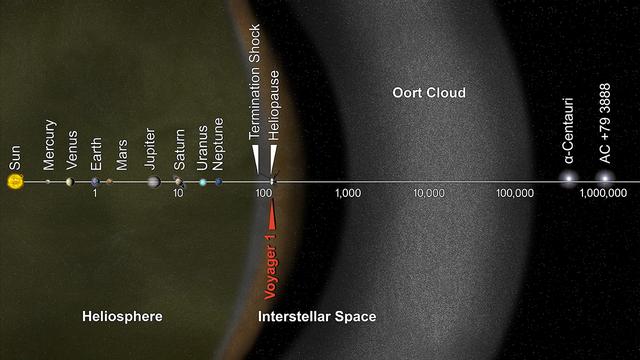
This artist's concept puts solar system distances in perspective. The scale bar is in astronomical units, with each set distance beyond 1 AU representing 10 times the previous distance. One AU is the distance from the sun to the Earth, which is about 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers. Neptune, the most distant planet from the sun, is about 30 AU. Informally, the term "solar system" is often used to mean the space out to the last planet. Scientific consensus, however, says the solar system goes out to the Oort Cloud, the source of the comets that swing by our sun on long time scales. Beyond the outer edge of the Oort Cloud, the gravity of other stars begins to dominate that of the sun. The inner edge of the main part of the Oort Cloud could be as close as 1,000 AU from our sun. The outer edge is estimated to be around 100,000 AU. NASA's Voyager 1, humankind's most distant spacecraft, is around 125 AU. Scientists believe it entered interstellar space, or the space between stars, on Aug. 25, 2012. Much of interstellar space is actually inside our solar system. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 1 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly about 30,000 years to fly beyond it. Alpha Centauri is currently the closest star to our solar system. But, in 40,000 years, Voyager 1 will be closer to the star AC +79 3888 than to our own sun. AC +79 3888 is actually traveling faster toward Voyager 1 than the spacecraft is traveling toward it. The Voyager spacecraft were built and continue to be operated by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, Calif. Caltech manages JPL for NASA. The Voyager missions are a part of NASA's Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. For more information about Voyager, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/voyager" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/voyager</a> and <a href="http://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">voyager.jpl.nasa.gov</a> . Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

These artist concepts show some of the best known objects found outside Neptune orbit. Included are Pluto and fellow plutinos, Kuiper Belt Objects, and an Oort Cloud object.
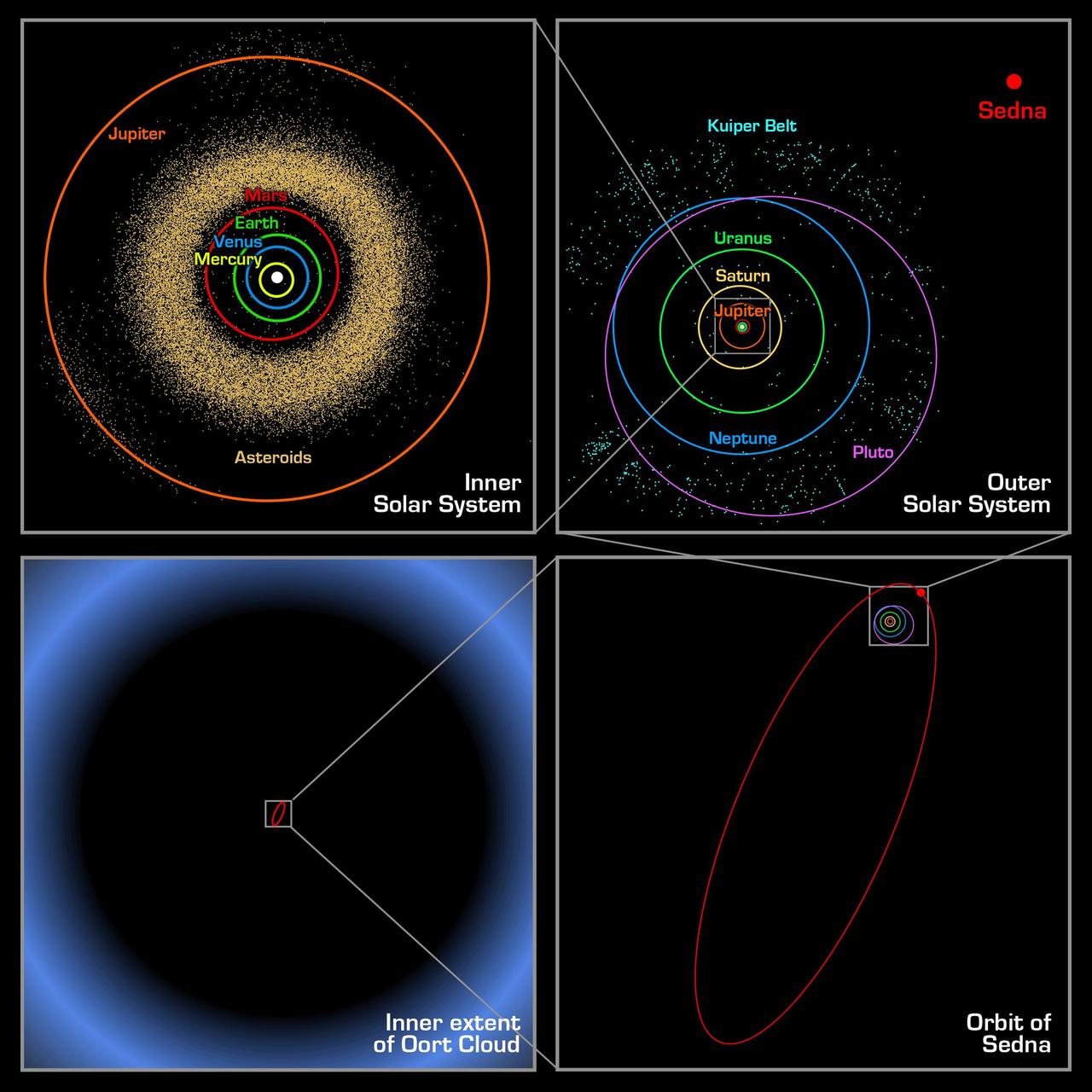
These four panels show the location of the newly discovered planet-like object, dubbed "Sedna," which lies in the farthest reaches of our solar system. Each panel, moving counterclockwise from the upper left, successively zooms out to place Sedna in context. The first panel shows the orbits of the inner planets, including Earth, and the asteroid belt that lies between Mars and Jupiter. In the second panel, Sedna is shown well outside the orbits of the outer planets and the more distant Kuiper Belt objects. Sedna's full orbit is illustrated in the third panel along with the object's current location. Sedna is nearing its closest approach to the Sun; its 10,000 year orbit typically takes it to far greater distances. The final panel zooms out much farther, showing that even this large elliptical orbit falls inside what was previously thought to be the inner edge of the Oort cloud. The Oort cloud is a spherical distribution of cold, icy bodies lying at the limits of the Sun's gravitational pull. Sedna's presence suggests that this Oort cloud is much closer than scientists believed. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05569

This artist's concept puts solar system distances -- and the travels of NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft -- in perspective. The scale bar is in astronomical units, with each set distance beyond 1 AU representing 10 times the previous distance. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth, which is about 93 million miles, or 150 million kilometers. Neptune, the most distant planet from the Sun, is about 30 AU. Much of the solar system is actually in interstellar space. Informally, the term "solar system" is often used to mean the space out to the last planet. Scientific consensus, however, says the solar system goes out to the Oort Cloud, the source of the comets that swing by our sun on long time scales. Beyond the outer edge of the Oort Cloud, the gravity of other stars begins to dominate that of the Sun. The inner edge of the main part of the Oort Cloud could be as close as 1,000 AU from our Sun. The outer edge is estimated to be around 100,000 AU. Voyager 2, the second farthest human-made object after Voyager 1, is around 119 AU from the Sun. Indications from the scientific instruments suggest Voyager 2 passed beyond our heliosphere (the bubble of plasma the Sun blows around itself) and into interstellar space (the space between stars) in November 2018. The heliosphere has a turbulent outer boundary known as the heliosheath. The termination shock is the inner boundary of the heliosheath and the heliopause is the outer boundary, beyond which lies interstellar space. Voyager 2 crossed the termination shock at 84 AU in August 2007. It will take about 300 years for Voyager 2 to reach the inner edge of the Oort Cloud and possibly about 30,000 years to fly beyond it. Voyager 2 is heading away from the Sun about 36 degrees out of the ecliptic plane (plane of the planets) to the south, toward the constellations of Sagittarius and Pavo. In about 40,000 years, Voyager 2 will be closer to another star than our own Sun, coming within about 1.7 light years of a star called Ross 248, a small star in the constellation of Andromeda. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22921
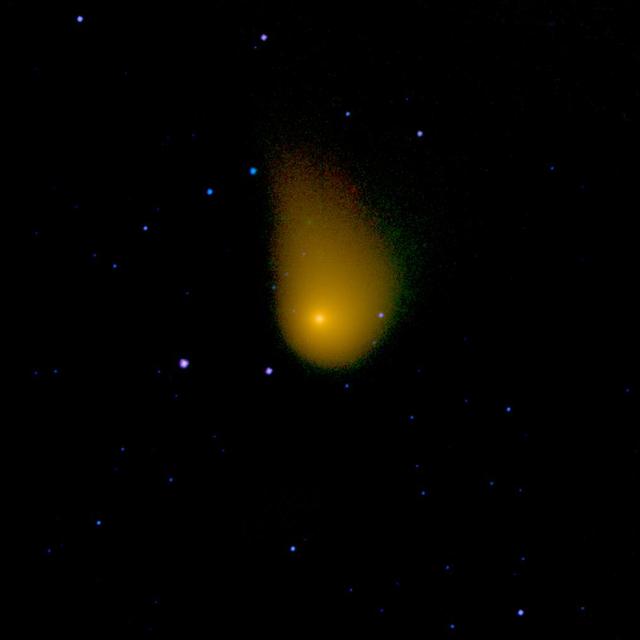
An infrared view from NASA's NEOWISE mission of the Oort cloud comet C/2006 W3 (Christensen). The spacecraft observed this comet on April 20th, 2010 as it traveled through the constellation Sagittarius. Comet Christensen was nearly 370 million miles (600 million kilometers) from Earth at the time. The image is half of a degree of the sky on each side. Infrared light with wavelengths of 3.4, 12 and 22 micron channels are mapped to blue, green, and red, respectively. The signal at these wavelengths is dominated primarily by the comet's dust thermal emission, giving it a golden hue. The WISE spacecraft was put into hibernation in 2011 upon completing its goal of surveying the entire sky in infrared light. WISE cataloged three quarters of a billion objects, including asteroids, stars and galaxies. In August 2013, NASA decided to reinstate the spacecraft on a mission to find and characterize more asteroids. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20118
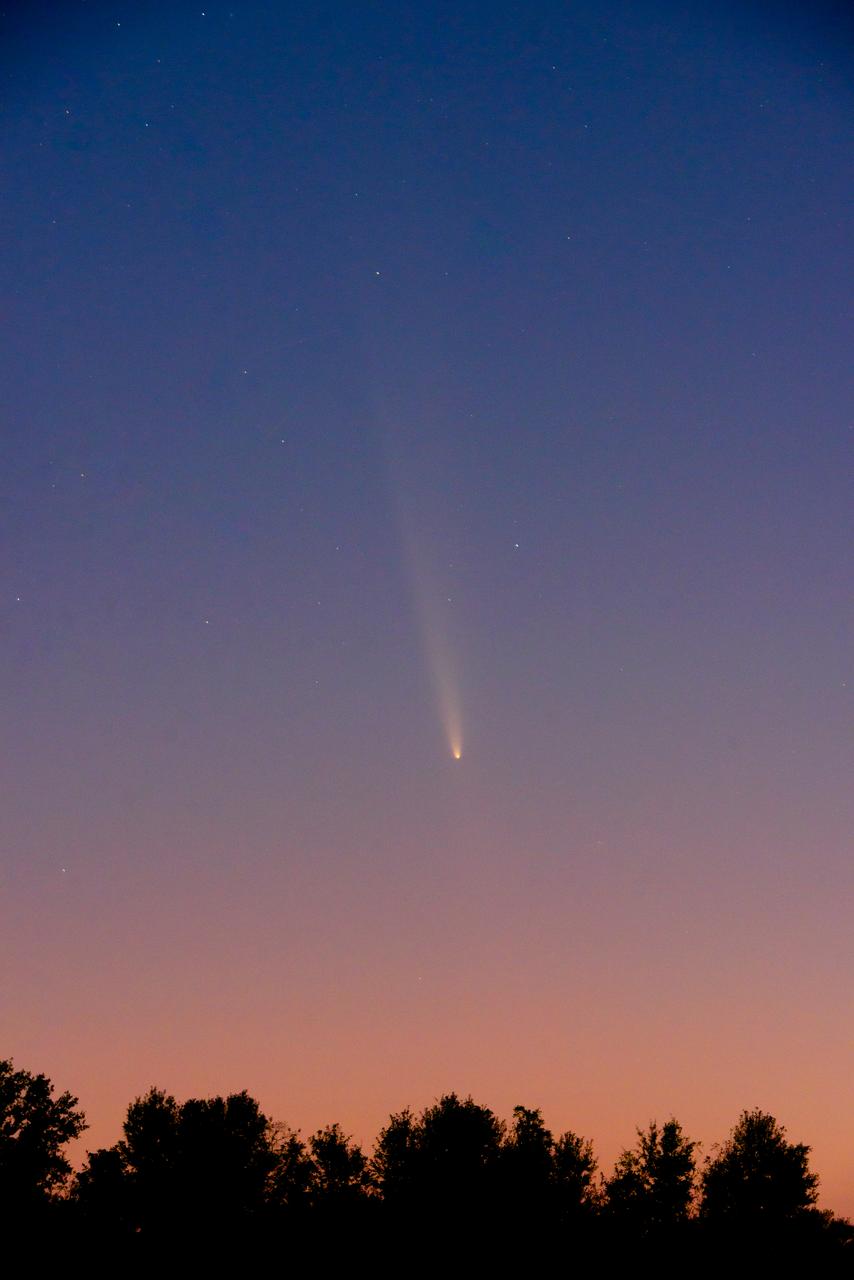

The Oort Cloud comet, called C/2023 A3 Tsuchinshan-ATLAS, passes over Southeast Louisiana near New Orleans, home of NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility, Sunday, Oct. 13, 2024. The comet is making its first appearance in documented human history; it was last seen in the night sky 80,000 years ago. The Tsuchinshan-ATLAS comet made its first close pass by Earth in mid-October and will remain visible to viewers in the Northern Hemisphere just between the star Arcturus and planet Venus through early November.
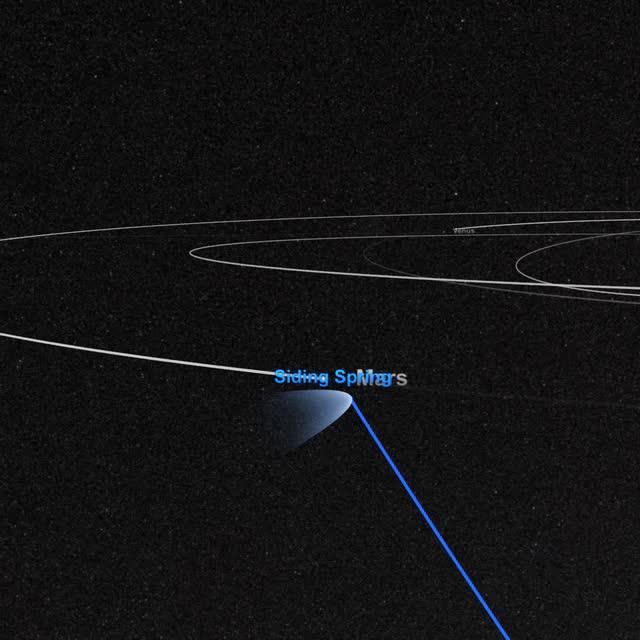
On October 19, Comet Siding Spring will pass within 88,000 miles of Mars – just one third of the distance from the Earth to the Moon! Traveling at 33 miles per second and weighing as much as a small mountain, the comet hails from the outer fringes of our solar system, originating in a region of icy debris known as the Oort cloud. Comets from the Oort cloud are both ancient and rare. Since this is Comet Siding Spring’s first trip through the inner solar system, scientists are excited to learn more about its composition and the effects of its gas and dust on the Mars upper atmosphere. NASA will be watching closely before, during, and after the flyby with its entire fleet of Mars orbiters and rovers, along with the Hubble Space Telescope and dozens of instruments on Earth. The encounter is certain to teach us more about Oort cloud comets, the Martian atmosphere, and the solar system’s earliest ingredients. Learn more: <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FG4KsatjFeI" rel="nofollow">www.youtube.com/watch?v=FG4KsatjFeI</a> Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Comet C/2018 Y1 Iwamoto as imaged in multiple exposures of infrared light by the NEOWISE space telescope. The infrared images were taken on Feb. 25, 2019, when the comet was about 56 million miles, or 90 million kilometers, from Earth. C/2018 Y1 Iwamoto is a long-period comet originally from the Oort Cloud and coming in near the Sun for the first time in over 1,000 years. Appearing as a string of red dots, this comet can be seen in a series of exposures captured by the spacecraft. Infrared light detected by the 3.4-micron channel is mapped to blue and green, while light from the 4.6-micron channel is mapped to red. In this image, stars show up as blue because they are hotter, whereas the cooler dust around the comet - with a temperature near the freezing point of water - glows red. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23165
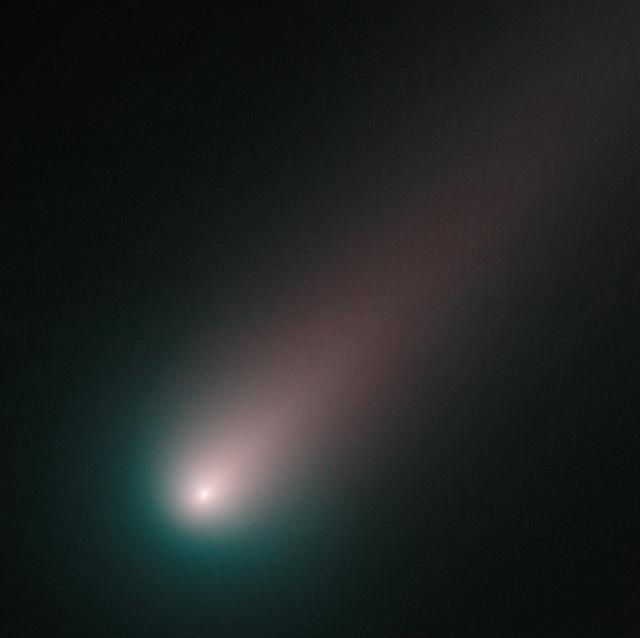

As of mid-November, ISON is officially upon us. Using Hubble, we've taken our closest look yet at the innermost region of the comet, where geysers of sublimating ice are fueling a spectacular tail. Made from observations on November 2nd, the image combines pictures of ISON taken through blue and red filters. As we expect, the round coma around ISON's nucleus is blue and the tail has a redder hue. Ice and gas in the coma reflect blue light from the Sun, while dust grains in the tail reflect more red light than blue light. This is the most color separation we've seen so far in ISON -- that's because the comet, nearer than ever to the Sun, is brighter and more structured than ever before. We've certainly come a long way since Hubble started observing Comet ISON, way back in April. Of course, our eight-month retrospective pales in comparison with ISON's own journey, which started some 10,000 years ago in the Oort cloud. ISON will come closest to the Sun on November 28, a point in its orbit known as perihelion. What's remarkable here is that the entire ISON, this awesome, shimmery space tadpole, is being produced from a dusty ball of ice estimated to be a few kilometers in diameter. Compared to ISON's full extent, Hubble's latest image is tiny. It only shows the very base of the tail. Yet even in this closest closeup we've ever had, a single pixel spans 24 km across the comet. Now that Comet ISON is close, amateur astromers rule the day. But Hubble observations, including this latest image, are still providing key insights into the science and spectacle of a comet we hope will continue to impress. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is
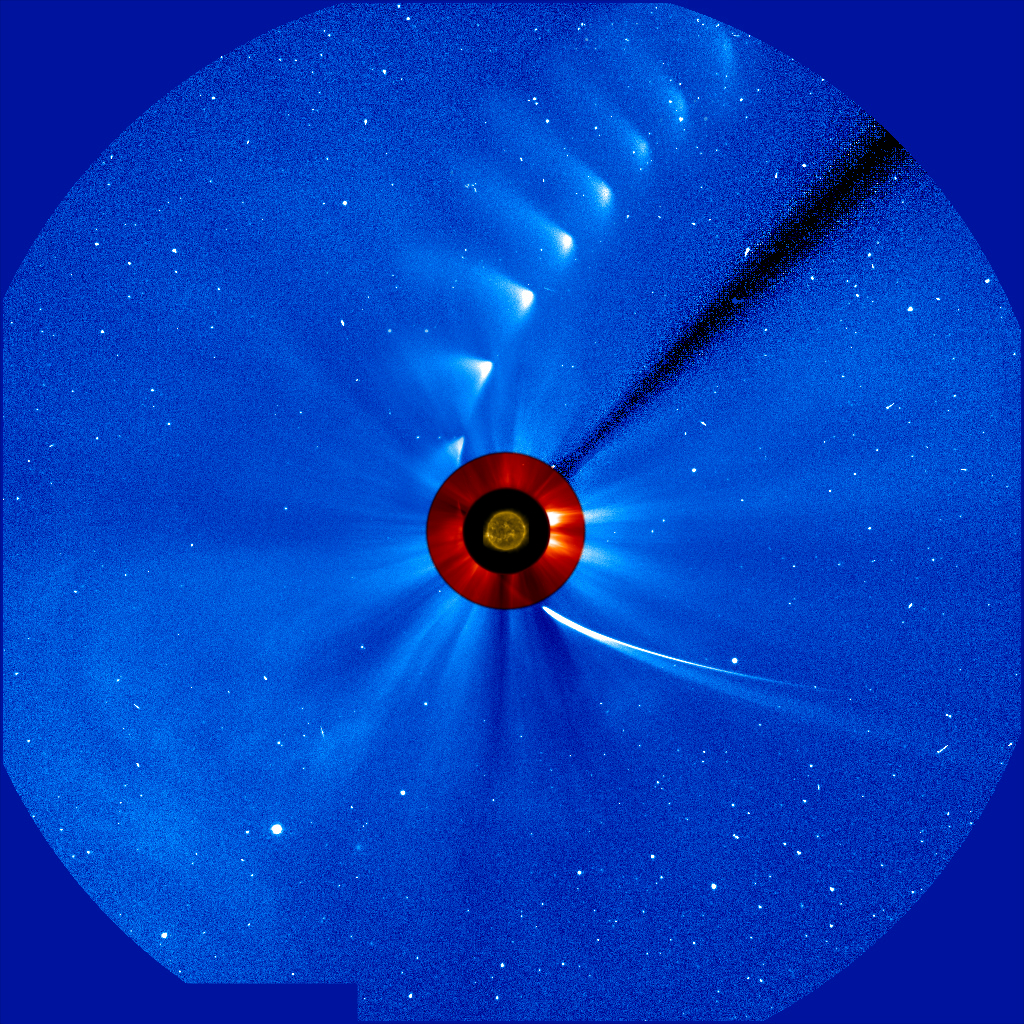
Comet ISON comes in from the bottom right and moves out toward the upper right, growing more faint, in this time-lapse image from the ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory. The image of the sun at the center is from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory. Credit: ESA/NASA/SOHO/SDO/GSFC After several days of fading, scientists continue to work to determine and to understand the fate of Comet ISON: There's no doubt that the comet shrank in size considerably as it rounded the sun and there's no doubt that something made it out on the other side to shoot back into space. The question remains as to whether the bright spot seen moving away from the sun was simply debris, or whether a small nucleus of the original ball of ice was still there. Regardless, it is likely that it is now only dust. Comet ISON, which began its journey from the Oort Cloud some 3 million years ago, made its closest approach to the sun on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet was visible in instruments on NASA's Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, and the joint European Space Agency/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO, via images called coronagraphs. Coronagraphs block out the sun and a considerable distance around it, in order to better observe the dim structures in the sun's atmosphere, the corona. As such, there was a period of several hours when the comet was obscured in these images, blocked from view along with the sun. During this period of time, NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory could not see the comet, leading many scientists to surmise that the comet had disintegrated completely. However, something did reappear in SOHO and STEREO coronagraphs some time later – though it was significantly less bright. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/18hGYag" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/18hGYag</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
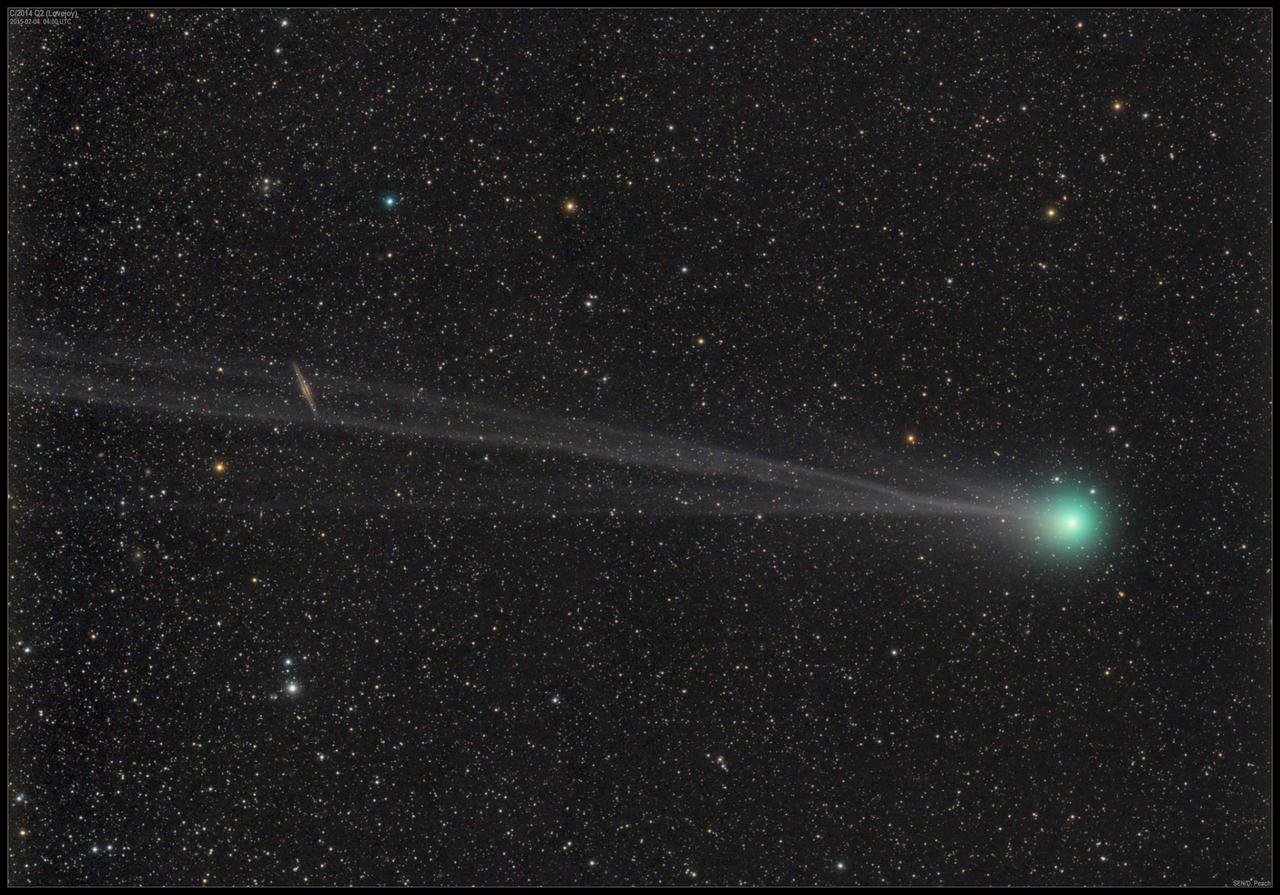

A trip past the sun may have selectively altered the production of one form of water in a comet – an effect not seen by astronomers before, a new NASA study suggests. Astronomers from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, observed the Oort cloud comet C/2014 Q2, also called Lovejoy, when it passed near Earth in early 2015. Through NASA’s partnership in the W. M. Keck Observatory on Mauna Kea, Hawaii, the team observed the comet at infrared wavelengths a few days after Lovejoy passed its perihelion – or closest point to the sun. The team focused on Lovejoy’s water, simultaneously measuring the release of H2O along with production of a heavier form of water, HDO. Water molecules consist of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. A hydrogen atom has one proton, but when it also includes a neutron, that heavier hydrogen isotope is called deuterium, or the “D” in HDO. From these measurements, the researchers calculated the D-to-H ratio – a chemical fingerprint that provides clues about exactly where comets (or asteroids) formed within the cloud of material that surrounded the young sun in the early days of the solar system. Researchers also use the D-to-H value to try to understand how much of Earth’s water may have come from comets versus asteroids. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2lvd6Vt" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2lvd6Vt</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
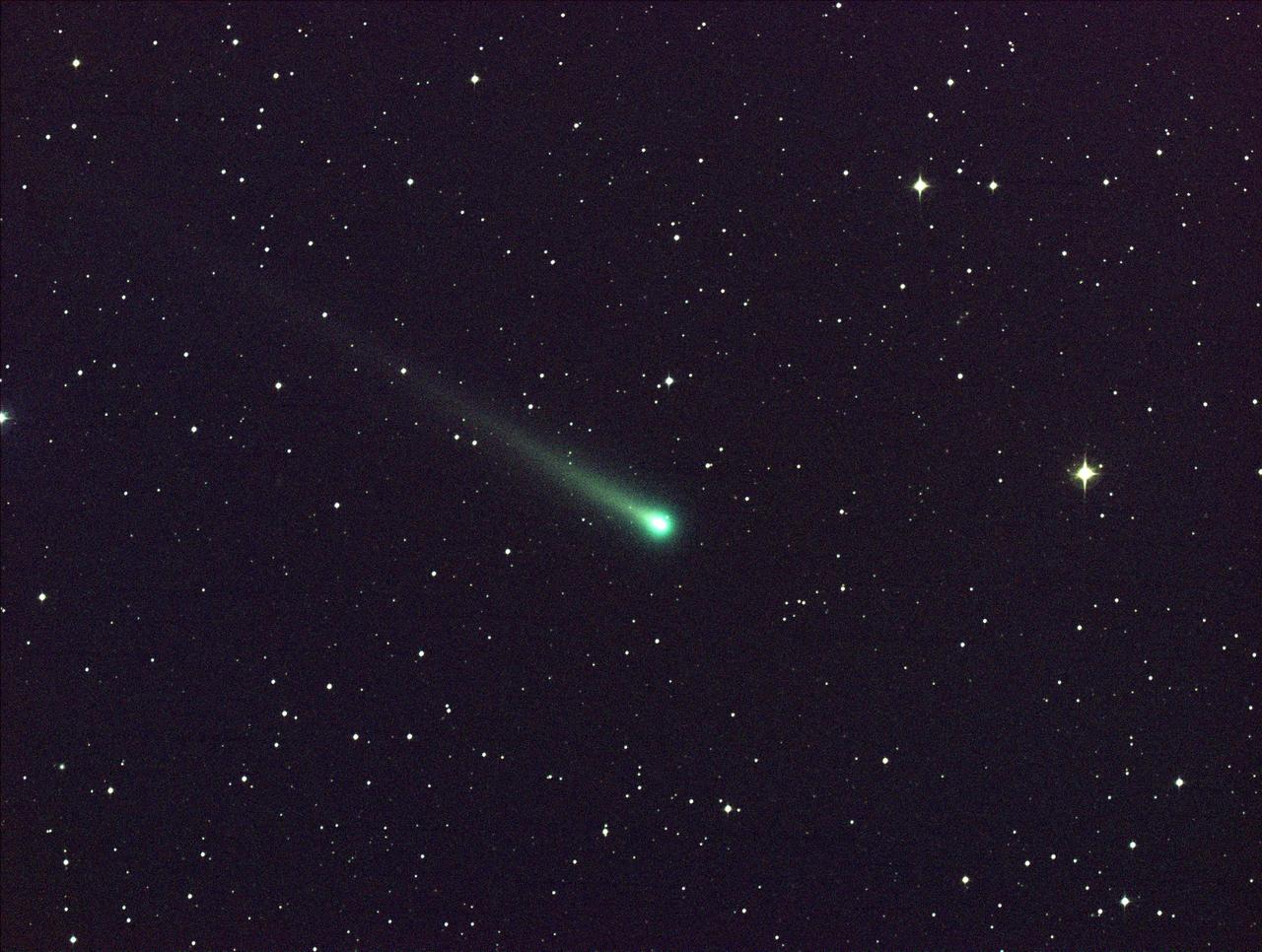

Date: 8 Nov 2013 - Comet ISON shines in this five-minute exposure taken at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center on Nov. 8, 2013.. The image was captured using a color CCD camera attached to a 14" telescope located at Marshall. At the time of this picture, comet ISON was 97 million miles from Earth, moving ever closer toward the sun. Credit: NASA/MSFC/Aaron Kingery -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
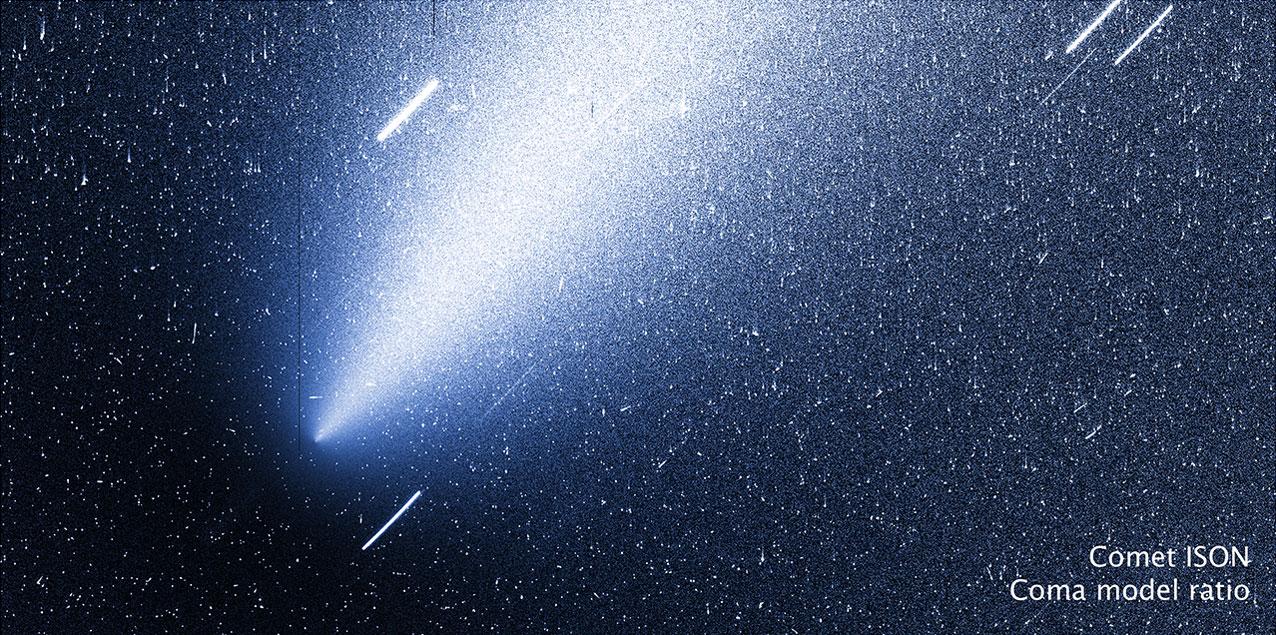

In this modeled image of ISON, the coma has been subtracted, leaving behind the nucleus. Credit: NASA, ESA, the Hubble Heritage Team (AURA/STScI) and Jian-Yang Li (Planetary Science Institute) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Taken on 19 Nov. 2013, this image shows a composite "stacked" image of comet ISON. These five stacked images of 10 seconds each were taken with the 20" Marshall Space Flight Center telescope in New Mexico. This technique allows the comet's sweeping tail to emerge with more detail. Credit: NASA/MSFC/MEO/Cameron McCarty -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>
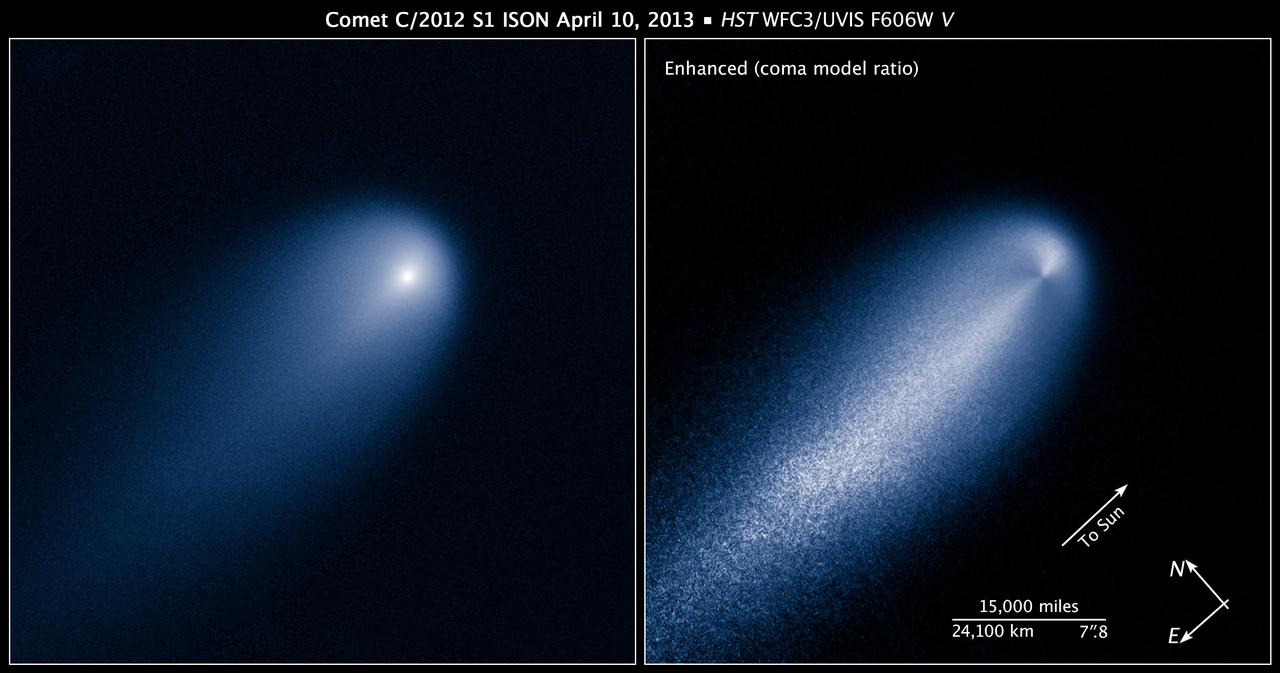

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of Comet (C/2012 S1) ISON was photographed on April 10, 2013, when the comet was slightly closer than Jupiter's orbit at a distance of 394 million miles from Earth. Even at that great distance the comet is already active as sunlight warms the surface and causes frozen volatiles to boil off. Astronomers used such early images to try to measure the size of the nucleus, in order to predict whether the comet would stay intact when it slingshots around the sun -- at 700,000 miles above the sun's surface -- on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet's dusty coma, or head of the comet, is approximately 3,100 miles across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 57,000 miles, far beyond Hubble's field of view. This image was taken in visible light. The blue false color was added to bring out details in the comet structure. Credit: NASA/ ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Godd</b>
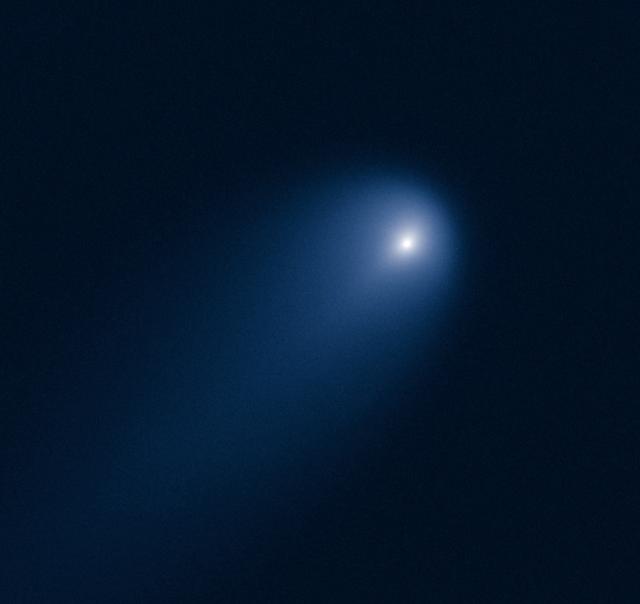

This NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of Comet (C/2012 S1) ISON was photographed on April 10, 2013, when the comet was slightly closer than Jupiter's orbit at a distance of 394 million miles from Earth. Even at that great distance the comet is already active as sunlight warms the surface and causes frozen volatiles to boil off. Astronomers used such early images to try to measure the size of the nucleus, in order to predict whether the comet would stay intact when it slingshots around the sun -- at 700,000 miles above the sun's surface -- on Nov. 28, 2013. The comet's dusty coma, or head of the comet, is approximately 3,100 miles across, or 1.2 times the width of Australia. A dust tail extends more than 57,000 miles, far beyond Hubble's field of view. This image was taken in visible light. The blue false color was added to bring out details in the comet structure. Credit: NASA/ ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Godd</b>
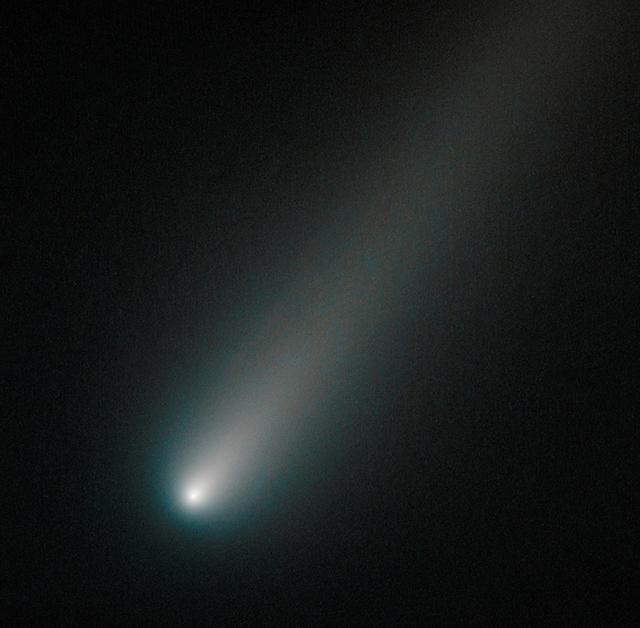

On Oct. 9, 2013, Hubble observed comet ISON once again, when it was inside the orbit of Mars, about 177 million miles from Earth. This image shows that the comet was still intact despite some predictions that the fragile icy nucleus might disintegrate closer to the sun. The comet will pass closest to the sun on Nov. 28, 2013. If the nucleus had broke apart then Hubble would have likely seen evidence of multiple fragments. Moreover, the coma, or head, surrounding the comet's nucleus is symmetric and smooth. This would probably not be the case if clusters of smaller fragments were flying along. This color composite image was assembled using two filters. The comet's coma appears cyan, a greenish-blue color due to gas, while the tail is reddish due to dust streaming off the nucleus. The tail forms as dust particles are pushed away from the nucleus by the pressure of sunlight. Credit: NASA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>
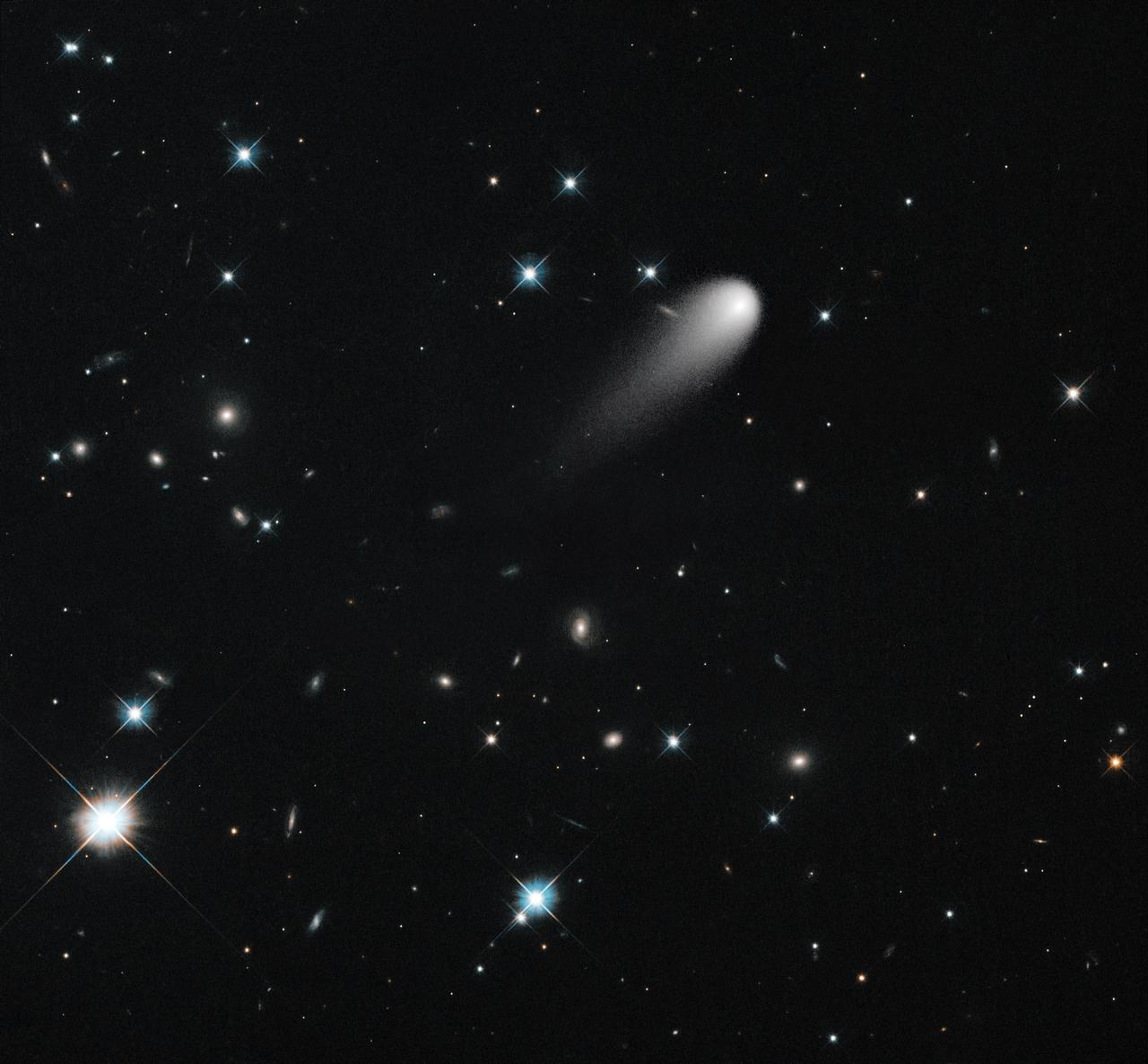

On April 30, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope observed Comet ISON again. The comet is in the upper middle, showing the long tail. Various galaxies and stars appear behind it. In this image, Hubble trained its telescope on the stars instead of following the comet. The result is that the comet appears fuzzier, but the stars and galaxies are more detailed and precise. These dimmer features don't pop out if the camera is moving, following along with ISON. To see them, you really need to dwell in one place until they emerge from the noise. Credit: NASA/ESA/STScI/AURA -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
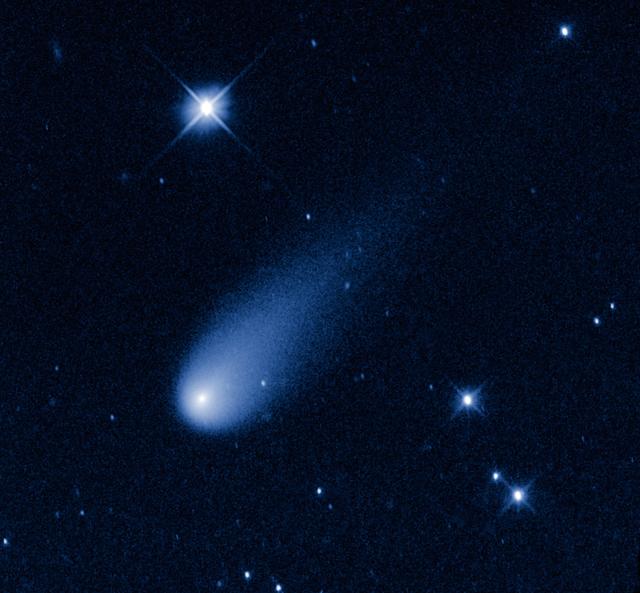

Superficially resembling a skyrocket, Comet ISON is hurtling toward the Sun at a whopping 48,000 miles per hour. Its swift motion is captured in this image taken May 8, 2013, by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. At the time the image was taken, the comet was 403 million miles from Earth, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Unlike a firework, the comet is not combusting, but in fact is pretty cold. Its skyrocket-looking tail is really a streamer of gas and dust bleeding off the icy nucleus, which is surrounded by a bright, star-like-looking coma. The pressure of the solar wind sweeps the material into a tail, like a breeze blowing a windsock. As the comet warms as it moves closer to the Sun, its rate of sublimation will increase. The comet will get brighter and the tail grows longer. The comet is predicted to reach naked-eye visibility in November. The comet is named after the organization that discovered it, the Russia-based International Scientific Optical Network. This false-color, visible-light image was taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3. Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scienti

Date: 19 Nov 2013 Comet ISON shows off its tail in this three-minute exposure taken on 19 Nov. 2013 at 6:10 a.m. EST, using a 14-inch telescope located at the Marshall Space Flight Center. The comet is just nine days away from its close encounter with the sun; hopefully it will survive to put on a nice show during the first week of December. The star images are trailed because the telescope is tracking on the comet, which is now exhibiting obvious motion with respect to the background stars over a period of minutes. At the time of this image, Comet ISON was some 44 million miles from the sun -- and 80 million miles from Earth -- moving at a speed of 136,700 miles per hour. Credit: NASA/MSFC/Aaron Kingery -------- More details on Comet ISON: Comet ISON began its trip from the Oort cloud region of our solar system and is now travelling toward the sun. The comet will reach its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- 28 Nov 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun's surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. Catalogued as C/2012 S1, Comet ISON was first spotted 585 million miles away in September 2012. This is ISON's very first trip around the sun, which means it is still made of pristine matter from the earliest days of the solar system’s formation, its top layers never having been lost by a trip near the sun. Comet ISON is, like all comets, a dirty snowball made up of dust and frozen gases like water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide -- some of the fundamental building blocks that scientists believe led to the formation of the planets 4.5 billion years ago. NASA has been using a vast fleet of spacecraft, instruments, and space- and Earth-based telescope, in order to learn more about this time capsule from when the solar system first formed. The journey along the way for such a sun-grazing comet can be dangerous. A giant ejection of solar material from the sun could rip its tail off. Before it reaches Mars -- at some 230 million miles away from the sun -- the radiation of the sun begins to boil its water, the first step toward breaking apart. And, if it survives all this, the intense radiation and pressure as it flies near the surface of the sun could destroy it altogether. This collection of images show ISON throughout that journey, as scientists watched to see whether the comet would break up or remain intact. The comet reaches its closest approach to the sun on Thanksgiving Day -- Nov. 28, 2013 -- skimming just 730,000 miles above the sun’s surface. If it comes around the sun without breaking up, the comet will be visible in the Northern Hemisphere with the naked eye, and from what we see now, ISON is predicted to be a particularly bright and beautiful comet. ISON stands for International Scientific Optical Network, a group of observatories in ten countries who have organized to detect, monitor, and track objects in space. ISON is managed by the Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, part of the Russian Academy of Sciences. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/39501</b>