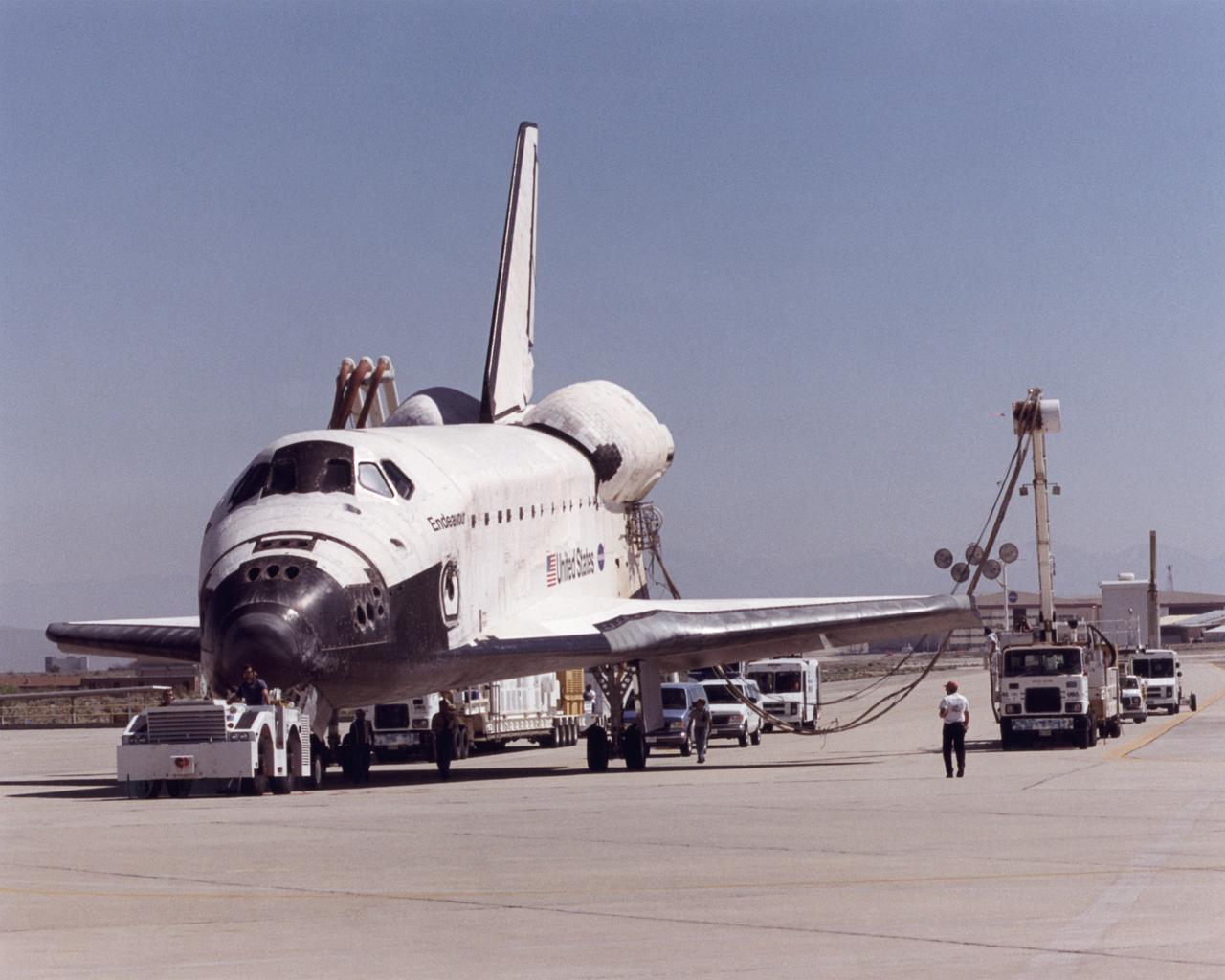

A convoy of specialized support vehicles follow the Space Shuttle Endeavour as it is towed up a taxiway at NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center on Edwards Air Force Base, California, after landing on May 1, 2001. The two largest vehicles trailing the shuttle provide electrical power and air conditioning to the shuttle's systems during post-flight recovery operations. The Endeavour had just completed mission STS-100, an almost 12-day mission to install the Canadarm 2 robotic arm and deliver some three tons of supplies and experiments to the International Space Station. The landing was the 48th shuttle landing at Edwards since shuttle flights began in 1981. After post-flight processing, the Endeavour was mounted atop one of NASA's modified Boeing 747 shuttle carrier aircraft and ferried back to the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 8, 2001.
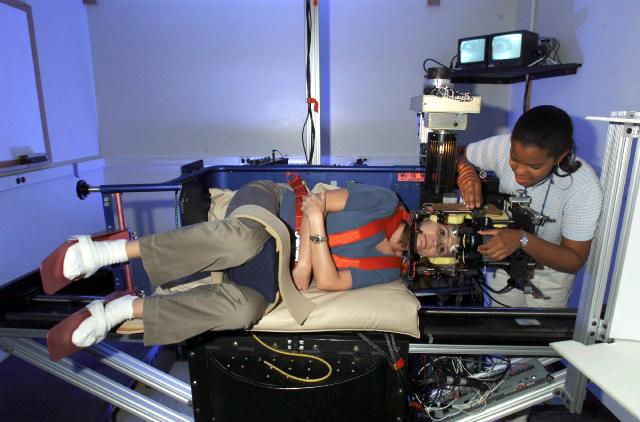
The short-arm centrifuge subjects an astronaut to conflicting sensory input and study the astronaut's perception of motion. It is one of several instruments used in the Spatial Reorientation Following Space Flight investigation to be conducted on crewmembers. During space flight, the vestibular organs no longer respond in a familiar way. Instead, inputs from the irner ear do not match those coming from the eyes. While on Earth, you can open your eyes to see if you truly are spinning, but astronauts do not have this luxury. Astronauts can see the floor, but have no sense of down; when they bend their heads forward, the otoliths are not stimulated properly. This state, called sensory conflict, must be resolved by the brain to maintain orientation. When they first return to Earth, astronauts are again disoriented because of sensory conflict. They undergo a period of spatial reorientation, as their brains reconcile what their eyes see and what their vestibular system senses. Recovery can take anywhere from hours to days depending on the length of the mission. Principal Investigator: Dr. William Paloski, Johnson Space Center, Houston, TX.
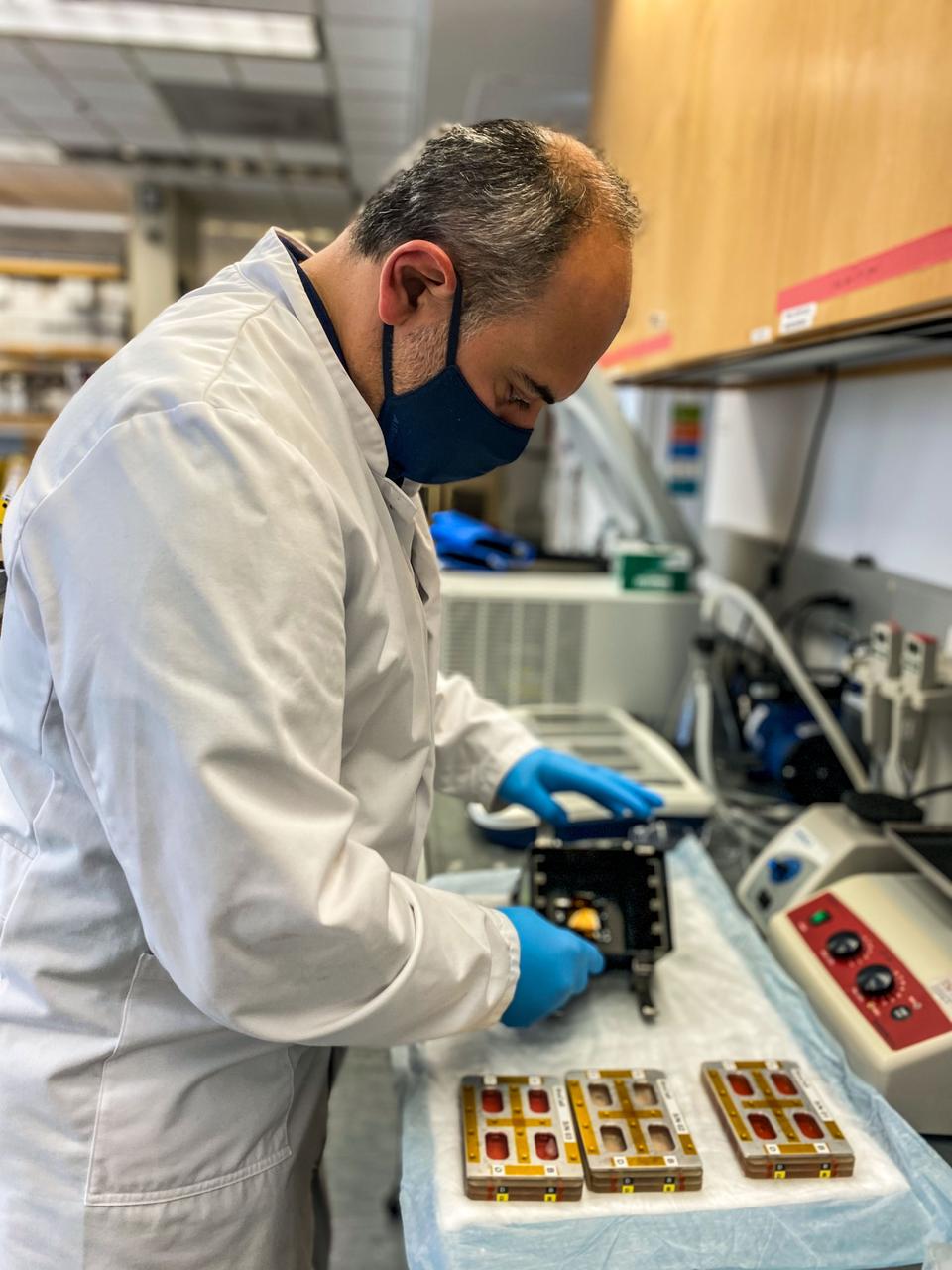

jsc2022e042485 (2/2/2022) --- Grigol Tediashvili conducts the EVT for the Microgravity as a Model for Immunological Senescense and its Impact on Tissue Stem Cells and Regeneration (Immunosenescence) investigation which studies the effects of microgravity on cells involved in tissue regeneration and whether recovery occurs post-flight. Image courtesy of UCSF.
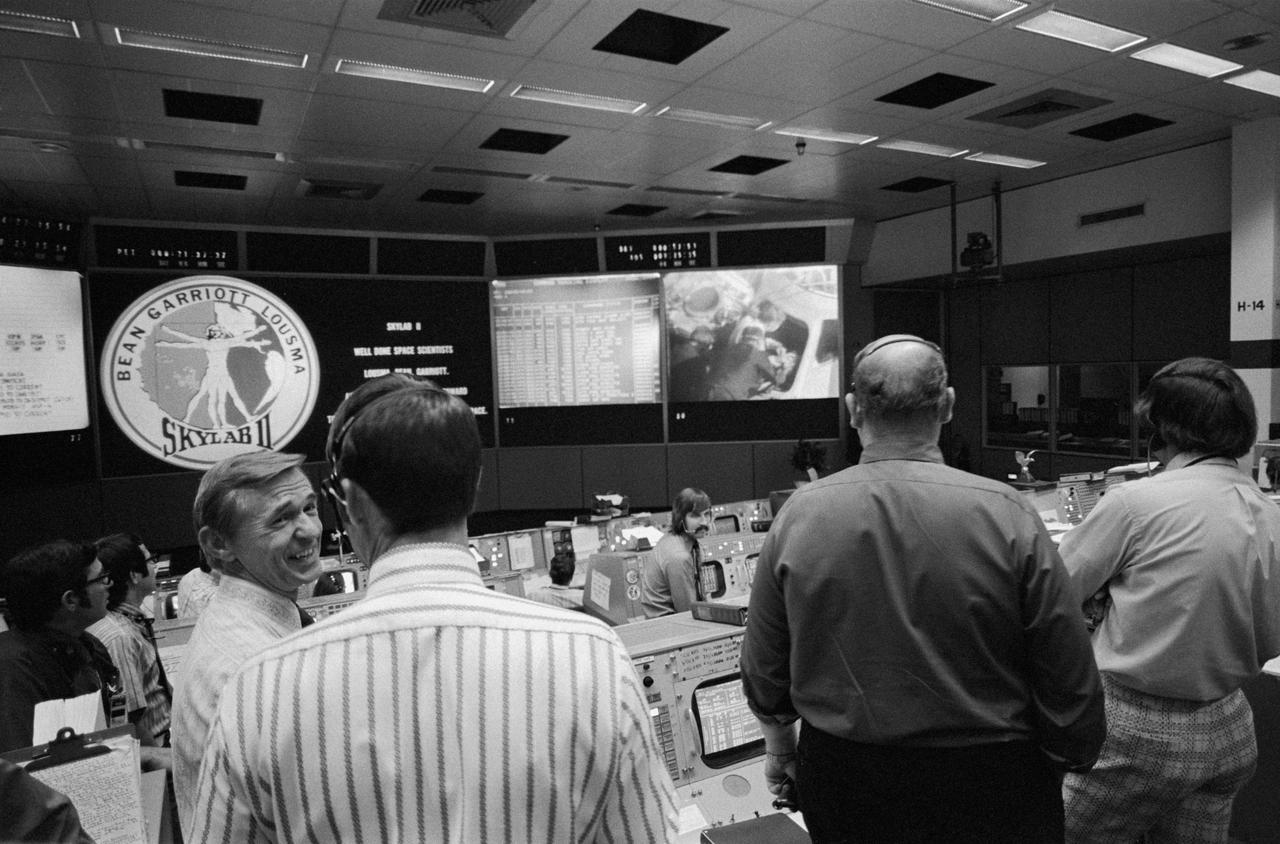

S73-34553 (25 Sept. 1973) --- Skylab flight directors (foreground) and flight controllers (background) view the large screen in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC) at JSC during recovery operations of the second manned Skylab mission. From left to right in the foreground are flight directors Charles R. Lewis, Donald R. Puffy, Phillip Shaffer and Neil B. Hutchinson. The Skylab 3 crewmen were preparing to egress the spacecraft aboard the USS New Orleans. Television cameras aboard the New Orleans recorded post-recovery activity. Photo credit: NASA
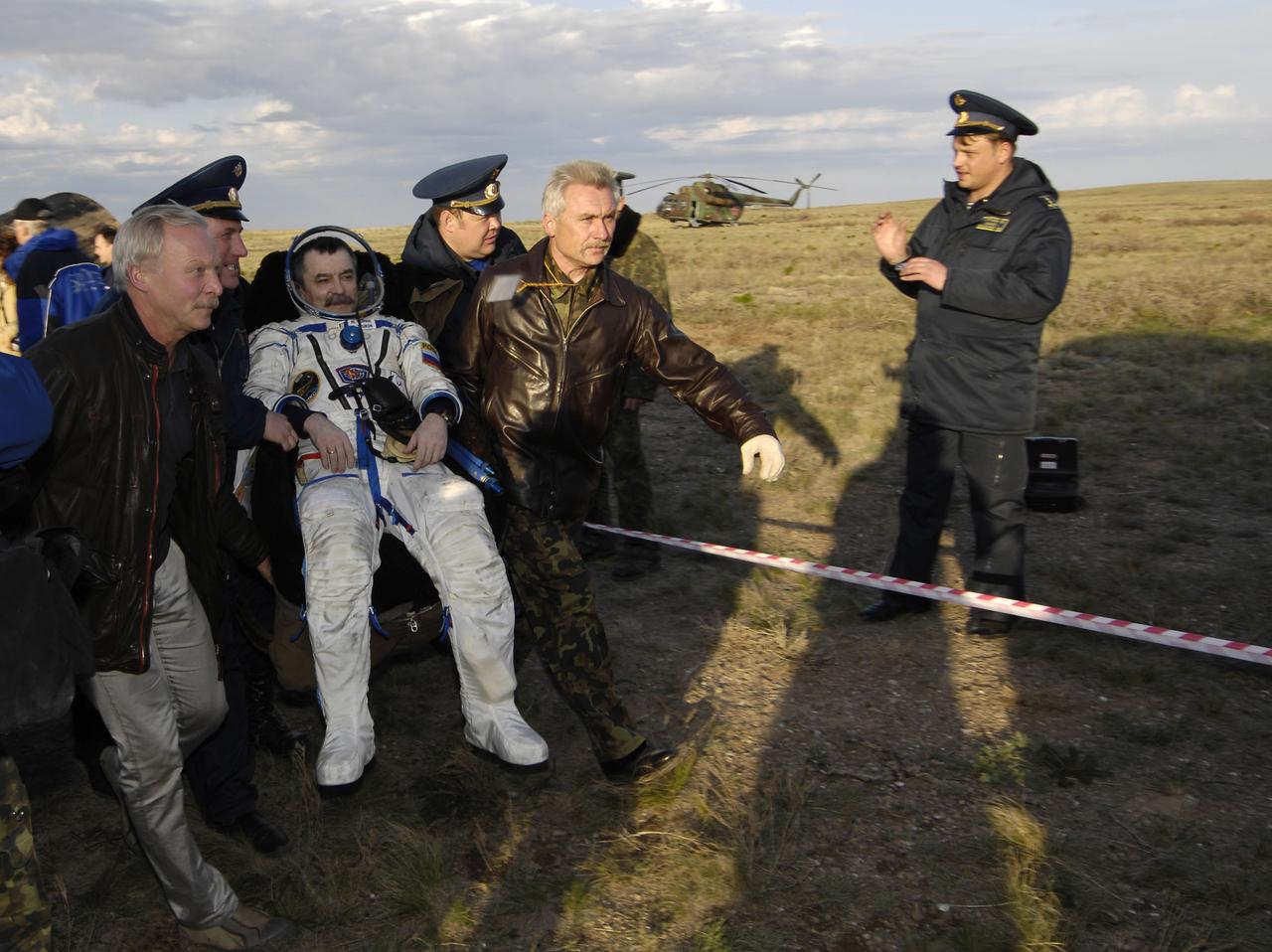

Expedition 14 Flight Engineer Mikhail Tyurin is taken in his chair to the medical tent near the Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft where the recovery officials conduct post-landing medical checks, Friday, April 21, 2007 in Kazakhstan. Expedition 14 Commander Michael Lopez-Alegria, Flight Engineer Mikhail Tyurin and American spaceflight participant Charles Simonyi landed in their Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft southwest of Karaganda, Kazakhstan at approximately 6:30 p.m. local time. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
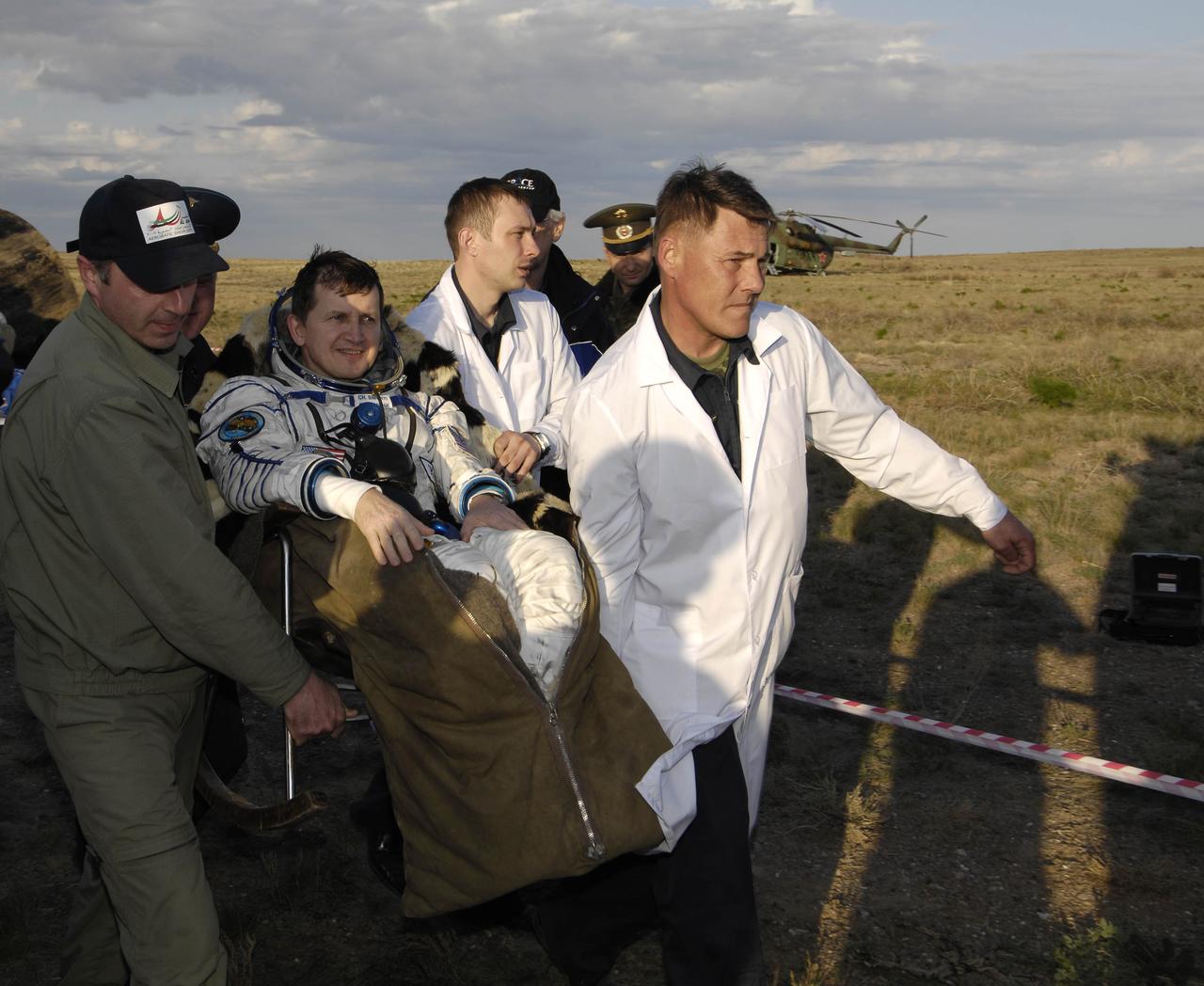

American spaceflight participant Charles Simonyi is taken in his chair to the medical tent near the Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft where the recovery officials conduct post-landing medical checks, Friday, April 21, 2007 in Kazakhstan. Expedition 14 Commander Michael Lopez-Alegria, Flight Engineer Mikhail Tyurin and American spaceflight participant Charles Simonyi landed in their Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft southwest of Karaganda, Kazakhstan at approximately 6:30 p.m. local time. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
