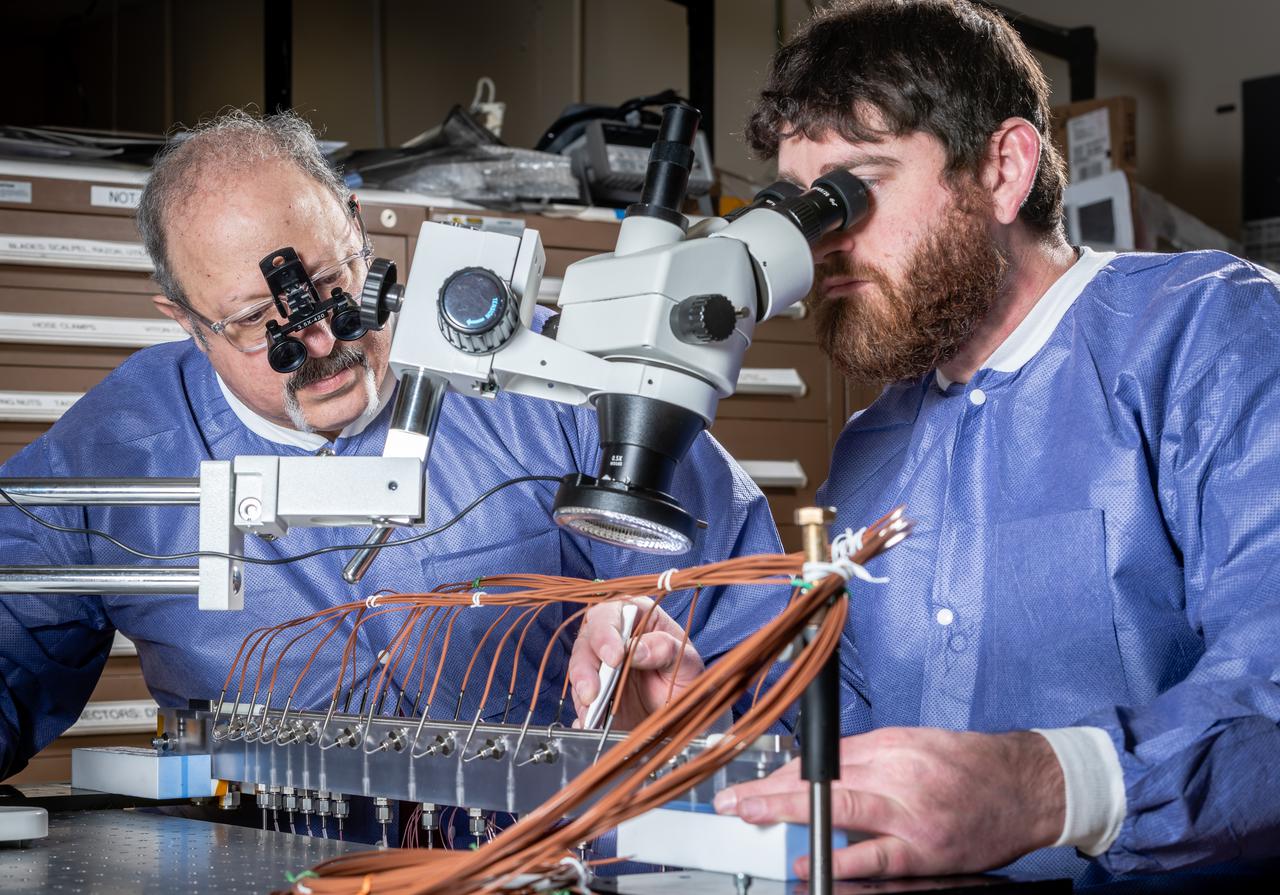

Flow Boiling Condensation Experiment, FBCE Micro Gravity Payload, Condensation Module – Heat Transfer (CM-HT) Test Section Hardware Fabrication
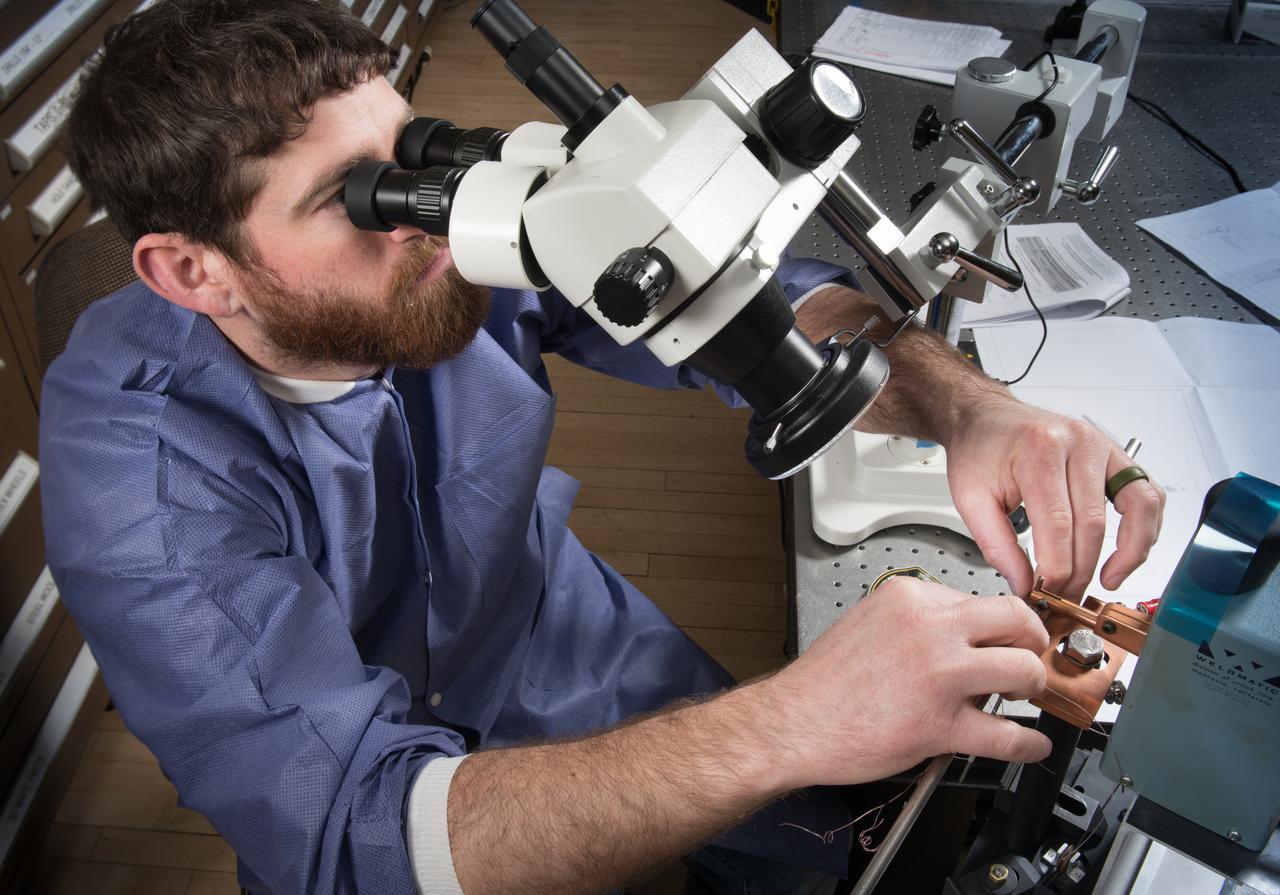

A technician in the Instrumentation Shop during the buildup of Flow Boiling Condensation Experiment, FBCE Micro Gravity Payload, Condensation Module – Heat Transfer, CM-HT, Test Section Hardware Fabrication
Interior of a combustion experiment apparatus used in the 2.2-second drop tower at NASA's Glenn Research Center. This was shown to students participating in the second Dropping in a Microgravity Environment (DIME) competition held April 23-25, 2002, at NASA's Glenn Research Center. Competitors included two teams from Sycamore High School, Cincinnati, OH, and one each from Bay High School, Bay Village, OH, and COSI Academy, Columbus, OH. DIME is part of NASA's education and outreach activities. Details are on line at http://microgravity.grc.nasa.gov/DIME_2002.html.
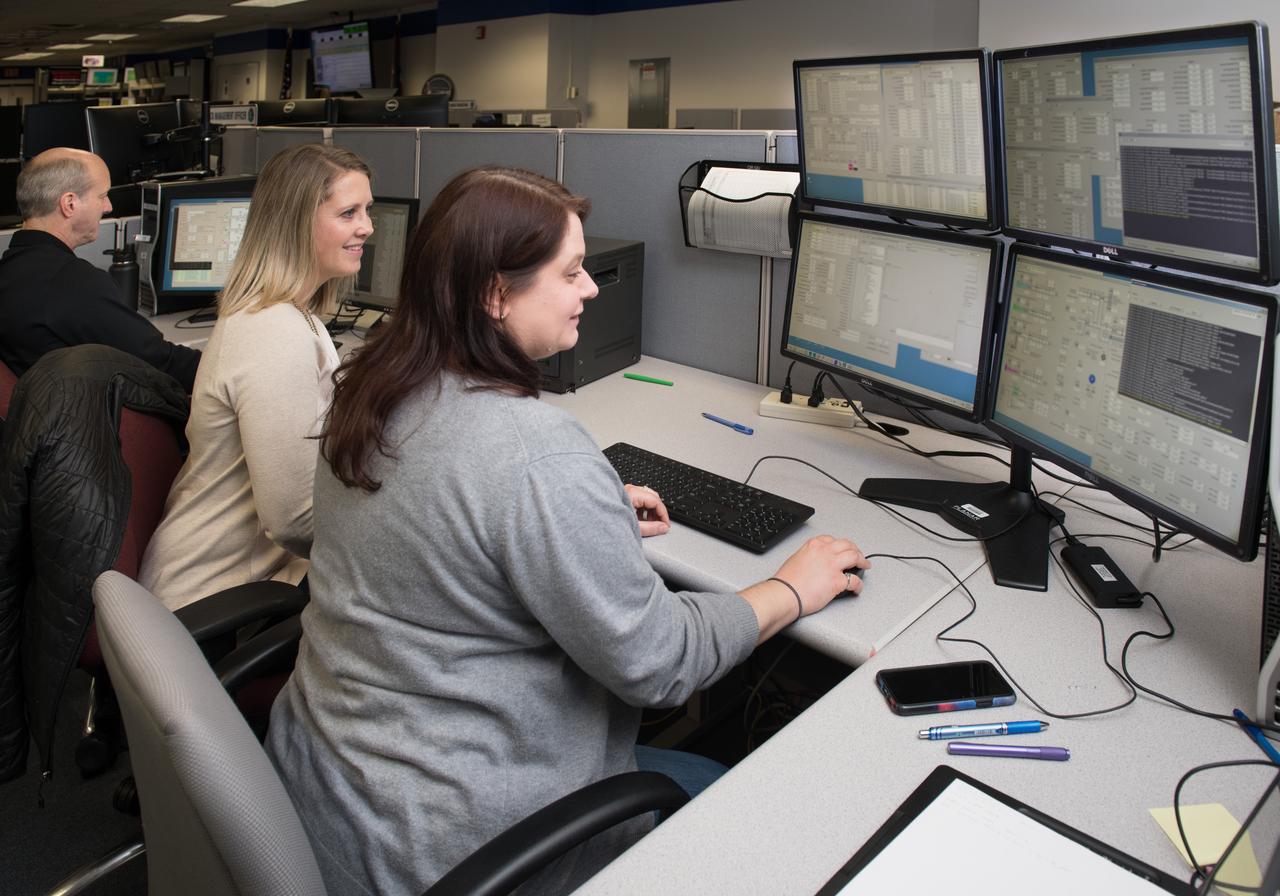

Testing of software with ground hardware for the Structue and Response of Spherical Diffusion Flames, s-Flame, experiment - of the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments, ACME, project conducted in the ISS Combustion Integrated Rack, CIR - by ACME Software Engineer Jeffrey Eggers, Operations Lead Angela Adams, and Planning Lead Melani Smajdek in the Telescience Support Center, TSC, also known as the Glenn ISS Payload Operations Center, GIPOC
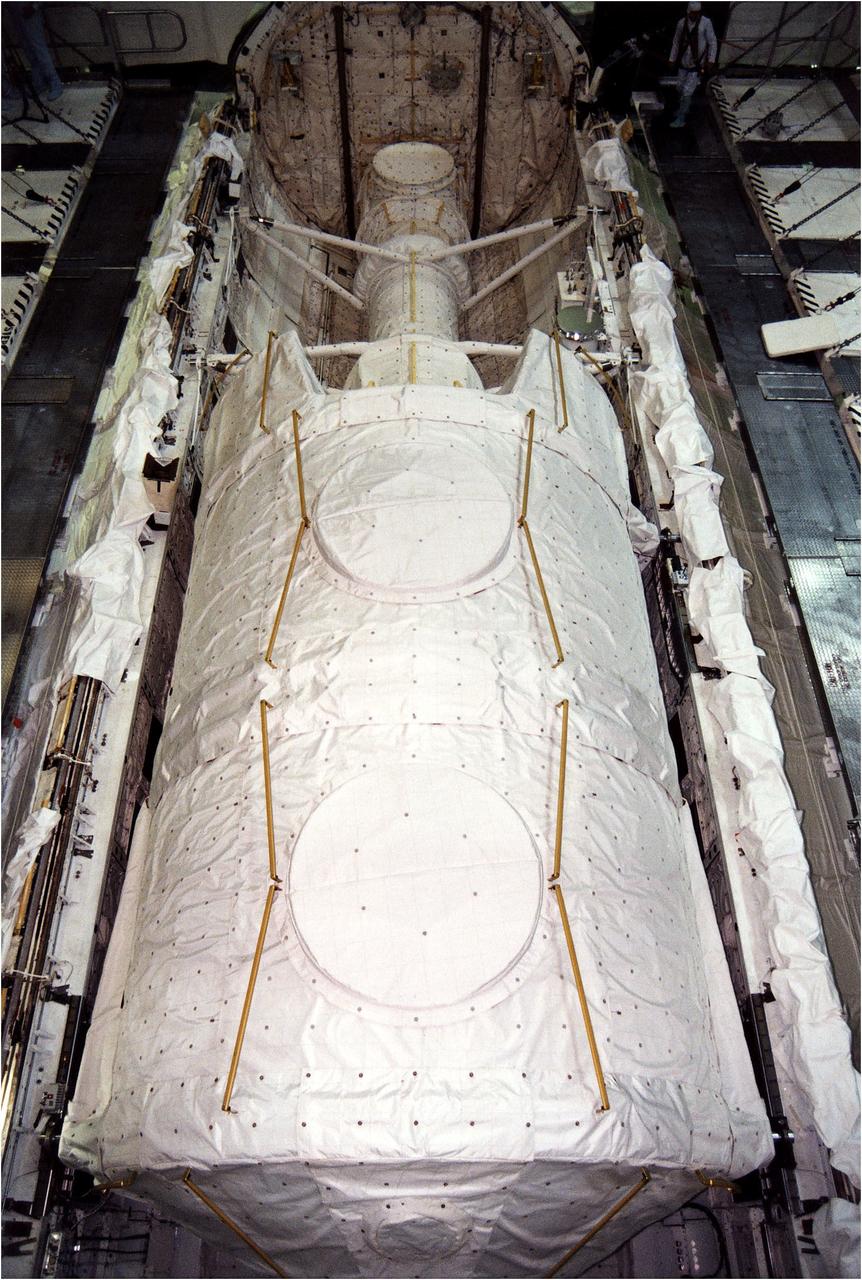
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
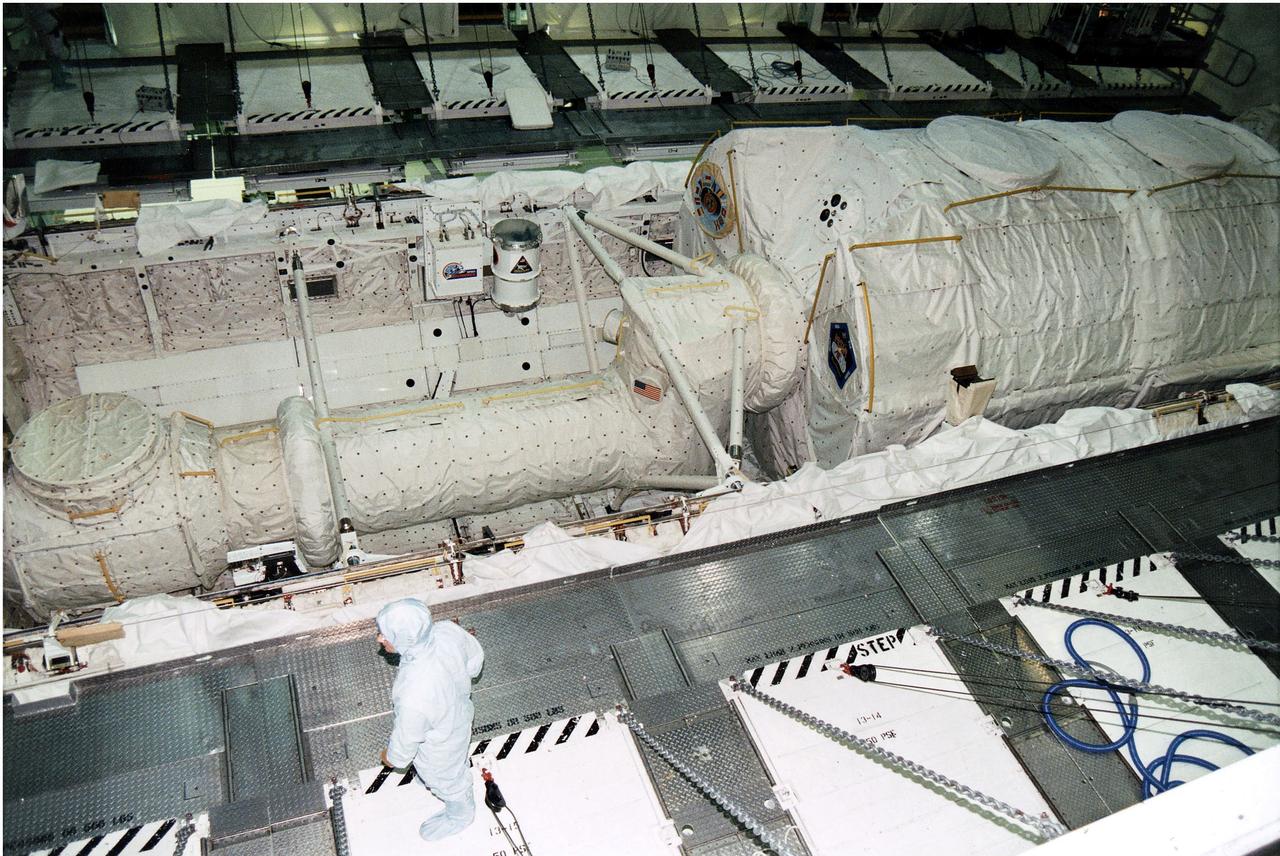
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Microgravity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) Spacelab module is installed into the payload bay of the Space Shuttle Orbiter Columbia in Orbiter Processing Facility 1. The Spacelab long crew transfer tunnel that leads from the orbiter's crew airlock to the module is also aboard, as well as the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attached to the right side of Columbia's payload bay. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments.
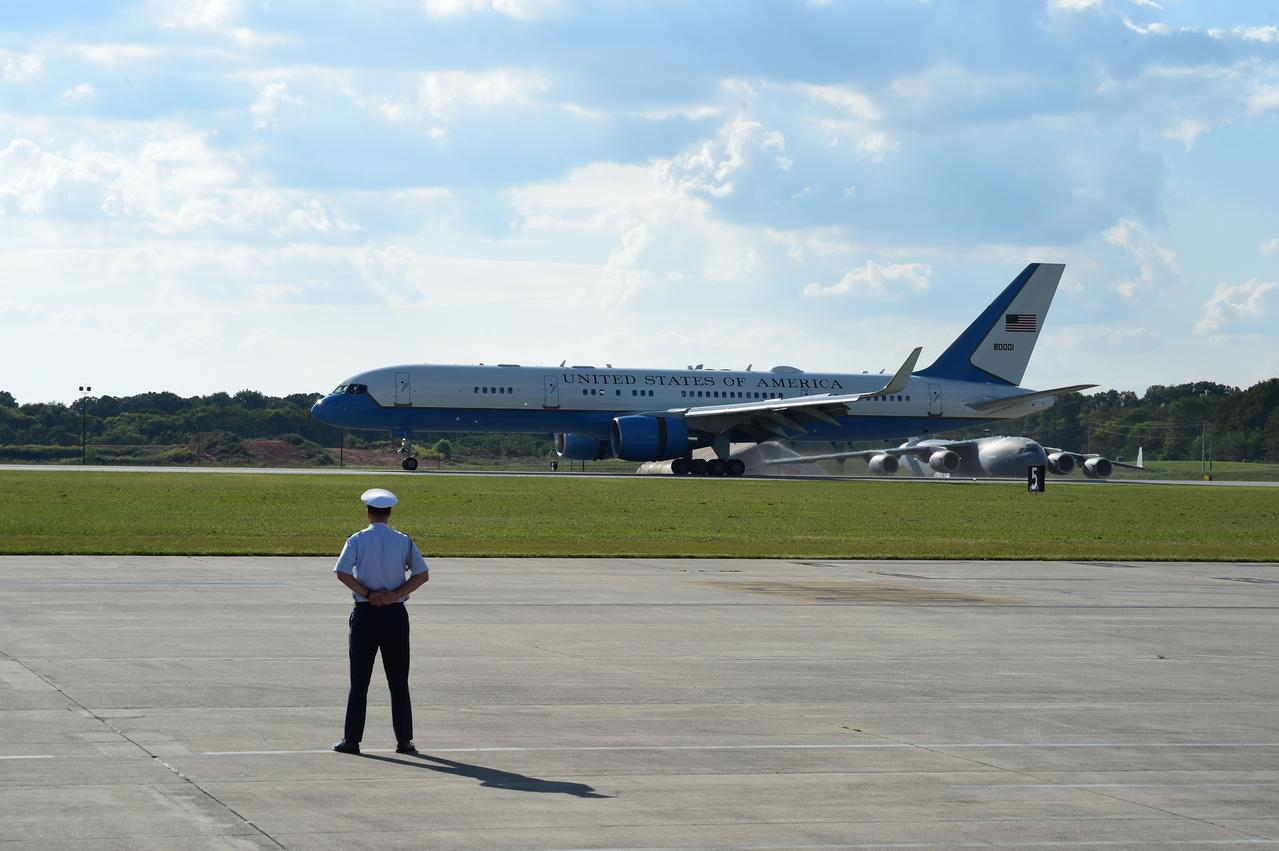

Air Force Two lands with Vice President Mike Pence along with Congressman Robert Aderholt at the Redstone Army Airfield in Huntsville, Alabama, on Monday, Sept. 25. The Vice President is visiting NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, located on Redstone Arsenal, to meet with employees, view test hardware for NASA’s Space Launch System — America’s new deep-space rocket, and tour the Payload Operations Integration Center, “science central” for the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Emmett Given)
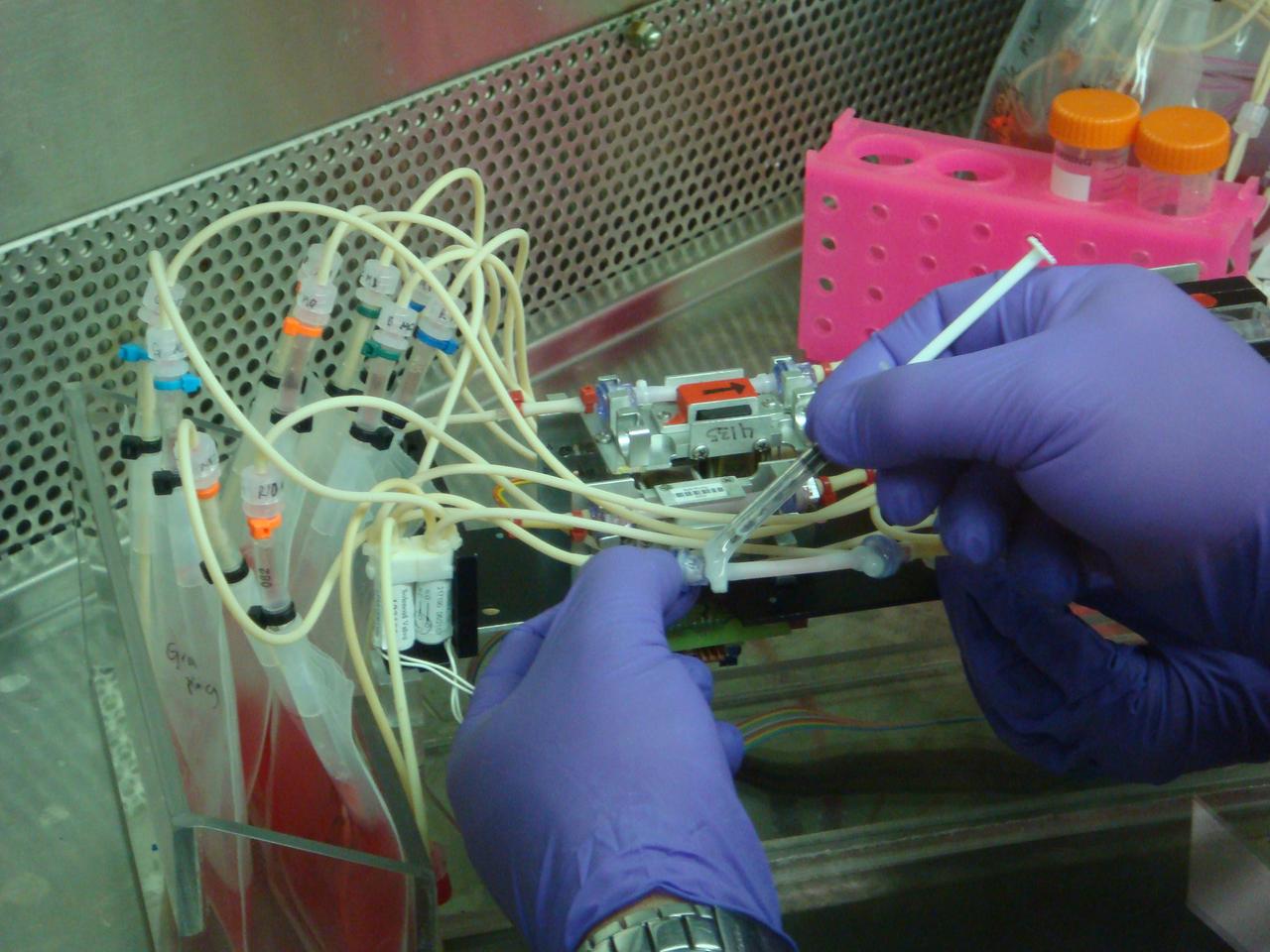

STS-131 payload; Ames Space Bio-Sciences Lab, Dr Eduardo Almeida P. I.; Assembly of Space Tissue Loss Hardware
STS-131 payload; Ames Space Bio-Sciences Lab, Dr Eduardo Almeida P. I.; Assembly of Space Tissue Loss hardware
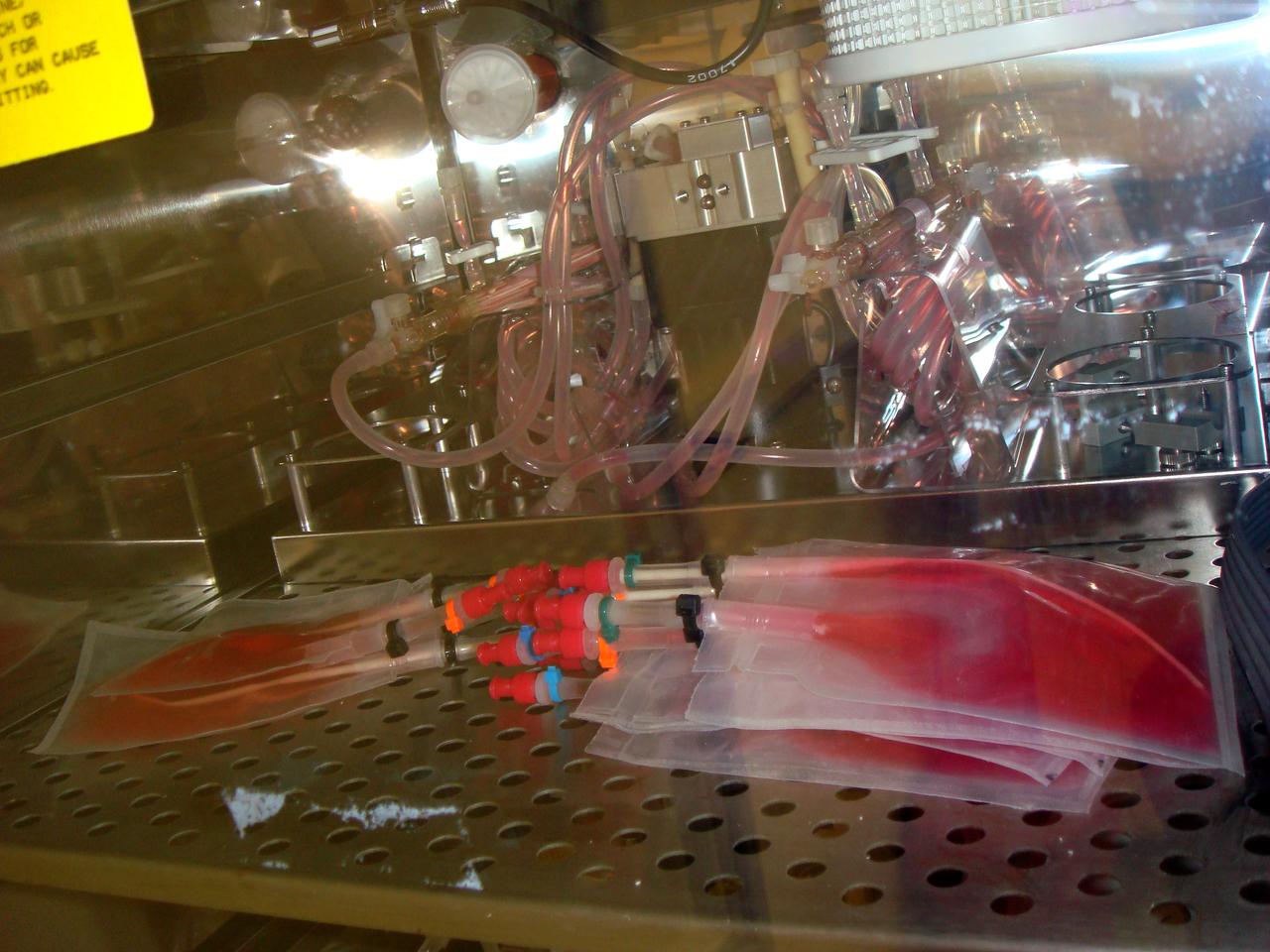

STS-131 payload; Ames Space Bio-Sciences Lab, Dr Eduardo Almeida P. I.; Media Bags: part of Space Tissue Loss hardware.
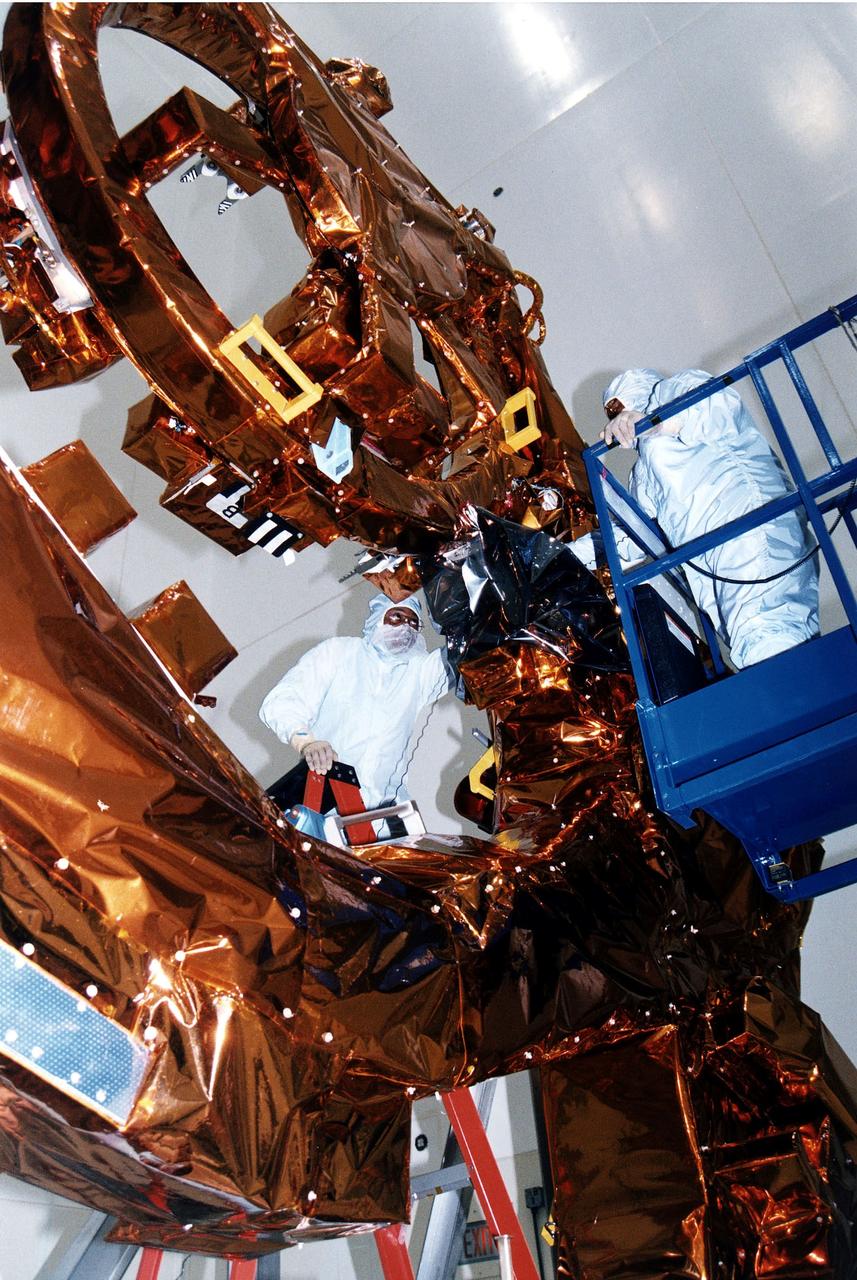

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in KSC's Vertical Processing Facility make final adjustments to the Flight Support System (FSS) for STS-82, the second Hubble Space Telescope servicing mission. The FSS is reusable flight hardware that provides the mechanical, structural and electrical interfaces between HST, the space support equipment and the orbiter for payload retrieval and on-orbit servicing. Liftoff aboard Discovery is targeted Feb. 11 with a crew of seven.
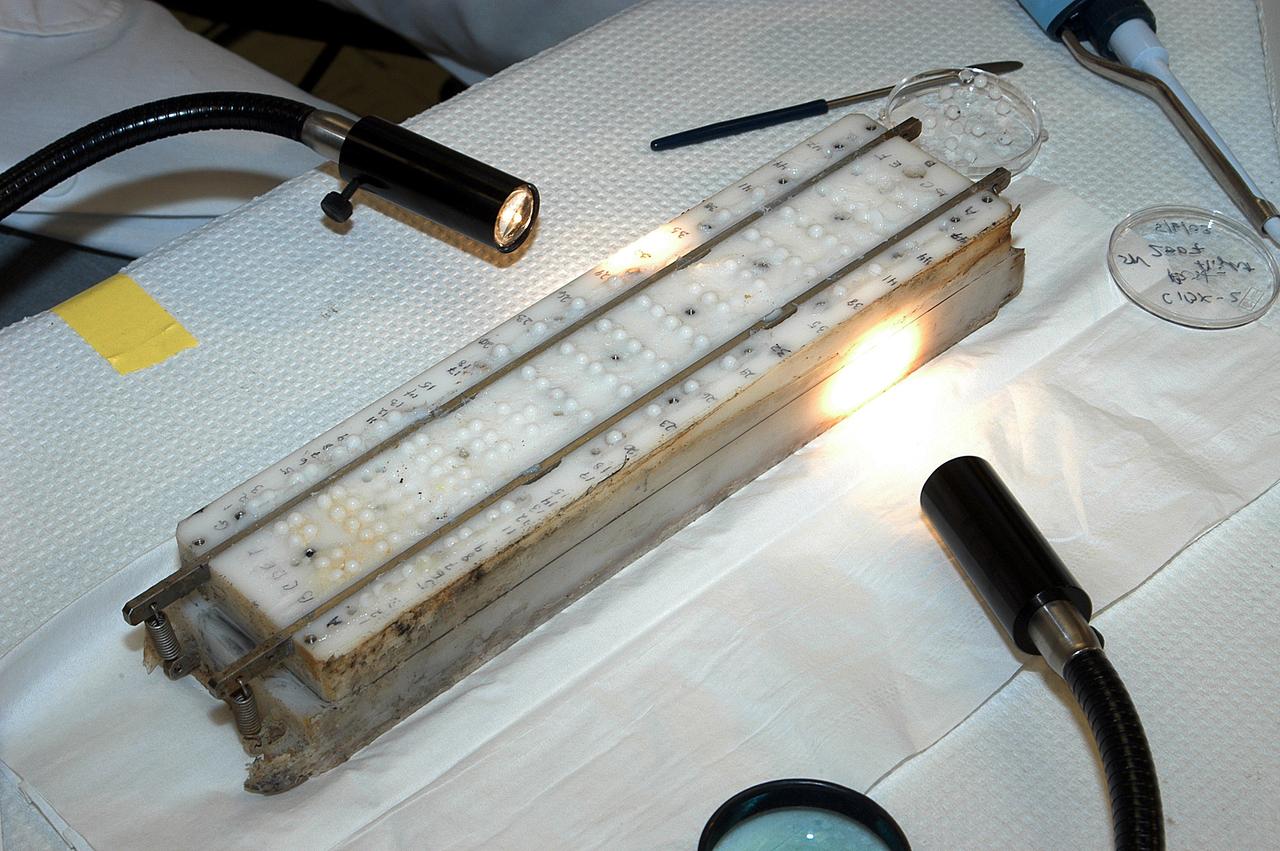

