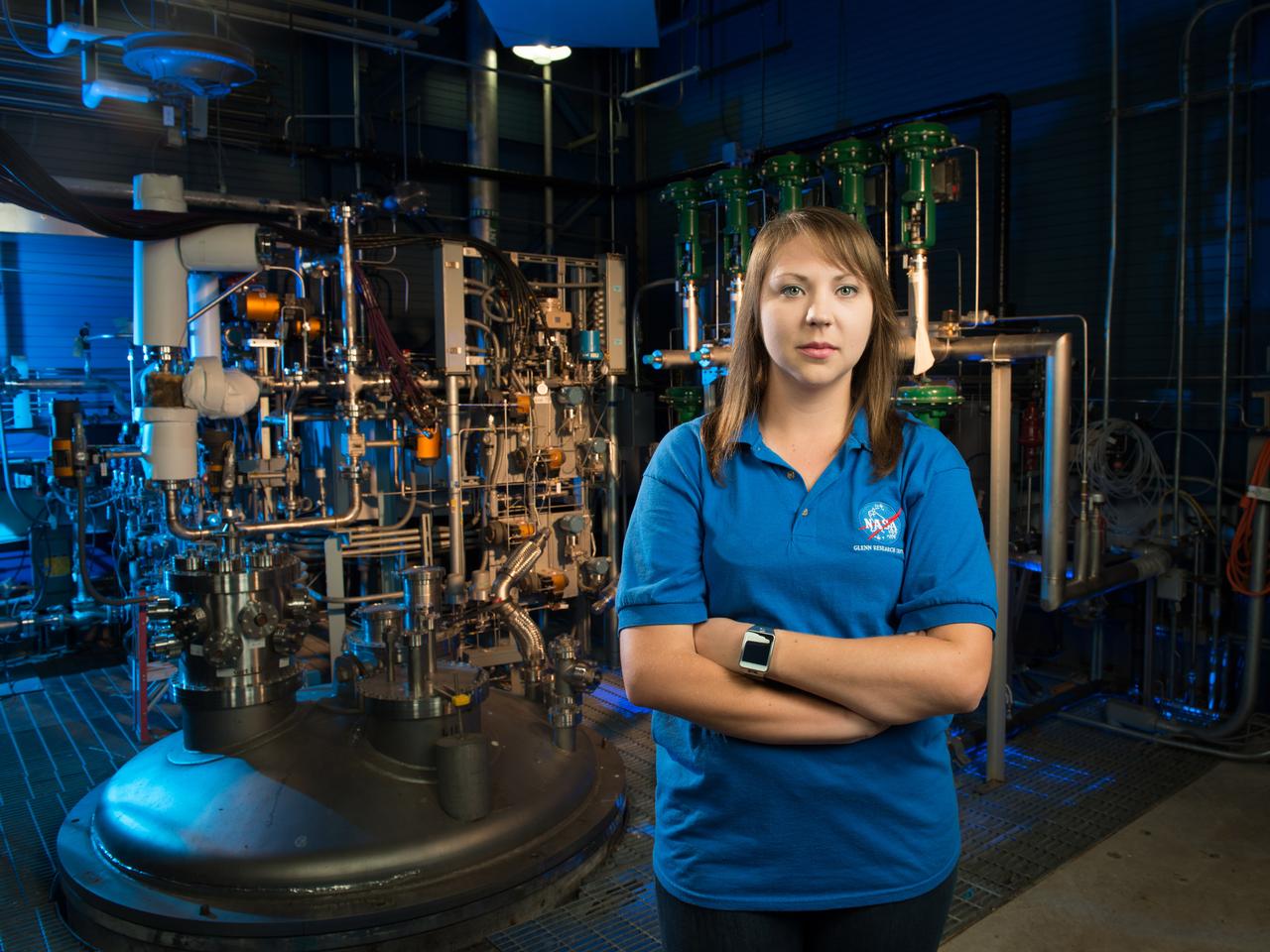
NASA Glenn engineer Monica Guzik in the Small Multi-Purpose Research Facility (SMiRF). The facility provides the ability to simulate the environmental conditions encountered in space for a variety of cryogenic applications such as thermal protection systems, fluid transfer operations and propellant level gauging. SMiRF is a low-cost, small-scale screening facility for concept and component testing of a wide variety of hardware and is capable of testing cryogenic hydrogen, oxygen, methane and nitrogen.
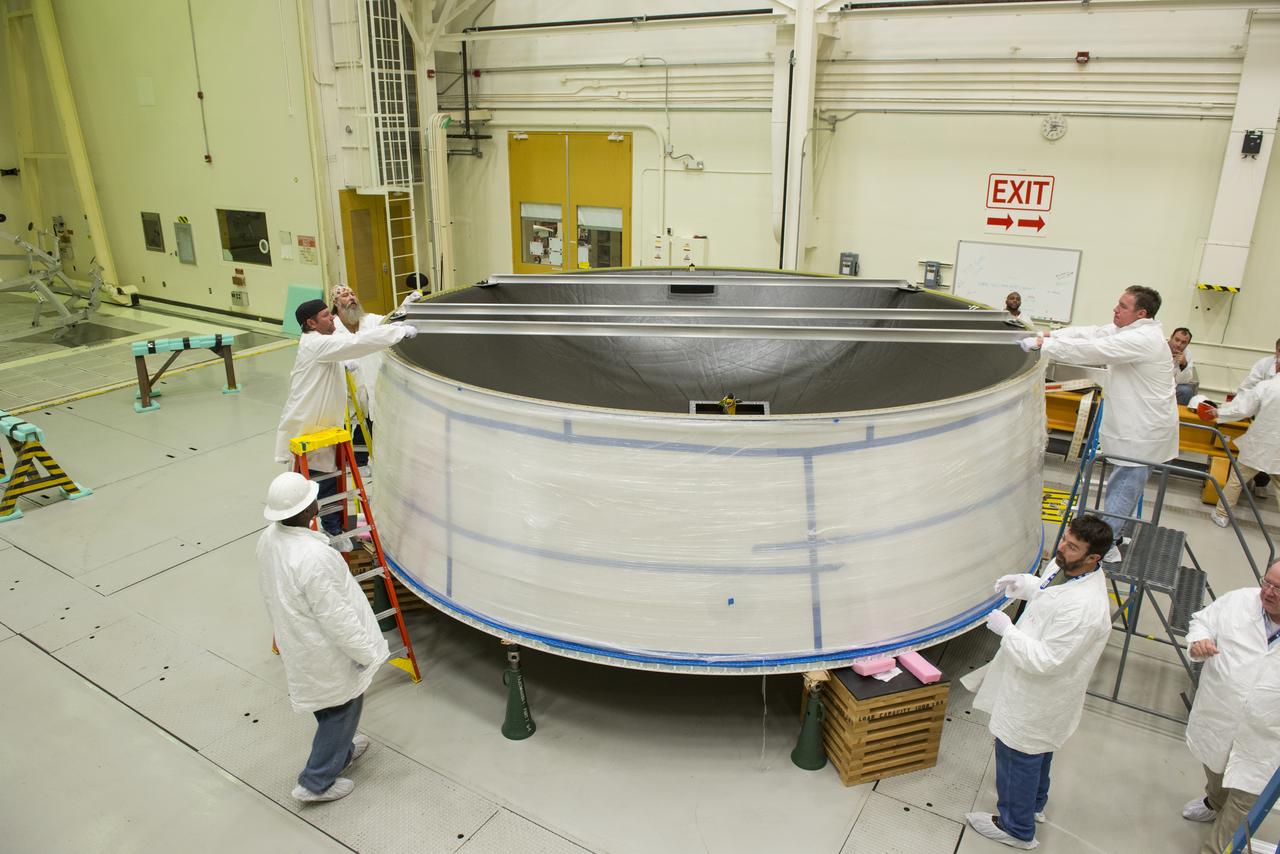

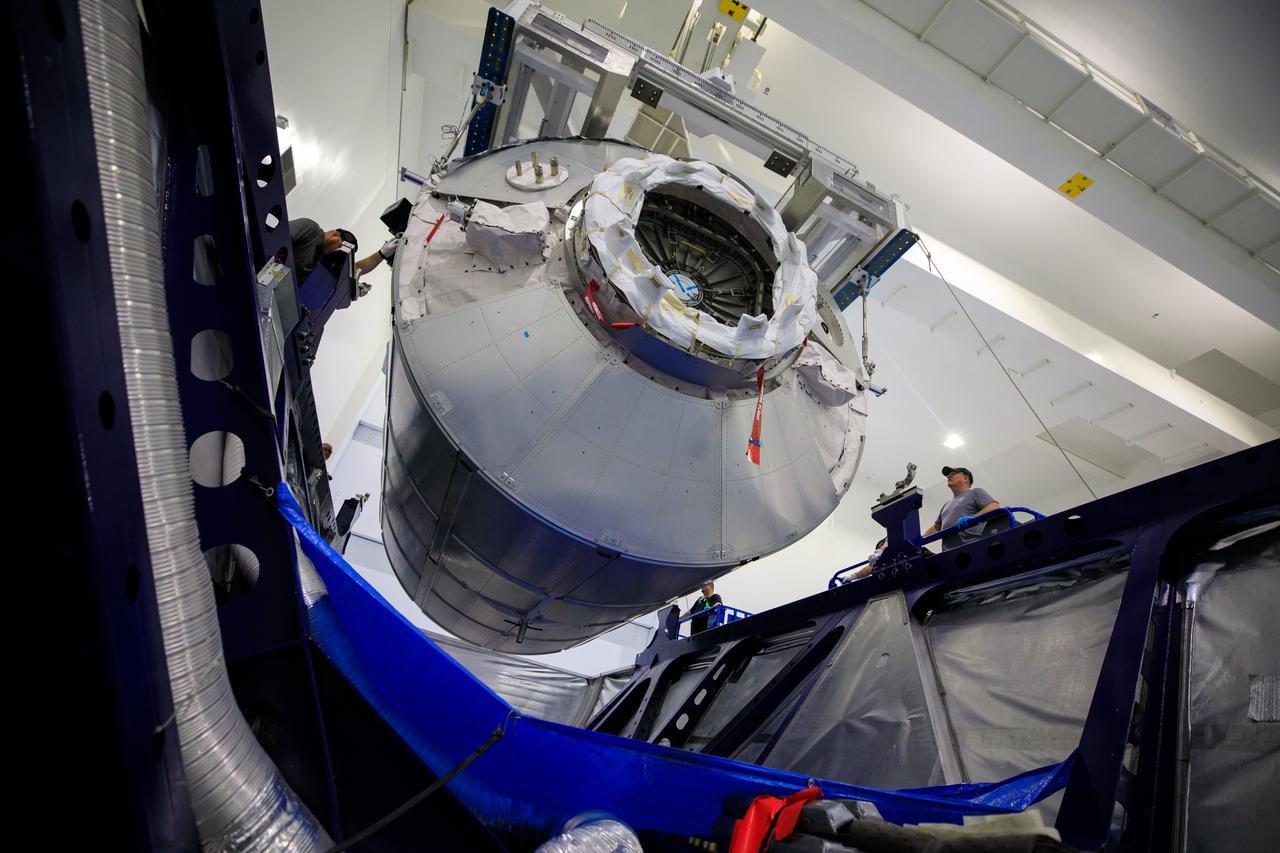
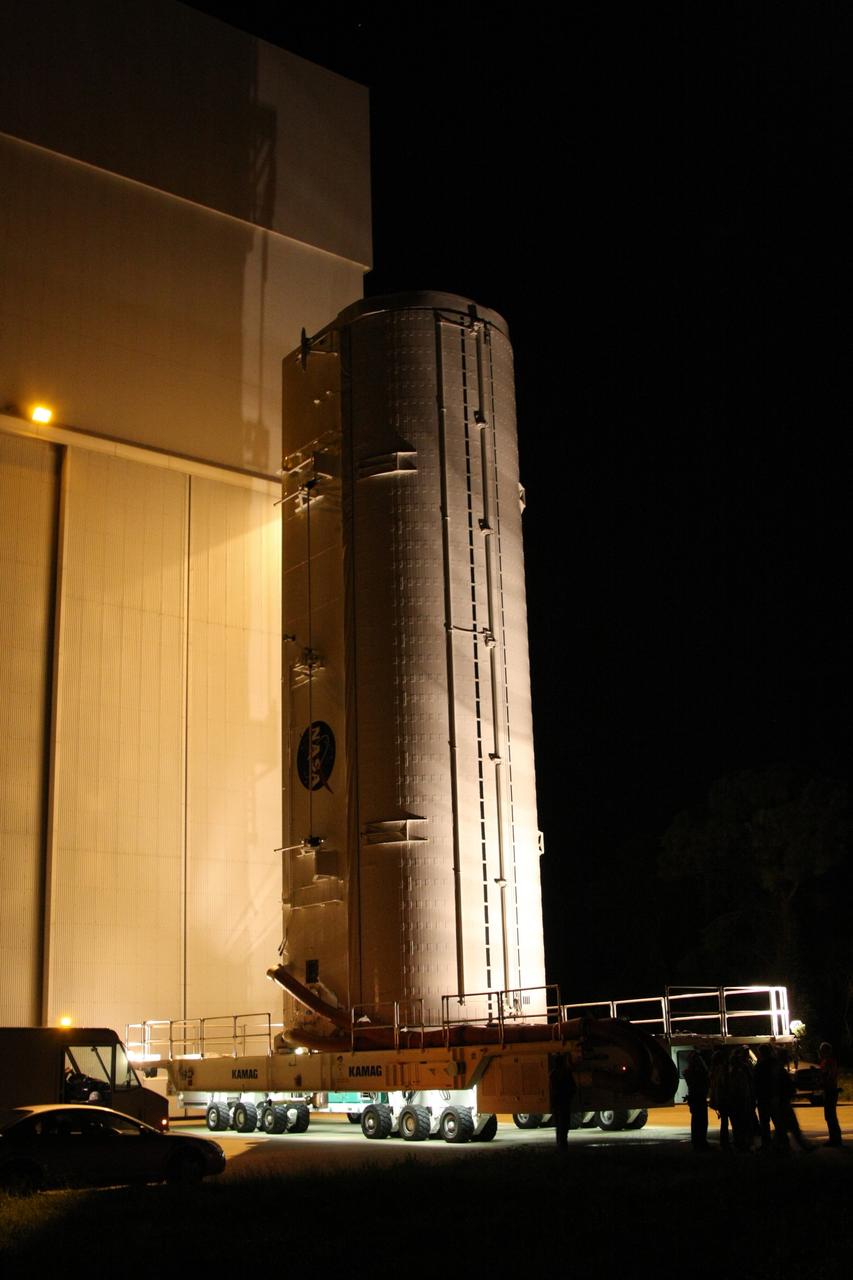
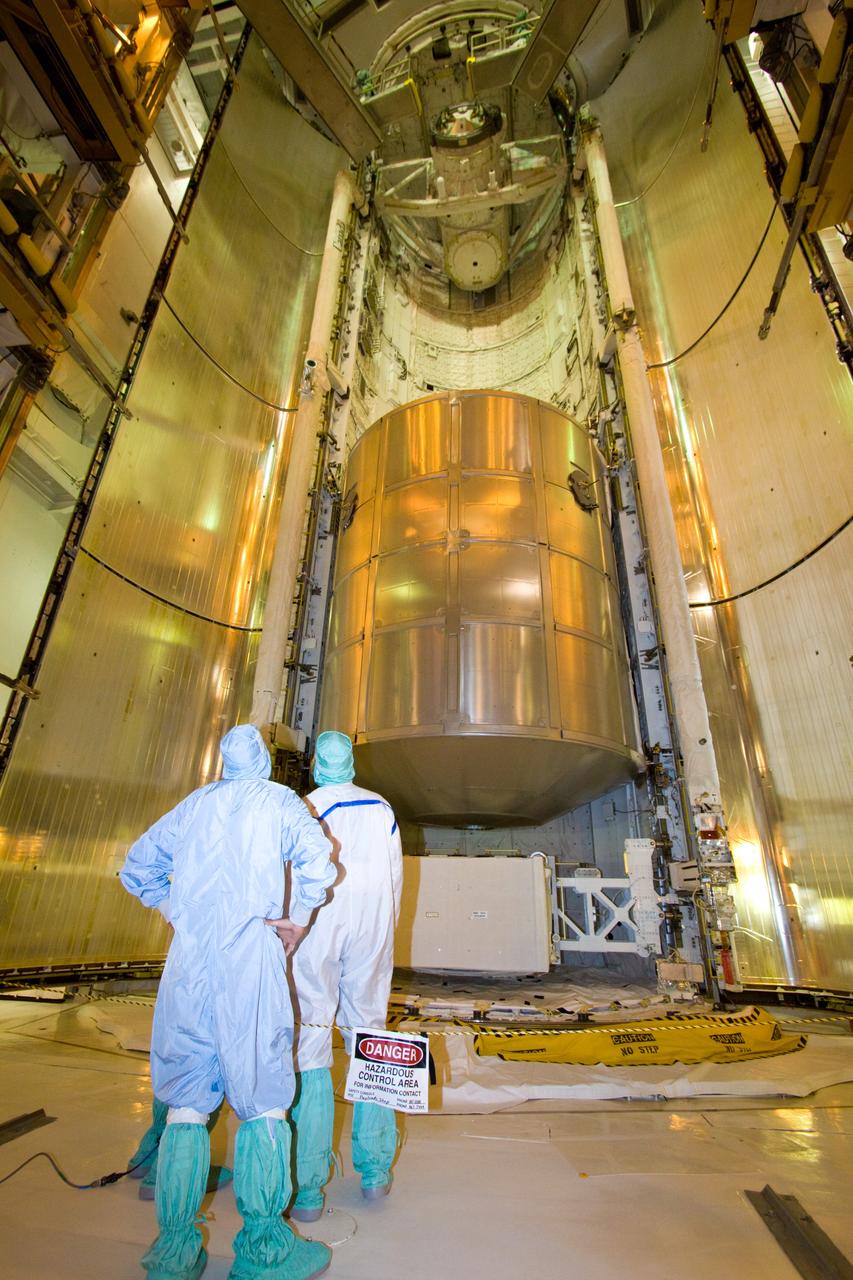
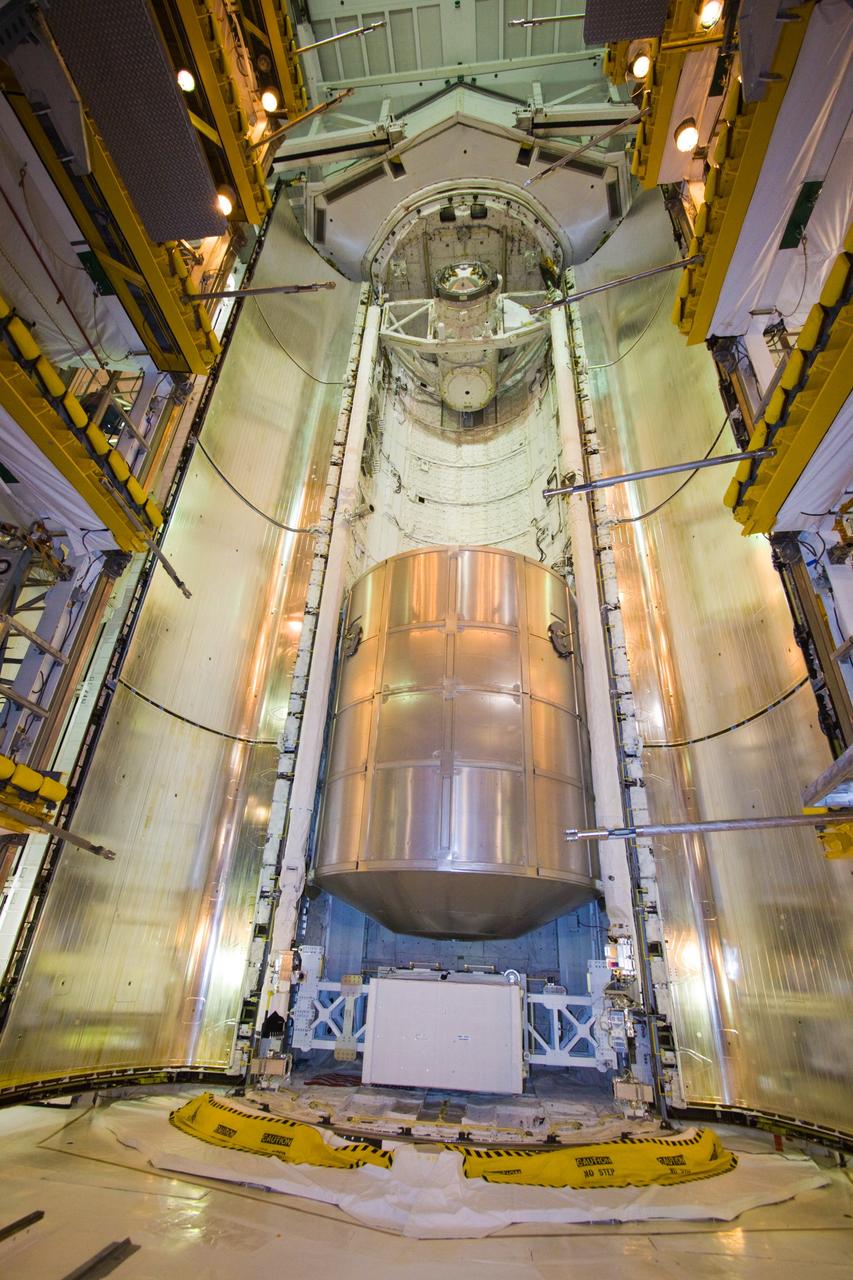
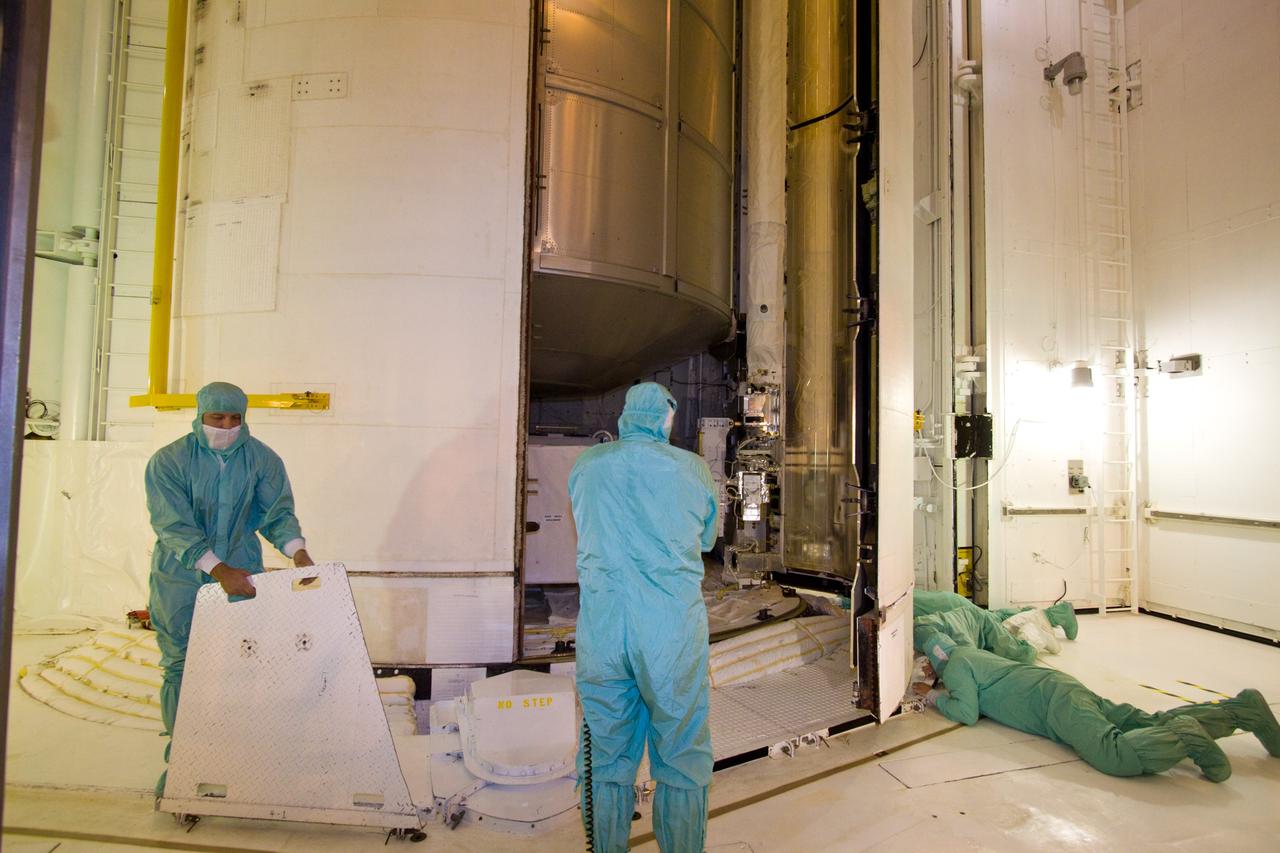
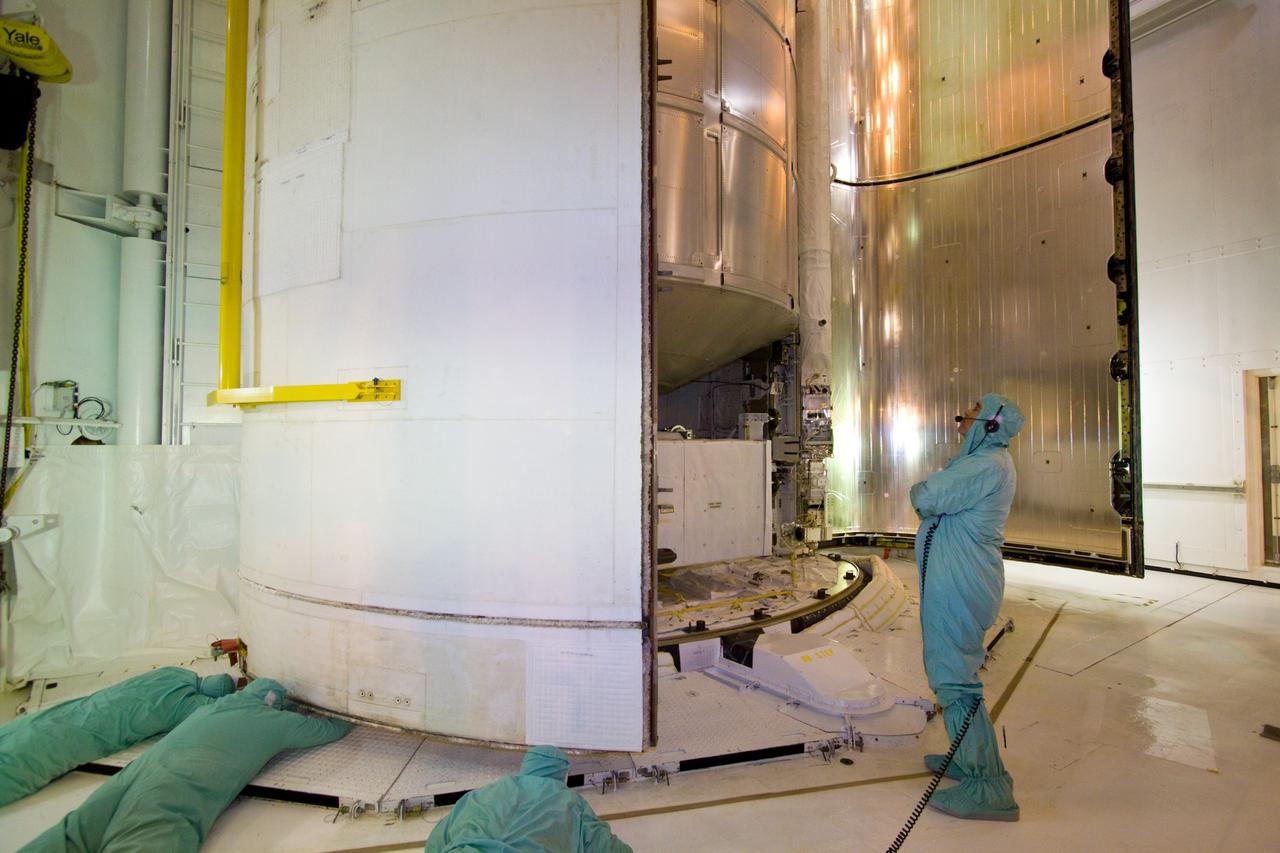
MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
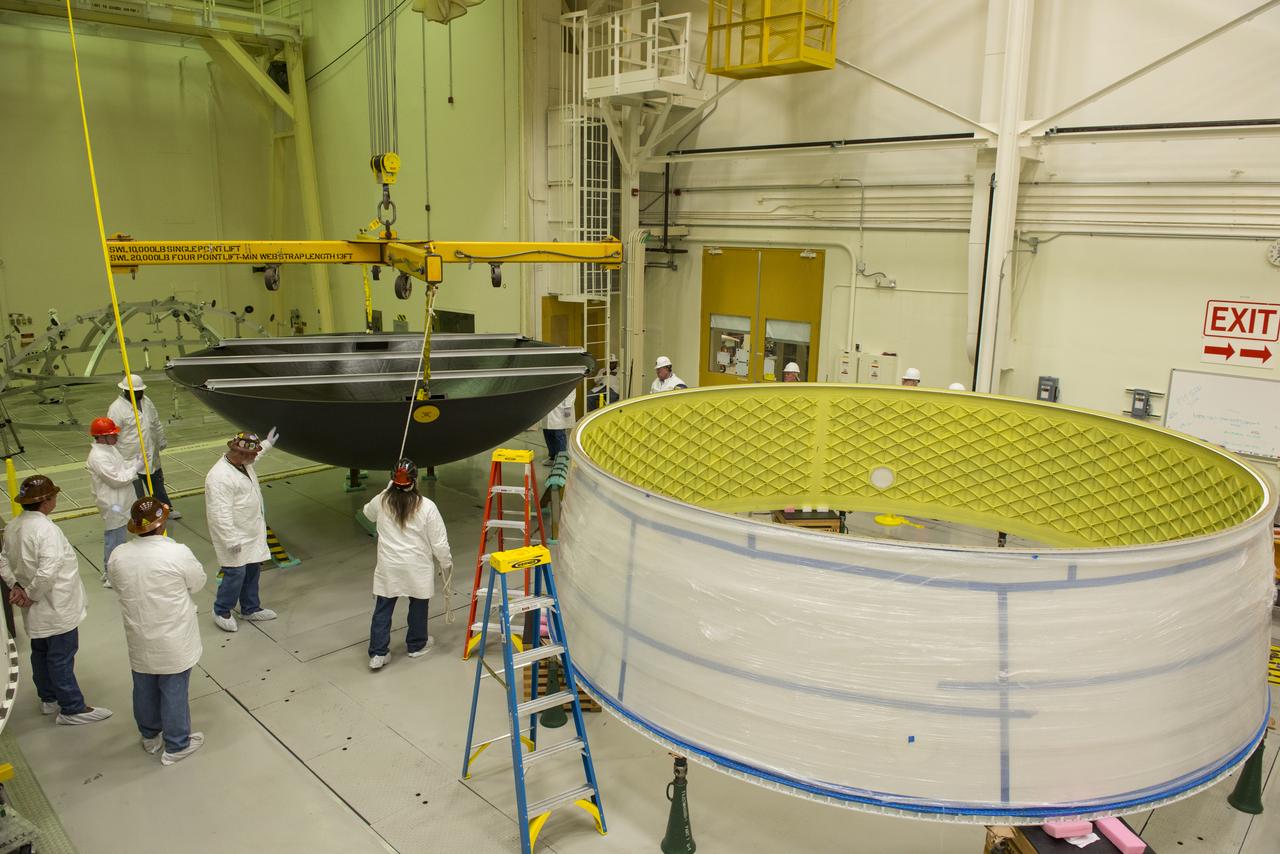

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.F
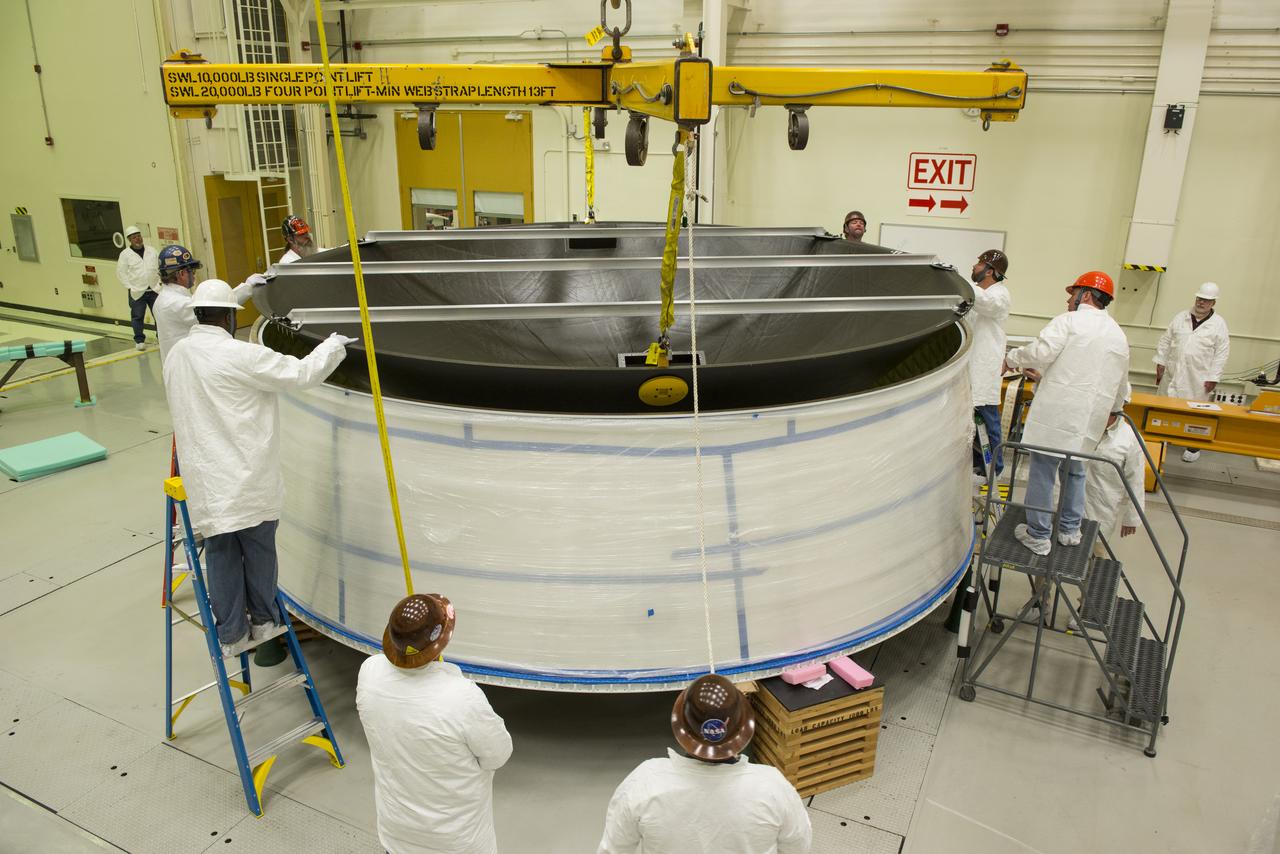

