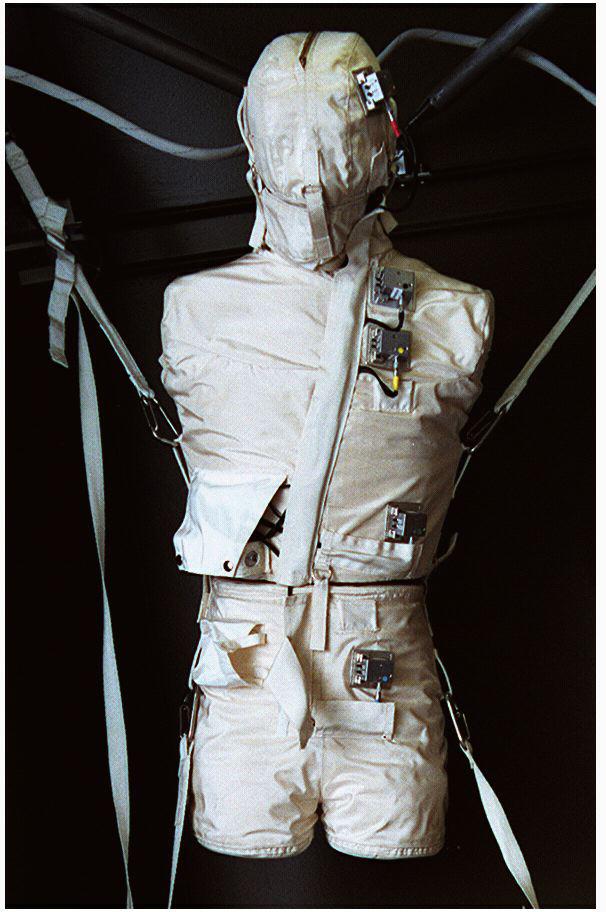
The Phantom Torso is a tissue-muscle plastic anatomical model of a torso and head. It contains over 350 radiation measuring devices to calculate the radiation that penetrates internal organs in space travel. The Phantom Torso is one of three radiation experiments in Expedition Two including the Borner Ball Neutron Detector and Dosimetric Mapping.
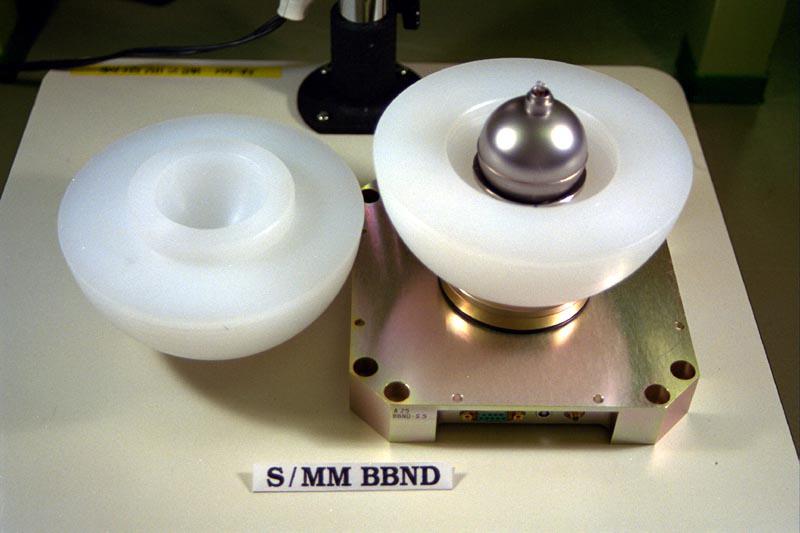

The Bonner Ball Neutron Detector measures neutron radiation. Neutrons are uncharged atomic particles that have the ability to penetrate living tissues, harming human beings in space. The Bonner Ball Neutron Detector is one of three radiation experiments during Expedition Two. The others are the Phantom Torso and Dosimetric Mapping.
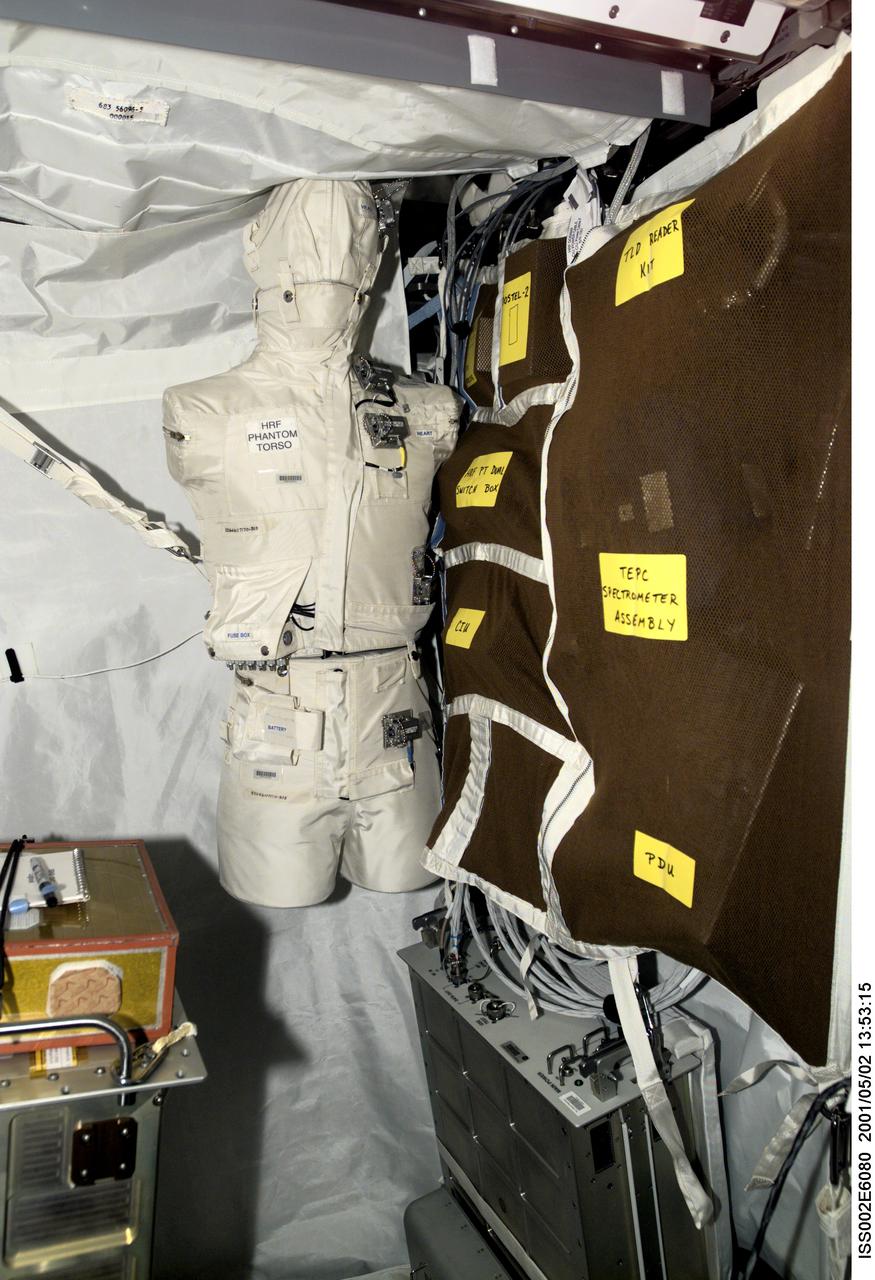

ISS002-E-6080 (2 May 2001) --- The Phantom Torso, seen here in the Human Research Facility (HRF) section of the Destiny/U.S. laboratory on the International Space Station (ISS), is designed to measure the effects of radiation on organs inside the body by using a torso that is similar to those used to train radiologists on Earth. The torso is equivalent in height and weight to an average adult male. It contains radiation detectors that will measure, in real-time, how much radiation the brain, thyroid, stomach, colon, and heart and lung area receive on a daily basis. The data will be used to determine how the body reacts to and shields its internal organs from radiation, which will be important for longer duration space flights. The experiment was delivered to the orbiting outpost during by the STS-100/6A crew in April 2001. Dr. Gautam Badhwar, NASA JSC, Houston, TX, is the principal investigator for this experiment. A digital still camera was used to record this image.
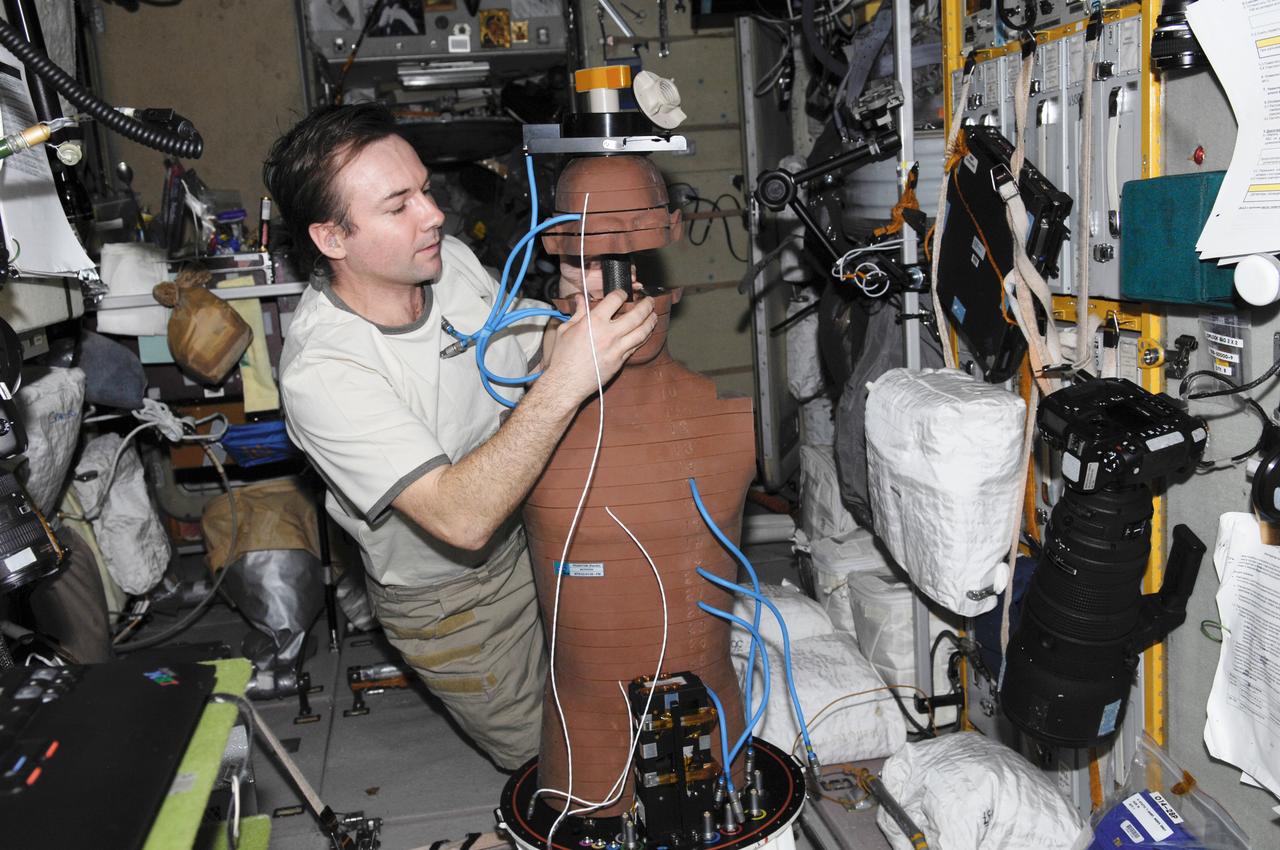

ISS018-E-040944 (18 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, works with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
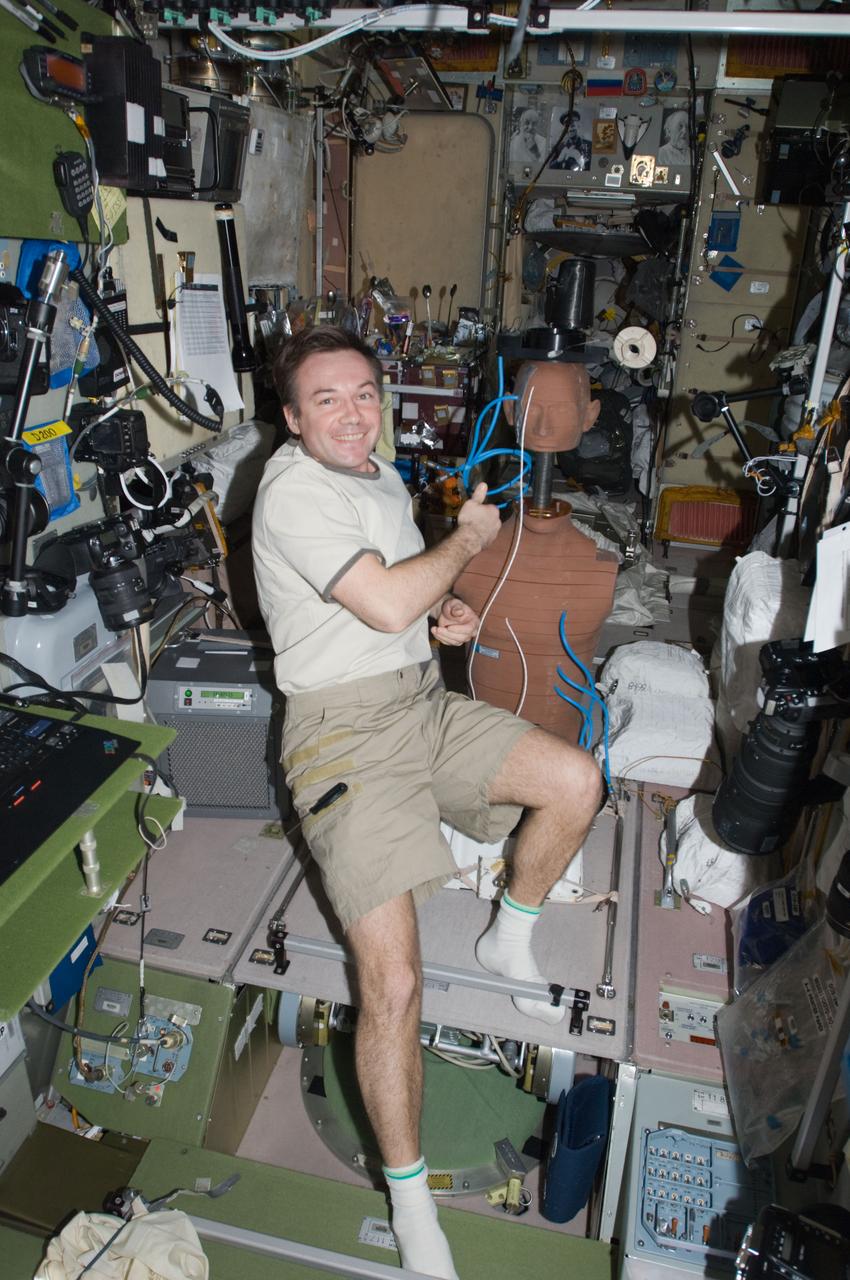

ISS018-E-040992 (18 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, works with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
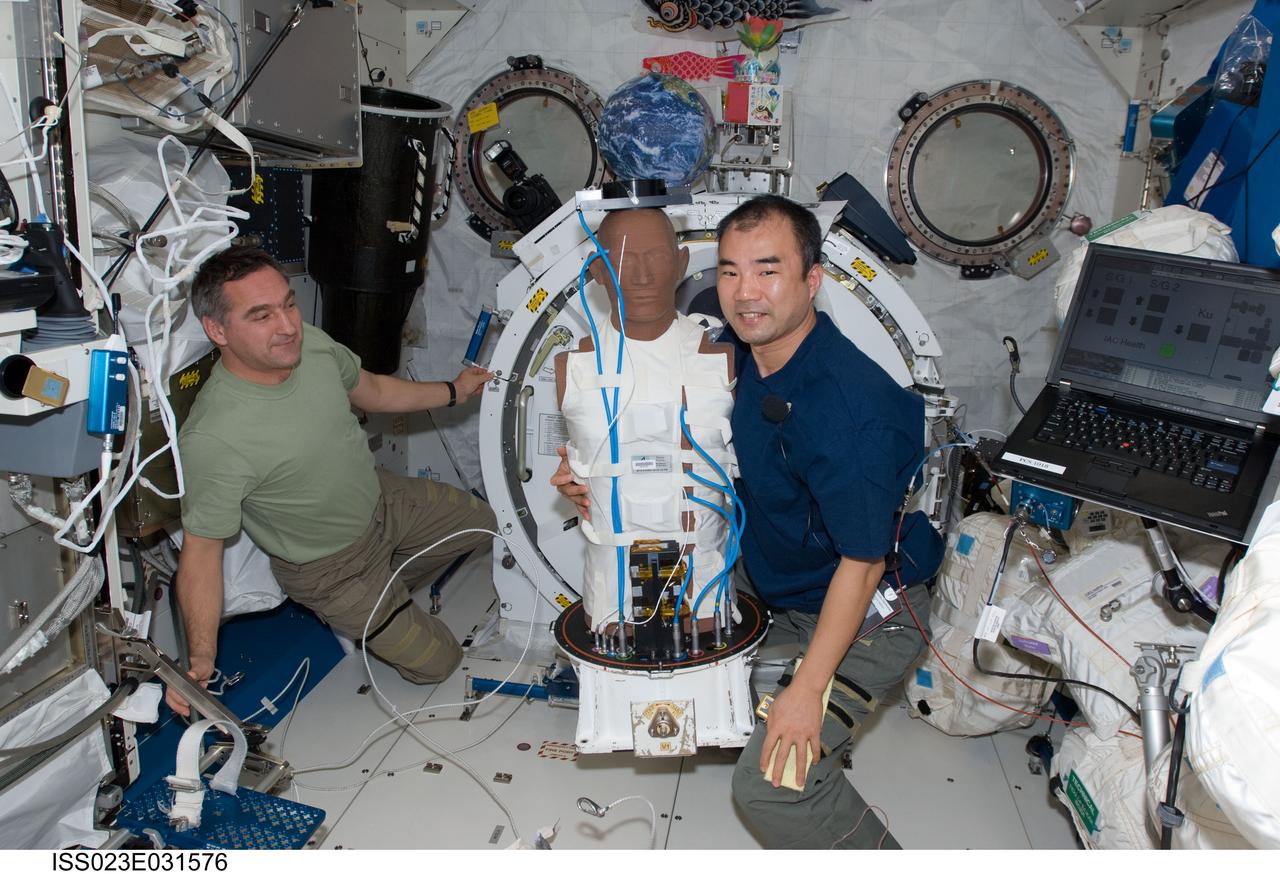

ISS023-E-031576 (4 May 2010) --- Russian cosmonaut Alexander Skvortsov (left) and Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) astronaut Soichi Noguchi, both Expedition 23 flight engineers, work with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
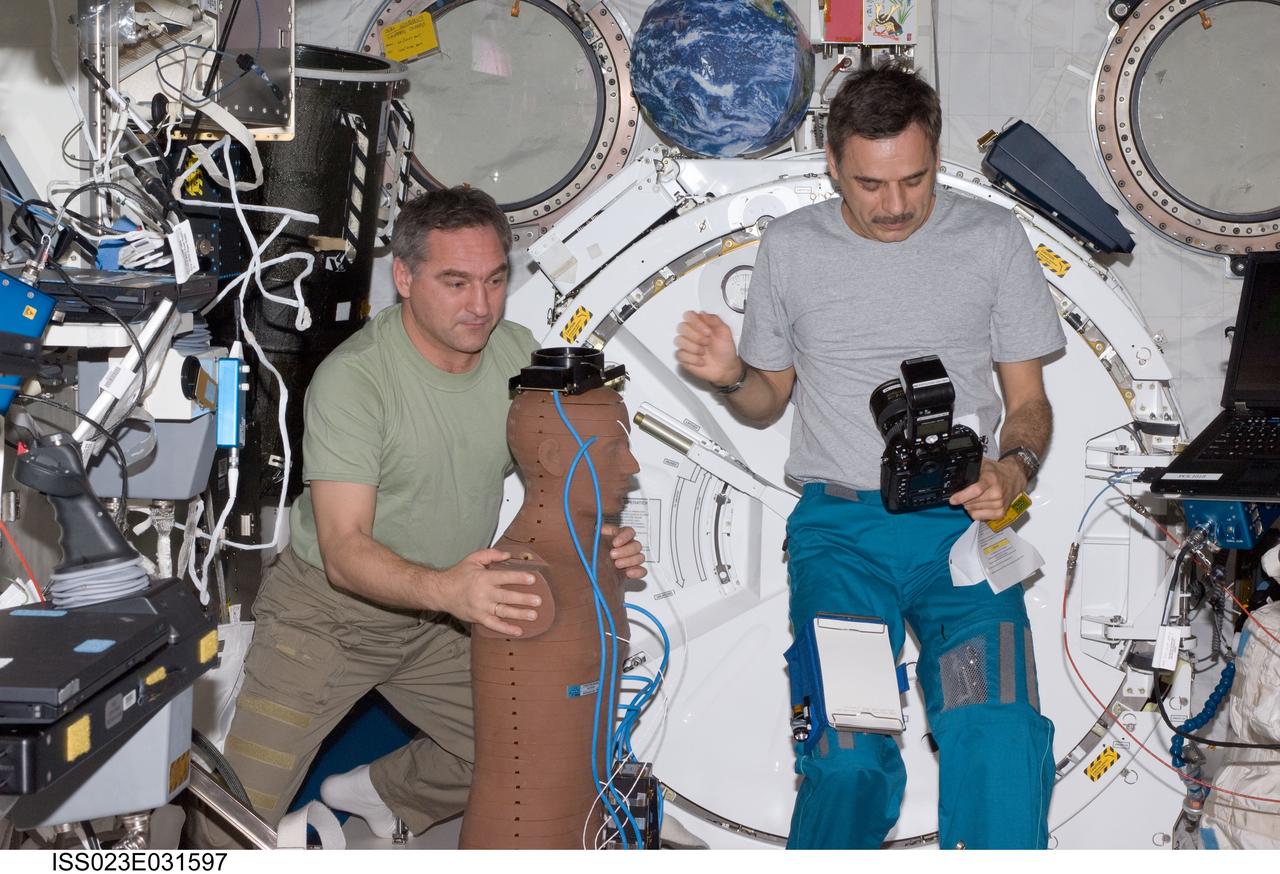

ISS023-E-031597 (4 May 2010) --- Russian cosmonauts Alexander Skvortsov (left) and Mikhail Kornienko, both Expedition 23 flight engineers, work with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
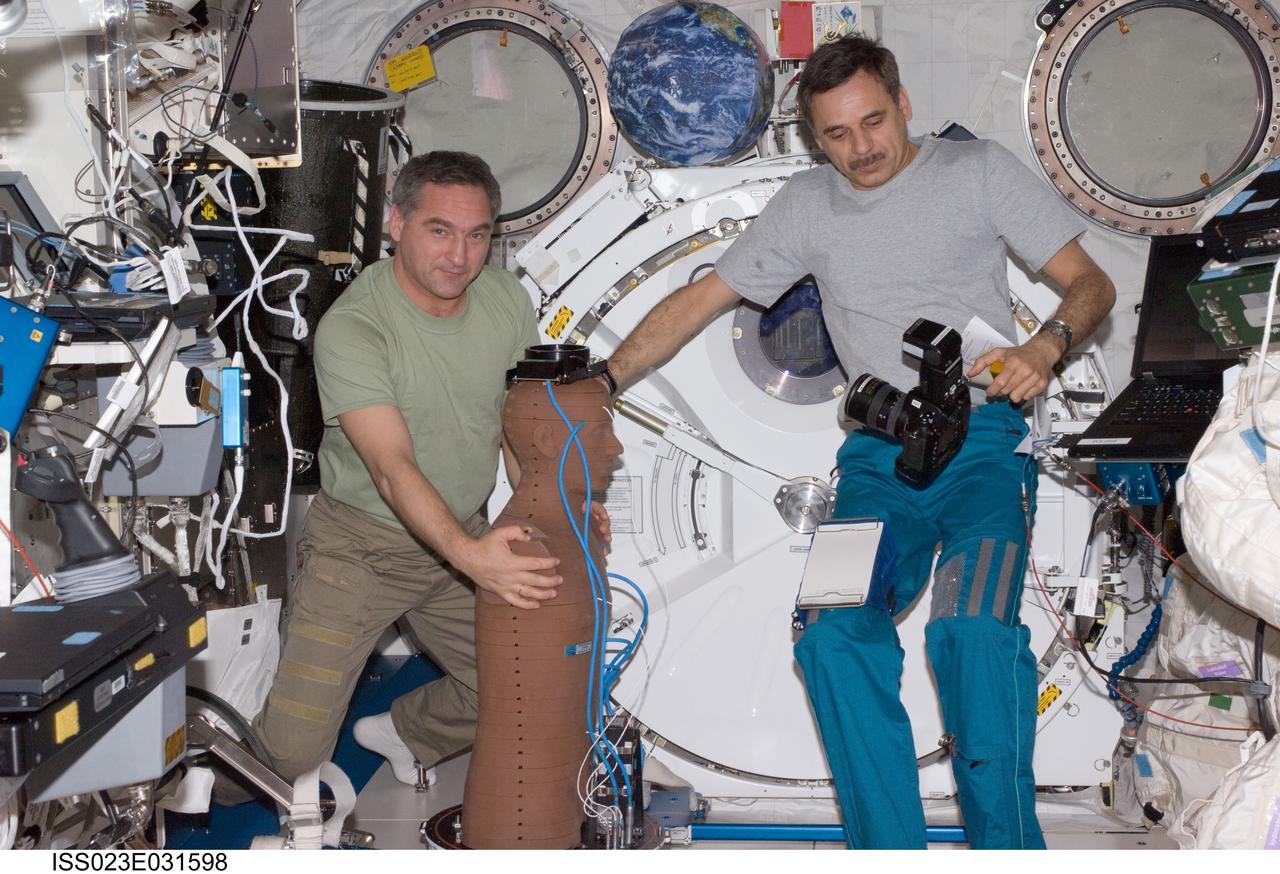

ISS023-E-031598 (4 May 2010) --- Russian cosmonauts Alexander Skvortsov (left) and Mikhail Kornienko, both Expedition 23 flight engineers, work with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
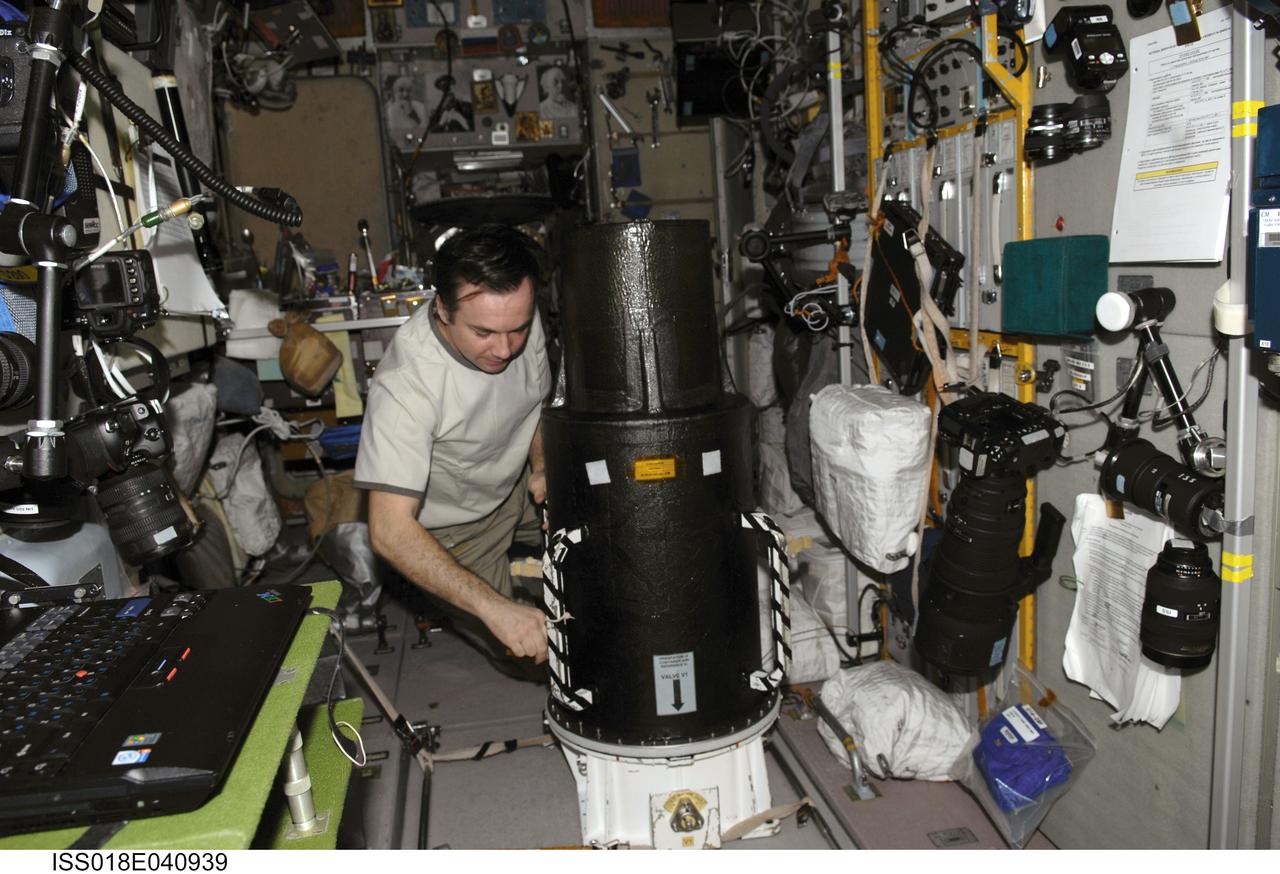

ISS018-E-040939 (18 March 2009) --- Cosmonaut Yury Lonchakov, Expedition 18 flight engineer, prepares to work with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station while Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-119) remains docked with the station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
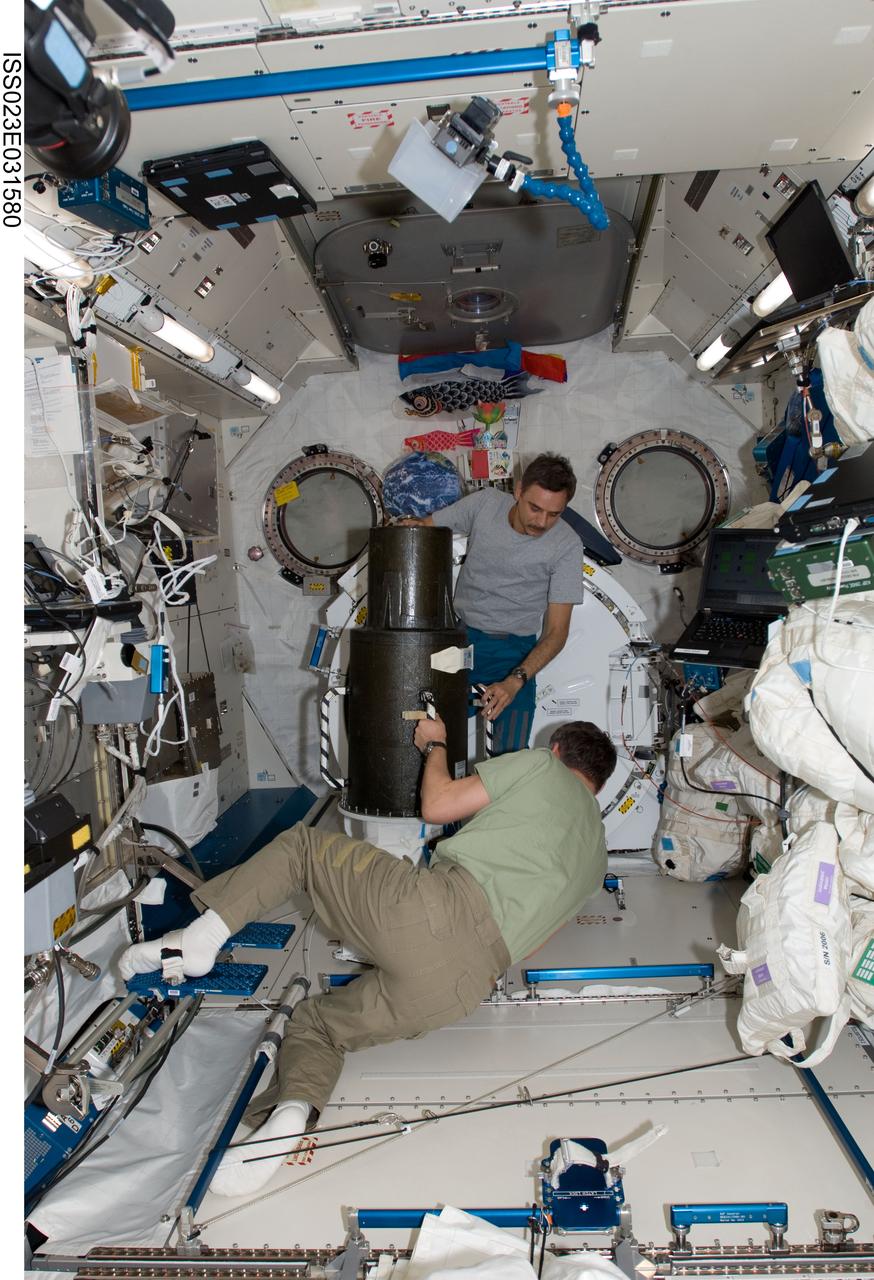

ISS023-E-031580 (4 May 2010) --- Russian cosmonauts Alexander Skvortsov (foreground) and Mikhail Kornienko, both Expedition 23 flight engineers, work with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Kibo laboratory of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
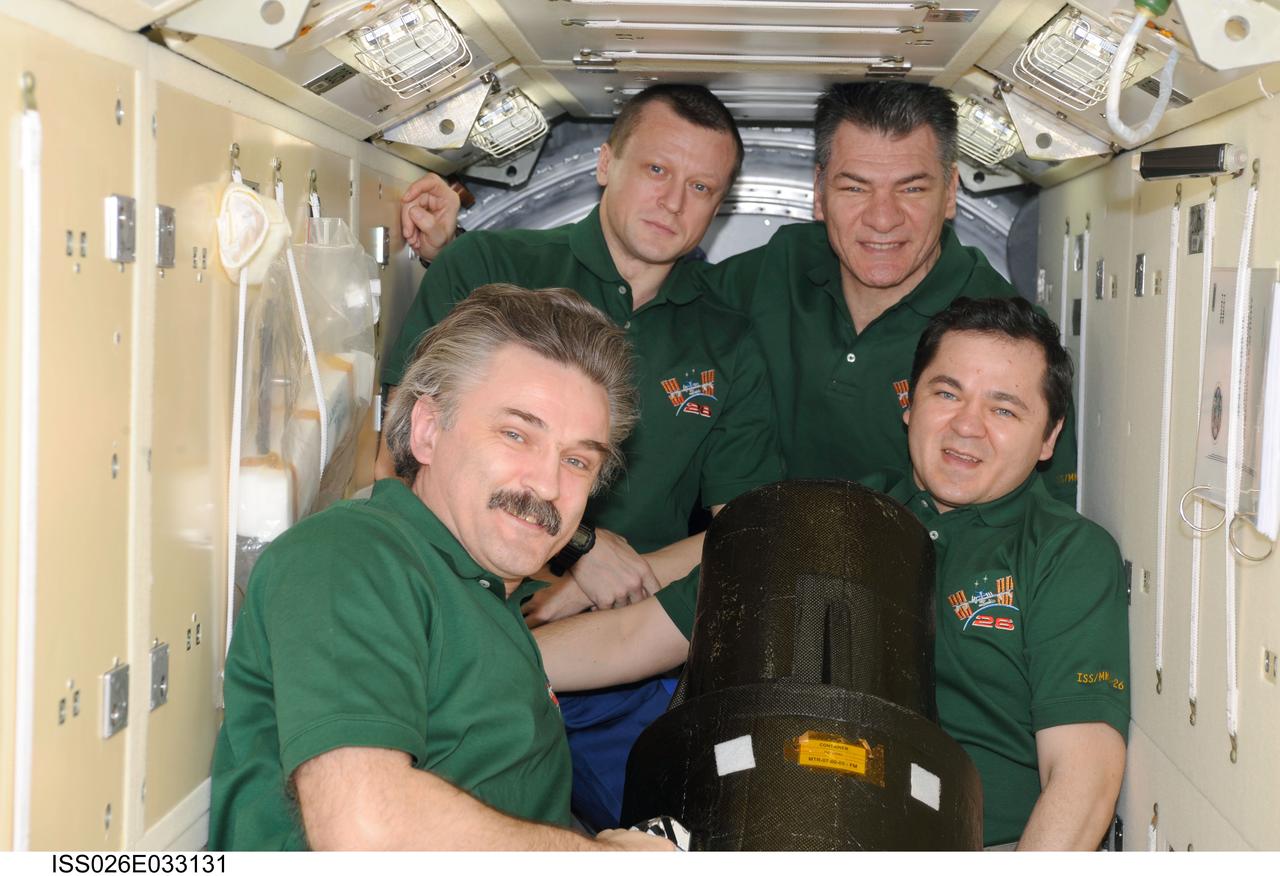

ISS026-E-033131 (11 March 2011) --- Russian cosmonauts Alexander Kaleri (left foreground), Oleg Skripochka (right foreground), Dmitry Kondratyev (left background) and European Space Agency astronaut Paolo Nespoli, all Expedition 26 flight engineers, pose for a photo with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Zarya Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies.
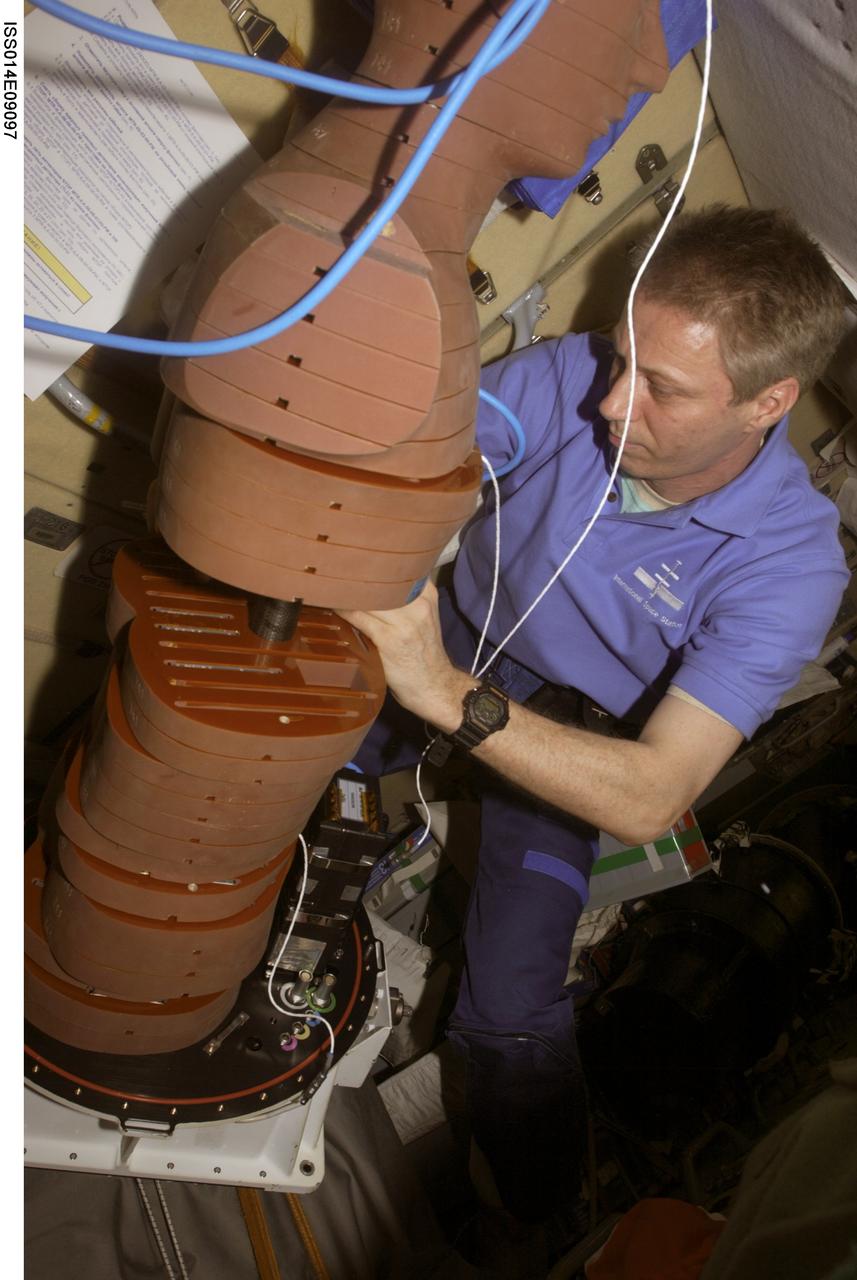

ISS014-E-09097 (December 2006) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Reiter, Expedition 14 flight engineer, works with the European Matroshka-R Phantom experiment in the Zvezda Service Module of the International Space Station. Matroshka, the name for the traditional Russian set of nestling dolls, is an antroph-amorphous model of a human torso designed for radiation studies. The activity, supported by ground specialist tag-up, requires equipping the torso's individual horizontal slice-like layers with 356 thermo luminescent detectors (TLDs) and five nuclear radiation tracking detectors (NTDPs). The mannequin was then to be reassembled, covered with poncho and hood and installed in the Pirs Docking Compartment for studies of on-orbit radiation and long-term dose accumulation.
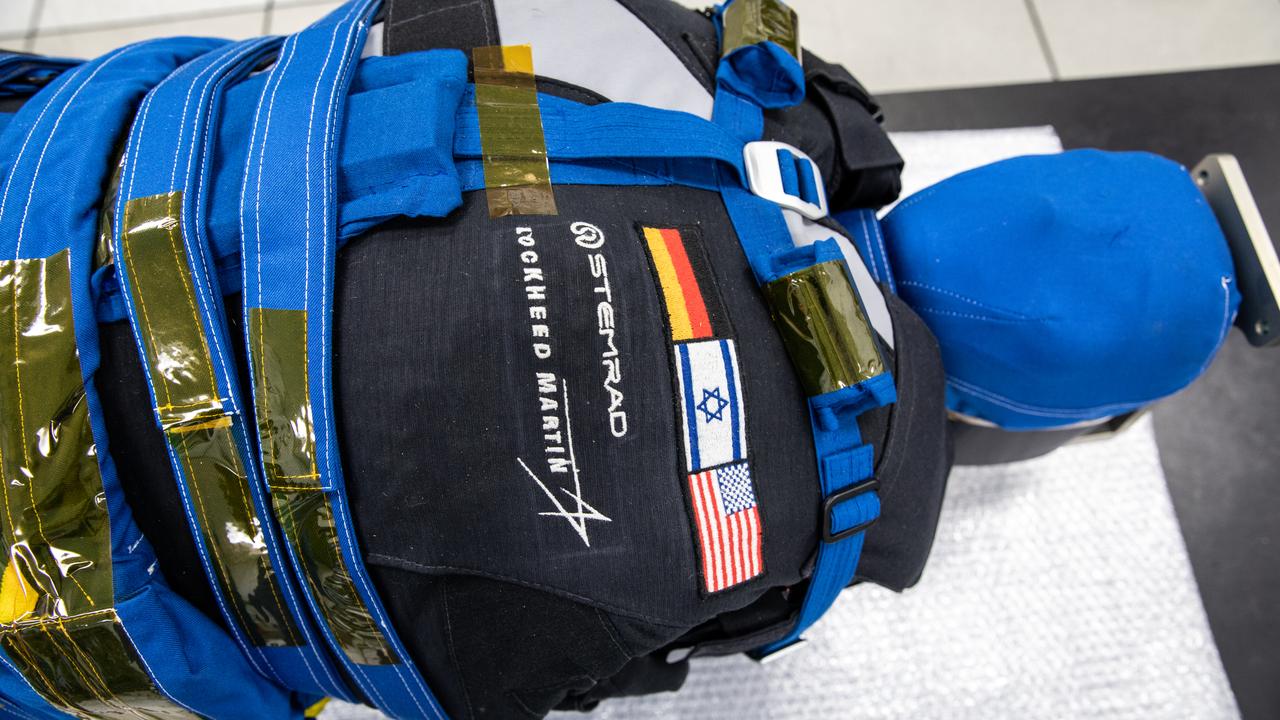

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.
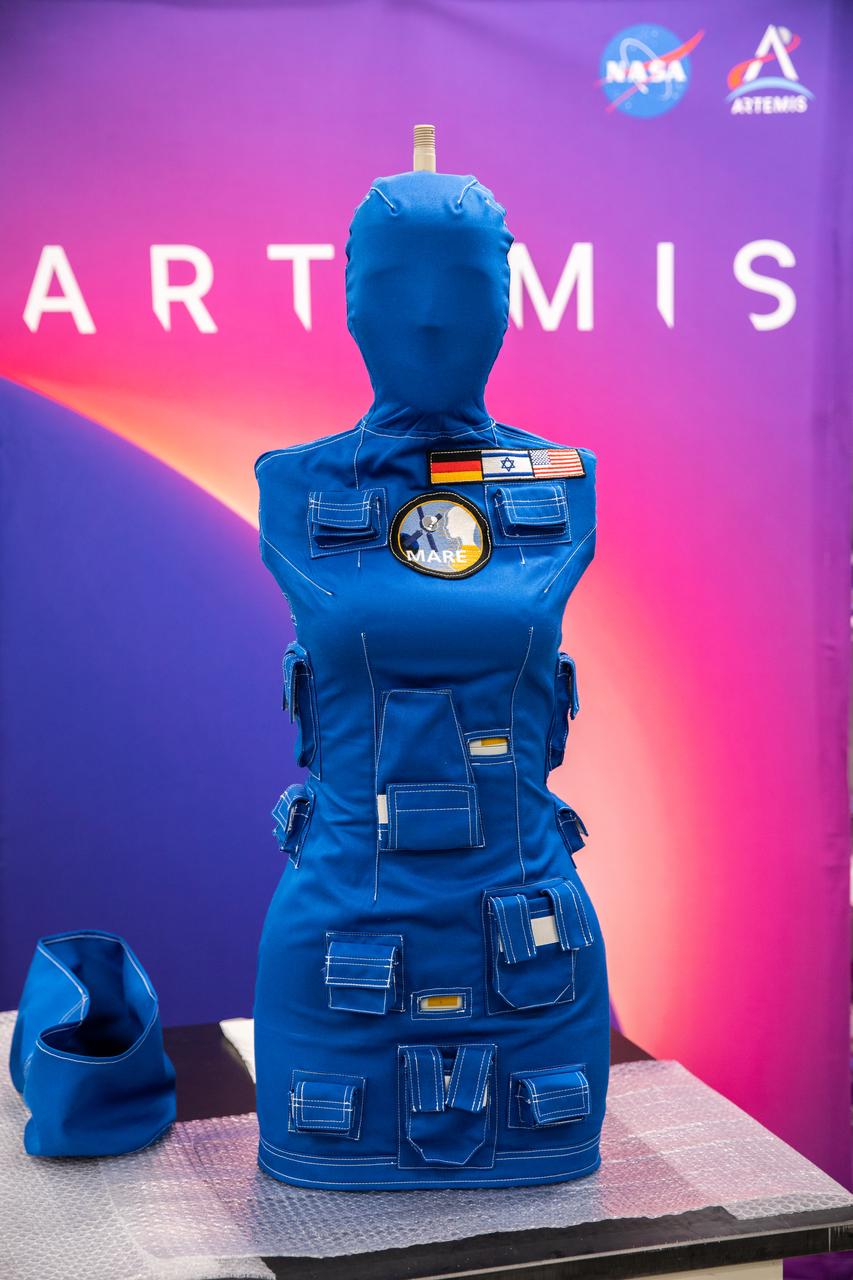

After a 25-day flight inside the Artemis I Orion crew module beyond the Moon and back, Helga, one of two identical phantom torsos, is shown without a radiation detection vest while undergoing post-flight payload inspections inside the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 11, 2023. The detectors will be removed at Kennedy and the torsos will return to teams at the German Space Agency for further analysis. As part of the Matroshka AstroRad Radiation Experiment (MARE) investigation, two female manikins – Helga and Zohar – were equipped with radiation detectors, while Zohar also wore a radiation protection vest, to determine the radiation risk during the Artemis I mission and potentially reduce exposure during future missions with astronauts. Artemis I Orion launched atop the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39B on Nov. 16, 2022, at 1:47 a.m. EST. During the flight, Orion flew farther than any spacecraft built for humans has ever flown, paving the way for human deep space exploration and demonstrating NASA’s commitment and capability to extend human presence to the Moon and beyond. The primary goal of Artemis I was to thoroughly test the SLS and Orion spacecraft’s integrated systems before crewed missions. Under Artemis, NASA aims to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon and establish sustainable lunar exploration.