
Phobos
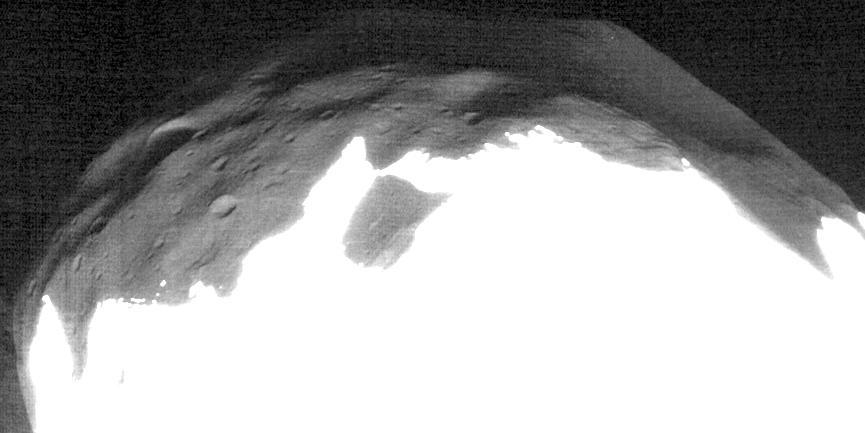
Marsshine on Shadowed Part of Phobos

Phobos from 6,800 Kilometers

Phobos from 5,800 Kilometers
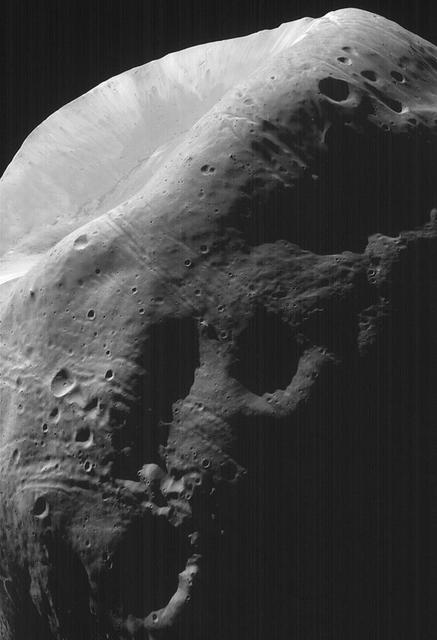

High-Resolution MOC Image of Phobos

Phobos from 5,800 Kilometers Color
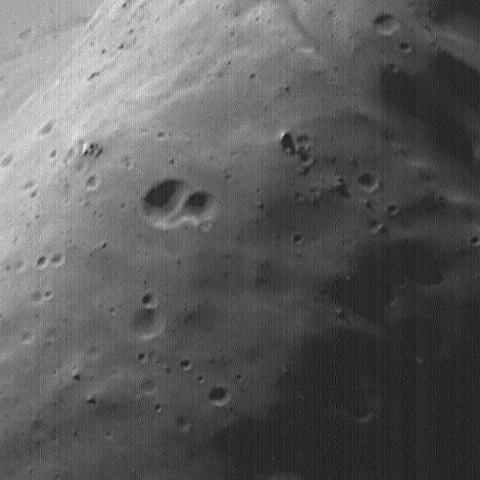

High-Resolution MOC Image of Phobos Face

Spirit View of Phobos Eclipse, Sol 675

Spirit Movie of Phobos Eclipse, Sol 675

MOC Image of Phobos with TES Temperature Overlay
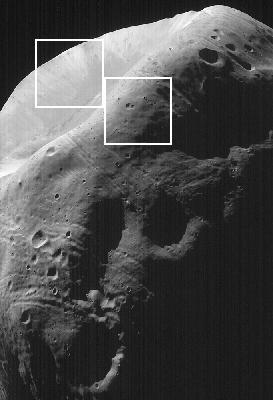
High-Resolution MOC Image of Phobos with Graphics Overlay
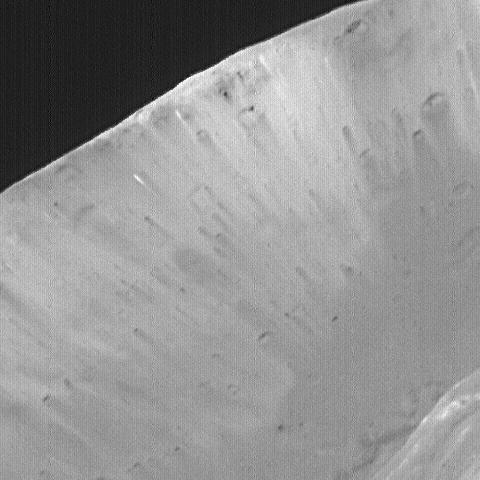

High-Resolution MOC Image of Phobos Stickney Crater

These six views of the Martian moon Phobos were captured by NASA's Odyssey orbiter as of March 2020. The orbiter's infrared camera, the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), is used to measure temperature variations that provide insight into the physical properties and composition of the moon. Chronologically, the views represent waxing, waning and full views of the moon. On Feb. 25, 2020, Phobos was observed during a lunar eclipse, where Mars' shadow completely blocked sunlight from reaching the moon's surface. This provided some of the coldest temperatures measured on Phobos to date: The coldest measured was about minus189 degrees Fahrenheit (minus123 degrees Celsius). On March 27, 2020, Phobos was observed exiting an eclipse, when the surface was still warming up. All of the THEMIS infrared images are colorized and overlain on THEMIS visible images taken at the same time, except for the eclipse image, which is overlain on a computer-generated visible image of what Phobos would have looked like if it wasn’t in complete shadow. Phobos is about 15 miles (about 25 kilometers) across. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23893

This image of Phobos is one product of the first pointing at that Martian moon by the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. The Sept. 29, 2017, observation also provided information about temperatures on different areas of Phobos. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. Phobos has an oblong shape with average diameter of about 14 miles (22 kilometers). Odyssey orbits Mars at an altitude of about 250 miles (400 kilometers), much closer to the planet than to Phobos, which orbits about 3,700 miles (6,000 kilometers) above the surface of Mars. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during this observation was about 3,424 miles (5,511 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22056

Colors in this image of the Martian moon Phobos indicate a range of surface temperatures detected by observing the moon on February 15, 2018, with the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. The left edge of the small moon is in darkness, and the right edge in sunlight. Phobos has an oblong shape with average diameter of about 14 miles (22 kilometers). Temperature information was derived from thermal-infrared imaging such as the grayscale image shown smaller at lower left with the moon in the same orientation. The color-coding merges information from THEMIS observations made in 10 thermal-infrared wavelength bands. This was the second observation of Phobos by Mars Odyssey; the first was on September 29, 2017. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22249
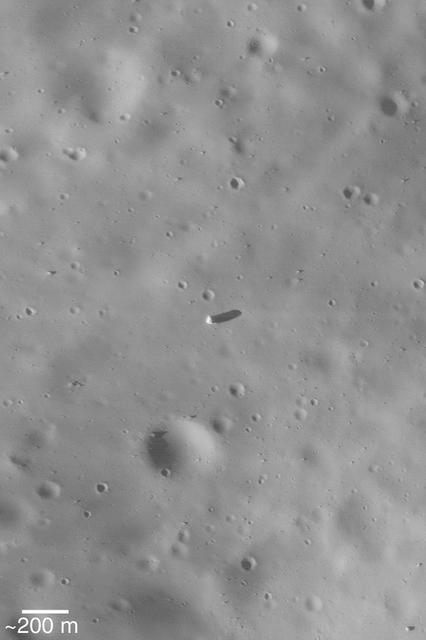

