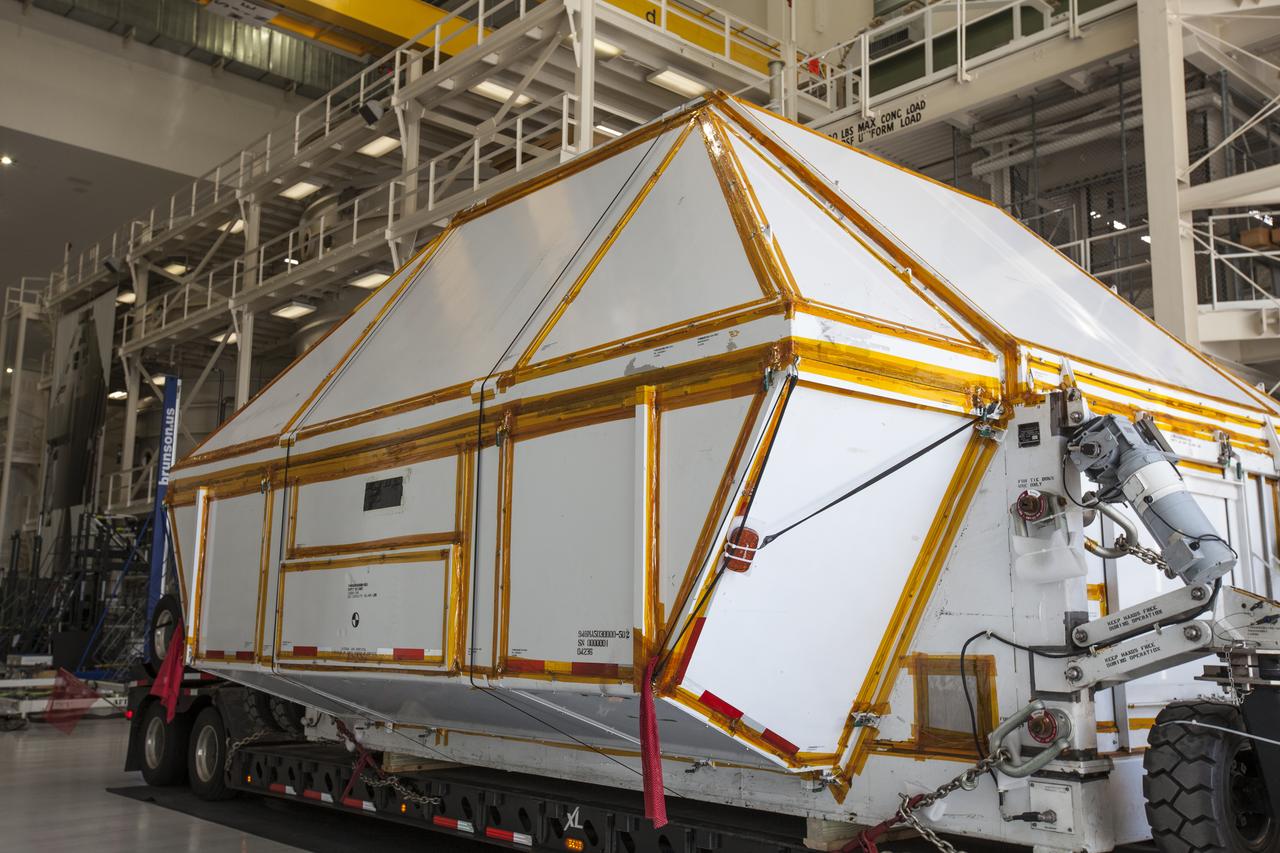

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 is backed into the high bay at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Inside the facility's high bay, the pressure vessel will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
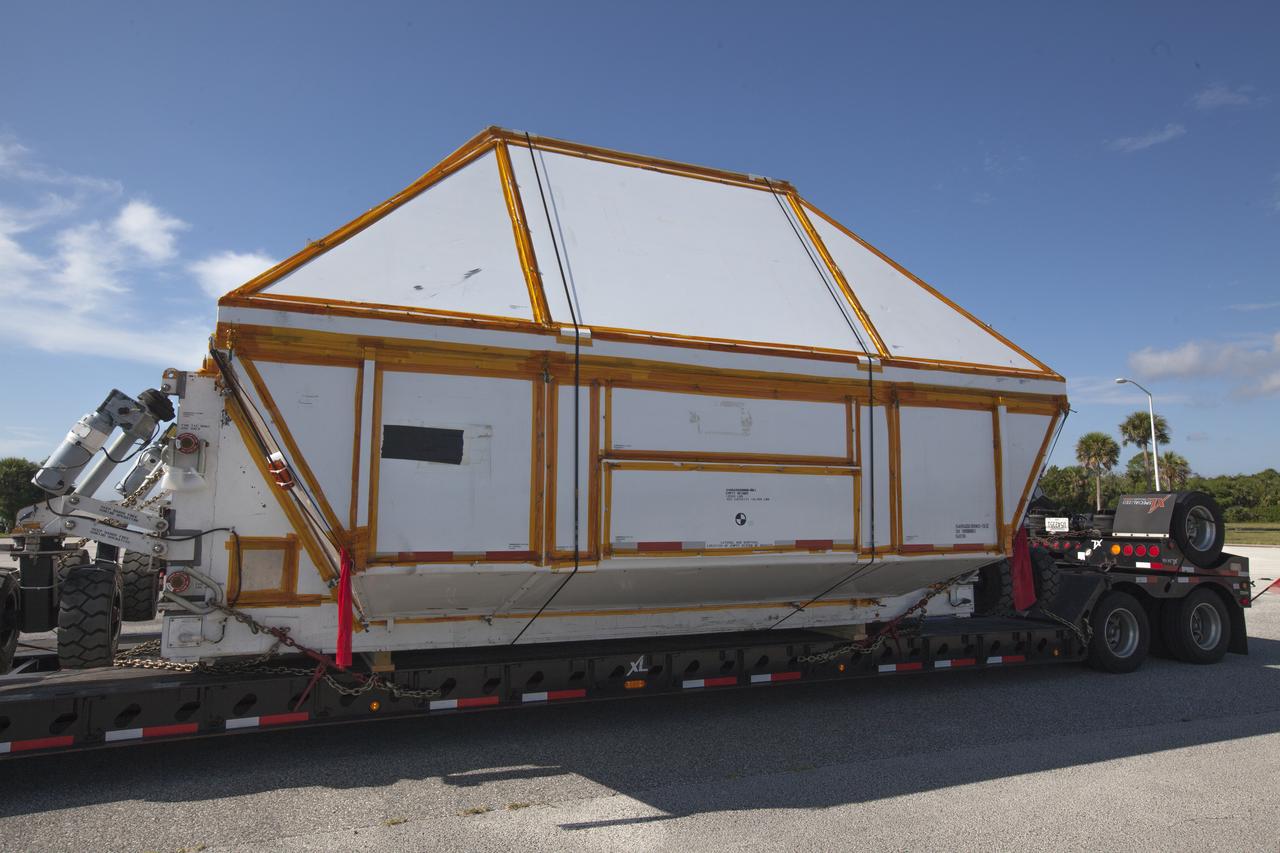

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
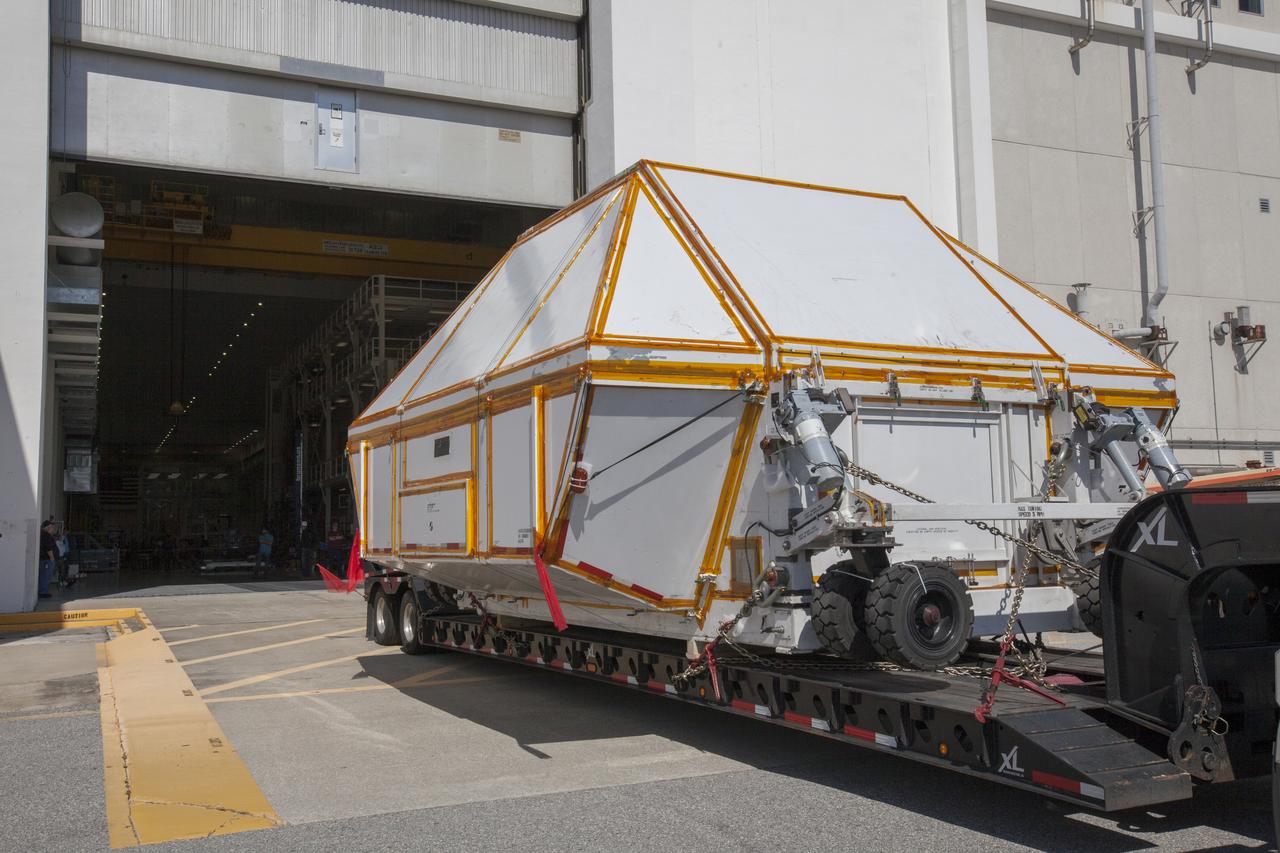

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the facility's high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
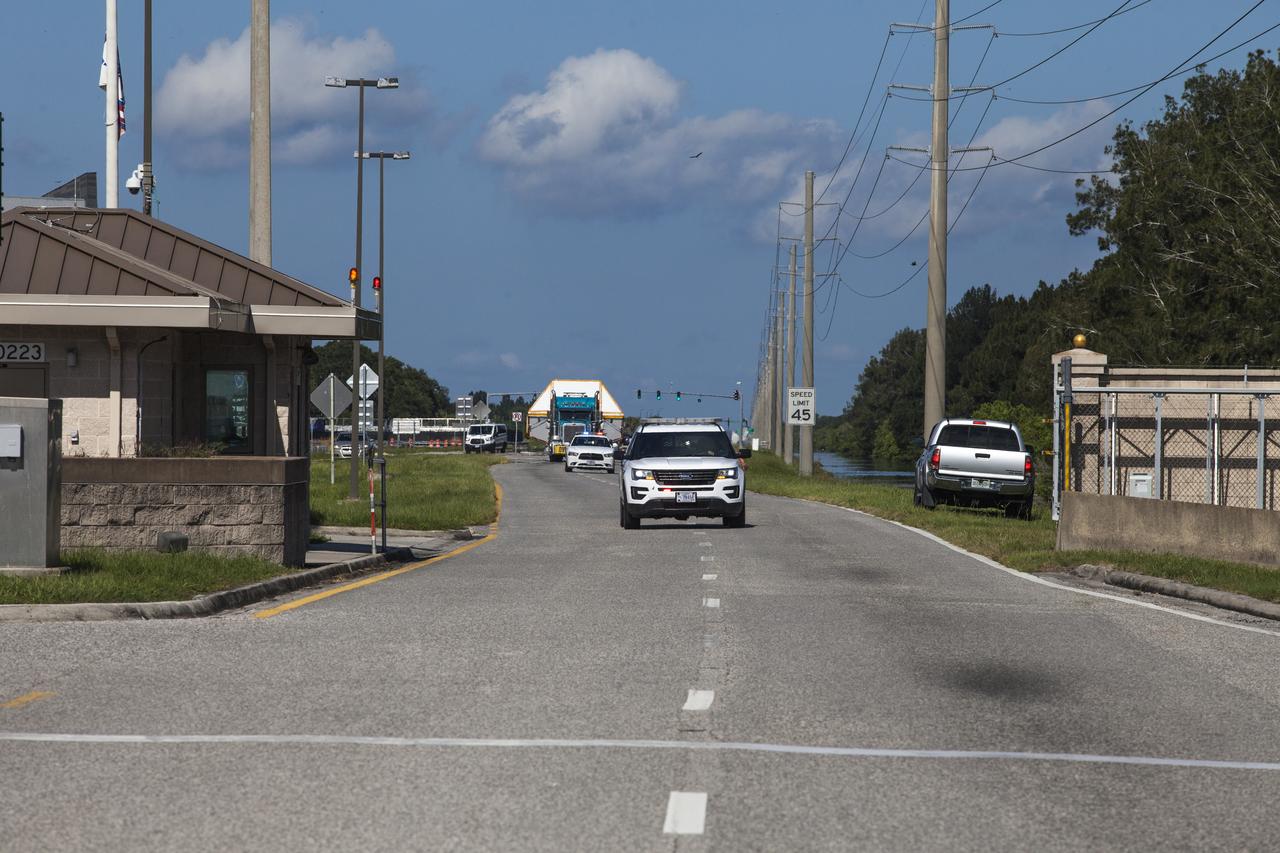

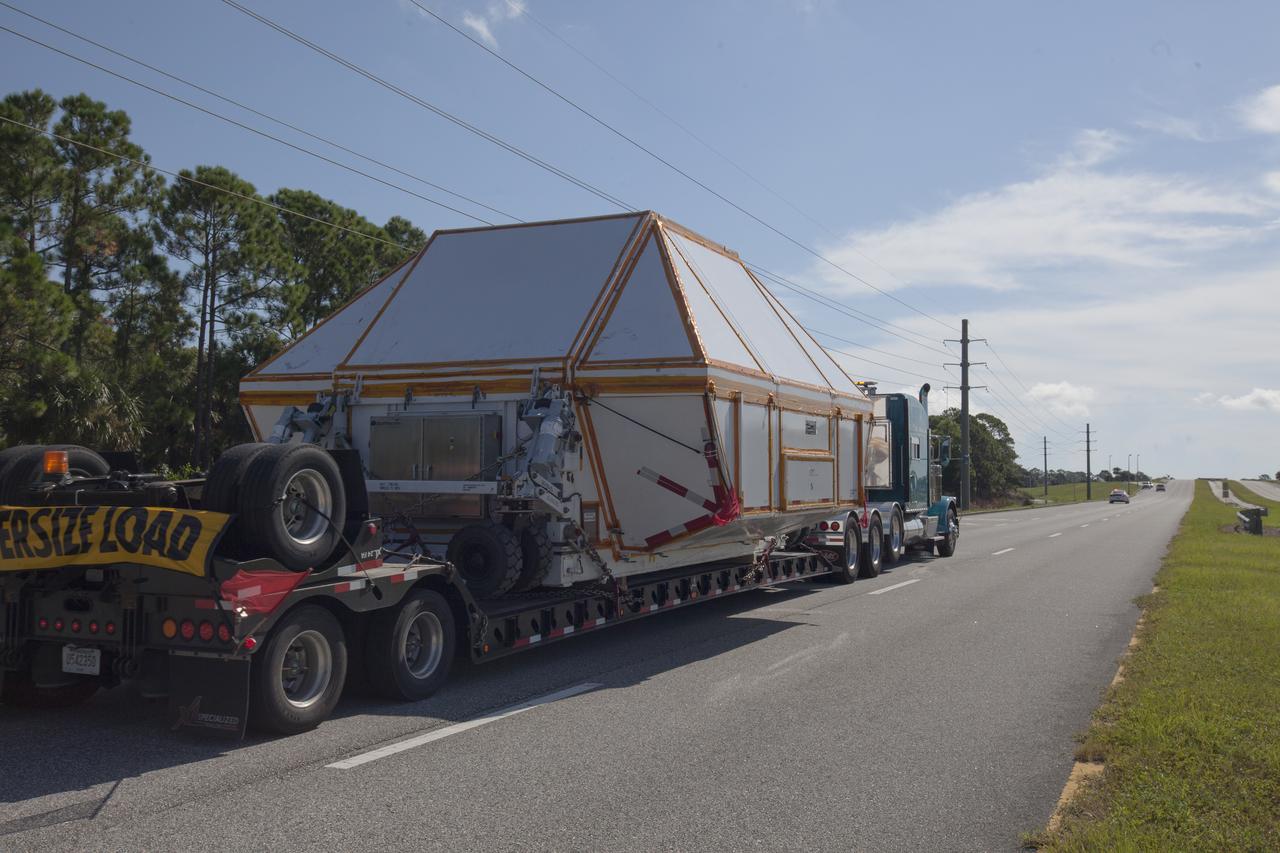
A super-wide truck carrying the Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 approaches the entrance gate at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
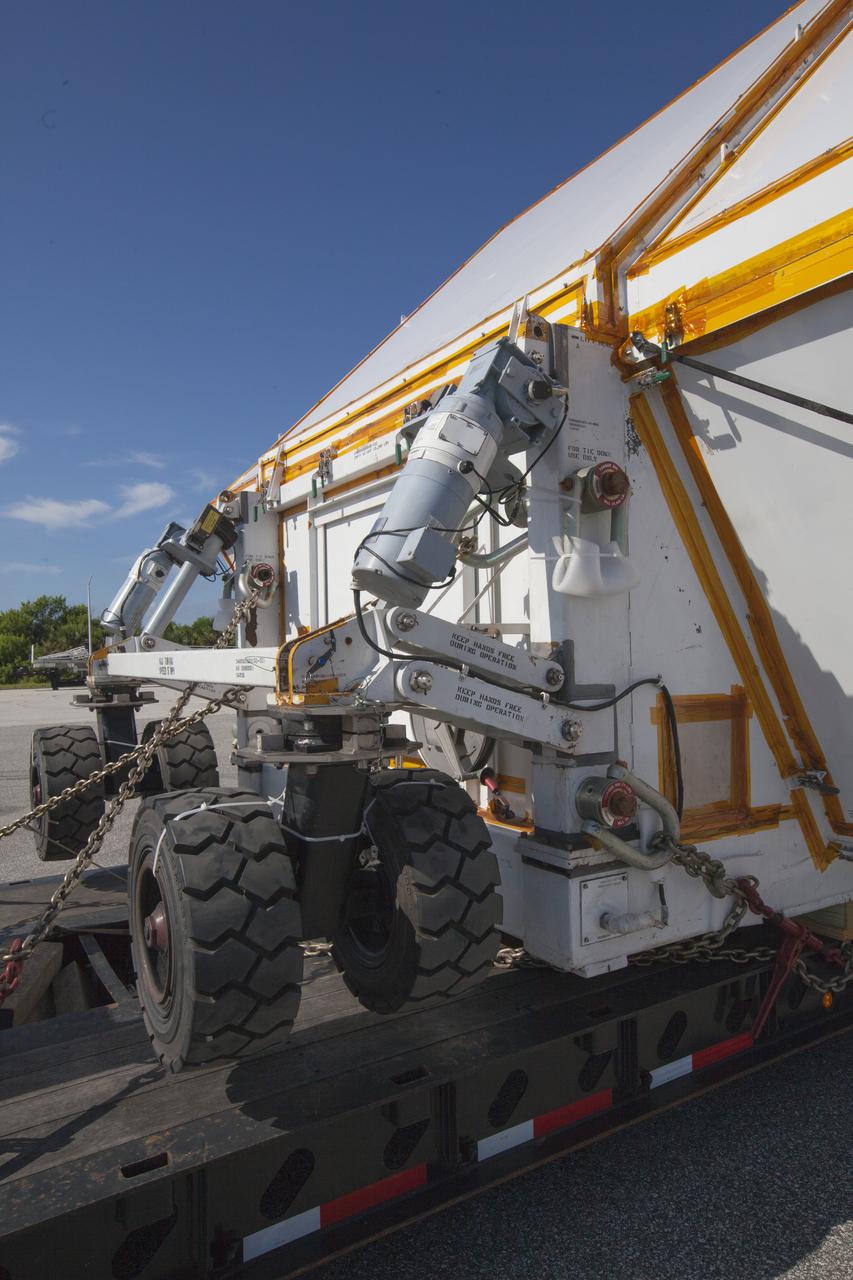

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
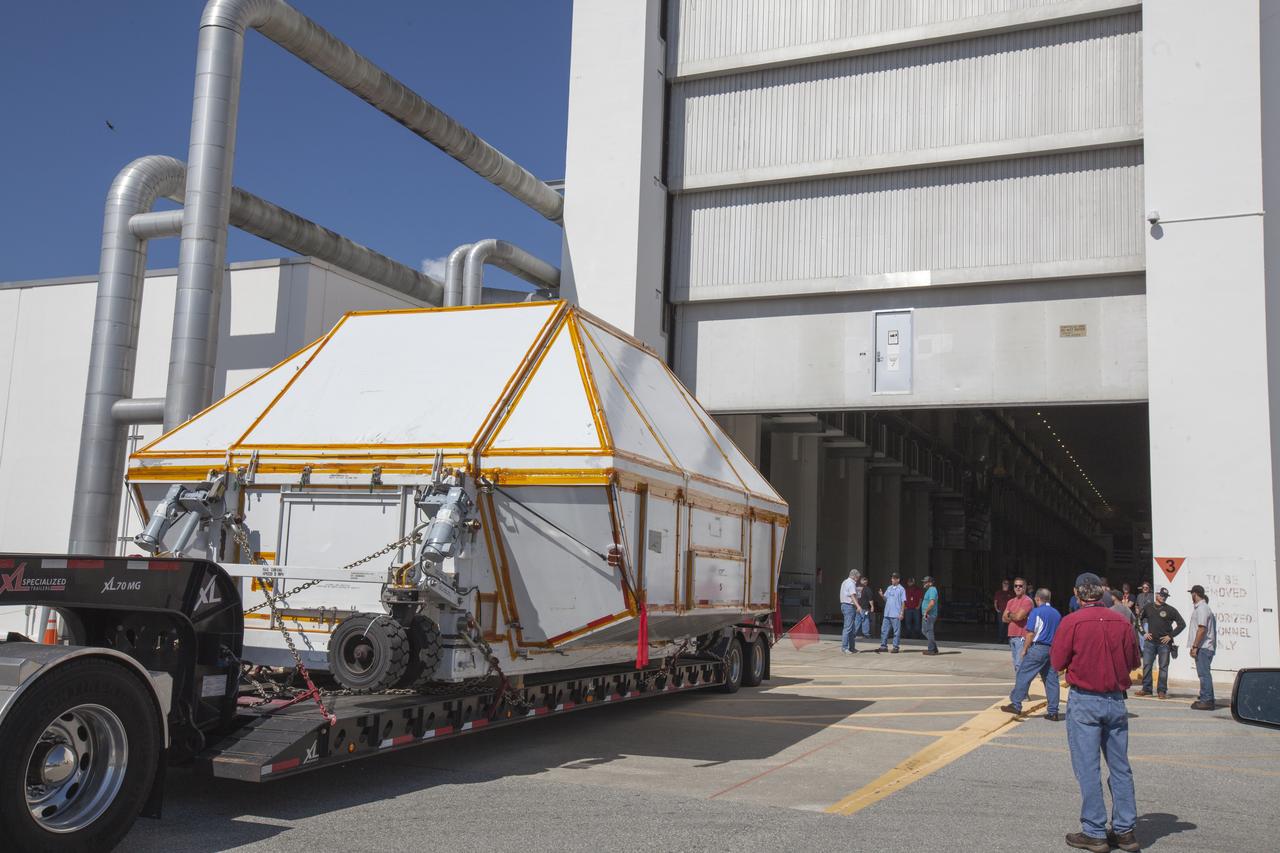

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 24, 2018. The pressure vessel was transported in its Crew Module Transportation Fixture by super-wide transport truck from Michoud Assembly Facility near New Orleans. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. It will be moved into the facility's high bay, where it will be secured on a precision alignment tool to begin preparing it for flight.
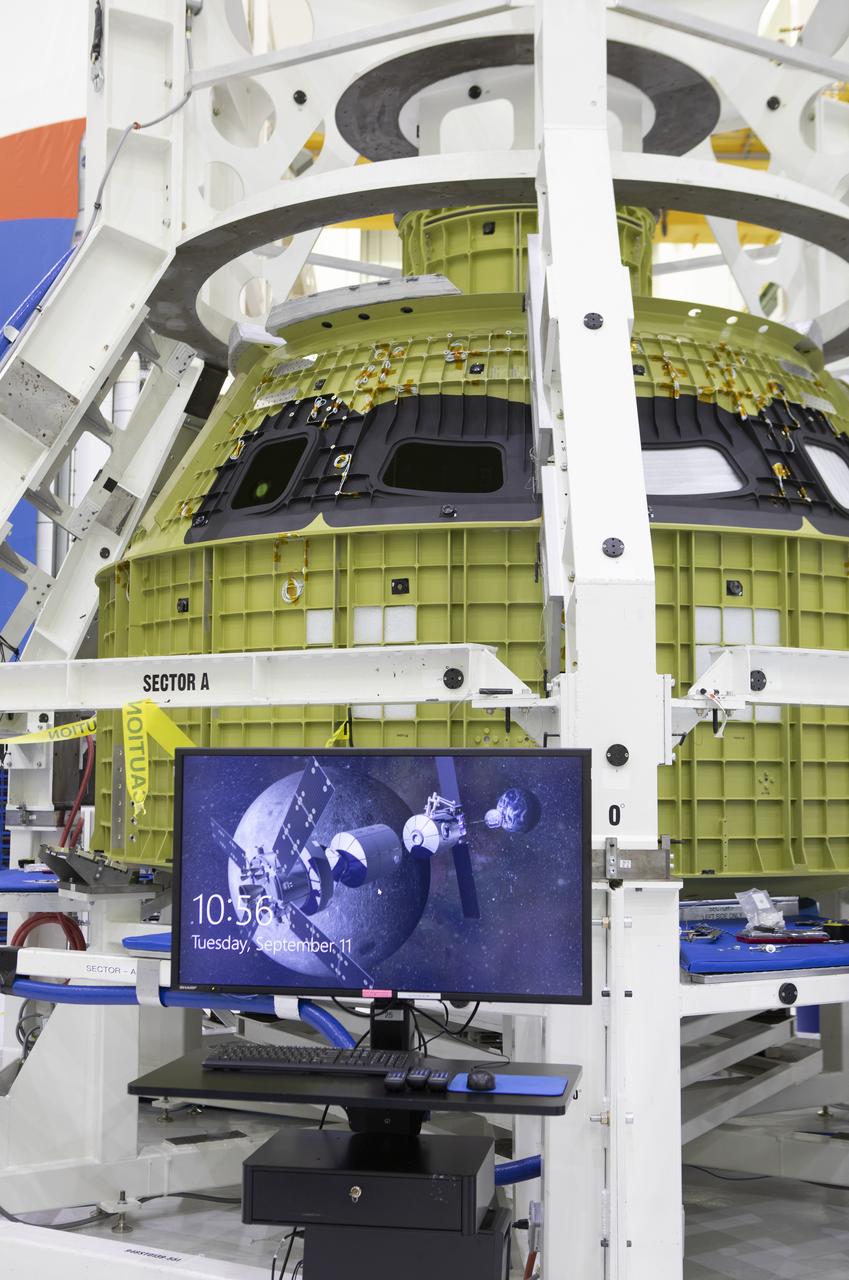

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.
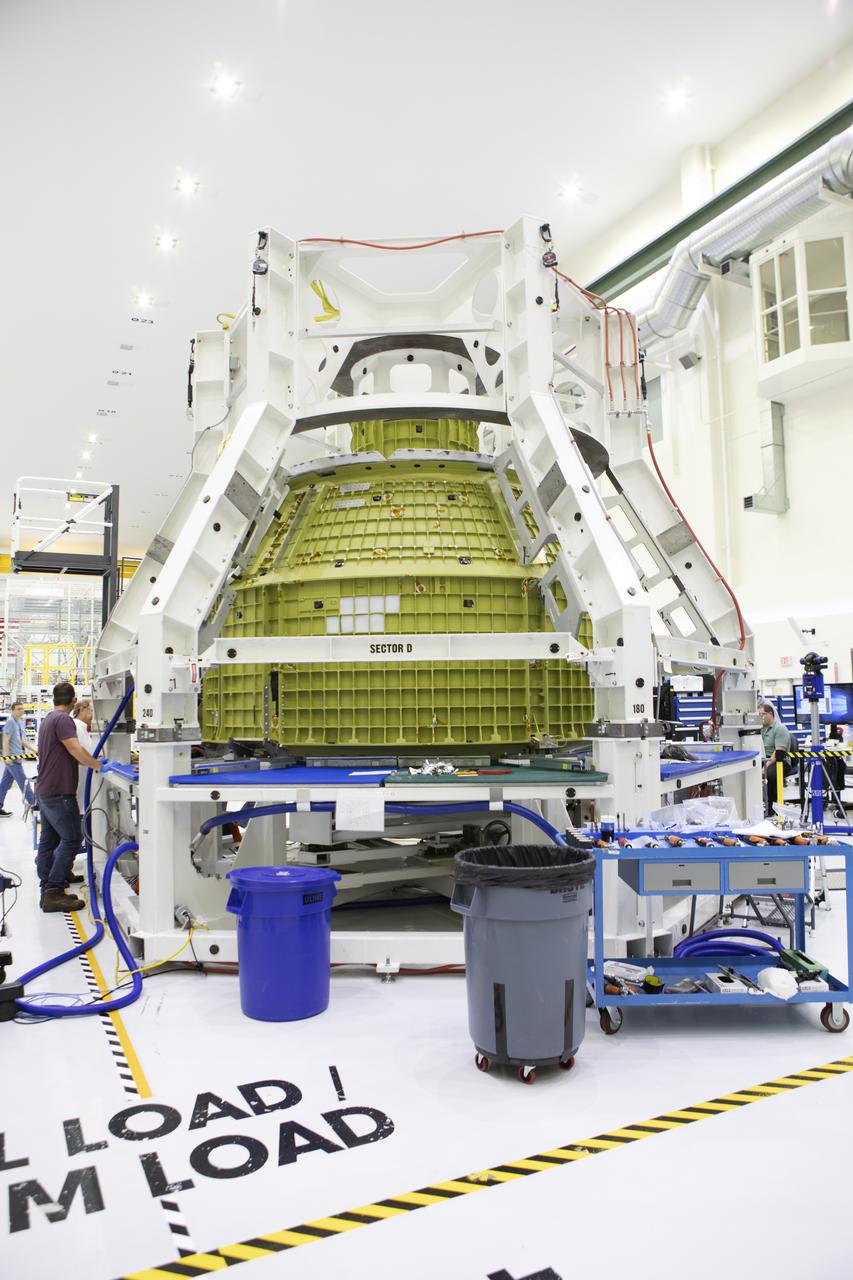

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.
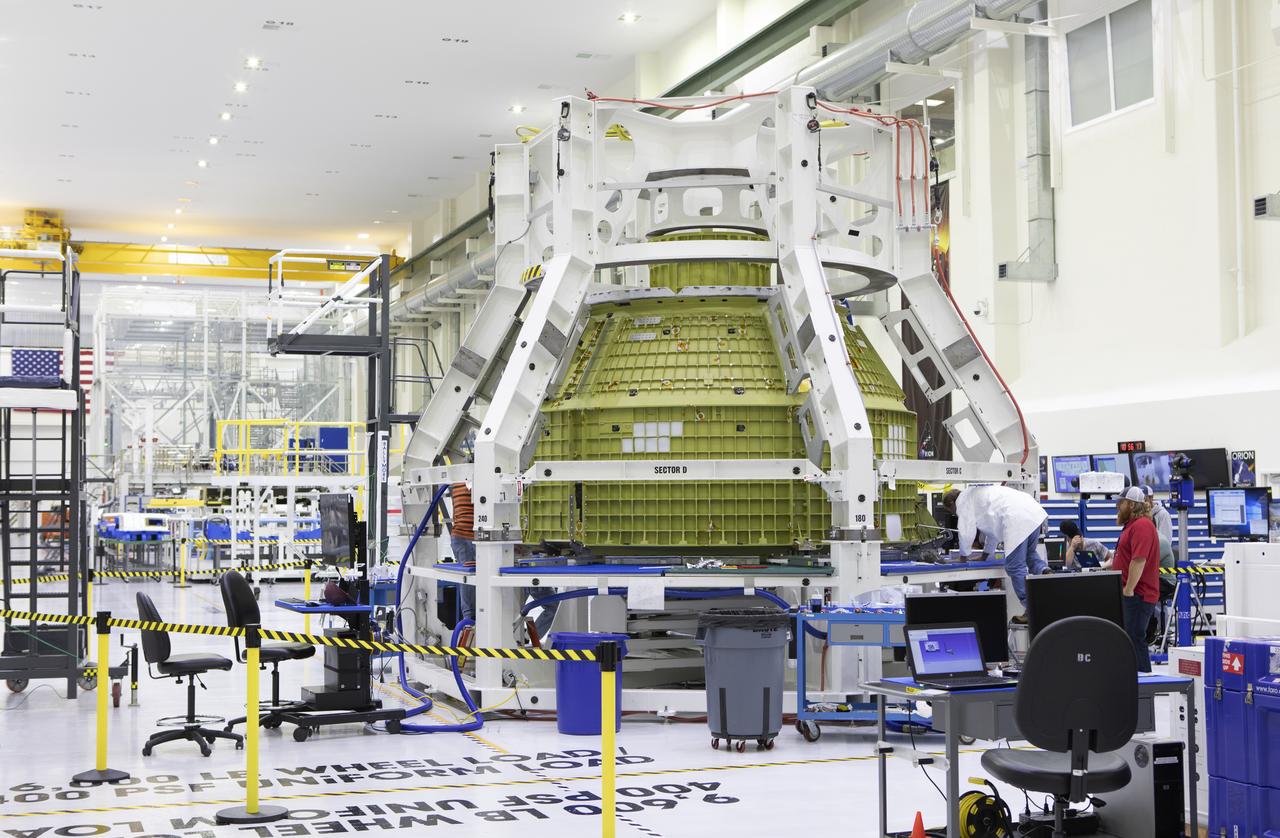

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.
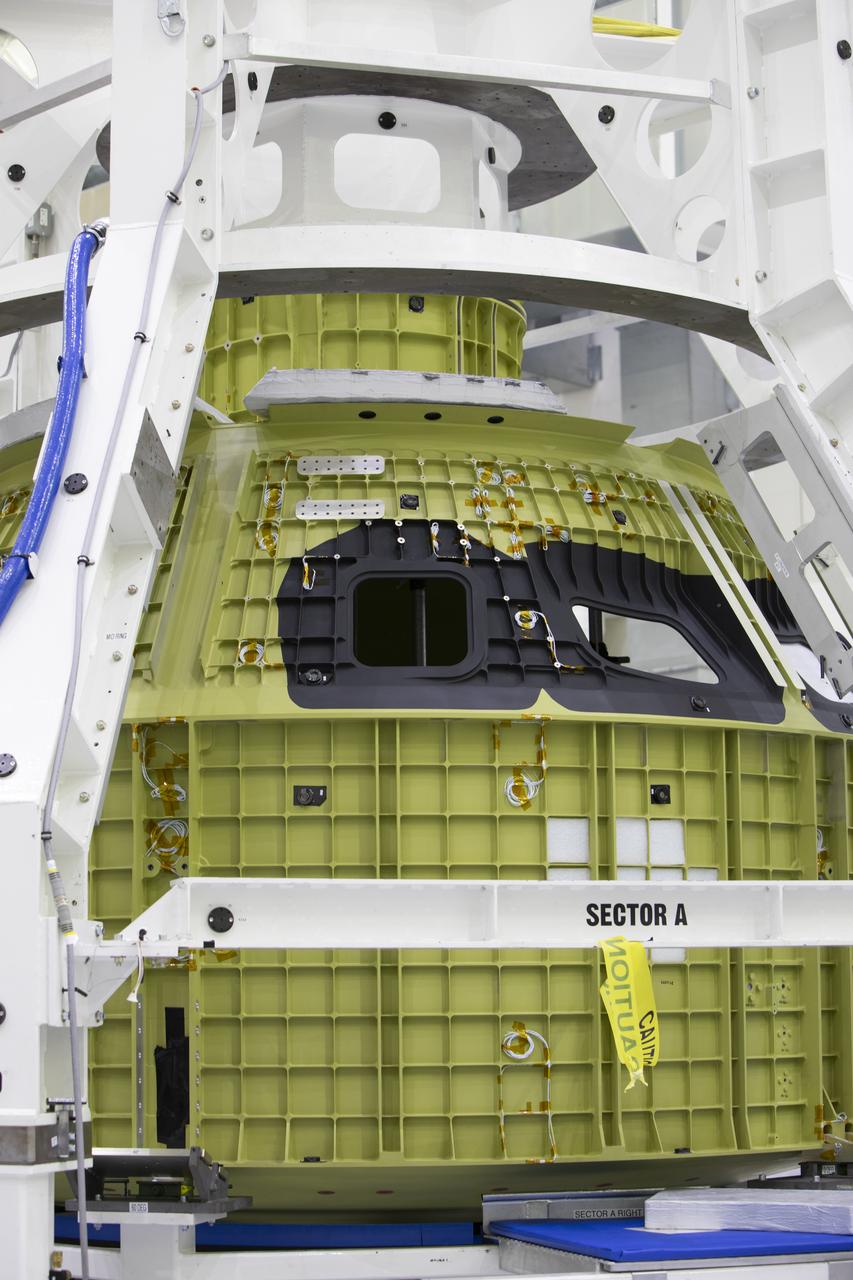

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.
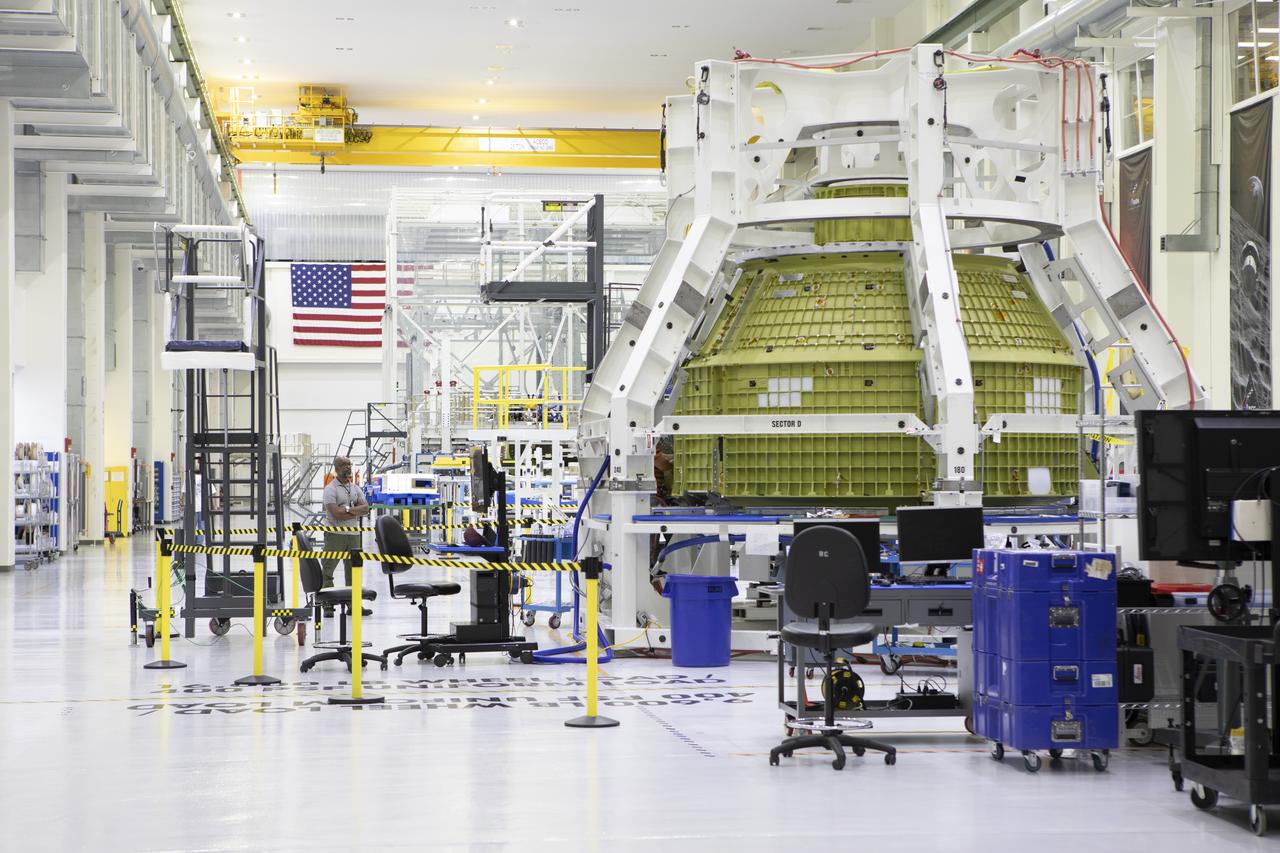

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.

The Orion pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is inside processing equipment where it is getting where it is getting initial processing done.

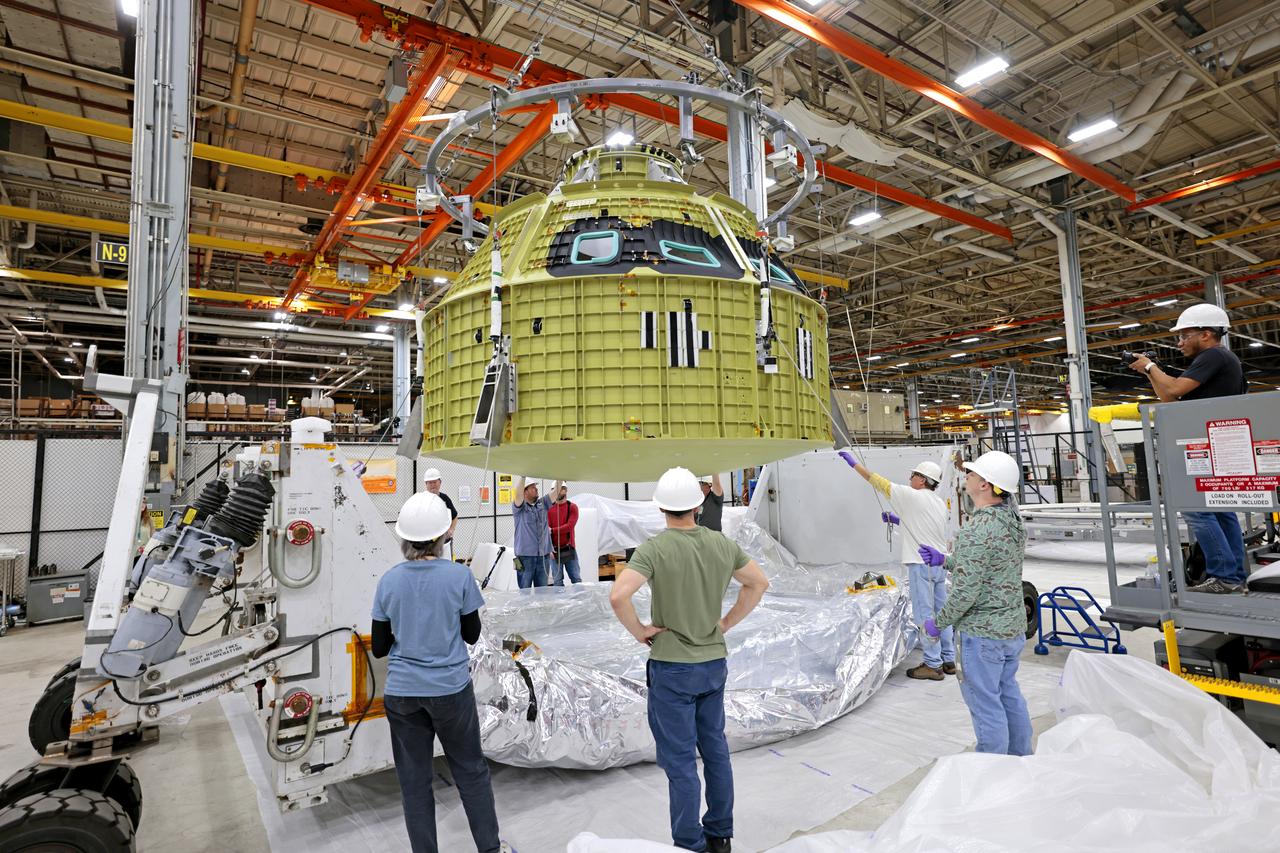
The Orion pressure vessel for NASA’s Artemis III mission is moved into the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The pressure vessel will be secured onto a work stand where Lockheed Matin technicians will begin the work to prepare the spacecraft for its launch atop a Space Launch System rocket. Artemis III will send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon by 2024.
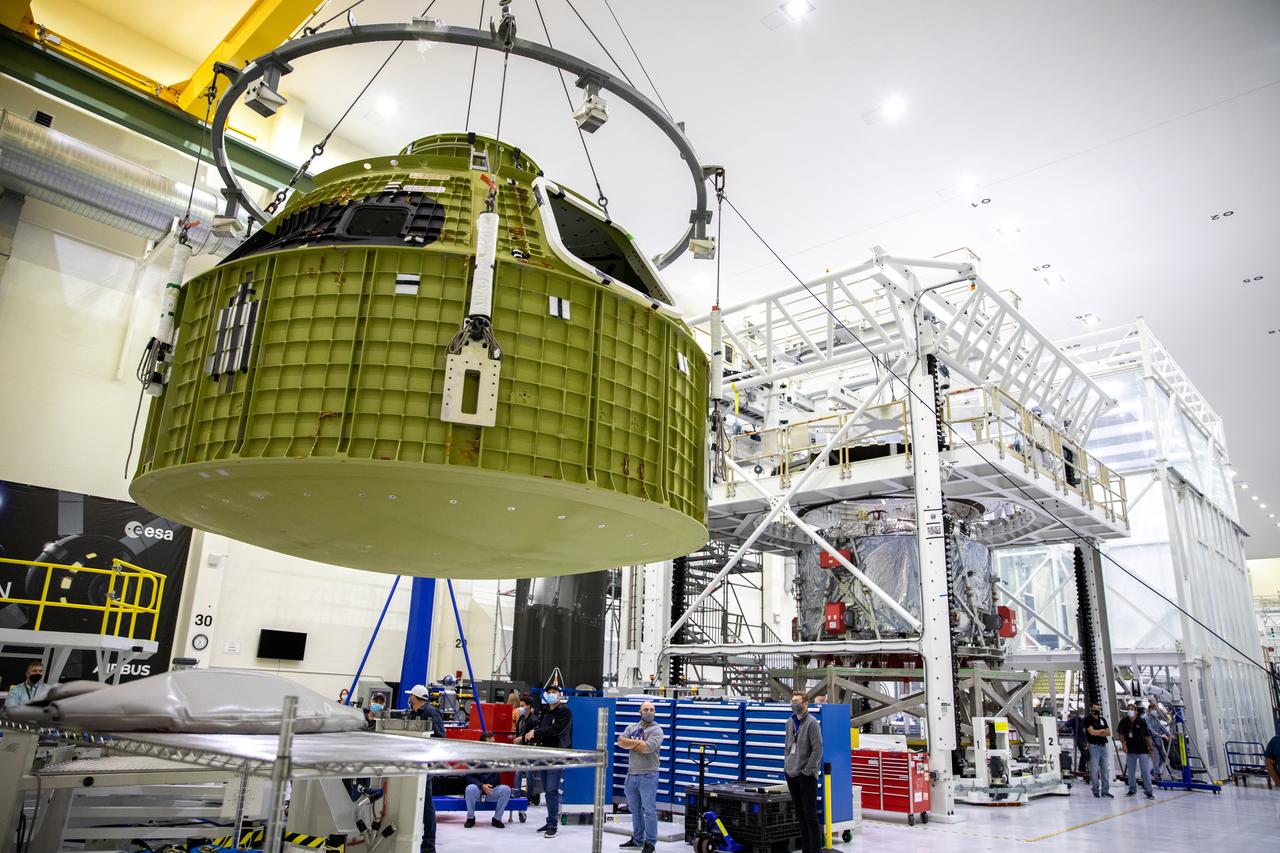

The Orion pressure vessel for NASA’s Artemis III mission is lifted by crane for its move onto a work stand in the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. The pressure vessel will be secured onto the work stand where Lockheed Matin technicians will begin the work to prepare the spacecraft for its launch atop a Space Launch System rocket. Artemis III will send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon by 2024.
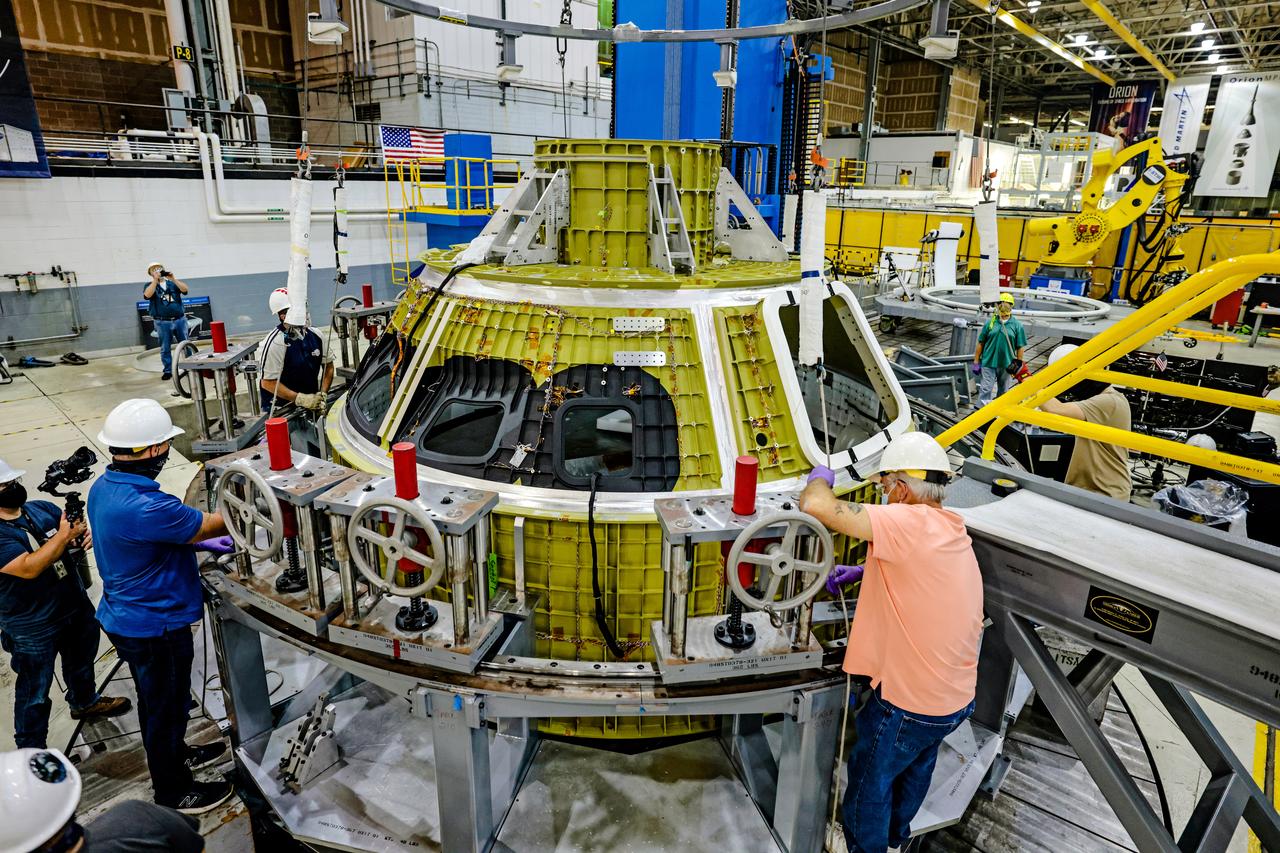

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
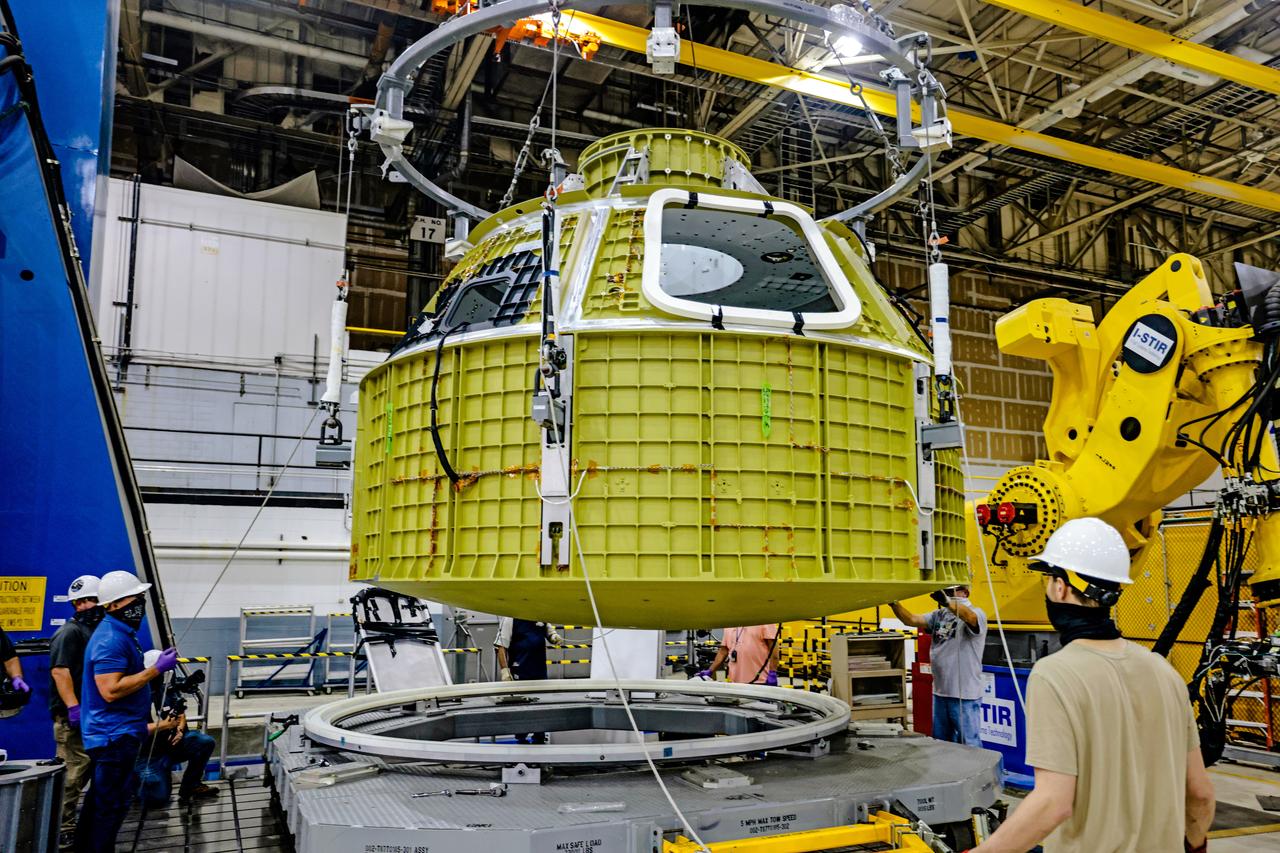

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
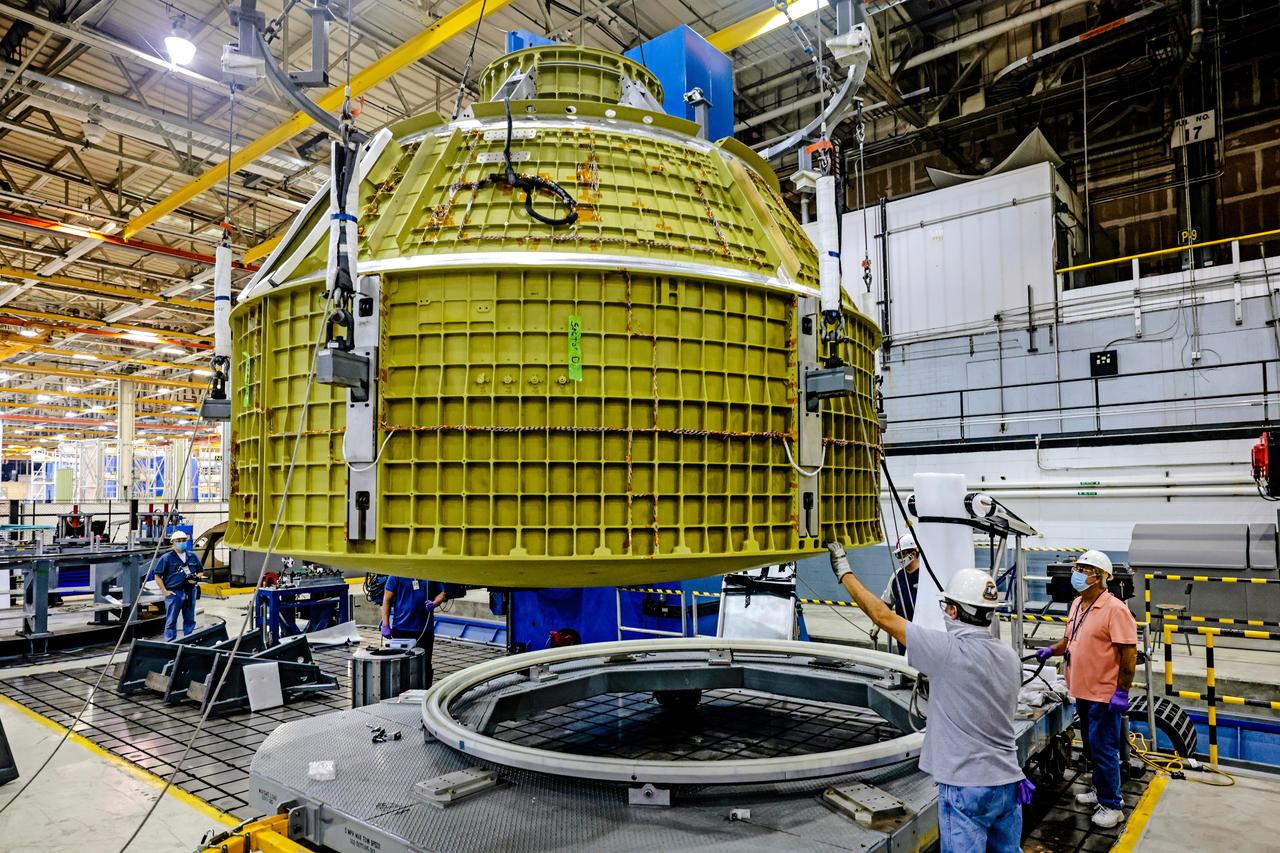

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
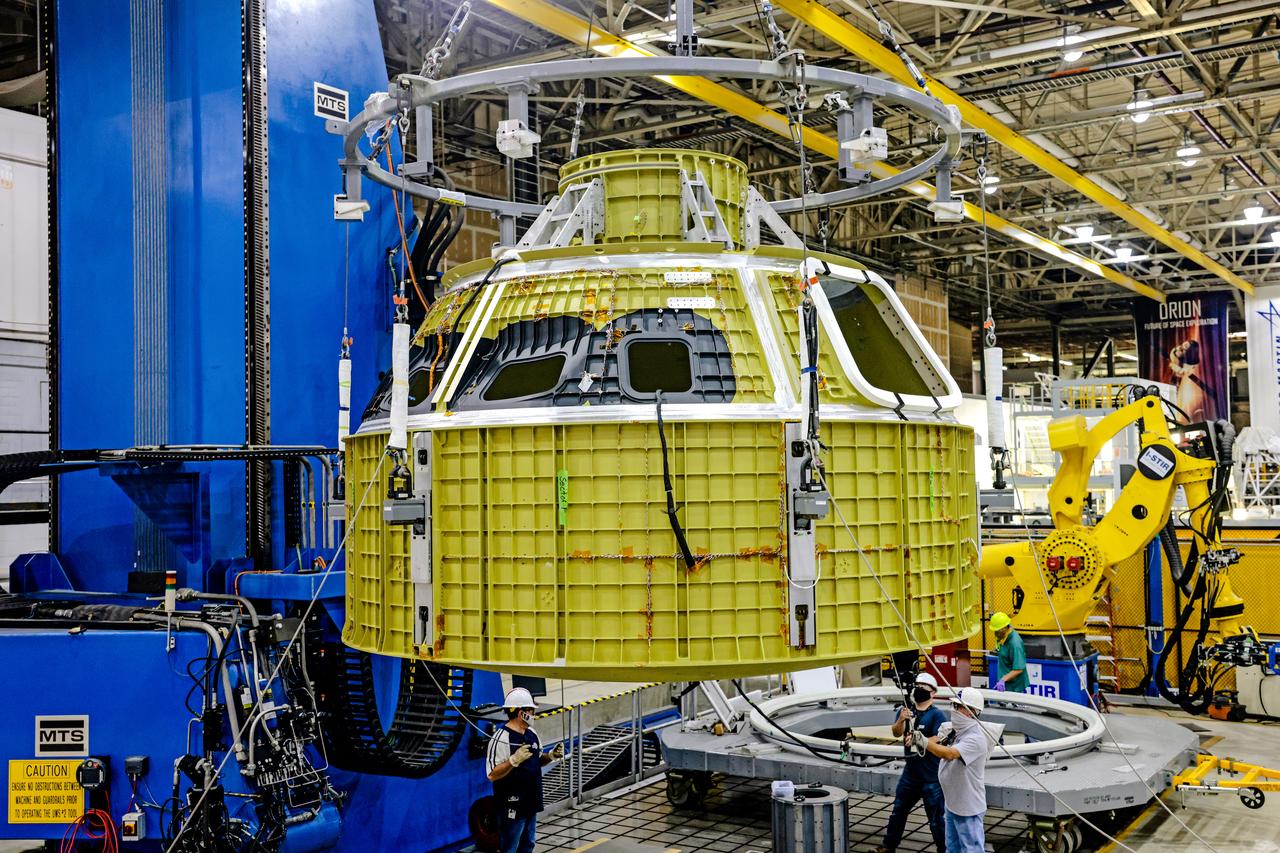

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
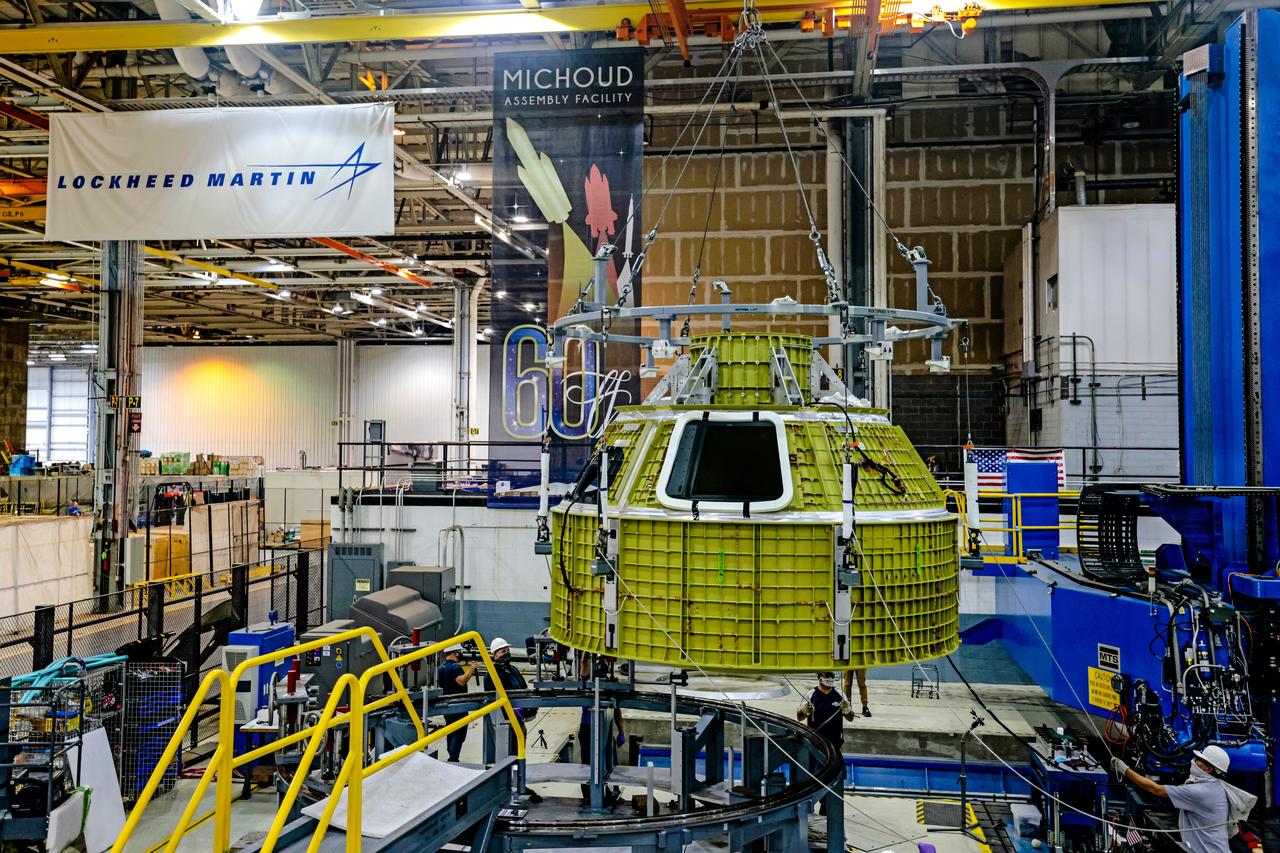

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
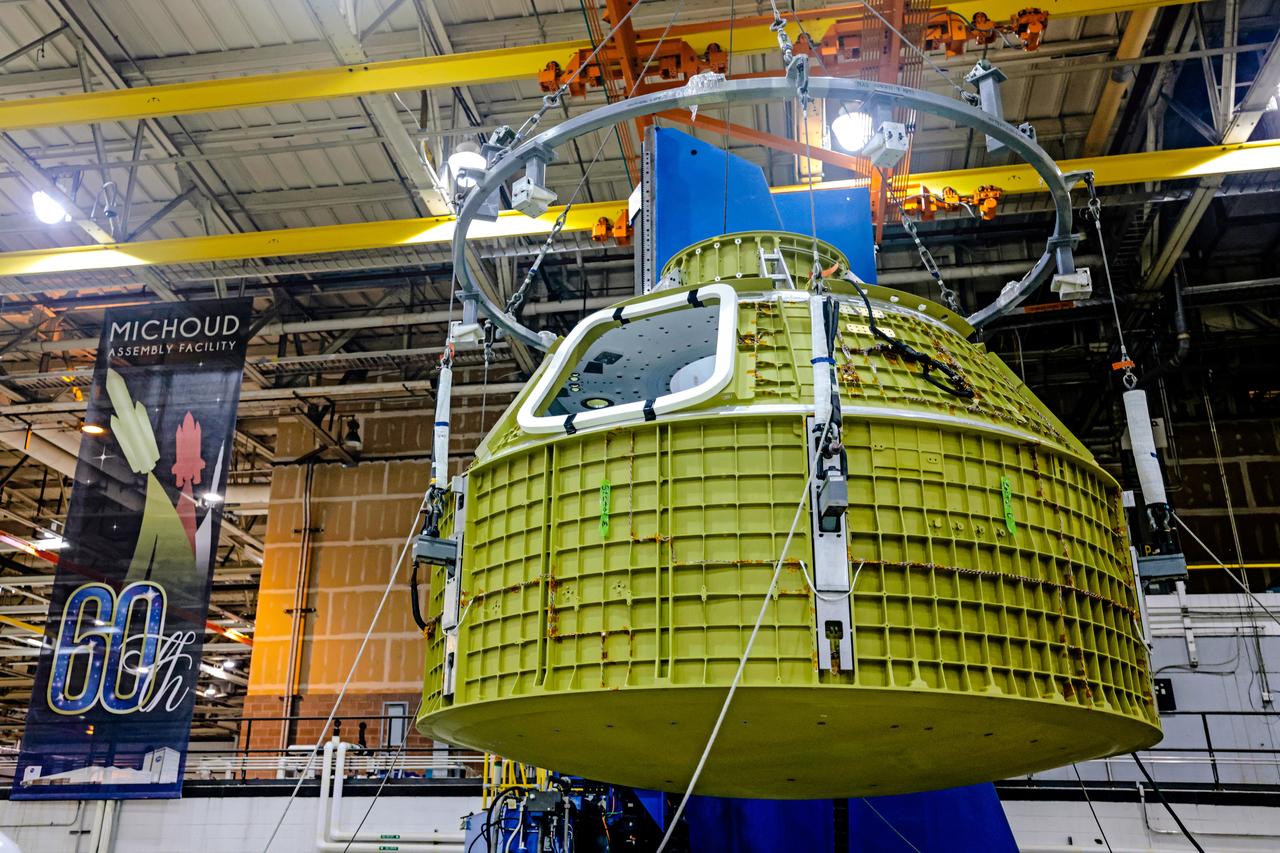

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
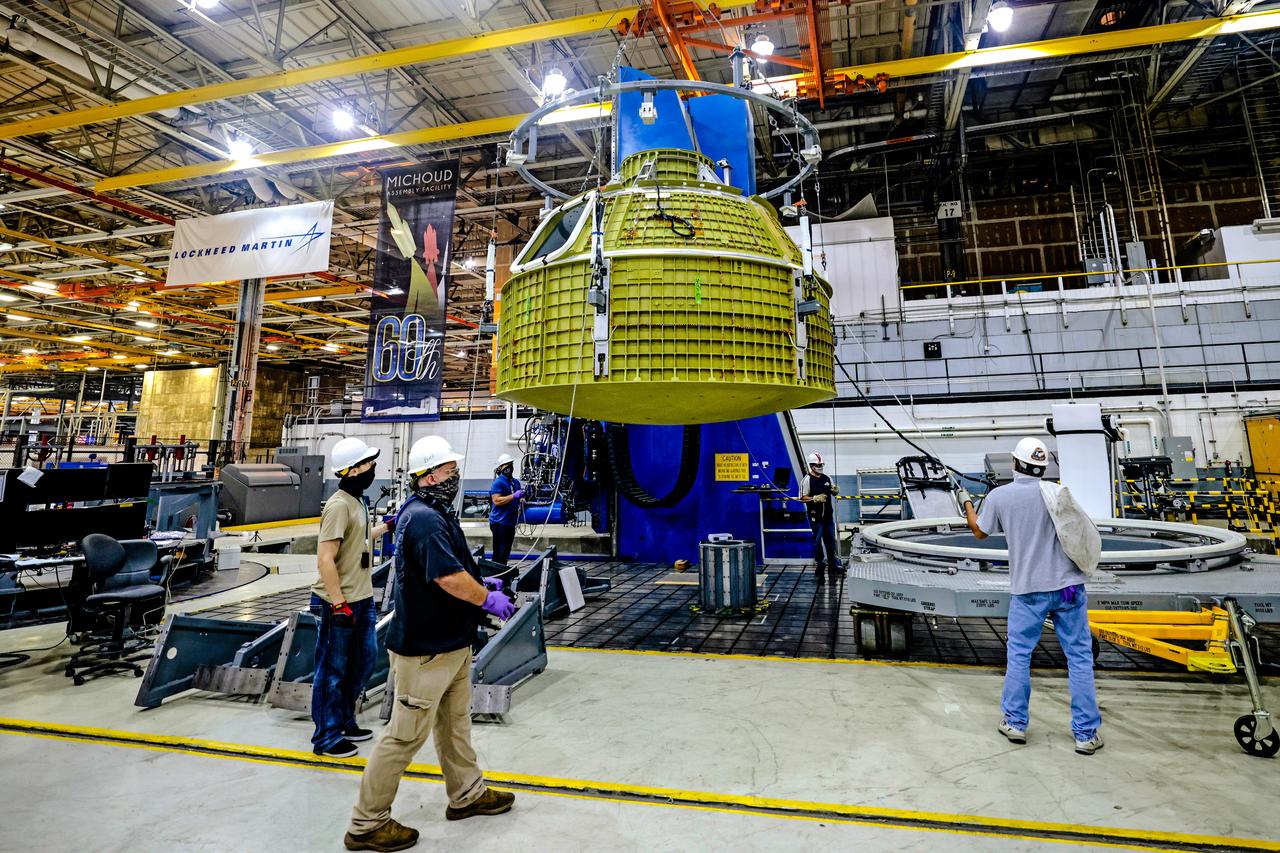

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
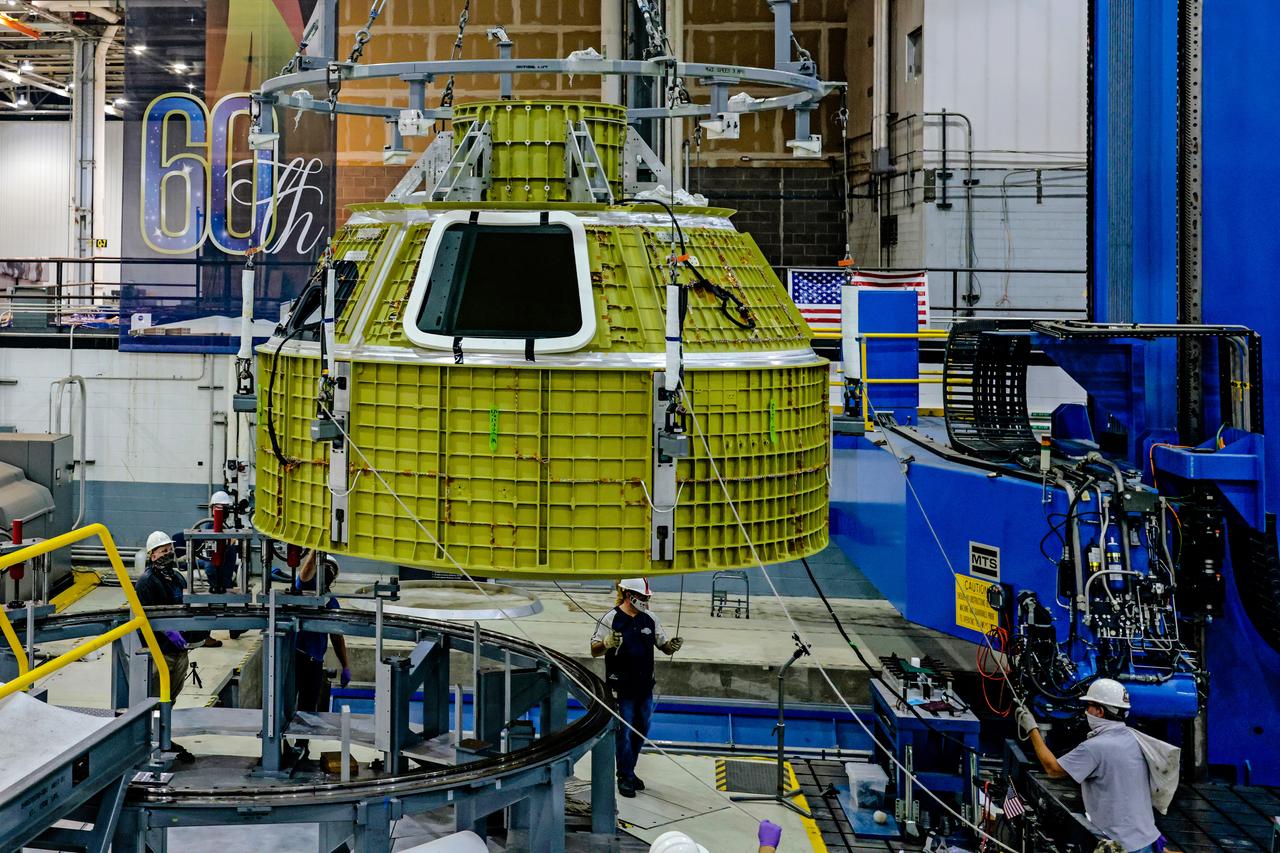

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
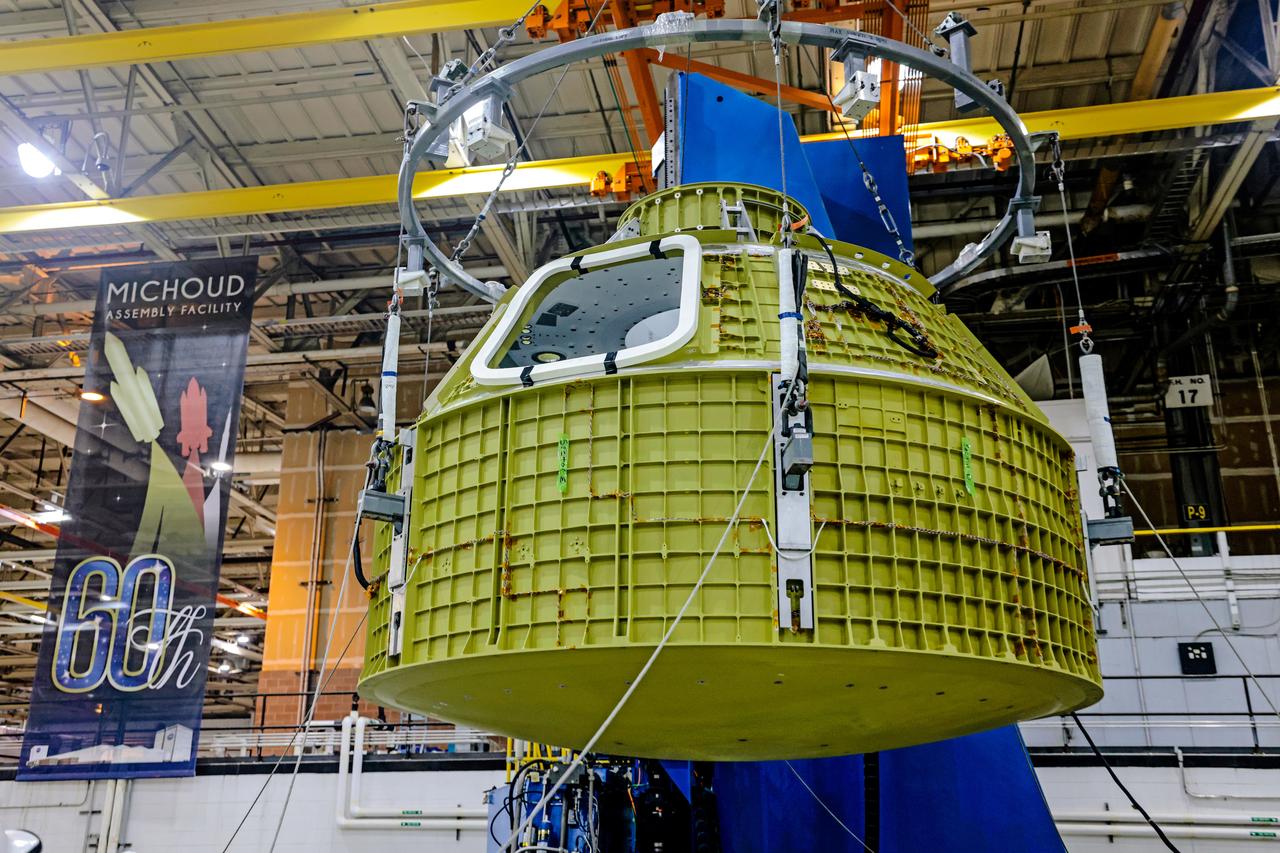

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
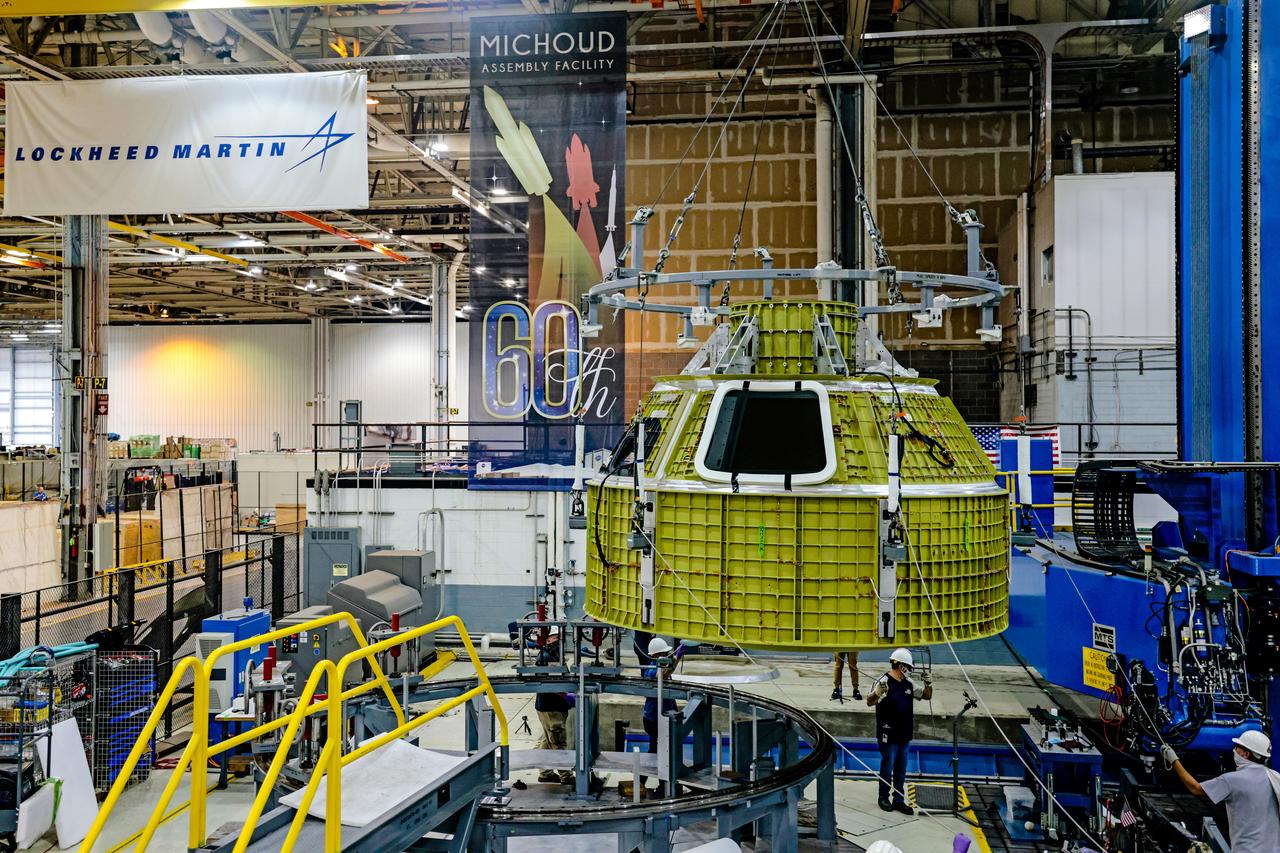

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
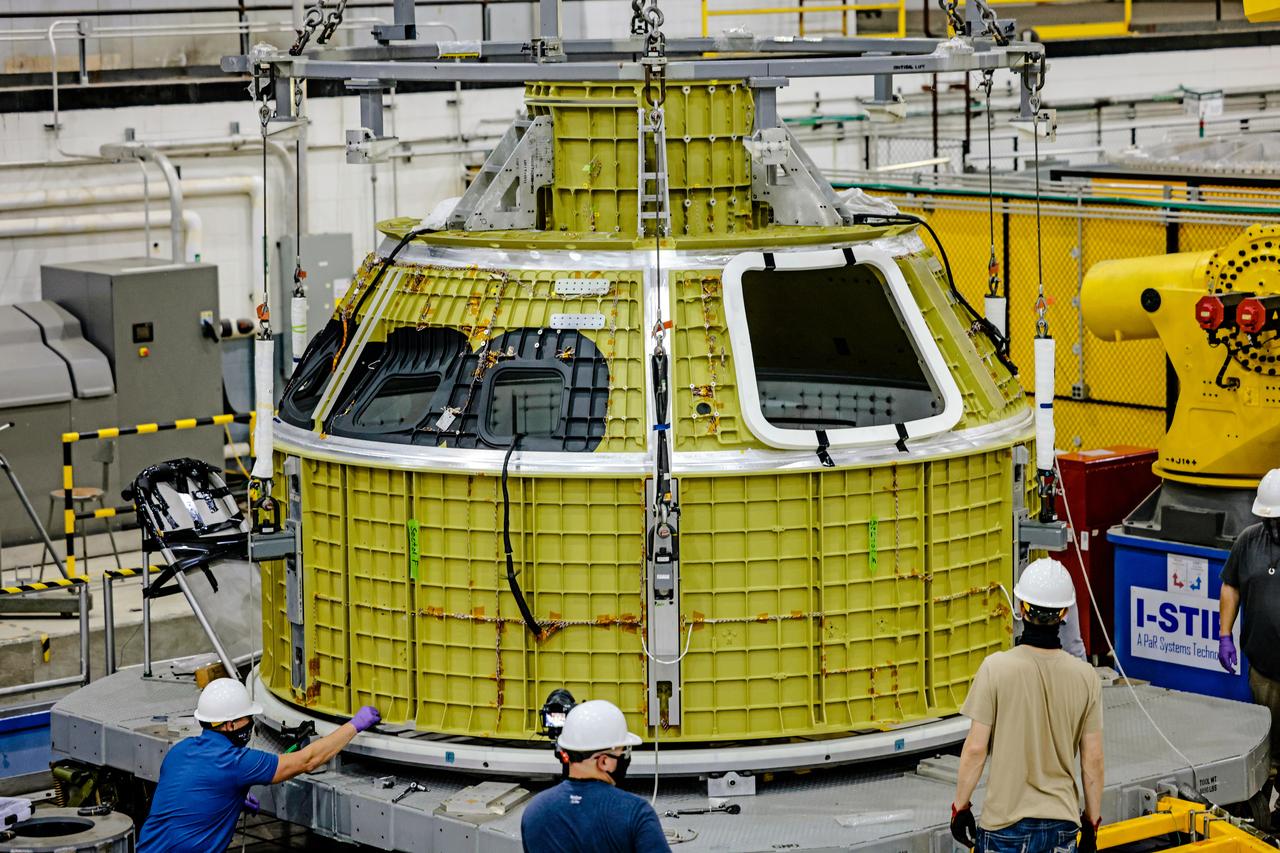
At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
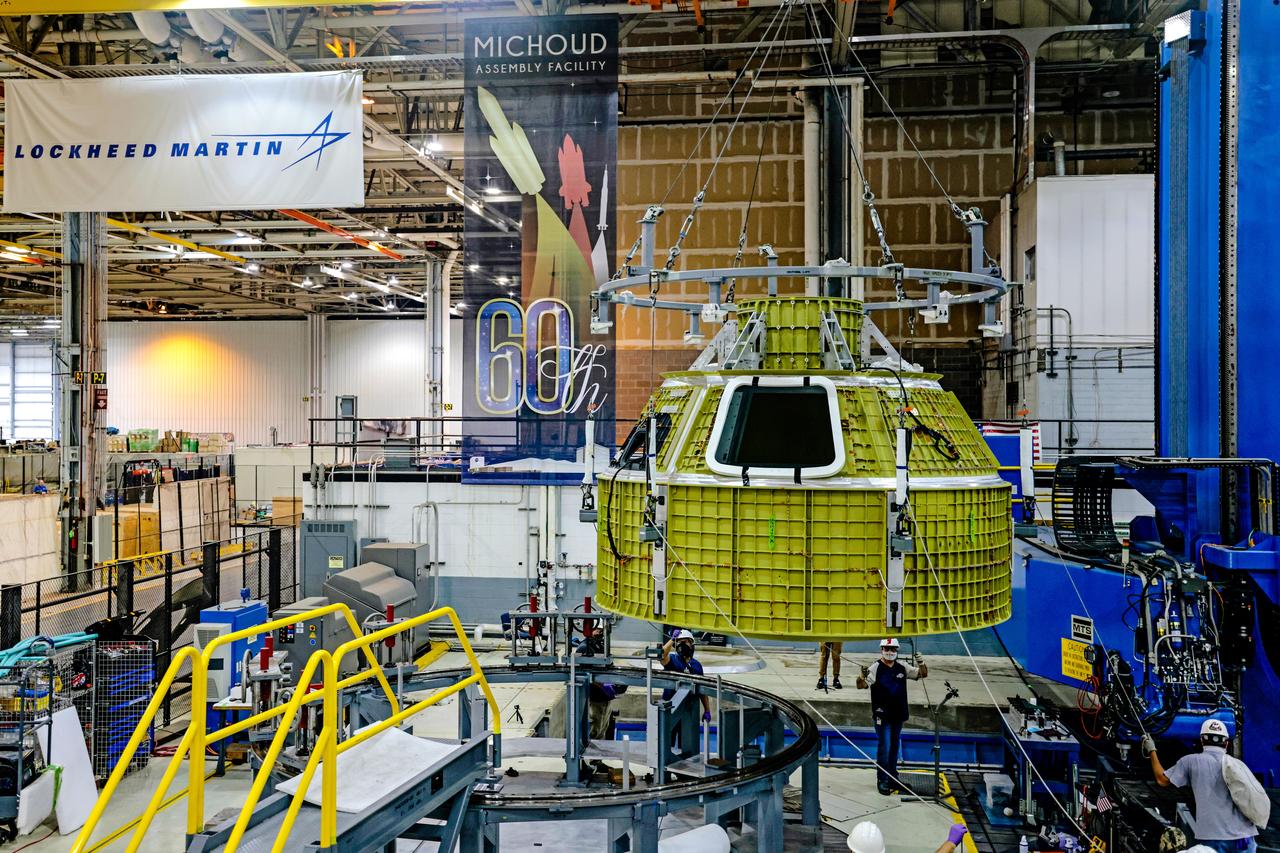

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
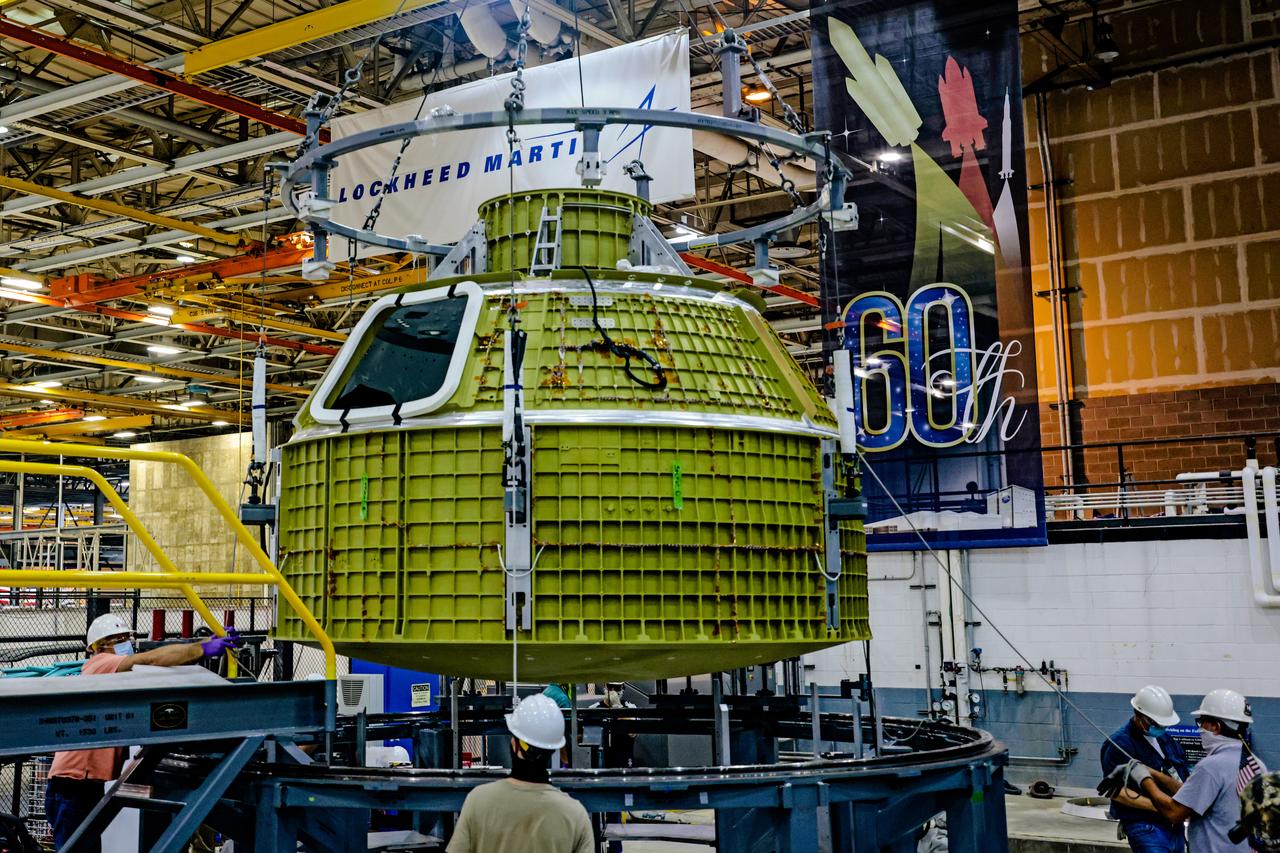

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
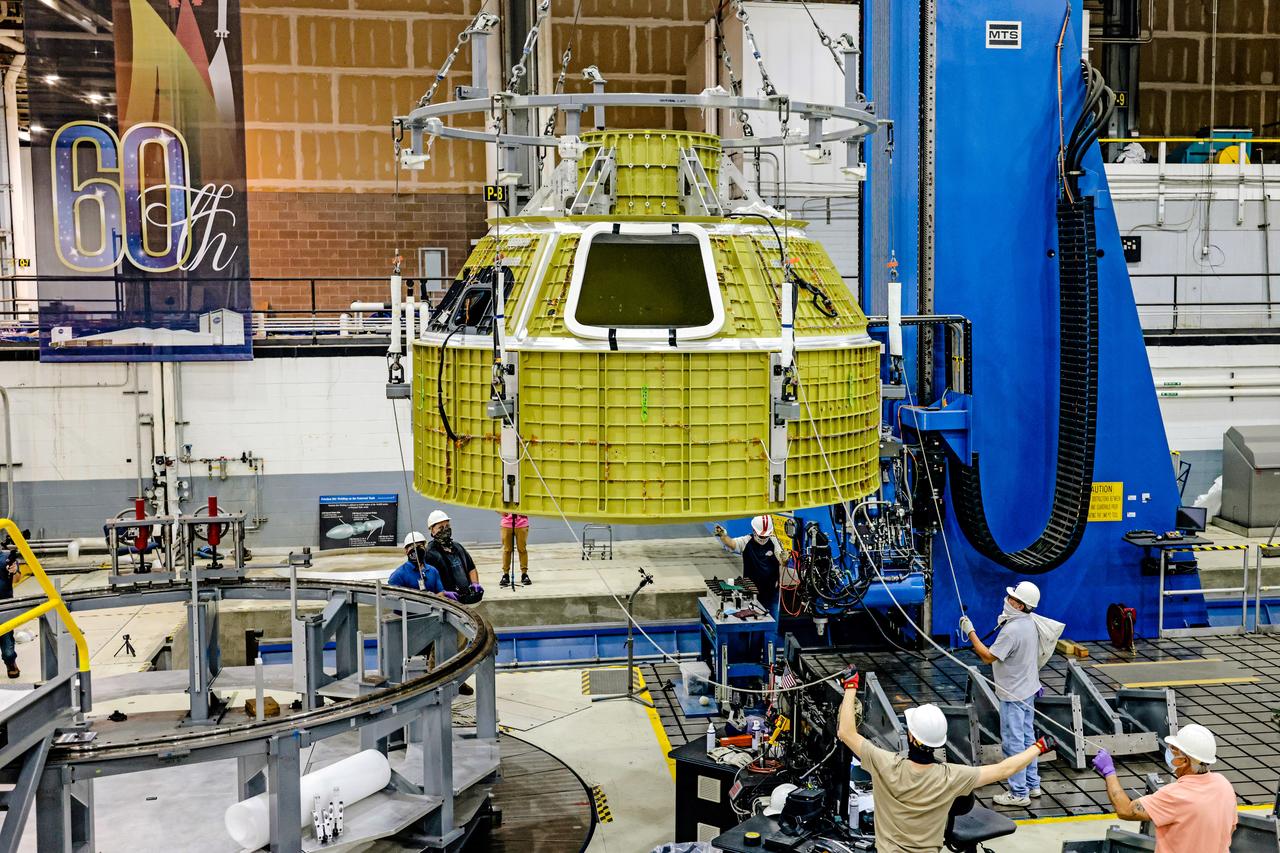

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
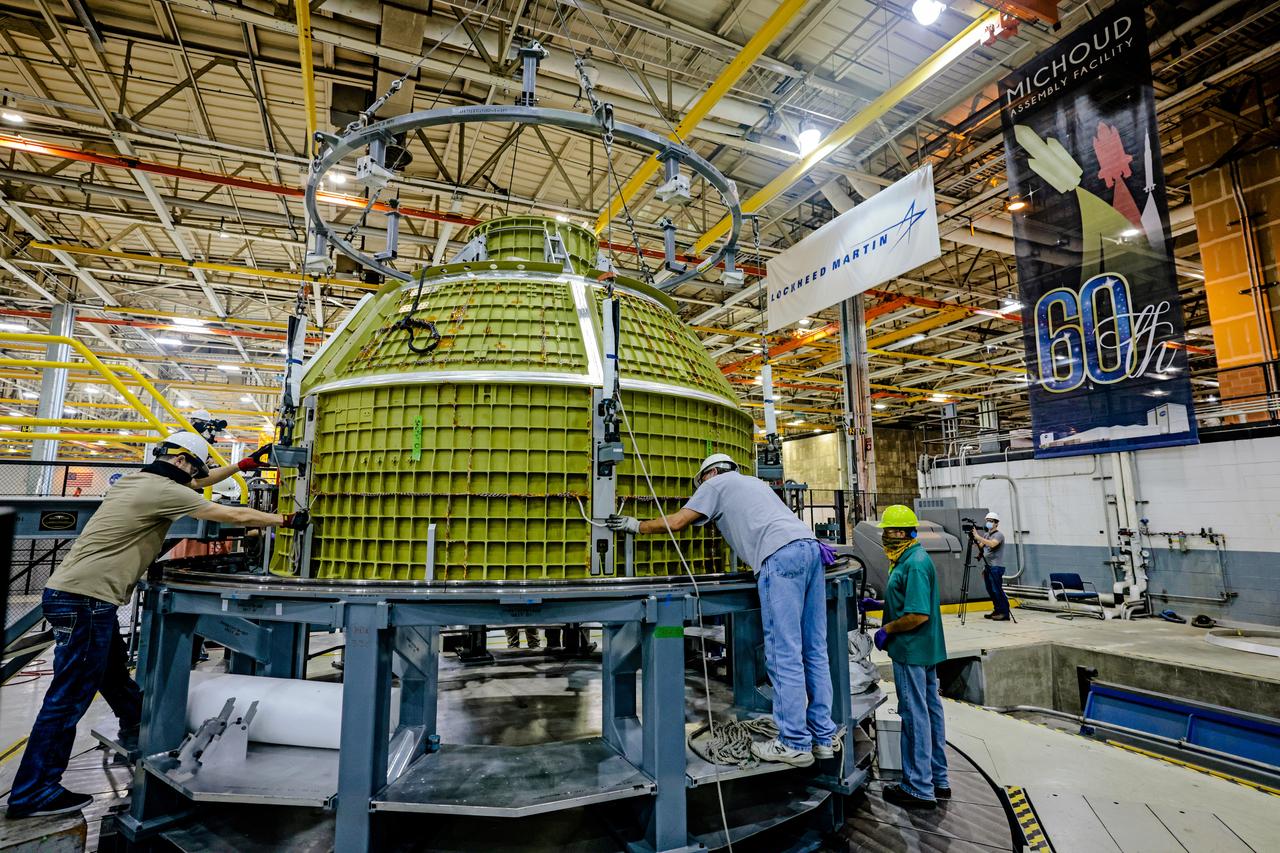

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
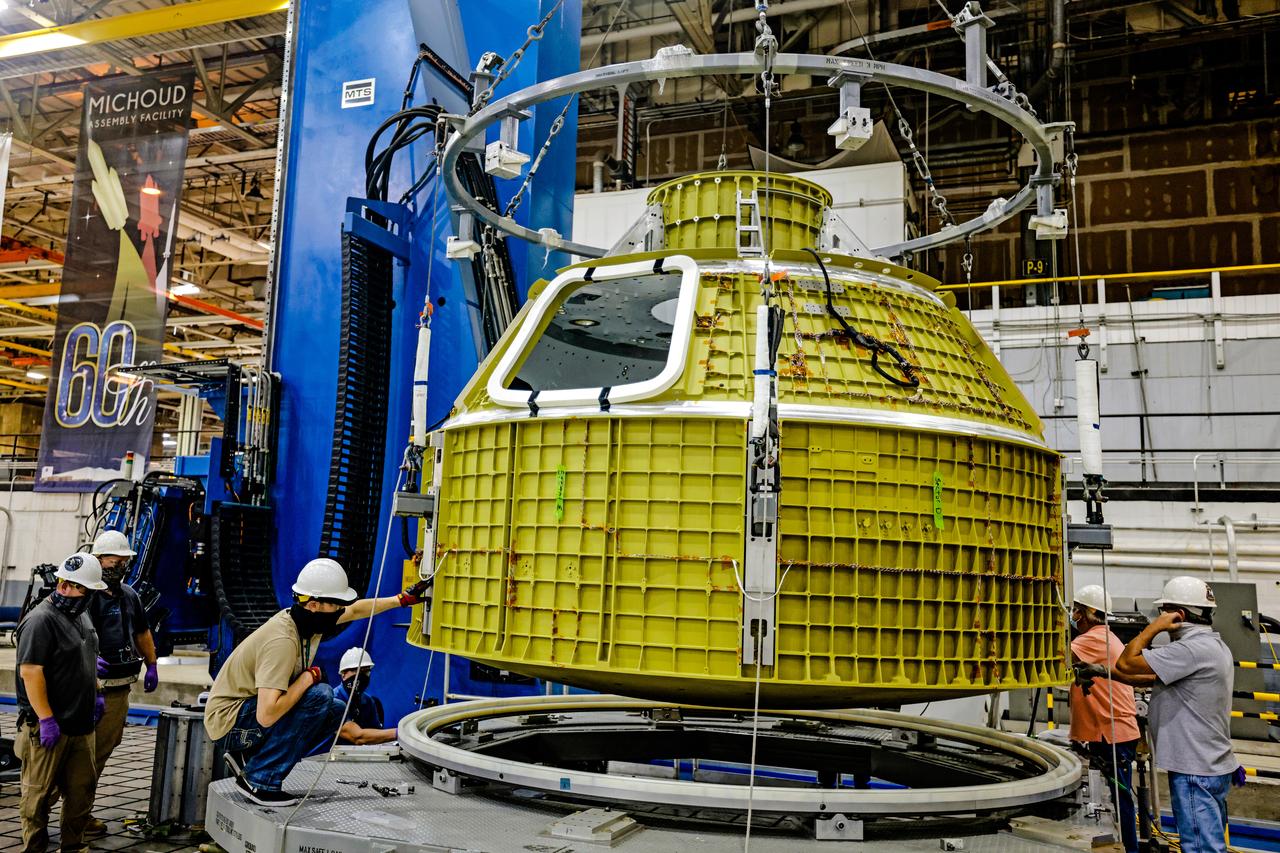

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
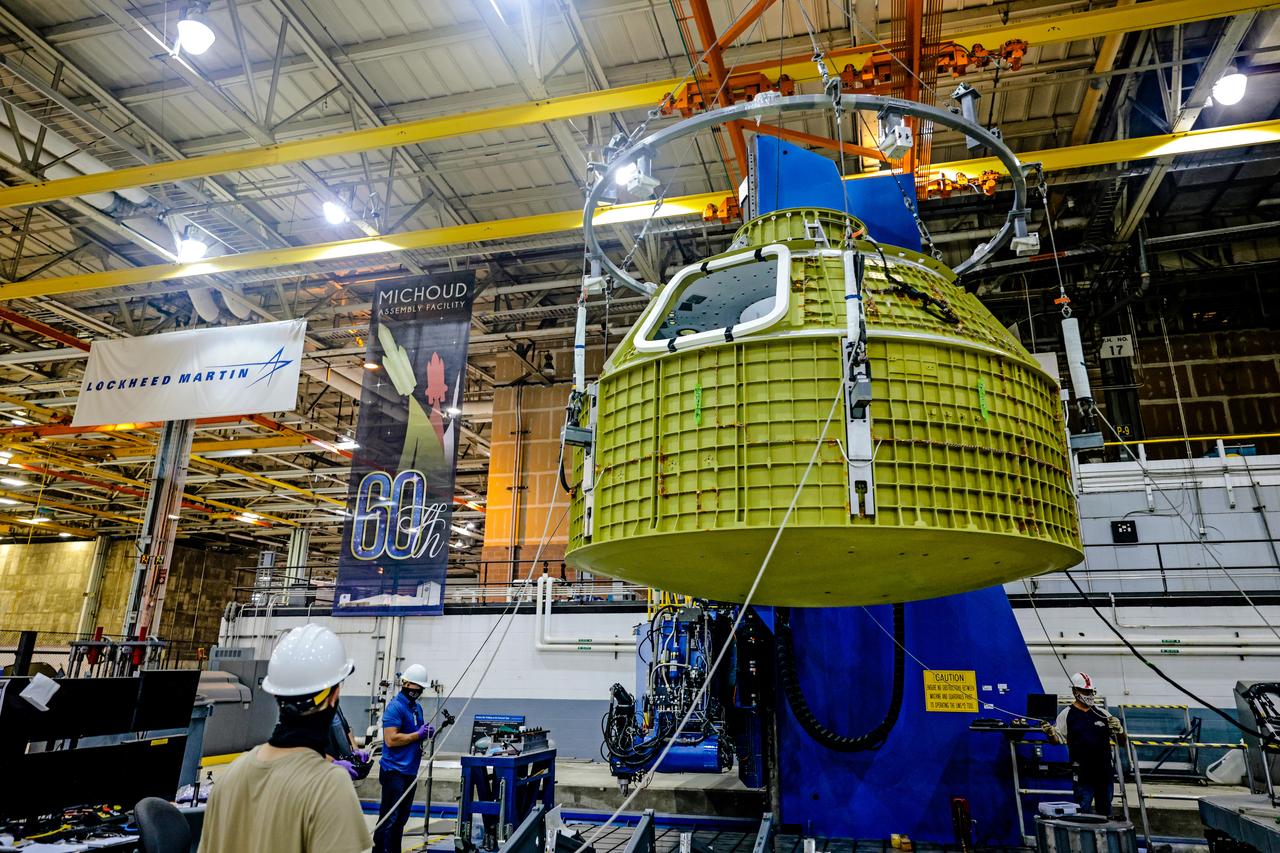

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
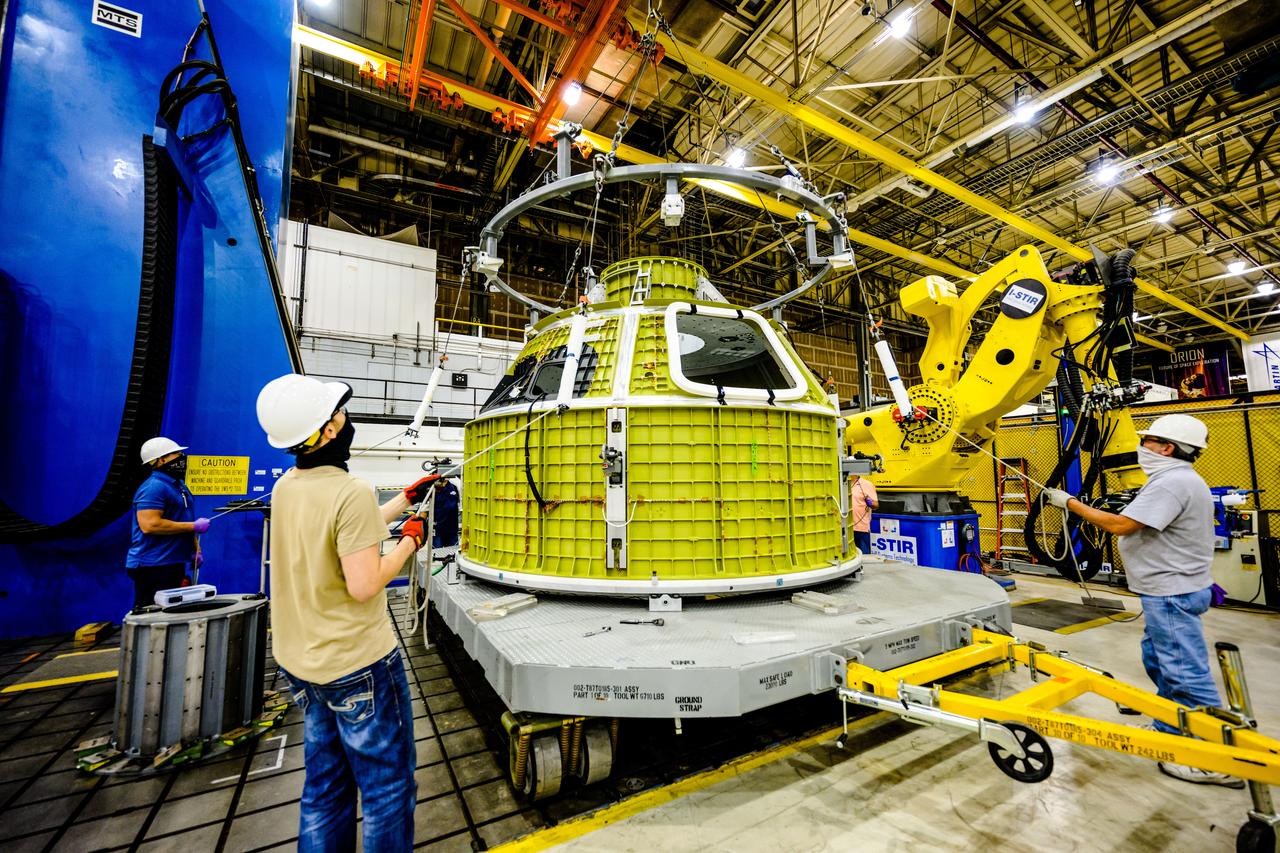

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
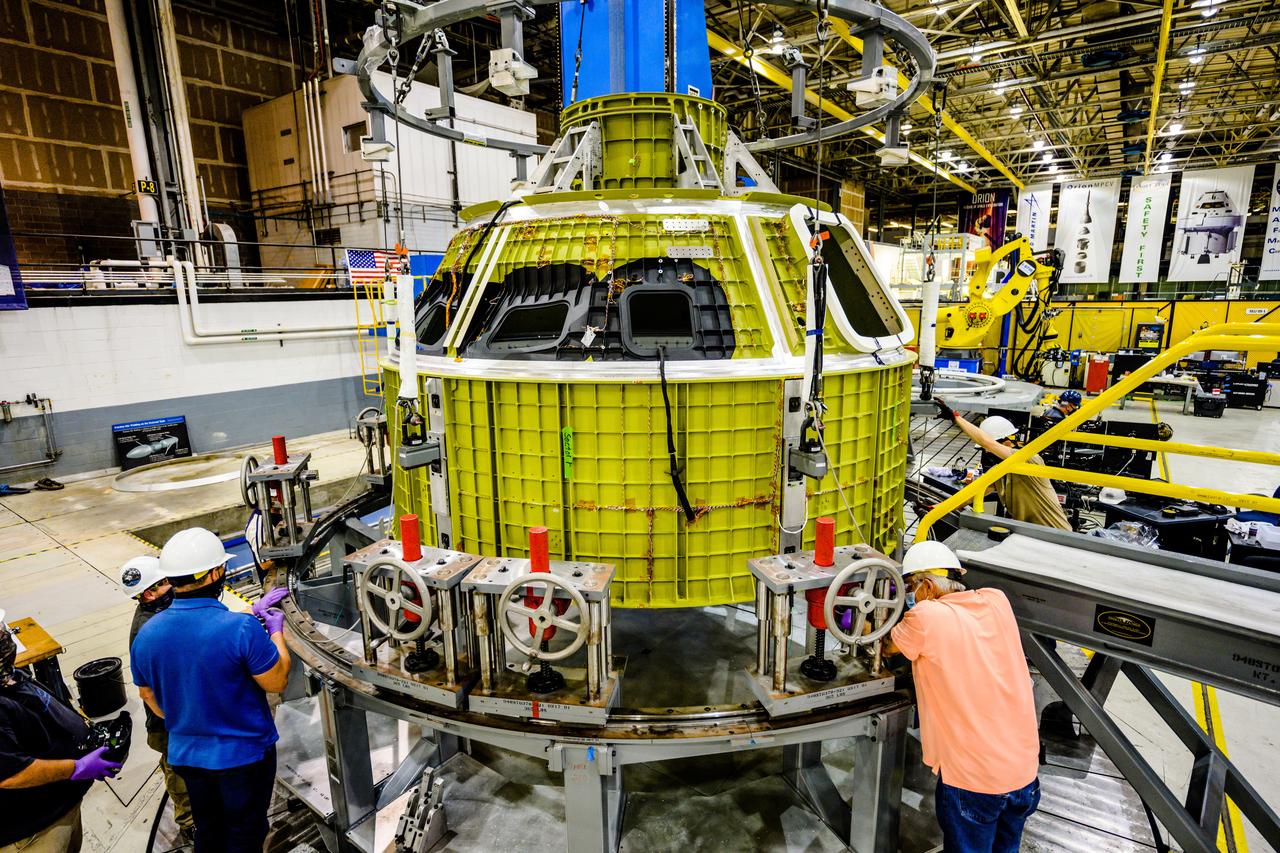

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
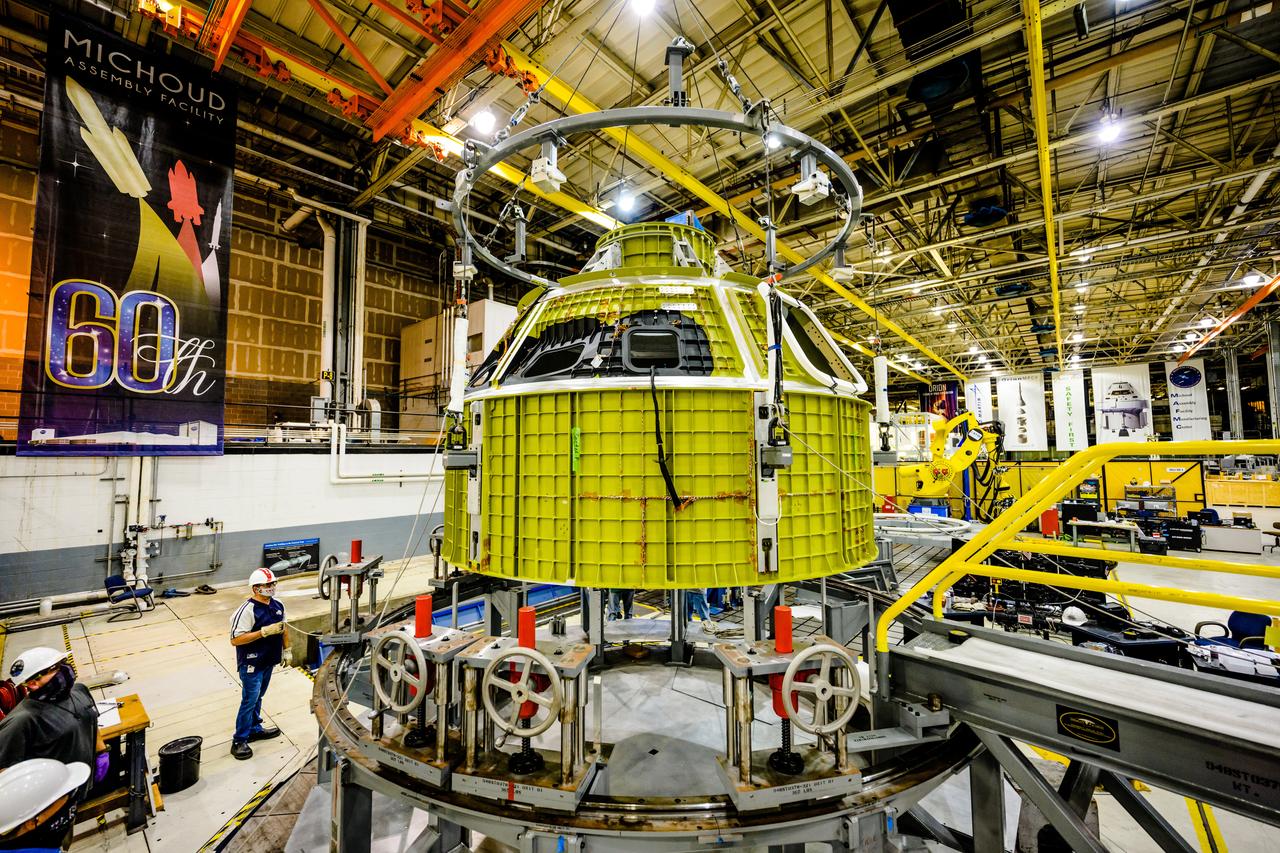

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
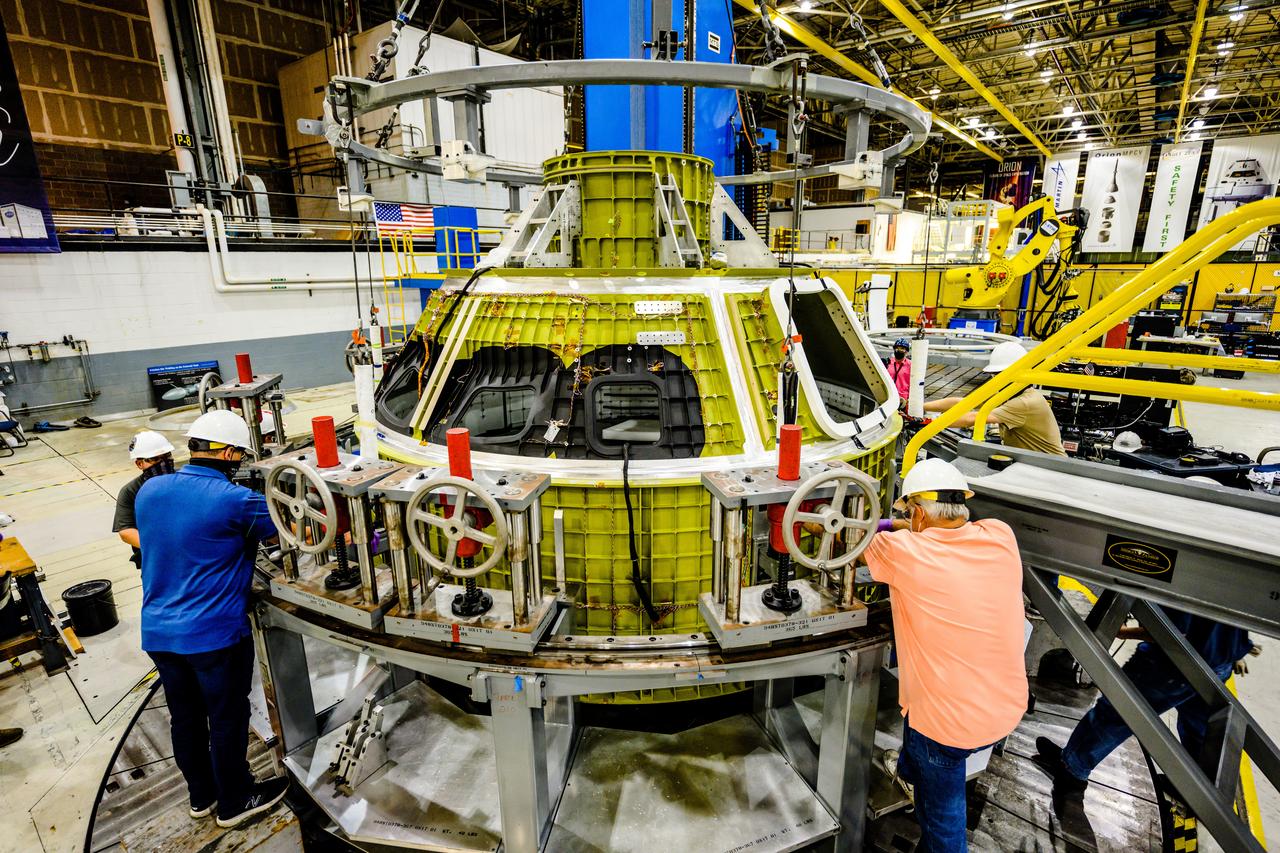

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
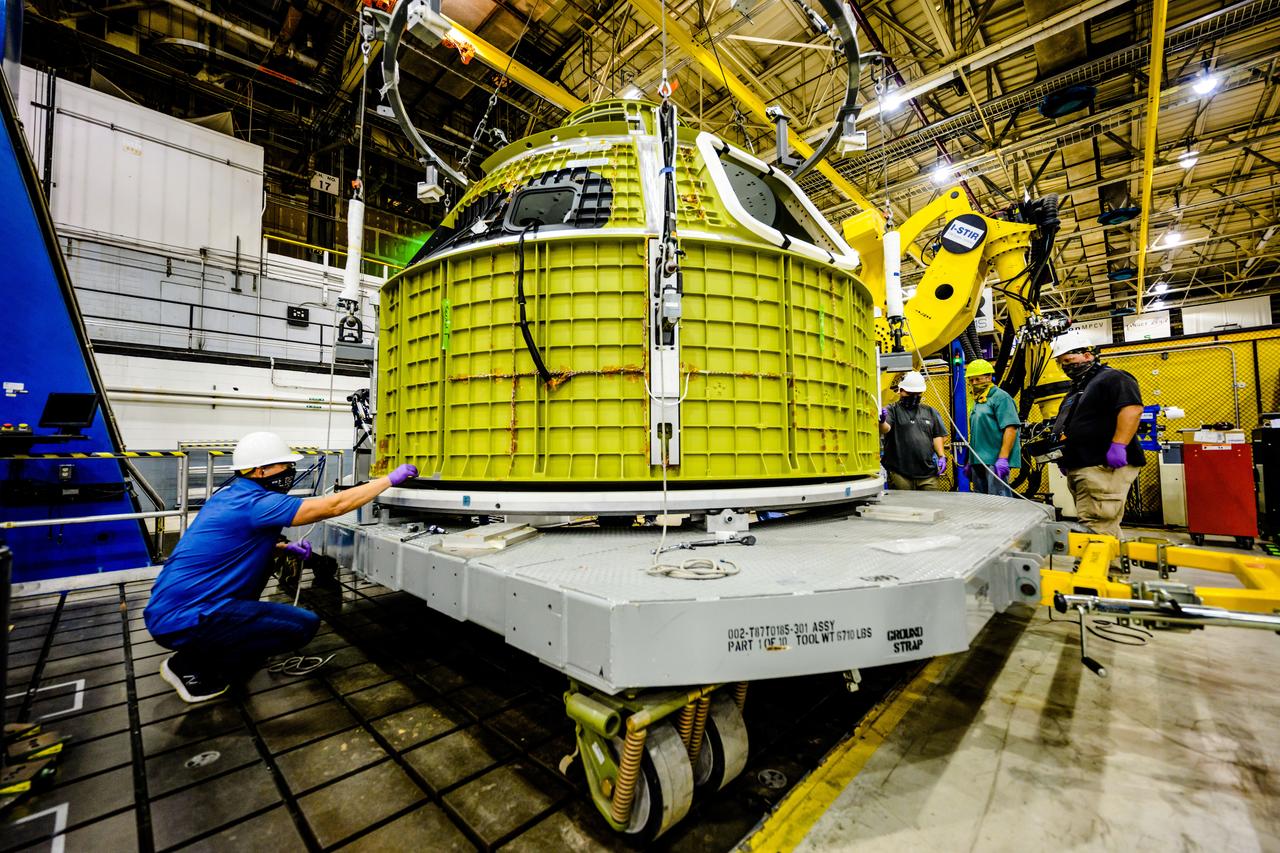

At NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans, Orion's newly completed pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission is lifted out of the welding tool on Aug. 27, 2021. The pressure vessel is the primary structure for Orion's crew module, joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin.
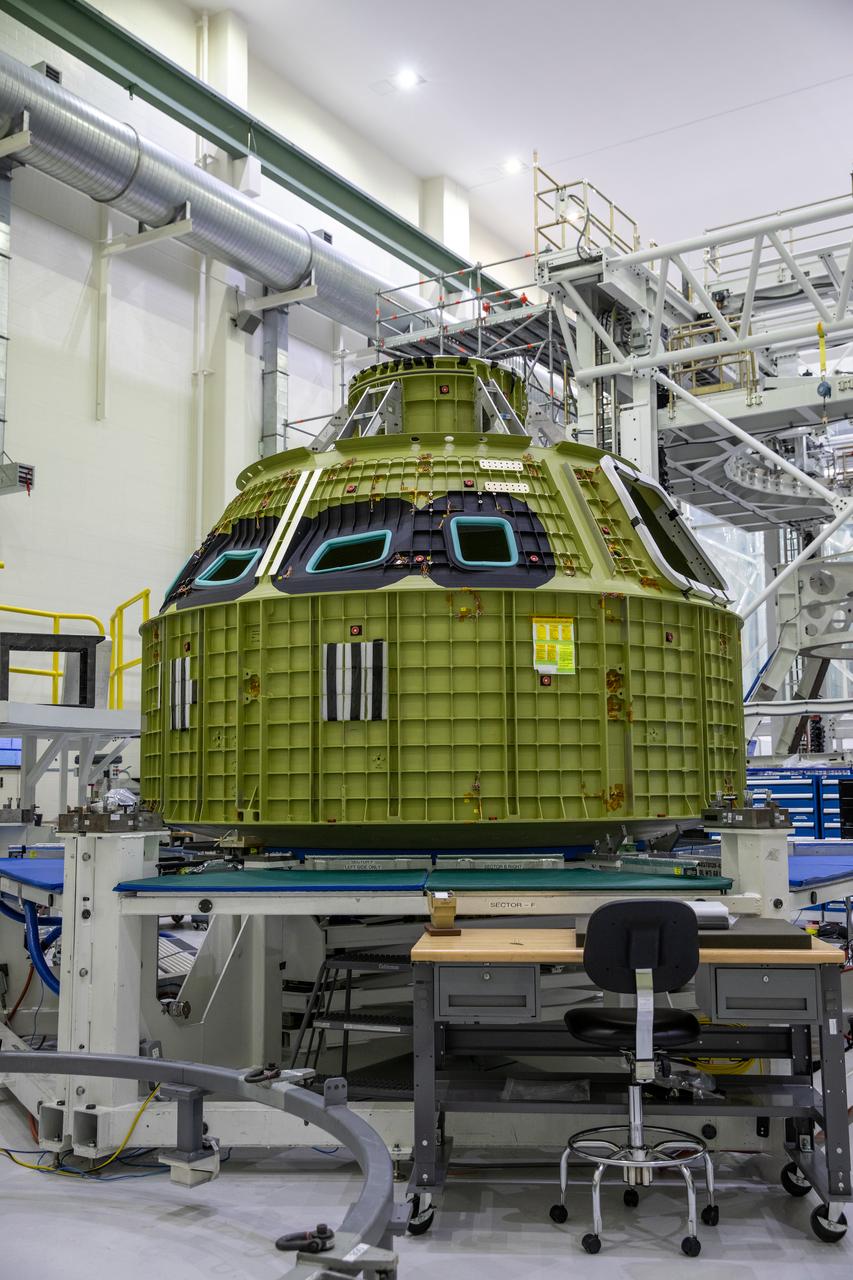

Seen here is the pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. The pressure vessel is the underlying structure of the Orion crew module, containing the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Artemis IV will be the first operational mission to Gateway – an outpost in lunar orbit serving as a staging point for deep space exploration – followed by a week-long surface mission on the Moon. Using Gateway, NASA will develop a long-term presence on the Moon, using this as a steppingstone before venturing on to Mars.

Seen here is the pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. The pressure vessel is the underlying structure of the Orion crew module, containing the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Artemis IV will be the first operational mission to Gateway – an outpost in lunar orbit serving as a staging point for deep space exploration – followed by a week-long surface mission on the Moon. Using Gateway, NASA will develop a long-term presence on the Moon, using this as a steppingstone before venturing on to Mars.
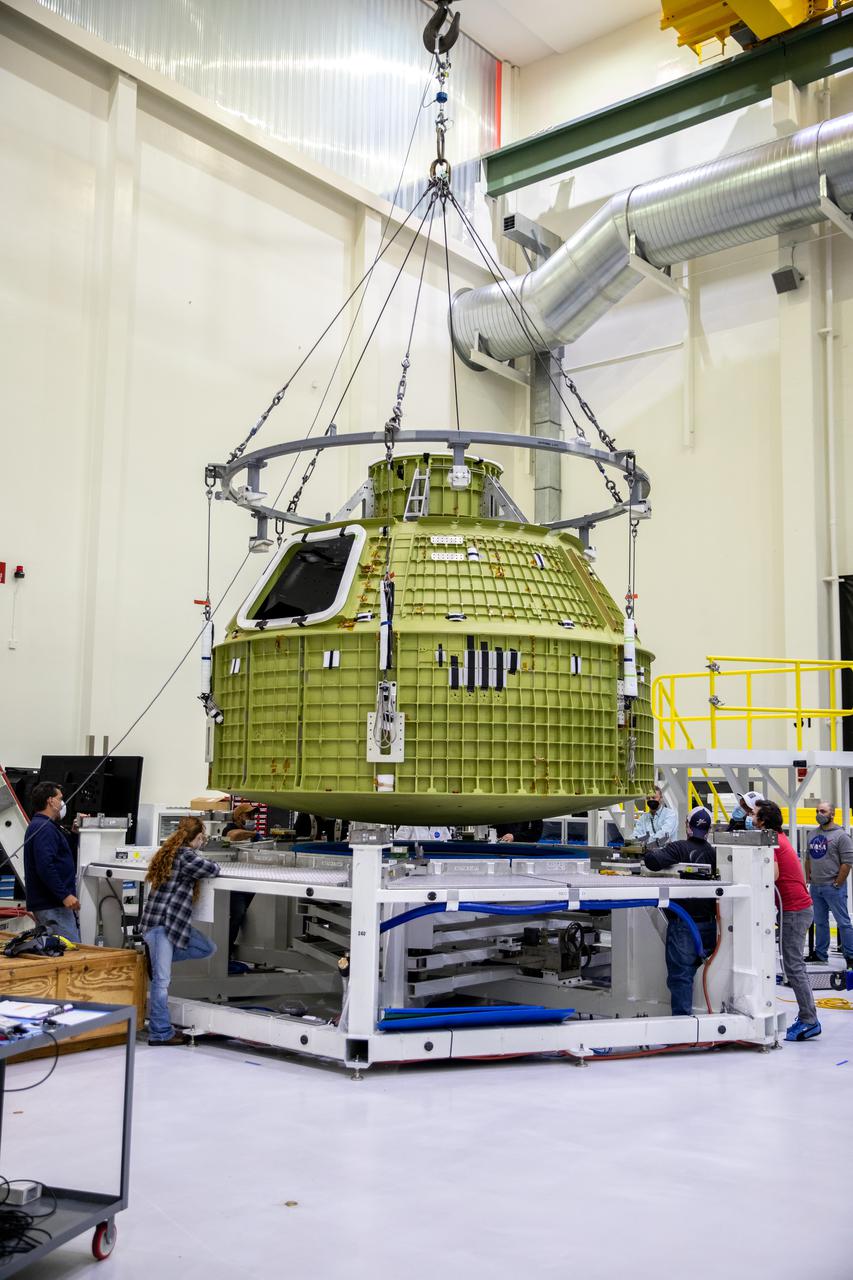

The Orion pressure vessel for NASA’s Artemis III mission is lowered onto a work stand in the high bay of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Oct. 20, 2021. Lockheed Matin technicians will begin the work to prepare the spacecraft for its launch atop a Space Launch System rocket. Artemis III will send astronauts, including the first woman and first person of color, on a mission to the surface of the Moon by 2024.
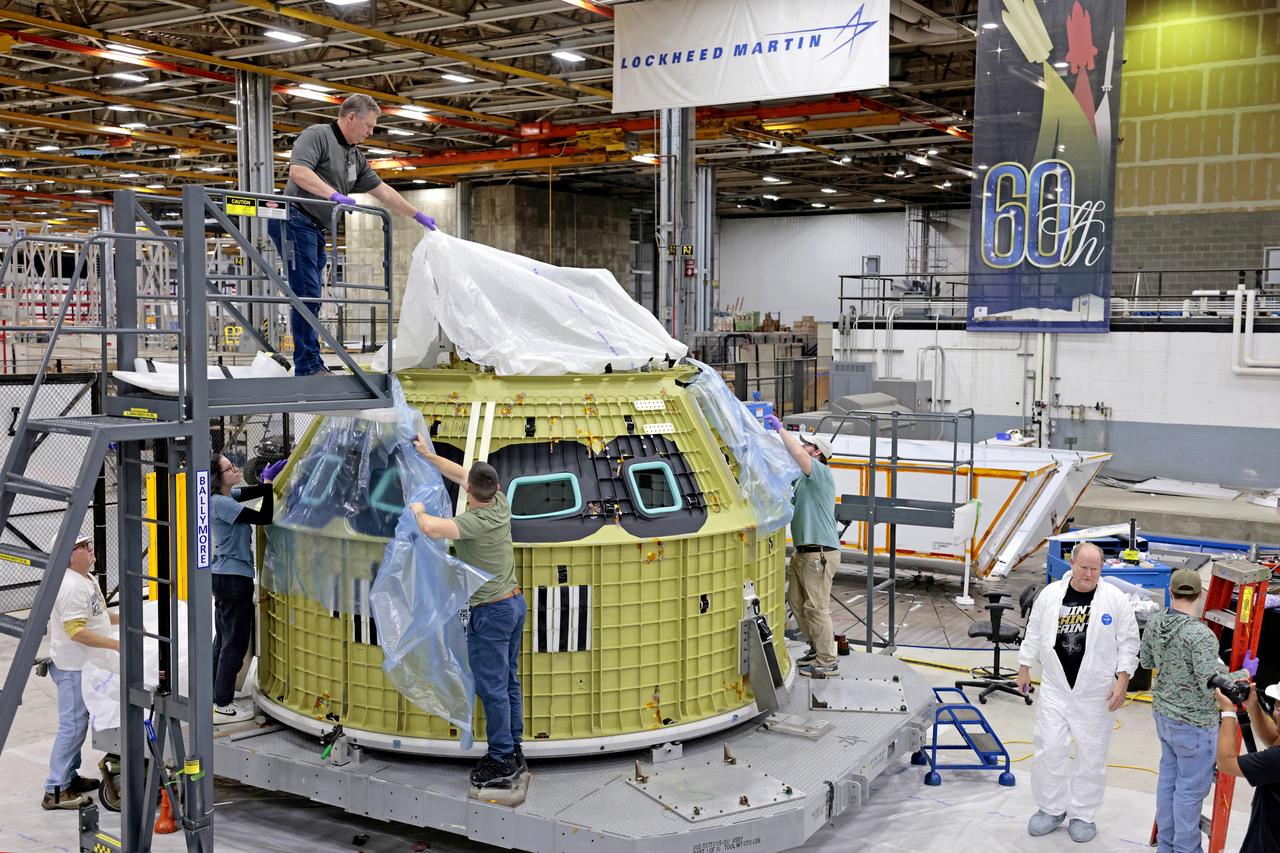

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
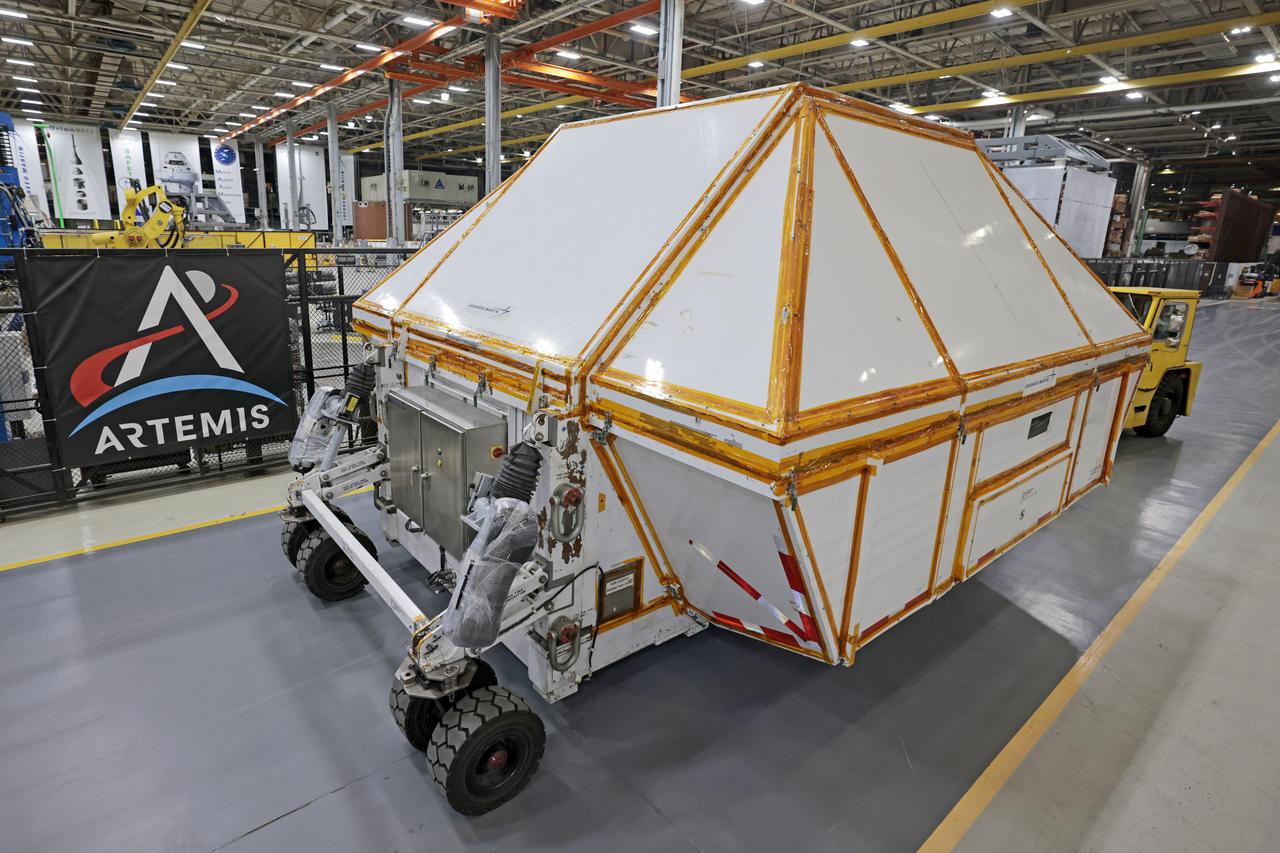

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
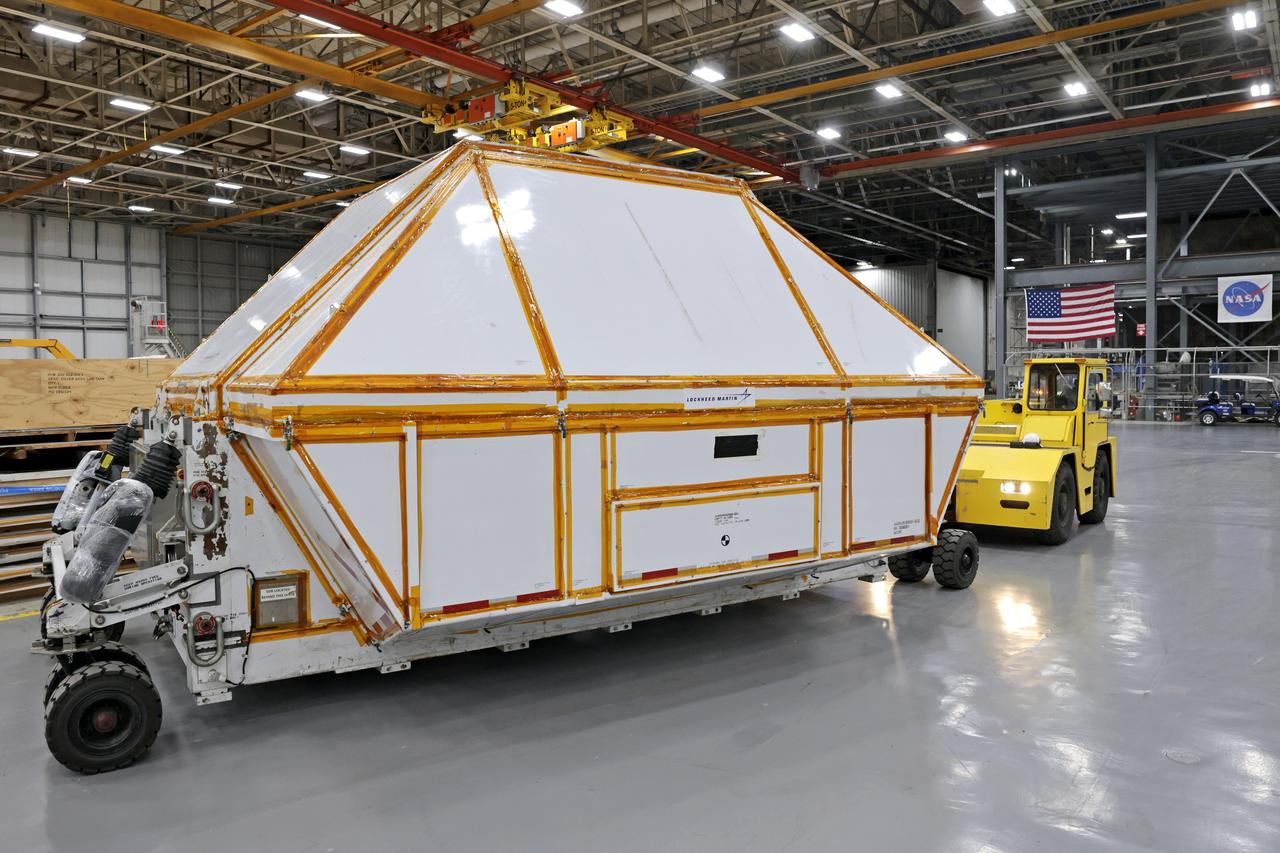

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
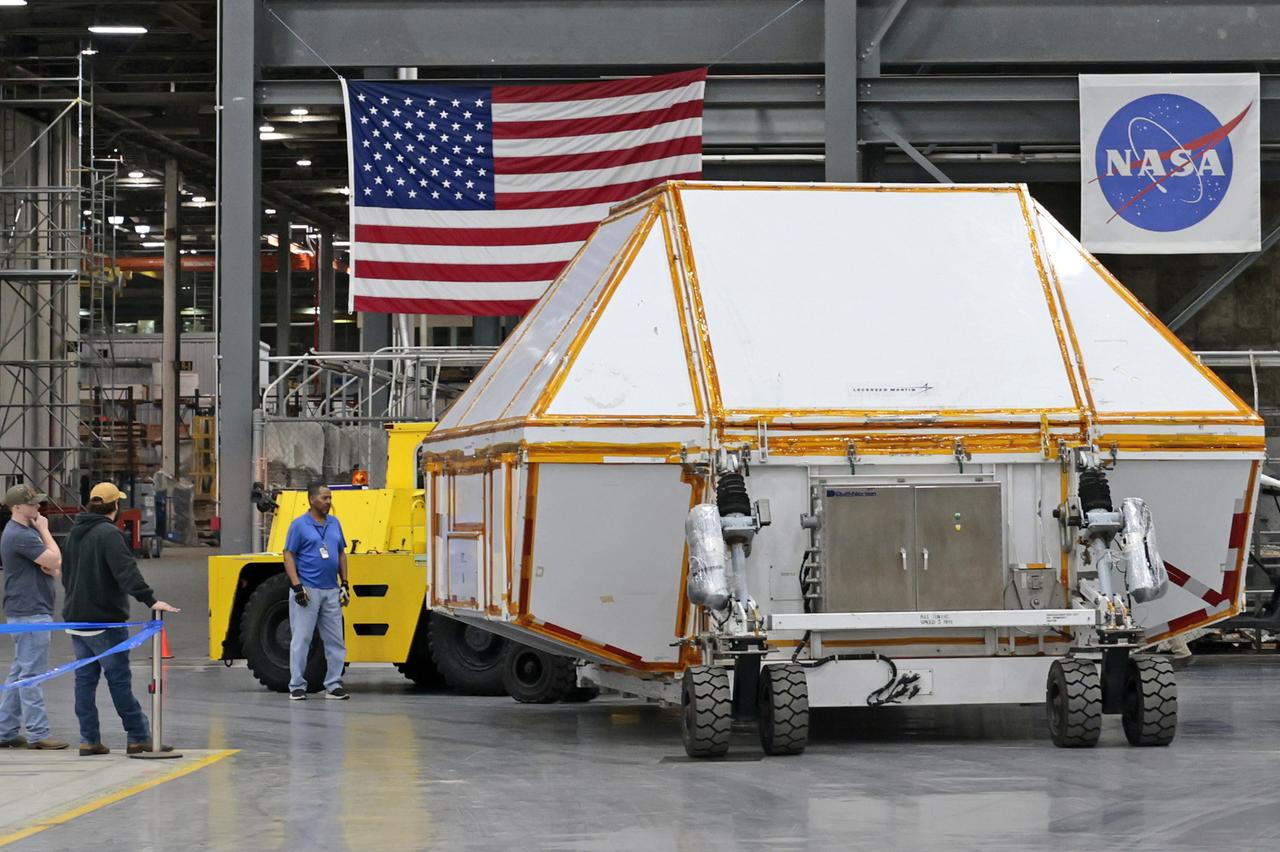

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepare the completed Orion pressure vessel for the Artemis IV mission for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel, which was assembled by lead contractor, Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is critical to Artemis crews as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in a while in the vacuum of deep space. Once the module arrives at Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the lunar surface, paving the way for human exploration of the Moon and on to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
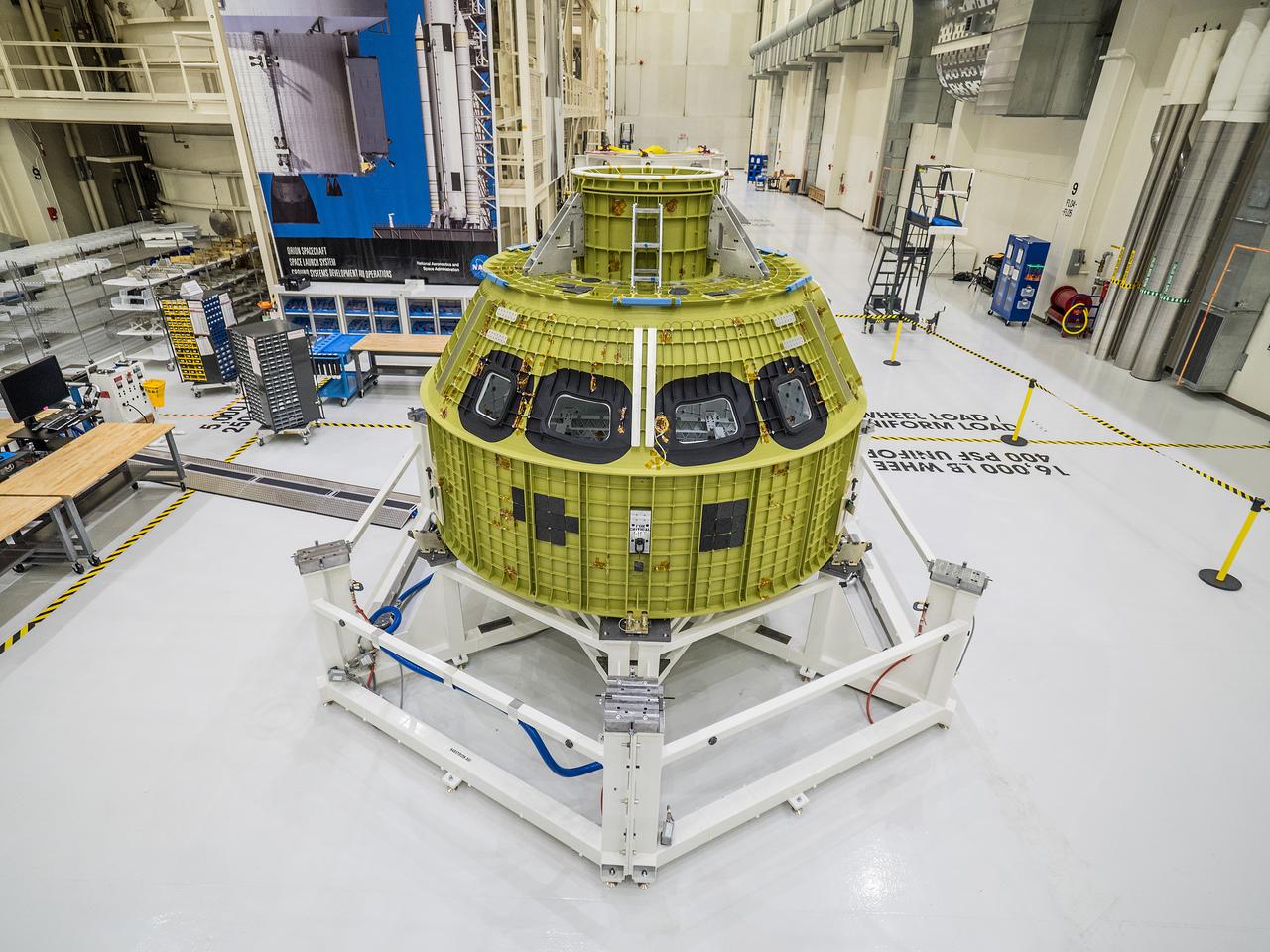

The Orion pressure vessel, which is the underlying structure of the crew module, arrived at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 2, 2016 and was maneuvered into a work stand. At Kennedy, engineers will outfit the pressure vessel with Orion's systems and subsystems ahead of Artemis I. The pressure vessel was welded together at the agency's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion pressure vessel, which is the underlying structure of the crew module, arrived at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 2, 2016. At Kennedy, engineers will outfit the pressure vessel with Orion's systems and subsystems ahead of Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
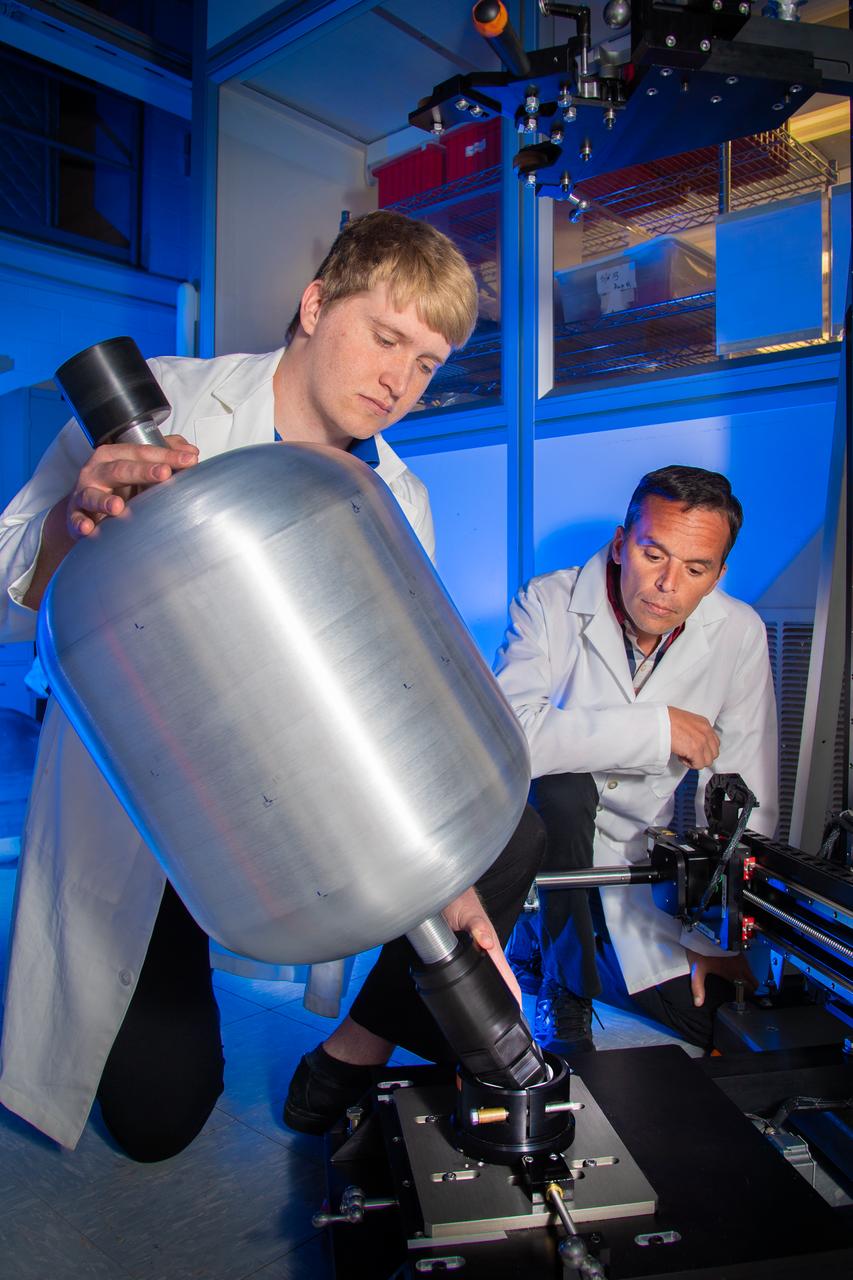

Engineers Ayrton Jordan (left) and Anthony Milana (right) at the NASA White Sands Test Facility (WSTF) in Las Cruces, N.M. install a metallic liner into the multipurpose pressure vessel scanner that could one day become part of a composite overwrapped pressure vessel. A slotted ball joint at the base of the rotary stage allows the tank to pivot resulting in helical scans that are more reliable when measuring interior and exterior 3D surface profiles. Photo Credit: (NASA/Reed P. Elliott)
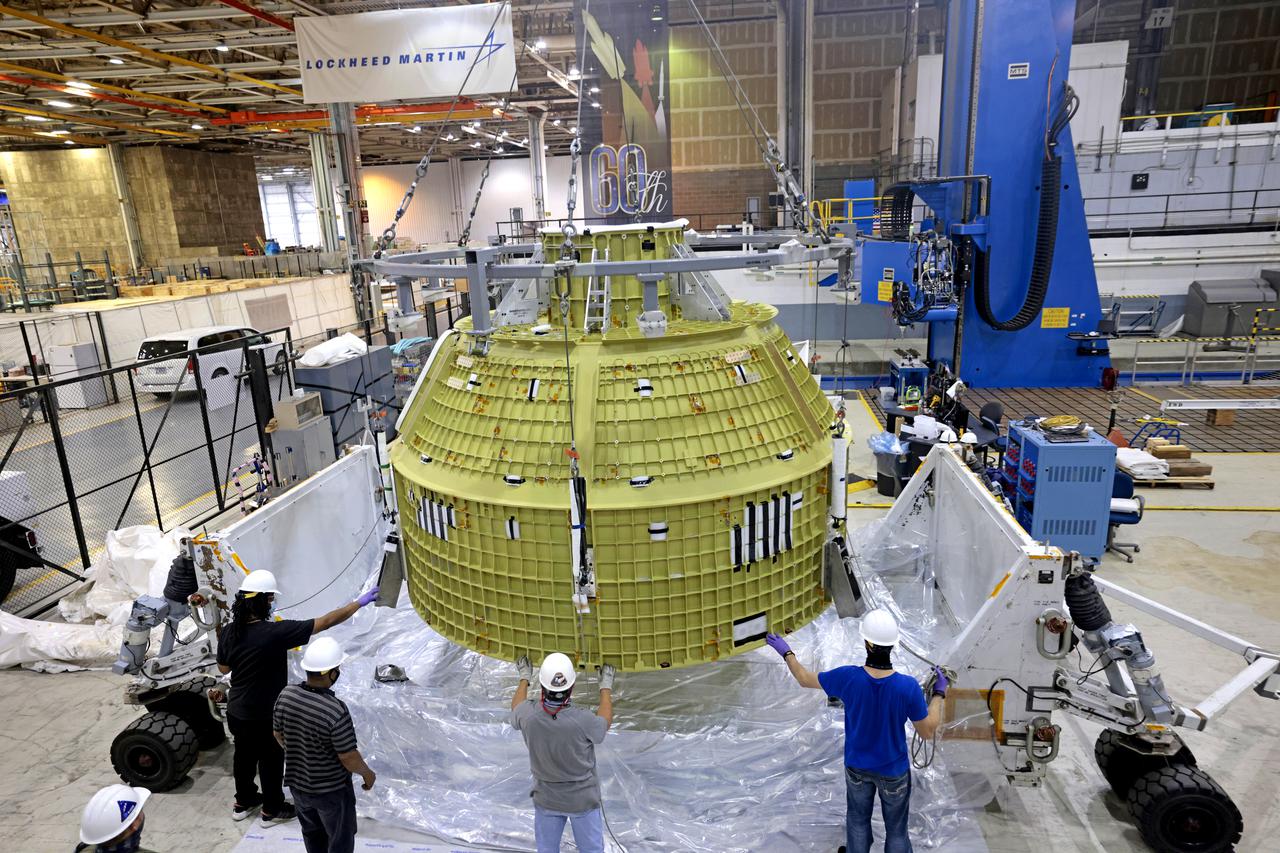

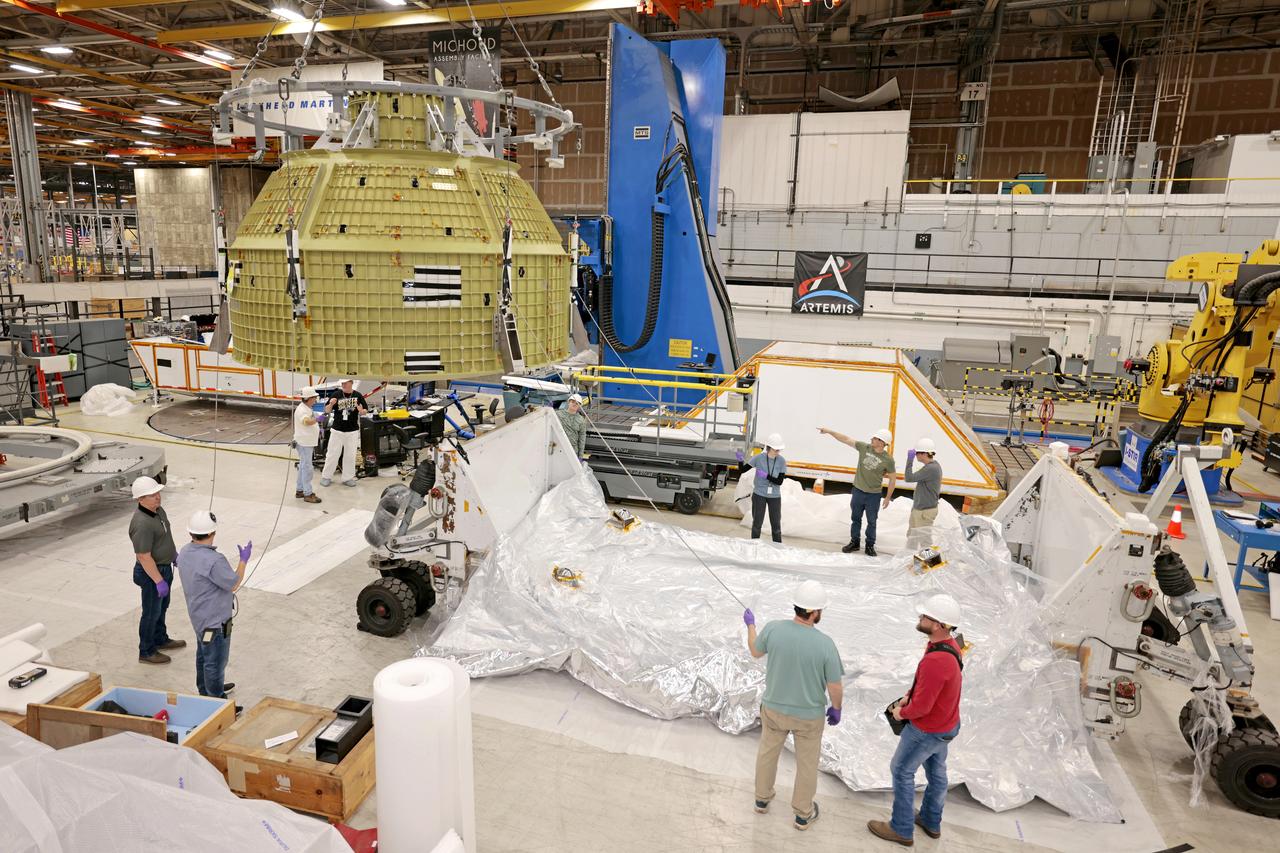
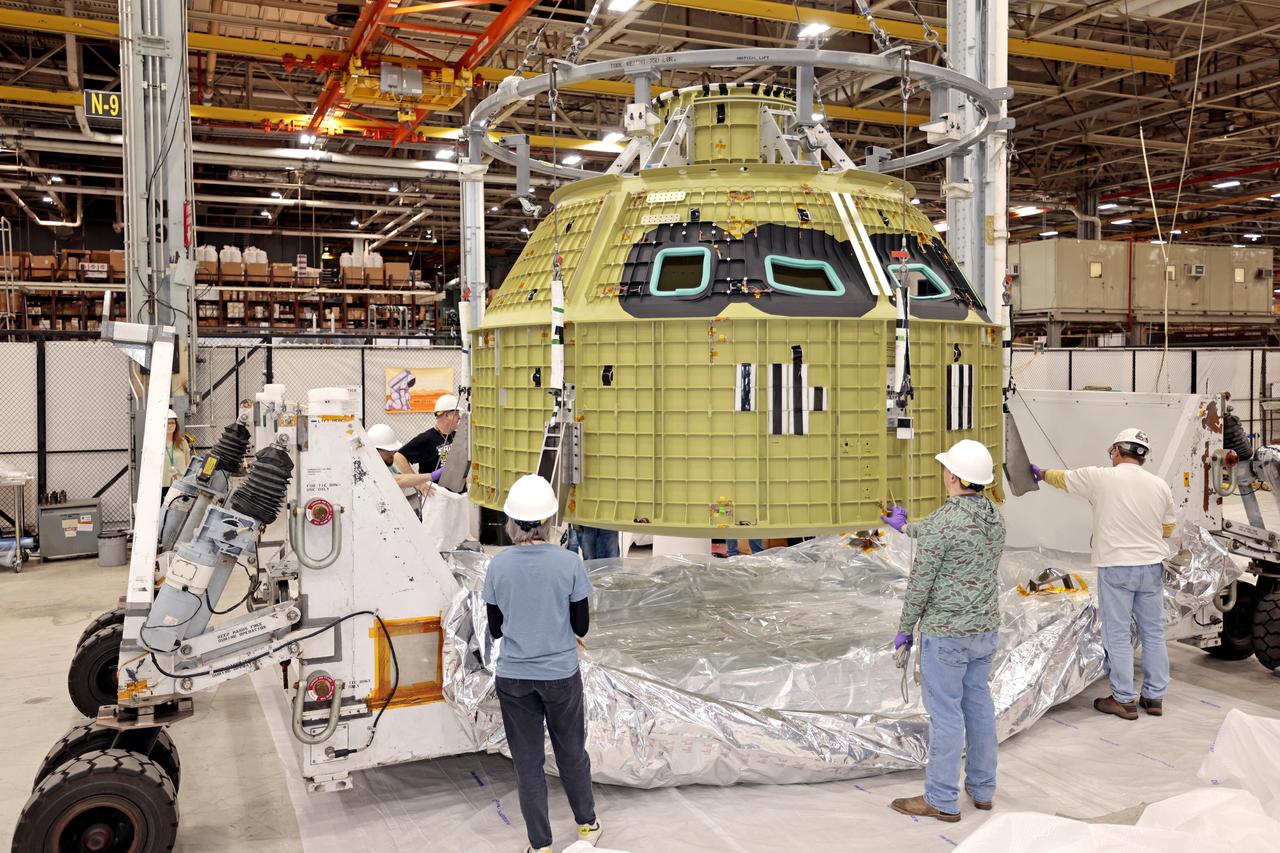
Technician’s at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepared the newly-welded Artemis III mission Orion pressure vessel for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s in Florida, where it later arrived on October 15 at Kennedy’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The pressure vessel, which was joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is a critical element for crew as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Once transported to Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. Photographed on Wednesday, October 13, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
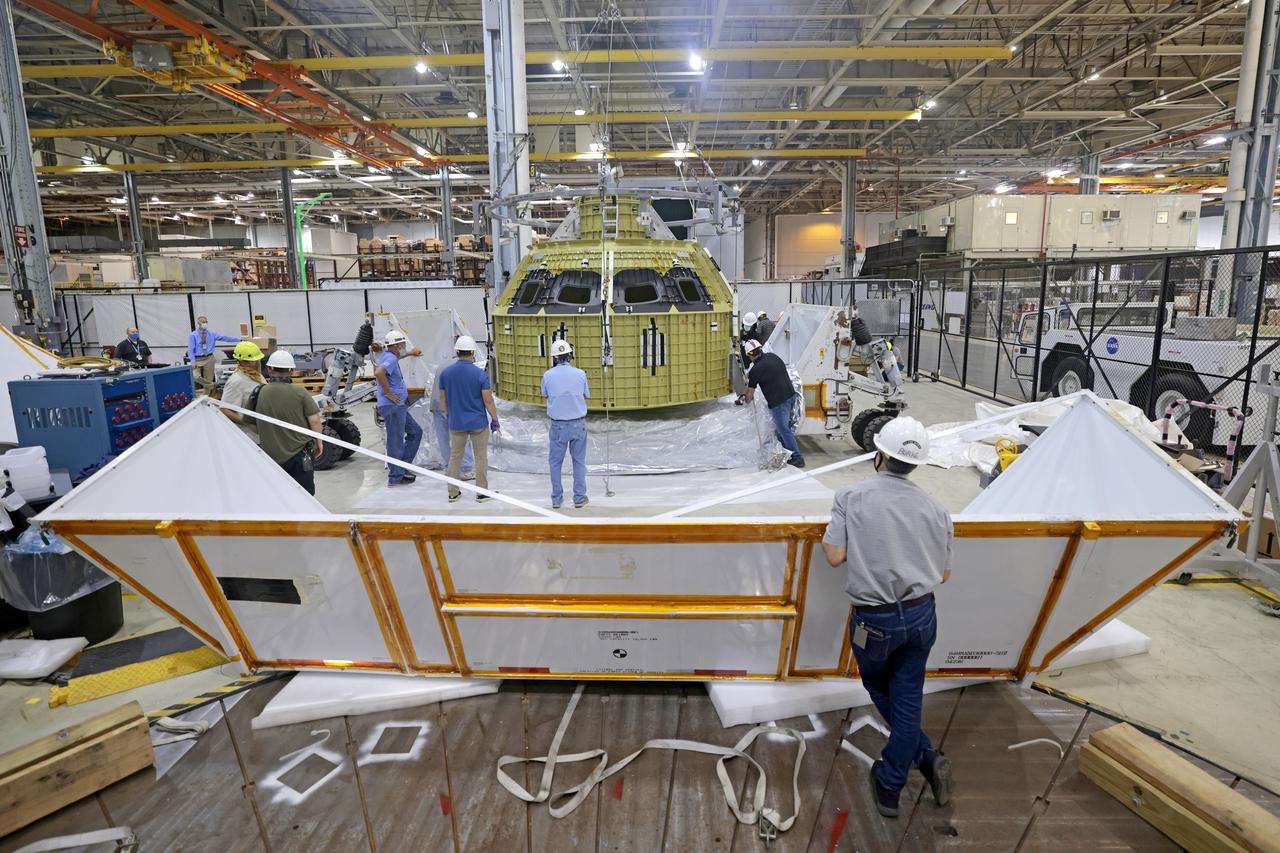

Technician’s at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepared the newly-welded Artemis III mission Orion pressure vessel for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s in Florida, where it later arrived on October 15 at Kennedy’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The pressure vessel, which was joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is a critical element for crew as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Once transported to Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. Photographed on Wednesday, October 13, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
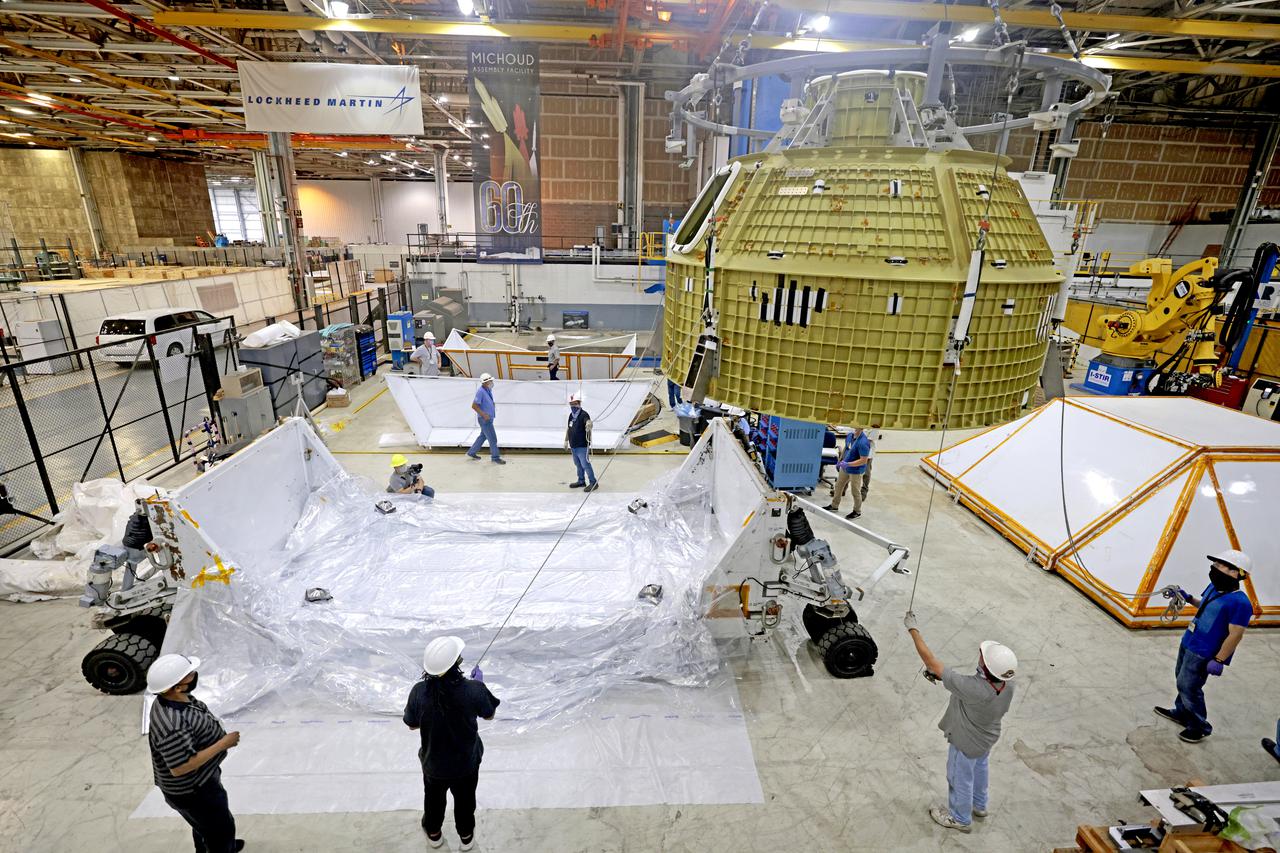

Technician’s at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepared the newly-welded Artemis III mission Orion pressure vessel for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s in Florida, where it later arrived on October 15 at Kennedy’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The pressure vessel, which was joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is a critical element for crew as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Once transported to Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. Photographed on Wednesday, October 13, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
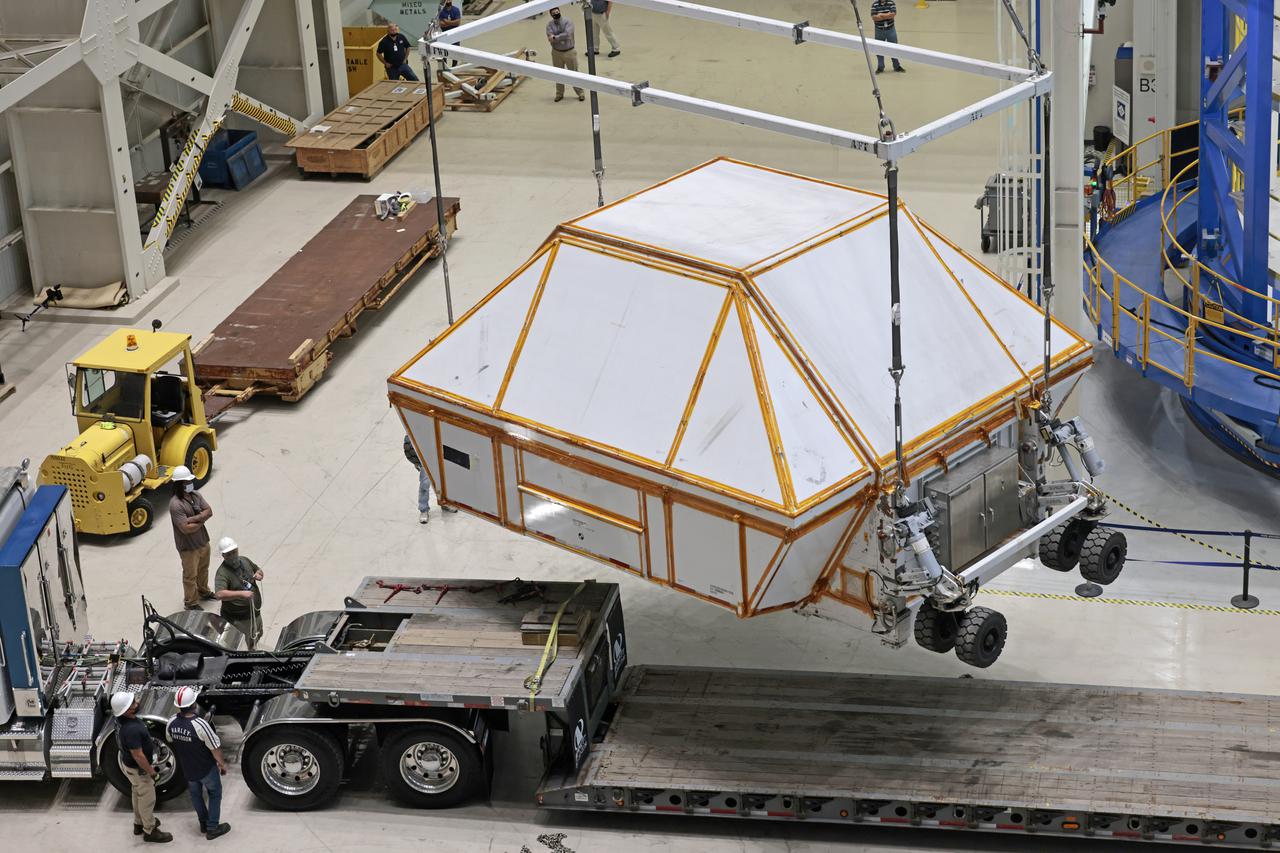

Technician’s at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepared the newly-welded Artemis III mission Orion pressure vessel for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s in Florida, where it later arrived on October 15 at Kennedy’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The pressure vessel, which was joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is a critical element for crew as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Once transported to Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. Photographed on Wednesday, October 13, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
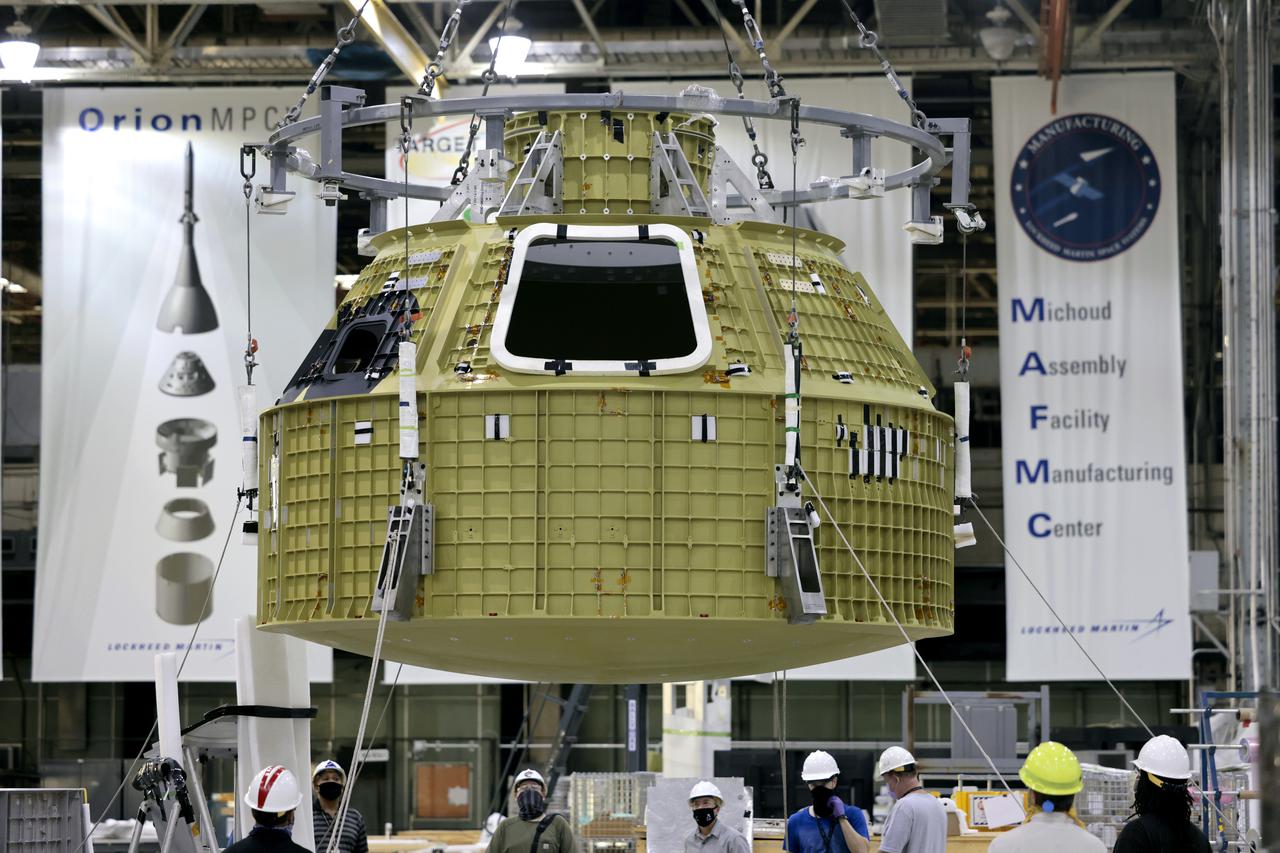

Technician’s at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans prepared the newly-welded Artemis III mission Orion pressure vessel for shipment to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center’s in Florida, where it later arrived on October 15 at Kennedy’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. The pressure vessel, which was joined together using state-of-the-art welding by technicians from lead contractor Lockheed Martin, is the Orion crew module primary structure – the core upon which all other elements of Orion’s crew module are integrated. The structure is a critical element for crew as it holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Once transported to Kennedy’s Vehicle Assembly Building high bay, teams will begin integration of the pressure vessel with the Orion spacecraft crew module adapter and other assembly. Photographed on Wednesday, October 13, 2021. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
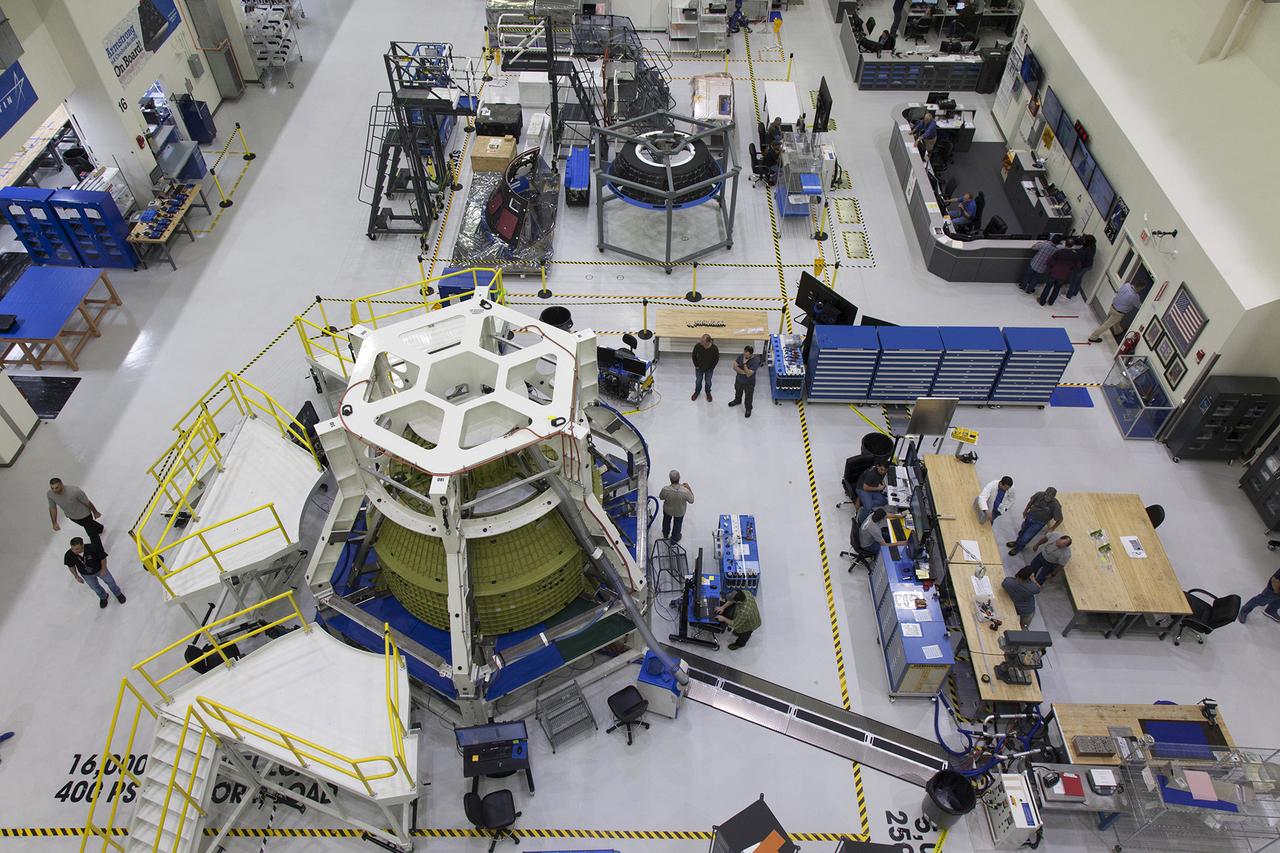

The Orion crew module pressure vessel for Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2) is secured in a work stand called the bird cage inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on March 21, 2019. The pressure vessel is Orion's primary structure that holds the pressurized atmosphere astronauts will breathe and work in while in the vacuum of deep space. Behind the pressure vessel, secured on a work stand is the Orion bay cover for Exploration Mission-1.
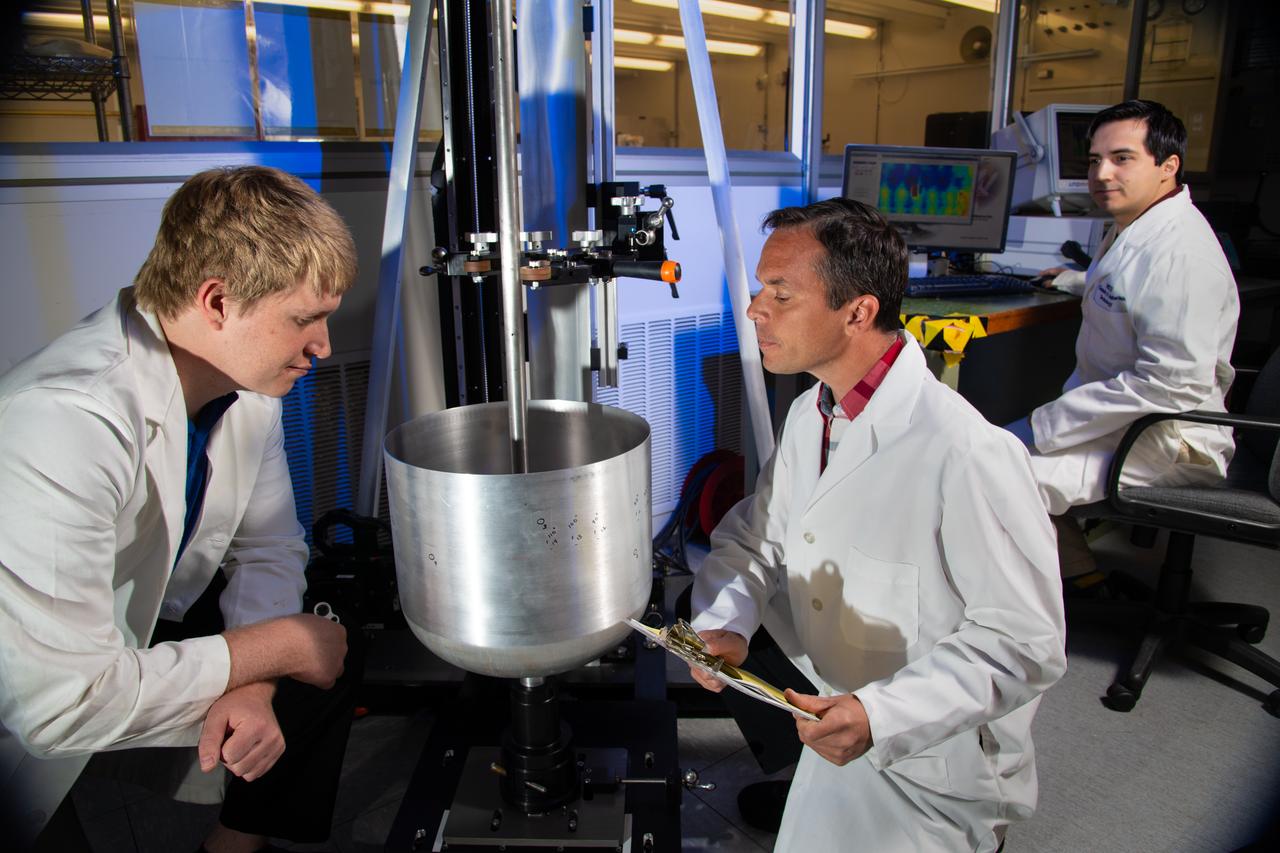

Engineers (from left) Ayrton Jordan, Anthony Milana and Edgar Reyes from the NASA White Sands Test Facility (WSTF) in Las Cruces, N.M. qualify an interior surface pressure vessel crack inspection using the eddy current nondestructive testing technique to find flaws smaller than more common and less capable penetrant testing methods. Detecting cracks smaller than the eye can detect is an important feature as manufacturers push performance limits to achieve lighter, more efficient spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Reed P. Elliott)
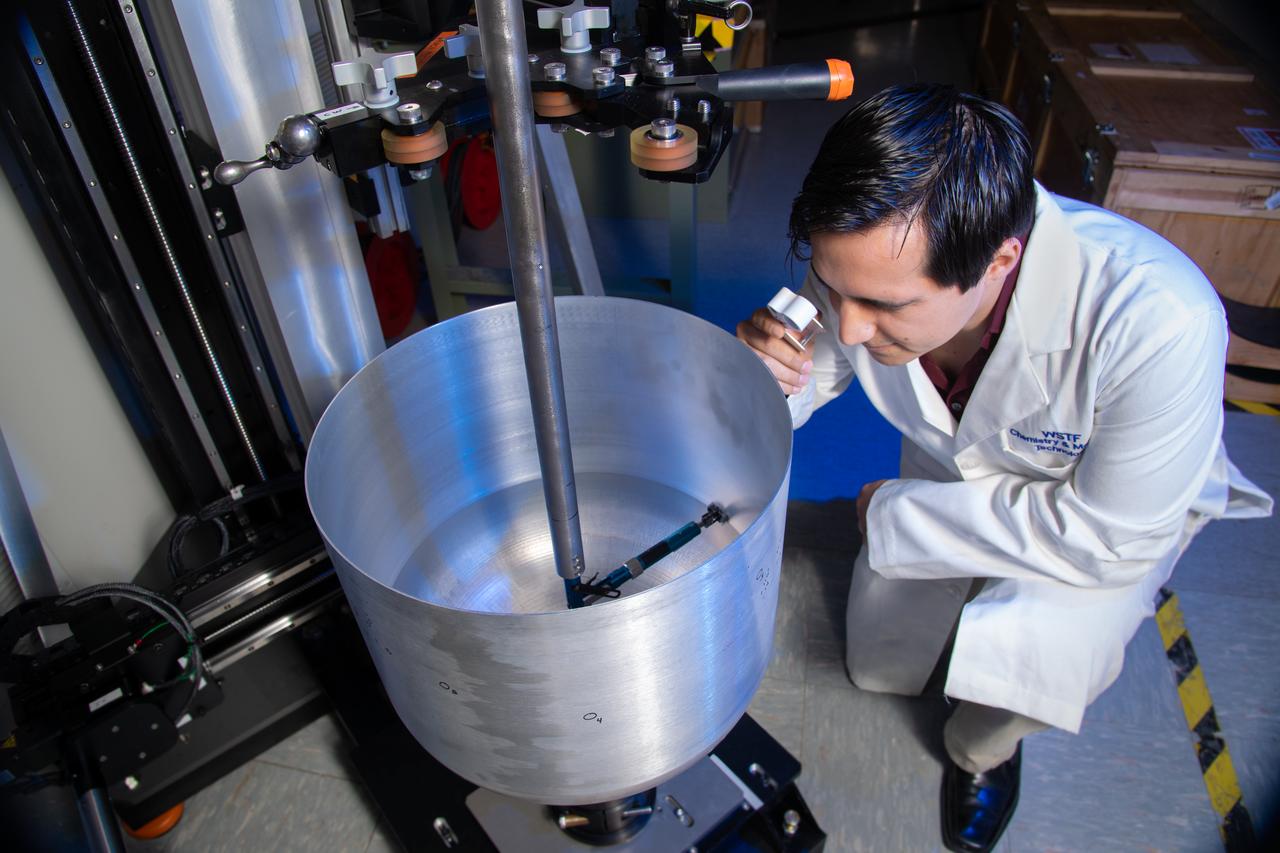

Edgar Reyes, a materials engineer and recent graduate of The University of Texas at El Paso, visually inspects a crack identified on the outer surface of a composite overwrapped pressure vessel (COPV) following an internal eddy-current through-wall nondestructive inspection conducted at the NASA White Sands Test Facility in Las Cruces, N.M. Eddy-current testing is one of many electromagnetic testing methods used in nondestructive testing to identify cracks in COPVS that can potentially threaten spacecraft crew and mission success. Photo Credit: (NASA/Reed P. Elliott)
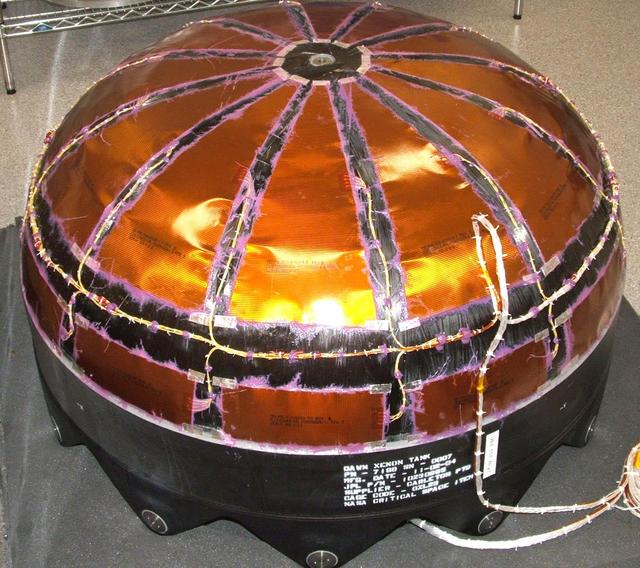

This image shows NASA Dawn spacecraft Xenon tank -- composite overwrapped pressure vessel with titanium liner.

The European Service Module for the Artemis II mission is photographed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. Artemis II will be the first crewed flight test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. The service module will provide the power necessary to propel Orion on a trip around the Moon, including the in-space maneuvering capability and other commodities necessary to sustain crew for the duration of the mission.
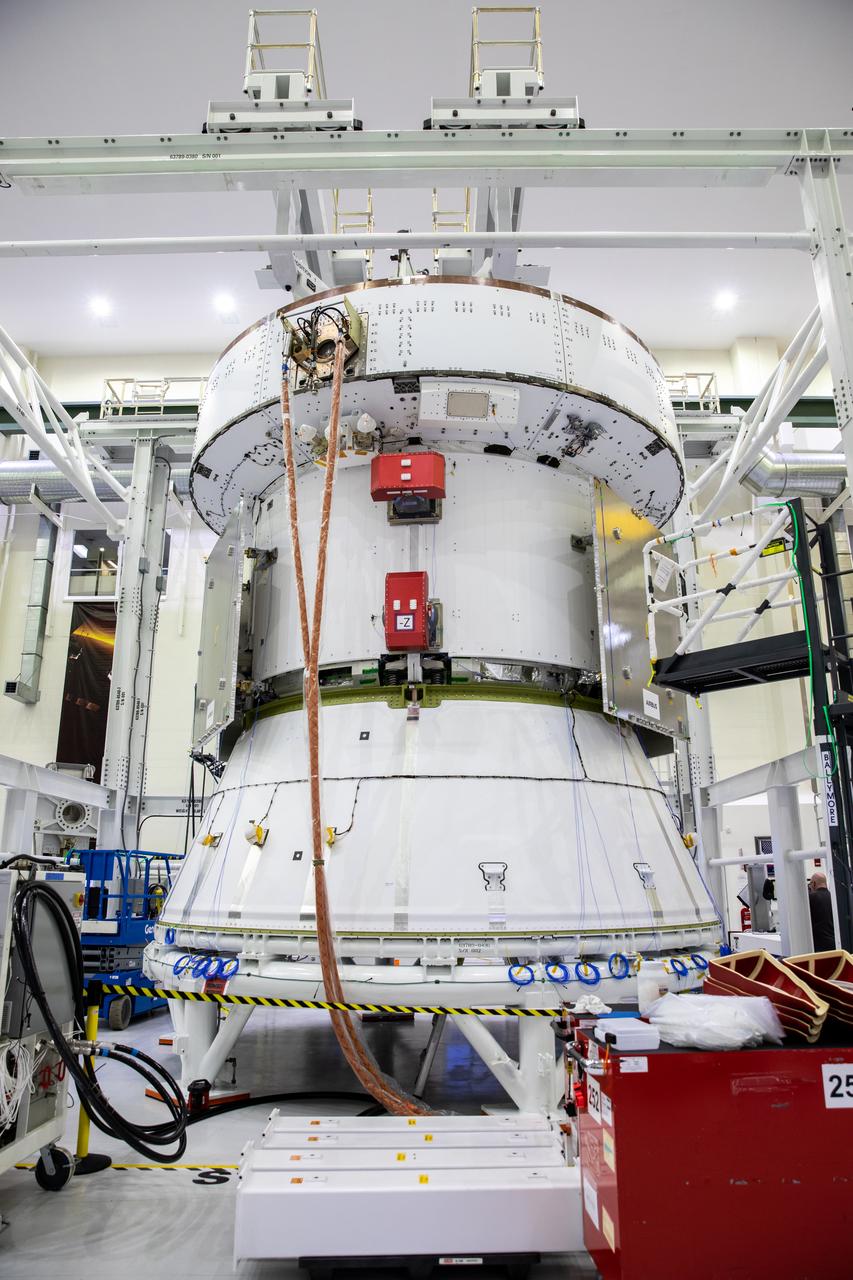

The European Service Module for the Artemis II mission is photographed inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Feb. 21, 2023. Artemis II will be the first crewed flight test of the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft. The service module will provide the power necessary to propel Orion on a trip around the Moon, including the in-space maneuvering capability and other commodities necessary to sustain crew for the duration of the mission.
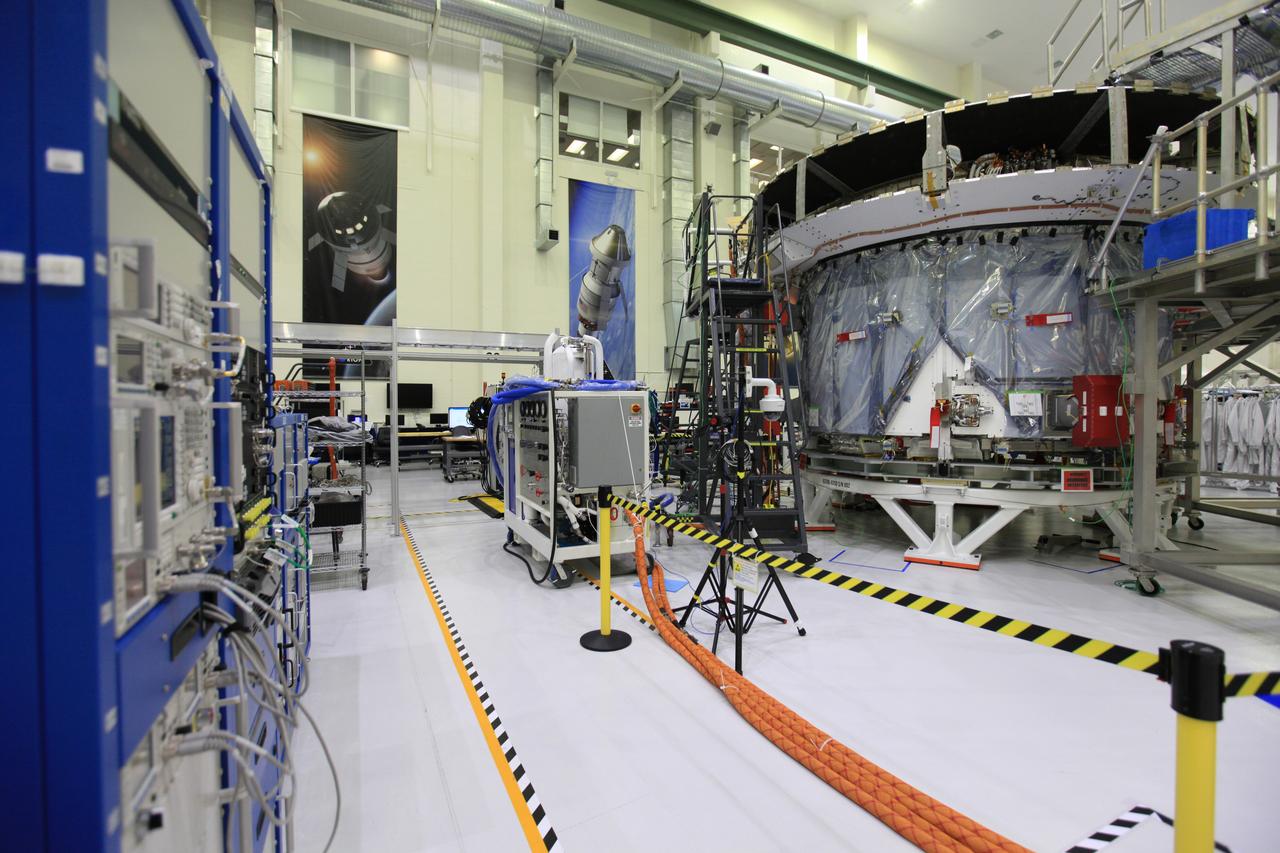

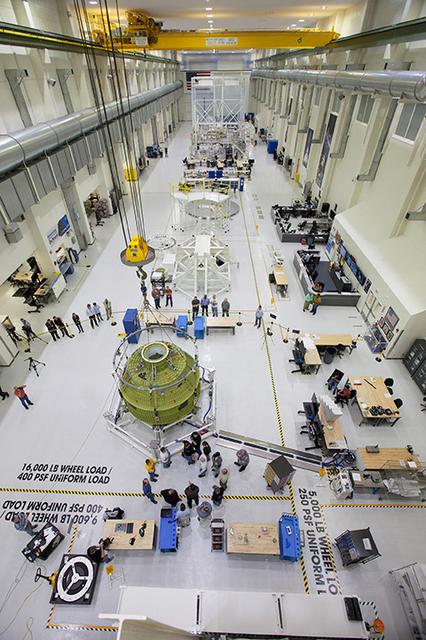
The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
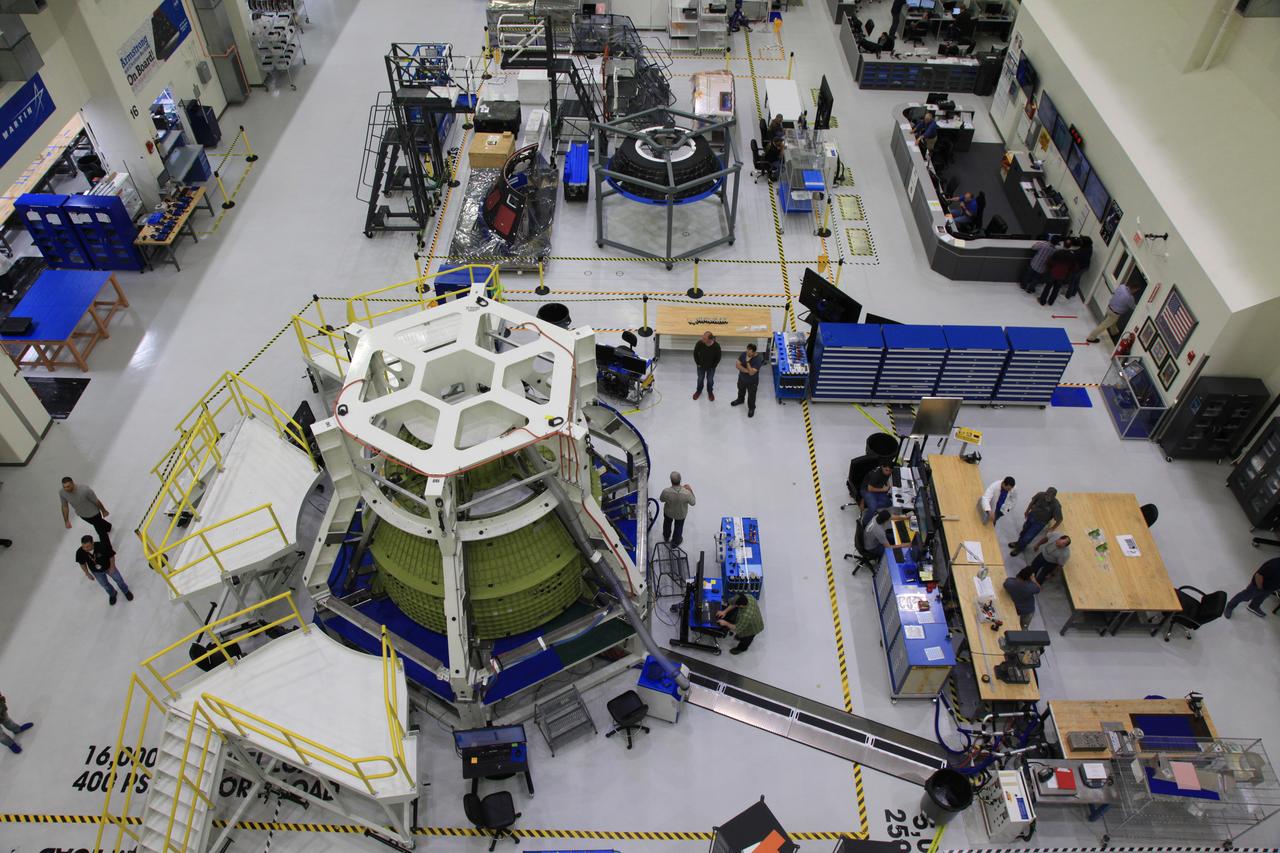

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
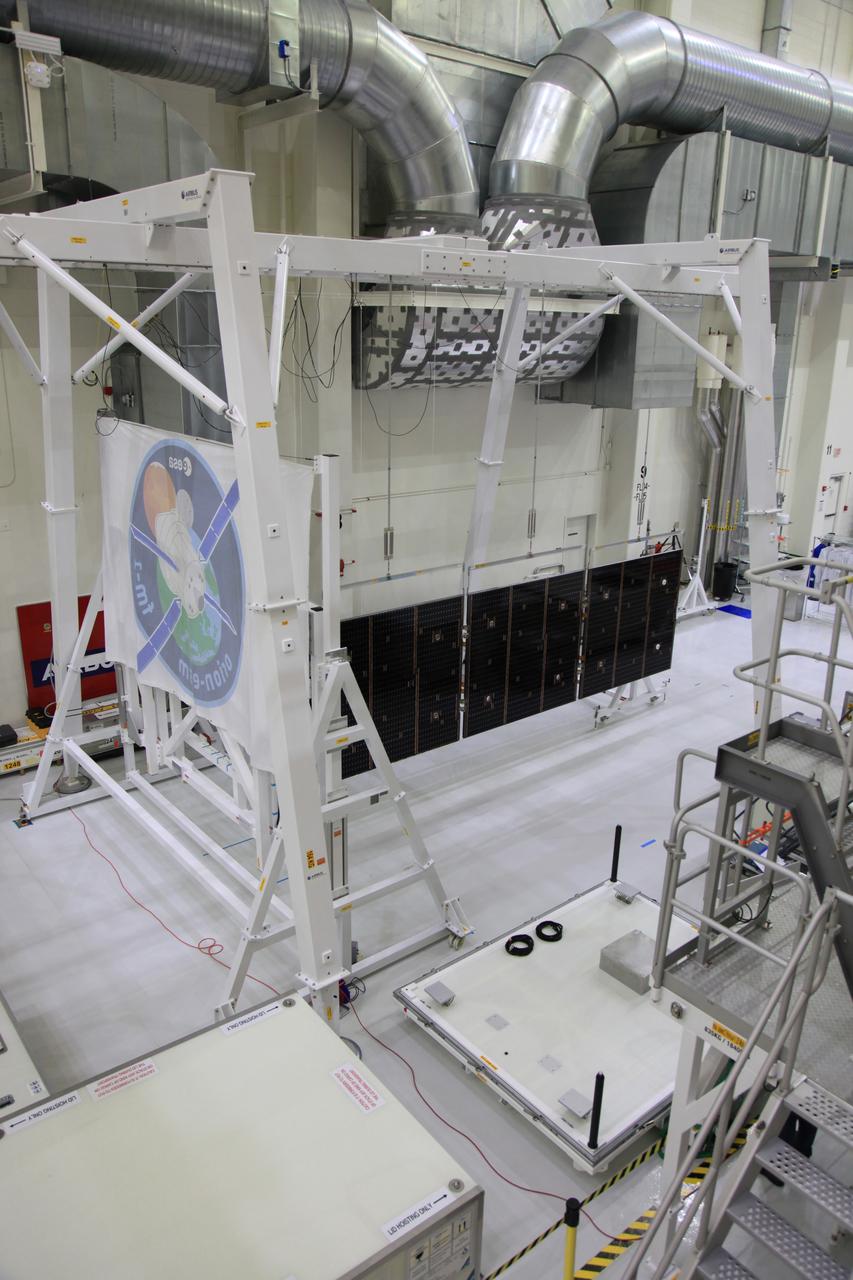

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
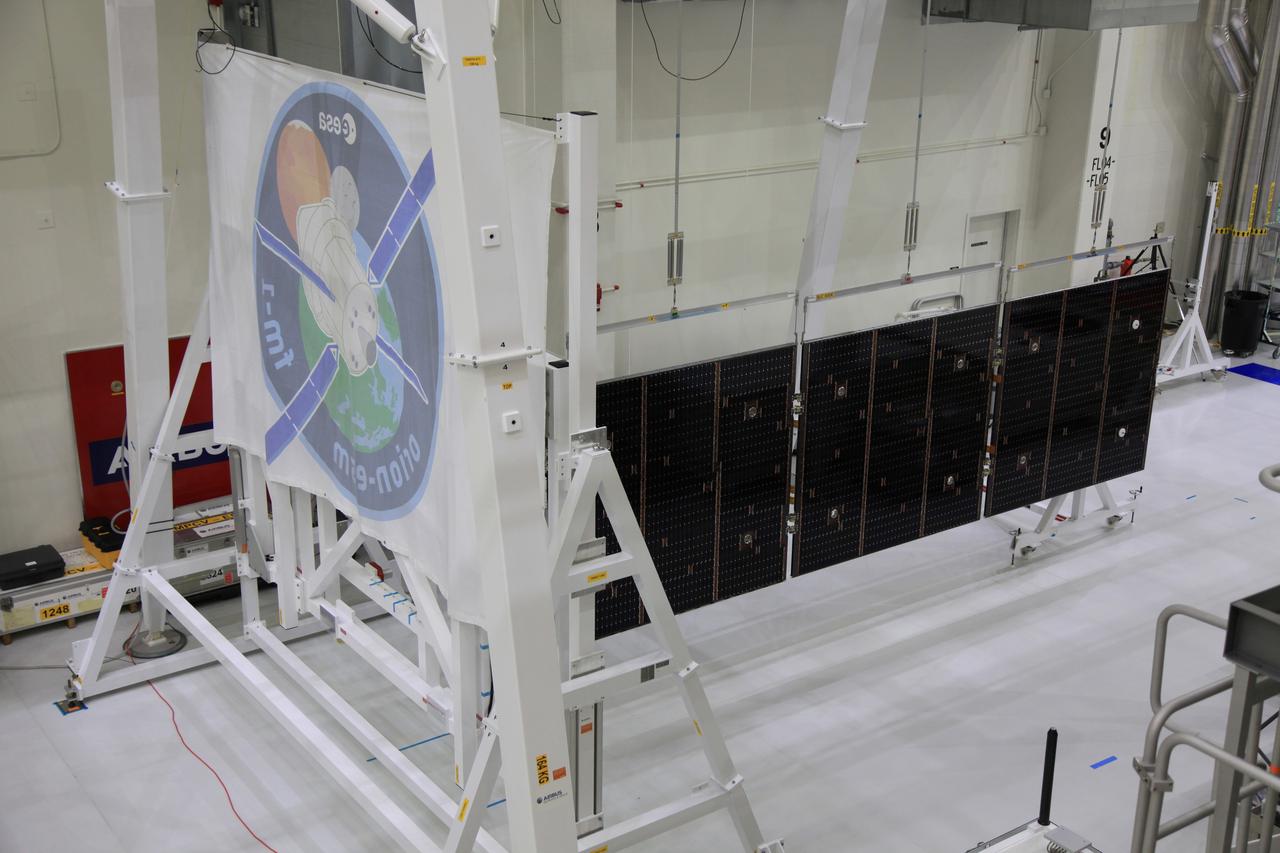

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
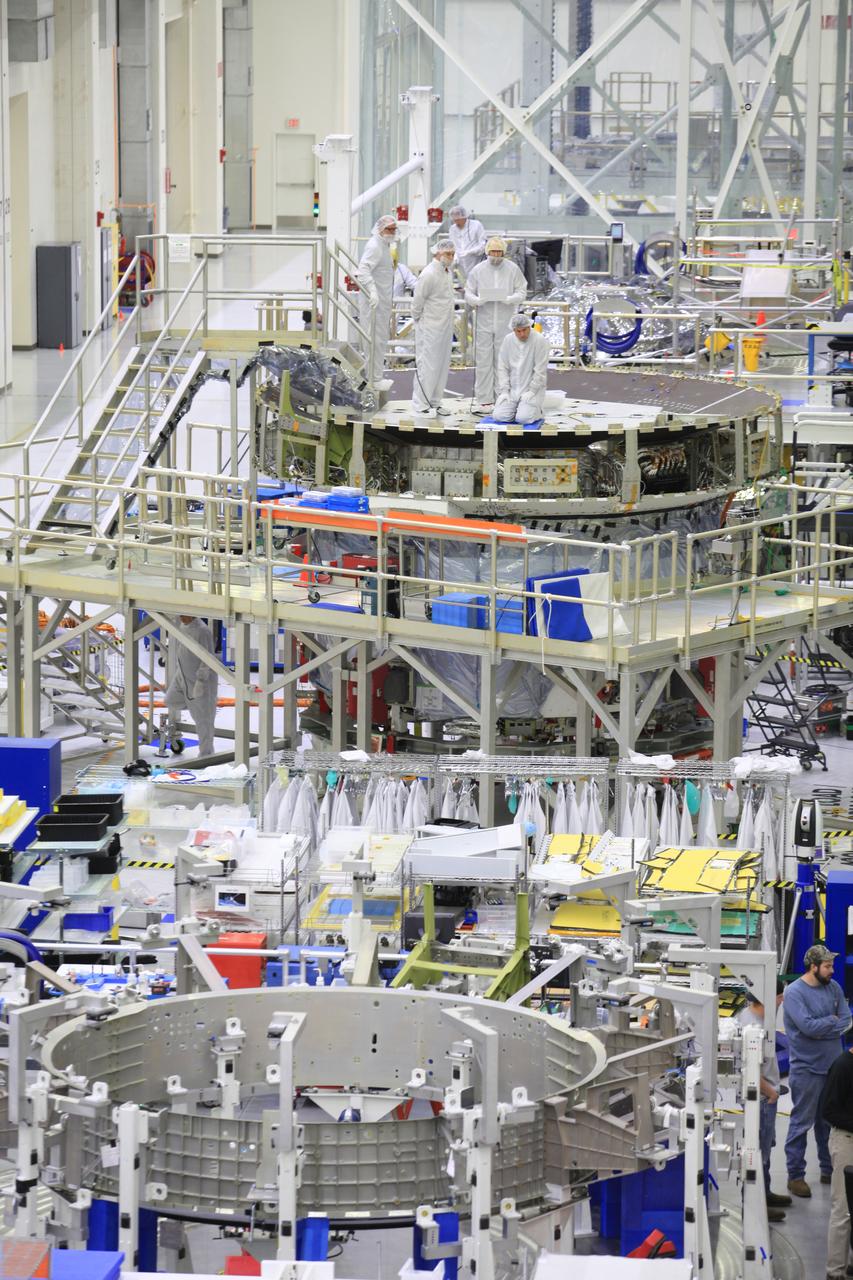

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
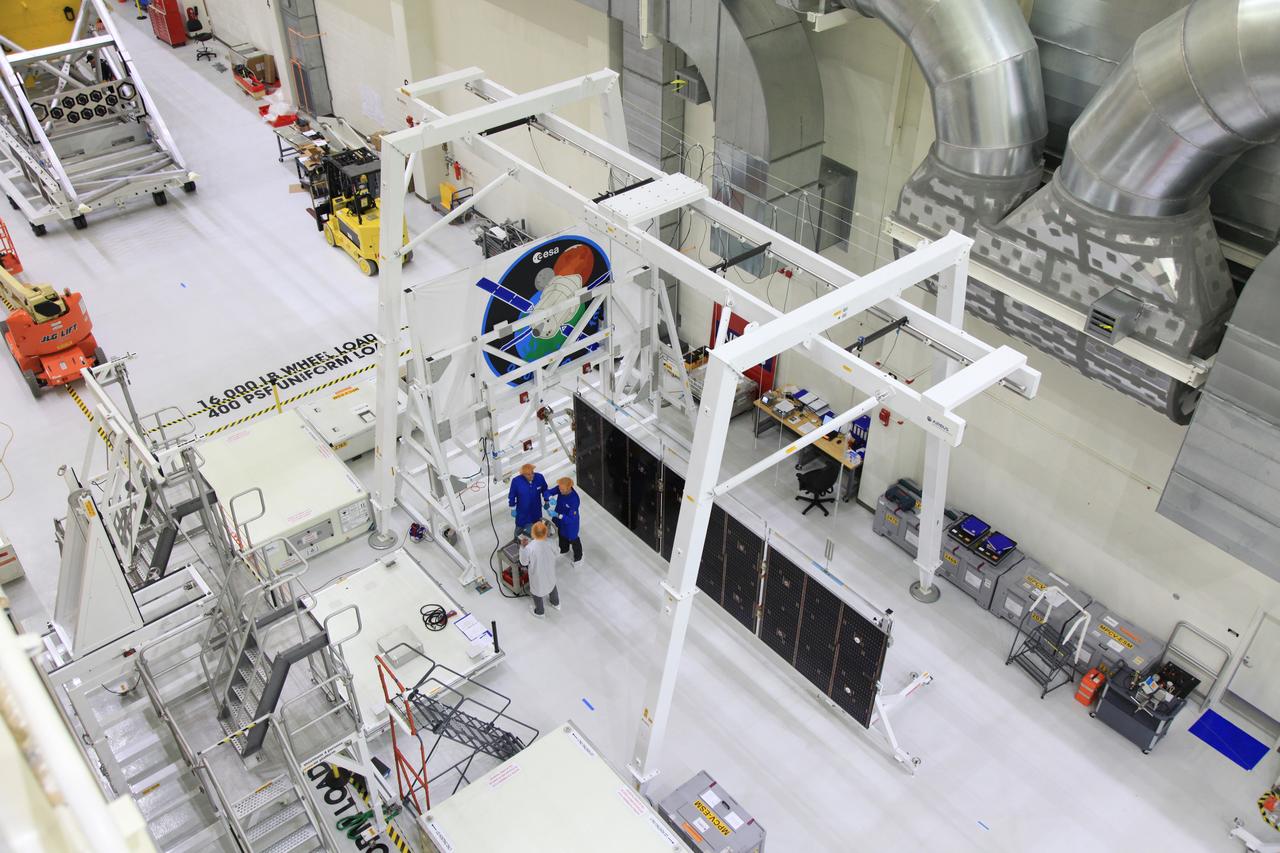

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
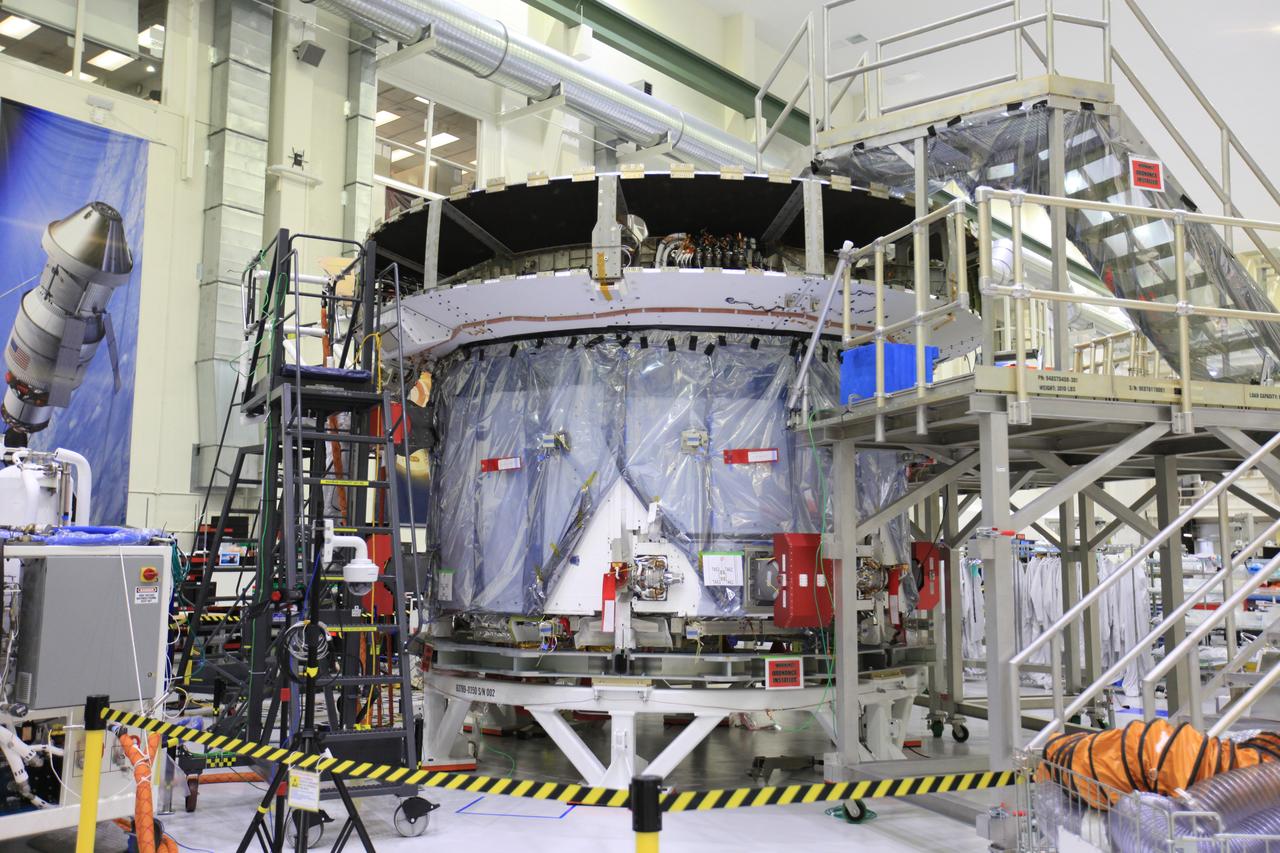

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
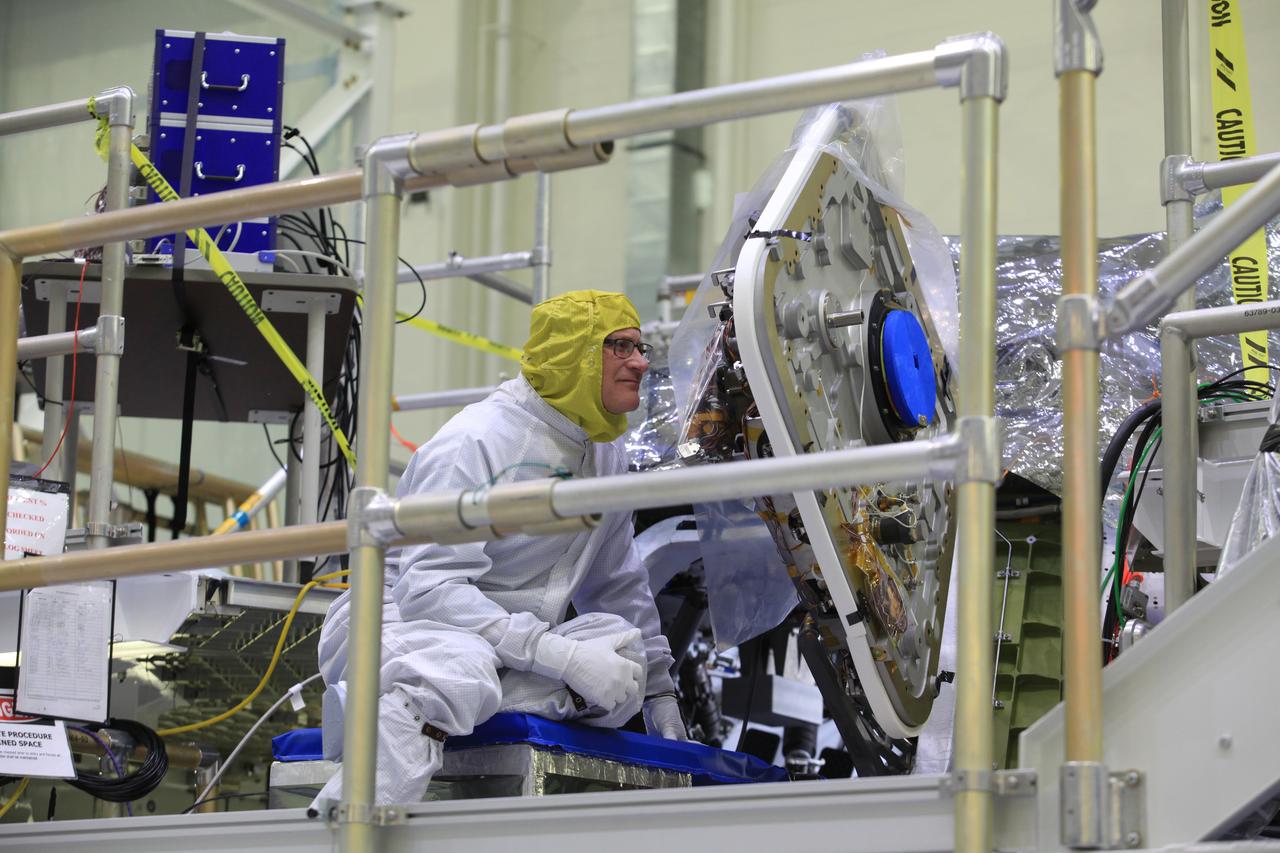

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
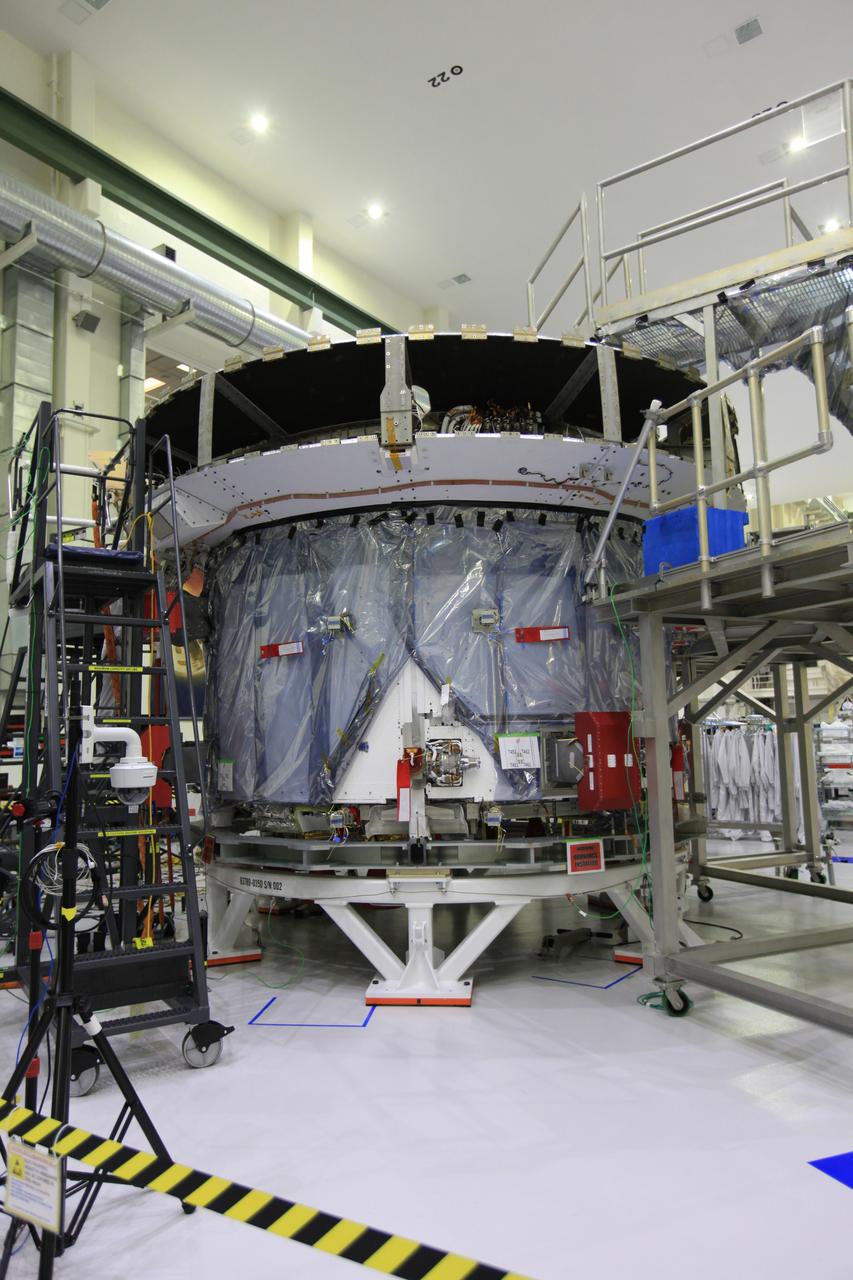

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
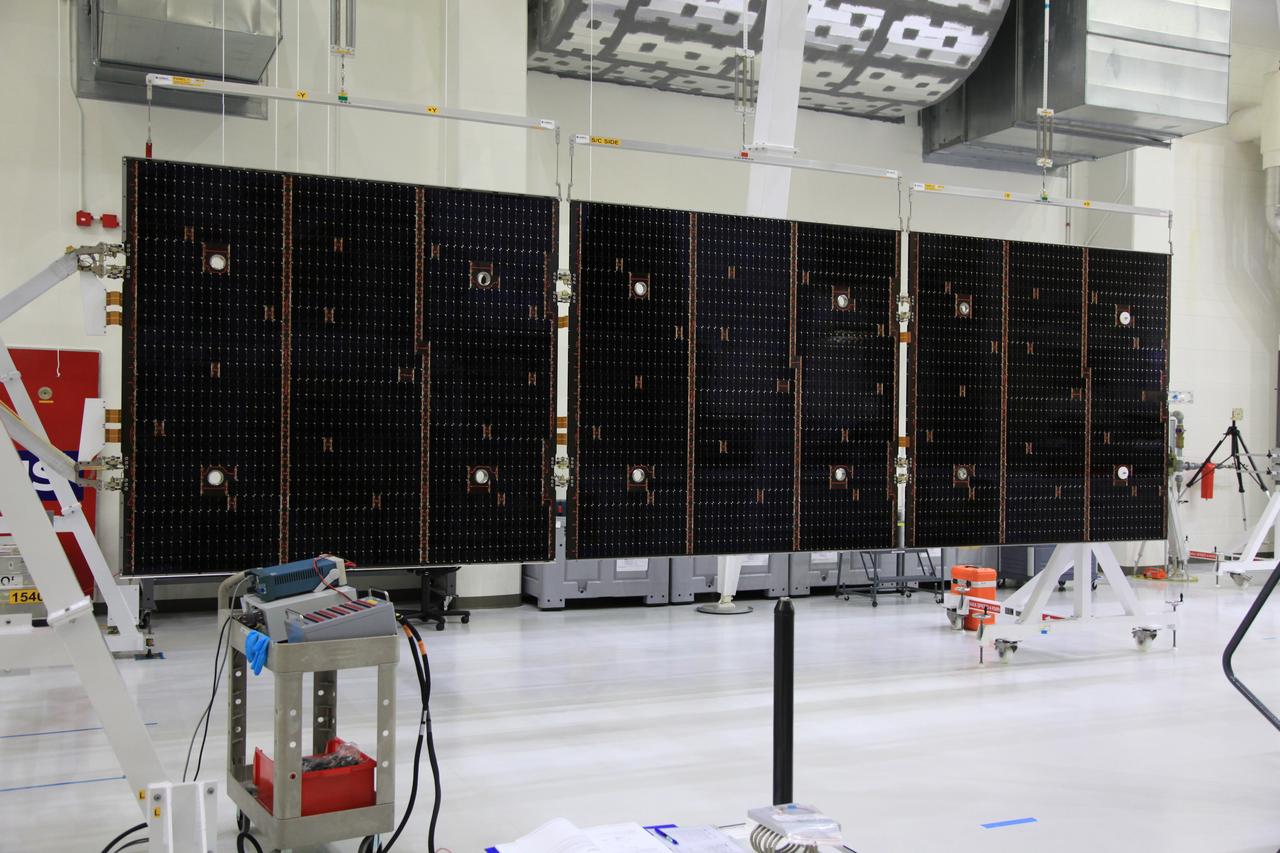

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
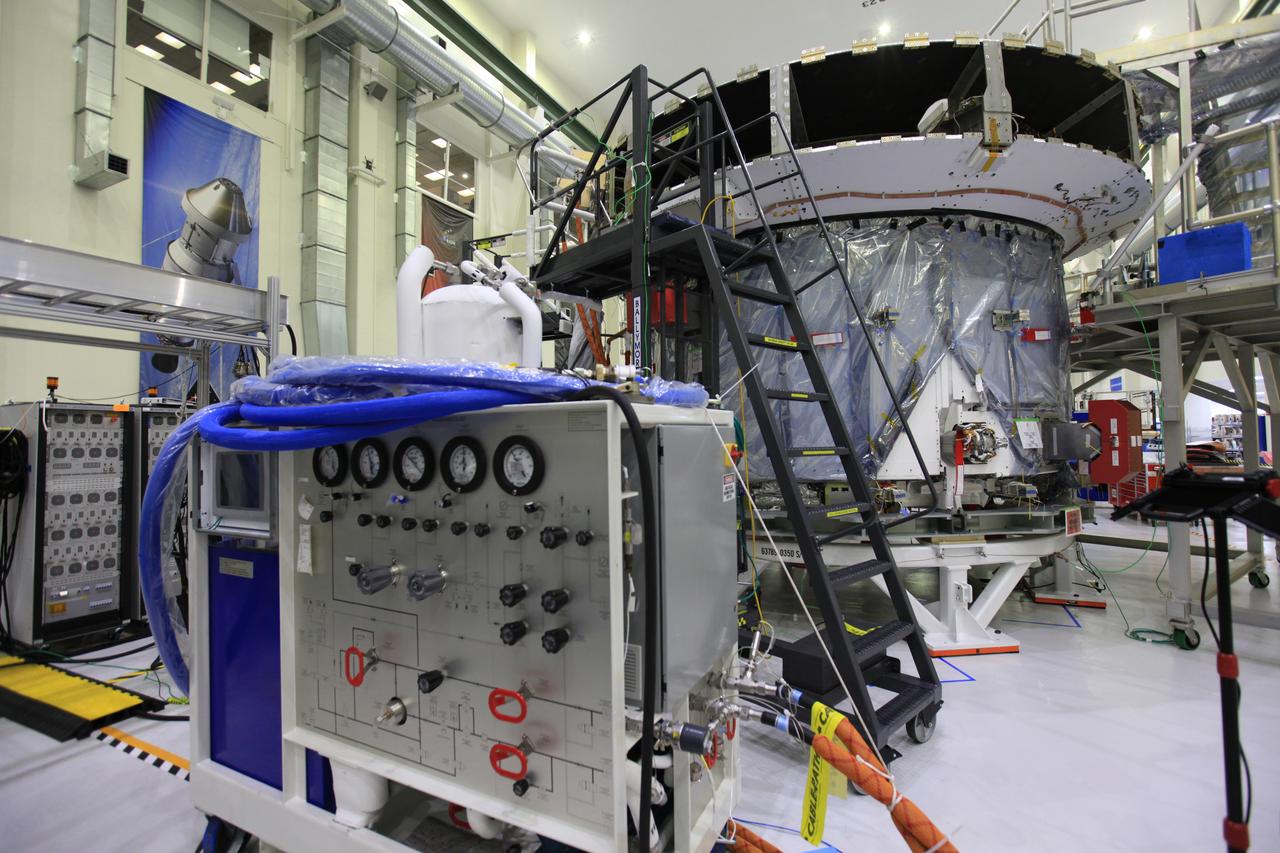
The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
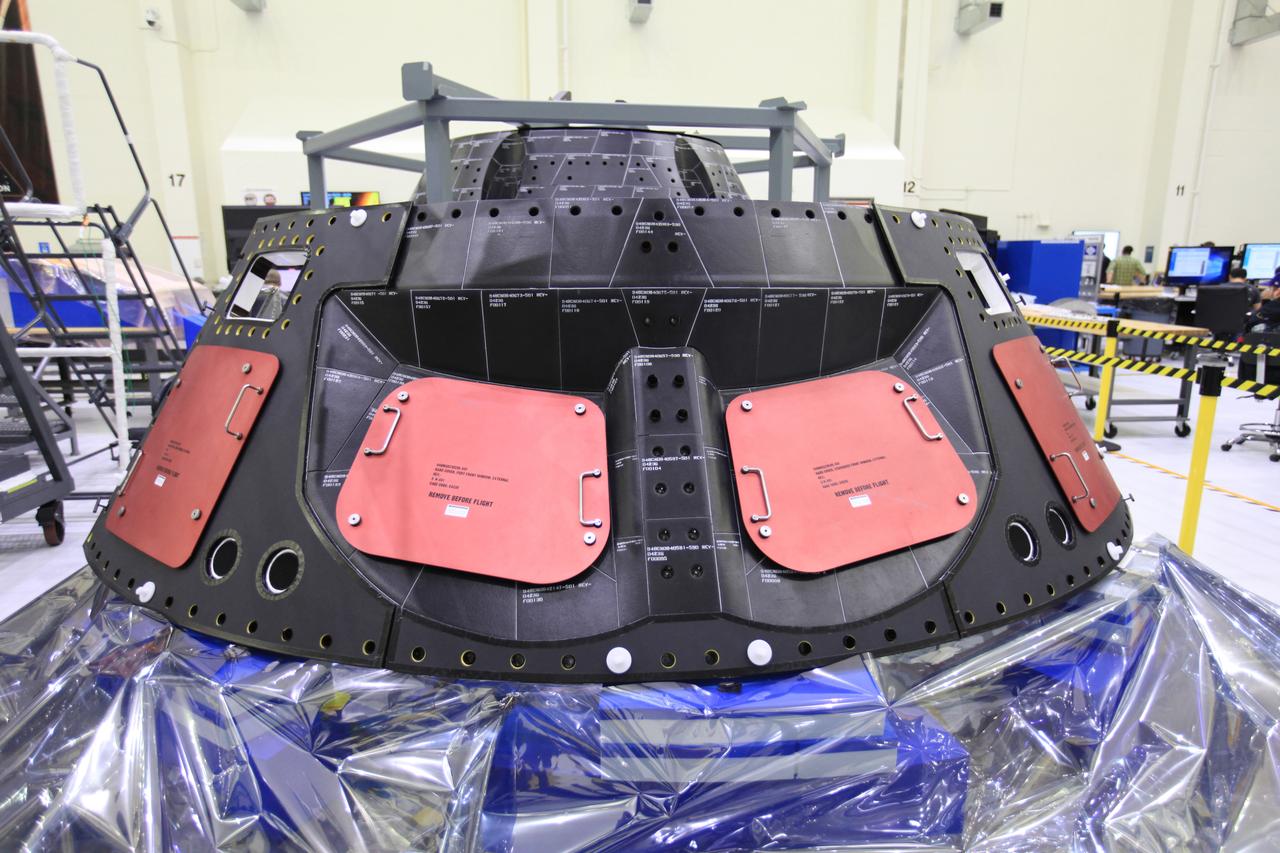
The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
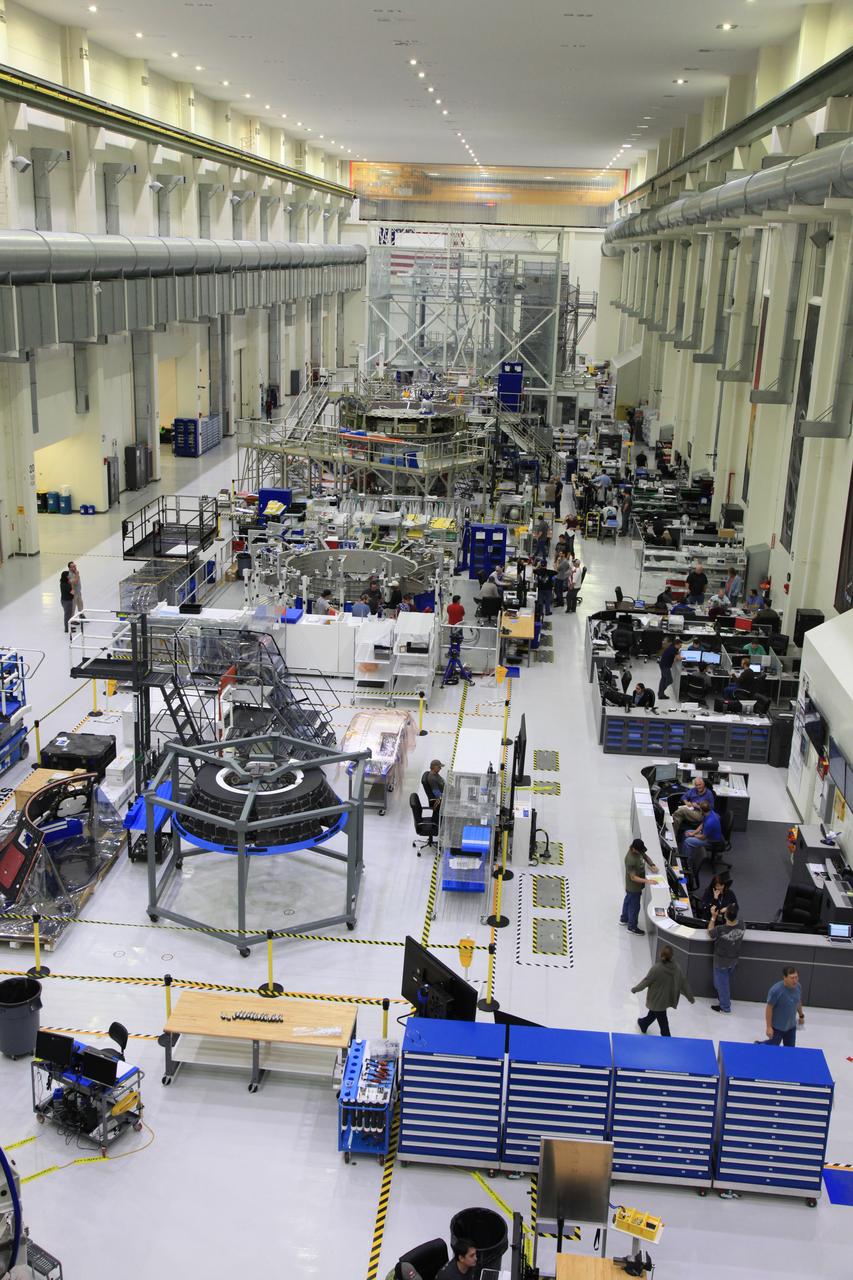

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
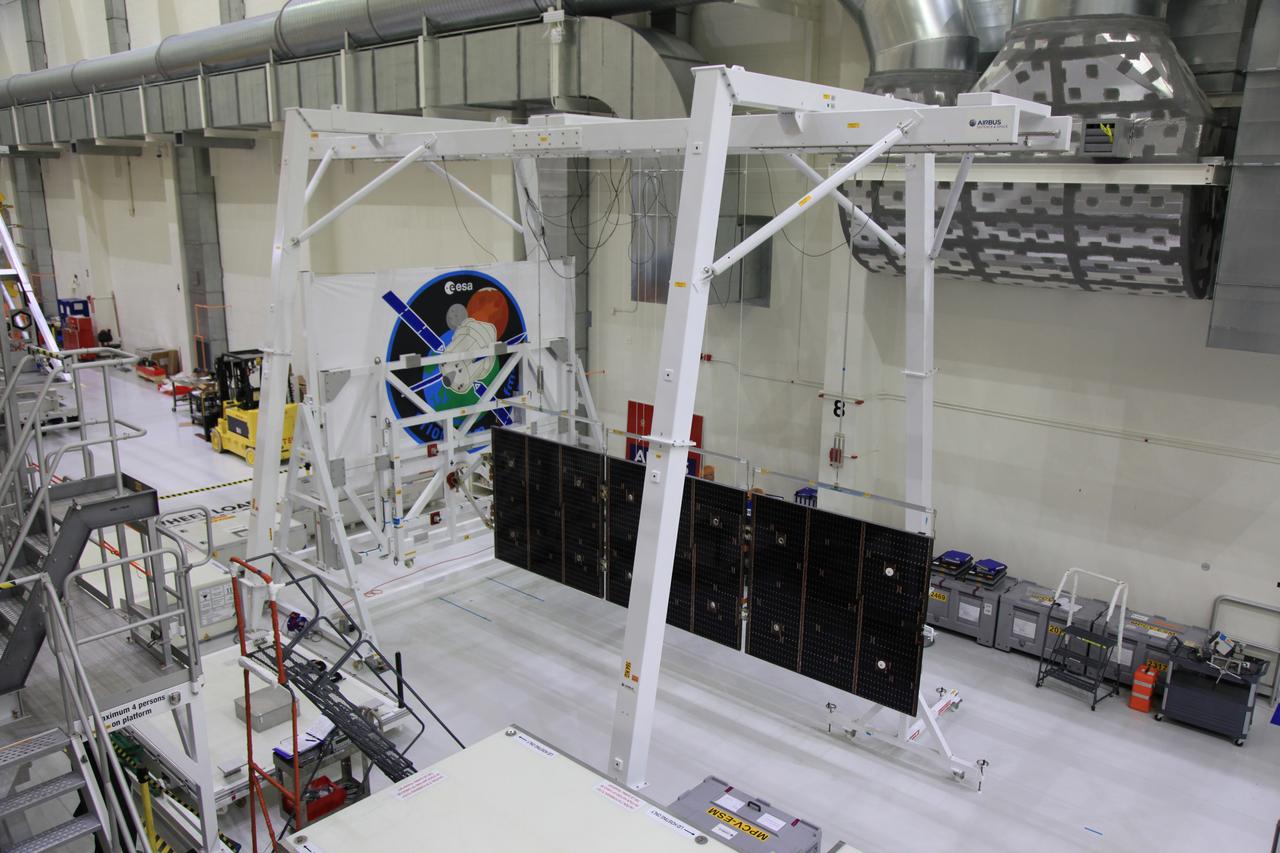

The crew and service module for Artemis I continue preparations for mating inside the Operations and Checkout (O&C) Building High Bay at Kennedy Space Center on March 21, 2019. Alongside, the pressure vessel for Artemis II is undergoing install of its secondary structure.
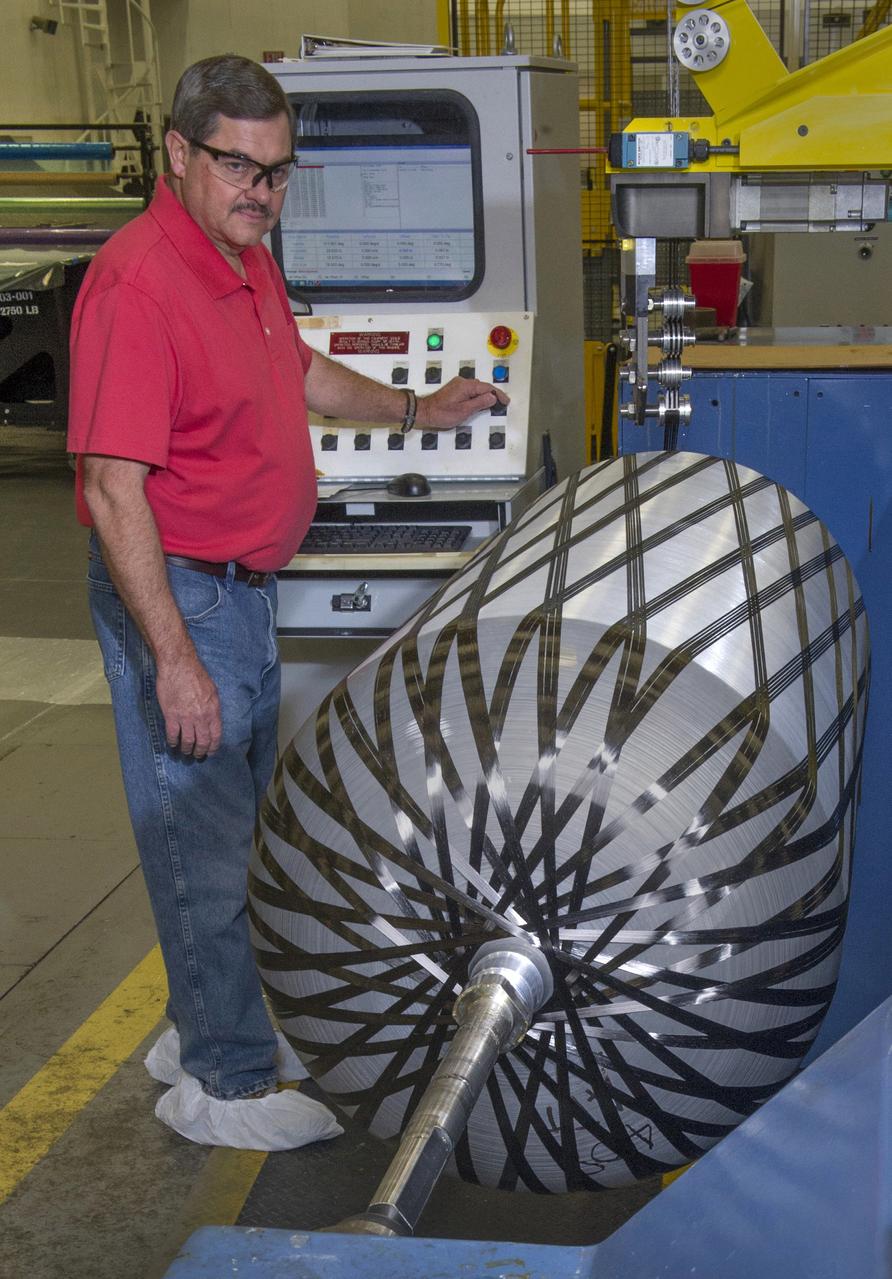

PHILLIP THOMPSON WRAPS PRESSURE VESSEL WITH COMPOSITE MATERIAL
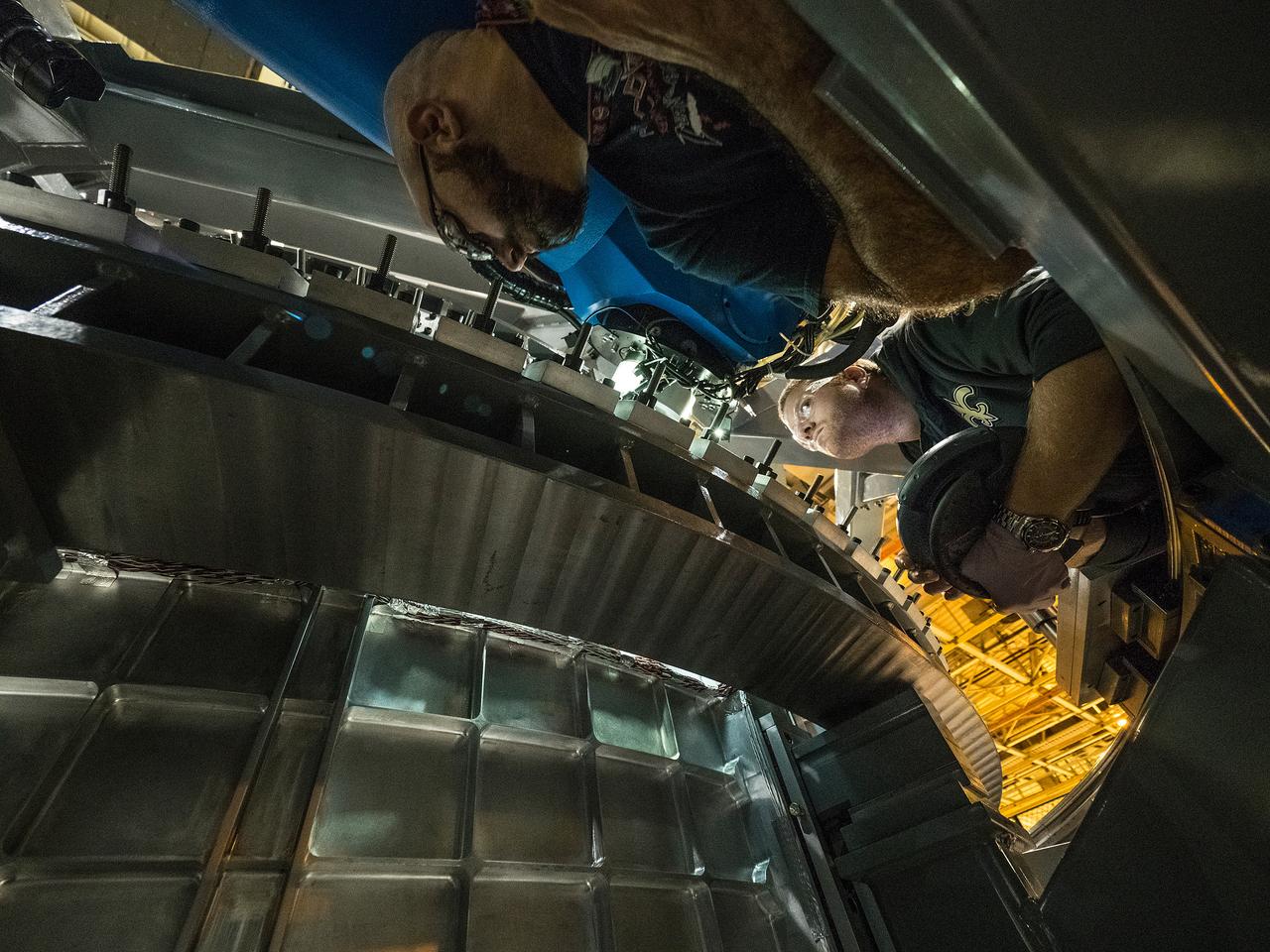

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 15, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
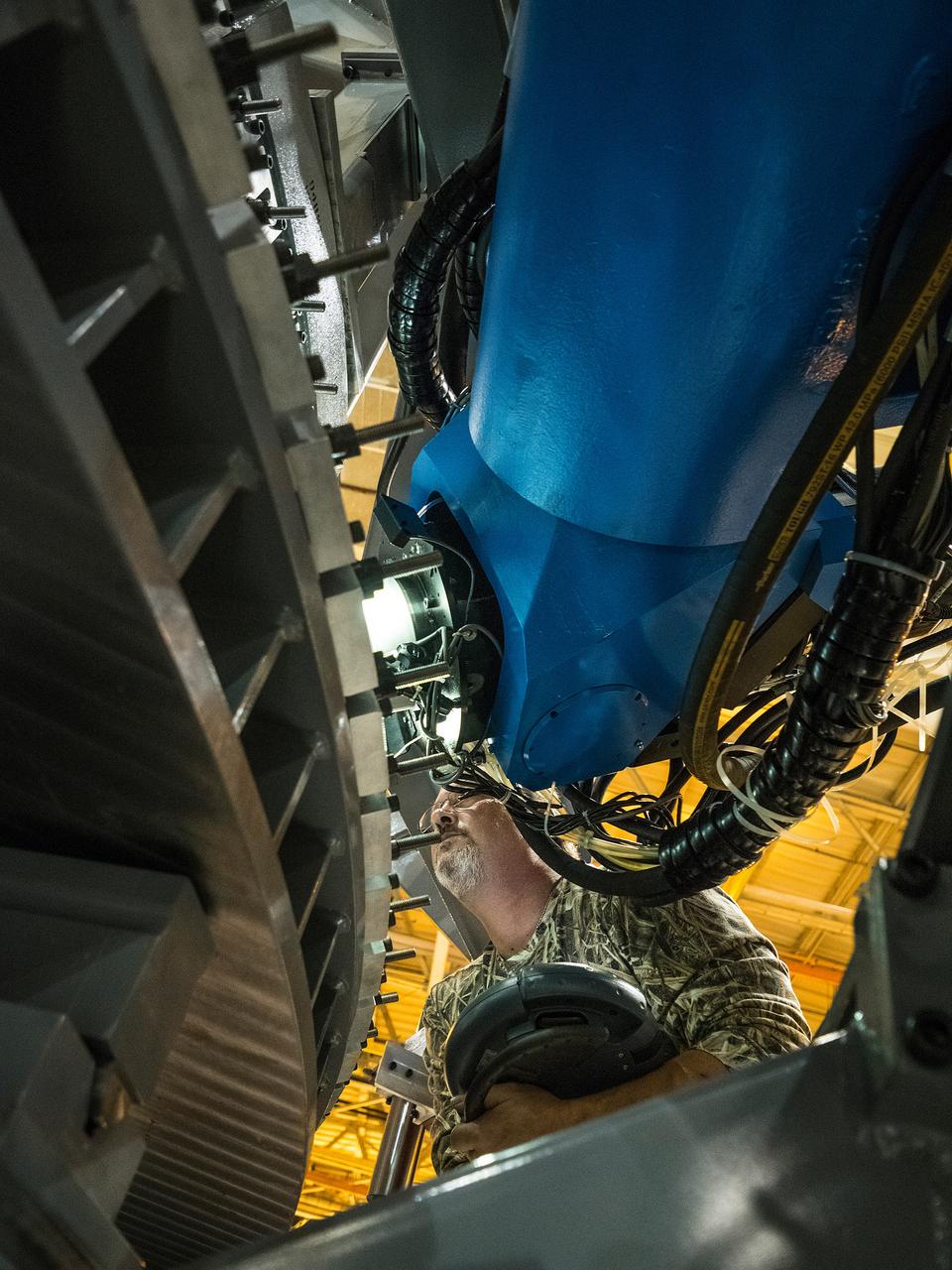

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 16, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
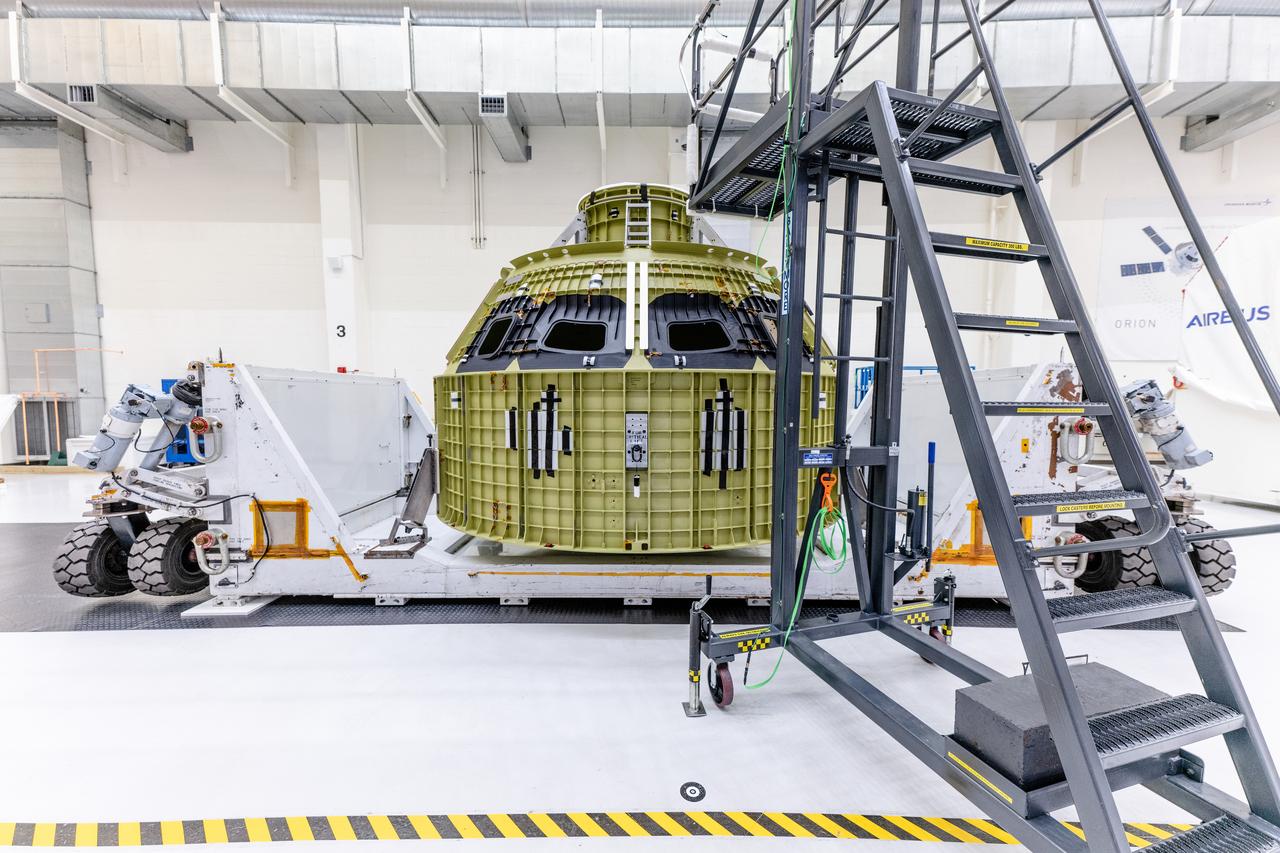

The pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission arrives at Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center on Oct. 19, 2021. The pieces for the pressure vessel were machined at AMRO in California and Ingersoll Machine Tools Inc. in Illinois and welded at the Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana.
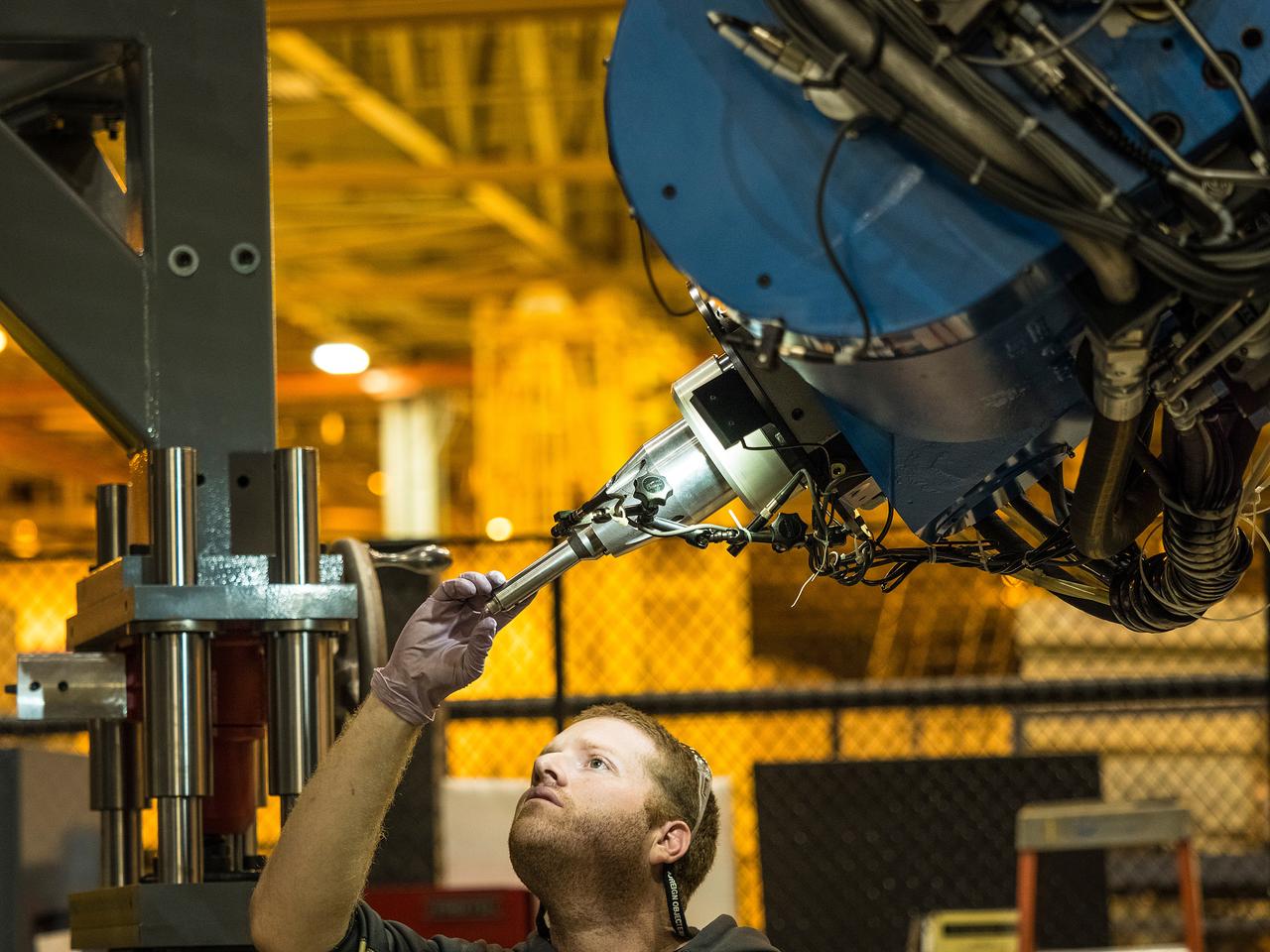

Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 15, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
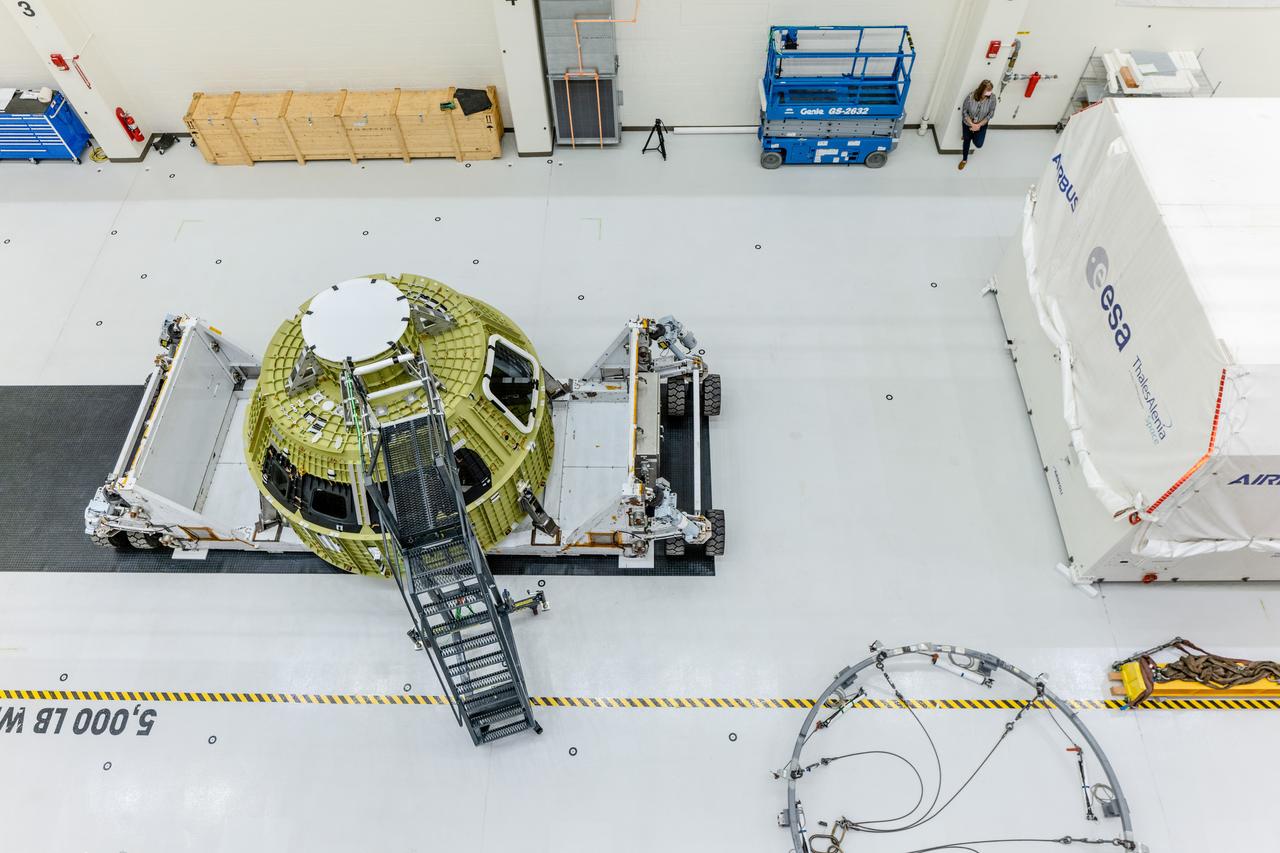

The pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission arrives at Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center on Oct. 19, 2021. The pieces for the pressure vessel were machined at AMRO in California and Ingersoll Machine Tools Inc. in Illinois and welded at the Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana
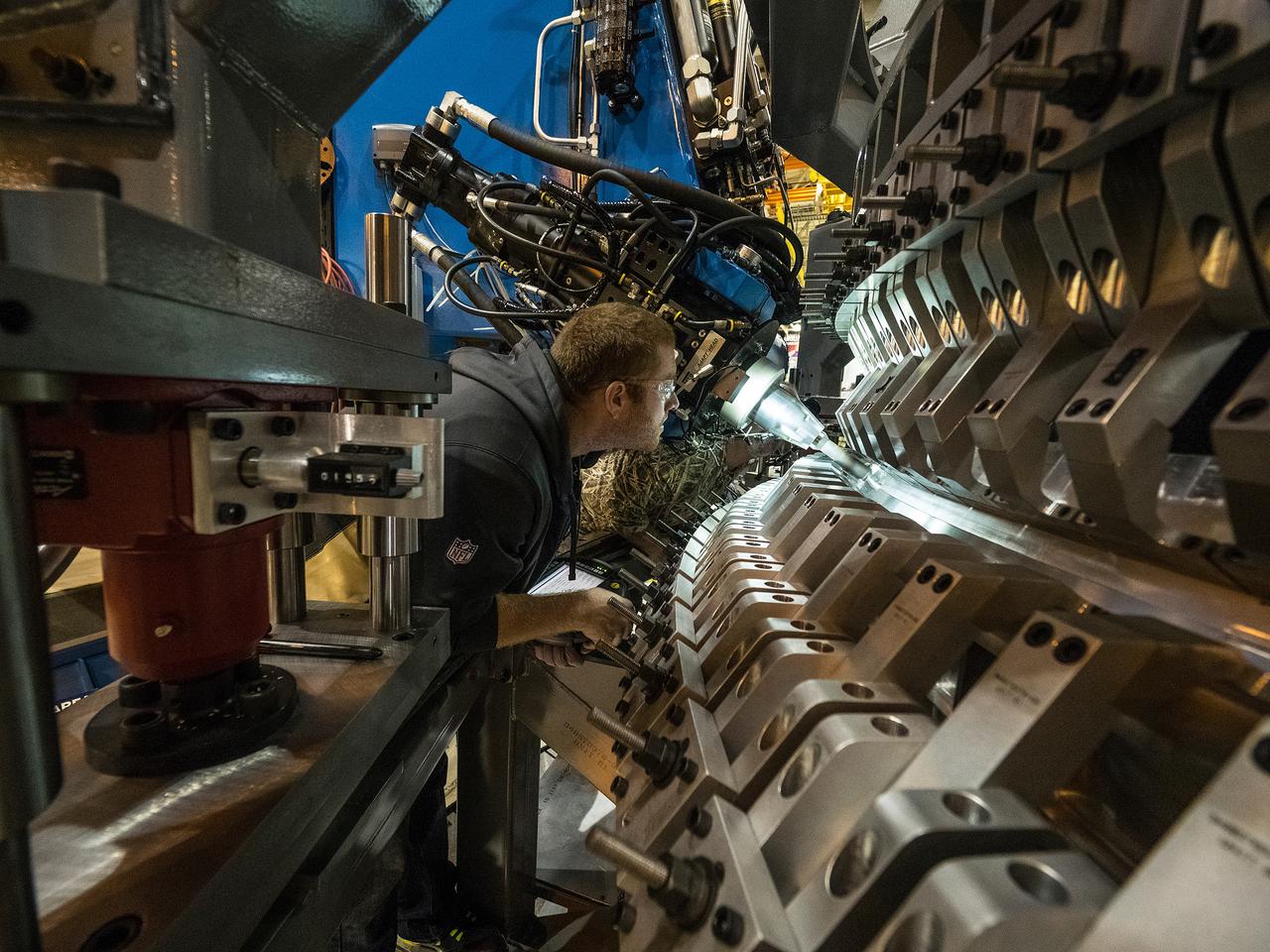
Lockheed Martin team completes the closeout weld of the pathfinder pressure vessel at NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Nov. 16, 2015. The pathfinder welds demonstrated the tools and processes required to safely perform the 7 welds required to assemble the pressure vessel for Artemis I. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
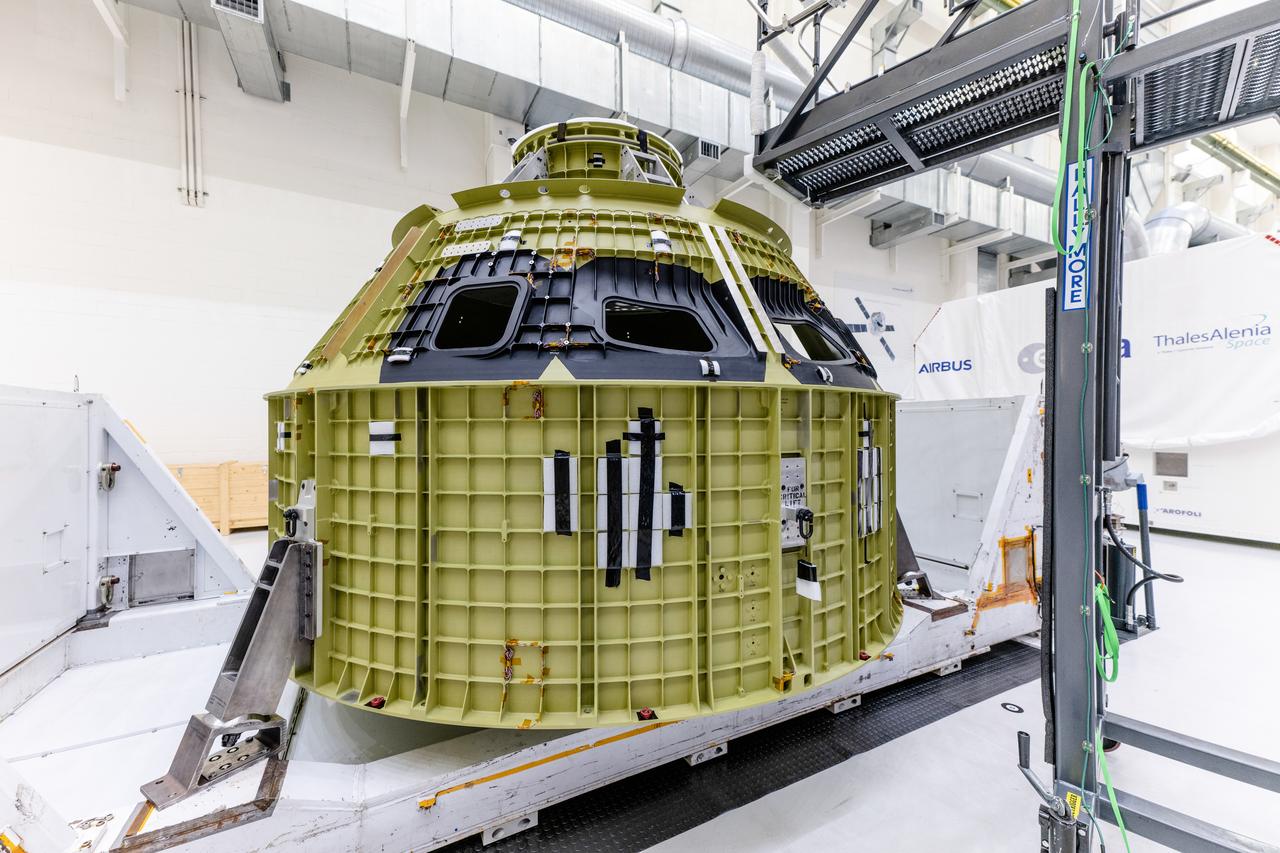

The pressure vessel for the Artemis III mission arrives at Operations and Checkout Building at Kennedy Space Center on Oct. 19, 2021. The pieces for the pressure vessel were machined at AMRO in California and Ingersoll Machine Tools Inc. in Illinois and welded at the Michoud Assembly Facility in Louisiana
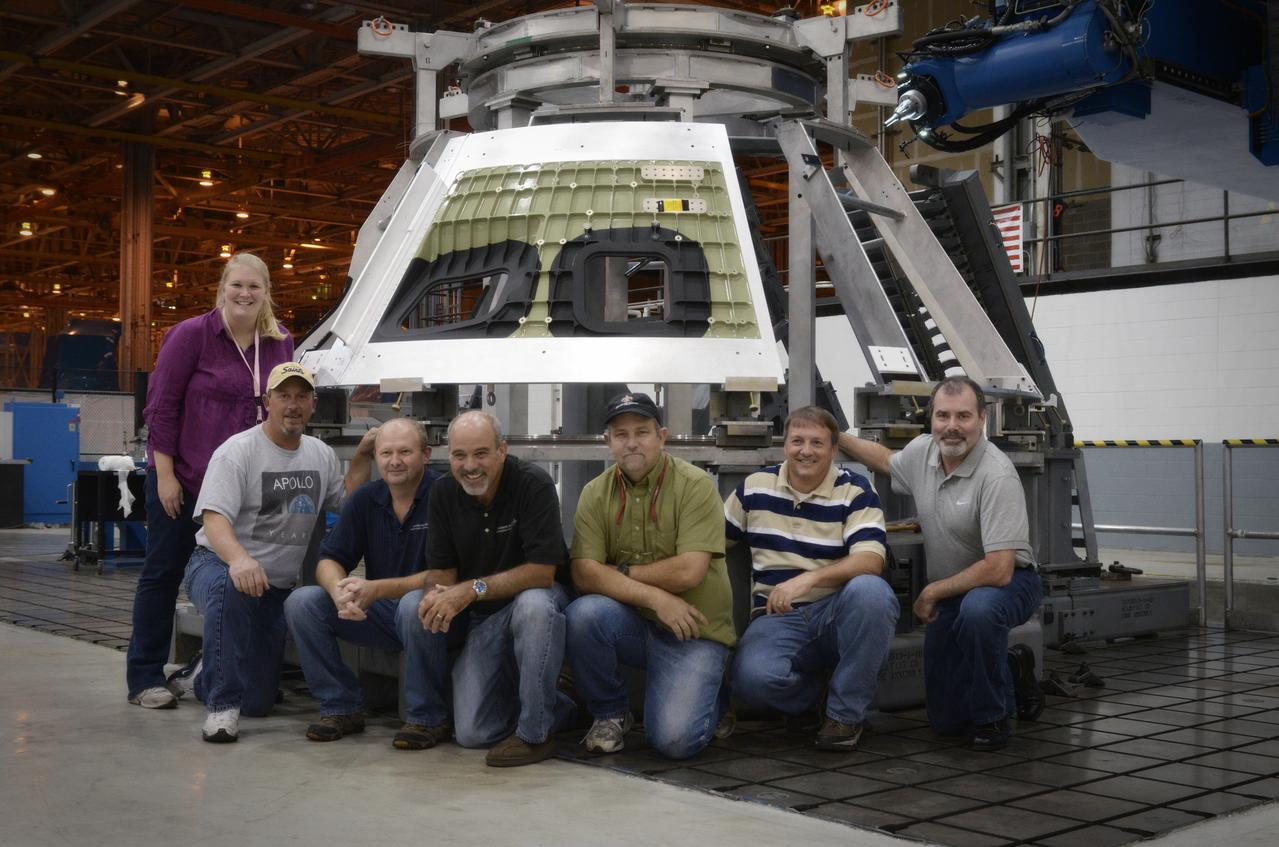

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
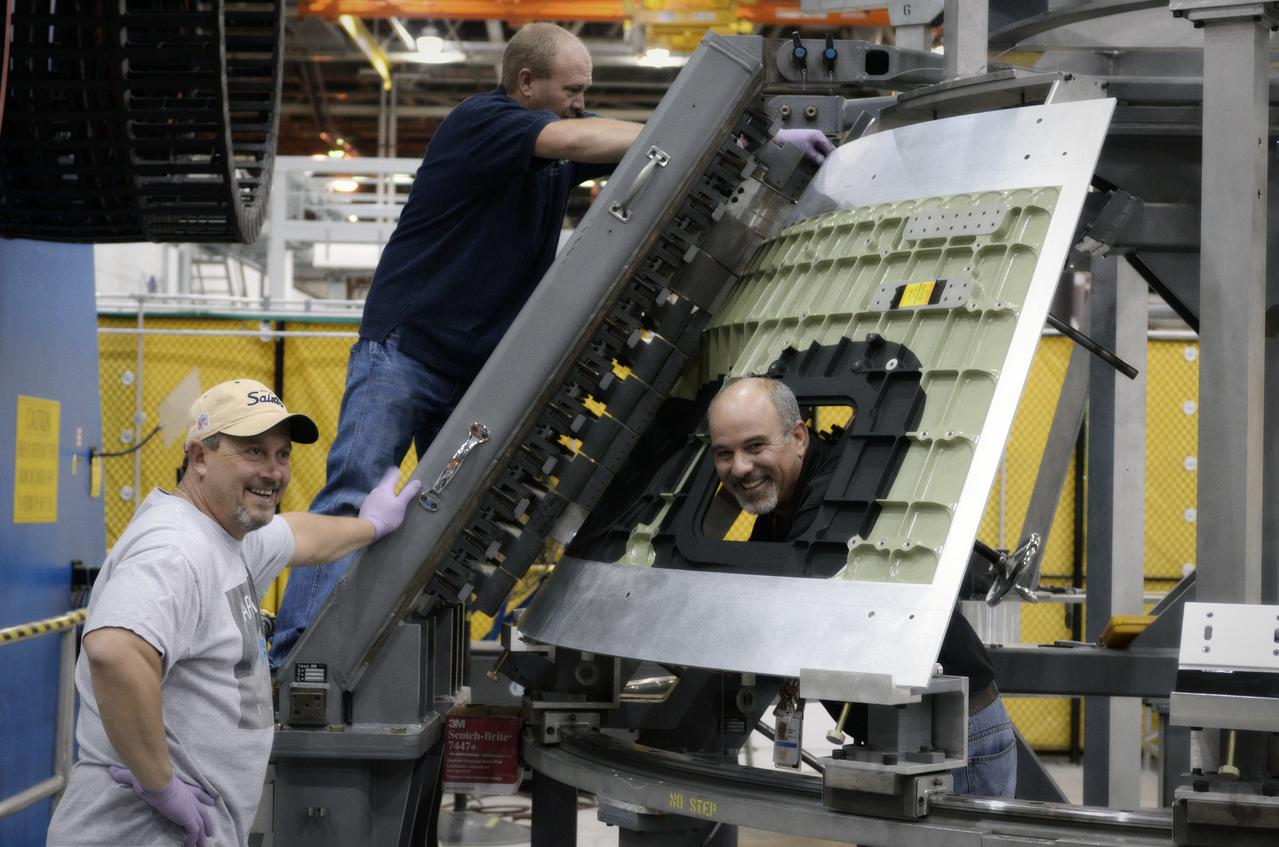

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
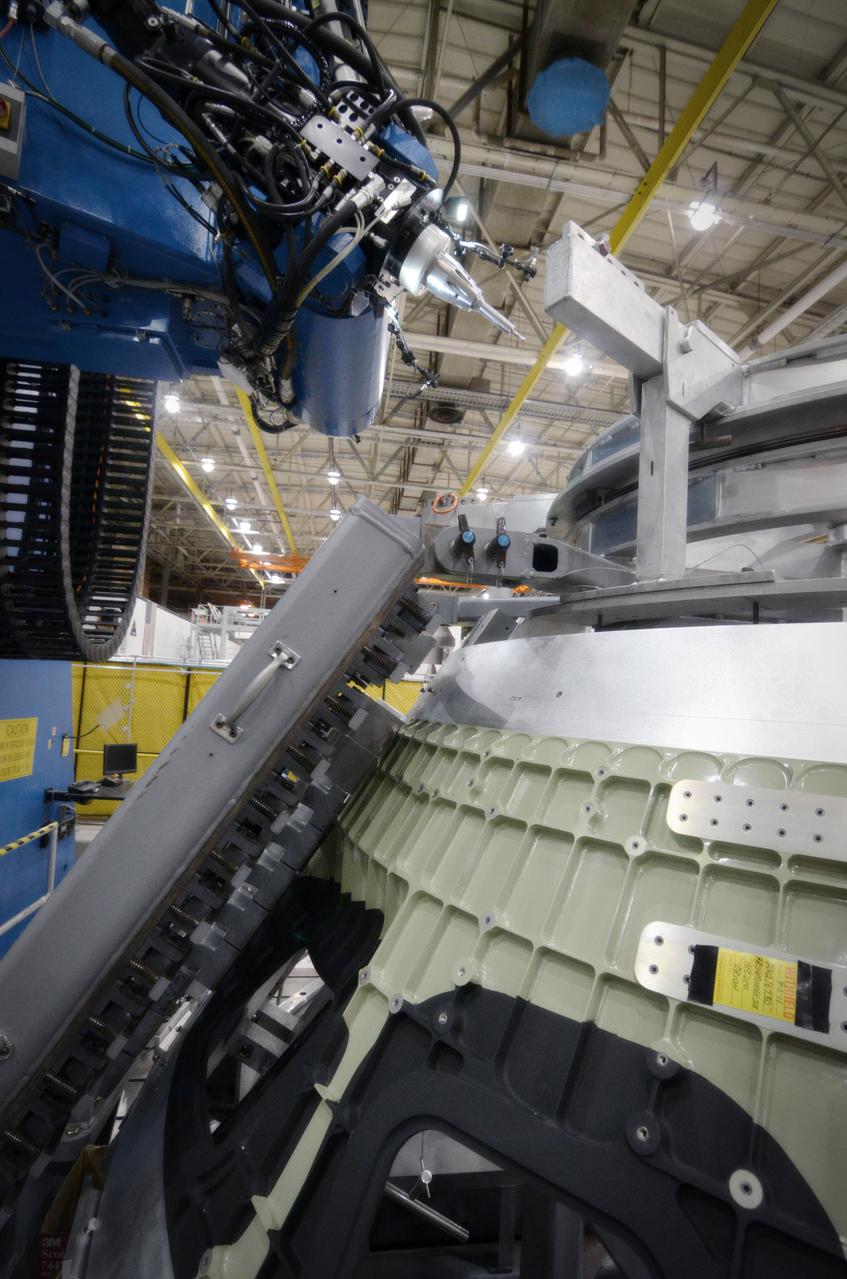

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
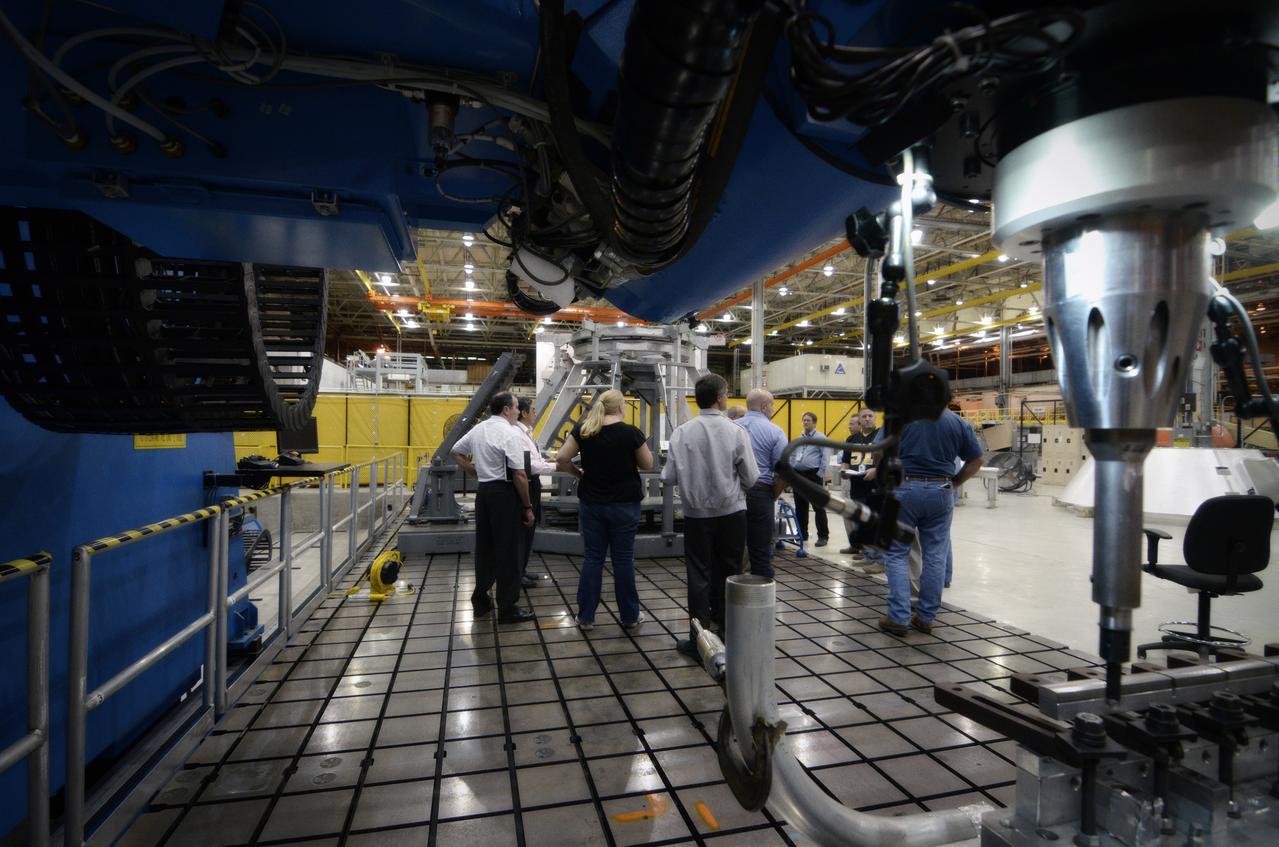

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
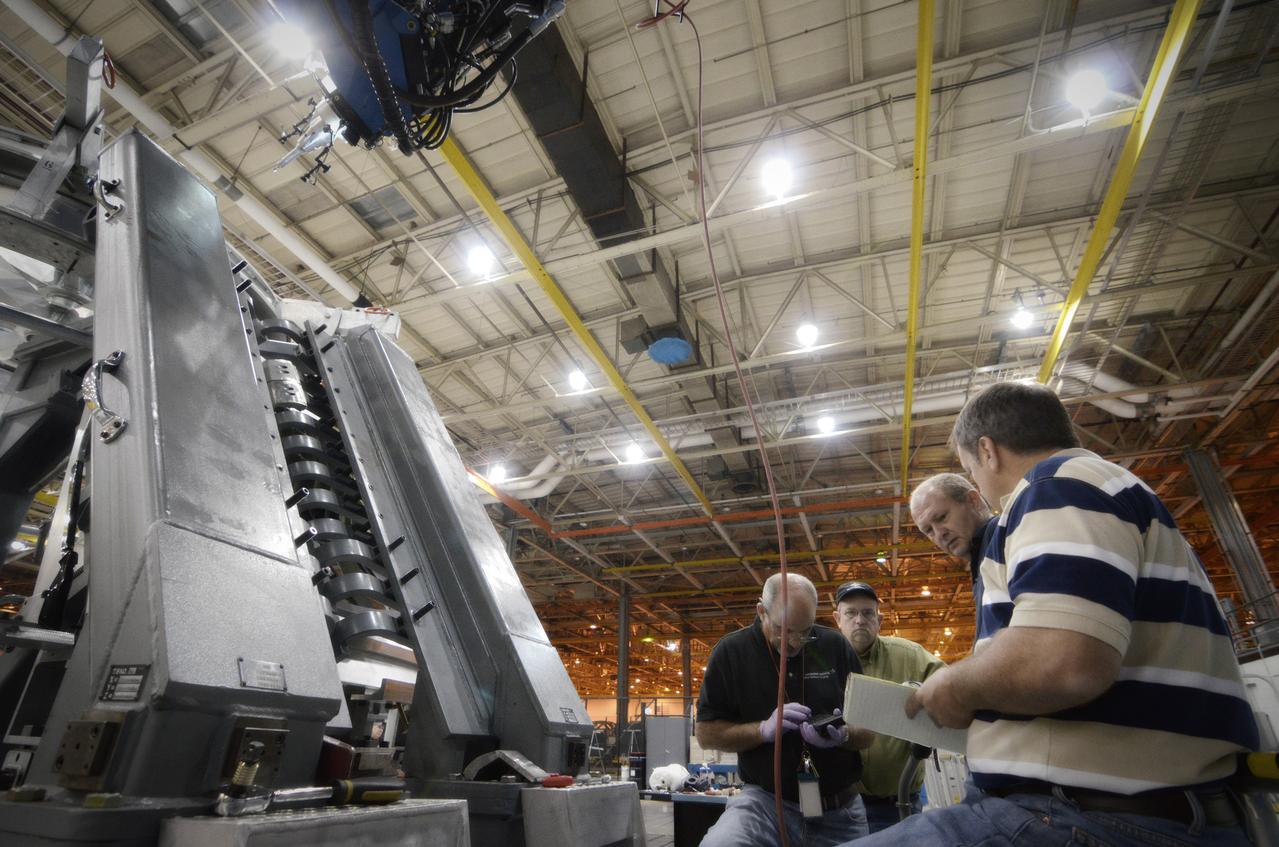

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
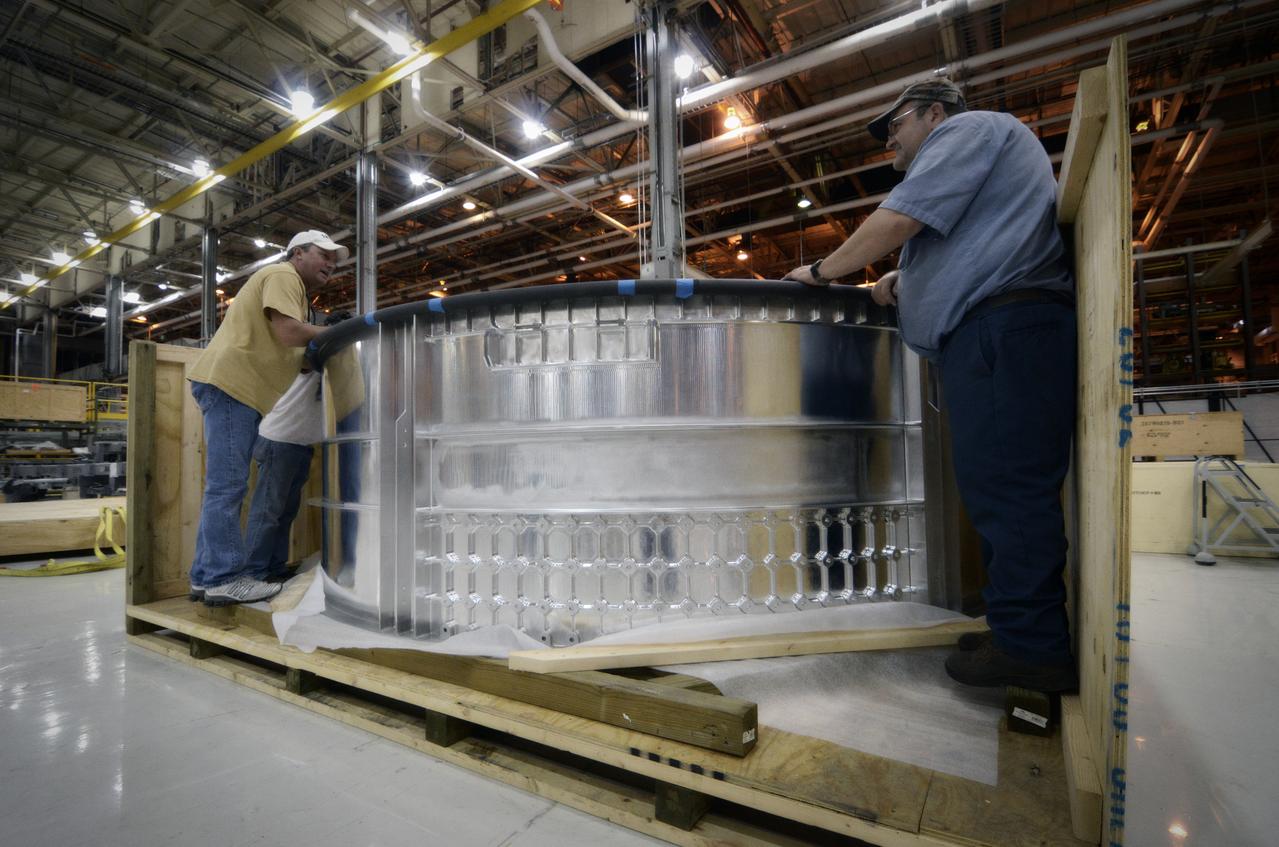

Elements for the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel are prepared for welding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 7, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
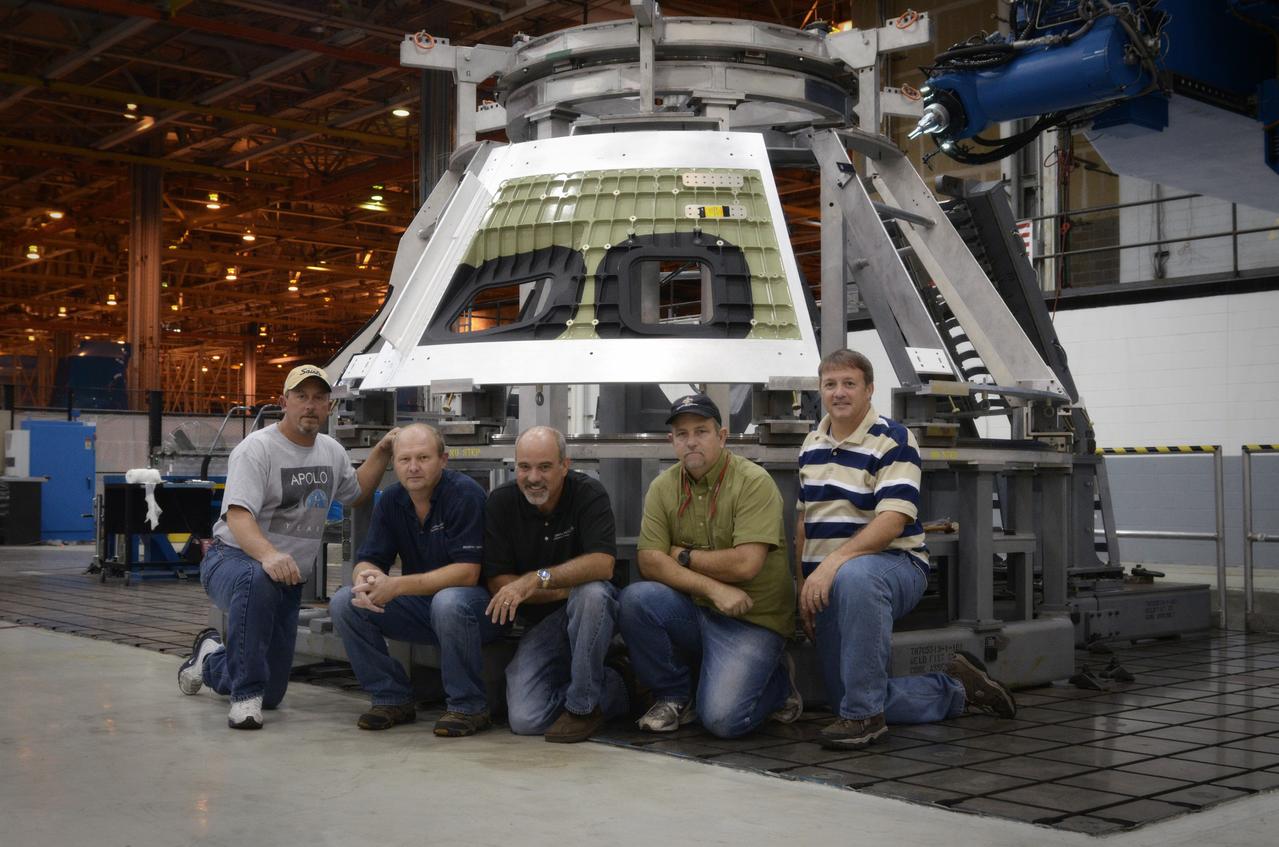

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
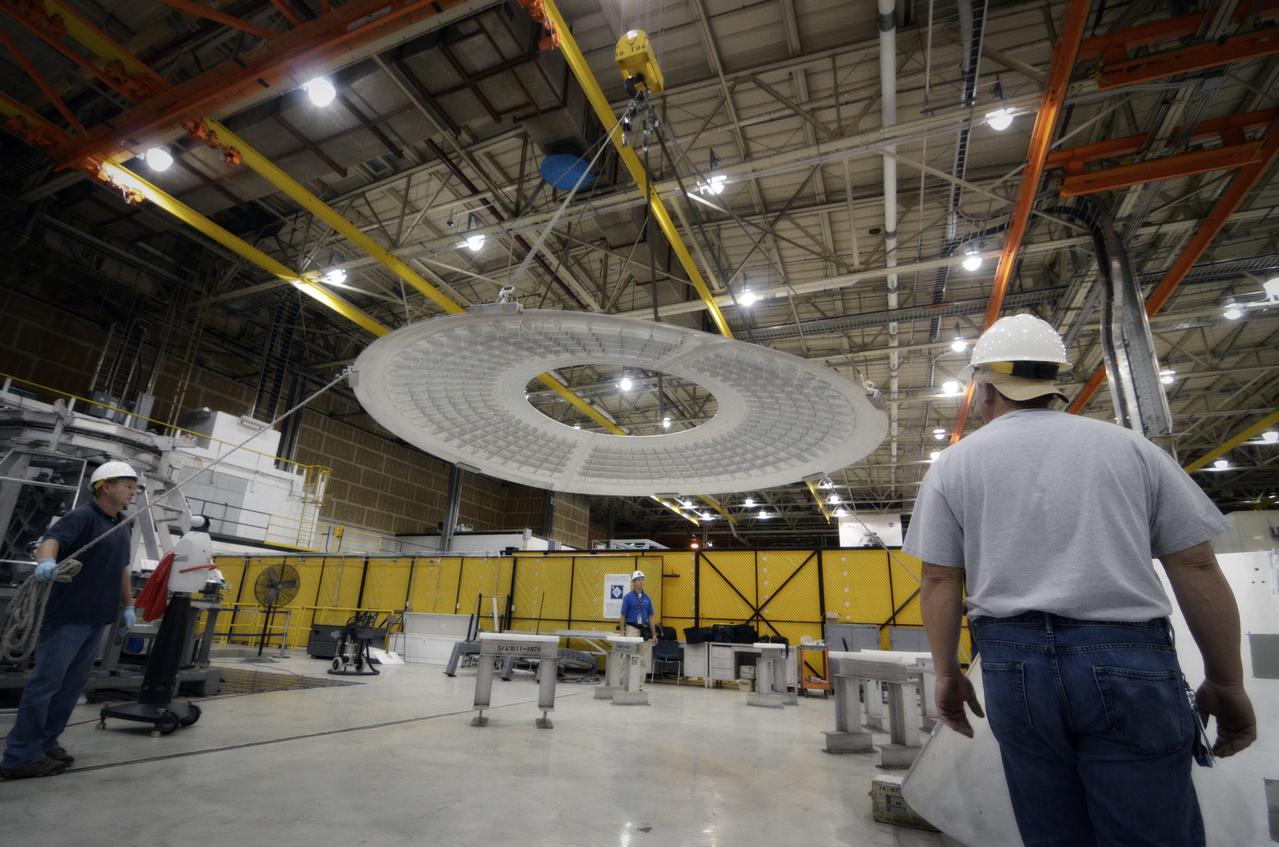

Elements for the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel are prepared for welding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 7, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
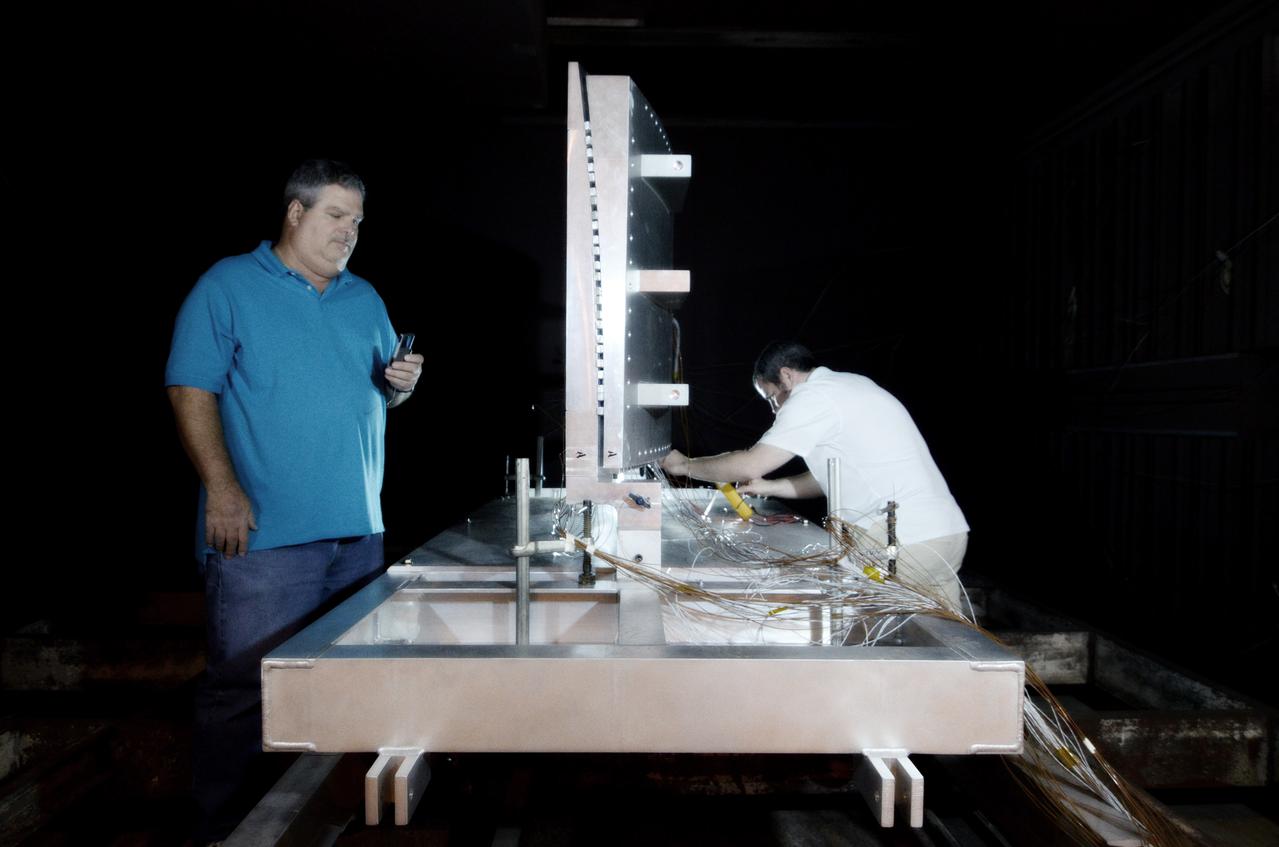
Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
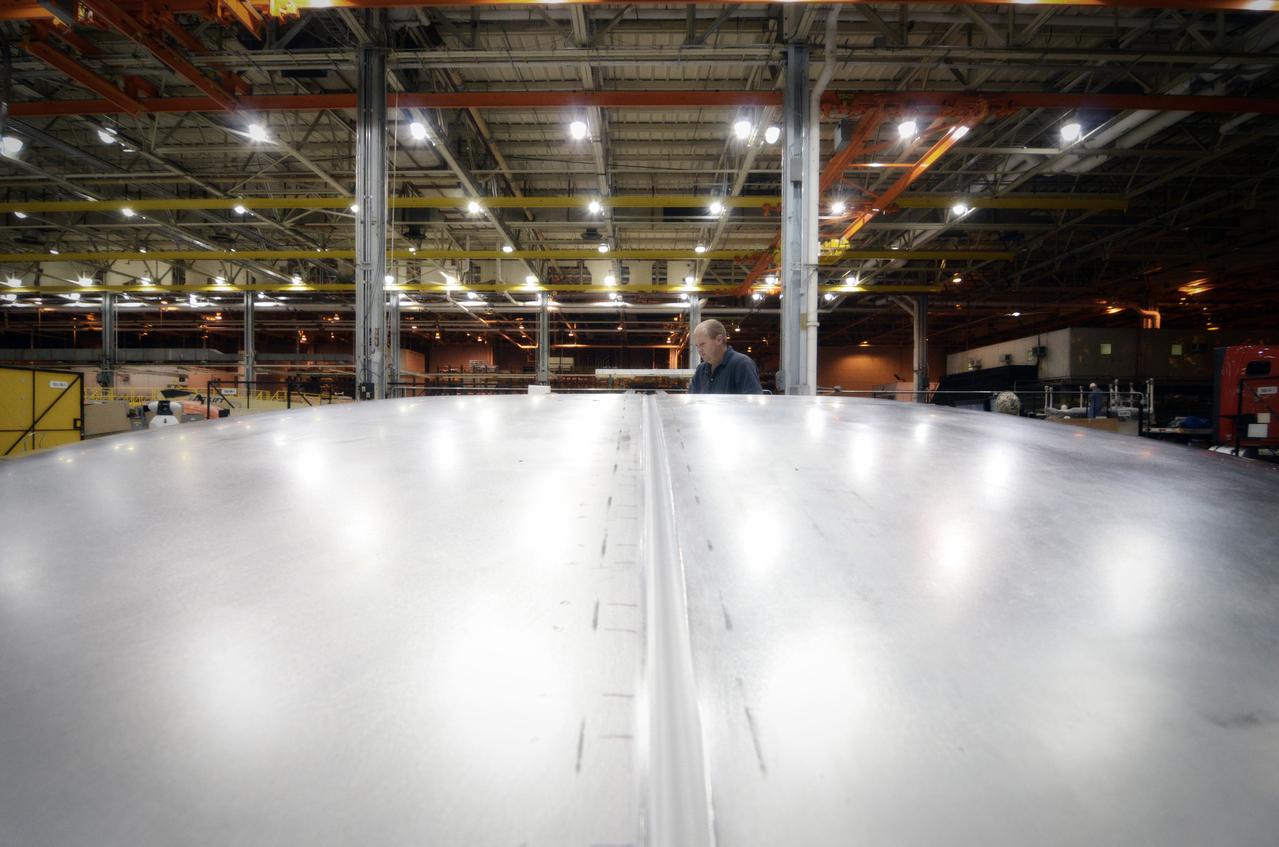

Elements for the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel are prepared for welding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 7, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
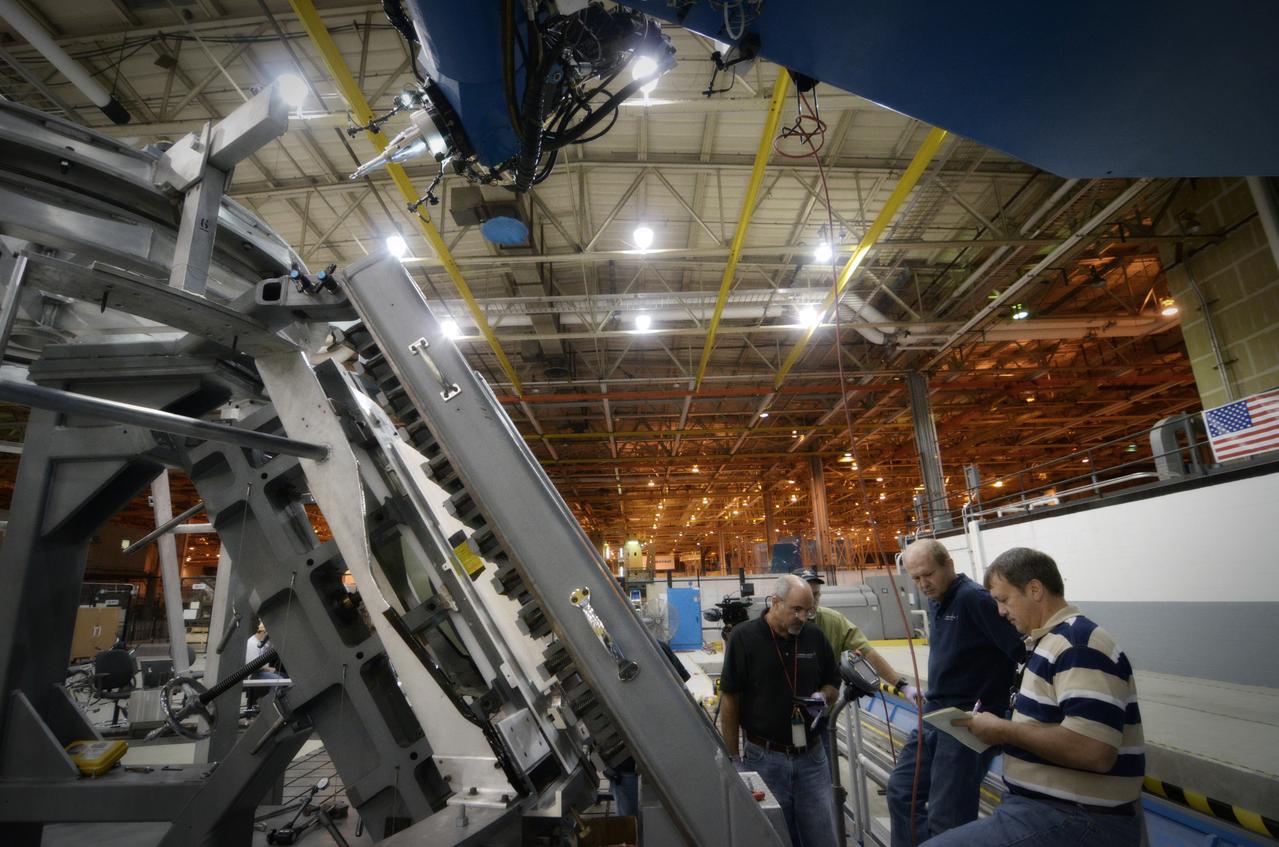

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
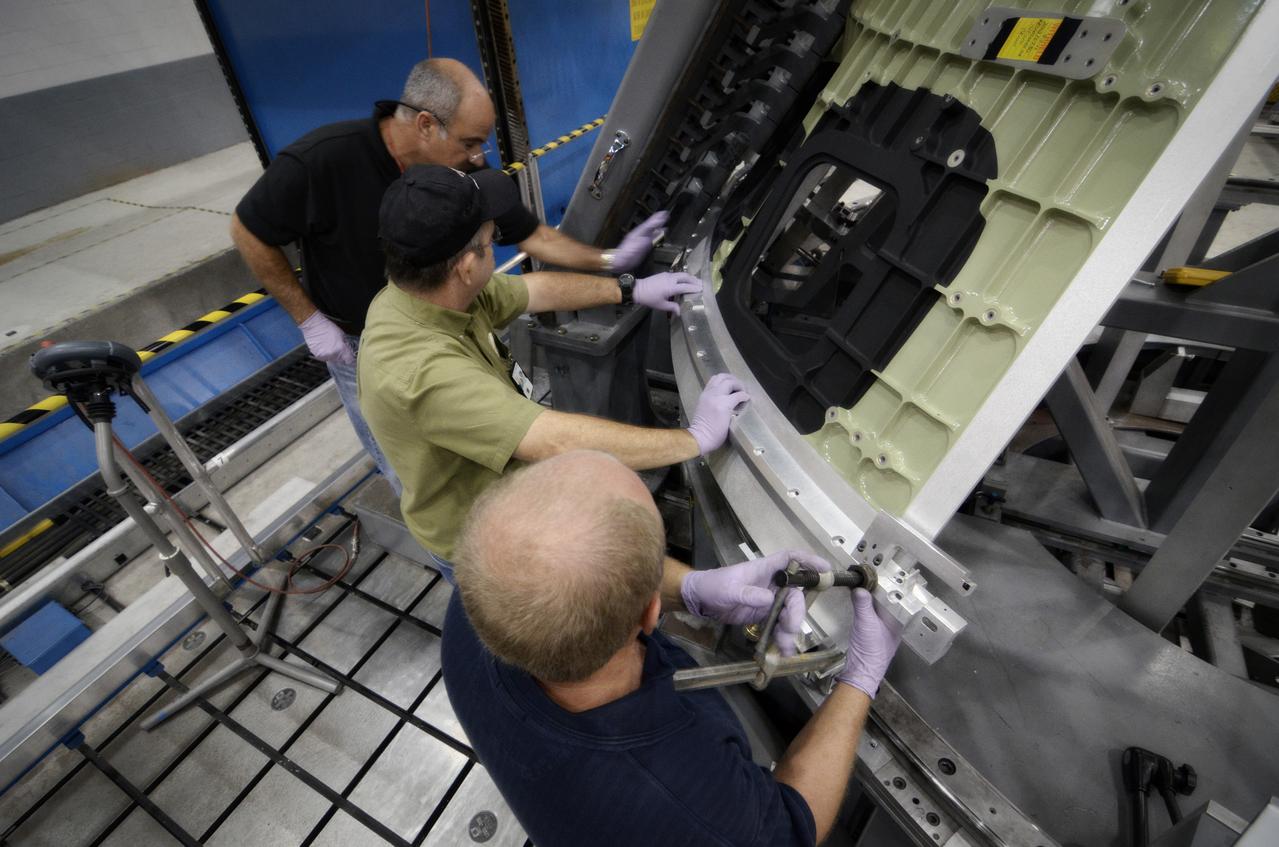

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
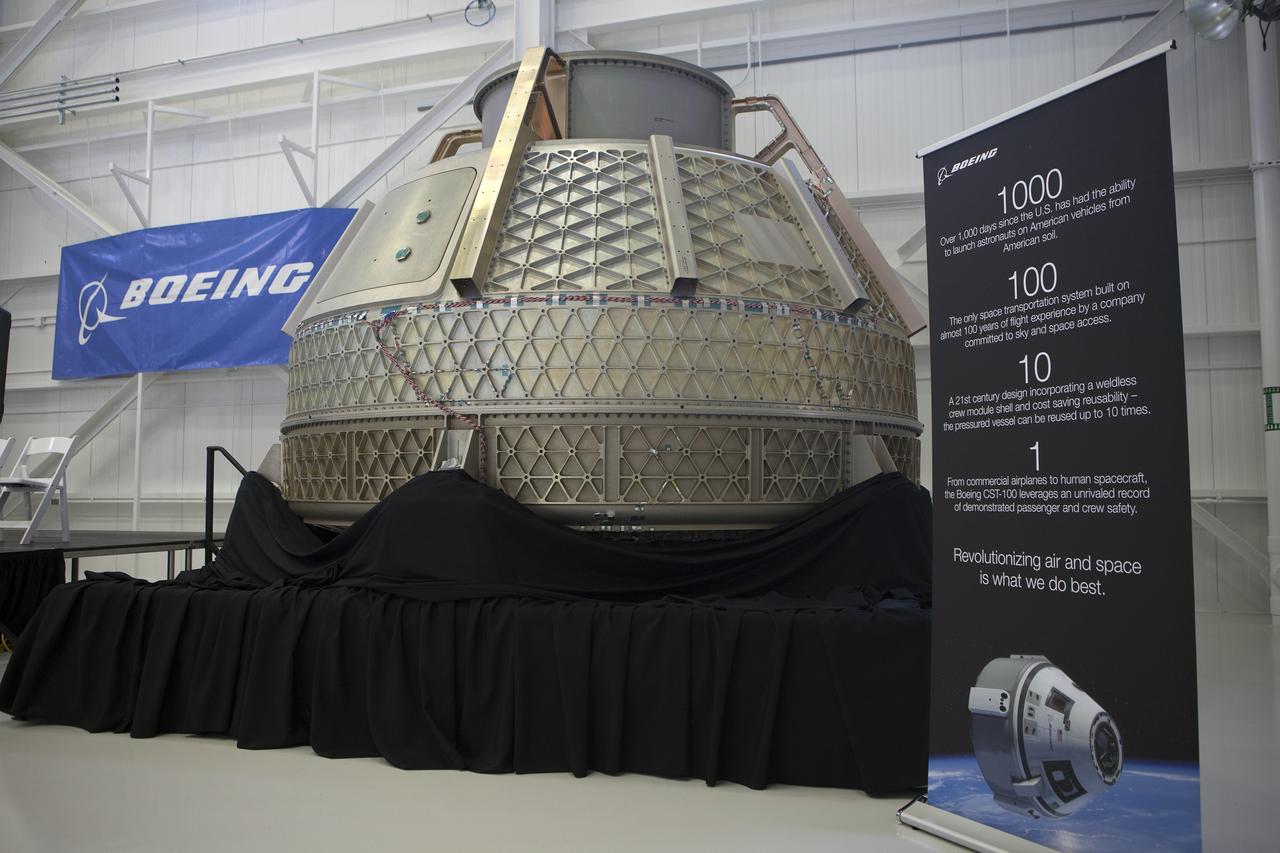

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The pressure vessel of The Boeing Company's CST-100 was displayed by the company during a ceremony inside Orbiter Processing Facility 3 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The pressure vessel is the shell of the finished spacecraft and encases the crew compartment and supplies on the inside. A heat shield and many other components are attached to the exterior to complete the spacecraft. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
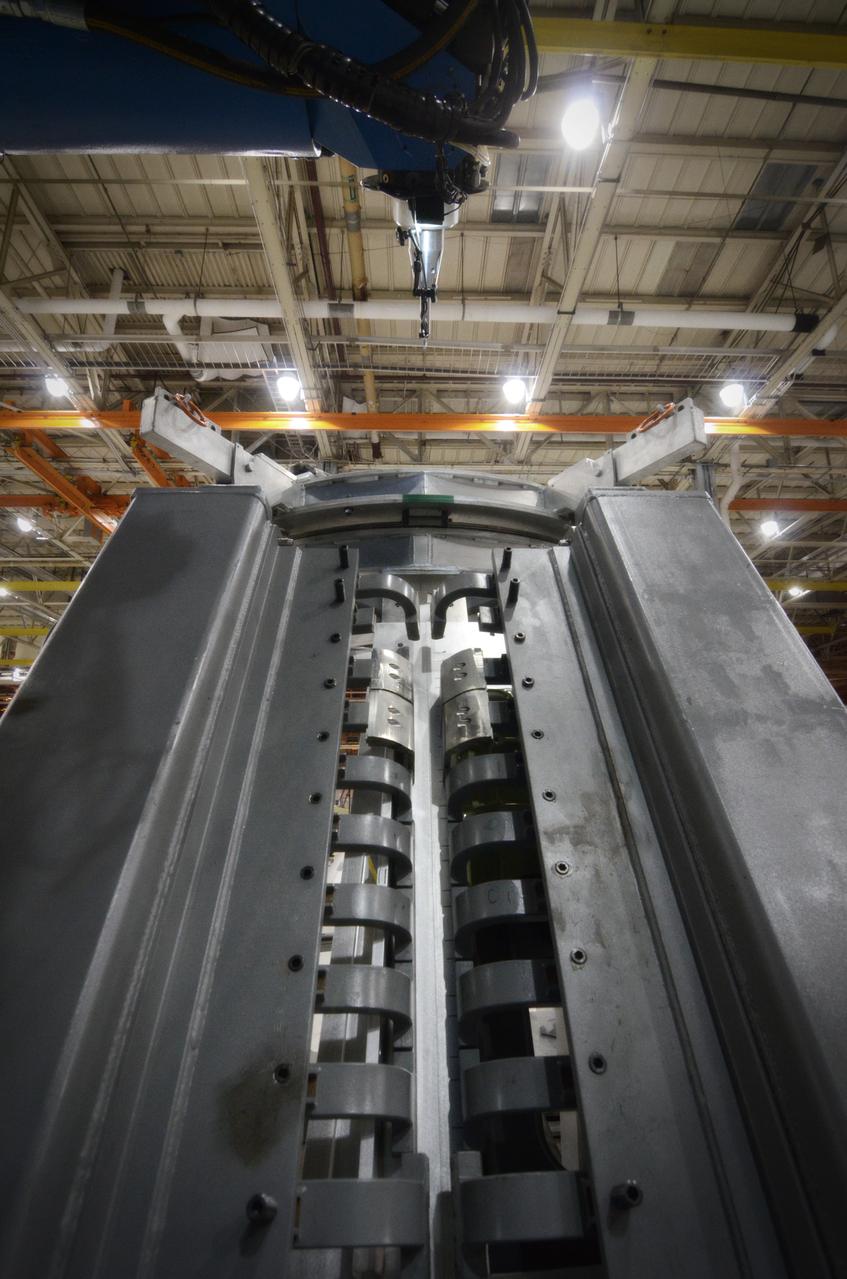

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
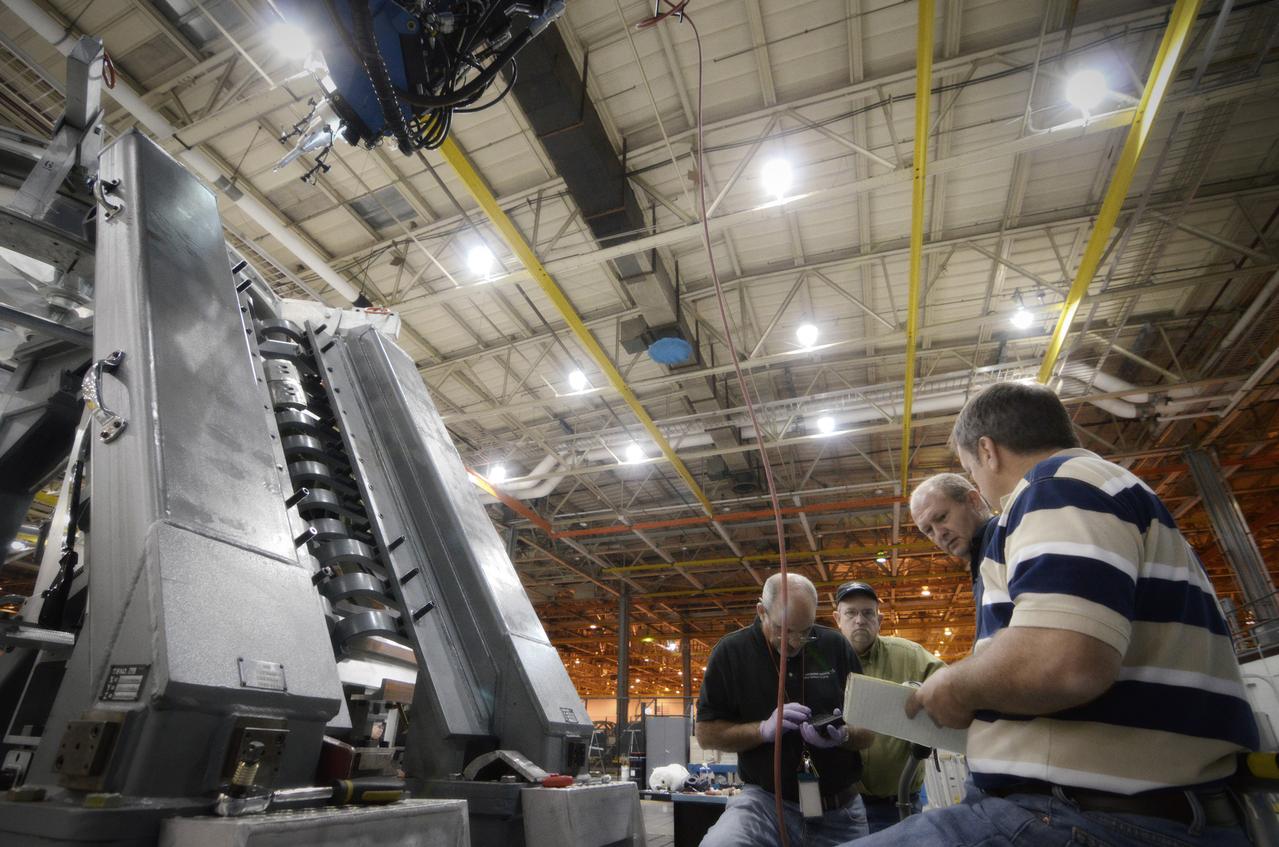

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
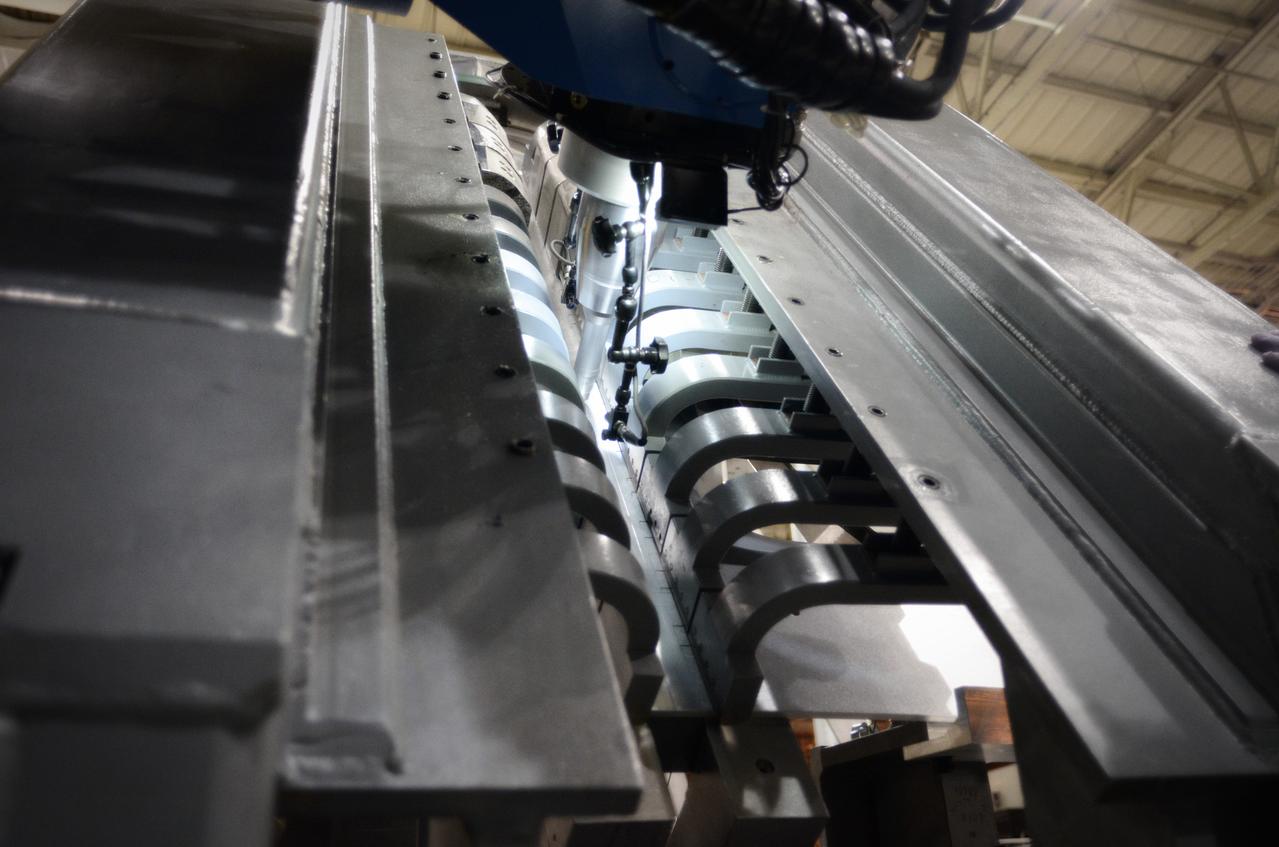

Technicians begin welding the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 9, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
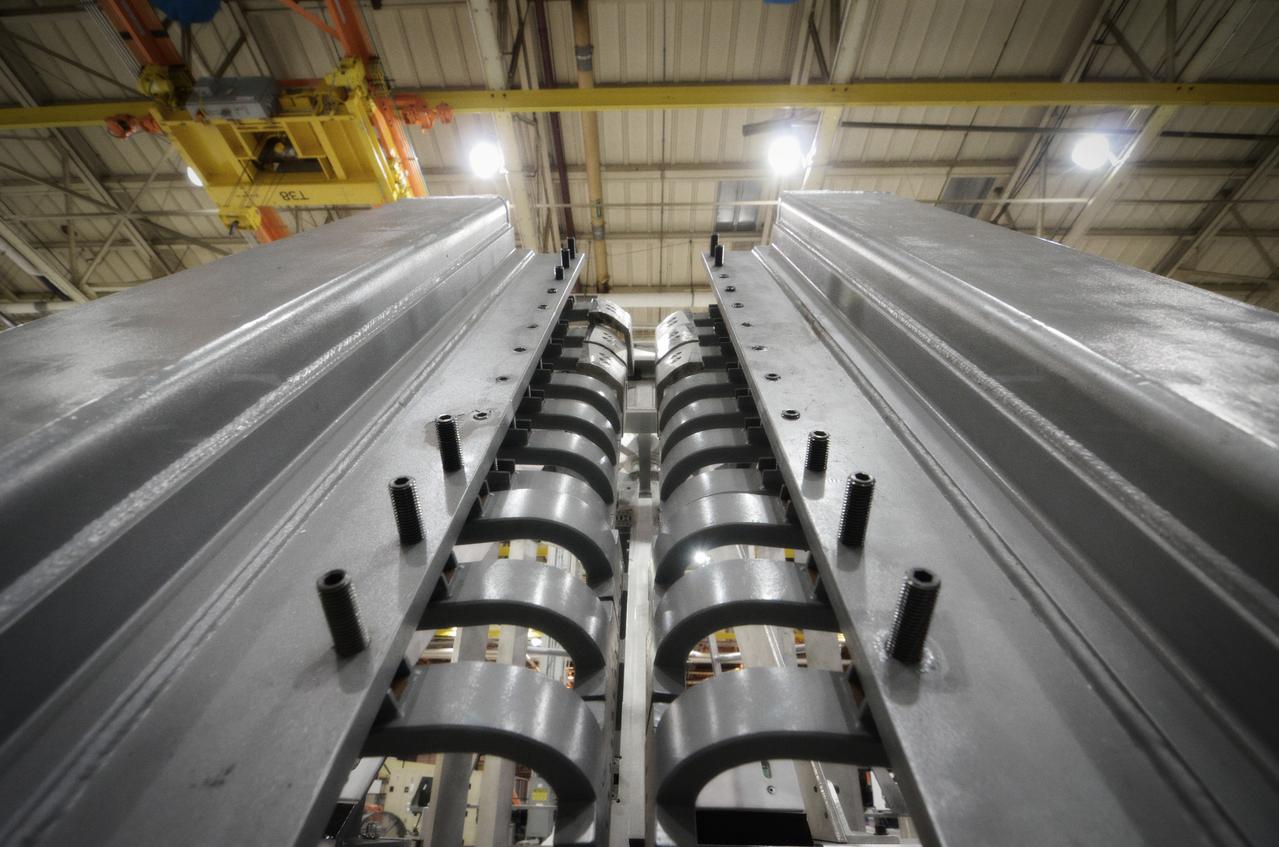

Elements for the Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) Orion pressure vessel are prepared for welding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Sept. 7, 2011. Orion’s pressure vessel is underlying frame of the crew module that will provide an air-tight, habitable space for astronauts on future missions to the Moon. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.