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
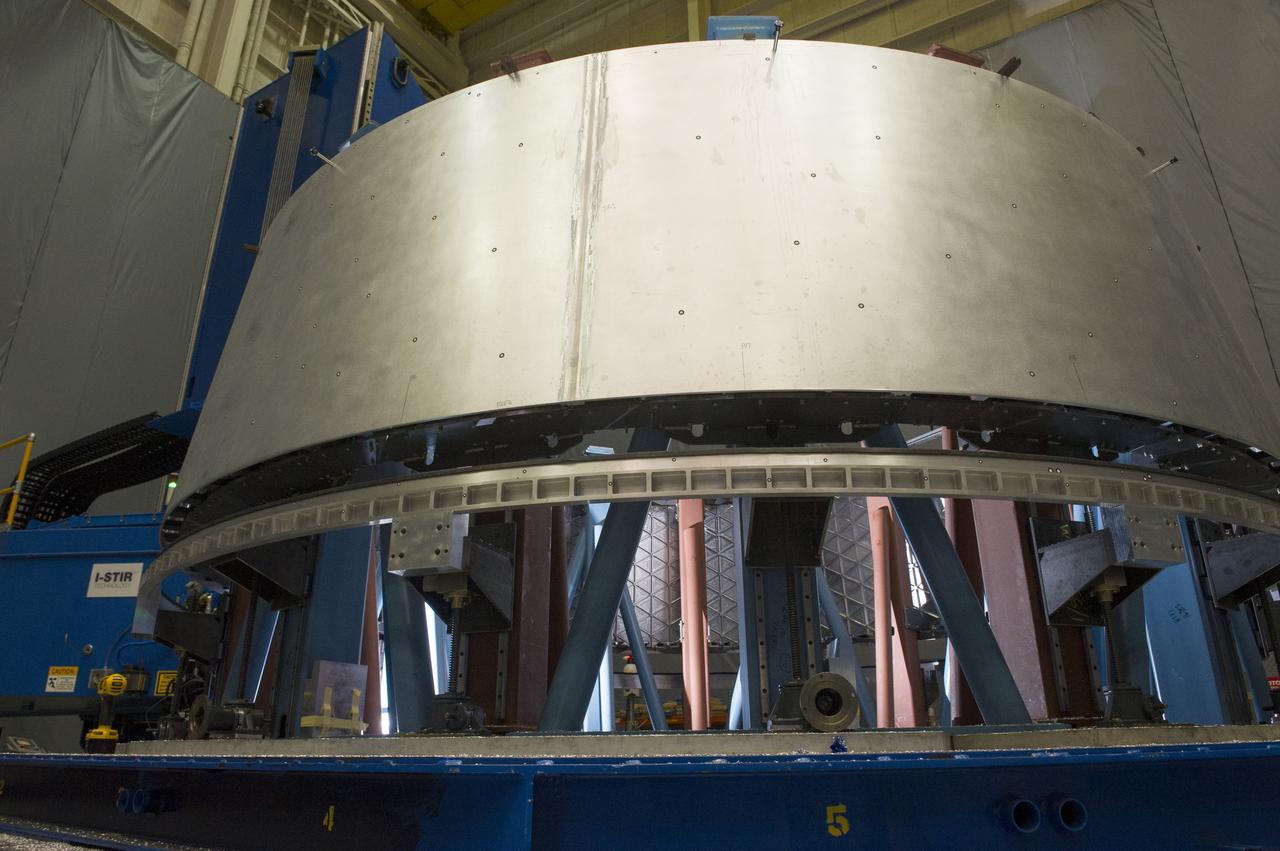
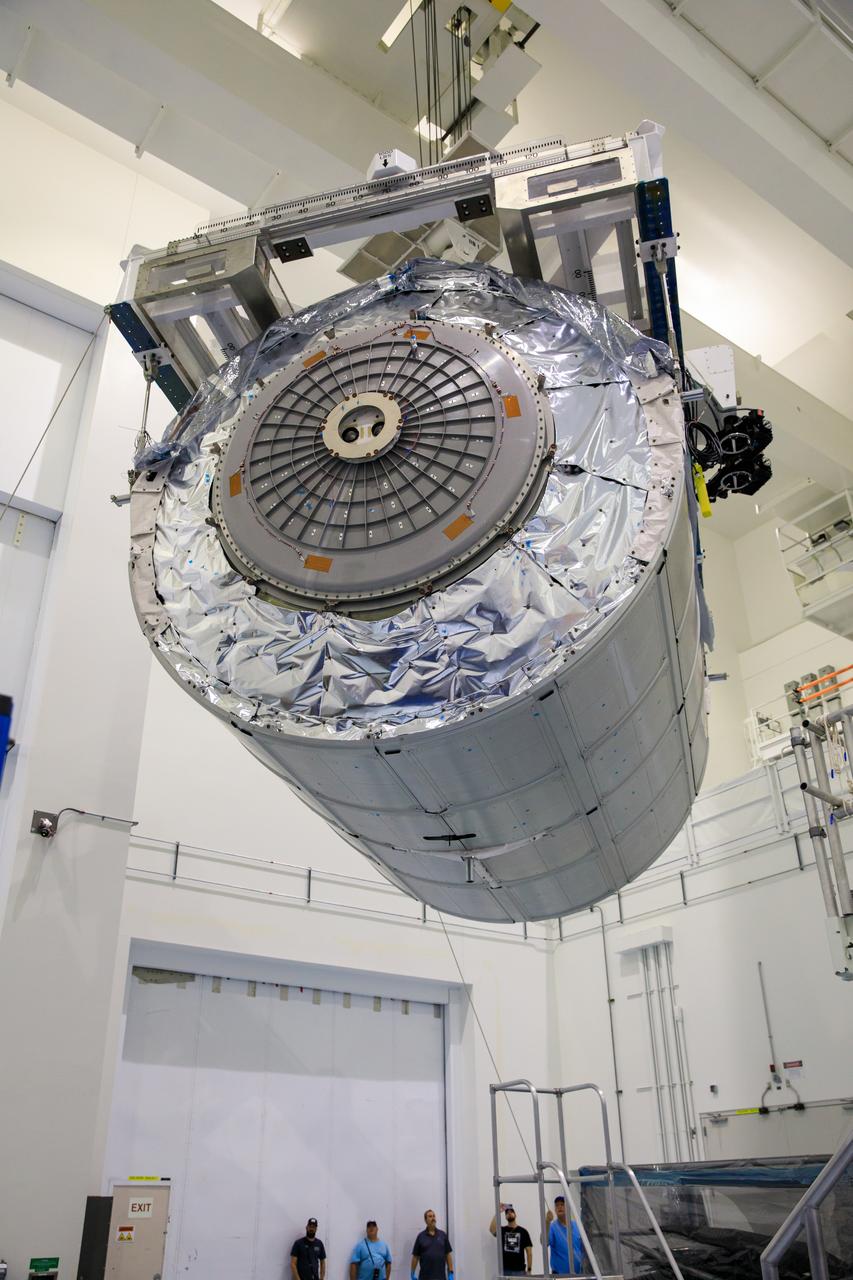
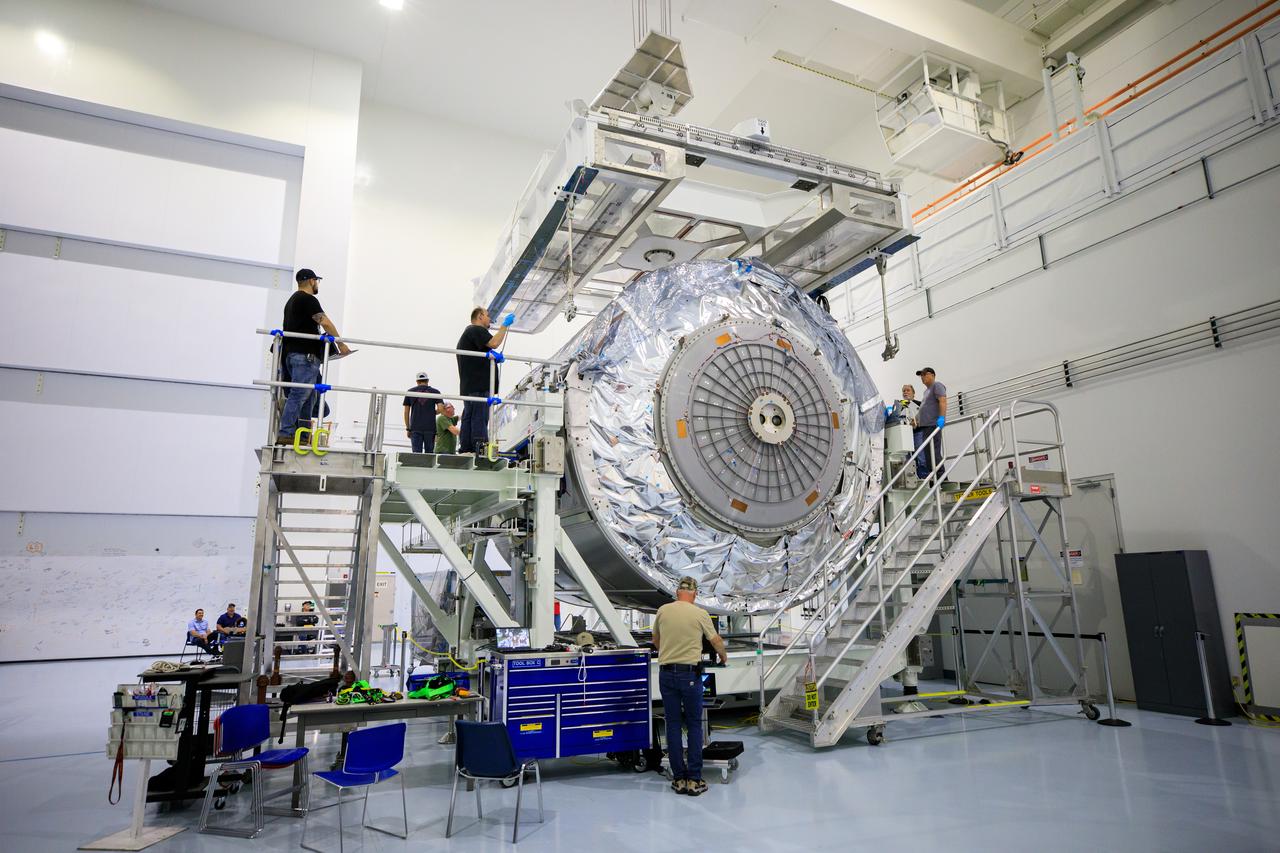
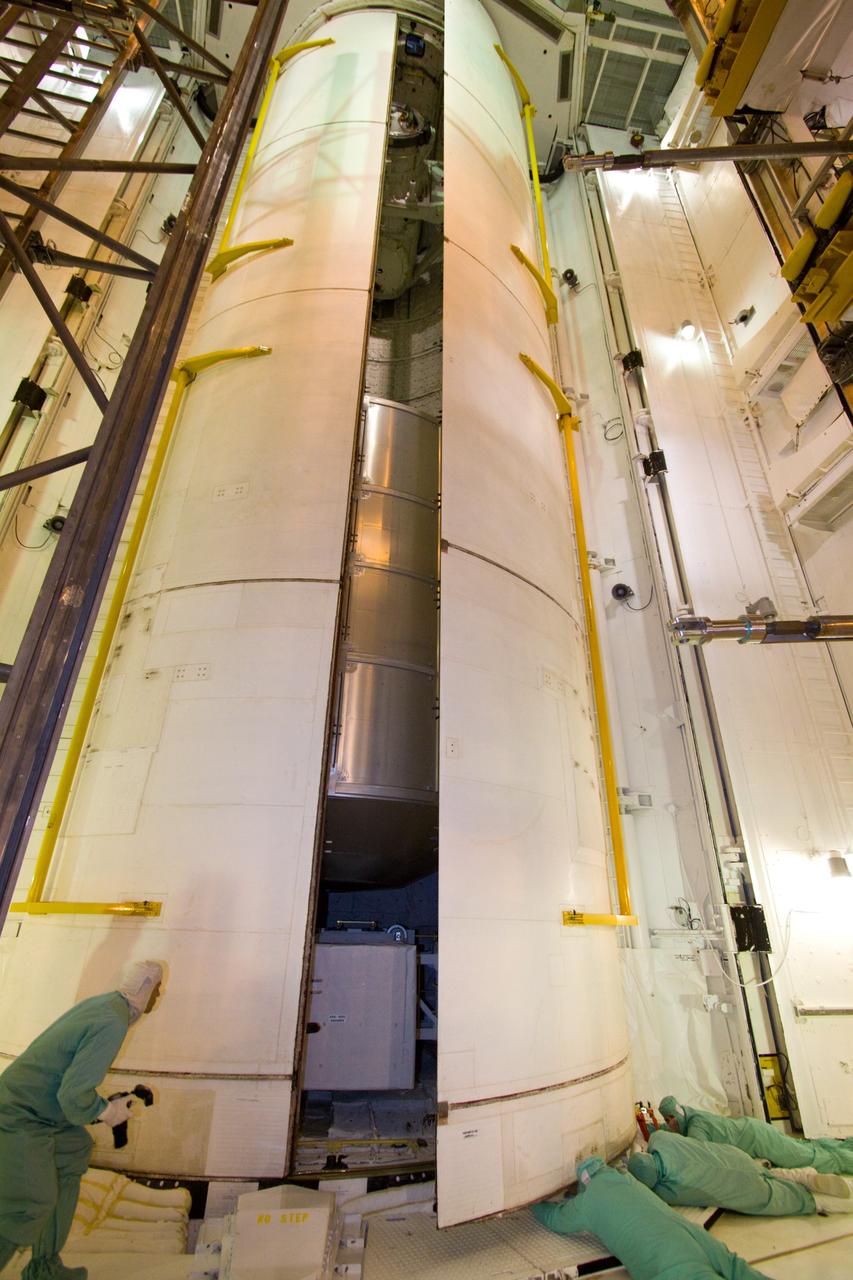
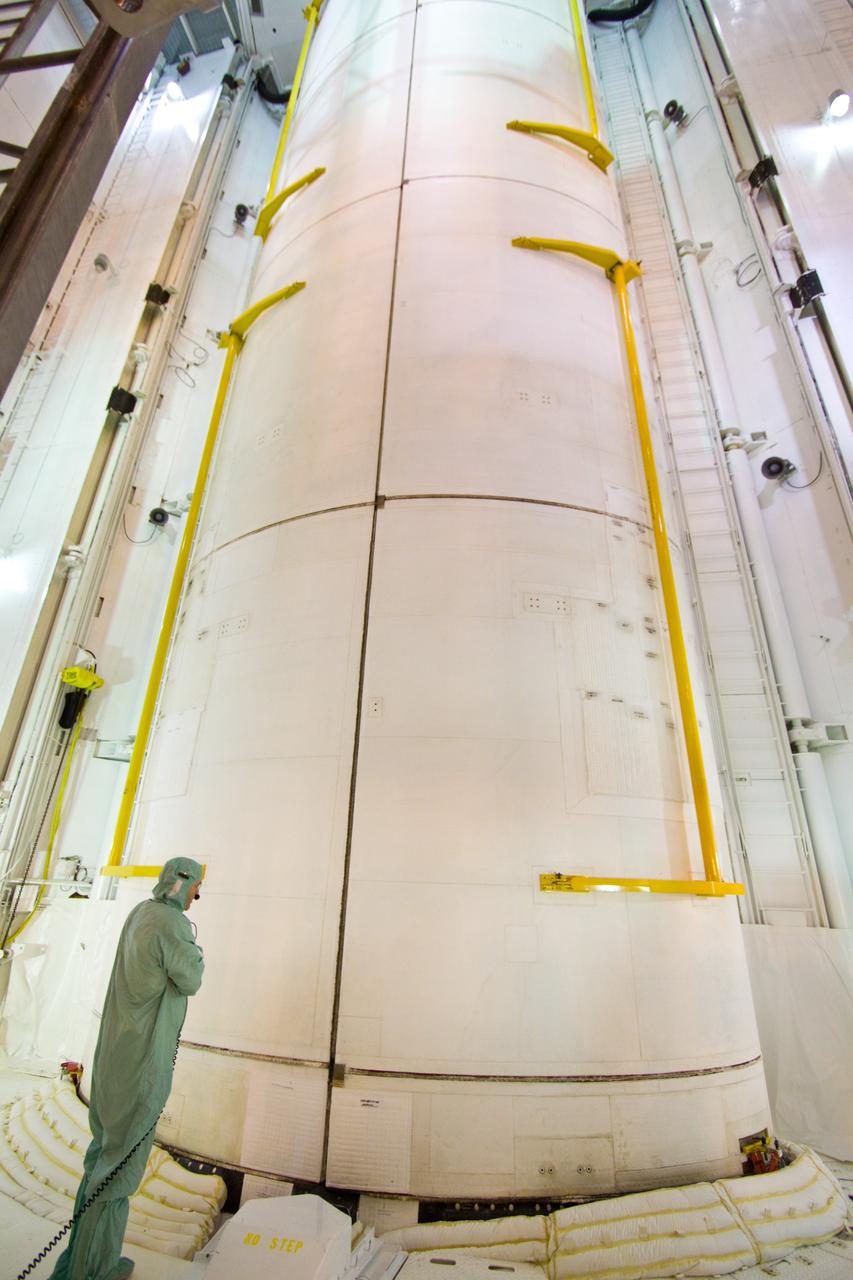
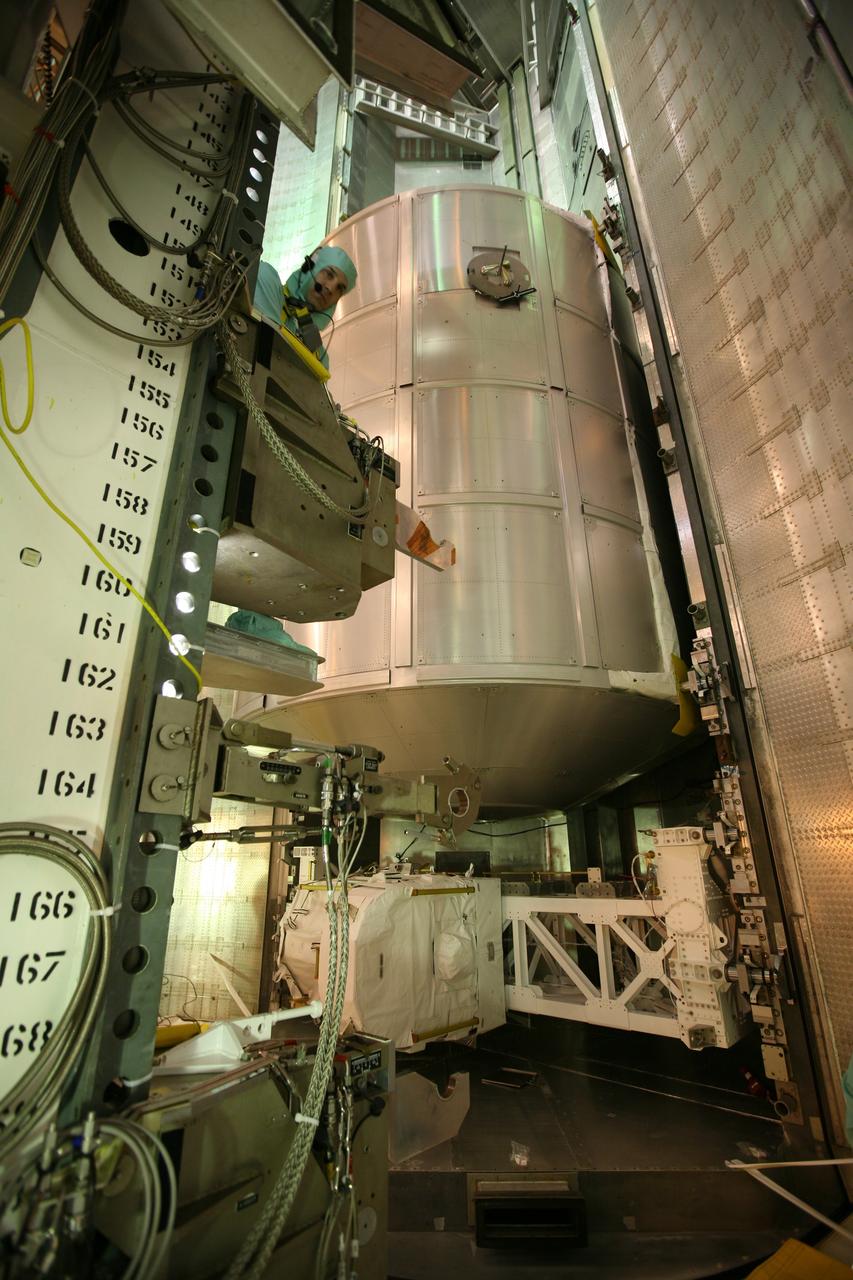
MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE-TO-STAGE ADAPTER(MSA) FLIGHT HARDWARE ON CIRCUMFERENTIAL WELD TOOL, FEBRUARY 27, 2013
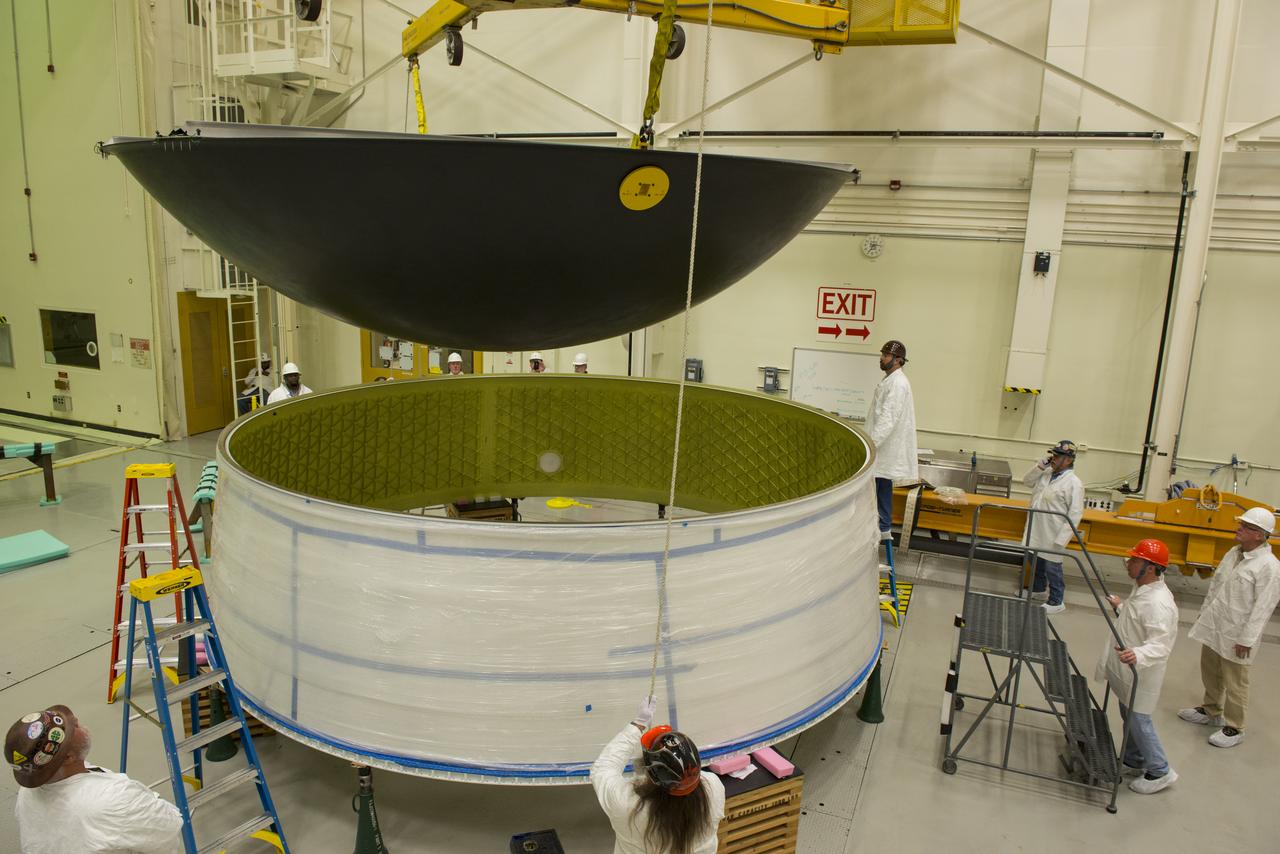

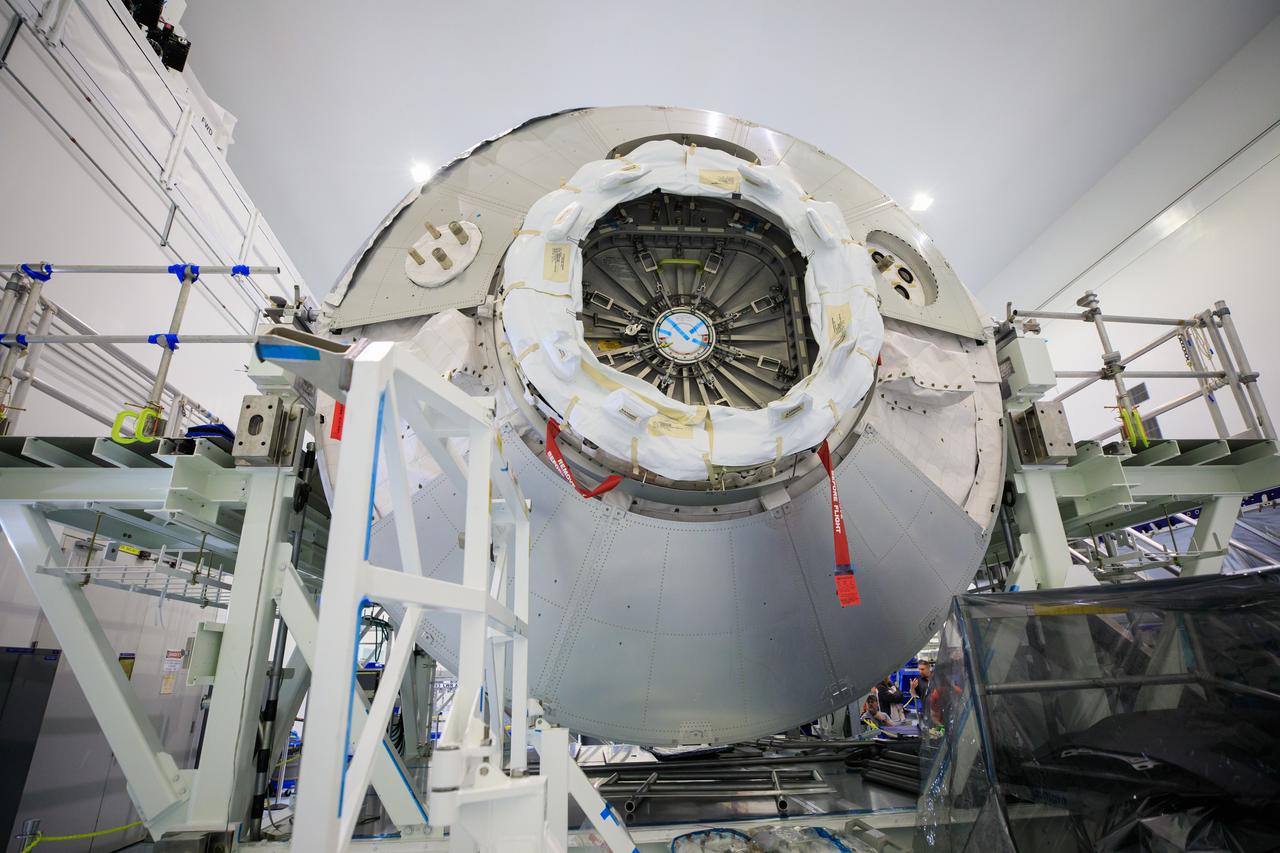
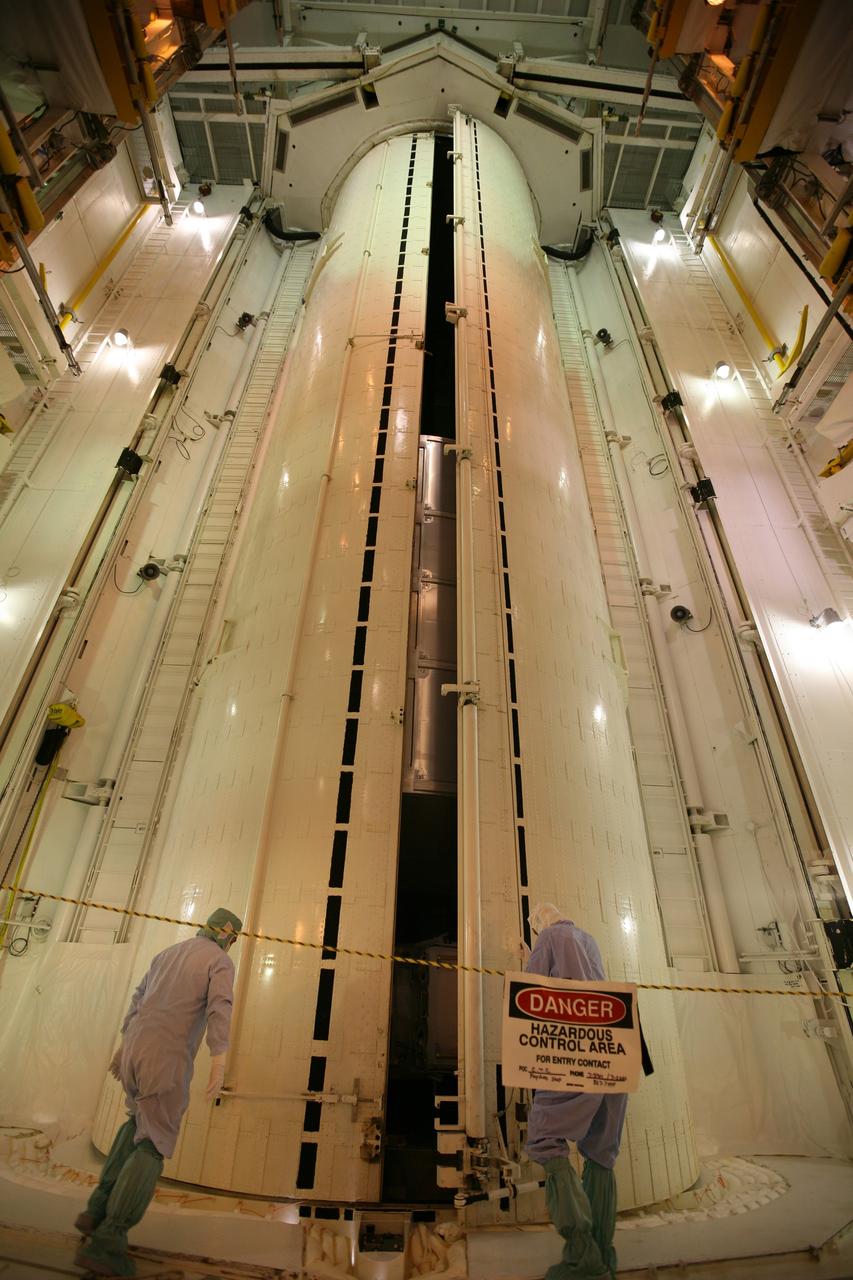
MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
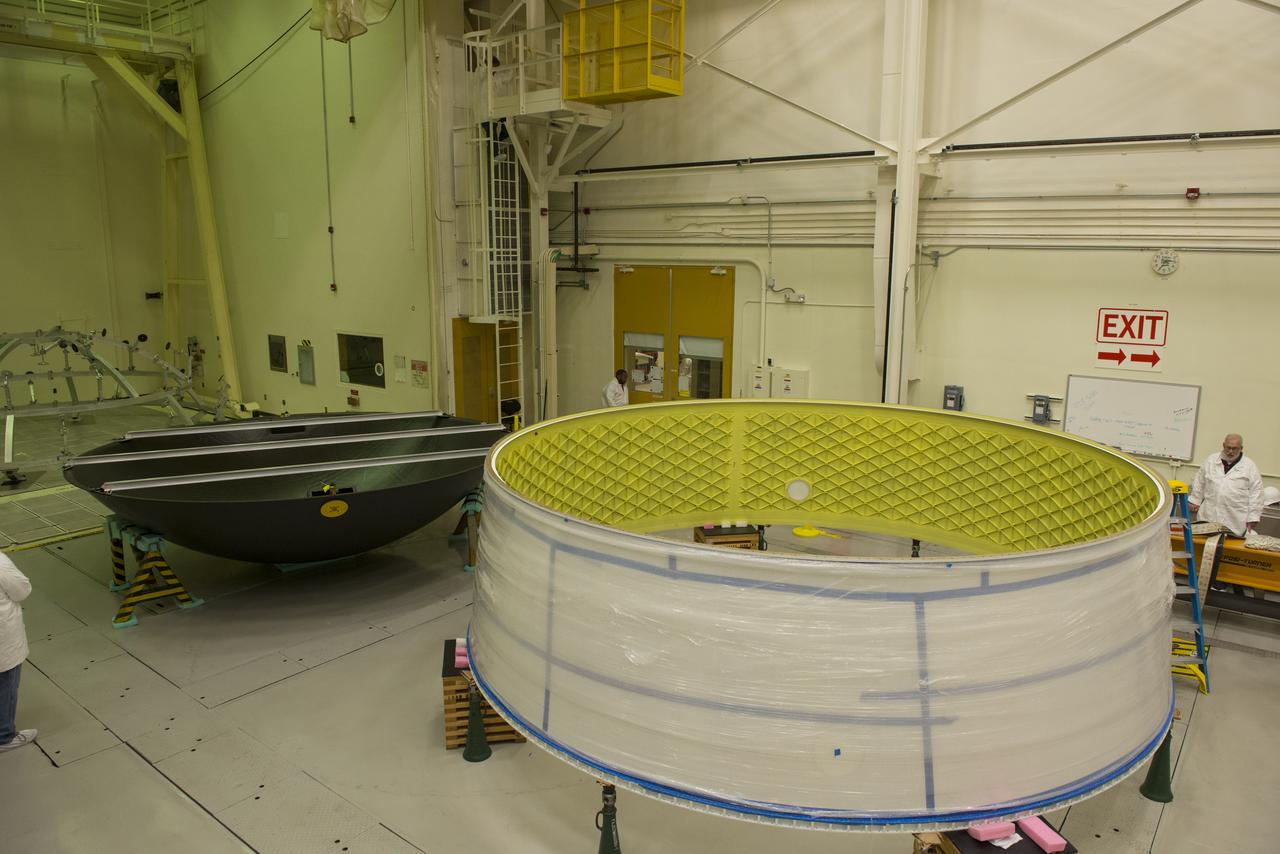

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
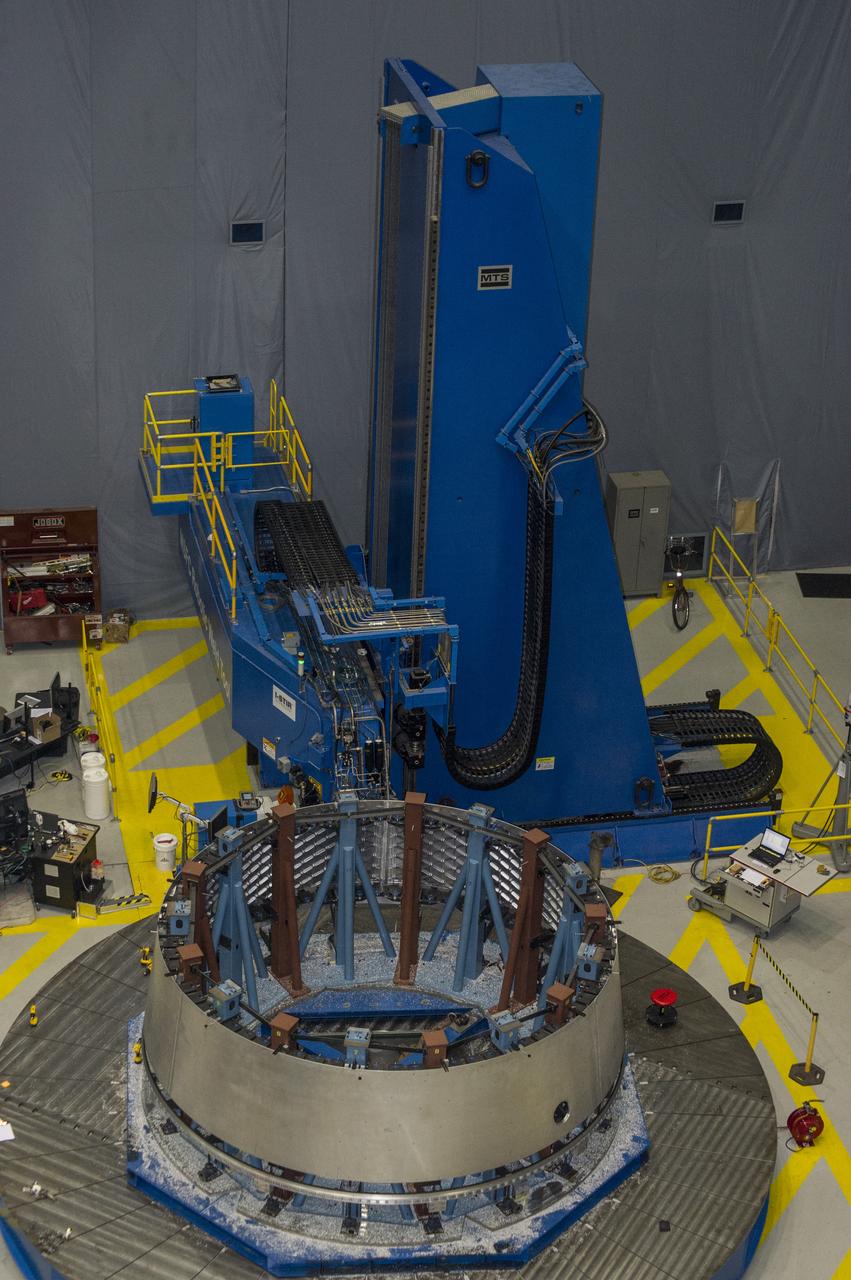
MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE-TO-STAGE ADAPTER(MSA) FLIGHT HARDWARE ON CIRCUMFERENTIAL WELD TOOL, FEBRUARY 27, 2013
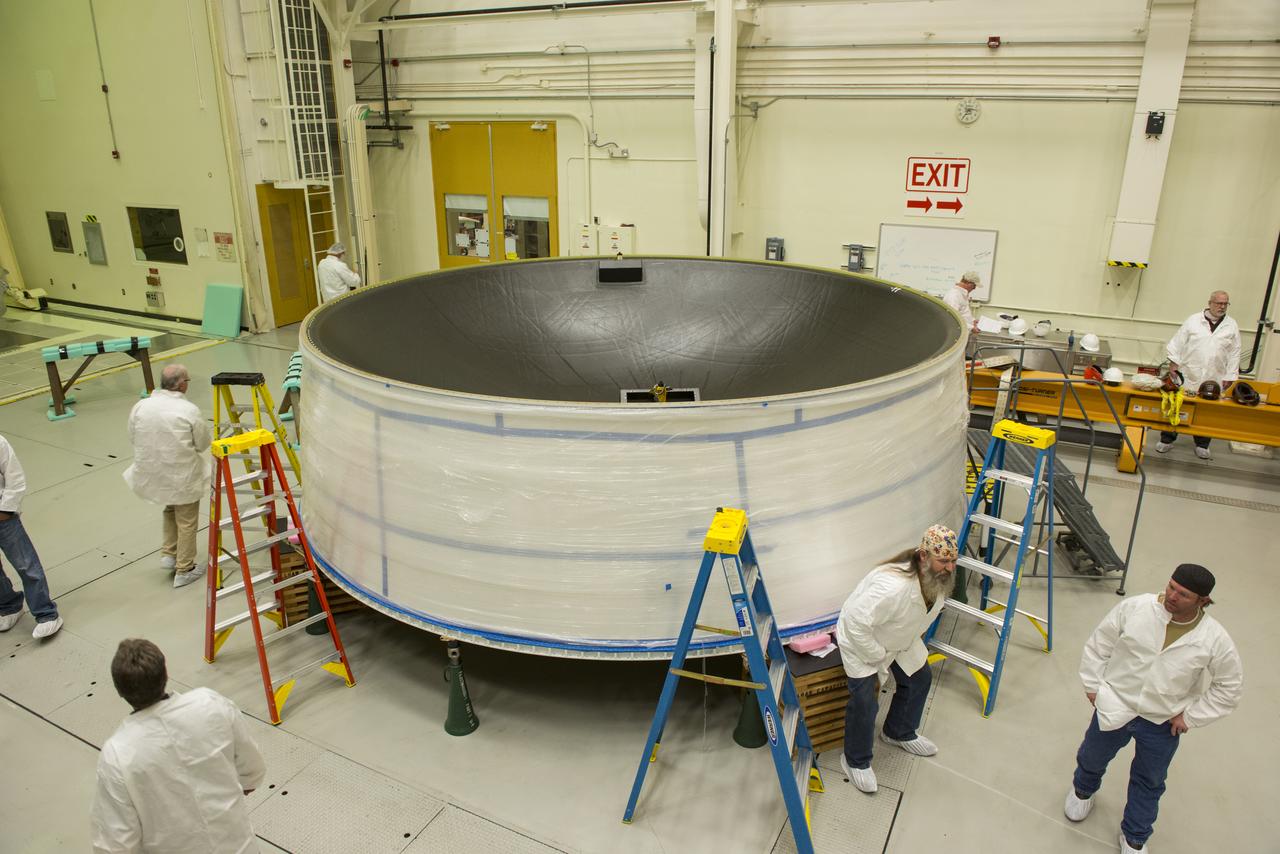

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
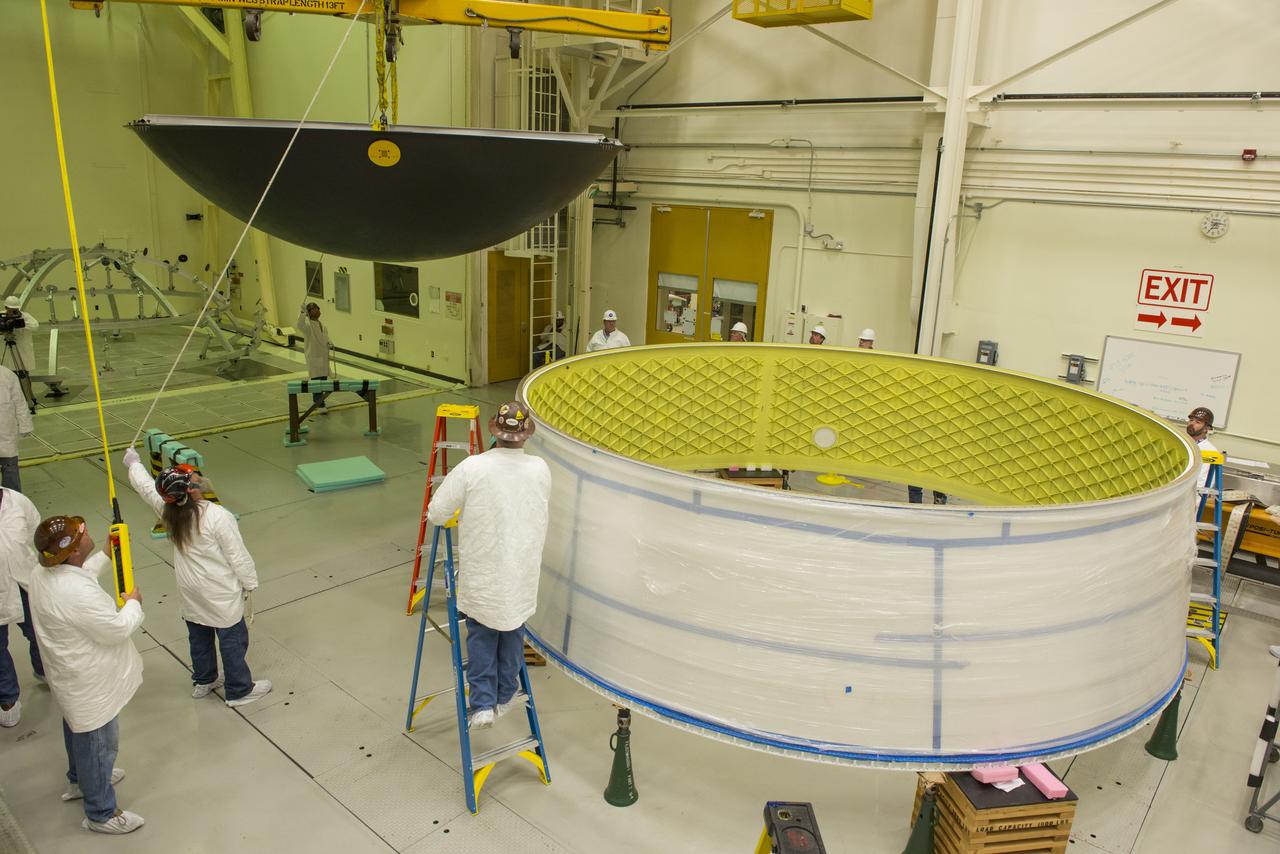

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.

MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
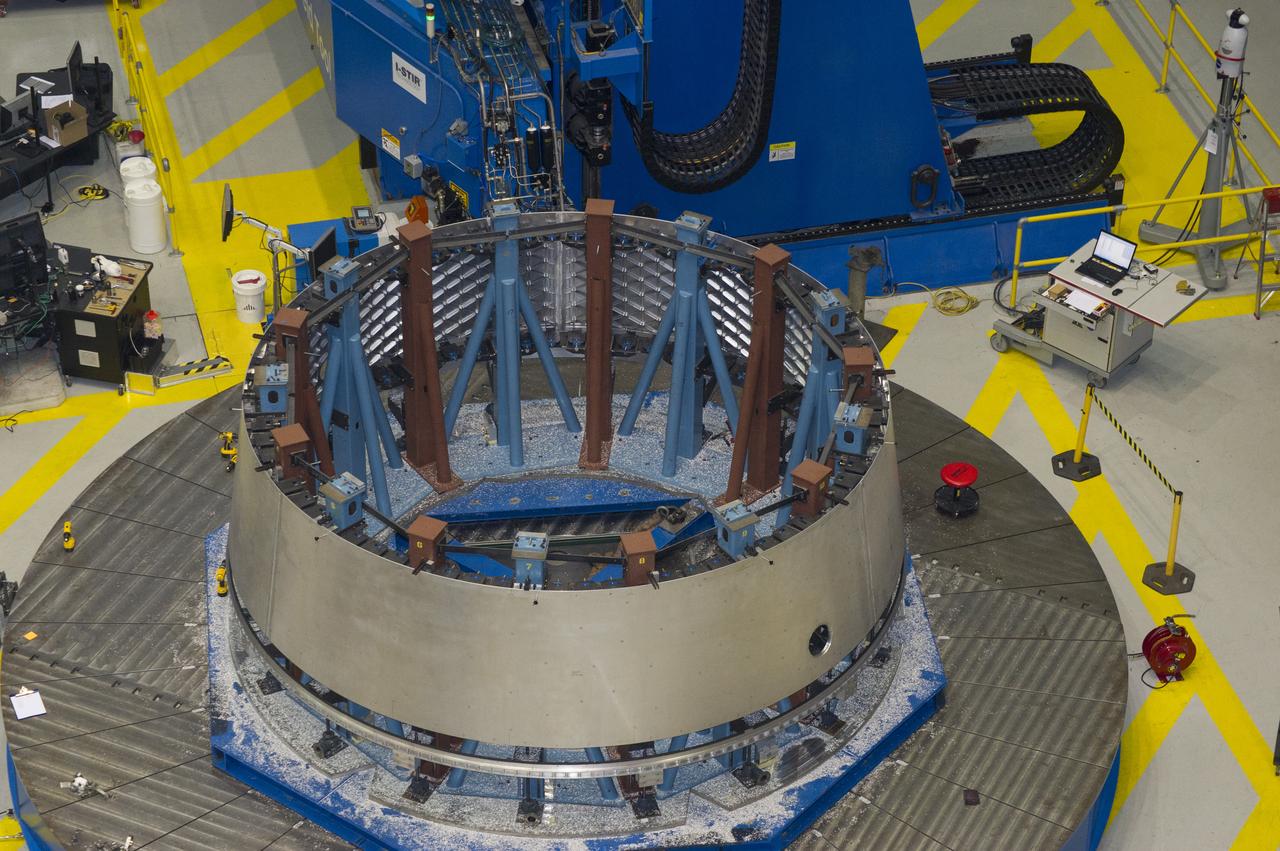
MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE-TO-STAGE ADAPTER(MSA) FLIGHT HARDWARE ON CIRCUMFERENTIAL WELD TOOL, FEBRUARY 27, 2013
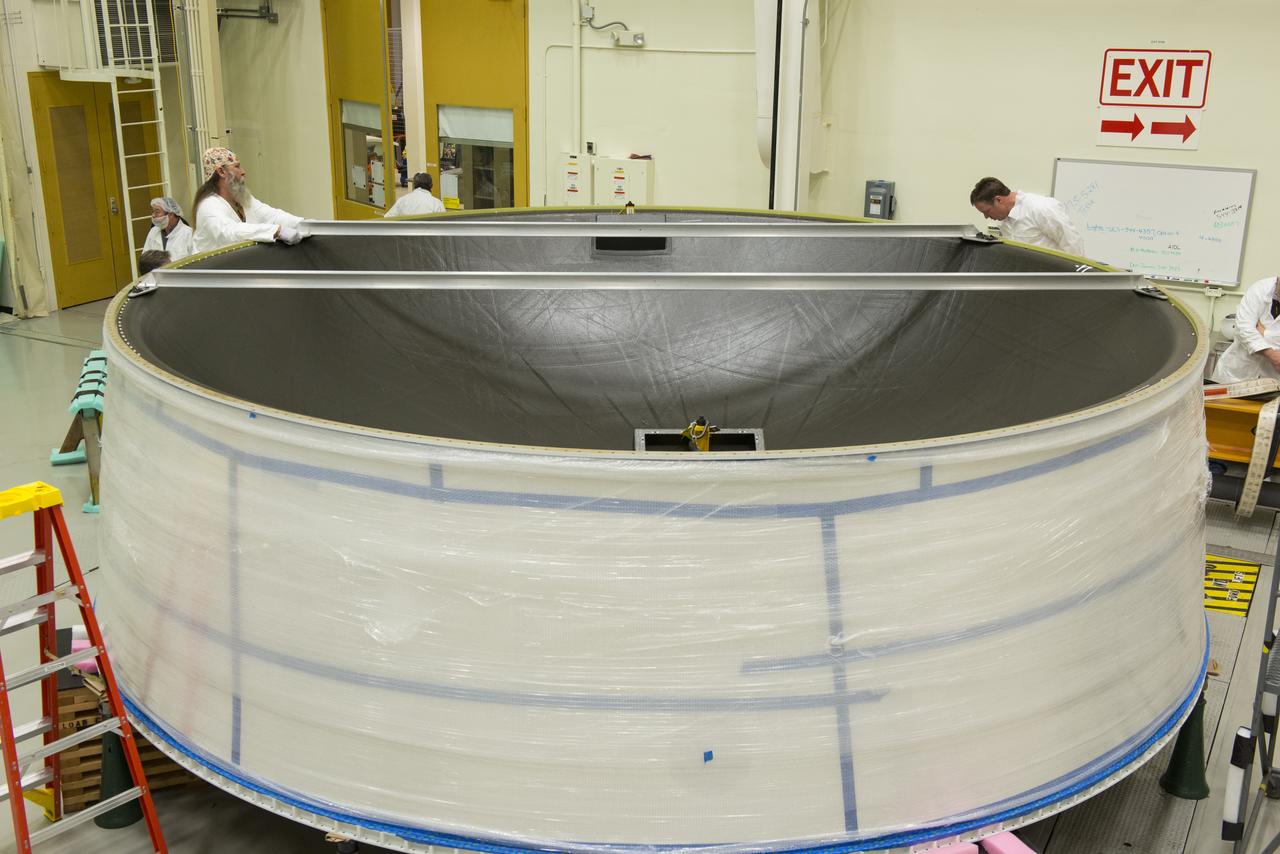
MATING OF THE MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE STAGE ADAPTER (MSA) WITH ITS DIAPHRAGM IN BLDG. 4708. DECEMBER 20, 2014.
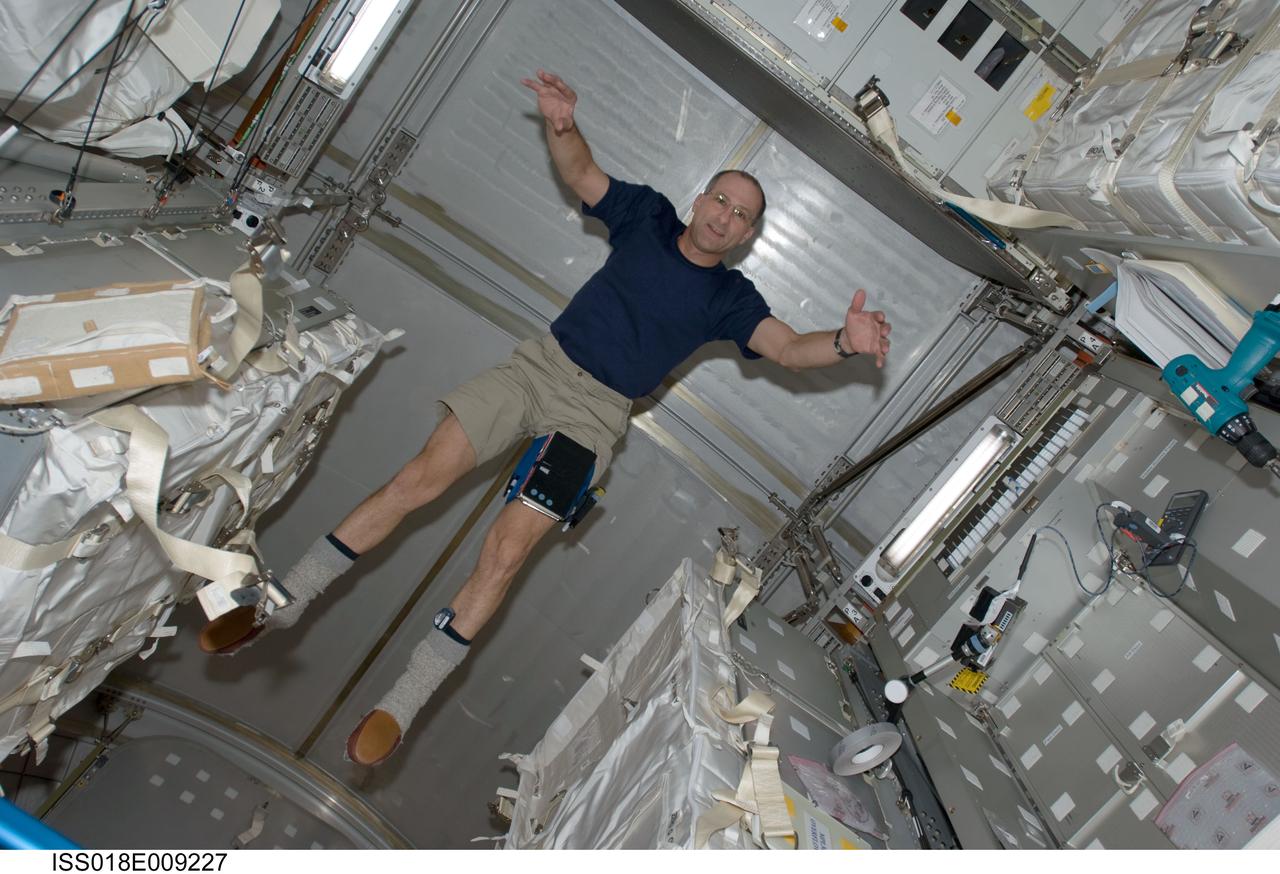

ISS018-E-009227 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Donald Pettit, STS-126 mission specialist, floats in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module attached to the Earth-facing port of the International Space Station's Harmony node while Space Shuttle Endeavour is docked with the station.
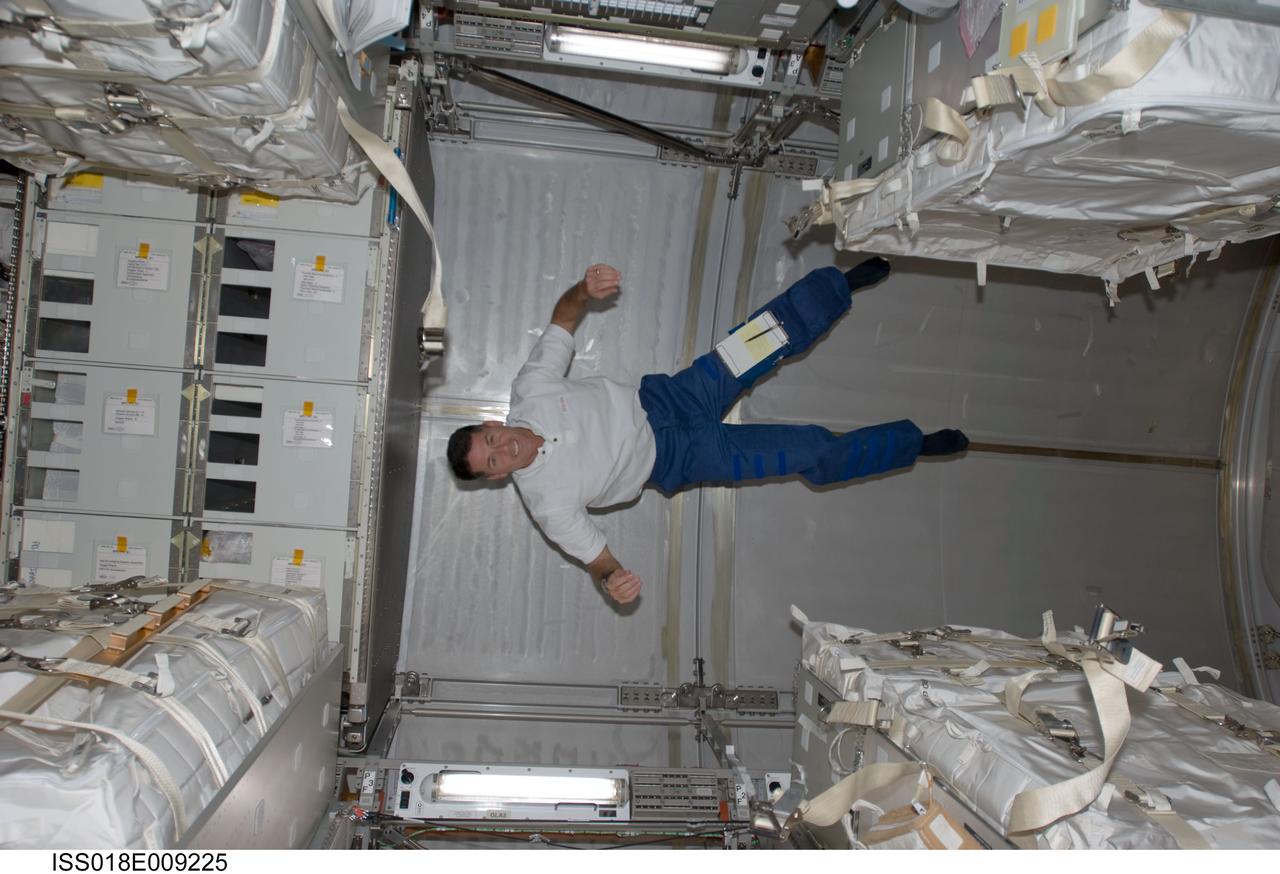

ISS018-E-009225 (18 Nov. 2008) --- Astronaut Shane Kimbrough, STS-126 mission specialist, floats in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module attached to the Earth-facing port of the International Space Station's Harmony node while Space Shuttle Endeavour is docked with the station.
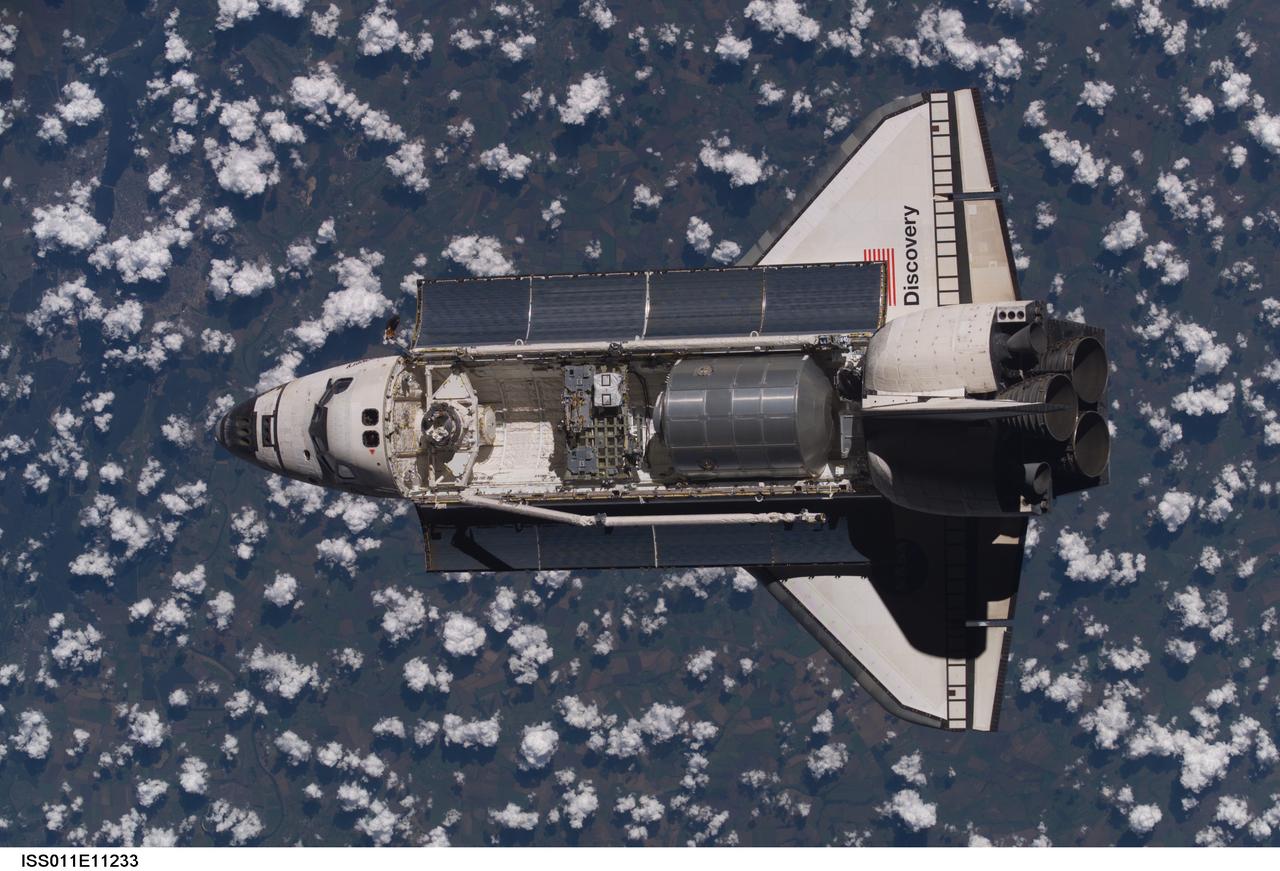

Launched on July 26, 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) and the External Stowage Platform-2. Back dropped by popcorn-like clouds, the MPLM can be seen in the cargo bay as Discovery undergoes rendezvous and docking operations. Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the spacecraft from the International Space Station (ISS).
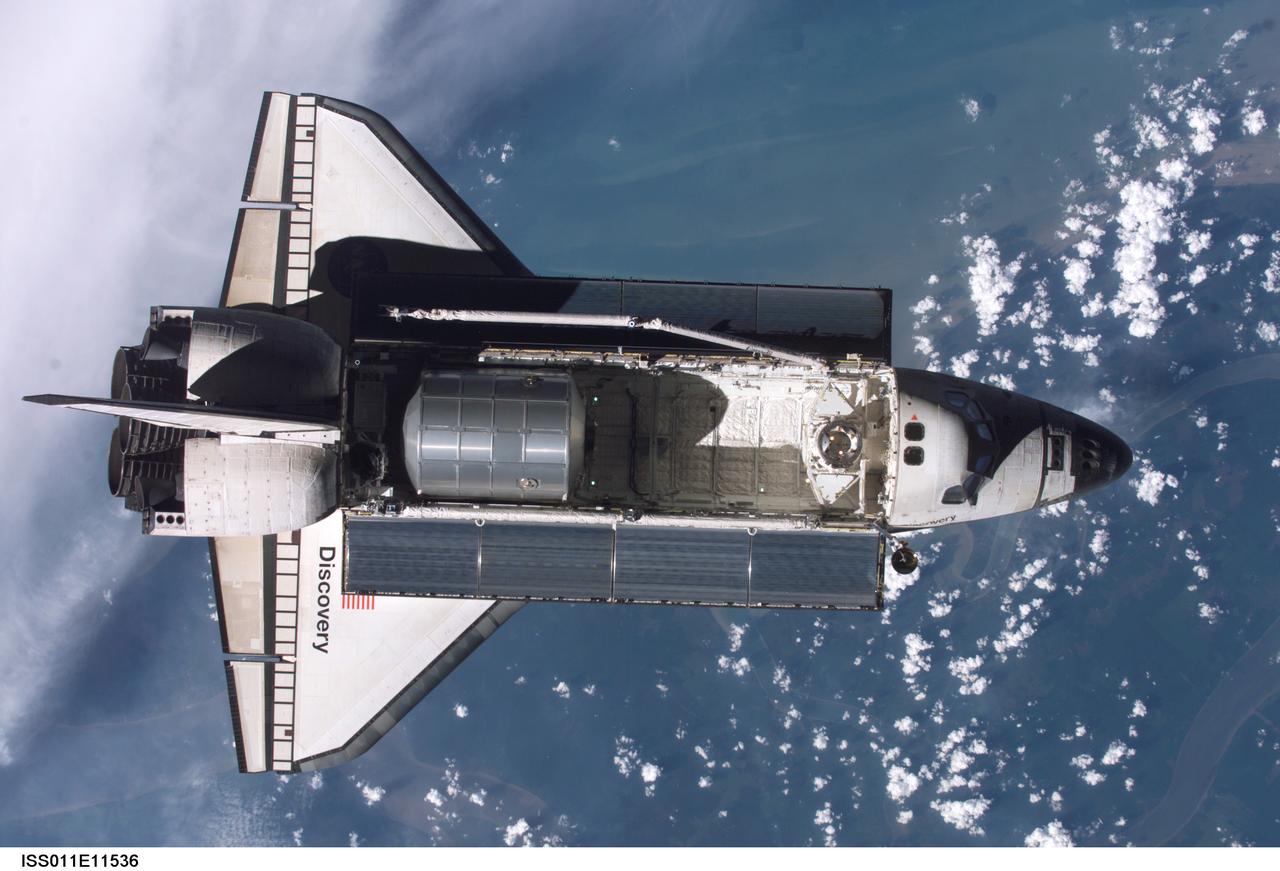

Launched on July 26 2005 from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-114 was classified as Logistics Flight 1. Among the Station-related activities of the mission were the delivery of new supplies and the replacement of one of the orbital outpost's Control Moment Gyroscopes (CMGs). STS-114 also carried the Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) and the External Stowage Platform-2. Back dropped by popcorn-like clouds, the MPLM can be seen in the cargo bay as Discovery undergoes rendezvous and docking operations. Cosmonaut Sergei K. Kriklev, Expedition 11 Commander, and John L. Phillips, NASA Space Station officer and flight engineer photographed the spacecraft from the International Space Station (ISS).
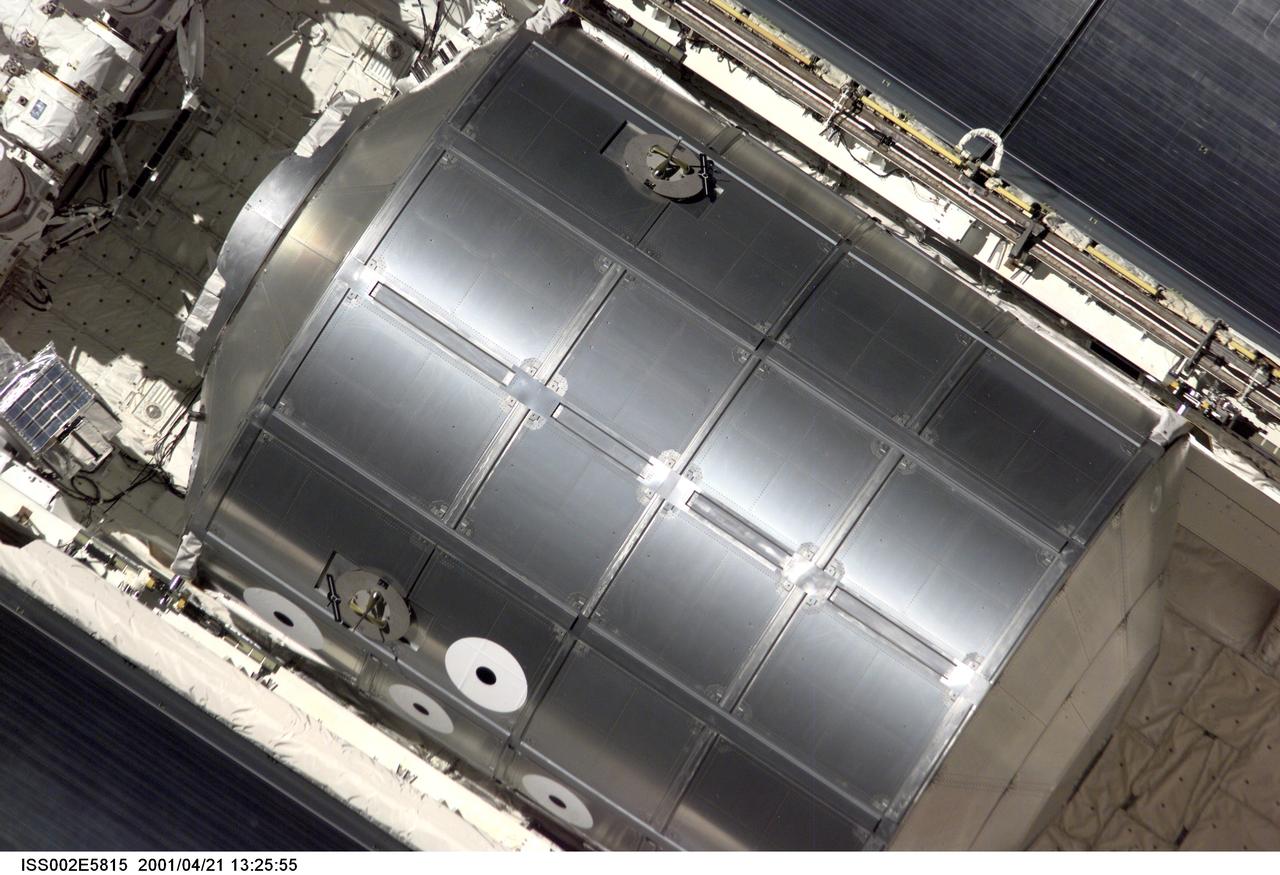

ISS002-E-5815 (21 April 2001) --- The Raffaello Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), built by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), sits in its berthed position in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour as the STS-100 crew eases the vehicle close to the International Space Station (ISS) for docking. The image was recorded with a digital still camera by one of the Expedition Two crew members aboard the Station.
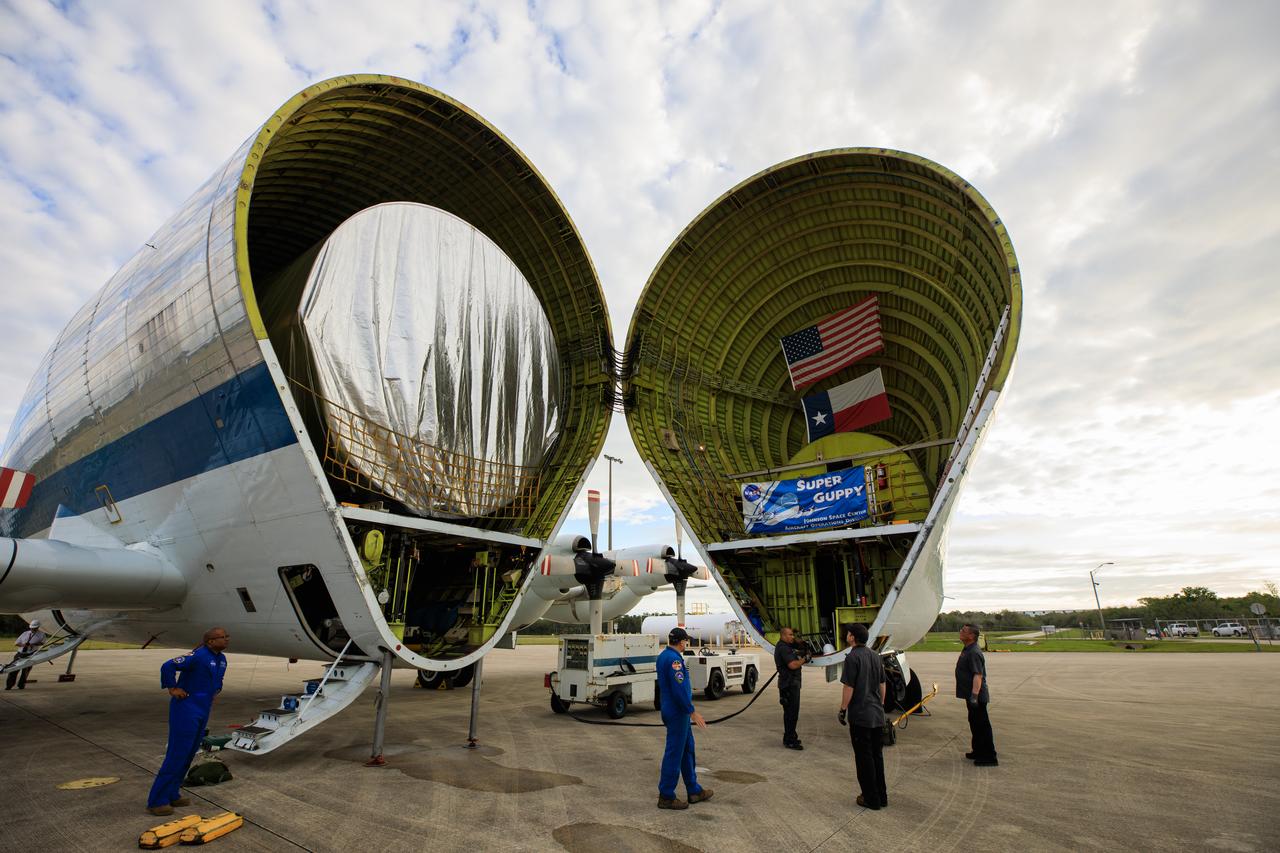

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is loaded into NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. The MPLM will be transported to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.
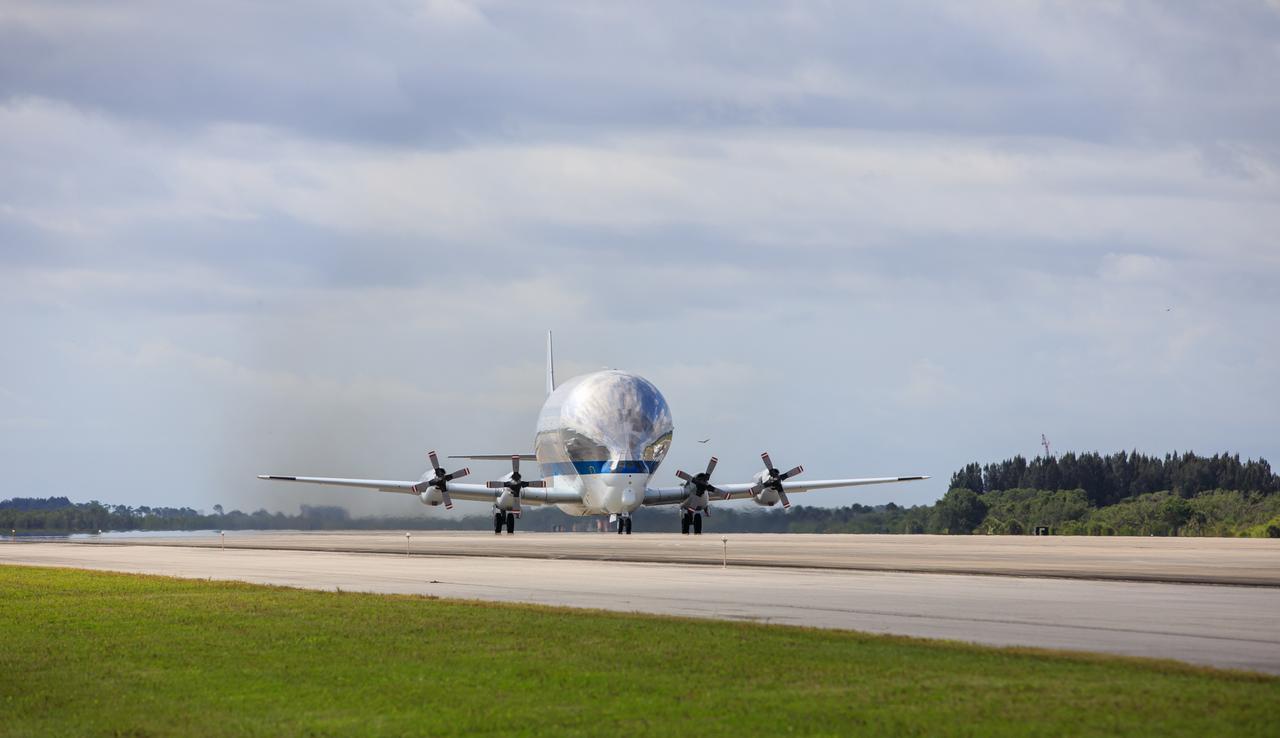

NASA's Super Guppy aircraft lifts off from the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. Carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, the aircraft is transporting the module to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.
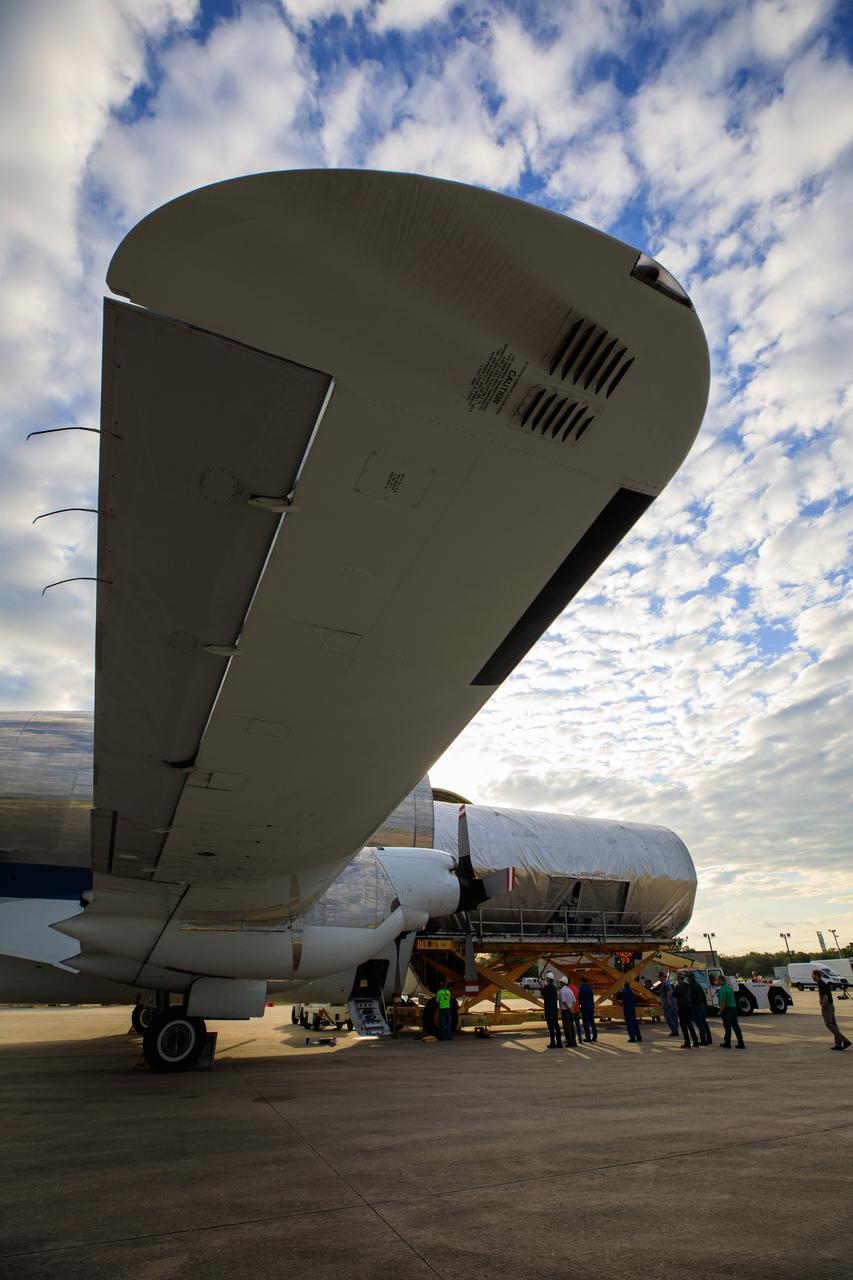

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is loaded into NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. The MPLM will be transported to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.
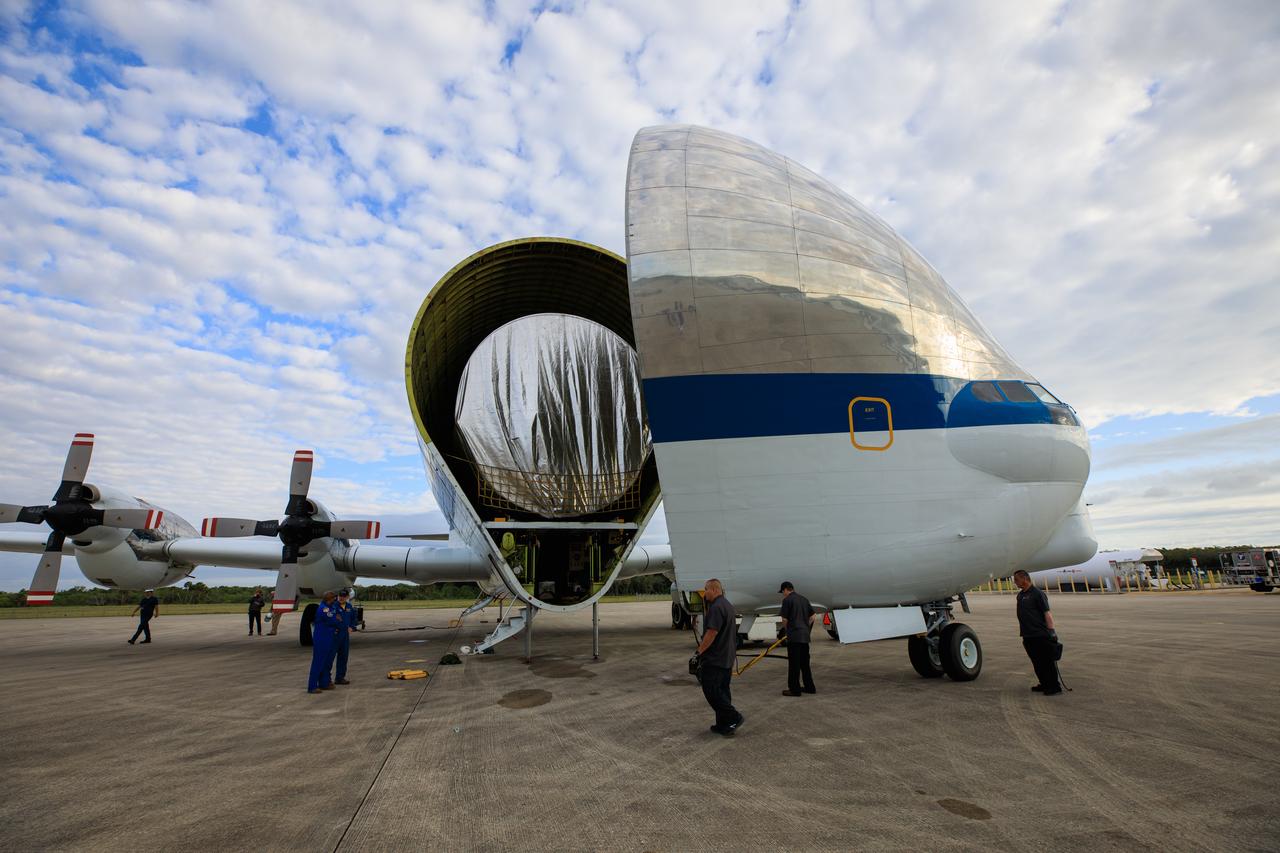

