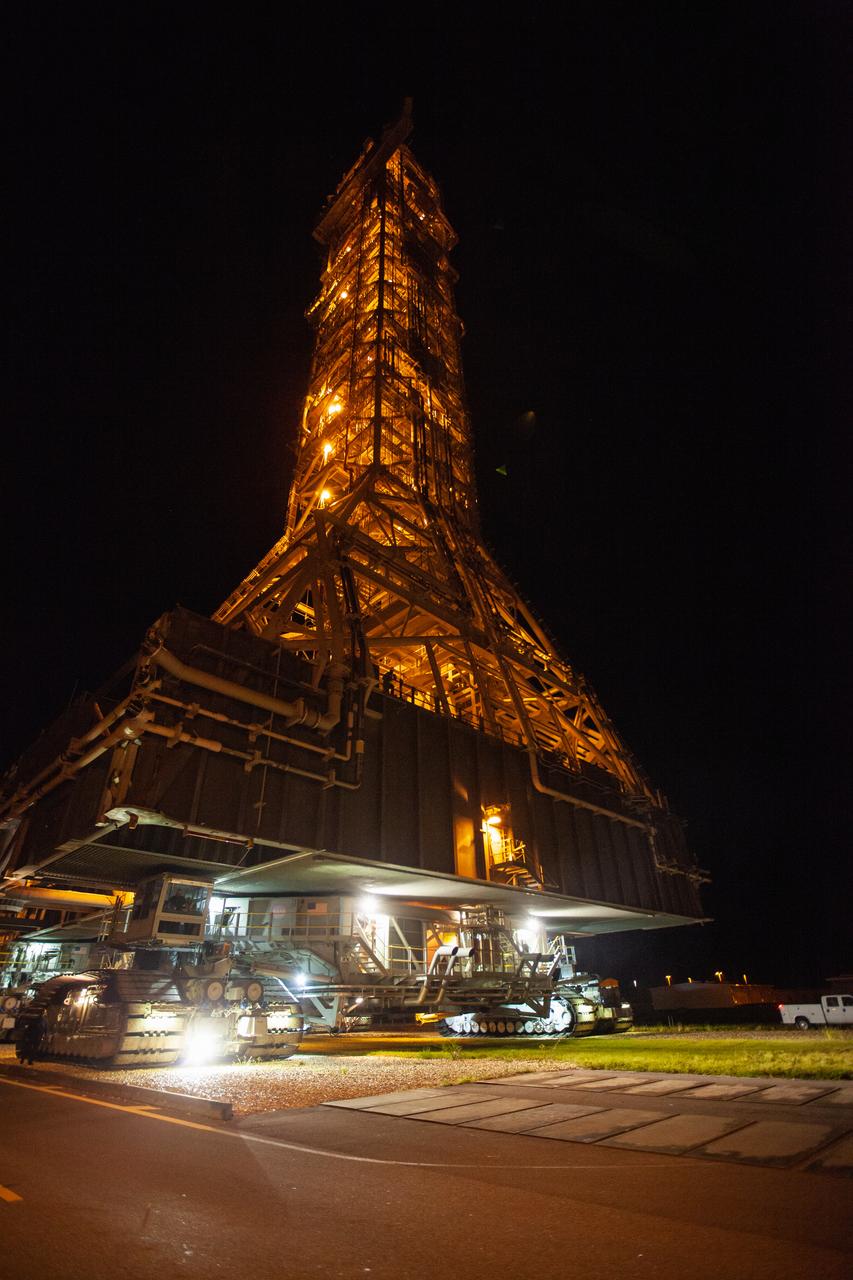

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher is illuminated in the night as it makes its last solo trek to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
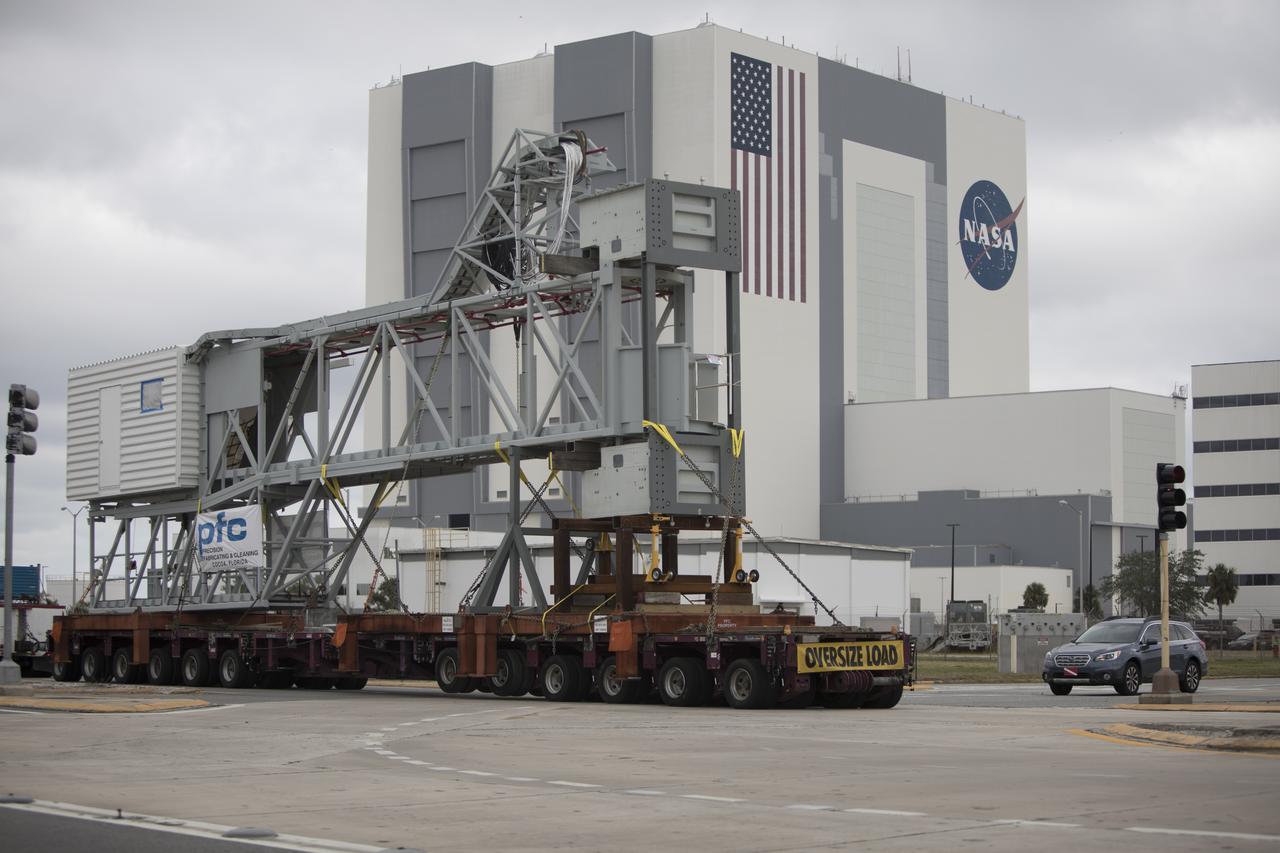

A heavy-load transport truck carrying the Orion crew access arm passes the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The access arm will be installed at about the 274-foot level on the mobile launcher tower. It will rotate from its retracted position and interface with the Orion crew hatch location to provide entry to the Orion crew module. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing installation of umbilicals and launch accessories on the ML tower to prepare for Exploration Mission-1.
