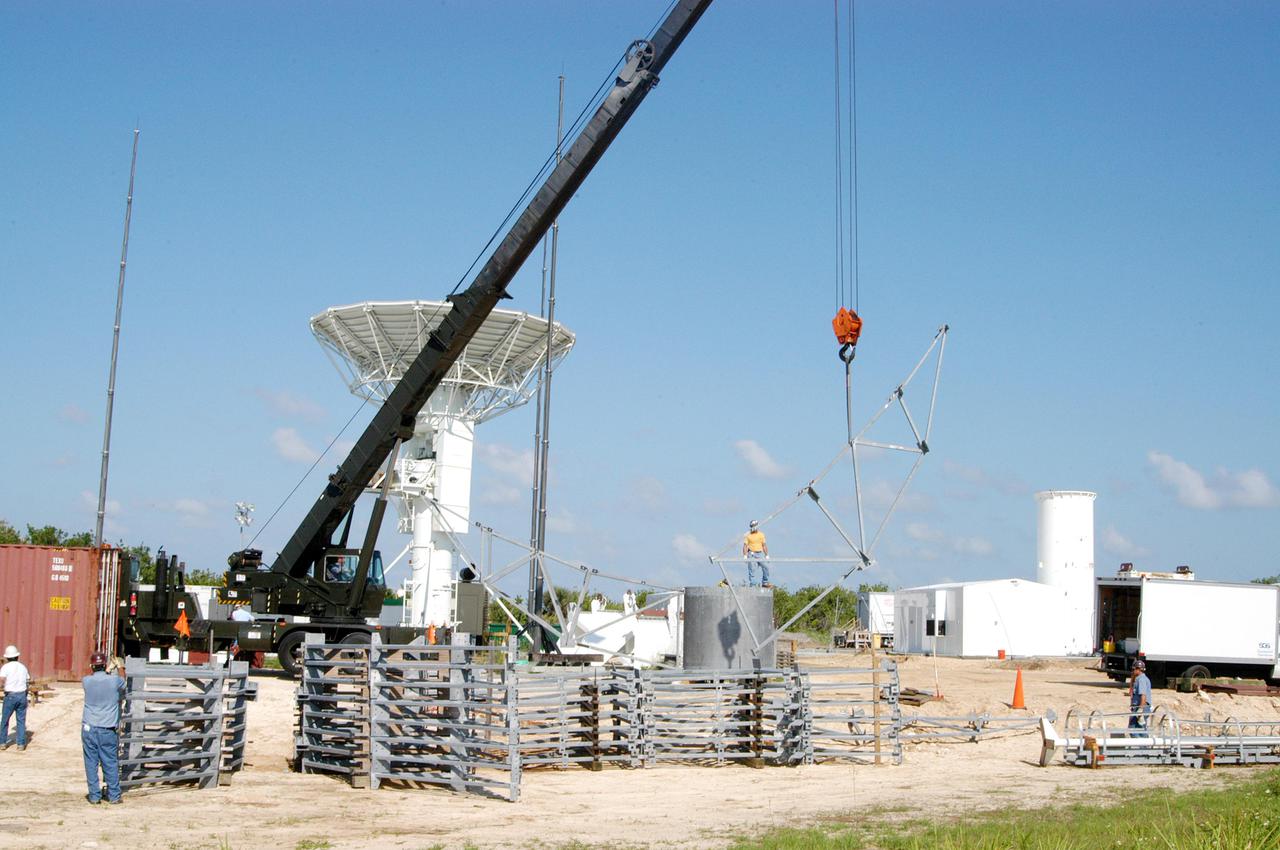

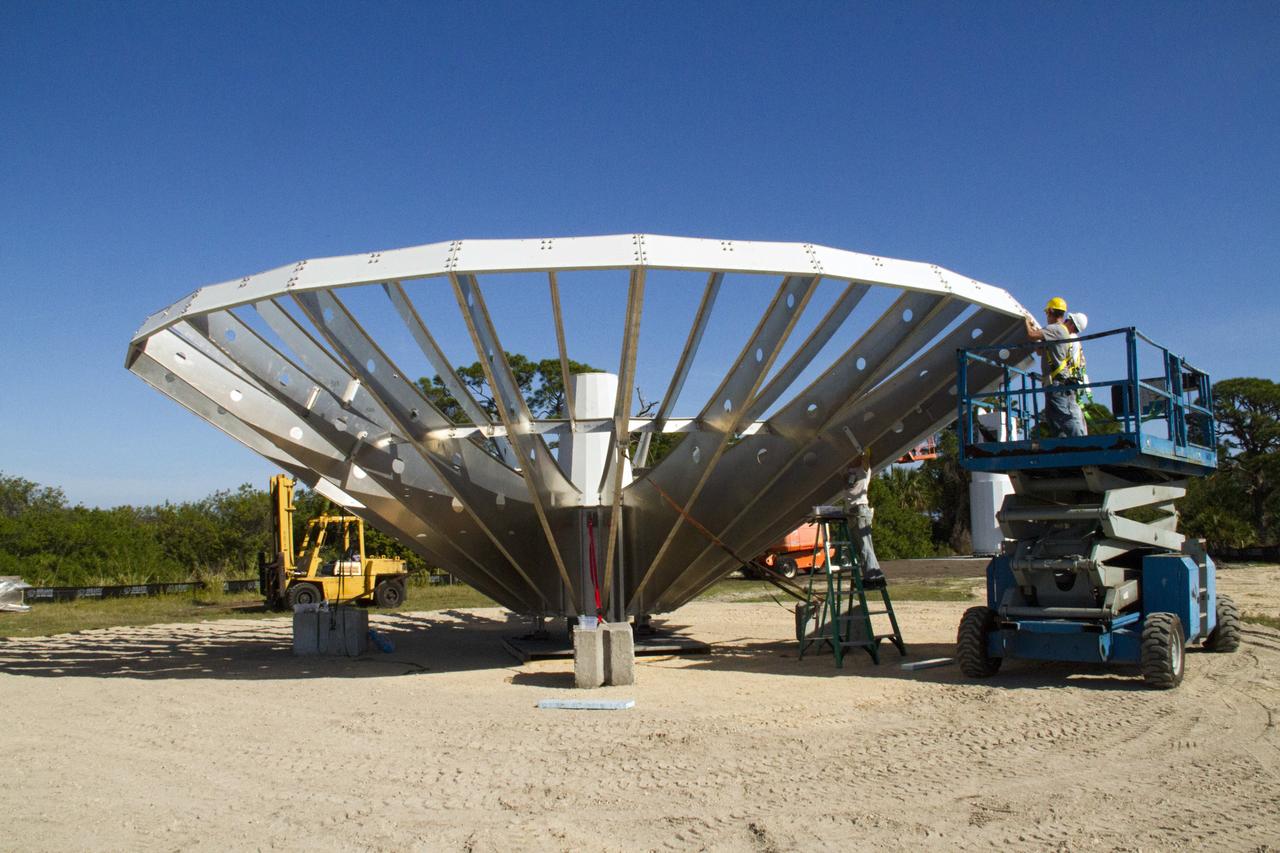
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, a 50-foot dish for NASA’s C-band radar is being assembled. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. Behind the dish is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31.

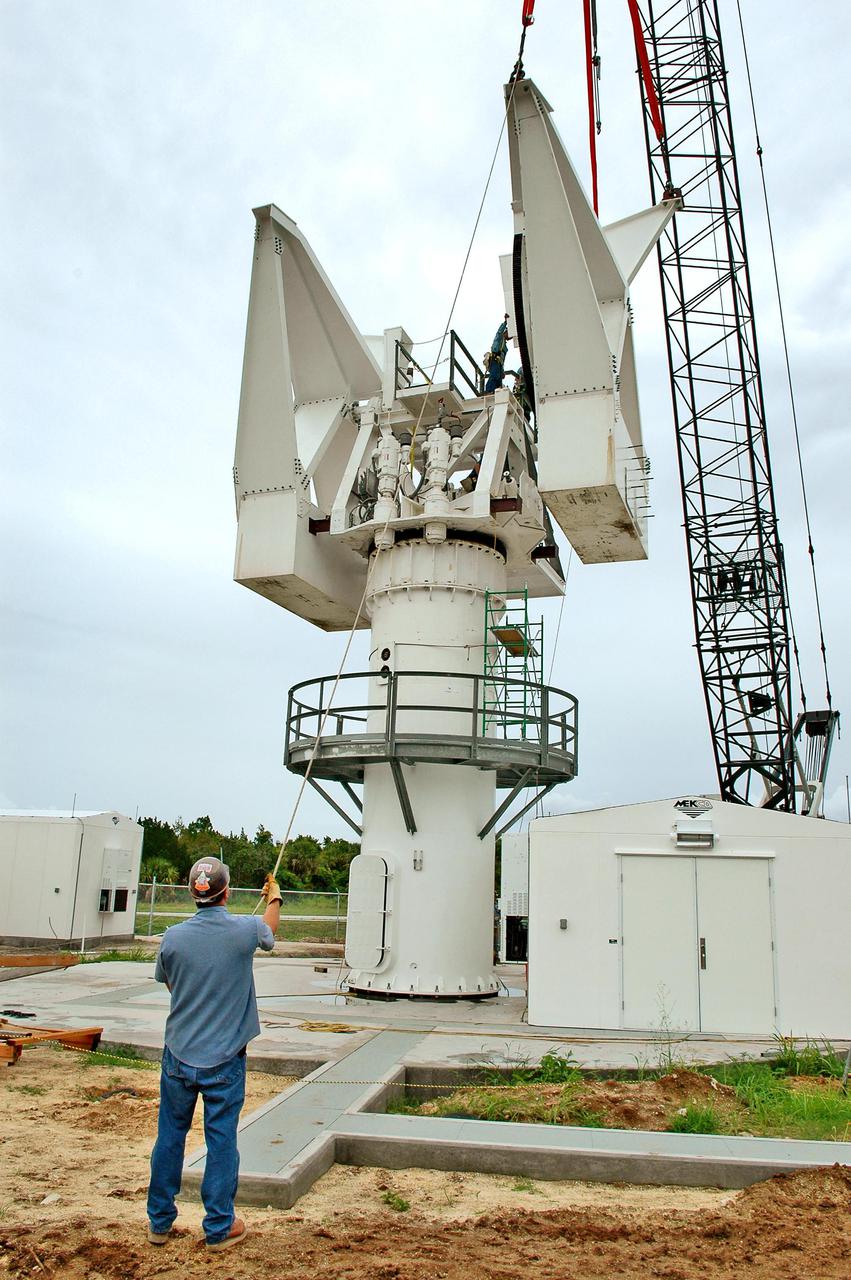
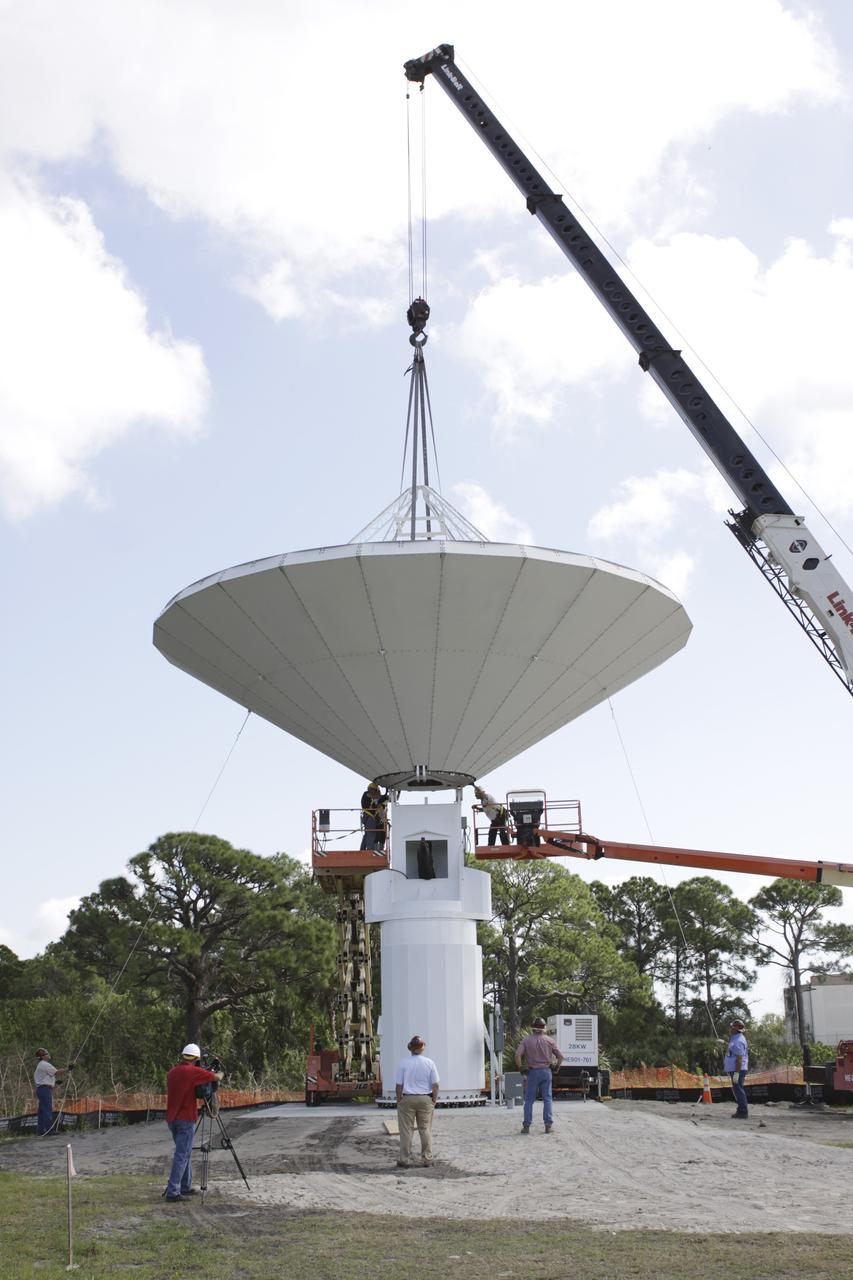
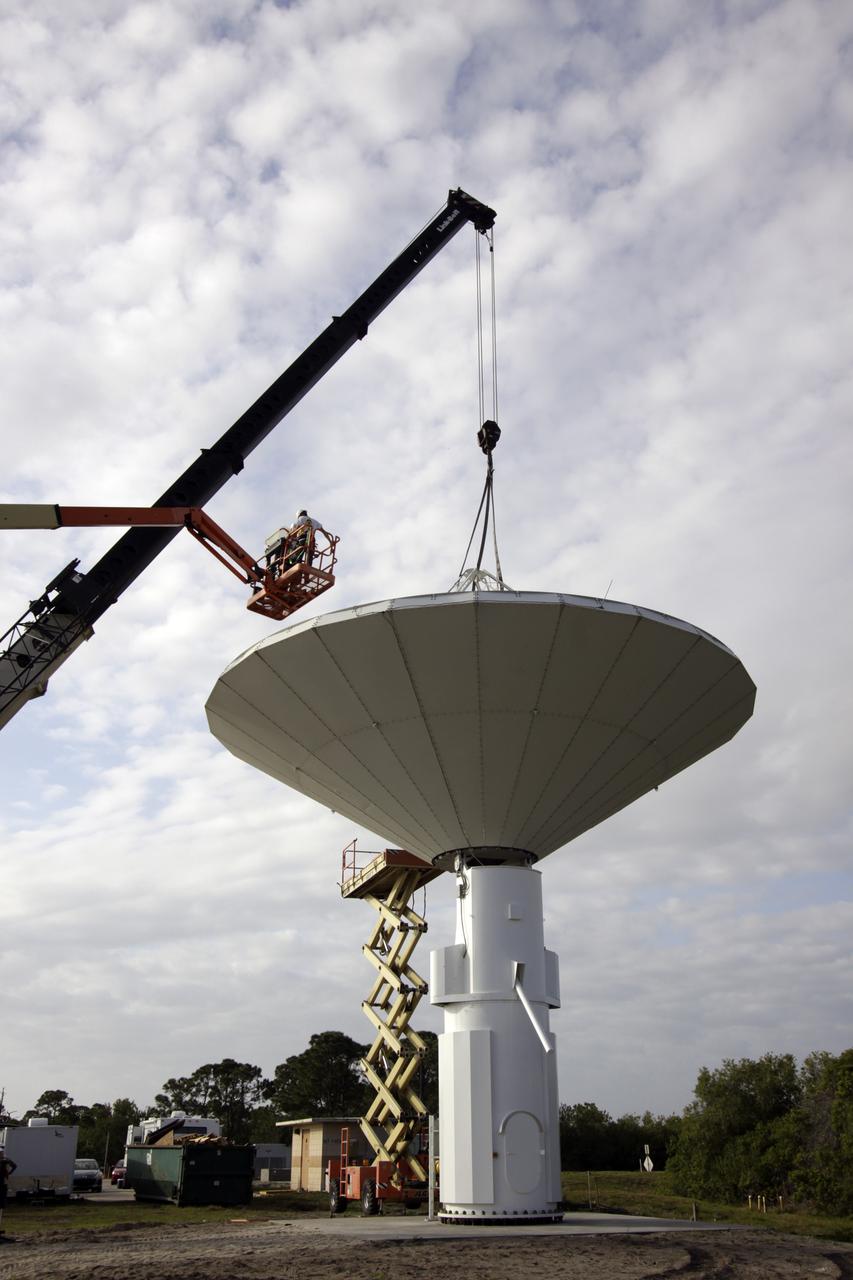
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lowered toward the top of the support structure. It will be placed on the counterweights installed there. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the second counterweight (right side) is lifted into place on the support structure for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
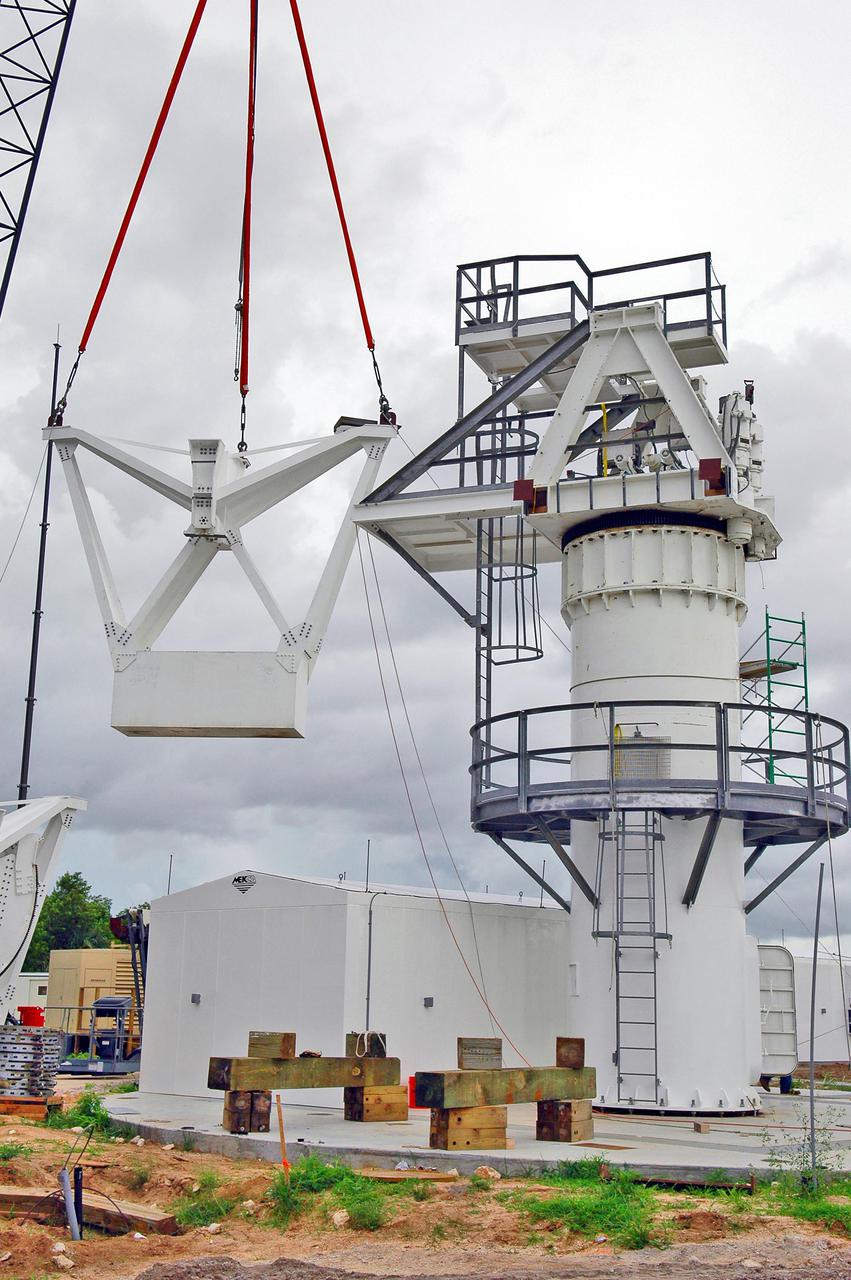

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., one of two counterweights is being lifted for installation on a support structure (right) for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
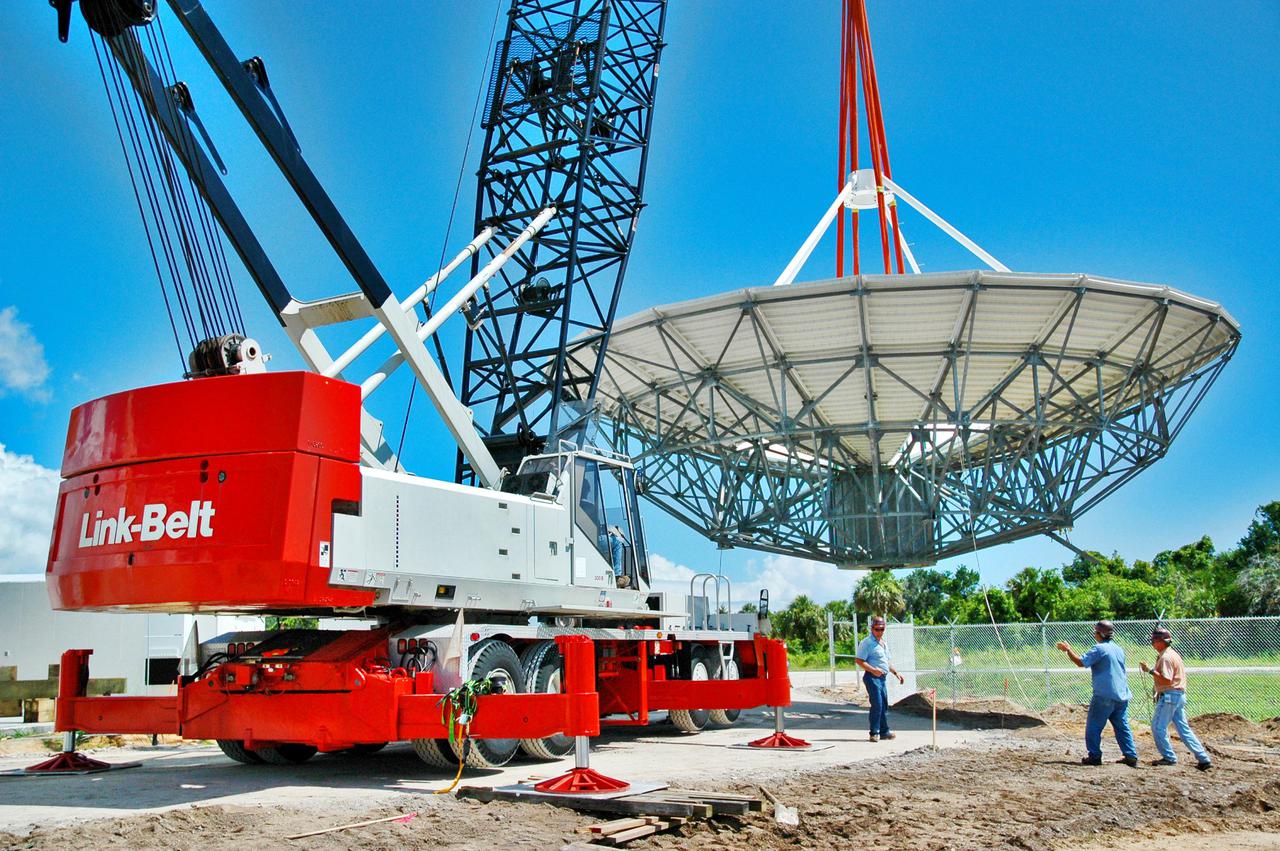

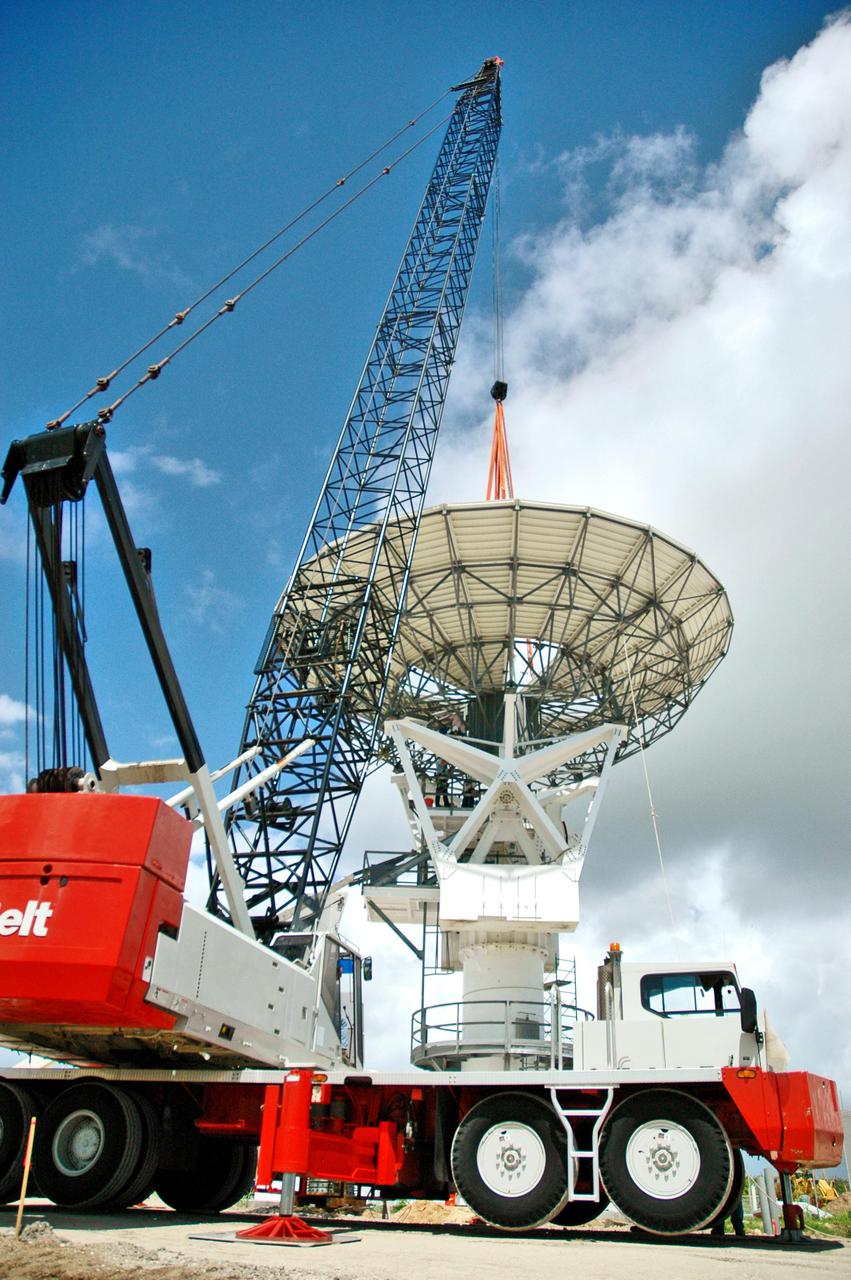
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lifted off the ground. It will be placed onto the top of a support structure.The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
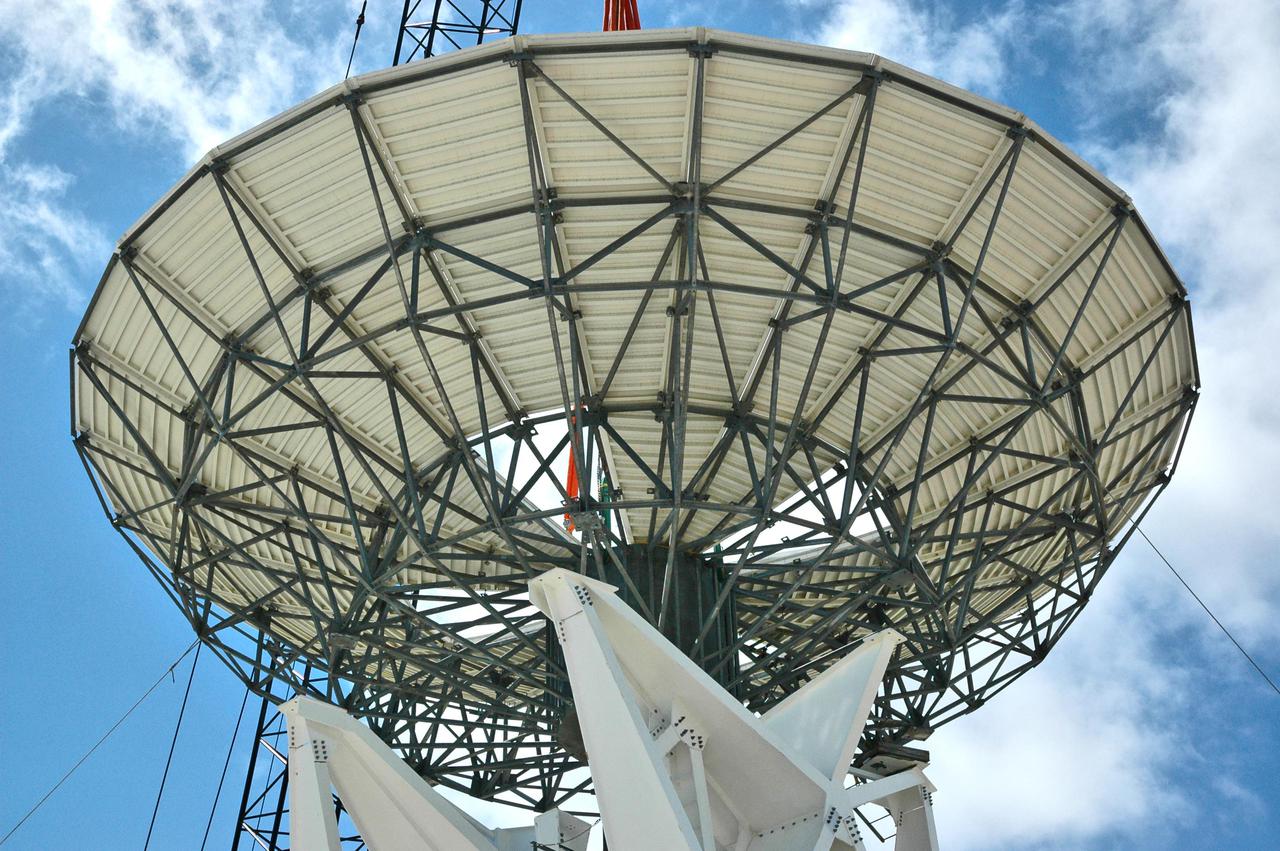

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lowered toward the top of the support structure. It will be placed on the counterweights installed there. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
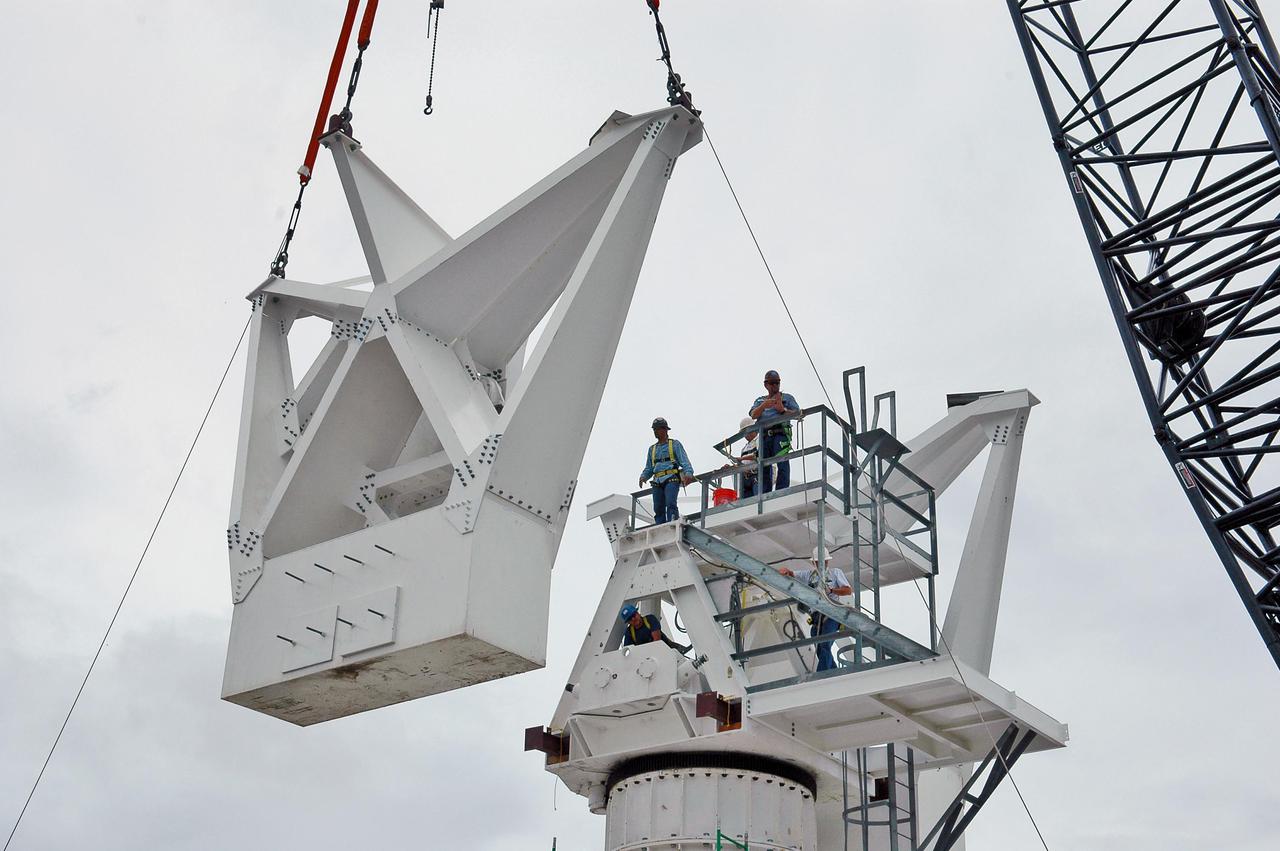

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the second counterweight is being lifted for installation on the support structure (right) for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
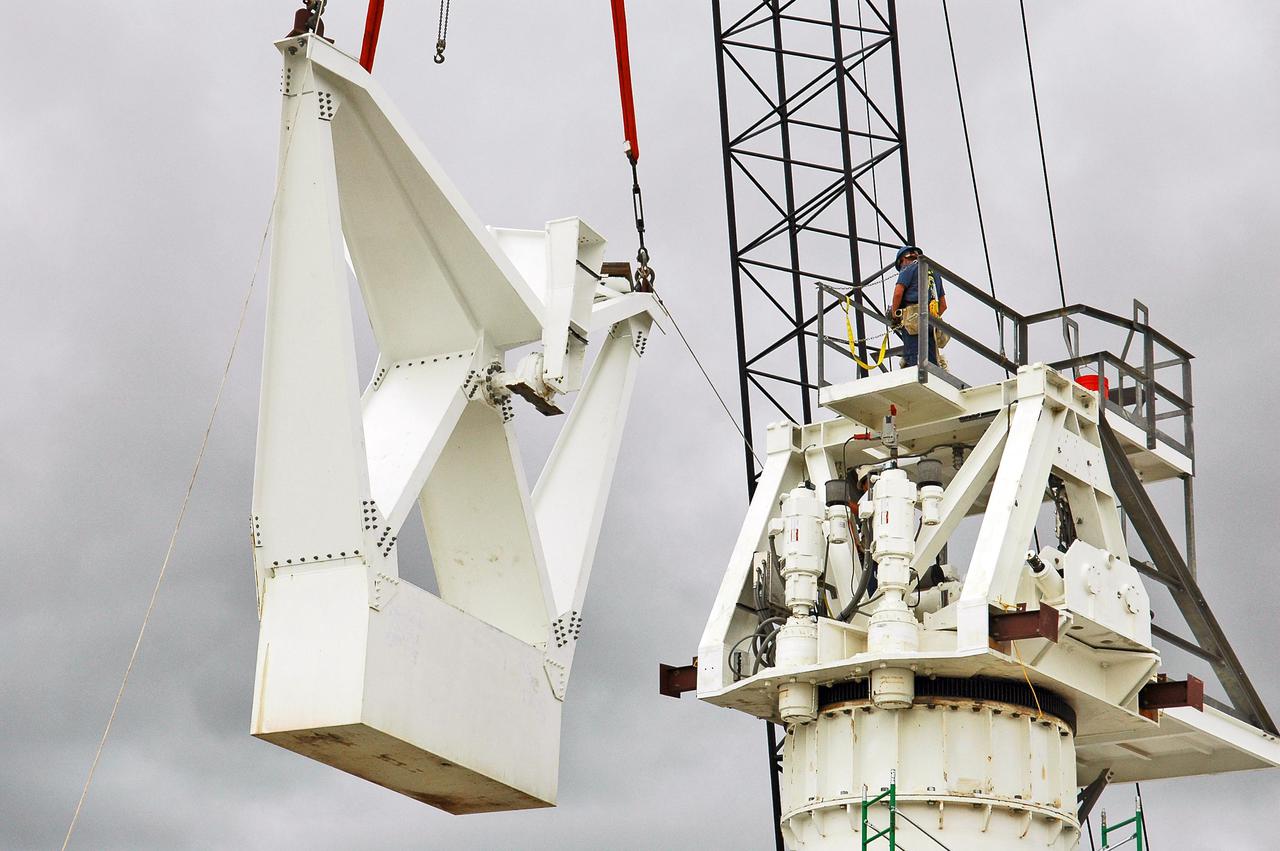