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is loaded into NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. The MPLM will be transported to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.
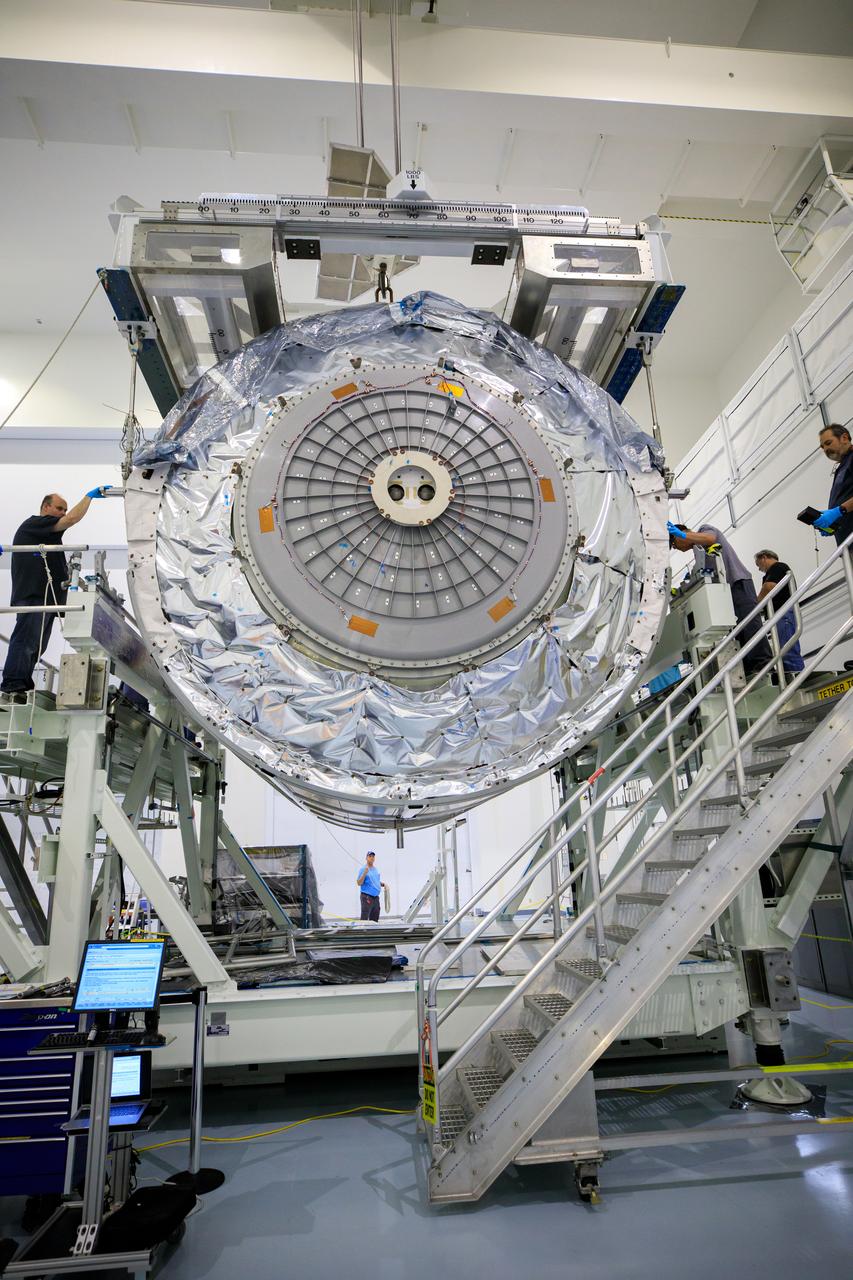

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is hoisted up by crane inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is lowered by crane into its transport container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is moved by crane inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is secured in a stand inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is lifted by crane inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.
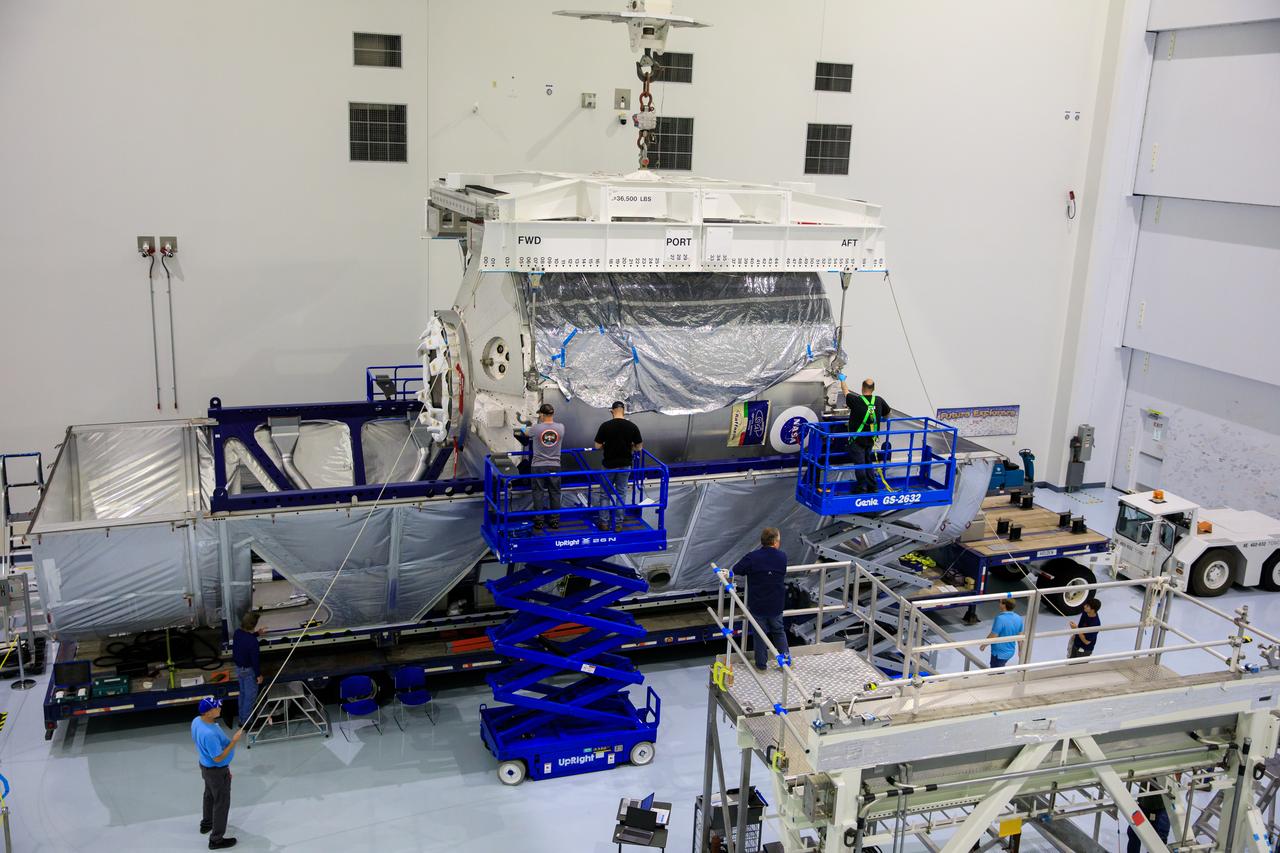

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is lowered by crane into its transport container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.
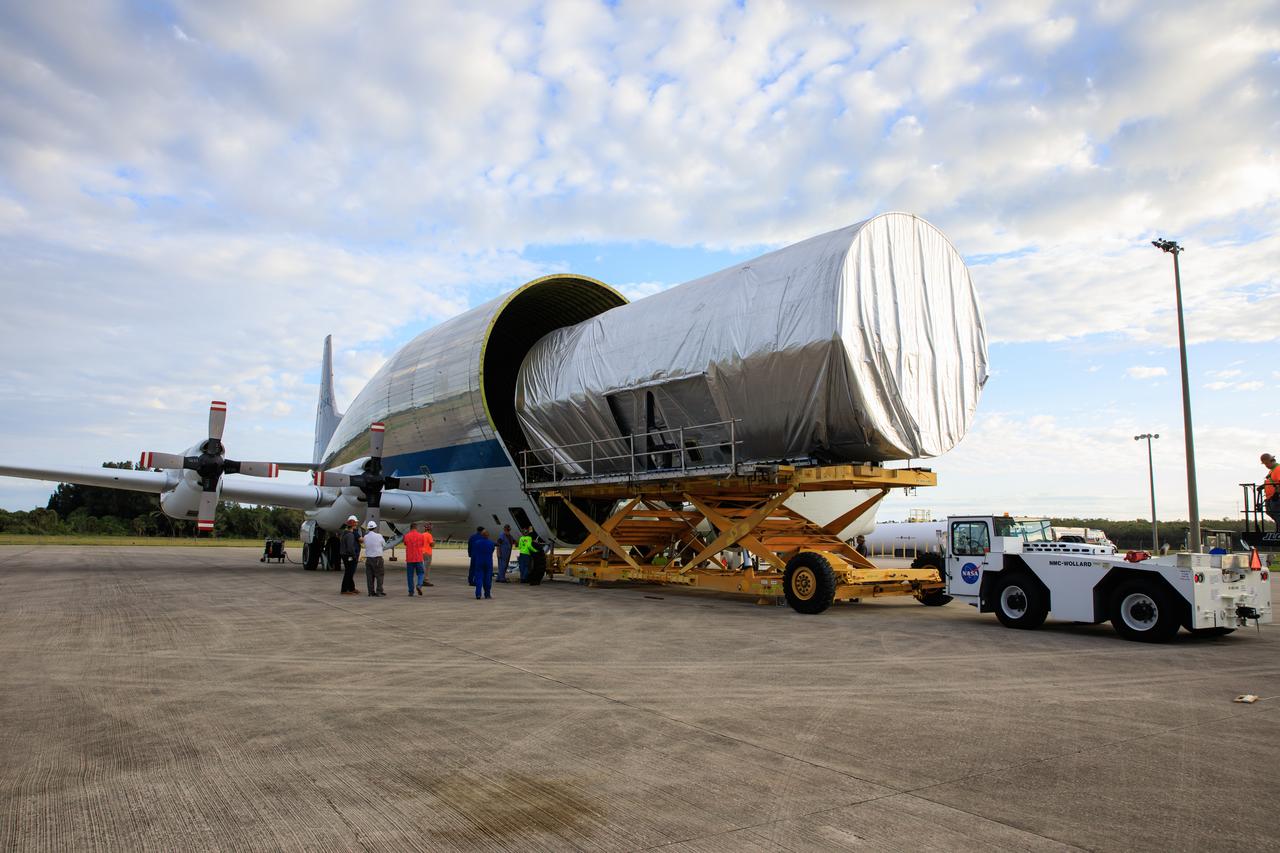

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is loaded into NASA's Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. The MPLM will be transported to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.
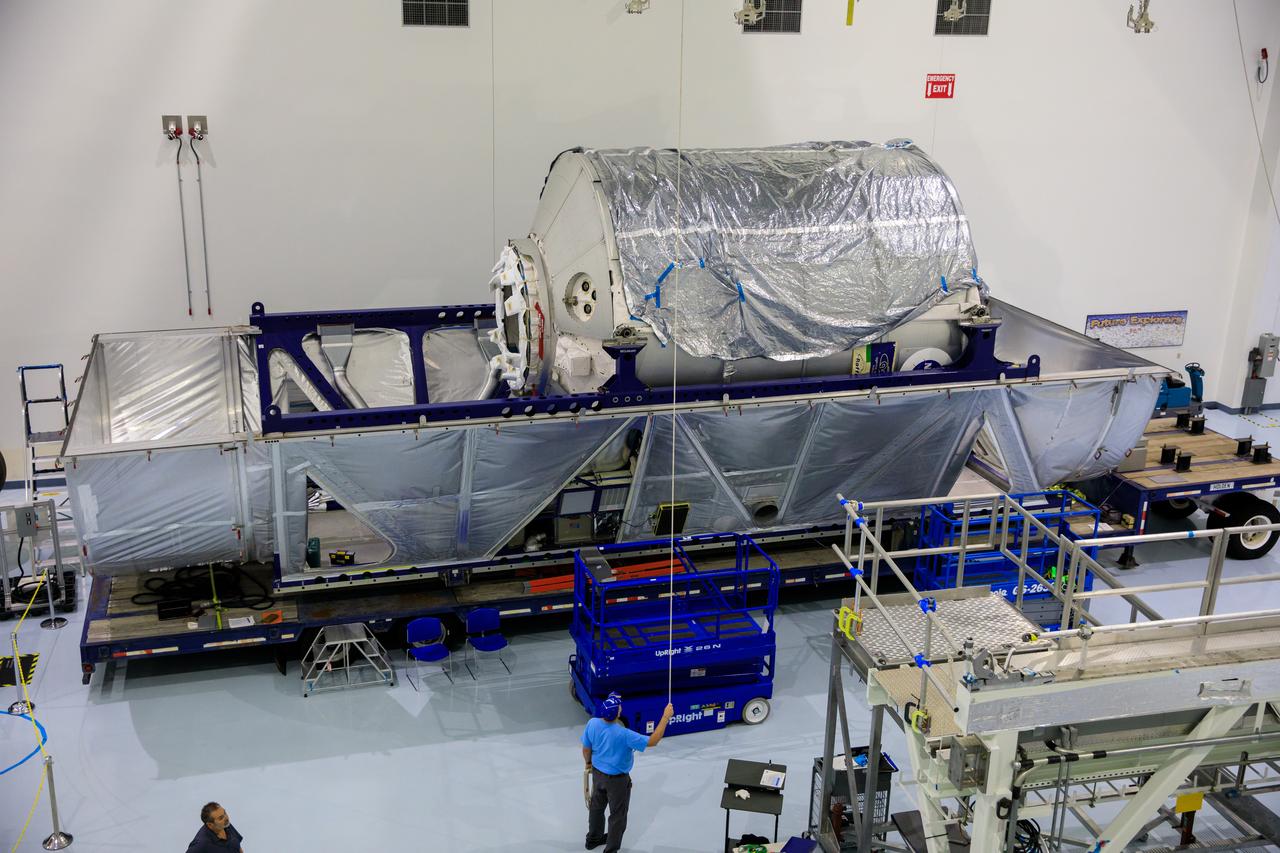

The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is secured in its transport container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.
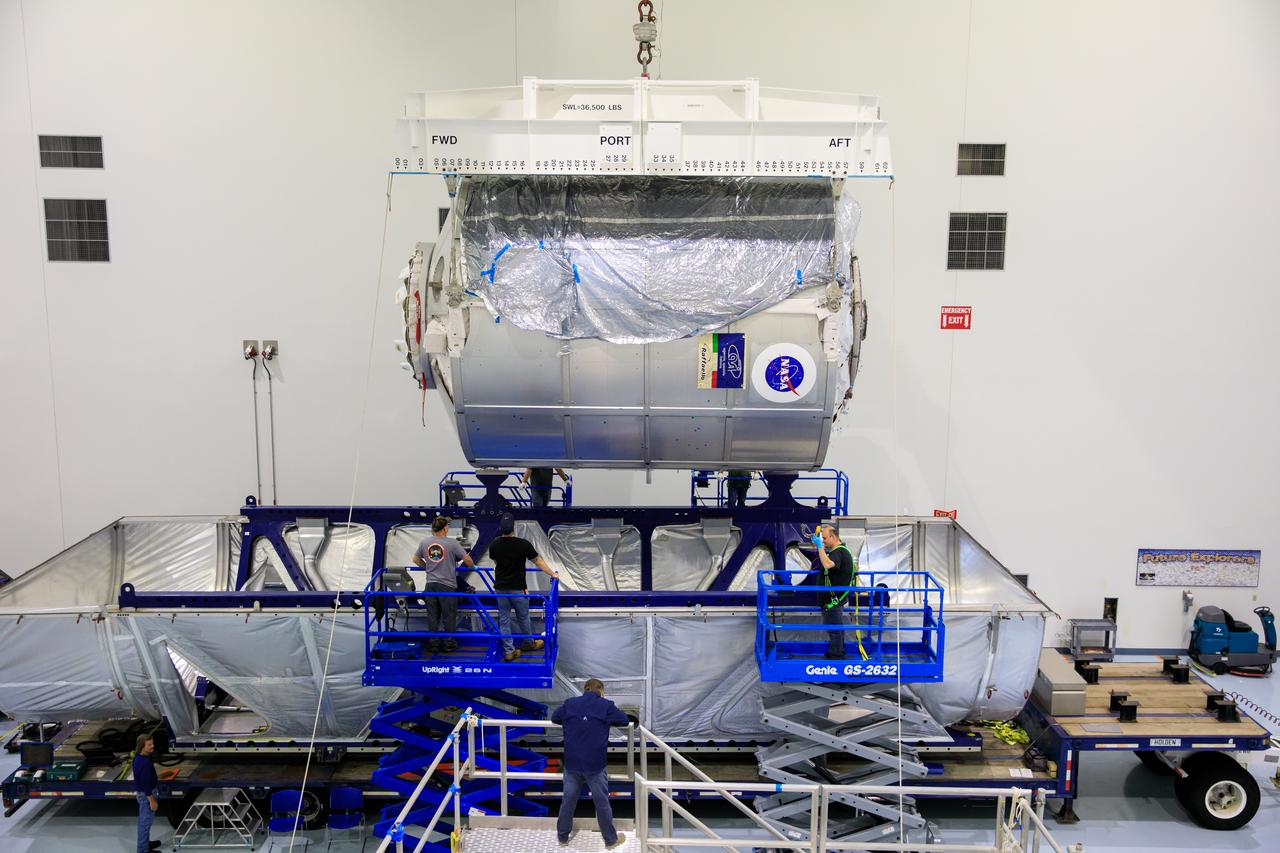
The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, is lowered by crane into its transport container inside the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 20, 2023. The MPLM is being prepared for transport to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use Raffaello as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the space station.

NASA's Super Guppy aircraft lifts off from the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 25, 2023. Carrying the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM), used during the Space Shuttle Program to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station, the aircraft is transporting the module to Ellington Field in Houston, where it will then be transported by road to Axiom’s facility near Ellington to be utilized to further commercialization of space. Three MPLMs were built by Thales Alenia Space Italia (TASI) for the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and named after Italian masters (Leonardo, Raffaello, and Donatello). Only two ever flew to the space station, Leonardo and Raffaello, with Axiom intending to use the Raffaello module as a future element that will attach to a segment being built by the company for addition to the station.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane lifts a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
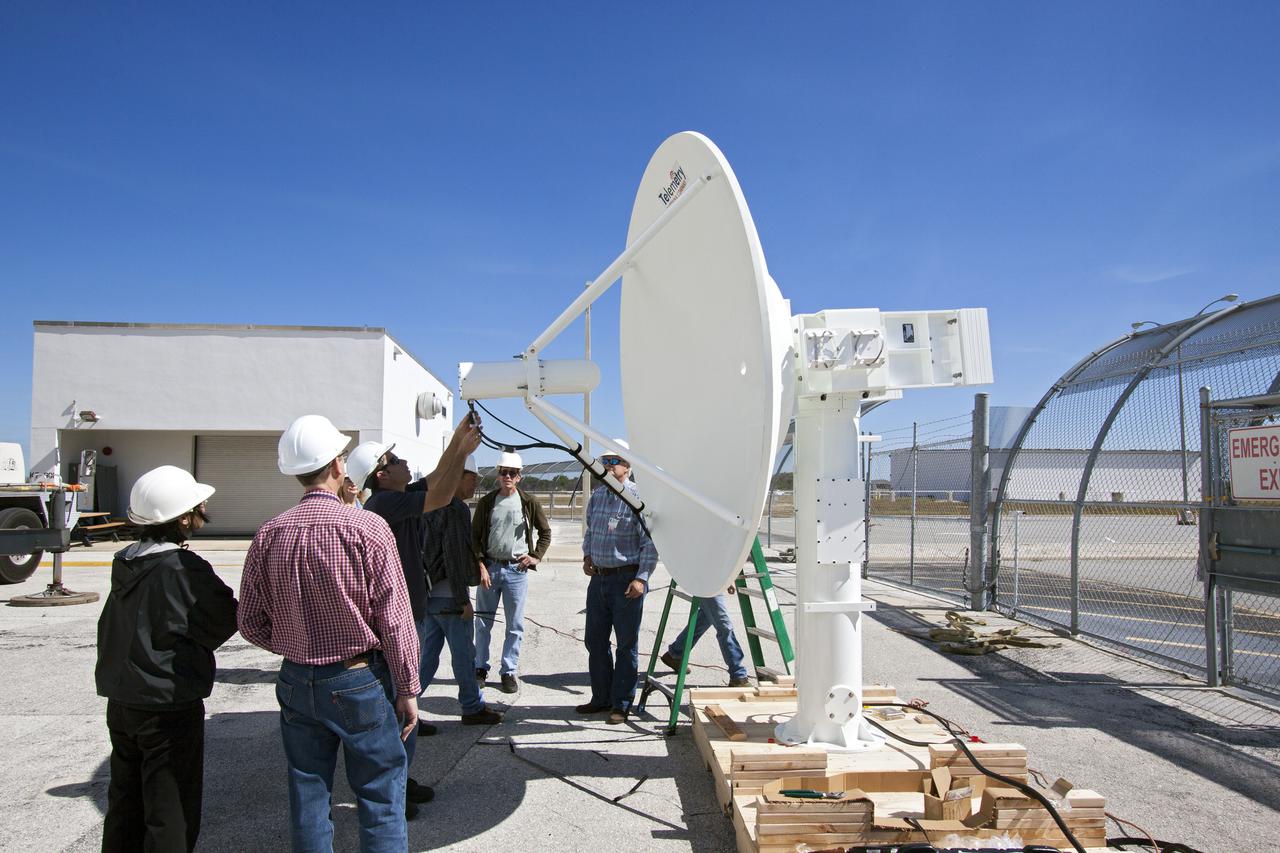

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers prepare to install a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
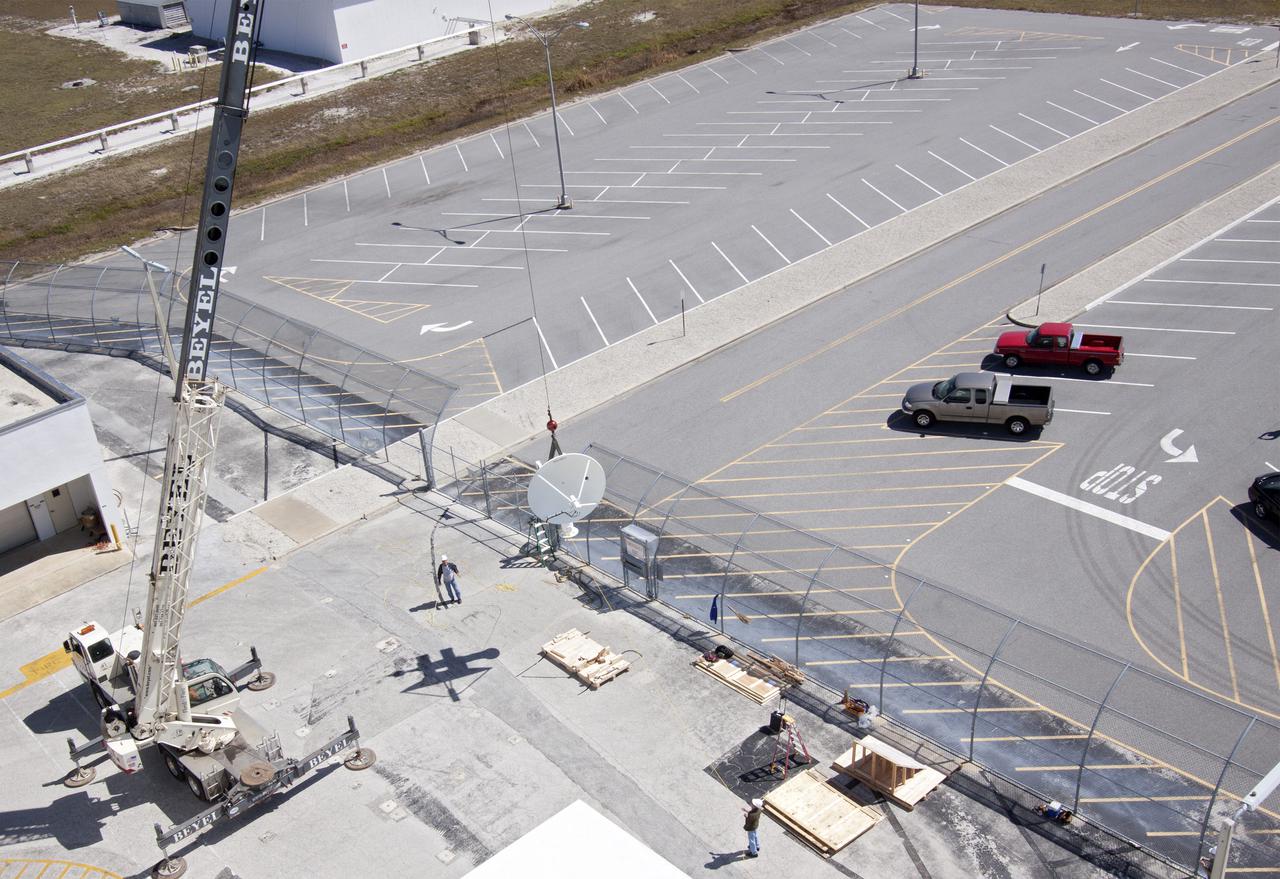

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers use a crane to install a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
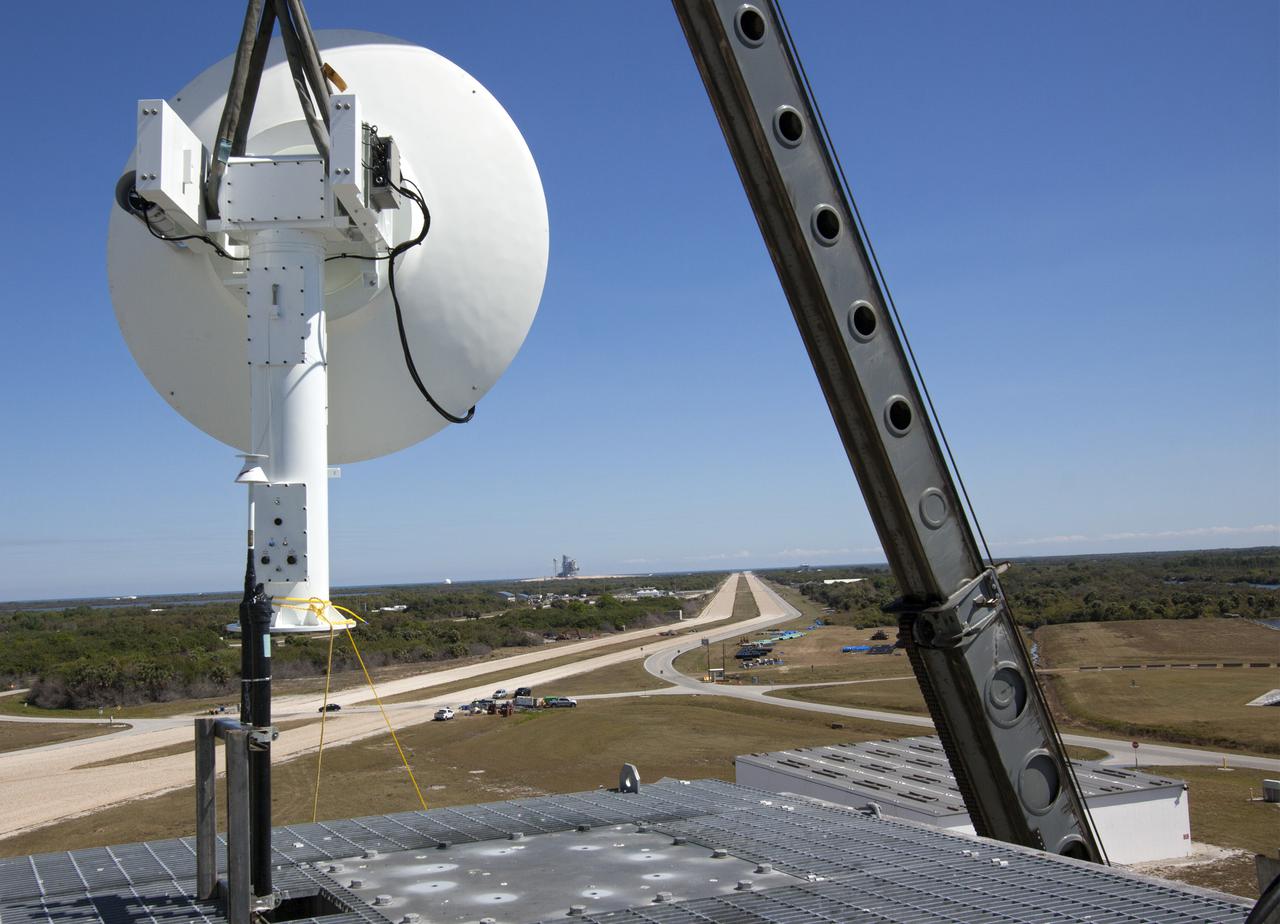

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A crane lifts a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
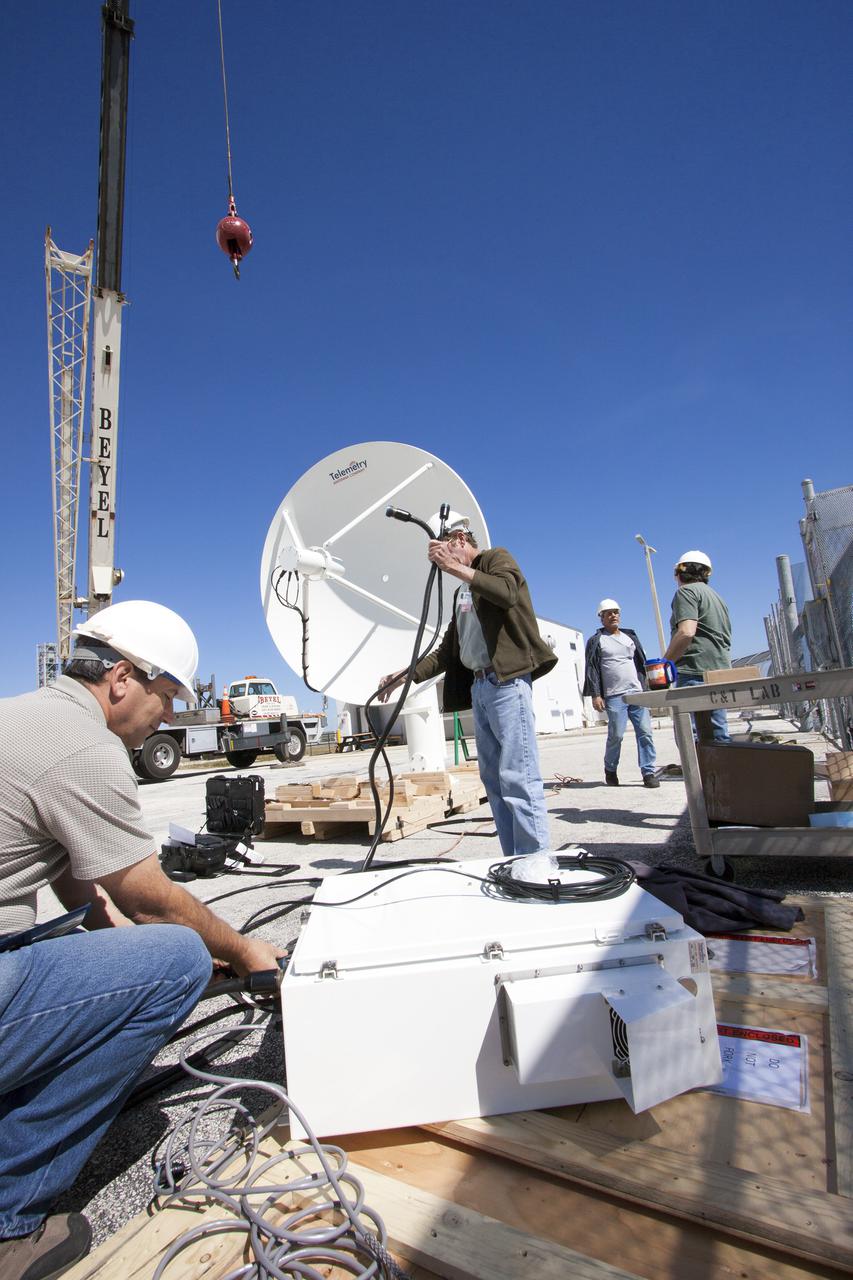

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers prepare to install a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera via crane to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
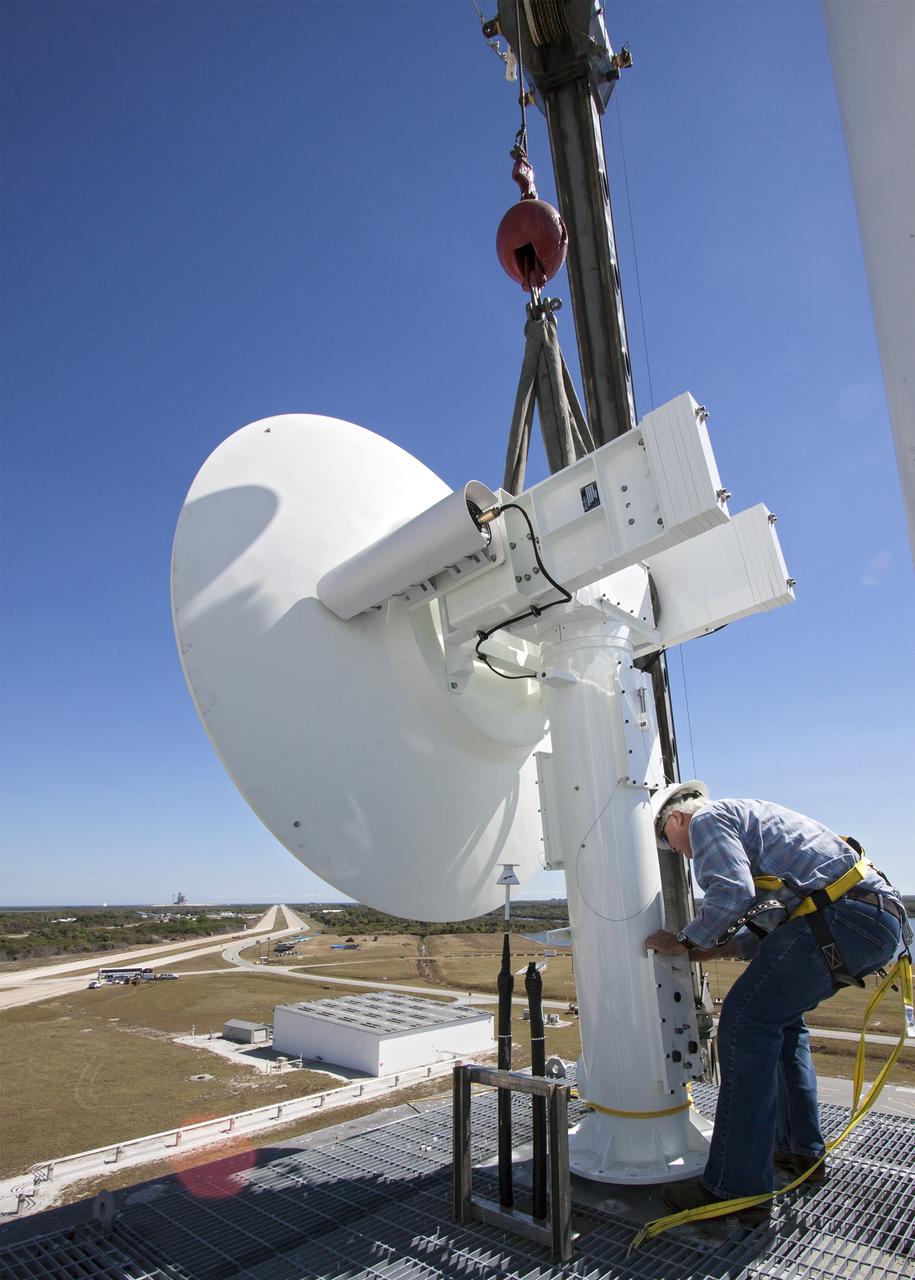

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – With the help of a crane, a worker helps guide a parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
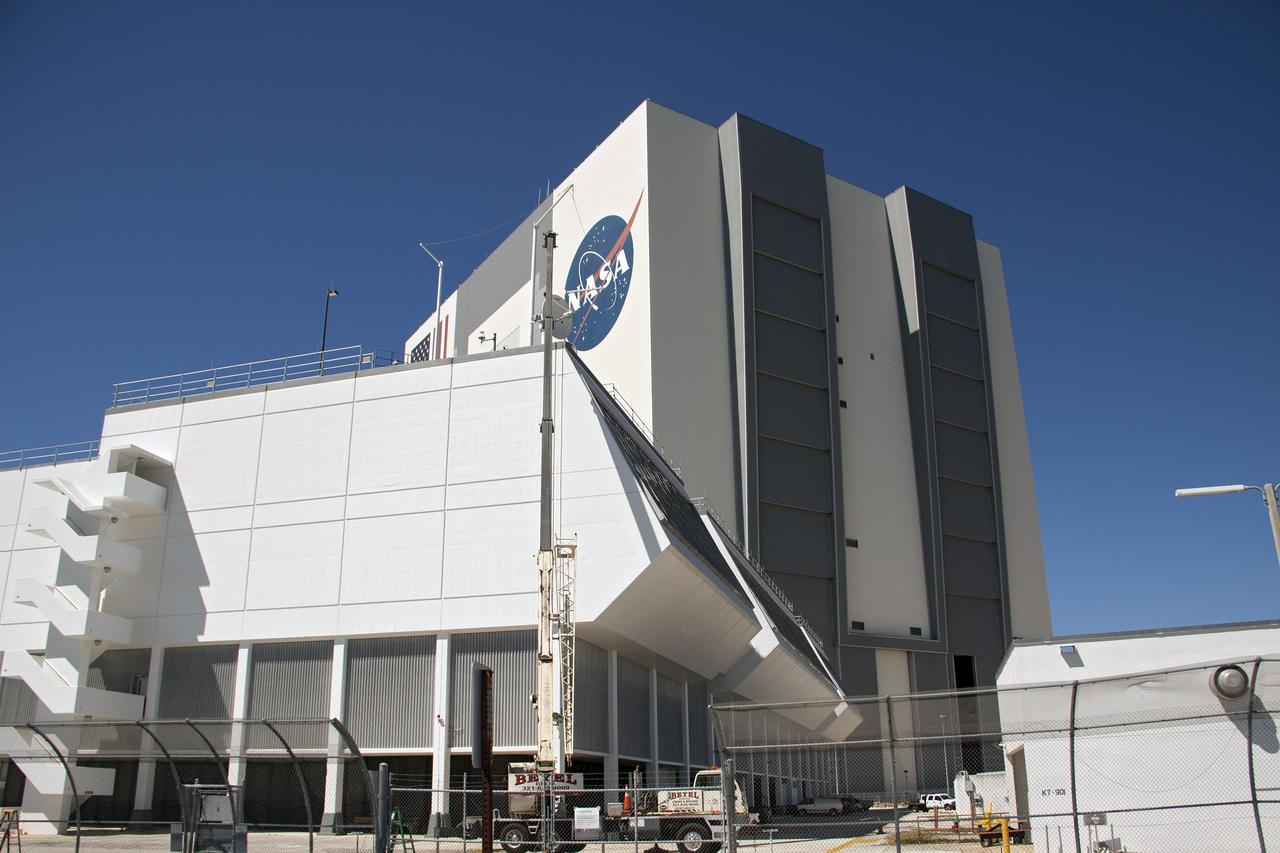

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A telemetry antenna and tracker camera is attached to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three to be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http://go.nasa.gov/groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
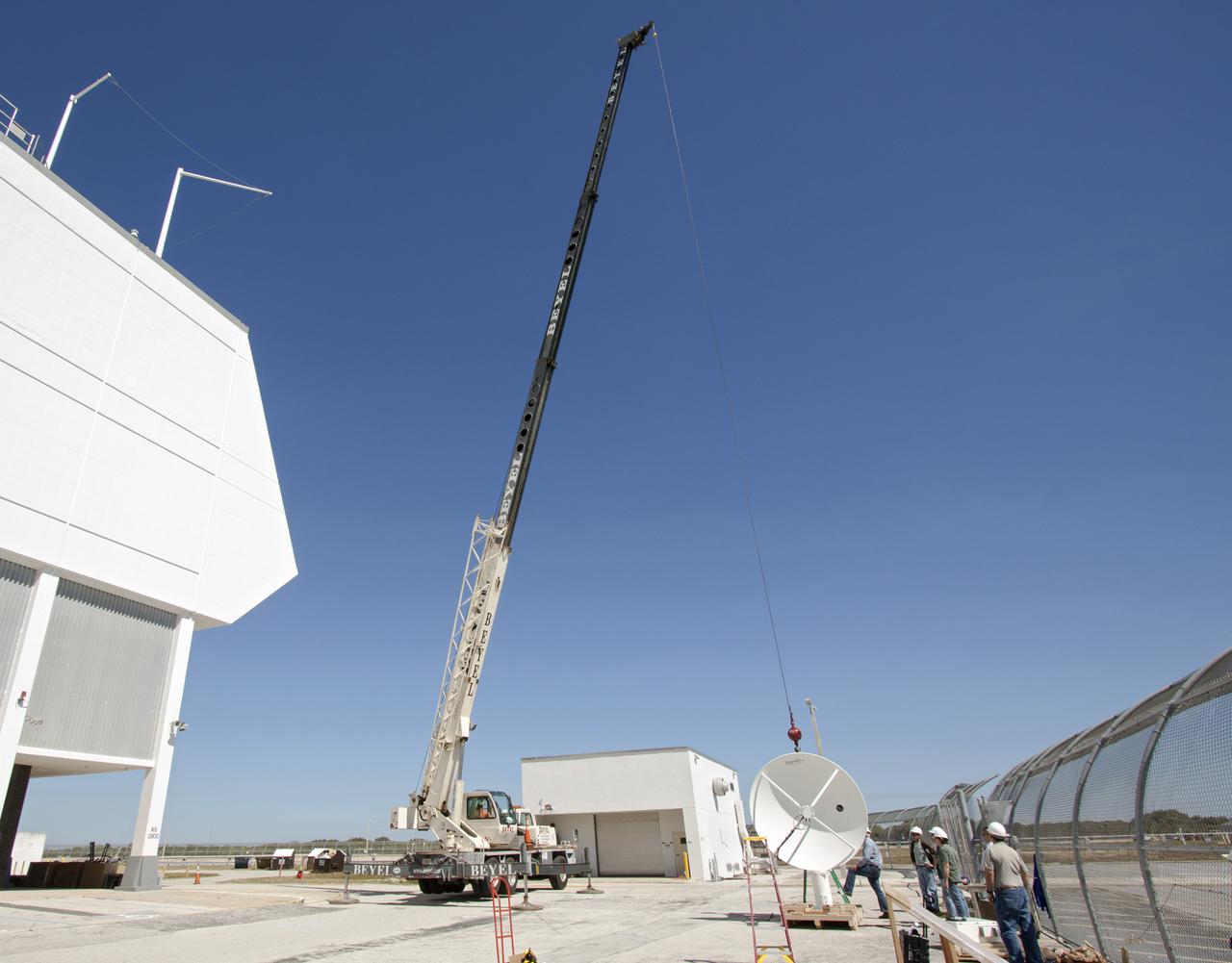

