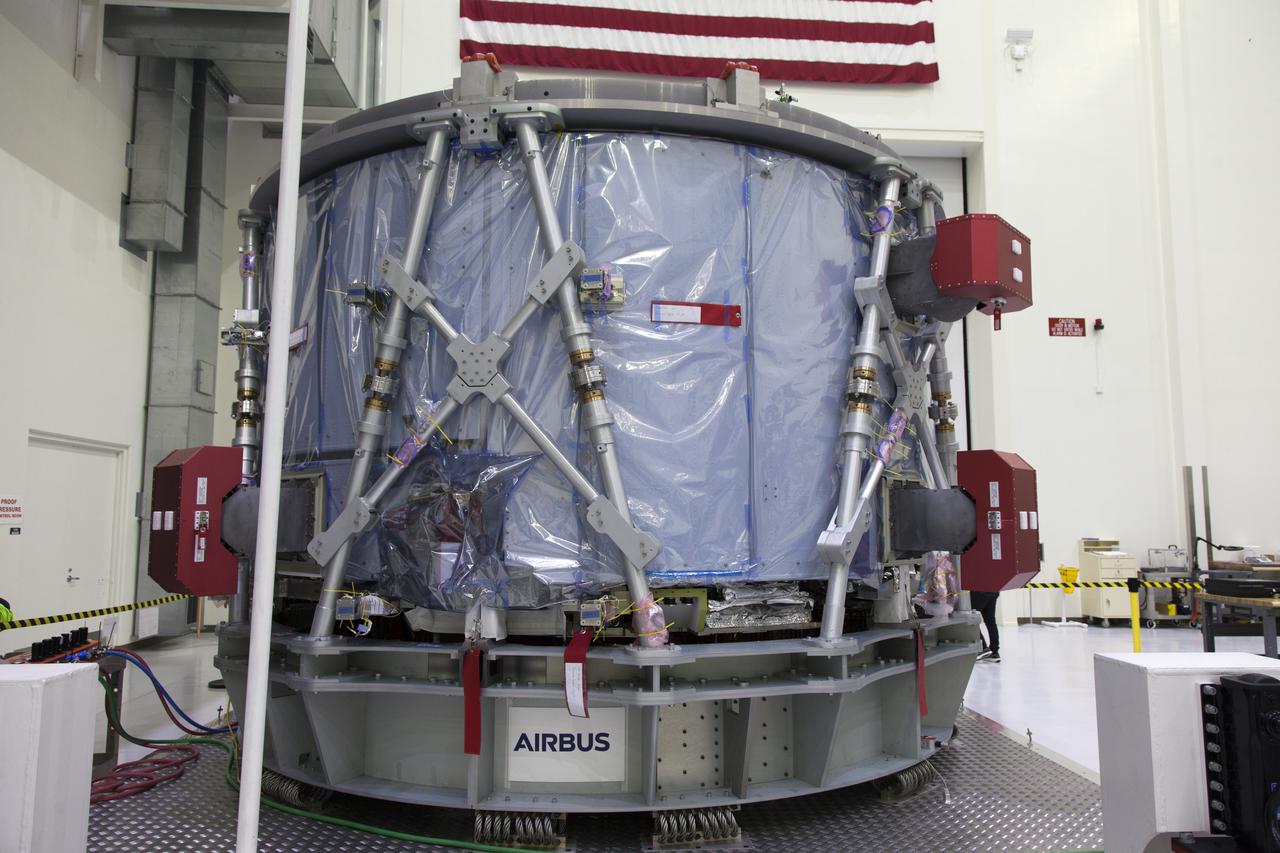

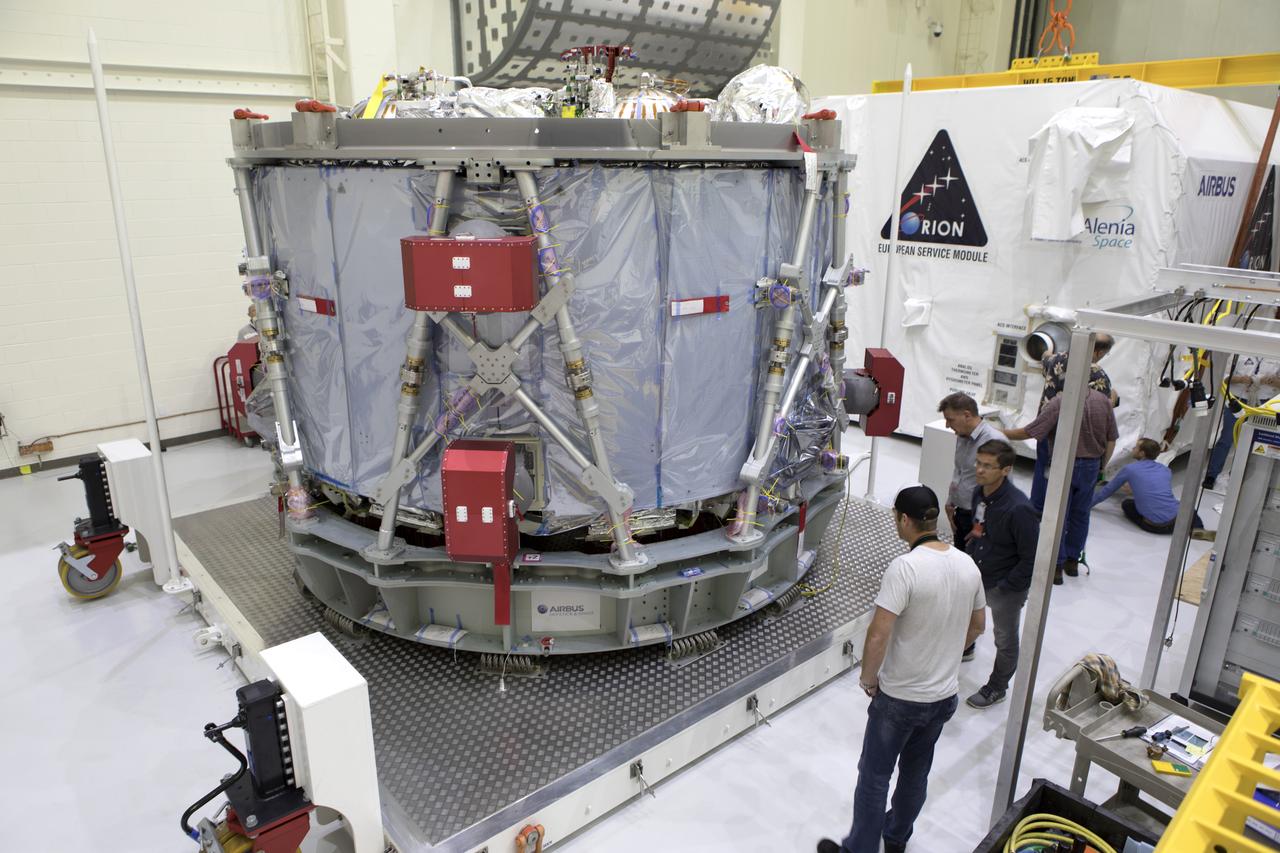
The European Service Module (ESM) is unpacked inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM is provided by the European Space Agency, and built by ESA contractor Airbus Defence and Space. It will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission around the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
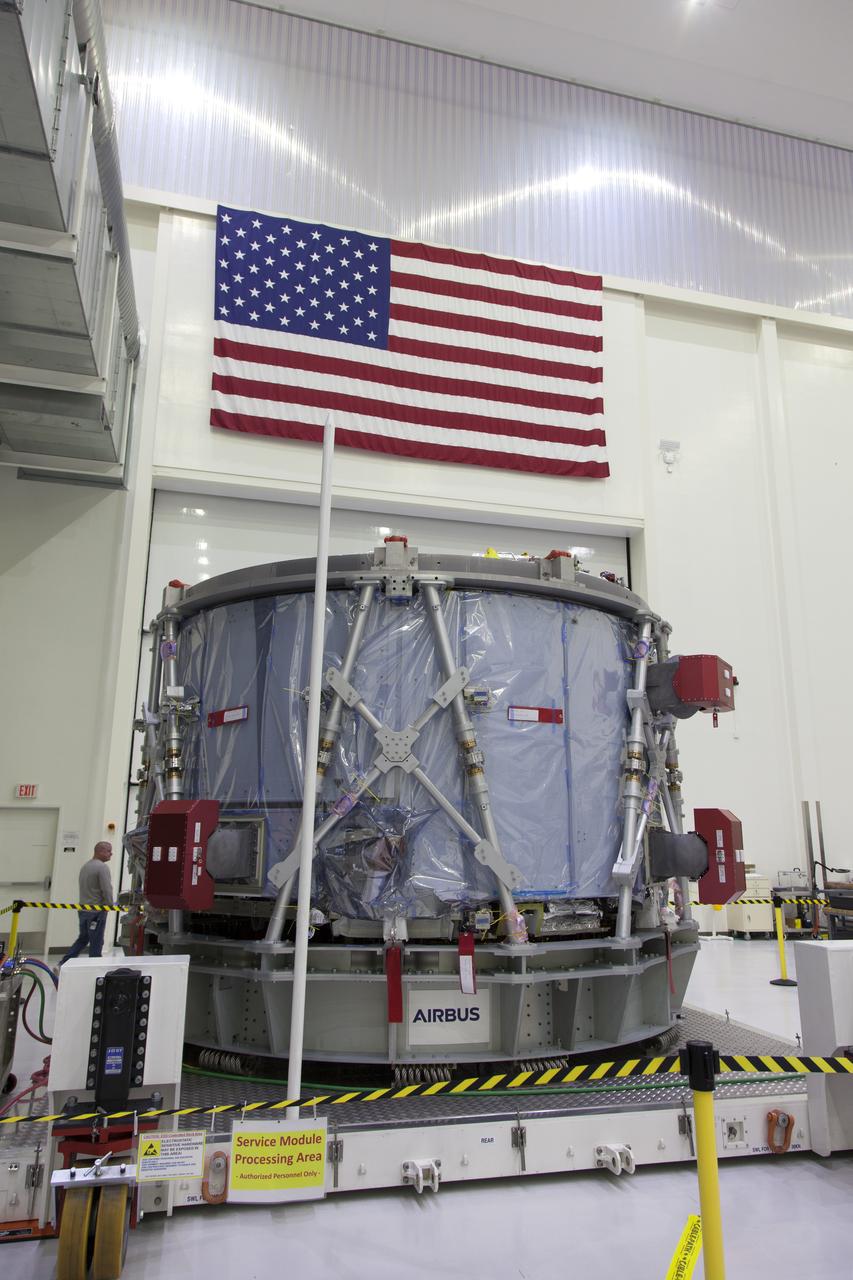

The European Service Module (ESM) is unpacked inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM is provided by the European Space Agency, and built by ESA contractor Airbus Defence and Space. It will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission around the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
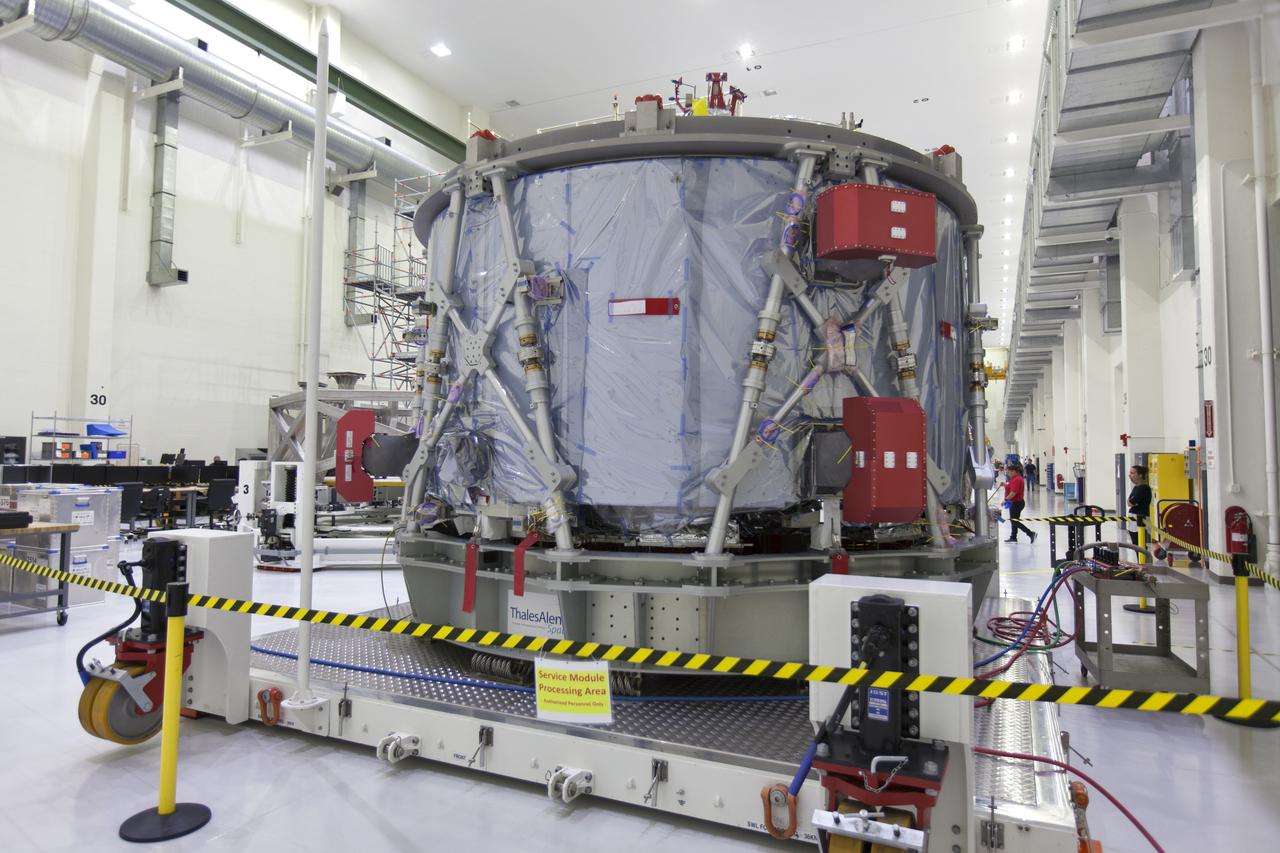

The European Service Module (ESM) is unpacked inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM is provided by the European Space Agency, and built by ESA contractor Airbus Defence and Space. It will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission around the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
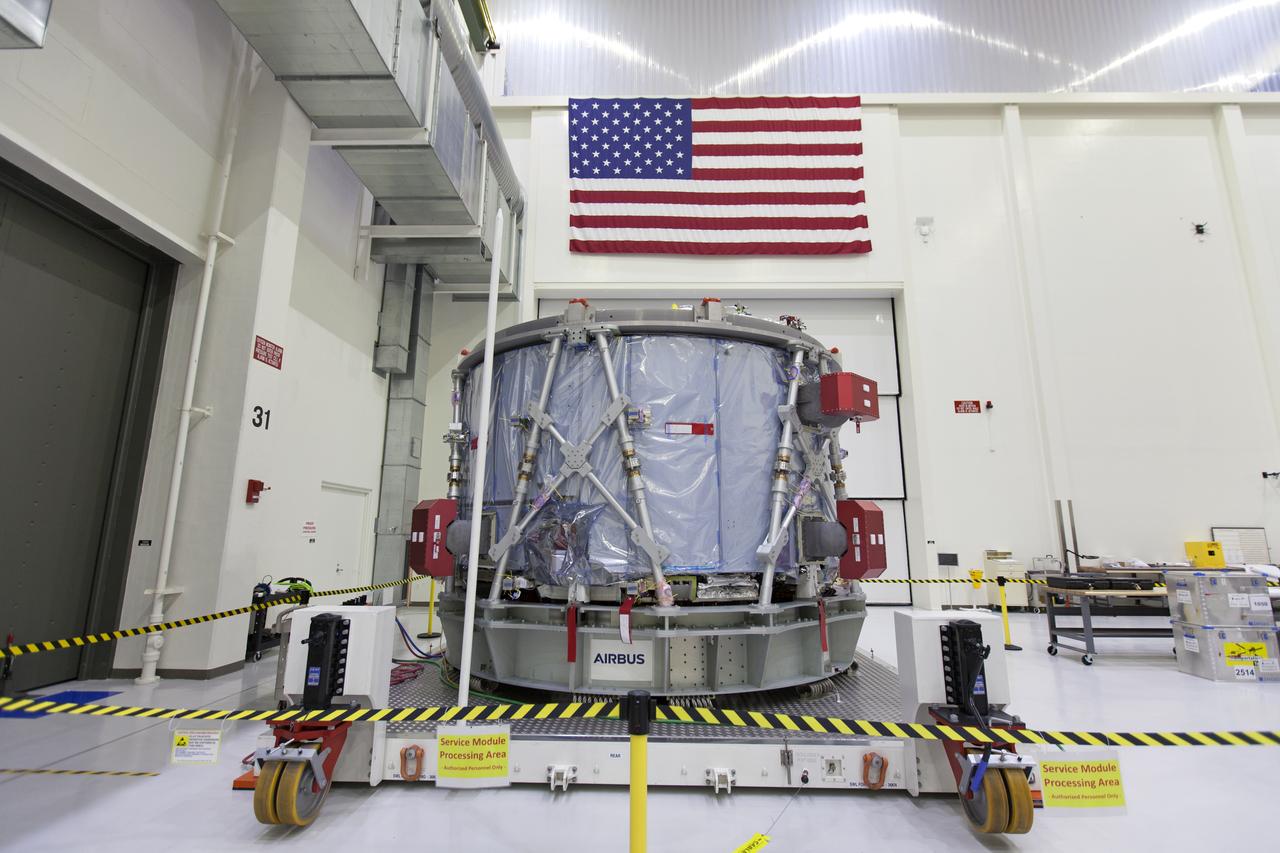

The European Service Module (ESM) is unpacked inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 7, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM is provided by the European Space Agency, and built by ESA contractor Airbus Defence and Space. It will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission around the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
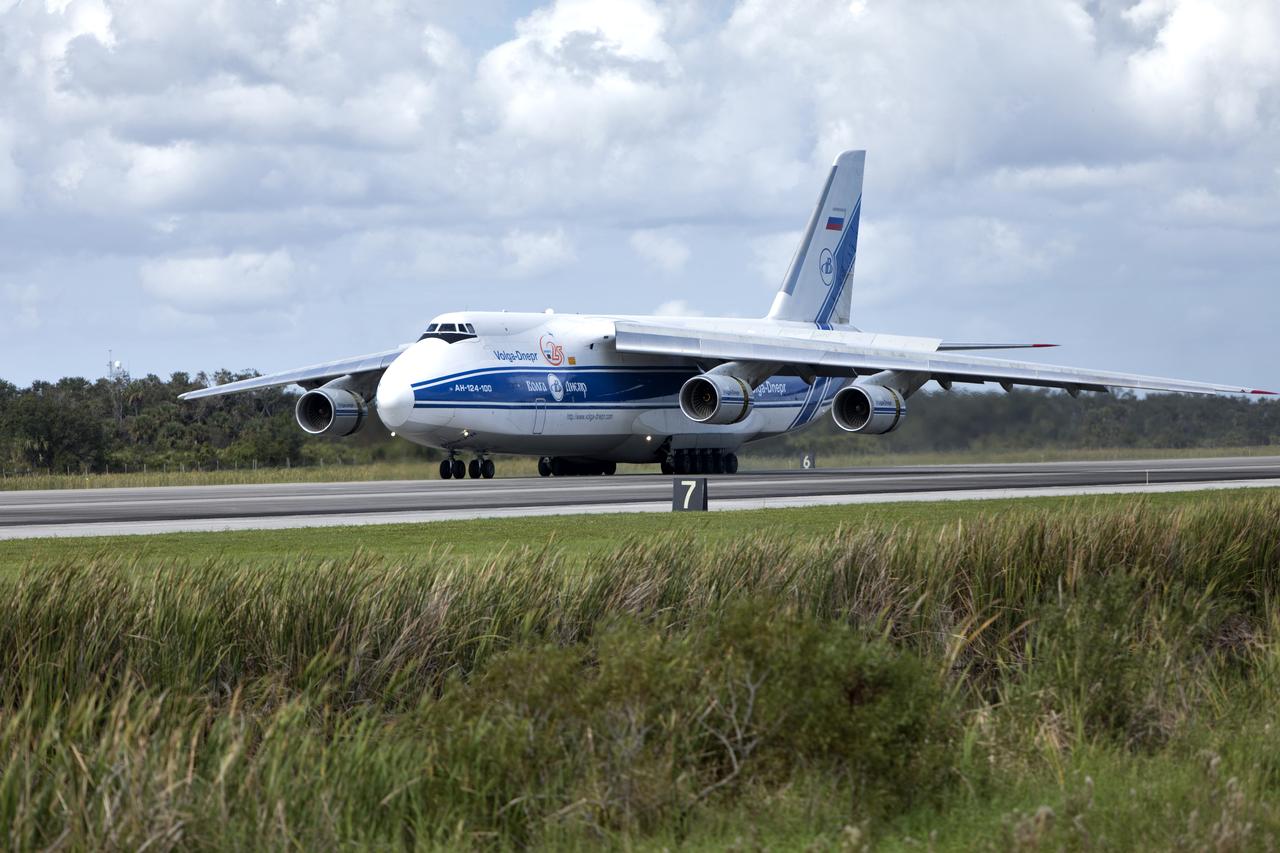

The Antonov cargo aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018, carrying the European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

The Antonov cargo aircraft touches down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018, carrying the European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
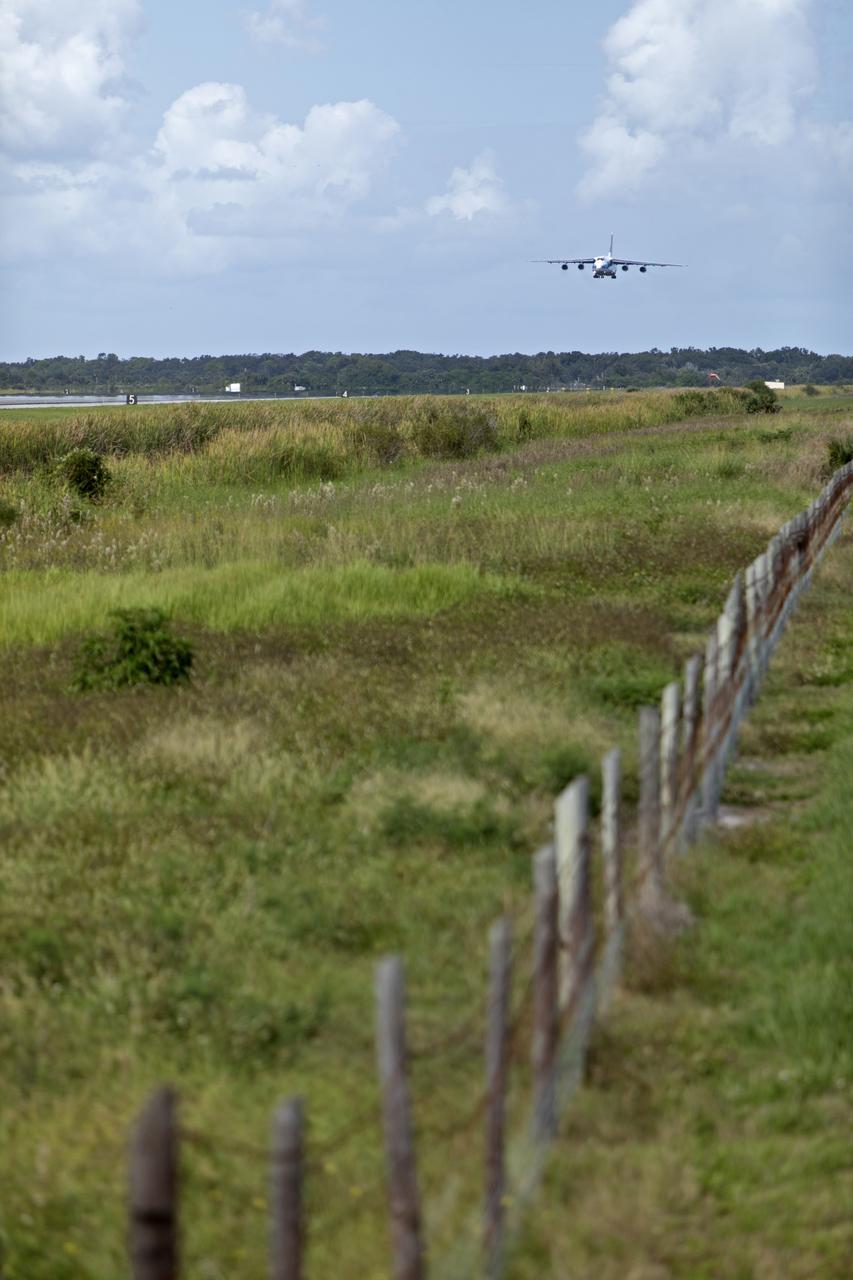

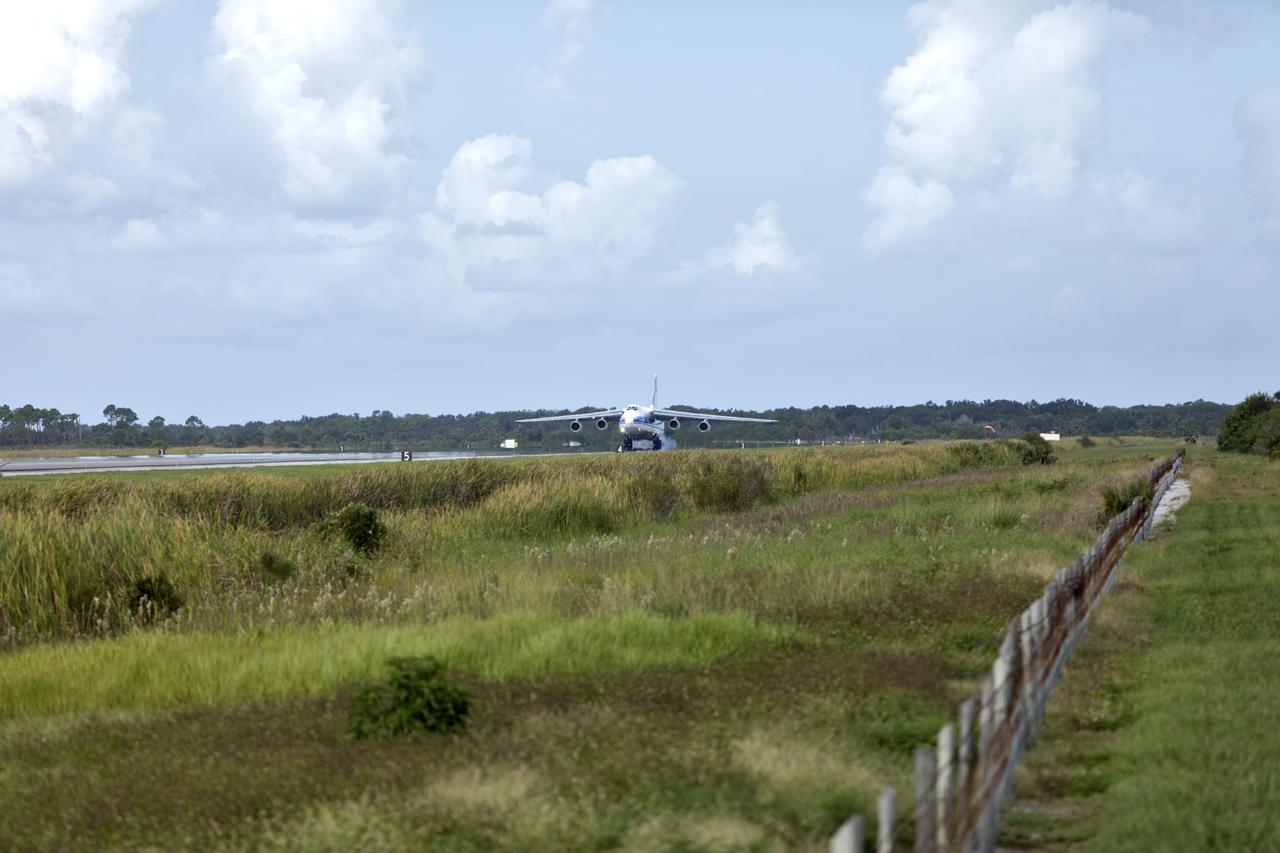
The Antonov cargo aircraft descends toward the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018, carrying the European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
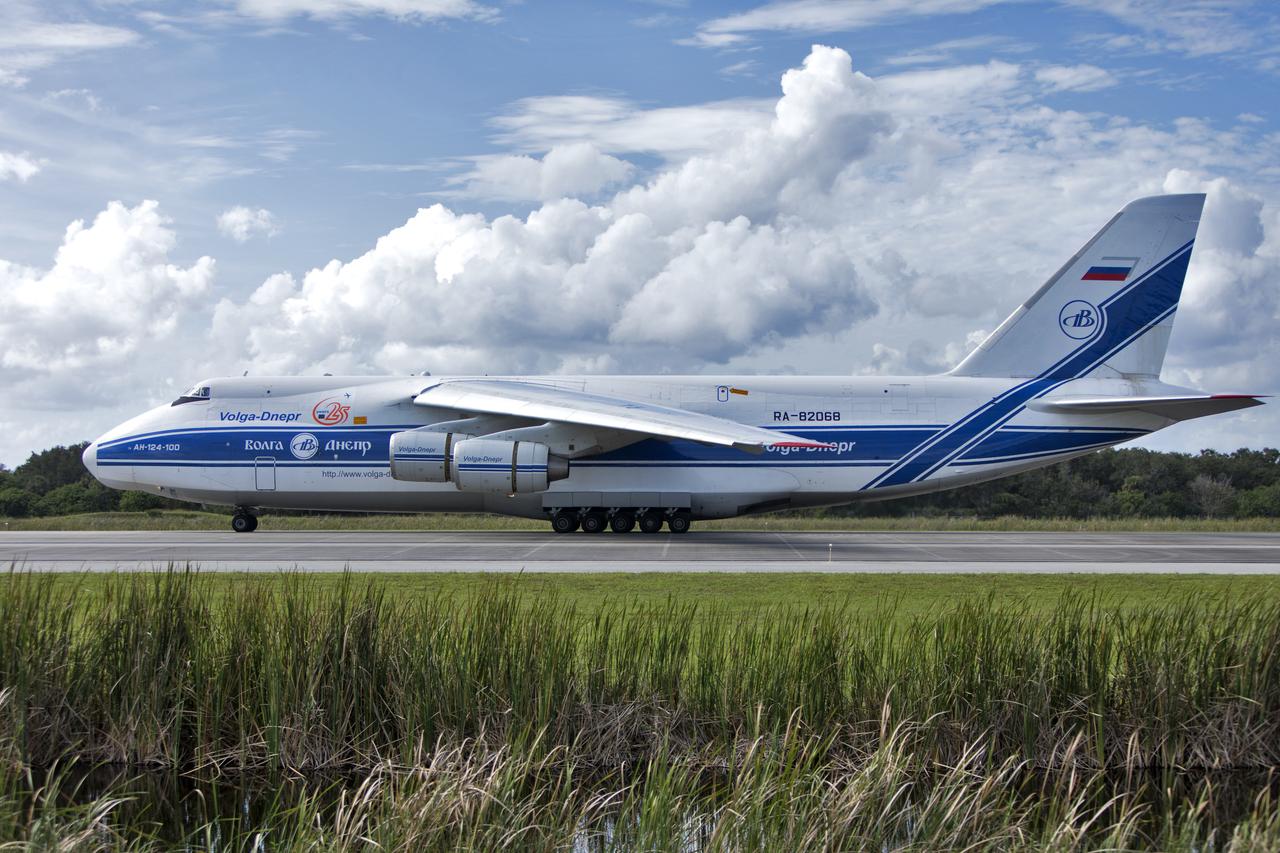

The Antonov cargo aircraft arrives at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018, carrying the European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
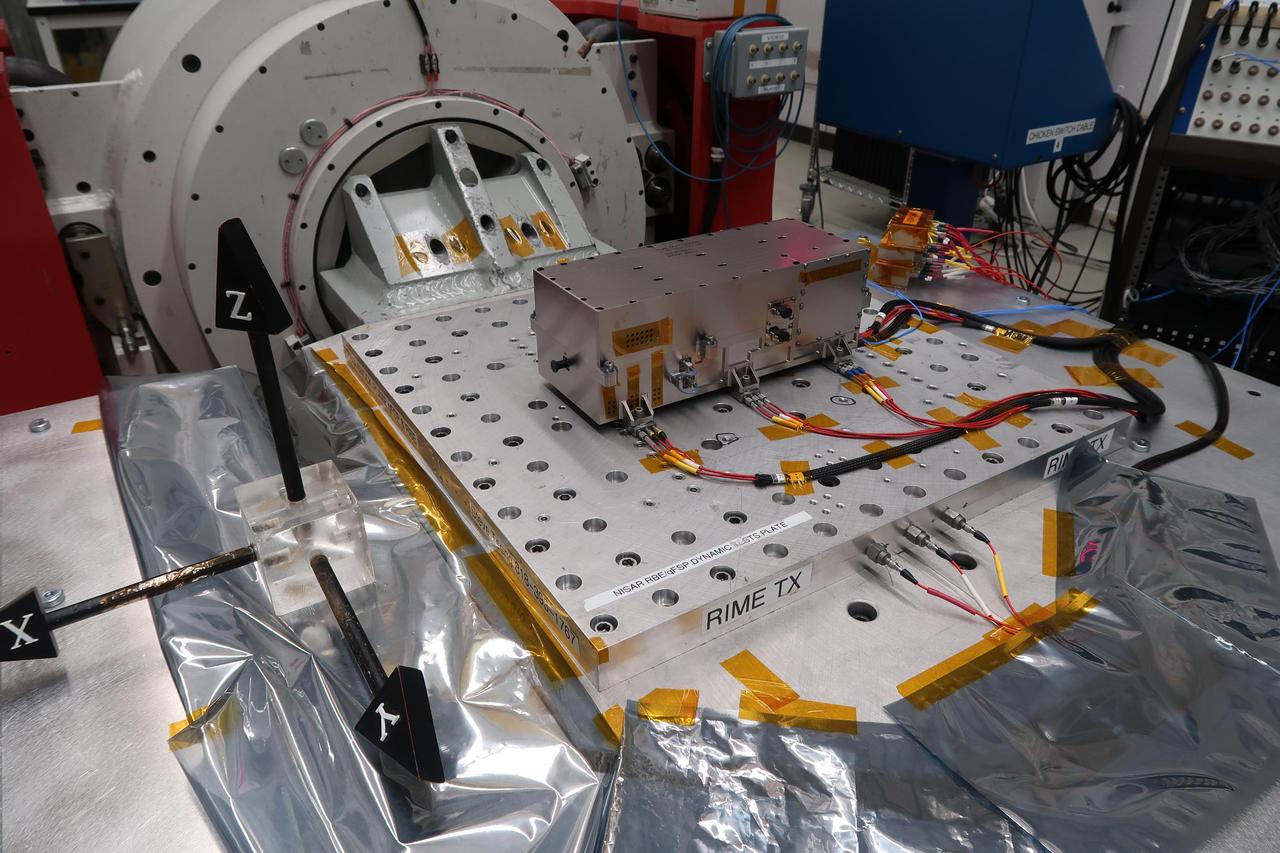
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and shipped the receiver, transmitter, and electronics necessary to complete the radar instrument for Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE), the ESA (European Space Agency) mission to explore Jupiter and its three large icy moons. In this photo, shot at JPL on April 27, 2020, the transmitter undergoes random vibration testing to ensure the instrument can survive the shaking that comes with launch. Part of an instrument called Radar for Icy Moon Exploration, or RIME, the transmitter sends out radio waves, which can penetrate surfaces of icy moons and help scientists "see" underneath. A collaboration between JPL and the Italian Space Agency (ASI), RIME is one of 10 instruments that will fly aboard ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission, set to launch in 2022. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24024
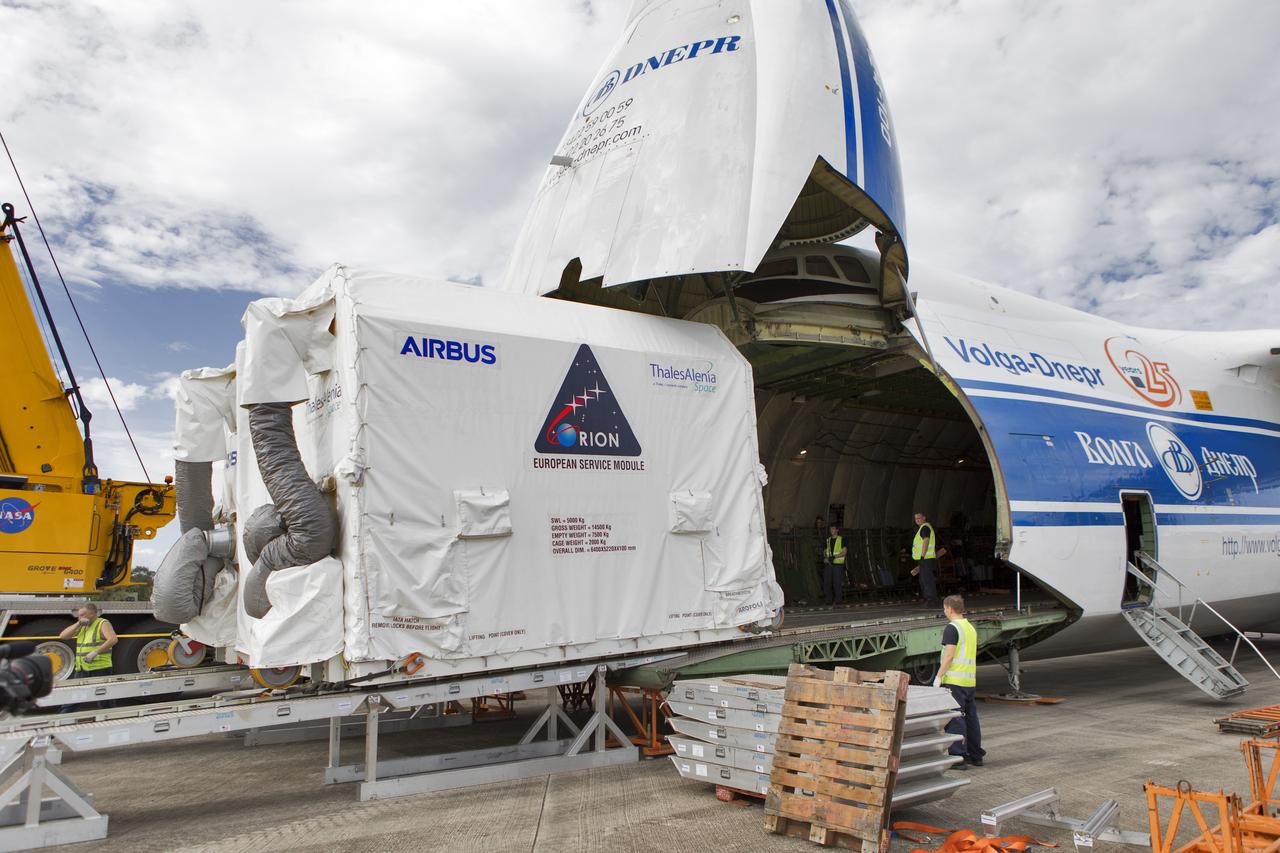

