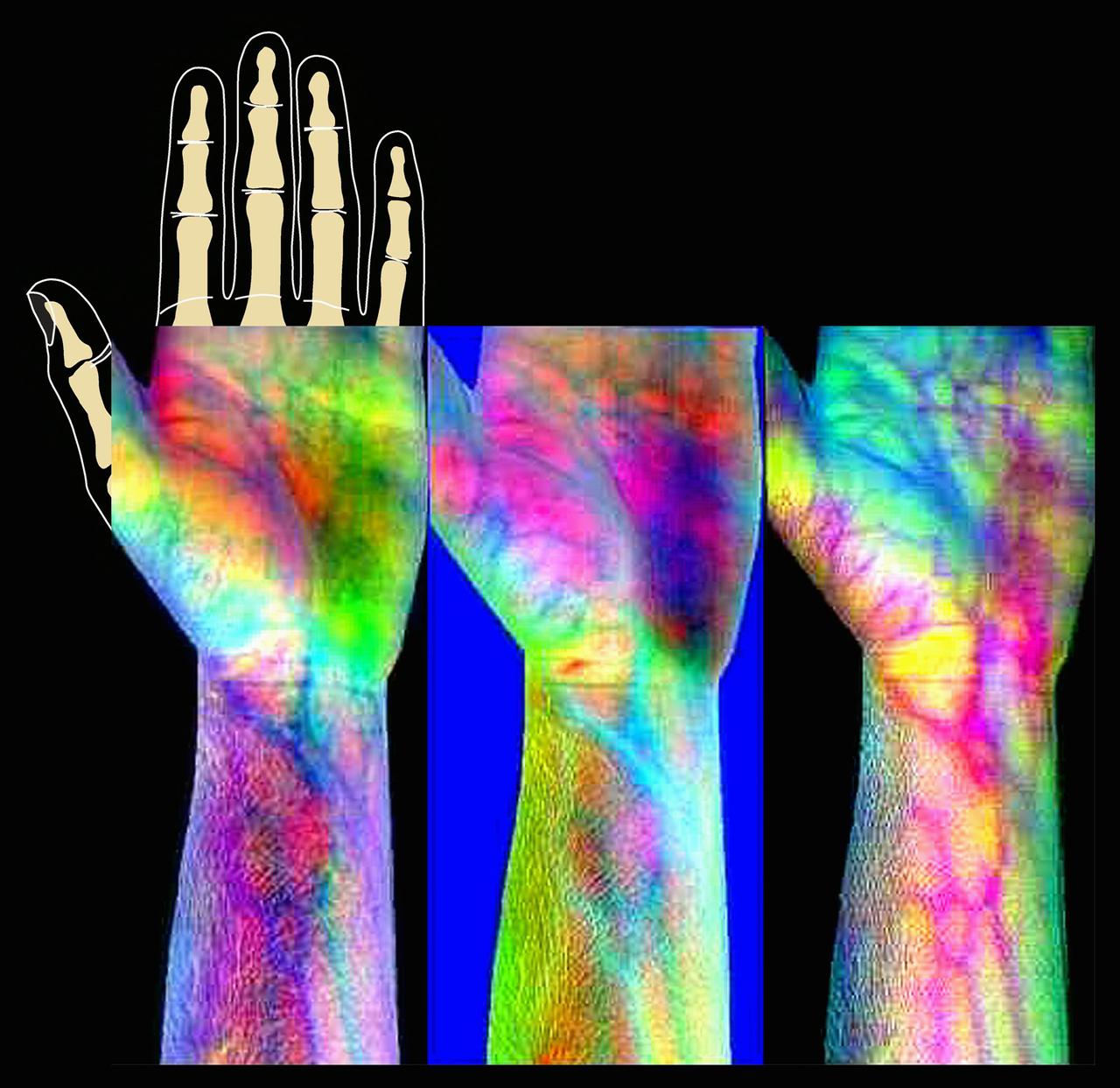
ProVision Technologies, a NASA research partnership center at Sternis Space Center in Mississippi, has developed a new hyperspectral imaging (HSI) system that is much smaller than the original large units used aboard remote sensing aircraft and satellites. The new apparatus is about the size of a breadbox. Health-related applications of HSI include non-invasive analysis of human skin to characterize wounds and wound healing rates (especially important for space travelers who heal more slowly), determining if burns are first-, second-, or third degree (rather than painful punch biopsies). The work is sponsored under NASA's Space Product Development (SPD) program.
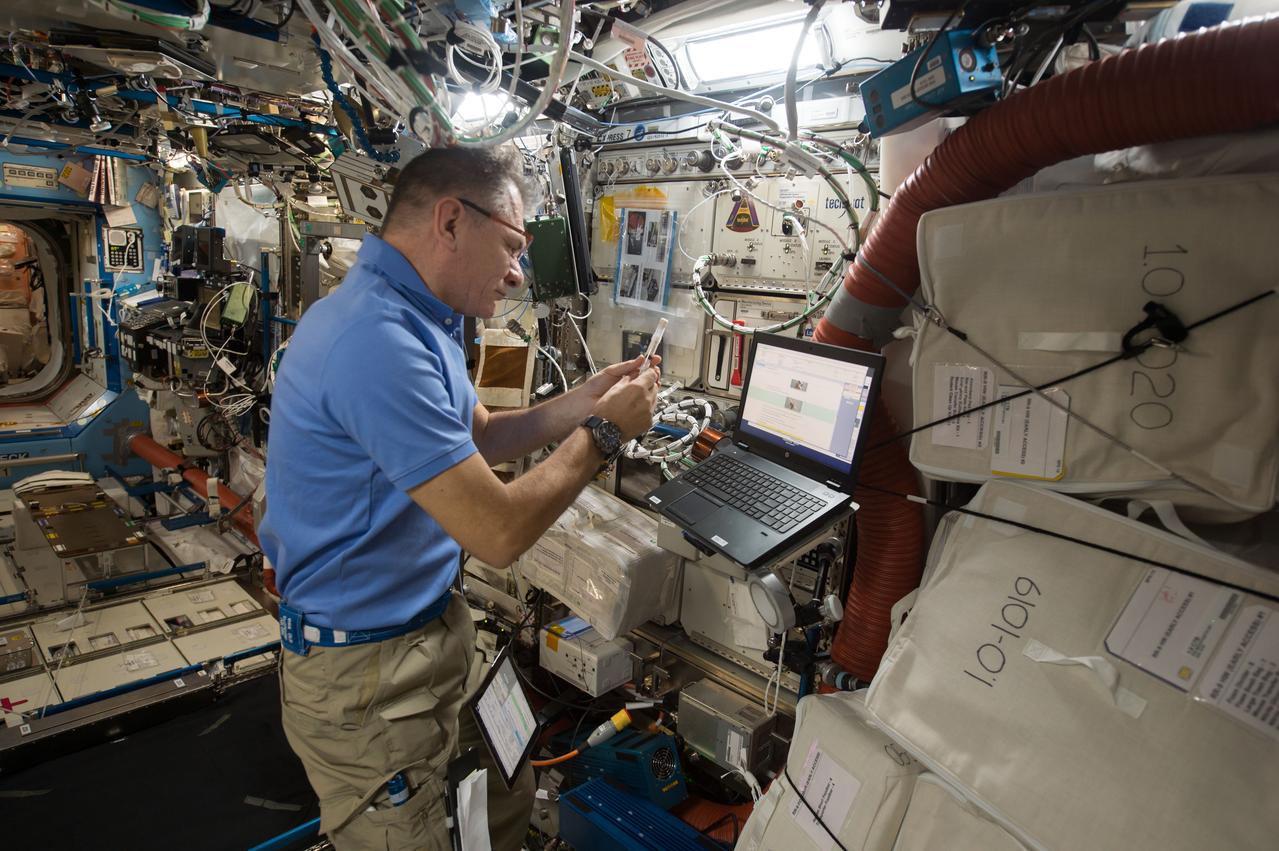

iss052e058828(8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
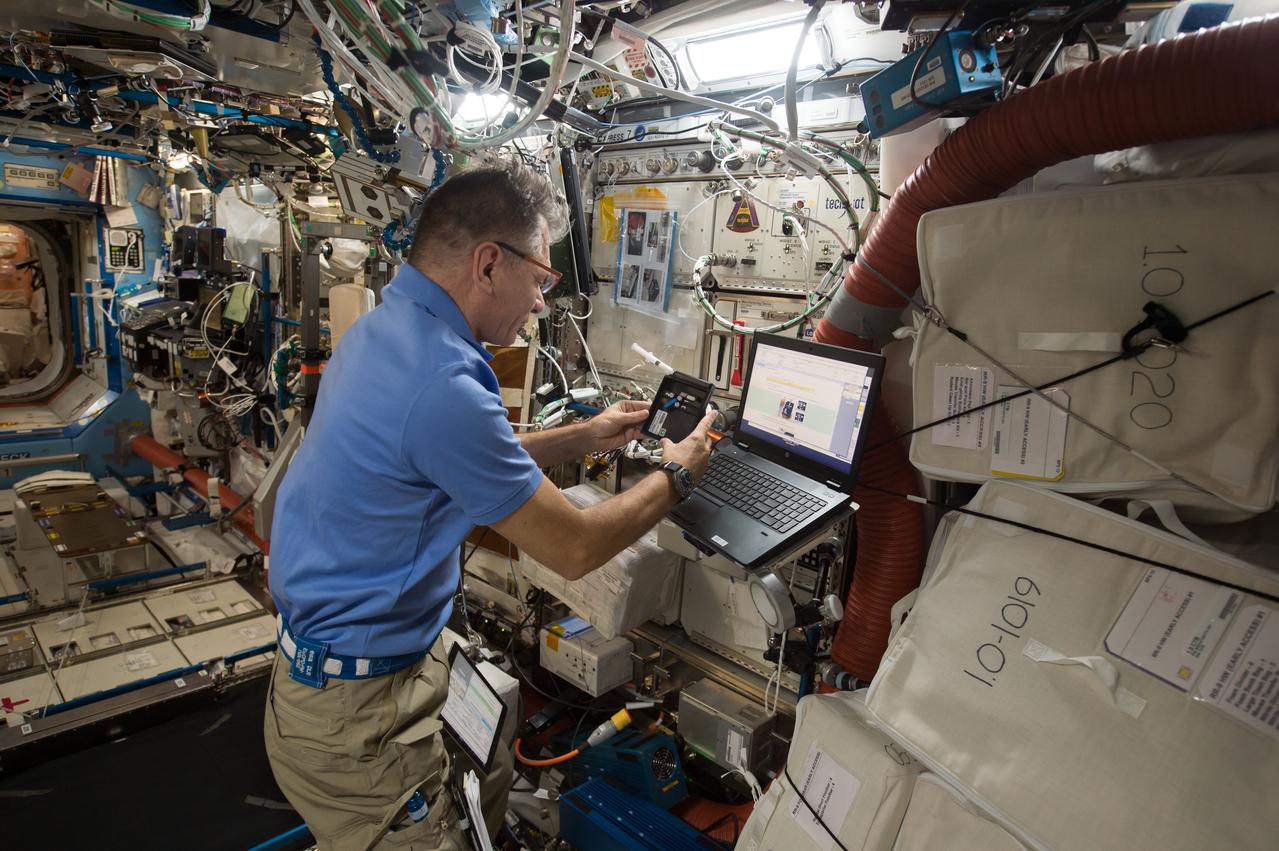

iss052e058906 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
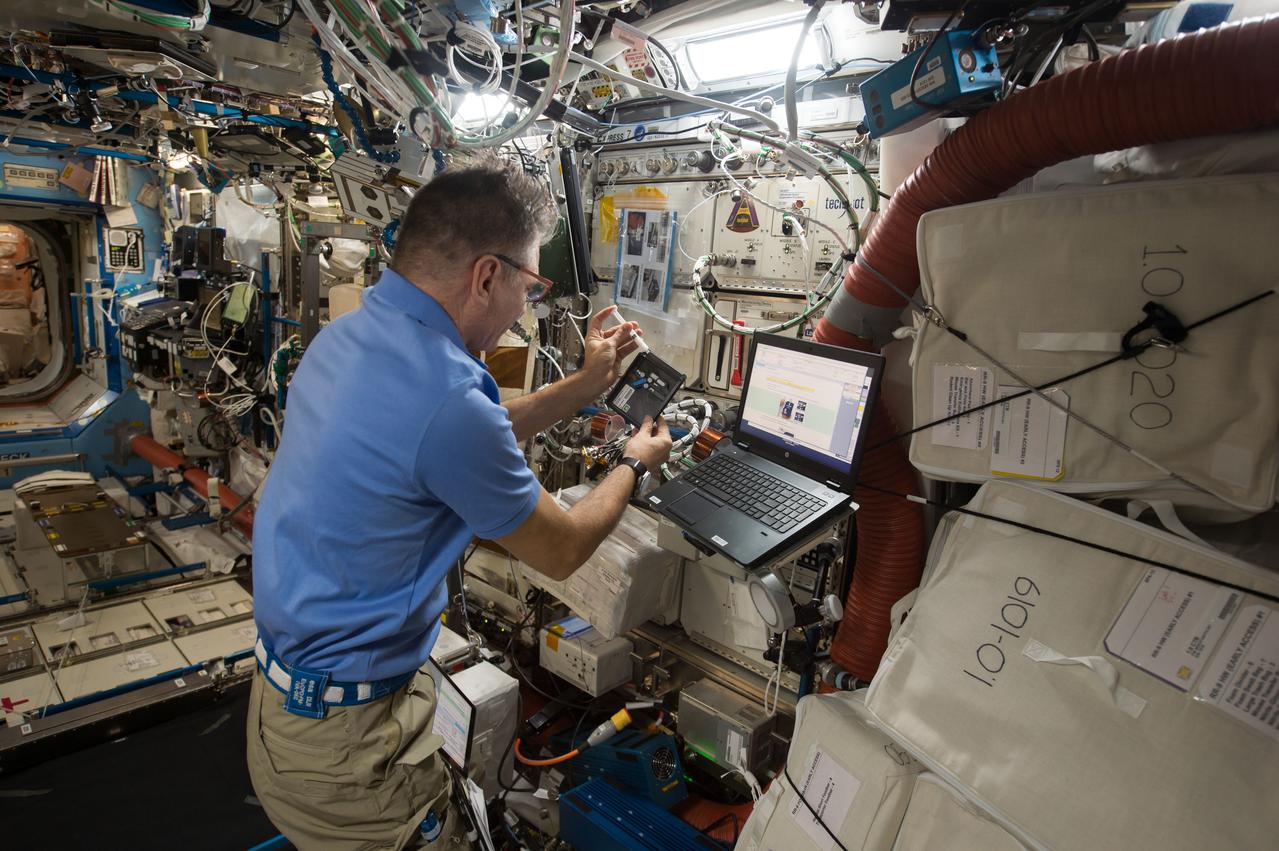

iss052e058893 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members
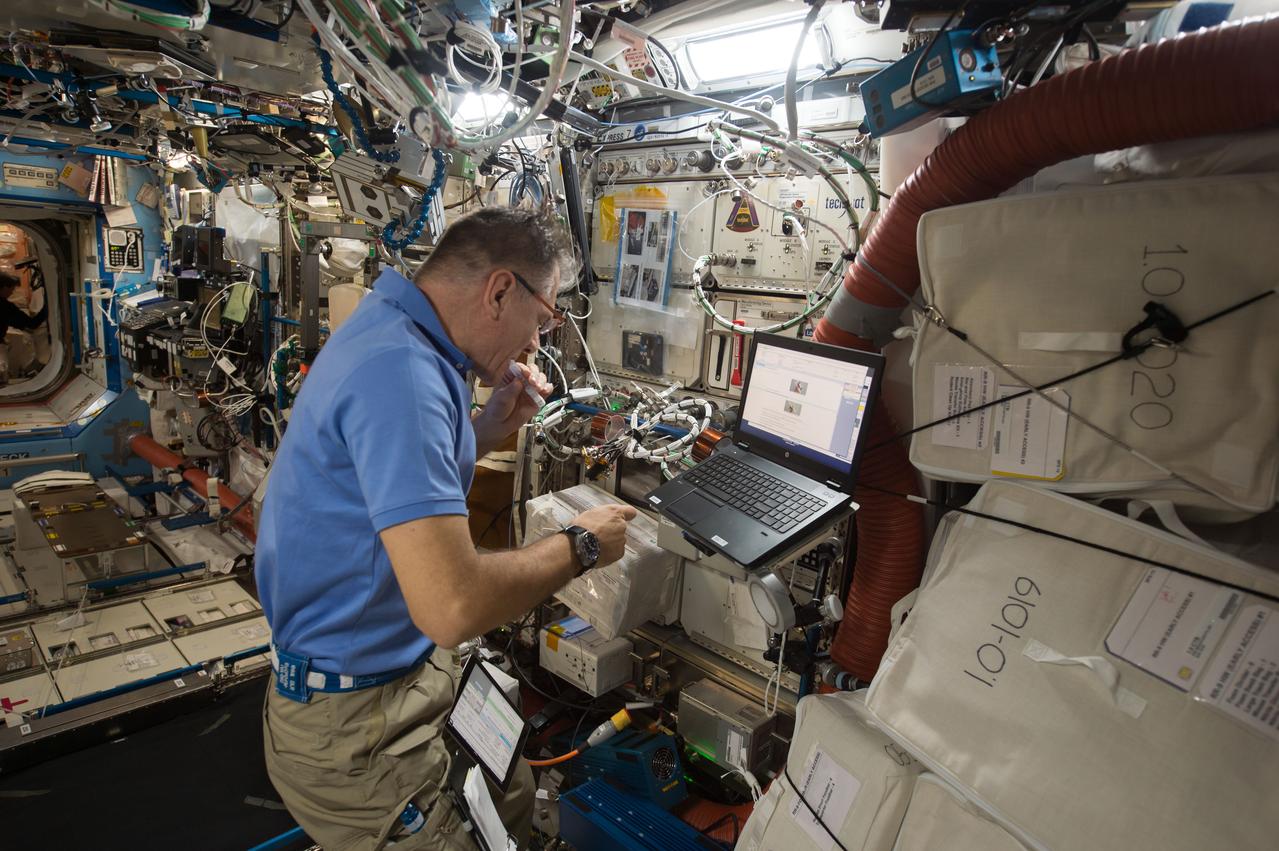

iss052e058815 (8/18/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Paolo Nespoli collects and processes saliva samples in the bioanalyzer for the ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and Results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (In Situ). Crew on the International Space Station (ISS) are continually monitored for health changes, and as part of these measurements, they take saliva samples that are stored and returned to Earth later. The ISS Non-invasive Sample Investigation and results Transmission to ground with the Utmost easiness (IN SITU) bioanalysis is a portable device that can check crew members’ saliva on board, enabling direct real-time analysis. The device’s first uses are to monitor stress levels and appetites among crew members