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers use a crane to install a new parabolic telemetry antenna and tracker camera to the roof of the Launch Control Center, or LCC, in Launch Complex 39 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This antenna and camera system is the first of three that will be installed on the LCC roof for the Radio Frequency and Telemetry Station RFTS, which will be used to monitor radio frequency communications from a launch vehicle at Launch Pad 39A or B as well as provide radio frequency relay for a launch vehicle in the Vehicle Assembly Building. The RFTS replaces the shuttle-era communications and tracking labs at Kennedy. The modern RFTS checkout station is designed to primarily support NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft, but can support multi-user radio frequency tests as the space center transitions to support a variety of rockets and spacecraft. For more information on the modernization efforts at Kennedy, visit the Ground Systems Development and Operations, or GSDO, website at http:__go.nasa.gov_groundsystems. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
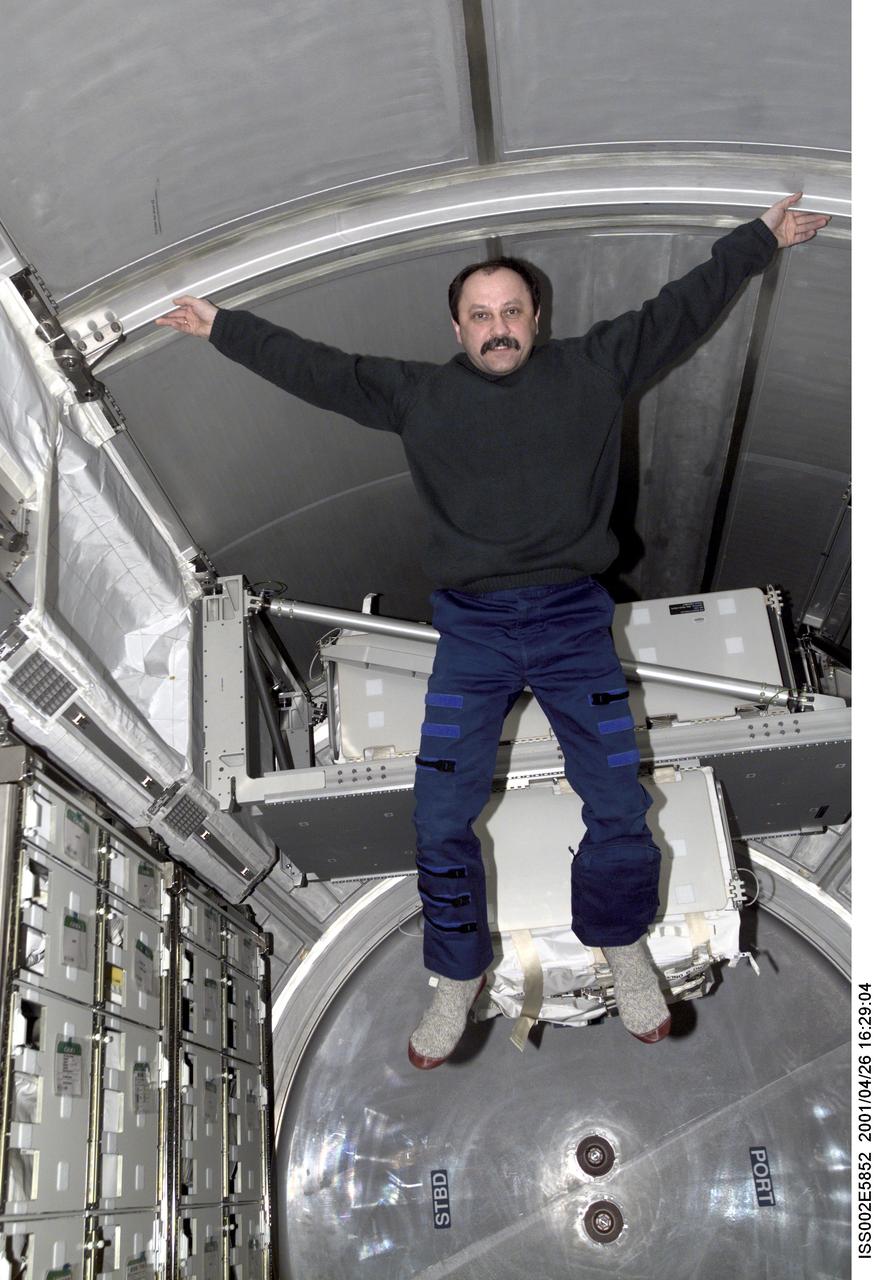

ISS002-E-5852 (26 April 2001) --- Yury V. Usachev of Rosaviakosmos, Expedtion Two mission commander, enjoys the extra space provided by the Multipurpose Logistics Module (MPLM) Raphaello which was mated to the International Space Station (ISS) during the STS-100 mission. The image was taken with a digital still camera.
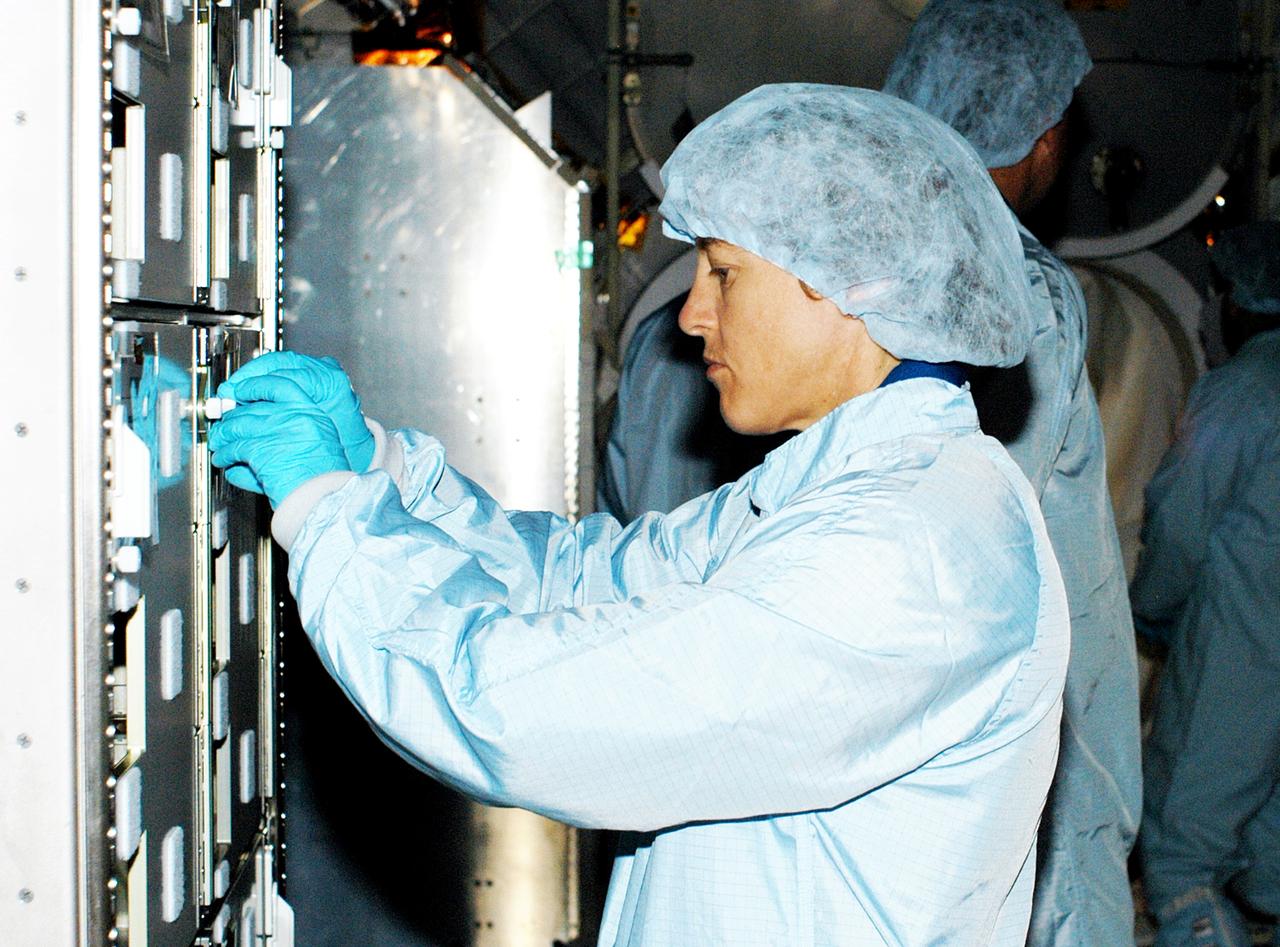

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-114 Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence manipulates part of a Multi-Purpose Logistics Module. Lawrence is a new addition to the mission crew. The STS-114 crew is at KSC to take part in crew equipment and orbiter familiarization.
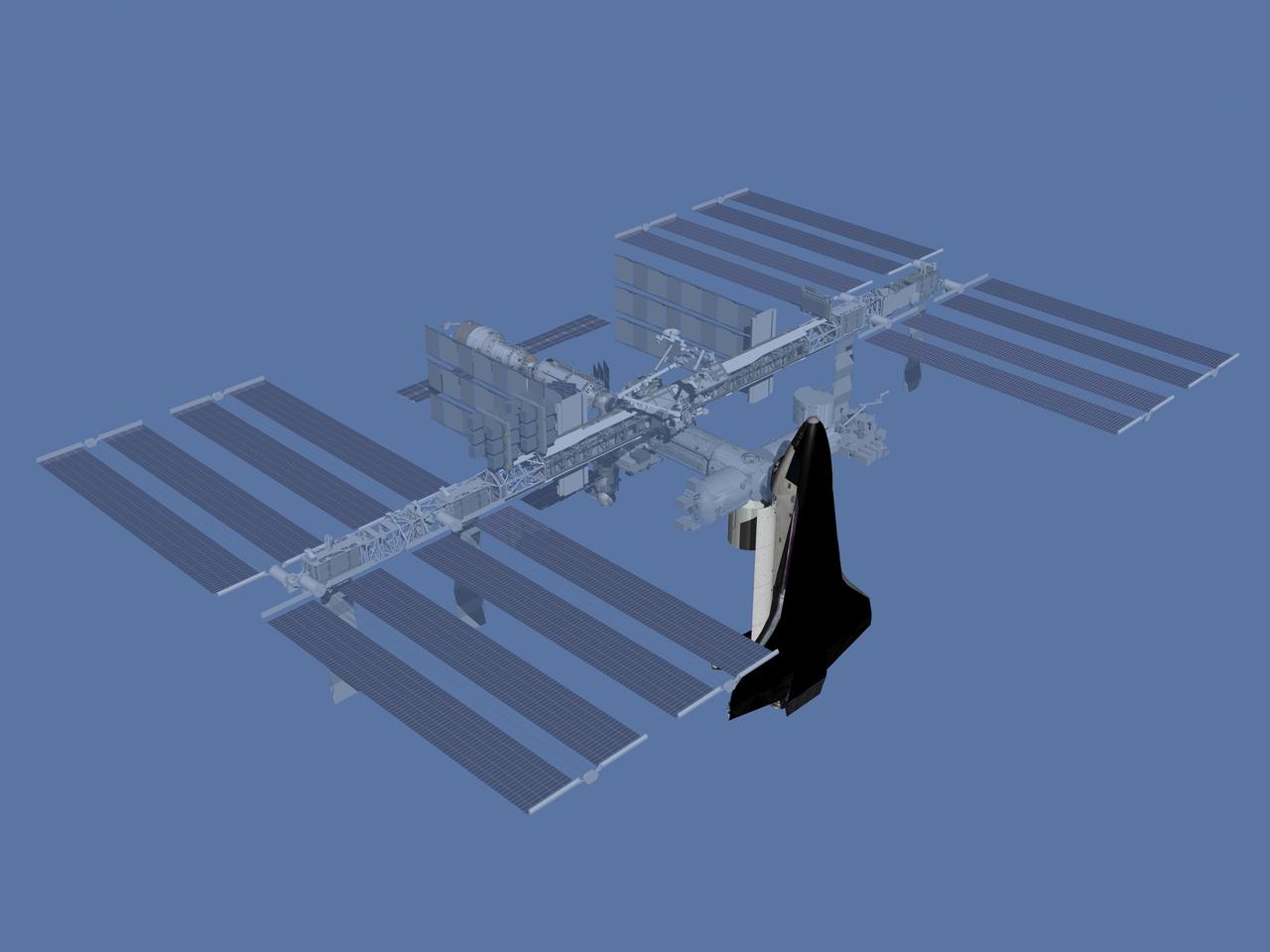
JSC2006-E-43514 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight 19A. U.S. Orbiter brings Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) and Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC).
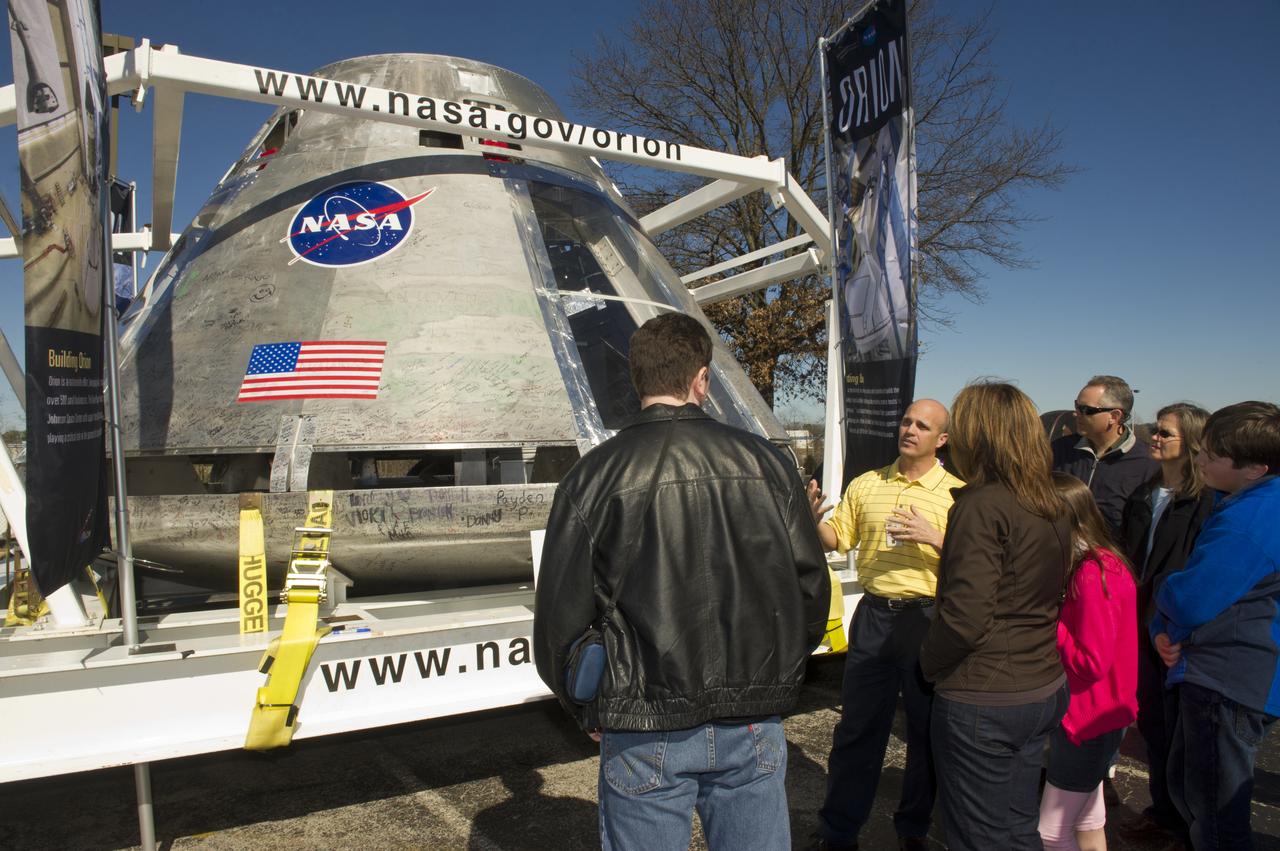

LARRY GAGLIANO SHARES INFORMATION ABOUT THE ORION MULTI-PURPOSE CREW VEHICLE WITH VISITORS TO THE USSRC
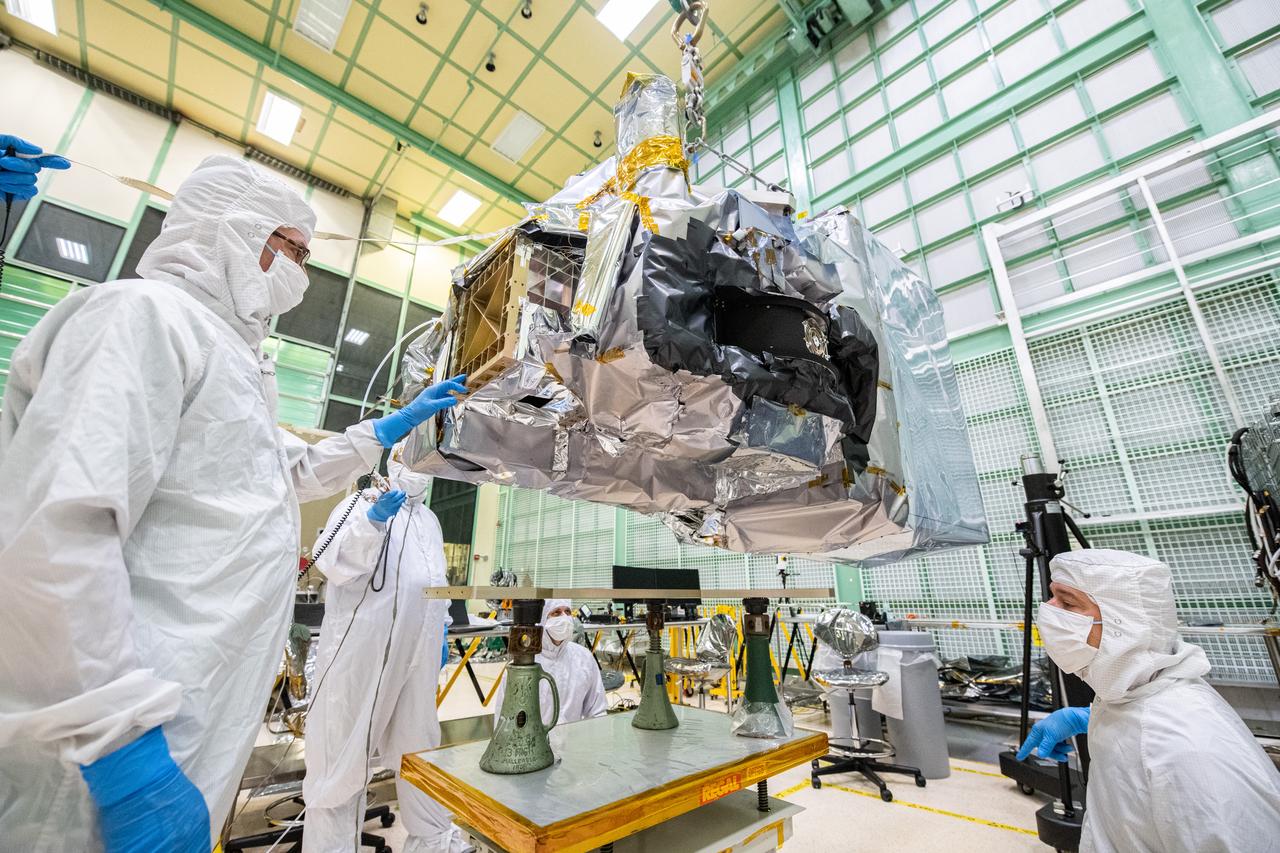

Mechanical technicians, Nicholas Kwiatkowski and Thomas Huber, guide the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) as it is suspended on a crane to install an adapter plate and for additional integration operations. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
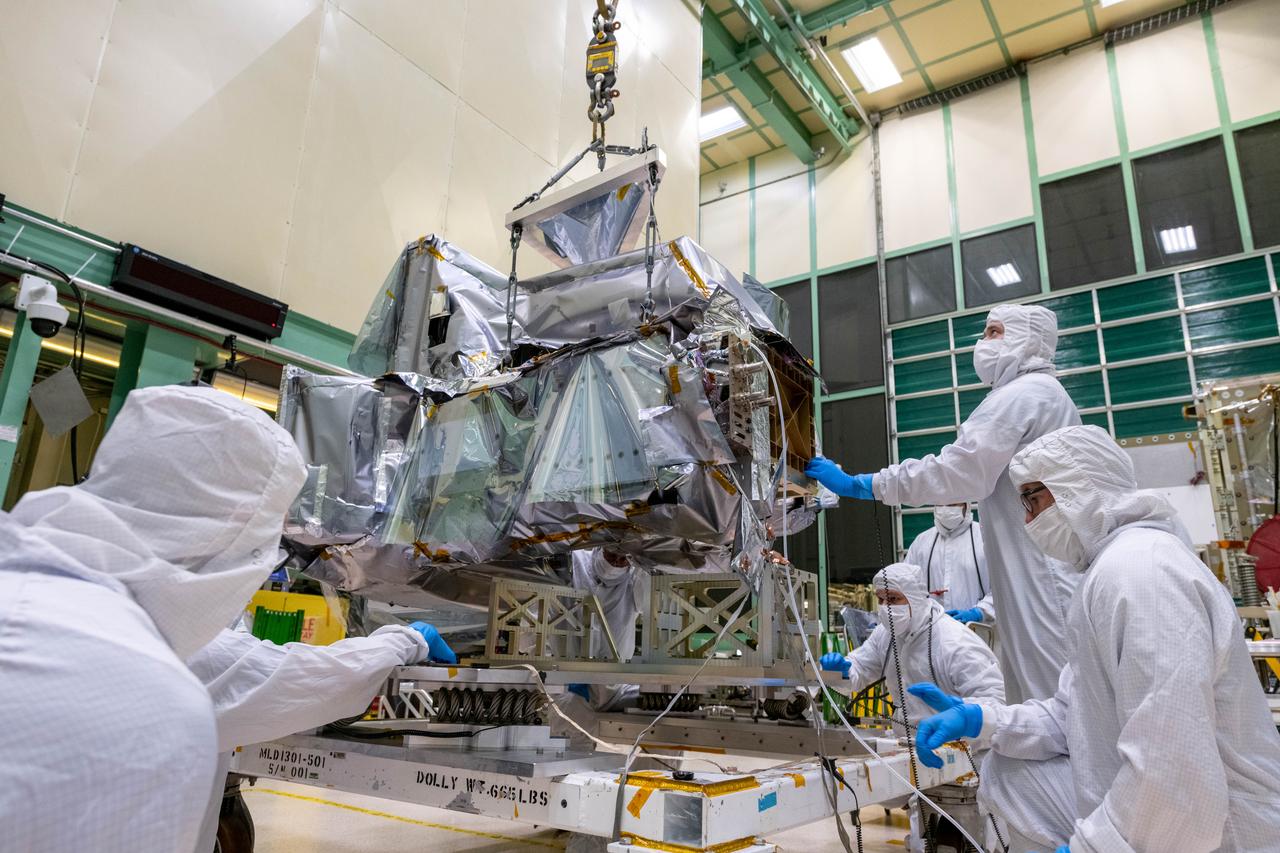

Mechanical technicians crane lift the Ocean Color Instrument (OCI) off of the transportation dolly. OCI is a highly advanced optical spectrometer that will be used to measure properties of light over portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. It will enable continuous measurement of light at finer wavelength resolution than previous NASA satellite sensors, extending key system ocean color data records for climate studies. OCI is PACE's (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem) primary sensor built at Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD.
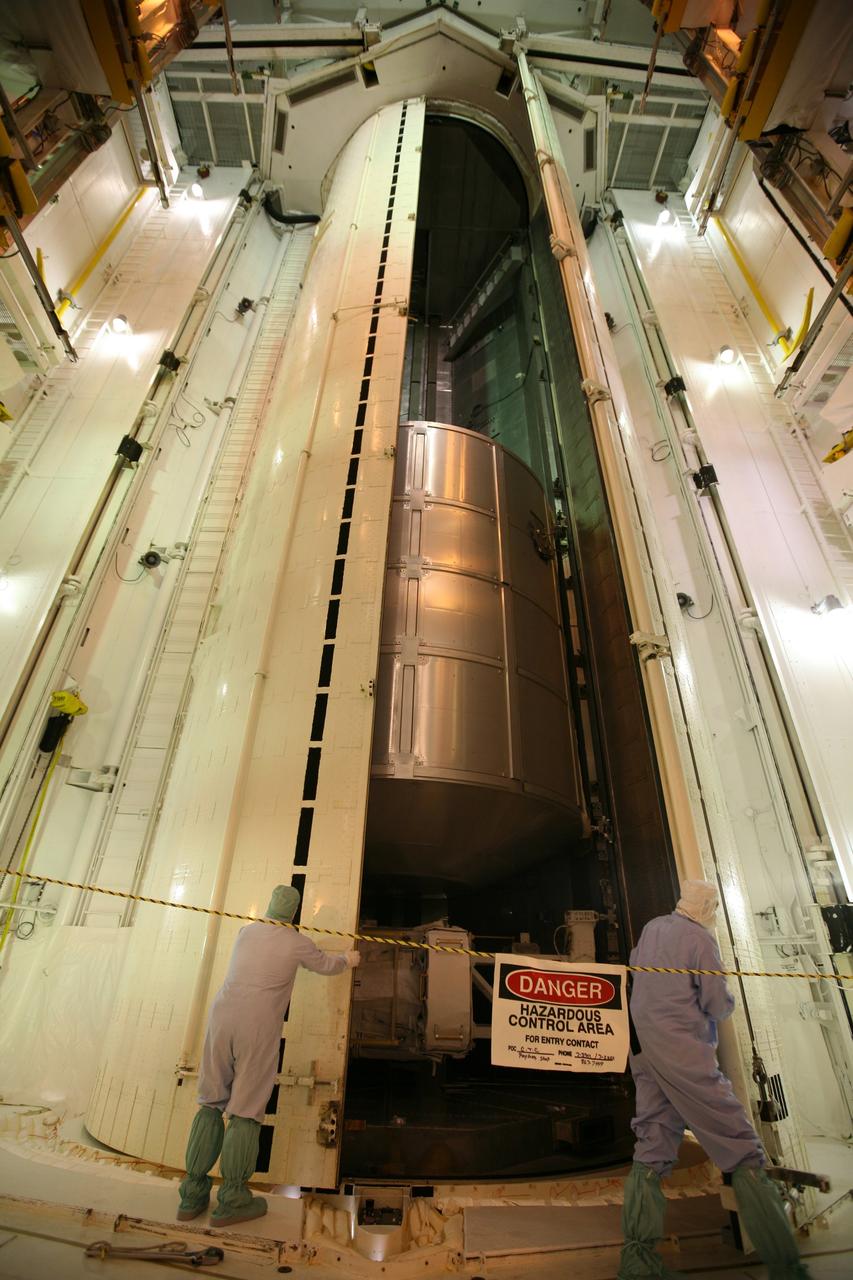

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - From inside the Payload Changeout Room on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers oversee the opening of the doors of the payload canister. The canister contains space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom). The payload will be moved into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In its vertical position, the payload canister with space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload inside leaves the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the canister are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, technicians ensure the payload bay door closes properly around the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier inside space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
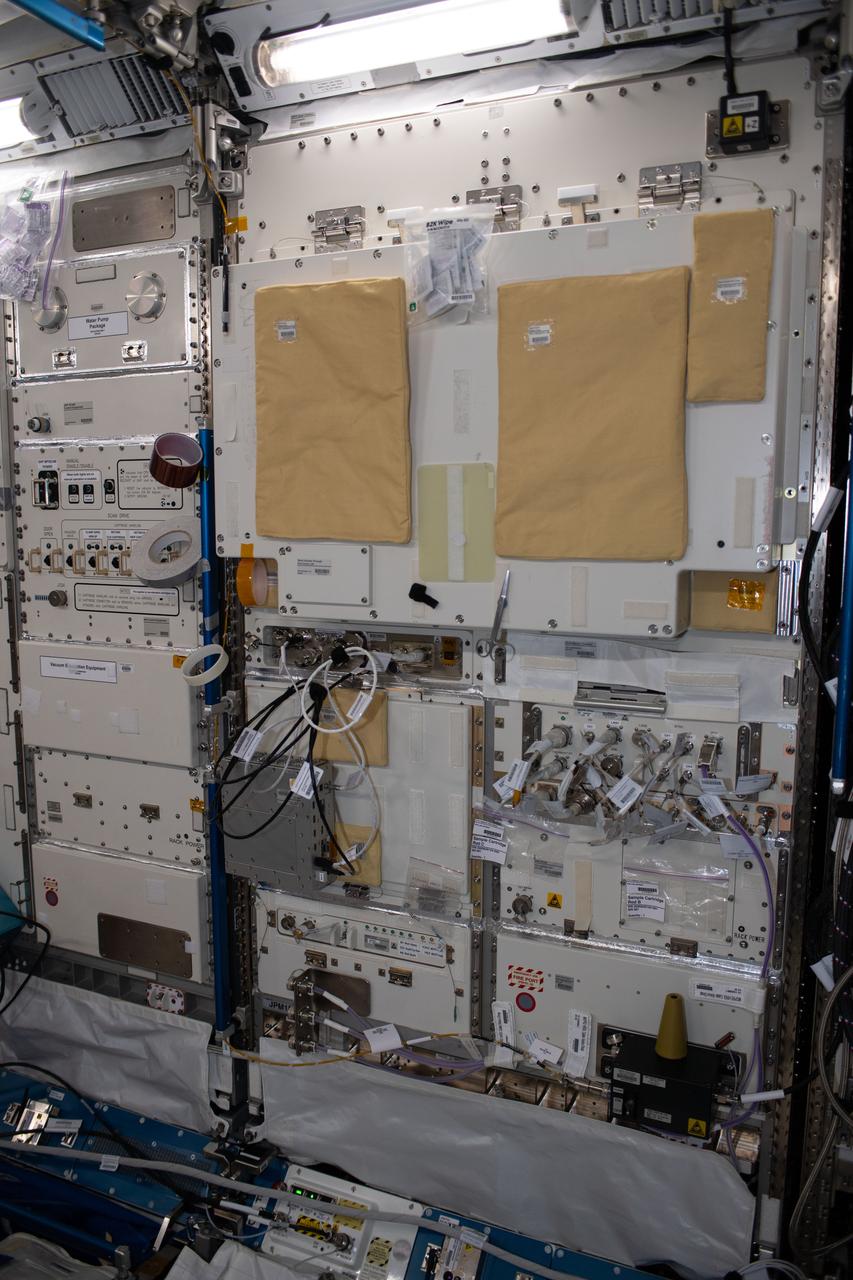

iss056e150256 (8/21/2018) --- A view of the Multi purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) 2 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Multi Purpose Small Payload Rack-2 (MSPR-2) is a second multipurpose payload rack system used in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Similar to the original MSPR (still in use), MSPR-2 has two workspaces and a work table that can be used for wide fields of space environment utilization including science and educational missions.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - From inside the Payload Changeout Room on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers oversee the opening of the doors of the payload canister. The canister contains space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. The payload will be moved into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the open doors of the payload canister in the Payload Changeout Room reveal the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom). The payload will be moved into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, a technician checks the closing of the payload bay door around the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier inside space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
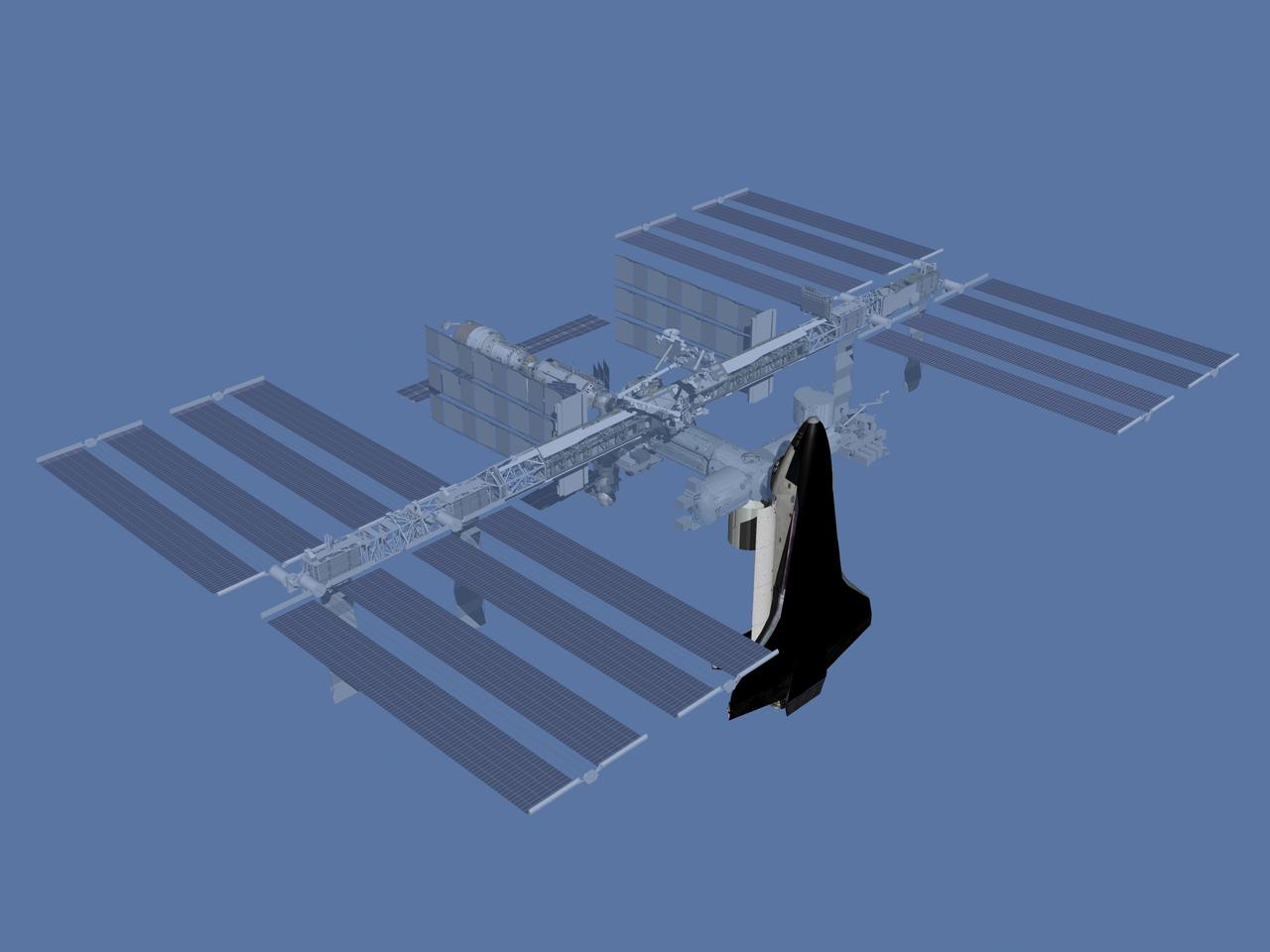
JSC2006-E-43511 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight 17A. U.S. Orbiter brings Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM); Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (LMC); three crew quarters; galley; second Treadmill Vibration Isolation System (TVIS); Crew Health Care System 2 (CHeCS 2).