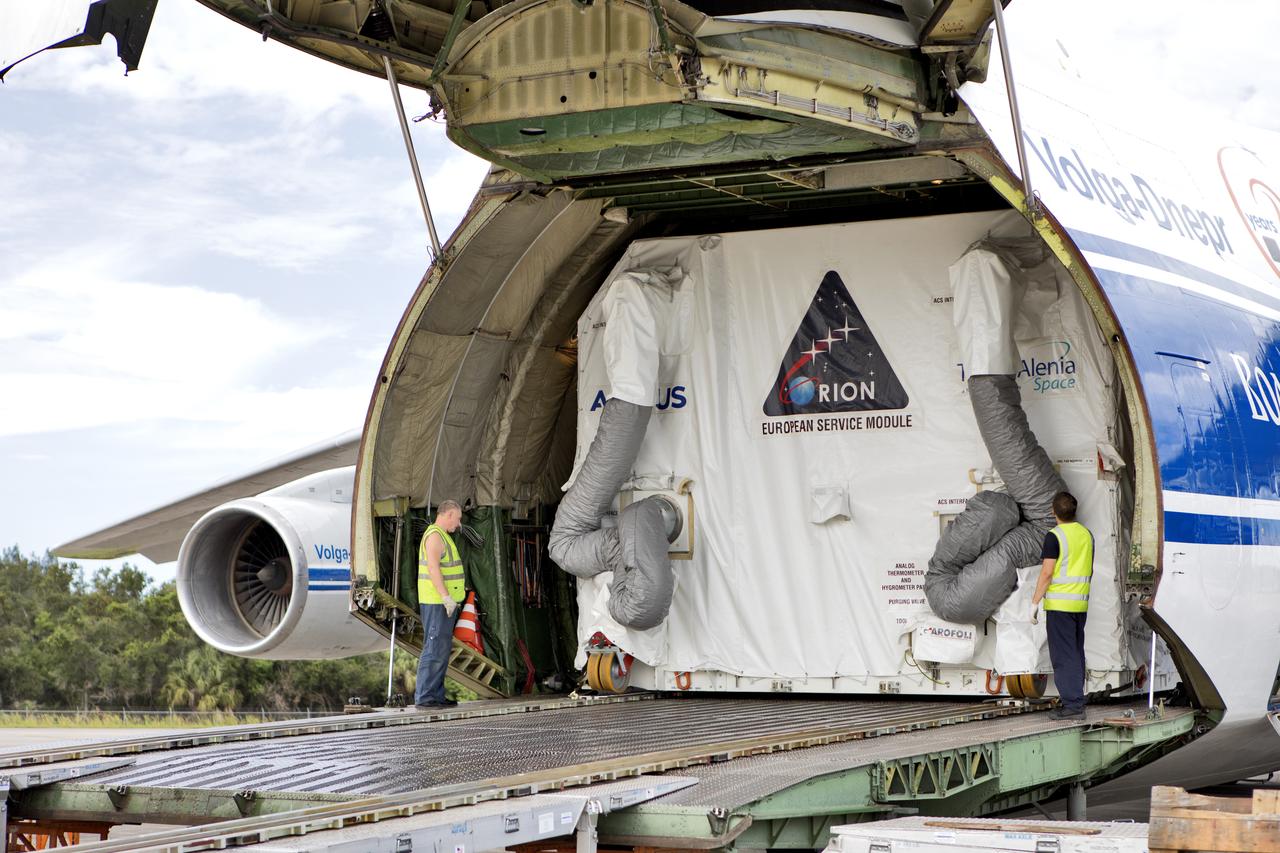
The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
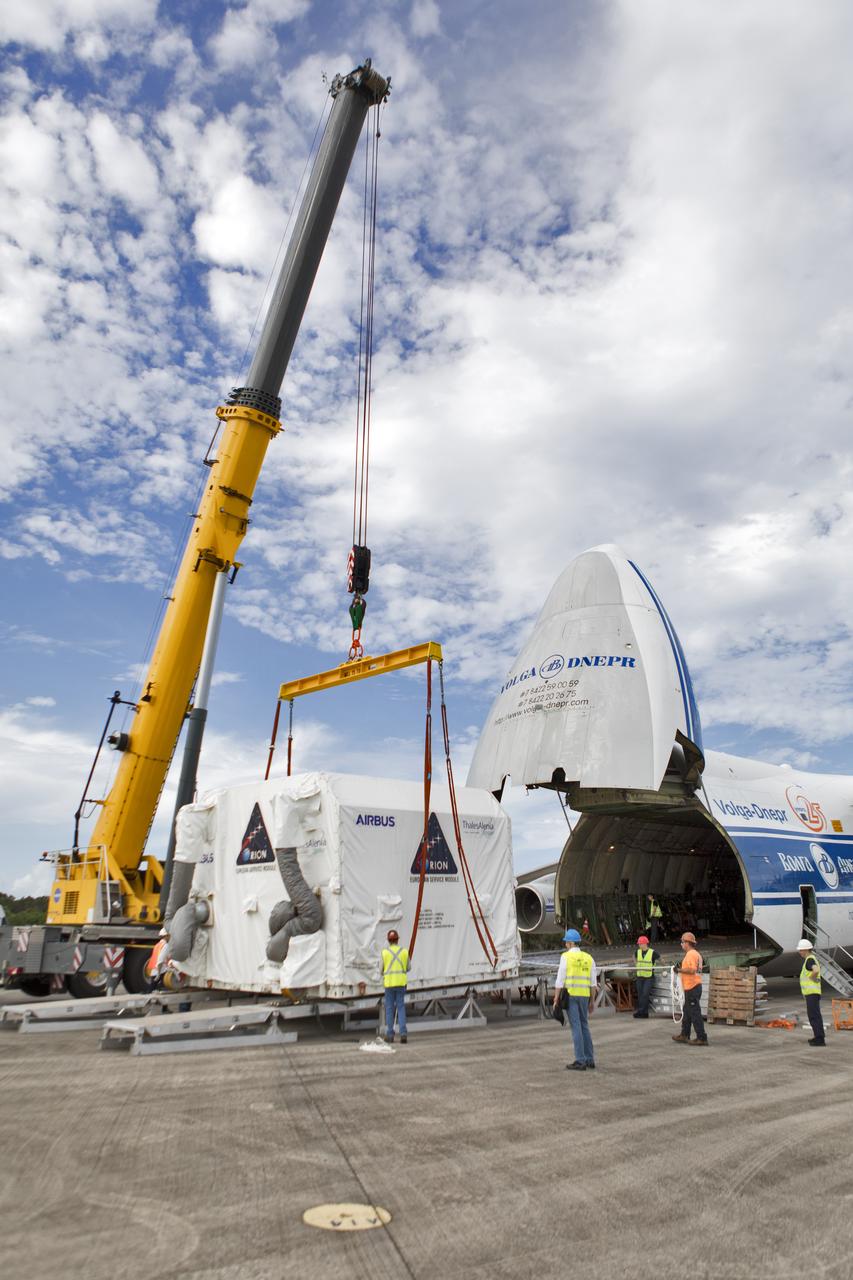

A crane is attached to the shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) after it was moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
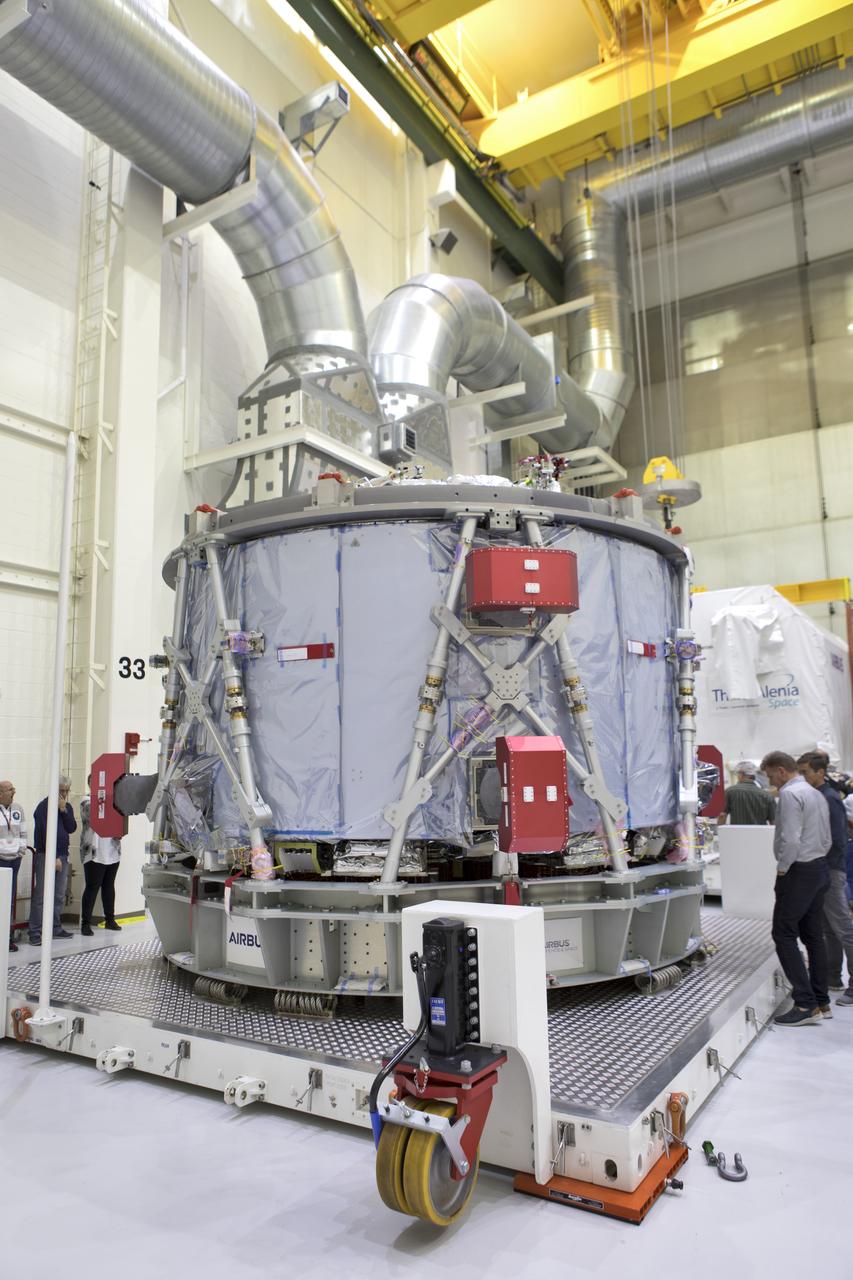

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
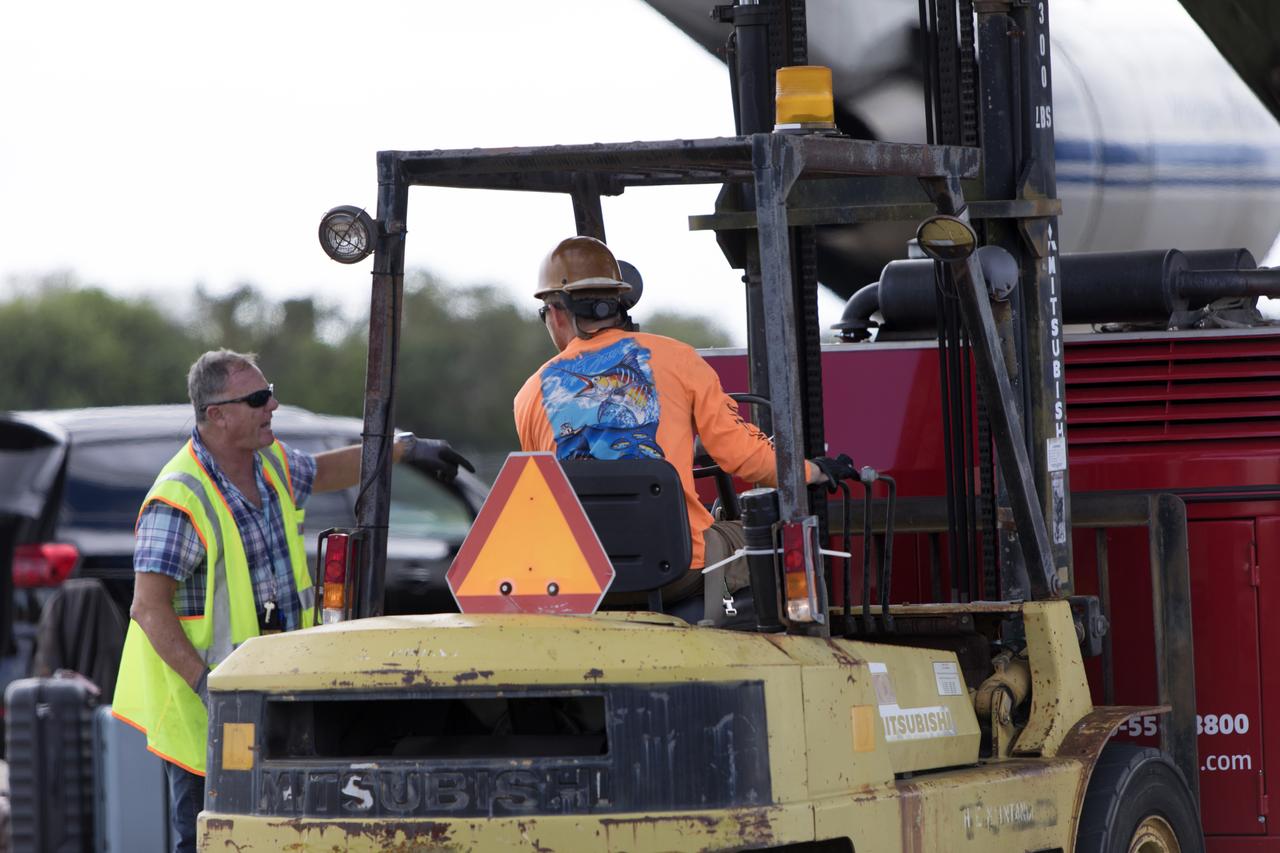

Technicians operate a forklift to lift the European Service Module (ESM) out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, a crane is used to uncrate the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
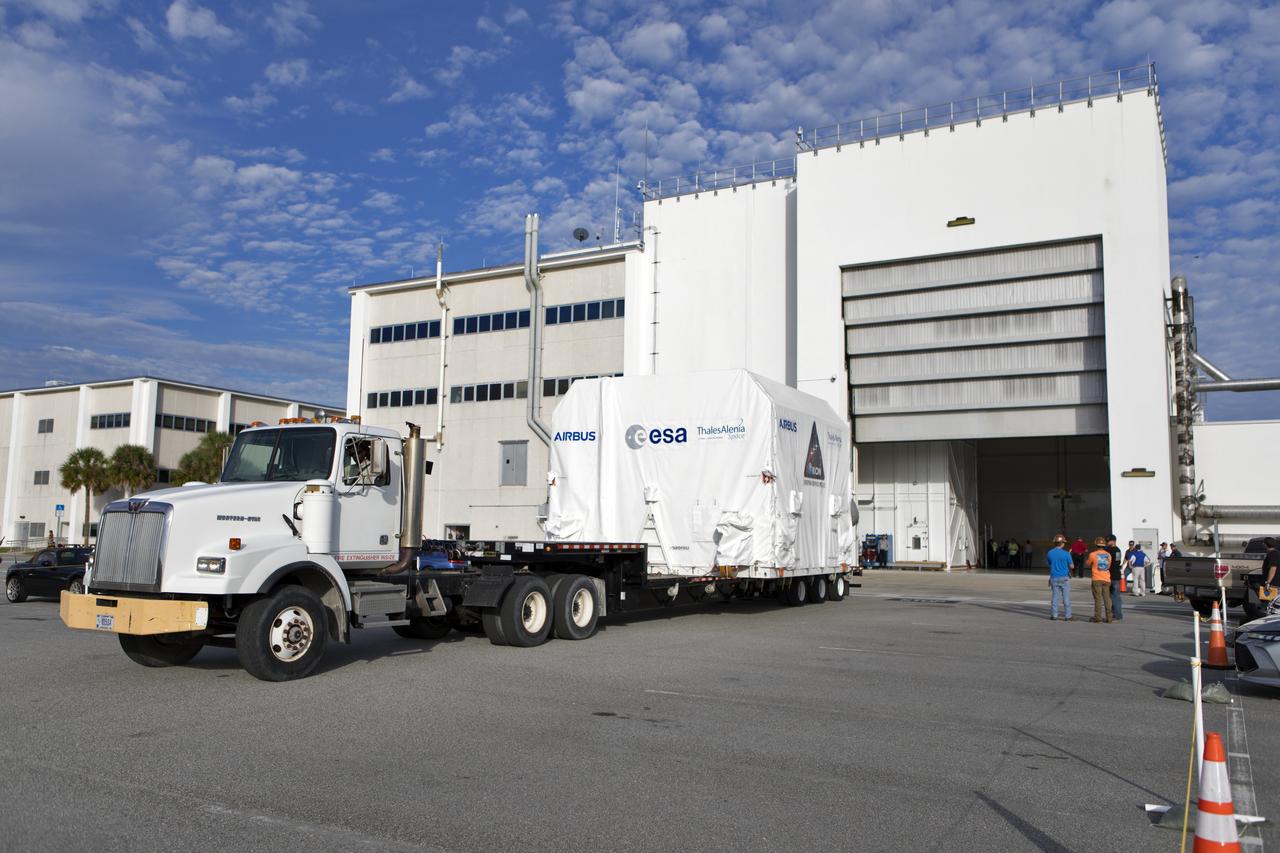

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container begins to back into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
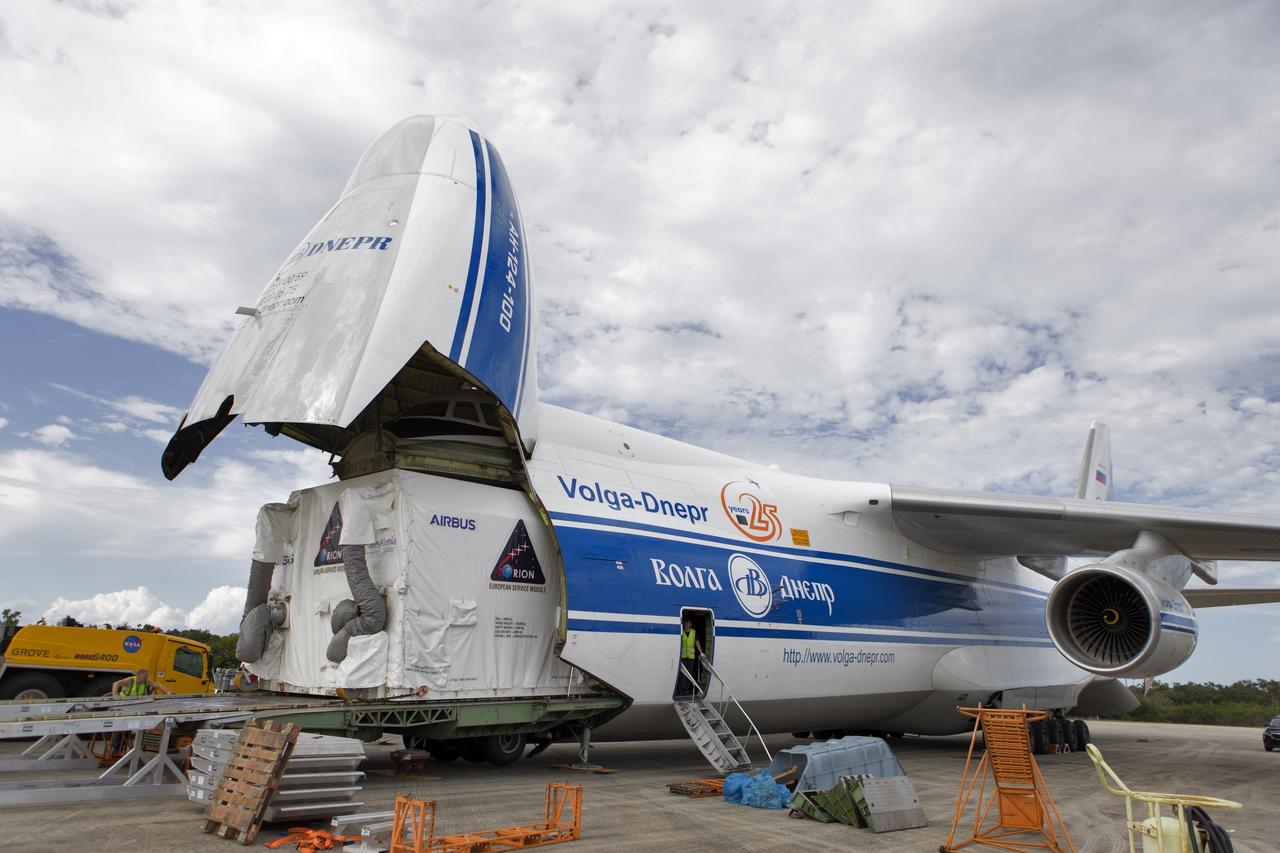

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
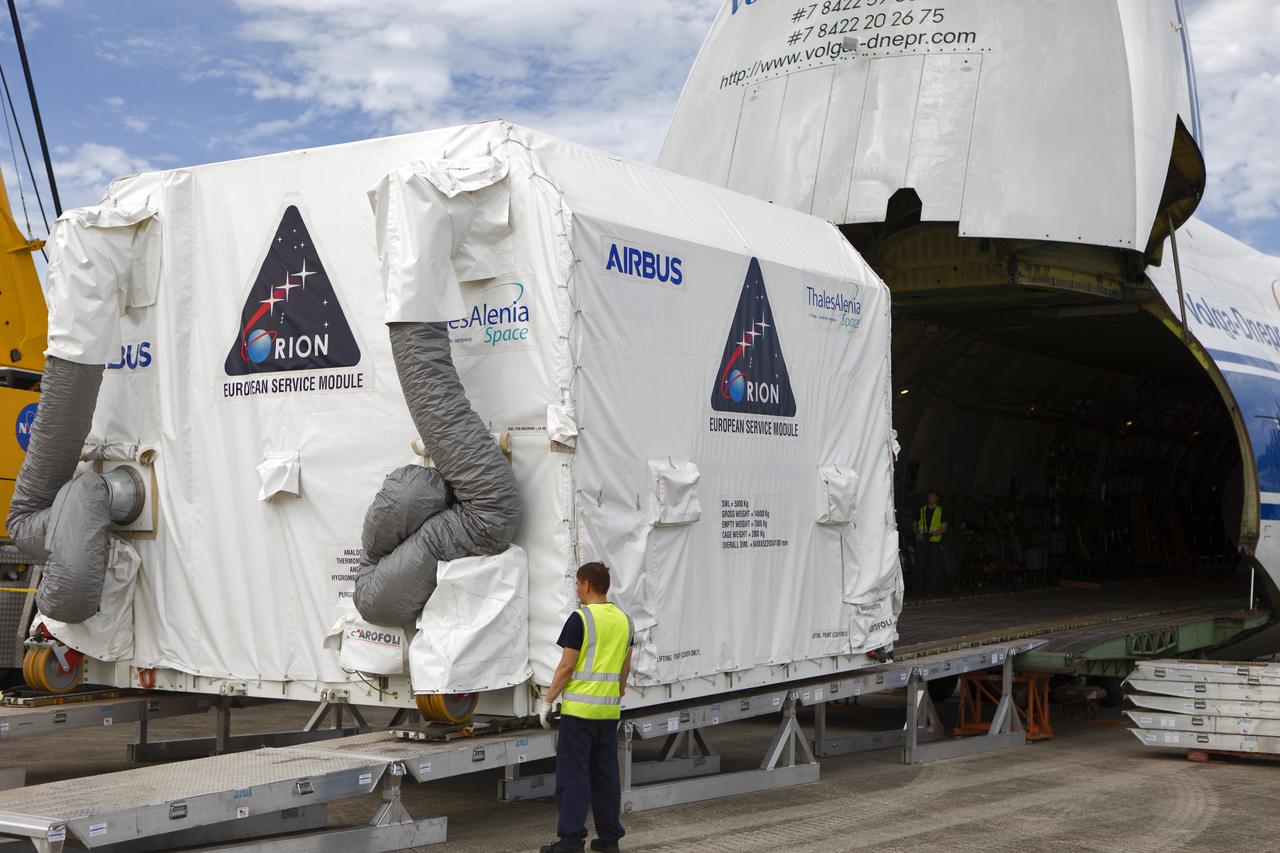

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
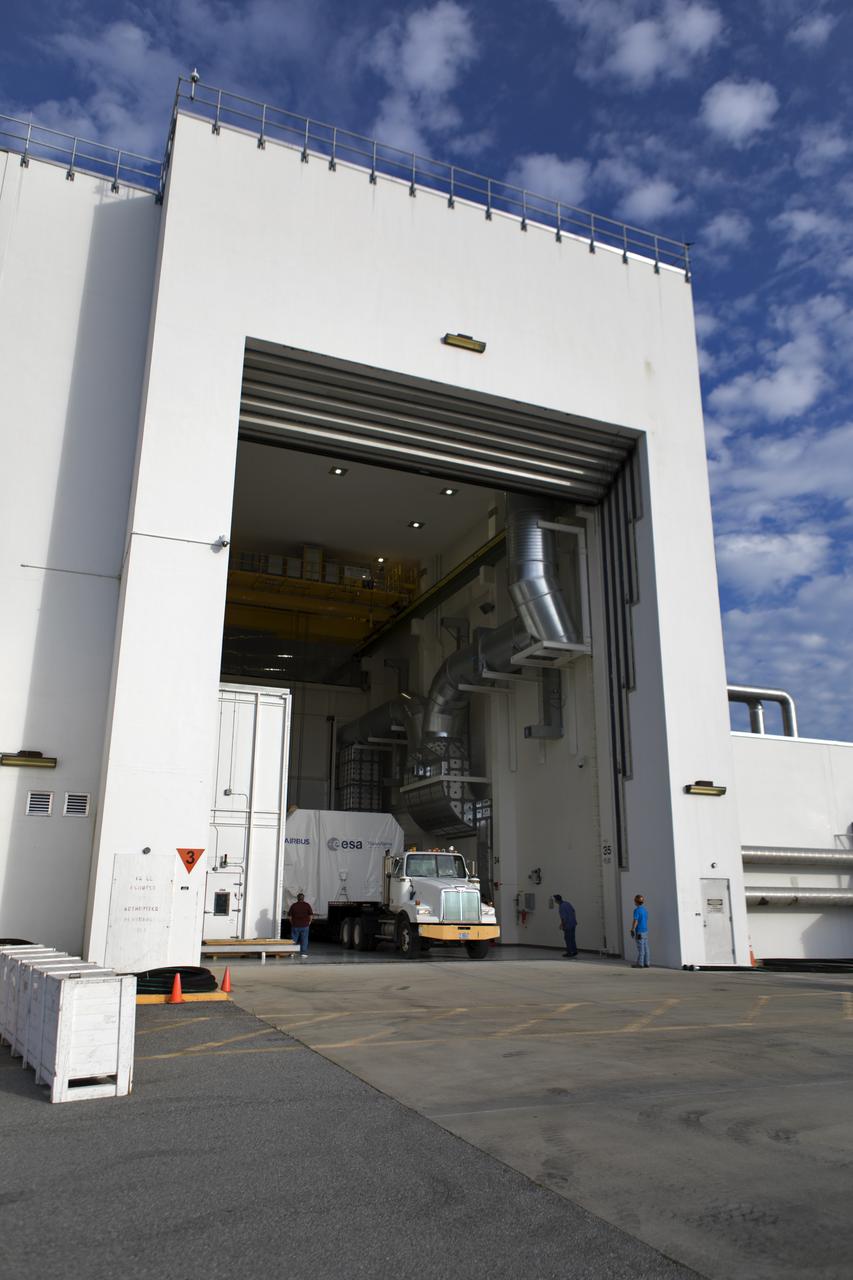

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container backs into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
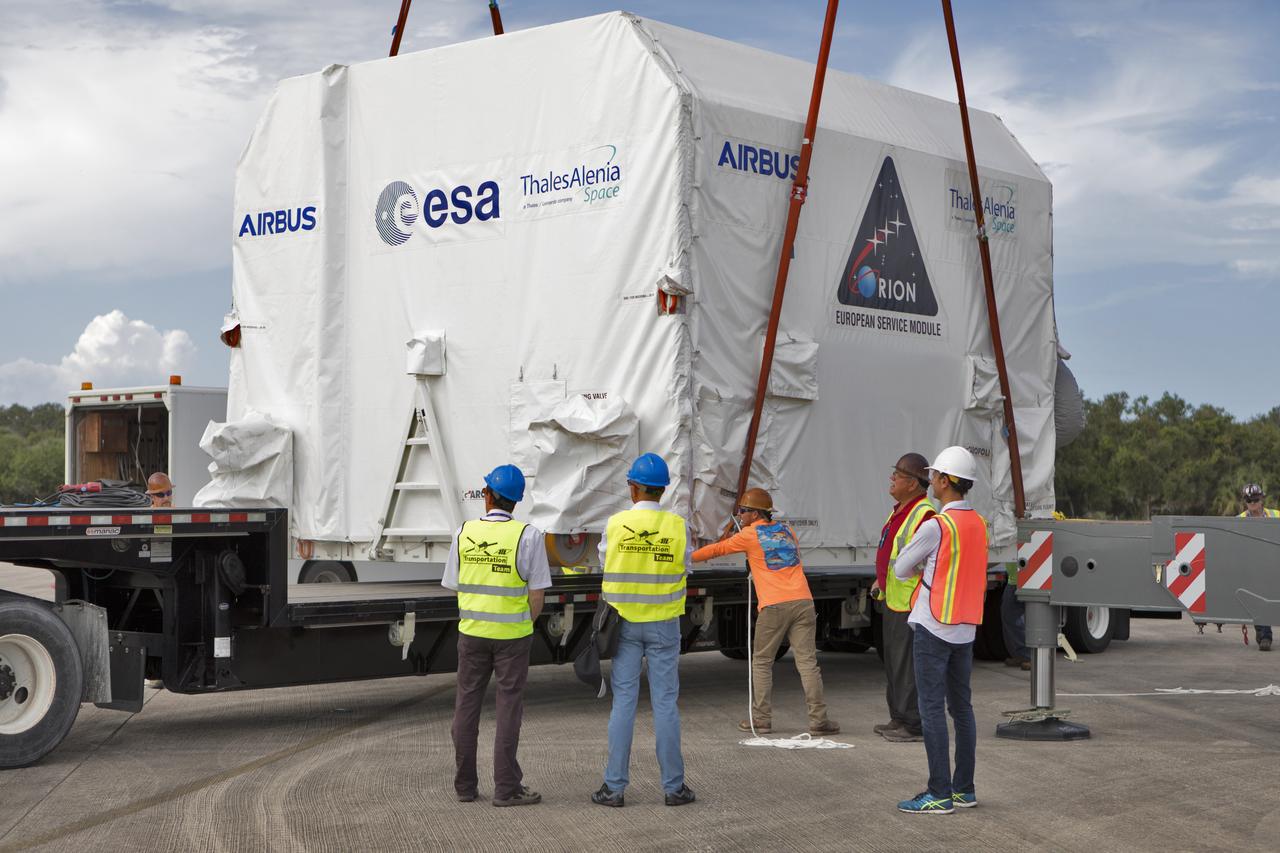

A crane lowers the shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) onto a flatbed truck at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
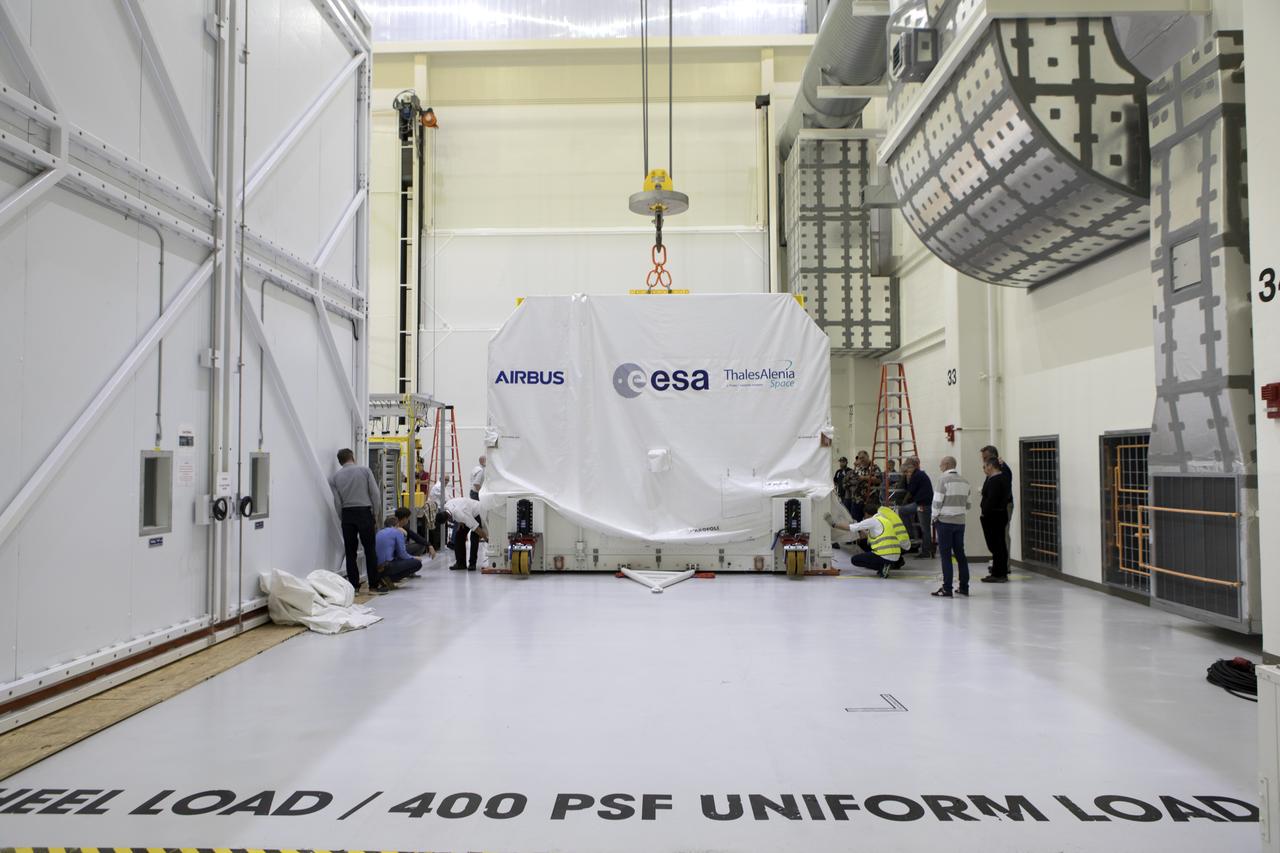