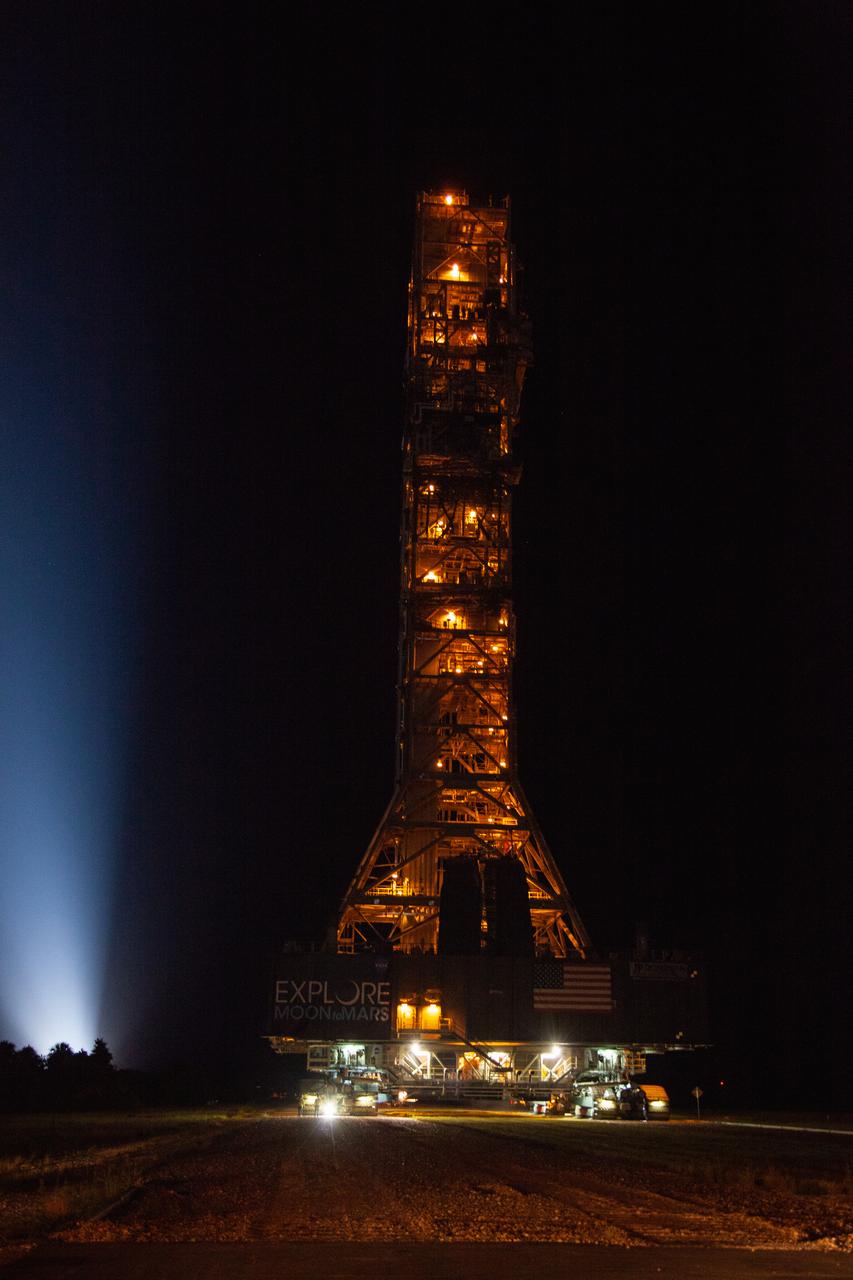

Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher makes its last solo trek along the crawlerway atop crawler-transporter 2 to Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B in Florida on June 27, 2019. The mobile launcher departed from the Vehicle Assembly Building at midnight on June 27 for the 10-hour journey to the pad, where it