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, technicians observe as space shuttle Discovery's payload bay doors begin closing. Seen in the payload bay are the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, space shuttle Discovery's payload bay doors begin closing. Seen in the payload bay are the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, on Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use the payload ground-handling mechanism to transfer space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload from the payload canister. The payload is the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. The payload later will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
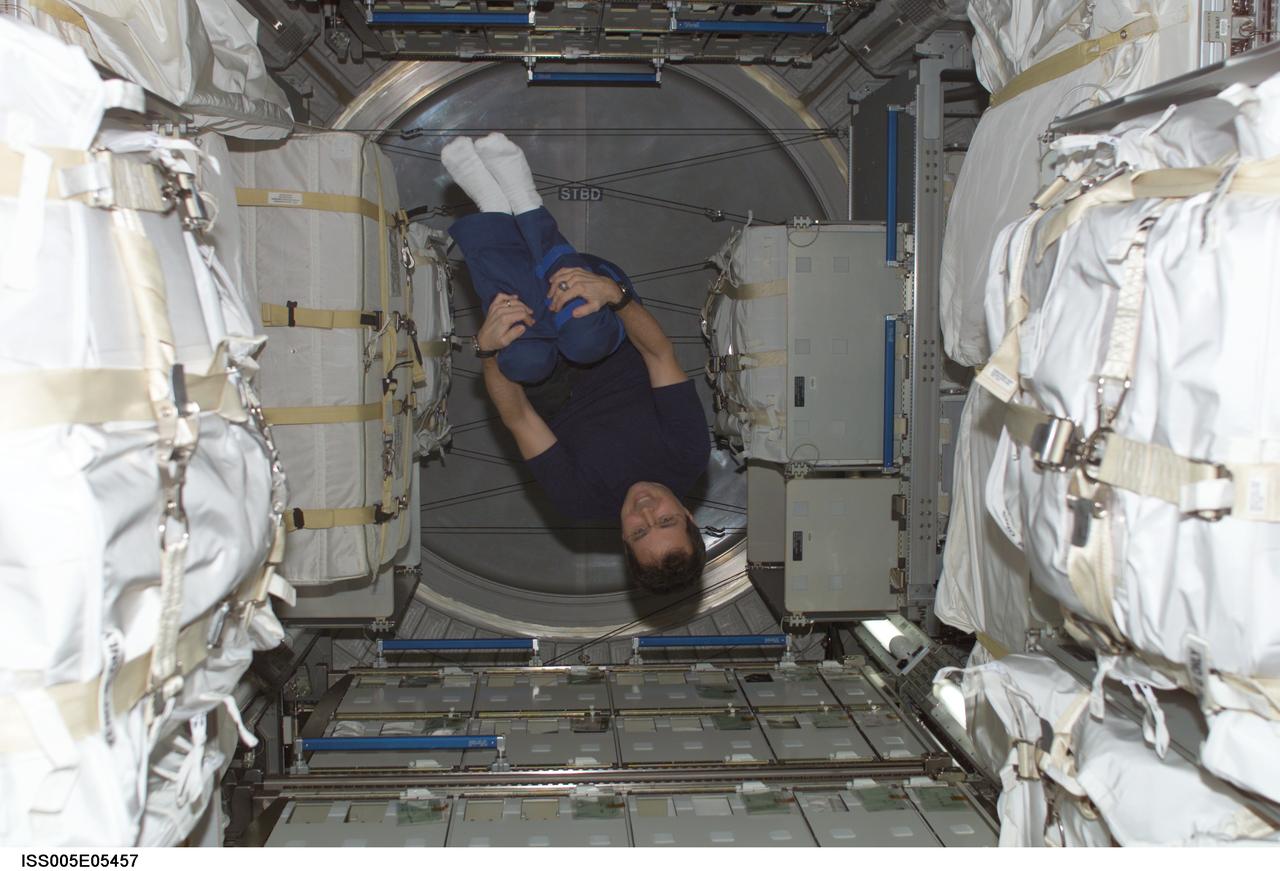

ISS005-E-05457 (June 2002) --- Astronaut Daniel W. Bursch, Expedition Four flight engineer, floats in the Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM). Leonardo is one of three Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules built by the Italian Space Agency that serve as pressurized, reusable cargo carriers to ferry supplies, equipment and experiments between the ground and the space station.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, the payload for space shuttle Discovery's STS-128 mission waits for closure of the payload bay doors. At the bottom is the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier. Above it is the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
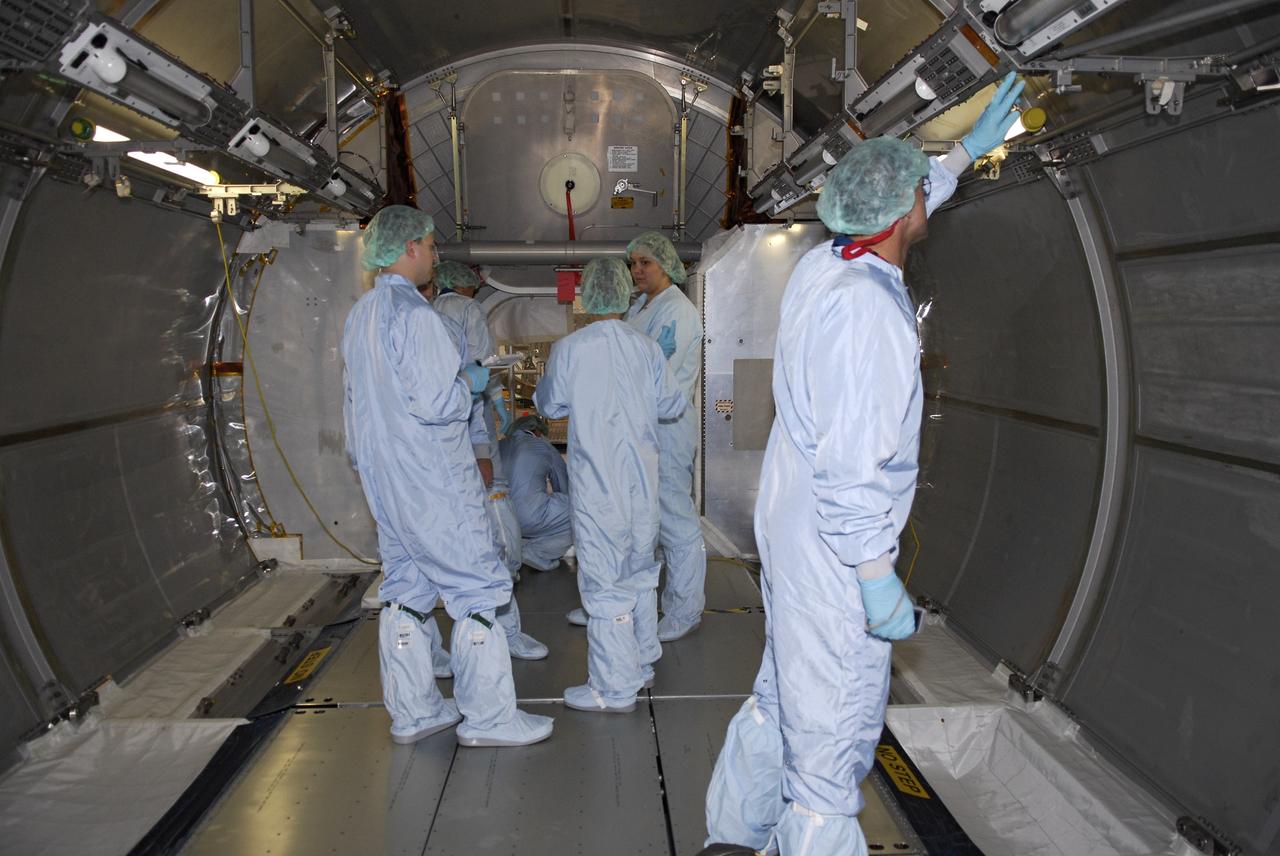

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, STS-126 crew members check out the interior of the multi-purpose logistics module that will fly on the mission. Shuttle crews frequently visit Kennedy to get hands-on experience, called a crew equipment interface test, with hardware and equipment for their missions. On STS-126, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
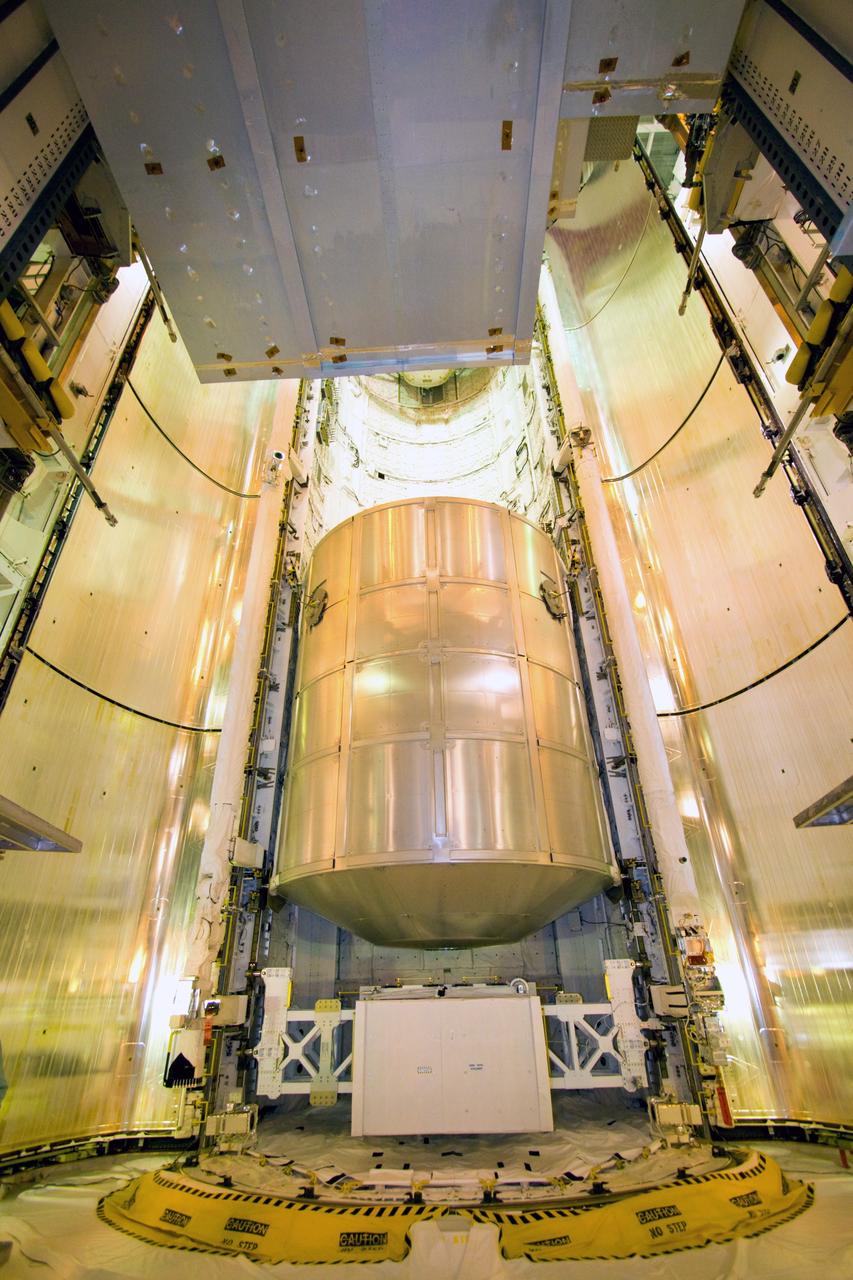

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, the payload for space shuttle Discovery's STS-128 mission has been installed in the payload bay. At the bottom is the Lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier. Above it is the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers in the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, oversee the transfer of the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom) from the payload canister into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
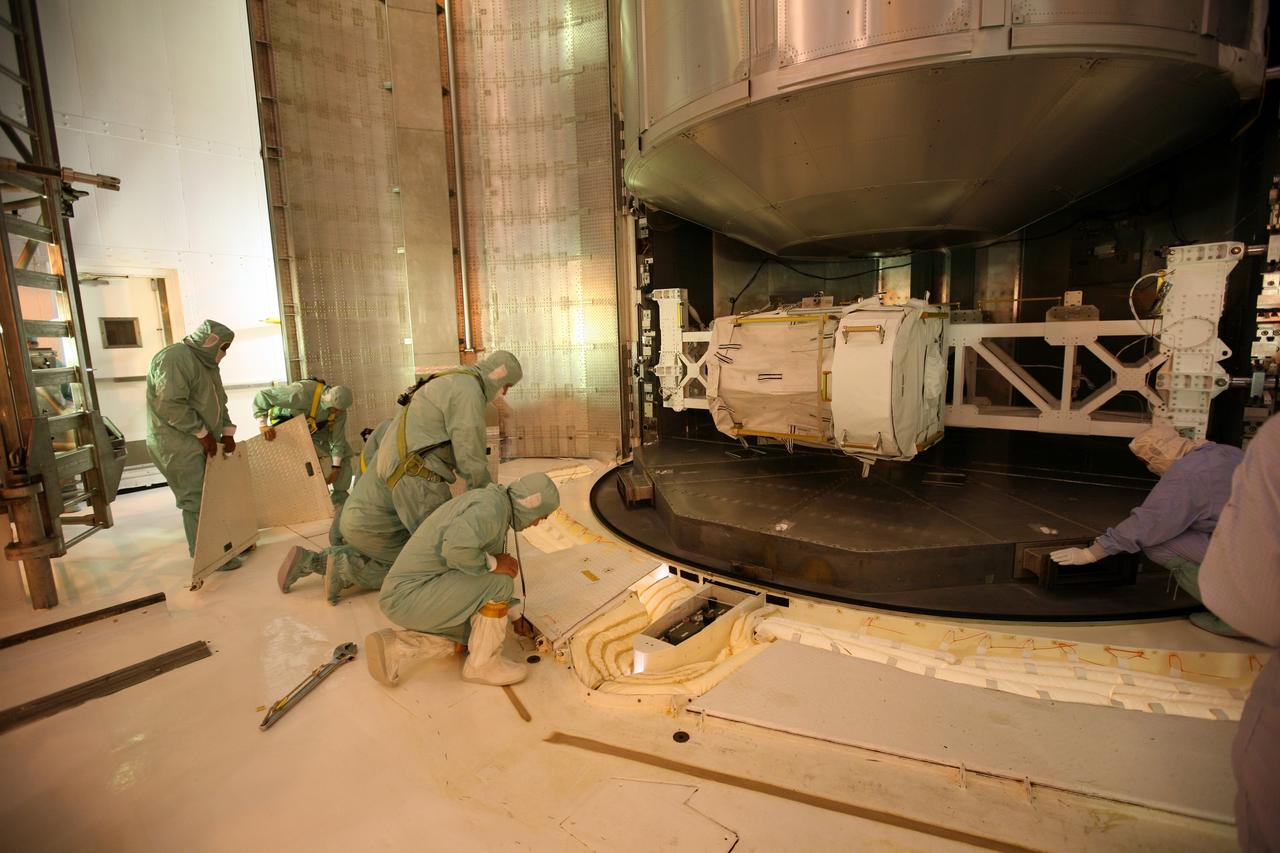

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers in the Payload Changeout Room prepare for the removal of the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom) from the payload canister. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
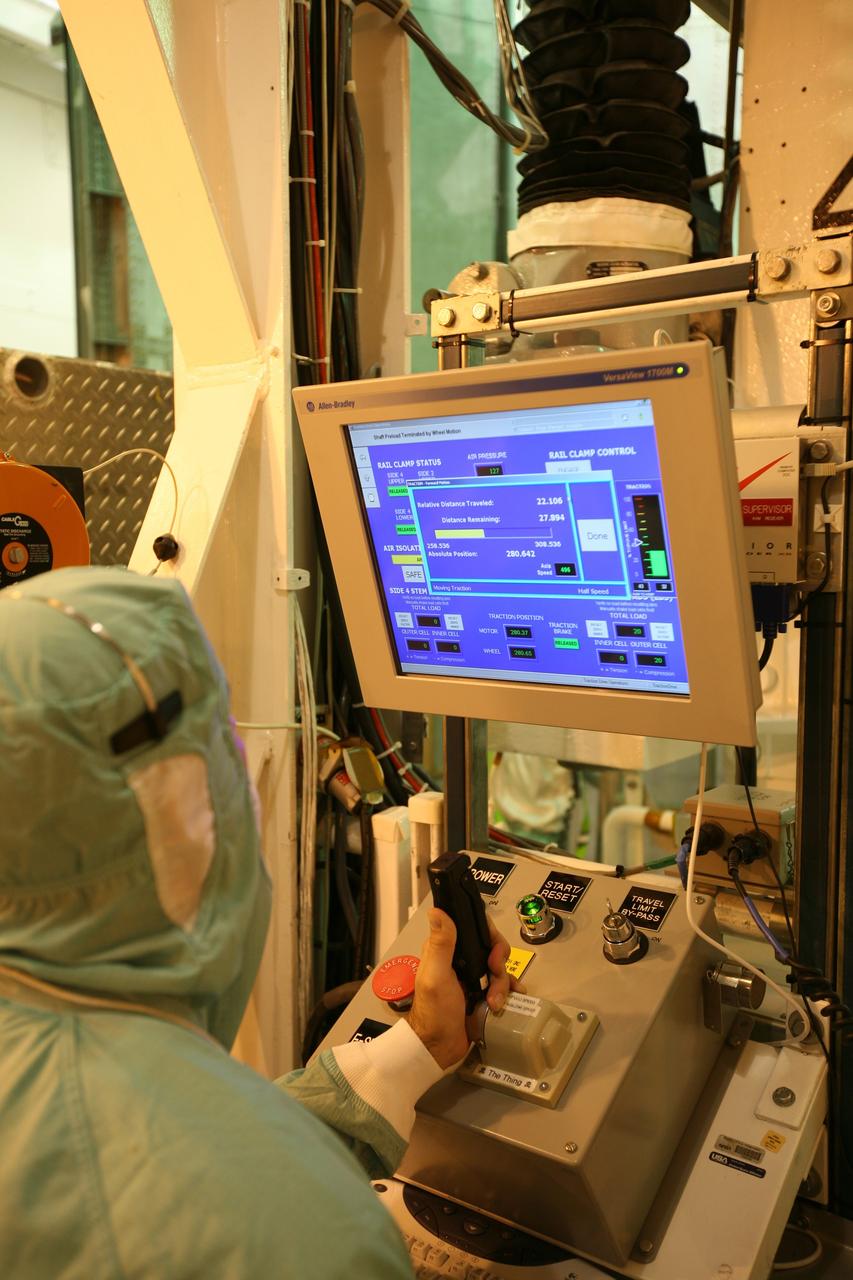
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a worker monitors use of the payload ground-handling mechanism in the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, to aid the transfer of the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom) from the payload canister into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, technicians check the clearance of the payload bay door as it closes around the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier inside space shuttle Discovery's payload bay. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A, technicians check underneath as space shuttle Discovery's payload bay doors begin closing. Seen in the payload bay are the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo and the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier. Discovery will deliver 33,000 pounds of equipment to the station, including science and storage racks, a freezer to store research samples, a new sleeping compartment and the COLBERT treadmill. Launch is targeted for late August. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers use the payload ground-handling mechanism in the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, to aid the transfer of the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo (center) and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier (bottom) from the payload canister into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the payload canister with space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload inside is in place to be lifted into the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, above. Inside the canister are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. The payload canister will release its cargo into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
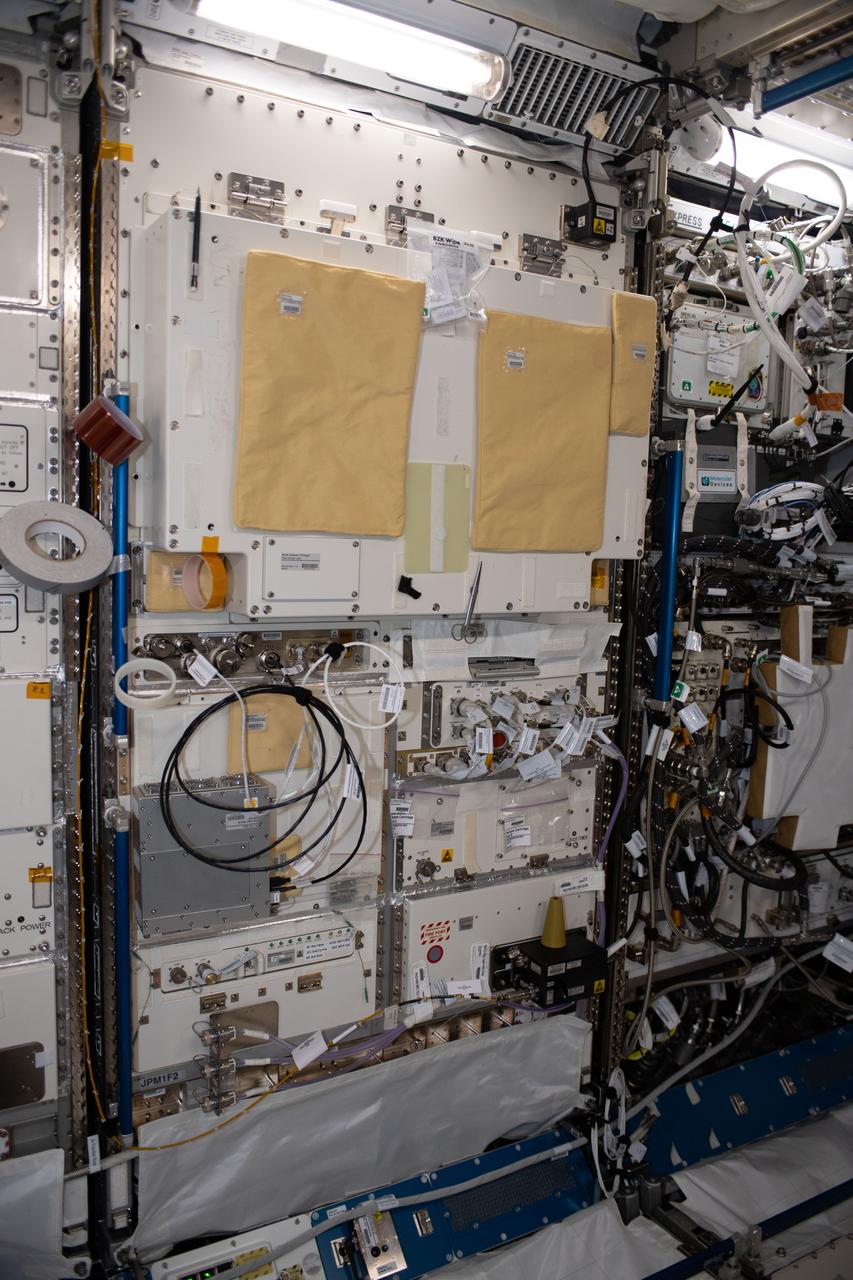

iss056e150255 (8/21/2018) --- A view of the Multi purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) 2 in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International Space Station (ISS). The Multi Purpose Small Payload Rack-2 (MSPR-2) is a second multipurpose payload rack system used in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Similar to the original MSPR (still in use), MSPR-2 has two workspaces and a work table that can be used for wide fields of space environment utilization including science and educational missions.
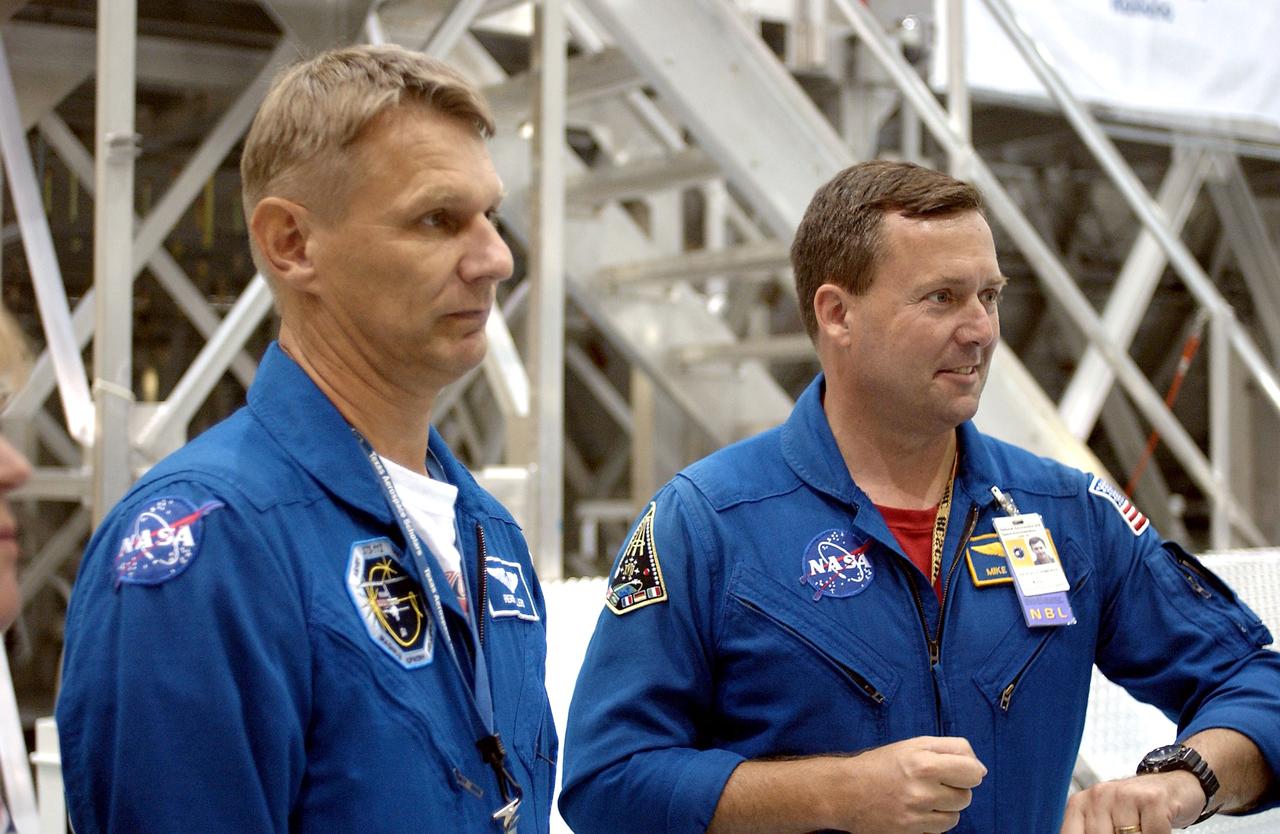

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-120 Mission Specialists Piers Sellers and Michael Foreman are in the Space Station Processing Facility for hardware familiarization. The mission will deliver the second of three Station connecting modules, Node 2, which attaches to the end of U.S. Lab. It will provide attach locations for the Japanese laboratory, European laboratory, the Centrifuge Accommodation Module and later Multi-Purpose Logistics Modules. The addition of Node 2 will complete the U.S. core of the International Space Station.
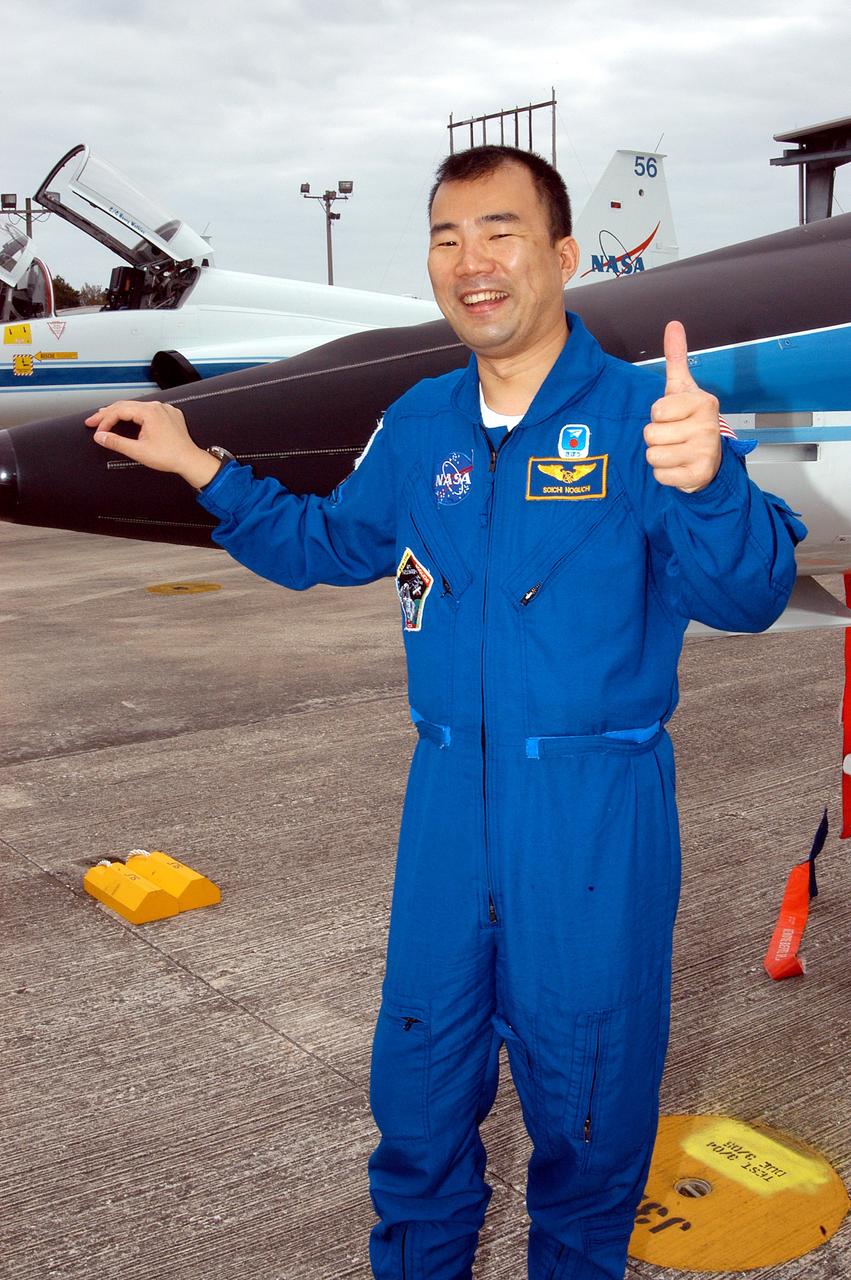

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Soichi Noguchi is happy to be back at KSC after arriving aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment to the Space Station and the external stowage platform.
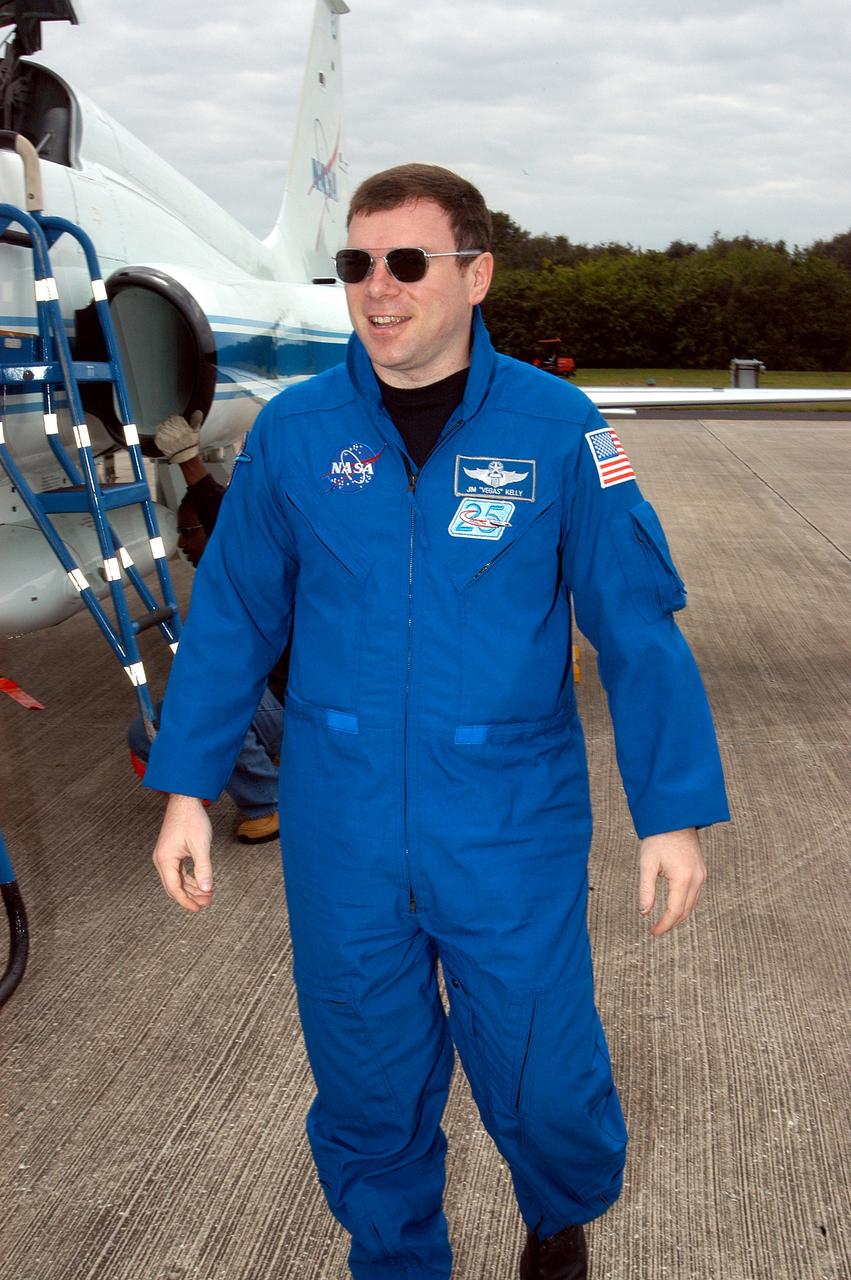

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Pilot Jim Kelly is pleased to be back at KSC after arriving aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment to the Space Station and the external stowage platform.
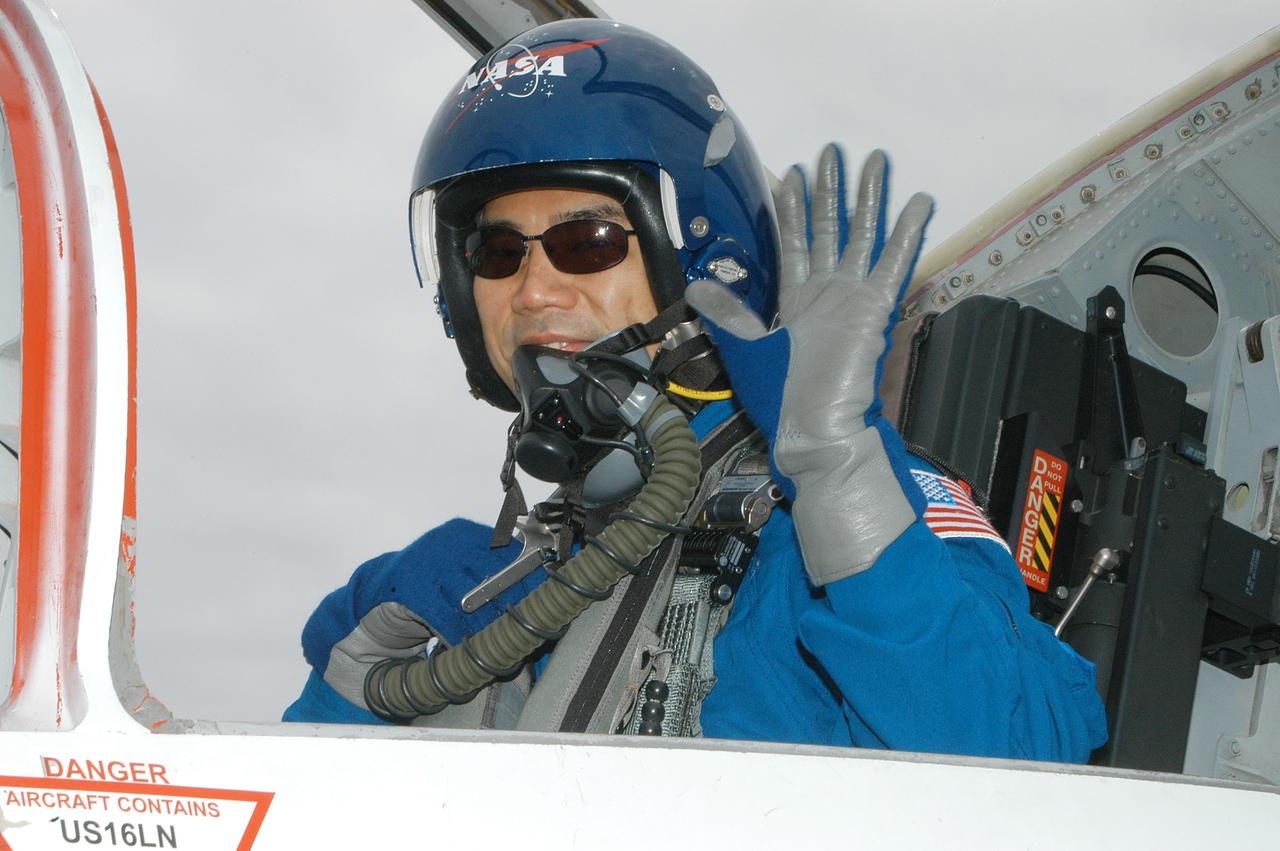

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Soichi Noguchi arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment to the Space Station and the external stowage platform.
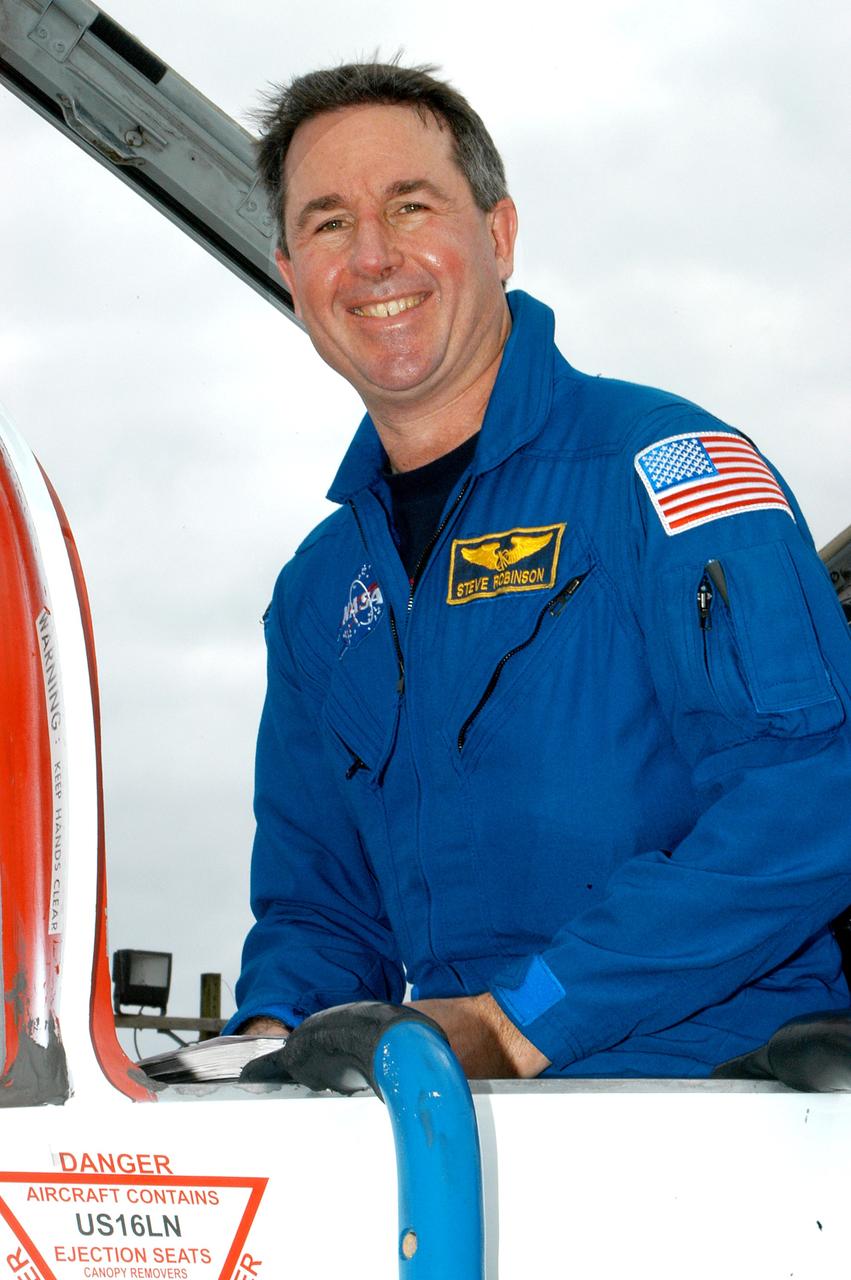

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment to the Space Station and the external stowage platform.
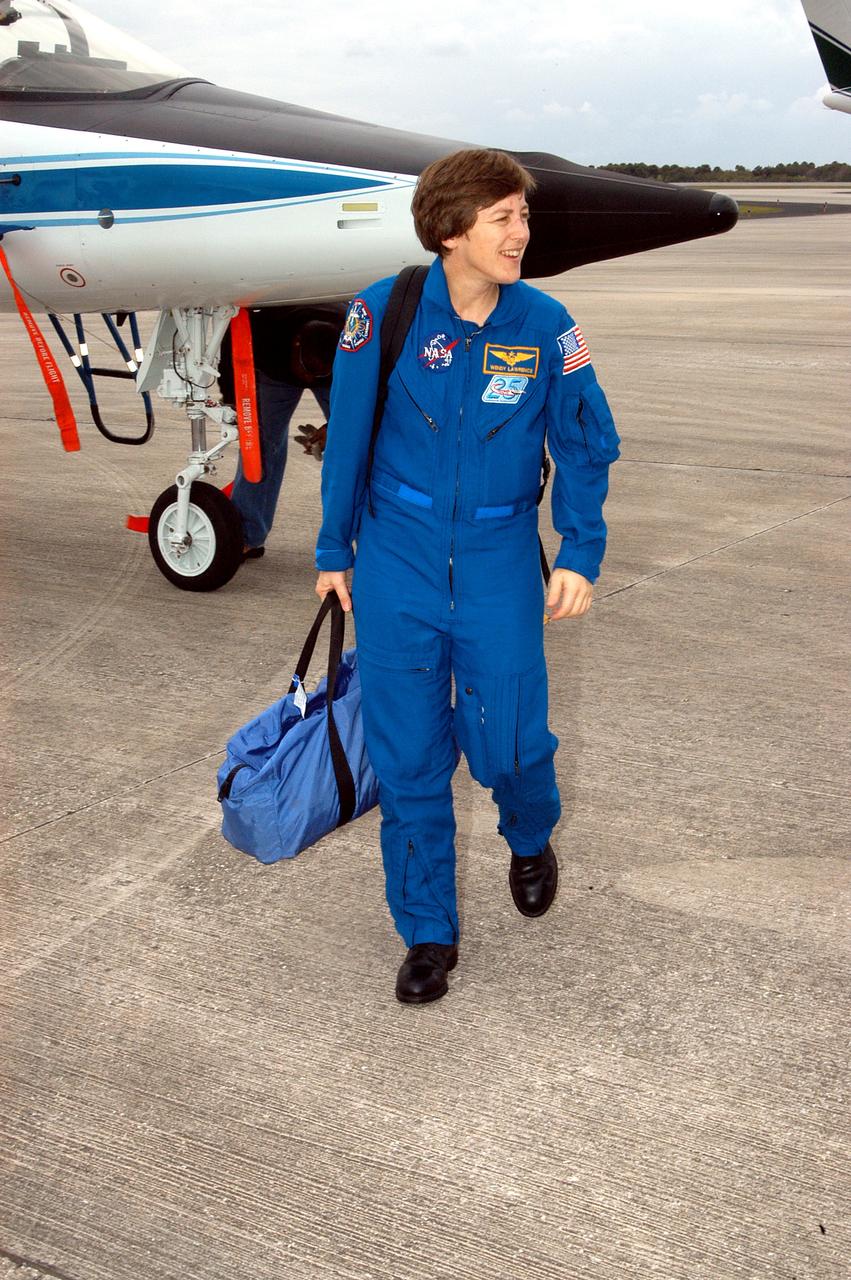

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Wendy Lawrence is pleased to be back at KSC after arriving aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. She and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment to the Space Station and the external stowage platform.
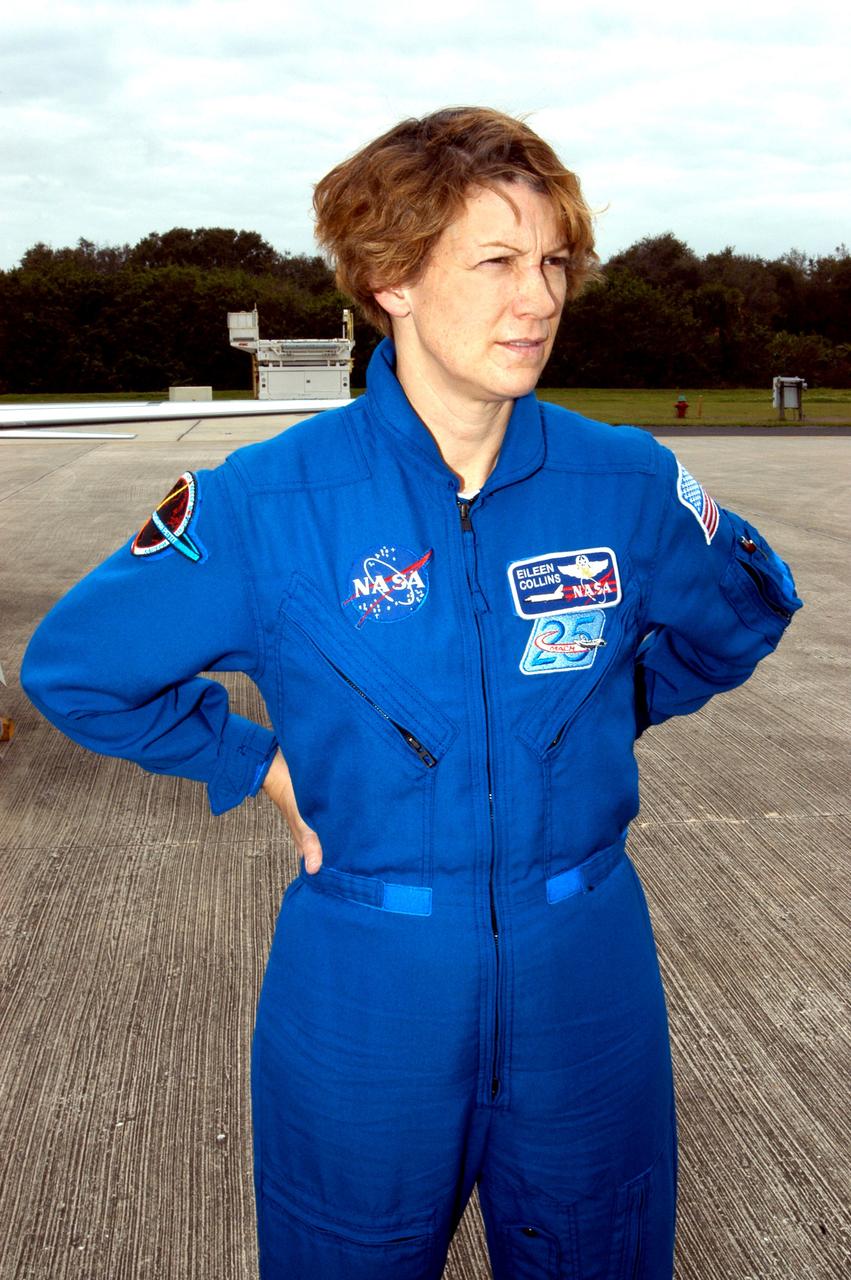

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Commander Eileen Collins is pleased to be back at KSC after arriving aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. She and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver to the Space Station the external stowage platform and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module with supplies and equipment.
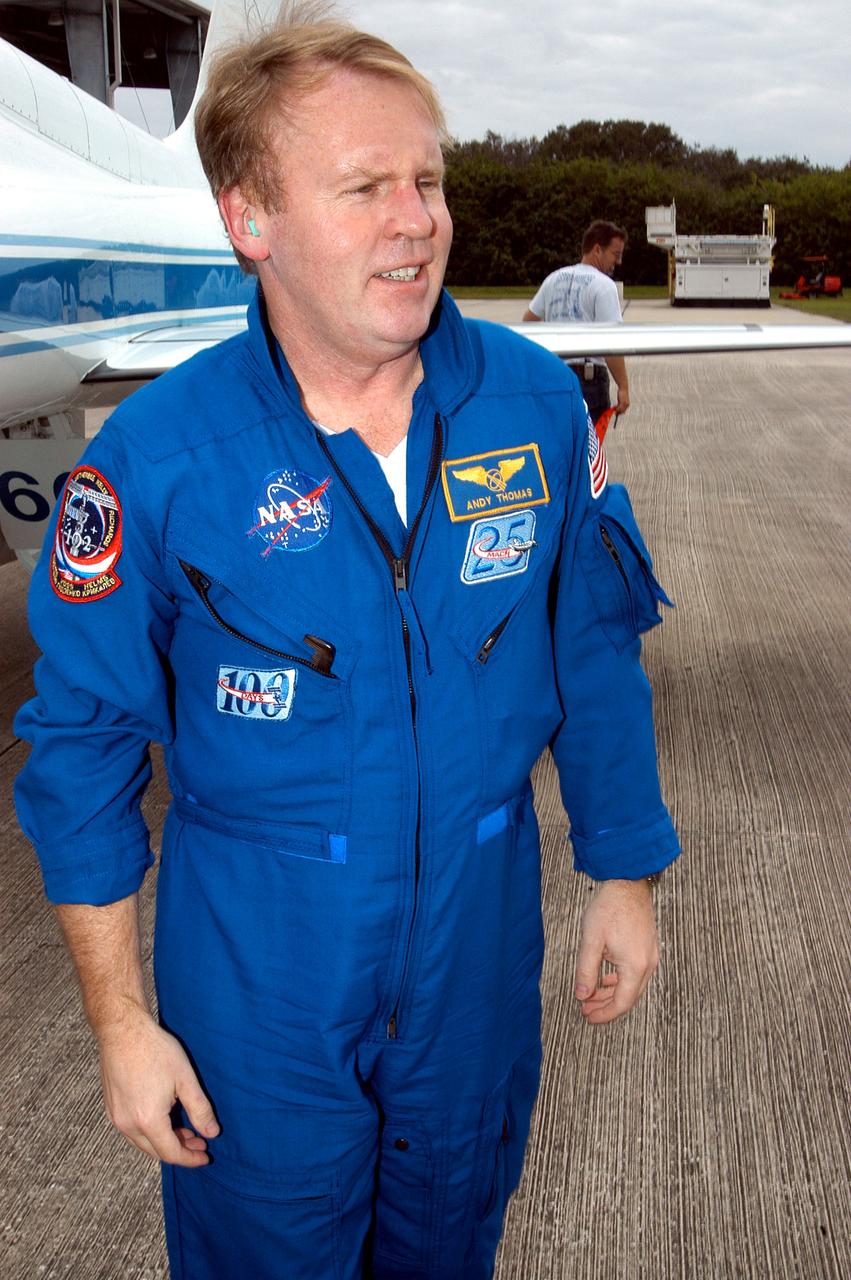

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas is pleased to be back at KSC after arriving aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver to the Space Station the external stowage platform and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module with supplies and equipment.
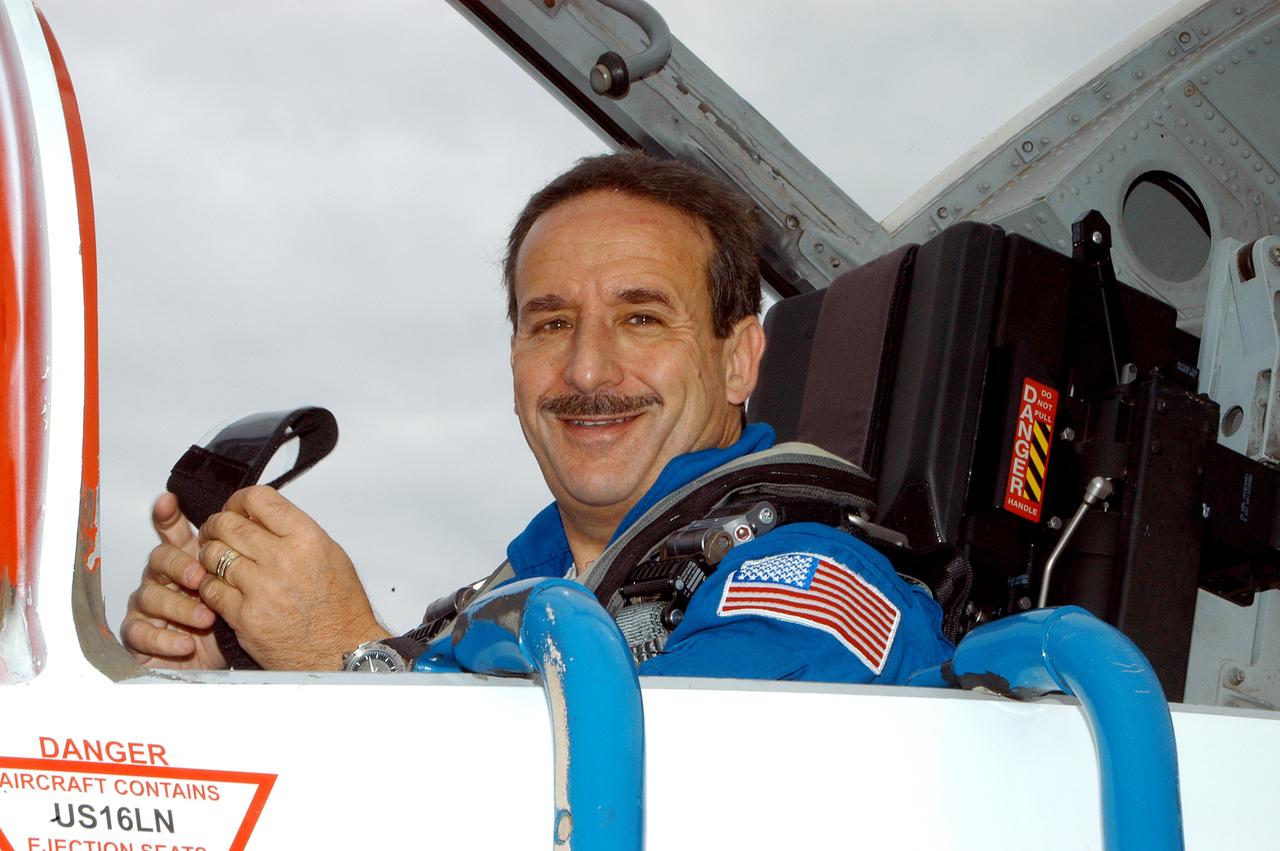

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-114 Mission Specialist Charles Camarda arrives at KSC aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He and other crew members are at the Center for familiarization activities with equipment. The mission is Logistics Flight 1, scheduled to deliver the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module carrying supplies and equipment,to the Space Station, and the external stowage platform.
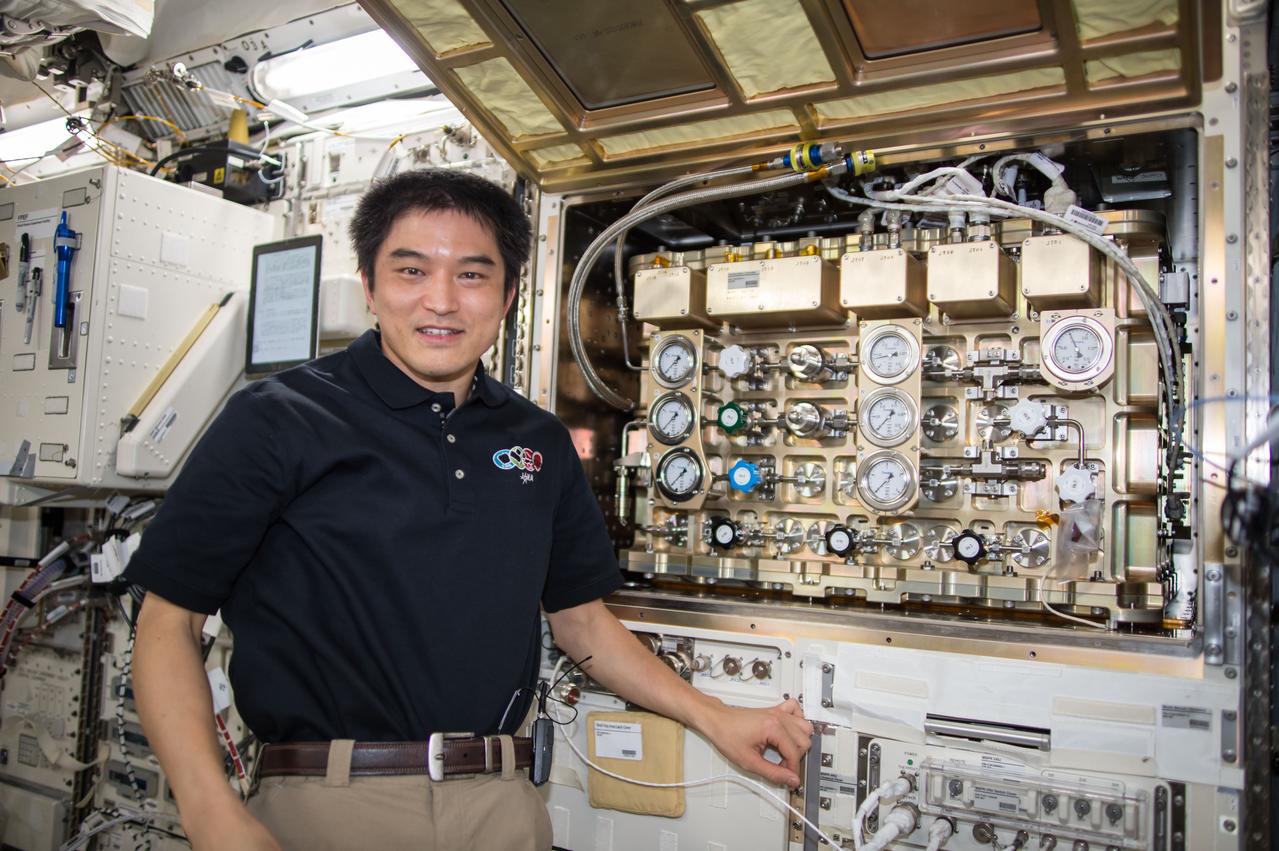

iss049e012031 (9/28/2016) --- Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Takuya Onishi with the Multi purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) Combustion Chamber (CC) in Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
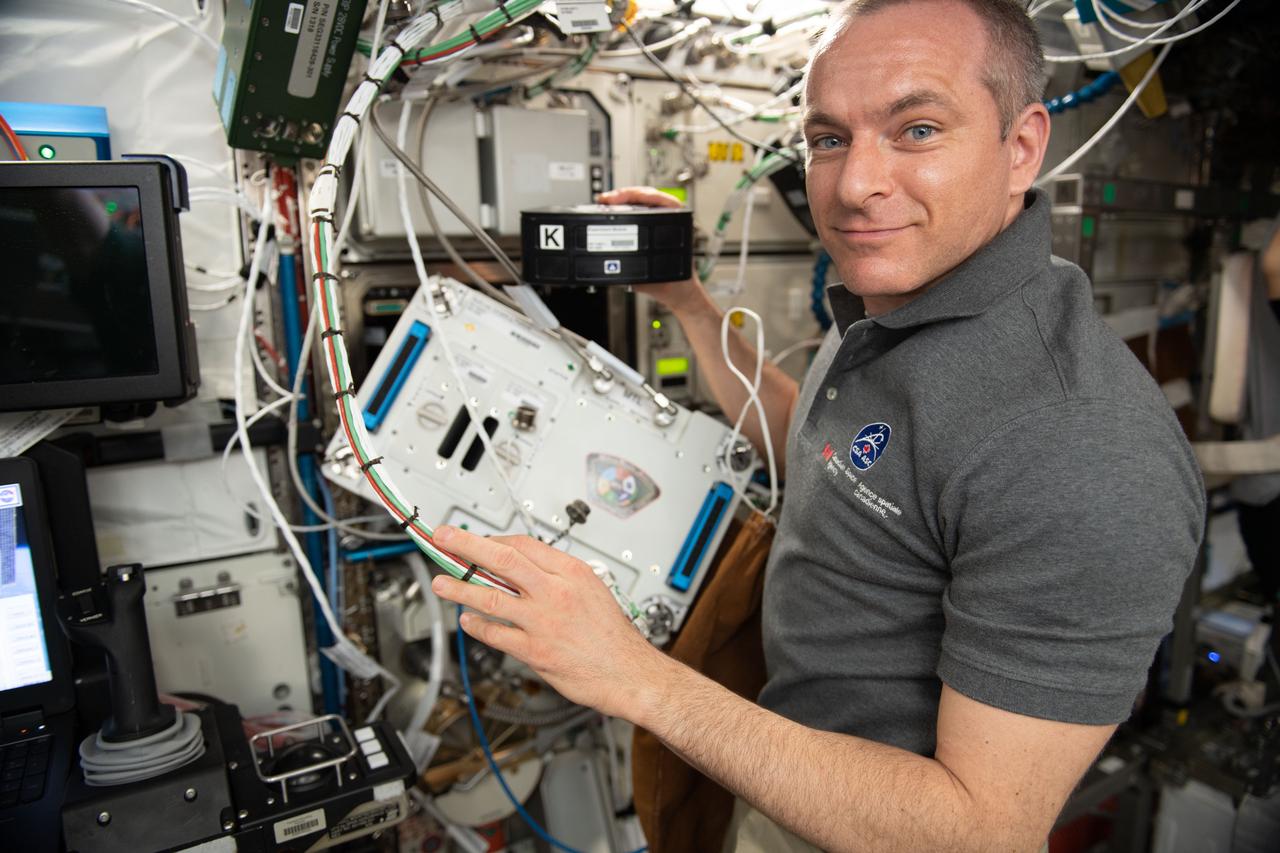

iss059e061366 (May 12, 2019) --- Canadian Space Agency astronaut David Saint-Jacques works with the Multi-purpose Variable-G Platform hardware exploring therapies for bone injuries and bone diseases on Earth and in space.

STS102-E-5095 (10 March 2001) --- The Leonardo Multi Purpose Logistics Module rests in Discovery's payload bay in this view taken from the station by a crew member using a digital still camera.
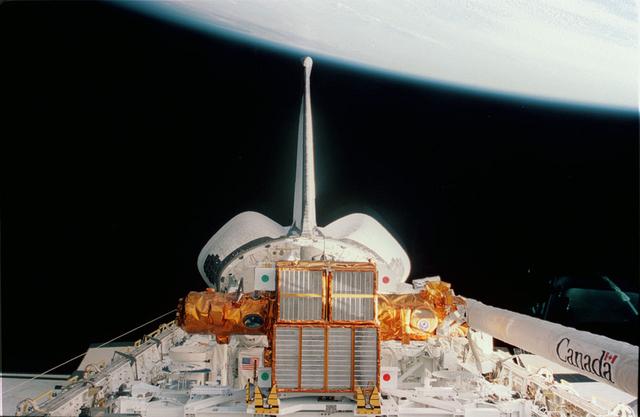

STS-87 Onboard Photo: The U. S. Microgravity Payload-4 (USMP-4) is carried aboard multi-purpose experiment support structures mounted in the shuttle payload bay and sparning the width of the orbiter.
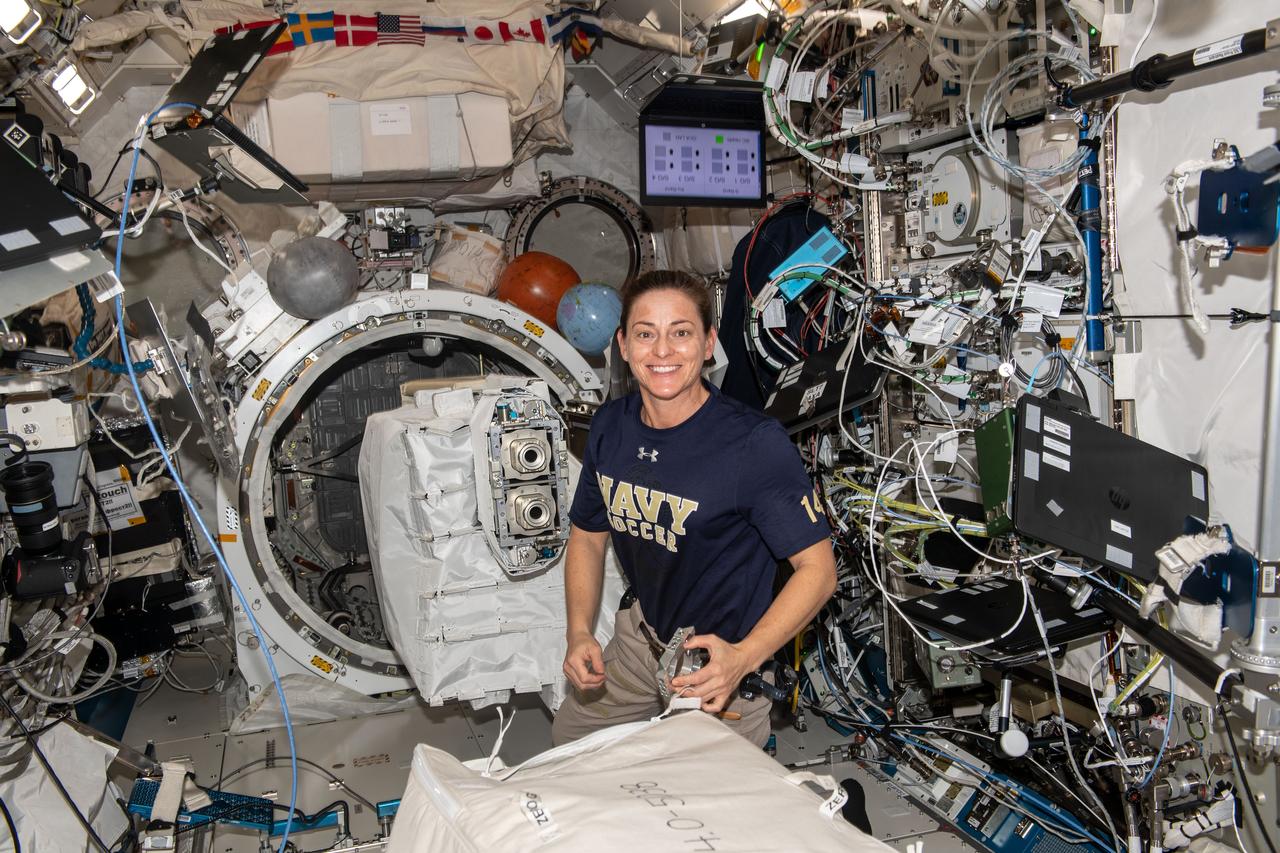

iss068e028254_alt (Dec. 9, 2022) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 68 Flight Engineer Nicole Mann removes a small satellite deployer from the Multi-Purpose Experiment Platform inside the Kibo laboratory module's airlock.
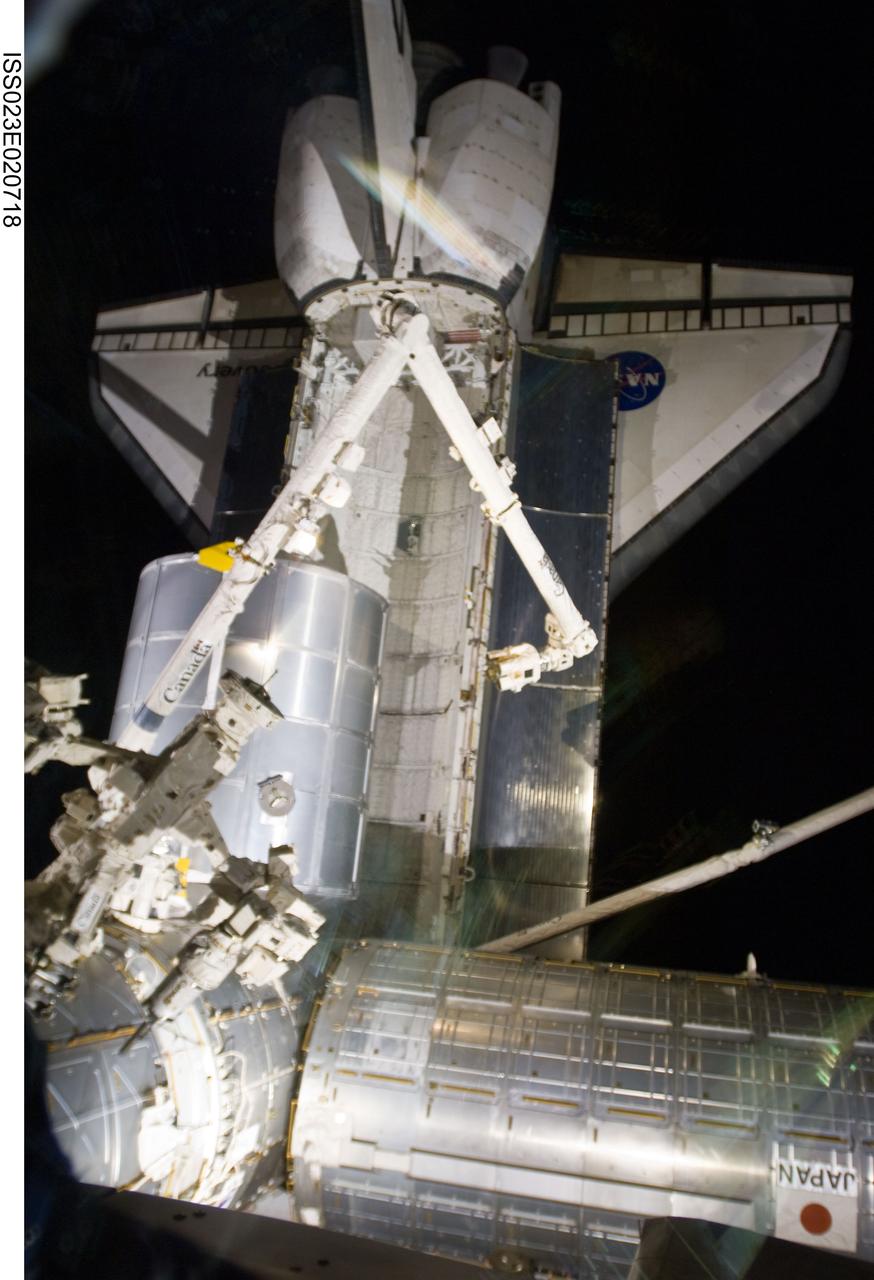

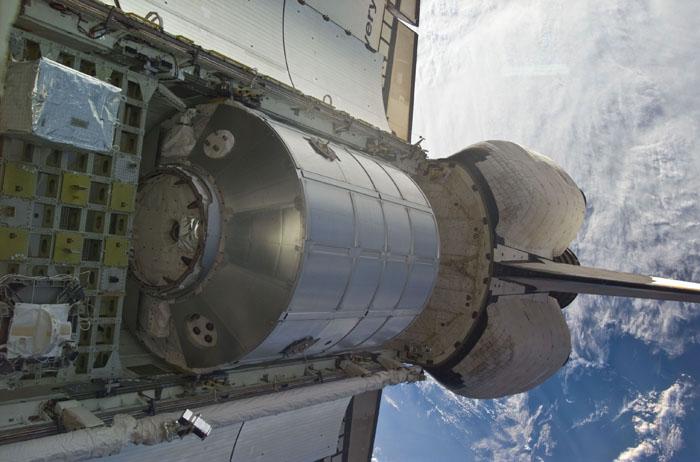
ISS023-E-020718 (8 April 2010) --- The station’s robotic Canadarm2 relocates the Leonardo Multi-purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) from space shuttle Discovery’s payload bay to a port on the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
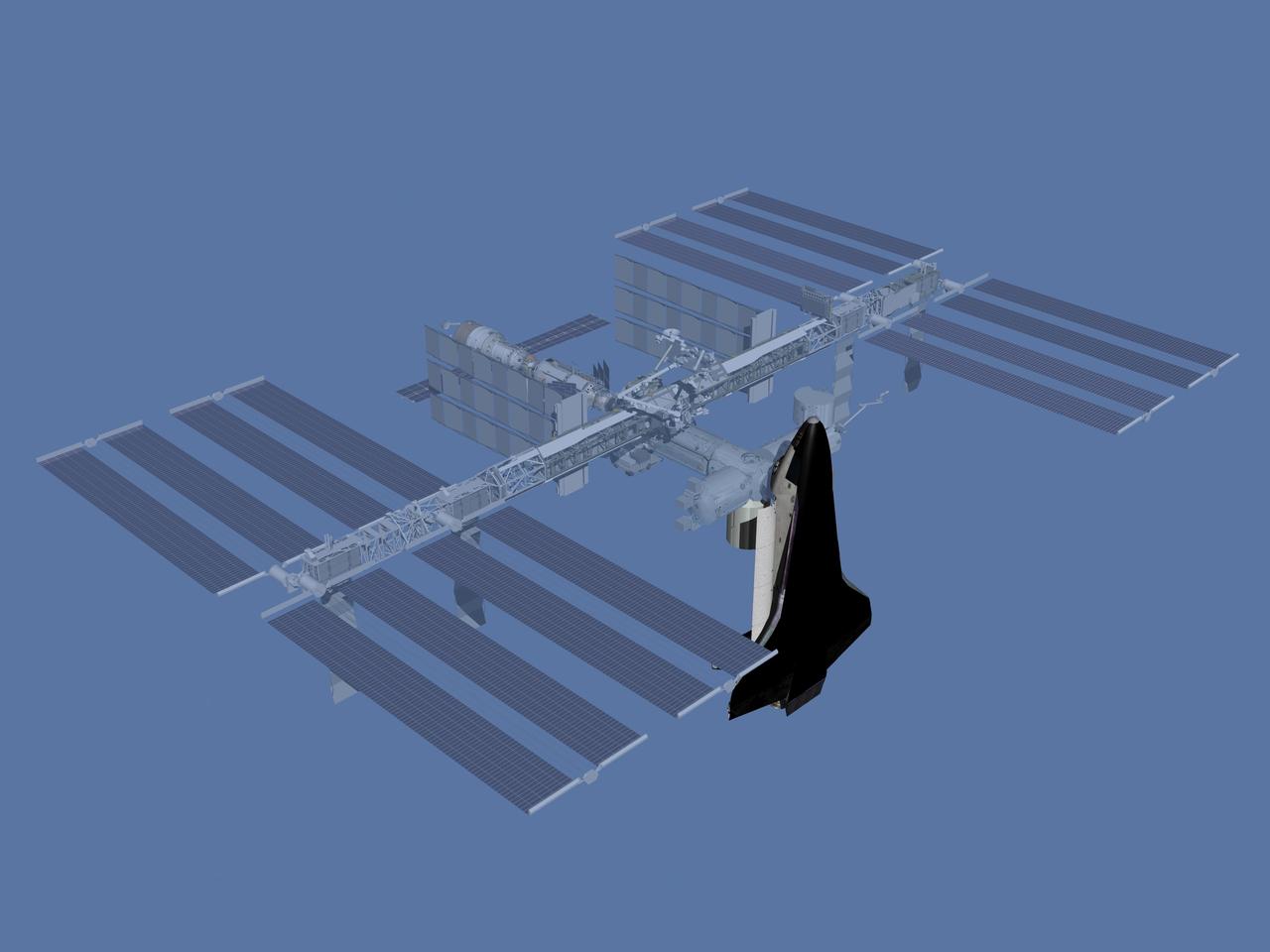
JSC2006-E-43508 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight ULF2. U.S. Orbiter brings Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM).
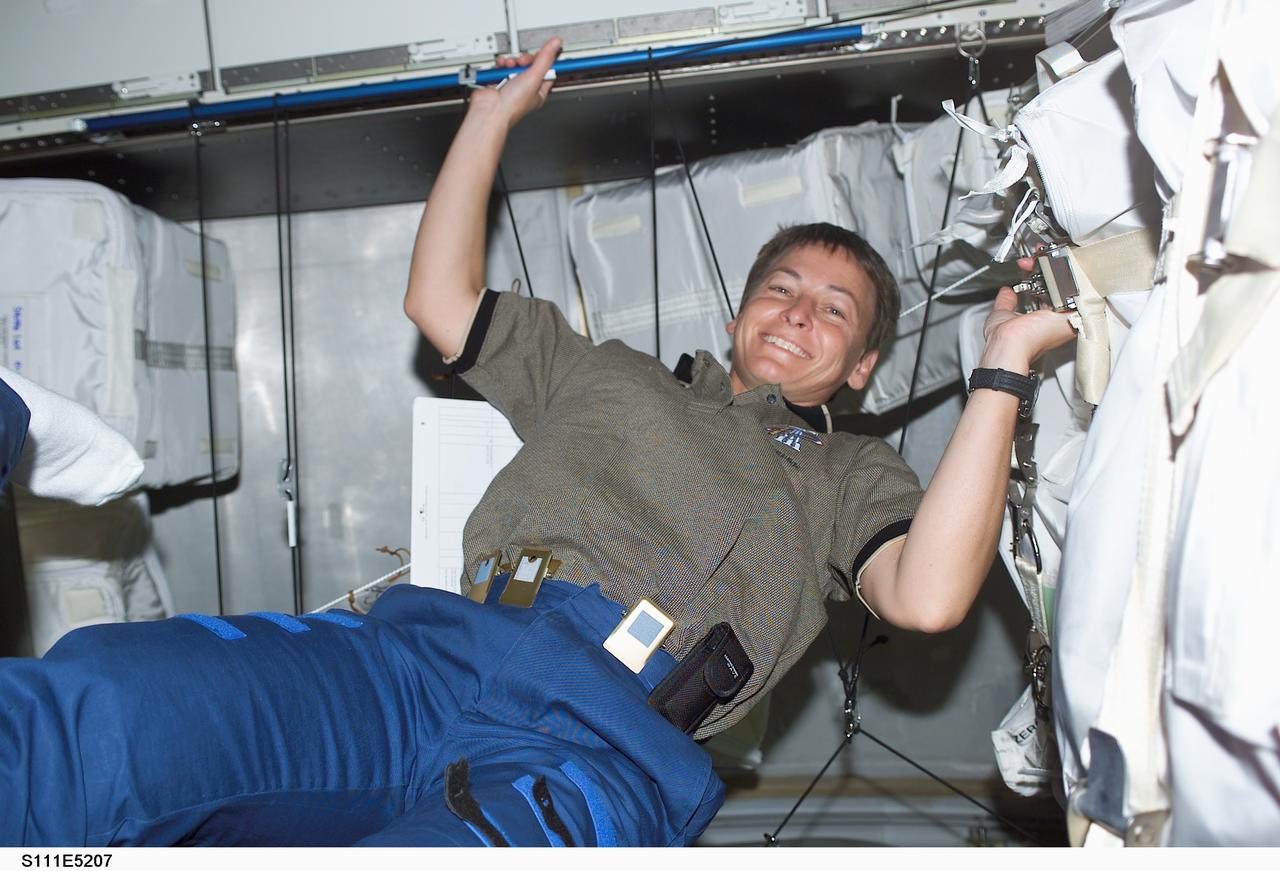

STS111-E-5207 (12 June 2002) --- Astronaut Peggy A. Whitson, Expedition Five flight engineer, is photographed in Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) on the International Space Station (ISS).
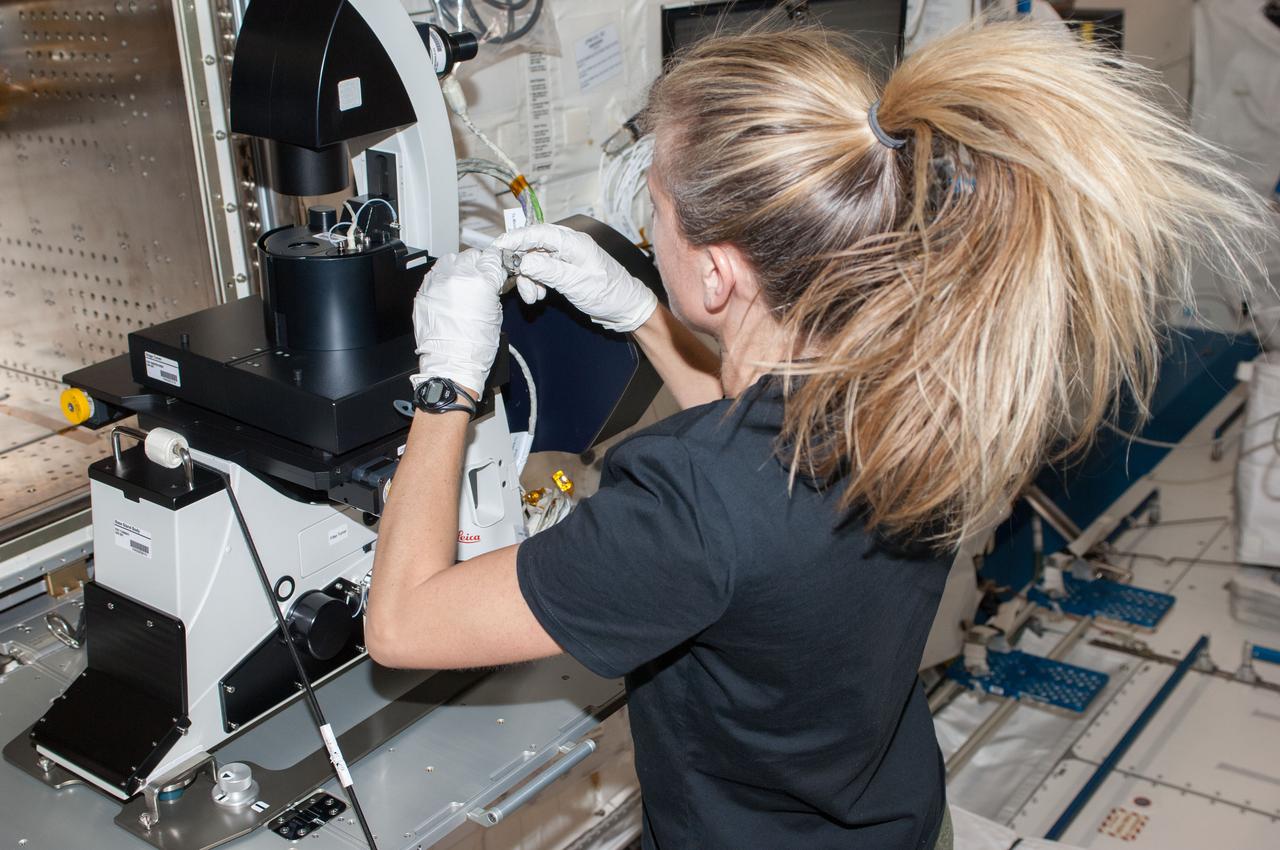

NASA astronaut Karen Nyberg, Expedition 36 flight engineer, works to setup the Multi-Purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) fluorescence microscope in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station.
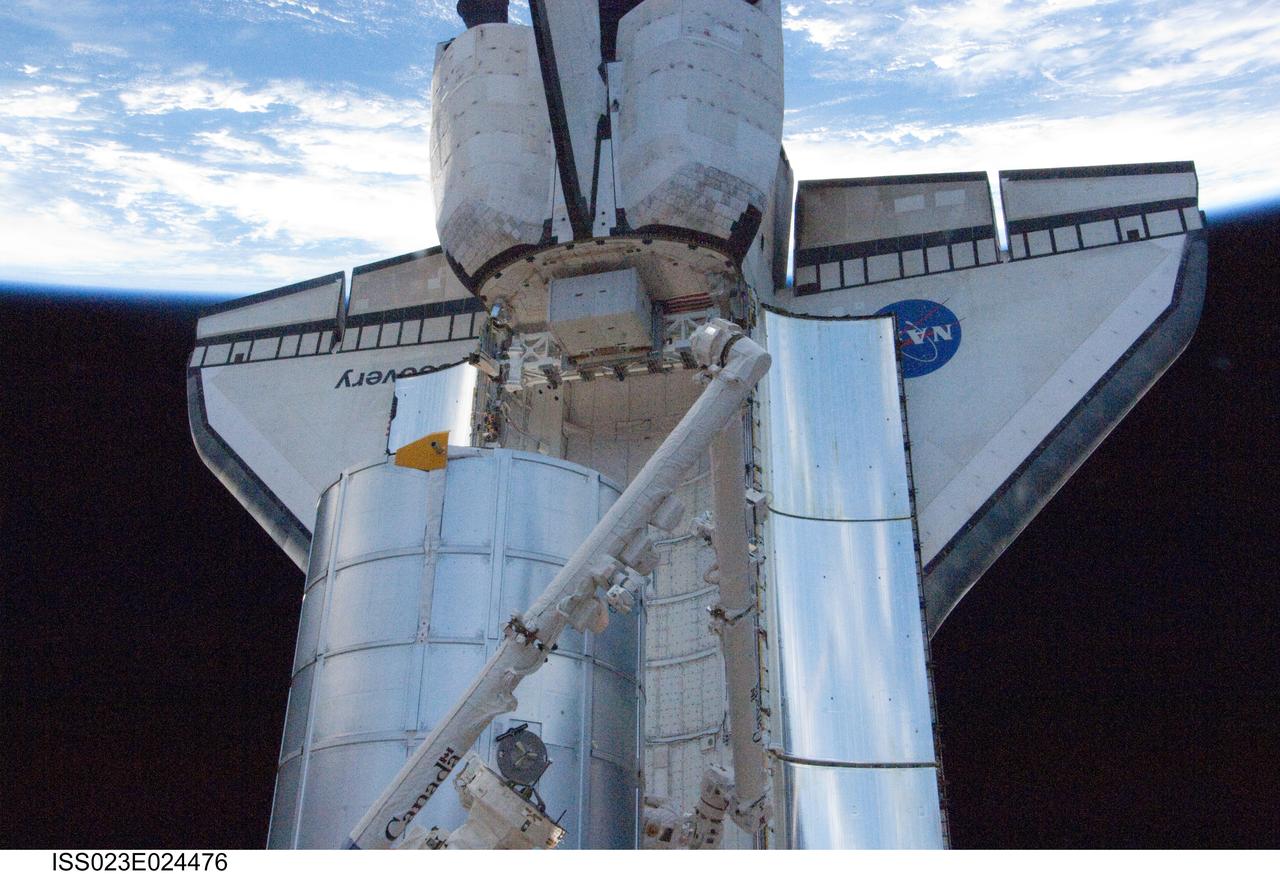

ISS023-E-024476 (15 April 2010) --- The Leonardo Multi-Purpose Logistics Module hovers over Discovery's payload bay awaiting its placement there for the trip back home.
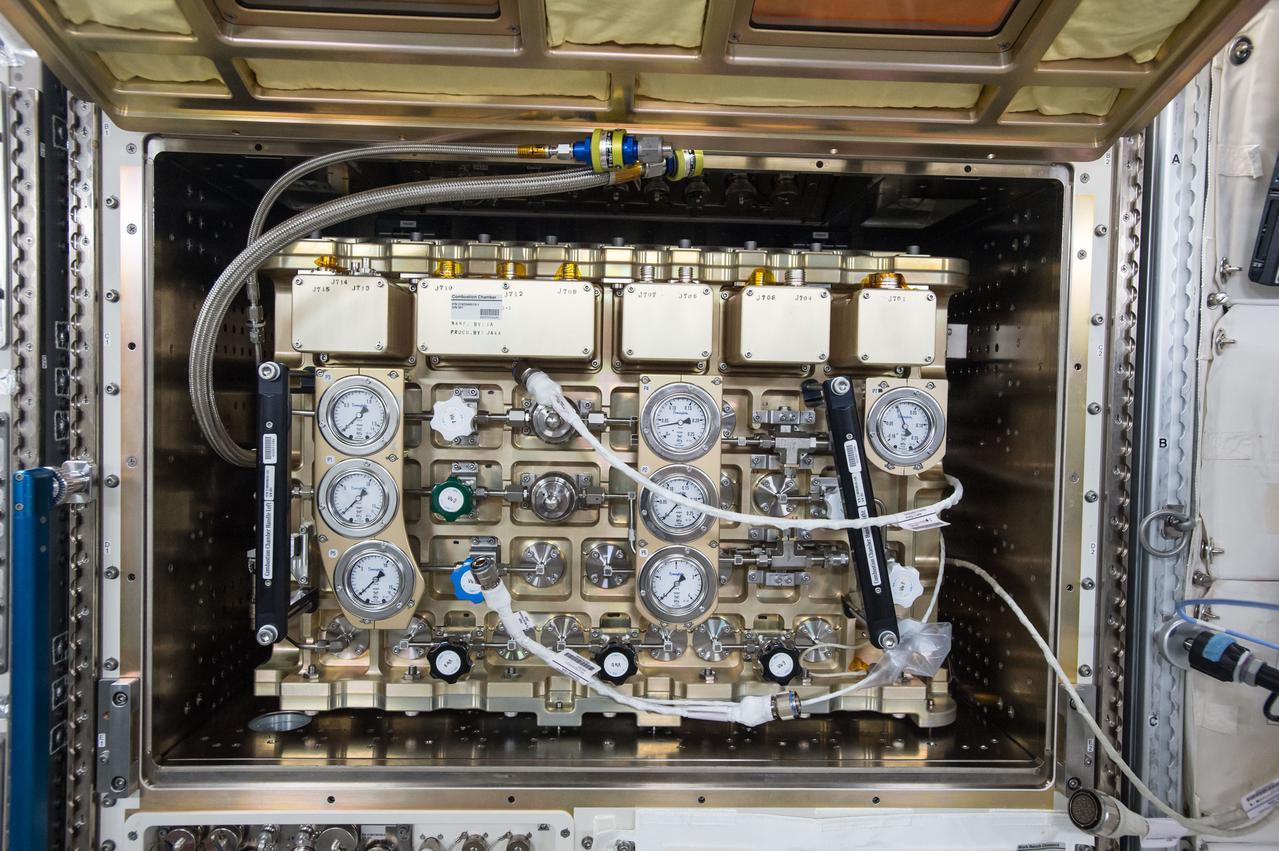
iss049e025077 (9/28/2016) --- View taken during Multi-Purpose Small Payload Rack (MSPR) Combustion Chamber (CC) installed in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
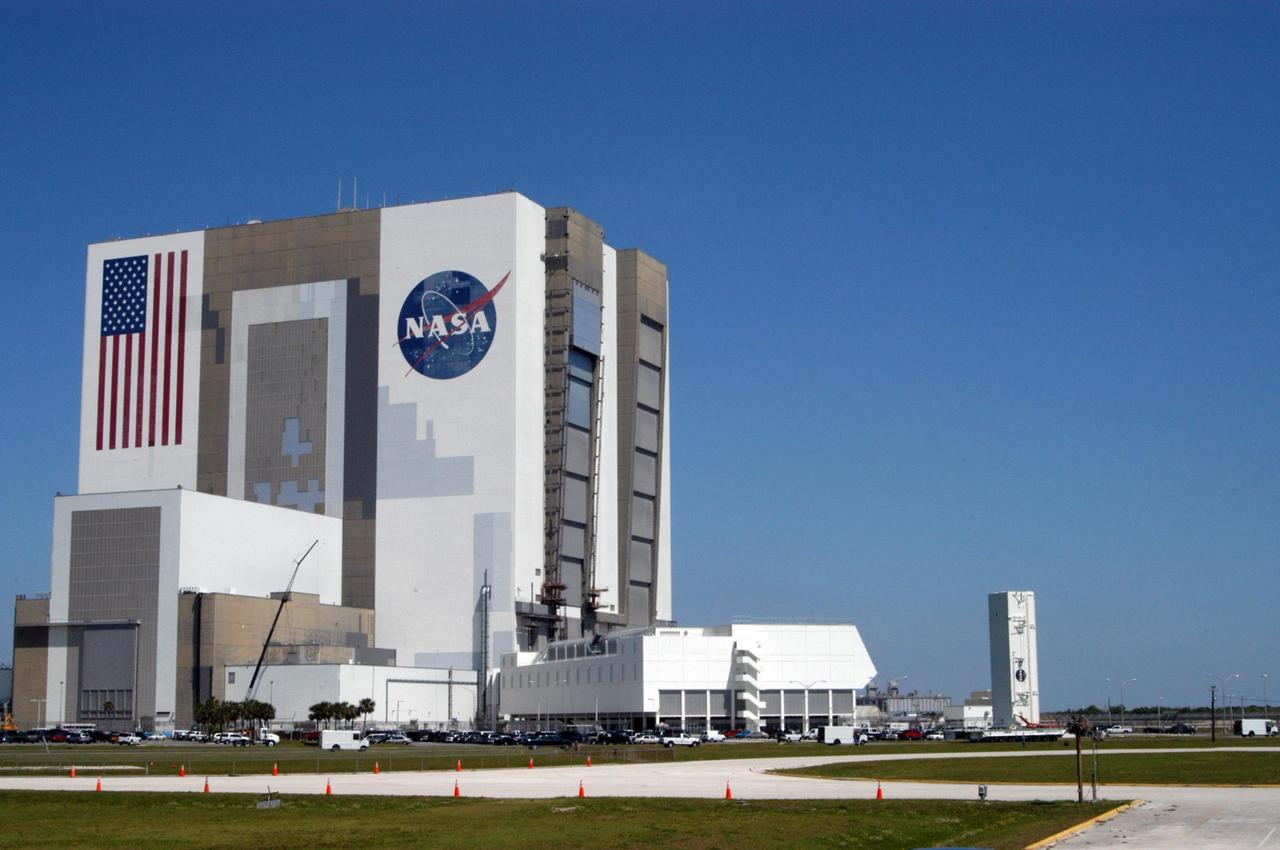

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister passes NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building and Launch Control Center on its way to Launch Pad 39B. Inside are the payloads for mission STS-121: the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, with supplies and equipment for the International Space Station; the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier; and the integrated cargo carrier, with the mobile transporter reel assembly and a spare pump module. The payload will be transferred from the canister to Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay at the pad. Discovery is scheduled to launch on mission STS-121 from Launch Pad 39B in a window that opens July 1 and extends to July 19. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
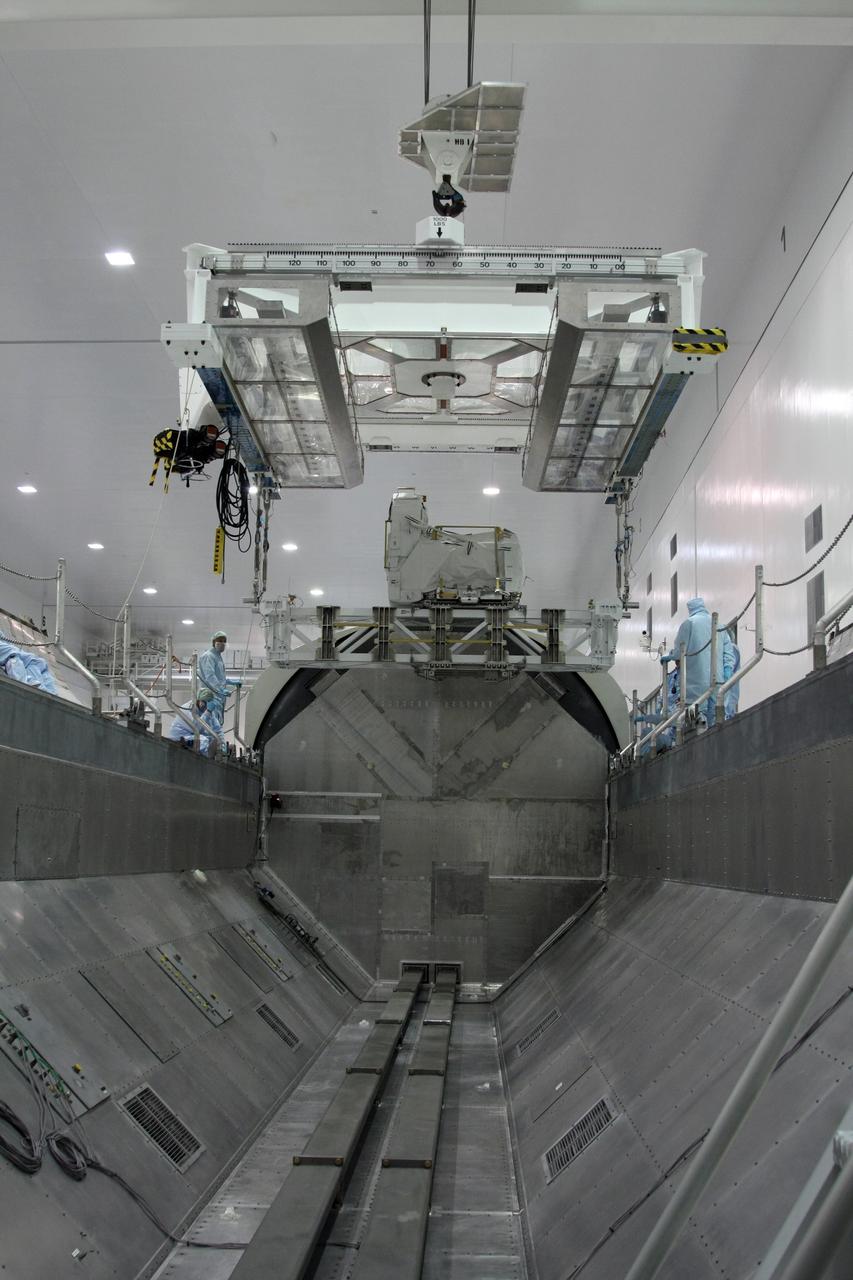

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier with the flexible hose rotary coupler is lowered into the payload canister in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The carrier is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. Endeavour will also carry the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo holding supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, equipment for the regenerative life support system and spare hardware. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
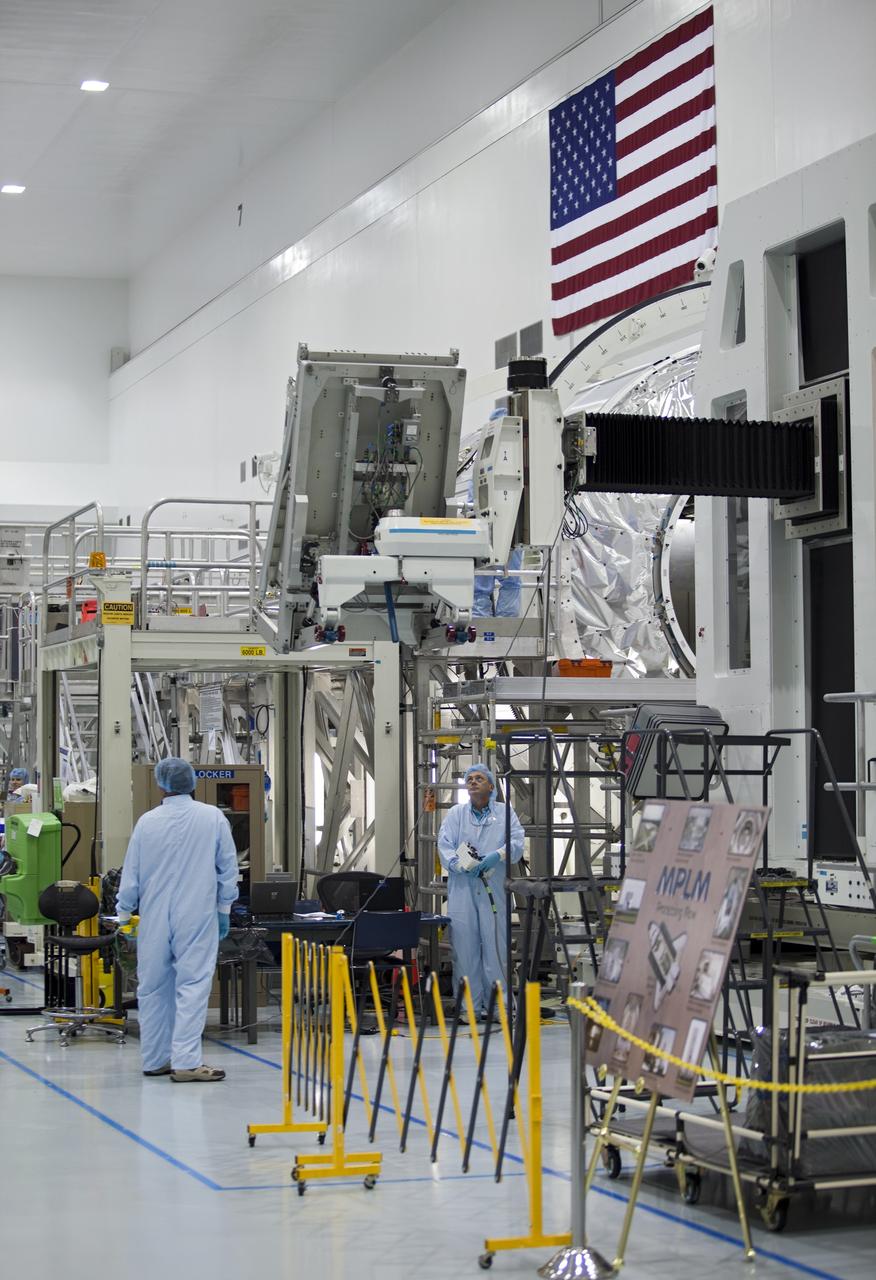

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress of cargo as it is being prepared for installation inside the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module for shuttle Atlantis' flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its payload is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last shuttle flight for the Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians garbed in protective wear, commonly known as 'bunny suits,' install cargo inside the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module for shuttle Atlantis' flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its payload is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last shuttle flight for the Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
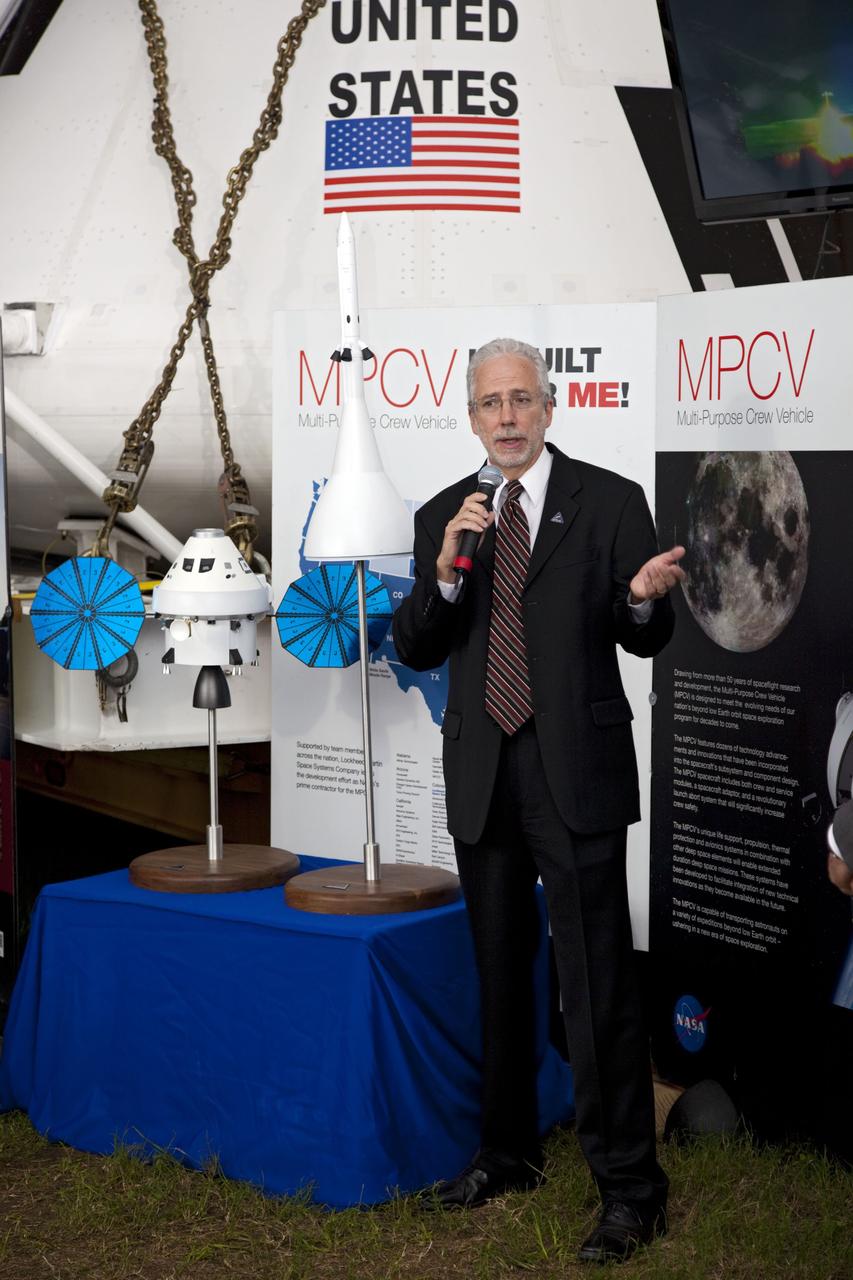

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A media event was held on the grounds near the Press Site at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida where a Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle (MPCV) is on display. The MPCV is based on the Orion design requirements for traveling beyond low Earth orbit and will serve as the exploration vehicle that will carry the crew to space, provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel, and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Seen here is Mark Geyer, Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle program manager speaking to media during a question-and-answer session. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
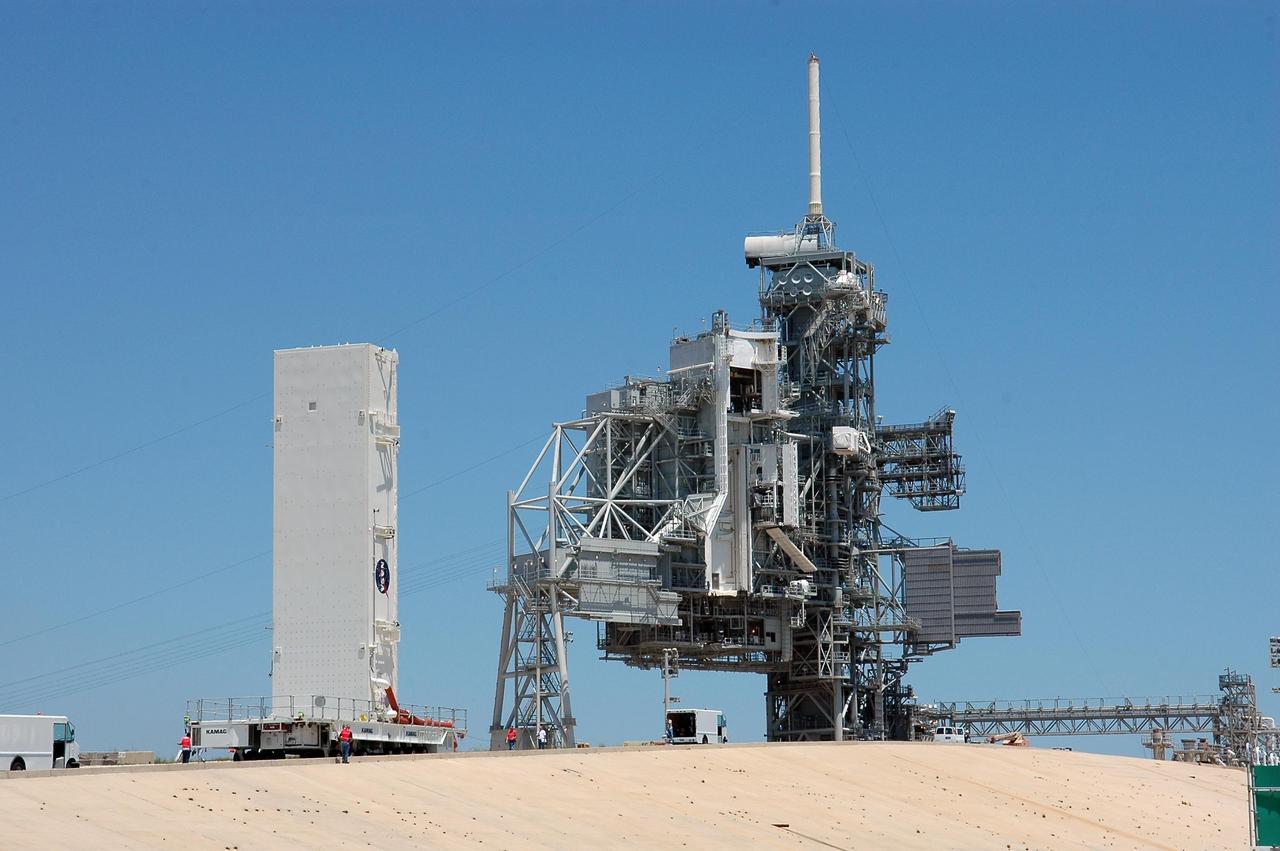

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister approaches the rotating service structure on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The canister holds the payloads for mission STS-121: the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, with supplies and equipment for the International Space Station; the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier; and the integrated cargo carrier, with the mobile transporter reel assembly and a spare pump module. The payload will be transferred from the canister to Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay at the pad. Discovery is scheduled to launch on mission STS-121 from Launch Pad 39B in a window that opens July 1 and extends to July 19. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload canister slowly climbs the ramp on Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The canister holds the payloads for mission STS-121: the multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo, with supplies and equipment for the International Space Station; the lightweight multi-purpose experiment support structure carrier; and the integrated cargo carrier, with the mobile transporter reel assembly and a spare pump module. The payload will be transferred from the canister to Space Shuttle Discovery's payload bay at the pad. Discovery is scheduled to launch on mission STS-121 from Launch Pad 39B in a window that opens July 1 and extends to July 19. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
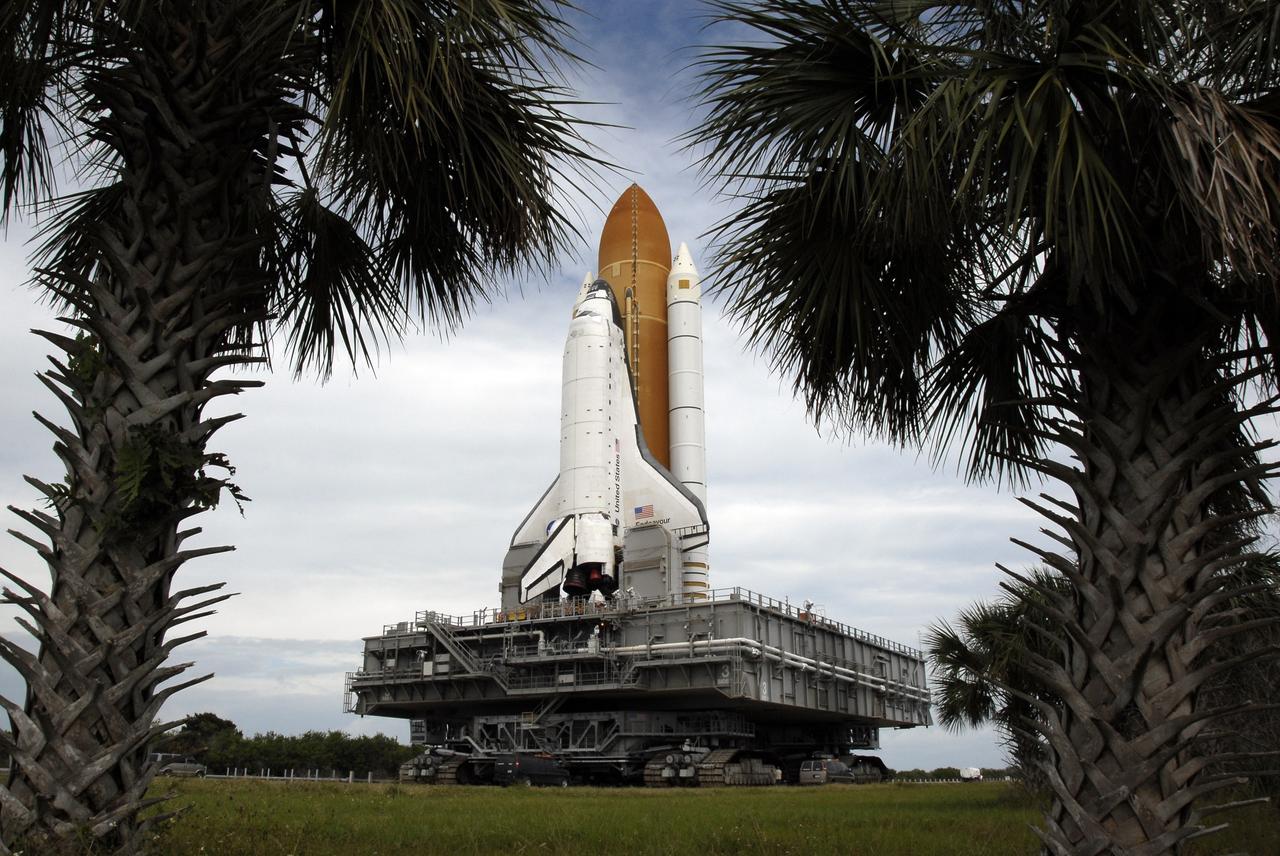

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Palmettos appear to frame space shuttle Endeavour as it rolls toward Launch Pad 39A on NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The shuttle earlier moved off Launch Pad 39B starting at 8:28 am. EDT and headed for pad 39A. Endeavour is targeted to launch Nov. 14 on the STS-126 mission. On this 27th mission to the International Space Station, Endeavour will carry the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo that will hold supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, additional exercise equipment, spare hardware and equipment for the regenerative life support system. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
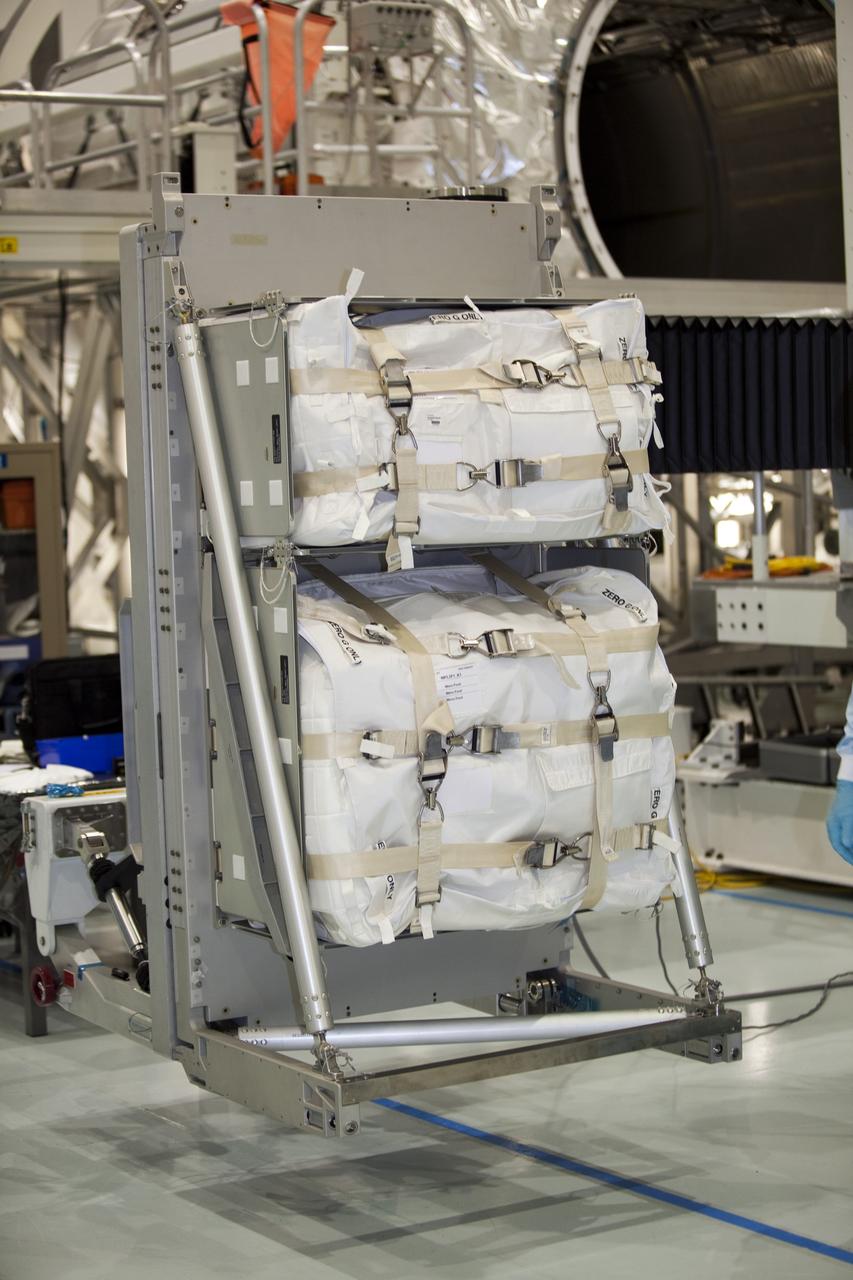

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, cargo is secured and ready to be installed inside the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module for shuttle Atlantis' flight to the International Space Station. Atlantis and its payload is being prepared for the STS-135 mission, which will deliver the Raffaello multi-purpose logistics module packed with supplies and spare parts to the station. Atlantis is targeted to launch June 28, and will be the last shuttle flight for the Space Shuttle Program. For more information visit, http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts135/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
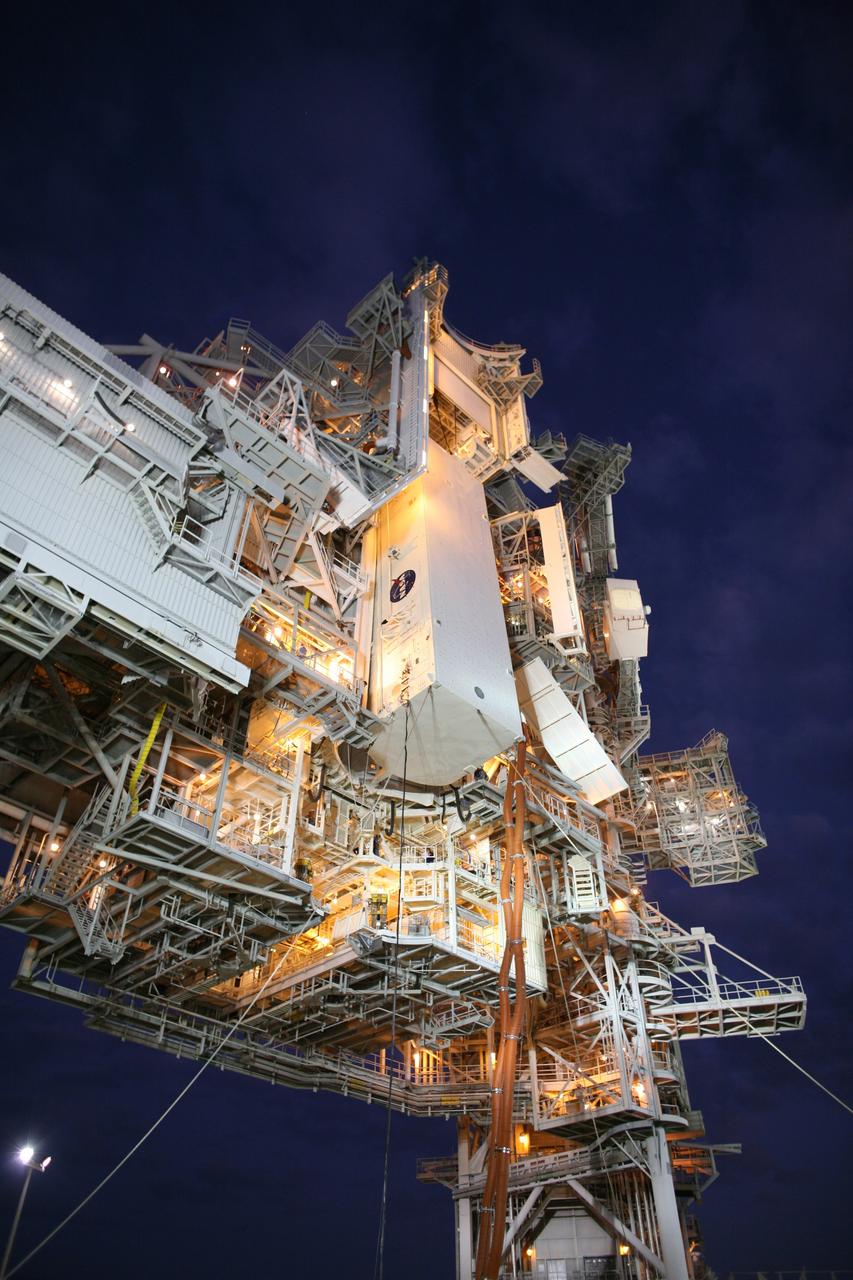

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the payload canister with space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission payload inside is lifted to the Payload Changeout Room, or PCR, above. Inside the canister are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. The red umbilical lines attached preserve the environmentally controlled interior. The payload canister will release its cargo into the PCR. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
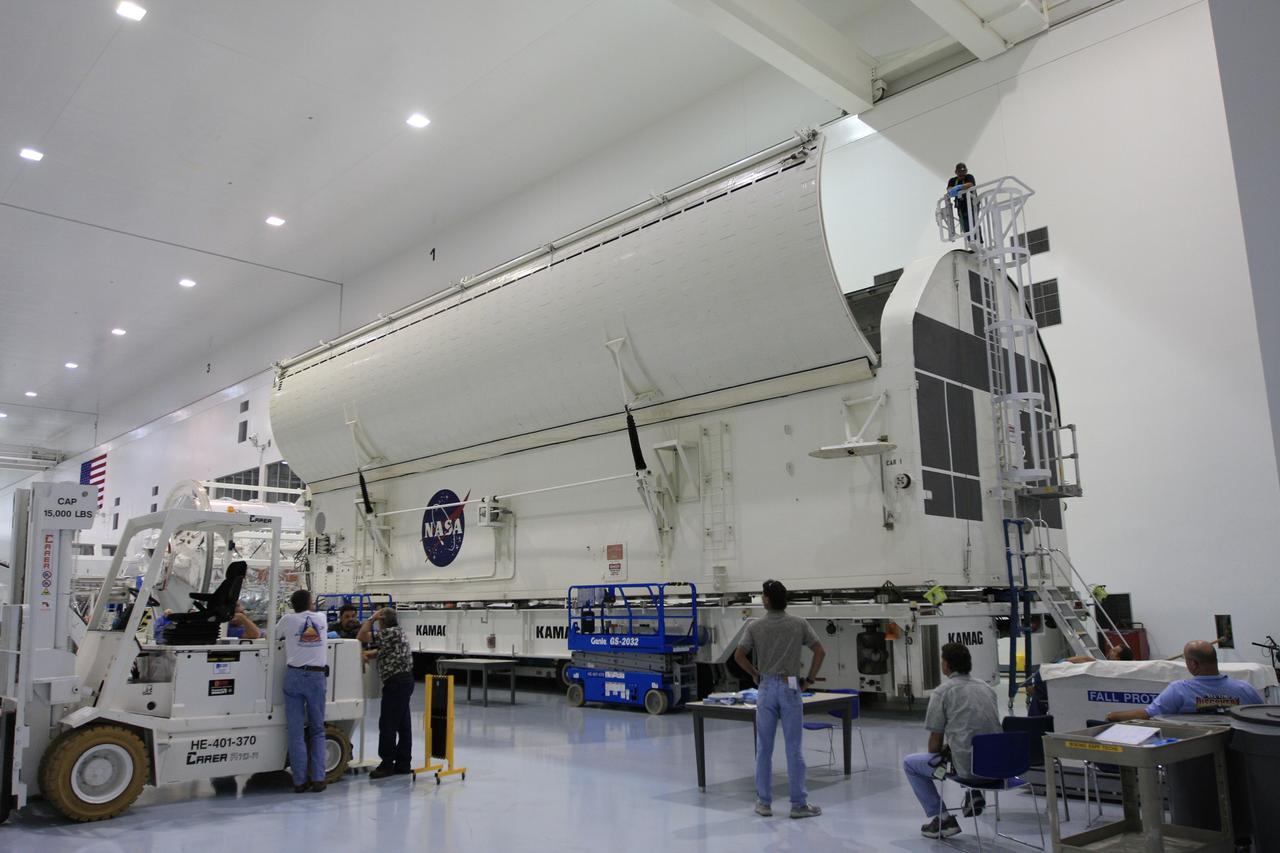

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the doors of the payload canister are closing over the payload for space shuttle Endeavour's STS-126 mission. Inside the canister are the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo and the Lightweight Multi-Purpose Experiment Support Structure Carrier. The canister next will be transported to the Canister Rotation Facility to raise it to vertical and then will be taken to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder