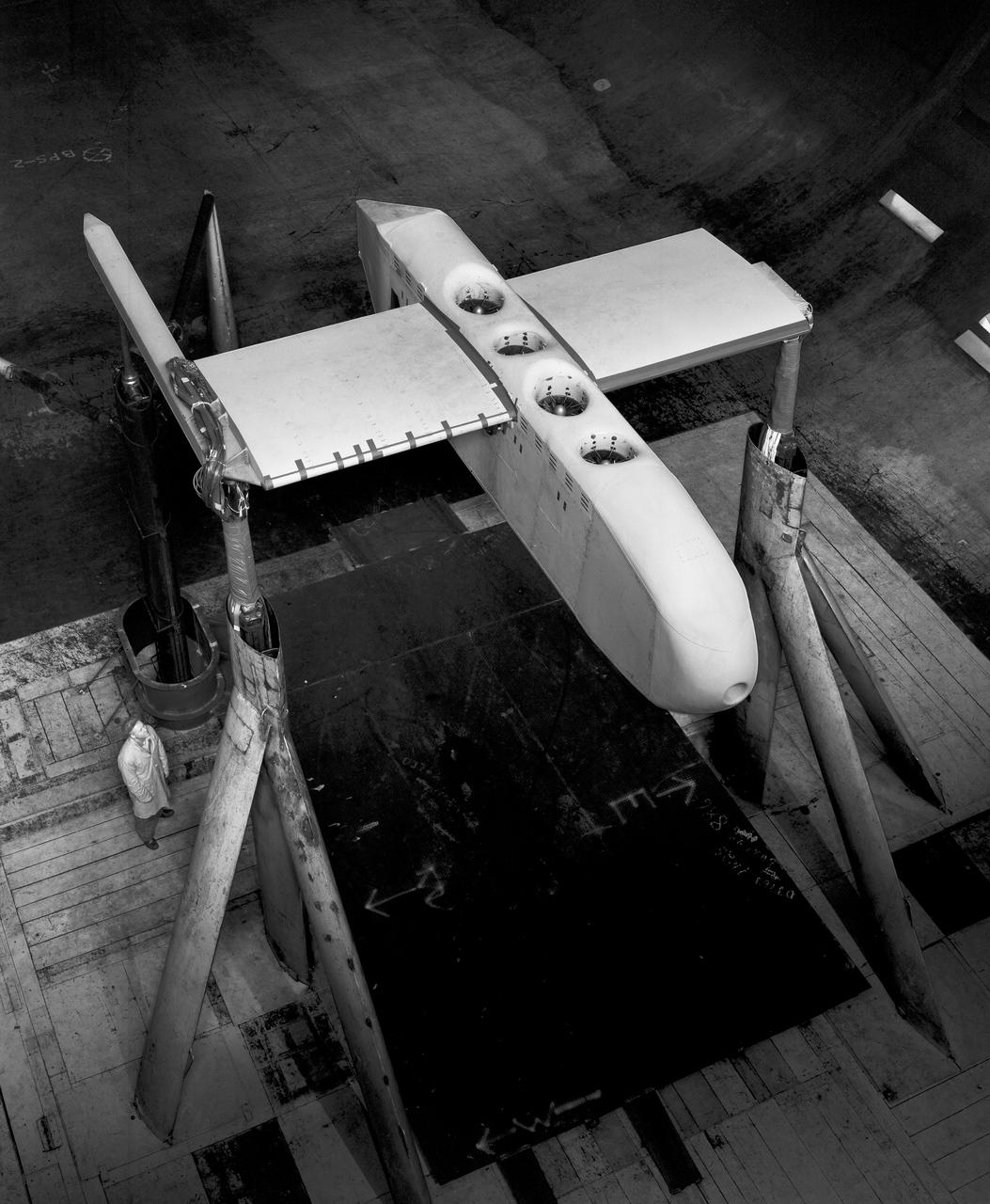

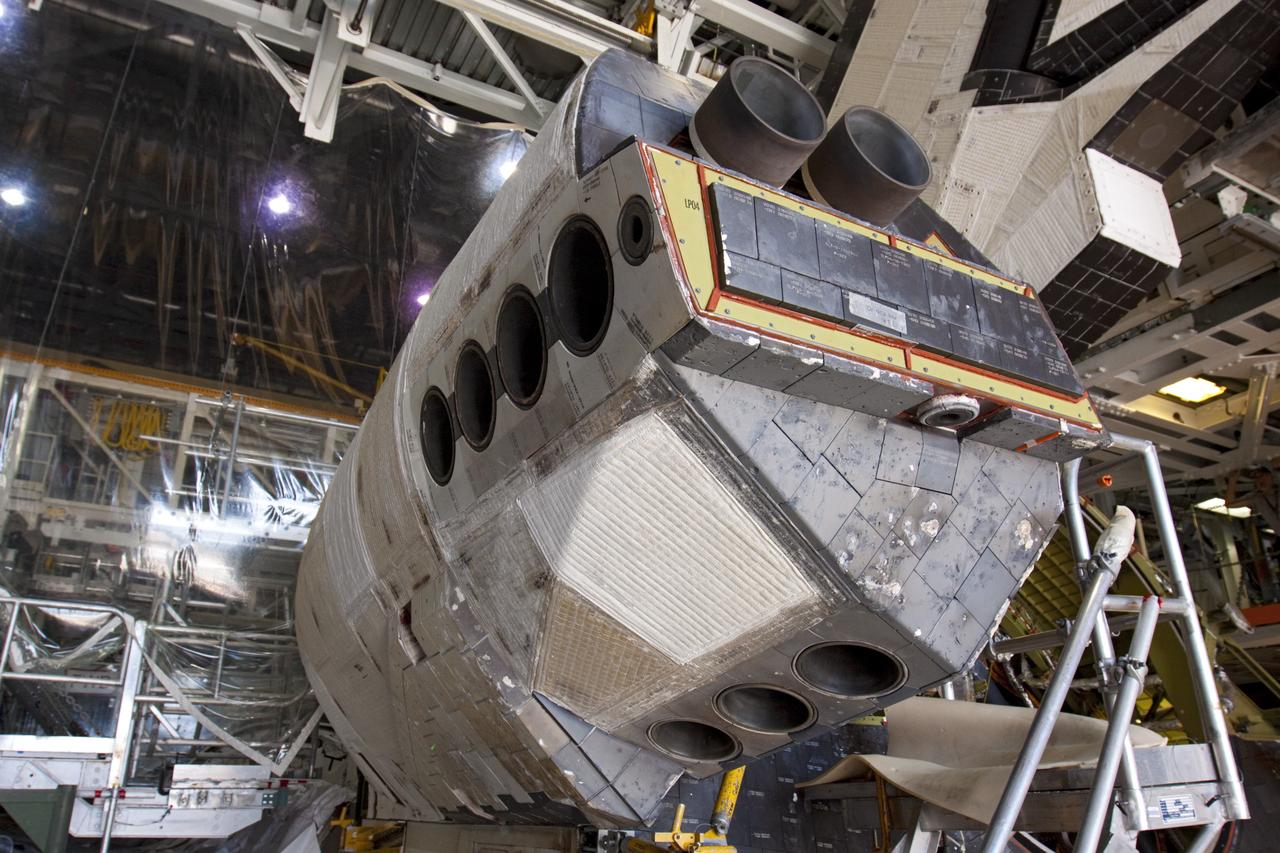
3/4 front, top view of Noriar Lift Engine Pod installation in Ames 40x80 foot wind tunnel

Official group photo of the new class of PODs (Payload Operations Directors) for 2019, taken in building 4663 Payload Operations Center. (L to R) Stacey Steele, Michael Vigo, Dr. Ian Howley, Luke Bingaman, Jennifer McMillian, Luke Mays, Carlos Barreto, David Nicholas Benjamin
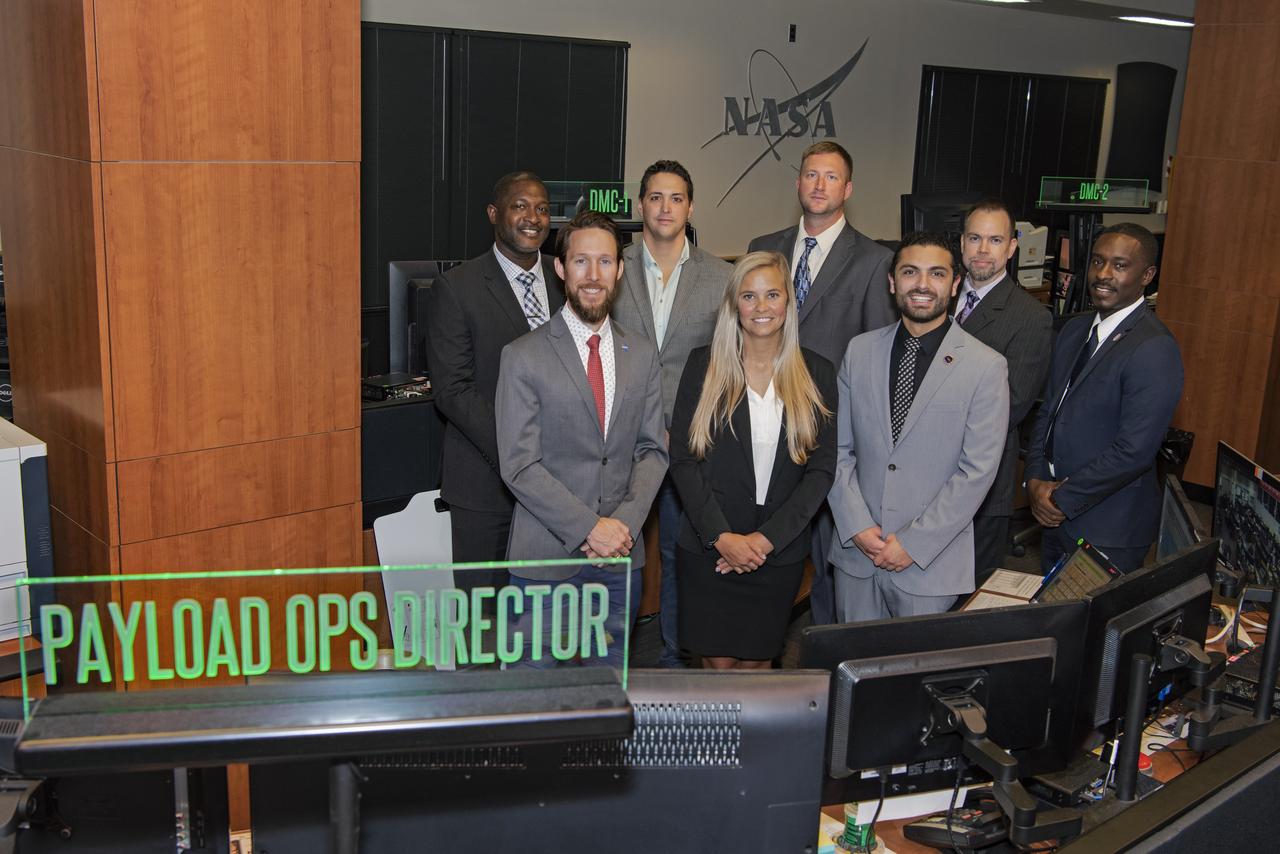

Official group photo of the new class of PODs (Payload Operations Directors) for 2019, taken in building 4663 Payload Operations Center. (L to R) Stacey Steele, Dr. Ian Howley, Michael Vigo, Jennifer McMillian, Luke Bingaman, Carlos Barreto, Luke Mays, David Nicholas Benjamin
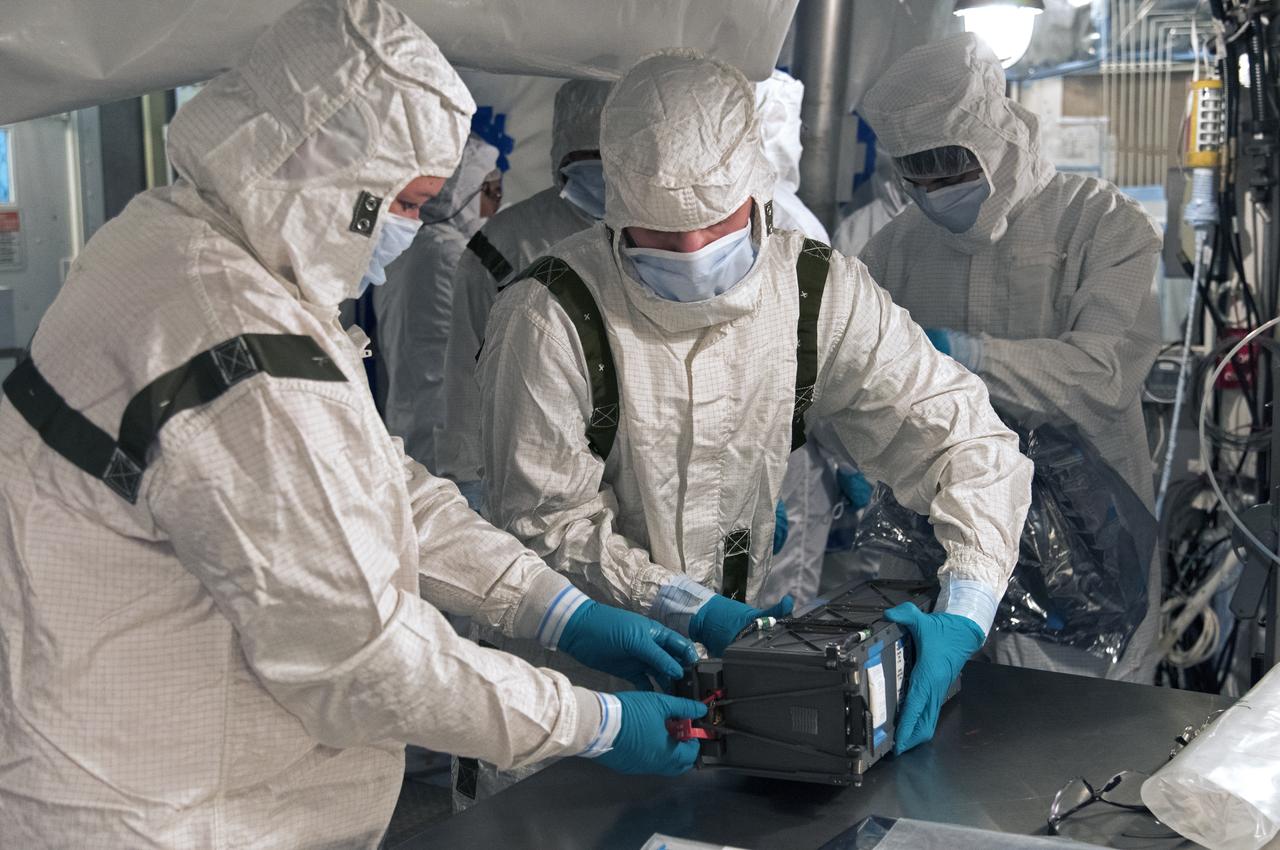

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare to install a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
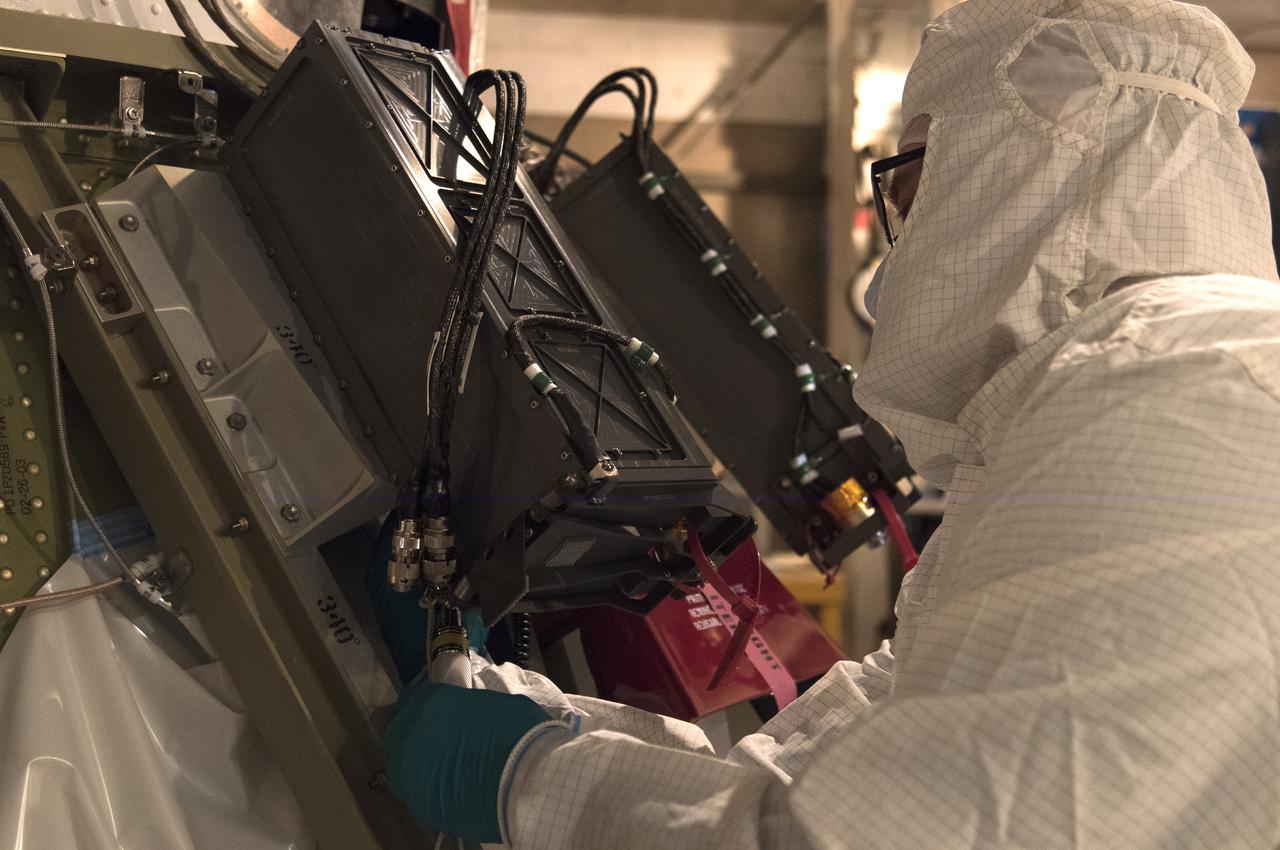

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
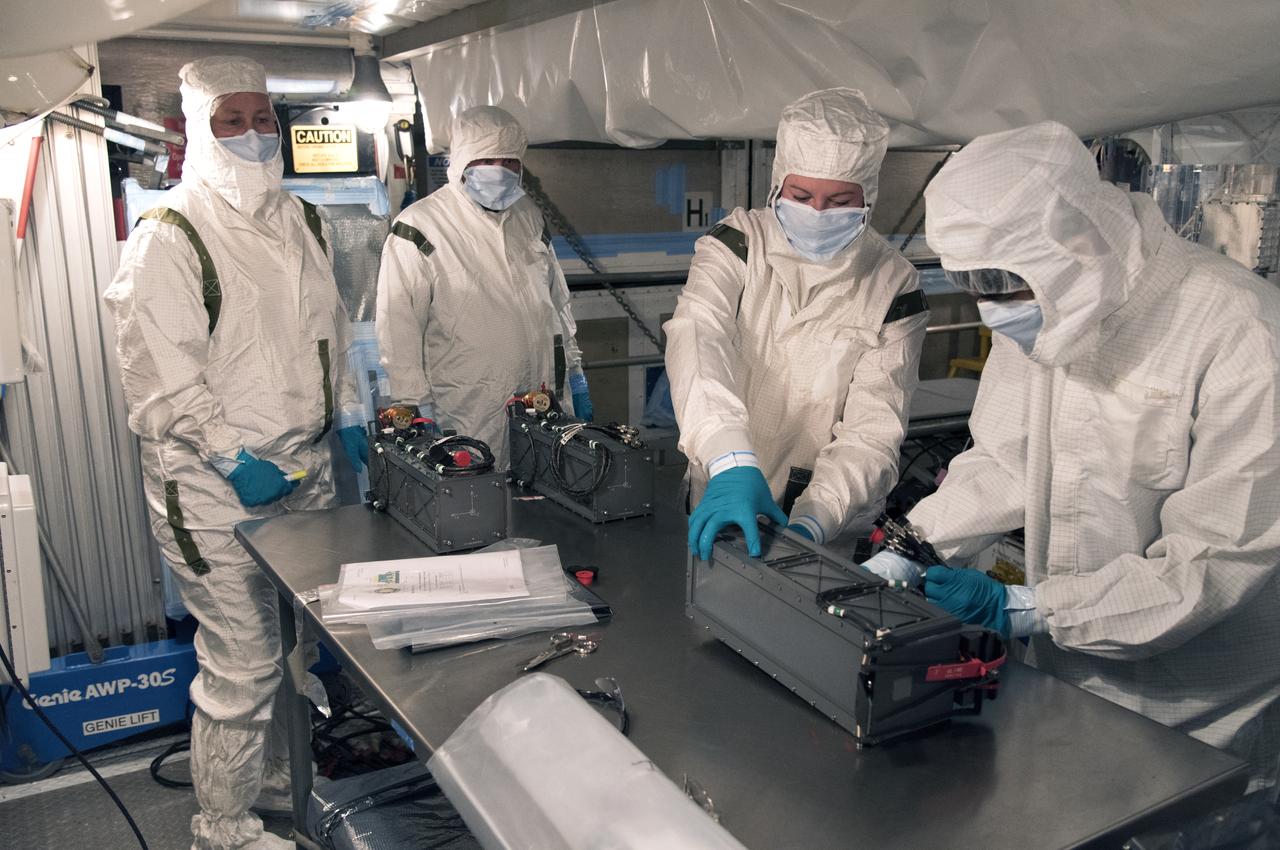

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
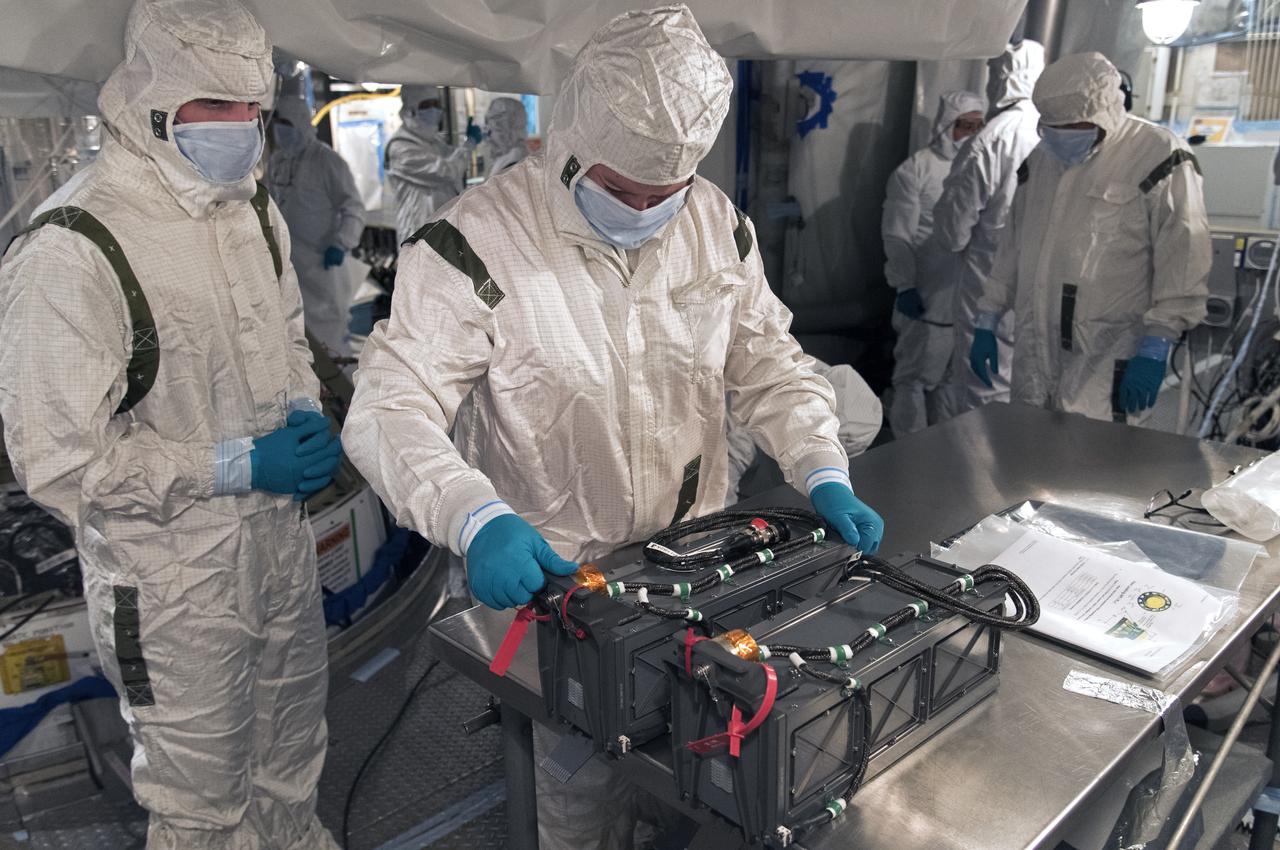

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
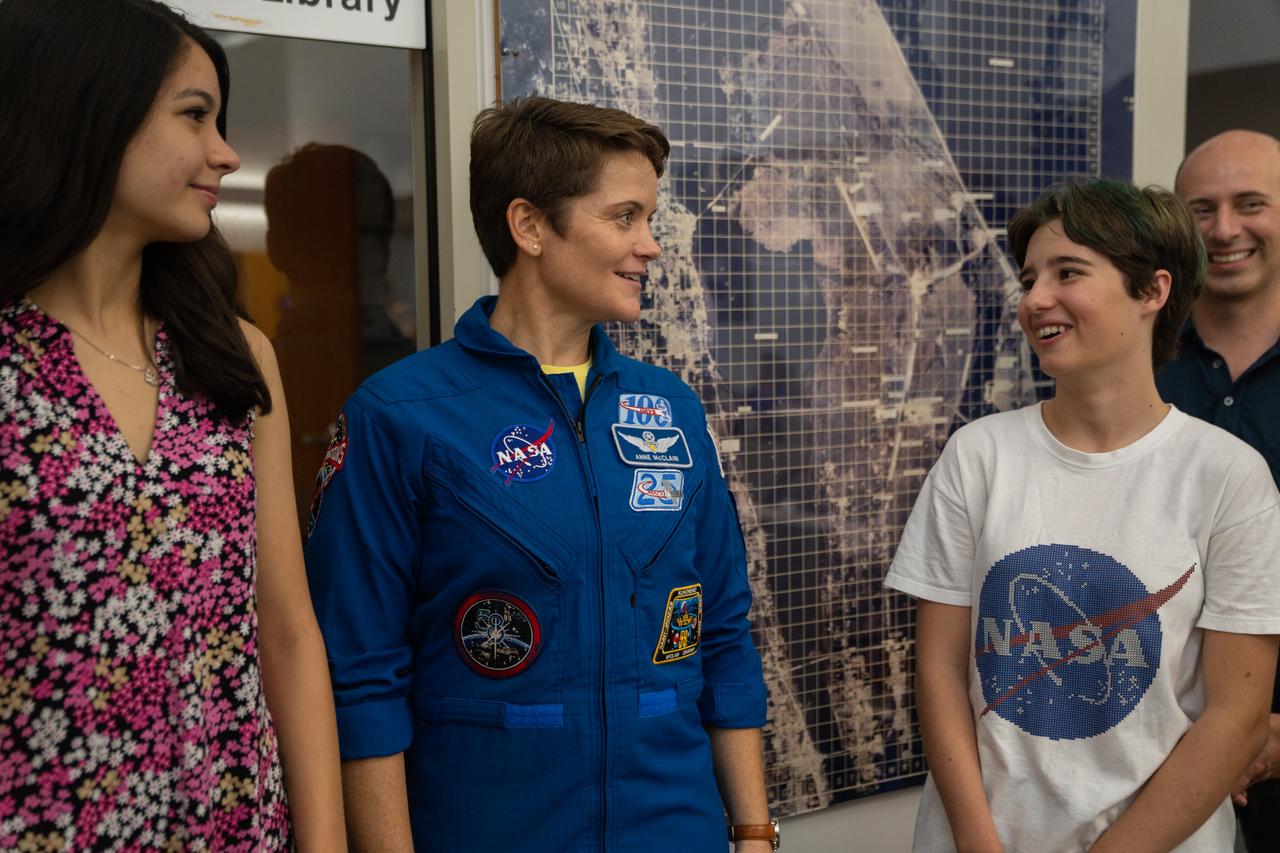

NASA astronaut Anne McClain talks with student essay winners Amanda Gutierrez, left, and Taia Saurer at the agency’s news center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 2, 2022. Gutierrez and Saurer won the Artemis Moon Pod Essay Contest – a nationwide event involving nearly 14,000 students – for their creative visions of a pioneering journey to the Moon. The grand prize was a trip to Kennedy to watch the launch of Artemis I. Gutierrez, 17, is an 11th-grader from Lincoln, Nebraska, while Saurer, 14, is an eighth-grader from Laguna Beach, California.
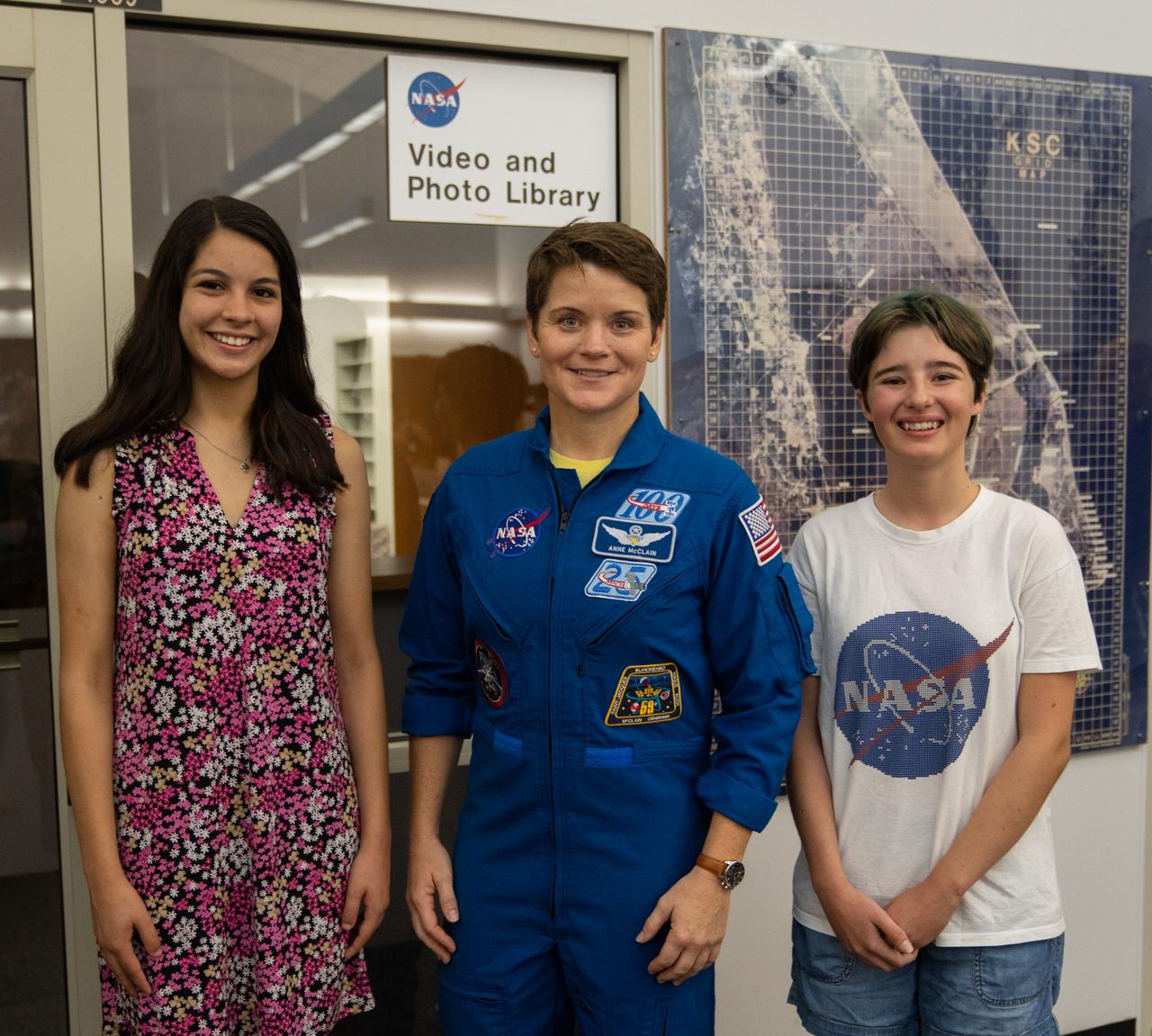

Student essay winners Amanda Gutierrez, left, and Taia Saurer pose with NASA astronaut Anne McClain at the agency’s news center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 2, 2022. Gutierrez and Saurer won the Artemis Moon Pod Essay Contest – a nationwide event involving nearly 14,000 students – for their creative visions of a pioneering journey to the Moon. The grand prize was a trip to Kennedy to watch the launch of Artemis I. Gutierrez, 17, is an 11th-grader from Lincoln, Nebraska, while Saurer, 14, is an eighth-grader from Laguna Beach, California.
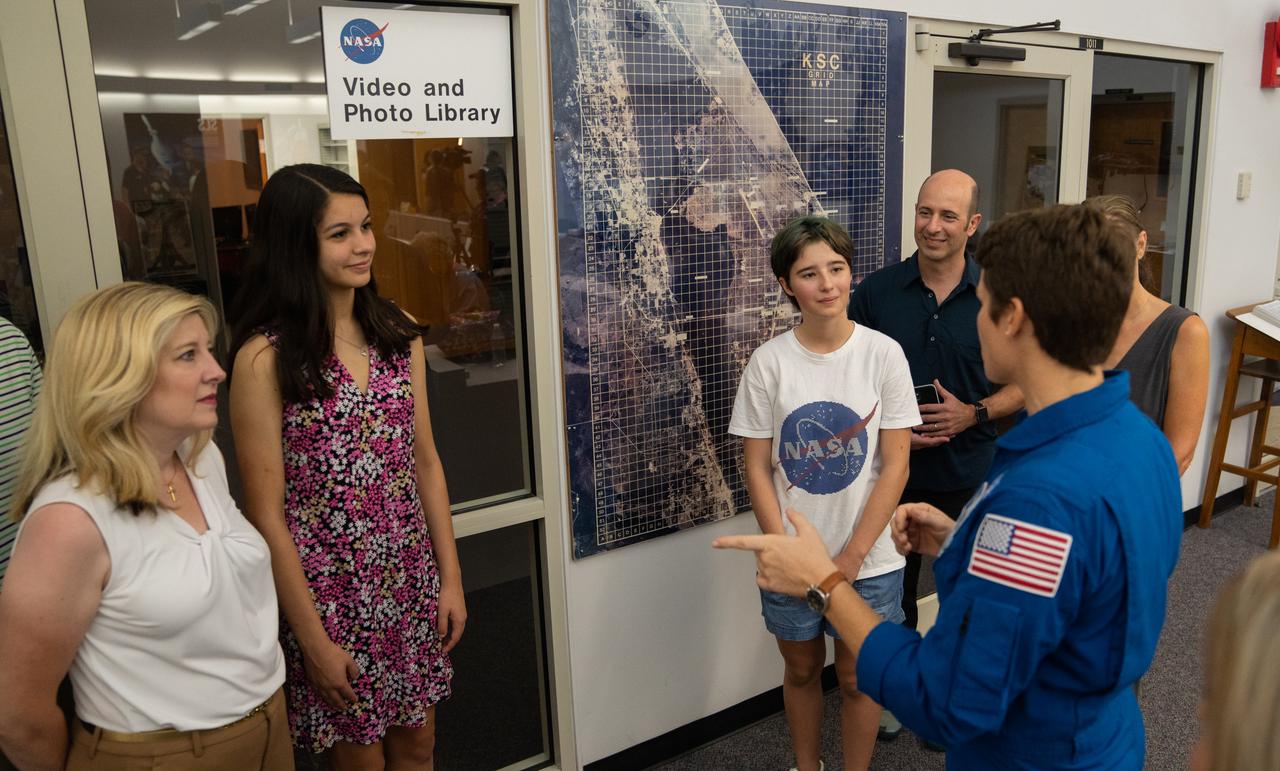

NASA astronaut Anne McClain talks with student essay winners Amanda Gutierrez, second from left, and Taia Saurer, white NASA shirt, at the agency’s news center at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 2, 2022. Gutierrez and Saurer won the Artemis Moon Pod Essay Contest – a nationwide event involving nearly 14,000 students – for their creative visions of a pioneering journey to the Moon. The grand prize was a trip to Kennedy to watch the launch of Artemis I. Gutierrez, 17, is an 11th-grader from Lincoln, Nebraska, while Saurer, 14, is an eighth-grader from Laguna Beach, California.
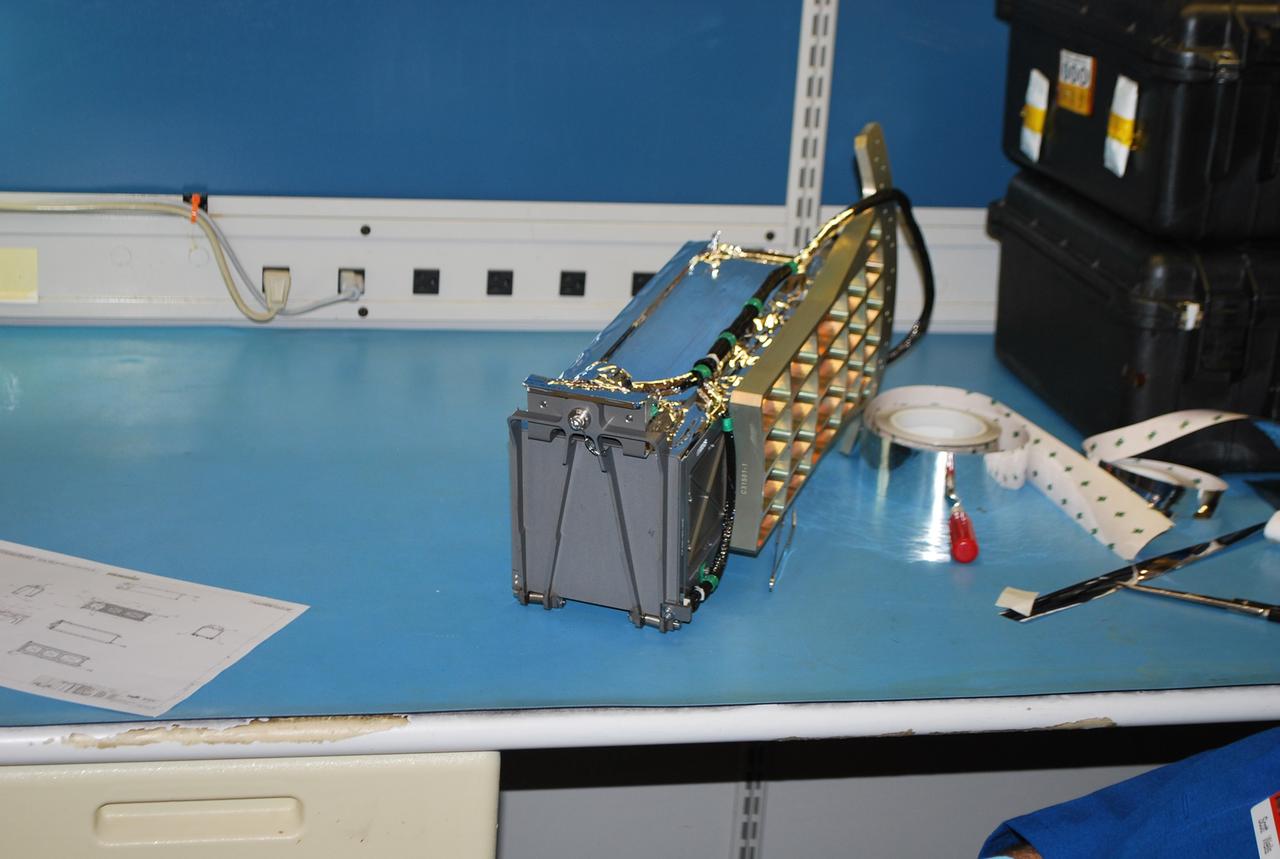

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is imaged here with the bracket interface installed. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin,VAFB
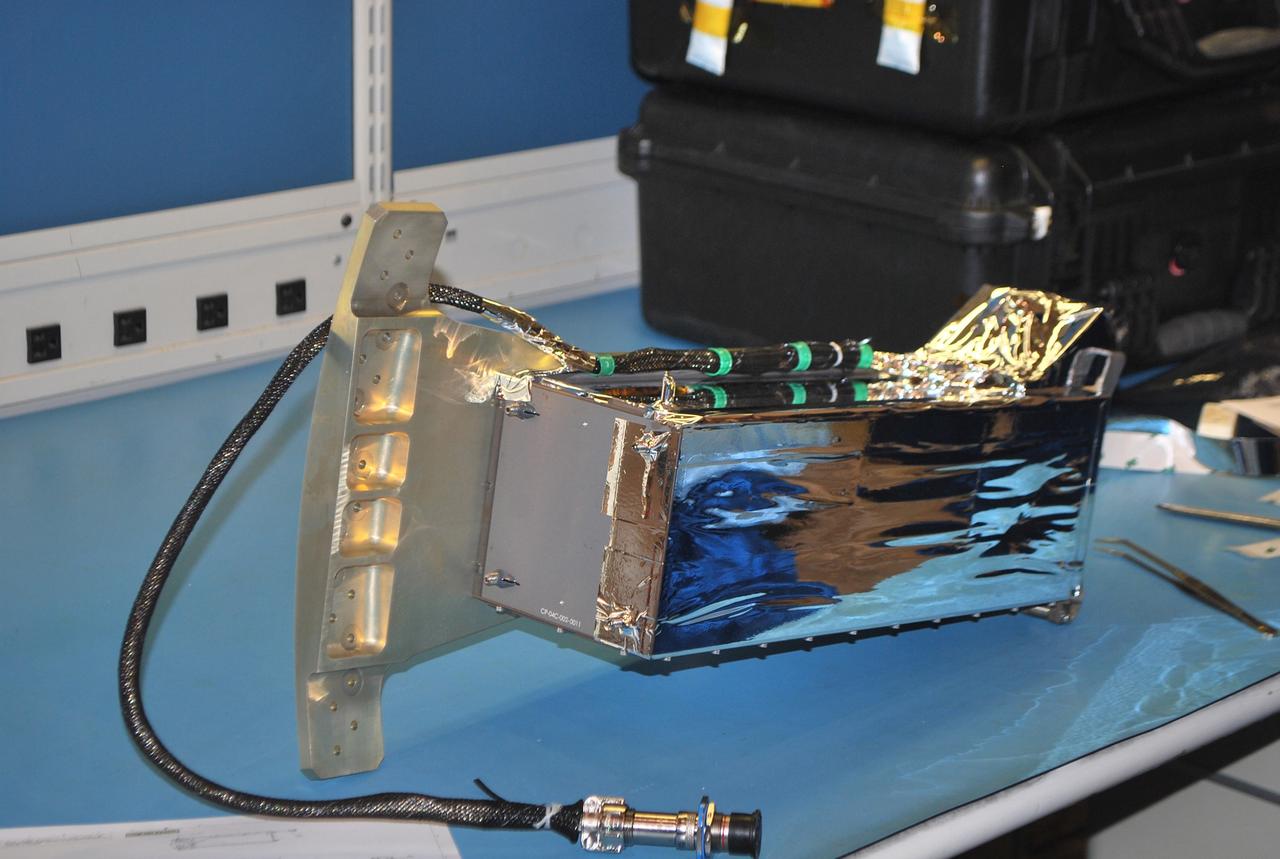

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is imaged here with the bracket interface installed. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
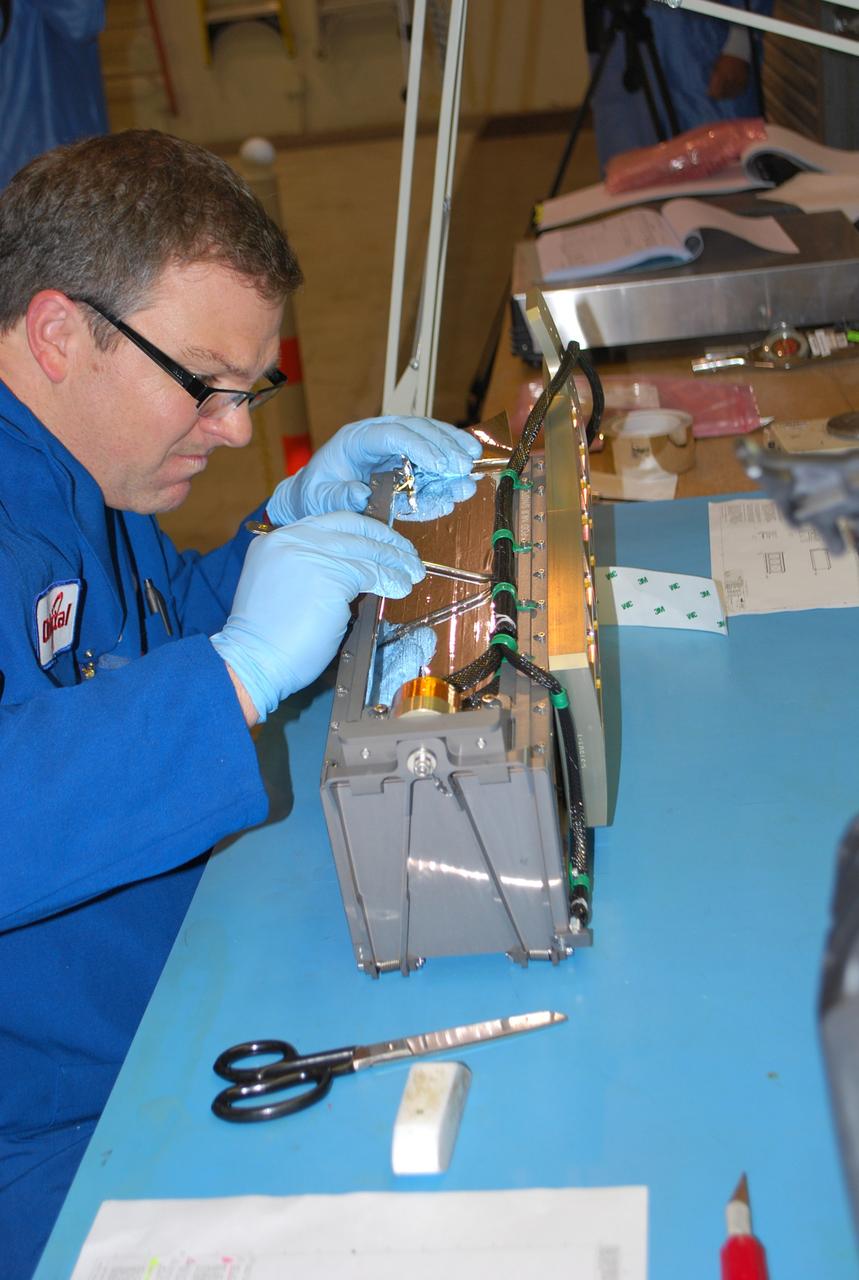

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician installs a bracket on a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
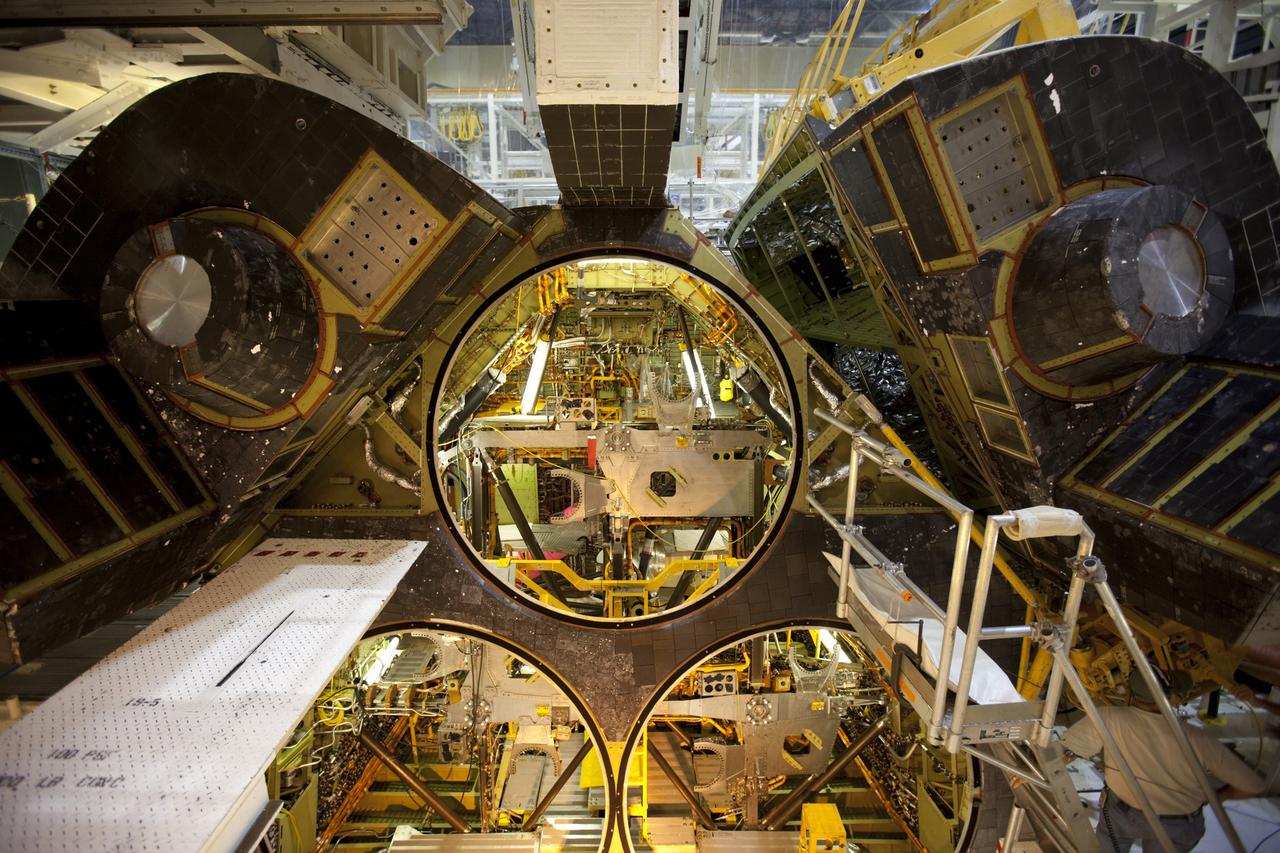

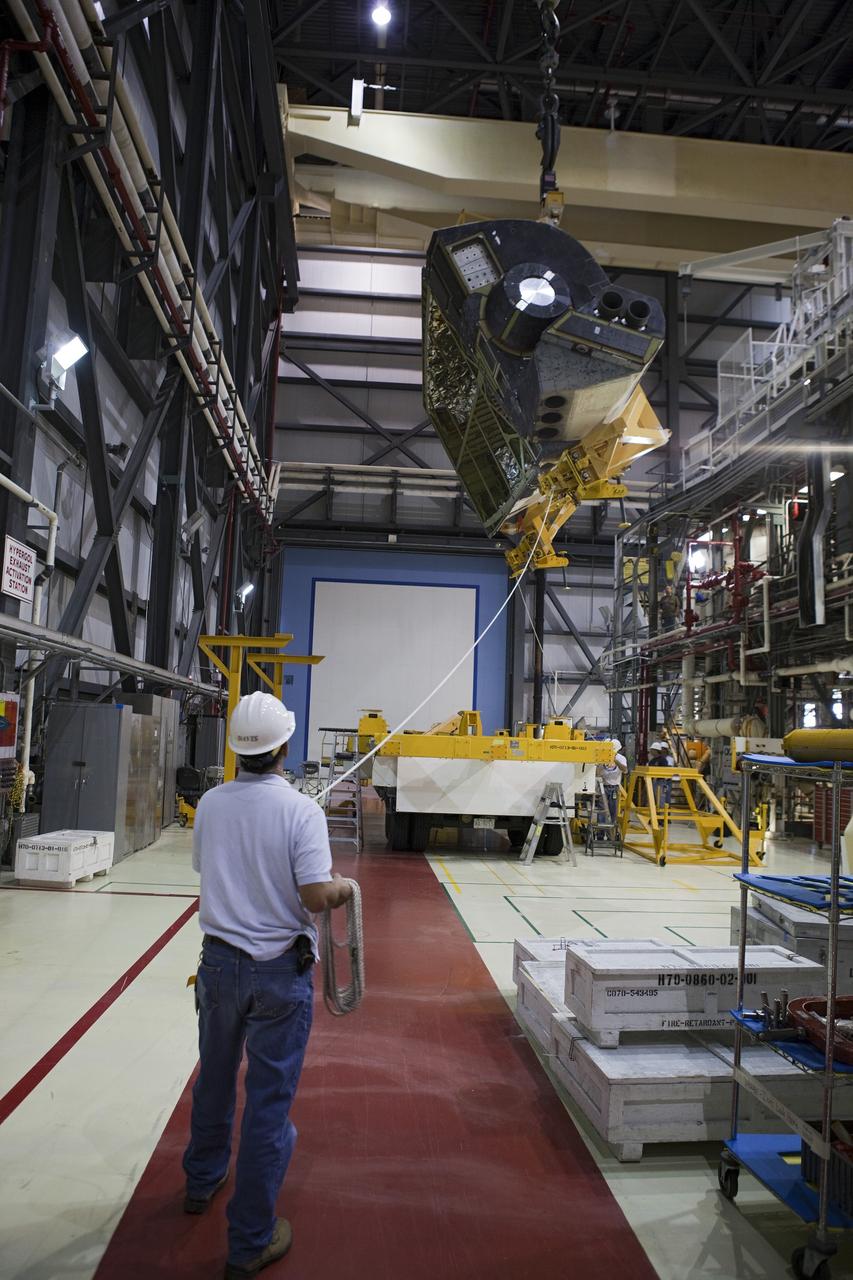
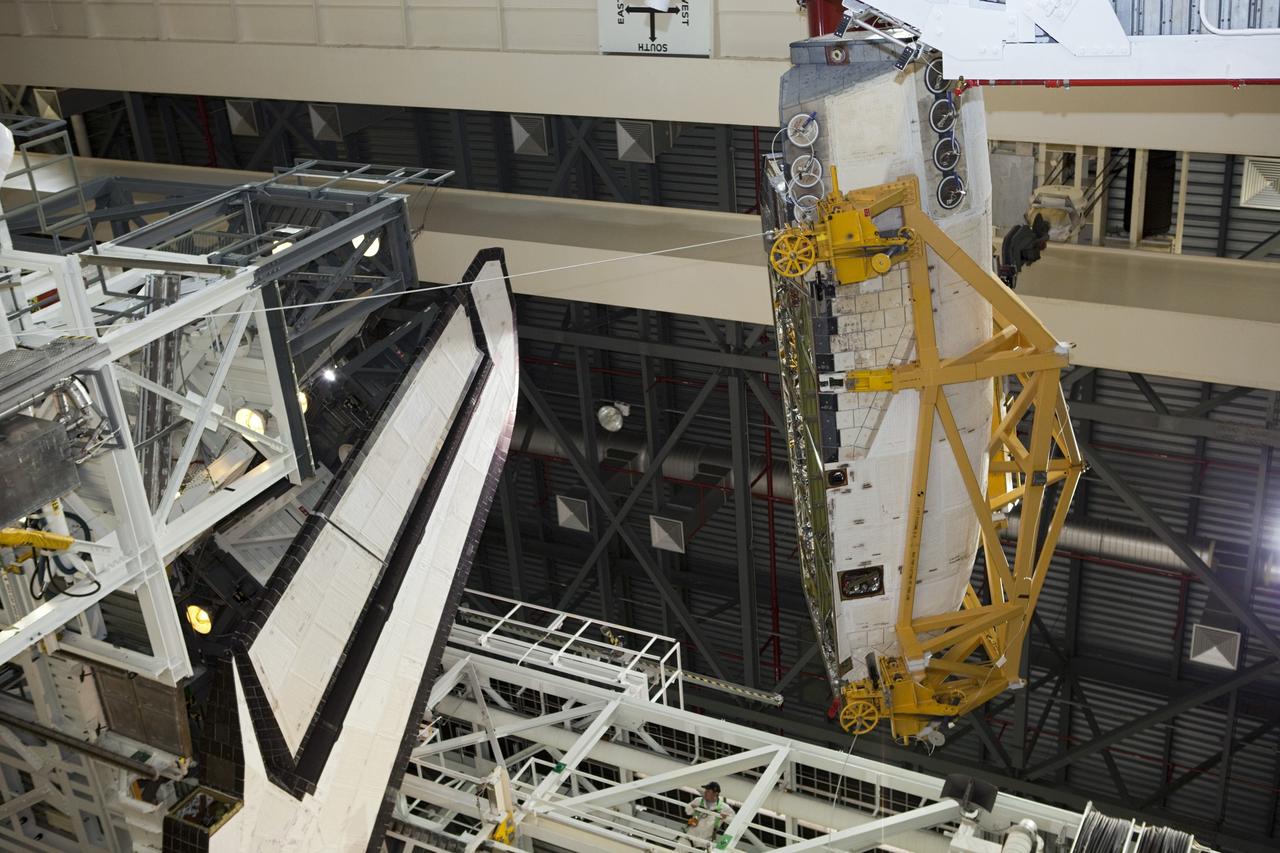
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a unique close-up view shows a large crane lowering the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis and the left OMS pod already installed. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane transports an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod closer to space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod will be installed on Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane carries an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod closer to space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod will be installed on Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane carries an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod closer to space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod will be installed on Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

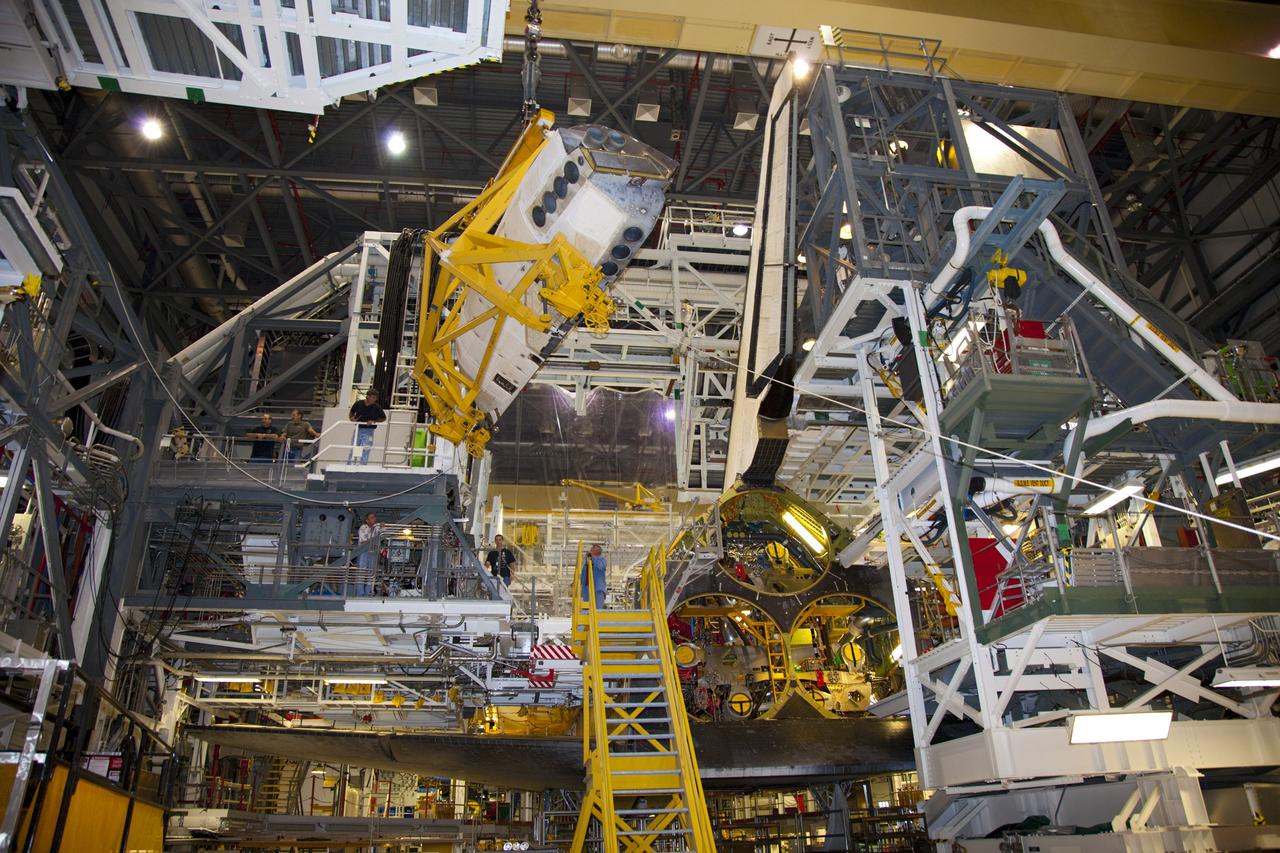
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane begins to lift the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a United Space Alliance technician monitors the progress as a large crane lifts the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
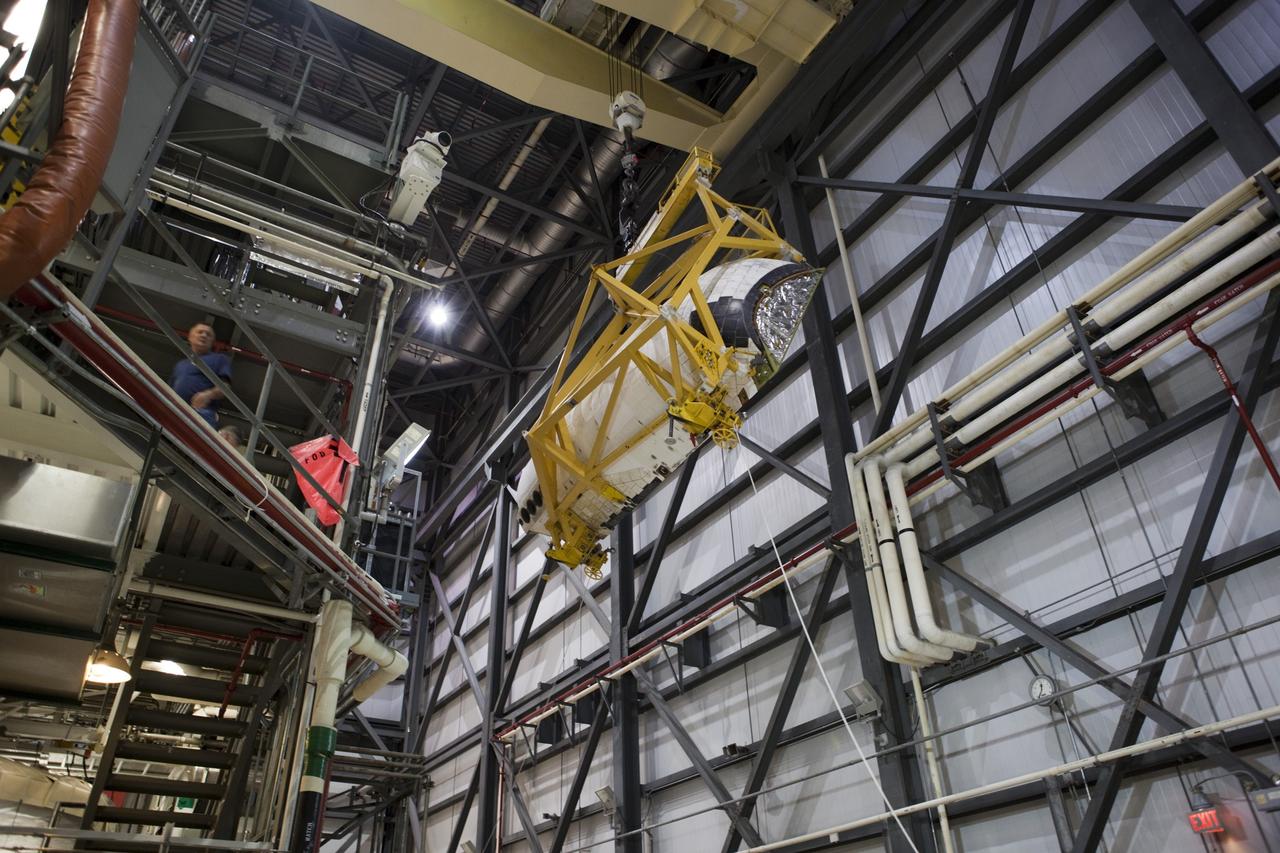

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a United Space Alliance technician monitors the progress as a large crane lifts the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

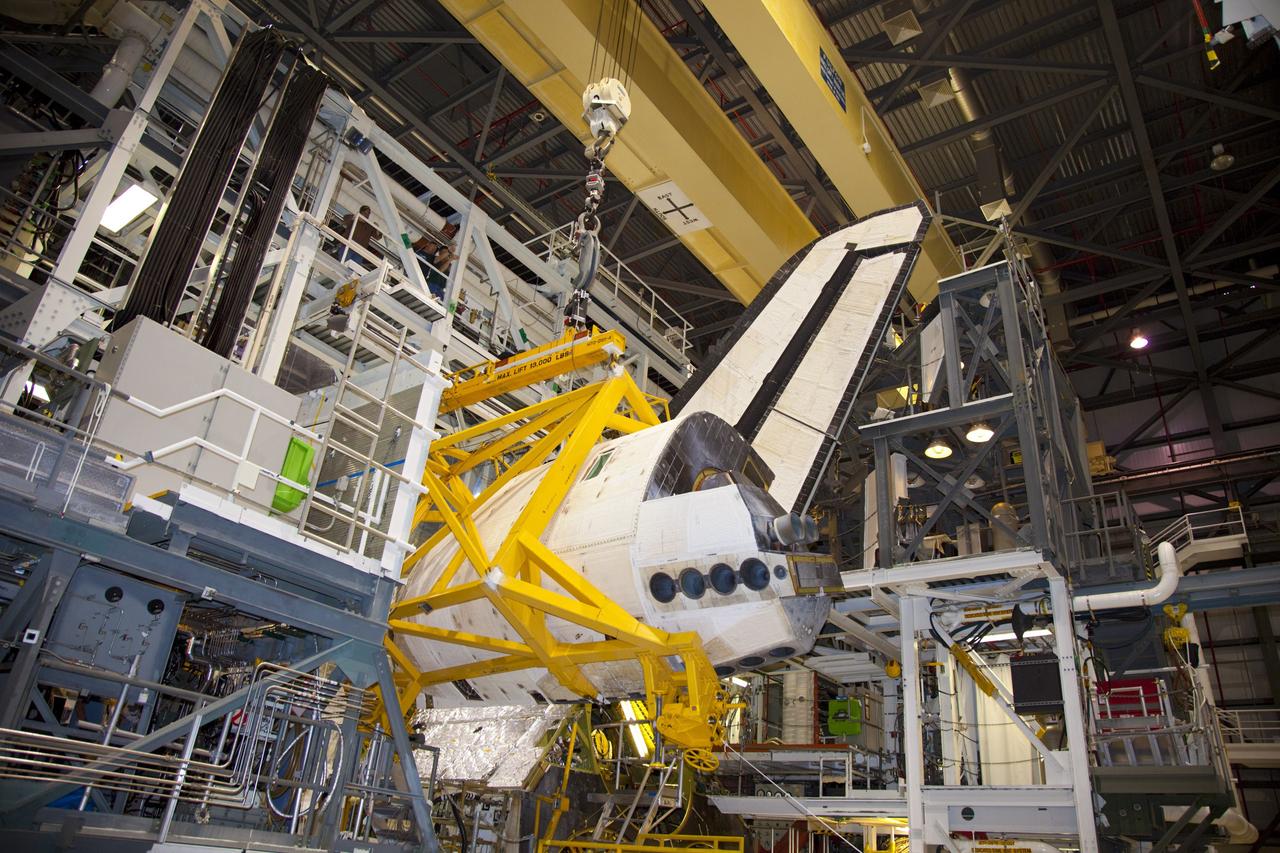
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane moves the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
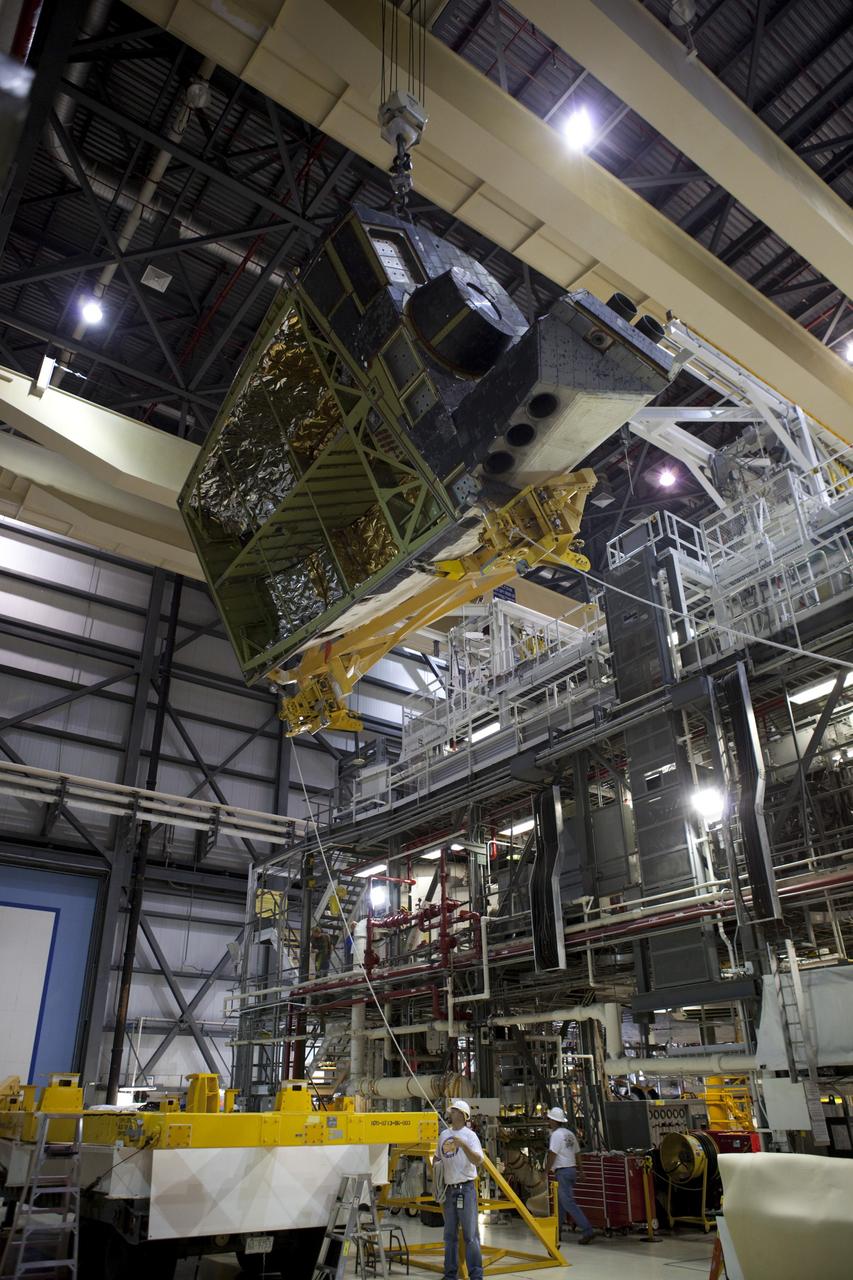

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lifts the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane lowers the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod onto space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a view from above inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a crane is attached to the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod onto space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
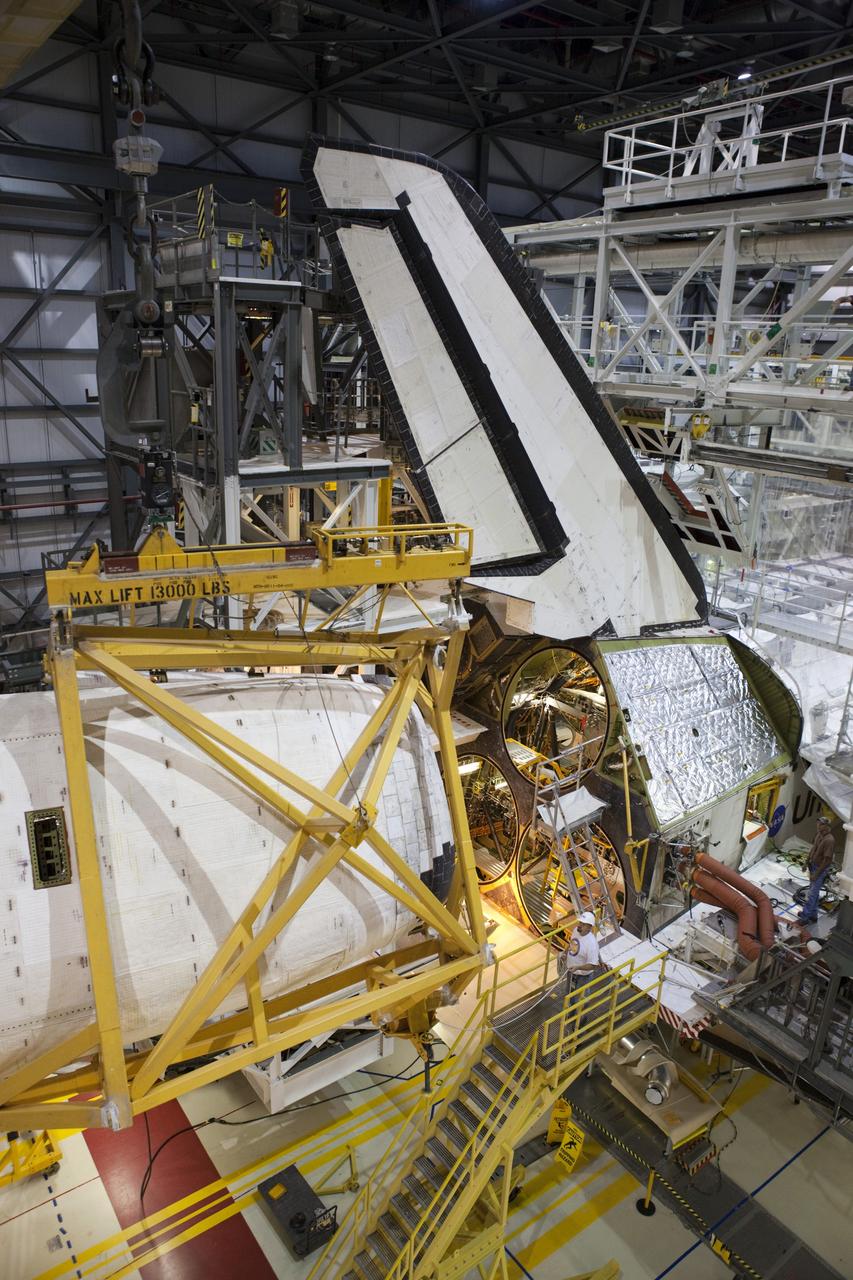

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane moves the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
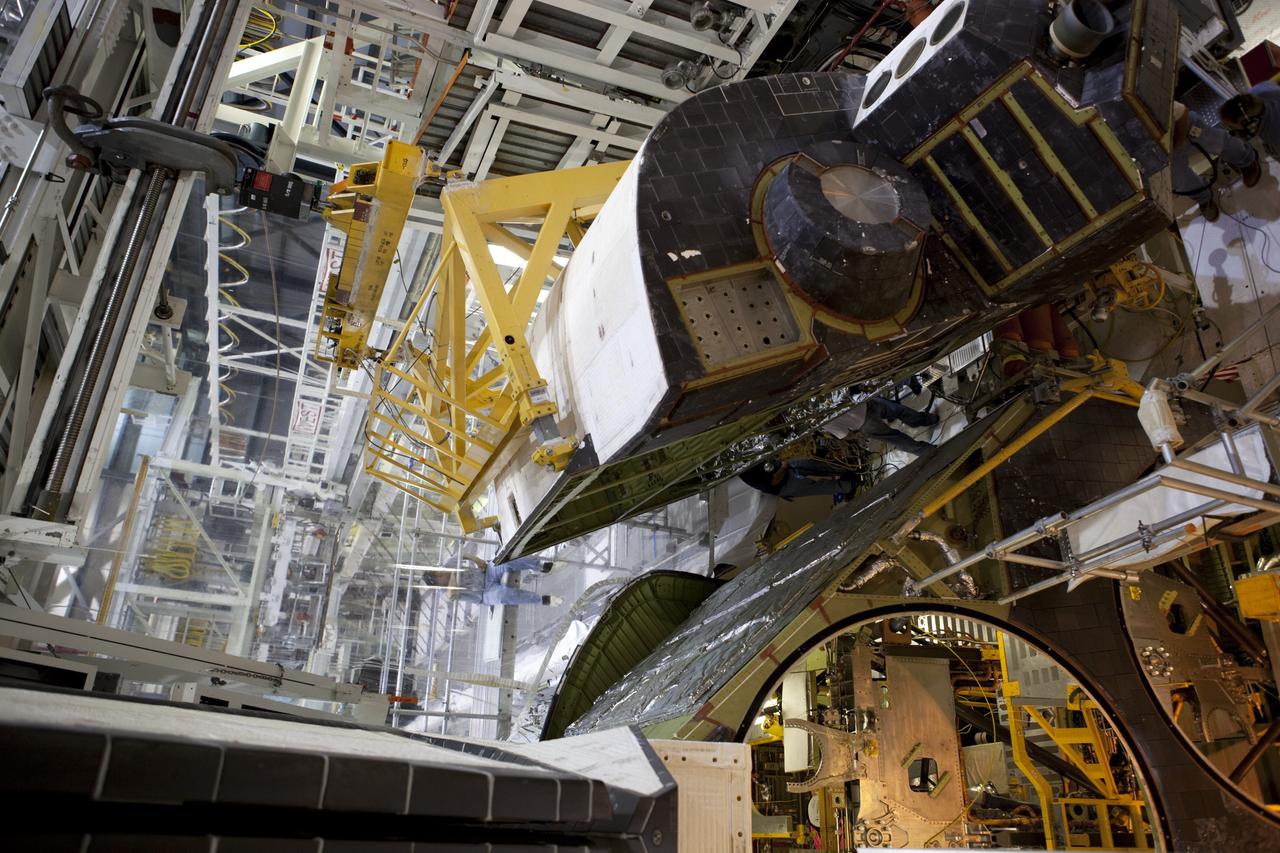

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a unique close-up view shows a large crane lowering the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
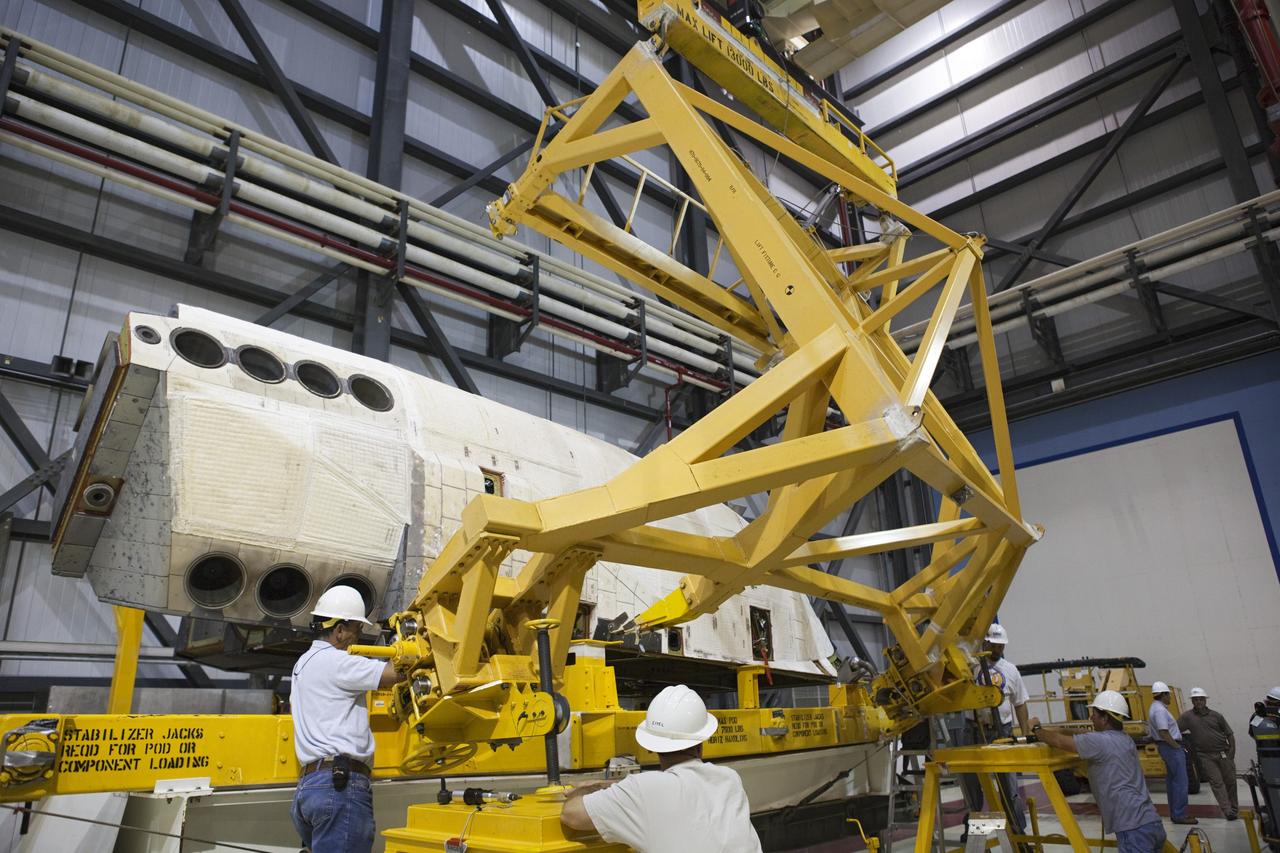

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Launch Alliance technicians provide assistance as a large crane is lowered toward the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for space shuttle Atlantis. It will be the last time an OMS pod is installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane lowers the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
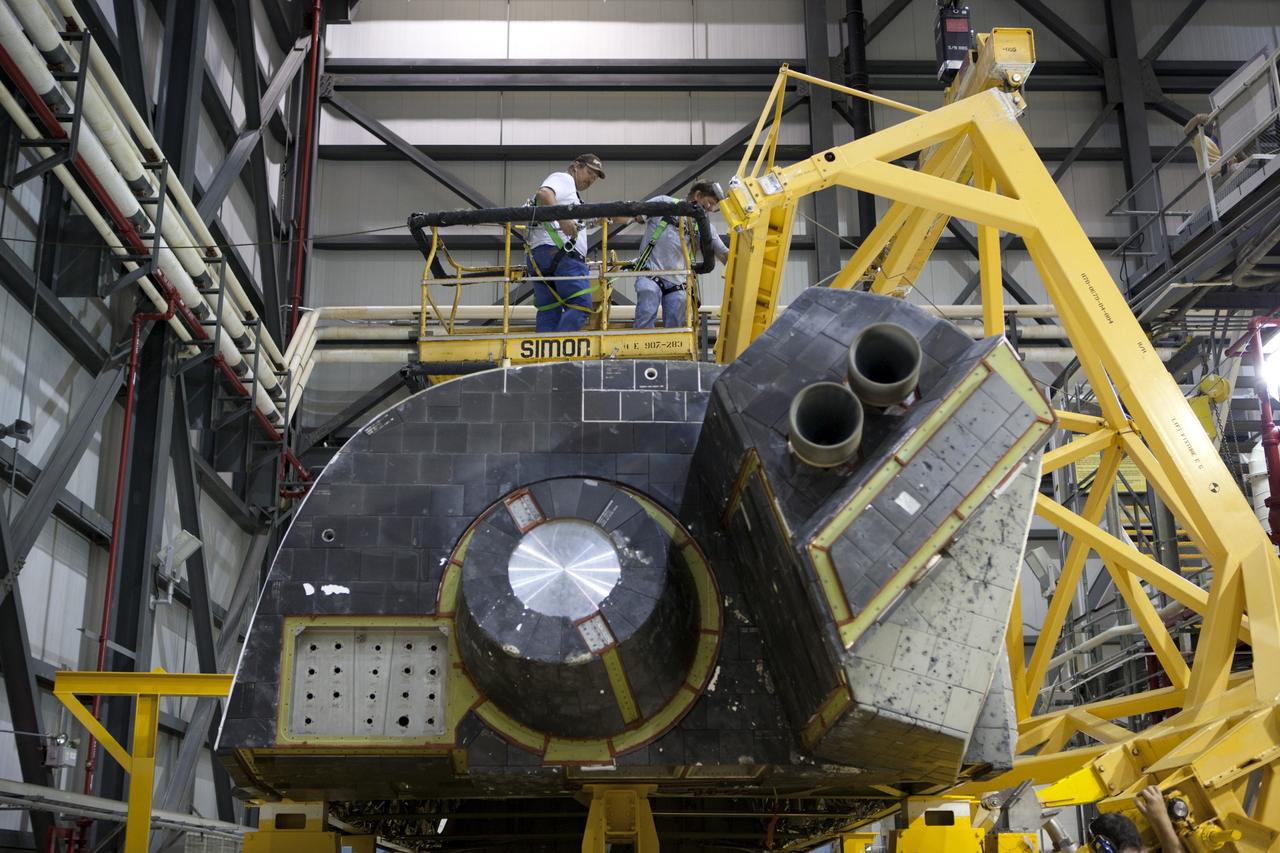

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Launch Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane moves the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It will be the last time an OMS pod is installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
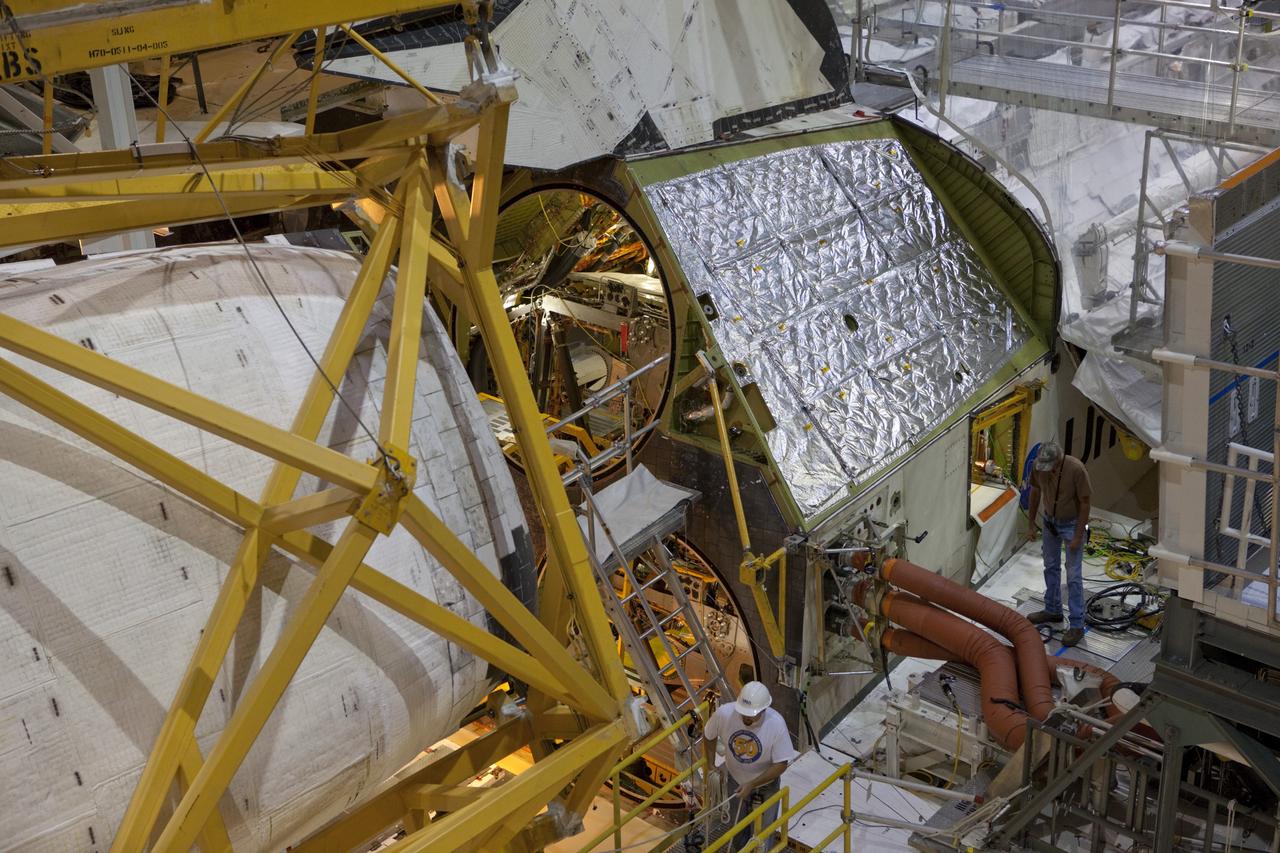

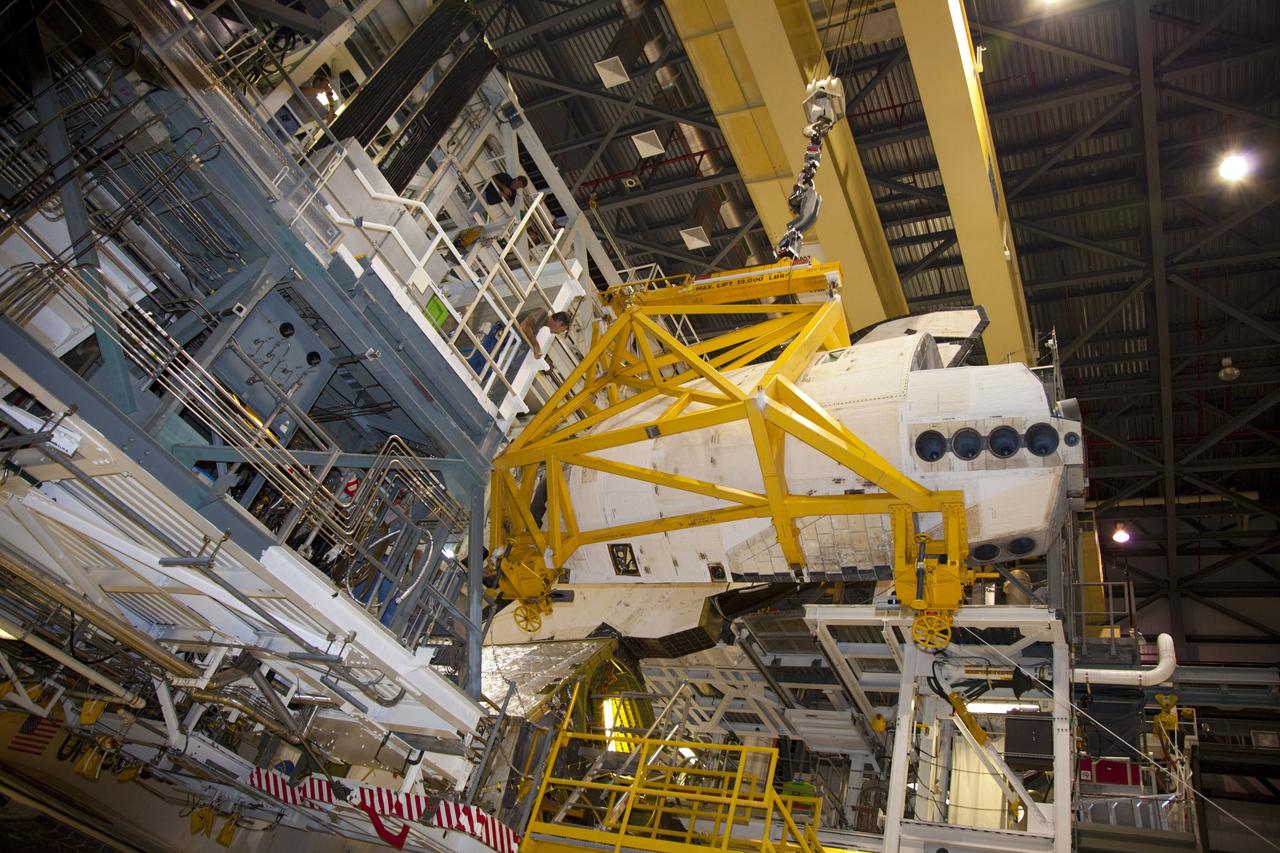
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane moves the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
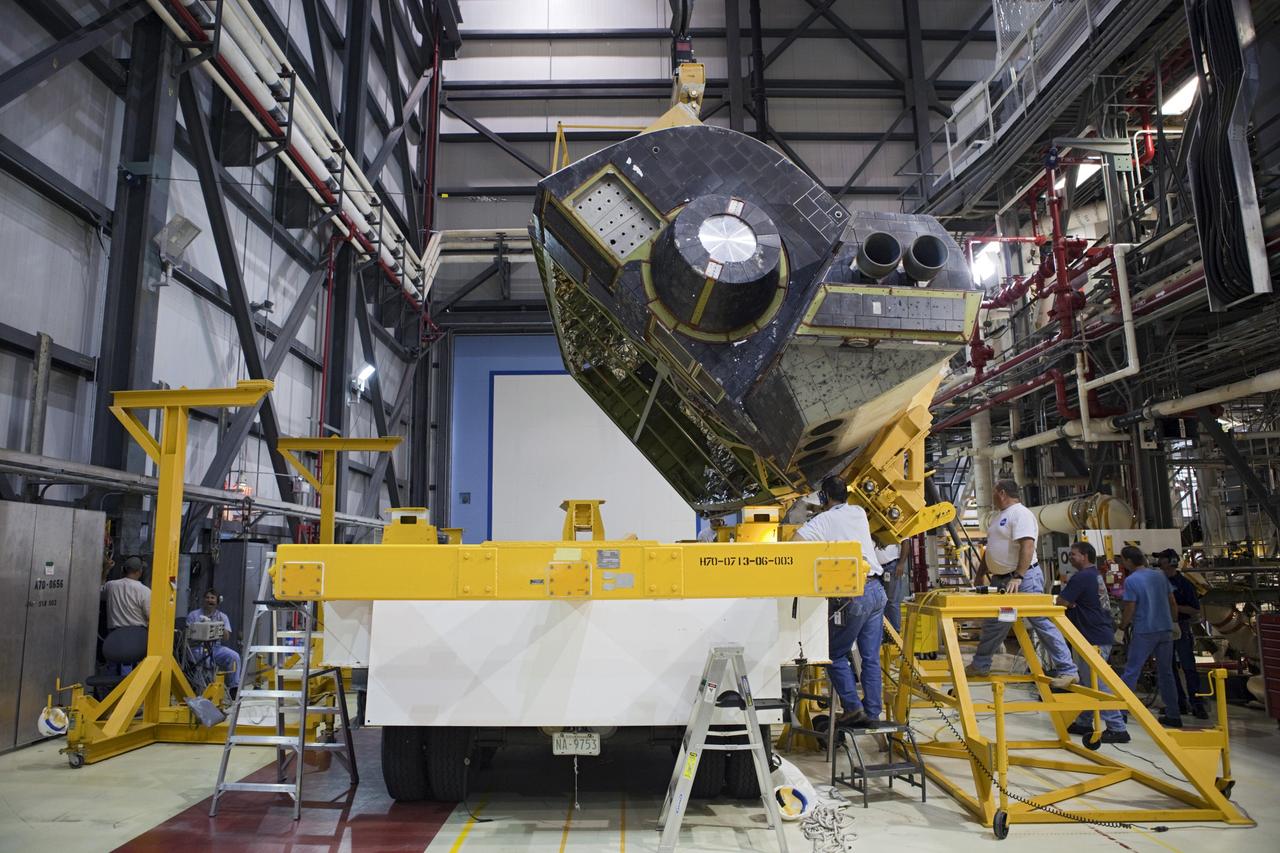

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane begins to lift the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for installation on space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
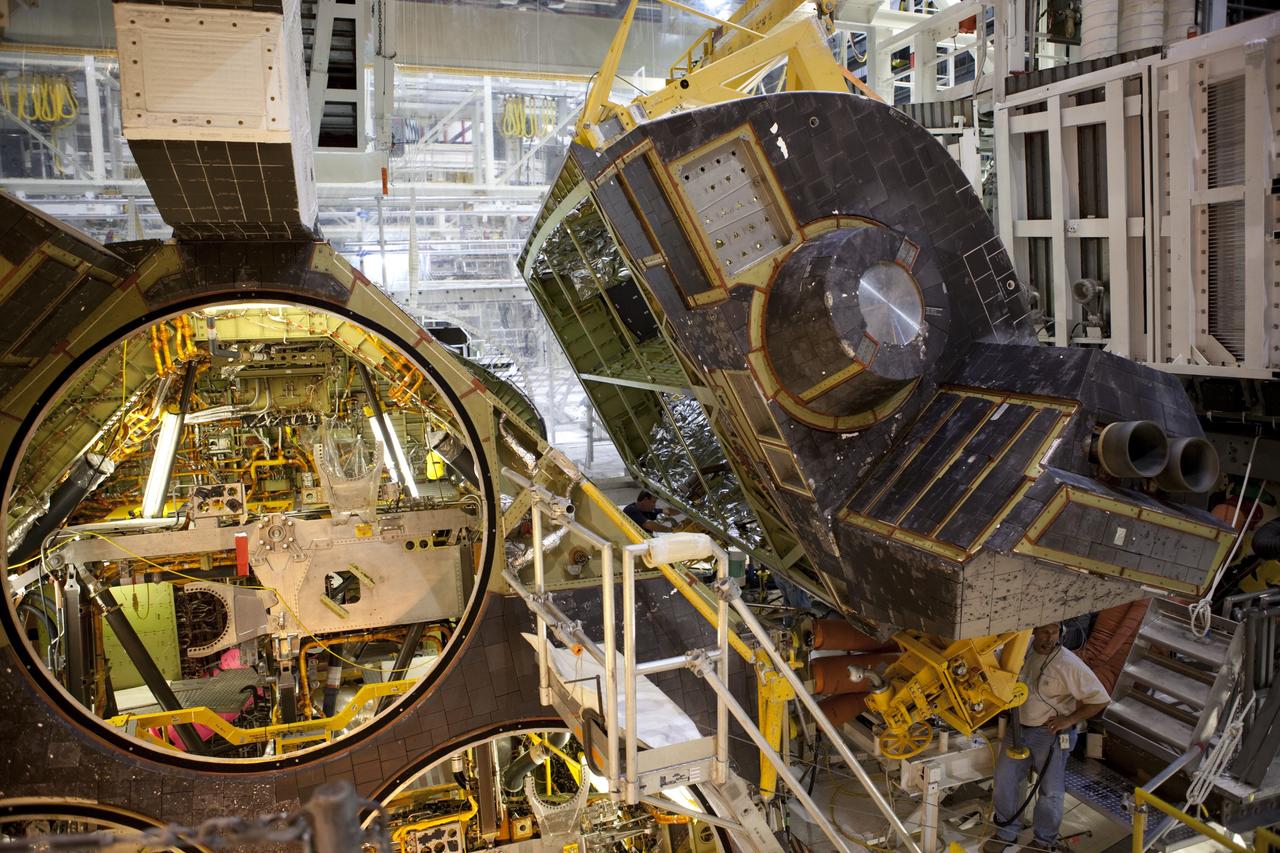

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a unique close-up view shows a large crane lowering the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
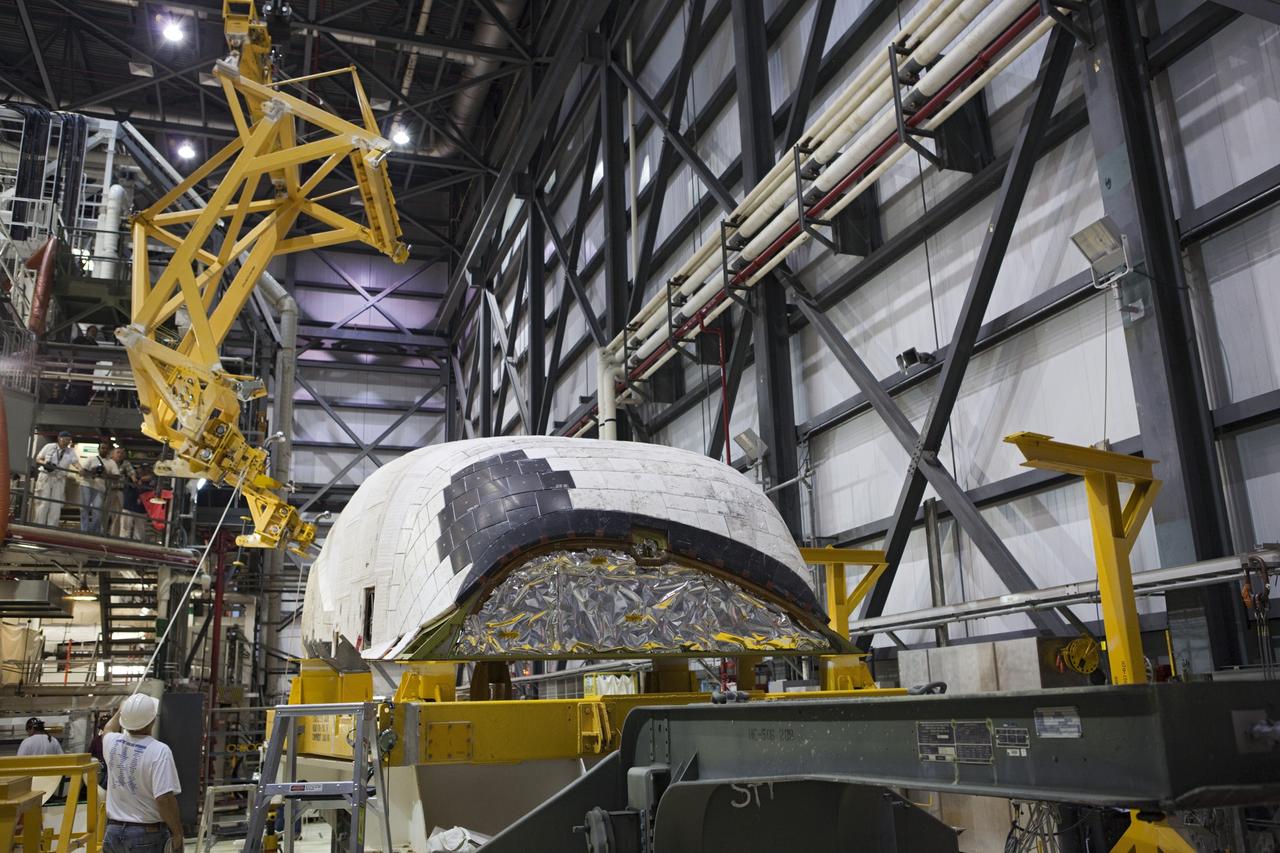

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane is lowered toward the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod for space shuttle Atlantis. It will be the last time an OMS pod is installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
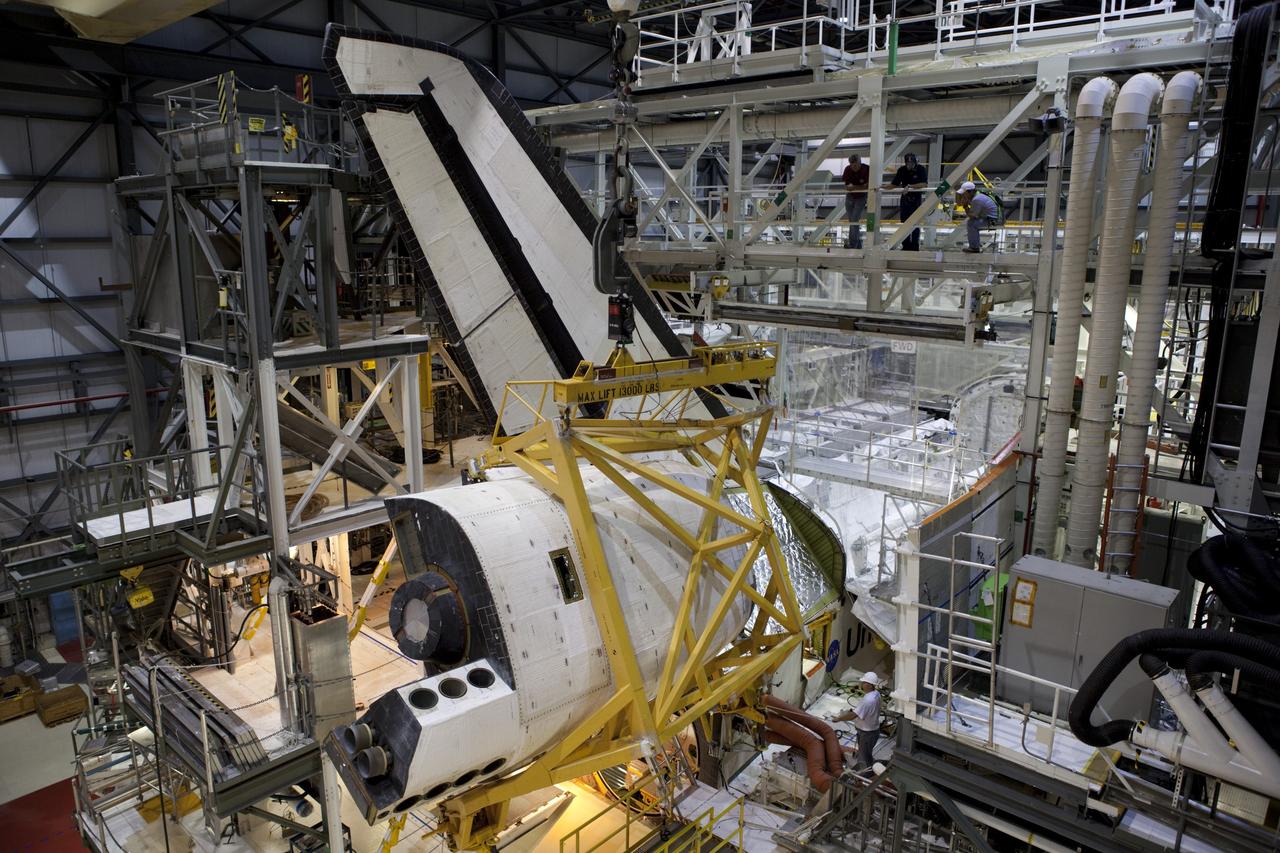

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress as a large crane moves the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod closer to space shuttle Atlantis. It is the last time an OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
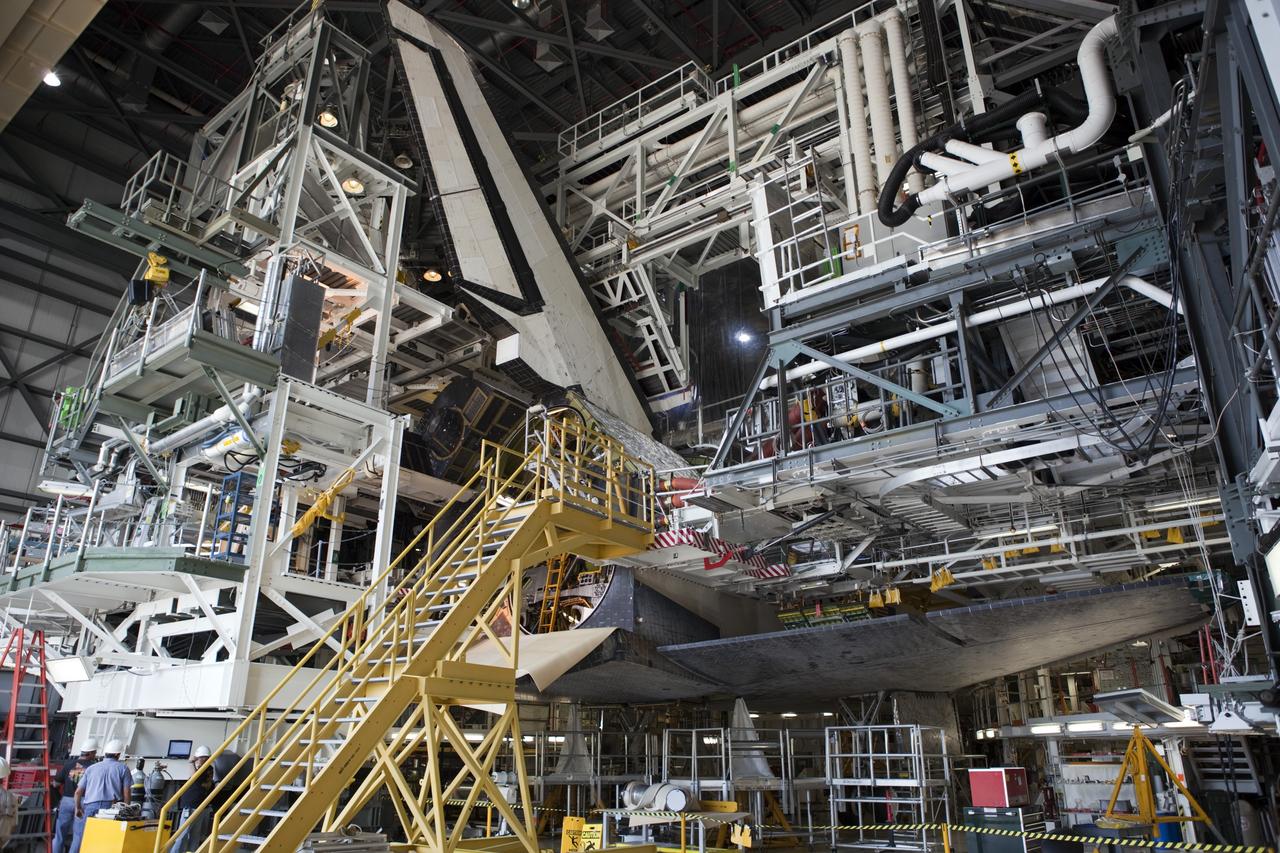

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, preparations are underway to install the right orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod on space shuttle Atlantis. It will be the last time an OMS pod is installed on Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to the test facility at White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
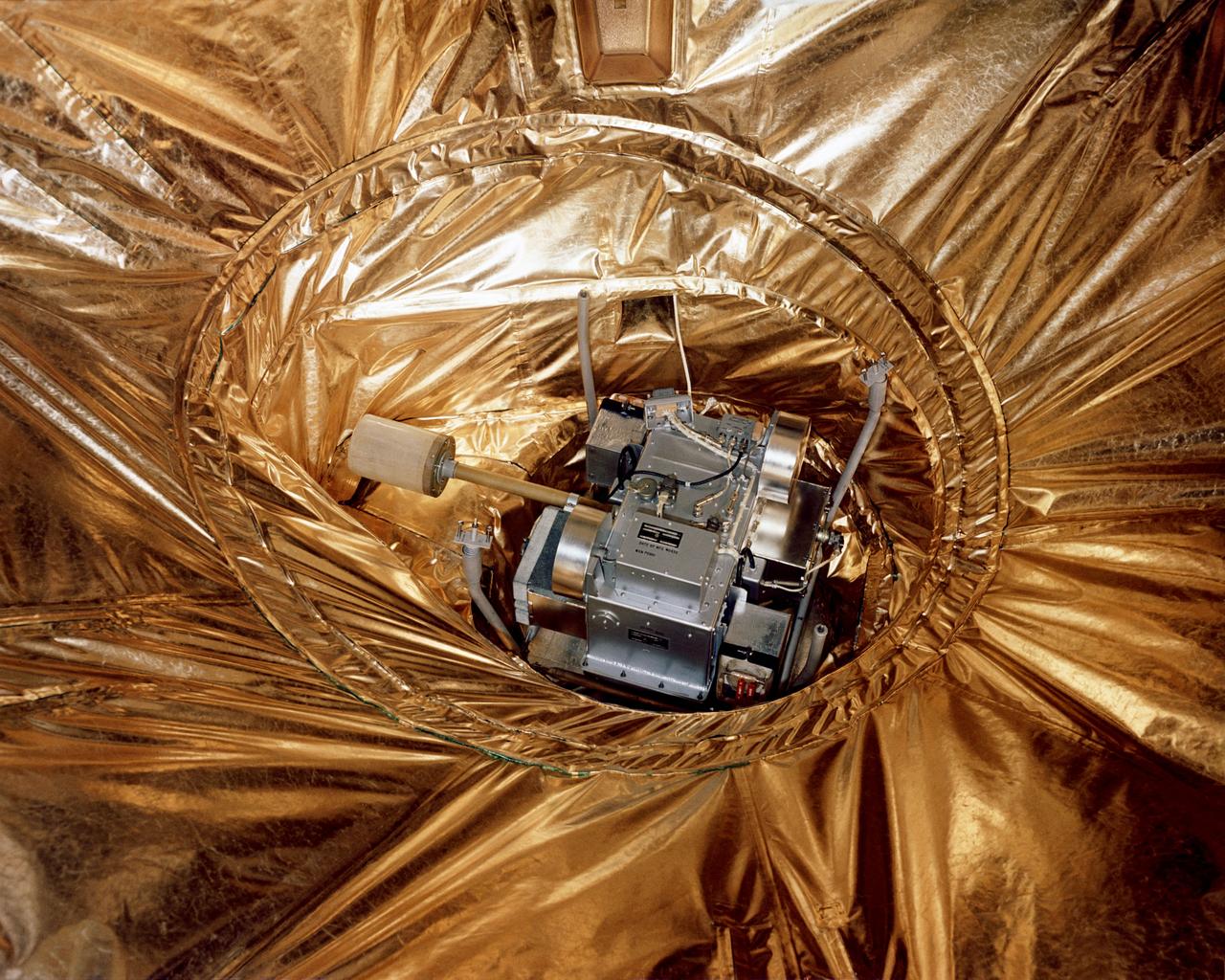

S65-42044 (28 July 1965) --- Close-up view of the Rendezvous Evaluation Pod installed in the equipment section of the Gemini-5 spacecraft at Pad 19.

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician applies a sheet of thermal insulation on a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
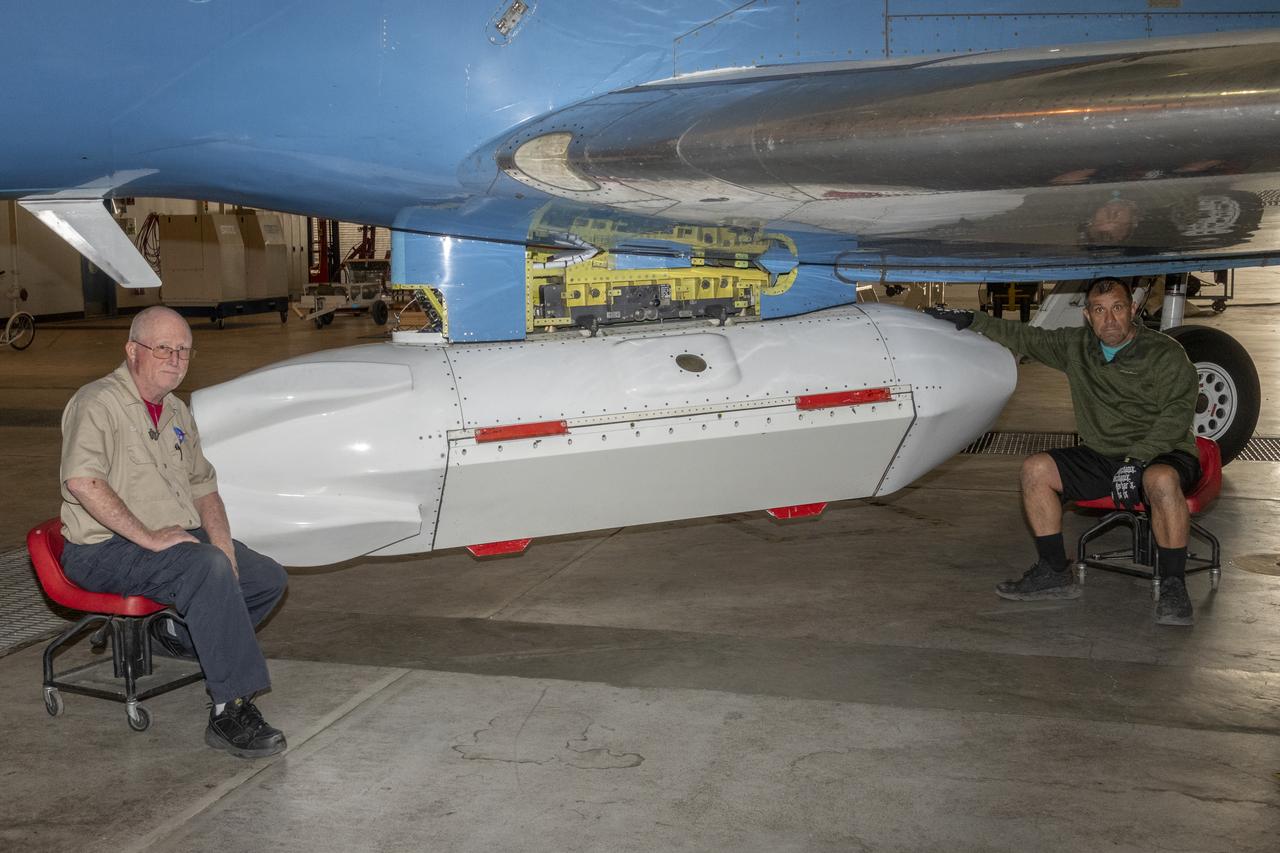

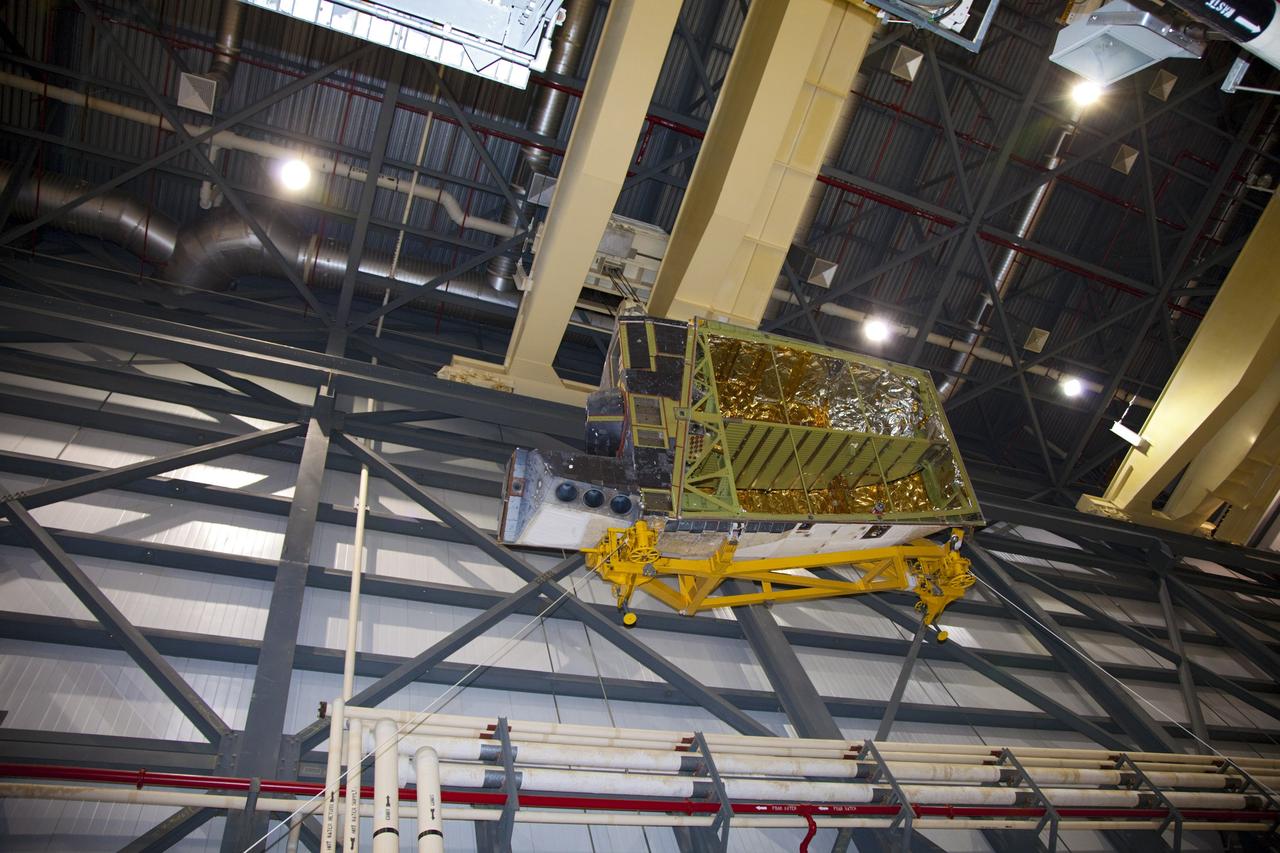
The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, UAVSAR, is prepared for installation onto NASA’s C-20A aircraft. THE UAVSAR uses a technique called interferometry to detect and measure very subtle deformations in the Earth’s surface, and the pod is specially designed to be interoperable with unmanned aircraft in the future. It will gather data from Gabon, Africa in September of 2023.

The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, UAVSAR, is prepared for installation onto NASA’s C-20A aircraft. THE UAVSAR uses a technique called interferometry to detect and measure very subtle deformations in the Earth’s surface, and the pod is specially designed to be interoperable with unmanned aircraft in the future. It will gather data from Gabon, Africa in September of 2023.
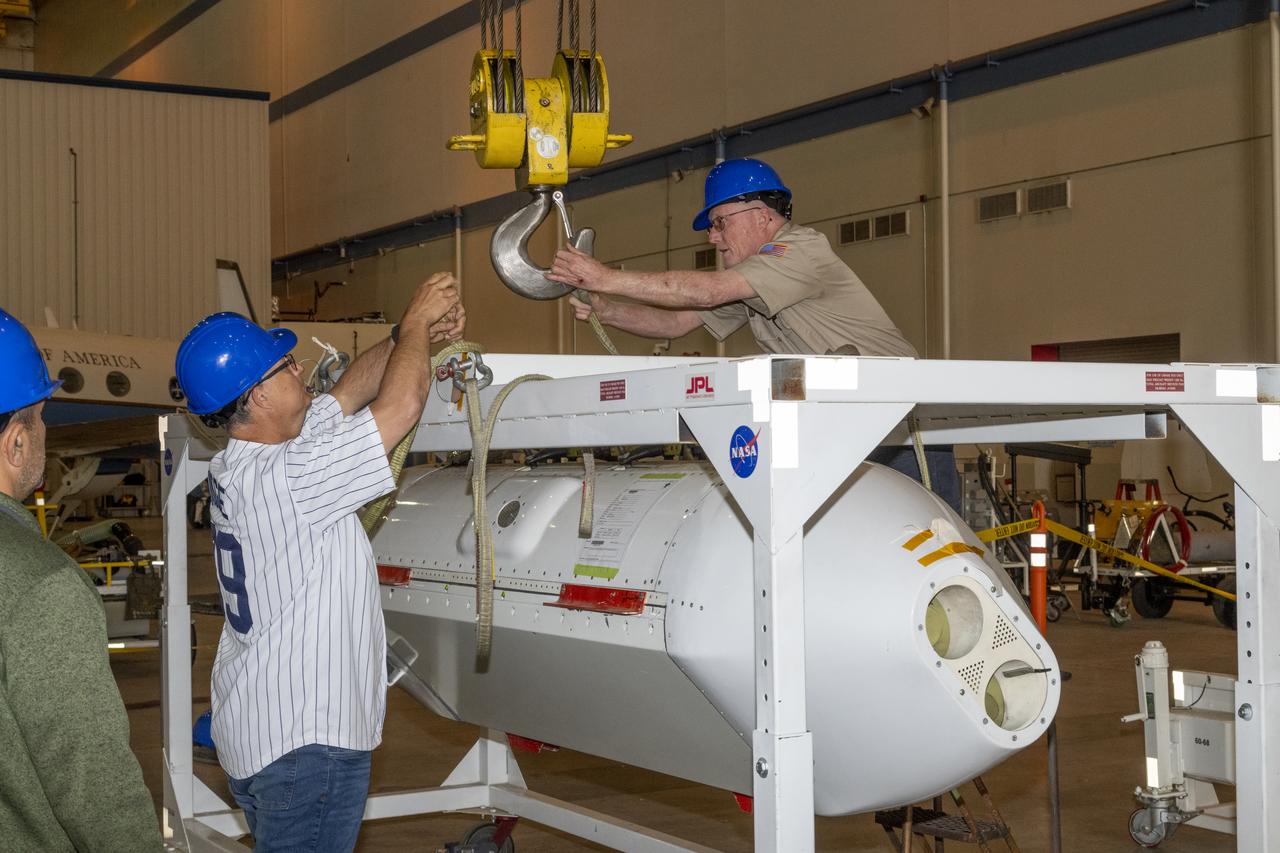

The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, UAVSAR, is prepared for installation onto NASA’s C-20A aircraft. THE UAVSAR uses a technique called interferometry to detect and measure very subtle deformations in the Earth’s surface, and the pod is specially designed to be interoperable with unmanned aircraft in the future. It will gather data from Gabon, Africa in September of 2023.
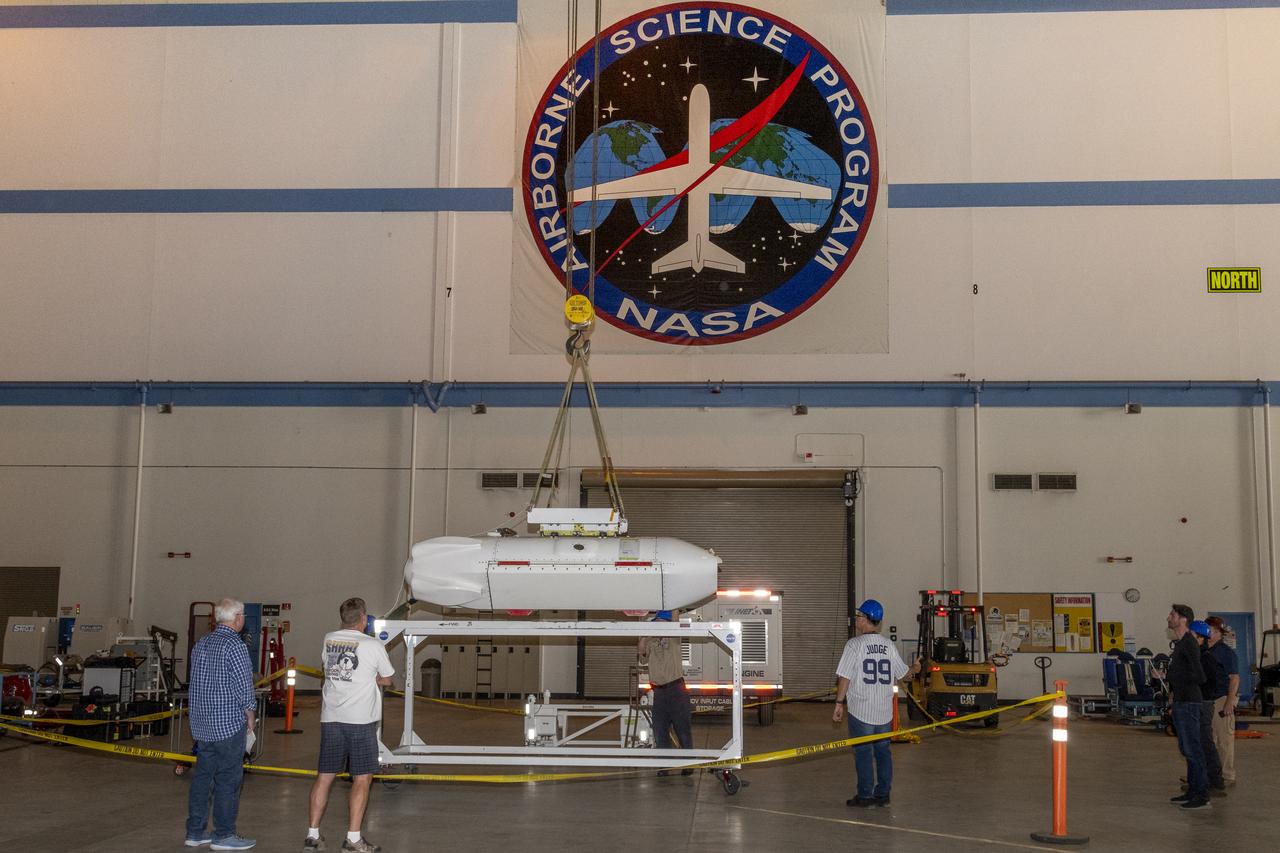

The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, UAVSAR, is prepared for installation onto NASA’s C-20A aircraft. THE UAVSAR uses a technique called interferometry to detect and measure very subtle deformations in the Earth’s surface, and the pod is specially designed to be interoperable with unmanned aircraft in the future. It will gather data from Gabon, Africa in September of 2023.
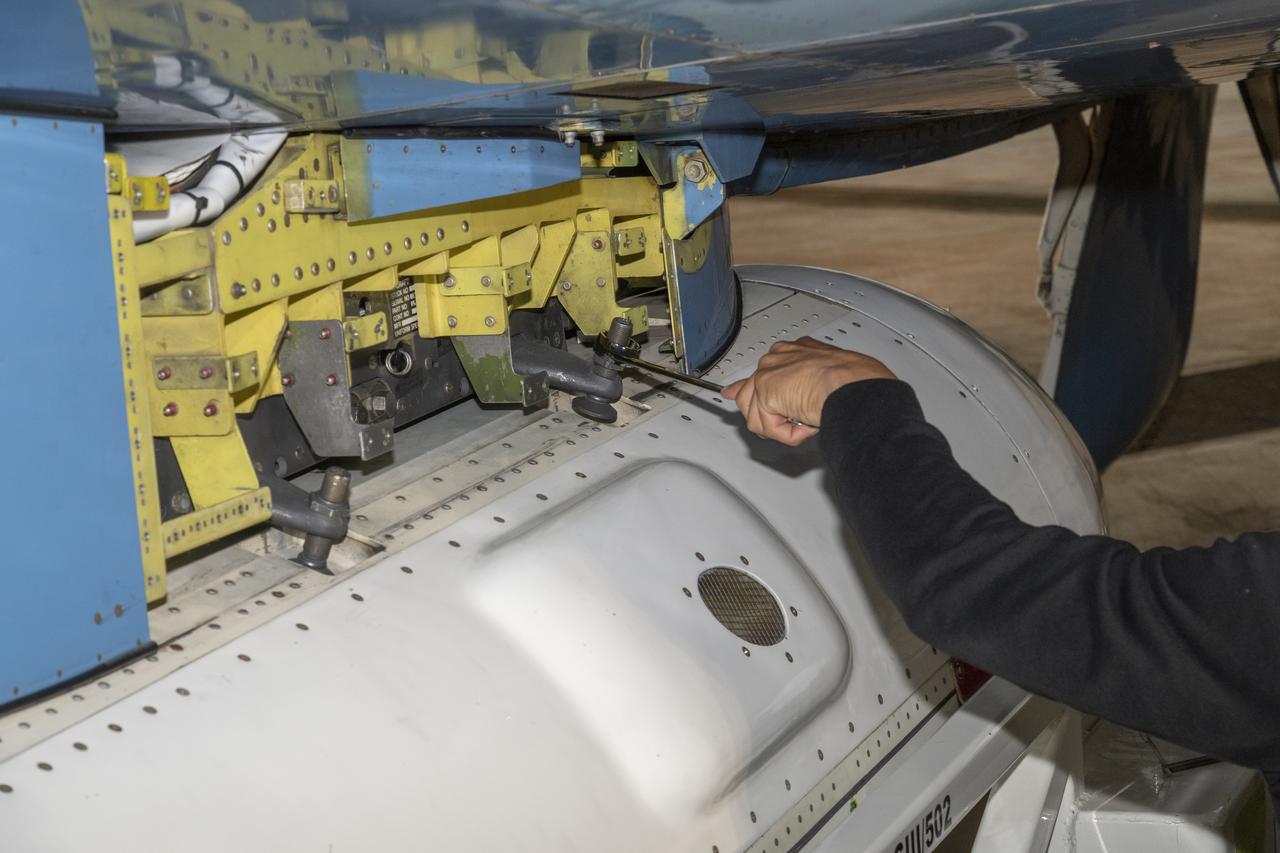

The Uninhabited Aerial Vehicle Synthetic Aperture Radar, UAVSAR, is prepared for installation onto NASA’s C-20A aircraft. THE UAVSAR uses a technique called interferometry to detect and measure very subtle deformations in the Earth’s surface, and the pod is specially designed to be interoperable with unmanned aircraft in the future. It will gather data from Gabon, Africa in September of 2023.
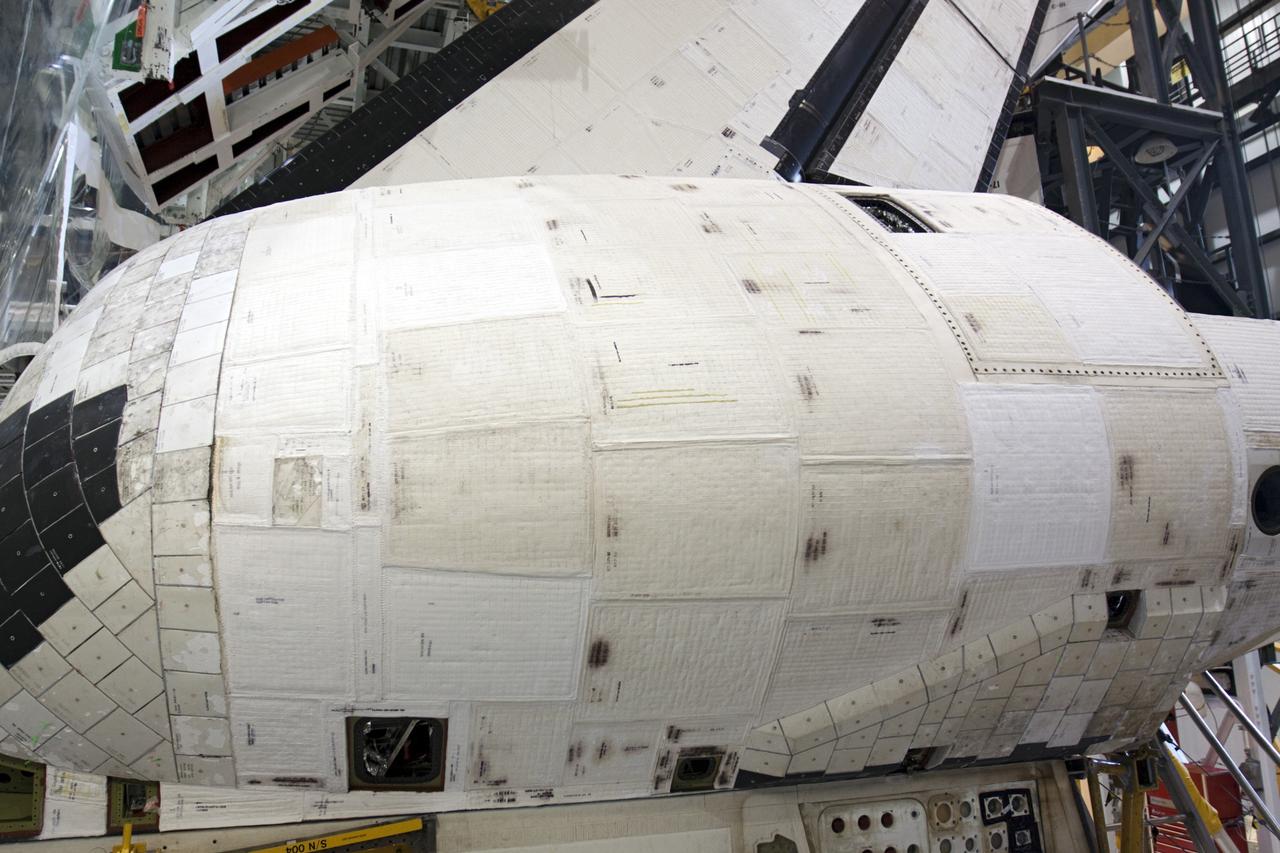

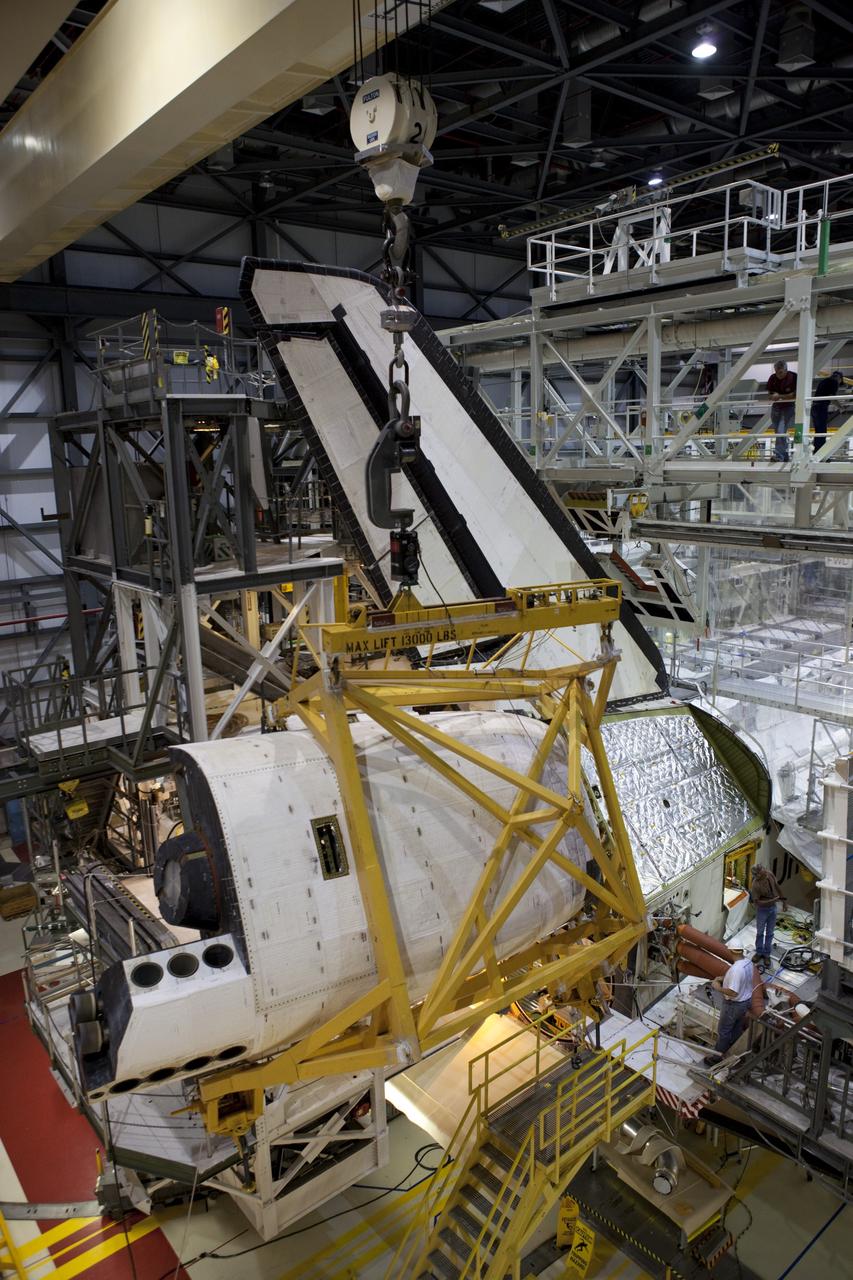
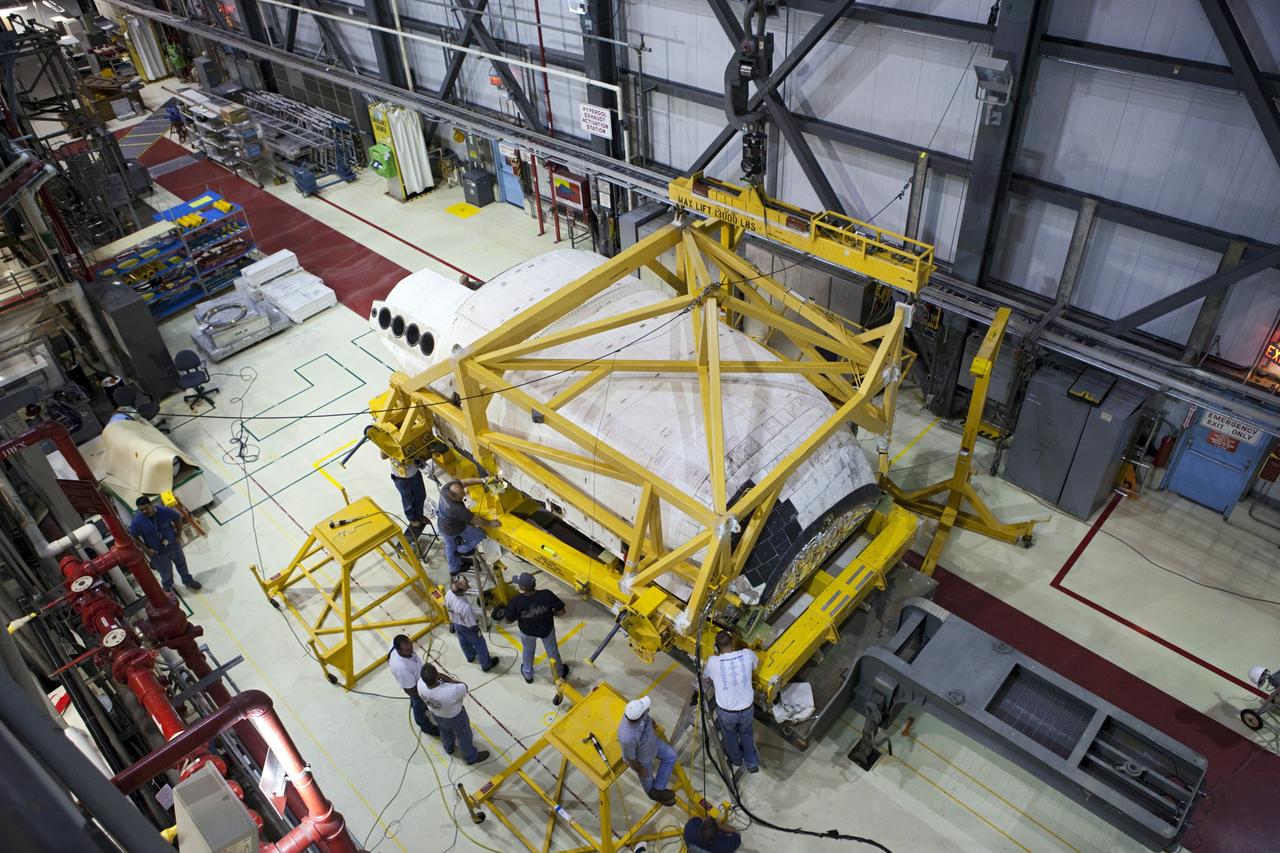
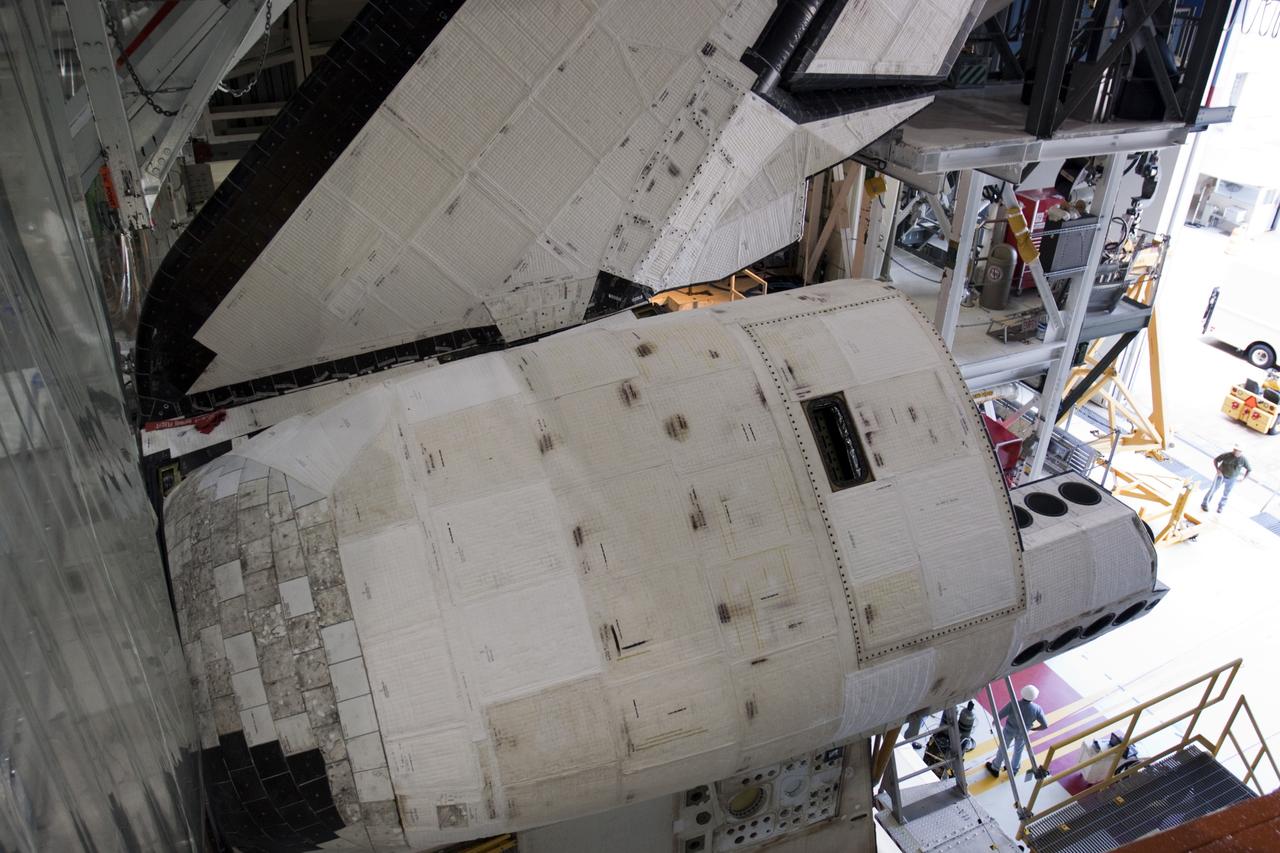
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
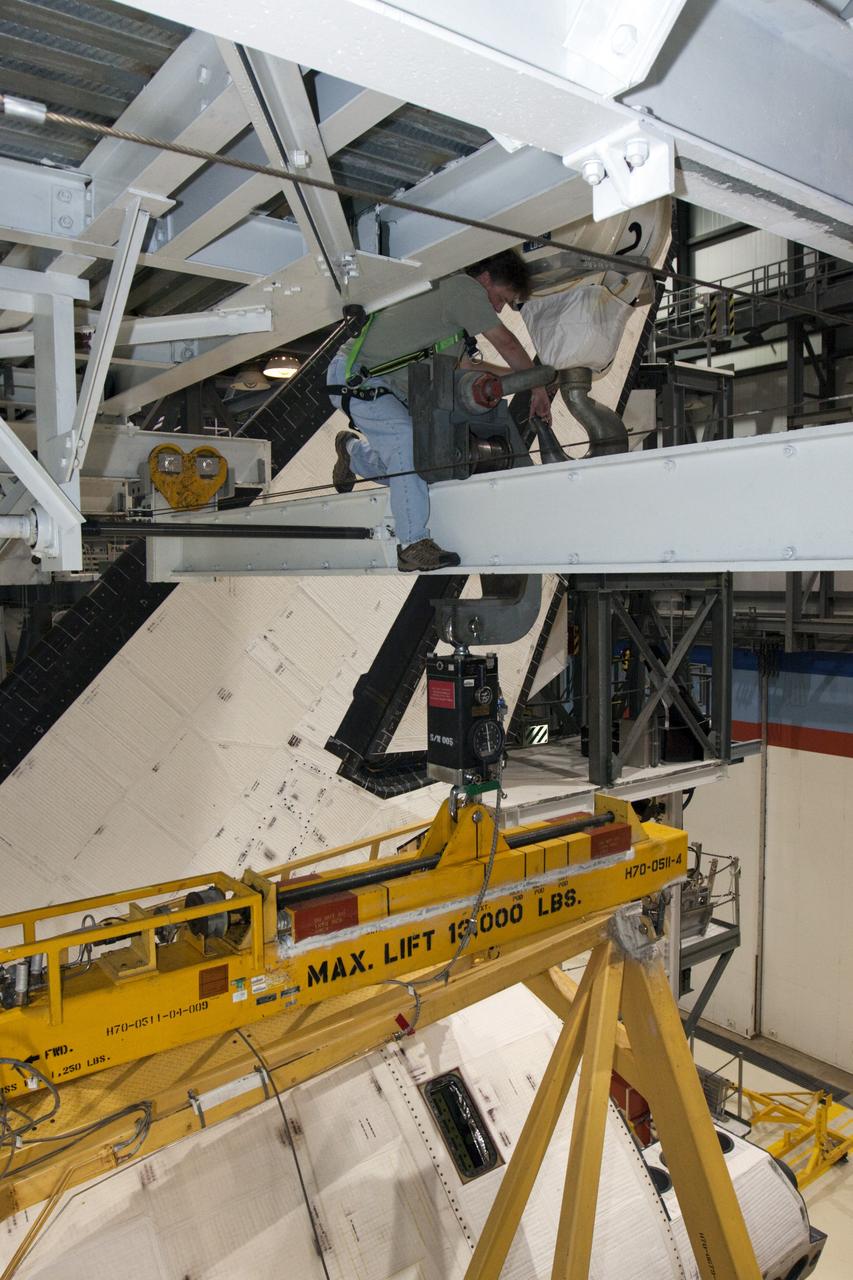

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a United Space Alliance technician assists as a large crane lowers the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod toward space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
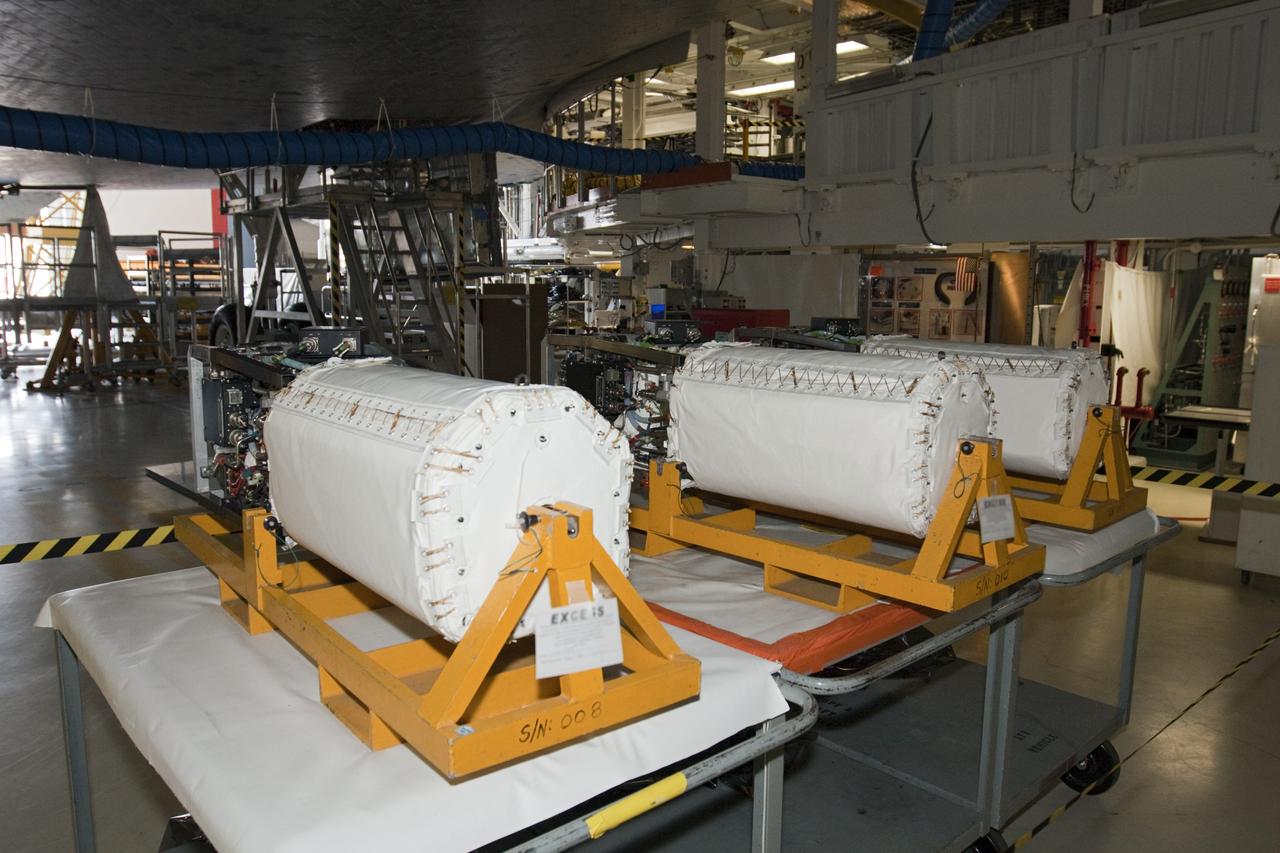

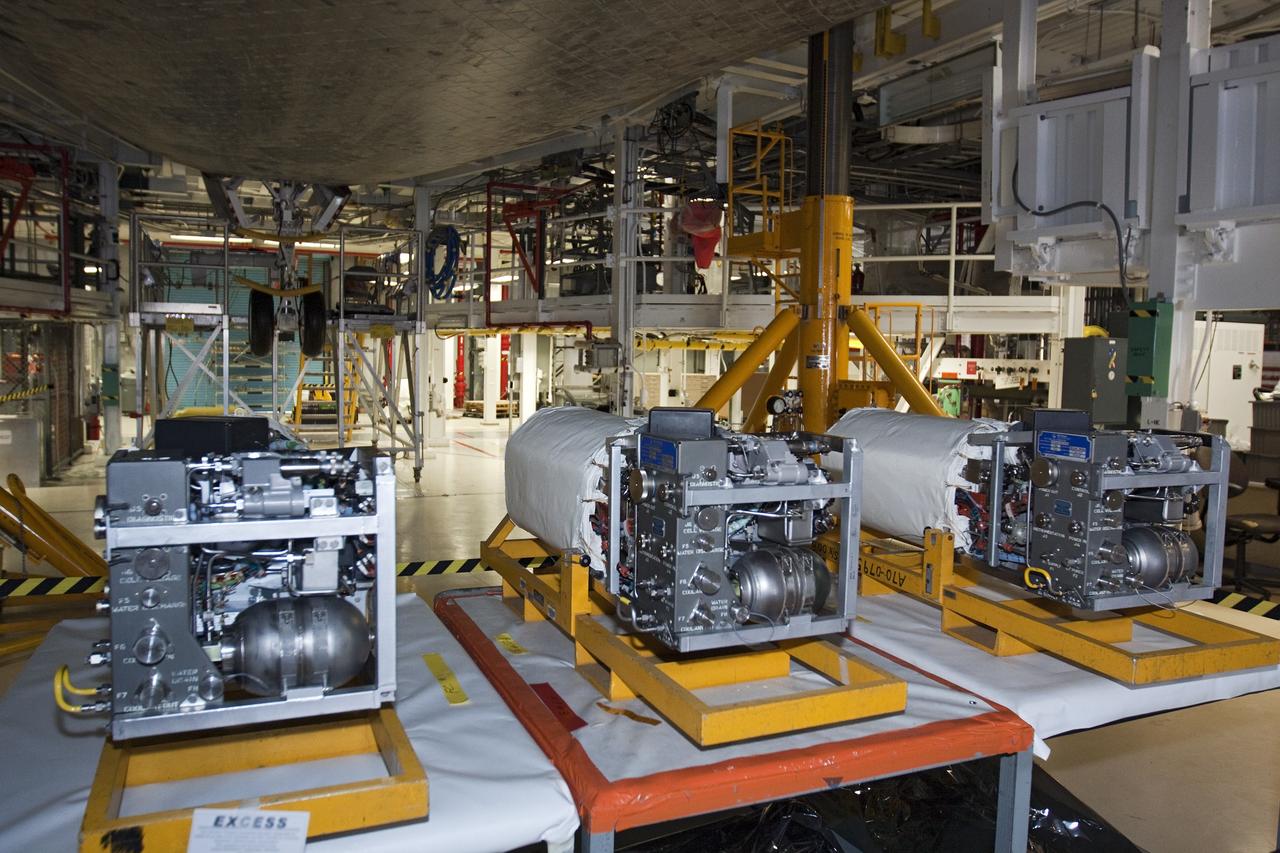
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, three excessed fuel cells are on a work bench beneath space shuttle Atlantis. The left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
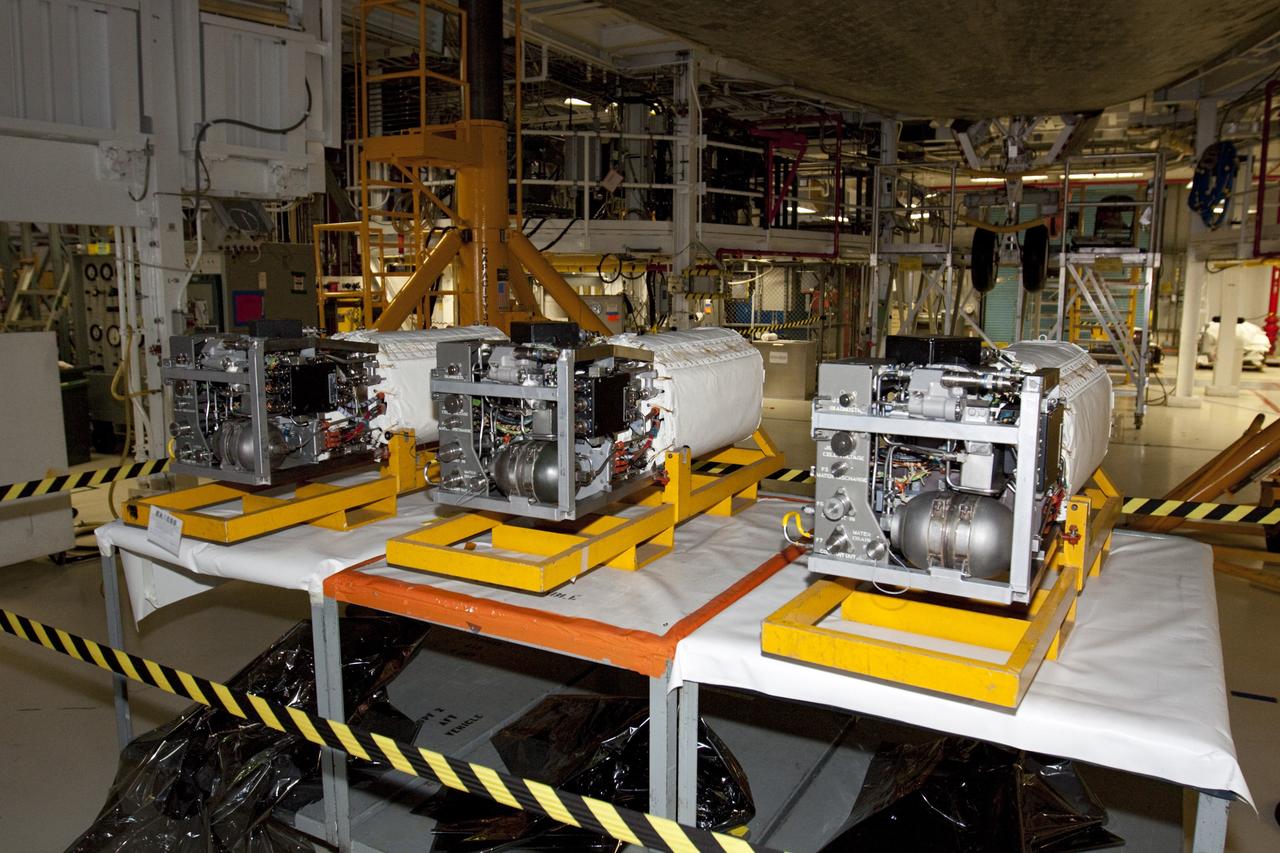

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, three excessed fuel cells are on a work bench beneath space shuttle Atlantis. The left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
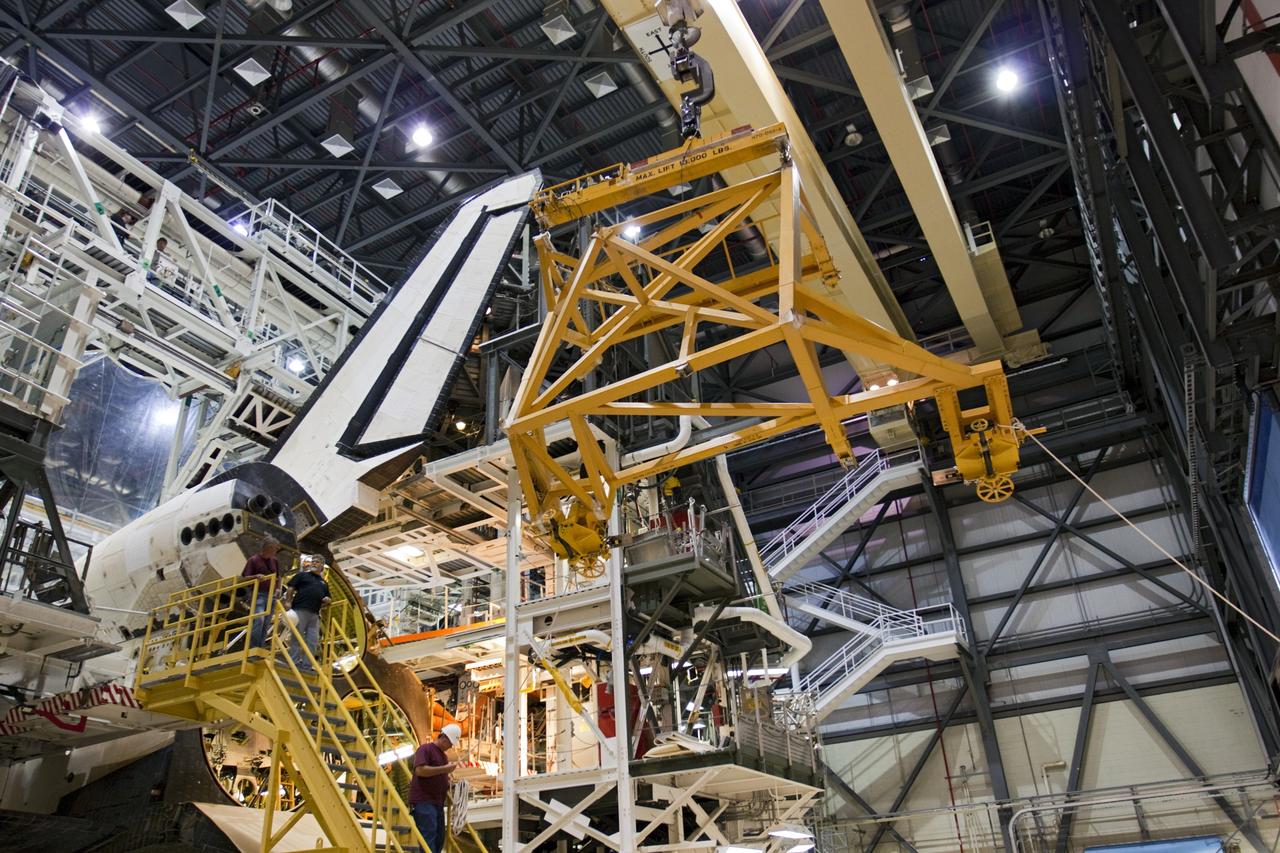

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane is moved away after it lowered the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, three excessed fuel cells are on a work bench beneath space shuttle Atlantis. The left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane was used to lower the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod has been installed onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress after a large crane lowers the left orbital maneuvering system, or OMS, pod onto space shuttle Atlantis. The OMS provided the shuttle with thrust for orbit insertion, rendezvous and deorbit, and could provide up to 1,000 pounds of propellant to the aft reaction control system. The OMS is housed in two independent pods located on each side of the shuttle’s aft fuselage. Each pod contains one OMS engine and the hardware needed to pressurize, store and distribute the propellants to perform the velocity maneuvers. Atlantis’ OMS pods were removed and sent to White Sands Test Facility in New Mexico to be cleaned of residual toxic propellant. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the space shuttle fleet. A groundbreaking was held Jan. 18 for Atlantis’ future home, a 65,000-square-foot exhibit hall in Shuttle Plaza at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Atlantis is scheduled to roll over to the visitor complex in November in preparation for the exhibit’s grand opening in July 2013. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is lowered toward an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that awaits installation on space shuttle Discovery in Orbiter Processing Facility-1. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to carry an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

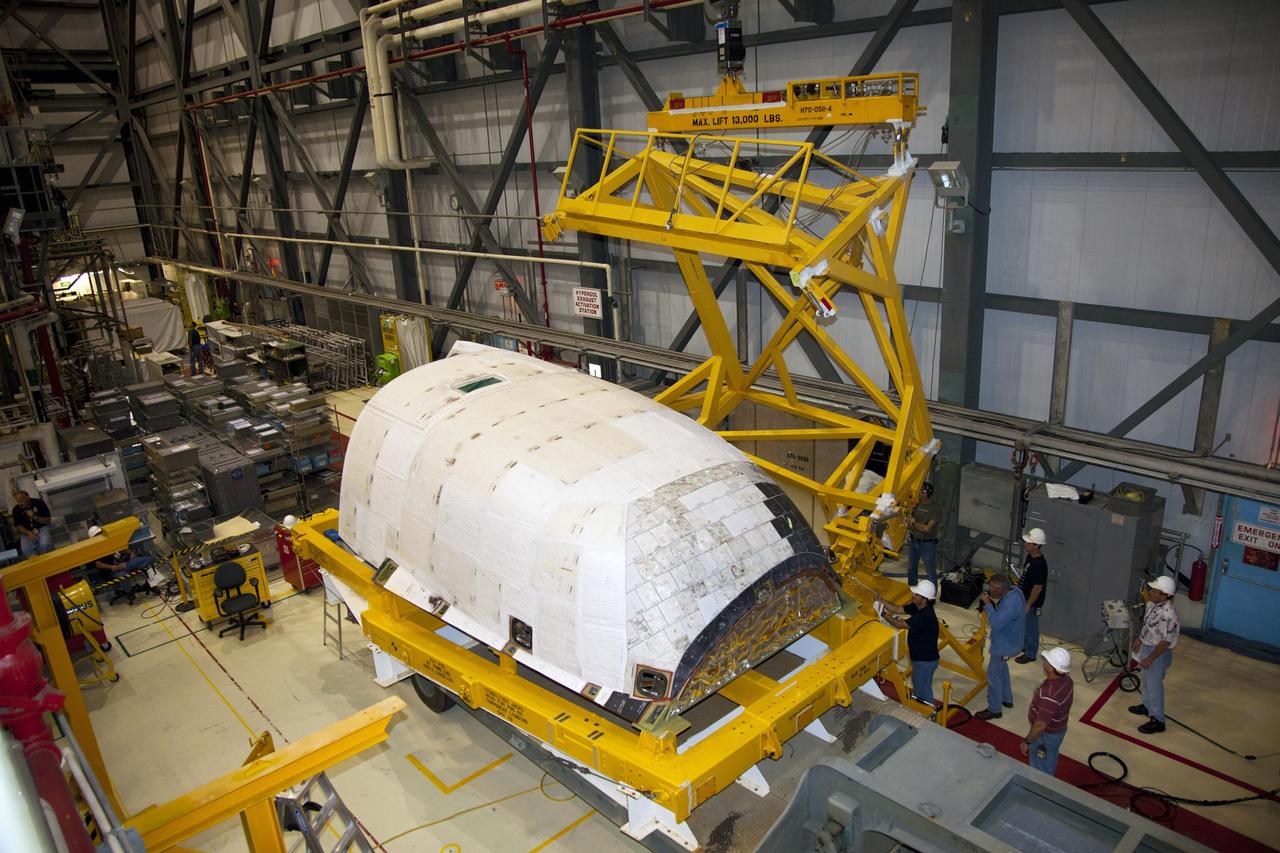
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane is being used to move the right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod away from space shuttle Atlantis. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod awaits installation on space shuttle Discovery in Orbiter Processing Facility-1. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane is lowered toward an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that awaits installation on space shuttle Discovery in Orbiter Processing Facility-1. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane carries an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
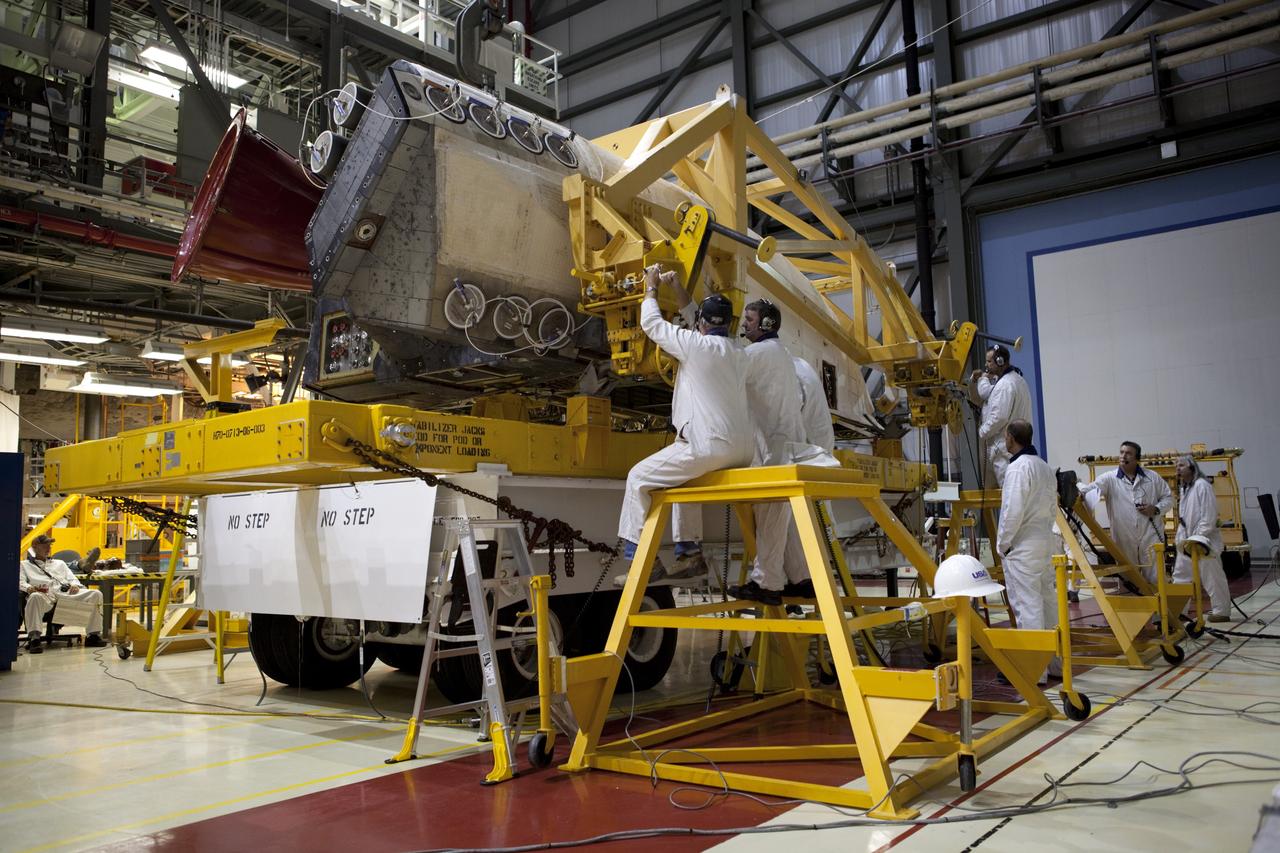

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help secure space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod onto a pallet. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
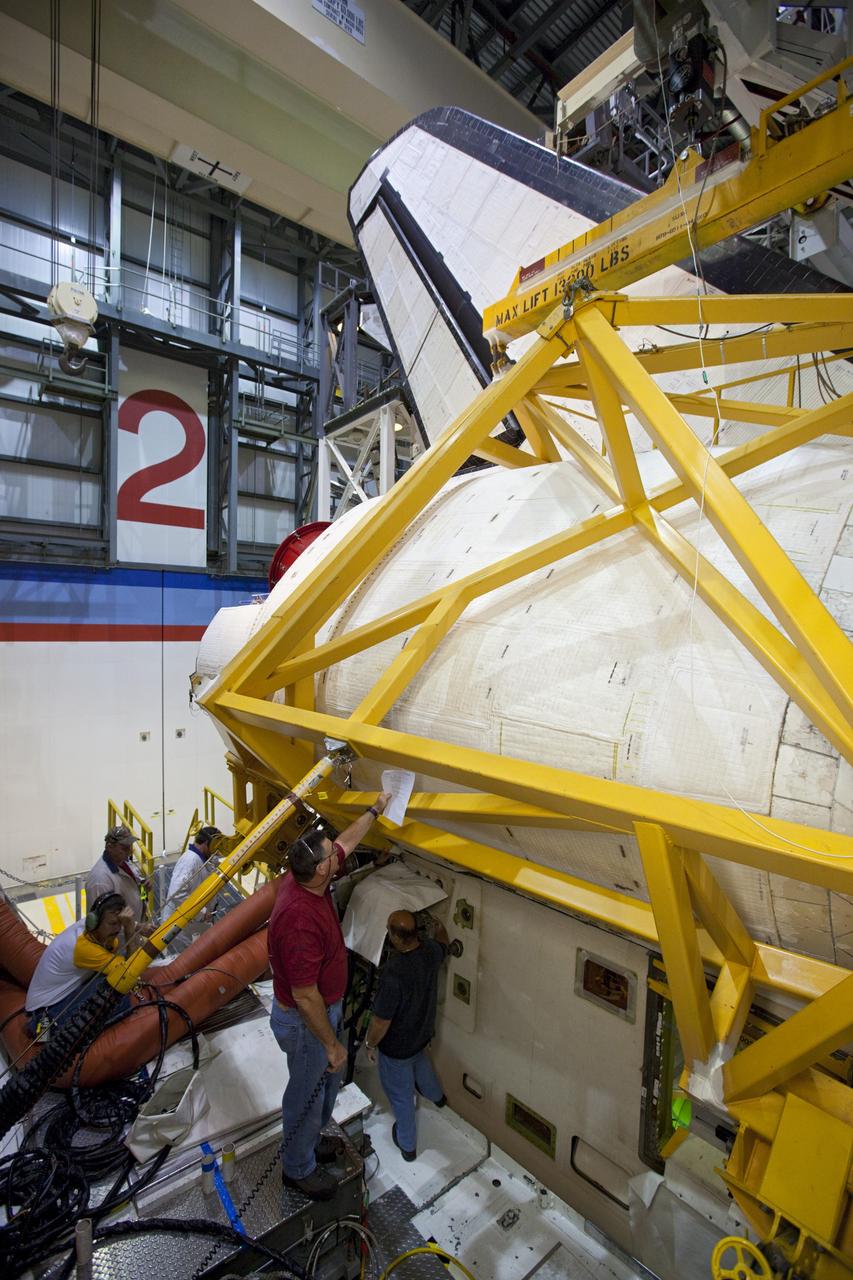

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help secure a sling around space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
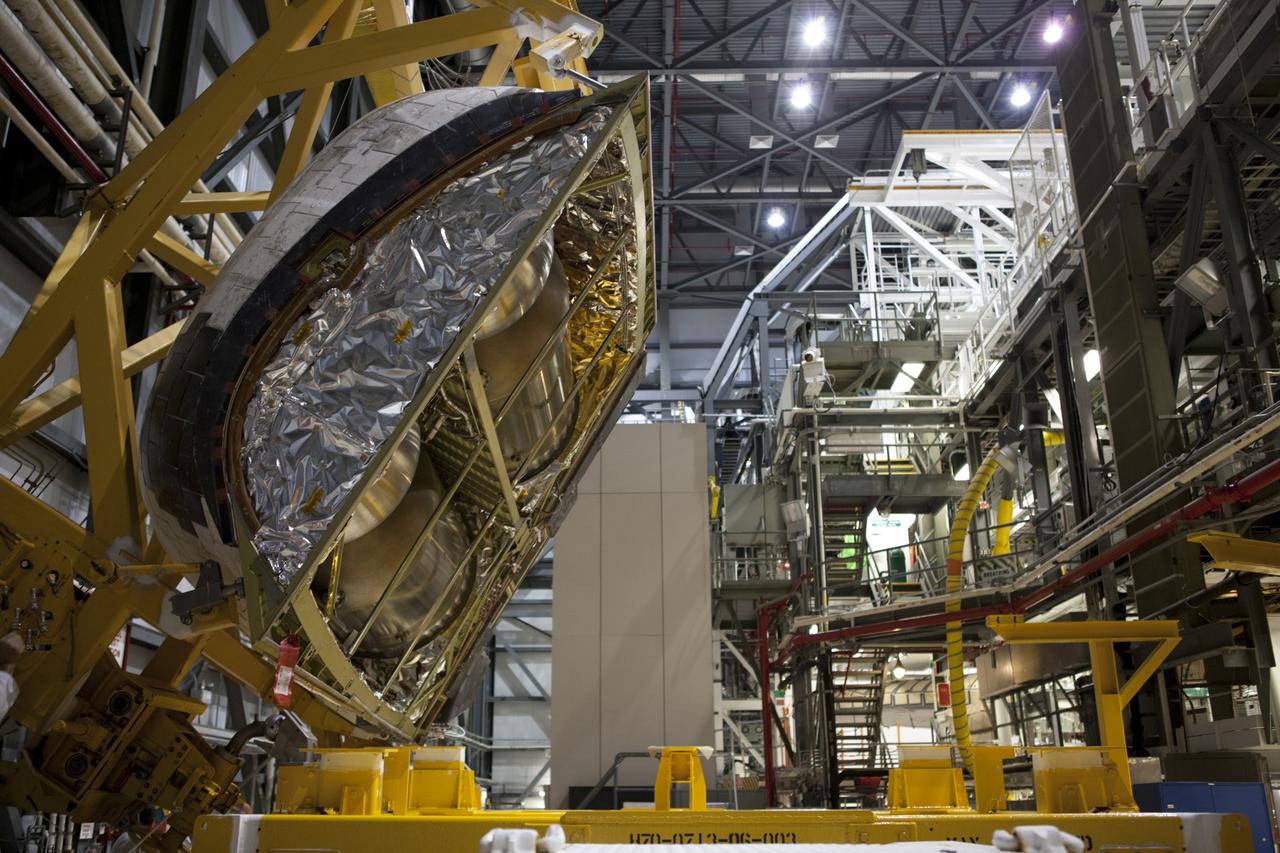

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod onto a pallet. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
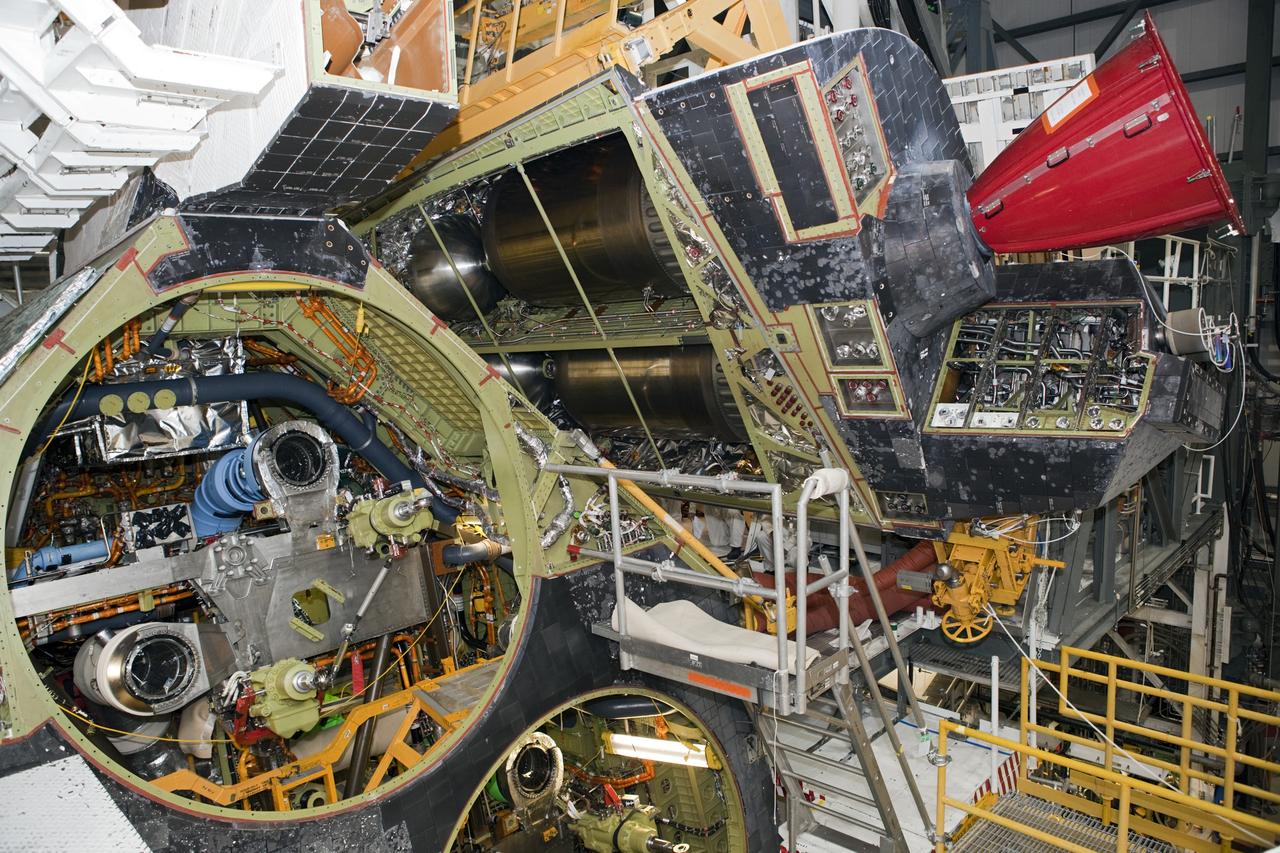

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane is being used to remove the right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod from space shuttle Atlantis. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
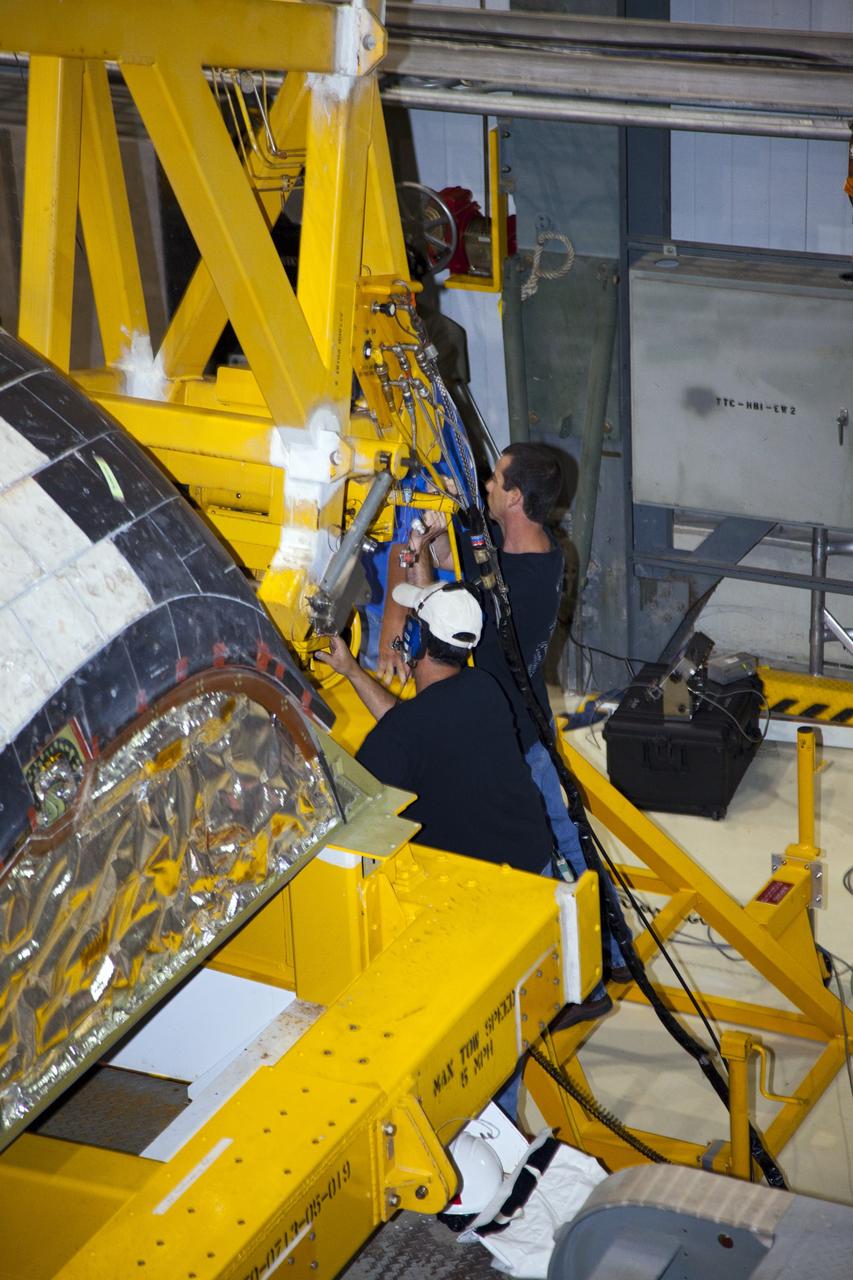

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is lowered toward an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod onto a pallet. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
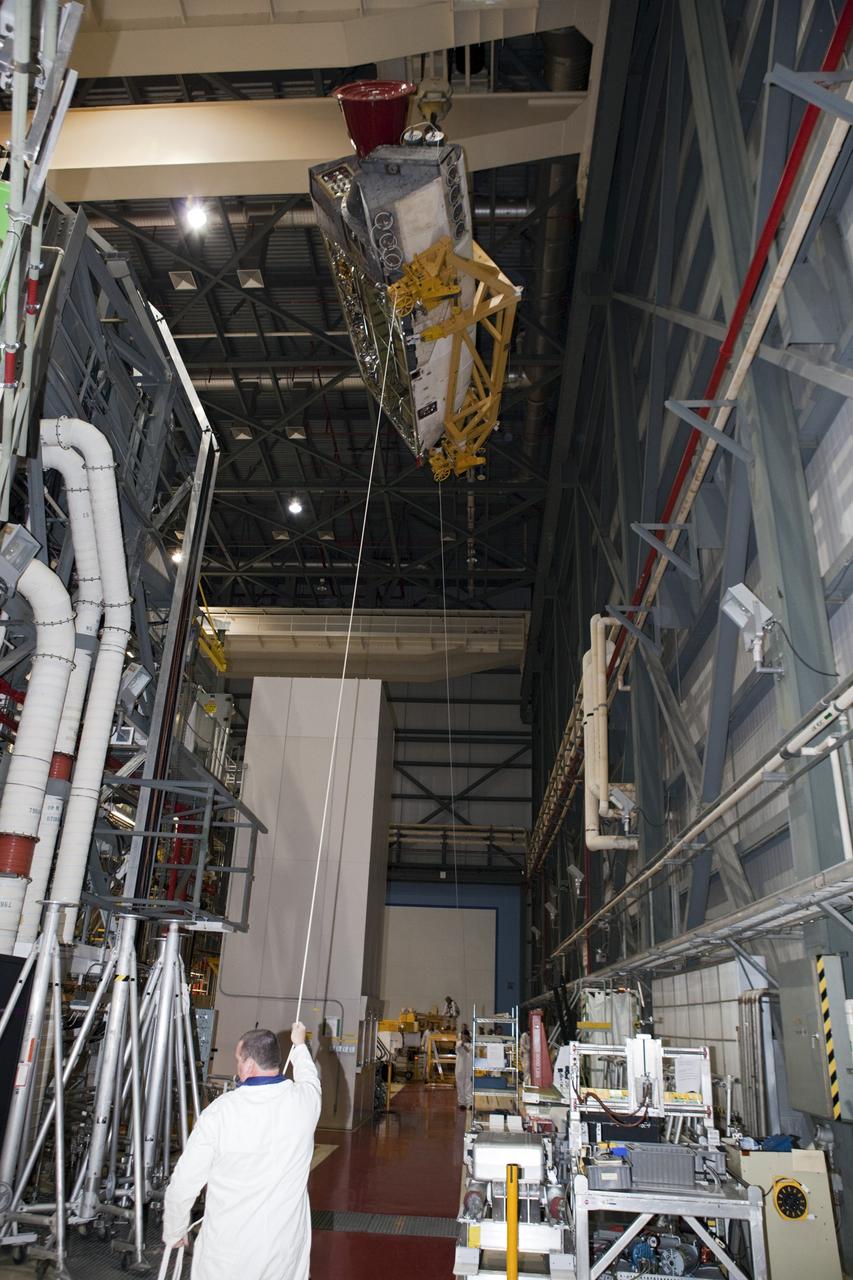

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a large crane is being used to move the right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod away from space shuttle Atlantis. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
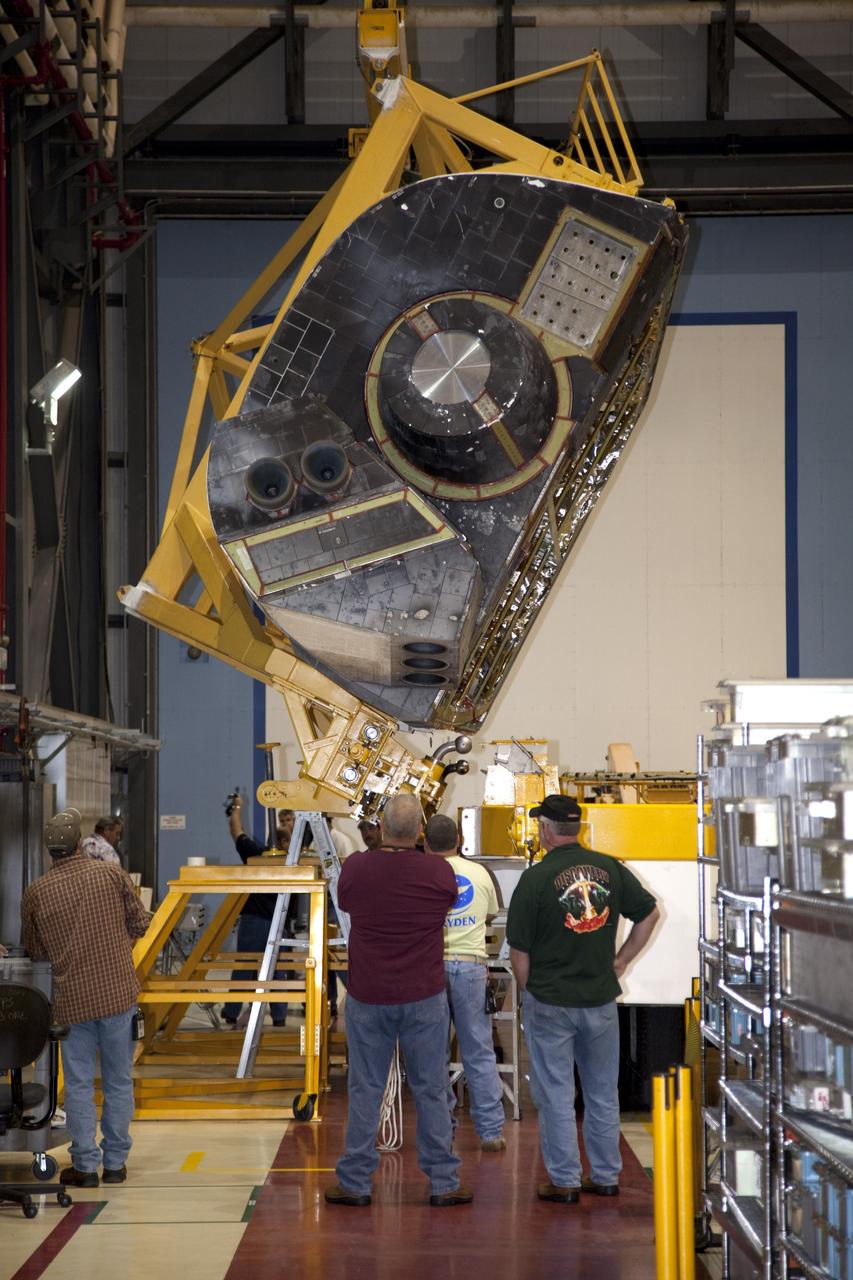

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane is used to carry an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
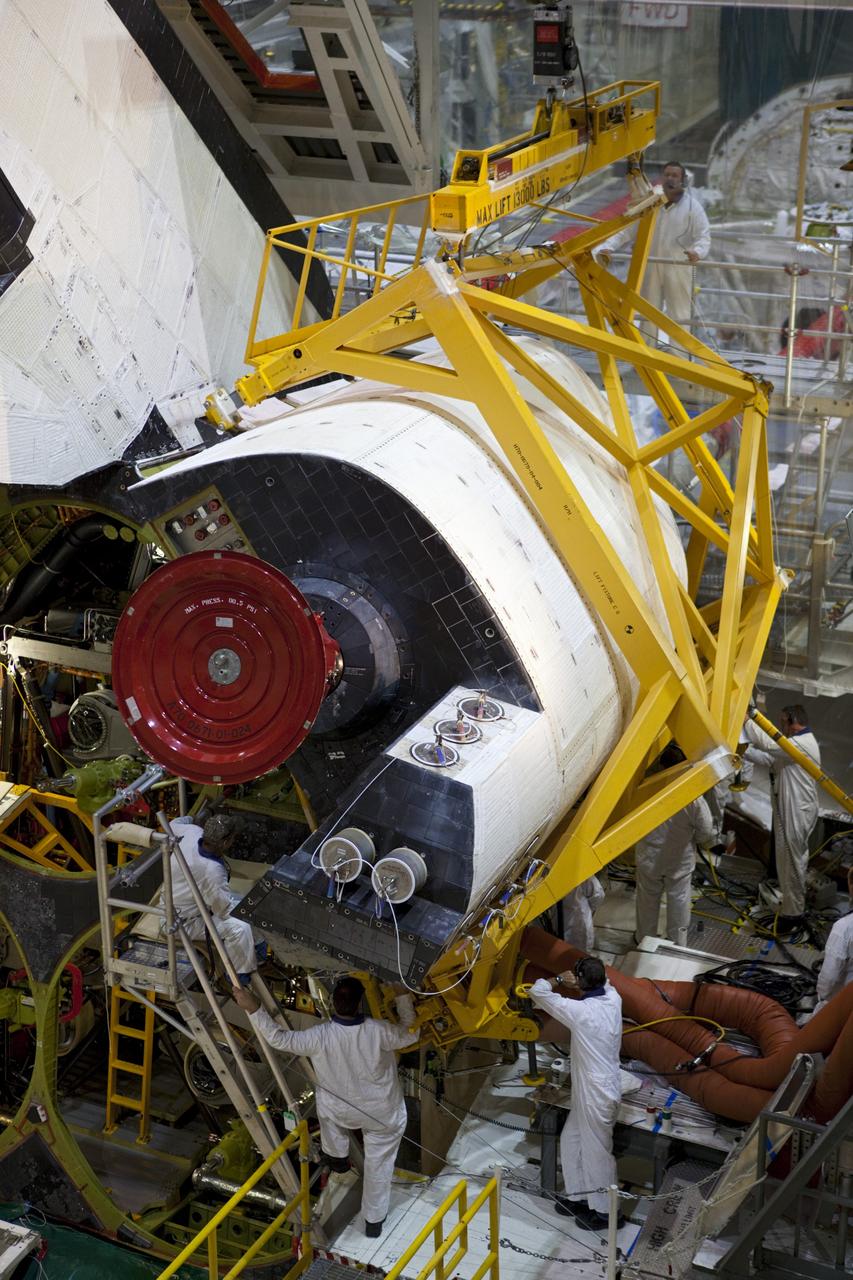

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help secure a sling around space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod and prepare it for removal. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
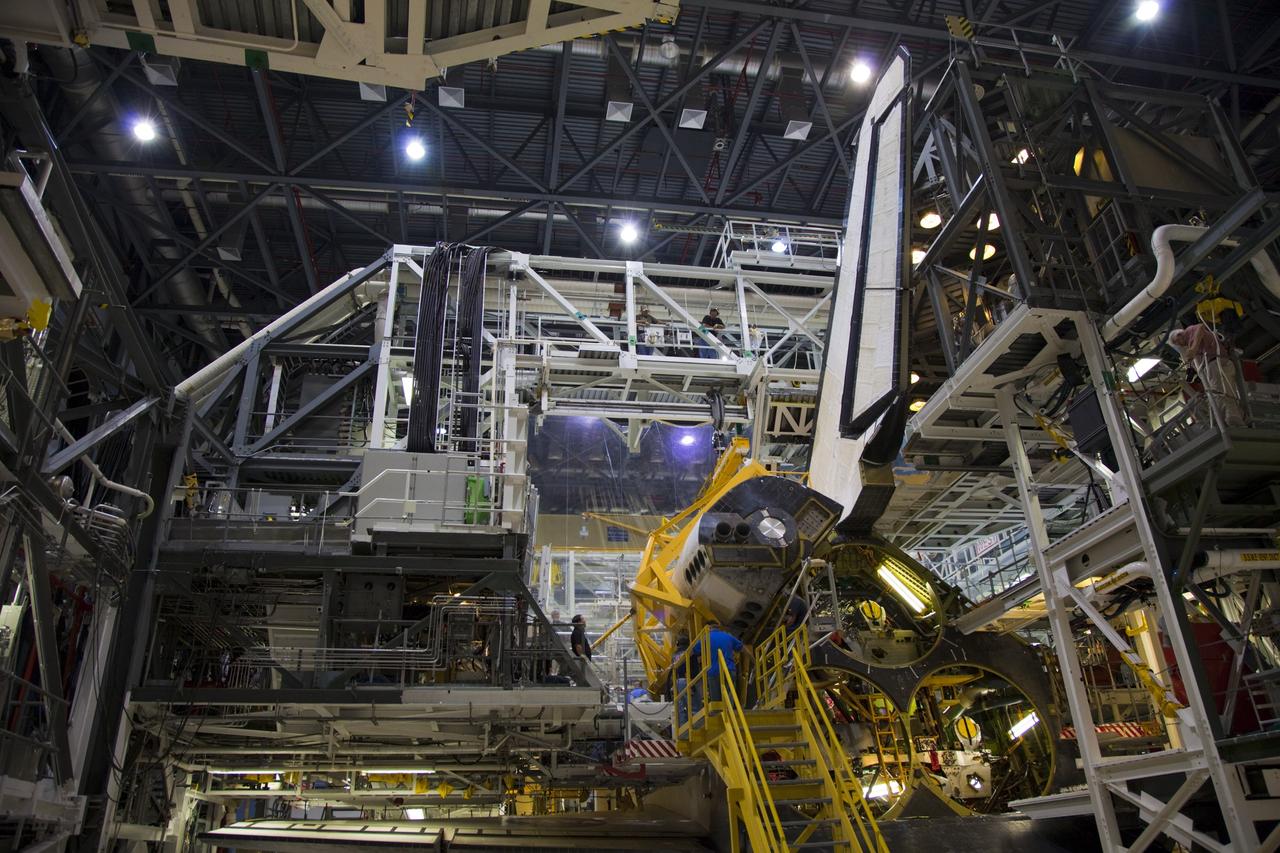

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
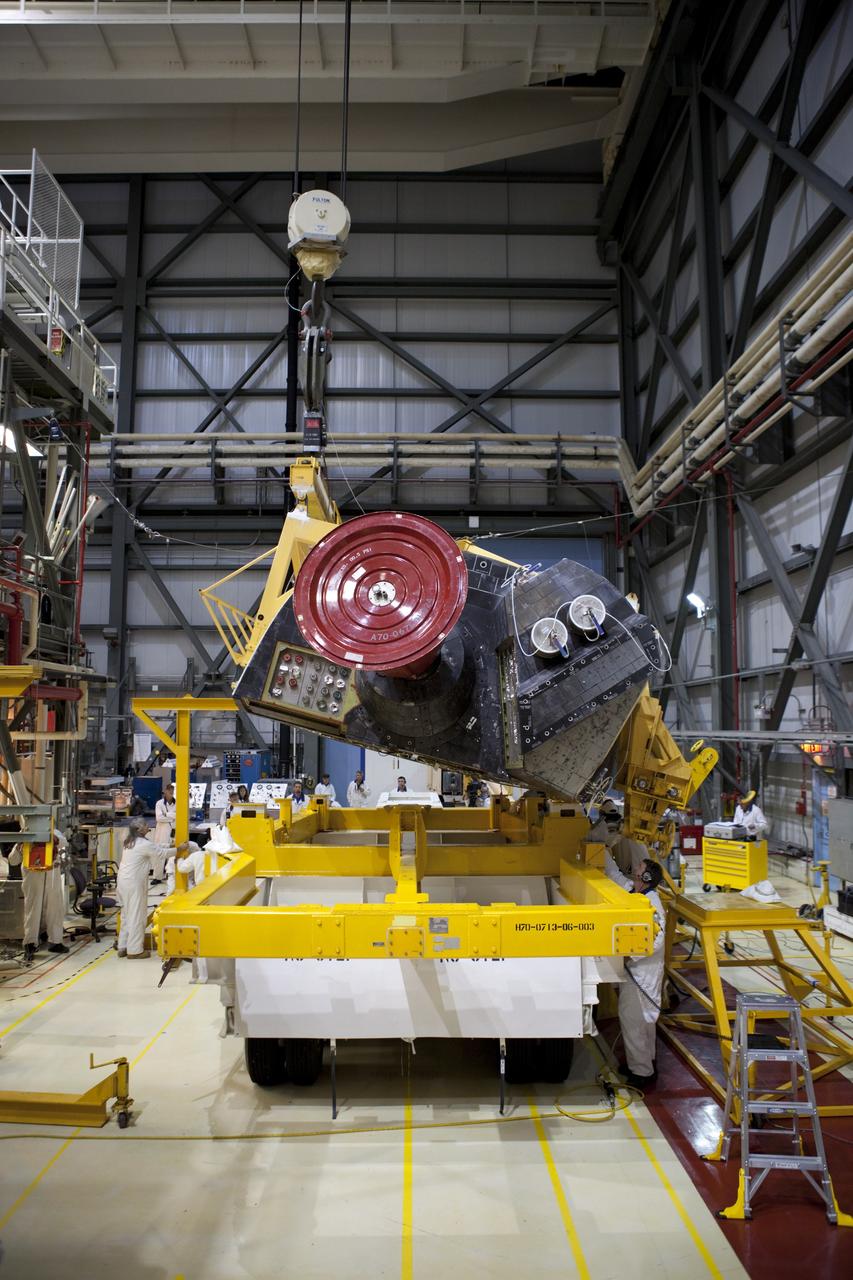

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod onto a pallet. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
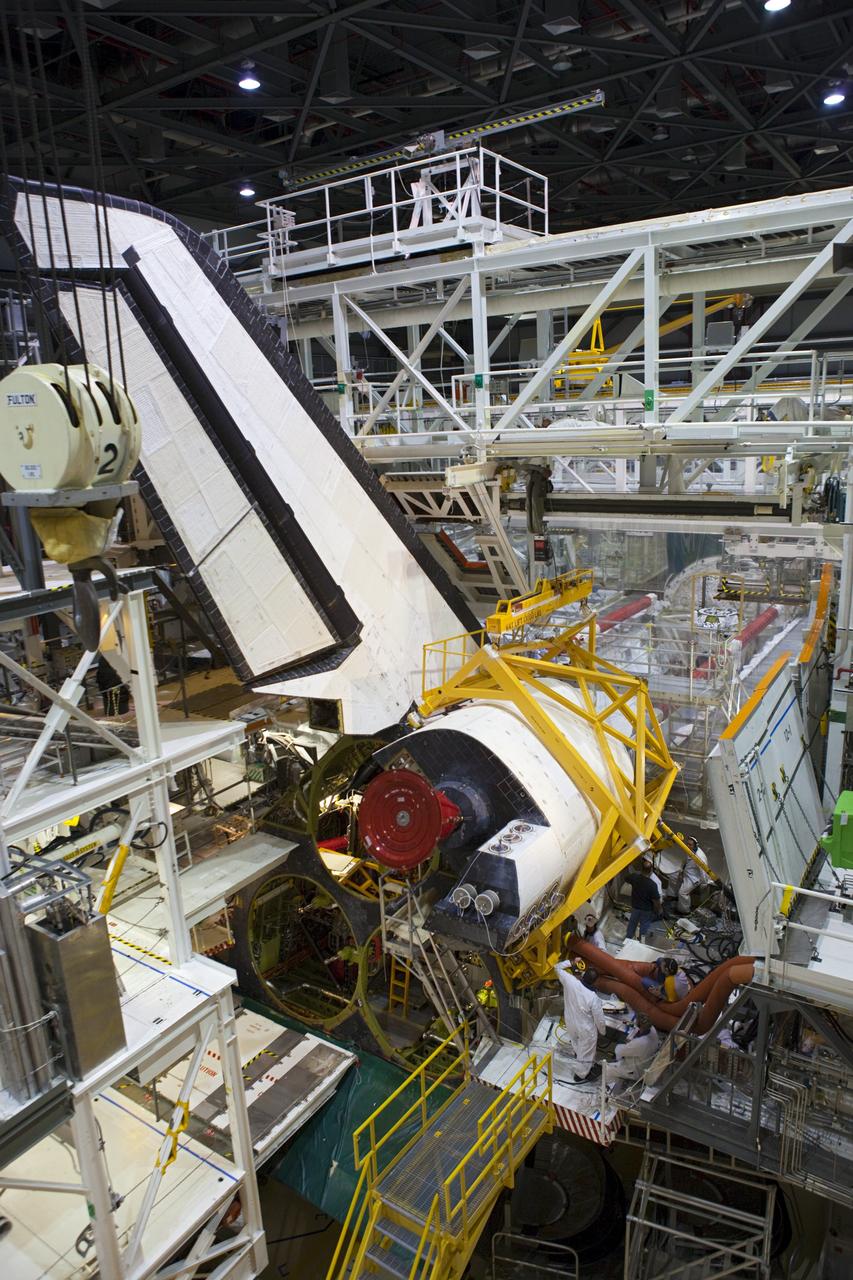

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help secure a sling around space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod and prepare it for removal. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
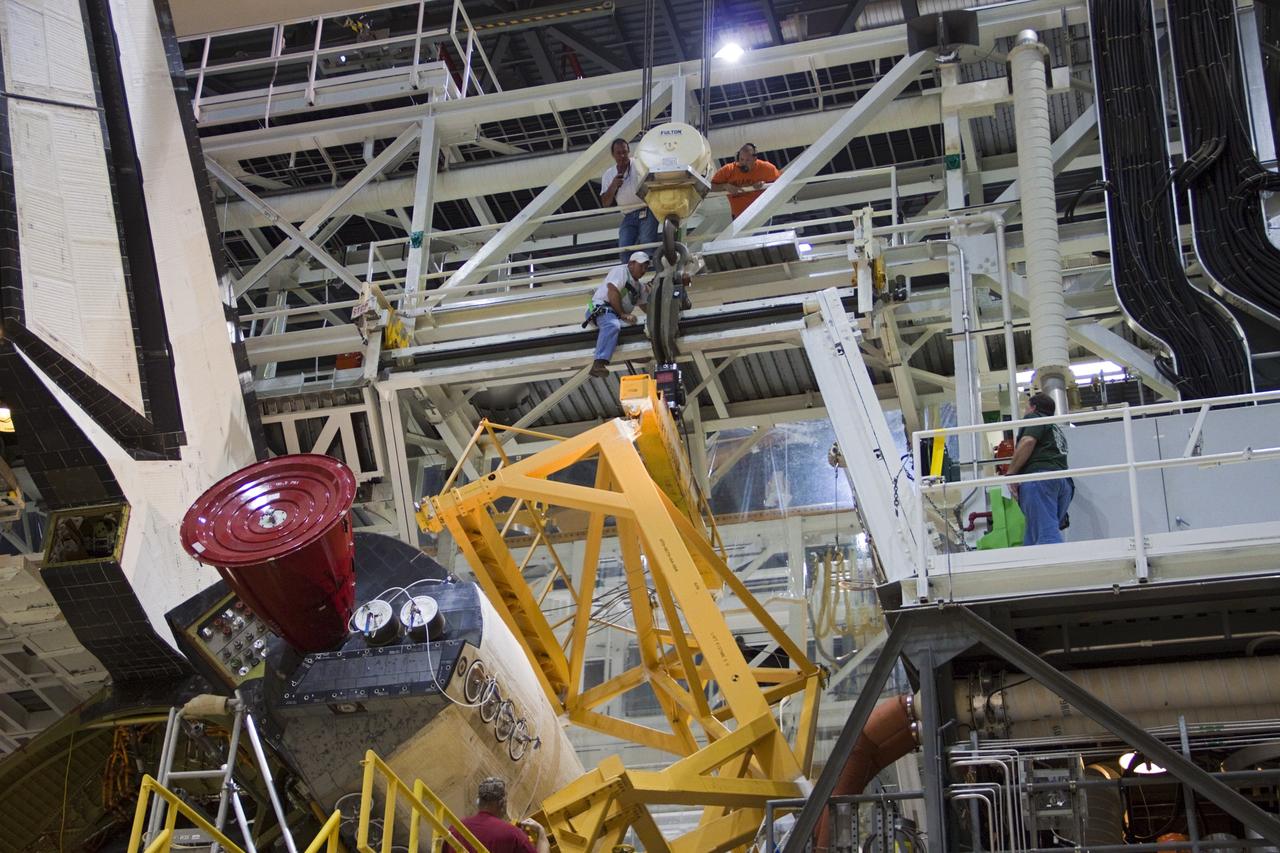

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers a sling toward space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod closer for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

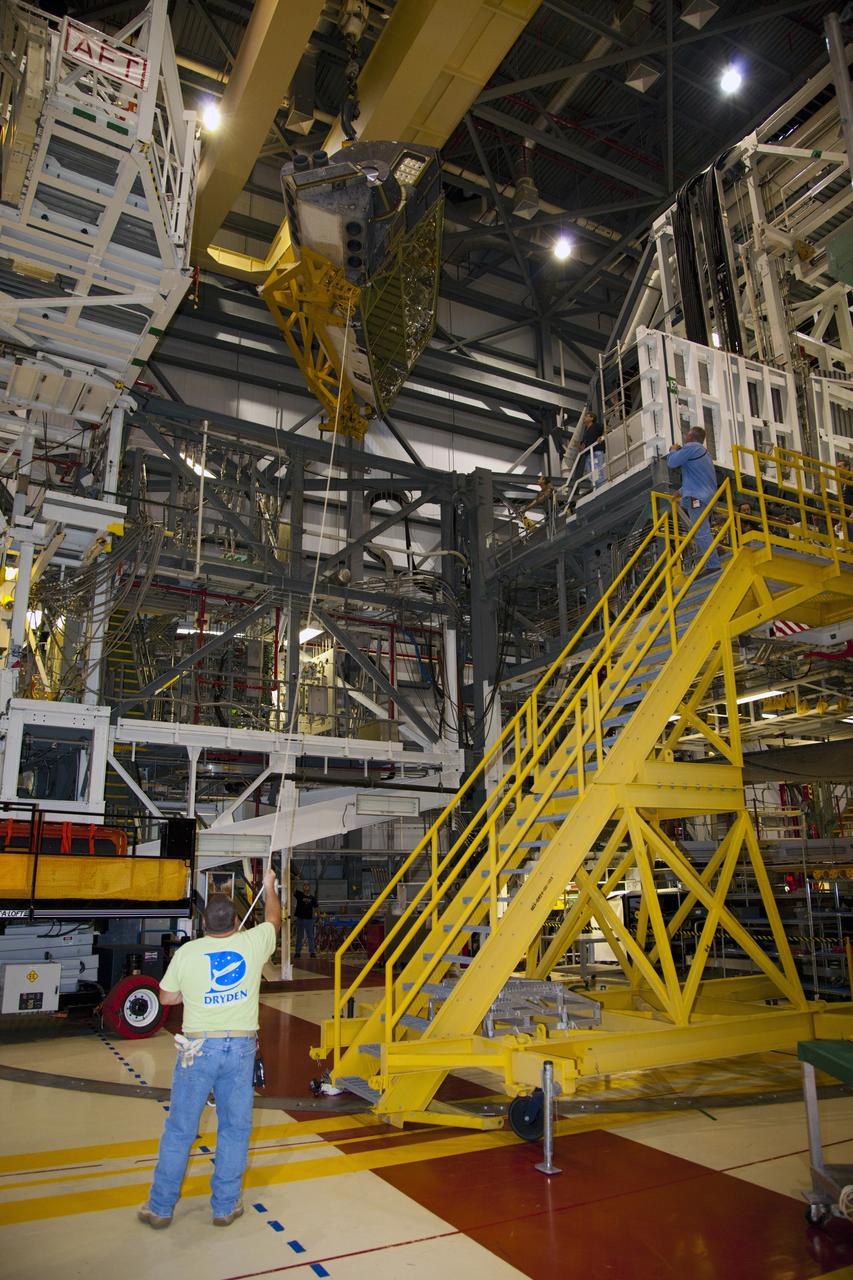
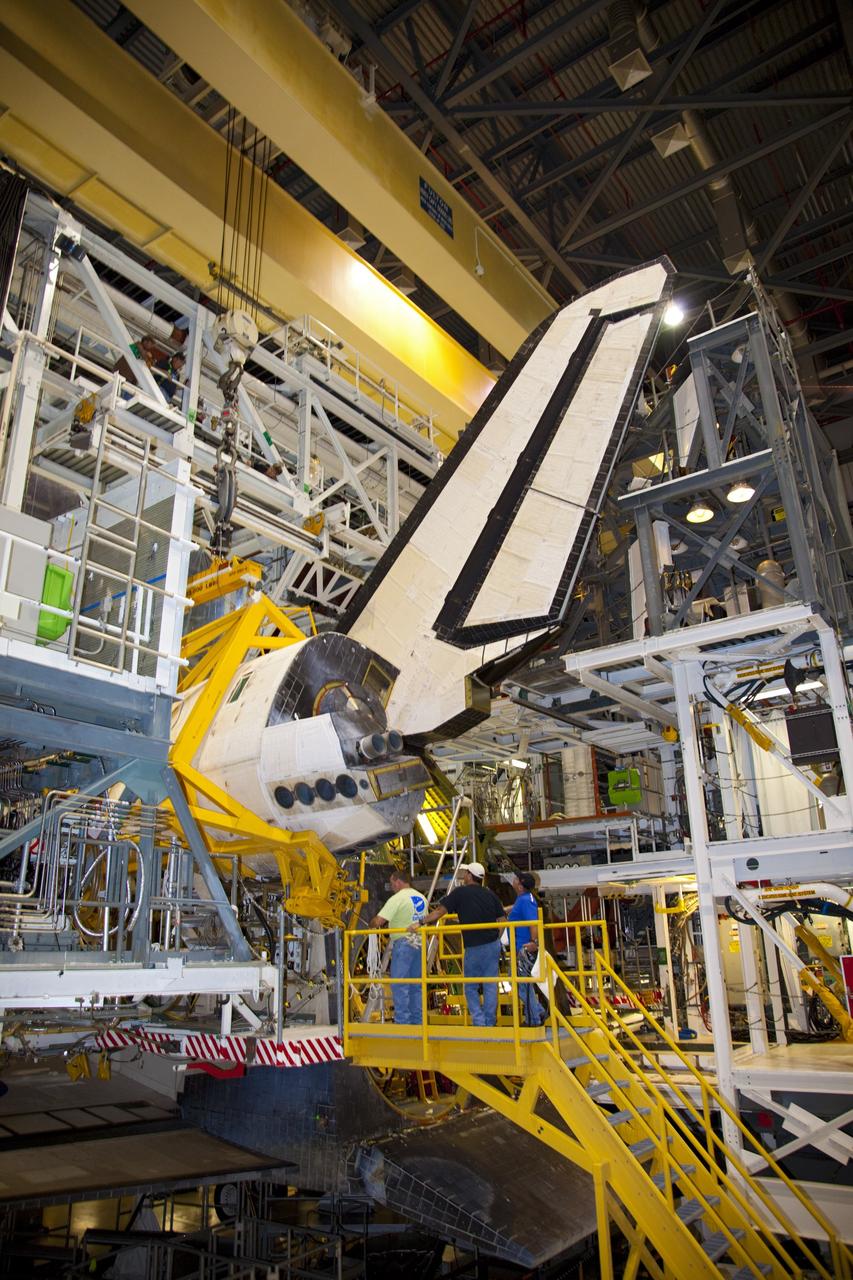
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lifts the right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod from space shuttle Atlantis. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. Both OMS pods will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where they will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician monitors the progress as a crane is used to carry an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod closer for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians monitor the progress as a large crane lowers a sling that will be secured around space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. --Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help secure a sling around space shuttle Atlantis’ right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Atlantis. The OMS pod will be removed and sent to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Atlantis. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane is secured around an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod that will be installed on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-1 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians assist as a crane lowers an orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod for installation on space shuttle Discovery. The OMS pod was returned from White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico where it underwent a complete deservicing and cleaning. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of space shuttle Discovery. The shuttle will go to the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum, Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Chantilly, Va., in April 2012. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
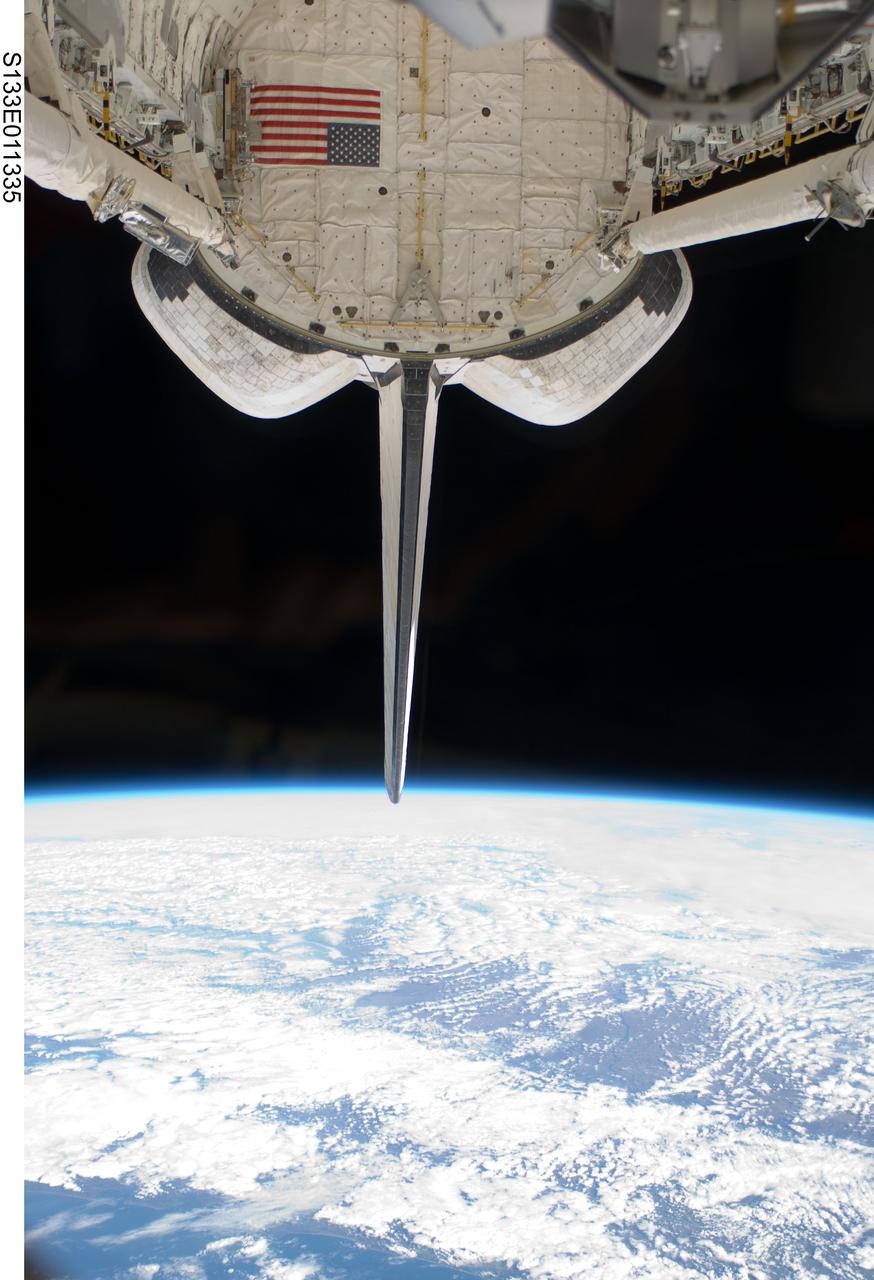

S133-E-011335 (7 March 2011) --- Space shuttle Discovery’s vertical stabilizer, orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, remote manipulator system/orbiter boom sensor system (RMS/OBSS) and payload bay are featured in this image photographed by an STS-133 crew member on the shuttle during flight day 12 activities. Earth's horizon and the blackness of space provide the backdrop for the scene. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
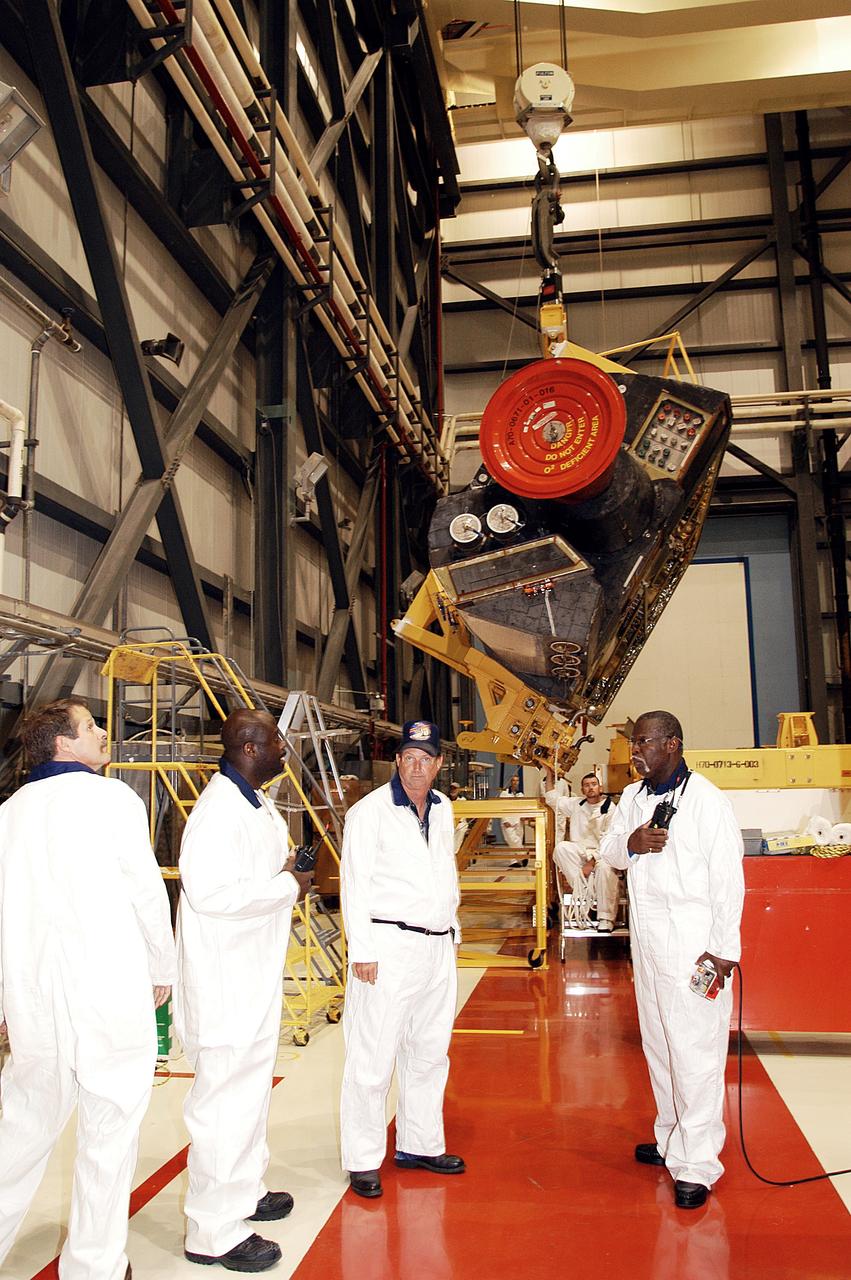