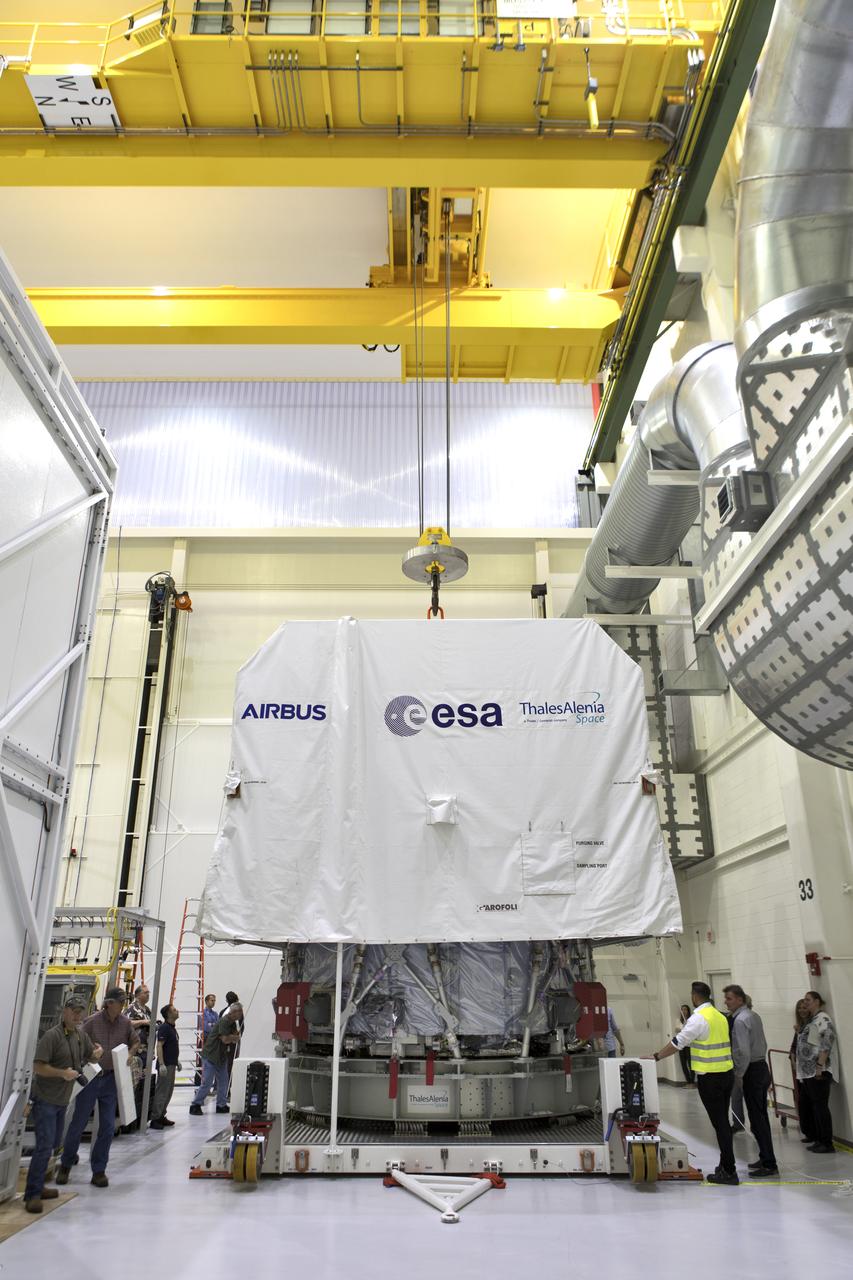
The European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM), in its shipping container, is inside the airlock at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
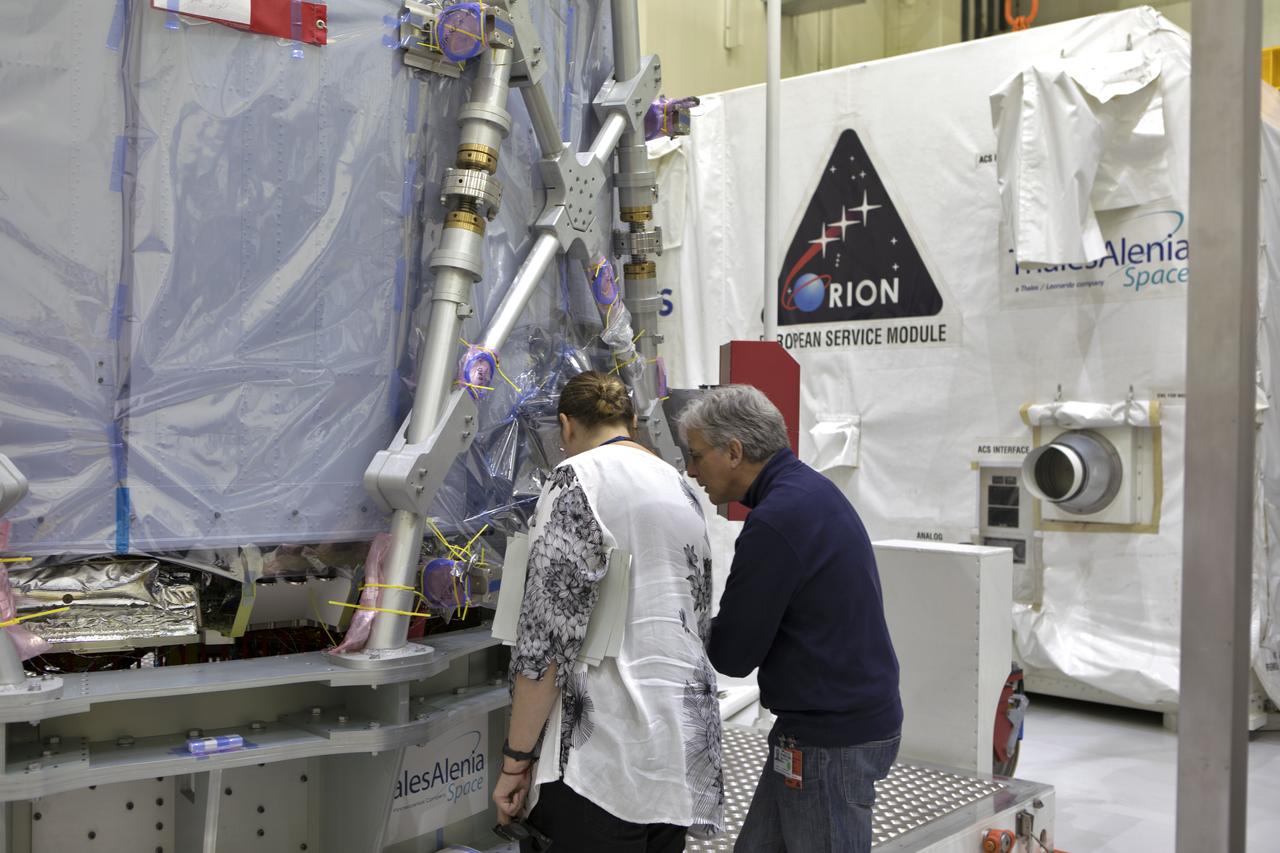

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers check the ESA European Service Module (ESM) after it is uncrated at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

The European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM), in its shipping container, is inside the airlock at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
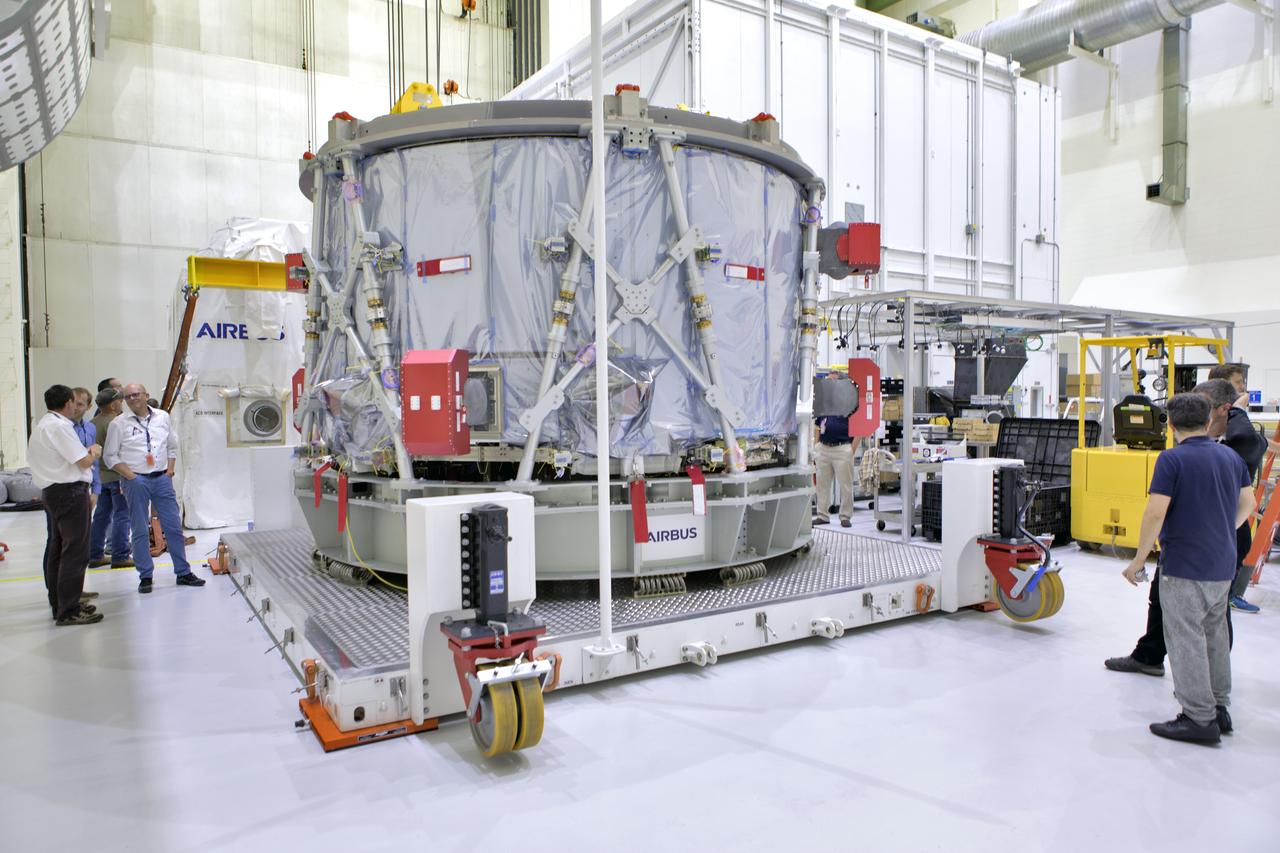

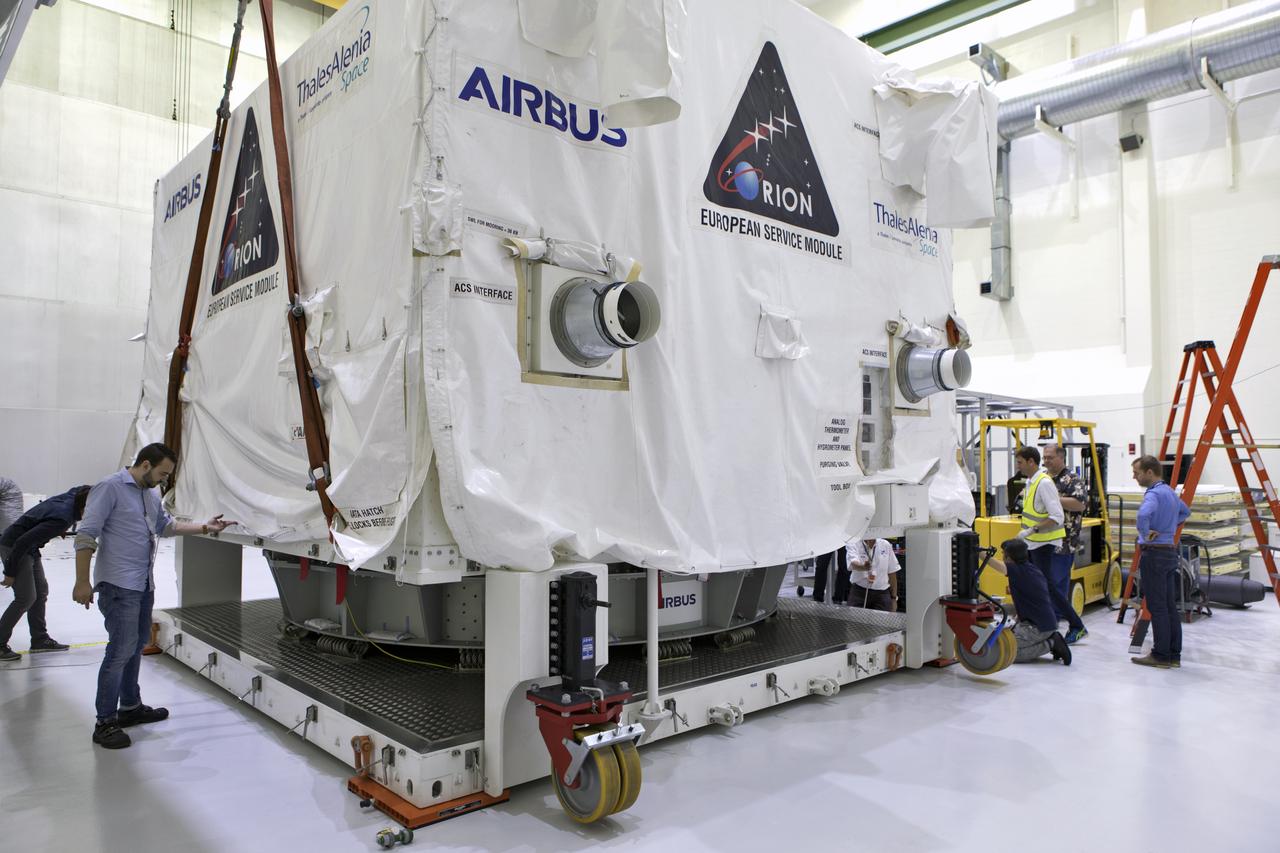
Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) is uncrated and ready for its move to the high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
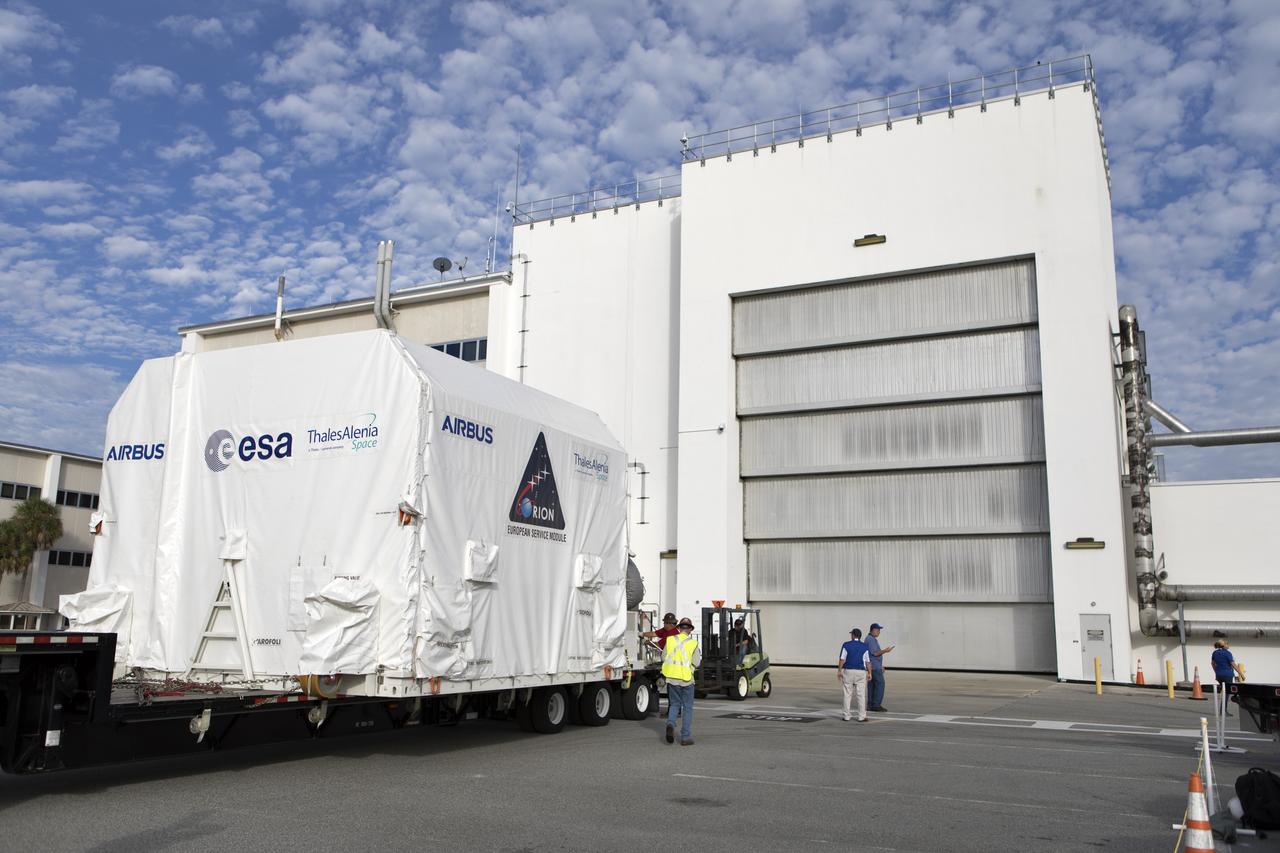

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
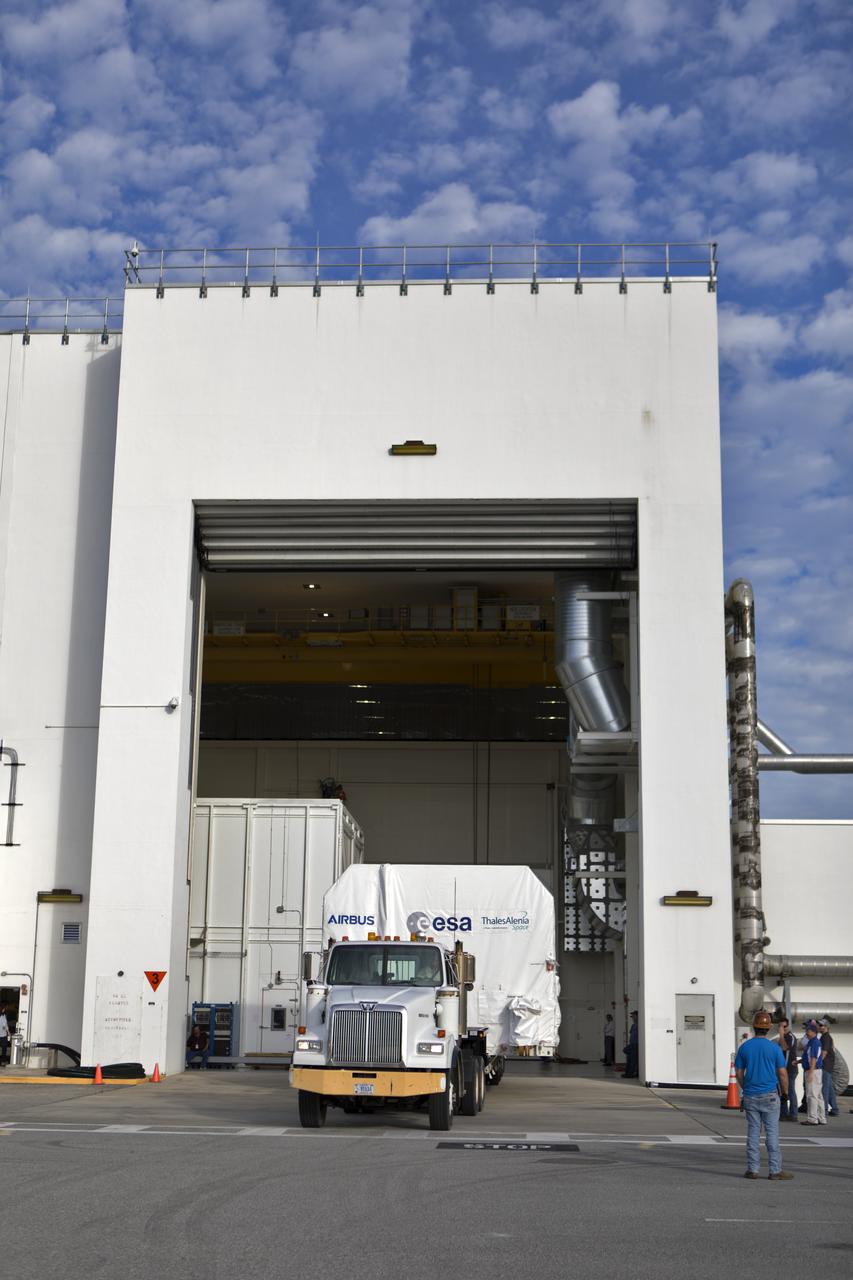

A flatbed truck carrying the European Space Agency's European Service Module (ESM) in its shipping container backs into the airlock of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on Nov. 6, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
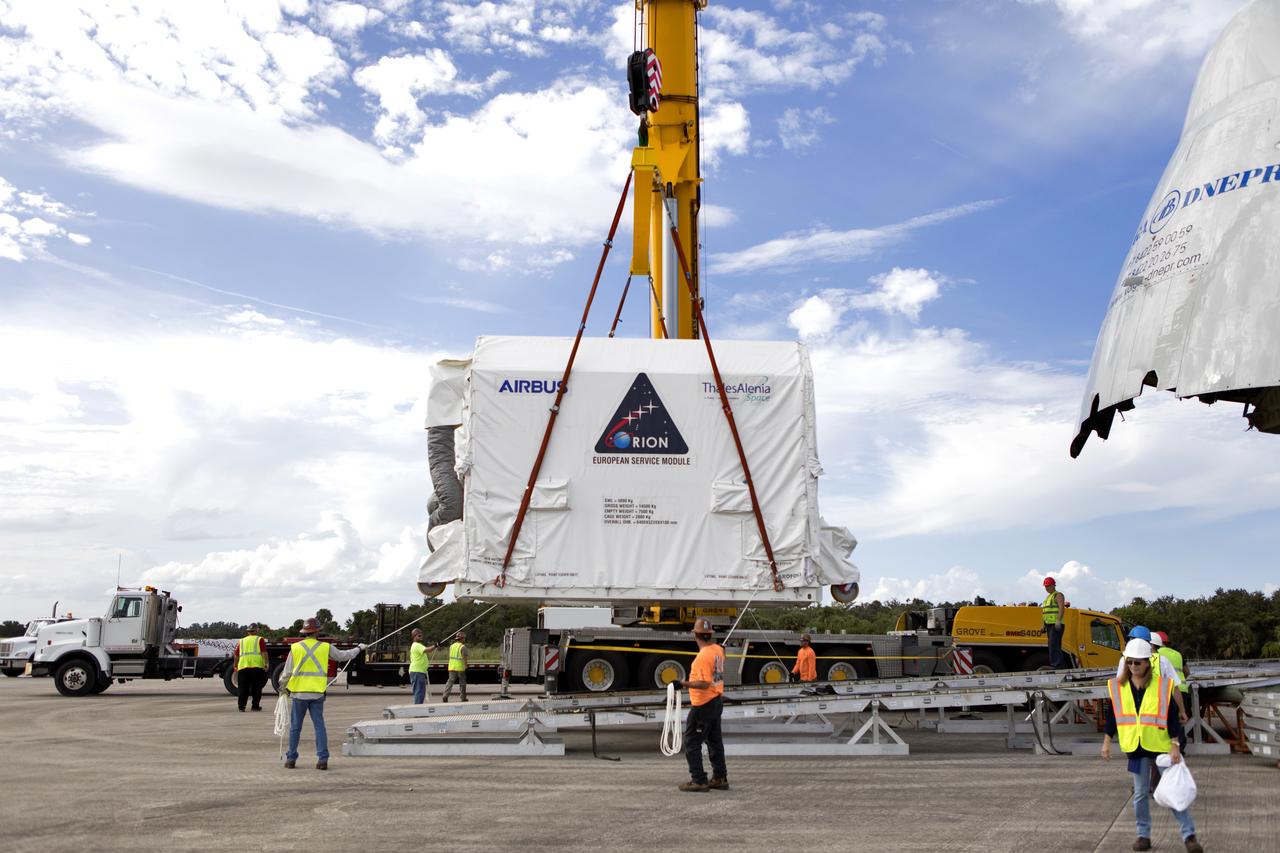

A crane lifts the shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) after it was moved out of the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay on Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus technicians begin to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
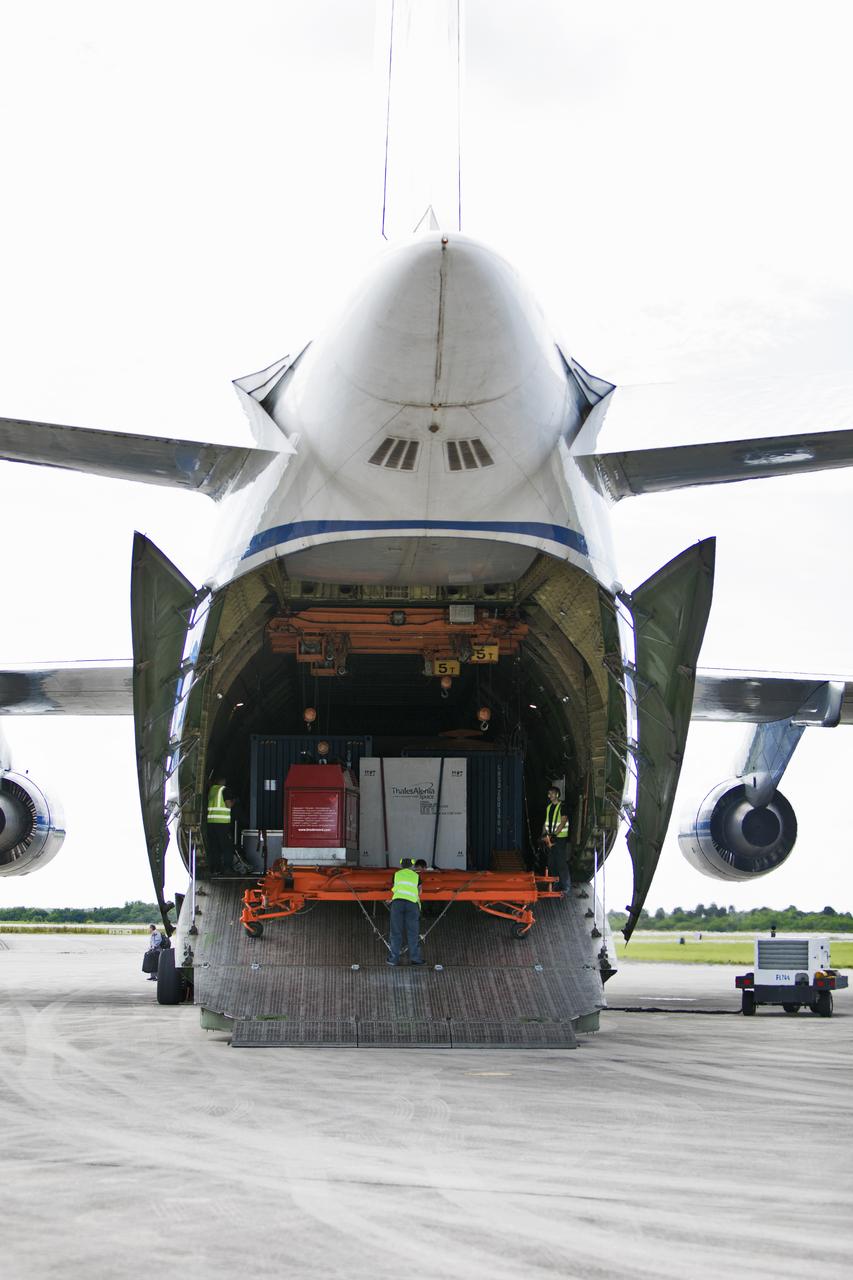

The Antonov cargo aircraft is open on the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) will be offloaded from the cargo hold. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
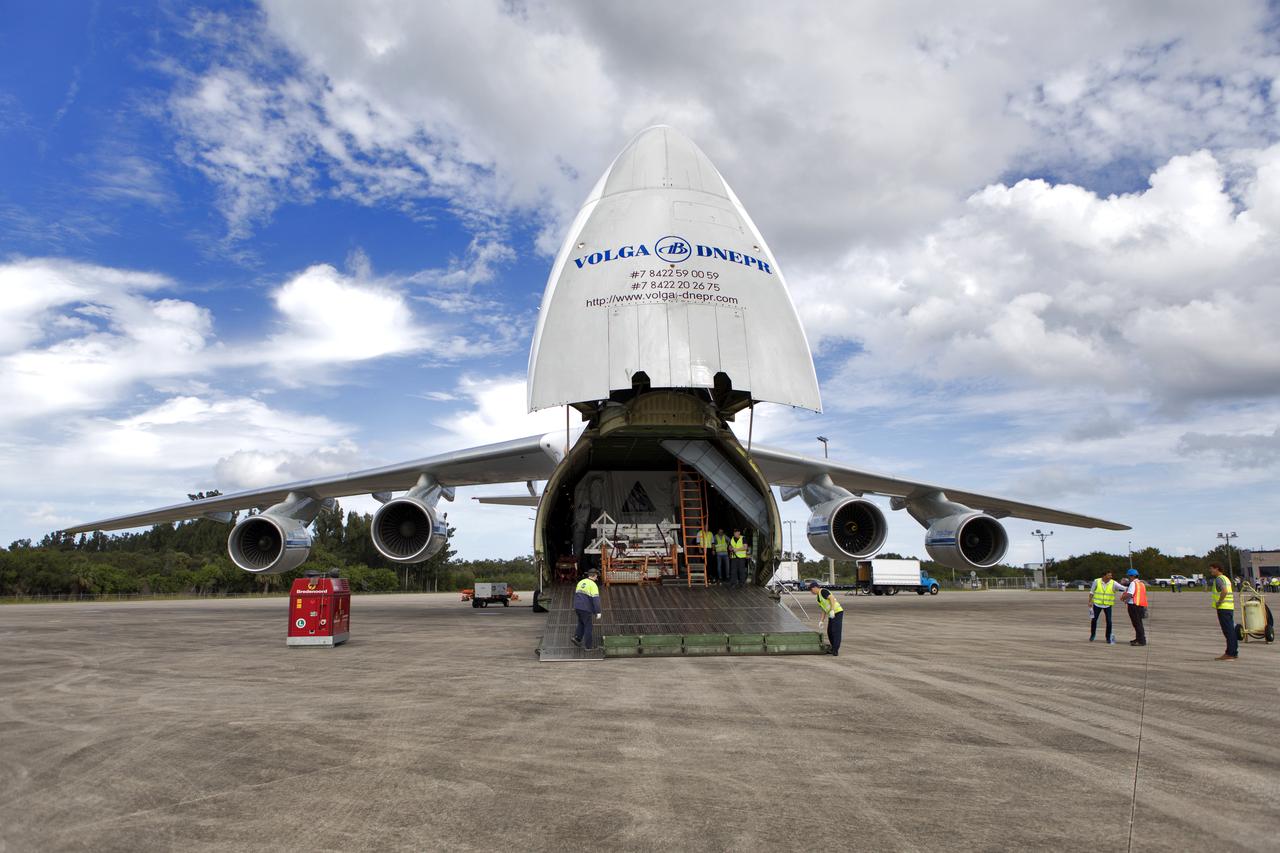

The Antonov cargo aircraft is open on the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) will be offloaded from the cargo hold. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
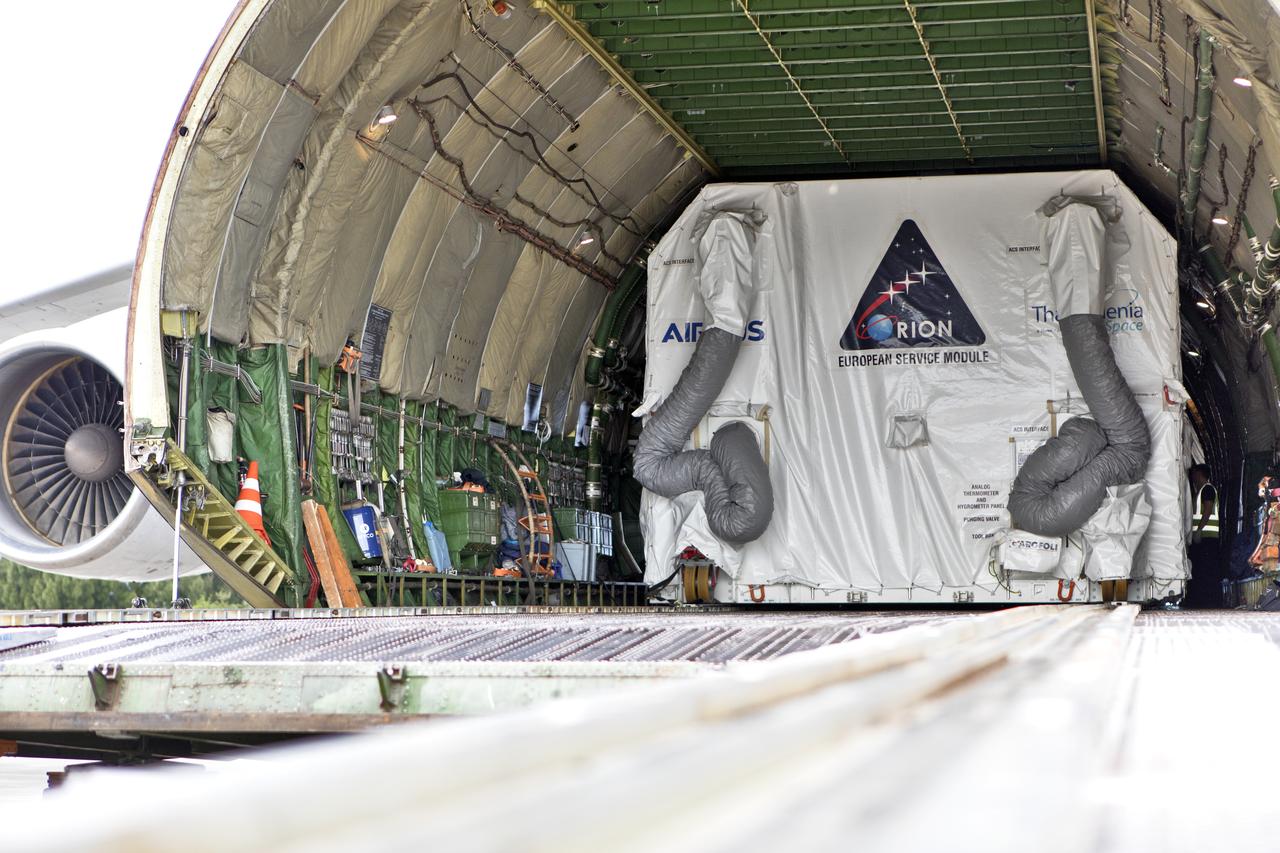

The shipping container holding the European Service Module (ESM) is in view inside the cargo hold of the Antonov cargo aircraft at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The ESM for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) will be offloaded from the cargo hold. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
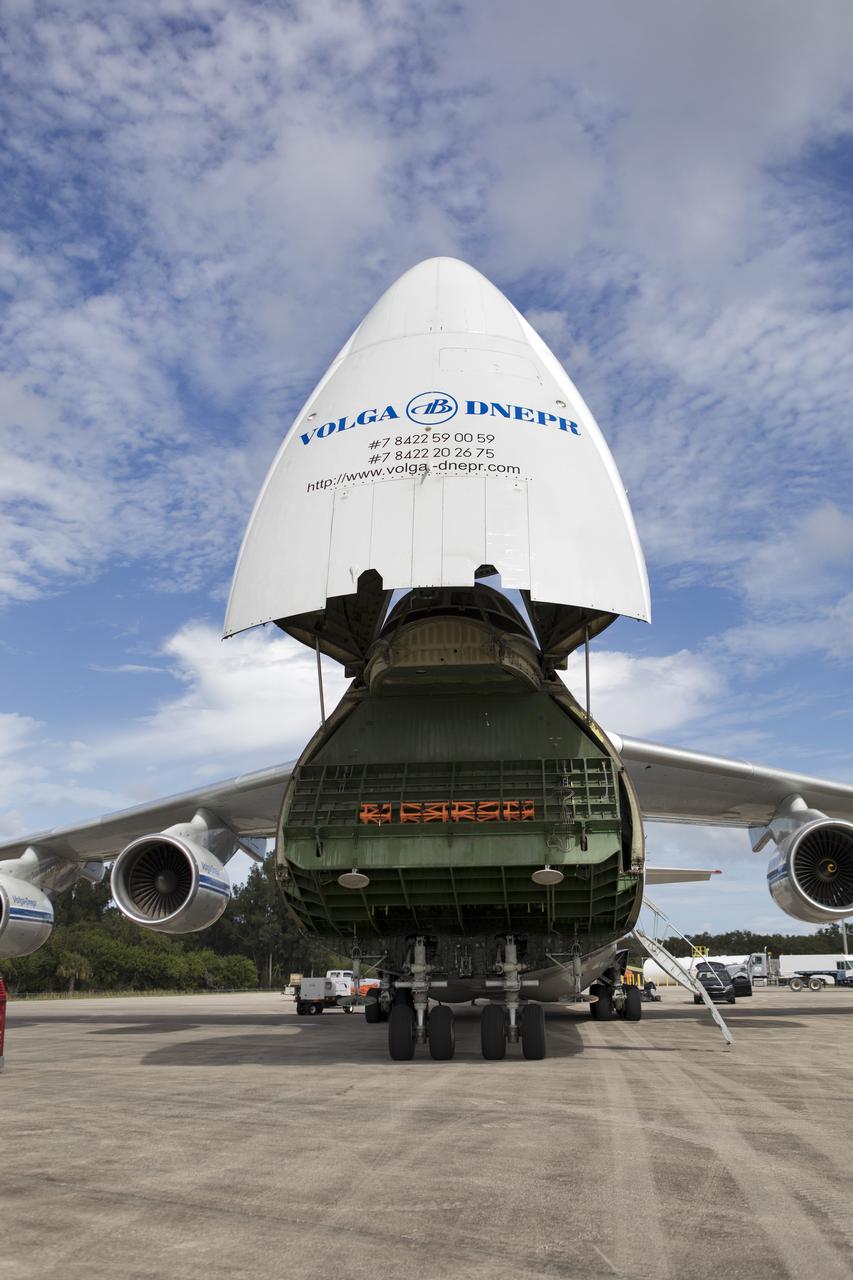