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The apparatus shown was designed to hold microcapsules for research on mission STS-107. It is one over several included in the Commercial ITA Biomedical Experiments payload. The box was recently recovered during the search for Columbia debris. The drug delivery system and spaceflight hardware was developed jointly by JSC, the Institute for Research Inc. and Instrumentation Technology Associates Inc. to conduct microencapsulation experiments under microgravity conditions.
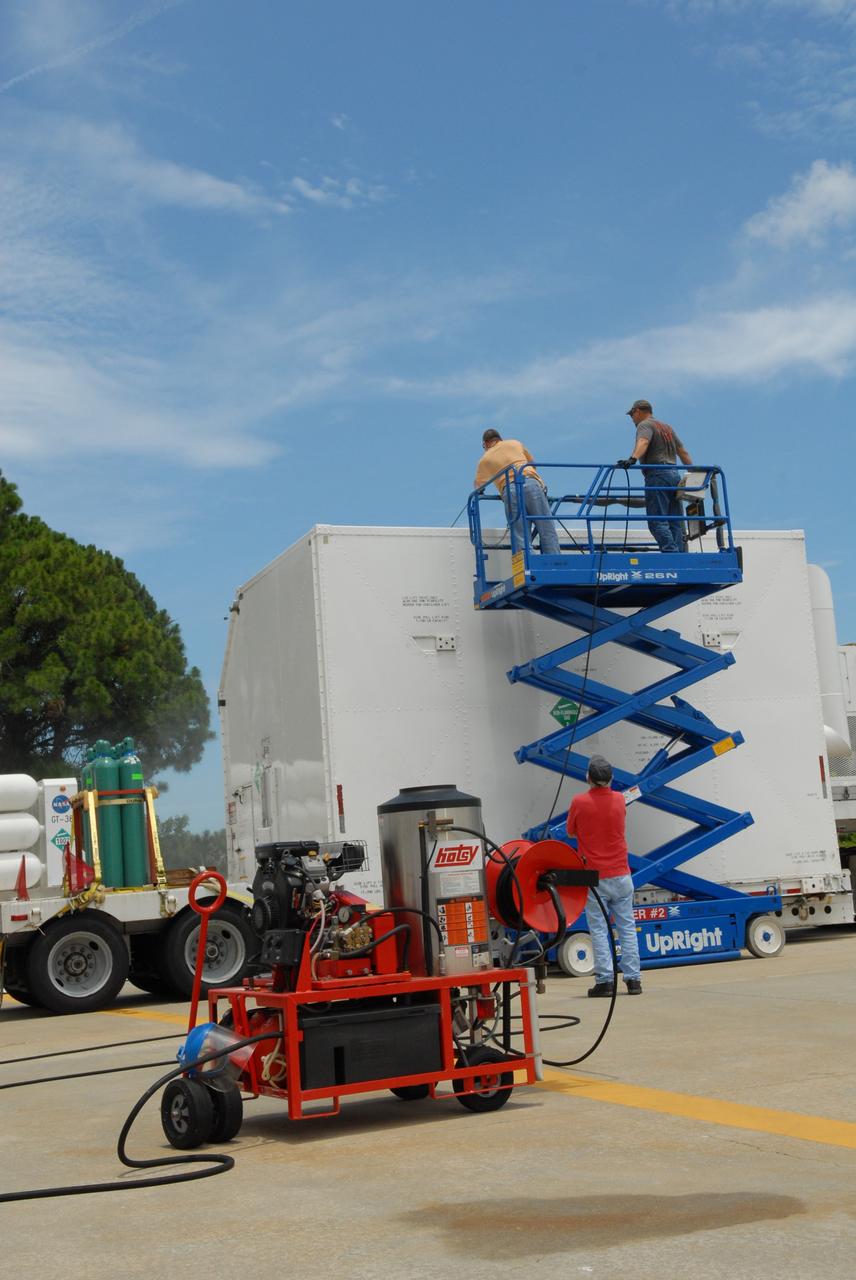

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
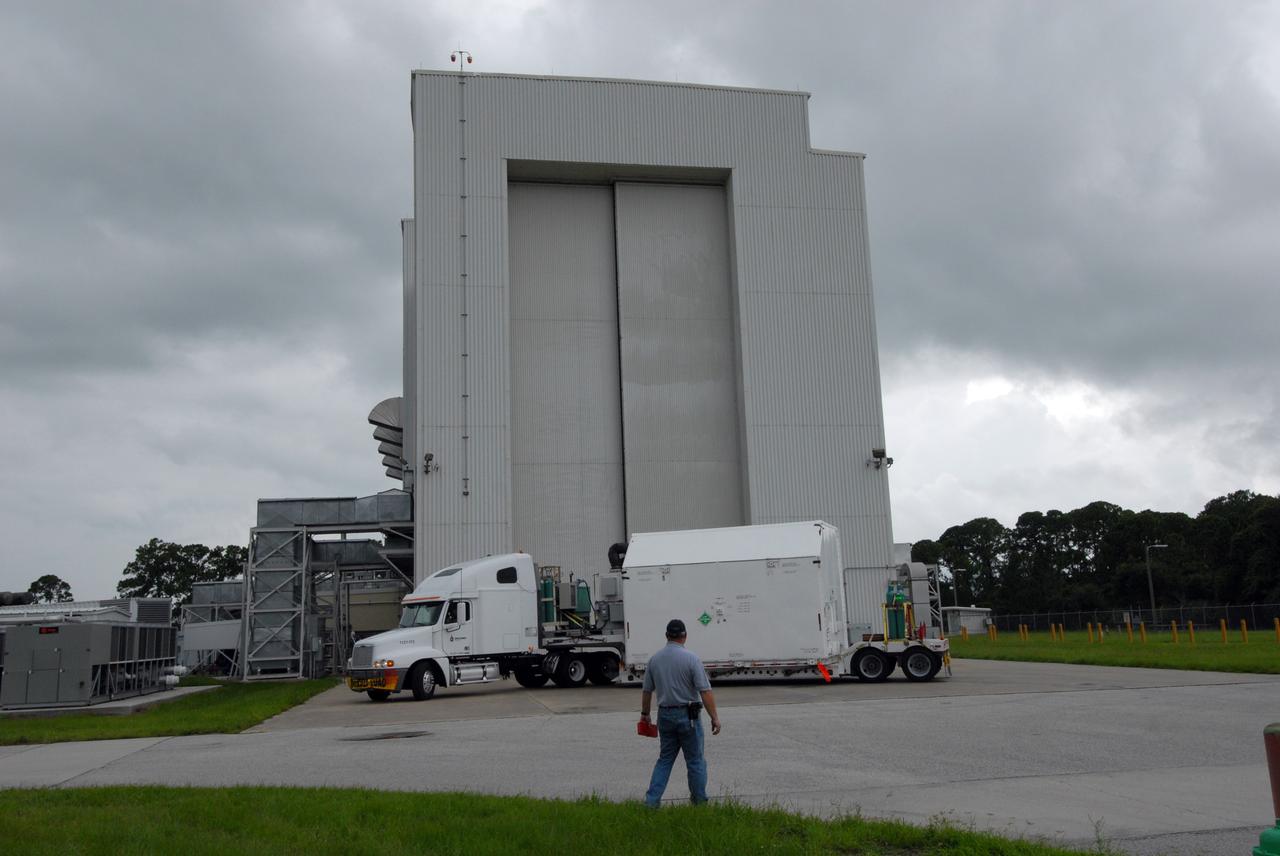

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Another container with flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is moved toward the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the facility, the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
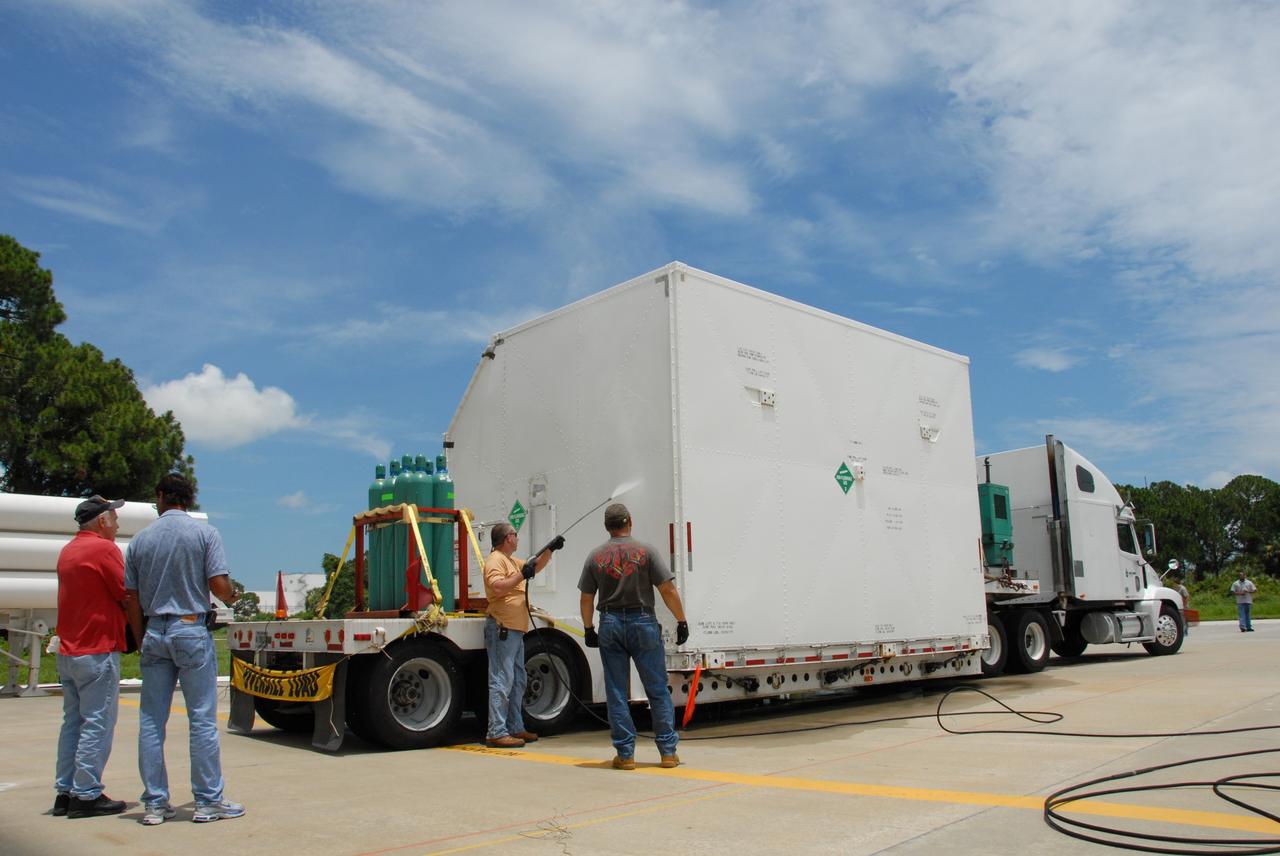

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
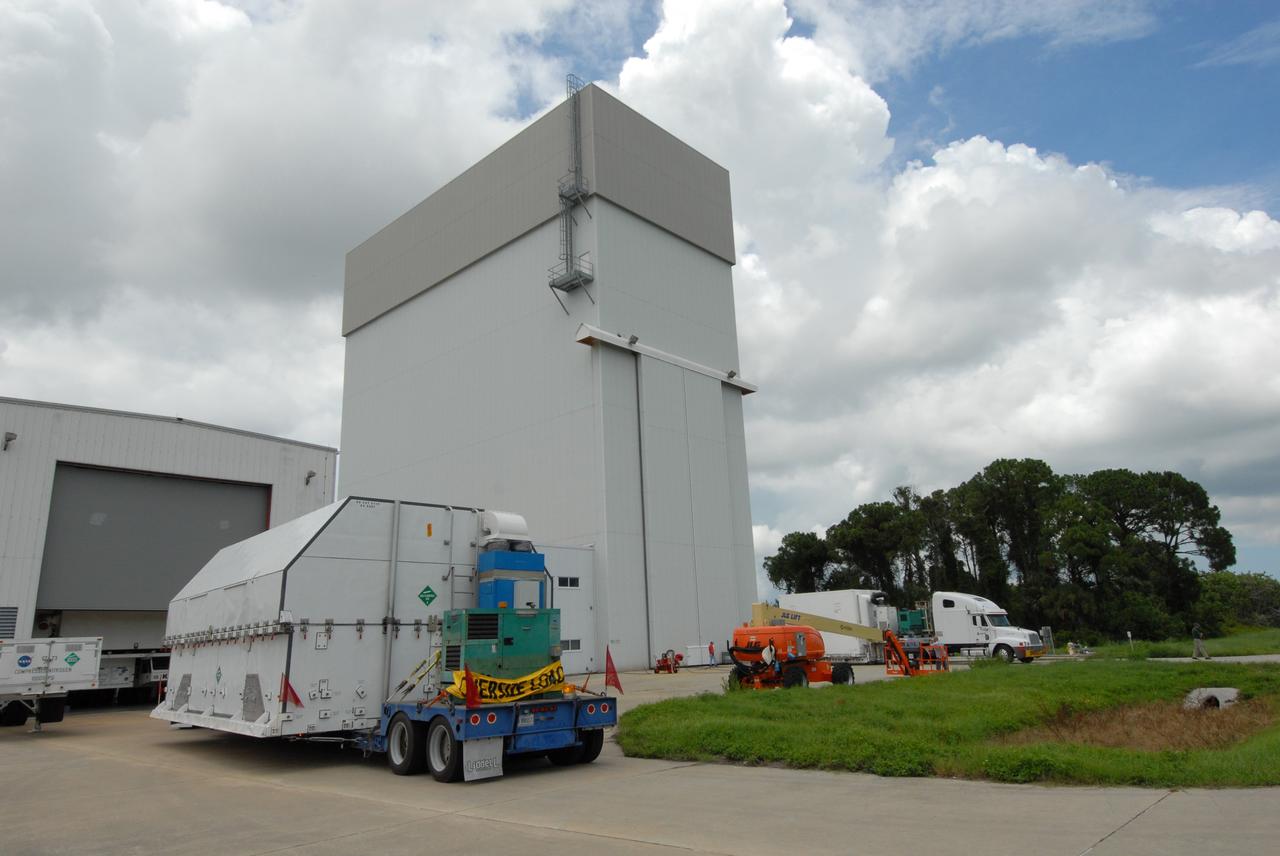

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A container with flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is moved toward the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the facility, the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
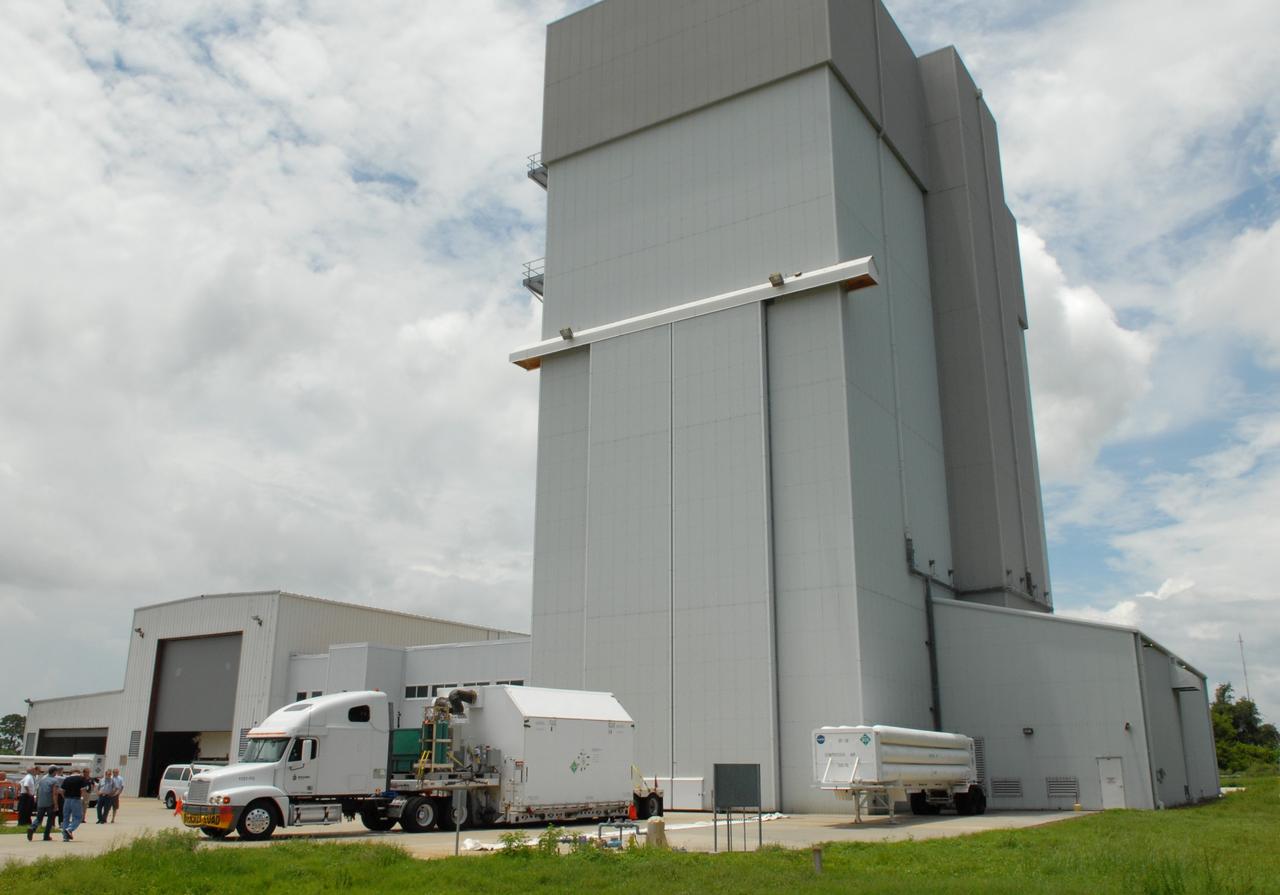

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope arrives at the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. After being steam cleaned, the hardware will be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
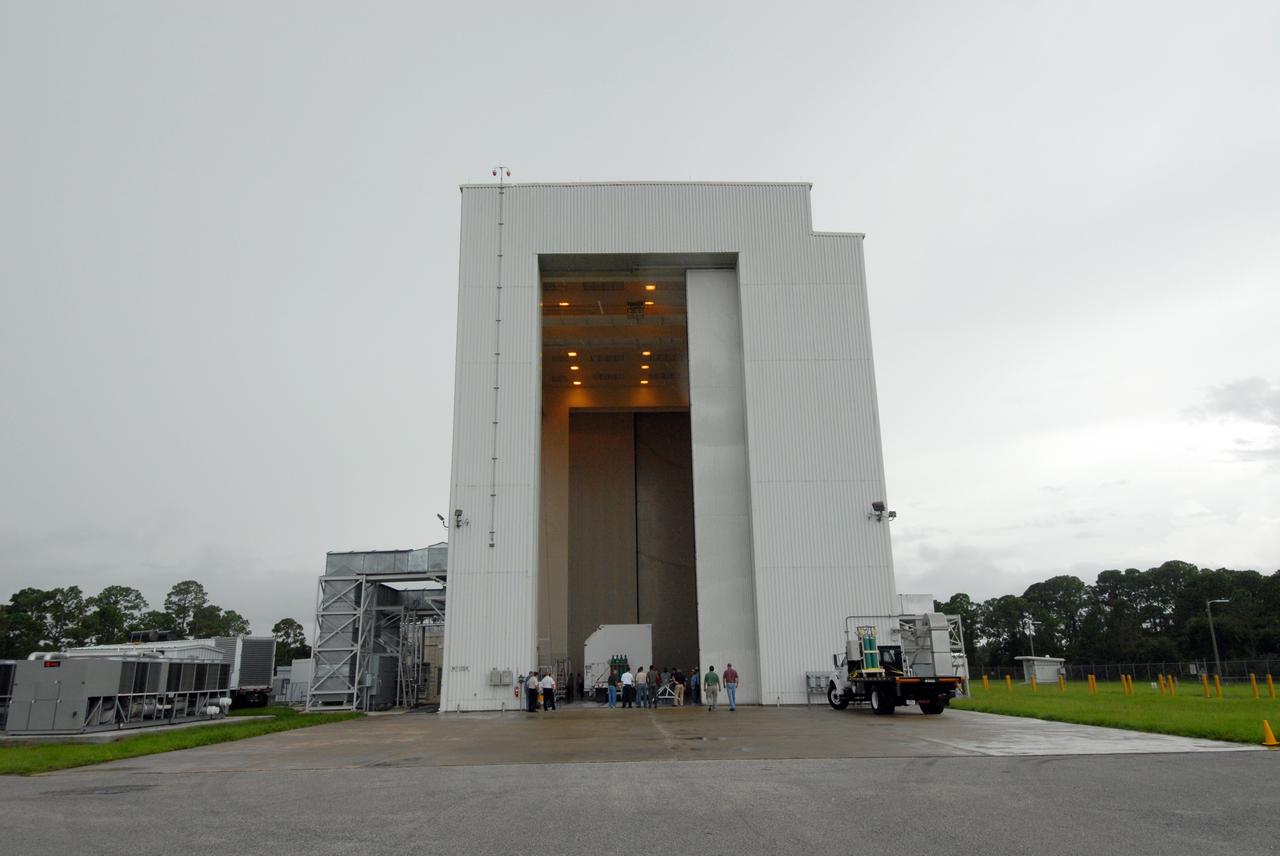

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A container with flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is moved into the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the facility, the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
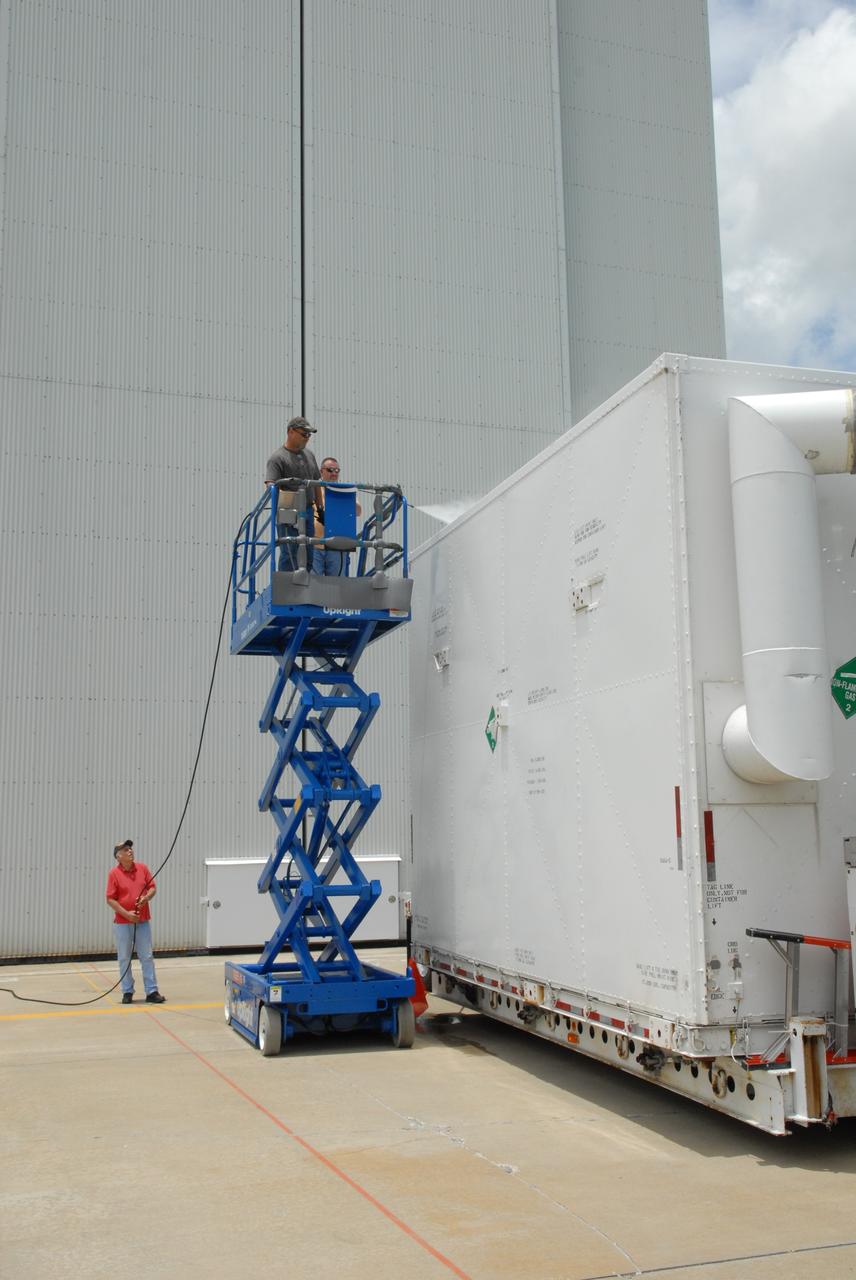

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
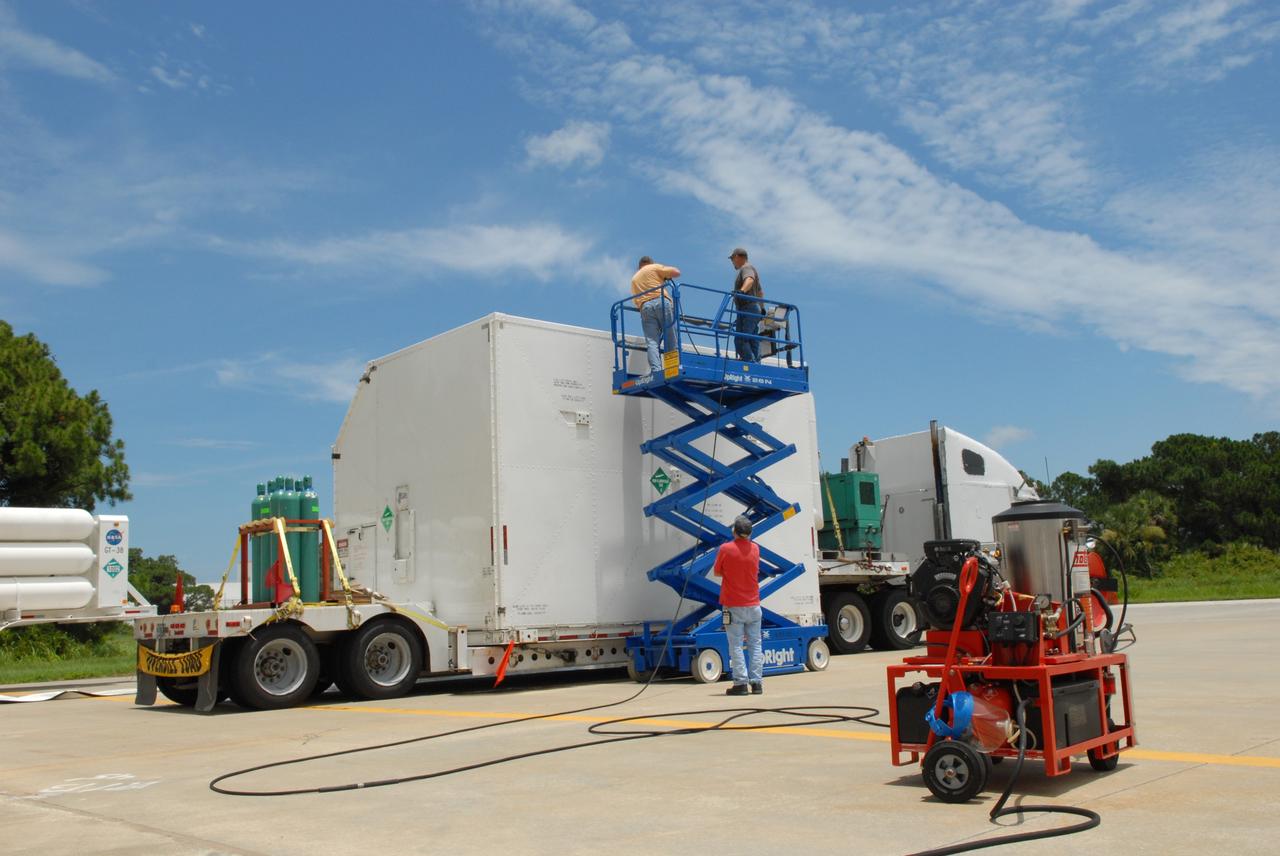

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
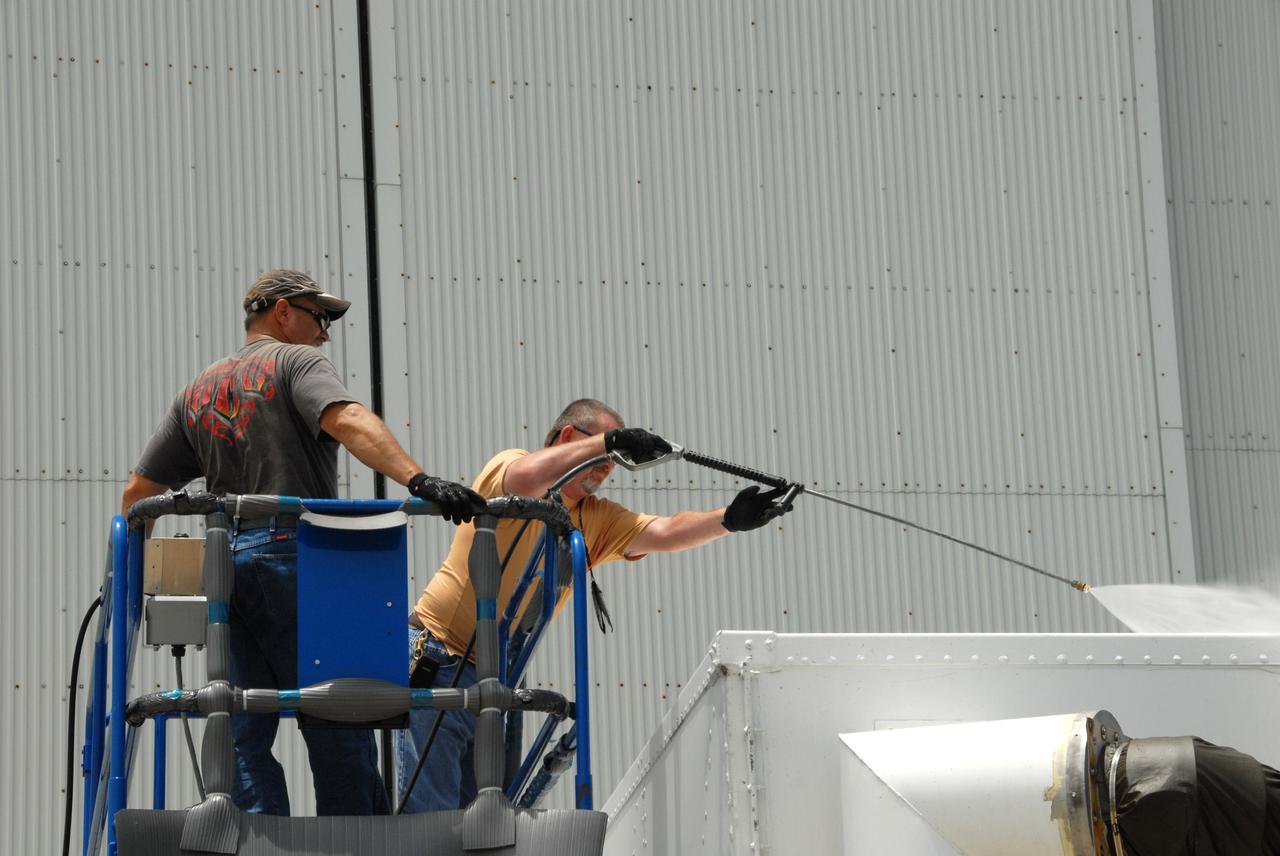

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At the Canister Rotation Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers steam clean the shipping containers holding the first major flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The containers will next be moved to the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing facility where the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
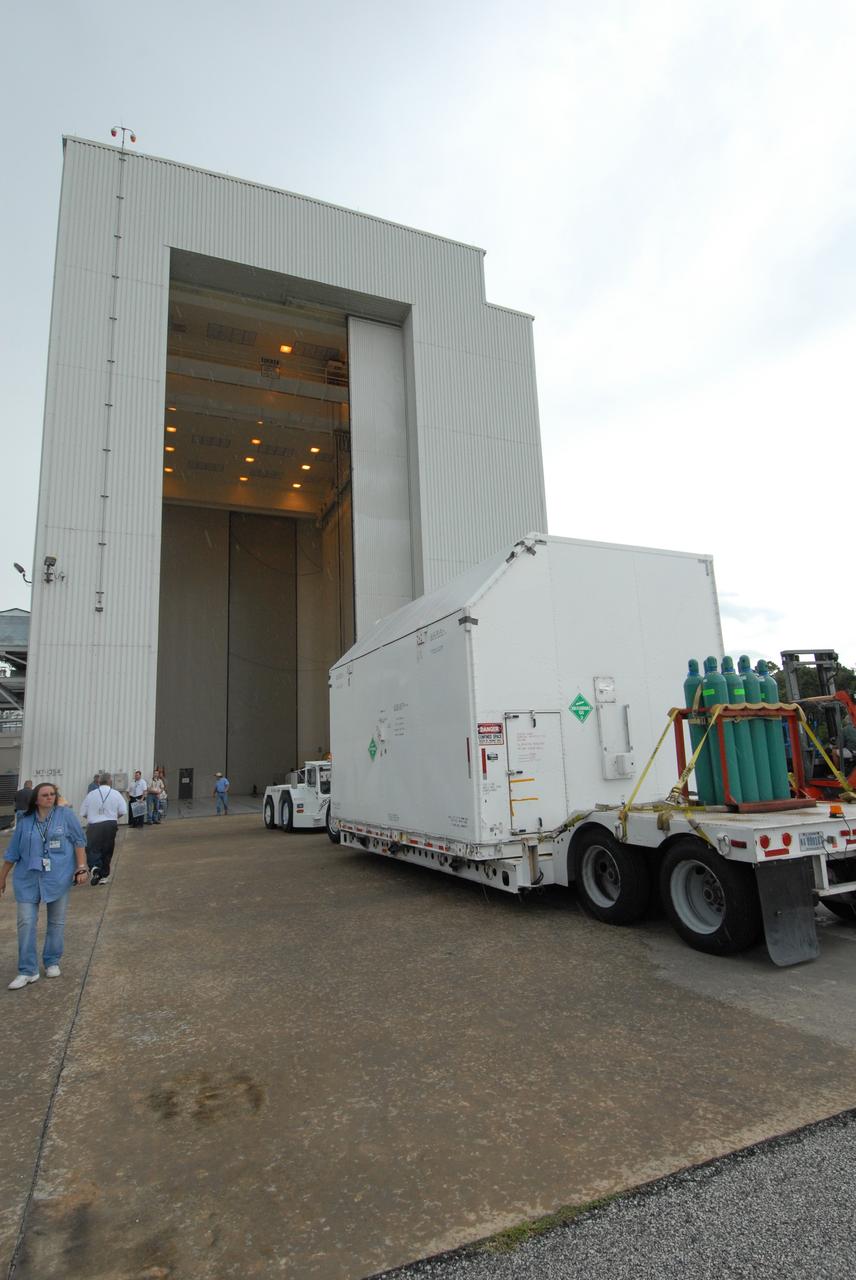

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A container with flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is moved toward the open door of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the facility, the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
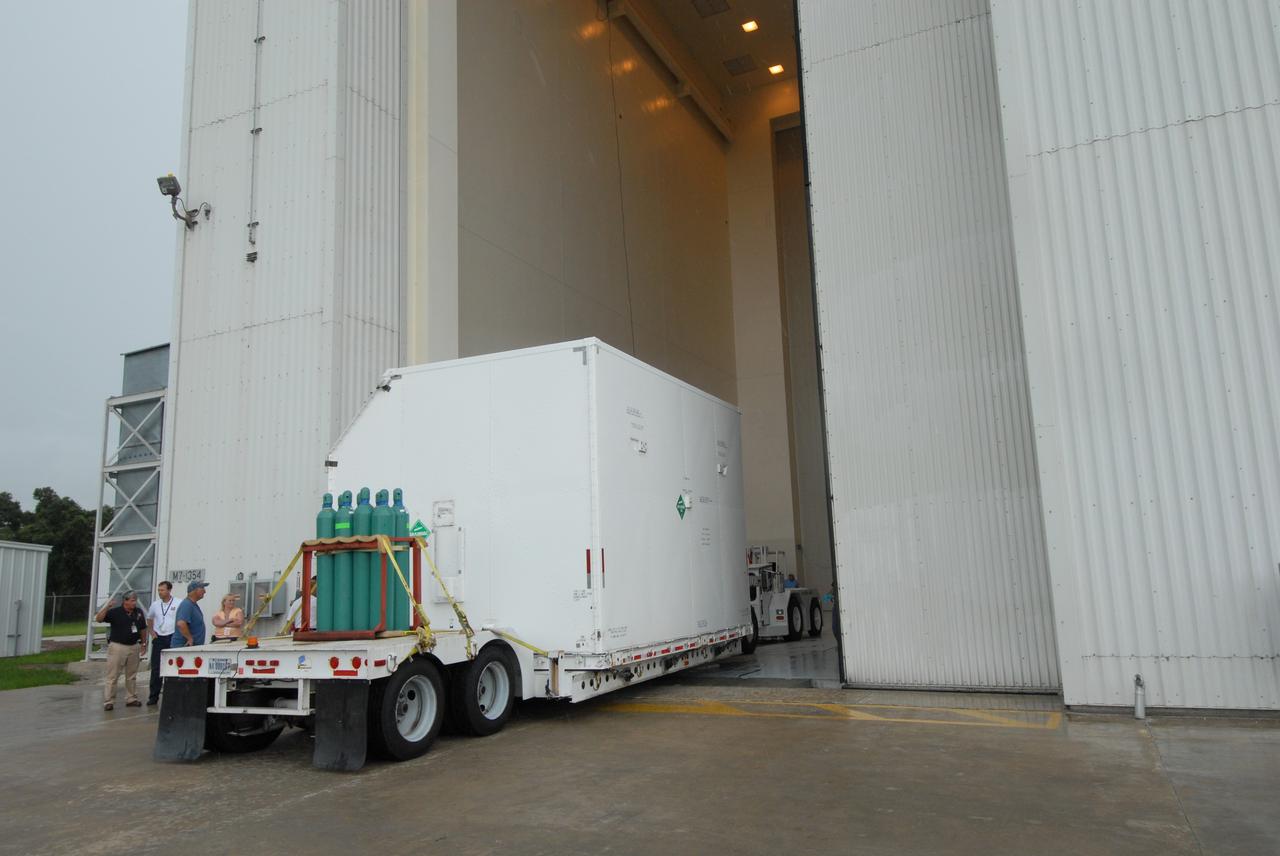