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., one of two counterweights is being lifted for installation on a support structure (right) for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
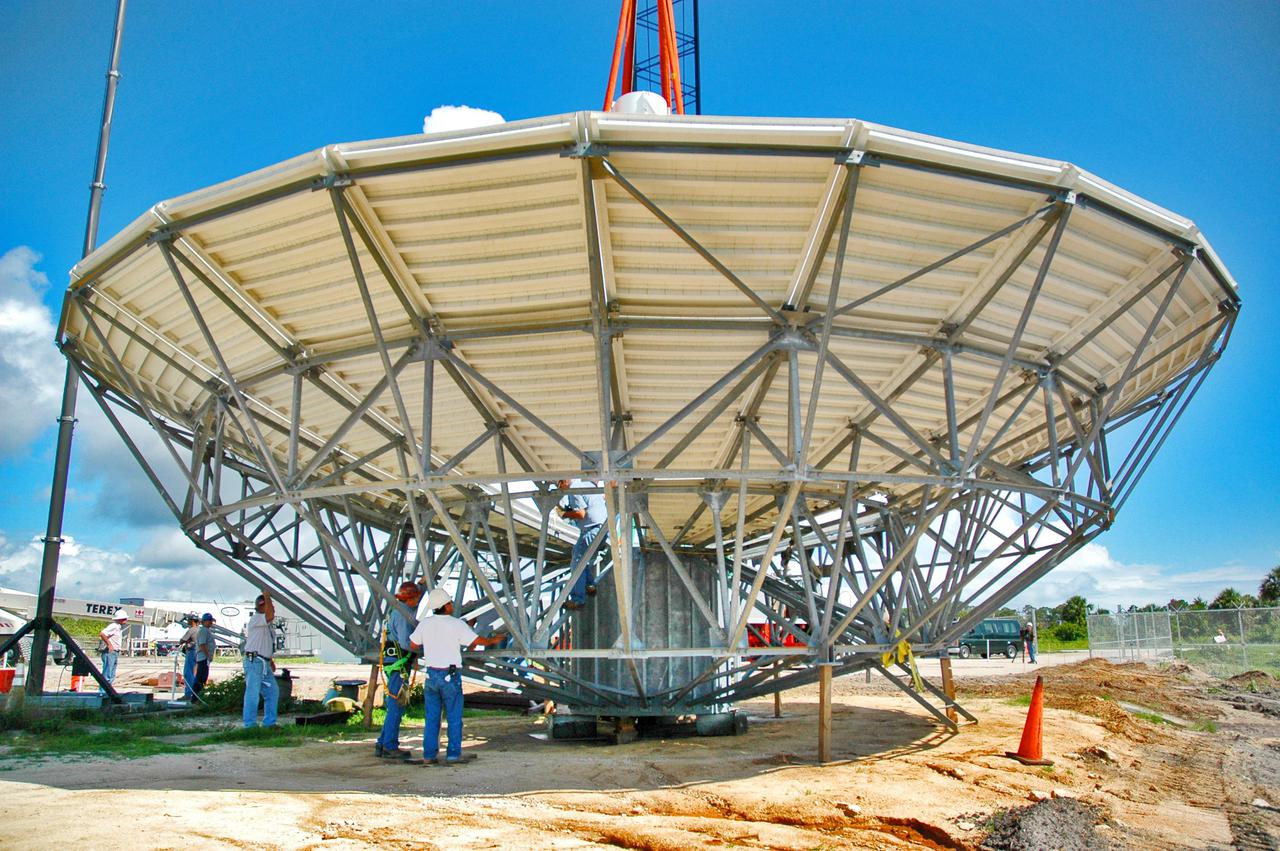

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is prepared to be lifted onto the top of a support structure. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
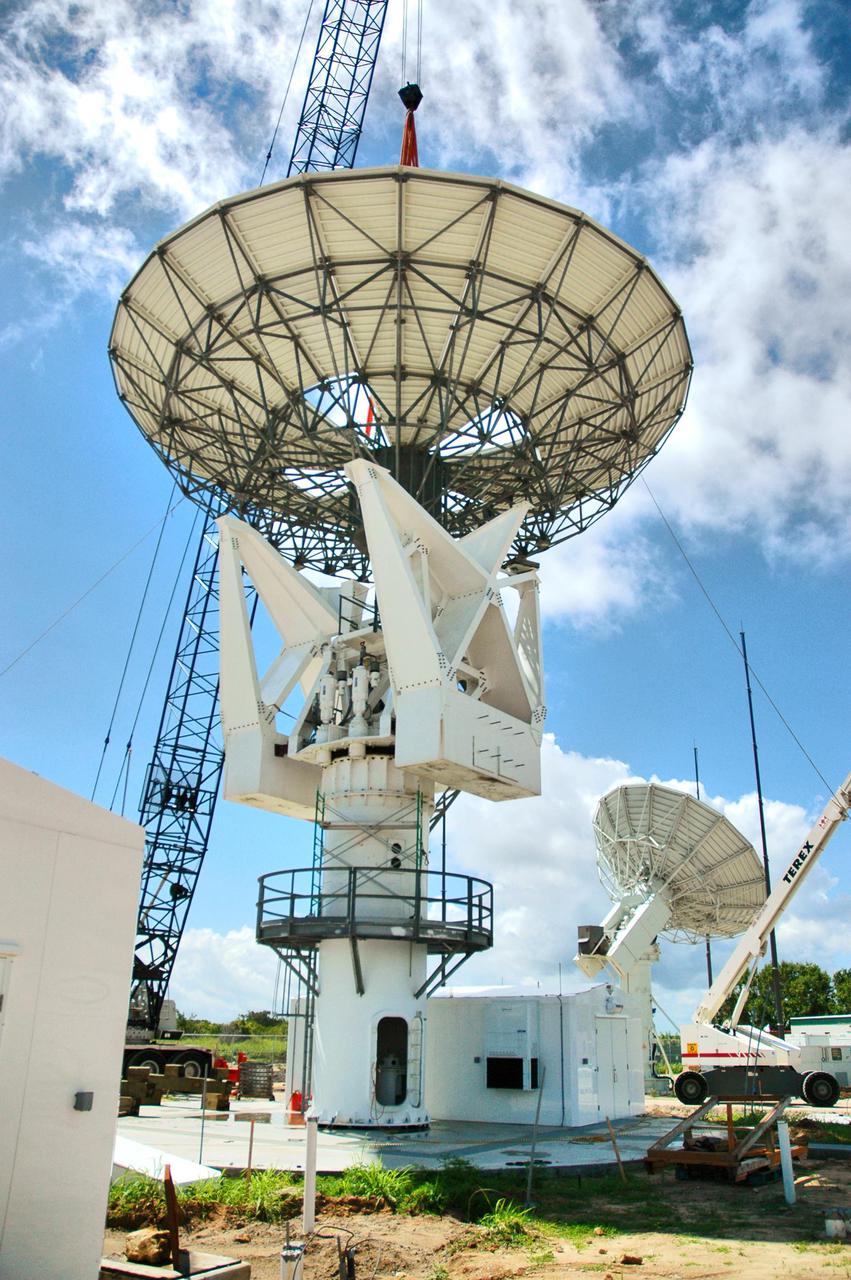

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lowered toward the top of the support structure. It will be placed on the counterweights installed there. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
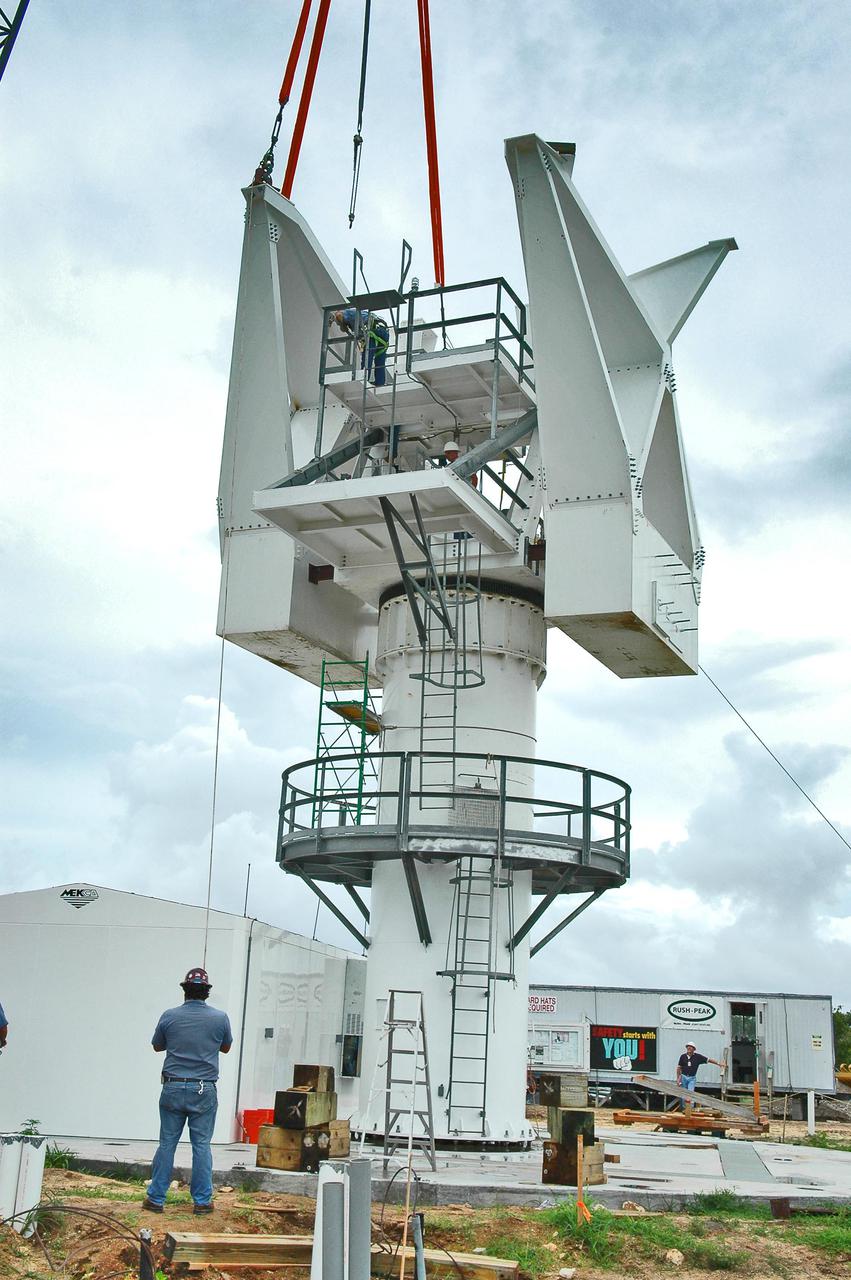

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the second counterweight (left side) is moved into place on the support structure for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
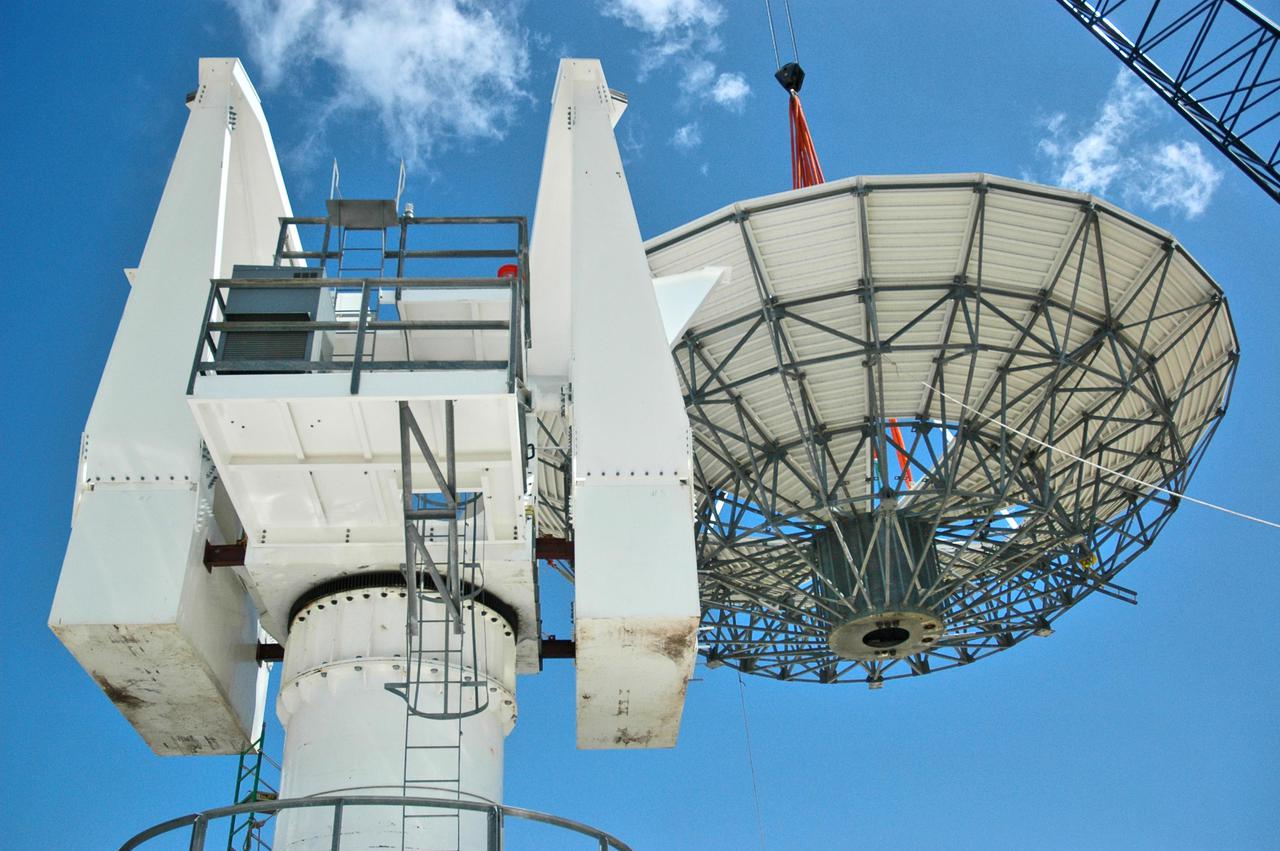

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lifted above the support structure, where it will be installed on top. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
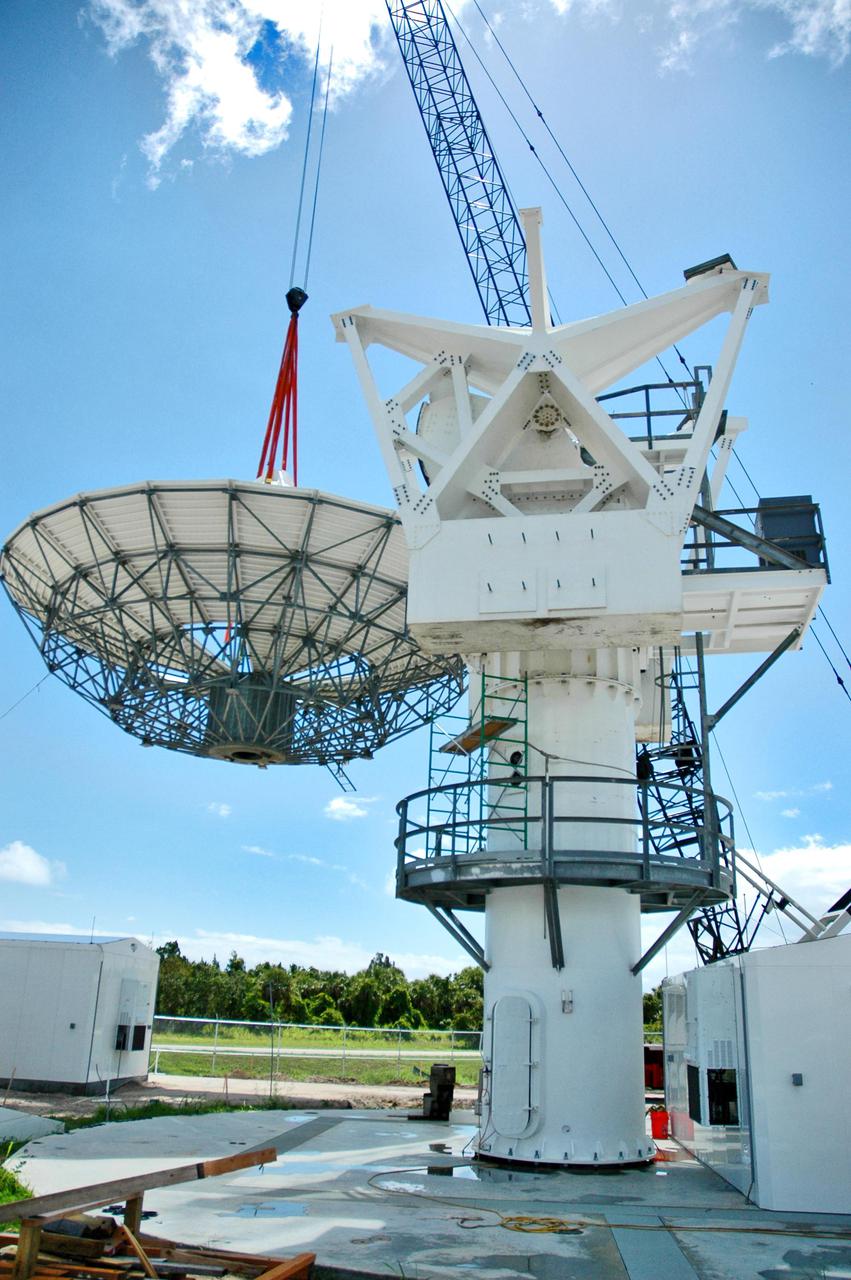

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., the 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish is lifted next to the support structure, where it will be installed on top. It will be placed onto the top of a support structure.The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
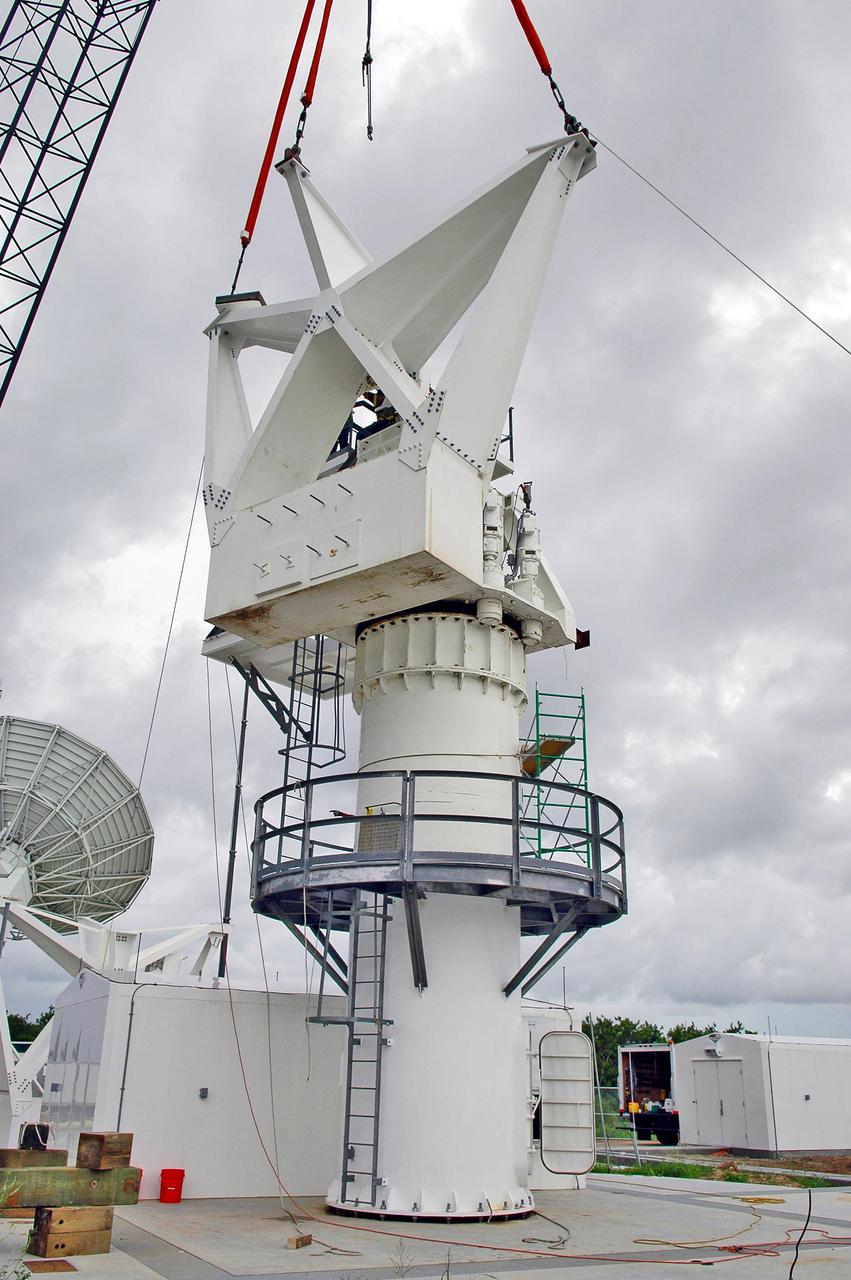

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., one of two counterweights is lifted into place on a support structure for a 50-foot C-band radar antenna dish. The radar will be used for Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. It will be used for the first time on STS-114. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission is July 13 to July 31.
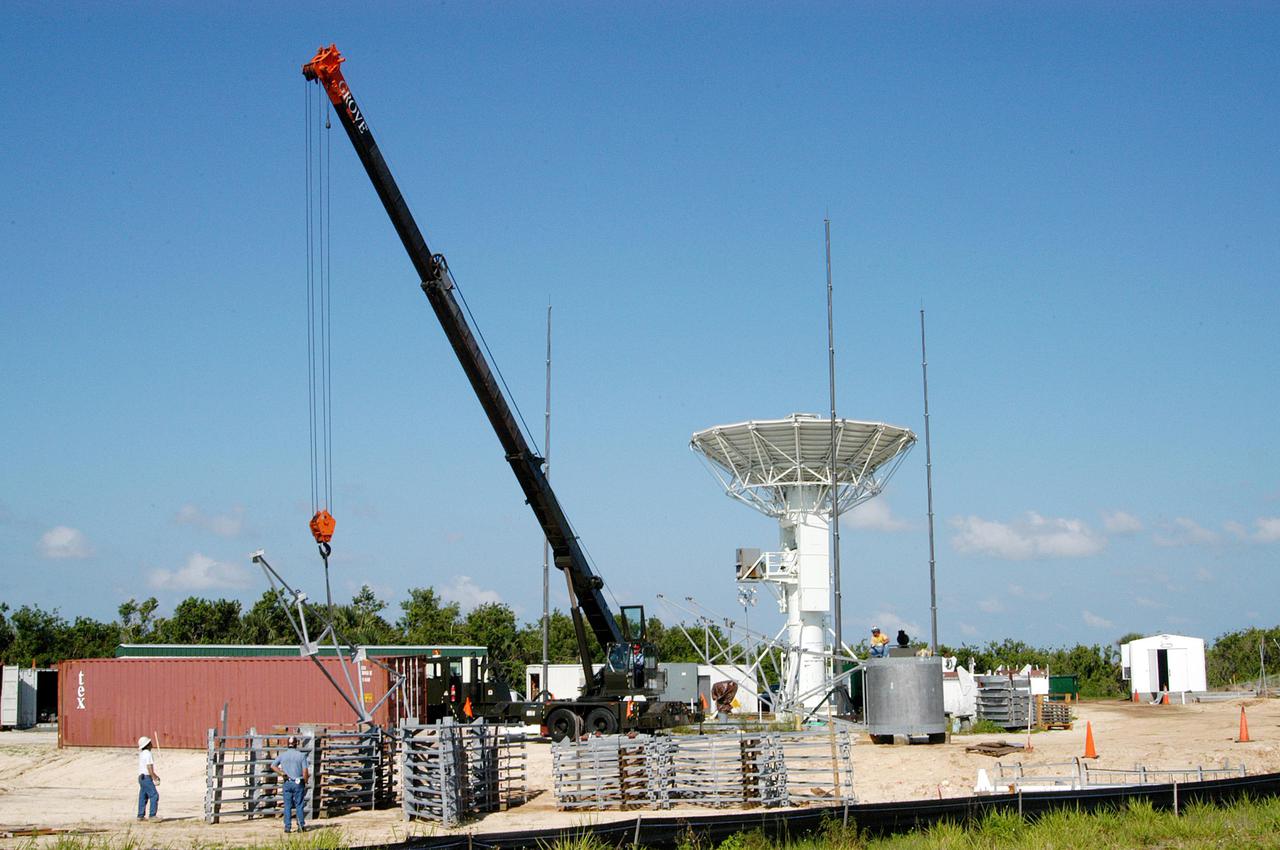

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, a 50-foot dish for NASA’s C-band radar is being assembled. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. In the background is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31.
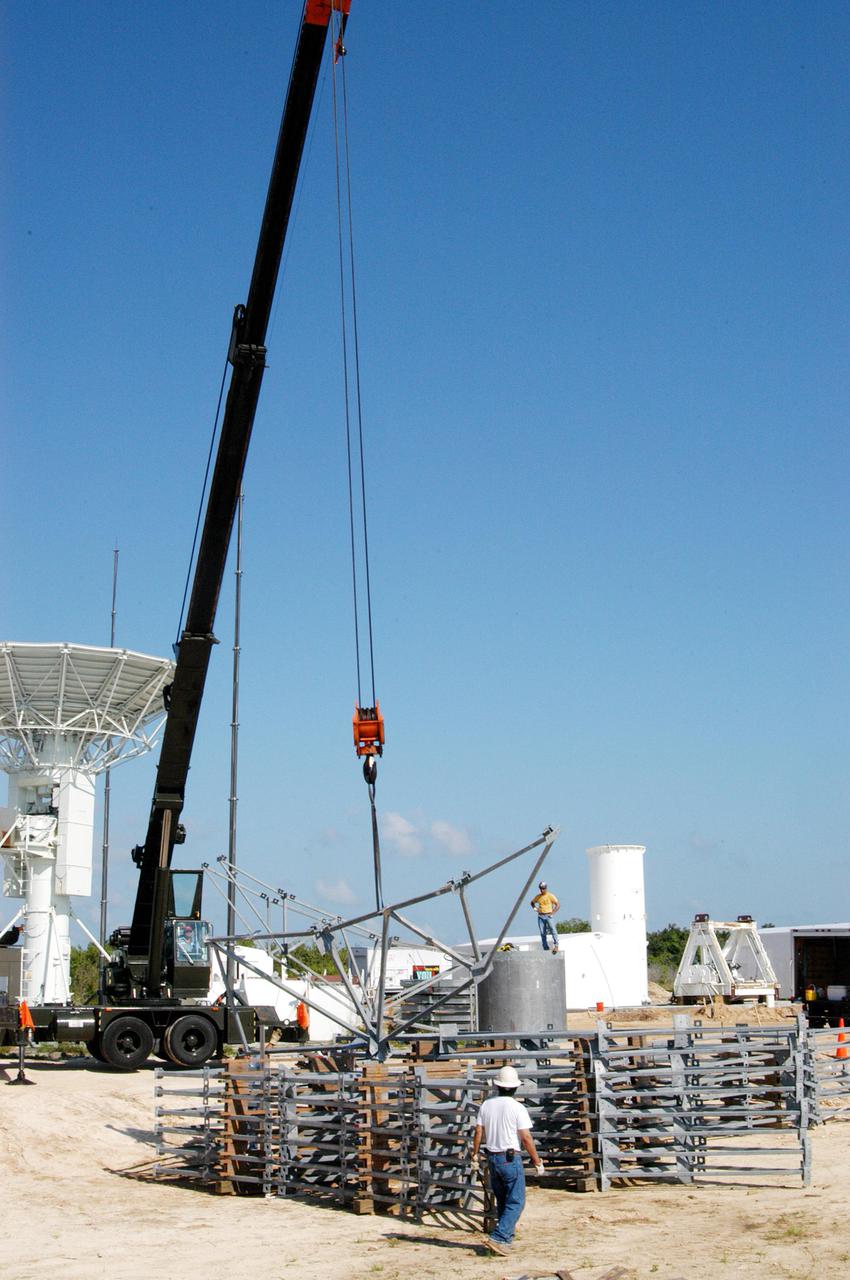

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, a 50-foot dish for NASA’s C-band radar is being assembled. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. At left is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31.
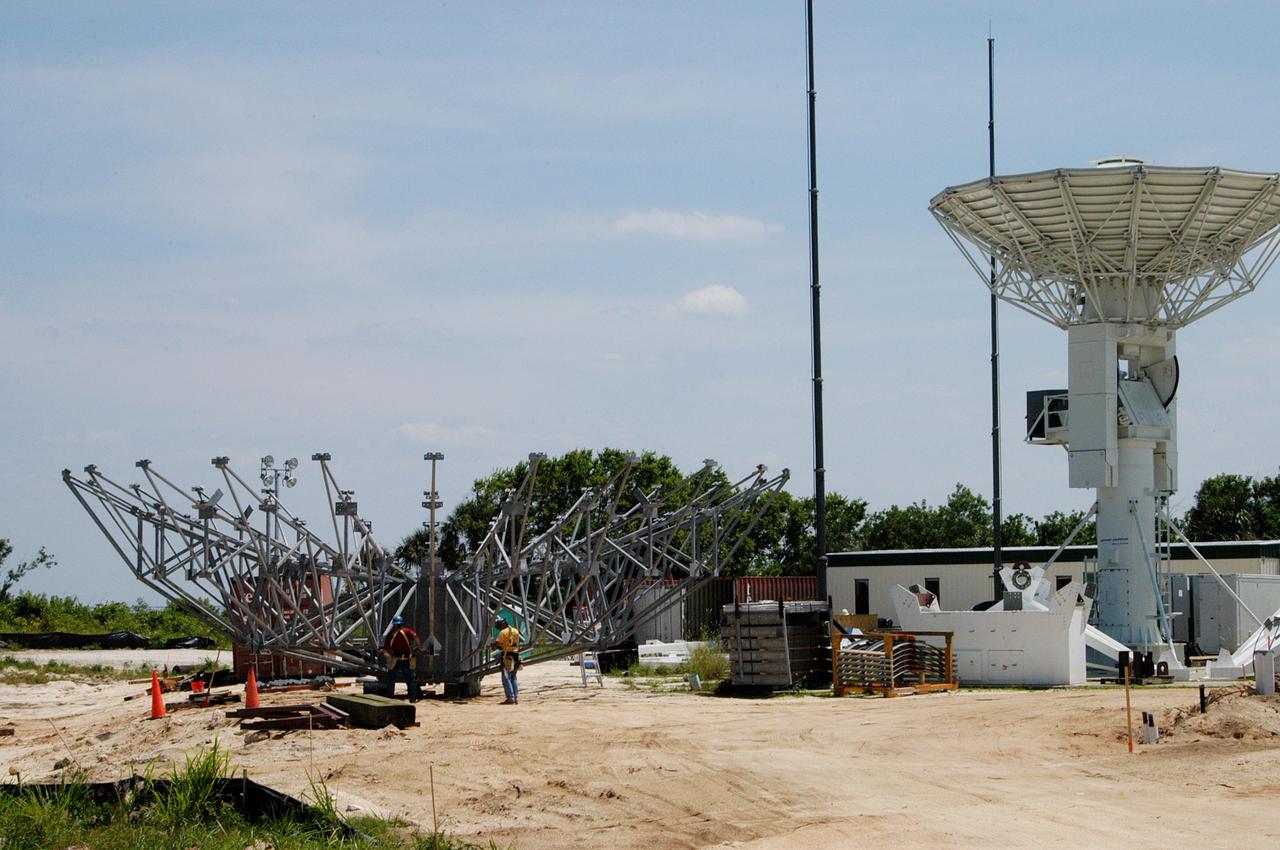

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, a 50-foot dish for NASA’s C-band radar is being assembled. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. On the right is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, workers are assembling the dish for the 50-foot NASA C-band radar. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. In the background is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31..
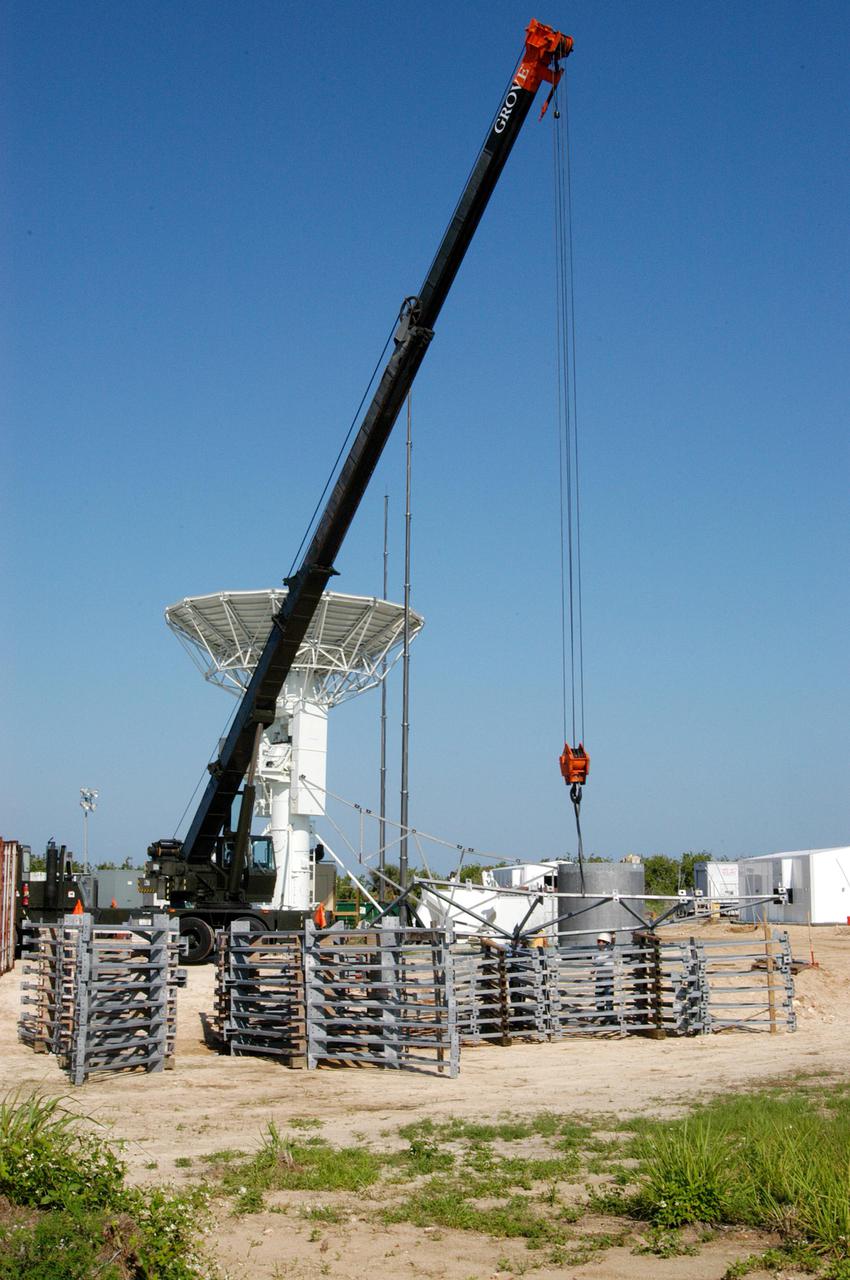

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At a radar site on North Merritt Island, Fla., north of the Haulover Canal, workers begin assembling the dish for the 50-foot NASA C-band radar. The radar will be used for long-term Shuttle missions to track the launches and observe possible debris coming from the Shuttle. In the background is an existing 30-foot C-band Pathfinder radar whose use was demonstrated on the Delta Messenger launch. It will be used on the upcoming two Return to Flight missions. The launch window for the first Return to Flight mission, STS-114, is July 13 to July 31.
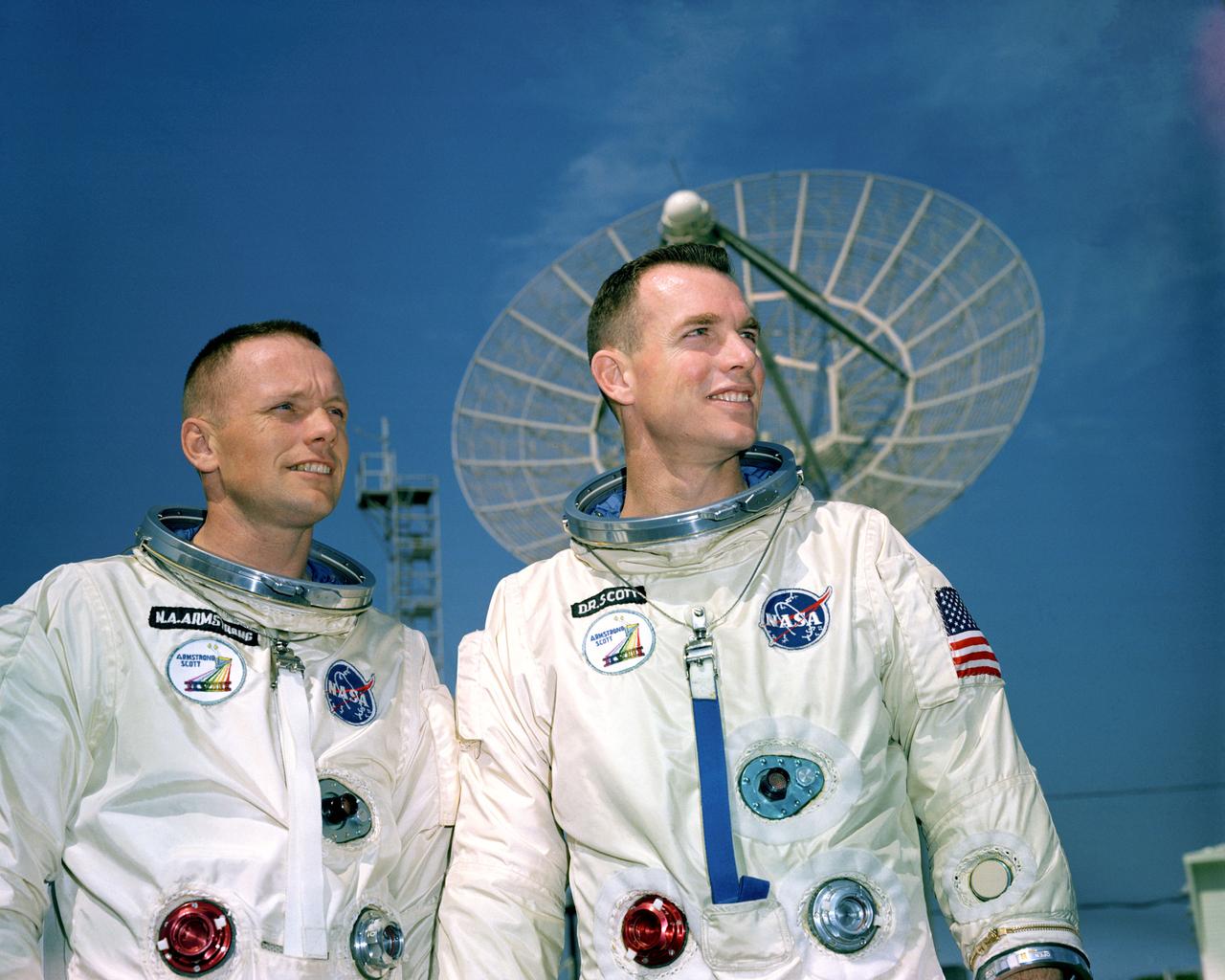