The Antonov cargo aircraft is open on the tarmac at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 6, 2018. The European Service Module (ESM) for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) will be offloaded from the cargo hold. The ESM, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
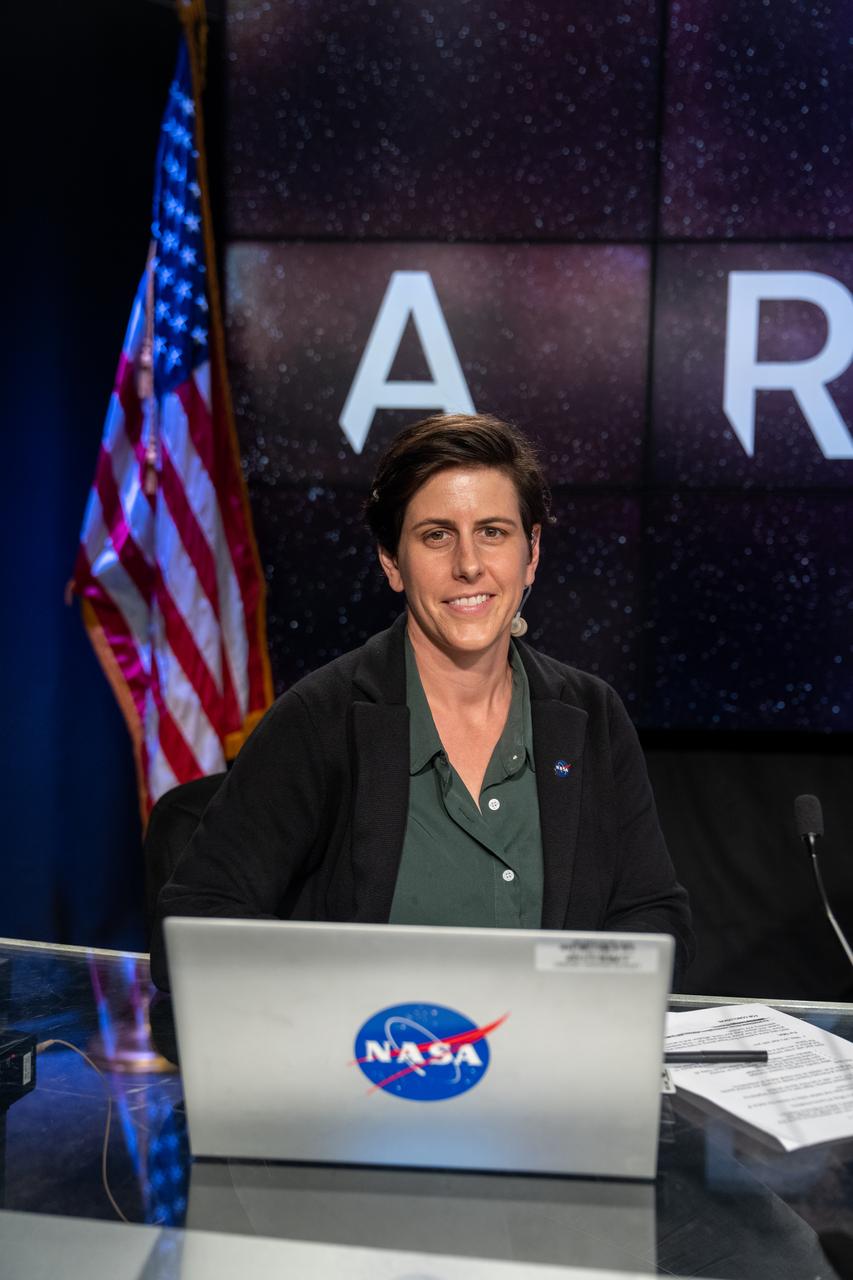

Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications, moderates a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
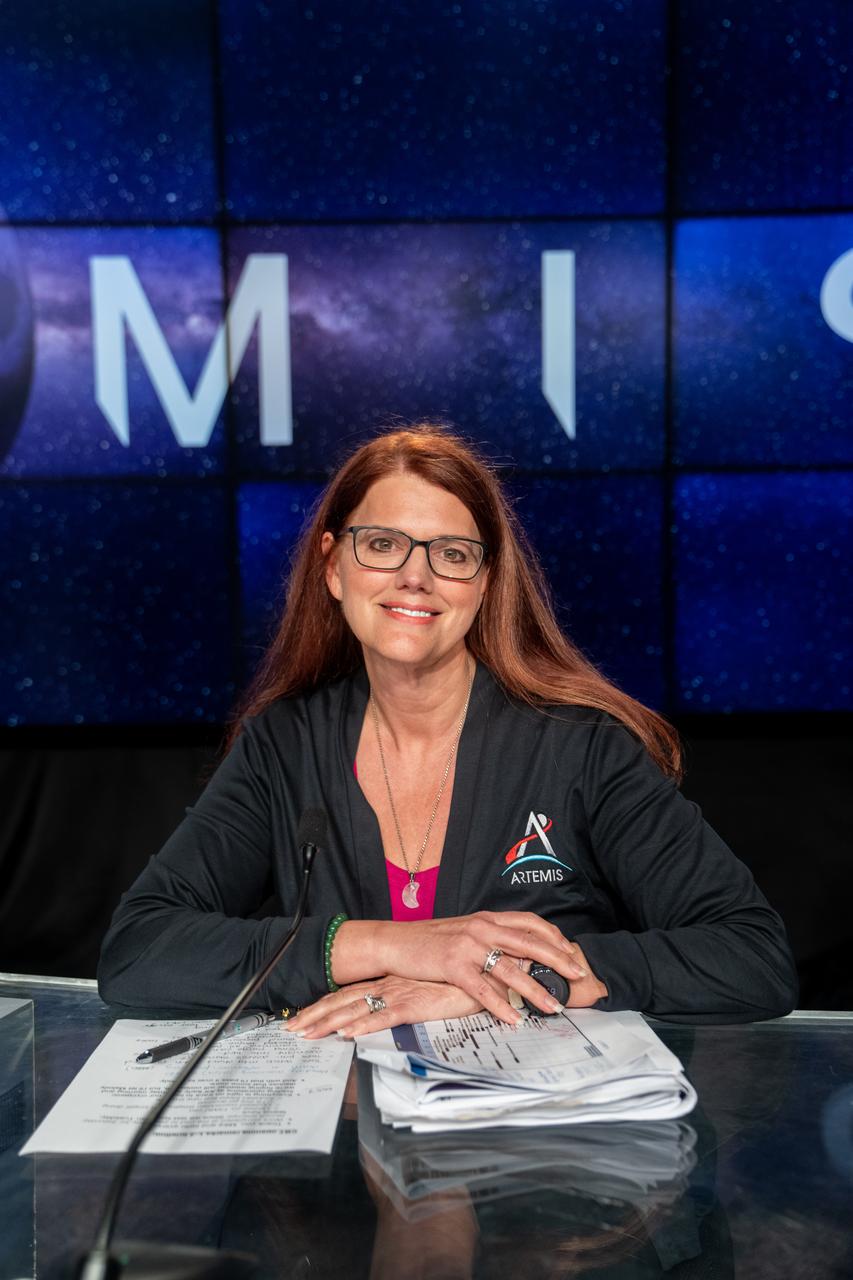

Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis I launch director, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
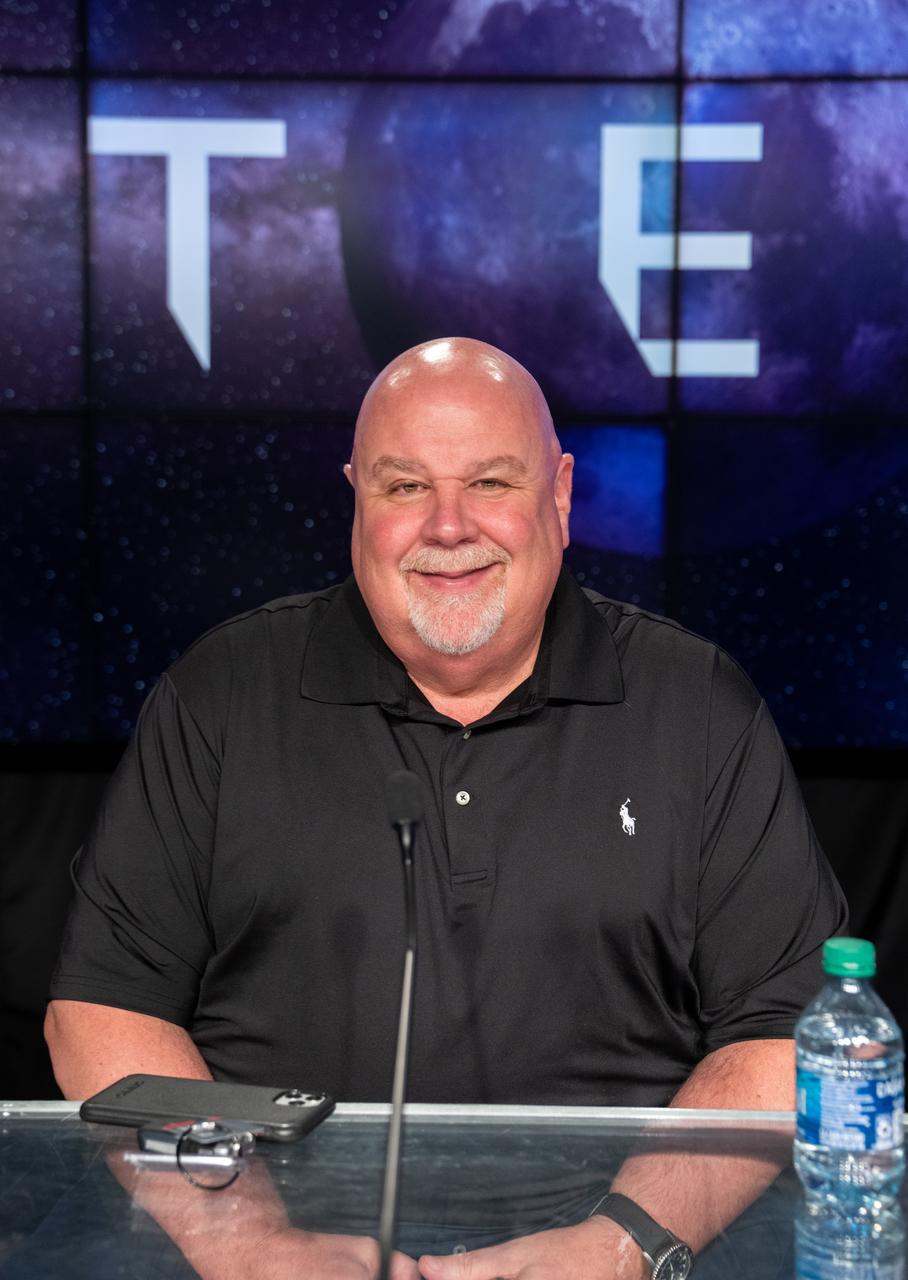

John Honeycutt, Space Launch System program manager, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
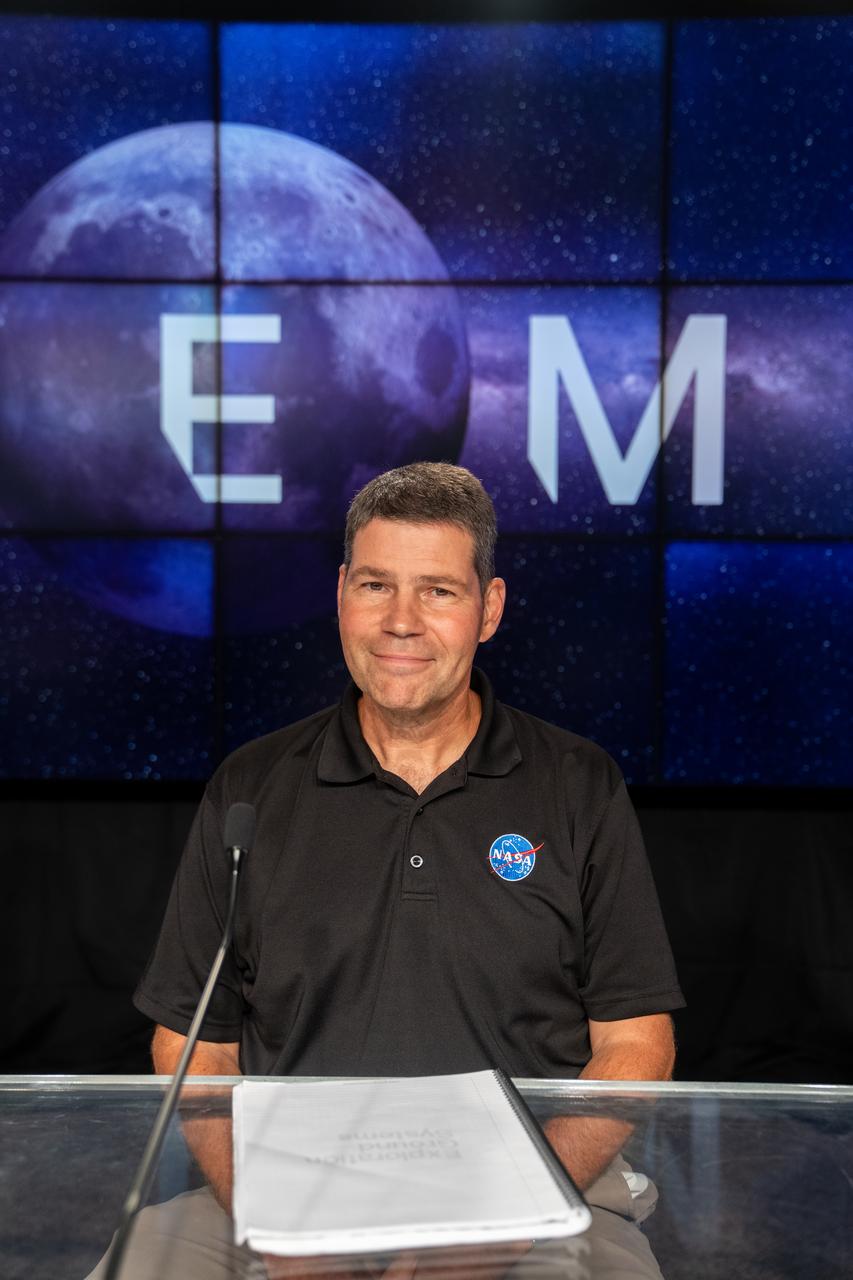

John Blevins, Space Launch System chief engineer, participates in a prelaunch media briefing following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
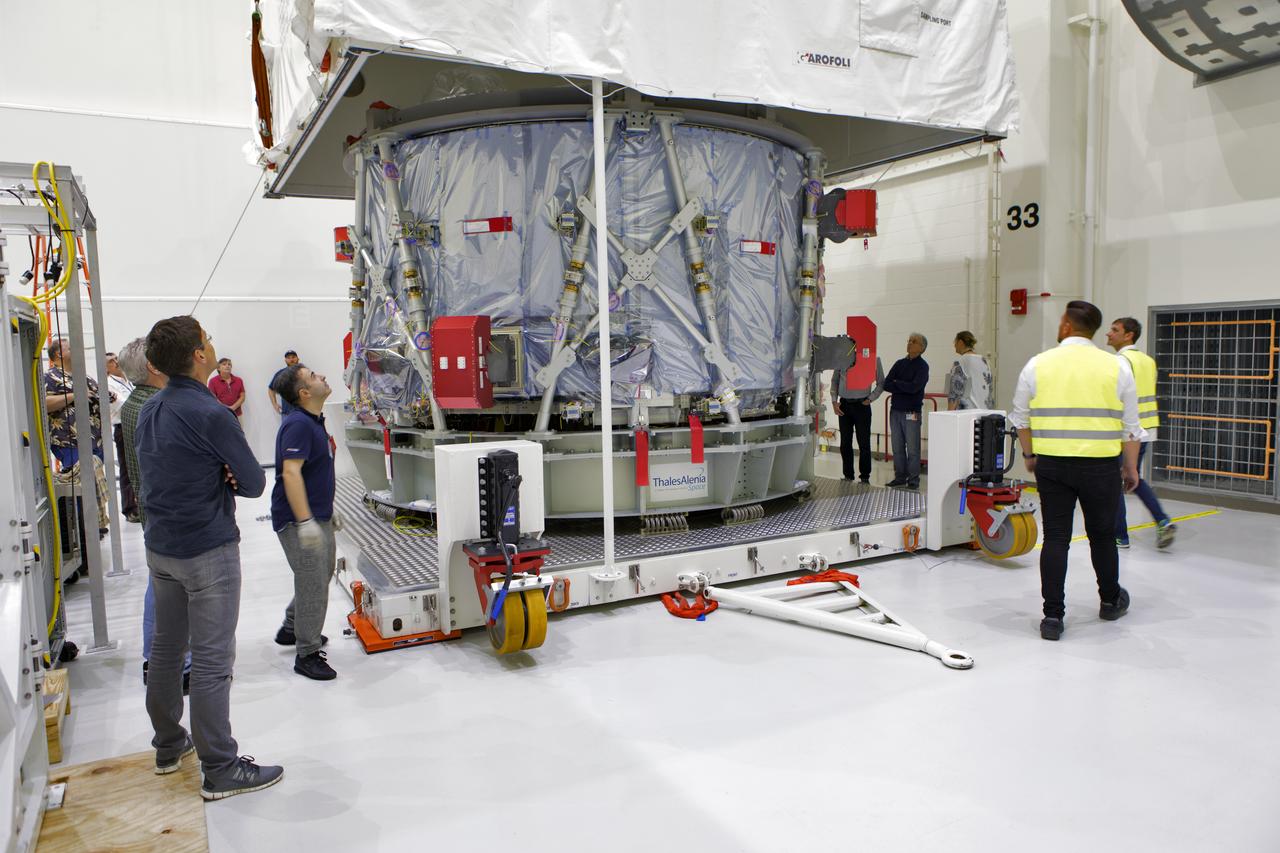

Inside the airlock in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay On Nov. 6, 2018, European Space Agency (ESA) and Airbus engineers and technicians watch as a crane is used to uncrate the ESA's European Service Module (ESM) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ESM will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.

Artist rendering of NASA’s Stardust returning to Earth. Stardust is the first U.S. space mission dedicated to the exploration of a comet, and the first robotic mission designed to return extraterrestrial material from outside the orbit of the Moon.
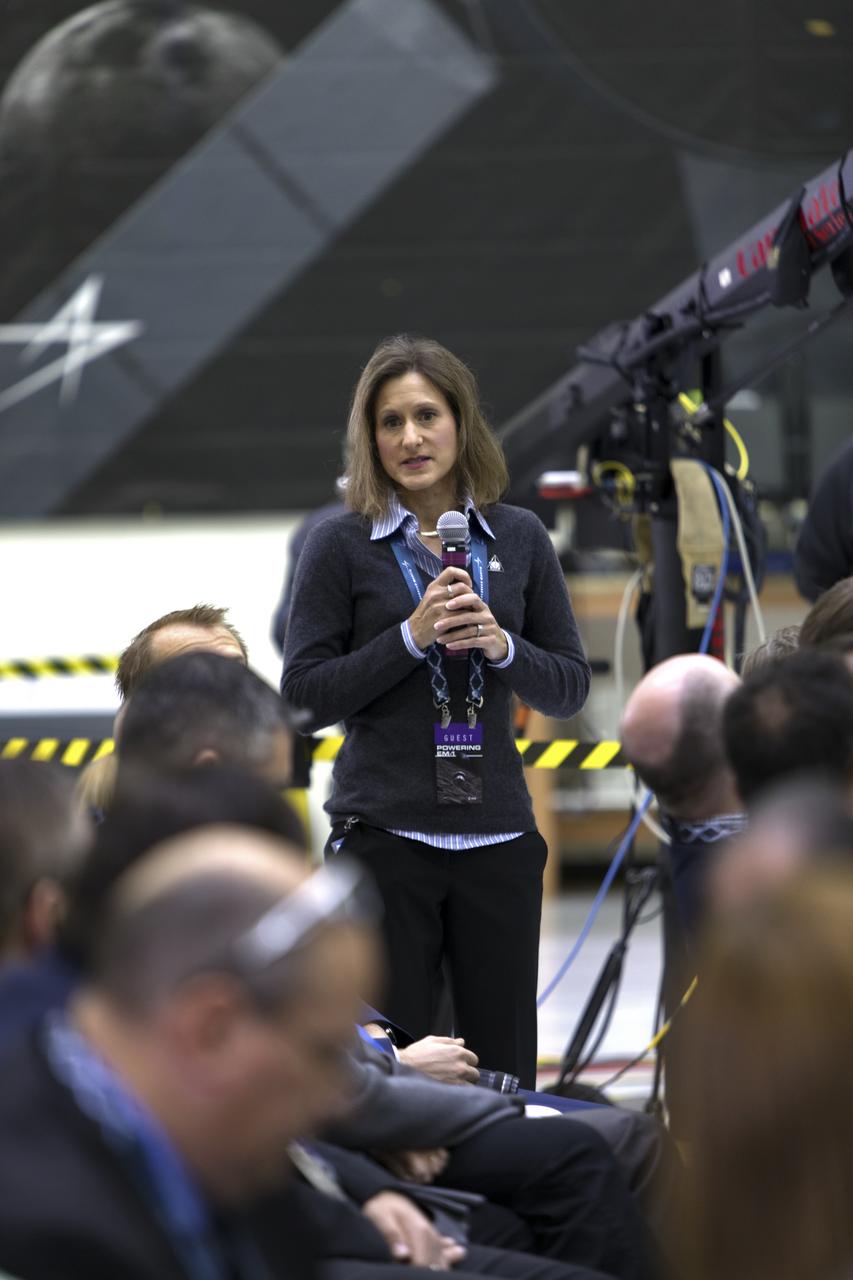

During a "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 16, 2018, Amy Marasia, Orion Crew Module assembly lead for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), explains the next steps in processing Orion and the European Service Module (ESM). The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
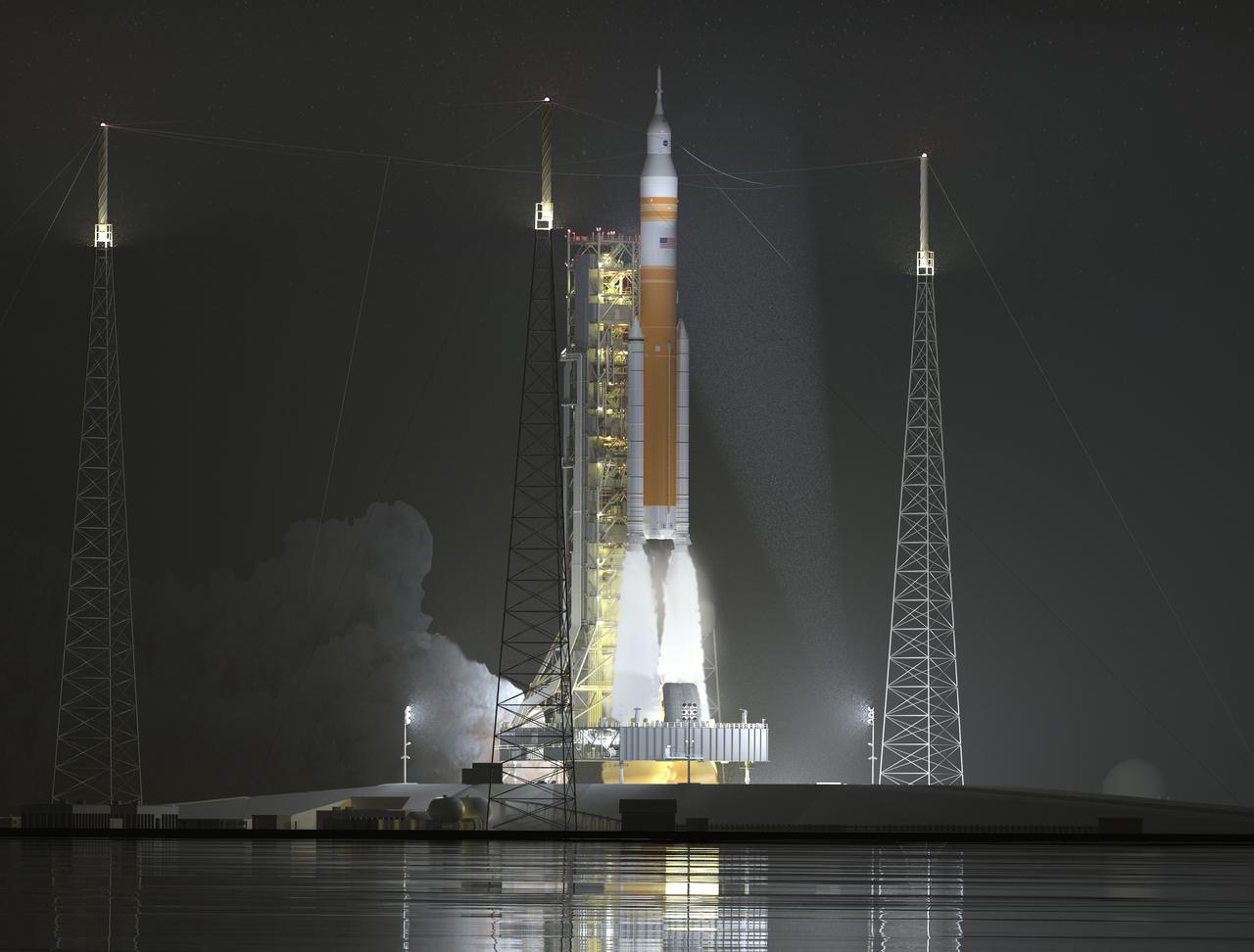

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant night launch. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA) In album: B1B_Crew_SLS
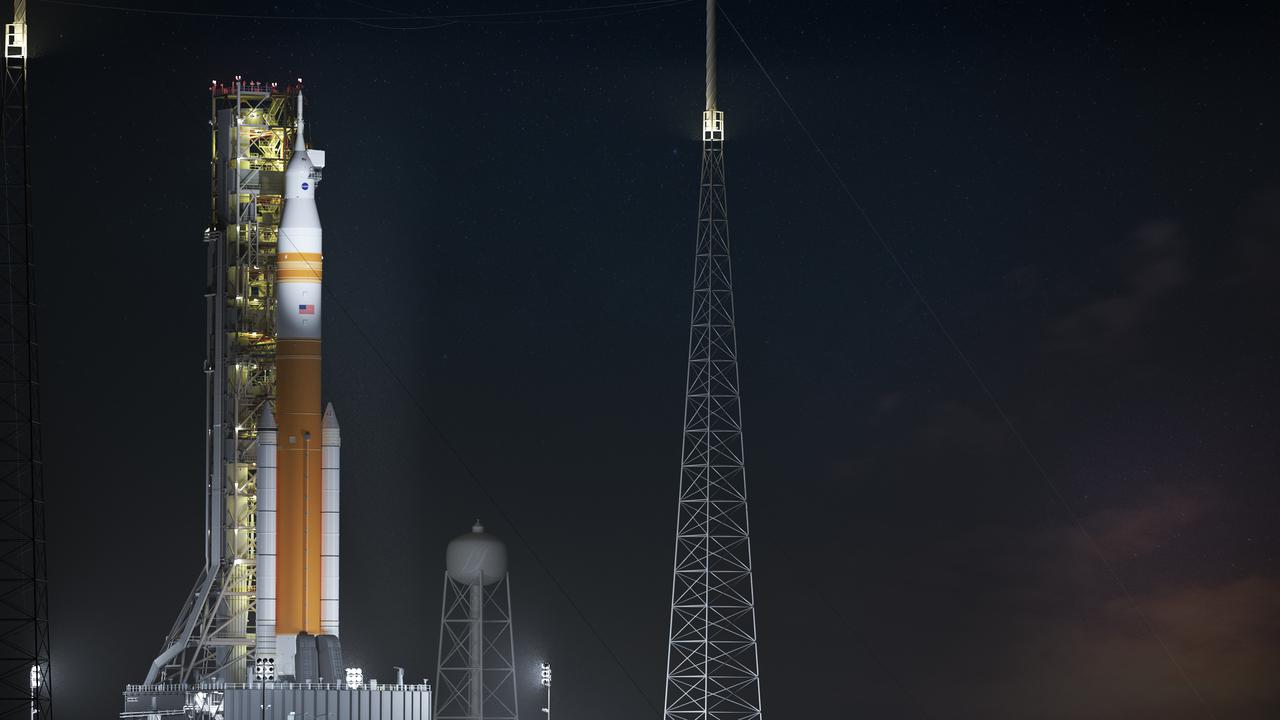

Illustration of nighttime scene of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant on Pad 39B.. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)

Seen here, is a nighttime rendering of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant positioned on the mobile launcher. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
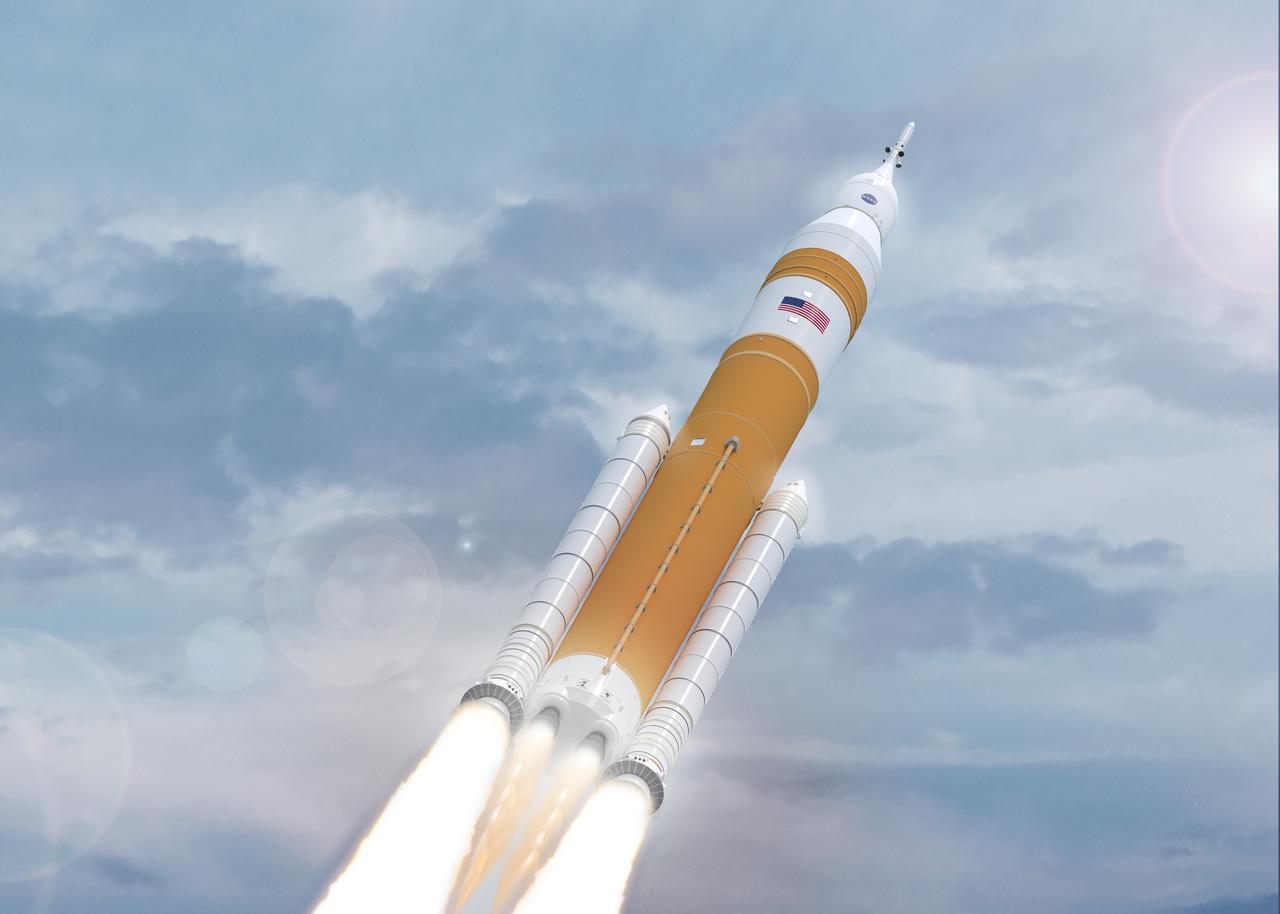

Illustration of evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant in flight. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
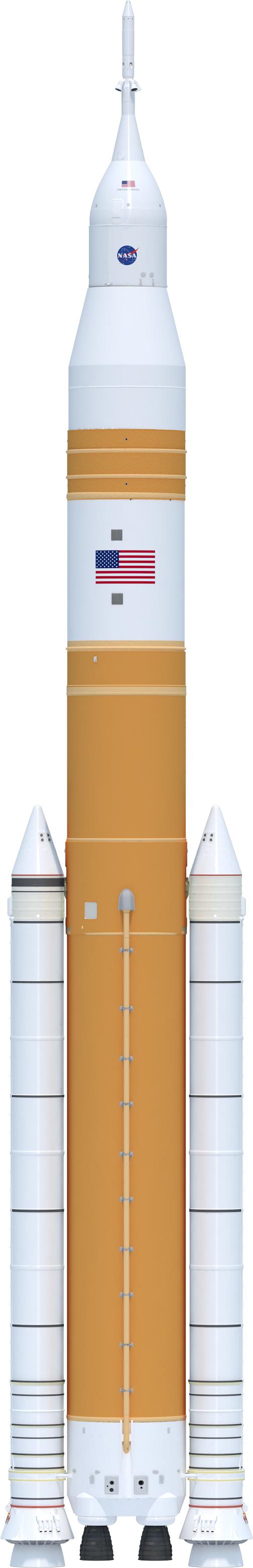