will remain for the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
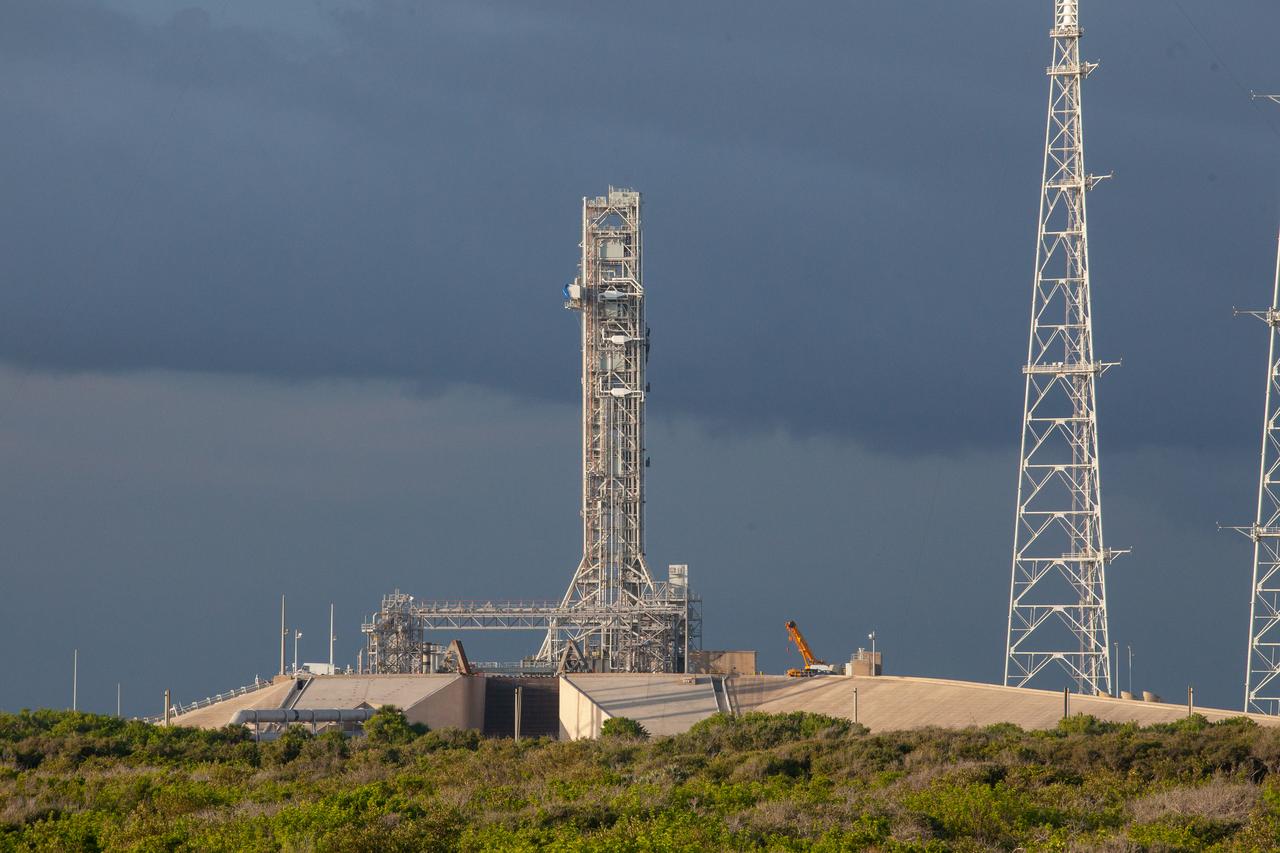

After successfully arriving at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch Complex 39B, Exploration Ground Systems’ mobile launcher is photographed at the pad surface on June 28, 2019. The mobile launcher began its final solo trek to the pad at midnight on June 