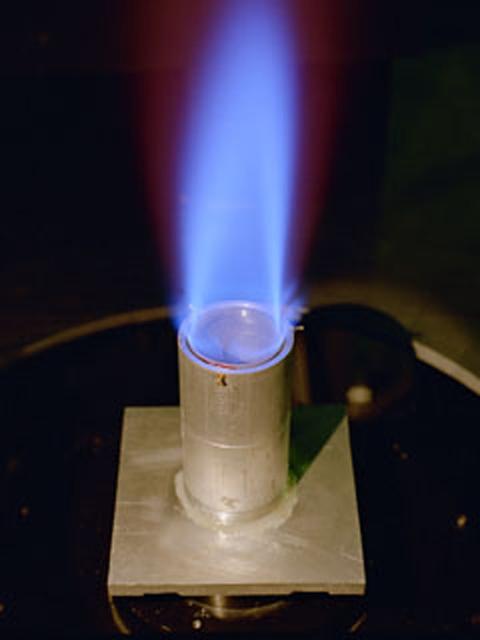

The Ring Flame Stabilizer has been developed in conjunction with Lewis Research Center. This device can lower pollutant emissions (which contribute to smog and air pollution) from natural-gas appliances such as furnaces and water heaters by 90 percent while improving energy efficiency by 2 percent.
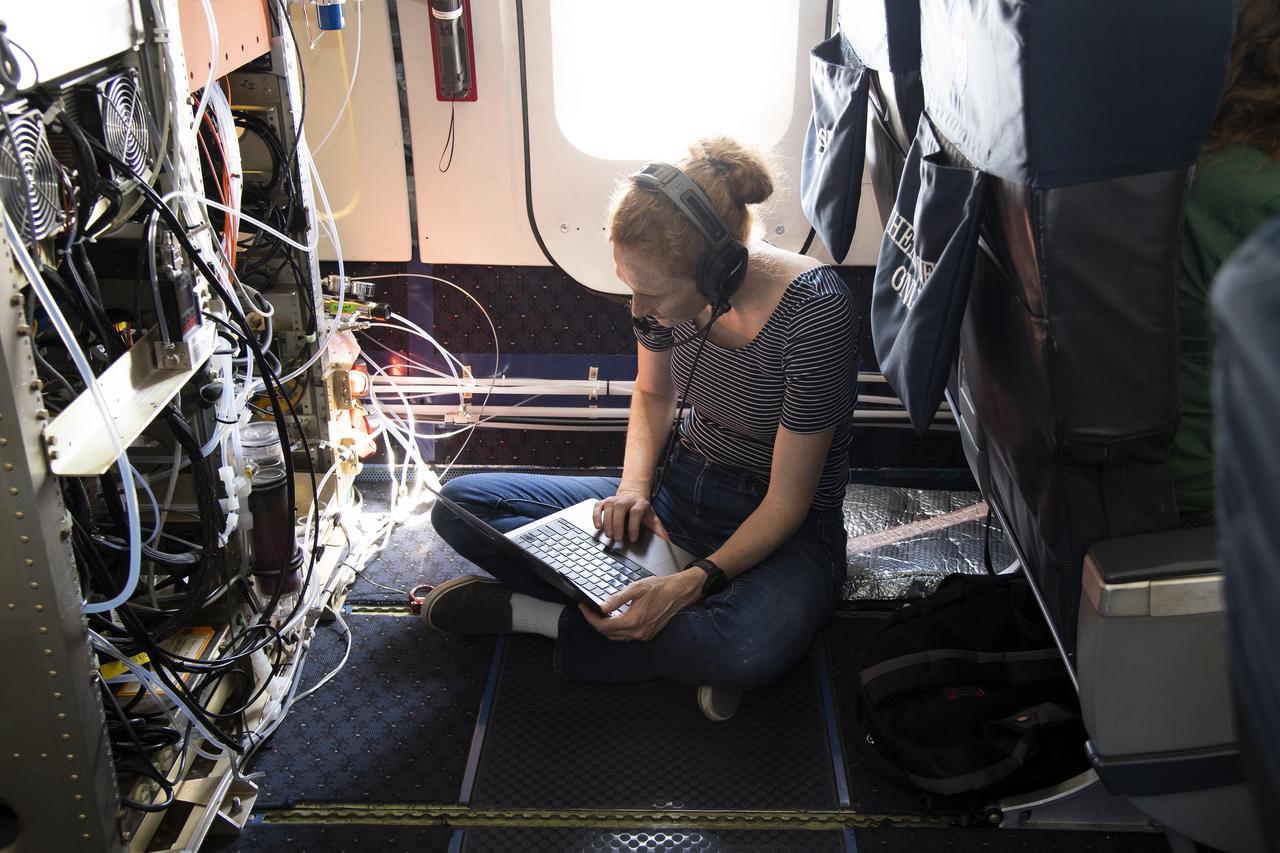

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
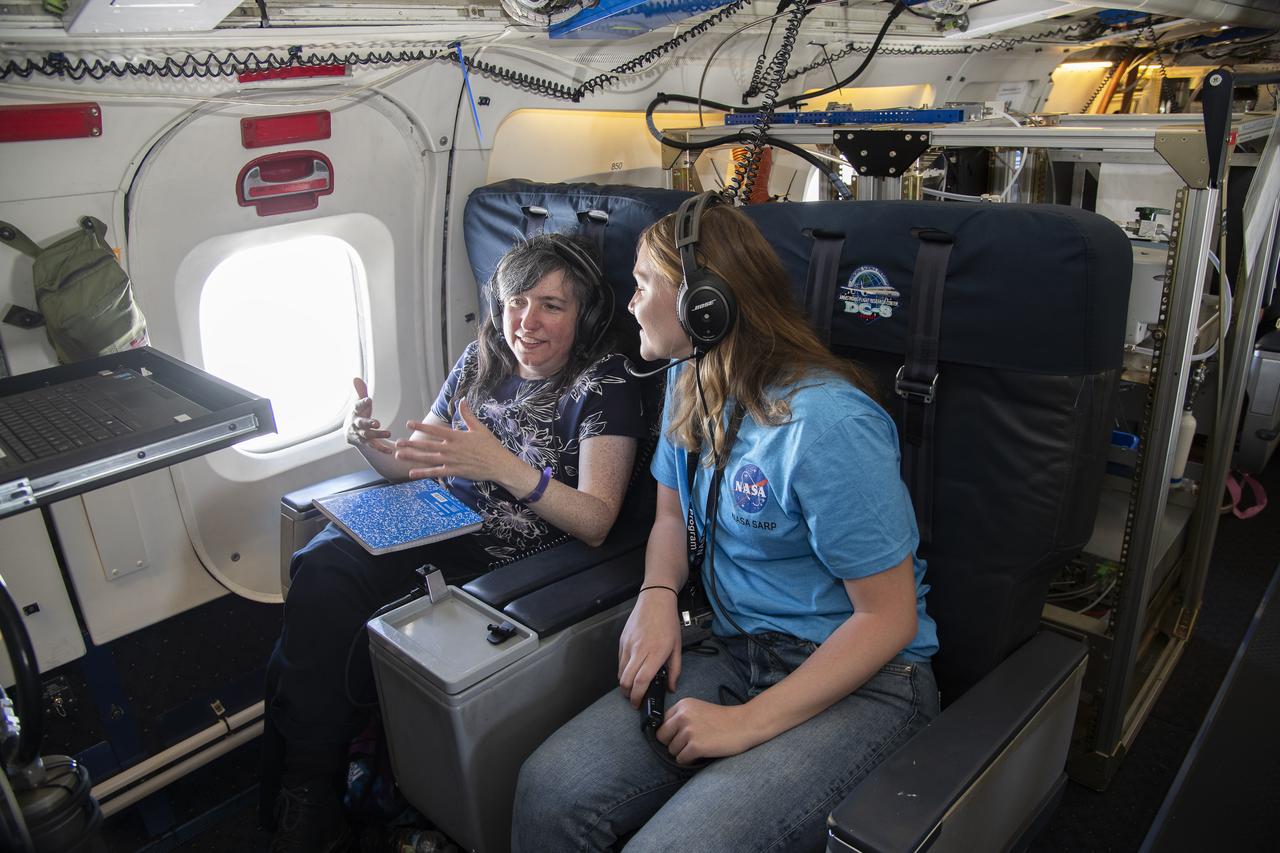

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
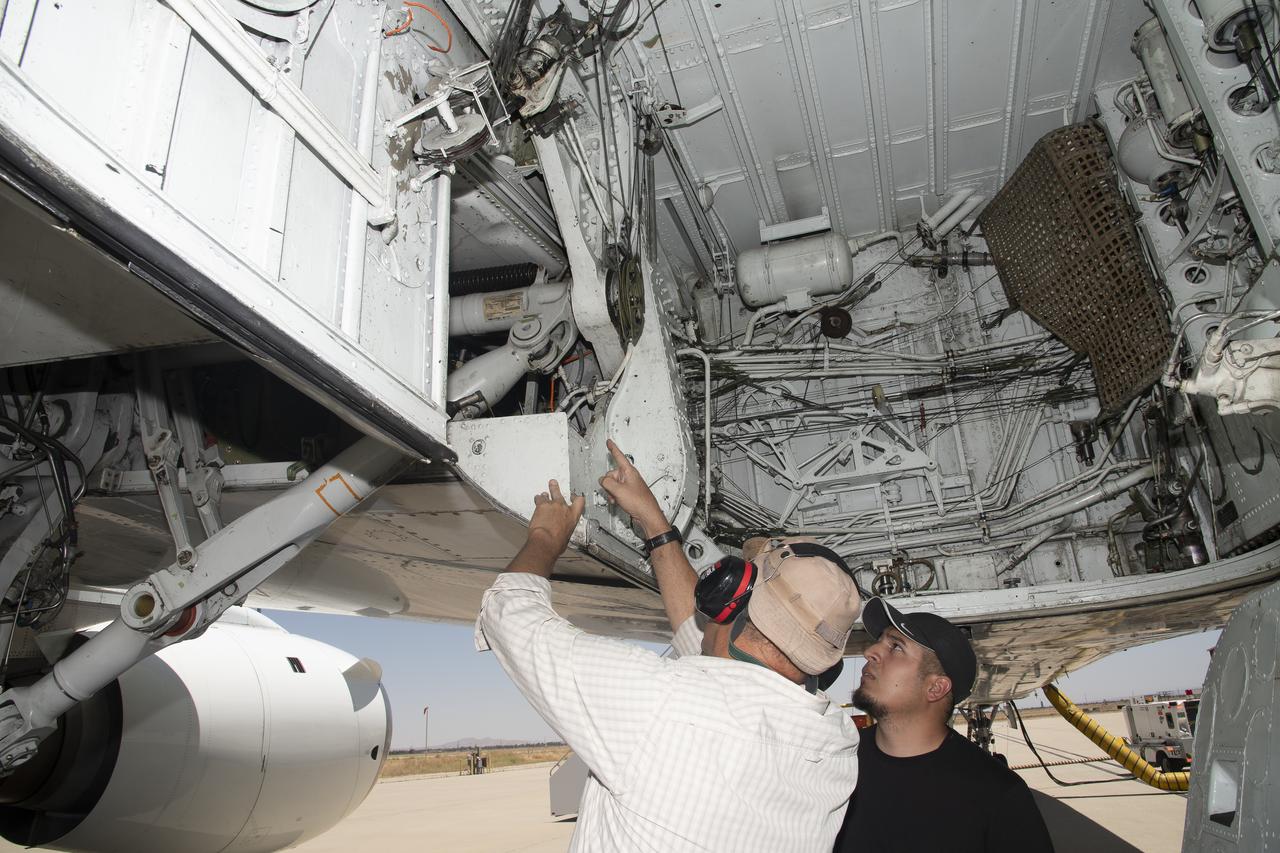

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
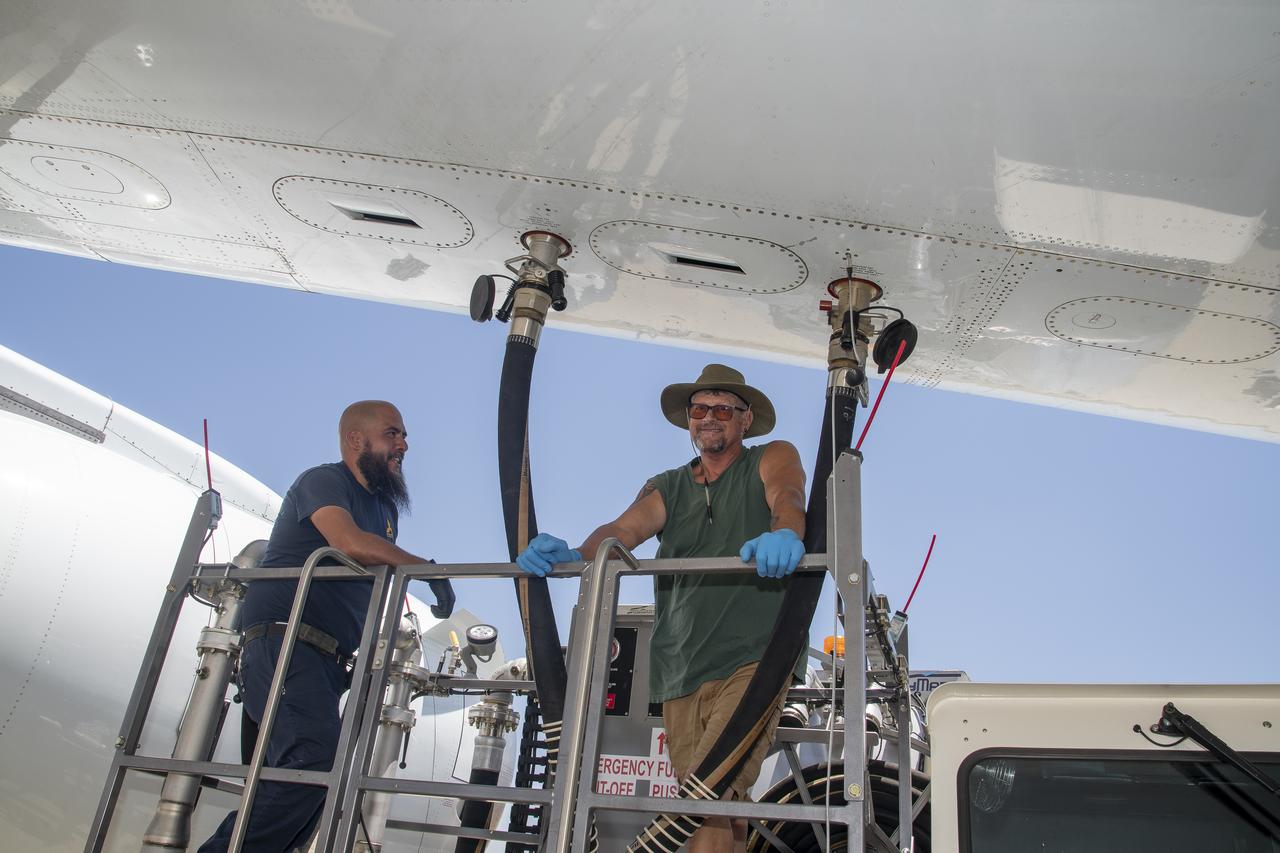

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
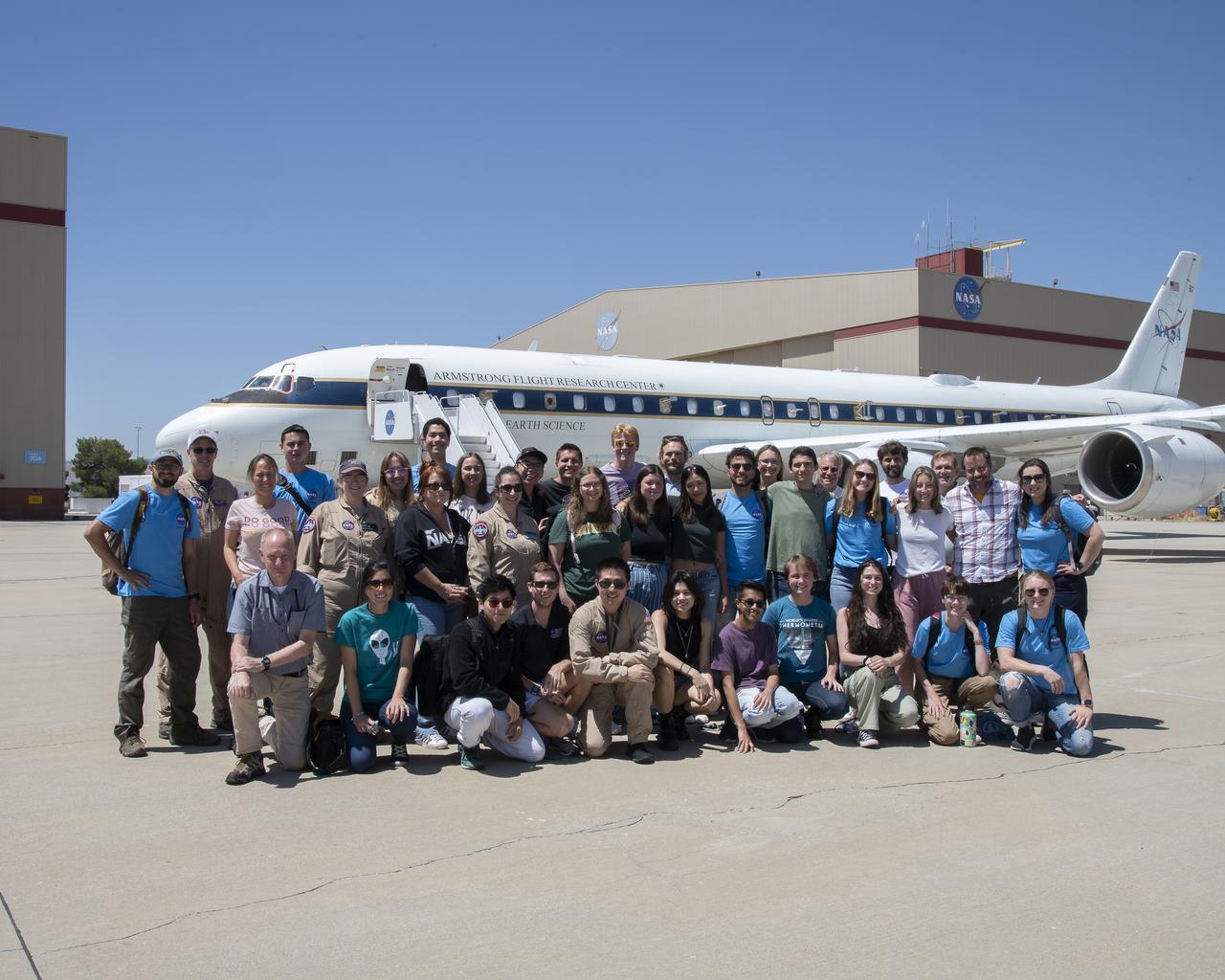

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
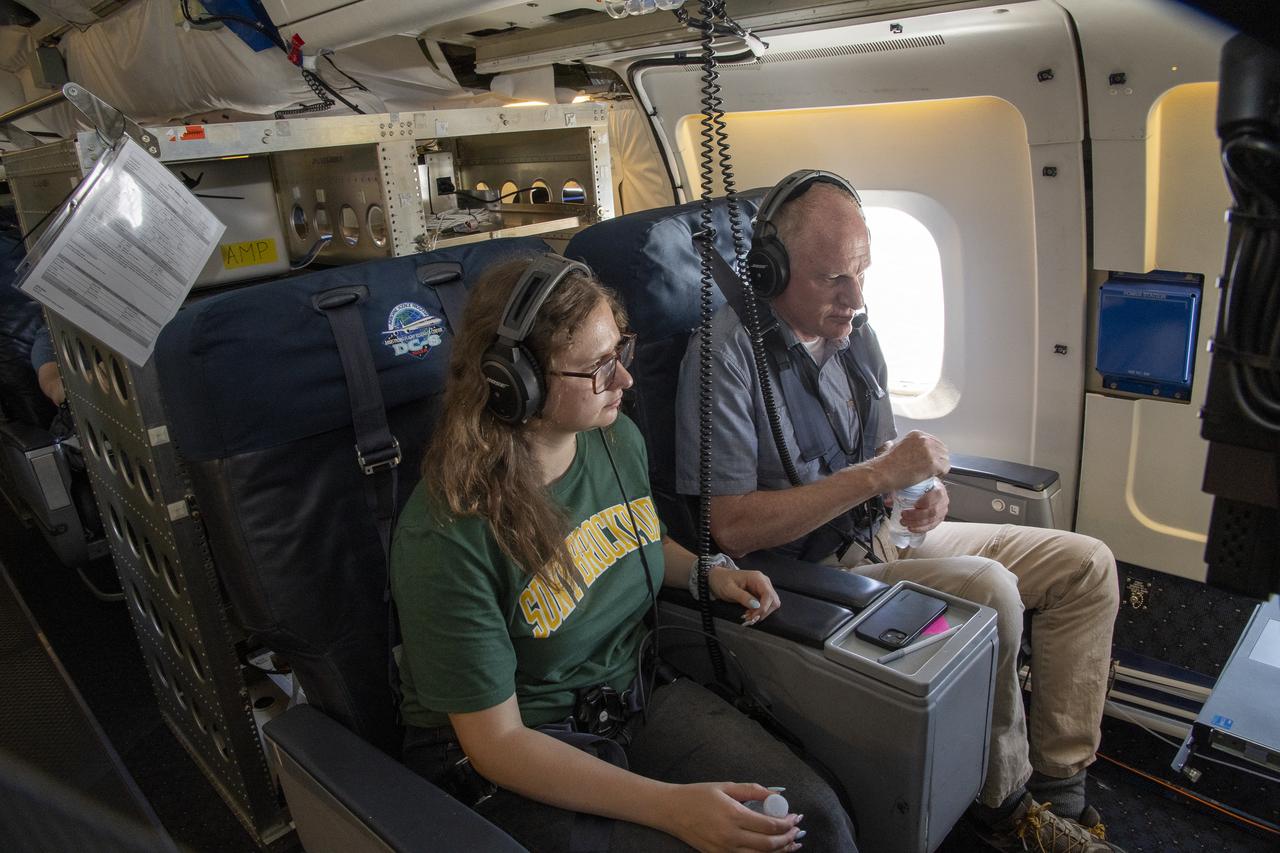

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
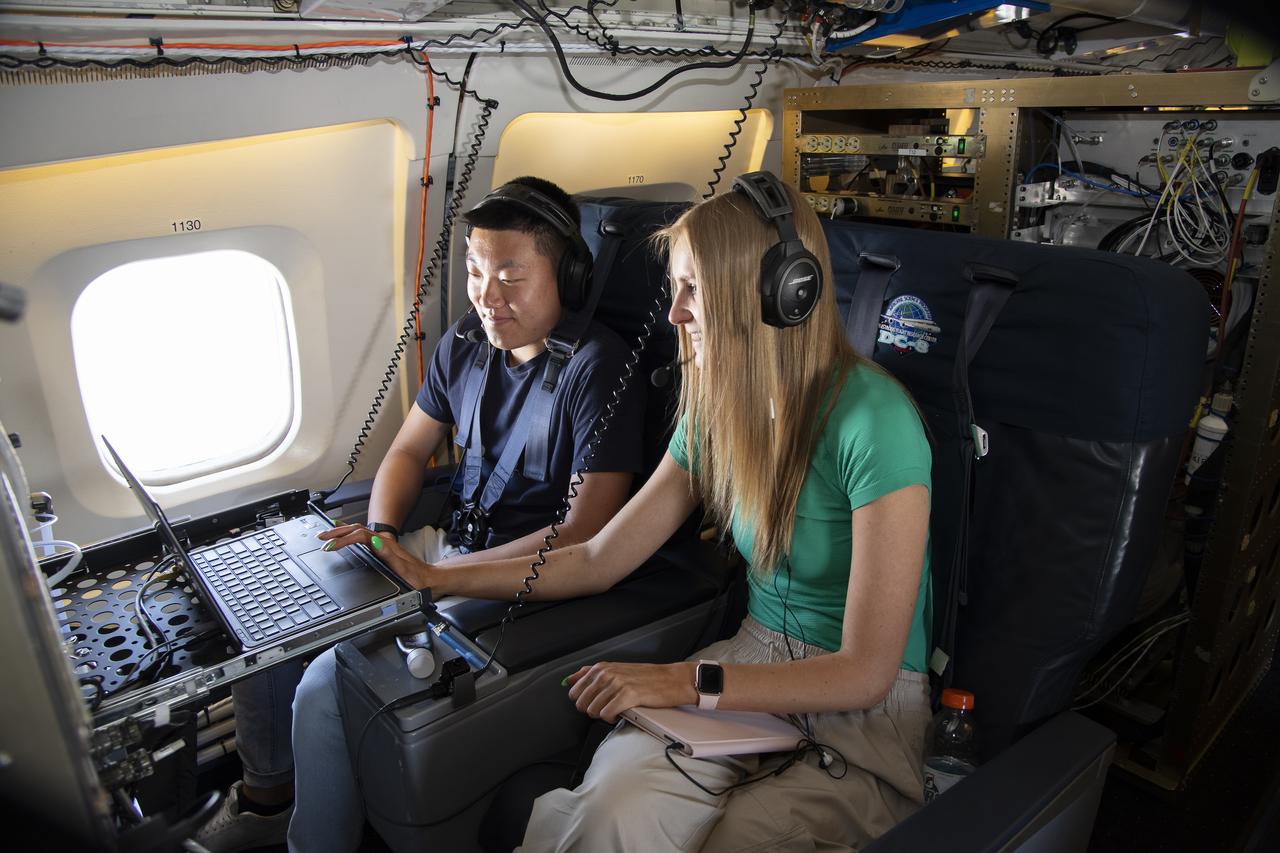

NASA Armstrong’s Student Airborne Research Program celebrates 15 years of success in 2023. An eight-week summer internship program, SARP offers upper-level undergraduate students the opportunity to acquire hands-on research experience as part of a scientific campaign using NASA Airborne Science Program flying science laboratories—aircraft outfitted specifically for research projects. Students onboard NASA’s DC-8 aircraft, the largest flying science laboratory in the world, help scientists from NOAA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with a science project investigating air quality and non-vehicular pollution sources called AEROMMA, which measures Atmospheric Emissions and Reactions Observed from Megacities to Marine Areas. In 2023, NASA also introduced a sister program, SARP East to complement the West Coast program.
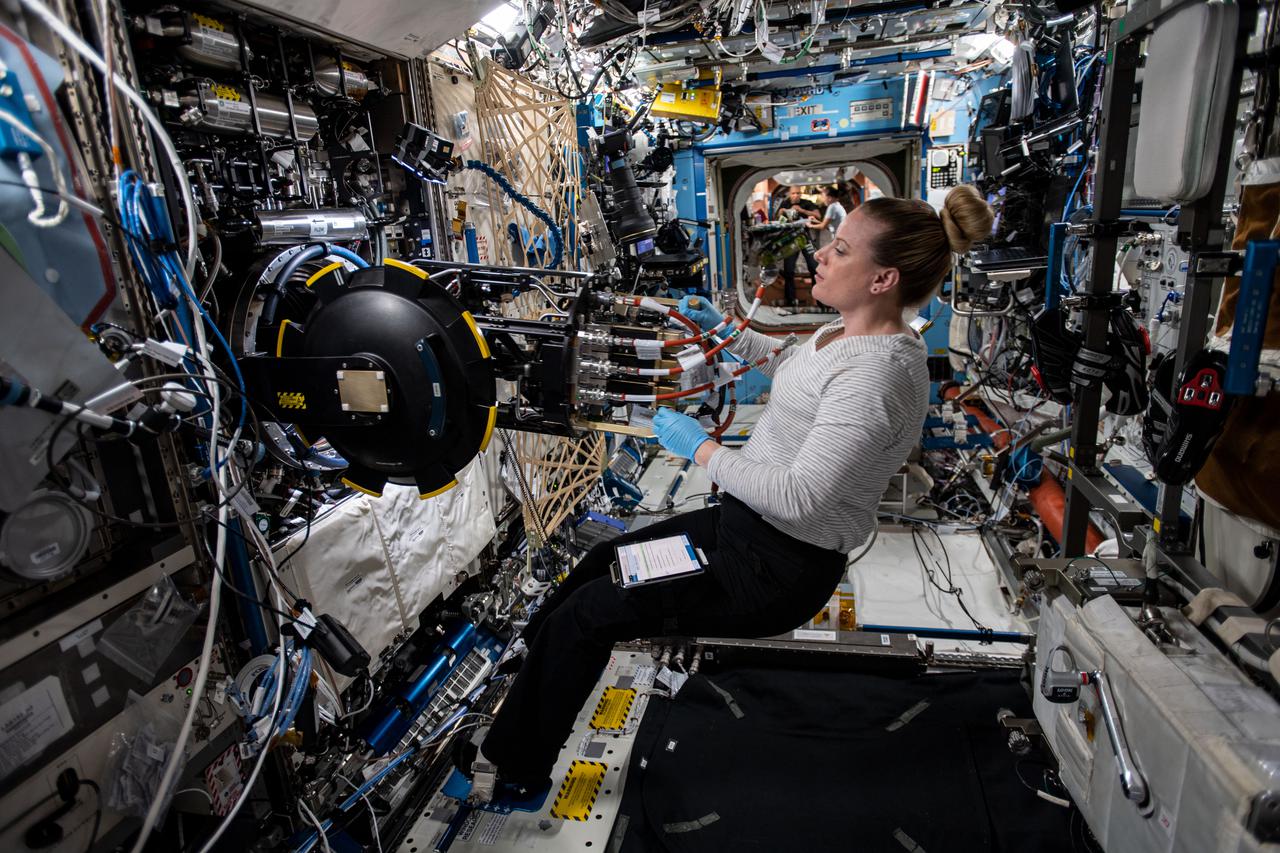

iss064e029405 (Feb. 3, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Kate Rubins removes research hardware from inside the Combustion Integrated Rack. She was replacing gear to support a suite of fuel efficiency, pollution and fire safety studies known as the Advanced Combustion in Microgravity Experiments, or ACME.
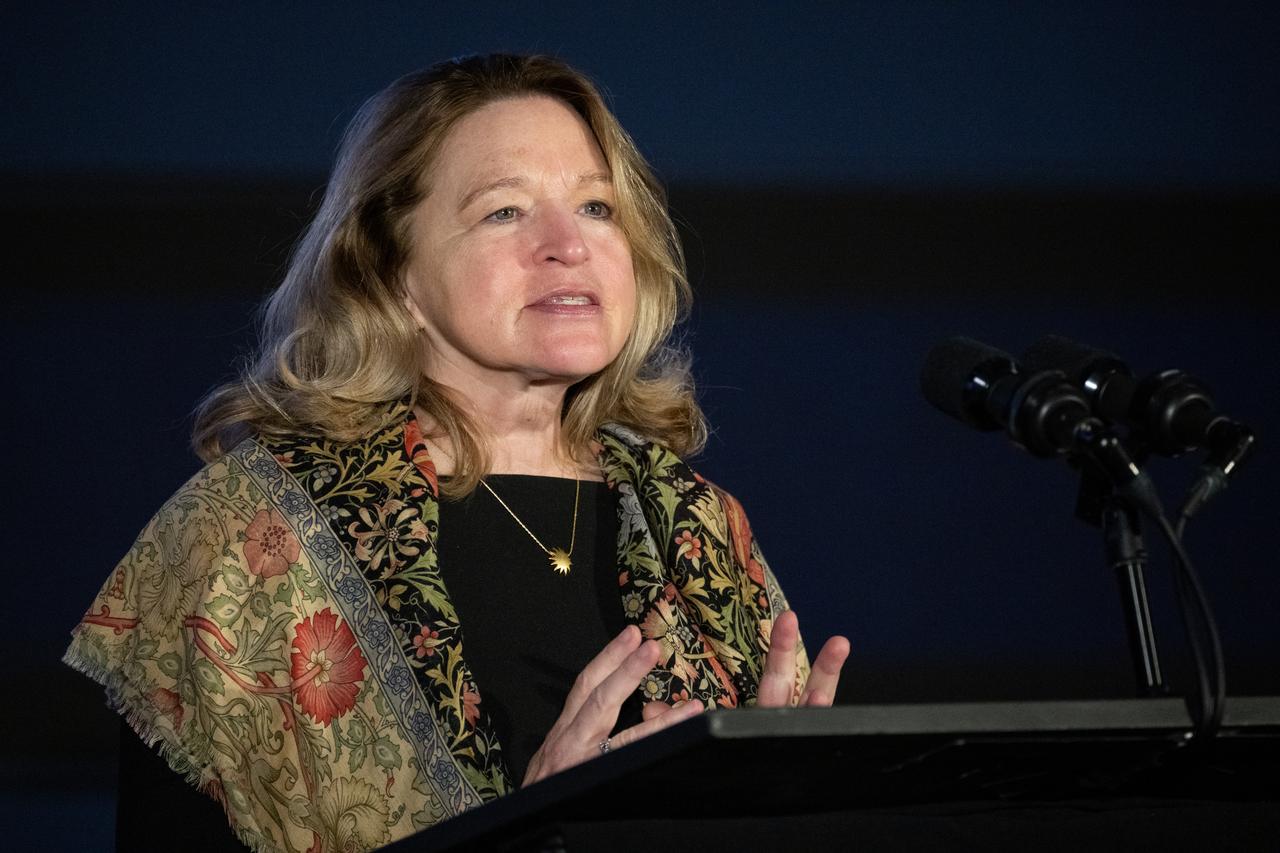