Illustration of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant outer mold line. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
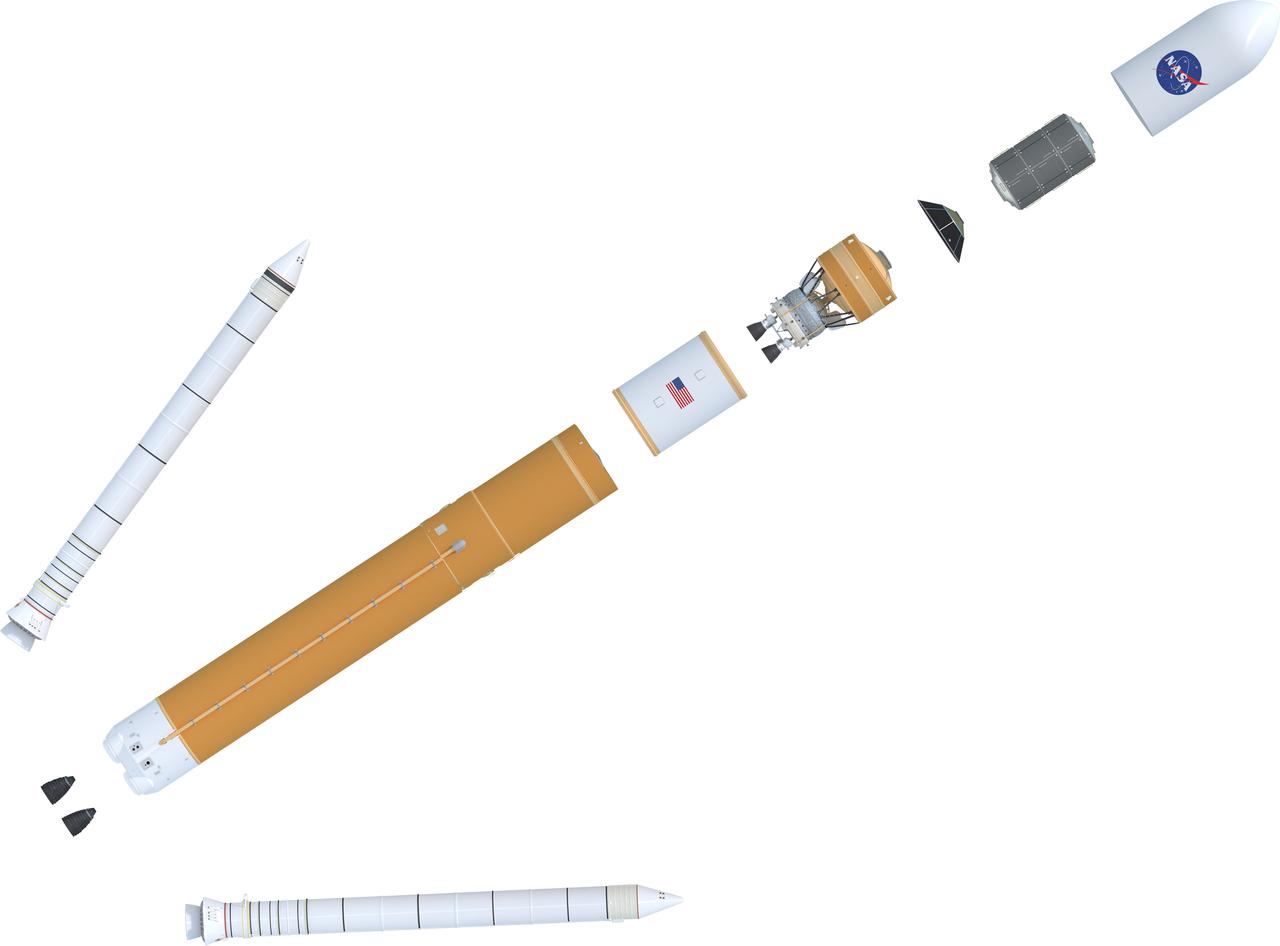
Expanded view illustration of elements of the evolved SLS Block 1B Crew variant. This configuration of the rocket, with the Exploration Upper Stage, will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
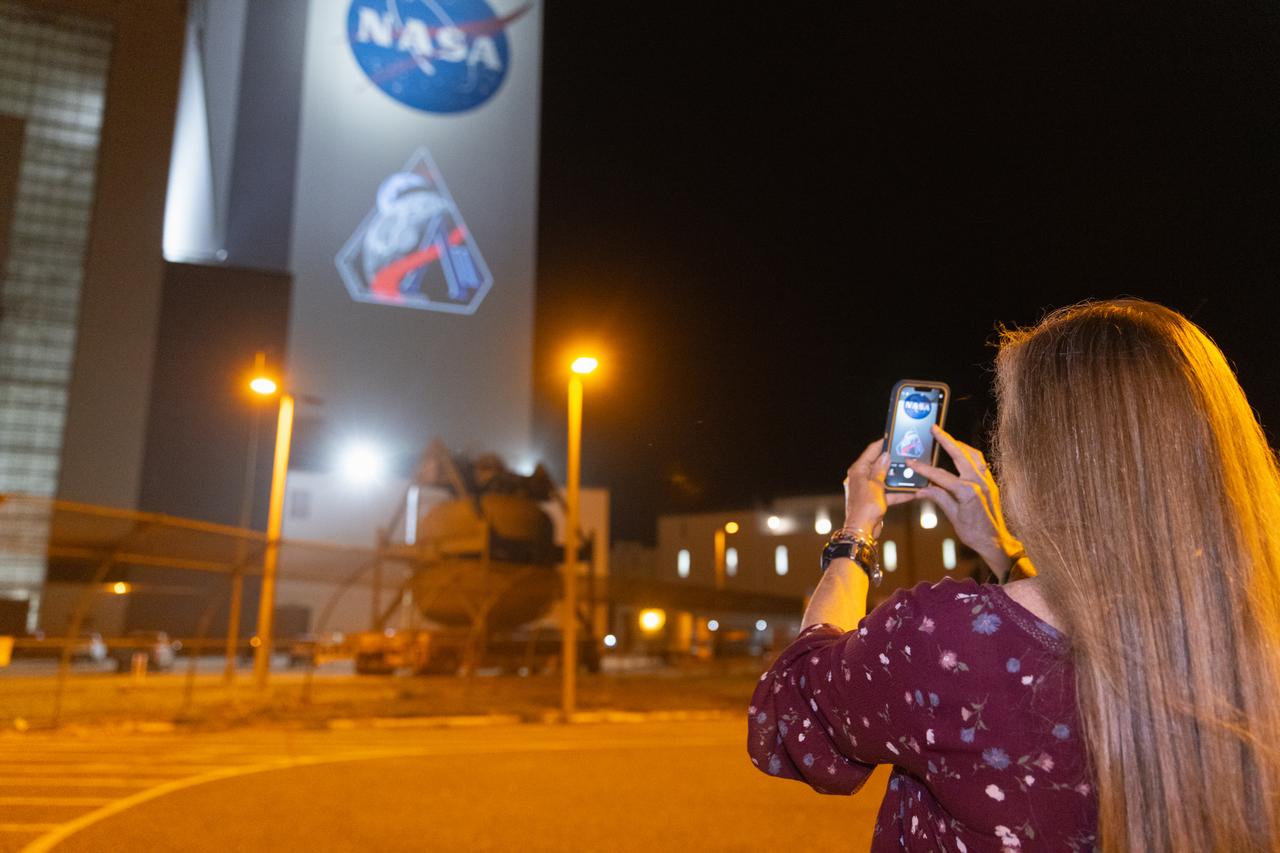

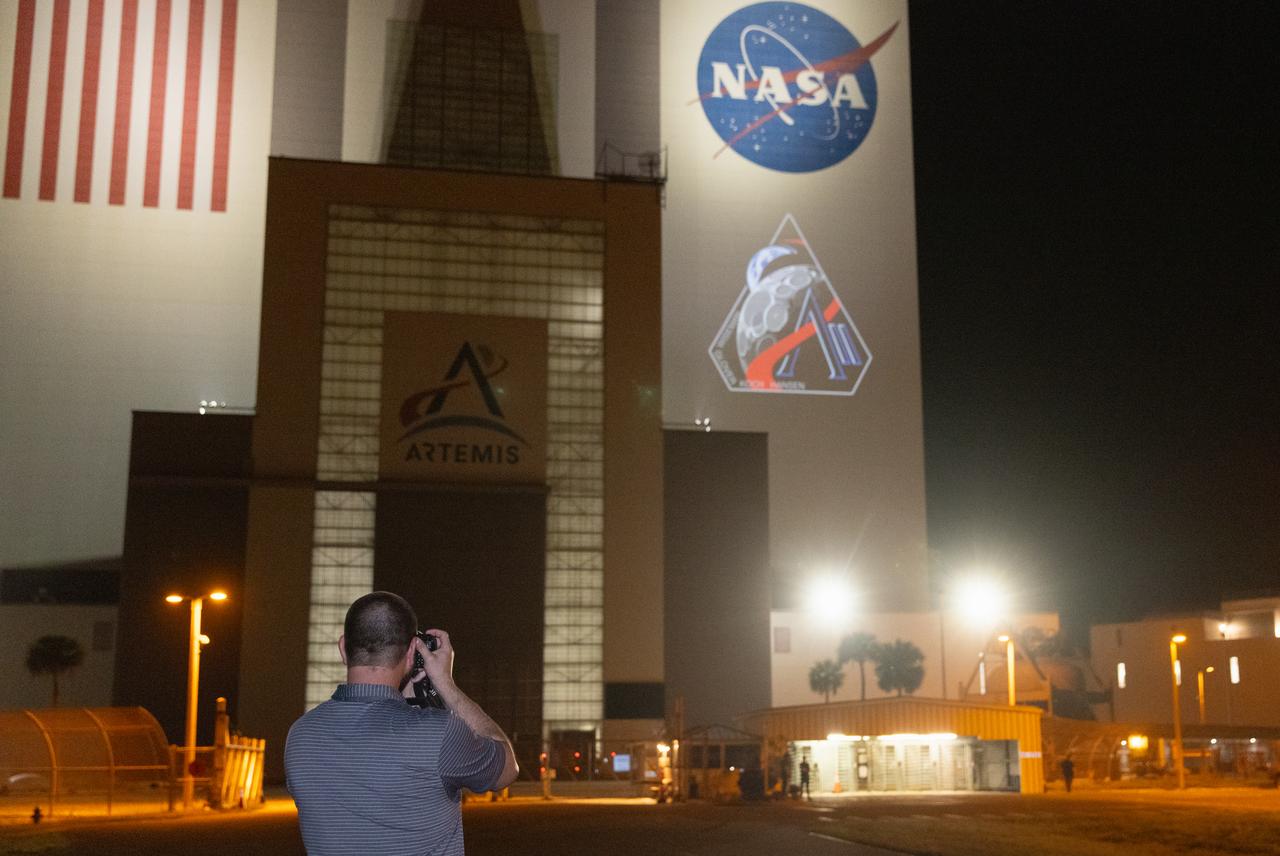
Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida take photos of the official Artemis II mission crew insignia projected on the exterior of the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
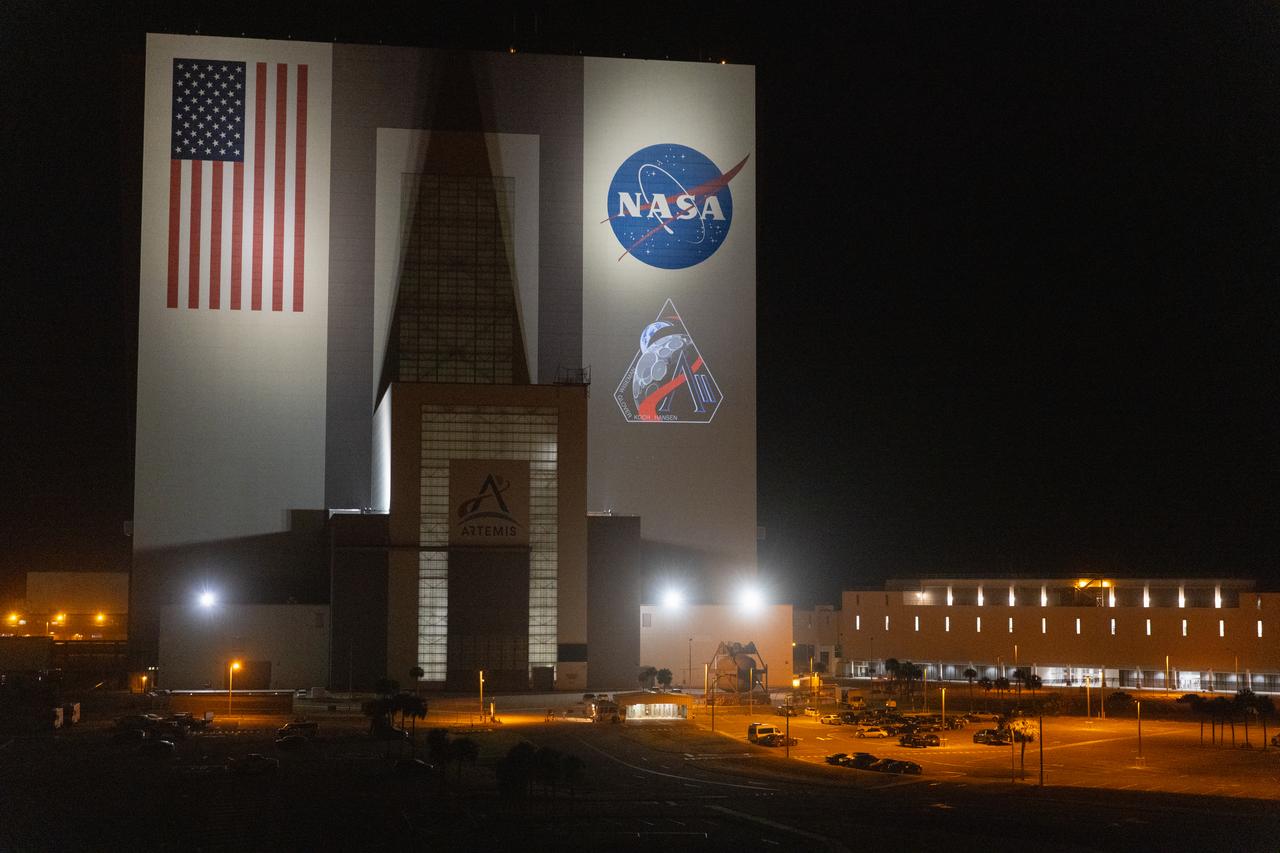

The official Artemis II mission crew insignia is projected on the exterior of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
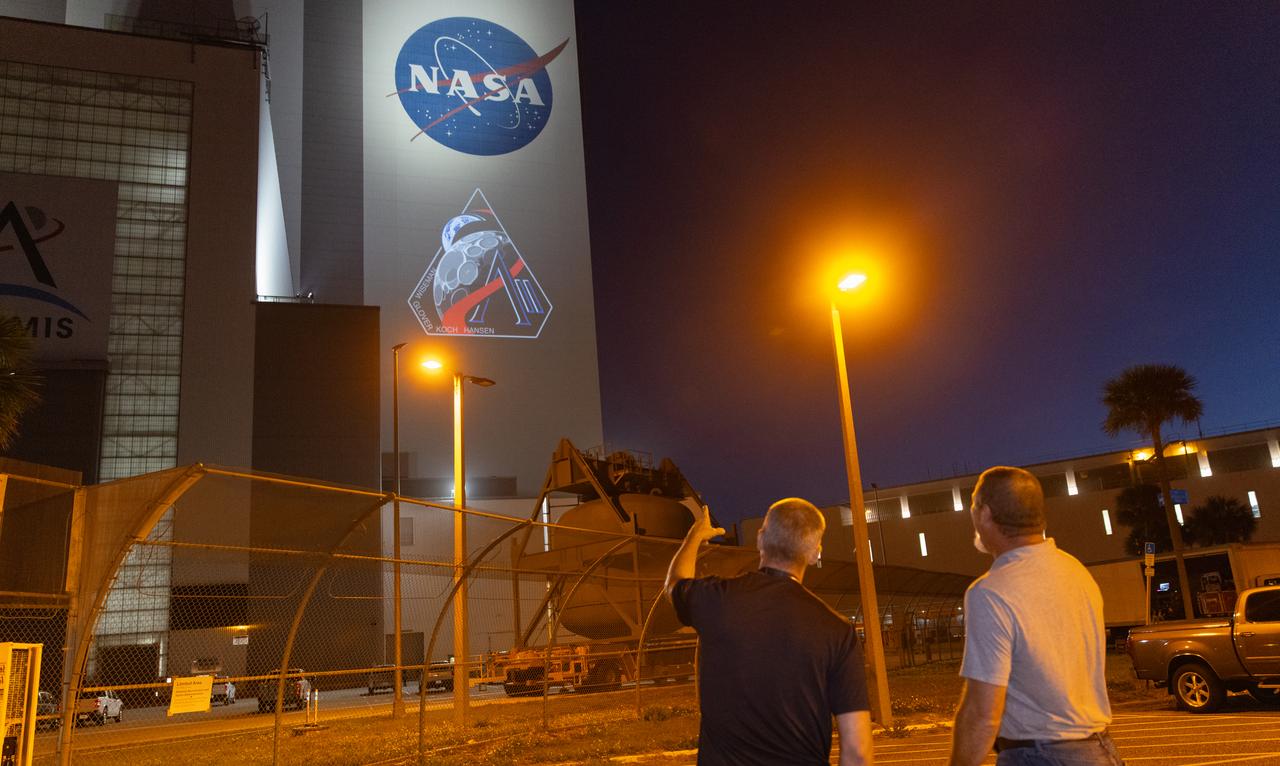

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida take photos of the official Artemis II mission crew insignia projected on the exterior of the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.

The official Artemis II mission crew insignia is projected on the exterior of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.

The official Artemis II mission crew insignia is projected on the exterior of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
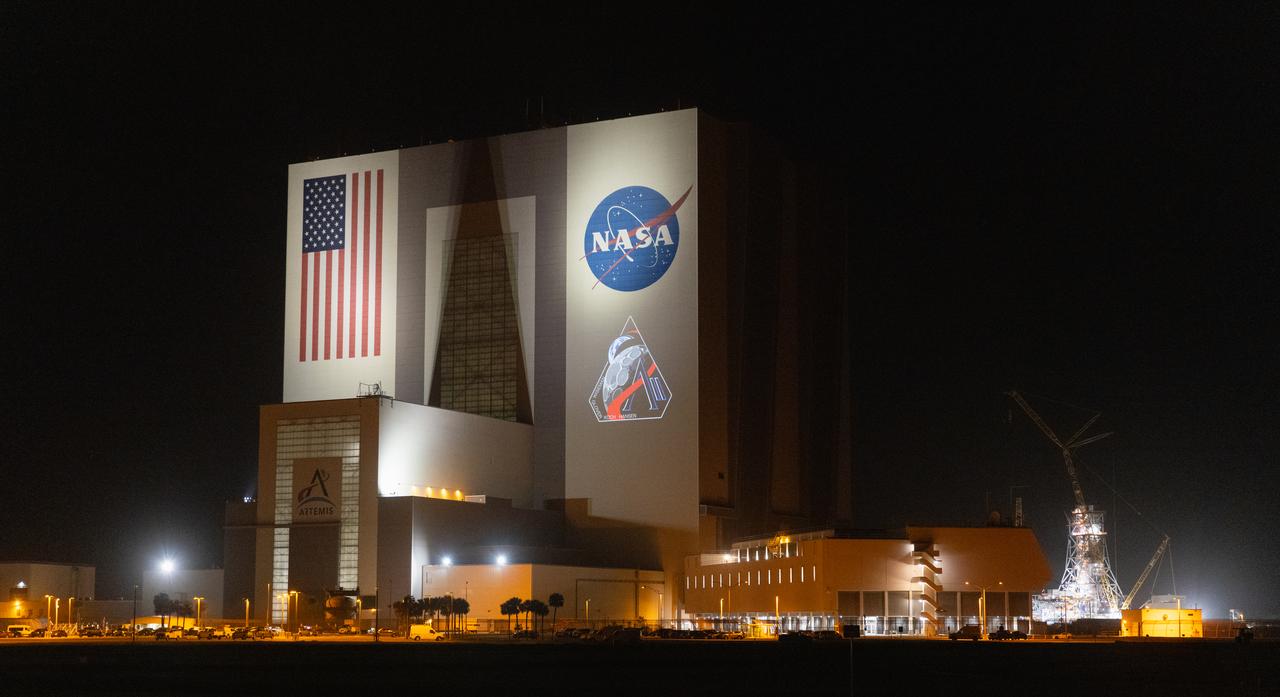

The official Artemis II mission crew insignia is projected on the exterior of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
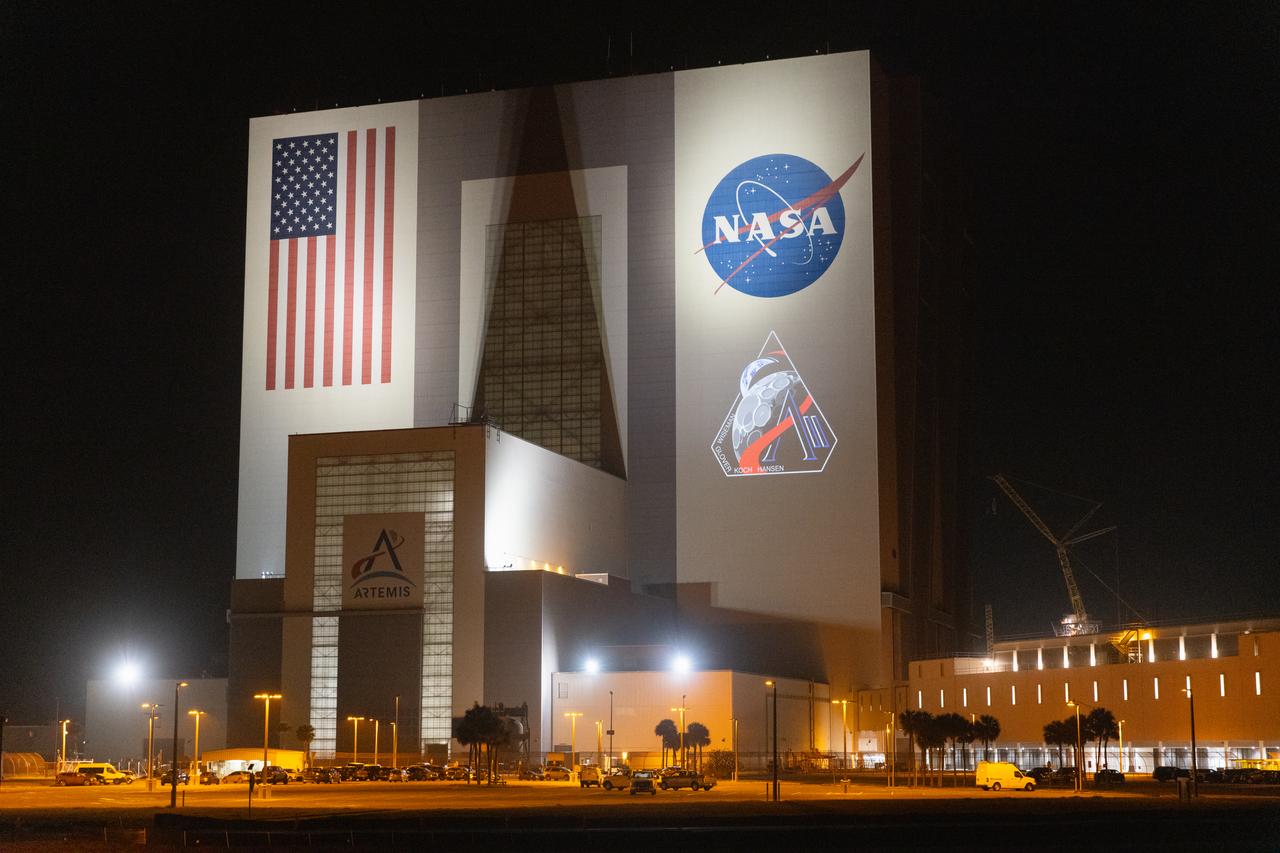

The official Artemis II mission crew insignia is projected on the exterior of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida take photos of the official Artemis II mission crew insignia projected on the exterior of the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
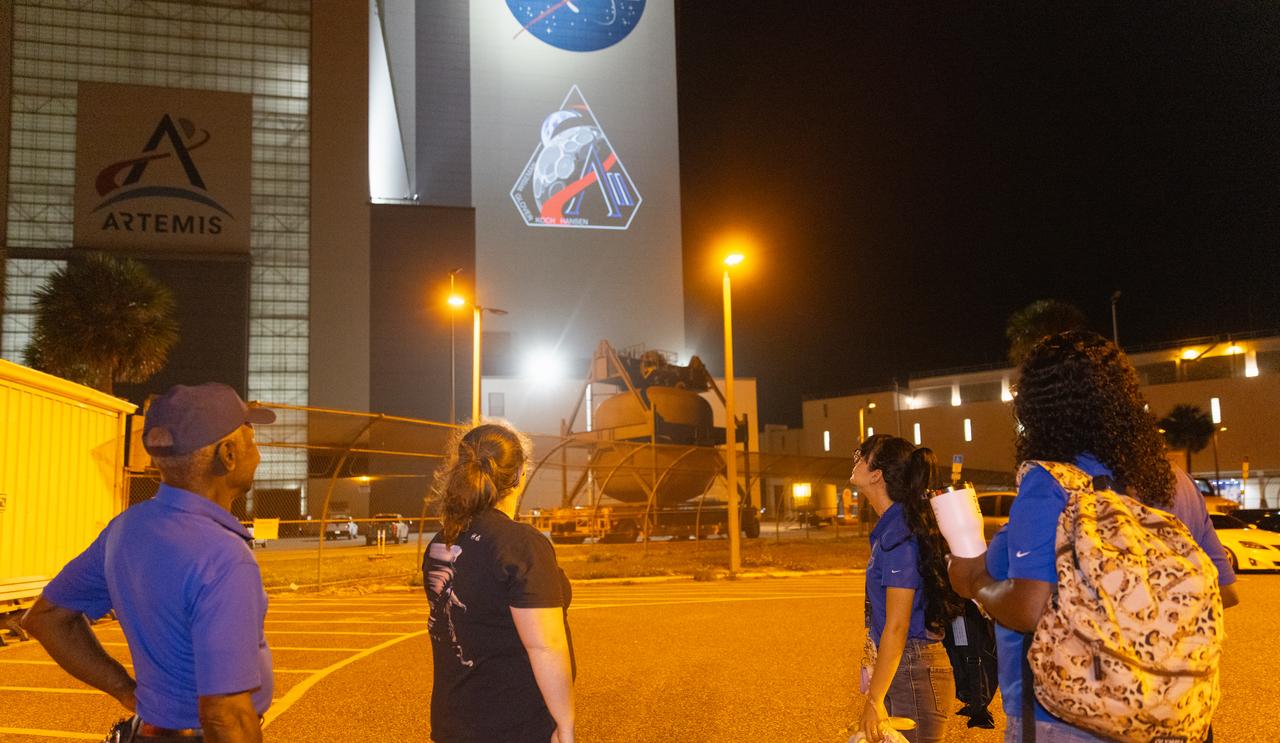

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida take photos of the official Artemis II mission crew insignia projected on the exterior of the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.
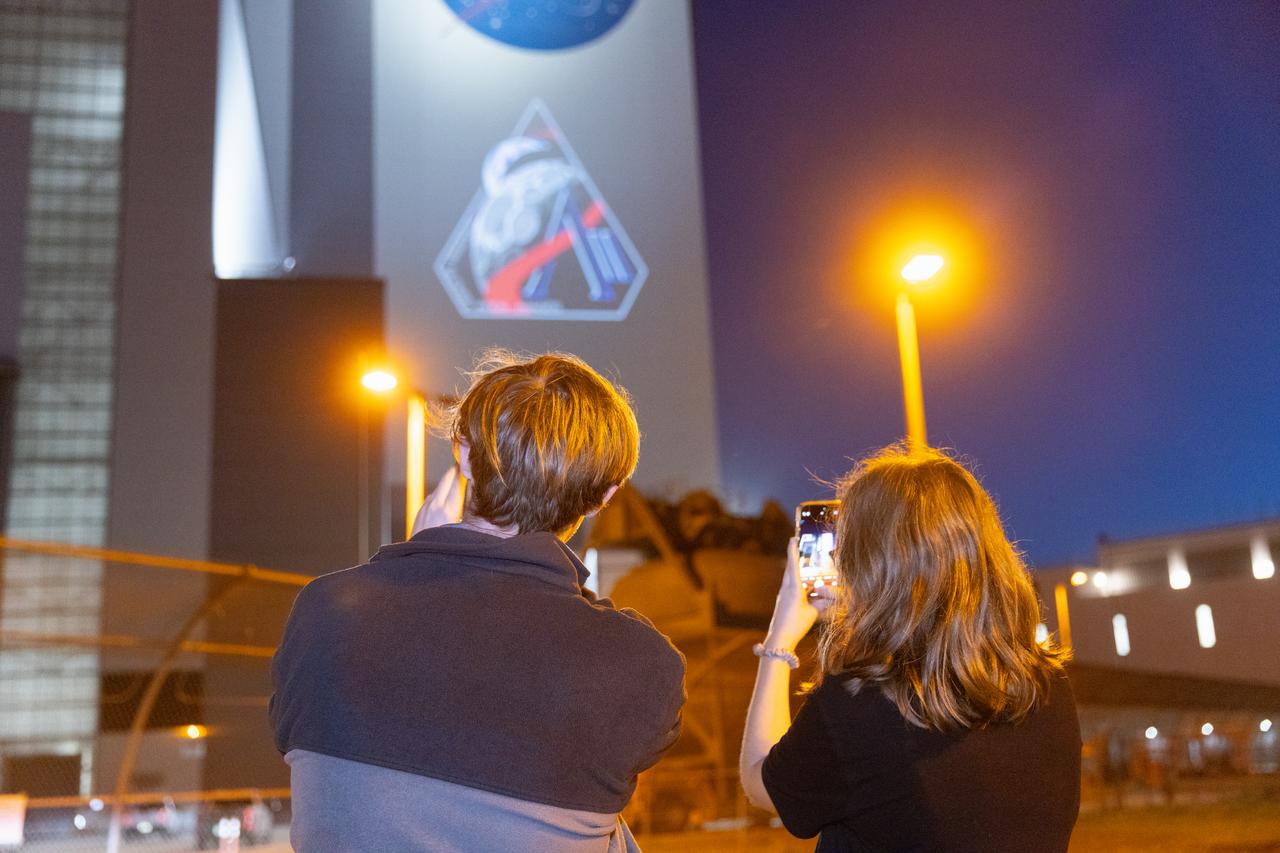

Employees at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida take photos of the official Artemis II mission crew insignia projected on the exterior of the spaceport’s Vehicle Assembly Building on Friday, April 4, 2025. The patch designates the mission as “AII,” signifying not only the second major flight of the Artemis campaign, but also an endeavor of discovery that seeks to explore for all and by all. Framed in Apollo 8’s famous Earthrise photo, the scene of the Earth and the Moon represents the dual nature of human spaceflight, both equally compelling: The Moon represents our exploration destination, focused on discovery of the unknown. The Earth represents home, focused on the perspective we gain when we look back at our shared planet and learn what it is to be uniquely human. The orbit around Earth highlights the ongoing exploration missions that have enabled Artemis to set sights on a long-term presence on the Moon and soon, Mars.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
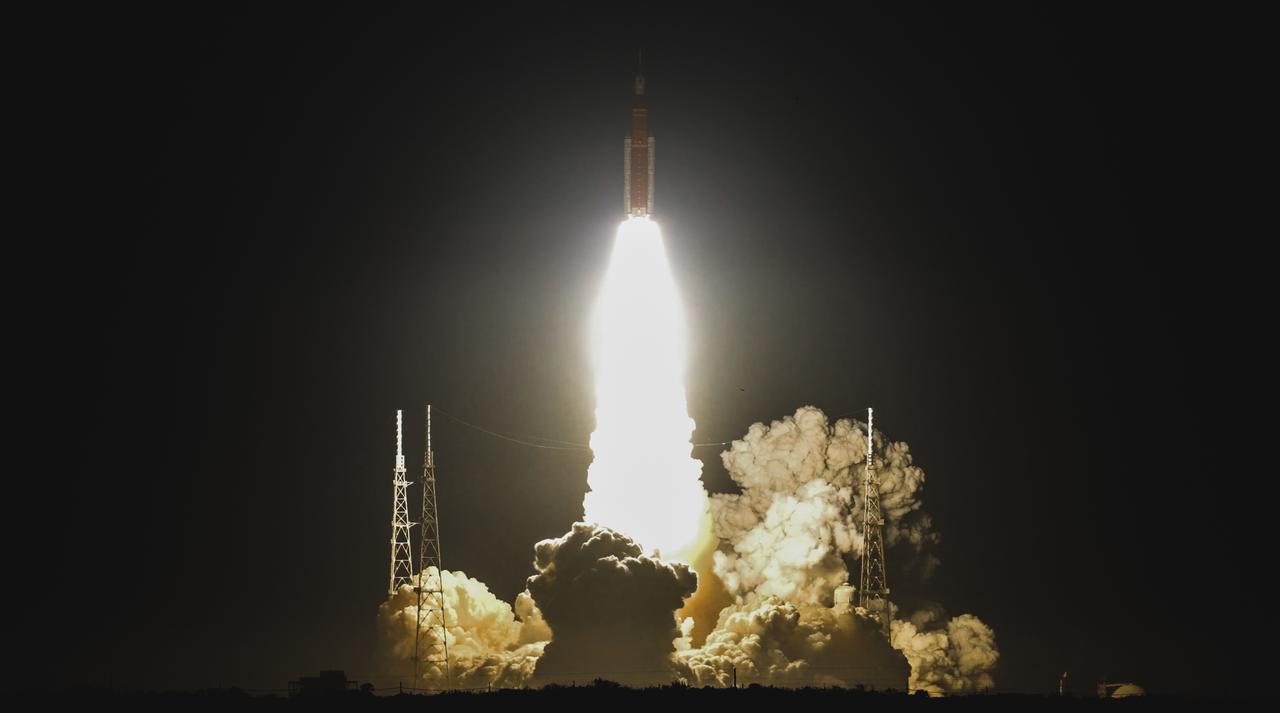

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
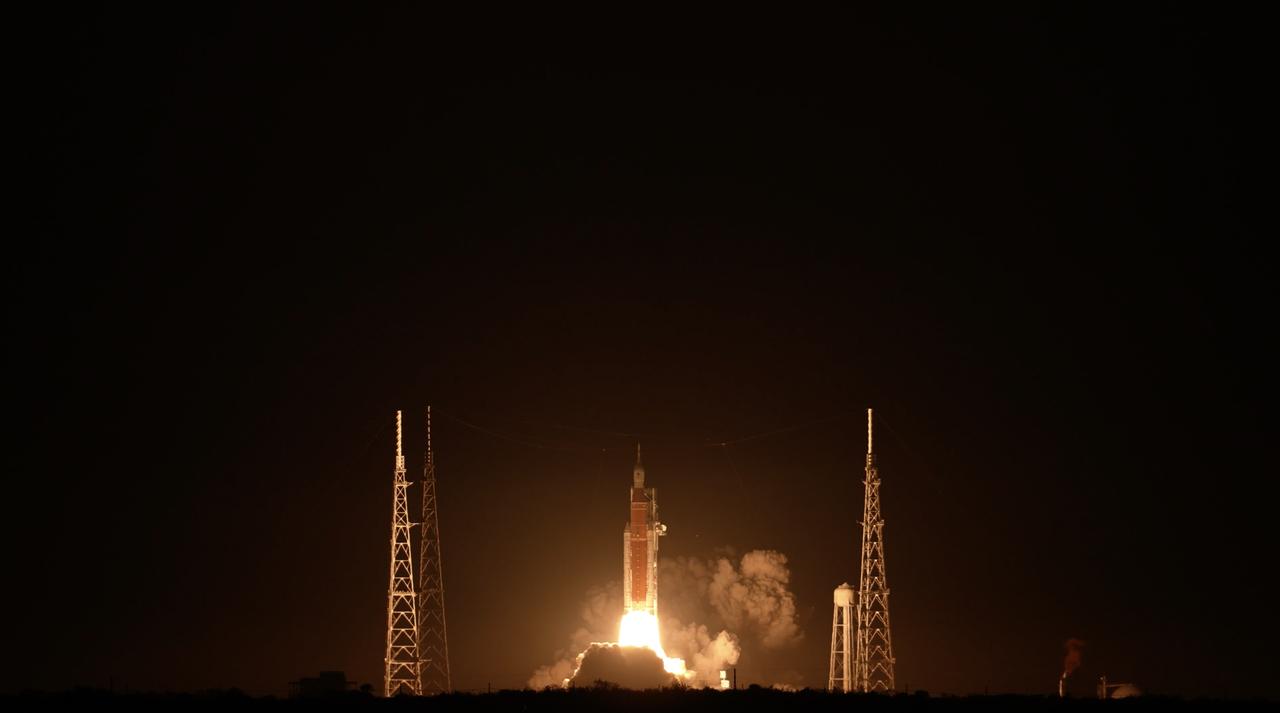

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
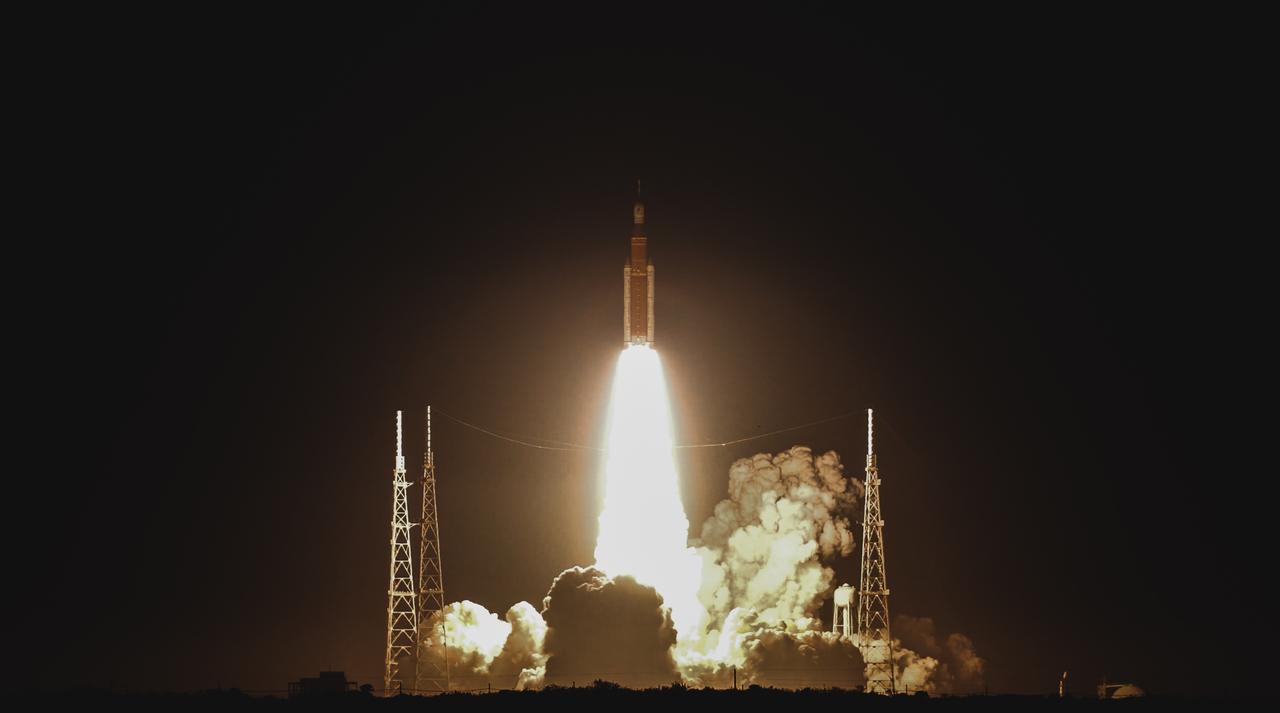