S66-27513 (11 March 1966) --- Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong (left), command pilot, and David R. Scott, pilot, the Gemini-8 prime crew, during a photo session outside the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Mission Control Center. They are standing in front of a radar dish. Photo credit: NASA
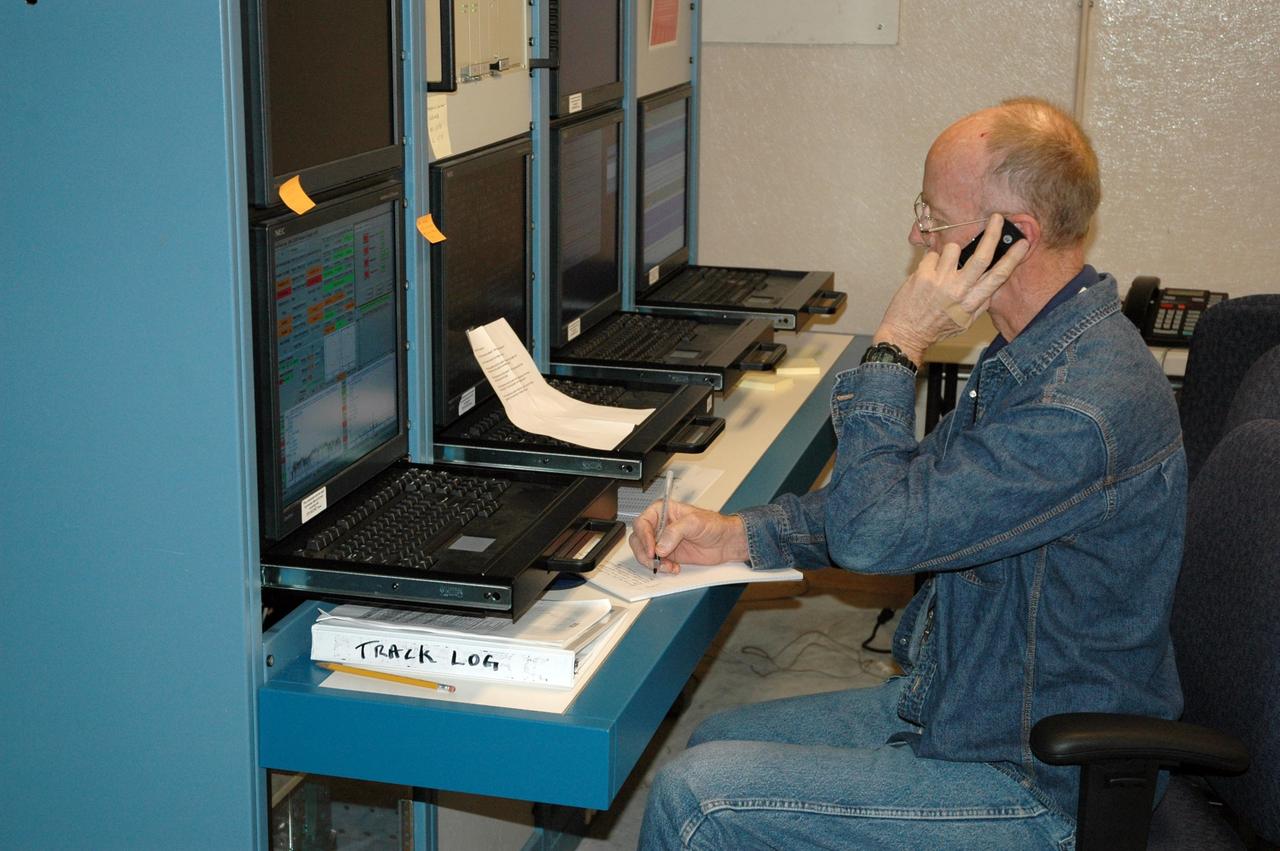

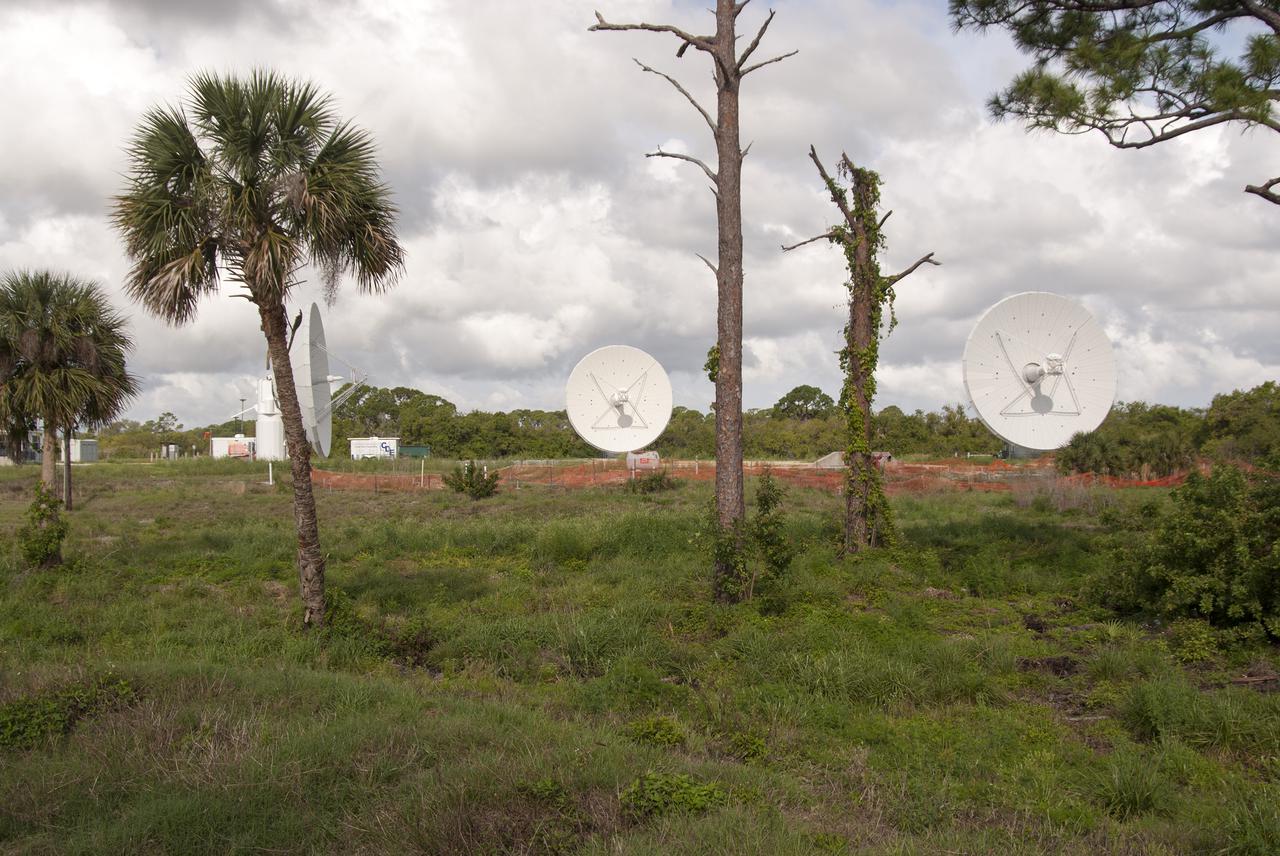
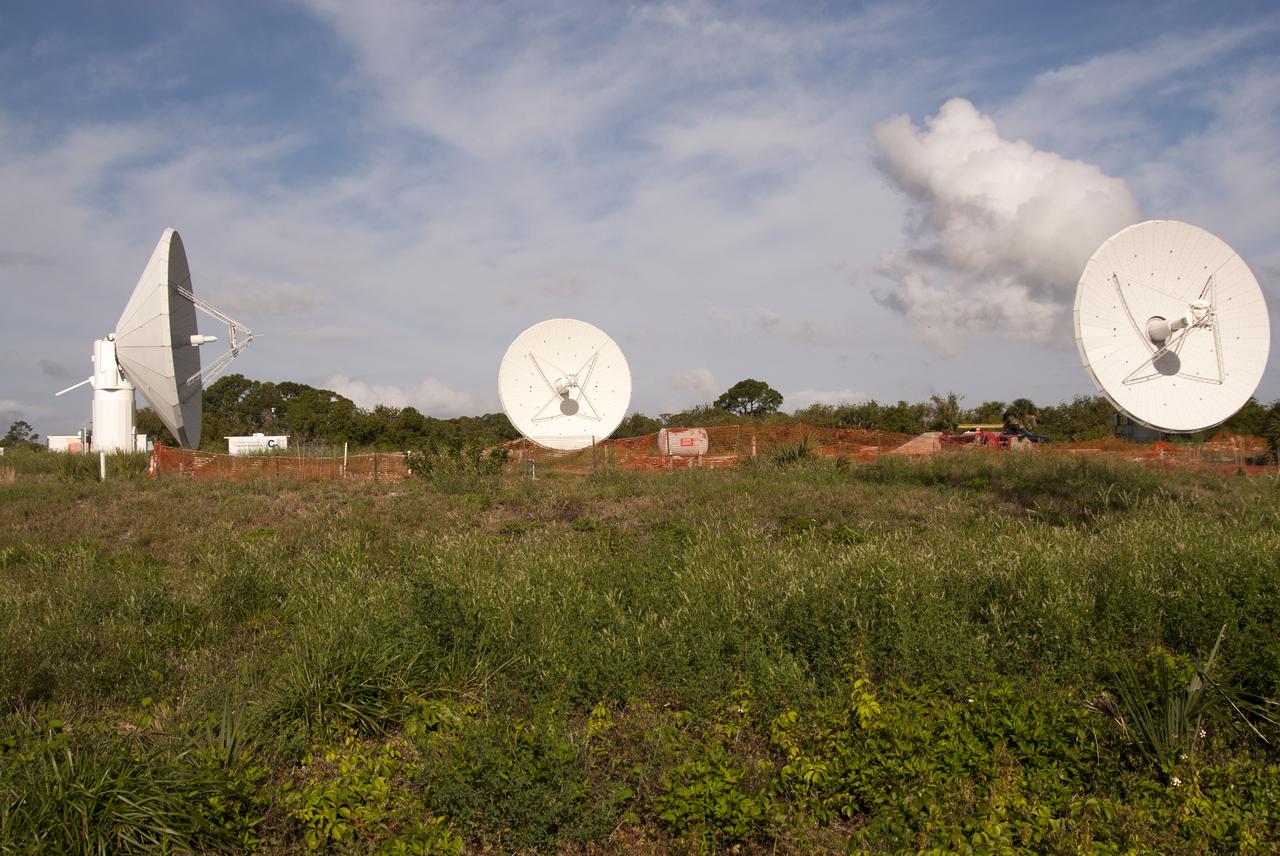
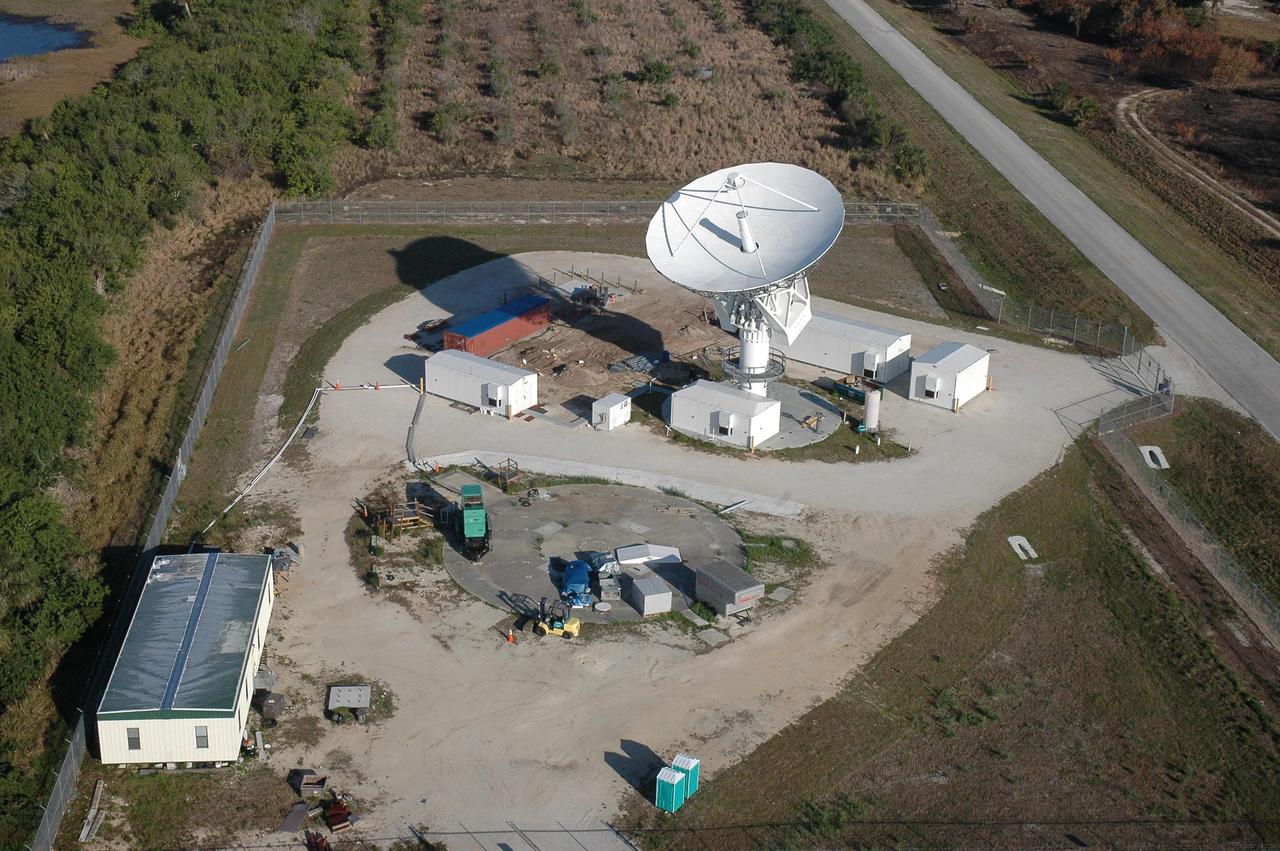
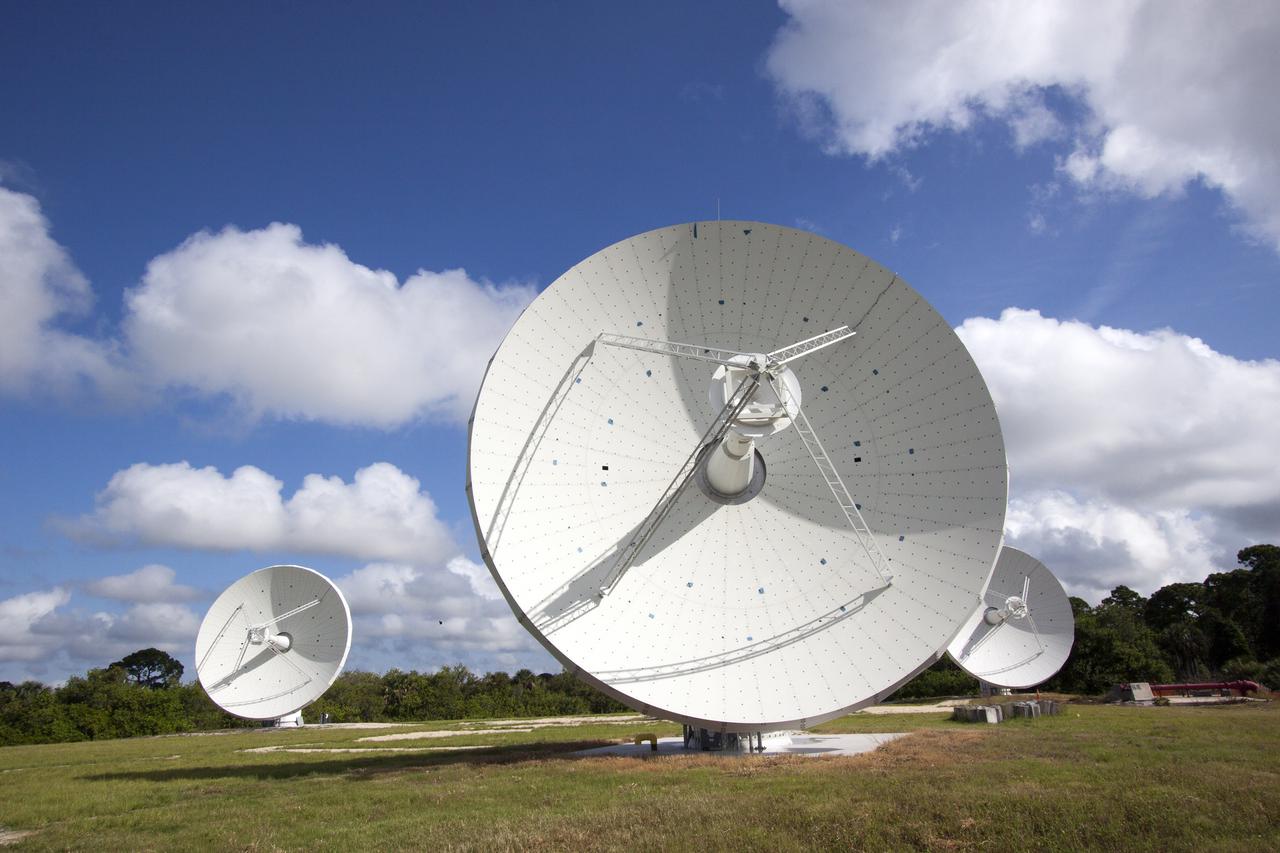
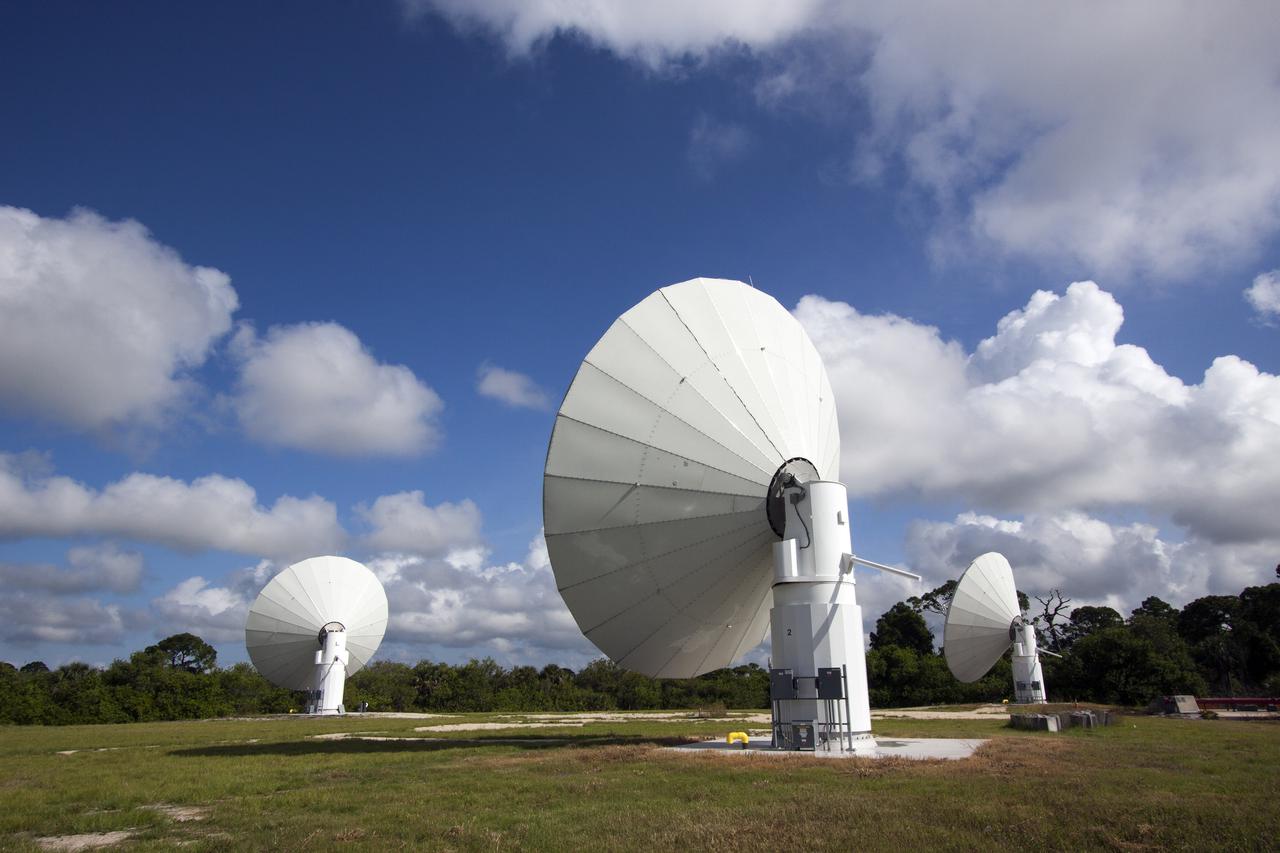
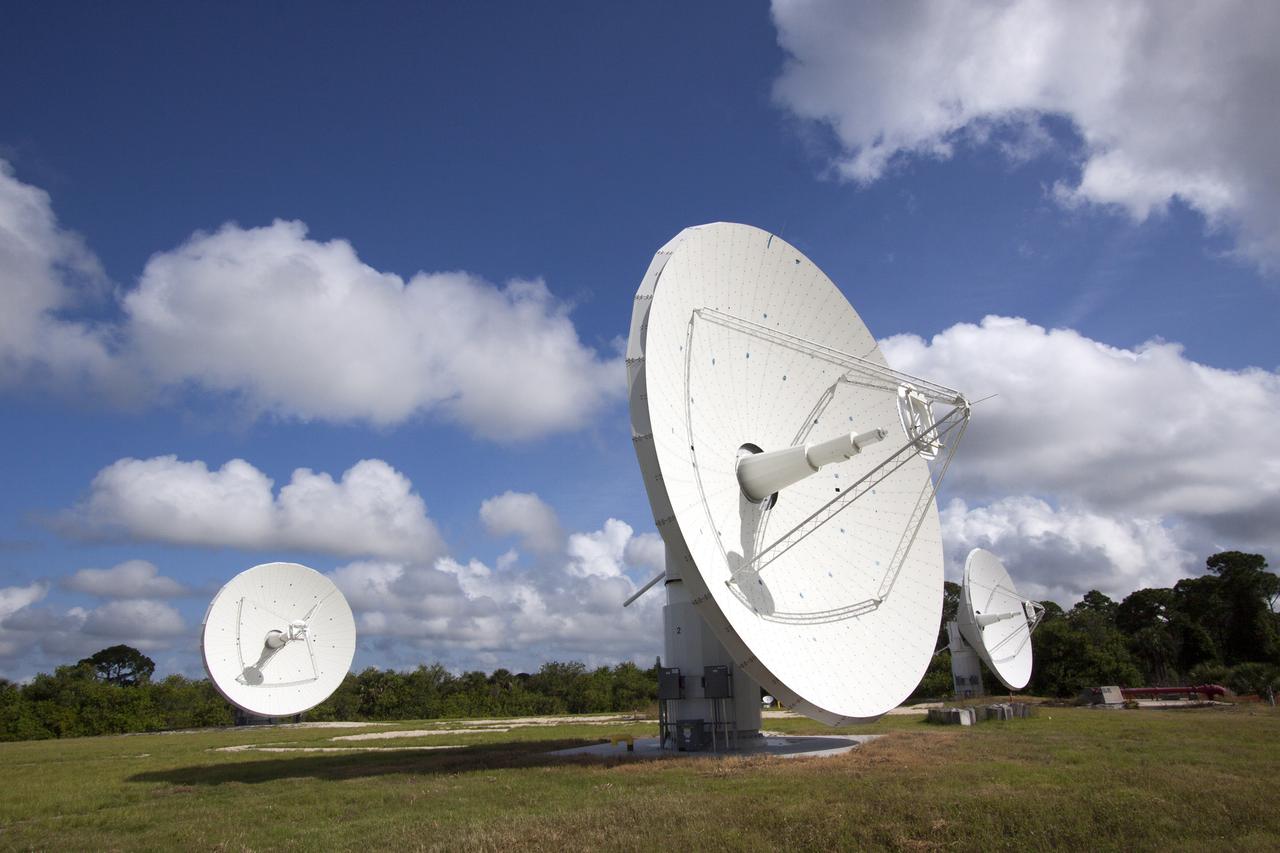
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Chuck Demming, with Northrop Grumman, works the console responsible for operation of the C-band, 3 megawatt radar and 50-foot dish antenna recently installed on north Kennedy Space Center. The radar is is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy, who owns the radar. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton/Demitrius Gerondidakas

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna has recently been installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.
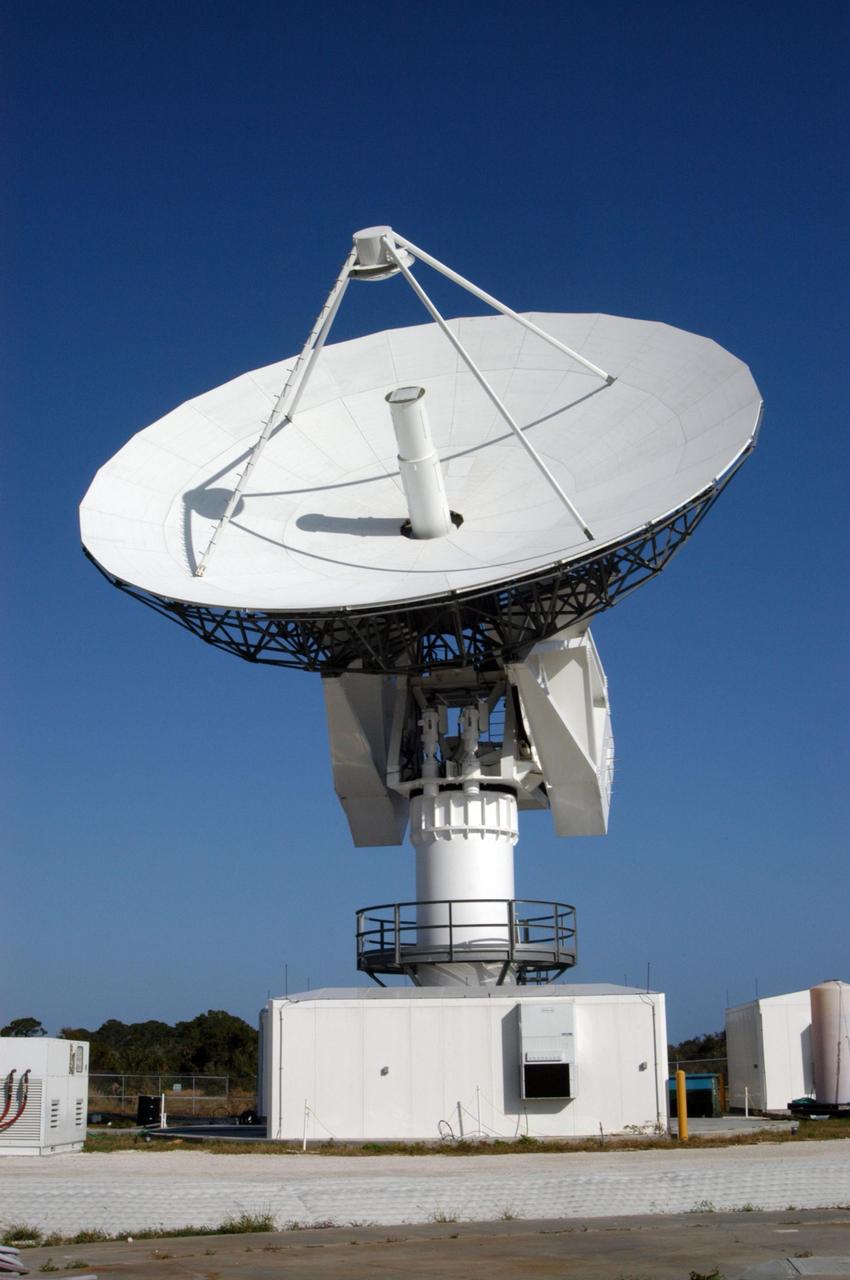

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna has recently been installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna has recently been installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.
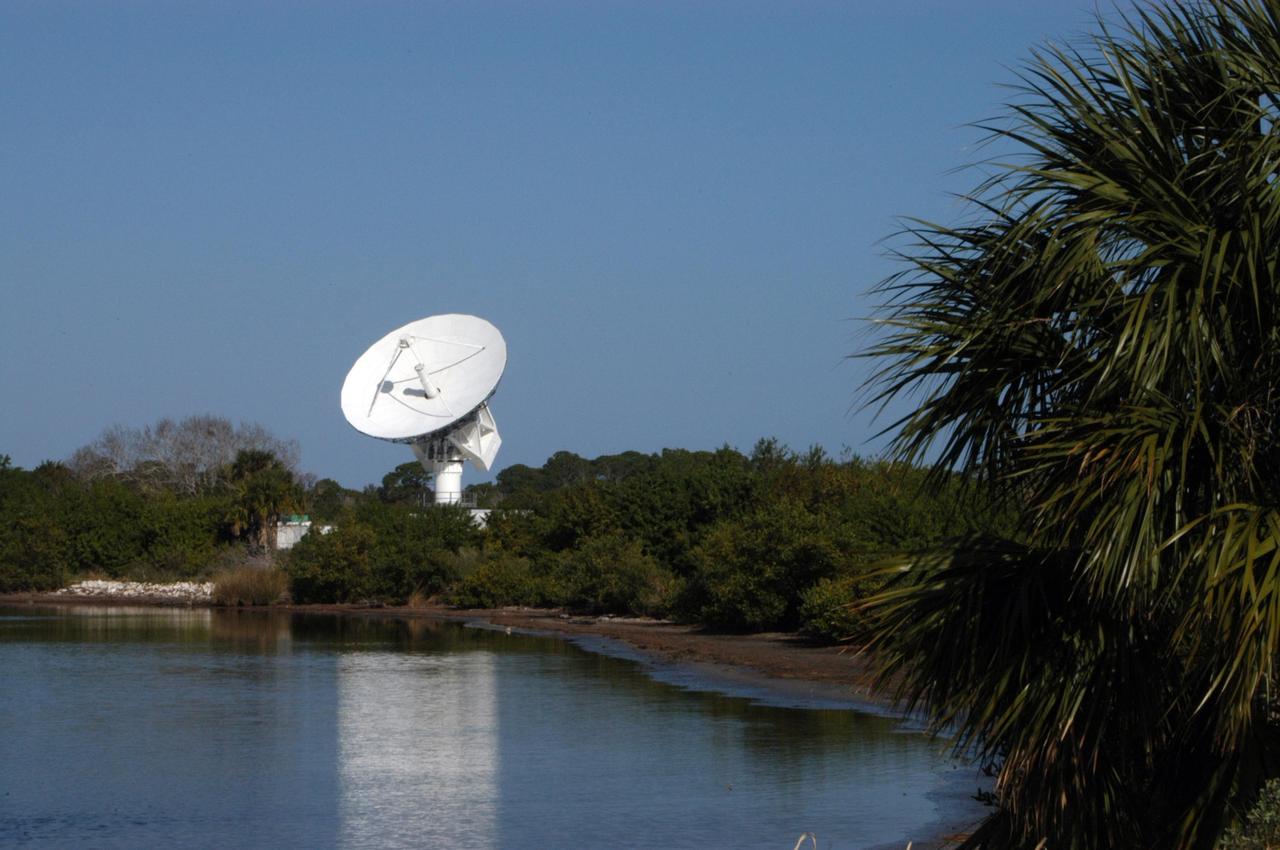

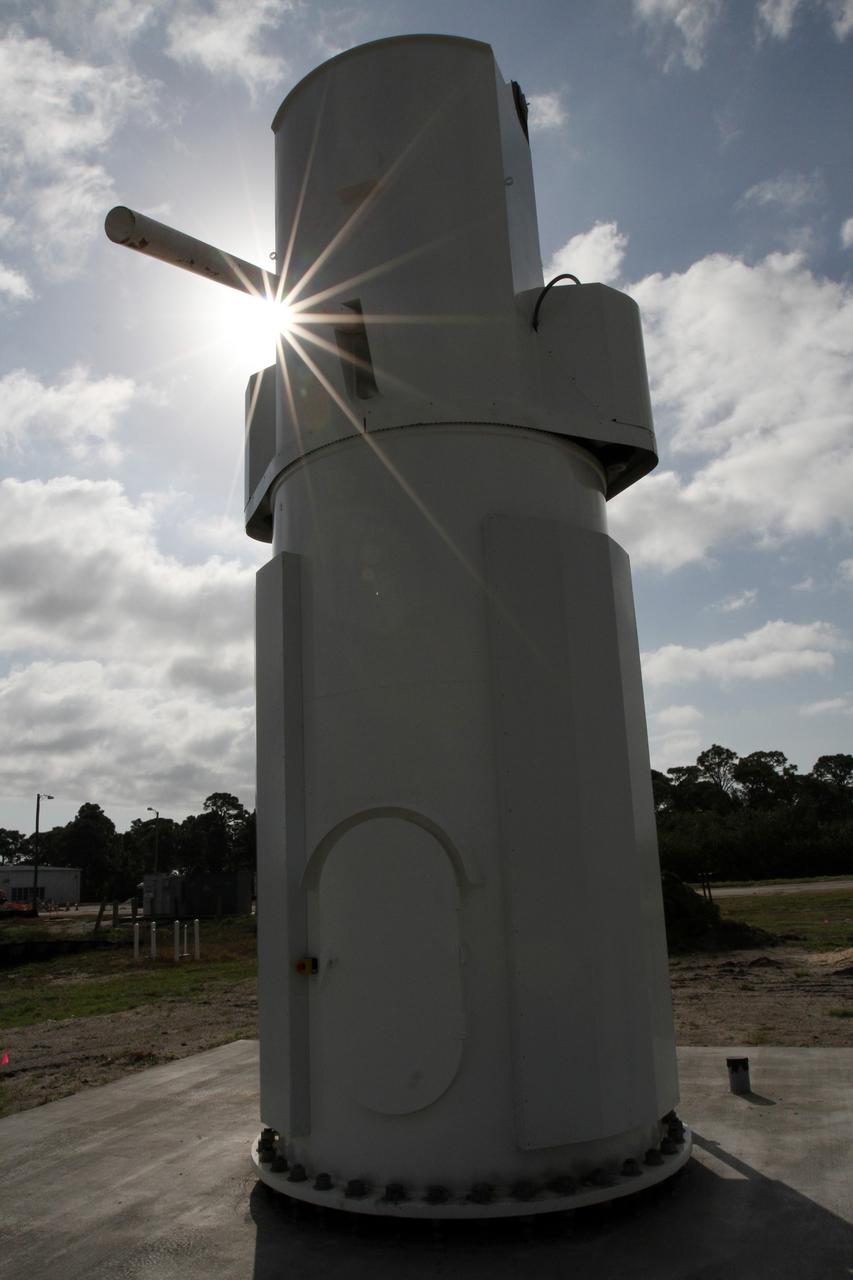
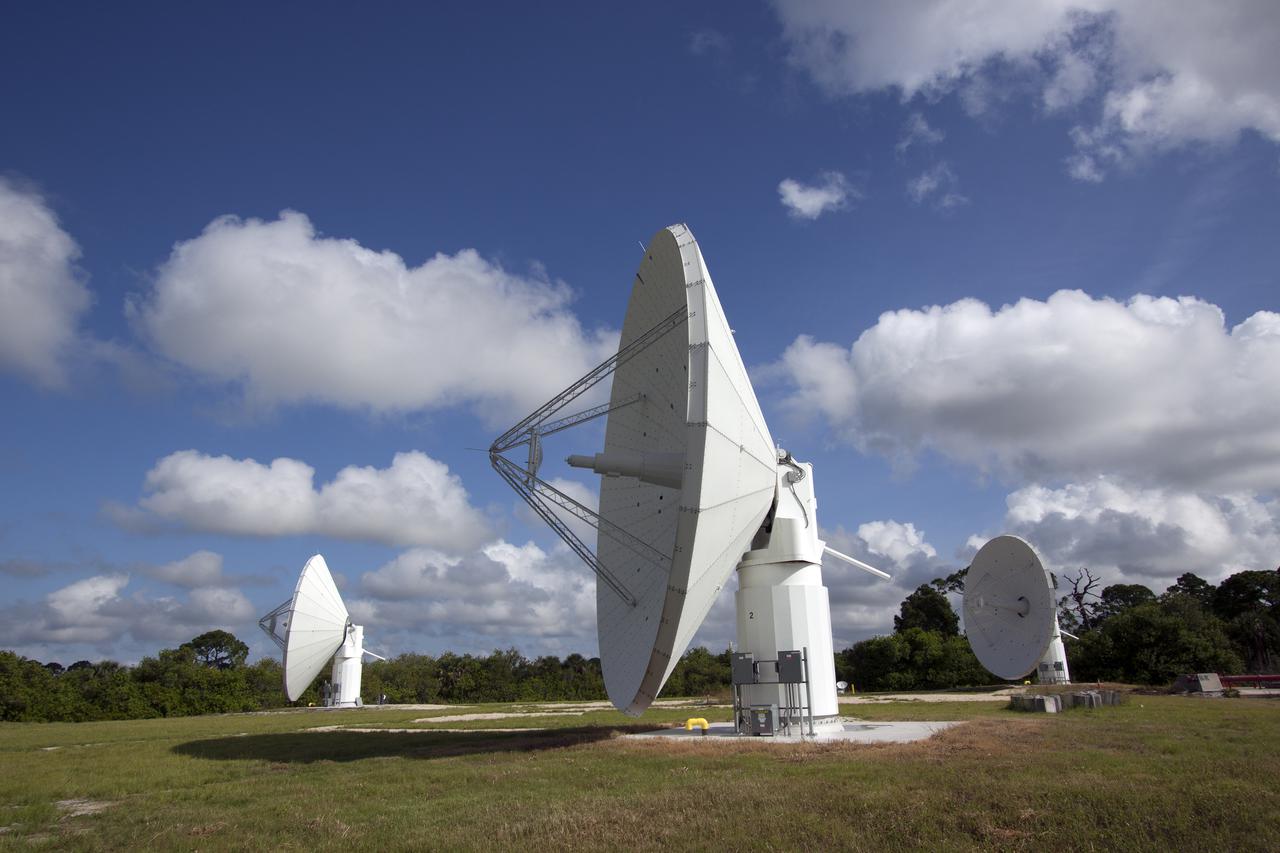
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna reflects on the marsh water nearby. The antenna has recently been installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.
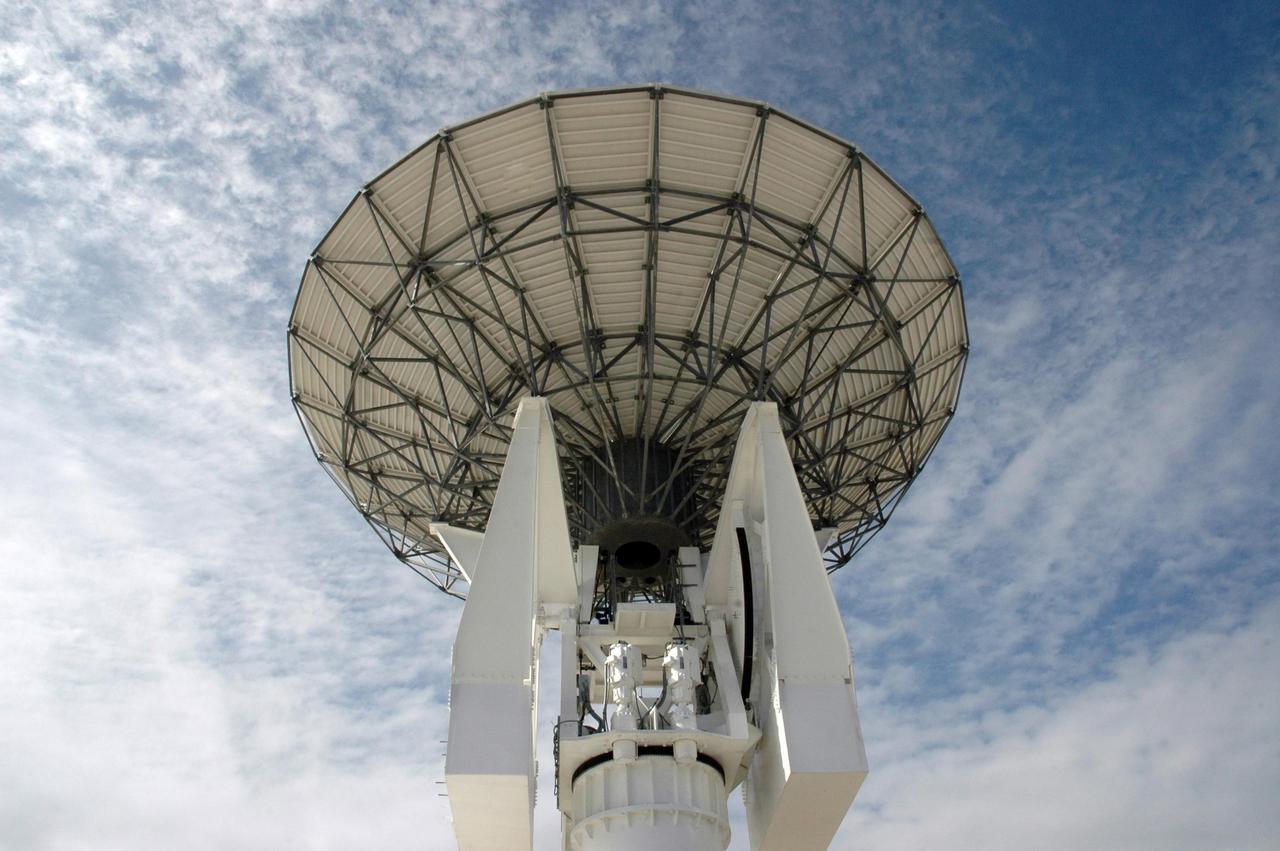

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Stretching into the cloud-streaked sky is this new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna recently installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna has recently been installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Working in concert with two new NASA-owned X-band radars mounted on the solid rocket booster retrieval ships, tracking the space shuttle and expendable launch vehicles with this new capability will provide more detail than NASA has ever observed by radar before. The first use of this C-band radar will be for the launch of the Atlas V rocket sending the New Horizons probe toward Pluto. The radar is operated under a NASA contract with the U.S. Navy who owns the radar.