27, departing from NASA’s Vehicle Assembly Building. The mobile launcher will remain at the pad over the summer, undergoing final testing and checkouts. Its next roll to the pad will be with the agency’s Space Launch System rocket and Orion in preparation for the launch of Artemis 1.
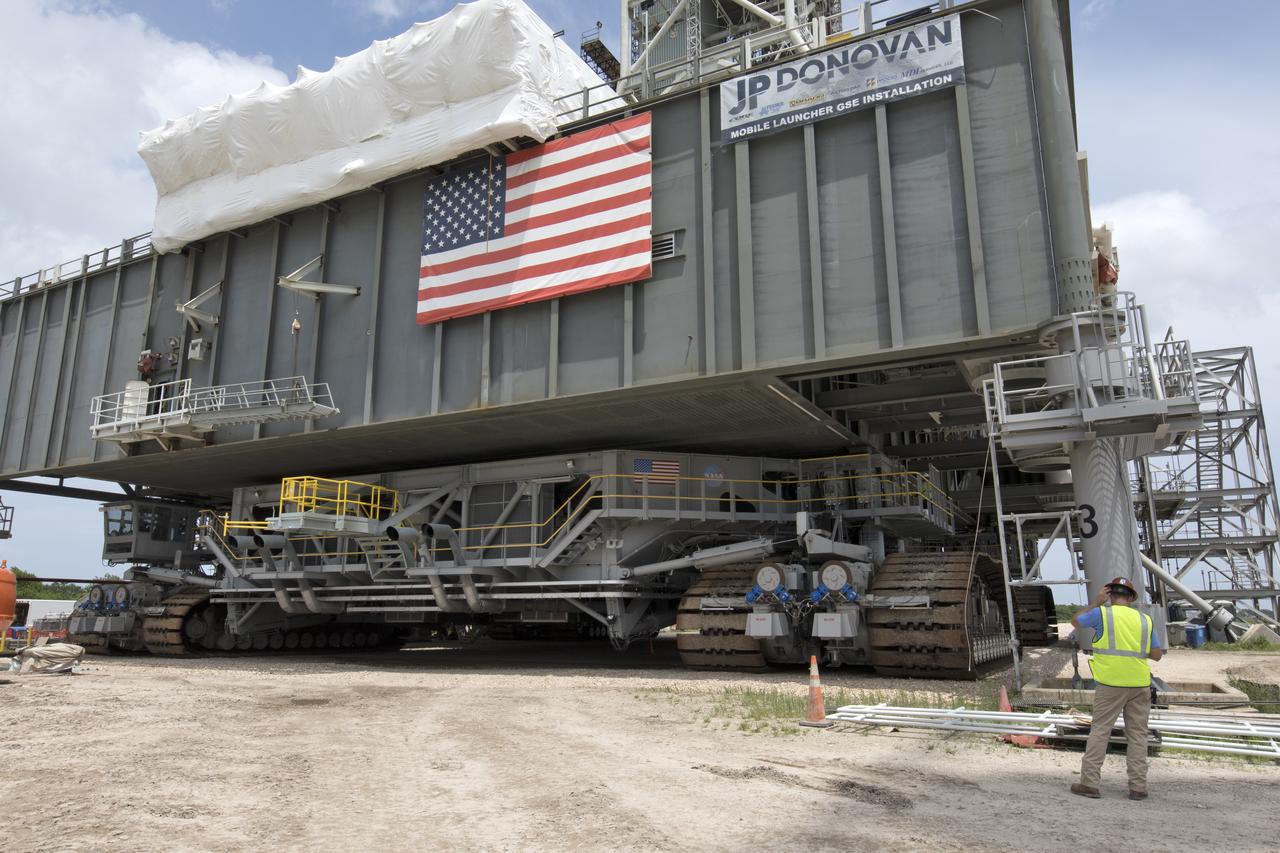

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is