Boulders on Phobos
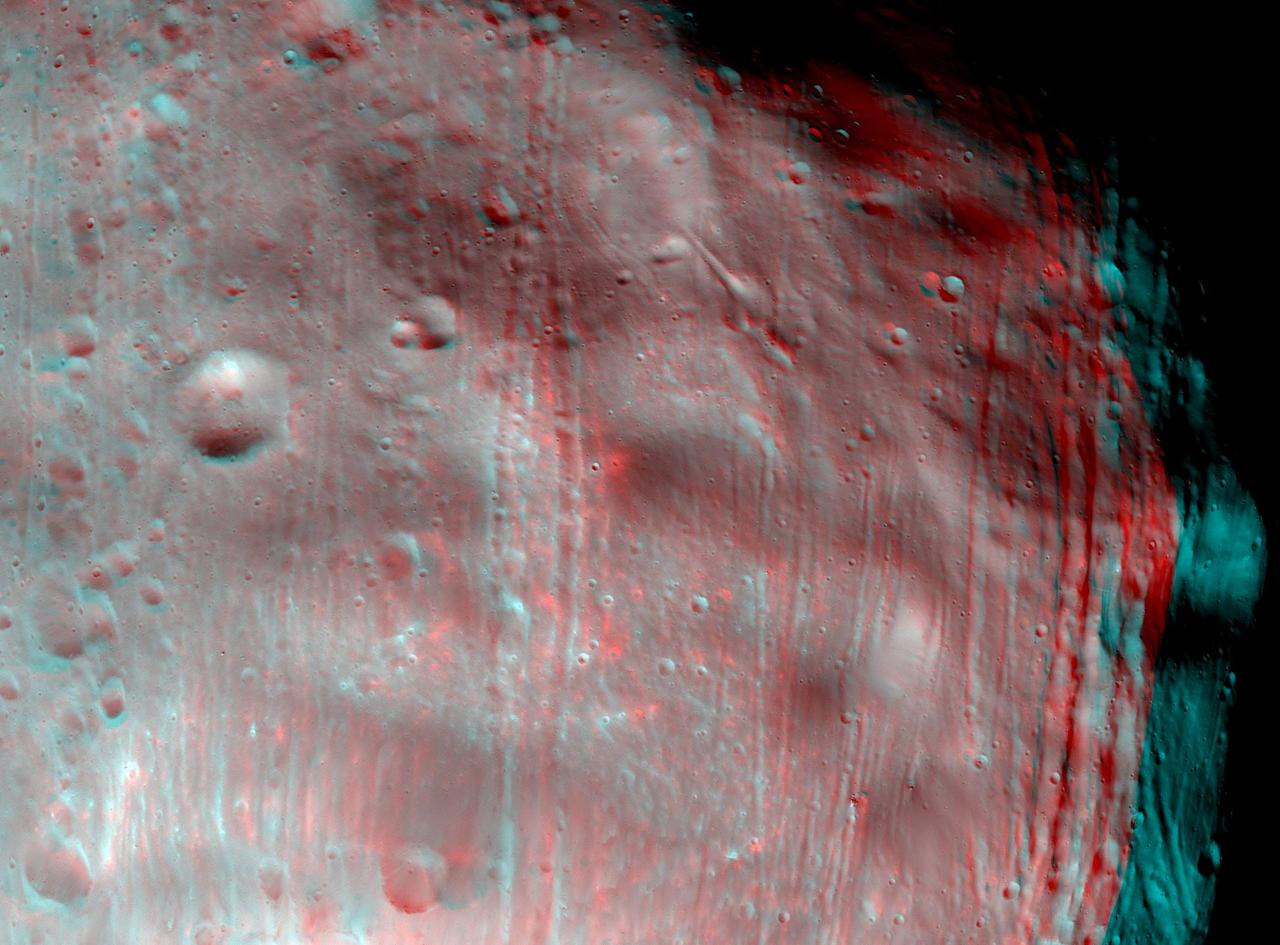

NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took two images of the larger of Mars two moons, Phobos, within 10 minutes of each other on March 23, 2008. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
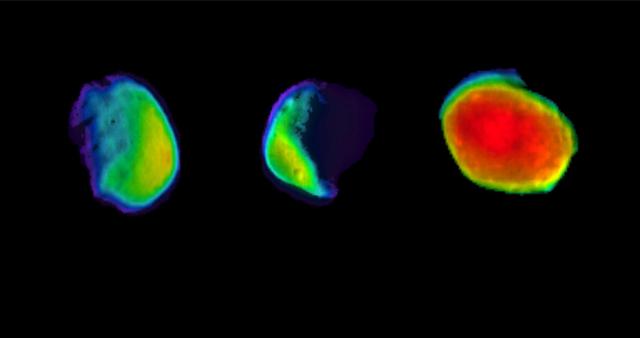
These are three different views of the Martian moon Phobos, as seen by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter using its infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). Each color represents a different temperature range. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23205

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to shoot video of Phobos, one of Mars' two moons, eclipsing the Sun. It's the most zoomed-in, highest-frame-rate observation of a Phobos solar eclipse ever taken from the Martian surface. Several Mars rovers have observed Phobos crossing in front of the Sun over the past 18 years. Spirit and Opportunity made the first observations in 2004; Curiosity in 2019 was the first to record video of the event. Each time these eclipses are observed, they allow scientists to measure subtle shifts in Phobos' orbit over time. The moon's tidal forces pull on the deep interior crust and mantle of the Red Planet; studying how much Phobos shifts over time reveals something about how resistant the crust and mantle are, and thus what kinds of materials they're made of. It's long been known that Phobos is drifting toward the Martian surface year by year; tens of millions of years from now, it is expected to crash into the planet or fragment into chunks that will impact the planet. Studying Phobos' orbit also allows scientists to refine predictions of when the doomed moon will crash into Mars. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25179

This movie shows the Martian moon Phobos as viewed in visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter on April 24, 2019. It was put together from 19 images taken 1 second apart by Odyssey's infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The apparent motion is due to progression of the camera's pointing during the observation. This was the third observation of Phobos by Mars Odyssey. While displayed here in visible-wavelength light, THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 5,692 miles (9,160 kilometers). Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23207

This frame from an animation shows Phobos, the larger of the two moons of Mars, passing overhead, as observed by NASA Mars rover Curiosity, centered straight overhead starting shortly after sunset.
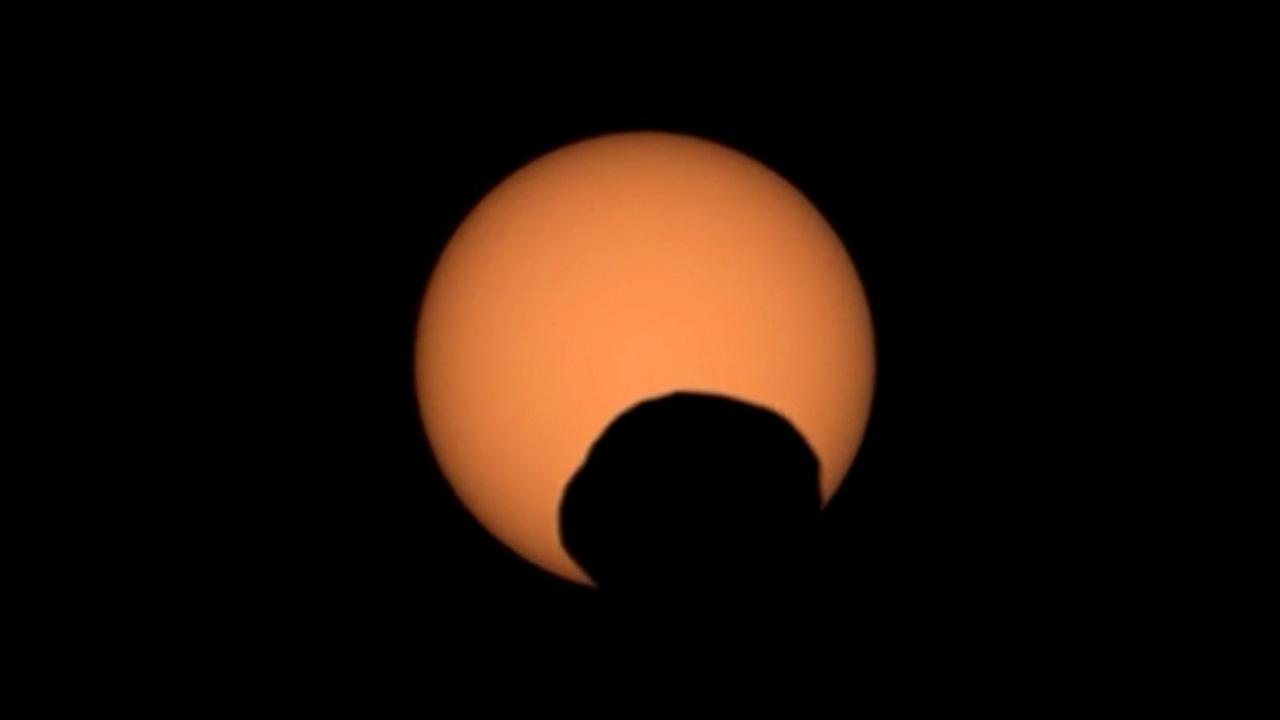

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture the silhouette of Phobos, one of the two Martian moons, as it passed in front of the Sun on Sept. 30, 2024, the 1,285th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Perseverance has captured several Phobos transits since its landing at Mars' Jezero Crater in February 2021. By comparing the various recordings, scientists can refine their understanding of the potato-shaped moon's orbit, learning how it is changing. Eons from now, Phobos' orbit is expected to eventually send the moon toward the Red Planet's surface. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26380
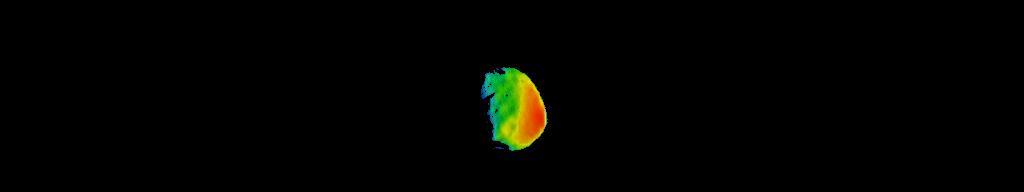
This image combines two products from the first pointing at the Martian moon Phobos by the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter, on Sept. 29, 2017. Surface-temperature information from observation in thermal-infrared wavelengths is overlaid on a more detailed image from a visible-light observation. The left edge of the small moon was in darkness, and the right edge in morning sunlight. Phobos has an oblong shape with average diameter of about 14 miles (22 kilometers). The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 3,424 miles (5,511 kilometers). Researchers will analyze the surface-temperature information from this observation and possible future THEMIS observations to learn how quickly the surface warms after sunup or cools after sundown. That could provide information about surface materials, because larger rocks heat or cool more slowly than smaller particles do. The thermal information in this image is from merging observations made in four thermal-infrared wavelength bands, centered from 11.04 microns to 14.88 microns. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. Odyssey orbits Mars at an altitude of about 250 miles (400 kilometers), much closer to the planet than to Phobos, which orbits about 3,700 miles (6,000 kilometers) above the surface of Mars. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22057
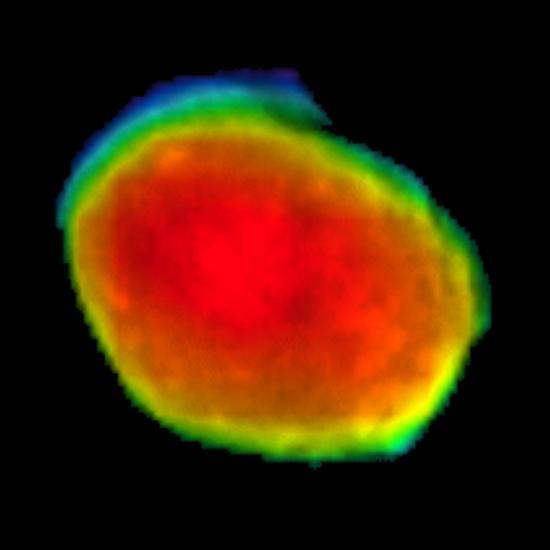
Taken on April 24, 2019, this rainbow-colored image shows the Martian moon Phobos, as viewed by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter using its infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). Each color represents a different temperature range, with the warmest in the center and coolest on the outer edge. This was the first time THEMIS was used to observe Phobos while in a full moon phase, which offers scientists a much better view for studying the composition of the Martian moon. Previous half-moon views, which can be seen here, were better for studying surface textures. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23204
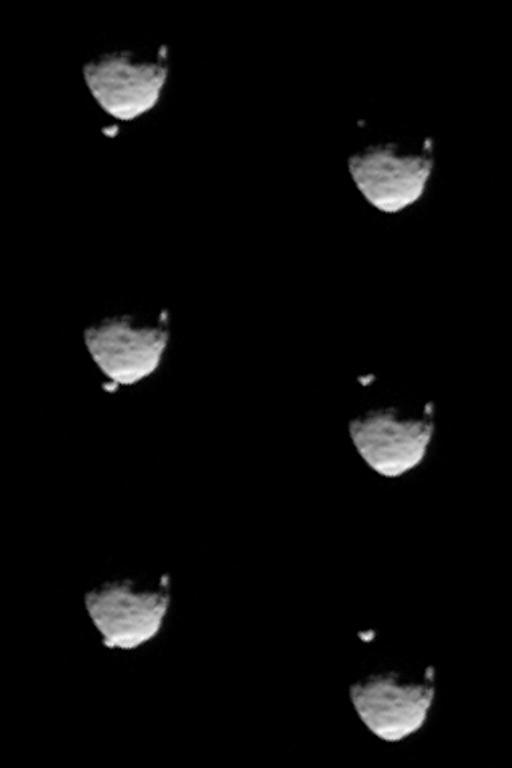

These six images from NASA Mars rover Curiosity show the two moons of Mars moments before left three and after right three the larger moon, Phobos, occulted Deimos on Aug. 1, 2013.

The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter took two images of the larger of Mars two moons, Phobos, within 10 minutes of each other on March 23, 2008. This is the first.

Phobos Over the Martian Limb
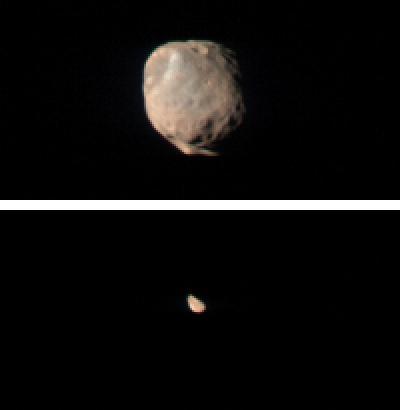
CRISM Views Phobos and Deimos

Martian Moon, Phobos
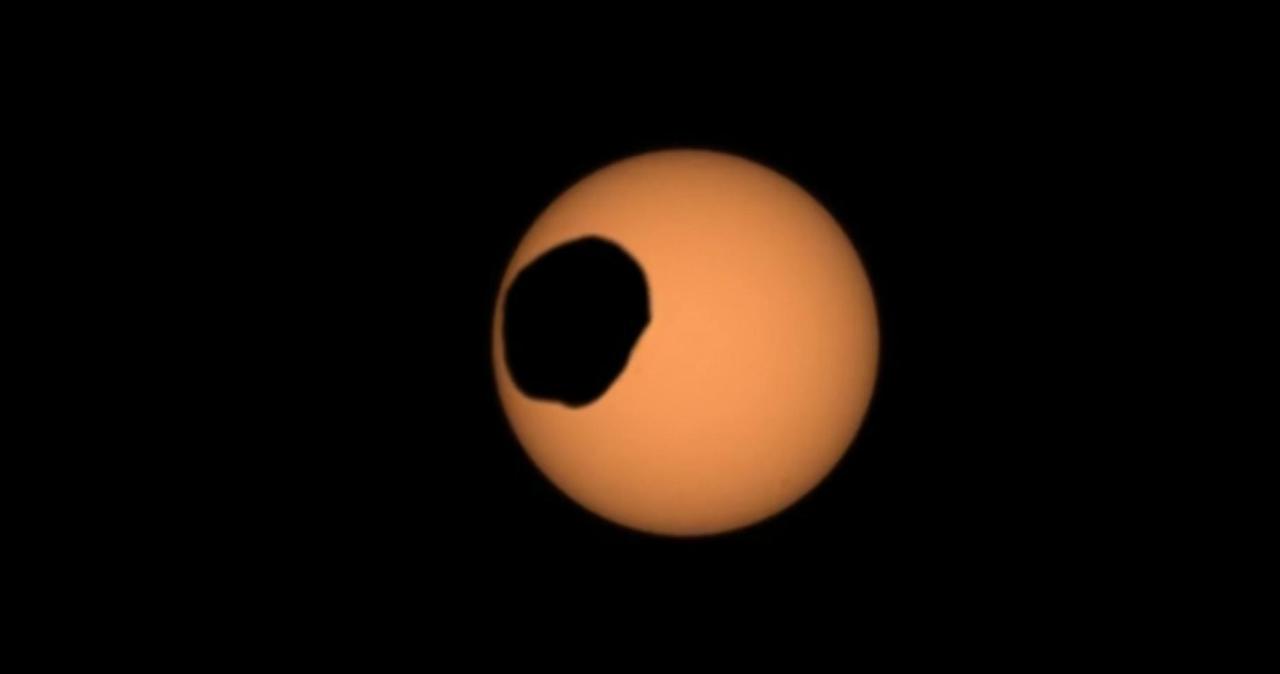
NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture the silhouette of Phobos, one of the two Martian moons, as it passed in front of the Sun on Feb. 8, 2024, the 1,056th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This is one of several transits of Phobos that NASA's Mars rovers have captured. By comparing the various recordings, scientists can refine their understanding of the potato-shaped moon's orbit, learning how it's changing. Eons from now, Phobos' orbit is expected to eventually send the moon toward the Red Planet's surface. The video shows the transit as it happened in real time. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26248

This image from a movie clip shows Phobos, the larger of the two moons of Mars, passing in front of the other Martian moon, Deimos, on Aug. 1, from the perspective of NASA Mars rover Curiosity.

This set of three images shows views three seconds apart as the larger of Mars two moons, Phobos, passed directly in front of the sun as seen by NASA Mars rover Curiosity.

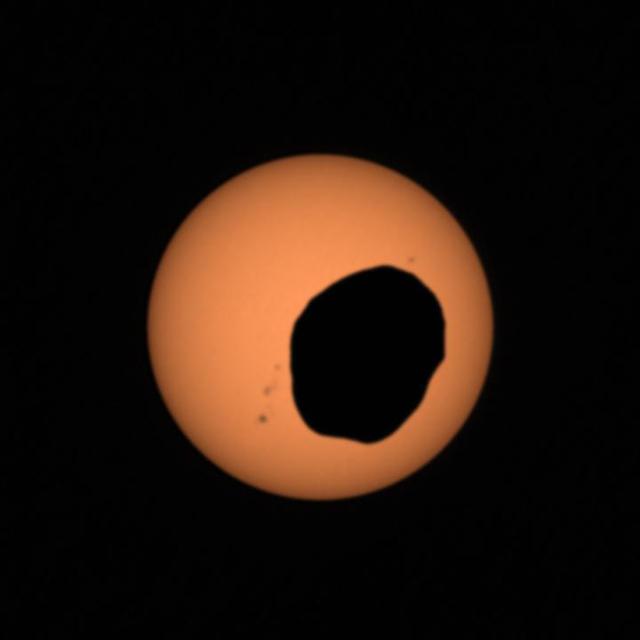
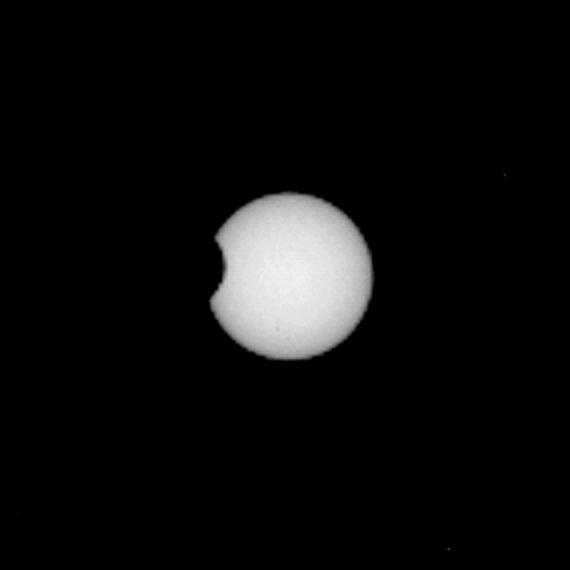
This image shows Phobos, the larger of Mars two moons, as it transits in front of the sun. This image was taken by NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity during the afternoon of the rover 3,078th Martian day, or sol.
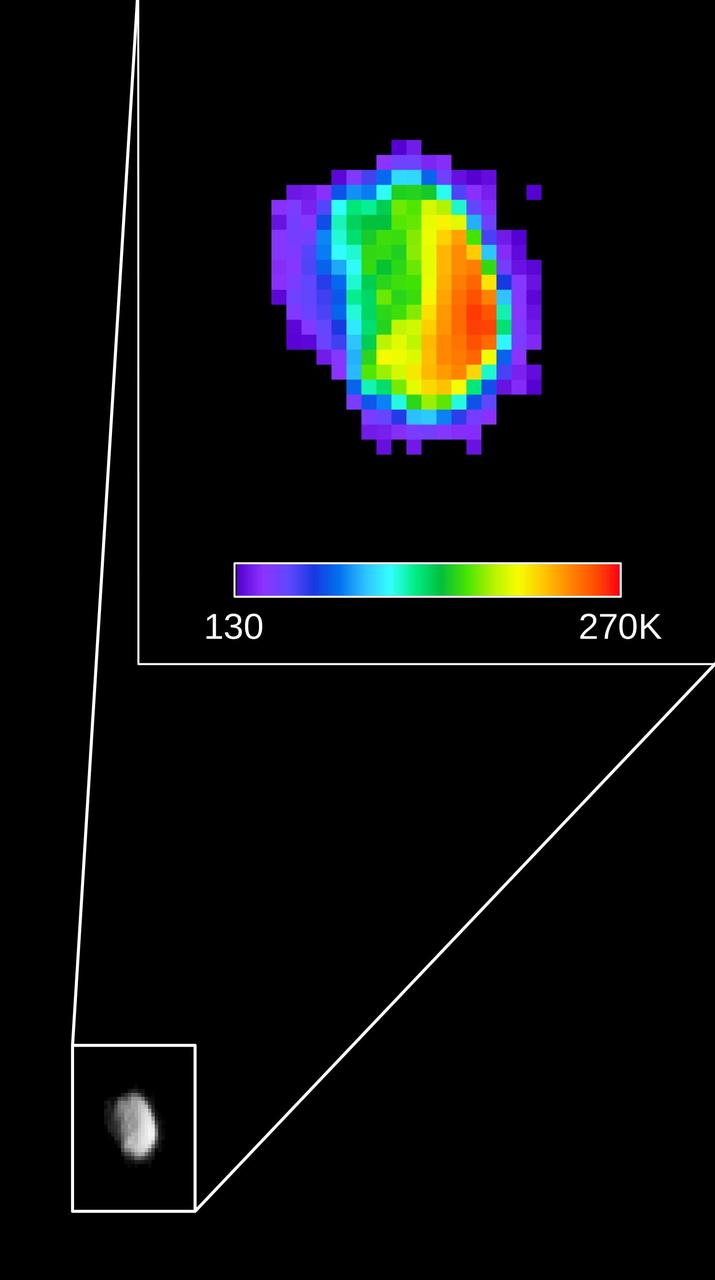
Colors in this image of the Martian moon Phobos indicate a range of surface temperatures detected by observing the moon on Sept. 29, 2017, with the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. The left edge of the small moon was in darkness, and the right edge in morning sunlight. Phobos has an oblong shape with average diameter of about 14 miles (22 kilometers). Temperature information was derived from thermal-infrared imaging such as the grayscale image shown smaller at lower left with the moon in the same orientation. The color-coding merges information from THEMIS observations made in four thermal-infrared wavelength bands, centered from 11.04 microns to 14.88 microns. The scale bar correlates color-coding to the temperature range on the Kelvin scale, from 130 K (minus 226 degrees Fahrenheit) for dark purple to 270 K (26 degrees F) for red. Researchers will analyze the surface-temperature information from this observation and possible future THEMIS observations to learn how quickly the surface warms after sunup or cools after sundown. That could provide information about surface materials, because larger rocks heat or cool more slowly than smaller particles do. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. Odyssey orbits Mars at an altitude of about 250 miles (400 kilometers), much closer to the planet than to Phobos, which orbits about 3,700 miles (6,000 kilometers) above the surface of Mars. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 3,424 miles (5,511 kilometers). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21858
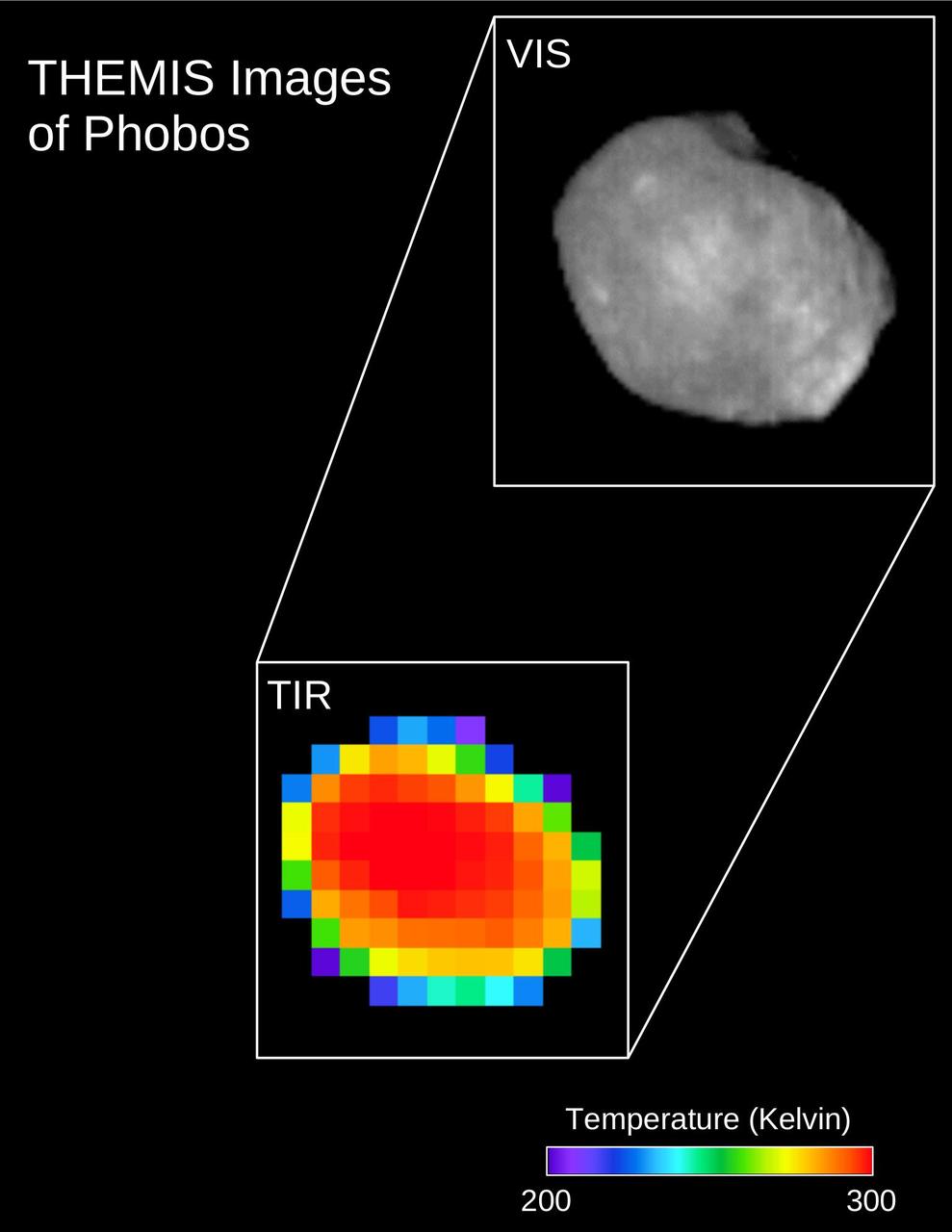
These are two views of the same observation of the Martian moon Phobos taken in both infrared and visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter using its infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS). The image was taken on April 24, 2019. The top view is what Phobos looked like in the visible light spectrum, as viewed by THEMIS. The bottom view is what it looks like in infrared, which reveals temperature differences. The warmest temperatures are in the center, and the coolest are on the outer edge. A scale bar is provided to reflect the temperatures, which range from 200 to 300 degrees Kelvin, or -100 degrees Fahrenheit (-73 Celsius) to 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 Celsius). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23206

This series of images shows the Martian moon Phobos as it crossed in front of the Sun, as seen by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover on Tuesday, March 26, 2019 (the 2,359th sol, or Martian day, of the mission). The images were captured by Curiosity's telephoto-lens camera, called its Mast Camera (Mastcam) using its right-eye solar filter. The images have been sped up by a factor of 10; the entire eclipse lasted about 35 seconds. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23133
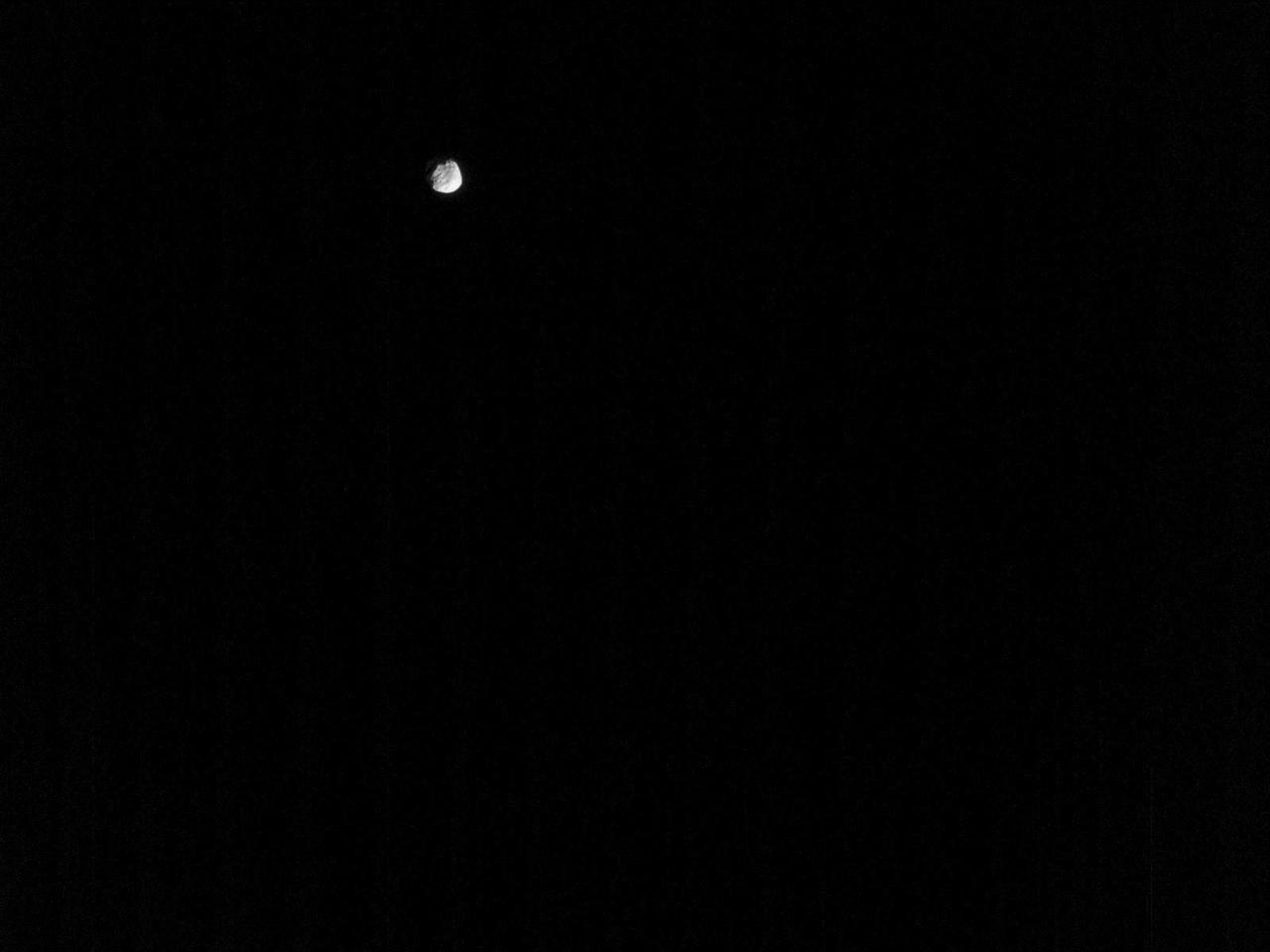

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to view Phobos, one of Mars' two moons, on Jan. 12, 2022, the 319th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The Perseverance team took this image to measure the amount of dust in the planet's nighttime atmosphere, which can be compared to similar measurements made by imaging the Sun during the day. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25419

Taking advantage of extra solar energy collected during the day, NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Spirit settled in for an evening of stargazing, photographing the two moons of Mars as they crossed the night sky. The first two images in this sequence show gradual enhancements in the surface detail of Mars' largest moon, Phobos, made possible through a combination technique known as "stacking." In "stacking," scientists use a mathematical process known as Laplacian sharpening to reinforce features that appear consistently in repetitive images and minimize features that show up only intermittently. In this view of Phobos, the large crater named Stickney is just out of sight on the moon's upper right limb. Spirit acquired the first two images with the panoramic camera on the night of sol 585 (Aug. 26,2005). The far right image of Phobos, for comparison, was taken by the High Resolution Stereo Camera on Mars Express, a European Space Agency orbiter. The third image in this sequence was derived from the far right image by making it blurrier for comparison with the panoramic camera images to the left http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA06335

The panoramic camera on NASA Opportunity combines the first photographs of solar eclipses by Mars two moons, Deimos and Phobos. Deimos appears as a speck in front of the Sun and Phobos grazes its edge.
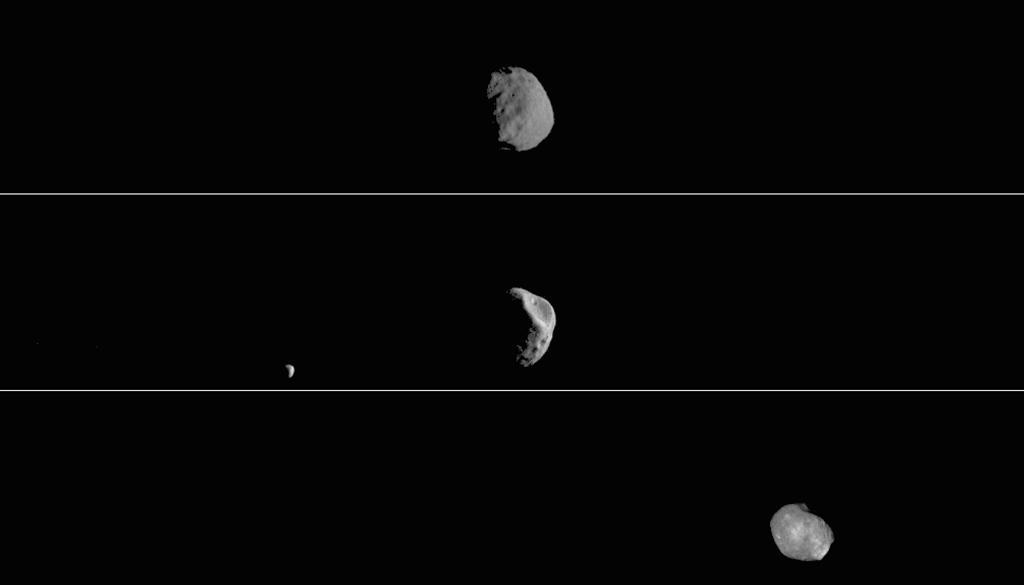

This movie shows three views of the Martian moon Phobos as viewed in visible light by NASA's 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter. The apparent motion is due to movement by Odyssey's infrared camera, Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS), rather than movement by the moon. Each of the three panels is a series of images taken on different dates (from top to bottom): Sept. 29, 2017; Feb. 15, 2018; and April 24, 2019. Deimos, Mars' other moon, can also be seen in the second panel. While displayed here in visible-wavelength light, THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23208
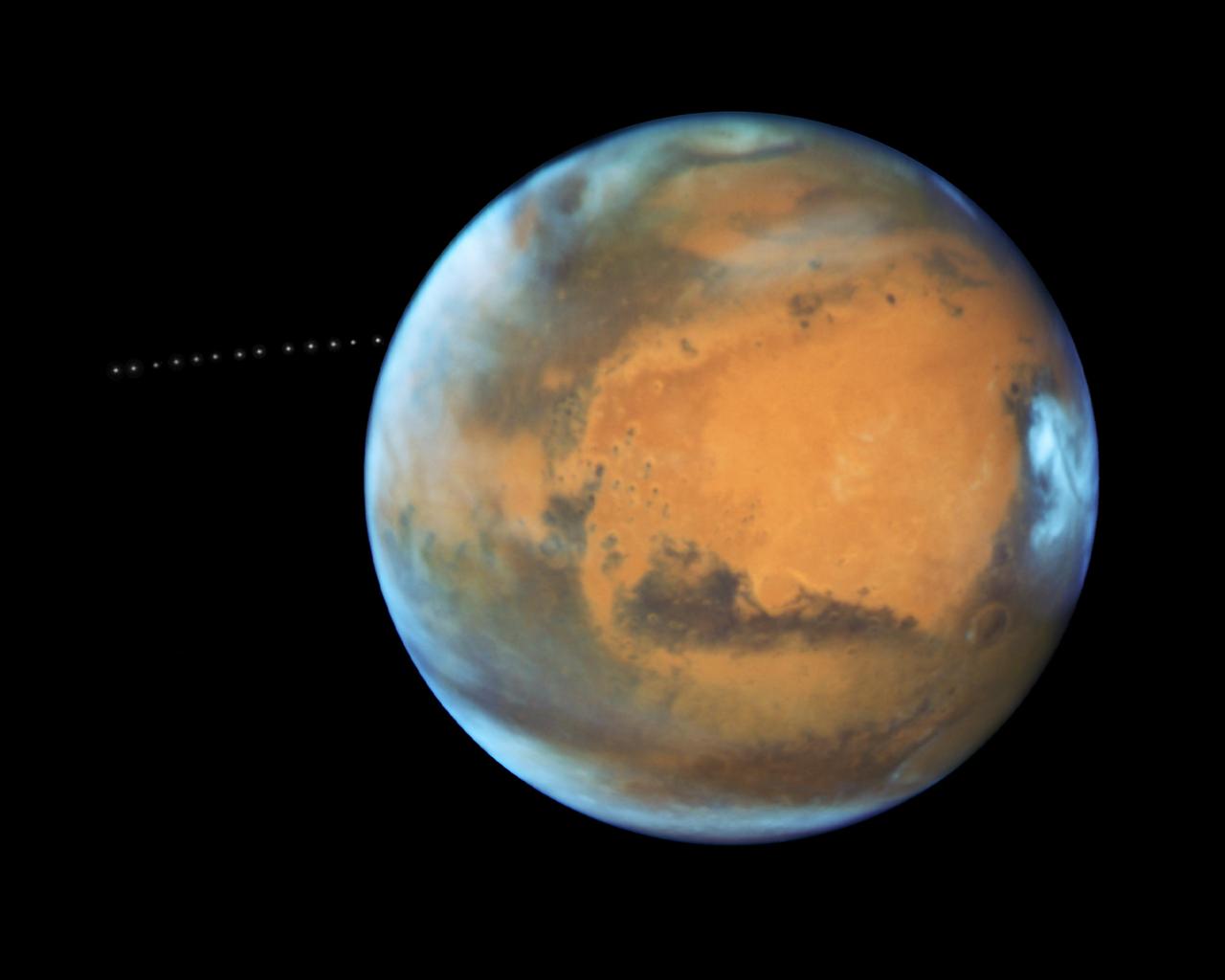
The sharp eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured the tiny moon Phobos during its orbital trek around Mars. Because the moon is so small, it appears star-like in the Hubble pictures. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble took 13 separate exposures, allowing astronomers to create a time-lapse video showing the diminutive moon's orbital path. The Hubble observations were intended to photograph Mars, and the moon's cameo appearance was a bonus. A football-shaped object just 16.5 miles by 13.5 miles by 11 miles, Phobos is one of the smallest moons in the solar system. It is so tiny that it would fit comfortably inside the Washington, D.C. Beltway. The little moon completes an orbit in just 7 hours and 39 minutes, which is faster than Mars rotates. Rising in the Martian west, it runs three laps around the Red Planet in the course of one Martian day, which is about 24 hours and 40 minutes. It is the only natural satellite in the solar system that circles its planet in a time shorter than the parent planet's day. About two weeks after the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing on July 20, 1969, NASA's Mariner 7 flew by the Red Planet and took the first crude close-up snapshot of Phobos. On July 20, 1976 NASA's Viking 1 lander touched down on the Martian surface. A year later, its parent craft, the Viking 1 orbiter, took the first detailed photograph of Phobos, revealing a gaping crater from an impact that nearly shattered the moon. Phobos was discovered by Asaph Hall on August 17, 1877 at the U.S. Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., six days after he found the smaller, outer moon, named Deimos. Hall was deliberately searching for Martian moons. Both moons are named after the sons of Ares, the Greek god of war, who was known as Mars in Roman mythology. Phobos (panic or fear) and Deimos (terror or dread) accompanied their father into battle. Close-up photos from Mars-orbiting spacecraft reveal that Phobos is apparently being torn apart by the gravitational pull of Mars. The moon is marred by long, shallow grooves that are probably caused by tidal interactions with its parent planet. Phobos draws nearer to Mars by about 6.5 feet every hundred years. Scientists predict that within 30 to 50 million years, it either will crash into the Red Planet or be torn to pieces and scattered as a ring around Mars. Orbiting 3,700 miles above the Martian surface, Phobos is closer to its parent planet than any other moon in the solar system. Despite its proximity, observers on Mars would see Phobos at just one-third the width of the full moon as seen from Earth. Conversely, someone standing on Phobos would see Mars dominating the horizon, enveloping a quarter of the sky. From the surface of Mars, Phobos can be seen eclipsing the sun. However, it is so tiny that it doesn't completely cover our host star. Transits of Phobos across the sun have been photographed by several Mars-faring spacecraft. The origin of Phobos and Deimos is still being debated. Scientists concluded that the two moons were made of the same material as asteroids. This composition and their irregular shapes led some astrophysicists to theorize that the Martian moons came from the asteroid belt. However, because of their stable, nearly circular orbits, other scientists doubt that the moons were born as asteroids. Such orbits are rare for captured objects, which tend to move erratically. An atmosphere could have slowed down Phobos and Deimos and settled them into their current orbits, but the Martian atmosphere is too thin to have circularized the orbits. Also, the moons are not as dense as members of the asteroid belt. Phobos may be a pile of rubble that is held together by a thin crust. It may have formed as dust and rocks encircling Mars were drawn together by gravity. Or, it may have experienced a more violent birth, where a large body smashing into Mars flung pieces skyward, and those pieces were brought together by gravity. Perhaps an existing moon was destroyed, reduced to the rubble that would become Phobos. Hubble took the images of Phobos orbiting the Red Planet on May 12, 2016, when Mars was 50 million miles from Earth. This was just a few days before the planet passed closer to Earth in its orbit than it had in the past 11 years. A time-lapse video captures a portion of the path that tiny Phobos takes around Mars. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble snapped 13 separate exposures of the little Martian moon. The video can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21837

This montage shows asteroid 951 Gaspra top compared with Deimos lower left and Phobos lower right, the moons of Mars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00078

Mars has two small, asteroid-sized moons named Phobos and Deimos. This frame from an animation shows the point of view of the rover, located near the equator of Mars, as these moons occasionally pass in front of, or transit, the disk of the sun.
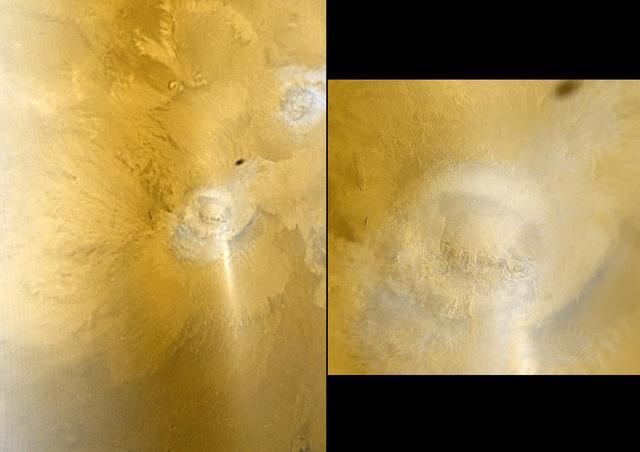

This pair of Mars Global Surveyor MGS Mars Orbiter Camera MOC color images shows early autumn clouds over the Arsia Mons volcano, plus the shadow of the innermost of the two martain moons, Phobos
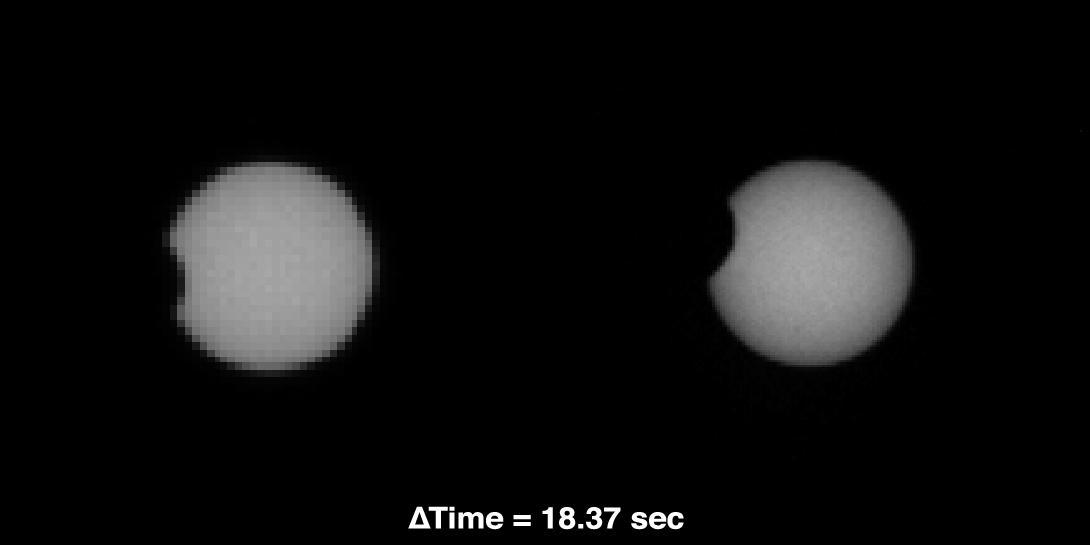

As part of a multi-mission campaign, NASA Curiosity rover is observing Martian moon transits, the first of which involved the moon Phobos grazing the sun disk.

Phobos and Deimos, the moons of Mars, are seen by the Mars Odyssey orbiter's Thermal Emission Imaging System, or THEMIS, camera. The images were taken in visible-wavelength light. THEMIS also recorded thermal-infrared imagery in the same scan. The apparent motion is due to progression of the camera's pointing during the 17-second span of the February 15, 2018, observation, not from motion of the two moons. This was the second observation of Phobos by Mars Odyssey; the first was on September 29, 2017. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. The distance to Phobos from Odyssey during the observation was about 3,489 miles (5,615 kilometers). The distance to Deimos from Odyssey during the observation was about 12,222 miles (19,670 kilometers). An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22248
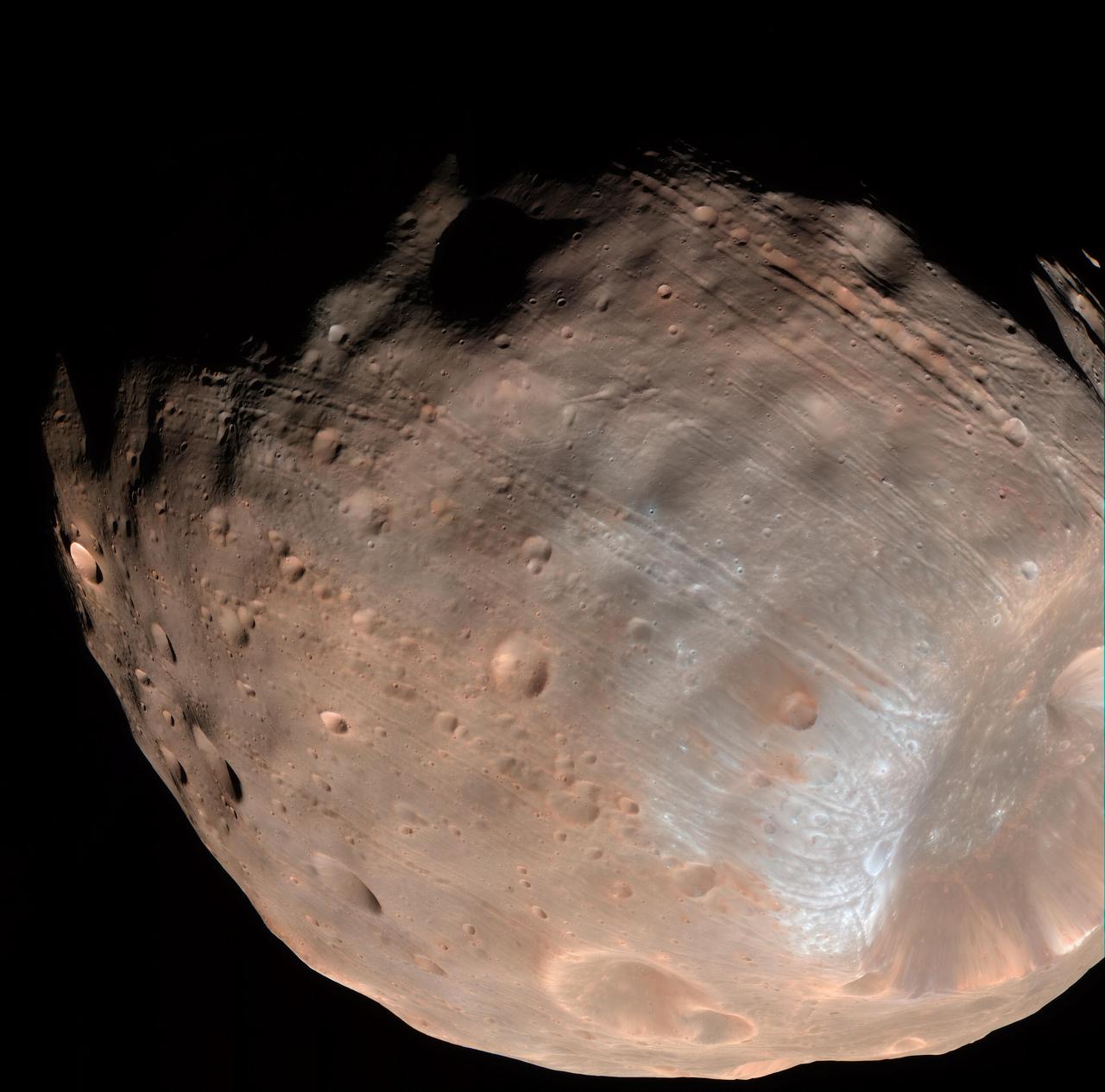
New modeling indicates that the grooves on Mars’ moon Phobos could be produced by tidal forces – the mutual gravitational pull of the planet and the moon. Initially, scientists had thought the grooves were created by the massive impact that made Stickney crater (lower right). Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Arizona Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1RLCS1v" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1RLCS1v</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
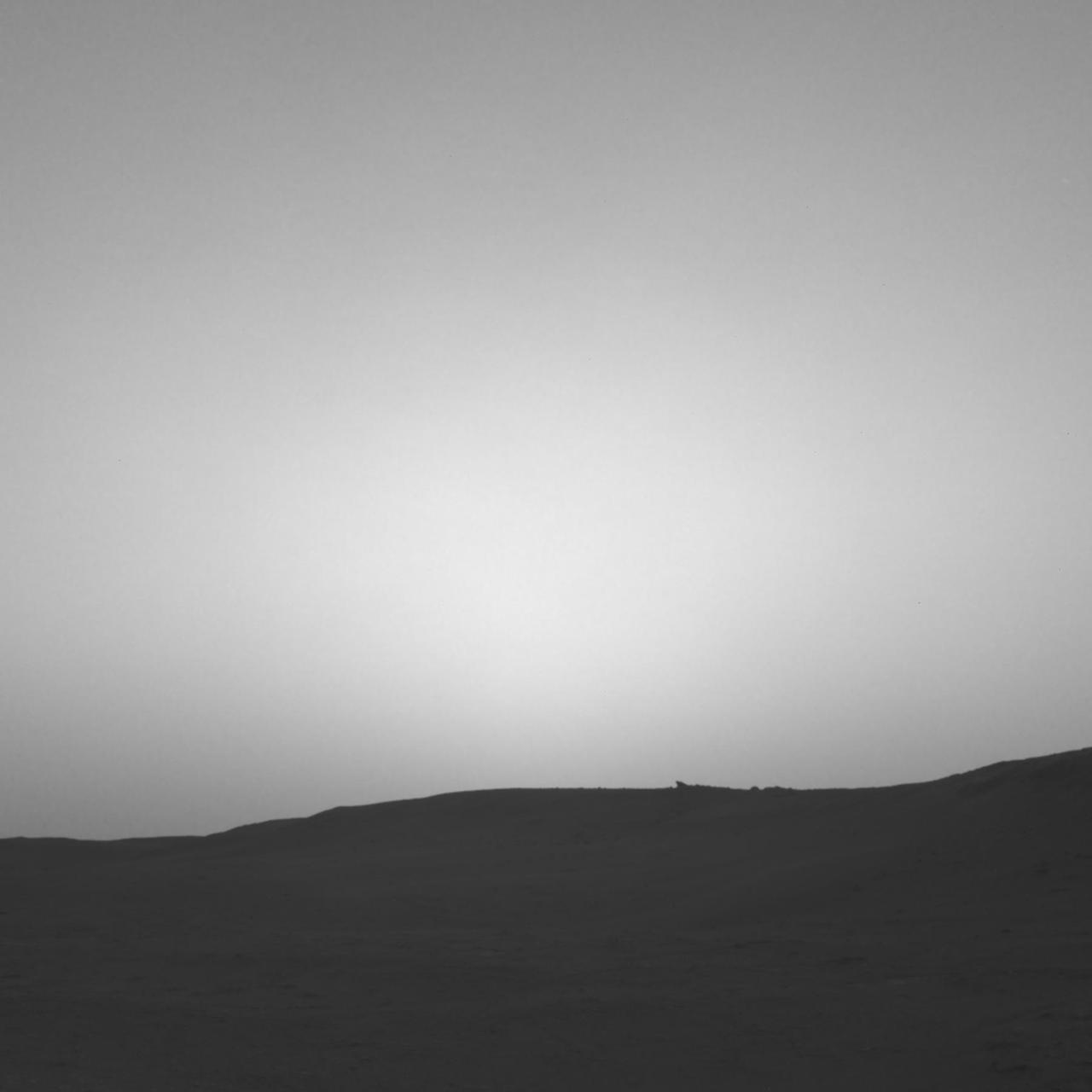

This series of images shows the shadow of Phobos as it sweeps over NASA's Curiosity Mars rover and darkens the sunlight on Monday, March 25, 2019 (the 2,358th sol, or Martian day, of the mission). This image was taken by one of Curiosity's Navigation Cameras (Navcams). The sequence has been contrast-enhanced and sped up by a factor of four. The image was taken after the Sun had descended behind the horizon, just as Phobos was rising and throwing its elongated shadow across the Martian surface. Dust particles in the atmosphere acted as a screen against which the shadow was projected. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23135
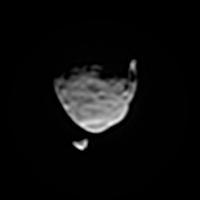
This view of the two moons of Mars comes from a set of images taken by NASA Mars rover Curiosity as the larger moon, Phobos, passed in front of the smaller one, Deimos, from Curiosity perspective, on Aug. 1, 2013.
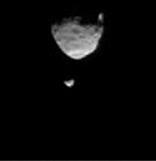
This frame from a movie clip shows the larger of Mars two moons, Phobos, passing in front of the smaller Martian moon, Deimos, as observed by NASA Mars rover Curiosity.

The larger of the two moons of Mars, Phobos, passes in front of the Sun face in this image from NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity. A movie is available at the Photojournal.

NASA's Curiosity Mars rover used its Mast Camera, or Mastcam, to capture this view of Earth setting while Phobos, one of Mars' two moons, is rising. It's the first time an image of the two celestial bodies have been captured together from the surface of Mars. The image is a composite of five short exposures and 12 long exposures all taken on Sept. 5, 2024, the 4,295th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's mission. An inset in the image shows Phobos on the left and Earth on the right. From the rover's perspective, the inset area would be about half the width of a thumb held at arm's length. The image shows the sky over Texoli, a butte on lower Mount Sharp, a 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) mountain that Curiosity has been ascending since 2014. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26362
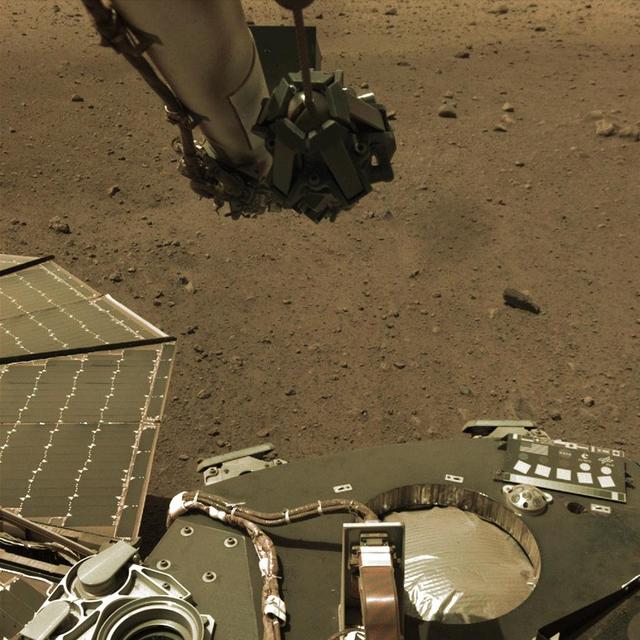

NASA's InSight lander took this series of images on Tuesday, March 5, 2019, capturing the moment when Phobos, one of Mars' moons, crossed in front of the Sun and darkened the ground around the lander. The images were taken by InSight's Instrument Deployment Camera (IDC), located on the lander's robotic arm. The images were taken at intervals of about 50 seconds in order to capture the eclipse, which on this day lasted 24.3 seconds. In the lower right corner of the frame, the shadow of the robotic arm can be seen moving to the right before the entire scene darkened during the moment of the eclipse. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23049
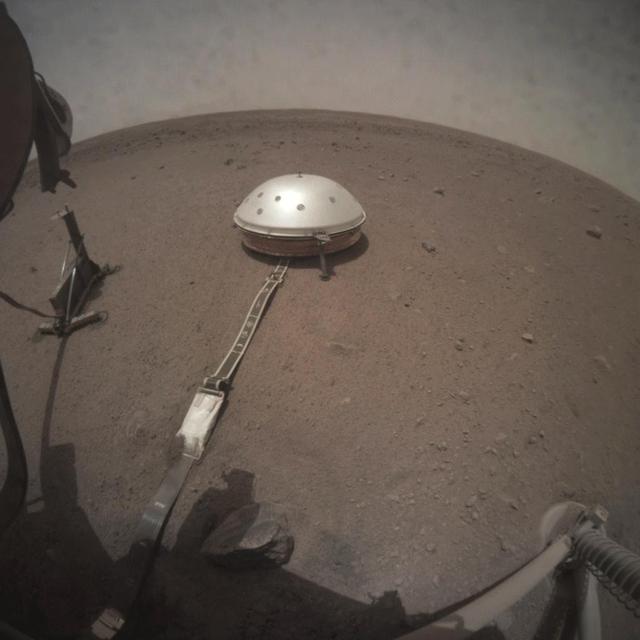

NASA's InSight lander took this series of images on Wednesday, March 6, 2019, capturing the moment when Phobos, one of Mars' moons, crossed in front of the Sun and darkened the ground around the lander. These images were taken by InSight's Instrument Context Camera (ICC), located under the lander's deck. The images were taken at intervals of about 50 seconds in order to capture the eclipse, which on this day lasted 26.7 seconds. The shadow of the lander can be seen moving to the right before the entire scene darkened during the moment of the eclipse. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23048
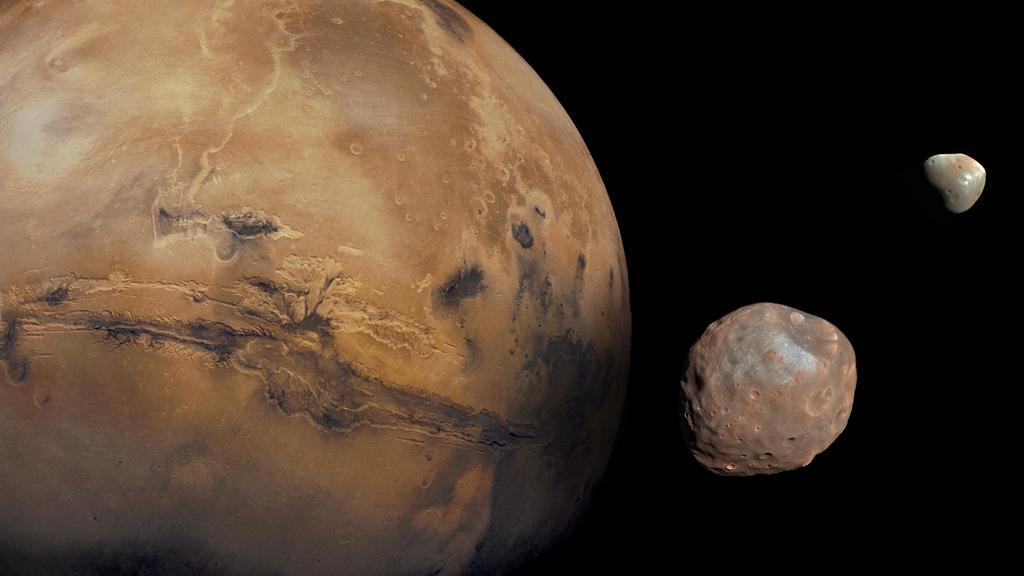

Mars is kept company by two cratered moons -- an inner moon named Phobos and an outer moon named Deimos.

This panel illustrates the transit of the martian moon Phobos across the Sun. It is made up of images taken by NASA Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity.

While photographing Mars, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured a cameo appearance of the tiny moon Phobos on its trek around the Red Planet. Discovered in 1877, the diminutive, potato-shaped moon is so small that it appears star-like in the Hubble pictures. Phobos orbits Mars in just 7 hours and 39 minutes, which is faster than Mars rotates. The moon’s orbit is very slowly shrinking, meaning it will eventually shatter under Mars’ gravitational pull, or crash onto the planet. Hubble took 13 separate exposures over 22 minutes to create a time-lapse video showing the moon’s orbital path. Credit: NASA, ESA, and Z. Levay (STScI) <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

NASA's Europa Clipper captured this infrared image of the heat radiation from Mars and its moons Phobos (closest to Mars) and Deimos (seen in upper left corner) on Feb. 28, 2025, as the spacecraft approached the Red Planet while en route to the Jupiter system to investigate the icy moon Europa. The mission flew by Mars the next day, using the planet's gravity to help shape the spacecraft's trajectory. When the image was taken by the mission's Europa Thermal Emission Imaging System (E-THEMIS), the spacecraft was about 560,000 miles (900,000 kilometers) from the Red Planet. The image is composed of 200 individual frames, part of a continuous scan of 1,100 frames taken roughly a second apart over a period of 20 minutes. Scientists are using the tiny, point-like images of the moons to check the camera's focus. The image was captured using the middle of E-THEMIS's three long-wave infrared wavelength bands, which extend from about 14 to 28 micrometers. (A previously released E-THEMIS image of Mars used the shortest of the instrument's wavelength bands, extending from 7 to 14 micrometers and showing Mars in higher contrast.) The dark oval near the top of Mars is the planet's cold northern polar cap and is about minus 190 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 125 degrees Celsius). The circular feature seen on Mars is the region around Elysium Mons. The faint halo seen around the planet is due to the processing of the image. The two moons are about 250 times fainter than Mars, so scientists brightened the image (except for a region circling the planet) to make the moons more visible. The brightening also makes image noise more visible; the area surrounding Mars within the halo appears comparatively dark because it wasn't brightened. Europa Clipper launched from NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 14, 2024, and will arrive at the Jupiter system in 2030 to conduct about 50 flybys of Europa. The mission's main science goal is to determine whether there are places below Europa's surface that could support life. The mission's three main science objectives are to determine the thickness of the moon's icy shell and its surface interactions with the ocean below, to investigate its composition, and to characterize its geology. The mission's detailed exploration of Europa will help scientists better understand the astrobiological potential for habitable worlds beyond our planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26567

The Two Moons of Mars as Seen from Mars

This image from NASA Mars rover Curiosity provides a comparison for how big the moons of Mars appear to be, as seen from the surface of Mars, in relation to the size that Earth moon appears to be when seen from the surface of Earth.
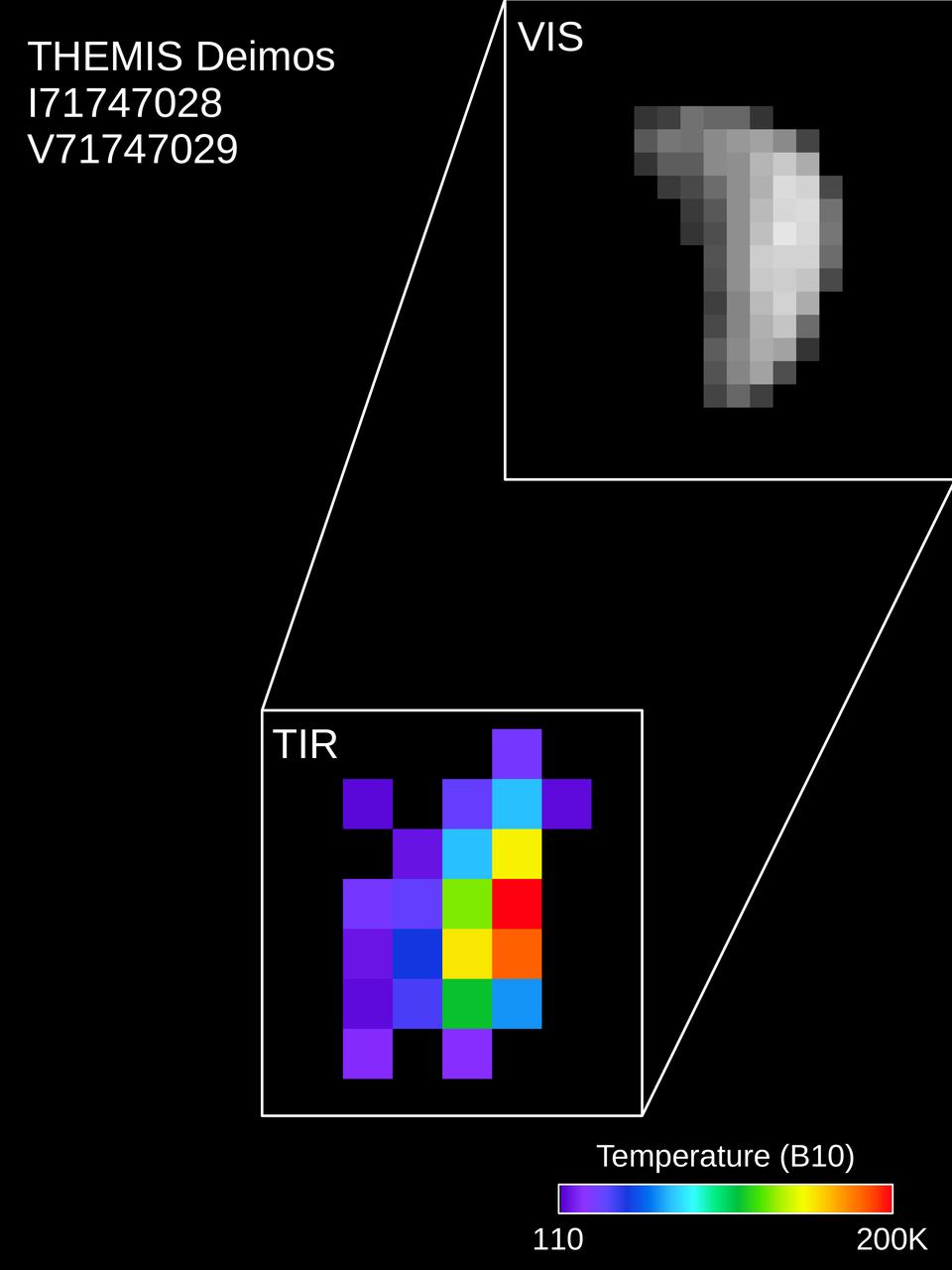
Colors in this image of the Martian moon Deimos indicate a range of surface temperatures detected by observing the moon on February 15, 2018, with the Thermal Emission Imaging System (THEMIS) camera on NASA's Mars Odyssey orbiter. The left edge of the small moon is in darkness, and the right edge in sunlight. Temperature information was derived from thermal-infrared imaging such as the grayscale image shown smaller at lower left with the moon in the same orientation. The color-coding merges information from THEMIS observations made in 10 thermal-infrared wavelength bands. This was the first observation of Deimos by Mars Odyssey; the spacecraft first imaged Mars' other moon, Phobos, on September 29, 2017. Researchers have been using THEMIS to examine Mars since early 2002, but the maneuver turning the orbiter around to point the camera at Phobos was developed only recently. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22250
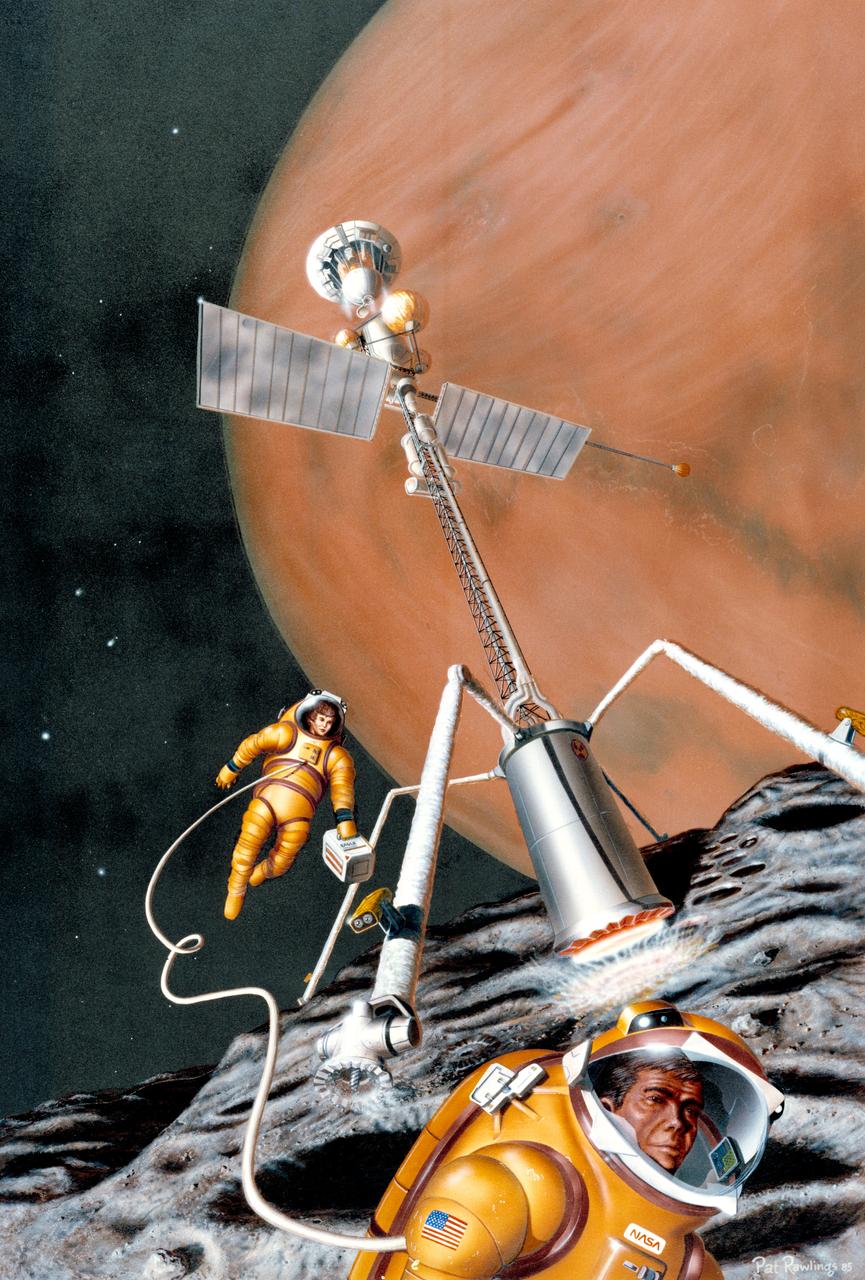

S86-25375 (1986) --- (Artist's concept of possible exploration programs.) On Phobos, the innermost moon of Mars and likely location for extraterrestrial resources, a mobile propellant-production plant lumbers across the irregular surface. Using a nuclear reactor the large tower melts into the surface, generating steam which is converted into liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen. Artwork by Pat Rawlings, of Eagle Engineering, Incorporated.
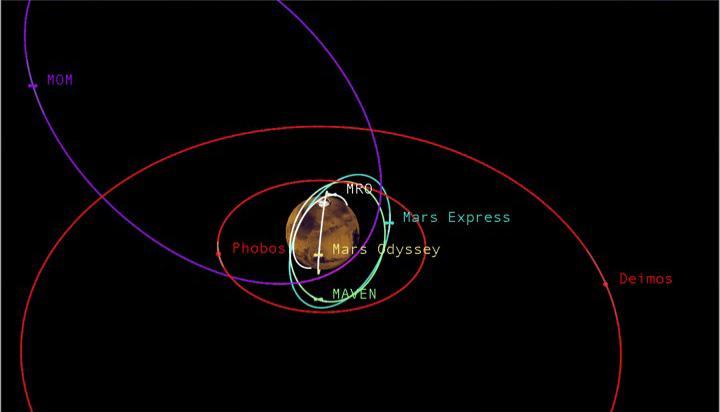

This graphic depicts the relative shapes and distances from Mars for five active orbiter missions plus the planet's two natural satellites. It illustrates the potential for intersections of the spacecraft orbits. The number of active orbiter missions at Mars increased from three to five in 2014. With the increased traffic, NASA has augmented a process for anticipating orbit intersections and avoiding collisions. NASA's Mars Odyssey and MRO (Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter) travel near-circular orbits. The European Space Agency's Mars Express, NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) and India's MOM (Mars Orbiter Mission), travel more elliptical orbits. Phobos and Deimos are the two natural moons of Mars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19396

The sharp eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured the tiny moon Phobos during its orbital trek around Mars. Because the moon is so small, it appears star-like in the Hubble pictures. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble took 13 separate exposures, allowing astronomers to create a time-lapse video showing the diminutive moon's orbital path. The Hubble observations were intended to photograph Mars, and the moon's cameo appearance was a bonus. More here: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2uDchSn" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2uDchSn</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>