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A container with flight hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is moved through the open door into the airlock in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. In the facility, the hardware will be prepared for its targeted October launch. The payload carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the servicing mission. The three payload carriers or pallets are the Flight Support System, the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier and the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier. At the end of July, a fourth and final carrier, the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will join the others in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where the Hubble payload is being prepared for launch. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
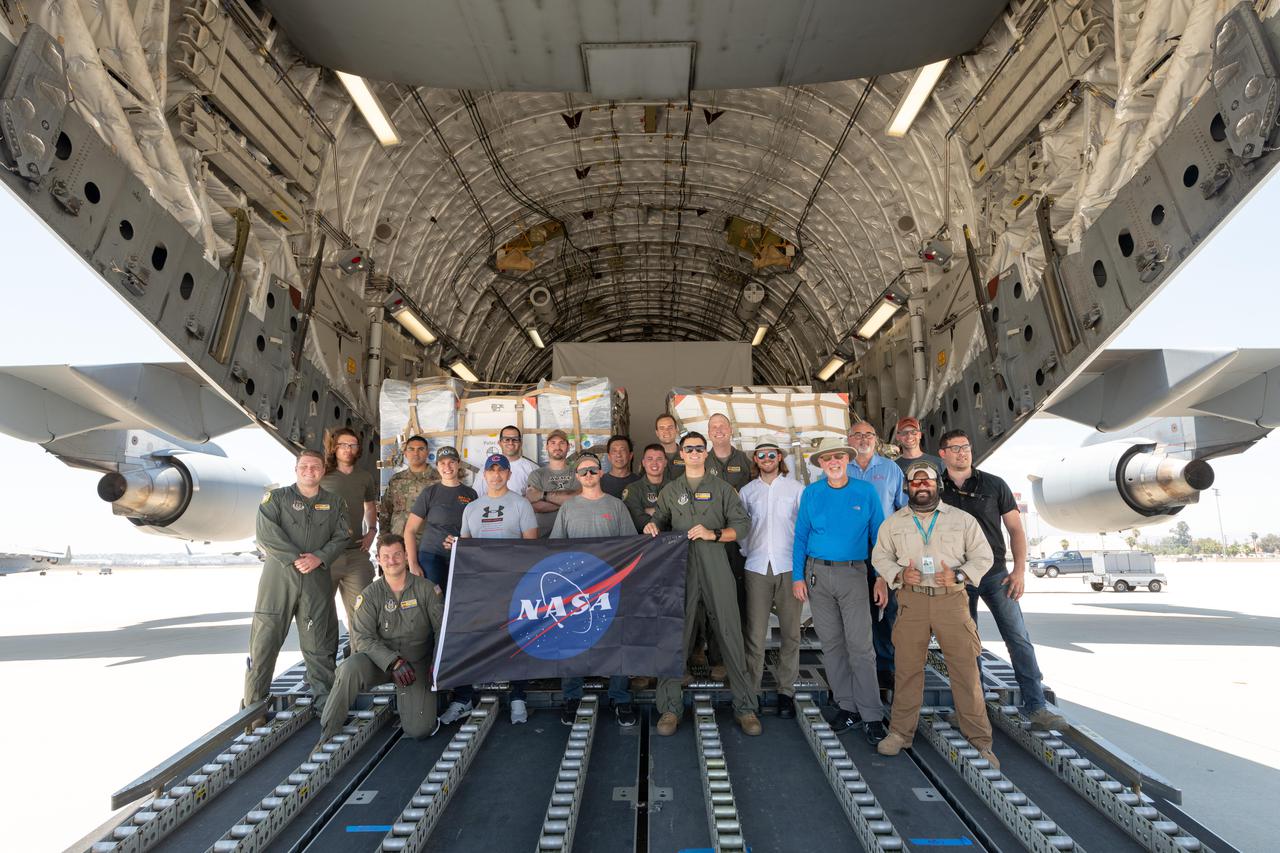

Some of the people who helped to load the hardware for the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite's research instruments onto a C-17 airplane pose for a picture. The payload left March Air Reserve Base in Riverside County, California, on June 27, 2021, and is headed to France. Once the SWOT research hardware arrives at a clean room facility near Cannes, France, engineers and technicians will complete assembly of the satellite over the next year. SWOT will make global surveys of Earth's surface water. By measuring its height, researchers can track the volume and location of the finite resource around the world. The data will help with monitoring changes in floodplains and wetlands, measure how much fresh water flows into and out of lakes and rivers and back to the ocean, and track regional shifts in sea level. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24535
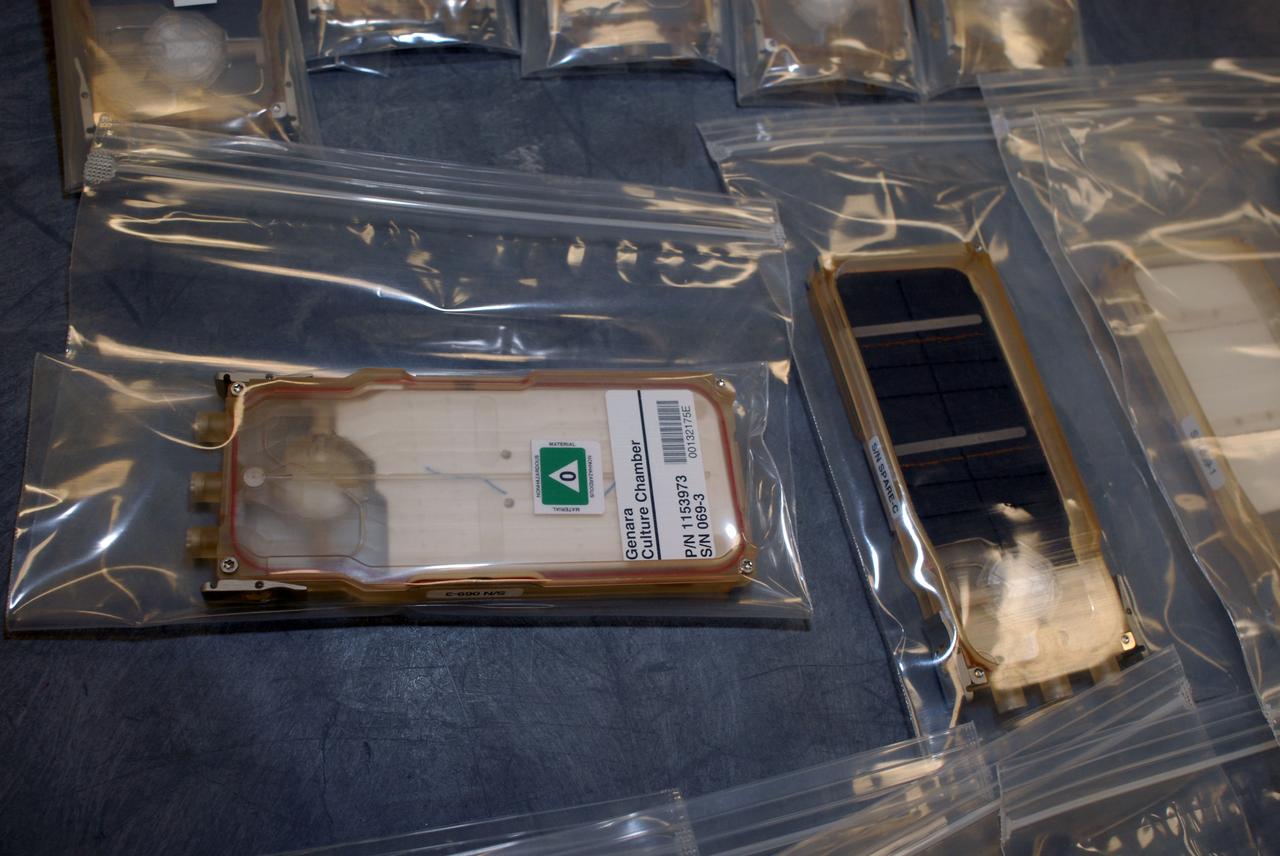

jsc2010e090140 (5/3/2010) --- Preflight photo of Gravity Related Genes in Arabidopsis GENARA-A middeck payload hardware taken in the KSC Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). Genara-A Culture Chambers.

jsc2010e090142 (5/3/2010) --- Preflight photo of Gravity Related Genes in Arabidopsis GENARA-A middeck payload hardware taken in the KSC Space Station Processing Facility (SSPF). Genara-A Experiment Containers (ECs).
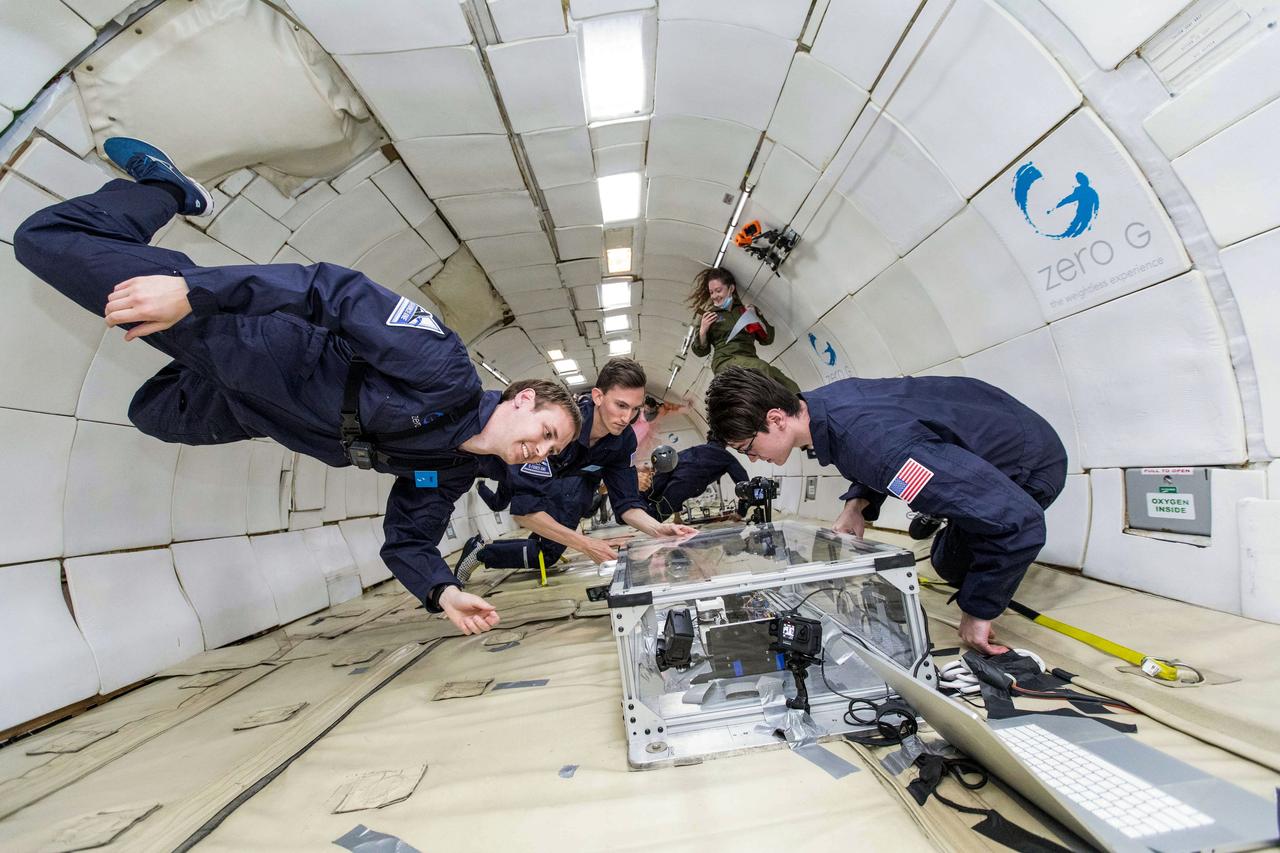

jsc2022e083566 (5/20/2022) --- The MIT Space Exploration Initiative team tests an early Extrusion payload hardware model on a parabolic flight in May 2021. Image courtesy of the MIT Space Exploration Initiative
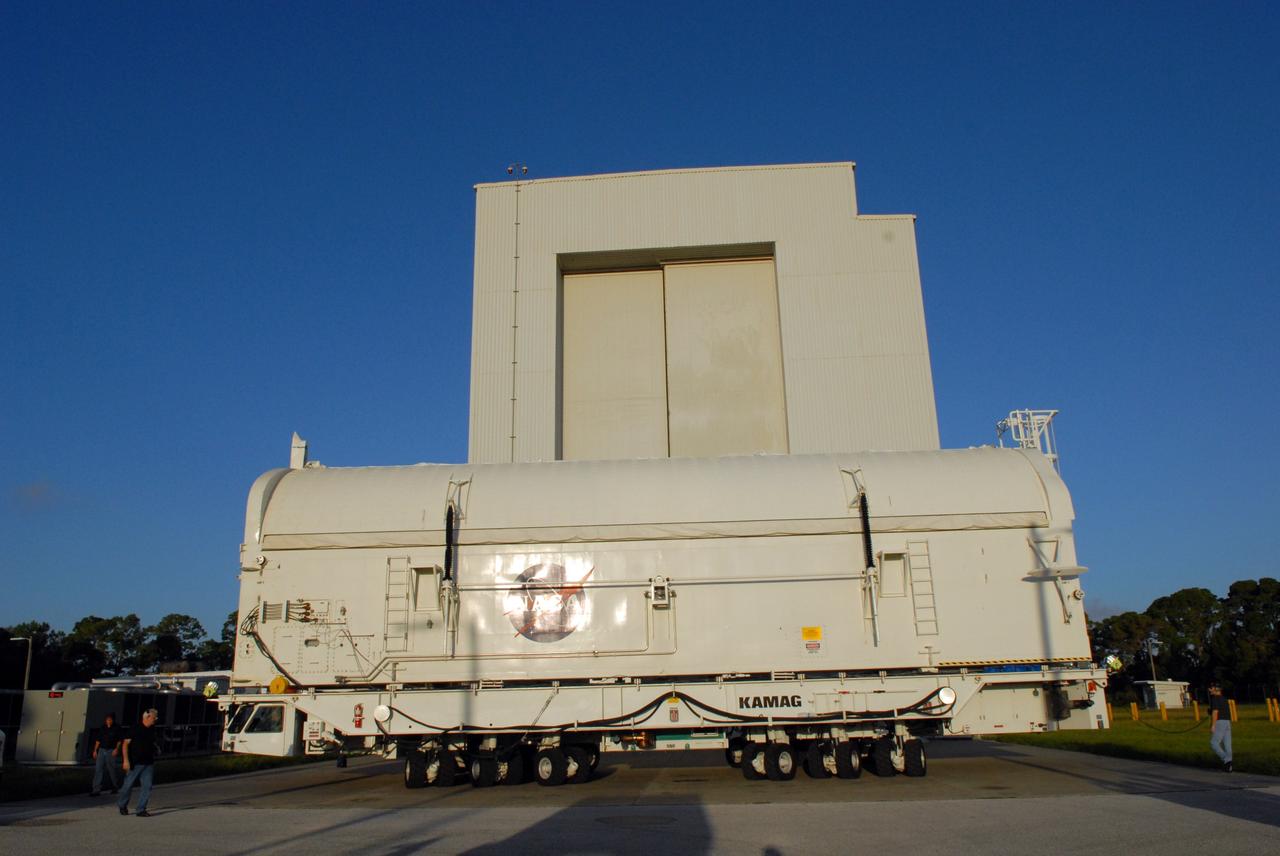

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
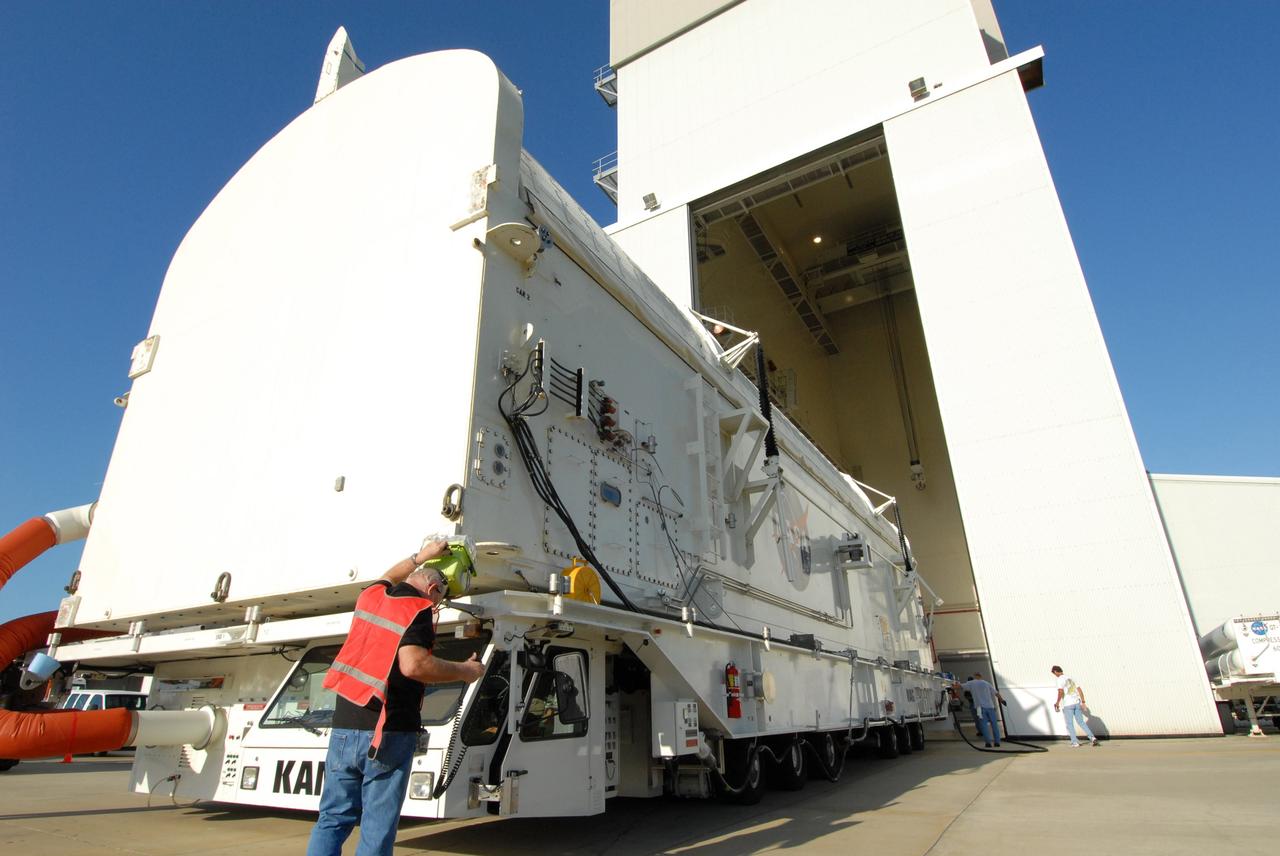

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
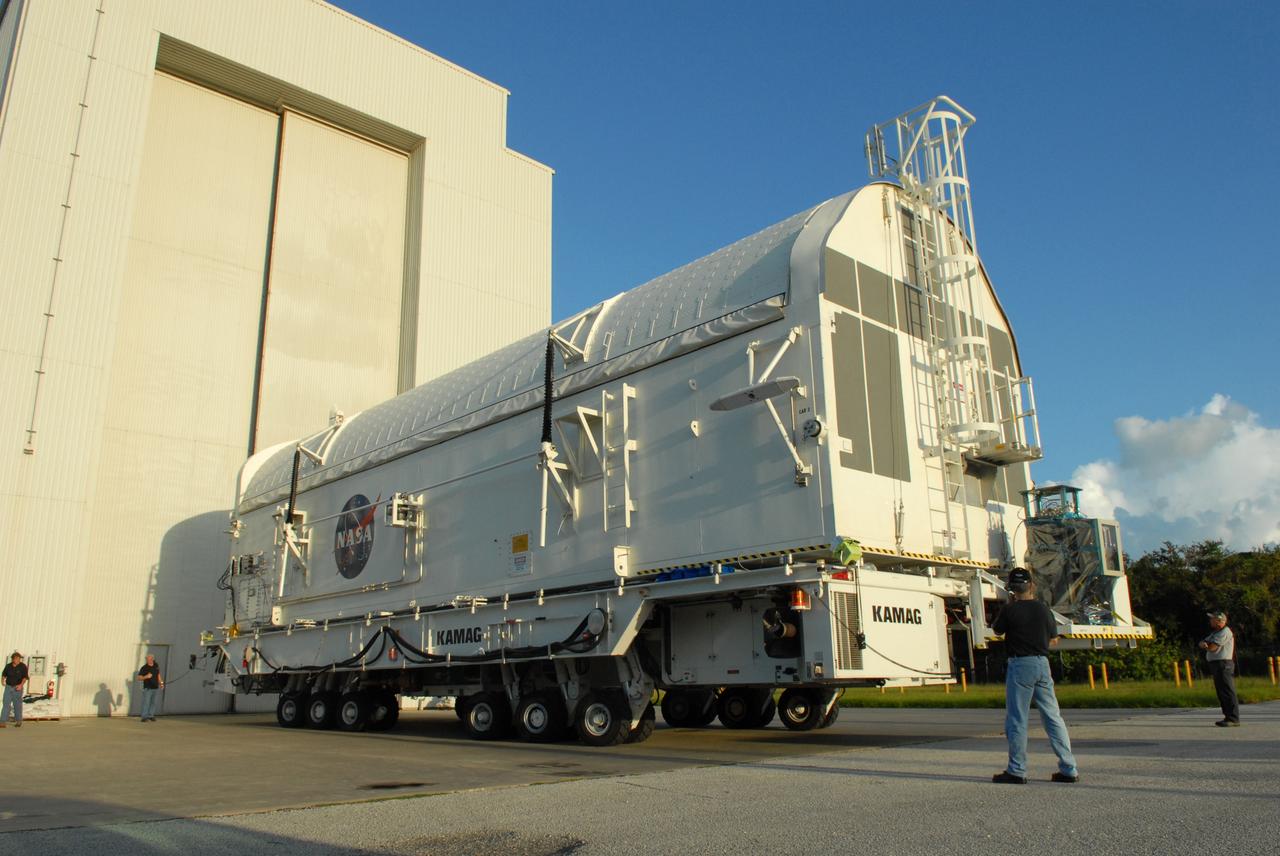

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
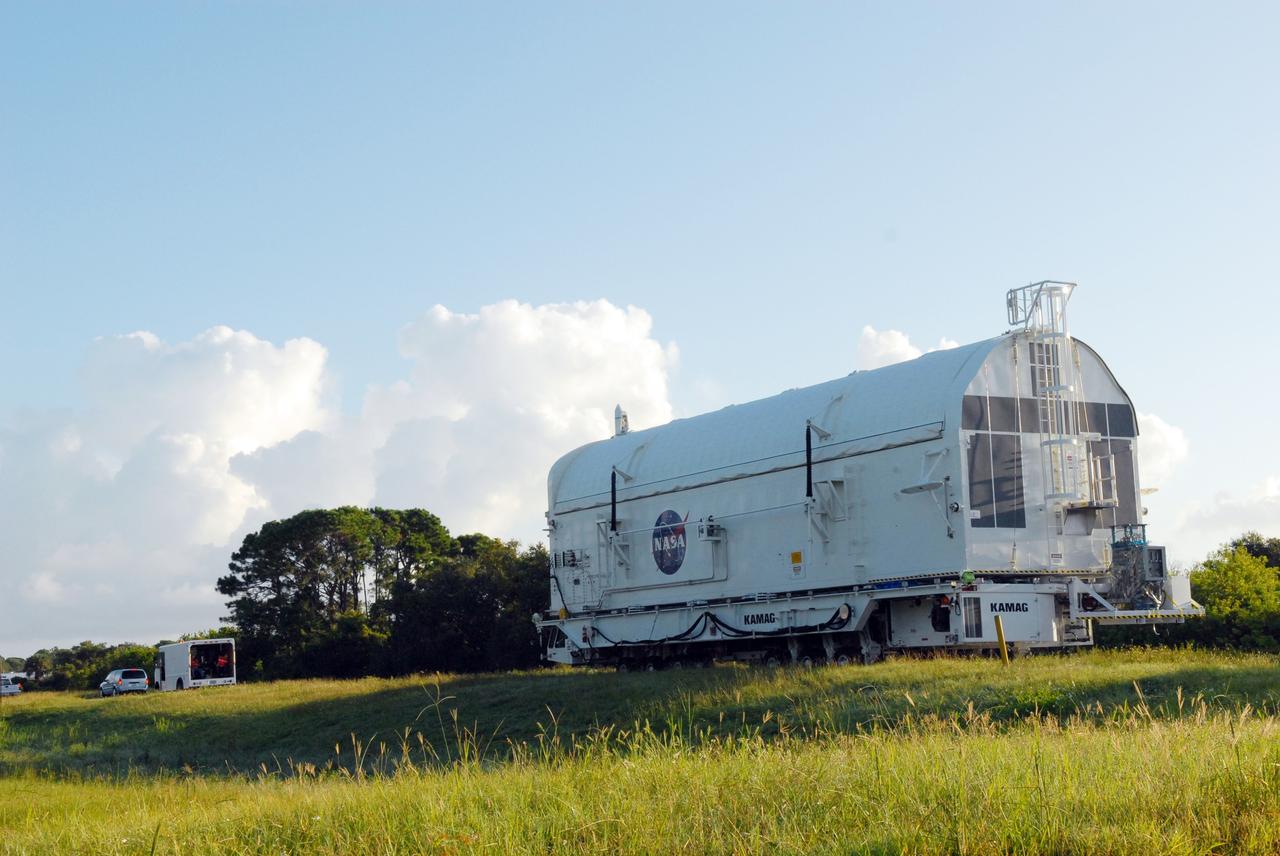

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
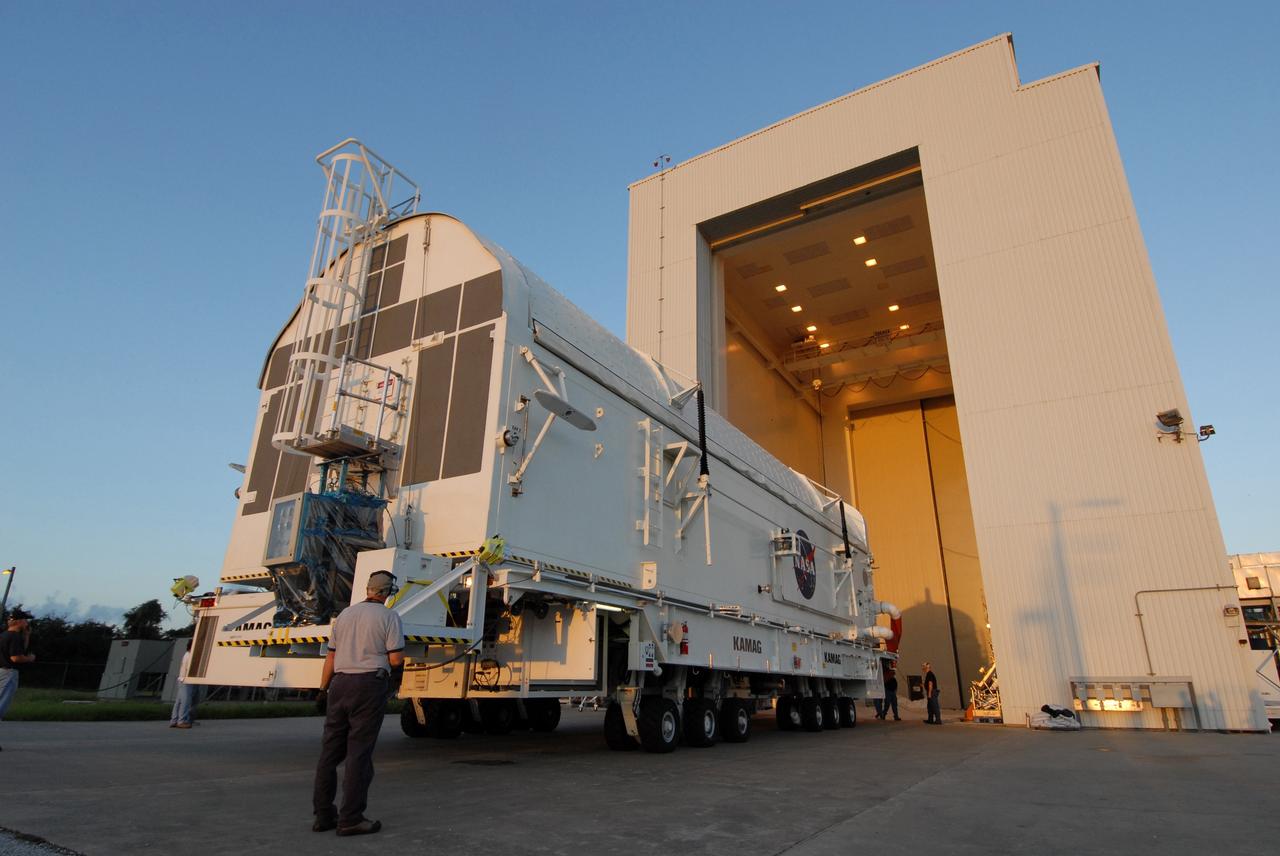

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
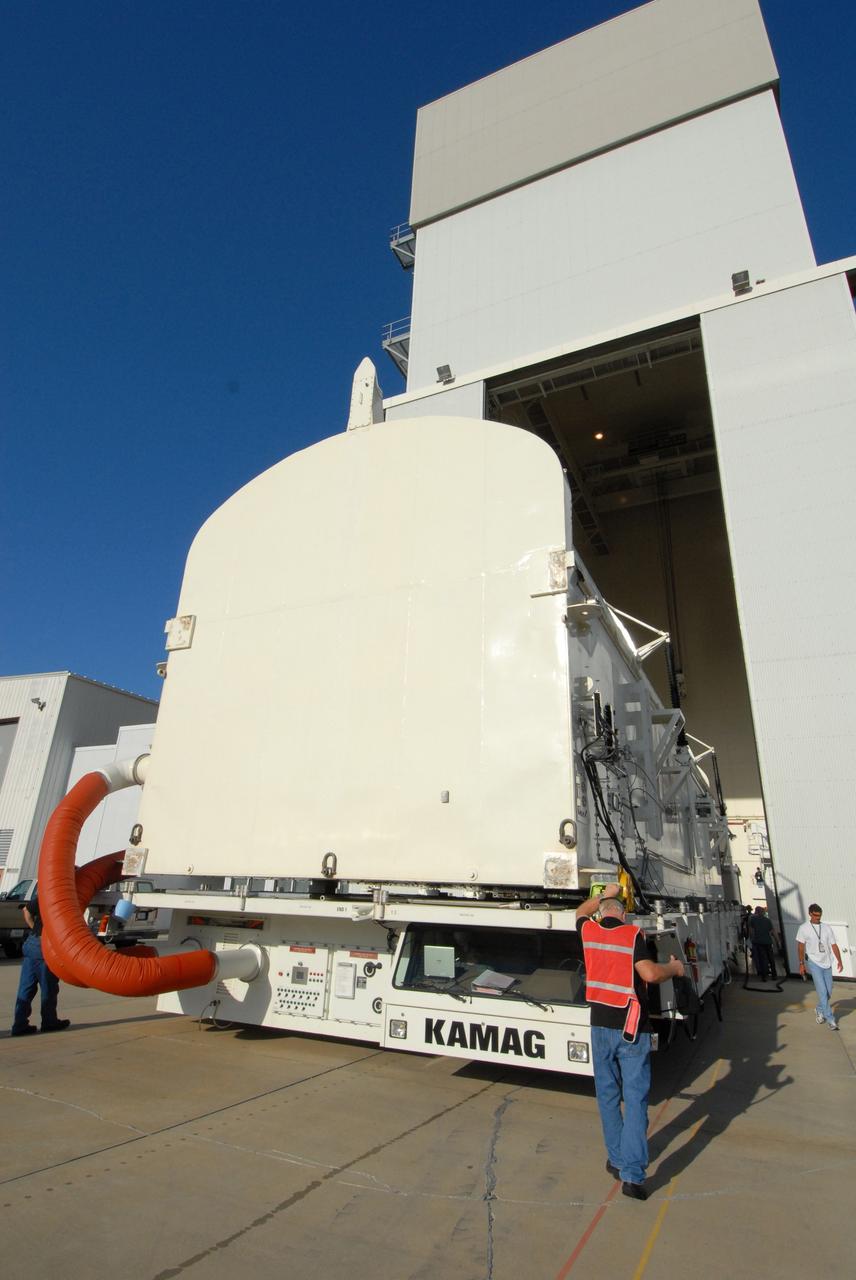

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The payload canister containing the equipment and hardware for space shuttle Atlantis’ STS-125 mission to the Hubble Space Telescope is moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, to the canister rotation facility. The canister will be transferred to Launch Pad 39A and the payload will be loaded into Atlantis’ payload bay. Launch of Atlantis is targeted for Oct 10. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
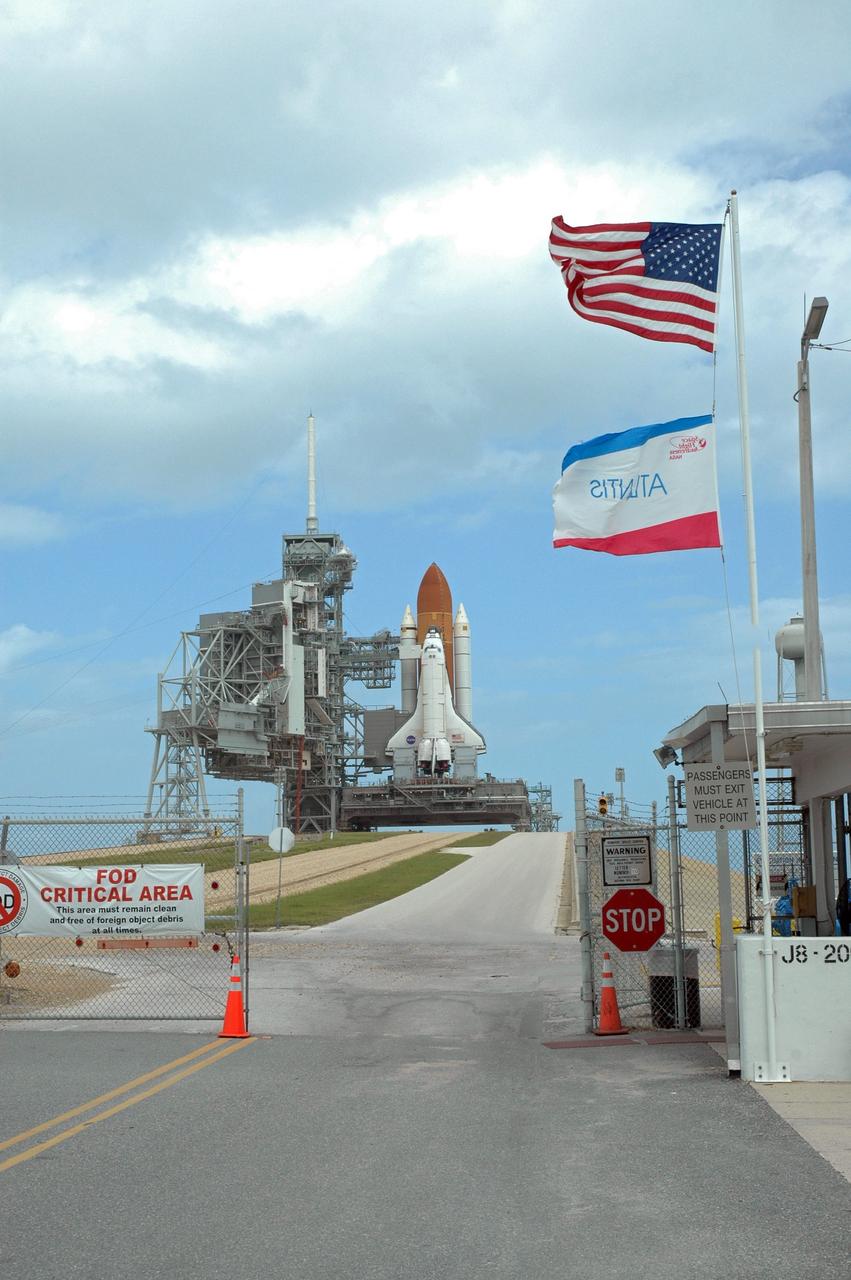

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the rotating service structure is open, revealing space shuttle Atlantis on the pad for the STS-125 mission, the fifth and final shuttle servicing mission for NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. On the RSS, the payload canister is in position at the payload changeout room to receive the Hubble hardware. High winds, however, have delayed the transfer. The payload comprises four carriers holding various equipment for the mission. The hardware will be transported back to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be stored until a new target launch date can be set for Atlantis’ STS-125 mission in 2009. Atlantis’ October target launch date was delayed after a device on board Hubble used in the storage and transmission of science data to Earth shut down on Sept. 27. Replacing the broken device will be added to Atlantis’ servicing mission to the telescope. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
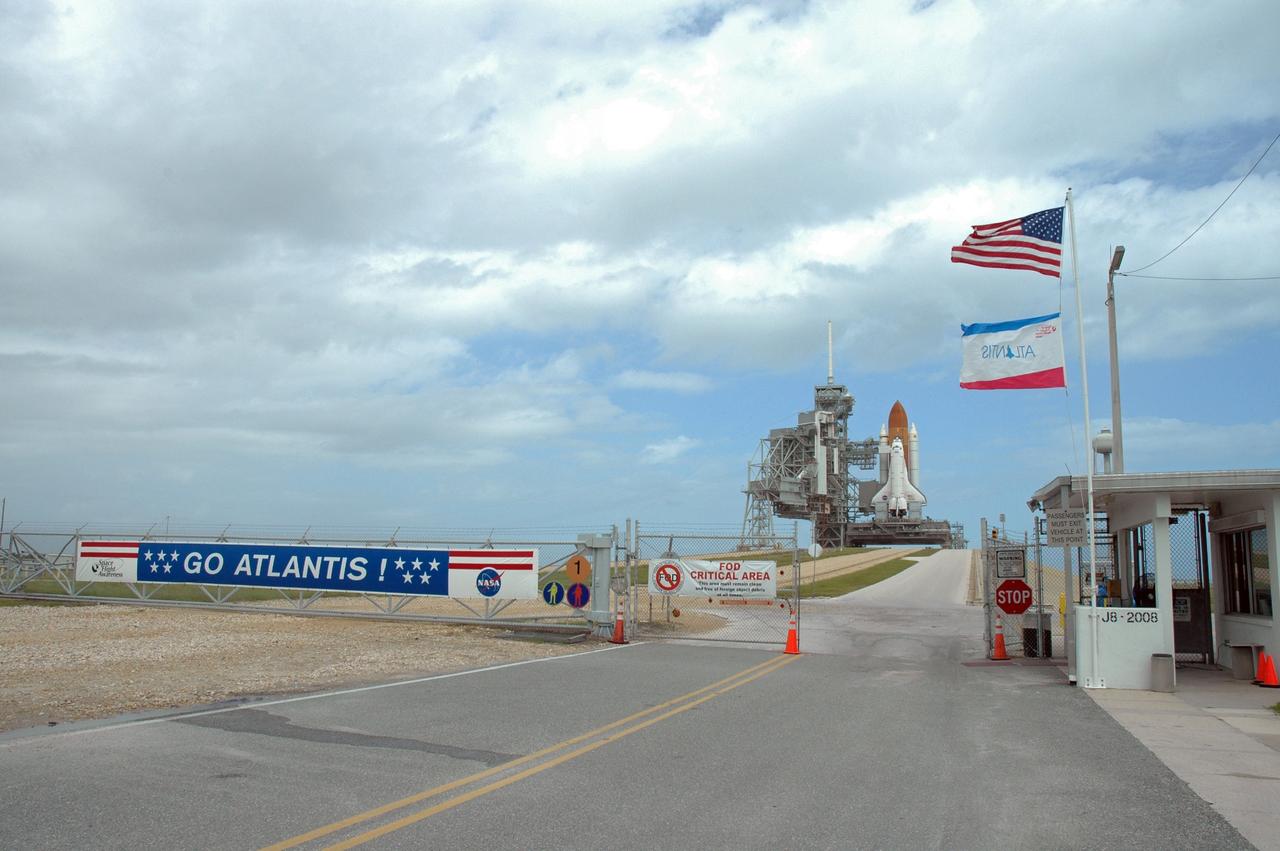

