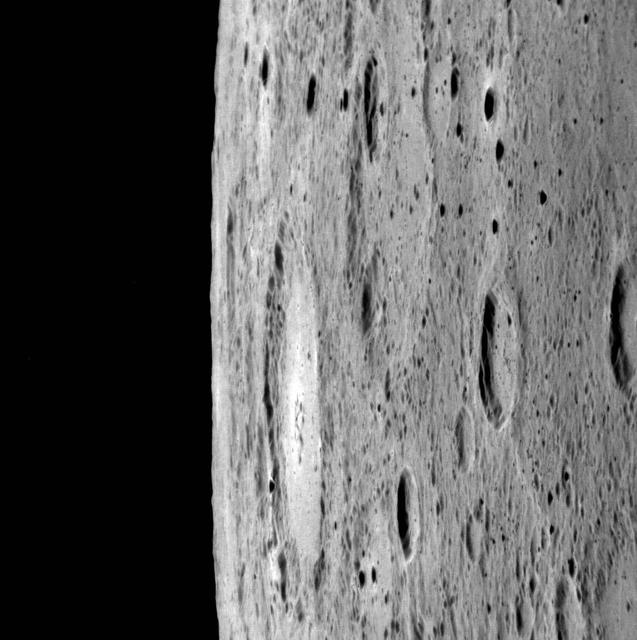
In High Phase
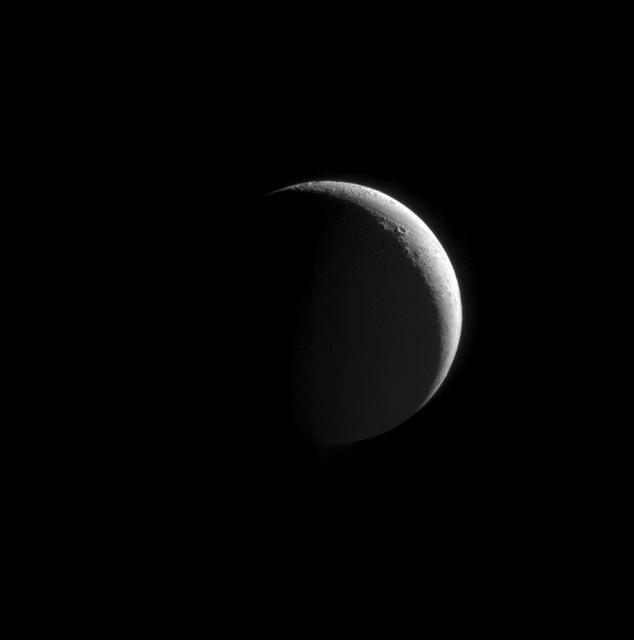

Just a Phase
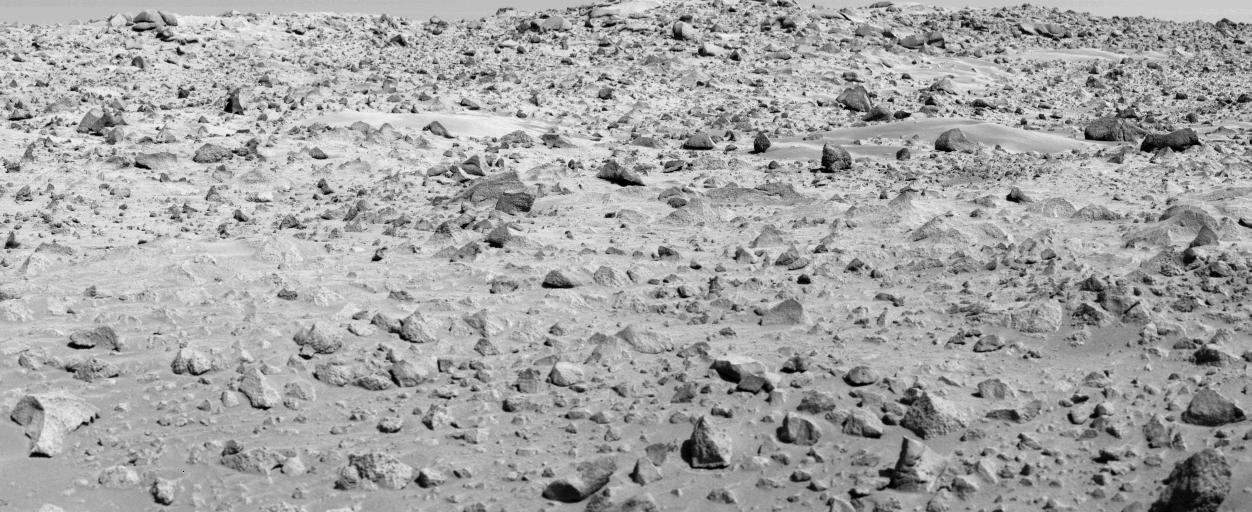

Viking Phase III
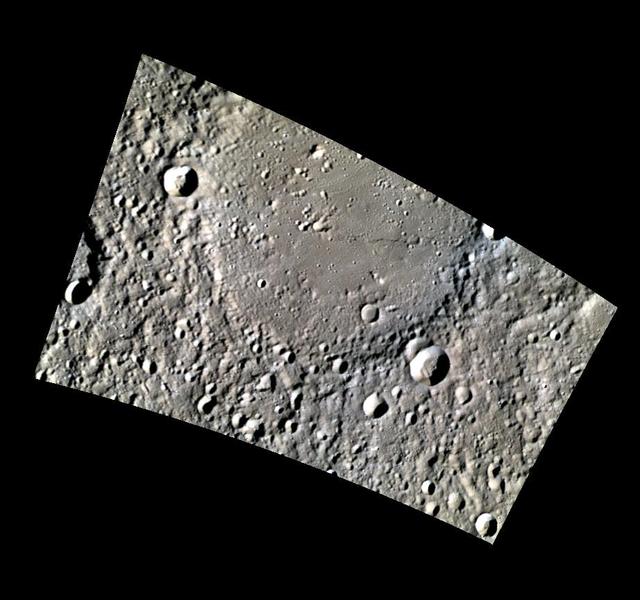

Botticelli in Low-Phase Color
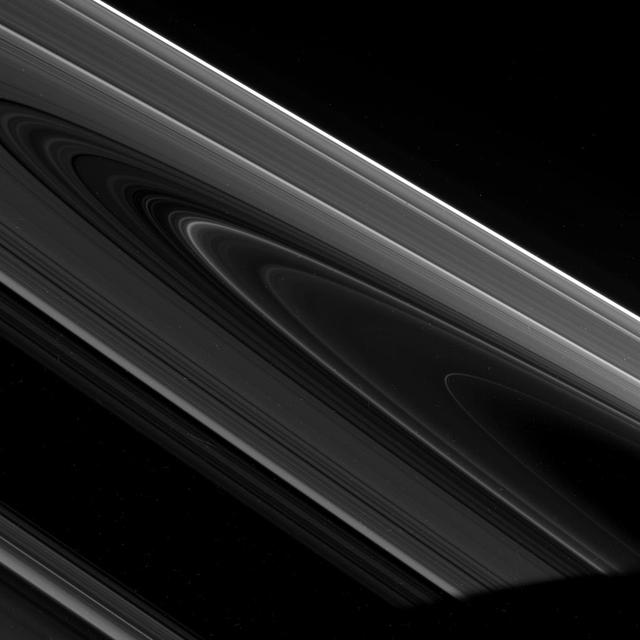

High-phase Rings
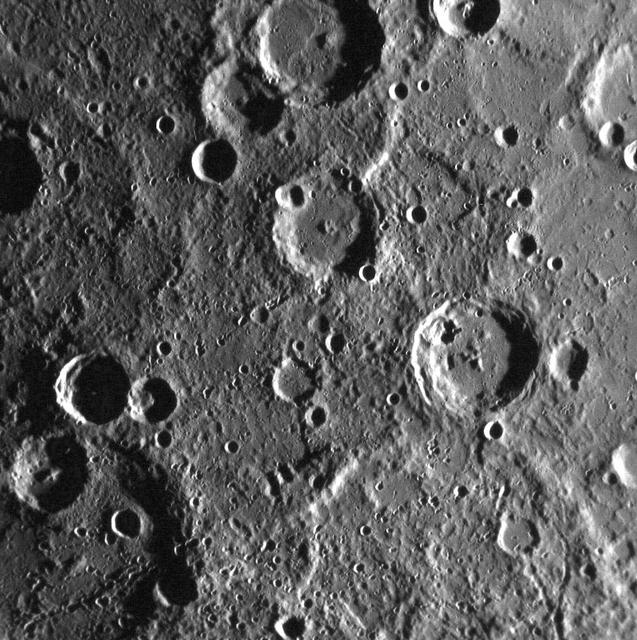

Let the Science Phase Begin!
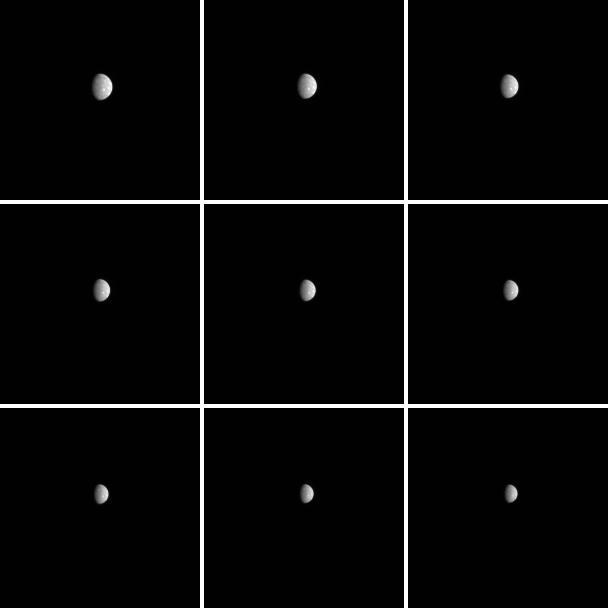
It Just a Phase that Mercury Going Through

This visualization shows the Moon's phase and libration at hourly intervals throughout 2015, as viewed from the northern hemisphere. Each frame represents one hour. Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) has been in orbit around the Moon since the summer of 2009. Its laser altimeter (LOLA) and camera (LROC) are recording the rugged, airless lunar terrain in exceptional detail, making it possible to visualize the Moon with unprecedented fidelity. This is especially evident in the long shadows cast near the terminator, or day-night line. The pummeled, craggy landscape thrown into high relief at the terminator would be impossible to recreate in the computer without global terrain maps like those from LRO. To download, learn more about this visualization, or to see what the Moon will look like at any hour in 2015, visit <a href="http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4236" rel="nofollow">svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/goto?4236</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
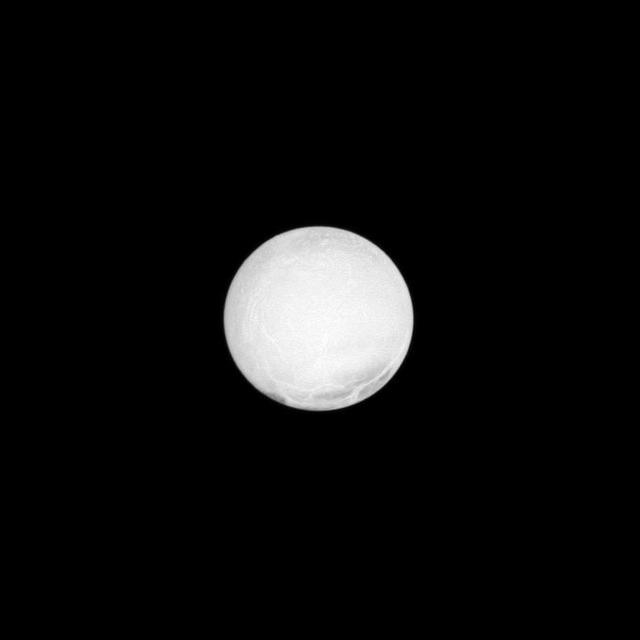

The highly reflective surface of Saturn moon Enceladus is almost completely illuminated in this NASA Cassini spacecraft image taken at a low phase angle.
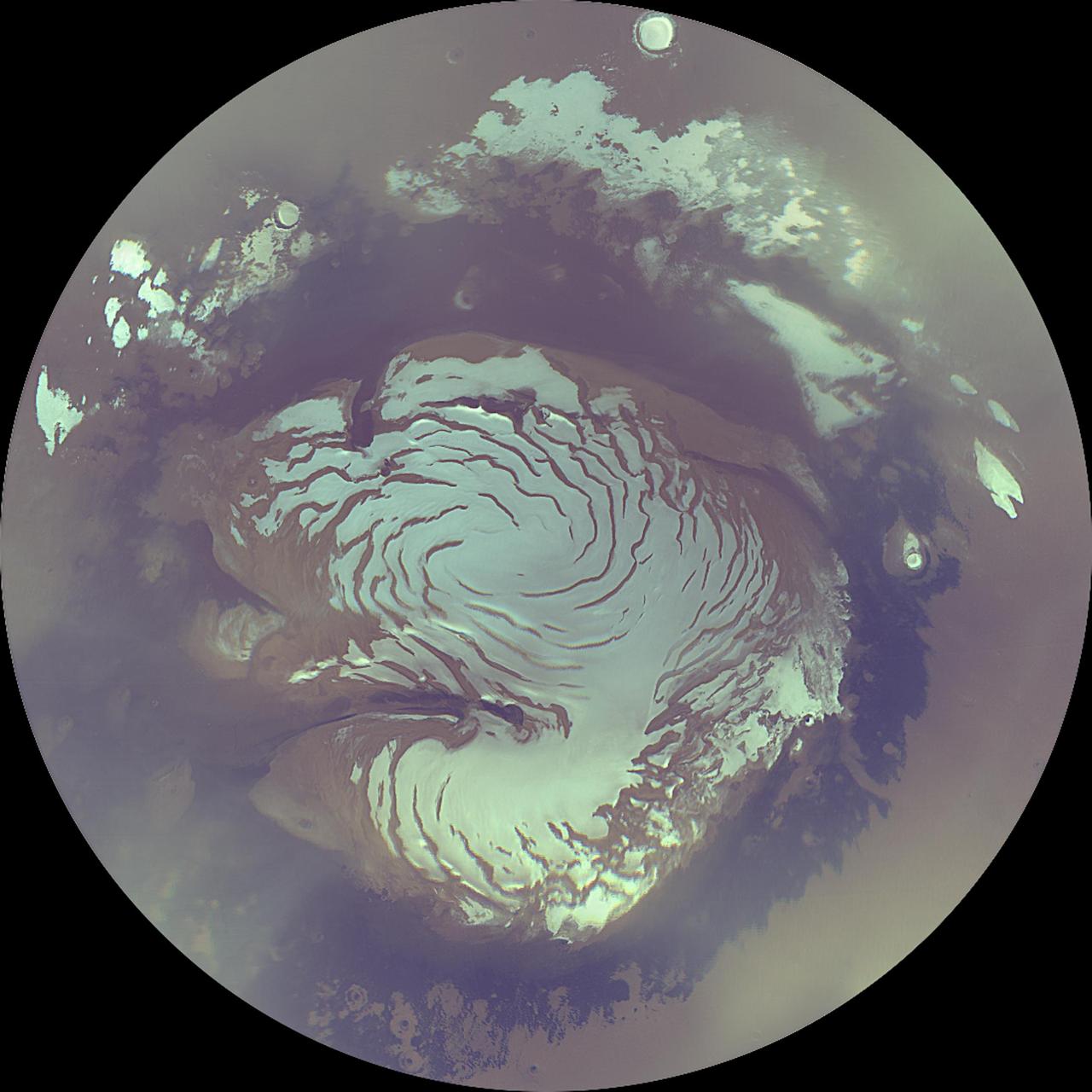
Mars Polar Cap During Transition Phase Instrument Checkout
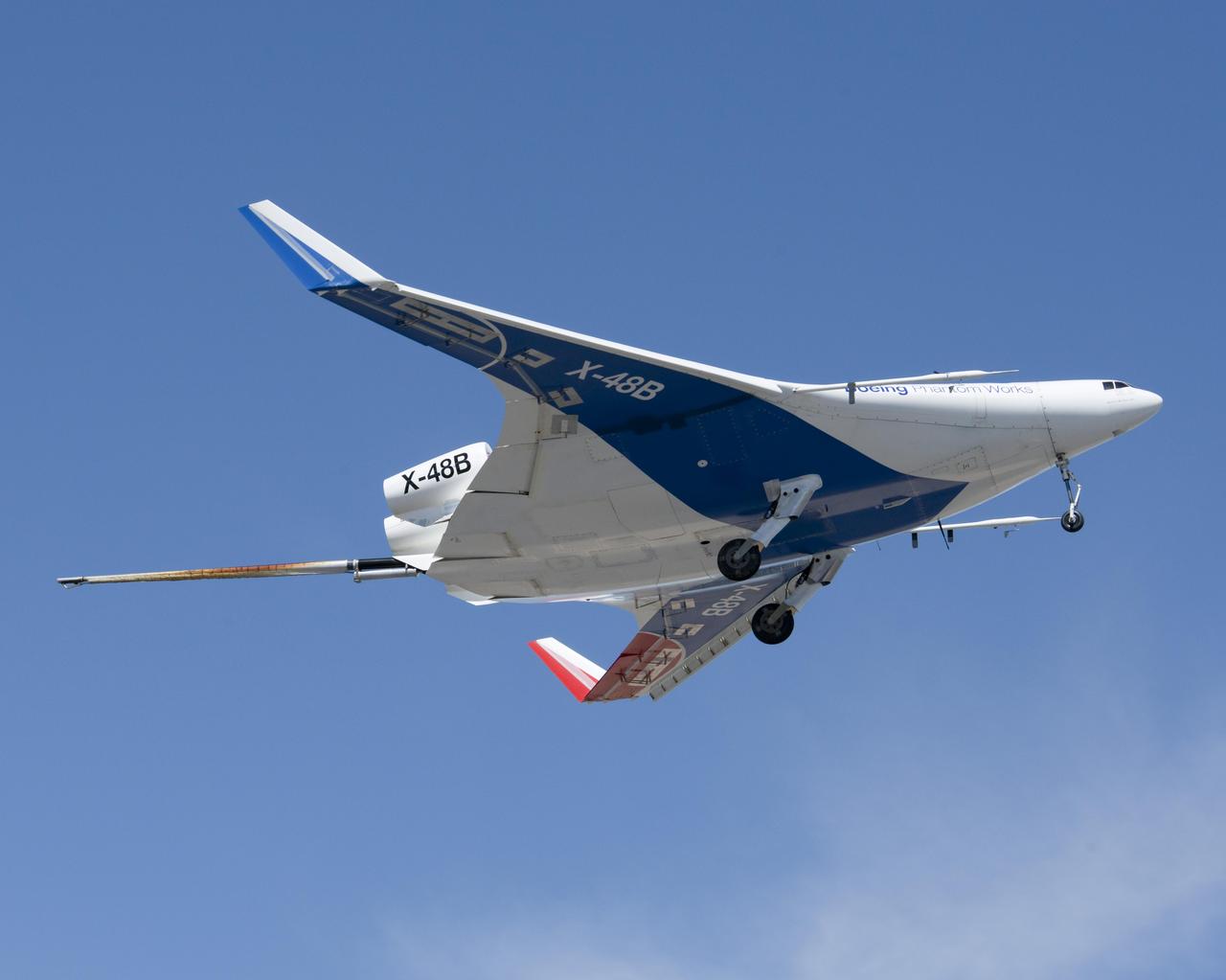

A joint NASA/Boeing team completed the first phase of flight tests on the unique X-48B Blended Wing Body aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, CA. The team completed the 80th and last flight of the project's first phase on March 19, 2010.
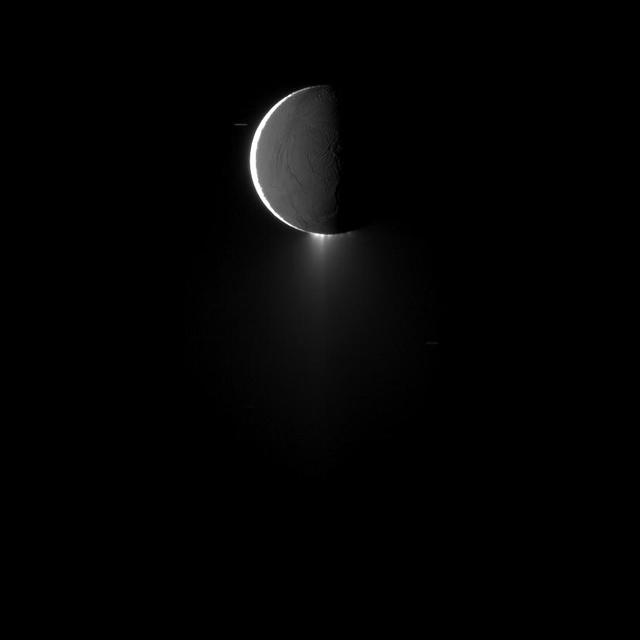

Saturn moon Enceladus, imaged at high phase, shows off its spectacular water ice plumes emanating from its south polar region in this image captured by NASA Cassini spacecraft.
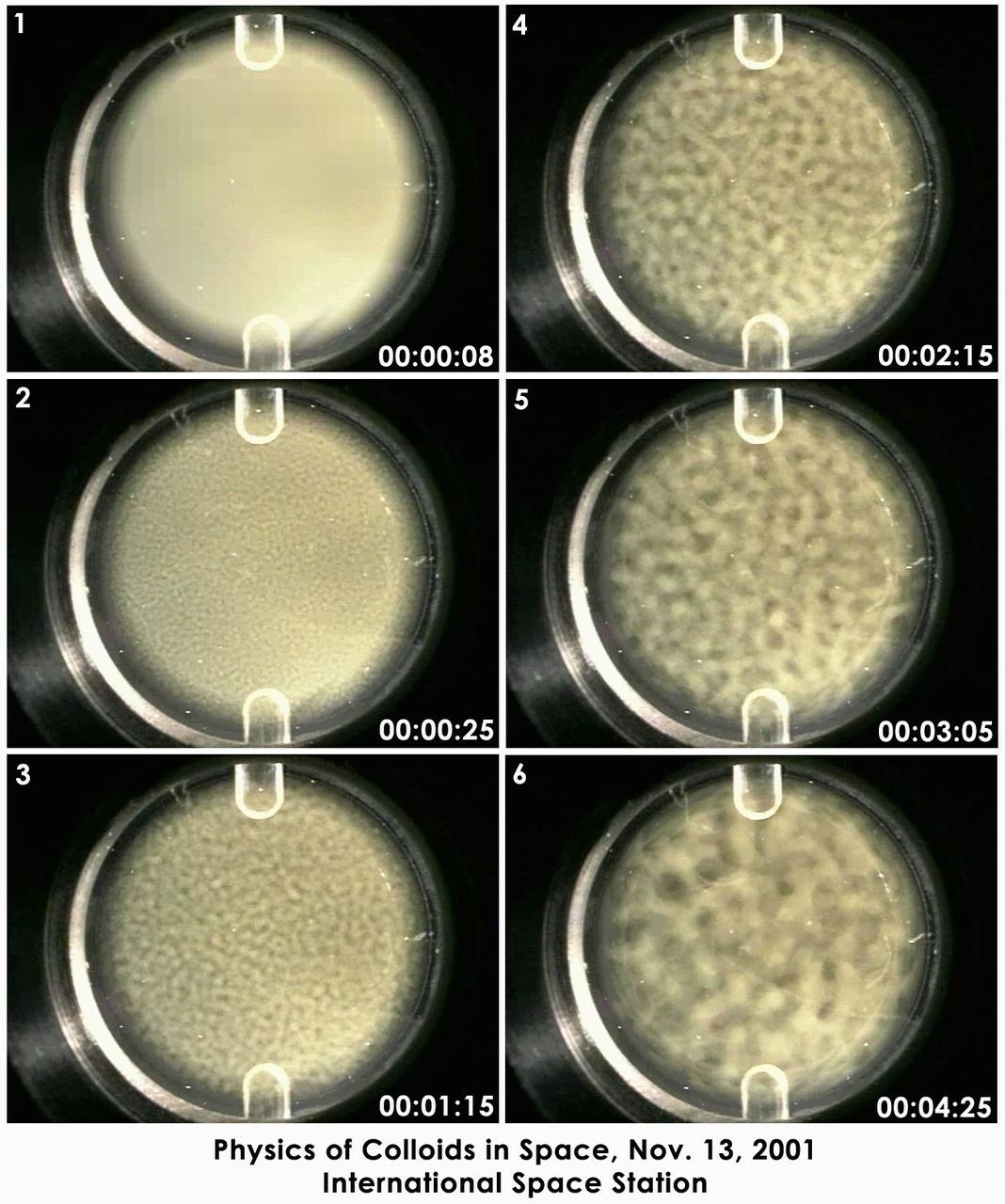
Still photographs taken over 16 hours on Nov. 13, 2001, on the International Space Station have been condensed into a few seconds to show the de-mixing -- or phase separation -- process studied by the Experiment on Physics of Colloids in Space. Commanded from the ground, dozens of similar tests have been conducted since the experiment arrived on ISS in 2000. The sample is a mix of polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA or acrylic) colloids, polystyrene polymers and solvents. The circular area is 2 cm (0.8 in.) in diameter. The phase separation process occurs spontaneously after the sample is mechanically mixed. The evolving lighter regions are rich in colloid and have the structure of a liquid. The dark regions are poor in colloids and have the structure of a gas. This behavior carnot be observed on Earth because gravity causes the particles to fall out of solution faster than the phase separation can occur. While similar to a gas-liquid phase transition, the growth rate observed in this test is different from any atomic gas-liquid or liquid-liquid phase transition ever measured experimentally. Ultimately, the sample separates into colloid-poor and colloid-rich areas, just as oil and vinegar separate. The fundamental science of de-mixing in this colloid-polymer sample is the same found in the annealing of metal alloys and plastic polymer blends. Improving the understanding of this process may lead to improving processing of these materials on Earth.
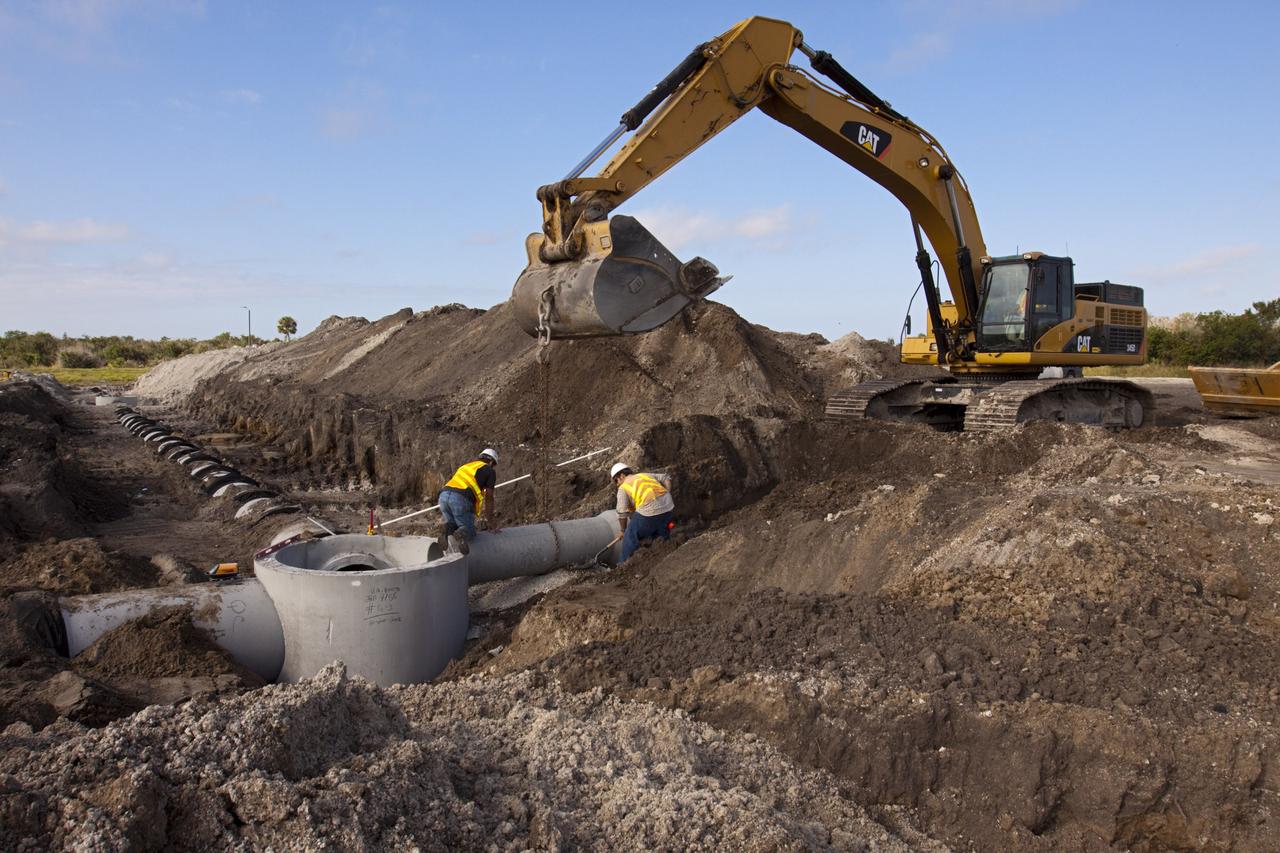

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
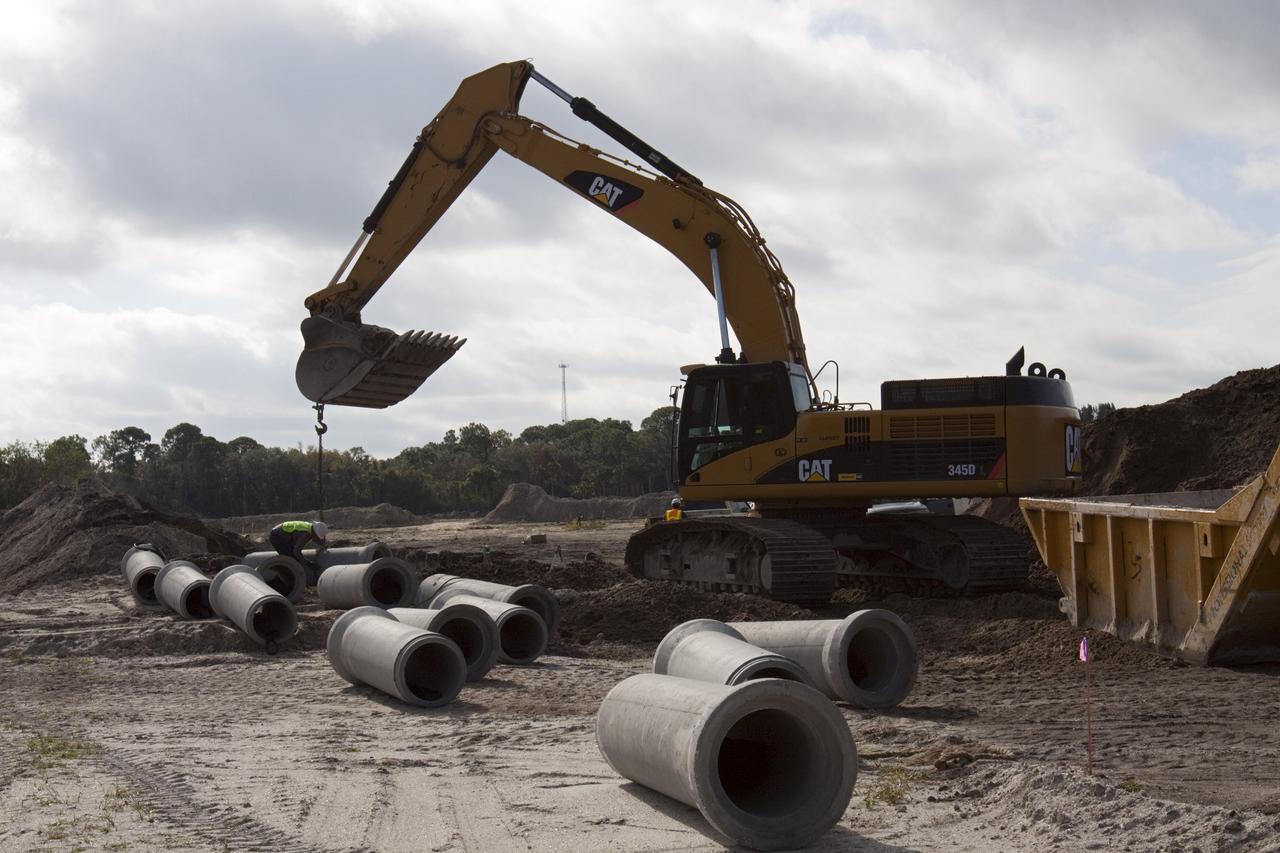

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
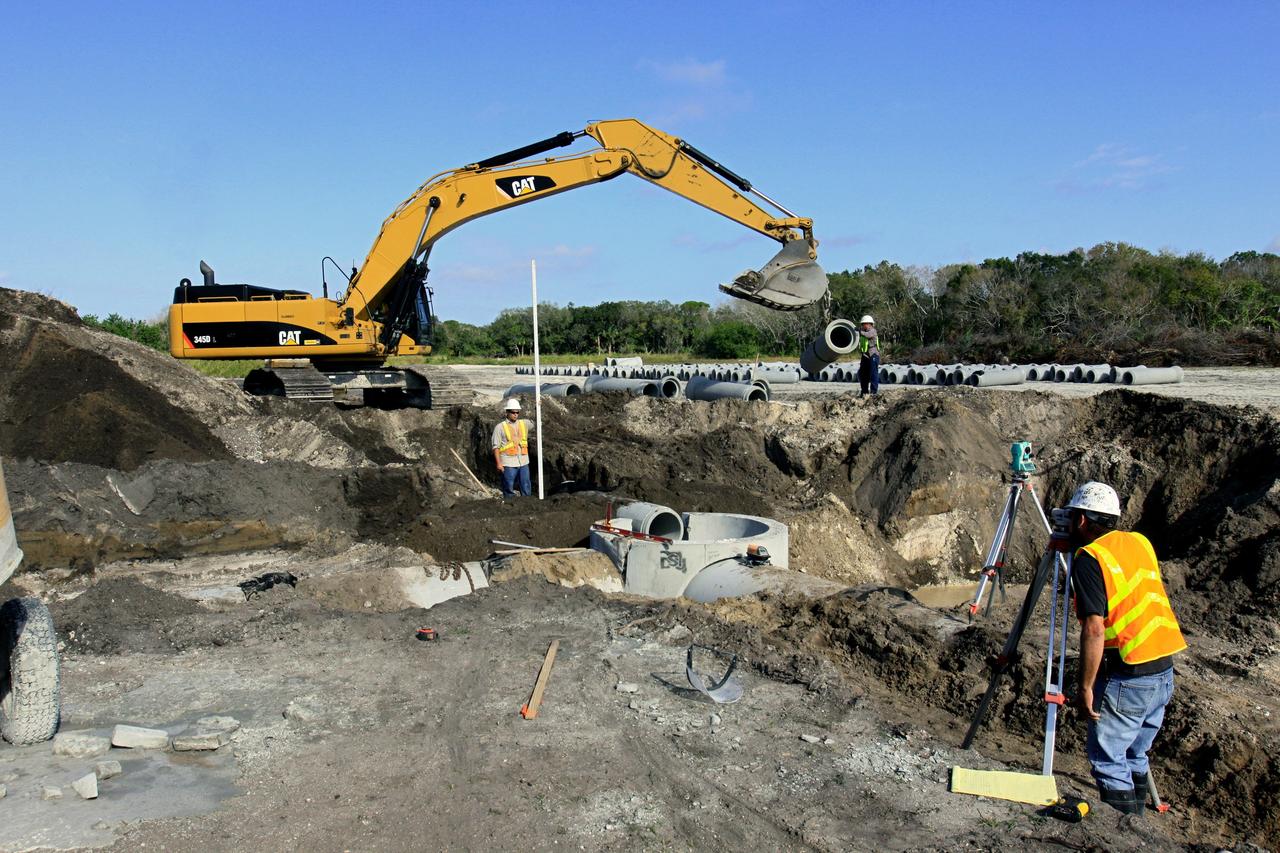