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
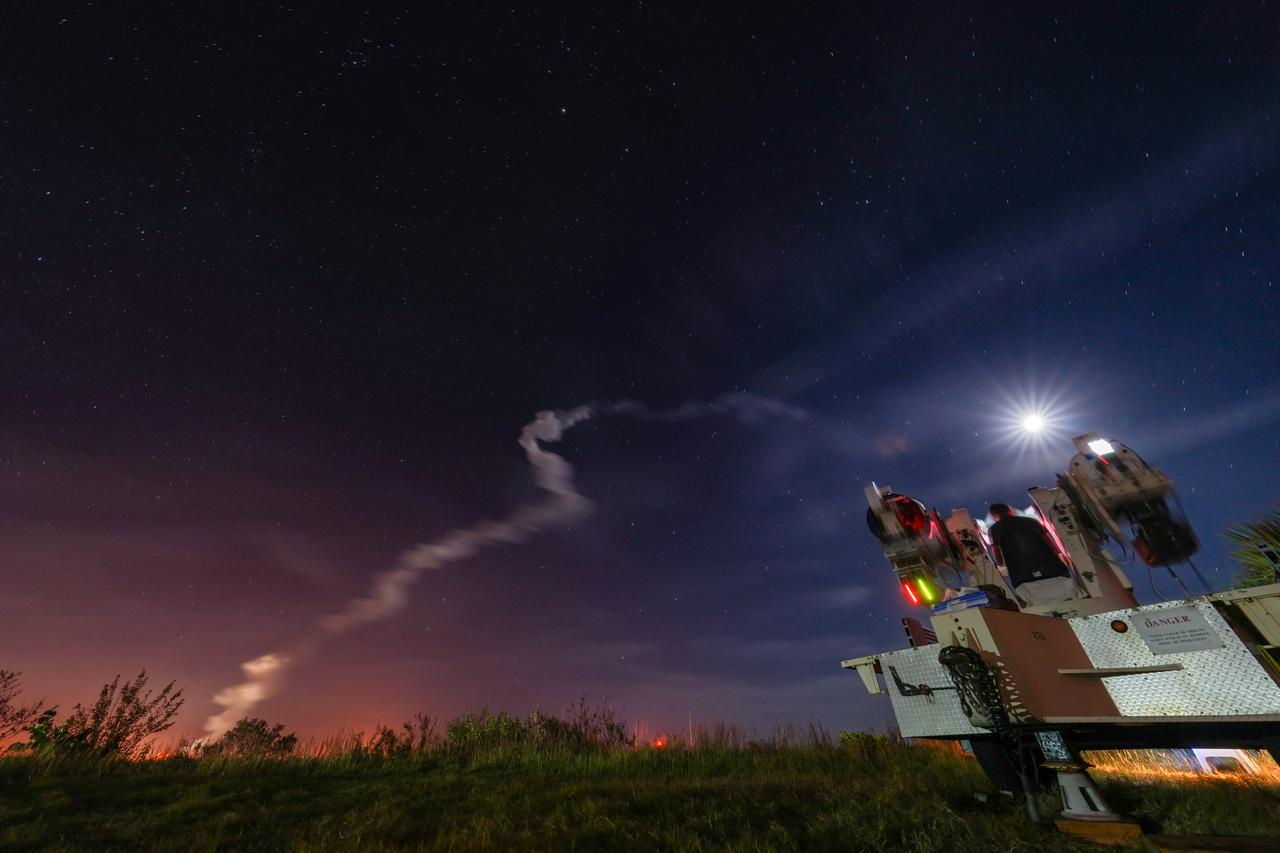

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
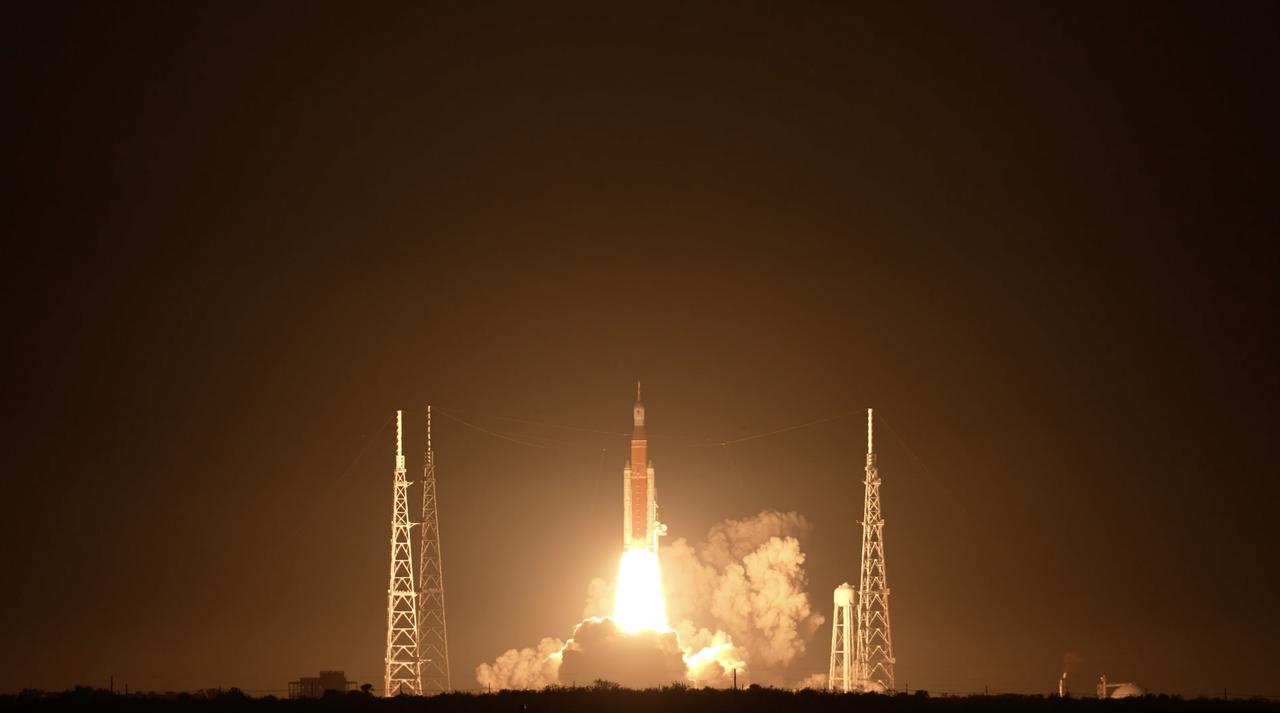

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
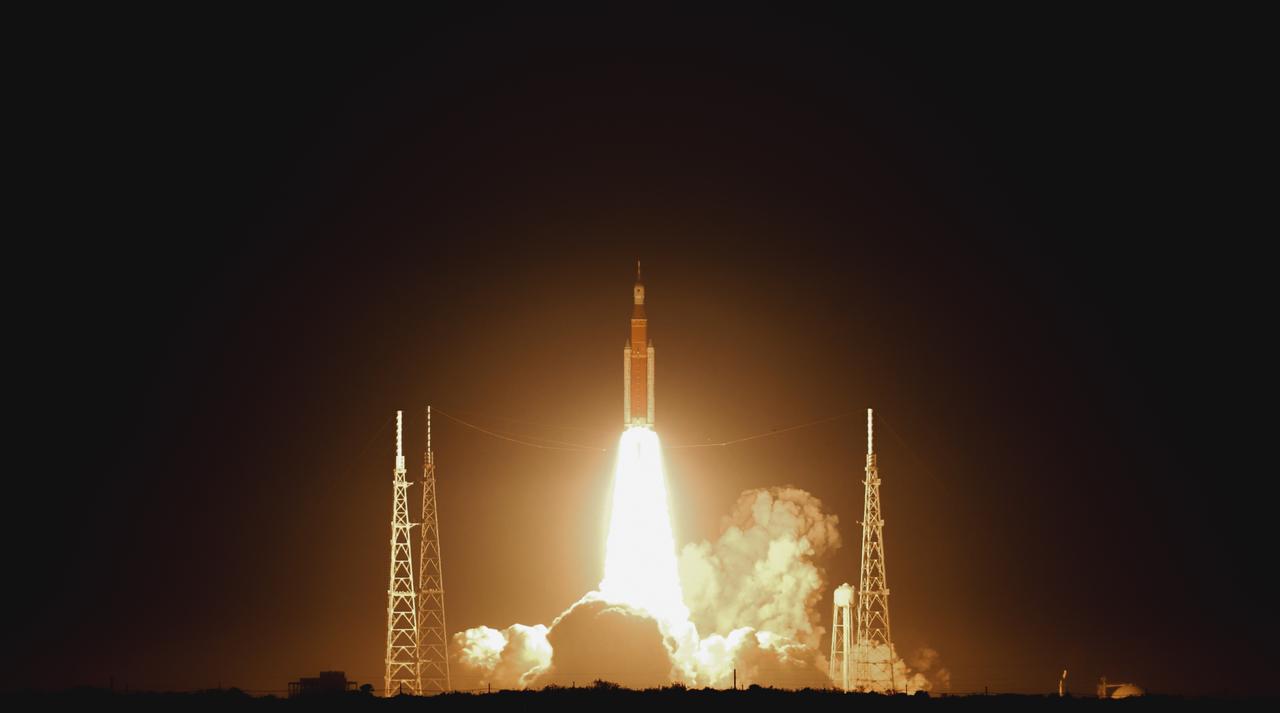

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft atop launches the agency’s Artemis I flight test, Wednesday, Nov. 16 from Launch Complex 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Moon rocket and spacecraft lifted off at 1:47 a.m. ET. The Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

Kennedy Space Center Associate Director Kelvin Manning speaks to guests at NASA's "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the center on Nov. 16, 2018. The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module (ESM) for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
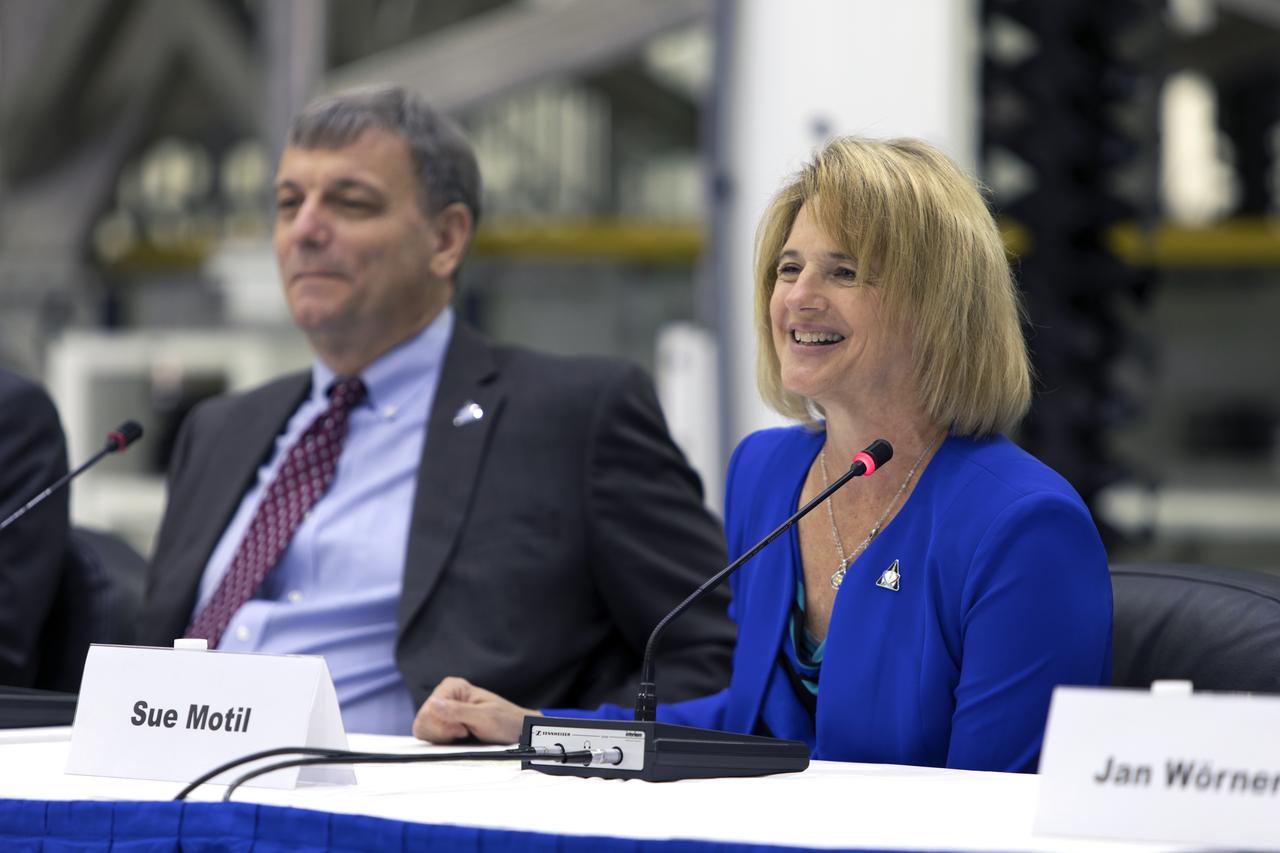

During a "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 16, 2018, Mark Kirasich, left, Orion Program manager at the agency's Johnson Space Center in Houston; and Sue Motil, Orion European Service Module integration manager at the agency's Glenn Research Center, answer questions. The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module (ESM) for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
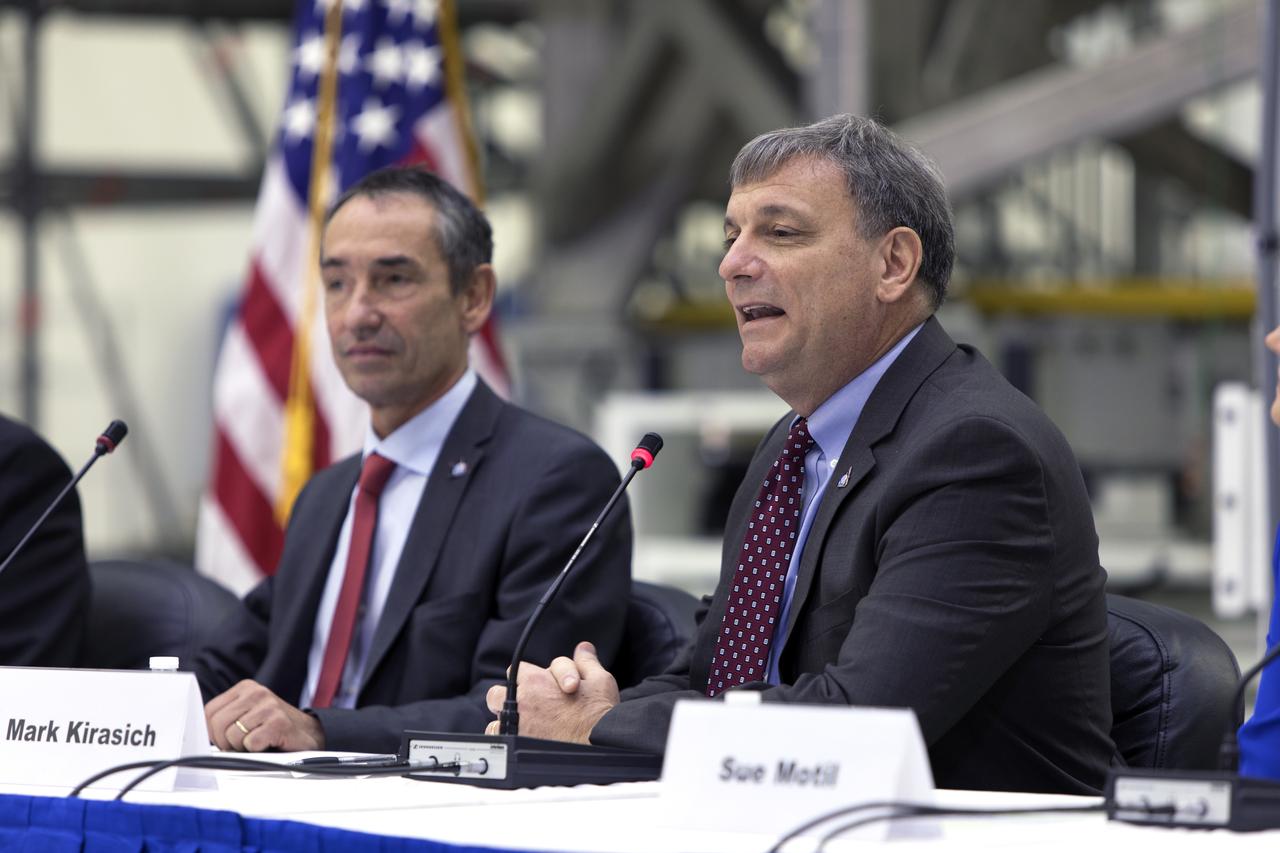

During a "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 16, 2018, Phillippe Deloo, left, European Service Module program manager at the European Space Agency (ESA); and Mark Kirasich, Orion Program manager at the agency's Johnson Space Center in Houston, answer questions. The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module (ESM) for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
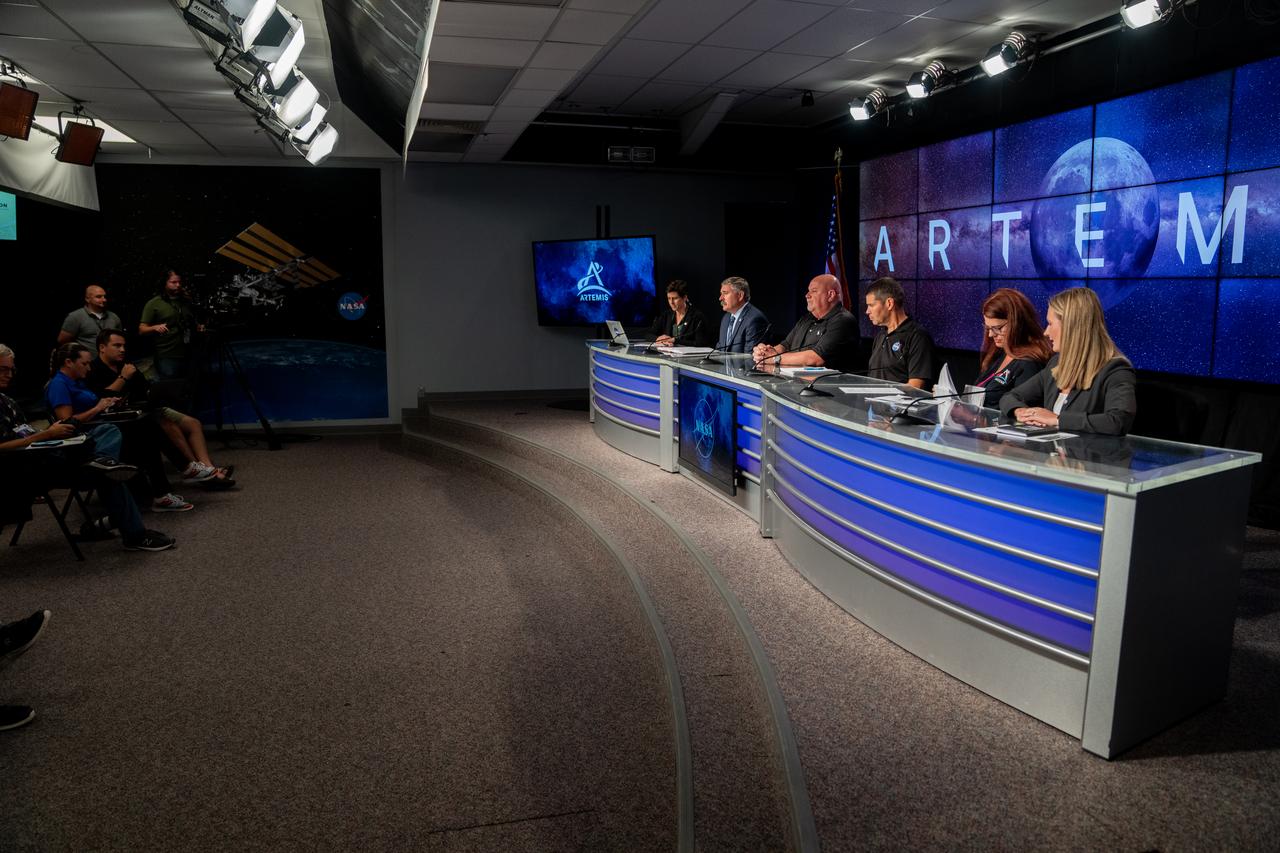

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, Rachel Kraft, NASA Communications; Mike Sarafin, Artemis mission manager; John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.
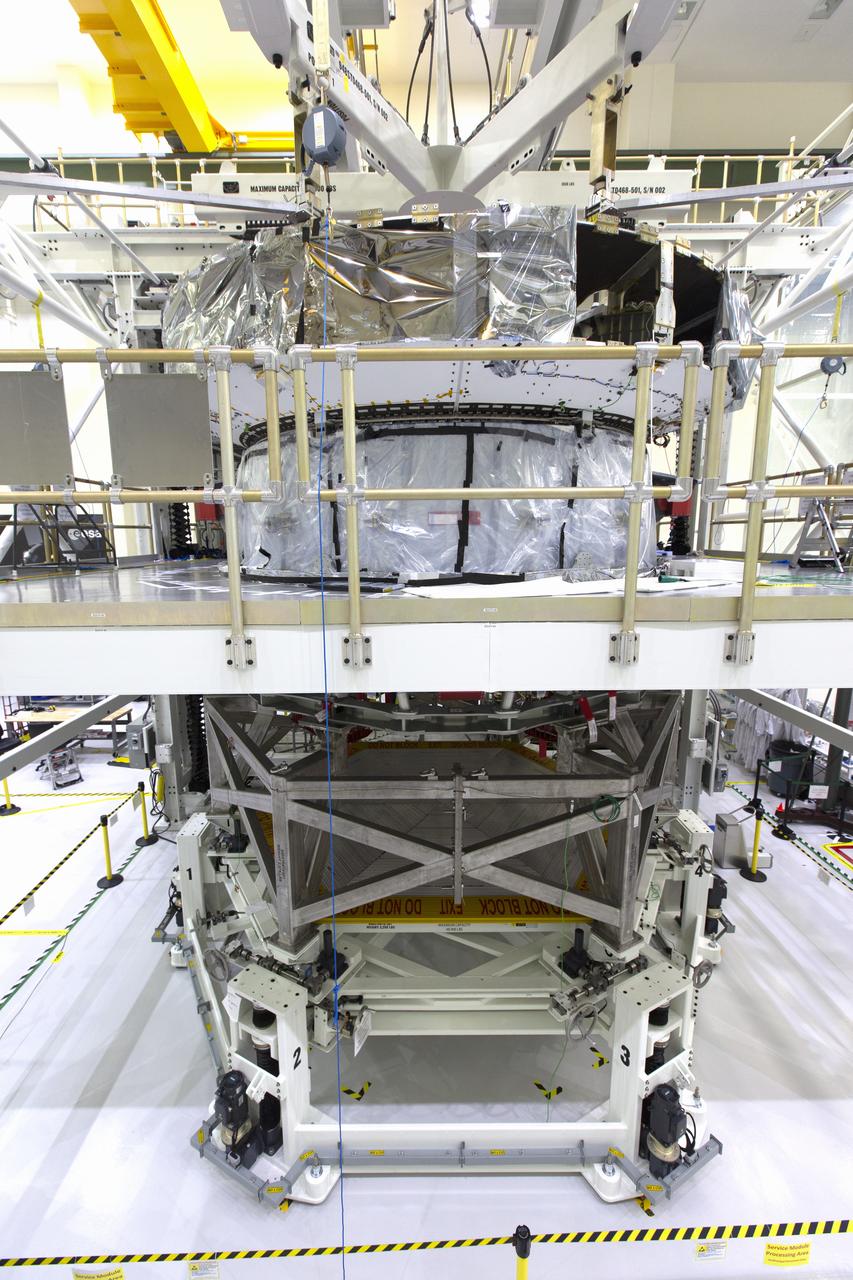

Inside the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion's crew module adapter is mated to the European Service Module on Nov. 26, 2018. For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry, including the European Space Agency's prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA's human deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
Inside the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion's crew module adapter is mated to the European Service Module on Nov. 26, 2018. For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry, including the European Space Agency's prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA's human deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
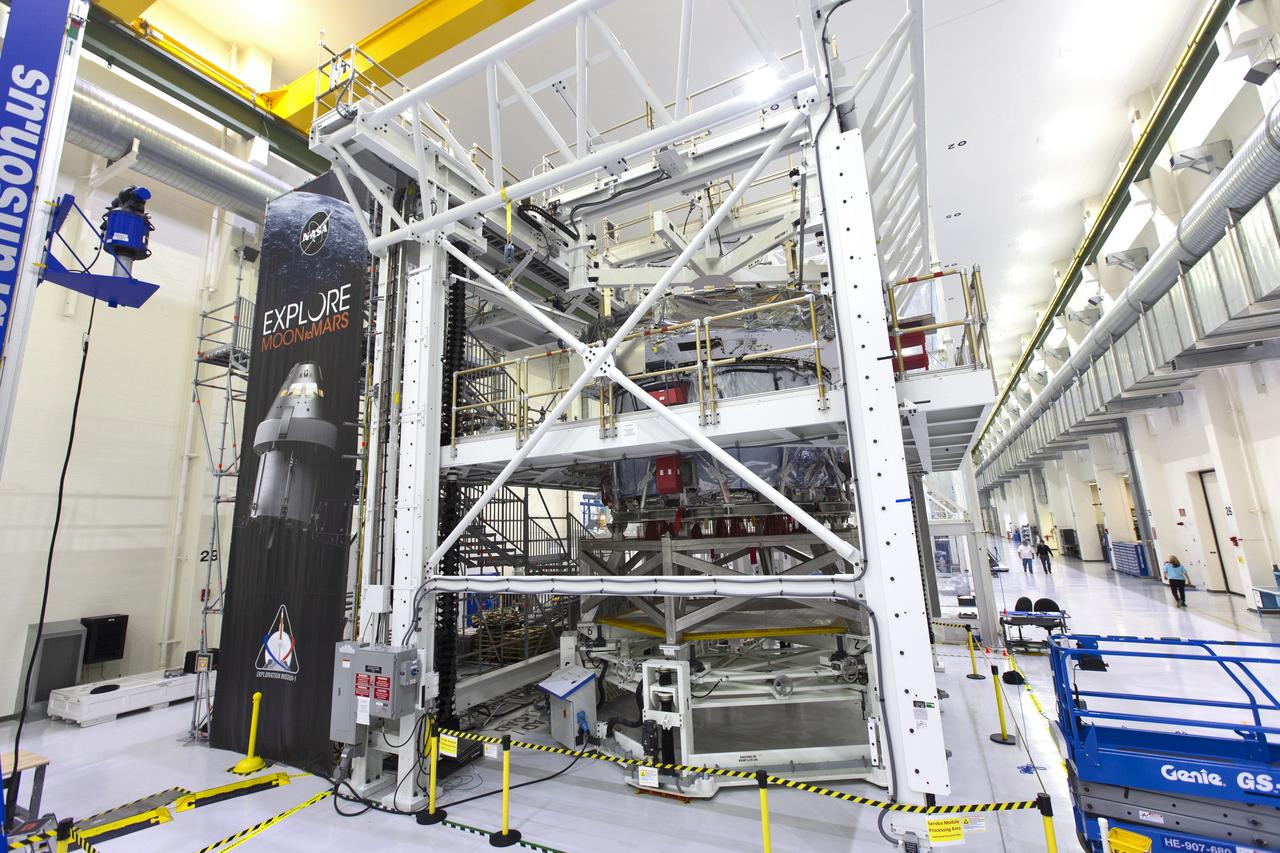

Inside the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion's crew module adapter is mated to the European Service Module on Nov. 26, 2018. For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry, including the European Space Agency's prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA's human deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
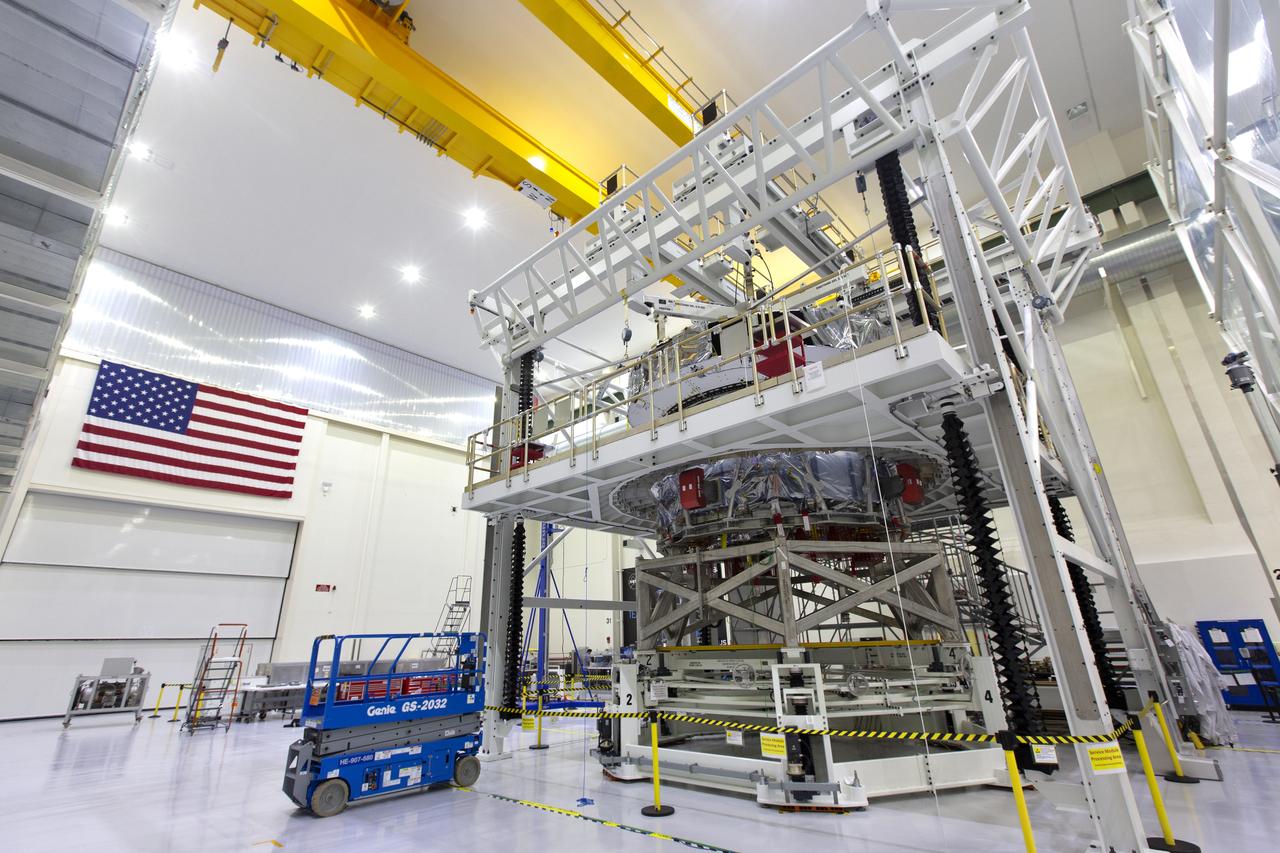

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion's crew module adapter is mated to the European Service Module on Nov. 16, 2018. For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry including ESA's prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA's deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
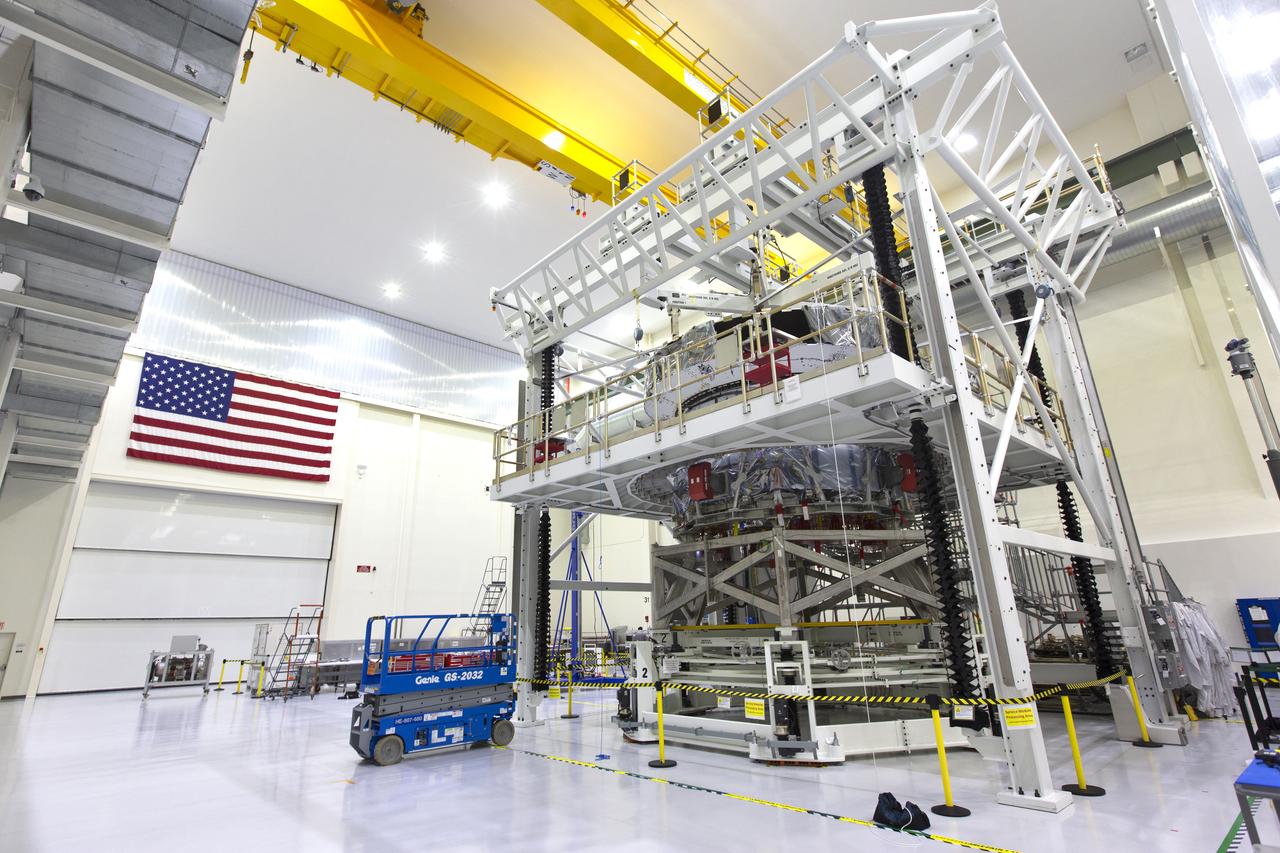

Inside the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Orion's crew module adapter is mated to the European Service Module on Nov. 26, 2018. For the first time, NASA will use a European-built system as a critical element to power an American spacecraft, extending the international cooperation of the International Space Station into deep space. The European Service Module is a unique collaboration across space agencies and industry, including the European Space Agency's prime contractor, Airbus, and 10 European countries. The completion of service module work in Europe and shipment to Kennedy signifies a major milestone toward NASA's human deep space exploration missions to the Moon and beyond.
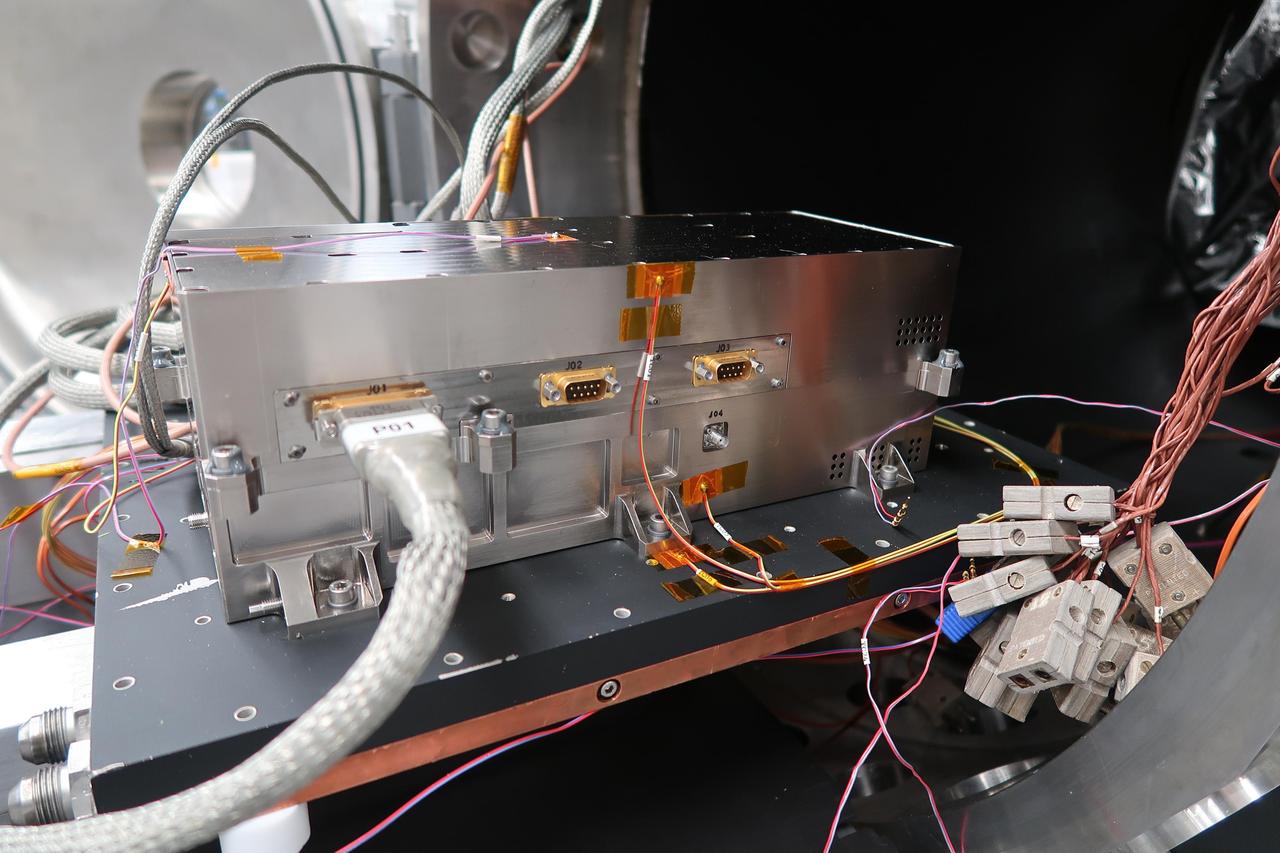
NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory built and shipped the receiver, transmitter and electronics necessary to complete the radar instrument for ESA's (European Space Agency's) Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) mission. Set to launch in 2022, JUICE will explore Jupiter and its three large icy moons. The transmitter works by sending out radio waves, which can penetrate surfaces of icy moons so that scientists "see" underneath. The instrument, called Radar for Icy Moon Exploration, or RIME, is a collaboration by JPL and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and is one of ten instruments that will fly aboard. This photo, shot at JPL on July 23, 2020, shows the transmitter as it exits a thermal vacuum chamber. The test is one of several designed to ensure the hardware can survive the conditions of space travel. The thermal chamber simulates deep space by creating a vacuum and by varying the temperatures to match those the instrument will experience over the life of the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24025

A prelaunch media briefing is held following a mission management team meeting for Artemis I on Sept. 1, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Participants are, from left, John Honeycutt, Space Launch System (SLS) program manager; John Blevins, SLS chief engineer; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, Artemis launch director; and Melody Lovin, Space Launch Delta 45 weather officer. Artemis I is scheduled to launch at 2:17 p.m. EDT on Sept. 3, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B. Launch was waved off on Aug. 29 due to an issue during tanking. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration and demonstrate NASA’s capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I is to thoroughly test the integrated systems before crewed missions by operating the spacecraft in a deep space environment, testing Orion’s heat shield, and recovering the crew module after reentry, descent, and splashdown.