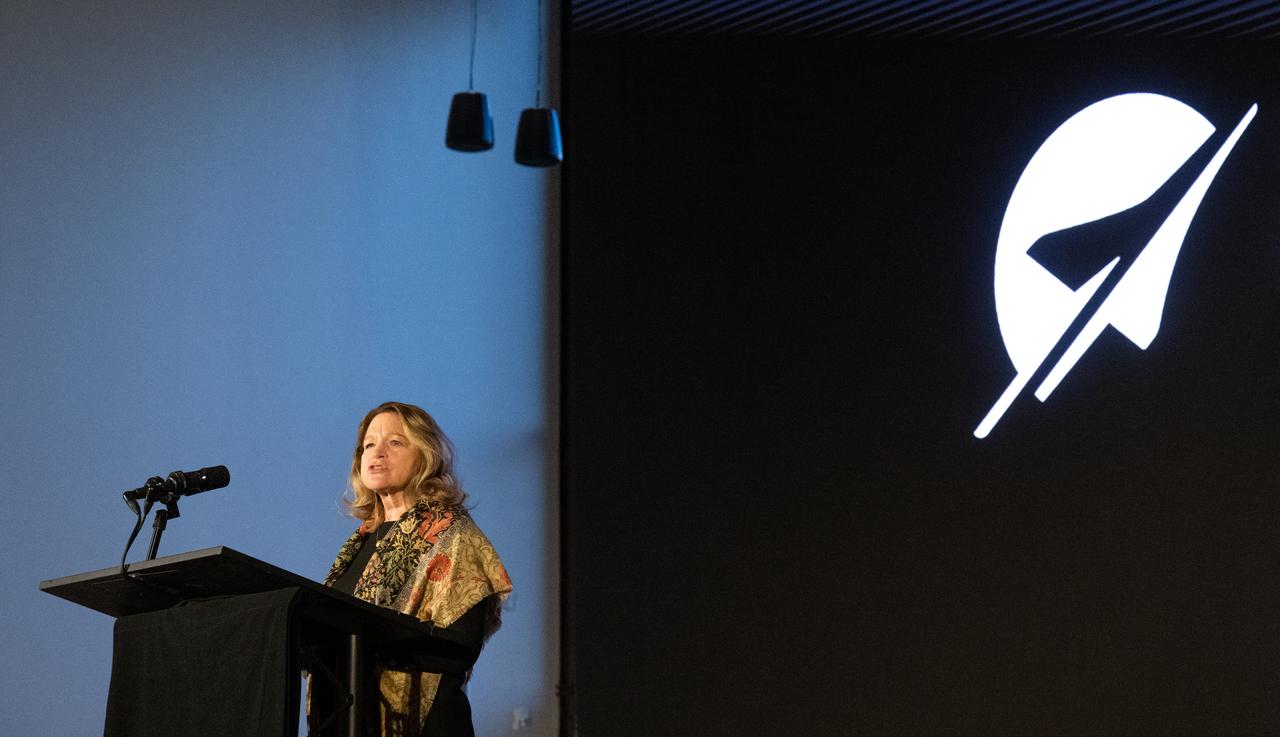
Ellen Stofan, under secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian Institution, speaks during a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Ellen Stofan, under secretary for Science and Research at the Smithsonian Institution, speaks during a briefing on NASA’s TEMPO (Tropospheric Emissions: Monitoring of Pollution) instrument, Tuesday, March 14, 2023 at the Smithsonian’s National Air and Space Museum in Washington. NASA’s TEMPO instrument, the first Earth Venture Instrument mission, will measure air pollution across North America from Mexico City to the Canadian oil sands and from the Atlantic to the Pacific hourly and at a high spatial resolution. A partnership between NASA and the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, TEMPO will launch on a commercial satellite to geostationary orbit as early as April. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
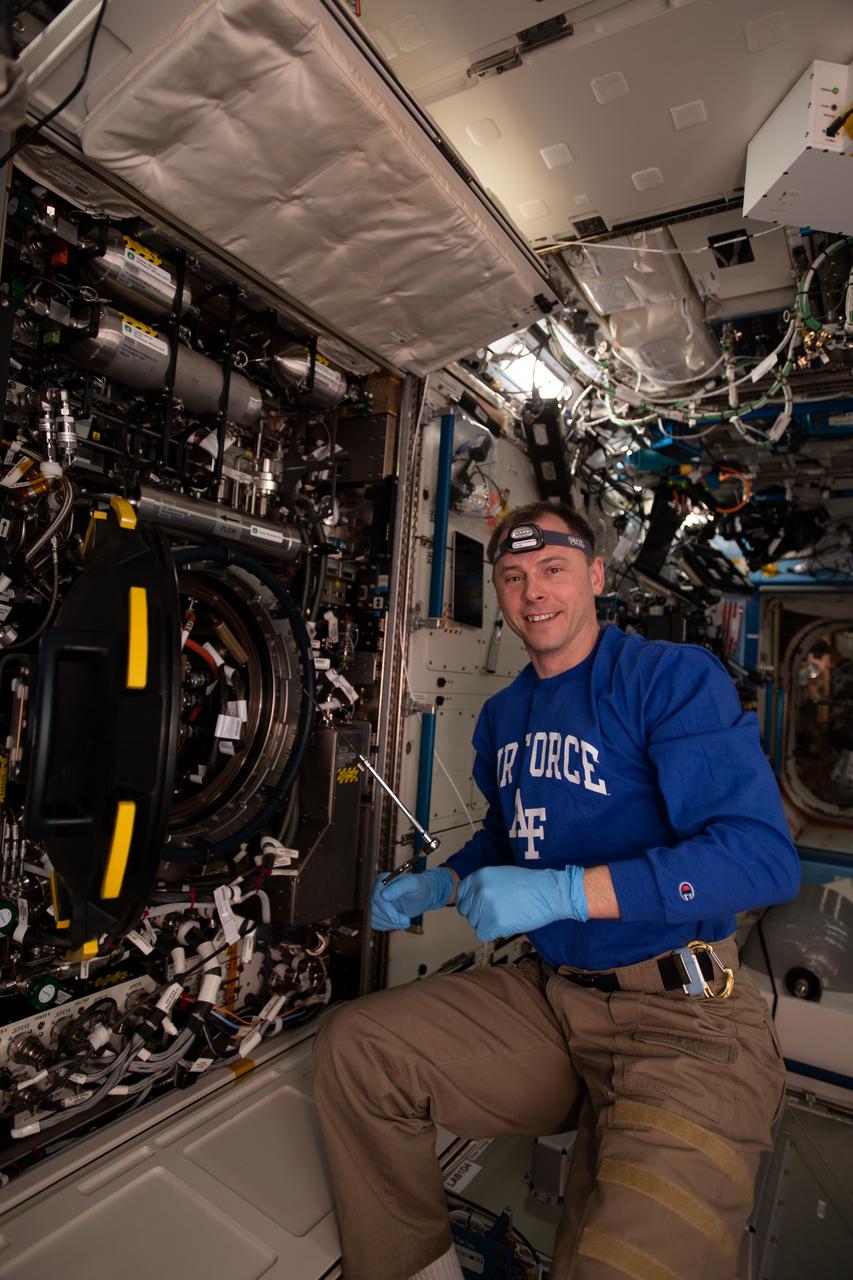

iss059e085880 (May 31, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague replaces hardware inside the Combustion Integrated Rack supporting the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME). ACME is a set of five independent studies researching improved fuel efficiency and reduced pollutant production in practical combustion on Earth, as well as spacecraft fire prevention through innovative research focused on materials flammability.
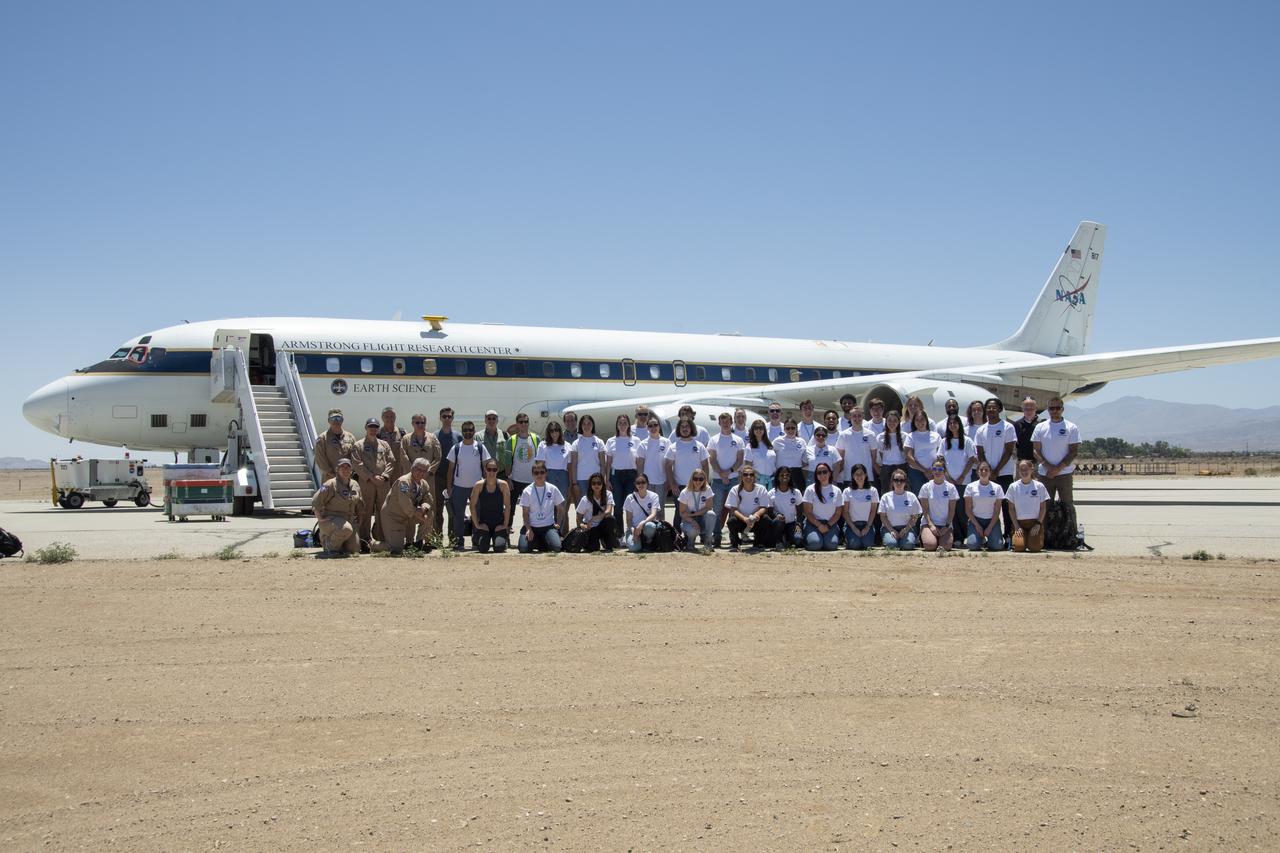

A group of university students and mentors flew aboard NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s DC-8 aircraft to study air quality as part of NASA’s Student Airborne Research Program (SARP). Based at NASA’s Armstrong Building 703 in Palmdale, California, the DC-8 flew over the Central Valley to measure pollution and monitor air quality on Tuesday, June 21, 2022.
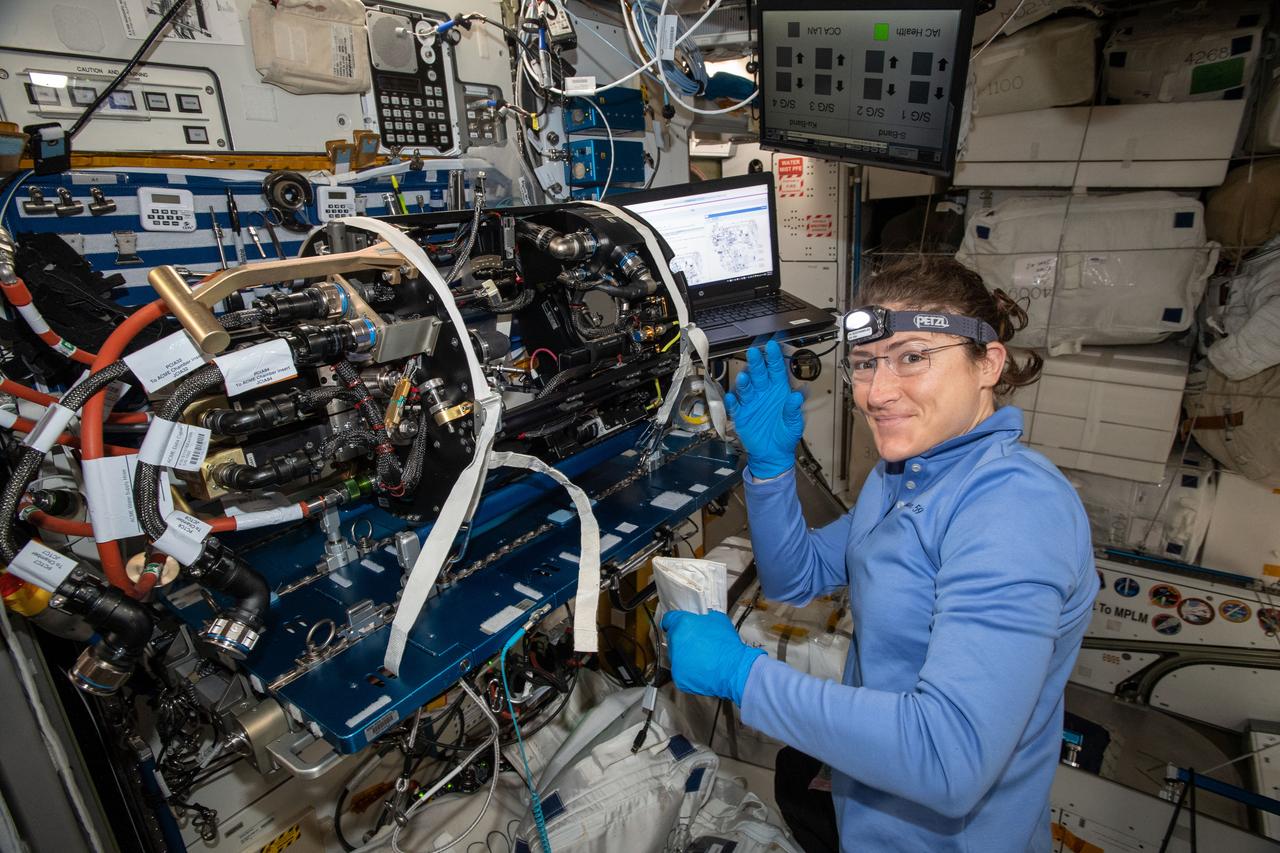

iss059e017072 (April 9, 2018) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 59 Flight Engineer Christina Koch works on the Unity module's Maintenance Work Area where the Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME) Chamber Insert was attached for hardware replacement. ACME is a set of five independent studies researching improved fuel efficiency and reduced pollutant production in practical combustion on Earth, as well as spacecraft fire prevention through innovative research focused on materials flammability.
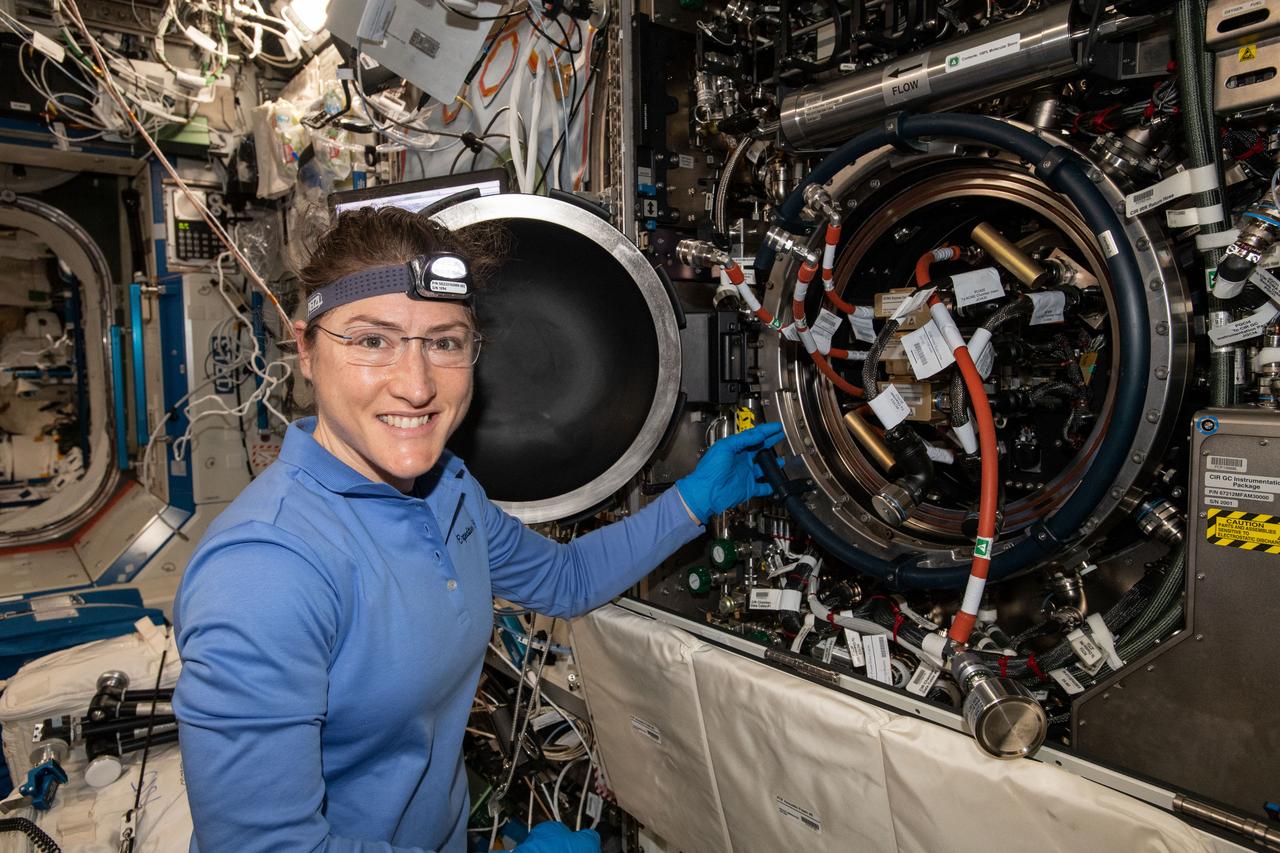

iss059e017127 (April 9, 2018) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 59 Flight Engineer Christina Koch works inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module's Combustion Integrated Rack. She was replacing hardware for a series of experiments collectively known as Advanced Combustion via Microgravity Experiments (ACME). ACME is a set of six independent studies researching improved fuel efficiency and reduced pollutant production in practical combustion on Earth, as well as spacecraft fire prevention through innovative research focused on materials flammability.
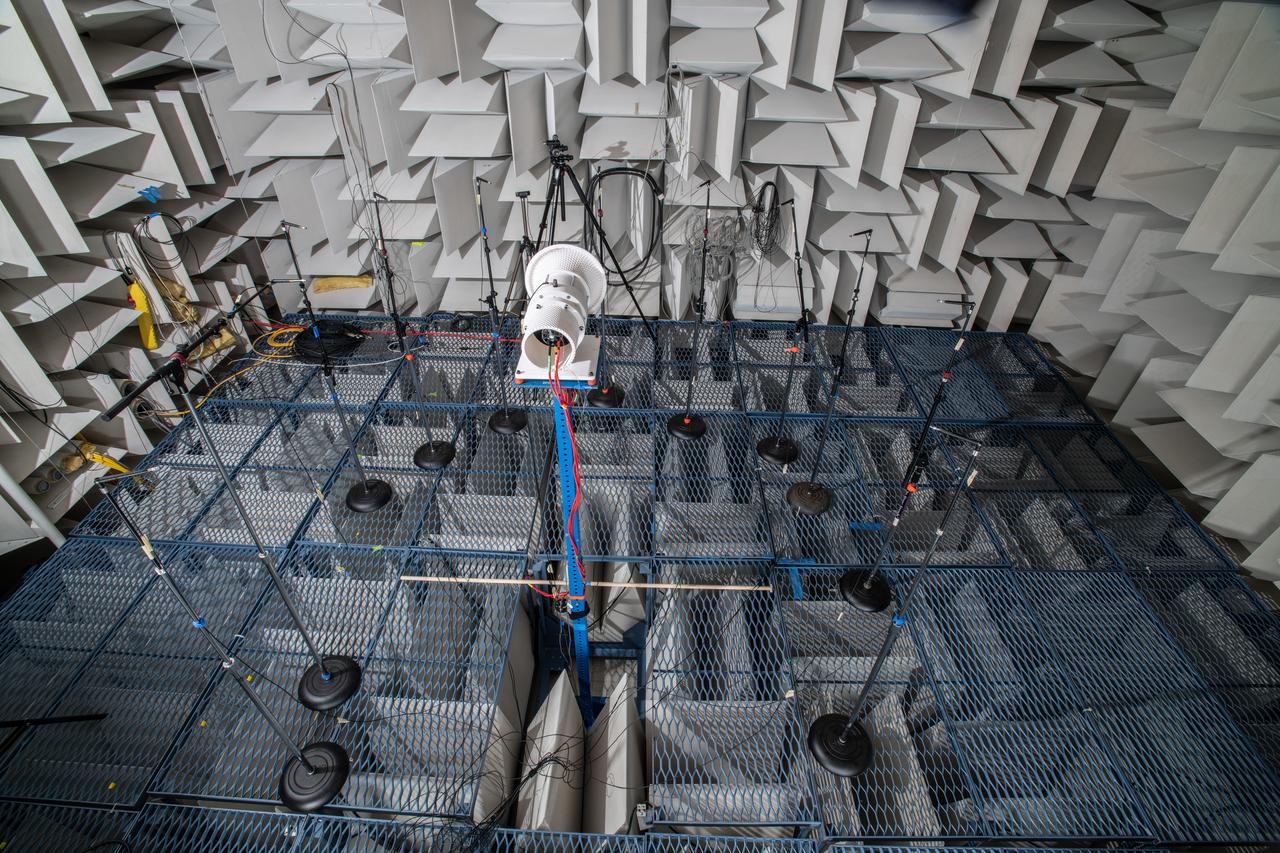

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.
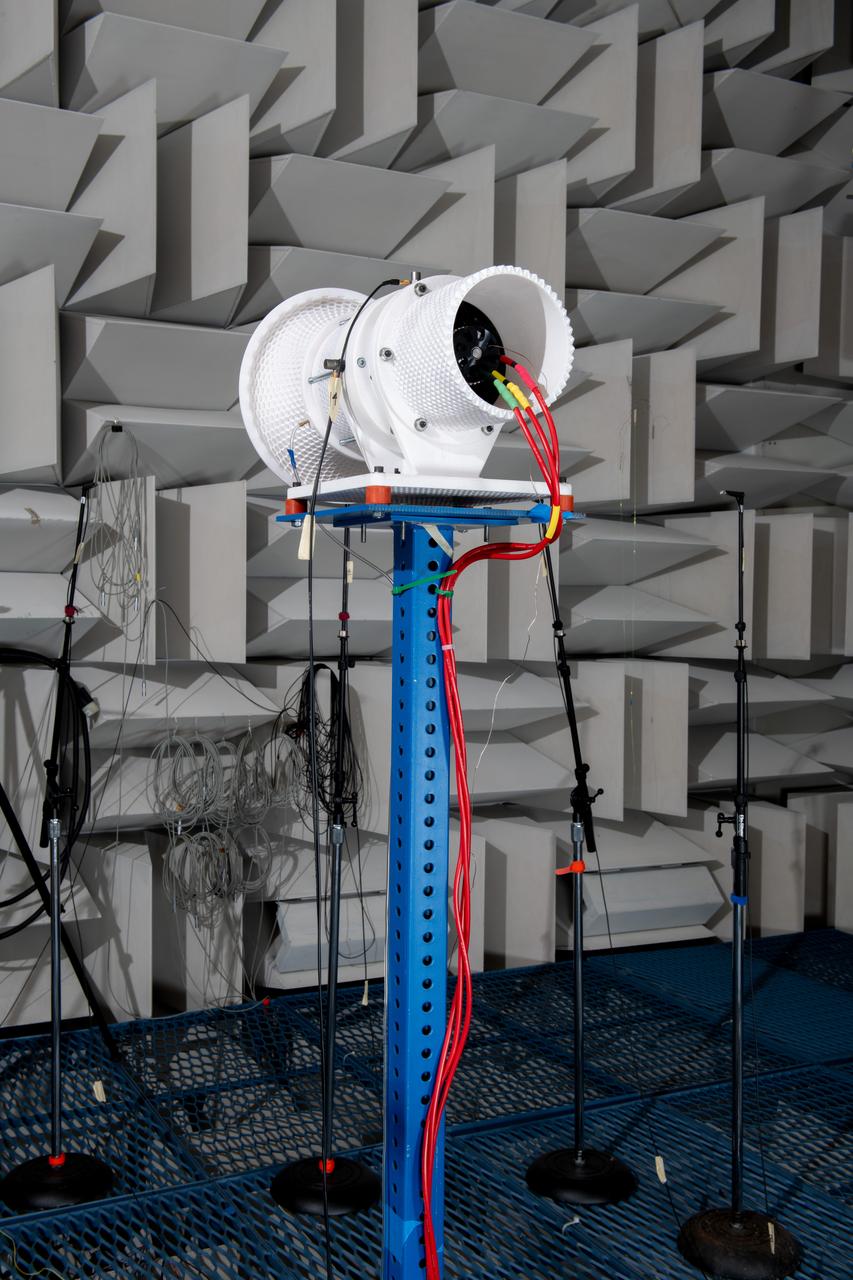
The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.
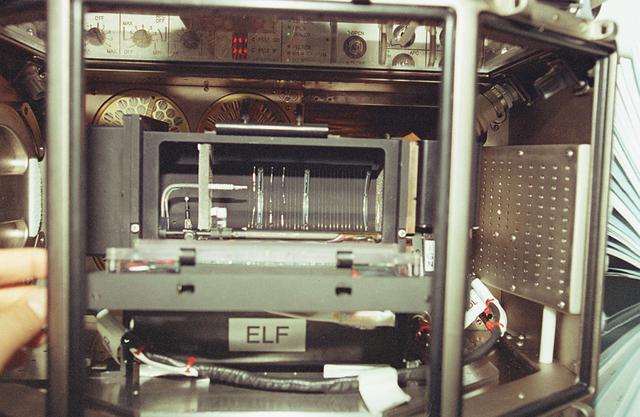

The goal of the ELF investigation is to improve our fundamental understanding of the effects of the flow environment on flame stability. The flame's stability refers to the position of its base and ultimately its continued existence. Combustion research focuses on understanding the important hidden processes of ignitions, flame spreading, and flame extinction. Understanding these processes will directly affect the efficiency of combustion operations in converting chemical energy to heat and will create a more balanced ecology and healthy environment by reducing pollutants emitted during combustion.
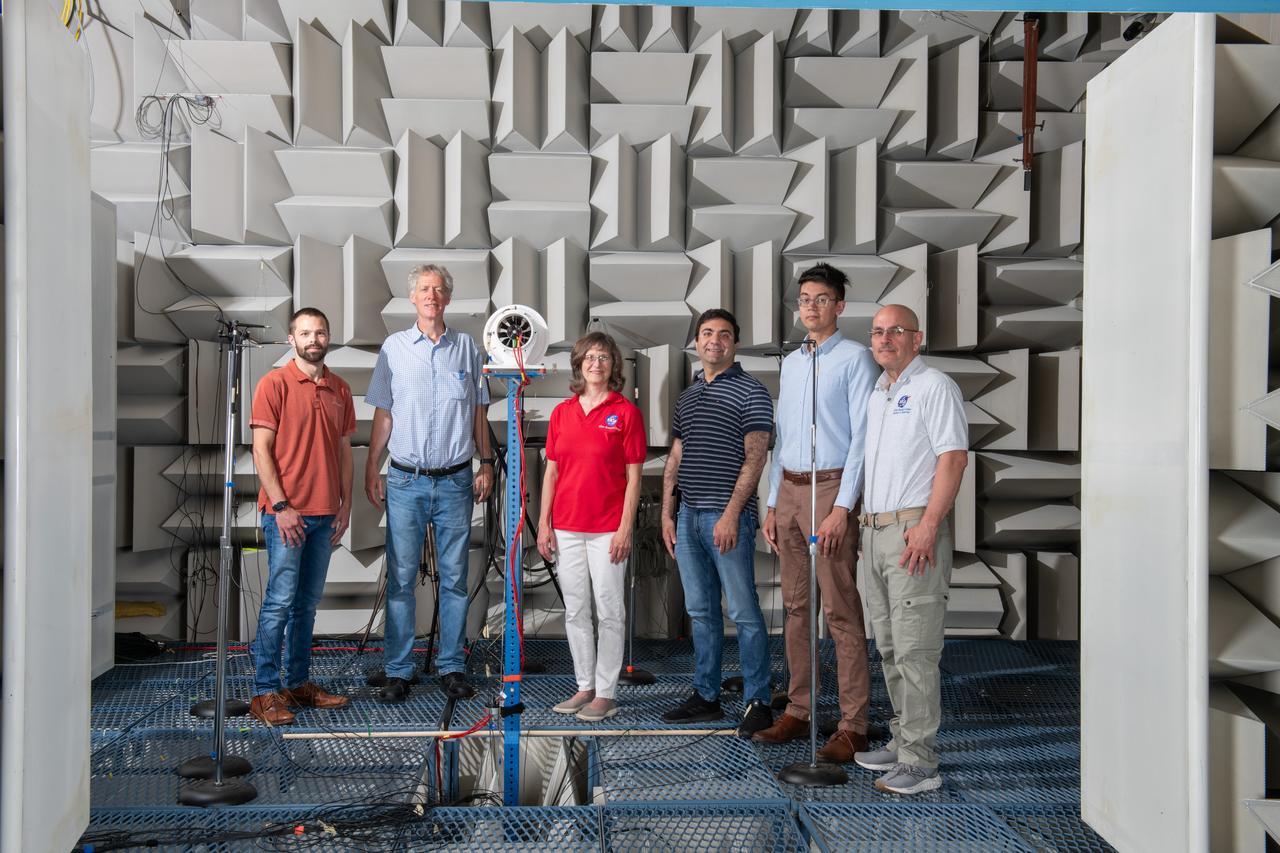

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter.
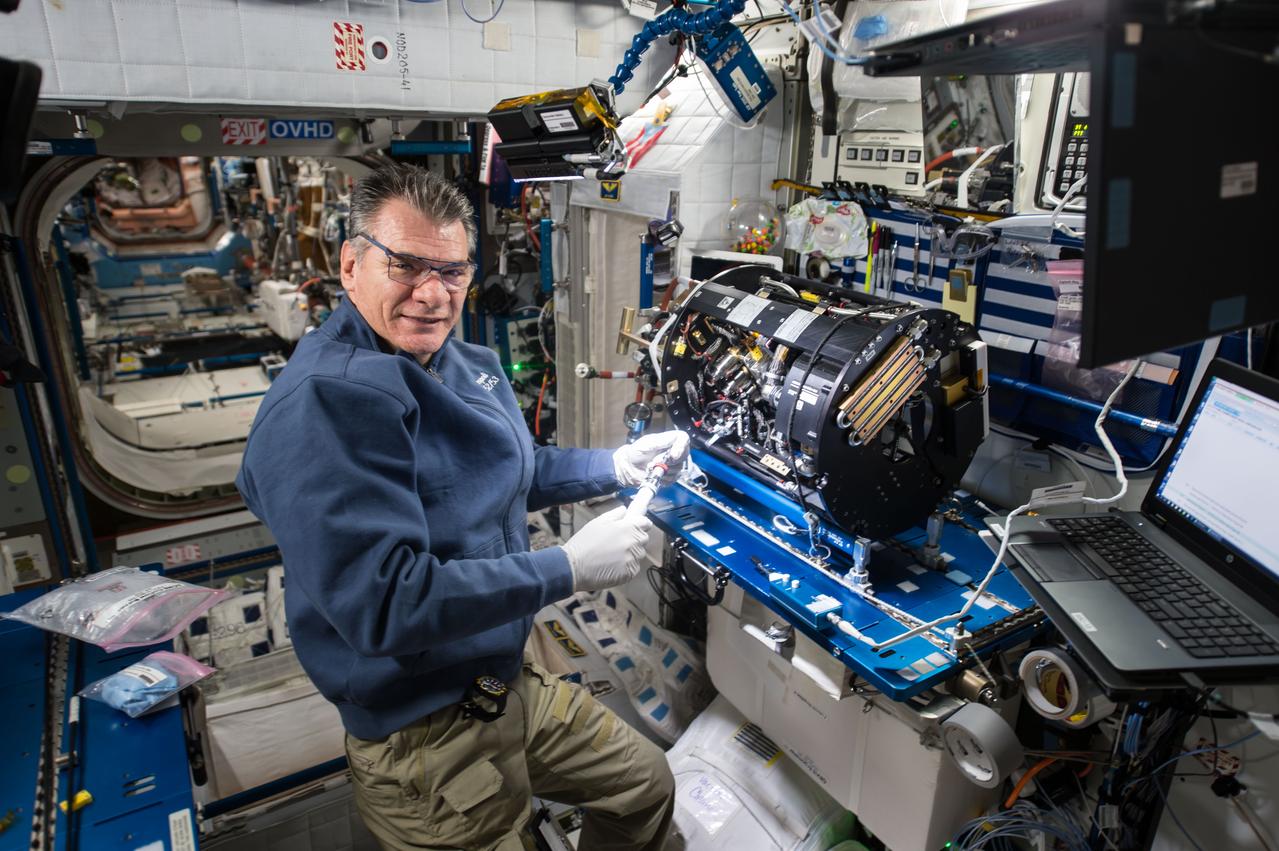
iss053e098185 (Oct. 12, 2017) --- Flight Engineer Paolo Nespoli works inside the Harmony module to configure the Combustion Integrated Rack and enable the Advanced Combustion Microgravity Experiment (ACME). The primary and secondary goals of ACME are the improved fuel efficiency and reduced pollutant production in practical combustion on Earth, and spacecraft fire prevention through innovative research focused on materials flammability.
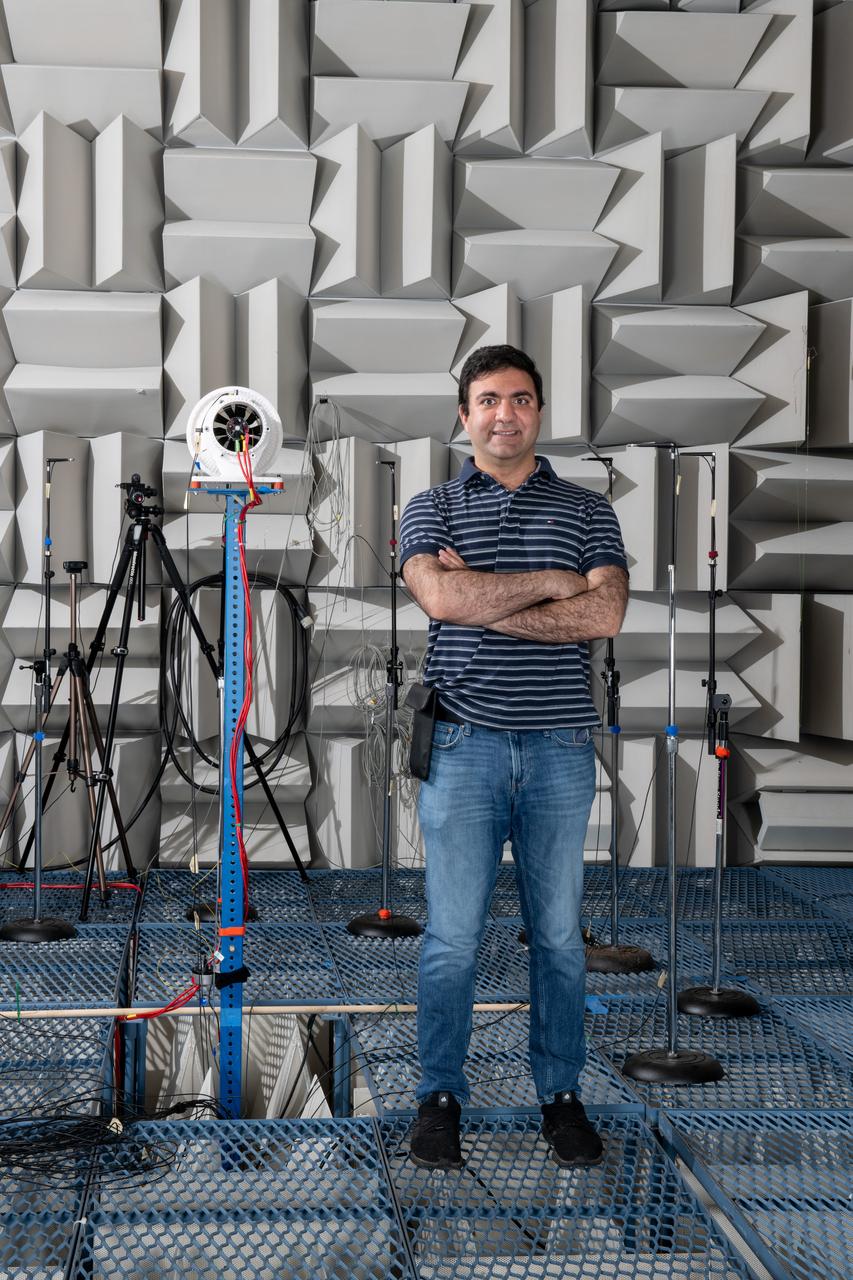

The Quiet Electric Engine V1 (QUEEN V1) experiment that was performed in the NASA GRC Acoustical Testing Laboratory (ATL). Equipment is installed in the anechoic chamber and in the adjacent control room. In response to the pervasive health and environmental problems associated with aviation noise and air pollution, NASA’s Quiet Electric Engine (QUEEN) team is working to increase the peace and quiet in the world by researching ways to make engines for large single-aisle aircraft safer, cleaner, and quieter. Posing with the experiment is aerospace engineer, Jonathan M. Goodman.
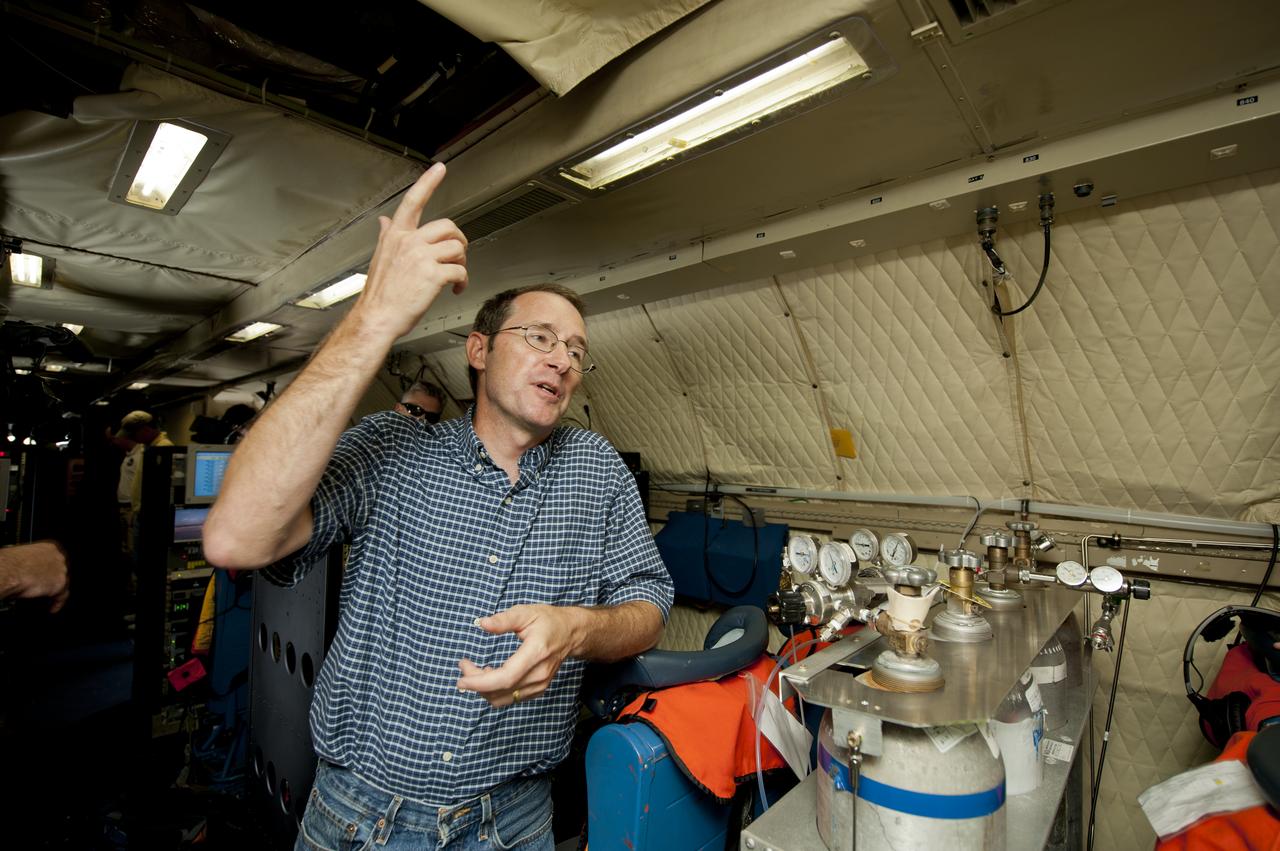

James Crawford, principal investigator and scientist based at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Va., talks about the DISCOVER-AQ project on board the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
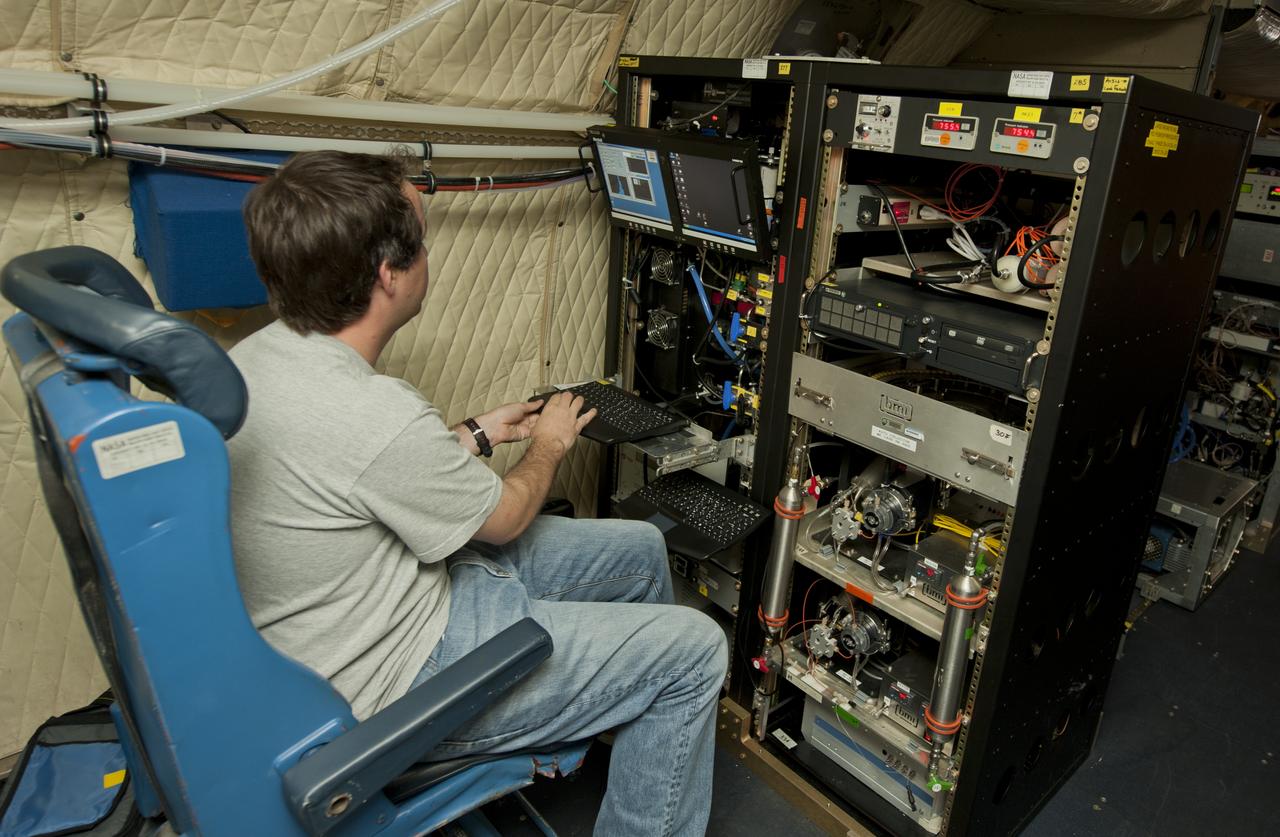

An unidentified researcher works aboard the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
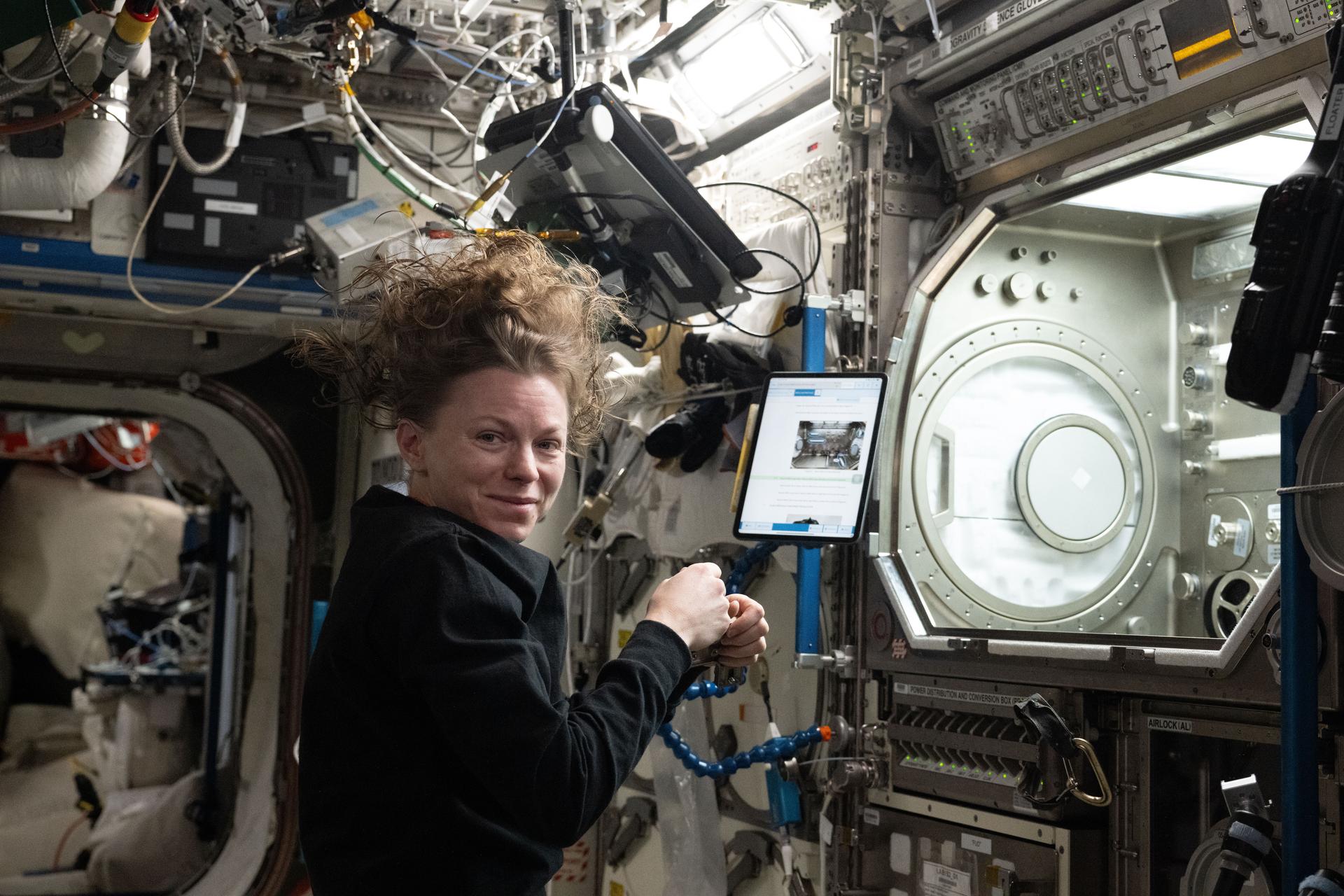

iss073e0886460 (Oct. 20, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Zena Cardman installs research hardware inside the Destiny laboratory module’s Microgravity Science Glovebox. The equipment supports the Fluid Particles experiment, which helps researchers understand how particles in a liquid interface come together to form larger structures or clusters in microgravity. Results could advance fire suppression, lunar dust control, and plant growth in space. Earth benefits may include insights into pollen behavior, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transfer during storms.
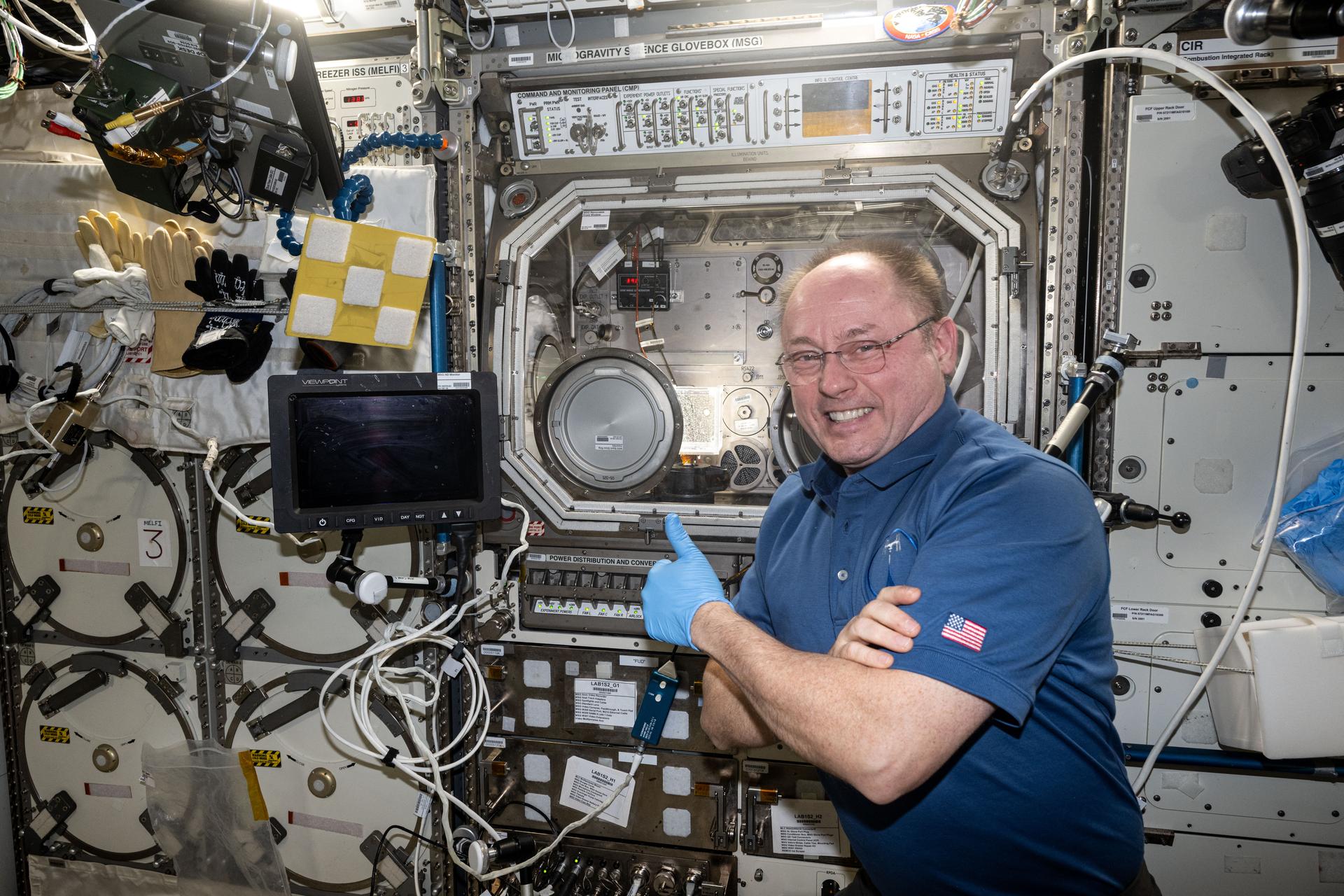

iss073e0917010 (Oct. 21, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Mike Fincke gives a thumbs-up in front of the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) inside the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. Fincke had just completed research operations for the Fluid Particles experiment, which helps researchers understand how particles in a liquid interface come together to form larger structures or clusters in microgravity. Results could advance fire suppression, lunar dust control, and plant growth in space. Earth benefits may include insights into pollen behavior, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transfer during storms.
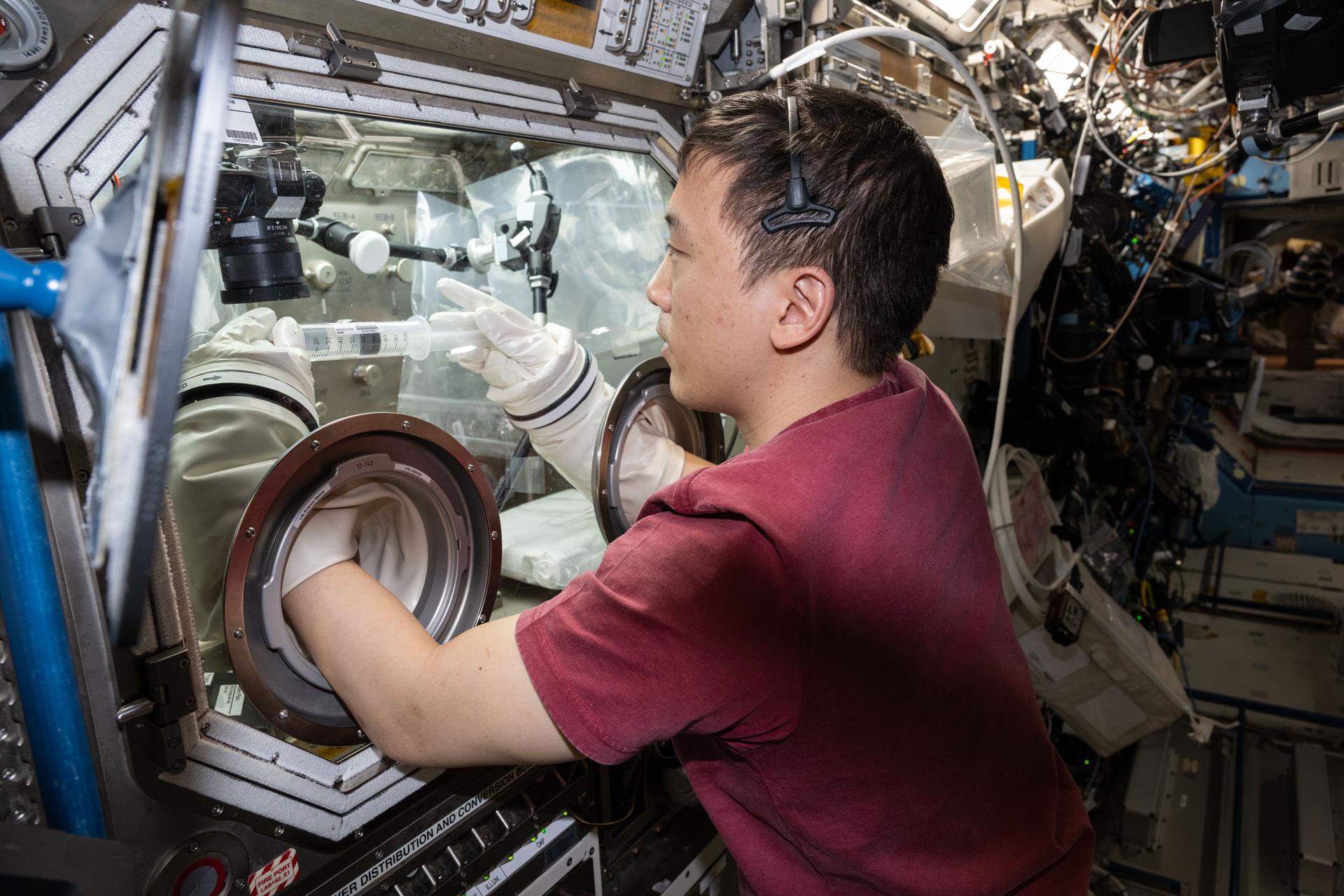

iss073e0917782 (Oct. 23, 2025) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 73 Flight Engineer Jonny Kim conducts research operations for the Fluid Particles investigation inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox aboard the International Space Station's Destiny laboratory module. The fluid physics experiment may help researchers understand how particles in a liquid interface come together to form larger structures or clusters in microgravity advancing fire suppression, lunar dust control, and plant growth in space. Earth benefits may include insights into pollen behavior, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transfer during storms.
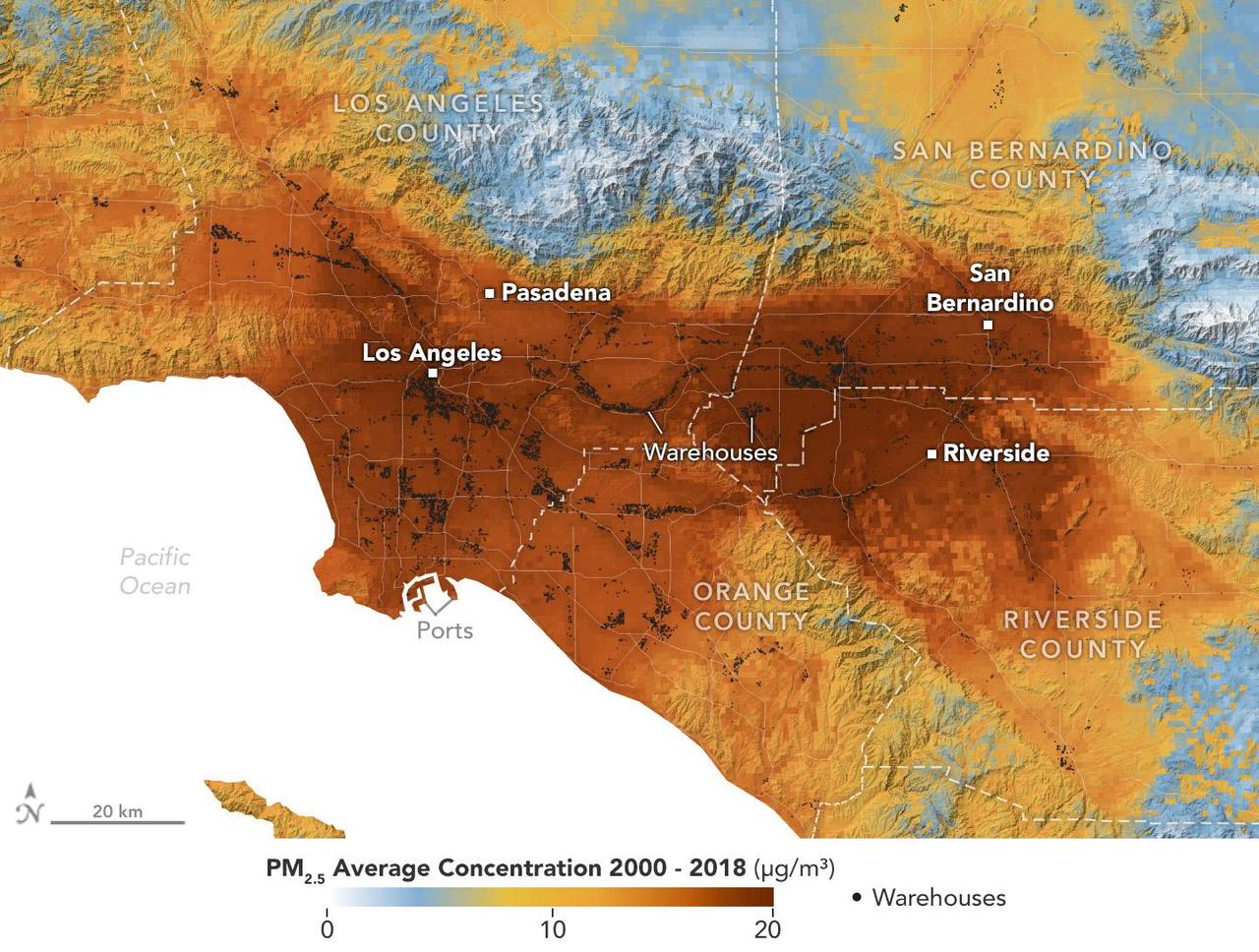
A data visualization shows the average concentration of PM2.5 particulate pollution in the Los Angeles region from 2000 to 2018, along with the locations of nearly 11,000 warehouses over the same time period. Particles measuring 2.5 micrometers or less, PM2.5 are pollutants that can be inhaled into the lungs and absorbed into the bloodstream. A NASA-funded study published in September 2024 in GeoHealth analyzed patterns and trends of atmospheric PM2.5 concentration and found that ZIP codes with more or larger warehouses had higher levels of PM2.5 and elemental carbon over time than those with fewer warehouses. Elemental carbon is a type of PM2.5 that is produced by heavy-duty diesel engines. In the visualization, areas with higher concentrations of PM2.5 are shown in darker red, and locations of warehouses are indicated by small black circles (many of them clustered closely together). The PM2.5 data came from models based on satellite observations, including from NASA's Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) instruments. The PM2.5 warehouse locations were derived from a commercial real estate database. Particulate pollution has been linked to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, some cancers, and adverse birth outcomes, including premature birth and low infant birth weight. As the e-commerce boom of recent decades has spurred warehouse construction, pollution in nearby neighborhoods has become a growing area for research. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26415
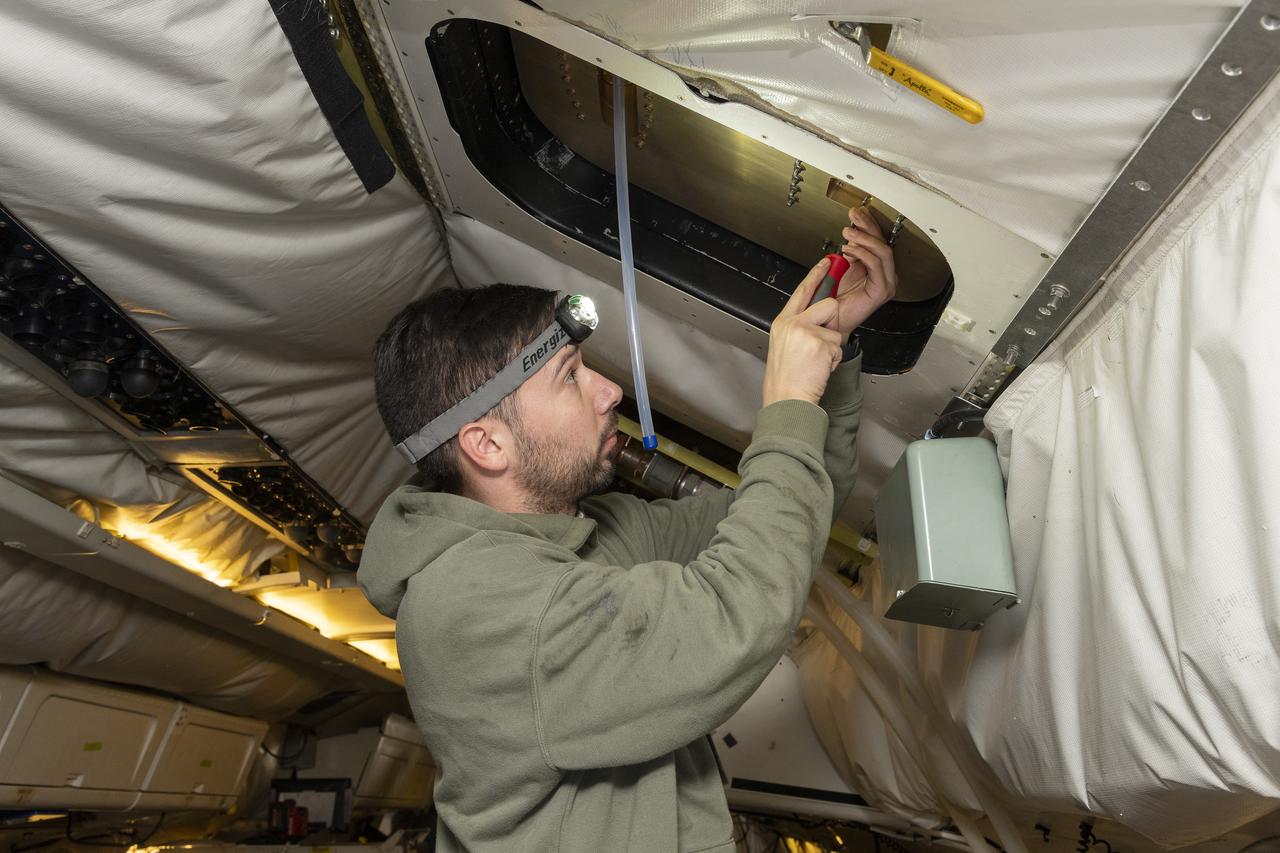

Isac Mata, engineering technician at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center, attends to the interior of the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
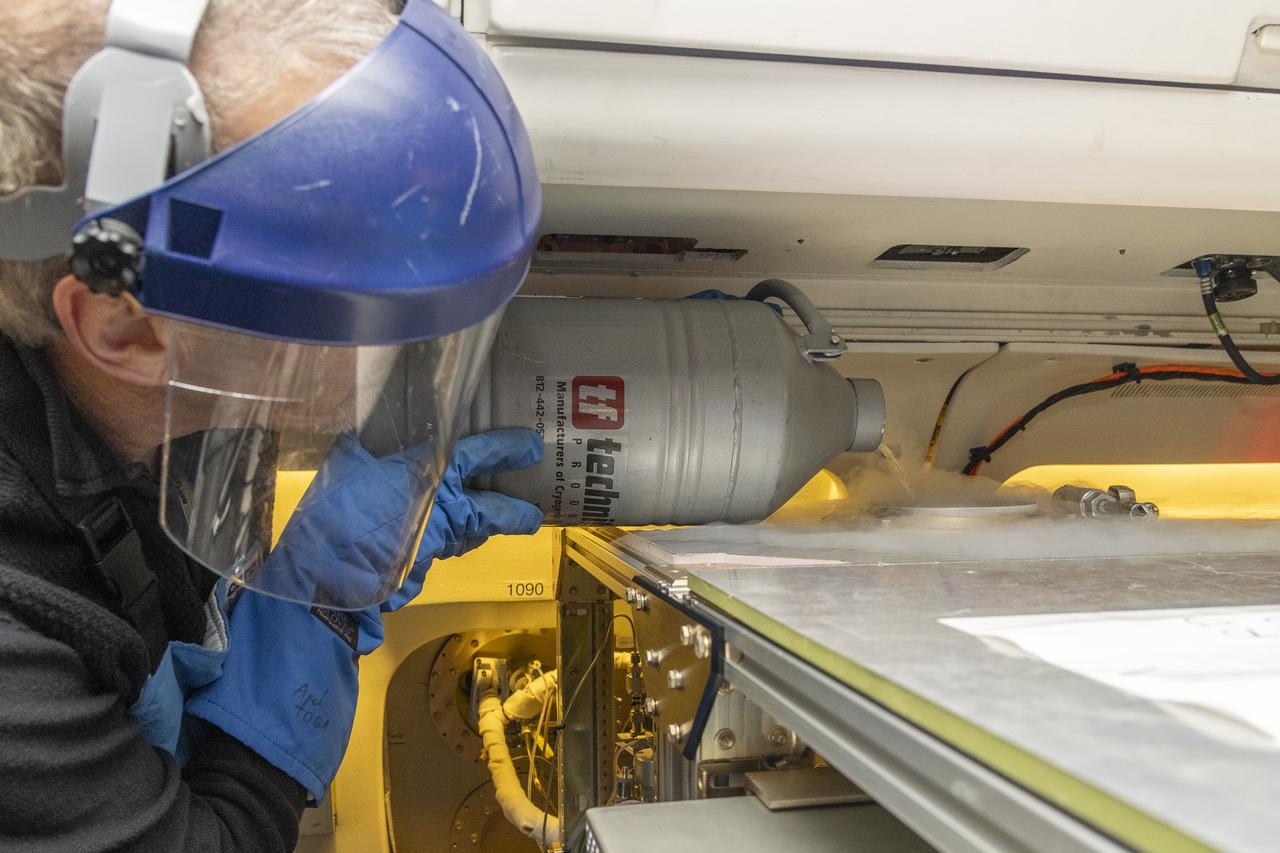

Alan Hills fills liquid nitrogen in the Trace Organic Gas Analyzer (TOGA) instrument onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. This instrument measures volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
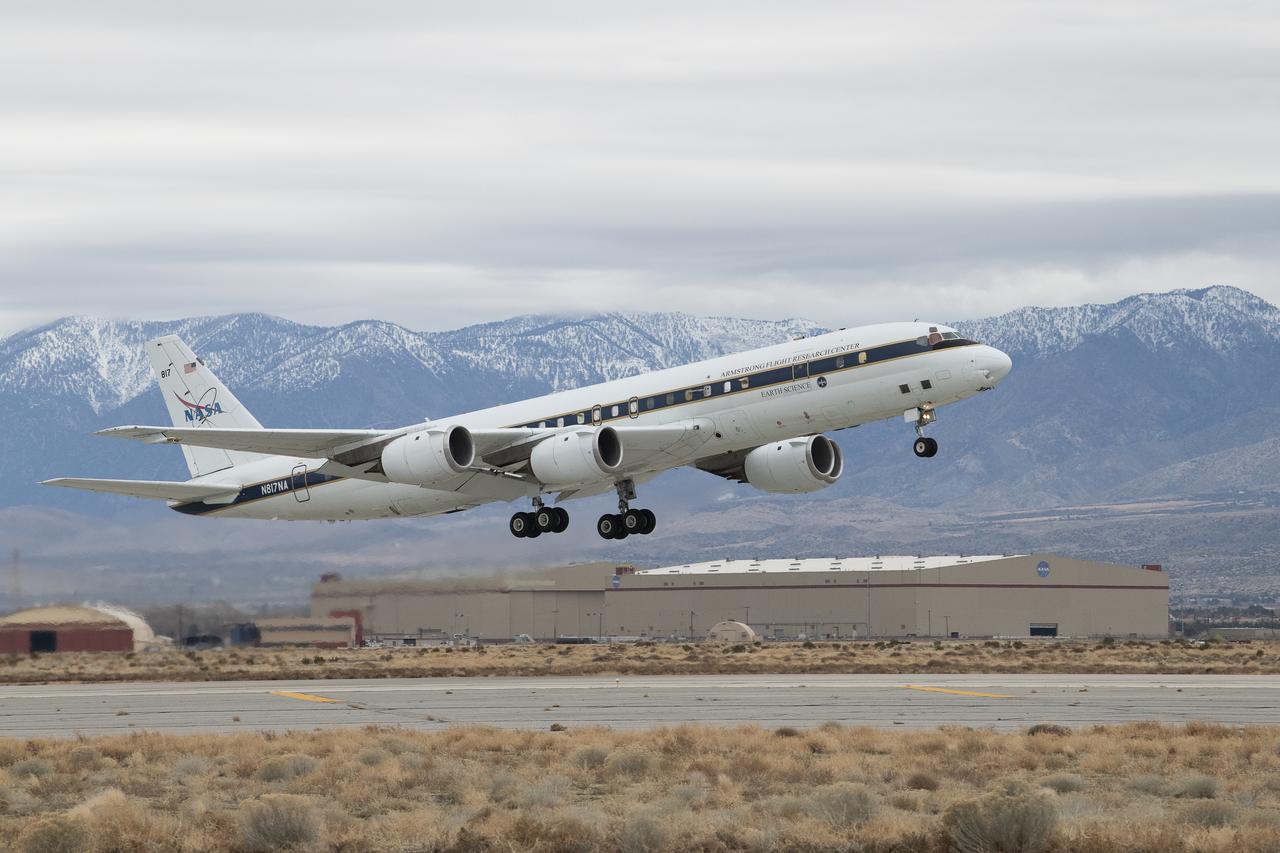

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
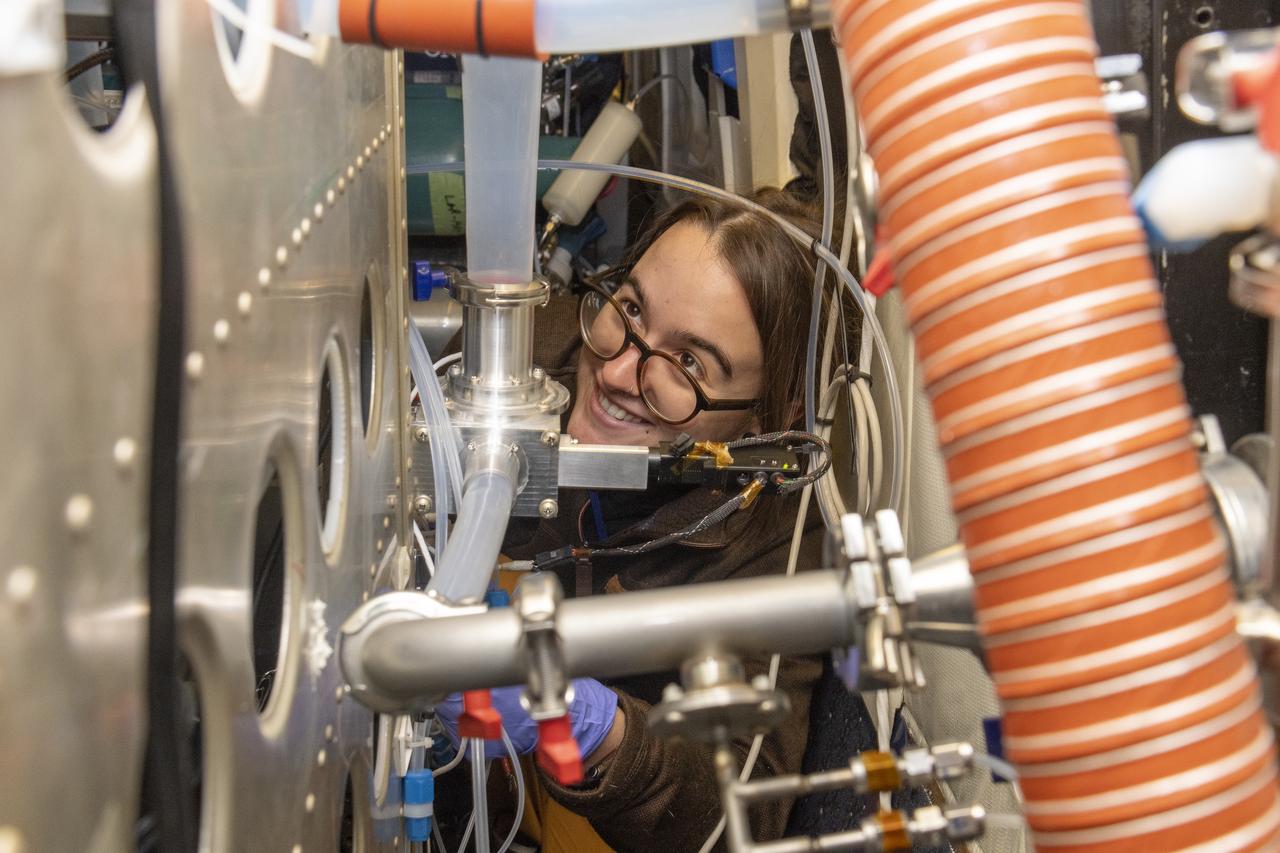
Kat Ball, Chemical Engineering Ph.D candidate at Caltech, attends to the Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer (CIMS) rack onboard the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
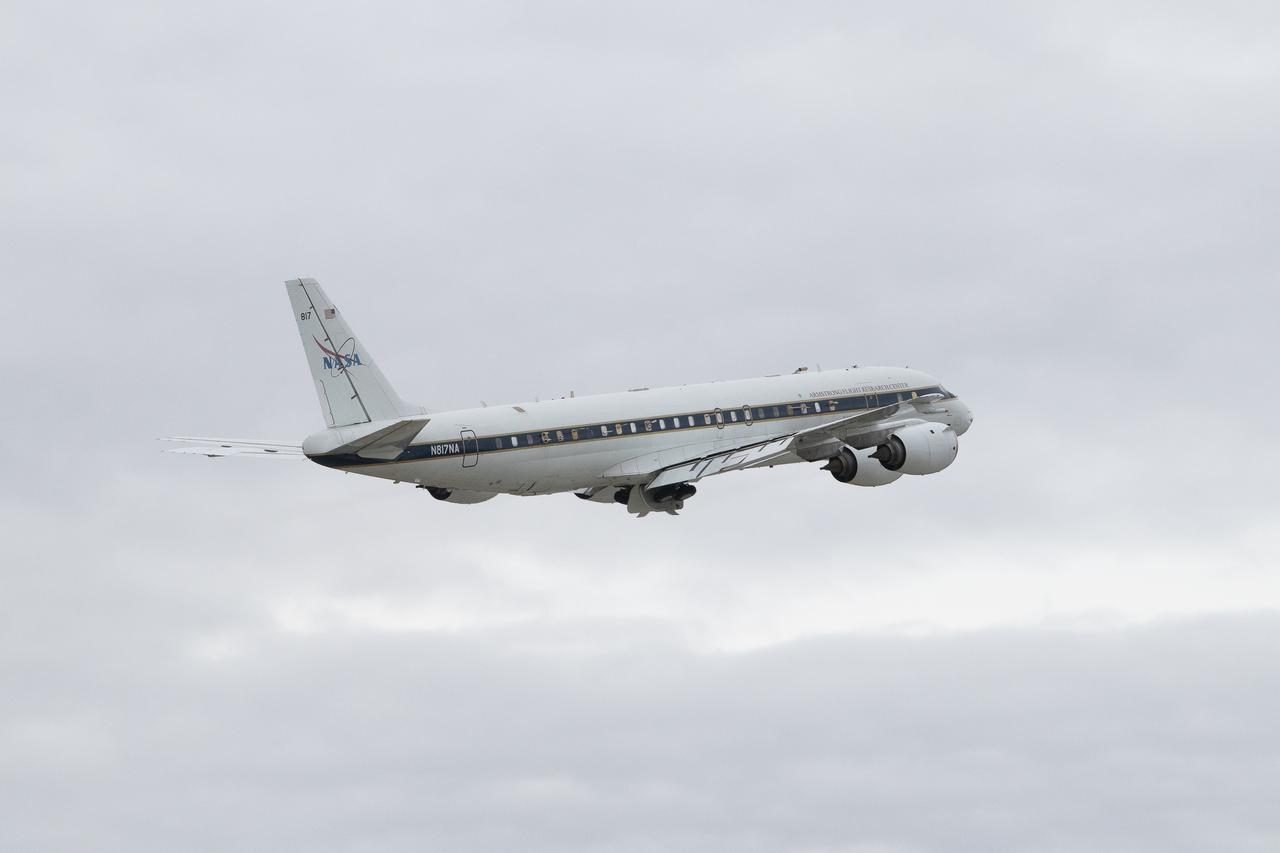

DC-8 aircraft conducts test flights at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
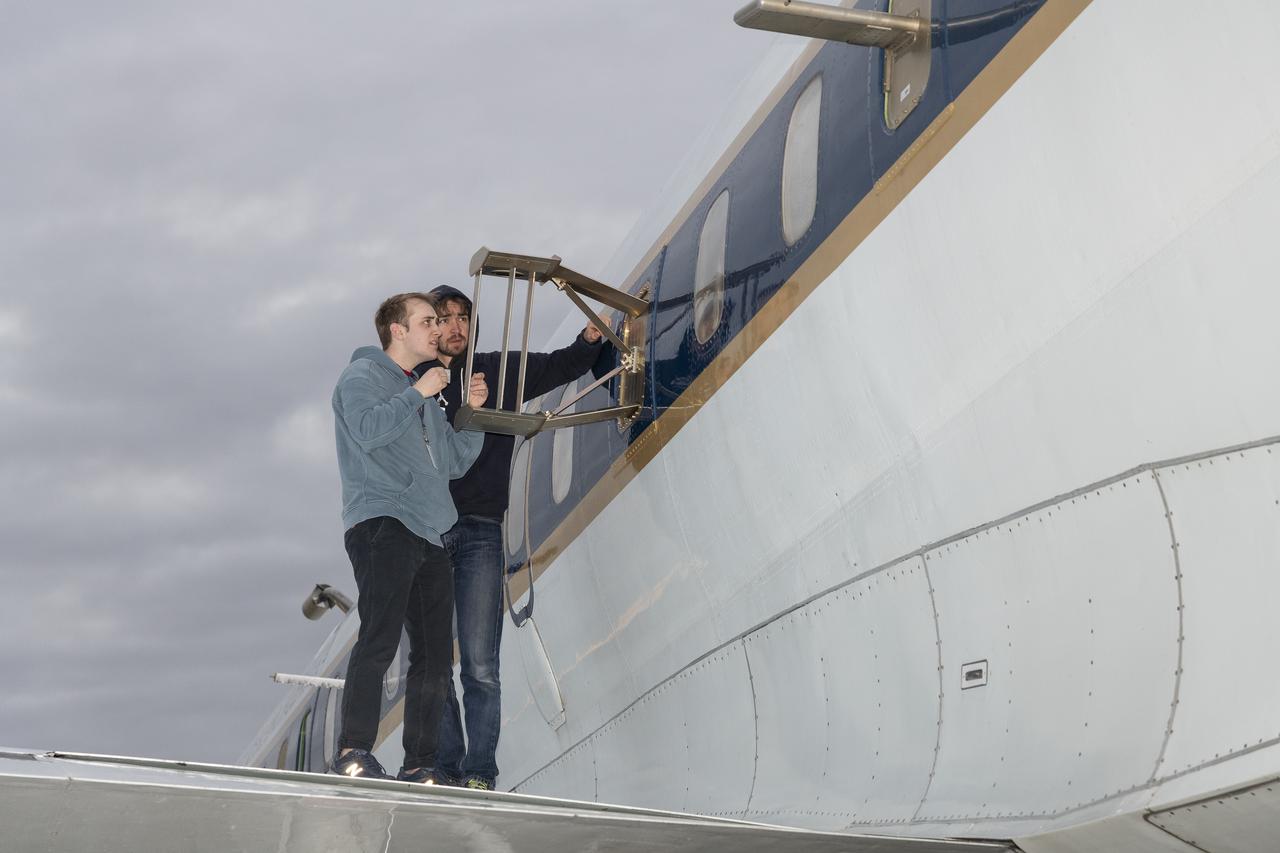

Scientists Ryan Boyd (left) and Vladislav Sevostianov (right) attend to the Optical Payload for Lasercomm Science (OPALS) instrument on the exterior the DC-8 aircraft at Building 703 in Palmdale, CA. The DC-8 aircraft is prepared for its last mission, ASIA-AQ (Airborne and Satellite Investigation of Asian Air Quality), that will collect detailed air quality data over several locations in Asia to improve the understanding of local air quality in collaboration with local scientists, air quality agencies, and government partners
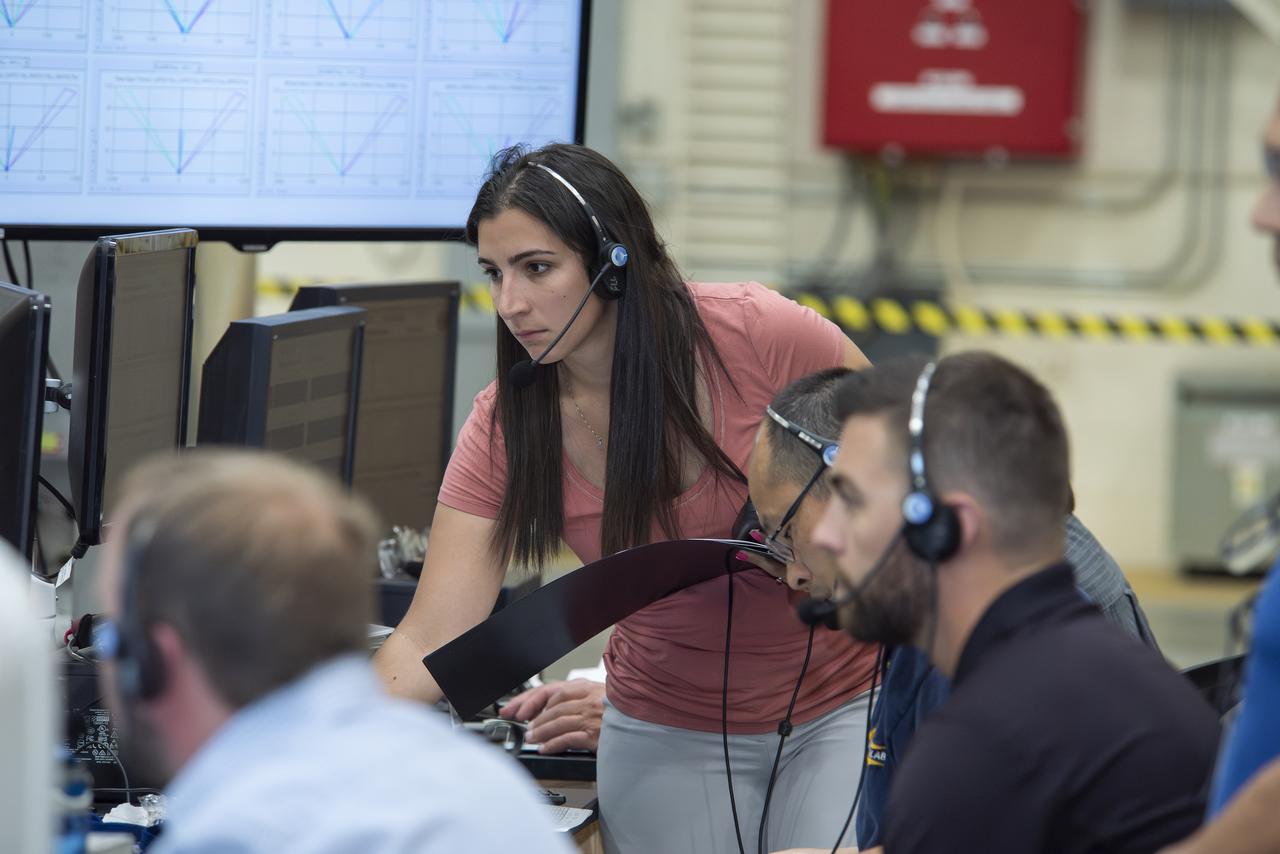

Kirsten Boogaard, Deputy Project Manager for the DC-8 aircraft, leads and manages project planning, integration and resources for airborne science missions since 2020
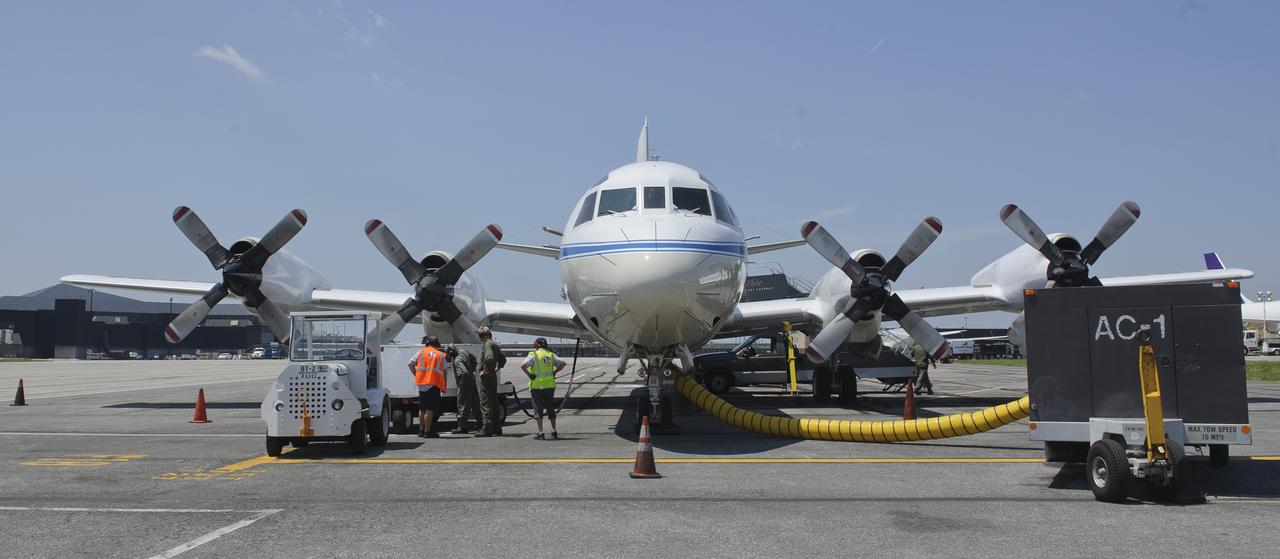

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
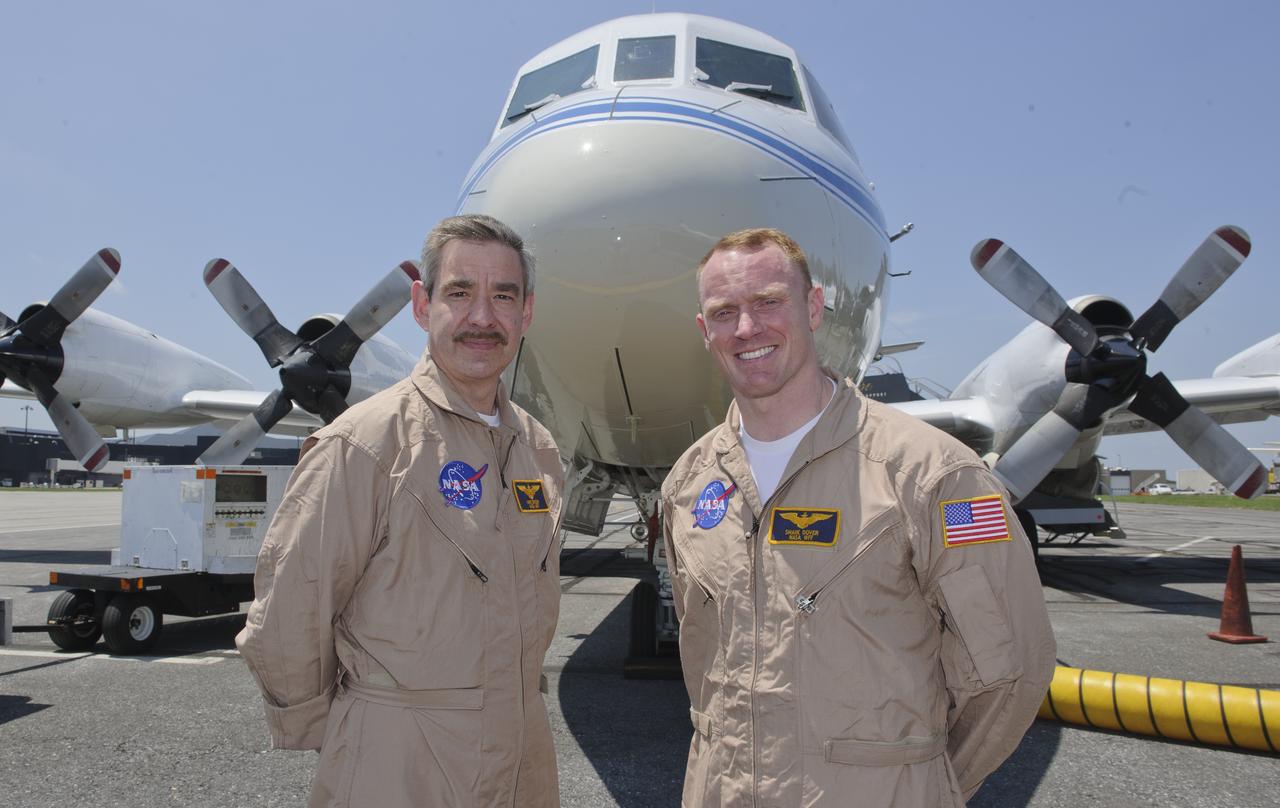

WFF Pilots Mike Singer, left, and Shane Dover stand in front of the 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
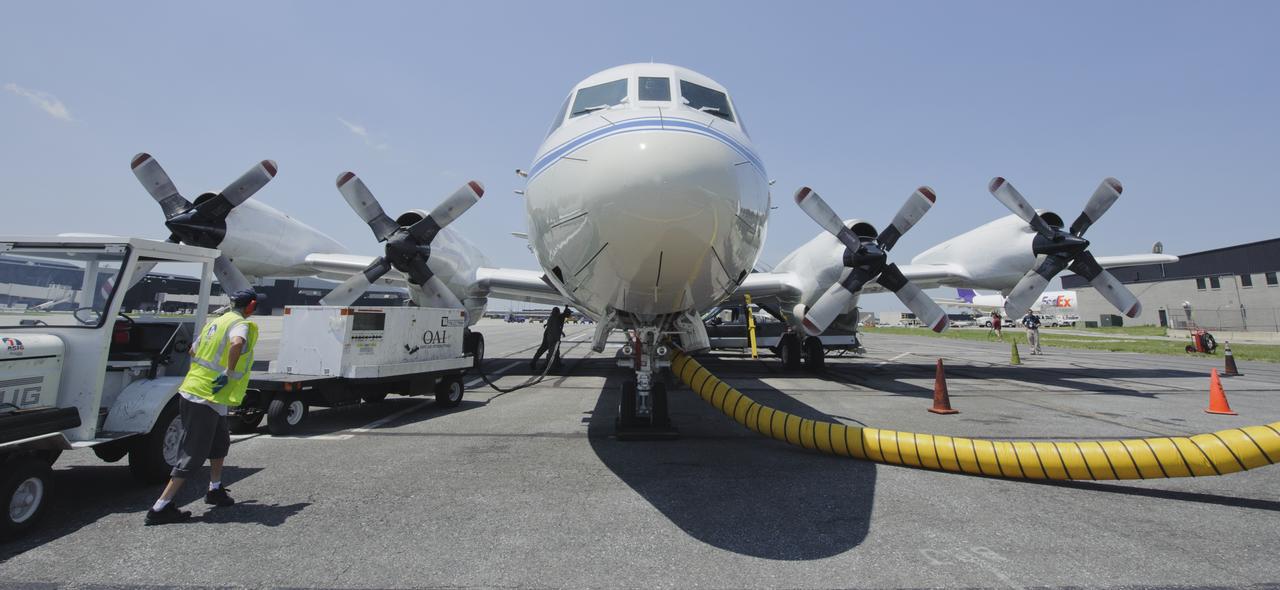

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
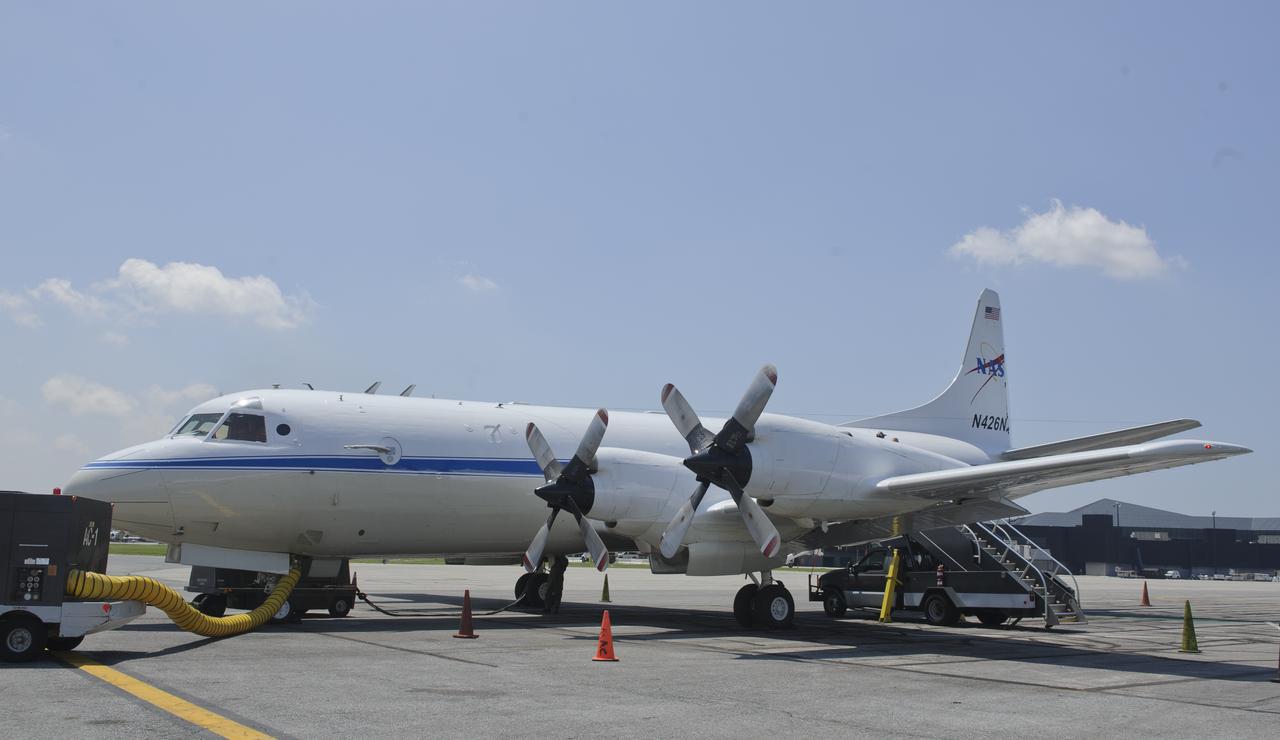

A 117-foot P-3B NASA research aircraft is seen on the tarmac at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Pilots Shane Dover, left, and Mike Singer are seen on the flight deck of the P-3B NASA research aircraft at Baltimore/Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport, Tuesday, June 28, 2011, in Baltimore, Md. The aircraft is part of a month-long field campaign designed to improve satellite measurements of air pollution. The name of the experiment -- Deriving Information on Surface conditions from Column and Vertically Resolved Observations Relevant to Air Quality (DISCOVER -- AQ) -- is a mouthful, but its purpose is simple. Come July, the aircraft will be flying spirals over six ground stations in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
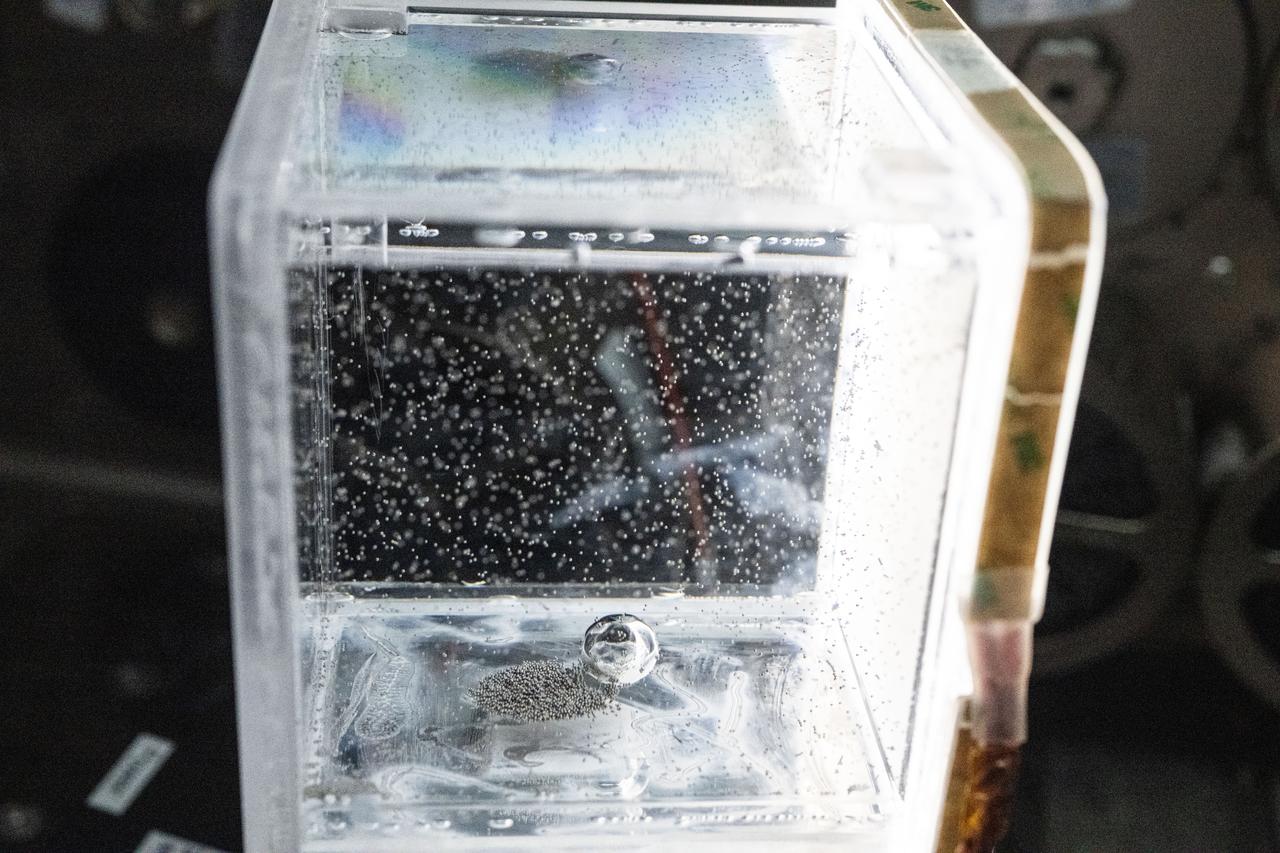

iss073e0917376 (Oct. 20, 2025) --- Tiny ball bearings surround a larger central bearing during the Fluid Particles experiment, conducted inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module. A bulk container installed in the MSG, filled with viscous fluid and embedded particles, is subjected to oscillating frequencies to observe how the particles cluster and form larger structures in microgravity. Insights from this research may advance fire suppression, lunar dust mitigation, and plant growth in space. On Earth, the findings could inform our understanding of pollen dispersion, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transport during storms.
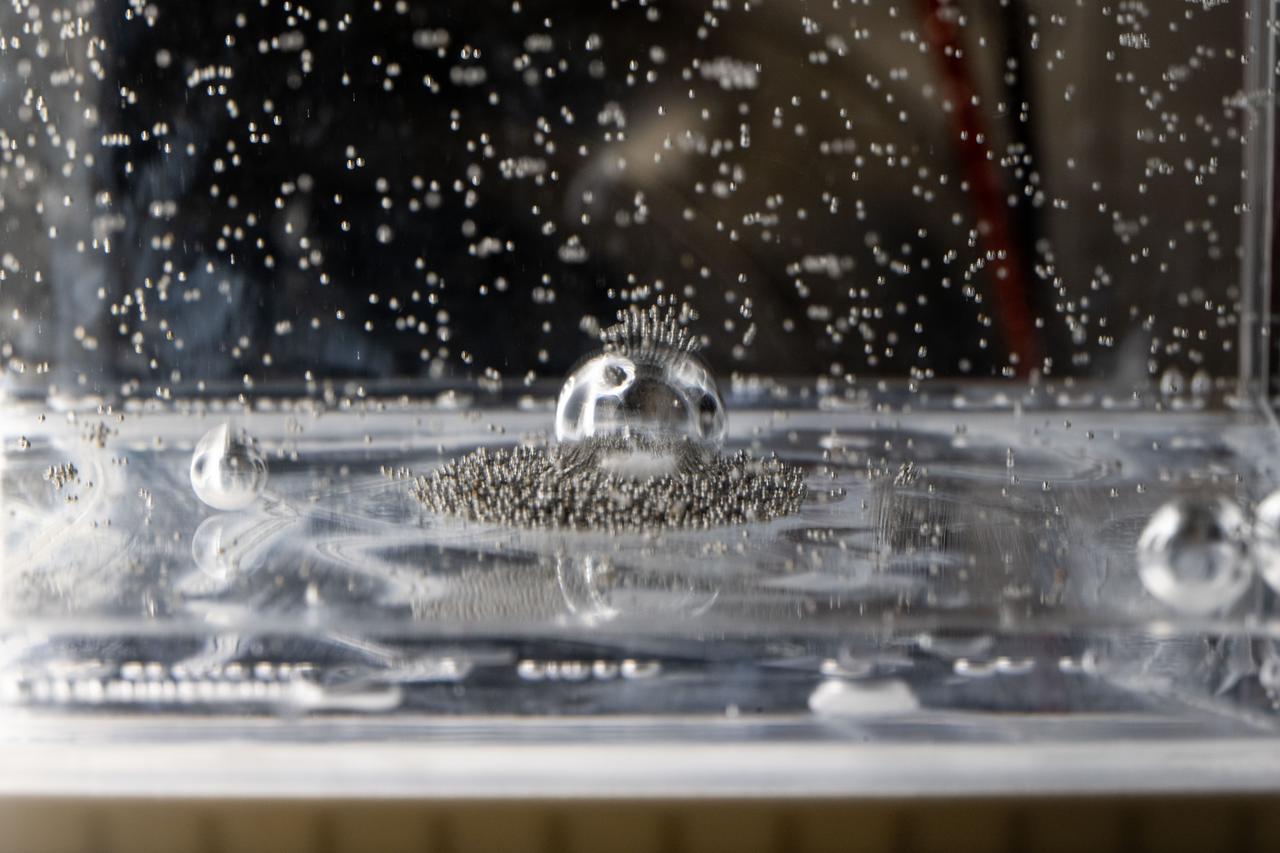

iss073e0917383 (Oct. 20, 2025) --- Tiny ball bearings surround a larger central bearing during the Fluid Particles experiment, conducted inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module. A bulk container installed in the MSG, filled with viscous fluid and embedded particles, is subjected to oscillating frequencies to observe how the particles cluster and form larger structures in microgravity. Insights from this research may advance fire suppression, lunar dust mitigation, and plant growth in space. On Earth, the findings could inform our understanding of pollen dispersion, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transport during storms.
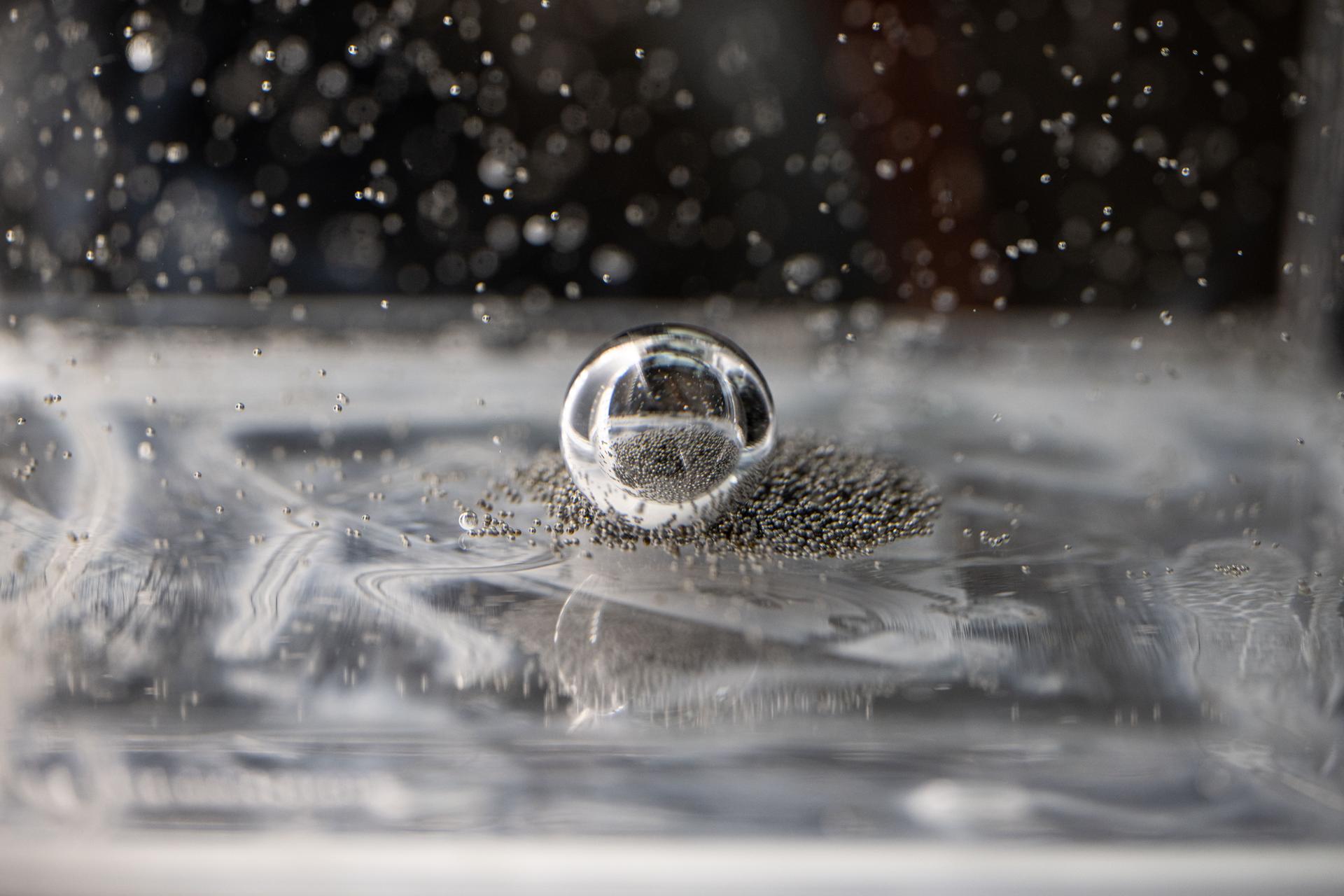

iss073e0917381 (Oct. 20, 2025) --- Tiny ball bearings surround a larger central bearing during the Fluid Particles experiment, conducted inside the Microgravity Science Glovebox (MSG) aboard the International Space Station’s Destiny laboratory module. A bulk container installed in the MSG, filled with viscous fluid and embedded particles, is subjected to oscillating frequencies to observe how the particles cluster and form larger structures in microgravity. Insights from this research may advance fire suppression, lunar dust mitigation, and plant growth in space. On Earth, the findings could inform our understanding of pollen dispersion, algae blooms, plastic pollution, and sea salt transport during storms.
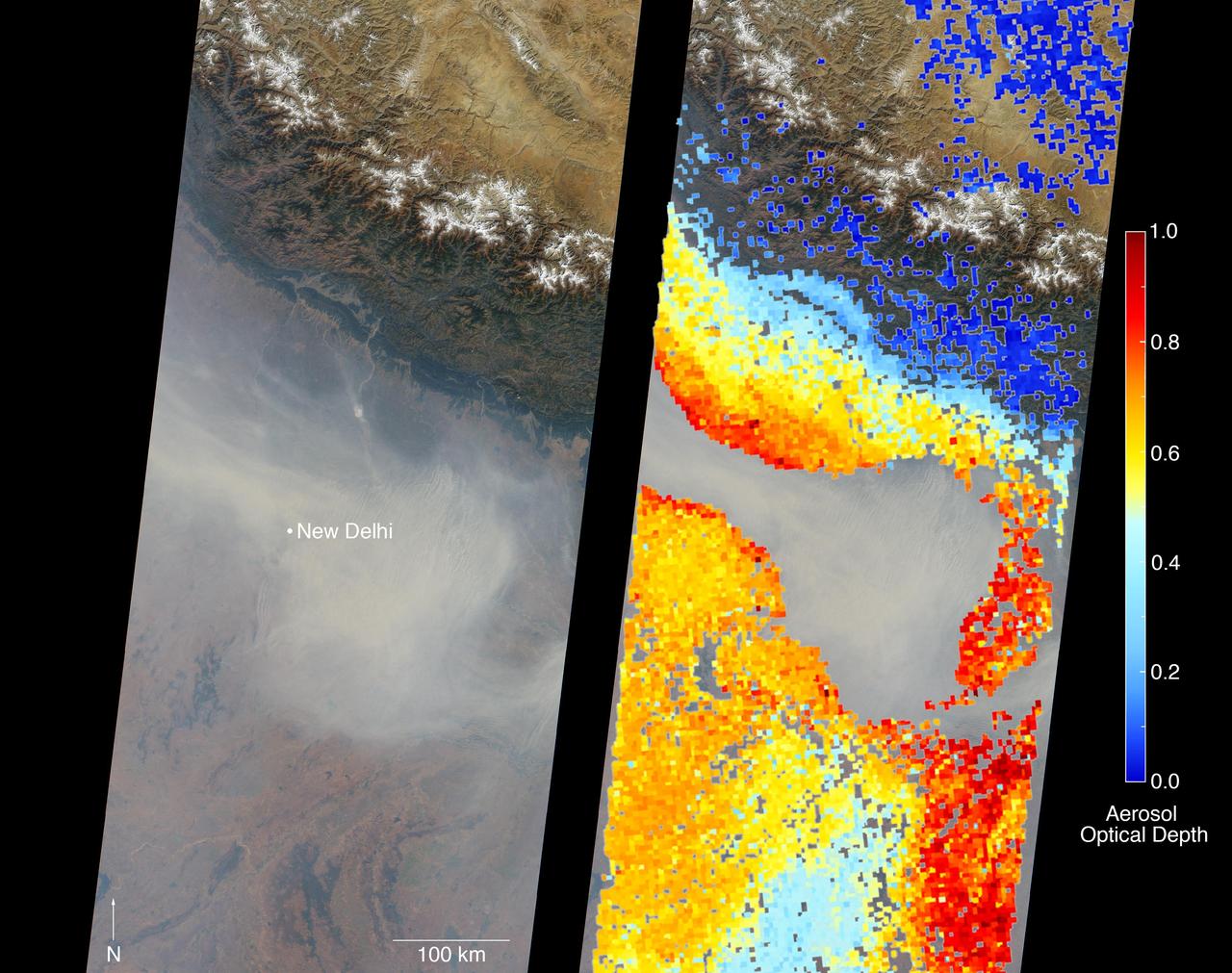
New Delhi, India's capital city, is currently suffering though a period of particularly poor air quality. In early November 2016, monitors at various locations in the area posted air quality index measurements as high as the 900s (the most severe ranking, "hazardous," is any air quality index measurement over 300). Thousands of schools have been closed, and a survey by the Associate Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India reports that 10 percent of the city's workers called in sick due to air-pollution-related health issues. According to several published news reports, the extreme air pollution may be due to a combination of nearby agricultural burning after harvest, urban construction and solid-waste burning, as well as remnants of firecracker smoke and additional car emissions after the celebration of Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, on October 30. The Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR) instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite passed over the region on Saturday, Nov. 5, 2016, at around 11:05 a.m. local time. At left is an image acquired from MISR's vertical viewing camera. The Himalayas stretch across the northern portion of the image. This towering mountain range tends to concentrate pollution in the region immediately to the south, including New Delhi, by preventing pollutants from blowing northwards. New Delhi, whose location is indicated on the image, is under a patch of especially thick haze. At 6:00 a.m. local time on that date, the U.S. Mission India NowCast Air Quality Index for New Delhi was reported at 751, more than twice the threshold for hazardous air quality. At right, a map of aerosol optical depth is superimposed on the image. Optical depth is a quantitative measure of the abundance of aerosols (tiny particles in the atmosphere). Optical depths for the area around New Delhi have not been calculated because the haze is so thick that the algorithm has classified the area as a cloud. In the region immediately surrounding the thick haze, optical depths approach 1.0. An optical depth of 1.0 means that only about 37 percent of direct sunlight reaches the surface due to interactions with particles in the atmosphere. These data were acquired during Terra orbit 89805. Other MISR data are available through the NASA Langley Research Center; for more information, go to https://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/project/misr/misr_table. MISR was built and is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington, D.C. The Terra spacecraft is managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland. The MISR data were obtained from the NASA Langley Research Center Atmospheric Science Data Center, Hampton, Virginia. JPL is a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21100
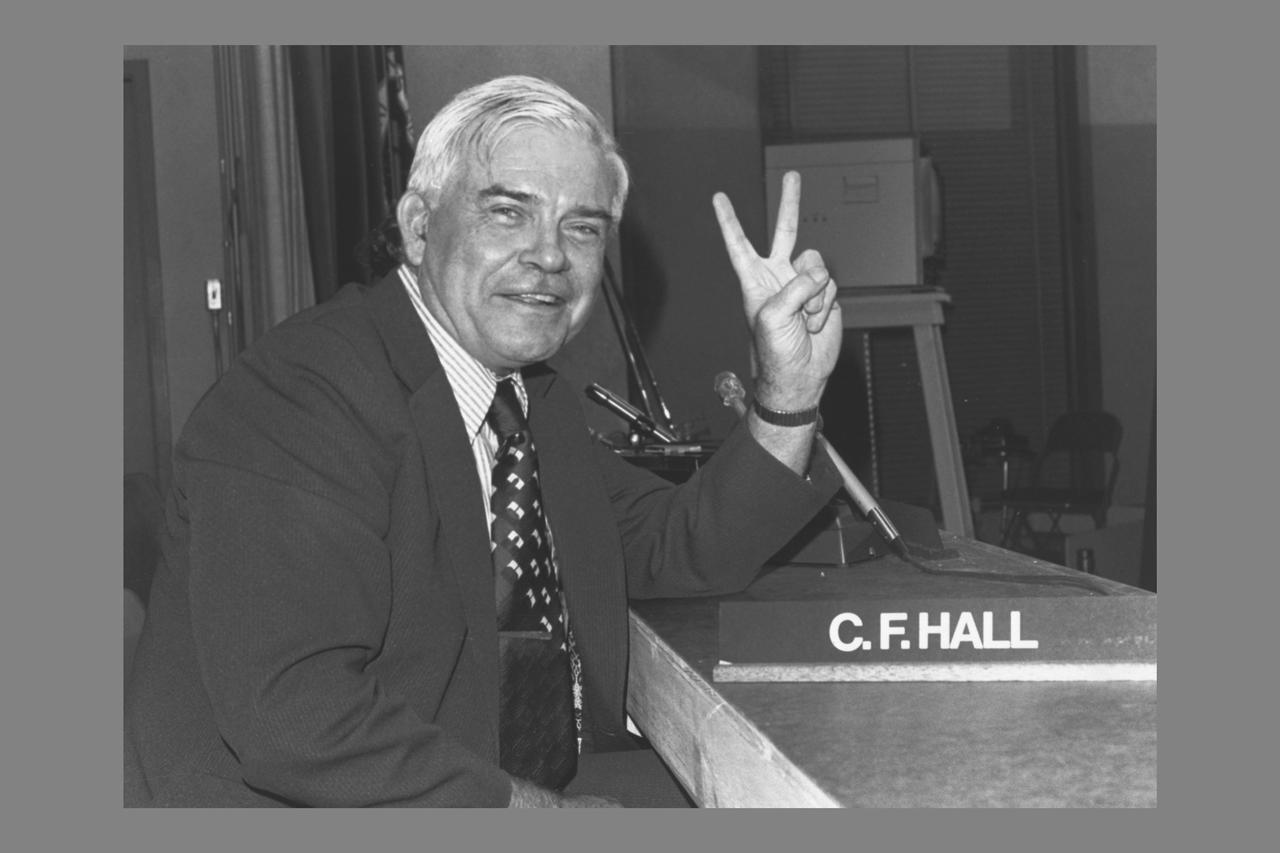

Photographs and Captions courtesy of Joseph and Donna Roizen Telegen, Palo Alto, CA (from) Pioneer 10 and 11 Missions Jupiter encounters - Activities at Ames Research Center December 1973 and December 1974 - As a memento of the highly successful Pioneer 10 and 11 missions to Jupiter, this collection of photographs represents a sampling of those taken at Ames Research Center during the Jupiter encounter periods in December 1973 and December 1974. The captions for these photographs are meant to suggest the lighter side of the intense activities that took place during these periods. I would like to express my gratitude to all participants in the Pioneer 10/11 program for their teamwork in accomplishing the scientific and technical objectives of the Pioneer 10 and 11 missions to Jupiter. (signed) Charles F. Hall - Manager, Pioneer Project Charles F. Hall ' Pioneers 10 and 11 not only made schedule, but they got 51,326.149 miles per gallon and met EPA environment pollution limits.'
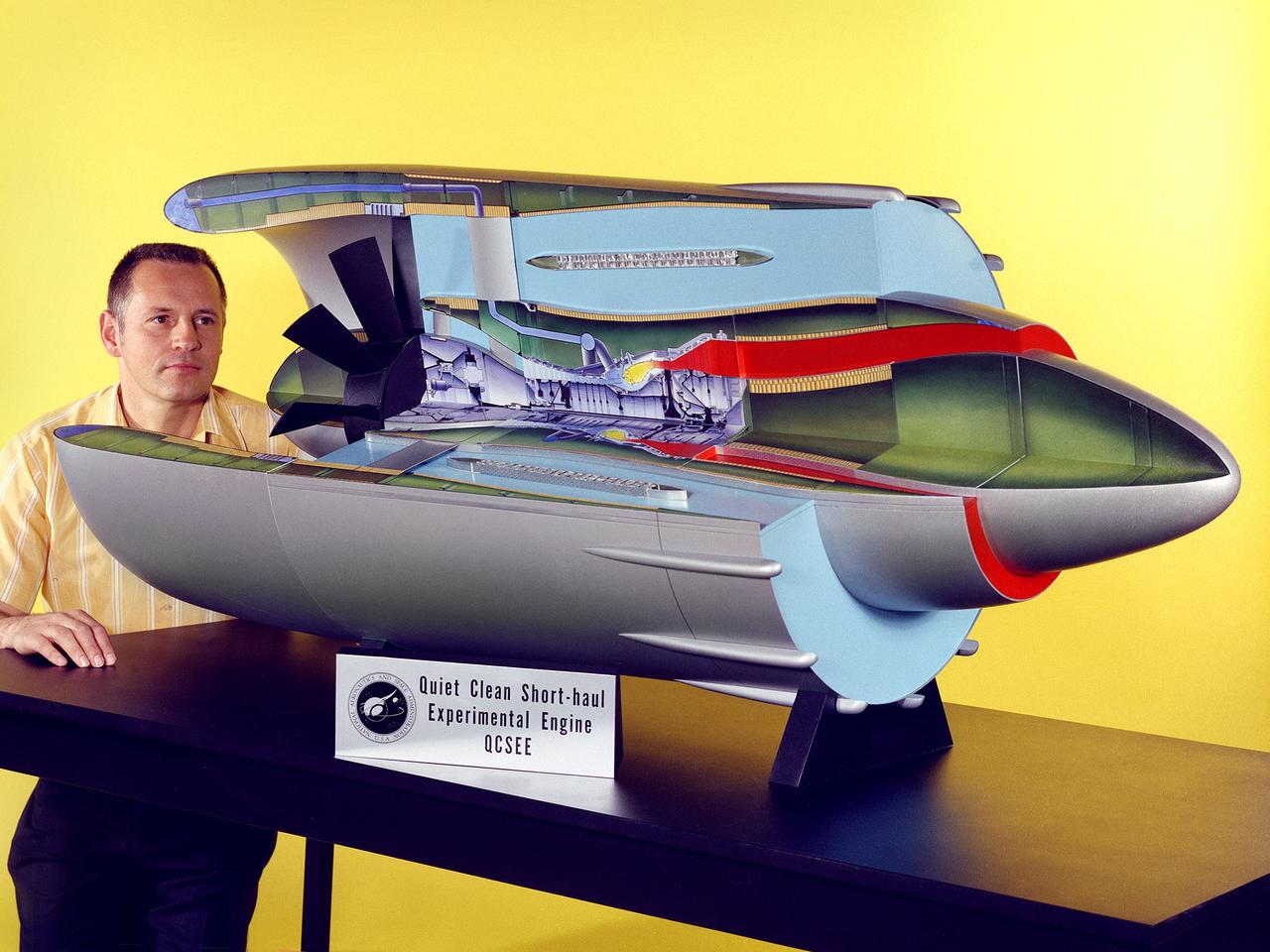

Program manager Carl Ciepluch poses with a model of the Quiet Clean Short Haul Experimental Engine (QCSEE) conceived by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The QCSEE engine was designed to power future short-distance transport aircraft without generating significant levels of noise or pollution and without hindering performance. The engines were designed to be utilized on aircraft operating from small airports with short runways. Lewis researchers investigated two powered-lift designs and an array of new technologies to deal with the shorter runways. Lewis contracted General Electric to design the two QCSEE engines—one with over-the-wing power-lift and one with an under-the-wing design. A scale model of the over-the-wing engine was tested in the Full Scale Tunnel at the Langley Research Center in 1975 and 1976. Lewis researchers investigated both versions in a specially-designed test stand, the Engine Noise Test Facility, on the hangar apron. The QCSEE engines met the goals set out by the NASA researchers. The aircraft industry, however, never built the short-distance transport aircraft for which the engines were intended. Different technological elements of the engine, however, were applied to some future General Electric engines.
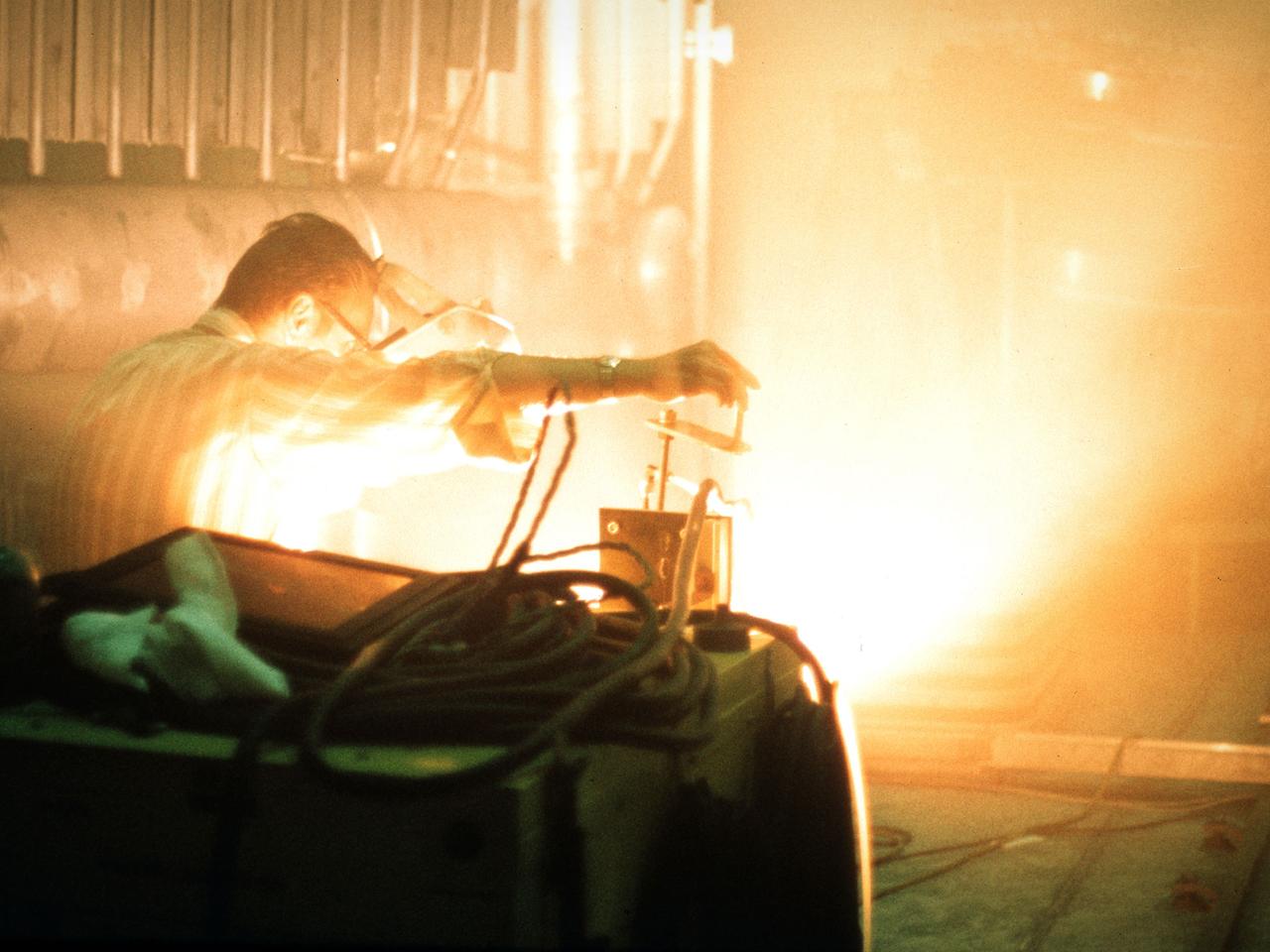

A researcher sets up equipment in the Space Power Chamber at National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Plum Brook Station to study the effects of contaminants on clouds. Drs. Rosa and Jorge Pena of Pennsylvania State University's Department of Meteorology initiated the program in an effort to develop methods of creating stable, long-lasting clouds in a test chamber in order to study their composition and formation. The researchers then wanted to use the artificially-created clouds to determine how they were affected by pollution. The 100-foot diameter and 122-foot high Space Power Chamber is the largest vacuum chamber in the world. The researchers covered the circular walls with muslin. A recirculating water system saturated the cloth. The facility engineers then reduced the chamber’s pressure which released the water from the muslin and generated a cloud. The researchers produced five different clouds in this first portion of this study. They discovered that they could not create stable clouds because of the heat generated by the water-pumping equipment. Nonetheless, they felt confident enough to commence planning the second phase of the program using a heat exchanger to cool the equipment.
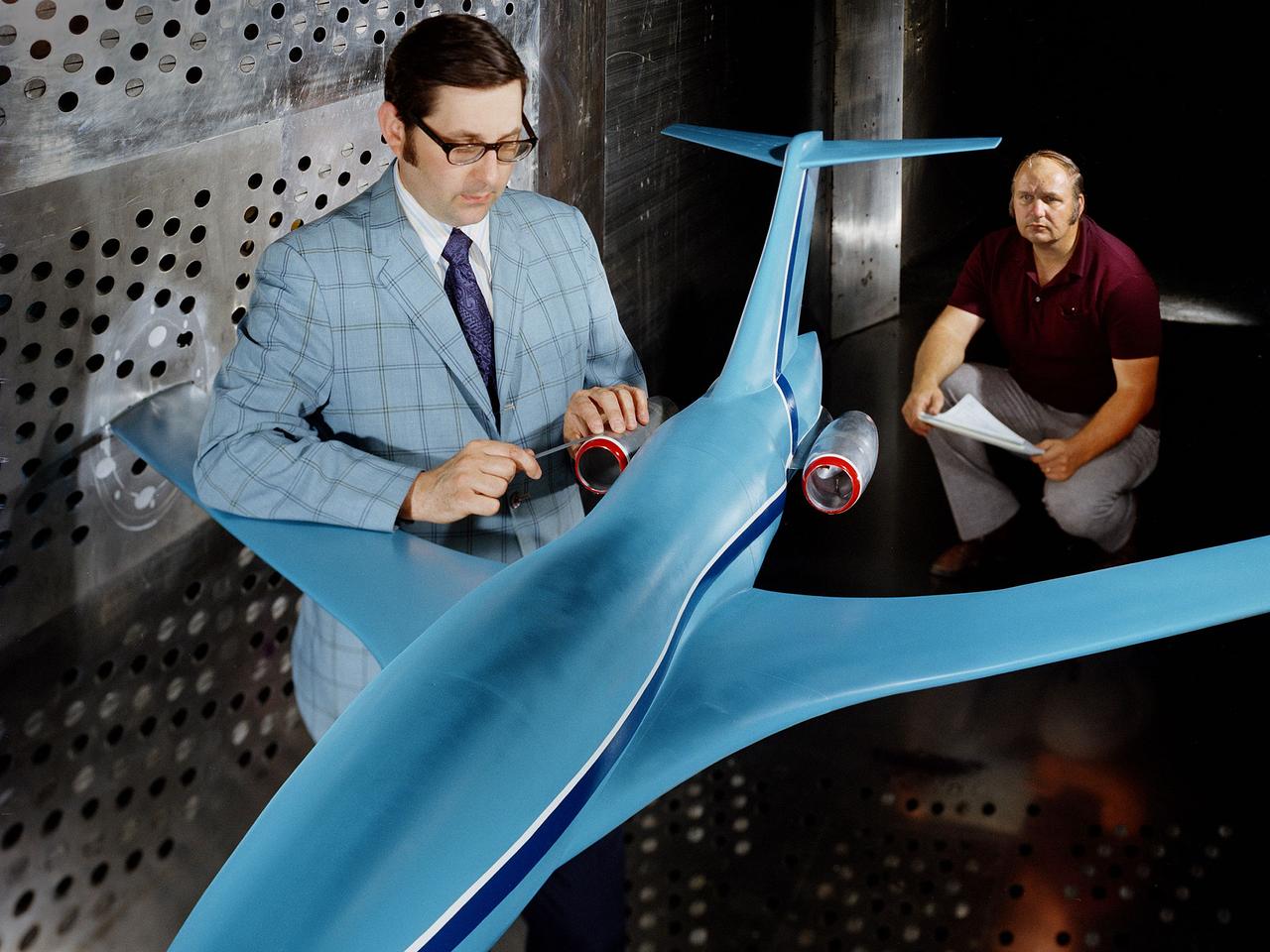

A researcher examines an Advanced Technology Transport model installed in the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The Advanced Technology Transport concept was a 200-person supersonic transport aircraft that could cruise at Mach 0.9 to 0.98 with low noise and pollution outputs. General Electric and Pratt and Whitney responded to NASA Lewis’ call to design a propulsion system for the aircraft. The integration of the propulsion system with the airframe was one of the greatest challenges facing the designers of supersonic aircraft. The aircraft’s flow patterns and engine nacelles could significantly affect the performance of the engines. NASA Lewis researchers undertook a study of this 0.30-scale model of the Advanced Technology Transport in the 8- by 6-foot tunnel. The flow-through nacelles were located near the rear of the fuselage during the initial tests, seen here, and then moved under the wings for ensuing runs. Different engine cowl shapes were also analyzed. The researchers determined that nacelles mounted at the rear of the aircraft produced more efficient airflow patterns during cruising conditions at the desired velocities. The concept of the Advanced Technology Transport, nor any other US supersonic transport, has ever come to fruition. The energy crisis, environmental concerns, and inadequate turbofan technology of the 1970s were among the most significant reasons.
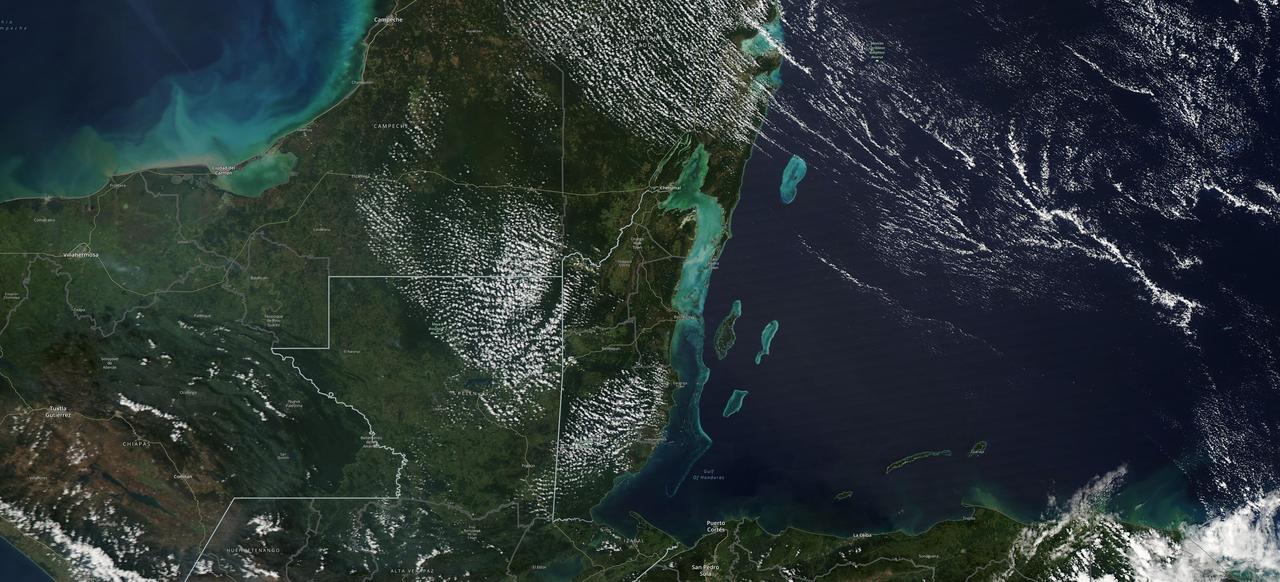

The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured this image of the Yucatán Peninsula on Feb. 3, 2022. At the center is Belize, a country whose Caribbean coast is home to the Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System, which encompasses a vibrant network of marine environments that supports thousands of animal and plant species and drives Belize's largest industry, tourism. The barrier reef system is among about 1,200 UNESCO World Heritage sites around the world. In a paper published in November 2022 in Frontiers in Remote Sensing, researchers used data from Aqua MODIS to rank 24 protected marine areas off the Belizean coast based on the risks coral face from murky water and rising temperatures. The research also outlined how researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and counterparts in Belize used free, cloud-based data on Google Earth Engine in their analysis. Analyzing imagery from 2002 to 2022, researchers developed a coral vulnerability index – a score between 2 and 12 that characterizes the risk to coral, with higher scores signifying greater risk. Their findings could help management authorities protect the reefs from human impacts such as development, overfishing, pollution, and climate change. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25861
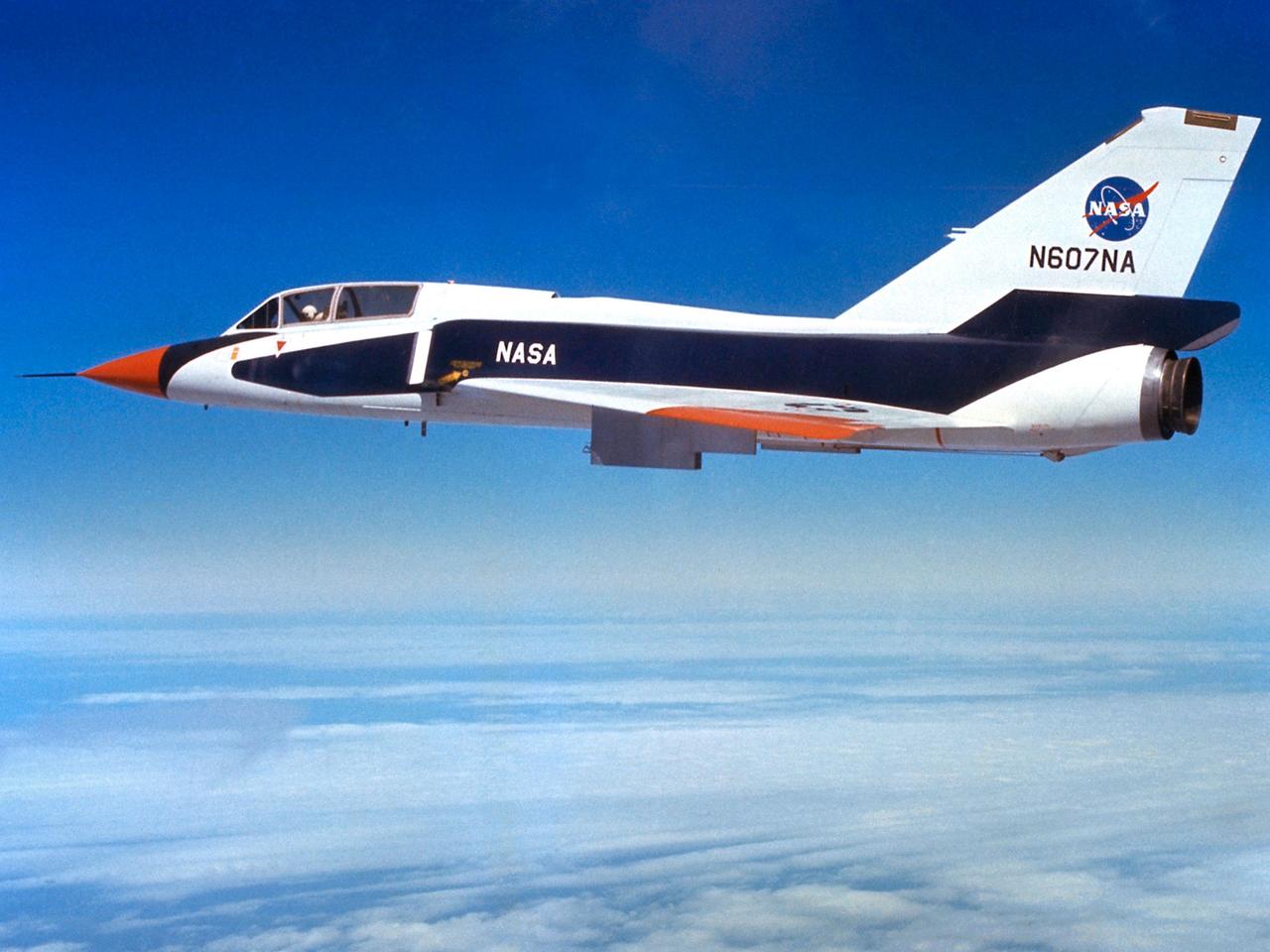

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center’s Convair F-106B Delta Dart equipped with air sampling equipment in the mid-1970s. NASA Lewis created and managed the Global Air Sampling Program (GASP) in 1972 in partnership with several airline companies. NASA researchers used the airliners’ Boeing 747 aircraft to gather air samples to determine the amount of pollution present in the stratosphere. Private companies developed the air sampling equipment for the GASP program, and Lewis created a particle collector. The collector was flight tested on NASA Lewis’ F-106B in the summer of 1973. The sampling equipment was automatically operated once the proper altitude was achieved. The sampling instruments collected dust particles in the air so their chemical composition could be analyzed. The equipment analyzed one second’s worth of data at a time. The researchers also monitored carbon monoxide, monozide, ozone, and water vapor. The 747 flights began in December 1974 and soon included four airlines flying routes all over the globe. The F-106B augmented the airline data with sampling of its own, seen here. It gathered samples throughout this period from locations such as New Mexico, Texas, Michigan, and Ohio. In July 1977 the F-106B flew eight GASP flights in nine days over Alaska to supplement the earlier data gathered by the airlines.

The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.

Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen became the first man to reach the South Pole in December 1911. More than 100 years later, an international team of scientists that includes a NASA researcher has proven that air pollution from industrial activities arrived to the planet’s southern pole long before any human. Using data from 16 ice cores collected from widely spaced locations around the Antarctic continent, including the South Pole, a group led by Joe McConnell of the Desert Research Institute (DRI) in Reno, Nevada, created the most accurate and precise reconstruction to date of lead pollution over Earth’s southernmost continent. The new record, described in an article published today in the online edition of the Nature Publishing Group’s journal Scientific Reports, spans a 410-year period from 1600 to 2010. More here: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1oB4p9U" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1oB4p9U</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
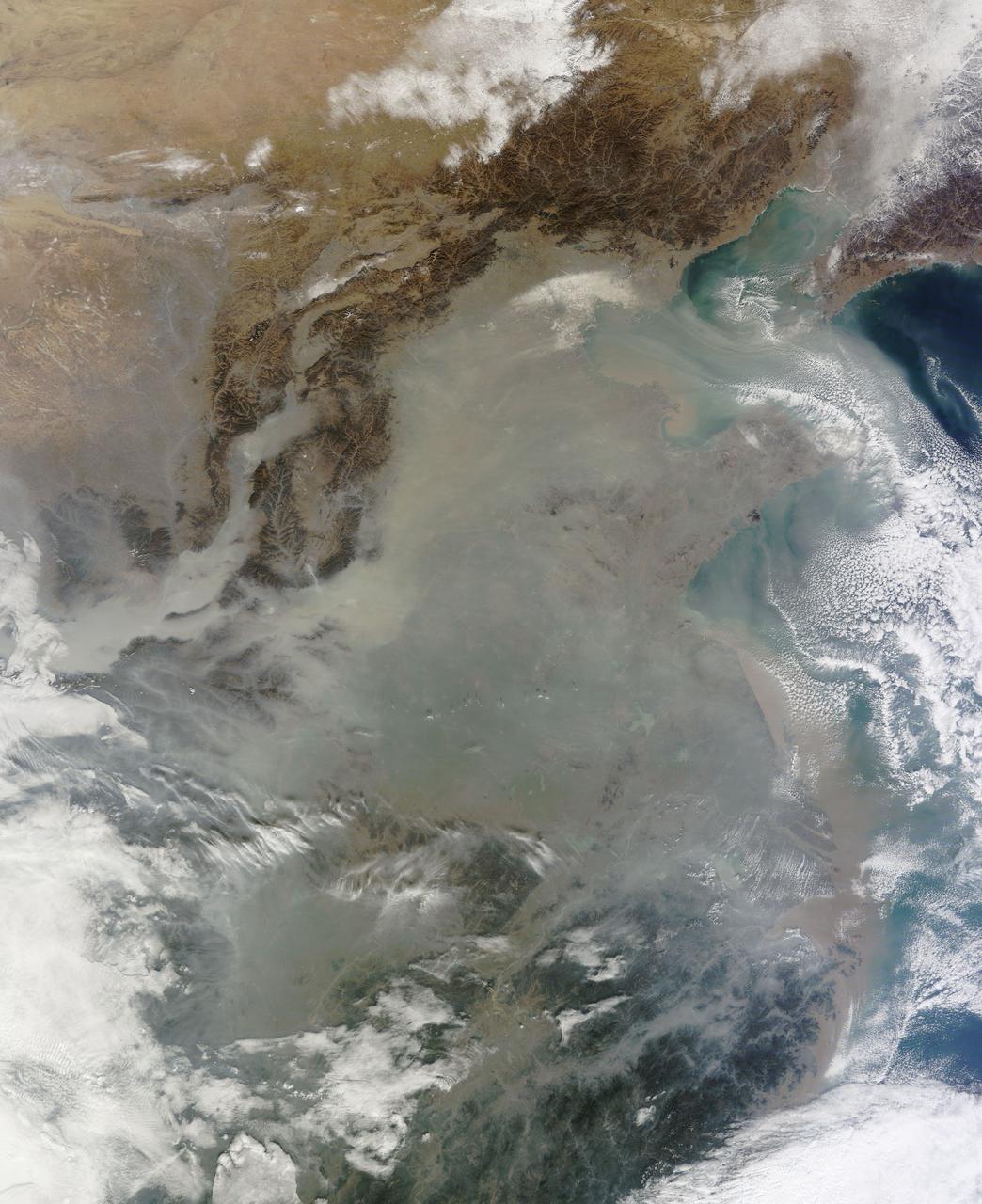
The skies over northern China were shrouded with a thick haze in late December, 2013. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite captured this true-color image on December 23. The dense, gray haze obscures almost all the land and much of the coastal waters from view south and east of the Taihang Mountains. Clearer air covers the region north of the mountains, although fingers of haze roll through most river valleys. The cities of Beijing and Hebei, both west of the Bohai Sea are complete enshrouded. By December 24 the smog levels in some area exceeded World Health Organization-recommended levels by 30 times, according to Bloomberg News. The concentration of PM2.5, which are fine air particulates, were reported at 421 micrograms per cubic meter at 2 p.m. near Tiananmen Square in Beijing, while levels were 795 in Xi’an and 740 in Zhengzhou. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 24-hour exposure to PM2.5 concentrations no higher than 25 micrograms per cubic meter. While not the sole cause of haze and pollution, the use of coal as a very cheap energy source adds to the problem, particularly north of the Huai River. Prior to 1980, the government policy provided free coal for fuel boilers for all people living north of the Huai River. The widespread use of coal allows people in the north to stay warm in winter, but they have paid a price in air quality. According to Michael Greenstone, a Professor of Environmental Economics at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), whose research team published a paper on sustained exposure to air pollution on life expectancy in the region, air pollution, as measured by total suspended particulates, was about 55% higher north of the Huai River than south of it, for a difference of around 184 micrograms of particulate matter per cubic meter. The research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences in July, 2013, also noted life expectancies were about 5.5 years lower in the north, owing to an increased incidence of cardiorespiratory mortality. Air pollution is an on-going issue for the government of China, and Beijing’s Five-Year Clean Air Action Plan aims to reduce overall particle density by over 25 percent on the PM2.5 scale by 2017, and also takes aim at shutting down all coal-burning plants. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
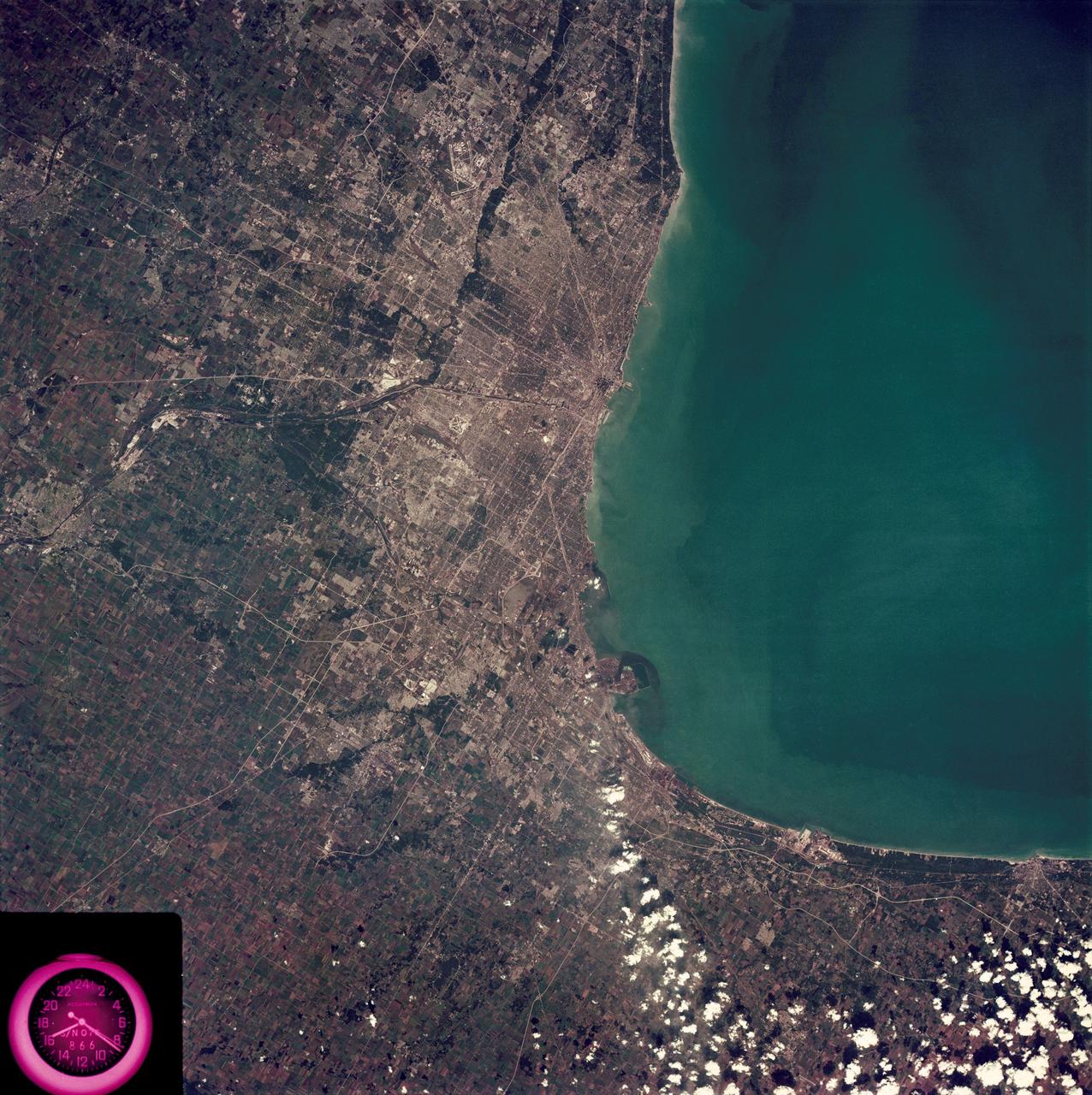

SL3-88-222 (18 Sept. 1973) --- The metropolitan area of Chicago is encompassed in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package (EREP) S190-B photograph taken on Sept. 18, 1973 from the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit. The surrounding major cities of Aurora and Joliet, Illinois; Hammond, Gary and East Chicago, Indiana, are easily delineated. The photograph reveals the following: (1) Cultural differentiation of commercial, industrial and residential areas for use in population and social studies in micro-macro community planning and in cultural pattern studies in the improvement of urban areas. (Aurora is one of 27 census cities of interest to Robert Alexander, a principal investigator. Alexander is with the U.S. Geological Survey). (2) The transportation network with major corridors and their interchanges, primary and feeder streets for use in network analysis and in the development of models for population movement and land use projection. (3) The agricultural lands for land use identification on crop inventory analysis; airports for use in delineation of service and infringement of major man-made features that affect ecosystem balance (support to environmental impact studies). (4) Air and water plumes for use in case studies, natural and man-made differentiation of pollution sources, in support of model development and in ecosystem research studies on the effects of pollution. (5) Recreational centers for use in relating recreational centers to population centers, establishing possible demands and in development of possible future recreational centers to support the demand. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
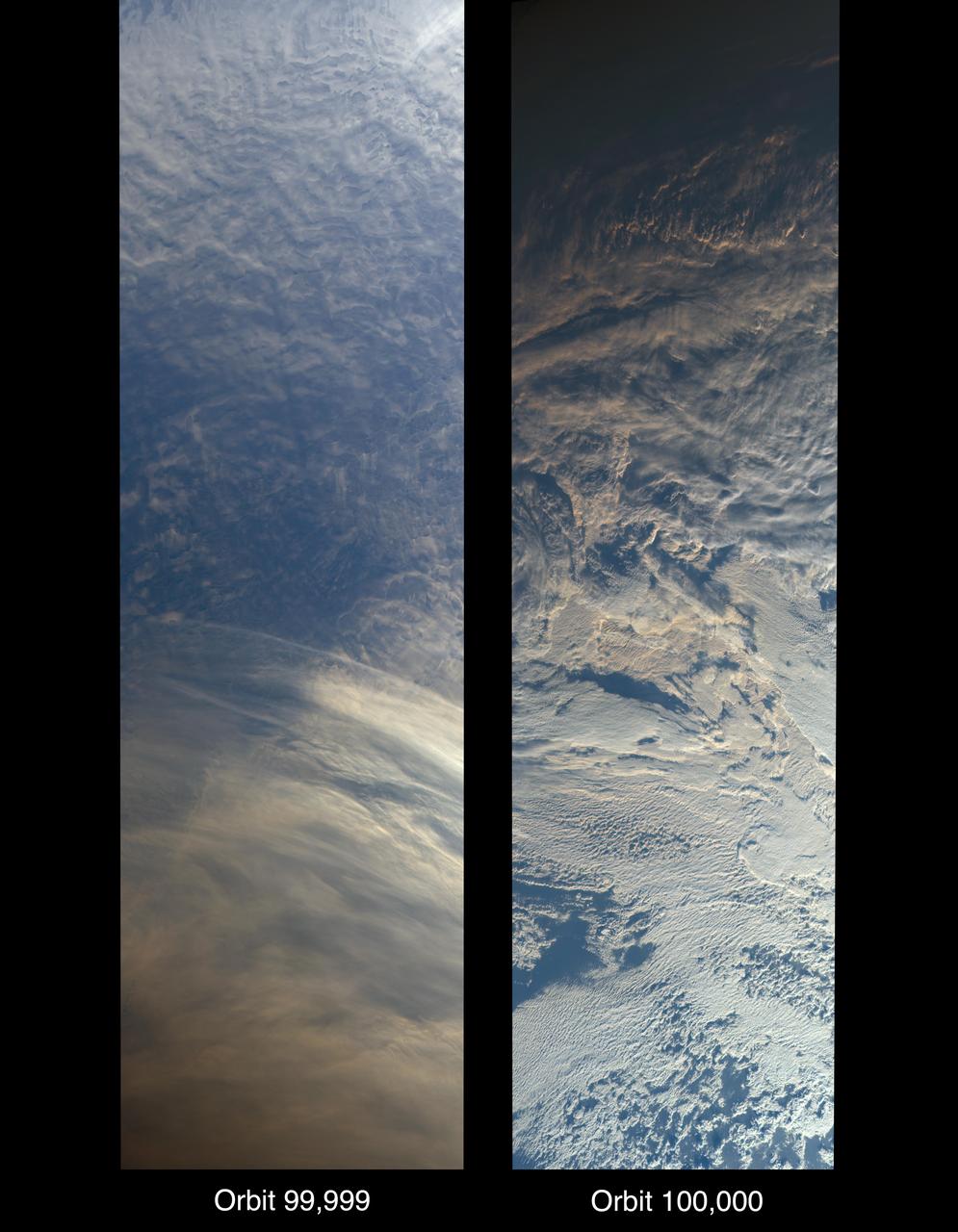
On Oct. 6, 2018, NASA's Terra satellite became one of a handful of NASA satellite ever to complete 100,000 orbits. Launched in 1999, Terra and its five scientific instruments were originally slated to last six years. More than 18 years later, the Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer (MISR), built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, and other instruments on Terra are still collecting data and are expected to continue into the 2020s, limited only by the amount of fuel in the spacecraft. MISR carries nine cameras that view the sunlit Earth simultaneously at widely spaced angles, providing global coverage with high spatial detail. The left image shows dusk falling over snowy Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, at the end of orbit 99,999, as captured by MISR's 70-degree backward-looking camera. On the right is MISR's first view from orbit 100,000, taken by its 70-degree forward-looking camera as sunrise illuminated clouds over the Kara Sea, north of Siberia. Over the years, researchers have used MISR's observations to construct a variety of global data sets that have advanced our understanding of Earth. These include the heights of clouds and wildfire smoke, the amounts of dangerous pollutants in the atmosphere, the movements of global wind systems, and the health of vegetation. The instrument remains as healthy as it was in 1999. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22836
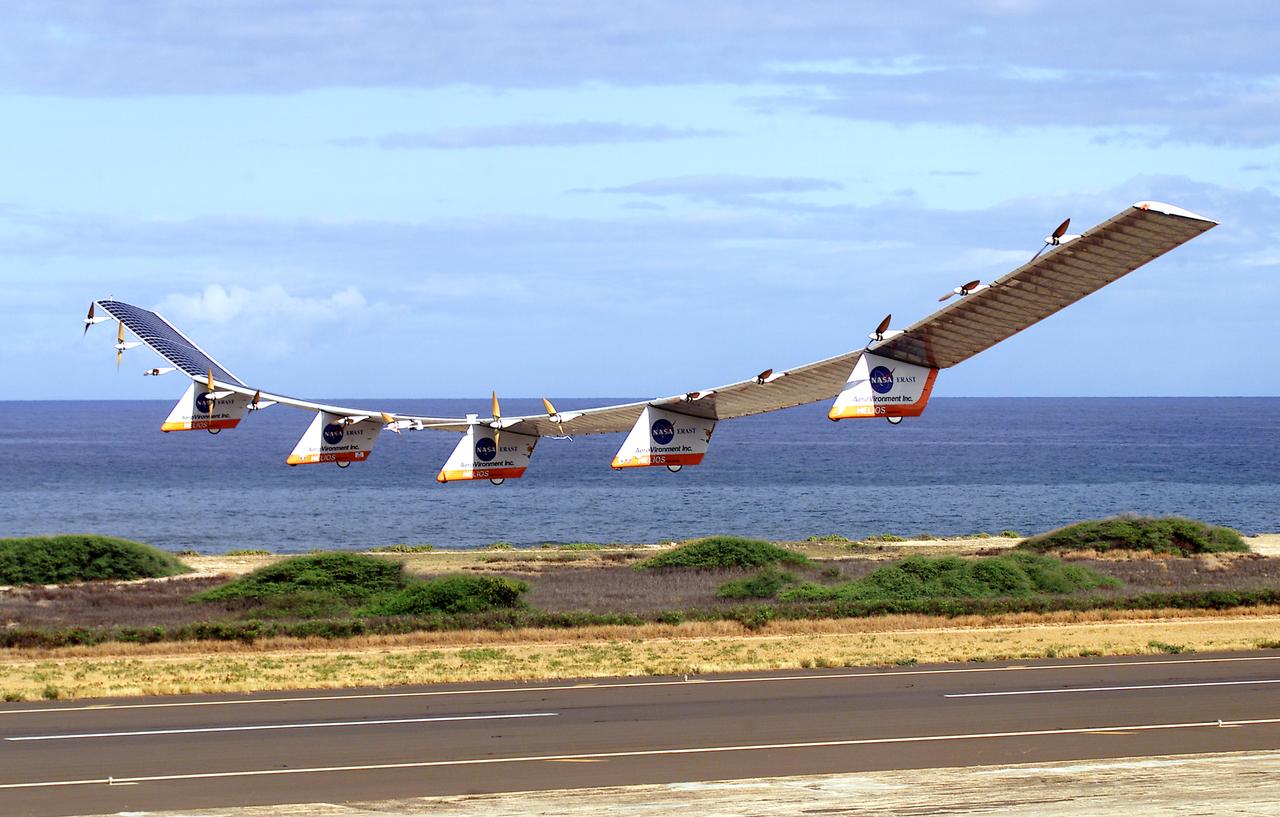

NASA's Helios Prototype aircraft taking off from the Pacific Missile Range Facility, Kauai, Hawaii, for the record flight. As a follow-on to the Centurion (and earlier Pathfinder and Pathfinder-Plus) aircraft, the solar-powered Helios Prototype is the latest and largest example of a slow-flying ultralight flying wing designed for long-duration, high-altitude Earth science or telecommunications relay missions in the stratosphere. Developed by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, California, under NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) project, the unique craft is intended to demonstrate two key missions: the ability to reach and sustain horizontal flight at 100,000 feet altitude on a single-day flight in 2001, and to maintain flight above 50,000 feet altitude for at least four days in 2003, with the aid of a regenerative fuel cell-based energy storage system now in development. Both of these missions will be powered by electricity derived from non-polluting solar energy. The Helios Prototype is an enlarged version of the Centurion flying wing, which flew a series of test flights at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in late 1998. The craft has a wingspan of 247 feet, 41 feet greater than the Centurion, 2 1/2 times that of its solar-powered Pathfinder flying wing, and longer than the wingspans of either the Boeing 747 jetliner or Lockheed C-5 transport aircraft. The remotely piloted, electrically powered Helios Prototype went aloft on its maiden low-altitude checkout flight Sept. 8, 1999, over Rogers Dry Lake adjacent to NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center in the Southern California desert. The initial flight series was flown on battery power as a risk-reduction measure. In all, six flights were flown in the Helios Protoype's initial development series. In upgrading the Centurion to the Helios Prototype configuration, AeroVironment added a sixth wing section and a fifth landing gear pod, among other improvements. The additional wingsp
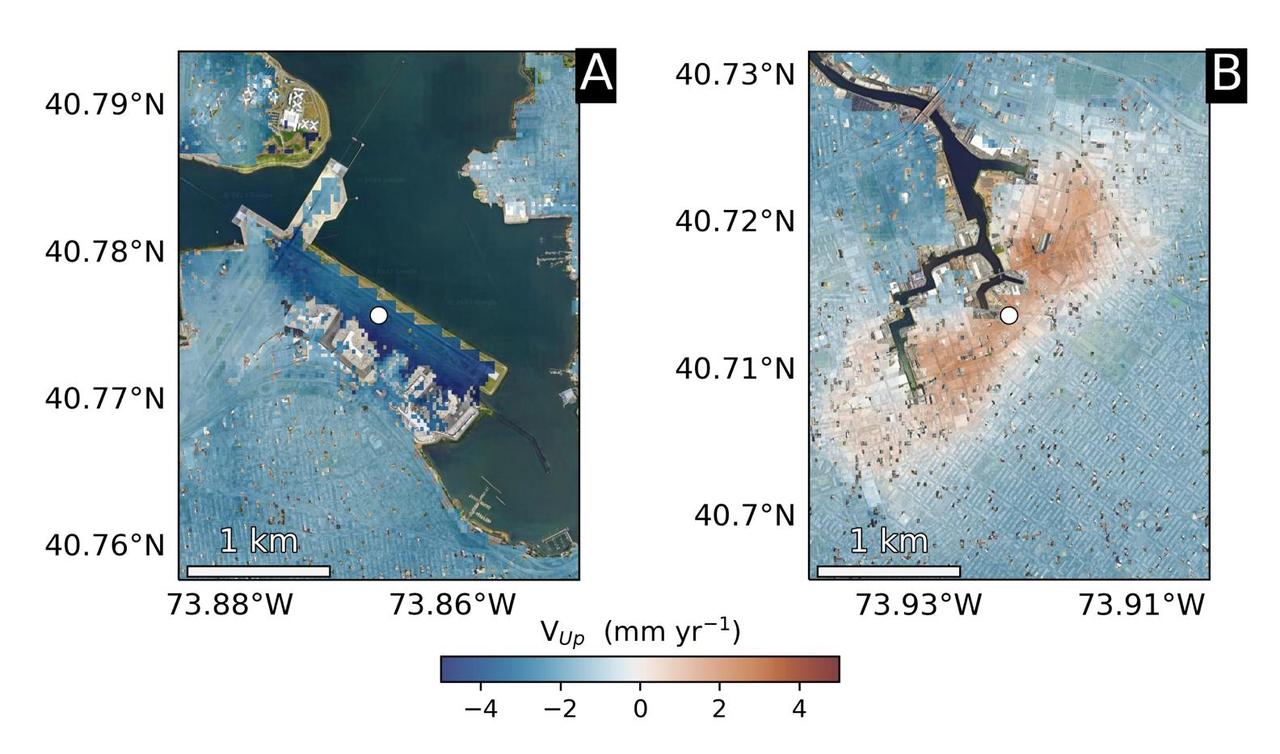
Using radars on the ESA (European Space Agency) Sentinel-1 satellites, along with advanced data processing techniques, a team of researchers measured upward and downward vertical land motion – also known as uplift and subsidence – across the New York City metropolitan area from 2016 to 2023. They mapped the motion in detail and pinpointed specific locations seen here – an airport runway and part of a Superfund site – that were notably sinking or rising. Runway 13/31 at LaGuardia Airport in Queens, left, is co-located with a former landfill and subsiding at a rate of about 0.15 inches (3.7 millimeters) per year. Part of the Newtown Creek Superfund site in East Williamsburg, Brooklyn, right, is rising unevenly by about 0.06 inches (1.6 millimeters) per year, possibly due to groundwater pumping and treatment activities. The site is undergoing extensive environmental remediation to address decades of pollution, including the Greenpoint oil spill that was discovered in the late 1970s. The researchers, from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and Rutgers University in New Jersey, found that on average the metropolitan area subsided by about (0.06 inches) (1.6 millimeters) per year – about the same amount that a toenail grows in a month. Causes for the observed motion include natural geologic adjustments that have been unfolding since the most recent ice age, as well as land-use practices such as the construction of landfills, which make the ground looser and more compressible beneath buildings. To create this map, the researchers employed a remote sensing technique called interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), which combines two or more three-dimensional observations of the same region to reveal surface motion down to fractions of inches. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25528
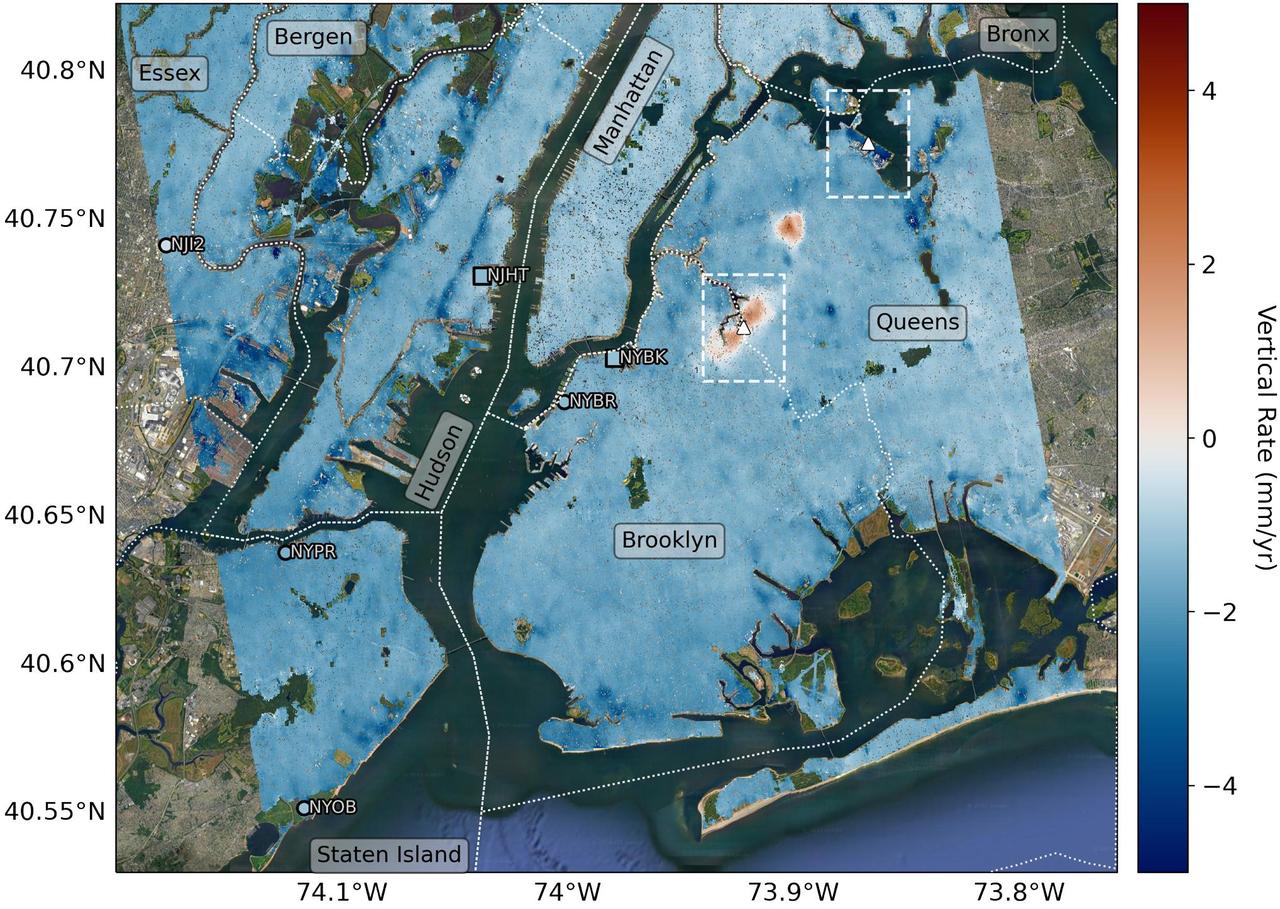
Researchers from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California and Rutgers University in New Jersey produced this map in their analysis of upward and downward vertical land motion – also known as uplift and subsidence – across the New York City metropolitan area from 2016 to 2023. Most of the study region was found to be gradually subsiding (indicated here in blue), while isolated locations of uplift (in red) were also observed. The white dotted lines indicate county/borough borders. The researchers found that on average the metropolitan area subsided by about 0.06 inches (1.6 millimeters) per year – about the same amount that a toenail grows in a month. They mapped the motion in detail and pinpointed neighborhoods and landmarks that were subsiding more rapidly than the average. Causes for the observed motion include natural geologic adjustments that have been unfolding since the most recent ice age, as well as human land-use practices such as the construction of landfills, which make the ground looser and more compressible beneath buildings. A few locations in Queens and Brooklyn were observed to rise due to activities that may include pollution remediation efforts and groundwater injection. To create this map, the researchers employed a remote sensing technique called interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR), which combines two or more three-dimensional observations of the same region to reveal surface motion down to fractions of inches. They used the radars on the ESA (European Space Agency) Sentinel-1 satellites, along with advanced data processing methods. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25527
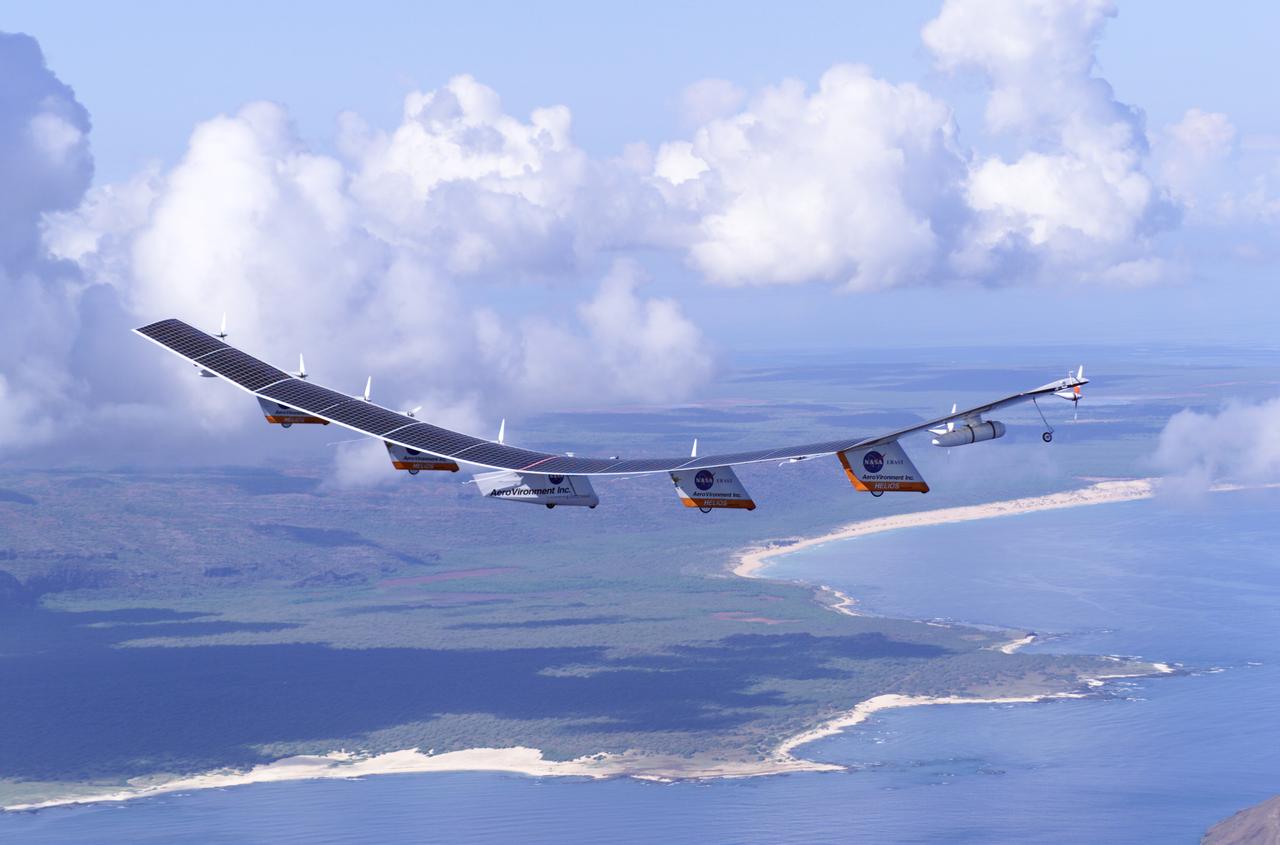

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
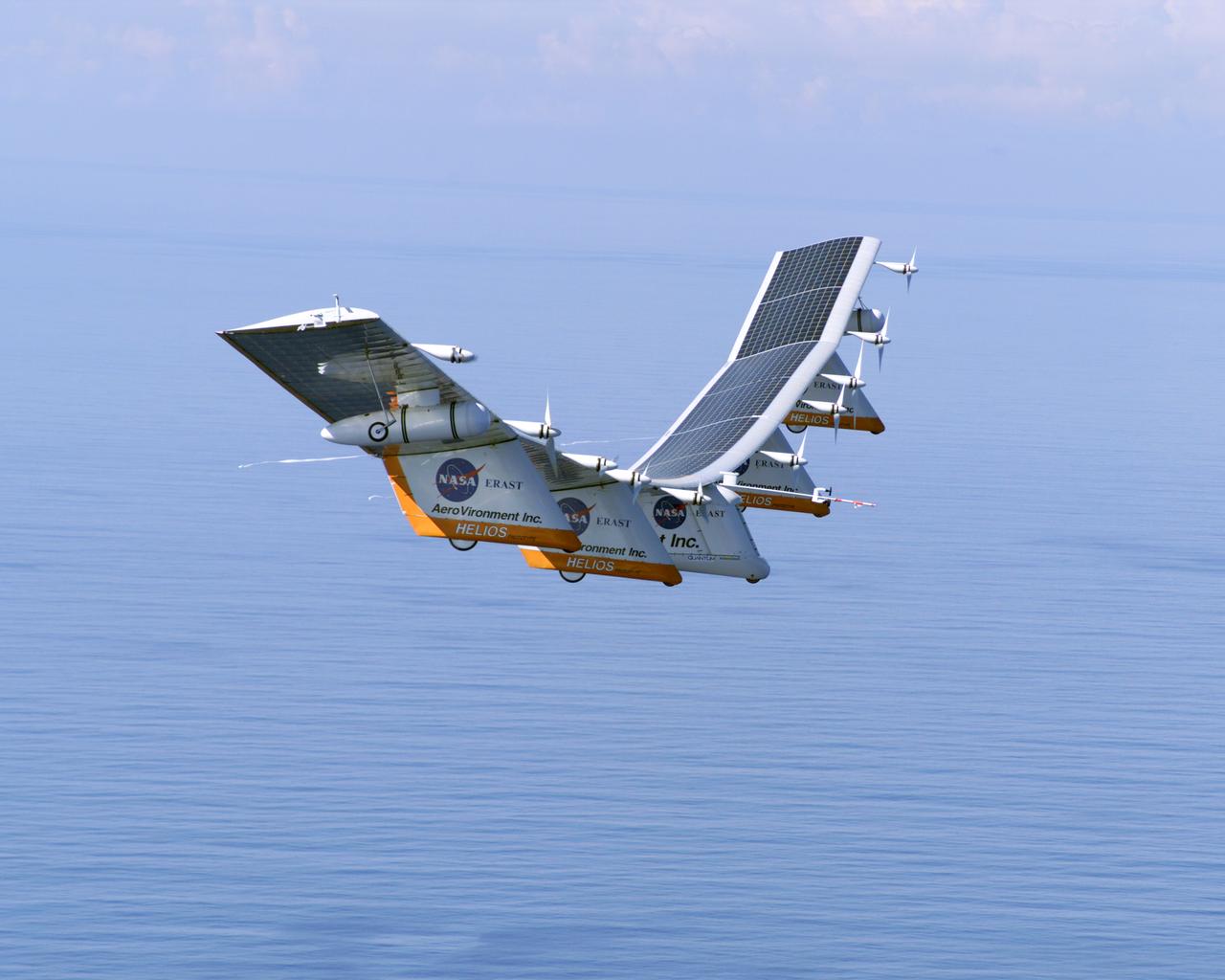

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
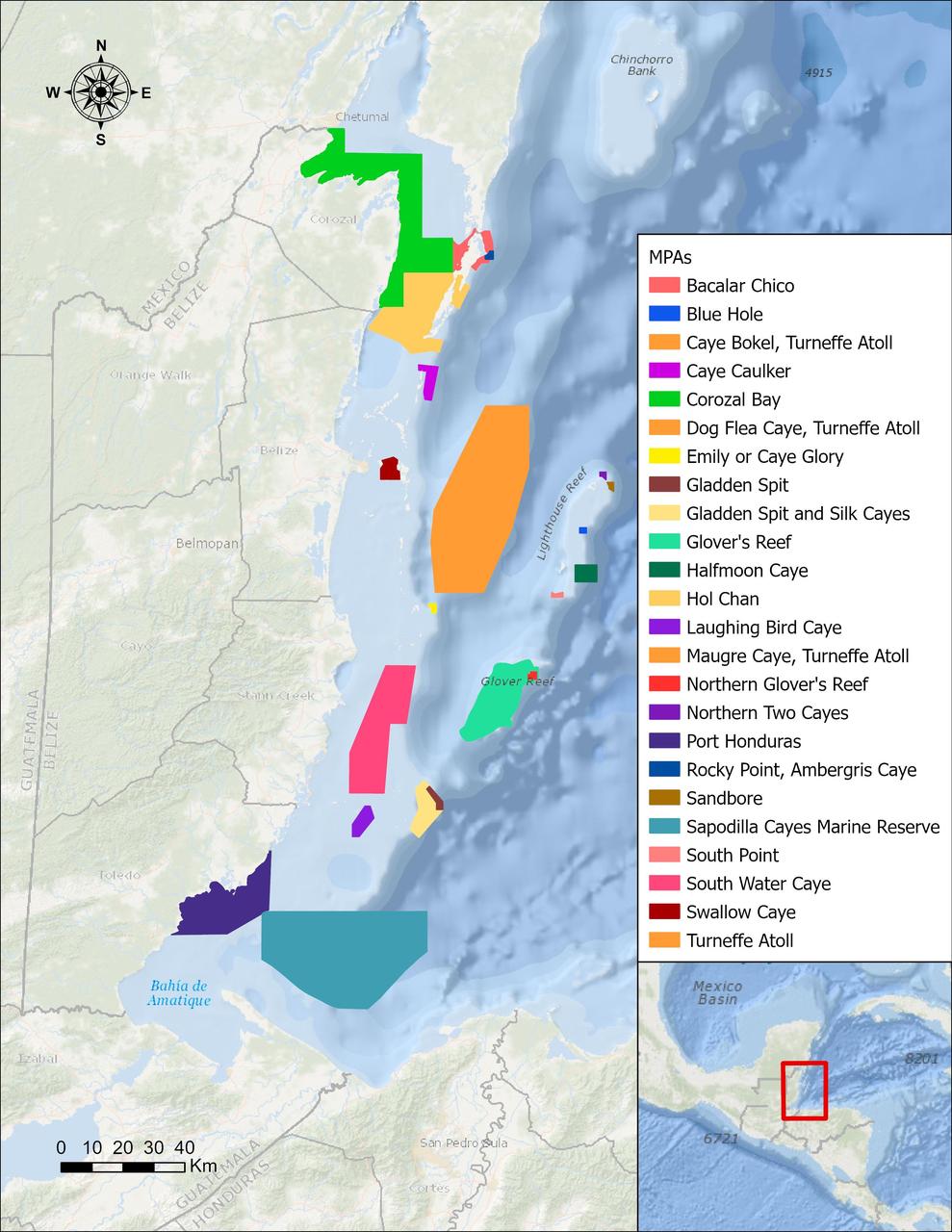
In a paper published in November 2022 in Frontiers in Remote Sensing, researchers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, with colleagues in Belize, used data from the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite to rank 24 protected marine areas off the Belizean coast based on the risks coral face from murky water and rising temperatures. All the areas are part of the 185-mile-long (298-kilometer-long) Belize Barrier Reef Reserve System, which encompasses a vibrant network of marine environments that supports thousands of animal and plant species and drives the Central American country's largest industry, tourism. The system is one of about 1,200 UNESCO World Heritage sites around the world. Analyzing imagery from 2002 to 2022, researchers developed a coral vulnerability index – a score between 2 and 12 that characterizes the risk to coral, with higher scores signifying greater risk. Their findings could help management authorities protect the reefs from human impacts such as development, overfishing, pollution, and climate change. Port Honduras Marine Reserve, a 156-square-mile (40,000-hectare) protected area in southern Belize, showed the highest coral vulnerability score: 10 out of 12. Based on the index, the study flags Port Honduras, Swallow Caye Wildlife Sanctuary, Sapodilla Cayes Marine Reserve, and Corozal Bay Wildlife Sanctuary as areas for concern. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25862
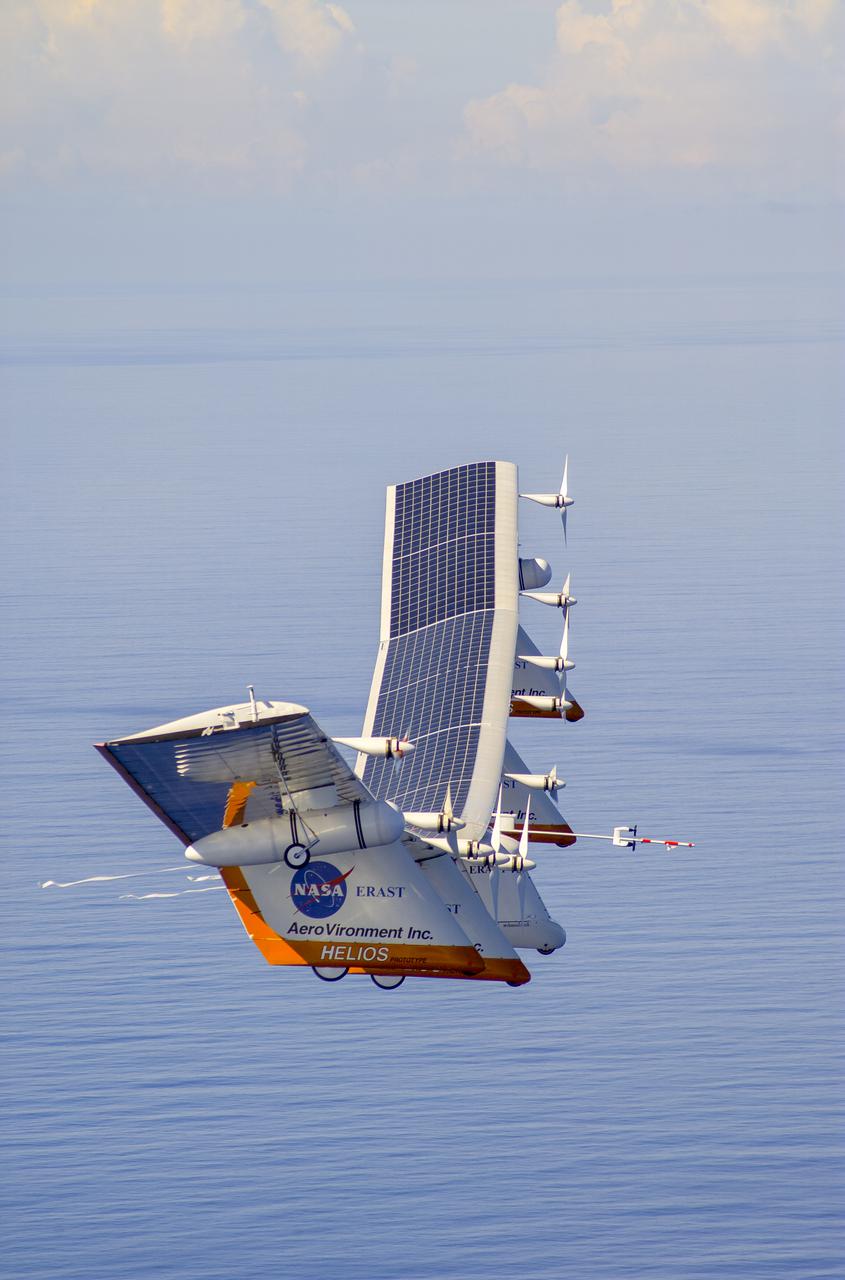

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
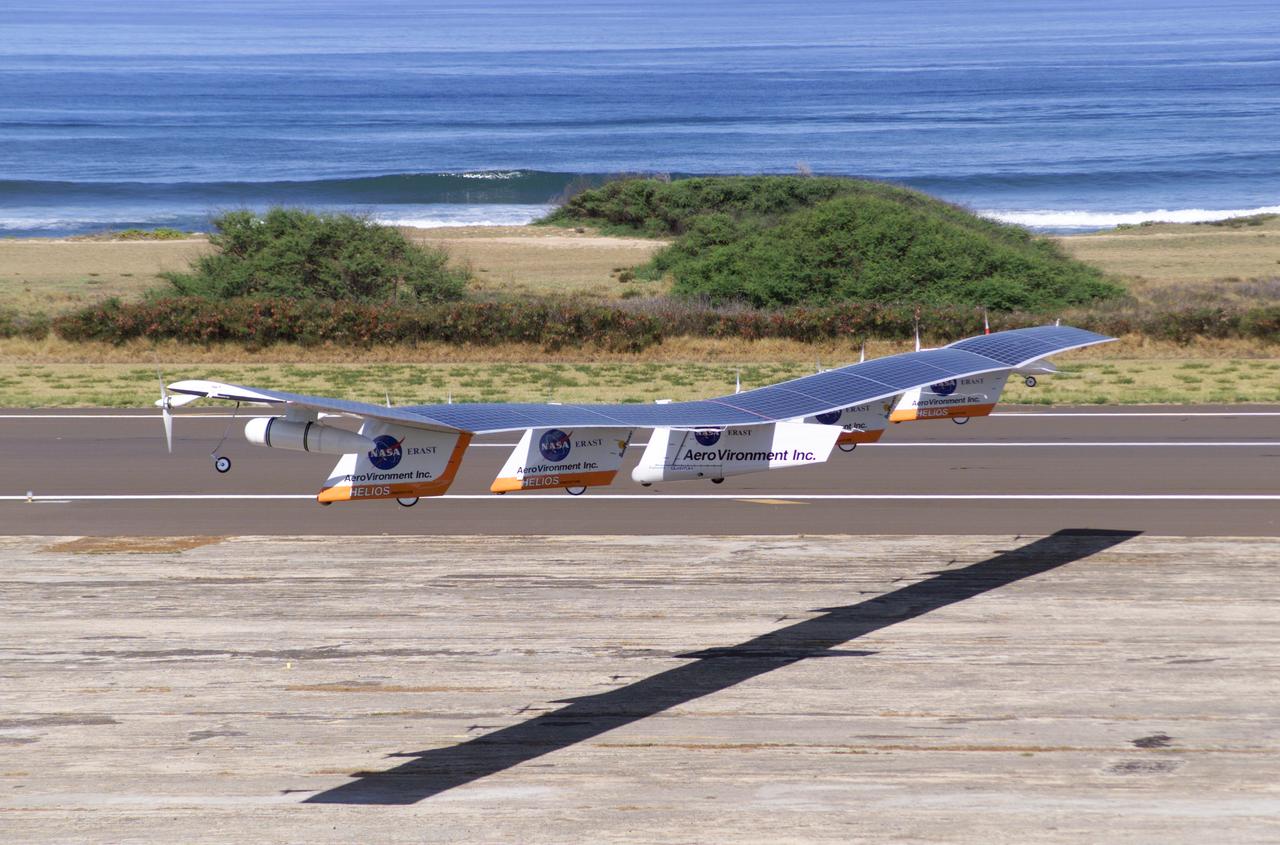

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, gave NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft would be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios was an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios flew above storms, and used the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft was the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
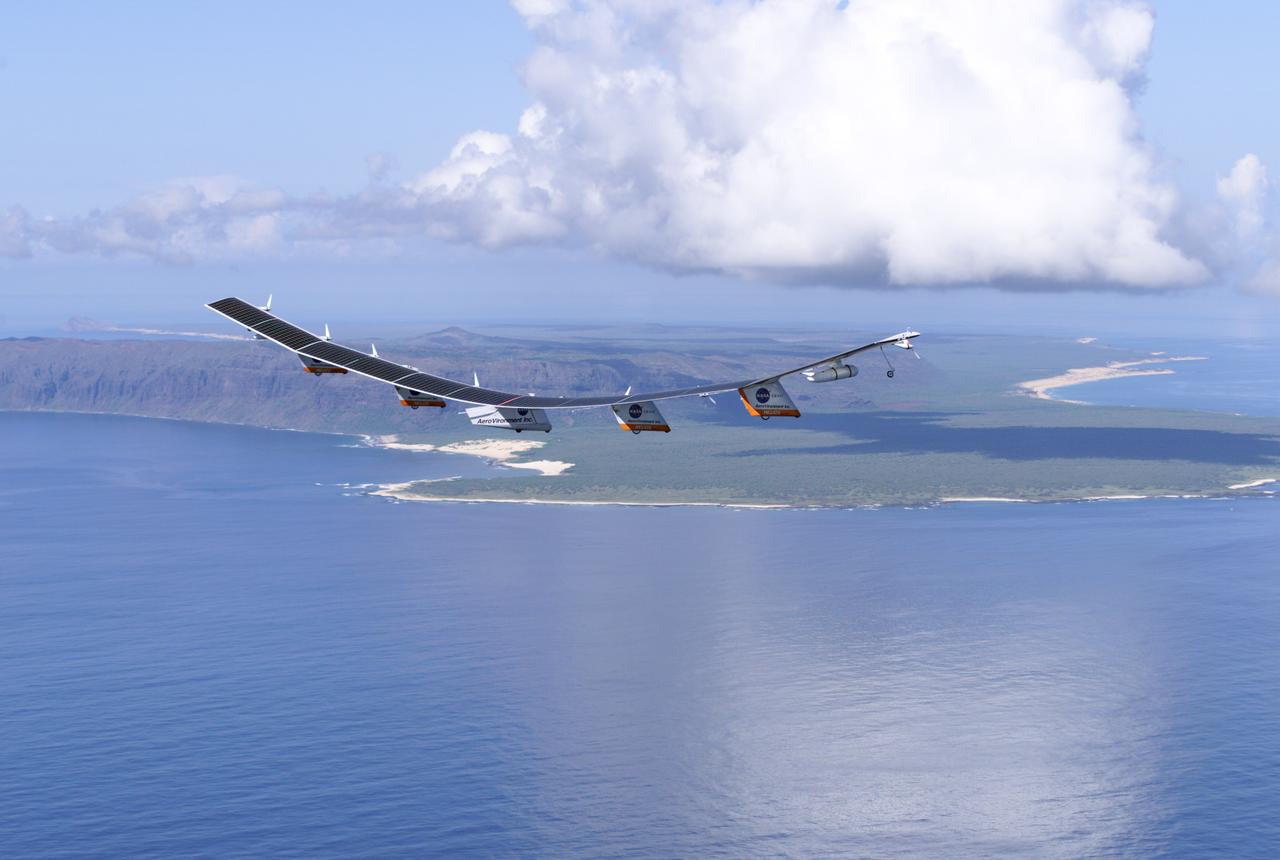

The first flight of a large aircraft to be powered by electric fuel cells began with a takeoff at 8:43 a.m. HST today from the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The Helios Prototype flying wing, built by AeroVironment, Inc., of Monrovia, Calif., as part of NASA's Environmental Research Aircraft and Sensor Technology (ERAST) program, used solar panels to power its 10 electric motors for takeoff and during daylight portions of its planned 20-hour shakedown flight. As sunlight diminishes, Helios will switch to a fuel cell system to continue flight into the night. The takeoff set the stage for a two-day Helios endurance flight in the stratosphere planned for mid-July. The Helios wing, spanning 247 feet and weighing about 2,400 pounds, is giving NASA and industry engineers confidence that remotely piloted aircraft will be able to stay aloft for weeks at a time, providing environmental monitoring capabilities and telecommunications relay services. Helios is an all-electric airplane. In addition to being non-polluting, Helios can fly above storms, and use the power of the sun to stay aloft during daylight. Key to the success of this type of aircraft is the ability to fly in darkness, using fuel cells when sunlight cannot furnish energy. Helios flew over the Navy's Pacific Missile Range Facility where favorable sun exposure and test ranges closed to other air traffic benefited the NASA research effort. In 2003 the aircraft was lost to a crash.
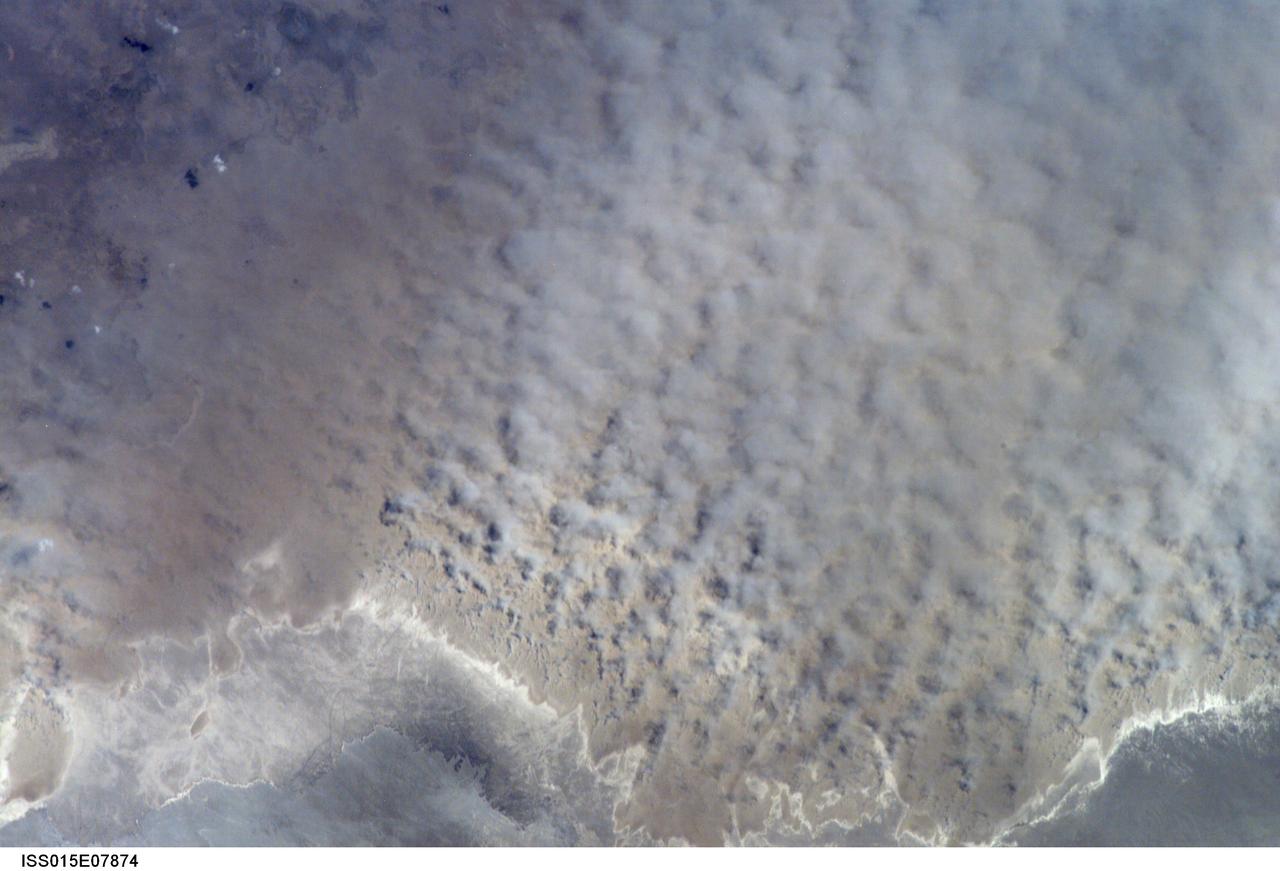

ISS015-E-07874 (12 May 2007) --- A major dust storm (center right) along the east side of the Aral Sea, Kazakhstan, is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 15 crewmember on the International Space Station while passing over central Asia. The white, irregular lines along the bottom of the image are salt and clay deposits on the present coastline. On the spring day when the ISS crew shot the image, winds were blowing from the west (lower left). The gray, puffy appearance is typical of dust clouds, allowing scientists to distinguish dust from fog and smog. The dust in this image is rising from the sea bed of the Aral Sea, from a point close to the middle of the original Aral Sea of 40--50 years ago, then the fourth largest inland sea on Earth. Heavy extraction of water from the main supply river, the Amu Dary'a, has resulted in rapid shrinking of the sea. According to scientists, dust storms have been occurring in the Aral Sea region for thousands of years, but since the drastic shrinking of the sea over the past half-century an important change in dust composition has occurred. The dust now includes fertilizer and pesticide washed into the Sea from the extensive cotton fields of the Amu Dary'a floodplain. Years of liberal application of agricultural chemicals have resulted in concentration of these pollutants on the sea bed. These are now exposed to the wind and transported hundreds of kilometers in a generally easterly direction. Research suggests that the remobilized chemicals are the cause of high rates of many diseases in the populations along the north, east and southern margins of the Aral Sea. This is one of the unintended consequences of the shrinking of the sea, which has made international news for many years due to the loss of the fishing industry and other significant ecological problems.
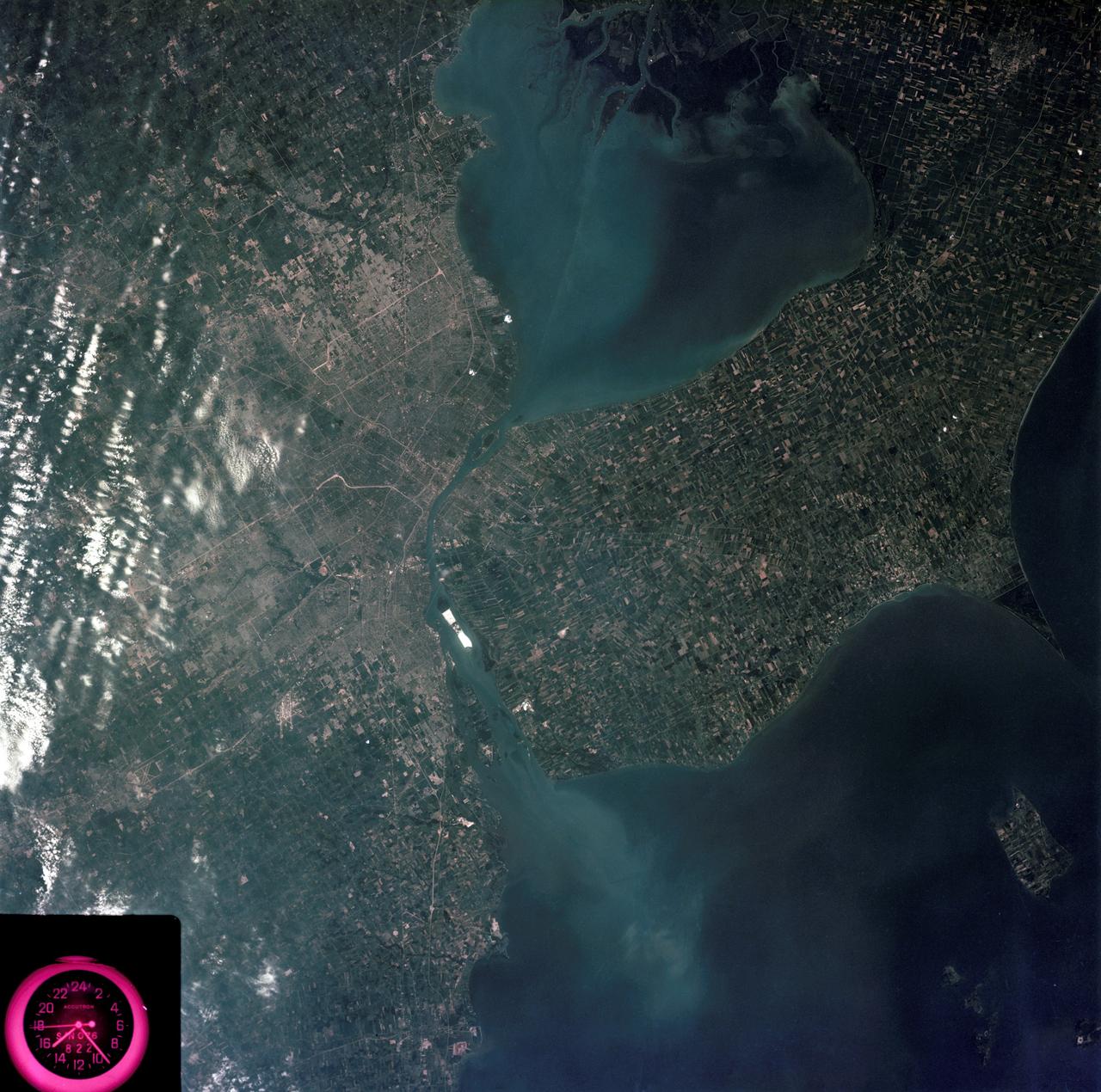

SL3-83-0152 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the metropolitan Detroit, Michigan area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The 25-mile long Detroit River drains the smaller body of water (Lake St. Clair) and flows southwestward separating Detroit from Windsor, Ontario, and empties into Lake Erie. The Detroit River handles a great deal of Great Lakes barge and ship traffic. Major streets and thoroughfares radiating from the city are clearly visible. Fighting Island is the highly reflective, white area located almost in the center of the picture. This high reflectivity is caused by the functional use of the island-disposal ponds for chemical salts. Sedimentation and/or pollution patterns in the area provide interesting visual phenomena for speculation and analysis. Distinct and rather unique cultivated field patterns can be observed south and east of Windsor, Ontario. This is a direct result of an English survey and land tenure system which was utilized when the area was settled. New areas of residential development are fairly easy to differentiate from older, established residential areas. Vegetation and extent of area coverage can be determined. The Oakland County Planning Commission and the Federal Bureau of Outdoor Recreation working closely with Irv Sattinger of the Environmental Research Institute of Michigan (University of Michigan) are presently processing and analyzing photographic and Multispectral scanner data to determine its usefulness for recreation and open space site studies for this area. Photo credit: NASA
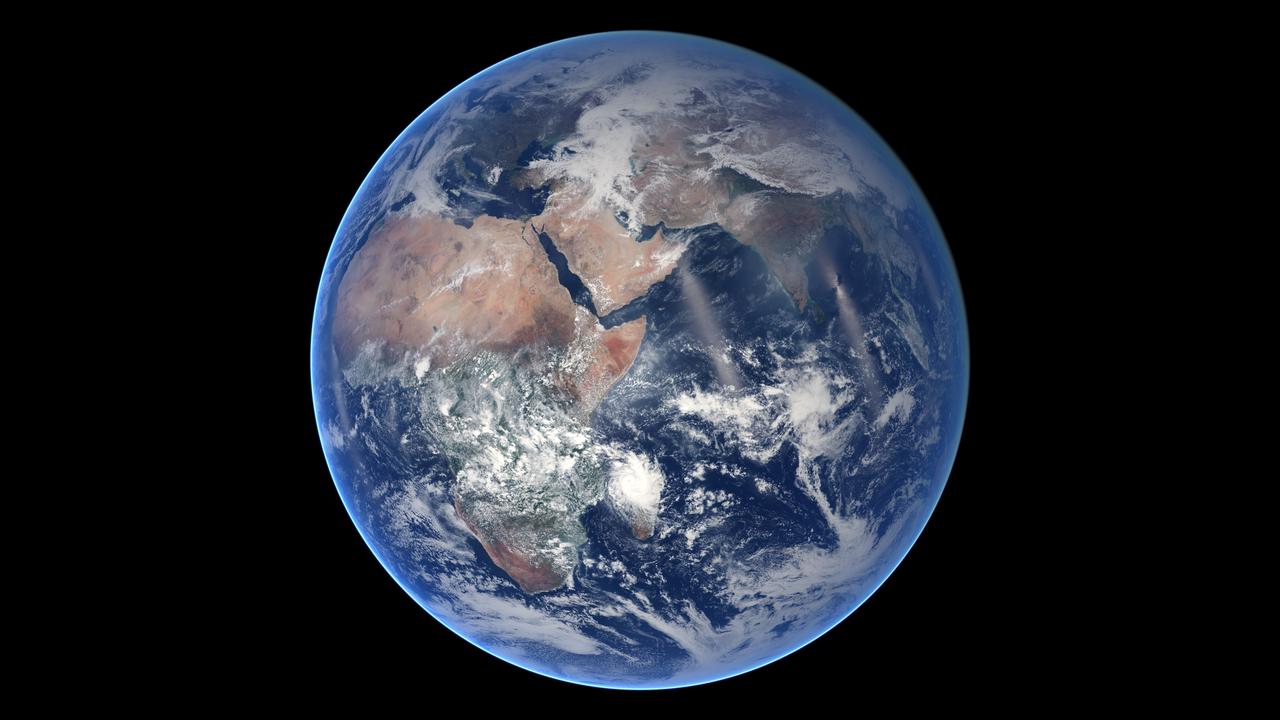

Of all the planets NASA has explored, none have matched the dynamic complexity of our own. Earth is constantly changing, and NASA are working constantly to explore and understand the planet on scales from local to global. Though Earth science has been a key part of NASA’s mission since the agency was founded in 1958, this year has been one of the peaks. Two new Earth-observing satellites have already been launched and put to work: the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) and the Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2). Three more missions are set to take off in the next six months: the wind-measuring ISS-RapidScat, the ISS Cloud-Aerosol Transport System (CATS), and the Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP). And research planes have been flying over polar ice, hurricanes, boreal forests, and pollution plumes. All of these new efforts complement an existing fleet of Earth-observing satellites. In visible light and many invisible wavelengths, NASA and its science partners are observing the entire planet every day. The image above was captured on March 30, 2014, by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on the Suomi NPP satellite. The composite image of the eastern hemisphere was compiled from eight orbits of the satellite and ten imaging channels, then stitched together to blend the edges of each satellite pass. Read more: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84214&eocn=home&eoci=iotd_title" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=84214&eocn...</a> NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using Suomi NPP VIIRS imagery from NOAA's Environmental Visualization Laboratory. Suomi NPP is the result of a partnership between NASA, NOAA and the Department of Defense. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
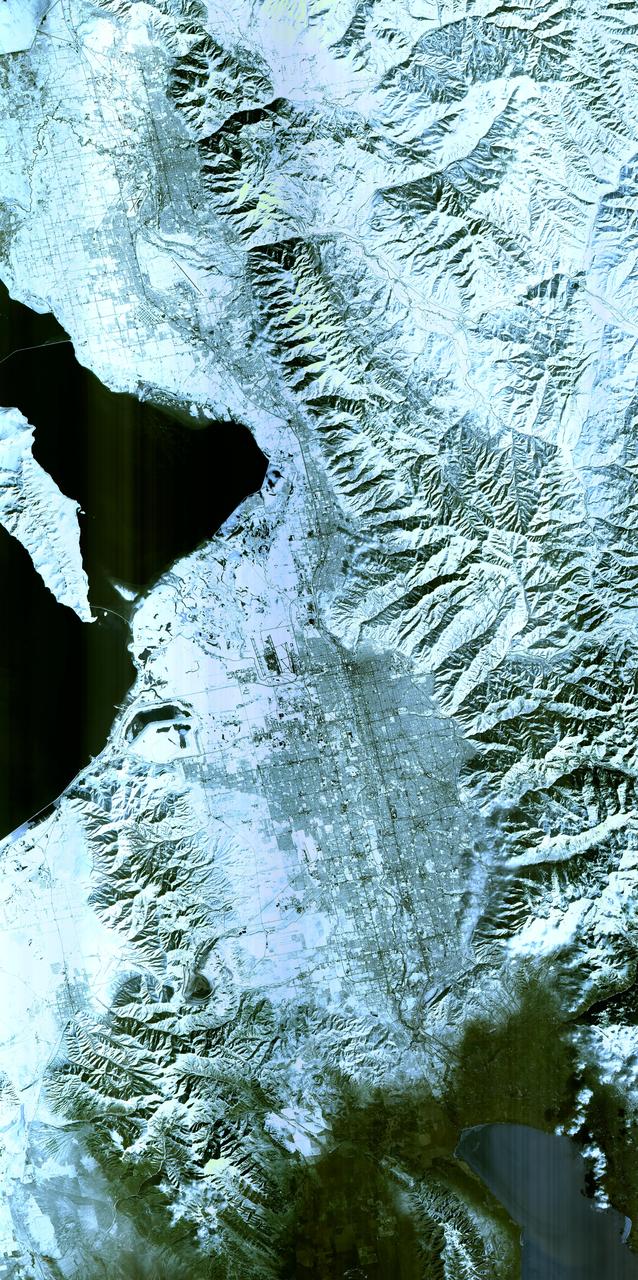

Salt Lake City, Utah, Winter 2001 The 2002 Winter Olympics are hosted by Salt Lake City at several venues within the city, in nearby cities, and within the adjacent Wasatch Mountains. This simulated natural color image presents a snowy, winter view of north central Utah that includes all of the Olympic sites. The image extends from Ogden in the north, to Provo in the south; and includes the snow-capped Wasatch Mountains and the eastern part of the Great Salt Lake. This image was acquired on February 8, 2001 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER will image Earth for the next 6 years to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. ASTER is one of five Earth-observing instruments launched December 18,1999, on NASA's Terra satellite. The instrument was built by Japan's Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. A joint U.S./Japan science team is responsible for validation and calibration of the instrument and the data products. Dr. Anne Kahle at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, is the U.S. Science team leader; Bjorn Eng of JPL is the project manager. ASTER is the only high resolution imaging sensor on Terra. The Terra mission is part of NASA's Earth Science Enterprise, along-term research and technology program designed to examine Earth's land, oceans, atmosphere, ice and life as a total integrated system. The broad spectral coverage and high spectral resolution of ASTER will provide scientists in numerous disciplines with critical information for surface mapping, and monitoring dynamic conditions and temporal change. Example applications are: monitoring glacial advances and retreats; monitoring potentially active volcanoes; identifying crop stress; determining cloud morphology and physical properties; wetlands evaluation; thermal pollution monitoring; coral reef degradation; surface temperature mapping of soils and geology; and measuring surface heat balance. Image credit: NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>