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
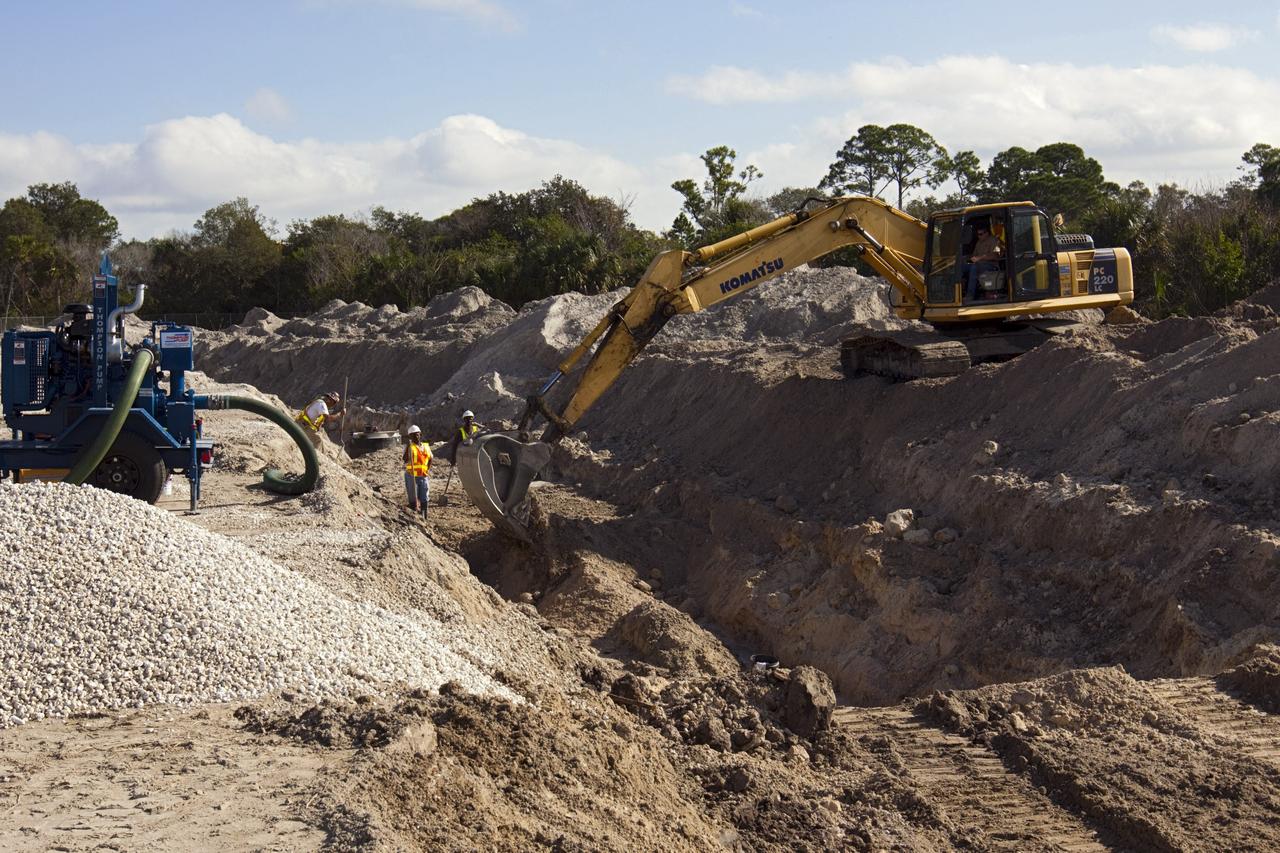

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
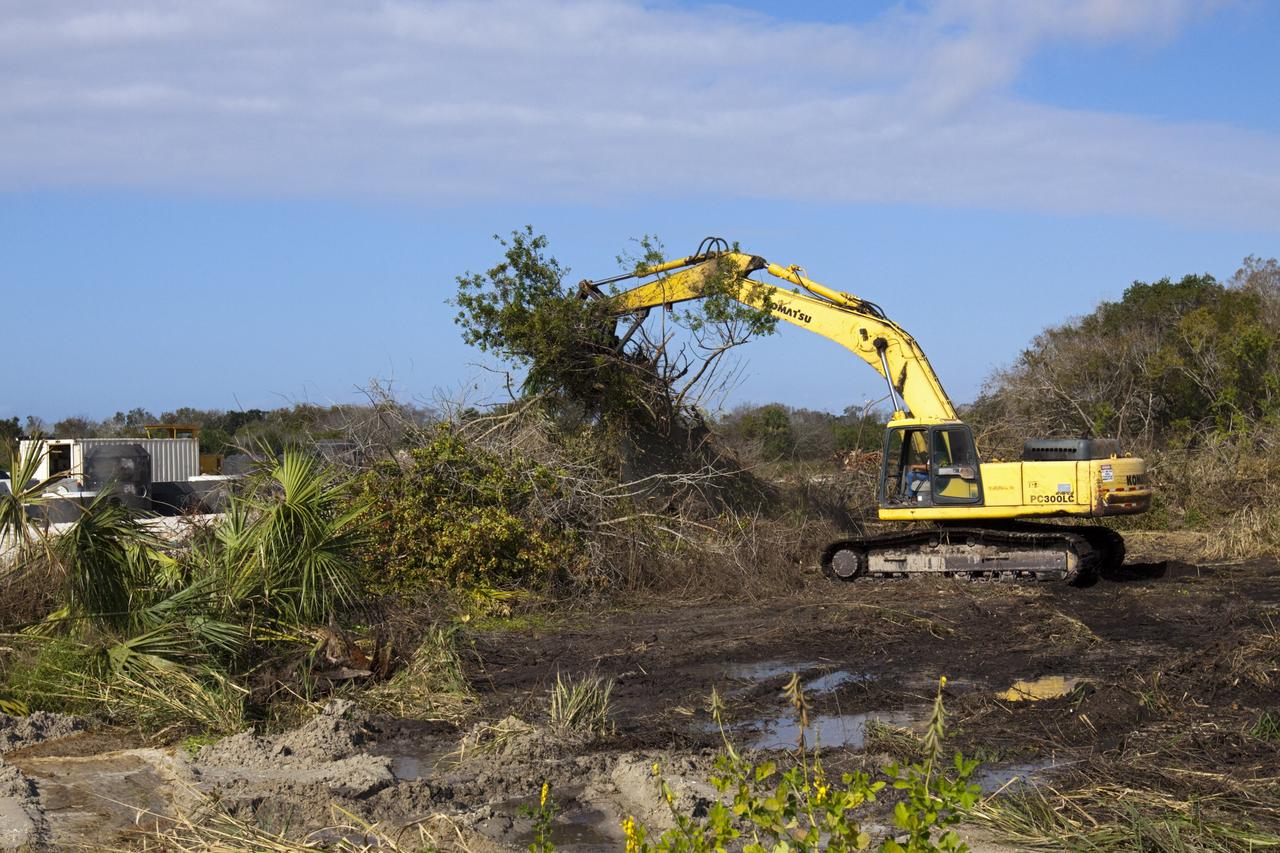

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Land is cleared as construction work progresses on Phase I of Exploration Park at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Exploration Park is near the Space Life Sciences Laboratory (SLSL). The first phase encompasses 60 acres just outside Kennedy’s security gates. Nine buildings will provide 350,000-square feet of work space, including educational, office, research and lab, and high-bay facilities. Each building is expected to be certified in the U.S. Green Building Council’s Leadership in Environmental and Energy Design (LEED). Exploration Park is designed to be a strategically located complex, adjacent to the SLSL, for servicing diverse tenants and uses that will engage in activities to support space-related activities of NASA, other government agencies and the U.S. commercial space industry. The SLSL will be the anchor facility for the park. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
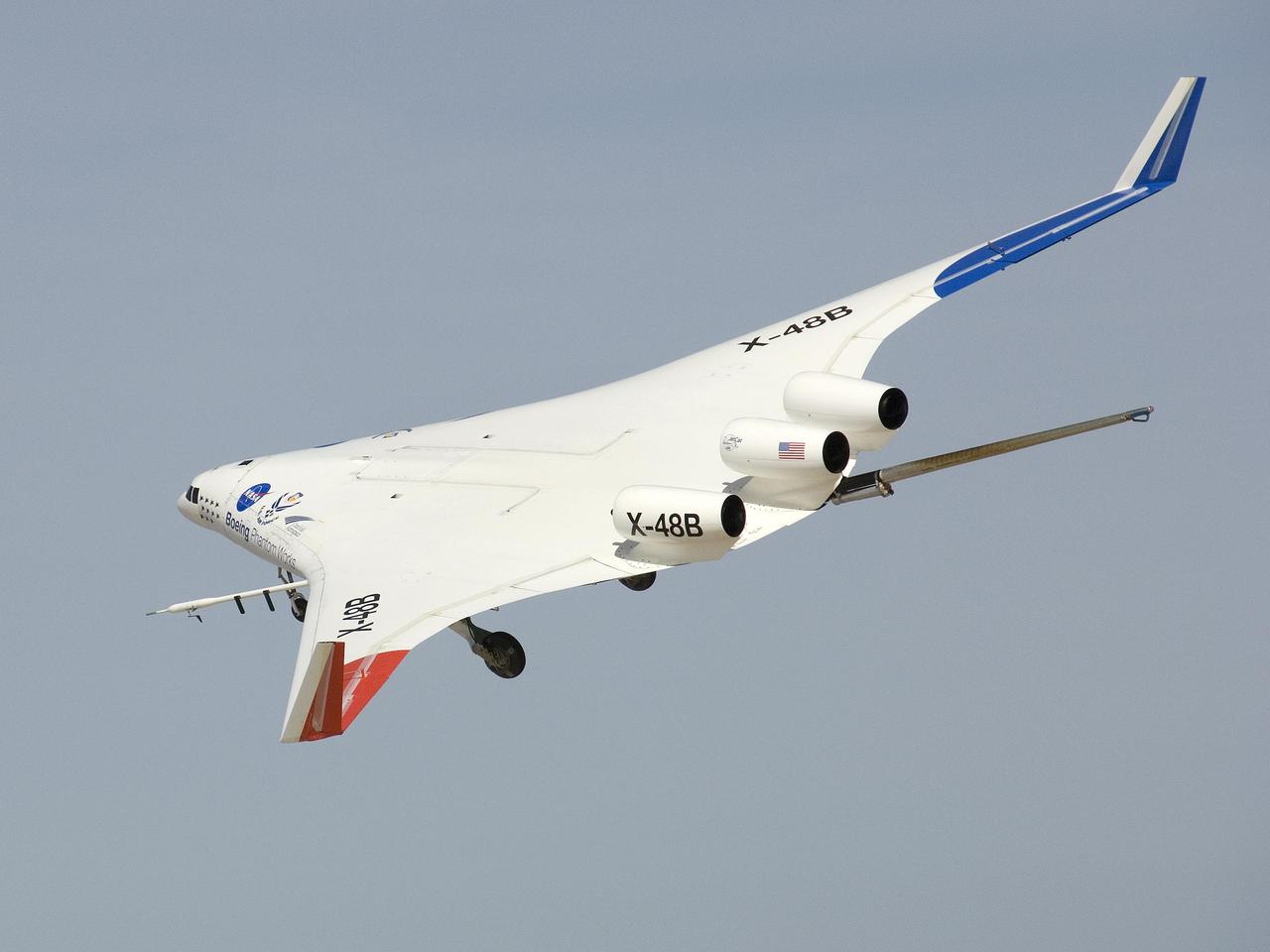

The X-48B Blended Wing Body research aircraft banked smartly in this Block 2 flight phase image.
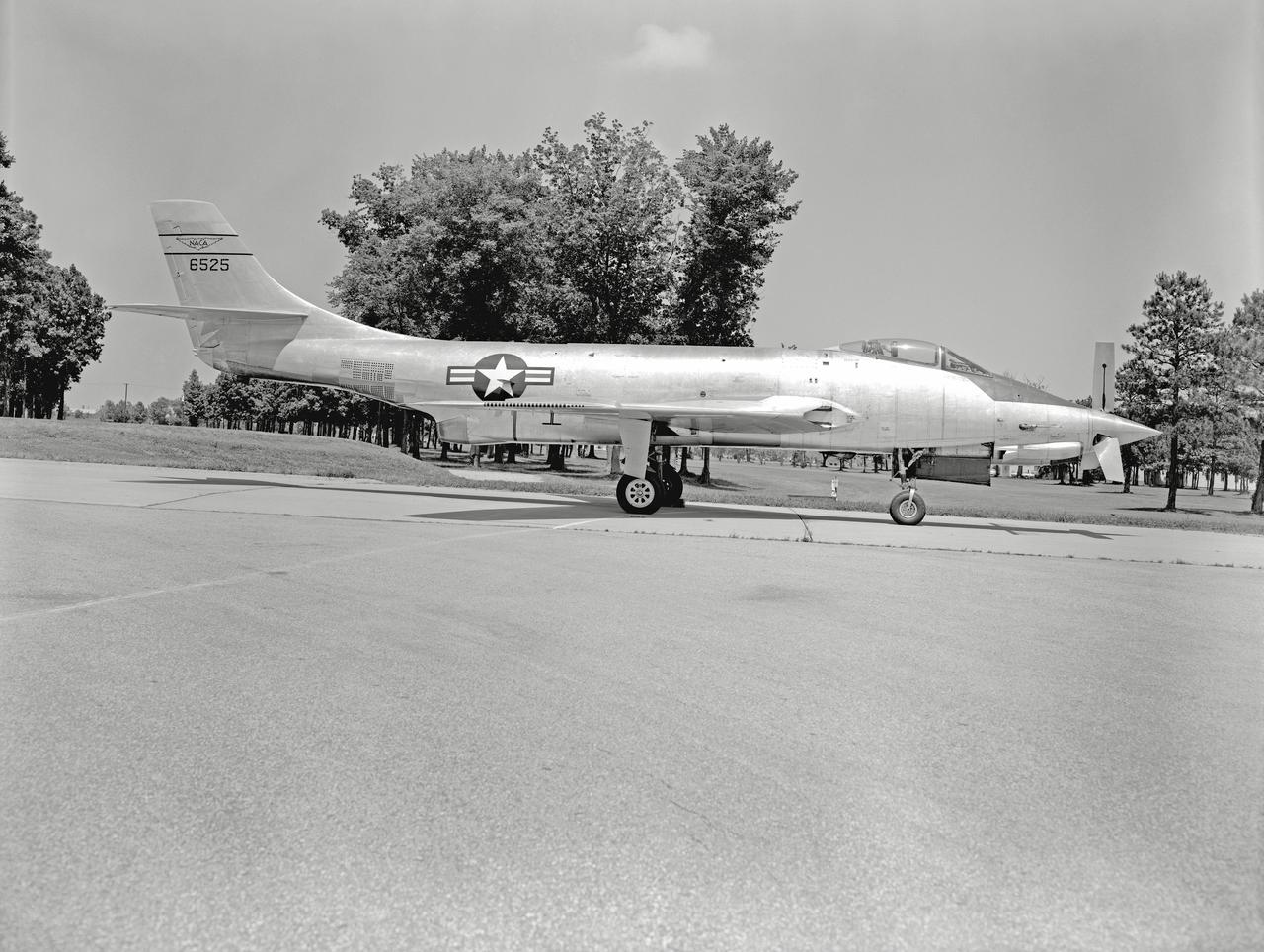

Phase SB Propeller installed on F88B

Phase SB Propeller installed on F88B
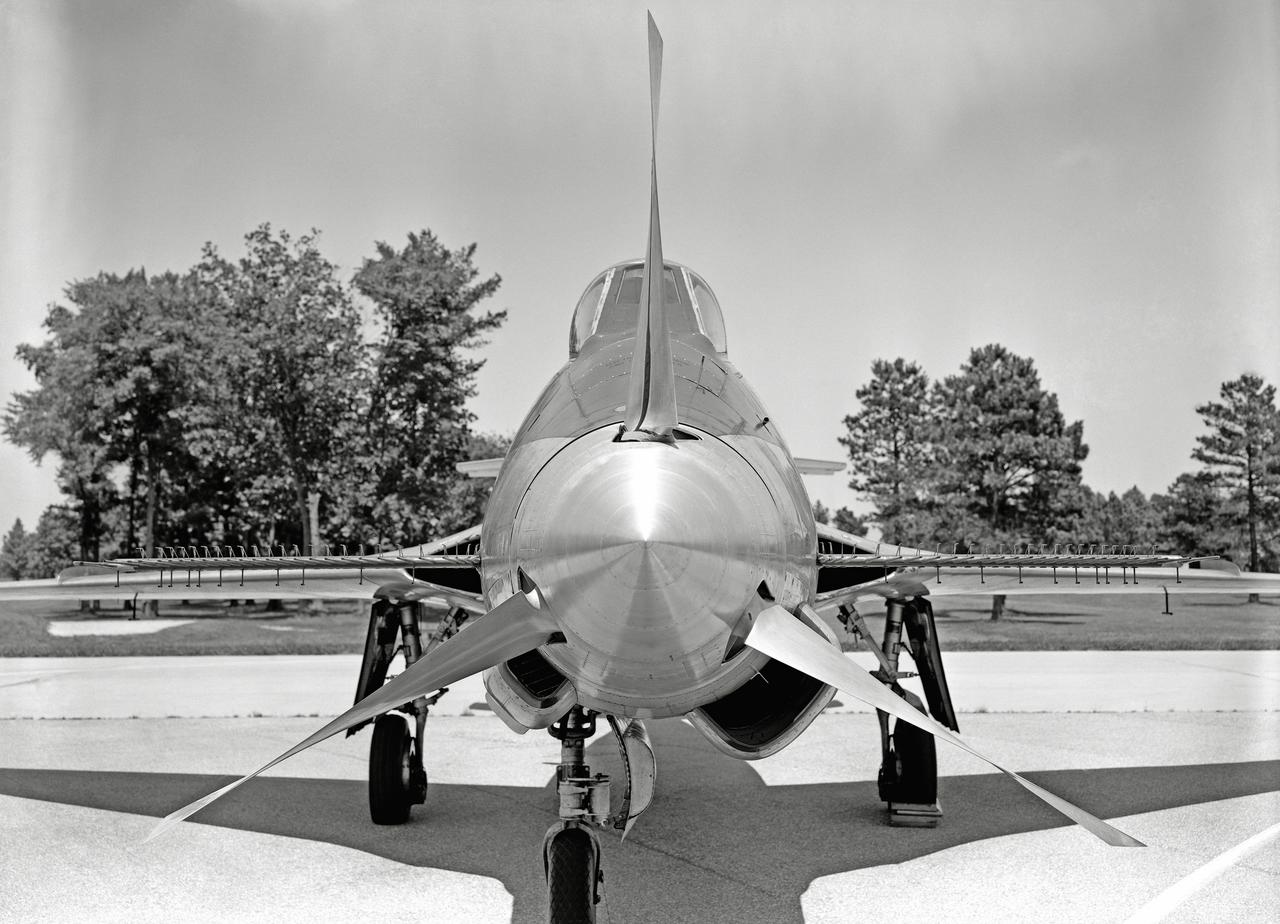

Phase SB Propeller installed on F88B
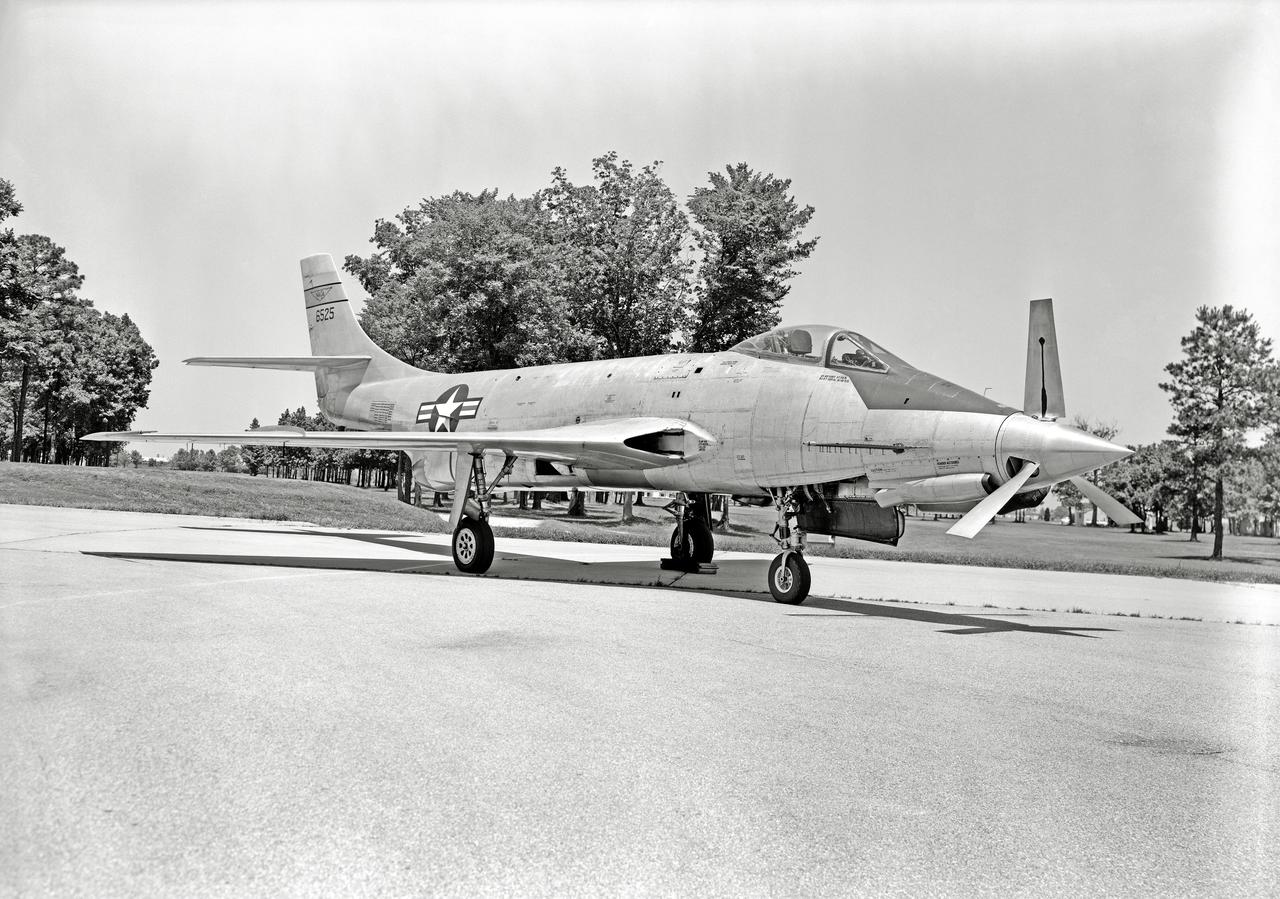

Phase SB Propeller installed on F88B
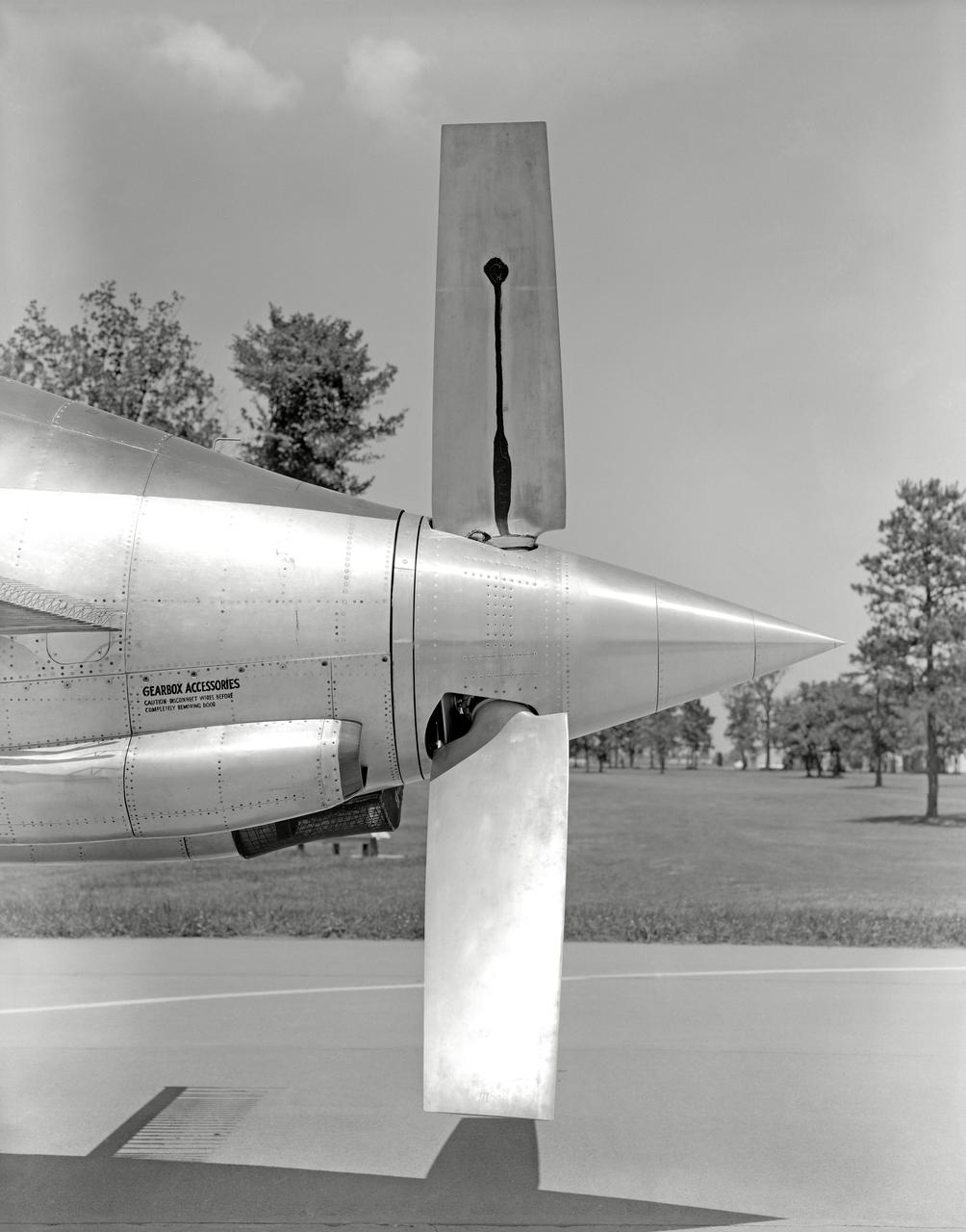

Phase SB Propeller installed on F88B

Launch Phase of ARCAS E1-239 Image taken at Wallops Island

NASA images acquired October 15, 2012 The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite captured these nighttime views of the Persian Gulf region on September 30, October 5, October 10, and October 15, 2012. The images are from the VIIRS “day-night band,” which detects light in a range of wavelengths from green to near-infrared and uses filtering techniques to observe signals such as gas flares, auroras, wildfires, city lights, and reflected moonlight. Each image includes an inset of the Moon in four different phases. September 30 shows the Persian Gulf by the light of the full Moon; October 15 shows the effects of a new Moon. As the amount of moonlight decreases, some land surface features become harder to detect, but the lights from cities and ships become more obvious. Urbanization is most apparent along the northeastern coast of Saudi Arabia, in Qatar, and in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). In Qatar and UAE, major highways can even be discerned by nighttime lights. In eighteenth-century England, a small group of entrepreneurs, inventors and free thinkers—James Watt and Charles Darwin’s grandfathers among them—started a club. They named it the Lunar Society, and the “lunaticks” scheduled their dinner meetings on evenings of the full Moon. The timing wasn’t based on any kind of superstition, it was based on practicality. In the days before electricity, seeing one’s way home after dark was far easier by the light of a full Moon. In the early twenty-first century, electricity has banished the need for such careful scheduling, but the light of the full Moon still makes a difference. NASA Earth Observatory image by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using VIIRS day-night band data from the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the Department of Defense. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: Suomi NPP - VIIRS Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b>Click here to view all of the <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/NightLights/" rel="nofollow"> Earth at Night 2012 images </a></b> <b>Click here to <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=79834" rel="nofollow"> read more </a> about this image </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
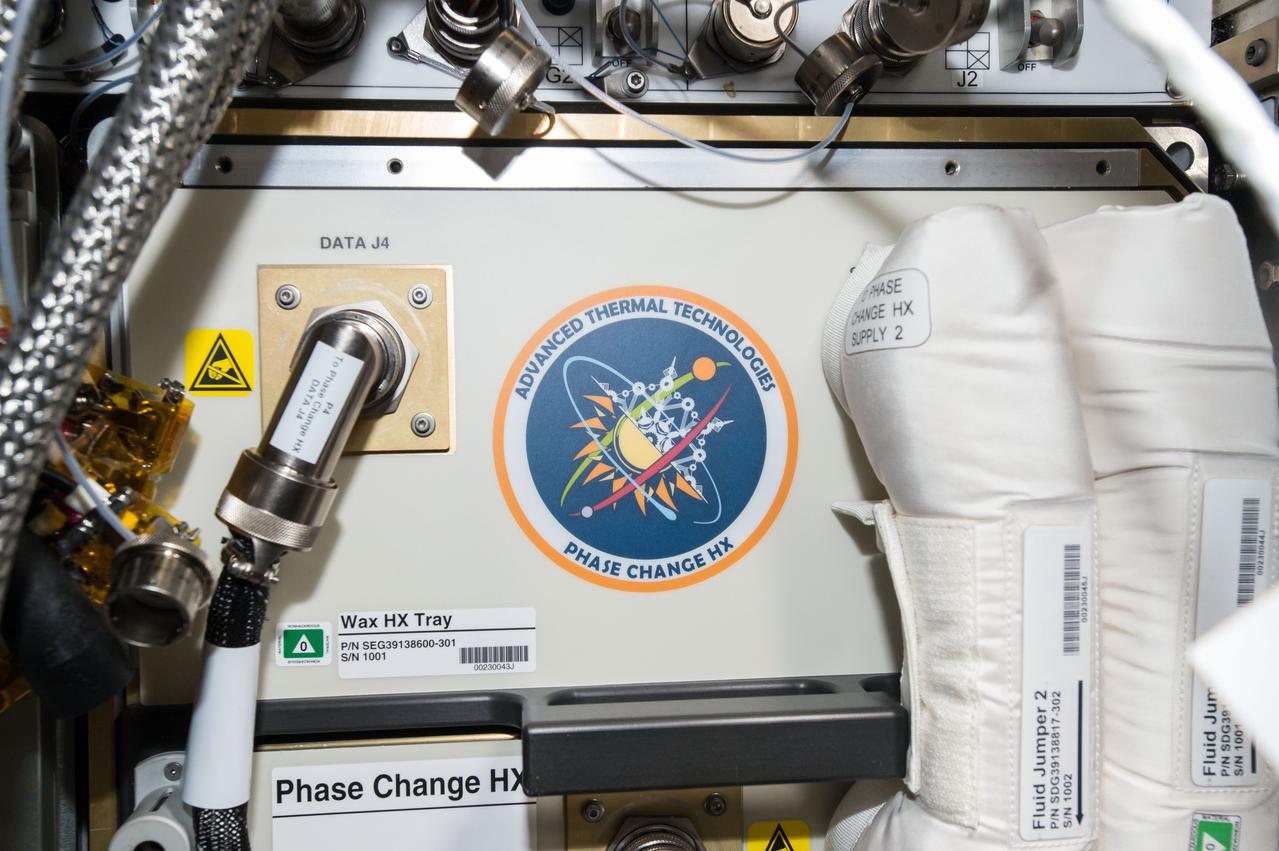

iss049e002221 (9/14/2016) --- Photographic documentation taken during installation of the Phase Change Heat Exchanger (PCHx) into EXpedite PRocessing of Experiments to Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack (ER)-8. The primary objective of the PCHx Project is to create a unique test platform utilizing the EXPRESS Rack on the ISS to advance the technology readiness level of phase change heat exchangers for infusion into future exploration vehicles.
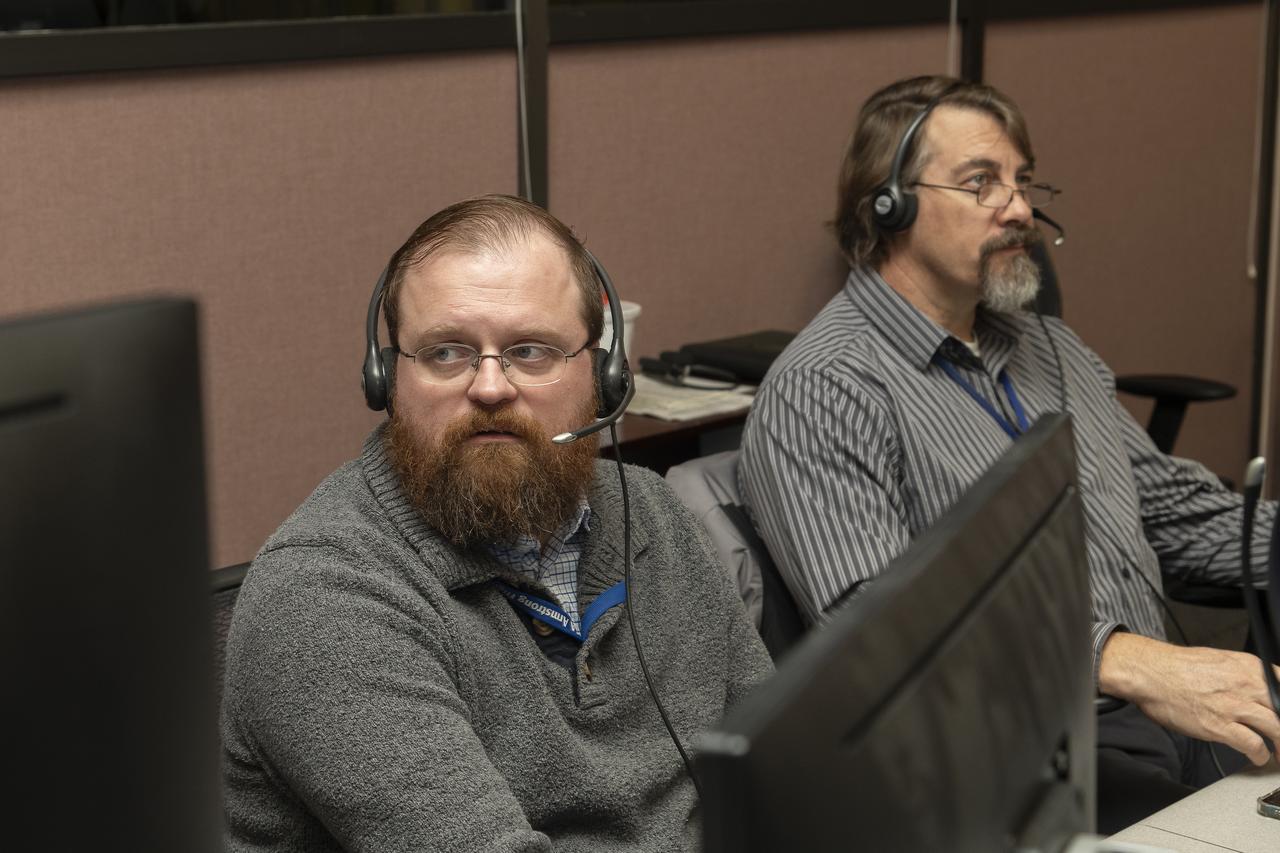

Dr. Forrest Carpenter, left, principal investigator for the third phase of CarpetDIEM, Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, monitors a test from one of the control rooms at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center. Next to Carpenter is Brian Strovers, chief engineer for Commercial Supersonic Technology. The third phase of CarpetDIEM tested logistics and upgraded ground recording systems in preparation for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission.
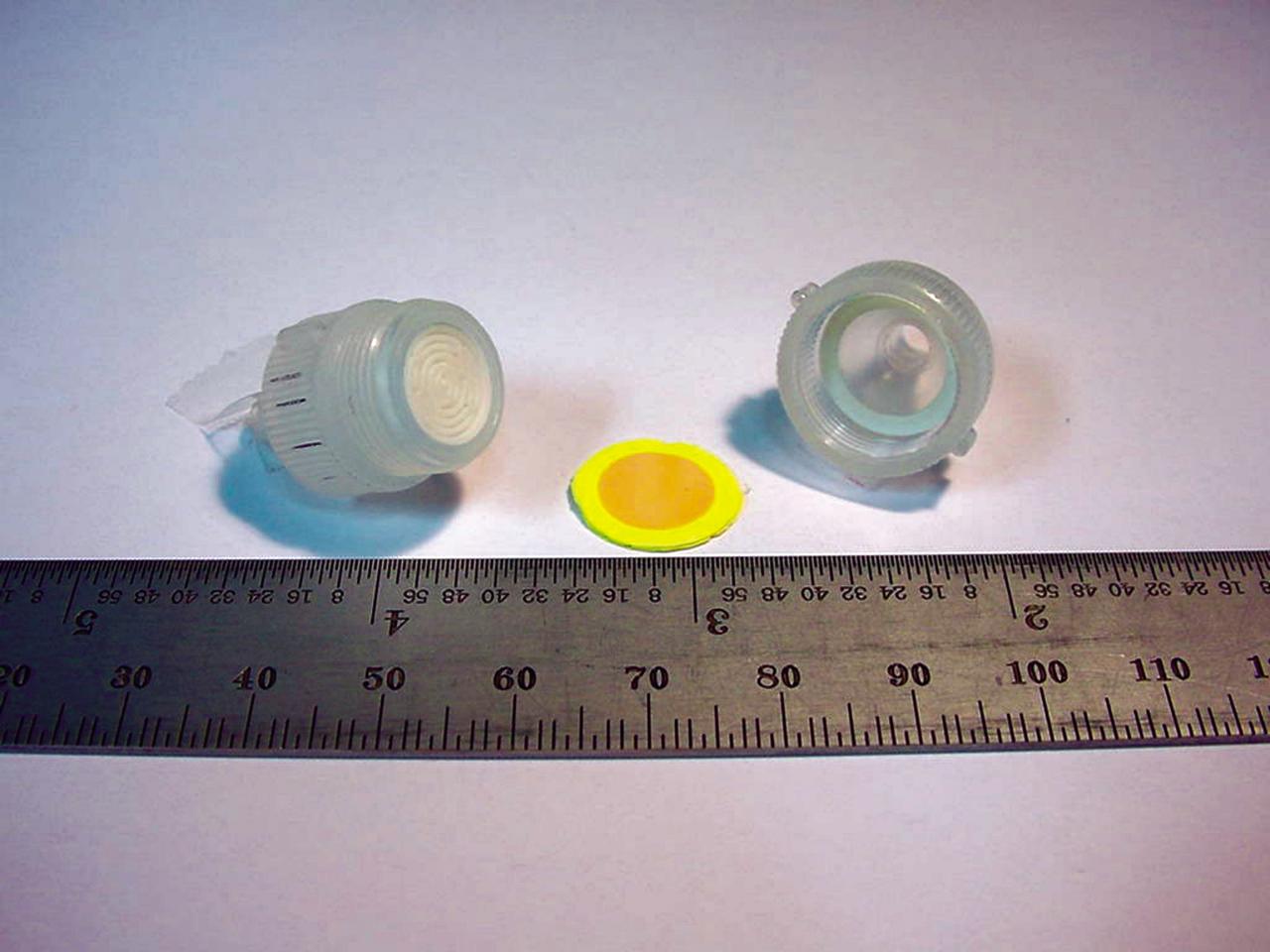