This mosaic is a view from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity of Yankee Clipper crater which carries the name of the command and service module of NASA 1969 Apollo 12 mission to the moon.
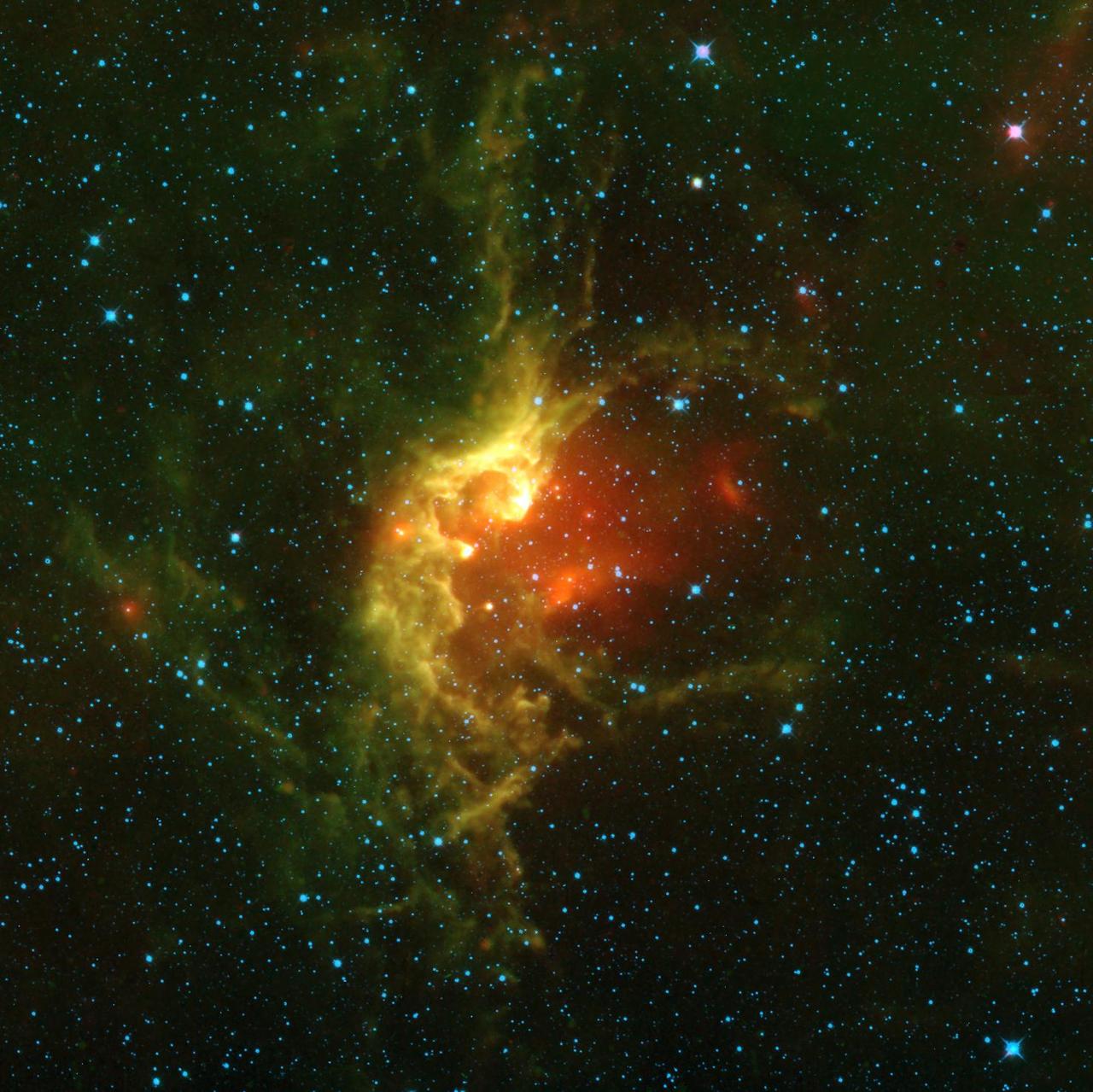

This picture of the open star cluster NGC 7380 is a mosaic of images from NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer mission spanning an area on the sky of about 5 times the size of the full Moon.
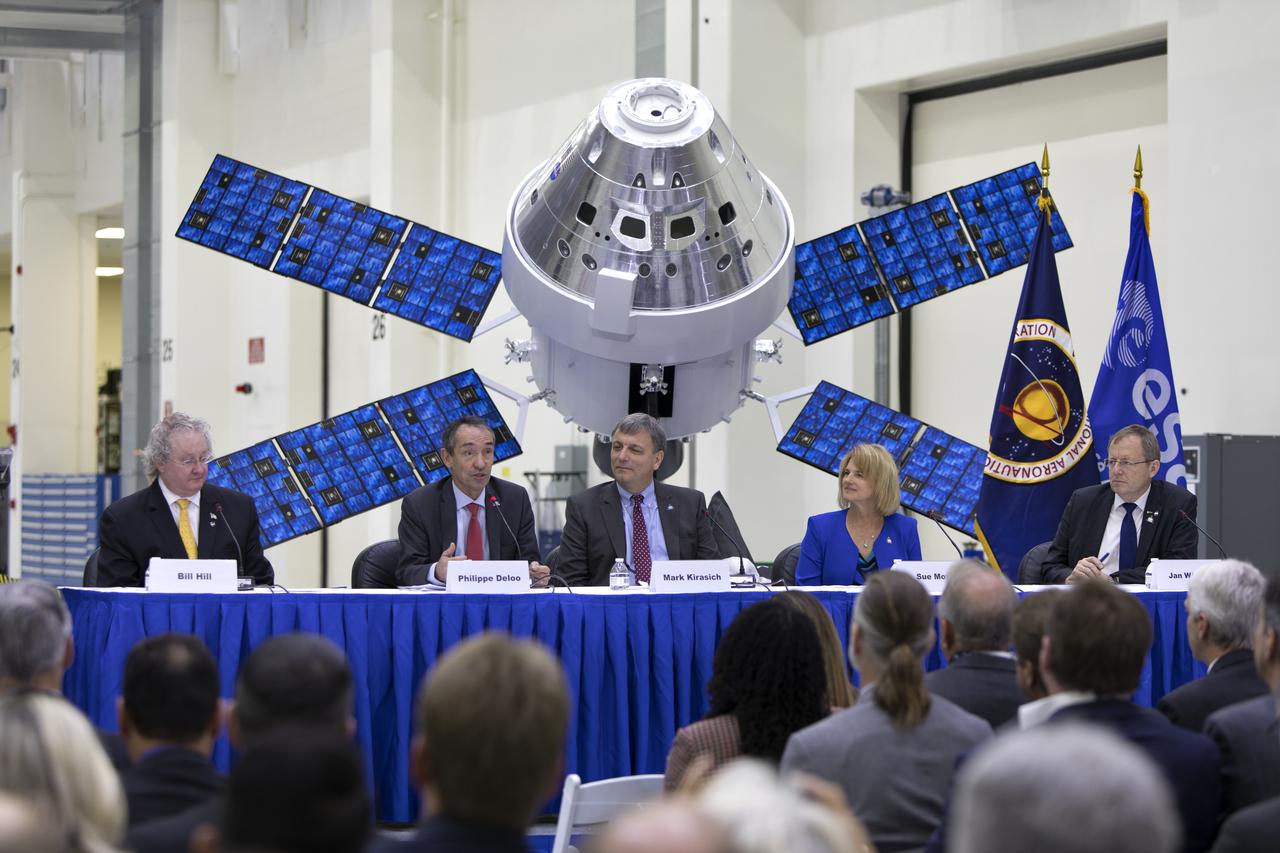

NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) senior managers answer questions during a "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 16, 2018. From left, are Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development; Phillippe Deloo, European Service Module program manager at ESA; Mark Kirasich, Orion Program manager at the agency's Johnson Space Center in Houston; Sue Motil, Orion European Service Module integration manager at the agency's Glenn Research Center; and Jan Worner, ESA director general. The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module (ESM) for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
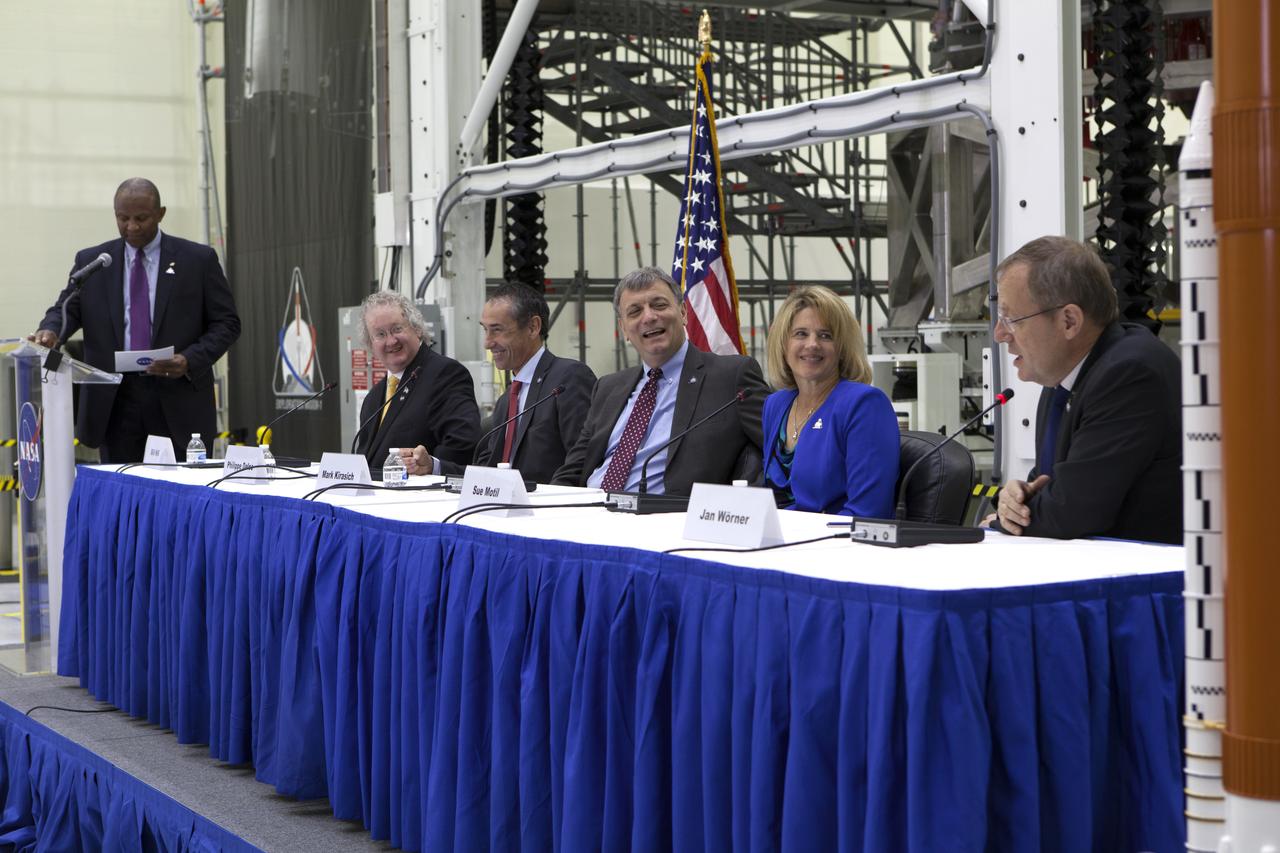

Kennedy Space Center Associate Director Kelvin Manning, far left, moderates questions to NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) senior managers during the "Powering Exploration Mission-1" ceremony in the high bay of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the center on Nov. 16, 2016. From left, are Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development; Phillippe Deloo, European Service Module program manager at ESA; Mark Kirasich, Orion Program manager at the agency's Johnson Space Center in Houston; Sue Motil, Orion European Service Module integration manager at the agency's Glenn Research Center; and Jan Worner, ESA director general. The event was held to mark a major milestone, the arrival of the European Service Module (ESM) for Orion's Exploration Mission-1. The service module, built by the European Space Agency, will supply the main propulsion system and power to the Orion spacecraft during EM-1, a mission to the Moon. The ESM also will house air and water for astronauts on future missions. EM-1 will be an uncrewed flight test that will provide a foundation for human deep space exploration to destinations beyond Earth orbit. EM-1 will be the first integrated test of NASA's Space Launch System, Orion and the ground systems at Kennedy.
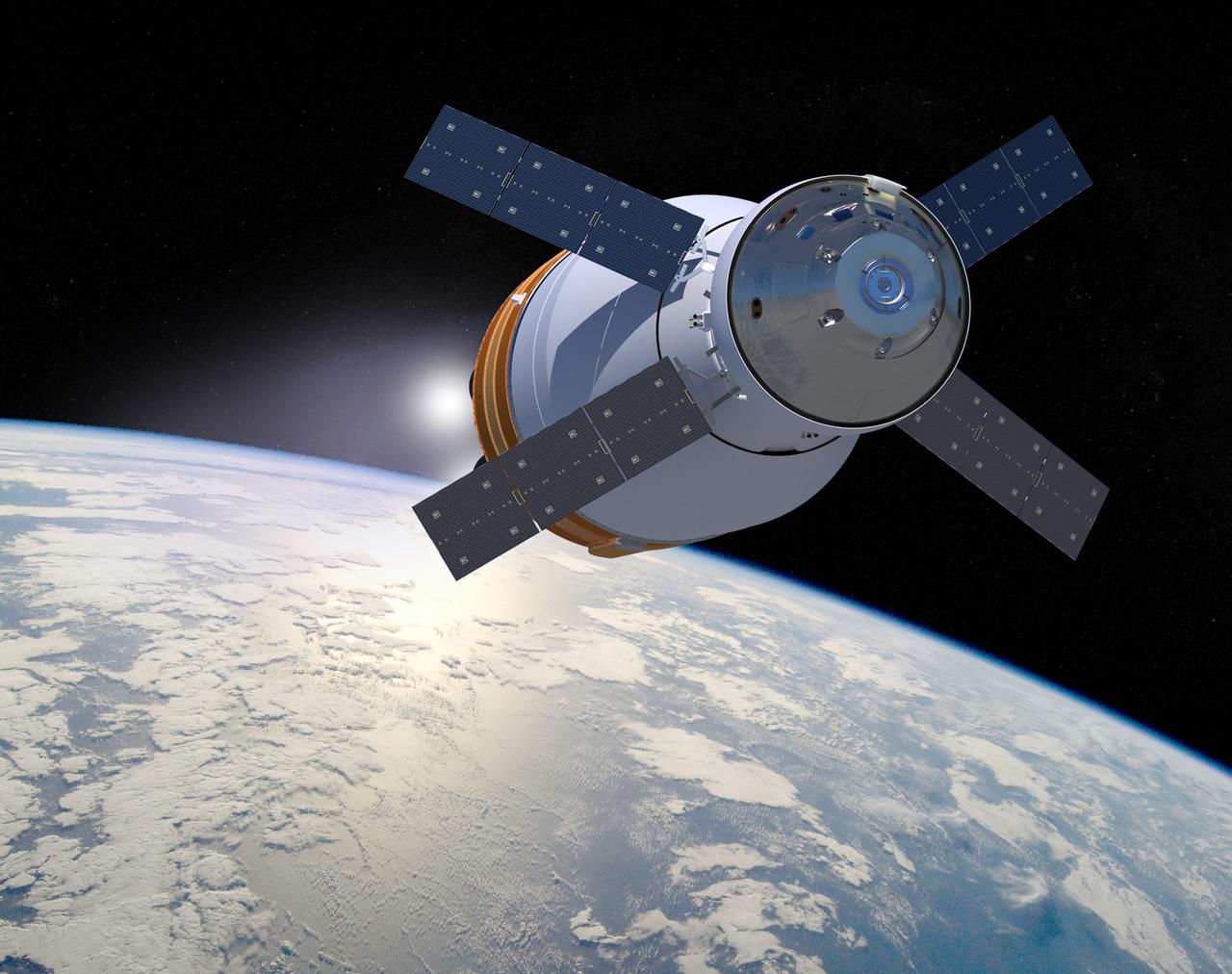

Seen here is an image of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage with the Orion Space craft on its way to a deep space mission. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
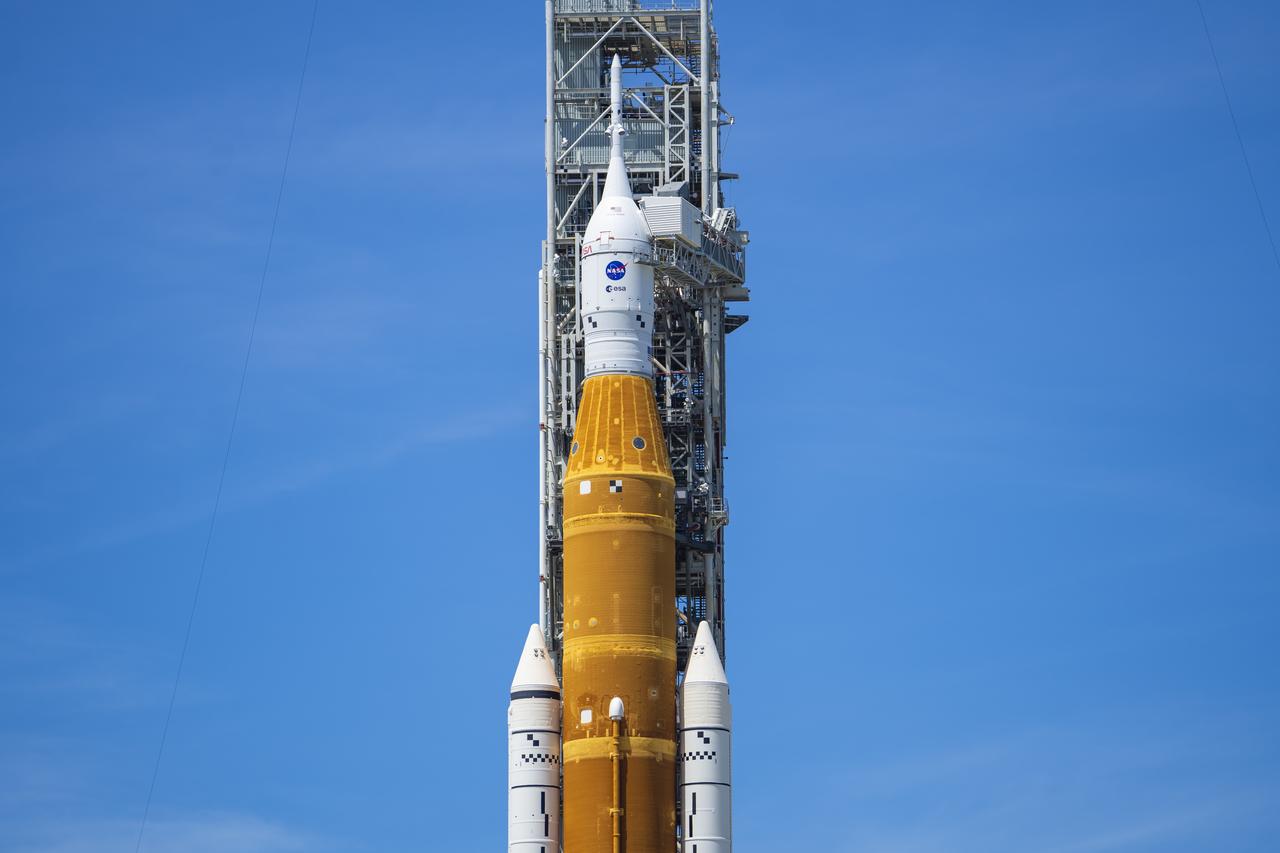

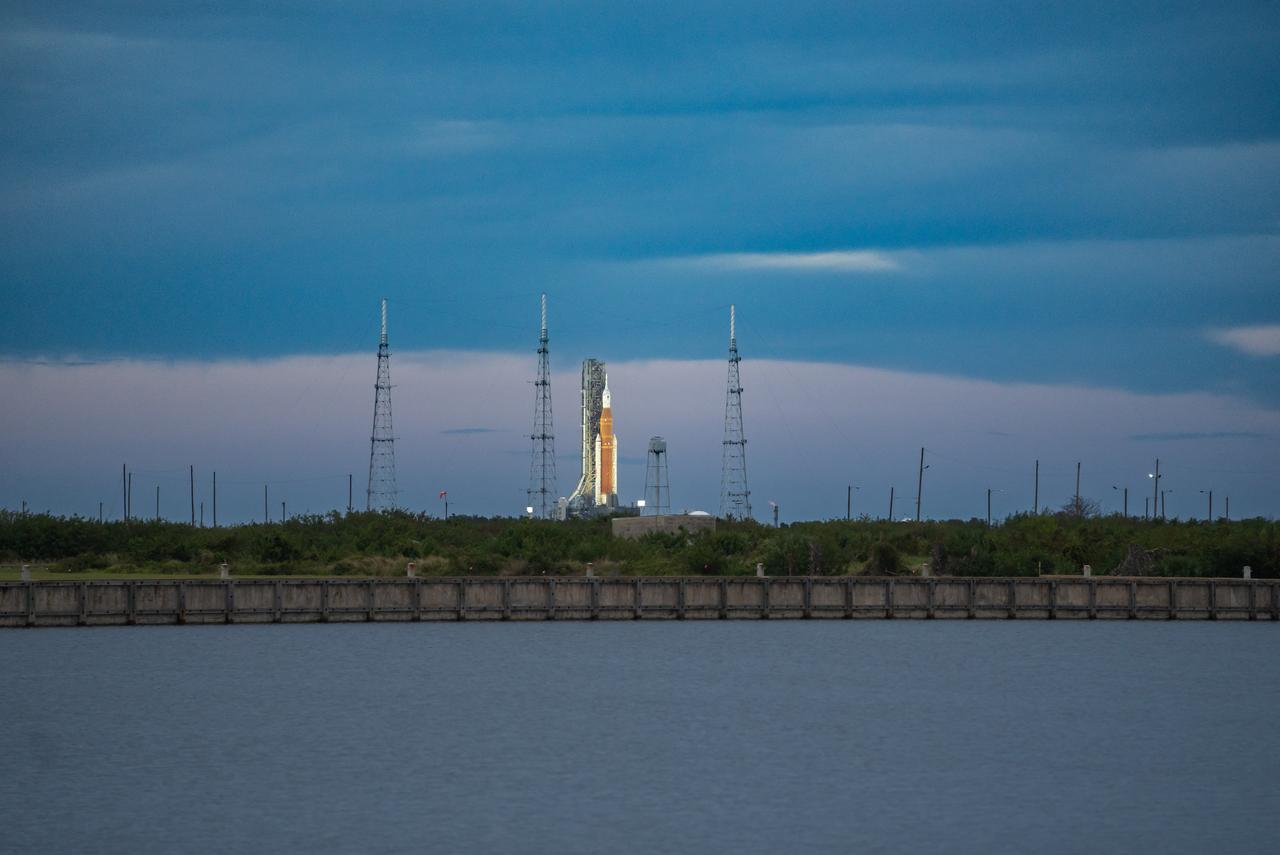
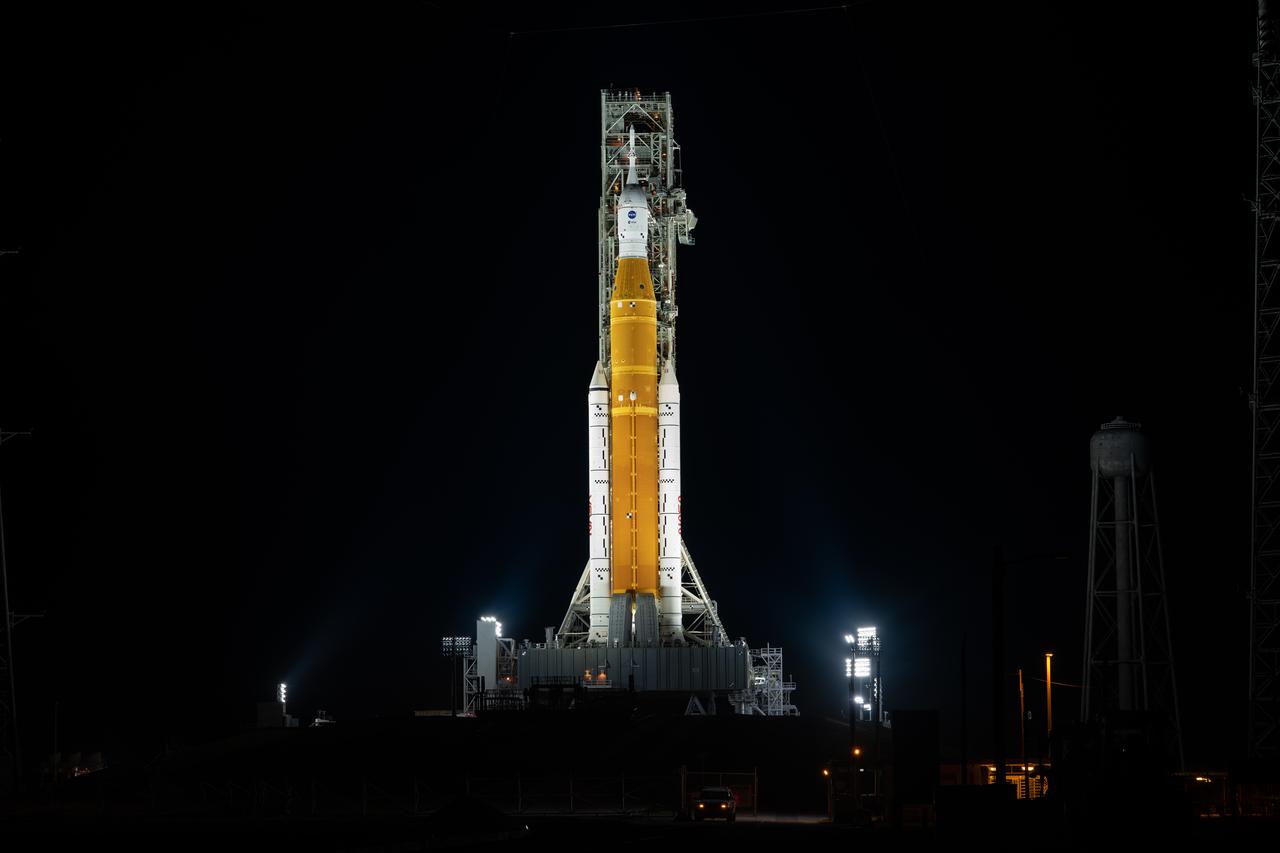
NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
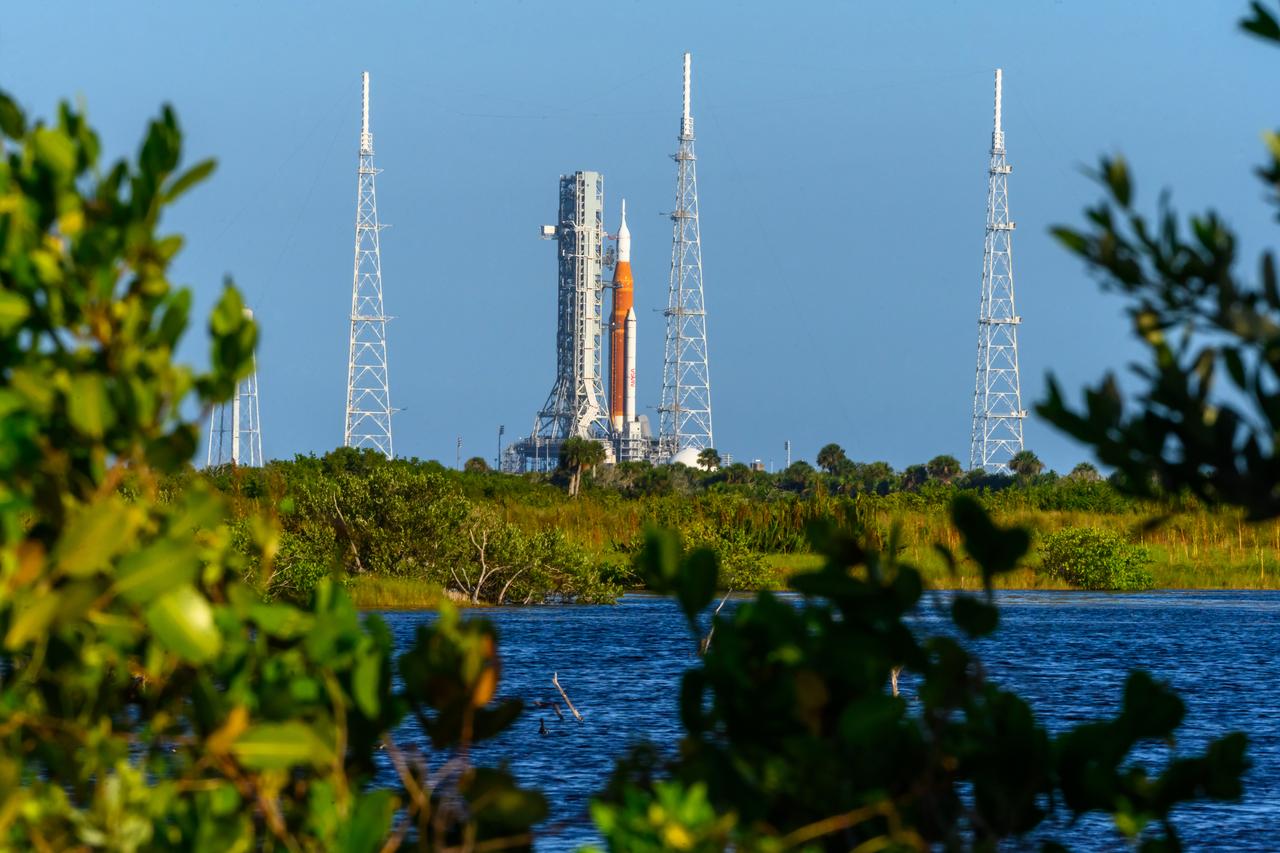

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
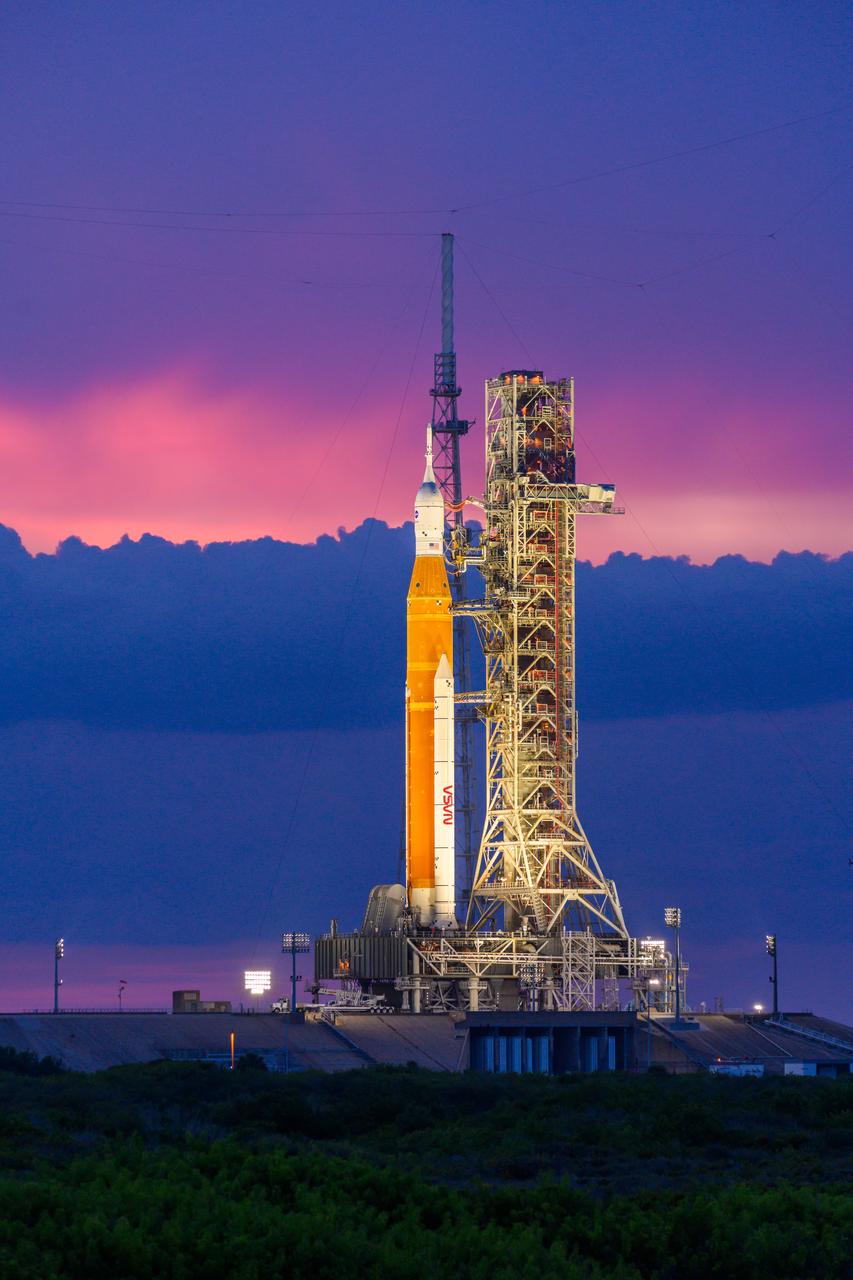

