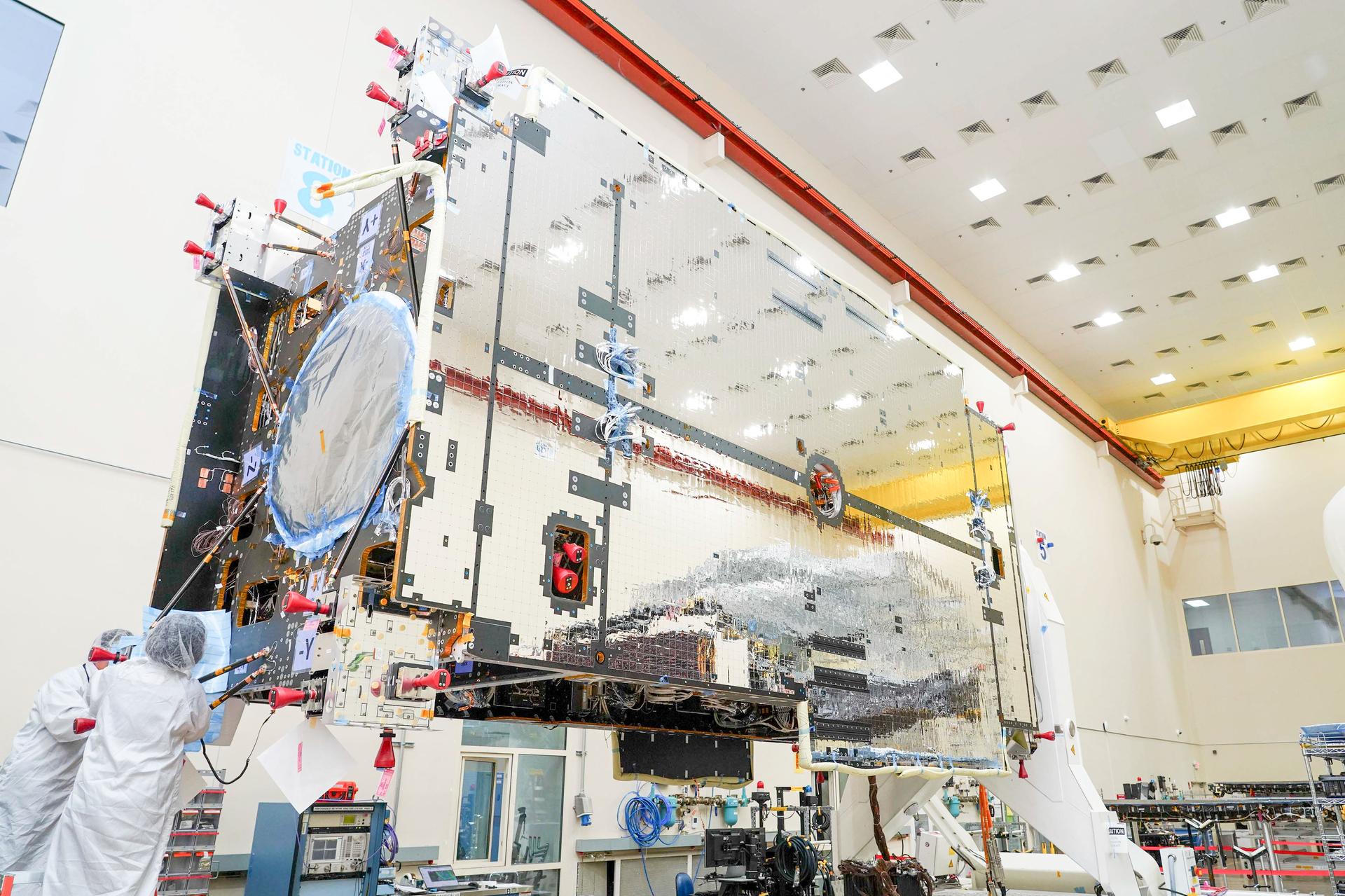
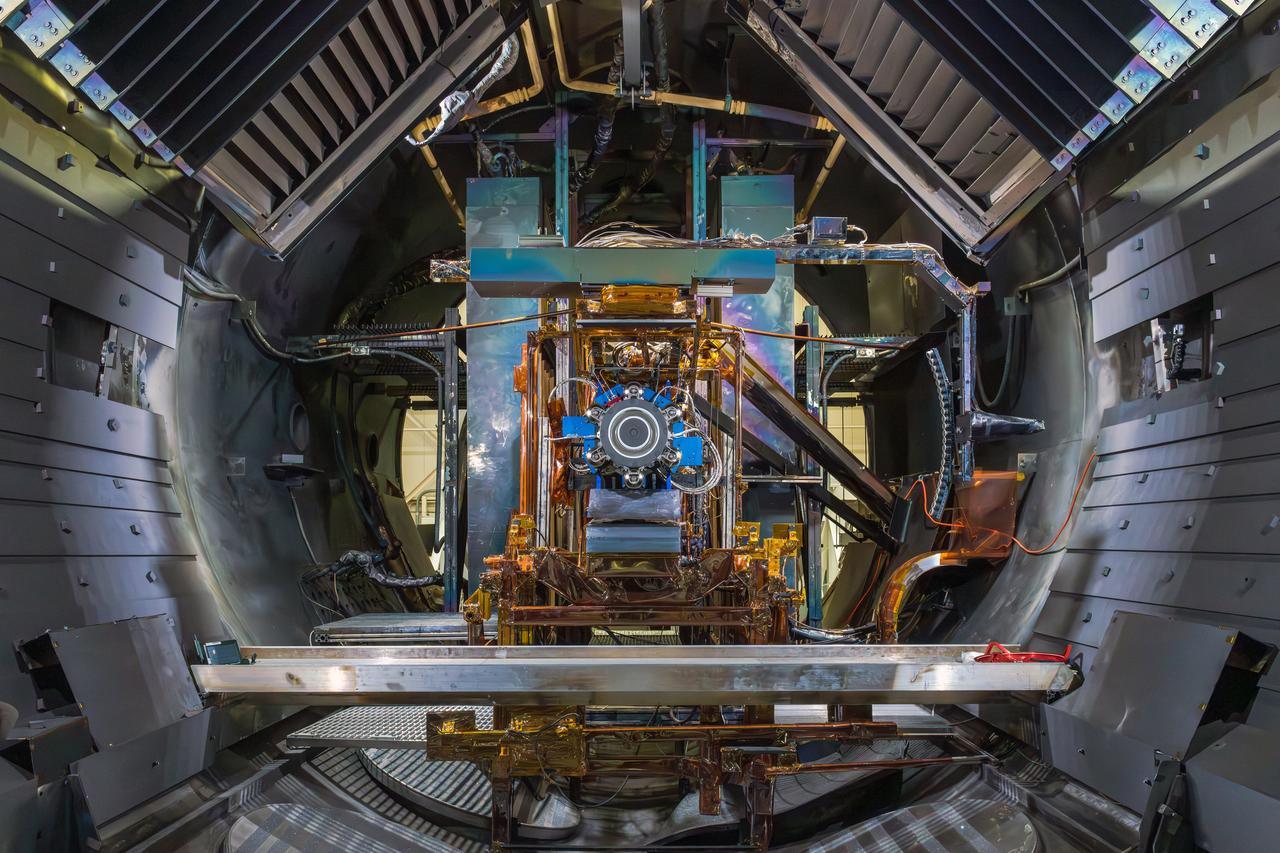
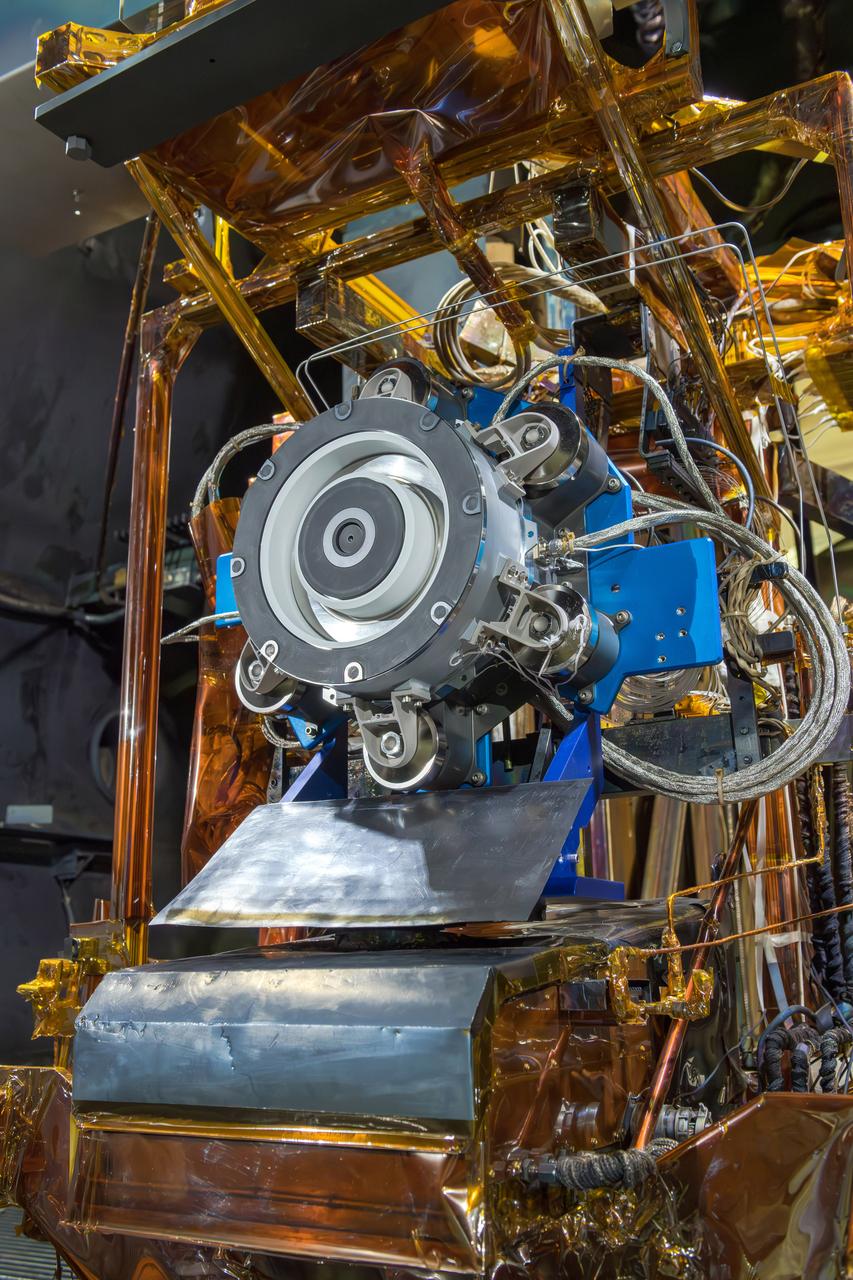
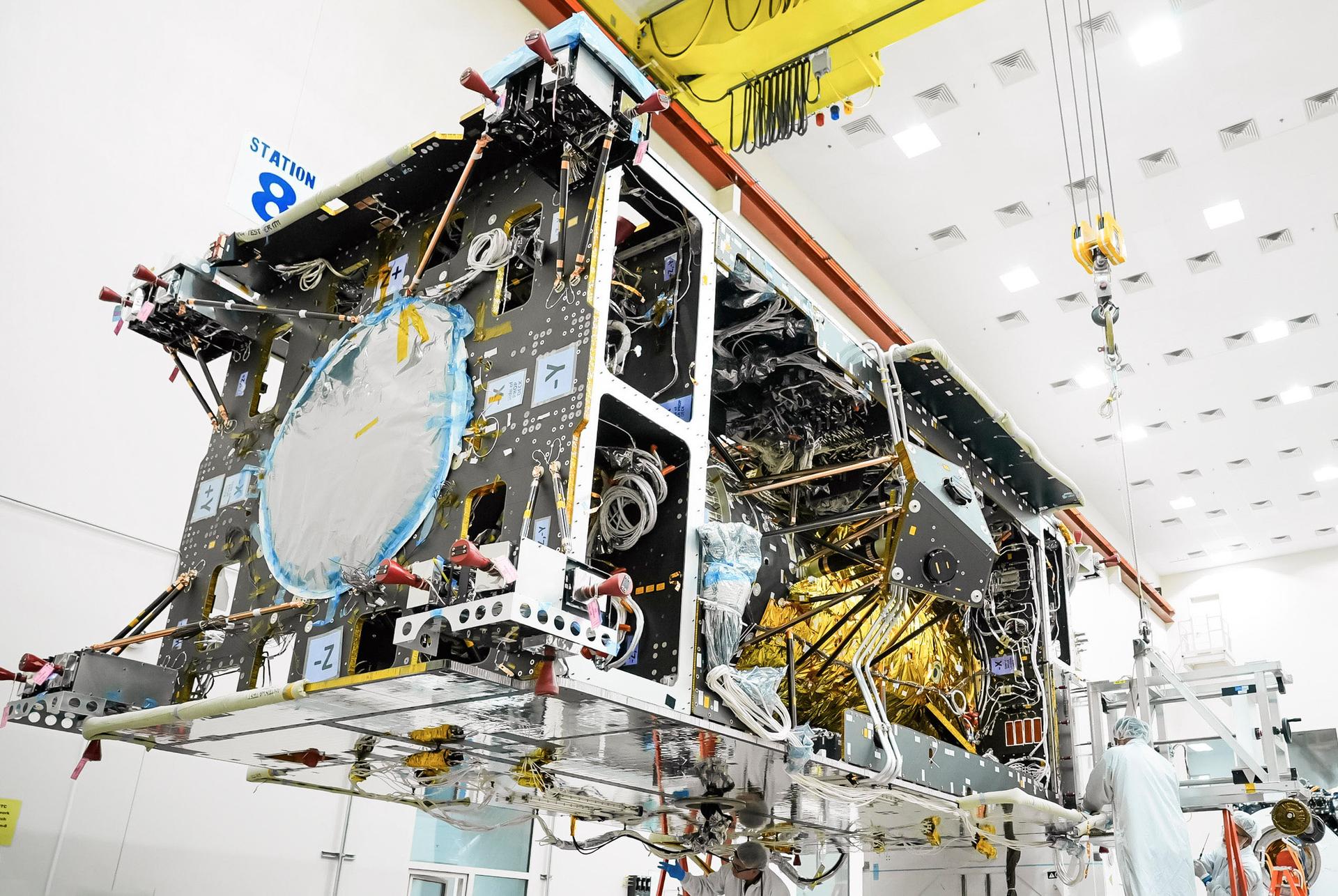
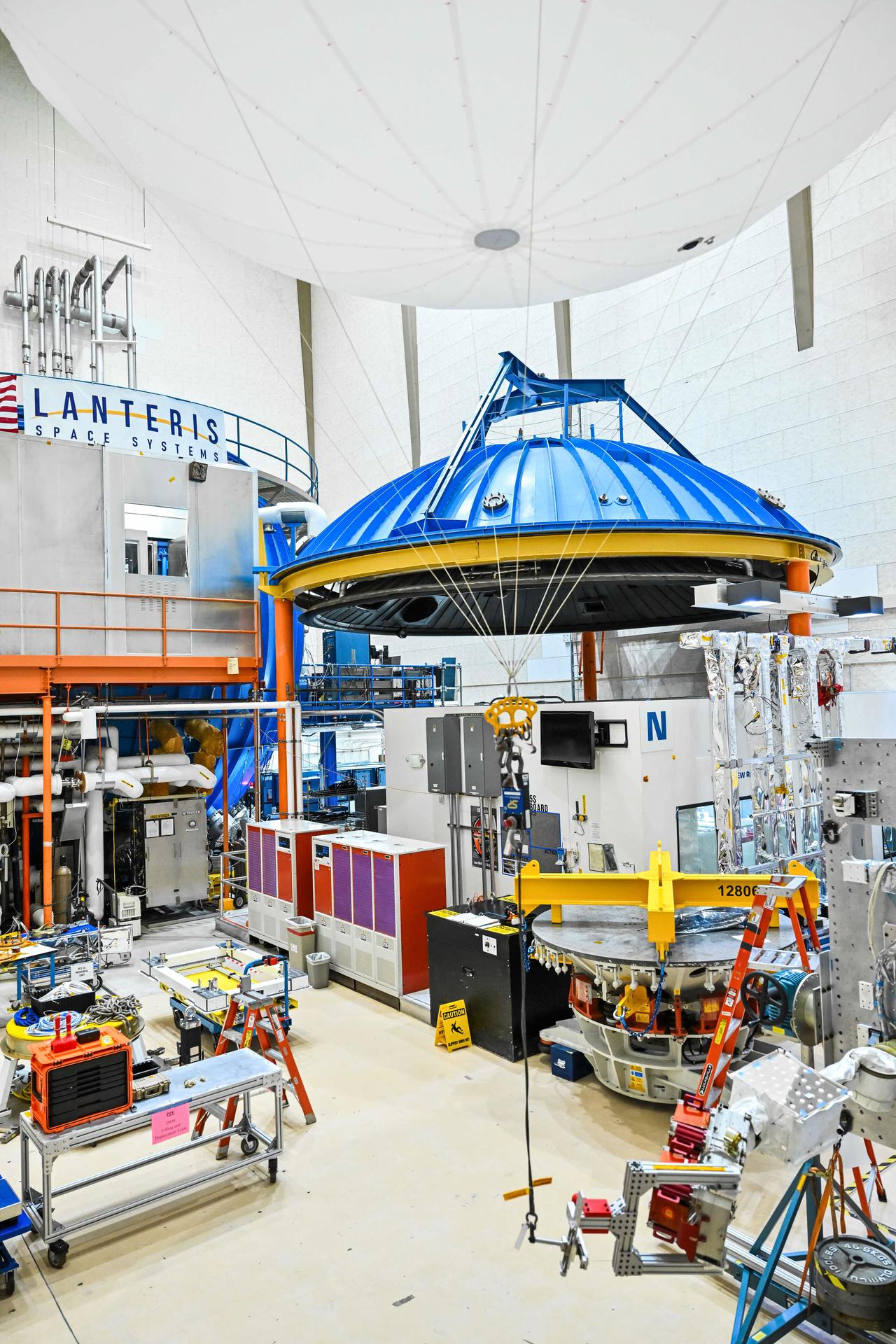
The primary structure of Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) undergoing assembly, integration, and testing at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, on September 29, 2025. Credit: Lanteris Space Systems

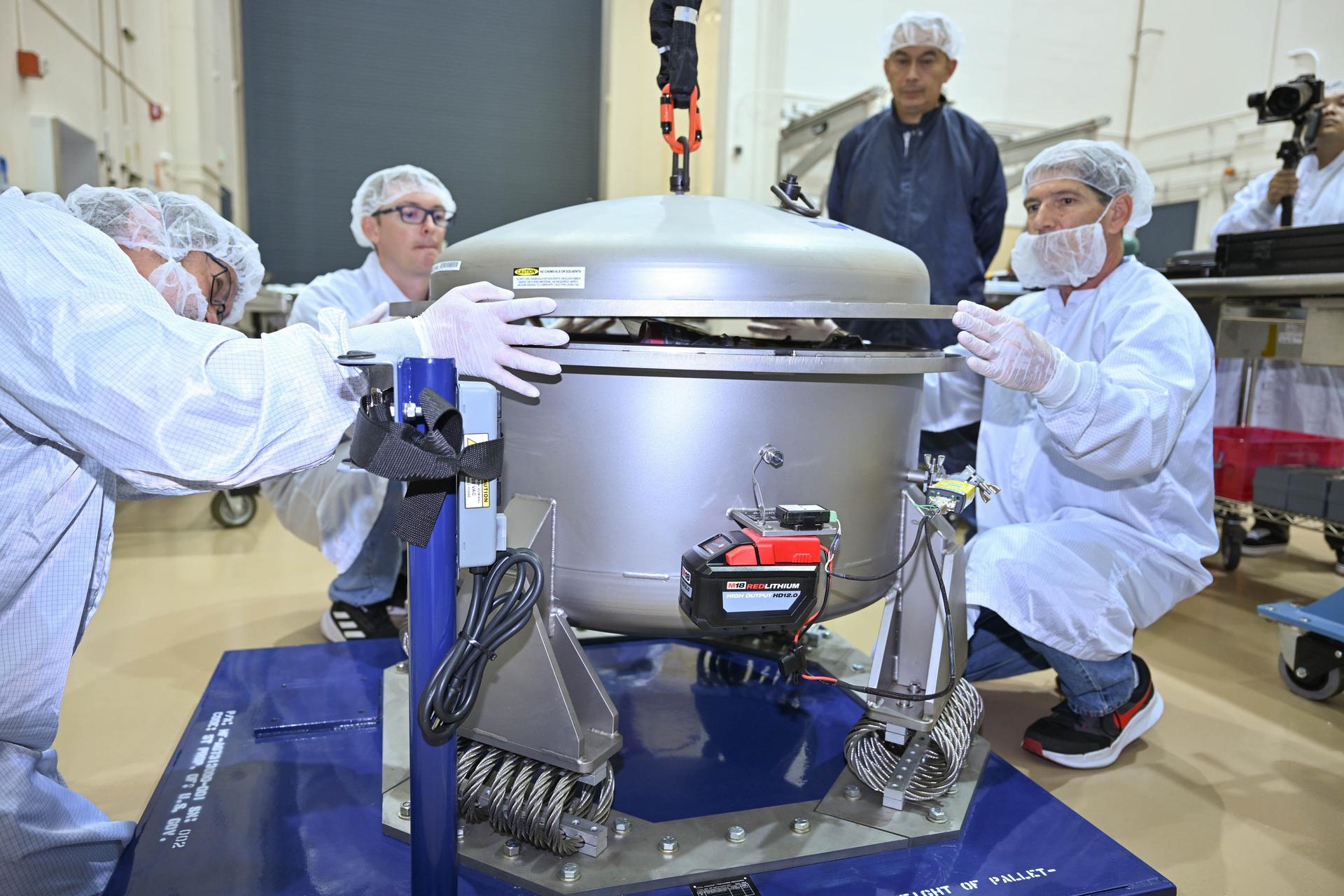
Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) undergoes battery installations at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, in January 2026. PPE is a 60-kilowatt solar electric propulsion spacecraft that will supply the lunar space station with power, high-rate communications, attitude control, orbit maintenance, and orbit transfer capabilities. Its design is based on Lanteris Space Systems’ commercial 1300 bus, enhanced with the most powerful Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters and the largest roll-out solar arrays (ROSAs) ever developed. Lanteris Space Systems is the lead industry partner for PPE’s design, manufacturing, and integration.
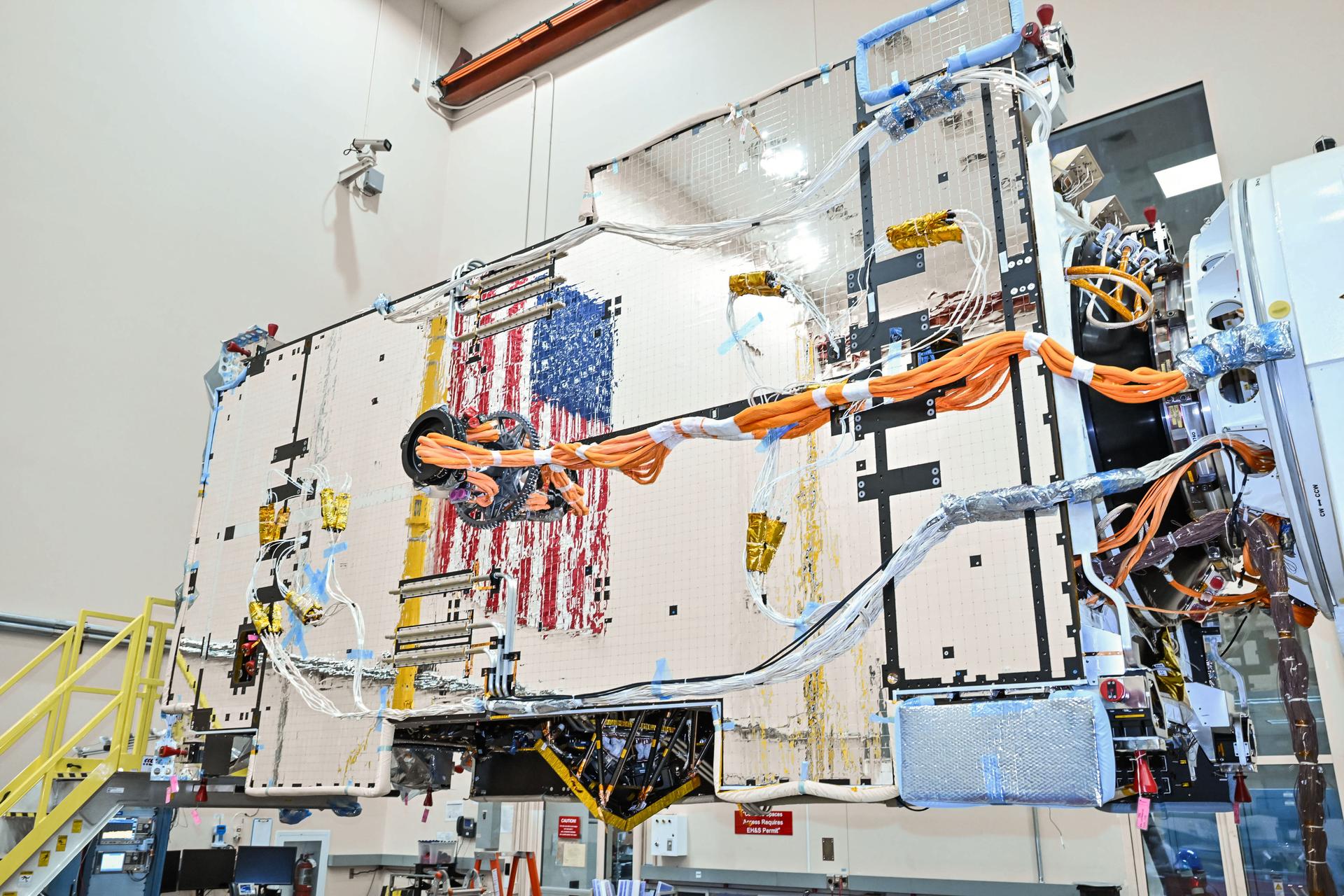
Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) undergoes flight software uploads at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, in January 2026. PPE is a 60-kilowatt solar electric propulsion spacecraft that will supply the lunar space station with power, high-rate communications, attitude control, orbit maintenance, and orbit transfer capabilities. Its design is based on Lanteris Space Systems’ commercial 1300 bus, enhanced with the most powerful Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters and the largest roll-out solar arrays (ROSAs) ever developed. Lanteris Space Systems is the lead industry partner for PPE’s design, manufacturing, and integration.
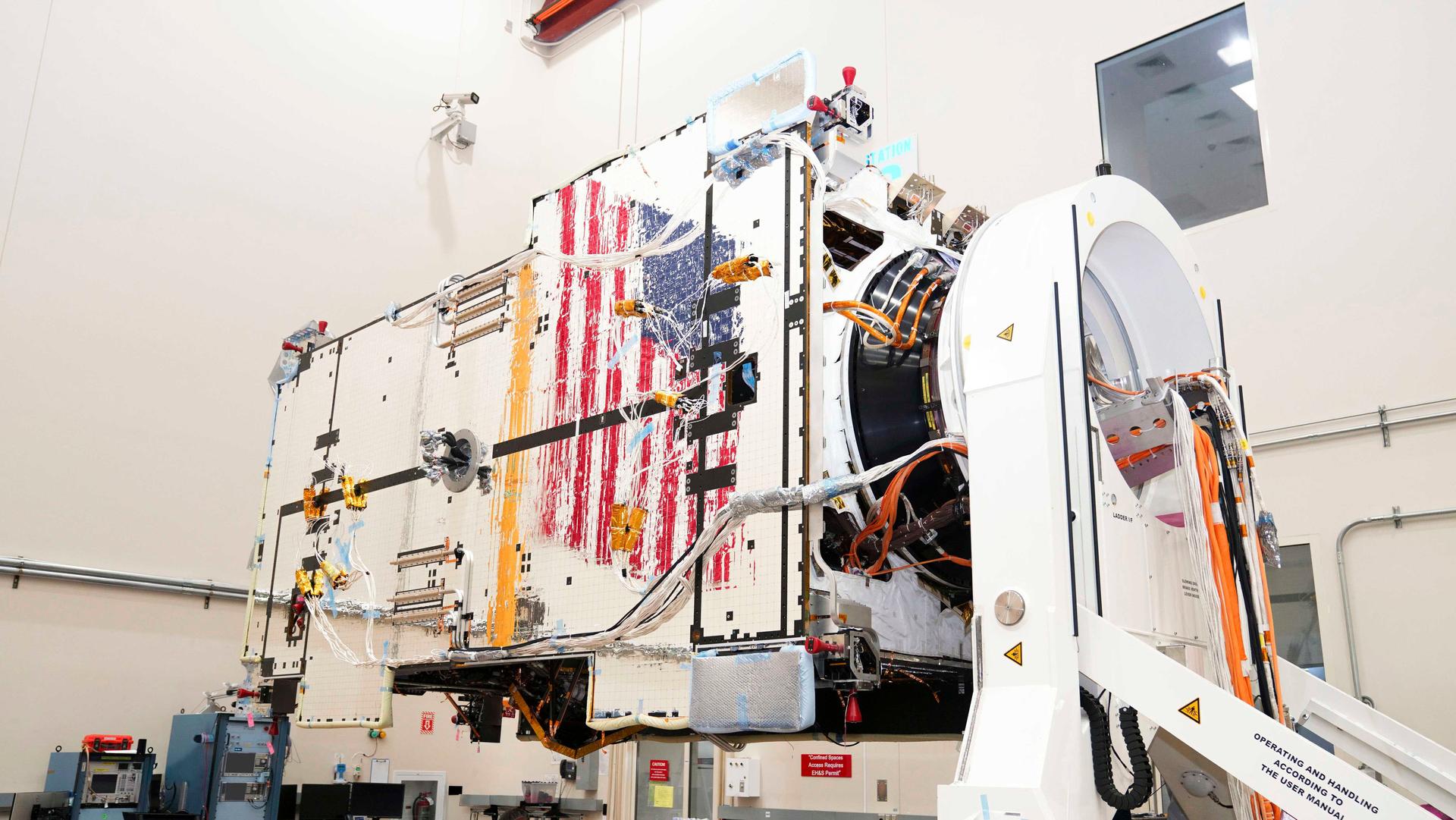

Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) undergoes battery installations at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, in January 2026. PPE is a 60-kilowatt solar electric propulsion spacecraft that will supply the lunar space station with power, high-rate communications, attitude control, orbit maintenance, and orbit transfer capabilities. Its design is based on Lanteris Space Systems’ commercial 1300 bus, enhanced with the most powerful Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters and the largest roll-out solar arrays (ROSAs) ever developed. Lanteris Space Systems is the lead industry partner for PPE’s design, manufacturing, and integration.
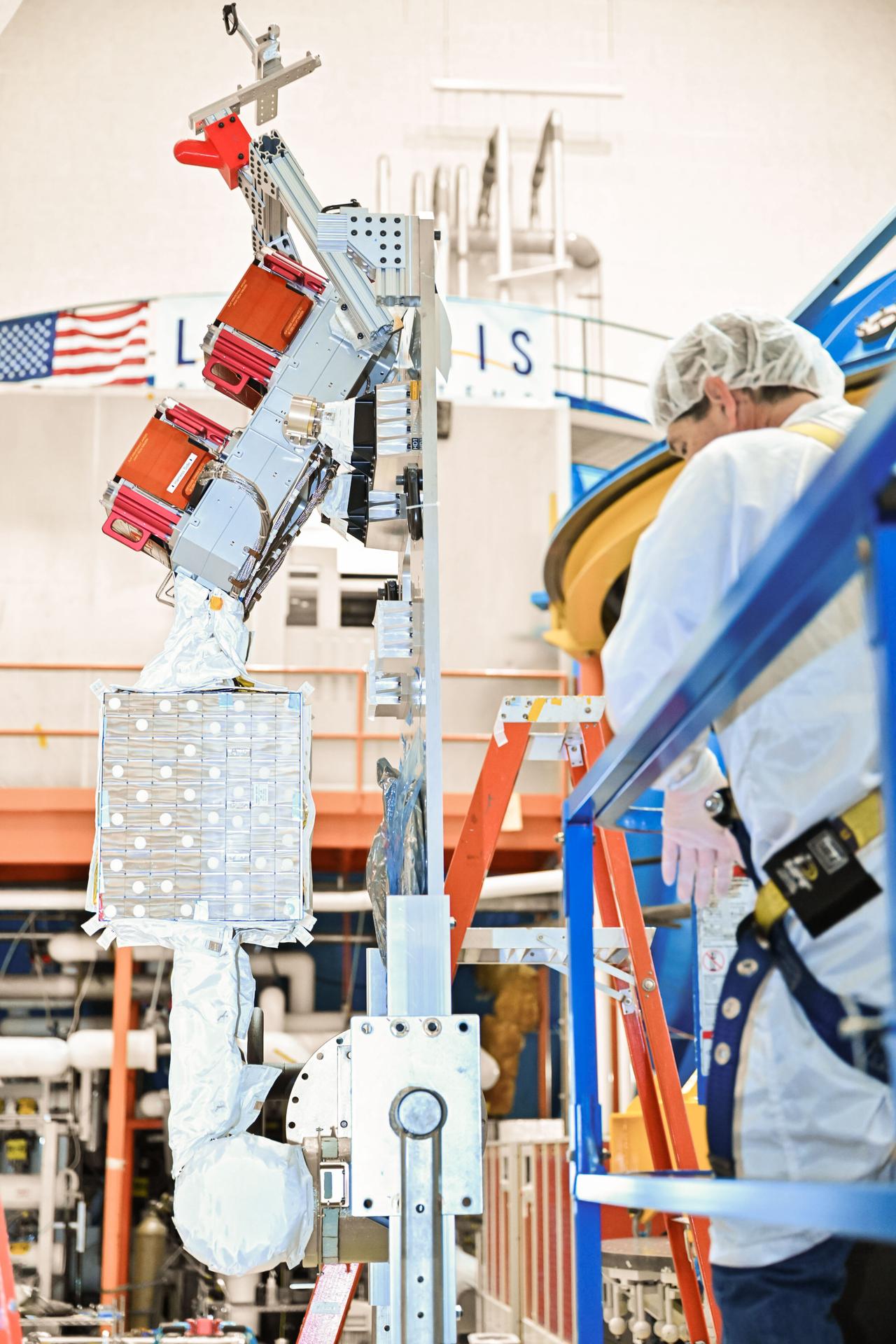