California's NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center photographer Carla Thomas takes photos on January 31 of the rare opportunity to capture a supermoon, a blue moon and a lunar eclipse at the same time. A supermoon occurs when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit and appearing 14 percent brighter than usual. As the second full moon of the month, this moon is also commonly known as a blue moon, though it will not be blue in appearance. The super blue moon passed through Earth's shadow and took on a reddish tint, known as a blood moon. This total lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and a full moon form a near-perfect lineup in space. The Moon passes directly behind the Earth into its umbra (shadow).
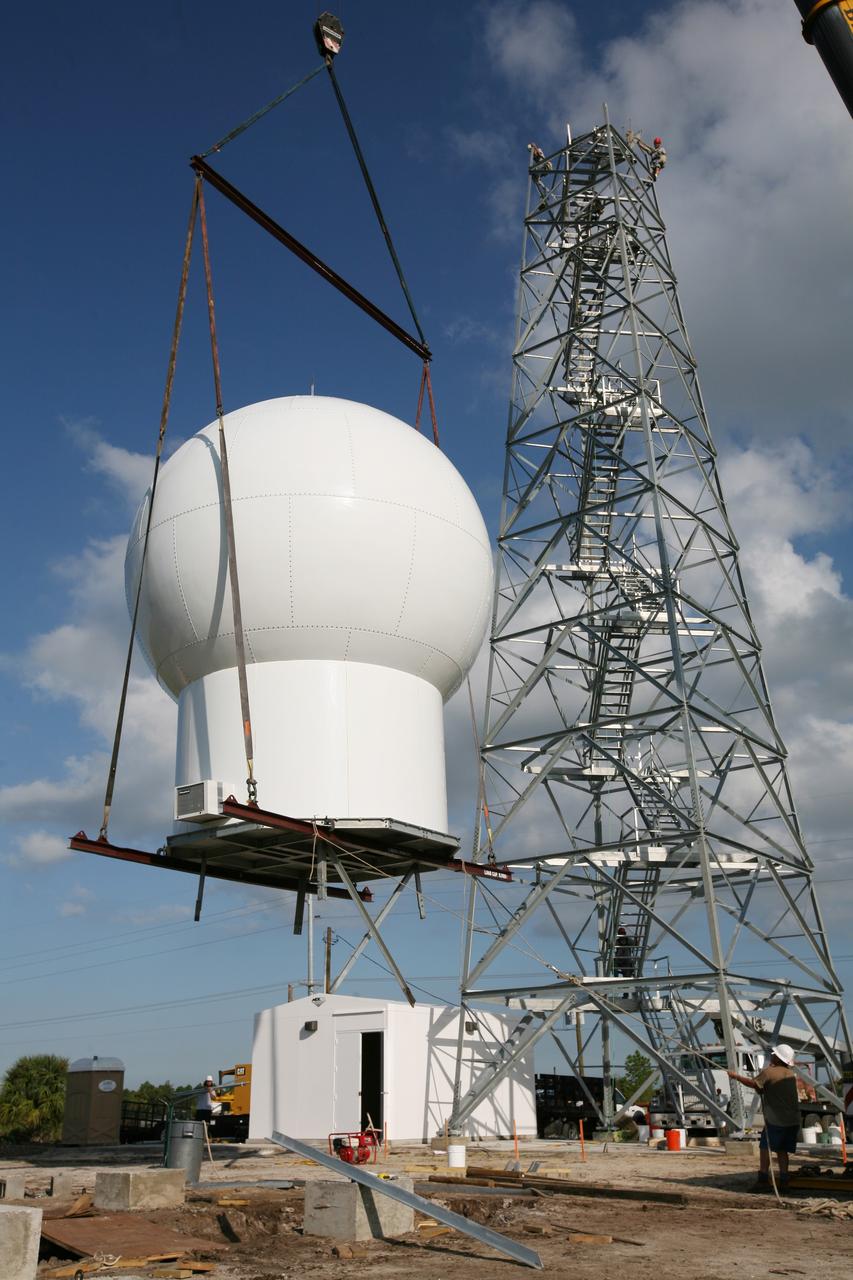

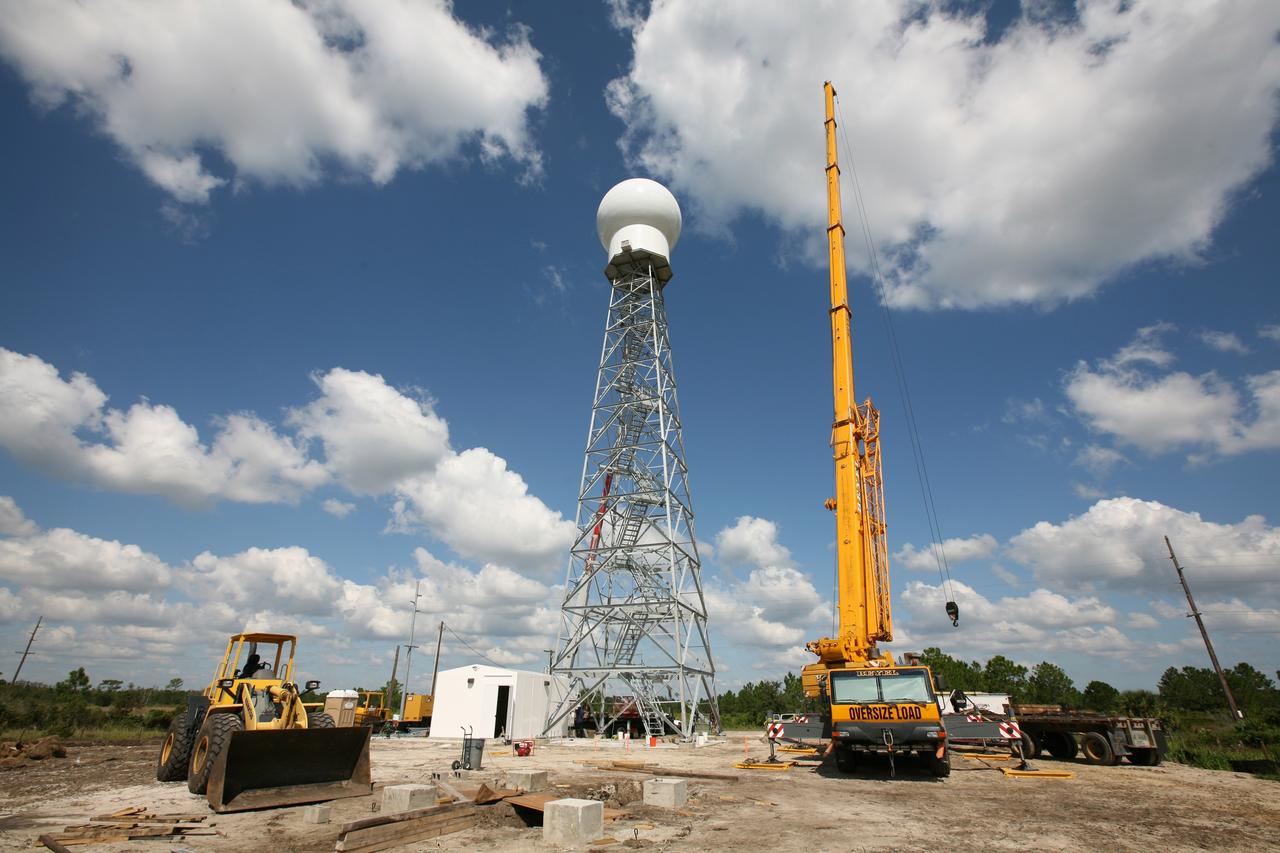
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane lifts the radome to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane positions the radome on top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The radome is secured atop a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
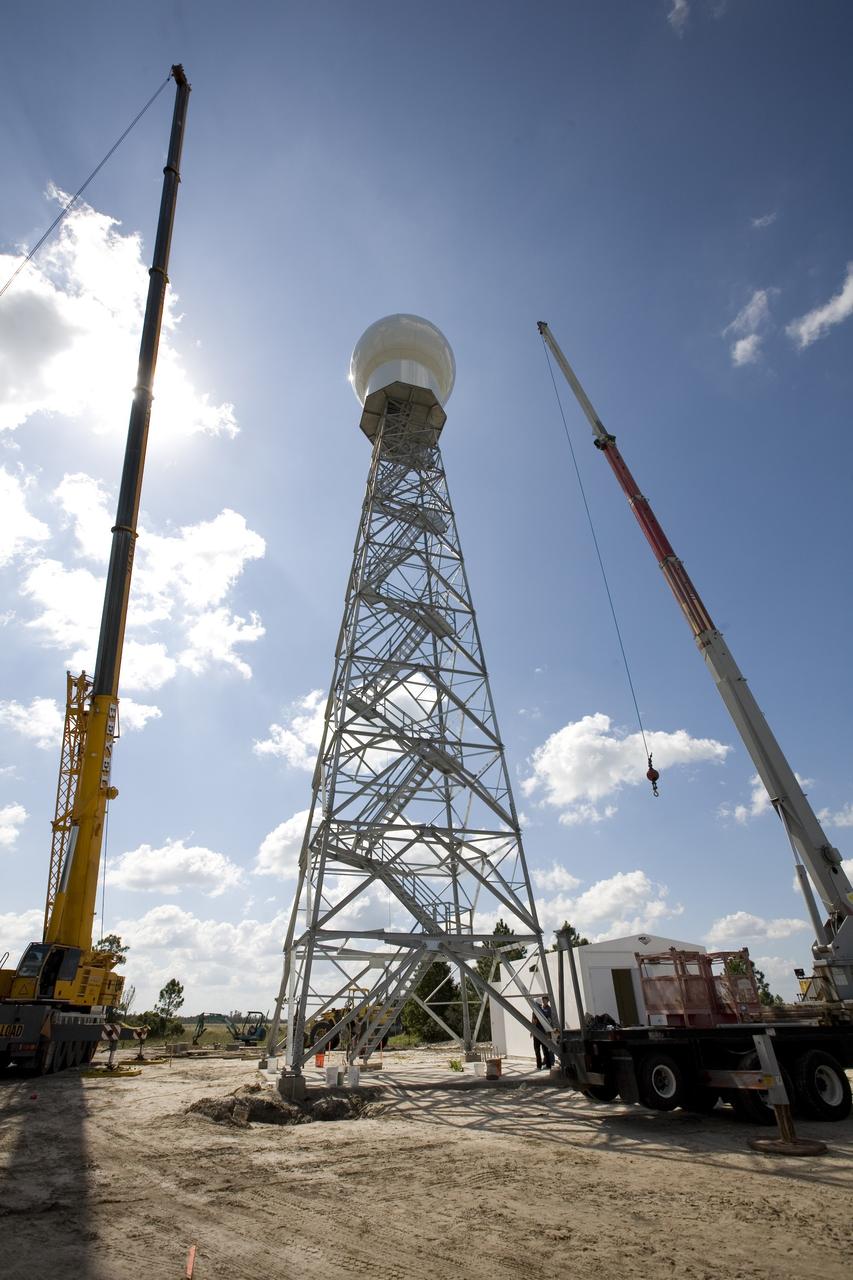

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The radome is secured atop a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
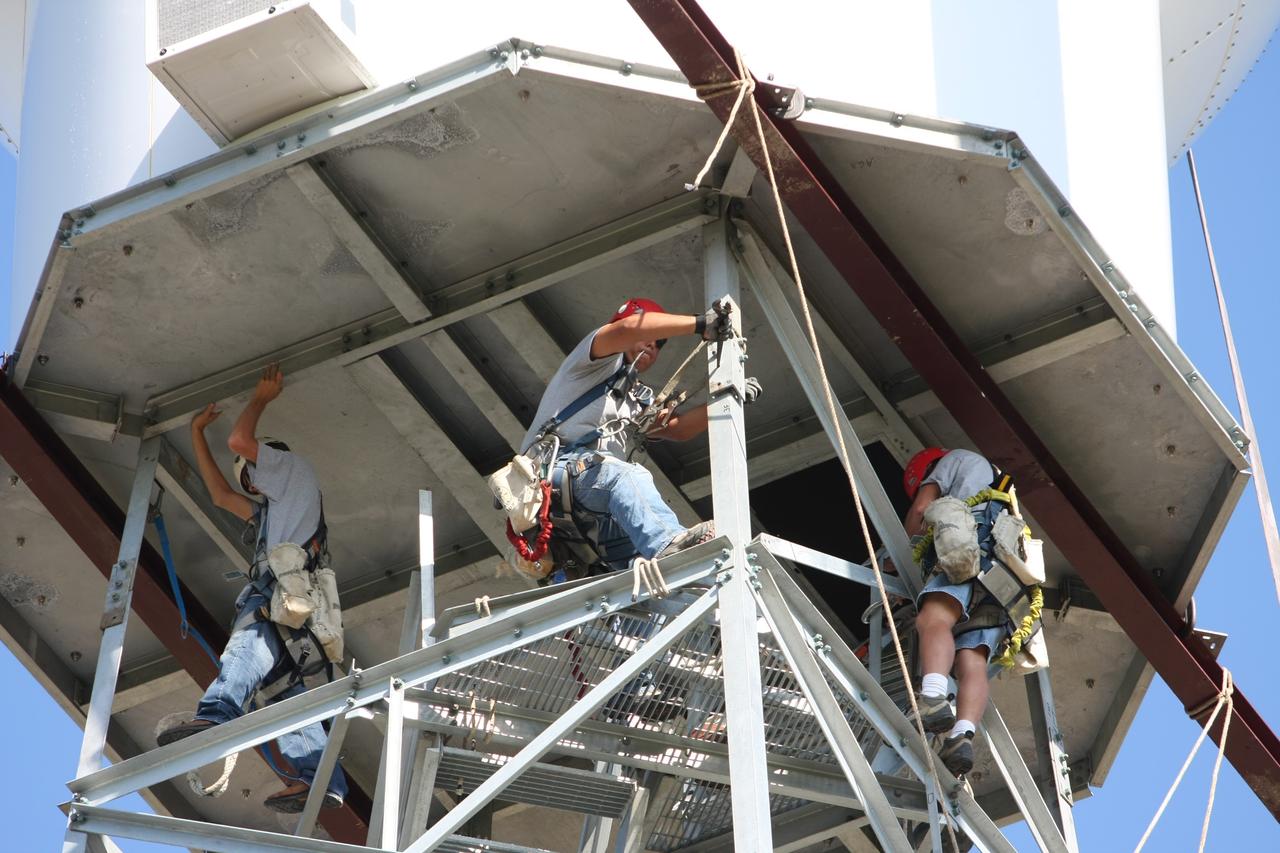

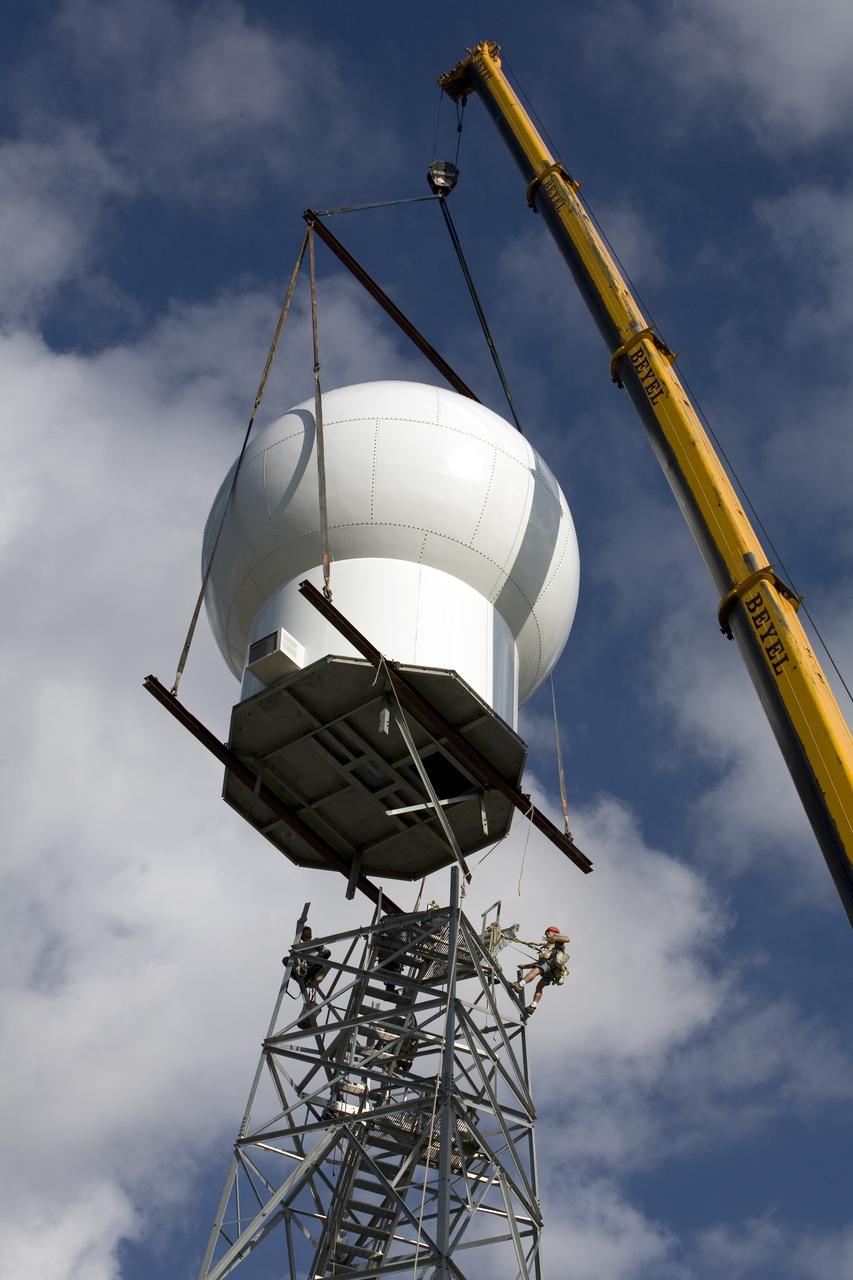
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers secure the radome to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
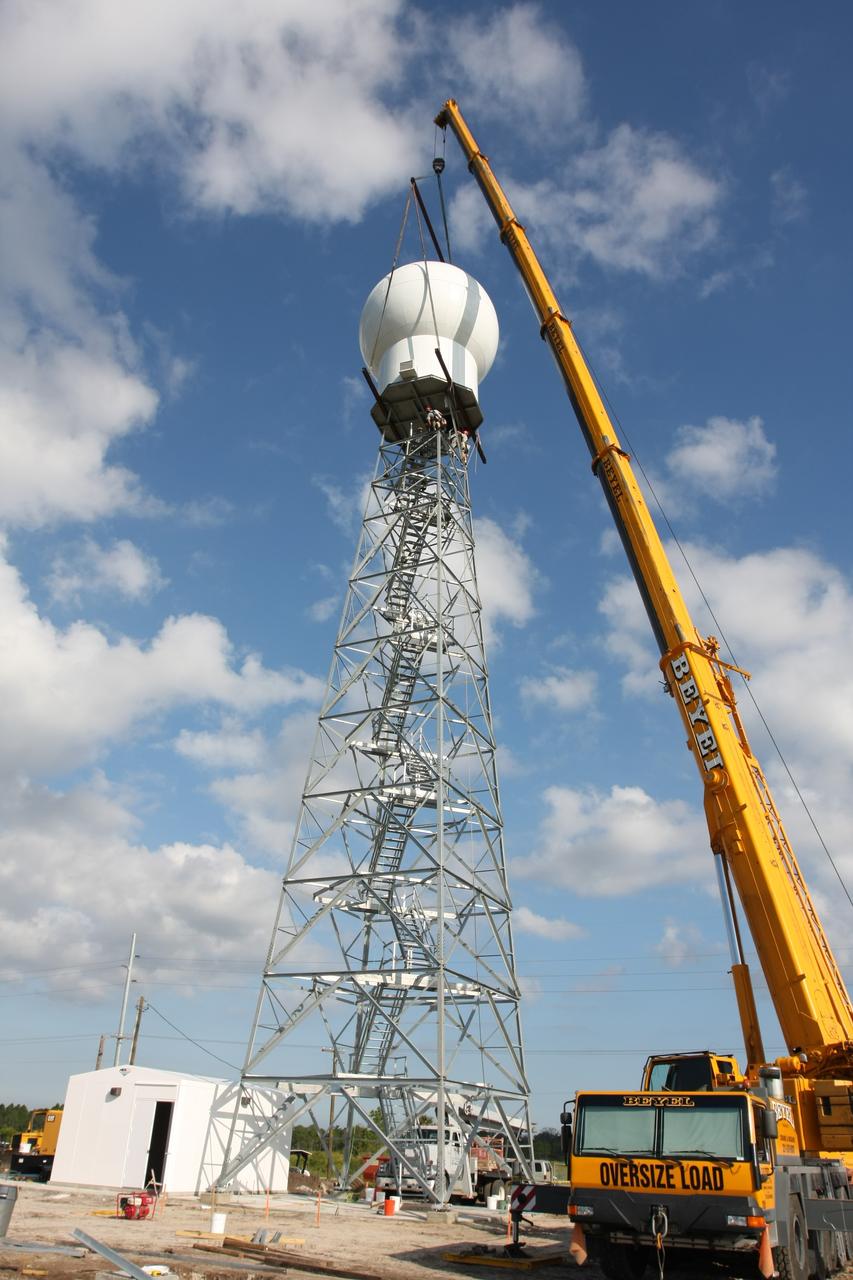

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane positions the radome on top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

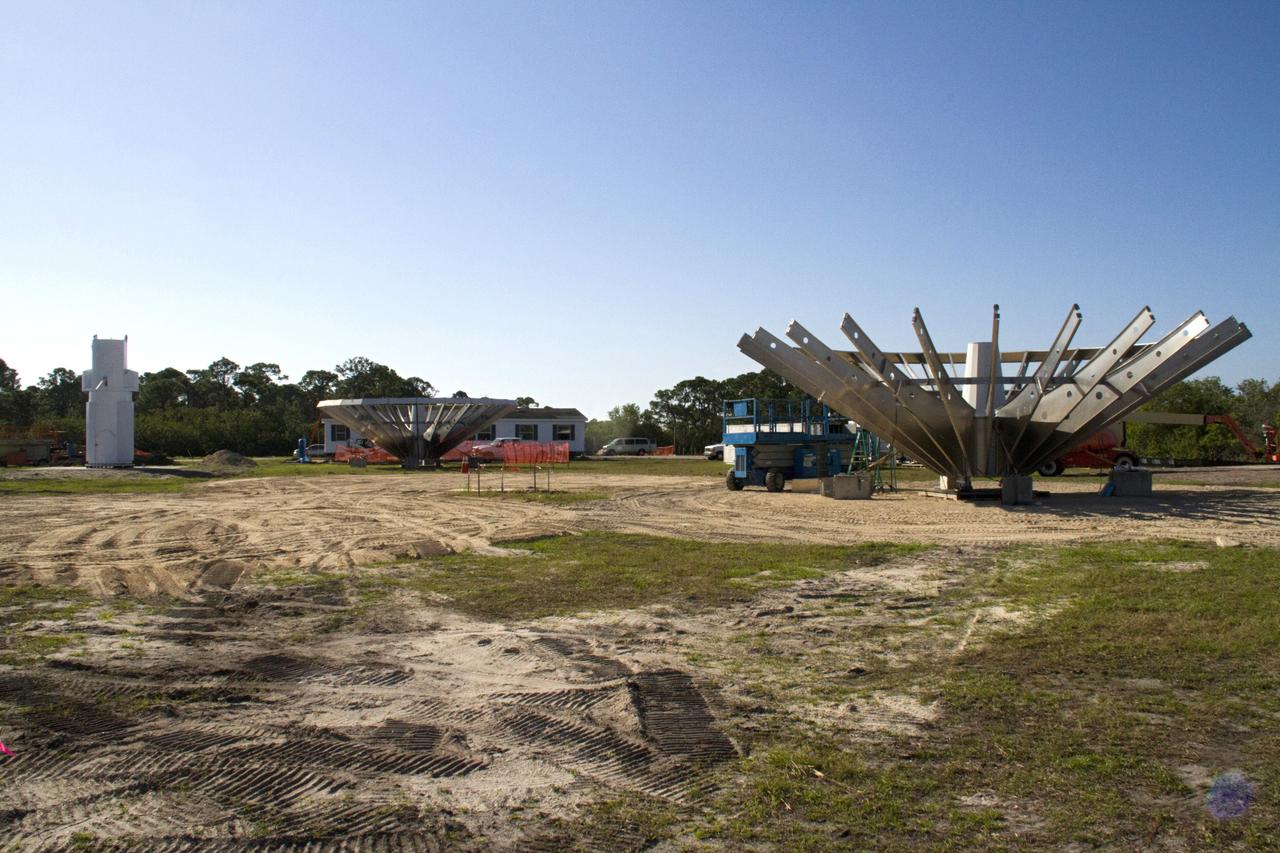
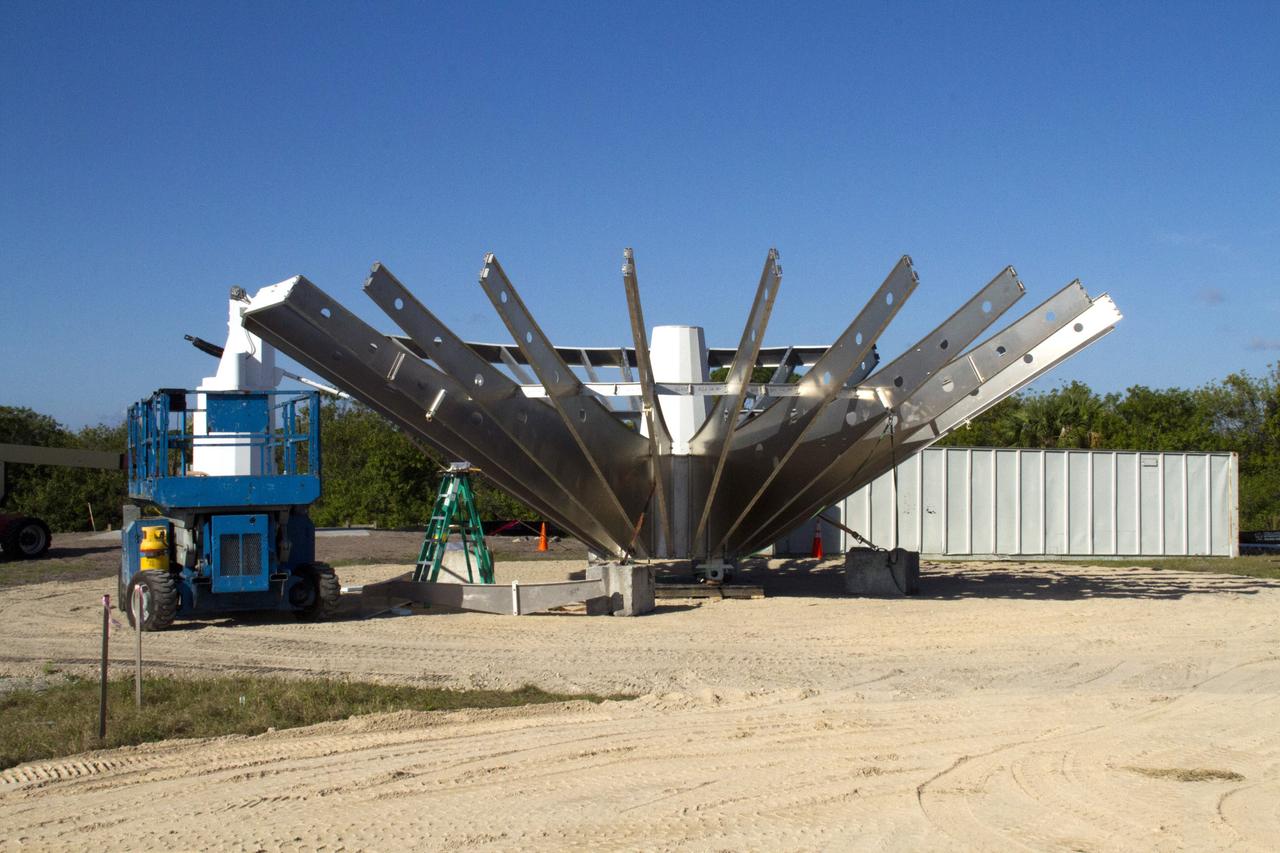
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are constructing 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
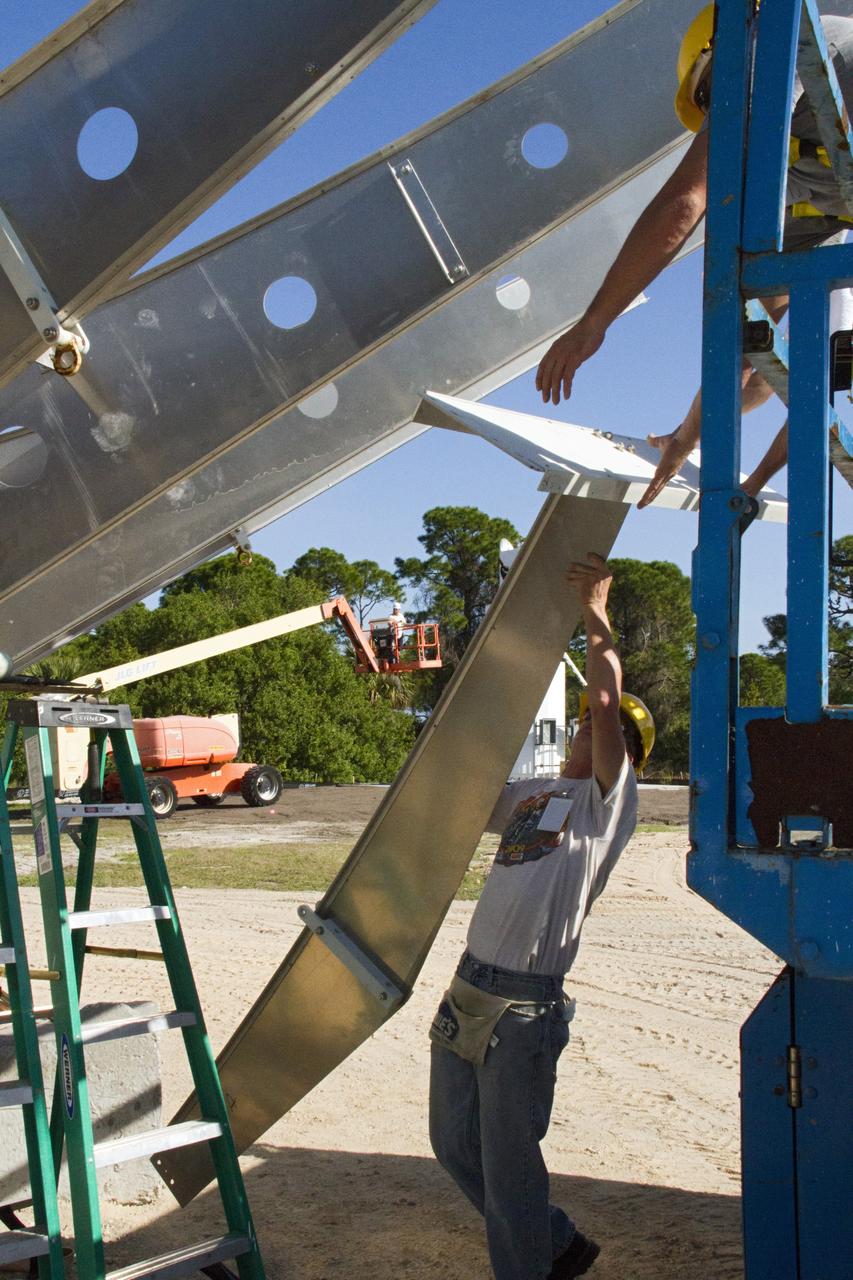

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are constructing 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
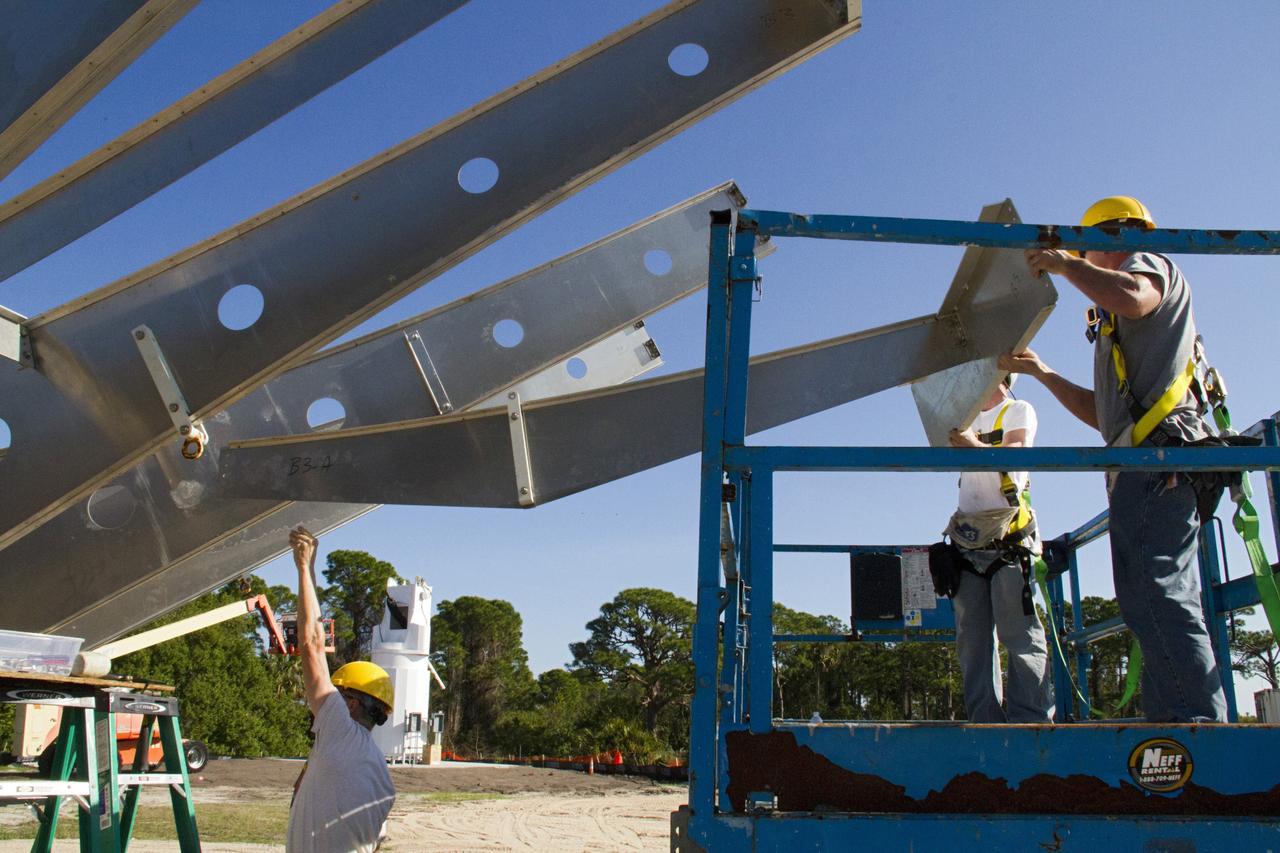

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are constructing 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers are constructing 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

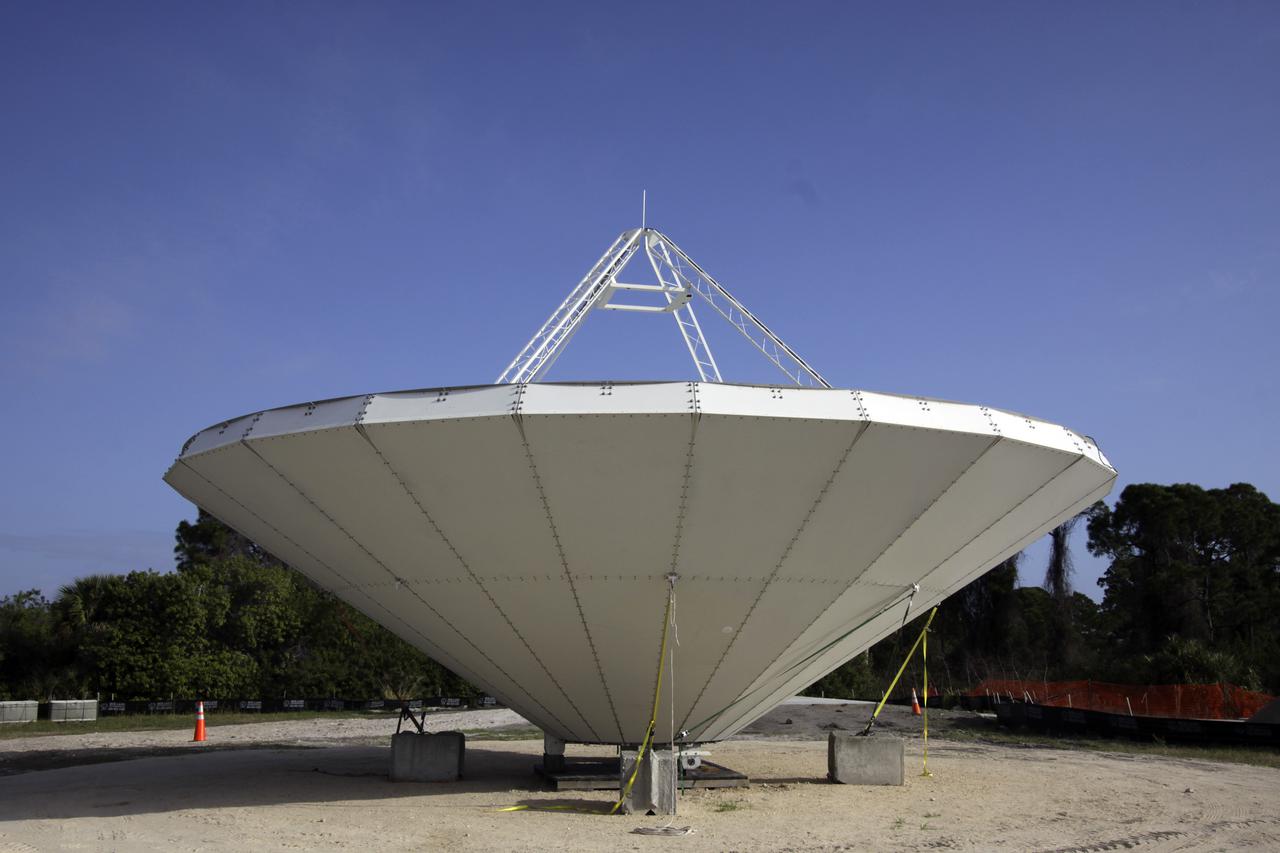
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction is almost complete on the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, system. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, construction is almost complete on the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, system. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser
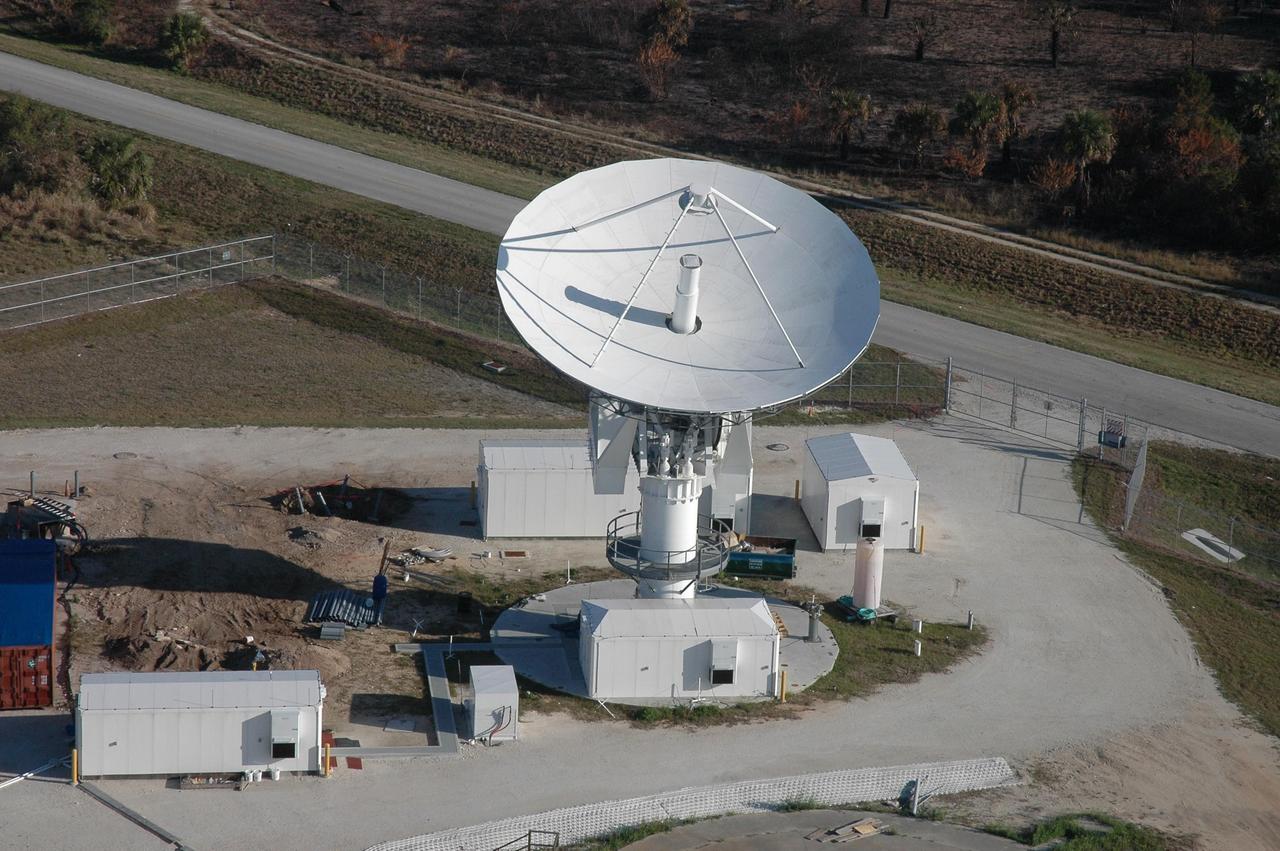

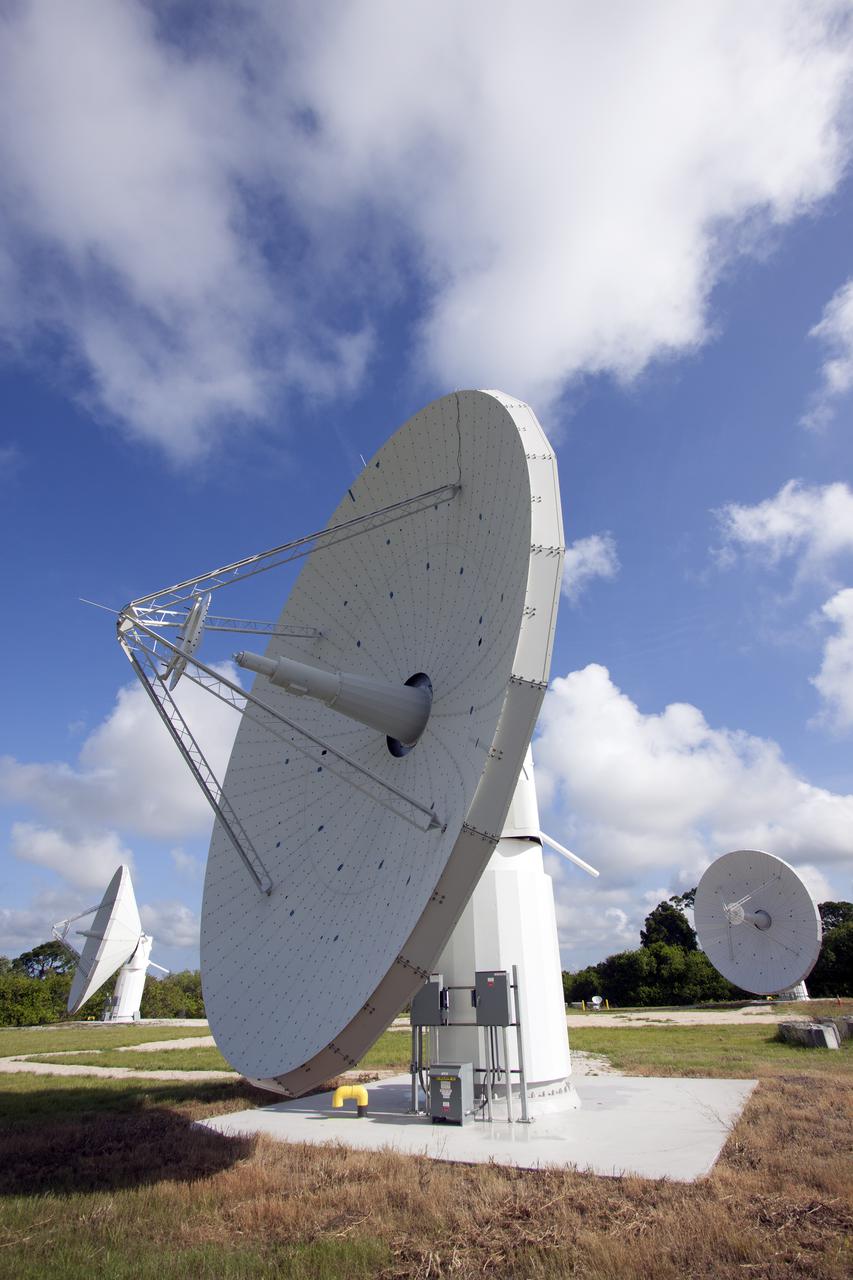
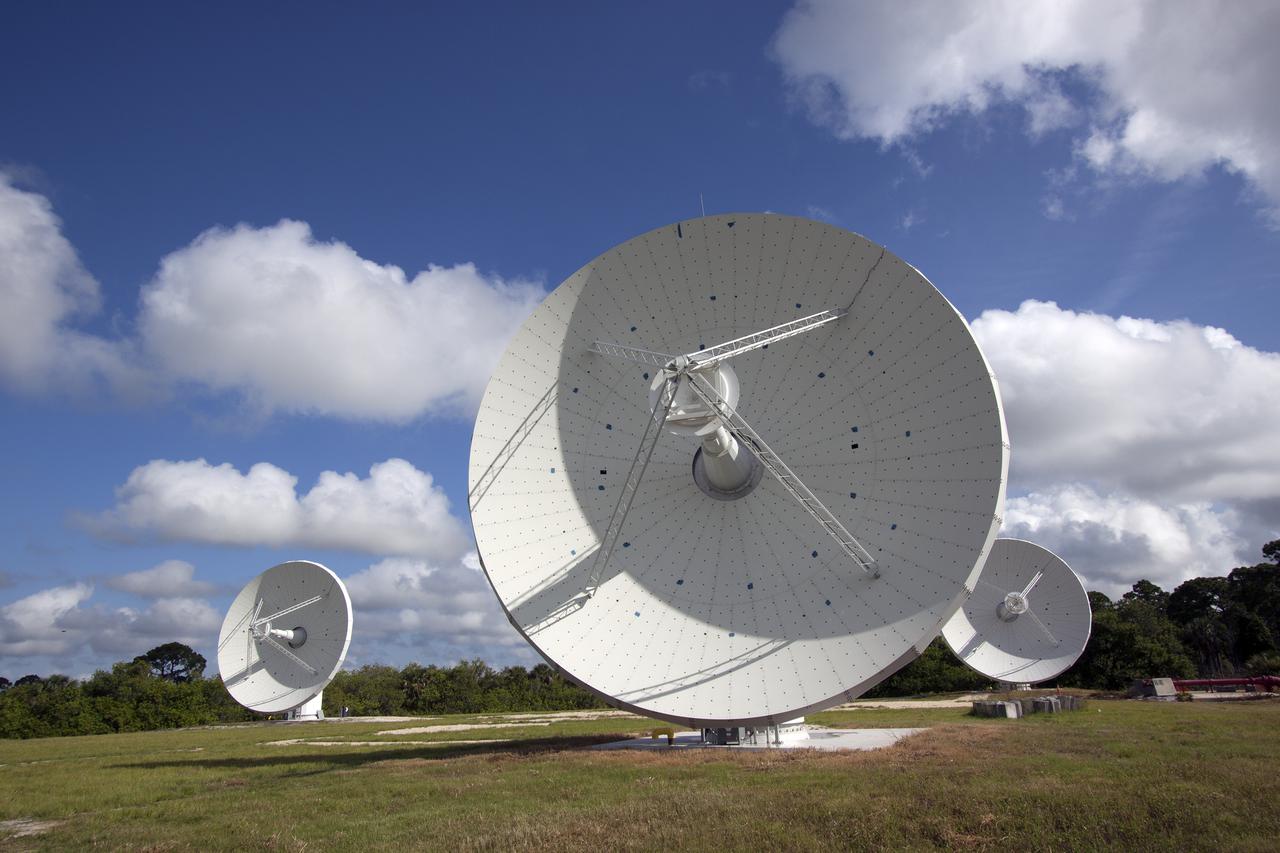
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view shows the new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna recently installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Photo credit: Cory Huston

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view shows the new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna recently installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest of its kind in the world, providing higher definition imagery than has ever been available before. Photo credit: Cory Huston
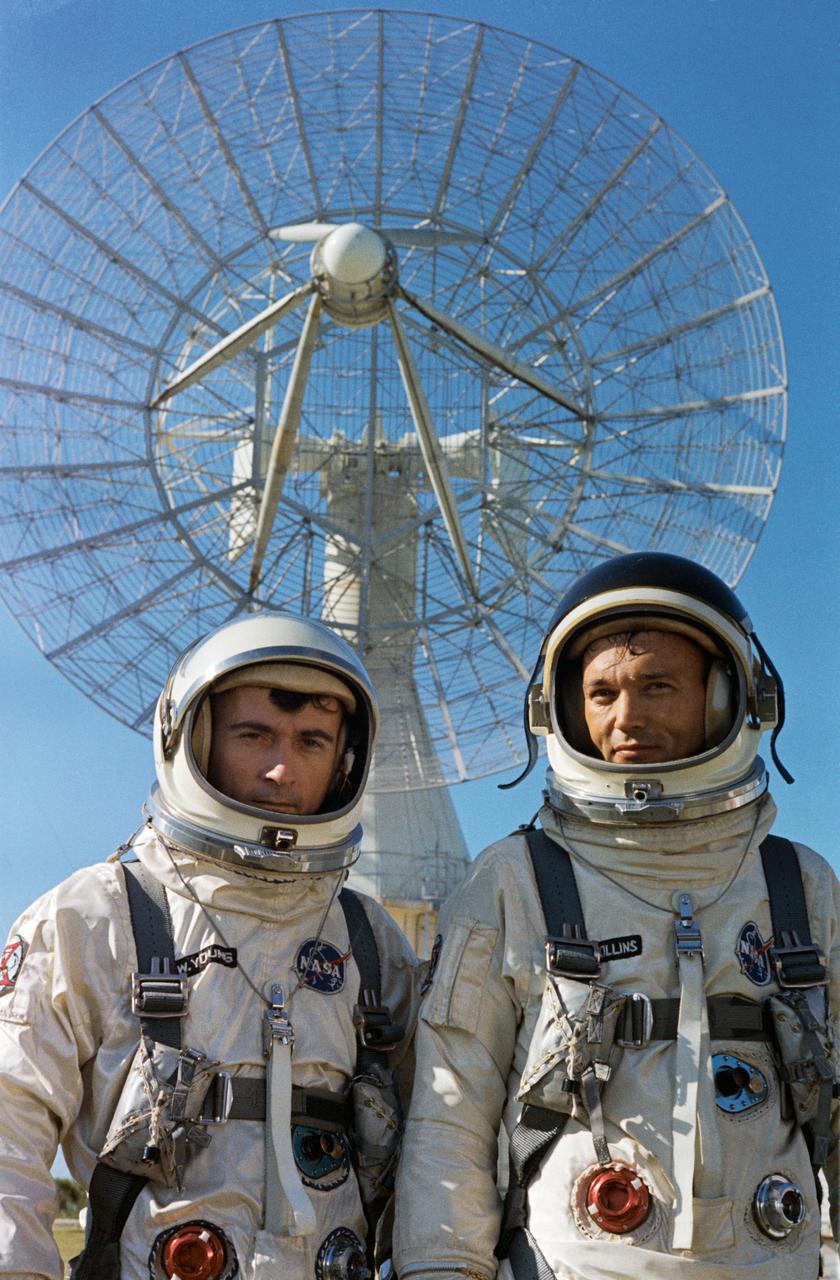

S66-42725 (16 July 1966) --- Astronauts John W. Young (left), command pilot, and Michael Collins, pilot, the Gemini-10 prime crew during a photo session for the press outside the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Mission Control Center. Both men are wearing their spacesuits including helmets. Behind them is a large radar dish. Photo credit: NASA
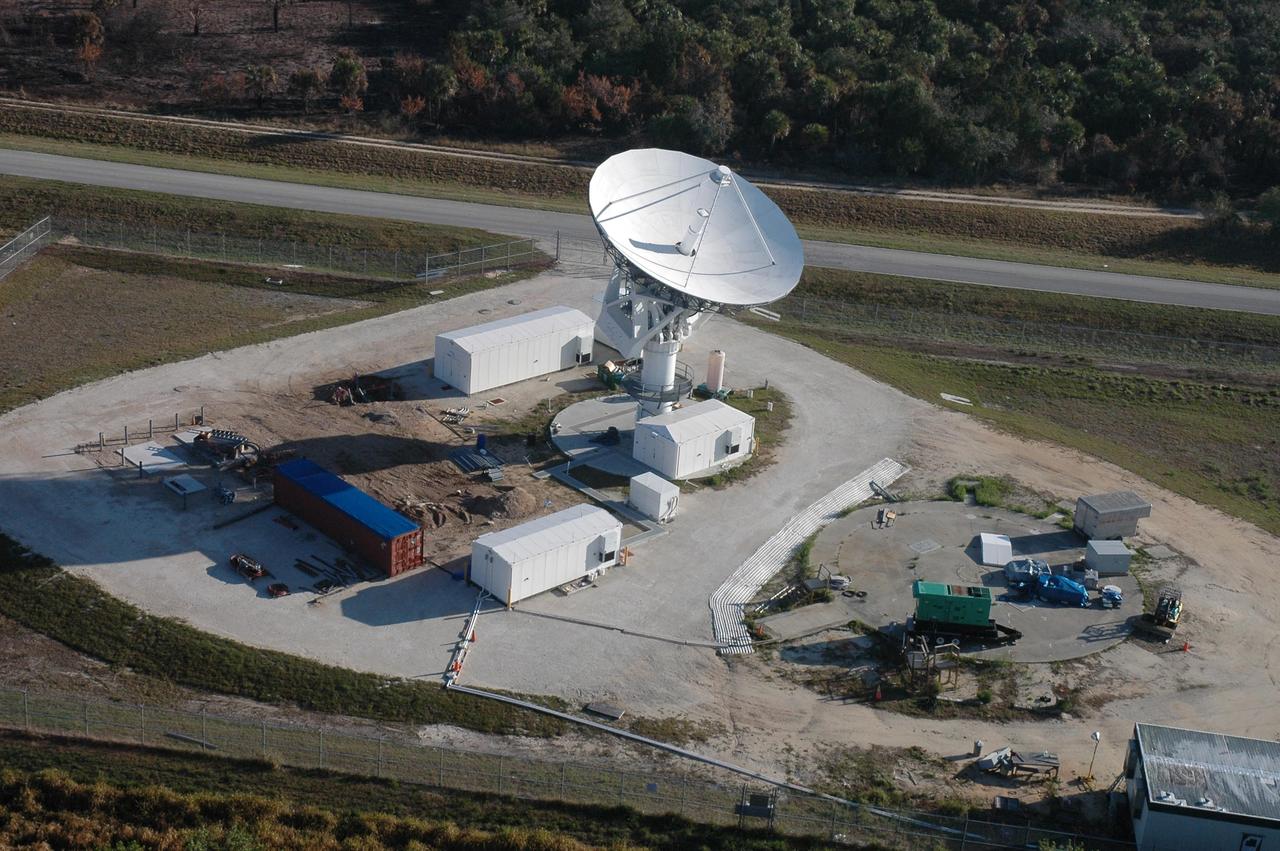

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - This view shows the new C-band, 3 megawatt radar with a 50-foot dish antenna recently installed on north Kennedy Space Center. It is one of the largest and most powerful of its kind in the world, providing higher definition launch imagery than has ever been available before. Photo credit: Cory Huston
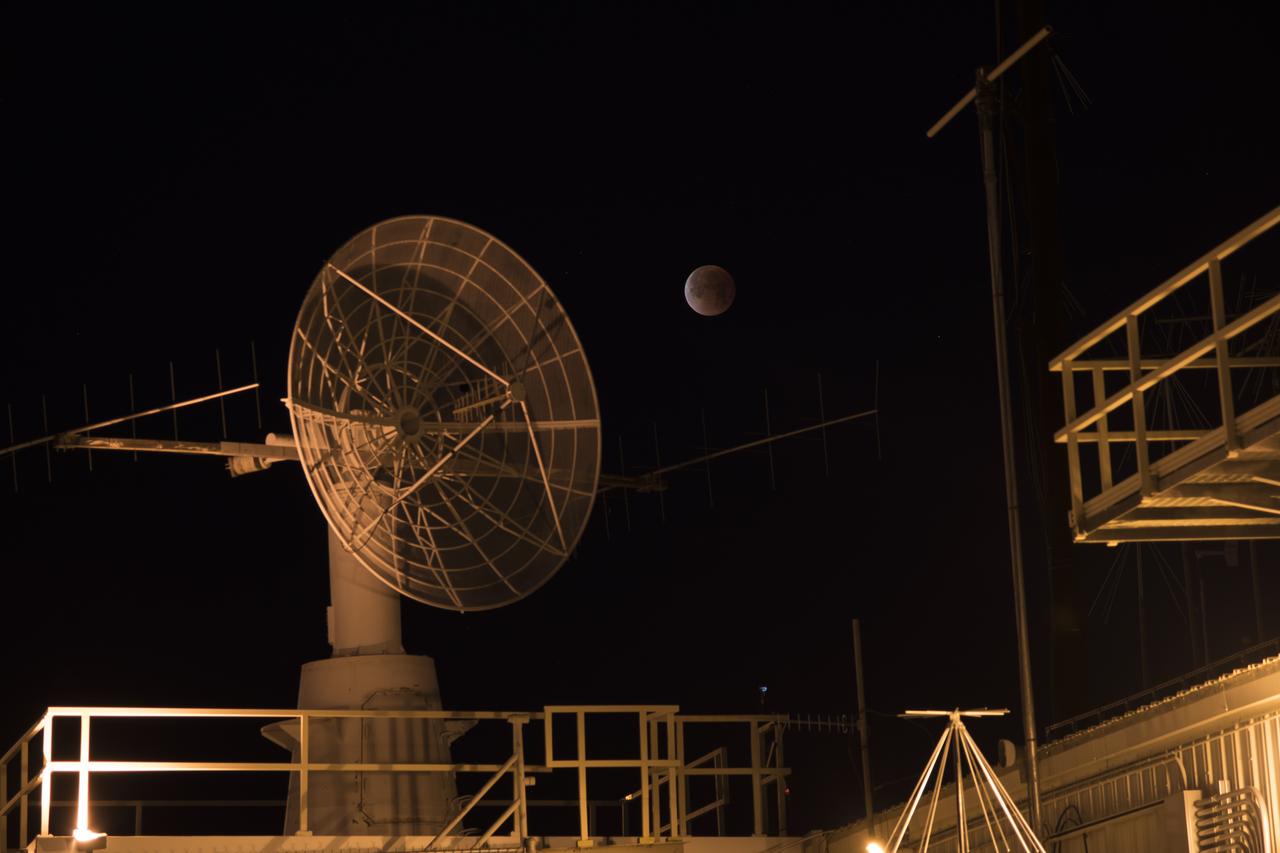

California’s NASA Armstrong Flight Research Center’s photographer Carla Thomas takes photos on January 31 of the rare opportunity to capture a supermoon, a blue moon and a lunar eclipse at the same time. A supermoon occurs when the Moon is closer to Earth in its orbit and appearing 14 percent brighter than usual. As the second full moon of the month, this moon is also commonly known as a blue moon, though it will not be blue in appearance. The super blue moon passed through Earth’s shadow and took on a reddish tint, known as a blood moon. This total lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and a full moon form a near-perfect lineup in space. The Moon passes directly behind the Earth into its umbra (shadow).
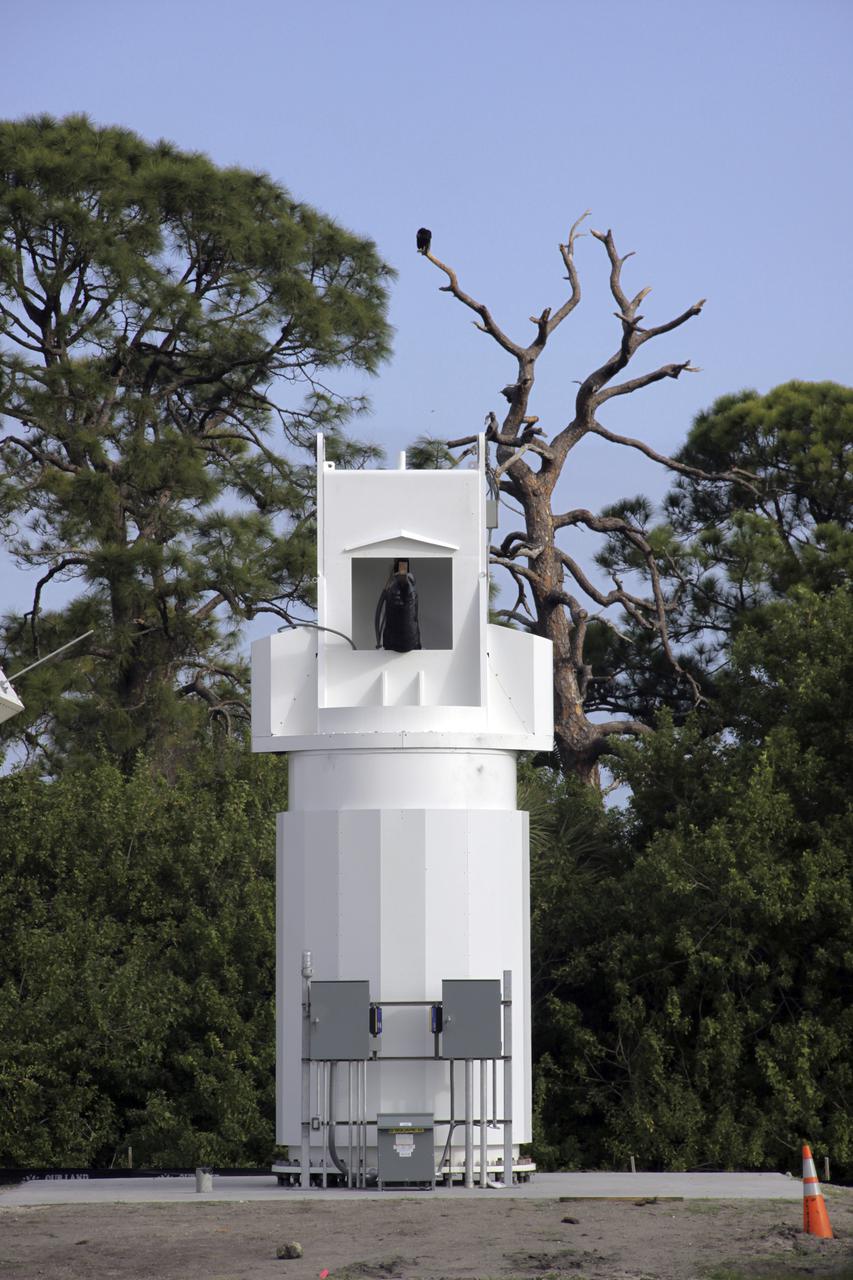

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
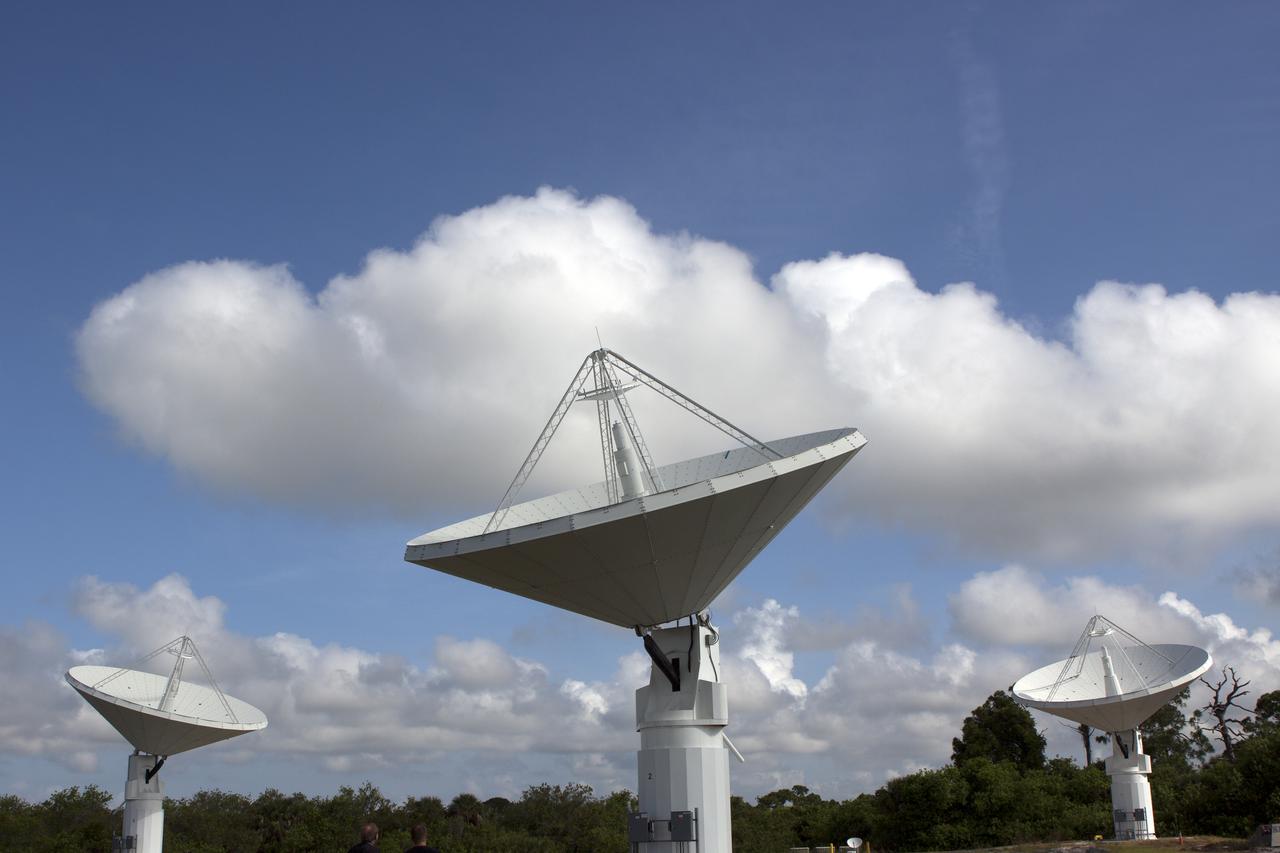

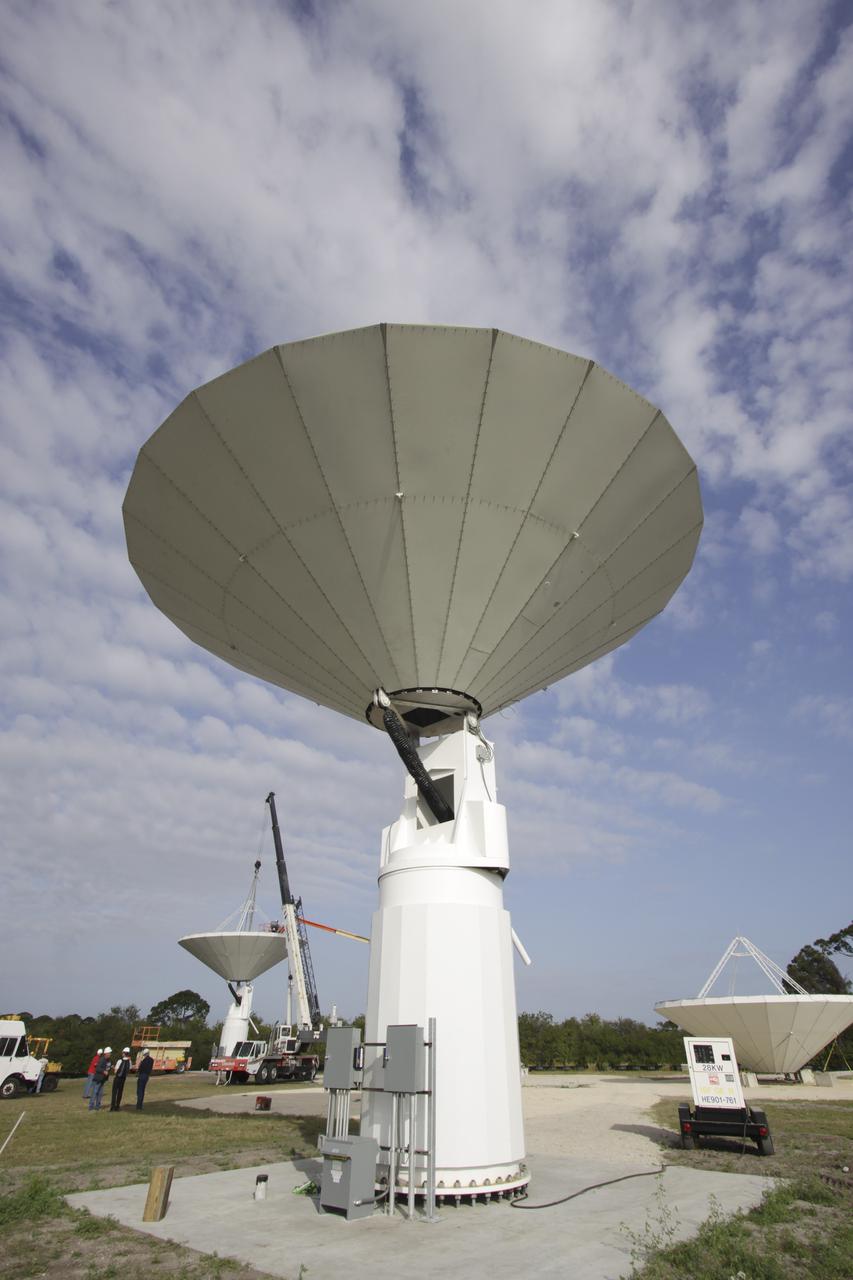
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
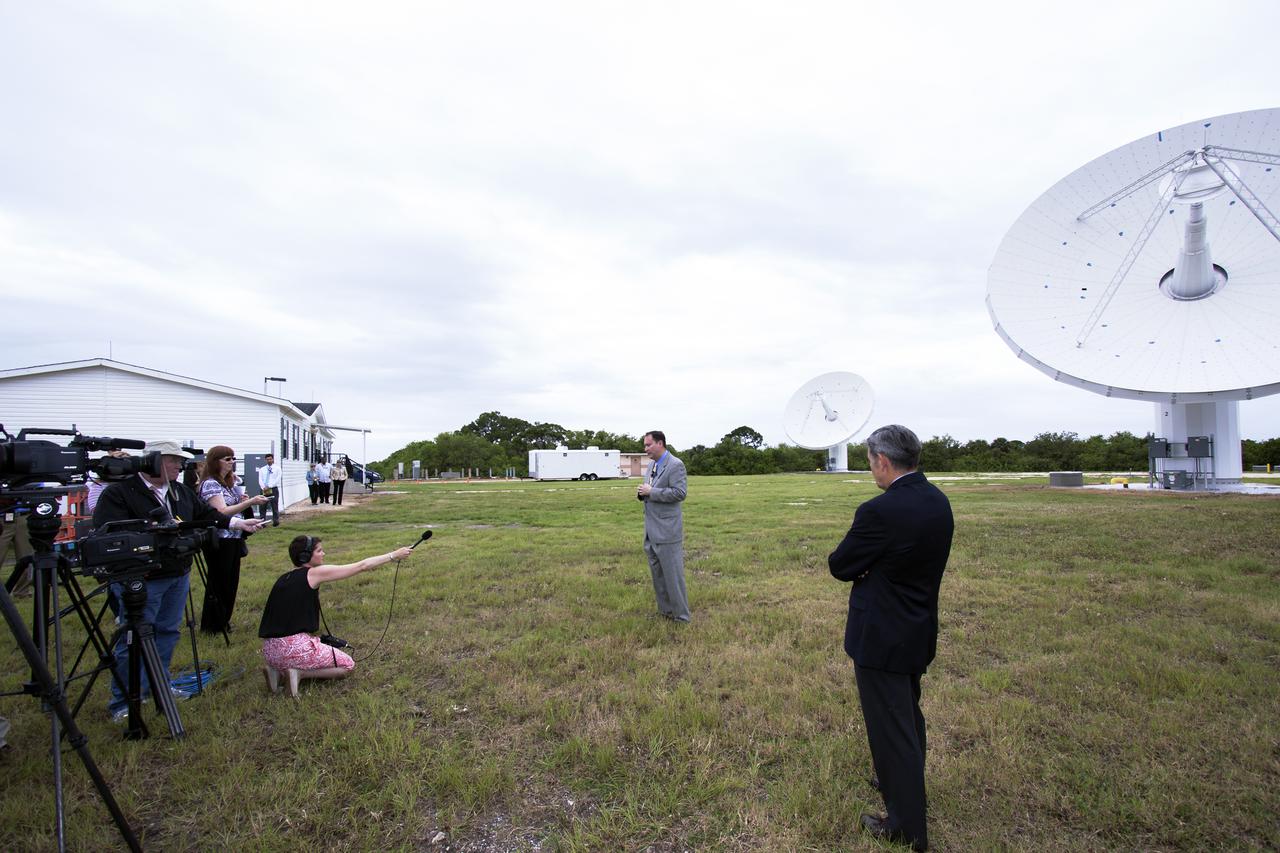

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Robert Lightfoot, NASA associate director, talks to members of the media at the Ka Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or KaBOOM, testbed antenna array site during a tour of Kennedy facilities. At right, in the foreground is Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. The goal of KaBOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas is used to track the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, new towers are being constructed for the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
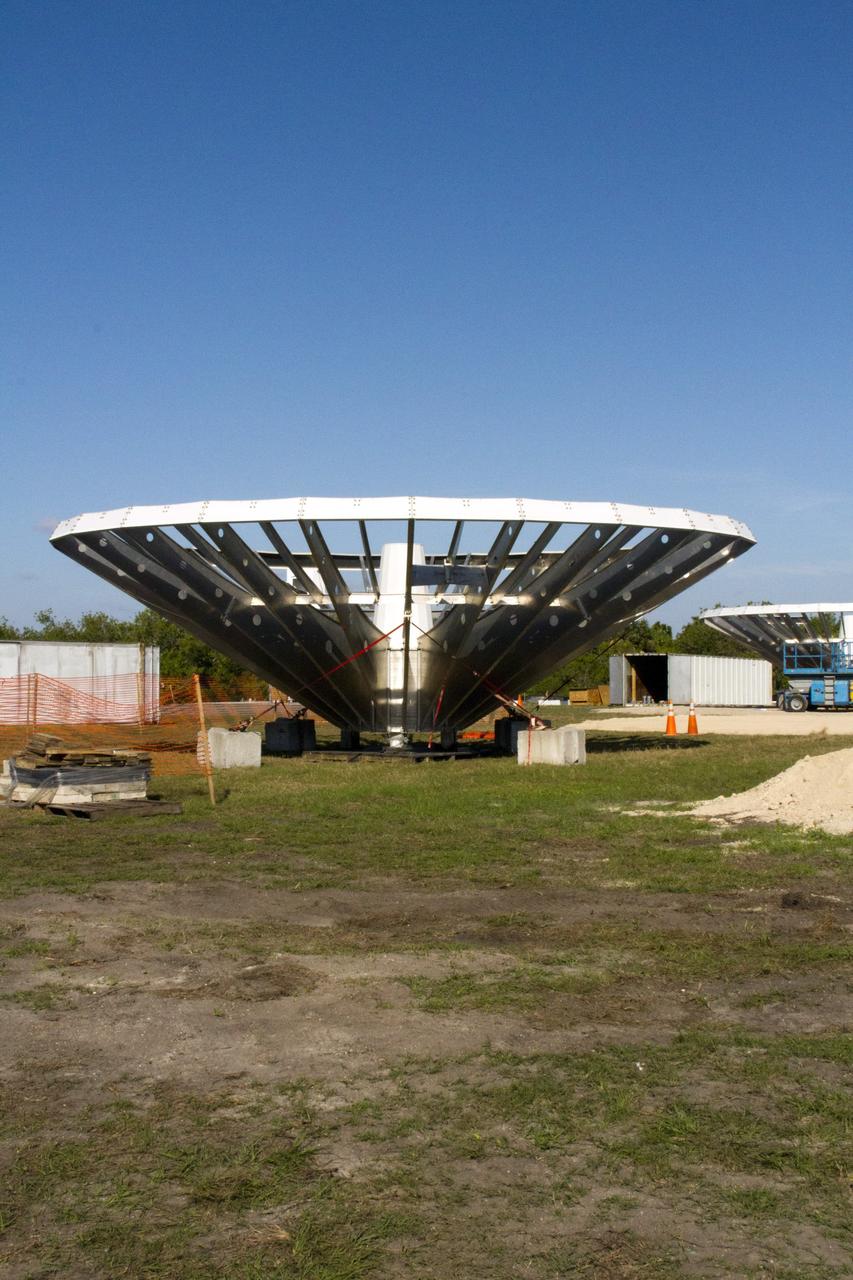

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
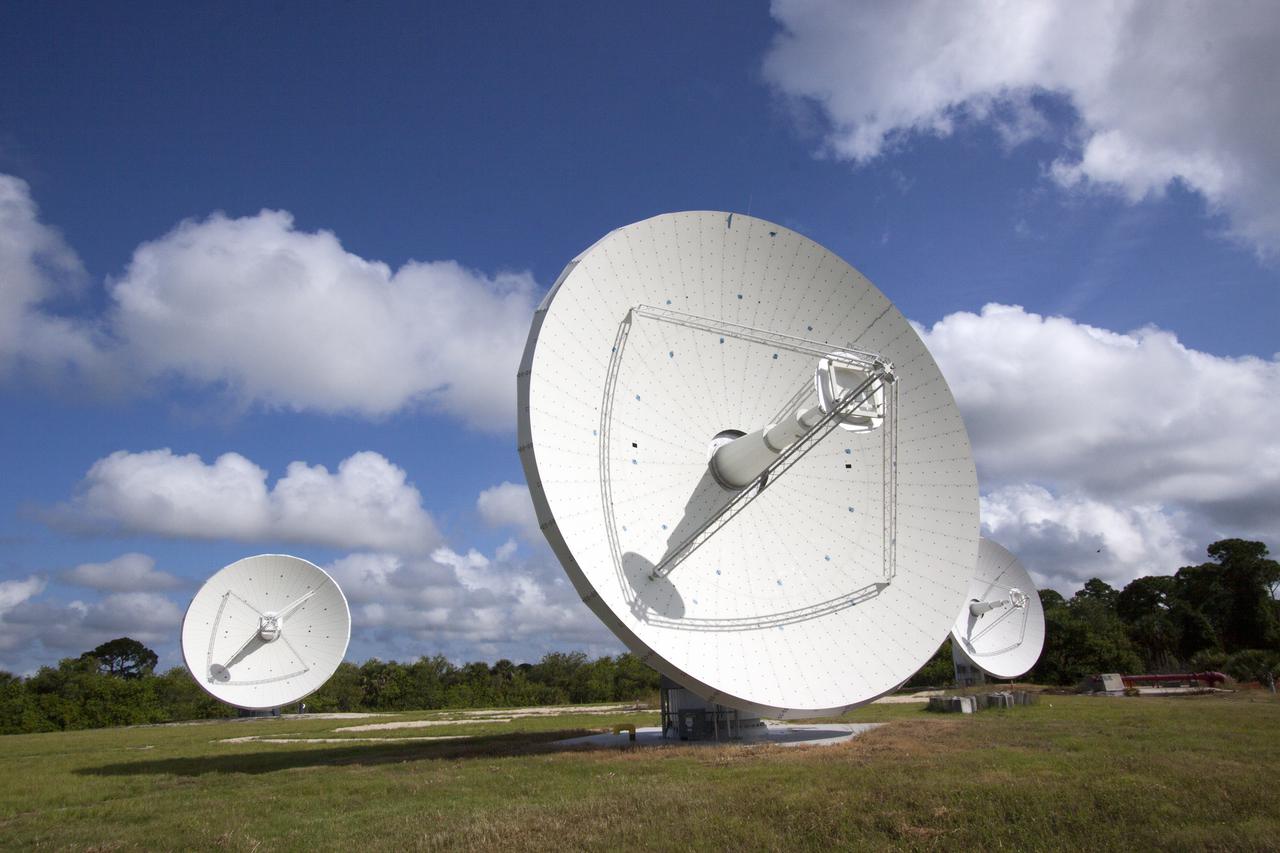

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
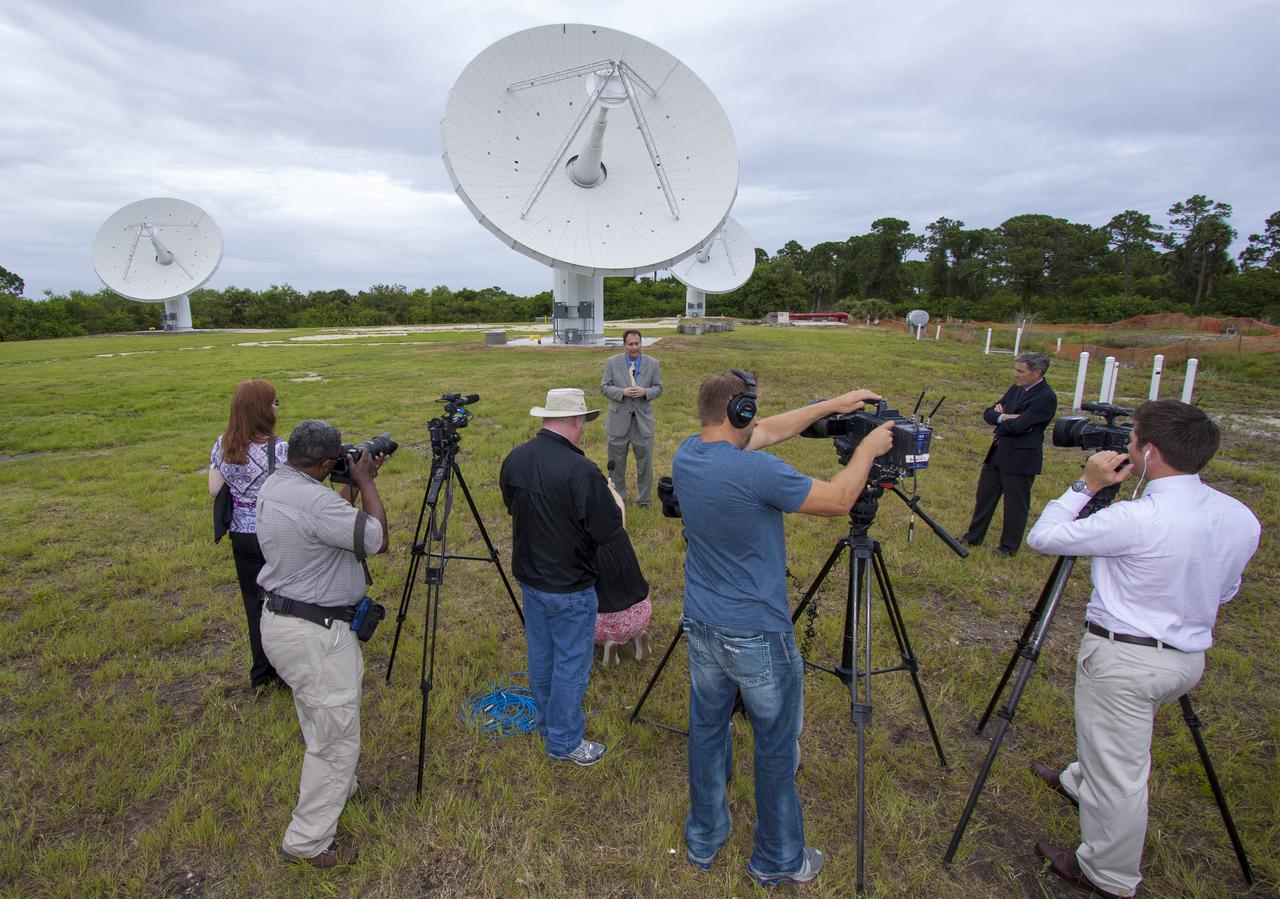

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Robert Lightfoot, NASA associate director, talks to members of the media at the Ka Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or KaBOOM, testbed antenna array site during a tour of Kennedy facilities. At right is Kennedy Director Bob Cabana. The goal of KaBOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
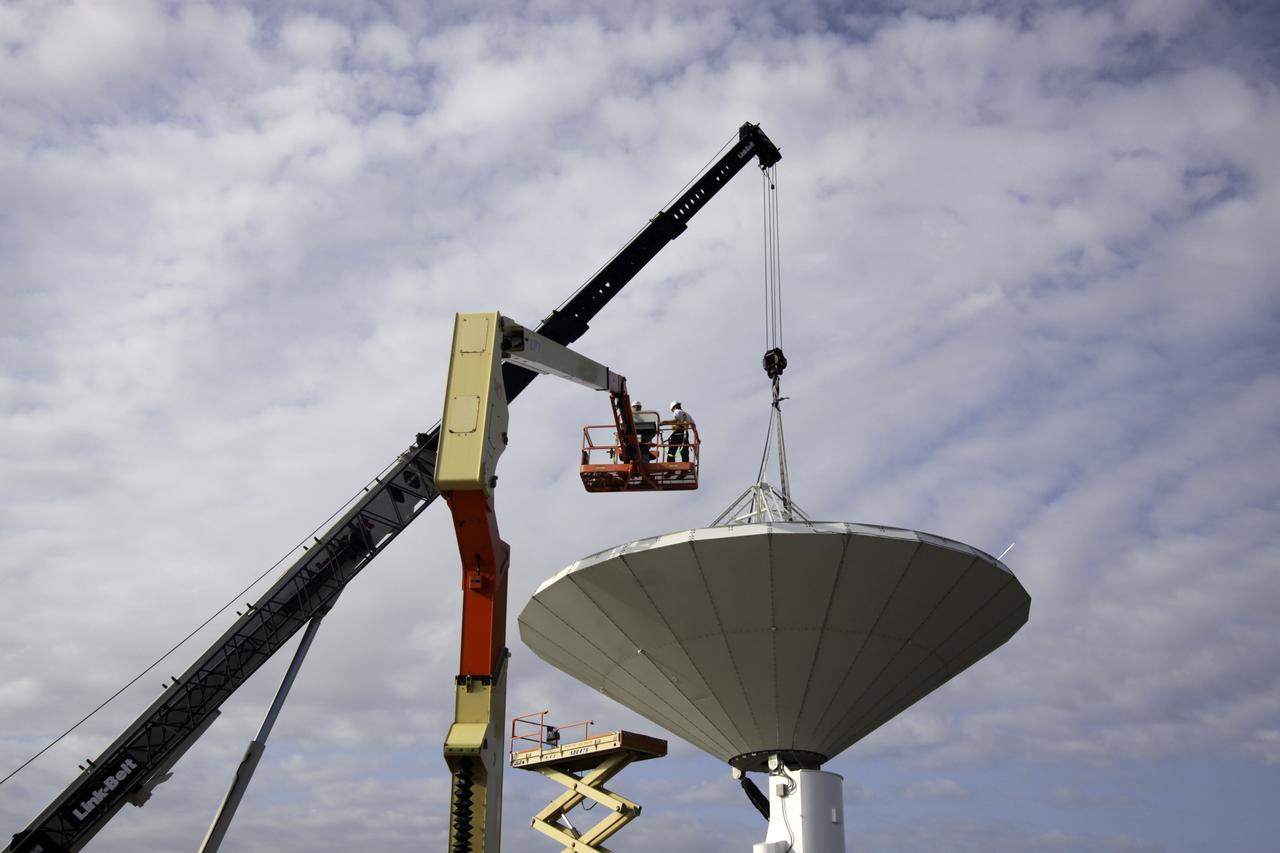

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
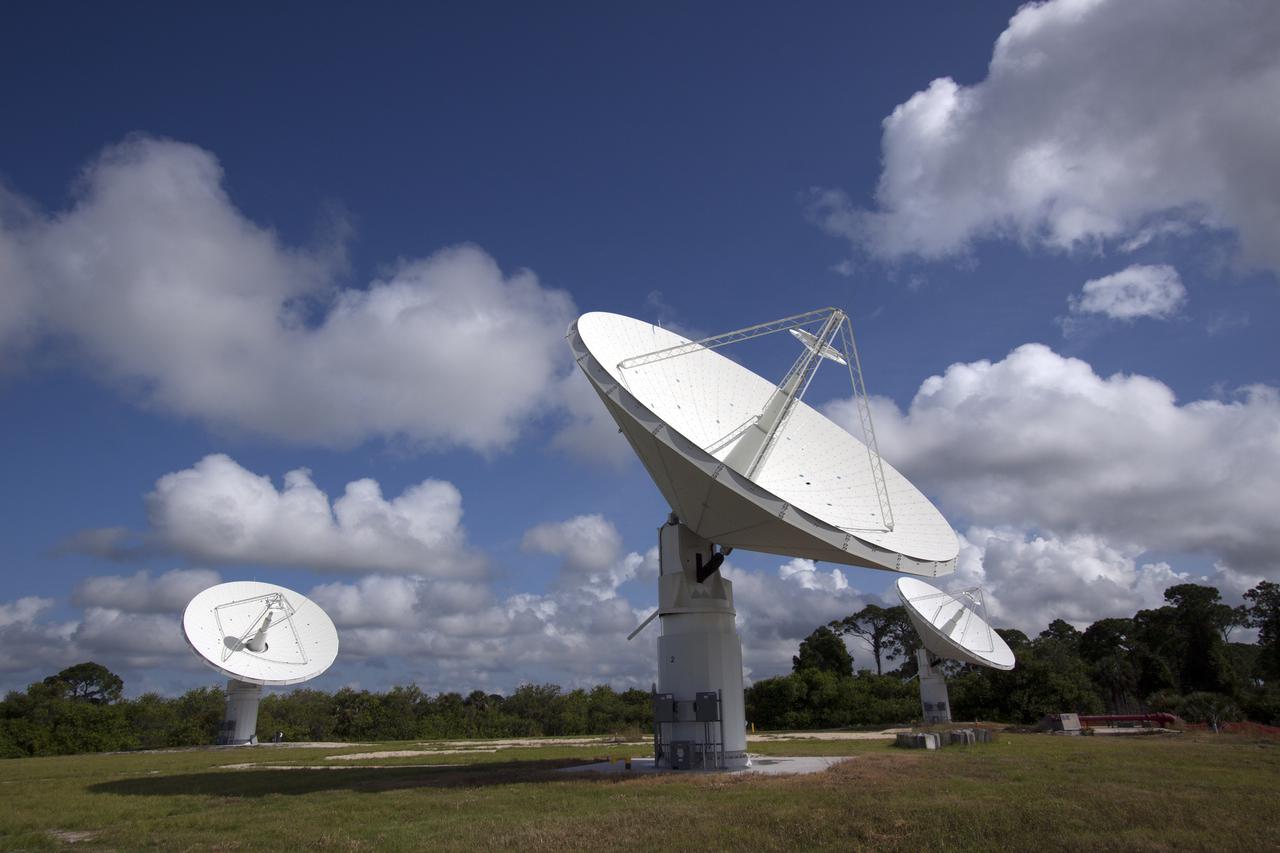

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, new towers are being constructed for the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
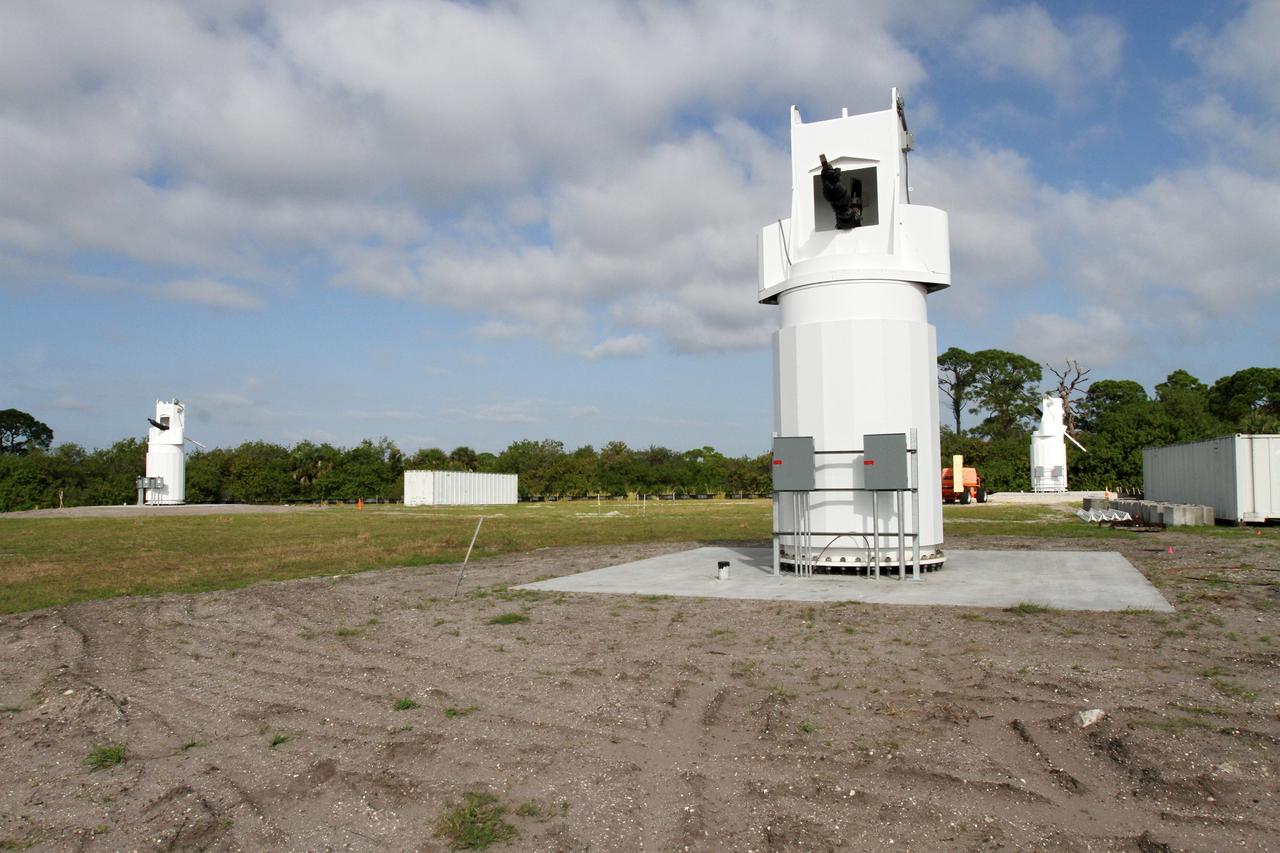

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, new towers are being constructed for the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
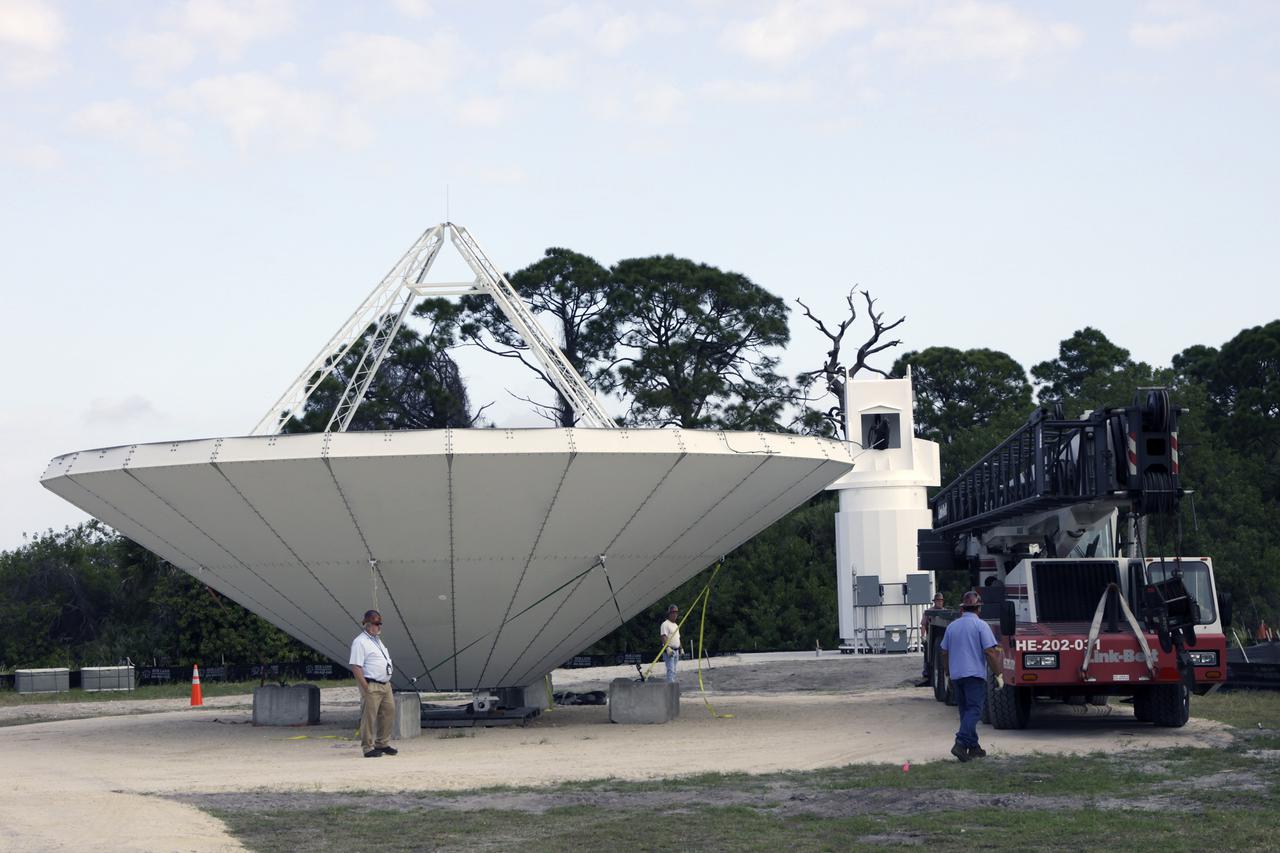

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
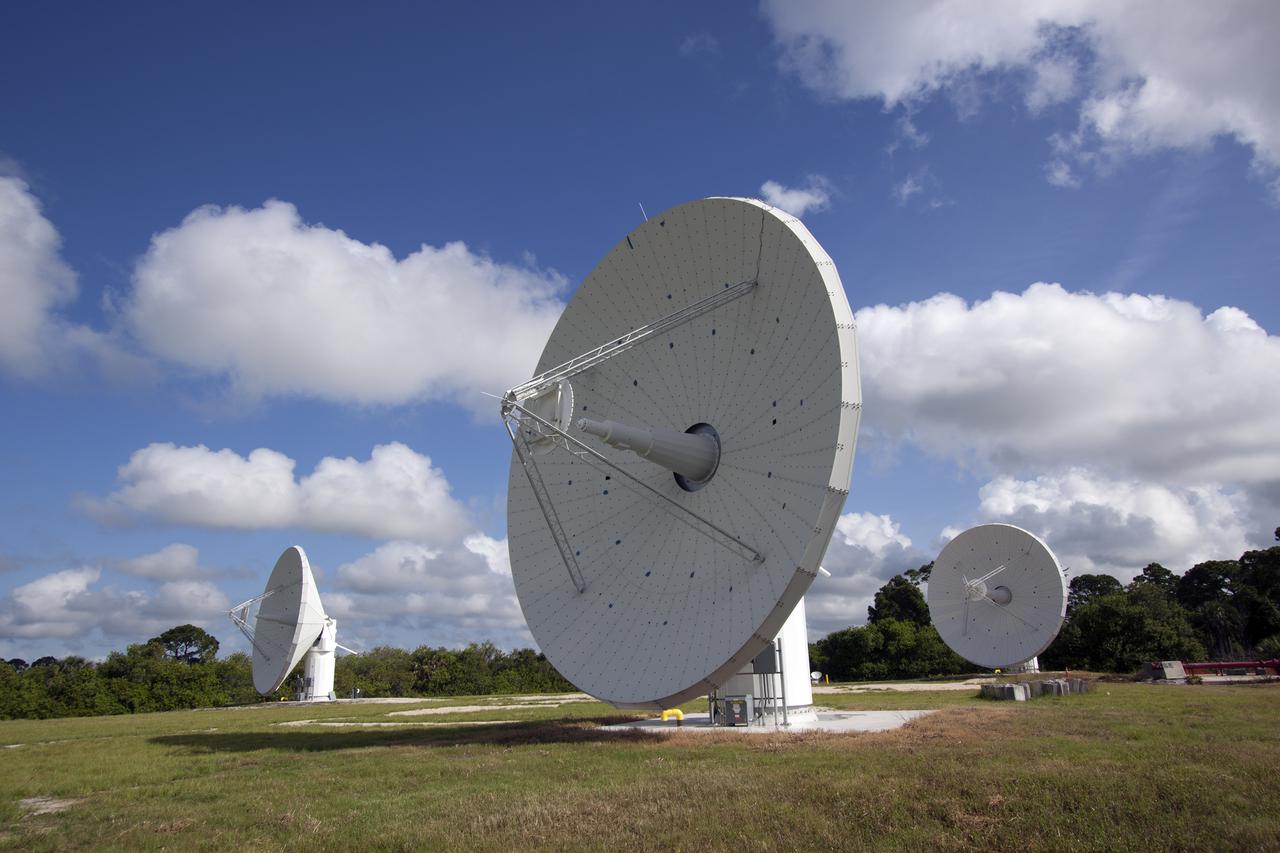

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas is used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
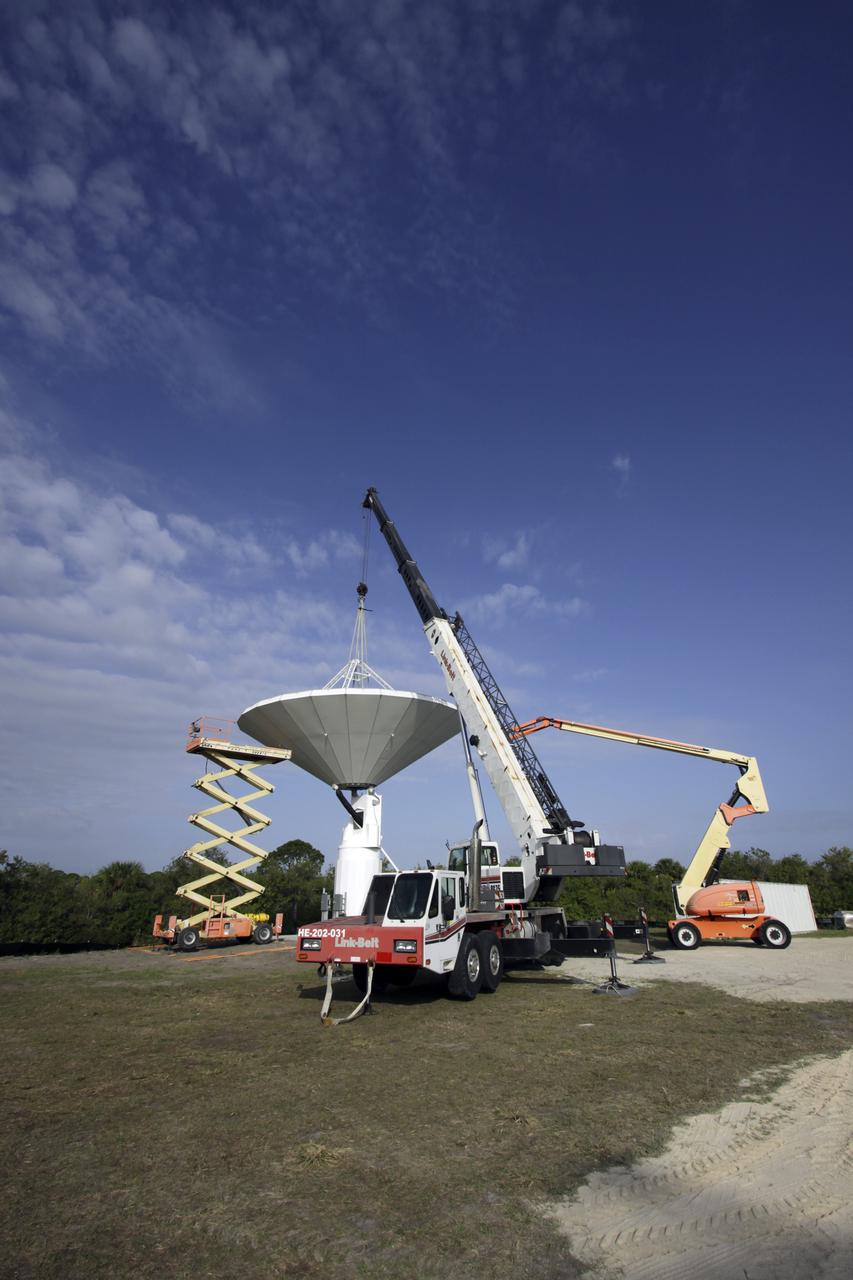

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
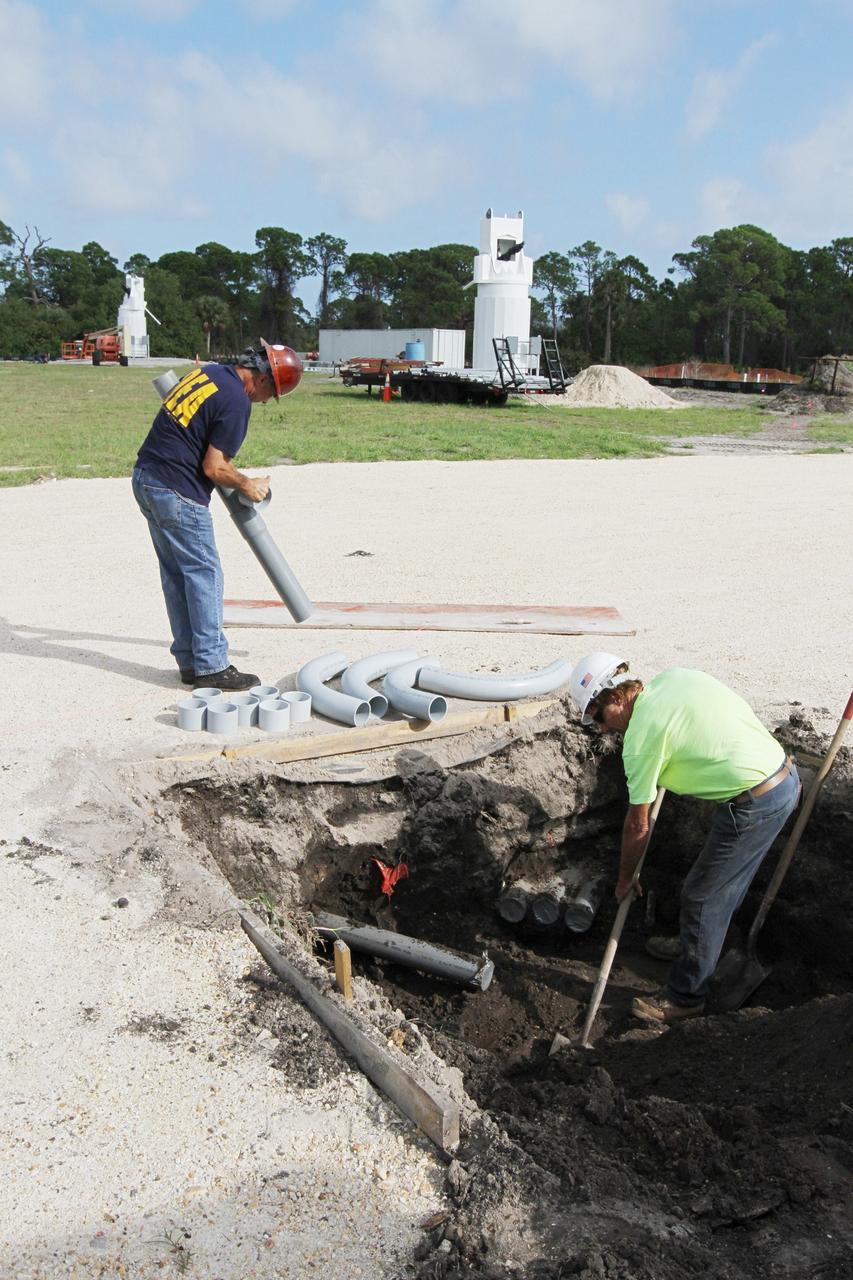

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers continue construction of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
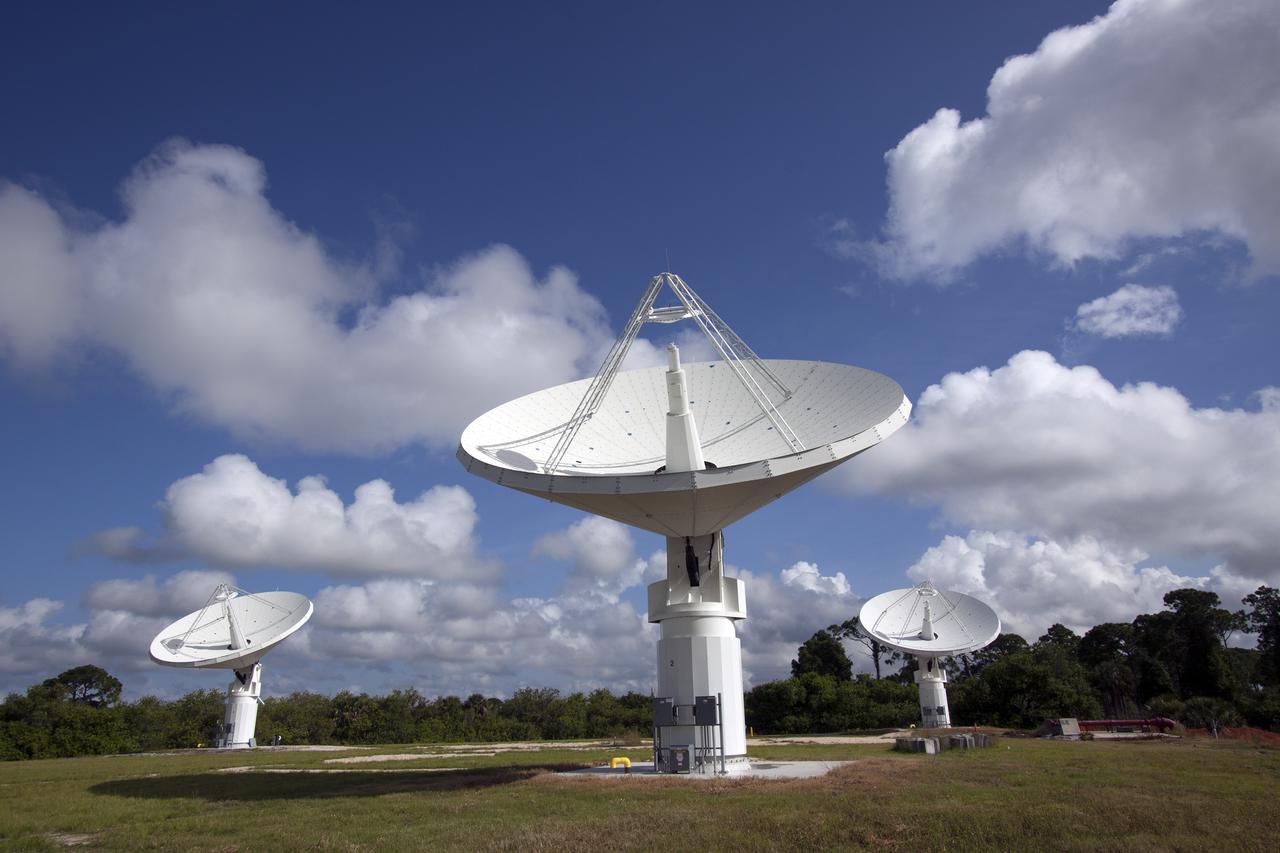

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
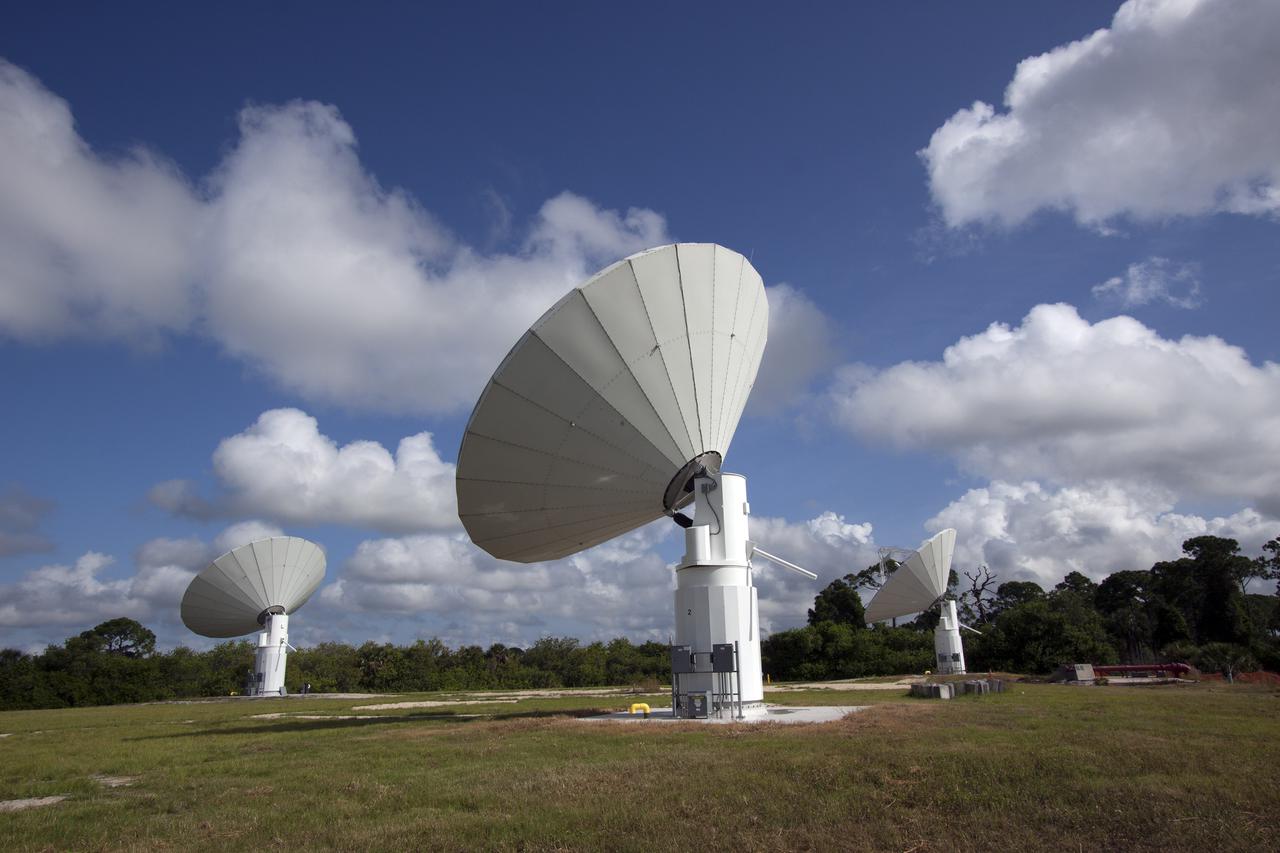

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
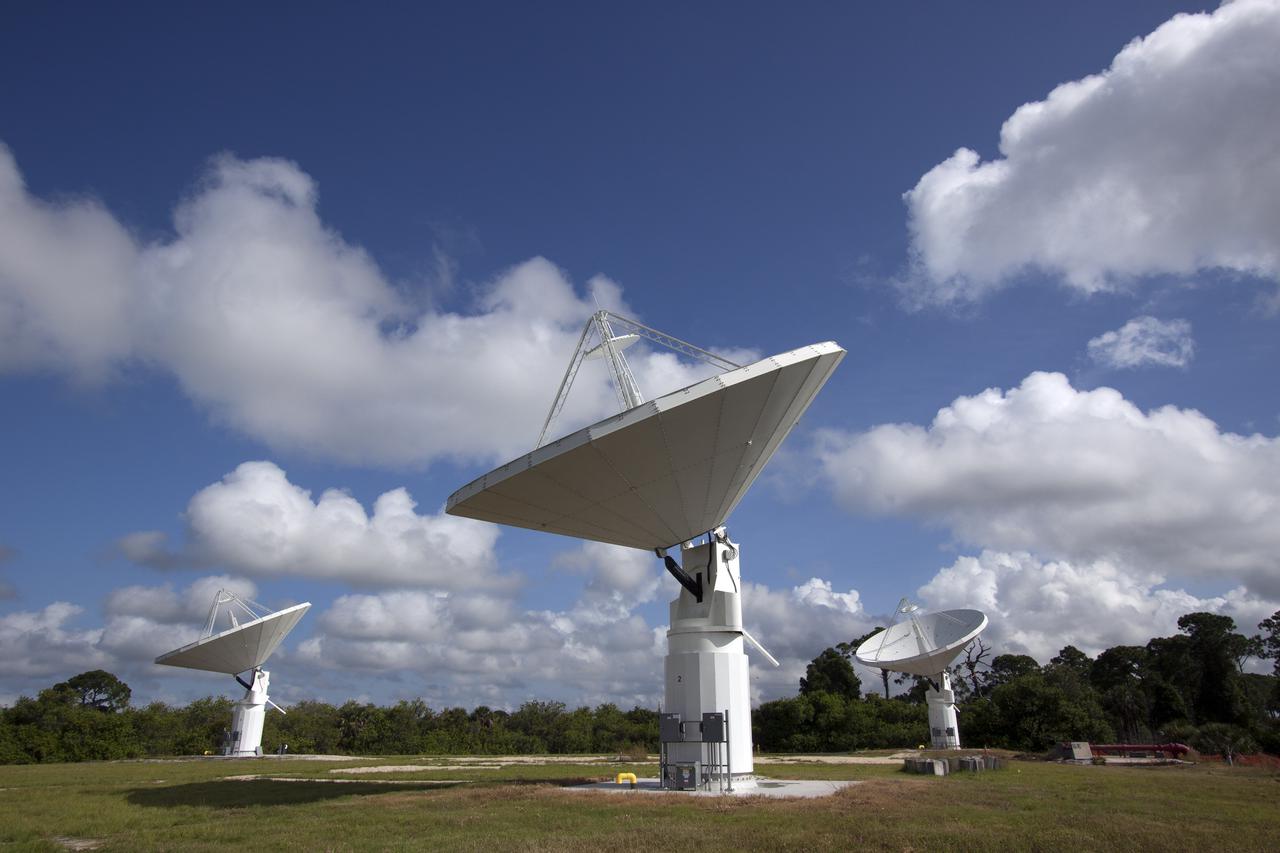

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
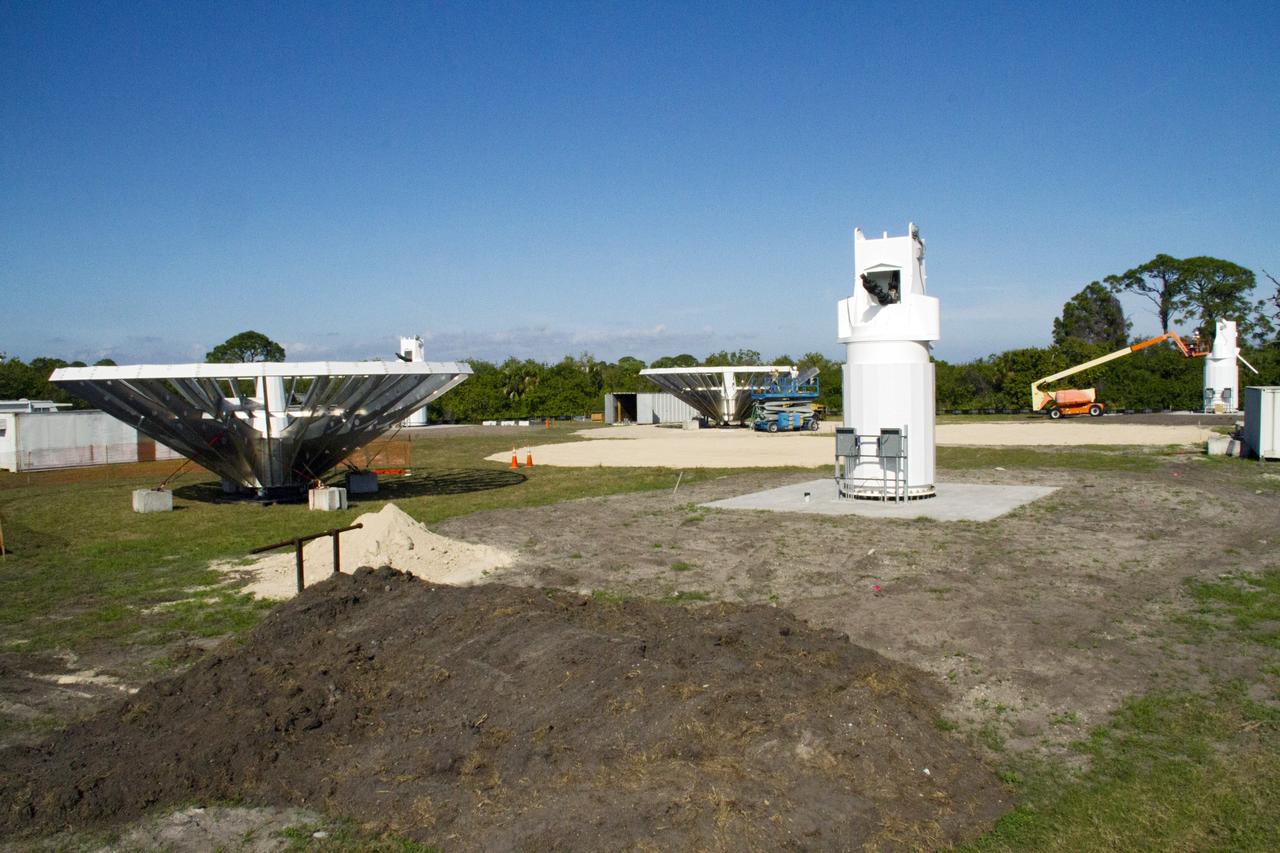

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
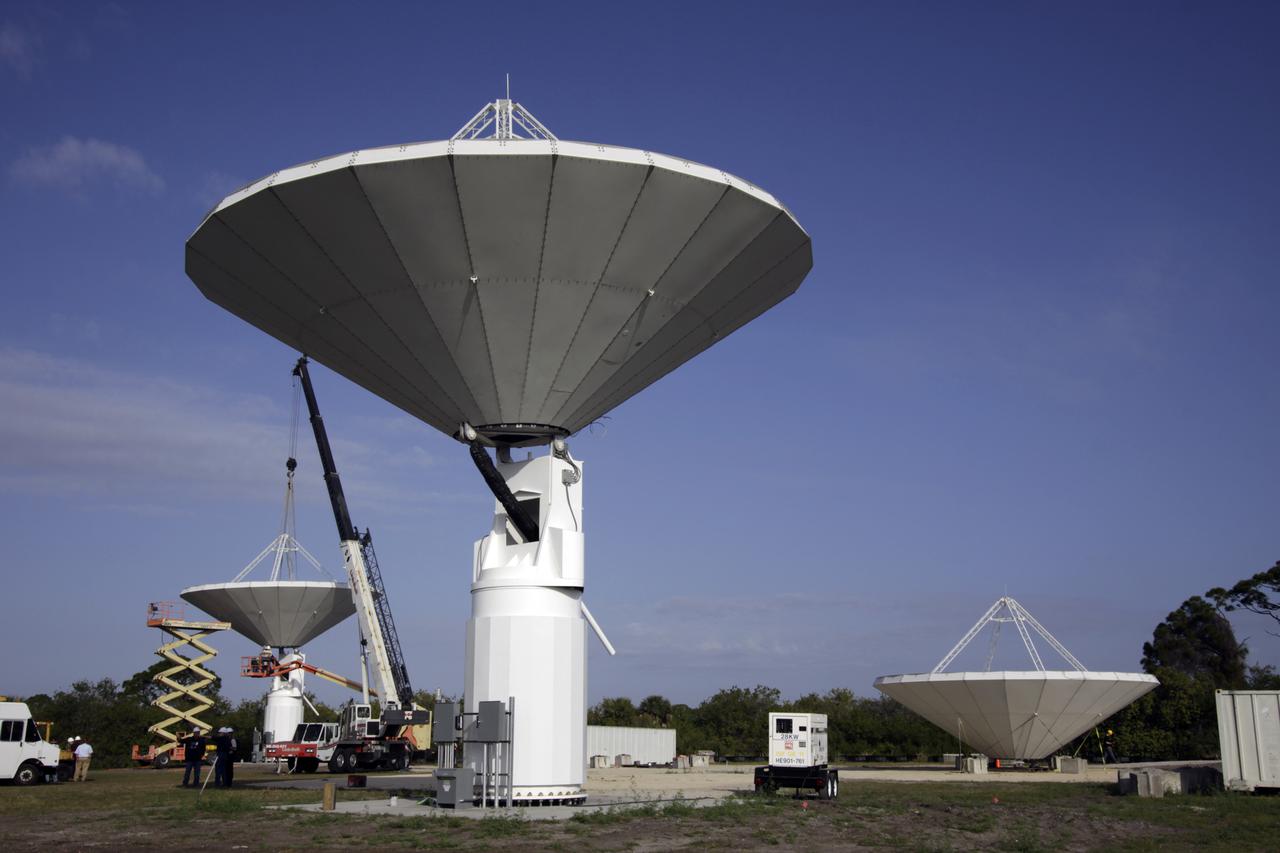

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
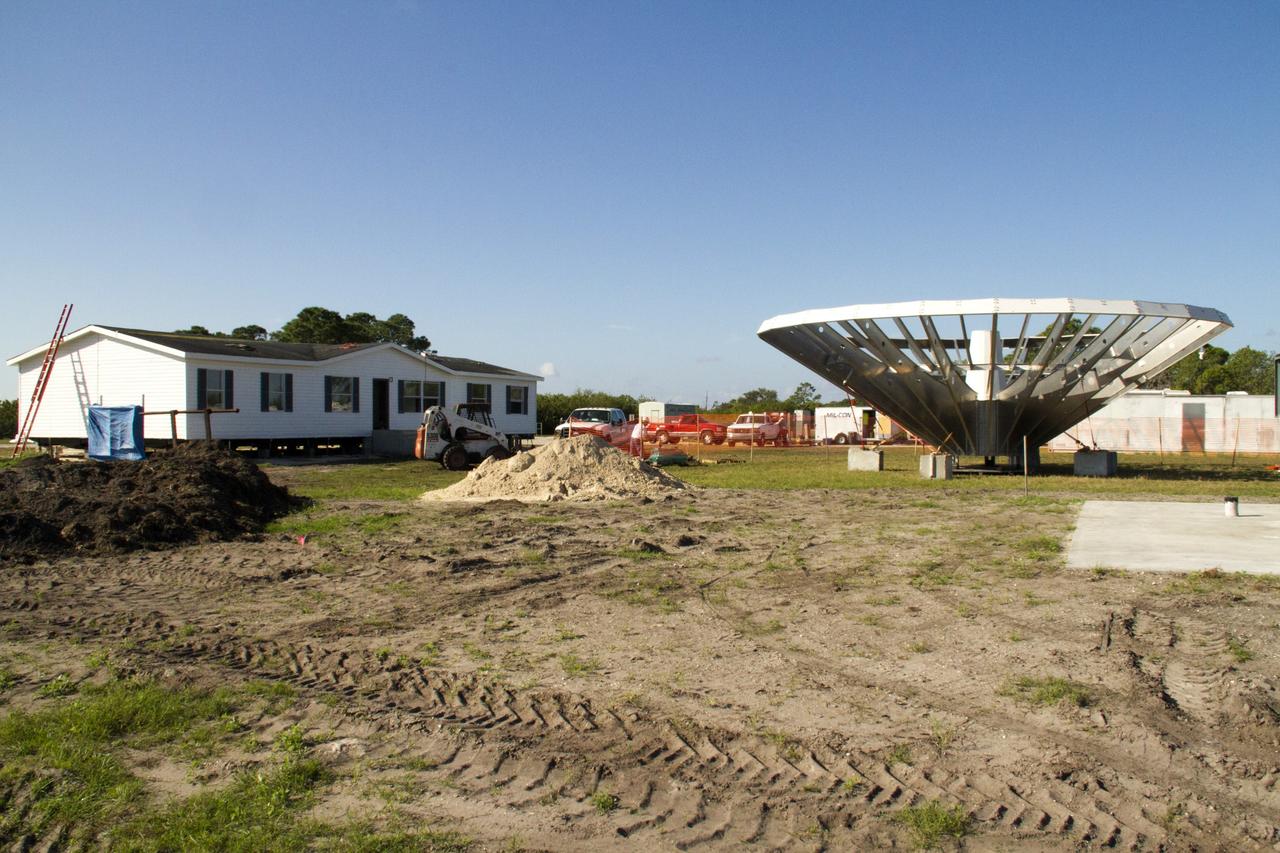

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
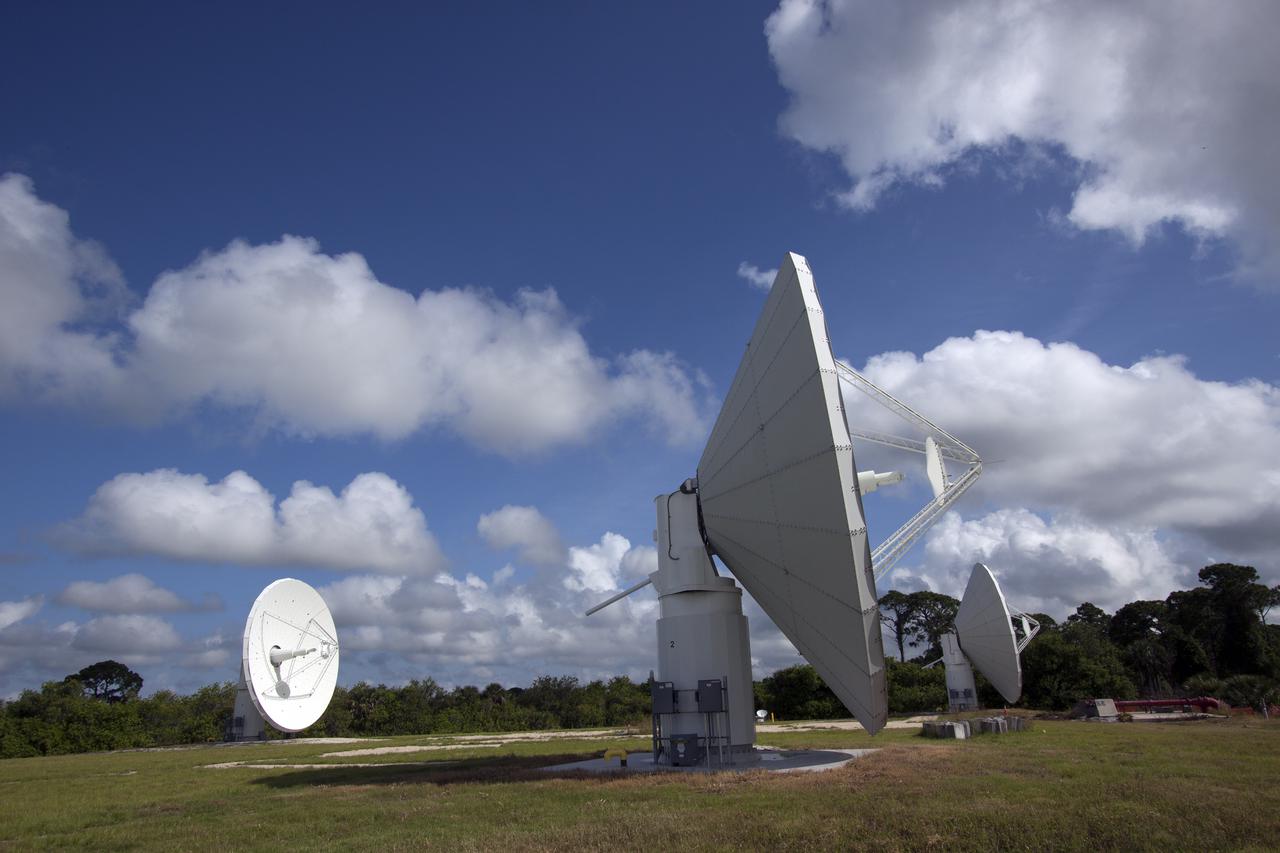

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
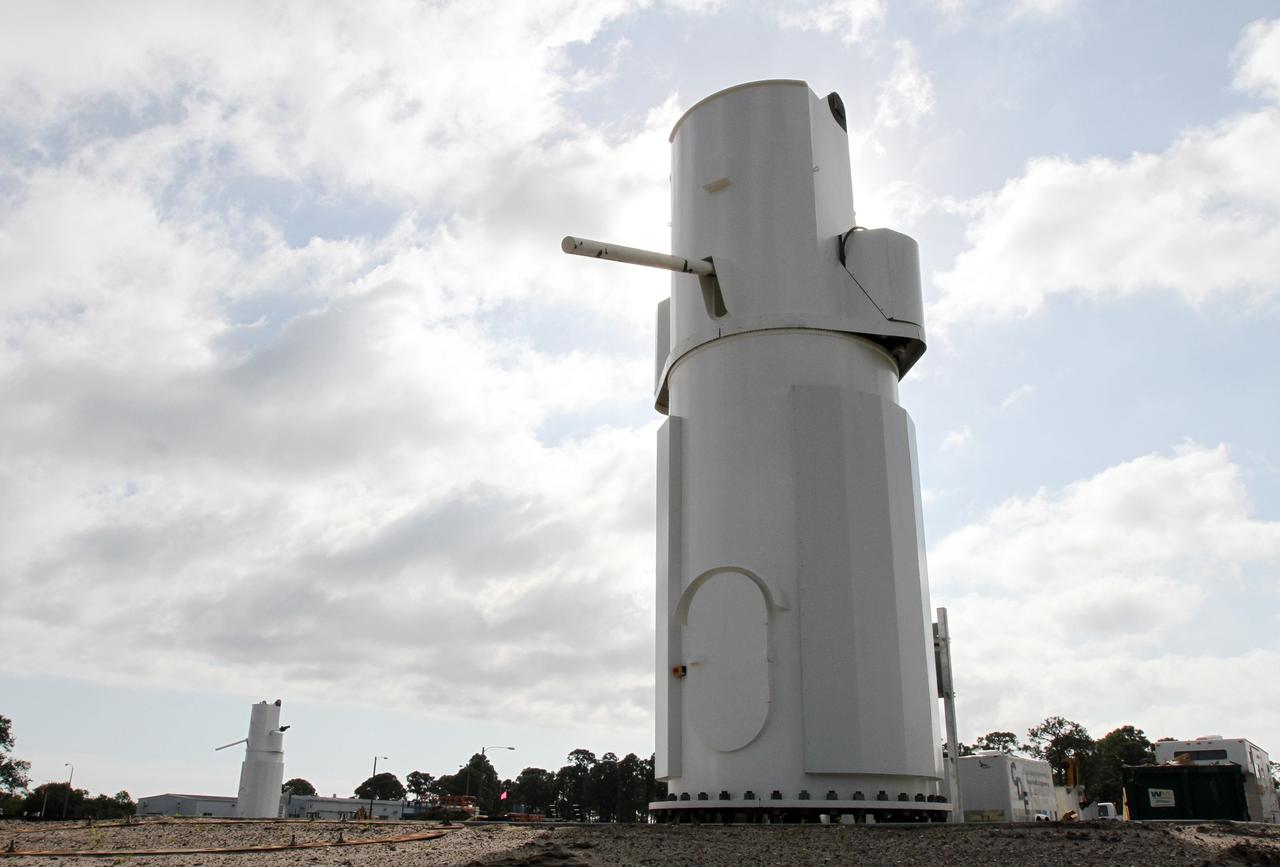

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, new towers are being constructed for the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
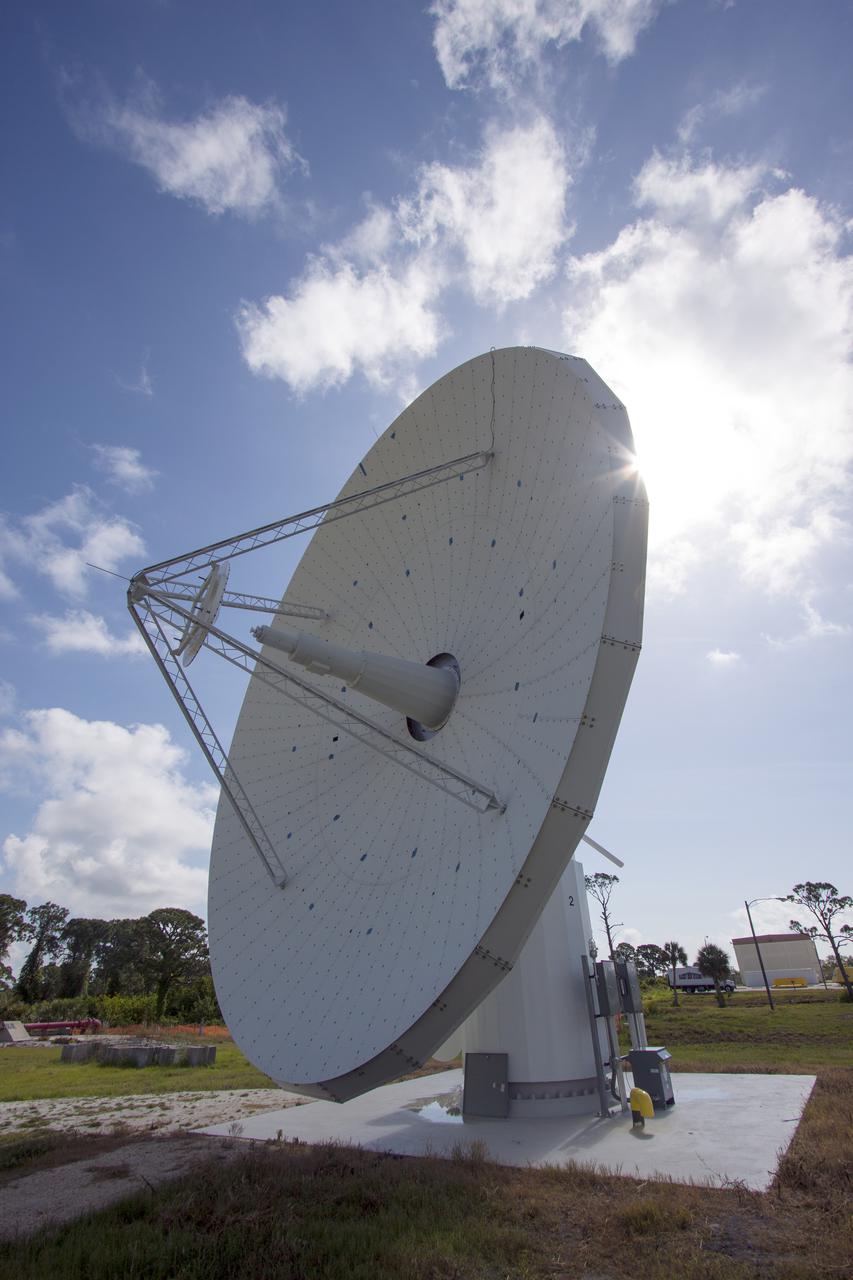

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas is used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
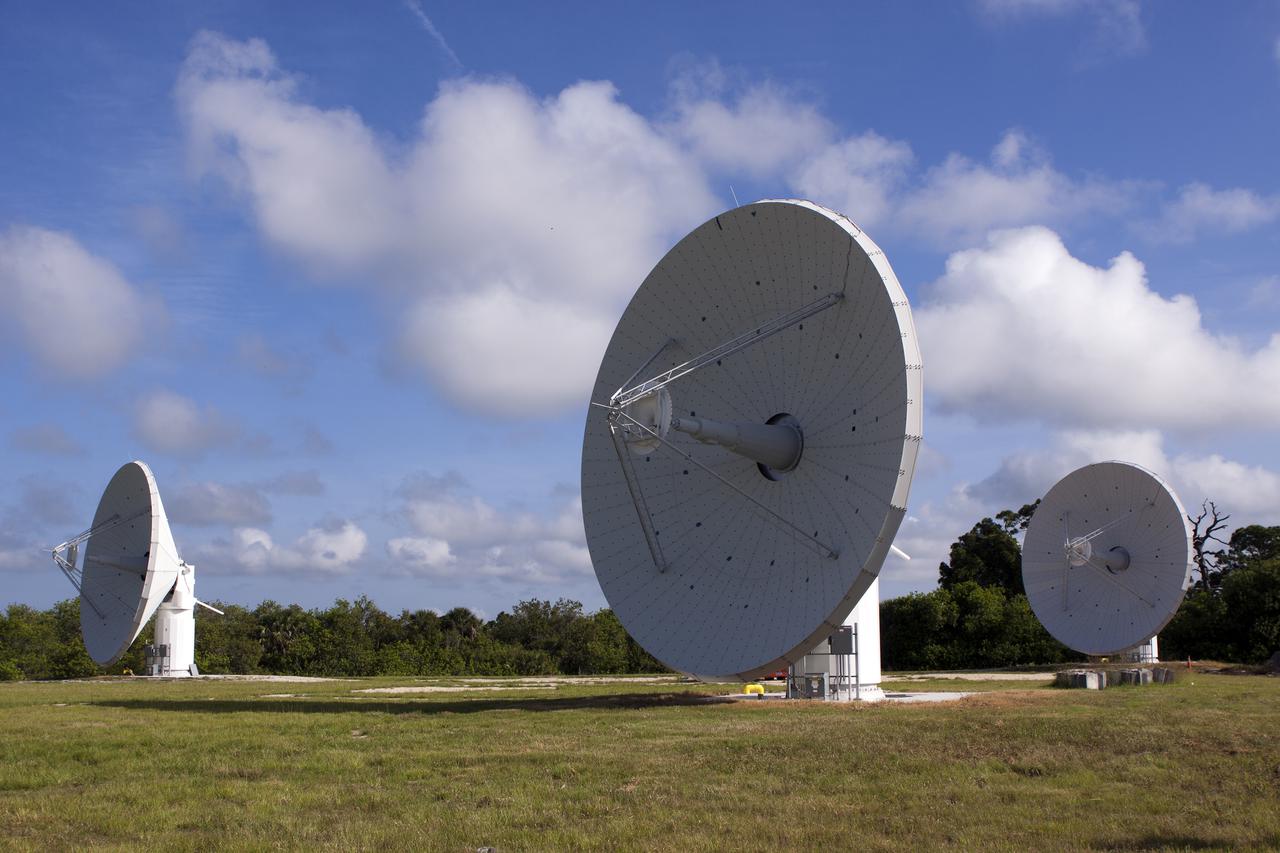

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas is used to track the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
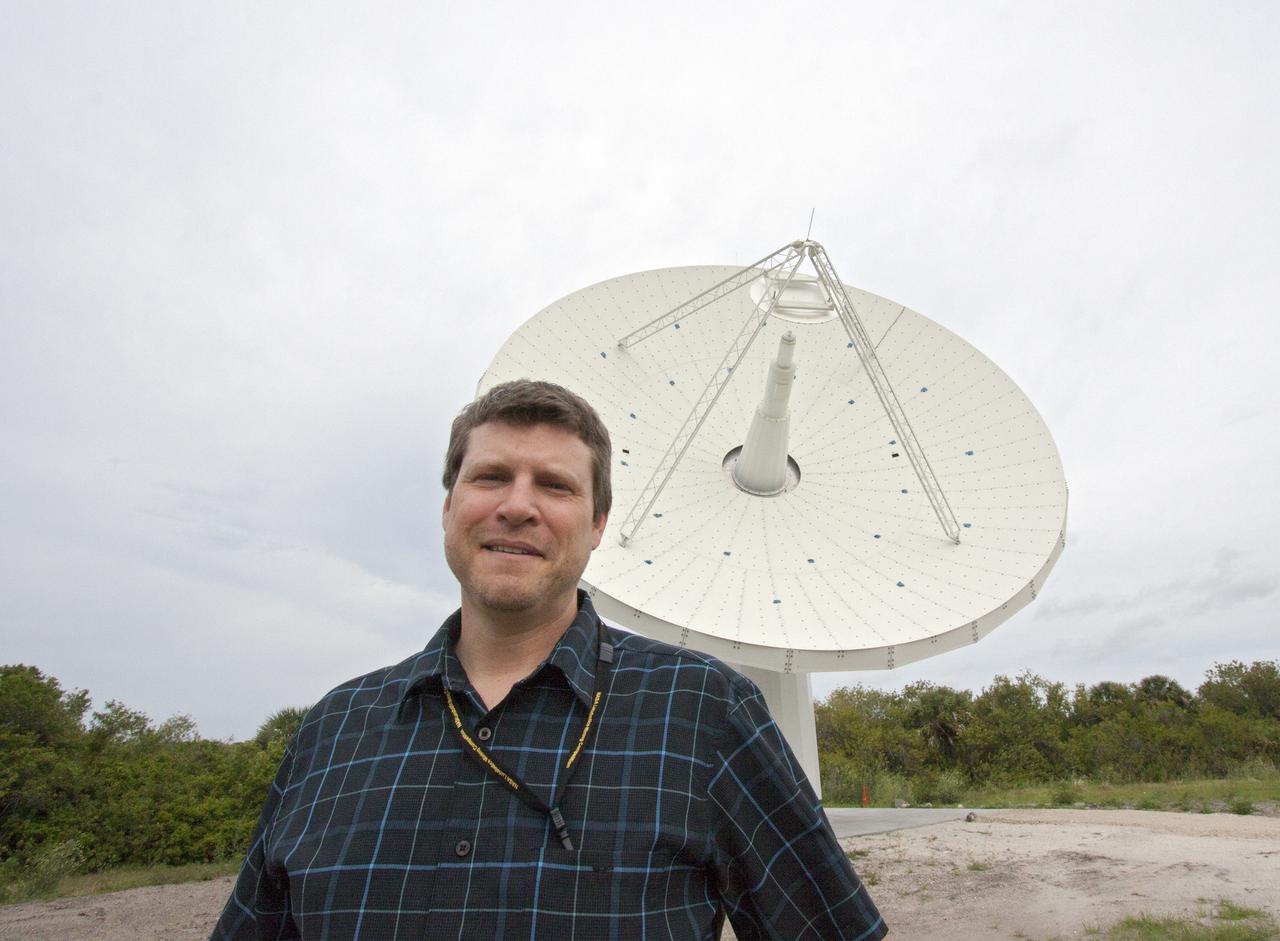

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Marc Seibert, the manager for Tracking and Timing Integration in the Research and Technology Management Office, stands near one of the three antennas that comprise the KA-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, System. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, new towers are being constructed for the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
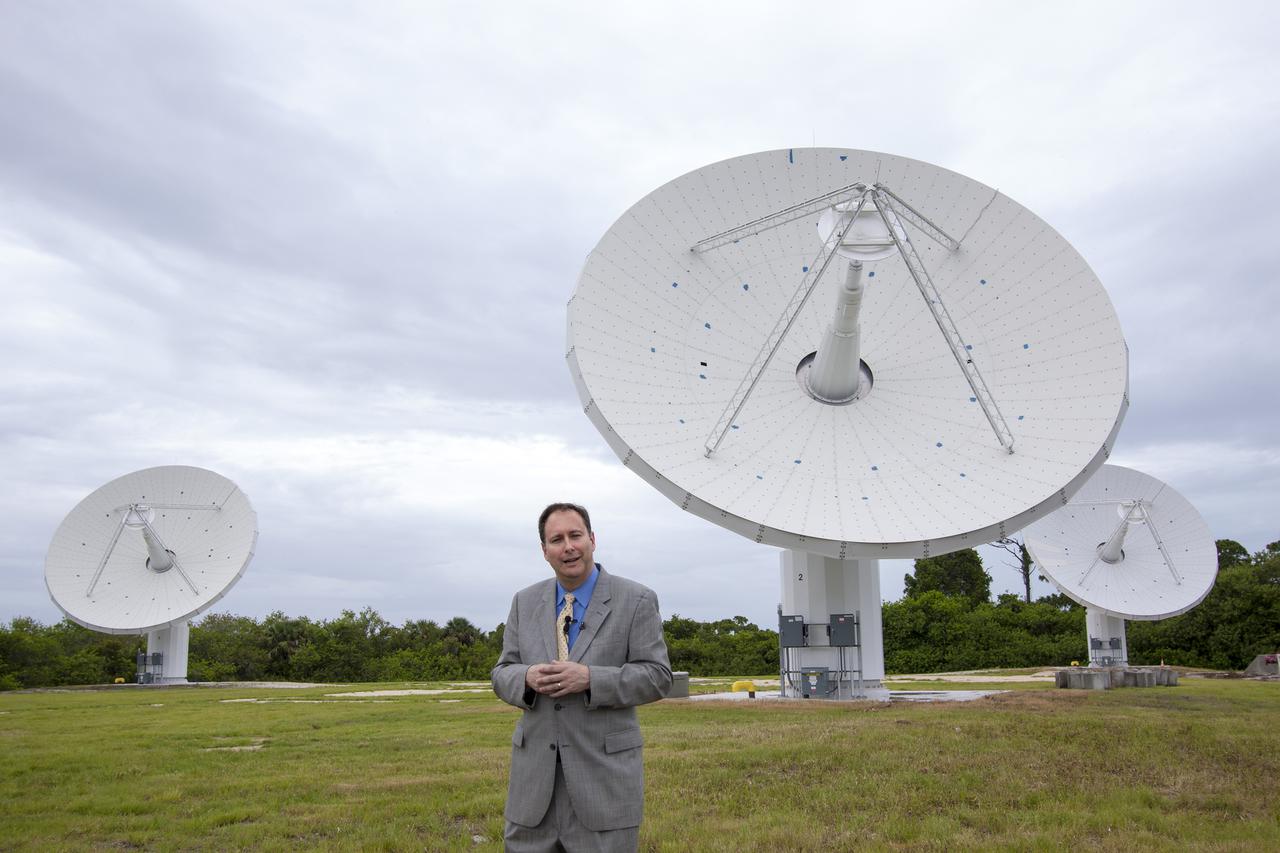

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Robert Lightfoot, NASA associate director, talks to members of the media at the Ka Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or KaBOOM, testbed antenna array site during a tour of Kennedy facilities. The goal of KaBOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
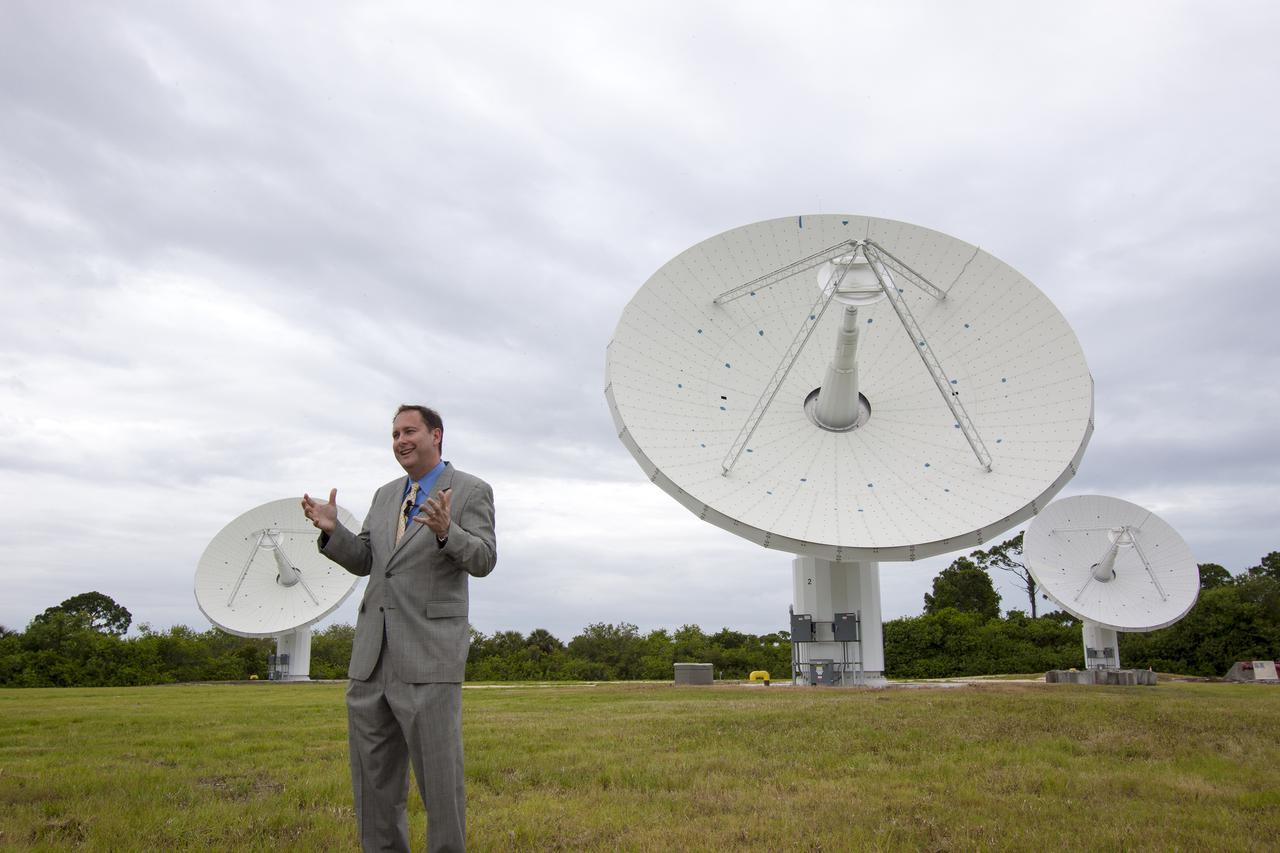

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Robert Lightfoot, NASA associate director, talks to members of the media at the Ka Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or KaBOOM, testbed antenna array site during a tour of Kennedy facilities. The goal of KaBOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
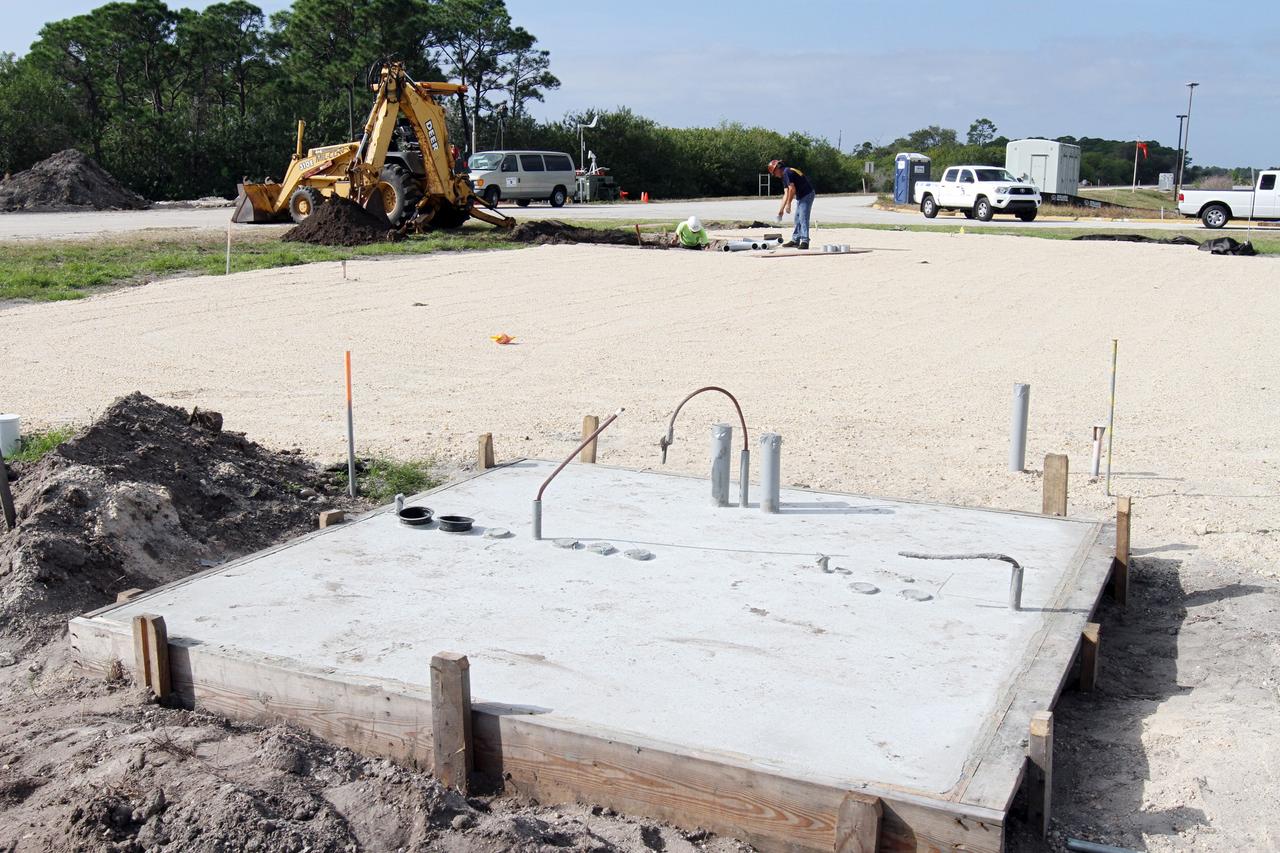

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers continue construction of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, system. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Workers soon will begin construction on the 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays and their associated utilities, and prepare the site for the operations command center facility. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky
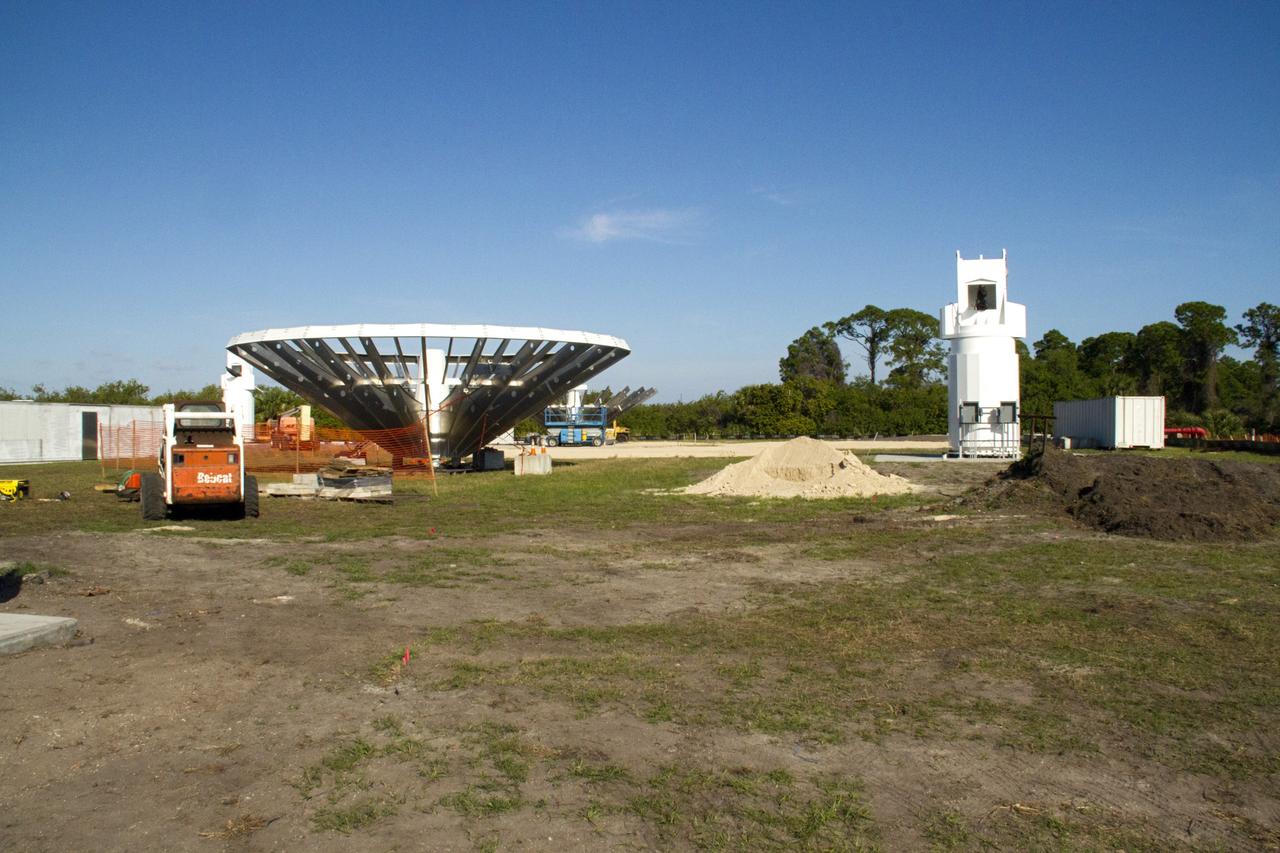

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the three Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM, testbed antennas are used to track the pattern of the sun during initial testing of the new system. The goal of Ka-BOOM is to prove technologies that will allow future systems to characterize near-Earth objects in terms of size, shape, rotation_tumble rate and to determine the trajectory of those objects. Radar studies can determine the trajectory 100,000 times more precisely than can optical methods. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. The 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are at the site of the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, 40-foot-diameter dish antenna arrays are being constructed as part of the Antenna Test Bed Array for the Ka-Band Objects Observation and Monitoring, or Ka-BOOM system. The antennas will be part of the operations command center facility. The construction site is near the former Vertical Processing Facility, which has been demolished. The Ka-BOOM project is one of the final steps in developing the techniques to build a high power, high resolution radar system capable of becoming a Near Earth Object Early Warning System. While also capable of space communication and radio science experiments, developing radar applications is the primary focus of the arrays. Photo credit: NASA/ Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A worker awaits the delivery by crane of the radome to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
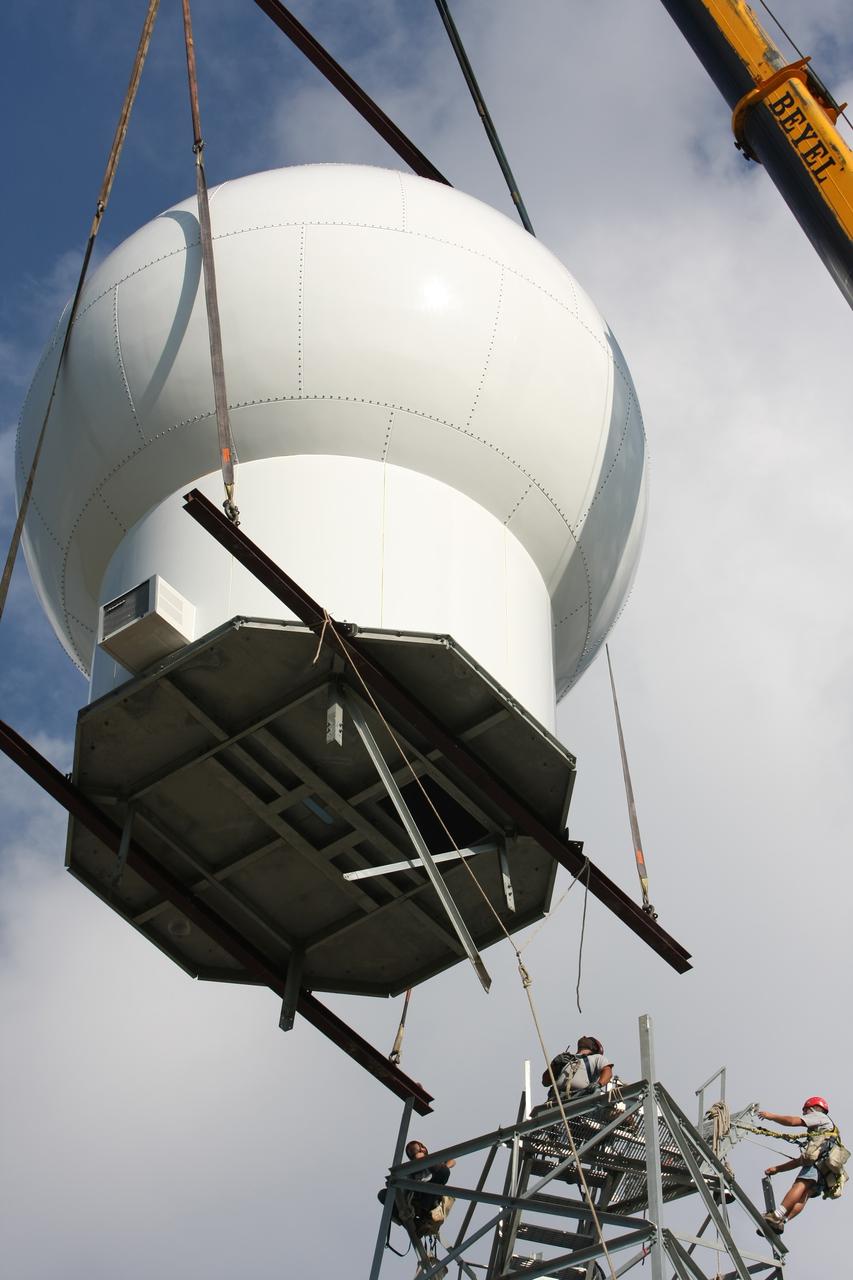

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers watch as the radome is delivered by crane to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
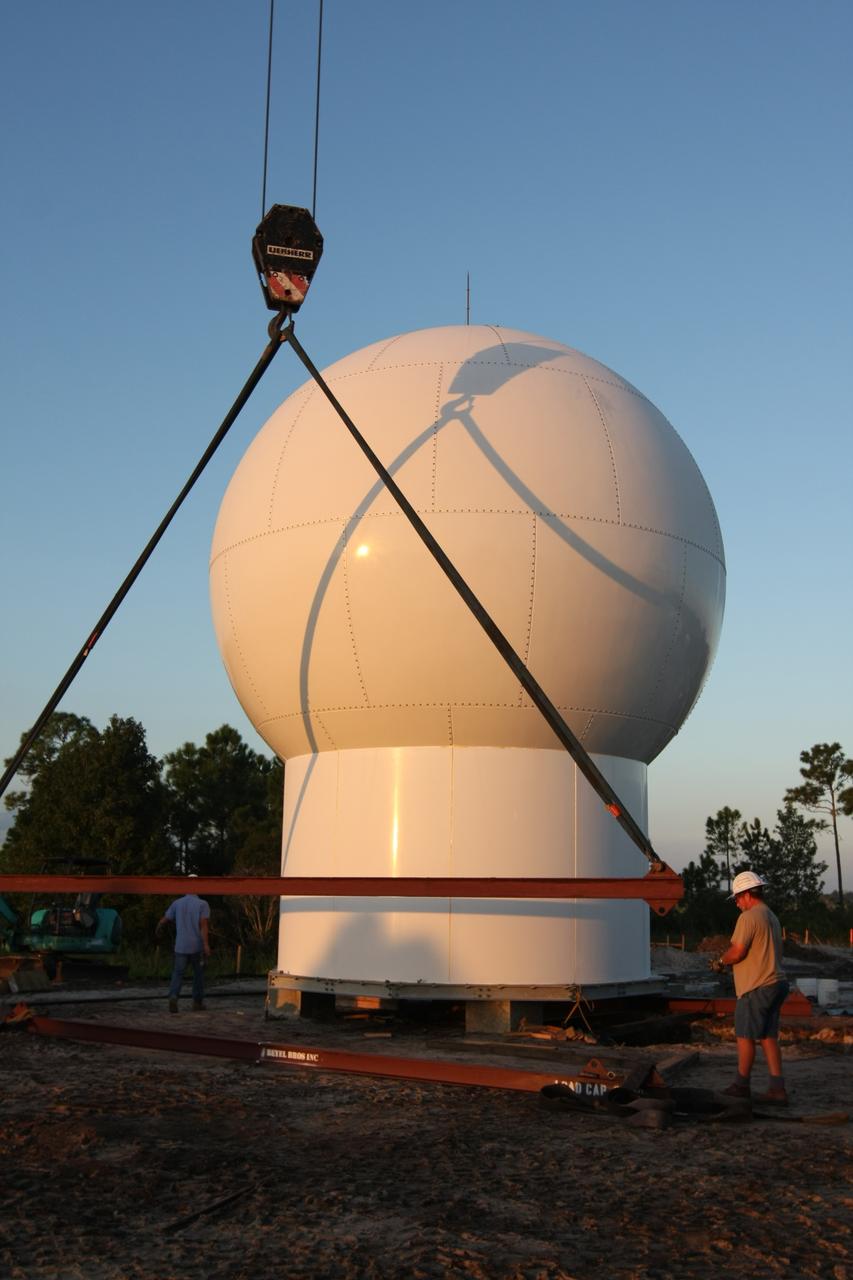

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers prepare the radome to be lifted by a crane to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
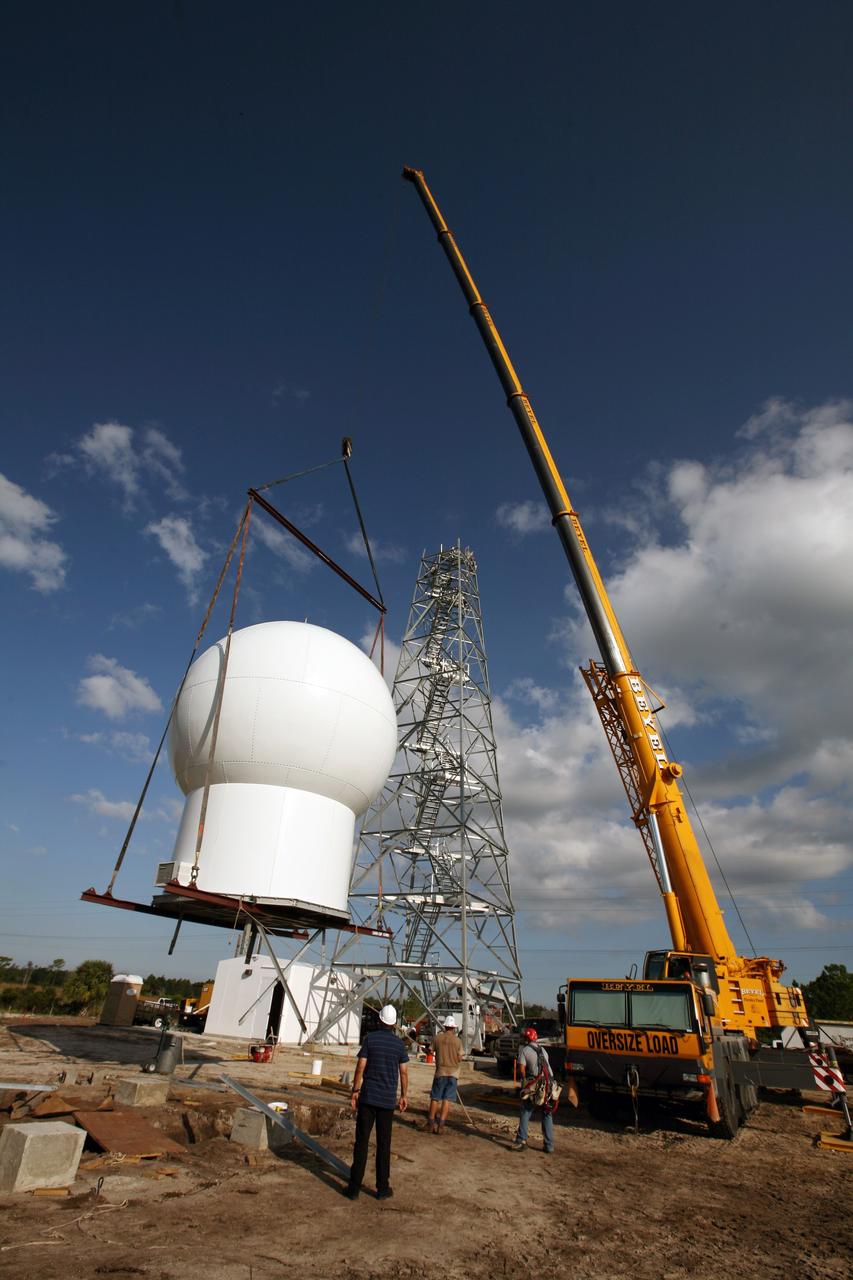

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Joe Buchanan (left), project lead with the ITT Corporation for the 45th Space Wing, supervises the lift of the radome to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
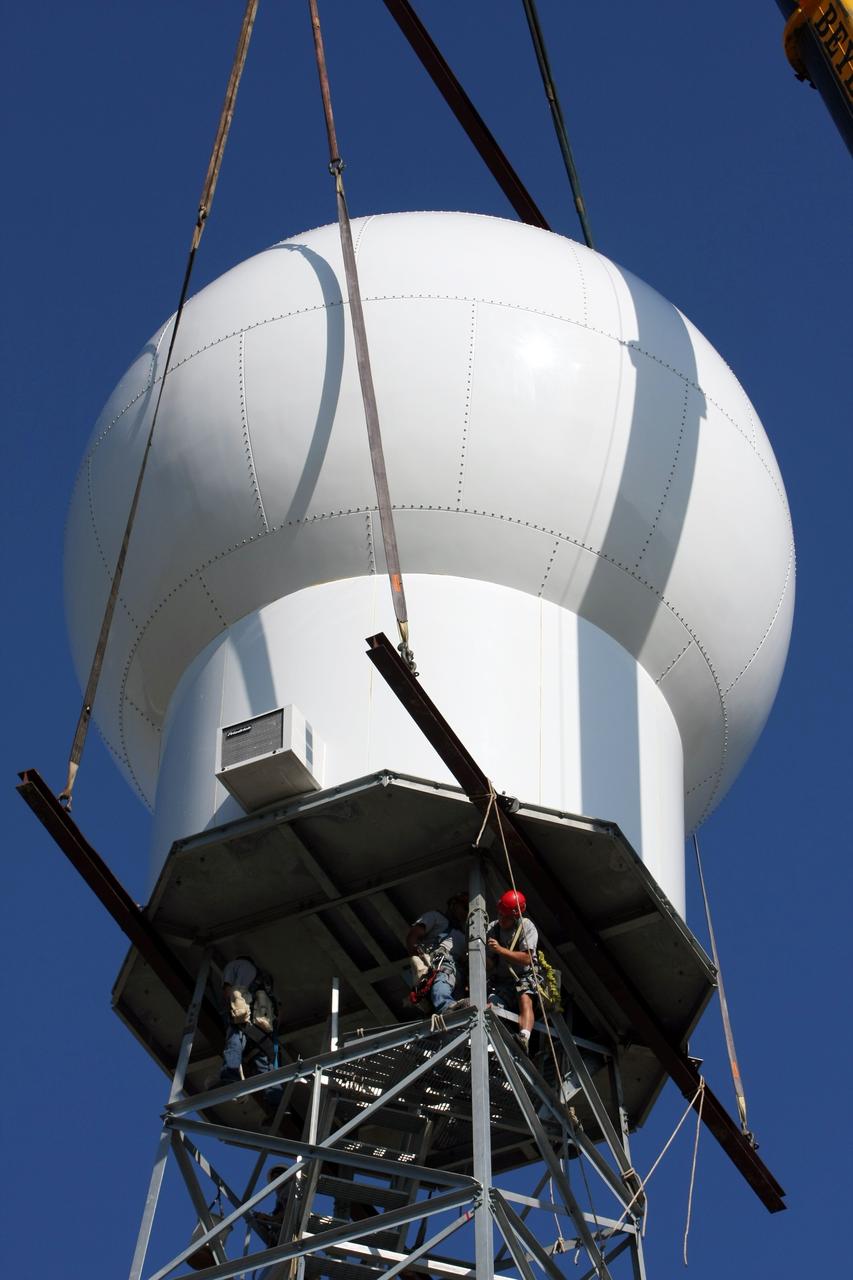

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Workers install the radome onto the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
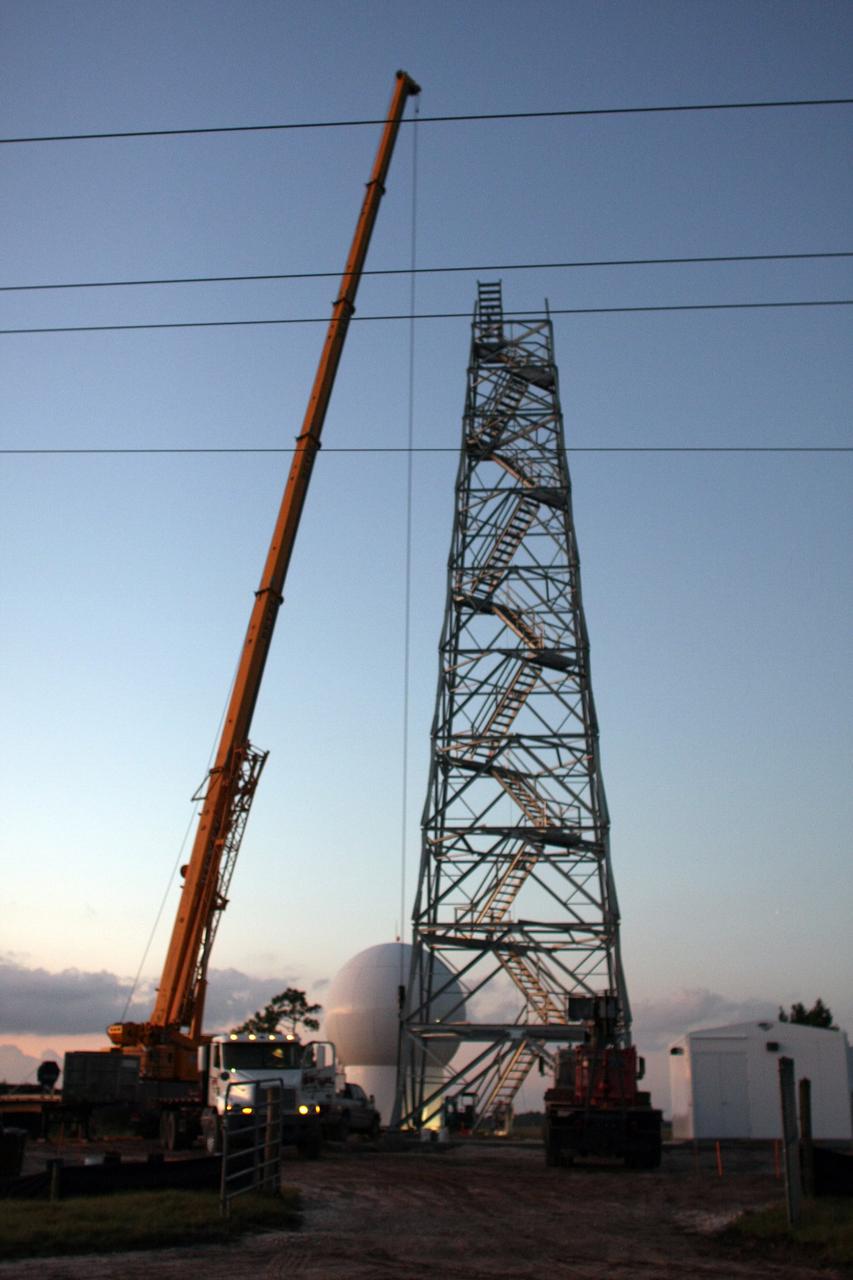

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - A crane is prepared to lift the radome to the top of a new Doppler weather radar tower being built in an area near S.R. 520 in Orange County, Fla. The dome houses the weather radar dish and pedestal and protects them from the elements. The new tower will replace one at nearby Patrick Air Force Base and will be used by NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the 45th Space Wing and their customers. The tower will be able to monitor weather conditions directly above the launch pads at Kennedy. The weather radar is essential in issuing lightning and other severe weather warnings and vital in evaluating lightning launch commit criteria. The new radar, replacing what was installed 25 years ago, includes Doppler capability to detect winds and identify the type, size and number of precipitation particles. The site is ideally distant from the launch pads and has unobstructed views of Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and Kennedy. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
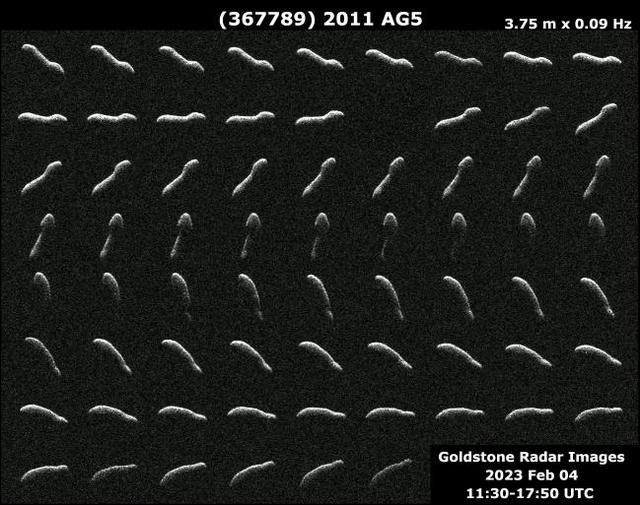
This collage represents NASA radar observations of near-Earth asteroid 2011 AG5 on Feb. 4, 2023, one day after its close approach to Earth brought it about 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers, or a little under five times the distance between the Moon and Earth) from our planet. While there was no risk of 2011 AG5 impacting Earth, scientists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California closely tracked the asteroid, making invaluable observations to help determine its size, rotation, surface details, and shape. More than three times as long as it is wide, 2011 AG5 is one of the most elongated asteroids to be observed by planetary radar to date. This close approach provided the first opportunity to take a detailed look at the asteroid since it was discovered in 2011, showing an object about 1,600 feet (500 meters) long and about 500 feet (150 meters) wide – dimensions comparable to the Empire State Building. The powerful 230-foot (70-meter) Goldstone Solar System Radar antenna dish at the Deep Space Network's facility near Barstow, California, revealed the asteroid's noteworthy dimensions. The Goldstone observations show that 2011 AG5 has a large concavity in one of its hemispheres and some subtle dark and lighter regions that may indicate small-scale surface features a few dozen meters across. If viewed by the human eye, 2011 AG5 would appear as dark as charcoal. The observations also confirmed the asteroid has a slow rotation rate, taking nine hours to fully rotate. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25259

Deep Space Station 13 (DSS-13) at NASA's Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex near Barstow, California – part of the agency's Deep Space Network – is a 34-meter (112-foot) experimental antenna that has been retrofitted with an optical terminal (the boxy instrument below the center of the antenna's dish). Since November 2023, DSS-13 has been tracking the downlink laser of the Deep Space Optical Communications (DSOC) experiment that is aboard NASA's Psyche mission, which launched on Oct. 13, 2023. In a first, the antenna also synchronously received radio-frequency signals from the spacecraft as it travels through deep space on its way to investigate the metal-rich asteroid Psyche. The laser signal collected by the camera is then transmitted through optical fiber that feeds into a cryogenically cooled semiconducting nanowire single photon detector. Designed and built by JPL's Microdevices Laboratory, the detector is identical to the one used at Caltech's Palomar Observatory, in San Diego County, California, that acts as DSOC's downlink ground station. Goldstone is one of three complexes that comprise NASA's Deep Space Network, which provides radio communications for all of the agency's interplanetary spacecraft and is also utilized for radio astronomy and radar observations of the solar system and the universe. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages the DSN for the agency. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26148
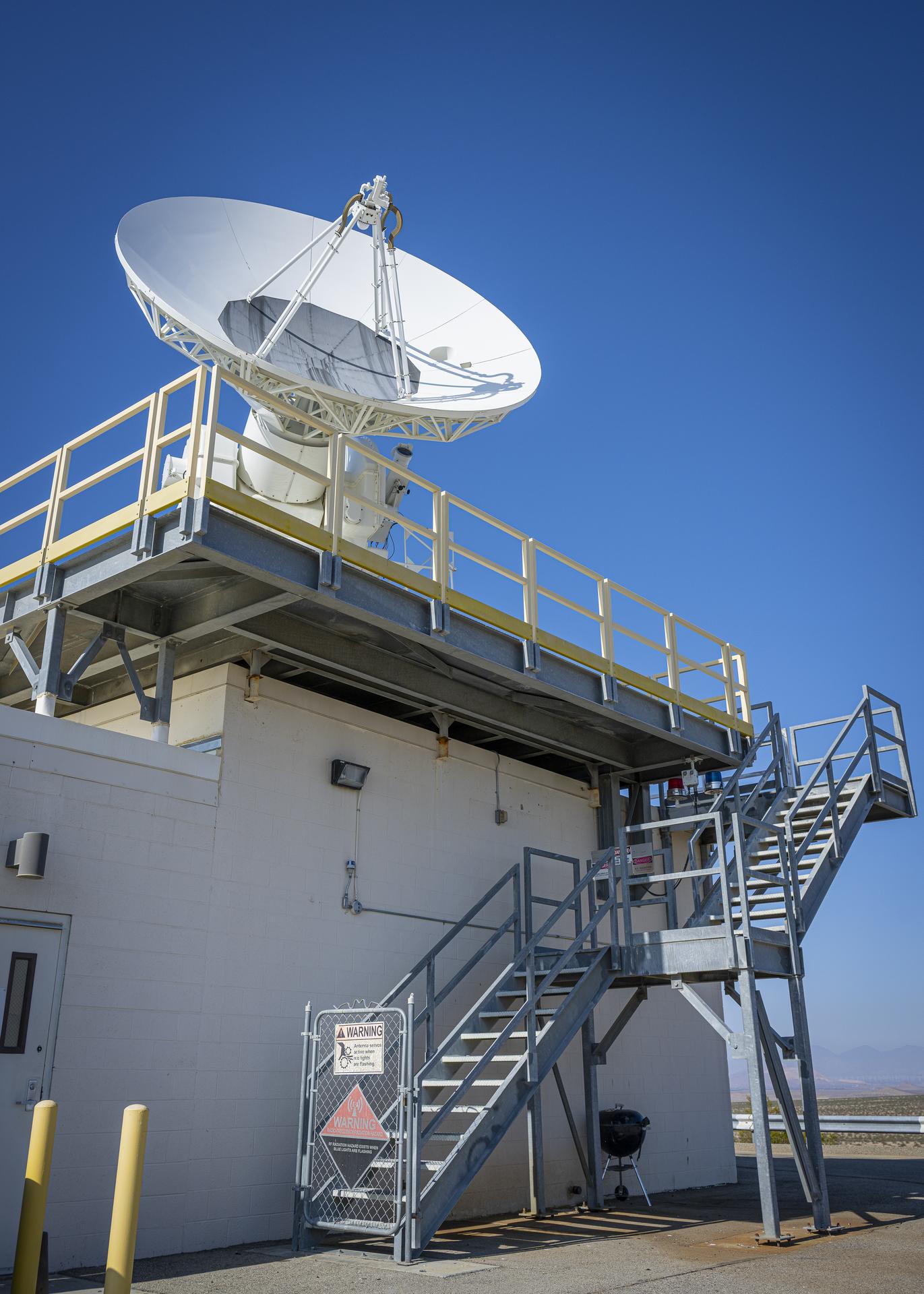

This is one of two radars that support radar tracking of the International Space Station at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, on Sept. 30, 2025. Radar tracking is one of the key capabilities of the center’s Dryden Aeronautical Test Range, which provides voice and tracking support to the International Space Station.

The Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) mission, scheduled for launch on Jan. 29, will measure the moisture in Earth's soil with greater accuracy and higher resolution than any preceding mission, producing a global map of soil moisture every three days. Here are five quick facts about the spacecraft and what it studies. 1. Soil moisture is a tiny fraction of water with a big punch. Only 0.001 percent of Earth's total water is lodged in the top few feet of soil. That tiny percentage, however, affects all living things on land and plays an important role in moving water, carbon and heat between land and atmosphere. 2. Soil moisture can compound water risks. A flood follows a heavy rainfall -- but only if the ground cannot soak up the rain. Waterlogged soil makes a region more flood-prone. Going to the opposite extreme, a drought can parch soil to such an extent that plants are unable to grow even after a few rains have fallen. Knowing soil moisture allows hydrologists to make better decisions related to the risk of flooding and drought, such as how much water to retain in reservoirs. 3. Soil moisture controls the on-off switch for carbon dioxide cleanup. The world's vast northern forests remove carbon dioxide from the air as they grow, helping to clean up our emissions from burning fossil fuels. But when the ground freezes, that process switches off. Carbon dioxide builds up in the atmosphere until the ground thaws in the spring and plants begin growing again. Knowing where and for how long the ground is frozen or thawed is an important part of understanding the role of the northern forests in reducing greenhouse warming. SMAP will map frozen and thawed soils north of 45 degrees north latitude (about the latitude of Minneapolis), around the globe. 4. SMAP is a twofer. The spacecraft's radiometer produces an accurate reading of how much moisture is in the top two inches (five centimeters) of soil, but it has low spatial resolution, that is, one measurement covers a large area. A radar instrument produces an image with higher spatial resolution, but it can't measure soil moisture as accurately as a radiometer. Through sophisticated data processing, SMAP combines observations from the two instruments into a very accurate measurement with high spatial resolution. 5. SMAP has a huge, folding, spinning antenna. At 19 feet 8 inches (6 meters) in diameter, SMAP's rotating mesh antenna dwarfs the size of the instruments and spacecraft and is the largest rotating antenna of its kind that NASA has yet deployed. But the entire dish furls into a cylinder one foot (diameter) by four feet (30 by 120 centimeters) to fit inside the rocket’s fairing for launch, and it weighs only 128 pounds (about 58 kilograms). For more information about SMAP, see: <a href="http://smap.jpl.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">smap.jpl.nasa.gov/</a> <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/smap/" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/smap/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>