underneath the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is being moved under the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
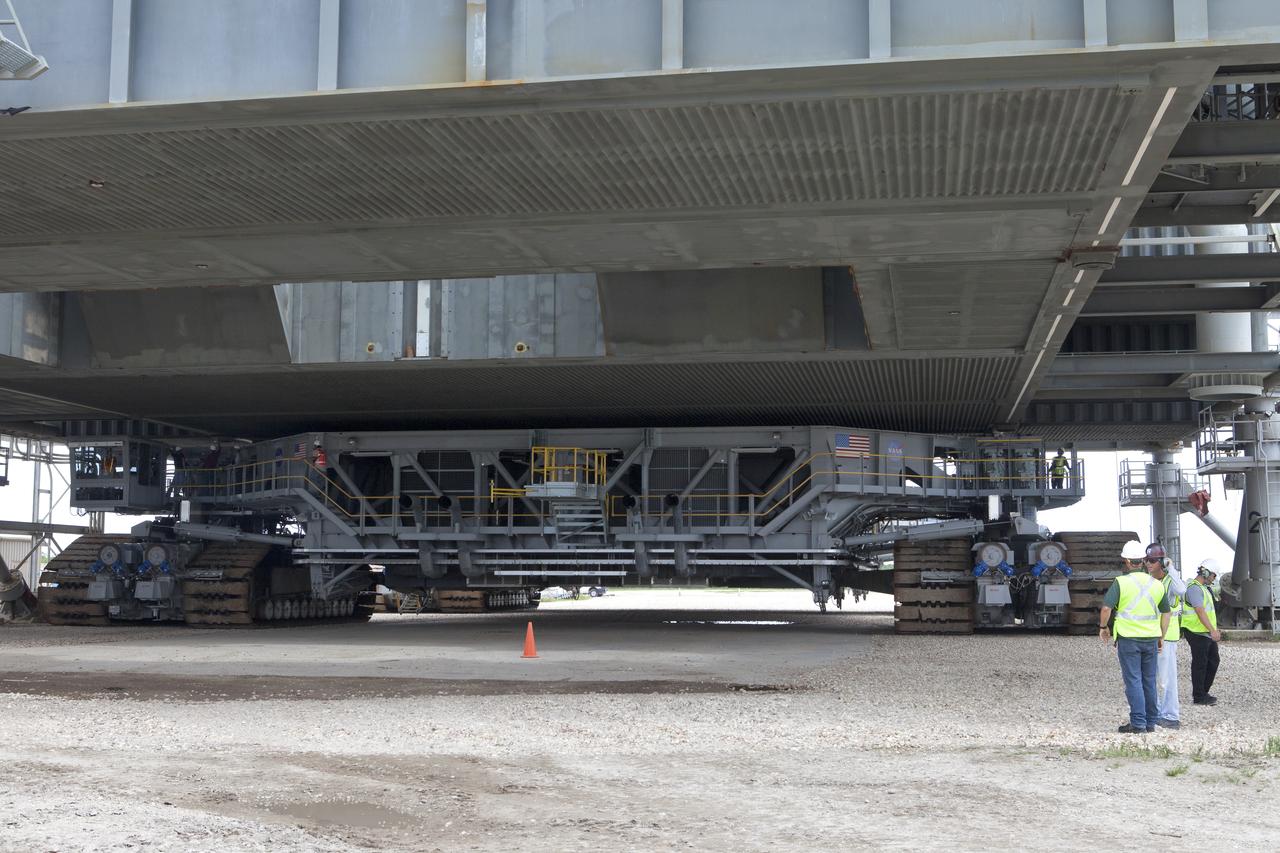

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is moved under the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
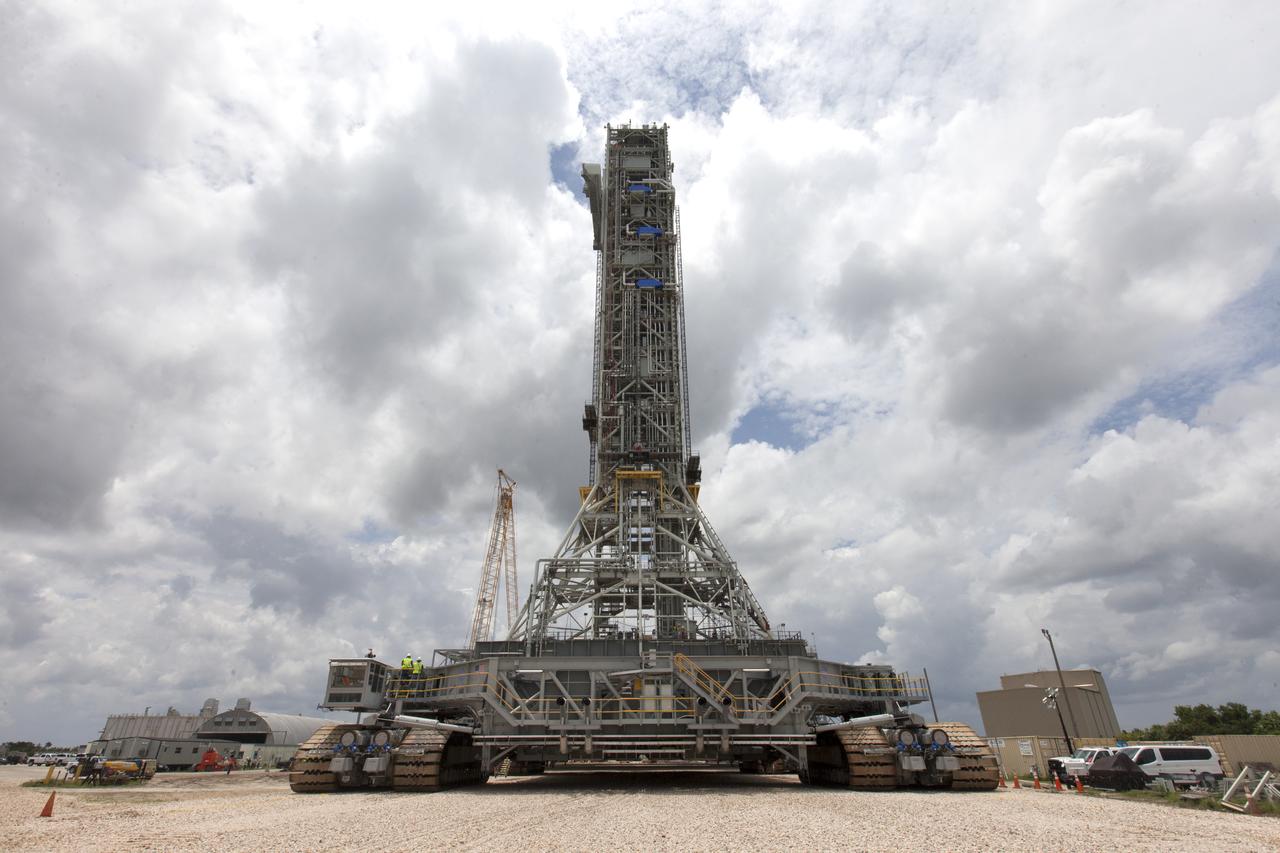

Preparations are underway May 31, 2018, to move crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) under the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
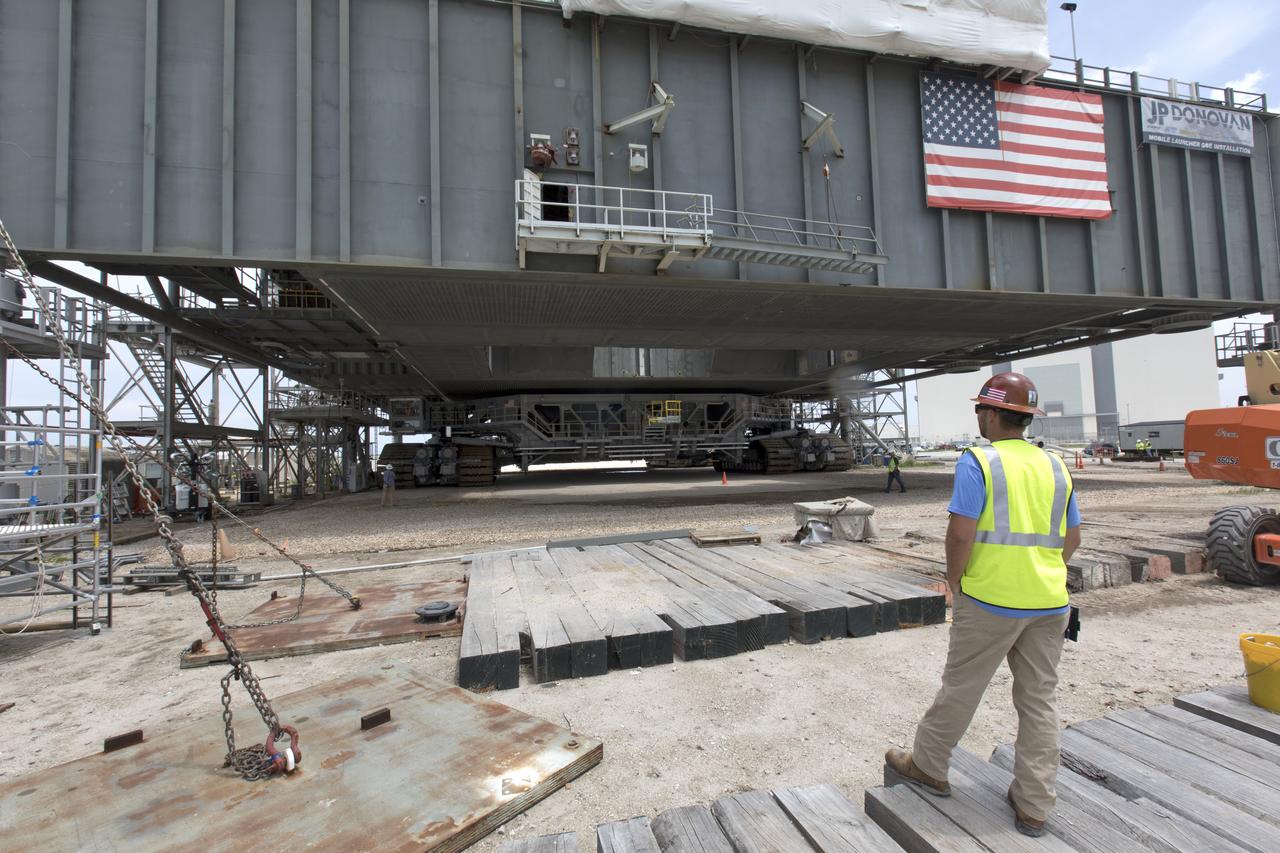

Crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) is underneath the mobile launcher May 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts were performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.
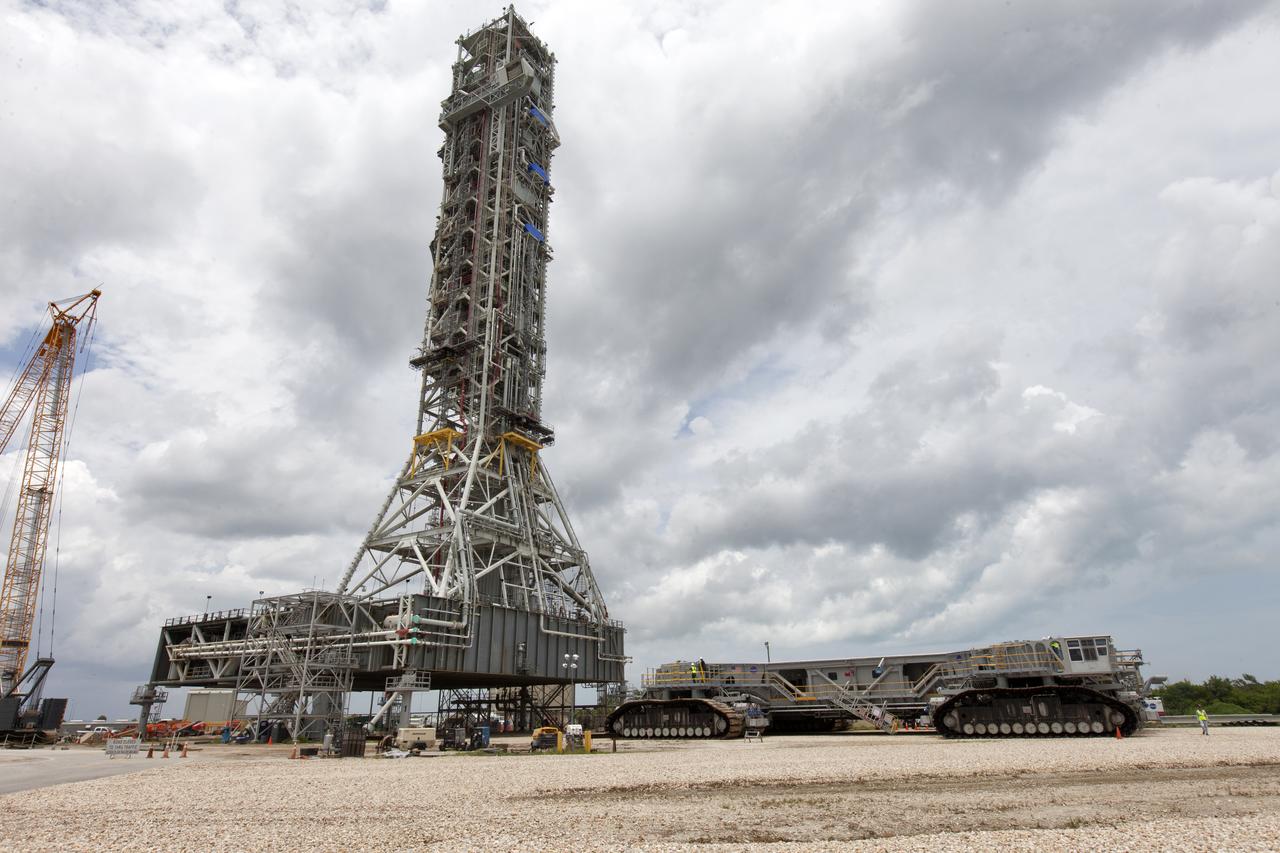

Preparations are underway May 31, 2018, to move crawler-transporter 2 (CT-2) under the mobile launcher at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Three lifts will be performed to practice lifting procedures, validate interface locations, confirm the weight of the mobile launcher, and develop a baseline for modal analysis. The mobile launcher is equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals, which will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and Orion. CT-2 has been upgraded to handle the weight of the mobile launcher with SLS and Orion atop. Exploration Ground Systems is preparing the ground systems necessary to support the SLS and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 and deep space missions.