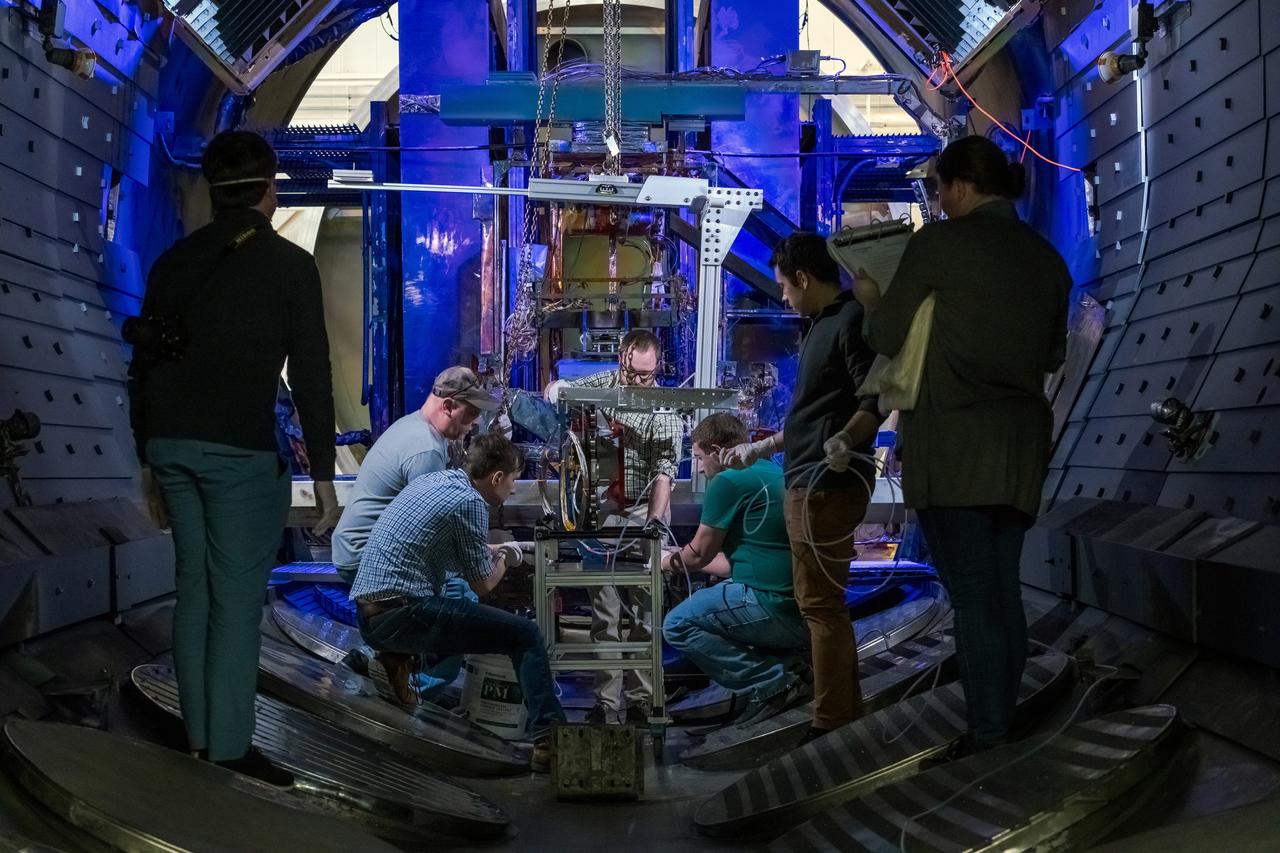
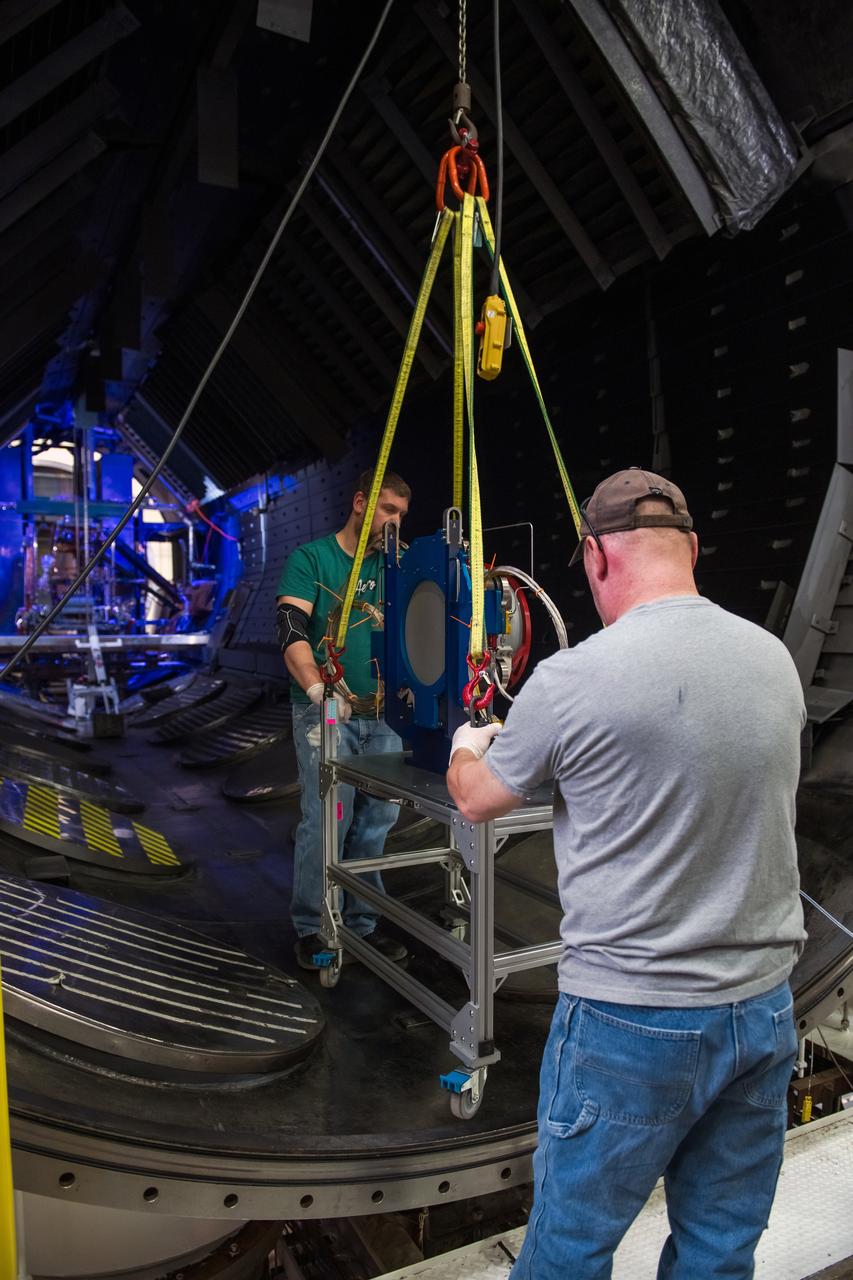
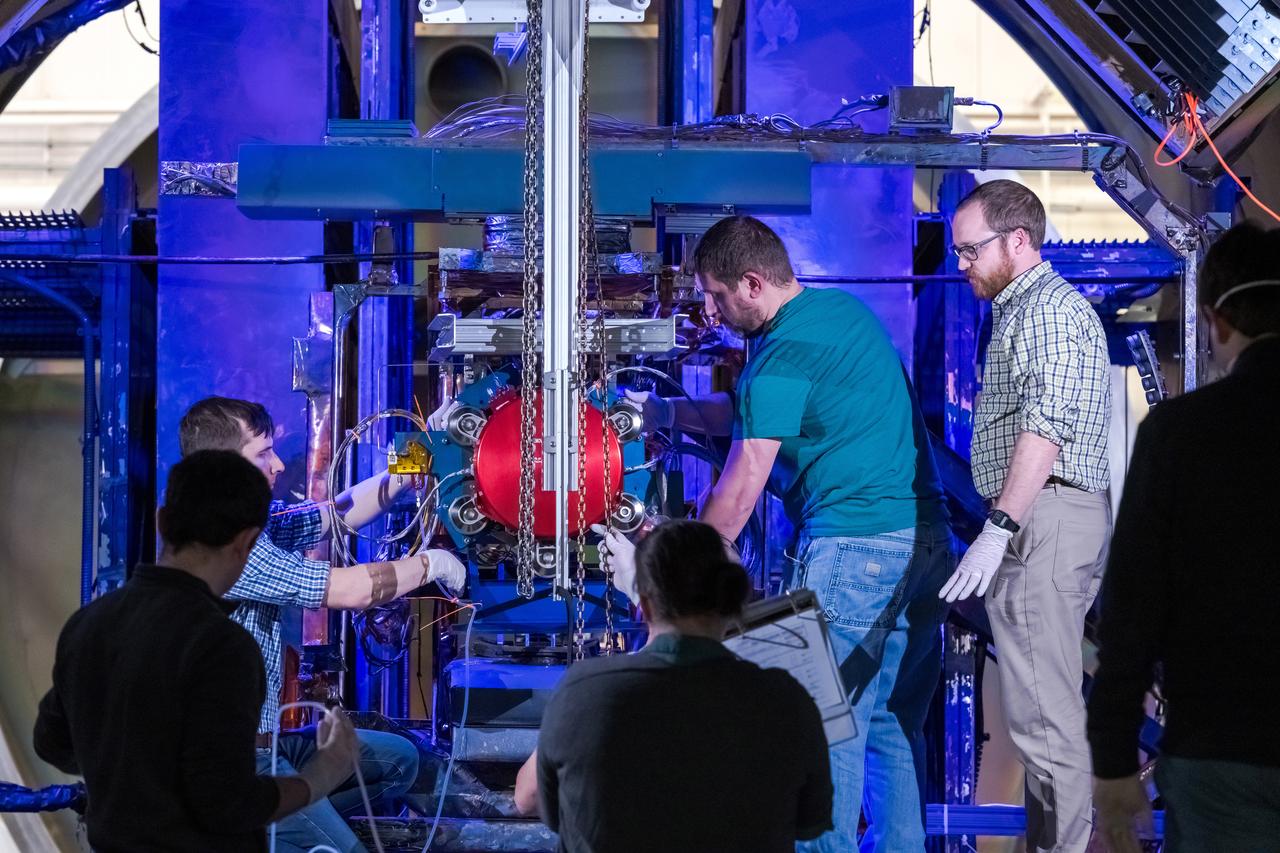
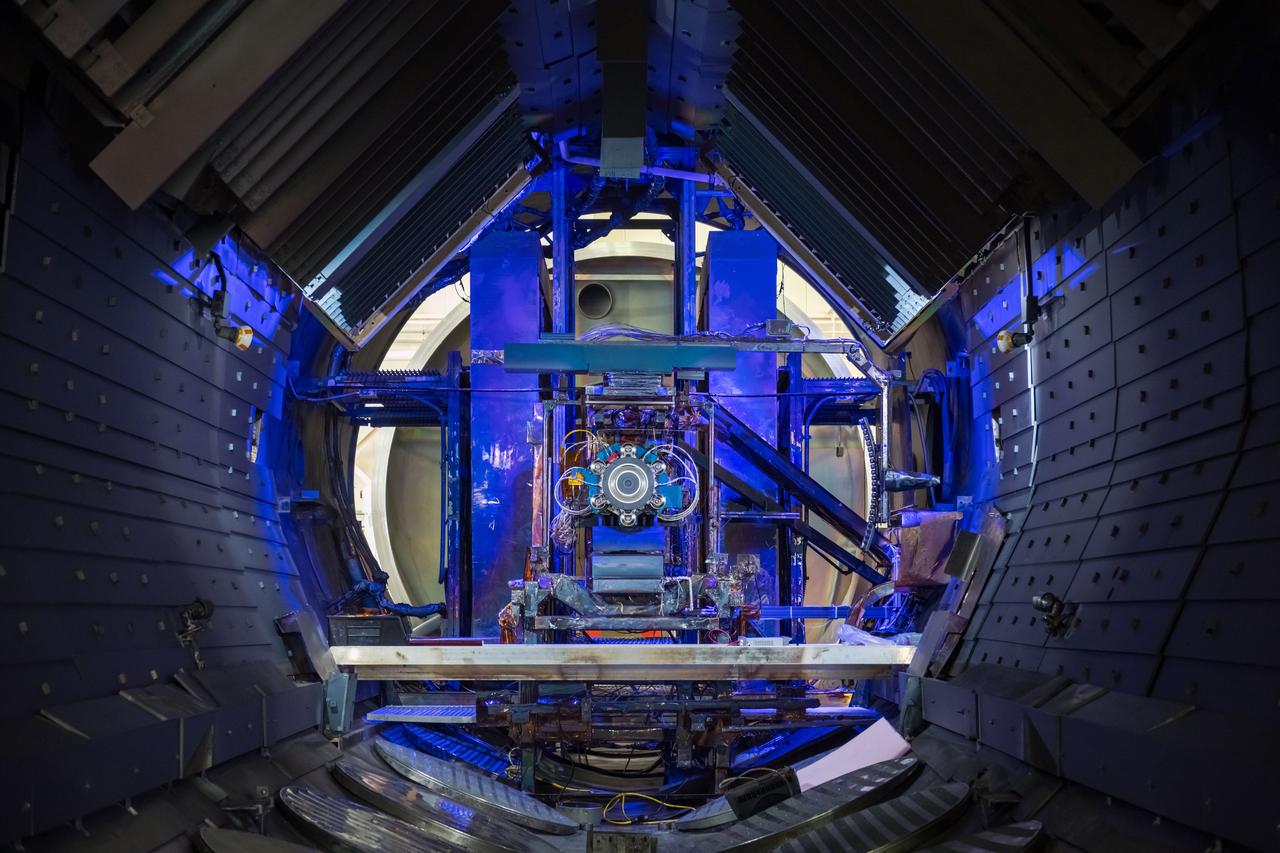
During this Engineering Qualification Module test, the gimbal platforms for the Busek-built BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters are exercised through their full range of motion to verify articulation performance and confirm the system can properly steer thrust once integrated with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE). On PPE, four BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters and three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters will use solar power generated by Gateway’s Roll-Out Solar Arrays (ROSAs) to ionize xenon gas. The resulting xenon ions are then accelerated to extremely high speeds and expelled from the thrusters, creating a steady and highly efficient stream of thrust. This propulsion system will enable the Gateway lunar space station to maneuver and maintain its orbit around the Moon.
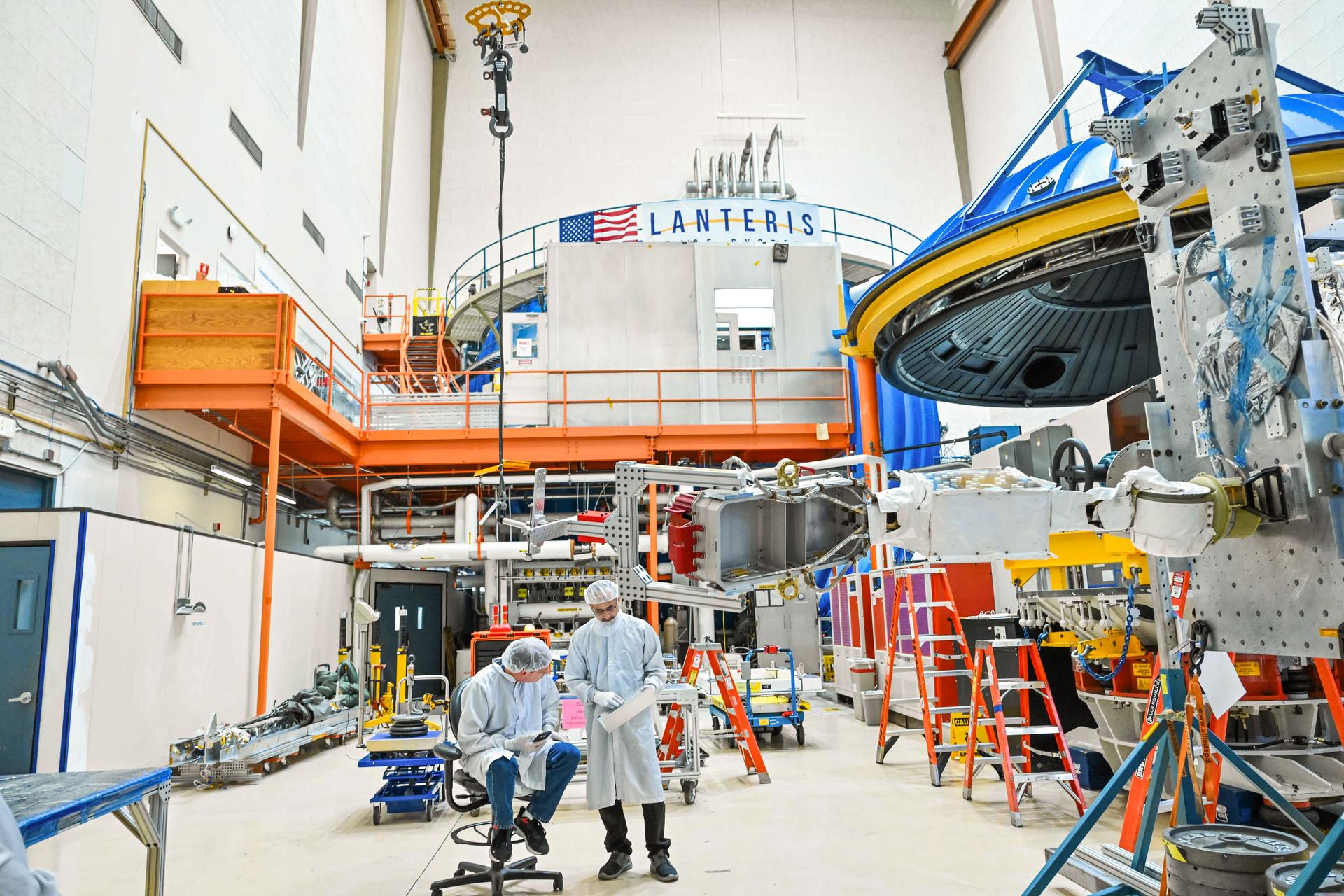

During this Engineering Qualification Module test, the gimbal platforms for the Busek-built BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters are exercised through their full range of motion to verify articulation performance and confirm the system can properly steer thrust once integrated with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE). On PPE, four BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters and three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters will use solar power generated by Gateway’s Roll-Out Solar Arrays (ROSAs) to ionize xenon gas. The resulting xenon ions are then accelerated to extremely high speeds and expelled from the thrusters, creating a steady and highly efficient stream of thrust. This propulsion system will enable the Gateway lunar space station to maneuver and maintain its orbit around the Moon.

During this Engineering Qualification Module test, the gimbal platforms for the Busek-built BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters are exercised through their full range of motion to verify articulation performance and confirm the system can properly steer thrust once integrated with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE). On PPE, four BHT-6000 Hall effect thrusters and three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters will use solar power generated by Gateway’s Roll-Out Solar Arrays (ROSAs) to ionize xenon gas. The resulting xenon ions are then accelerated to extremely high speeds and expelled from the thrusters, creating a steady and highly efficient stream of thrust. This propulsion system will enable the Gateway lunar space station to maneuver and maintain its orbit around the Moon.

Technicians at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, remove the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) flight thrusters from its transport container following delivery from NASA’s Glenn Research Center. The thruster previously completed acceptance testing at Glenn and will be prepared for integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE). Credit: Lanteris Space Systems

Technicians carefully install a piece of equipment to house Gateway’s xenon fuel tanks, part of its advanced electric propulsion system.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
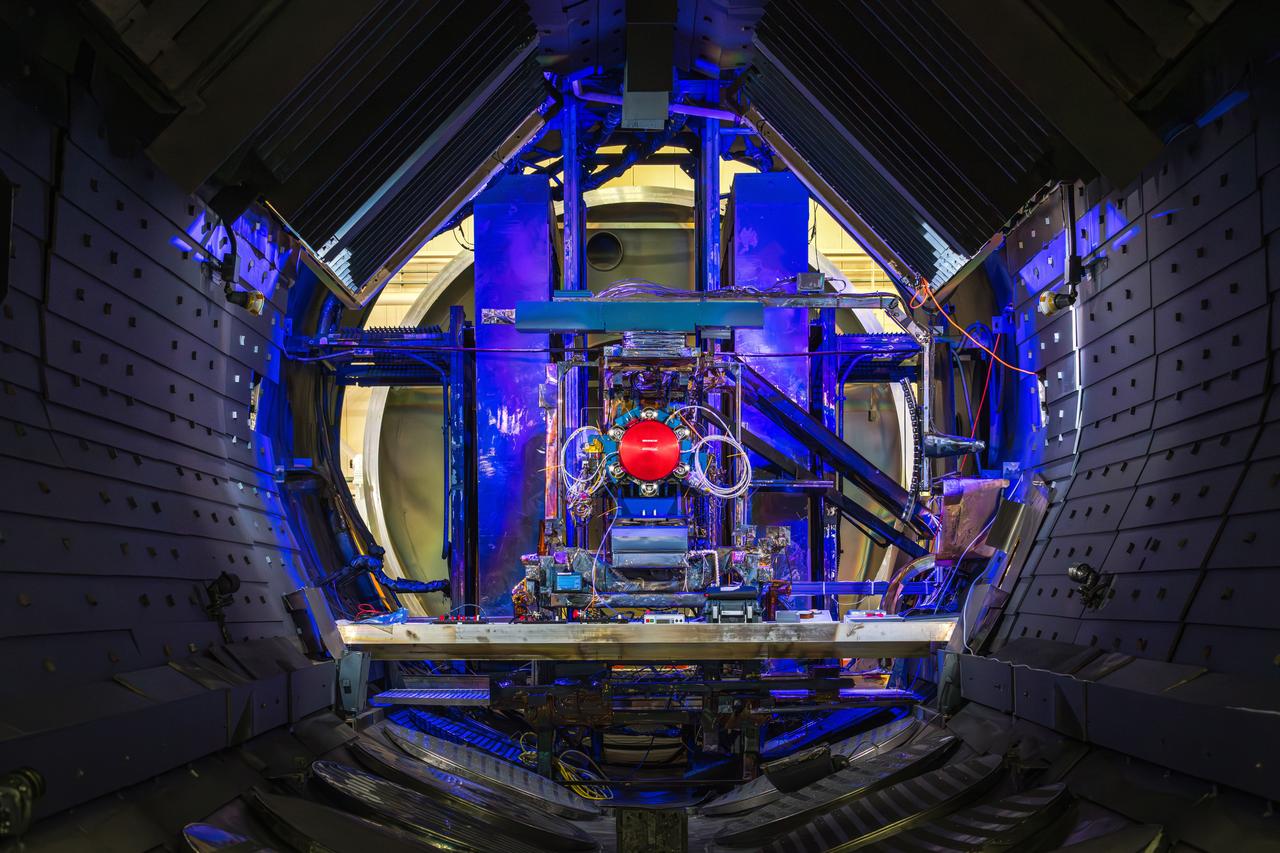
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
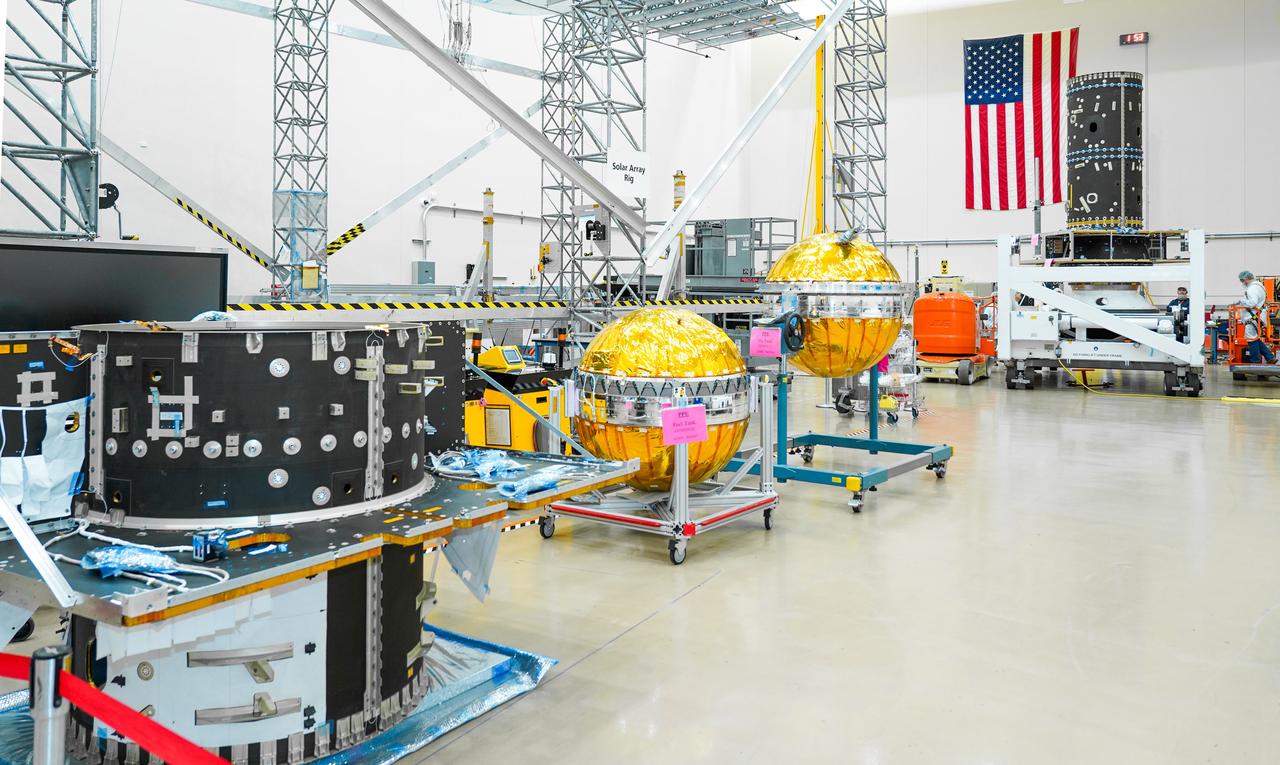

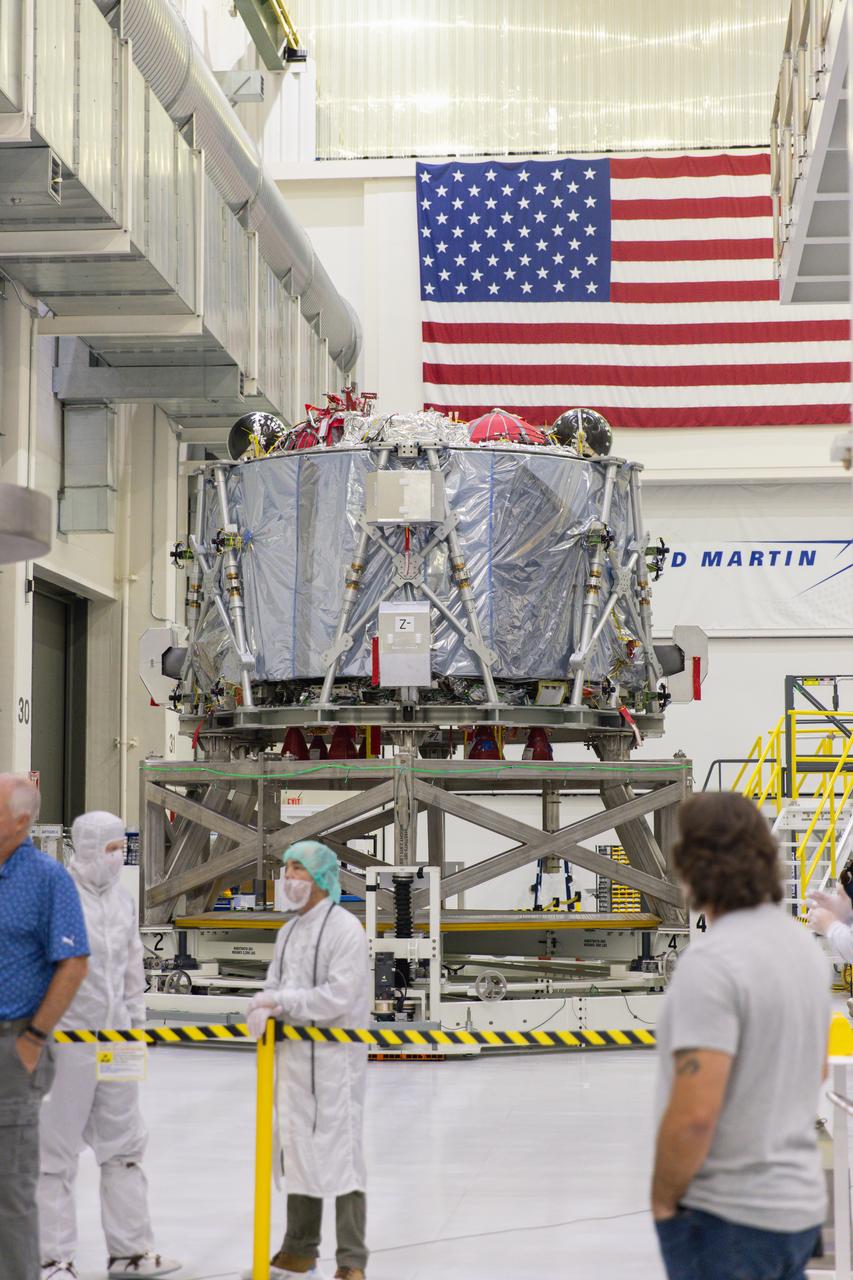
Hardware for the Gateway space station’s Power and Propulsion element, including its primary structure and fuel tanks ready for assembly, are shown at Maxar Space Systems in Palo Alto, California.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.

NASA Glenn Research Center has received the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for the Gateway lunar space station. Built by L3Harris Technologies, the thruster will undergo testing before integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element, launching with the HALO module ahead of Artemis IV.
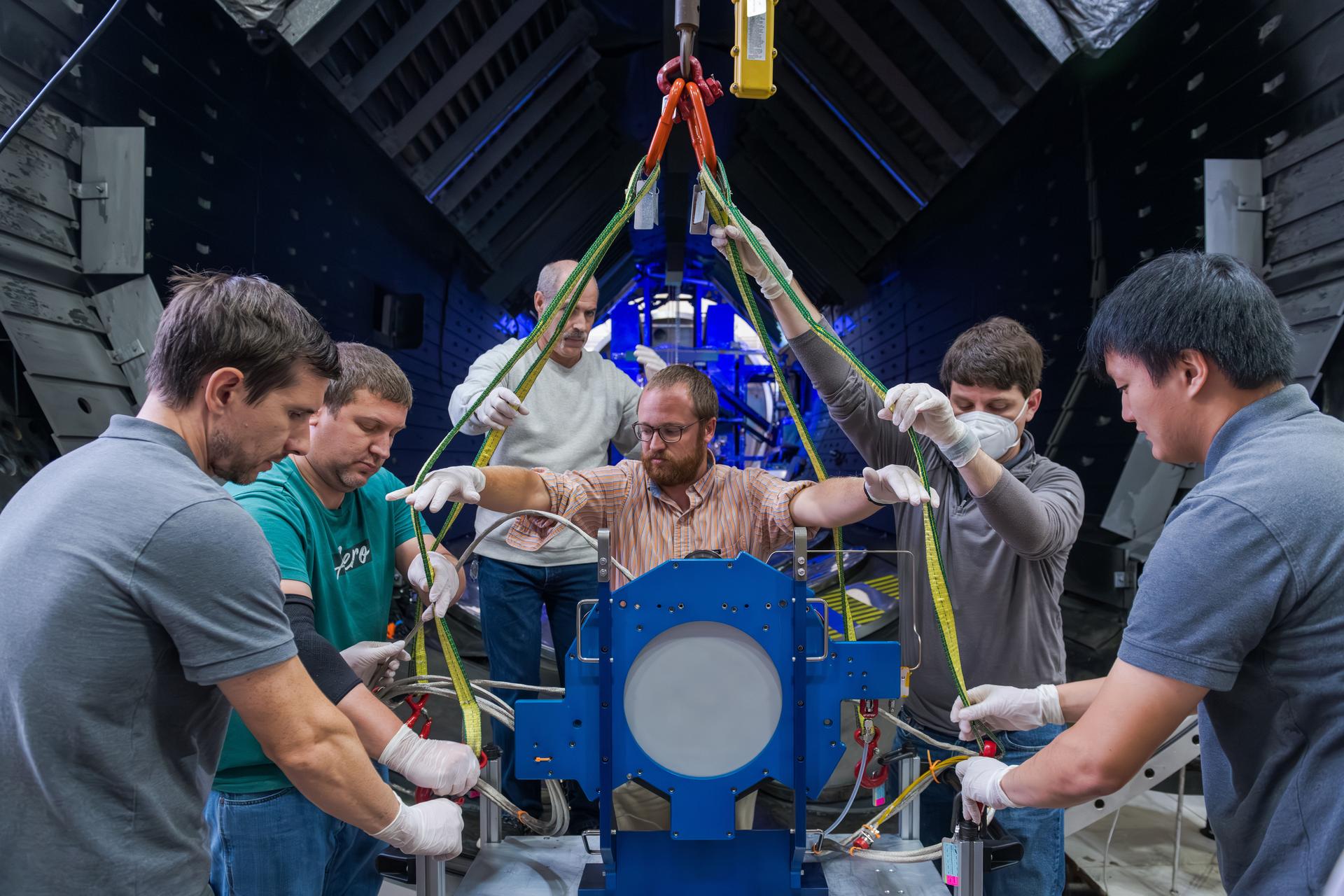

Teams at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland conduct acceptance testing on the third and final Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE). After successfully completing testing, the thruster was delivered to Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, for installation on PPE’s primary structure. Credit: NASA
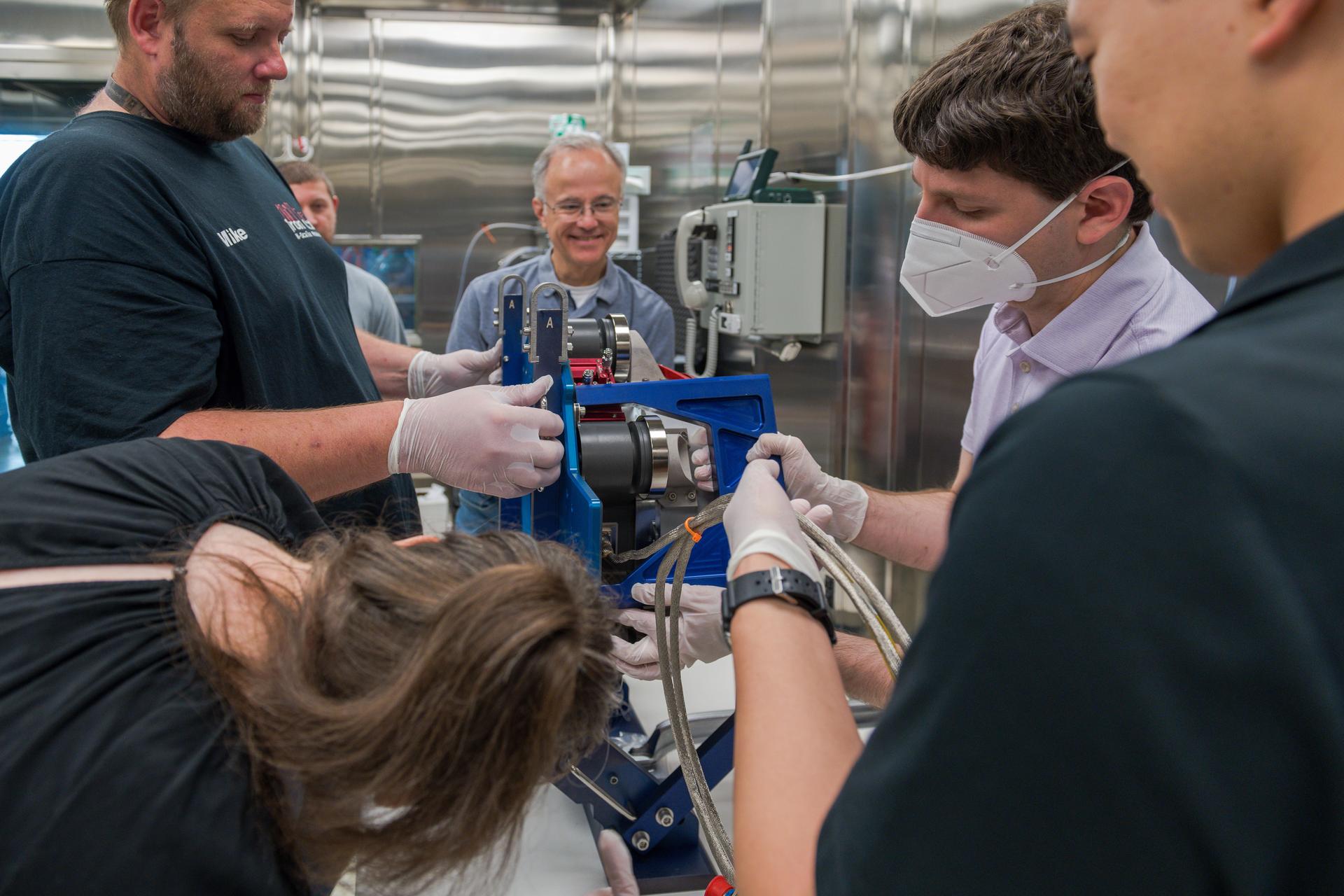

Engineers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland work together to position and secure the second of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for acceptance testing. Following testing, the thruster was delivered to Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, for installation on Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element. Credit: NASA
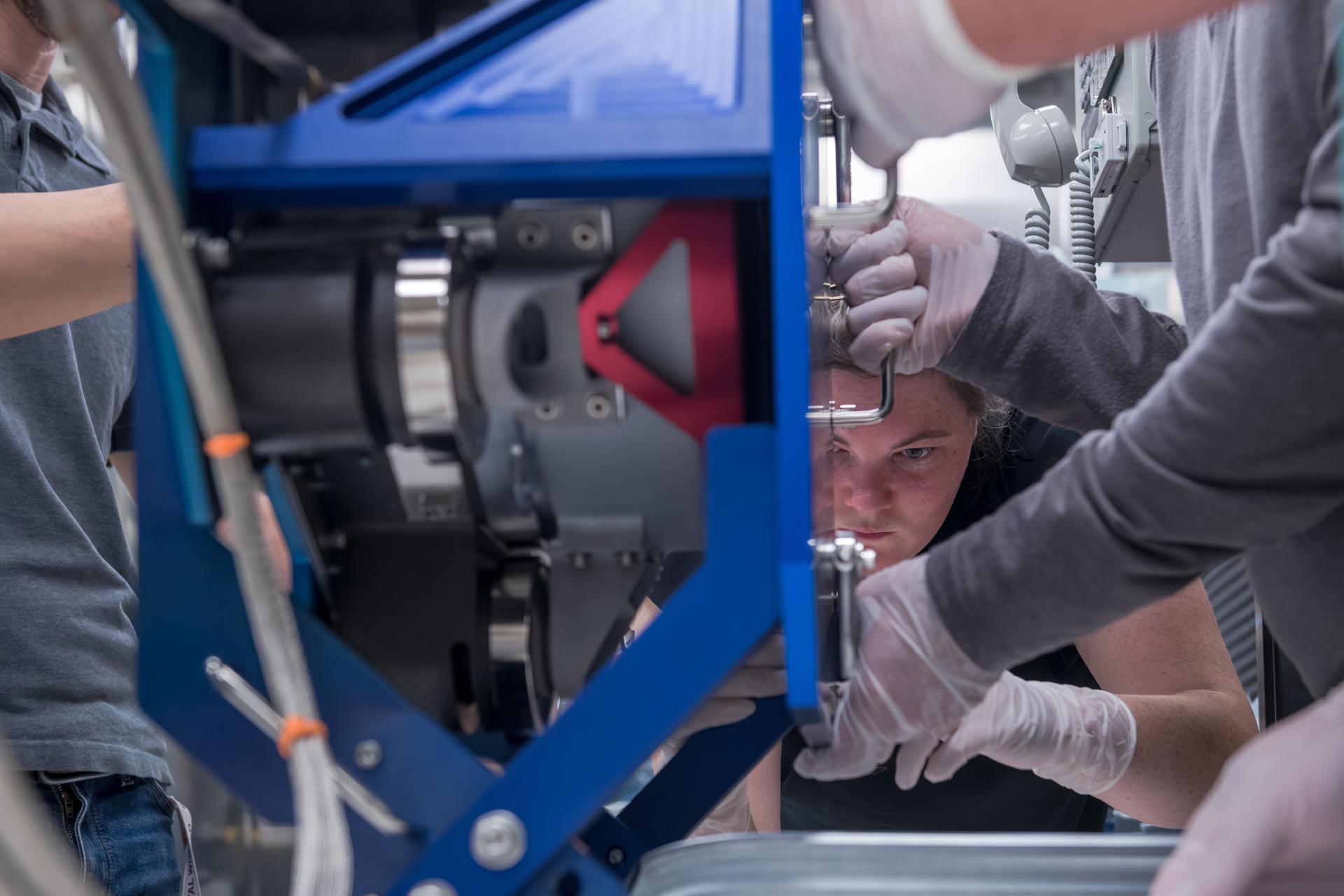