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
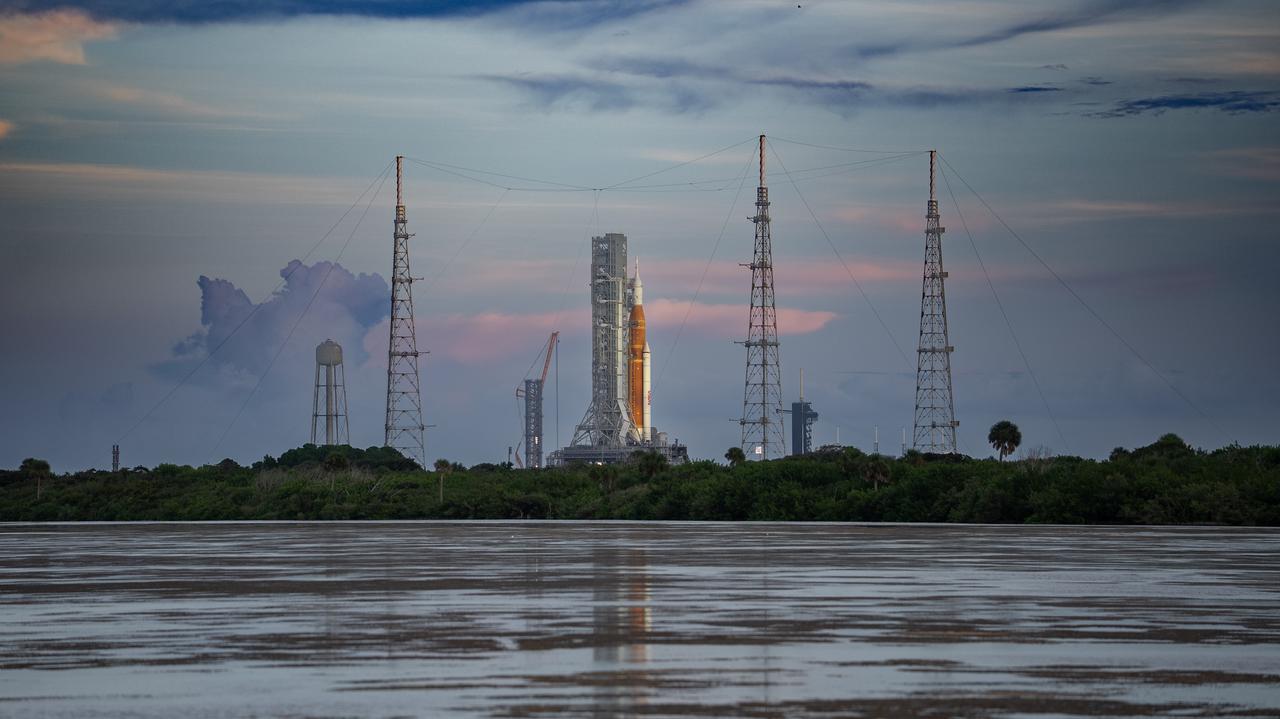

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launchpad 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
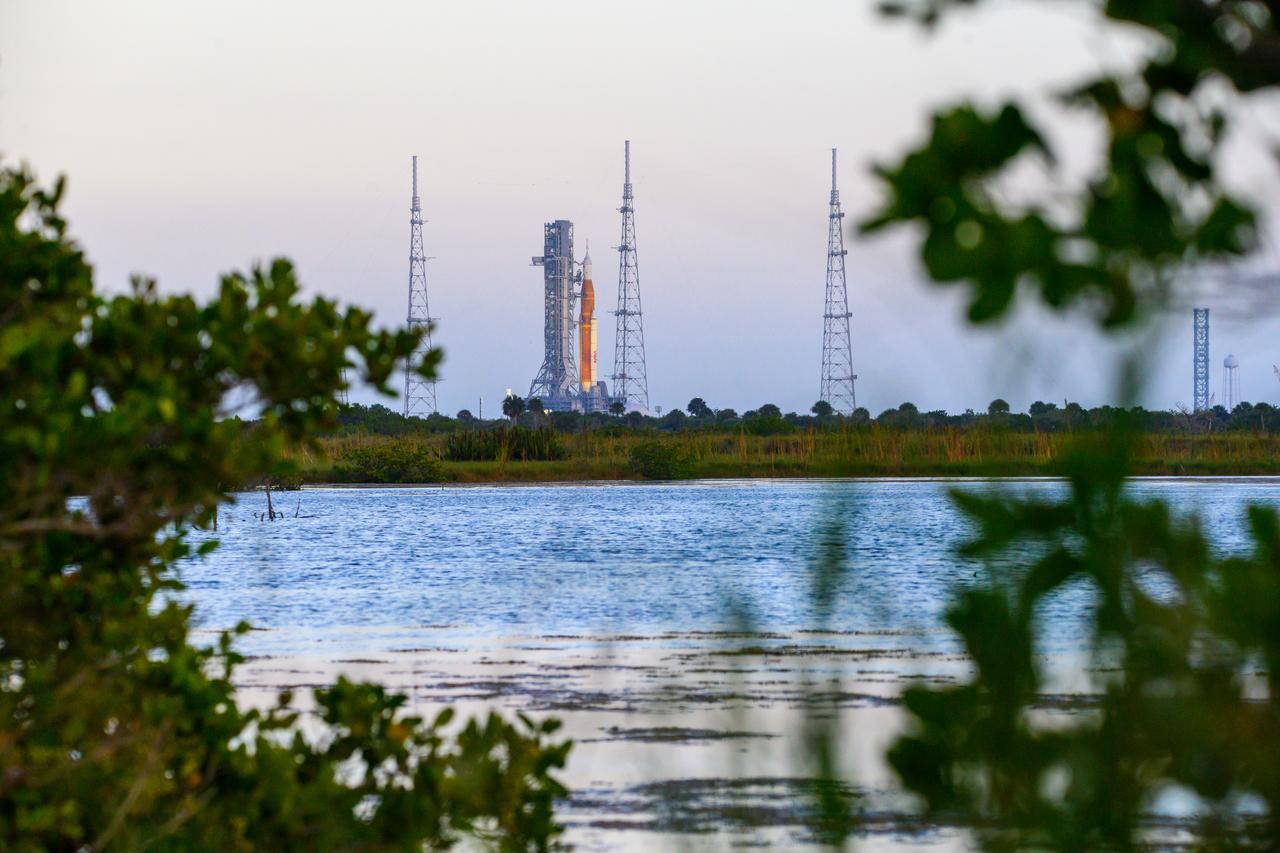

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
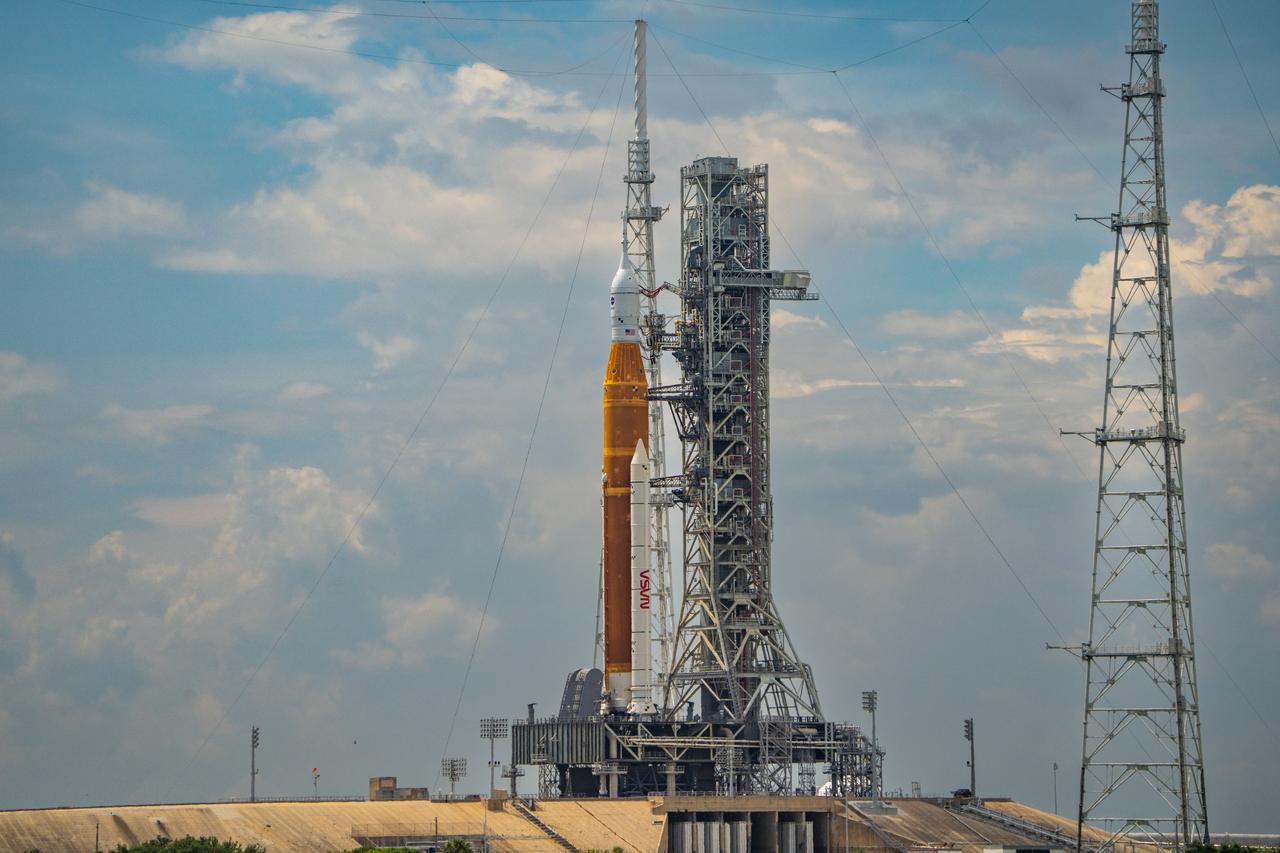

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
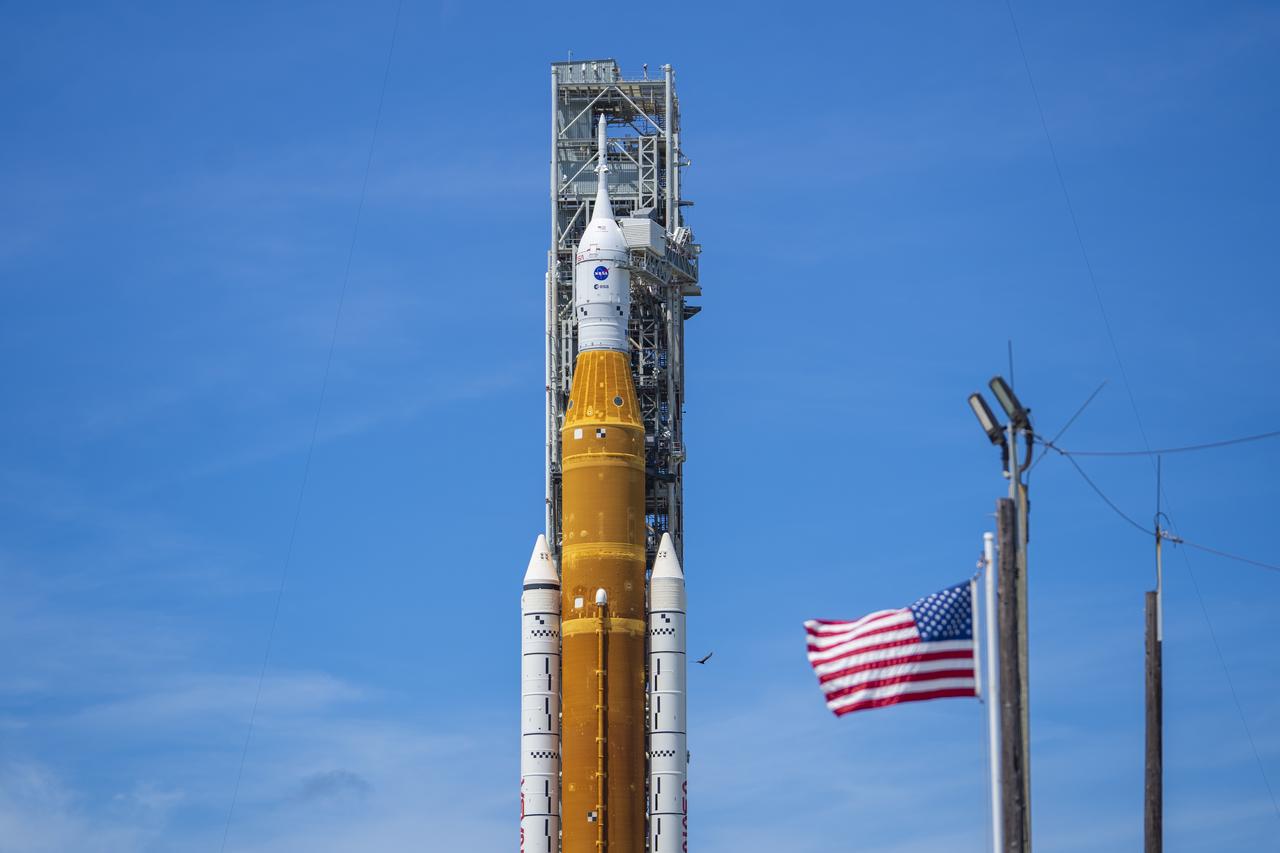

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
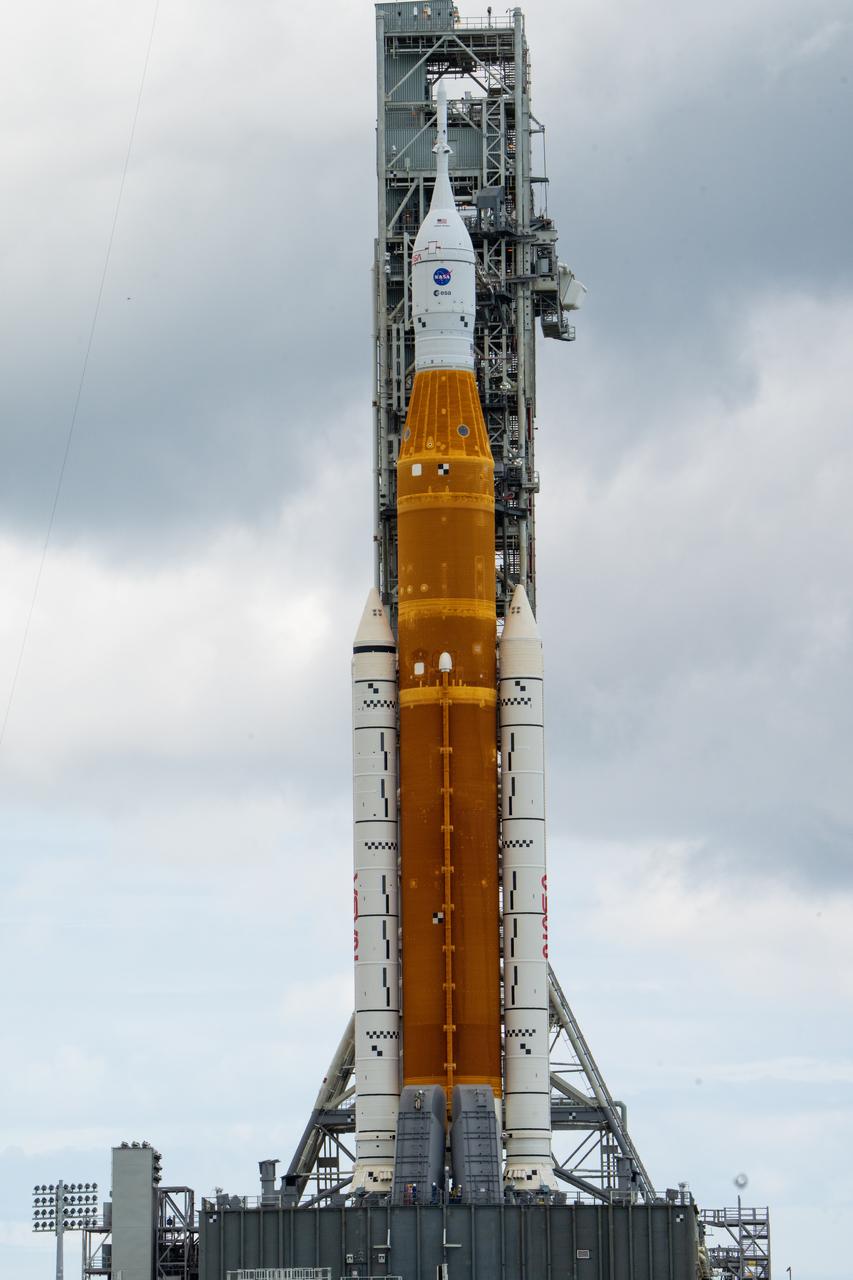

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
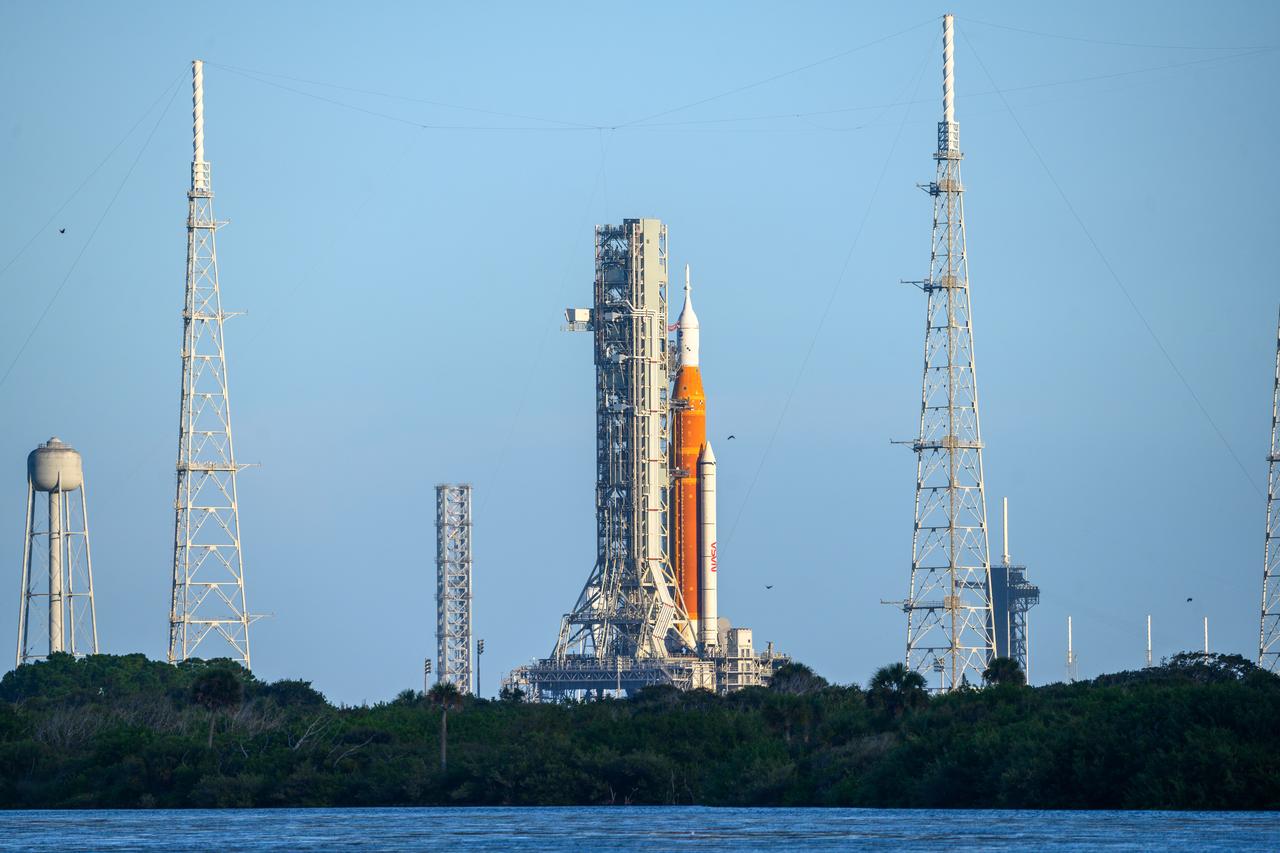

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
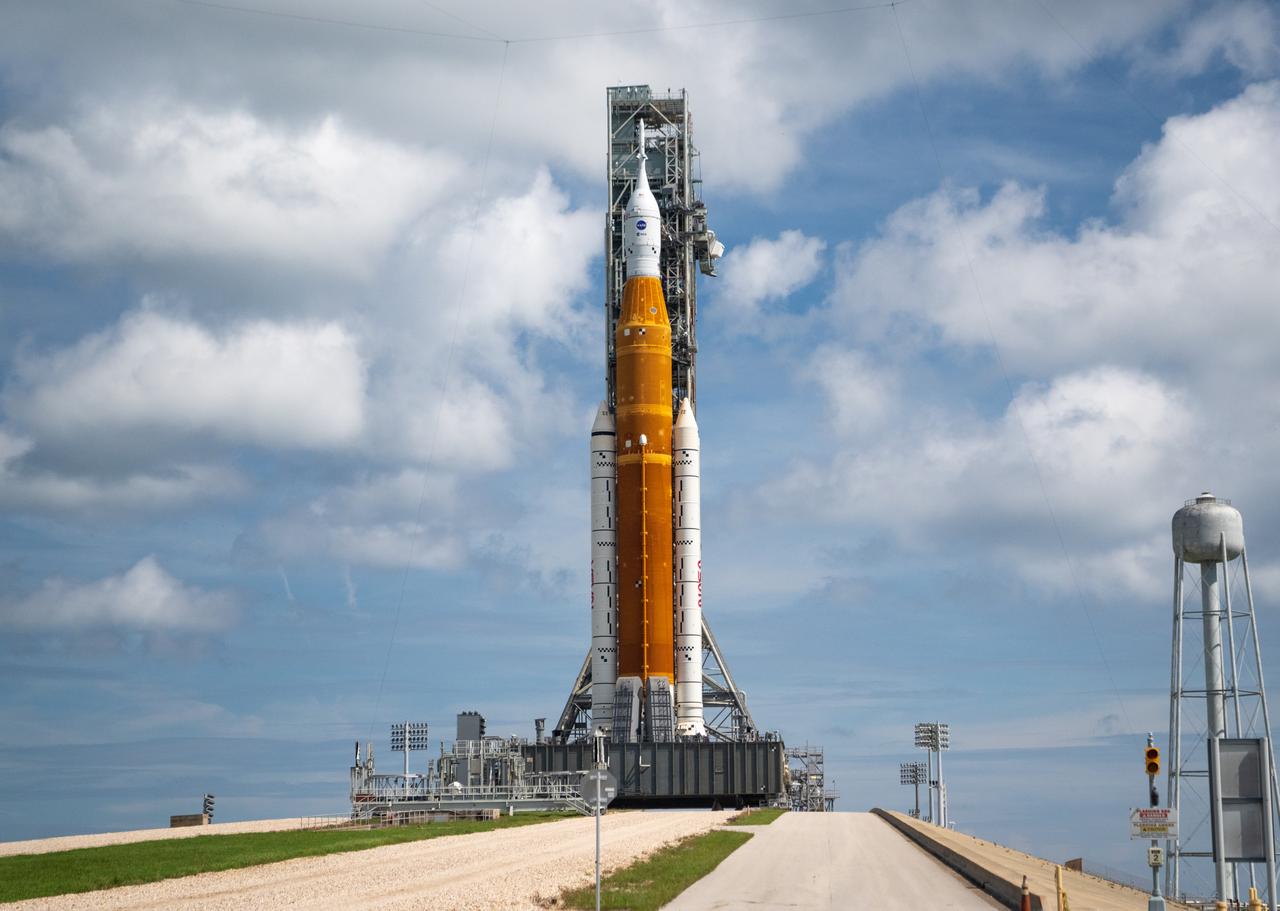

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
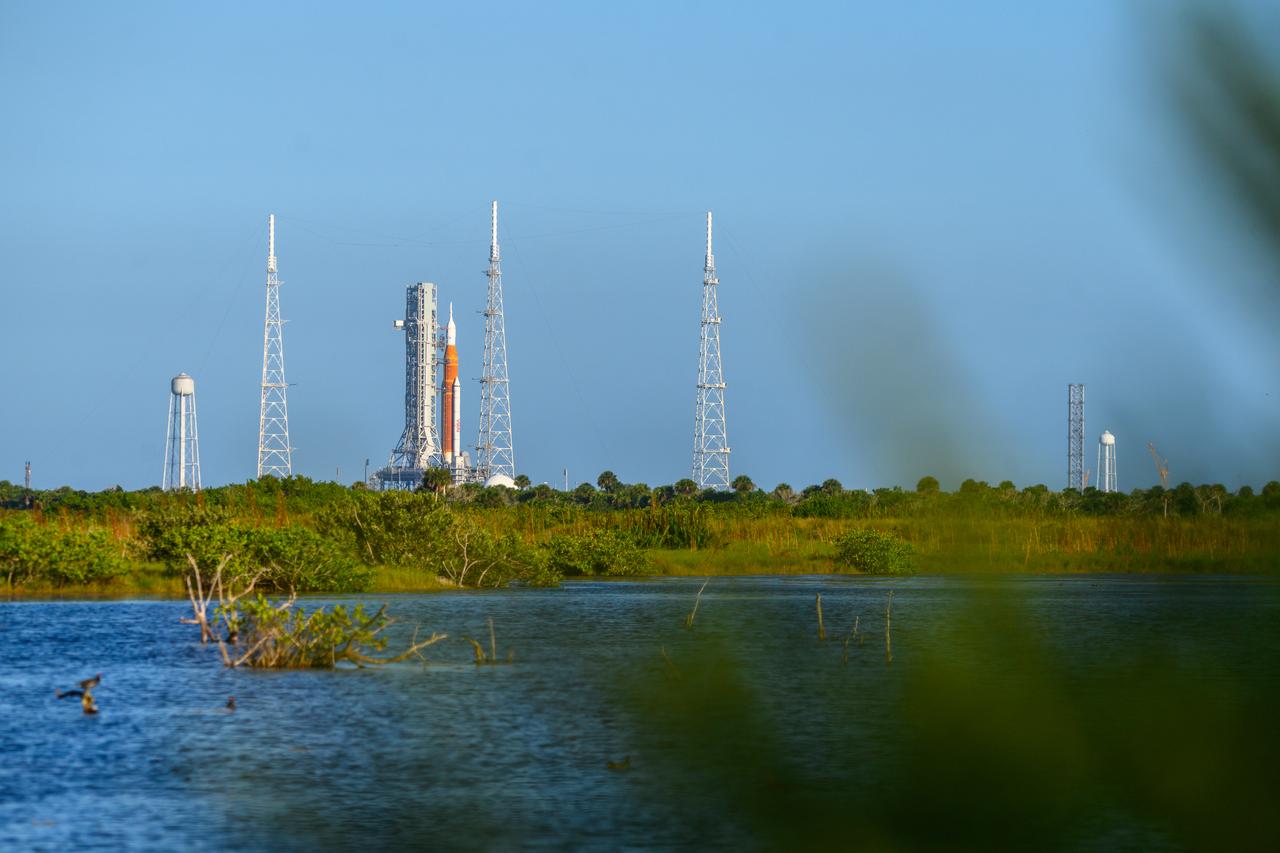

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
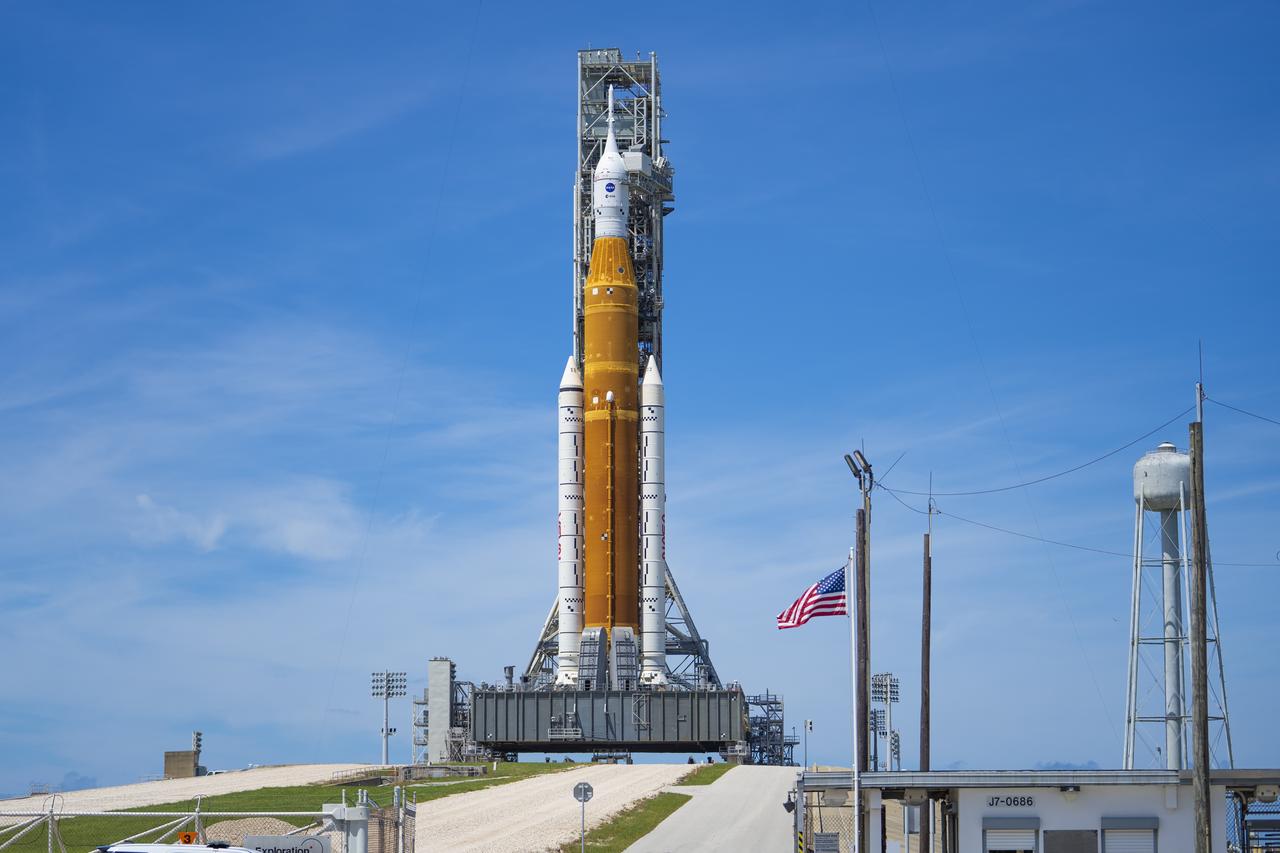

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
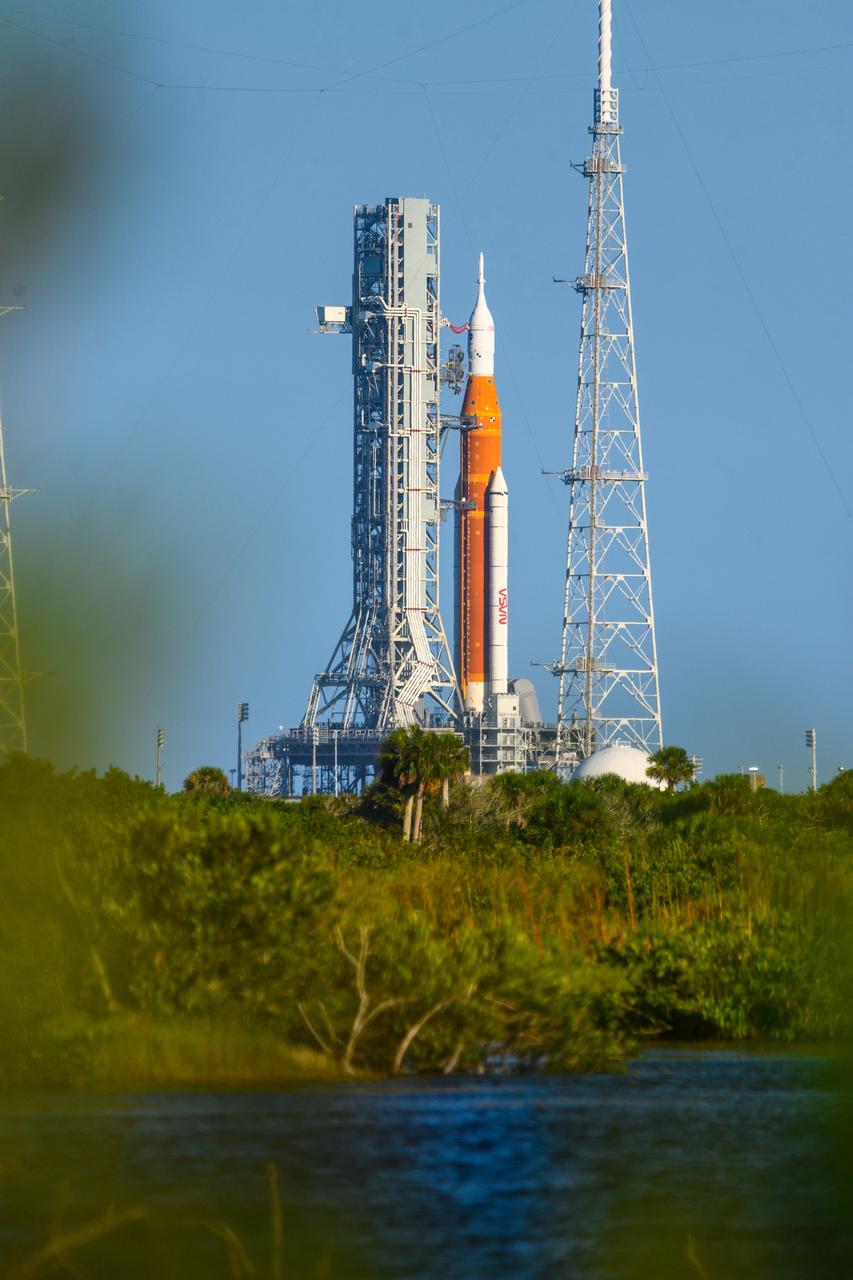

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Sept. 3 at 2:17 p.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
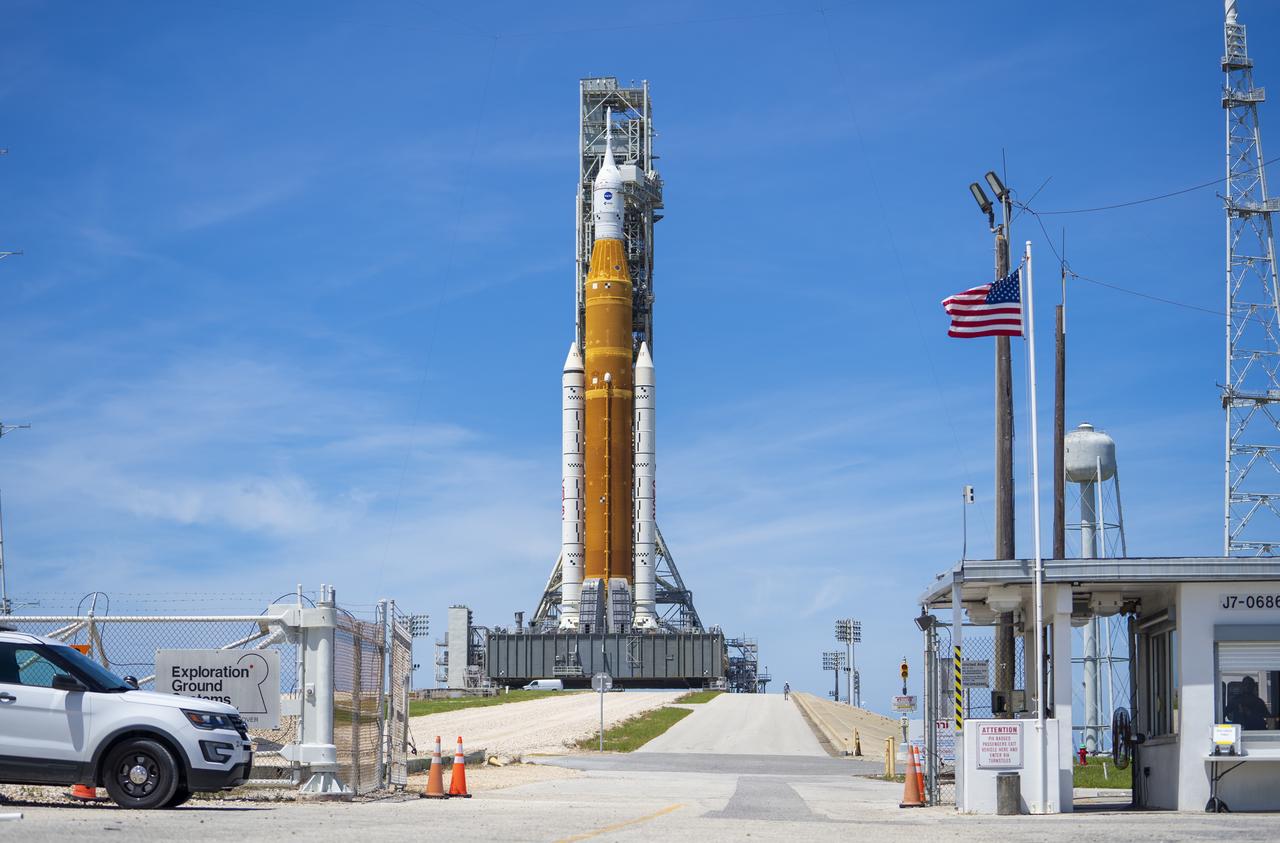

NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket with the Orion spacecraft aboard is seen atop the mobile launcher at Launch 39B at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Artemis I mission is the first integrated test of the agency’s deep space exploration systems: the Space Launch System rocket, Orion spacecraft, and supporting ground systems. The mission is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon. Launch of the uncrewed flight test is targeted for no earlier than Aug. 29 at 8:33 a.m. ET. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.