The heart of a colorimetric solid phase extractor (CSPE) test kit quickly measures the concentration of the biocides silver or iodine in astronauts’ drinking water to determine whether concentrations are safe. When 10 milliliters (ml) of water is drawn through the disk, the disk will turn color (yellow in this picture for iodine) indicating the presence of the biocides. The device could someday be used to test water safety at reservoirs and water treatment plants on Earth. (photo credit: Microanalytical Instrumentation Center, Iowa State University).
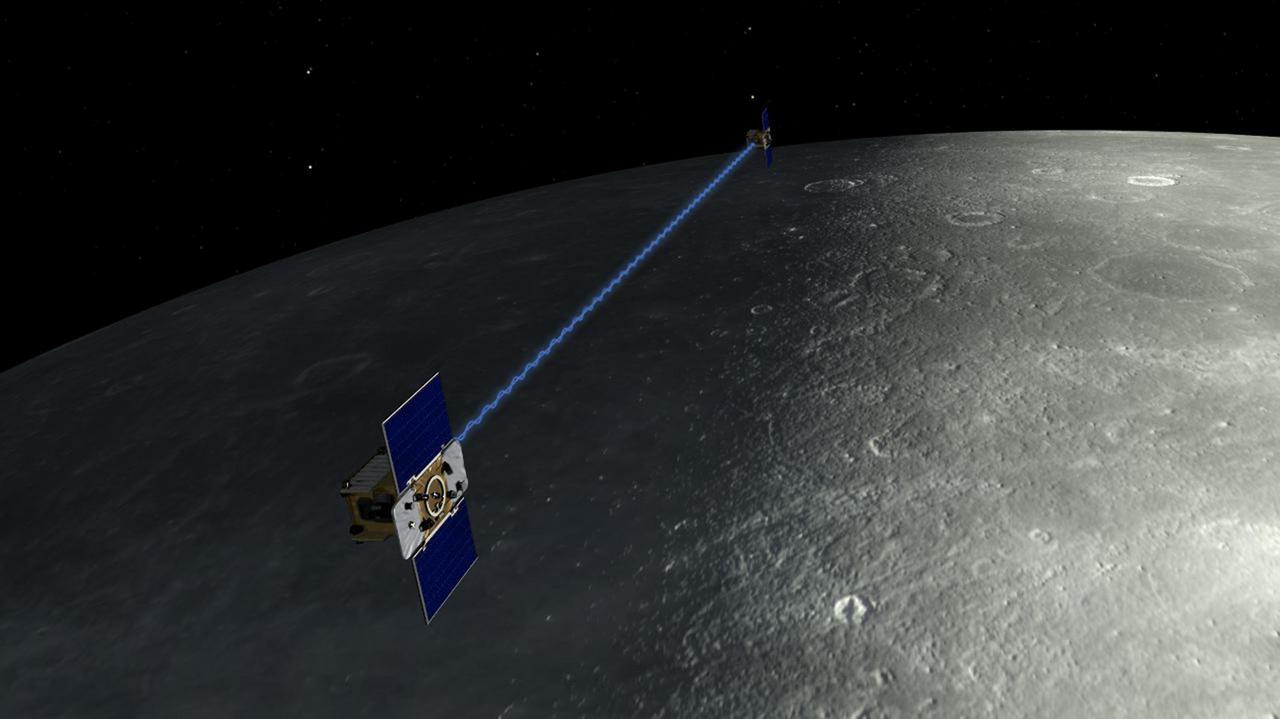

An artist depiction of the twin spacecraft that comprise NASA GRAIL mission. During the GRAIL mission science phase, spacecraft Ebb and Flow transmit radio signals precisely defining the distance between them as they orbit the moon in formation.
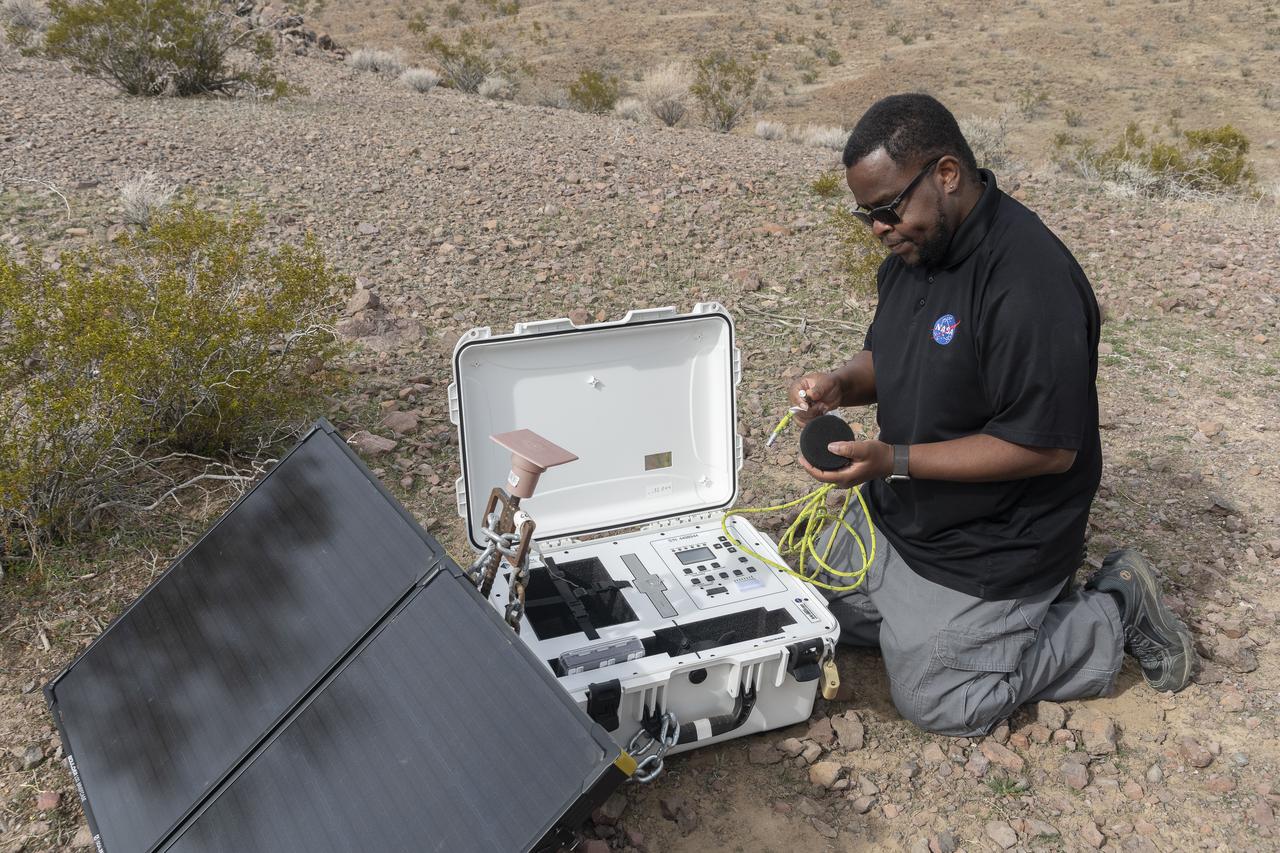

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager and technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
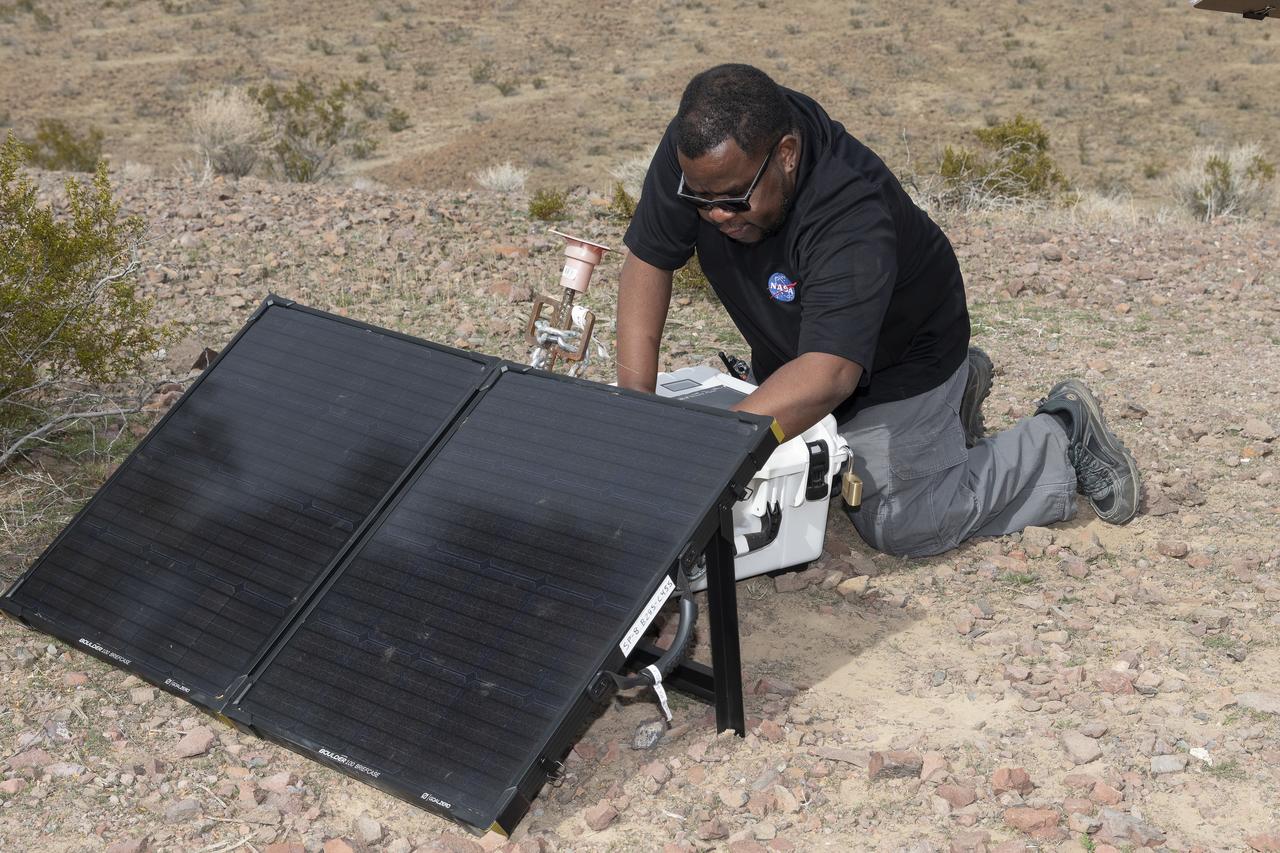

Aerospace engineer Larry Cliatt, Quesst Phase 2 Sub-Project Manager abd technical lead for the acoustic validation phase of the Quesst mission, sets up a ground recording system in the California desert. The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
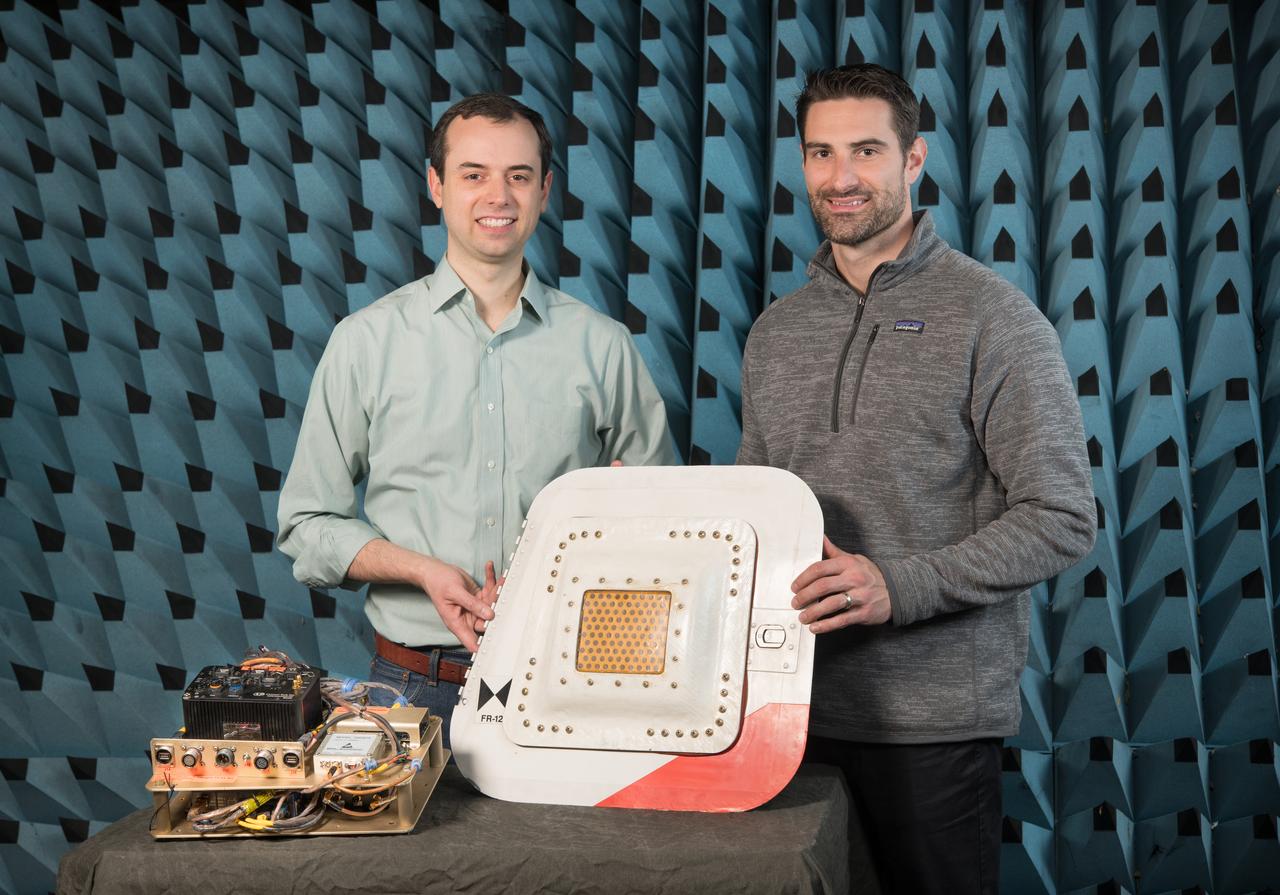
Flight Electronics Payload for Curved Confocal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies, CLAS-ACT, Phased Array Antenna on T-34-C Aircraft Door Flight Curved Confocal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies, CLAS-ACT, Phased Array Antenna Control / Flight Testing
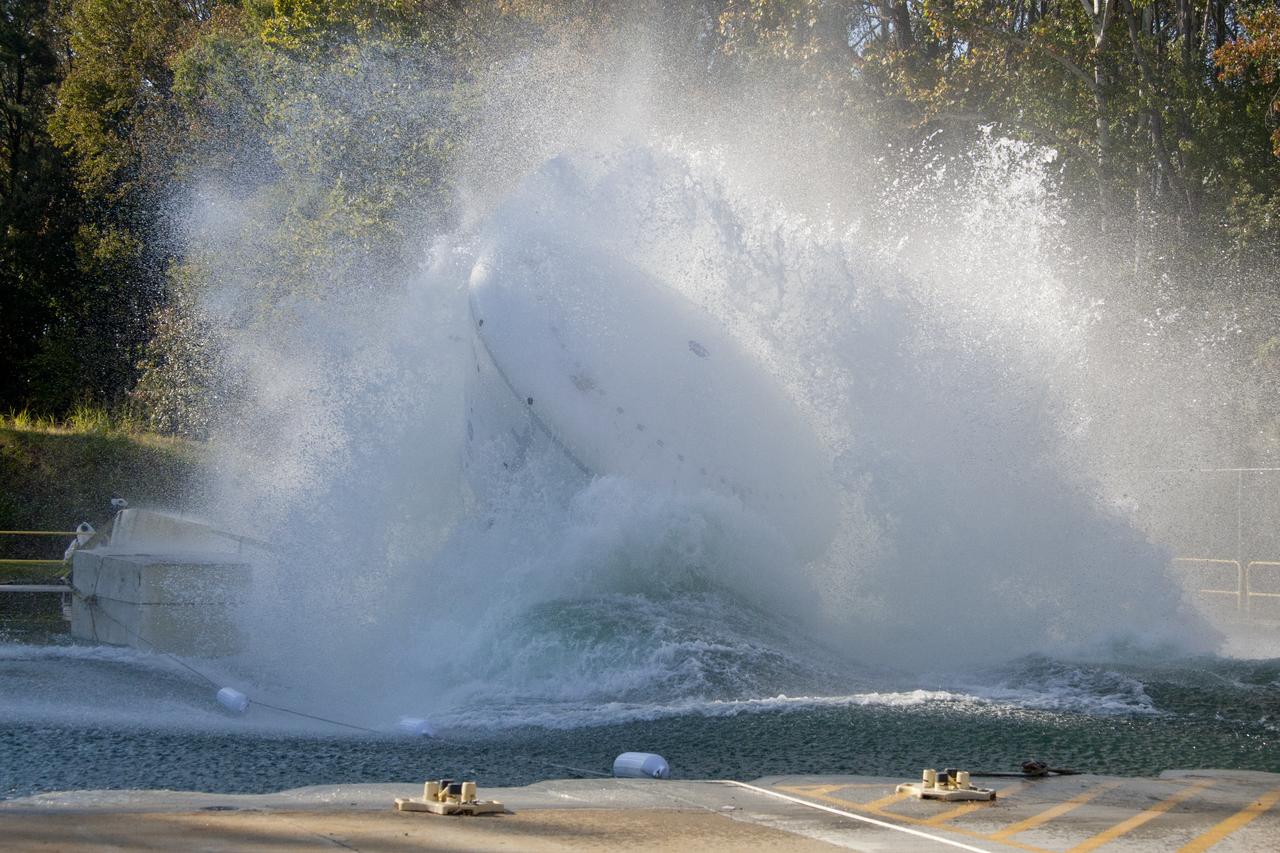

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
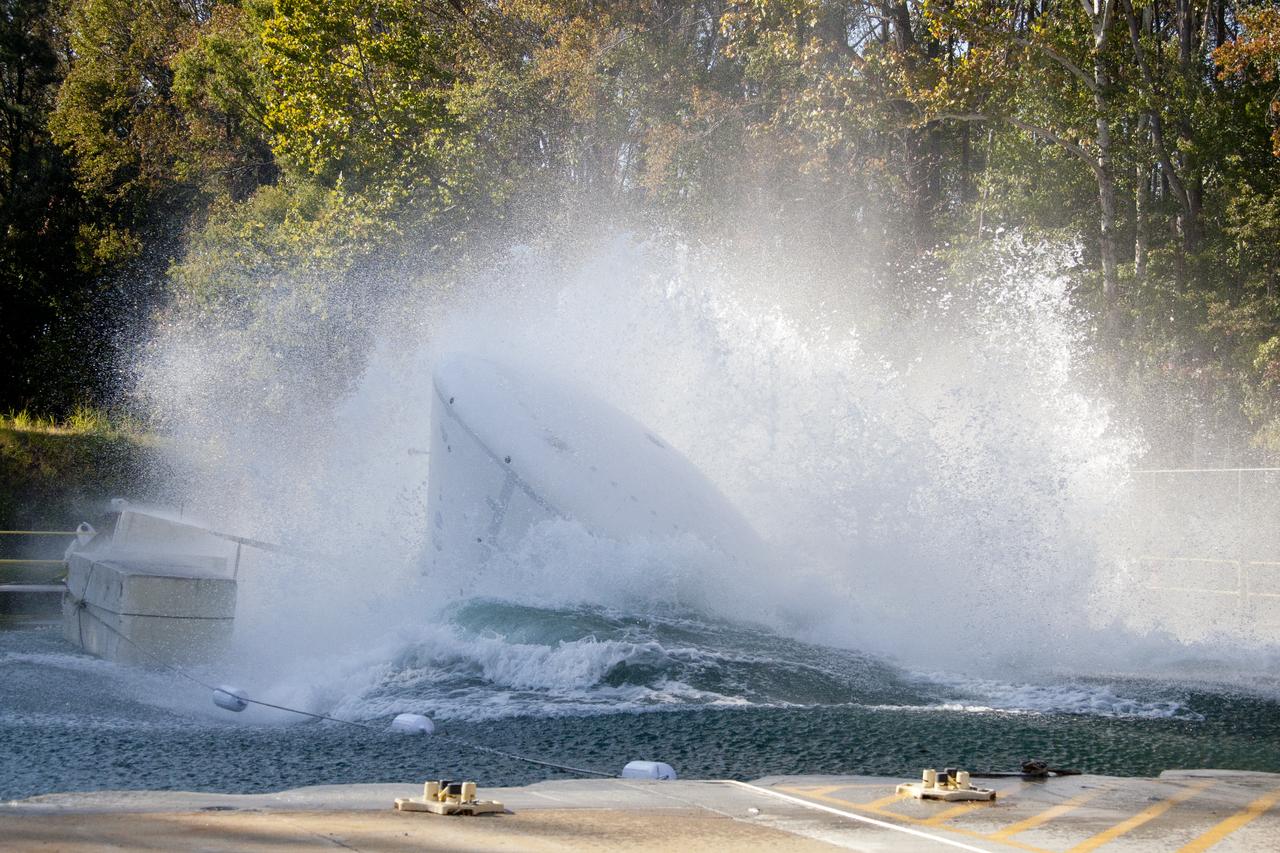

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
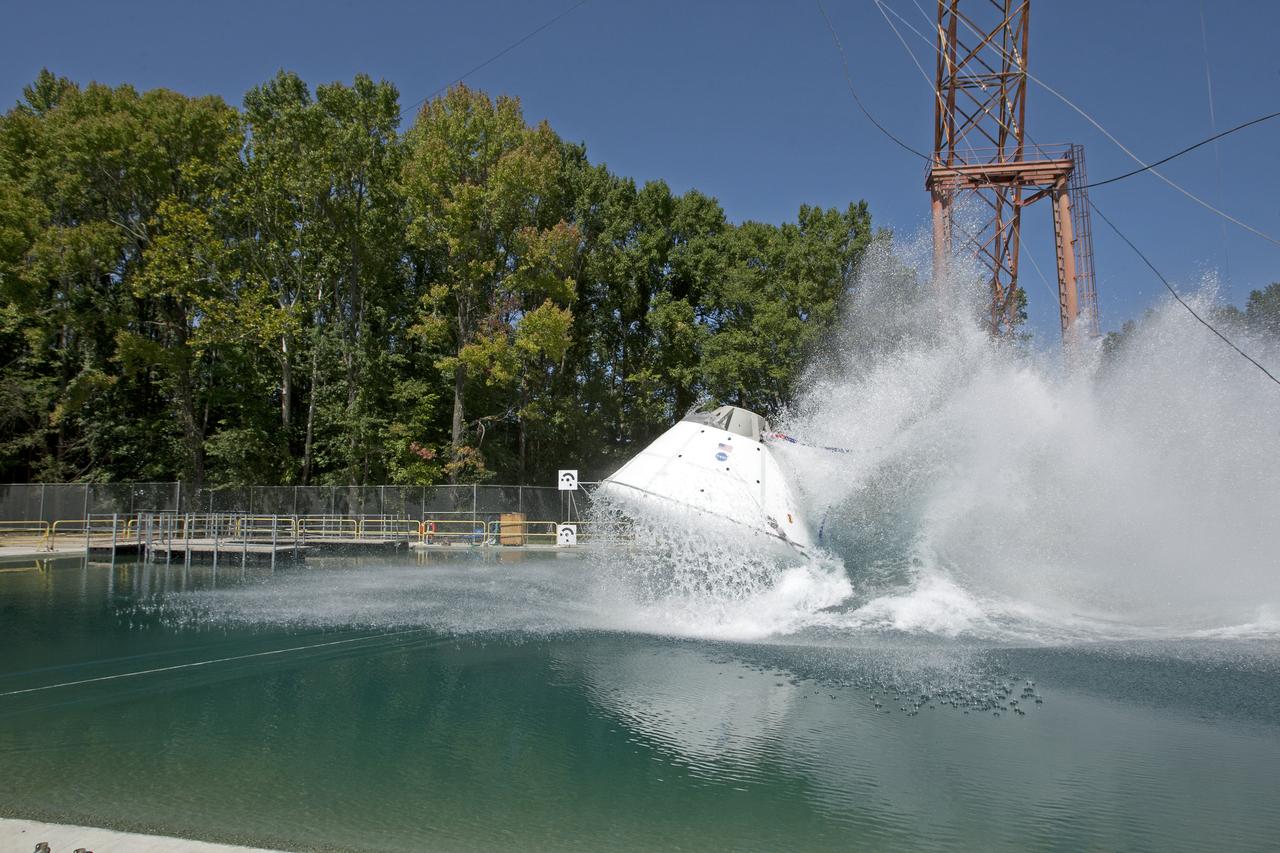

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
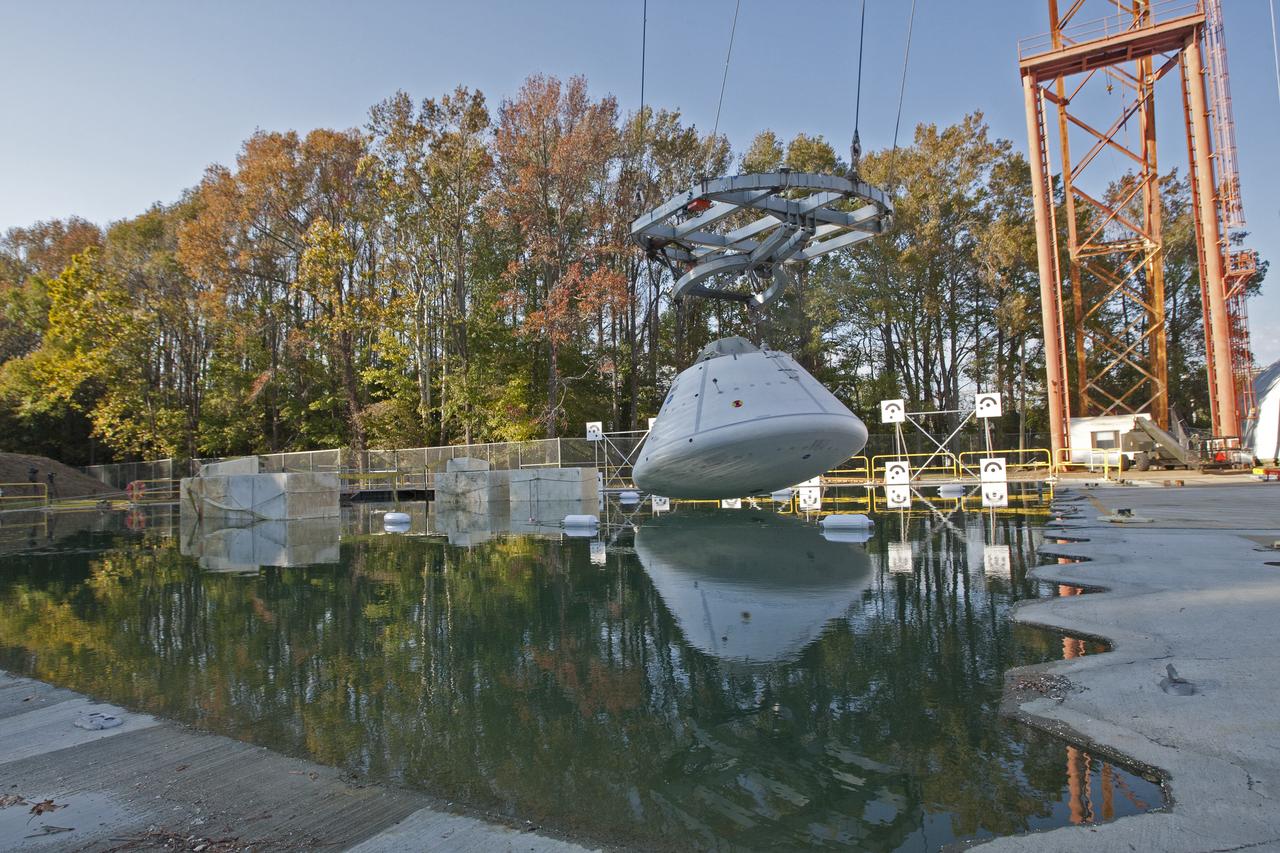

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
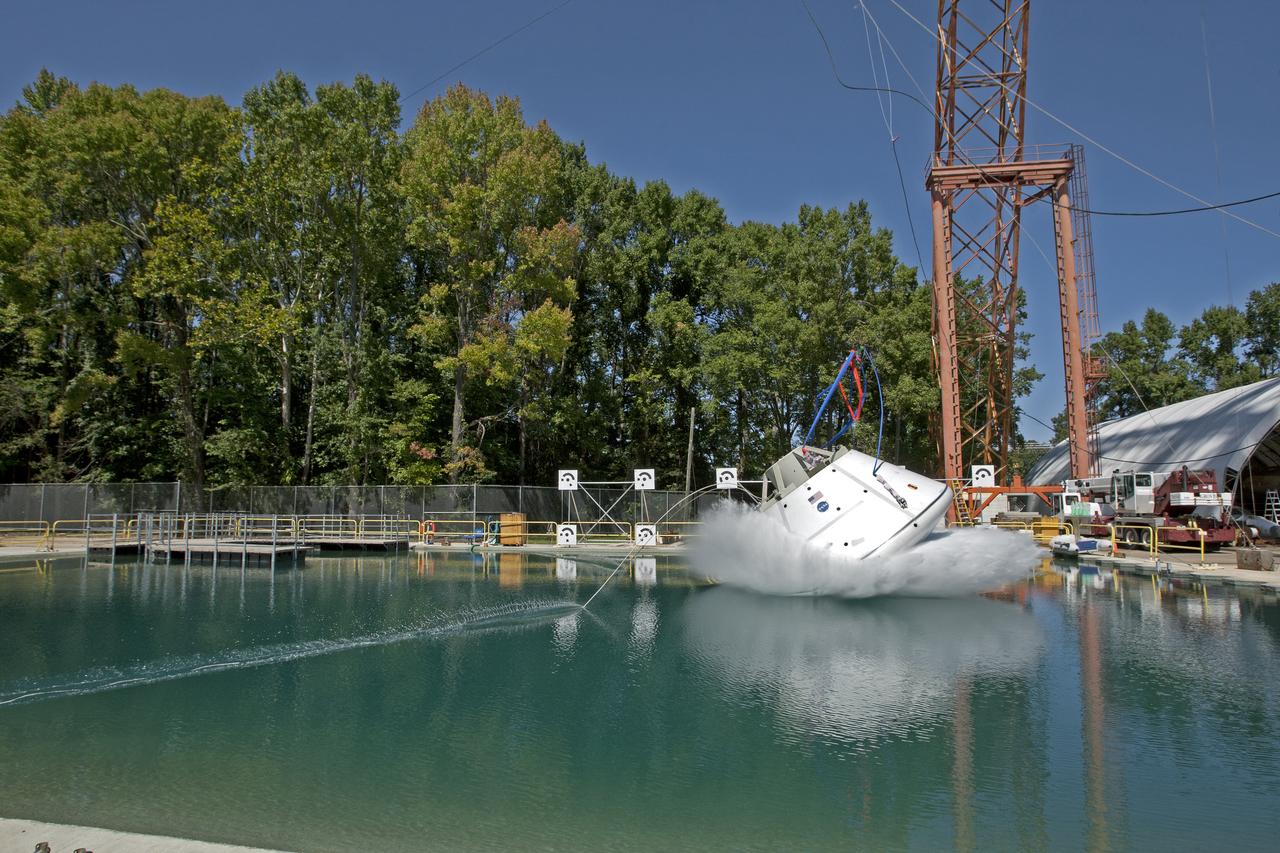

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
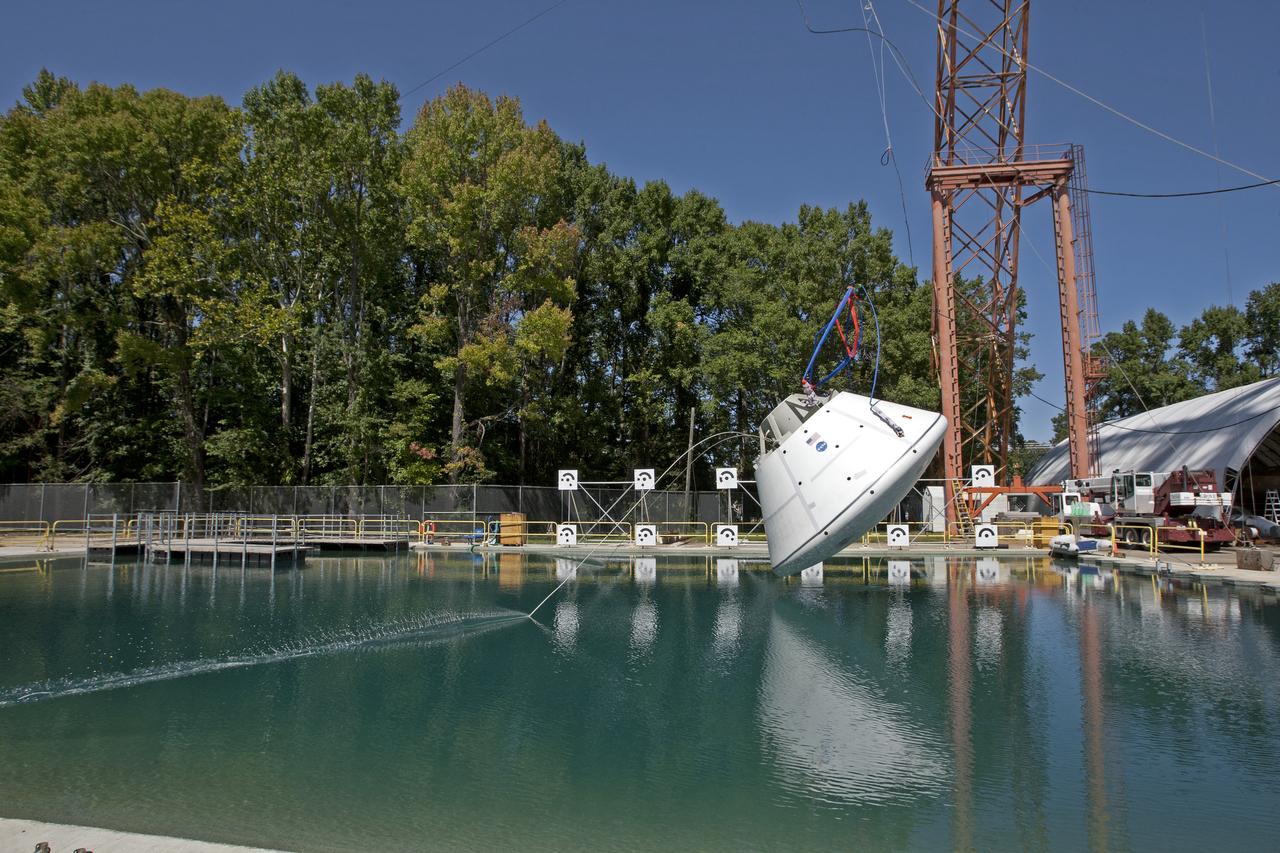

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
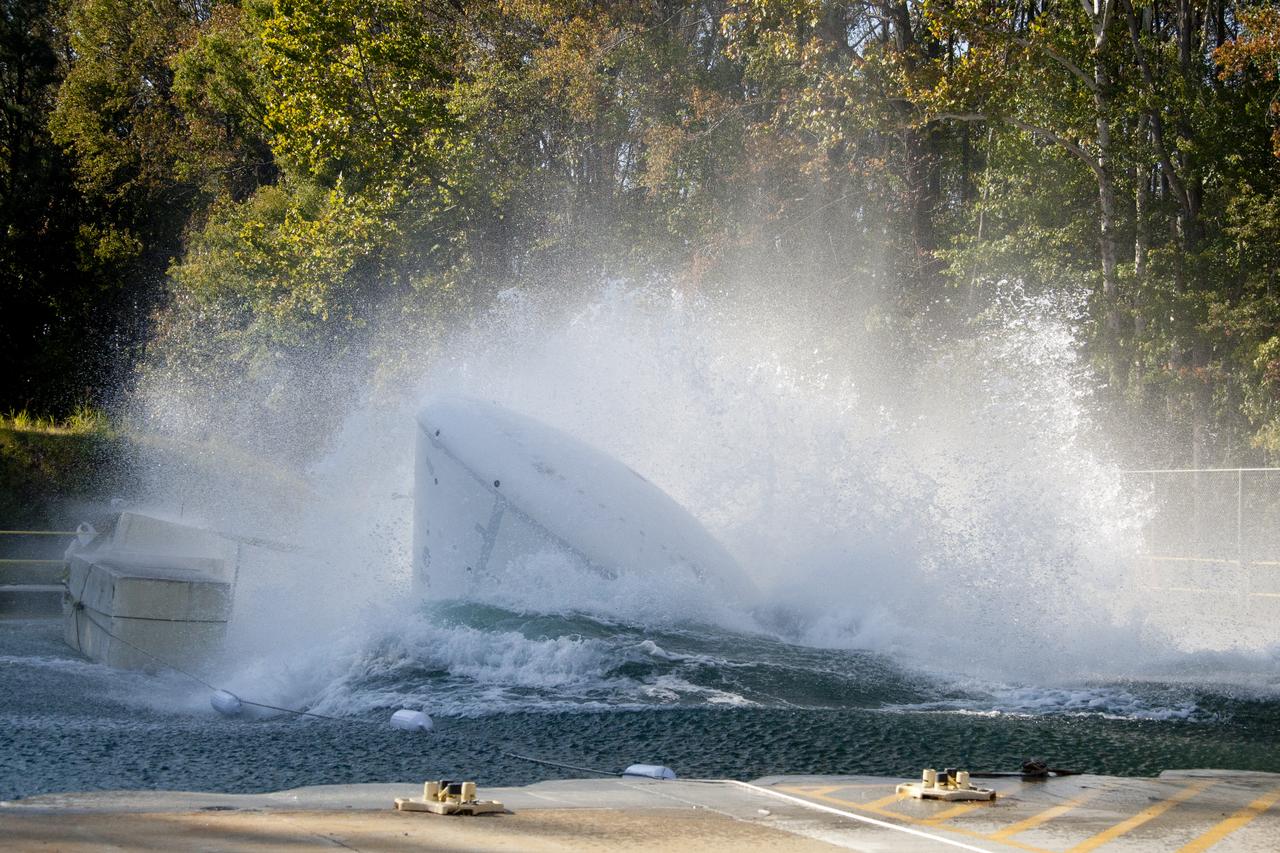

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
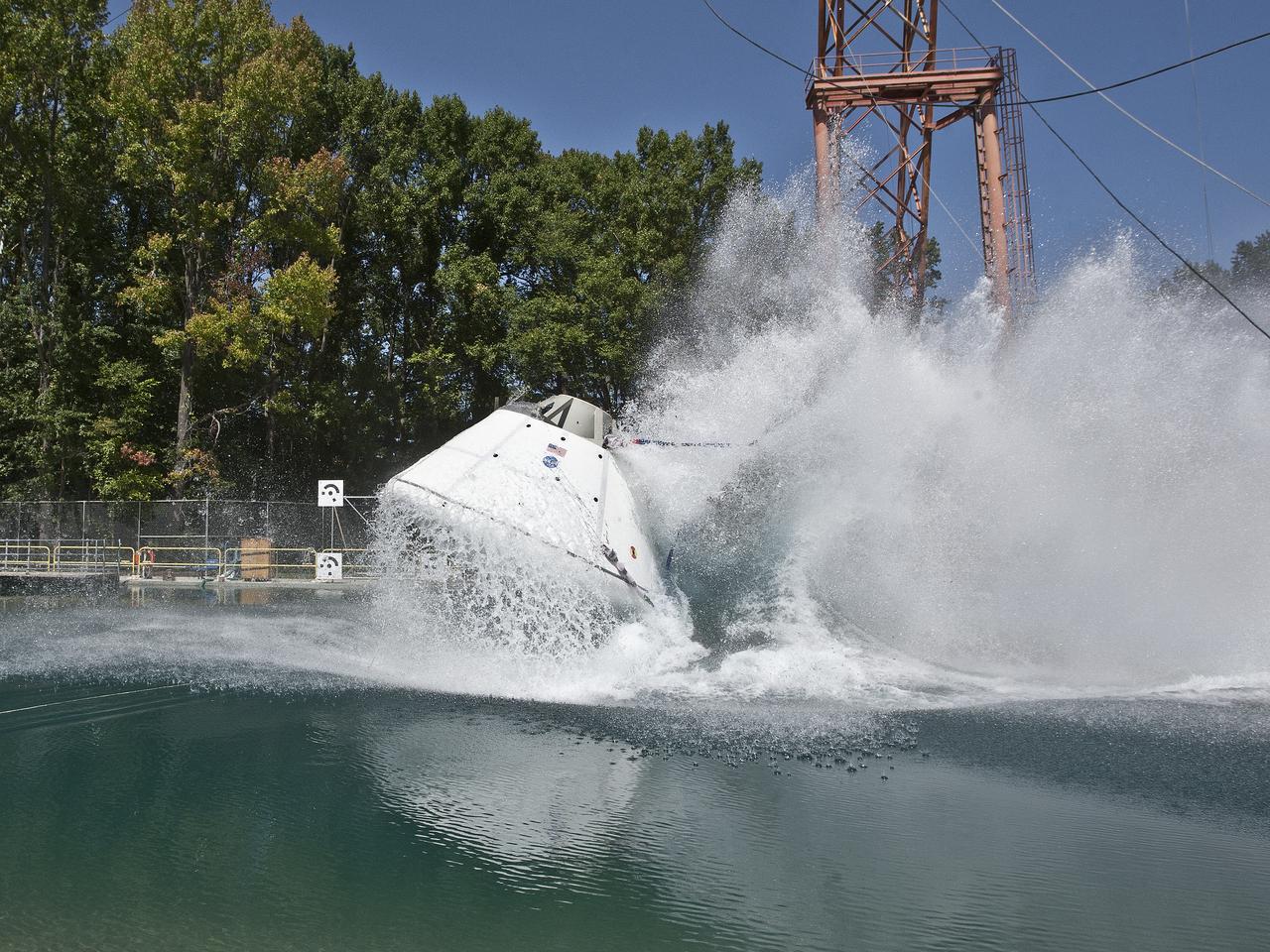

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
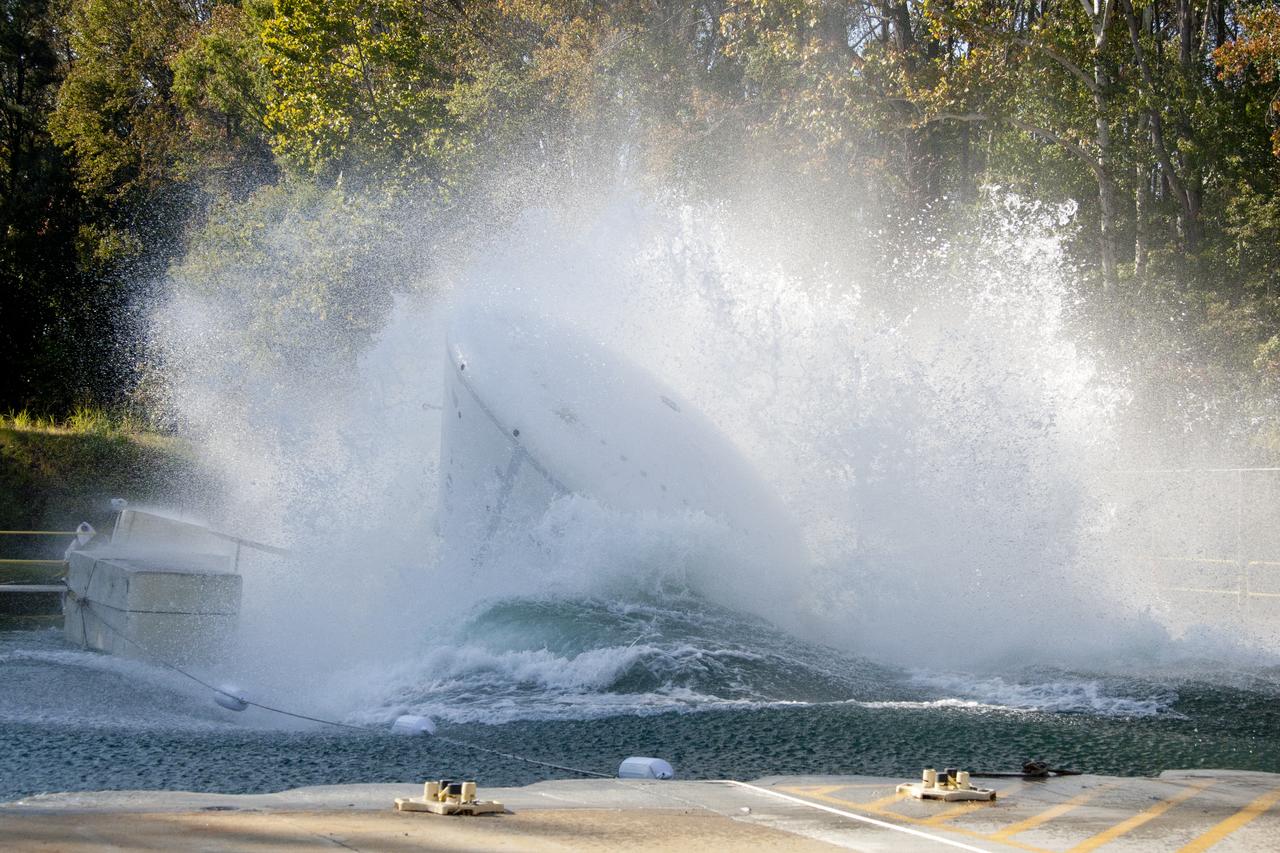

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
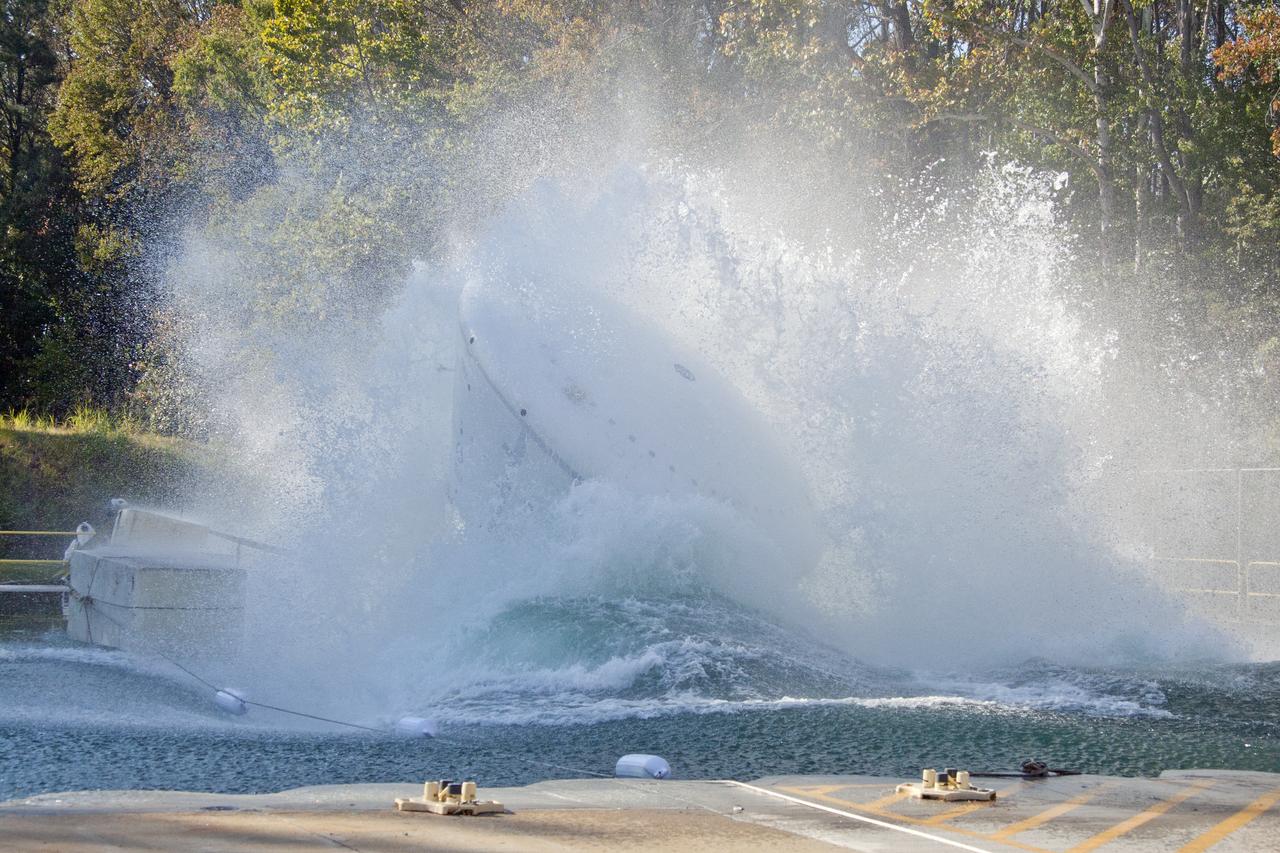

Orion at Hydro Impact Basin Engineers conducted the first test as part of Phase 1 of the Orion boilerplate test article at NASA's Langley Research Center, on Oct. 18.
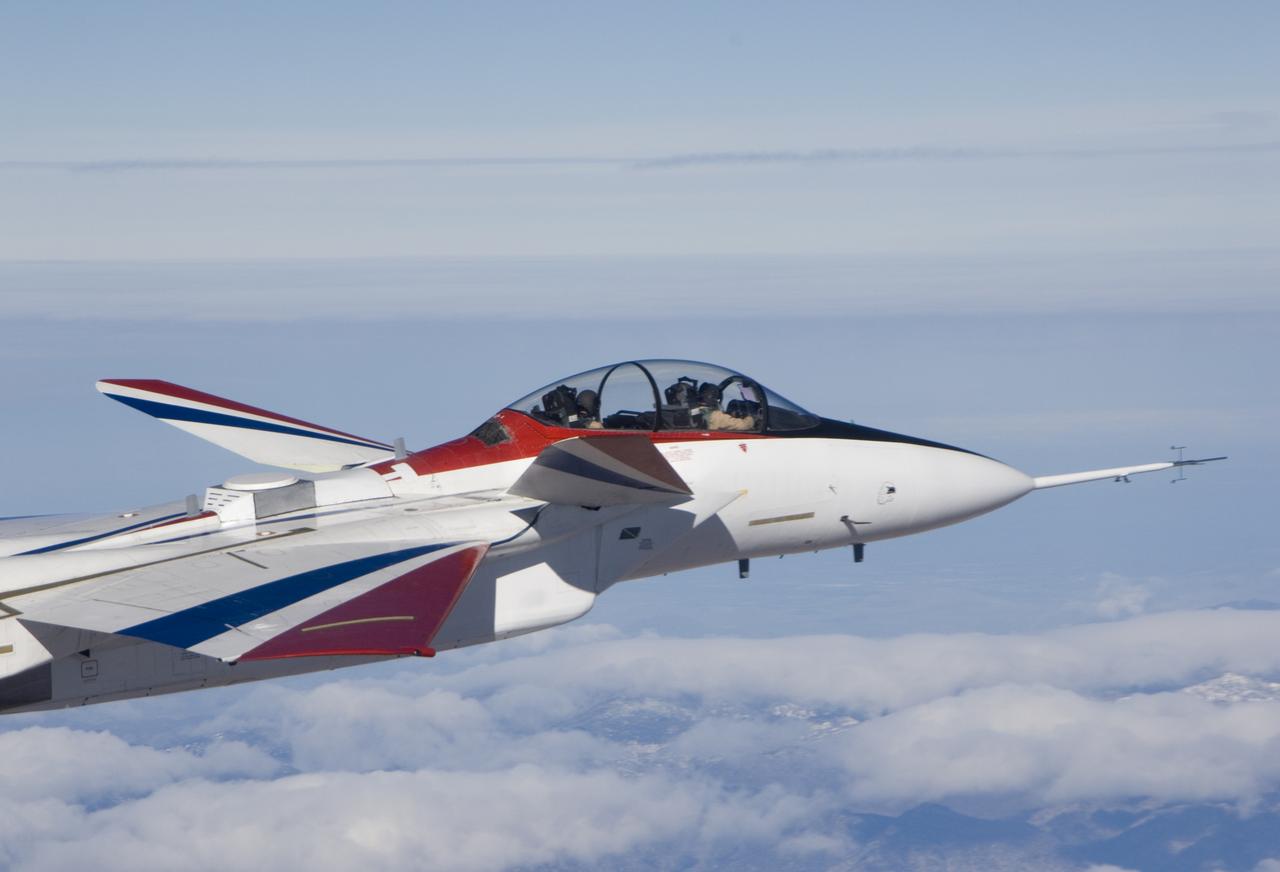

Range safety and phased-array range user system antennas validated in the ECANS project can be seen just behind the cockpit on NASA's NF-15B research aircraft.
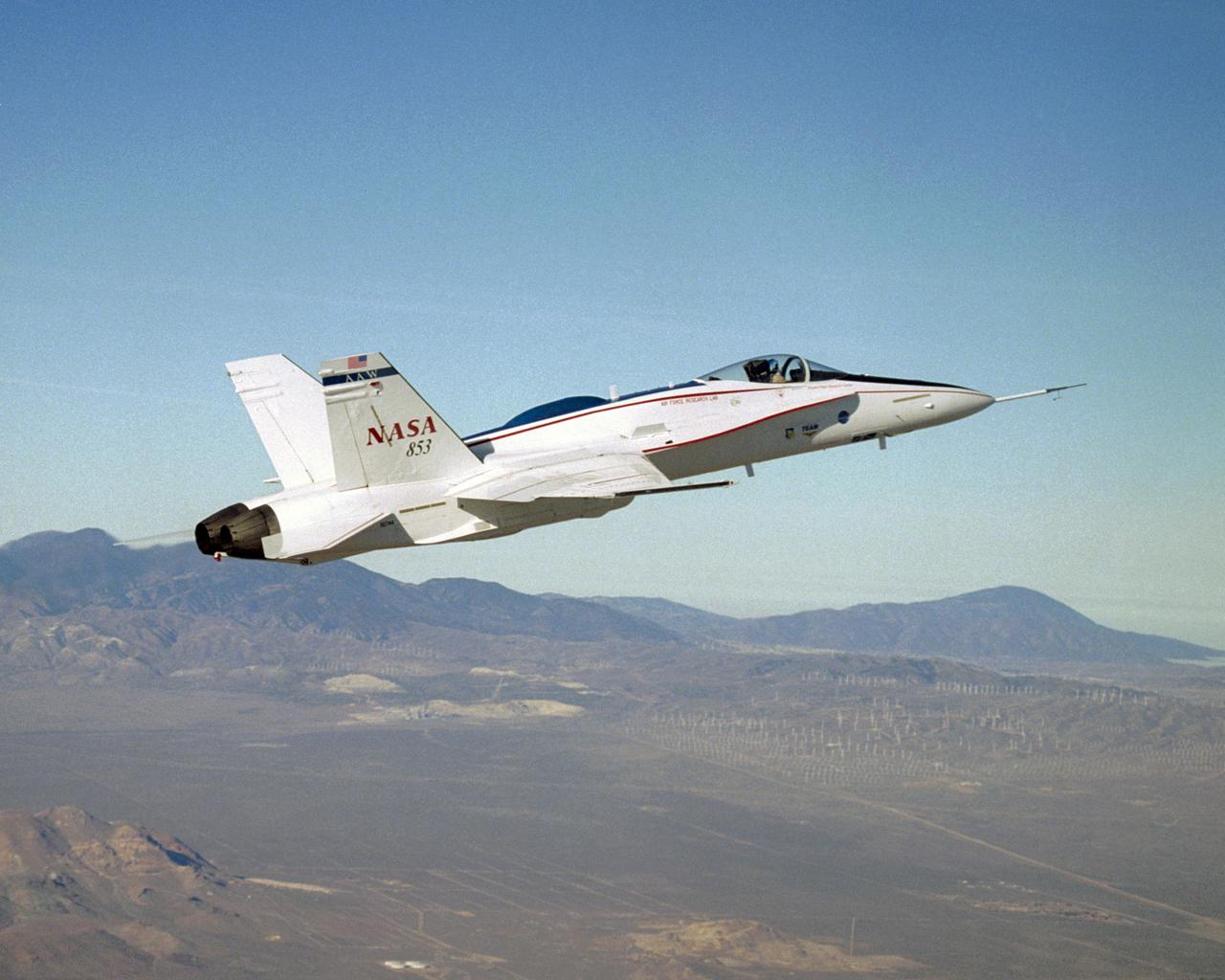

NASA's Active Aeroelastic Wing F/A-18 resumed flight tests in the second phase of the program at the Dryden Flight Research Center in early December 2004.
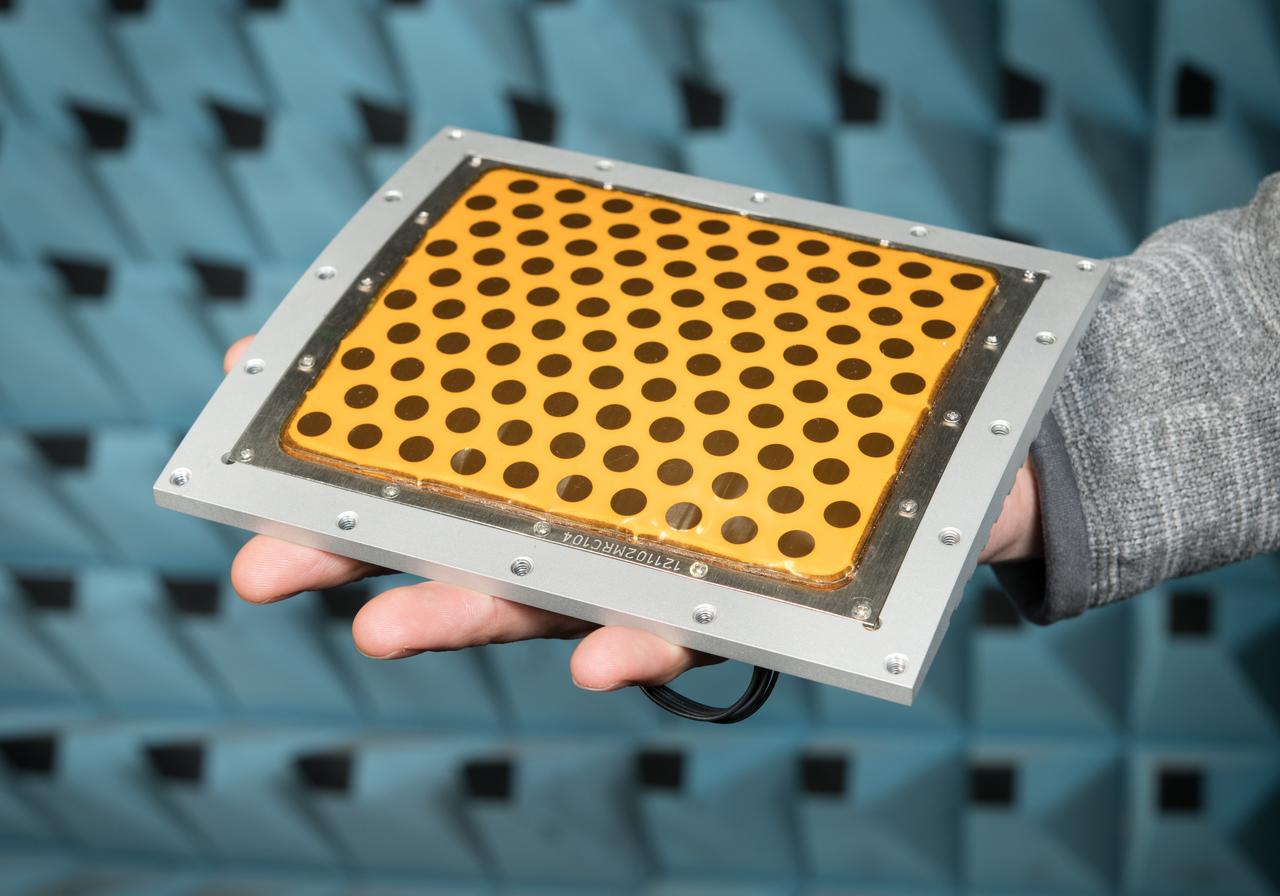
Curved Confocal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies, CLAS-ACT, Phased Array Antenna on Mock Carbon Fiber Fuselage
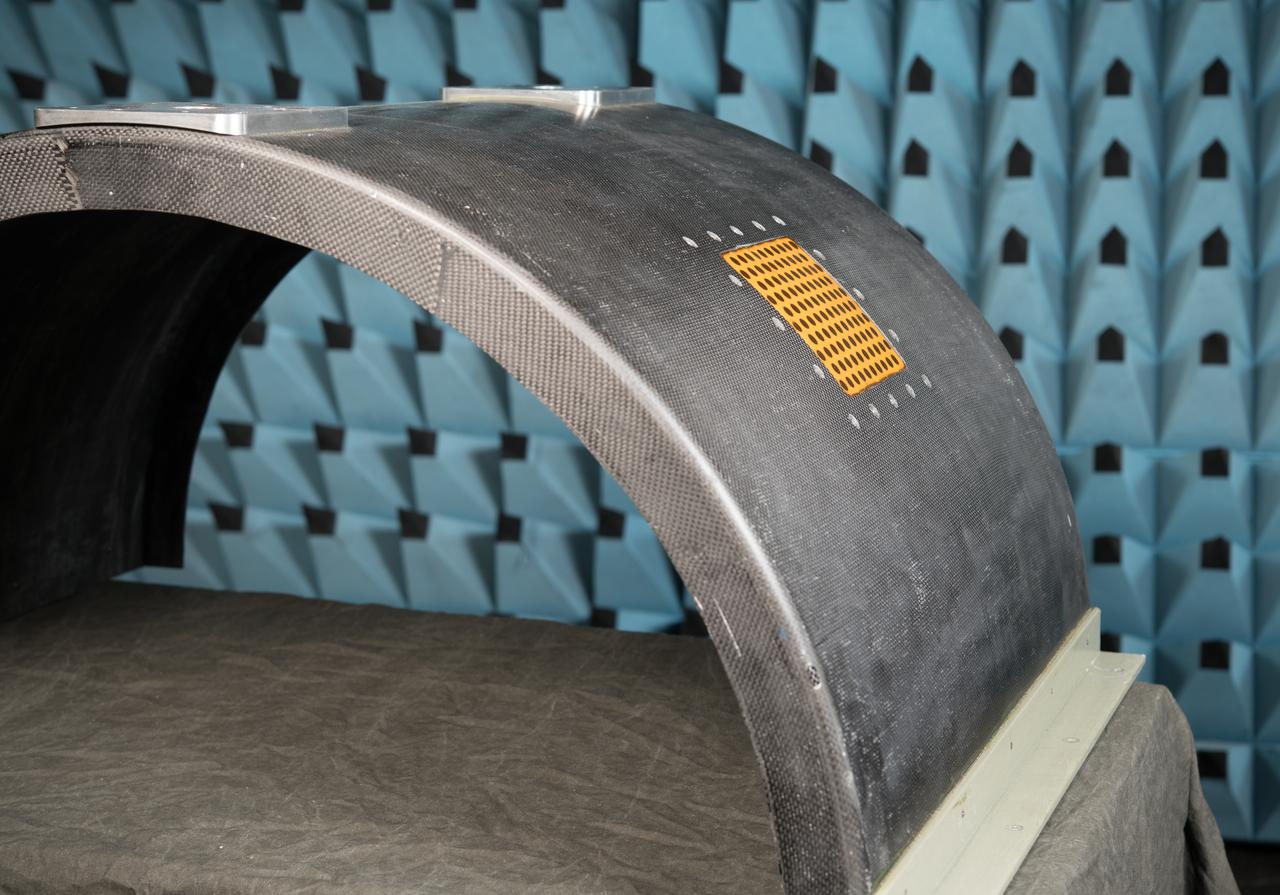

Curved Confocal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies, CLAS-ACT, Phased Array Antenna on Mock Carbon Fiber Fuselage
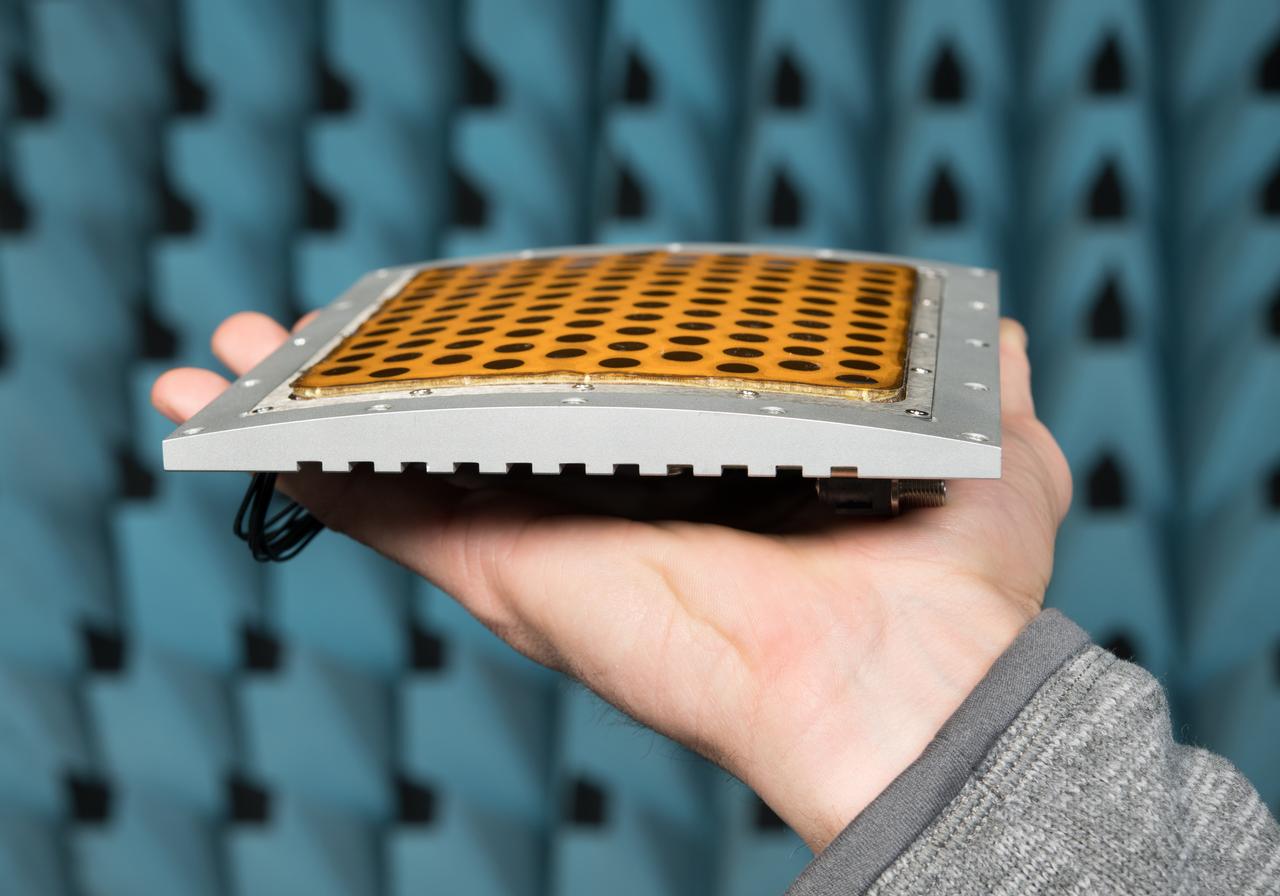
Curved Confocal Lightweight Antenna Structures for Aeronautical Communications Technologies, CLAS-ACT, Phased Array Antenna on Mock Carbon Fiber Fuselage
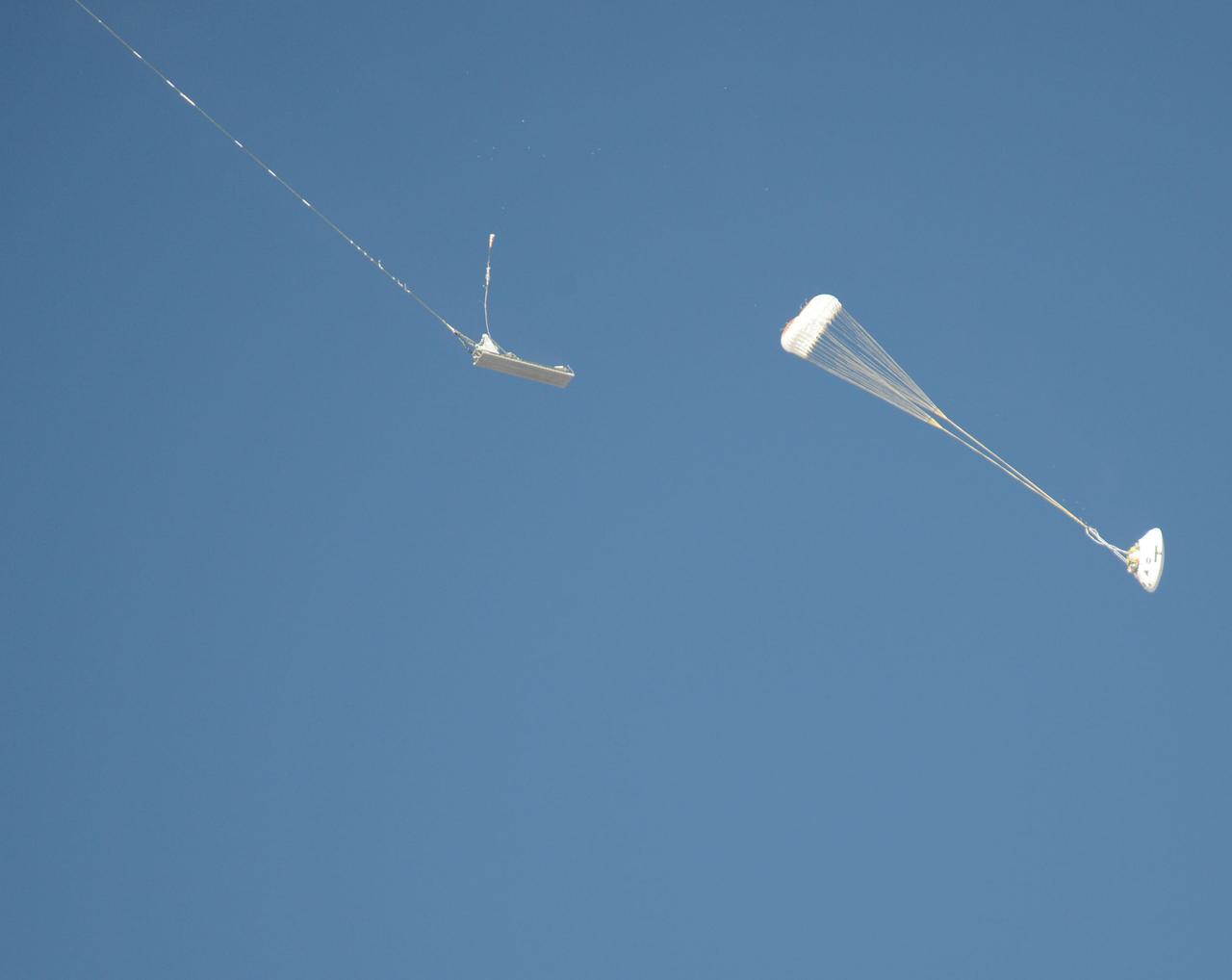

An Orion parachute test enters a new phase following separation from a platform.
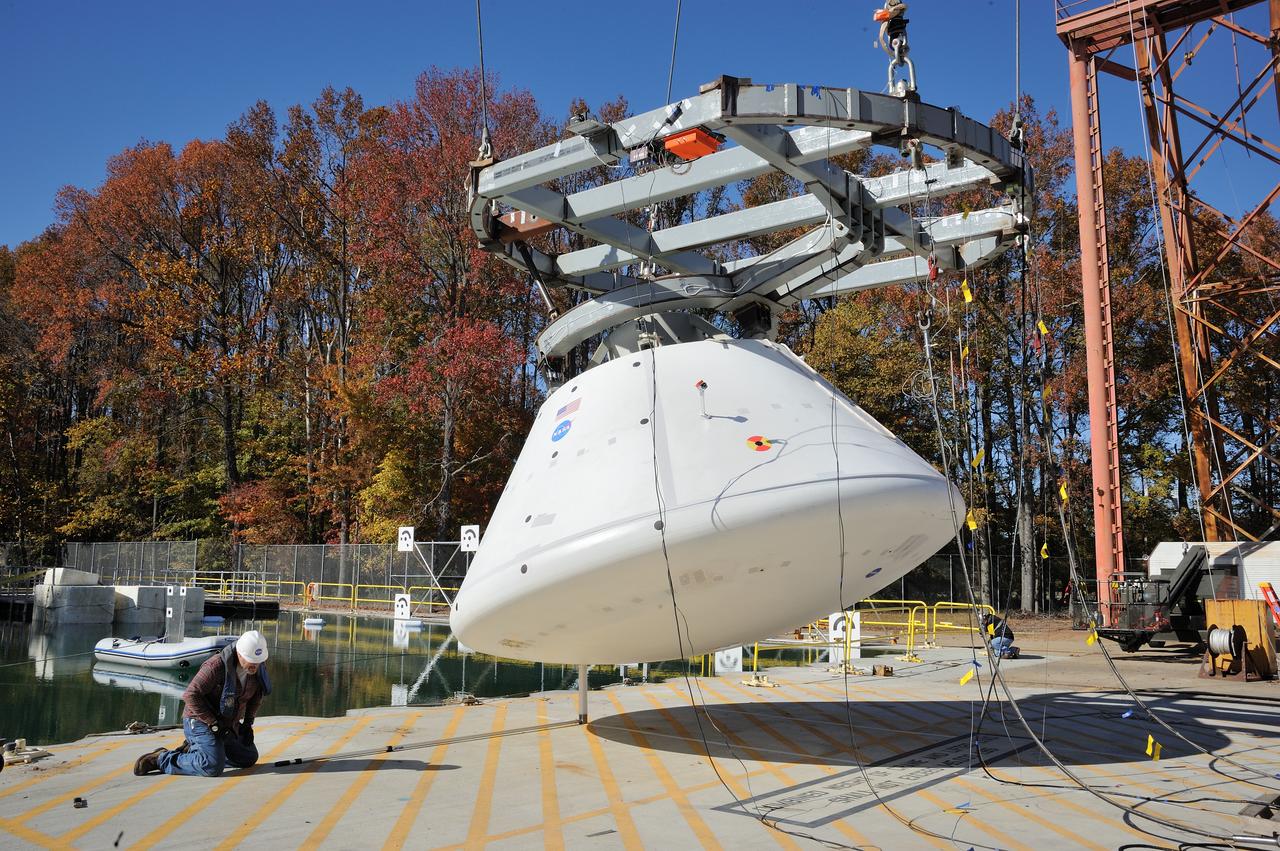

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
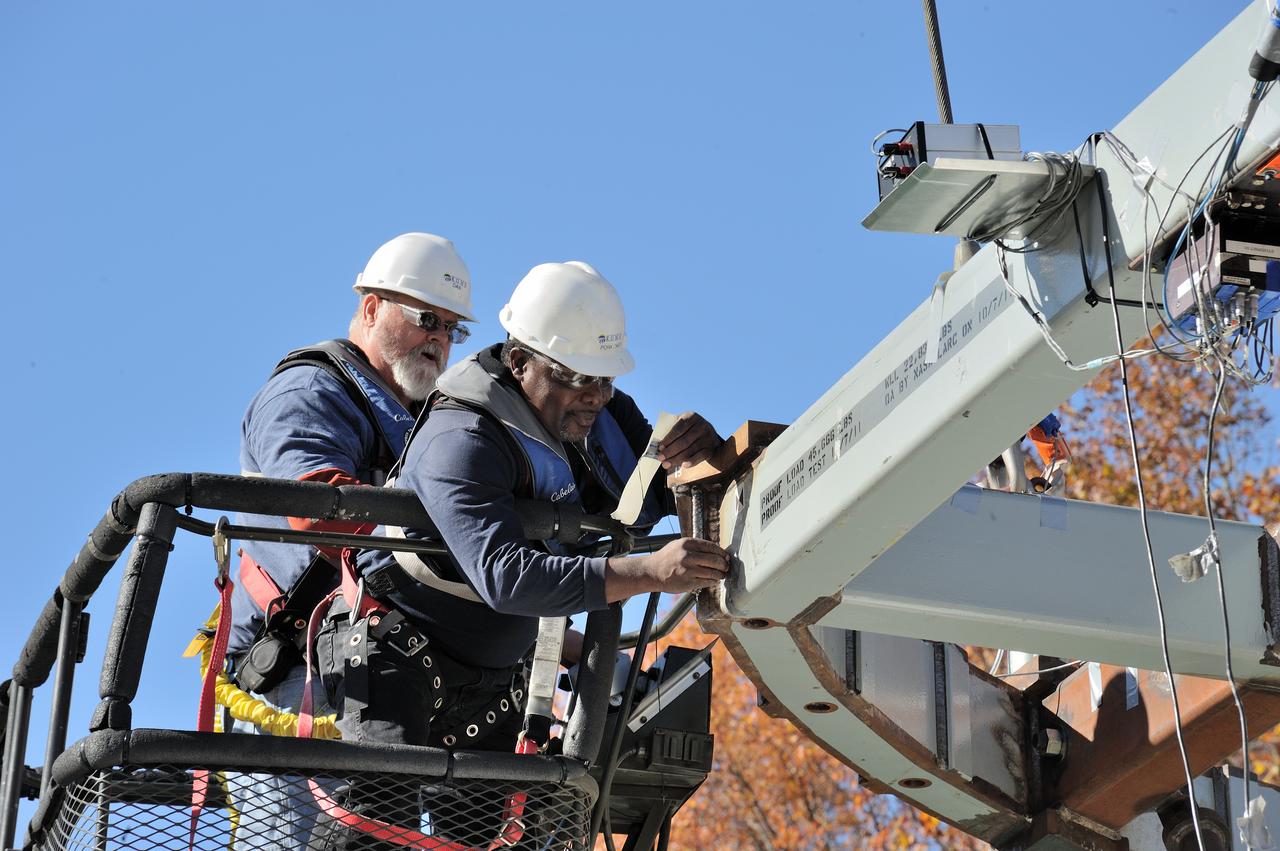

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
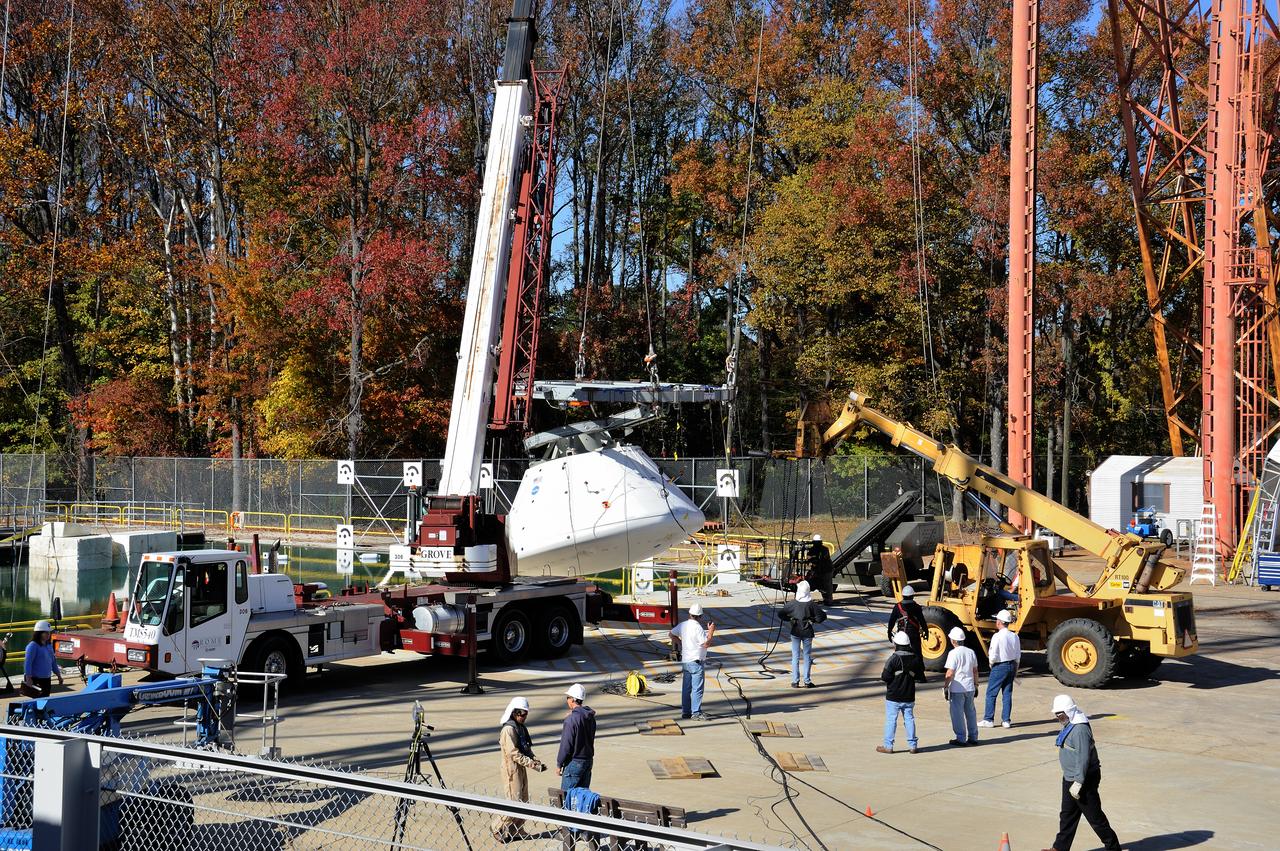

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
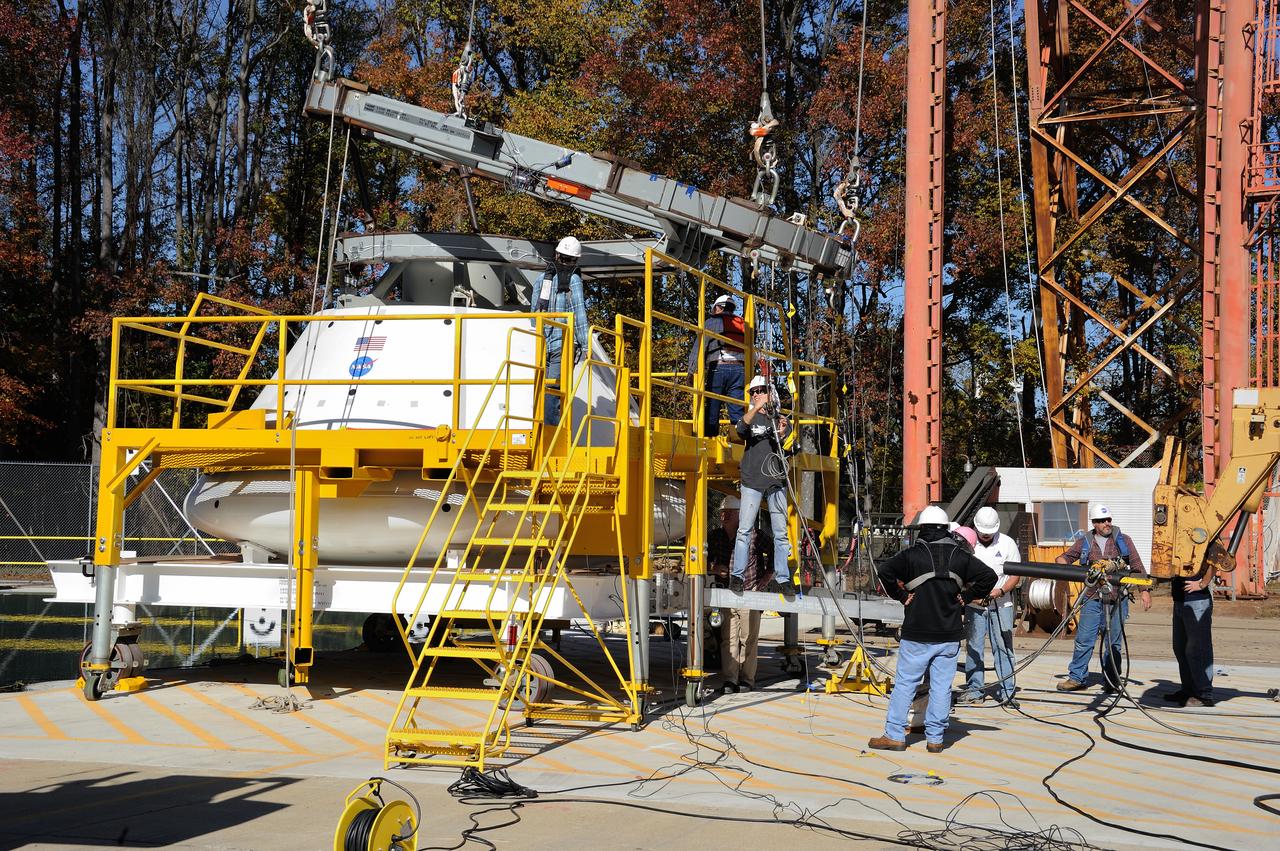

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
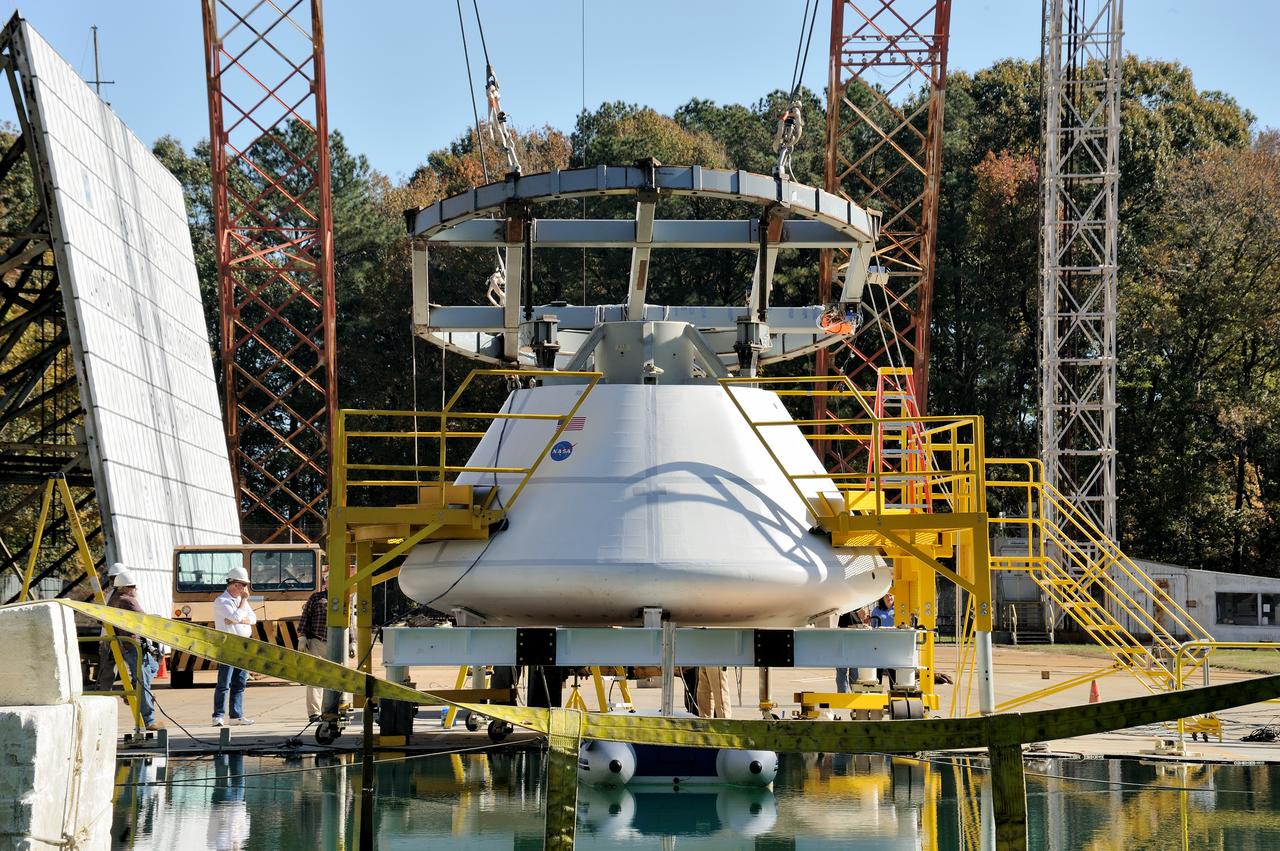

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
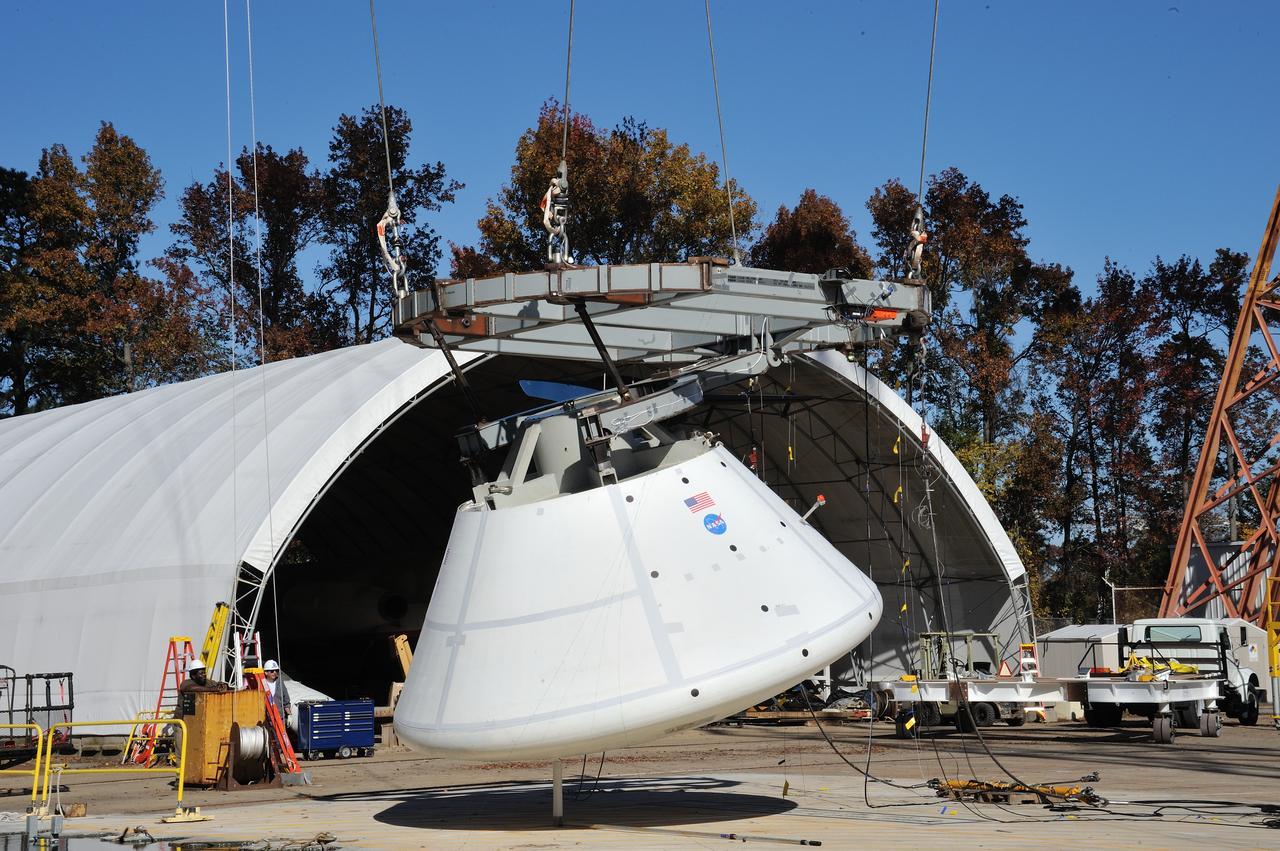

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
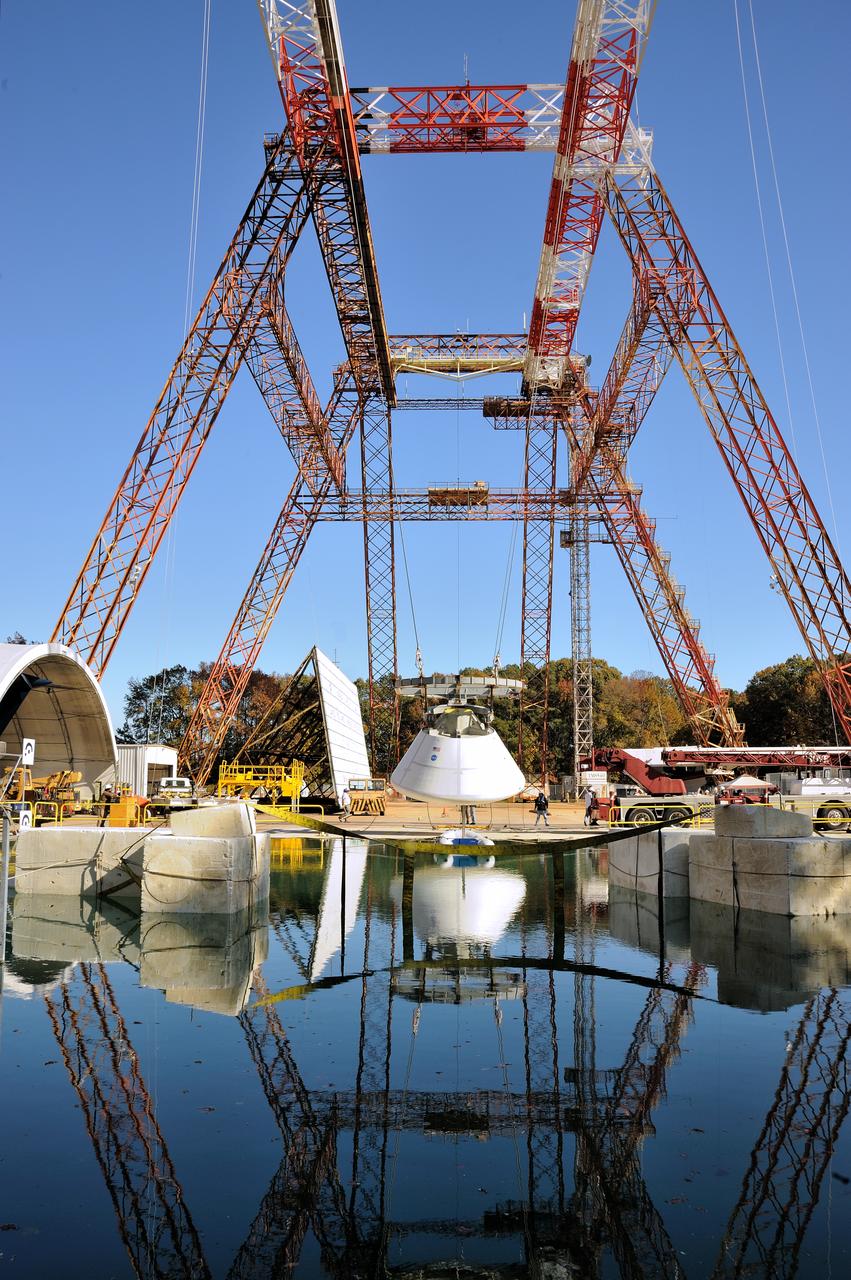

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
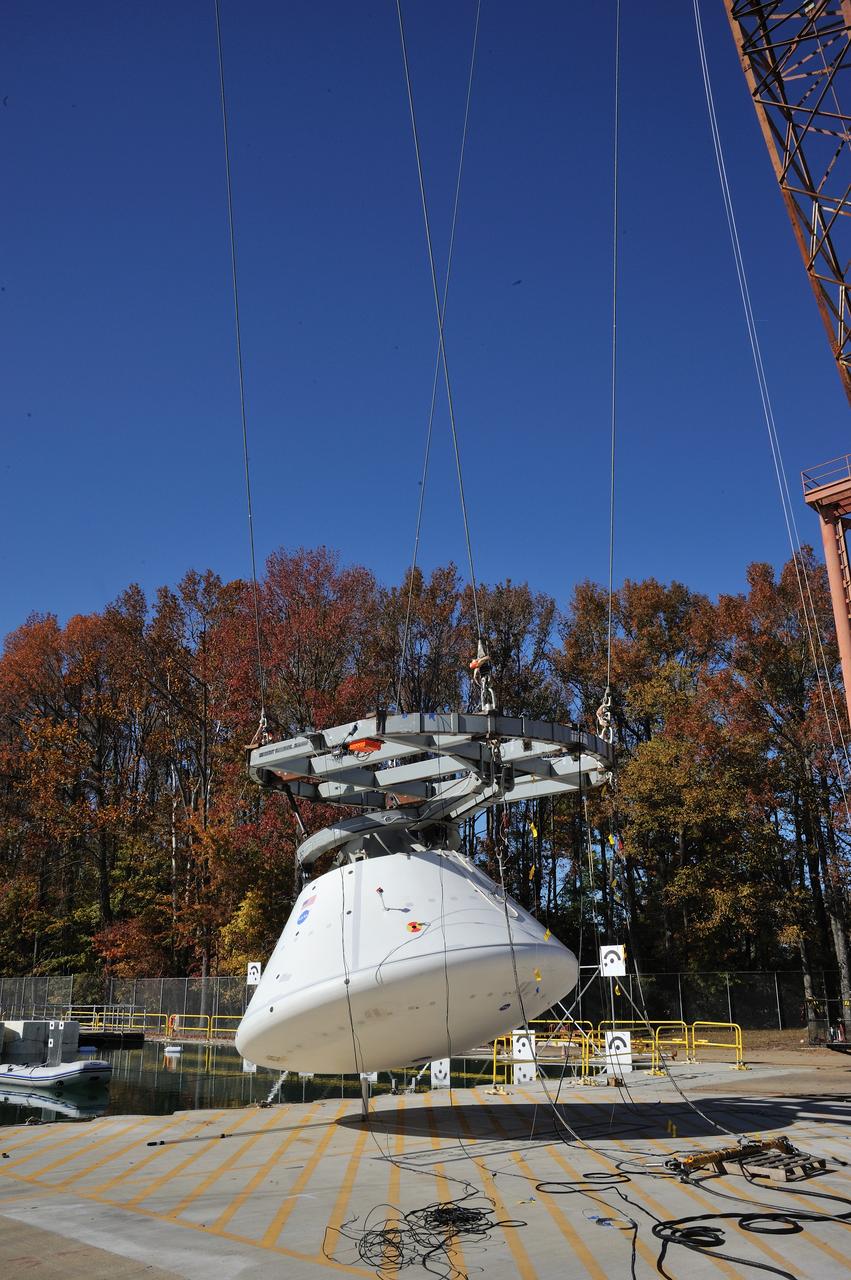

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
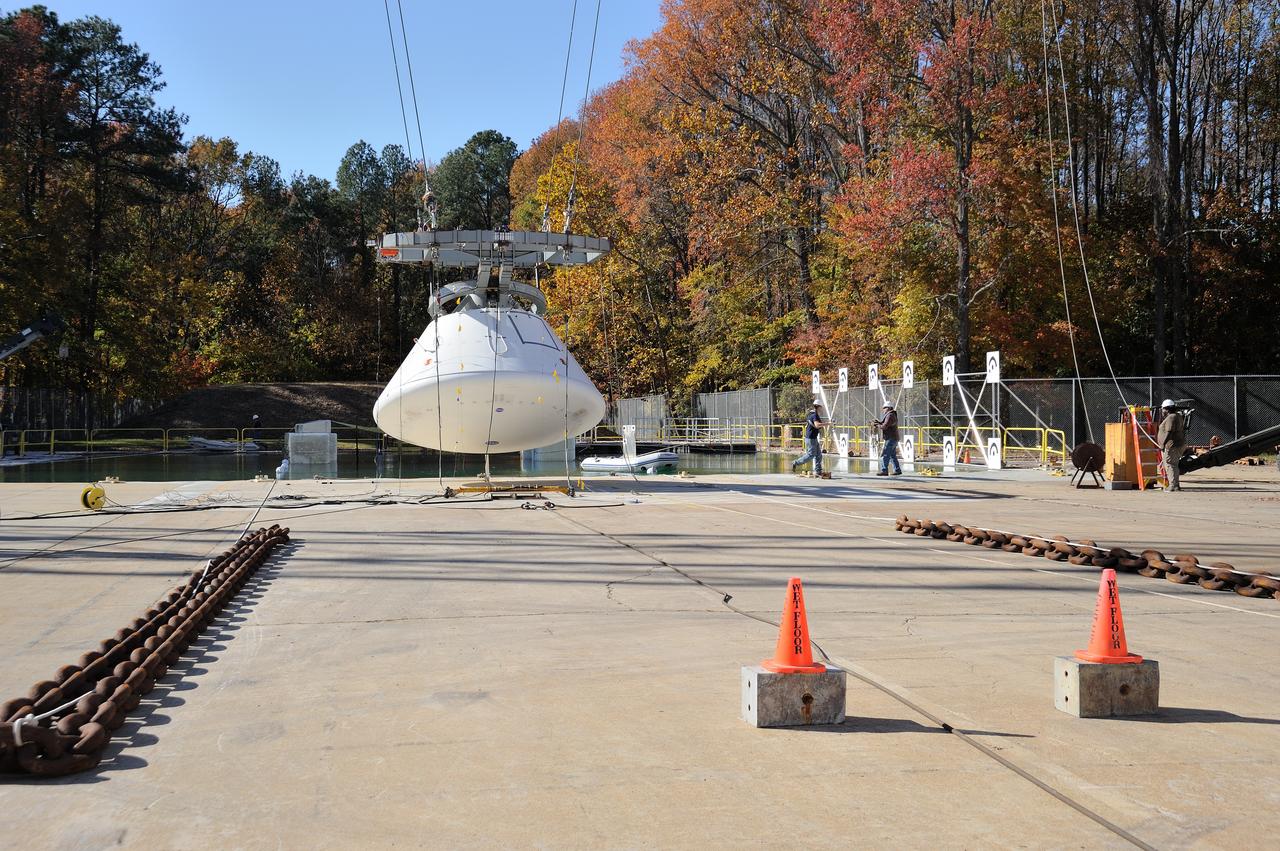

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
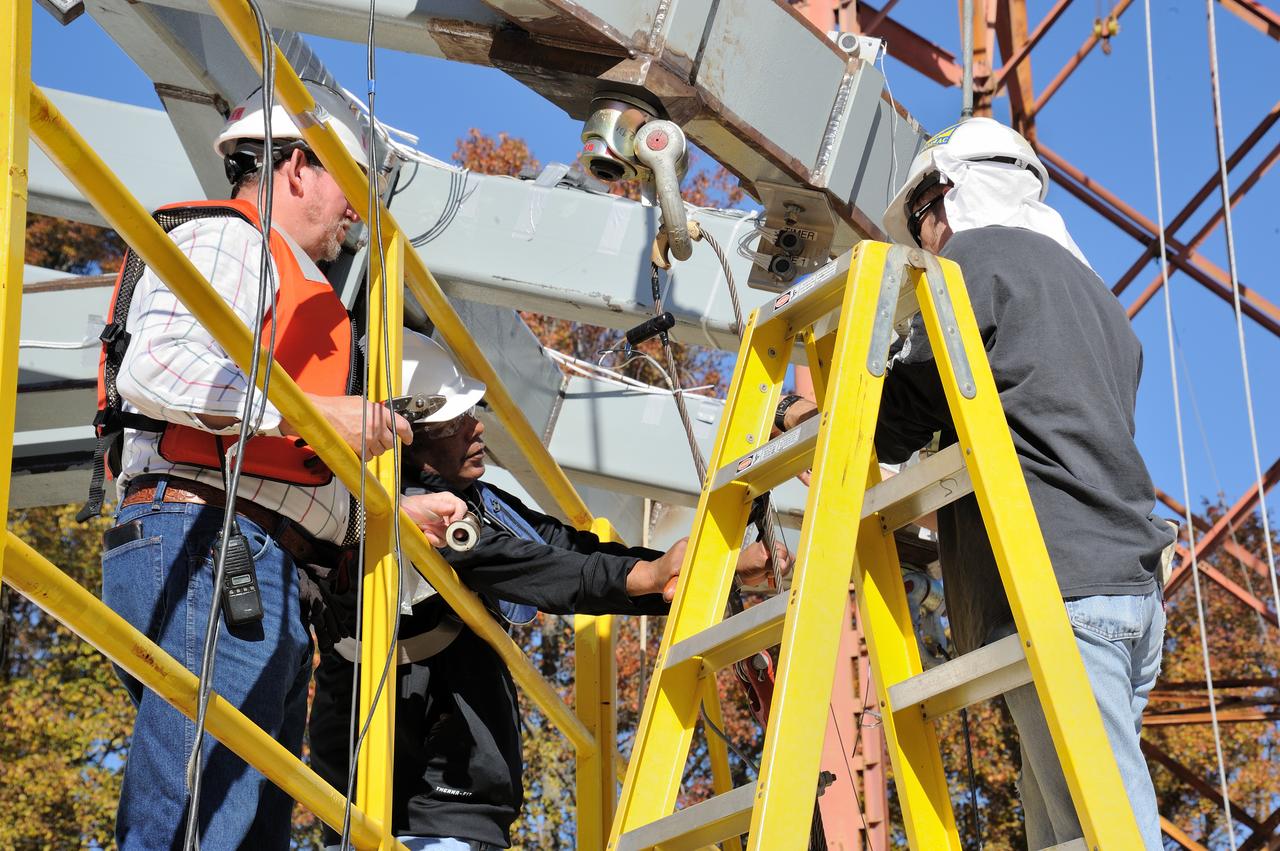

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
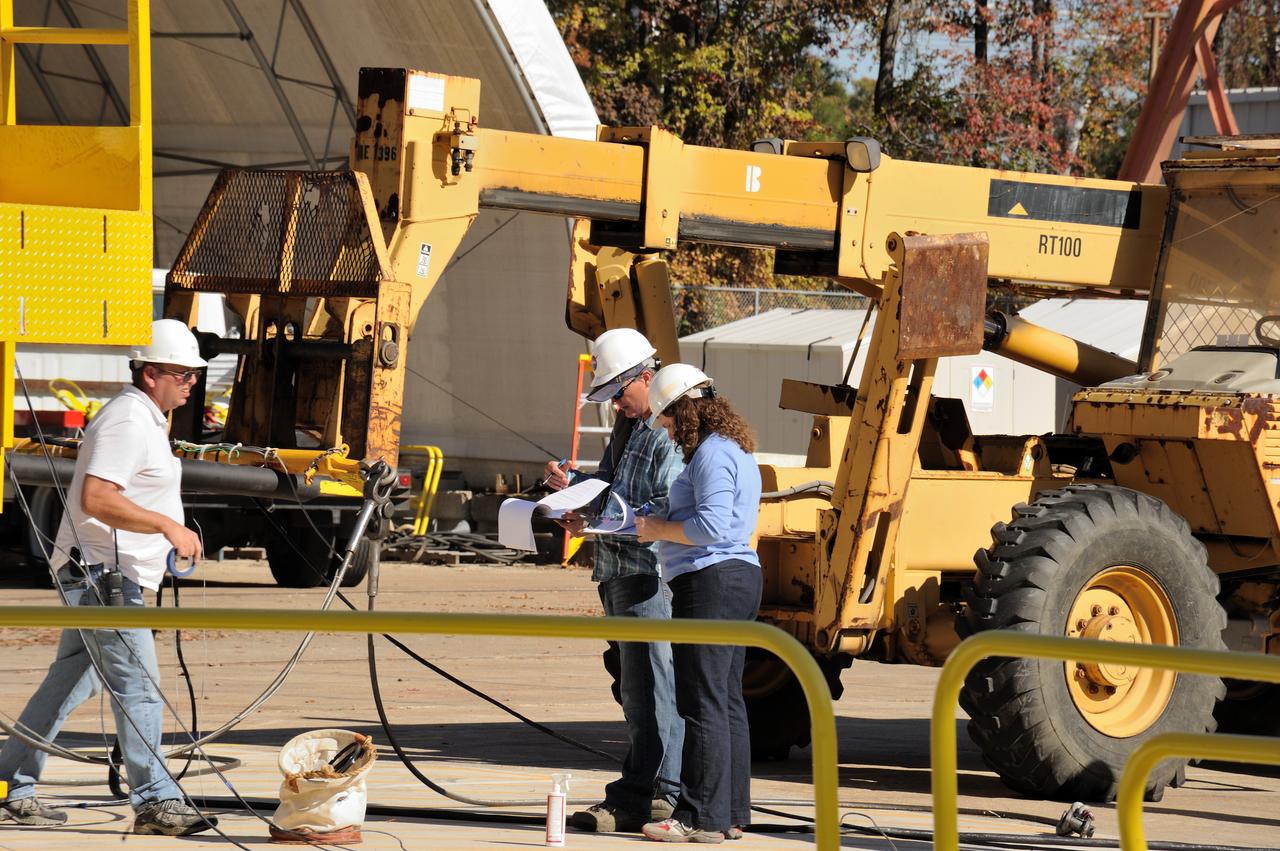

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
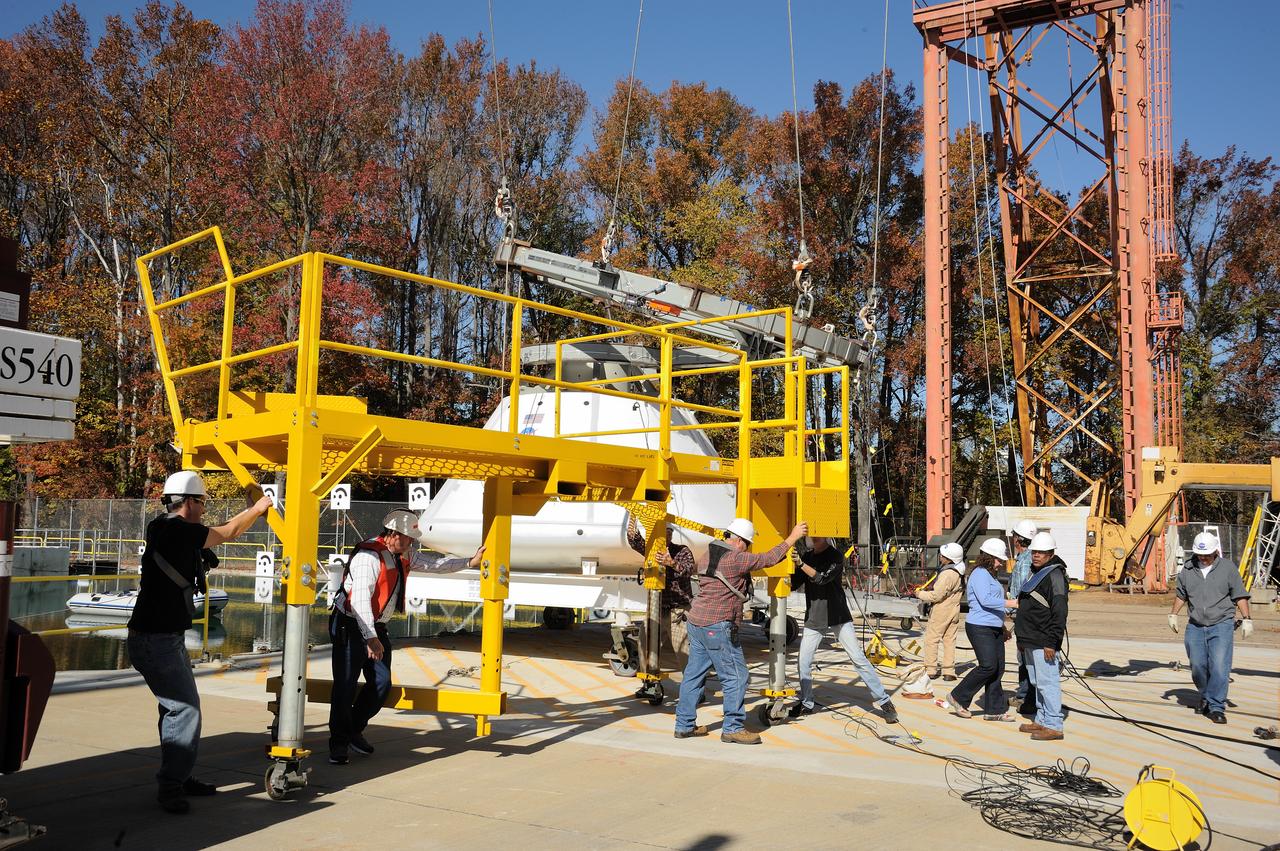

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
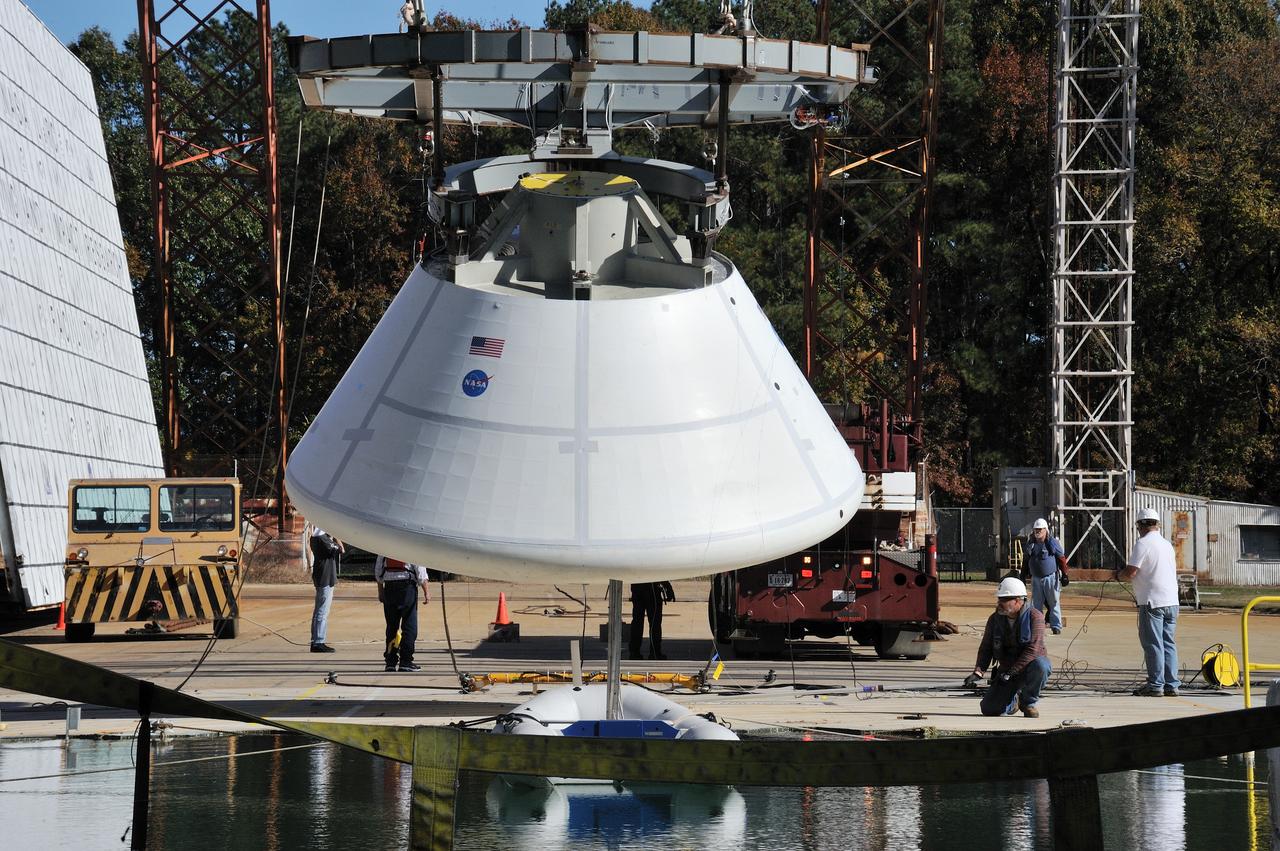

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
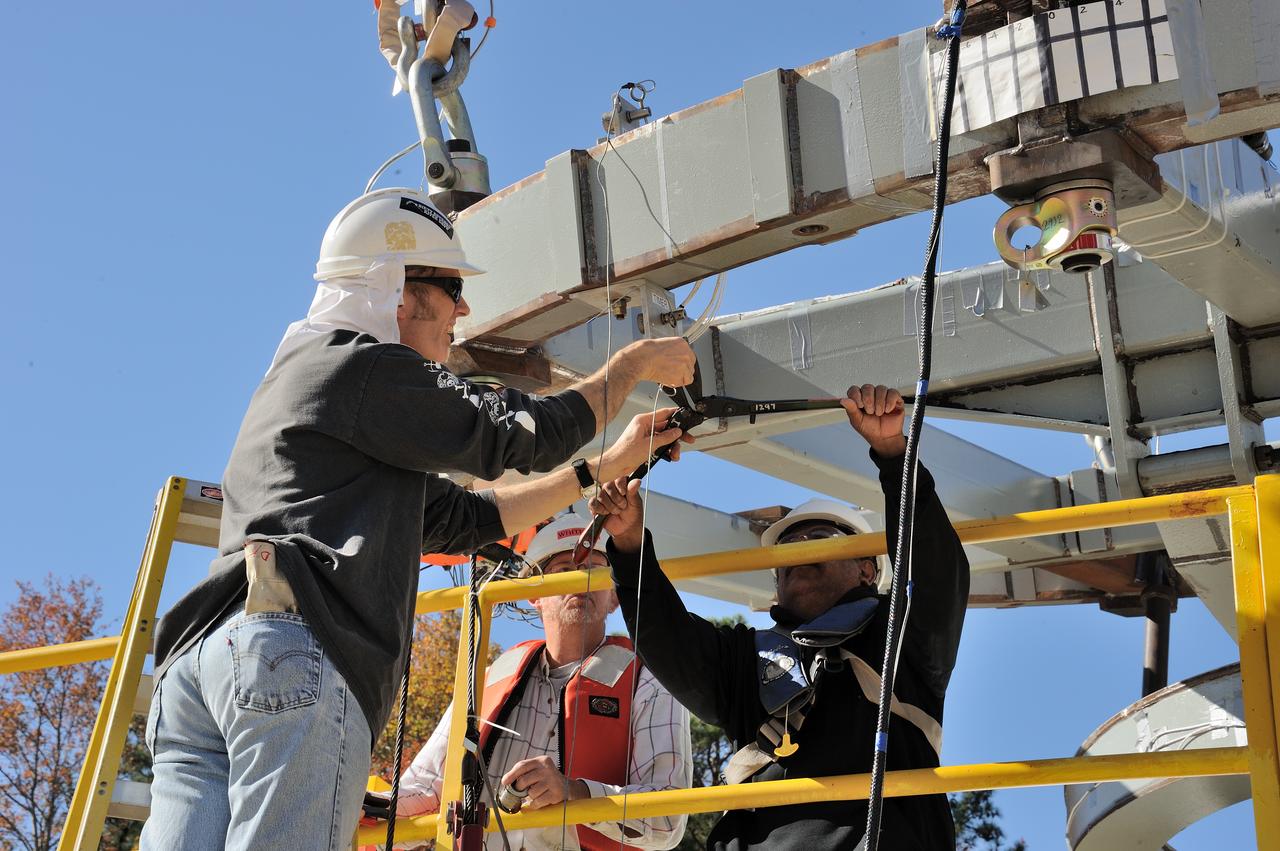

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
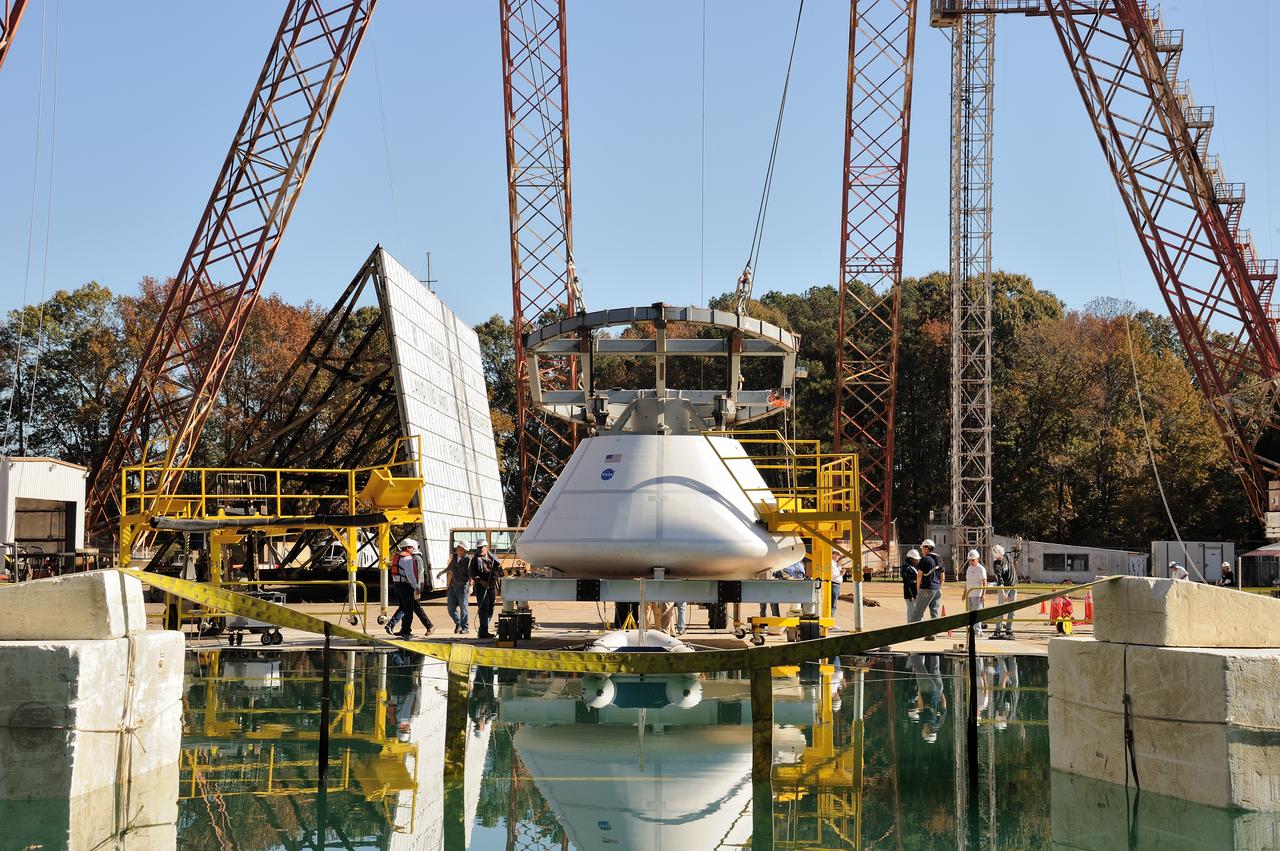

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
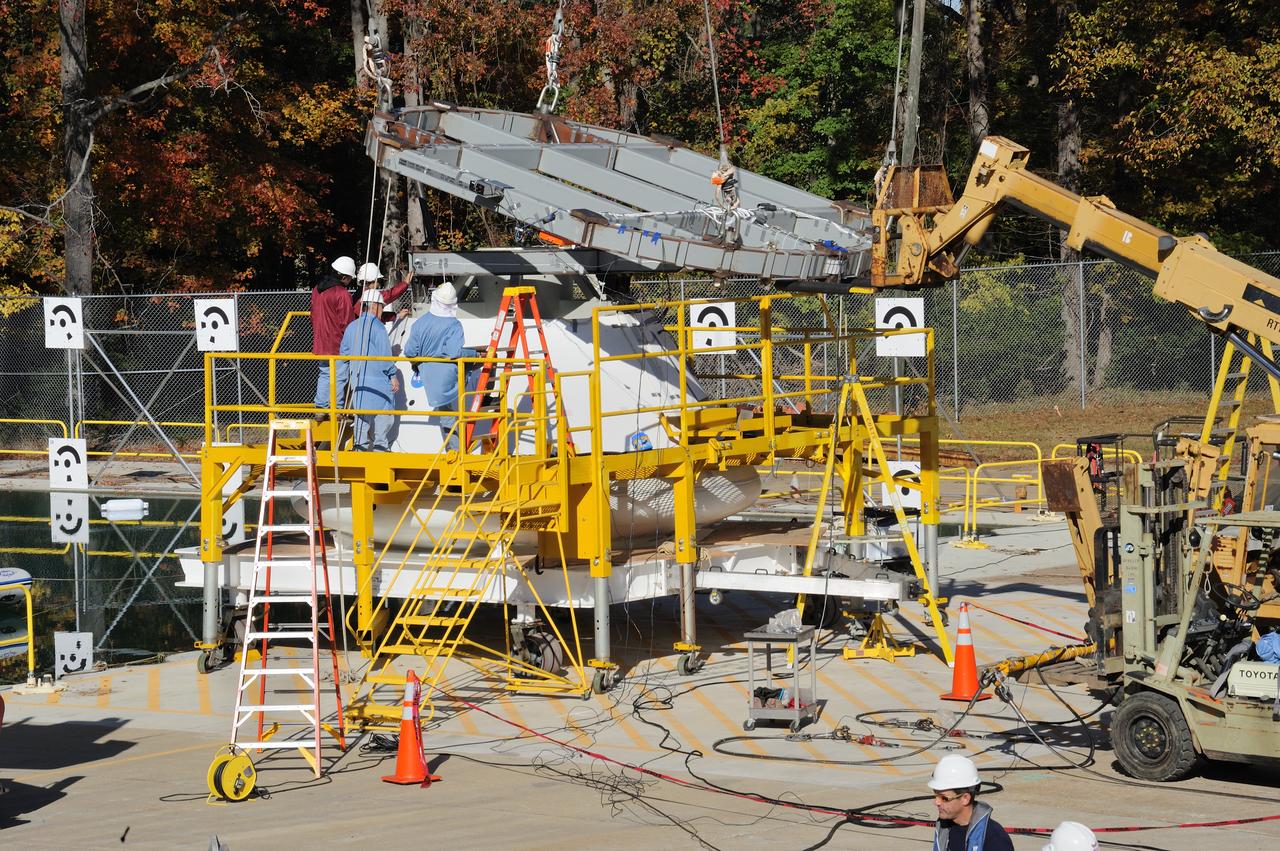

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
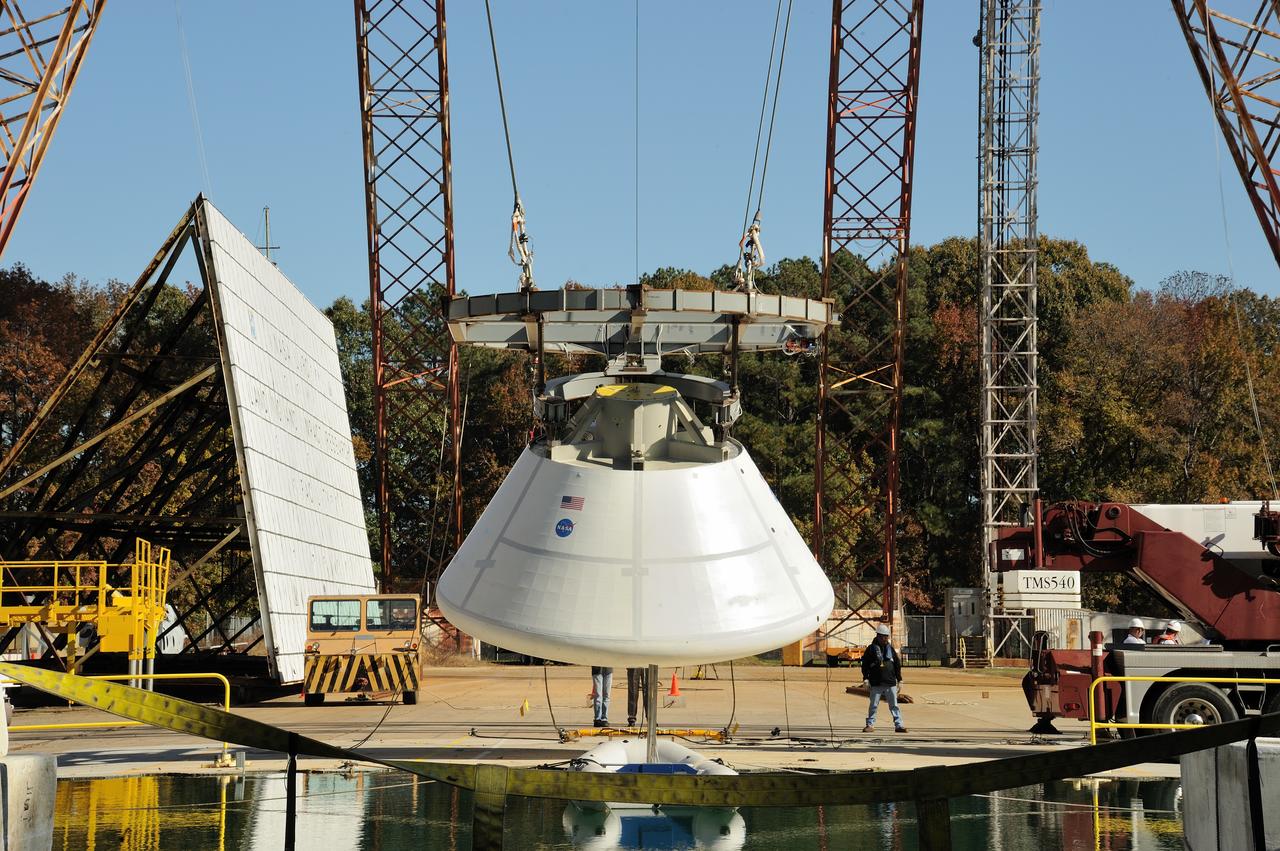

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
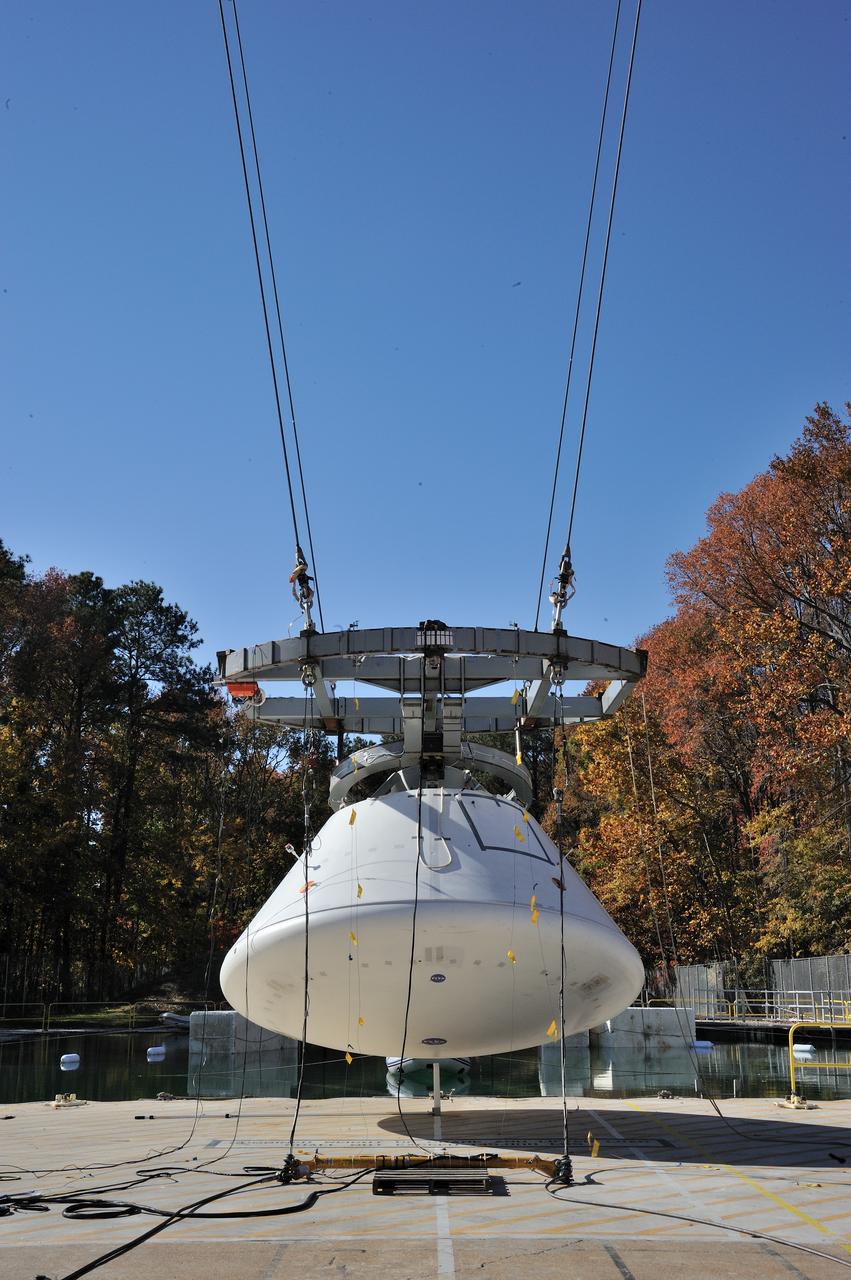

ORION Project-(SPLASH) Structural Passive Landing Attenuation for Survivability of Human Crew (BTA) Boiler Plate Test Article Water Impact Test-Pot Phase"0" Test Tested at the Hydro Impact Basin at the Landing and Impact Research Facility (Gantry)
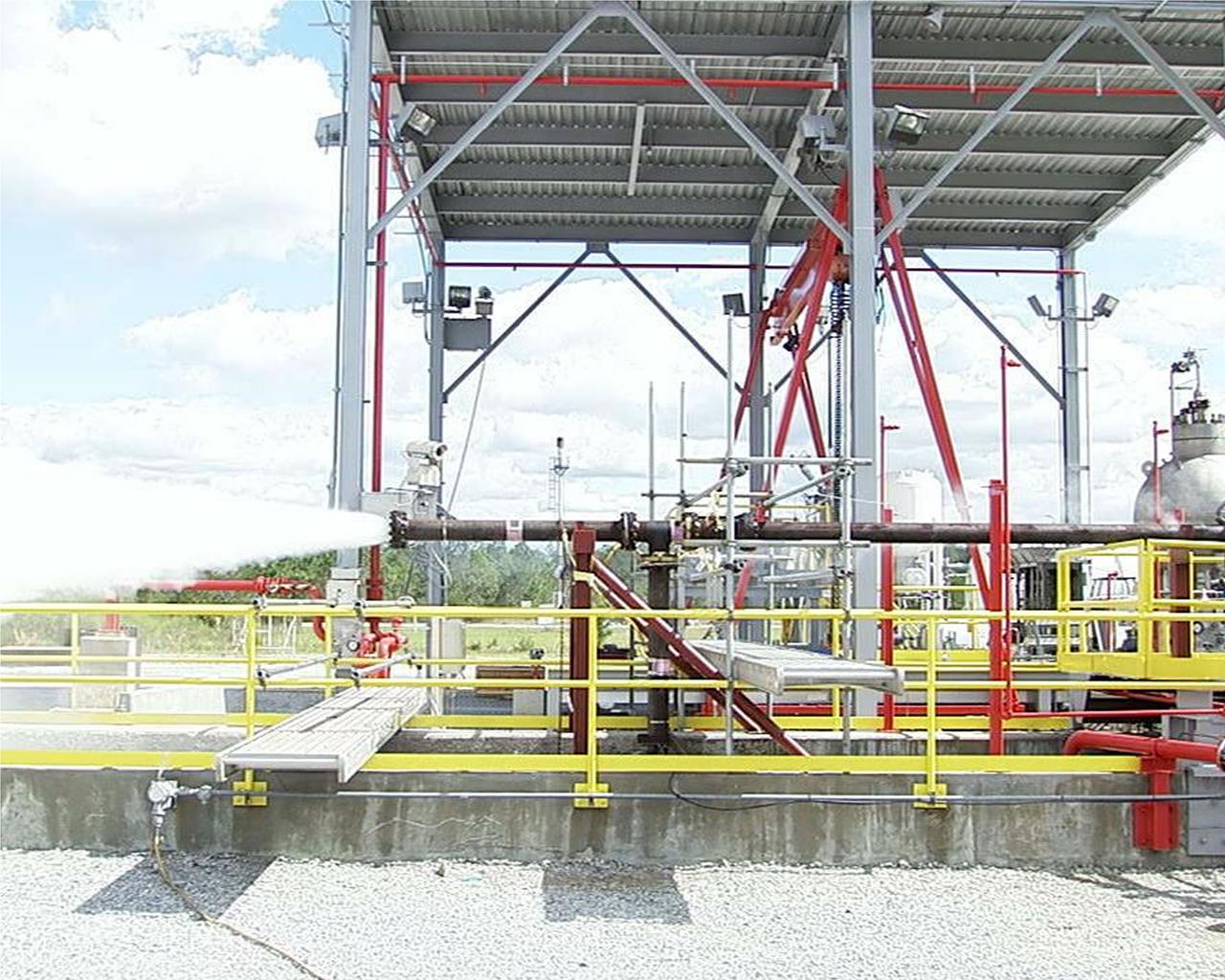

Phase 2 of the A-3 Test Facility Subscale Diffuser Risk Mitigation Project at Stennis Space Center reached a milestone Oct. 25 when the E-3 Test Facility produced superheated (500+ degrees) steam for approximately 3 seconds at more than 400 psi. The test team, led by Barry Robinson of NASA's Test Projects Office, followed that success with further tests to lengthen the duration of steam production. On Nov. 1, they were able to maintain a consistent pressure and temperature of steam for 60 seconds. In December, the team began Phase 3 of the testing, providing data for the design and procurement to build the full-scale version of the steam diffuser for SSC's A-3 Test Stand.
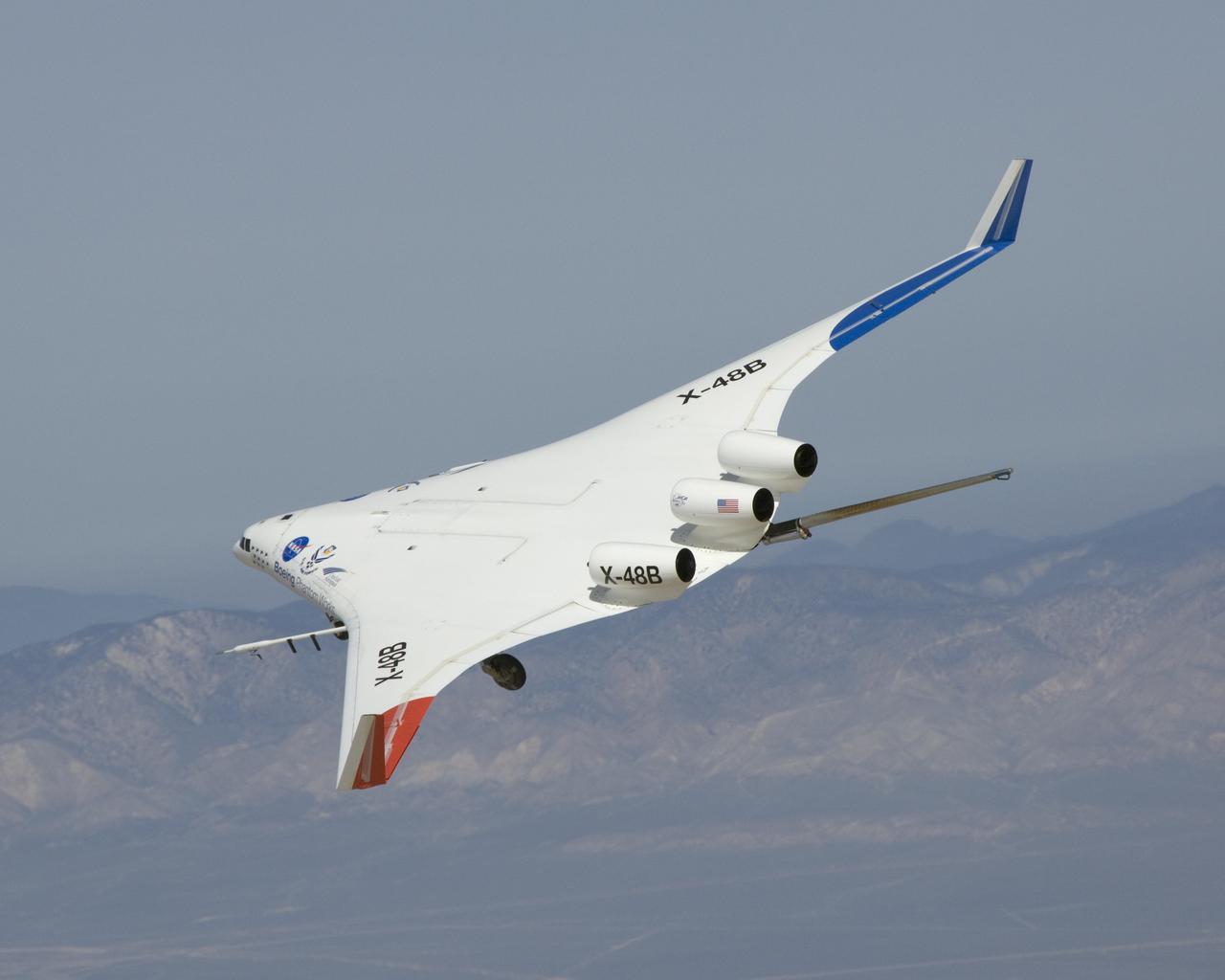

The X-48B Blended Wing Body research aircraft banks smartly in this Block 2 flight phase image.
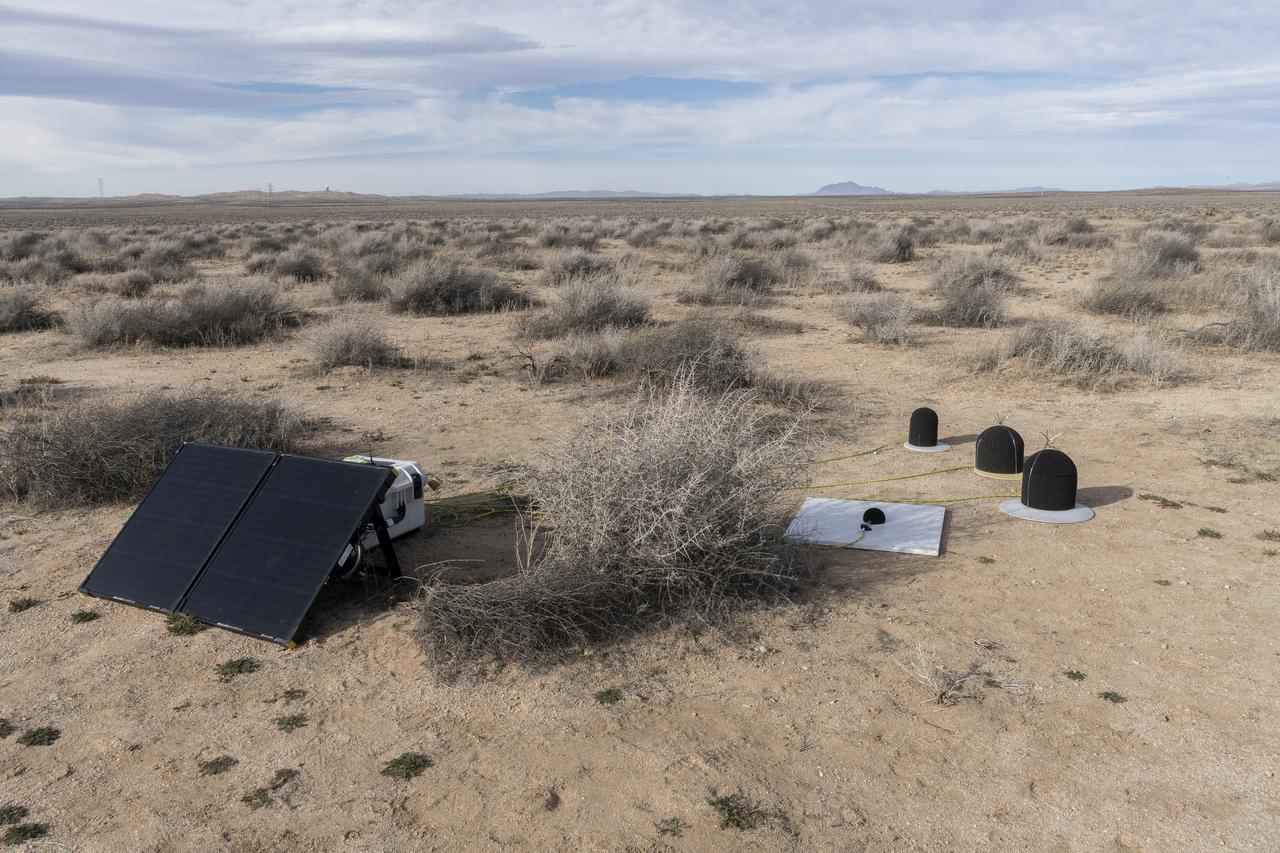

The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. Shown is one of 10 ground recording stations set up along a 30-mile stretch of desert to record sonic booms during the third phase of the of CarpetDIEM, Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems.
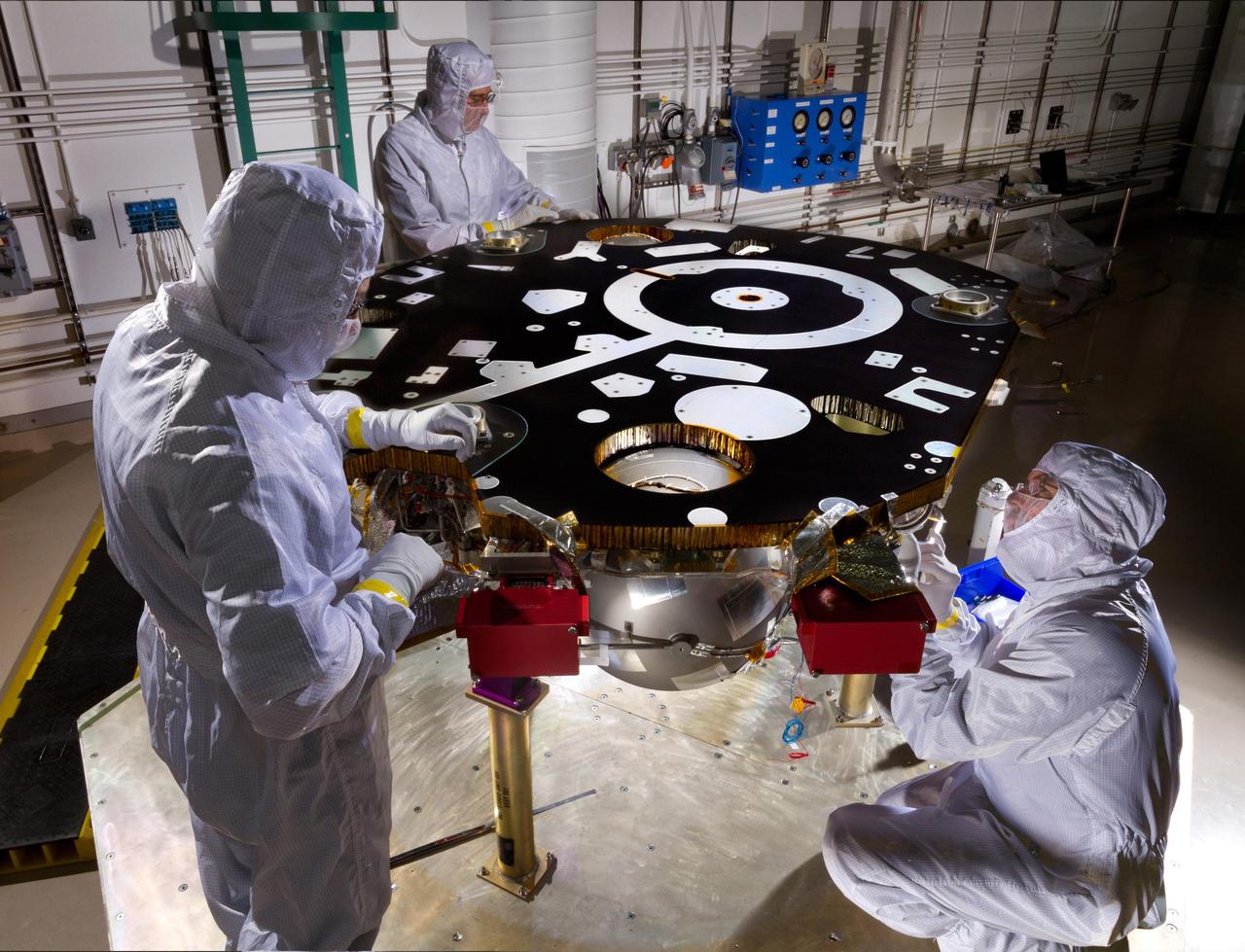

Technicians in a Lockheed Martin clean room near Denver prepare NASA's InSight Mars lander for propulsion proof and leak testing on Oct. 31, 2014. Following the test, the lander was moved to another clean room for the start of the mission's assembly, test and launch operations (ATLO) phase. The assembly portion of ATLO will last about six months. The InSight mission (for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) is scheduled to launch in March 2016 and land on Mars six months later. It will investigate processes that formed and shaped Mars and will help scientists better understand the evolution of our inner solar system's rocky planets, including Earth. Note: After thorough examination, NASA managers have decided to suspend the planned March 2016 launch of the Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy and Heat Transport (InSight) mission. The decision follows unsuccessful attempts to repair a leak in a section of the prime instrument in the science payload. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18884
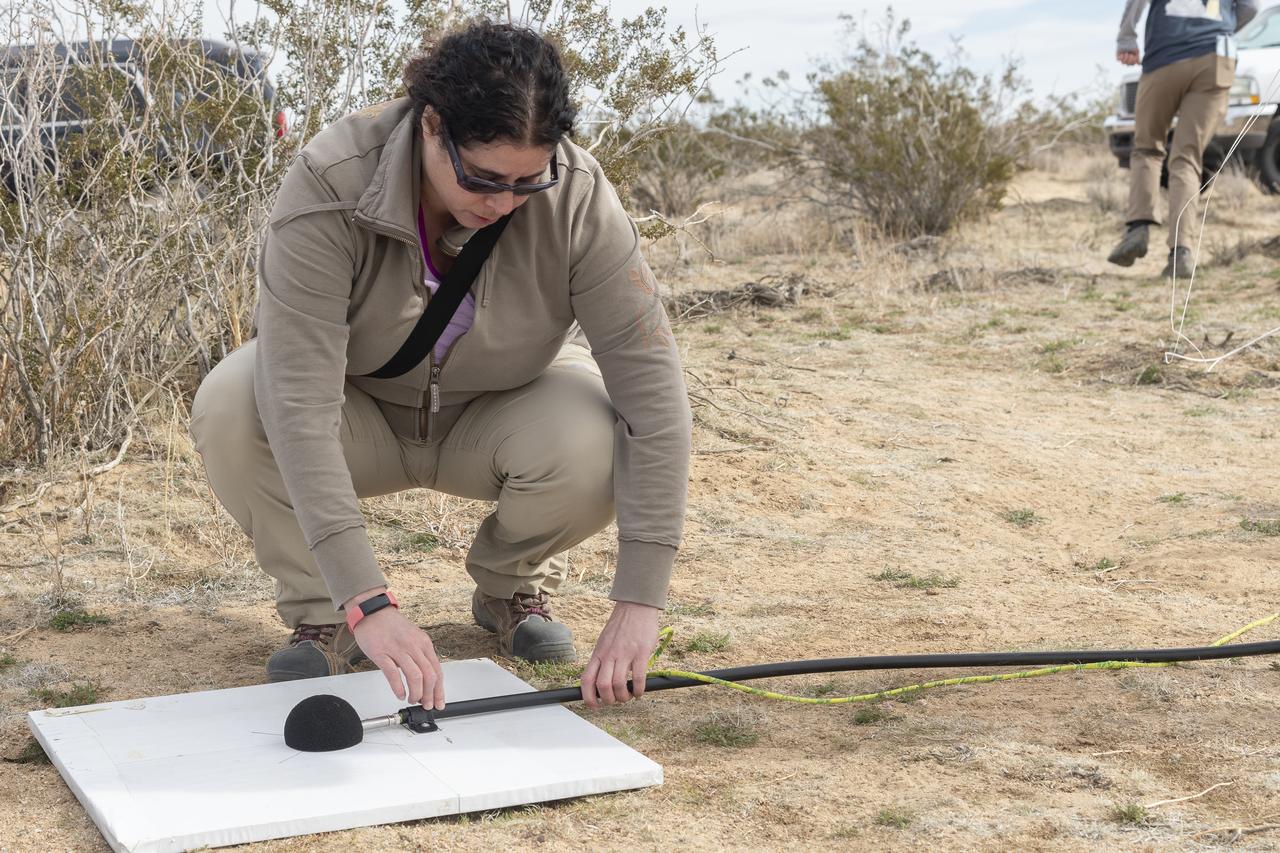

Dr. Alexandra Loubeau, one of the technical co-leads for sonic boom community testing for the Quesst mission, sets out a microphone in the California desert. . The Quesst mission recently completed testing of operations and equipment to be used in recording the sonic thumps of the X-59. The testing was the third phase of Carpet Determination in Entirety Measurements flights, called CarpetDIEM for short. An F-15 and an F-18 from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center created sonic booms, both loud and soft, to verify the operations of ground recording systems spread out across 30 miles of open desert.
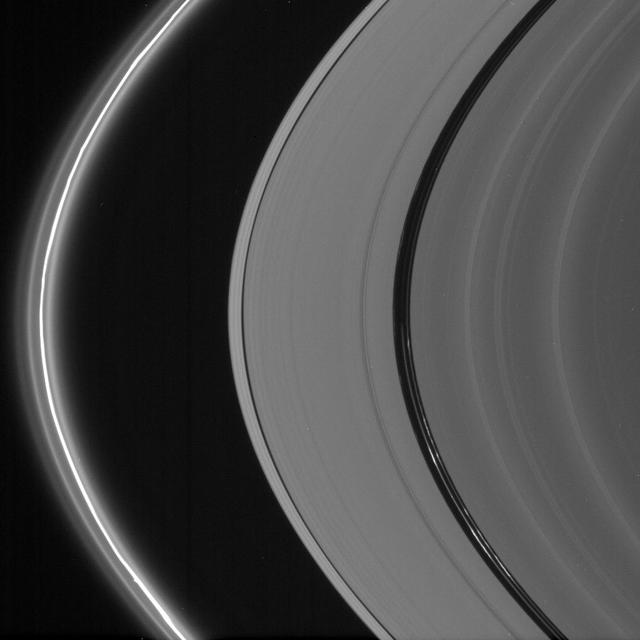

Saturn bright ringlets seen here are populated with microscopic icy particles and are among the brightest features in the rings at high phase angles

The battered features of the moon Rhea, seen at low phase, appear washed out by the sun.
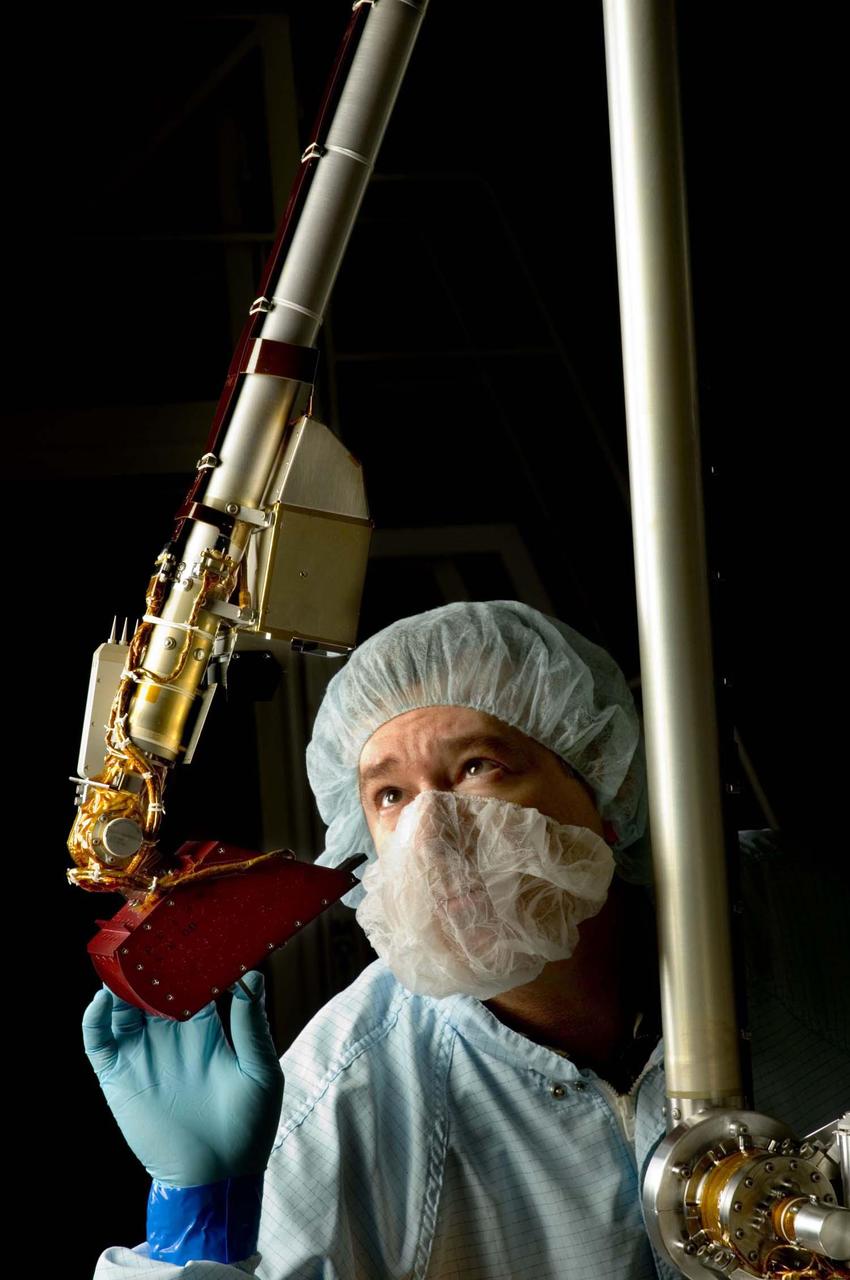
A spacecraft technician inspected the vital robotic arm of NASA Phoenix Mars Lander during the assembly phase of the mission
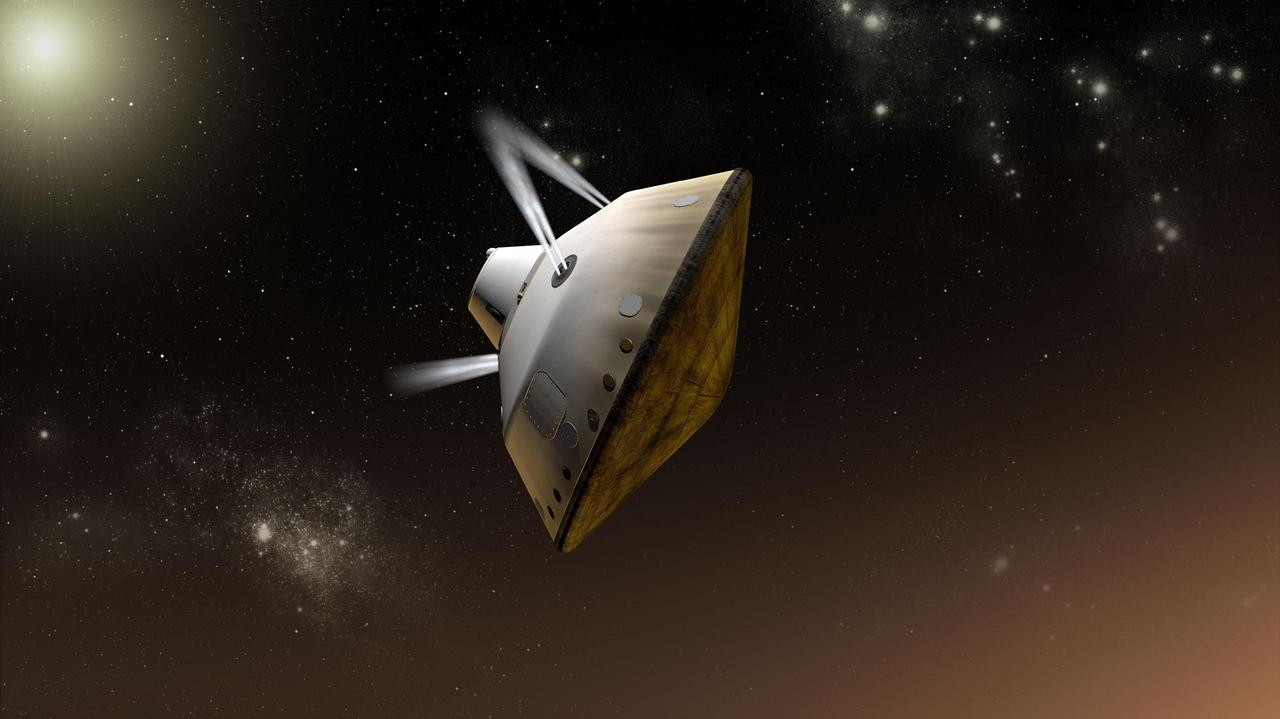

This artist concept shows thrusters firing during the entry, descent and landing phase for NASA Mars Science Laboratory mission to Mars.

A joint NASA/Boeing team completed the first phase of flight tests on the unique X-48B Blended Wing Body aircraft at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center at Edwards, CA. The team completed the 80th and last flight of the project's first phase on March 19, 2010.
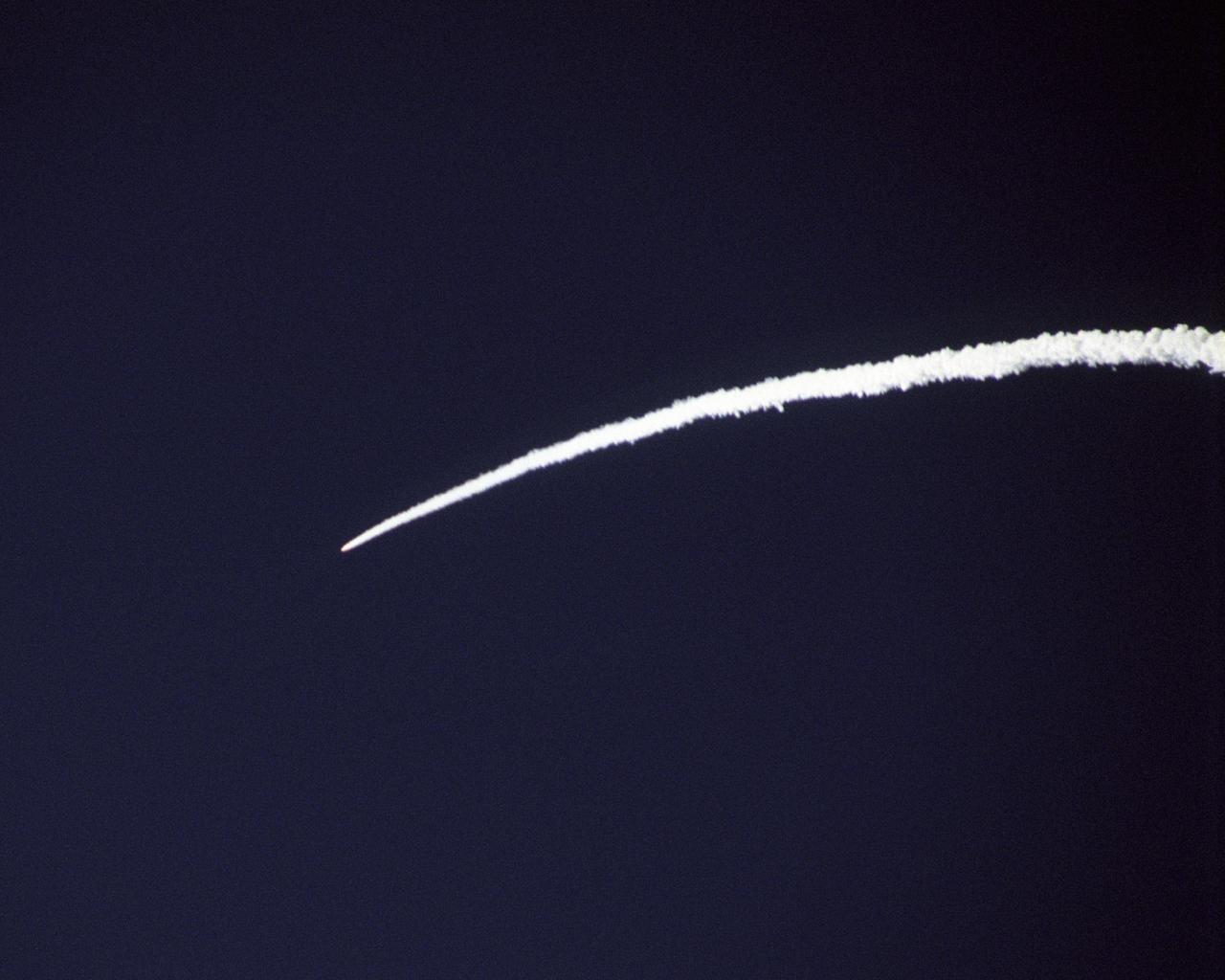

The Pegasus rocket that powered NASA's X-43A scramjet to almost Mach 10 test conditions leaves a bright arc in the Pacific sky during the boost phase.

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
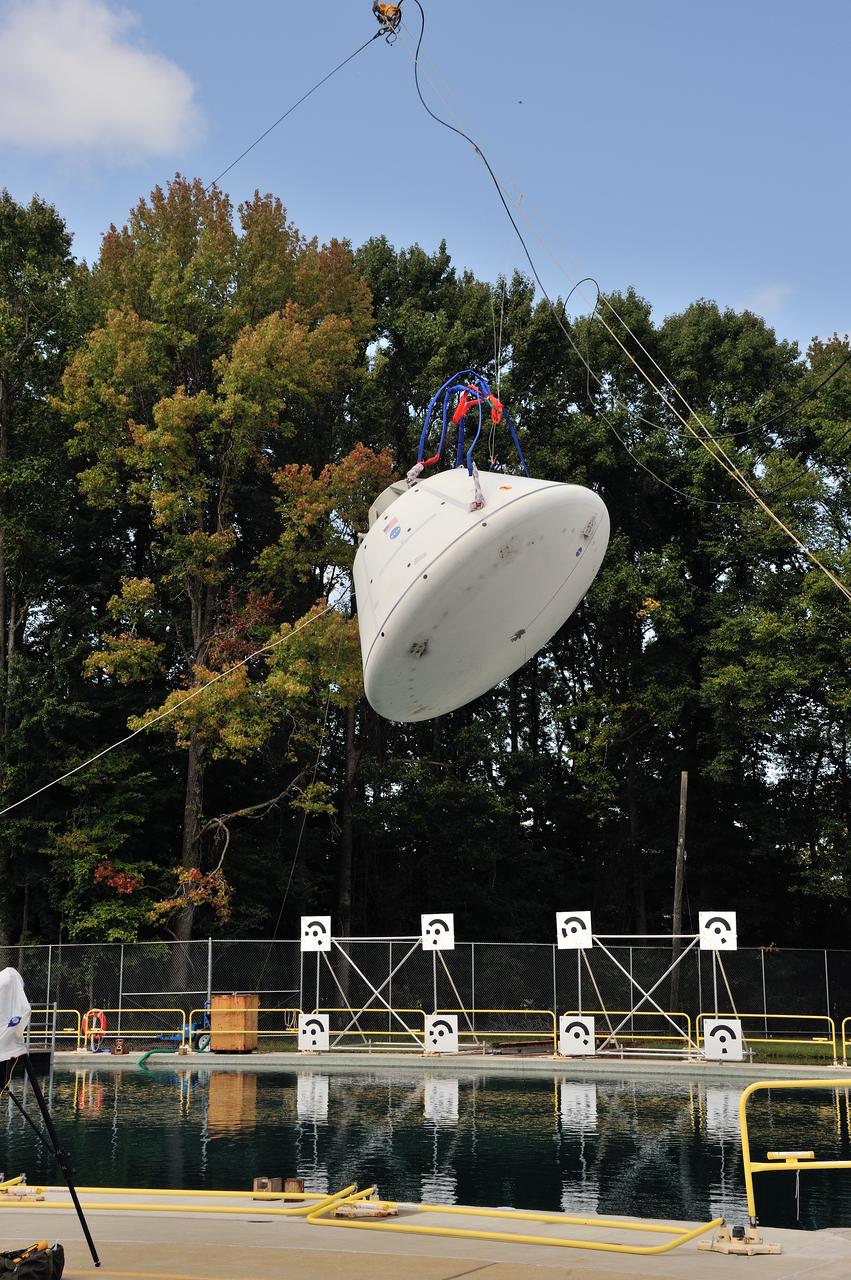

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
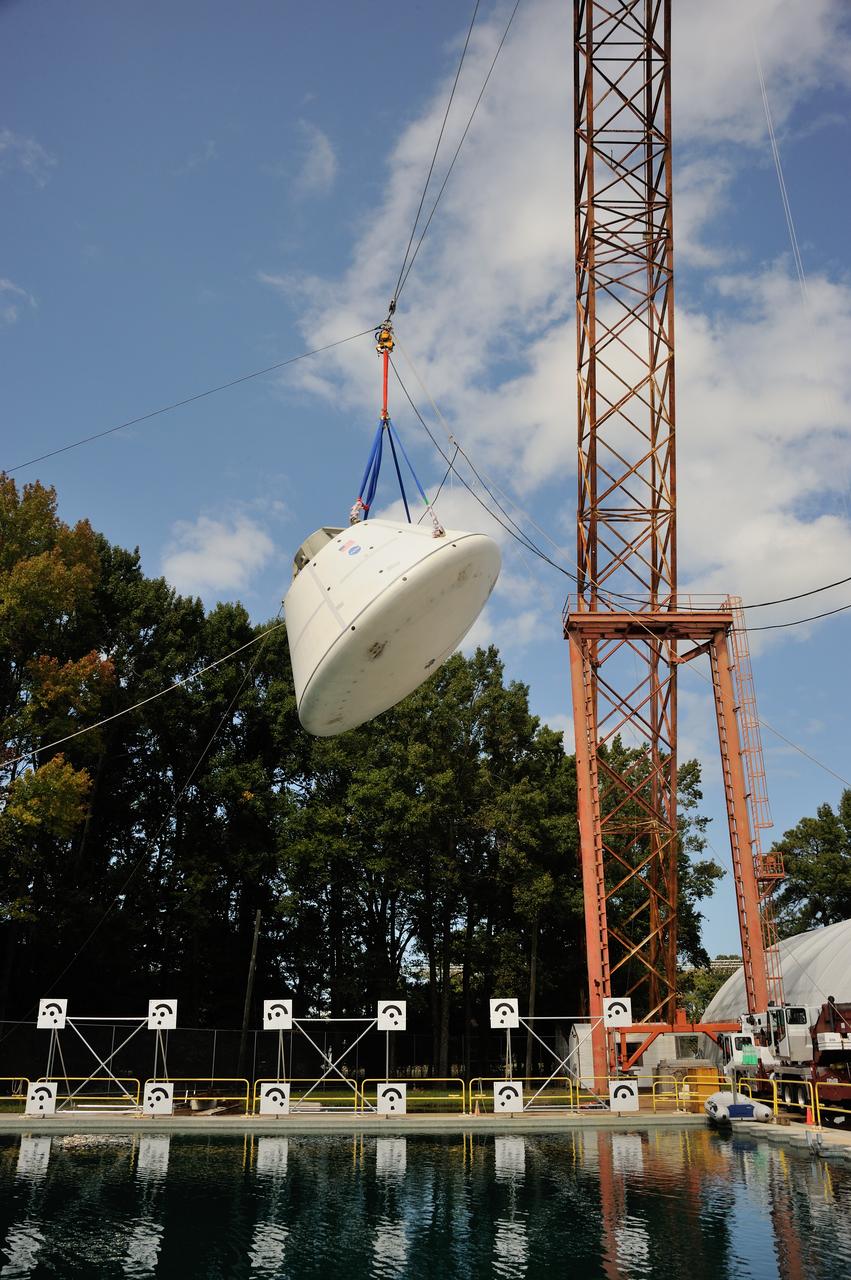

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
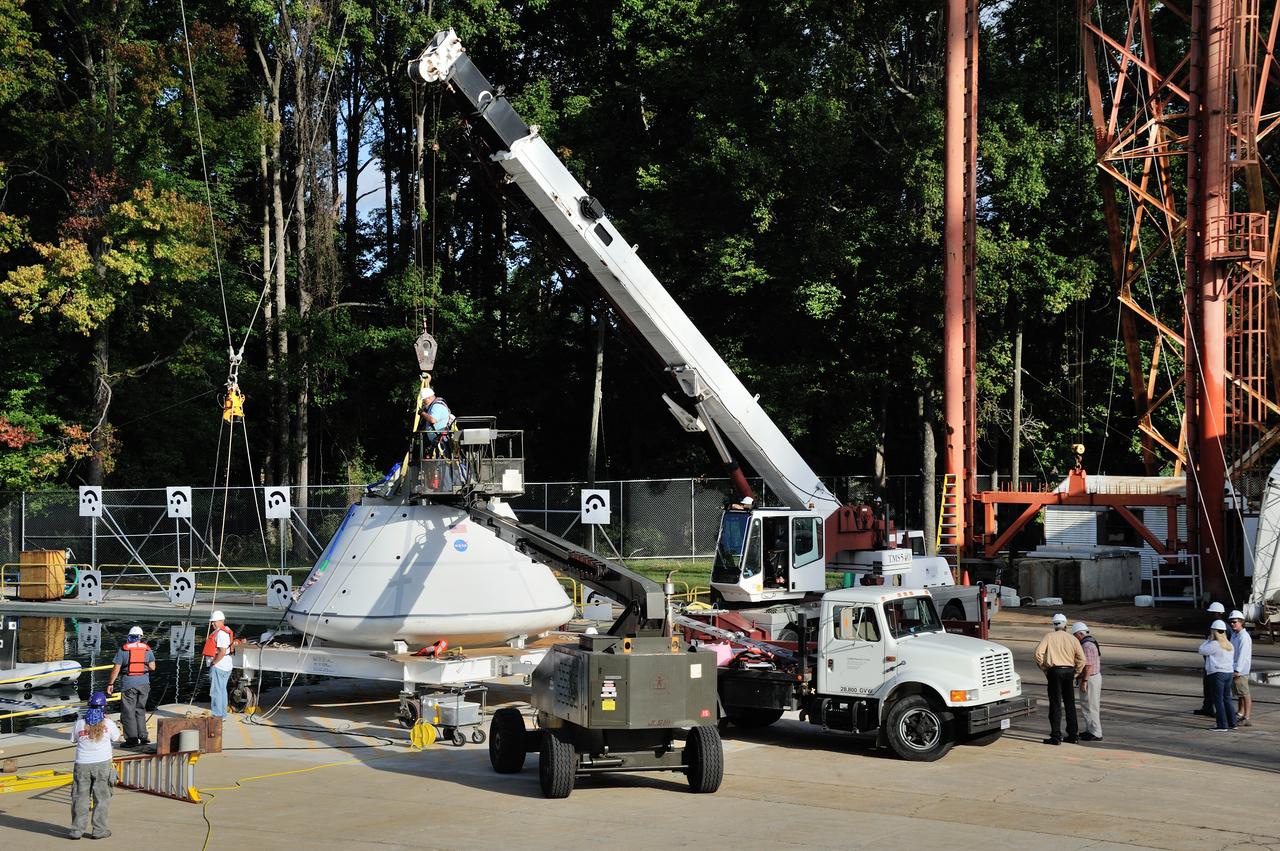

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
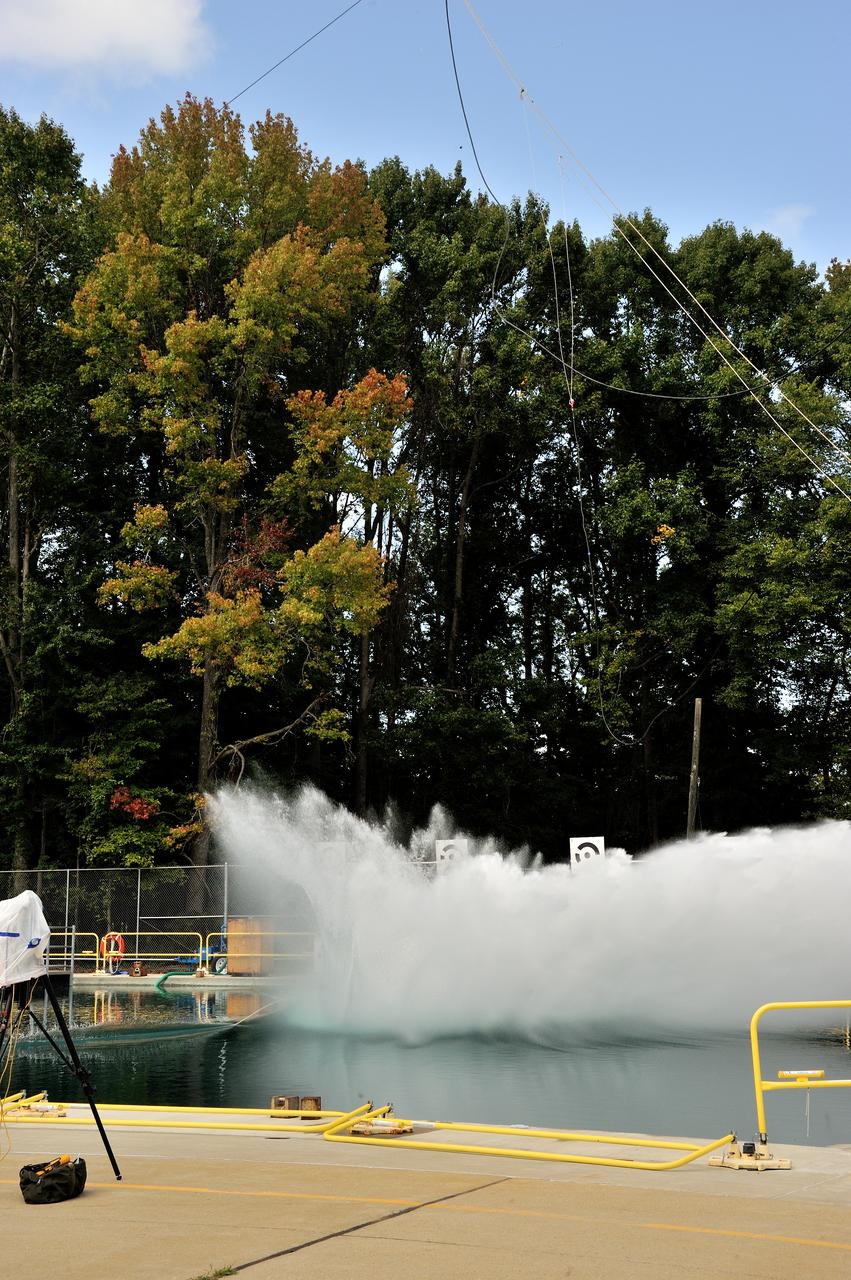

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
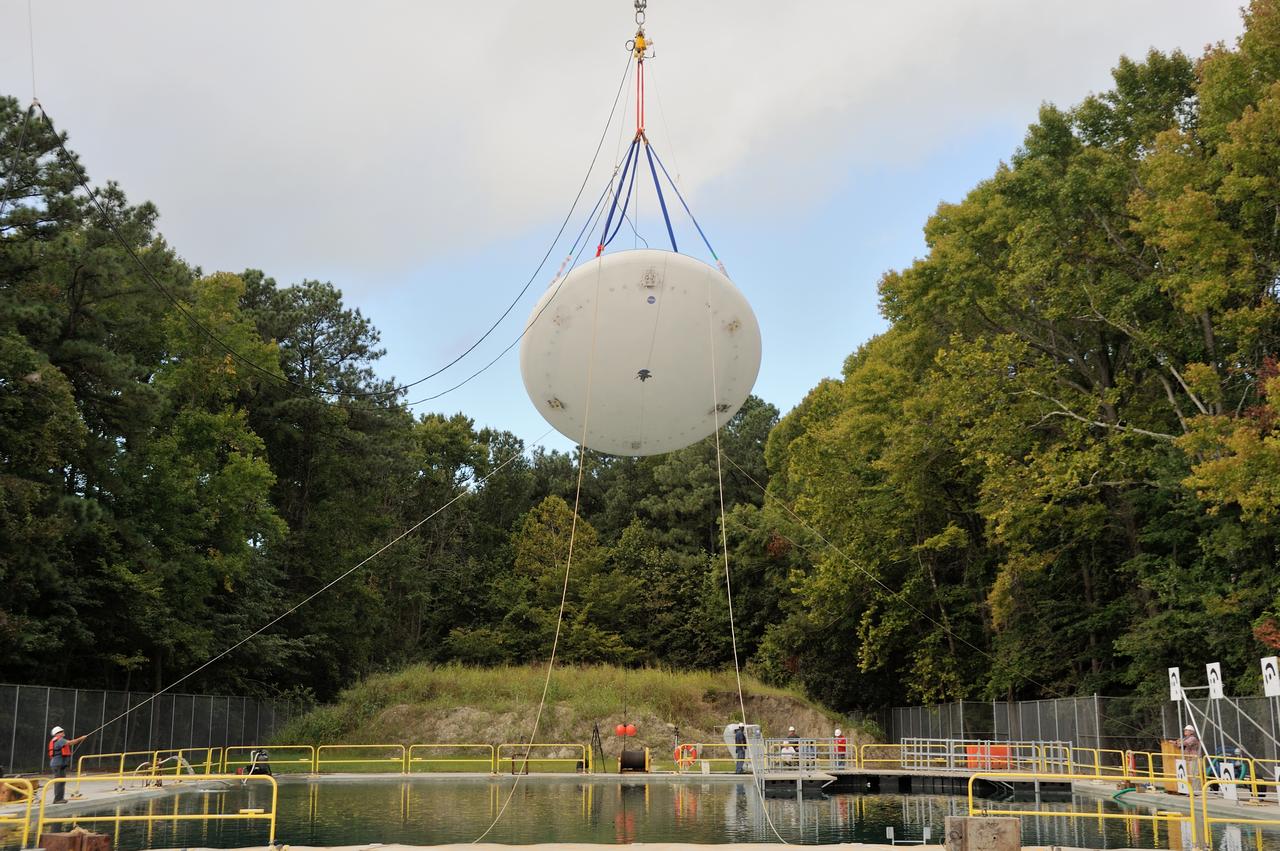

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
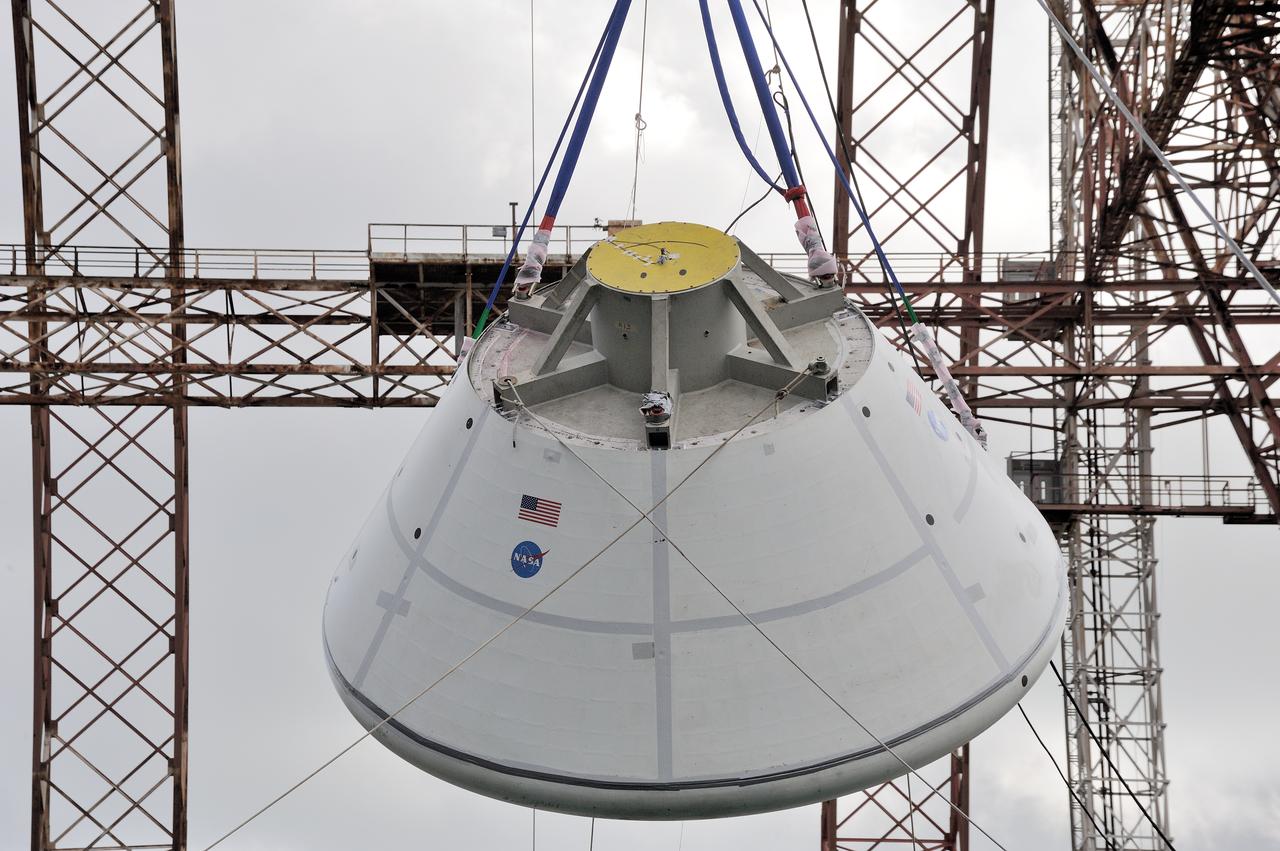

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
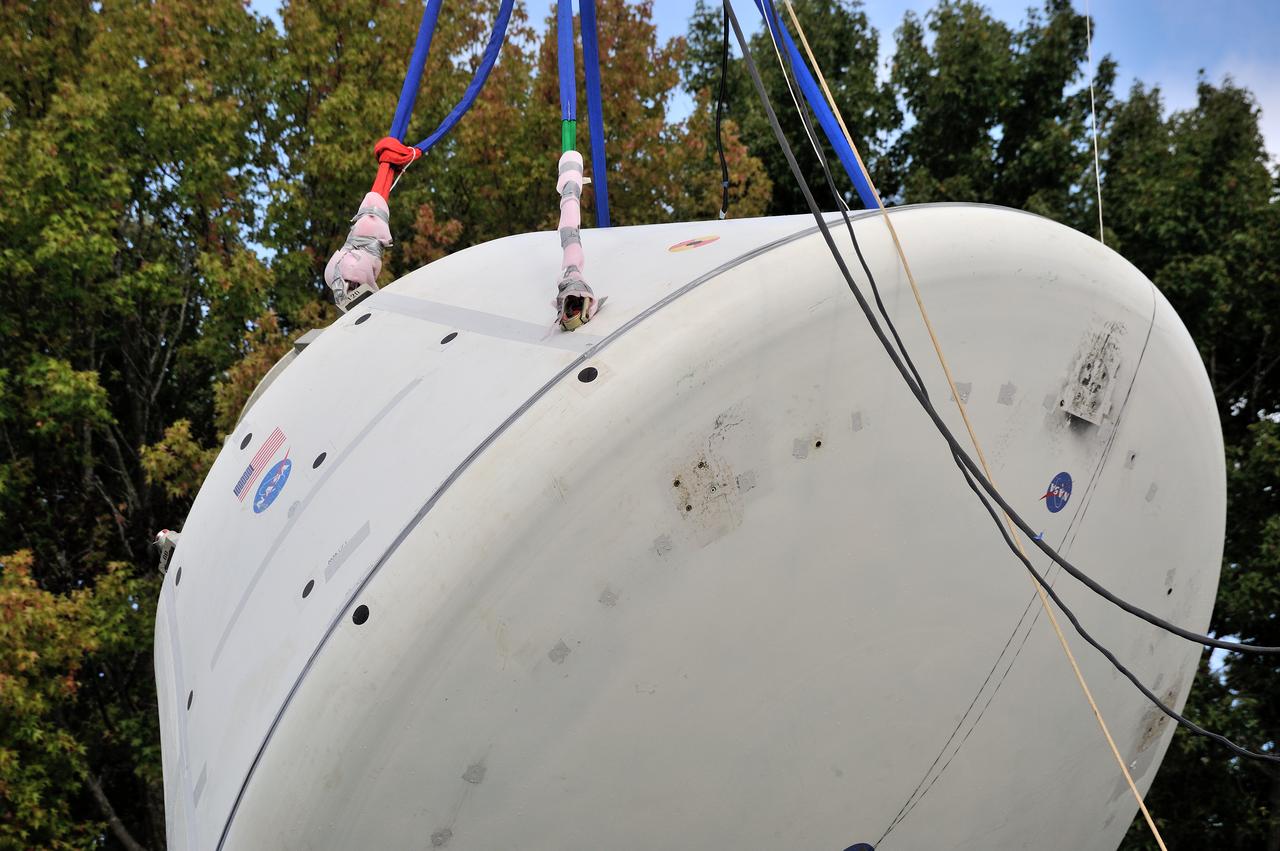

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
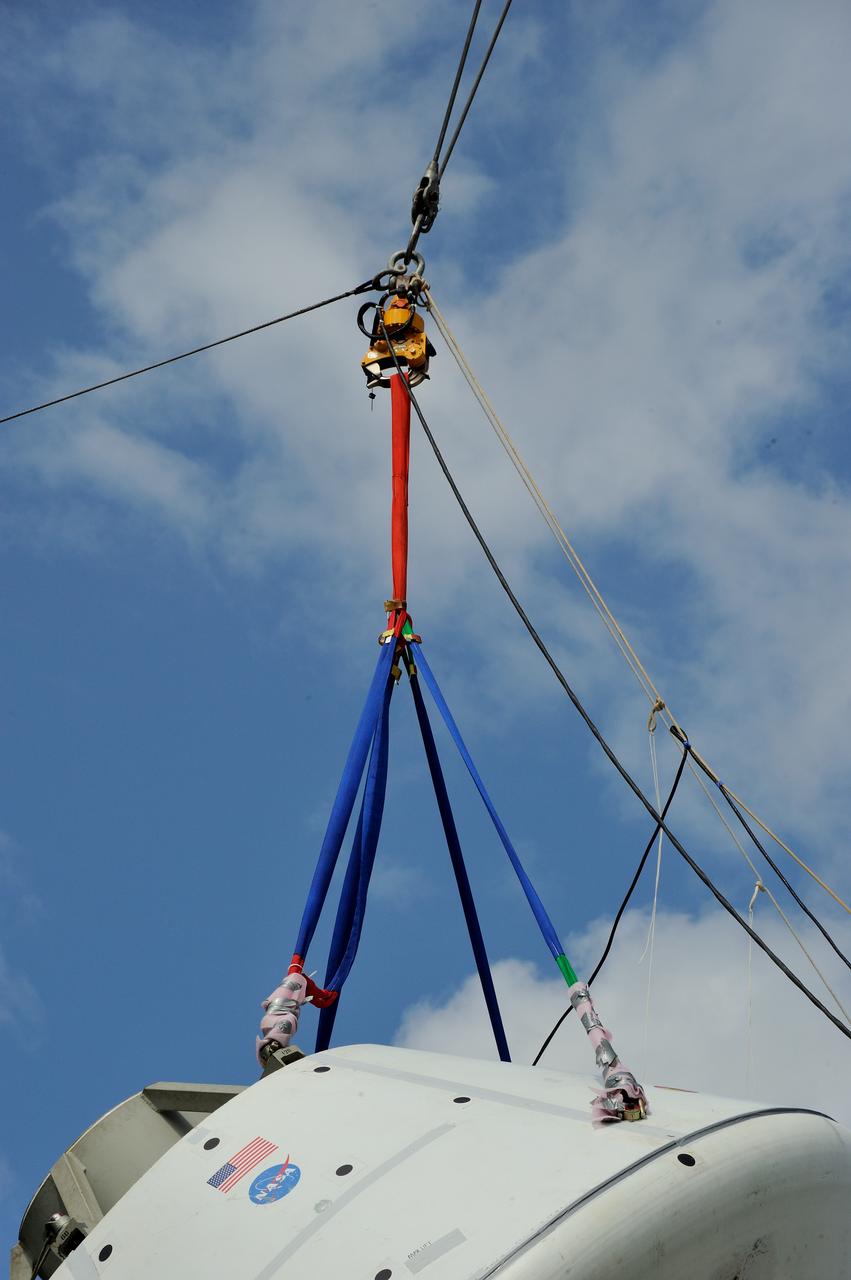

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
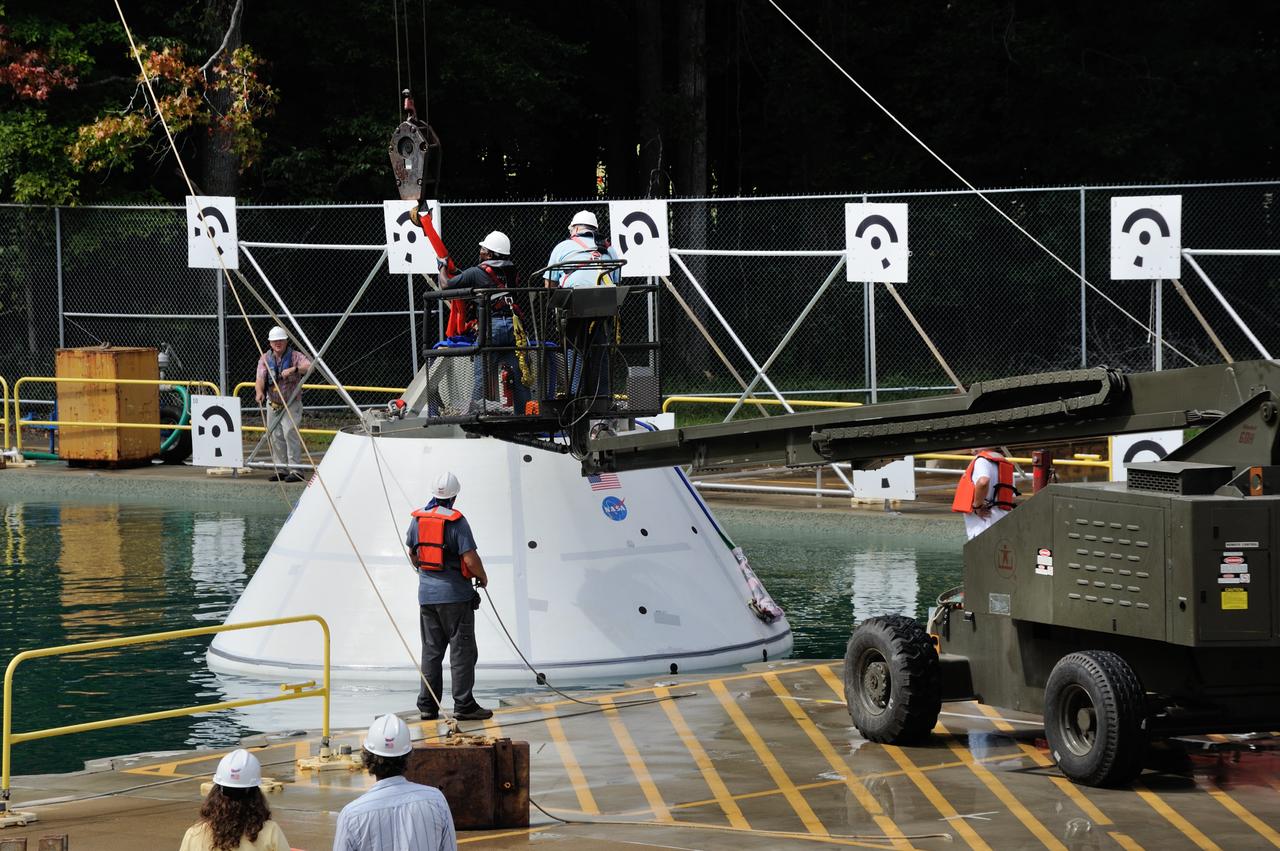

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
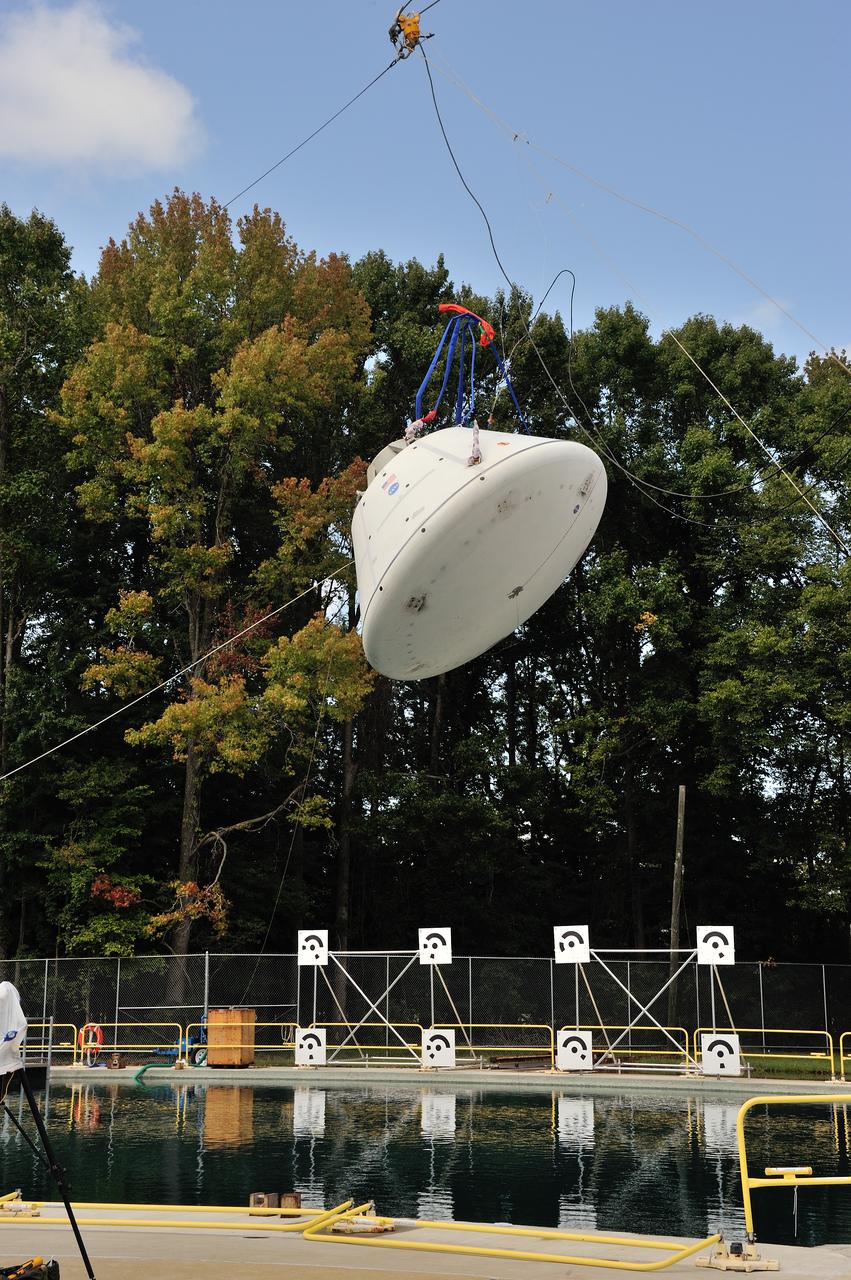

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
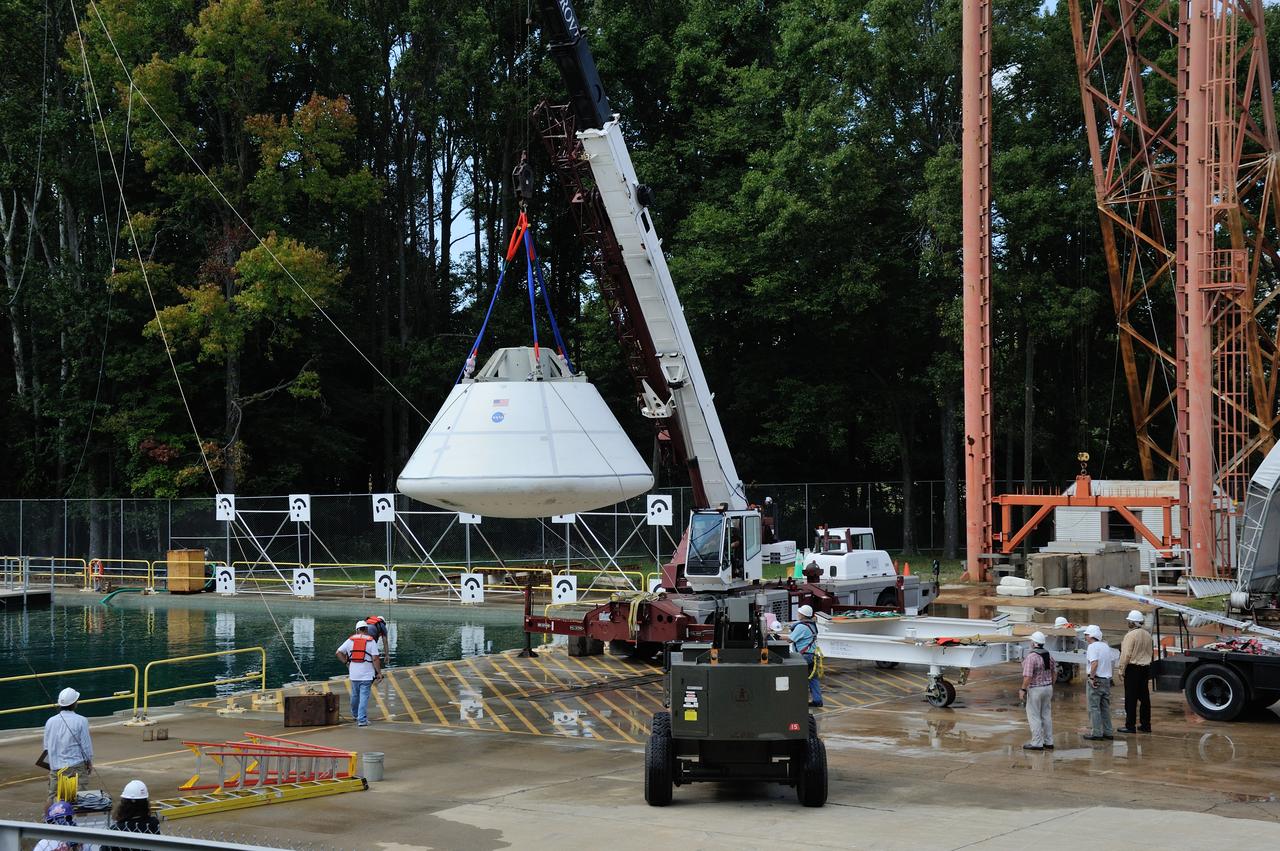

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
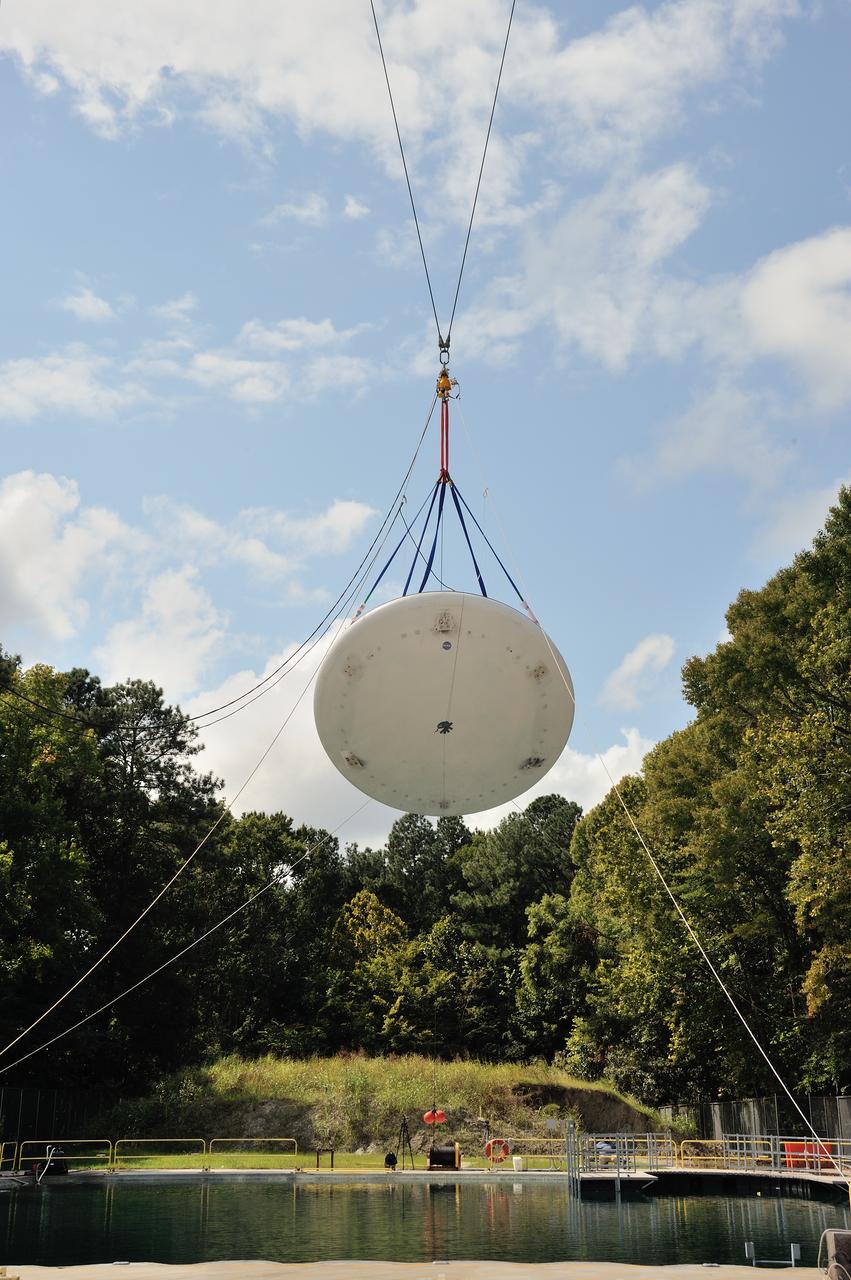

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
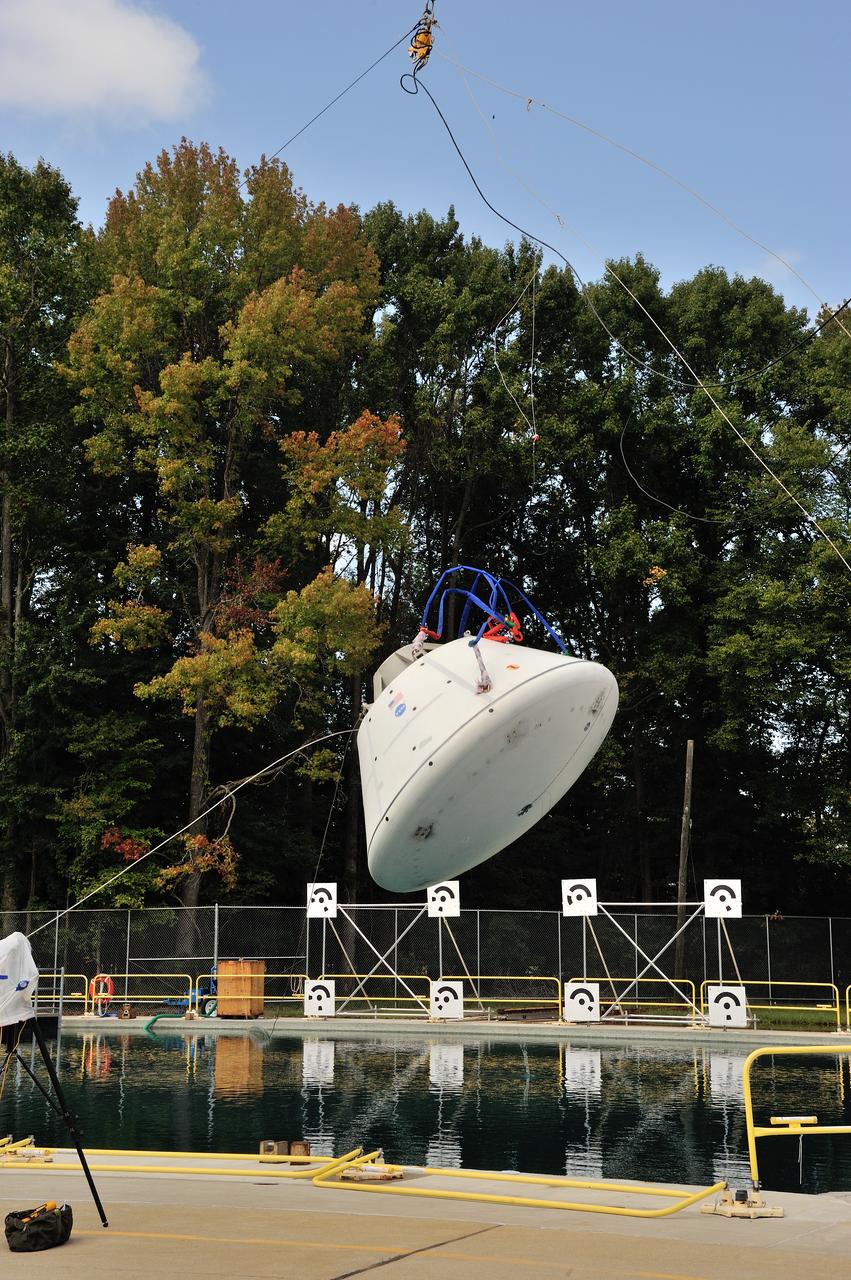

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
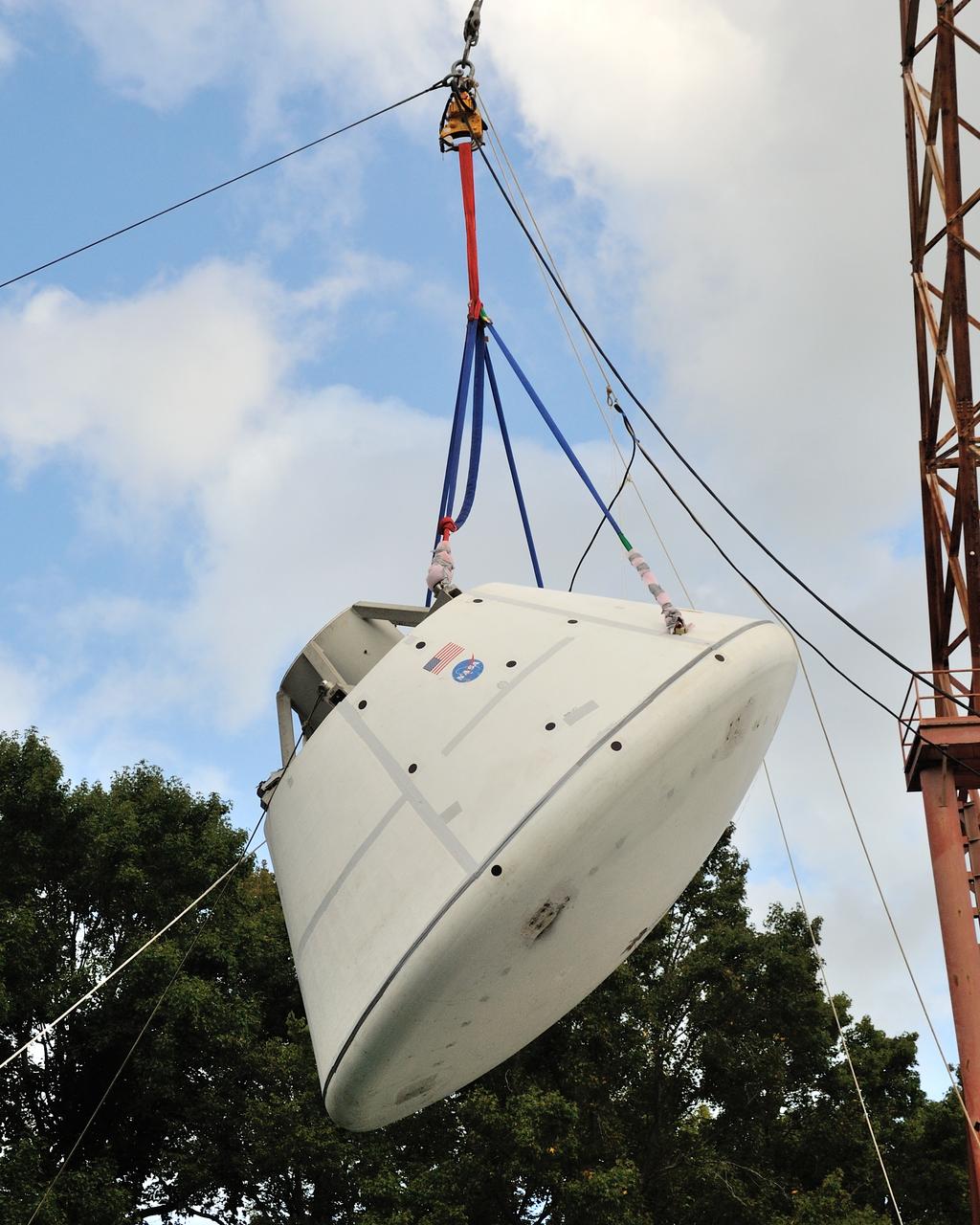

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
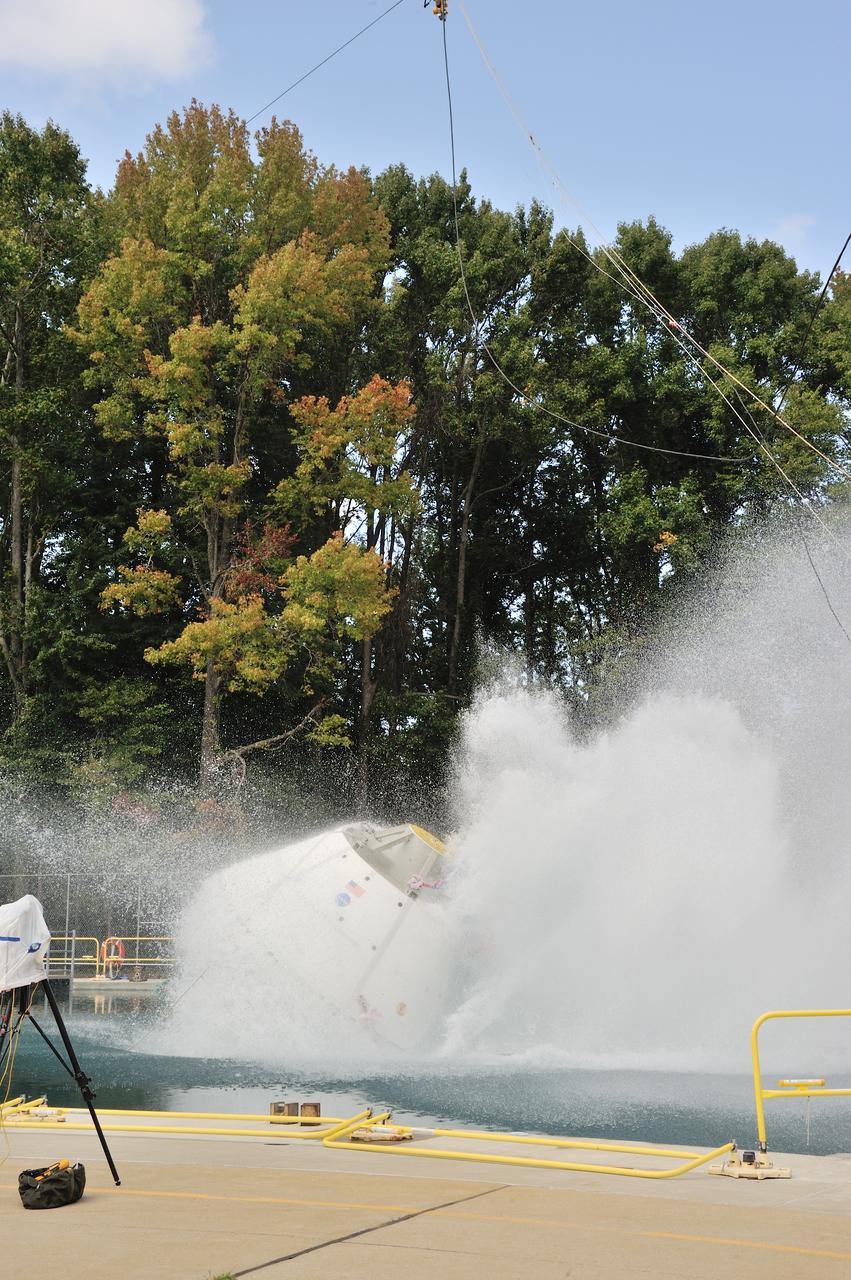

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)
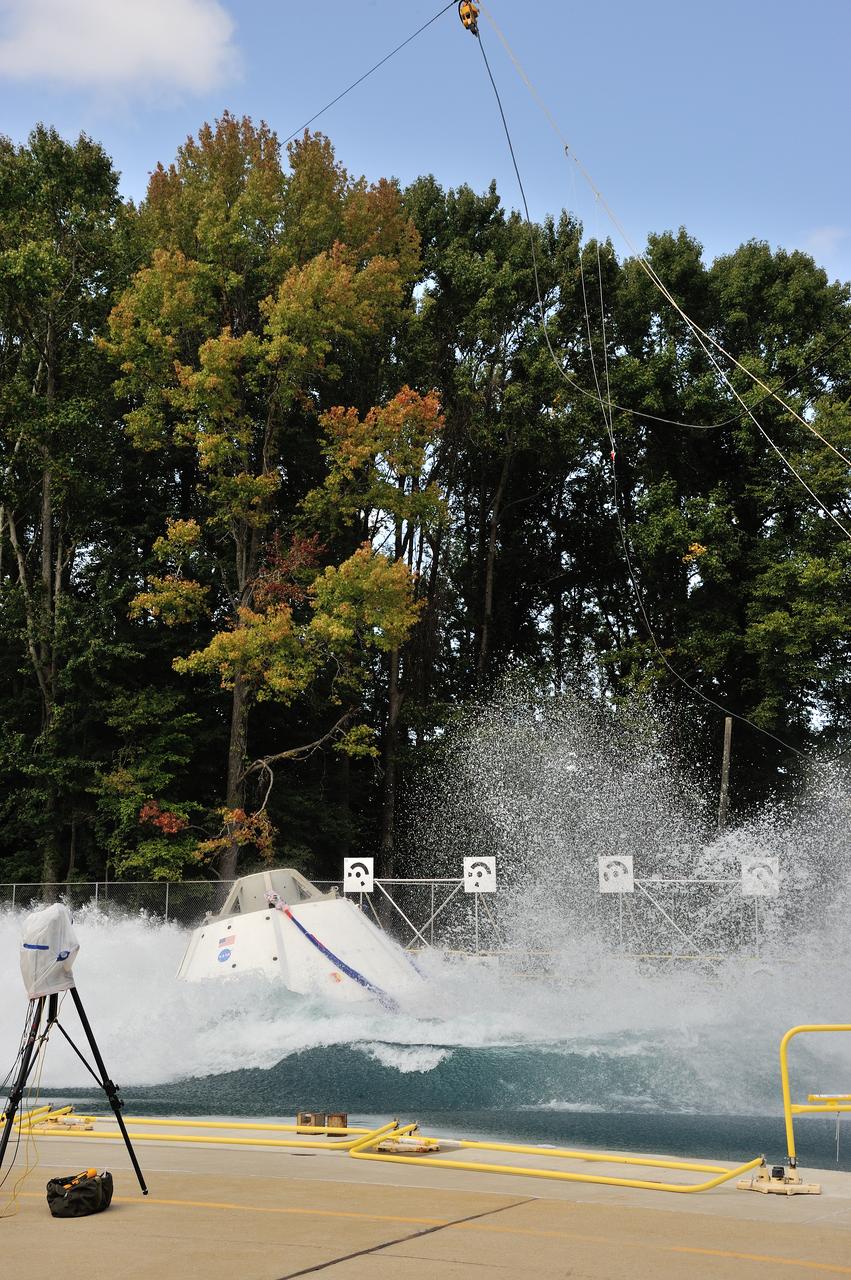

SPLASH BTA Phase 2 Vertical Tests 9: Documentation of preparation, set up and results of full scale BTA (Boilerplate Test Article) vertical drop test series performed in 2012 at the LaRC Hydro Impact Basin (HIB)