Engineers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland prepare the third and final Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thruster for acceptance testing. Following successful testing, the thruster was delivered to Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, for installation on the primary structure Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element. Credit: NASA
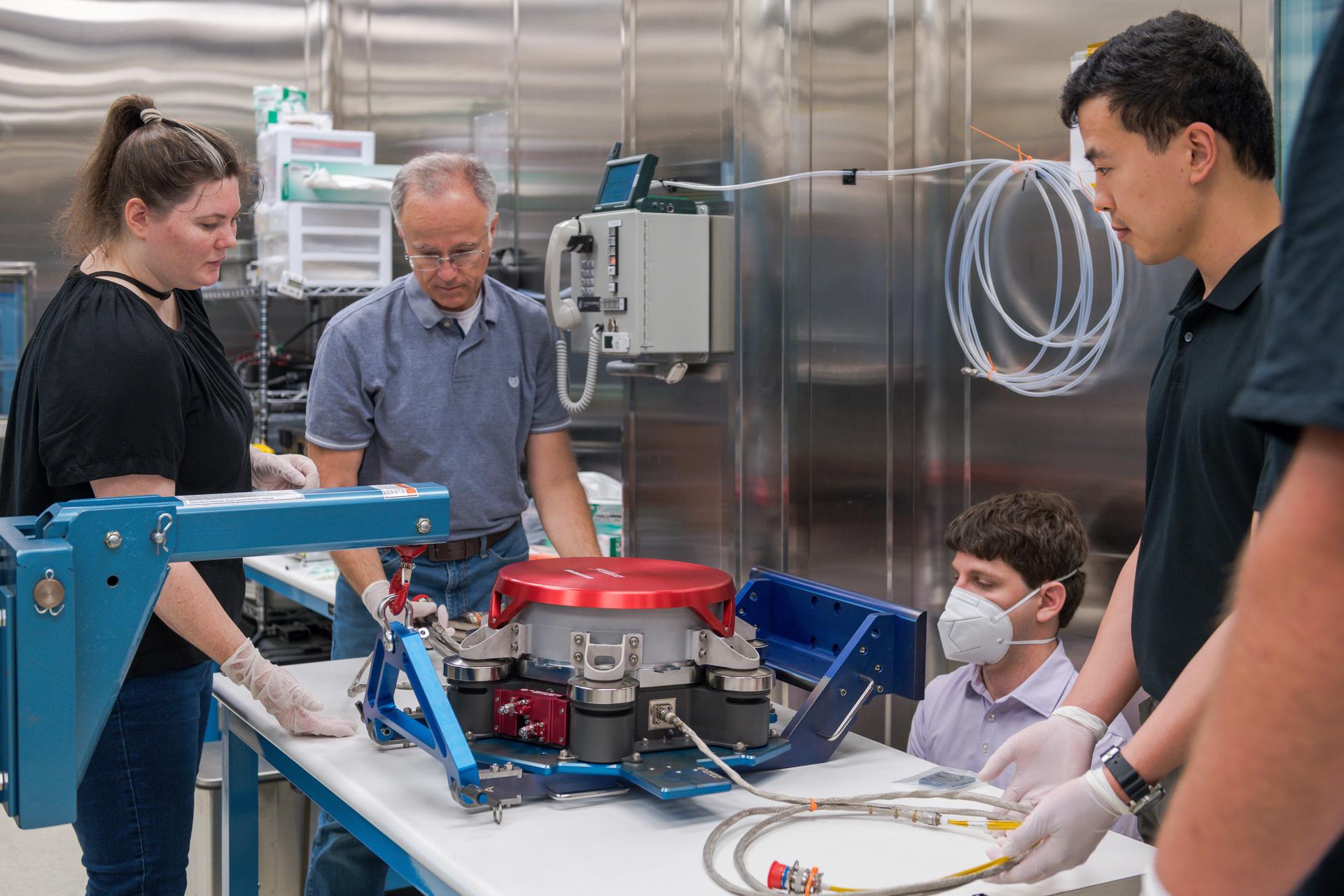

Engineers at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland work together to position and secure the second of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) thrusters for acceptance testing. Following testing, the thruster was delivered to Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, for installation on Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element. Credit: NASA
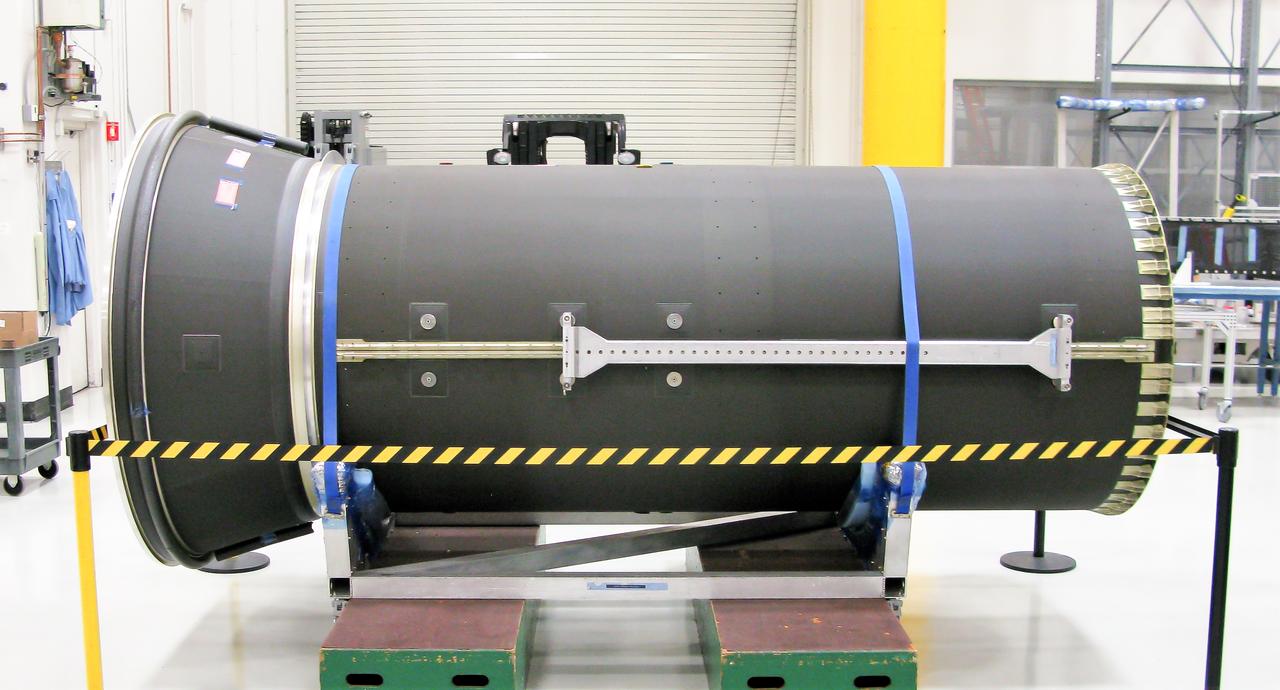

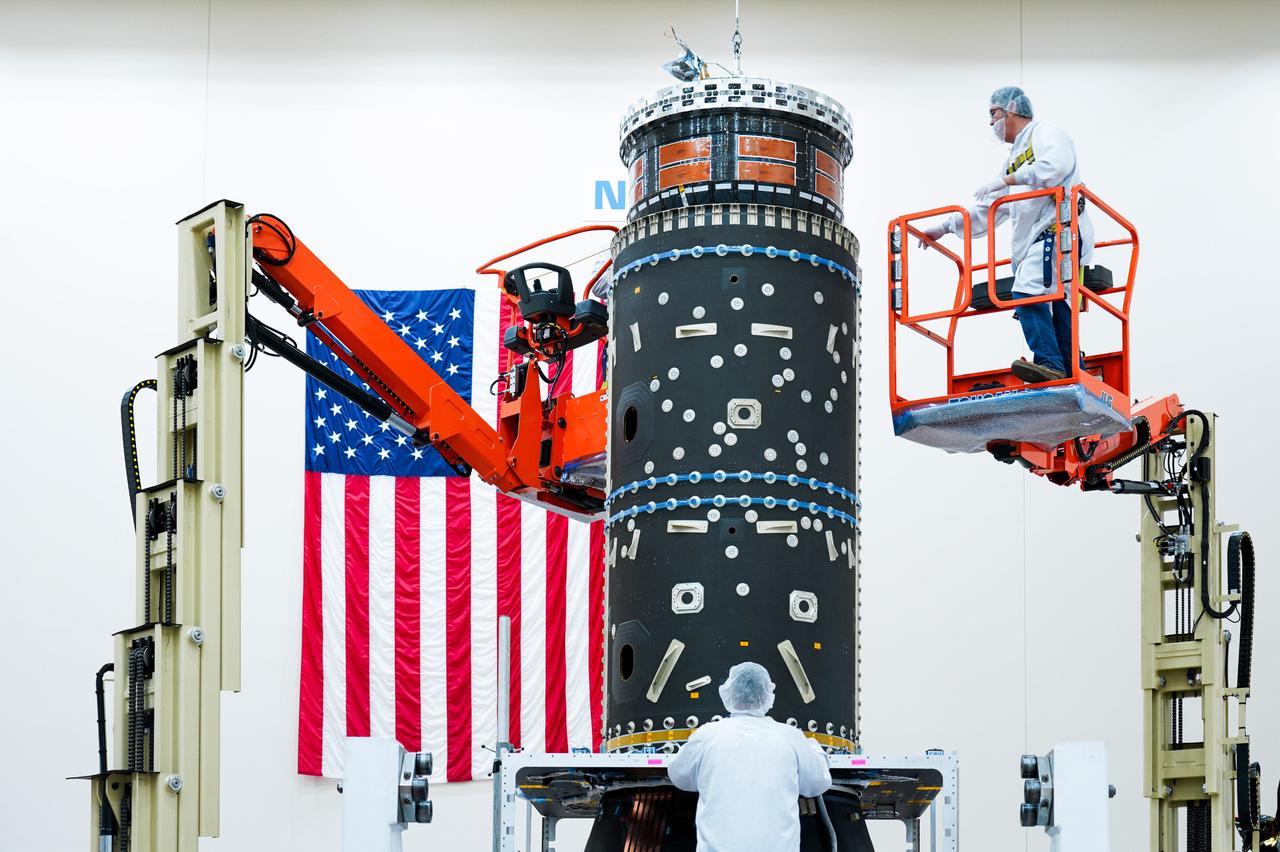
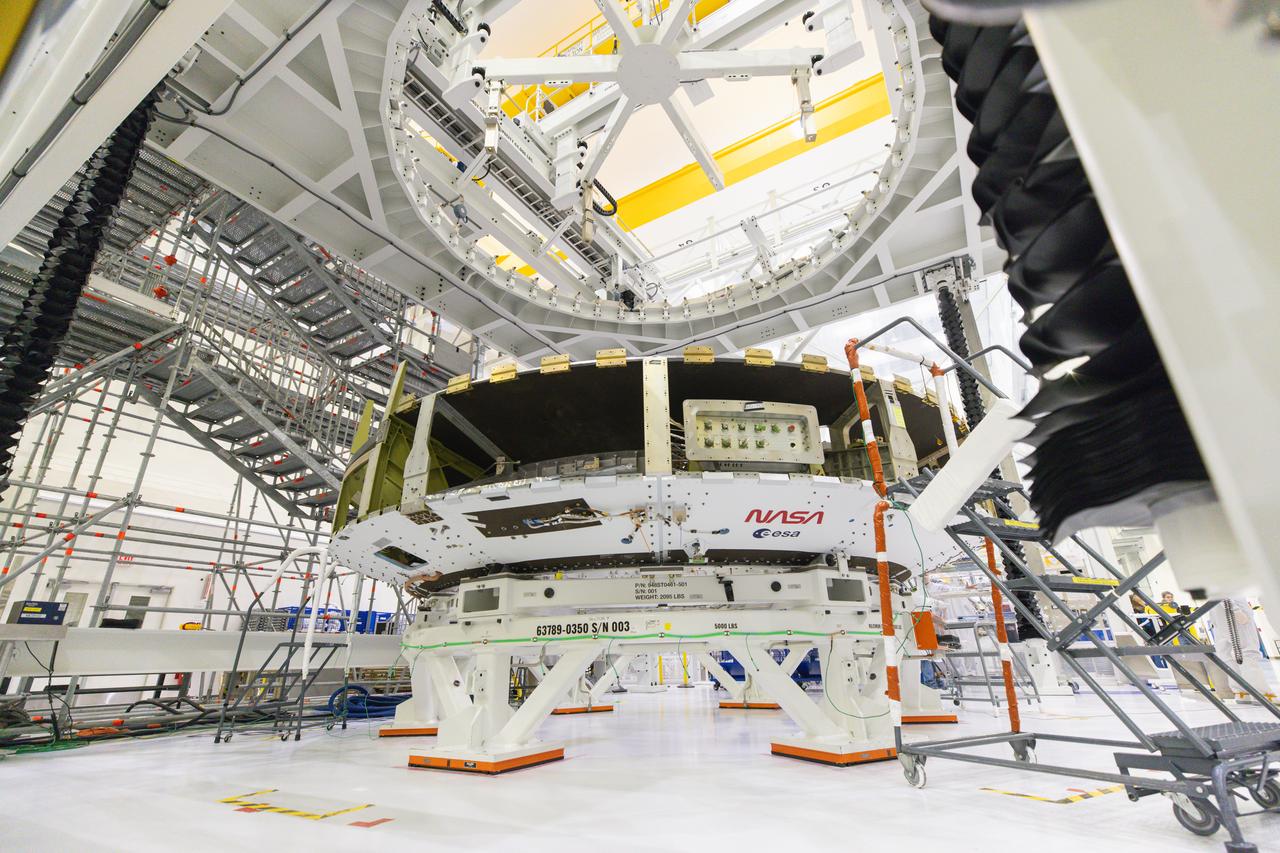
Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
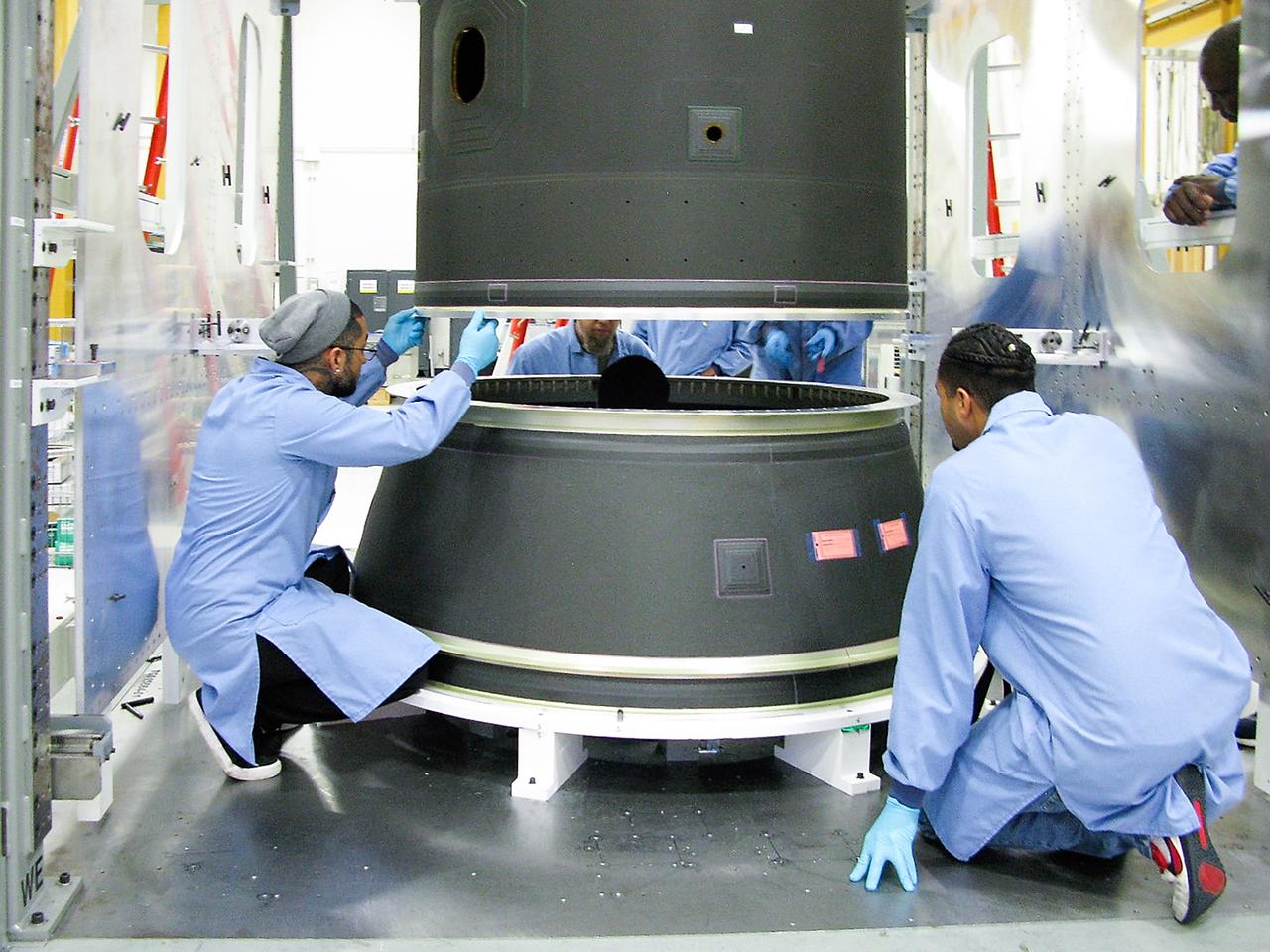

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
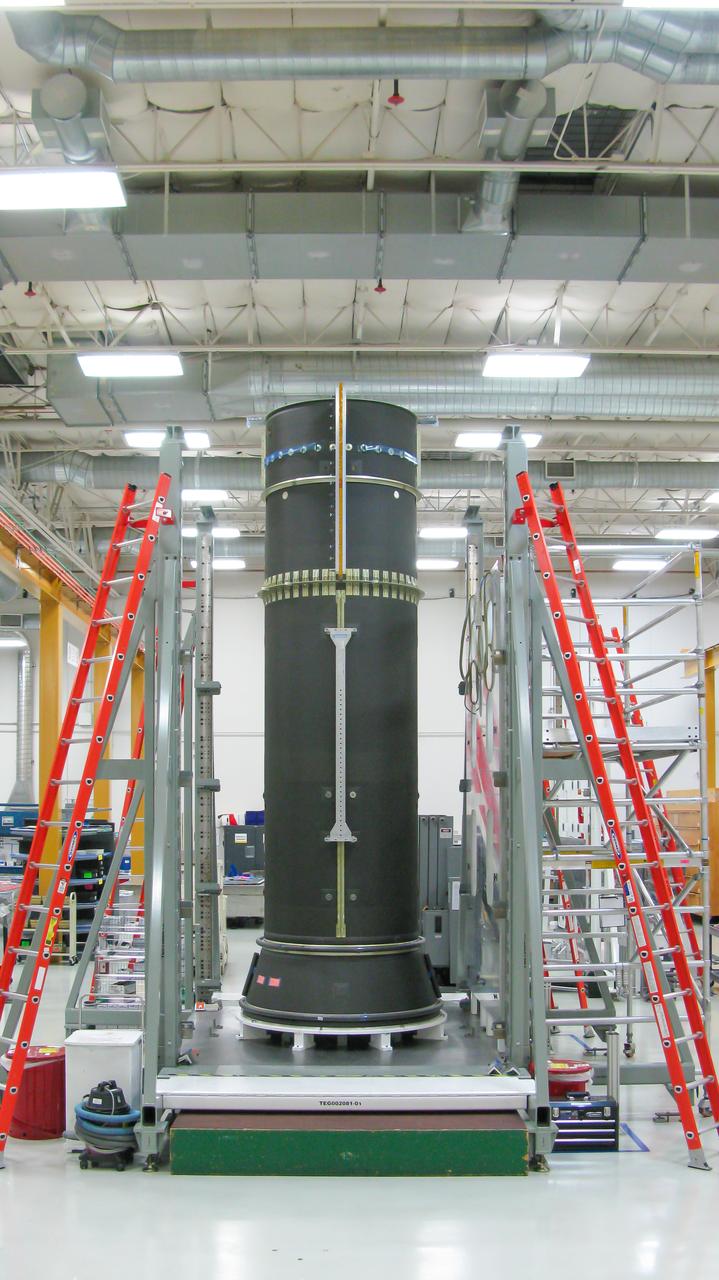

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
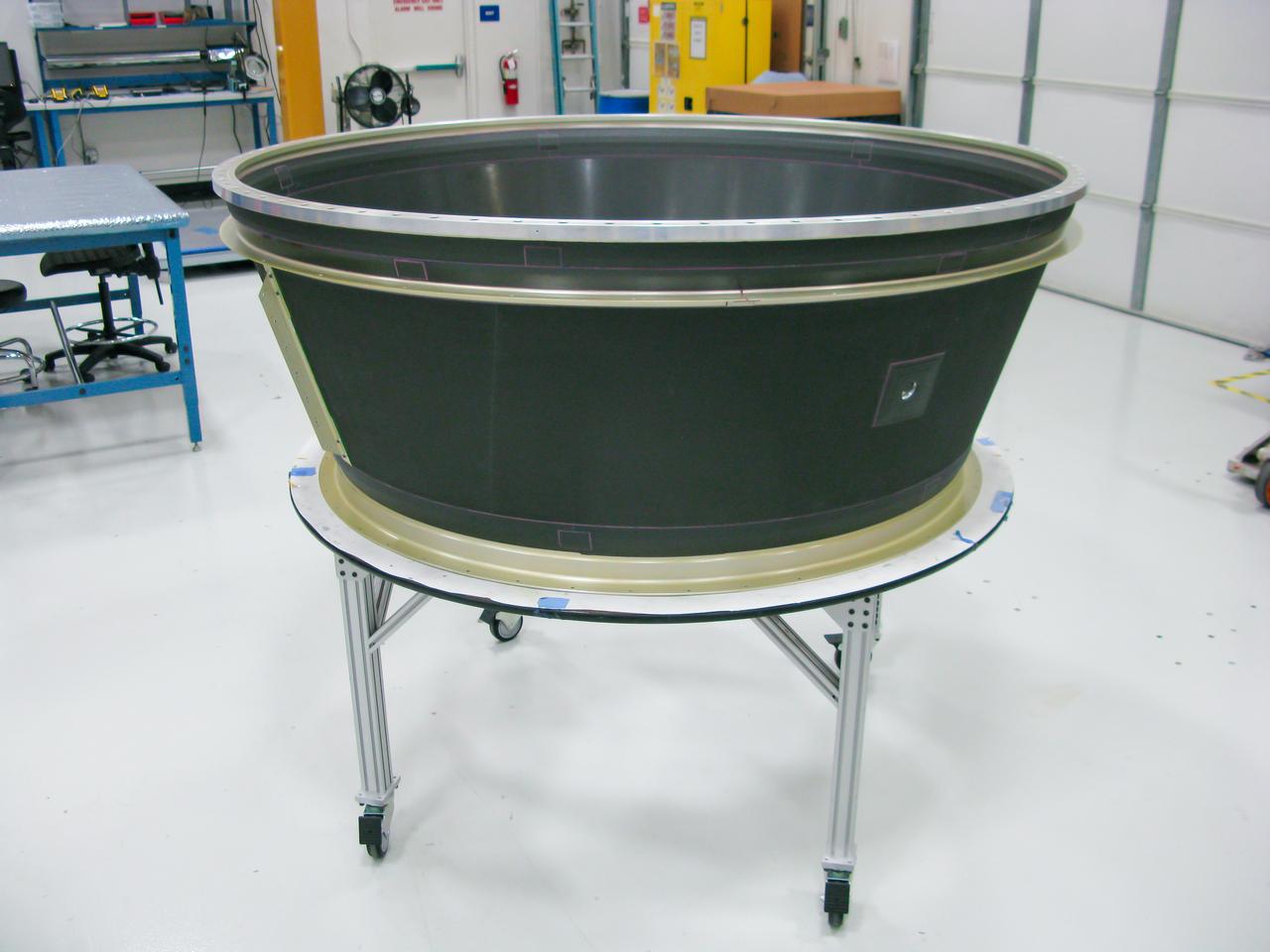

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
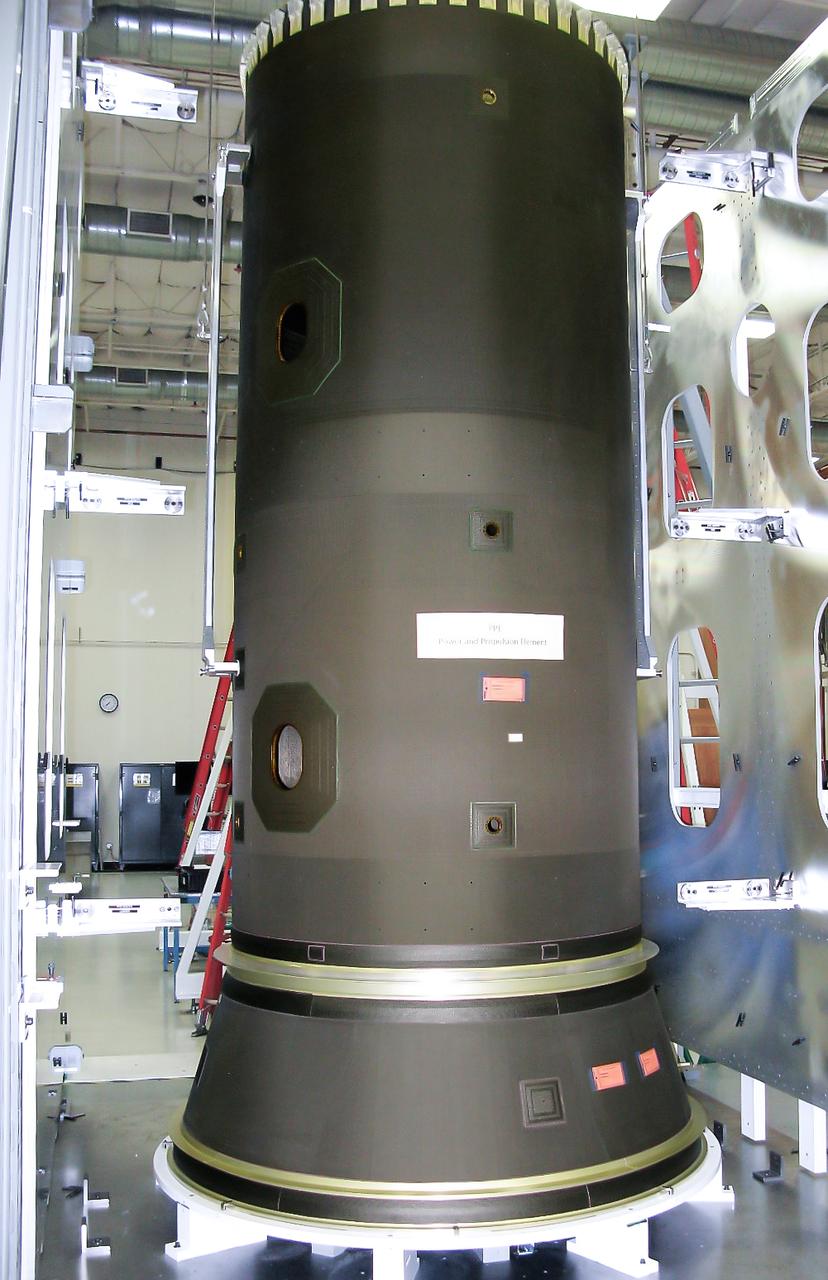

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
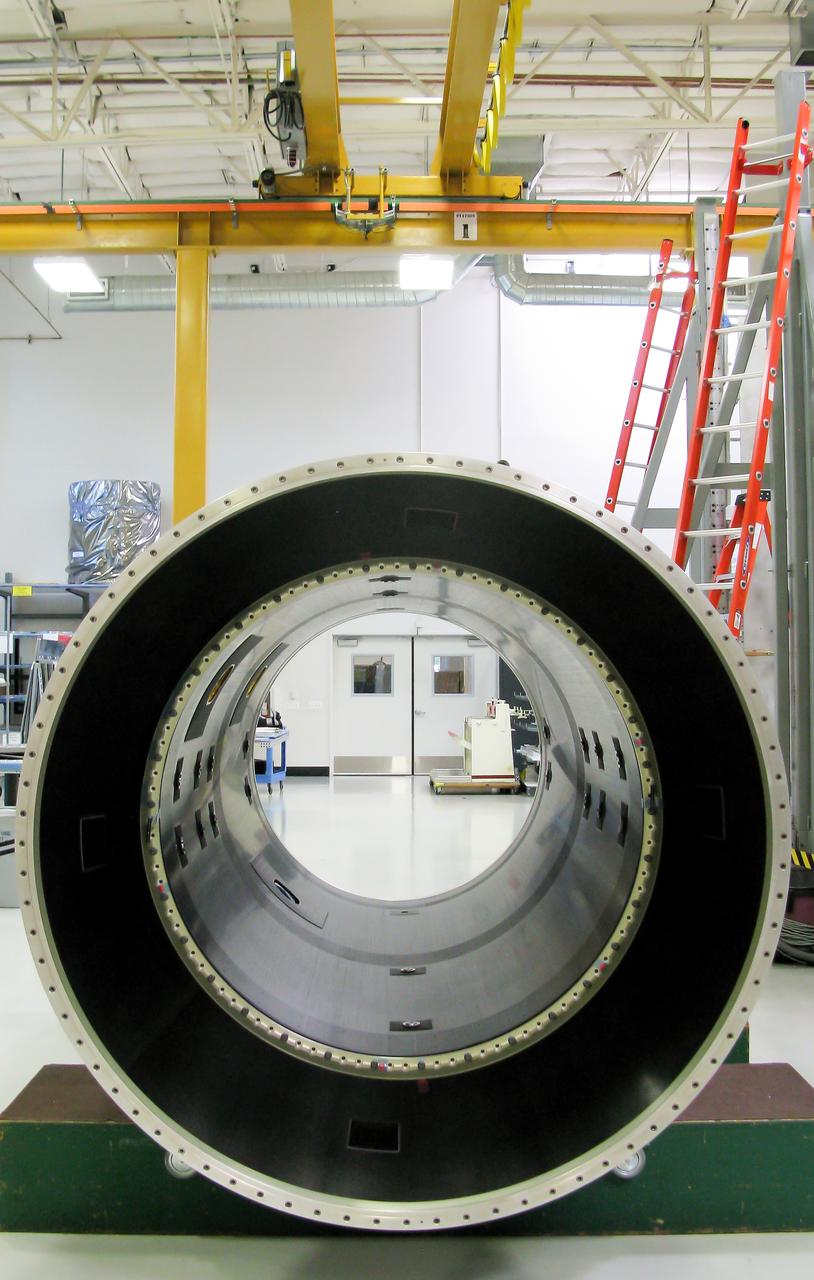

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
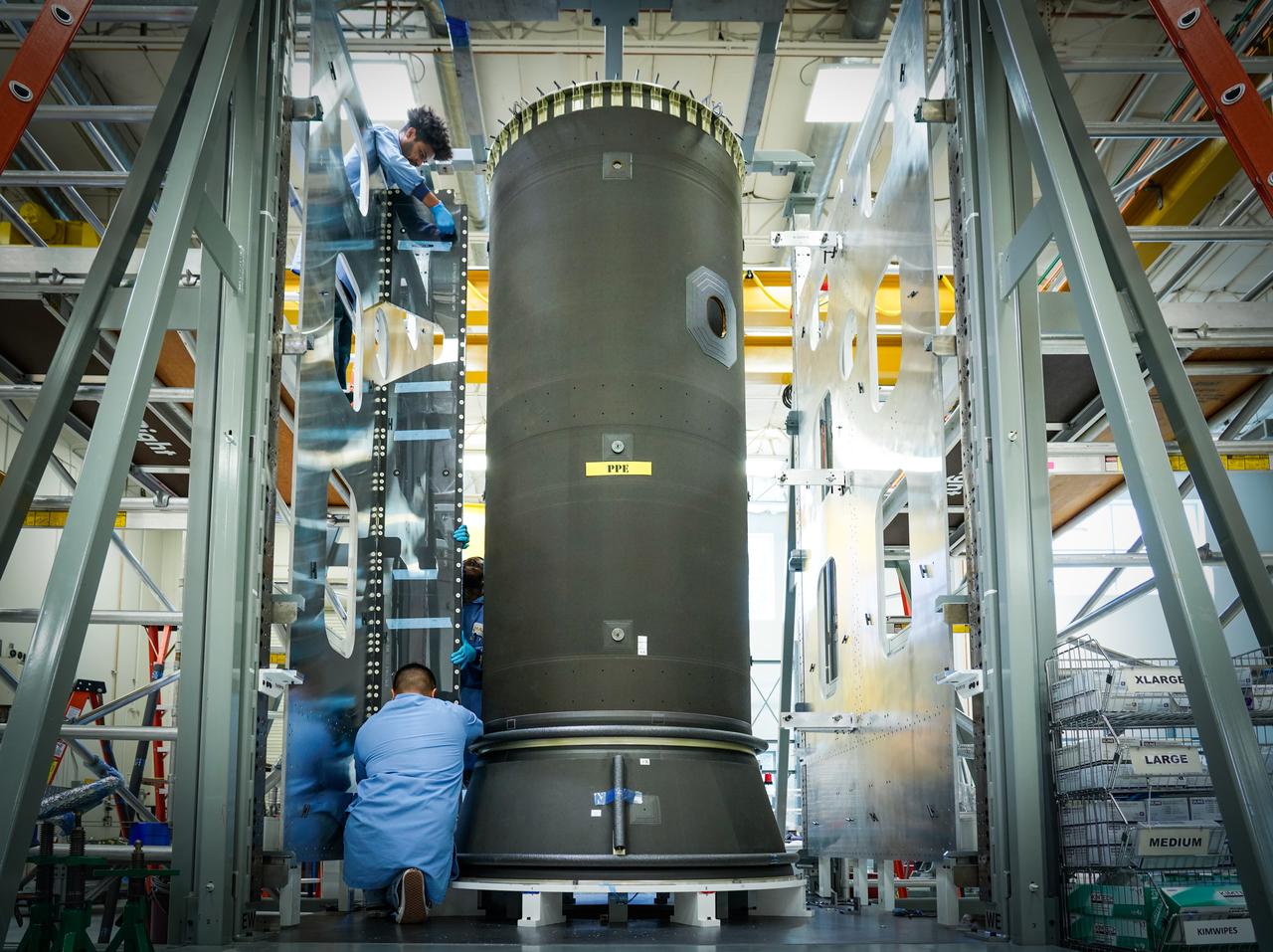

Maxar Technologies completes early fabrication work on the central cylinder structure of the Gateway space station's Power and Propulsion Element (PPE) that will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
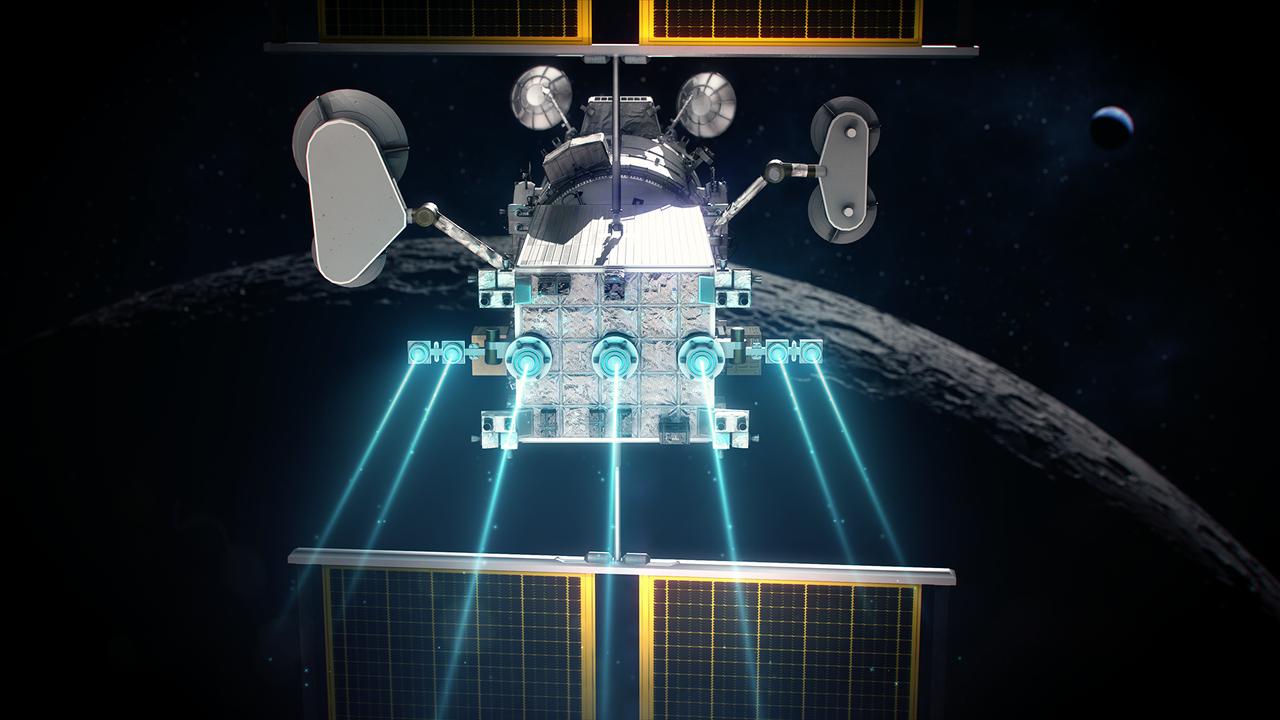
The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
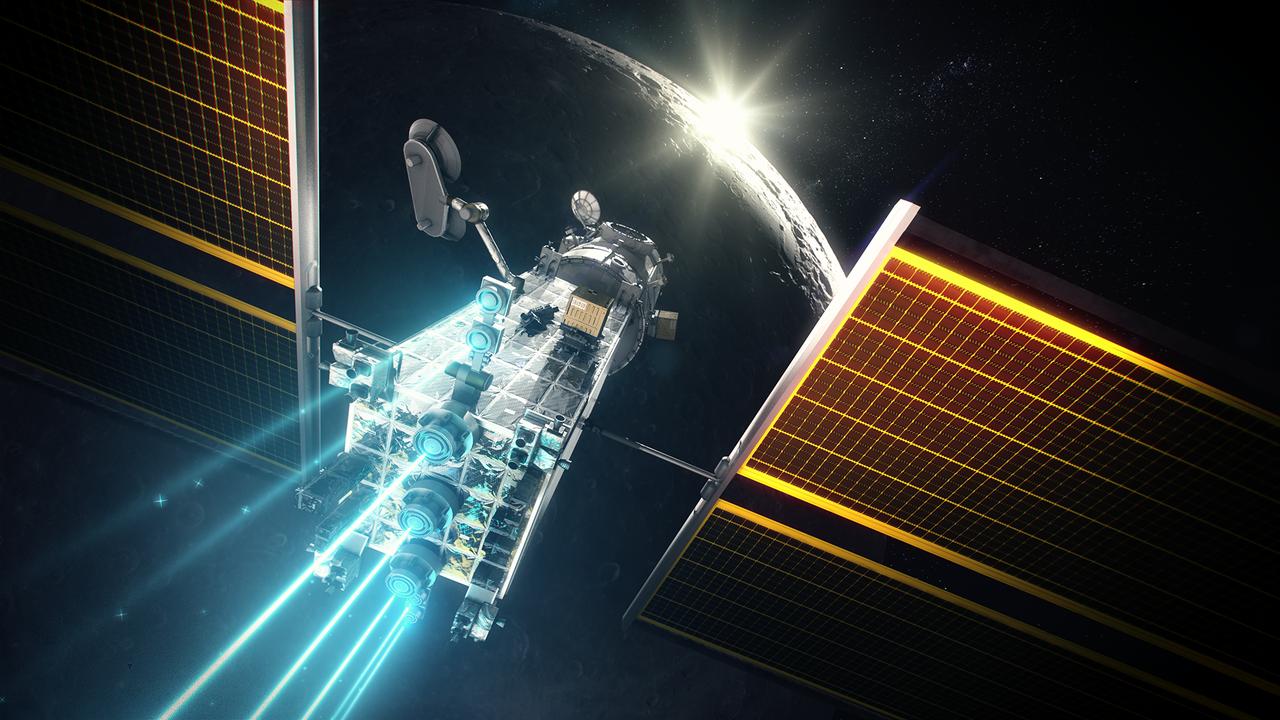

The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.
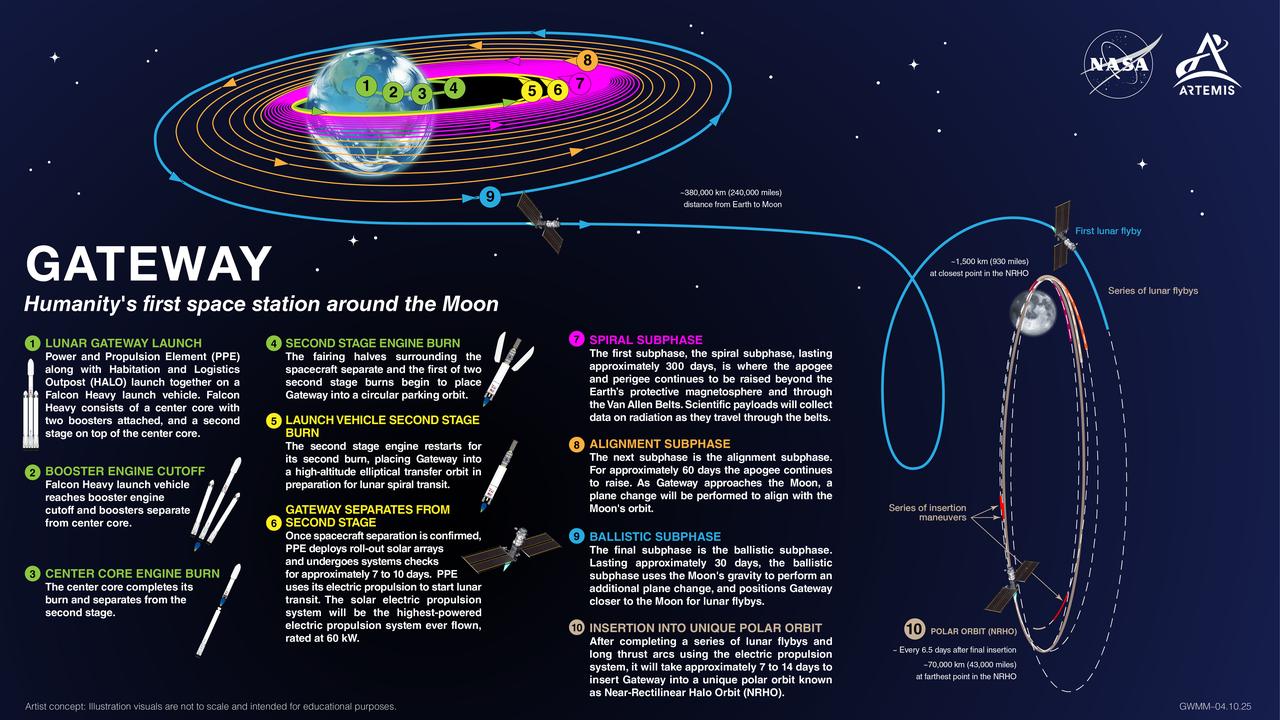
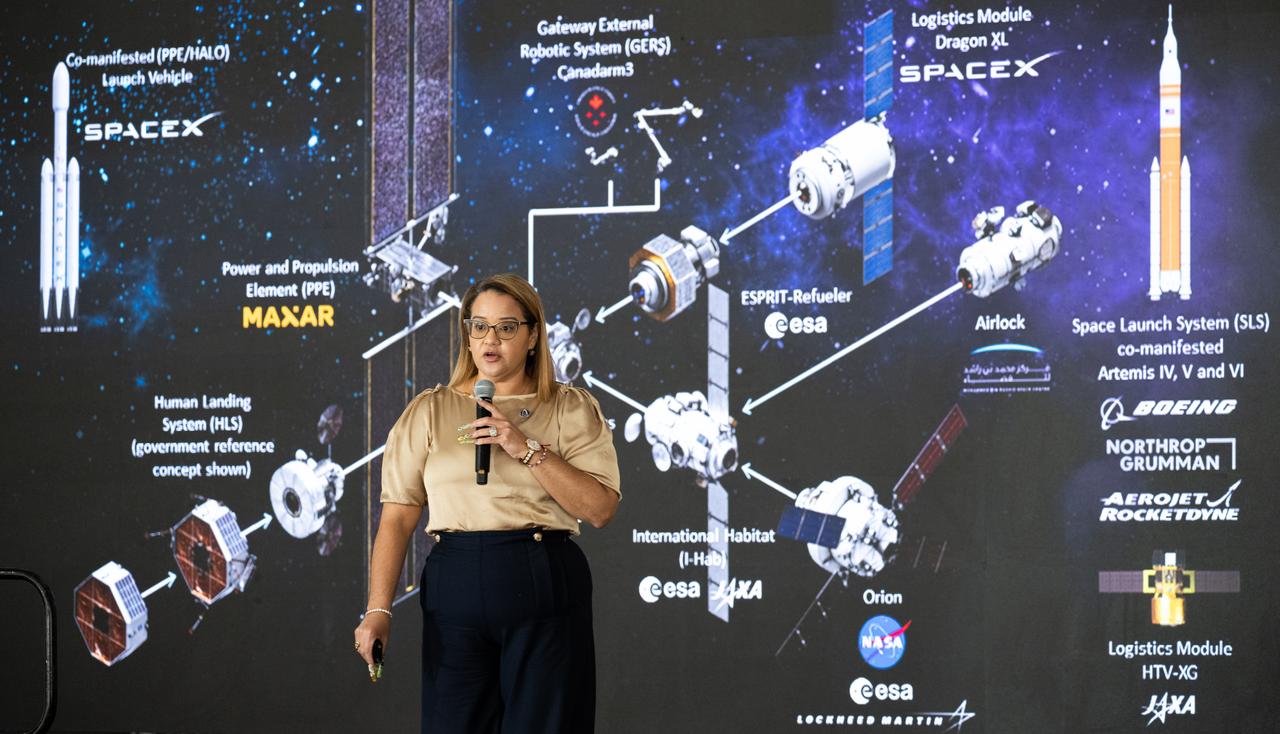
The Lunar Gateway Launch, mapped. Gateway's first elements, the Power and Propulsion Element and HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost), will launch together to lunar orbit, where they’ll set the stage for Artemis IV: the first Gateway assembly mission. During this milestone mission, the Artemis IV crew will deliver the European Space Agency's Lunar I-Hab, dock it to HALO, and enter the space station for the very first time. NASA is currently targeting a 2027 launch for HALO and the Power and Propulsion Element. This timeline allows for the roughly year-long journey to lunar orbit and ensures everything is in place ahead of Artemis IV.
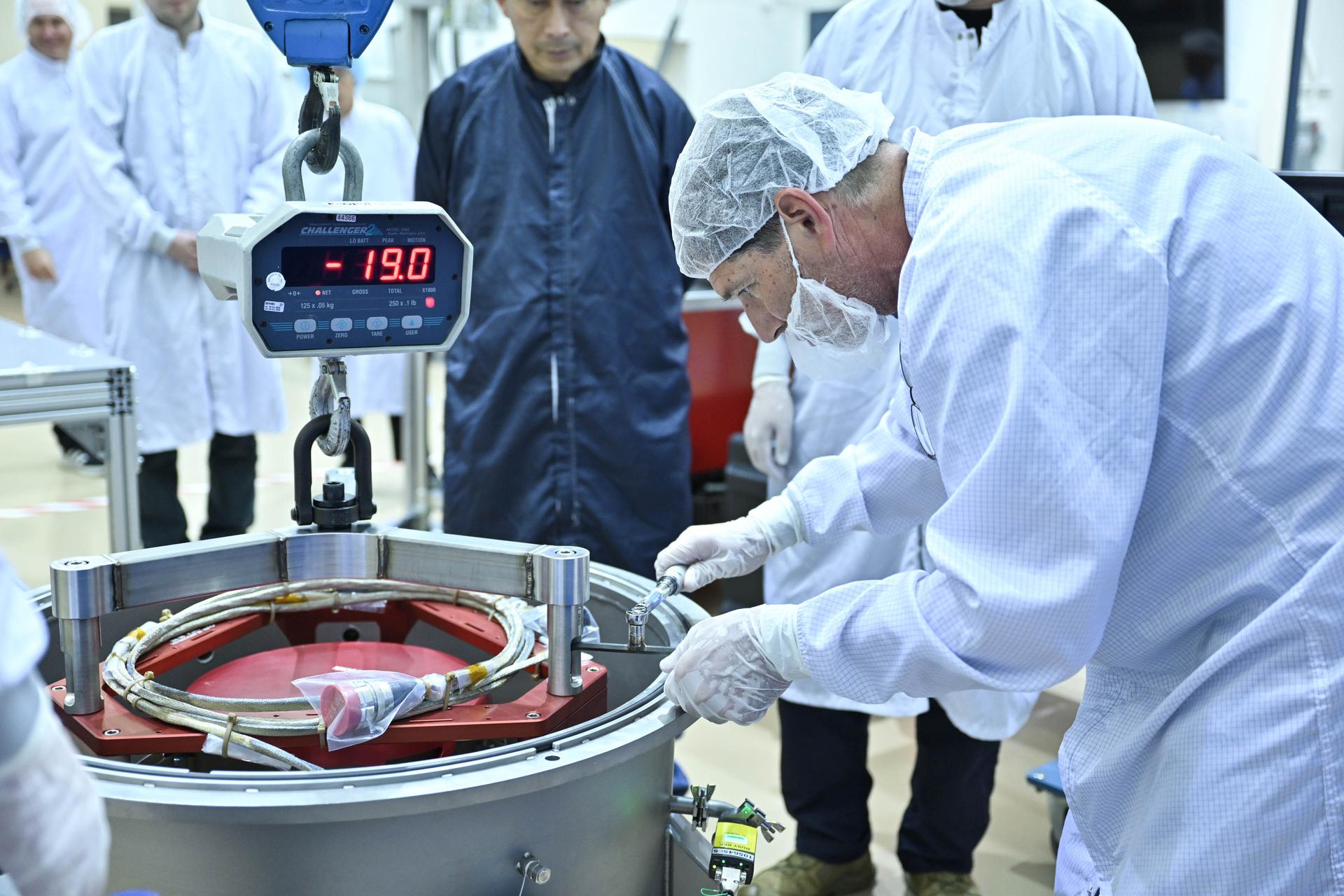

Technicians at Lanteris Space Systems in Palo Alto, California, remove the first of three Advanced Electric Propulsion System (AEPS) flight thrusters from its transport container following delivery from NASA’s Glenn Research Center. The thruster previously completed acceptance testing at Glenn and will be prepared for integration with Gateway’s Power and Propulsion Element (PPE).
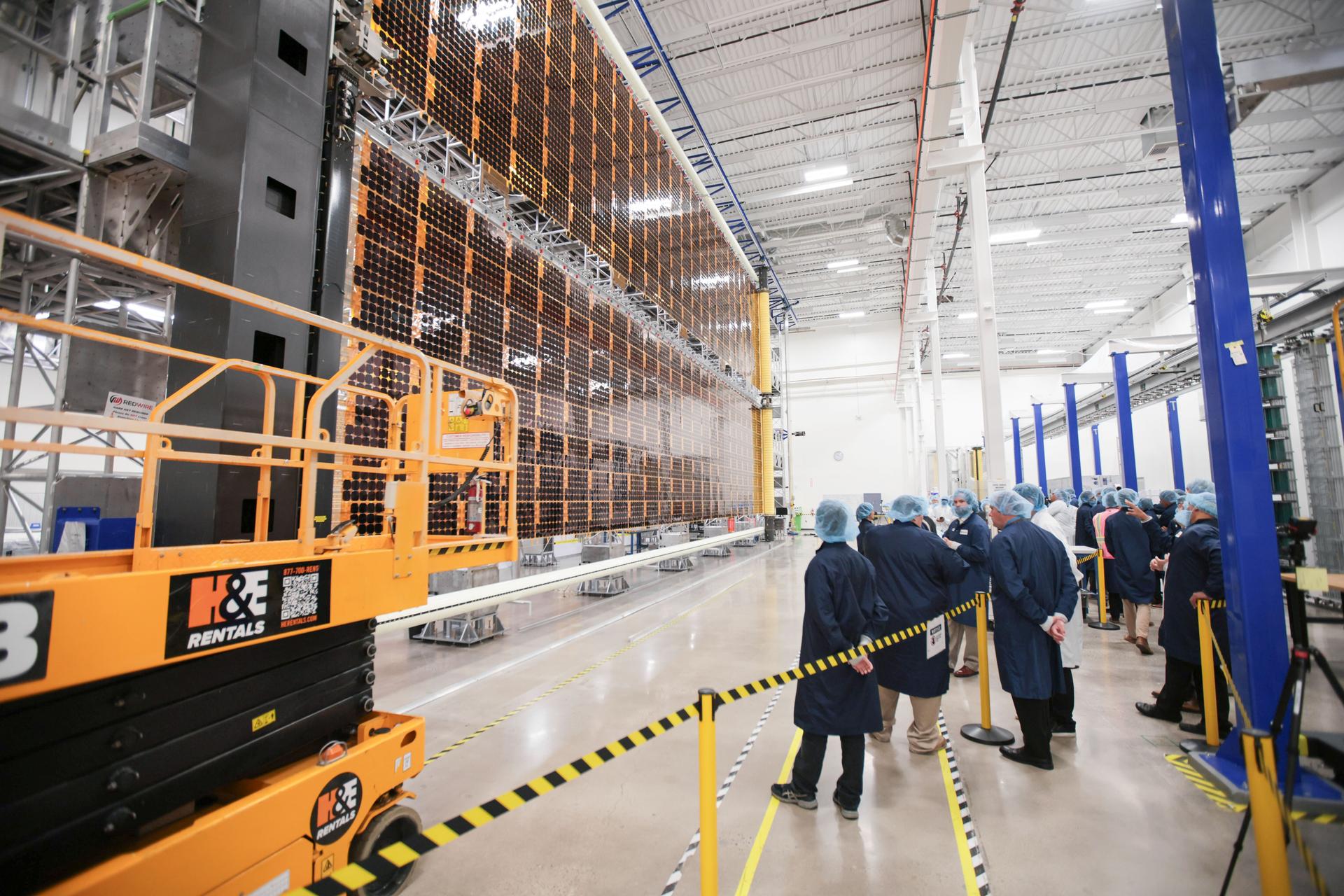

A Roll-Out Solar Array (ROSA) wing for Gateway stands fully deployed inside Redwire’s high-bay facility in Goleta, California, following a successful deployment test on June 30, 2025. The image shows the extended solar array structure as NASA’s Gateway Program leadership and representatives from industry and international partners observe the test from the facility floor. Credit: NASA

NASA and industry team members observe a Roll-Out Solar Array (ROSA) wing for Gateway as it deploys inside Redwire’s high-bay facility in Goleta, California, during a test on June 30, 2025. The image shows the solar array partially extended as technicians monitor the process from the facility floor and elevated work platforms. Credit: Lanteris Space Systems

The Power and Propulsion Element's 12 kw thrusters will make Gateway the most powerful solar electric spacecraft ever flown.

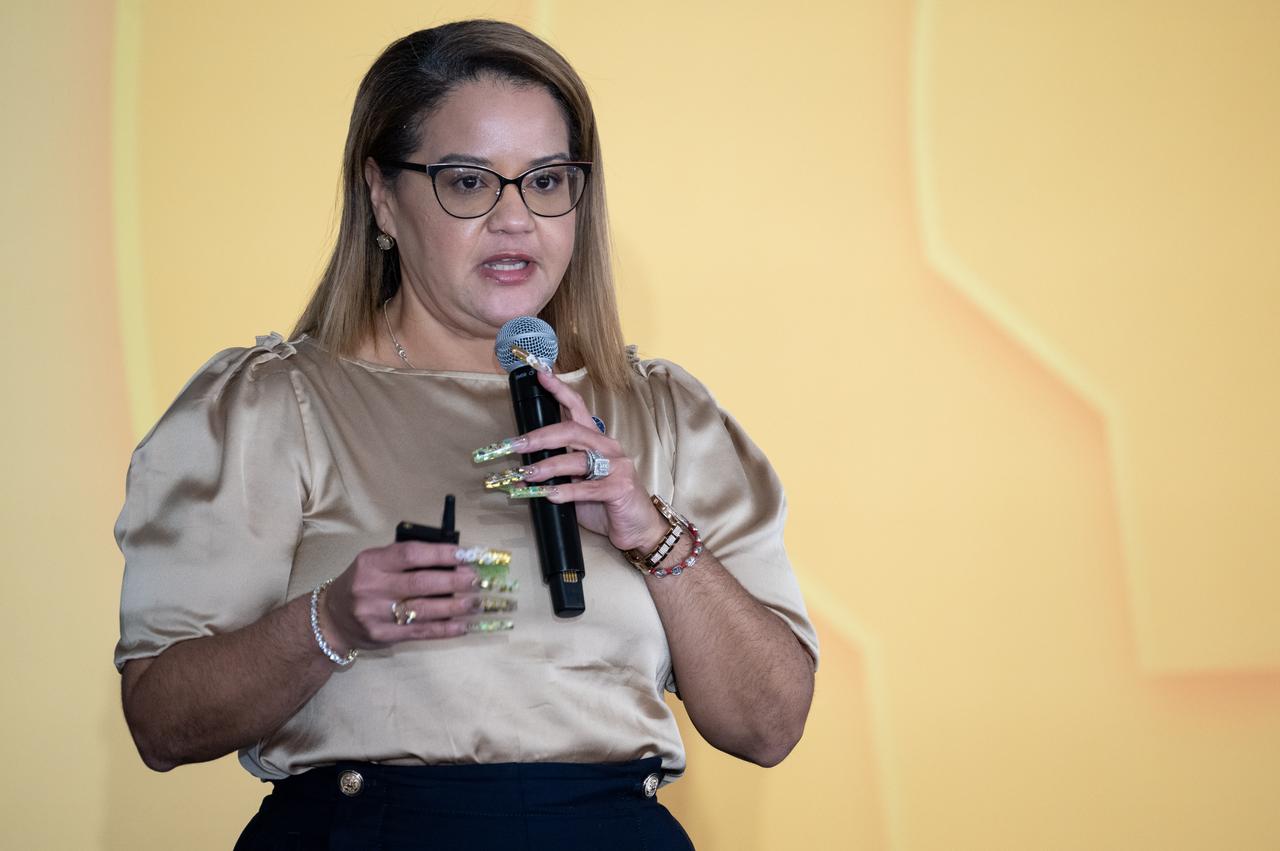
Dr. Dionne Hernandez-Lugo, Power and Propulsion Element Contracting Officer Representative in the Gateway & Power and Propulsion Element Office of NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
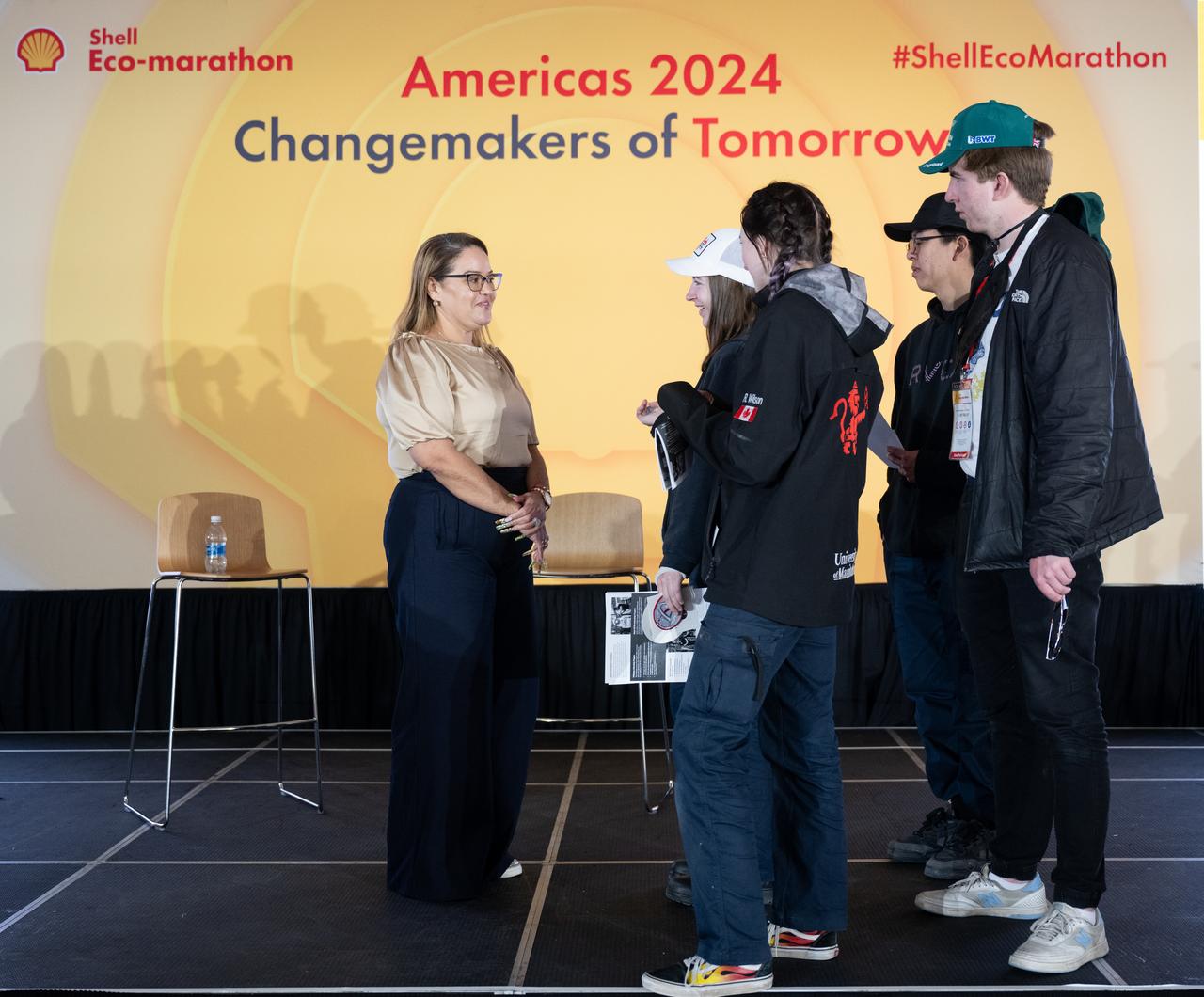

Dr. Dionne Hernandez-Lugo, Power and Propulsion Element Contracting Officer Representative in the Gateway & Power and Propulsion Element Office of NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students after discussing about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Dr. Dionne Hernandez-Lugo, Power and Propulsion Element Contracting Officer Representative in the Gateway & Power and Propulsion Element Office of NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Dr. Dionne Hernandez-Lugo, Power and Propulsion Element Contracting Officer Representative in the Gateway & Power and Propulsion Element Office of NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, left, and Logan Kennedy, surface lead for Human Landing System Programs in NASA's Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, right, speaks to students about power production and energy for the Artemis Program at the Shell Eco-marathon Americas, Saturday, April 6, 2024, at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway in Indianapolis, Ind. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
/jsc2024e044856 (1)~medium.jpg)
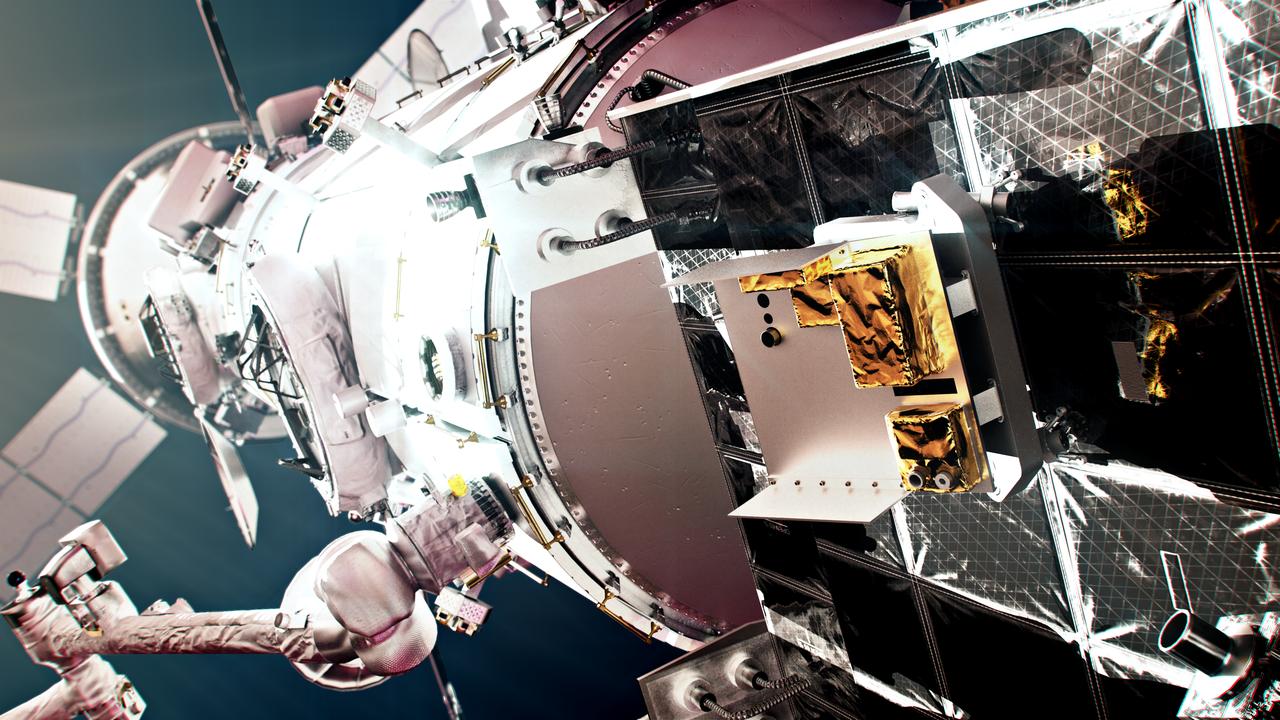
jsc2024e044856 (July 1, 2024) -- Two engineers in cleanroom suits work on the Power and Propulsion Element at Maxar Space Systems in Palo Alto, California. Photo Credit: Maxar Space Systems
/Gateway - Intermodule Element Adaptor (IEA)~medium.jpg)
The Intermodule Element Adaptor (IEA) is attached to the aft bulkhead of the Habitation Element (HE) to support mechanical integration of HALO and PPE. The IEA is also used to provide an enclosure to protect the HALO batteries.

The European Radiation Sensors Array is one of the first three science payloads selected to fly on the Gateway space station. ERSA will study solar and cosmic radiation to help the science community better understand this primary concern for people and hardware during deep space travels.
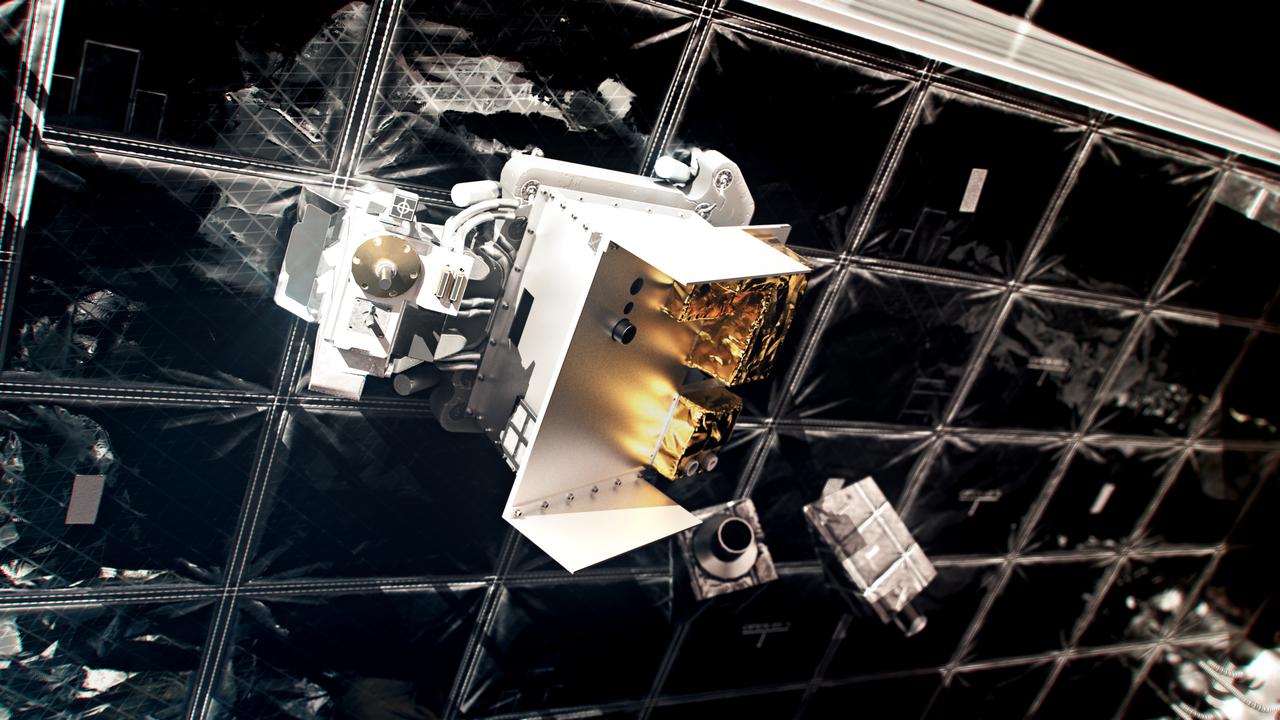

The European Radiation Sensors Array is one of the first three science payloads selected to fly on the Gateway space station. ERSA will study solar and cosmic radiation to help the science community better understand this primary concern for people and hardware during deep space travels.
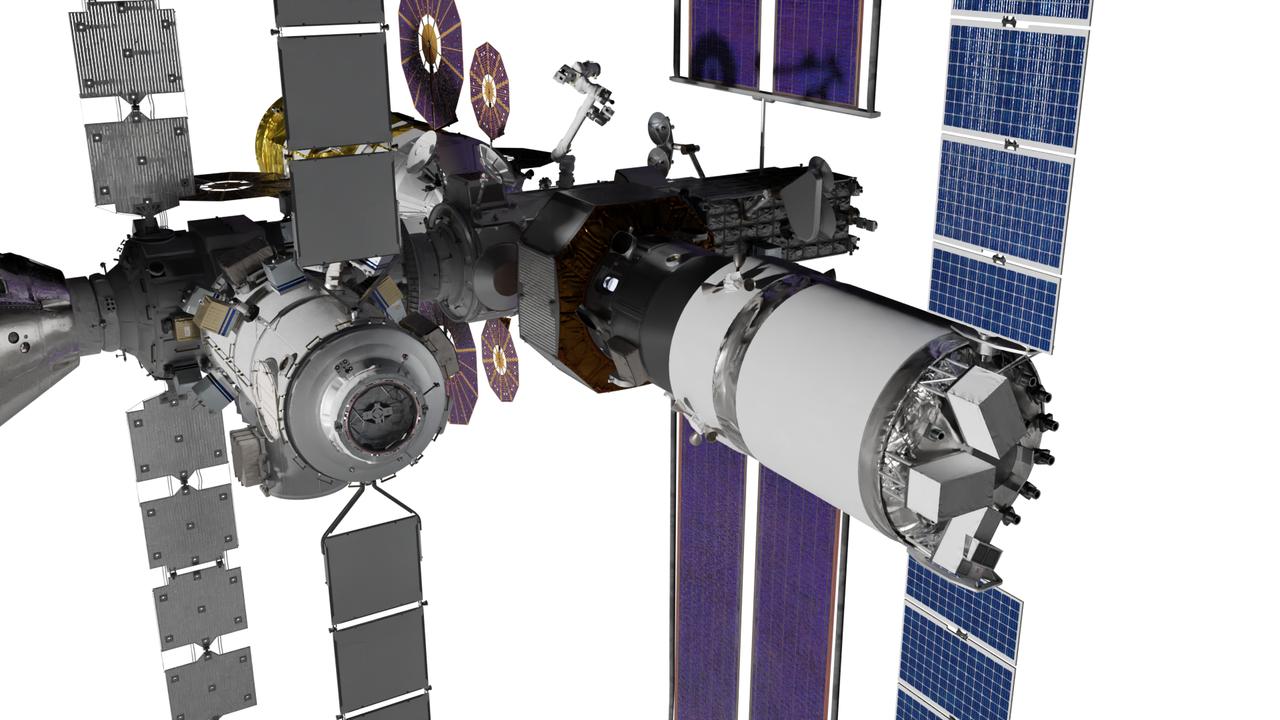
An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
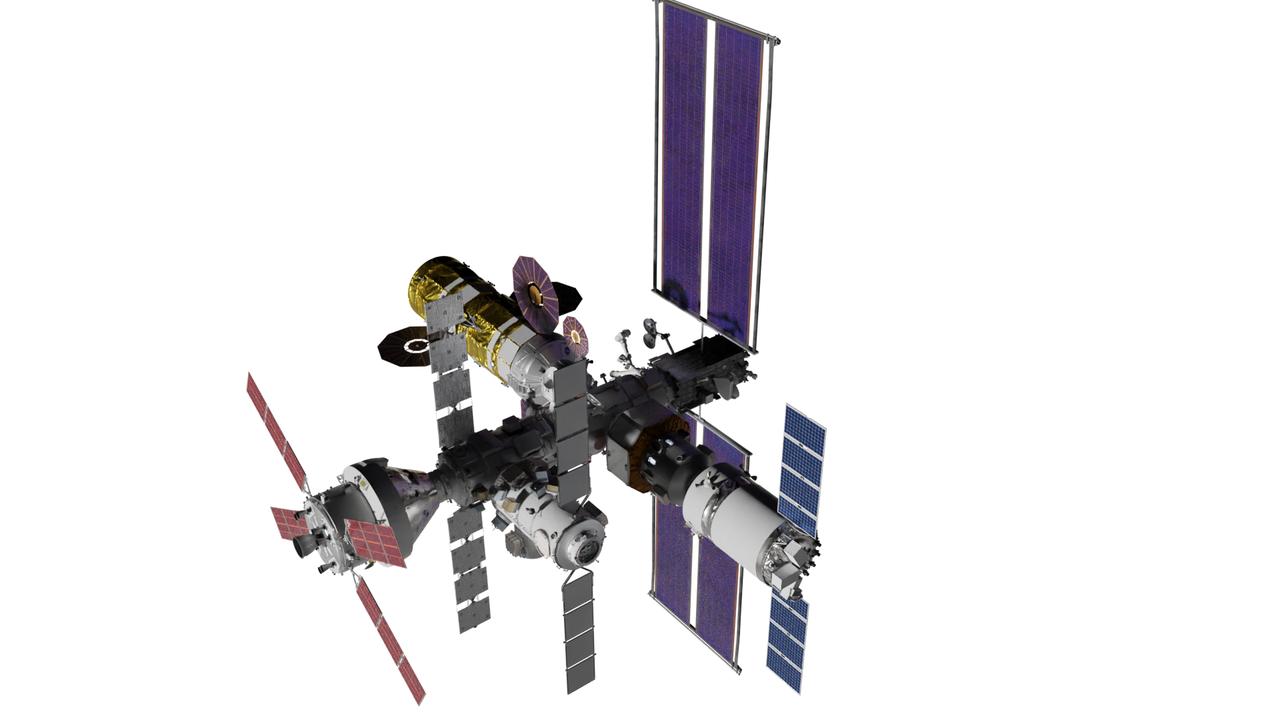

An artist’s rendering displays a configuration of the lunar-orbiting Gateway space station’s modules and visiting spacecraft. The core elements of Gateway consist of the Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) element, the Power and Propulsion Element (PPE), and Lunar I-Hab. Visiting vehicles include the Orion spacecraft, the Logistics Module, and the Human Landing System. Gateway is built in collaboration with NASA’s commercial and international partners to serve as a multiuse space port for lunar science as humanity’s first place to live and work in lunar orbit.
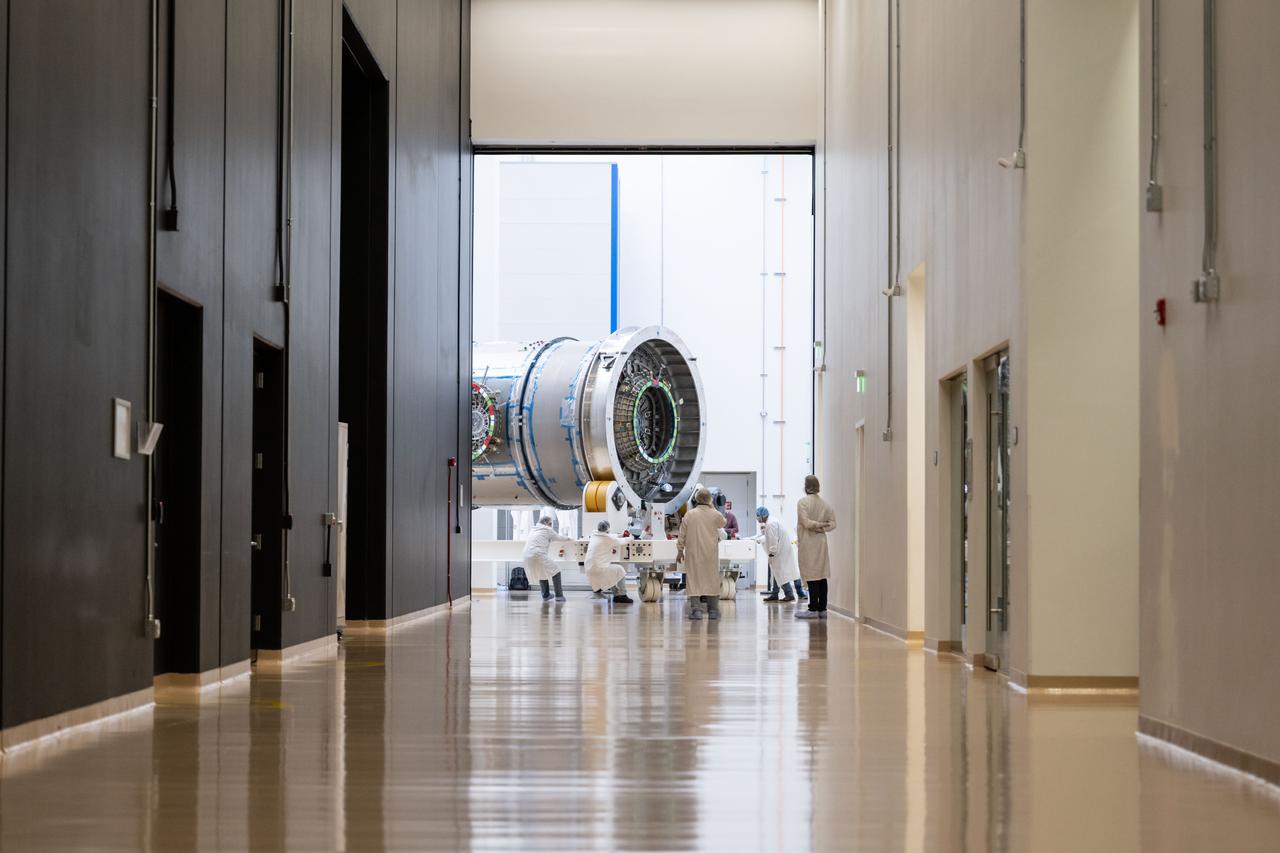

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams transport Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost). HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
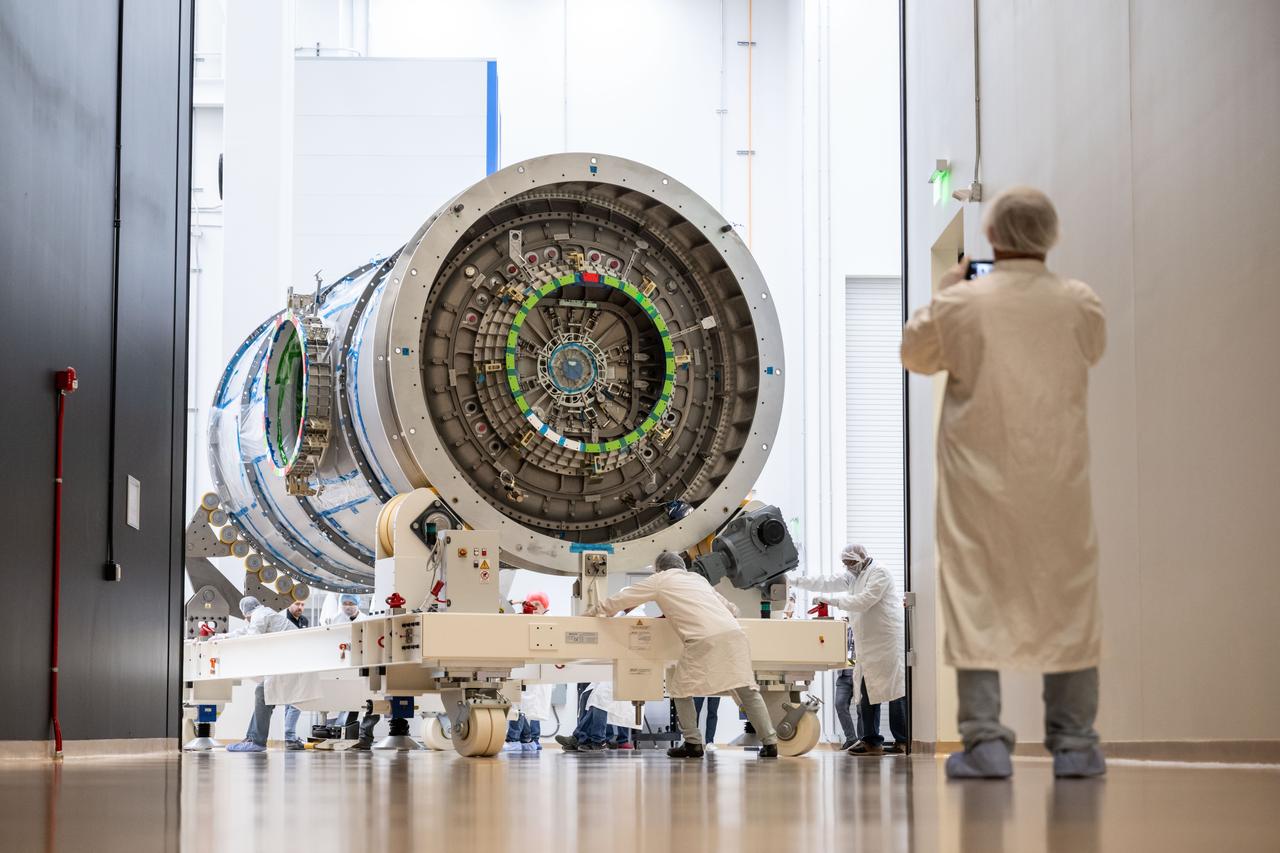

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams transport Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost). HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
/jsc2018e081150 (3)~medium.jpg)
Official NASA Portrait of Jon B. Olansen. Photo Date: September 12, 2018. Location: Building 8, Room 183 - Photo Studio. Photographer: Robert Markowitz
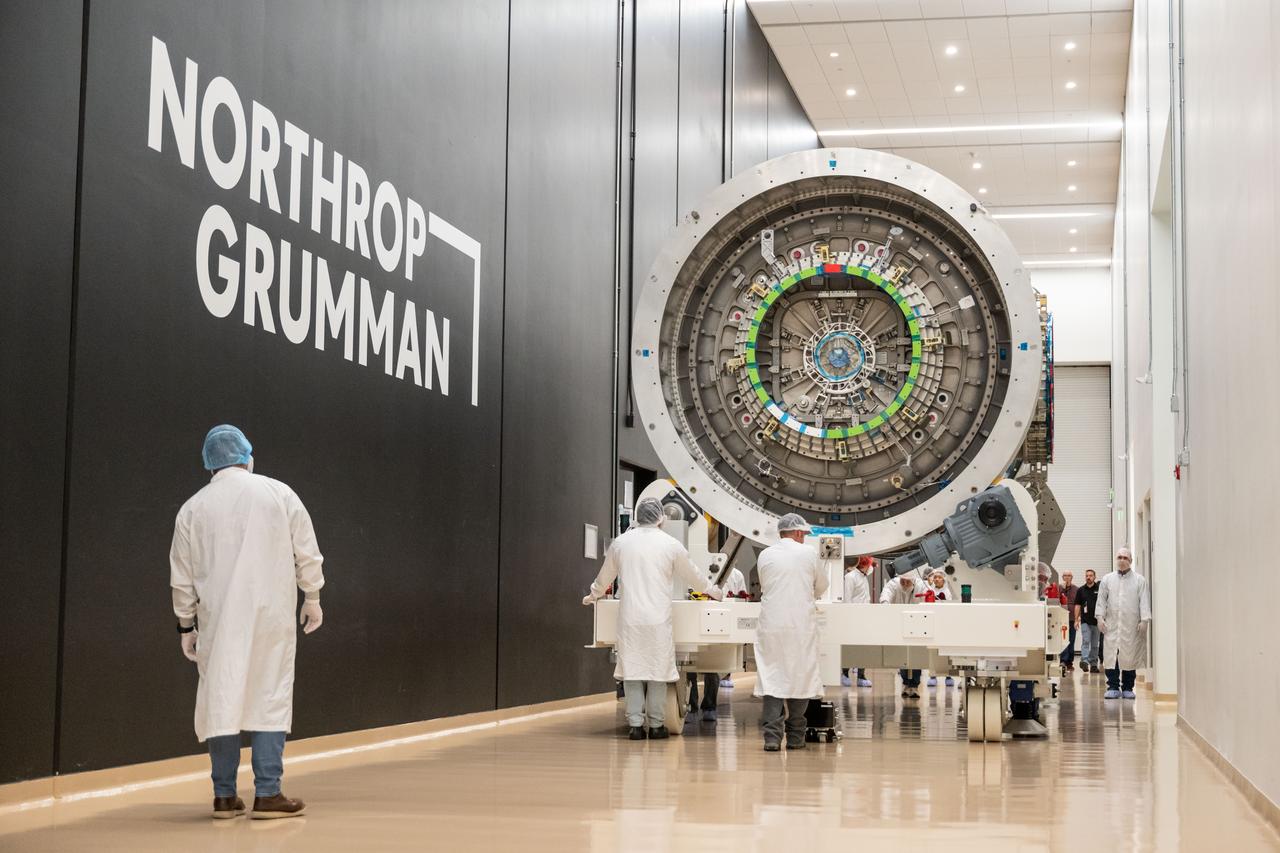

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams guide Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) down a hallway. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
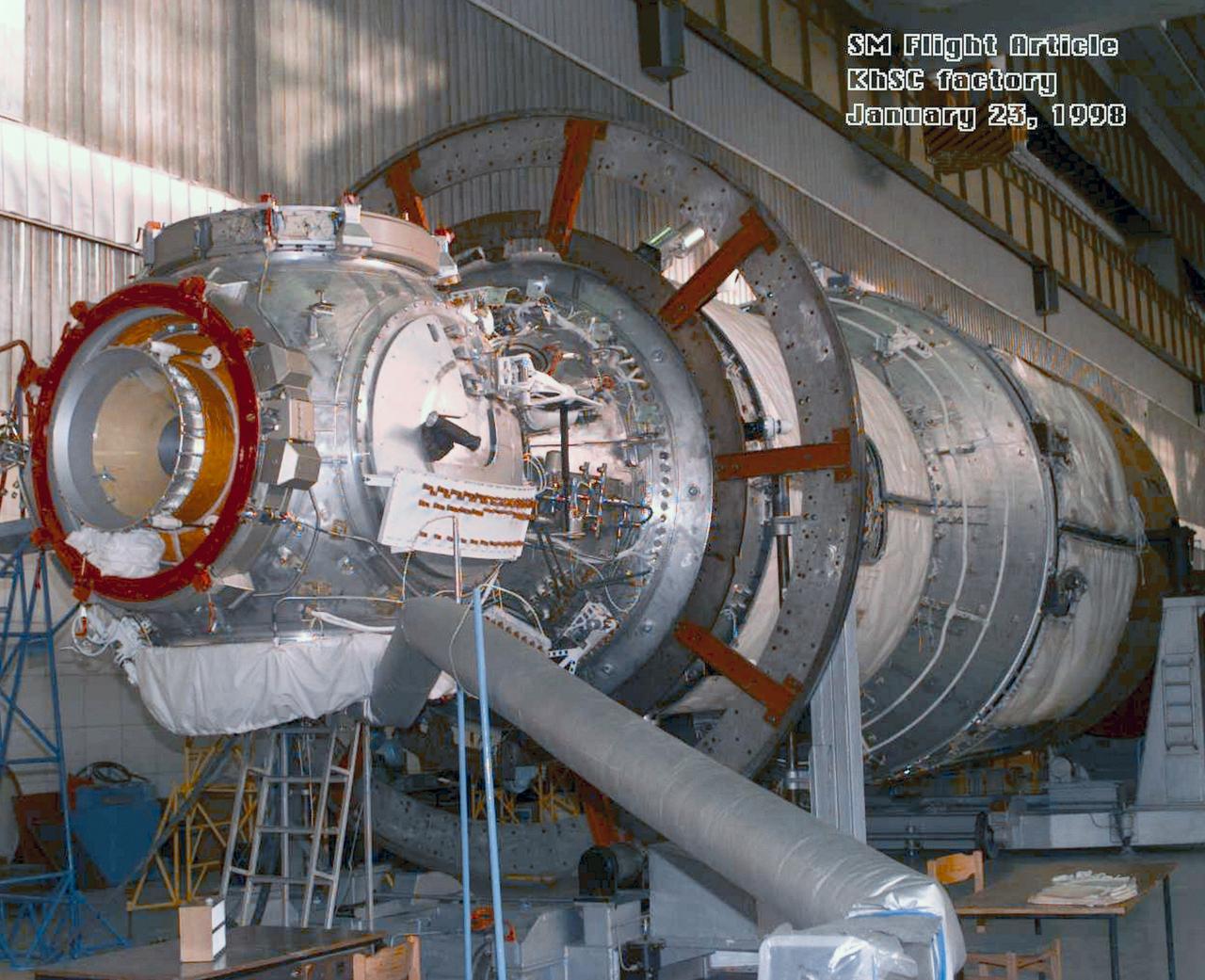
S98-04906 (23 Jan. 1998) --- A three-quarter frontal view of the flight article of the Service Module (SM) for the International Space Station (ISS). The first fully Russian contribution to ISS, the SM will provide early power, propulsion, life support, communications and living quarters for the station. It will be the third station element to be launched and join the United States-funded, Russian-built Functional Cargo Block (FGB) and the United States connecting module Node 1 in orbit.
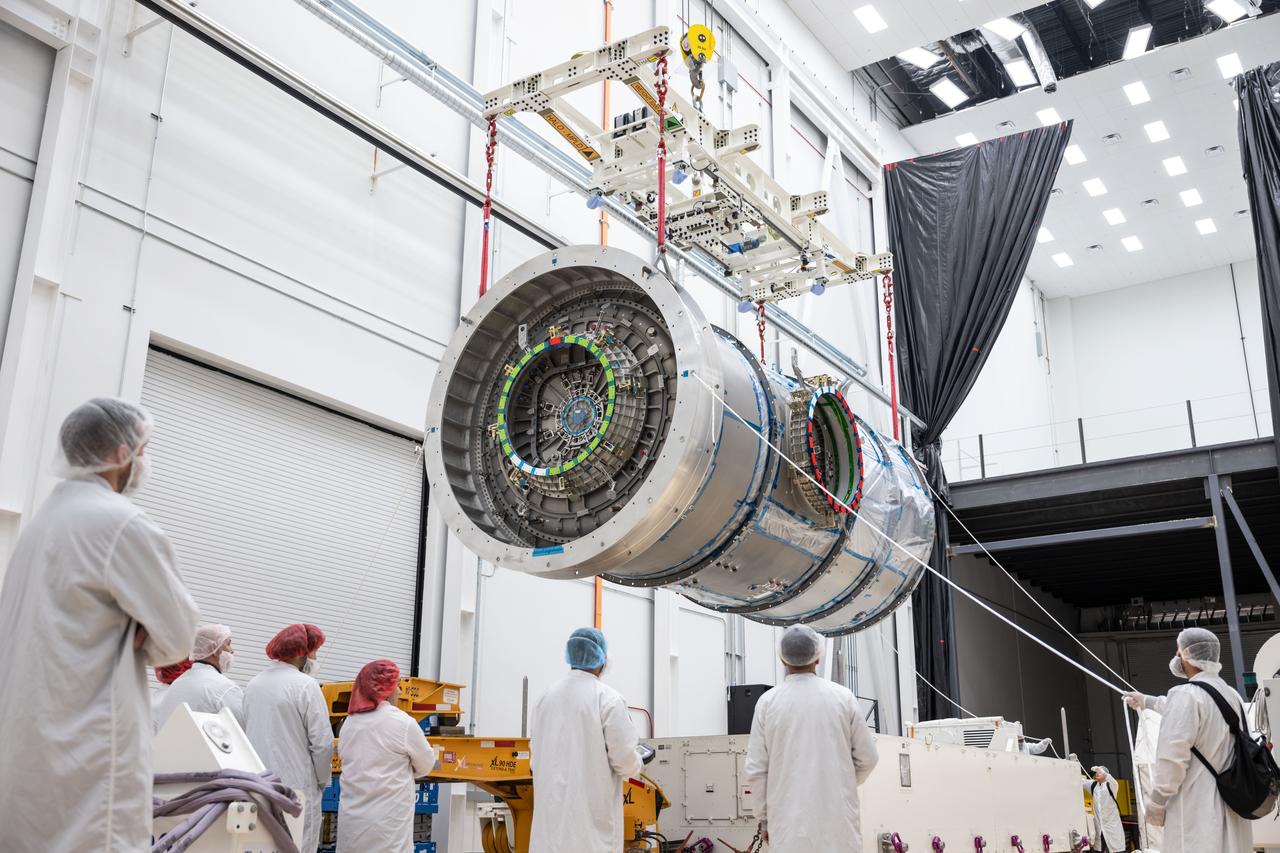

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
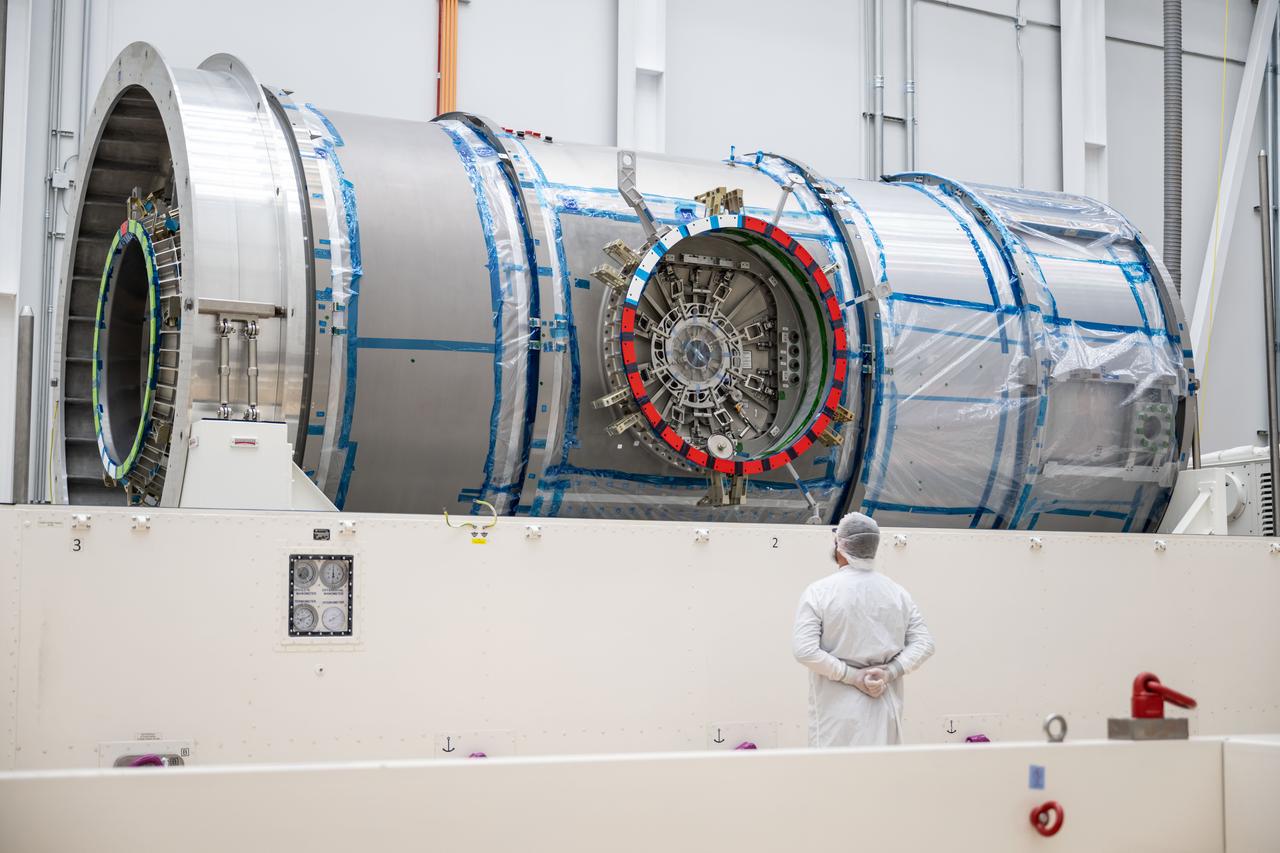

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
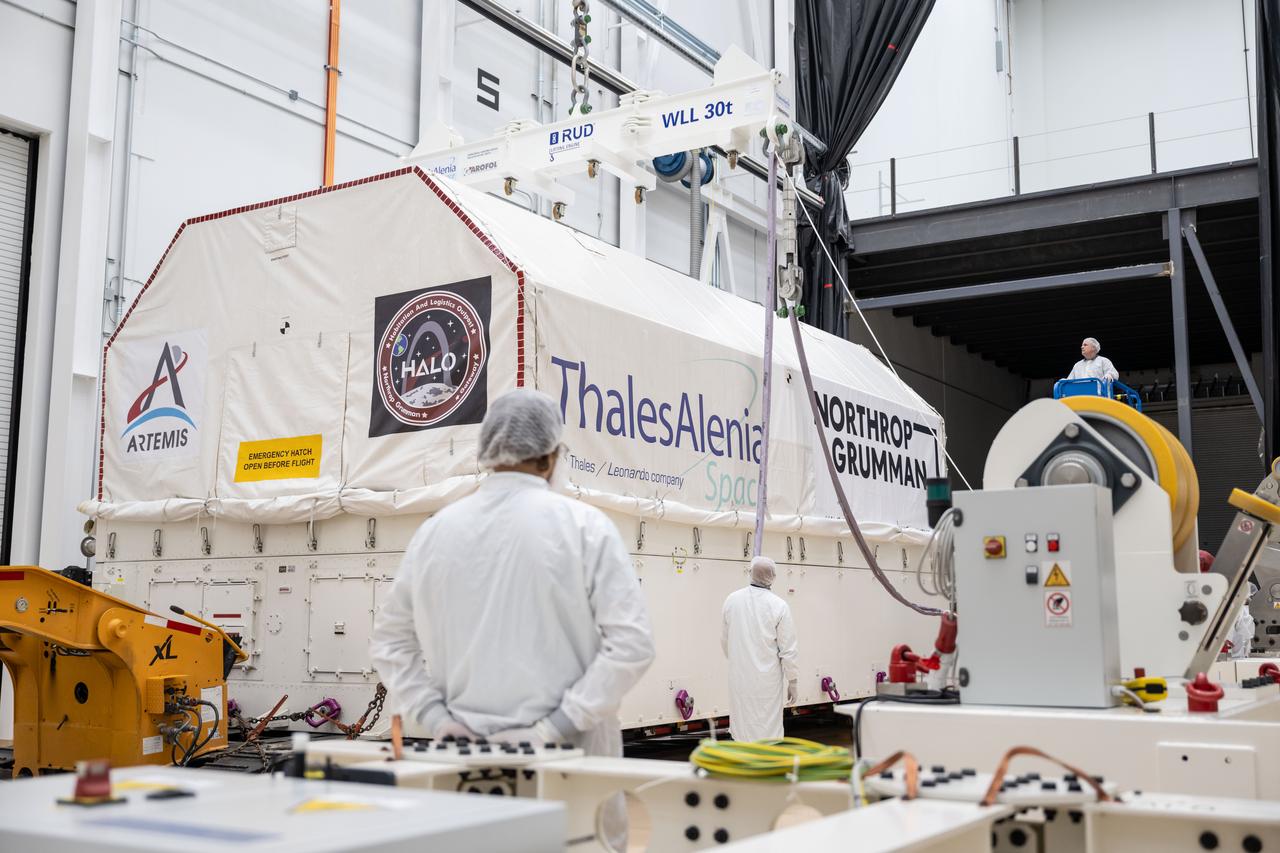

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
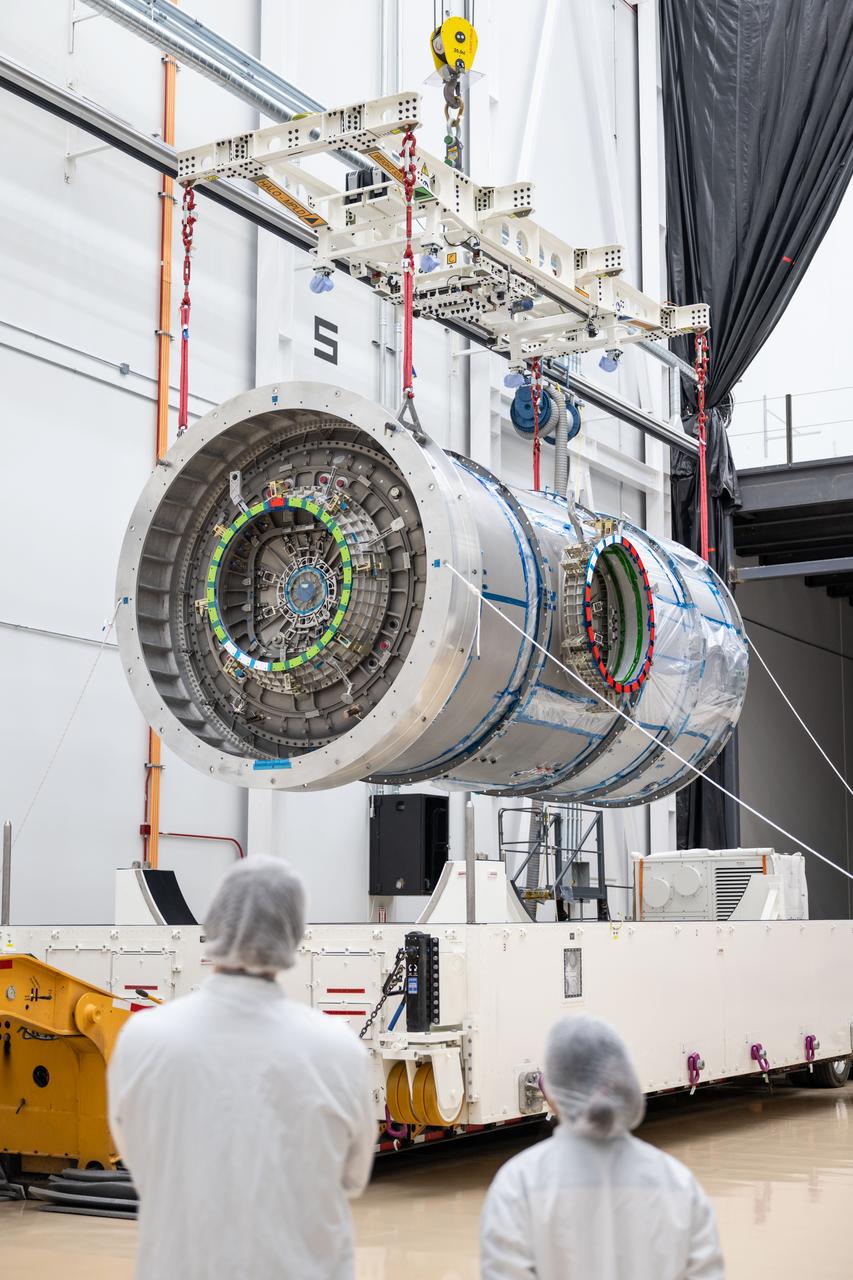

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
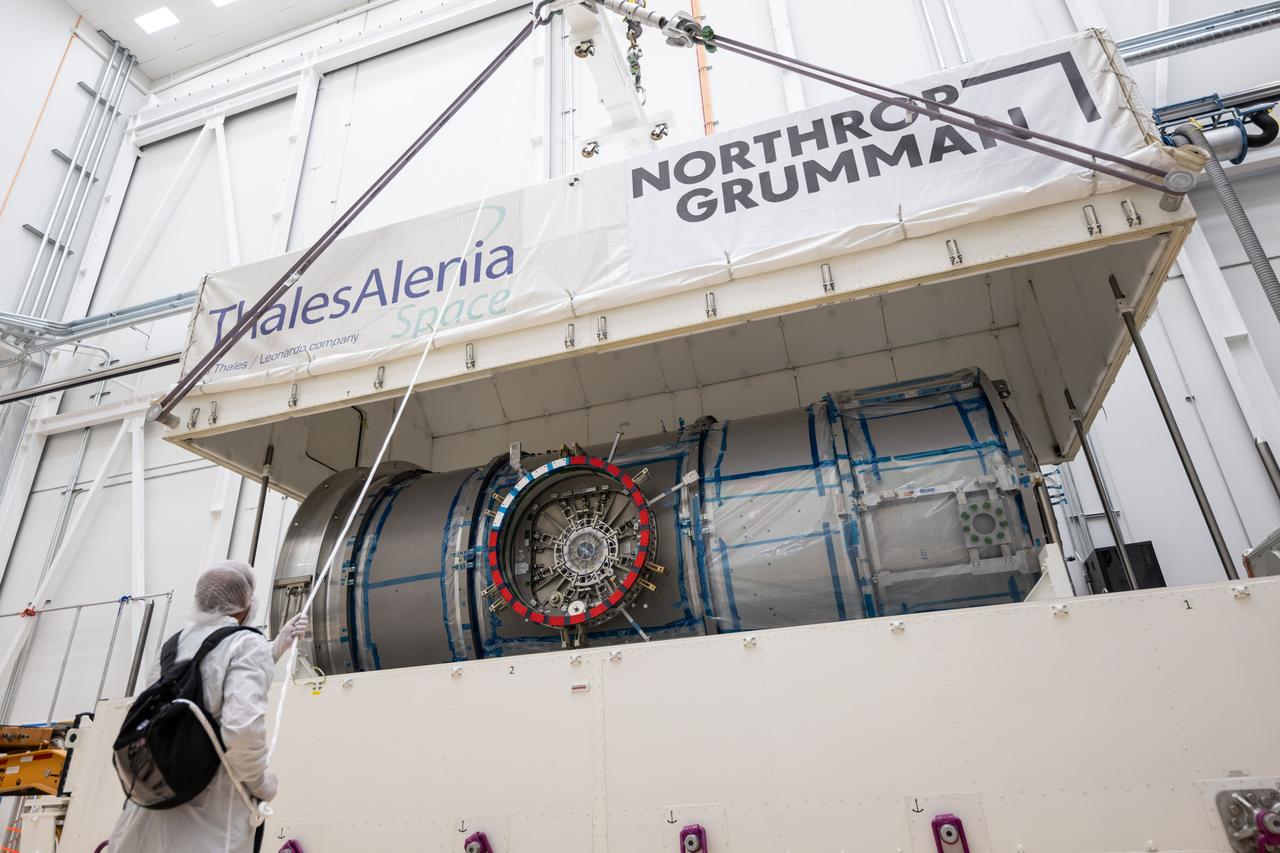

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams begin removing Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
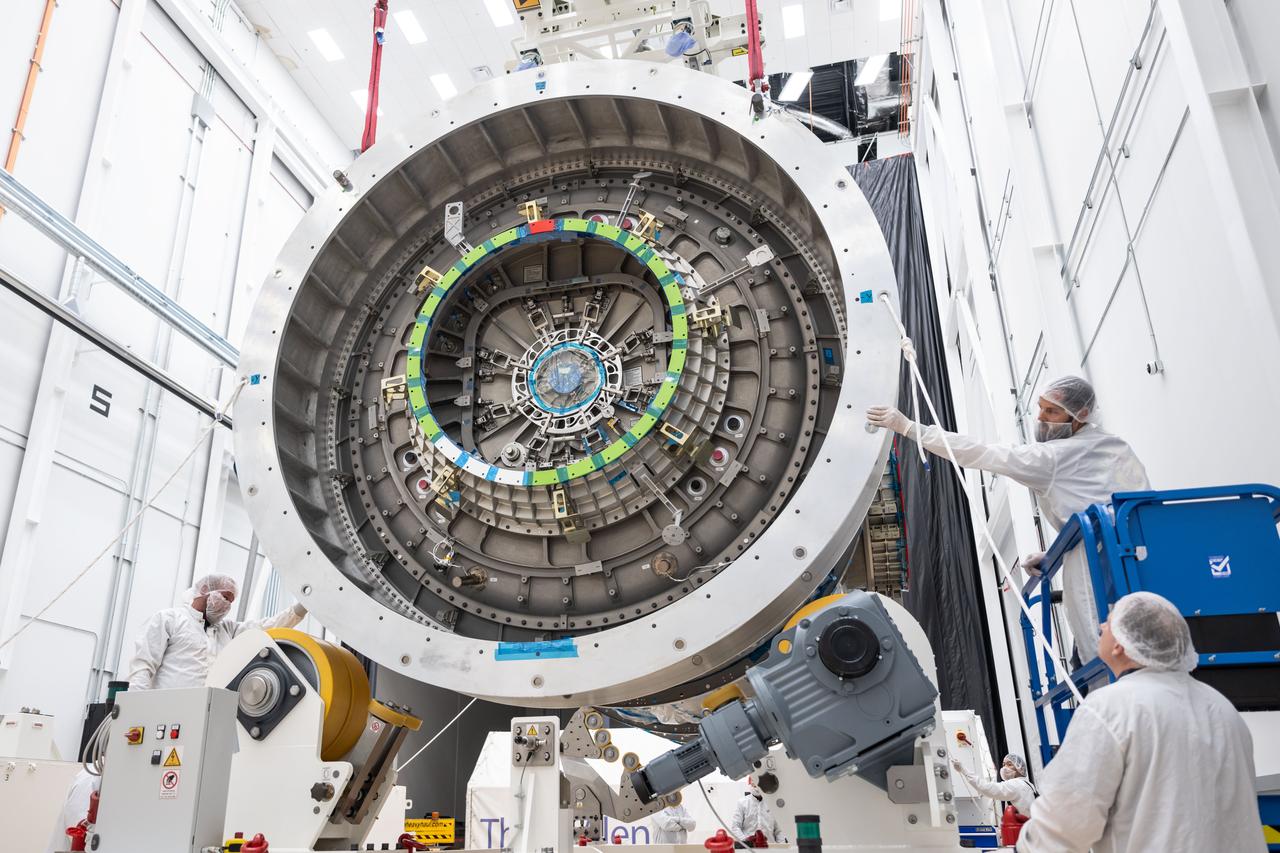
At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
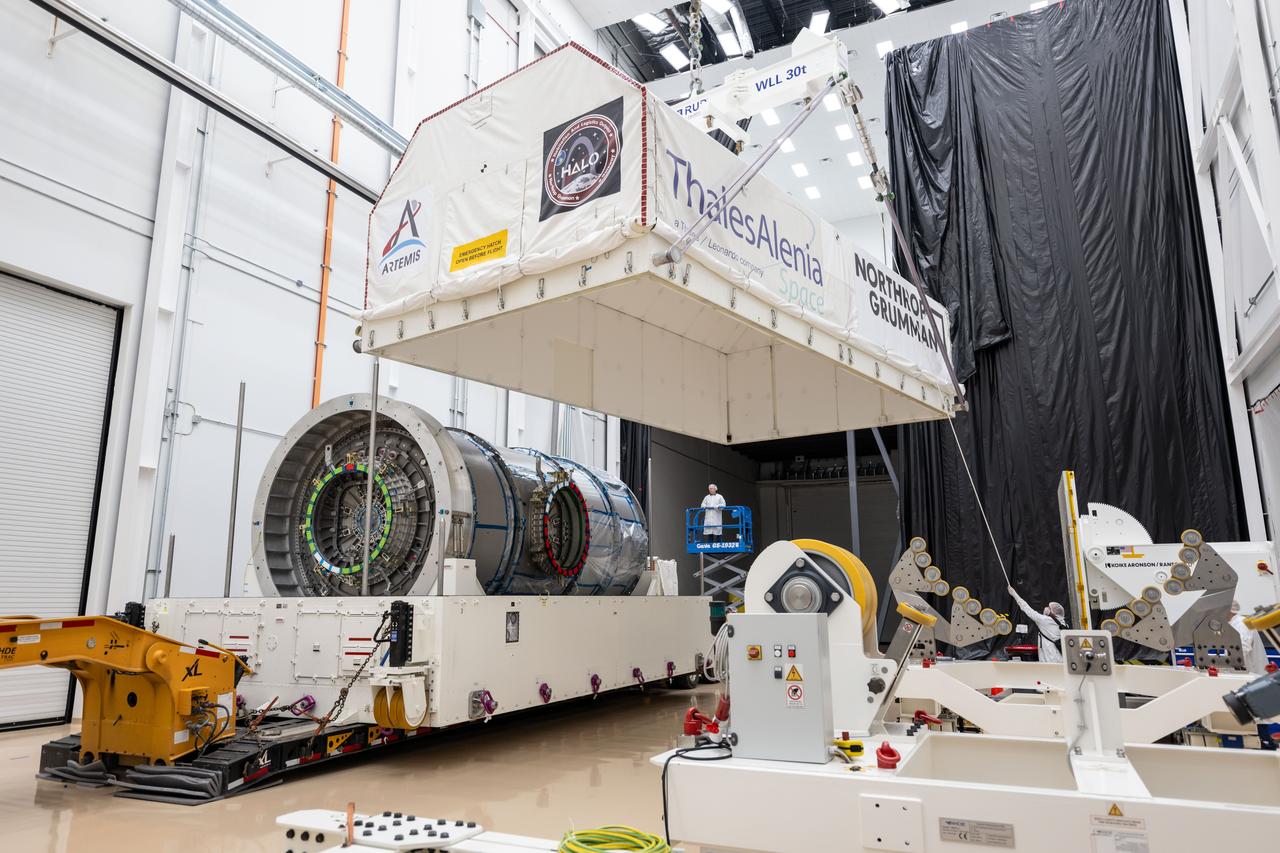

At Northrop Grumman’s Gilbert, Arizona, facility, teams remove Gateway’s HALO (Habitation and Logistics Outpost) from its transport container. HALO arrived from Turin, Italy, where Thales Alenia Space fabricated its primary structure. The module will undergo final outfitting in Gilbert before being integrated with the Power and Propulsion Element and launched to lunar orbit.
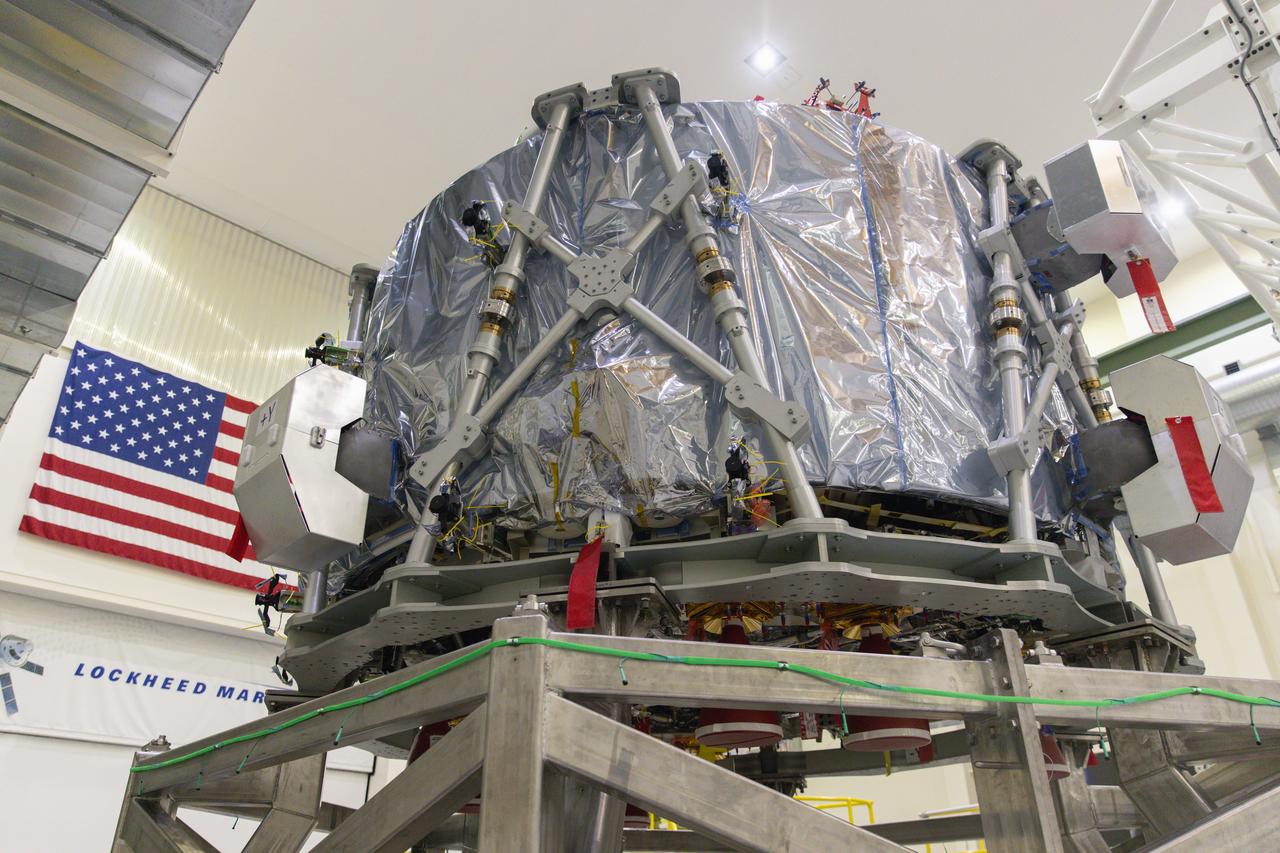

Teams from NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and Airbus prepare to integrate European Service Module 3 to the crew module adapter on Tuesday, Sept. 17, 2024, inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The integrated hardware provides propulsion, electrical power, and other important elements for the Orion spacecraft’s Artemis III campaign to the lunar South Pole region of the Moon.

Teams from NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and Airbus prepare to integrate European Service Module 3 to the crew module adapter on Tuesday, Sept. 17, 2024, inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The integrated hardware provides propulsion, electrical power, and other important elements for the Orion spacecraft’s Artemis III campaign to the lunar South Pole region of the Moon.

Teams from NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and Airbus prepare to integrate European Service Module 3 to the crew module adapter on Tuesday, Sept. 17, 2024, inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The integrated hardware provides propulsion, electrical power, and other important elements for the Orion spacecraft’s Artemis III campaign to the lunar South Pole region of the Moon.
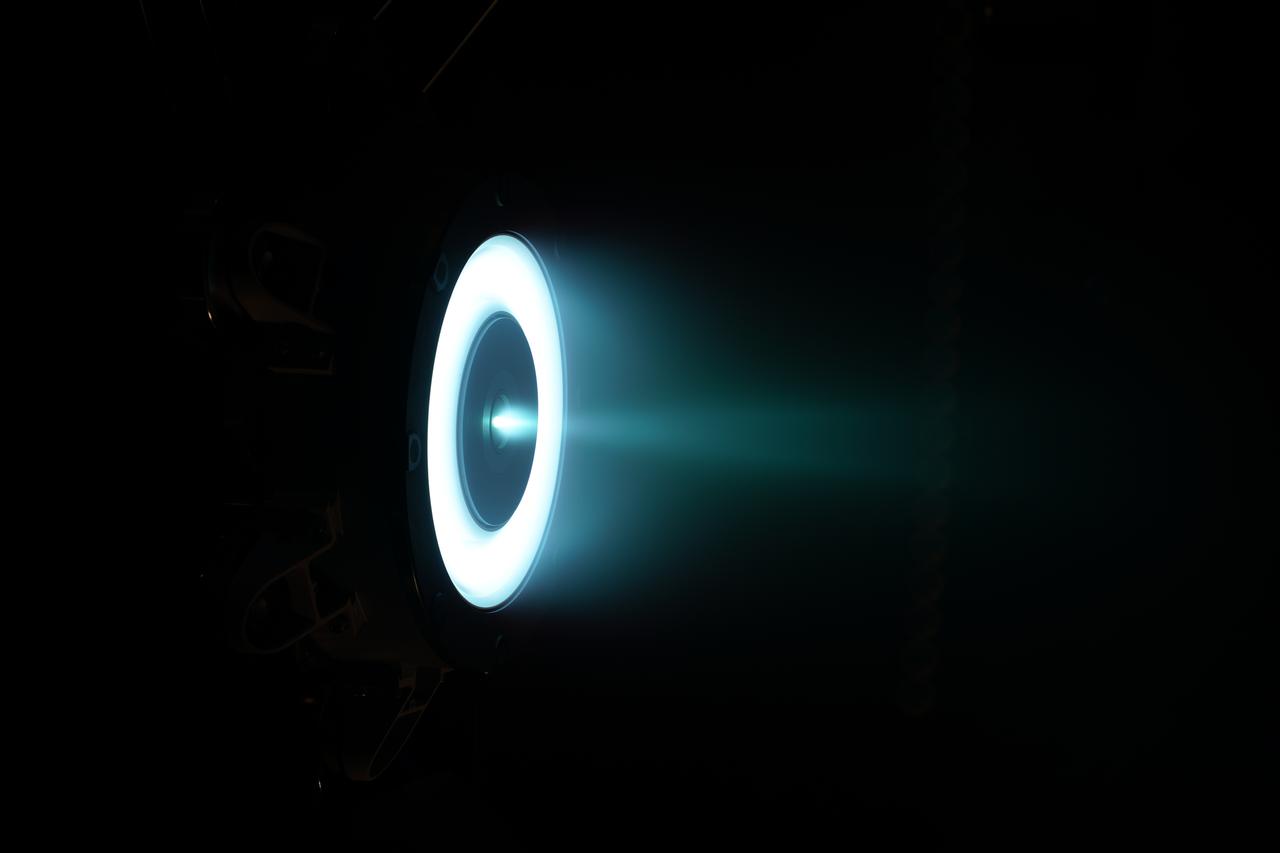
NASA and Aerojet
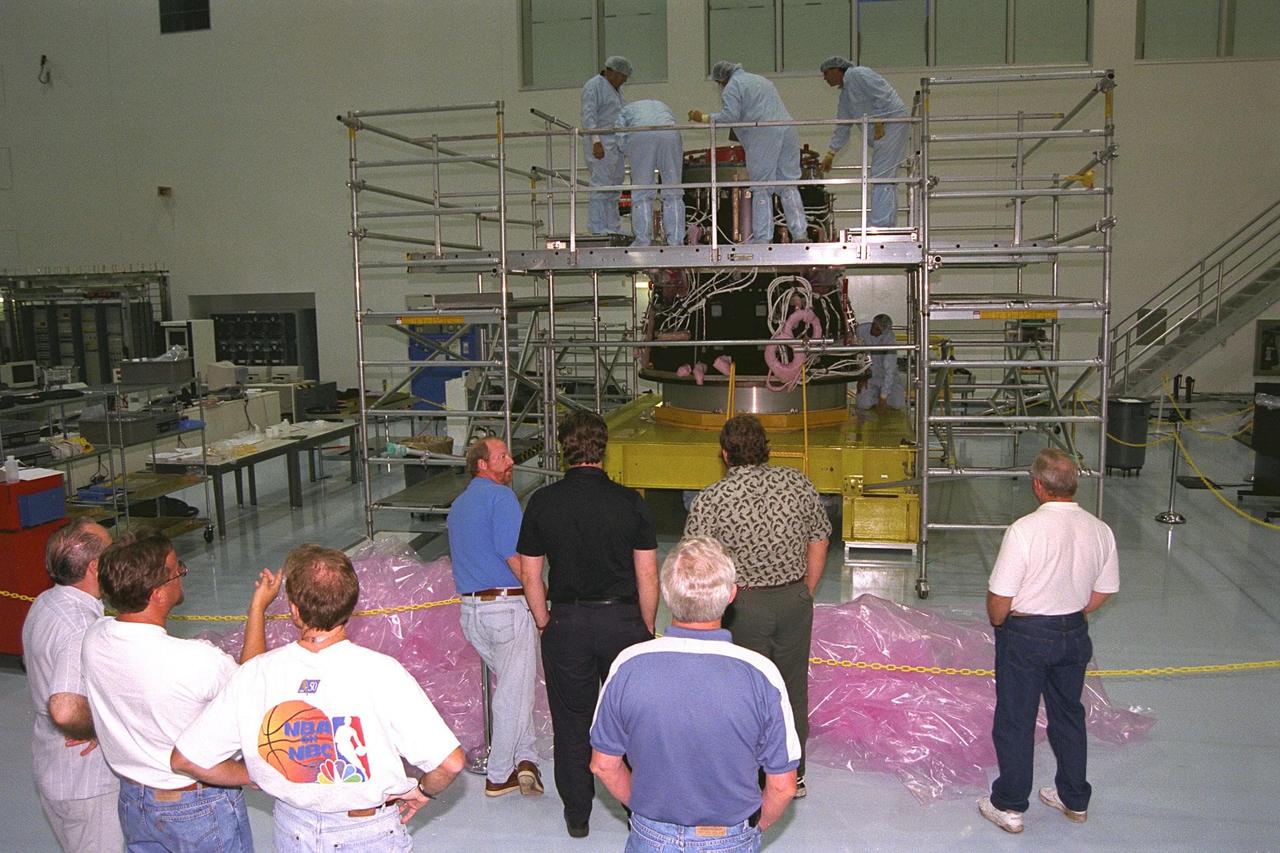

International Space Station (ISS) contractors erect access scaffolding around the Pressurized Mating Adapter-1 (PMA-1) for the ISS in KSC’s Space Station Processing Facility. A PMA is a cone-shaped connector that will be attached to Node 1, the space station’s structural building block, during ground processing. The white flight cables around PMA-1 will assist in connecting the node to the U.S.-financed, Russian-built Functional Cargo Block, a component that supplies early power and propulsion systems for the station. Node 1 with two adapters attached will be the first element of the station to be launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 in July 1998
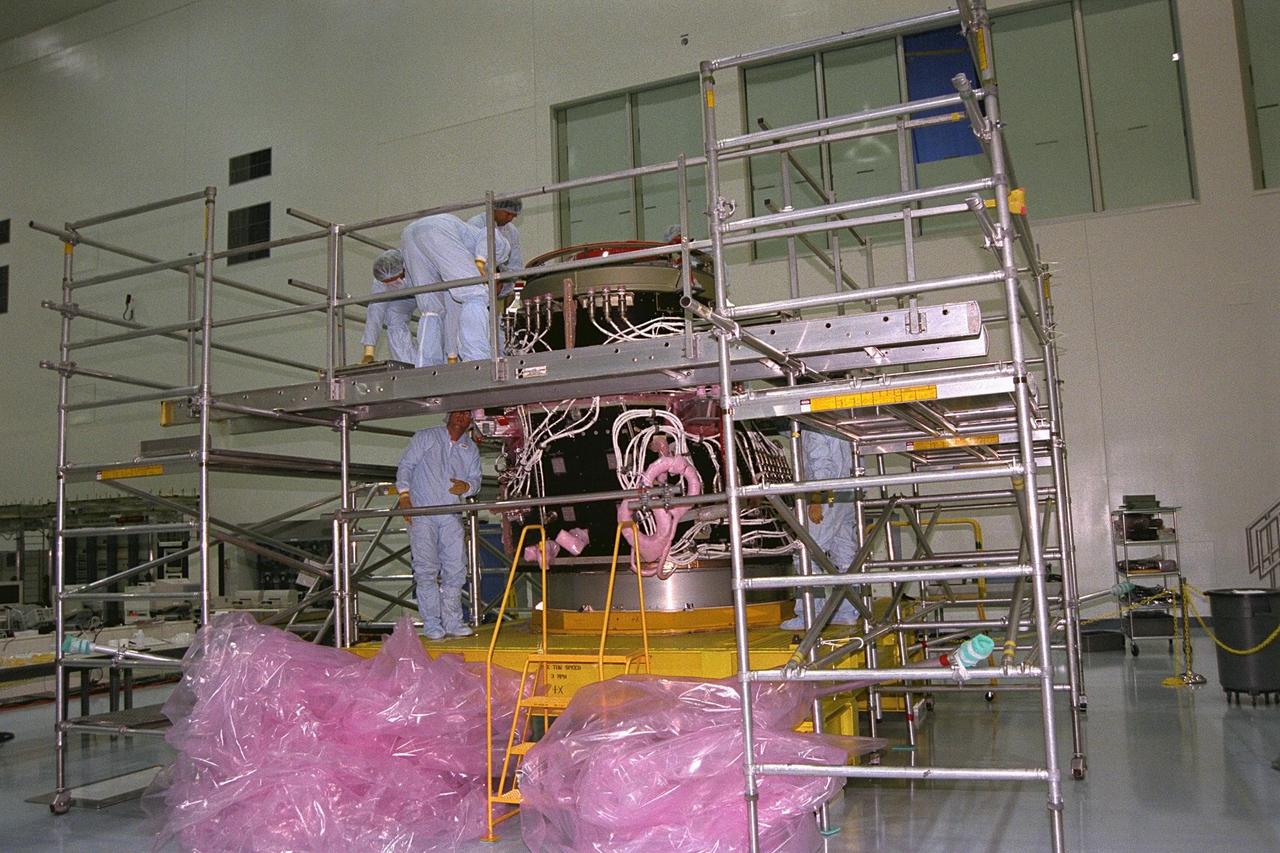

International Space Station (ISS) contractors erect access scaffolding around the Pressurized Mating Adapter-1 (PMA-1) for the ISS in KSC’s Space Station Processing Facility. A PMA is a cone-shaped connector that will be attached to Node 1, the space station’s structural building block, during ground processing. The white flight cables around PMA-1 will assist in connecting the node to the U.S.-financed, Russian-built Functional Cargo Block, a component that supplies early power and propulsion systems for the station. Node 1 with two adapters attached will be the first element of the station to be launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on STS-88 in July 1998
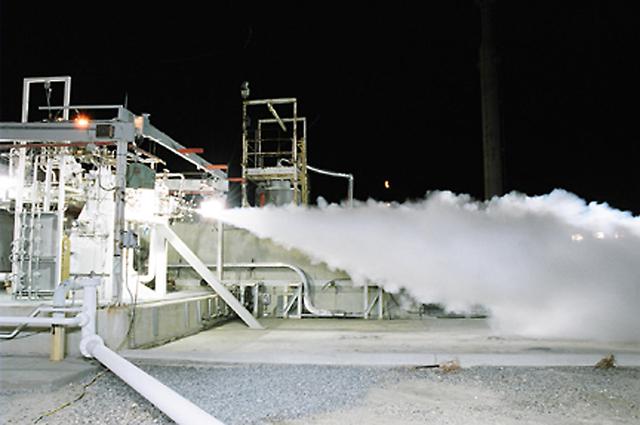

NASA Stennis Space Center engineers conducted a successful cold-flow test of an RS-84 engine component Sept. 24. The RS-84 is a reusable engine fueled by rocket propellant - a special blend of kerosene - designed to power future flight vehicles. Liquid oxygen was blown through the RS-84 subscale preburner to characterize the test facility's performance and the hardware's resistance. Engineers are now moving into the next phase, hot-fire testing, which is expected to continue into February 2004. The RS-84 engine prototype, developed by the Rocketdyne Propulsion and Power division of The Boeing Co. of Canoga Park, Calif., is one of two competing Rocket Engine Prototype technologies - a key element of NASA's Next Generation Launch Technology program.

The Gateway space station hosts the Orion spacecraft in a polar orbit around the Moon, supporting scientific discovery on the lunar surface during the Artemis IV mission.

The Gateway space station hosts the Orion spacecraft in a polar orbit around the Moon, supporting scientific discovery on the lunar surface during the Artemis IV mission.
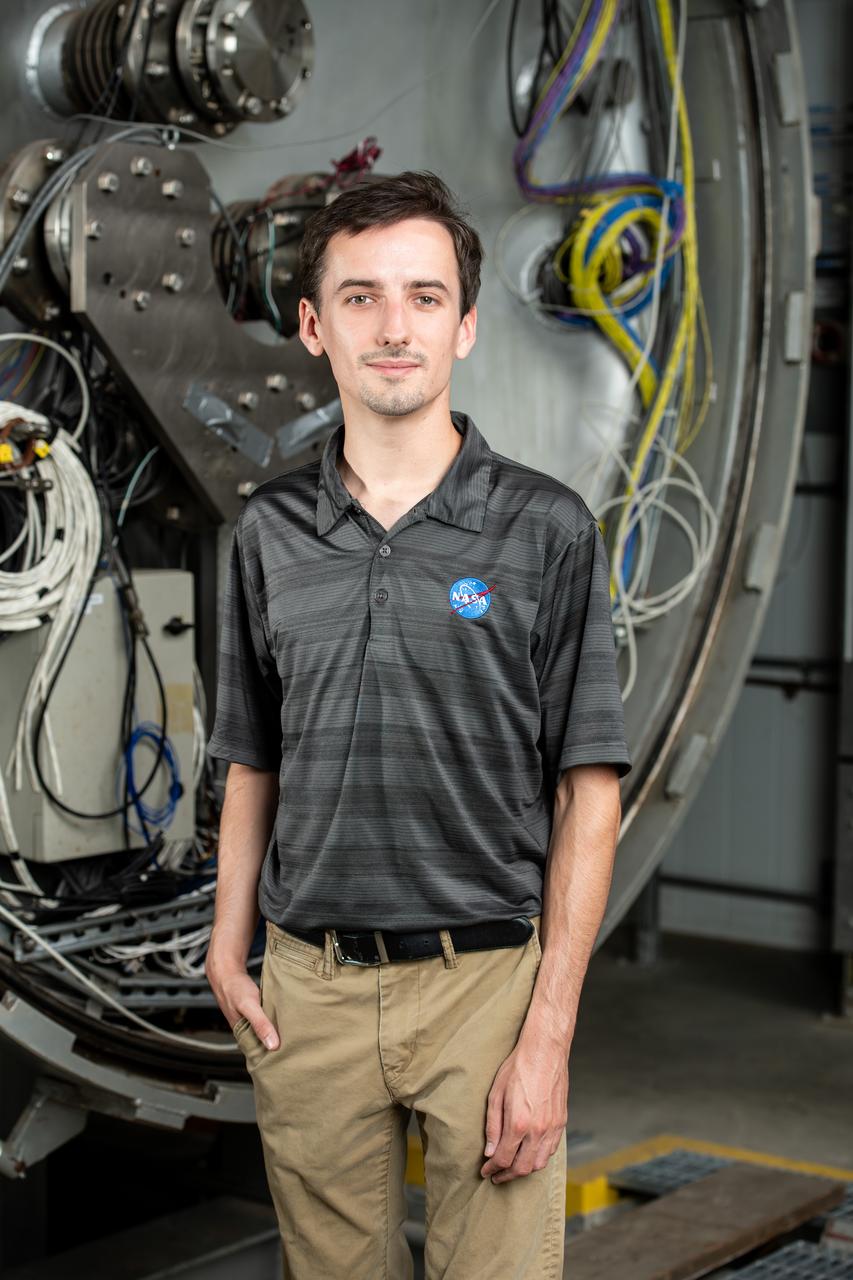

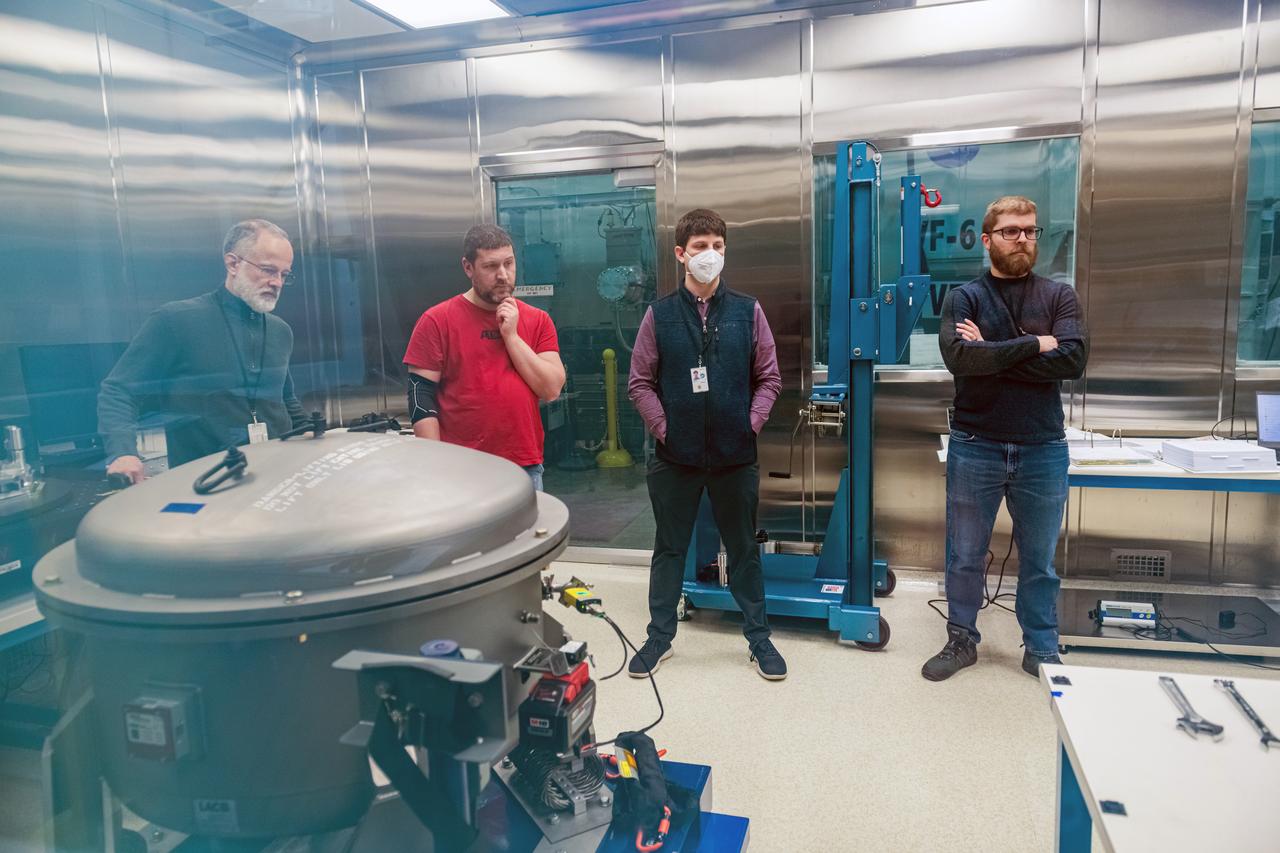
Each year, the NESC produces the NESC Technical Update, which highlights two or three individuals from each Center and includes assessments throughout the year. Because of the critical contributions to the NESC mission this year, Rob Jankovsky, NESC Chief Engineer at GRC, chose two individuals to be highlighted. This year, it is Andrew Ring and Michael Cooper. The Lead Analyst for GRC’s Chemical and Thermal Propulsion Systems branch, Mr. Michael Cooper, is supporting NESC test operations on reaction control system thrusters for Gateway’s Power & Propulsion Element. “These thrusters are small with few moving parts, but the heat and mass transfers involved are very complex,” he said. The test campaign is putting the thrusters through a rigorous profile to simulate the lifetime they will experience over decades in space. Mr. Cooper is analyzing test data gathered on chamber pressure, temperature, flow rates, and more to develop models on thruster performance. He also built the tool that read in that data from the test stand instrumentation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
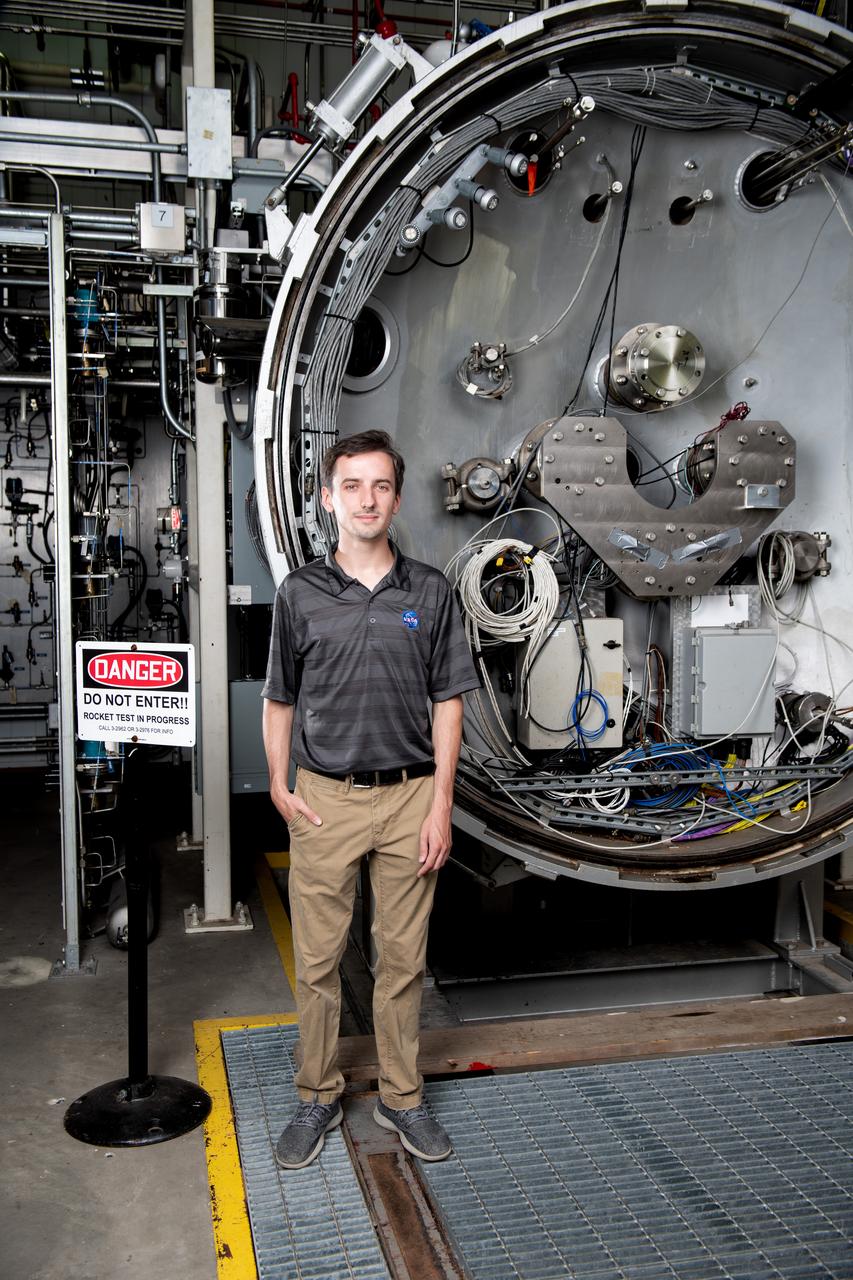

Each year, the NESC produces the NESC Technical Update, which highlights two or three individuals from each Center and includes assessments throughout the year. Because of the critical contributions to the NESC mission this year, Rob Jankovsky, NESC Chief Engineer at GRC, chose two individuals to be highlighted. This year, it is Andrew Ring and Michael Cooper. The Lead Analyst for GRC’s Chemical and Thermal Propulsion Systems branch, Mr. Michael Cooper, is supporting NESC test operations on reaction control system thrusters for Gateway’s Power & Propulsion Element. “These thrusters are small with few moving parts, but the heat and mass transfers involved are very complex,” he said. The test campaign is putting the thrusters through a rigorous profile to simulate the lifetime they will experience over decades in space. Mr. Cooper is analyzing test data gathered on chamber pressure, temperature, flow rates, and more to develop models on thruster performance. He also built the tool that read in that data from the test stand instrumentation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
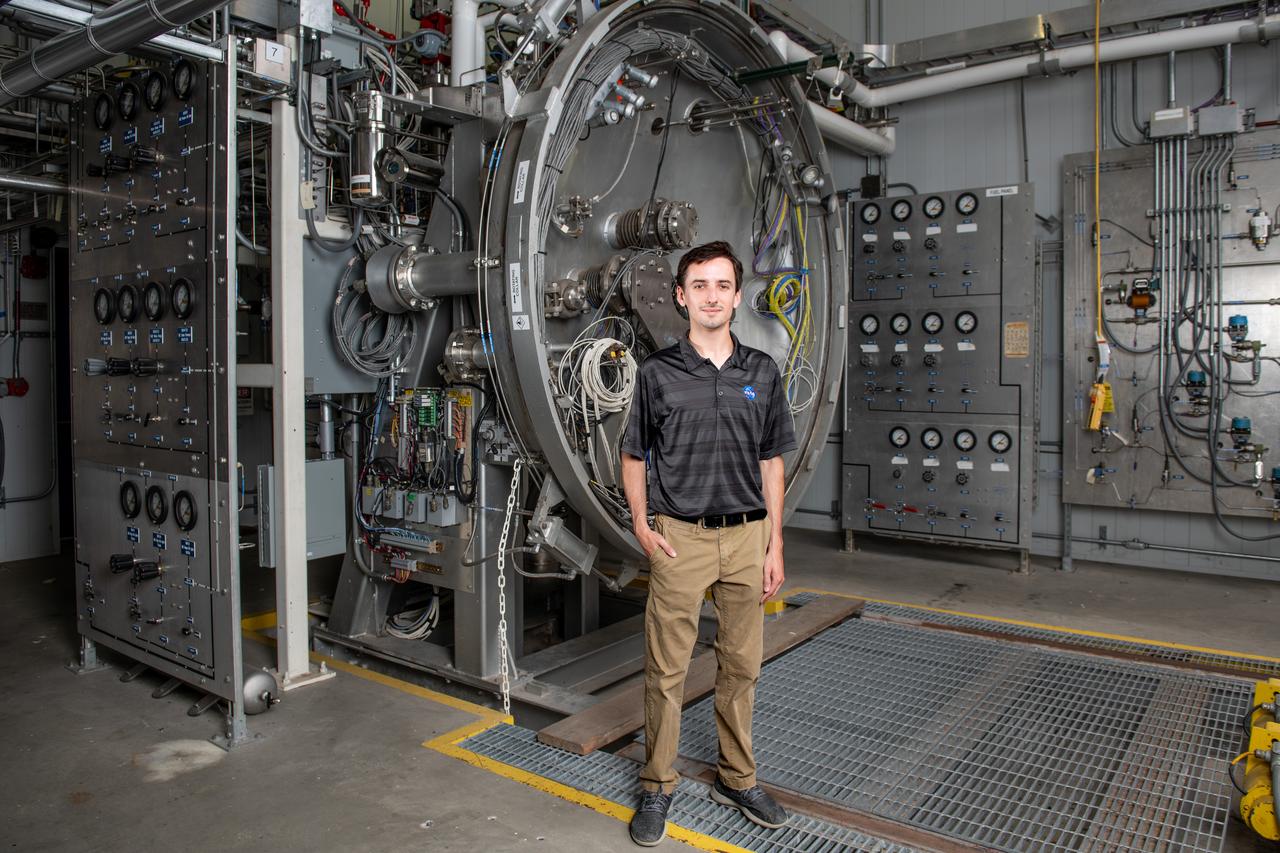

Each year, the NESC produces the NESC Technical Update, which highlights two or three individuals from each Center and includes assessments throughout the year. Because of the critical contributions to the NESC mission this year, Rob Jankovsky, NESC Chief Engineer at GRC, chose two individuals to be highlighted. This year, it is Andrew Ring and Michael Cooper. The Lead Analyst for GRC’s Chemical and Thermal Propulsion Systems branch, Mr. Michael Cooper pictured here in this environmental portrait on August 16, 2024. He is supporting NESC test operations on reaction control system thrusters for Gateway’s Power & Propulsion Element. “These thrusters are small with few moving parts, but the heat and mass transfers involved are very complex,” he said. The test campaign is putting the thrusters through a rigorous profile to simulate the lifetime they will experience over decades in space. Mr. Cooper is analyzing test data gathered on chamber pressure, temperature, flow rates, and more to develop models on thruster performance. He also built the tool that read in that data from the test stand instrumentation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
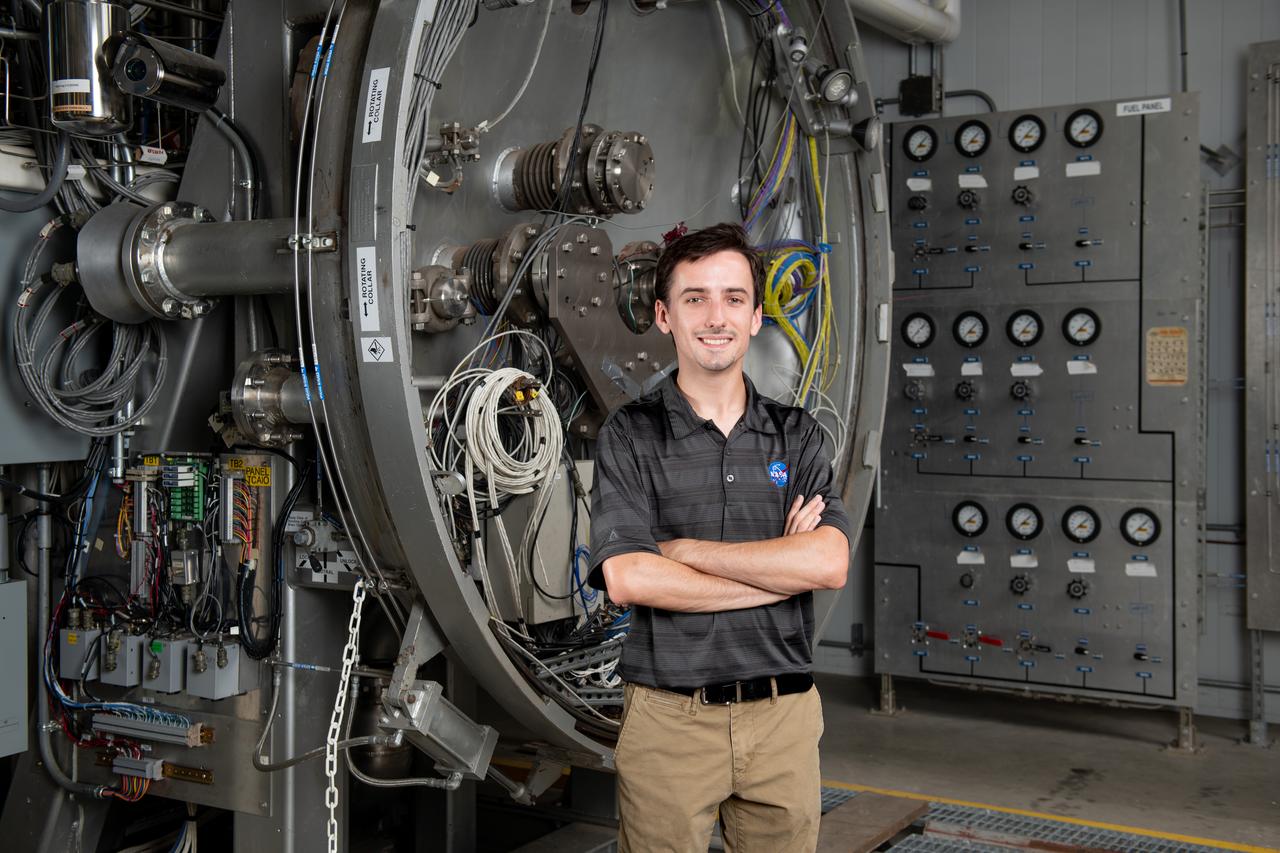

Each year, the NESC produces the NESC Technical Update, which highlights two or three individuals from each Center and includes assessments throughout the year. Because of the critical contributions to the NESC mission this year, Rob Jankovsky, NESC Chief Engineer at GRC, chose two individuals to be highlighted. This year, it is Andrew Ring and Michael Cooper. The Lead Analyst for GRC’s Chemical and Thermal Propulsion Systems branch, Mr. Michael Cooper, is supporting NESC test operations on reaction control system thrusters for Gateway’s Power & Propulsion Element. “These thrusters are small with few moving parts, but the heat and mass transfers involved are very complex,” he said. The test campaign is putting the thrusters through a rigorous profile to simulate the lifetime they will experience over decades in space. Mr. Cooper is analyzing test data gathered on chamber pressure, temperature, flow rates, and more to develop models on thruster performance. He also built the tool that read in that data from the test stand instrumentation. Photo Credit: (NASA/Sara Lowthian-Hanna)
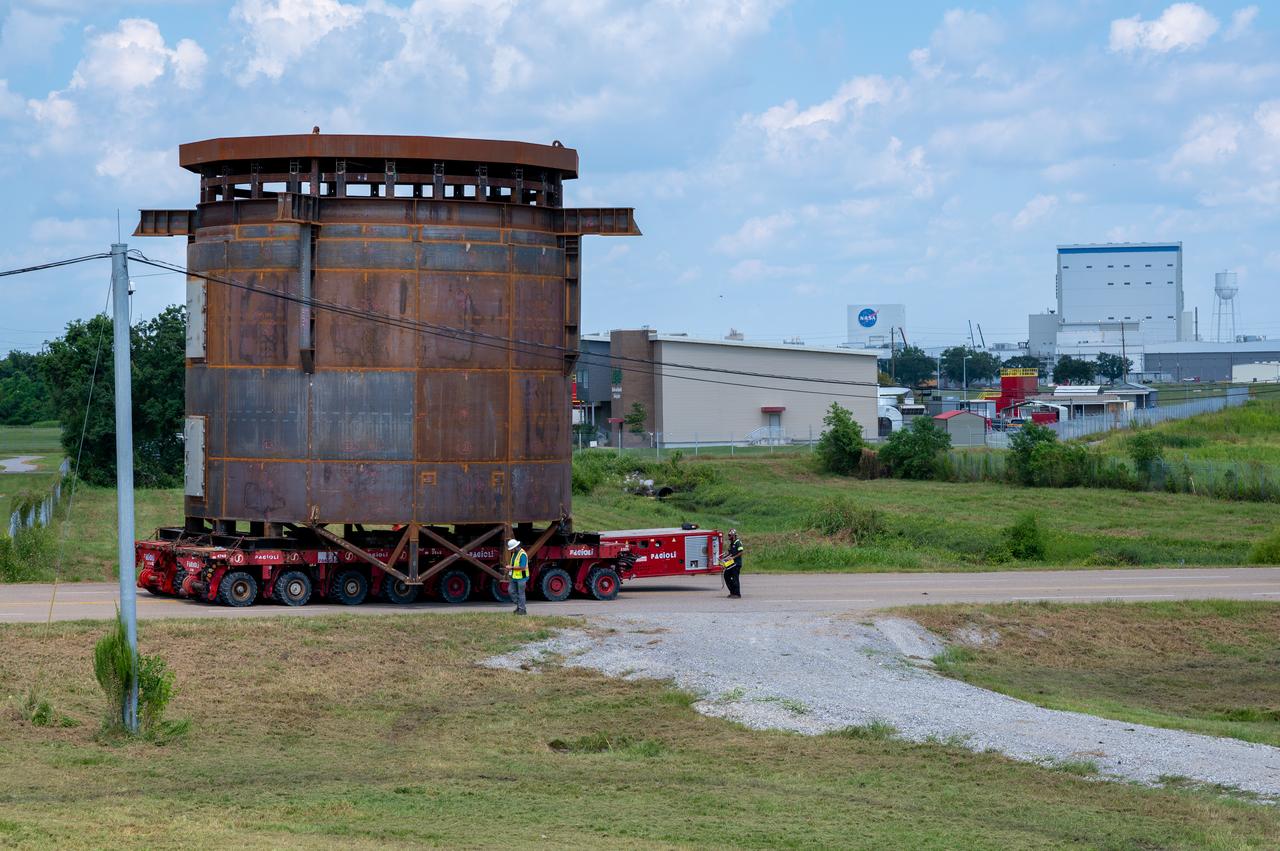

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
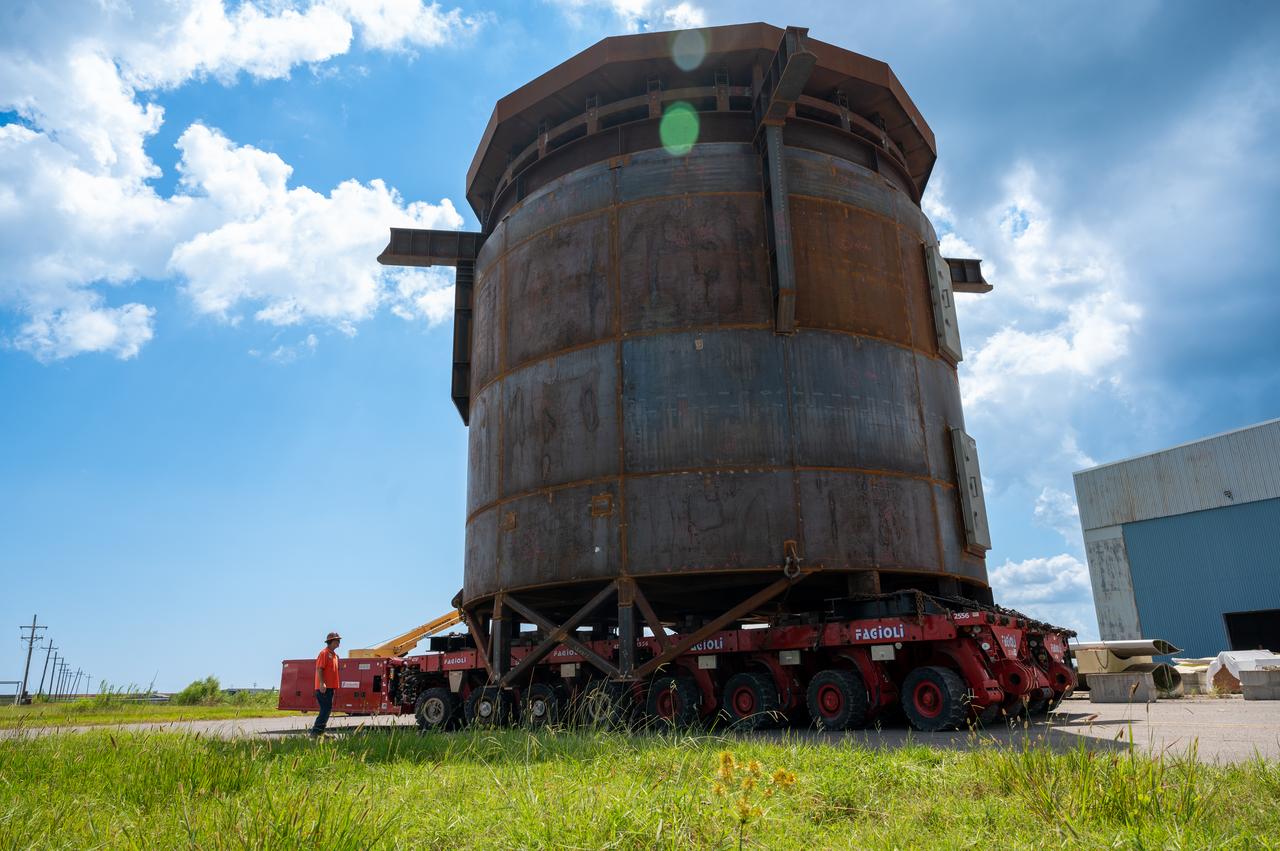

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
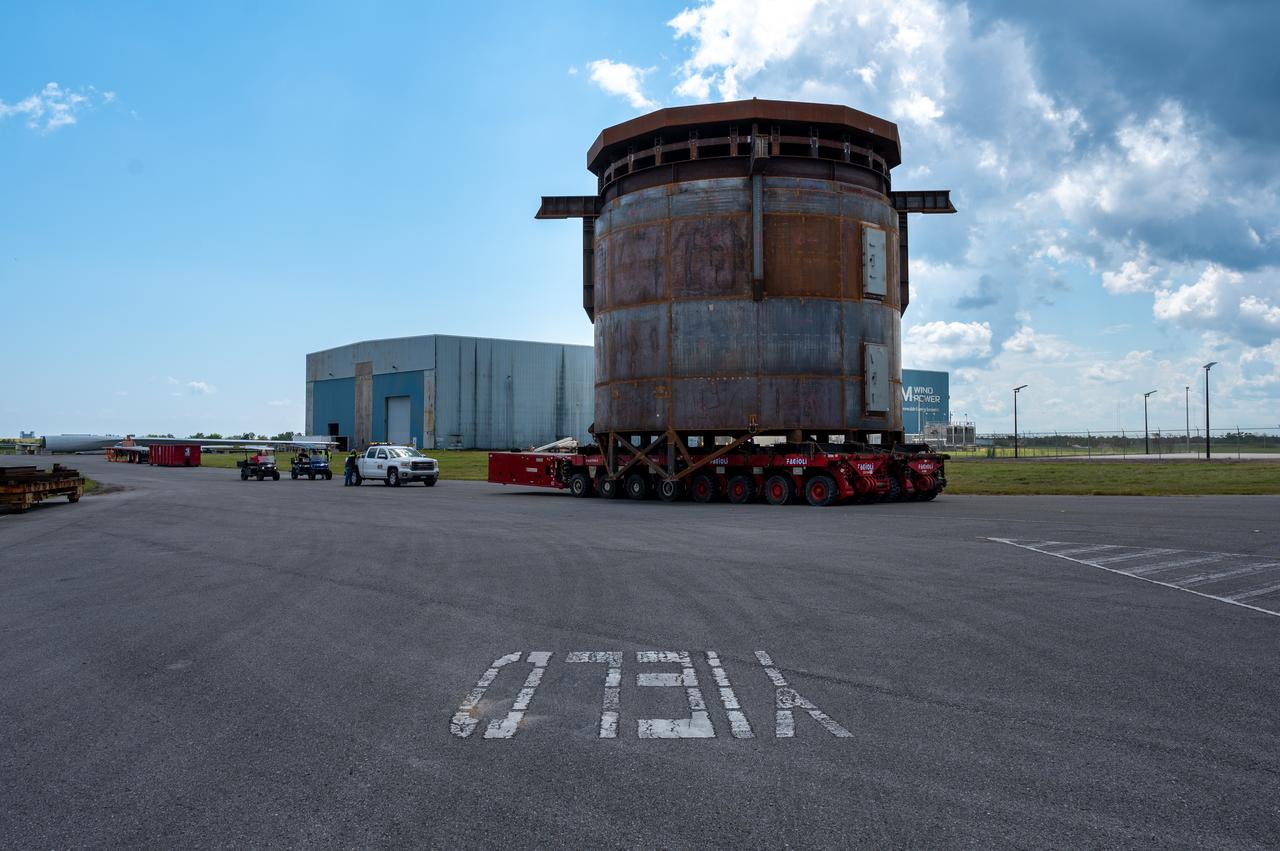

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
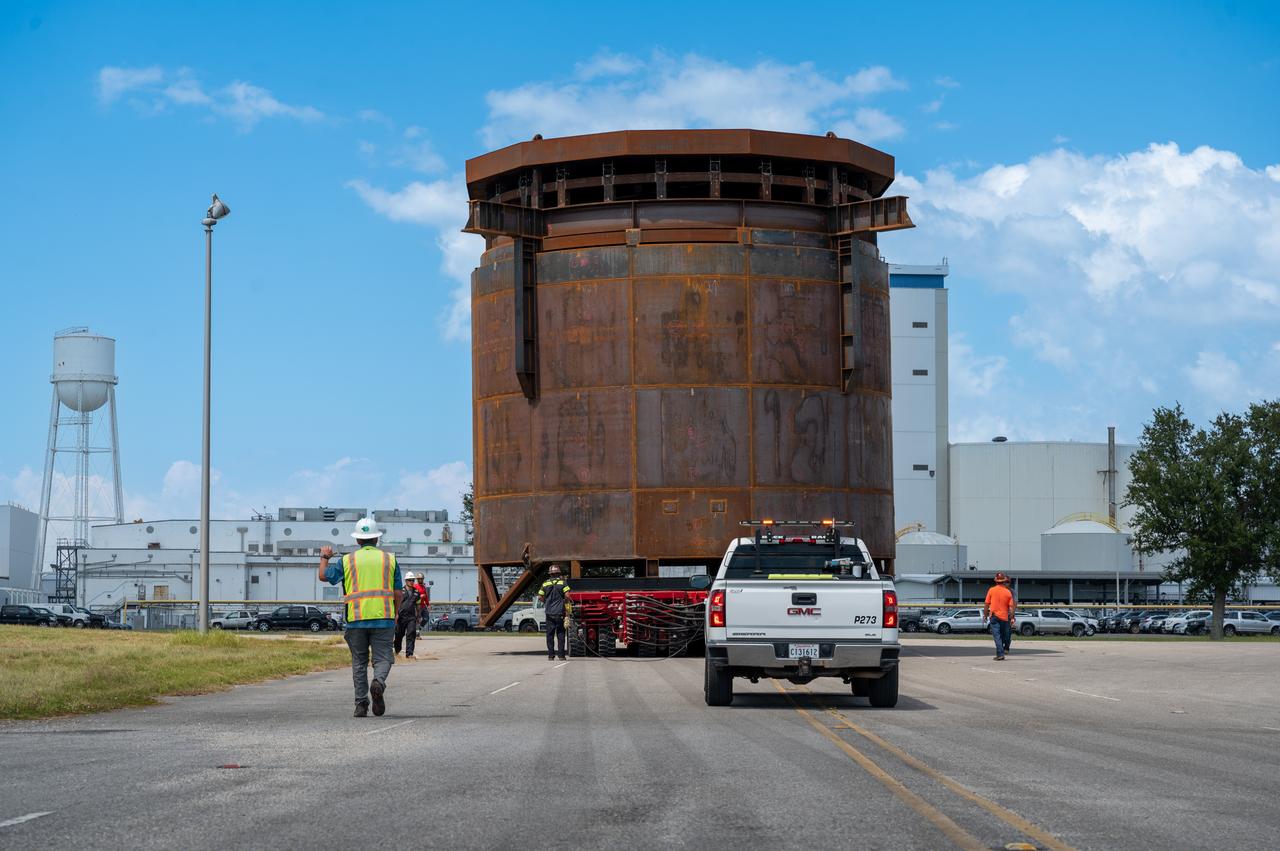

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

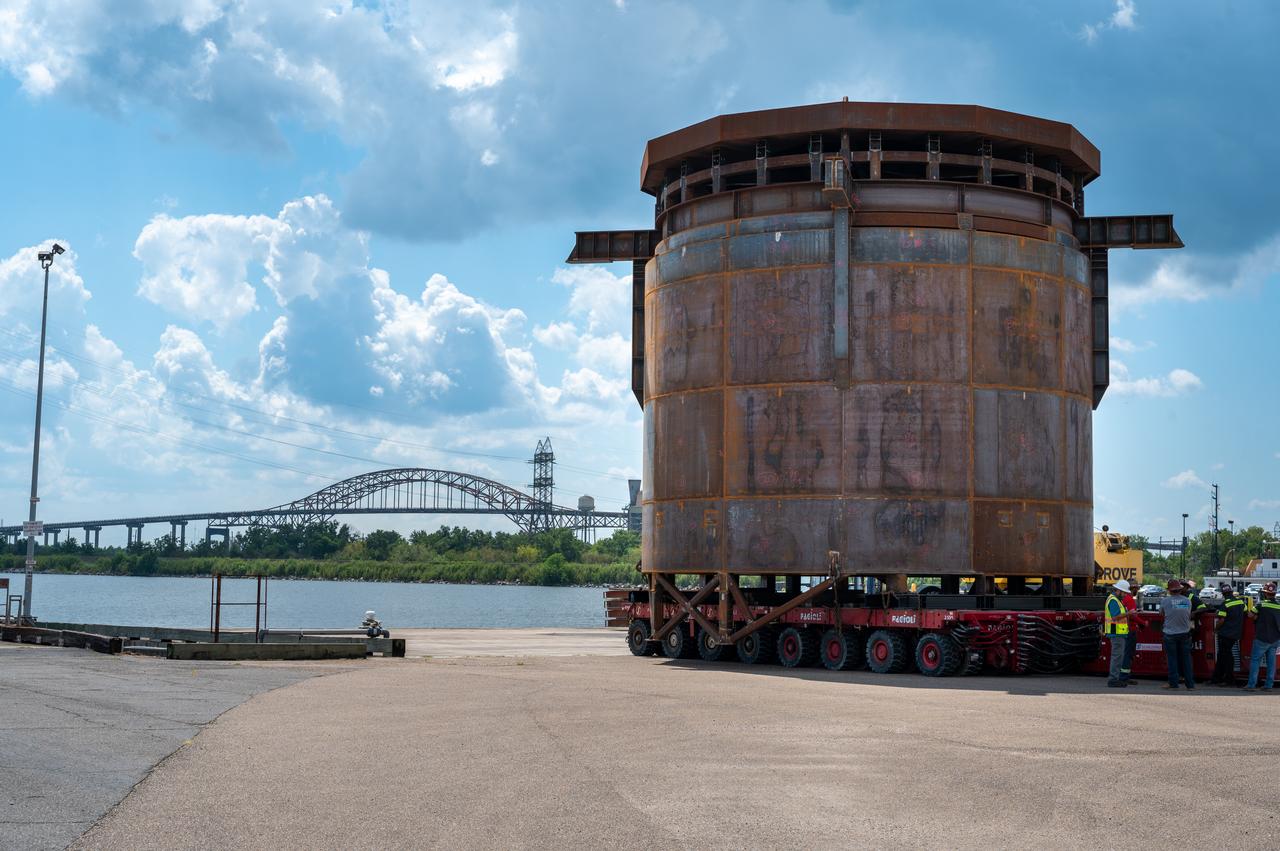
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.

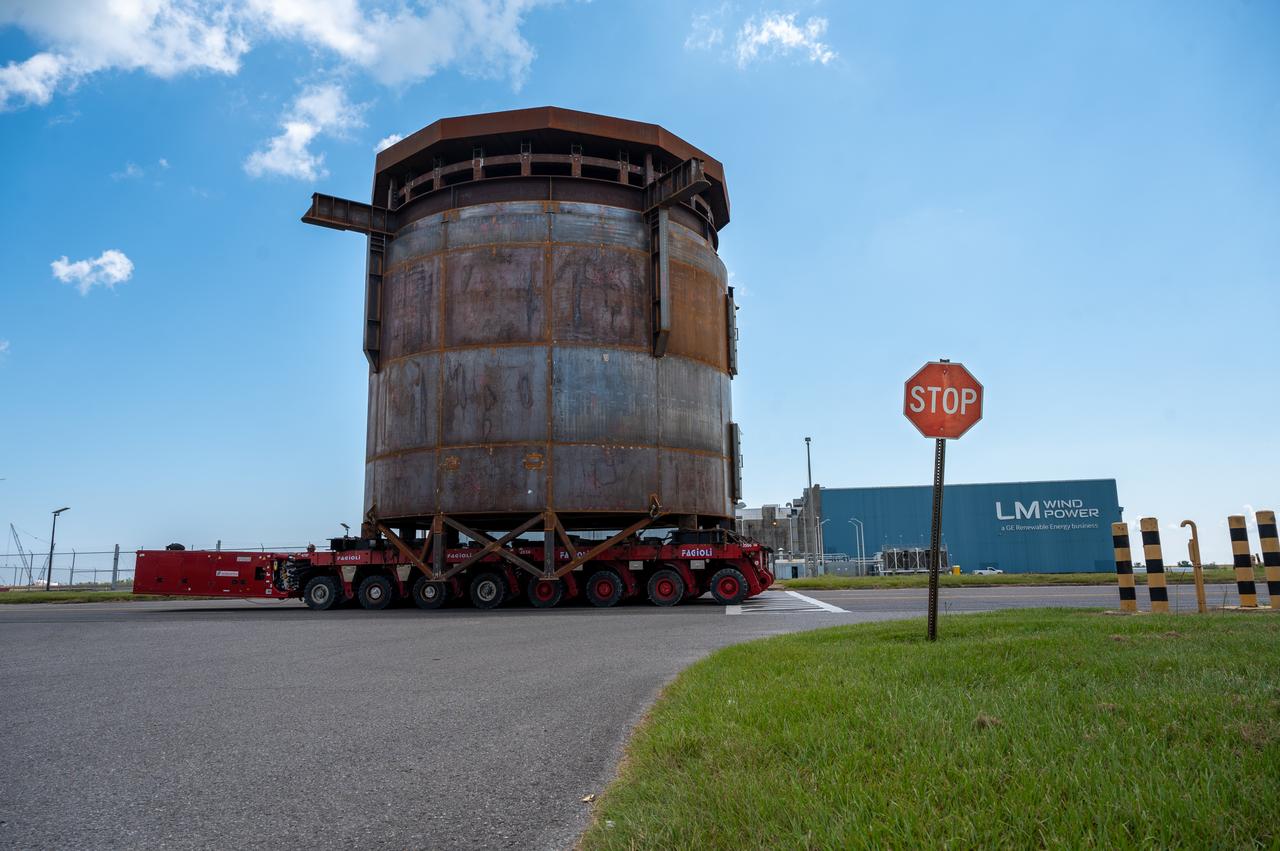
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Once it arrives at Stennis, the simulator will be lifted into the B2 Test Stand, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
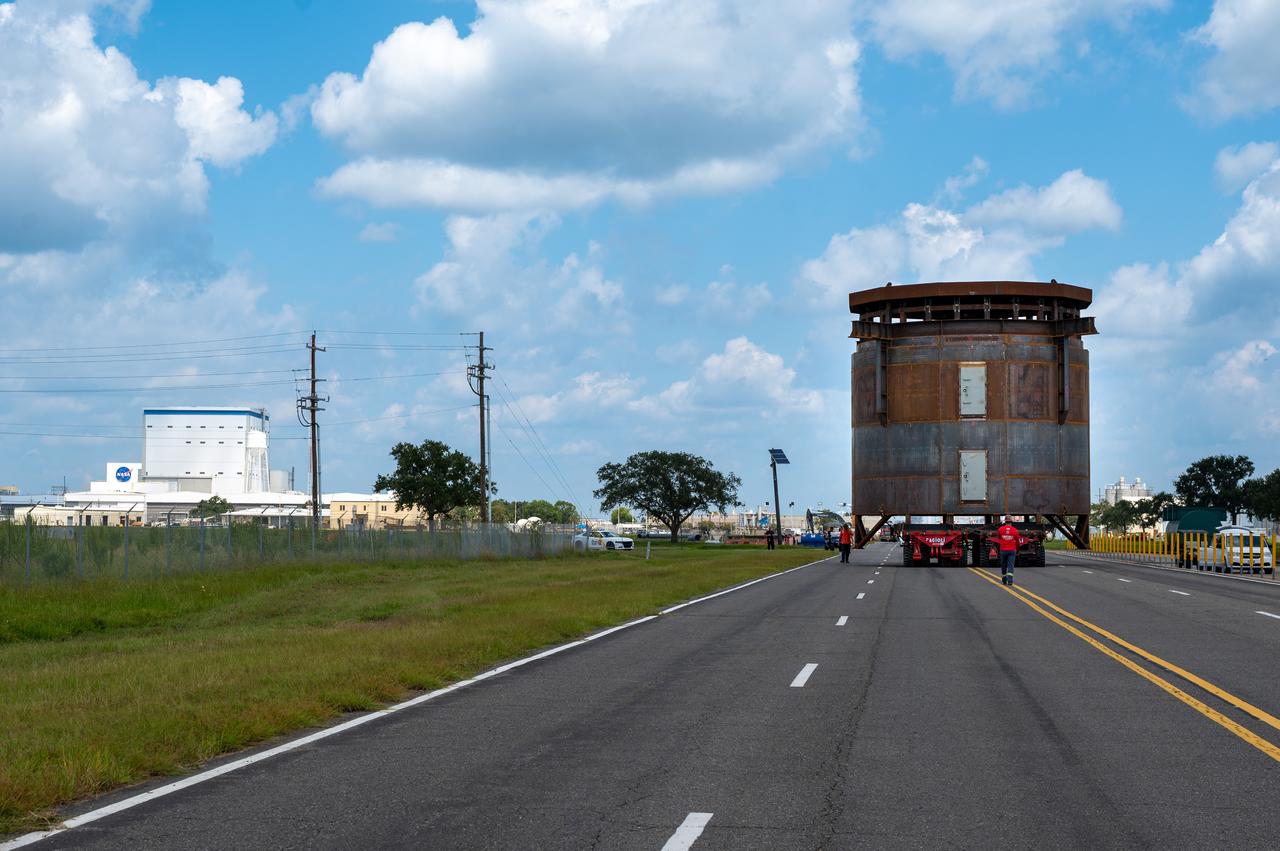

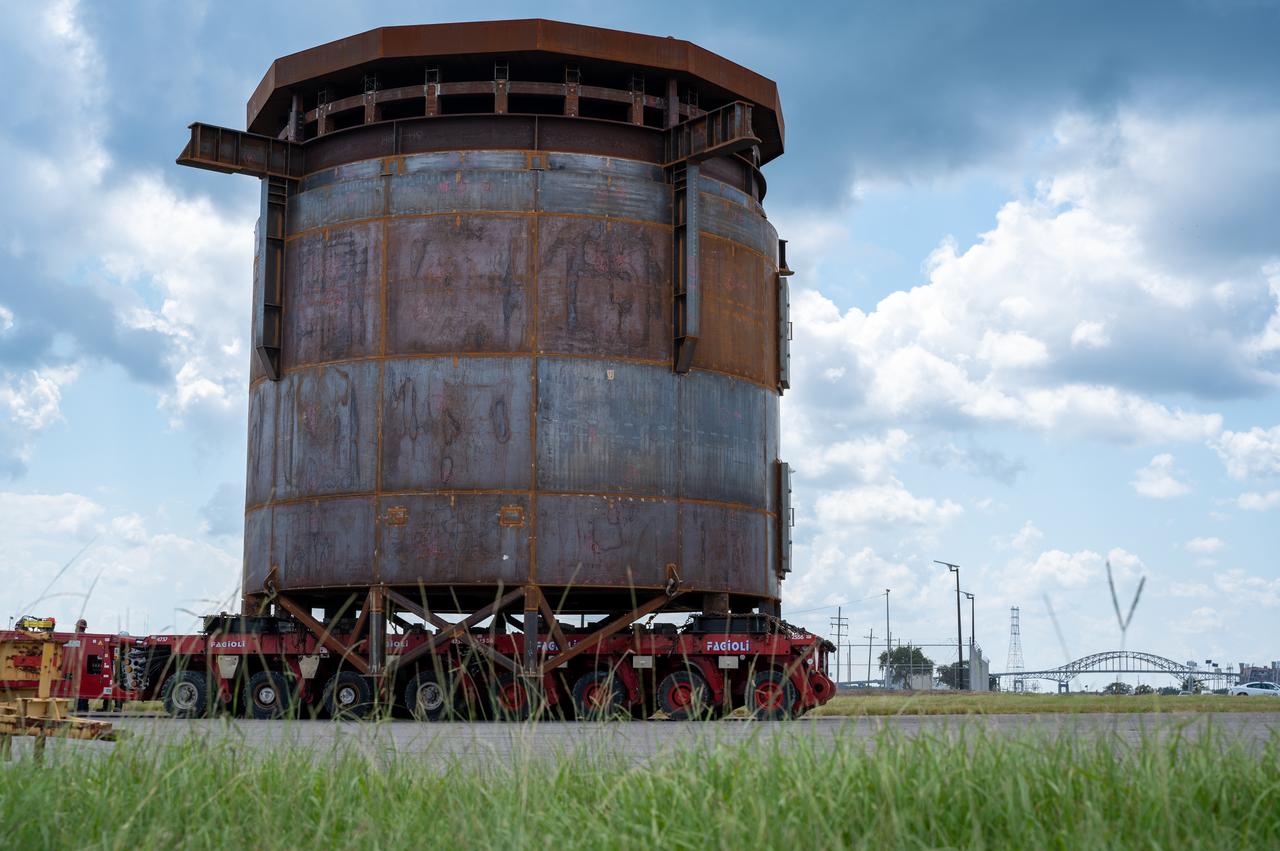
Move crews at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans guide the Inter-Stage Simulator (ISS) to the Michoud deep water port on Monday, Sept. 19 in preparation for transportation by barge to the agency’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Crews will lift the simulator into the B2 Test Stand at Stennis, where it holds the Exploration Upper Stage (EUS) in place and acts as a thrust takeout. ISS protects the lower portion of the EUS from environmental elements during its Green Run tests. The term “green” refers to the new hardware, and “run” refers to operation all the components together for the first time. During tanking and launch for its future mission, the lower portion is shrouded in a flight interstage. EUS is part of the SLS Block 1B configuration. The more powerful configuration of the SLS rocket will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and 40% more cargo mass on a precise trajectory to the Moon. Through the Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon to pave the way for a sustainable presence on the Moon and future missions beyond.
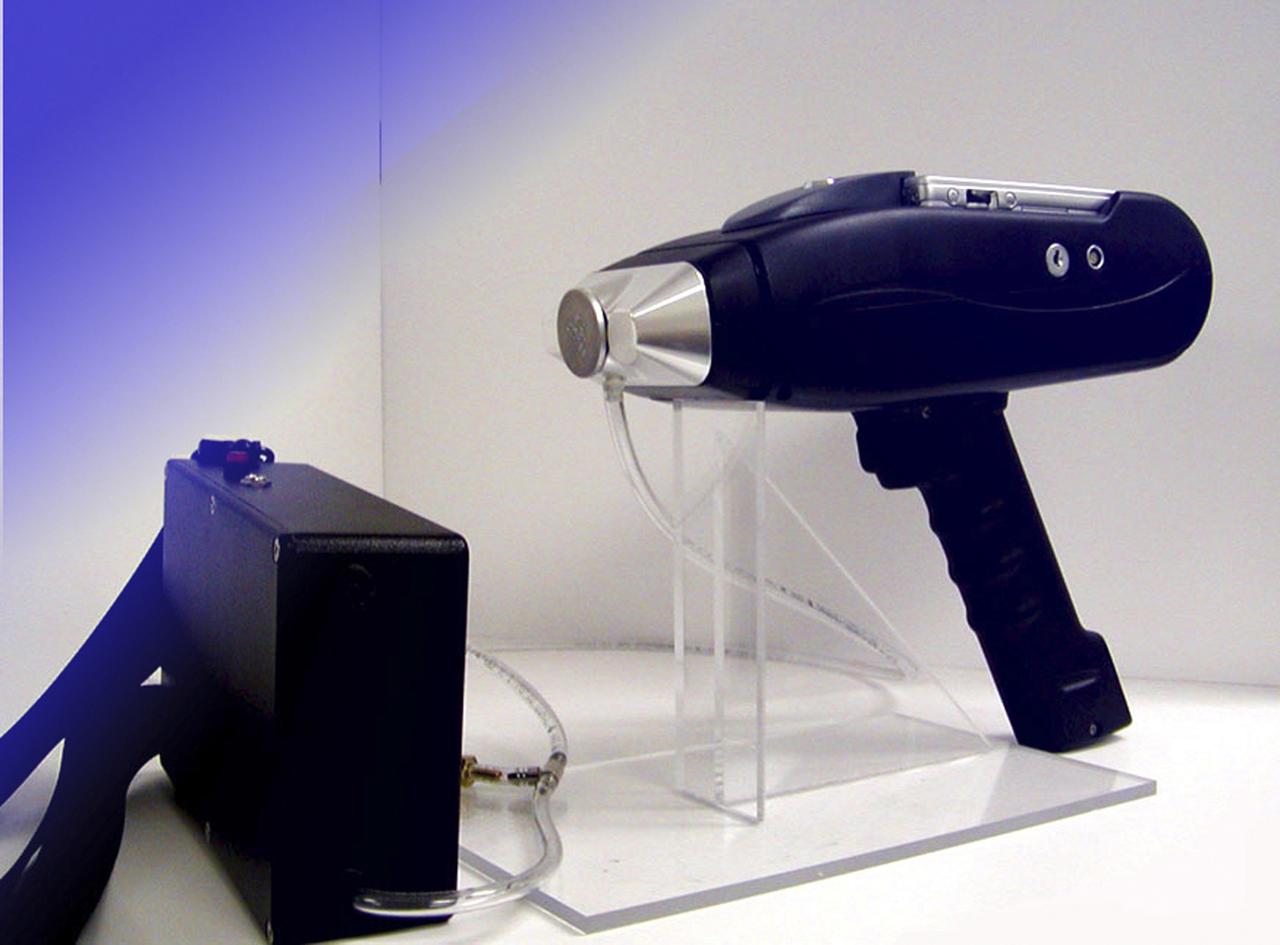

Marshall Space Flight Center engineers have teamed with KeyMaster Technologies, Kennewick, Washington, to develop a portable vacuum analyzer that performs on-the-spot chemical analyses under field conditions, a task previously only possible in a chemical laboratory. The new capability is important not only to the aerospace industry, but holds potential for broad applications in any industry that depends on materials analysis, such as the automotive and pharmaceutical industries. Weighing in at a mere 4 pounds, the newly developed handheld vacuum X-ray fluorescent analyzer can identify and characterize a wide range of elements, and is capable of detecting chemical elements with low atomic numbers, such as sodium, aluminum and silicon. It is the only handheld product on the market with that capability. Aluminum alloy verification is of particular interest to NASA because vast amounts of high-strength aluminum alloys are used in the Space Shuttle propulsion system such as the External Tank, Main Engine, and Solid Rocket Boosters. This capability promises to be a boom to the aerospace community because of unique requirements, for instance, the need to analyze Space Shuttle propulsion systems on the launch pad. Those systems provide the awe-inspiring rocket power that propels the Space Shuttle from Earth into orbit in mere minutes. The scanner development also marks a major improvement in the quality assurance field, because screws, nuts, bolts, fasteners, and other items can now be evaluated upon receipt and rejected if found to be substandard. The same holds true for aluminum weld rods. The ability to validate the integrity of raw materials and partially finished products before adding value to them in the manufacturing process will be of benefit not only to businesses, but also to the consumer, who will have access to a higher value product at a cheaper price. Three vacuum X-ray scanners are already being used in the Space Shuttle Program. The External Tank Project Office is using one for aluminum alloy analysis, while a Marshall contractor is evaluating alloys with another unit purchased for the Space Shuttle Main Engine Office. The Reusable Solid Rocket Motor Project Office has obtained a scanner that is being used to test hardware and analyze materials.
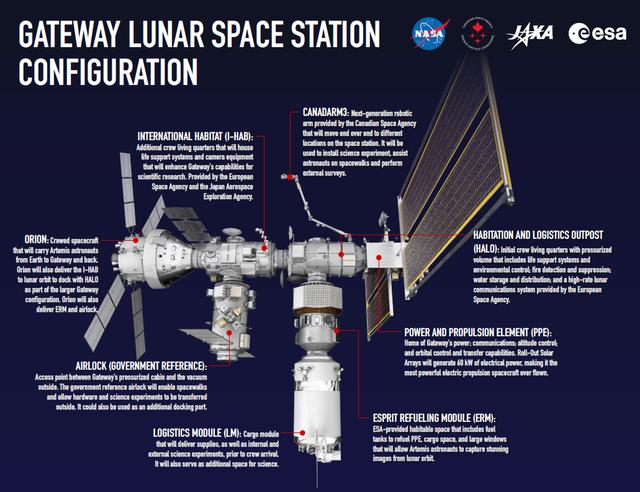
This infographic shows each element of Gateway, humanity's first space station in lunar orbit as a vital component of the Artemis missions to return to the Moon for scientific discovery and chart the path for the first human missions to Mars.
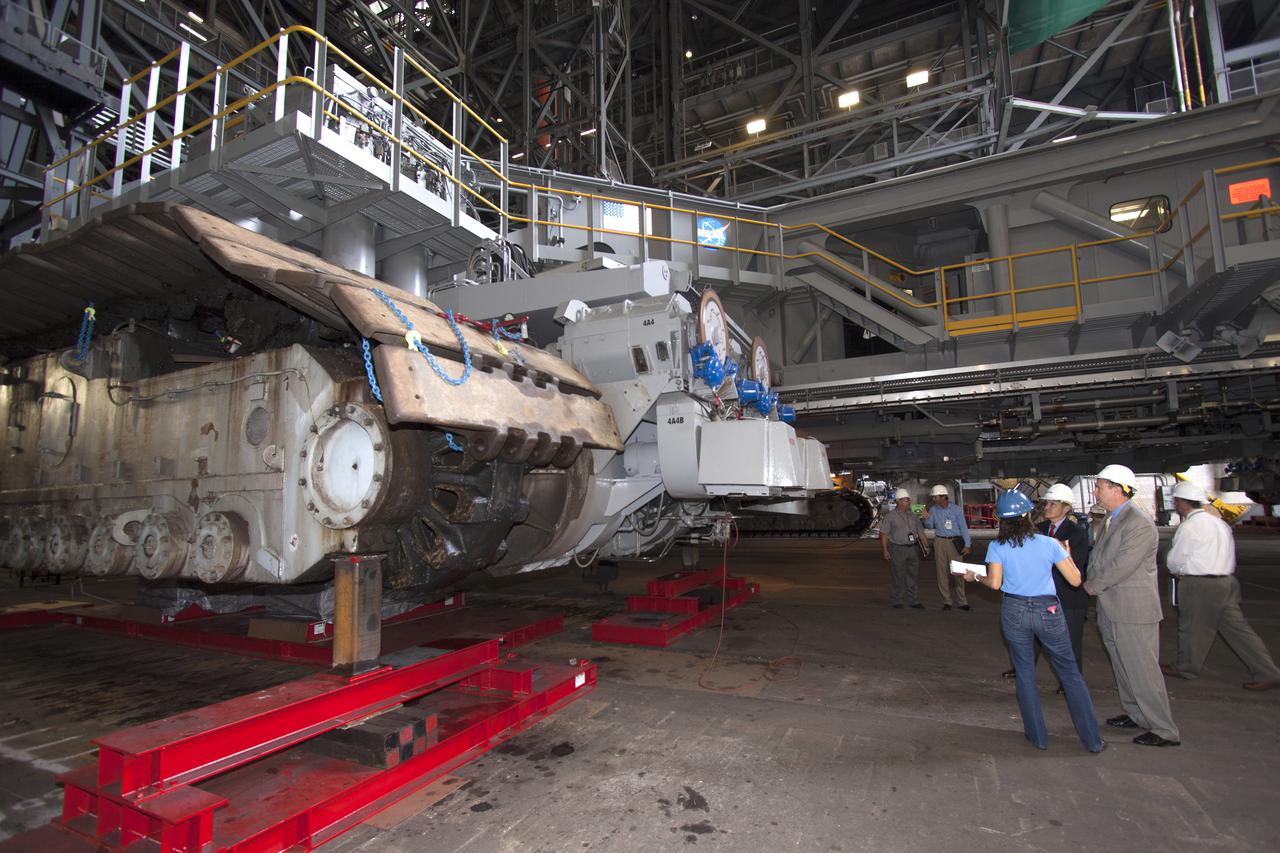

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot, second from right, is briefed on the modifications to crawler-transporter 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building, or VAB, during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Mary Hanna, crawler-transporter project manager, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, Lightfoot, and Shawn Quinn, Vehicle Integration and Launch Integration Product Team, or IPT, manager. Crawler-transporter 2 is being readied to support NASA's new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket, the SLS. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
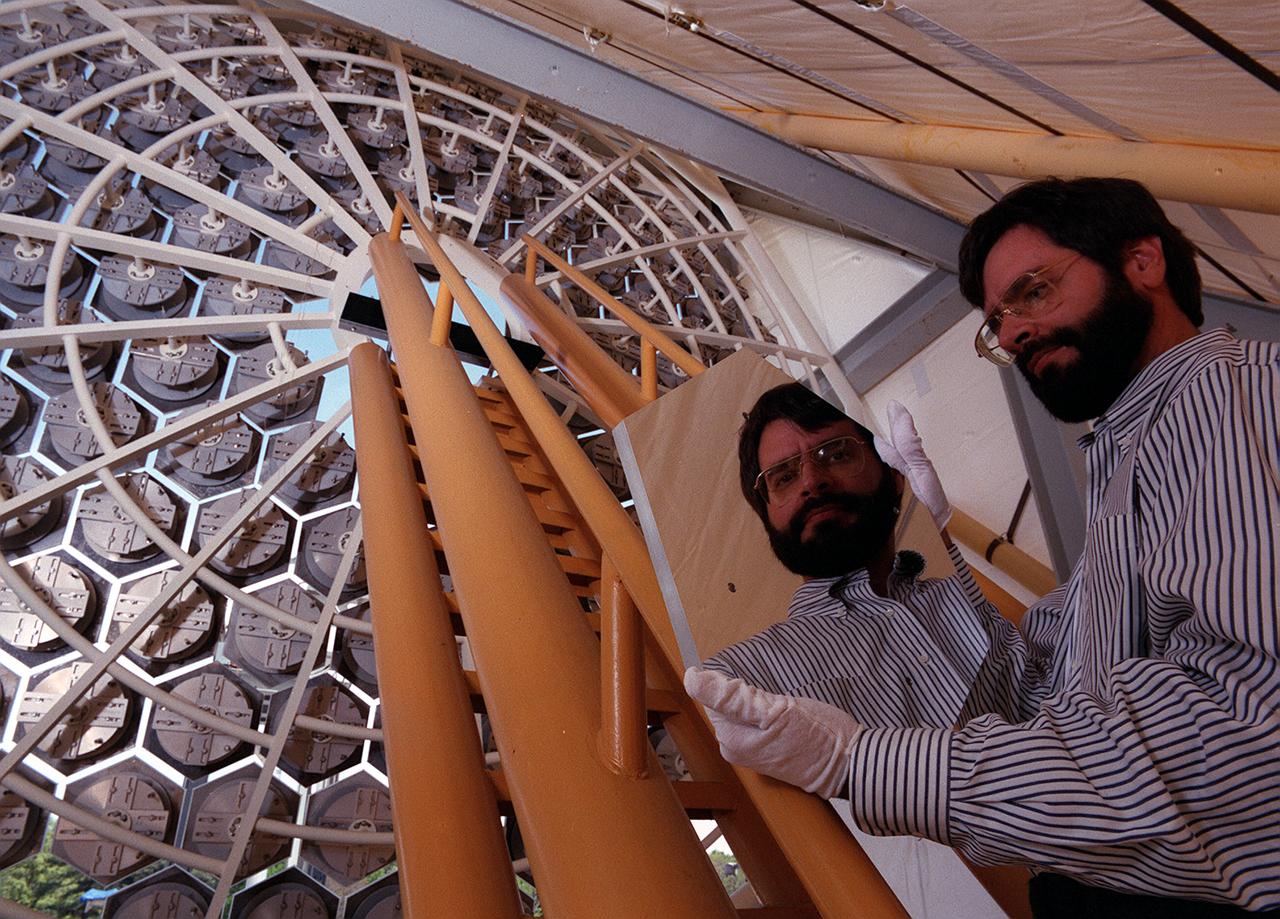

NASA's Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center has been working to expand our view of the universe via sophisticated new telescopes. The Optics Center's goal is to develop low-cost, advanced space optics technologies for the NASA program in the 21st century, including the long-term goal of imaging Earth-like planets in distant solar systems. A segmented array of mirrors was designed by the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center for solar the concentrator test stand at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) for powering solar thermal propulsion engines. Each hexagon mirror has a spherical surface to approximate a parabolic concentrator when combined into the entire 18-foot diameter array. The aluminum mirrors were polished with a diamond turning machine, that creates a glass-like reflective finish on metal. The precision fabrication machinery at the Space Optics Manufacturing Technology Center at MSFC can polish specialized optical elements to a world class quality of smoothness. This image shows optics physicist, Vince Huegele, examining one of the 144-segment hexagonal mirrors of the 18-foot diameter array at the MSFC solar concentrator test stand.
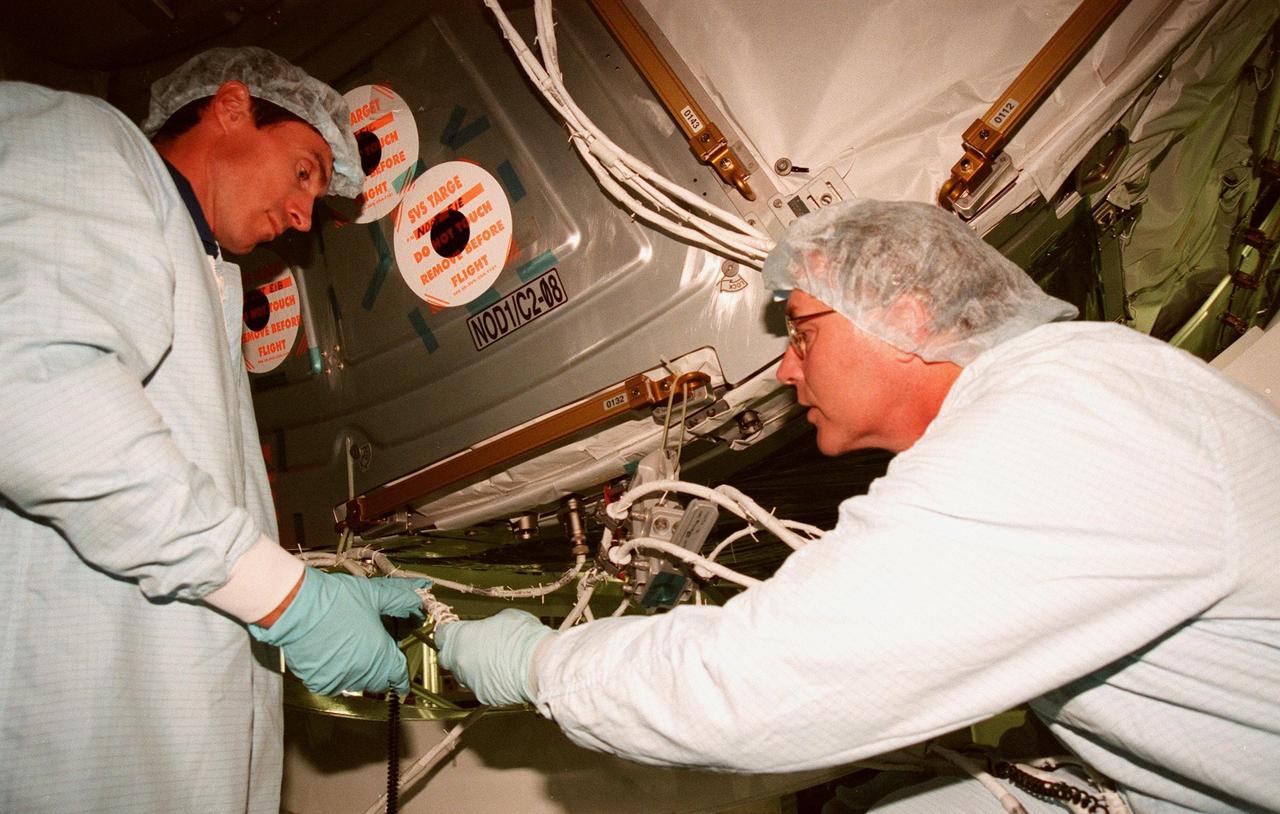
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, STS-88 Mission Specialists Sergei Krikalev, a Russian cosmonaut, and Jerry L. Ross check out equipment on the Unity connecting module, primary payload on the mission. The STS-88 crew members are participating in a Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT), familiarizing themselves with the orbiter's midbody and crew compartments. Scheduled for launch on Dec. 3, 1998, STS-88 will be the first Space Shuttle launch for the International Space Station. The Unity connecting module will be mated to the Russian-built Zarya control module, already on orbit after a November launch. Unity will have two Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs) attached and 1 stowage rack installed inside. PMA-1 will connect U.S. and Russian elements; PMA-2 will provide a Shuttle docking location. Eventually, Unity's six ports will provide connecting points for the Z1 truss exterior framework, U.S. lab, airlock, cupola, Node 3, and the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module, as well as the control module. Zarya is a self-supporting active vehicle, providing propulsive control capability and power through the early assembly stages. It provides fuel storage capability and a rendezvous and docking capability to the Service Module
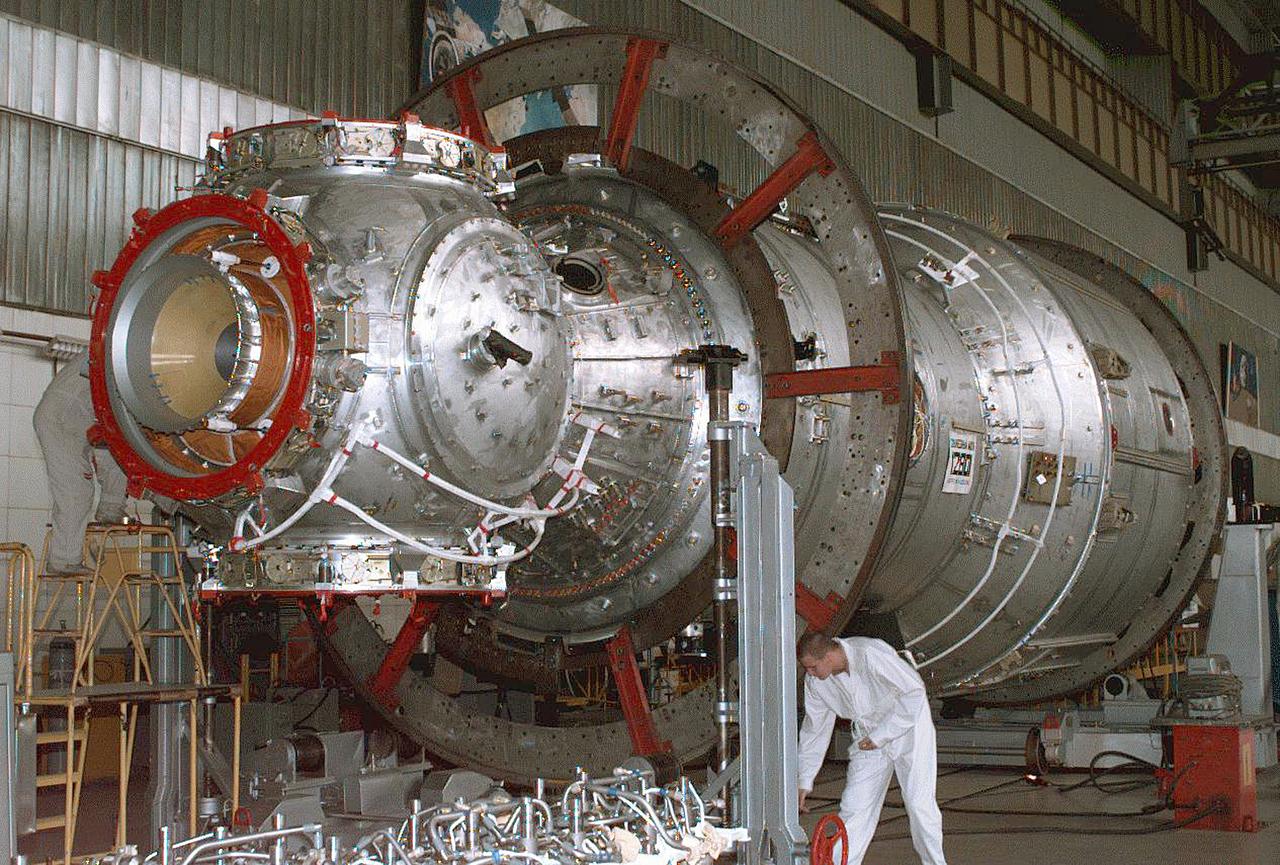
The Zvezda Service Module, the first Russian contribution and third element to the International Space Station (ISS), is shown under construction in the Krunichev State Research and Production Facility (KhSC) in Moscow. Russian technicians work on the module shortly after it completed a pressurization test. In the foreground is the forward portion of the module, including the spherical transfer compartment and its three docking ports. The forward port docked with the cornected Functional Cargo Block, followed by Node 1. Launched via a three-stage Proton rocket on July 12, 2000, the Zvezda Service Module serves as the cornerstone for early human habitation of the Station, providing living quarters, life support system, electrical power distribution, data processing system, flight control system, and propulsion system. It also provides a communications system that includes remote command capabilities from ground flight controllers. The 42,000-pound module measures 43 feet in length and has a wing span of 98 feet. Similar in layout to the core module of Russia's Mir space station, it contains 3 pressurized compartments and 13 windows that allow ultimate viewing of Earth and space.
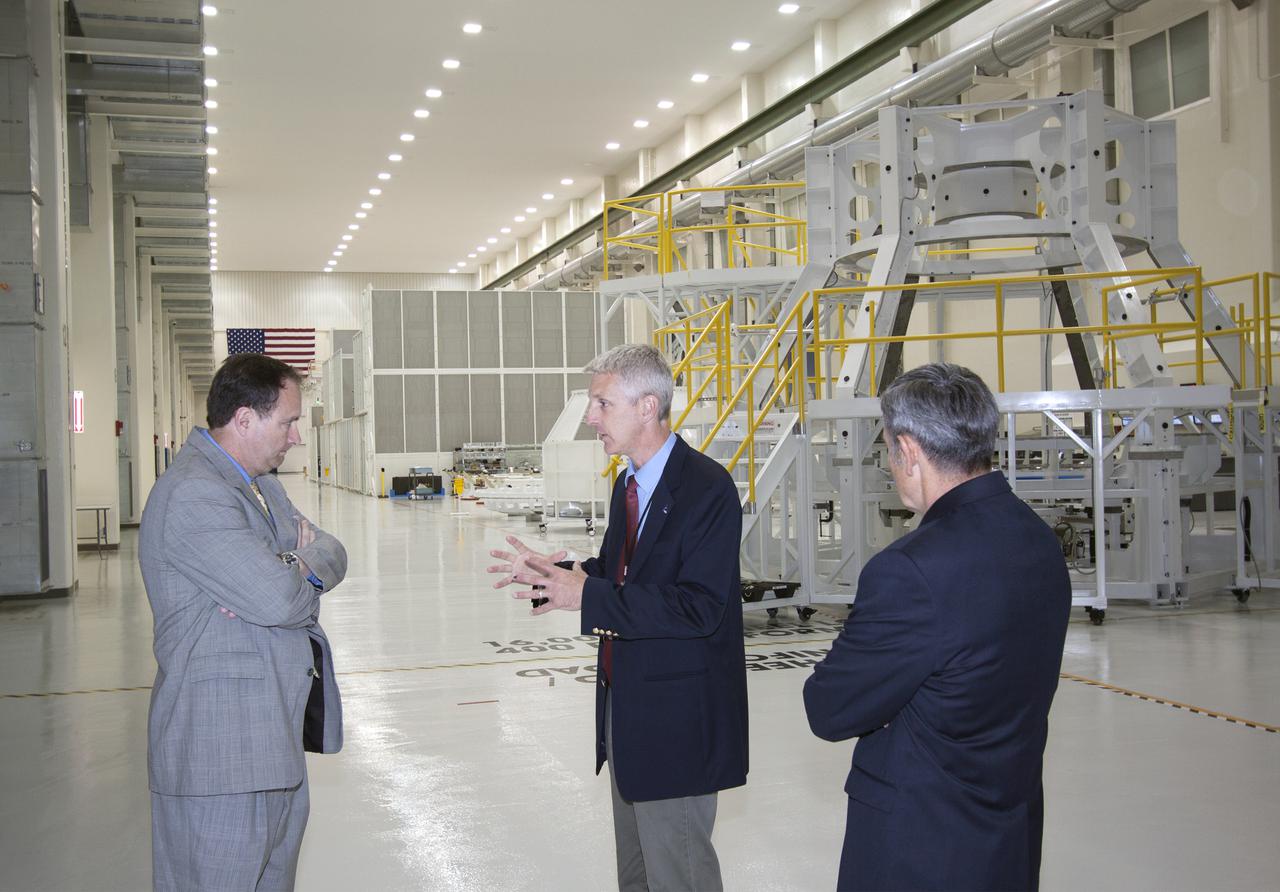

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot tours the Operations and Checkout Building high bay where the first Orion capsule, NASA's multi-purpose crew vehicle, is being prepared for flight on Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, in 2014. From left are Lightfoot, Kennedy's manager of Orion Production Operations Scott Wilson, and Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. Orion is NASA's next-generation transport for astronauts to destinations beyond Earth orbit. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
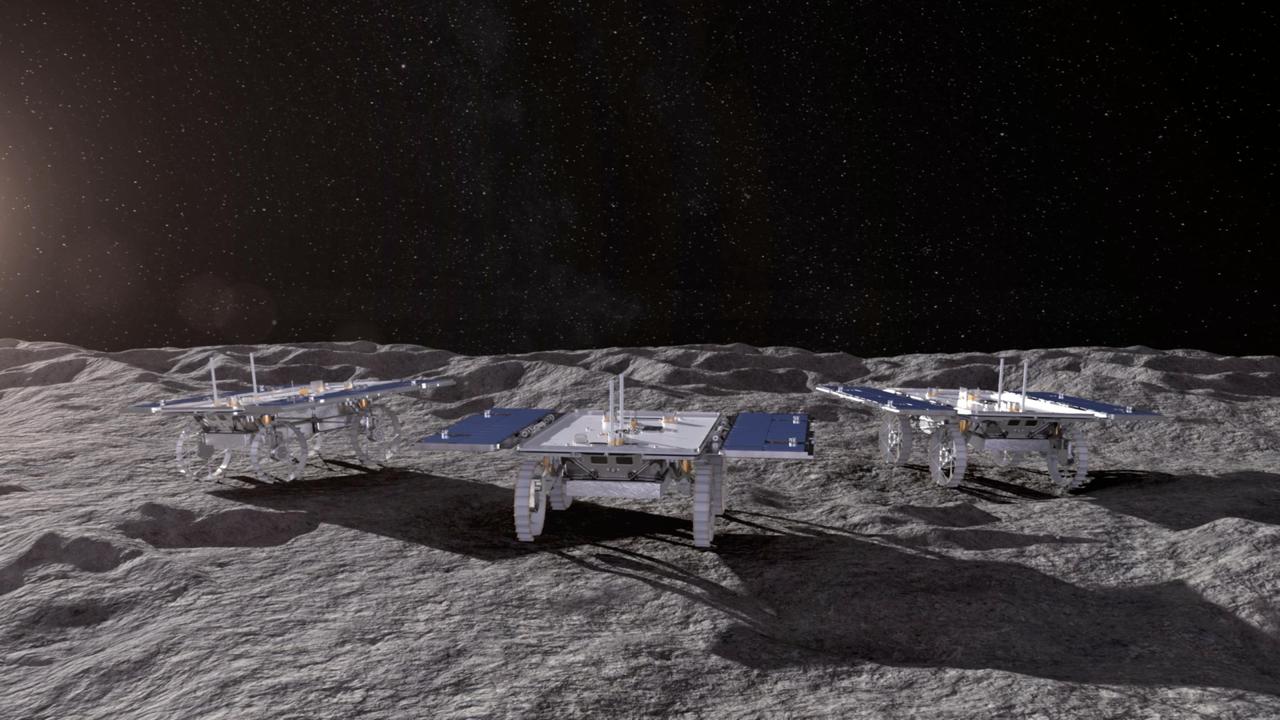
This animated artist's concept depicts three small rovers – part of NASA's CADRE (Cooperative Autonomous Distributed Robotic Exploration) technology demonstration headed for the Moon – driving together on the lunar surface. Motiv Space Systems in Pasadena, California, created the rendering and collaborated with NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory on critical rover and mobility functions. Slated to arrive aboard a lunar lander at the Reiner Gamma region of the Moon under NASA's CLPS (Commercial Lunar Payload Services) initiative, CADRE is designed to demonstrate that multiple robots can cooperate and explore together autonomously – without direct input from human mission controllers. A trio of the miniature solar-powered rovers, each about the size of a carry-on suitcase, will explore the Moon as a team, communicating via radio with each other and a base station aboard the lander. By taking simultaneous measurements from multiple locations, CADRE will also demonstrate how multirobot missions can record data impossible for a single robot to achieve – a tantalizing prospect for future missions. Motiv contributed subsystems and hardware elements for three of four CADRE systems, including designing and building the mobility system and rover chassis, the base station, the rover deployers, and the motor controller boards. The company also procured and tested the actuators with the flight motor controller boards. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26296
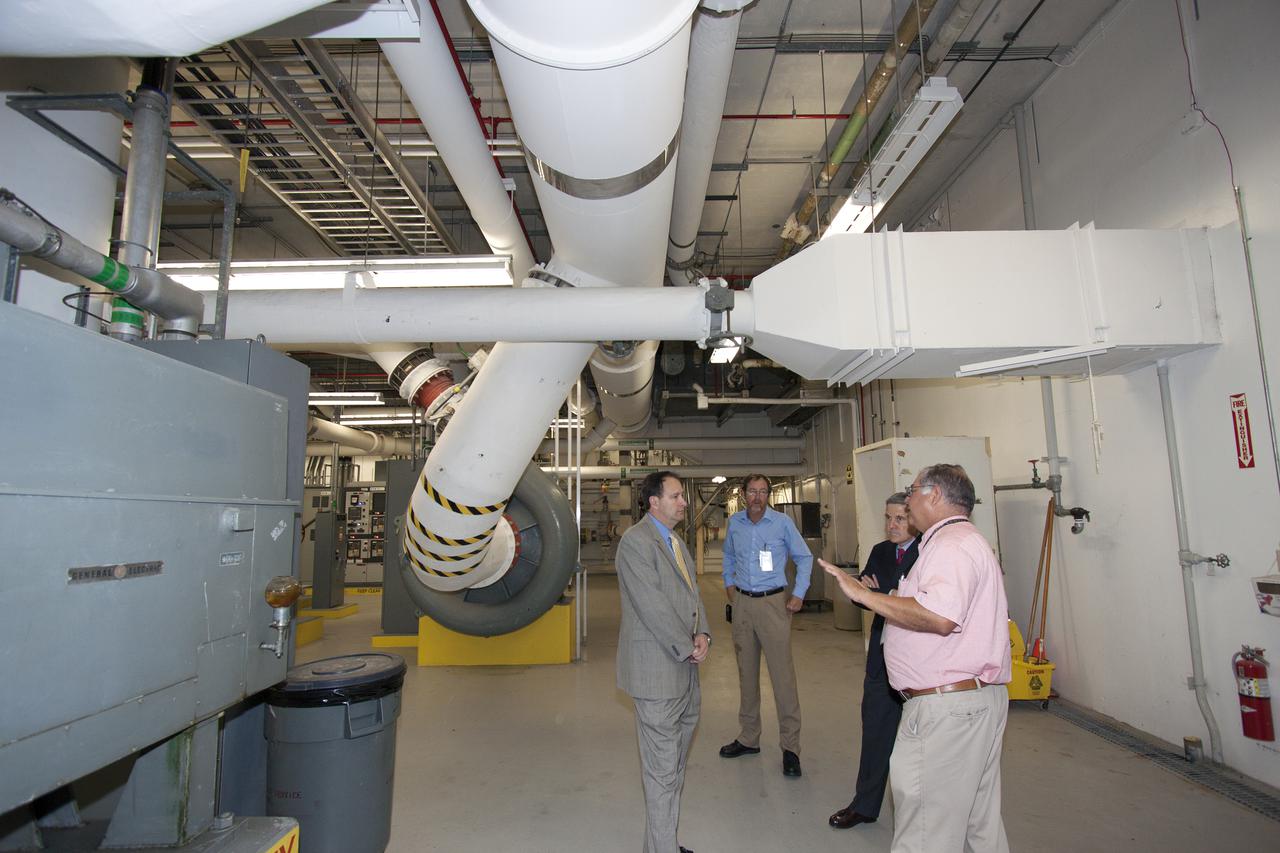

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot tours the Environmental Control System Room under the surface of Launch Pad 39B during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Lightfoot, Alan Littlefield, Vehicle Integration and Launch chief engineer, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, and Jose Perez Morales, launch pad project manager. The pad is being modified to support NASA's new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket, the SLS. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
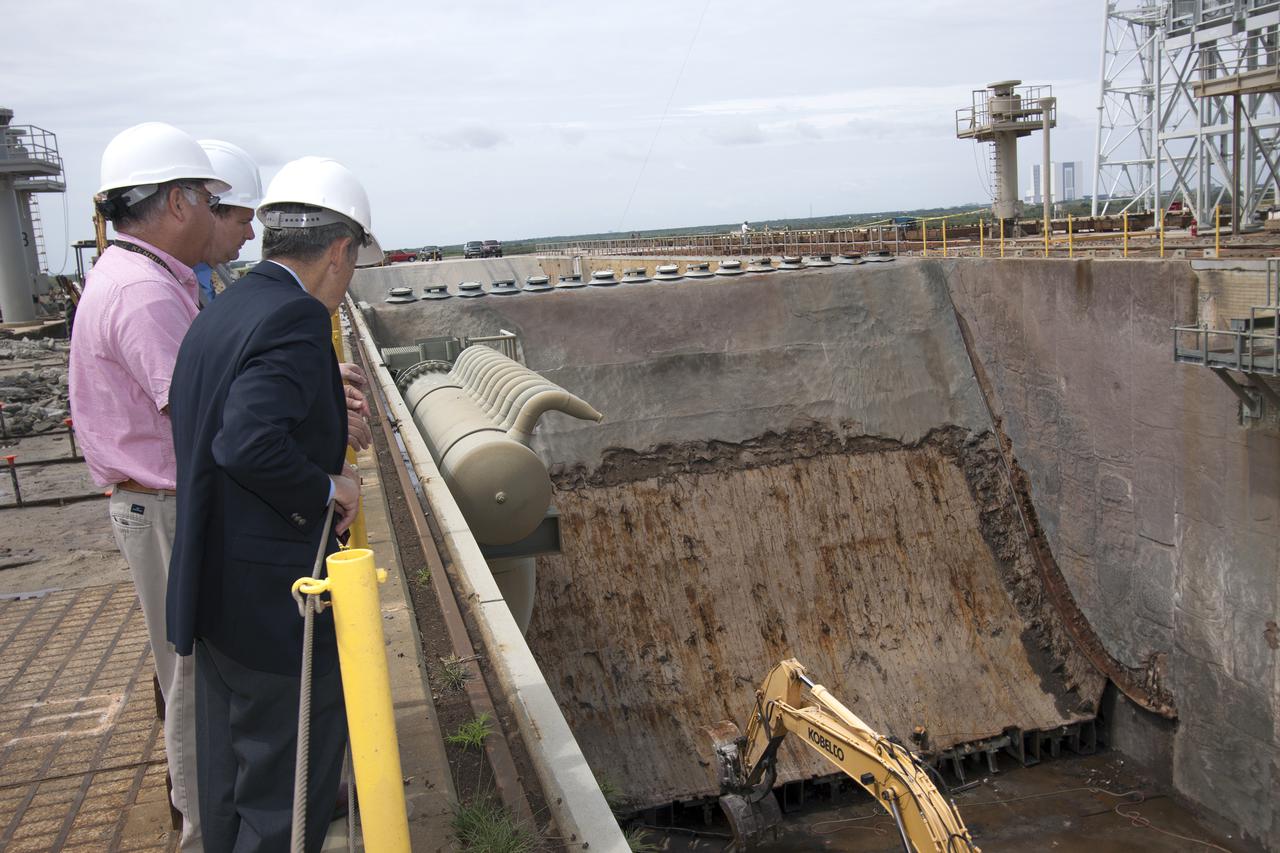

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot gets a close look at the flame deflector on Launch Pad 39B during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Lightfoot, Jose Perez Morales, launch pad project manager, and Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. The pad is being modified to support NASA's new Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System heavy-lift rocket, the SLS. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
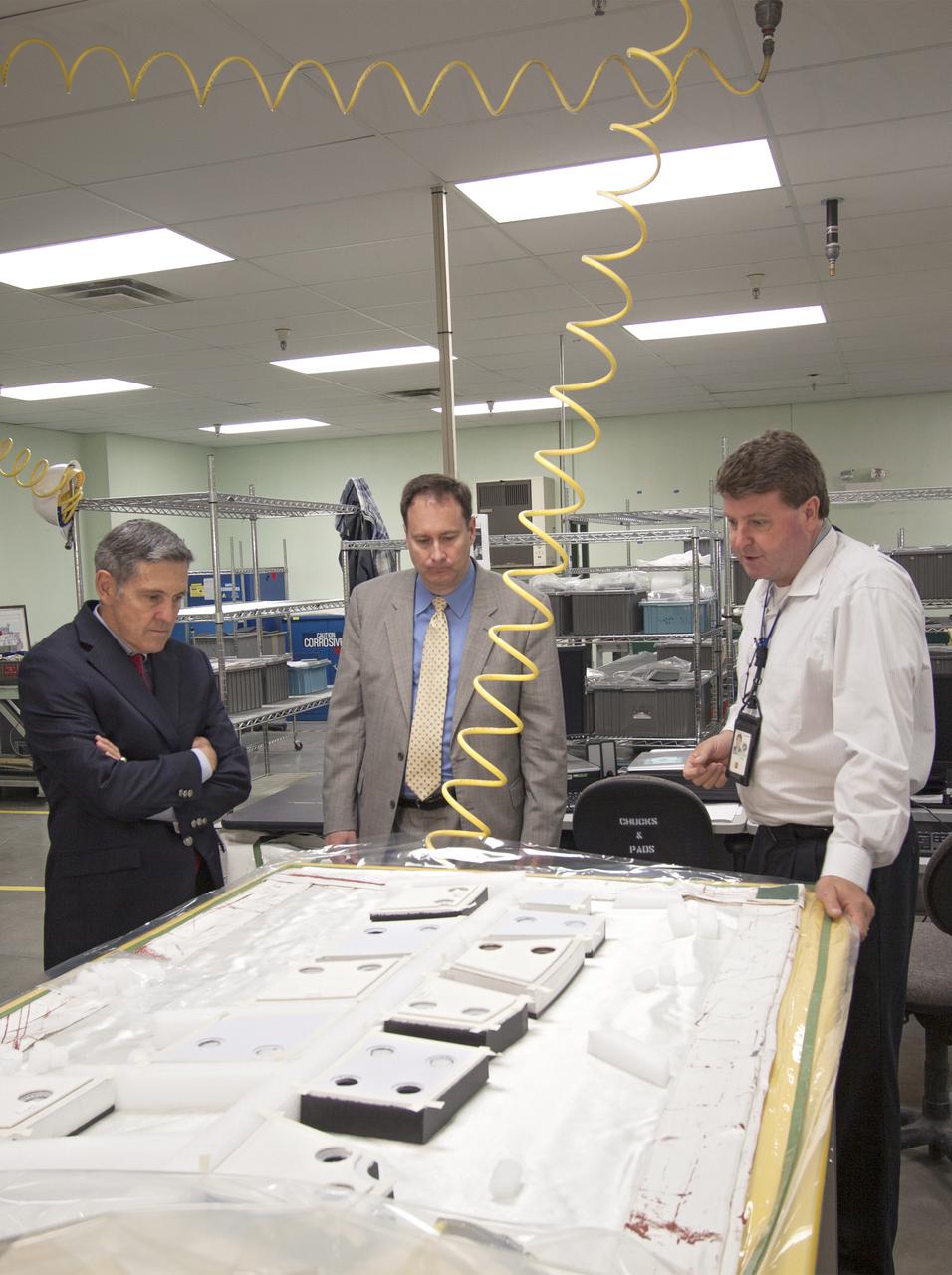

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA Associate Administrator Robert Lightfoot, center, tours the Thermal Protection System Facility, or TPSF, during a visit to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are Kennedy Director Bob Cabana, Lightfoot, and Martin Boyd, TPSF manager with Jacobs Technologies, briefing his guests on the production of TPS tile for NASA's new Orion spacecraft. NASA's FY2014 budget proposal includes a plan to robotically capture a small near-Earth asteroid and redirect it safely to a stable orbit in the Earth-moon system where astronauts can visit and explore it. Performing these elements for the proposed asteroid initiative integrates the best of NASA's science, technology and human exploration capabilities and draws on the innovation of America's brightest scientists and engineers. It uses current and developing capabilities to find both large asteroids that pose a hazard to Earth and small asteroids that could be candidates for the initiative, accelerates our technology development activities in high-powered solar electric propulsion and takes advantage of our hard work on the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft, helping to keep NASA on target to reach the President's goal of sending humans to Mars in the 2030s. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann