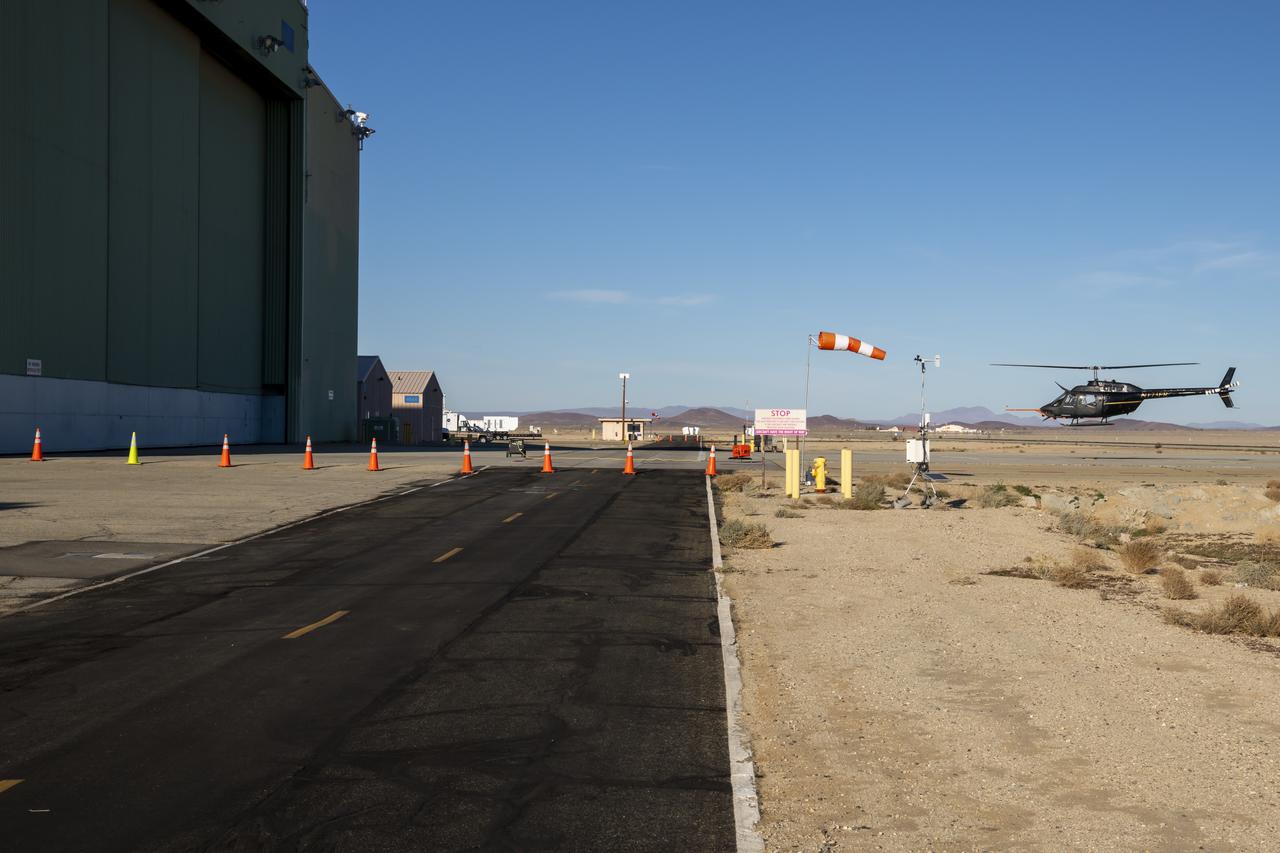

NASA's Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign conducts testing to study controllability characteristics when operating near buildings during heavy wind conditions at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Dec. 6 and 8-10. The Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. was used to study urban air mobility vehicle performance and flying qualities requirements.
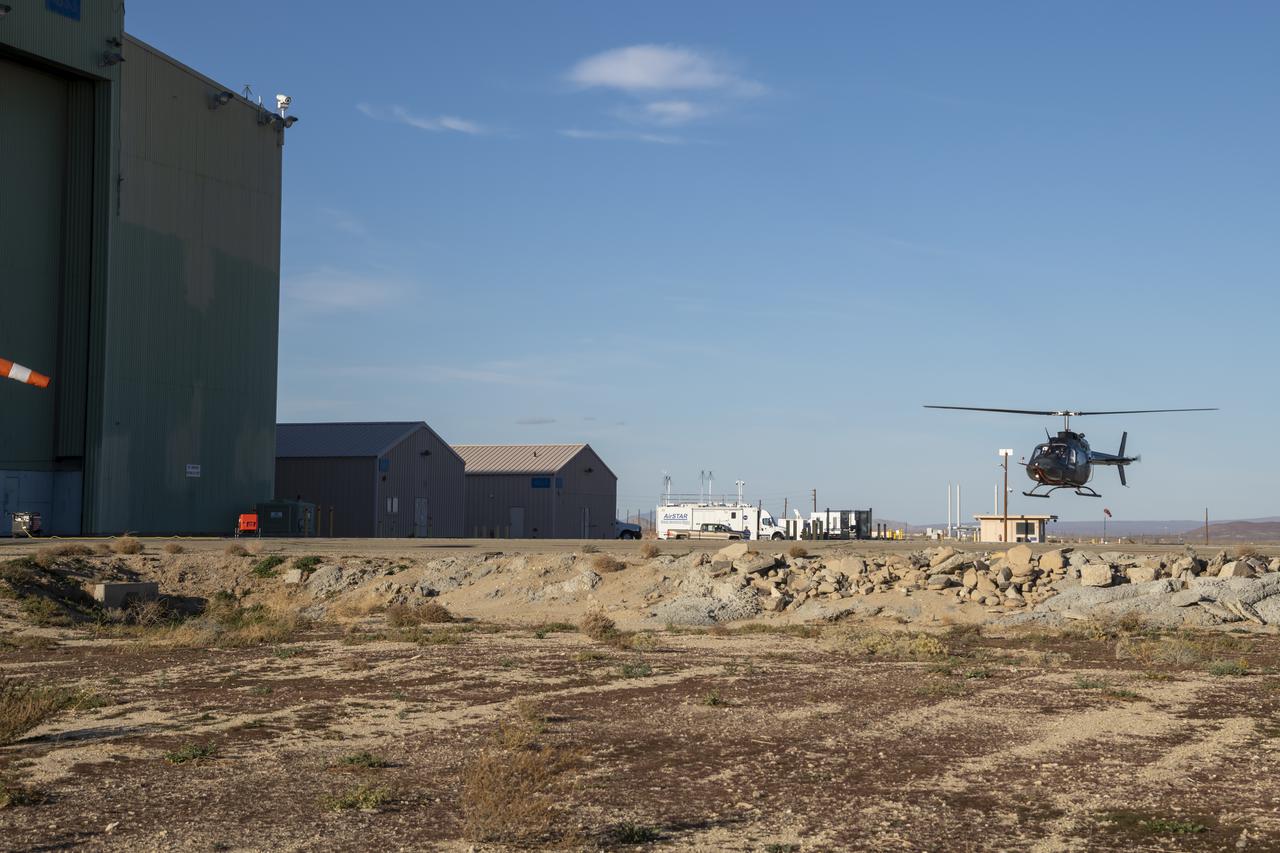

NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign flies maneuvers at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Dec. 6, and 8-10. During this testing, the helicopter is used to study controllability characteristics when operating near buildings during heavy wind conditions. The Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. was used to study urban air mobility vehicle performance and flying qualities requirements.
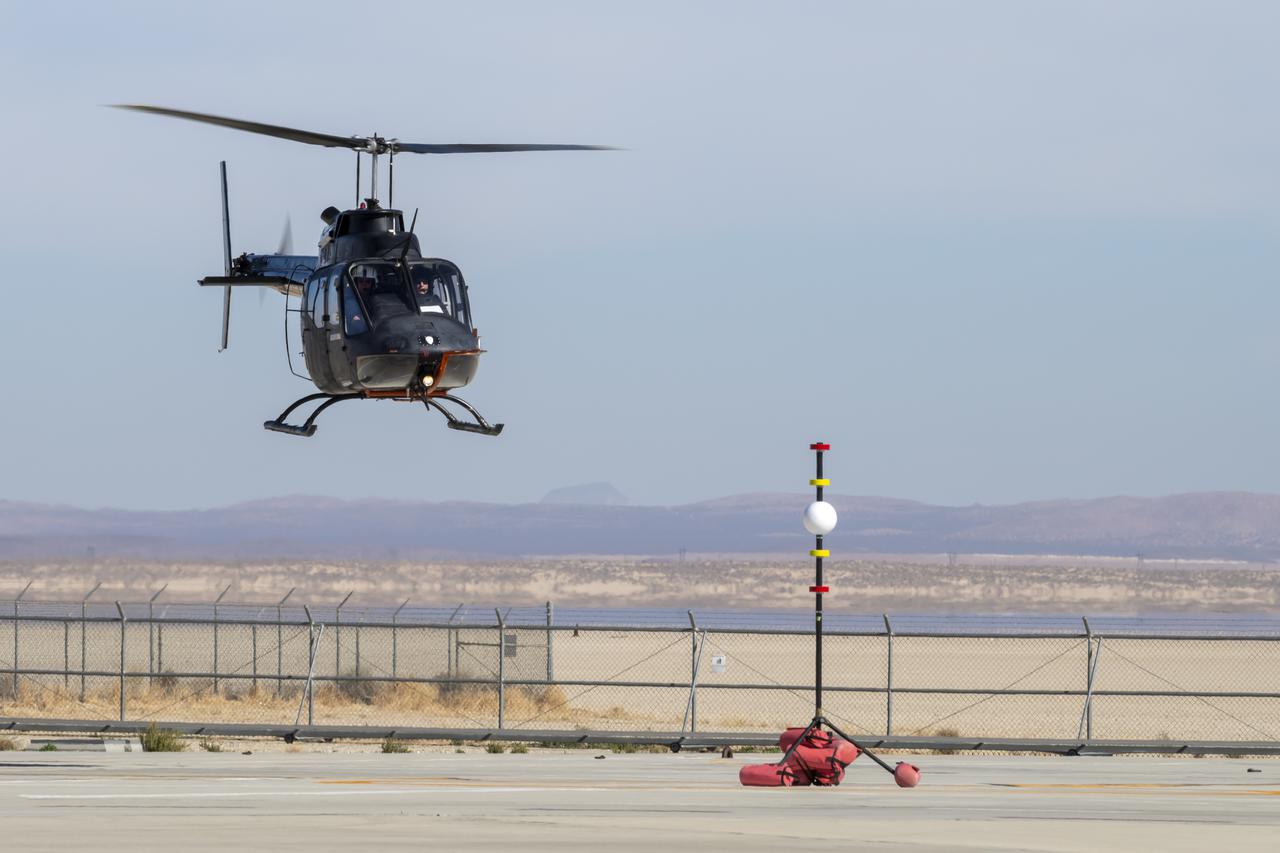

NASA's Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign created a visual aid, known as a tetherball, to serve as the helicopter pilot's height reference while flying different task elements at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Nov. 8-10. The Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. was used to study urban air mobility vehicle performance and flying qualities requirements.
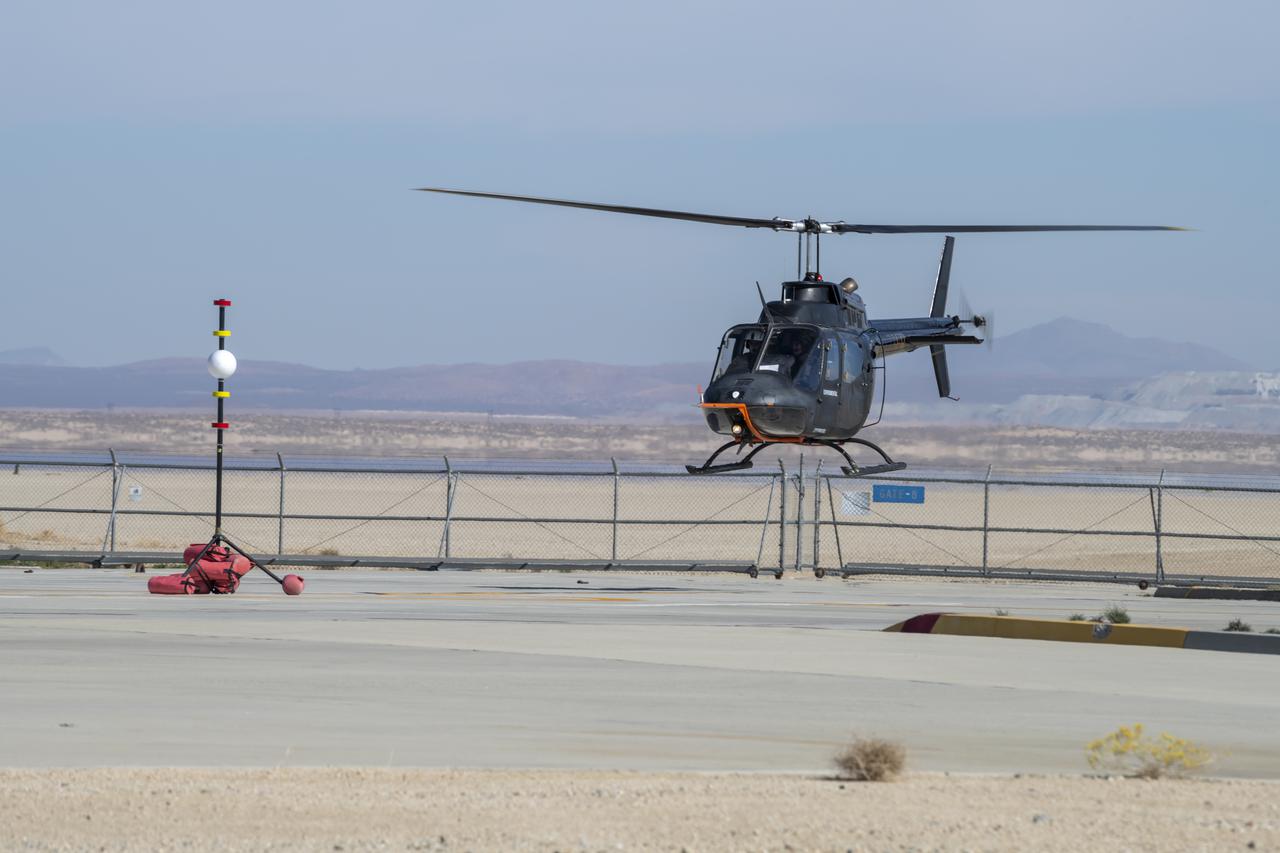

Flight Research Inc.'s Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopter flies around a visual aid, known as a tetherball, created to serve as the pilot's visual height reference while performing handling qualities testing at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Nov. 8-10. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used the helicopter to study urban air mobility vehicle and airspace requirements.
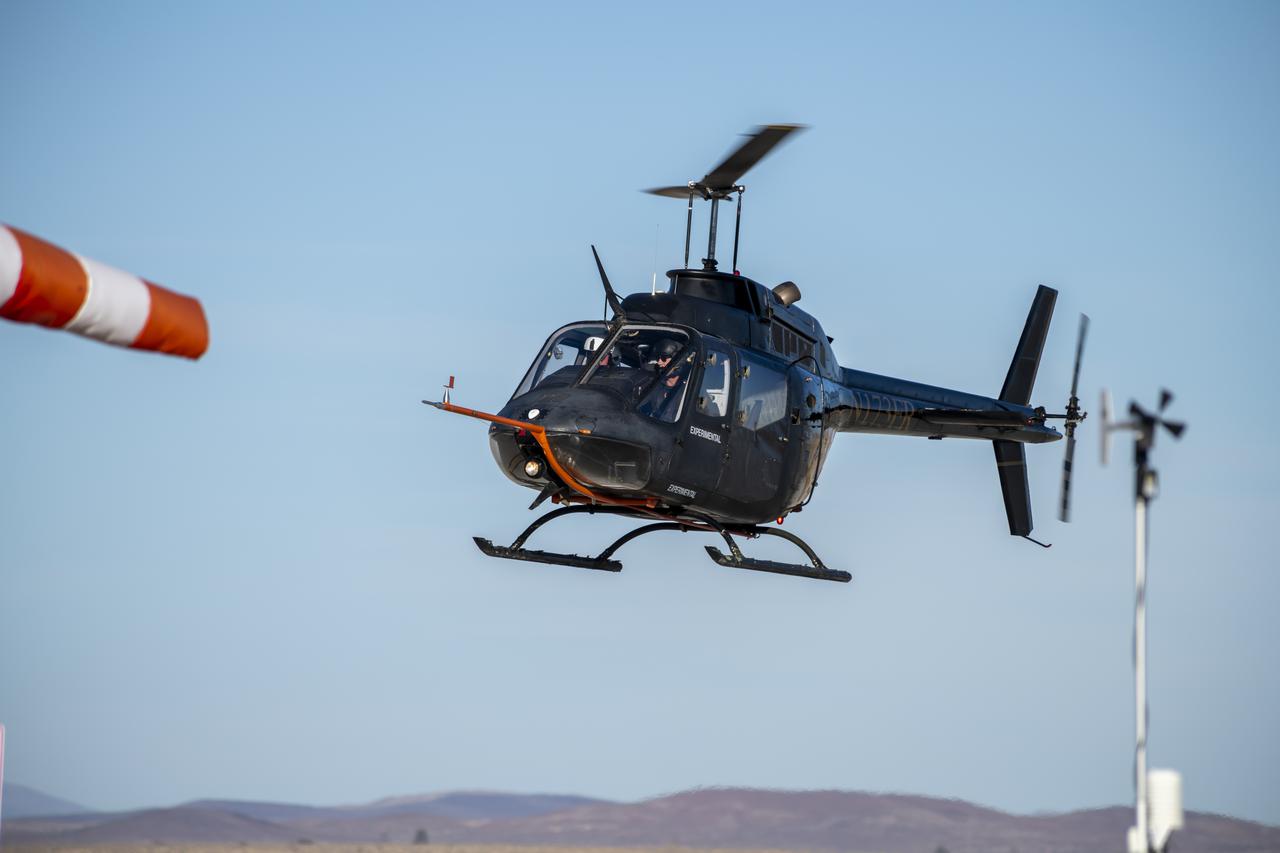

Flight Research Inc.'s Bell OH-58 helicopter performs different test maneuvers at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Nov. 8-10, and Dec. 6, and 8-10. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used the helicopter to study urban air mobility vehicle performance and flying qualities requirements.
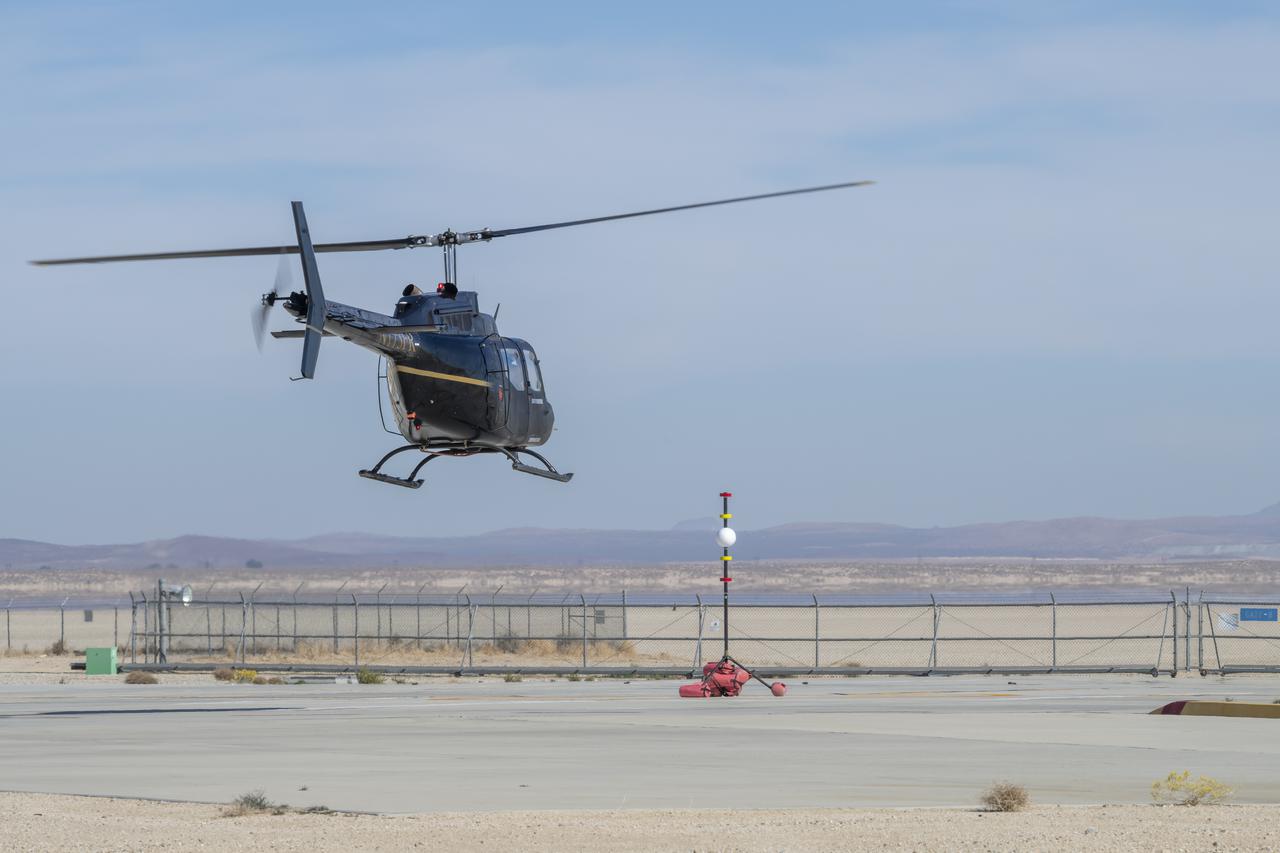

A Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. flies around a visual aid, known as a tetherball, created to serve as the pilot's visual height reference while performing handling qualities testing at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, Nov. 8-10. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used the helicopter to study urban air mobility vehicle and airspace requirements.
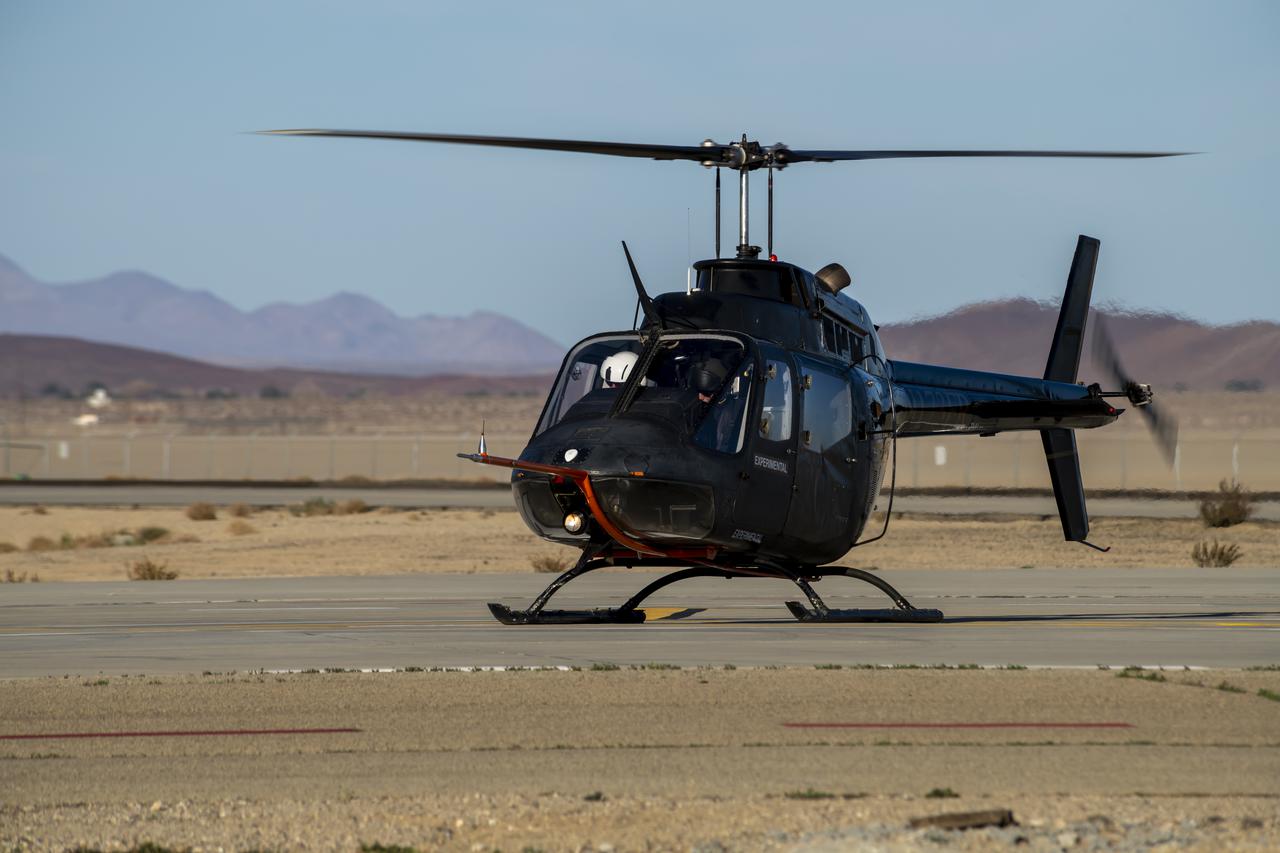

NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used this Bell OH-58 helicopter owned by Flight Research Inc. to study urban air mobility vehicle performance, flying qualities, and airspace requirements. The helicopter performed test maneuvers at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, during two sessions Nov, 8-10, and Dec. 6, and 8-10.
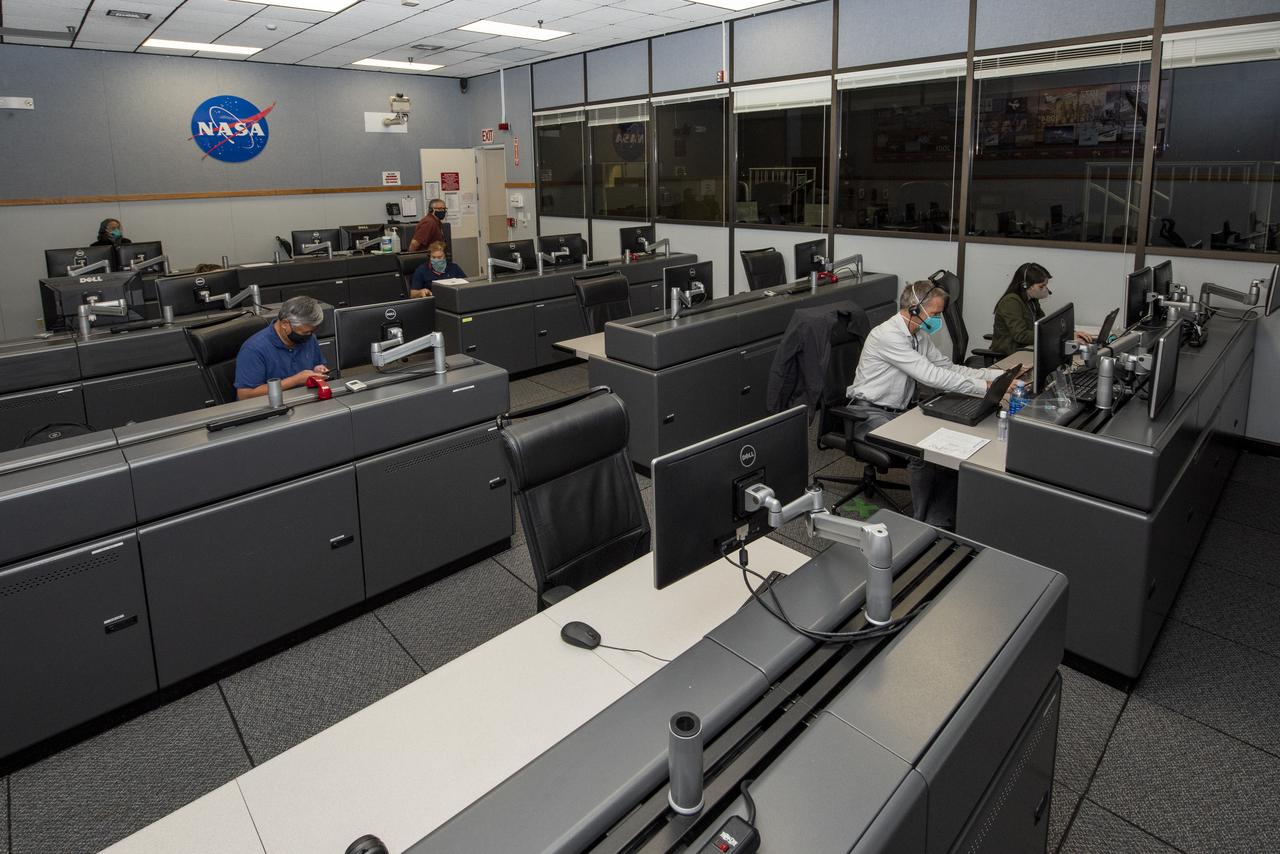

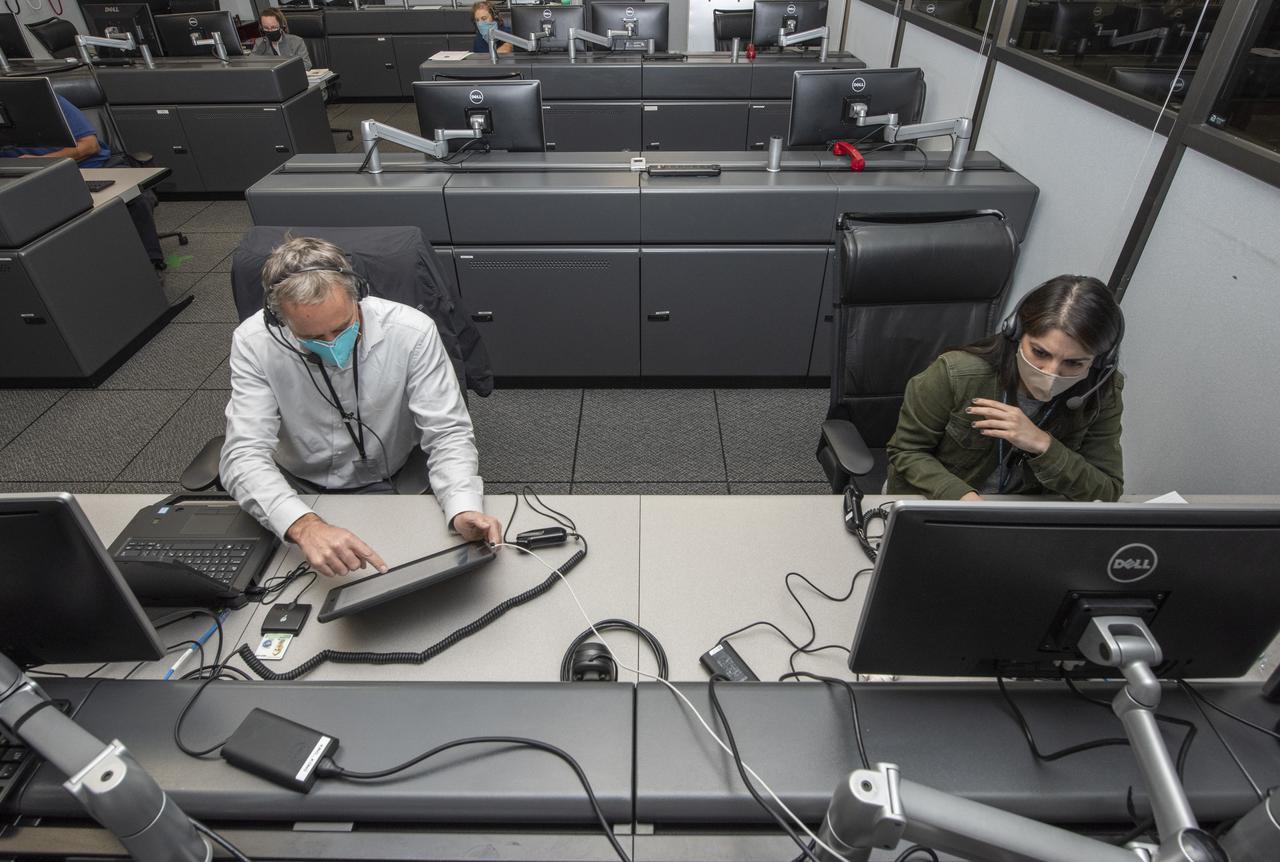
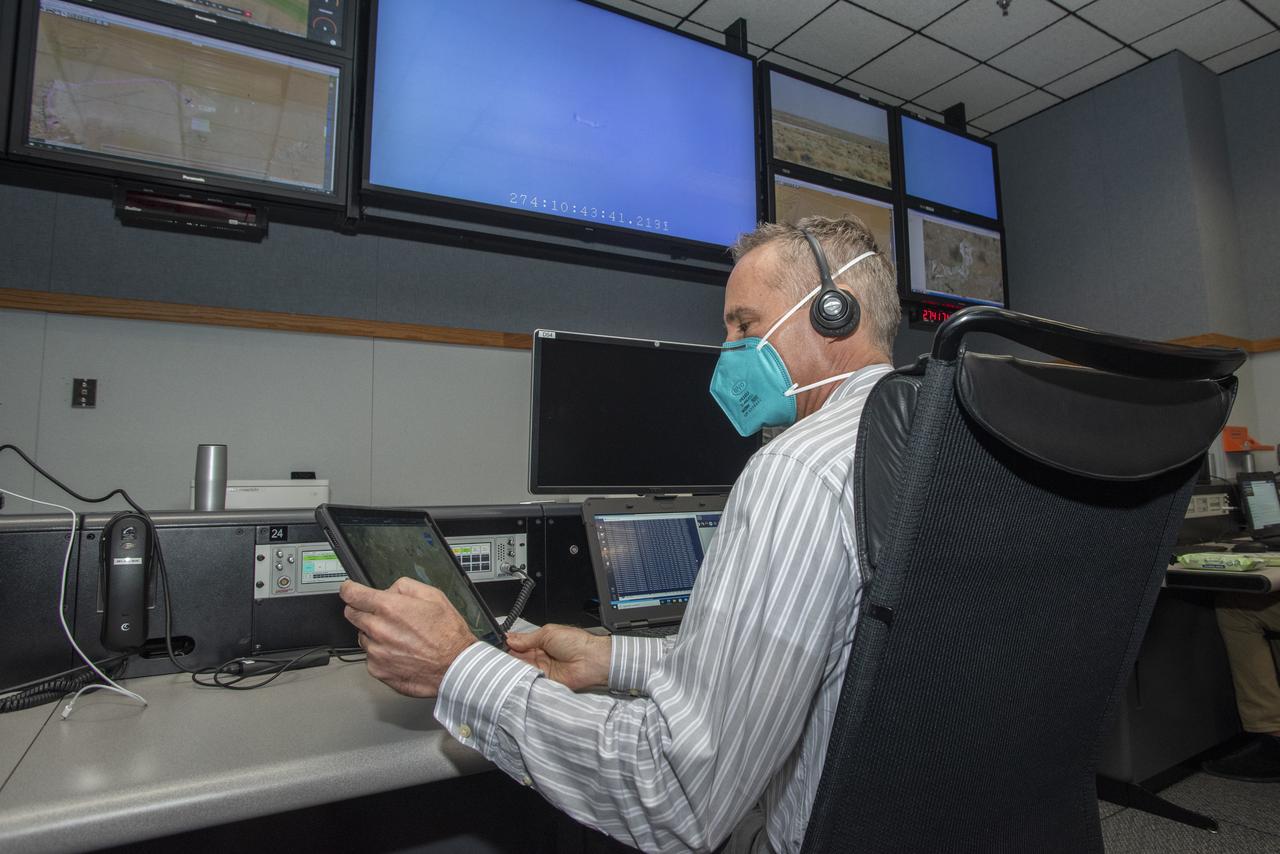
Ames Research Center researchers on the Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project's Airspace Test Infrastructure (ATI) team monitor surveillance data and metrics from the helicopter in real time during the NC Integrated Dry Run Test team the first week of December 2020 at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
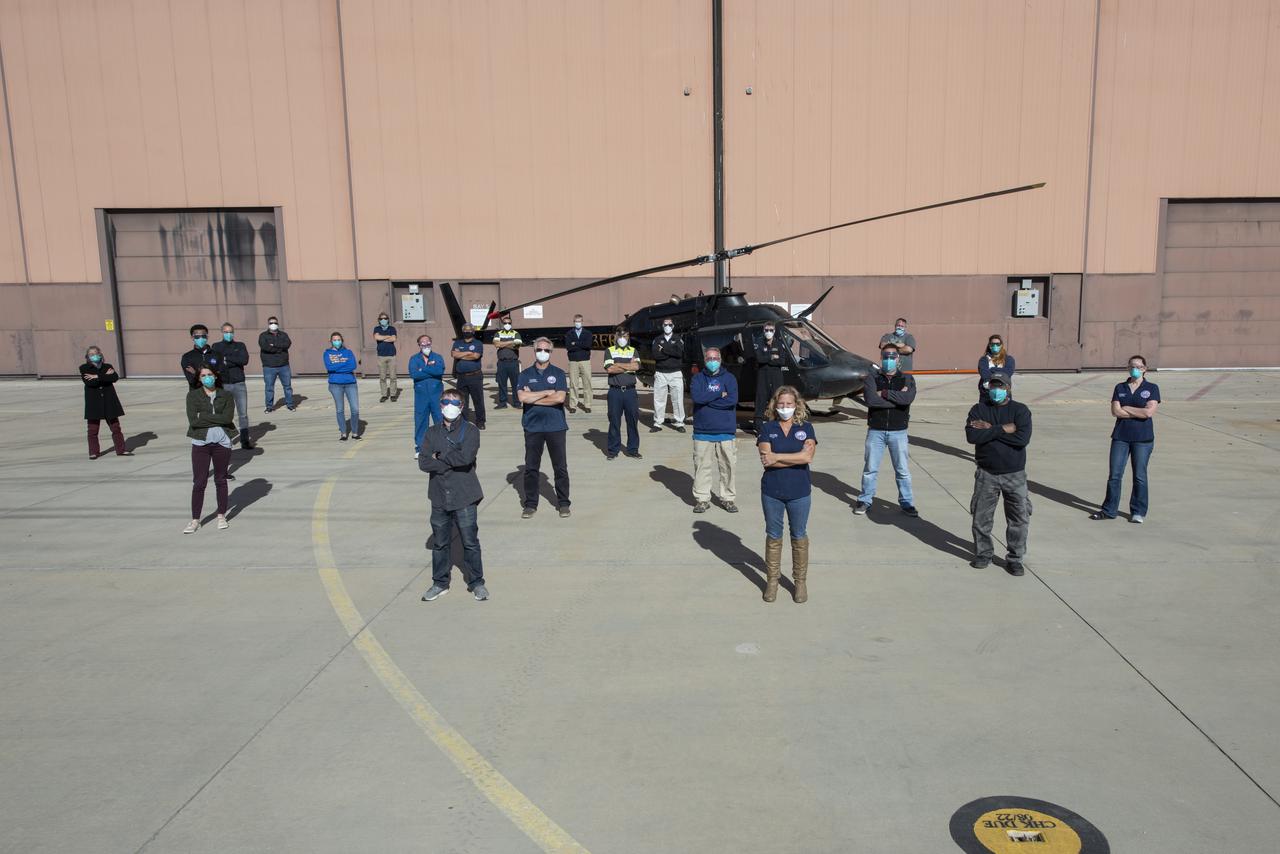

The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project’s NC Integrated Dry Run Test team is pictured in front of a Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California the first week of December 2020 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
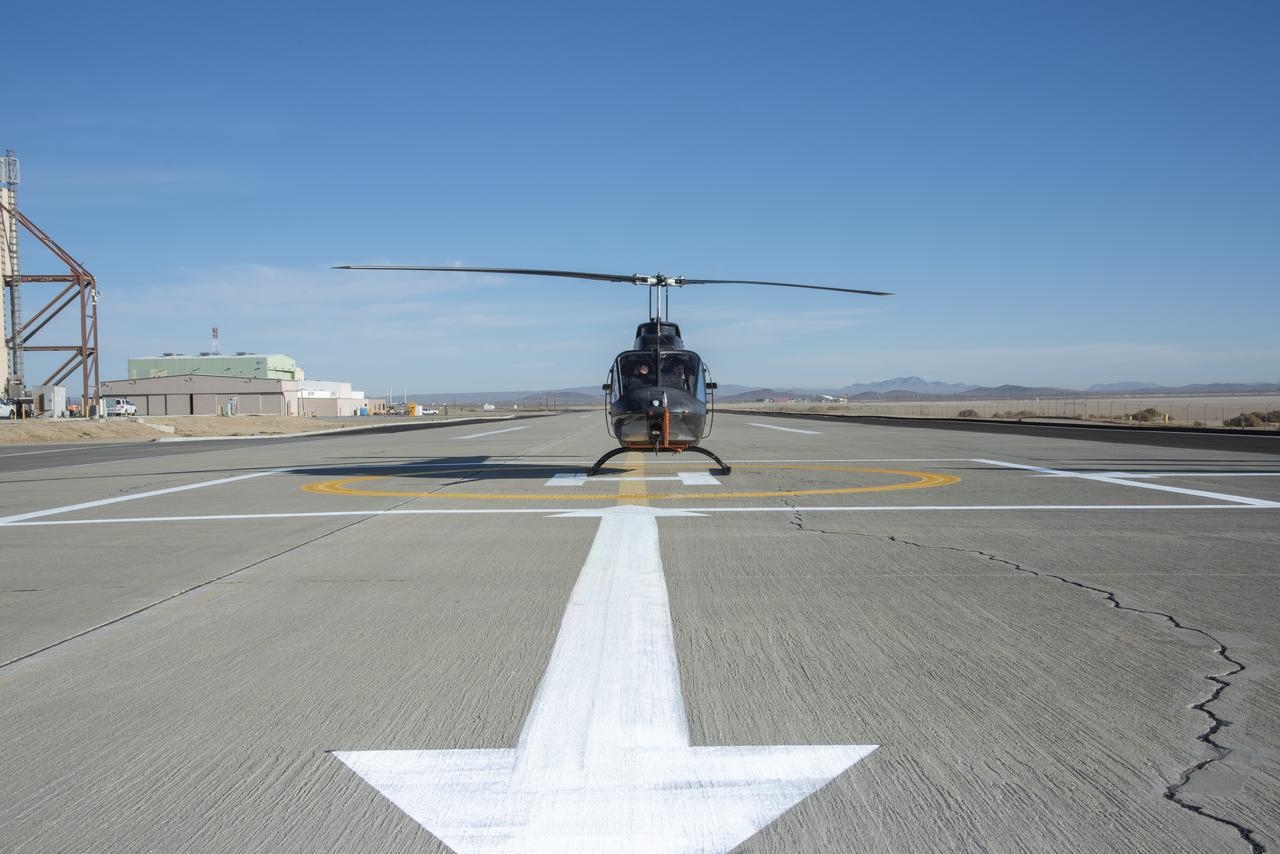

A Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California, sits on a helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California the first week of December 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project used the helicopter as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to develop and implement infrastructure, including the markings seen in the image, to support safe operations of these vehicles. Â
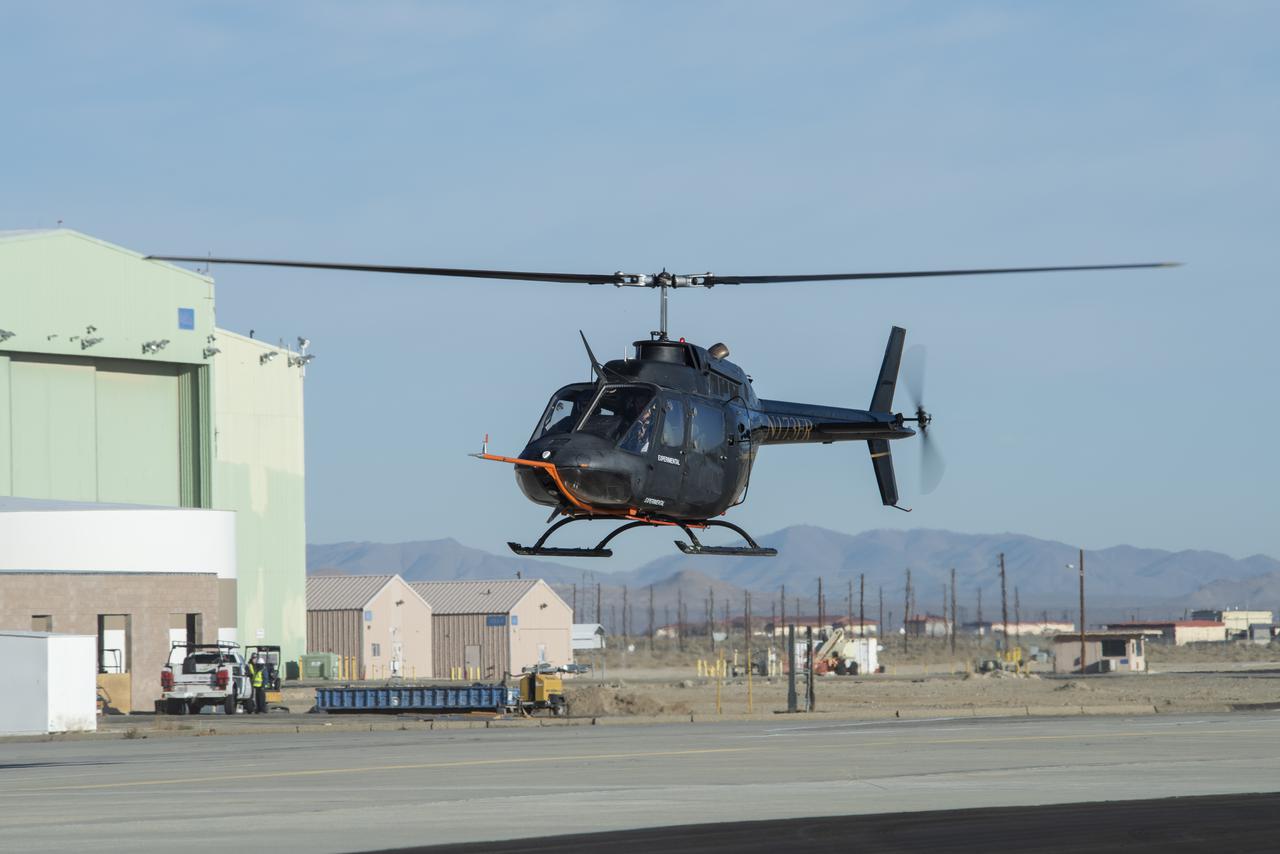

A Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California, flies at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California the first week of December 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project used the helicopter as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to develop a data baseline for future flight testing. Â
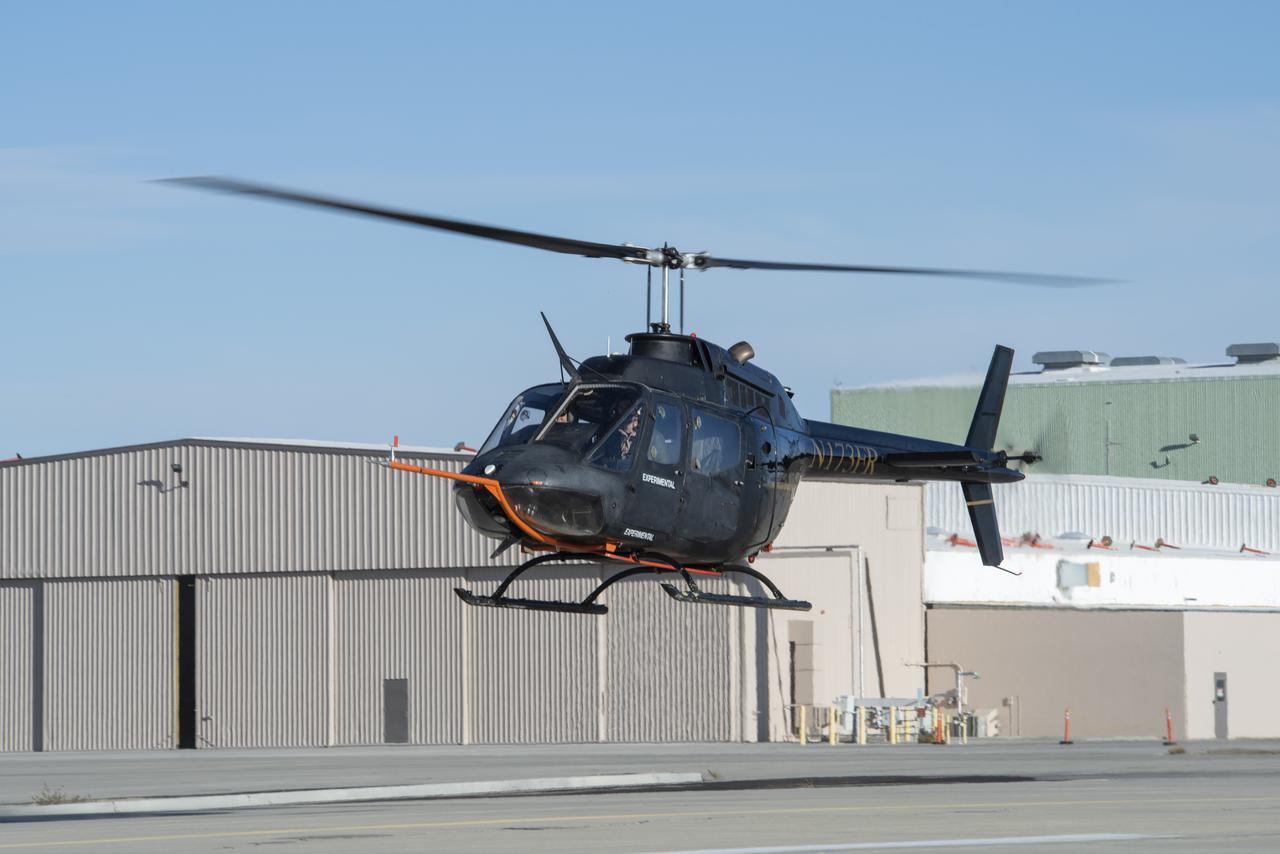

A Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter provided by Flight Research Inc. in Mojave, California, prepares to land at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California the first week of December 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project used the helicopter as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to develop a data baseline for future flight testing.
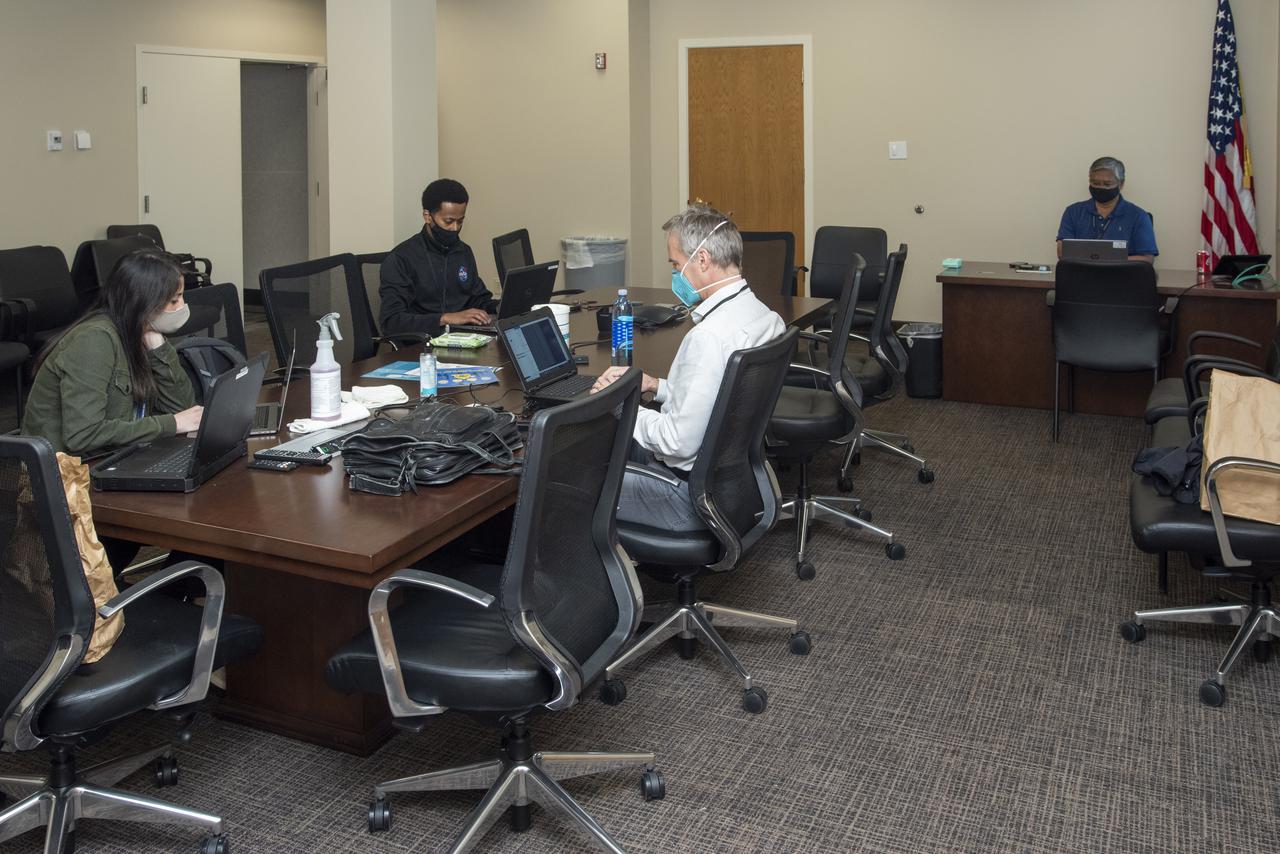

Ames Research Center researchers from left to right Yasmin Arbab,  Faisal Omar and Mark Snycerski on the Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project’s Airspace Test Infrastructure (ATI) team as well as Armstrong’s Sam Simpliciano in the background. The researchers monitor surveillance data from the helicopter in real time during the NC Integrated Dry Run Test the first week of December 2020 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter lands on a helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021 at the completion of an urban air mobility scenario. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted a second phase of research called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility vehicle to study aspects of a future air taxi mission.
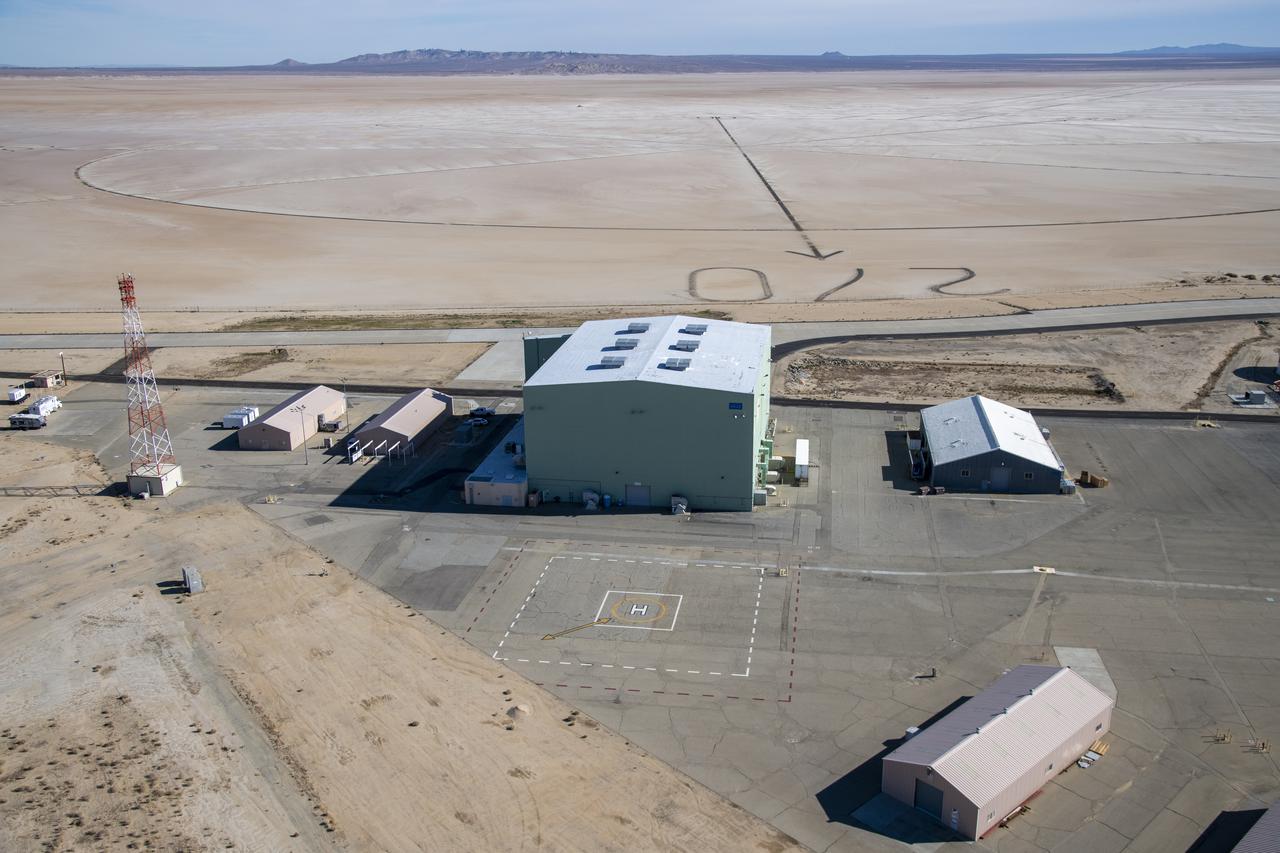

An aerial image taken by one of NASA's photographers during recent helicopter flights shows a view of the windward helipad and surrounding areas and structures that the Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign used during flight research at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. Part of the compass rose on the Edwards Air Force Base dry lakebed can also be seen.
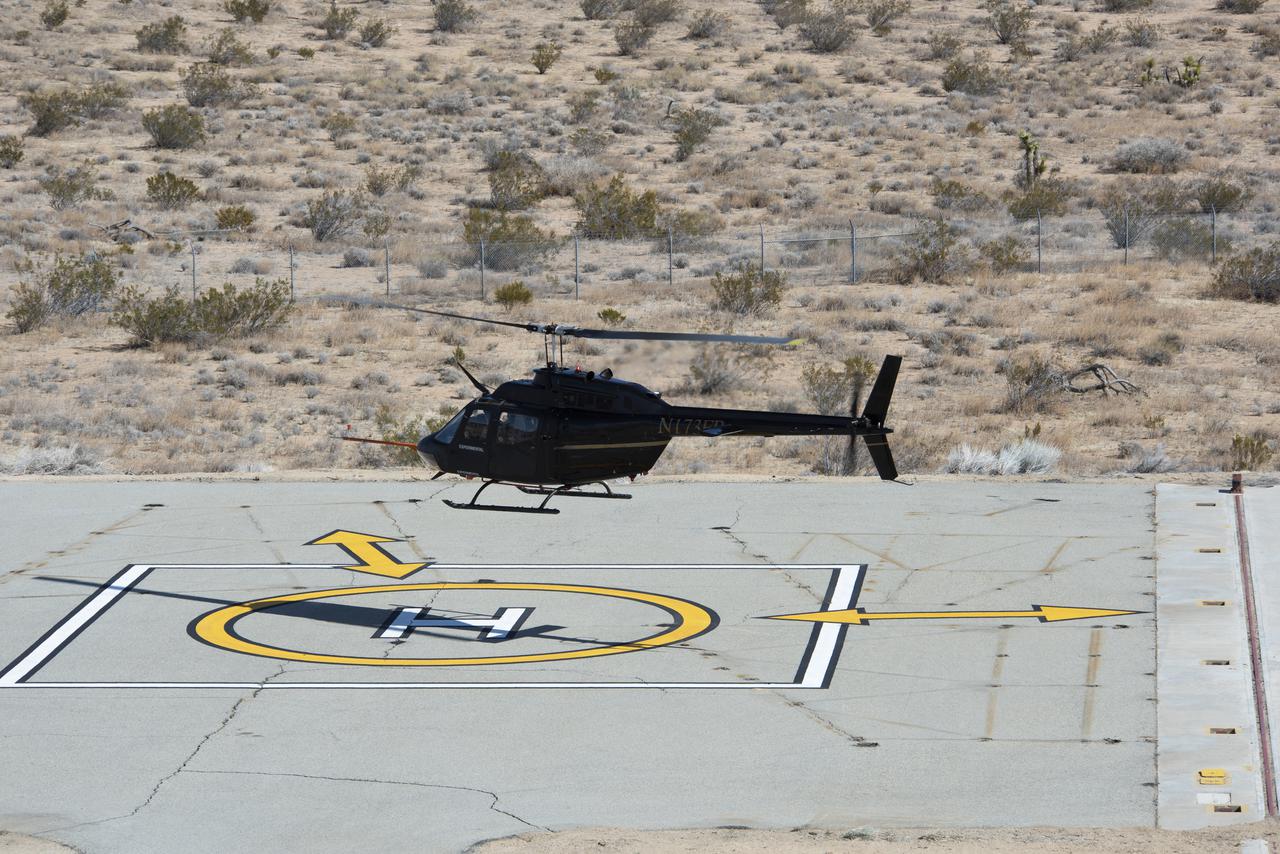

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter takes off from a research helipad at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project utilized several heliports and vertiports to study airspace management evolutions that could enable future urban air mobility operations. Tests were conducted during build II where this helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility or air taxi vehicle.
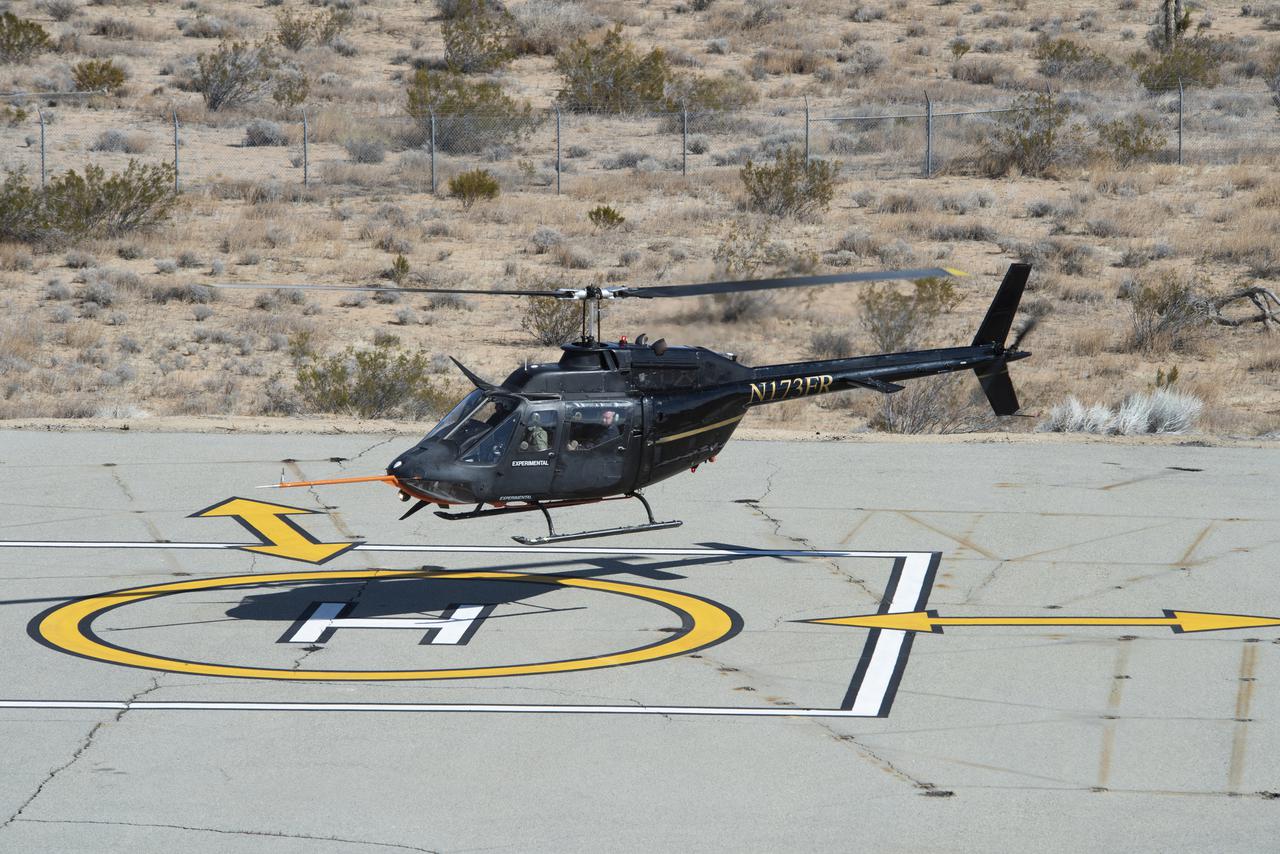

Flight Research Inc.’s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter hovers over a helipad after completing an urban air mobility approach at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign studied the viability of various urban air mobility approach options during a second phase called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility or air taxi vehicle.

Ames Research Center researchers Yasmin Arbab and Mark Snycerski on the Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project's Airspace Test Infrastructure (ATI) team monitor surveillance data and connectivity of the flight test infrastructure to a cloud based system in real time during the NC Integrated Dry Run Test team the first week of December 2020 at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California.
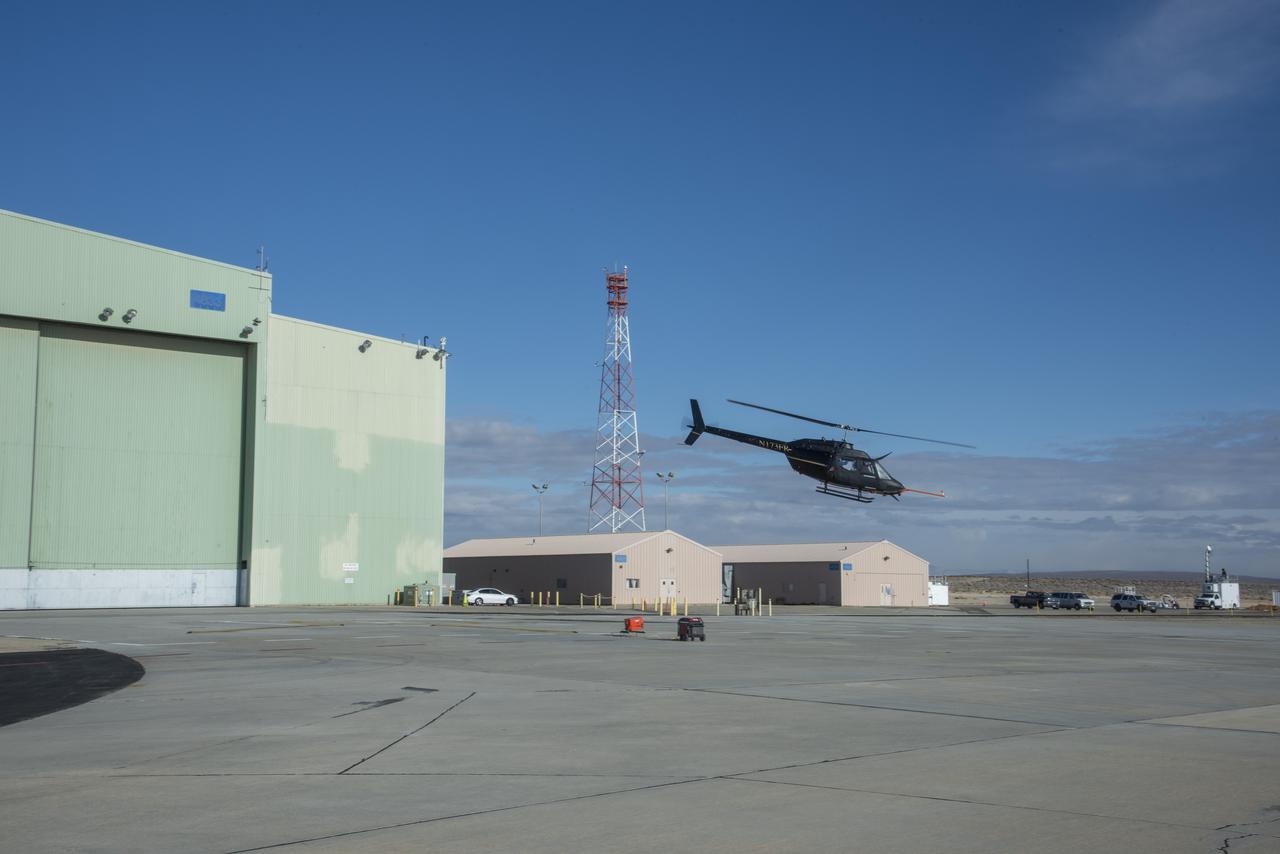

Flight Research Inc.'s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter departs the leeward heliport at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project studied wind and structure interactions as part of a second phase of testing called build II. This helicopter was used as a surrogate urban air mobility or air taxi vehicle.
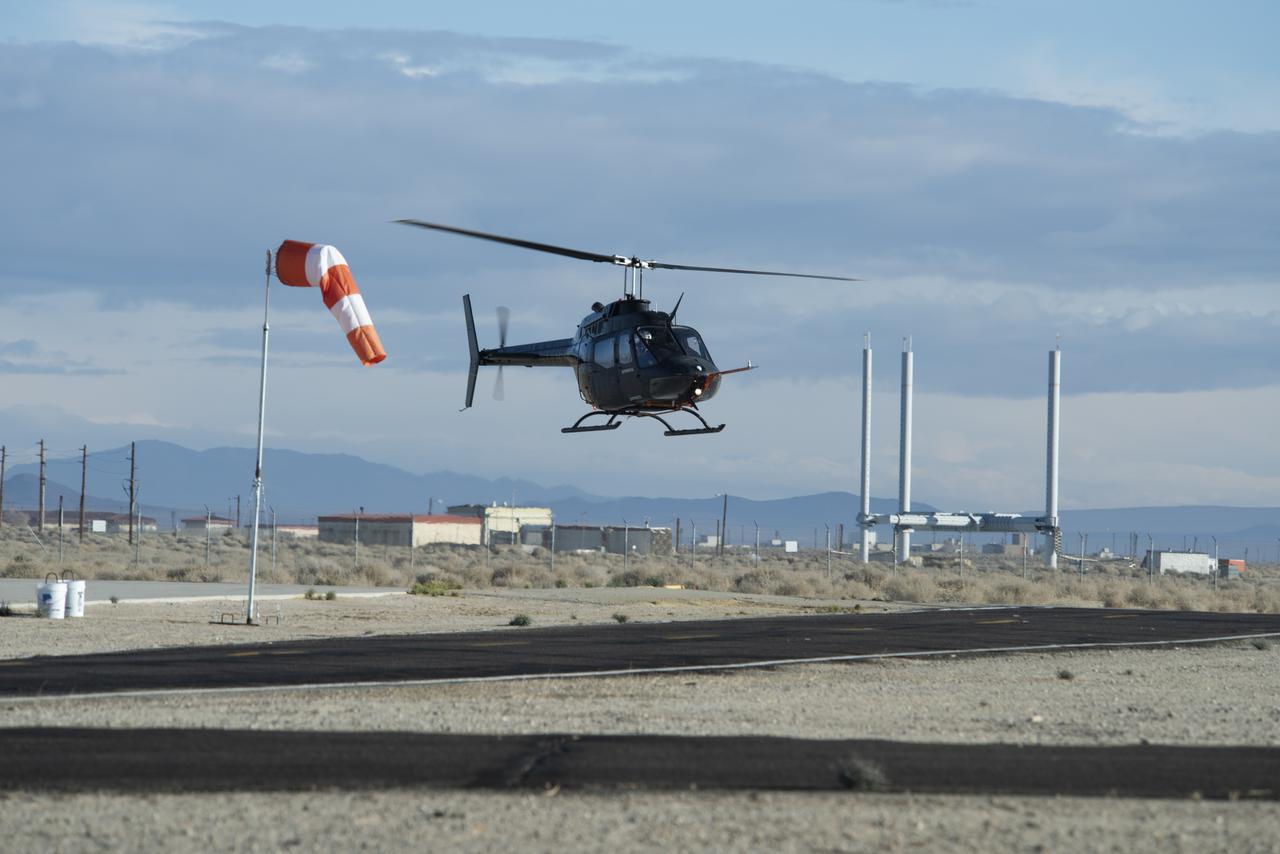

Flight Research Inc.'s Bell OH-58C Kiowa helicopter flies vehicle characteristics maneuvers for comparison to developmental urban air mobility (UAM) test maneuvers at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California in March 2021. The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign studied flight test techniques that may be used for future UAM certification.
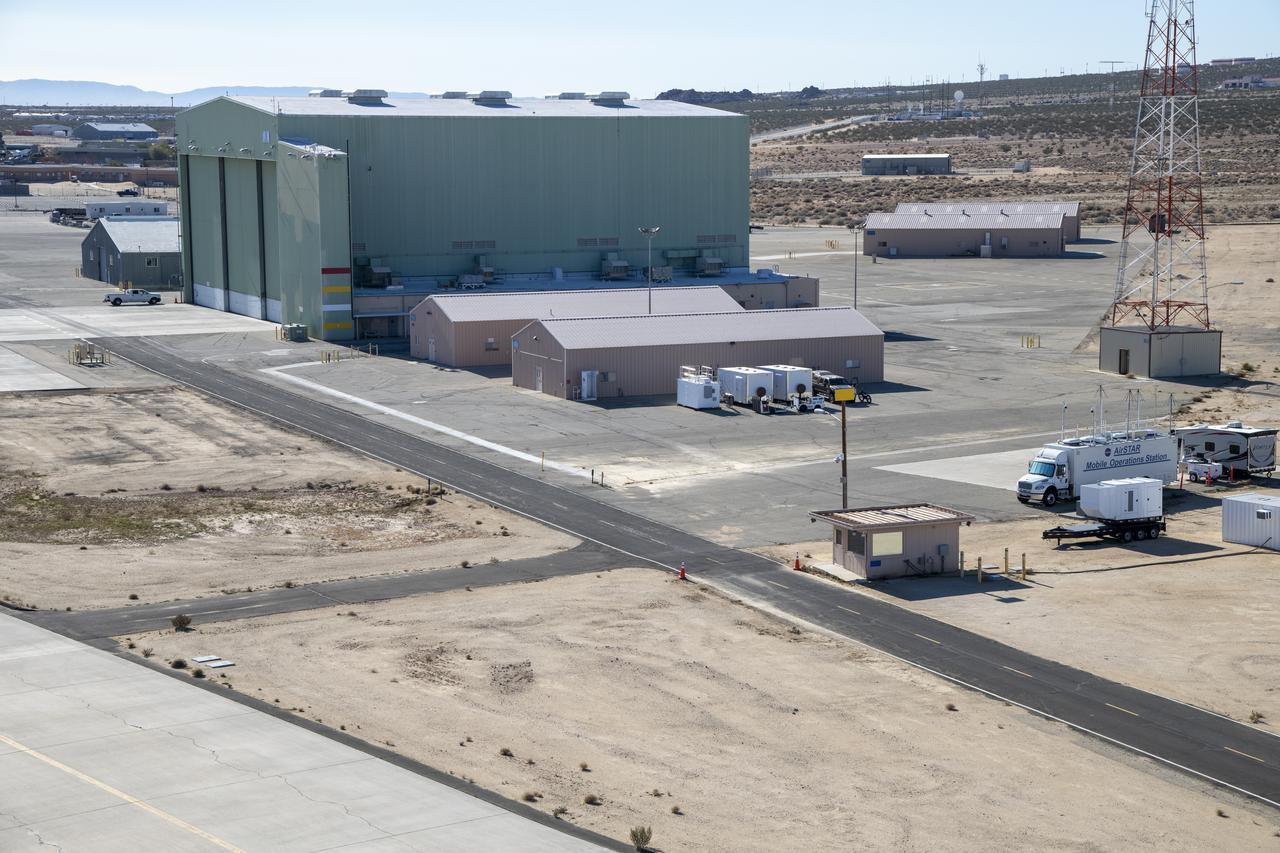

An aerial image taken by one of NASA’s photographers during recent helicopter flights shows a view of the building 4833 structure and the mobile operating facility at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. NASA’s Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign uses the mobile operations facility vehicle shown in the lower right corner during test operations. The red, yellow, and white building markings applied to building 4833 are used to provide visual aids to the pilot during handling qualities testing used to research advanced air mobility flight requirements.
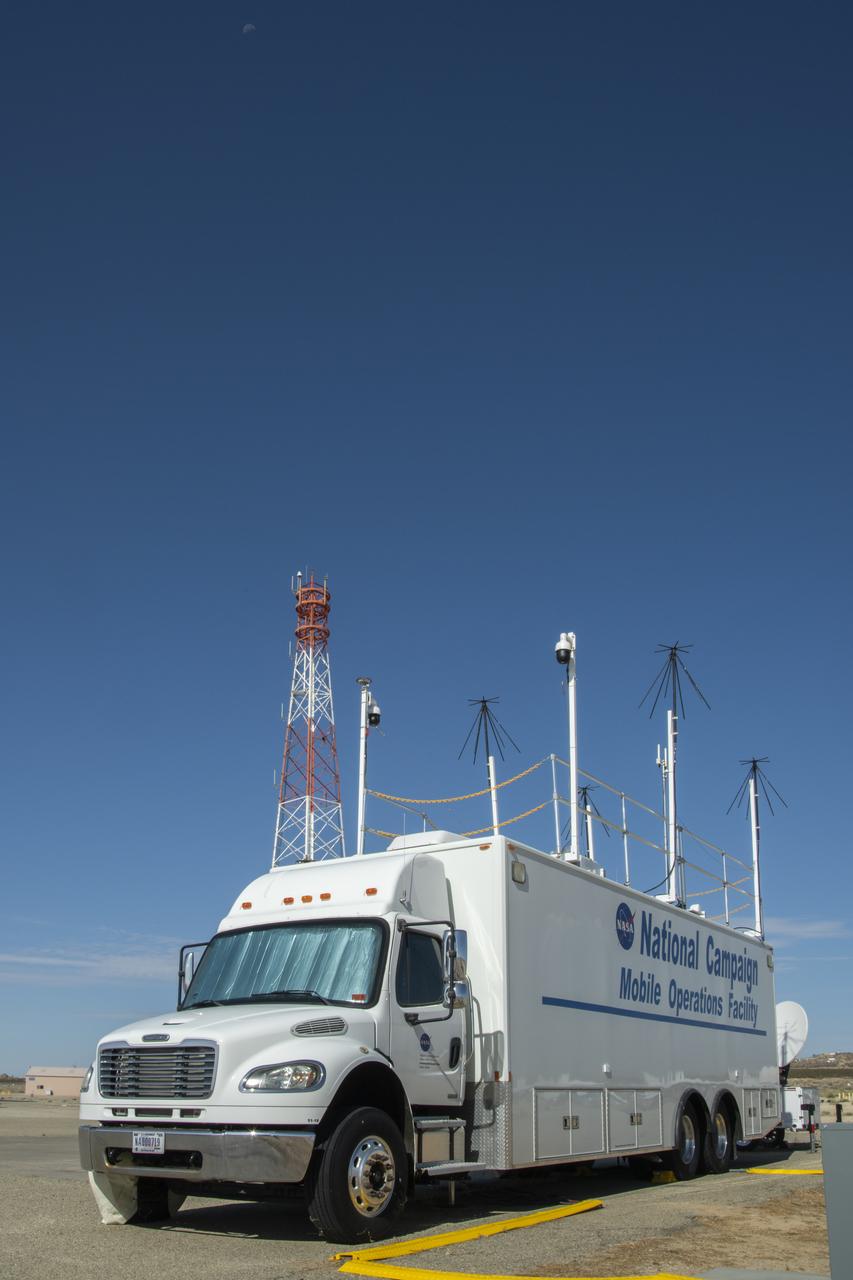

Housed at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, the Advanced Air Mobility project's National Campaign upgraded the Mobile Operations Facility, pictured here on July 20, 2022. This command center on wheels is a key piece of NASA's AAM testing.

New decals are shown in this image of NASA's Mobile Operations Facility at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on July 20, 2022. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility Project’s National Campaign uses the vehicle for mobile testing efforts.
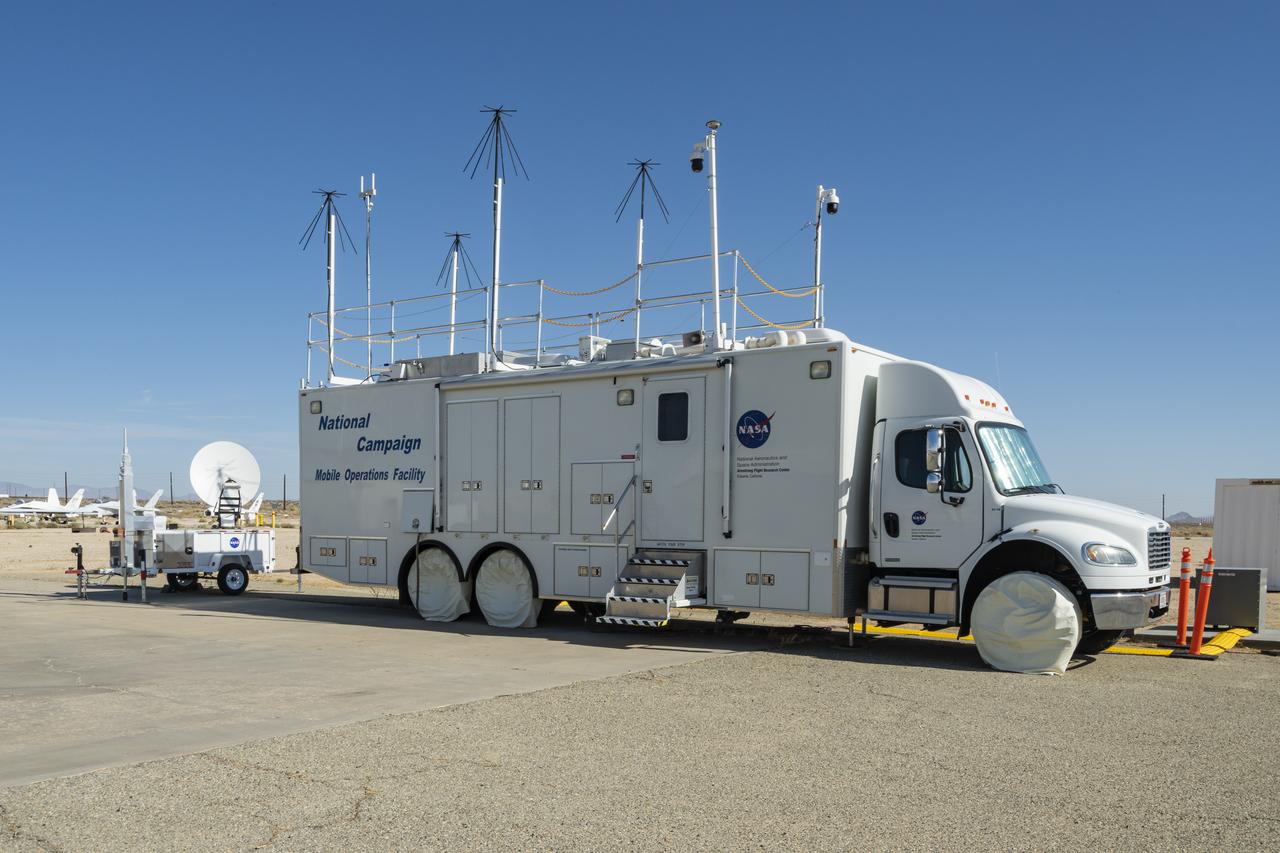

The upgraded NASA Mobile Operations Facility, a mission control and data collection center on wheels, is shown parked at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on July 20, 2022. This vehicle is used for NASA's Advanced Air Mobility project’s National Campaign testing.
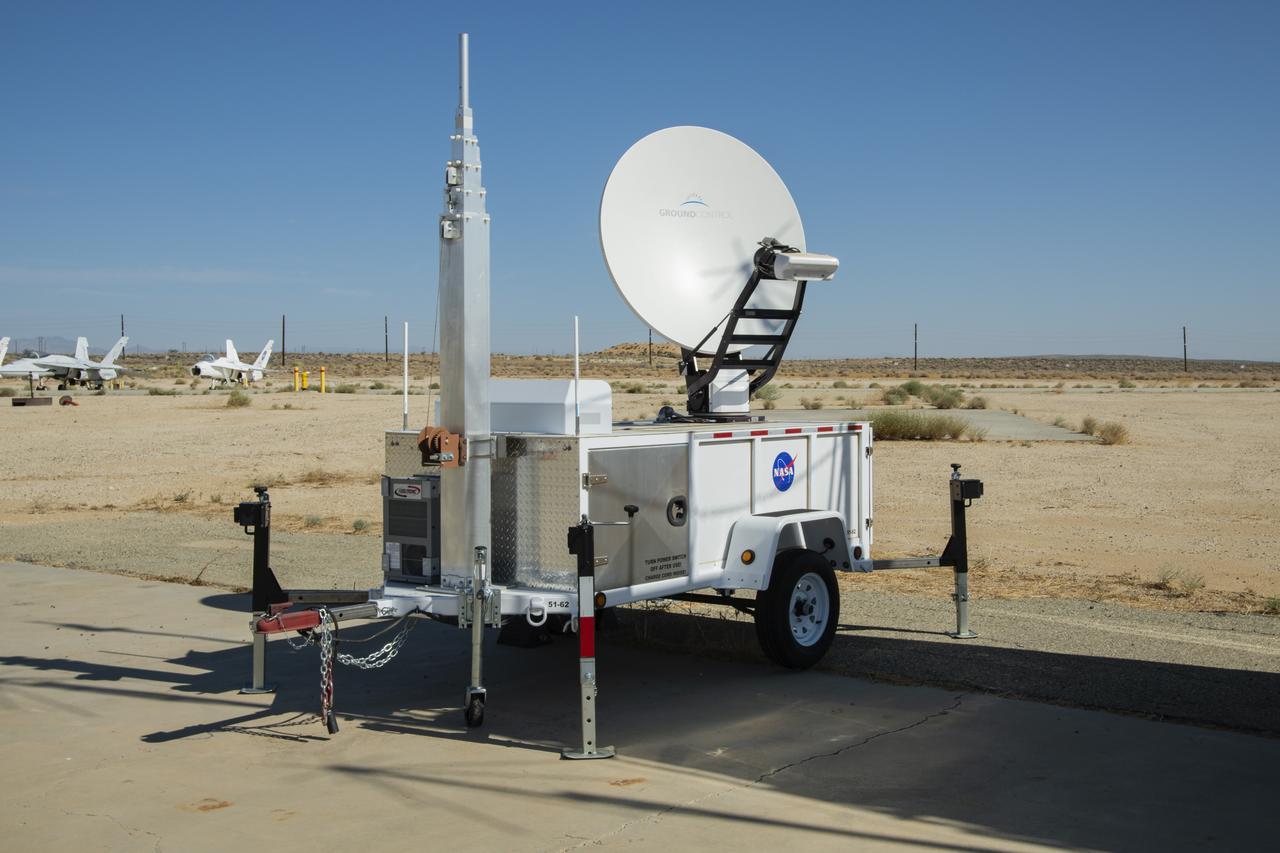

NASA Advanced Air Mobility project’s National Campaign mobile testing trailer is pictured at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards California on July 20, 2022. This trailer supports the Mobile Operations Facility’s data transmission when deployed to test locations.
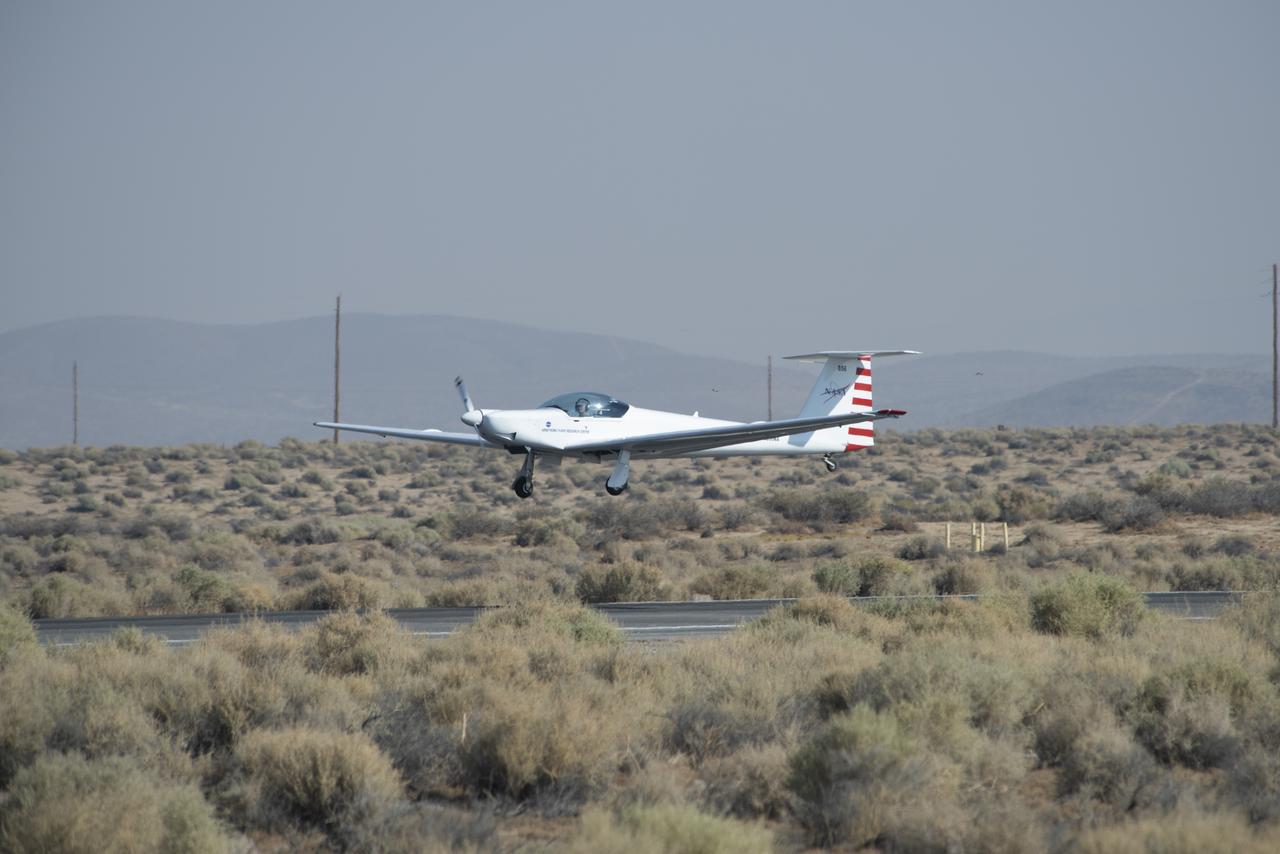

The Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign project conducted connectivity and infrastructure flight tests with a NASA TG-14 glider aircraft at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Sept. 30-Oct. 1, 2020. The flights were preparation for the NC Integrated Dry Run Test in December and allowed pilots to view the routes they will fly during the helicopter test.

Mark Snycerski, senior research associate at NASA's Ames Research Center in California, monitored inbound telemetry data through collection servers during the Advanced Air Mobility National Campaign's connectivity and infrastructure flight tests. The test used a NASA TG-14 glider aircraft based at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in California Sept. 30-Oct. 1, 2020. The exercise was in preparation for the NC Integrated Dry Run Test in December.
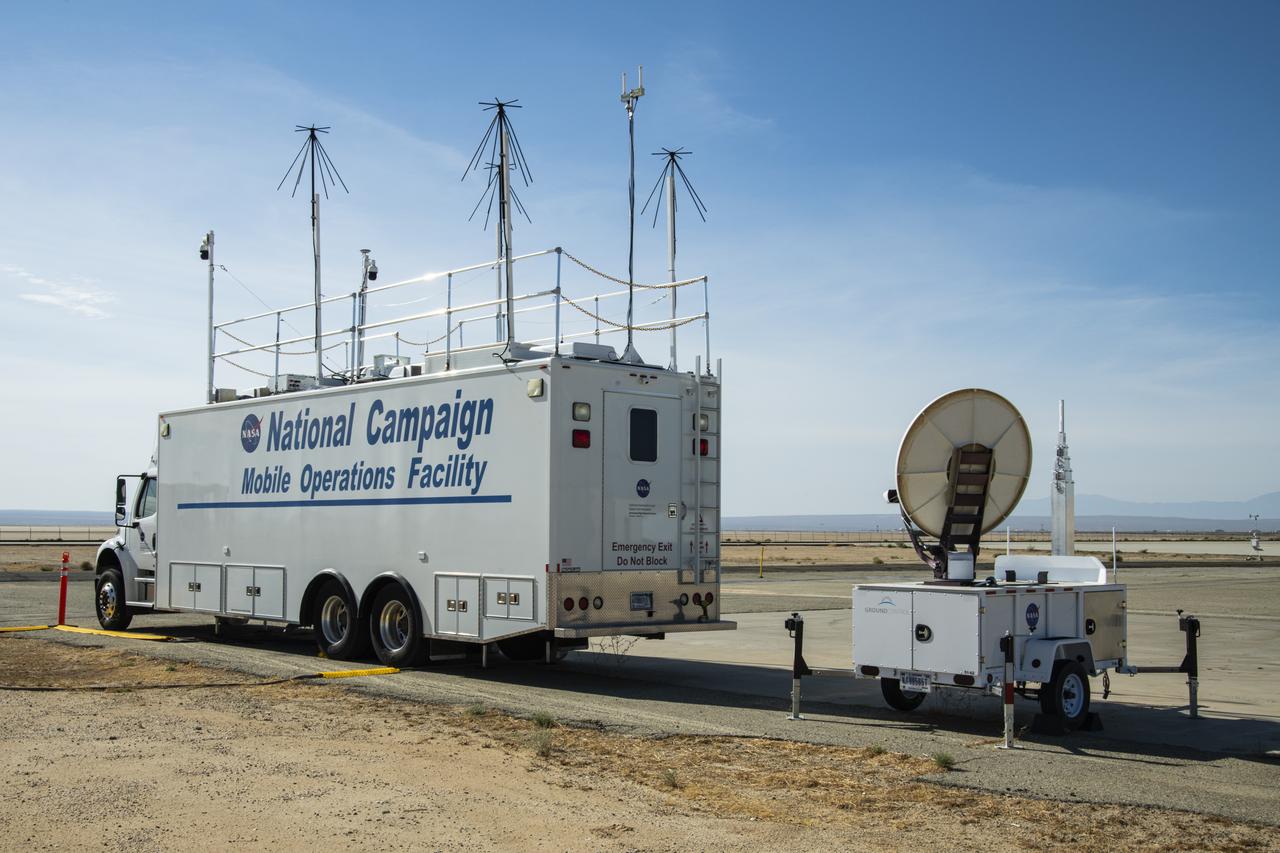

NASA's Mobile Operations Facility is shown here with new decals at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on July 20, 2022. Antennas, sensors, and radar communications, housed inside and outside of the vehicle, help monitor aircraft and transmit data. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility project’s National Campaign uses the vehicle for testing.
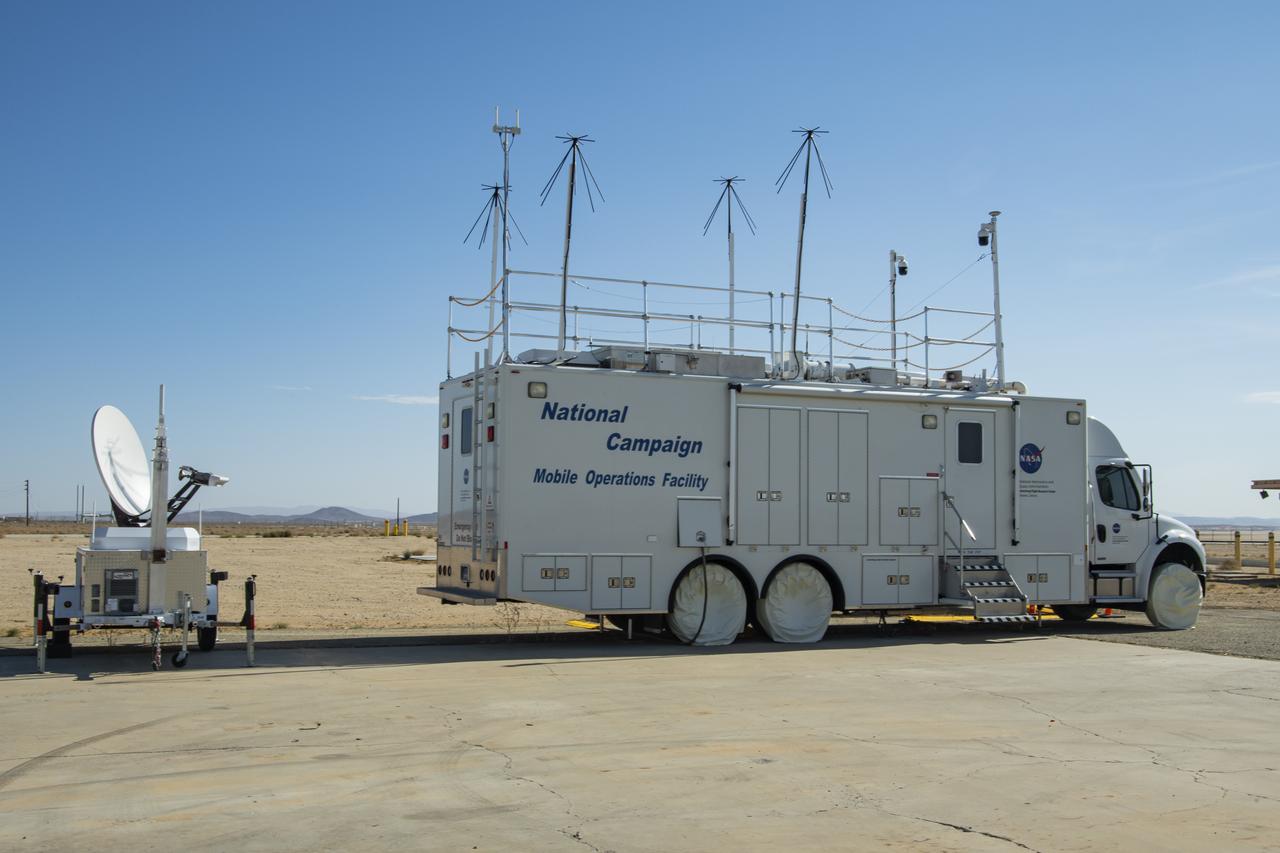

This specially outfitted mission control center, called the Mobile Operations Facility, can travel to any flight-testing site to obtain and transmit critical data. Here it is shown at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on July 20, 2022. The data collected from the vehicle is used by NASA's Advanced Air Mobility project’s National Campaign.

Vertiports and helipads were painted Oct. 6-14, 2020 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center to support future flight testing for the Advanced Air Mobility project’s National Campaign.
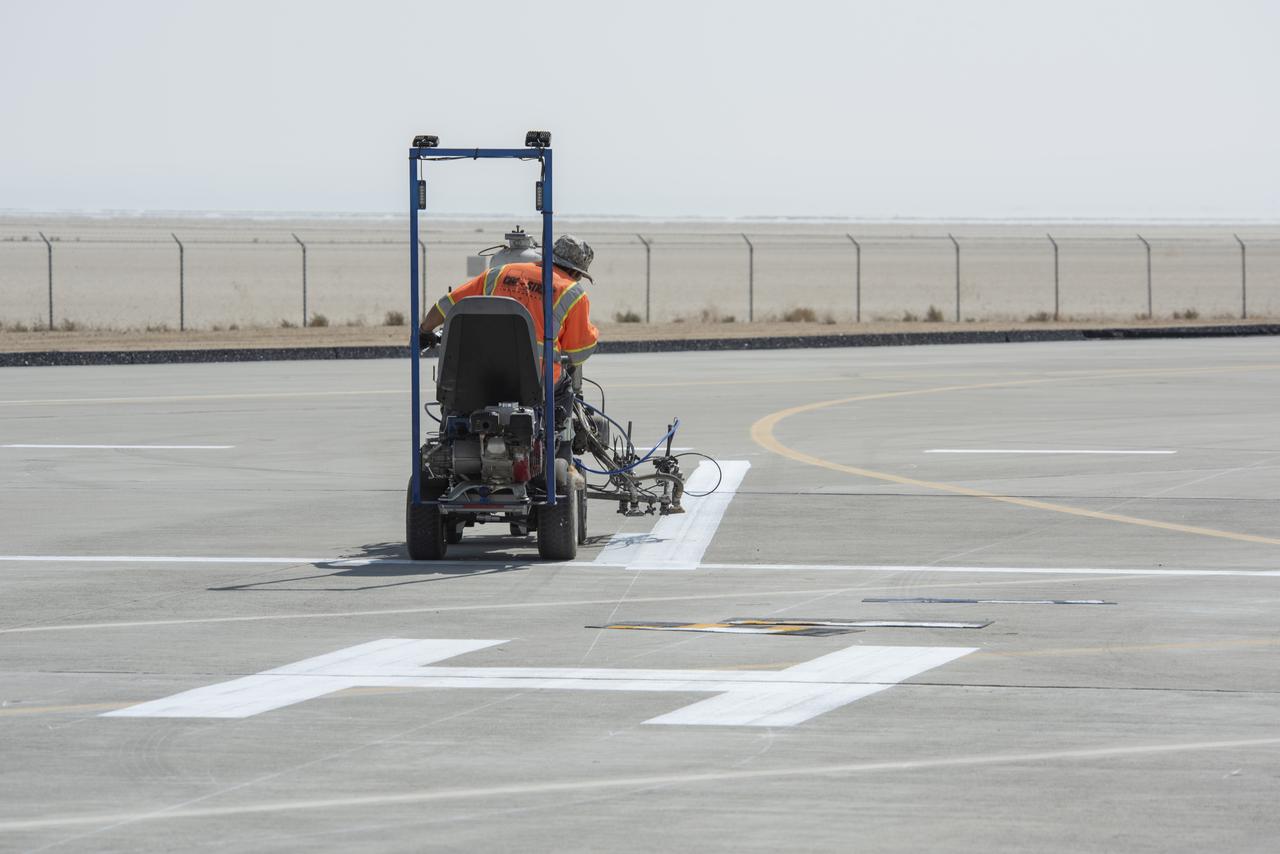

A worker painted vertiports and helipads at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center Oct. 6-14, 2020. The Advanced Air Mobility project's National Campaign will use these areas for future flight testing.
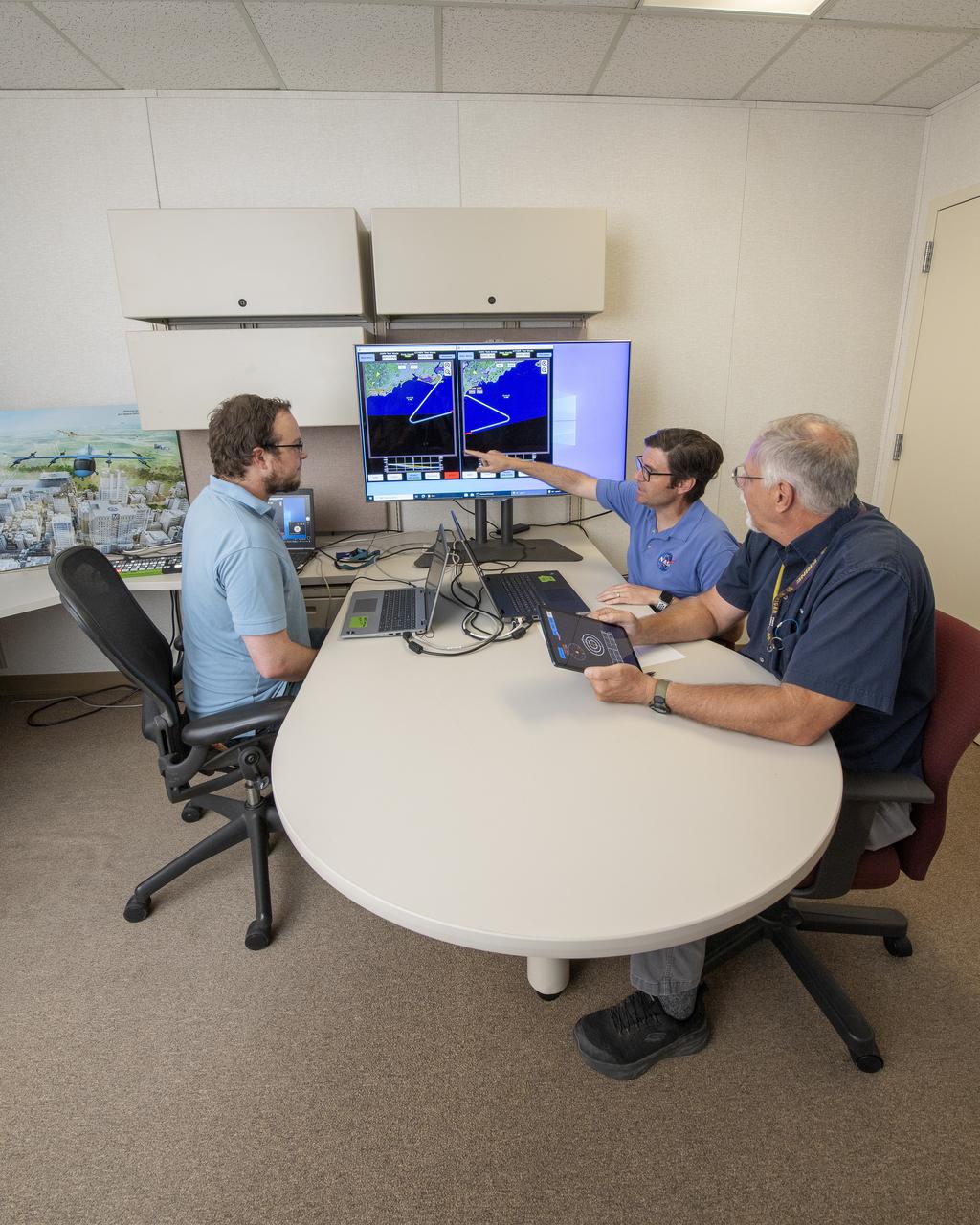

NASA software developer, Ethan Williams, left, pilot Scott Howe, and operations test consultant Jan Scofield run a flight path management software simulation at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California in May 2023. This simulation research supports the integration of automated systems for the advanced air mobility mission.
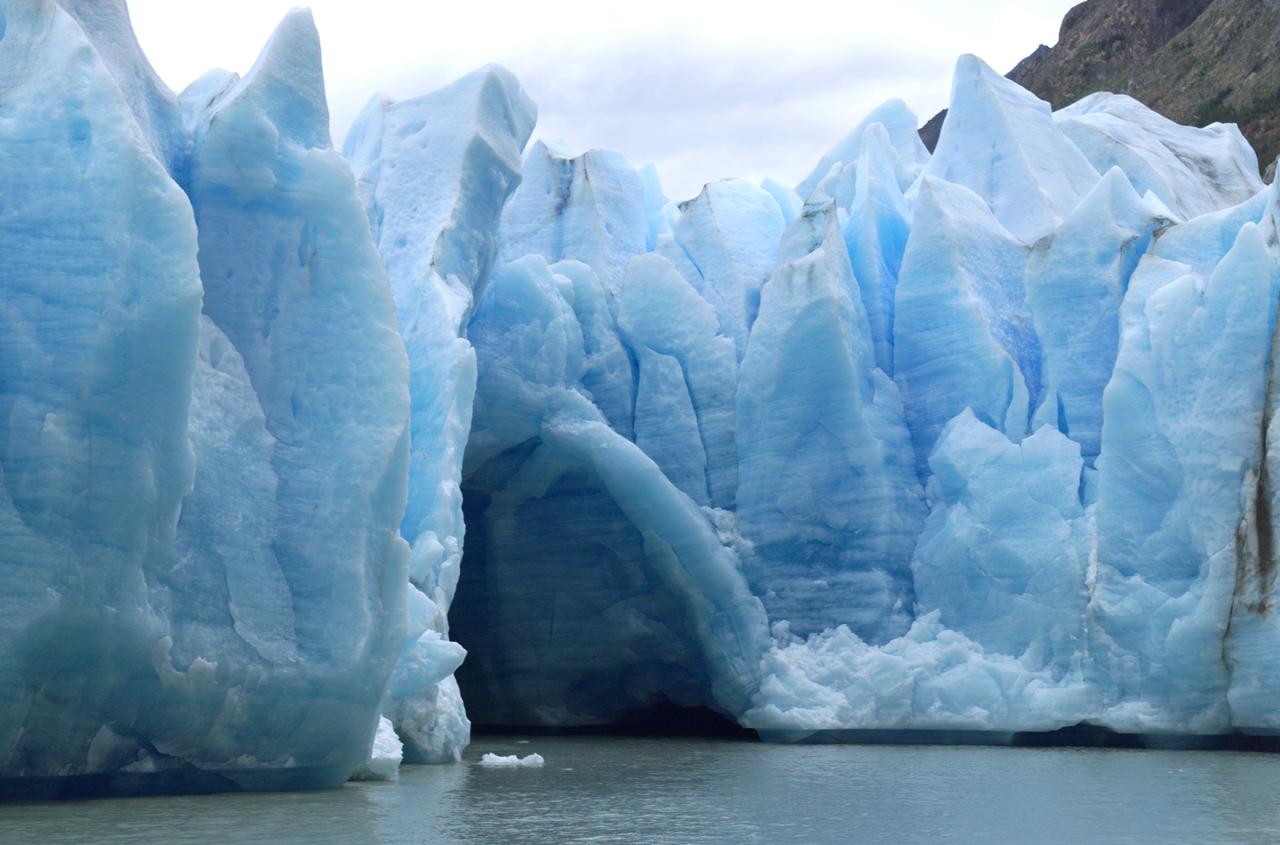

A cave in Glacier Grey in Torres del Paine National Park, seen during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
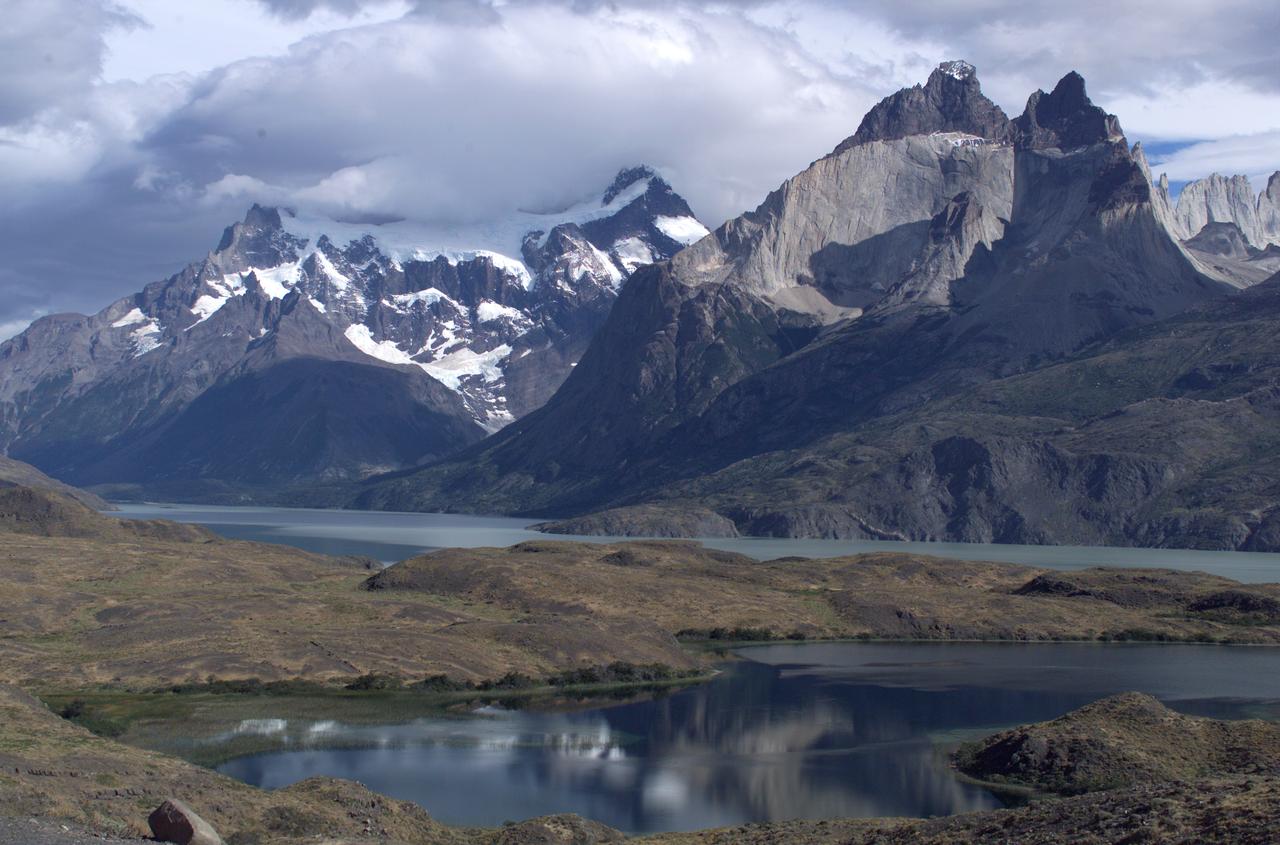

The Cuernos del Paine mountains in Torres del Paine National Park, Chile, during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
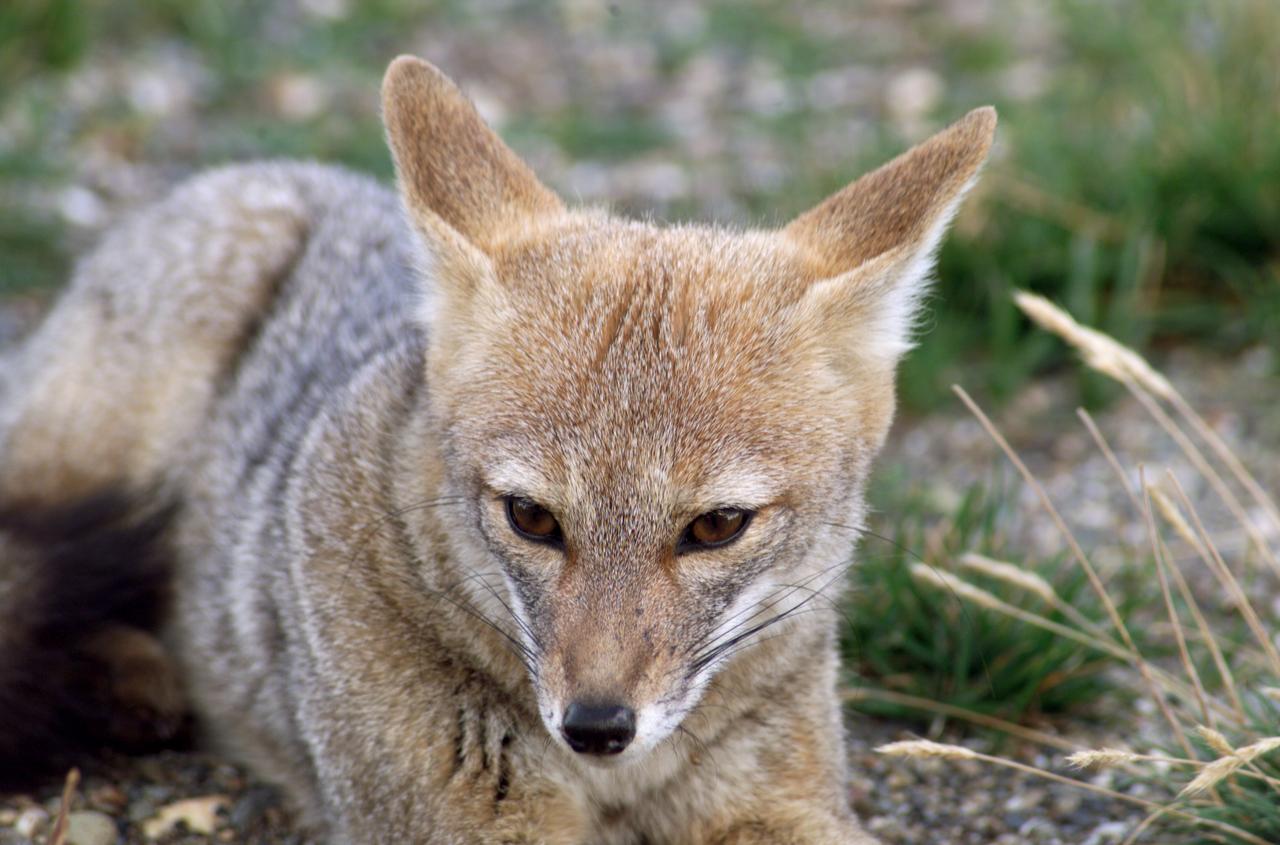

A fox at Torres del Paine National Park in Chile during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
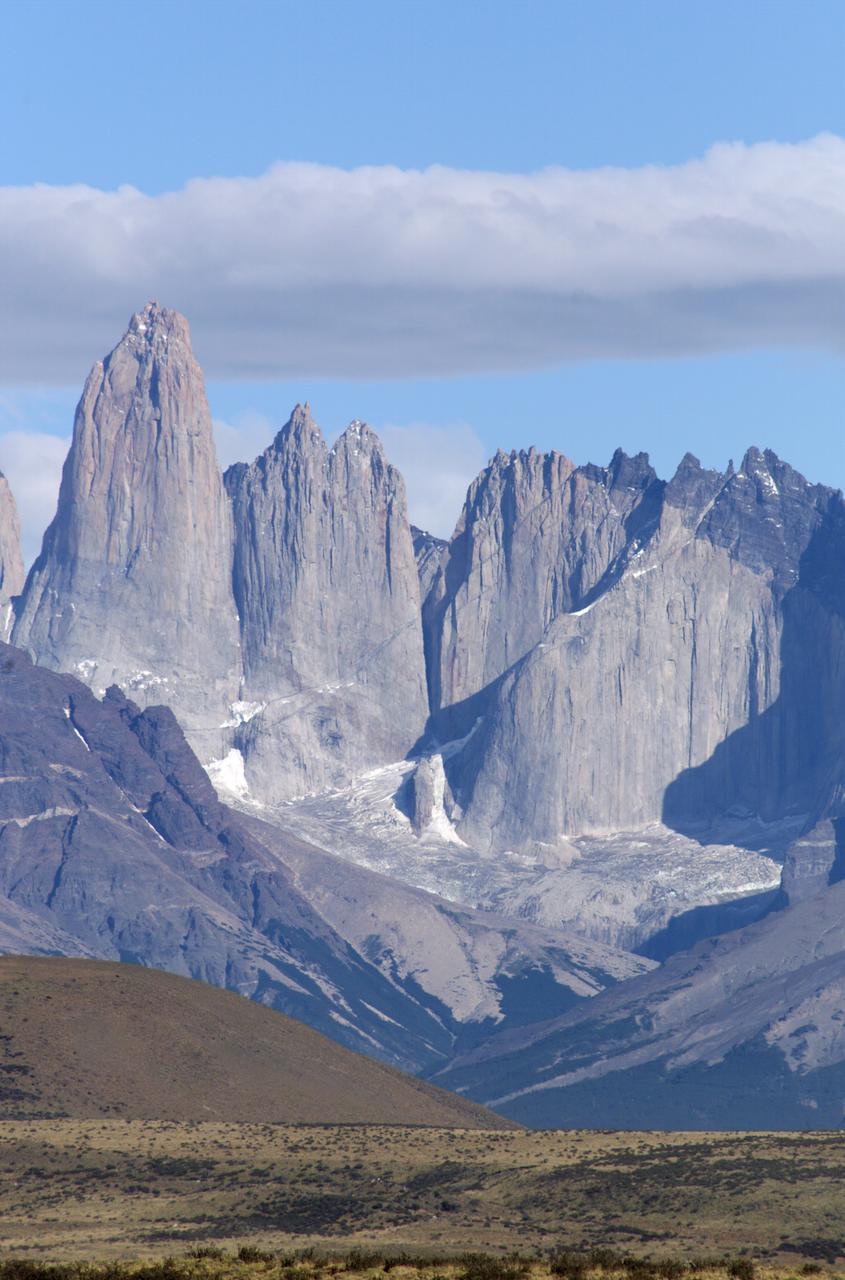

The Cuernos del Paine mountains in Torres del Paine National Park in Chile, photographed during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
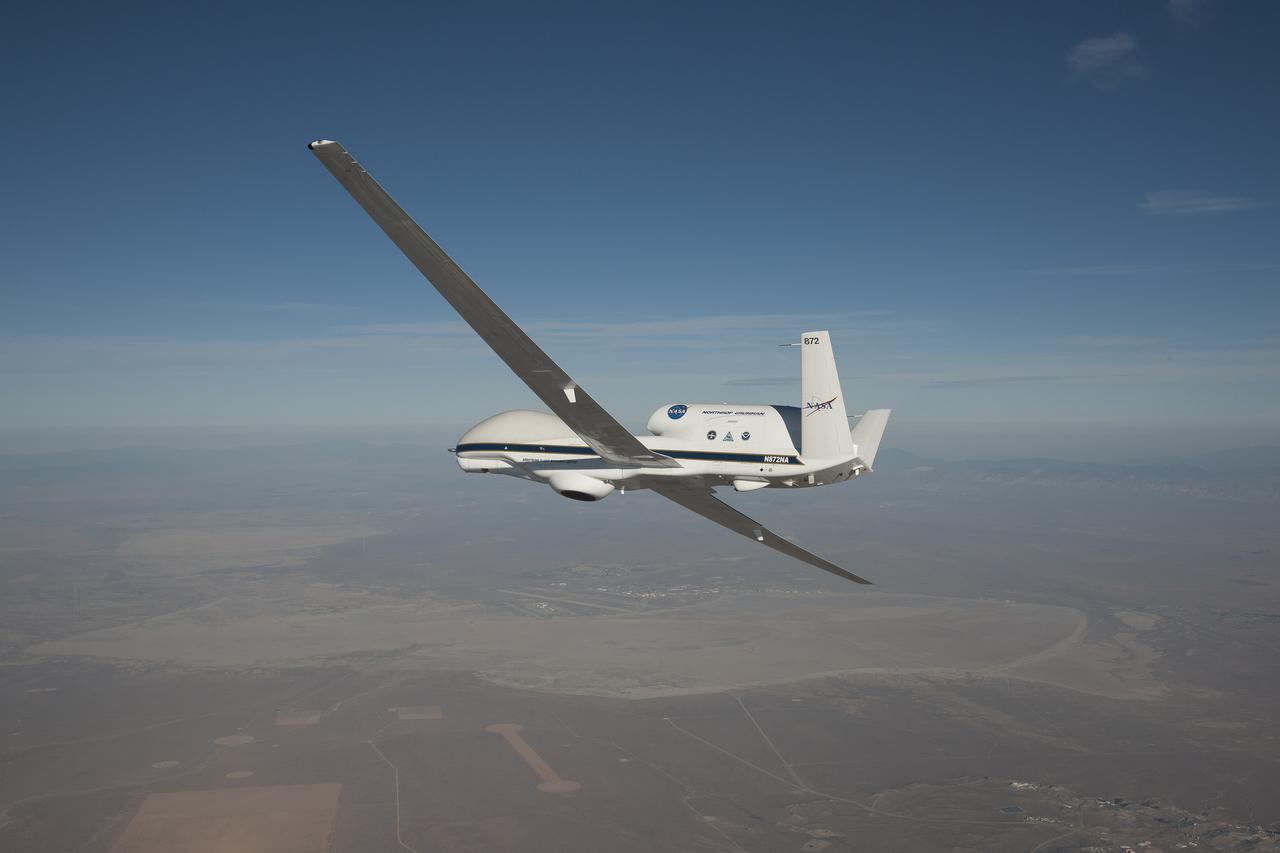

A NASA remotely piloted Global Hawk aircraft completes a flight in February 2015 to support the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s El Niño Rapid Response field campaign. The mission, called the Sensing Hazards Operational Unmanned Technology, gathered El Niño storm data over the Pacific Ocean. The flight originated from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
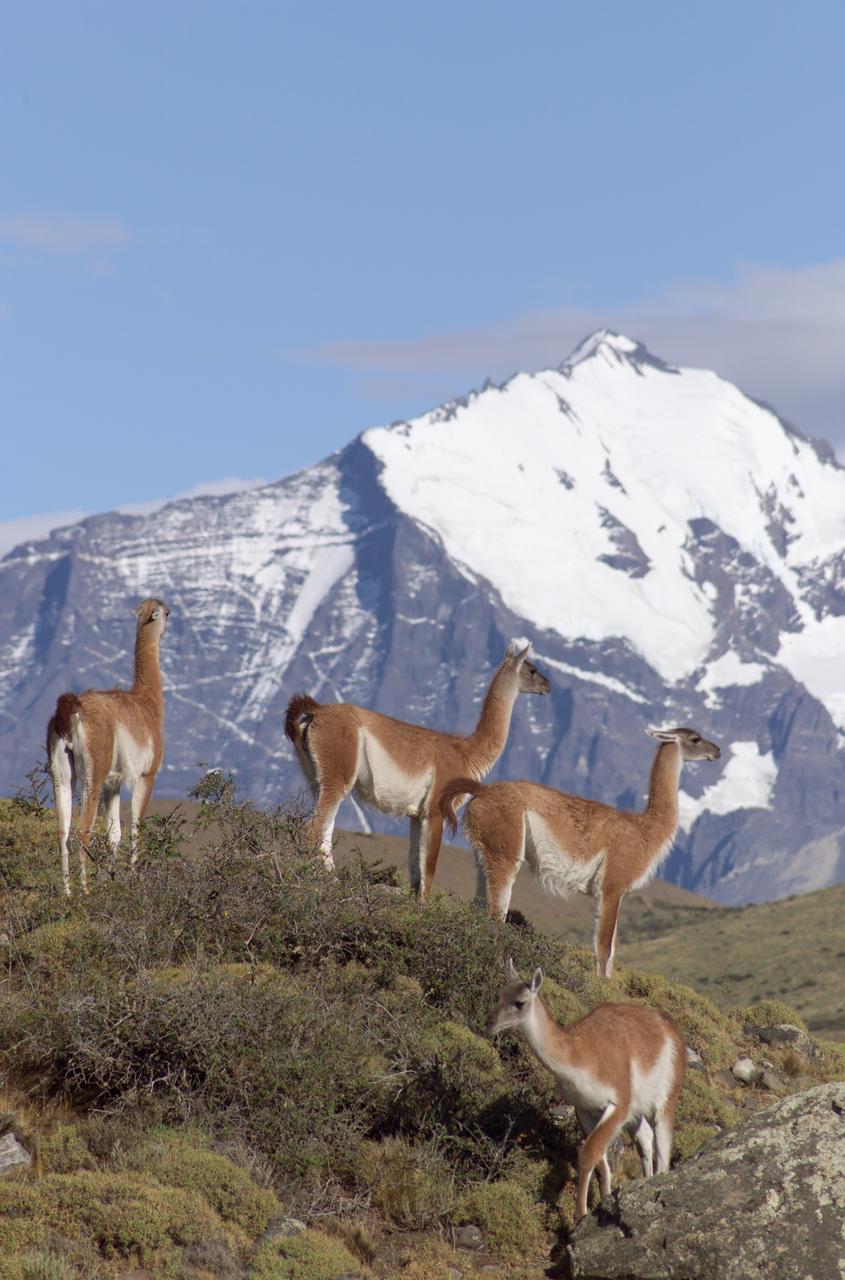

The Cuernos del Paine mountains in Torres del Paine National Park in Chile provide a backdrop to a herd of guanacos during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
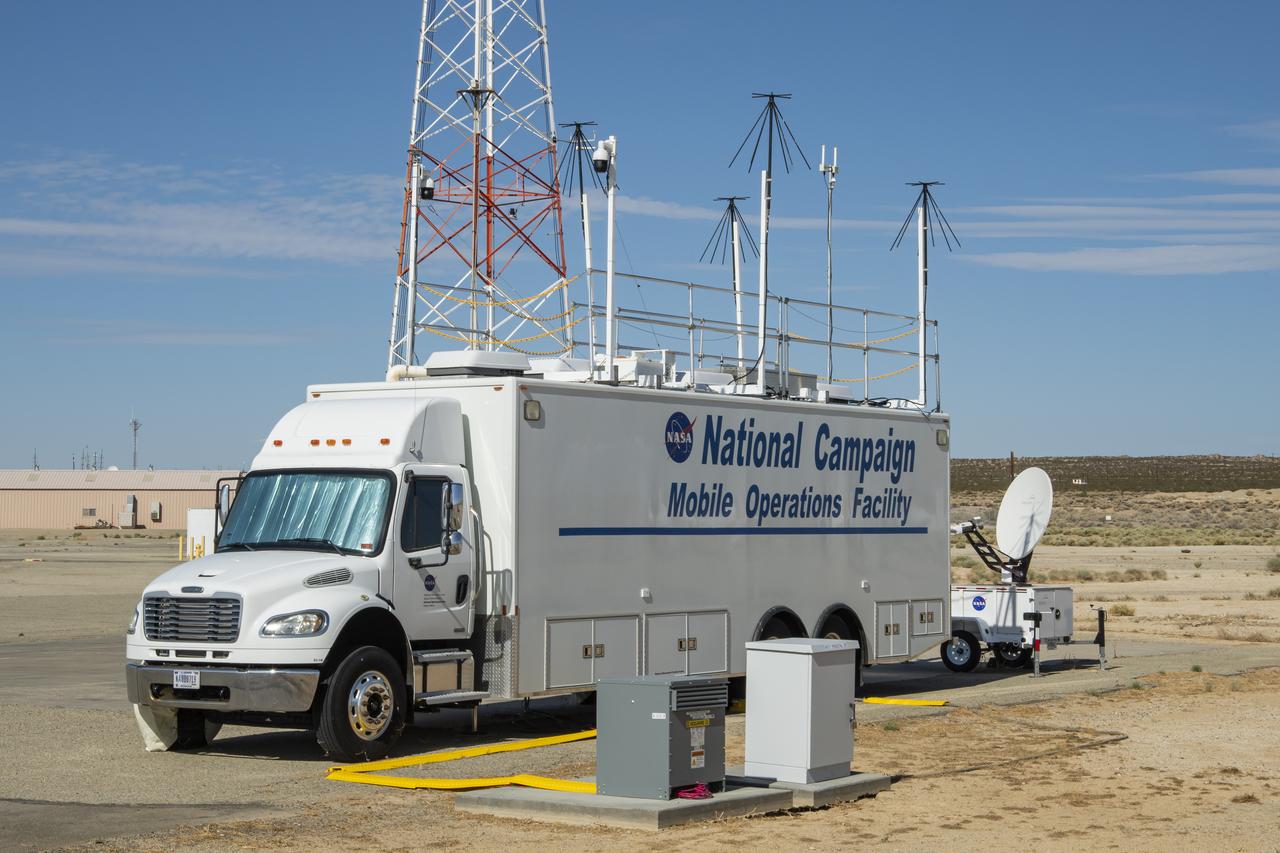

Photos taken on July 20, 2022, show new logos added to the side of the National Campaign’s upgraded Mobile Operations Facility, which has been outfitted to obtain and transmit data from anywhere in the country. This mobile command unit is housed at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
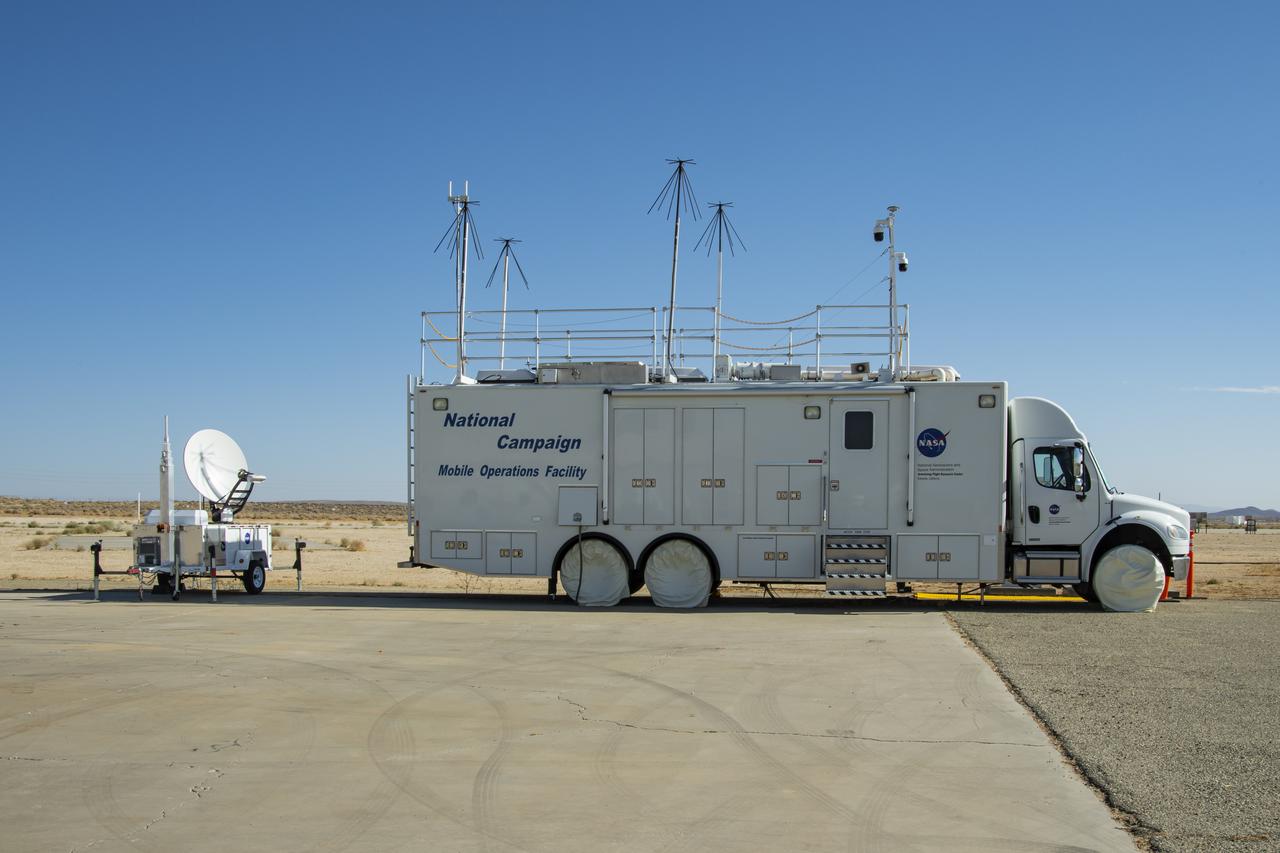

The NASA Mobile Operations Facility sports new decals while parked at NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California on July 20, 2022. This vehicle, also known as the MOF, is a mission control and data collection center on wheels. NASA's Advanced Air Mobility project uses it for testing.
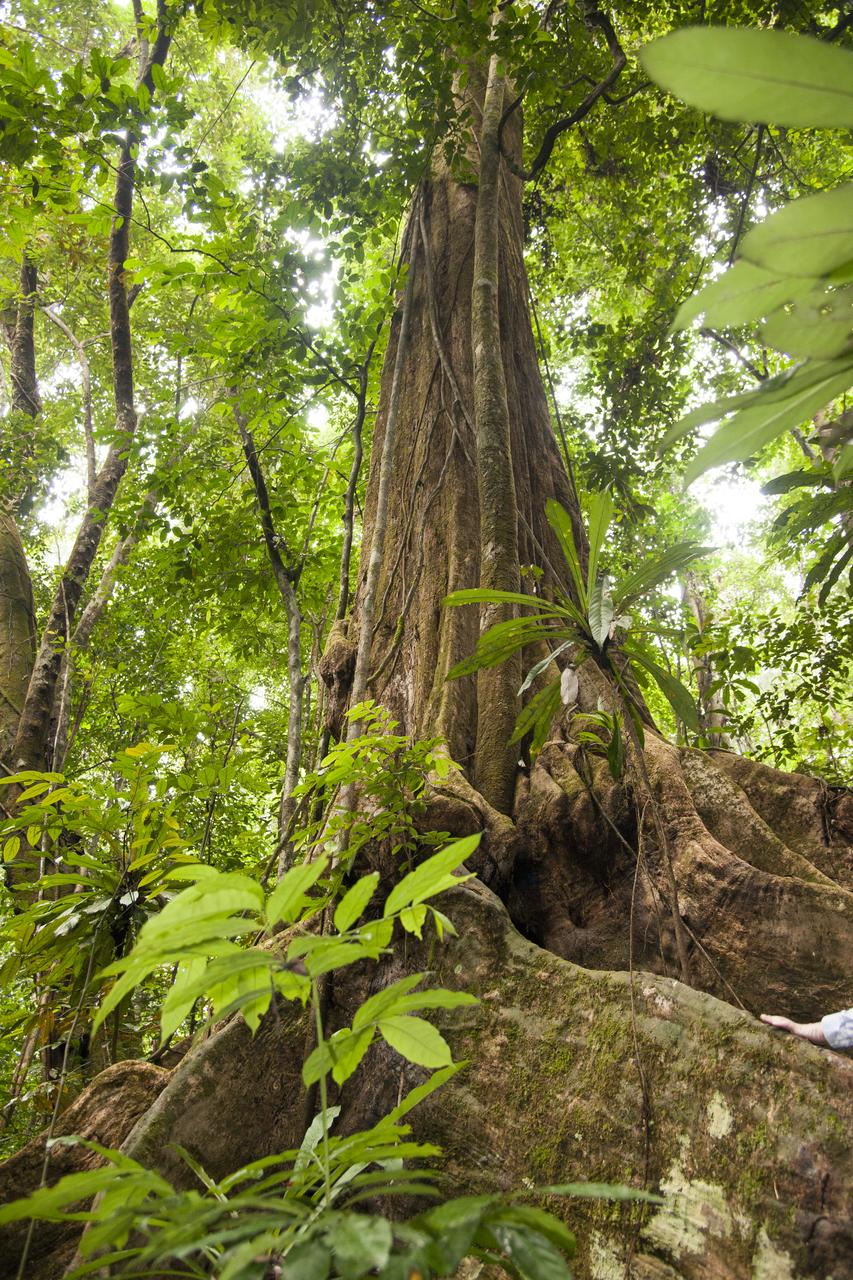

The Okoumé tree is large, as compared to a hand seen in the bottom right portion of the image. The Mondah National Park is one of the field research sites for NASA’s AfriSAR campaign.

NASA’s flight systems engineer, Kassidy Mclaughlin conducts environmental testing on an instrumentation pallet. The pallet was used during NASA’s National Campaign project in 2020 at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California.
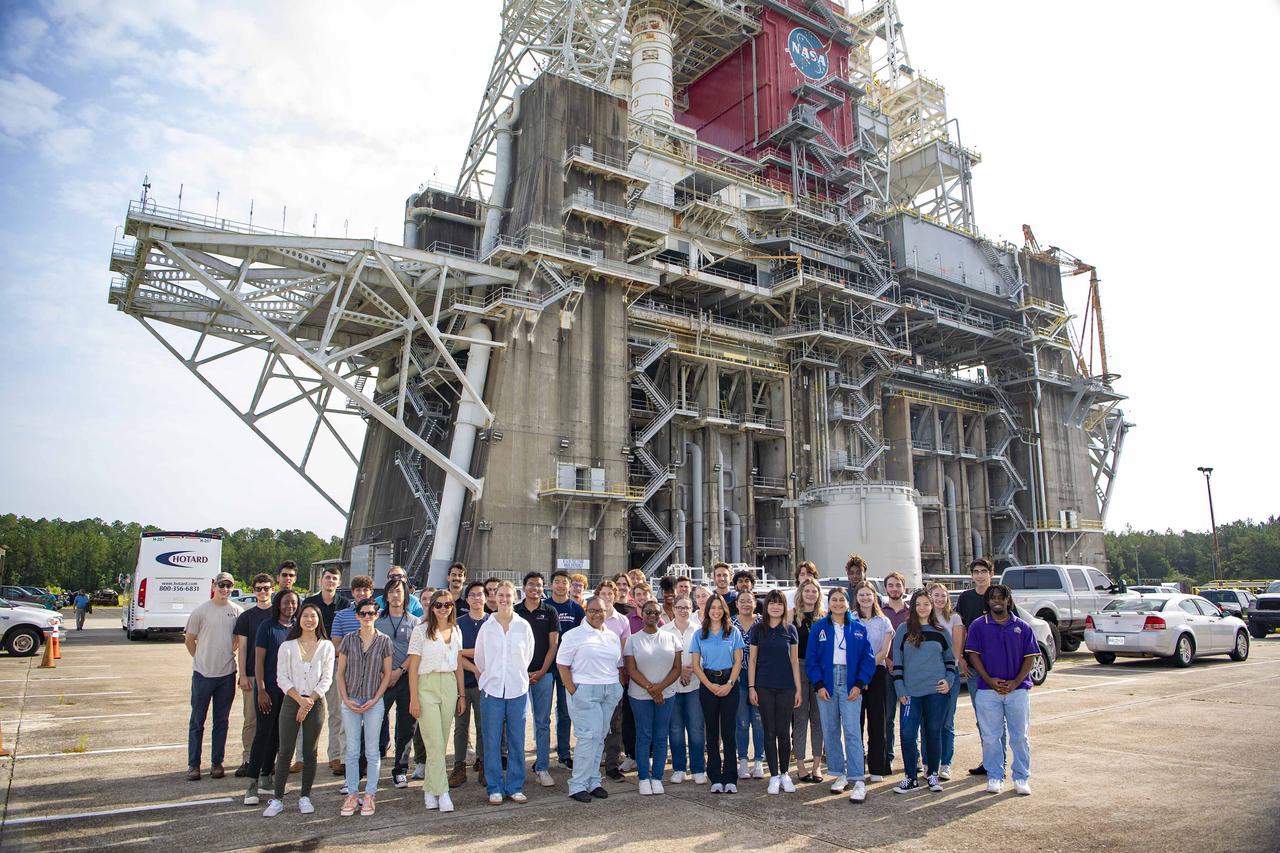

Interns at NASA Stennis visit the Thad Cochran Test Stand (B-1/B-2) on July 25 during a test complex tour on National Intern Day. As NASA continues to progress with the Artemis campaign, students across the nation are invited to join the journey. NASA’s internships aim to inspire the Artemis Generation to pursue STEM careers across the nation.

SPARKY THE FIRE DOG, MASCOT FOR THE NATIONAL FIRE PROTECTION ASSOCIATION, TEAMS UP WITH PATRICK SCHEUERMANN AT THE MARSHALL CENTER SEPT. 26 TO PROMOTE THE NATIONWIDE FIRE PREVENTION WEEK CAMPAIGN, “WORKING SMOKE ALARMS SAVE LIVES: TEST YOURS EVERY MONTH!”-
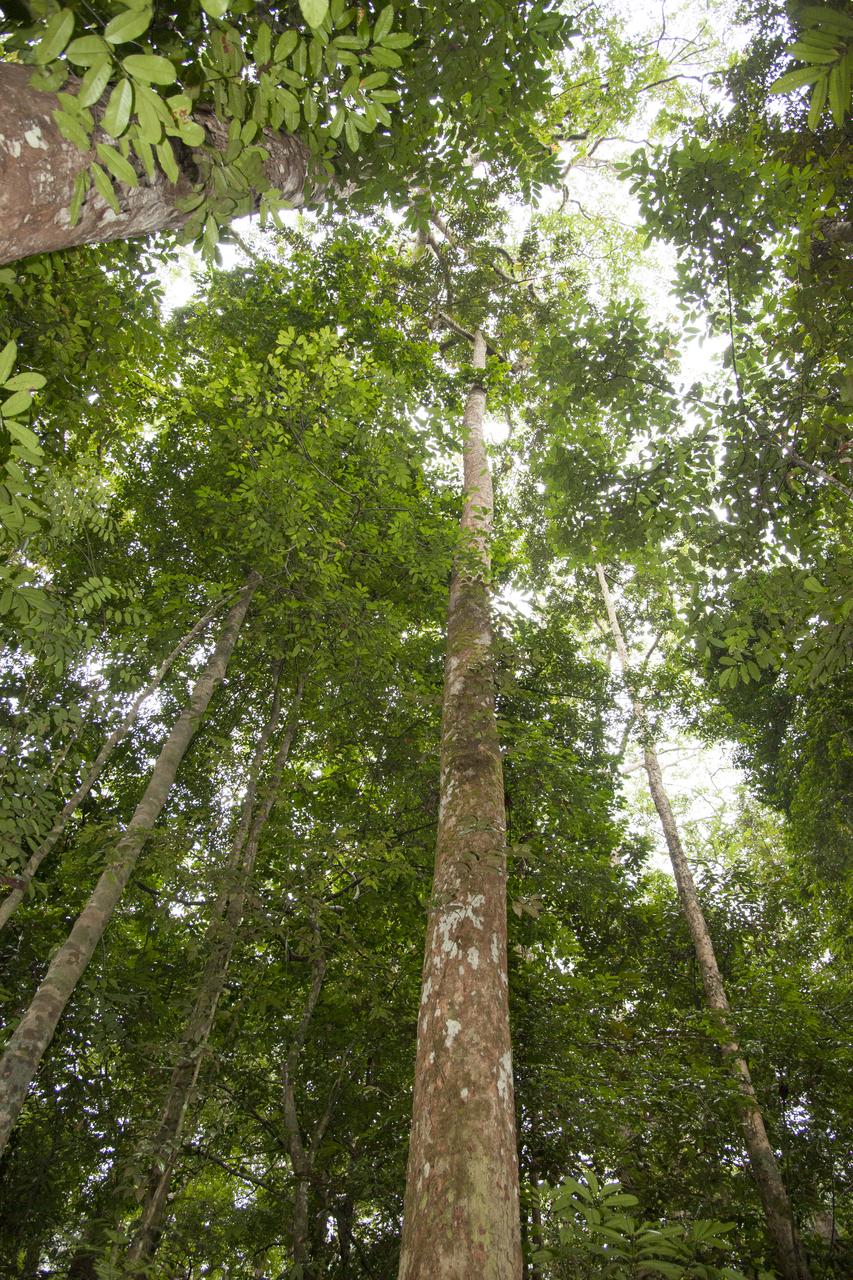

In Gabon, Africa, the Mondah National Park is one of the field research sites for NASA’s AfriSAR campaign. Gabon is a Central African country slightly smaller than the state of Colorado that features the world’s second largest rainforest. In addition to environmental measurements, the flights were used for calibrating satellites for current and upcoming missions.
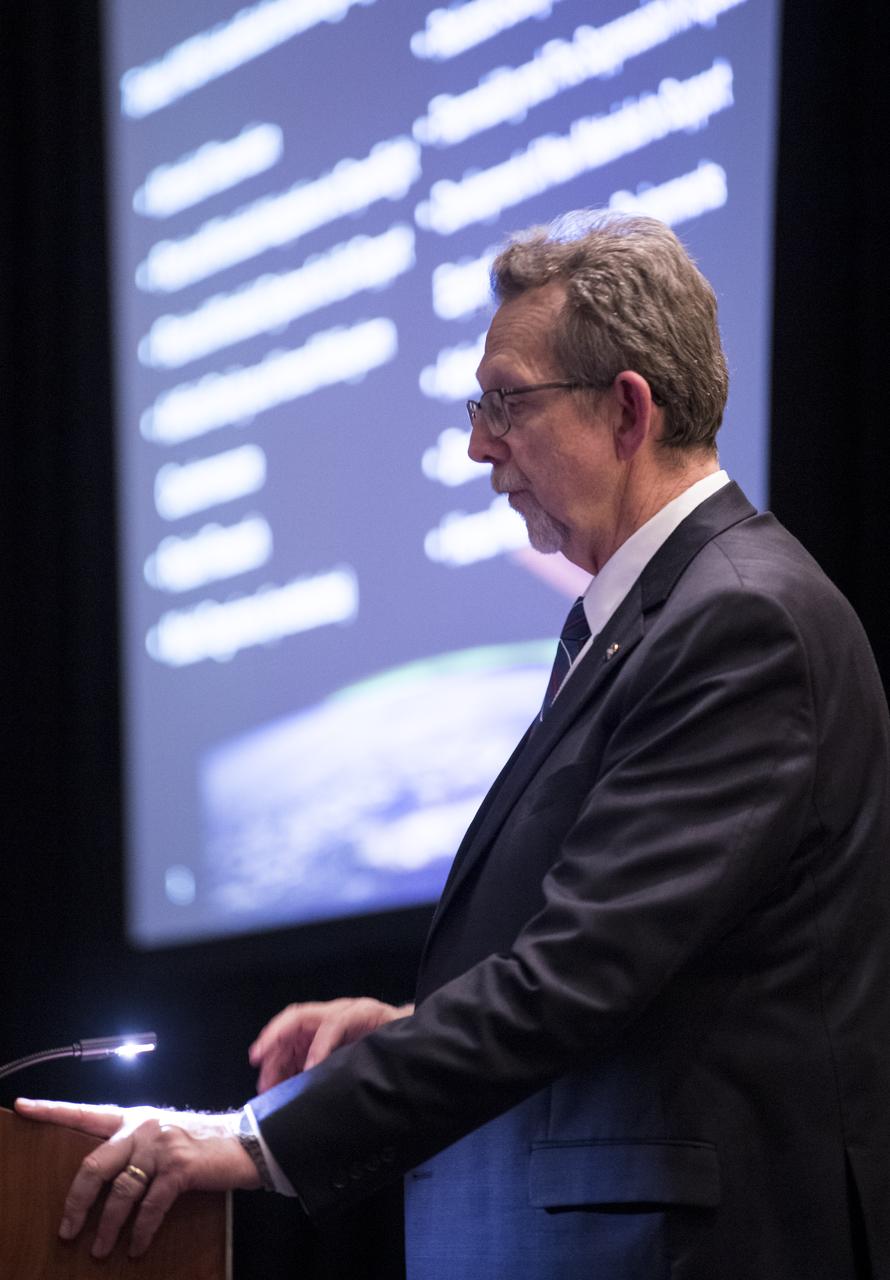

NASA Chief Scientist Jim Green speaks about NASA Science under the National Space Exploration Campaign during a keynote at the 70th International Astronautical Congress, Monday, Oct. 21, 2019 at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
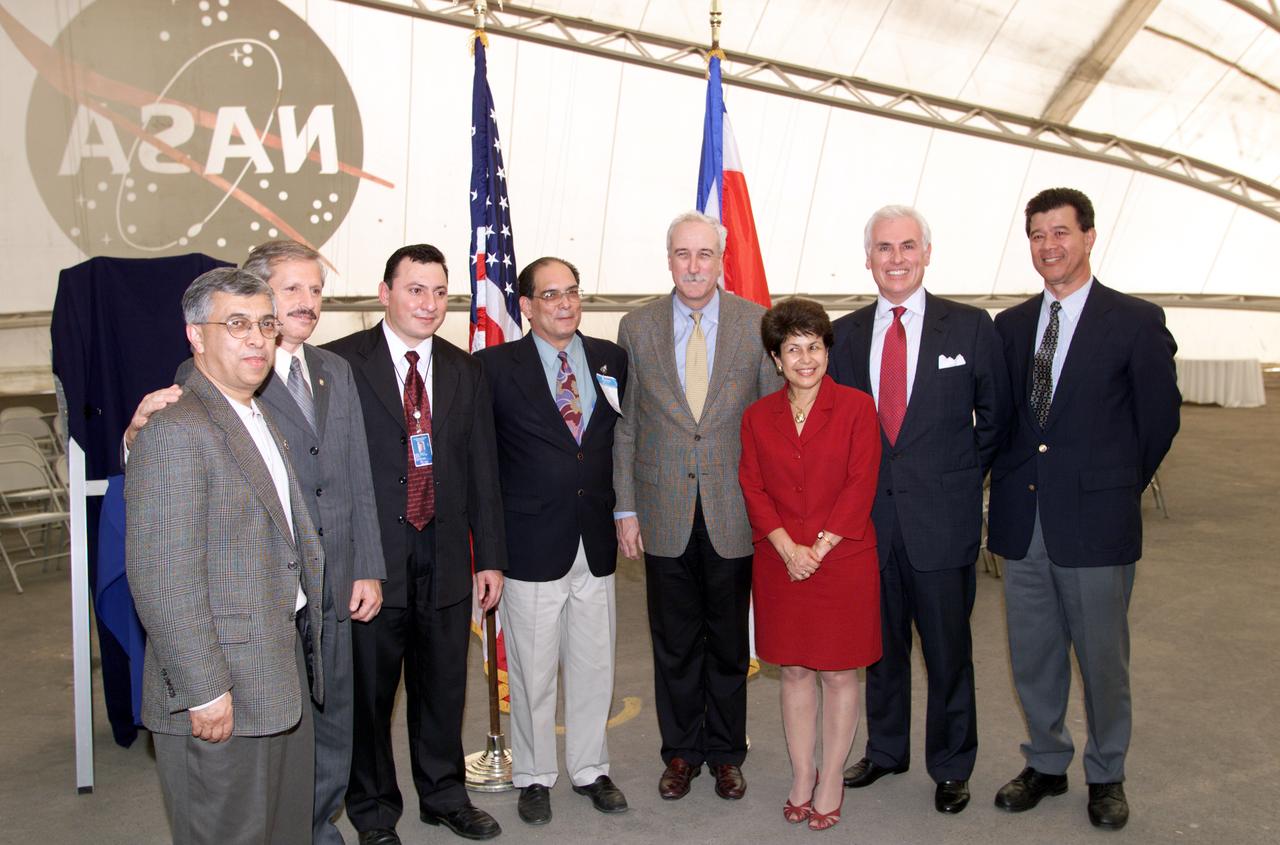

VIP group in hangar during AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign, L-R: Dr. Gahssem Asrar, NASA Associate Administrator for Earth Science Enterprises; Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT); Jorge Andres Diaz, Director of the Costa Rican National Hangar for Airborne Research division of the National Center for High Technology(CENAT); Dr. Pedro Leon, General Director for the Costa Rican National Center for High Technology(CENAT); NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe; Dr. Sonia Marta Mora, President of the Costa Rican National Rector’s Council(CONARE); Mr. John Danilovich, US Ambassador to Costa Rica; and unknown. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
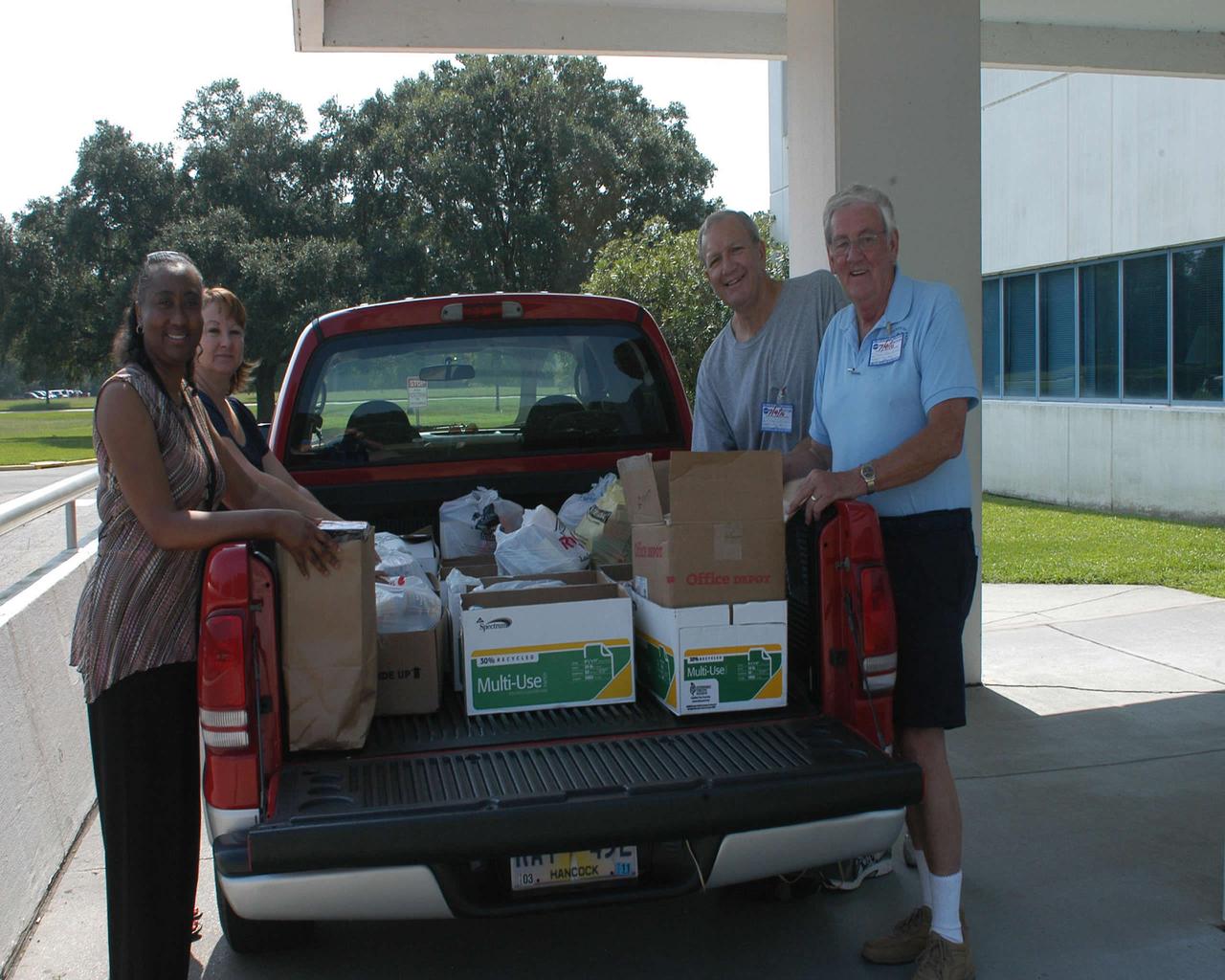

Cabrina Bell (l to r) and Jeanie Frederick with the Stennis Space Center Office of Human Capital help Hancock County Food Pantry representatives Edward Catone and Frank Manchester load collected food items July 9 as part of the 2010 Feds Feed Families campaign. The second annual national food drive was launched last month and involves federal agencies and employees across the country. Organizers hope to collect 1.2 million pounds of food items throughout the summer.
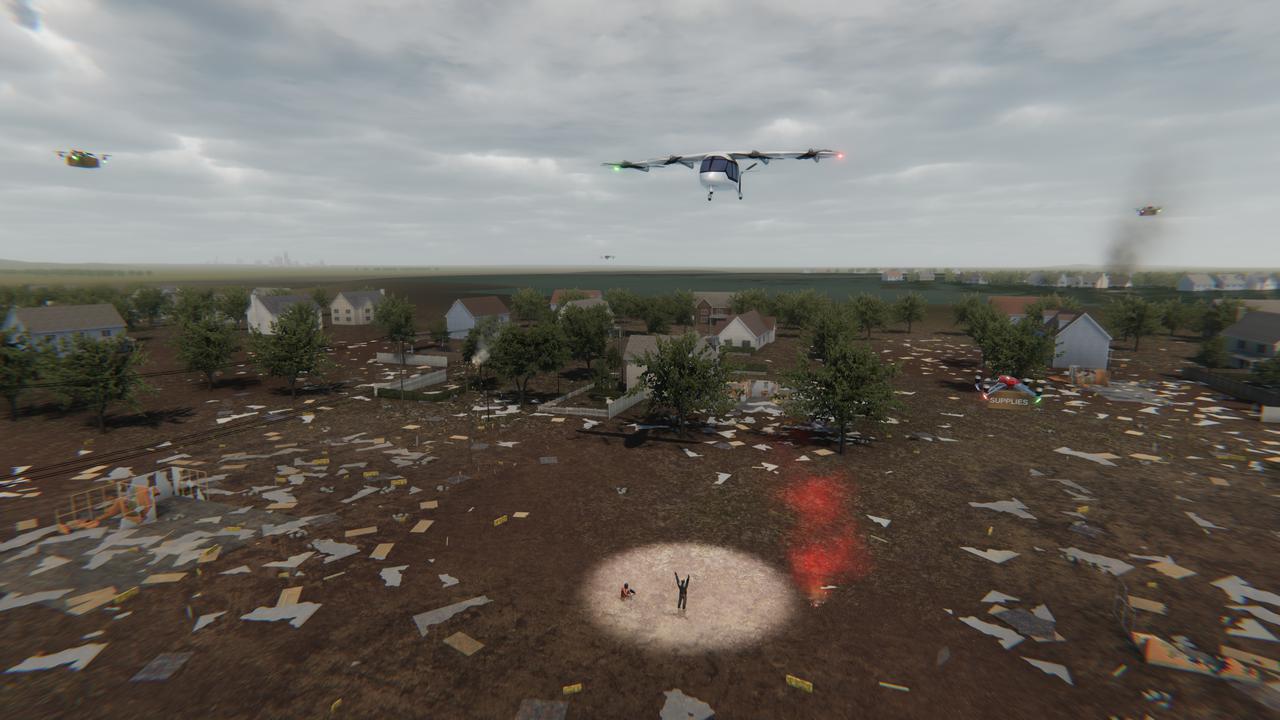

Several projects under NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality in emergency operations. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in disaster response.
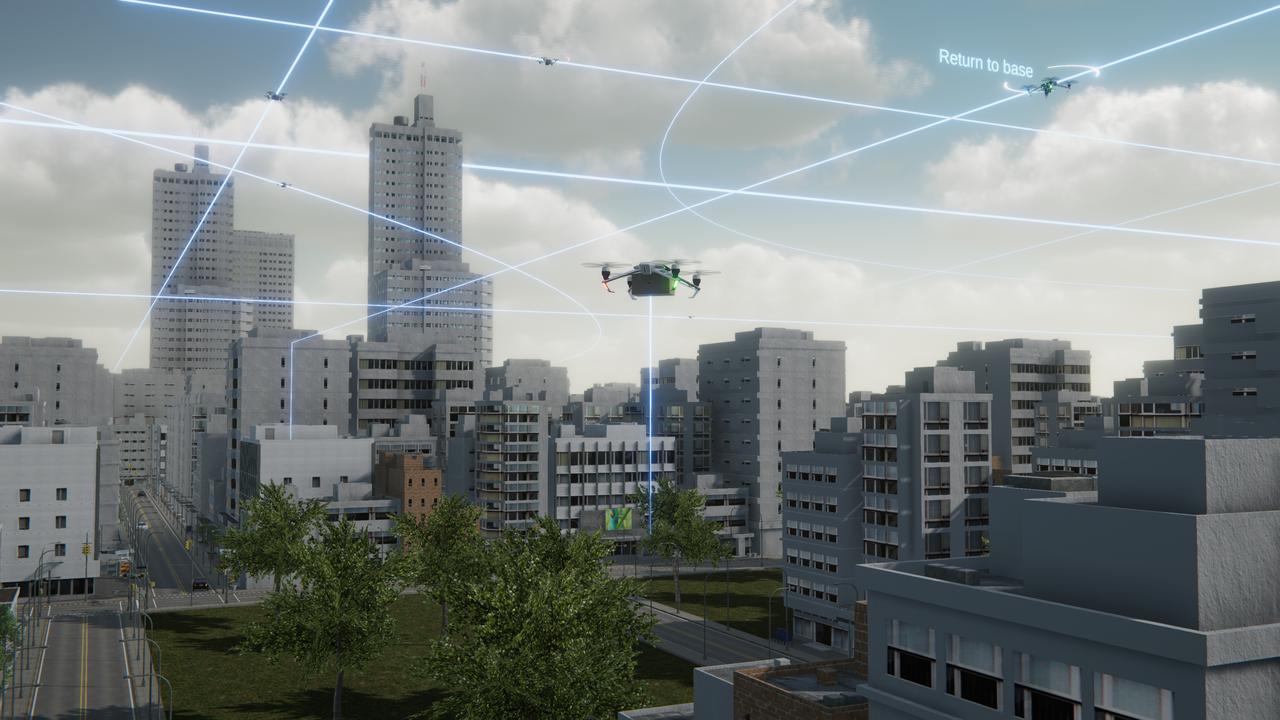

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality and one of these research areas is automation. This concept graphic shows how elements of automation could be integrated into a future airspace. Technology like this could enable vehicles to operate without a pilot, or if a pilot is in the loop, increase the safety.
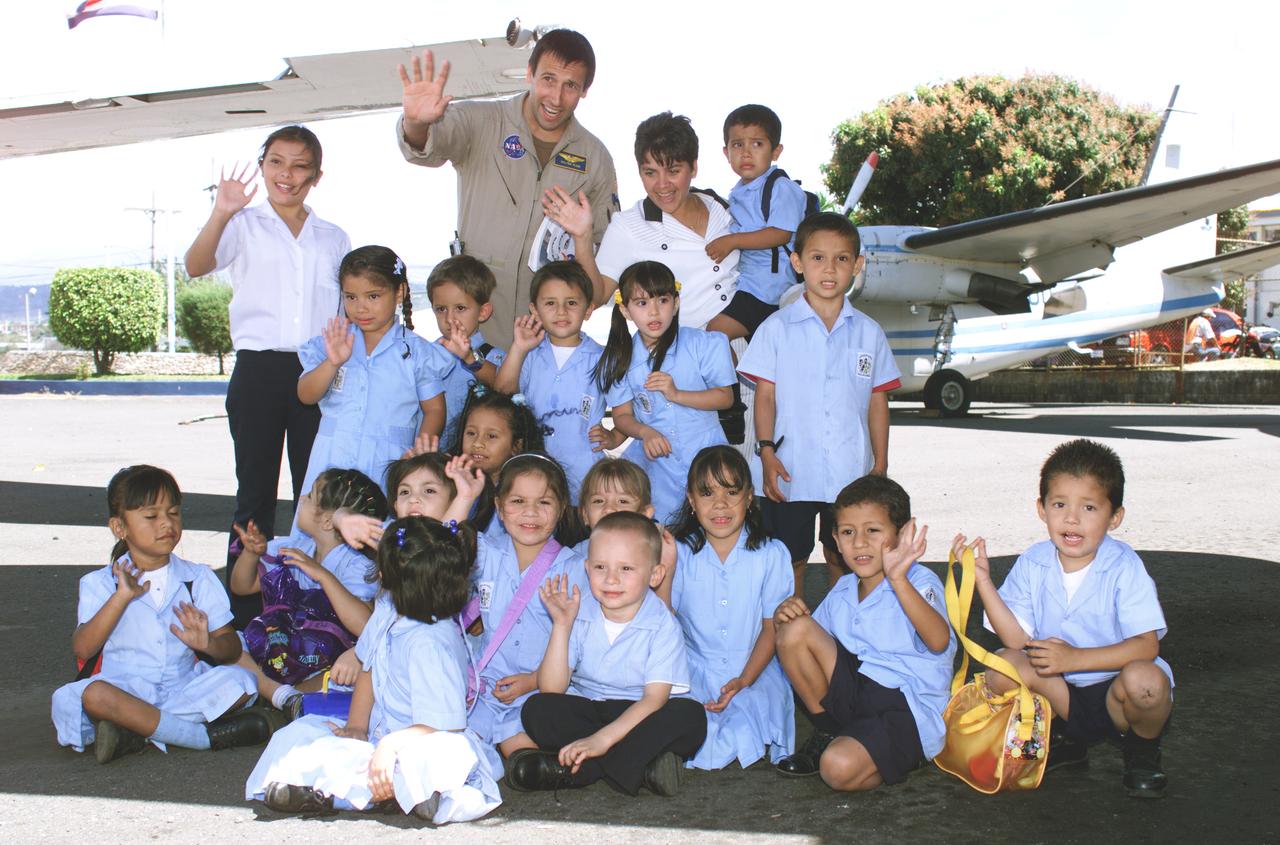

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein poses with school children that visited the airport during AirSAR 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
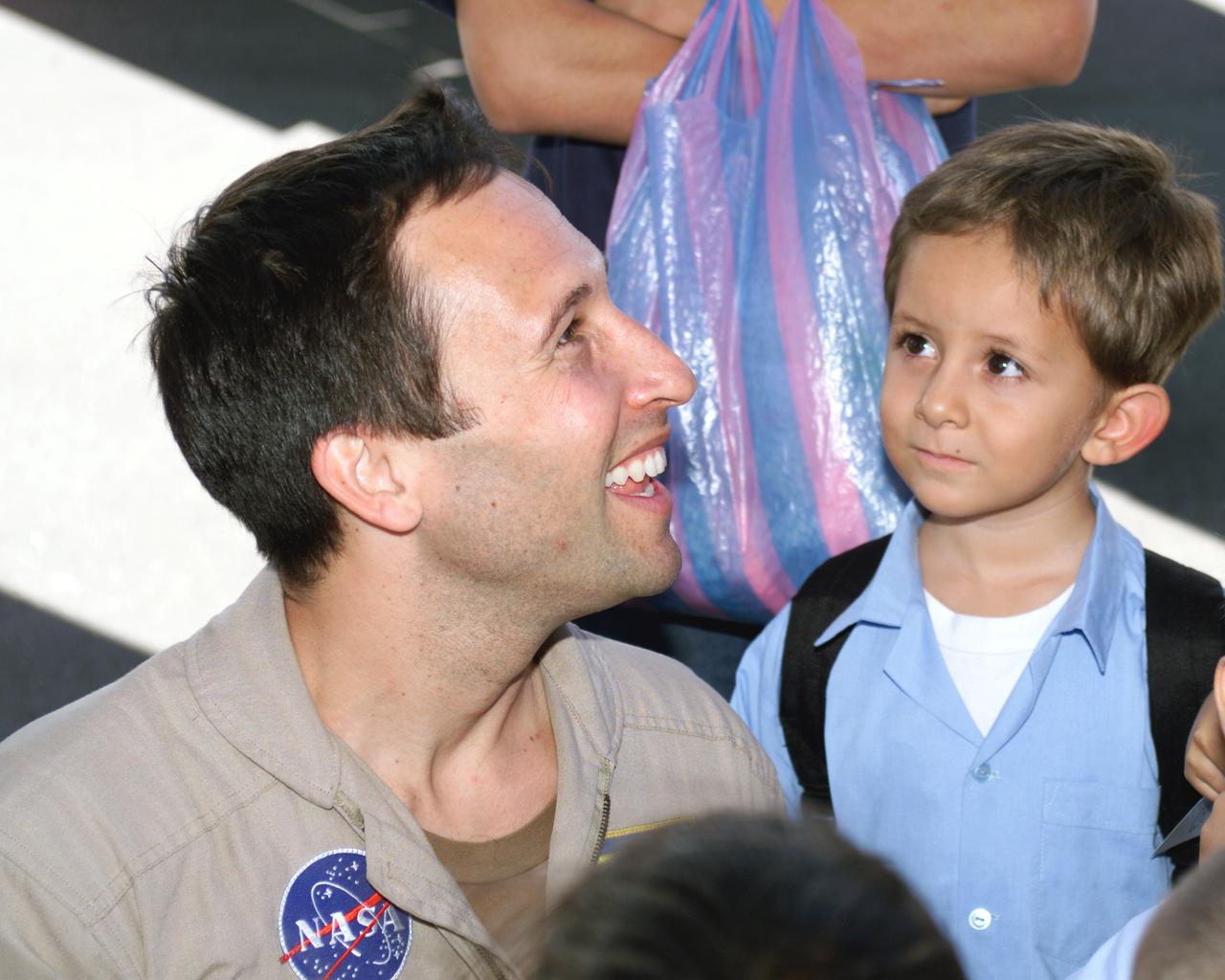

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
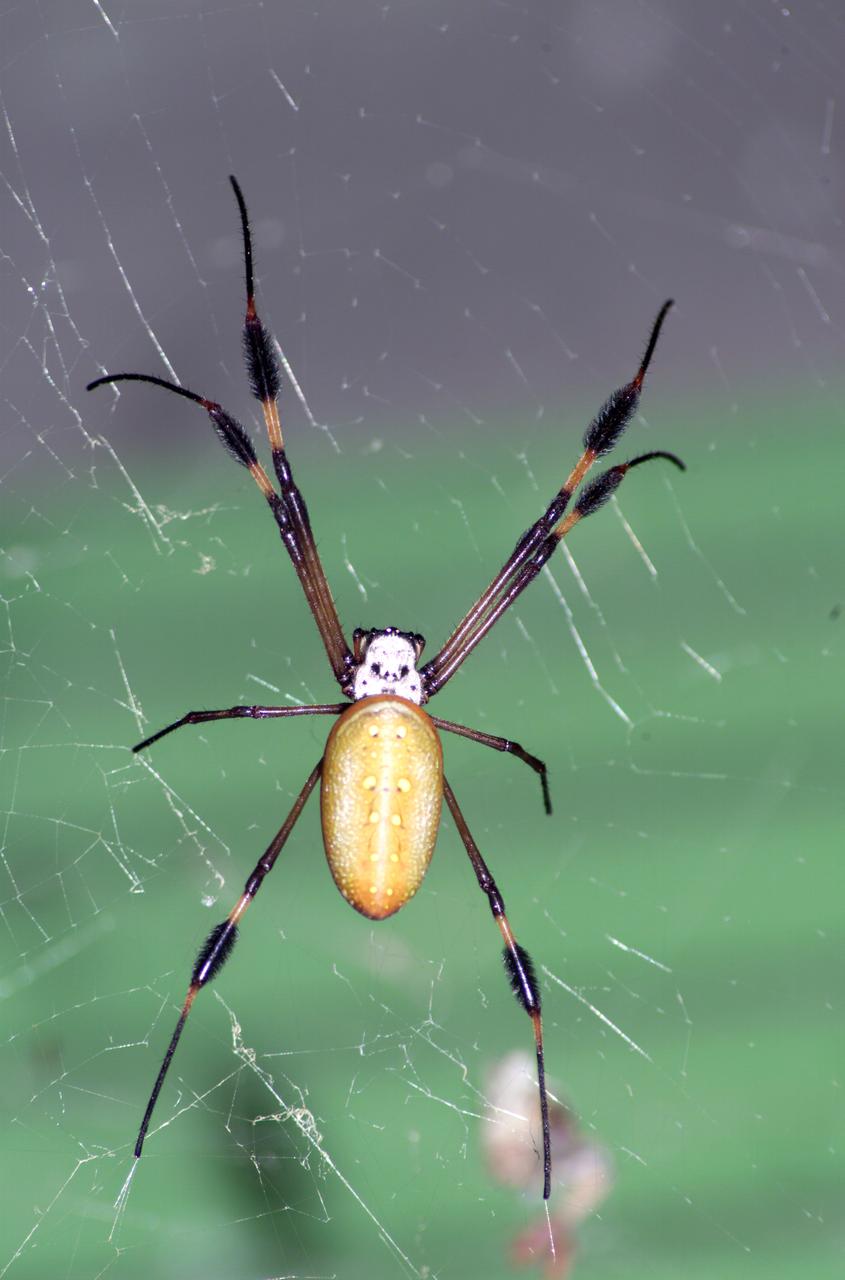

A spider photographed during NASA's AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
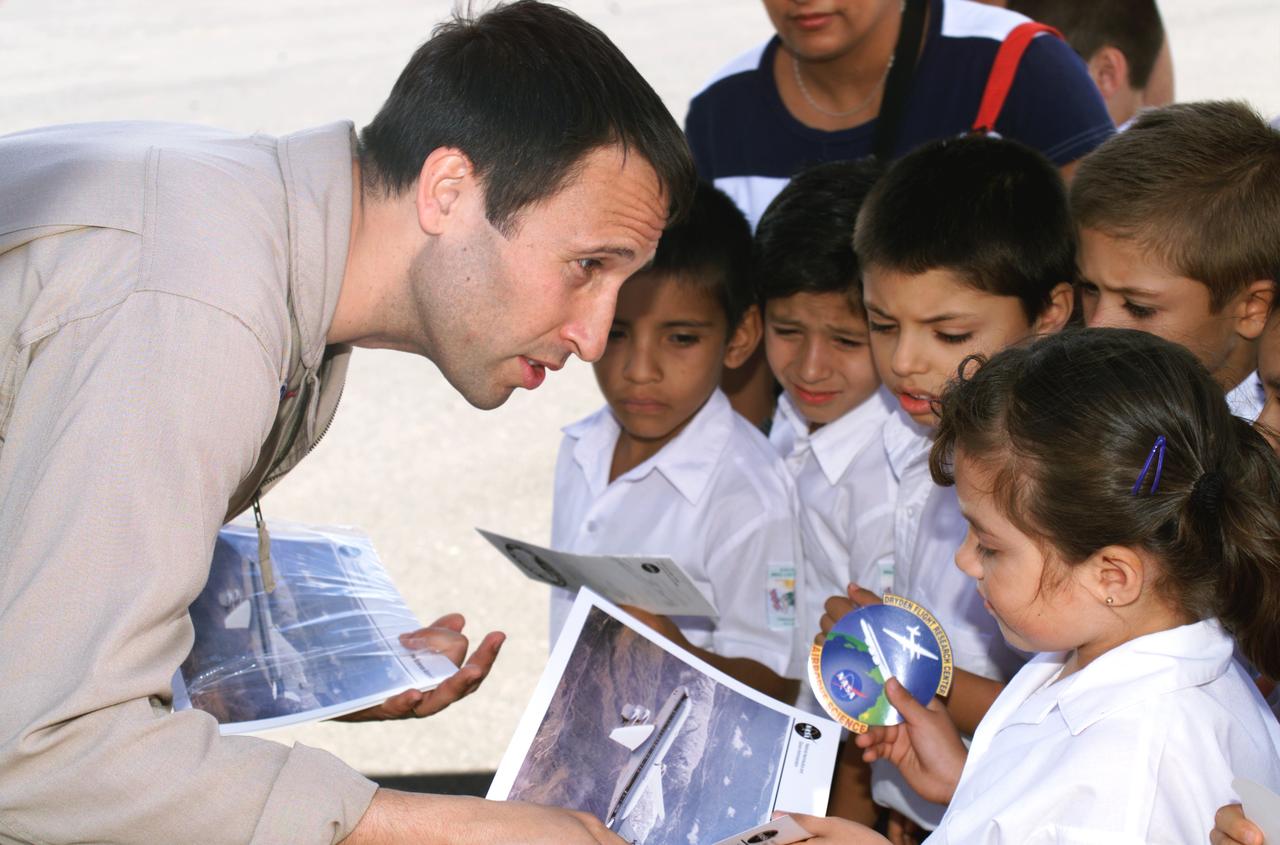

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
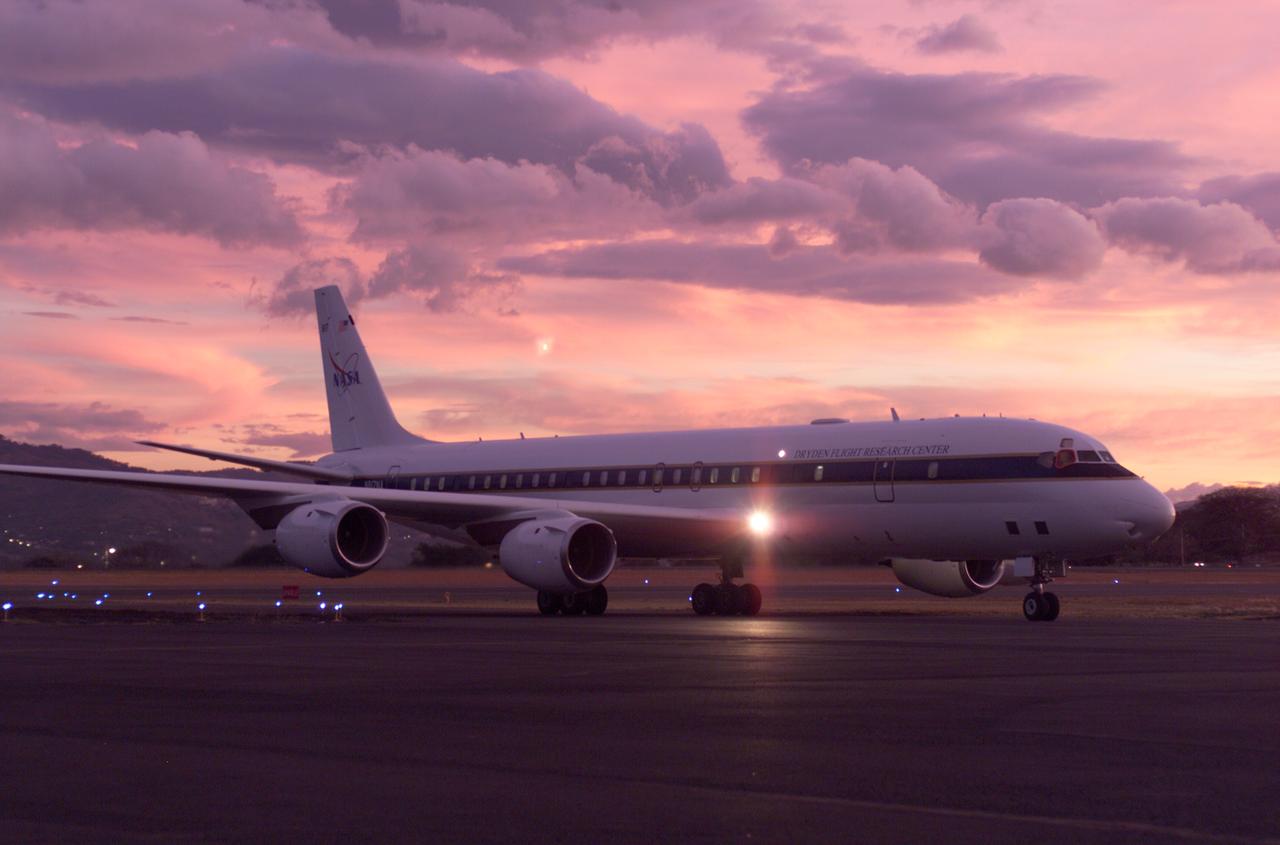

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory seen at sunset after a flight supporting the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
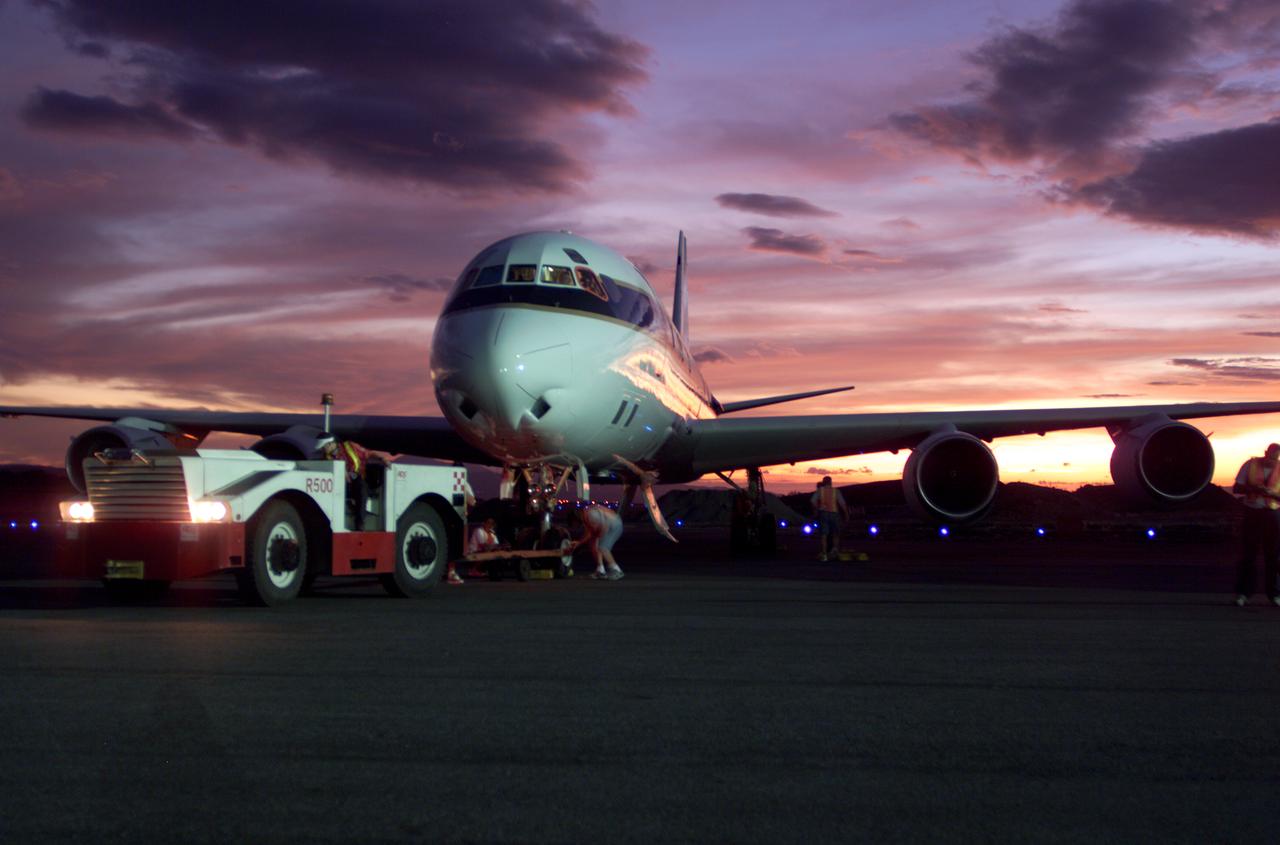

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory seen at sunset after a flight supporting the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
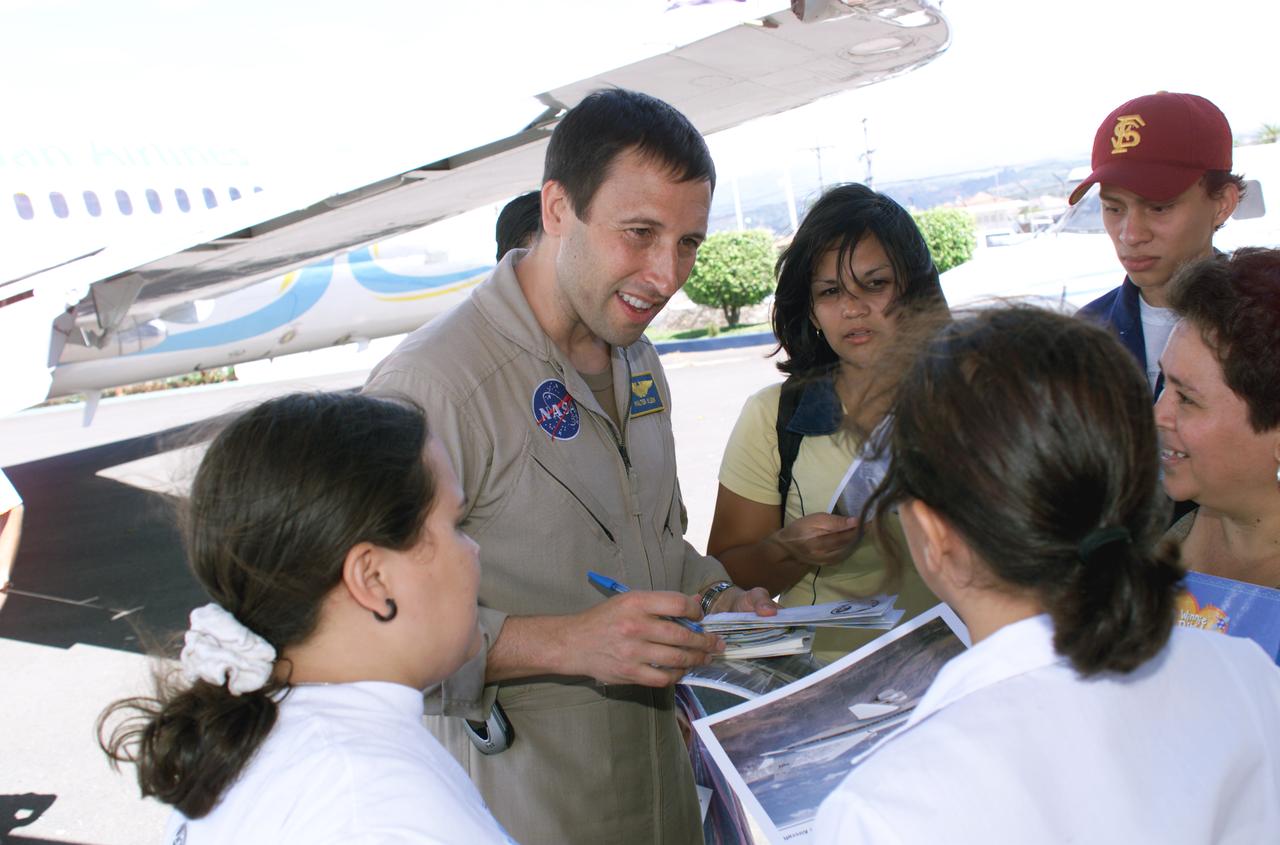

NASA Dryden Mission Manager Walter Klein passes out Airborne Science stickers and lithographs to underprivileged school children that visited the airport on Monday March 8, 2004. In spanish, he explained to them the mission of the DC-8 AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerican campaign in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
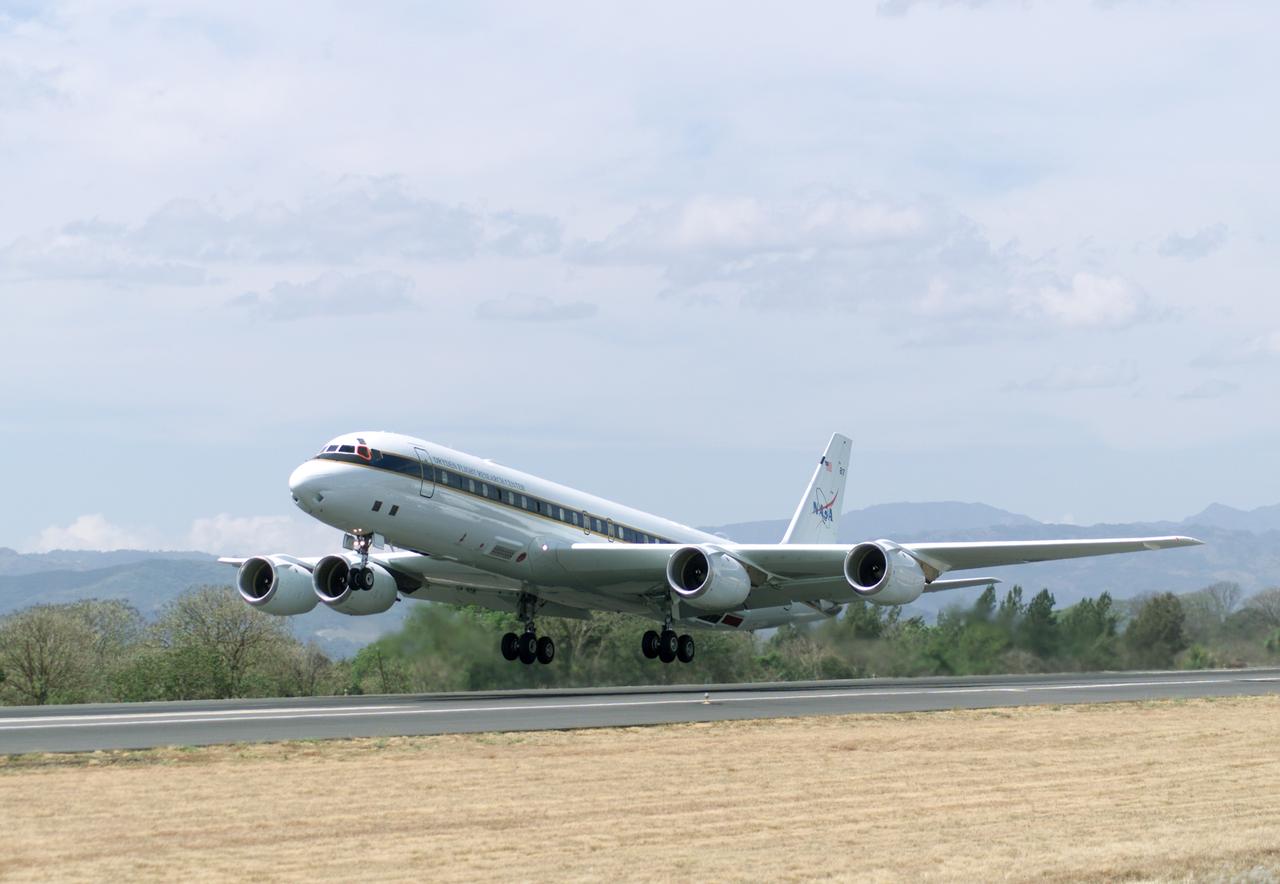

NASA's DC-8 flying laboratory takes off from Juan Santamaria International Airport in San Jose, Costa Rica, on NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
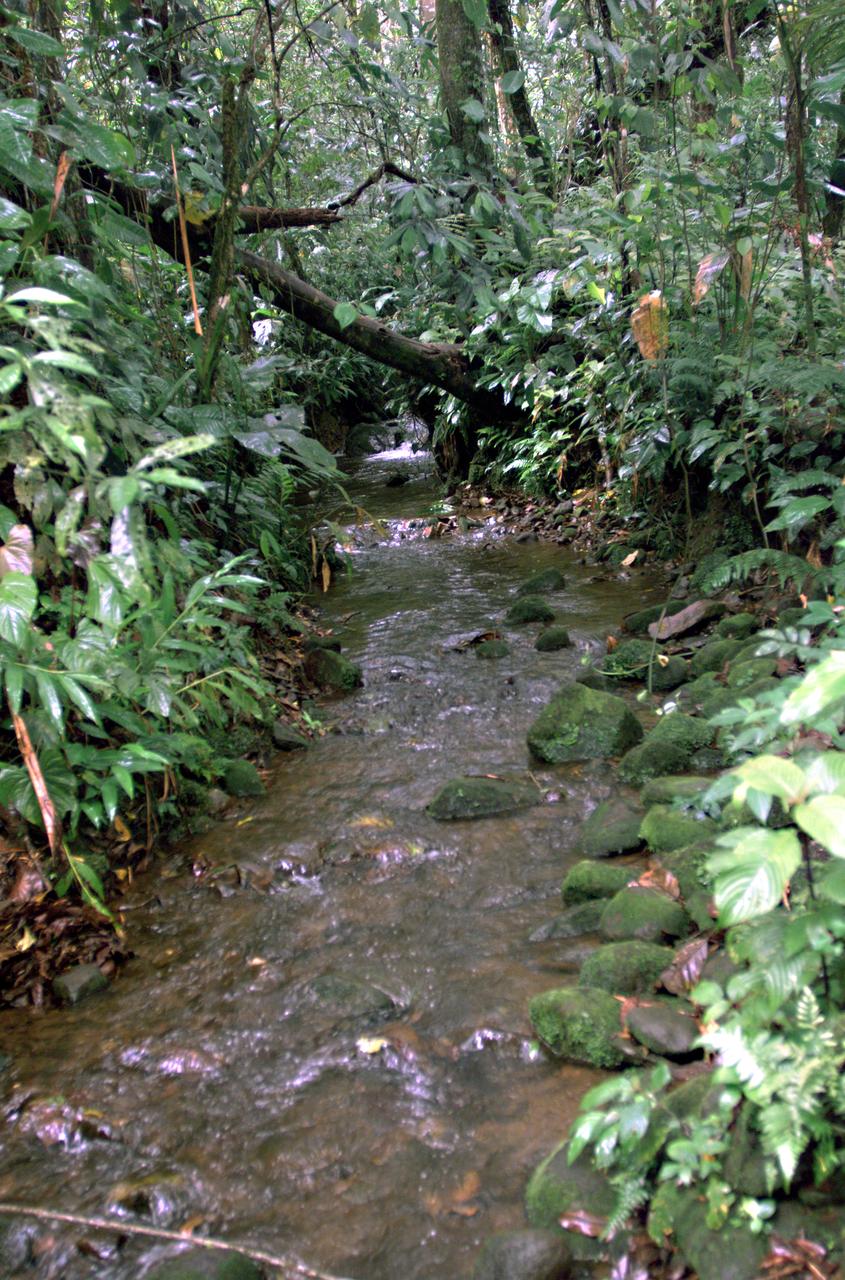

This photograph shows a stream in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest, taken during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
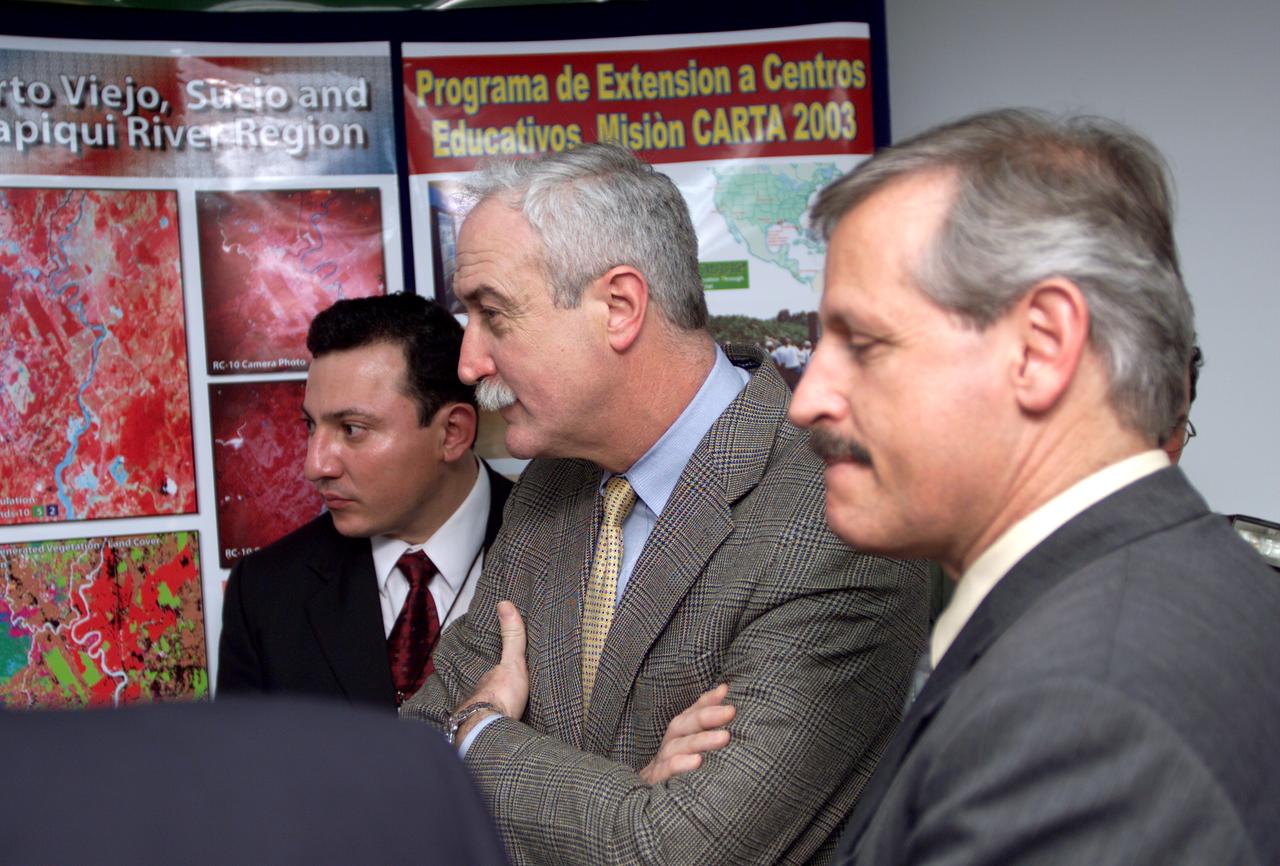

L-R; Jorge Andres Diaz, Director of the Costa Rican National Hangar for Airborne Research division of the National Center for High Technology(CENAT); NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe; and Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT), viewing posters showing how NASA activities have made an impact on Costa Rican people. Mr. O'Keefe was in Costa Rica to participate in the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign, which used NASA DFRC's DC-8 airborne laboratory aircraft. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
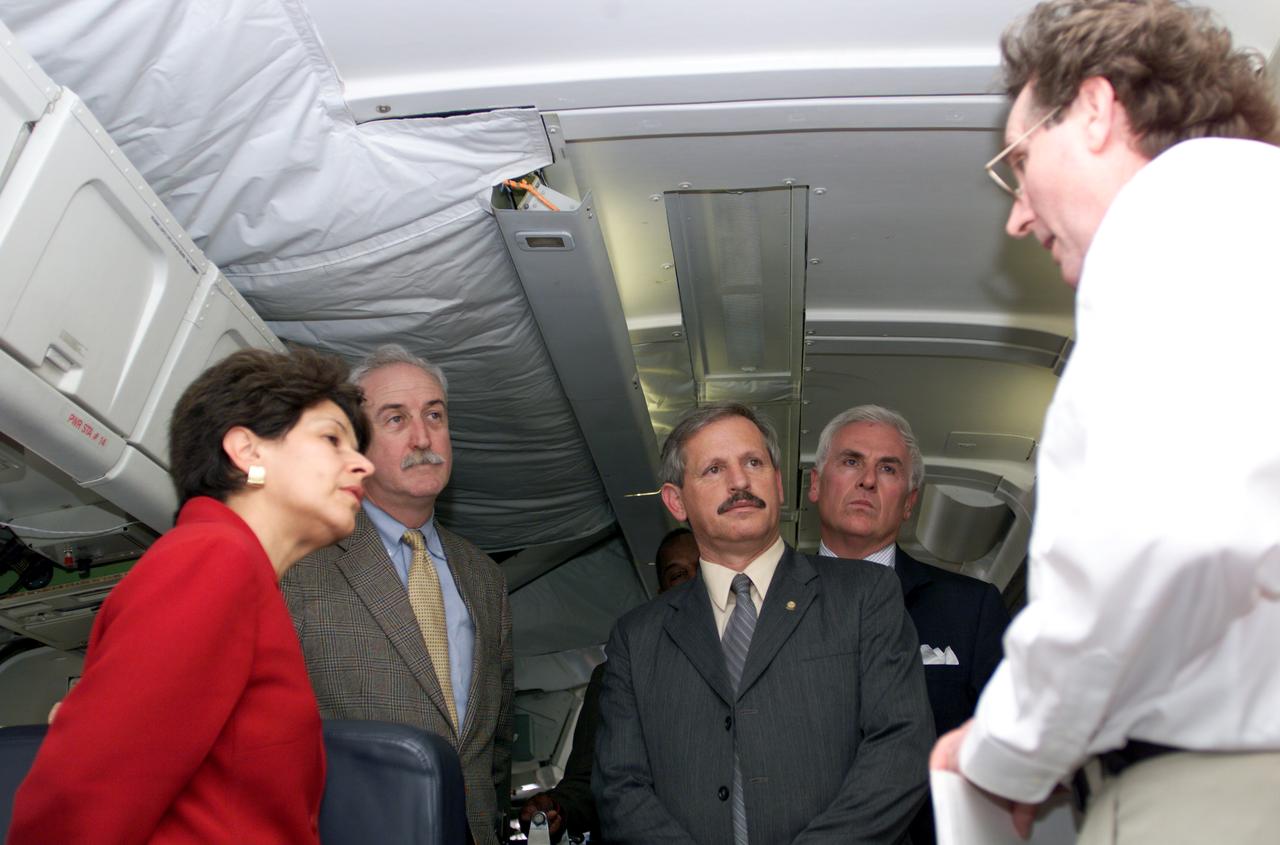

VIP tour of NASA DFRC's DC-8 airborne laboratory during the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign given by Craig Dobson, NASA Program Manager for AirSAR, L-R: Dr. Sonia Marta Mora, President of the Costa Rican National Rector’s Council; NASA Administrator Sean O'Keefe; Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT); Mr. John Danilovich, US Ambassador to Costa Rica; and Dobson. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
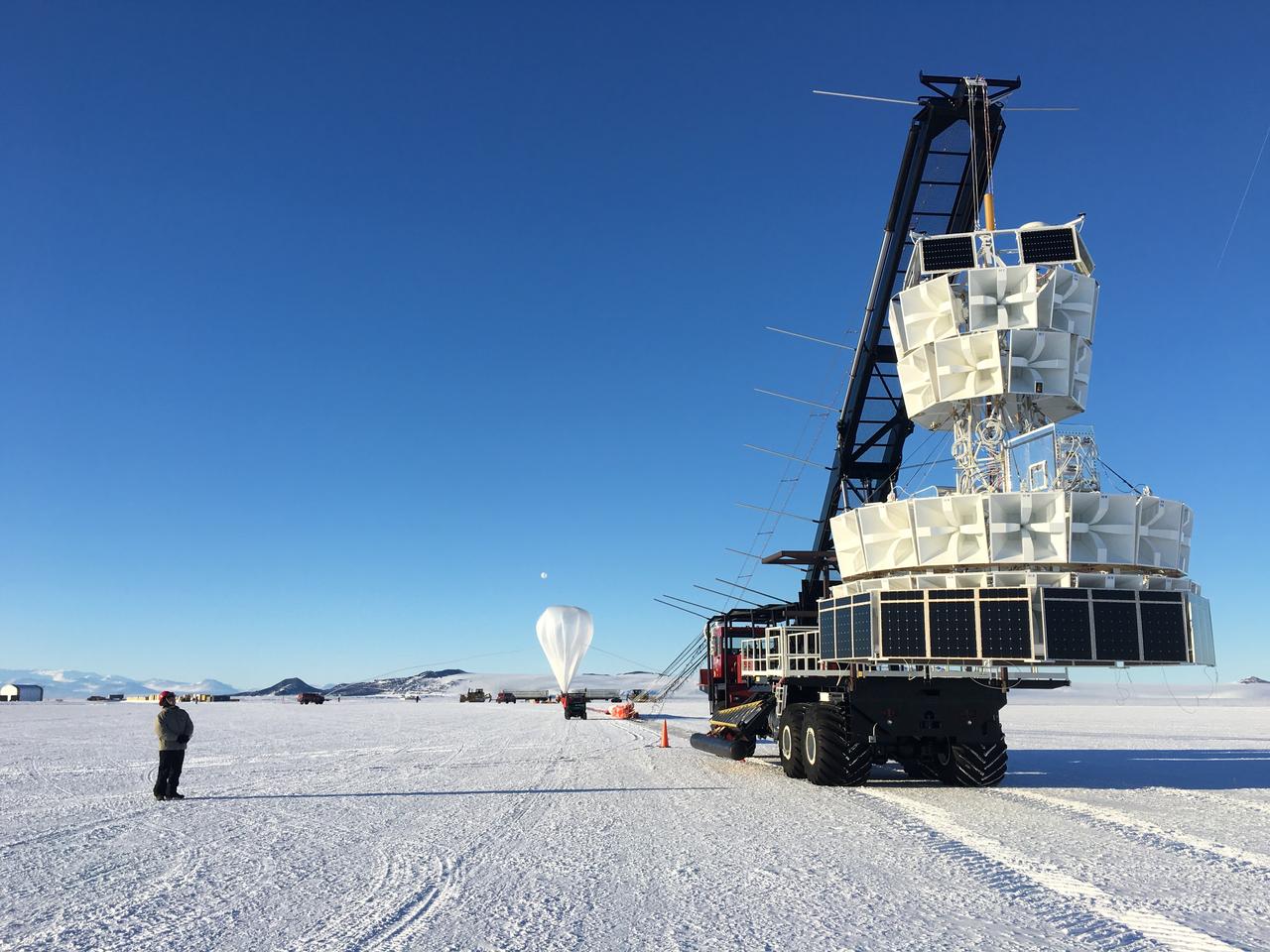

The second of three missions as part of NASA’s Antarctica Long Duration Balloon Flight Campaign was successfully launched at 8:10 a.m. EDT, Dec. 2. The Antarctic Impulsive Transient Antenna (ANITA) from the University of Hawaii at Manoa was launched from Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf near McMurdo Station with support from the National Science Foundation’s United States Antarctic Program. Scientists will use ANITA’s instruments to study the reactions in the core of stars and as they explode via the release of neutrinos that travel to Earth and interact with the Antarctica ice. More: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2ghR6Le" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2ghR6Le</a>
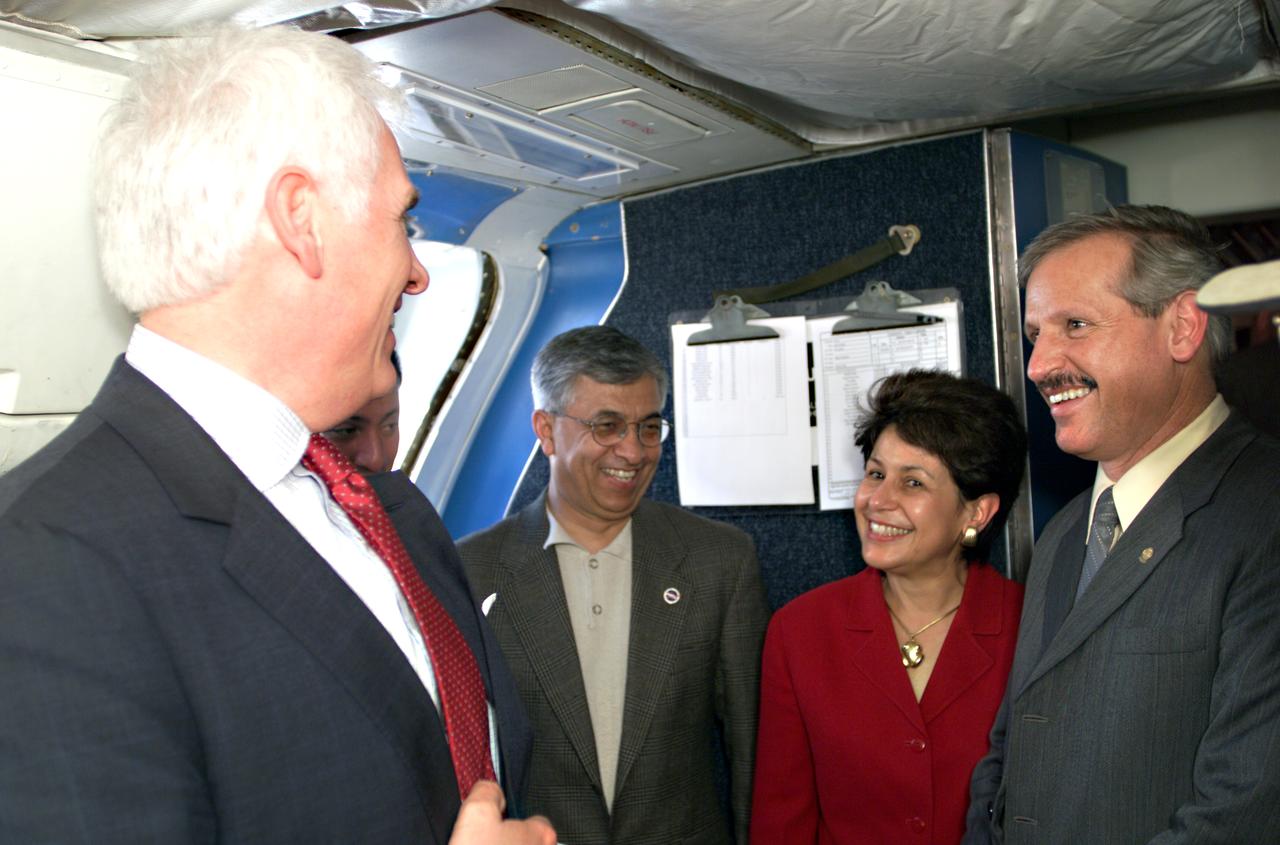

VIP’s onboard NASA's DC-8 aircraft during the AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica campaign, L-R: Mr. John Danilovich, US Ambassador to Costa Rica; Dr. Gahssem Asrar, NASA Associate Administrator for Earth Science Enterprises; Dr. Sonia Marta Mora, President of the Costa Rican National Rector’s Council; and Fernando Gutierrez, Costa Rican Minister of Science and Technology(MICIT). AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that will use an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), in a mission ranging from the tropical rain forests of Central America to frigid Antarctica.
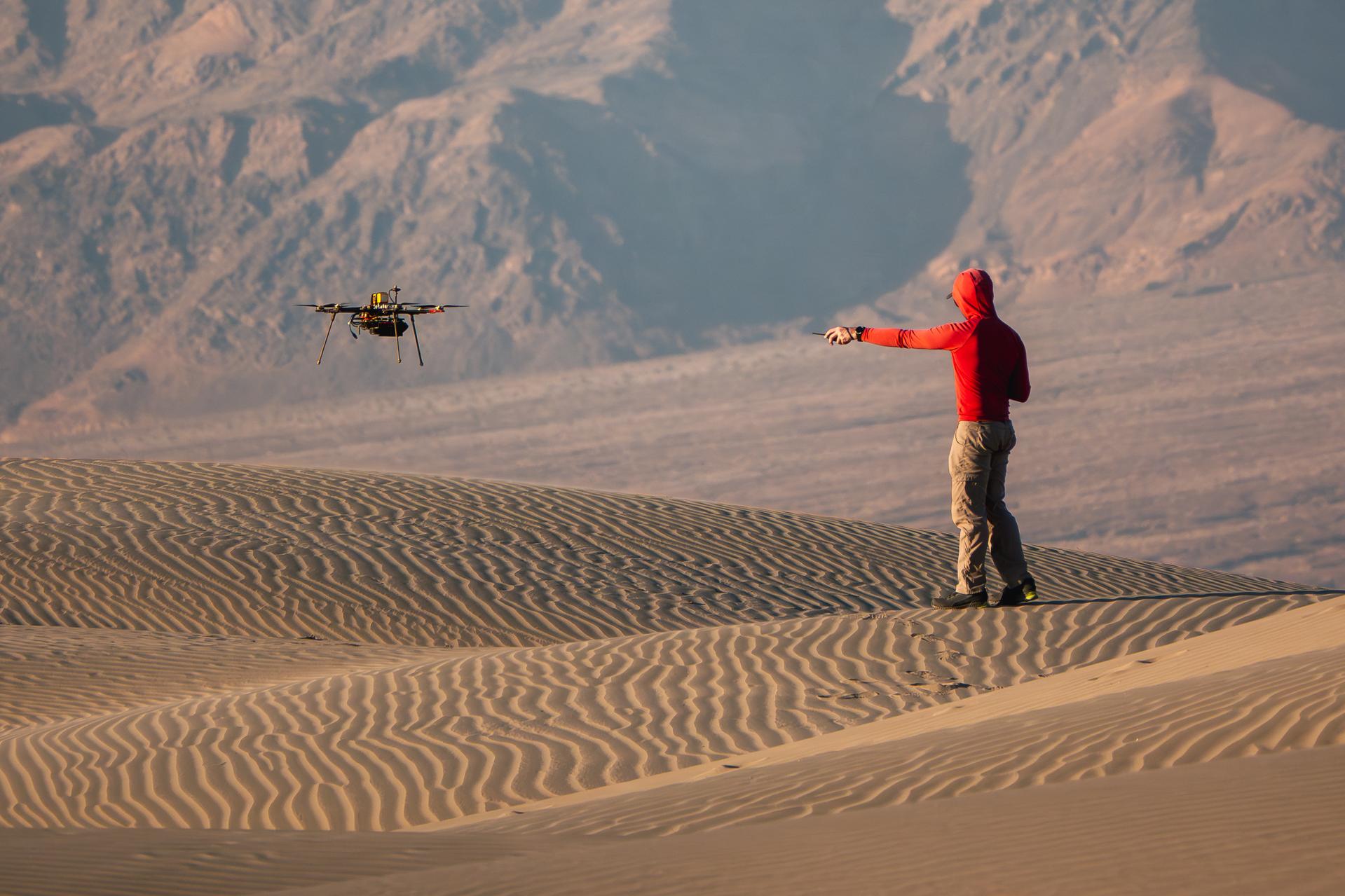

A researcher from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California monitors a drone as it flies over sand dunes in September 2025. This image was captured in Death Valley National Park during a larger test campaign to develop navigation software that would guide future rotorcraft on Mars. The work was among 25 projects funded by NASA’s Mars Exploration Program this past year to push the limits of future technologies. Sand dunes confused the navigation algorithm of the Ingenuity Mars helicopter during several of its last flights, including its 72nd and final flight on the Red Planet in January 2024. The navigation software in development would help future rotorcraft track the surface of especially bland, featureless terrain similar to the barren sand dunes seen in parts of Death Valley. Tests also included flights over a region of the park called Mars Hill, which is littered with rubbly volcanic rocks and has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, during preparations for the Viking lander missions.
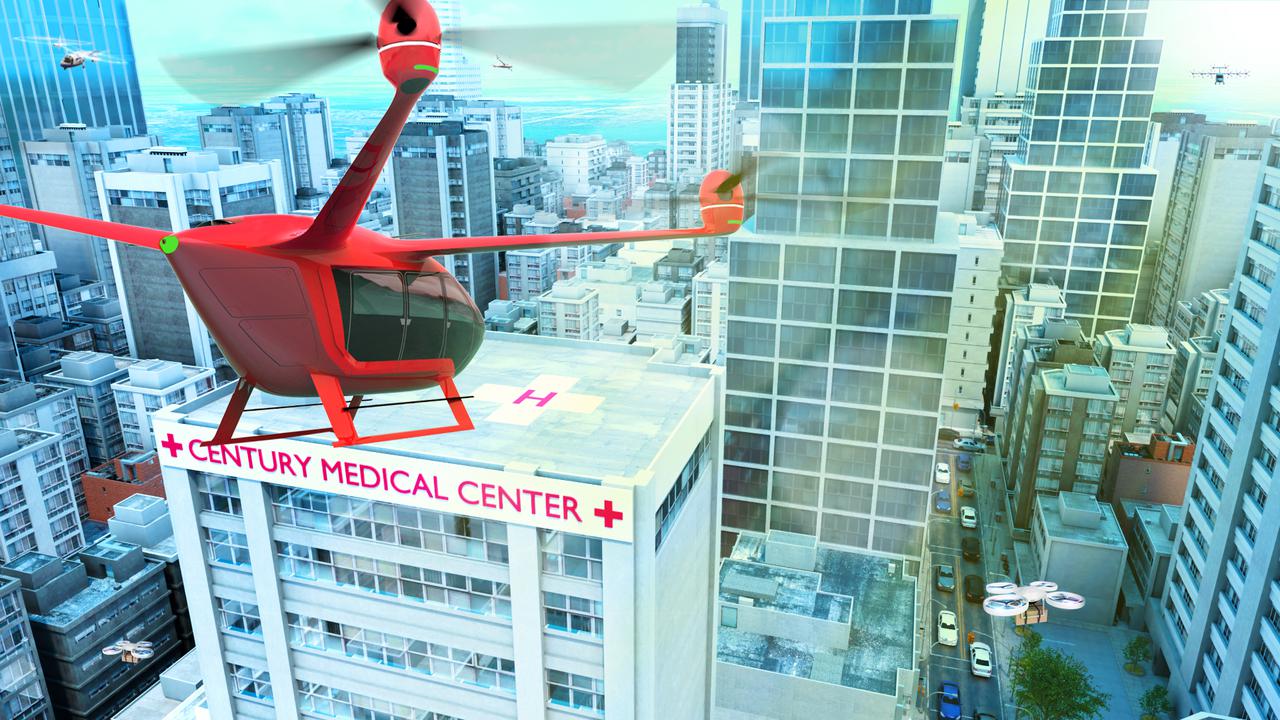

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility or AAM mission are working on different research initiatives to help make AAM a reality. AAM could be used in healthcare operations in the form of air taxi ambulances or medical supply delivery in the future. This concept graphic shows how a future AAM vehicle could aid in healthcare by carrying passengers to a hospital.
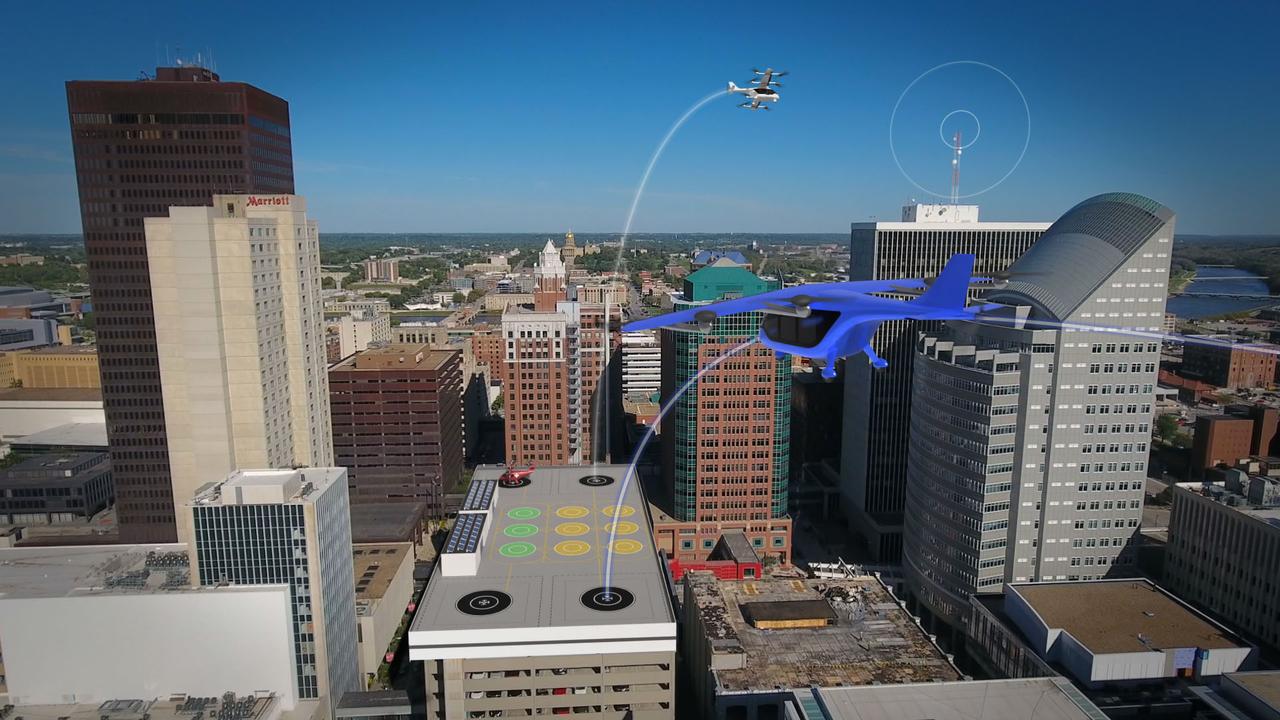

Several projects supporting NASA's Advanced Air Mobility, or AAM mission, are working on different elements to help make AAM a reality. The team is researching how the addition of AAM could cut traffic commutes, make travel more sustainable, and make road trips shorter. With the addition of AAM, we would be using another dimension in the sky for travel below traditional aircraft and above cars, buses, or trains below.
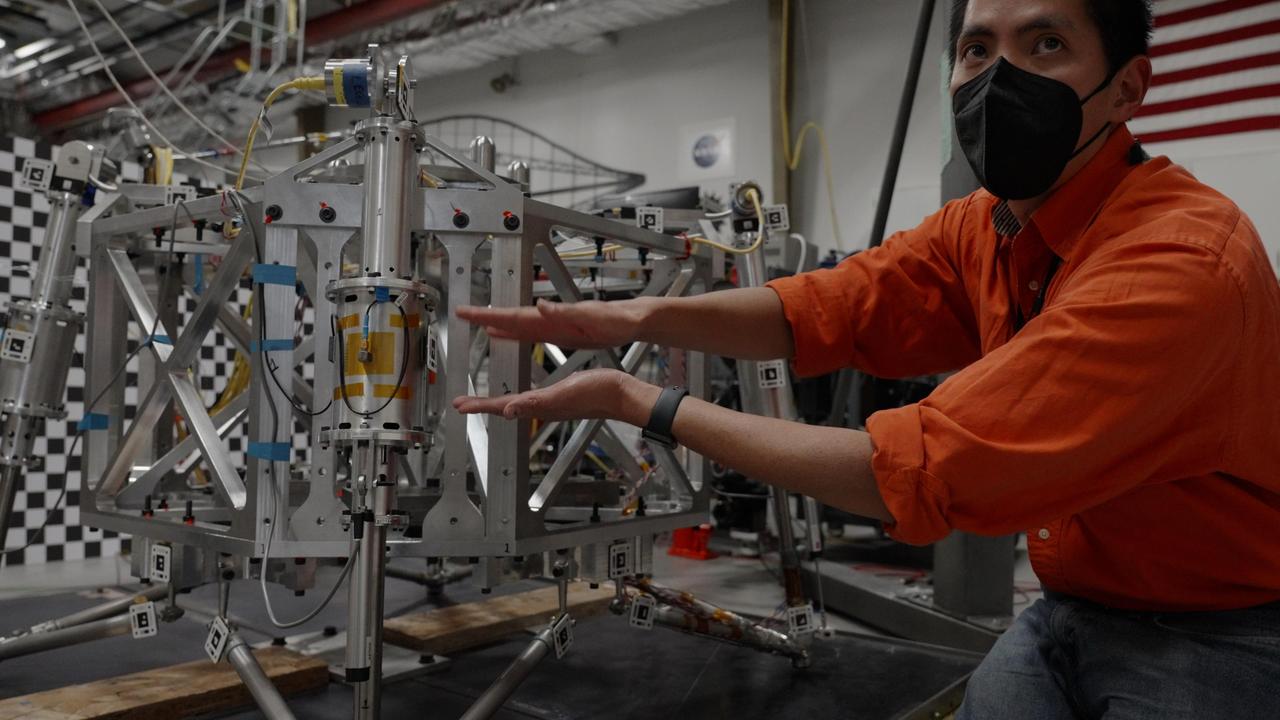

Engineer Abel Dizon explains how drop tests are conducted for a prototype lander being designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory for the planned Mars Sample Return campaign. The Sample Retrieval Lander, estimated to weigh as much as 5,016 pounds (2,275 kilograms), would be the heaviest spacecraft ever to land on the Red Planet. To study the physics involved in landing such a massive spacecraft, engineers have been testing a lander prototype that's about one-third the size it would be on Mars. Mars Sample Return will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by bringing scientifically selected samples to Earth for study using the most sophisticated instrumentation around the world. NASA's planned Mars Sample Return (MSR) campaign would fulfill one of the highest priority solar system exploration goals identified by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine in the past three decadal surveys. This strategic partnership with the ESA (European Space Agency) features the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch from the surface of another planet. The samples being collected by NASA's Perseverance rover during its exploration of an ancient river delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for ancient life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25822
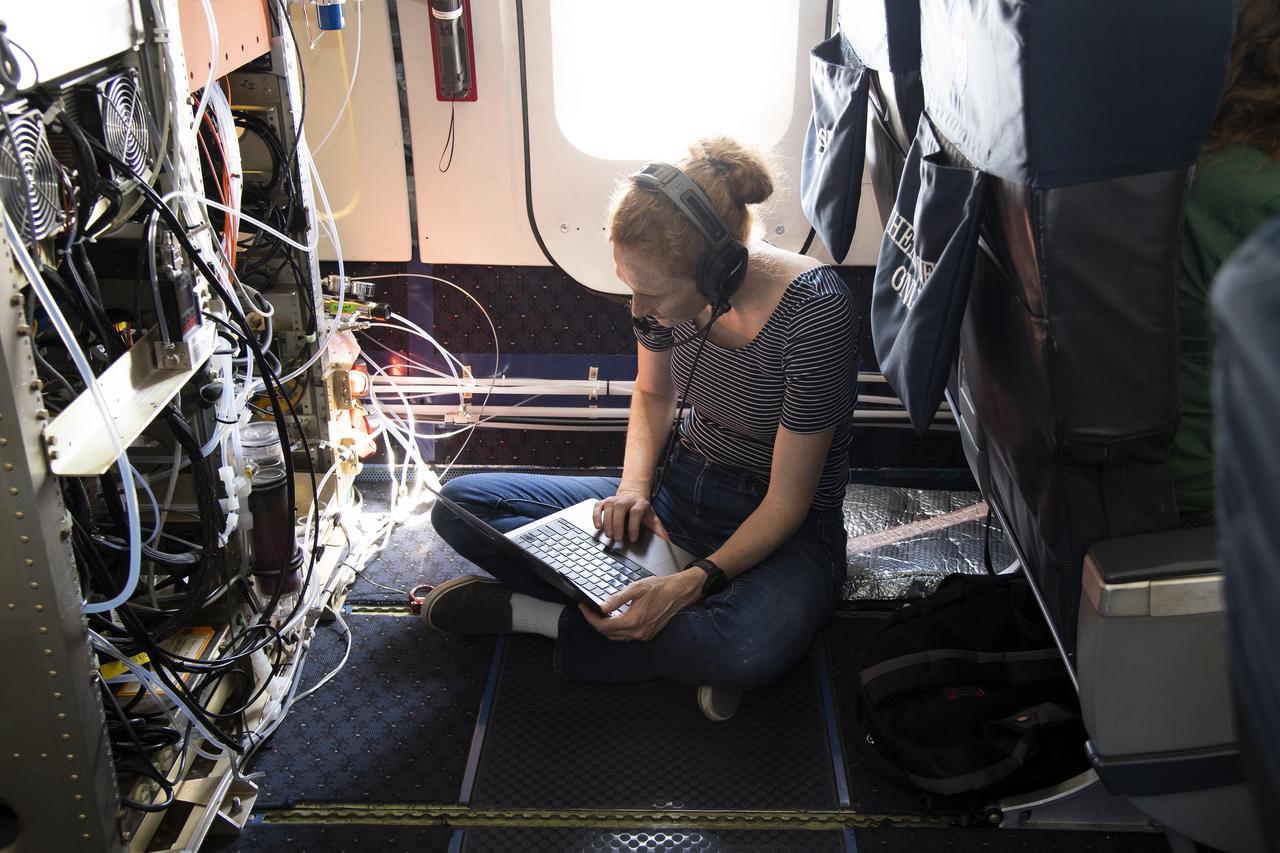

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
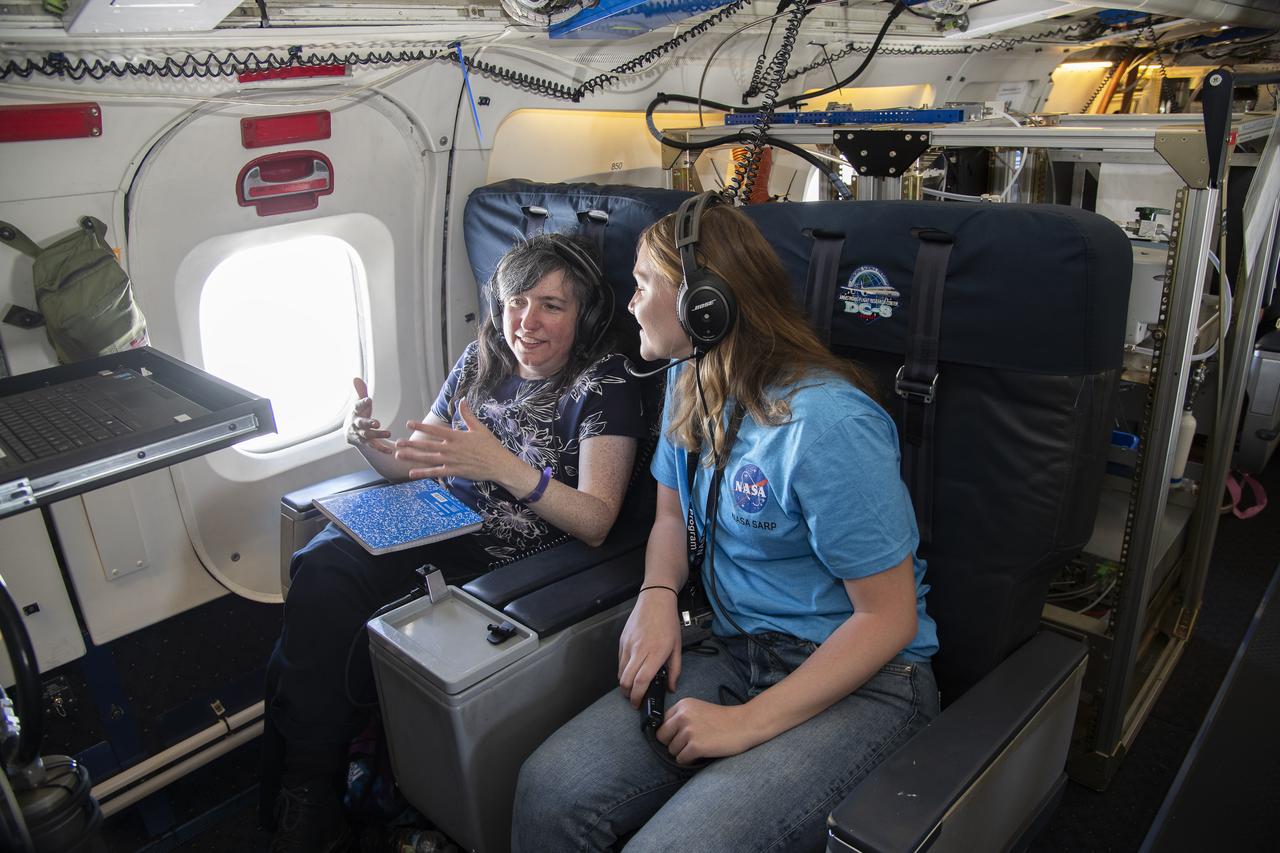

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
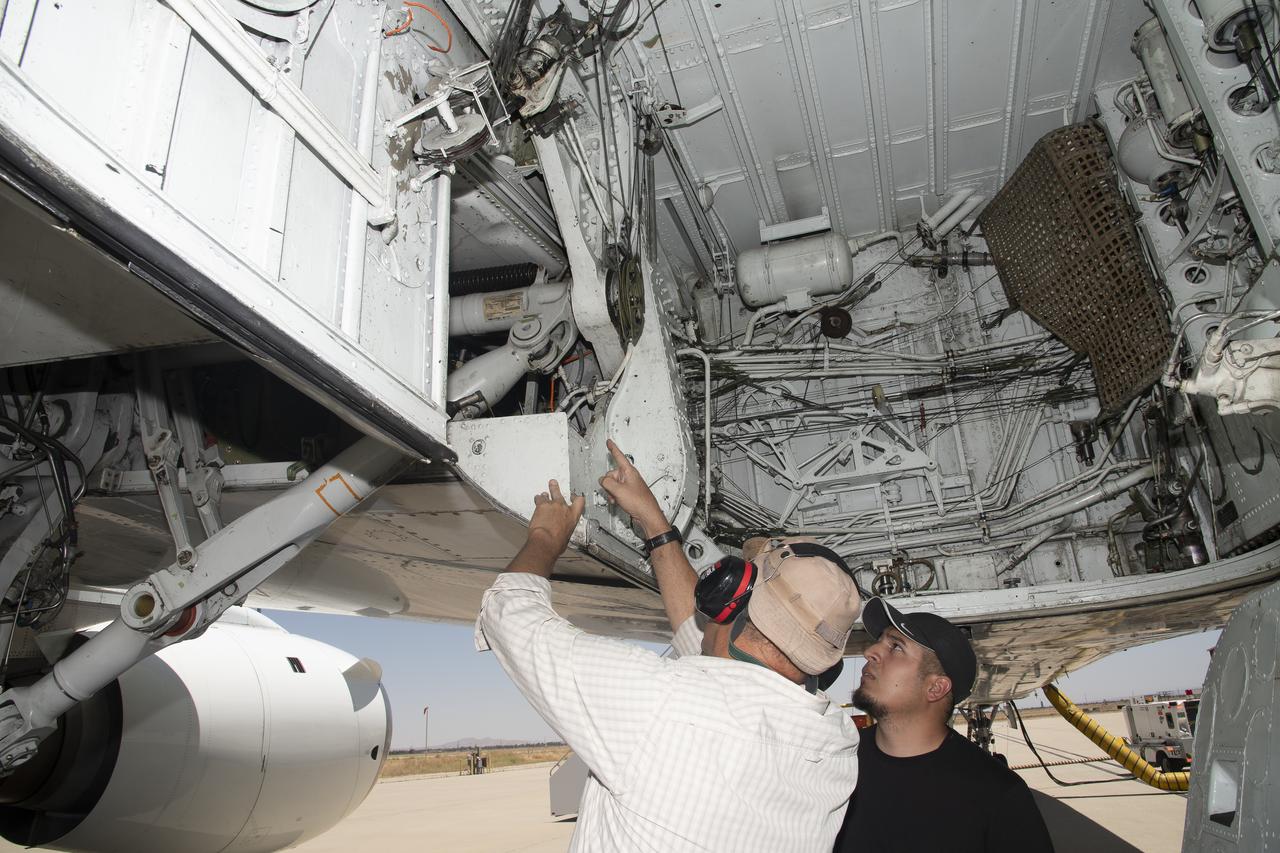

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
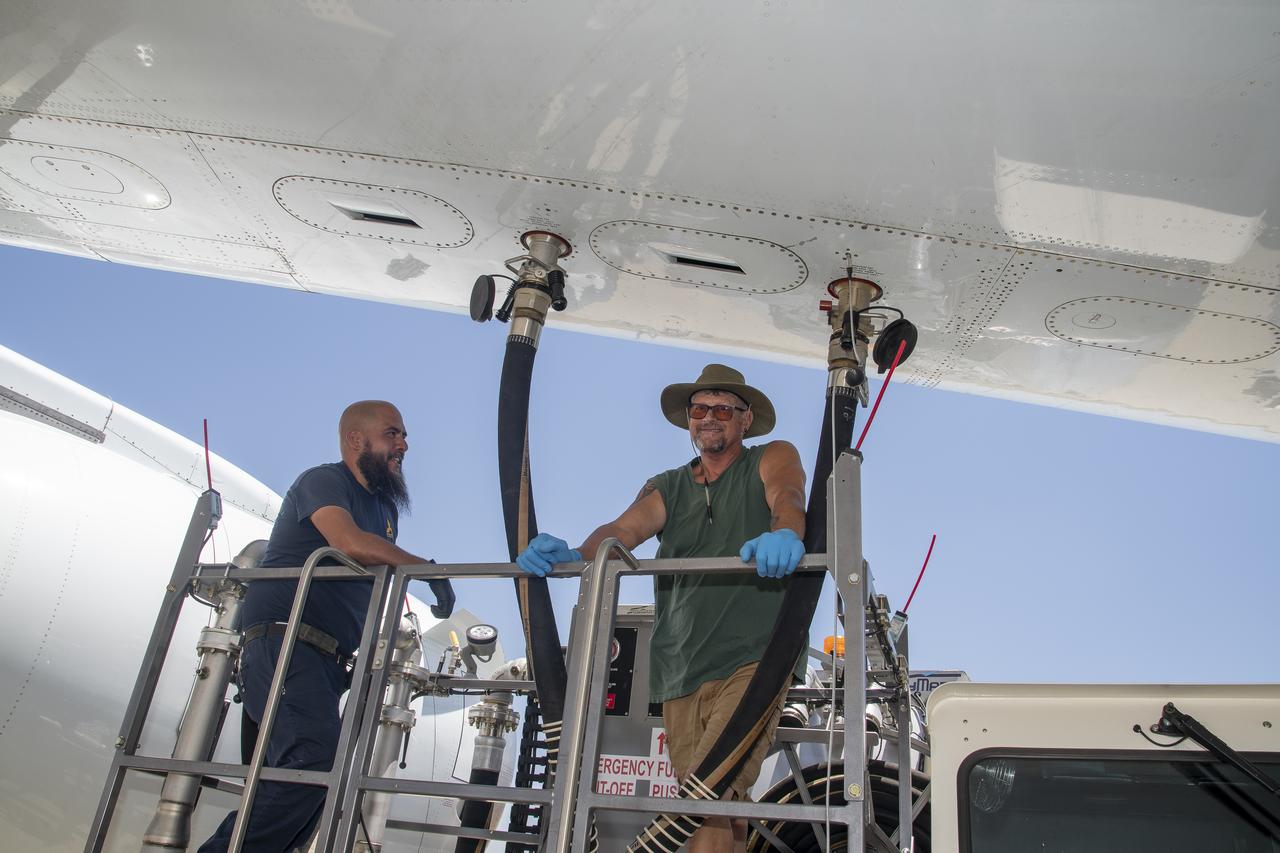

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory dropped this prototype to learn how a future Sample Return Lander could safely touch down on Mars. The lander would be part of the Mars Sample Return campaign. NASA's Mars Sample Return will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by returning scientifically-selected samples for study using the most sophisticated instruments around the world. The mission will fulfill a solar system exploration goal, a high priority since 1980 and the last two National Academy of Sciences Planetary Decadal Surveys. This strategic partnership of NASA and ESA (European Space Agency) will be the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch and return from the surface of another planet. These samples collected by Perseverance during its exploration of an ancient river-delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for life. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24766

This illustration depicts the Mars Earth Entry System for the Mars Sample Return campaign. The system would contain the orbiting sample inside a disk-shaped vehicle with a heat shield for safe entry through the Earth's atmosphere. NASA's Mars Sample Return (MSR) will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by returning scientifically-selected samples for study using the most sophisticated instruments around the world. The mission will fulfill a solar system exploration goal as identified by the National Academy of Sciences. This strategic partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA) will be the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch from the surface of another planet. These samples collected by Perseverance during its exploration of an ancient river-delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25336
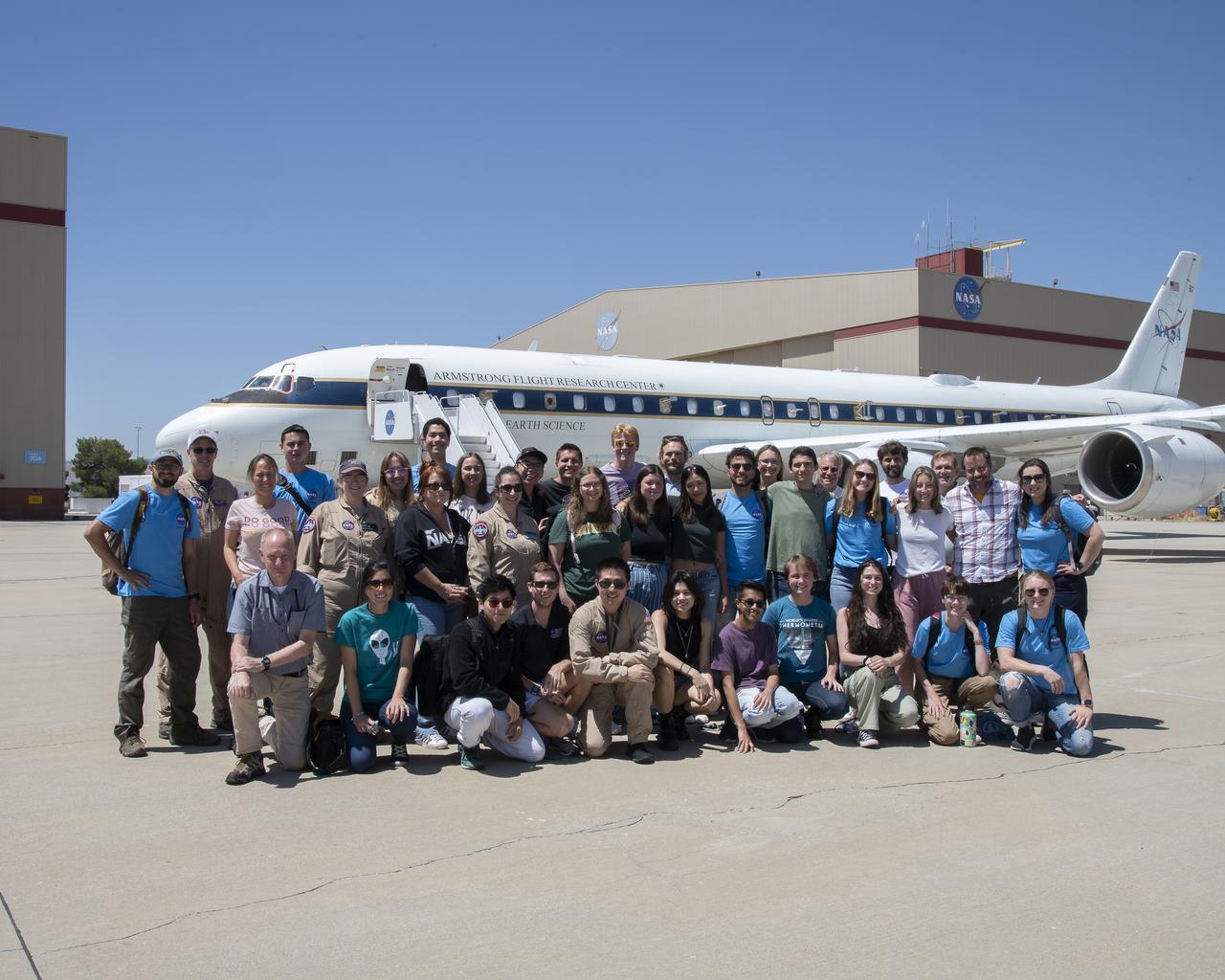

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
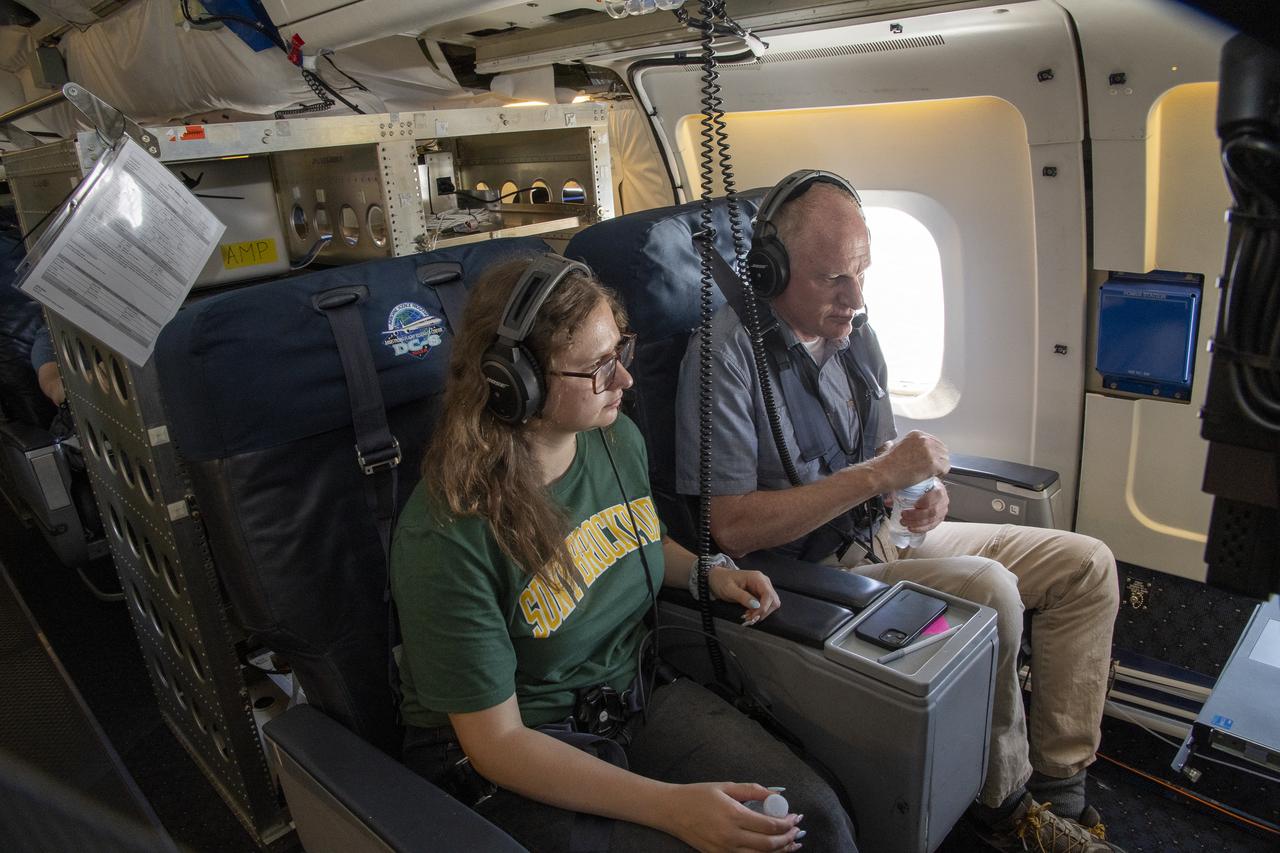

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
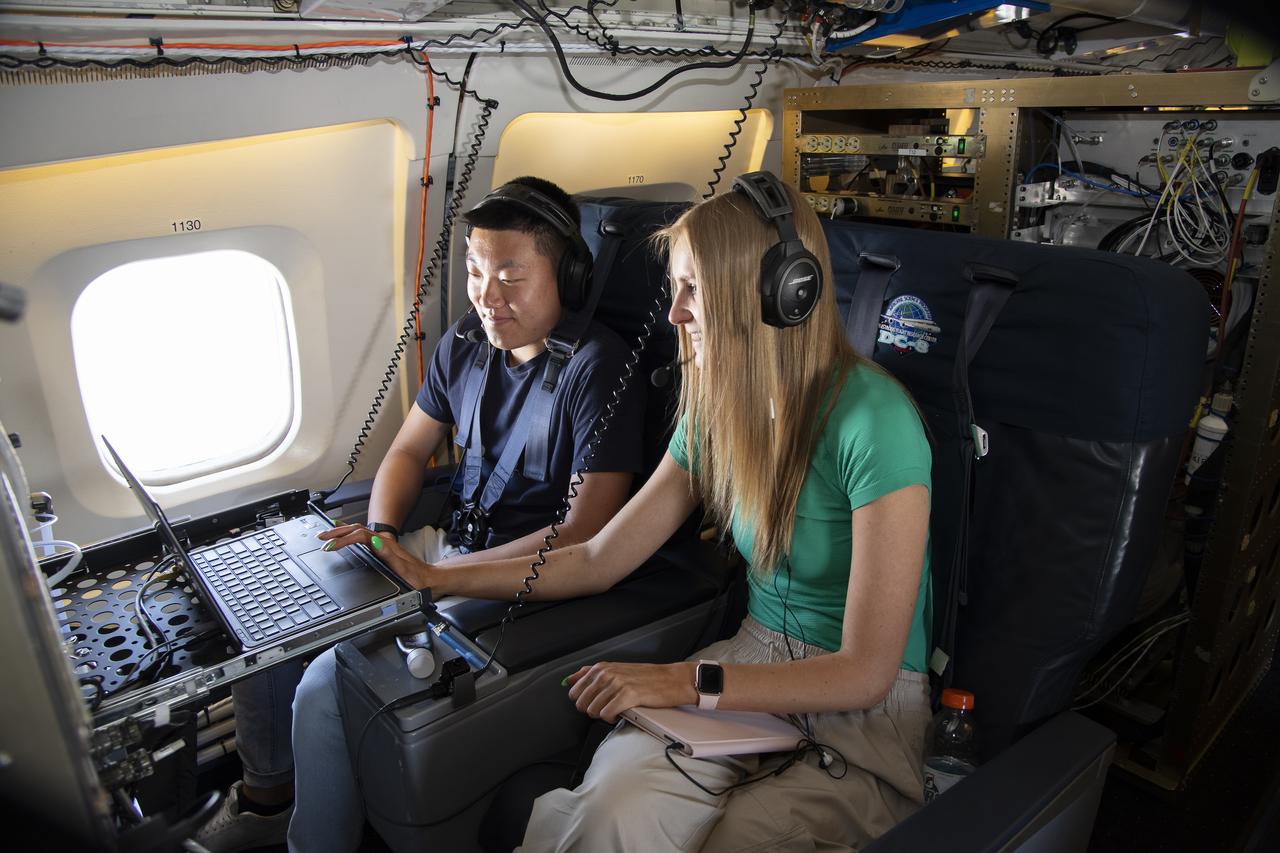

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
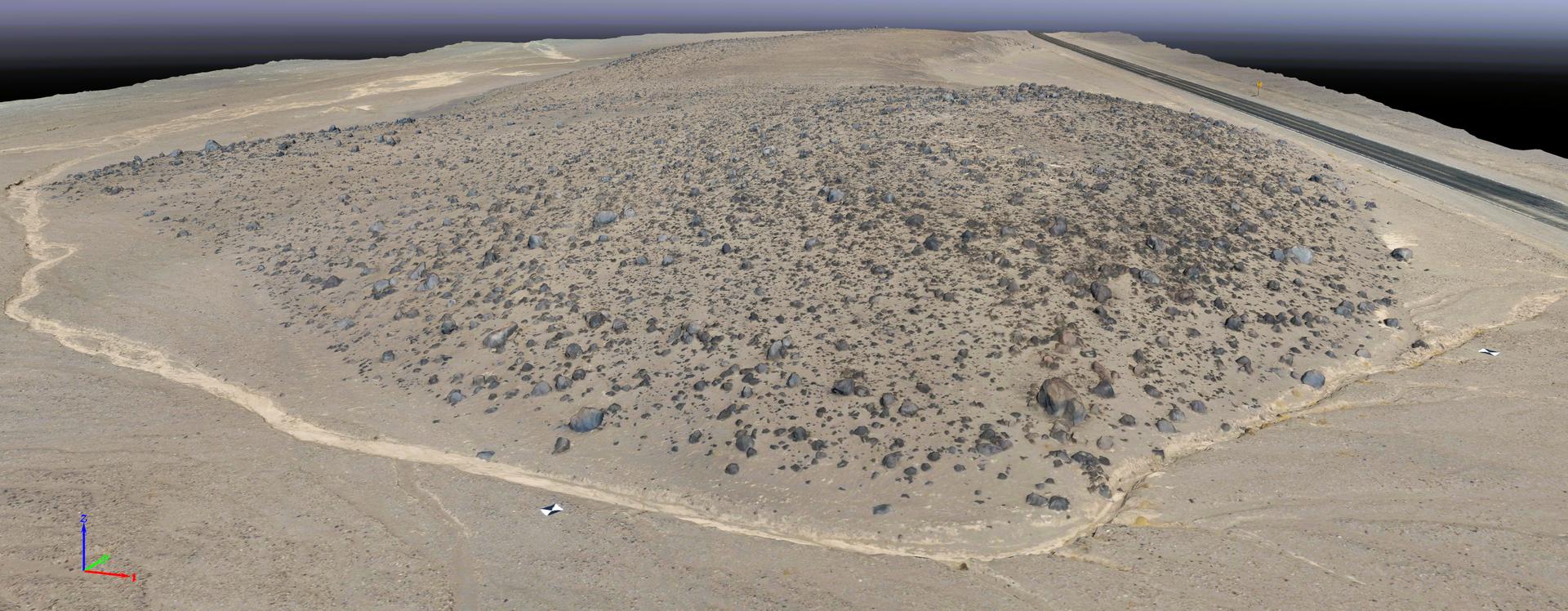

This rendering was created by research drones flying over Mars Hill, a region of Death Valley National Park that has been used by NASA’s Mars researchers since the 1970s, when the agency was preparing to land the twin Viking spacecraft. The hill’s rubbly, volcanic rock resembles the kind of inhospitable terrain that Mars rovers must navigate around and which posed a landing hazard for the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. In September 2025, researchers from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California flew research drones over Mars Hill as part of a test campaign to develop navigation software for future Mars rotorcraft. Being able to precisely land between rocks like those seen here is a critical capability to access similar Martian terrain in the future.
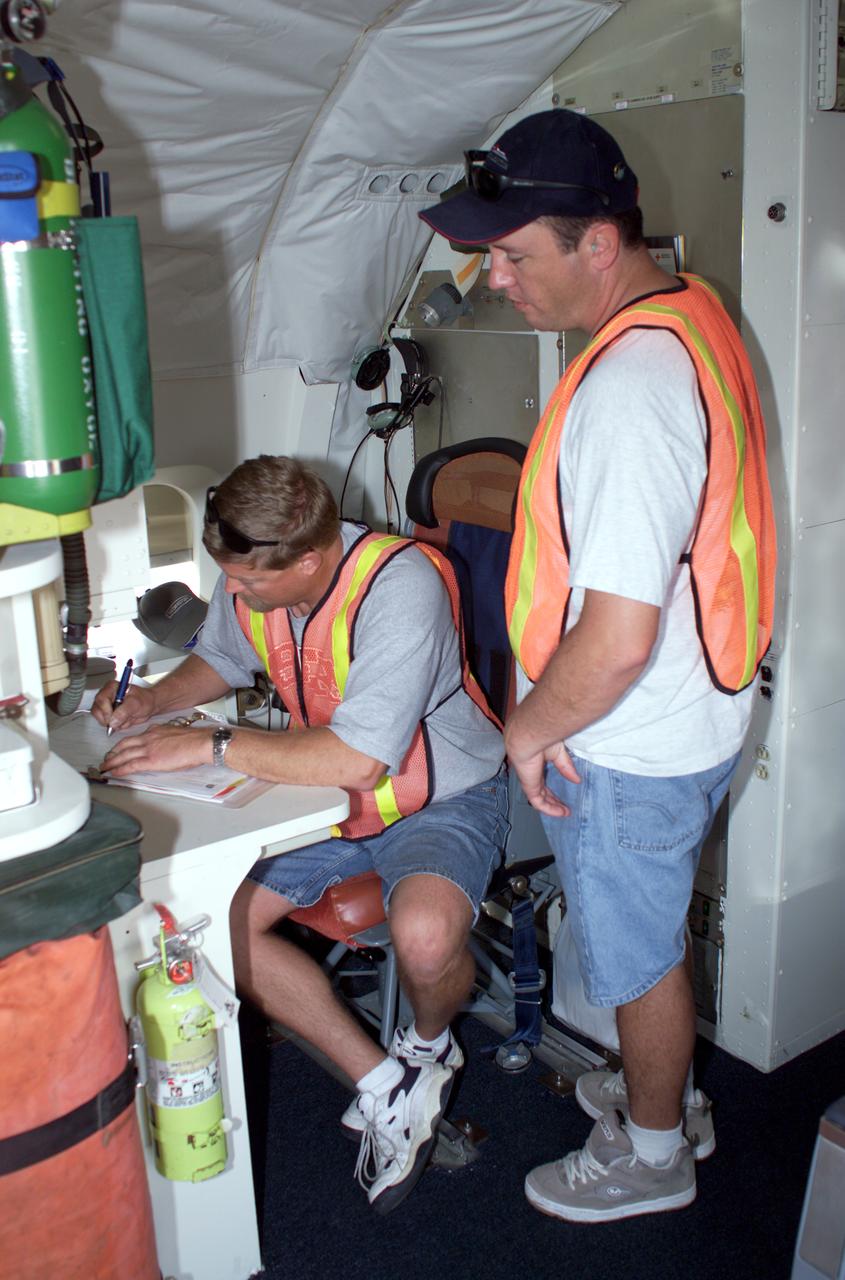

DC-8 Quality Inspector Scott Silver signs documents while Acting Crew Chief Mike Bereda looks on prior to a DC-8 AirSAR flight in Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
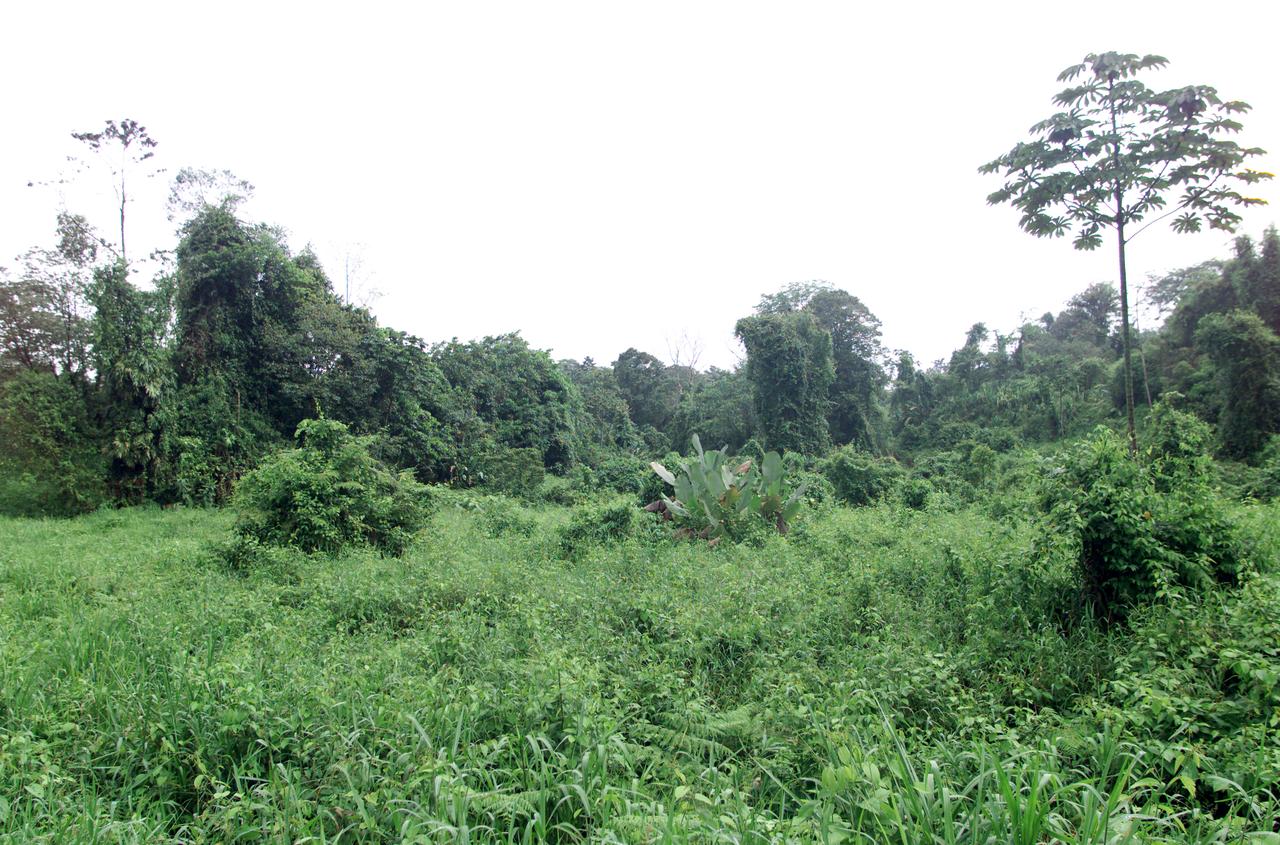

Dense rain forest in the La Selva region of Costa Rica. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
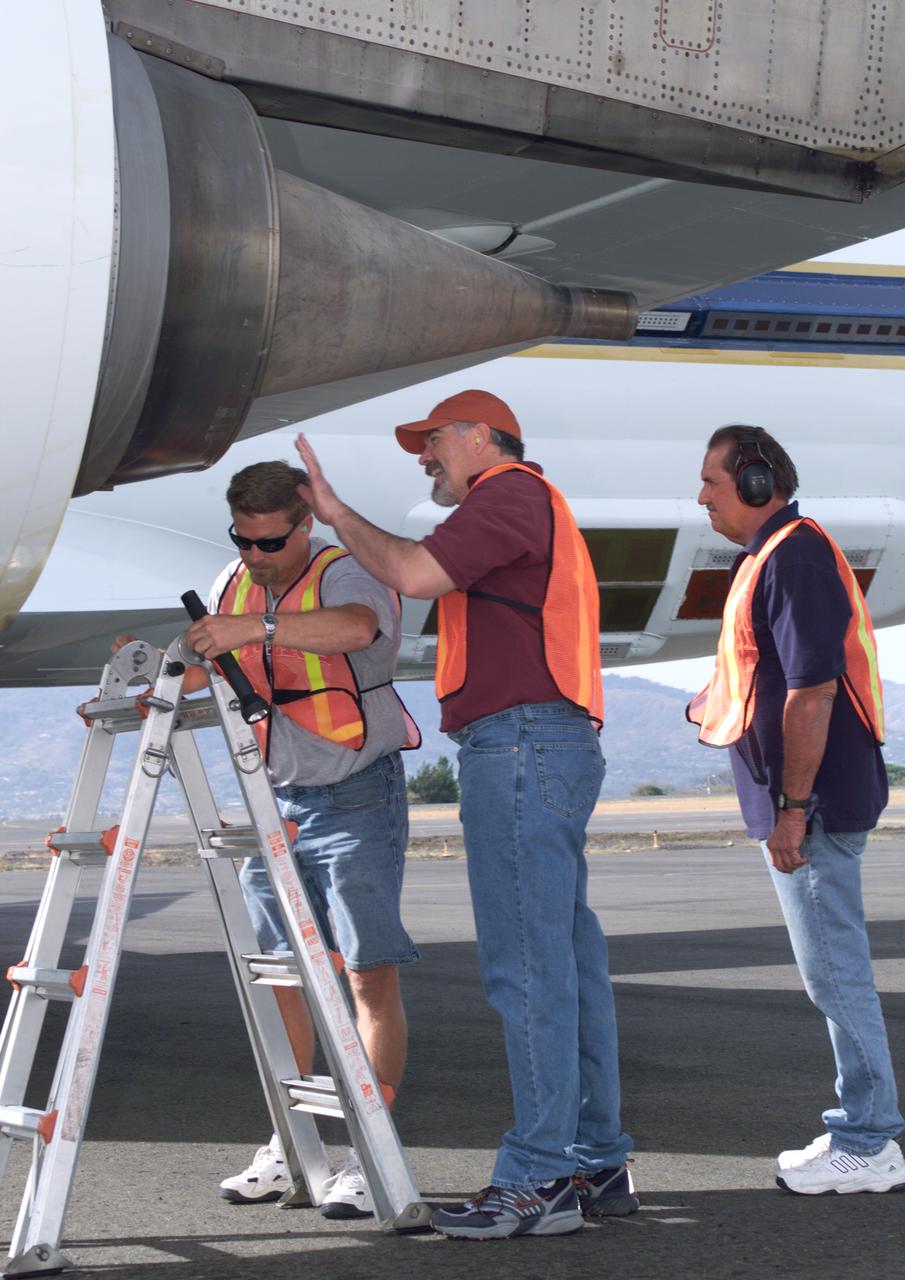

NASA Dryden DC-8 maintenance crew members inspect the aircraft prior to take-off. L-R; Scott Silver, Paul Ristrim and Mike Lakowski. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.

NASA image captured December 25, 2011 A NASA scientific balloon awaits launch in McMurdo, Antarctica. The balloon, carrying Indiana University's Cosmic Ray Electron Synchrotron Telescope (CREST), was launched on December 25. After a circum-navigational flight around the South Pole, the payload landed on January 5. The CREST payload is one of two scheduled as part of this seasons' annual NASA Antarctic balloon Campaign which is conducted in cooperation with the National Science Foundation's Office of Polar Programs. The campaign's second payload is the University of Arizona's Stratospheric Terahertz Observatory (STO). You can follow the flights at the Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility's web site at <a href="http://www.csbf.nasa.gov/antarctica/ice.htm" rel="nofollow">www.csbf.nasa.gov/antarctica/ice.htm</a> Credit: NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
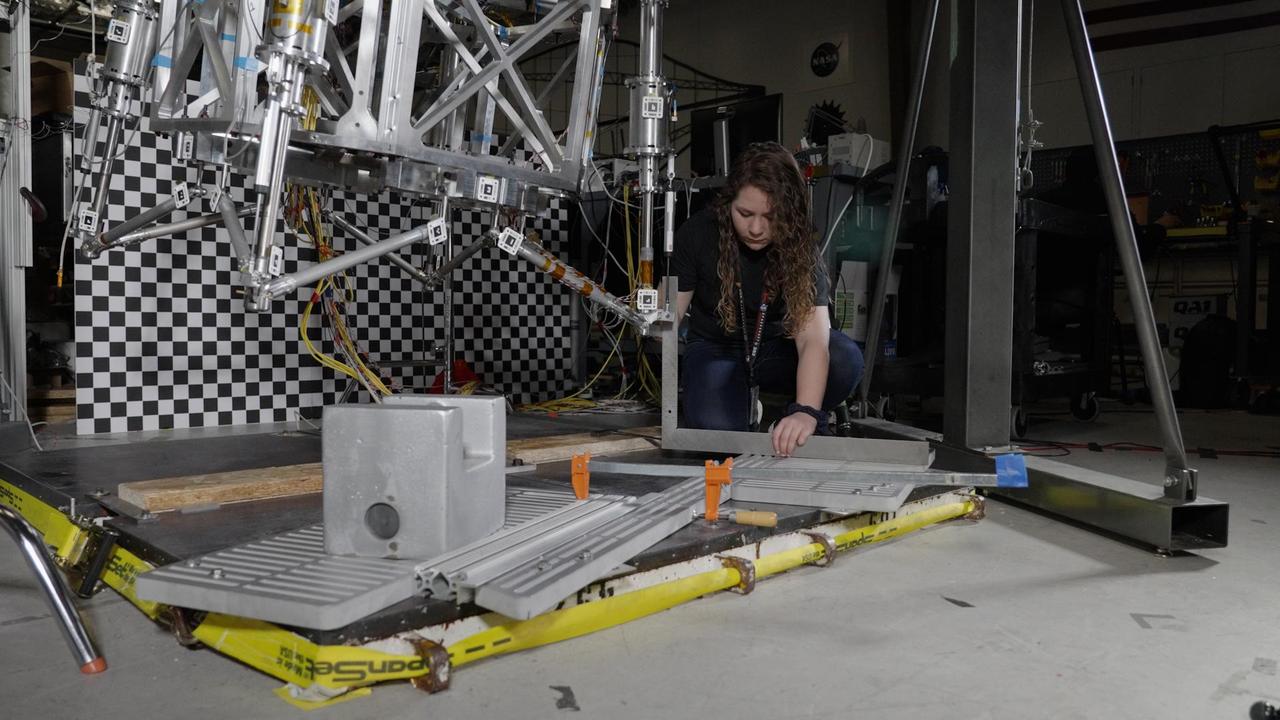

Morgan Montalvo, an engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, sets guardrails on the floor below a prototype of the lander being designed for the agency's Mars Sample Return campaign. These guardrails were used to test a scenario where the lander would "stub a toe" against a rock while touching down on Mars. The Sample Retrieval Lander, estimated to weigh as much as 5,016 pounds (2,275 kilograms), would be the heaviest spacecraft ever to land on the Red Planet. To study the physics involved in landing such a massive spacecraft, engineers have been testing a lander prototype that's about one-third the size it would be on Mars. Mars Sample Return will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by bringing scientifically selected samples to Earth for study using the most sophisticated instrumentation around the world. NASA's planned Mars Sample Return (MSR) campaign would fulfill one of the highest priority solar system exploration goals identified by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine in the past three decadal surveys. This strategic partnership with the ESA (European Space Agency) features the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch from the surface of another planet. The samples being collected by NASA's Perseverance rover during its exploration of an ancient river delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for ancient life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25823
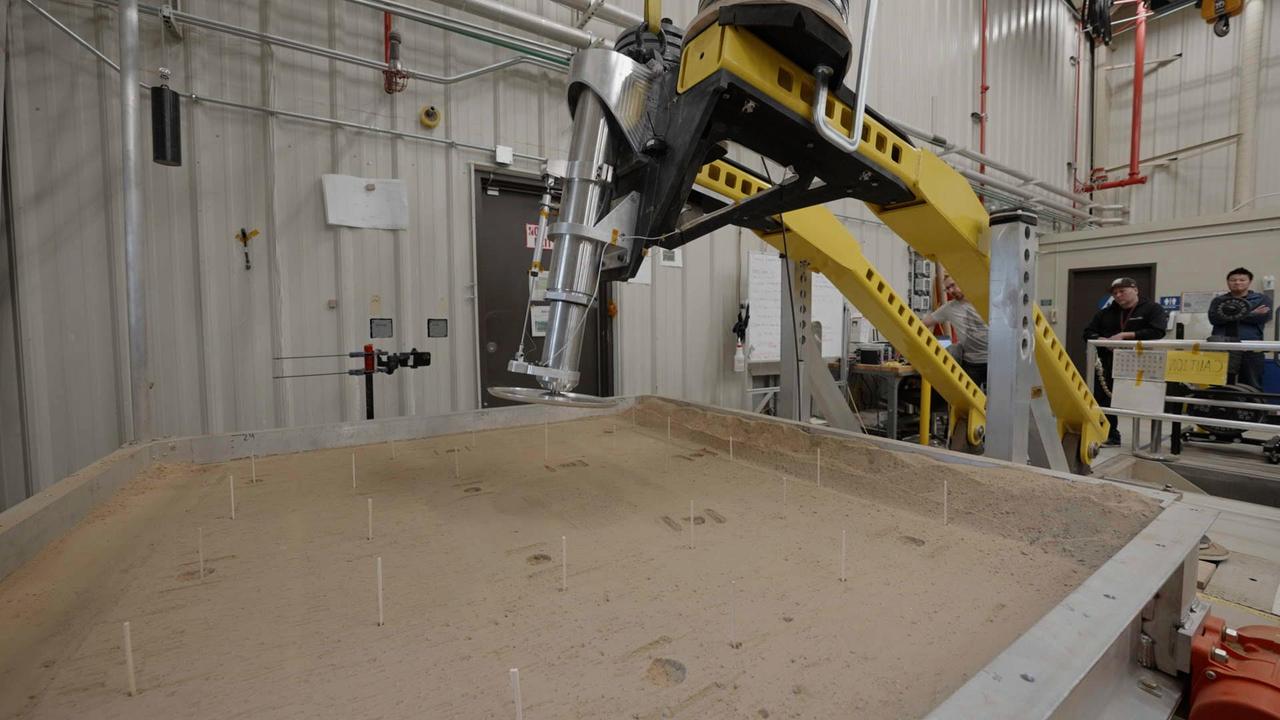

This setup is being used at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to test a 16-inch-diameter (40-centimeter-diameter) footpad for a future Mars lander. The footpad was plunged into a test bed filled with 10,000 pounds (4,536 kilograms) of simulated Martian soil in order to see how deep it would sink – too far, and the lander's belly could scrape against the ground during touchdown, damaging it. The Sample Retrieval Lander, which would be central to NASA's Mars Sample Return campaign, is estimated to weigh as much as 5,016 pounds (2,275 kilograms). It would be the heaviest spacecraft ever to land on the Red Planet. In order to understand how energy would be absorbed during the landing of such a massive spacecraft, JPL engineers have been conducting drop tests of a full-size footpad. Mars Sample Return will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by bringing scientifically selected samples to Earth for study using the most sophisticated instrumentation around the world. NASA's planned Mars Sample Return (MSR) campaign would fulfill one of the highest priority solar system exploration goals identified by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine in the past three decadal surveys. This strategic partnership with the ESA (European Space Agency) features the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch from the surface of another planet. The samples being collected by NASA's Perseverance rover during its exploration of an ancient river delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for ancient life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25824

NASA image captured December 25, 2011 A NASA scientific balloon awaits launch in McMurdo, Antarctica. The balloon, carrying Indiana University's Cosmic Ray Electron Synchrotron Telescope (CREST), was launched on December 25. After a circum-navigational flight around the South Pole, the payload landed on January 5. The CREST payload is one of two scheduled as part of this seasons' annual NASA Antarctic balloon Campaign which is conducted in cooperation with the National Science Foundation's Office of Polar Programs. The campaign's second payload is the University of Arizona's Stratospheric Terahertz Observatory (STO). You can follow the flights at the Columbia Scientific Balloon Facility's web site at <a href="http://www.csbf.nasa.gov/antarctica/ice.htm" rel="nofollow">www.csbf.nasa.gov/antarctica/ice.htm</a> Credit: NASA <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Patrick DeGrosse and fellow engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory review data from a recent test of a full-size footpad for a future Mars lander. The 16-inch-diameter (40-centimeter-diameter) footpad was plunged into a test bed filled with 10,000 pounds (4,536 kilograms) of simulated Martian soil in order to see how deep it would sink – too far, and the lander's belly could scrape against the ground during touchdown, damaging it. The Sample Retrieval Lander, which would be central to NASA's Mars Sample Return campaign, is estimated to weigh as much as 5,016 pounds (2,275 kilograms). It would be the heaviest spacecraft ever to land on the Red Planet. In order to understand how energy would be absorbed during the landing of such a massive spacecraft, JPL engineers have been conducting these footpad drop tests. Mars Sample Return will revolutionize our understanding of Mars by bringing scientifically selected samples to Earth for study using the most sophisticated instrumentation around the world. NASA's planned Mars Sample Return (MSR) campaign would fulfill one of the highest priority solar system exploration goals identified by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine in the past three decadal surveys. This strategic partnership with the ESA (European Space Agency) features the first mission to return samples from another planet, including the first launch from the surface of another planet. The samples being collected by NASA's Perseverance rover during its exploration of an ancient river delta are thought to be the best opportunity to reveal the early evolution of Mars, including the potential for ancient life. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25826
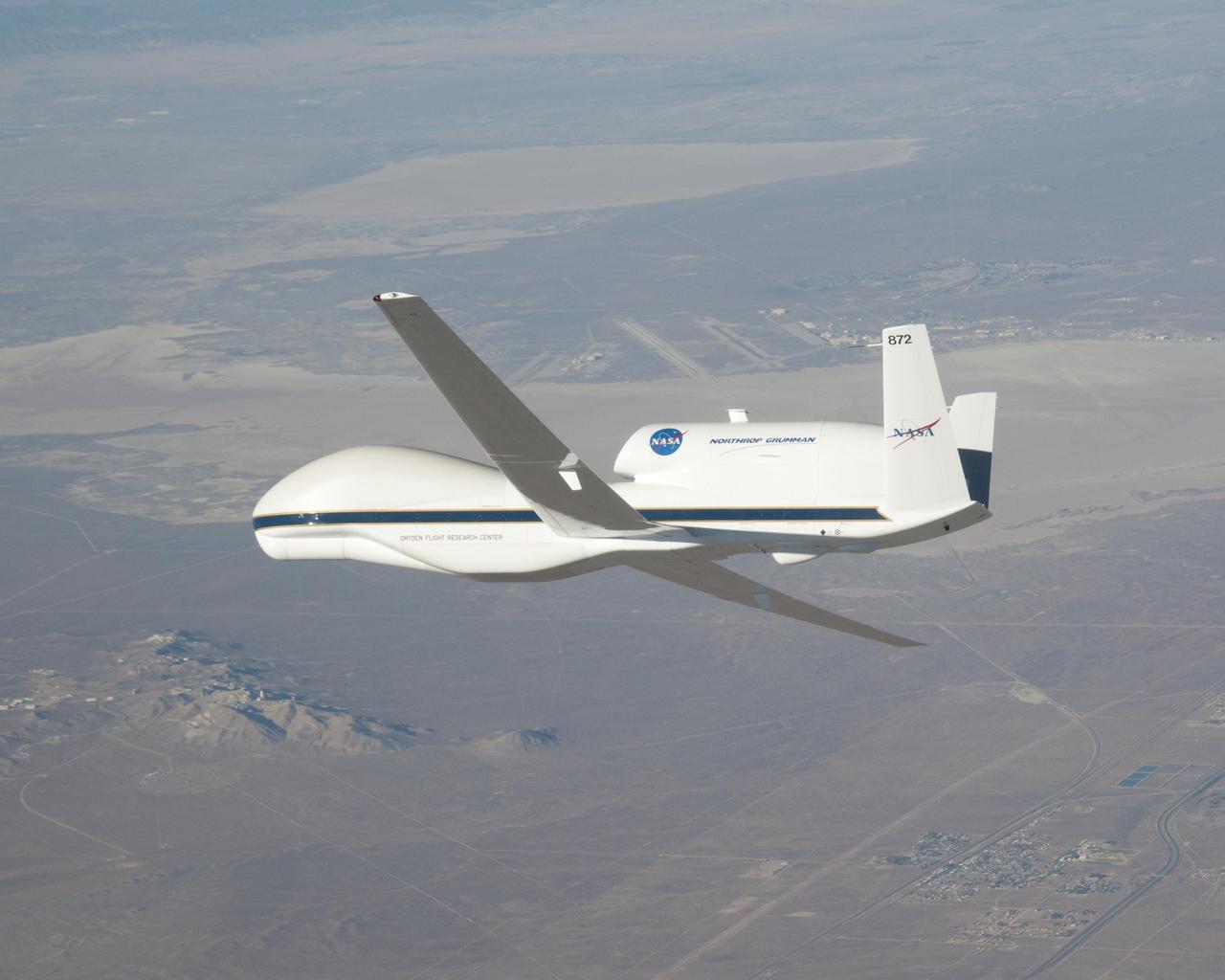

NASA image acquired October 23, 2009. At NASA’s Dryden Research Center in California, a group of engineers, scientists, and aviation technicians have set up camp in a noisy, chilly hangar on Edwards Air Force base. For the past two weeks, they have been working to mount equipment—from HD video cameras to ozone sensors—onto NASA’s Global Hawk, a remote-controlled airplane that can fly for up to 30 hours at altitudes up to 65,000 feet. The team is gearing up for the Global Hawk Pacific campaign, a series of four or five scientific research flights that will take the Global Hawk over the Pacific Ocean and Arctic regions. The 44-foot-long aircraft, with its comically large nose and 116-foot wingspan is pictured in the photograph above, banking for landing over Rogers Dry Lake in California at the end of a test flight on October 23, 2009. The long wings carry the plane’s fuel, and the bulbous nose is one of the payload bays, which house the science instruments. For the Global Hawk Pacific campaign, the robotic aircraft will carry ten science instruments that will sample the chemical composition of air in the troposphere (the atmospheric layer closest to Earth) and the stratosphere (the layer above the troposphere). The mission will also observe clouds and aerosol particles in the troposphere. The primary purpose of the mission is to collect observations that can be used to check the accuracy of simultaneous observations collected by NASA’s Aura satellite. Co-lead scientist Paul Newman from Goddard Space Flight Center is writing about the ground-breaking mission for the Earth Observatory’s Notes from the Field blog. NASA Photograph by Carla Thomas. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43291" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=43291</a>

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Logos affixed to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California represent the principal players in the launch campaign underway at the pad. From the top are the logos for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, or NASA the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2 and the United Launch Alliance, or ULA. Launch of NASA's OCO-2 satellite aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
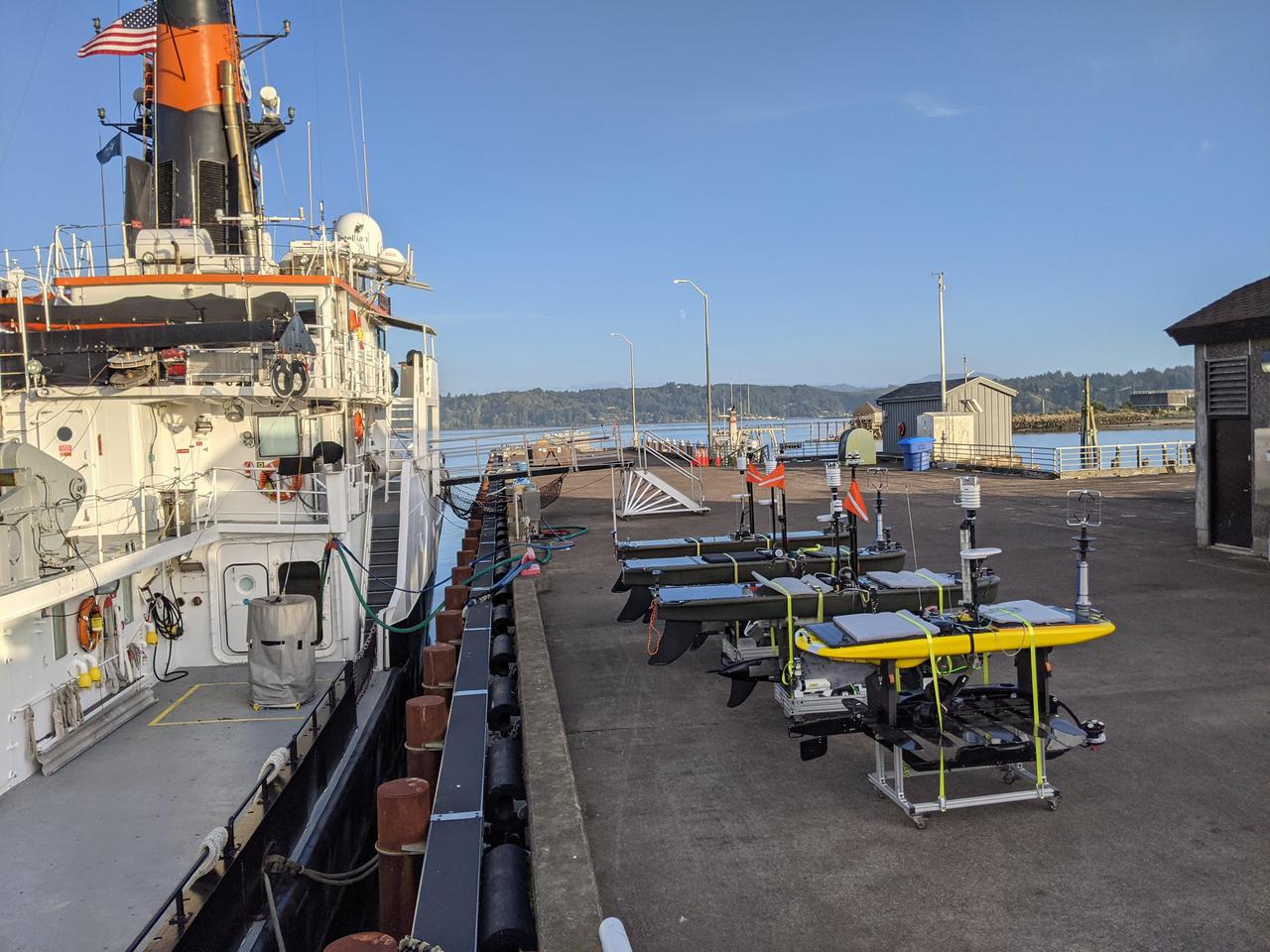

As part of NASA's Sub-Mesoscale Ocean Dynamics Experiment (S-MODE) pilot campaign in 2021, the research vessel Oceanus, owned by the National Science Foundation, set sail to an area 110 nautical miles off the coast of San Francisco, accompanied by a fleet of several types of autonomous marine research vessels. The wave gliders pictured here on the dock carry a variety of sensors and instruments. Because they're autonomous, their use reduces the risk posed to human researchers who could be exposed to large storms at sea. S-MODE is a NASA Earth mission to use newly developed in-situ and remote-sensing techniques to look at small-scale ocean whirlpools, eddies, and currents. The observations could help scientists better understand how these dynamics drive the give-and-take of material and energy between the ocean and atmosphere and, ultimately, help shape Earth's climate. More information about S-MODE is at https://espo.nasa.gov/s-mode/content/S-MODE https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25524
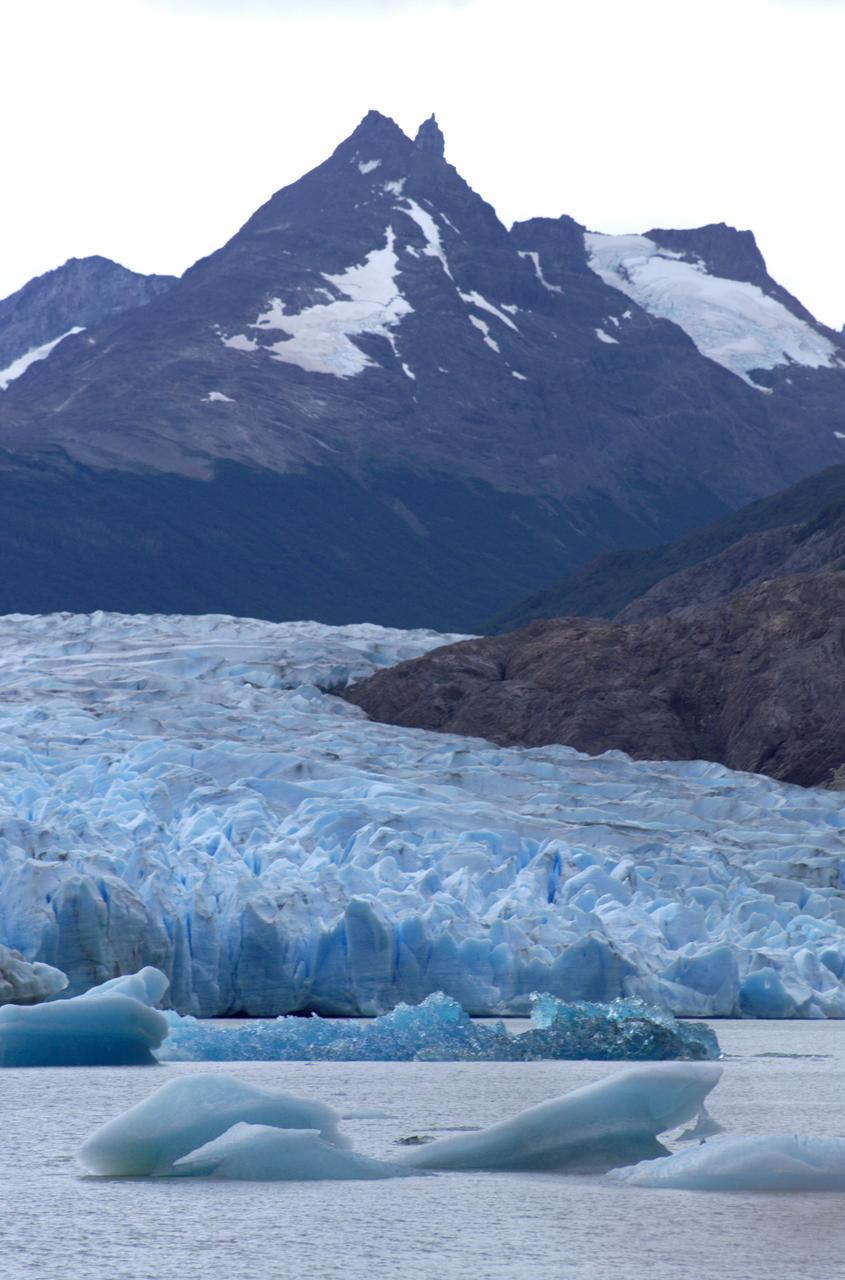

Glacier Grey in front of the Cuernos del Paine mountains, photographed from Lago Grey (Grey Lake) during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
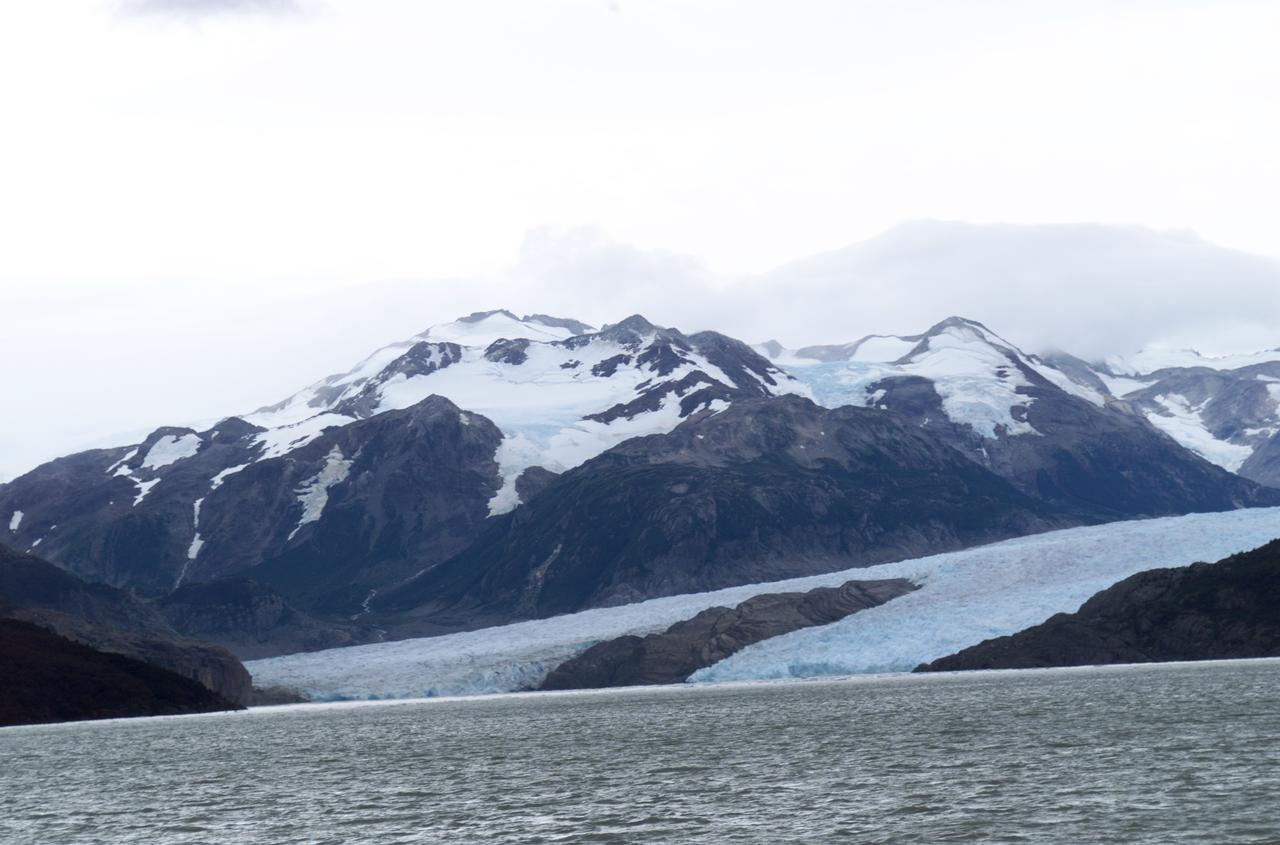

Glacier Grey view from Lago Grey (Grey Lake), photographed during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign in Chile. Land visible in this photo was covered by glacier just 6 years earlier. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.

View of Glacier Grey from Lago Grey (Grey Lake), with the Cuernos del Paine mountains in the background, seen during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
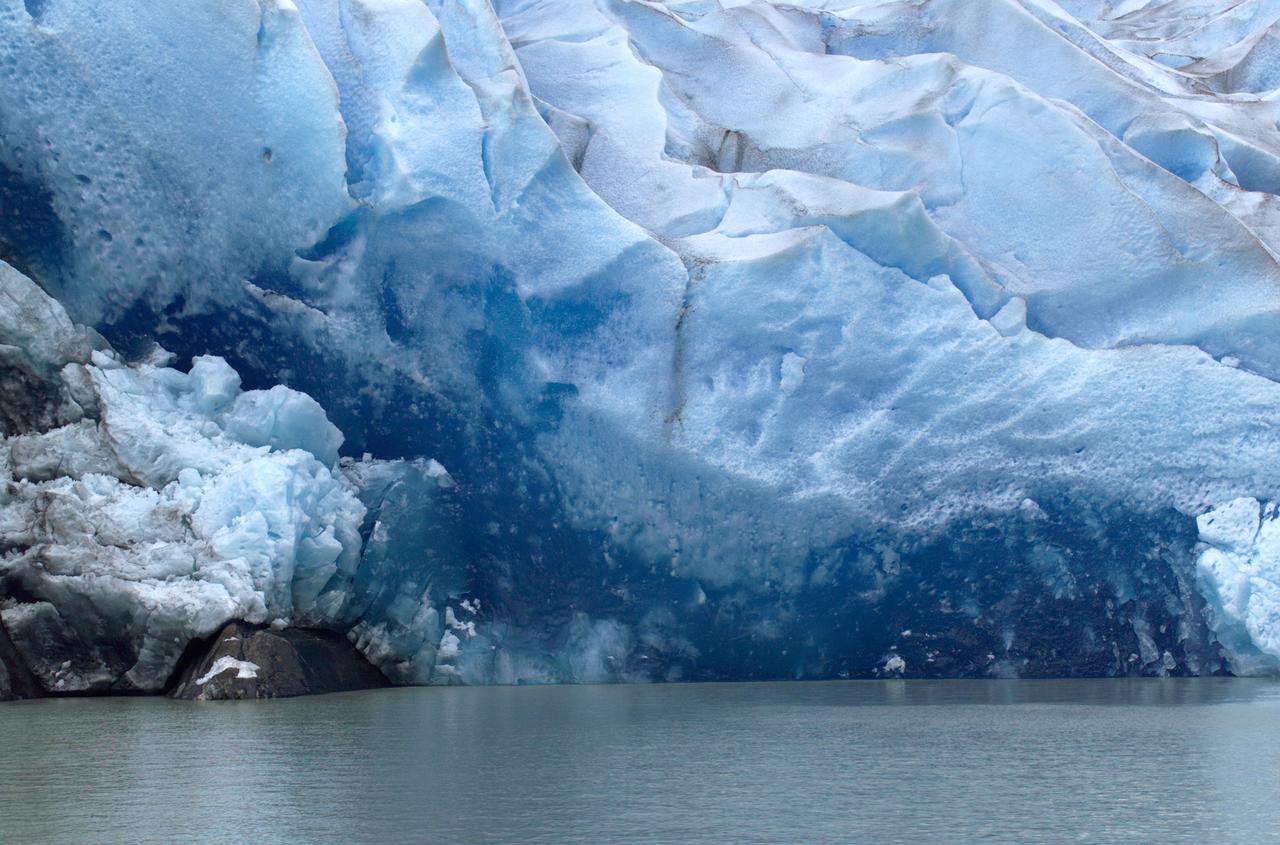

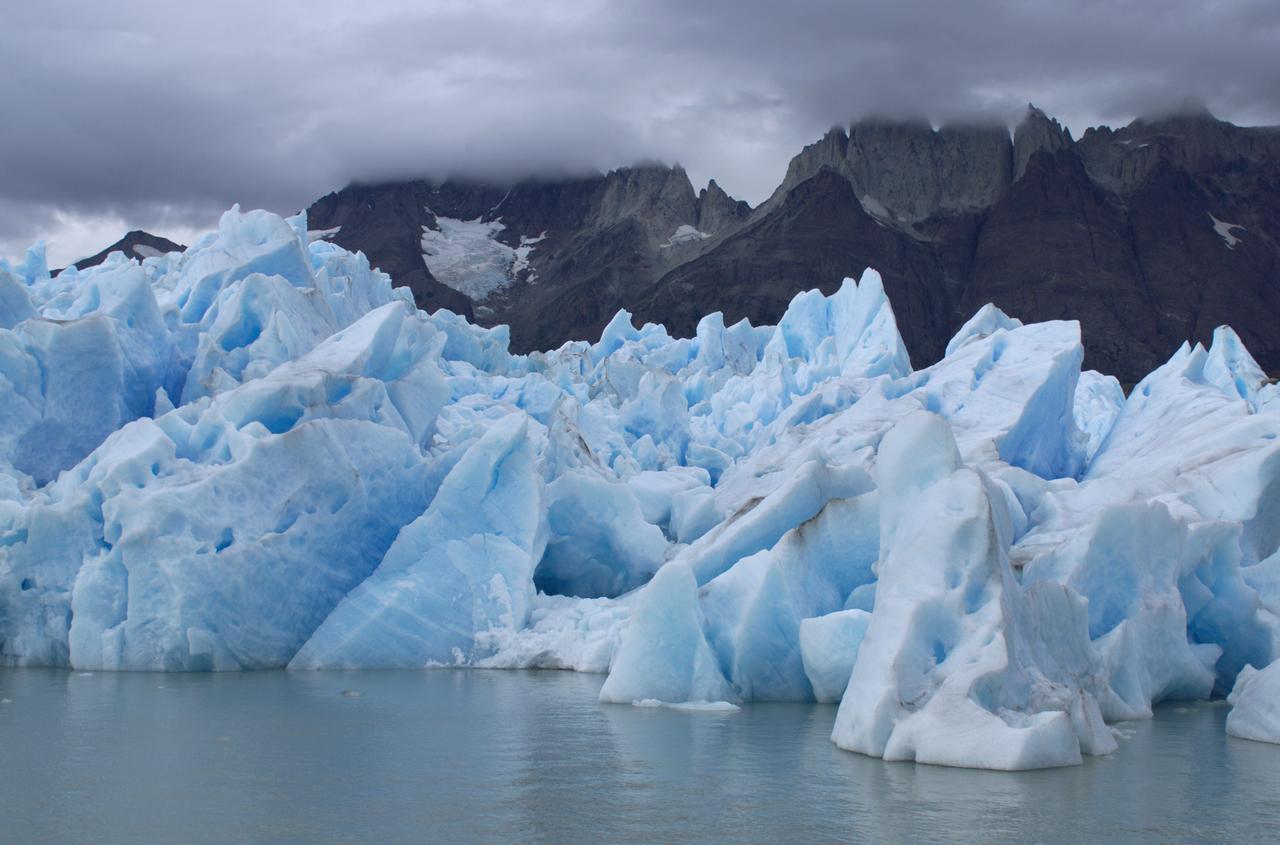
Close-up view of Grey Glacier from Lago Grey (Grey Lake), taken during NASA's AirSAR 2004 campaign in Chile. AirSAR 2004 is a three-week expedition in Central and South America by an international team of scientists that is using an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR), located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world are combining ground research with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. Founded in 1959, Torres del Paine National Park encompasses 450,000 acres in the Patagonia region of Chile. This region is being studied by NASA using a DC-8 equipped with an Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) developed by scientists from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. This is a very sensitive region that is important to scientists because the temperature has been consistently rising causing a subsequent melting of the region’s glaciers. AirSAR will provide a baseline model and unprecedented mapping of the region. This data will make it possible to determine whether the warming trend is slowing, continuing or accelerating. AirSAR will also provide reliable information on ice shelf thickness to measure the contribution of the glaciers to sea level.
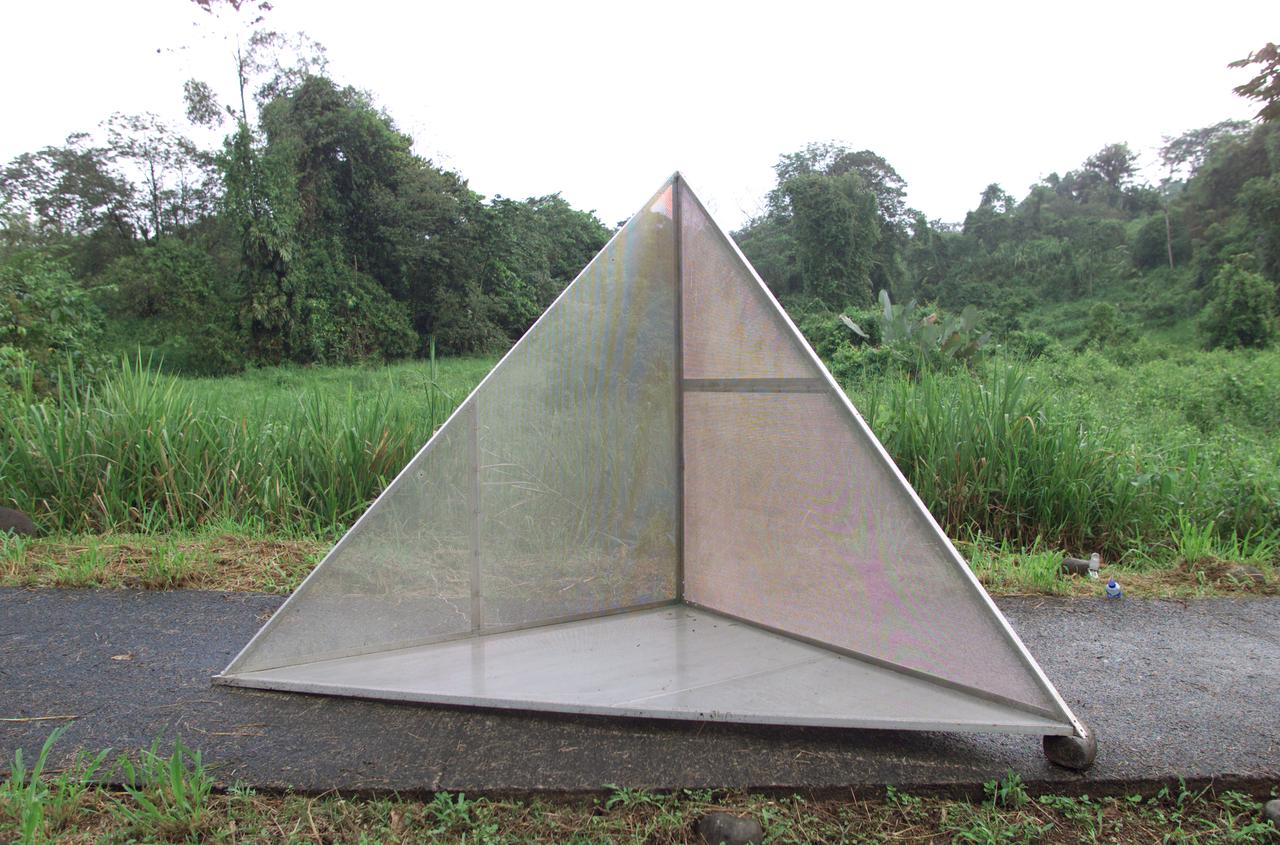

Reflectors setup in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest by scientist Paul Siqueira from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab. These reflectors are used by JPL scientists onboard Dryden's DC-8 aircraft to calibrate the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) system. Scientists place these reflectors at known points on the ground, allowing researchers onboard the aircraft to verify their data. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
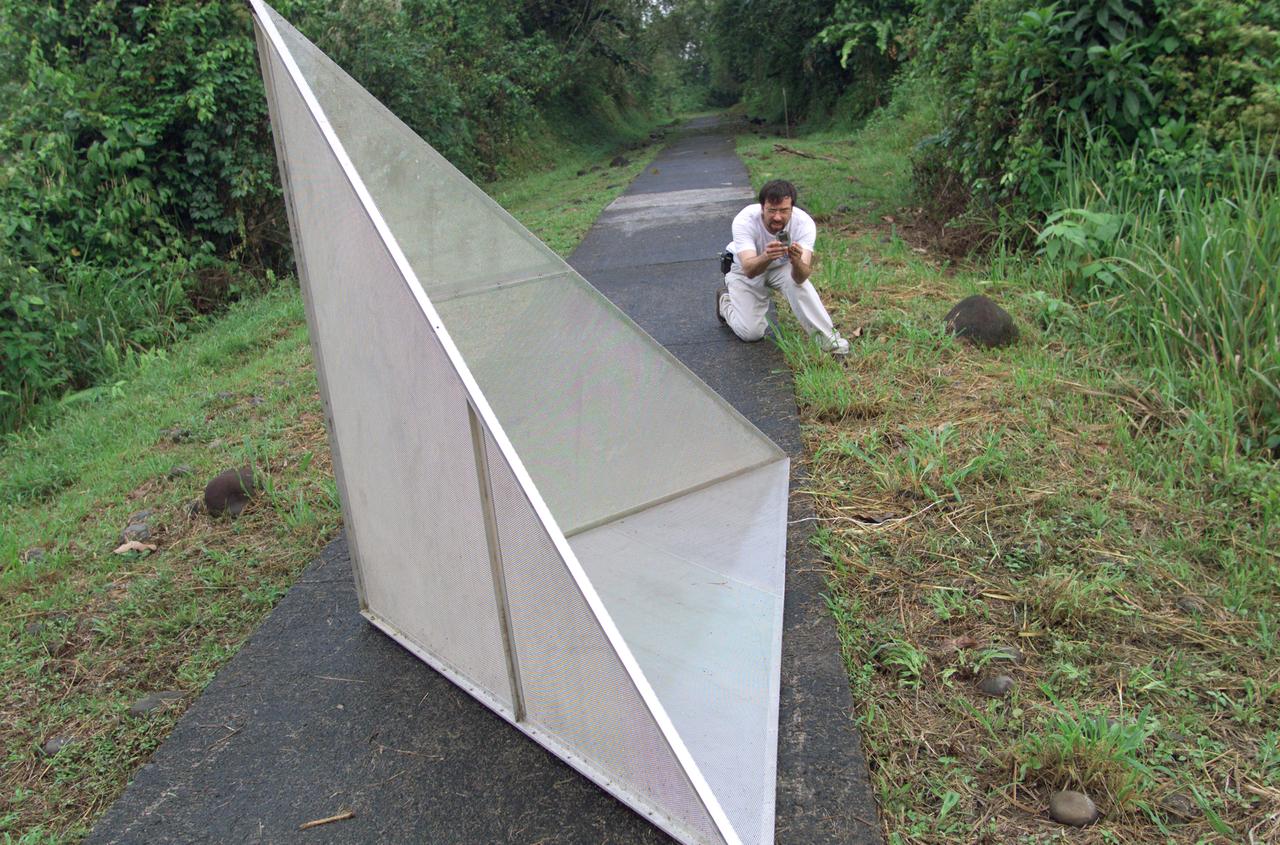

Reflectors setup in the La Selva region of the Costa Rican rain forest by scientist Paul Siqueira from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab. These reflectors are used by JPL scientists onboard Dryden's DC-8 aircraft to calibrate the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) system. Scientists place these reflectors at known points on the ground, allowing researchers onboard the aircraft to verify their data. AirSAR 2004 Mesoamerica is a three-week expedition by an international team of scientists that uses an all-weather imaging tool, called the Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AirSAR) which is located onboard NASA's DC-8 airborne laboratory. Scientists from many parts of the world including NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory are combining ground research done in several areas in Central America with NASA's AirSAR technology to improve and expand on the quality of research they are able to conduct. The radar, developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, can penetrate clouds and also collect data at night. Its high-resolution sensors operate at multiple wavelengths and modes, allowing AirSAR to see beneath treetops, through thin sand, and dry snow pack. AirSAR's 2004 campaign is a collaboration of many U.S. and Central American institutions and scientists, including NASA; the National Science Foundation; the Smithsonian Institution; National Geographic; Conservation International; the Organization of Tropical Studies; the Central American Commission for Environment and Development; and the Inter-American Development Bank.
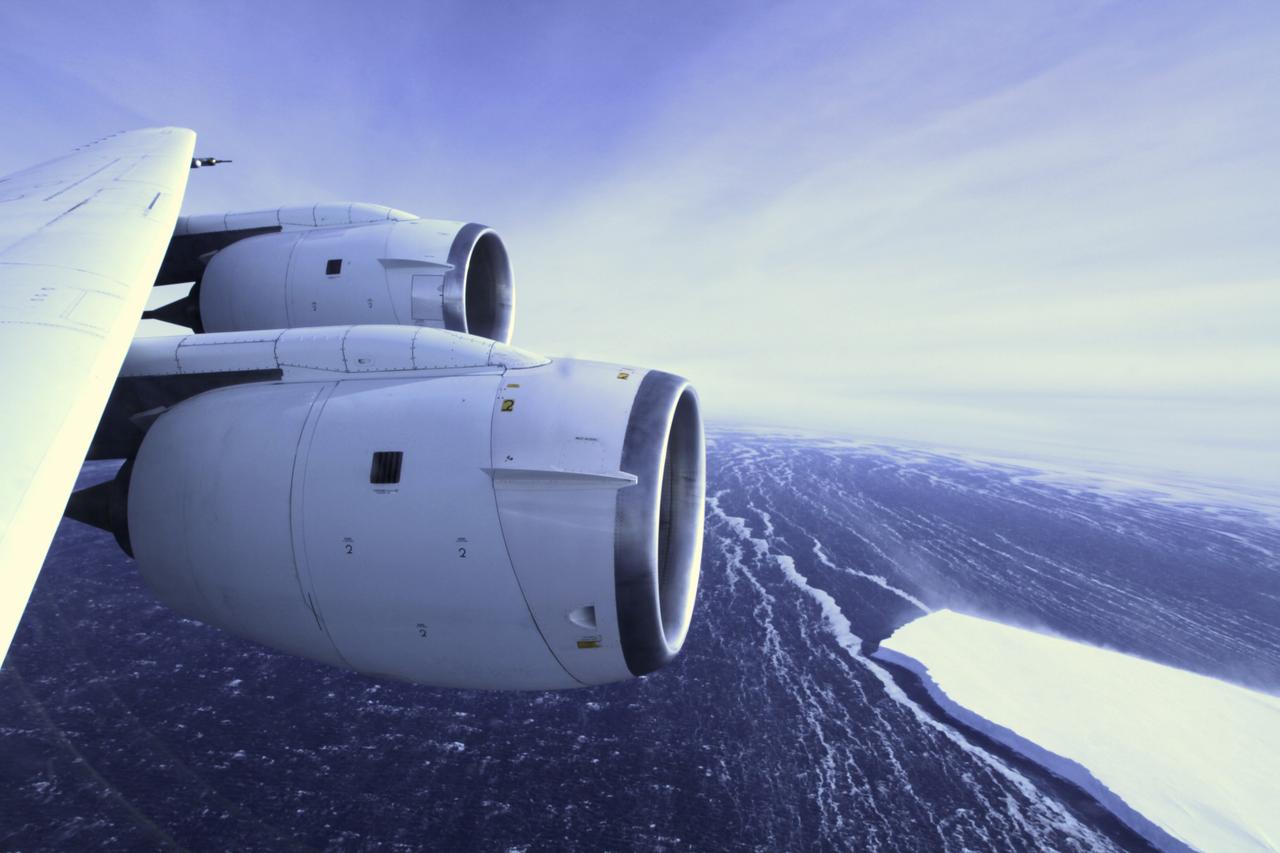

During a flight over the Pine Island Glacier ice shelf, the DC-8 banks over the Amundsen Sea and the clean edge of the ice shelf front. The shelf drops about 200 feet from its surface to sea level. This image was taken on Oct. 26, 2011. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jefferson Beck NASA's Operation IceBridge returns to a base camp of Punta Arenas, Chile for the third year of flights over Antarctica's changing sea ice, glaciers and ice sheets. NASA's DC-8, outfitted with seven remote-sensing instruments, and a Gulfstream 5 operated by the National Science Foundation and National Center for Atmospheric Research and outfitted with a high-altitude laser-ranging mapper, will fly from Chile over Antarctica in October and November. The mission is designed to record changes to Antarctica's ice sheets and give scientists insight into what is driving those changes. Follow the progress of the mission: Campaign News site: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/icebridge/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/icebridge/index.html</a> IceBridge blog: <a href="http://blogs.nasa.gov/cm/newui/blog/viewpostlist.jsp?blogname=icebridge" rel="nofollow">blogs.nasa.gov/cm/newui/blog/viewpostlist.jsp?blogname=ic...</a> Twitter: @nasa_ice <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

In May 2014, two new studies concluded that a section of the land-based West Antarctic ice sheet had reached a point of inevitable collapse. Meanwhile, fresh observations from September 2014 showed sea ice around Antarctica had reached its greatest extent since the late 1970s. To better understand such dynamic and dramatic differences in the region's land and sea ice, researchers are travelling south to Antarctica this month for the sixth campaign of NASA’s Operation IceBridge. The airborne campaign, which also flies each year over Greenland, makes annual surveys of the ice with instrumented research aircraft. Instruments range from lasers that map the elevation of the ice surface, radars that "see" below it, and downward looking cameras to provide a natural-color perspective. The Digital Mapping System (DMS) camera acquired the above photo during the mission’s first science flight on October 16, 2009. At the time of the image, the DC-8 aircraft was flying at an altitude of 515 meters (1,700 feet) over heavily compacted first-year sea ice along the edge of the Amundsen Sea. Since that first flight, much has been gleaned from IceBridge data. For example, images from an IceBridge flight in October 2011 revealed a massive crack running about 29 kilometers (18 miles) across the floating tongue of Antarctica's Pine Island Glacier. The crack ultimately led to a 725-square-kilometer (280-square-mile) iceberg. In 2012, IceBridge data was a key part of a new map of Antarctica called Bedmap2. By combining surface elevation, ice thickness, and bedrock topography, Bedmap2 gives a clearer picture of Antarctica from the ice surface down to the land surface. Discoveries have been made in Greenland, too, including the identification of a 740-kilometer-long (460-mile-long) mega canyon below the ice sheet. Repeated measurements of land and sea ice from aircraft extend the record of observations once made by NASA’s Ice, Cloud, and Land Elevation Satellite, or ICESat, which stopped functioning in 2009. In addition to extending the ICESat record, IceBridge also sets the stage for ICESat-2, which is scheduled for launch in 2017. Credit: IceBridge DMS L0 Raw Imagery courtesy of the Digital Mapping System (DMS) team/NASA DAAC at the National Snow and Ice Data Center More info: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84549" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84549</a> <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84549" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84549</a>
California, reveals the devastating effect of California's ongoing drought on Sierra Nevada conifer forests. The map will be used to help the U.S. Forest Service assess and respond to the impacts of increased tree mortality caused by the drought, particularly where wildlands meet urban areas within the Sierra National Forest. After several years of extreme drought, the highly stressed conifers (trees or bushes that produce cones and are usually green year-round) of the Sierra Nevada are now more susceptible to bark beetles (Dendroctonus spp.). While bark beetles killing trees in the Sierra Nevada is a natural phenomenon, the scale of mortality in the last couple of years is far greater than previously observed. The U.S. Forest Service is using recent airborne spectroscopic measurements from NASA's Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS) instrument aboard NASA's ER-2 aircraft, together with new advanced algorithms, to quantify this impact over this large region of rugged terrain. The high-altitude ER-2 aircraft is based at NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center, Edwards, California. The image was created by scientists at the USFS's Pacific Southwest Region Remote Sensing Lab, McClellan, California, by performing a time series analysis of AVIRIS images. Scientists evaluated baseline tree mortality on public lands in the summer of 2015 using a machine learning algorithm called "random forest." This algorithm classifies the AVIRIS measurements as dominated by either shrubs, healthy trees or newly dead conifer trees. To quantify how much the amount of dead vegetation increased during the fall of 2015, the Forest Service scientists conducted an advanced spectral mixture analysis. This analysis evaluates each spectrum to determine the fraction of green vegetation, dead vegetation and soil. The full spectral range of AVIRIS is important to separate the signatures of soil and dead vegetation. To produce this comprehensive Sierra National Forest tree mortality map, the result from the summer of 2015 was evaluated to look for increases of more than 10 percent in dead vegetation during the fall of 2015. AVIRIS measures spectra of the Earth system to conduct advanced science research. These western U.S. AVIRIS measurements were acquired as part of NASA's Hyperspectral Infrared Imager (HyspIRI) preparatory airborne campaign. HyspIRI was one of the space missions suggested to NASA by the National Academy of Sciences in its 2007 decadal survey for Earth Science. In the future, HyspIRI could provide spectral and thermal measurements of this type globally for ecosystem research and additional science objectives. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20717

A close-up image of the crack spreading across the ice shelf of Pine Island Glacier shows the details of the boulder-like blocks of ice that fell into the rift when it split. For most of the 18-mile stretch of the crack that NASA’s DC-8 flew over on Oct. 26, 2011, it stretched about 240 feet wide, as roughly seen here. The deepest points ranged from about 165 to 190 feet, roughly equal to the top of the ice shelf down to sea level. Scientists expect the crack to propagate and the ice shelf to calve an iceberg of more than 300 square miles in the coming months. This image was captured by the Digital Mapping System (DMS) aboard the DC-8. Credit: NASA/DMS NASA's Operation IceBridge returns to a base camp of Punta Arenas, Chile for the third year of flights over Antarctica's changing sea ice, glaciers and ice sheets. NASA's DC-8, outfitted with seven remote-sensing instruments, and a Gulfstream 5 operated by the National Science Foundation and National Center for Atmospheric Research and outfitted with a high-altitude laser-ranging mapper, will fly from Chile over Antarctica in October and November. The mission is designed to record changes to Antarctica's ice sheets and give scientists insight into what is driving those changes. Follow the progress of the mission: Campaign News site: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/icebridge/index.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/icebridge/index.html</a> IceBridge blog: <a href="http://blogs.nasa.gov/cm/newui/blog/viewpostlist.jsp?blogname=icebridge" rel="nofollow">blogs.nasa.gov/cm/newui/blog/viewpostlist.jsp?blogname=ic...</a> Twitter: @nasa_ice <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Cosmic rays and the chemicals and atoms that make up the interstellar space between stars are the focus of this year’s NASA Antarctica Long Duration Balloon Flight Campaign, which kicked into high gear with the launch of the Boron And Carbon Cosmic rays in the Upper Stratosphere (BACCUS) payload Nov. 28. The University of Maryland’s BACCUS mission is the first of three payloads taking flight from a balloon launch site on Antarctica’s Ross Ice Shelf near McMurdo Station with support from the National Science Foundation’s United States Antarctic Program. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2gCMtyP" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2gCMtyP</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>