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the rotating service structure is open, revealing space shuttle Atlantis on the pad for the STS-125 mission, the fifth and final shuttle servicing mission for NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. On the RSS, the payload canister is in position at the payload changeout room to receive the Hubble hardware. High winds, however, have delayed the transfer. The payload comprises four carriers holding various equipment for the mission. The hardware will be transported back to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be stored until a new target launch date can be set for Atlantis’ STS-125 mission in 2009. Atlantis’ October target launch date was delayed after a device on board Hubble used in the storage and transmission of science data to Earth shut down on Sept. 27. Replacing the broken device will be added to Atlantis’ servicing mission to the telescope. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
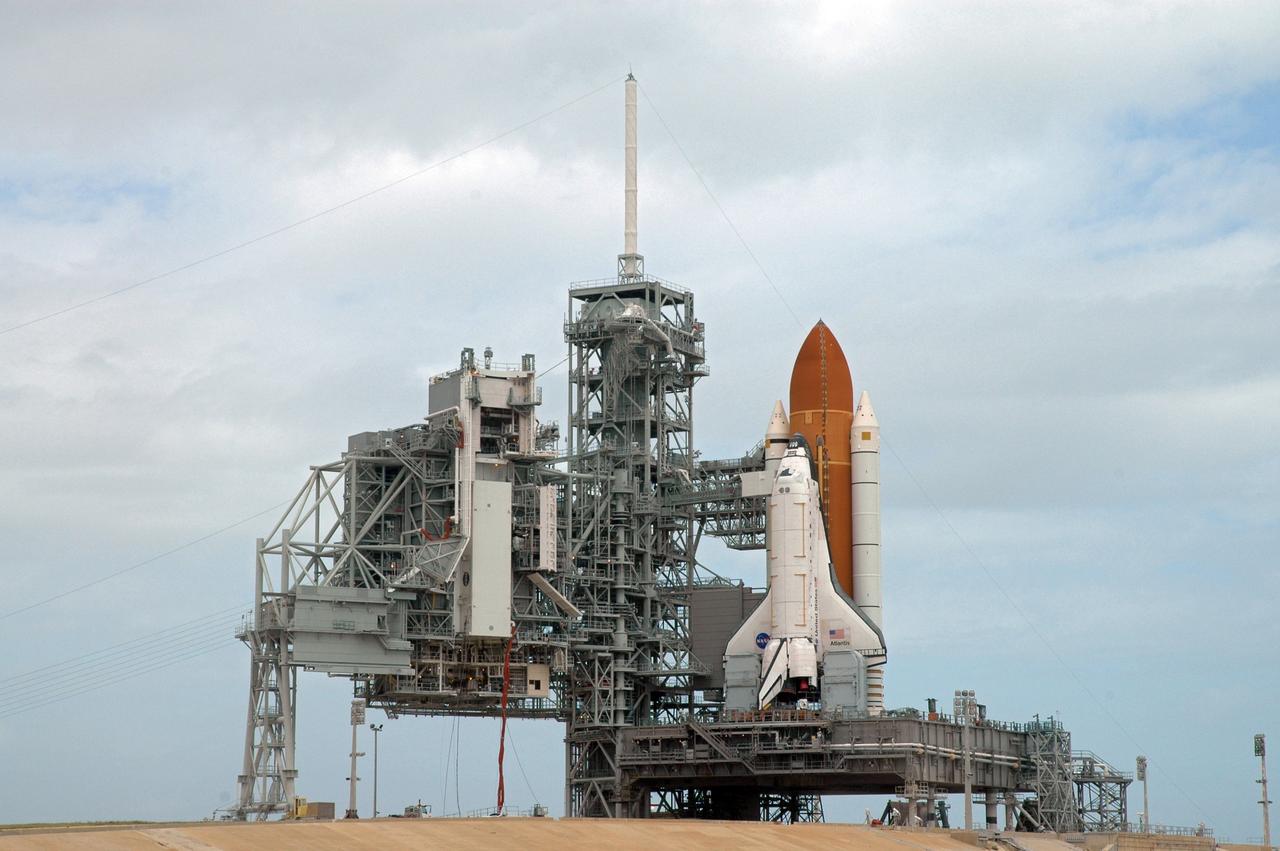

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the rotating service structure is open, revealing space shuttle Atlantis on the pad for the STS-125 mission, the fifth and final shuttle servicing mission for NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. On the RSS, the payload canister is in position at the payload changeout room to receive the Hubble hardware. The payload comprises four carriers holding various equipment for the mission. The hardware will be transported back to Kennedy’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be stored until a new target launch date can be set for Atlantis’ STS-125 mission in 2009. Atlantis’ October target launch date was delayed after a device on board Hubble used in the storage and transmission of science data to Earth shut down on Sept. 27. Replacing the broken device will be added to Atlantis’ servicing mission to the telescope. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
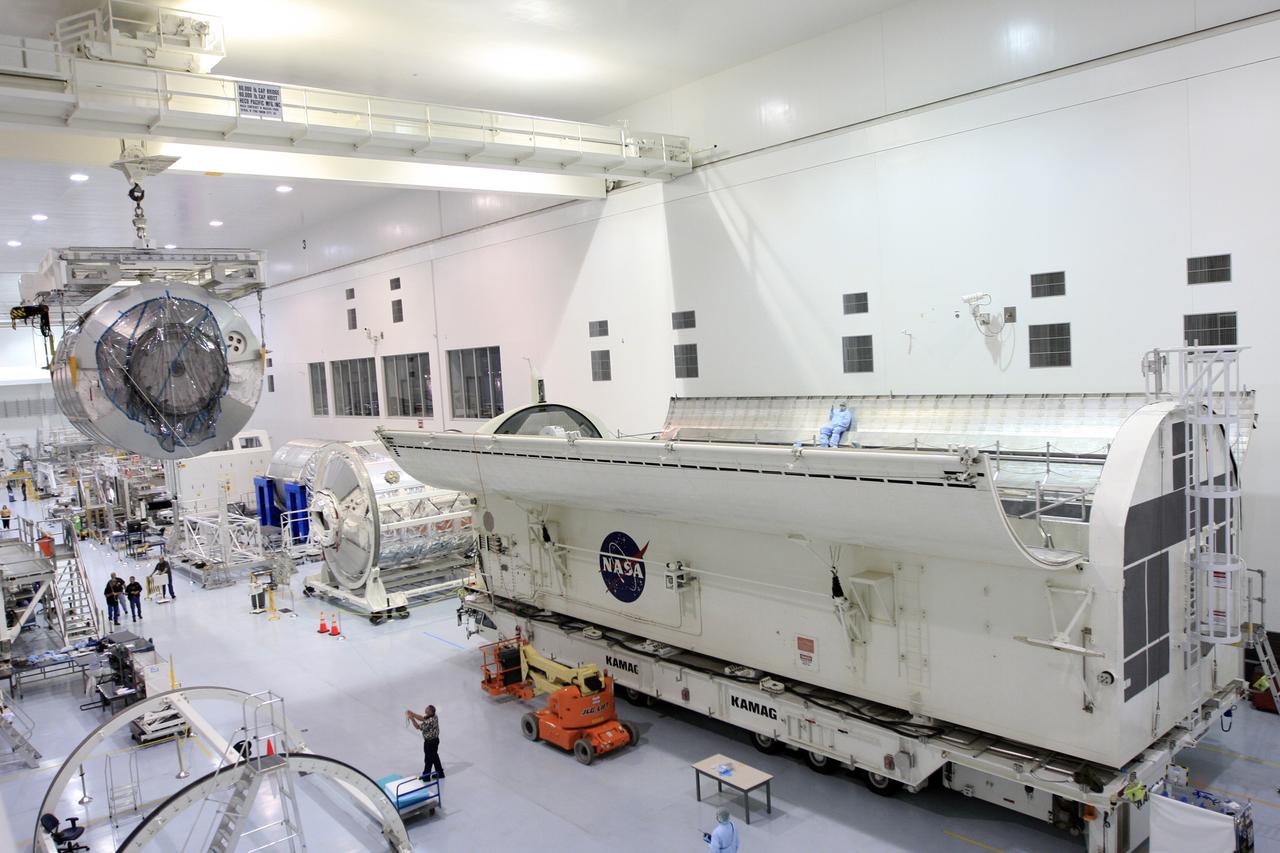

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is moved toward the payload canister at right. Leonardo is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. The payload canister will transfer the module to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The module contains supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, equipment for the regenerative life support system and spare hardware. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
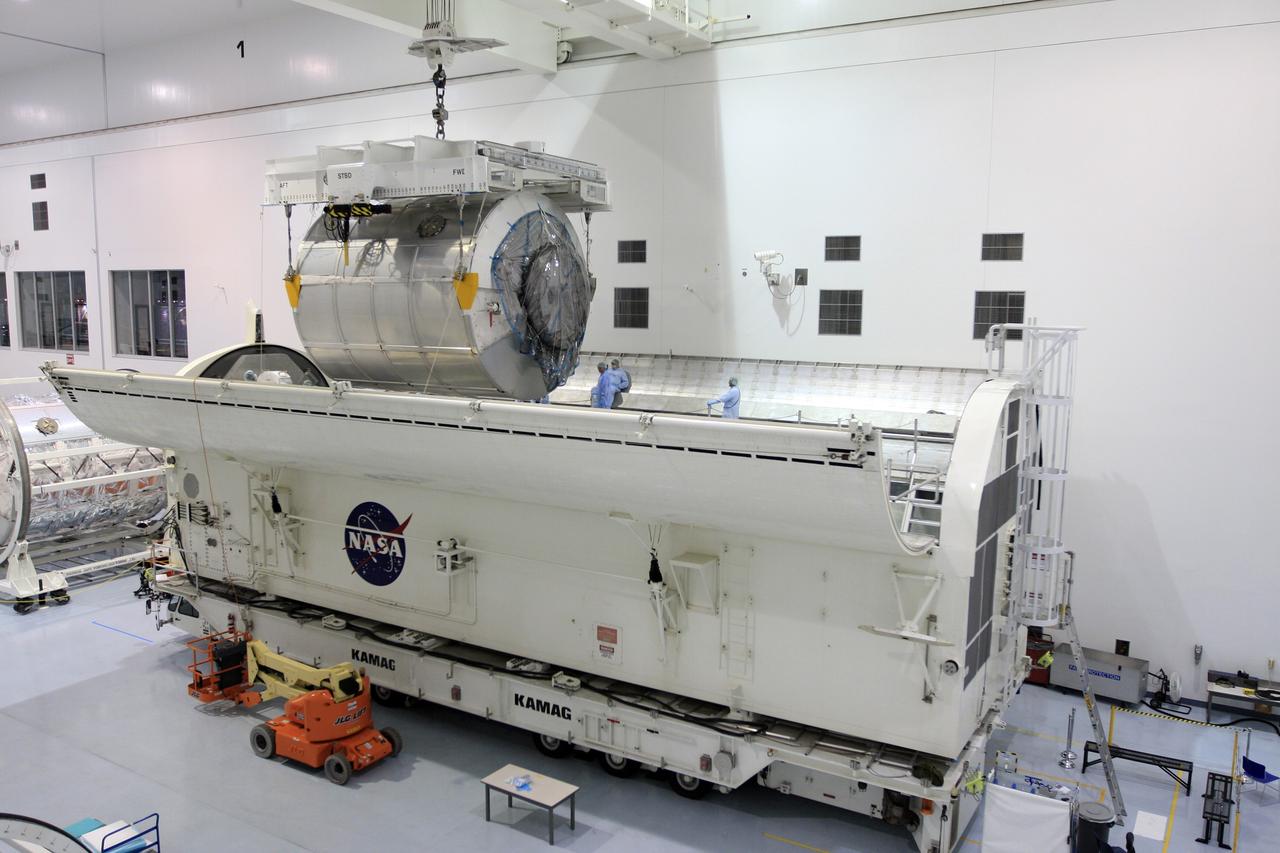

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is lowered into the payload canister for transfer to Launch Pad 39A. Leonardo is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The module contains supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, equipment for the regenerative life support system and spare hardware. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
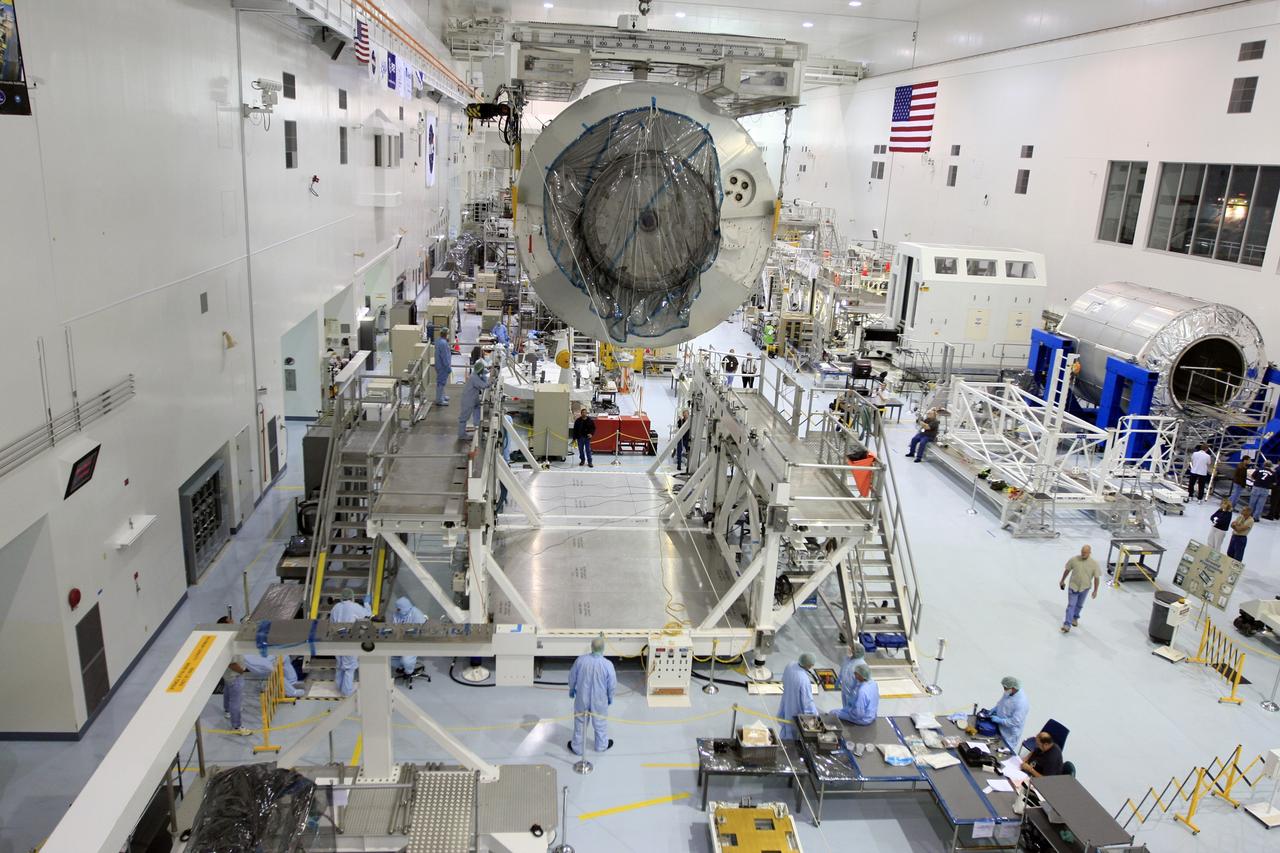

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is moved across the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Leonardo is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. The module will be installed in the waiting payload canister for transfer to Launch Pad 39A. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The module contains supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, equipment for the regenerative life support system and spare hardware. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
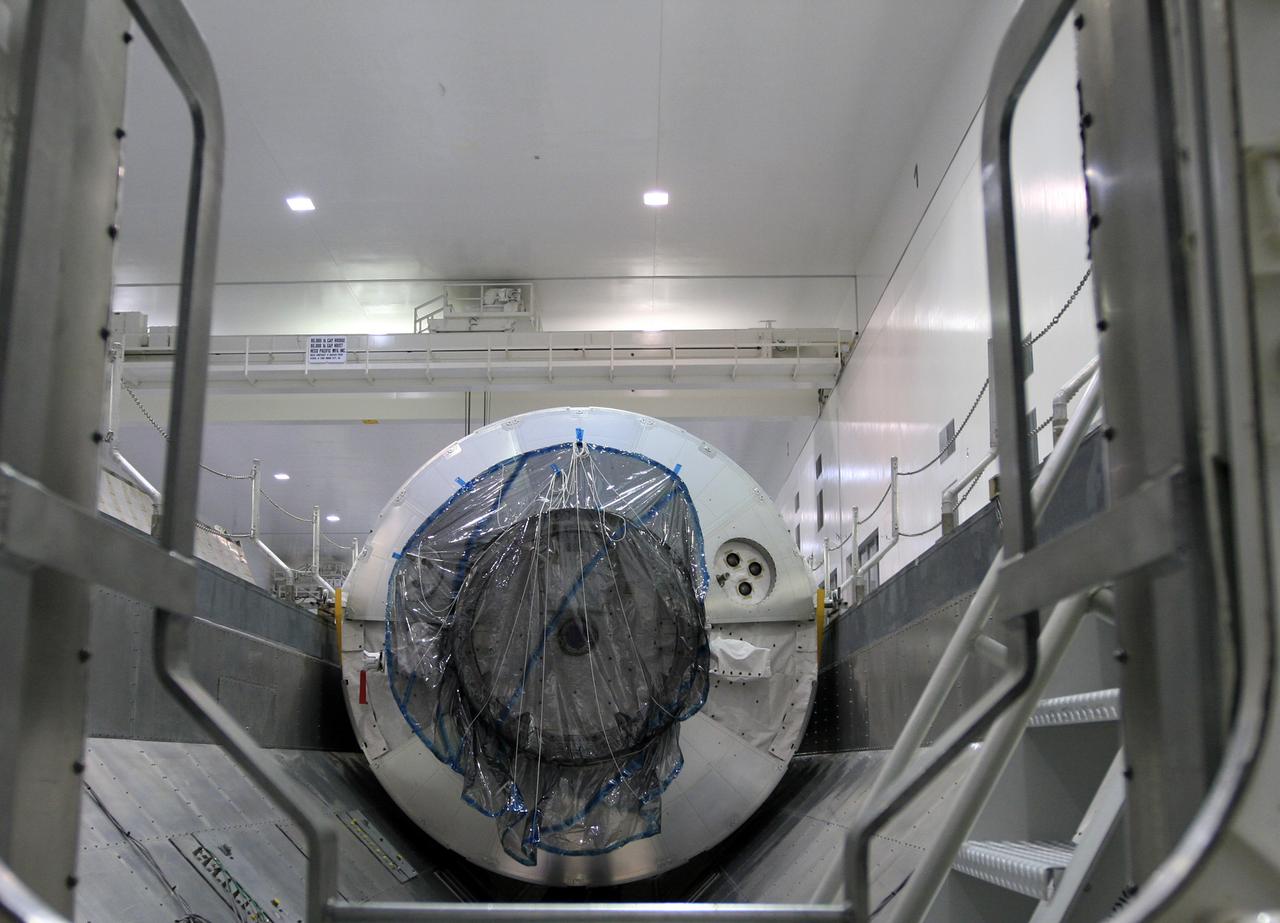

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is installed in the payload canister for transfer to Launch Pad 39A. Leonardo is part of space shuttle Endeavour's payload on the STS-126 mission to the International Space Station. At the pad, the payload canister will release its cargo into the Payload Changeout Room. Later, the payload will be installed in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The module contains supplies and equipment, including additional crew quarters, equipment for the regenerative life support system and spare hardware. Endeavour is targeted for launch on Nov. 14. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
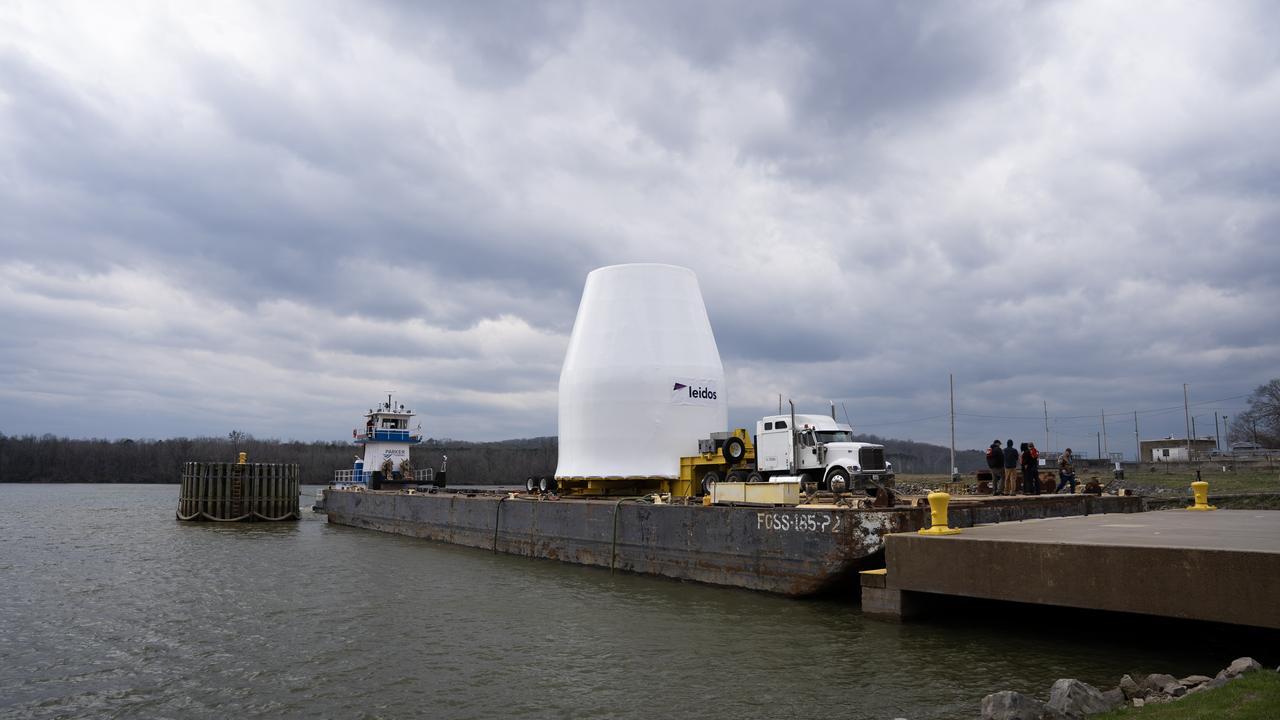

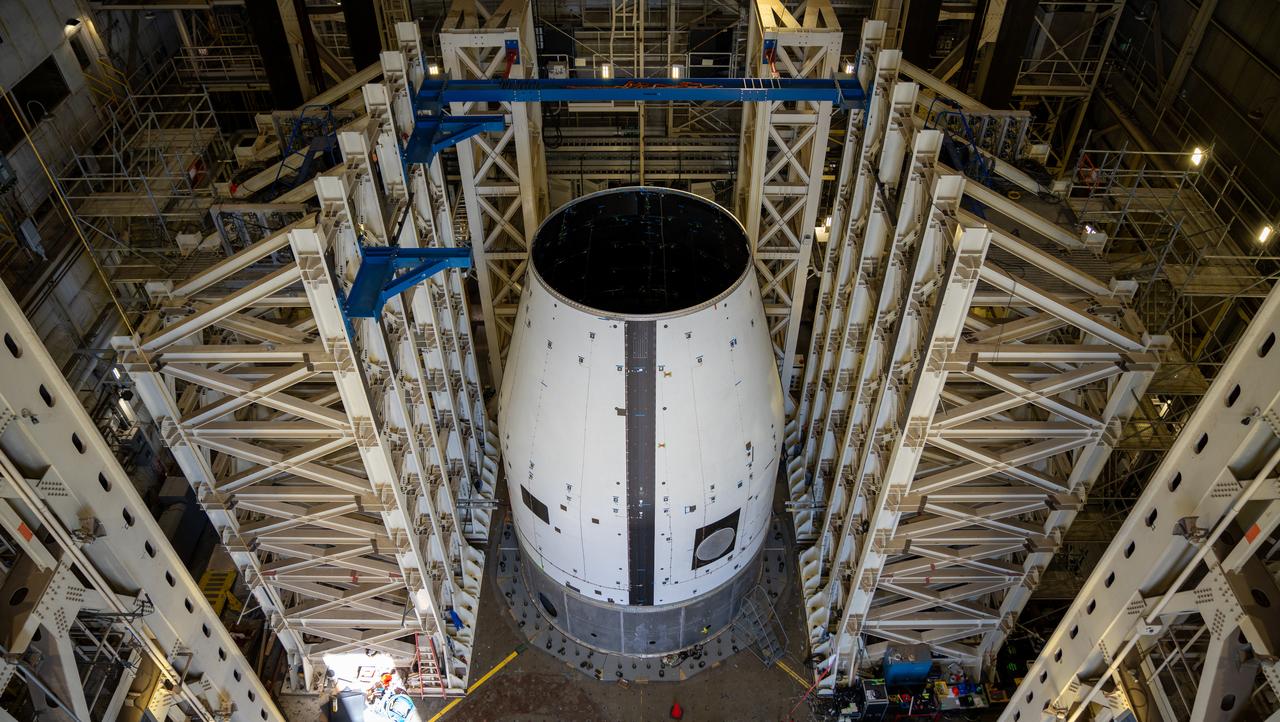
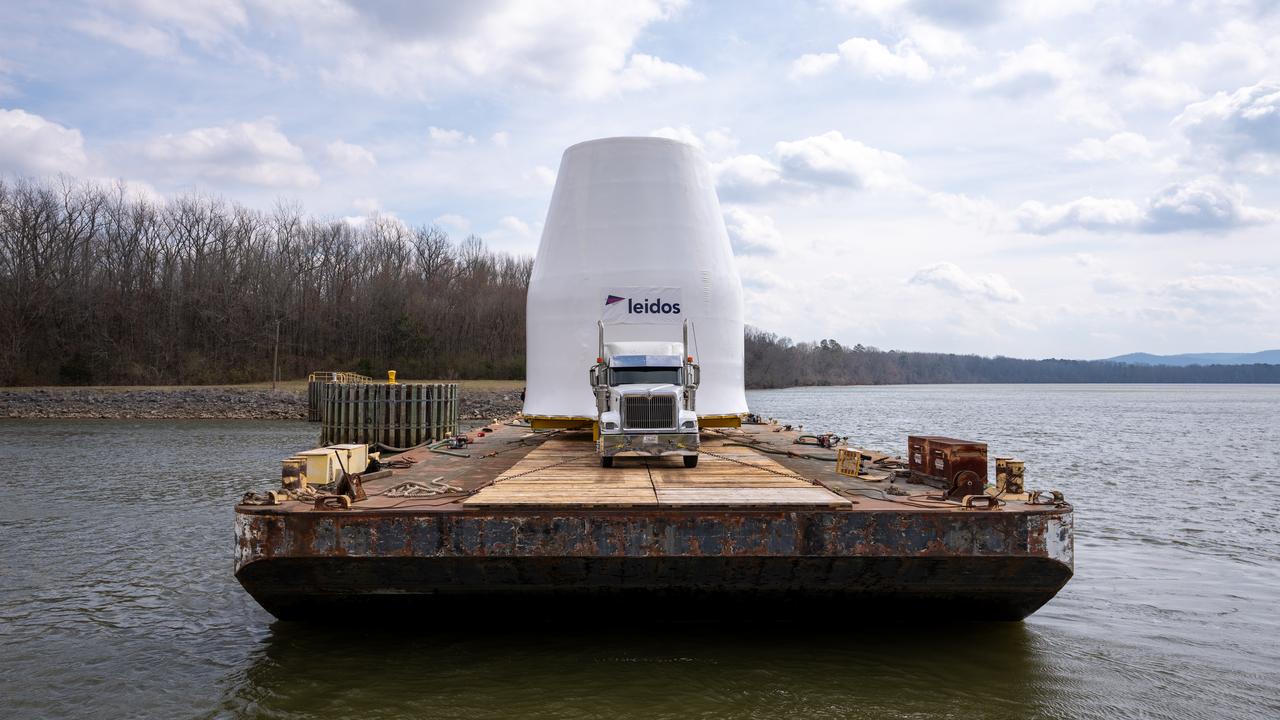
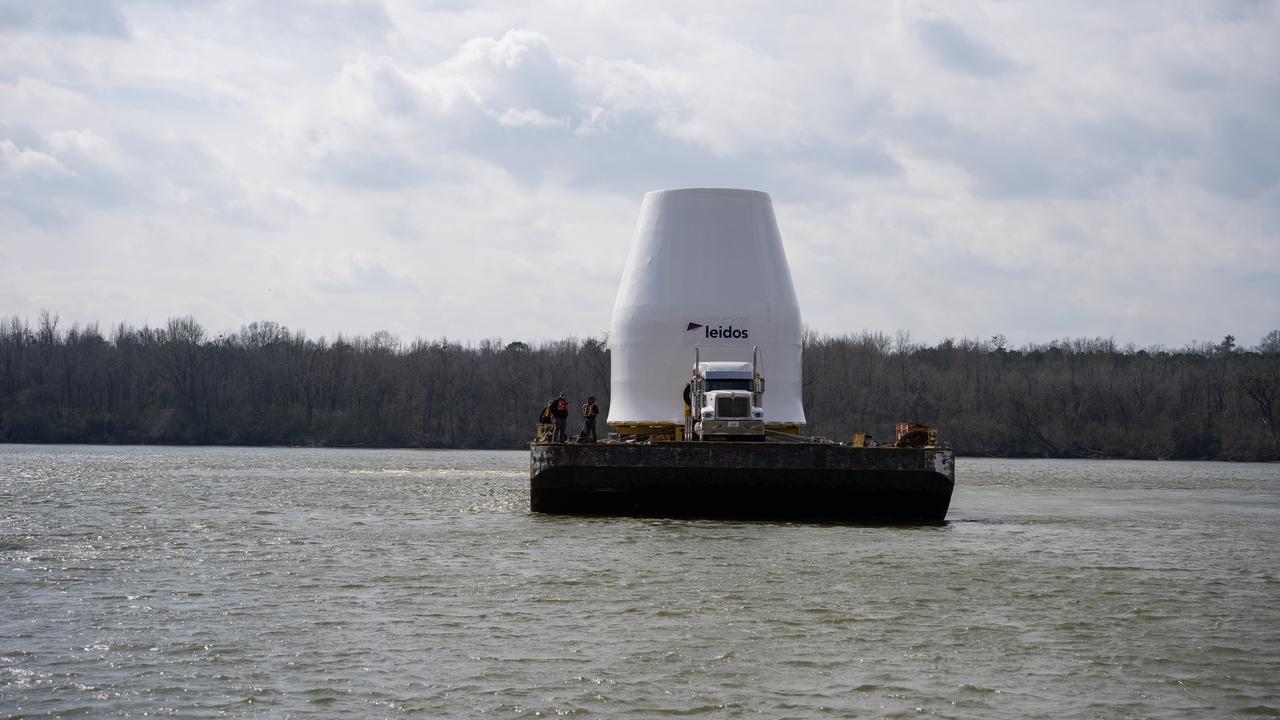
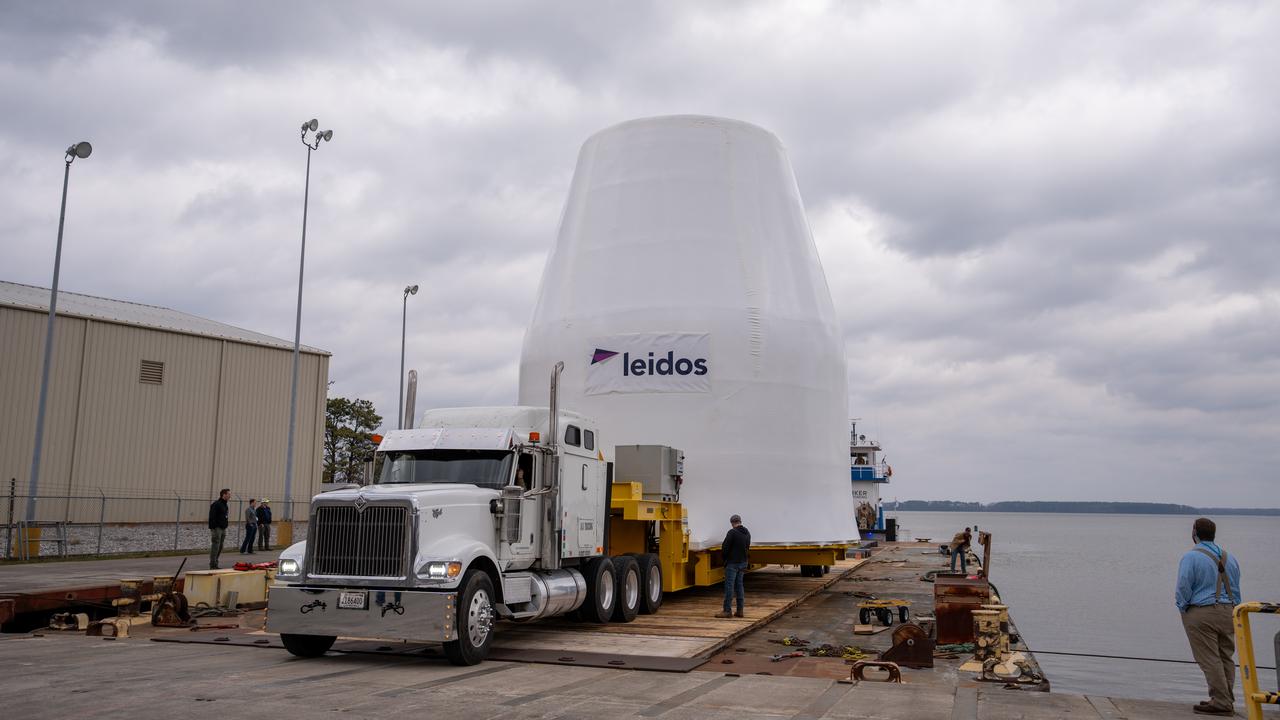
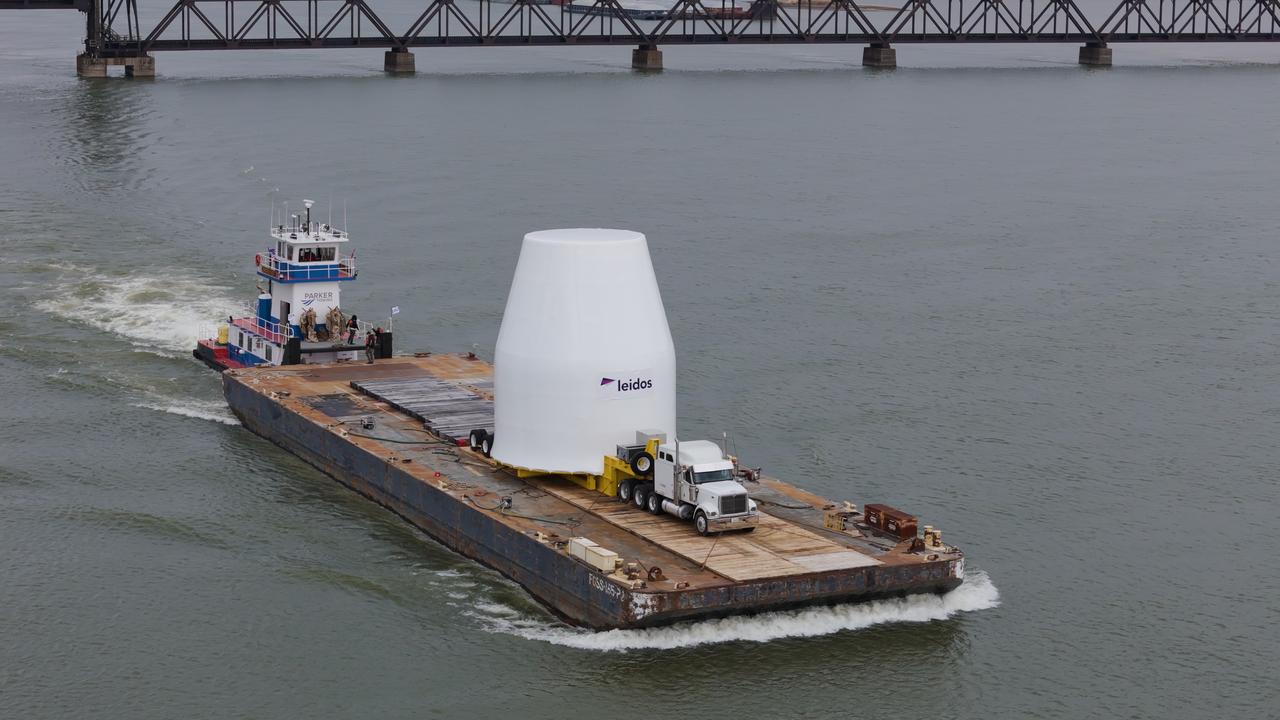
These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
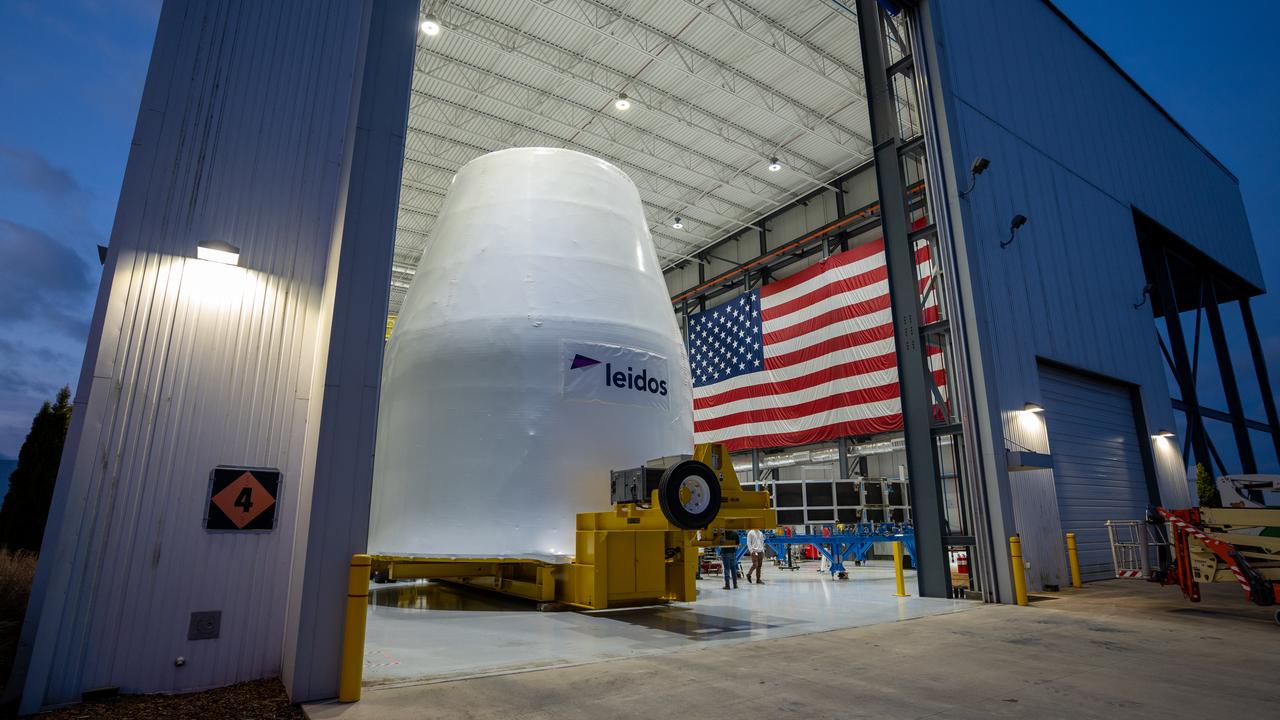

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
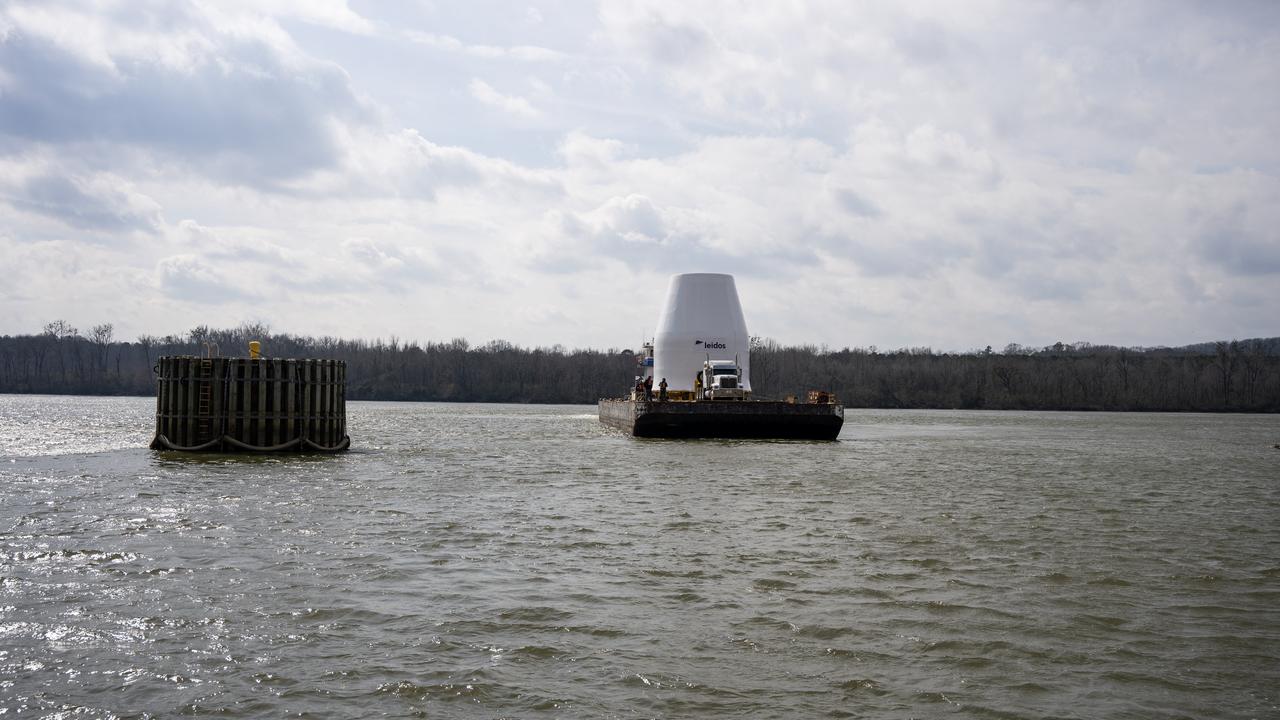

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
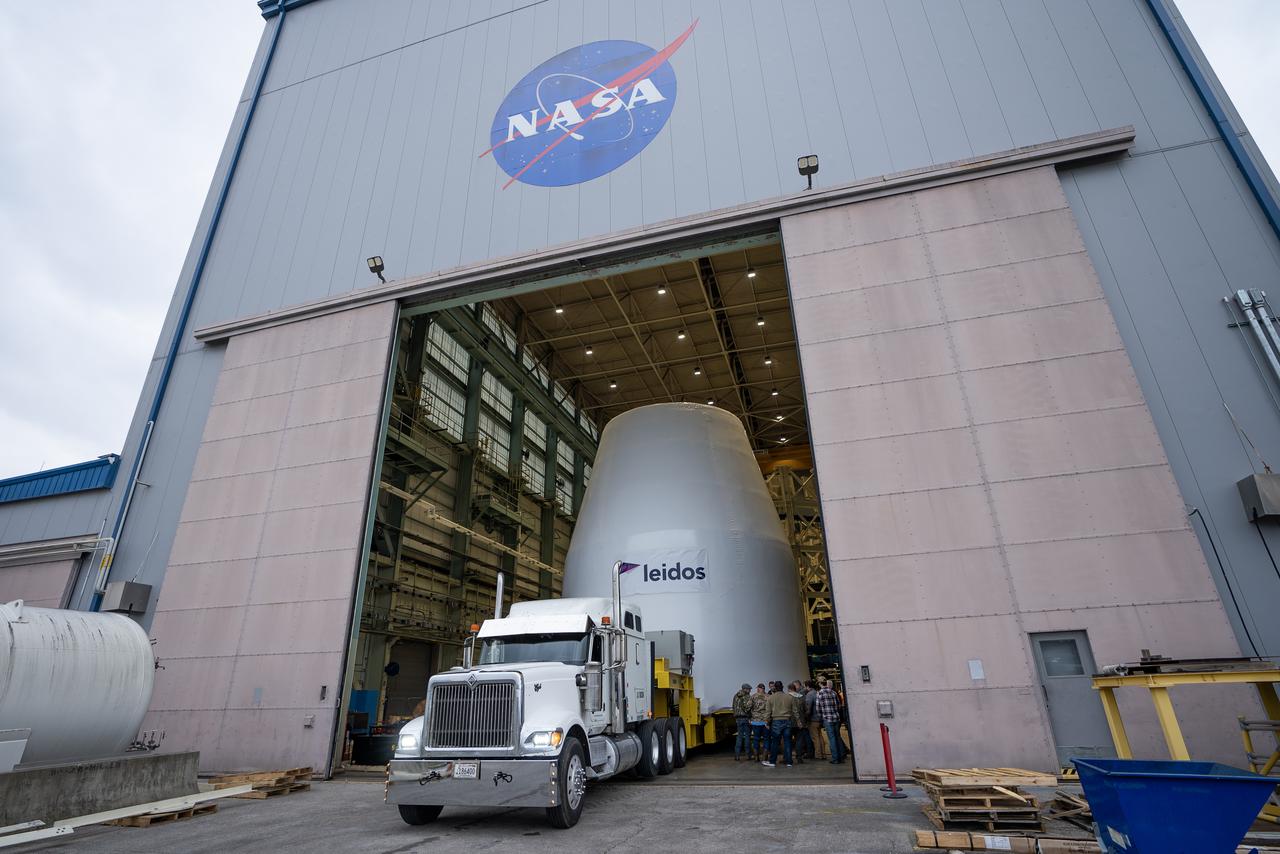

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
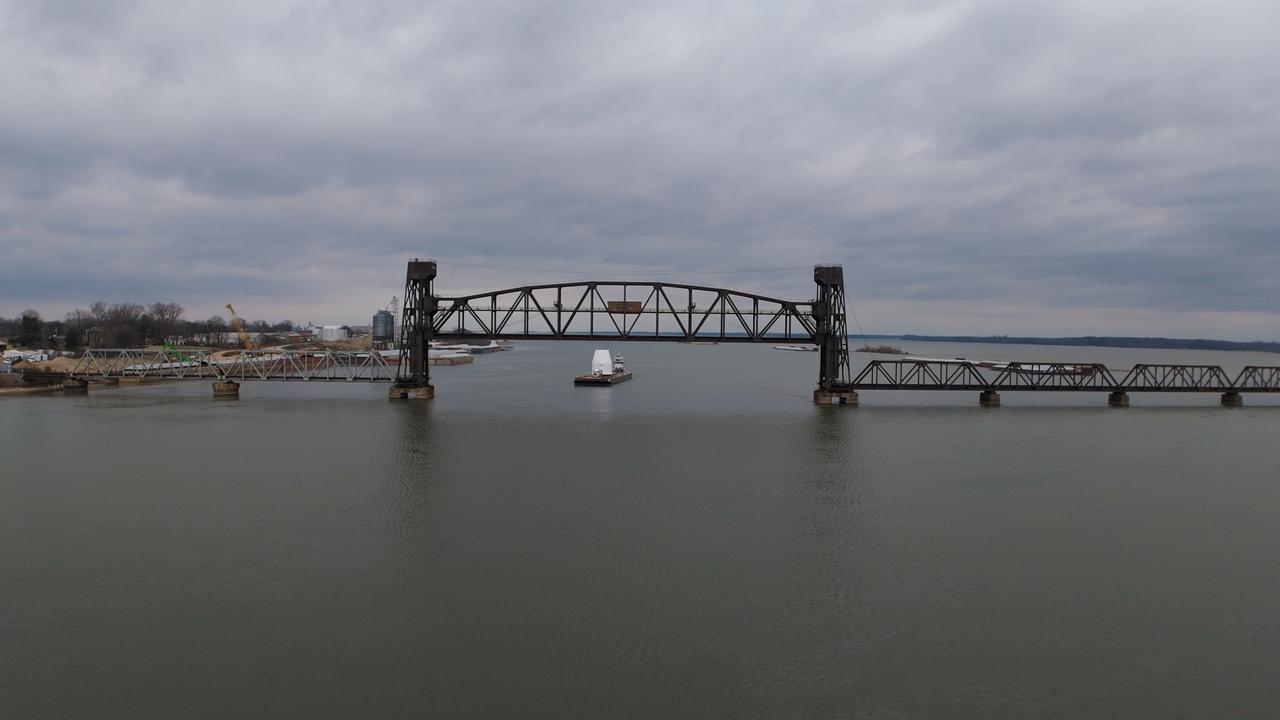

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
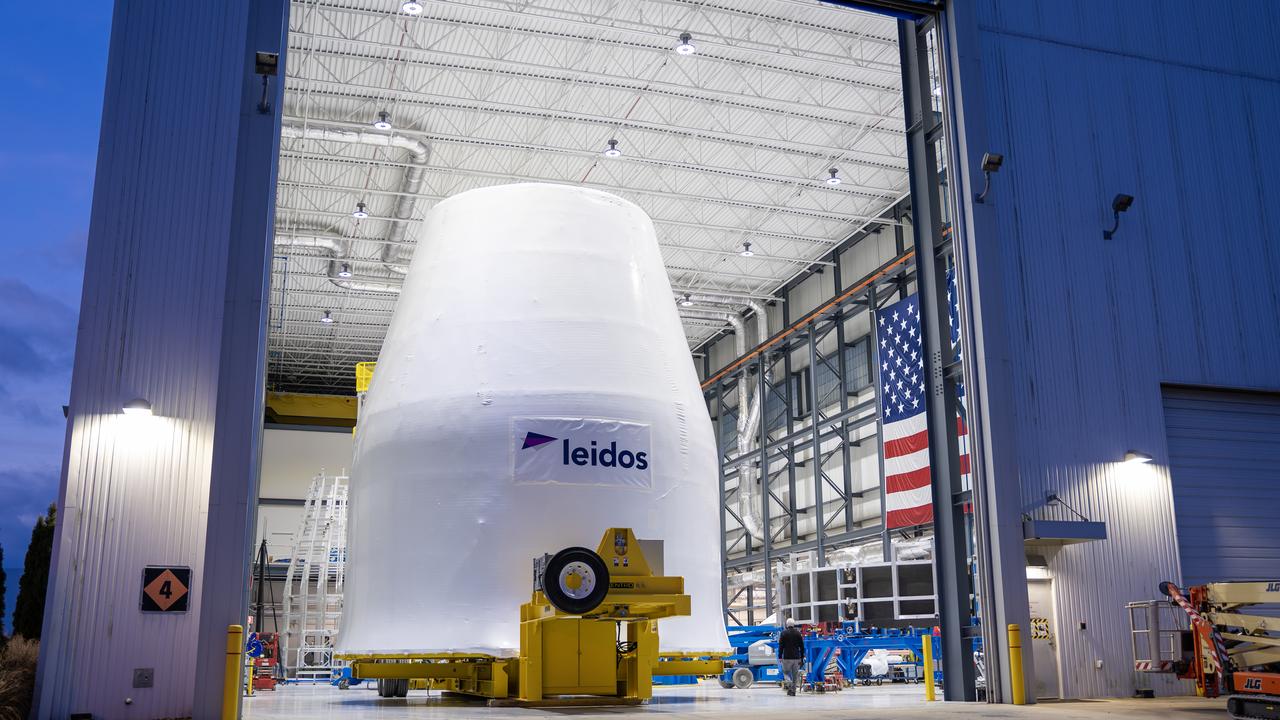

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
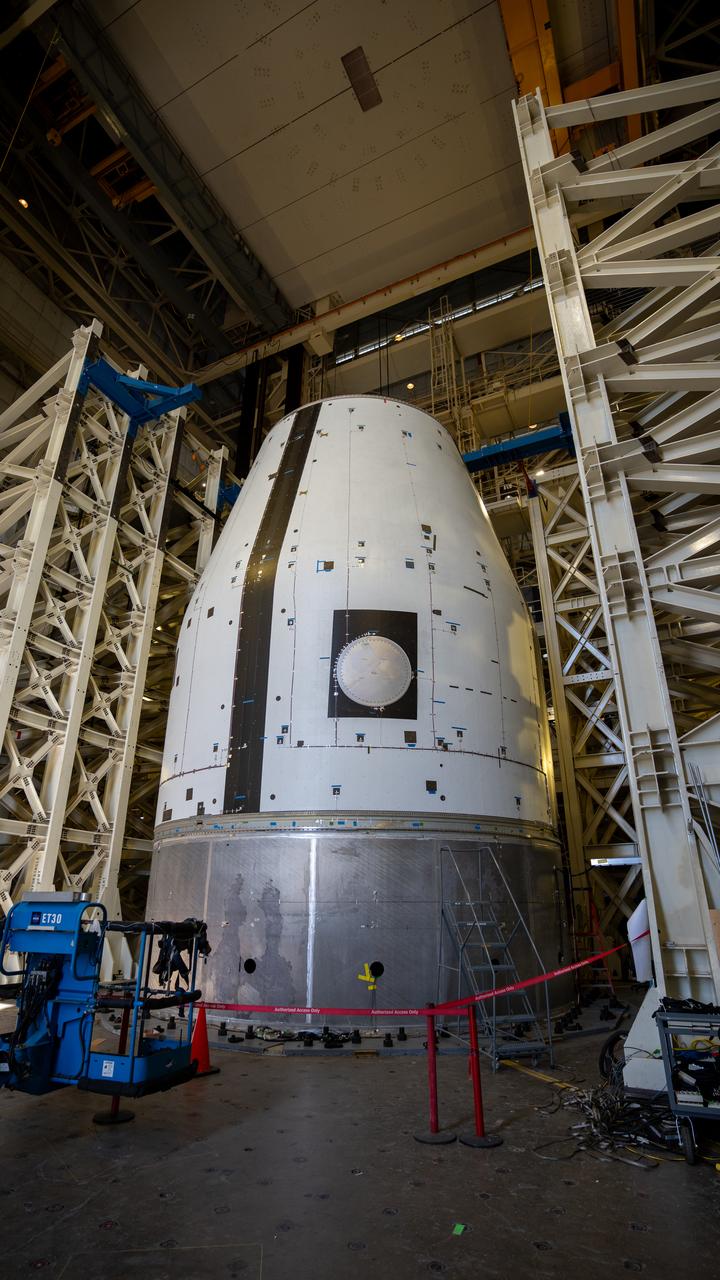

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
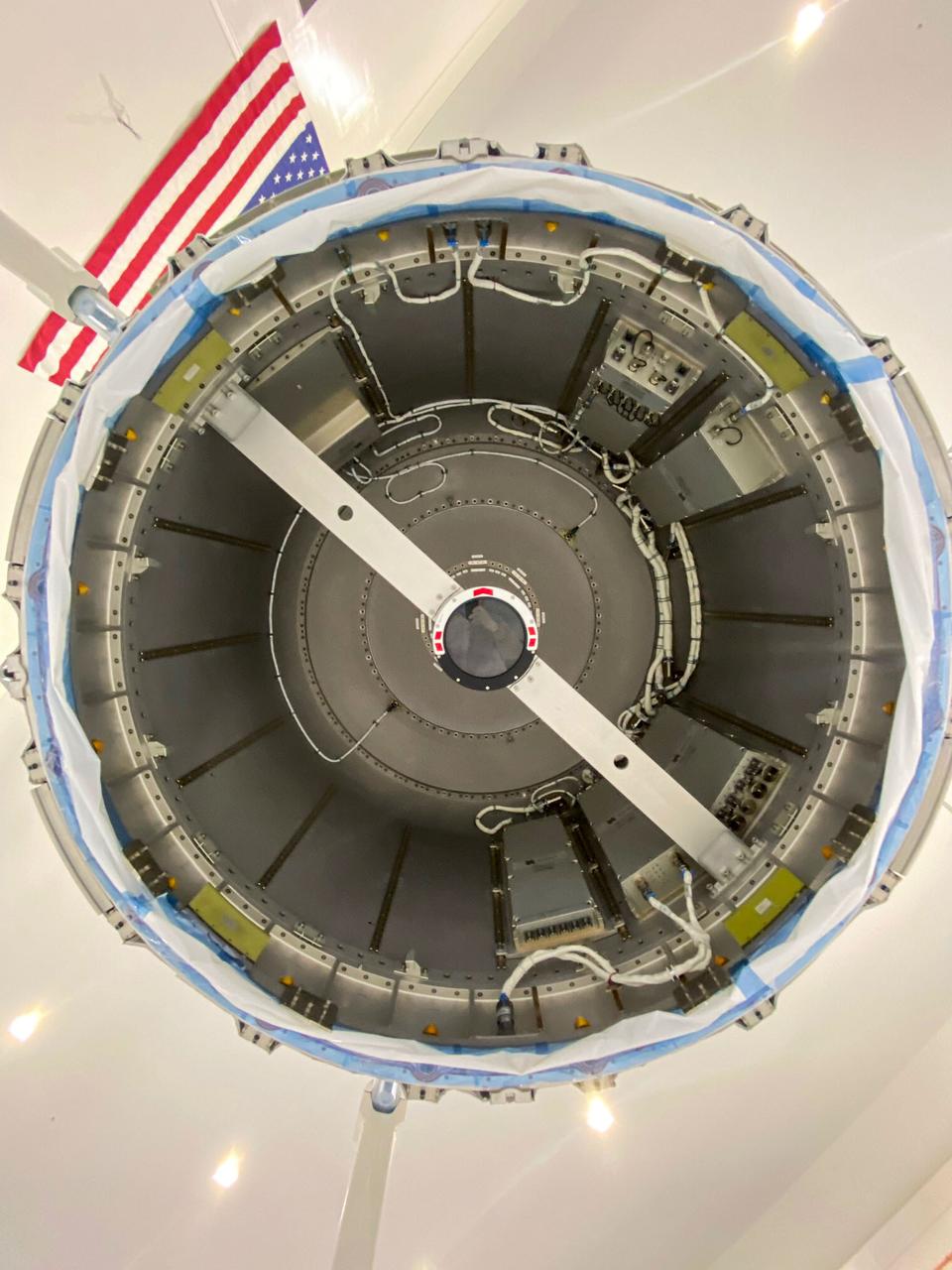

jsc2020e044492 (10/6/2020) —- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.
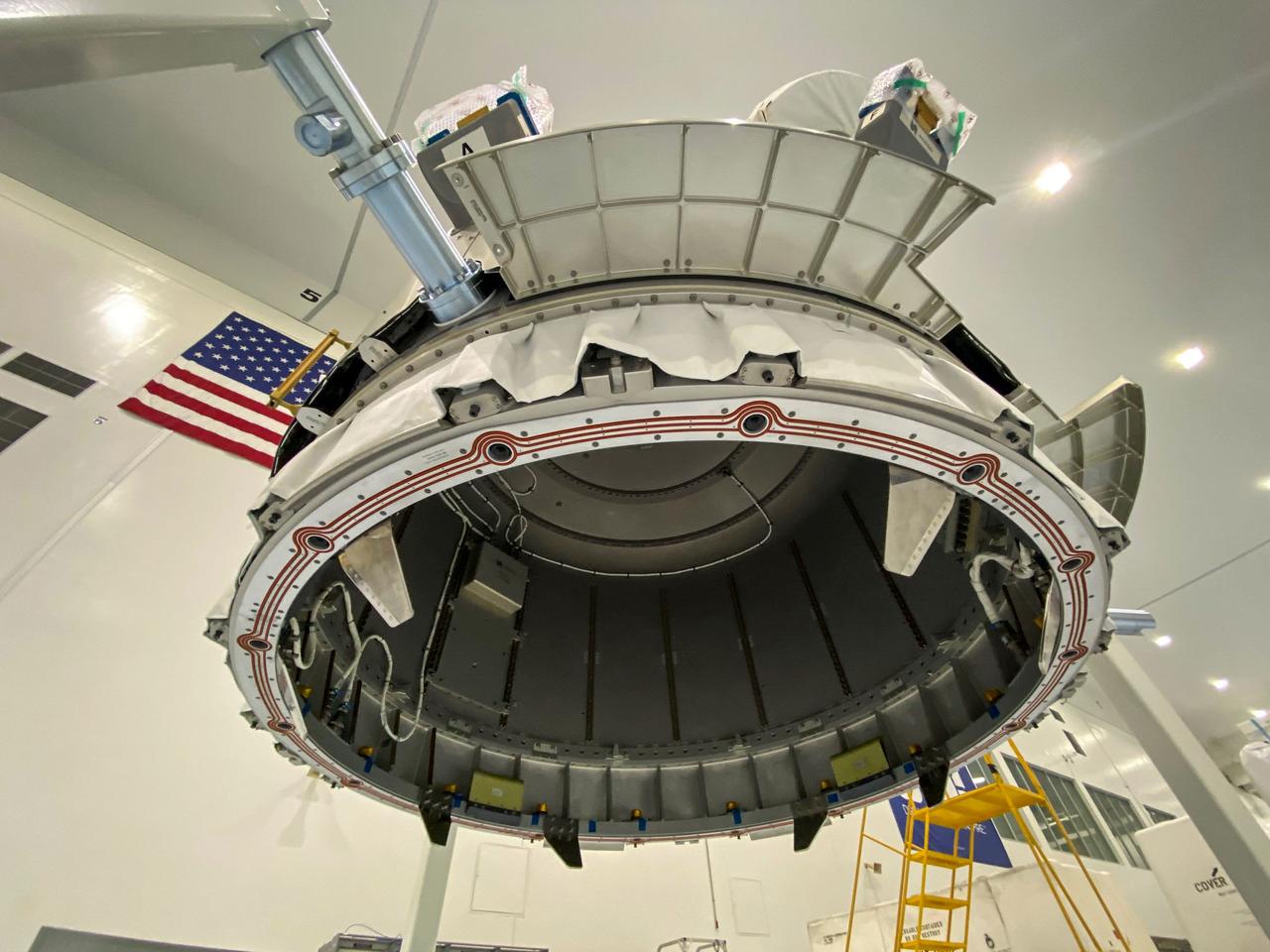

jsc2020e044494 (10/1/2020) --- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.
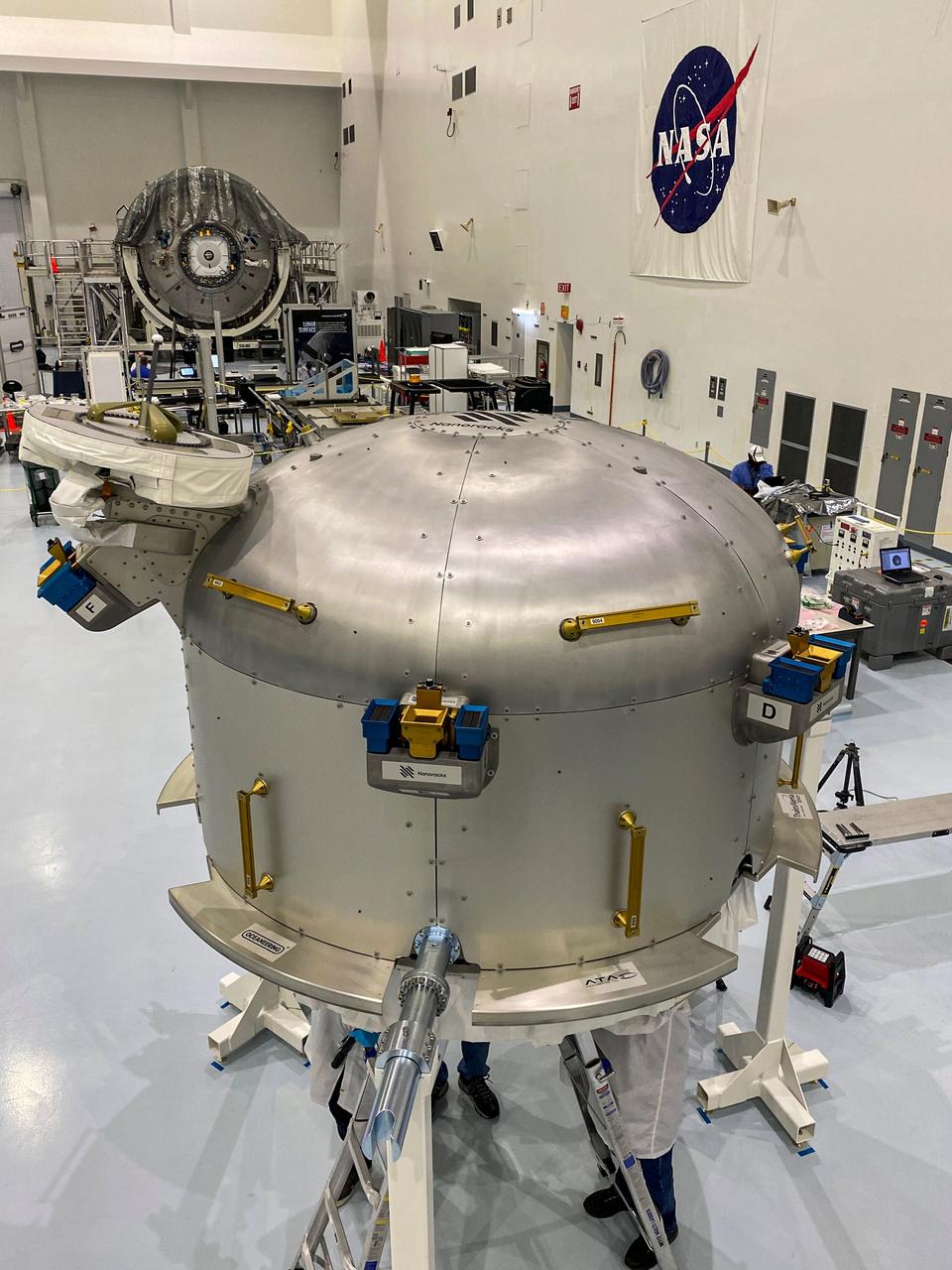

jsc2020e044491 (10/5/2020) —- A preflight view of the Nanoracks Airlock. The Nanoracks Bishop Airlock (Nanoracks Airlock) is the first-ever commercially owned and operated airlock on the International Space Station. It provides a variety of capabilities including jettisoning of payloads such as Cubesats, deployment of external payloads, support for small exterior payloads and locker-sized internal payloads, recovery of external on-orbit replaceable units (ORUs), and the ability to move hardware outside in support of extravehicular activities (EVAs). It is approximately five times larger than the Japanense Experiment Module (JEM) Airlock so it can accommodate more and larger payloads. The Airlock’s capabilities support many different types of scientific investigations.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Greeted by cheers from wellwishers at KSC and eager for their ventur into space on the Microgrvity Science Laboratory-1 (MSL-1) mission, the STS-83 astronauts depart the Operations and Checkout Building on their way to Launch Pad 39A. Leading the seven-member crew is Mission Commander James D. Halsell Jr. Behind Halsell and to his right is Pilot Susan L. Still. Behind Still is Payload Commander Janice Voss, with Mission Specialist Donald A. Thomas to her left. Behind Thomas, in order, are Mission Specialist Michael L. Gernhardt and Payload Specialists Roger K. Crouch and Gregory T. Linteris. During the scheduled 16-day STS-83 mission, the MSL-1 will be used to test some of the hardware, facilities and procedures that are planned for use on the International Space Station while the flight crew conducts combustion, protein crystal growth and materials processing experiments. Also onboard is the Hitchhiker Cryogenic Flexible Diode (CRYOFD) experiment payload, which is attched to the right side of Columbia's payload bay.
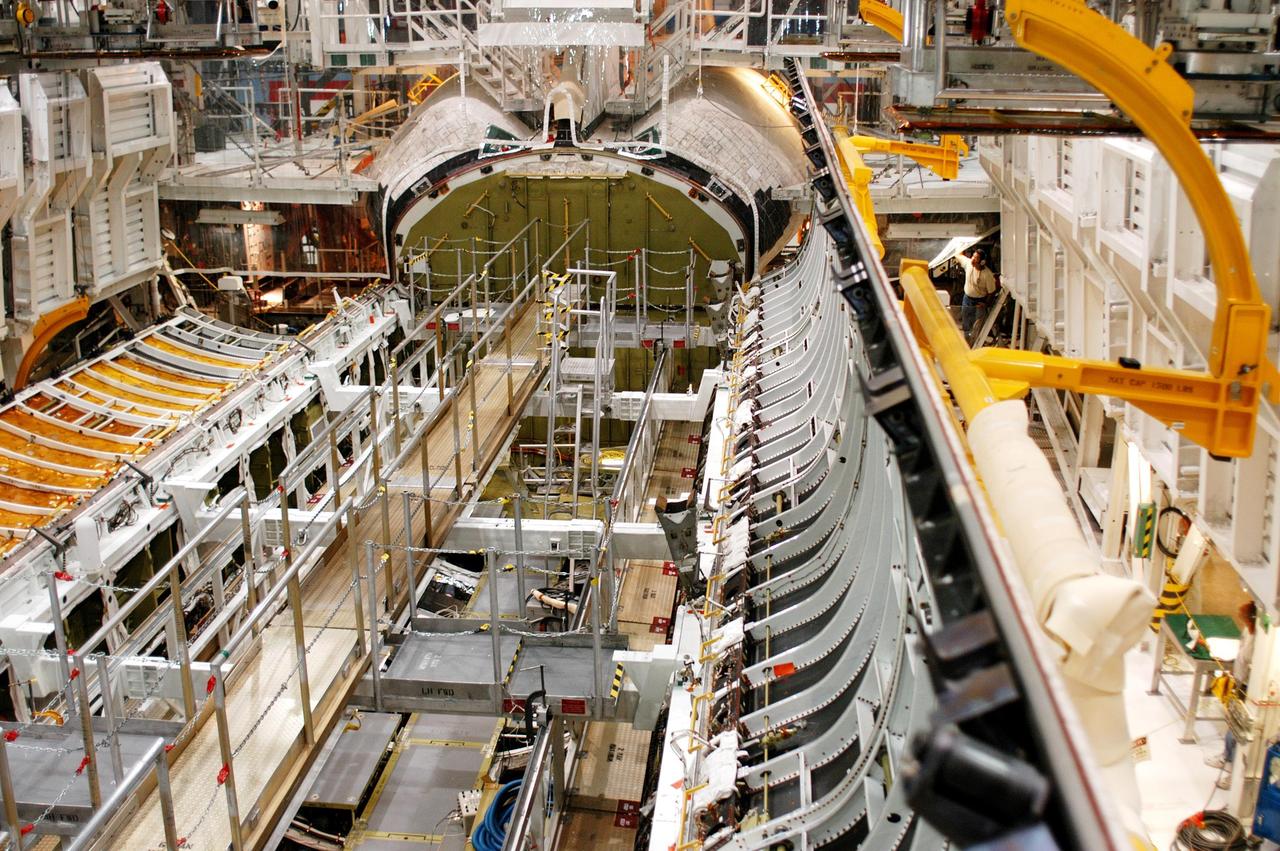

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers prepare to close the payload bay doors on Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
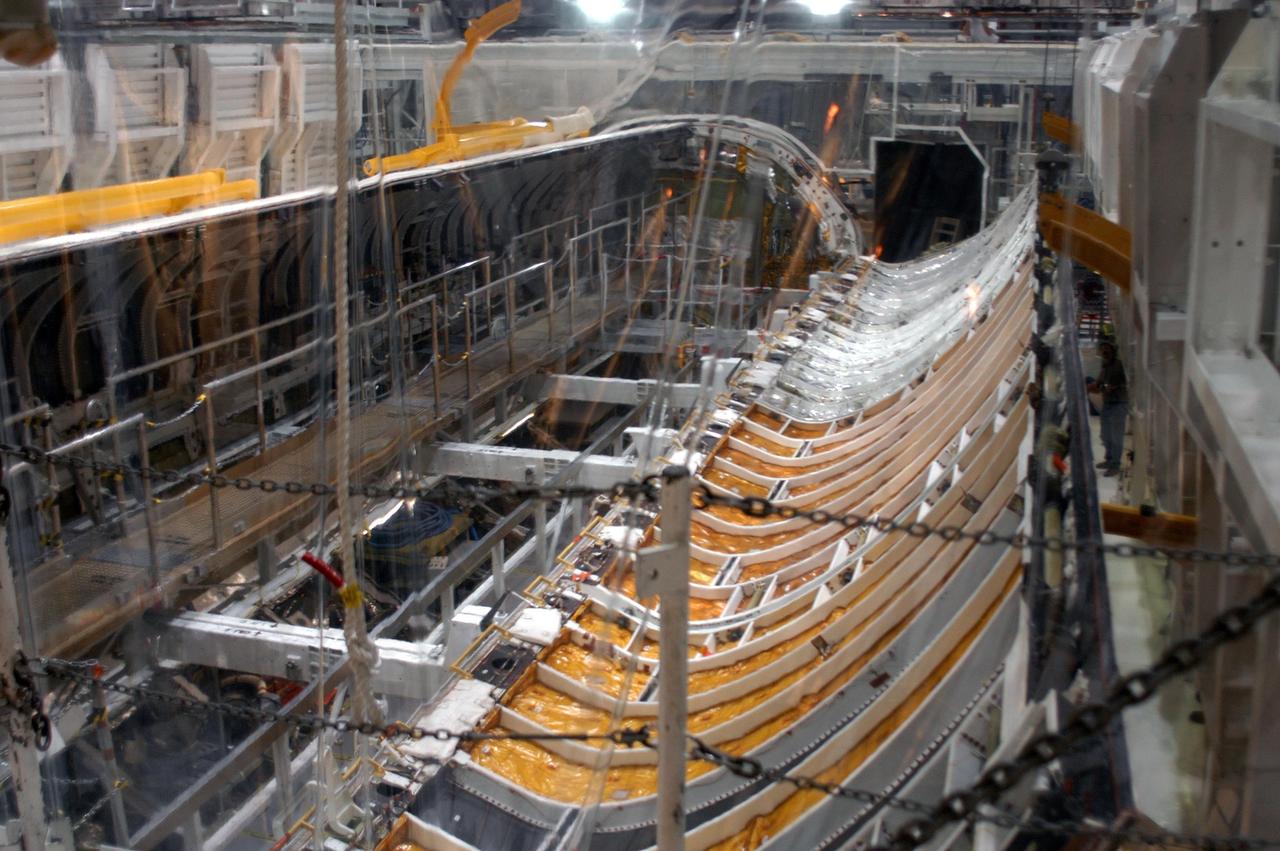

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the payload bay doors on Atlantis are being closed in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
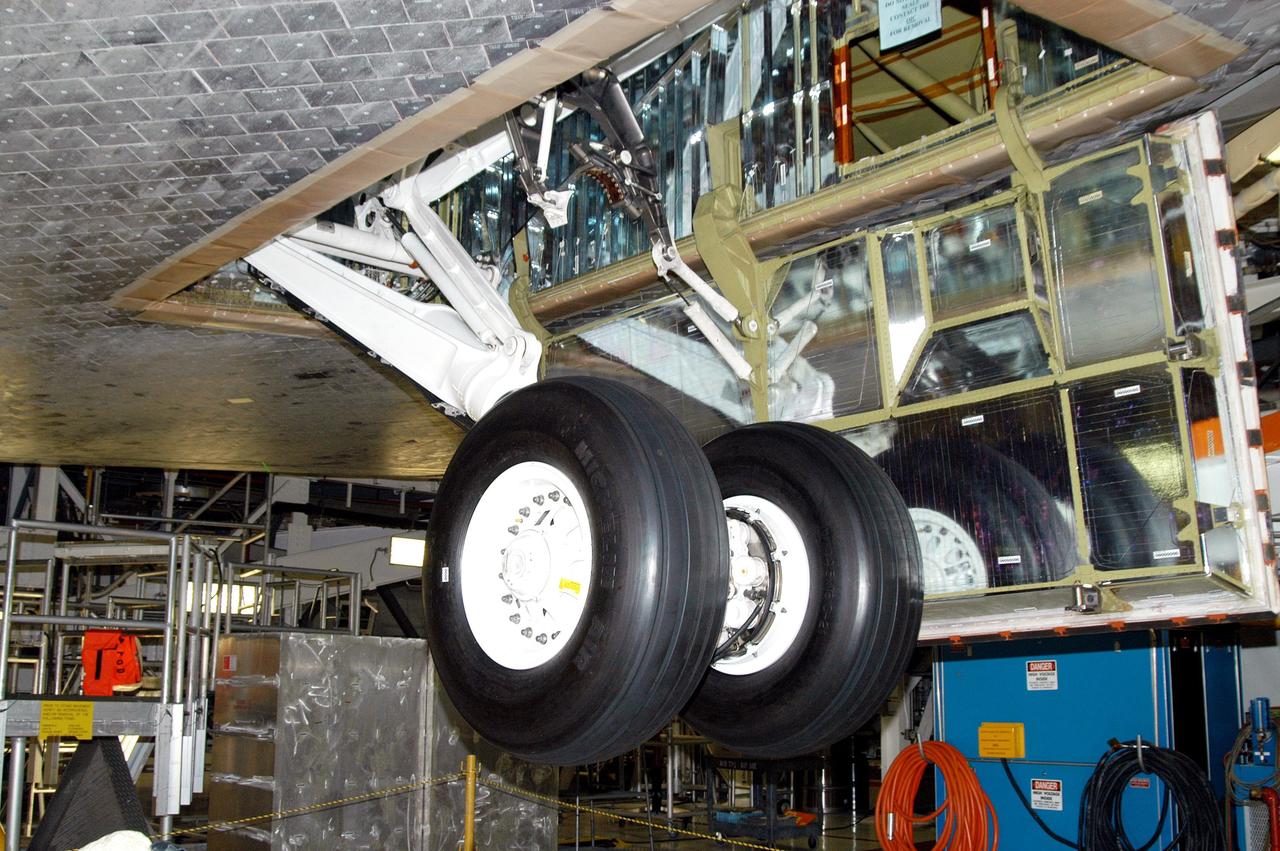