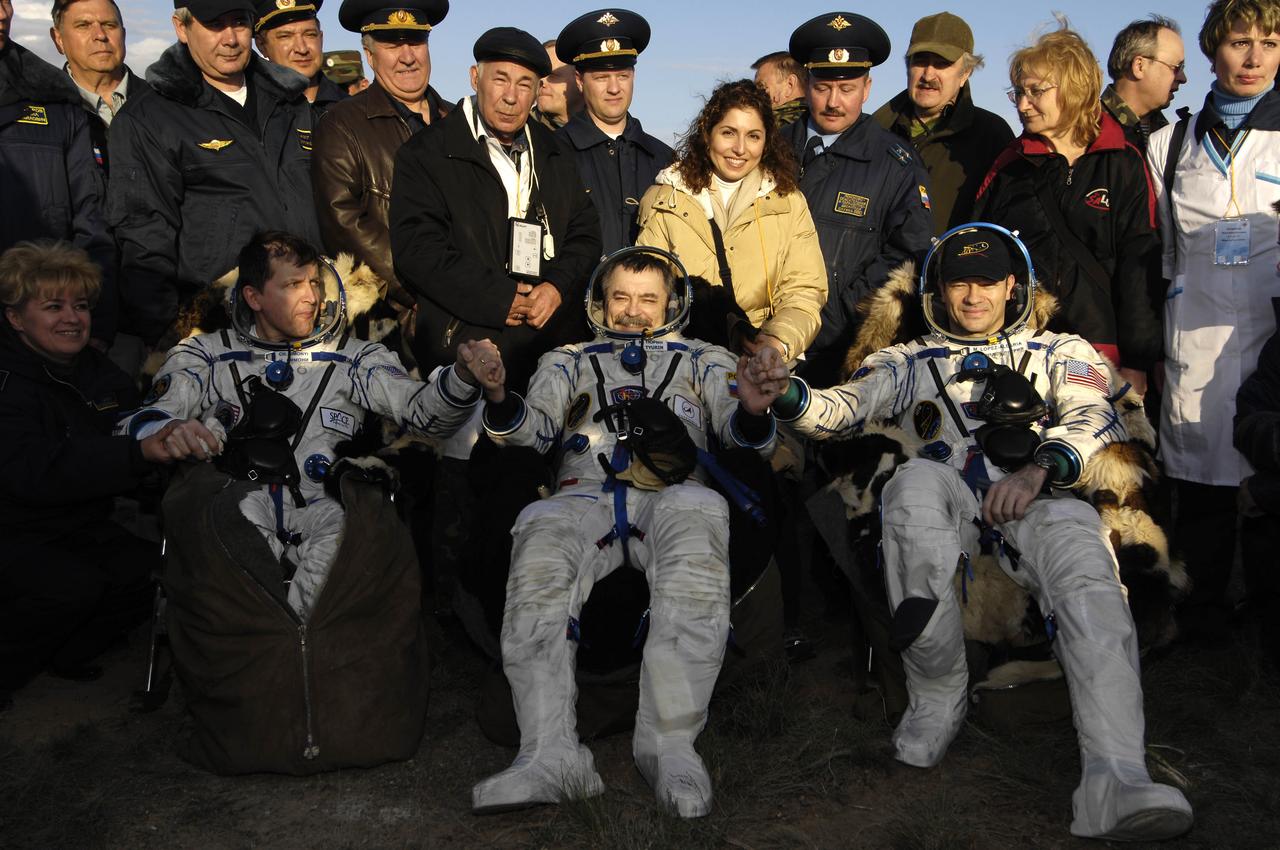

American spaceflight participant Charles Simonyi, left, Expedition 14 Flight Engineer Mikhail Tyurin and Expedition 14 Commander Michael Lopez-Alegria, right, sit in chairs in near their Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft at their landing site as landing and recovery officials conduct post-landing medical checks, Friday, April 21, 2007 in Kazakhstan. The Soyuz spacecraft landed southwest of Karaganda, Kazakhstan at approximately 6:30 p.m. local time. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
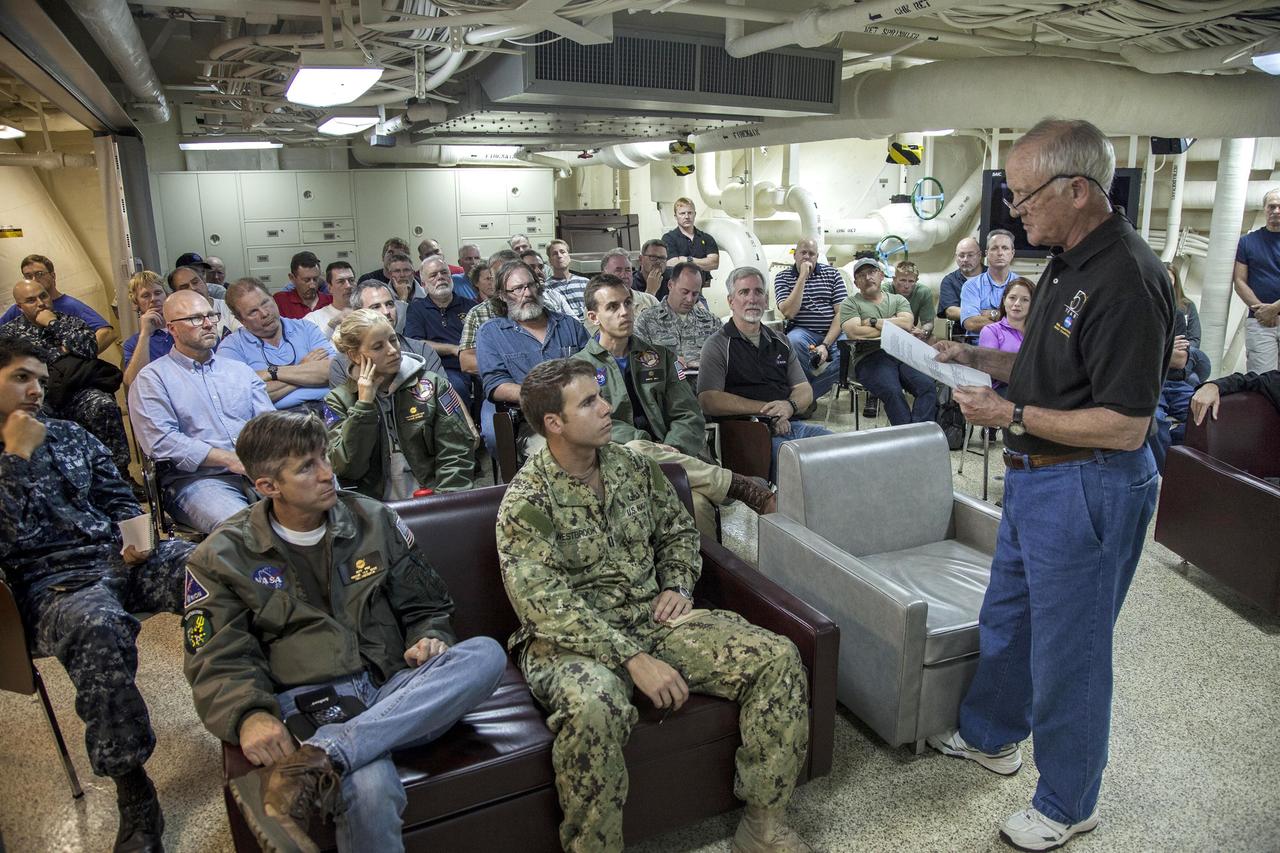

SAN DIEGO, Calif. – NASA, Lockheed Martin and U.S. Navy personnel listen to former space shuttle flight director and mission operations executive Milt Heflin during Orion recovery preparations aboard the USS Anchorage in the Pacific Ocean. Heflin was on prime recovery ships during the splashdowns and post-landing activities of Apollo 8, 10, 16 and 17, each of the three Skylab missions and the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project. NASA and the U.S. Navy are preparing for recovery of the Orion crew module, forward bay cover and parachutes on its return from space and splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is leading the recovery efforts. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch this week atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket. During its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight, Orion will venture 3,600 miles in altitude and travel nearly 60,000 miles before returning to Earth for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
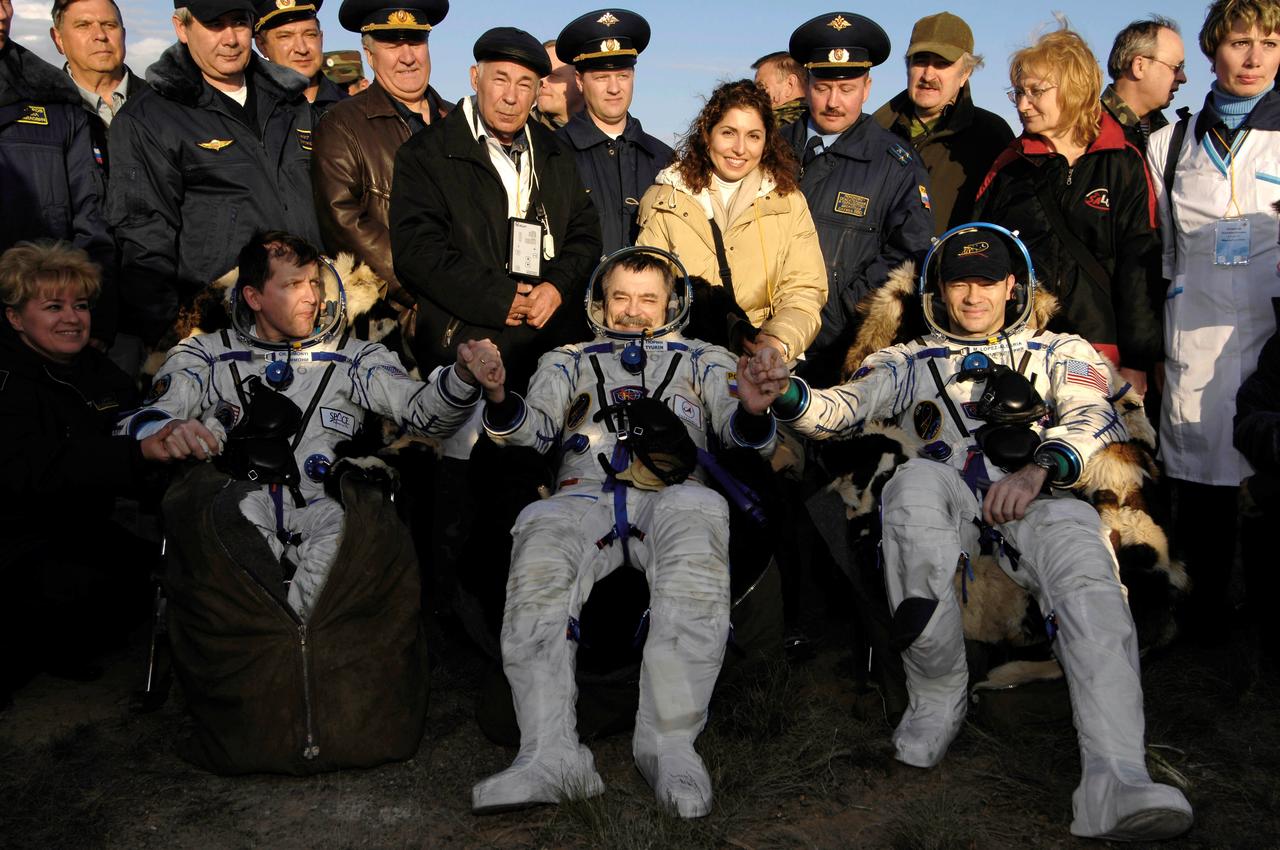

JSC2007-E-19320 (21 April 2007) --- From the left, U.S. spaceflight participant Charles Simonyi; cosmonaut Mikhail Tyurin, Expedition 14 Flight Engineer and Soyuz commander; and astronaut Michael E. Lopez-Alegria, Expedition 14 commander and NASA ISS science officer, sit in chairs near their Soyuz TMA-9 spacecraft at their landing site. Landing and recovery officials were conducting post-landing medical checks on the three crewmembers. The Soyuz spacecraft landed southwest of Karaganda, Kazakhstan at approximately 6:30 pm local time, April 21, 2007. Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
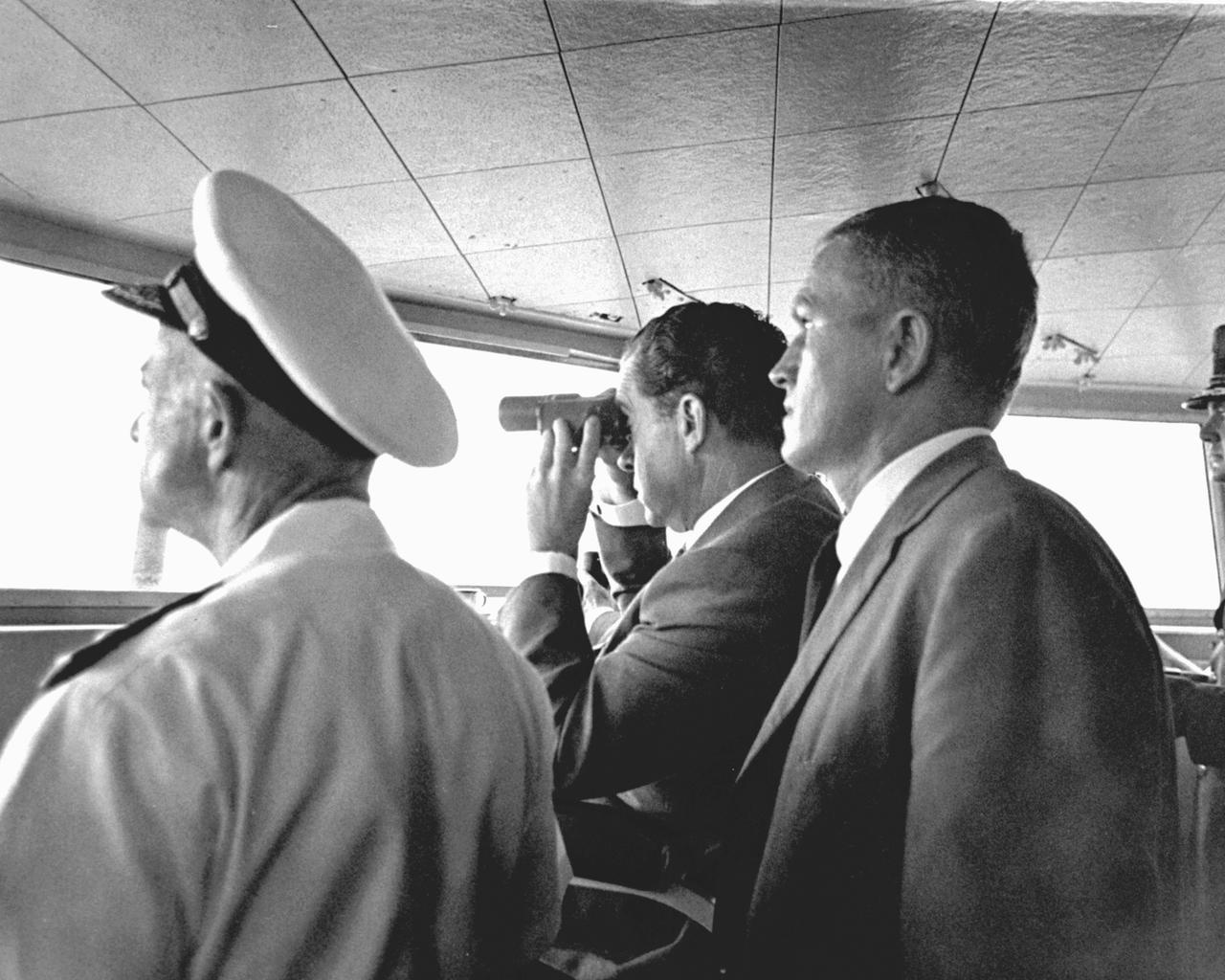

U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon (center), aboard the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft carrier, used binoculars to watch the Apollo 11 Lunar Mission Recovery. Standing next to the President is astronaut Frank Borman, Apollo 8 Commander. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days post mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
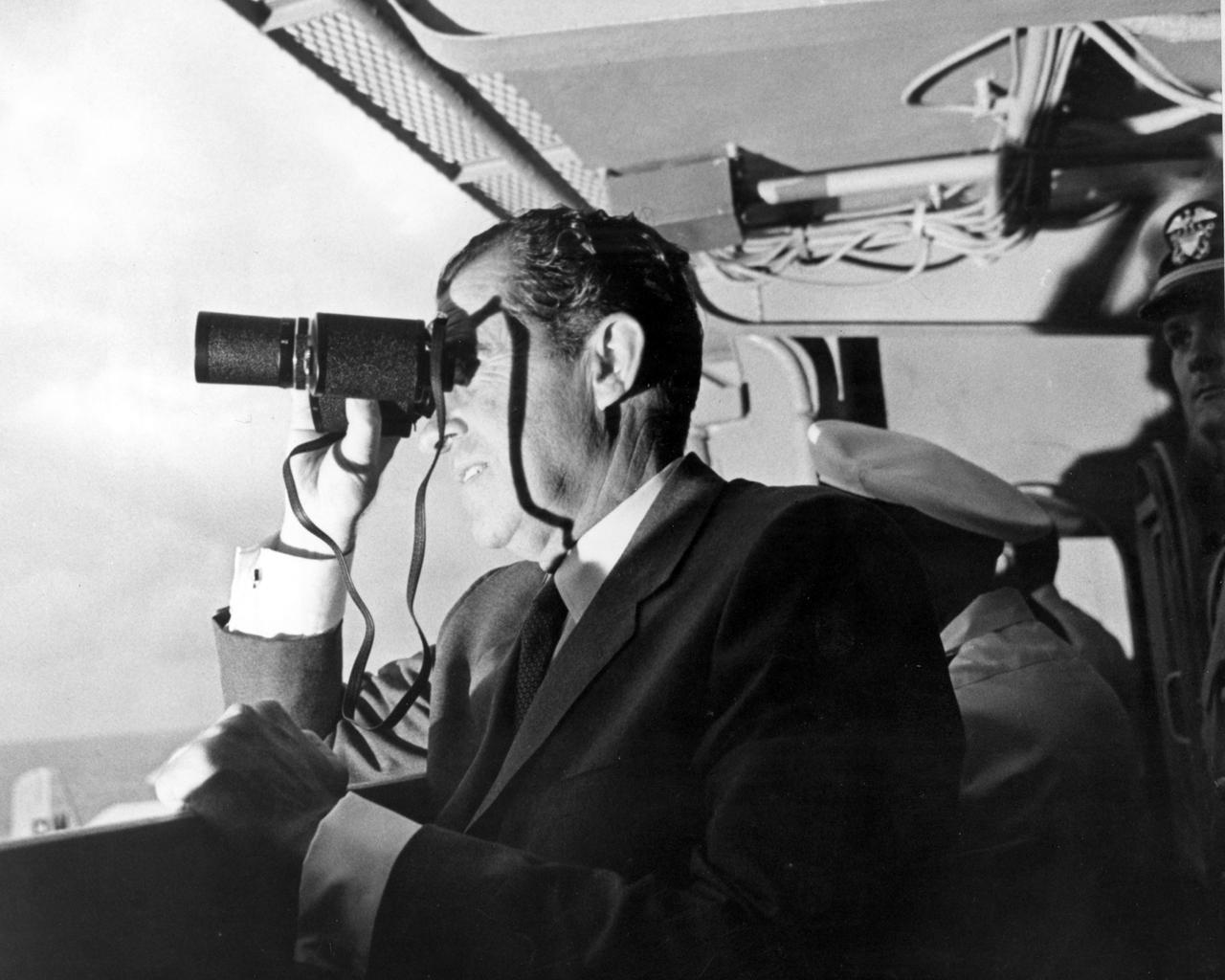

U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon, aboard the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft carrier, used binoculars to watch the Apollo 11 Lunar Mission recovery. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days post mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
![A swirling Eastern Pacific Ocean storm system headed for California was spotted by NOAA's GOES-West satellite on February 28. According to the National Weather Service, this storm system has the potential to bring heavy rainfall to the drought-stricken state. The storm was captured using visible data from NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite on Feb. 28 at 1915 UTC/11:15 a.m. PST was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The storm's center appeared as a tight swirl, with bands of clouds and showers already sweeping over the state extending from northern California to Baja California, Mexico. At 11:30 a.m. PST on February 28, Bill Patzert, climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. said, "Right now from northern to southern California we are being battered by very heavy rain, strong winds and our coastal communities are being battered by high surf. Through the weekend we are bracing for mud and rock slides in areas that recently burned [from wildfires]. Flooding is looming up and down the state." The National Weather Service (NWS) serving Los Angeles posted a Flood Watch for the region on Friday, February 28. The Flood Watch notes the "potential for flash flooding and debris flows for some 2013 and 2014 burn areas in Los Angeles County from this morning through Saturday evening (March 1).” The NWS Flood Watch also noted "a very strong and dynamic storm will bring a significant amount of rain to much of southwestern California through Saturday evening. A flash flood watch has been issued for several recent burn areas in Los Angeles County due to the abundant rainfall expected. Rain rates at times are expected to range from a half inch to one inch per hour which could cause significant mud and debris flows. There will be a chance of thunderstorms with locally higher rainfall rates." "Californians haven't seen rain and wind this powerful in 3 years," Patzert said. "By early next week, as this system moves east, this powerful system will wreak havoc causing snow and ice storms through the Midwest into the Northeast." GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. On a positive note, Patzert noted, "This is a nice down payment on drought recovery in the parched Western U.S." For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's National Weather Service website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or <a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e001192/GSFC_20171208_Archive_e001192~medium.jpg)
A swirling Eastern Pacific Ocean storm system headed for California was spotted by NOAA's GOES-West satellite on February 28. According to the National Weather Service, this storm system has the potential to bring heavy rainfall to the drought-stricken state. The storm was captured using visible data from NOAA's GOES-West or GOES-15 satellite on Feb. 28 at 1915 UTC/11:15 a.m. PST was made into an image by NASA/NOAA's GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The storm's center appeared as a tight swirl, with bands of clouds and showers already sweeping over the state extending from northern California to Baja California, Mexico. At 11:30 a.m. PST on February 28, Bill Patzert, climatologist at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif. said, "Right now from northern to southern California we are being battered by very heavy rain, strong winds and our coastal communities are being battered by high surf. Through the weekend we are bracing for mud and rock slides in areas that recently burned [from wildfires]. Flooding is looming up and down the state." The National Weather Service (NWS) serving Los Angeles posted a Flood Watch for the region on Friday, February 28. The Flood Watch notes the "potential for flash flooding and debris flows for some 2013 and 2014 burn areas in Los Angeles County from this morning through Saturday evening (March 1).” The NWS Flood Watch also noted "a very strong and dynamic storm will bring a significant amount of rain to much of southwestern California through Saturday evening. A flash flood watch has been issued for several recent burn areas in Los Angeles County due to the abundant rainfall expected. Rain rates at times are expected to range from a half inch to one inch per hour which could cause significant mud and debris flows. There will be a chance of thunderstorms with locally higher rainfall rates." "Californians haven't seen rain and wind this powerful in 3 years," Patzert said. "By early next week, as this system moves east, this powerful system will wreak havoc causing snow and ice storms through the Midwest into the Northeast." GOES satellites provide the kind of continuous monitoring necessary for intensive data analysis. Geostationary describes an orbit in which a satellite is always in the same position with respect to the rotating Earth. This allows GOES to hover continuously over one position on Earth's surface, appearing stationary. As a result, GOES provide a constant vigil for the atmospheric "triggers" for severe weather conditions such as tornadoes, flash floods, hail storms and hurricanes. On a positive note, Patzert noted, "This is a nice down payment on drought recovery in the parched Western U.S." For updated information about the storm system, visit NOAA's National Weather Service website: <a href="http://www.weather.gov" rel="nofollow">www.weather.gov</a> For more information about GOES satellites, visit: <a href="http://www.goes.noaa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.goes.noaa.gov/</a> or <a href="http://goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">goes.gsfc.nasa.gov/</a> Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>