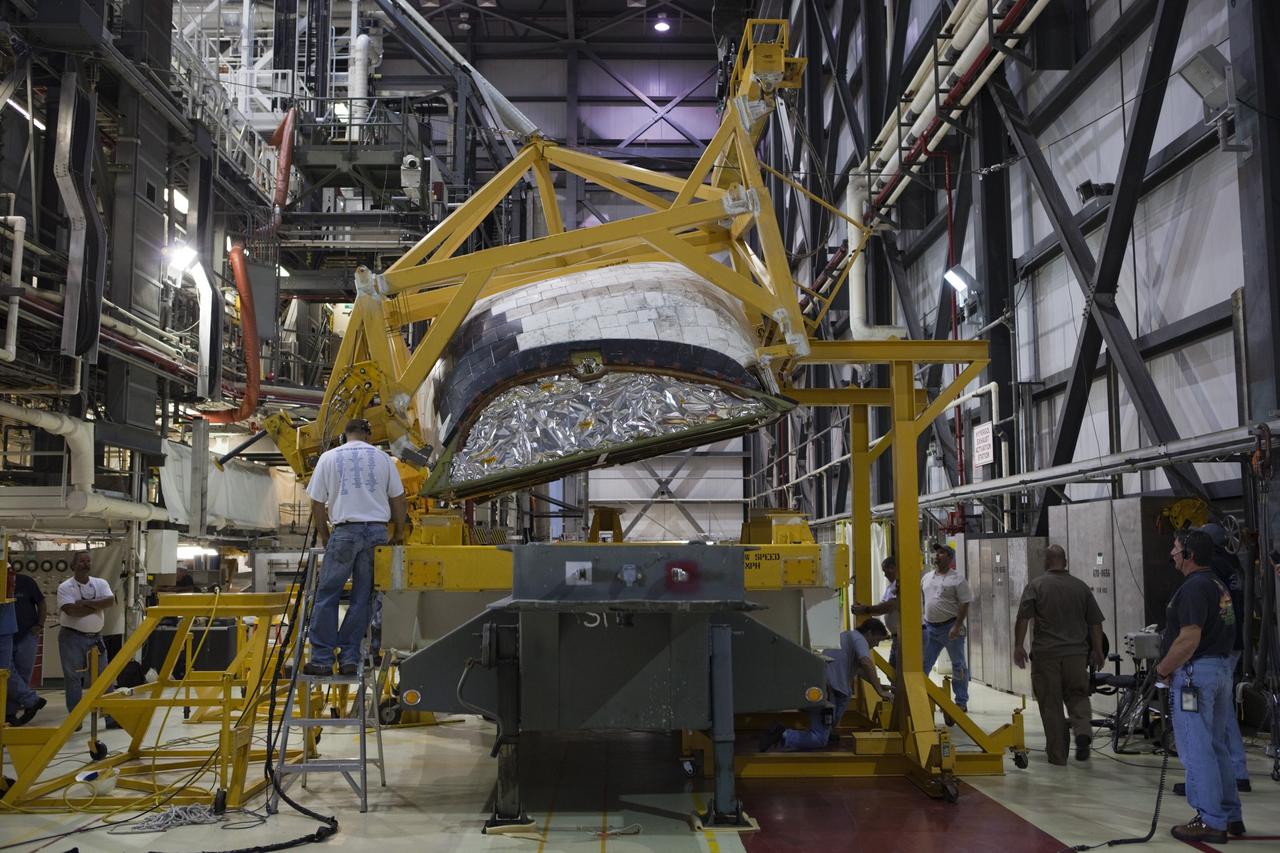
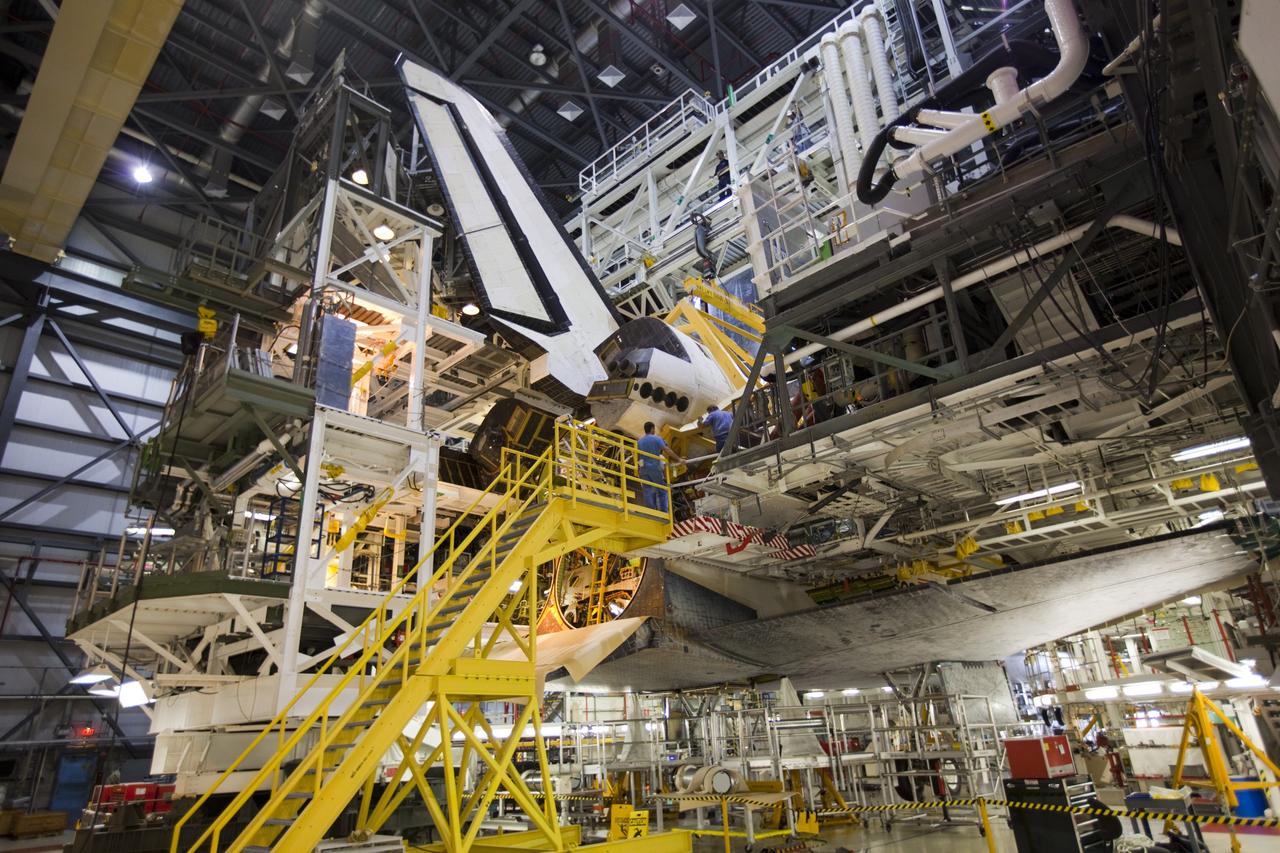
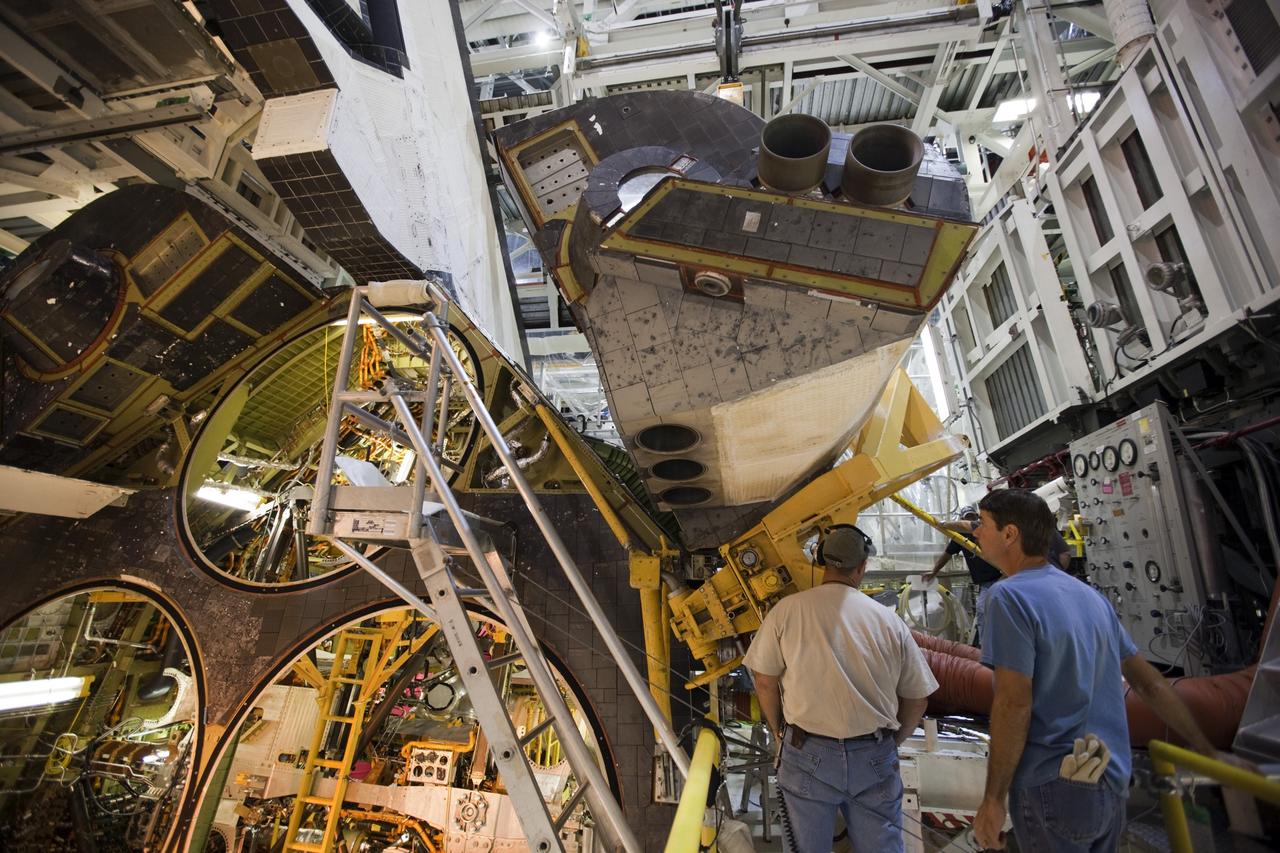
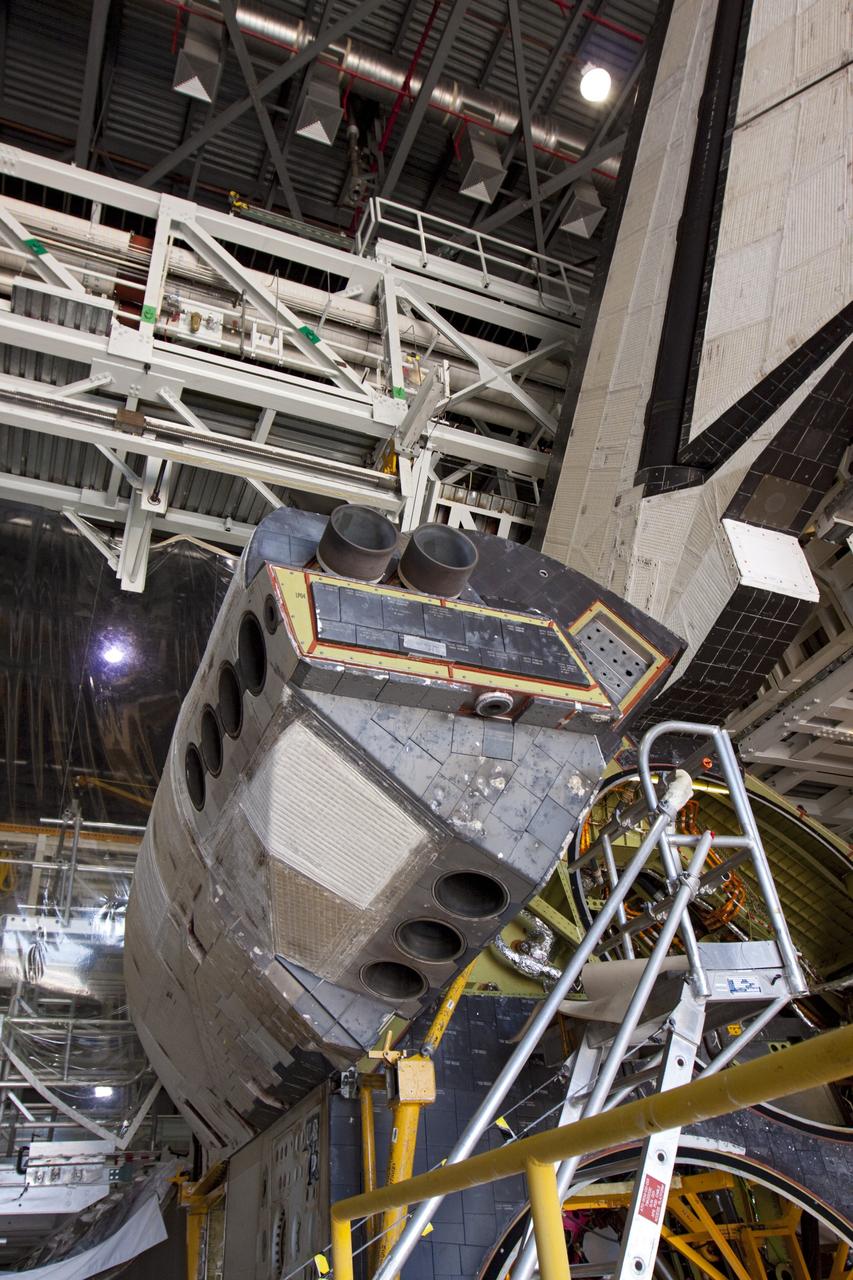
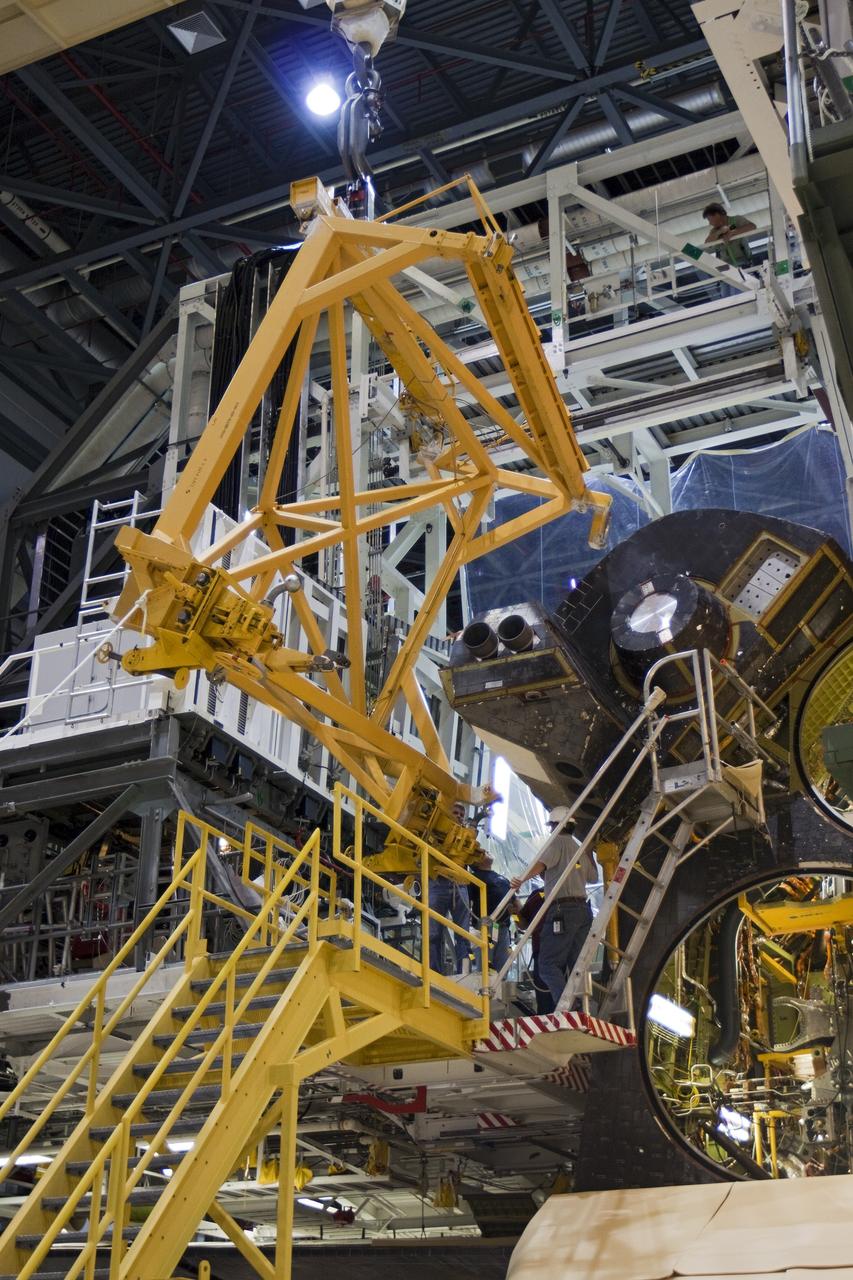
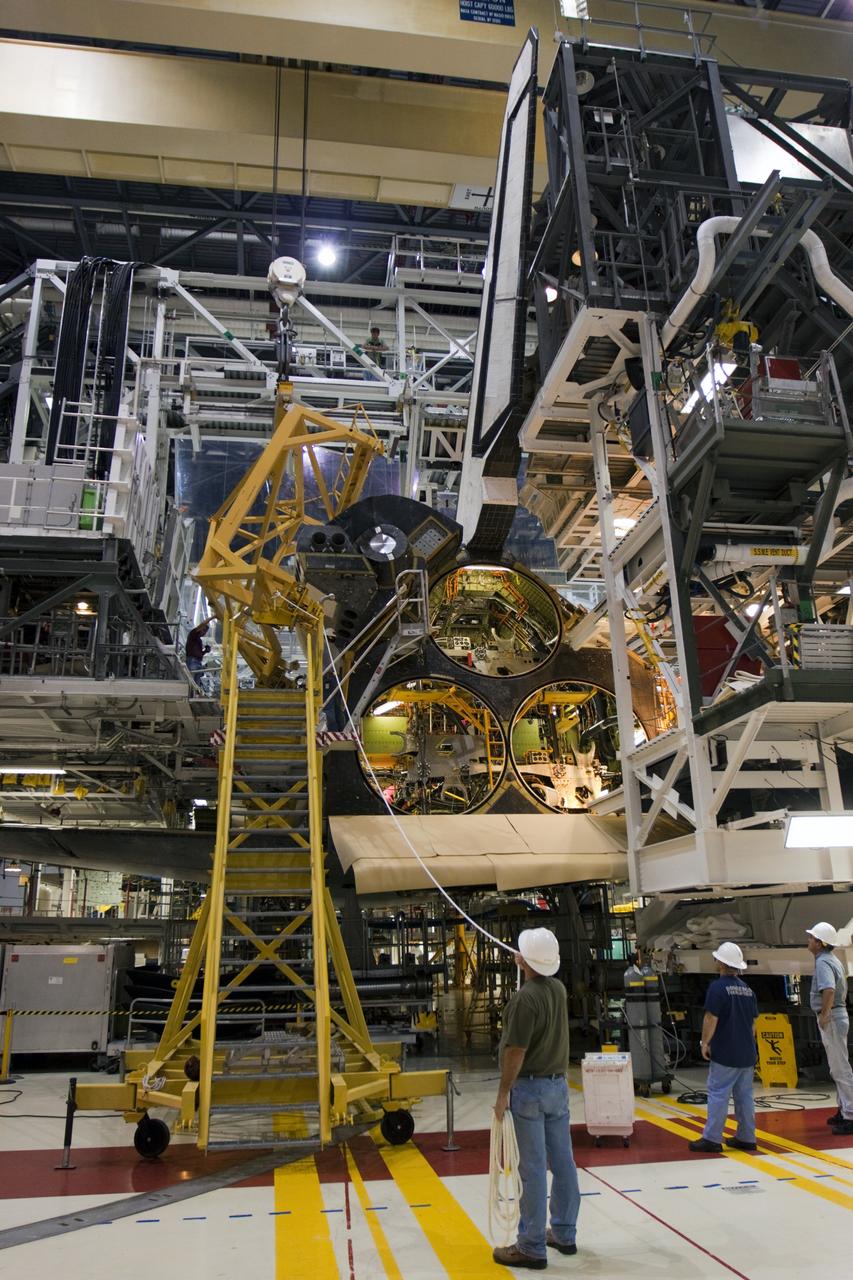
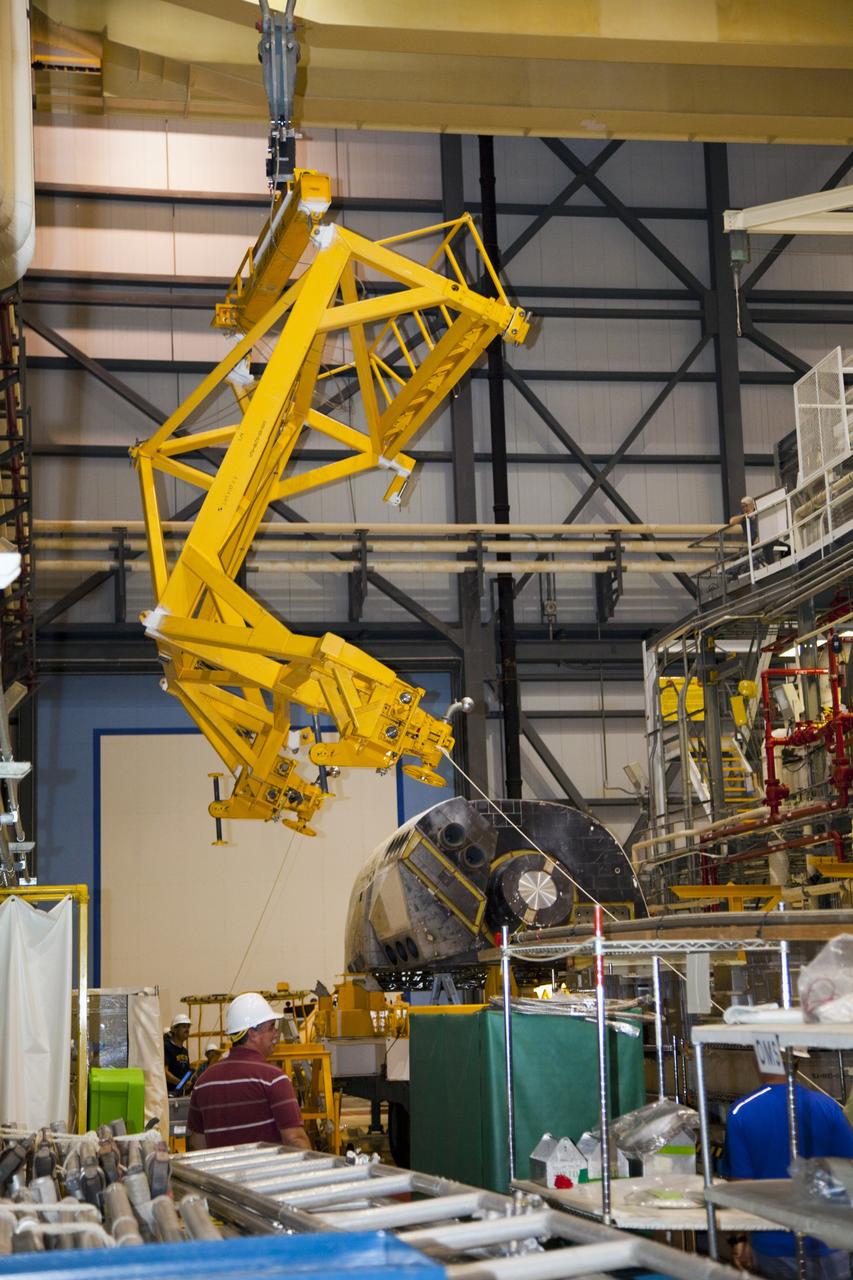
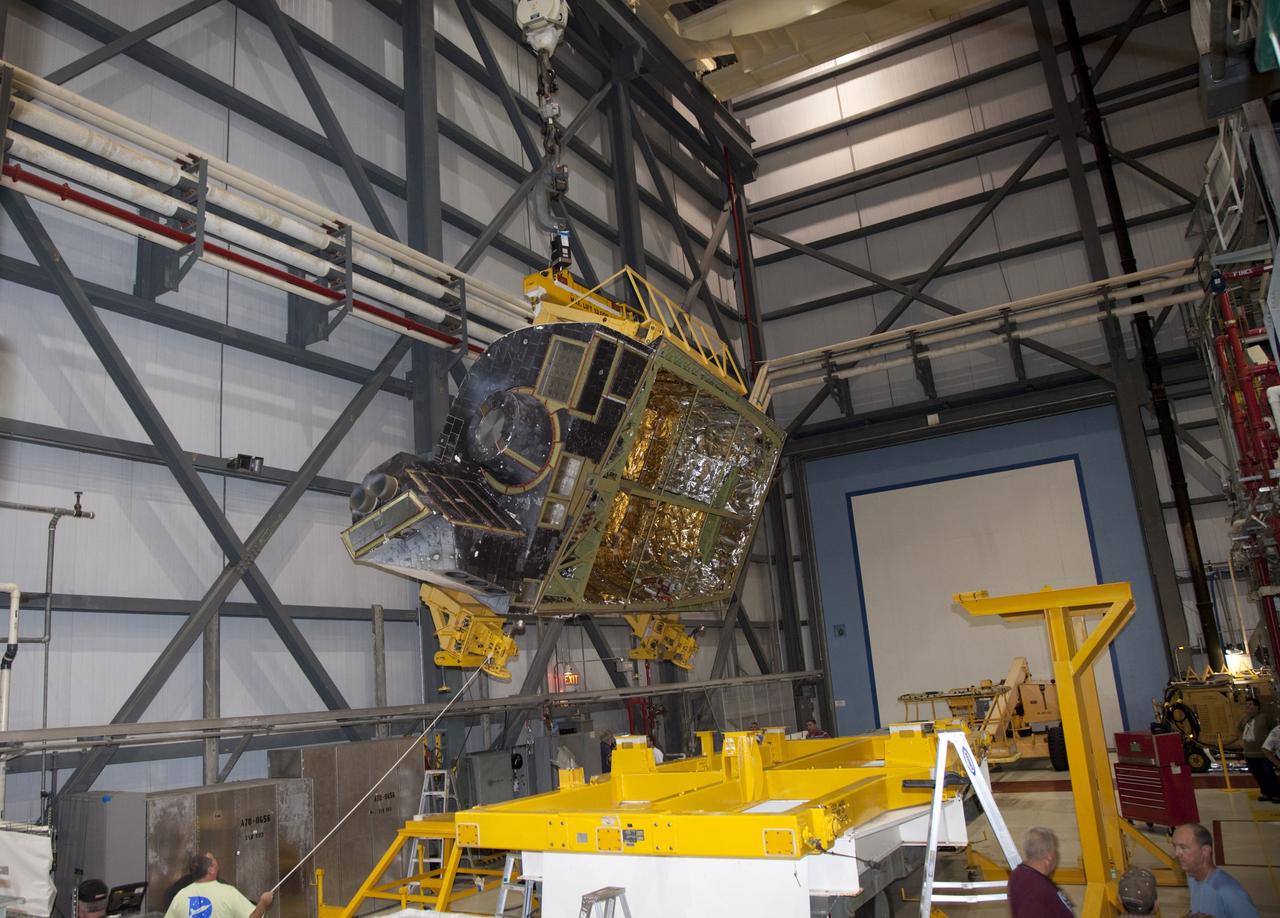
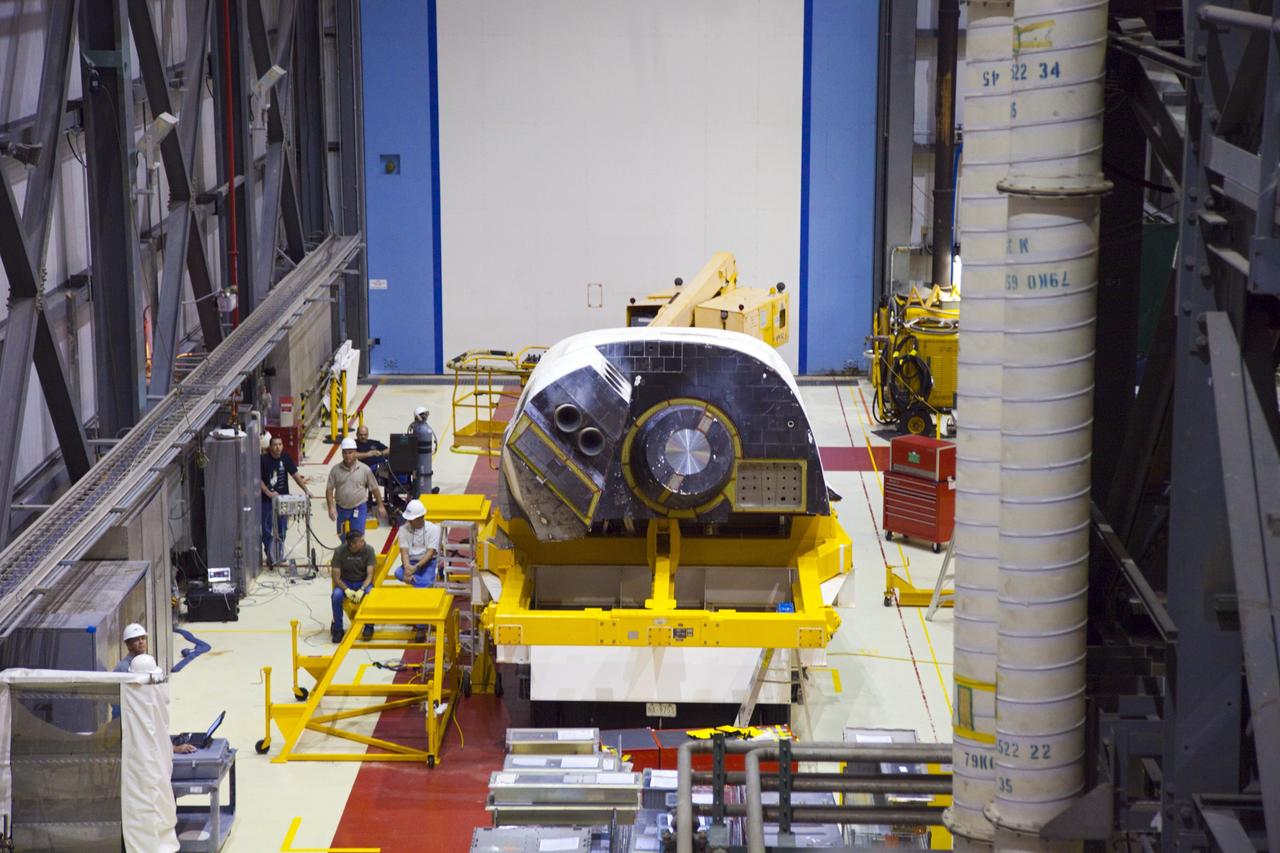
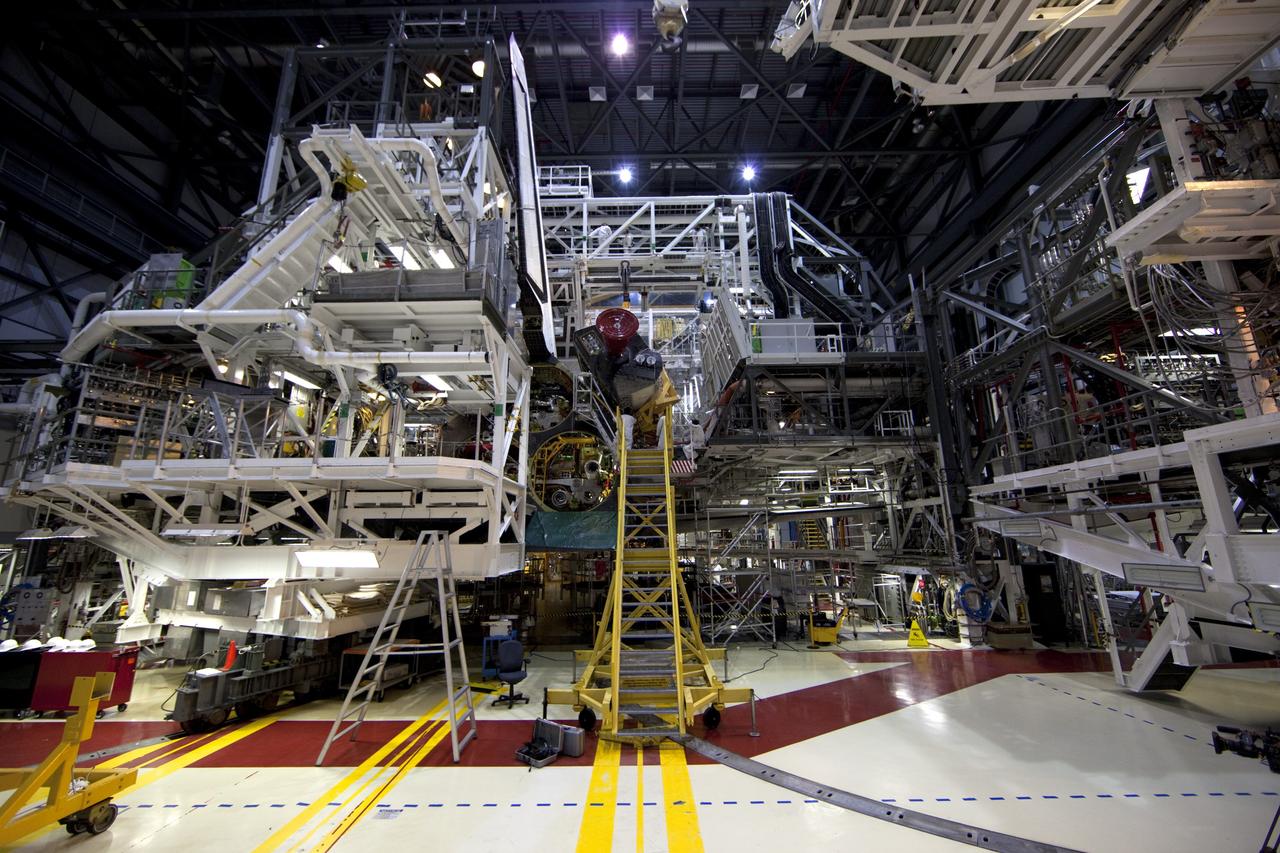
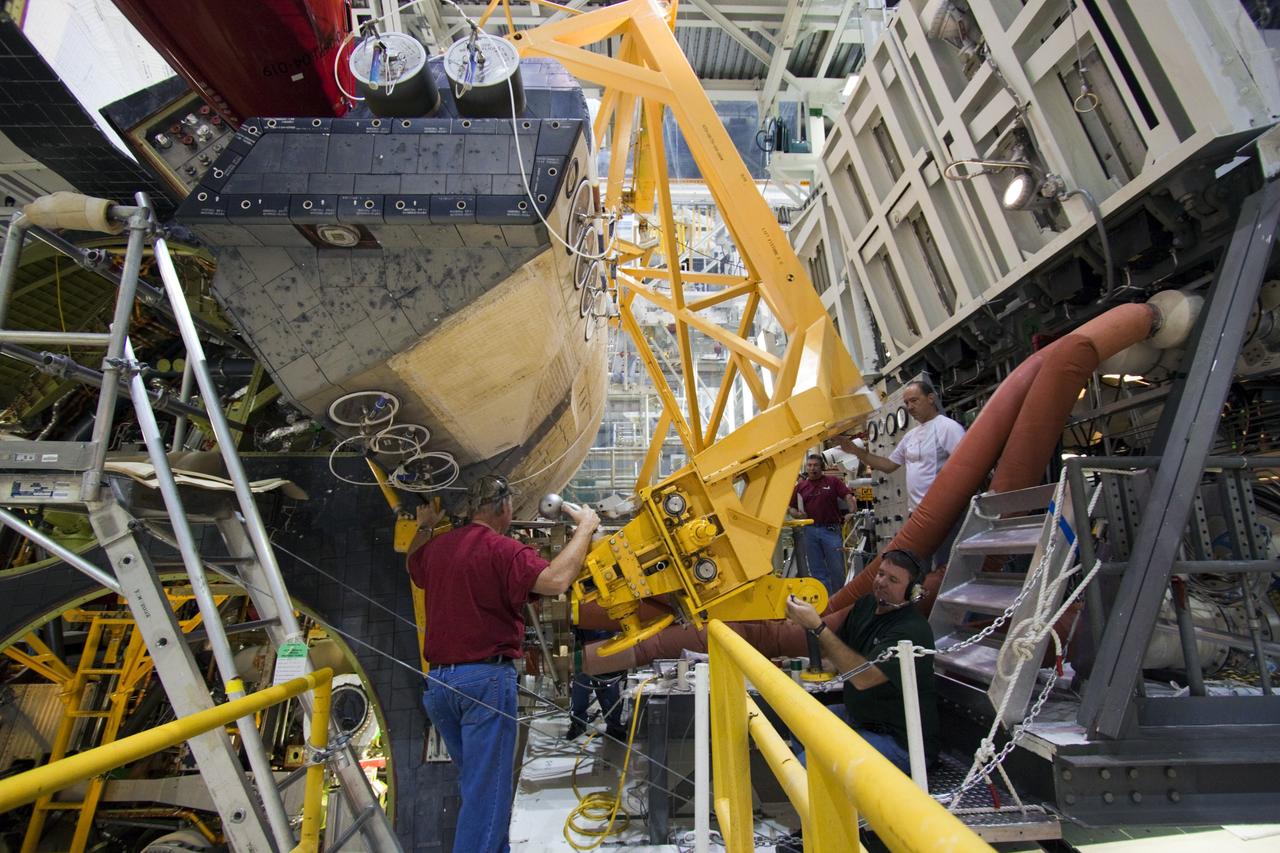
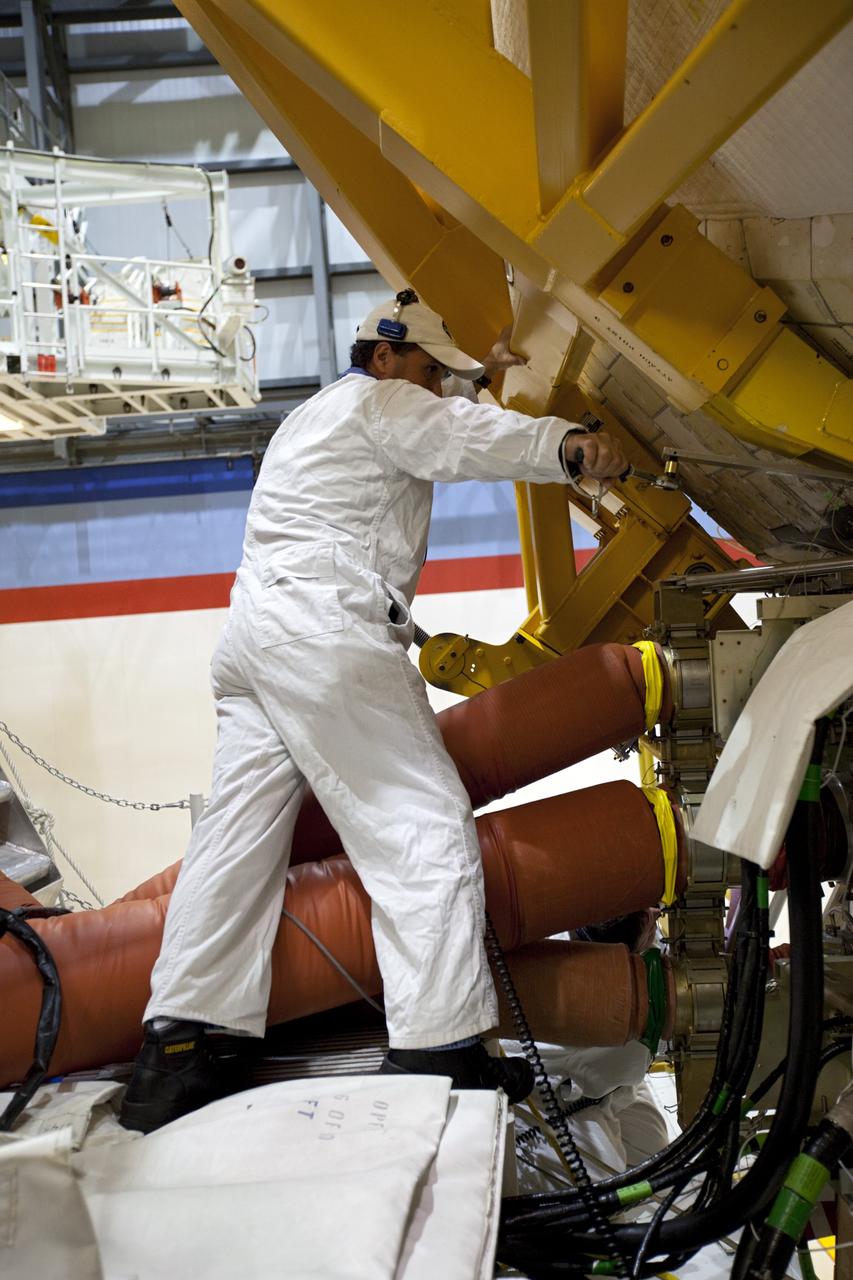
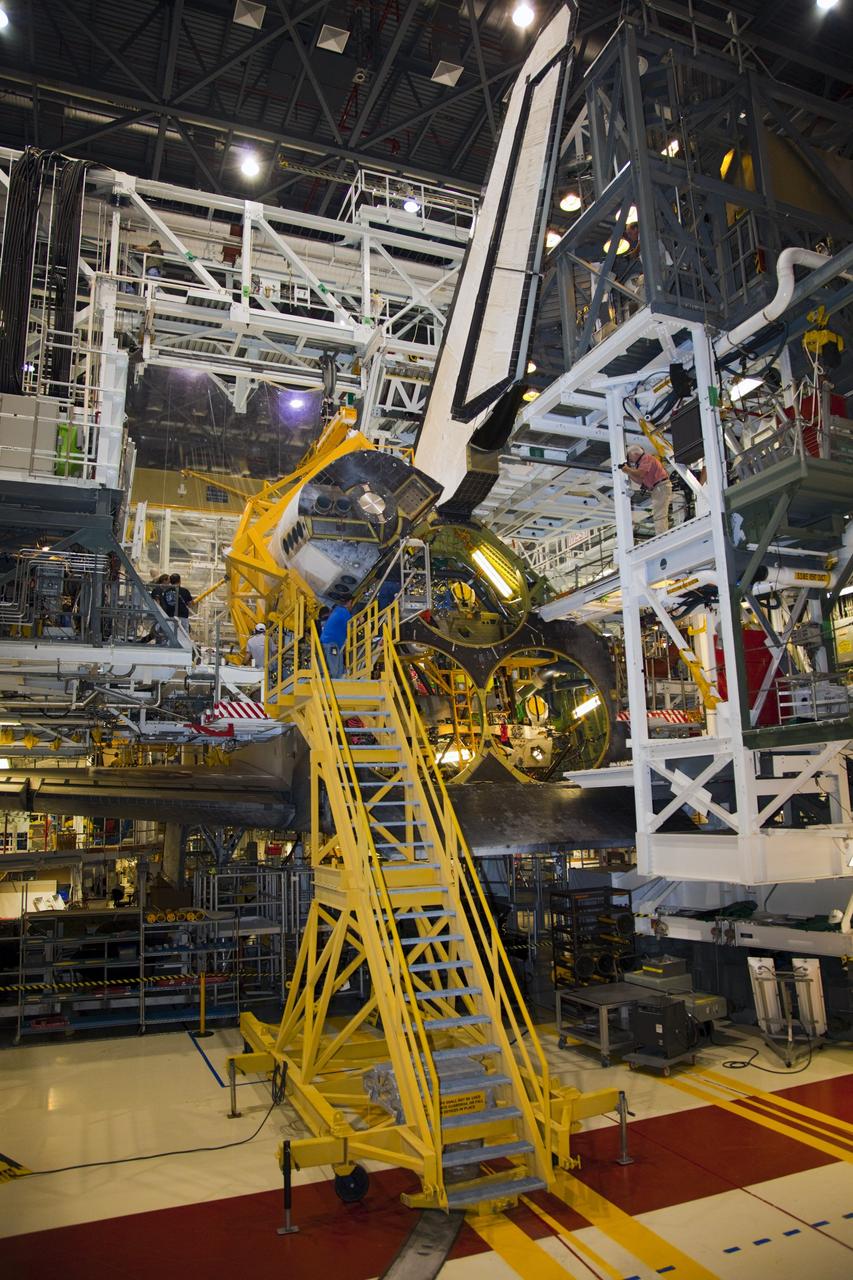
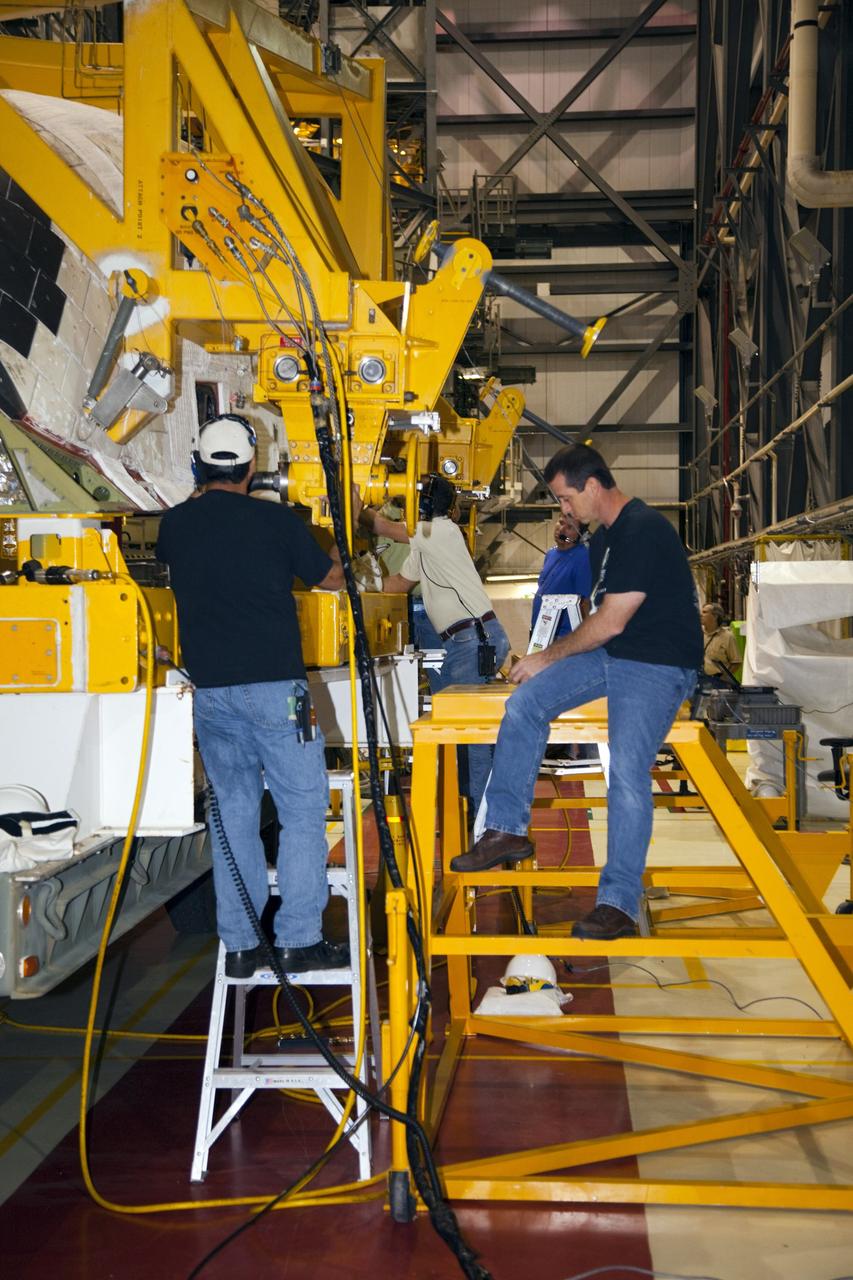
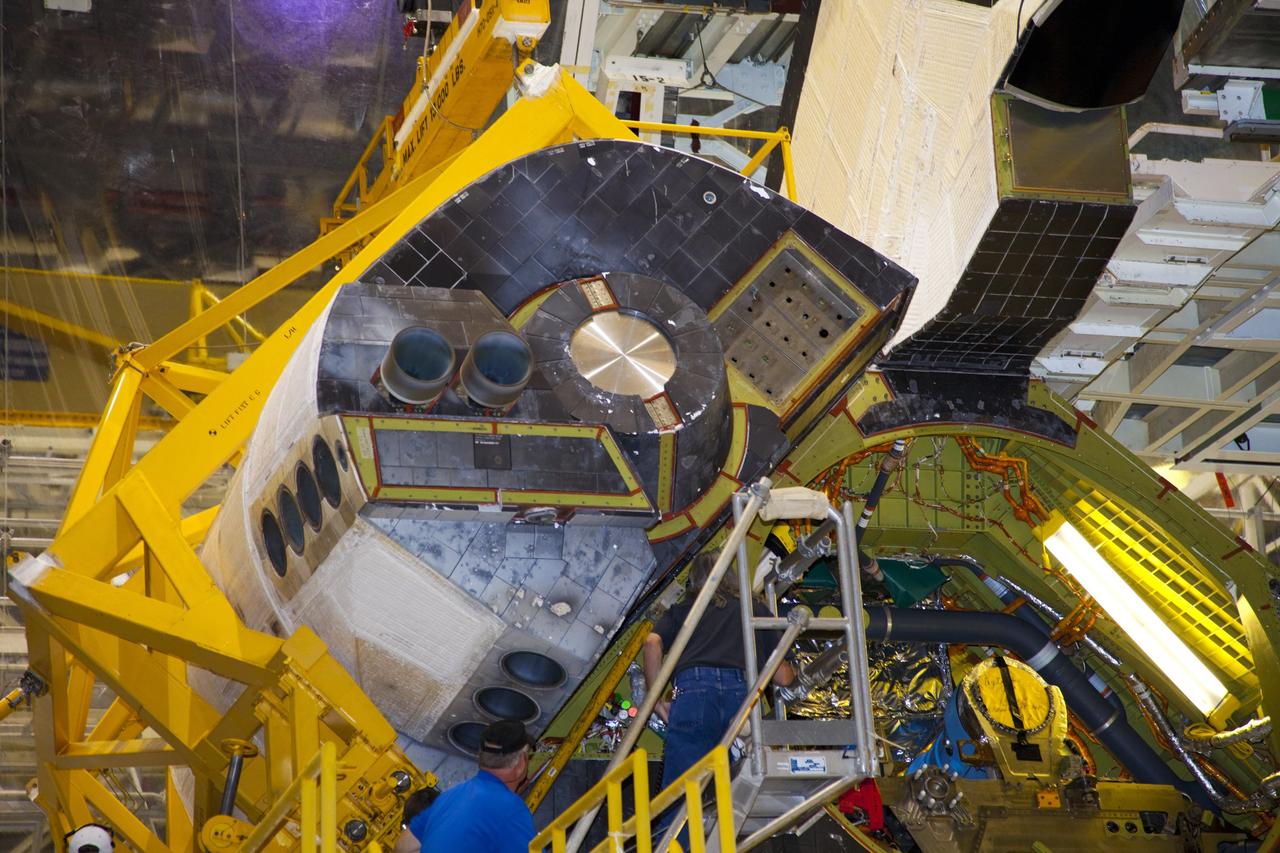
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers discuss the next step in moving the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pod behind them. The OMS pod will be installed on Atlantis. Two OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts.
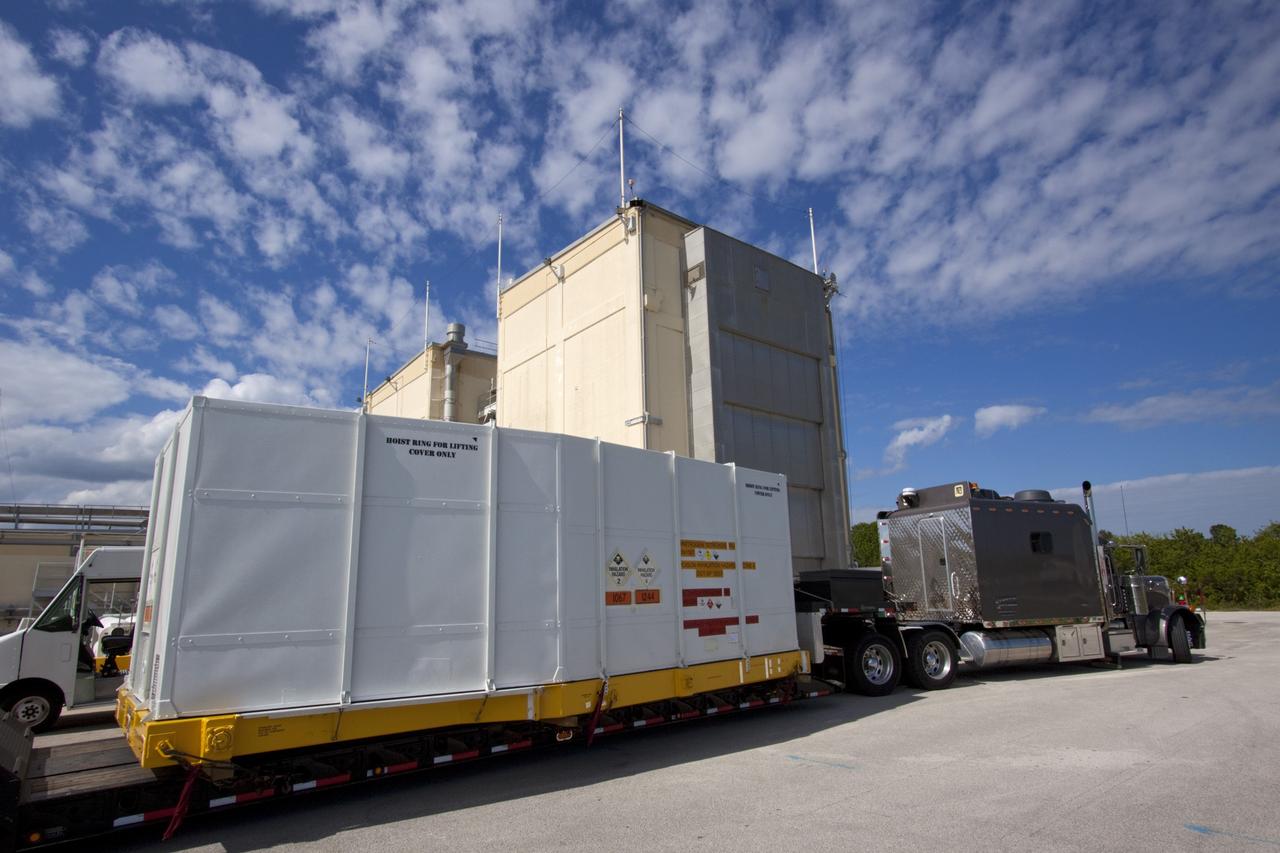

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outside the Hazardous Maintenance Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour’s left and right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and forward reaction control system (FRCS) are secured in several containers and ready for transport to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Endeavour. At White Sands the OMS pods and FRCS will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Endeavour. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
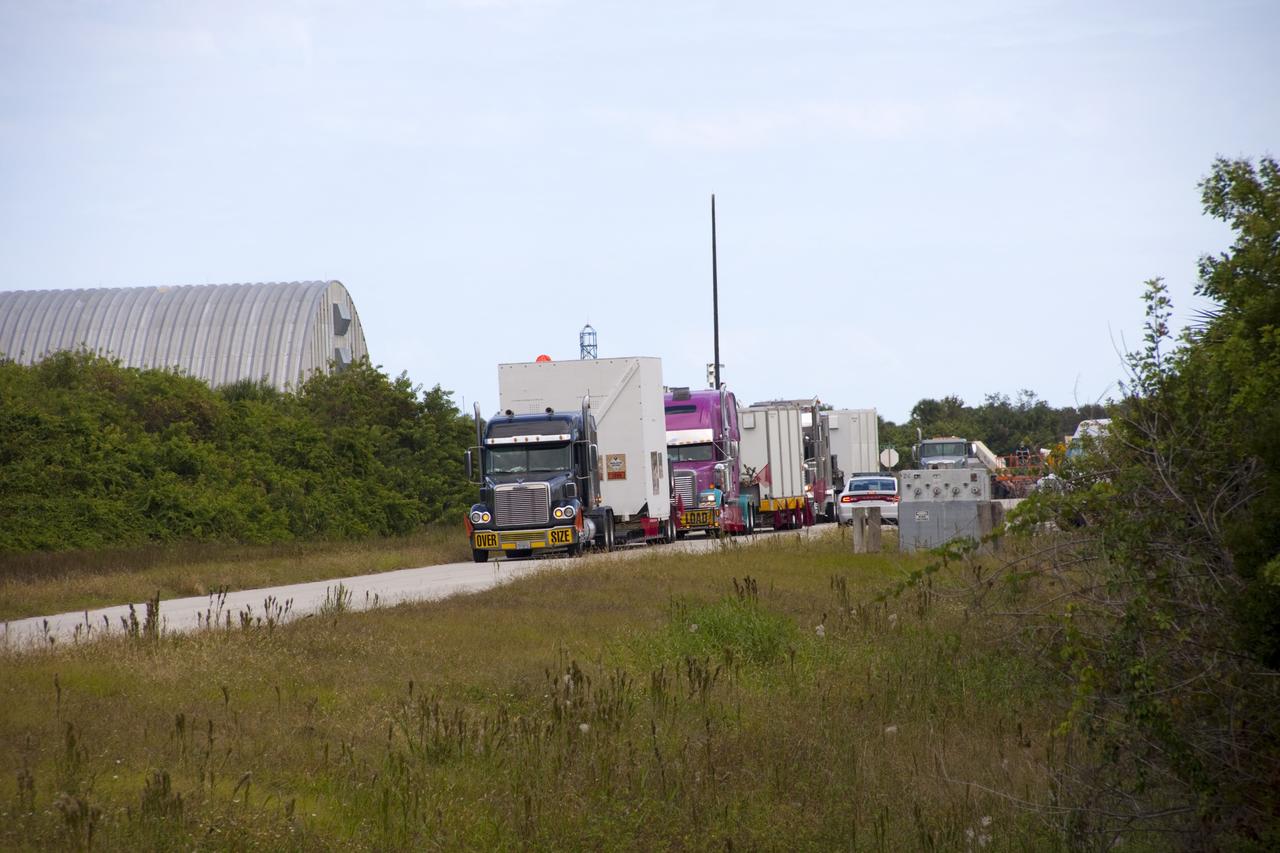

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outside the Hazardous Maintenance Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour’s left and right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and forward reaction control system (FRCS) are secured in several containers and ready for transport to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Endeavour. At White Sands the OMS pods and FRCS will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Endeavour. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
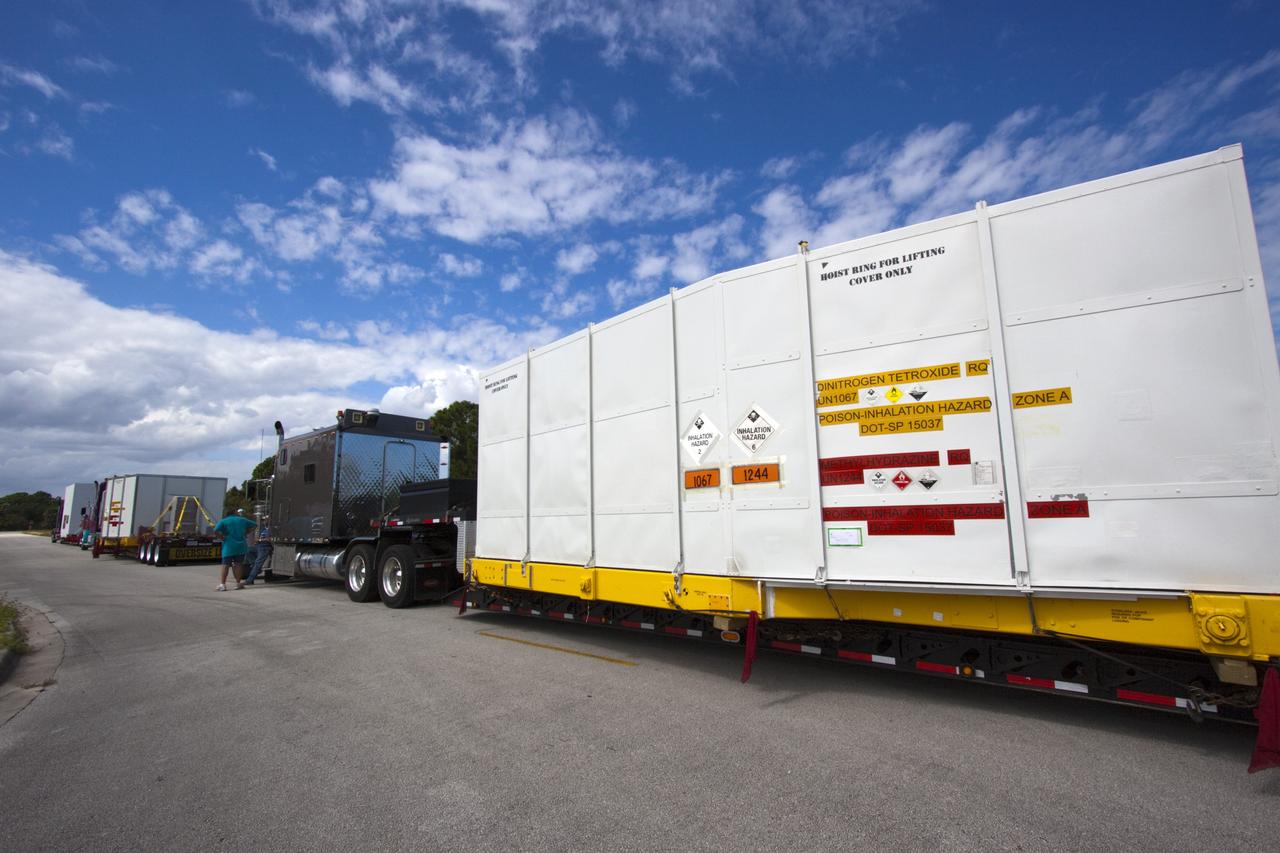

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outside the Hazardous Maintenance Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour’s left and right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and forward reaction control system (FRCS) are secured in several containers and ready for transport to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Endeavour. At White Sands the OMS pods and FRCS will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Endeavour. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
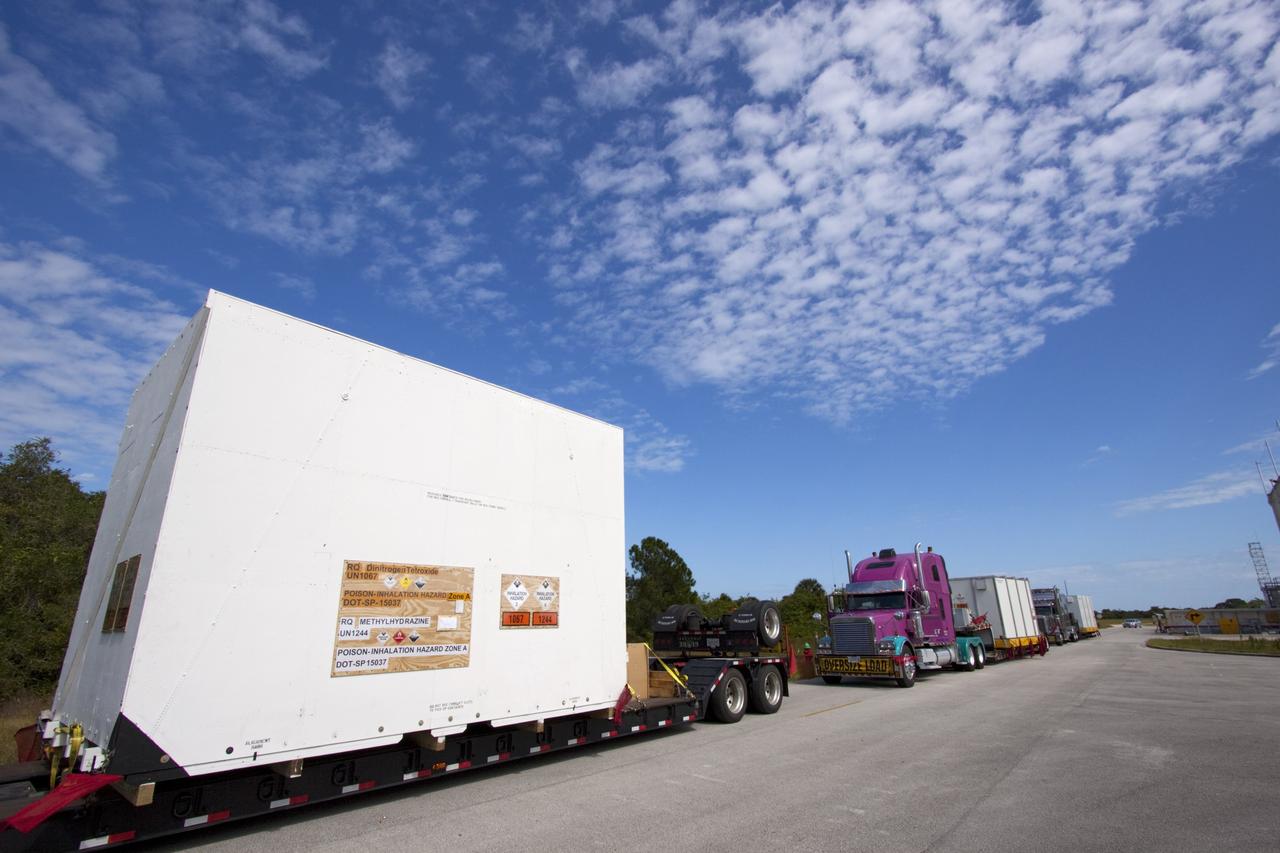

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Outside the Hazardous Maintenance Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour’s left and right orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and forward reaction control system (FRCS) are secured in several containers and ready for transport to White Sands Space Harbor in New Mexico. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of shuttle Endeavour. At White Sands the OMS pods and FRCS will undergo a complete deservicing and cleaning and then be returned to Kennedy for reinstallation on Endeavour. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
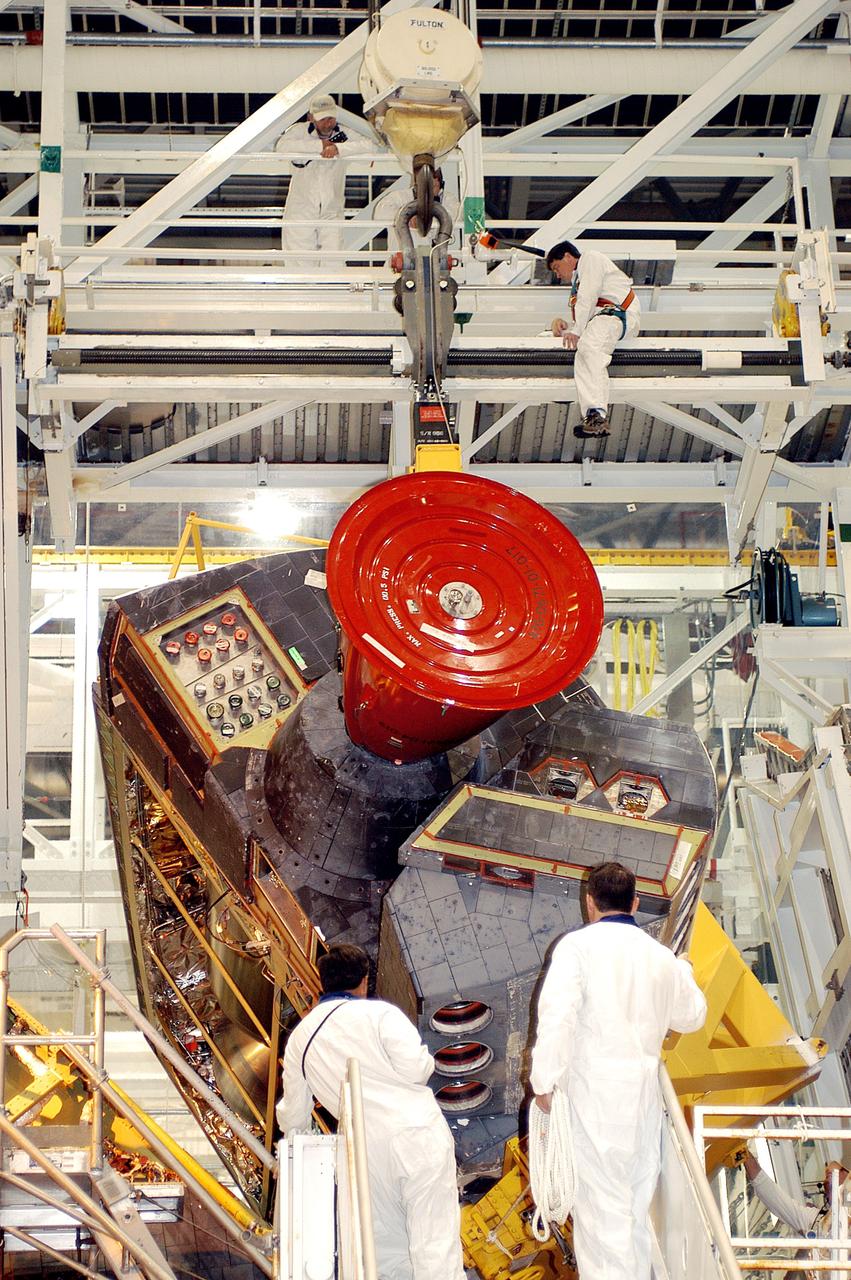
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians in the Orbiter Processing Facility oversee removal of one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods from Endeavour. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.
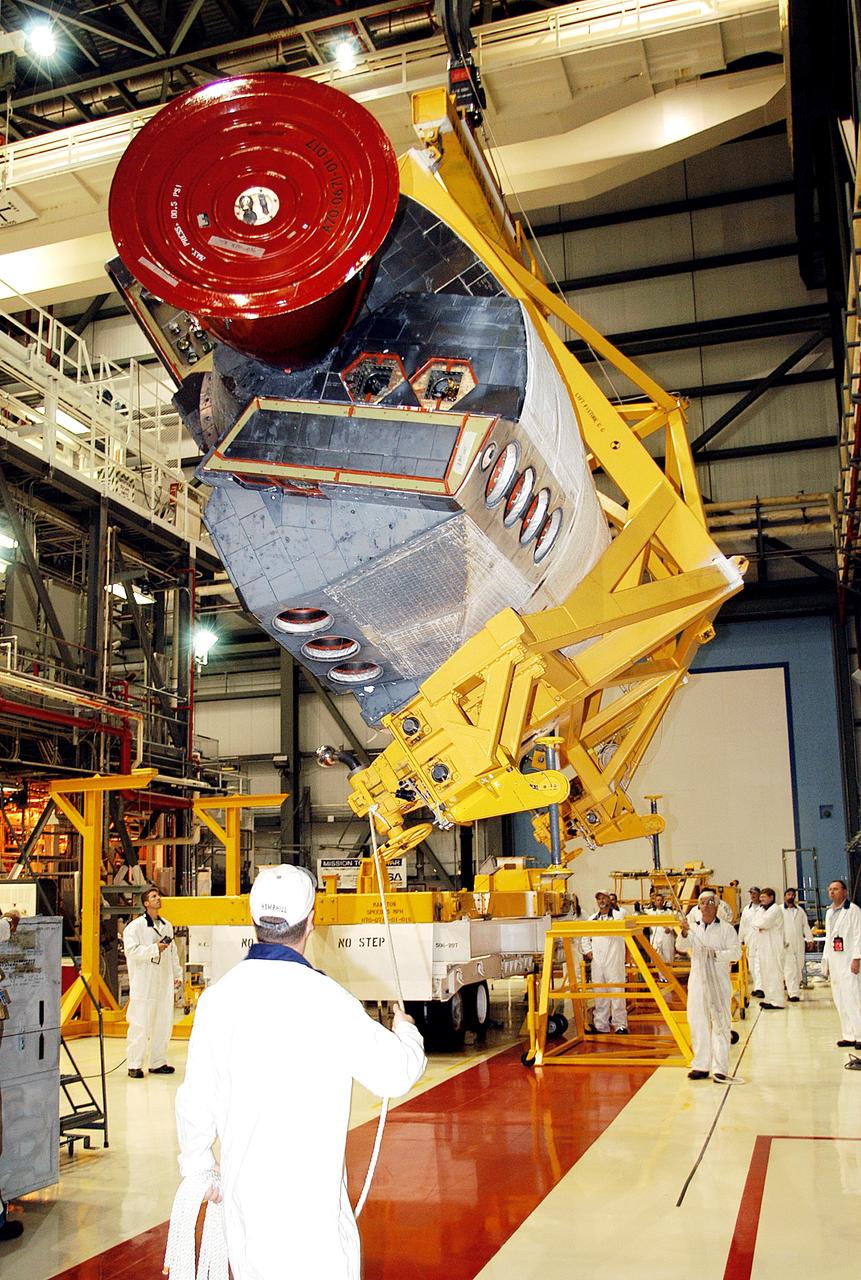

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods removed from Endeavour is lowered toward a transporter. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods removed from Endeavour is lowered onto a transporter. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.
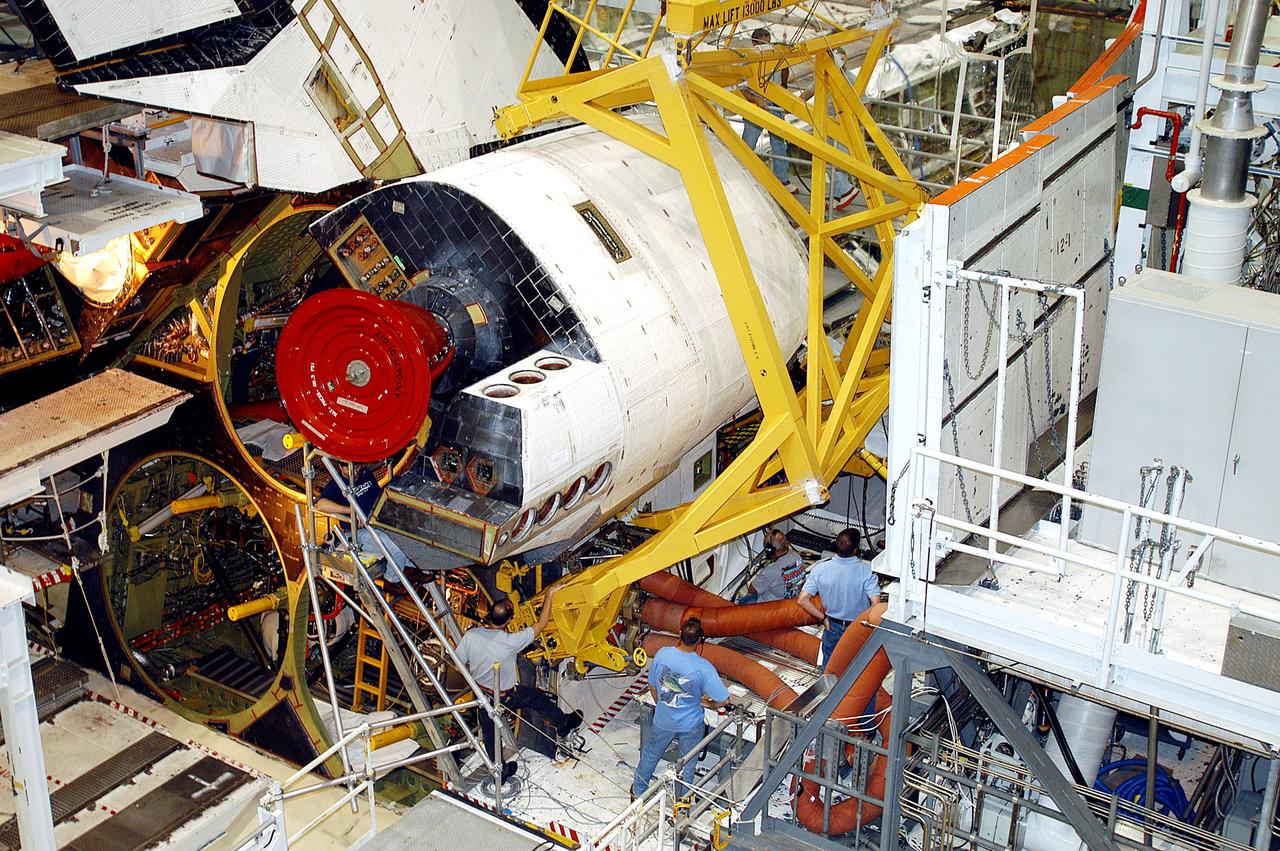

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to remove one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods from Endeavour. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.
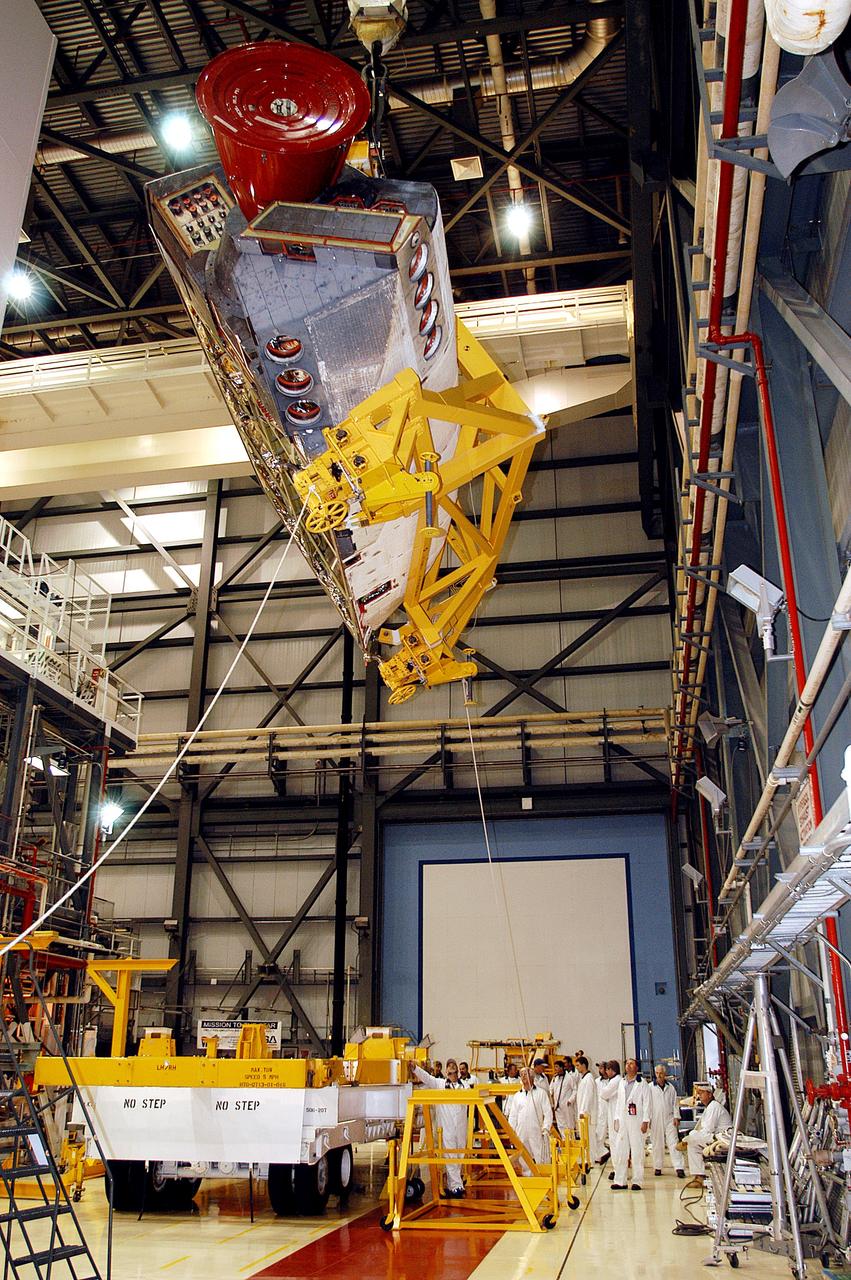

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods removed from Endeavour is suspended overhead. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.
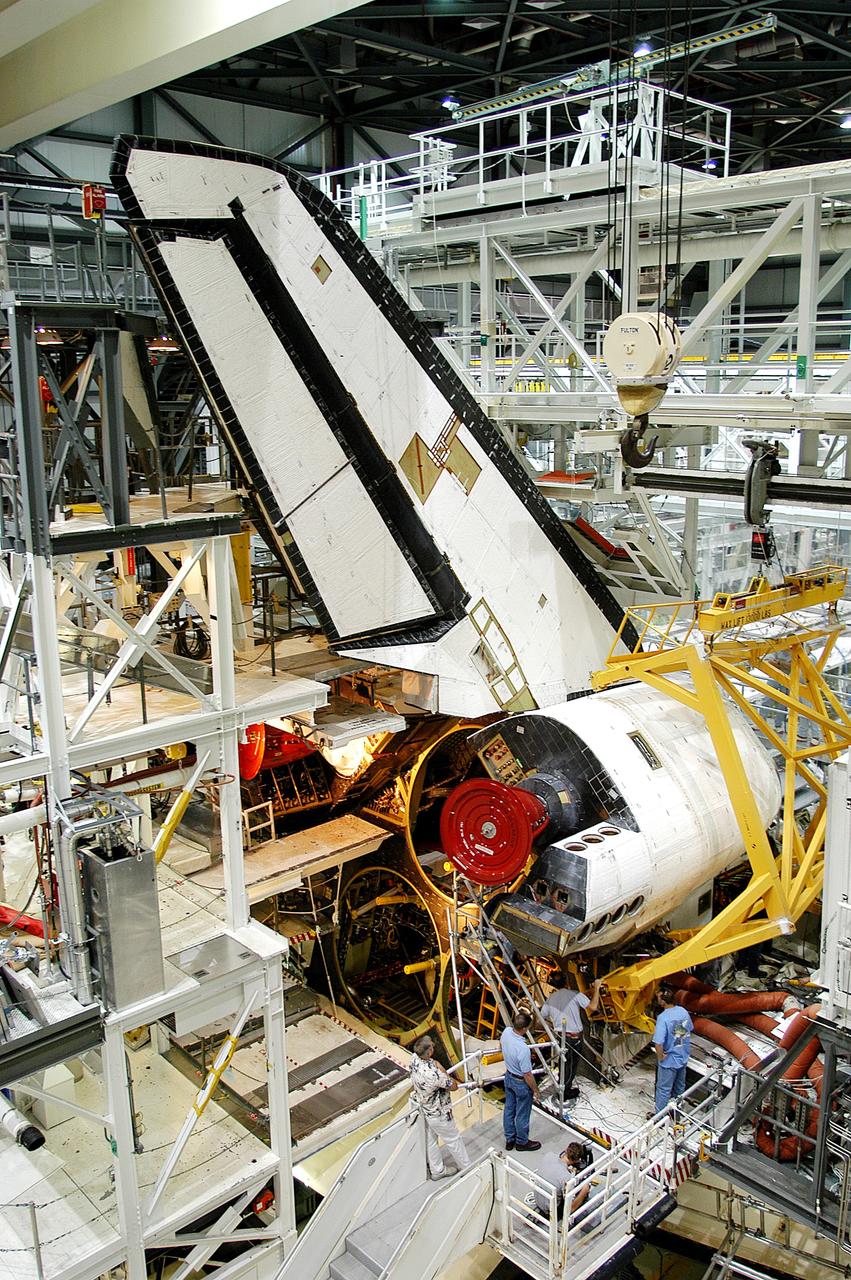

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to remove one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods from Endeavour. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.
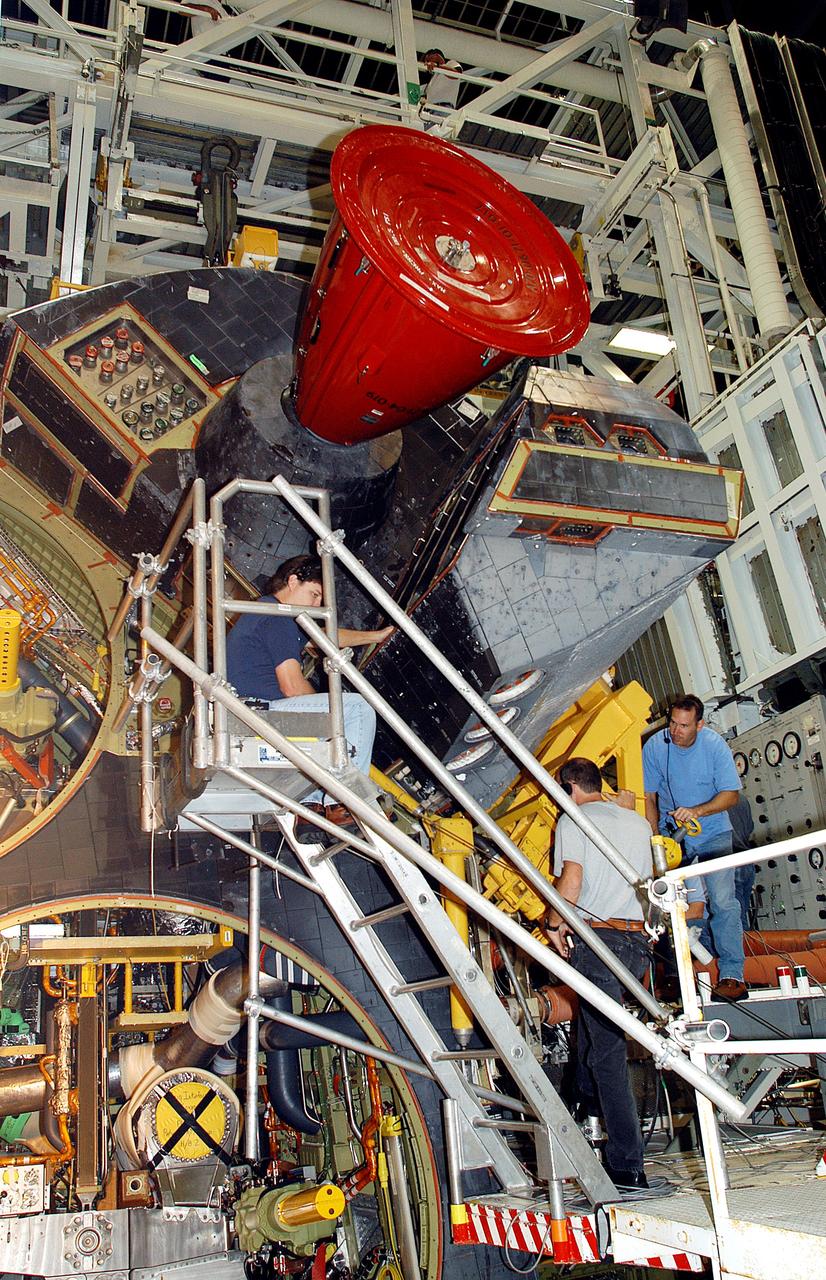

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility prepare to remove one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods from Endeavour. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Technicians in the Orbiter Processing Facility oversee removal of one of two orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods from Endeavour. The OMS pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum, each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. Each pod houses the Reaction Control System propulsion components used for inflight maneuvering and is attached to the aft fuselage with 11 bolts. OMS pods are removed during Orbiter Major Modifications. Once removed, the OMS pods undergo in-depth structural inspections, system checks and the thrusters are changed out.