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, Atlantis’ wheels are raised into their wheel bays in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and closing their payload bay doors. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
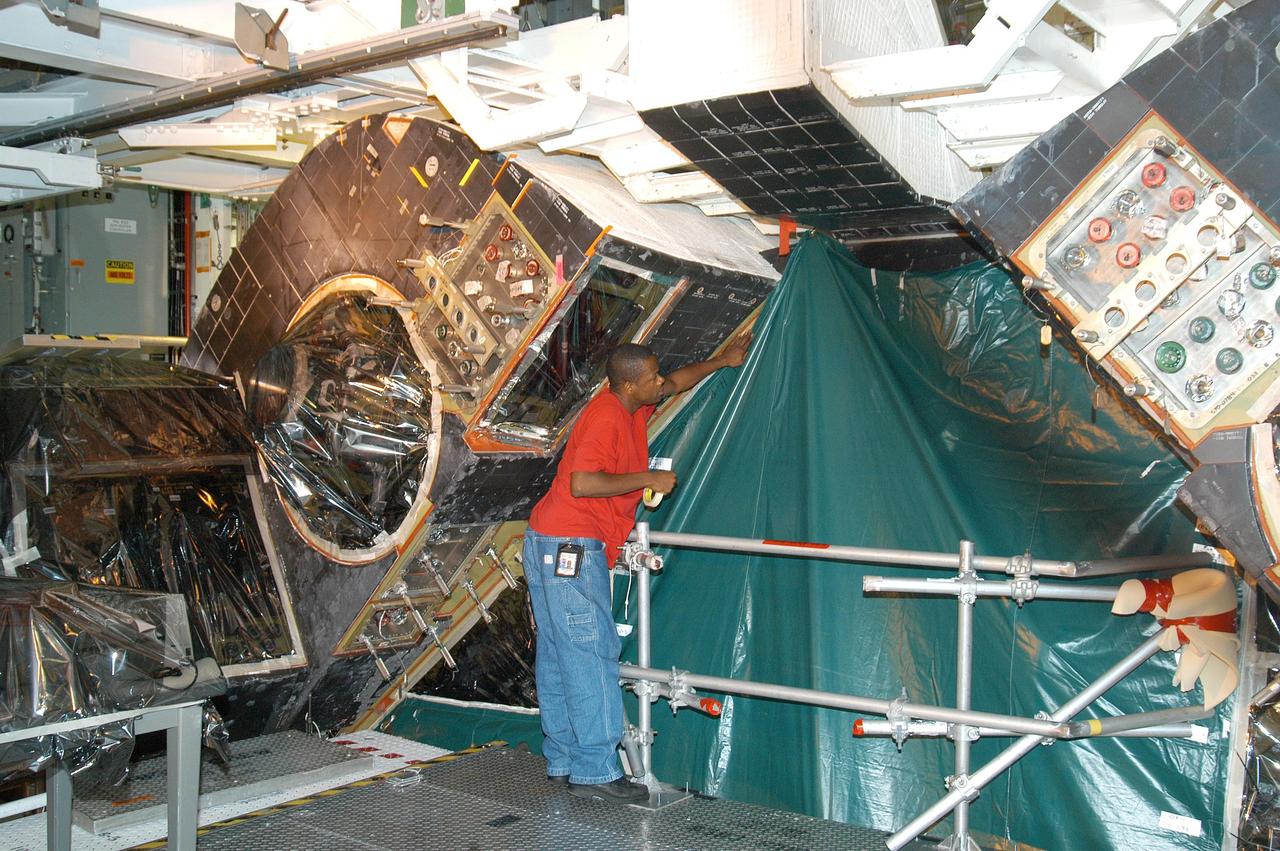

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility cover up areas of Atlantis with plastic, preparing for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing the payload bay doors and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
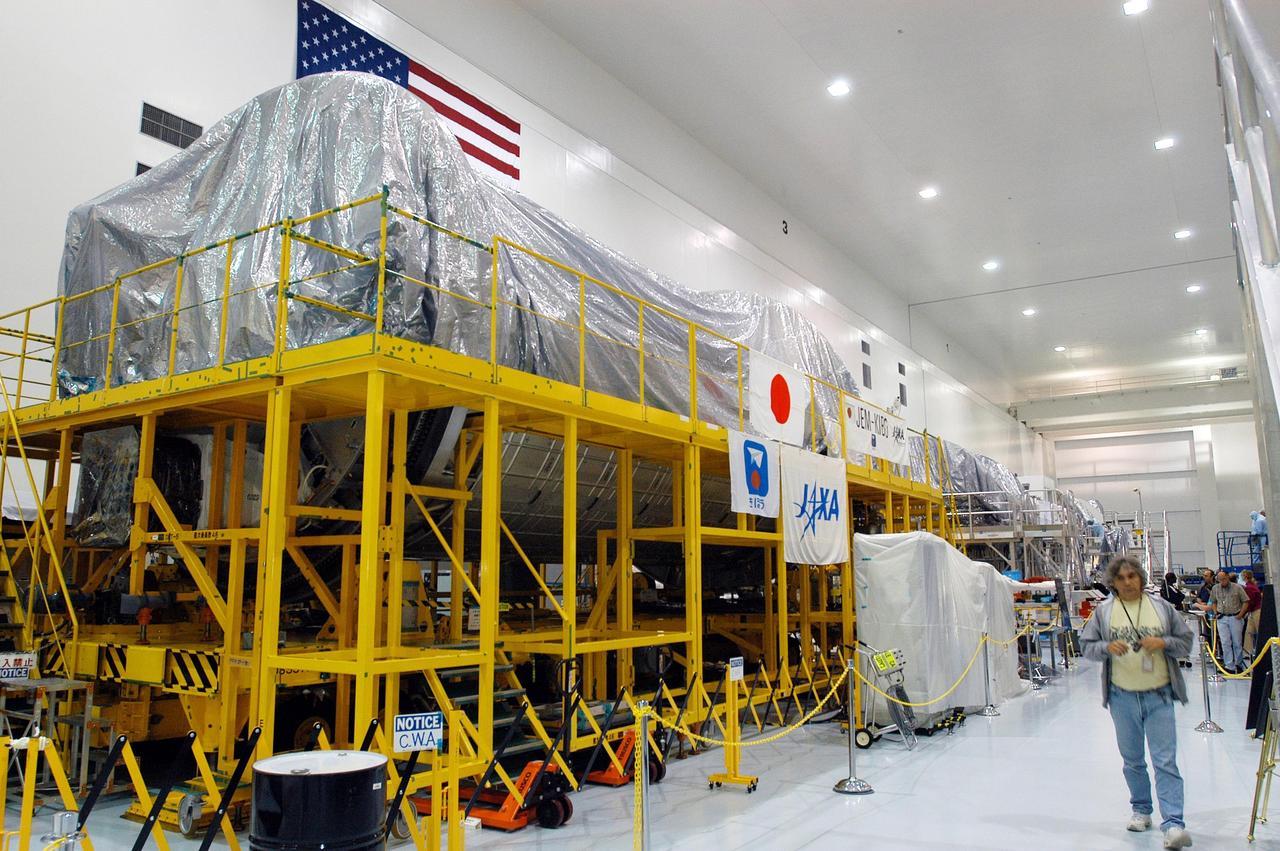

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, modules wrapped in plastic line one wall. The modules and equipment are being covered in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. KSC workers also have powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closed their payload bay doors and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The SSPF can withstand sustained winds of 110 mph and wind gusts up to 132 mph. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
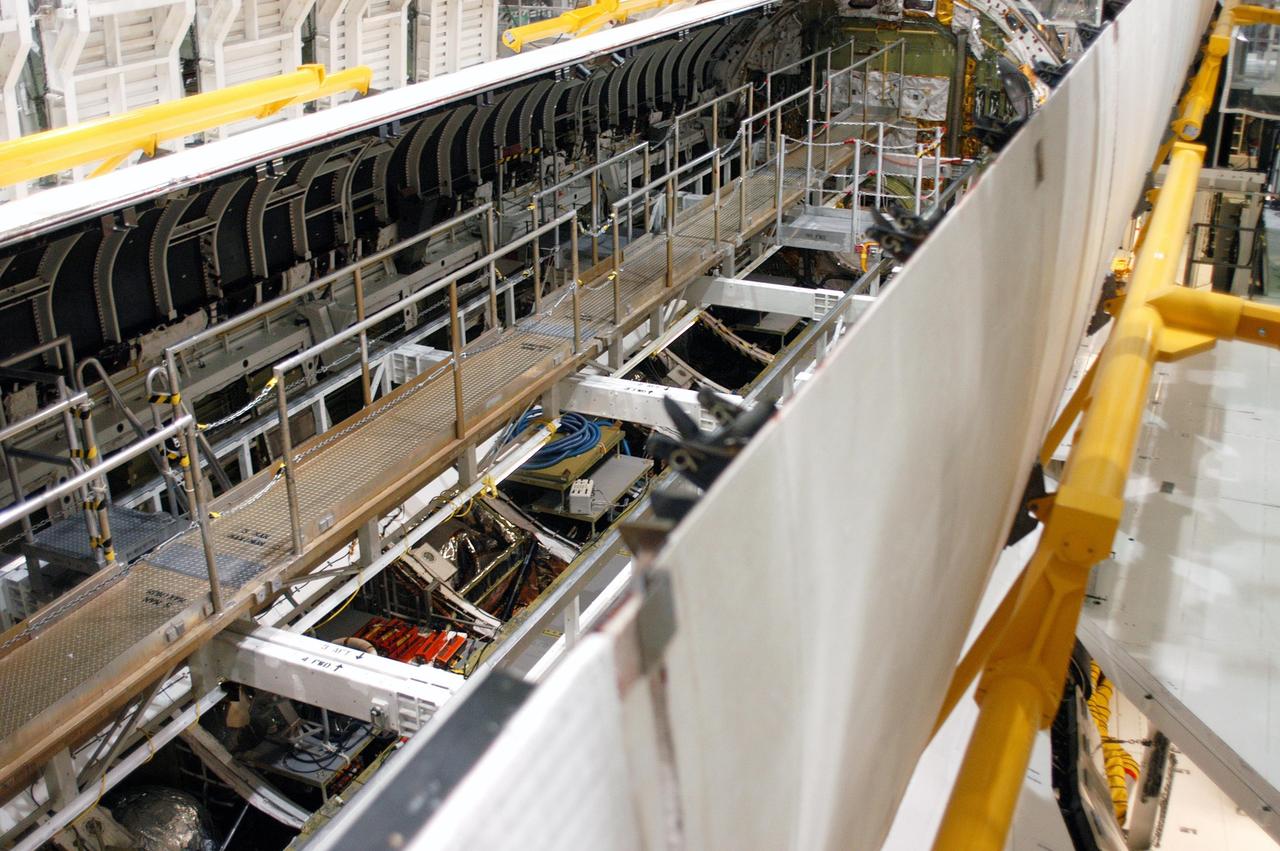

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the payload bay doors on Atlantis are being closed in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
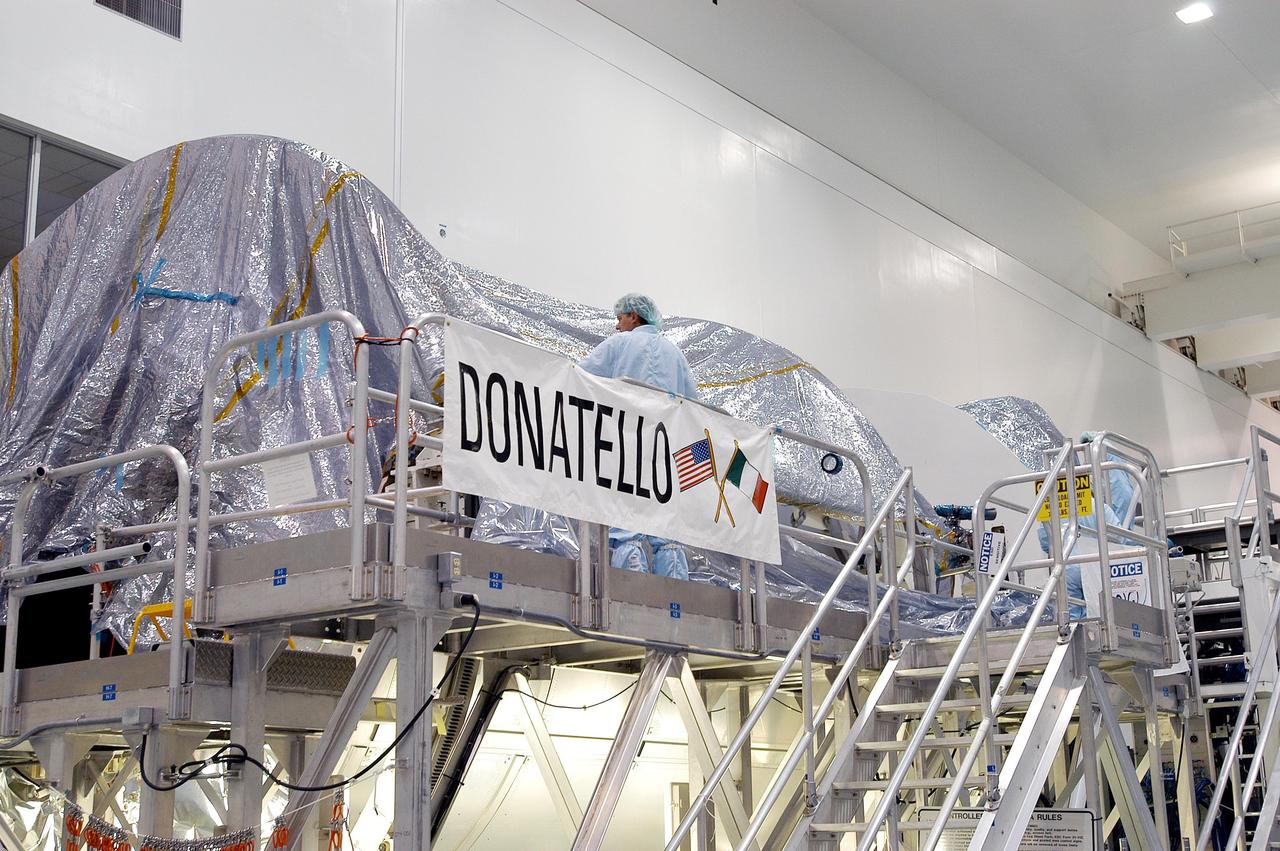

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers cover with plastic the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Donatello in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other modules and equipment are being covered as well. Workers also have powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closed their payload bay doors and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The SSPF can withstand sustained winds of 110 mph and wind gusts up to 132 mph. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to close the nose wheel doors on Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing their payload bay doors and stowing their landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
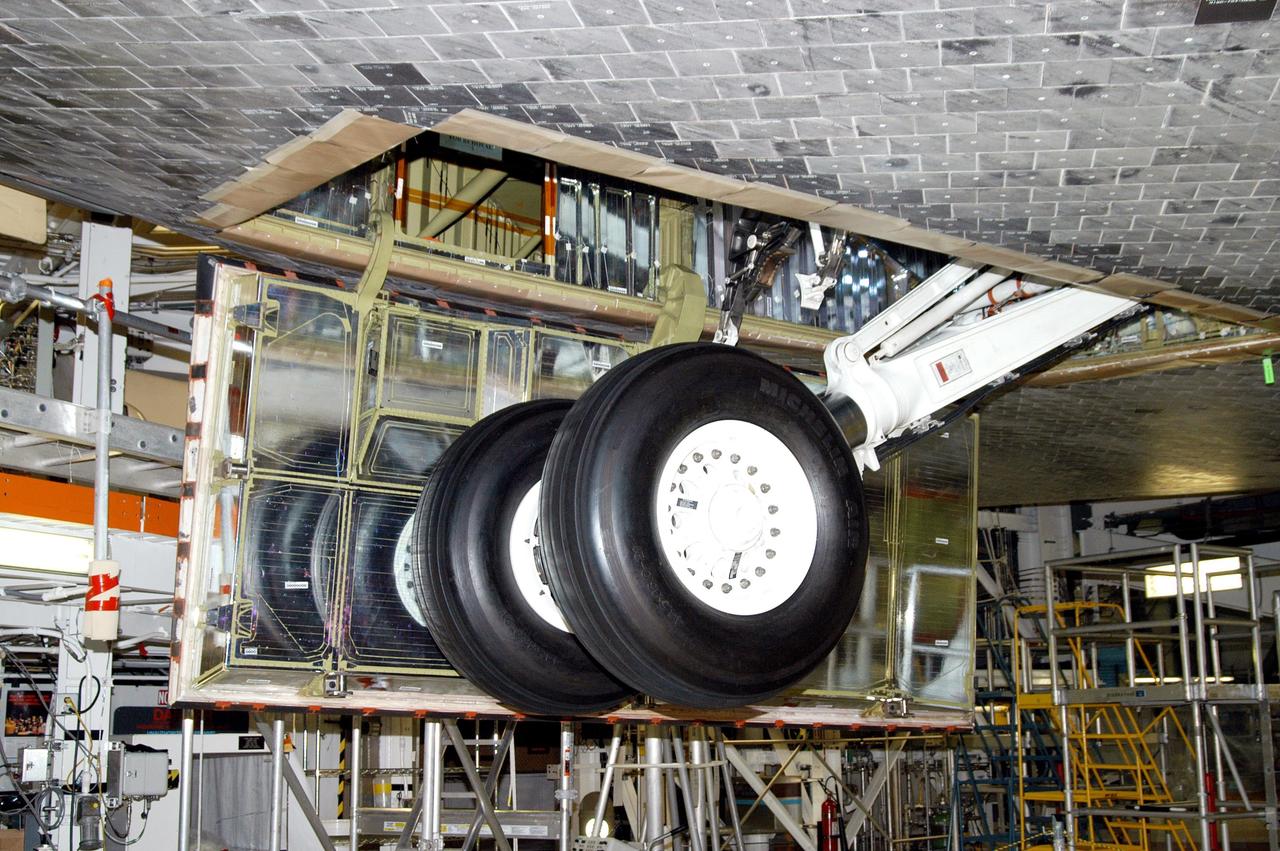

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, Atlantis’ wheels are raised into their wheel bays in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and closing their payload bay doors. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
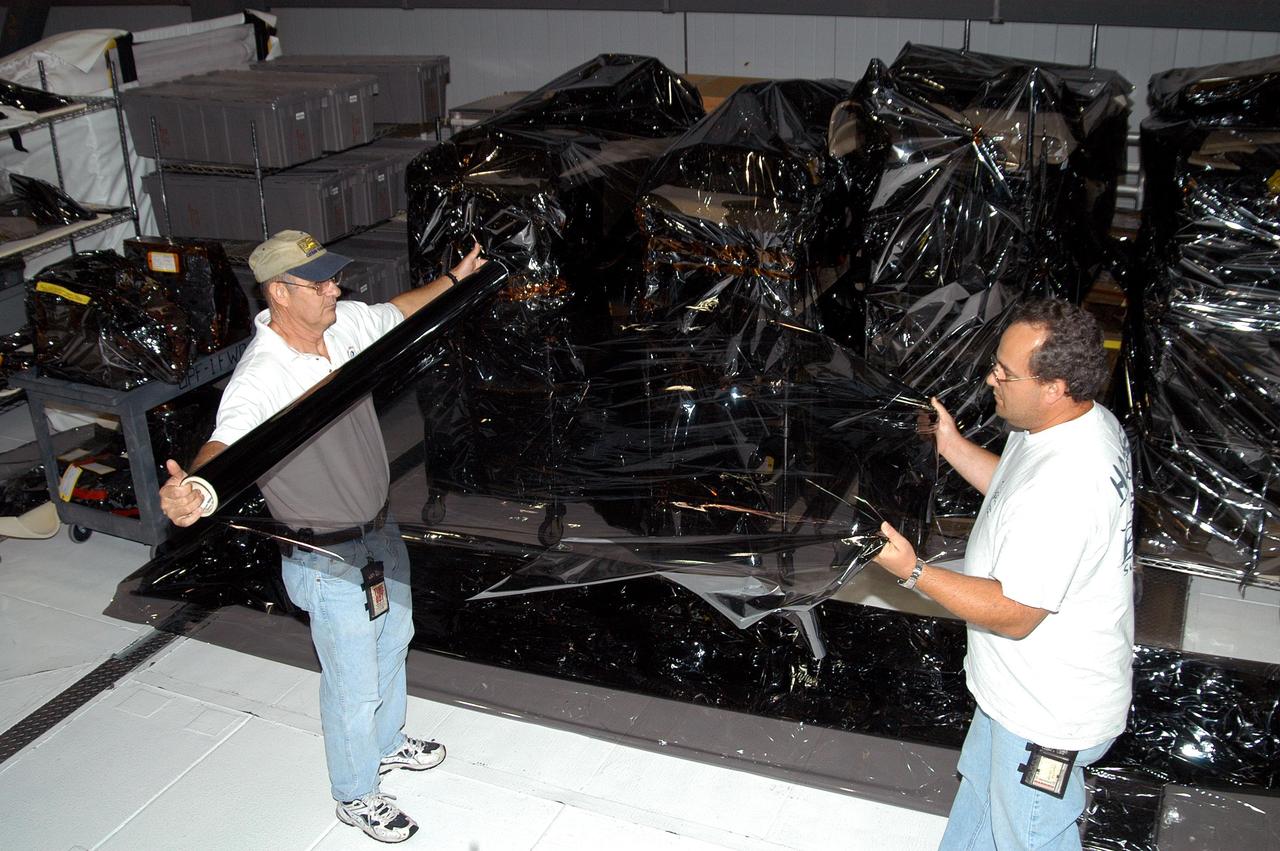

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility unwrap plastic for use in covering equipment as part of preparations for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing the payload bay doors and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
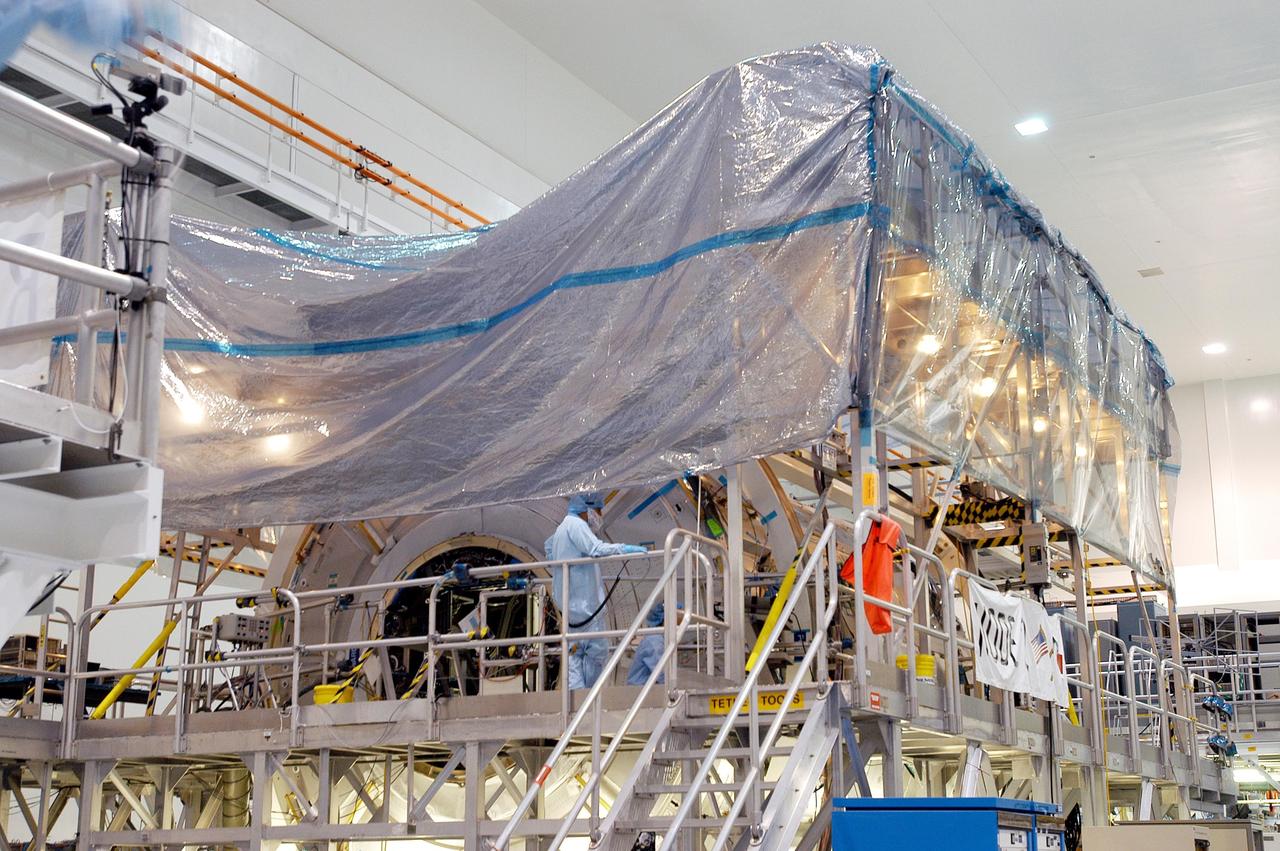

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers cover with plastic the U.S. Node 2 in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other modules and equipment are being covered as well. Workers also have powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closed their payload bay doors and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The SSPF can withstand sustained winds of 110 mph and wind gusts up to 132 mph. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to stow the landing gear on the orbiter Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and closing their payload bay doors. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
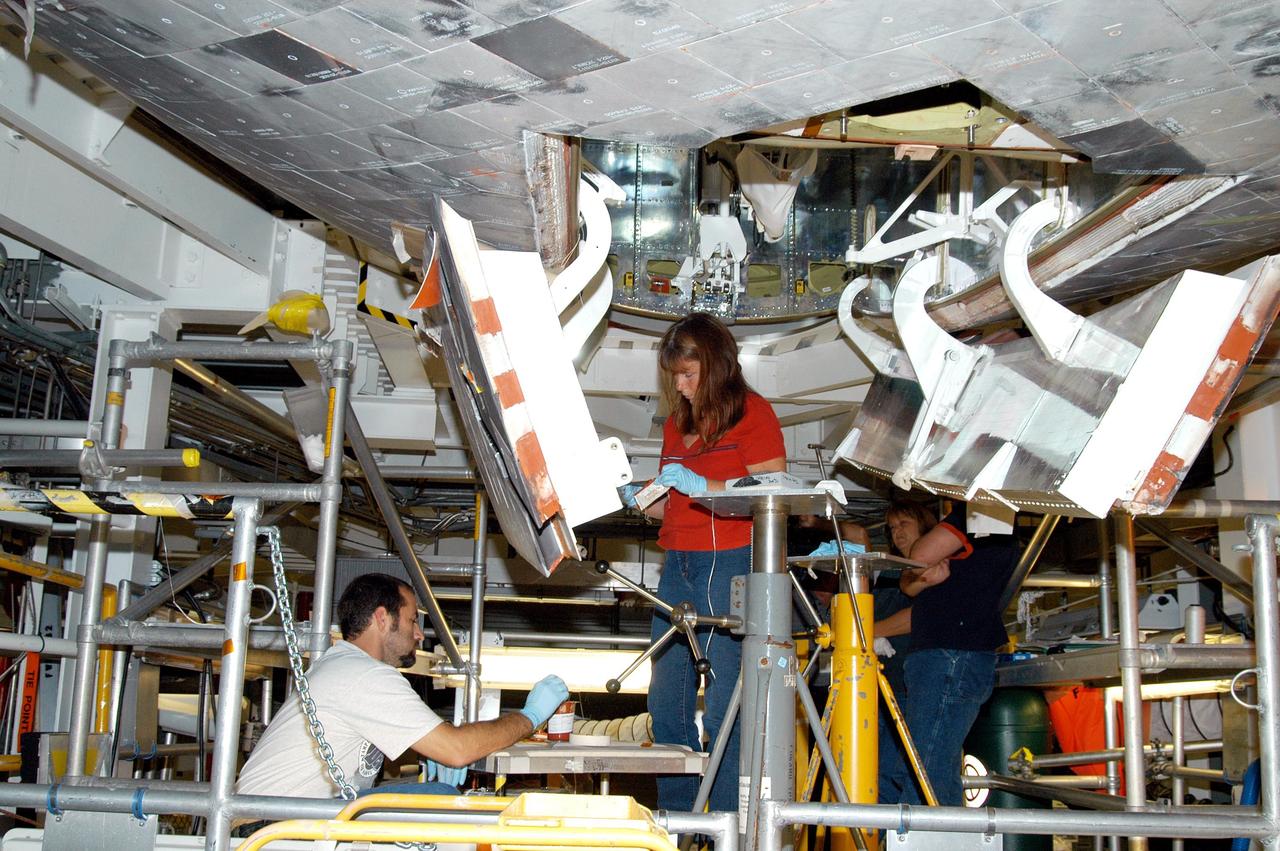

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to close the nose wheel doors on Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing their payload bay doors and stowing their landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
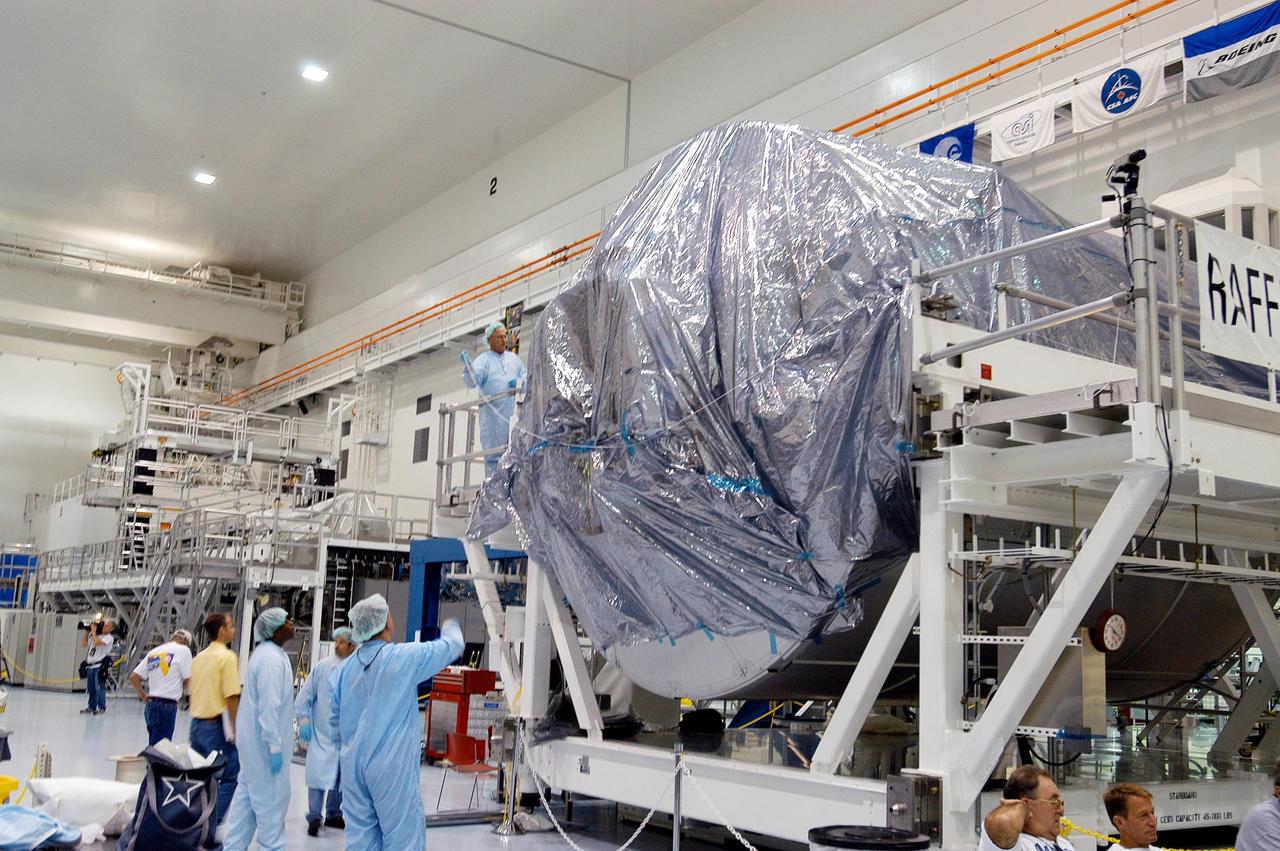

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, workers cover with plastic the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other modules and equipment are being covered as well. Workers also have powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closed their payload bay doors and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The SSPF can withstand sustained winds of 110 mph and wind gusts up to 132 mph. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
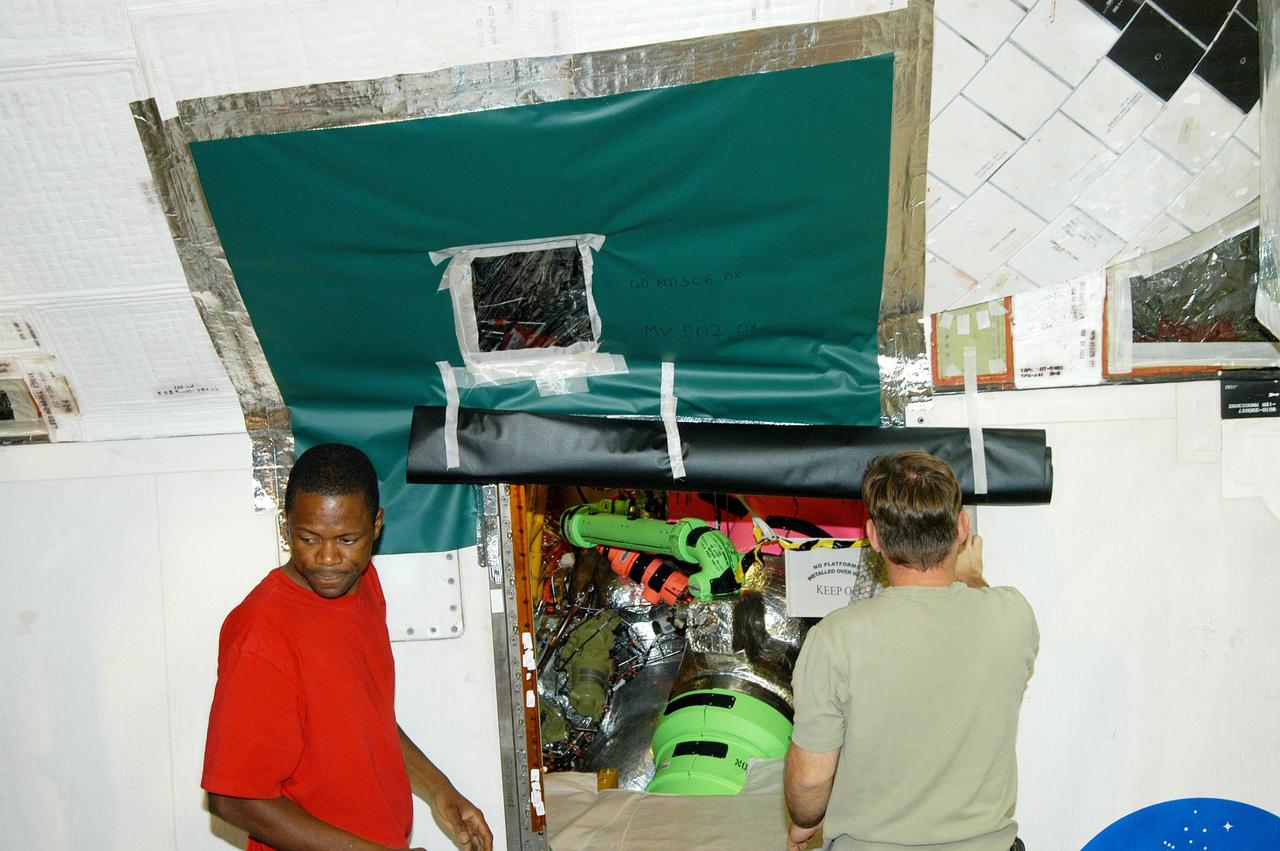

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility cover up areas of Atlantis, preparing for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing the payload bay doors and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to close the nose wheel doors on Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing their payload bay doors and stowing their landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
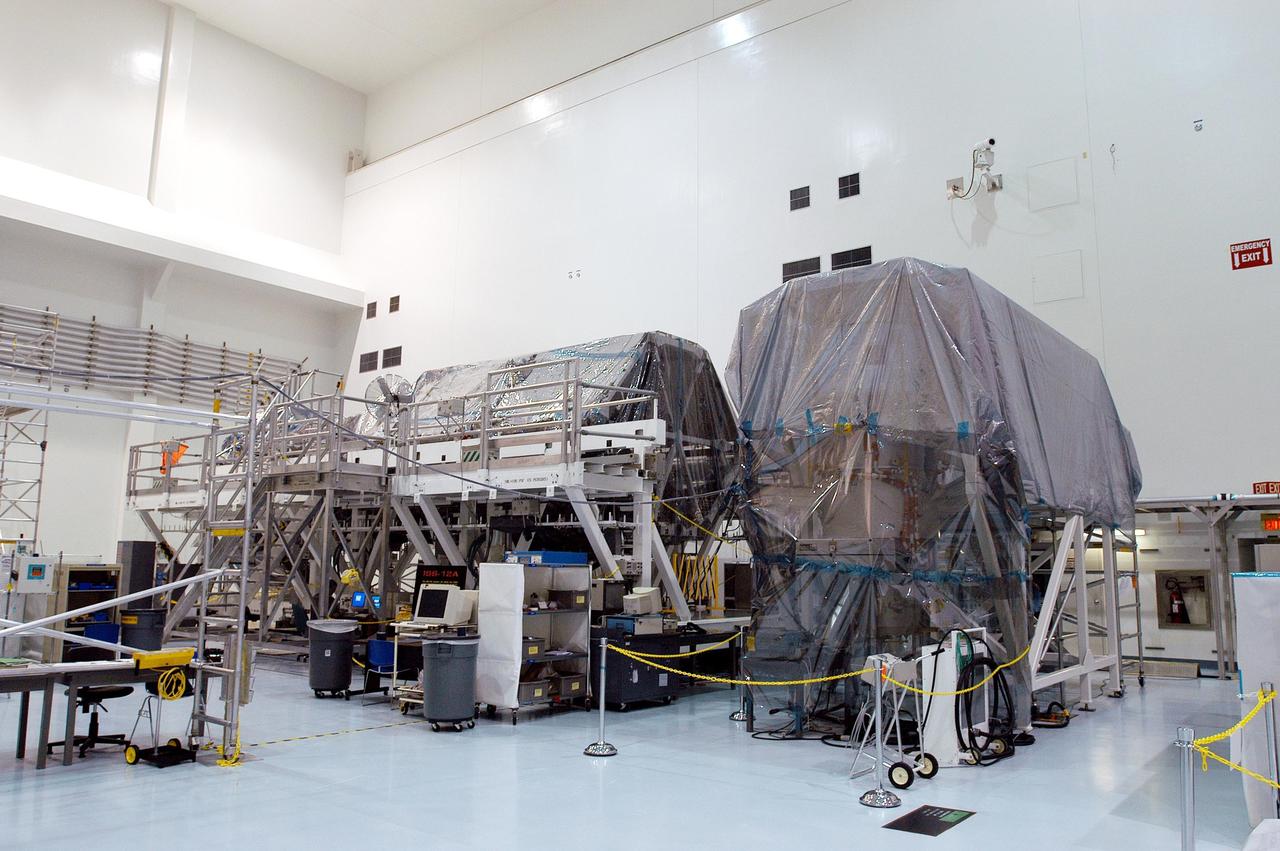

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Space Station Processing Facility, modules and equipment are being covered in plastic in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. KSC workers also have powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closed their payload bay doors and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The SSPF can withstand sustained winds of 110 mph and wind gusts up to 132 mph. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.

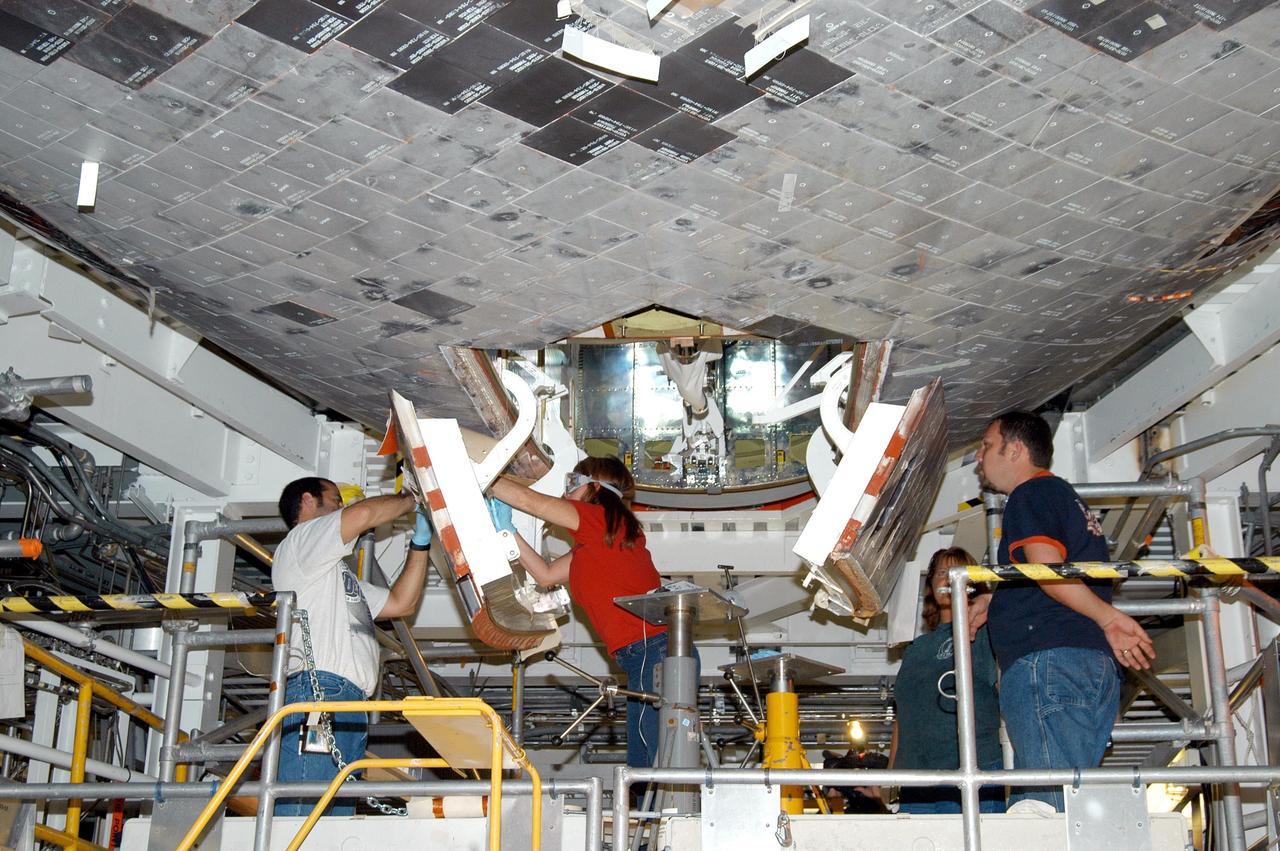
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility finish Hurricane preparations on the payload bay doors of Atlantis. Preparing for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday, workers also powered down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and stowed the landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
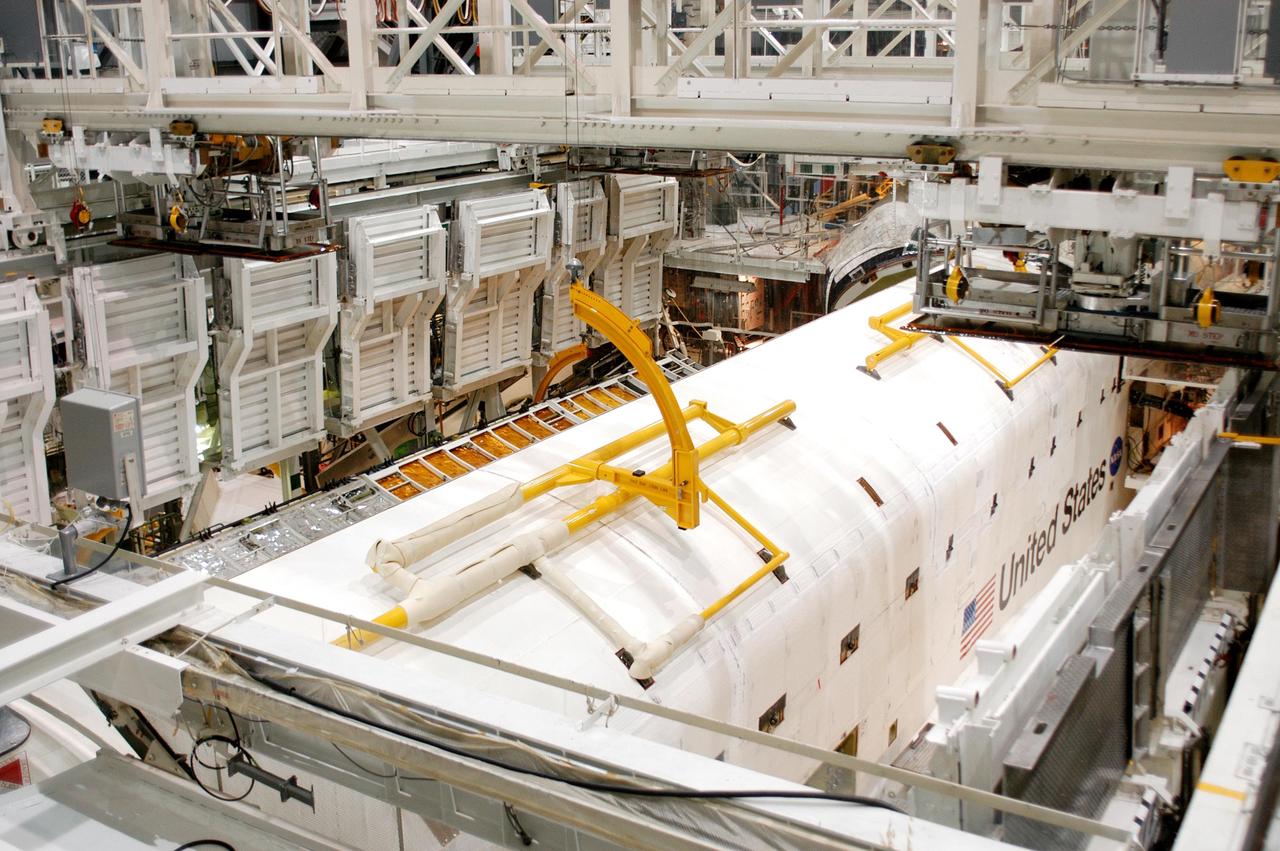

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the payload bay doors on Atlantis are being closed in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
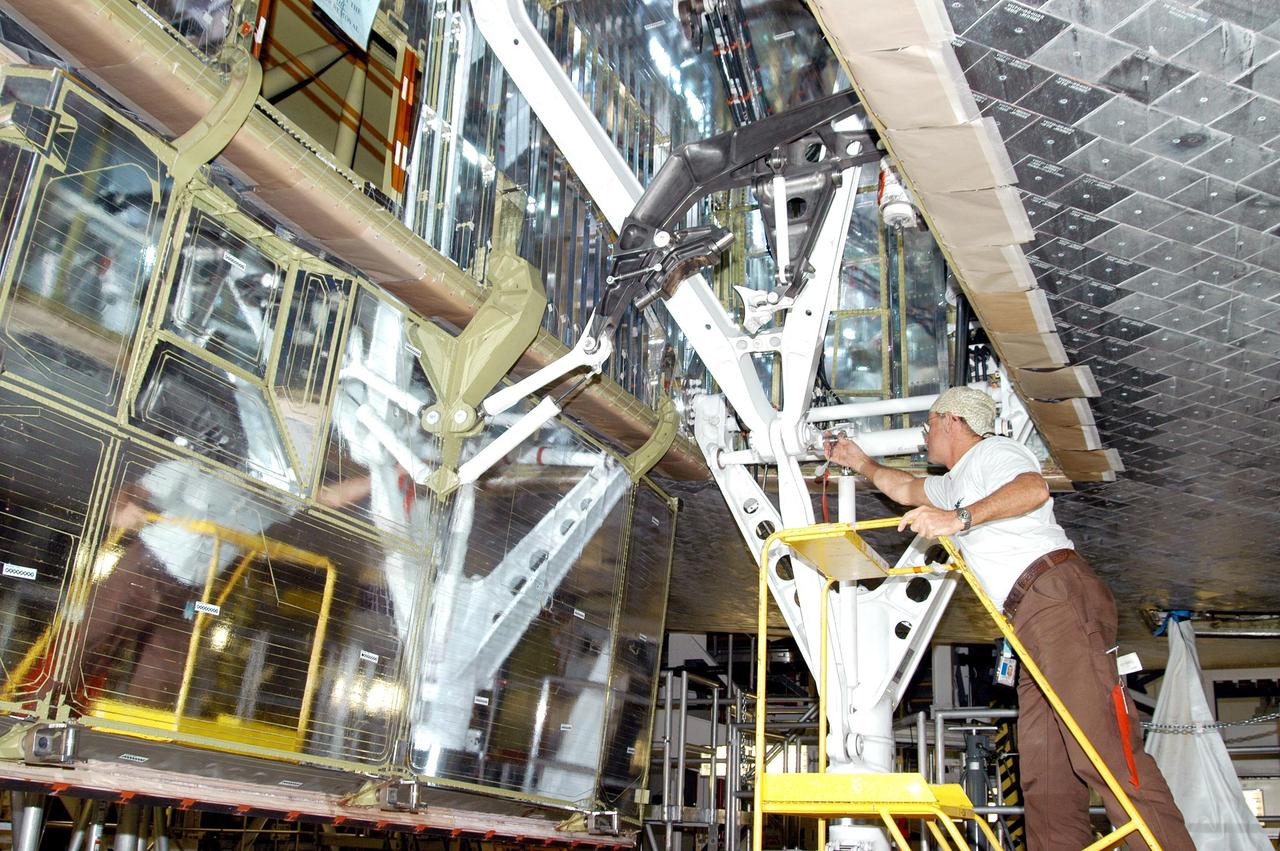

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare the wheel bay to stow Atlantis’ landing gear in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and closing their payload bay doors. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
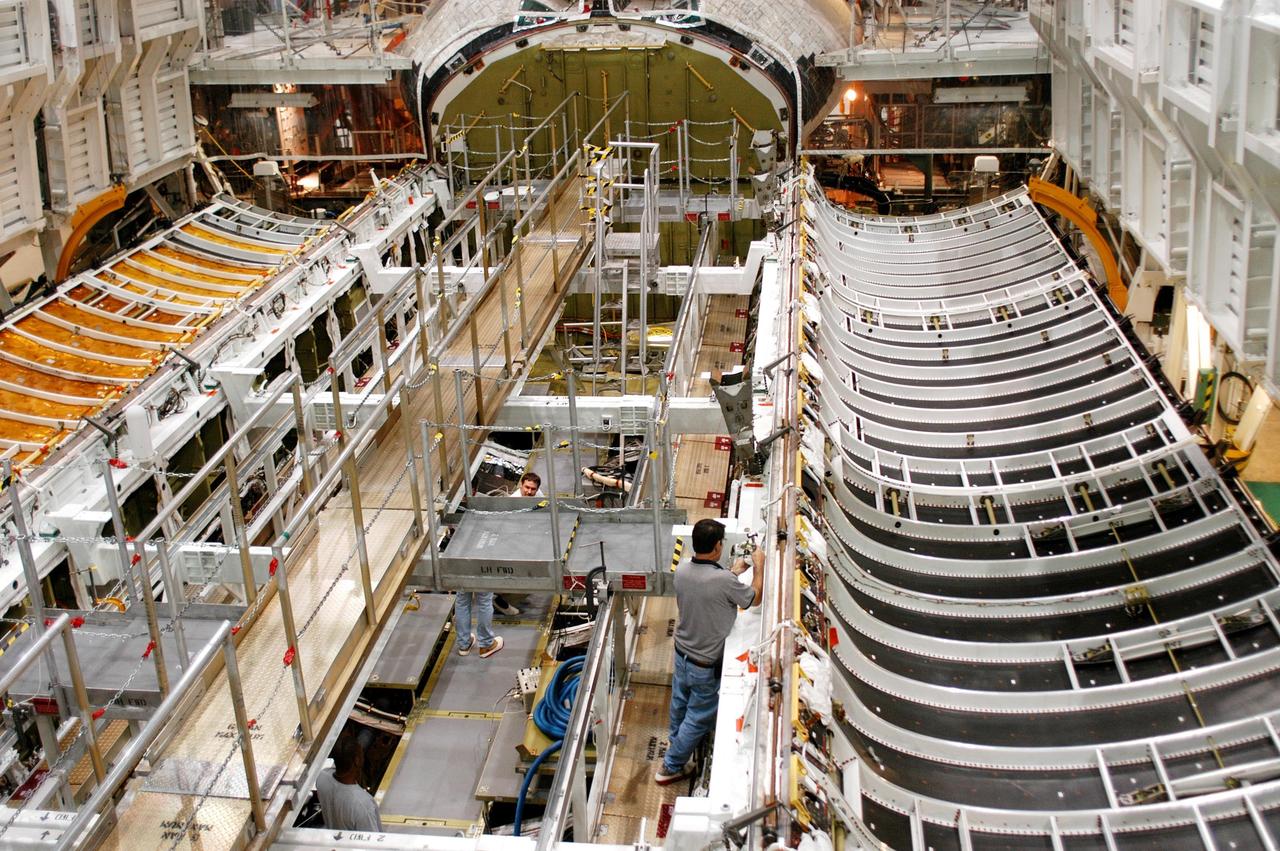

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers prepare to close the payload bay doors on Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare the orbiter Atlantis and related equipment for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing their payload bay doors and stowing their landing gear. They are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility cover up areas of Atlantis with plastic, preparing for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, closing the payload bay doors and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
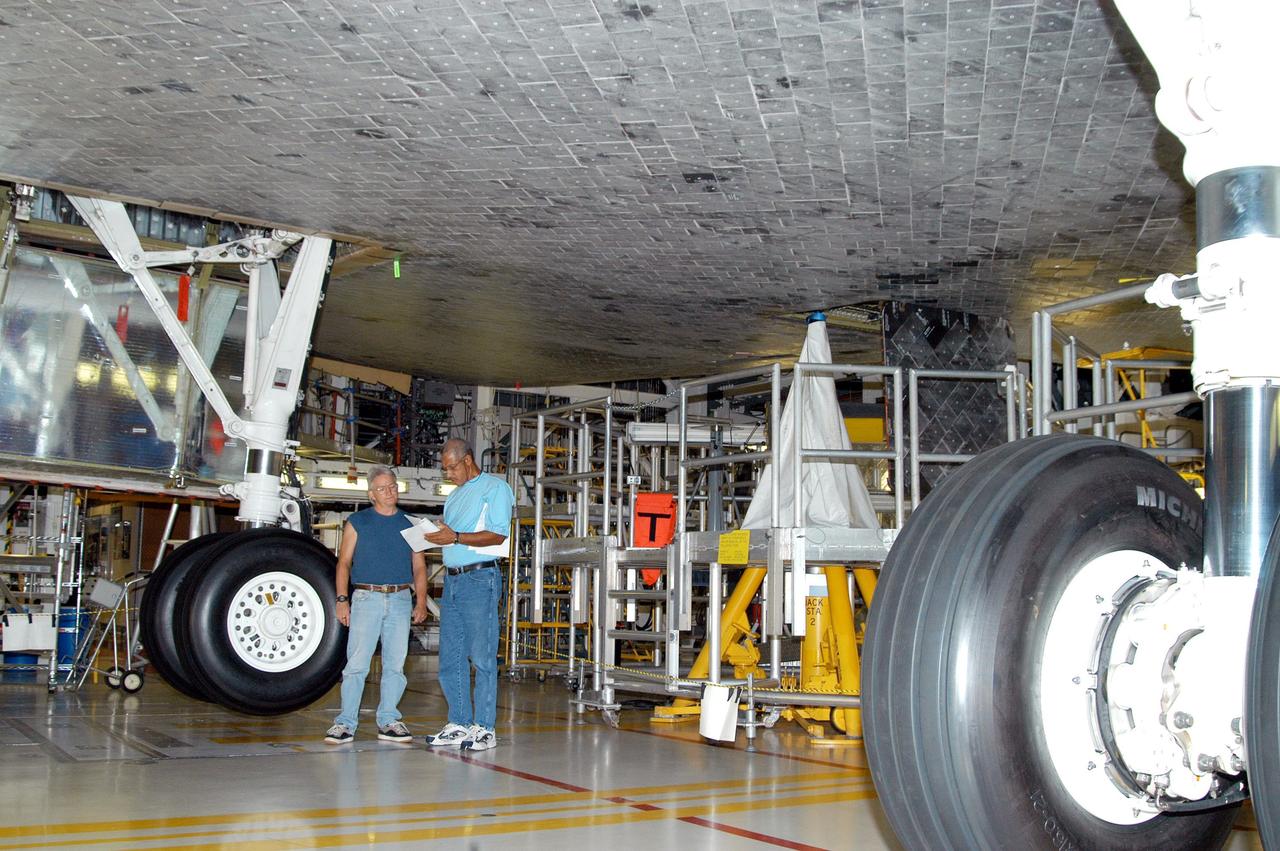

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to stow the landing gear on the orbiter Atlantis in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters, and closing their payload bay doors. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
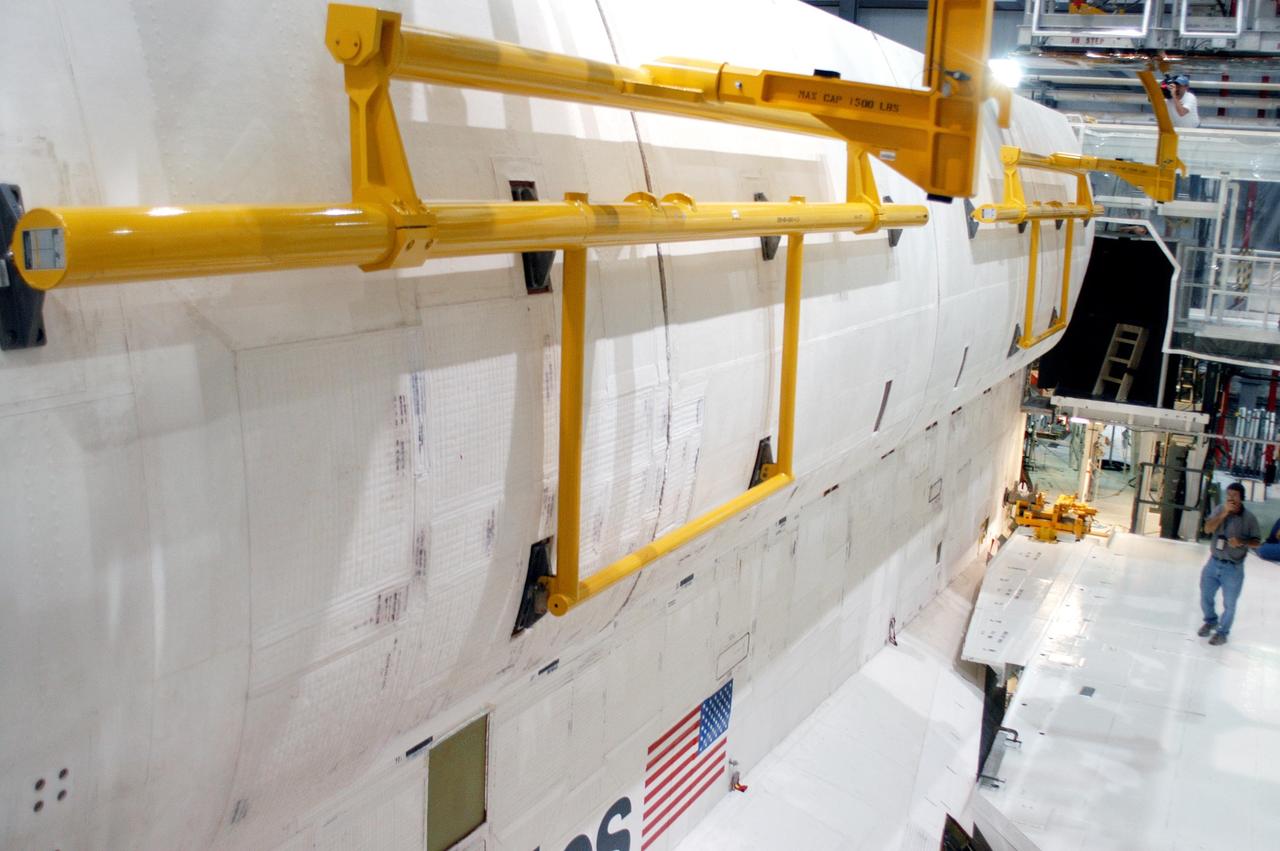

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the payload bay doors on Atlantis are being closed in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
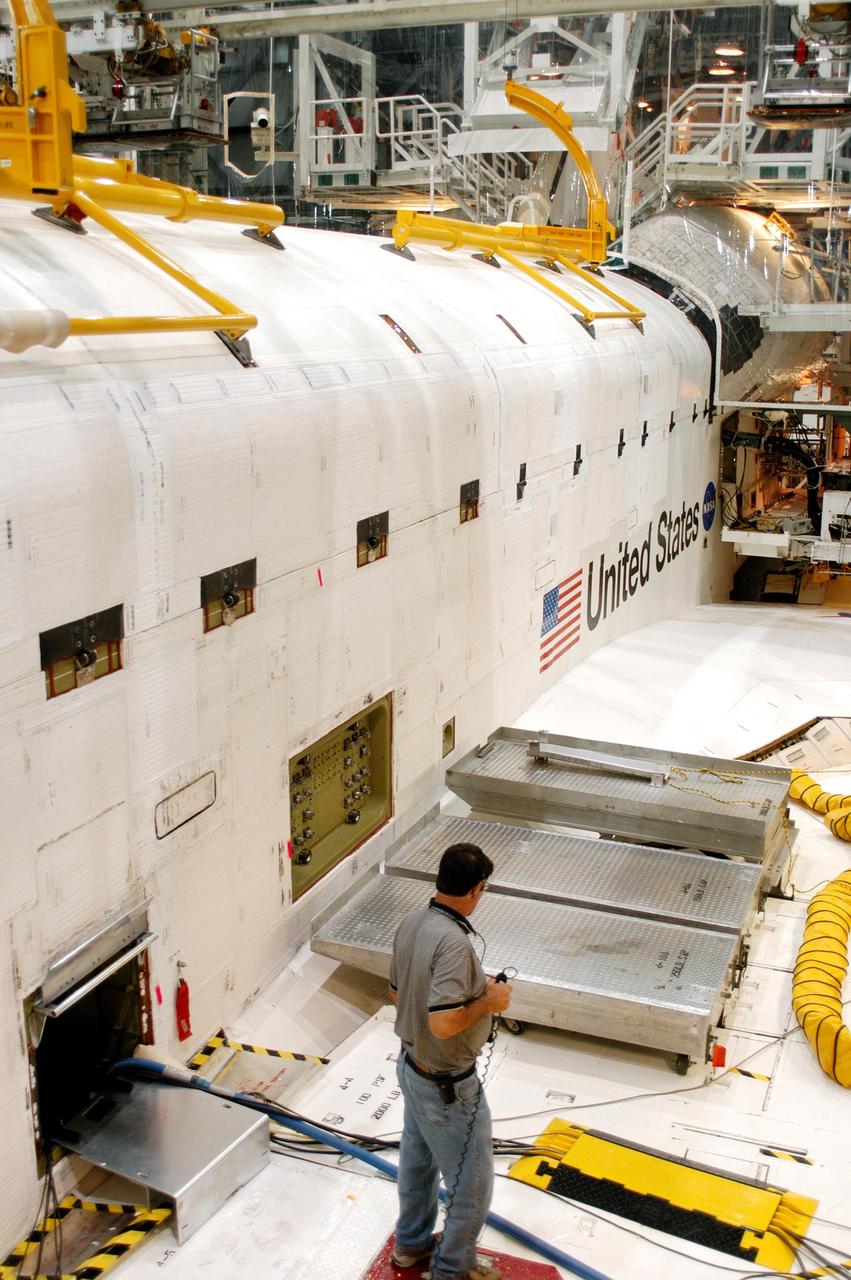

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, a worker checks out part of Atlantis after payload bay doors were closed in preparation for the expected impact of Hurricane Frances on Saturday. Other preparations at KSC include powering down the Space Shuttle orbiters and stowing the landing gear. Workers are also taking precautions against flooding by moving spacecraft hardware off the ground and sandbagging facilities. The Orbiter Processing Facility is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 105 mph. The Vehicle Assembly Building is constructed of concrete and steel and was designed to withstand winds of 125 mph. Other payload and flight hardware support facilities can endure winds of 110 mph. Launch pads and the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility can withstand 125-mph winds.
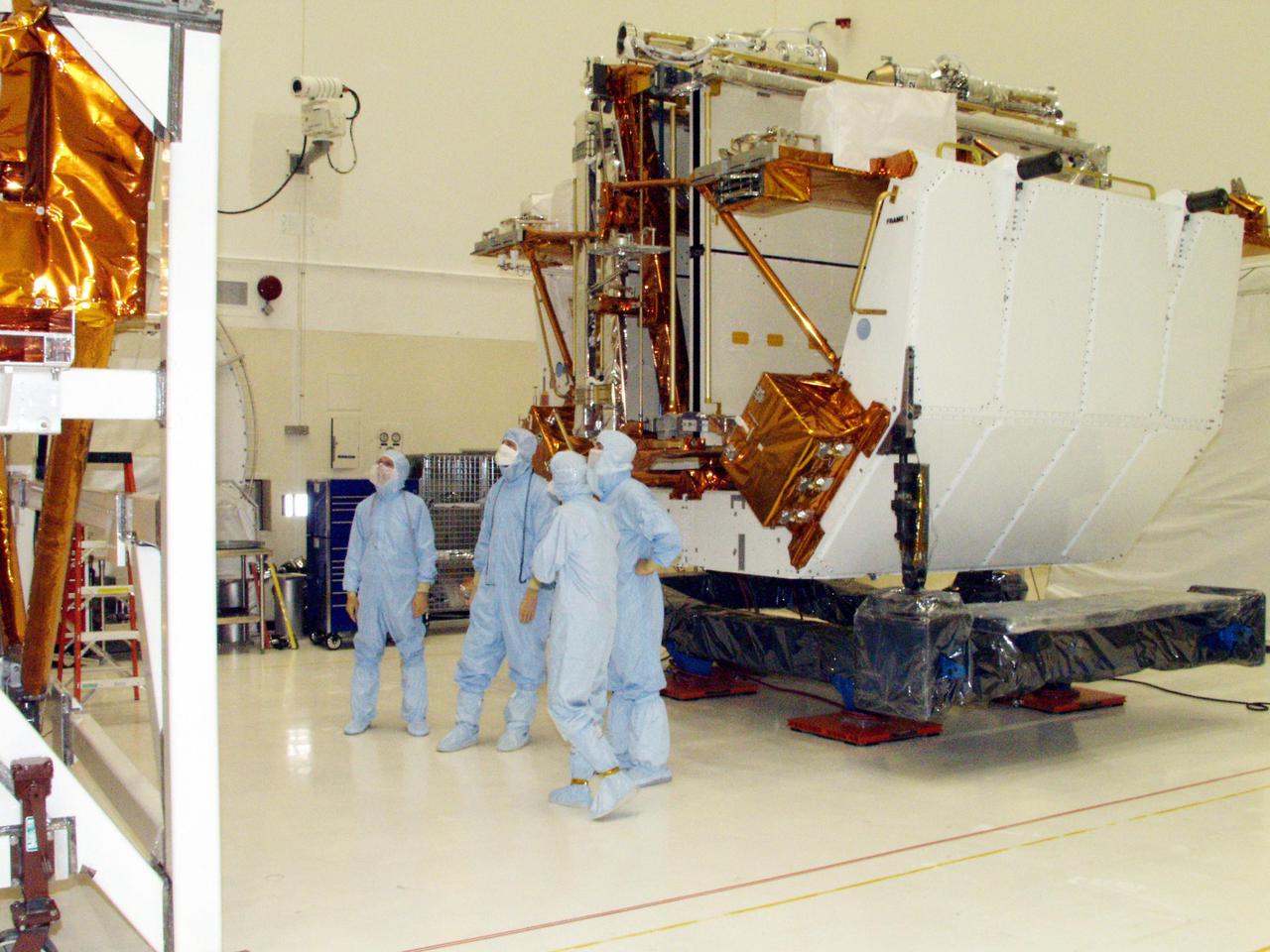

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility look over the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Solar Array 3 panels behind them, and other HST hardware, are installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
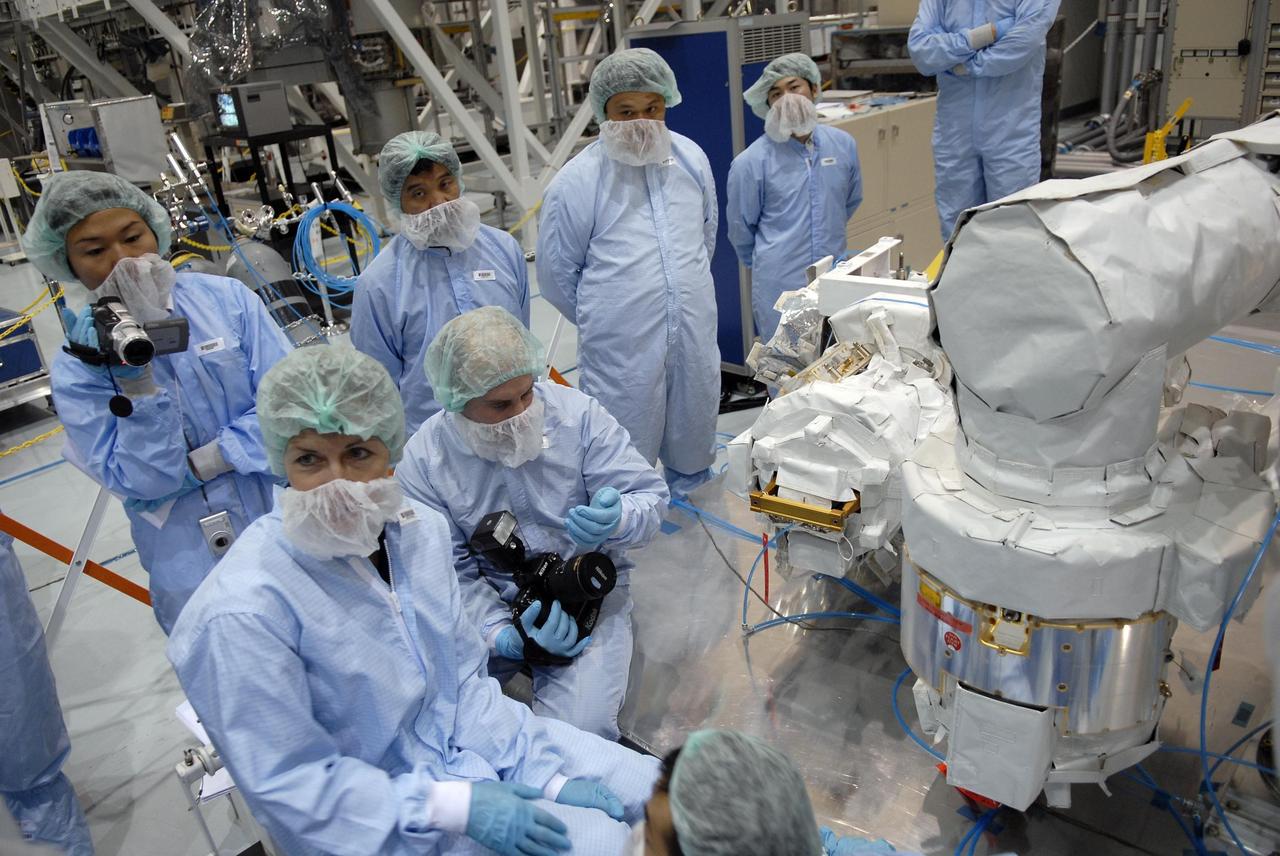

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, astronauts familiarize themselves with hardware and modules to be flown on upcoming shuttle flights. In the front is Peggy Whitson, looking at the Japanese remote manipulator system, part of the payload on a 2008 mission. With construction of the Space Station the primary focus of future shuttle missions, astronaut crews will be working with one or more of the elements and hardware already being processed in the SSPF. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
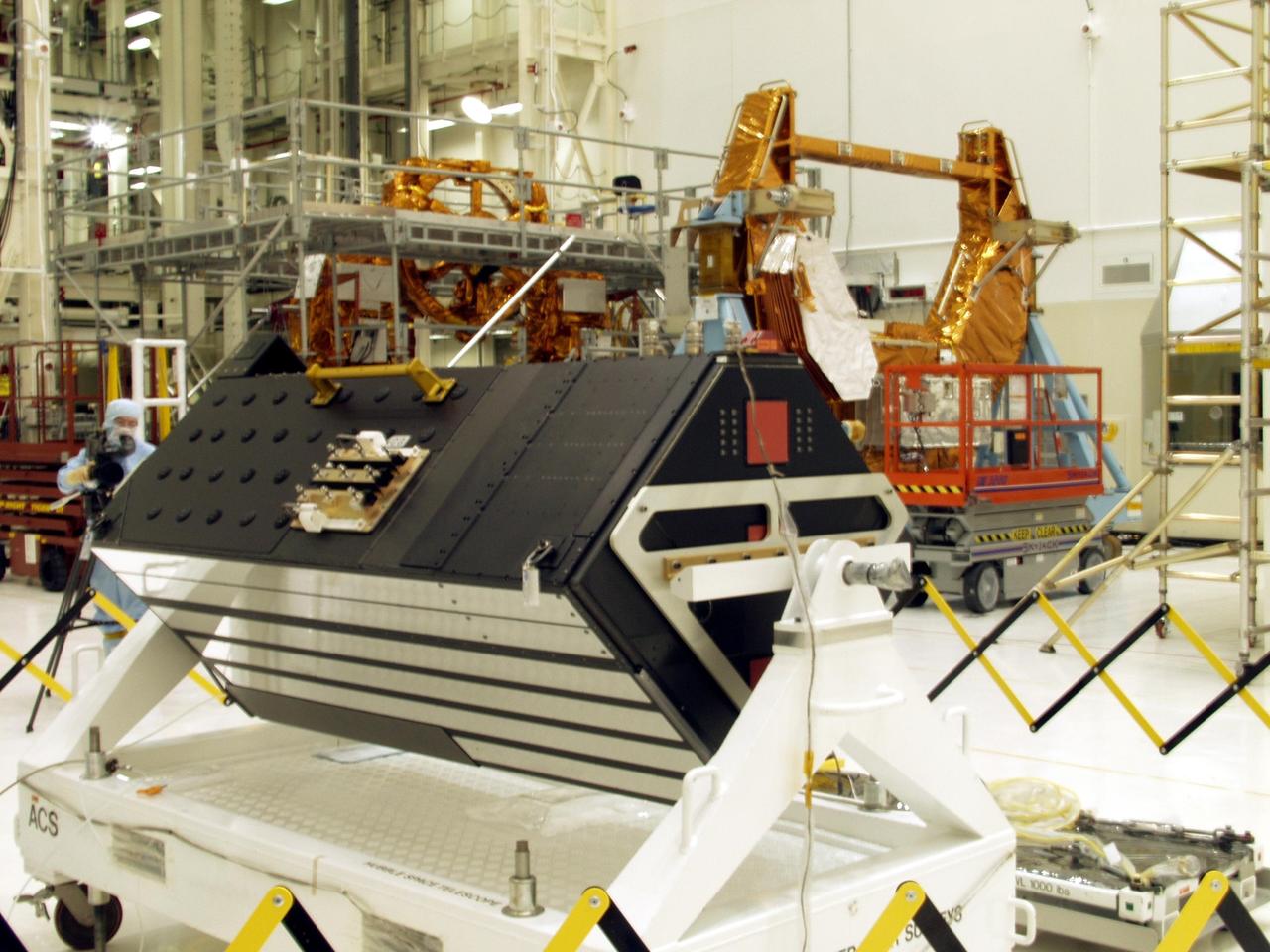

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), foreground, is part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The ACS and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The Solar Array 3 panels are part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The panels and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility take a close look at the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The hardware is installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
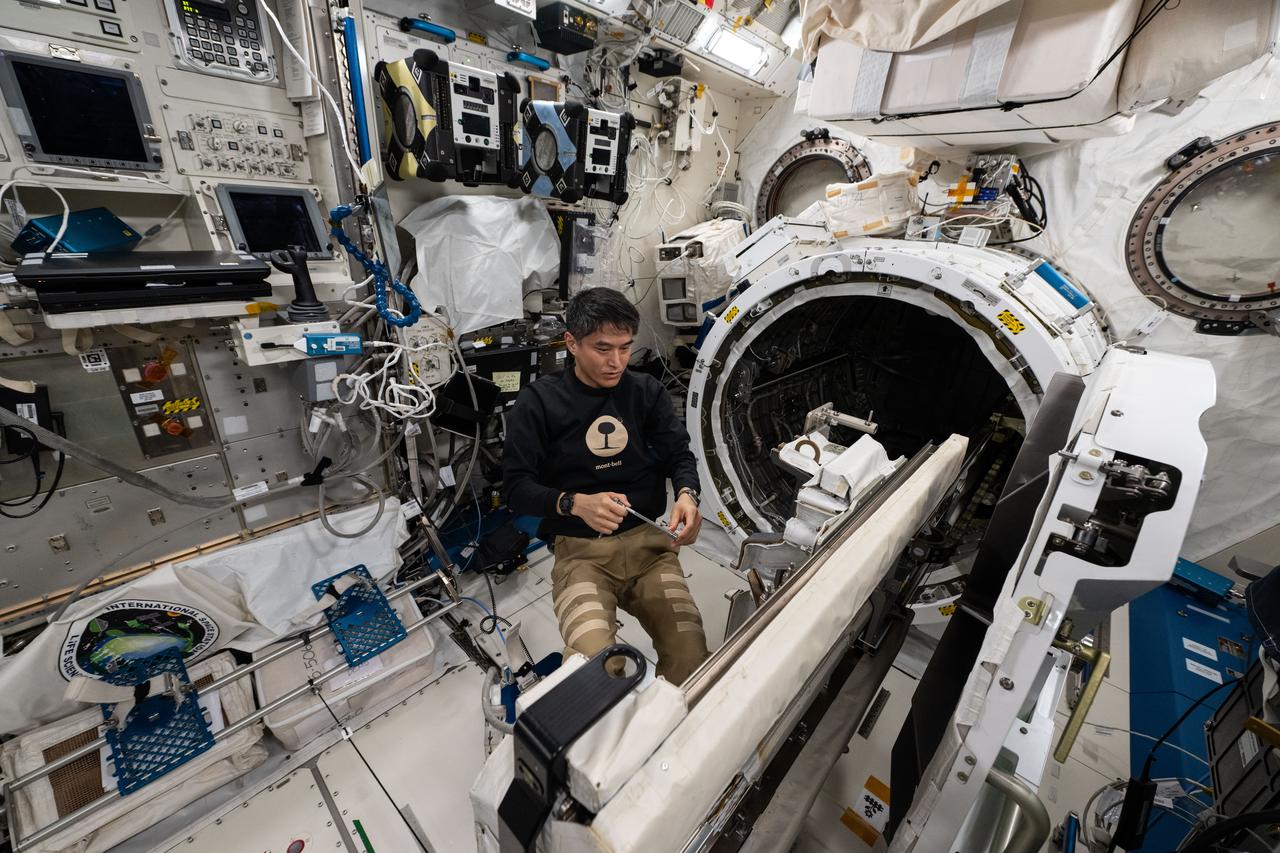

iss073e0383933 (July 4, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi removes research hardware attached to the Kibo laboratory module's airlock slide table aboard the International Space Station. The slide table can be retracted back and forth into the airlock where the Japanese robotic arm can grapple a variety of payloads and hardware for installation on the outside of Kibo for exposure to the external space environment.
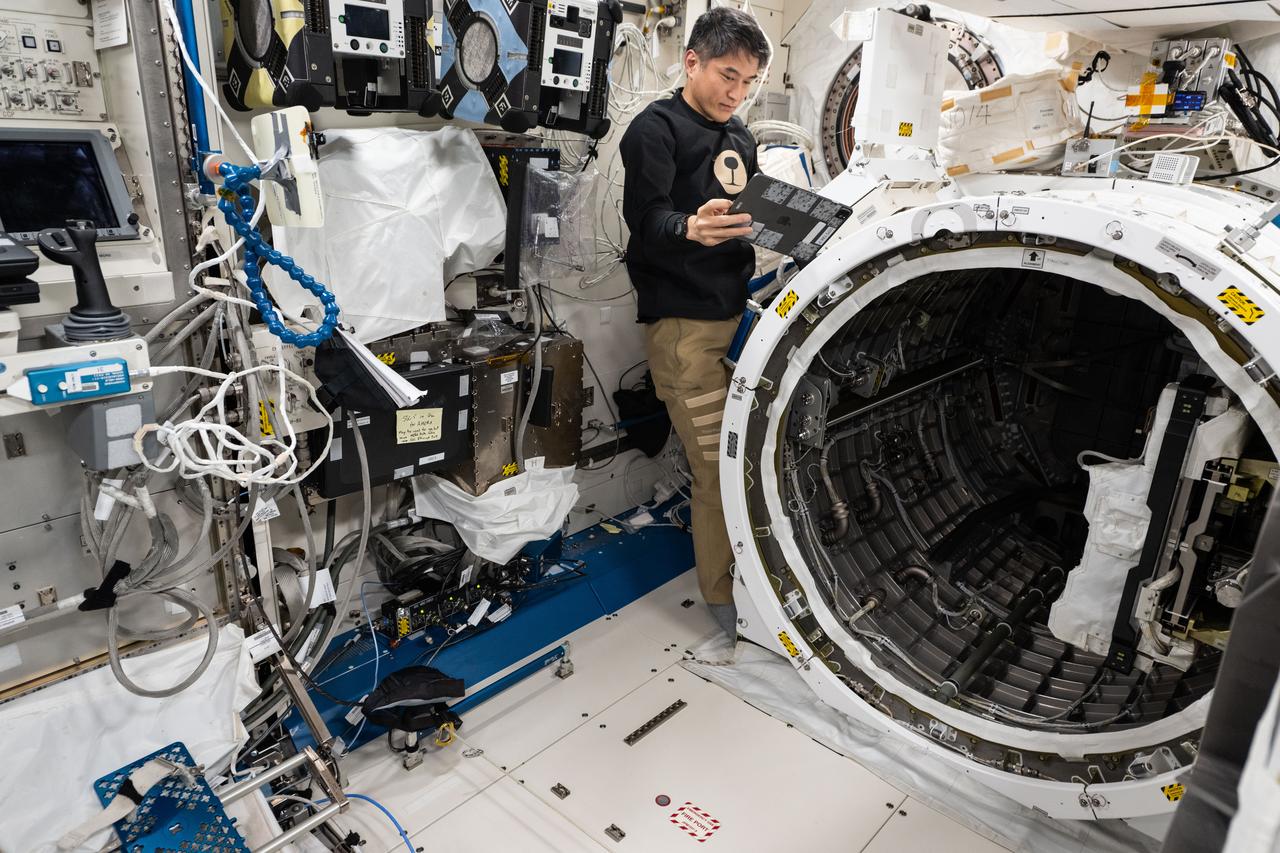

iss073e0383929 (July 4, 2025) --- JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut and Expedition 73 Commander Takuya Onishi prepares to retract a slide table that contains research hardware from inside the Kibo laboratory module's airlock. The slide table can be retracted back and forth into the airlock where the Japanese robotic arm can grapple a variety of payloads and hardware for installation on the outside of Kibo for exposure to the external space environment.
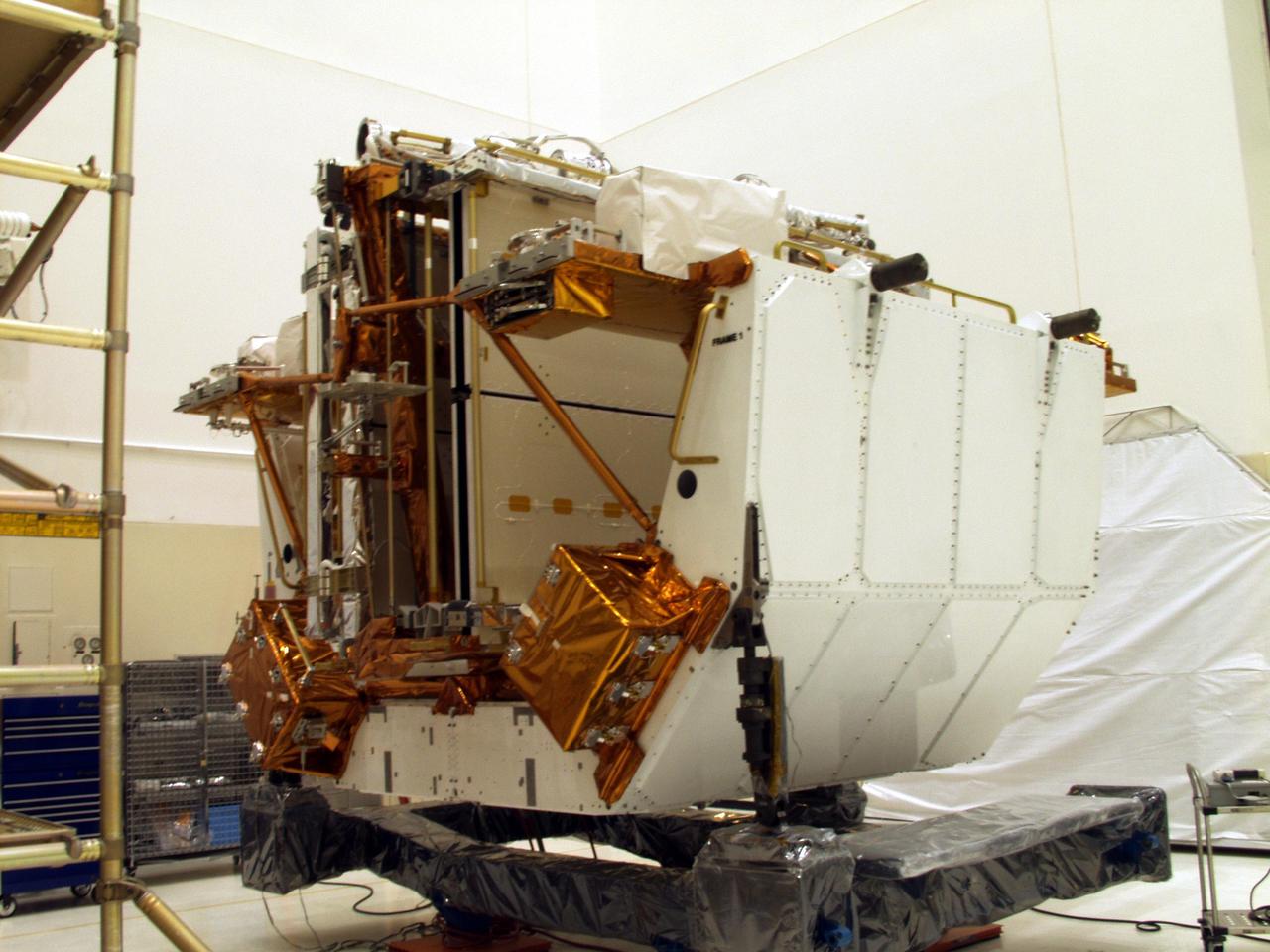

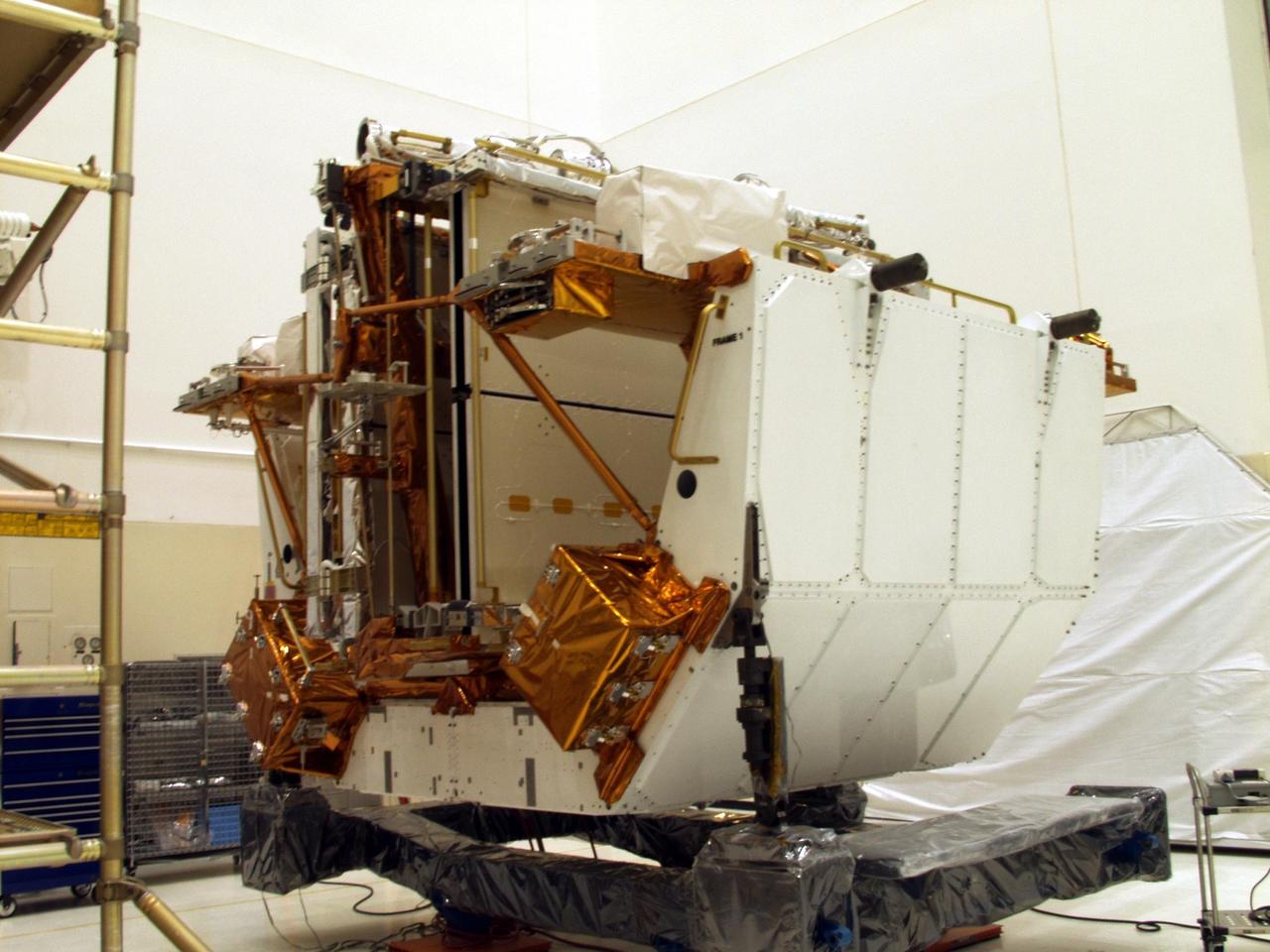
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The Solar Array 3 panels are part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The panels and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
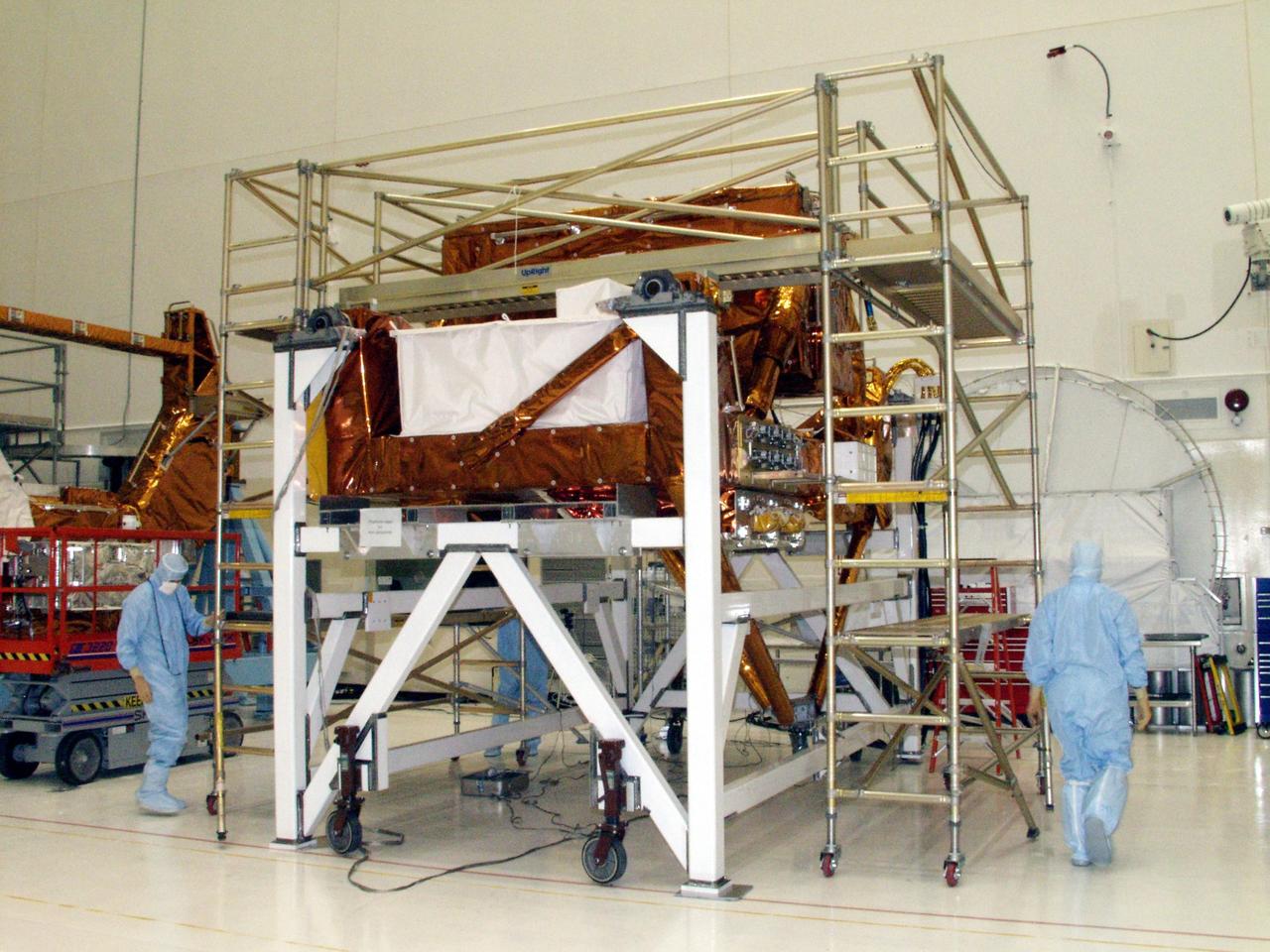

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). Seen here is the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The hardware will be installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
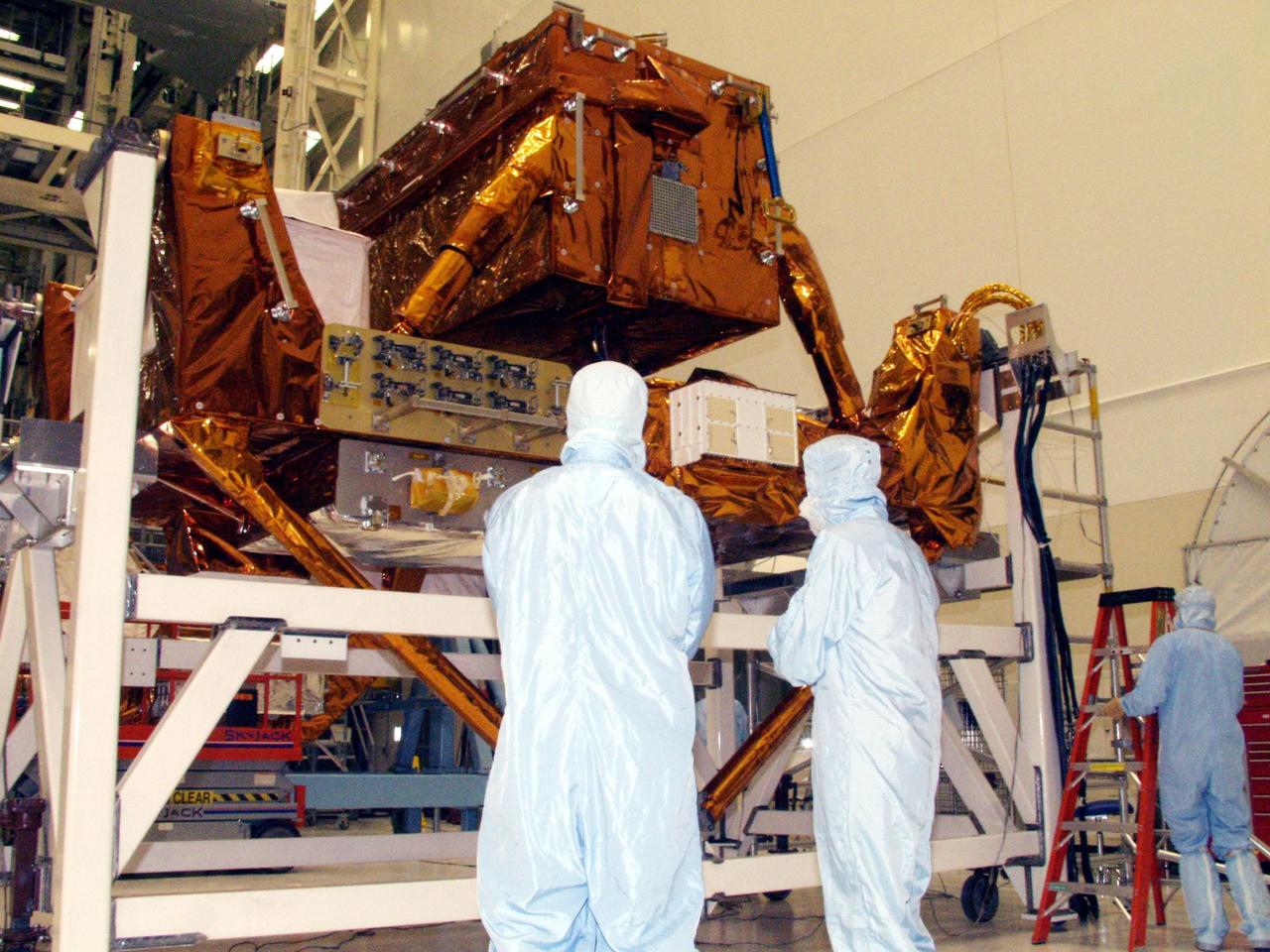

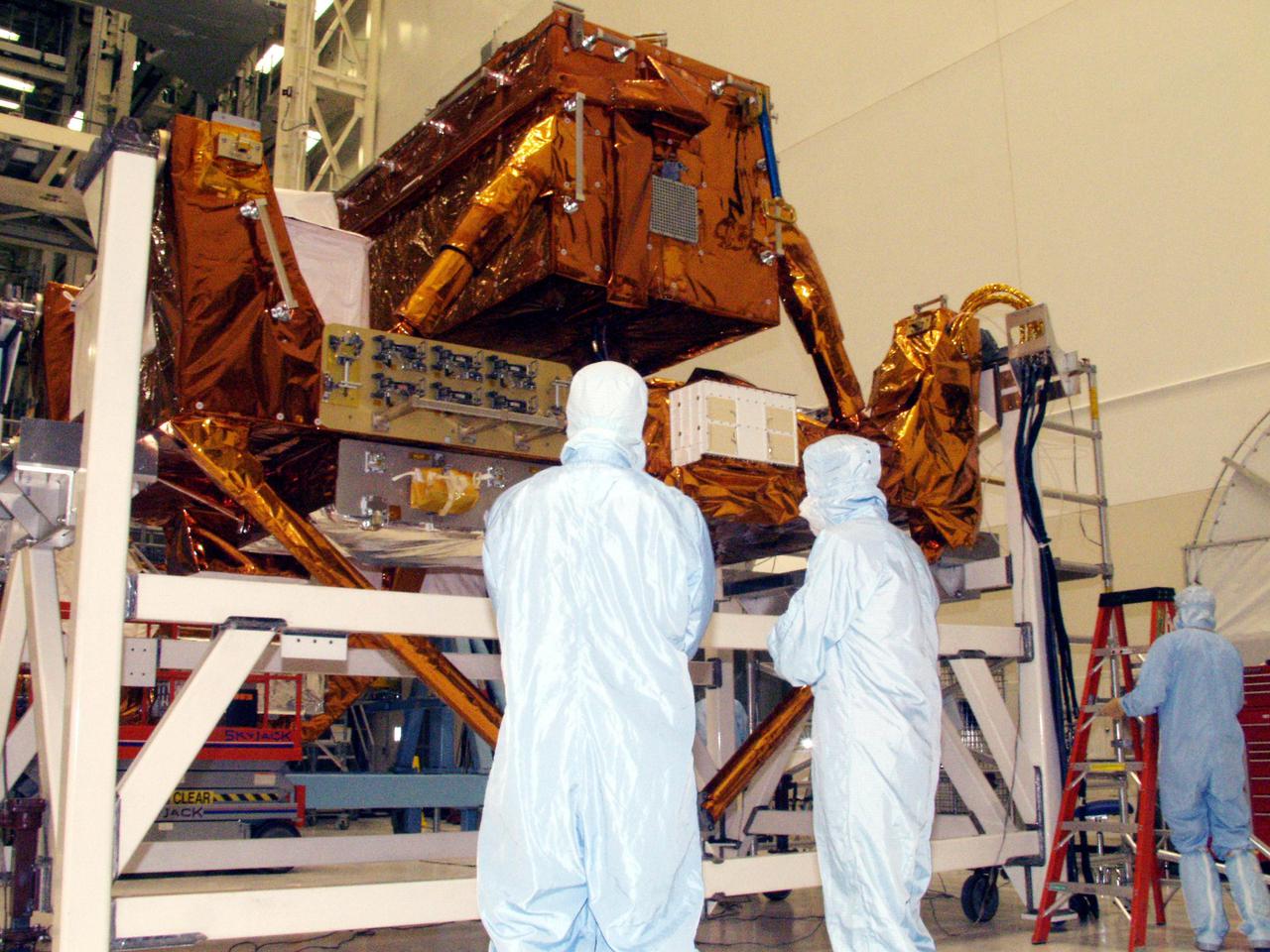
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility take a close look at the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The hardware is installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
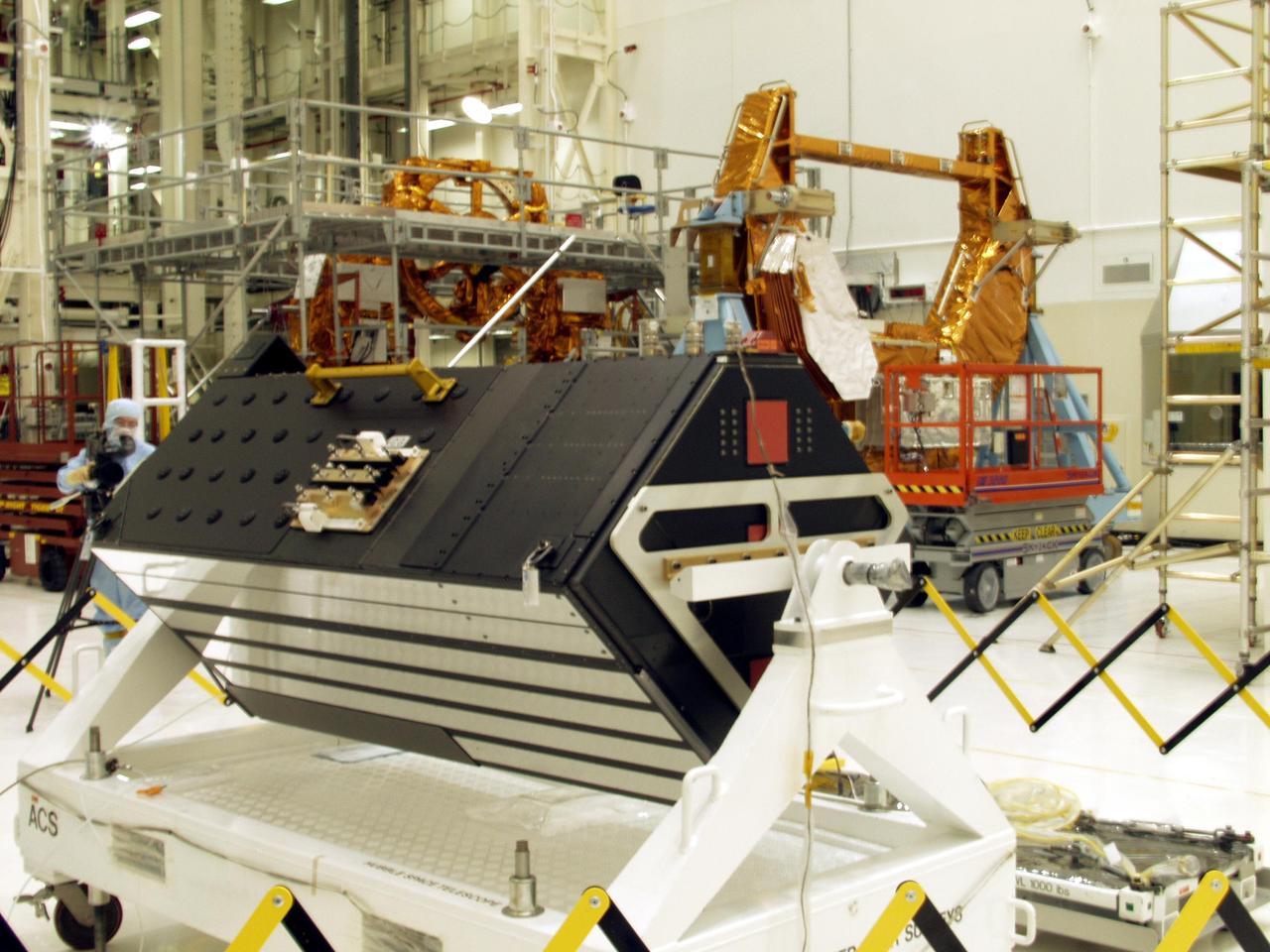

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), foreground, is part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The ACS and other hardware, installed on four principle payload carriers, are being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program

jsc2025e044727 (5/12/2025) --- Image of complete SEED payload, includes space-qualified lens, Image Sensor, and POBC. Space Test Program – Houston 10 – Space Edge Experiments and Demonstrations (STP-H10-SEED) tests hardware to deliver near-real time actionable information using machine learning algorithms. Results could validate the low size, weight, and power of this commercial off-the-shelf edge processing hardware for various applications. Image courtesy of NOVI LLC.
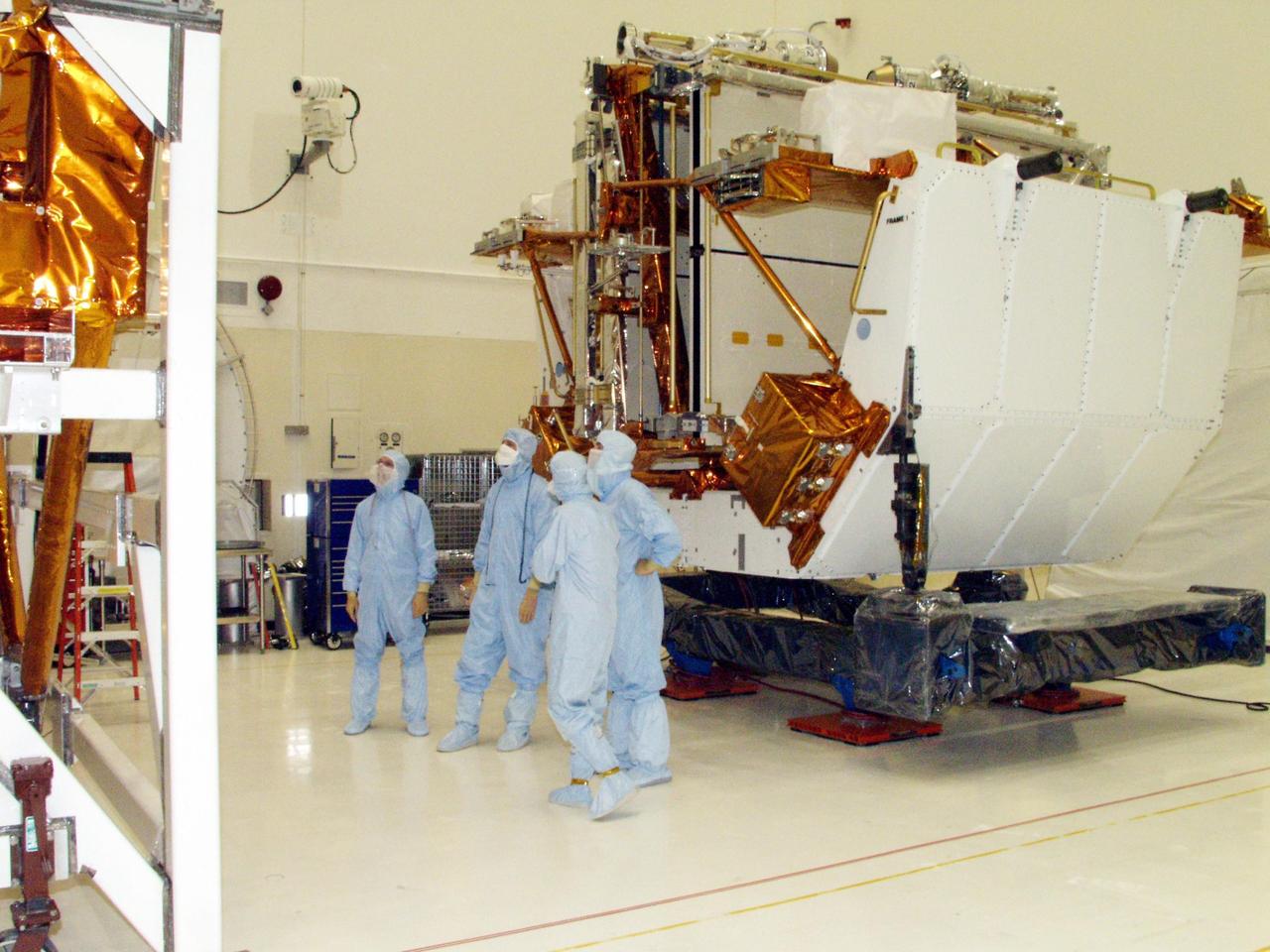

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Workers in the Vertical Processing Facility look over the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), part of the STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The Solar Array 3 panels behind them, and other HST hardware, are installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
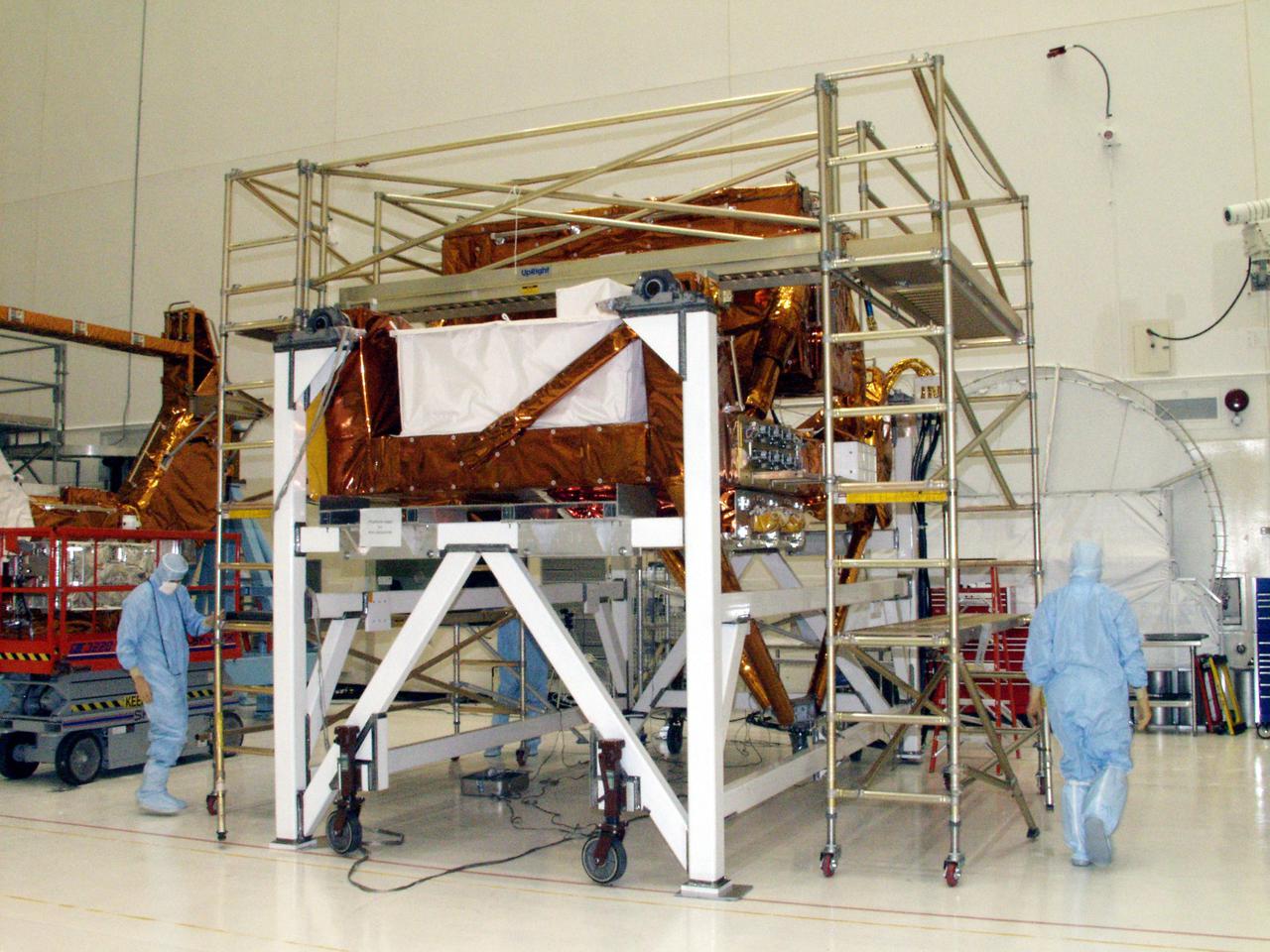

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. --The STS-109 flight hardware for maintenance of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is being processed inside the clean room at the Vertical Processing Facility (VPF). Seen here is the Axial Science Instrument Protective Enclosure (ASIPE), which will house the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS). The hardware will be installed on four principle payload carriers. The STS-109 launch aboard Columbia is targeted for Feb. 14, 2002, and will be the 108th flight in the Space Shuttle program
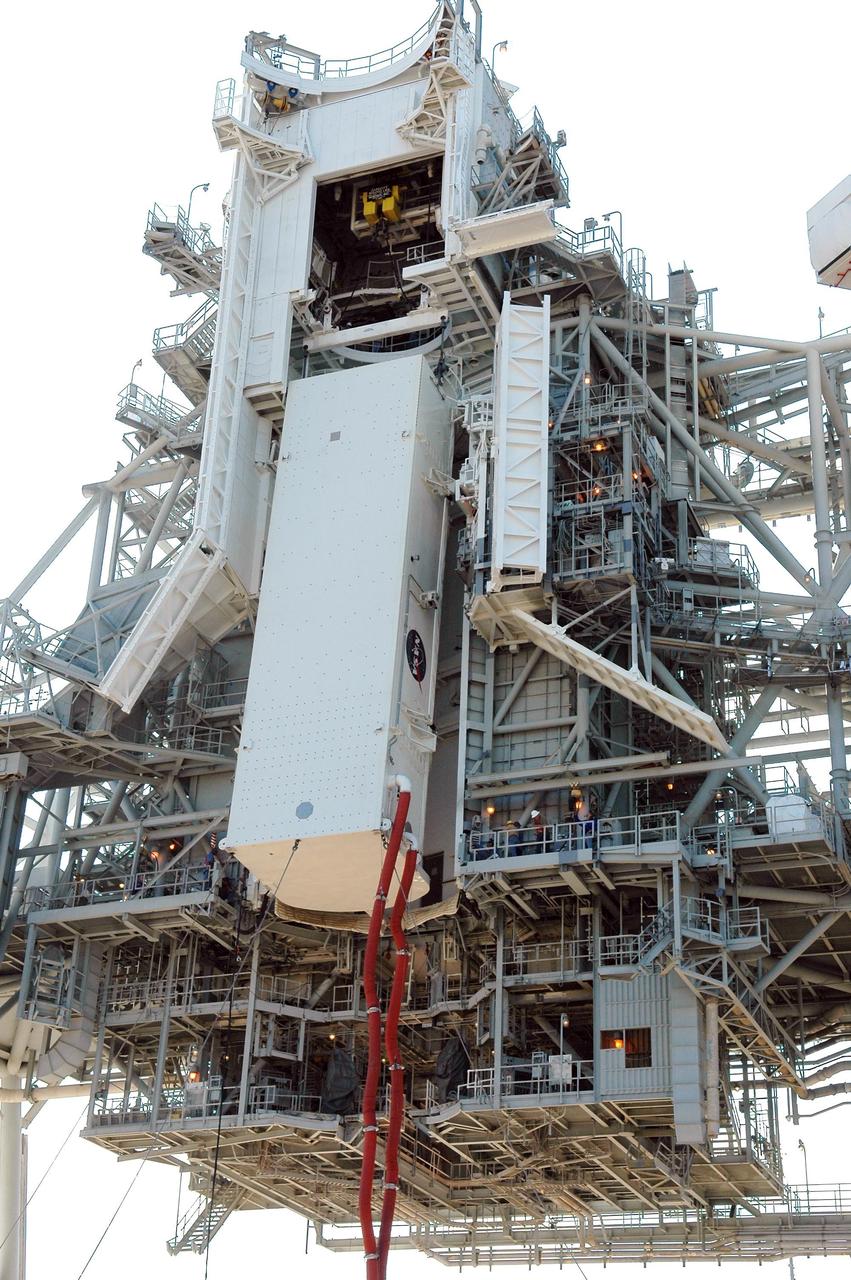

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the payload canister holding Space Shuttle Discovery's payloads nears the payload changeout room on the rotating service structure. The red umbilical lines are still attached. The payload changeout room provides an environmentally clean or "white room" condition in which to receive a payload transferred from a protective payload canister. After the shuttle arrives at the pad, the rotating service structure will close around it and the payloads, which include the multi-purpose logistics module and integrated cargo carrier, will then be transferred from the changeout room into Discovery's payload bay. Discovery's launch to the International Space Station on mission STS-121 is targeted for July 1 in a launch window that extends to July 19. During the 12-day mission, crew members will test new hardware and techniques to improve shuttle safety. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett